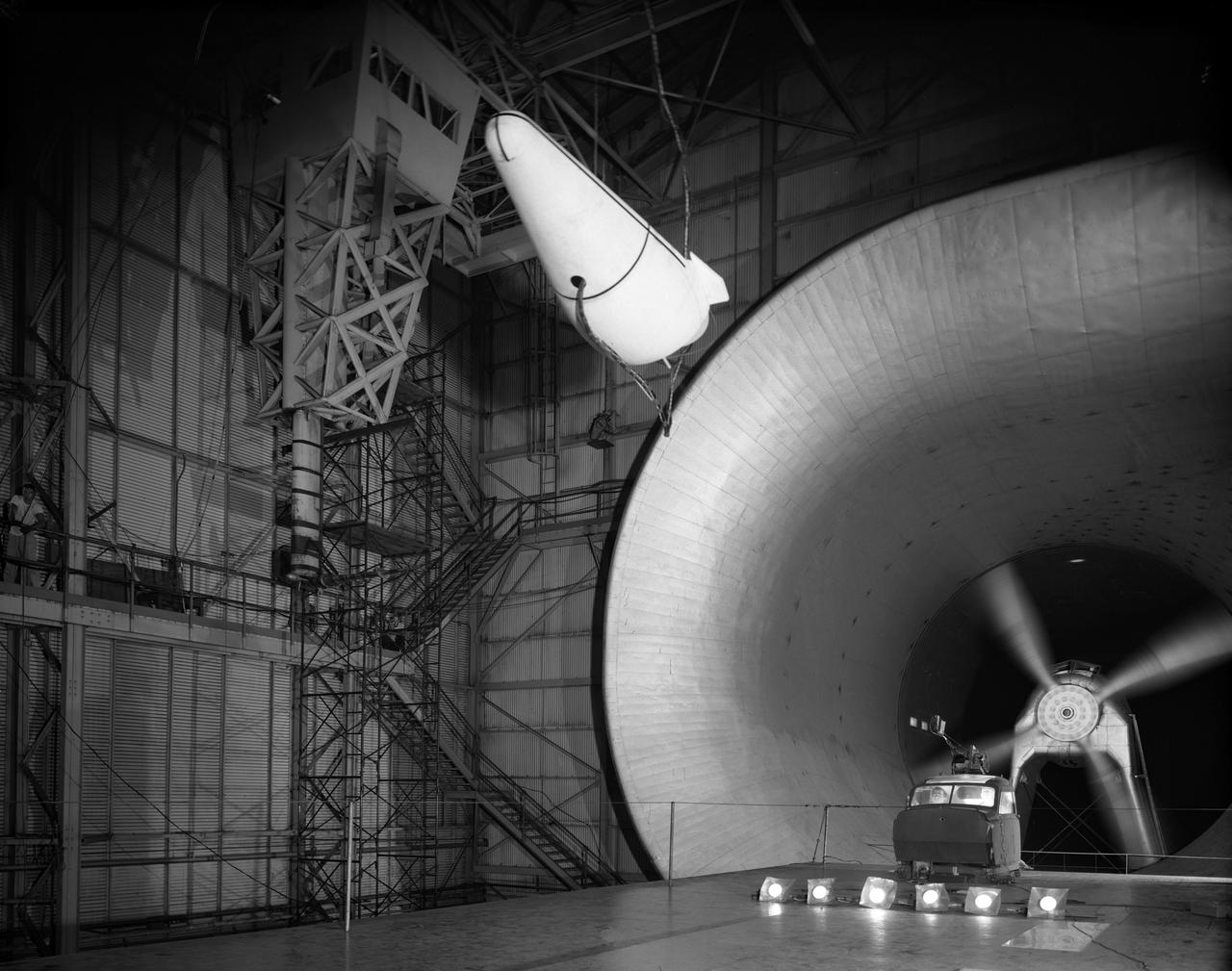

Re-entry vehicle on Full Scale Tunnel (FST)
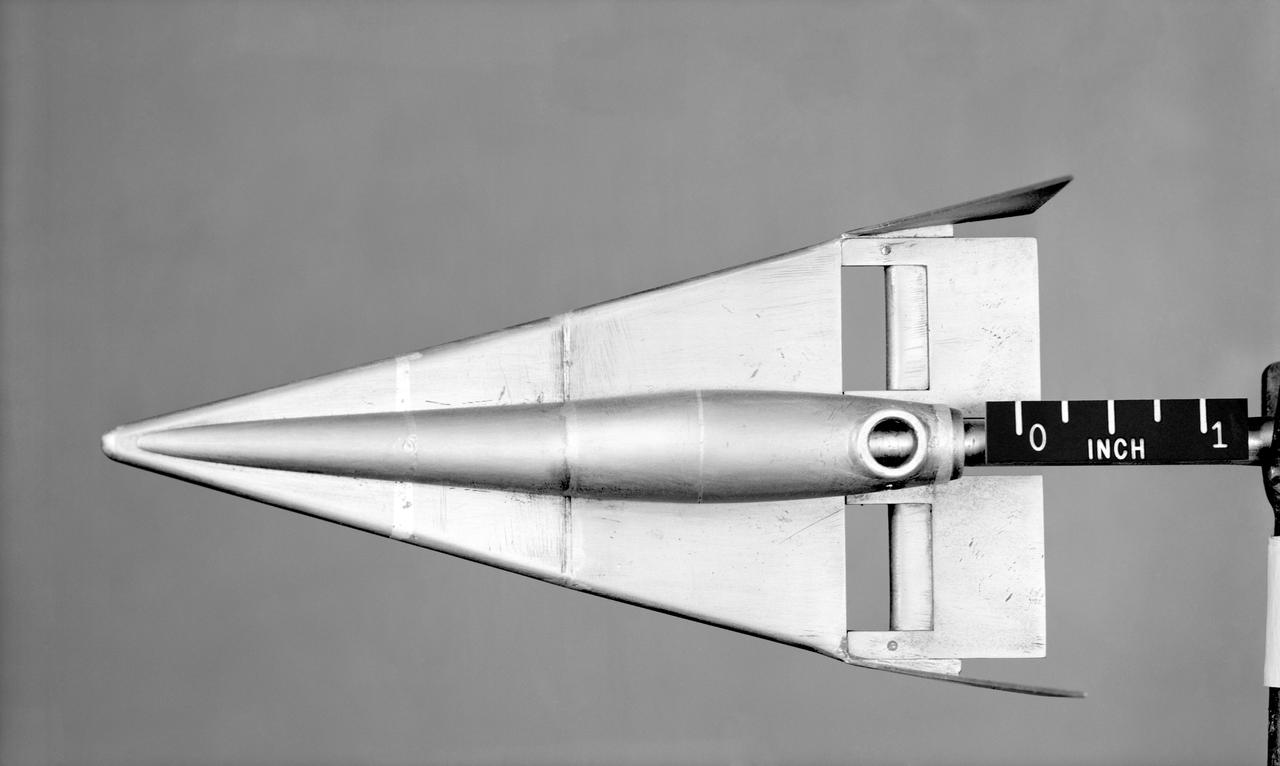

Lifting Type Re-Entry Vehicle
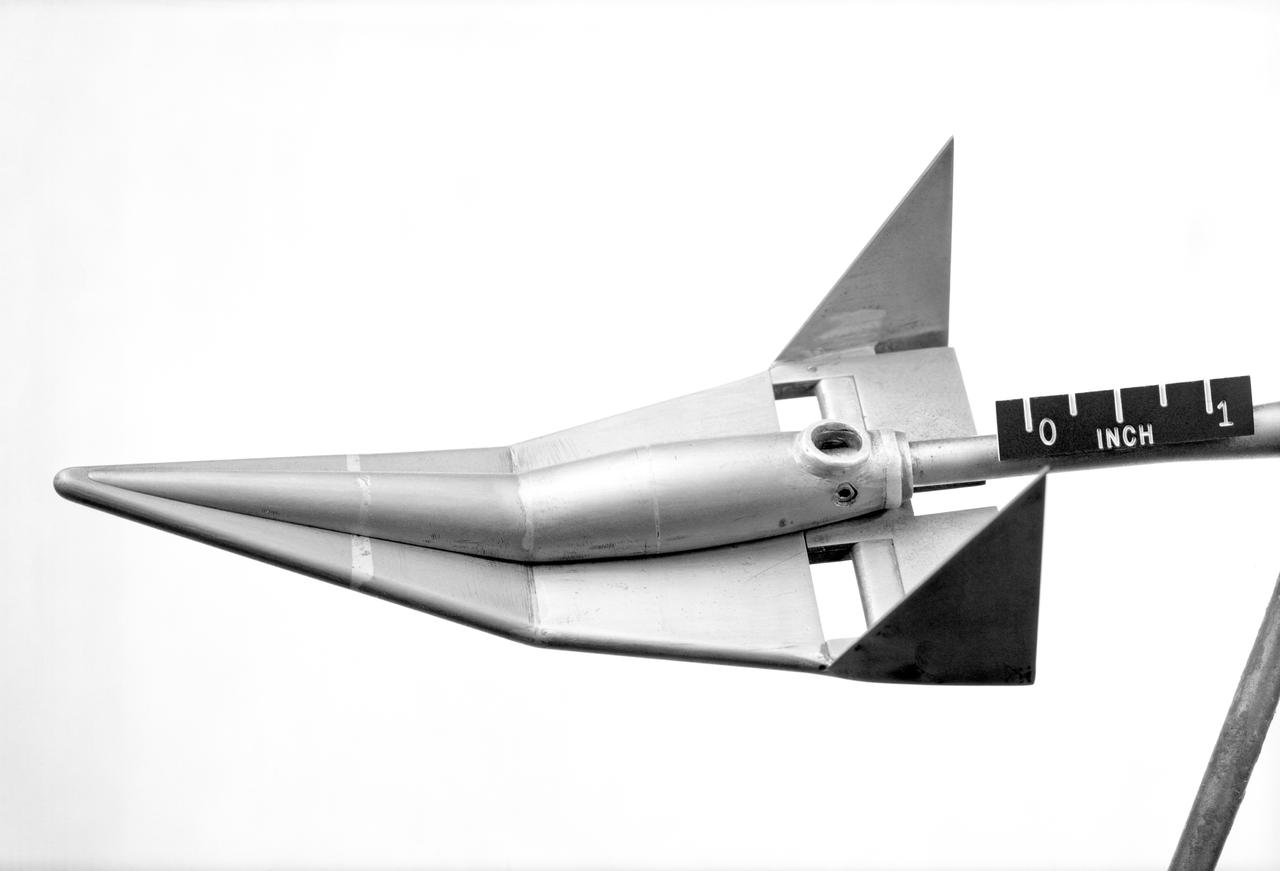

Lifting Type Re-Entry Vehicle
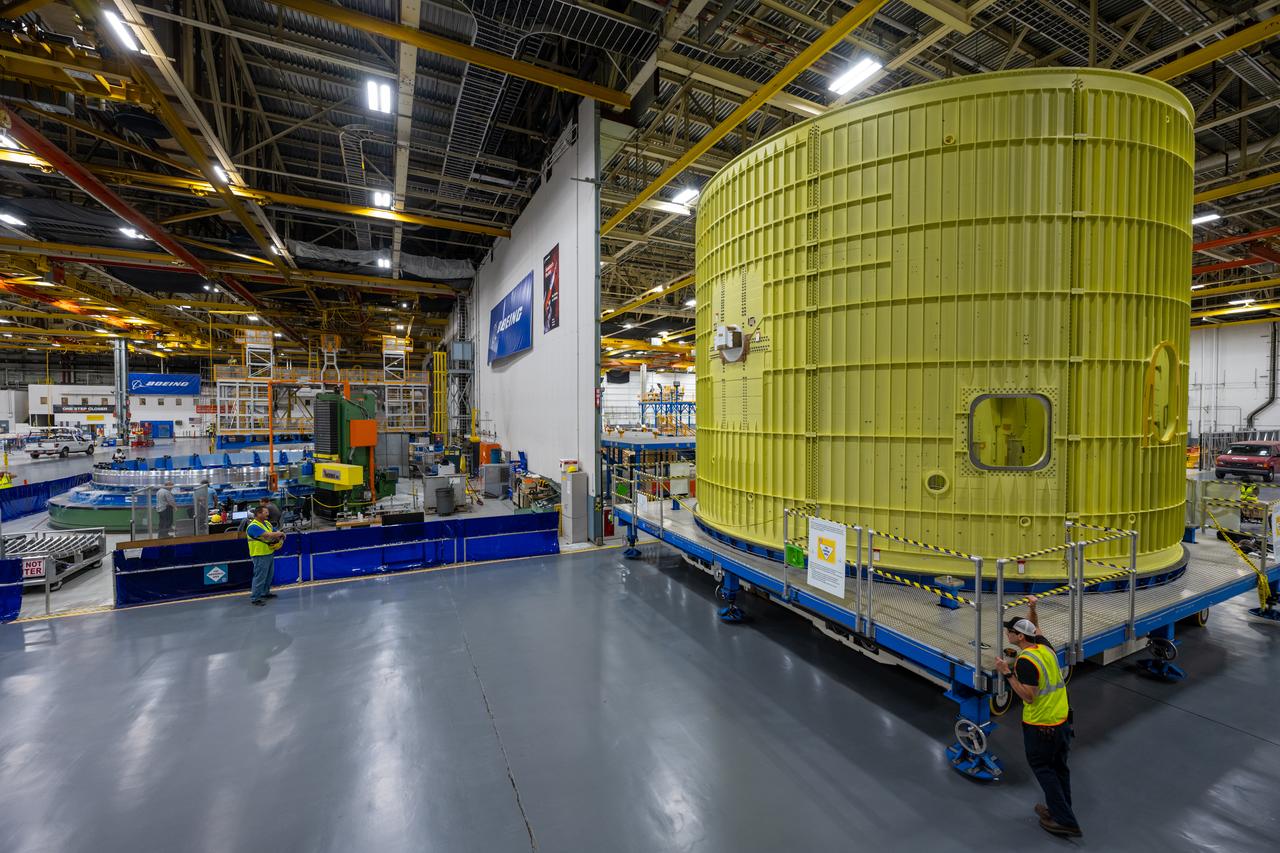

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere.
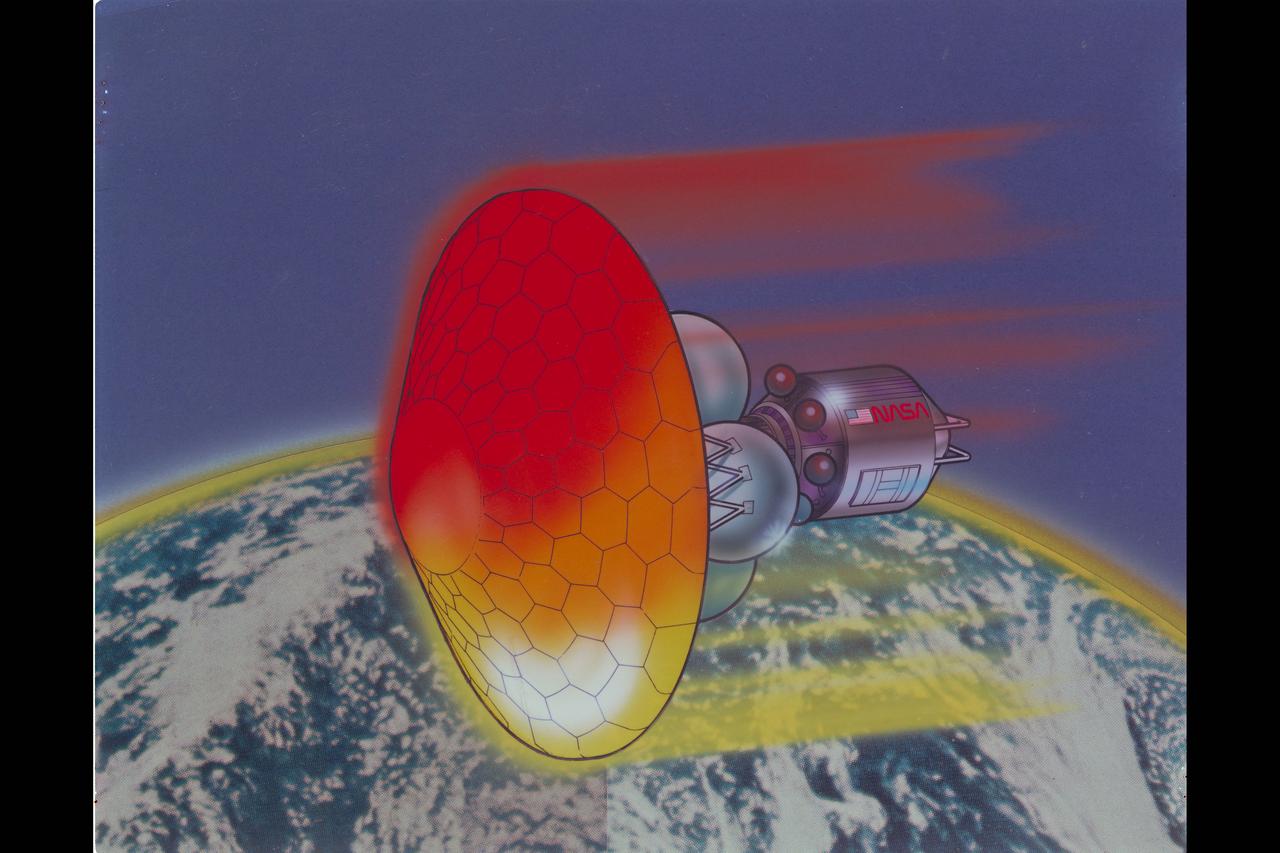
Artwork AOTV Aeroassisted orbital transfer vehicle re-entry
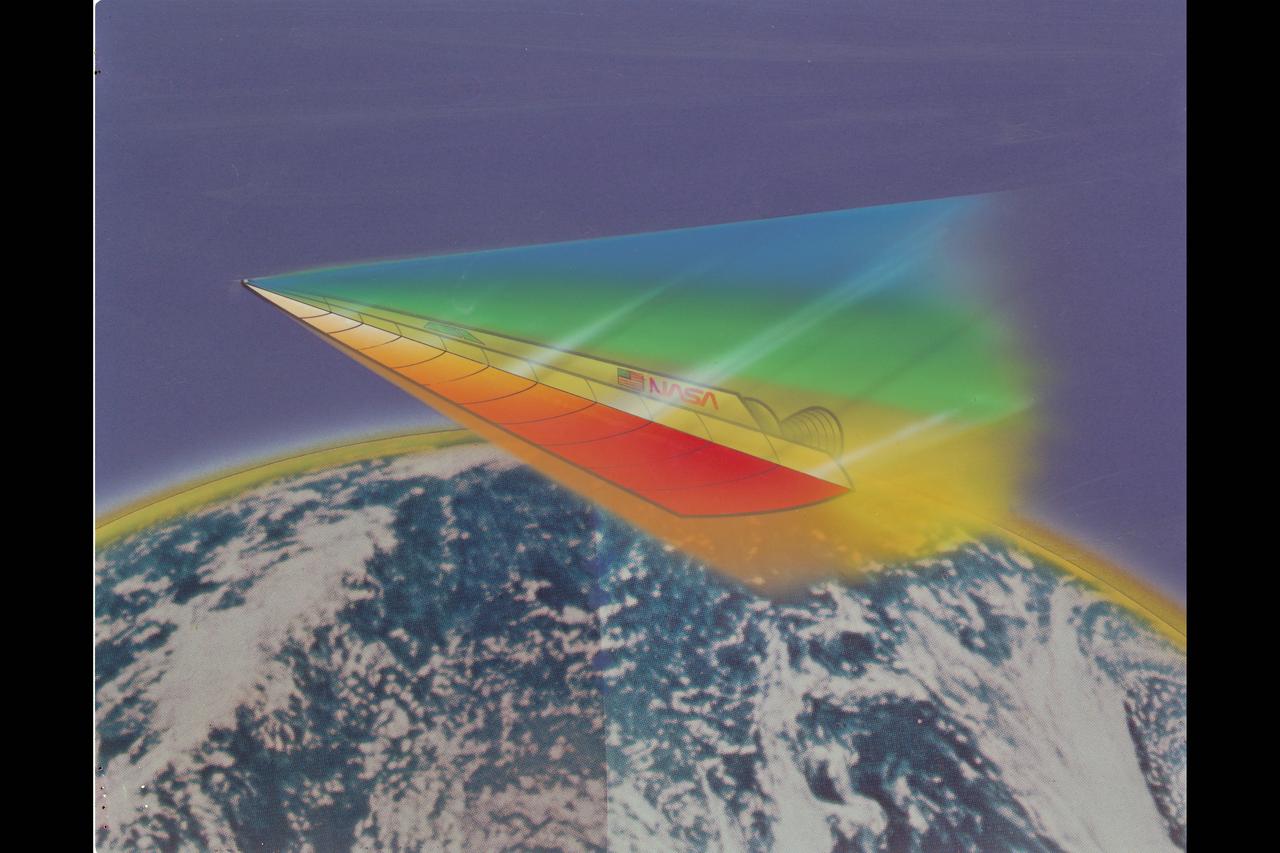
Artwork Artist conception of a hypersonic futuristic space vehicle re-entry
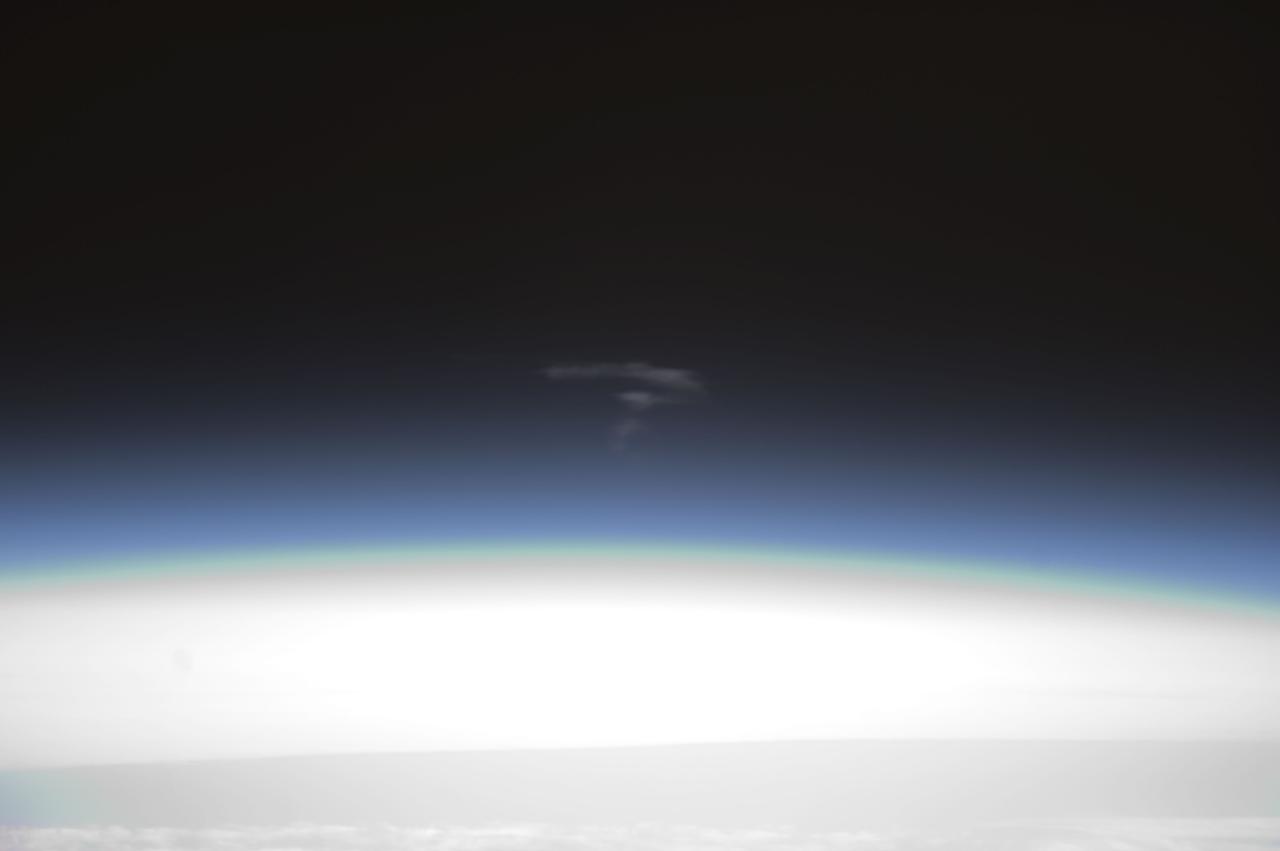

ISS033-E-009232 (3 Oct. 2012) --- This still photo taken by the Expedition 33 crew members aboard the International Space Station shows evidence of the fiery plunge through Earth?s atmosphere and the destructive re-entry of the European Automated Transfer Vehicle-3 (ATV-3) spacecraft, also known as ?Edoardo Amaldi.? The end of the ATV took place over a remote swath of the Pacific Ocean where any surviving debris safely splashed down a short time later, at around 1:30 a.m. (GMT) on Oct. 3, thus concluding the highly successful ATV-3 mission. Aboard the craft during re-entry was the Re Entry Breakup Recorder (REBR), a spacecraft ?black box? designed to gather data on vehicle disintegration during re-entry in order to improve future spacecraft re-entry models.

THIS IS A TEST OF THE 1ST STAGE RE-ENTRY VEHICLE. HEAT TESTING OF A 3% MODEL TO SUPPORT THE ARES/ CLV FIRST STAGE RE-ENTRY. THIS TEST OCCURRED AT ARNOLD AIR FORCE BASE, TENNESSEE. THIS TESTING SUPPORTS THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE CONSTELLATION/ARES PROJECT. THIS IMAGE IS EXTRACTED FROM A HIGH DEFINITION VIDEO FILE AND IS THE HIGHEST RESOLUTION AVAILABLE.
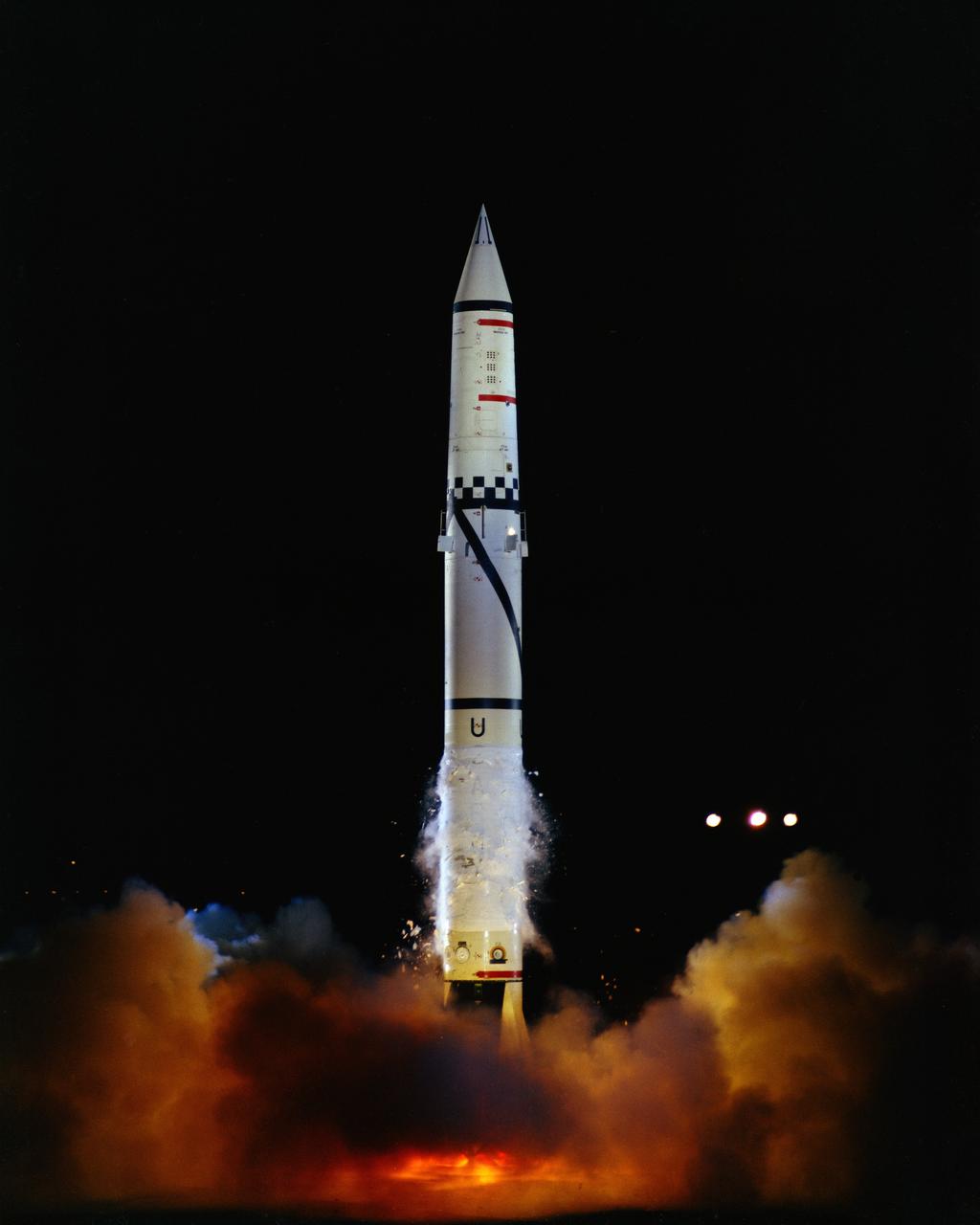

Pad 6. Launch of US Army Redstone (2040) for accuracy and vehicle re-entry observation, at 9: 30 P.M. EST. (Lift-off) Photo by: Bundy.

Columbia, which opened the era of the Space Transportation System with four orbital flight tests, is featured in re-entry in the emblem designed by the STS-61C crew representing the seven team members who manned the vehicle for its seventh STS mission. Gold lettering against black background honors the astronaut crewmembers on the delta pattern surrounding colorful re-entry shock waves, and the payload specialists are honored similarly below the sphere
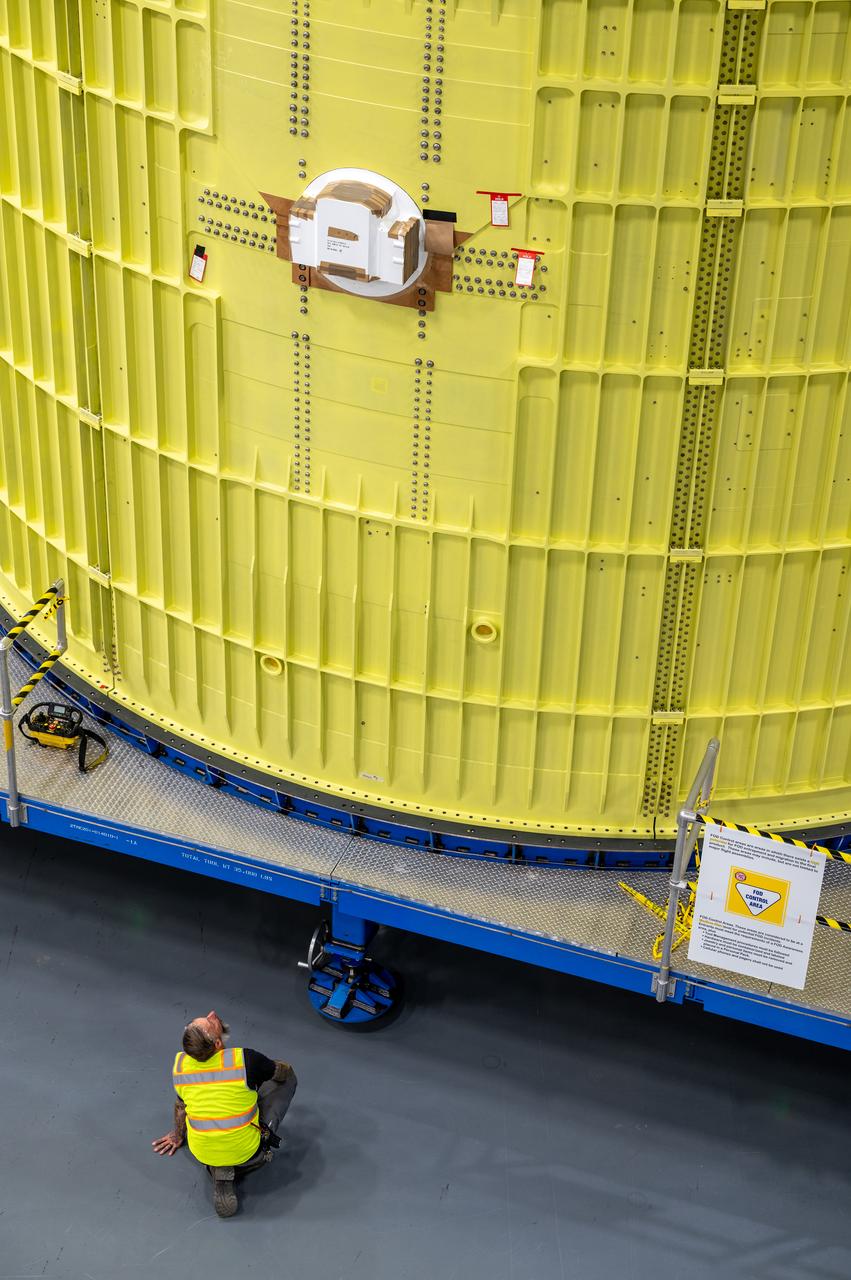

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
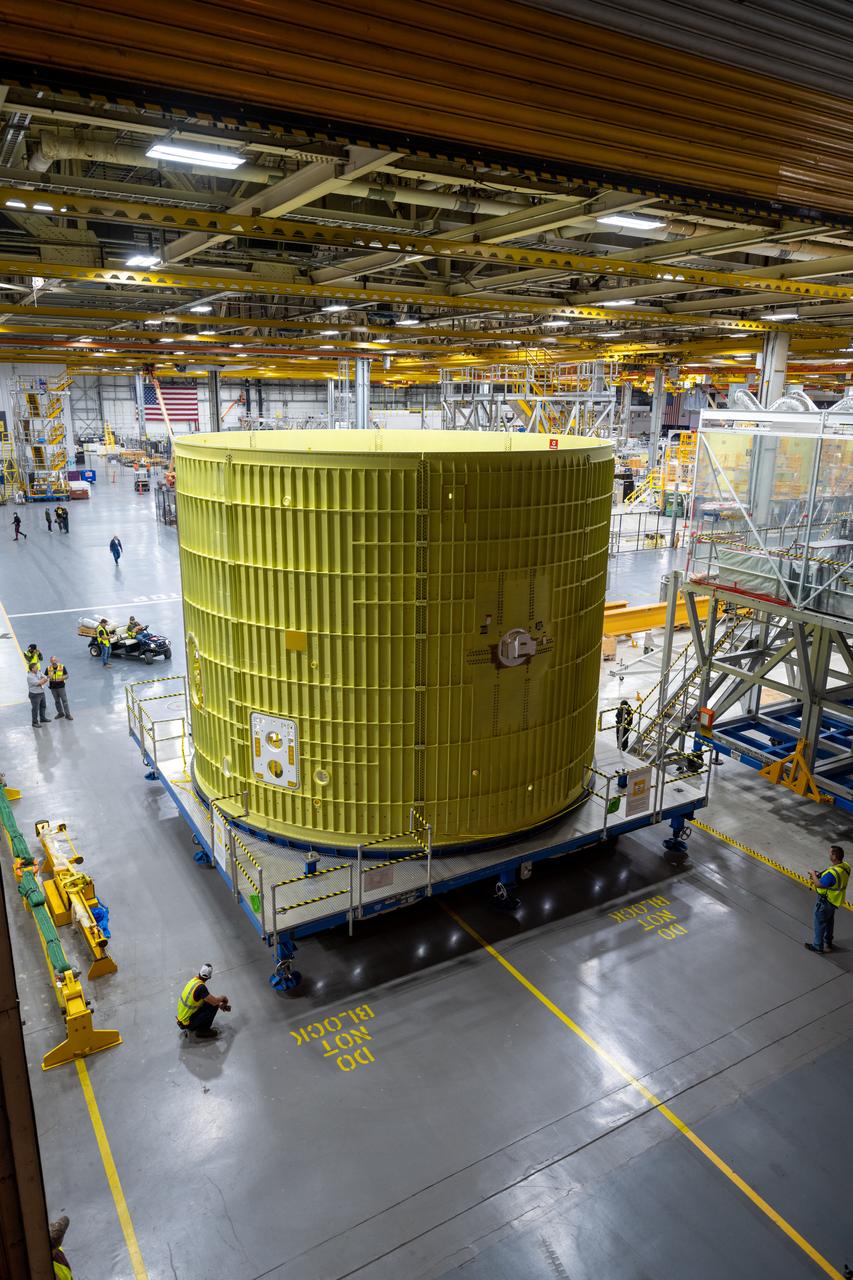

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
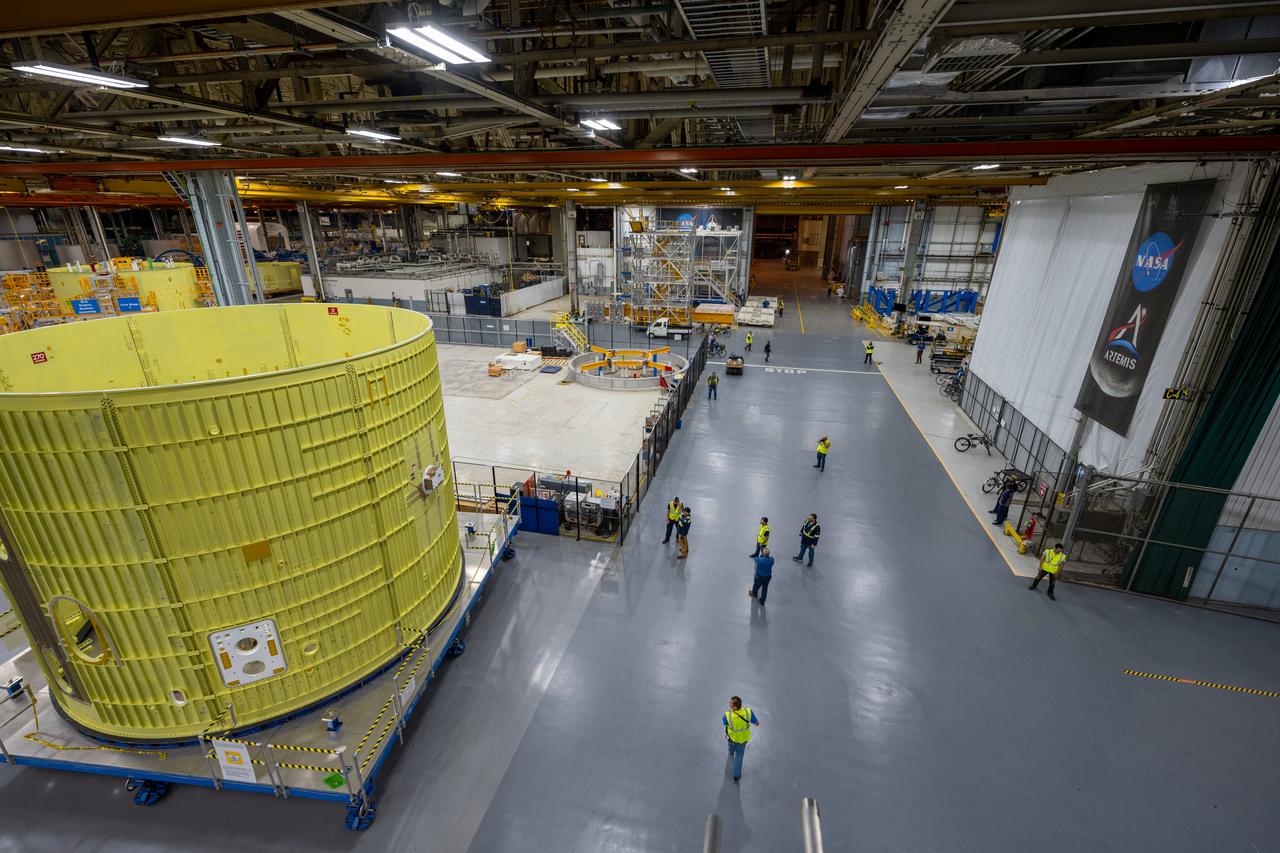

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
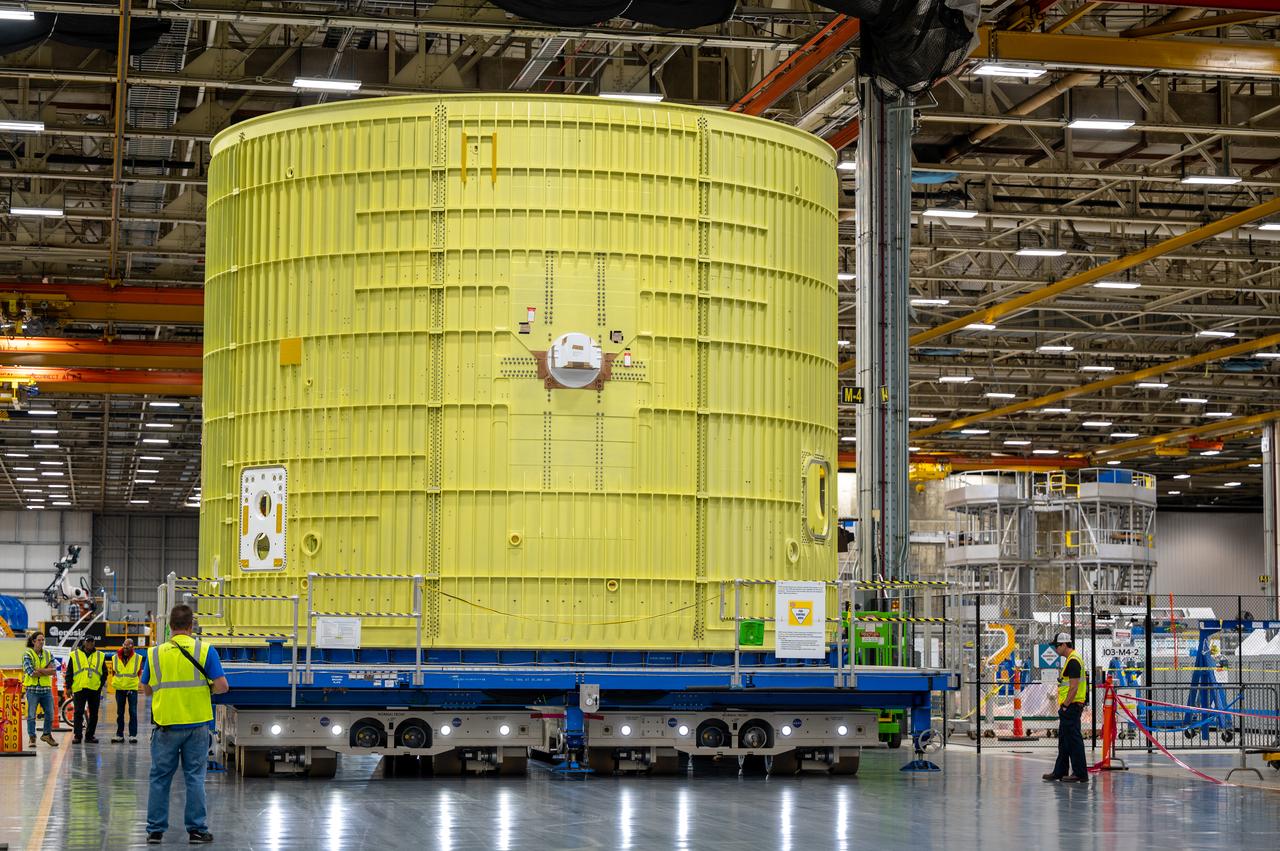

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
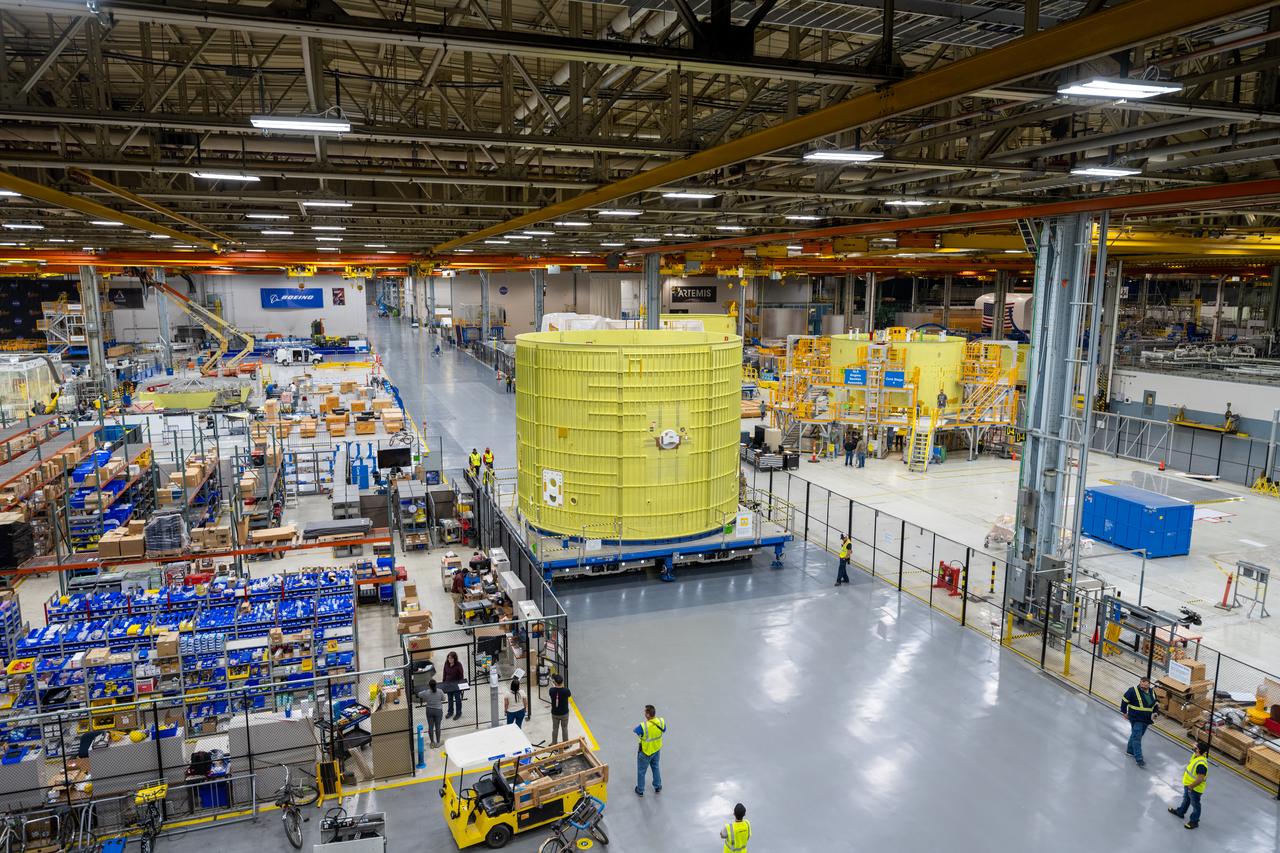

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
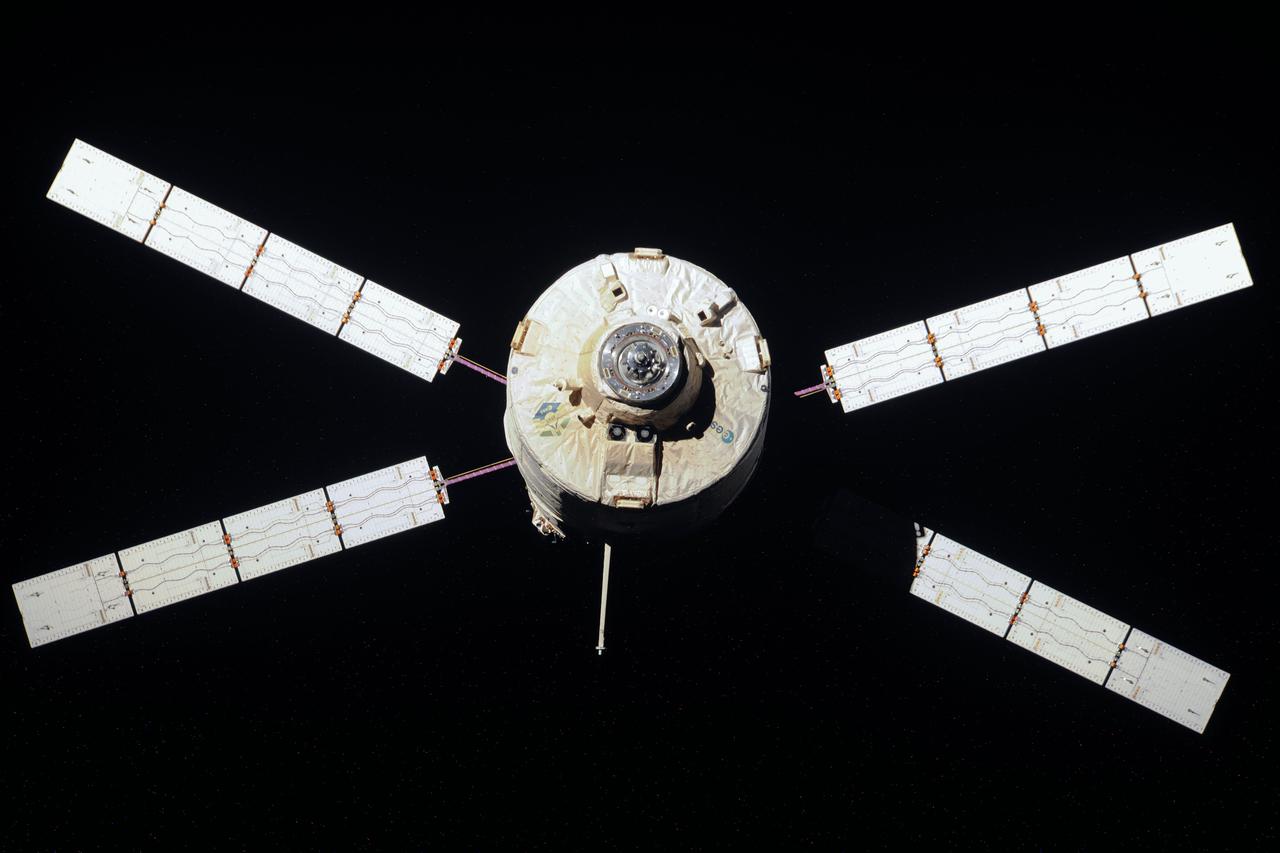

ISS033-E-007915 (28 Sept. 2012) --- European Space Agency's "Edoardo Amaldi" Automated Transfer Vehicle-3 (ATV-3) begins its relative separation from the International Space Station during the Expedition 33 mission. The ATV-3 undocked from the aft port of the Zvezda Service Module at 5:44 p.m. (EDT) on Sept. 28, 2012. The ATV-3 is scheduled to deorbit on Oct. 2 for a fiery re-entry over the Pacific Ocean that will destroy the trash-filled spacecraft. Inside the ATV-3 is the Re-Entry Breakup Recorder that will record various data such as temperature, pressure and speed as the resupply craft burns up during its return to Earth. Experts will use that data to design safer and more predictable destructive re-entry techniques.
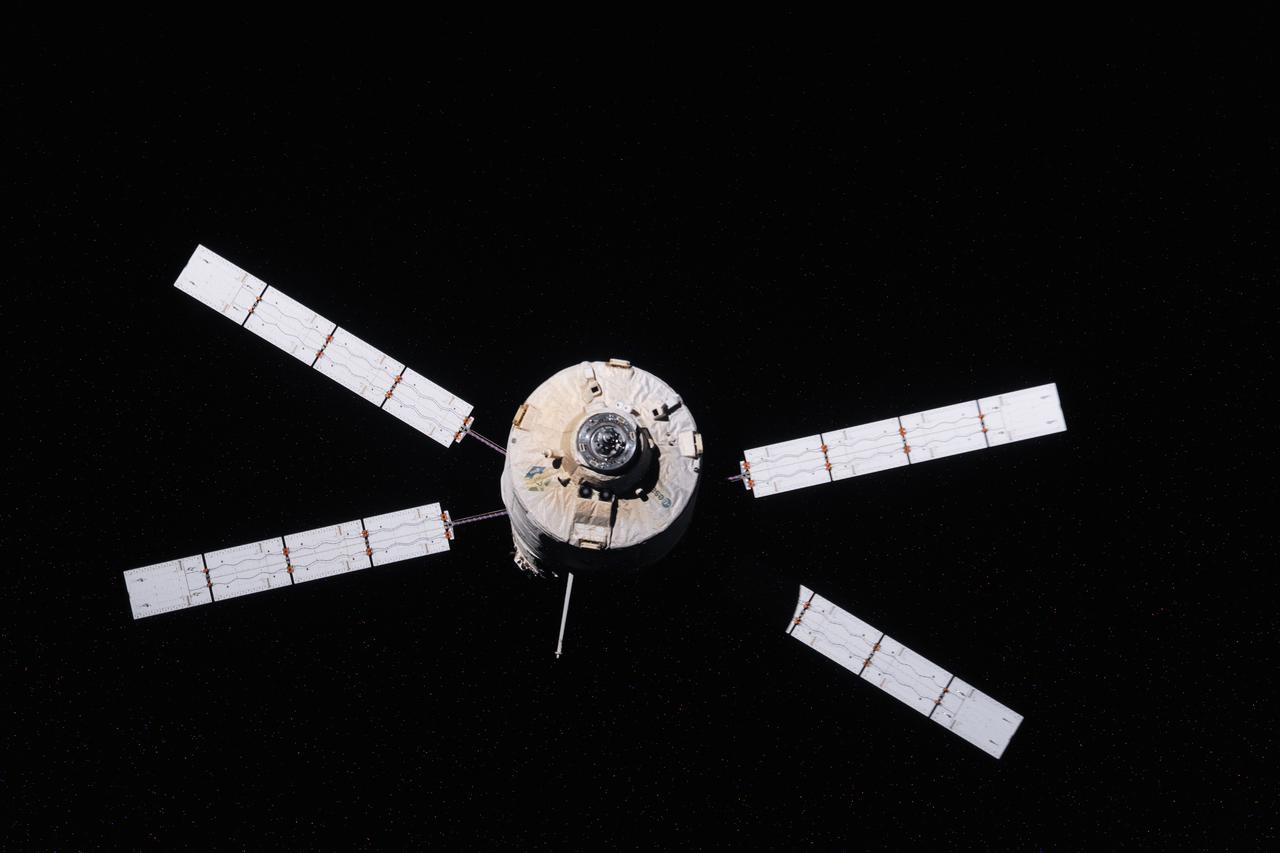

ISS033-E-007920 (28 Sept. 2012) --- European Space Agency's "Edoardo Amaldi" Automated Transfer Vehicle-3 (ATV-3) begins its relative separation from the International Space Station during the Expedition 33 mission. The ATV-3 undocked from the aft port of the Zvezda Service Module at 5:44 p.m. (EDT) on Sept. 28, 2012. The ATV-3 is scheduled to deorbit on Oct. 2 for a fiery re-entry over the Pacific Ocean that will destroy the trash-filled spacecraft. Inside the ATV-3 is the Re-Entry Breakup Recorder that will record various data such as temperature, pressure and speed as the resupply craft burns up during its return to Earth. Experts will use that data to design safer and more predictable destructive re-entry techniques.
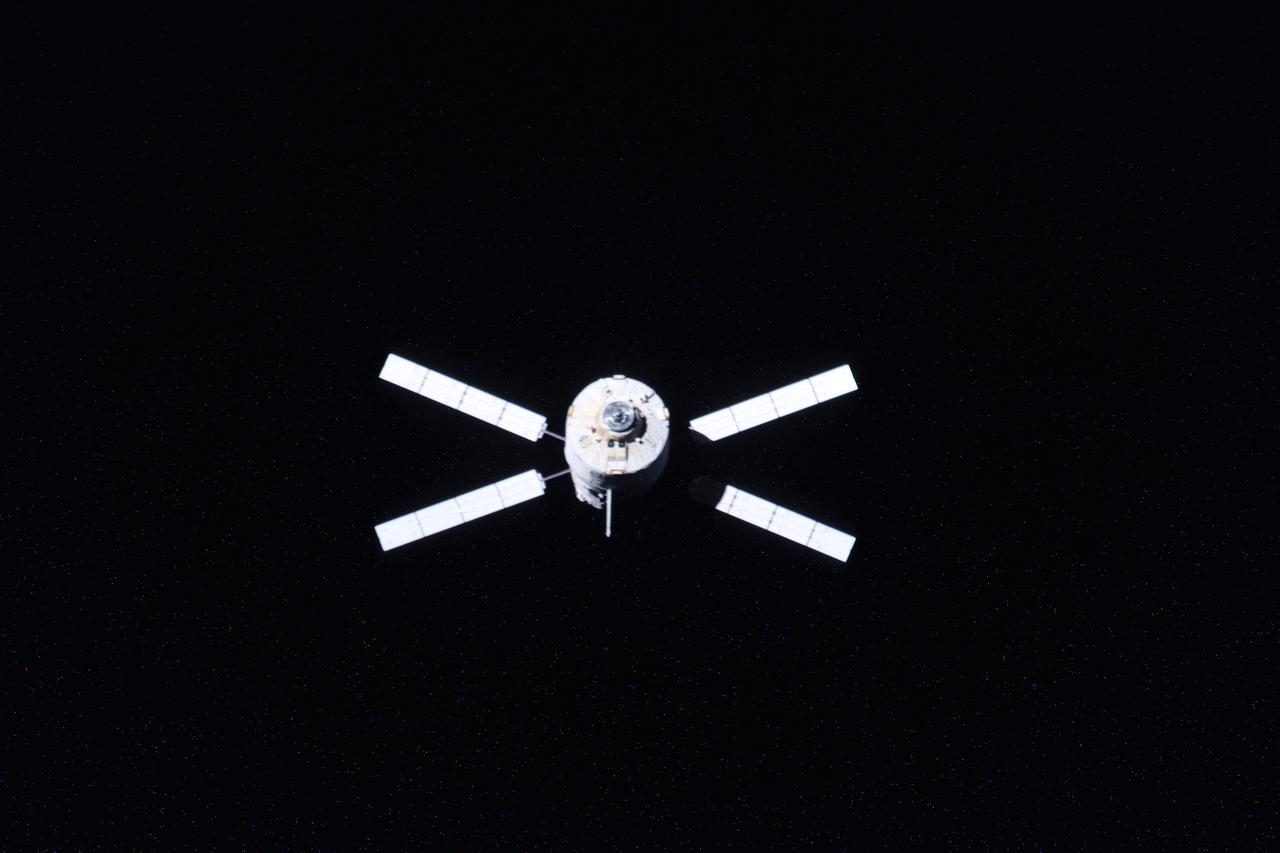
ISS033-E-007980 (28 Sept. 2012) --- European Space Agency's "Edoardo Amaldi" Automated Transfer Vehicle-3 (ATV-3) begins its relative separation from the International Space Station during the Expedition 33 mission. The ATV-3 undocked from the aft port of the Zvezda Service Module at 5:44 p.m. (EDT) on Sept. 28, 2012. The ATV-3 is scheduled to deorbit on Oct. 2 for a fiery re-entry over the Pacific Ocean that will destroy the trash-filled spacecraft. Inside the ATV-3 is the Re-Entry Breakup Recorder that will record various data such as temperature, pressure and speed as the resupply craft burns up during its return to Earth. Experts will use that data to design safer and more predictable destructive re-entry techniques.
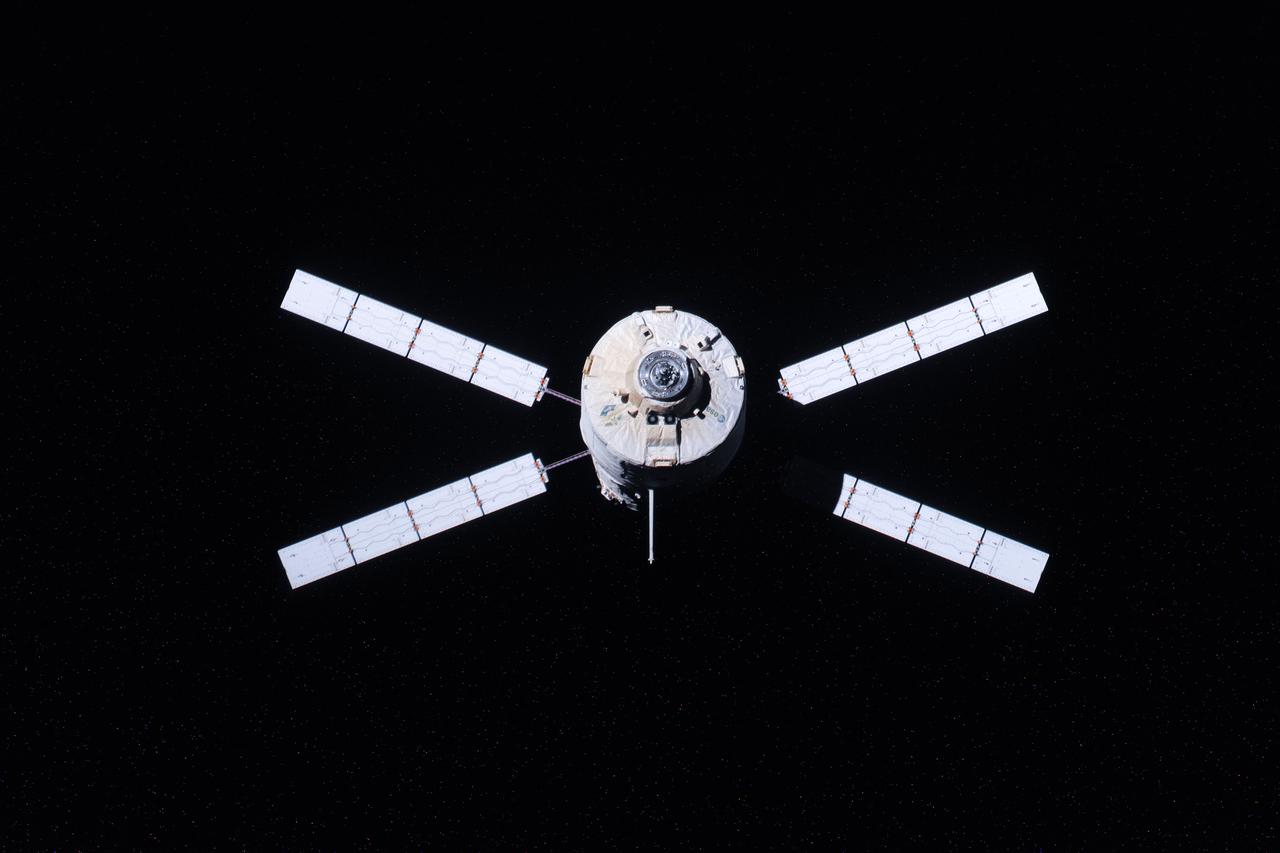

ISS033-E-007940 (28 Sept. 2012) --- European Space Agency's "Edoardo Amaldi" Automated Transfer Vehicle-3 (ATV-3) begins its relative separation from the International Space Station during the Expedition 33 mission. The ATV-3 undocked from the aft port of the Zvezda Service Module at 5:44 p.m. (EDT) on Sept. 28, 2012. The ATV-3 is scheduled to deorbit on Oct. 2 for a fiery re-entry over the Pacific Ocean that will destroy the trash-filled spacecraft. Inside the ATV-3 is the Re-Entry Breakup Recorder that will record various data such as temperature, pressure and speed as the resupply craft burns up during its return to Earth. Experts will use that data to design safer and more predictable destructive re-entry techniques.

ISS033-E-008016 (28 Sept. 2012) --- European Space Agency's "Edoardo Amaldi" Automated Transfer Vehicle-3 (ATV-3) begins its relative separation from the International Space Station during the Expedition 33 mission. The ATV-3 undocked from the aft port of the Zvezda Service Module at 5:44 p.m. (EDT) on Sept. 28, 2012. The ATV-3 is scheduled to deorbit on Oct. 2 for a fiery re-entry over the Pacific Ocean that will destroy the trash-filled spacecraft. Inside the ATV-3 is the Re-Entry Breakup Recorder that will record various data such as temperature, pressure and speed as the resupply craft burns up during its return to Earth. Experts will use that data to design safer and more predictable destructive re-entry techniques.
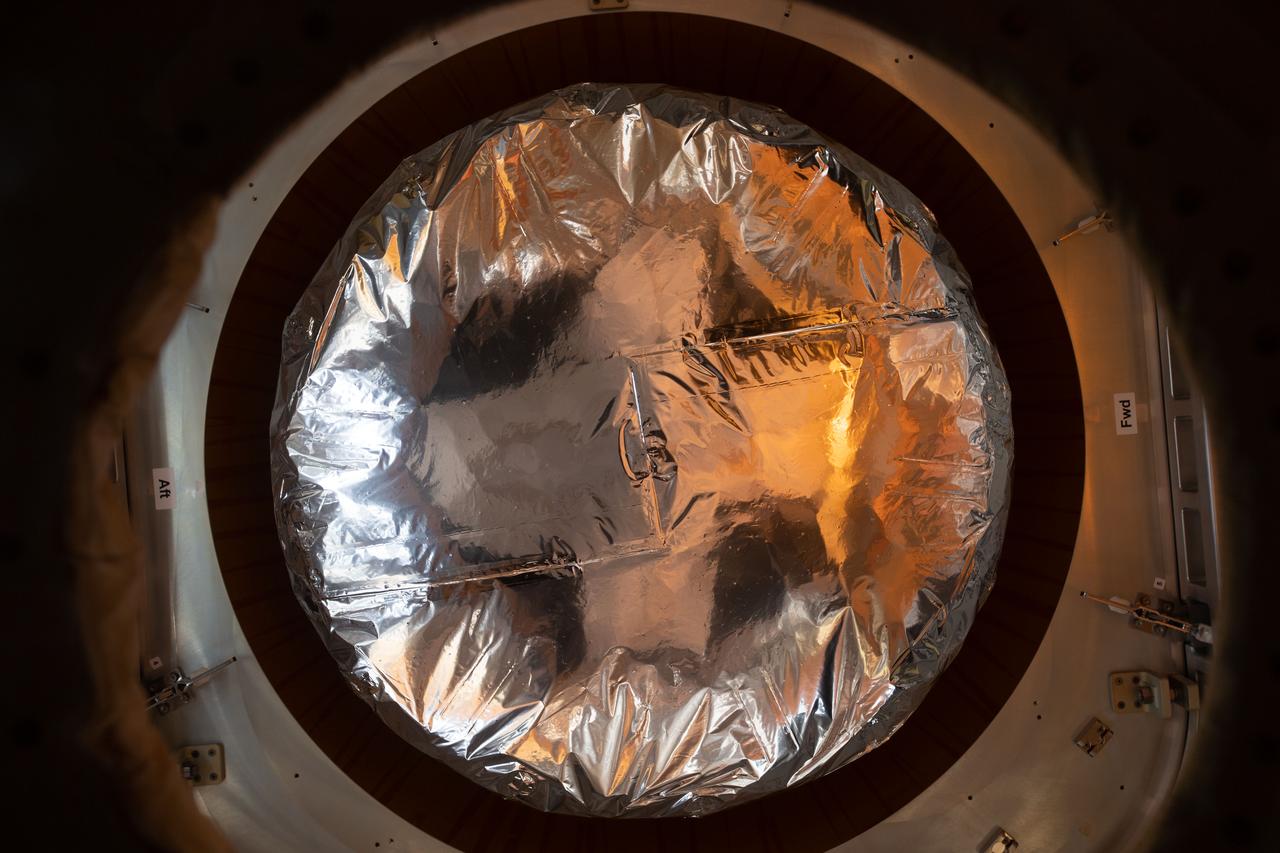

iss057e059221 (11/7/2018) --- A view taken through the Harmony Node 2 nadir hatch window of the Kounotori H-II Transfer Vehicle 7 (HTV-7), with the HTV Small Re-entry Capsule (HSRC) in view, during unberthing and backing away from the International Space Station (ISS).
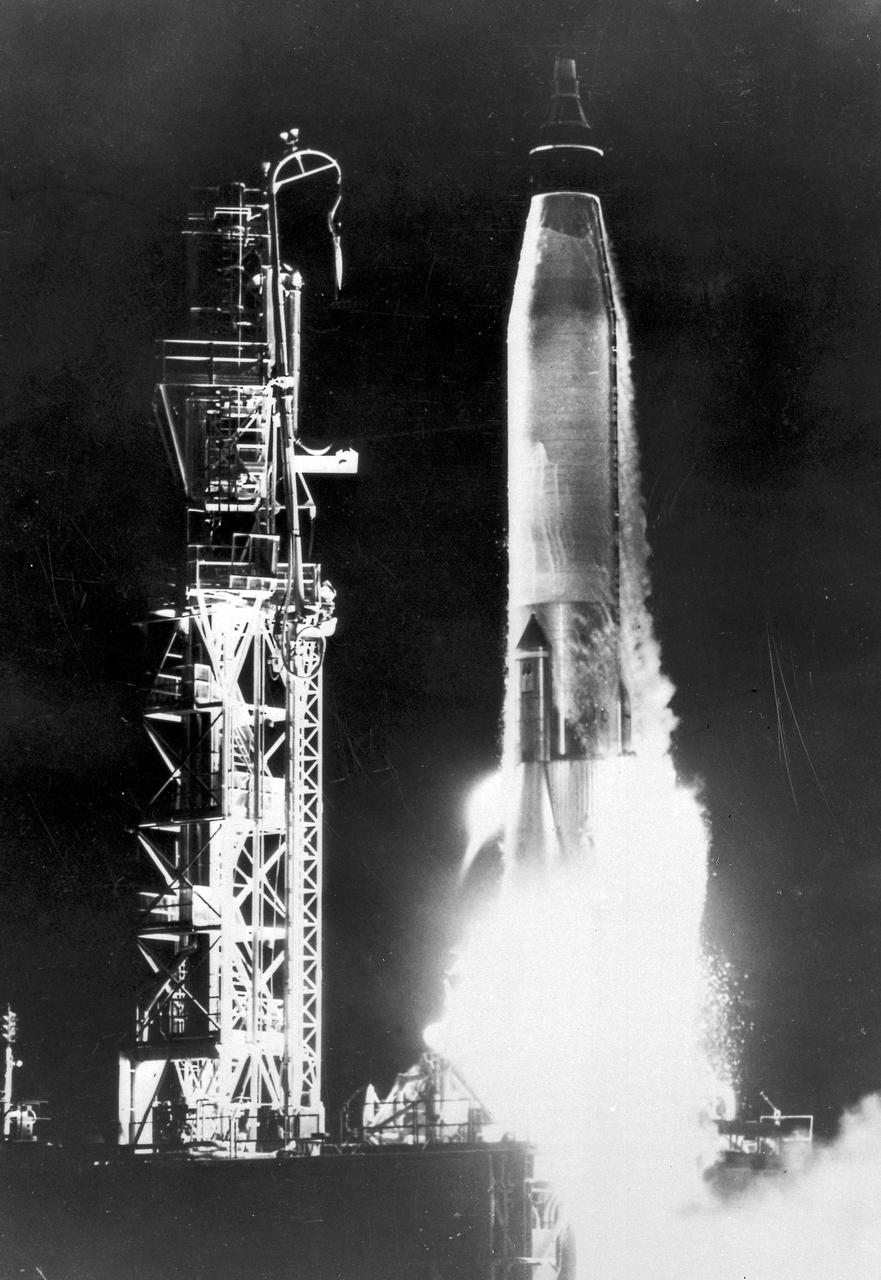

An Atlas launch vehicle carrying the Big Joe capsule leaves its launching pad on a 2,000-mile ballistic flight to the altitude of 100 miles. The Big Joe capsule is a boilerplate model of the marned orbital capsule under NASA's Project Mercury. The capsule was recovered and studied for the effect of re-entry heat and other flight stresses.

European Space Agency's 'Jules Verne' Automated Transfer Vehicle ATV-1 re-entry in Earth's atmosphere over Pacific Ocean. The breakup ad fragmentation of the ESA's ATV-1 was captured in dramatic fashion by scientists aboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory and a Gulfstream V aircraft as it re-entered the atmosphere early Monday morning over the South Pacific. Photo Credit: NASA Ames Research Center/ESA/Jesse Carpenter/Bill Moede
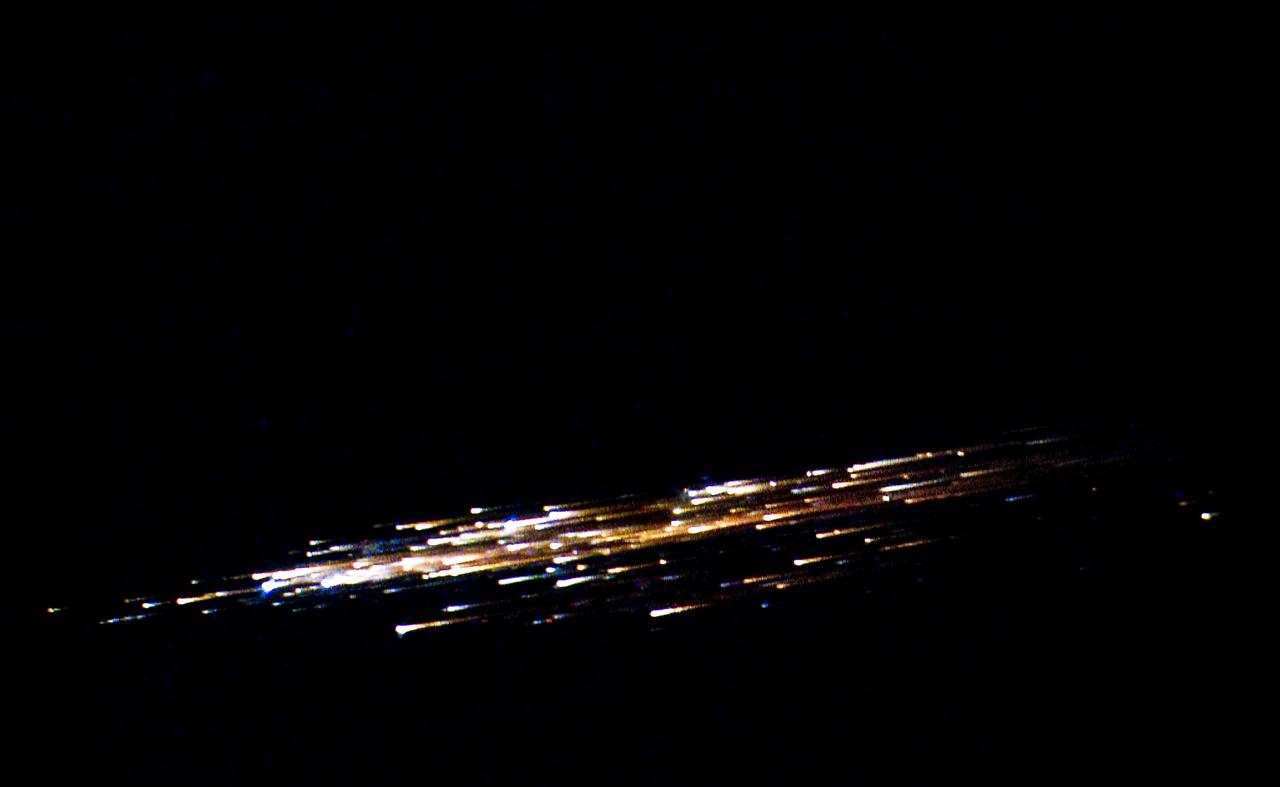

European Space Agency's 'Jules Verne' Automated Transfer Vehicle ATV-1 re-entry in Earth's atmosphere over Pacific Ocean. The breakup ad fragmentation of the ESA's ATV-1 was captured in dramatic fashion by scientists aboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory and a Gulfstream V aircraft as it re-entered the atmosphere early Monday morning over the South Pacific. Photo Credit: NASA Ames Research Center/ESA/Jesse Carpenter/Bill Moede
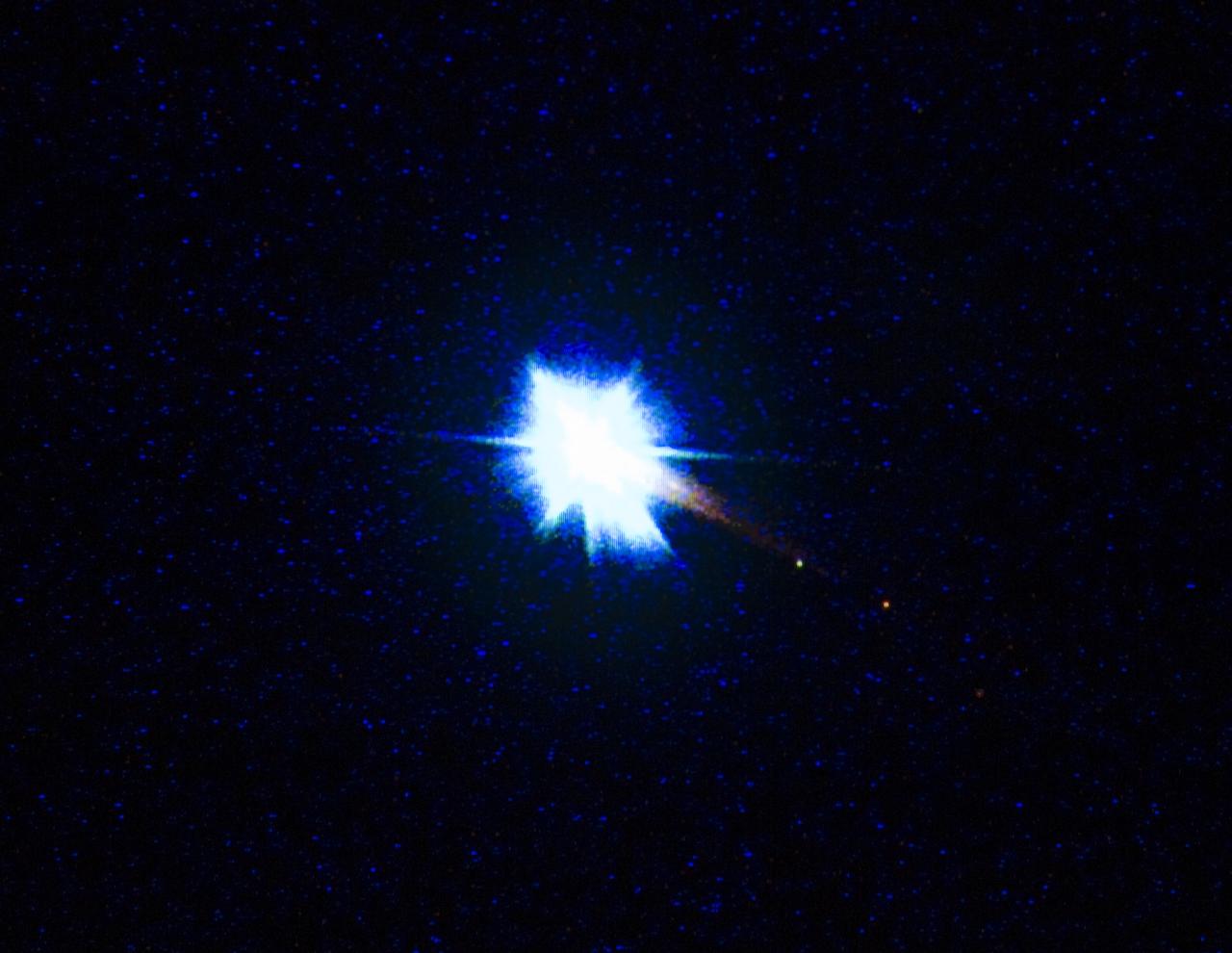

European Space Agency's 'Jules Verne' Automated Transfer Vehicle ATV-1 re-entry in Earth's atmosphere over Pacific Ocean. The breakup ad fragmentation of the ESA's ATV-1 was captured in dramatic fashion by scientists aboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory and a Gulfstream V aircraft as it re-entered the atmosphere early Monday morning over the South Pacific. Photo Credit: NASA Ames Research Center/ESA/Jesse Carpenter/Bill Moede

European Space Agency's 'Jules Verne' Automated Transfer Vehicle ATV-1 re-entry in Earth's atmosphere over Pacific Ocean. The breakup ad fragmentation of the ESA's ATV-1 was captured in dramatic fashion by scientists aboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory and a Gulfstream V aircraft as it re-entered the atmosphere early Monday morning over the South Pacific. Photo Credit: NASA Ames Research Center/ESA/Jesse Carpenter/Bill Moede
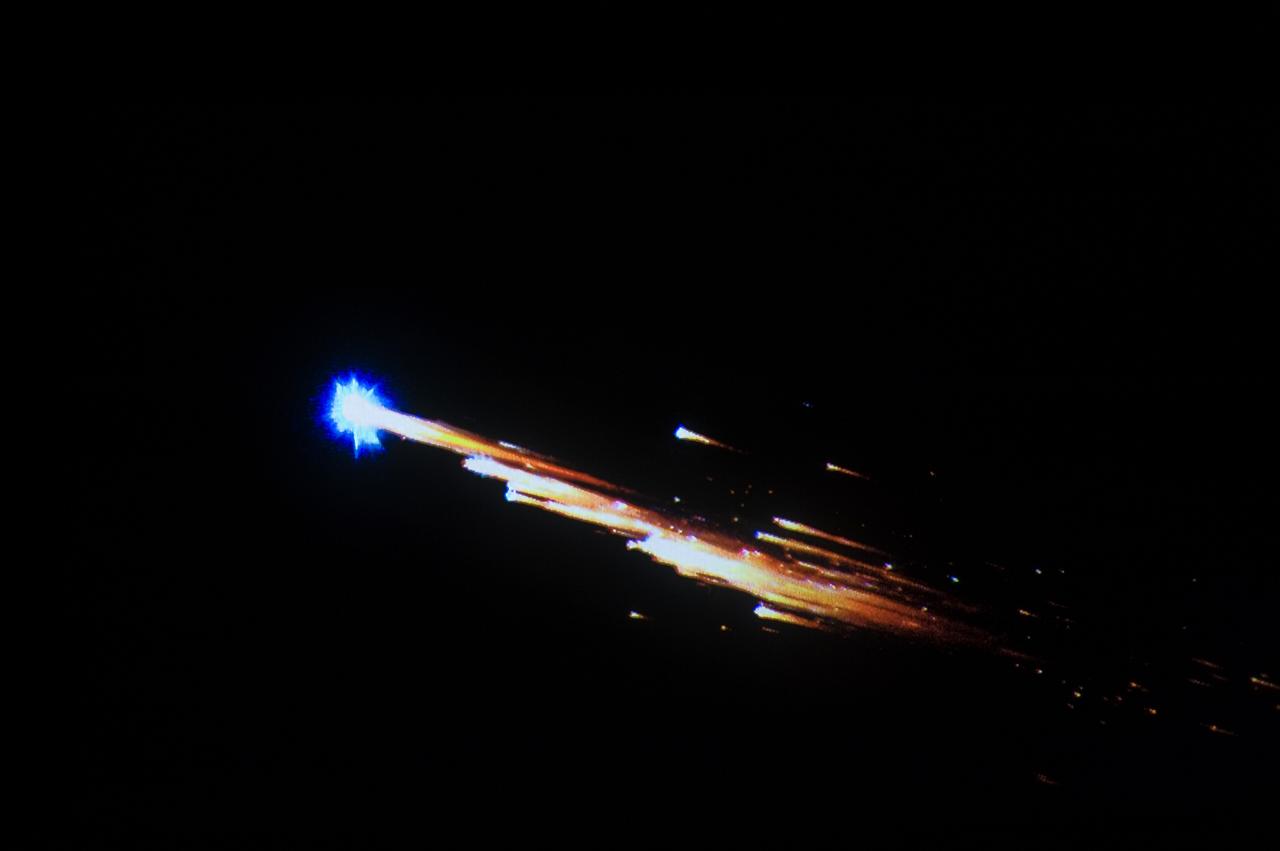

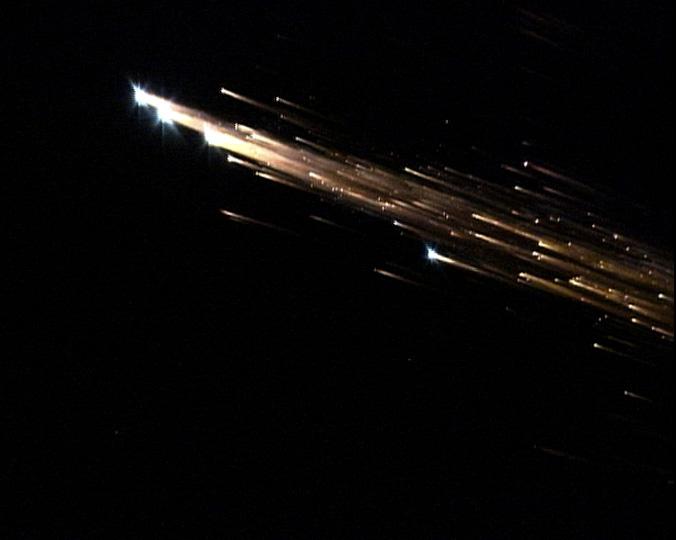
European Space Agency's 'Jules Verne' Automated Transfer Vehicle ATV-1 re-entry in Earth's atmosphere over Pacific Ocean. The breakup ad fragmentation of the ESA's ATV-1 was captured in dramatic fashion by scientists aboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory and a Gulfstream V aircraft as it re-entered the atmosphere early Monday morning over the South Pacific. Photo Credit: NASA Ames Research Center/ESA/Jesse Carpenter/Bill Moede
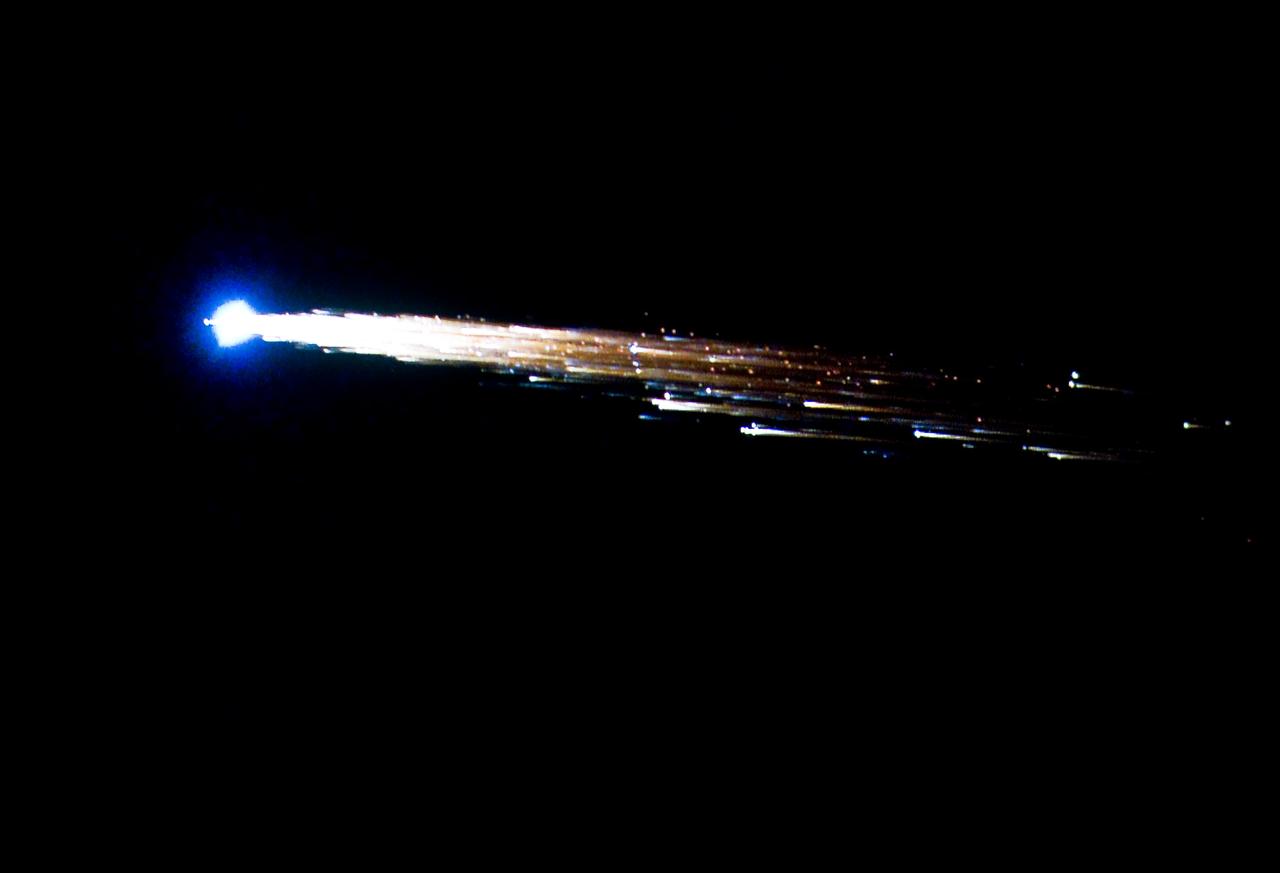

European Space Agency's 'Jules Verne' Automated Transfer Vehicle ATV-1 re-entry in Earth's atmosphere over Pacific Ocean. The breakup ad fragmentation of the ESA's ATV-1 was captured in dramatic fashion by scientists aboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory and a Gulfstream V aircraft as it re-entered the atmosphere early Monday morning over the South Pacific. Photo Credit: NASA Ames Research Center/ESA/Jesse Carpenter/Bill Moede
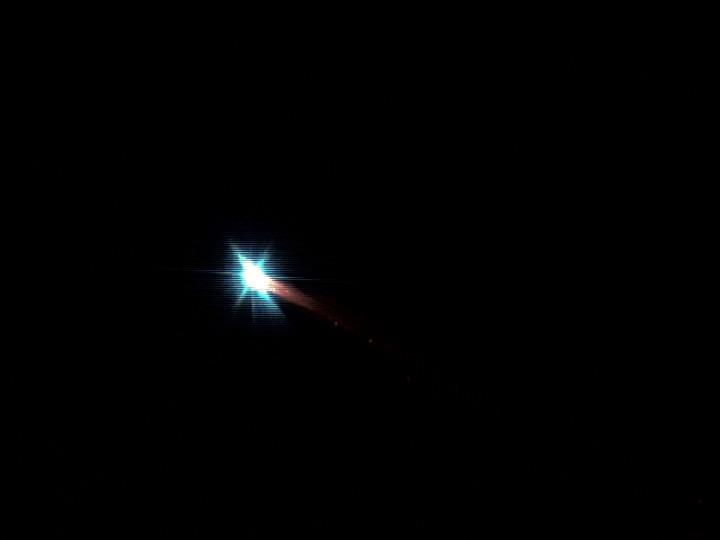

European Space Agency's 'Jules Verne' Automated Transfer Vehicle ATV-1 re-entry in Earth's atmosphere over Pacific Ocean. The breakup ad fragmentation of the ESA's ATV-1 was captured in dramatic fashion by scientists aboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory and a Gulfstream V aircraft as it re-entered the atmosphere early Monday morning over the South Pacific. Photo Credit: NASA Ames Research Center/ESA/Jesse Carpenter/Bill Moede
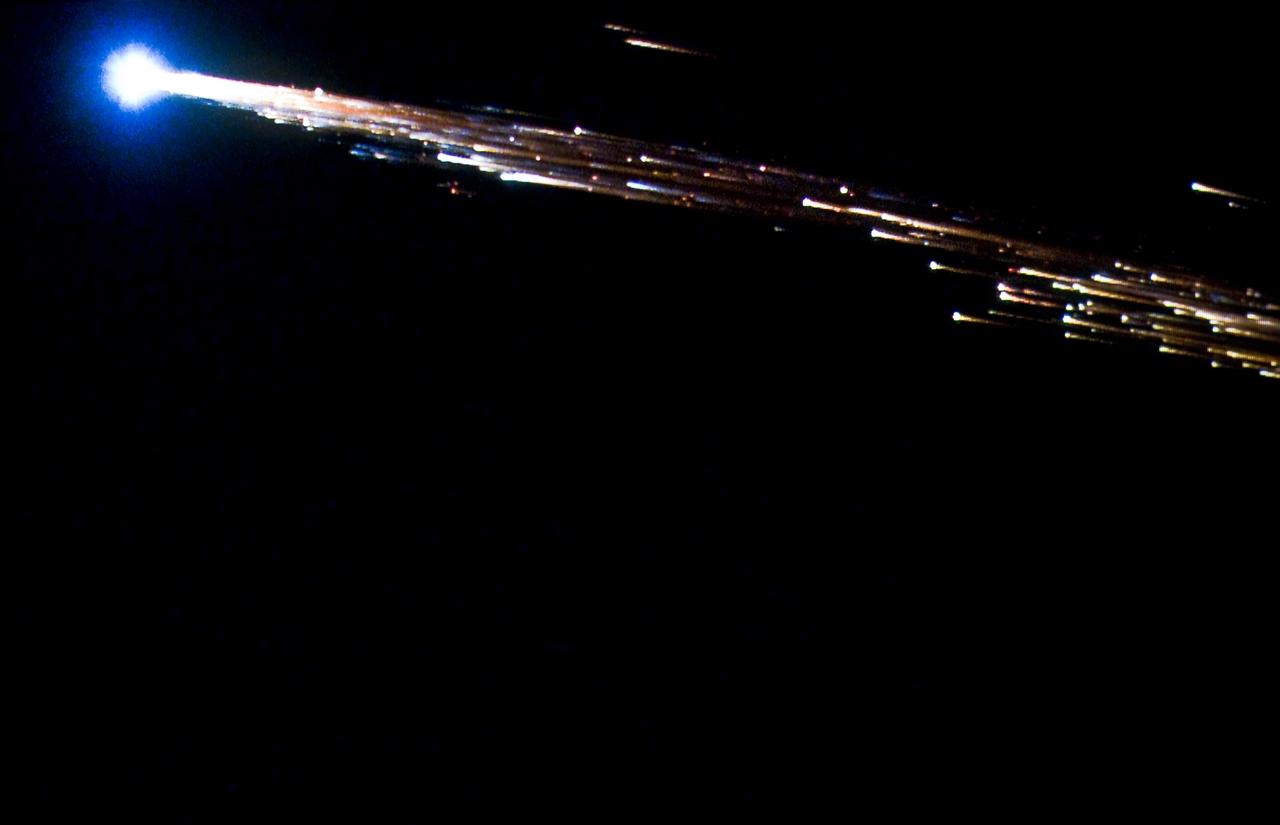

European Space Agency's 'Jules Verne' Automated Transfer Vehicle ATV-1 re-entry in Earth's atmosphere over Pacific Ocean. The breakup ad fragmentation of the ESA's ATV-1 was captured in dramatic fashion by scientists aboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory and a Gulfstream V aircraft as it re-entered the atmosphere early Monday morning over the South Pacific. Photo Credit: NASA Ames Research Center/ESA/Jesse Carpenter/Bill Moede
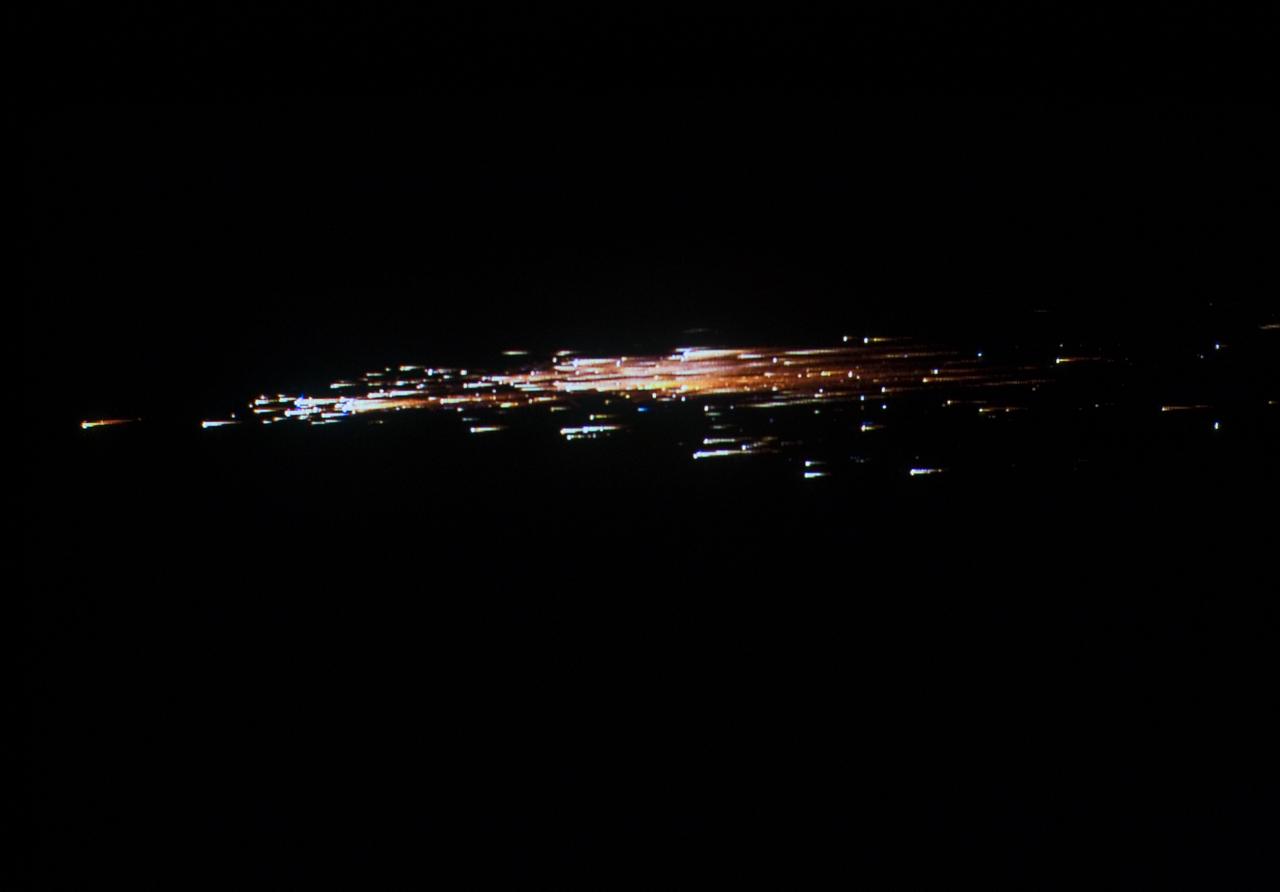

European Space Agency's 'Jules Verne' Automated Transfer Vehicle ATV-1 re-entry in Earth's atmosphere over Pacific Ocean. The breakup ad fragmentation of the ESA's ATV-1 was captured in dramatic fashion by scientists aboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory and a Gulfstream V aircraft as it re-entered the atmosphere early Monday morning over the South Pacific. Photo Credit: NASA Ames Research Center/ESA/Jesse Carpenter/Bill Moede
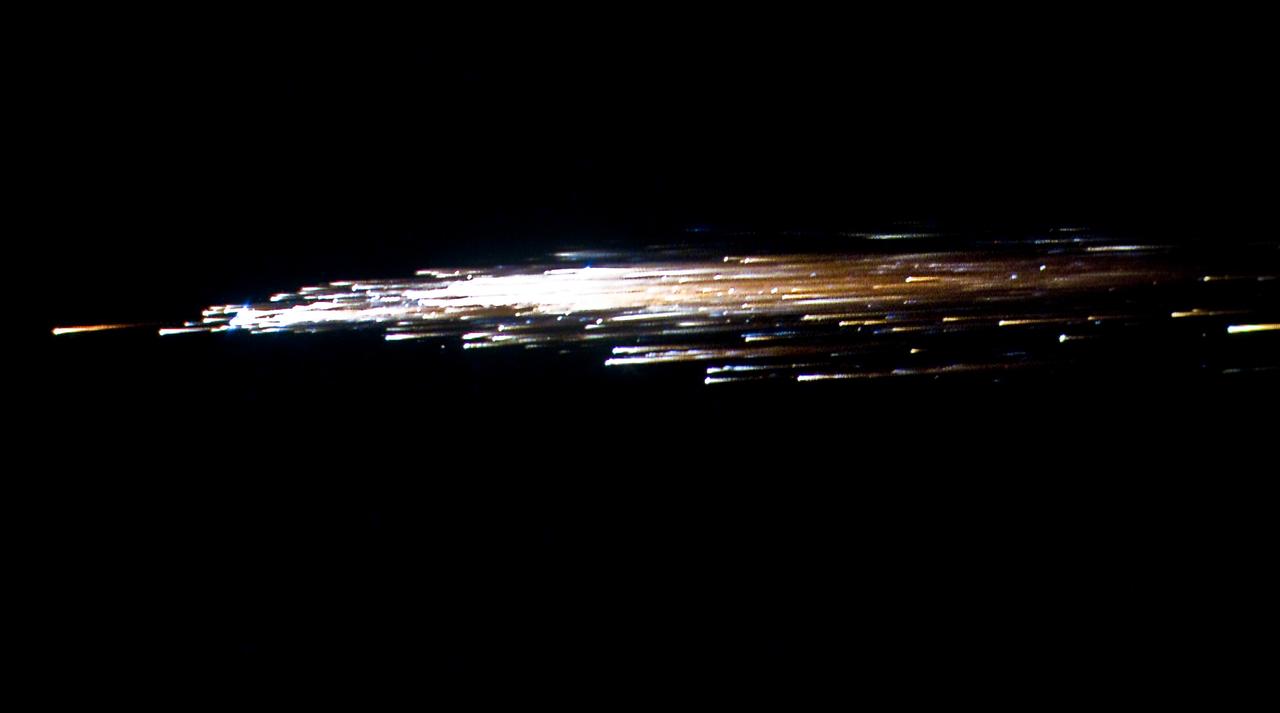

European Space Agency's 'Jules Verne' Automated Transfer Vehicle ATV-1 re-entry in Earth's atmosphere over Pacific Ocean. The breakup ad fragmentation of the ESA's ATV-1 was captured in dramatic fashion by scientists aboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory and a Gulfstream V aircraft as it re-entered the atmosphere early Monday morning over the South Pacific. Photo Credit: NASA Ames Research Center/ESA/Jesse Carpenter/Bill Moede
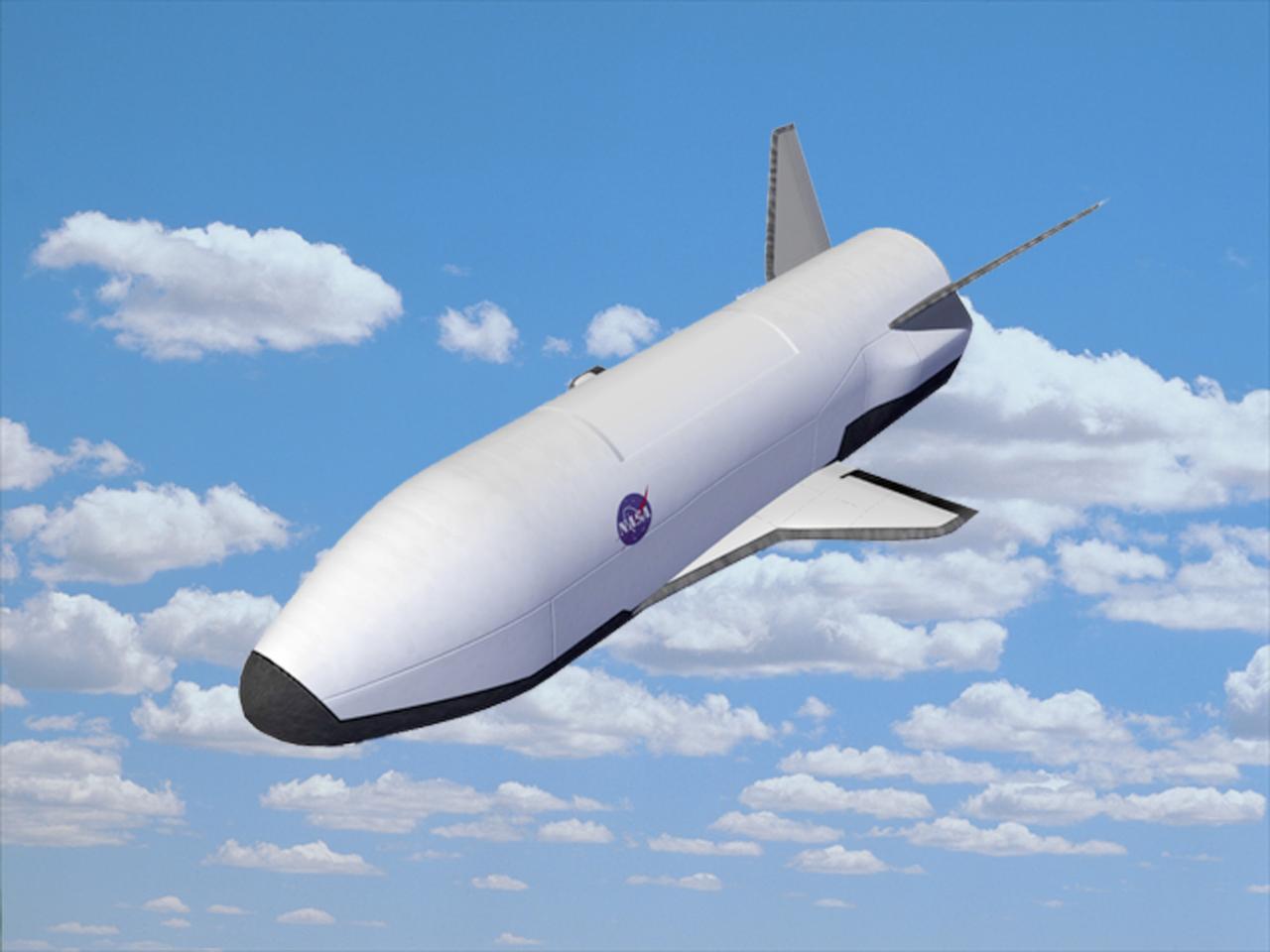

Pictured is an artist's concept of the X-37 Demonstrator re-entry. After being launched from the cargo bay of a Shuttle as a secondary payload, the X-37 remains on-orbit up to 21 days performing a variety of experiments before re-entering the Earth's atmosphere and landing. These vehicles supported the Agency's goal of dramatically reducing the cost of access to space in attempt to define the future of space transportation. The X-37 program was discontinued in 2003.

European Space Agency's 'Jules Verne' Automated Transfer Vehicle ATV-1 re-entry in Earth's atmosphere over Pacific Ocean. The breakup ad fragmentation of the ESA's ATV-1 was captured in dramatic fashion by scientists aboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory and a Gulfstream V aircraft as it re-entered the atmosphere early Monday morning over the South Pacific. Photo Credit: NASA Ames Research Center/ESA/Jesse Carpenter/Bill Moede
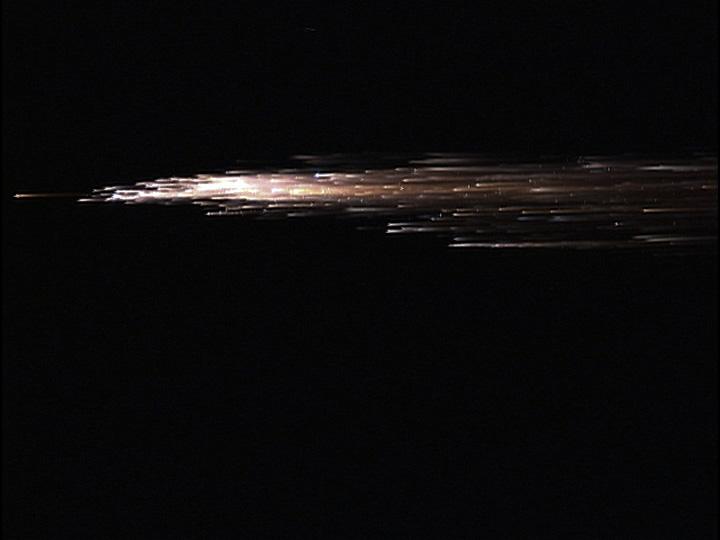

European Space Agency's 'Jules Verne' Automated Transfer Vehicle ATV-1 re-entry in Earth's atmosphere over Pacific Ocean. The breakup ad fragmentation of the ESA's ATV-1 was captured in dramatic fashion by scientists aboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory and a Gulfstream V aircraft as it re-entered the atmosphere early Monday morning over the South Pacific. Photo Credit: NASA Ames Research Center/ESA/Jesse Carpenter/Bill Moede
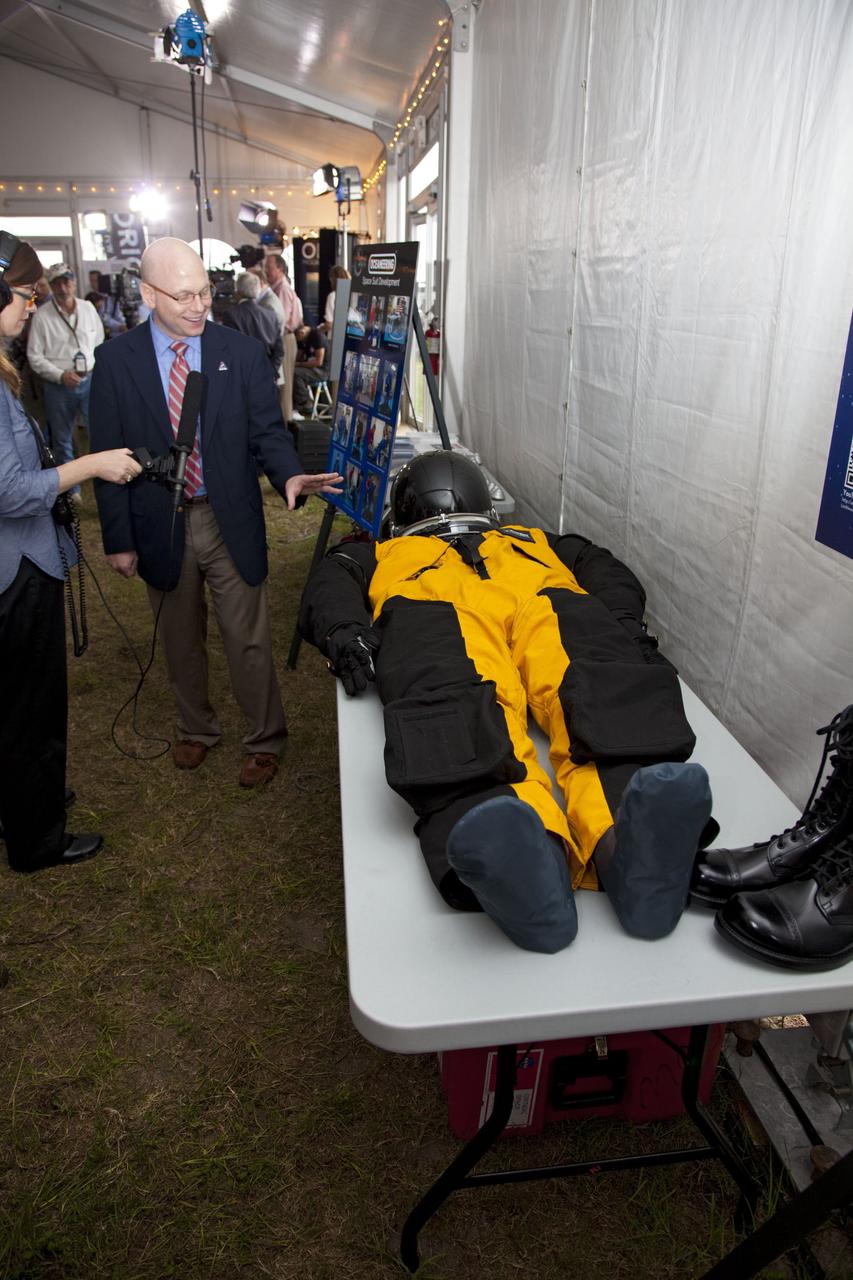

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A media event was held on the grounds near the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida where a Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle (MPCV) is on display. The MPCV is based on the Orion design requirements for traveling beyond low Earth orbit and will serve as the exploration vehicle that will carry the crew to space, provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel, and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Seen here is a sample of the Orion launch-and-entry suit on display. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
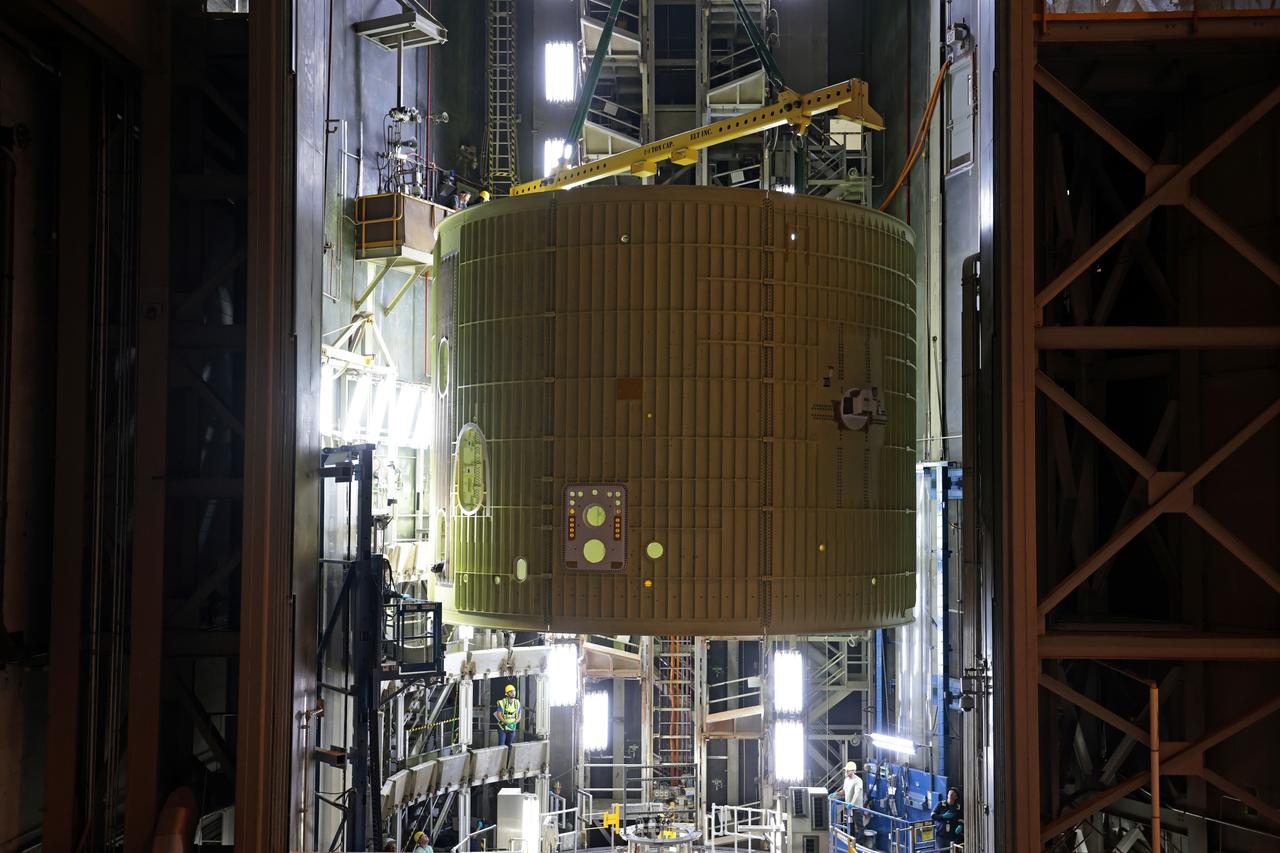

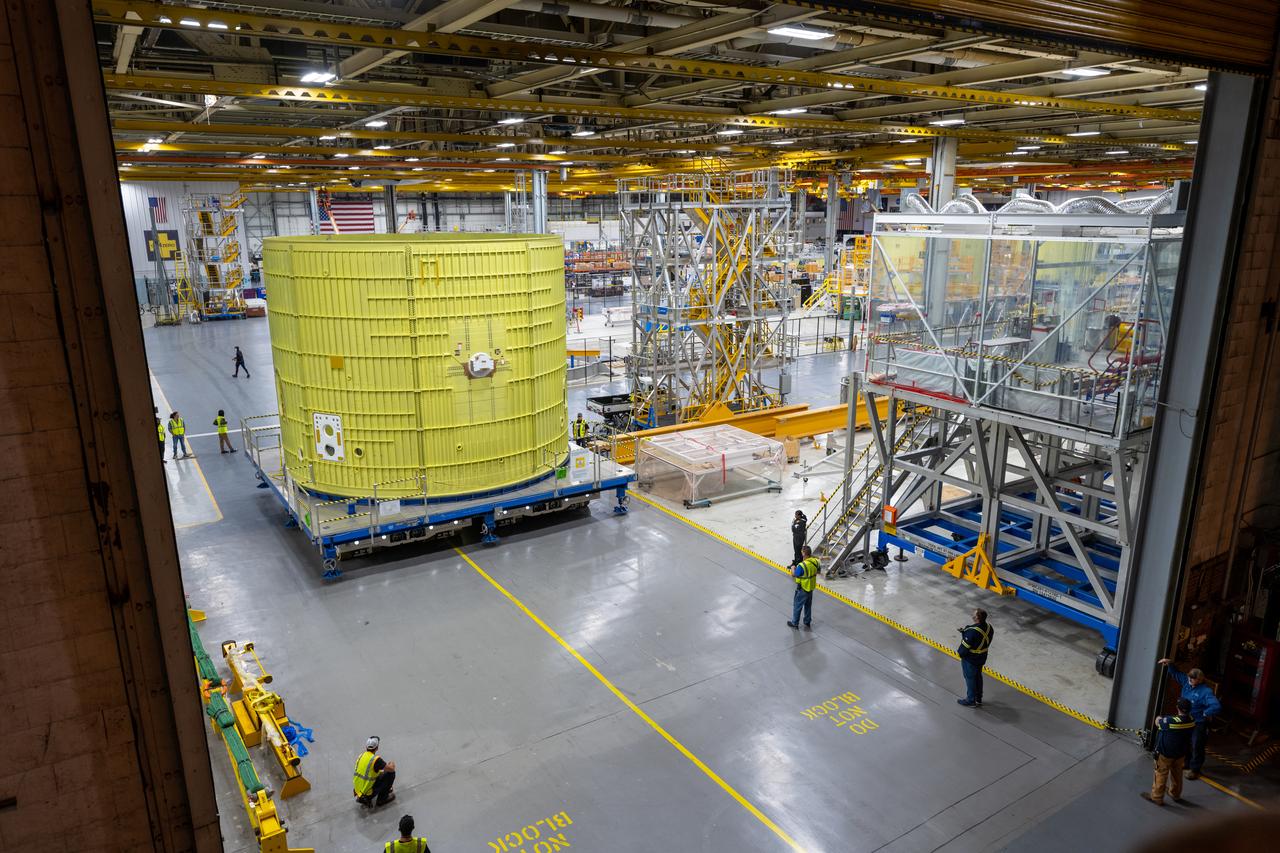
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
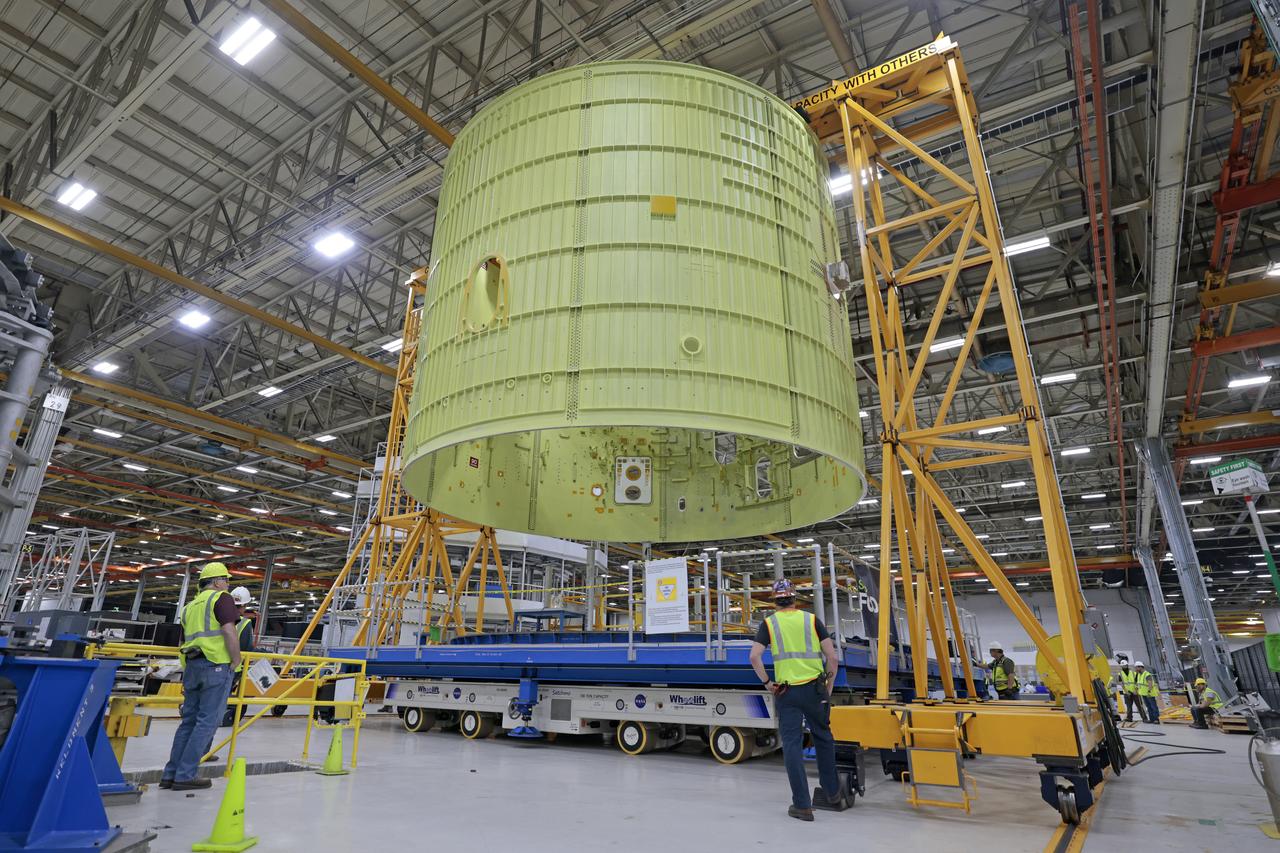

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
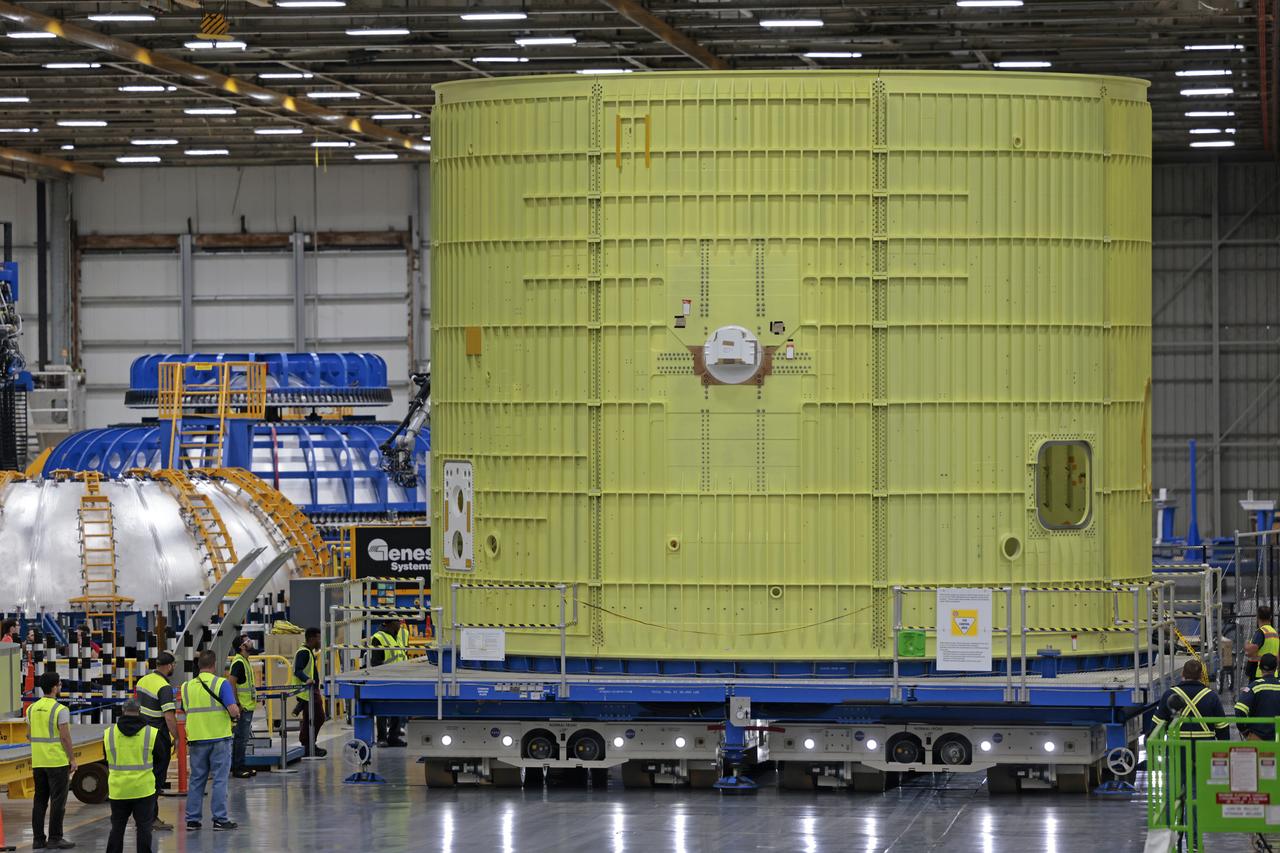

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
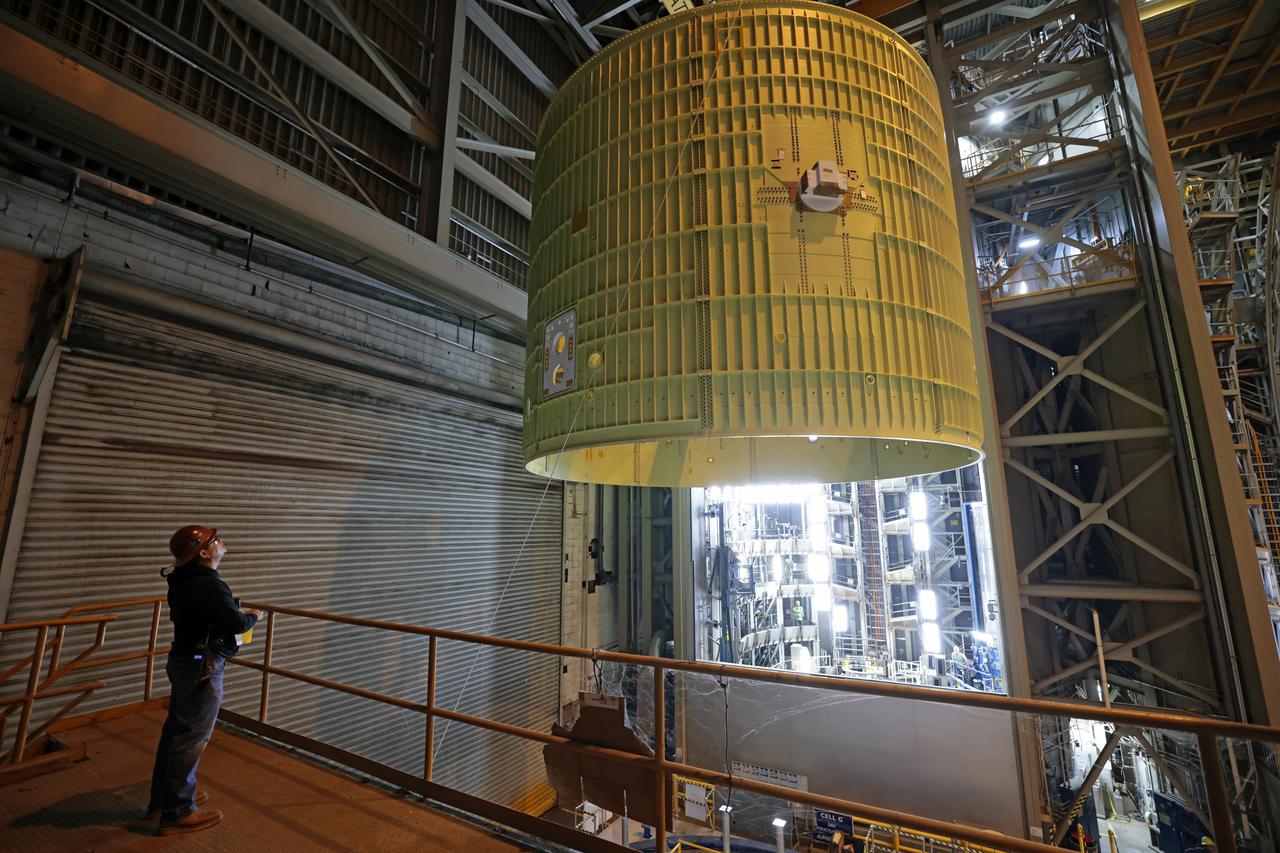

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
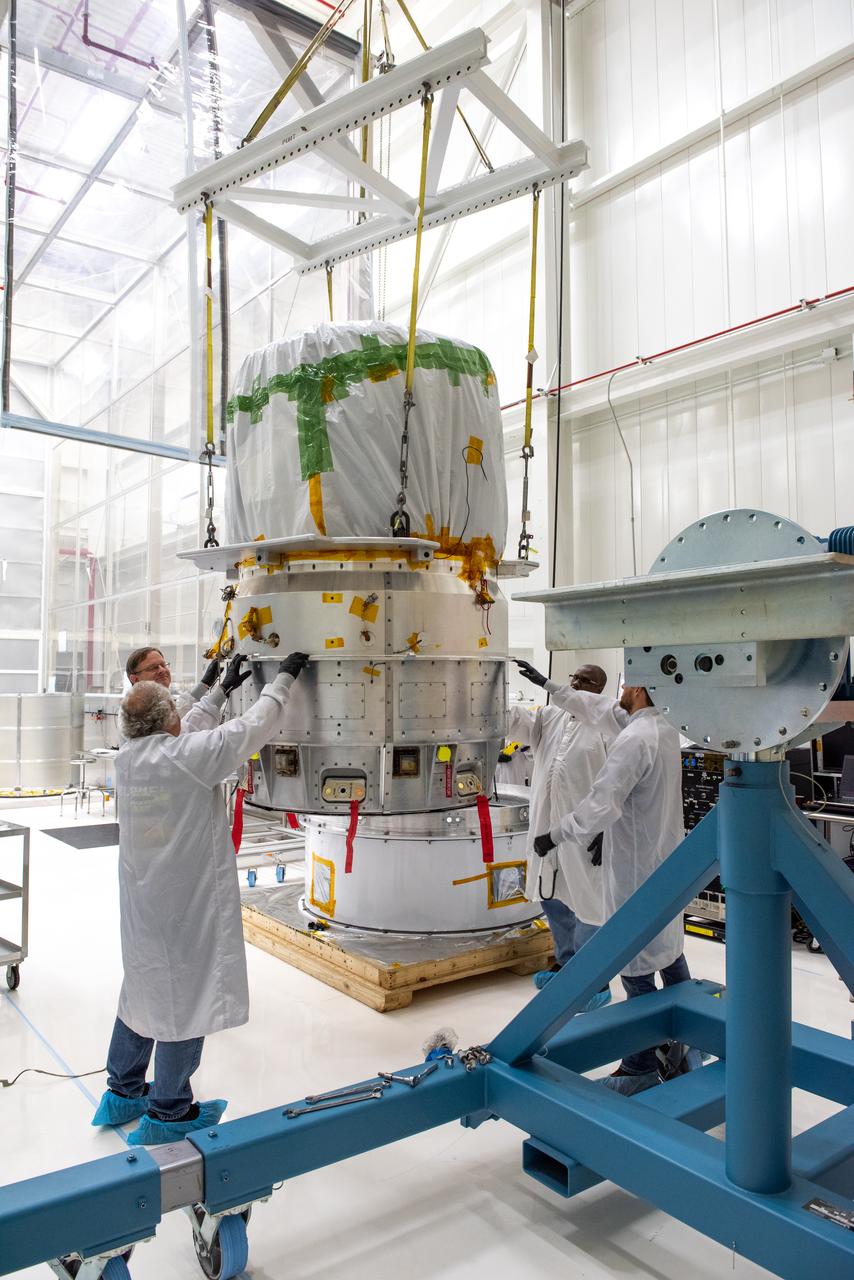

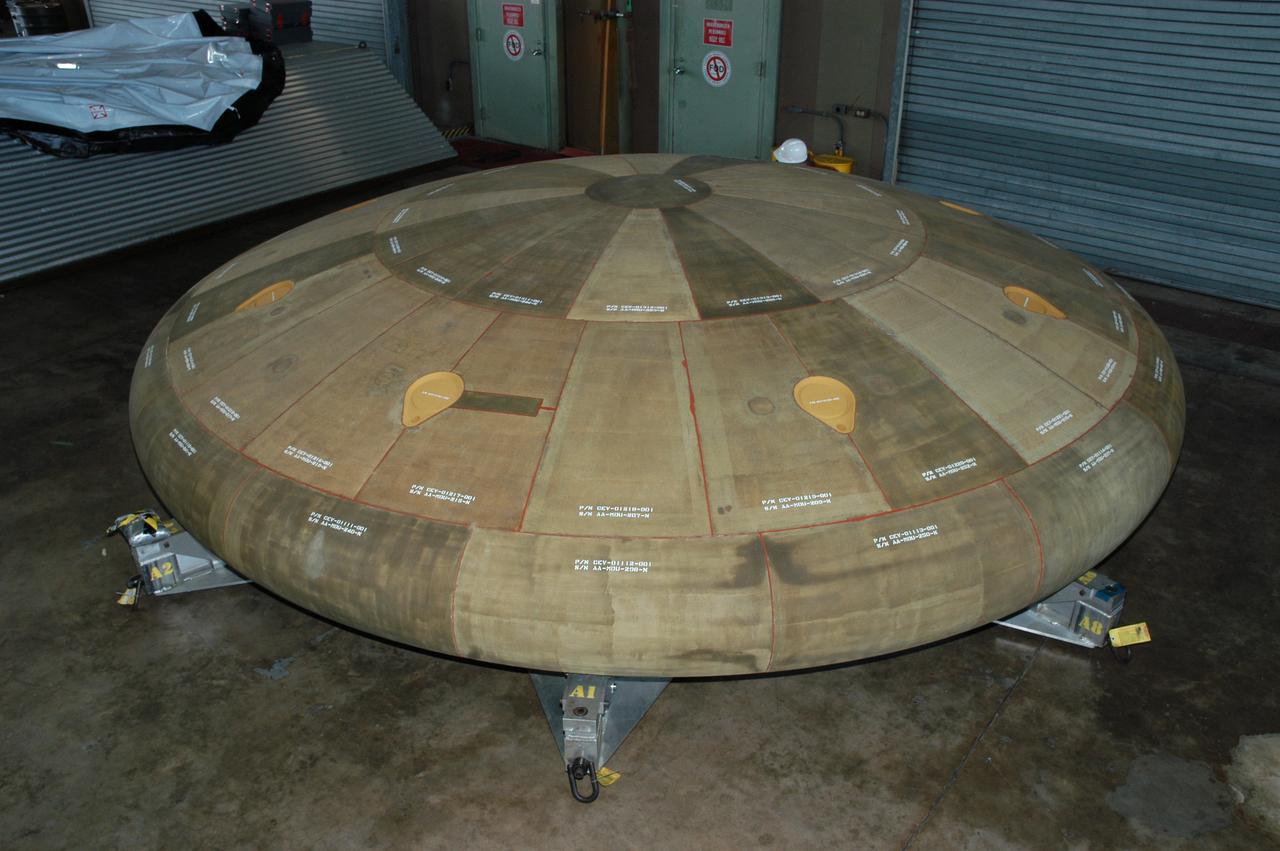
Technicians move NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) re-entry vehicle over to a turnover fixture for prelaunch processing inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Aug. 19, 2022. Dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter, LOFTID is a technology demonstration mission aimed at validating inflatable heat shield technology for atmospheric re-entry. This technology could enable missions to other planetary bodies, as well as allow NASA to return heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit. LOFTID is a rideshare launching with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite. NASA and NOAA are targeting Nov. 1, 2022, for the launch of JPSS-2 on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex-3 at Vandenberg.

Technicians move NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) re-entry vehicle onto a turnover fixture for prelaunch processing inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Aug. 19, 2022. Dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter, LOFTID is a technology demonstration mission aimed at validating inflatable heat shield technology for atmospheric re-entry. This technology could enable missions to other planetary bodies, as well as allow NASA to return heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit. LOFTID is a rideshare launching with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite. NASA and NOAA are targeting Nov. 1, 2022, for the launch of JPSS-2 on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex-3 at Vandenberg.
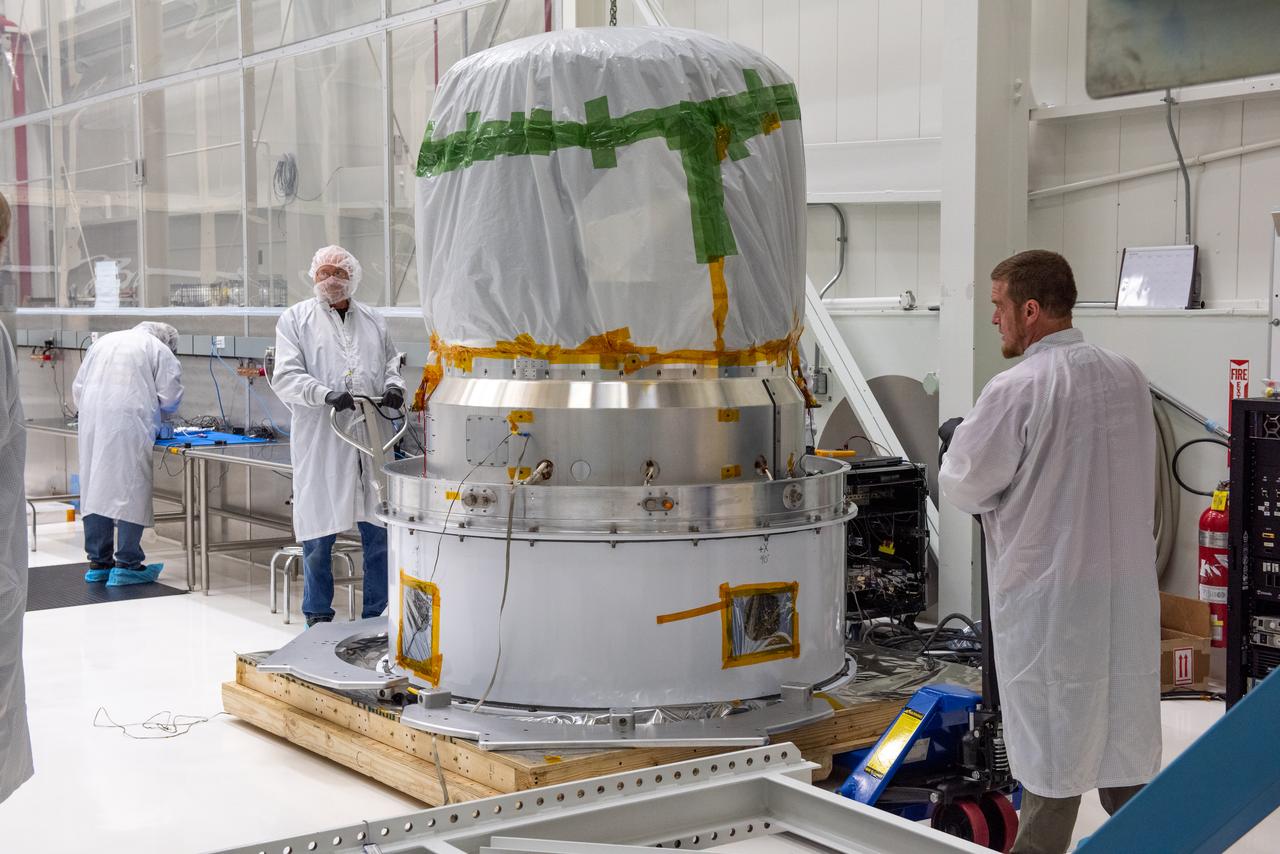

Technicians prepare to move NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) re-entry vehicle onto a turnover fixture for prelaunch processing inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Aug. 19, 2022. Dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter, LOFTID is a technology demonstration mission aimed at validating inflatable heat shield technology for atmospheric re-entry. This technology could enable missions to other planetary bodies, as well as allow NASA to return heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit. LOFTID is a rideshare launching with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite. NASA and NOAA are targeting Nov. 1, 2022, for the launch of JPSS-2 on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex-3 at Vandenberg.

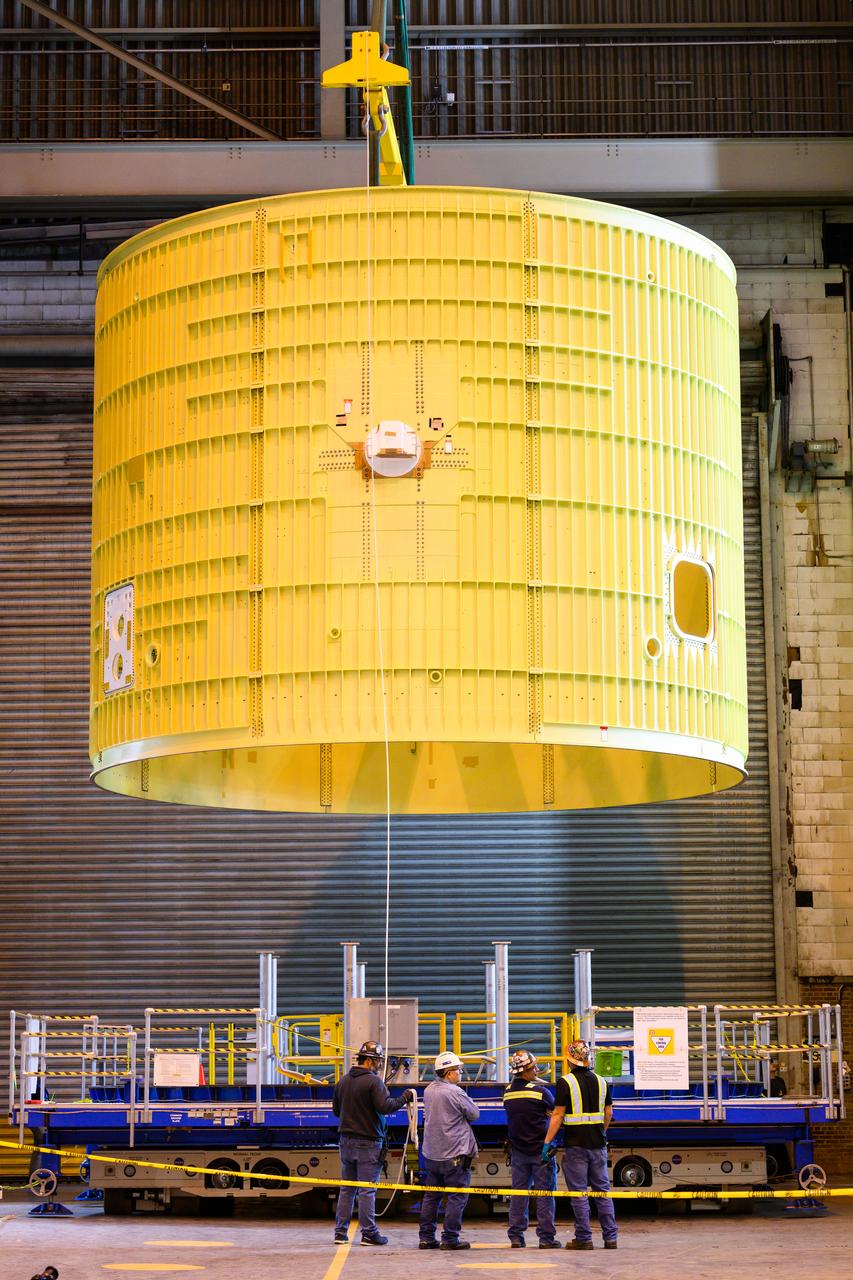
Technicians prepare the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) re-entry payload adapter interface ring for mating to the re-entry vehicle as part of launch preparations occurring inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 7, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily.

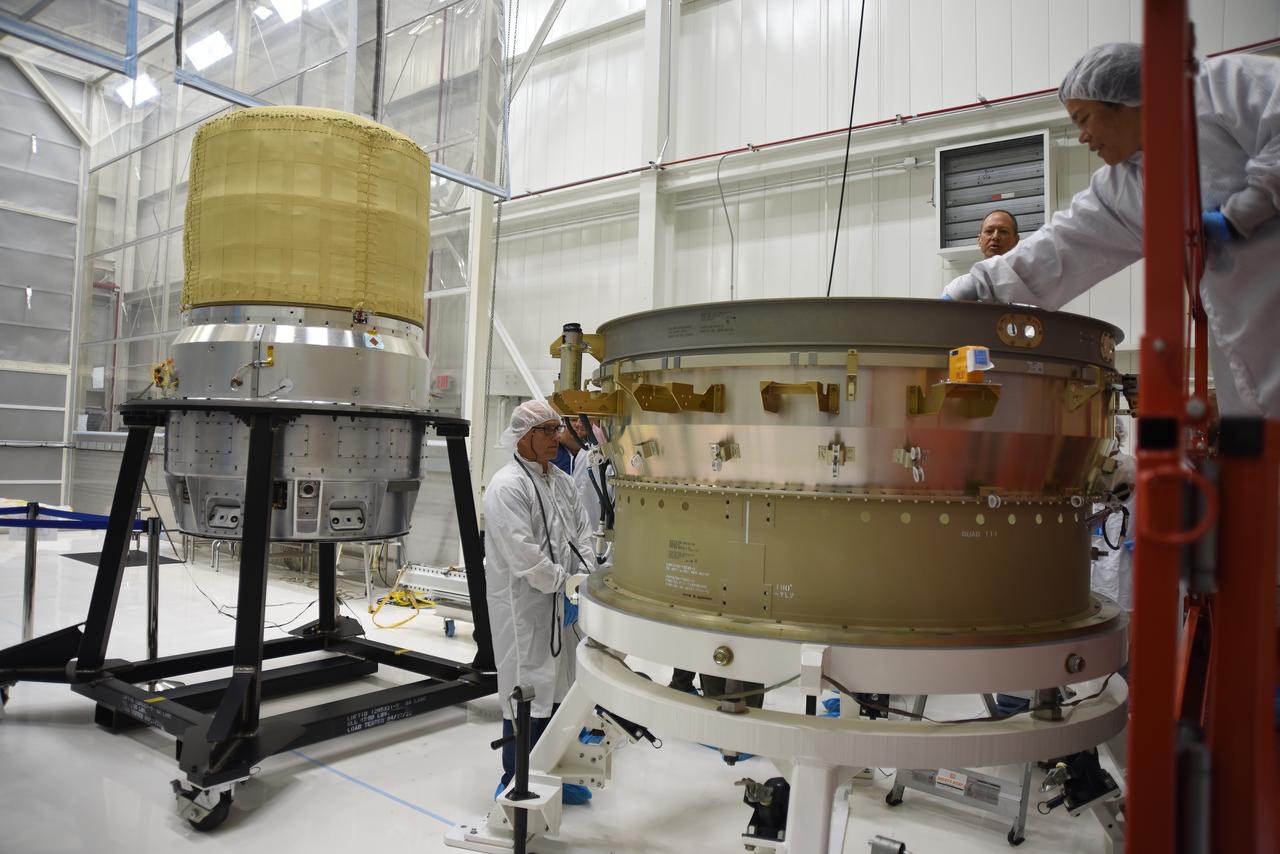
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.

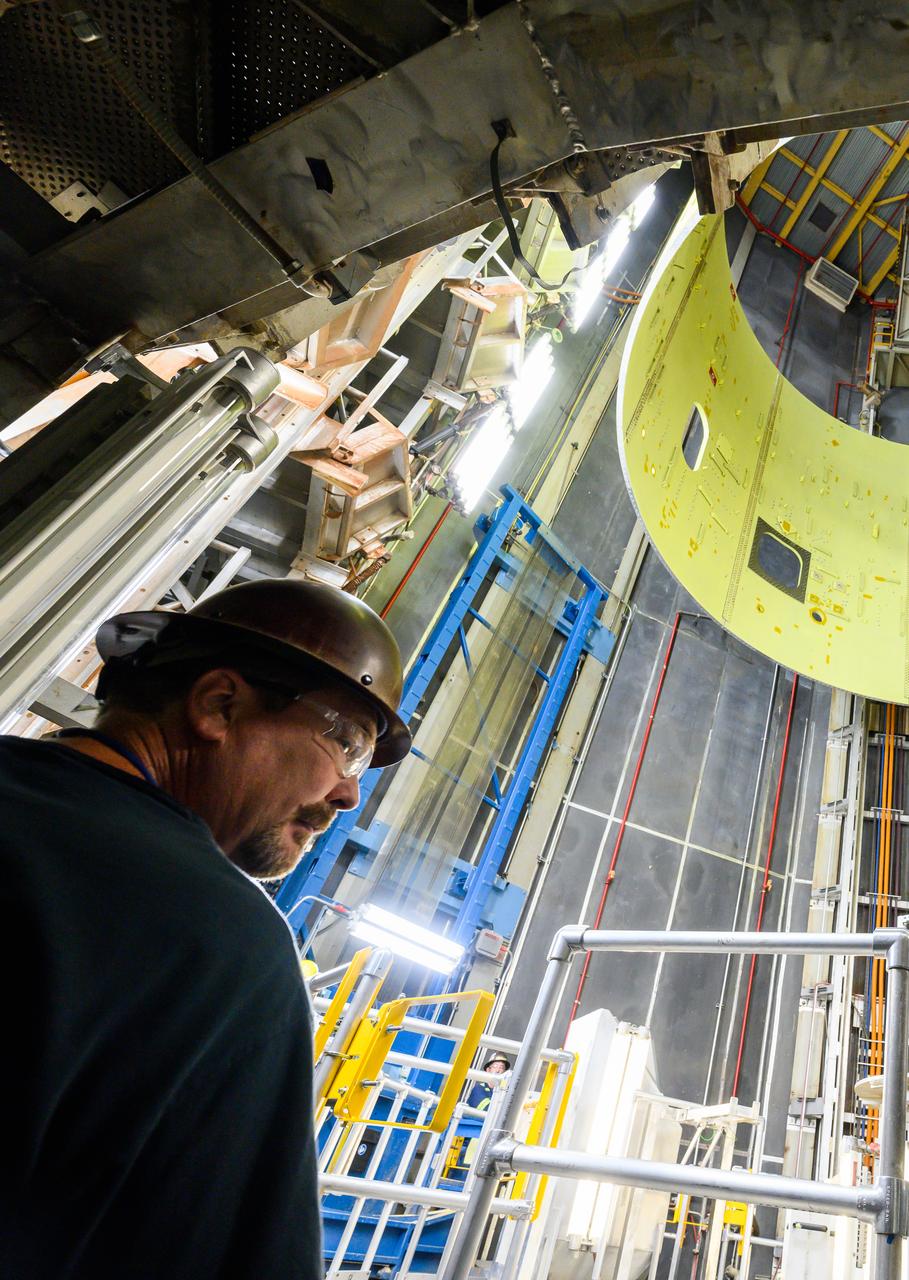
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.

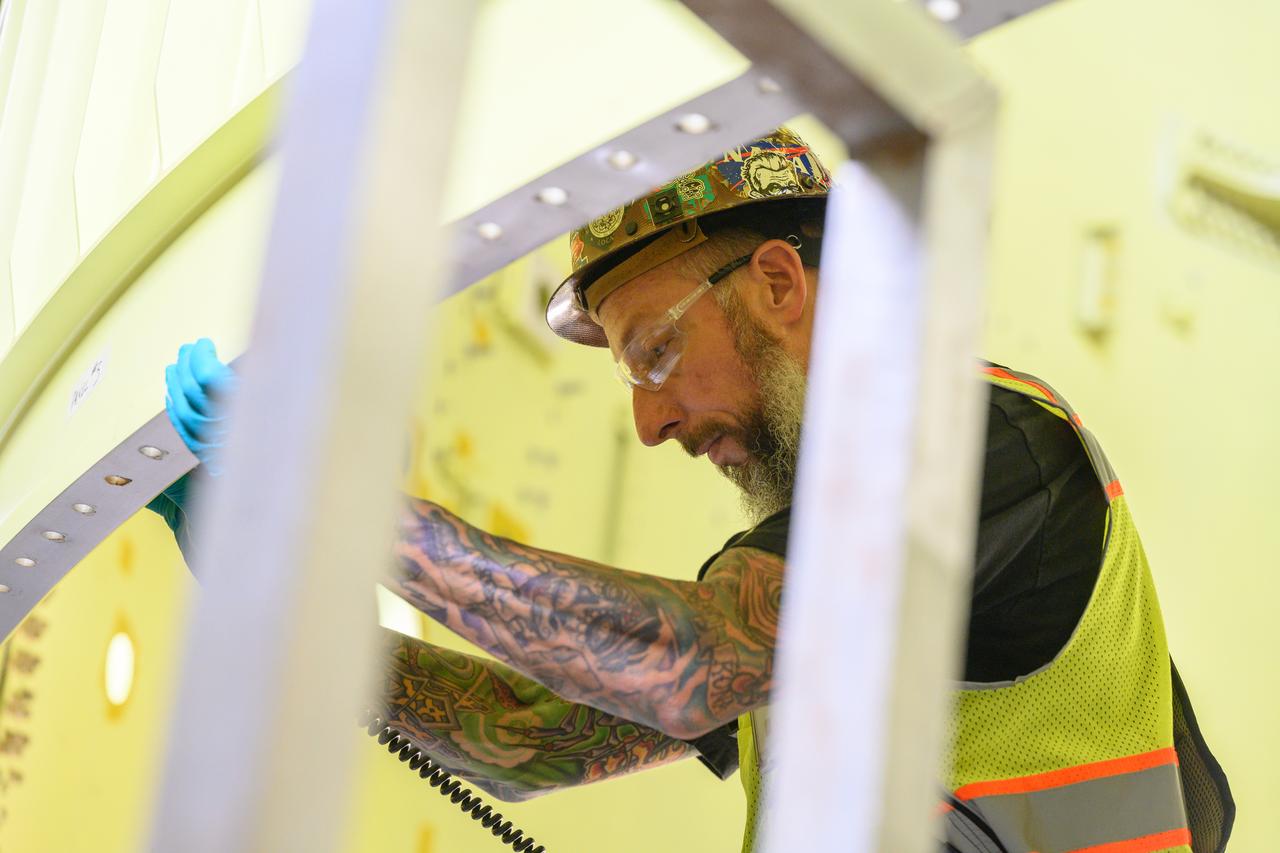
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
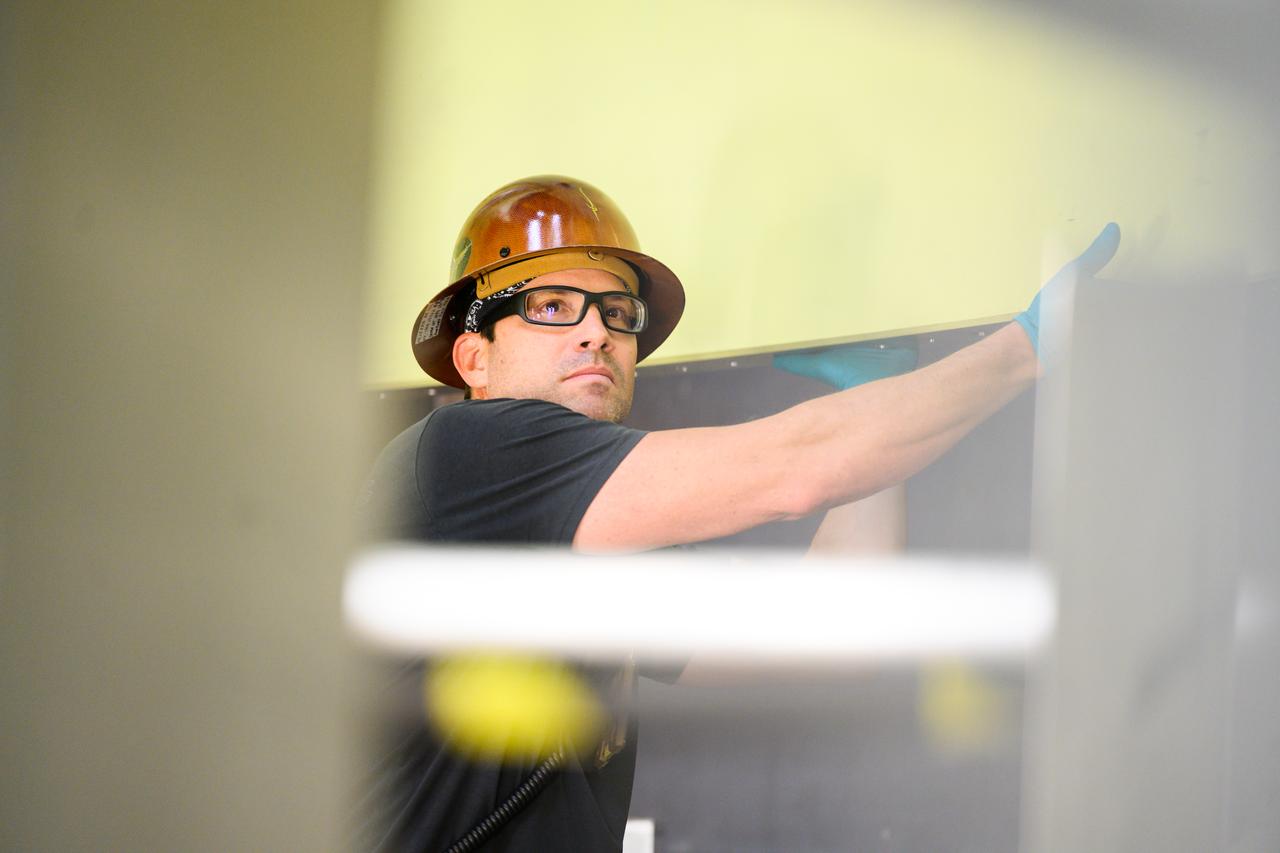

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
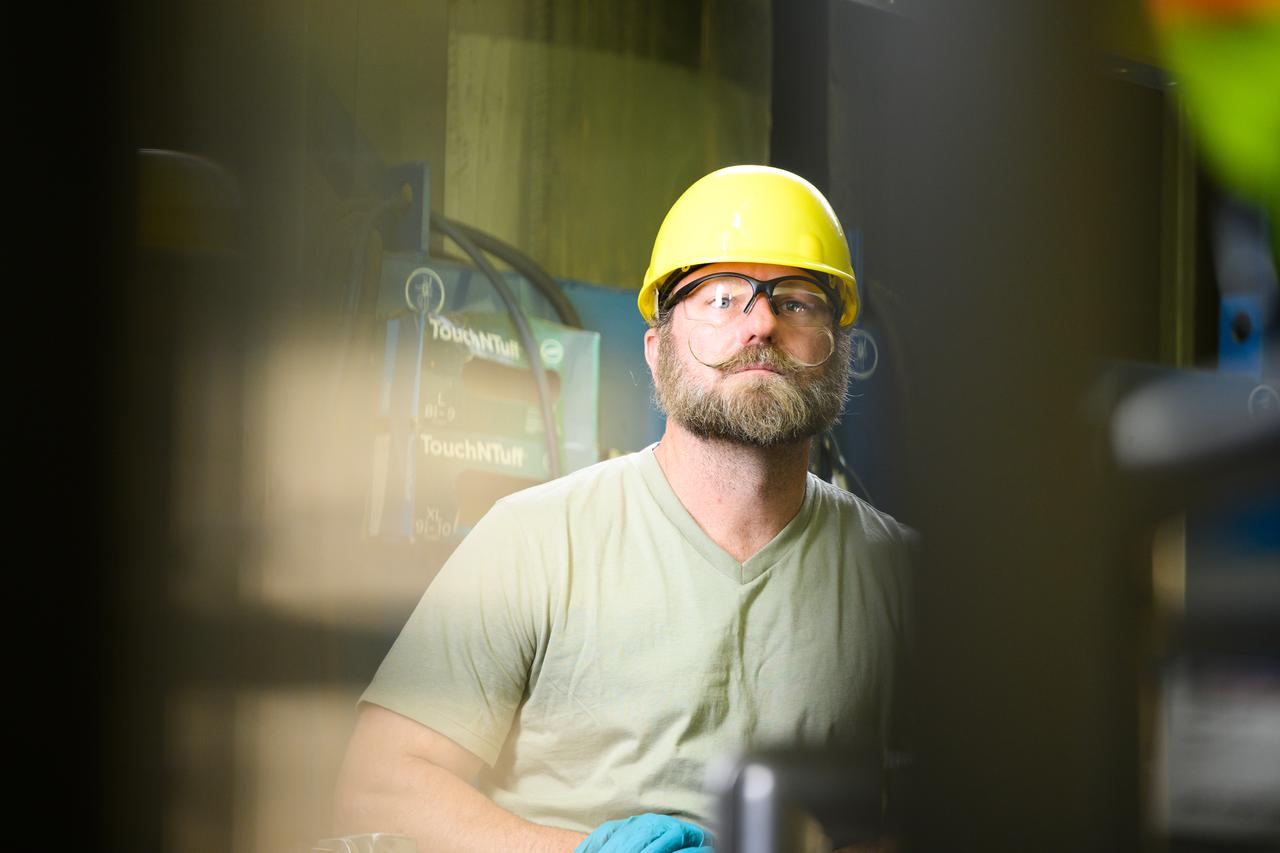

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
/MAF_20221027_CS3_IT_lifttoG-epb_004(1)~medium.jpg)
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
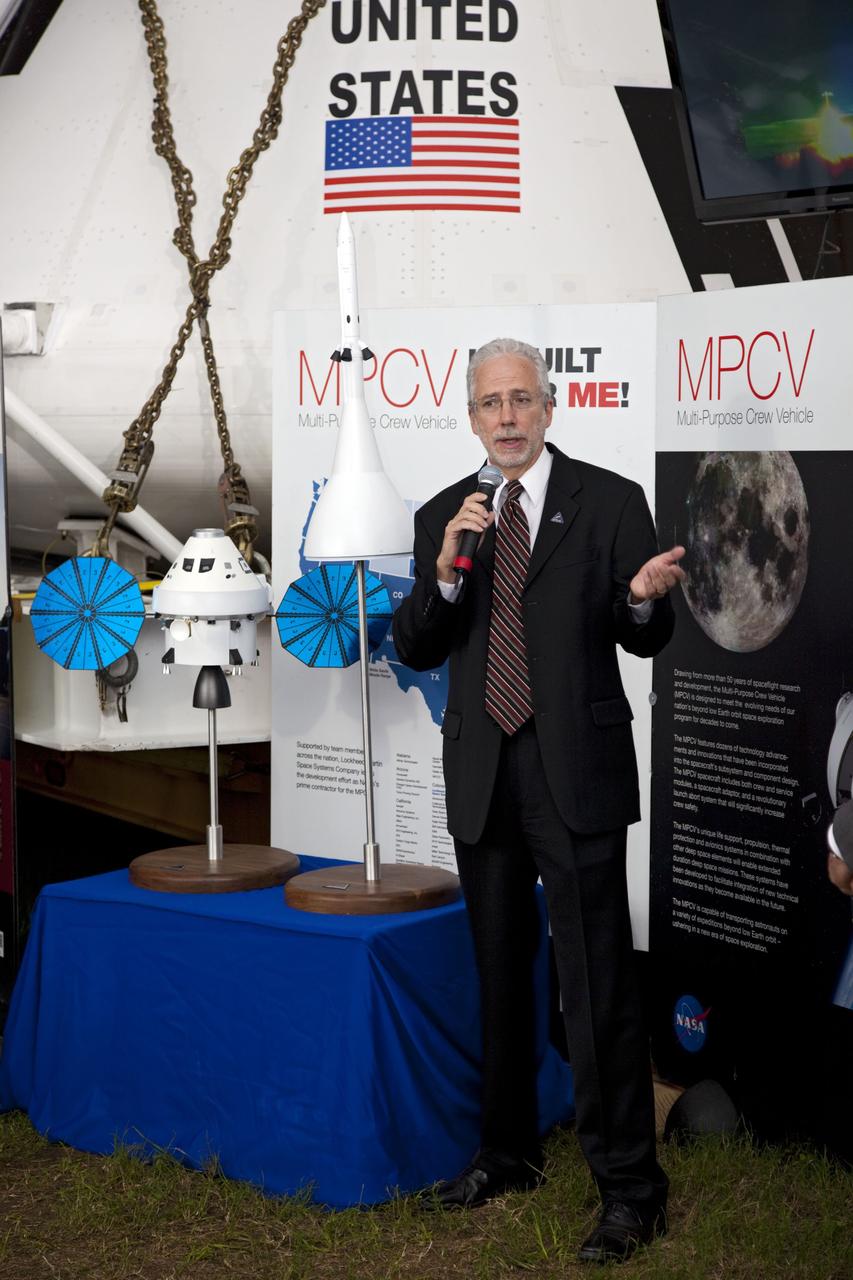

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A media event was held on the grounds near the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida where a Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle (MPCV) is on display. The MPCV is based on the Orion design requirements for traveling beyond low Earth orbit and will serve as the exploration vehicle that will carry the crew to space, provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel, and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Seen here is Mark Geyer, Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle program manager speaking to media during a question-and-answer session. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

ISS026-E-028490 (20 Feb. 2011) --- Backdropped by a blue and white part of Earth, the unpiloted ISS Progress 39 supply vehicle appears to be very small as it departs from the International Space Station at 8:12 a.m. (EST) on Feb. 20, 2011. At 11:12 a.m., the deorbit burn braked the trash-loaded cargo ship into its re-entry trajectory over the Pacific Ocean, where it was burned up in Earth’s atmosphere.

iss057e059103 (11/7/2018) --- Photo documentation of the area behind the Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM) Center Disk Cover in the Harmony Node 2 nadir hatch during part 2 of Kounotori H-II Transfer Vehicle 7 (HTV-7) Vestibule configuration for demating. The HTV Small Re-entry Capsule (HSRC) Protective Cover has been removed.

ISS028-E-028817 (23 Aug. 2011) --- The unpiloted ISS Progress 43 supply vehicle departs from the International Space Station on Aug. 23, 2011. Filled with trash and discarded items, Progress 43 will remain in orbit a safe distance from the station for engineering tests before being commanded by flight controllers to descend to a destructive re-entry into Earth's atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean.
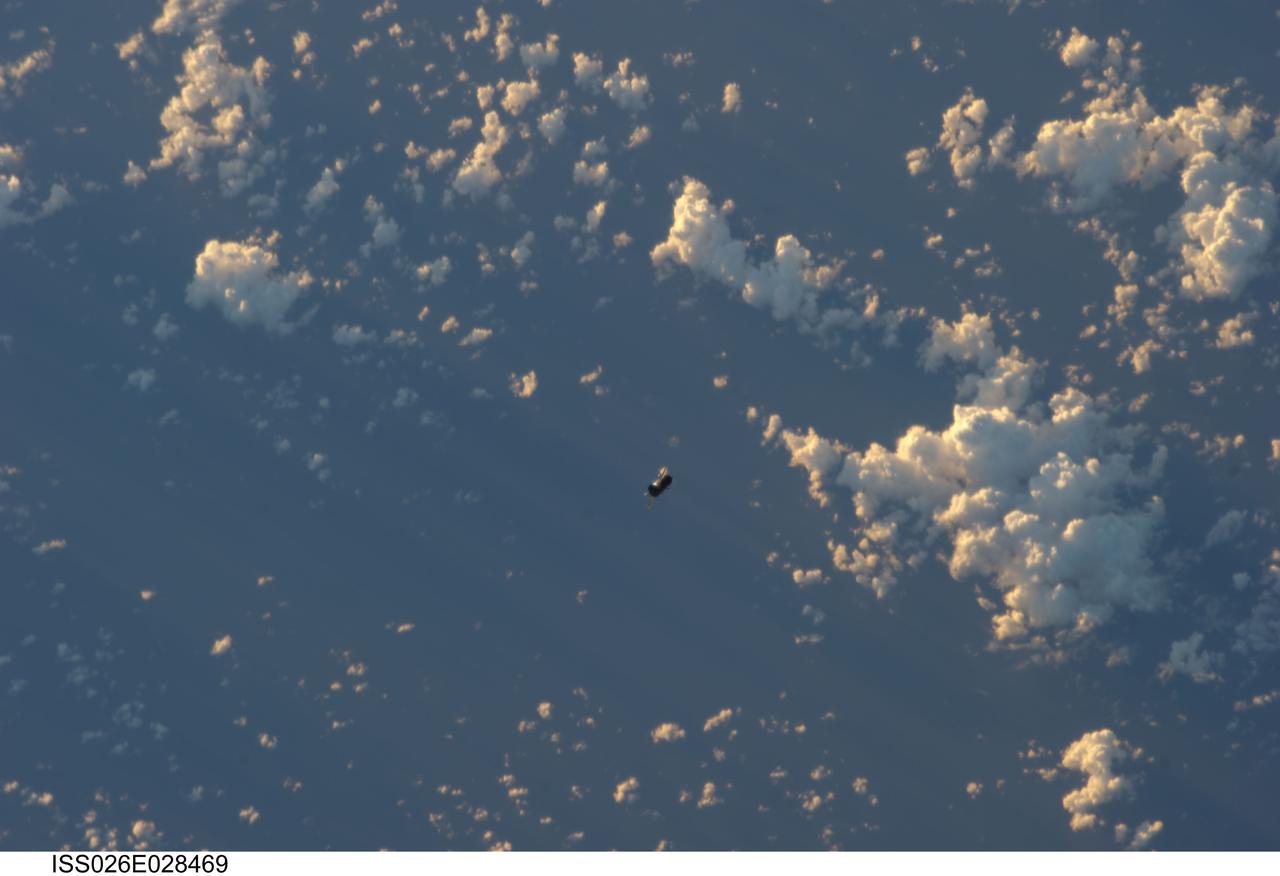

ISS026-E-028469 (20 Feb. 2011) --- Backdropped by a blue and white part of Earth, the unpiloted ISS Progress 39 supply vehicle appears to be very small as it departs from the International Space Station at 8:12 a.m. (EST) on Feb. 20, 2011. At 11:12 a.m., the deorbit burn braked the trash-loaded cargo ship into its re-entry trajectory over the Pacific Ocean, where it was burned up in Earth’s atmosphere.
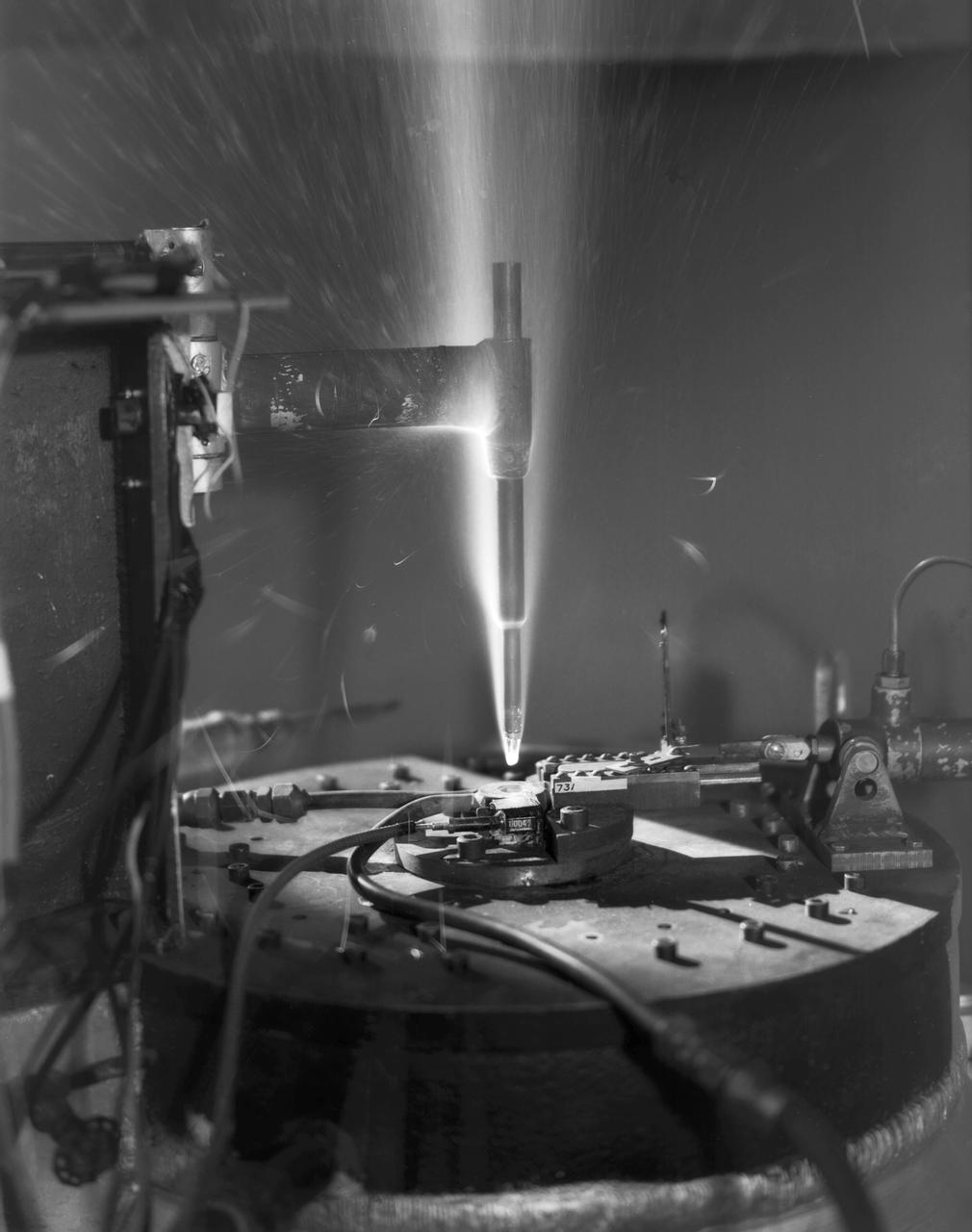

L57-5383 Hot-air jets employing ceramic heat exchangers played an important role at Langley in the study of materials for ballistic missile nose cones and re-entry vehicles. Here a model is being tested in one of theses jets at 4000 degrees Fahrenheit in 1957. Photograph published in Engineer in Charge: A History of the Langley Aeronautical Laboratory, 1917-1958 by James R. Hansen. Page 477.
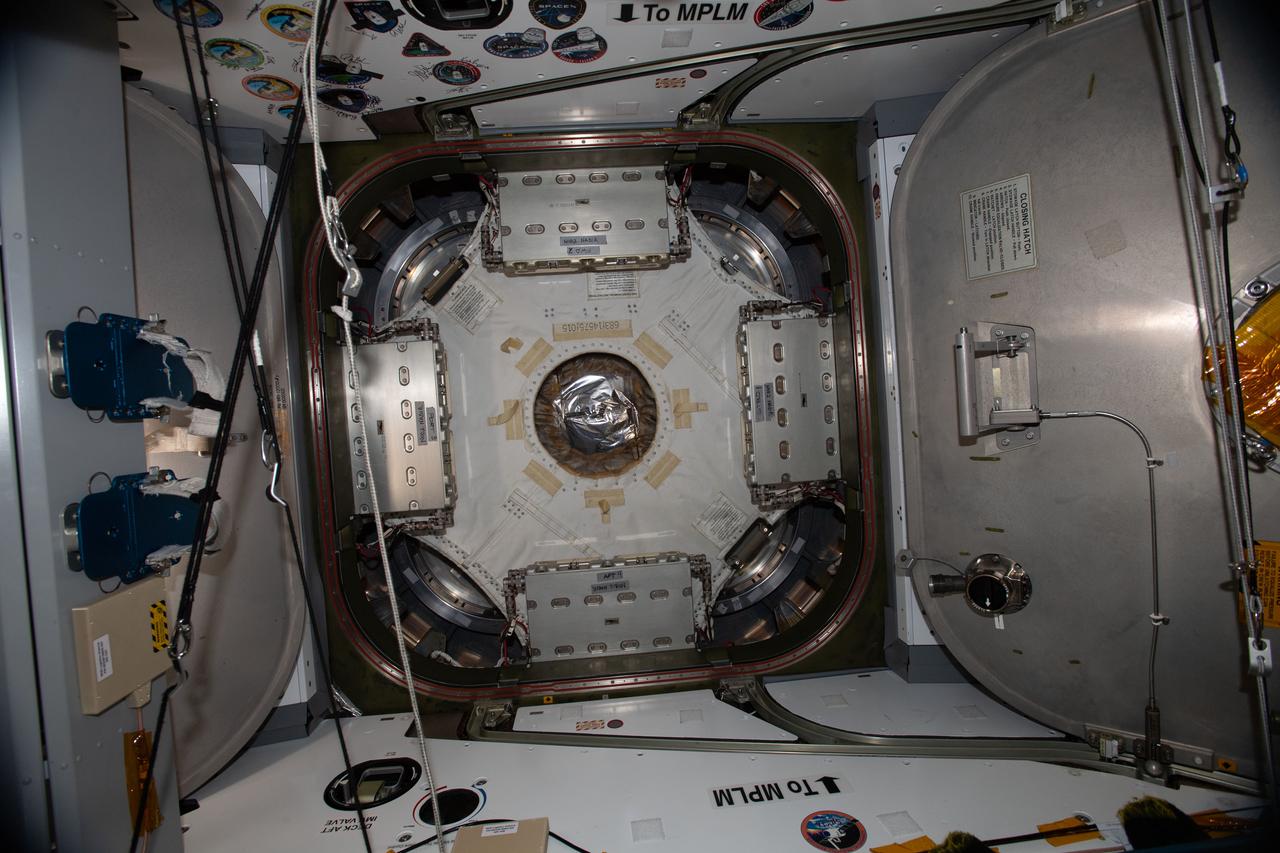

iss057e059085 (11/7/2018) --- Photo documentation of the Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM) Center Disk Cover in the Harmony Node 2 nadir hatch during part 2 of Kounotori H-II Transfer Vehicle 7 (HTV-7) Vestibule configuration for demating. The HTV Small Re-entry Capsule (HSRC) Protective Cover has been removed.

A/S 201 was launched from the Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 34 at 11:12 a.m., 02/26/1966. The instrumented Apollo Command and Service Module, and, a spacecraft Lunar Excursion Module Adapter, was successfully launched on the unmanned suborbital mission by the Saturn 1B to check spacecraft launch vehicle mechanical compatibility and to test the spacecraft heat shield in a high-velocity re-entry mode. CAPE KENNEDY, FL
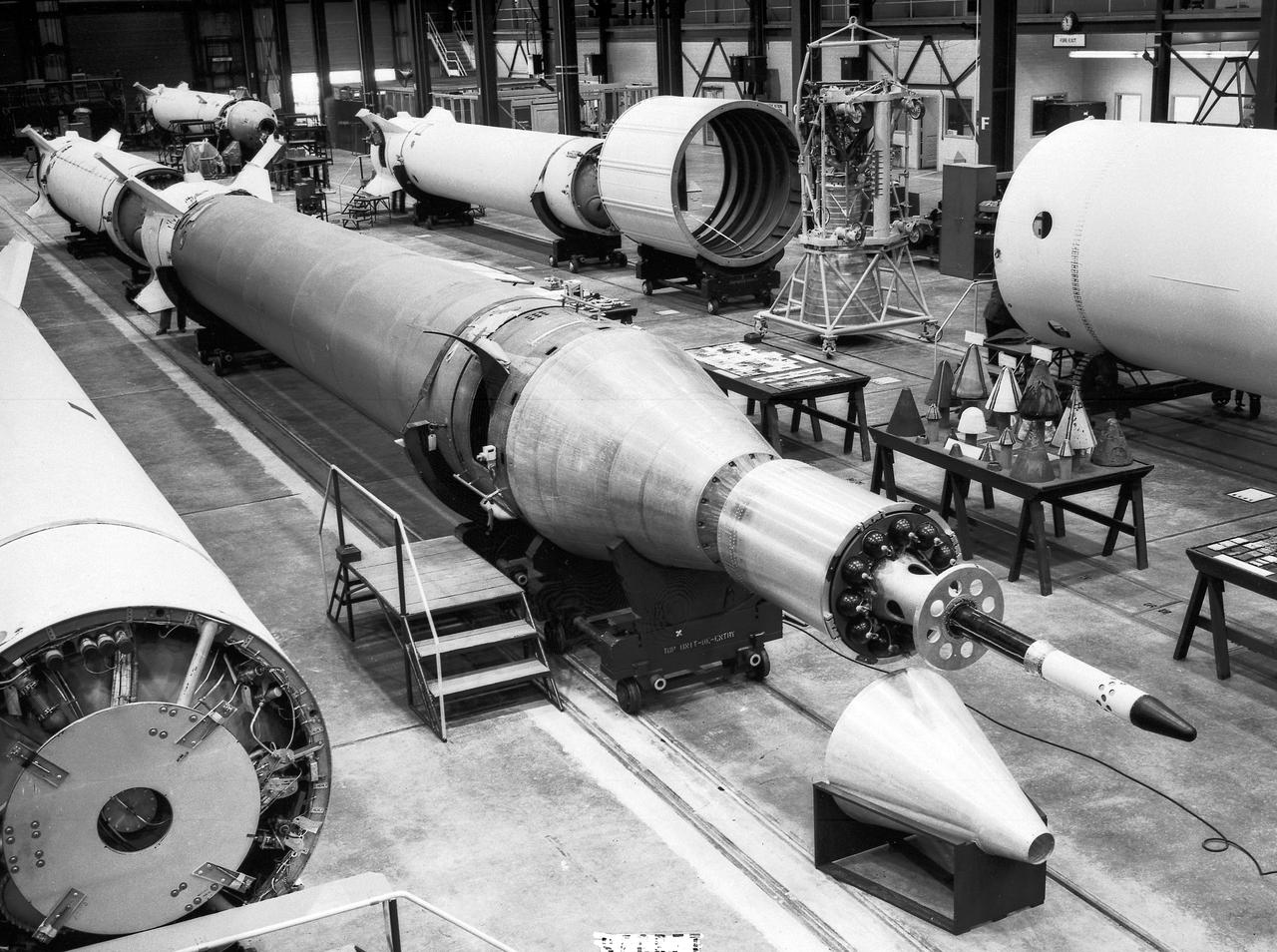

Jupiter-C Missile No. 27 assembly at the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA), Redstone Arsenal, in Huntsville, Aalabama. The Jupiter-C was a modification of the Redstone Missile, and originally developed as a nose cone re-entry test vehicle for the Jupiter Intermediate Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM). Jupiter-C successfully launched the first American Satellite, Explorer 1, in orbit on January 31, 1958.
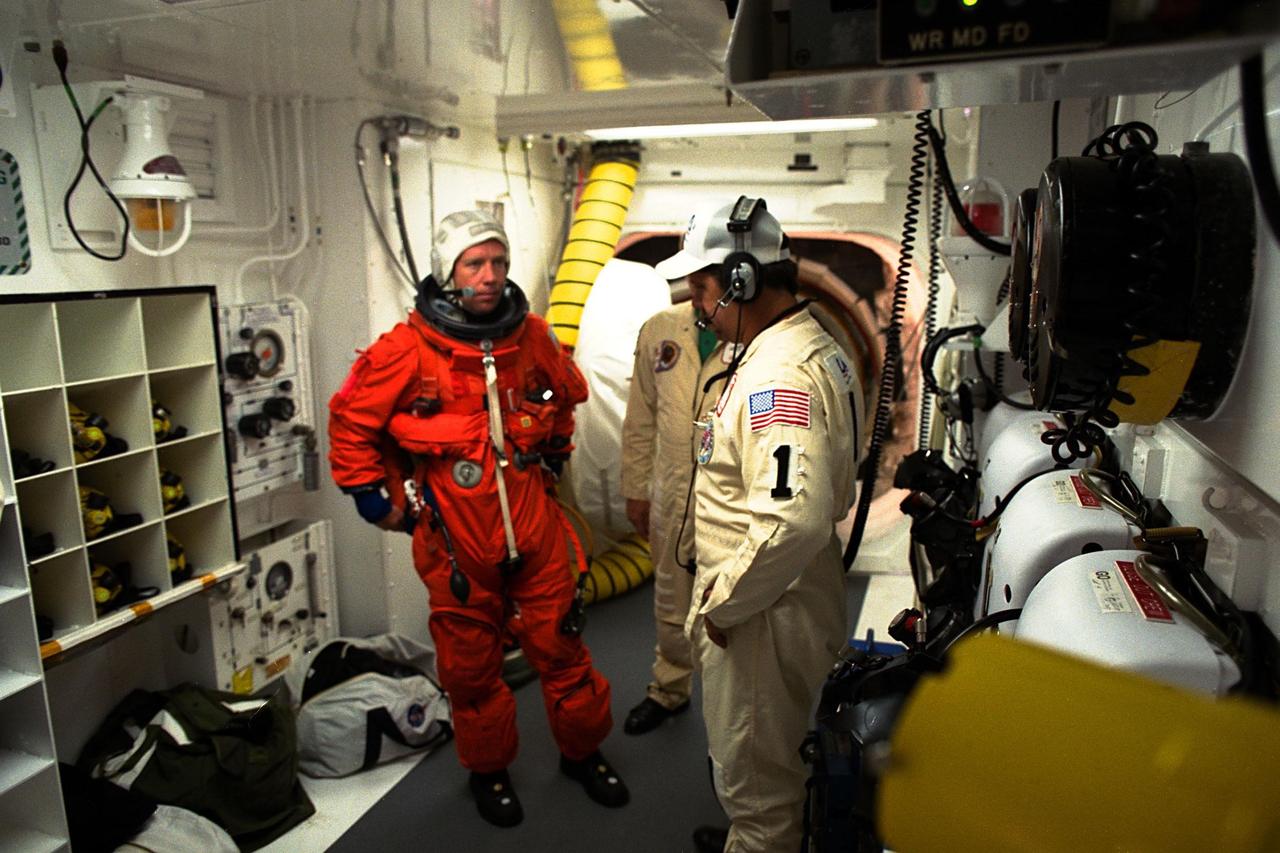

STS-87 Pilot Steven Lindsey is inspected before launch in his ascent and re-entry flight suit in the white room at Launch Pad 39B by Travis Thompson, USA orbiter vehicle closeout chief. STS-87 is the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201. Although this is his first Shuttle flight, Lindsey has logged more than 2,700 hours of flying time in 49 different types of aircraft
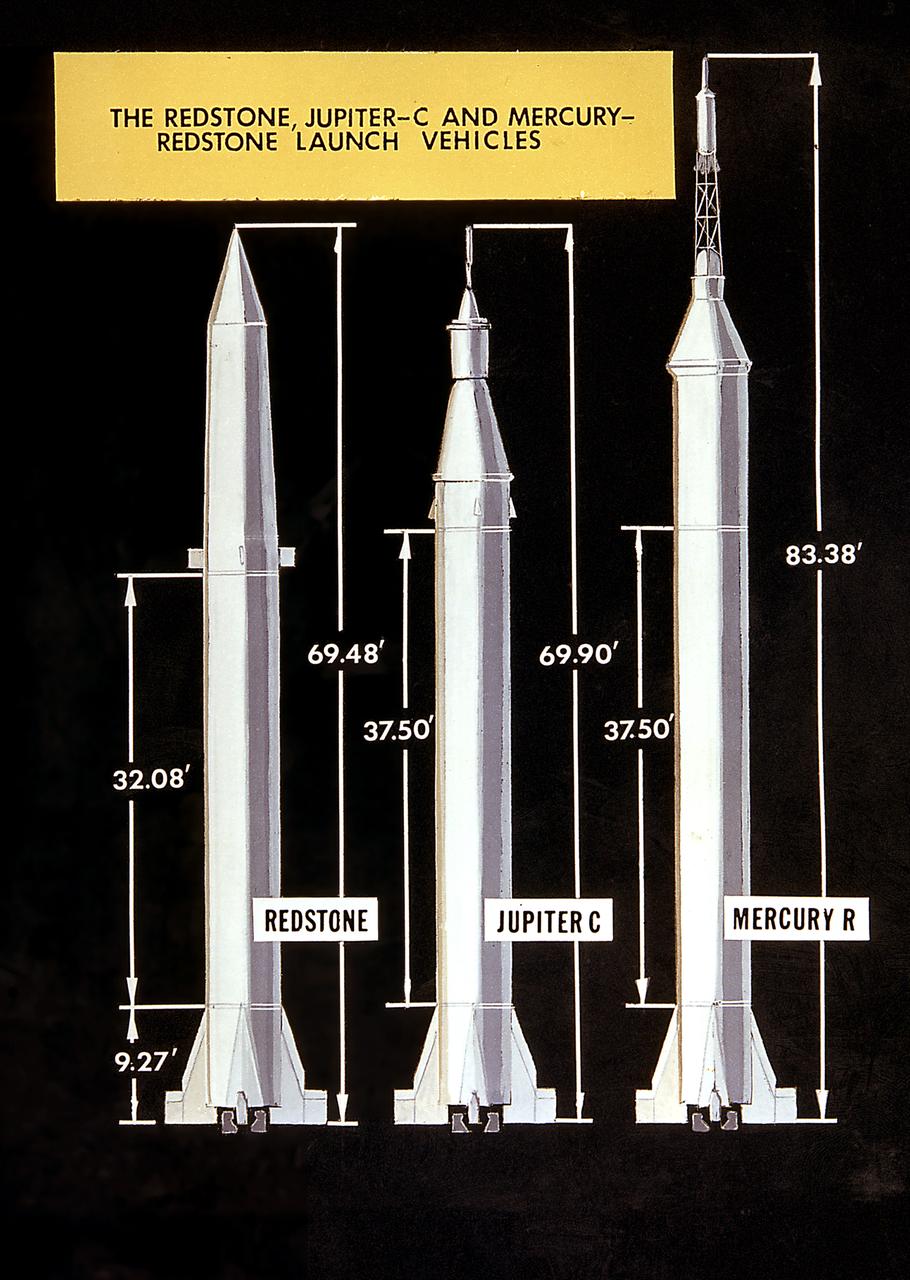

This is a comparison illustration of the Redstone, Jupiter-C, and Mercury Redstone launch vehicles. The Redstone ballistic missile was a high-accuracy, liquid-propelled, surface-to-surface missile. Originally developed as a nose cone re-entry test vehicle for the Jupiter intermediate range ballistic missile, the Jupiter-C was a modification of the Redstone missile and successfully launched the first American Satellite, Explorer-1, in orbit on January 31, 1958. The Mercury Redstone lifted off carrying the first American, astronaut Alan Shepard, in his Mercury spacecraft Freedom 7, on May 5, 1961.
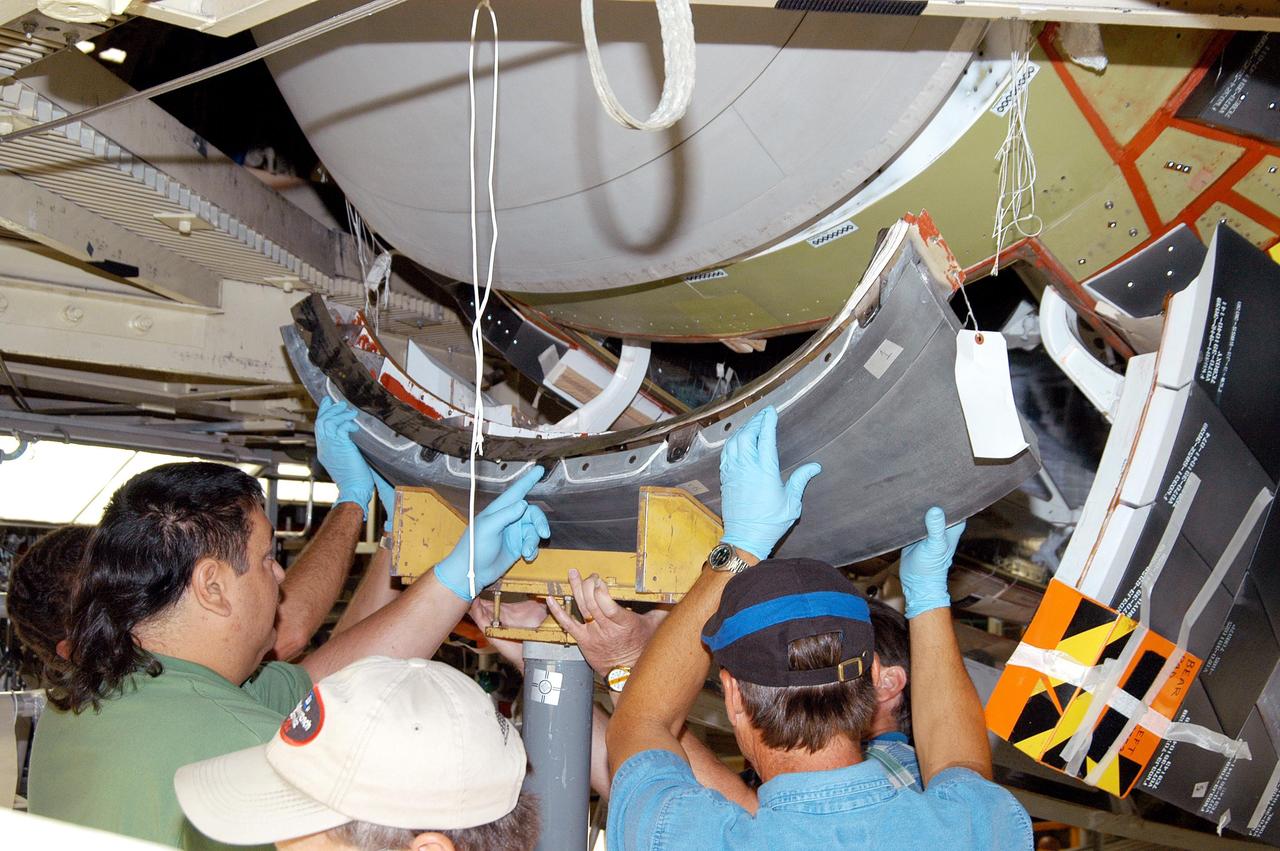

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility check the placement of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) chin panel on Discovery. . The chin panel is the smile-shaped section of RCC directly below the nose cap that provides a thermal barrier during re-entry. The nose cap, with chin panel, was removed from the vehicle in the summer of 2003 and returned to the vendor, where it underwent numerous forms of Non-Destructive Evaluation. These tests included X-ray, ultrasound and eddy current to ensure its structural integrity prior to reinstallation. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility prepare the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) chin panel to install on Discovery. The chin panel is the smile-shaped section of RCC directly below the nose cap that provides a thermal barrier during re-entry. The nose cap, with chin panel, was removed from the vehicle in the summer of 2003 and returned to the vendor, where it underwent numerous forms of Non-Destructive Evaluation. These tests included X-ray, ultrasound and eddy current to ensure its structural integrity prior to reinstallation. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.
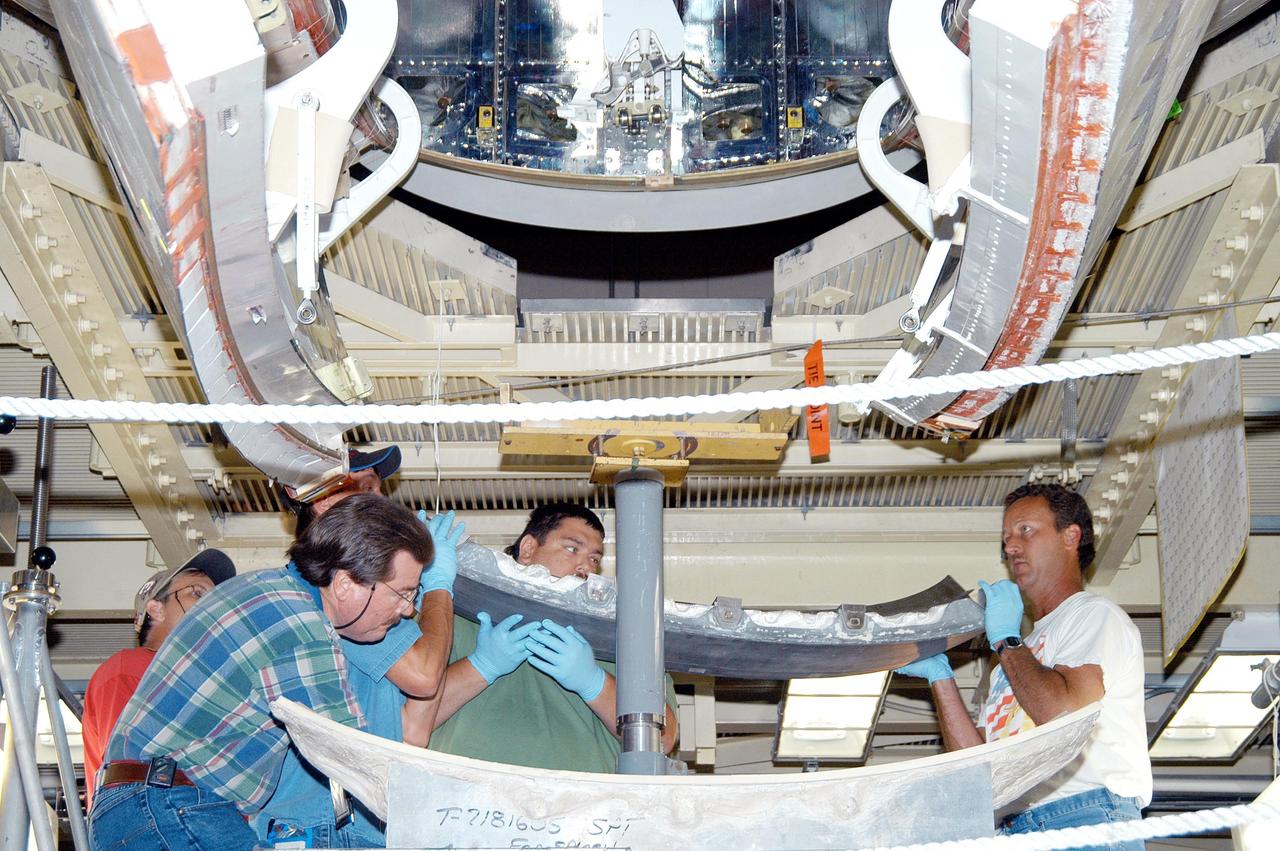

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility lift the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) chin panel to install on Discovery. The chin panel is the smile-shaped section of RCC directly below the nose cap that provides a thermal barrier during re-entry. The nose cap, with chin panel, was removed from the vehicle in the summer of 2003 and returned to the vendor, where it underwent numerous forms of Non-Destructive Evaluation. These tests included X-ray, ultrasound and eddy current to ensure its structural integrity prior to reinstallation. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.
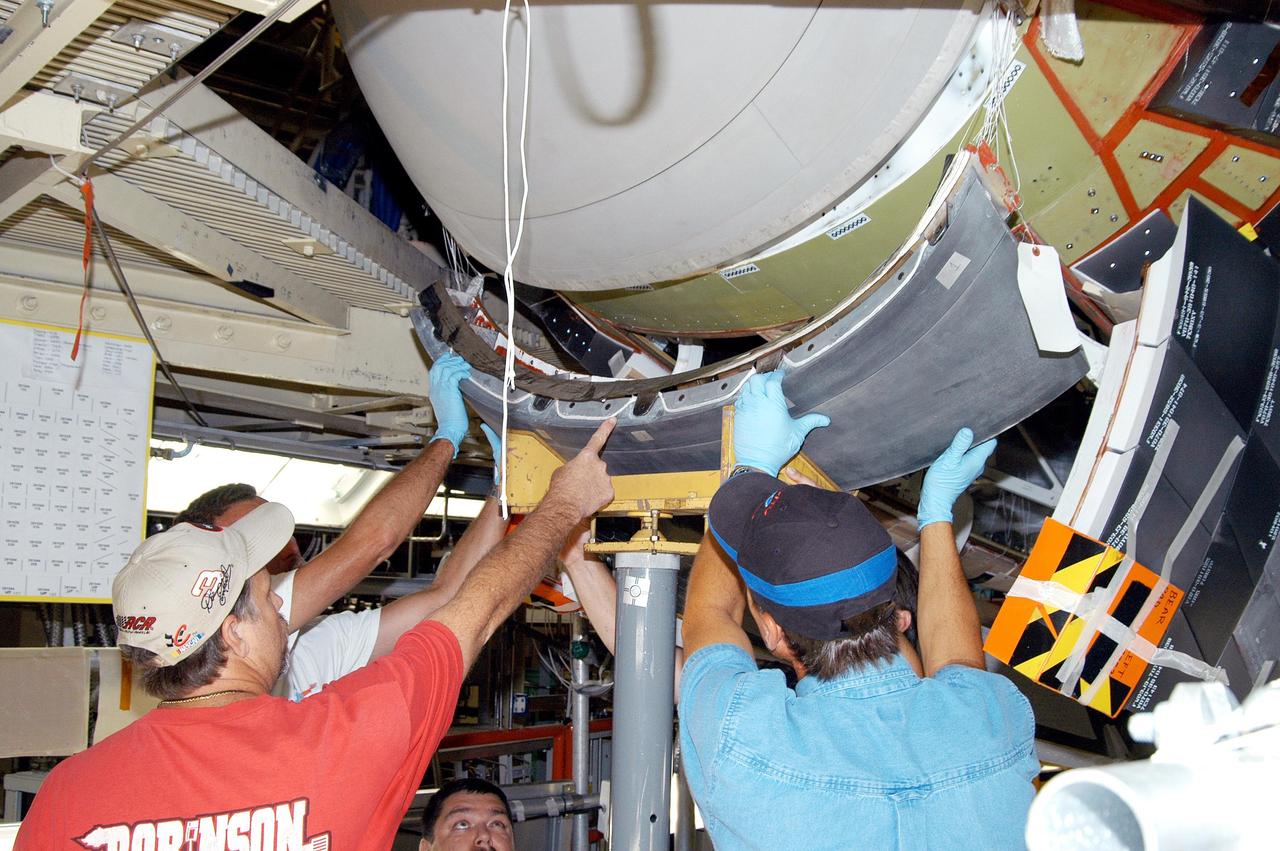

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility check the placement of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon chin panel on Discovery. The chin panel is the smile-shaped section of RCC directly below the nose cap that provides a thermal barrier during re-entry. The nose cap, with chin panel, was removed from the vehicle in the summer of 2003 and returned to the vendor, where it underwent numerous forms of Non-Destructive Evaluation. These tests included X-ray, ultrasound and eddy current to ensure its structural integrity prior to reinstallation. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.
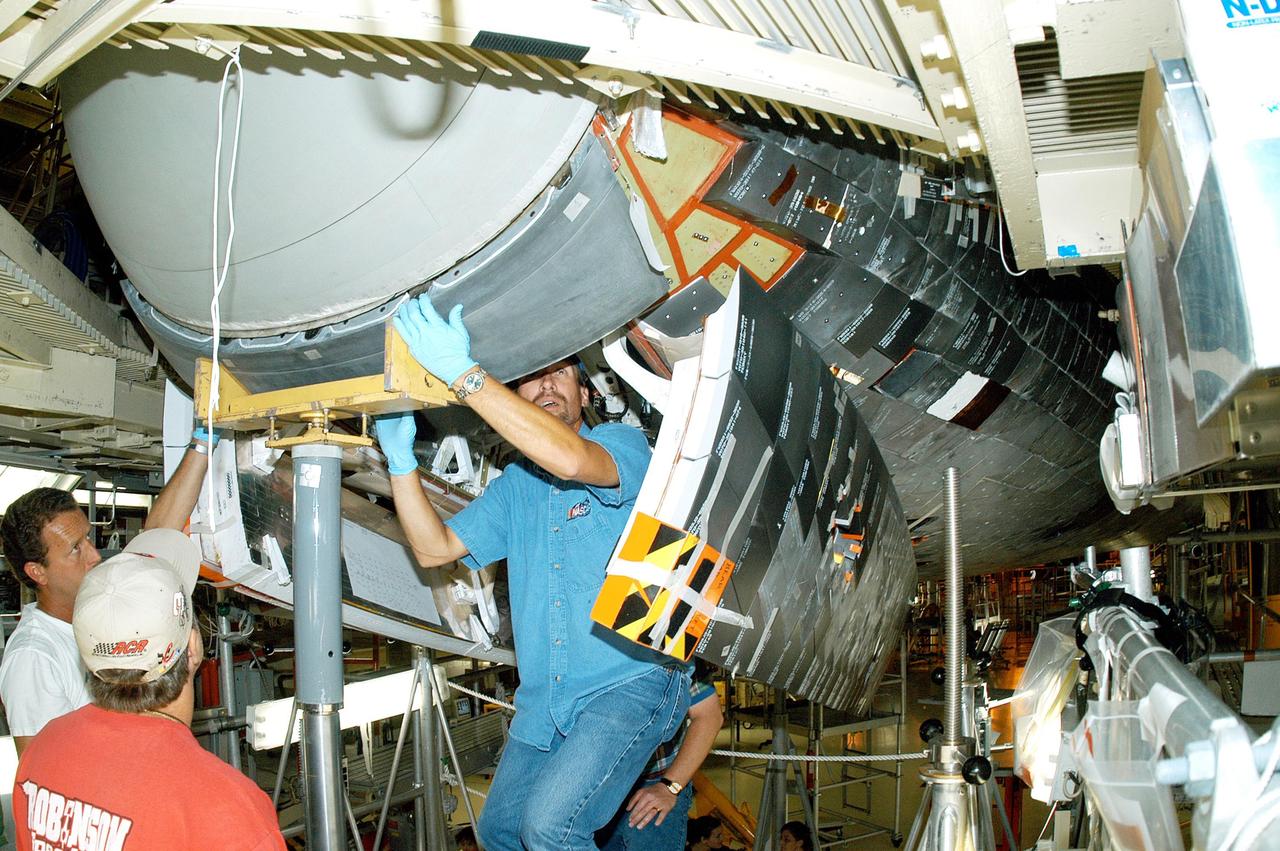

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility complete the installation of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panel on Discovery. The chin panel is the smile-shaped section of RCC directly below the nose cap that provides a thermal barrier during re-entry. The nose cap, with chin panel, was removed from the vehicle in the summer of 2003 and returned to the vendor, where it underwent numerous forms of Non-Destructive Evaluation. These tests included X-ray, ultrasound and eddy current to ensure its structural integrity prior to reinstallation. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.
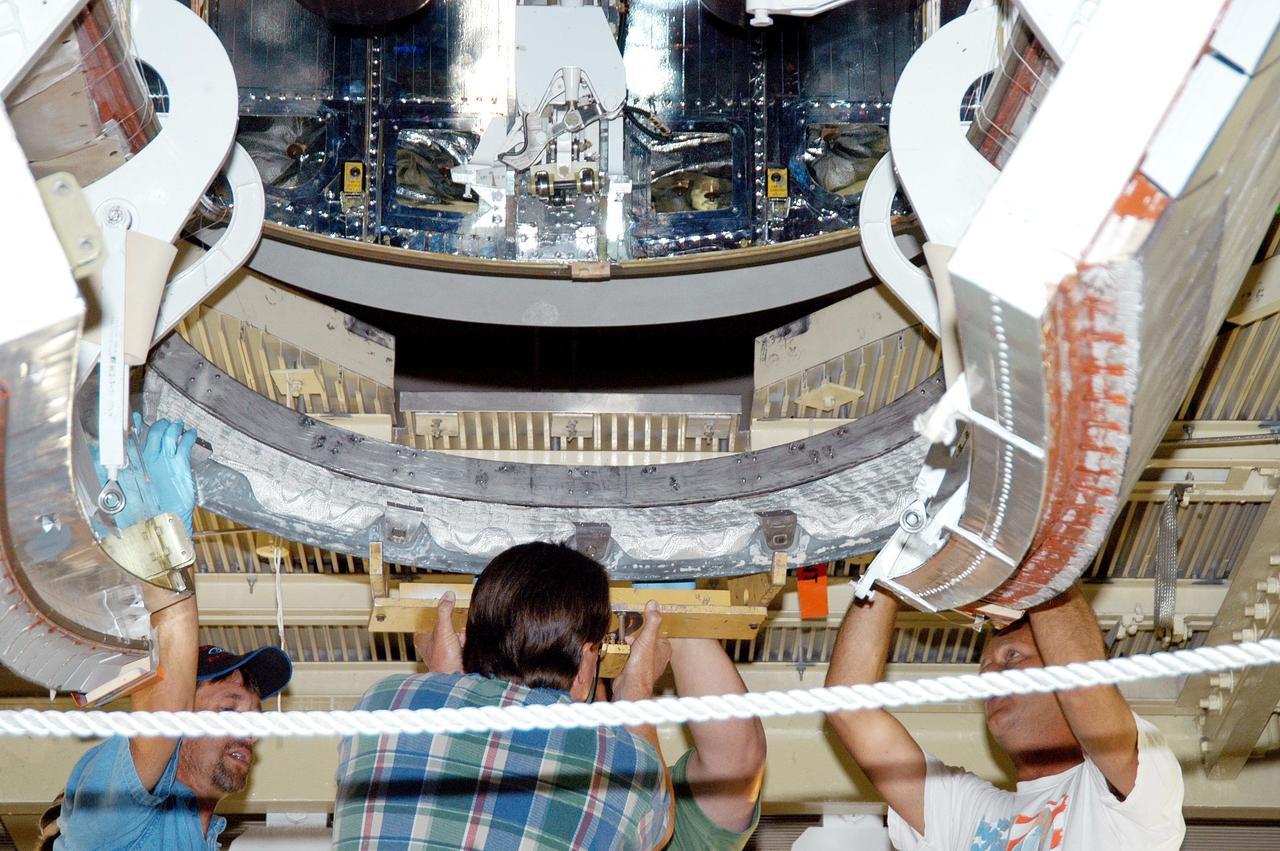

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility lift the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) chin panel into place on Discovery. The chin panel is the smile-shaped section of RCC directly below the nose cap that provides a thermal barrier during re-entry. The nose cap, with chin panel, was removed from the vehicle in the summer of 2003 and returned to the vendor, where it underwent numerous forms of Non-Destructive Evaluation. These tests included X-ray, ultrasound and eddy current to ensure its structural integrity prior to reinstallation. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.
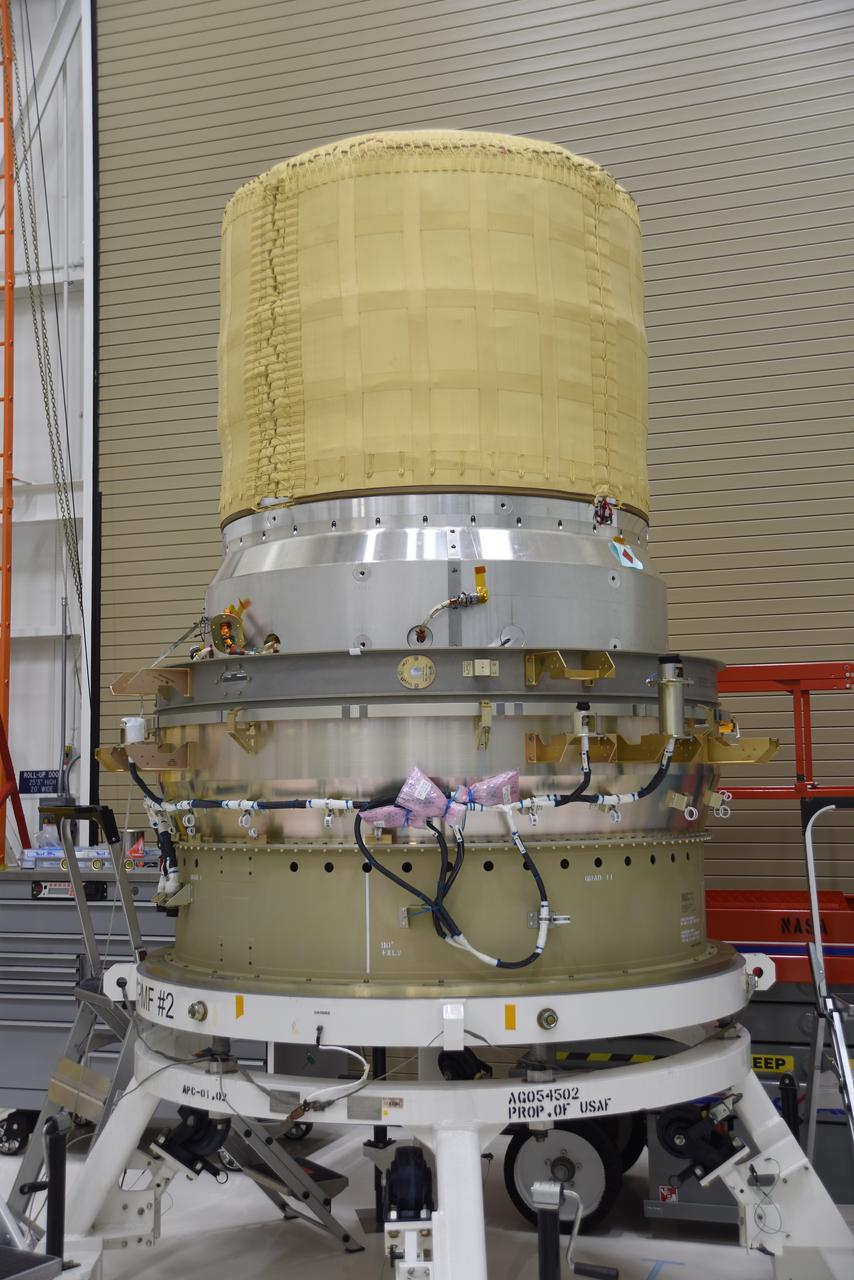

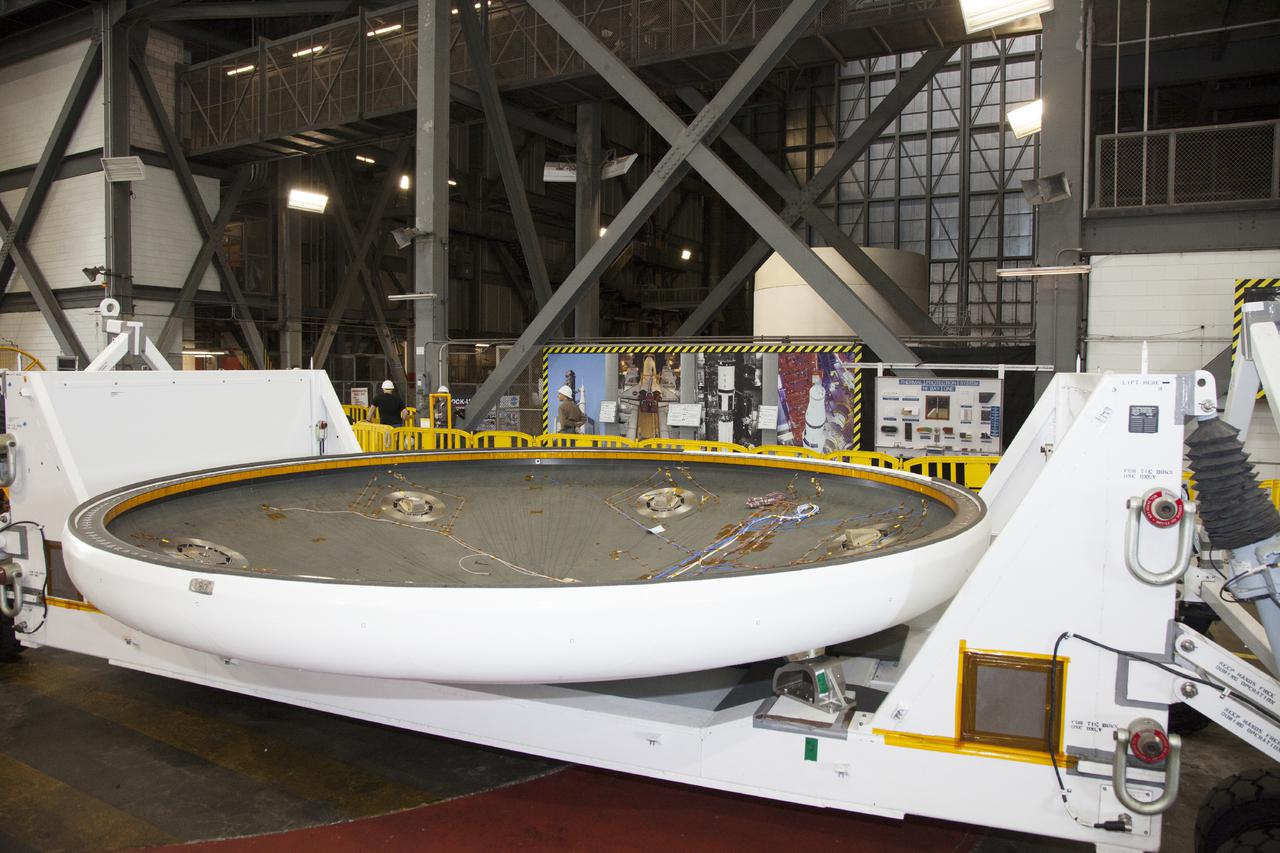
The re-entry vehicle for the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) is now mated to the re-entry vehicle payload adapter interface ring and secured on a work stand as part of launch preparations inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 7, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.
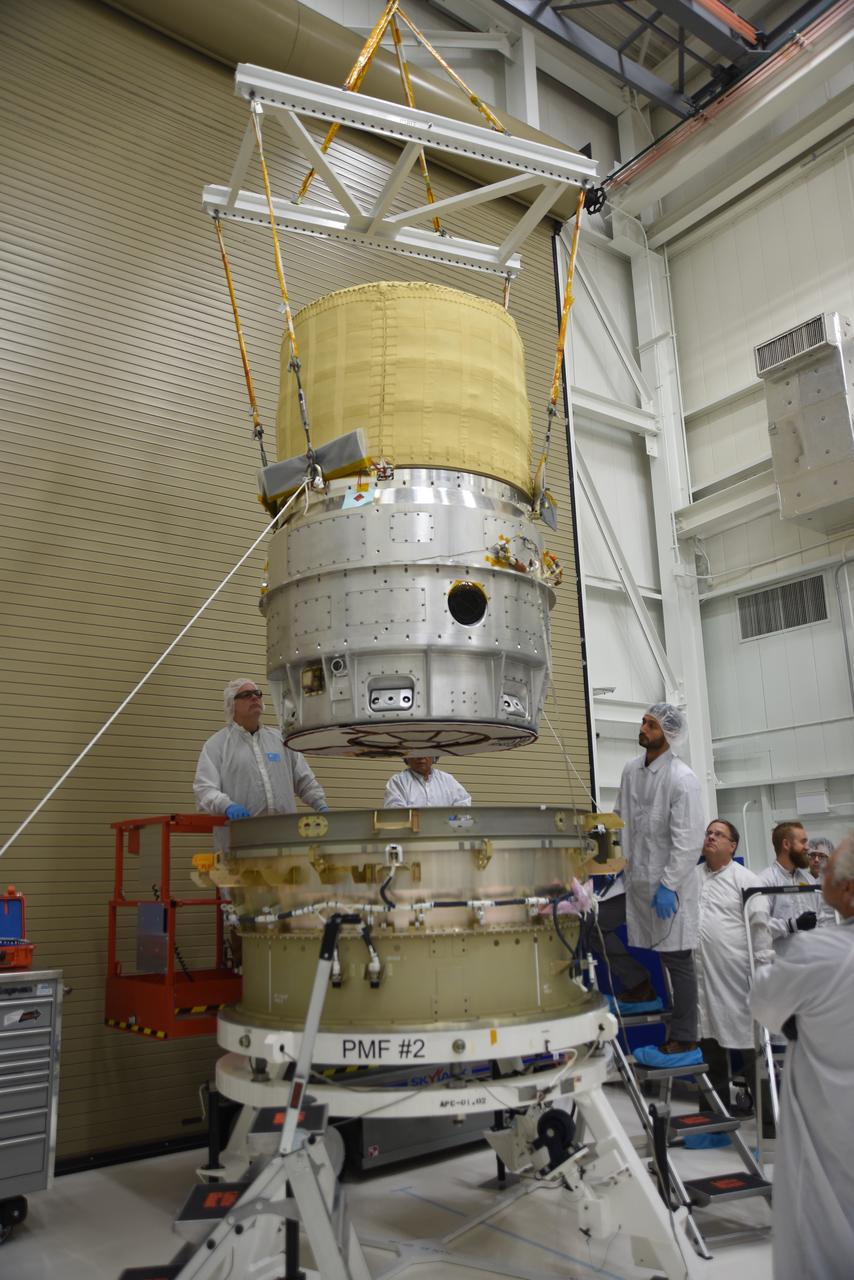

Technicians use a crane to lower the re-entry vehicle for the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) into the re-entry vehicle payload adapter interface ring as part of launch preparations inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 7, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.
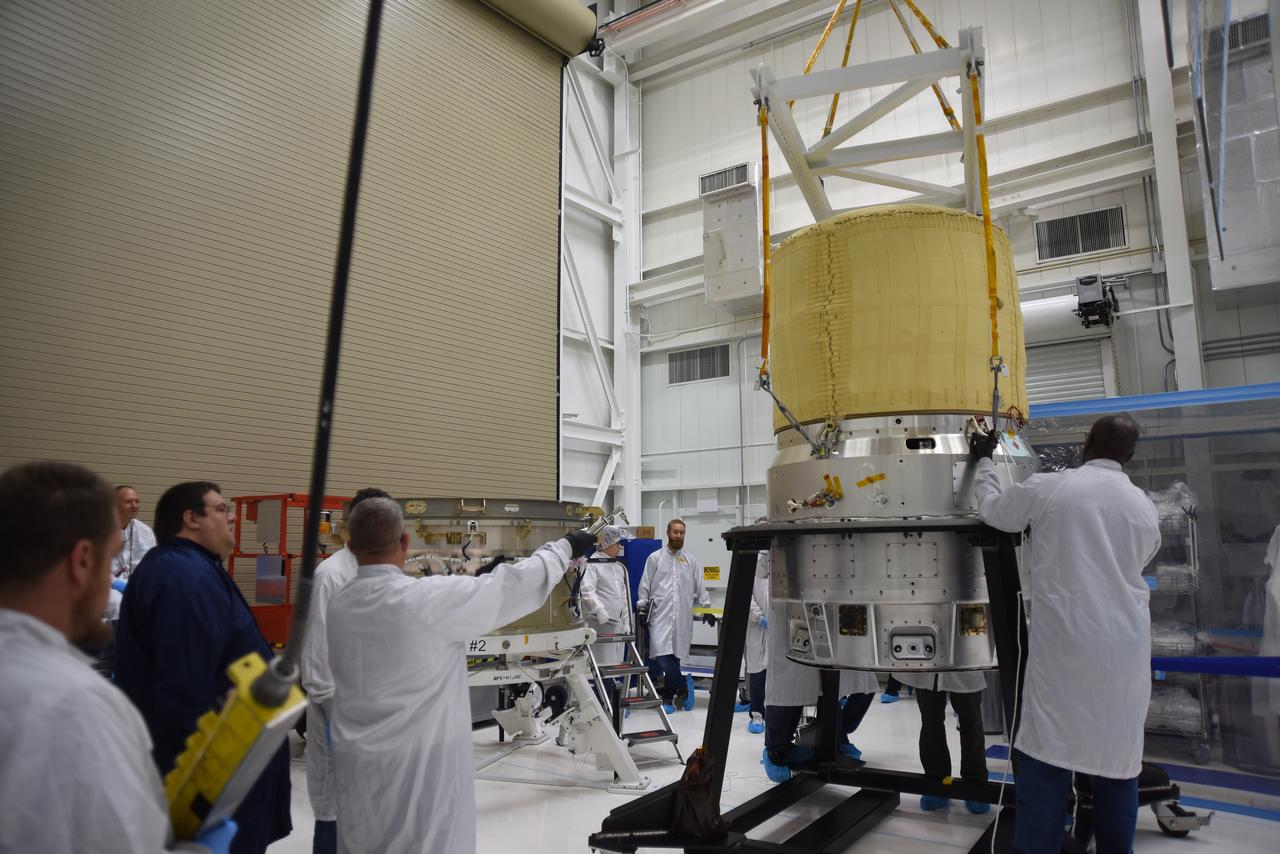

Technicians use a crane to lift the re-entry vehicle for the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) for mating to the re-entry vehicle payload adapter interface ring as part of launch preparations inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 7, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. The LOFTID is dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.
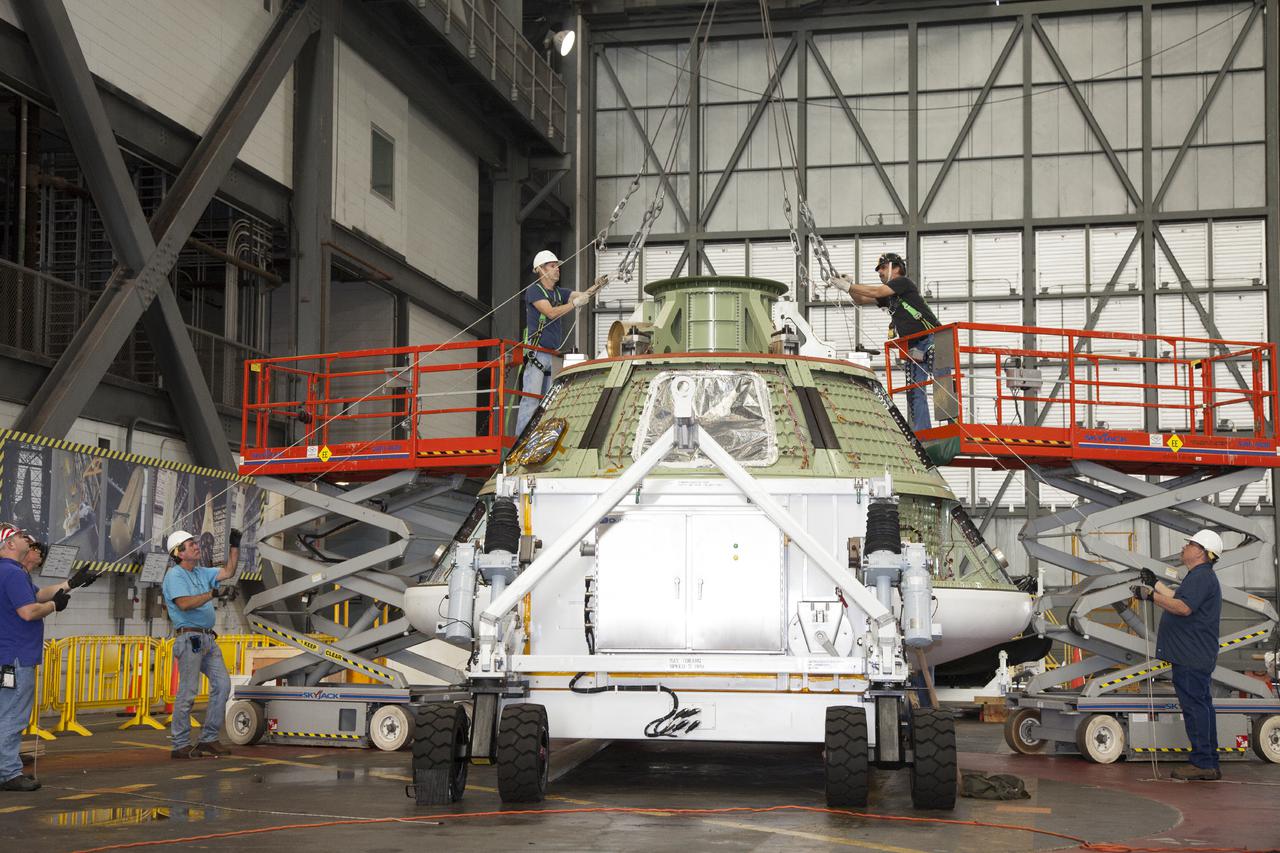

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians on scissor lifts prepare to attach a bridge crane to the Orion ground test vehicle for heat shield removal. The ground test vehicle is being prepared for its move to Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va., for a water test. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: Daniel Casper
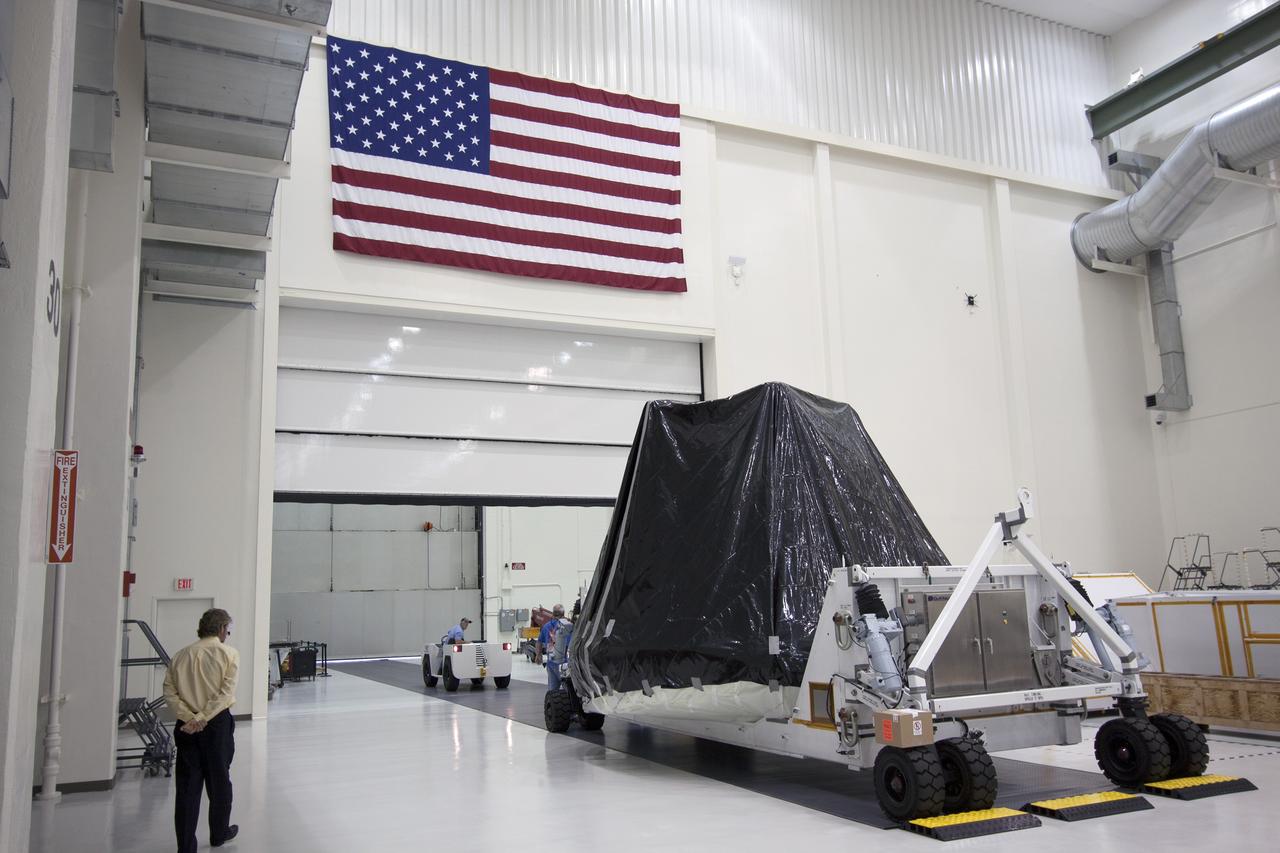

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers prepare to move the Orion ground test vehicle, or GTA, from the Operations and Checkout Building to the Launch Equipment Test Facility, or LETF. At the LETF, Lockheed Martin will put the GTA through a series of pyrotechnic bolt tests. The ground test vehicle is being used for path finding operations in the O&C, including simulated manufacturing and assembly procedures. Launching atop NASA's heavy-lift Space Launch System SLS, which also is under development, the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle MPCV will serve as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronaut crews beyond low Earth orbit. It also will provide emergency abort capabilities, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Jim Grossman
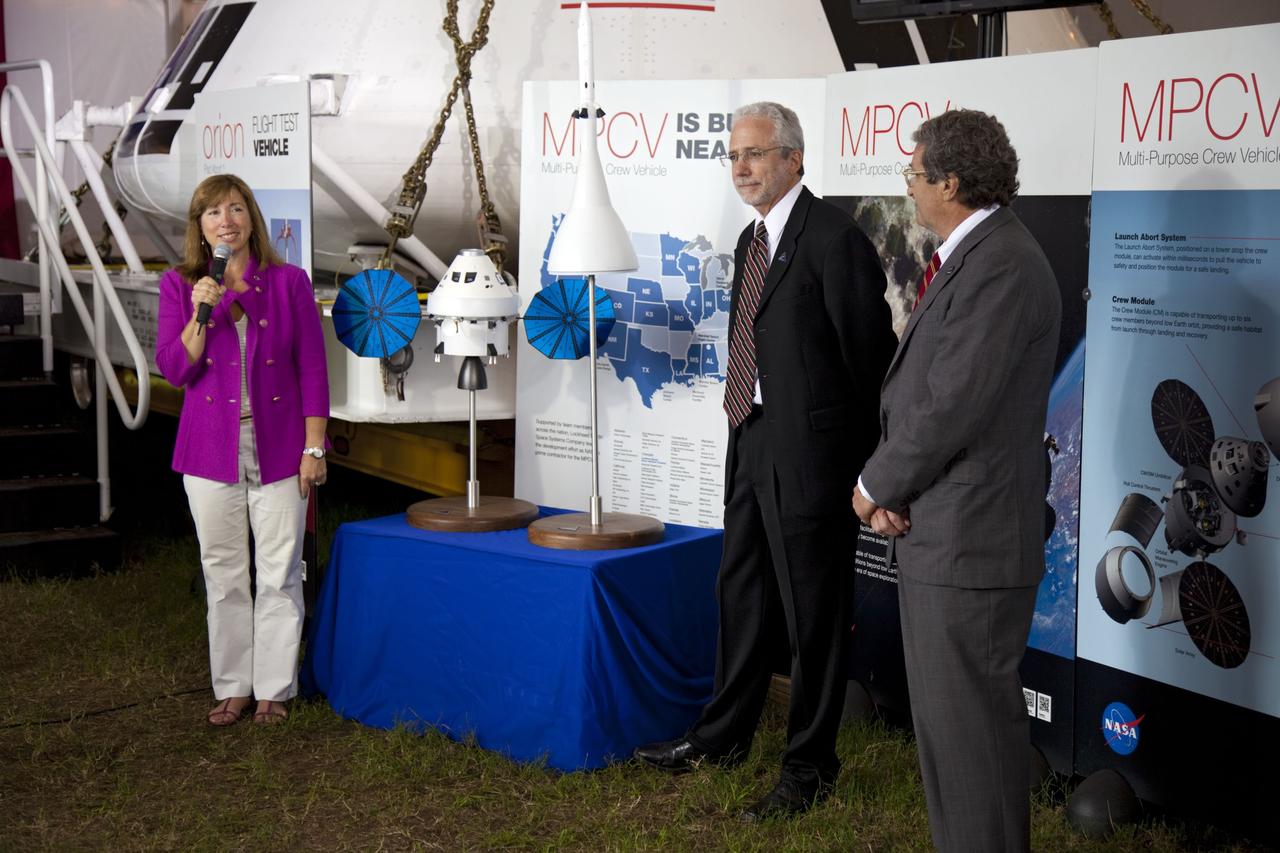

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A media event was held on the grounds near the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida where a Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle (MPCV) is on display. The MPCV is based on the Orion design requirements for traveling beyond low Earth orbit and will serve as the exploration vehicle that will carry the crew to space, provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel, and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Seen here is Lori Garver, NASA deputy administrator, Mark Geyer, Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle program manager and Laurence A. Price, Orion deputy program manager with Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company to talk about the vehicle during a question-and-answer session. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
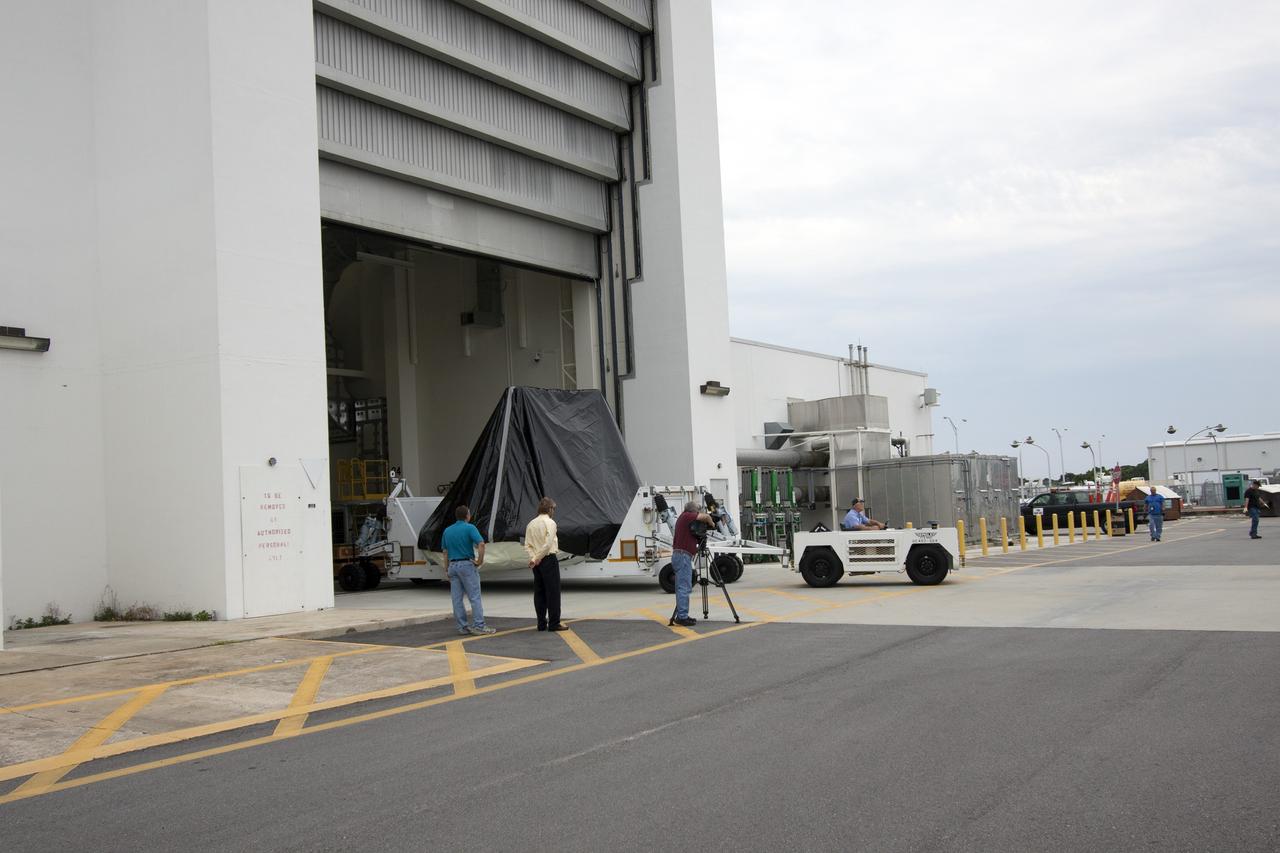

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers move the Orion ground test vehicle, or GTA, from the Operations and Checkout Building to the Launch Equipment Test Facility, or LETF. At the LETF, Lockheed Martin will put the GTA through a series of pyrotechnic bolt tests. The ground test vehicle is being used for path finding operations in the O&C, including simulated manufacturing and assembly procedures. Launching atop NASA's heavy-lift Space Launch System SLS, which also is under development, the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle MPCV will serve as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronaut crews beyond low Earth orbit. It also will provide emergency abort capabilities, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Jim Grossman
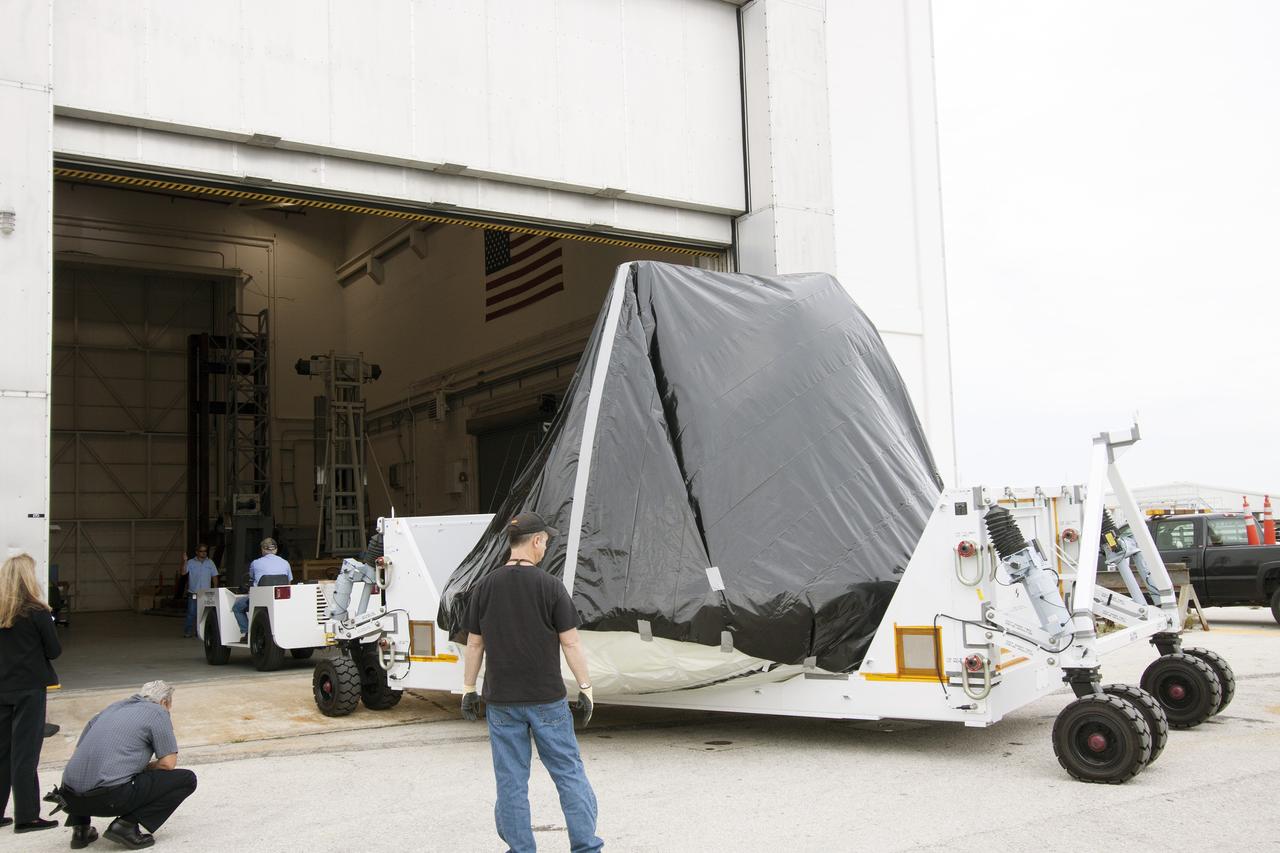

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers move the Orion ground test vehicle, or GTA, into the Launch Equipment Test Facility, or LETF, from the Operations and Checkout Building. At the LETF, Lockheed Martin will put the GTA through a series of pyrotechnic bolt tests. The ground test vehicle is being used for path finding operations in the O&C, including simulated manufacturing and assembly procedures. Launching atop NASA's heavy-lift Space Launch System SLS, which also is under development, the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle MPCV will serve as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronaut crews beyond low Earth orbit. It also will provide emergency abort capabilities, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Jim Grossman
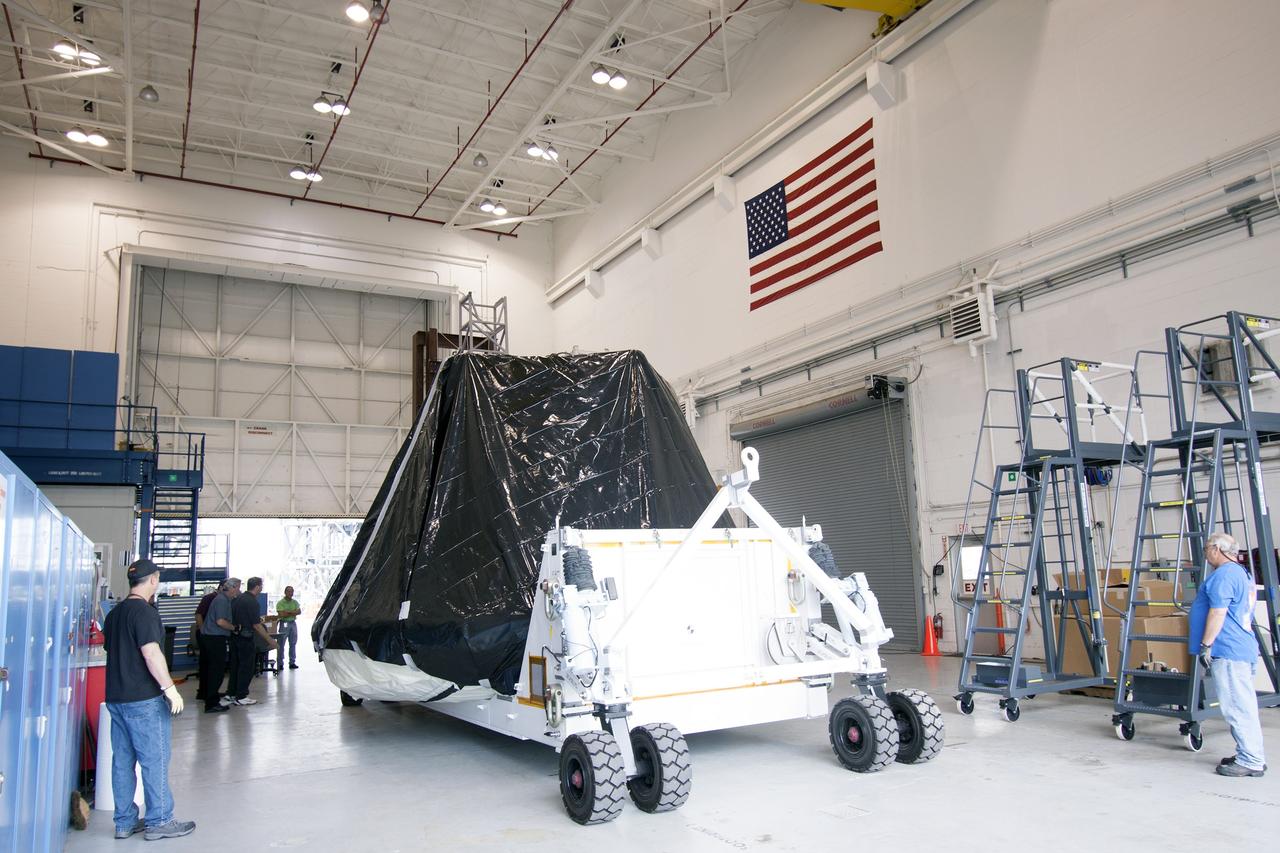

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers move the Orion ground test vehicle, or GTA, into the Launch Equipment Test Facility, or LETF, from the Operations and Checkout Building. At the LETF, Lockheed Martin will put the GTA through a series of pyrotechnic bolt tests. The ground test vehicle is being used for path finding operations in the O&C, including simulated manufacturing and assembly procedures. Launching atop NASA's heavy-lift Space Launch System SLS, which also is under development, the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle MPCV will serve as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronaut crews beyond low Earth orbit. It also will provide emergency abort capabilities, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Jim Grossman

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion ground test vehicle has been lifted away from the heat shield. The ground test vehicle is being prepared for its move to Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va., for a water test. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: Daniel Casper
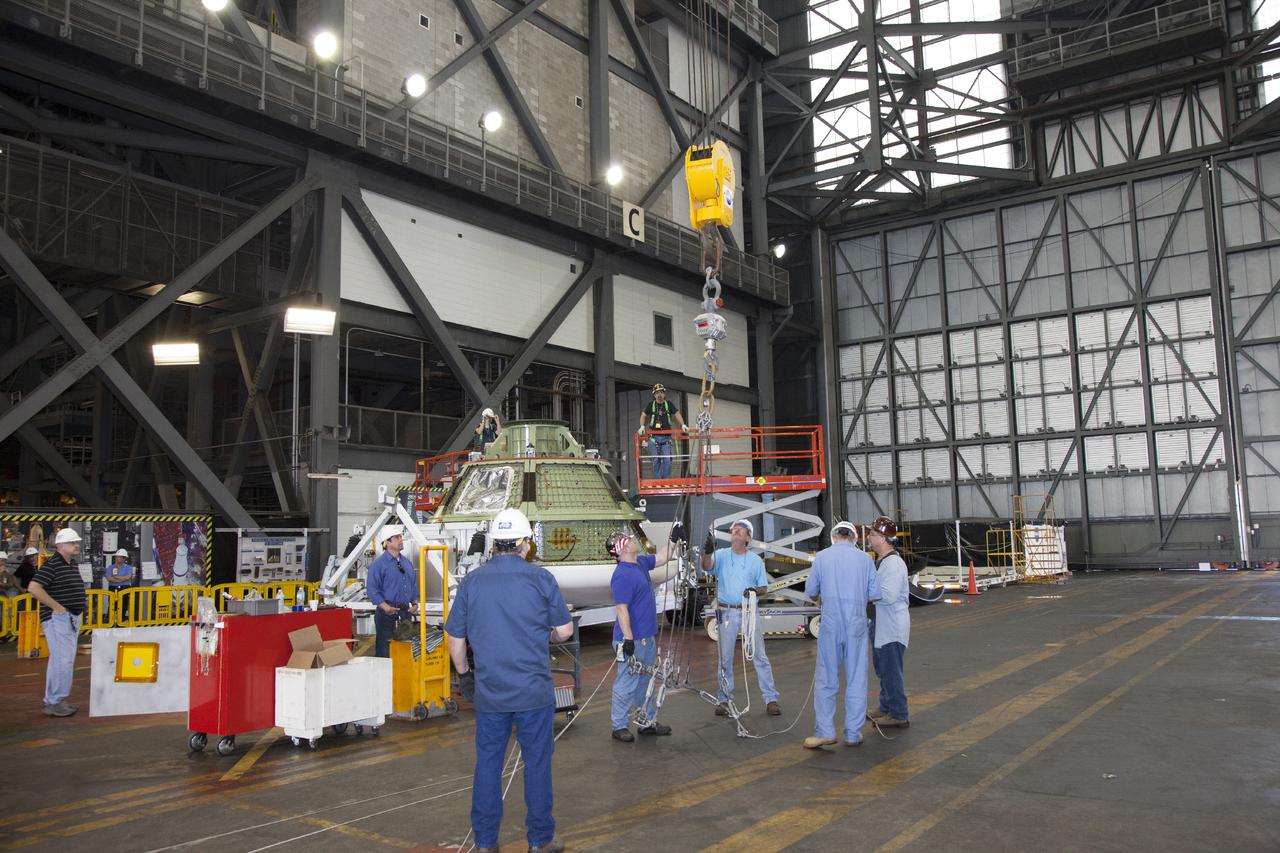

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to attach a bridge crane to the Orion ground test vehicle for heat shield removal inside the Vehicle Assembly Building. The ground test vehicle is being prepared for its move to Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va., for a water test. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: Daniel Casper

In Hangar N at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a heat shield for the Constellation crew exploration vehicle, or CEV, is being prepared for a demonstration. A developmental heat shield for the Orion spacecraft is being tested and evaluated at Kennedy. The shield was designed and assembled by the Boeing Company in Huntington Beach, Calif., for NASA's Constellation Program. The thermal protection system manufacturing demonstration unit is designed to protect astronauts from extreme heat during re-entry to Earth's atmosphere from low Earth orbit and lunar missions. The CEV will be used to dock and gain access to the International Space Station, travel to the moon in the 2018 timeframe and play a crucial role in exploring Mars.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Orbiter Experiment Support System (OEX) recorder from Columbia, in protective covering, rests inside a transport vehicle after its arrival at KSC aboard a T-38 jet aircraft. Search teams near Hemphill, Texas, recovered the recorder, which stores sensor information about temperature, aerodynamic pressure, vibrations and other data from dozens of sensor locations on the orbiter, operating only during launch and re-entry. The OEX uses magnetic tape to record data that is not sent to the ground by telemetry.
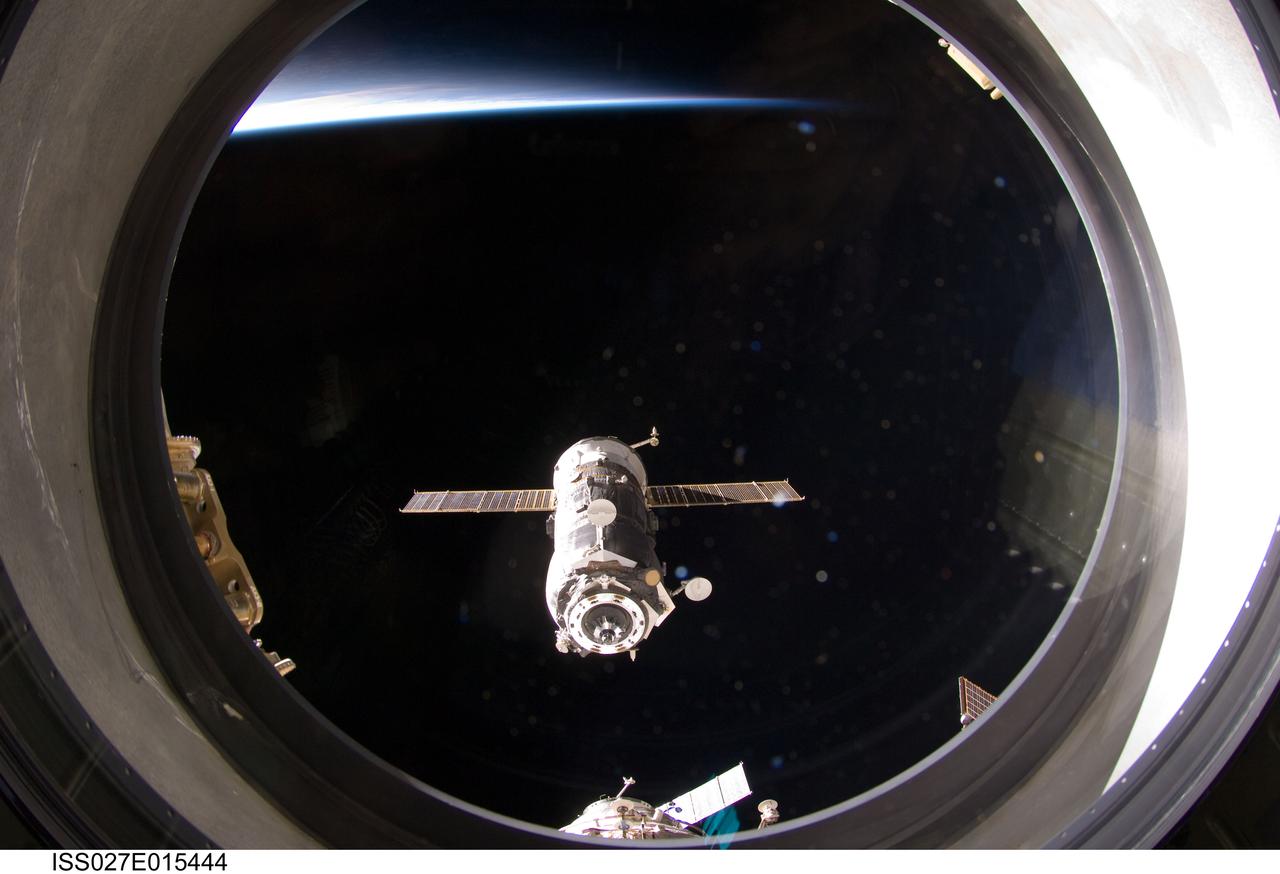

ISS027-E-015444 (22 April 2011) --- The unpiloted ISS Progress 41 supply vehicle departs from the International Space Station at 7:41 a.m. (EDT) on April 22, 2011. Filled with trash and discarded items, Progress 41 will remain in orbit a safe distance from the station for engineering tests before being commanded by flight controllers to descend to a destructive re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean. The departure of Progress 41 clears the way for the next unpiloted supply ship, ISS Progress 42, which is set to launch April 27 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, delivering three tons of food, fuel and supplies for the Expedition 27 crew.
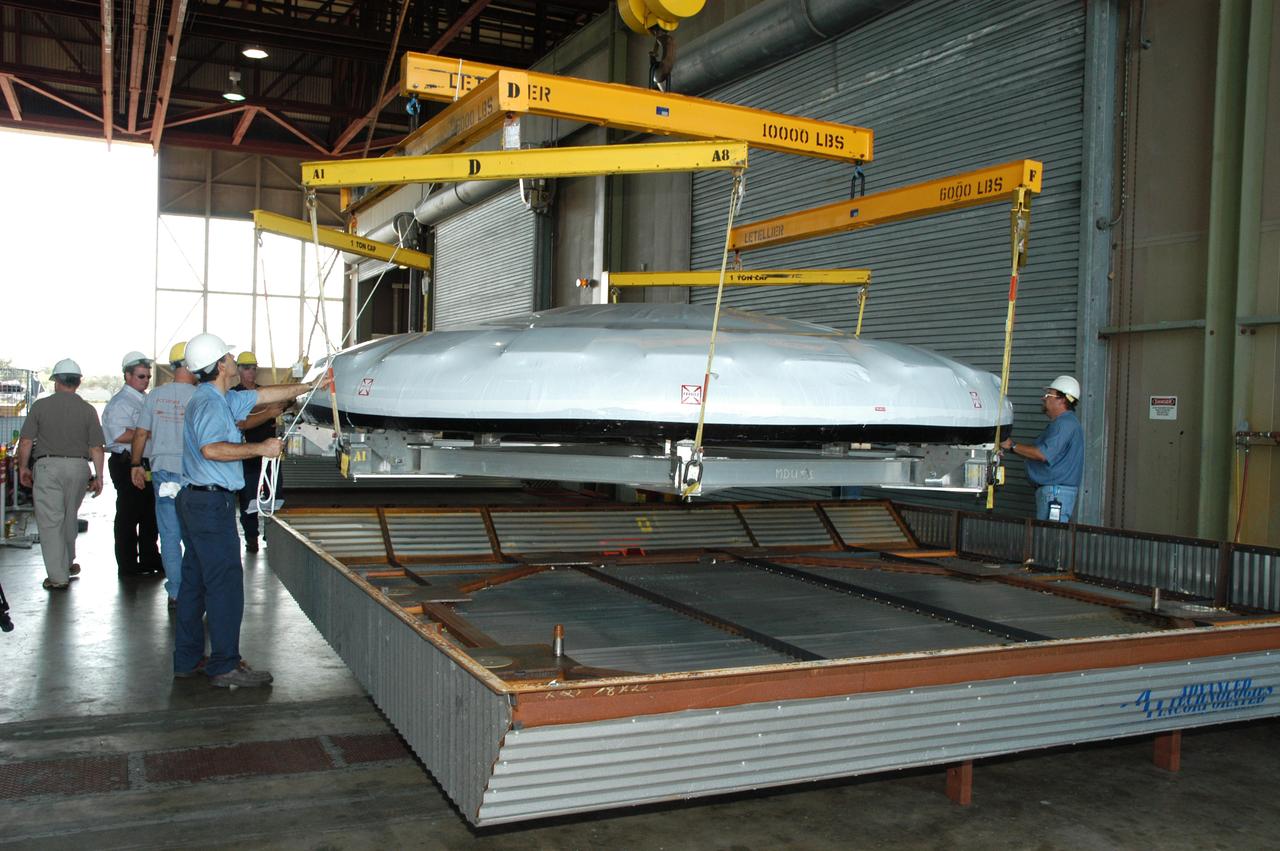

In Hangar N at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a heat shield for the Constellation crew exploration vehicle, or CEV, is being prepared for a demonstration. A developmental heat shield for the Orion spacecraft is being tested and evaluated at Kennedy. The shield was designed and assembled by the Boeing Company in Huntington Beach, Calif., for NASA's Constellation Program. The thermal protection system manufacturing demonstration unit is designed to protect astronauts from extreme heat during re-entry to Earth's atmosphere from low Earth orbit and lunar missions. The CEV will be used to dock and gain access to the International Space Station, travel to the moon in the 2018 timeframe and play a crucial role in exploring Mars.
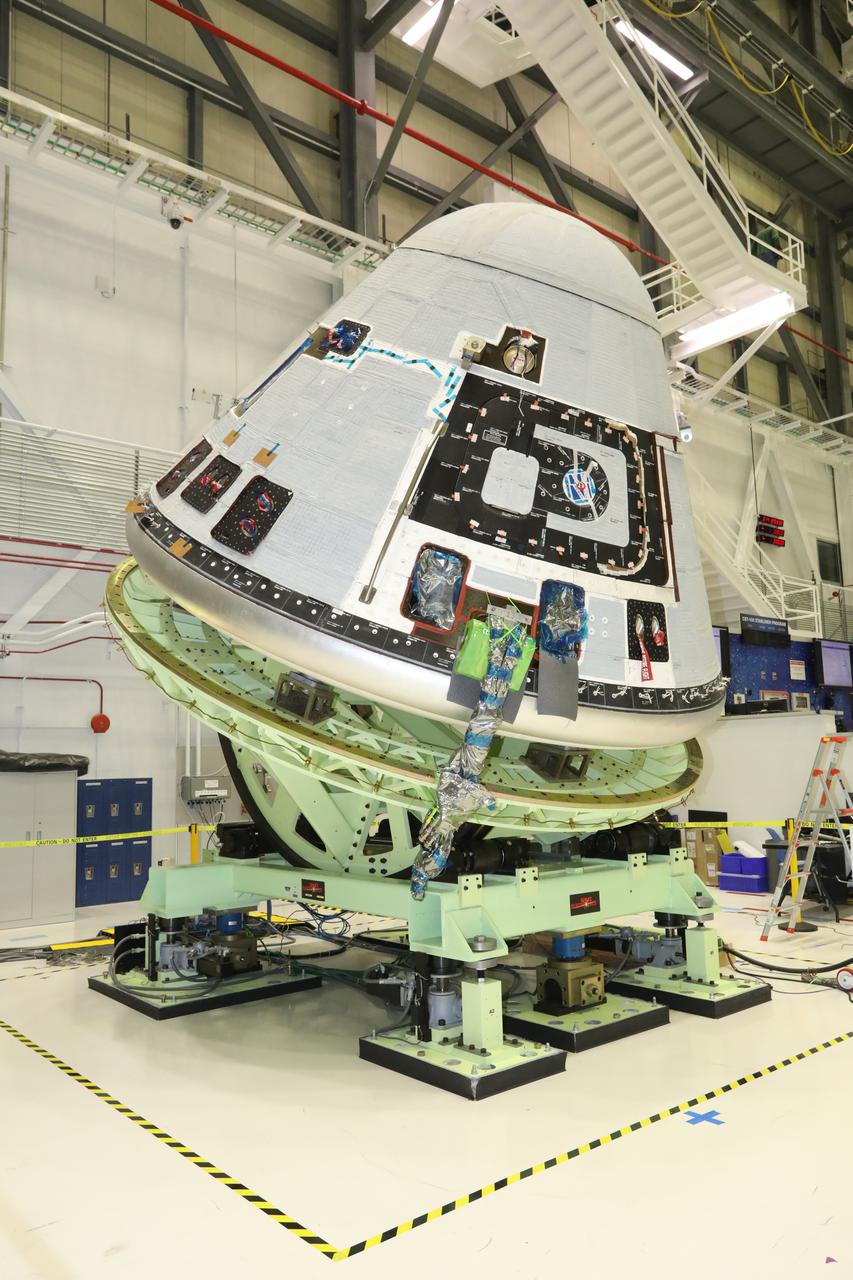

Boeing’s Starliner crew module is weighed in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for the company’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2), as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.. The Weight and Center of Gravity test measures the weight and balance of the spacecraft to ensure optimal performance during launch and re-entry. The test helps to validate parameters required for launching on United Launch Alliance’s Atlas V rocket, docking to the International Space Station and for navigation of the vehicle, among others.

ISS016-E-035178 (7 April 2008) --- An unpiloted Progress 28 resupply vehicle departs from the Pirs Docking Compartment of the International Space Station at 4:50 a.m. (EDT) on Monday, April 7, 2008, and headed into its deorbit and destructive re-entry into Earth's atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean. The Progress, which has been attached to the station since February, had been loaded with trash and discards before its departure. The undocking clears the way for the arrival Thursday of the Soyuz TMA-12 spacecraft carrying the Expedition 17 crew and a South Korean spaceflight participant.
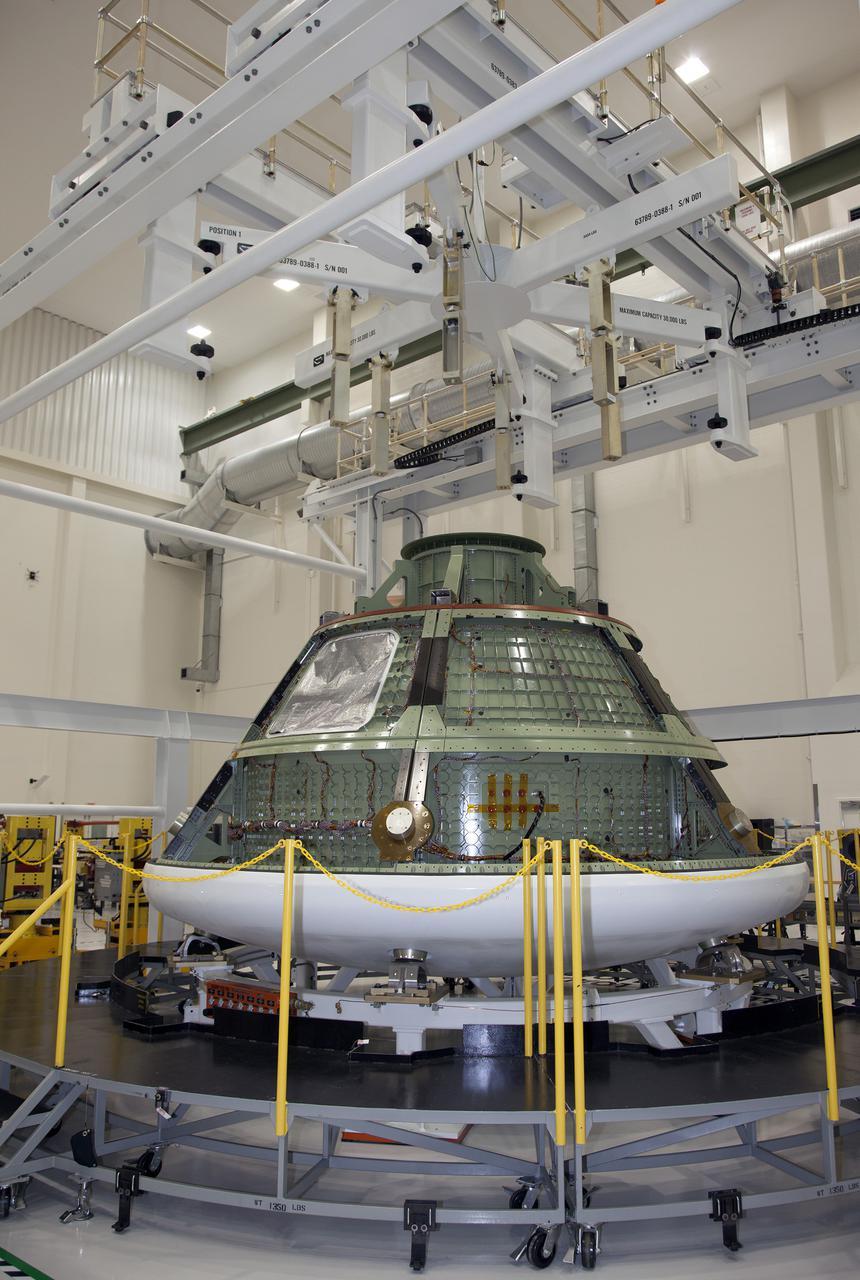

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Orion Ground Test Vehicle is on display in the high bay of the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a tour for media representatives. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low-Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket, and in 2017, on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Frankie Martin
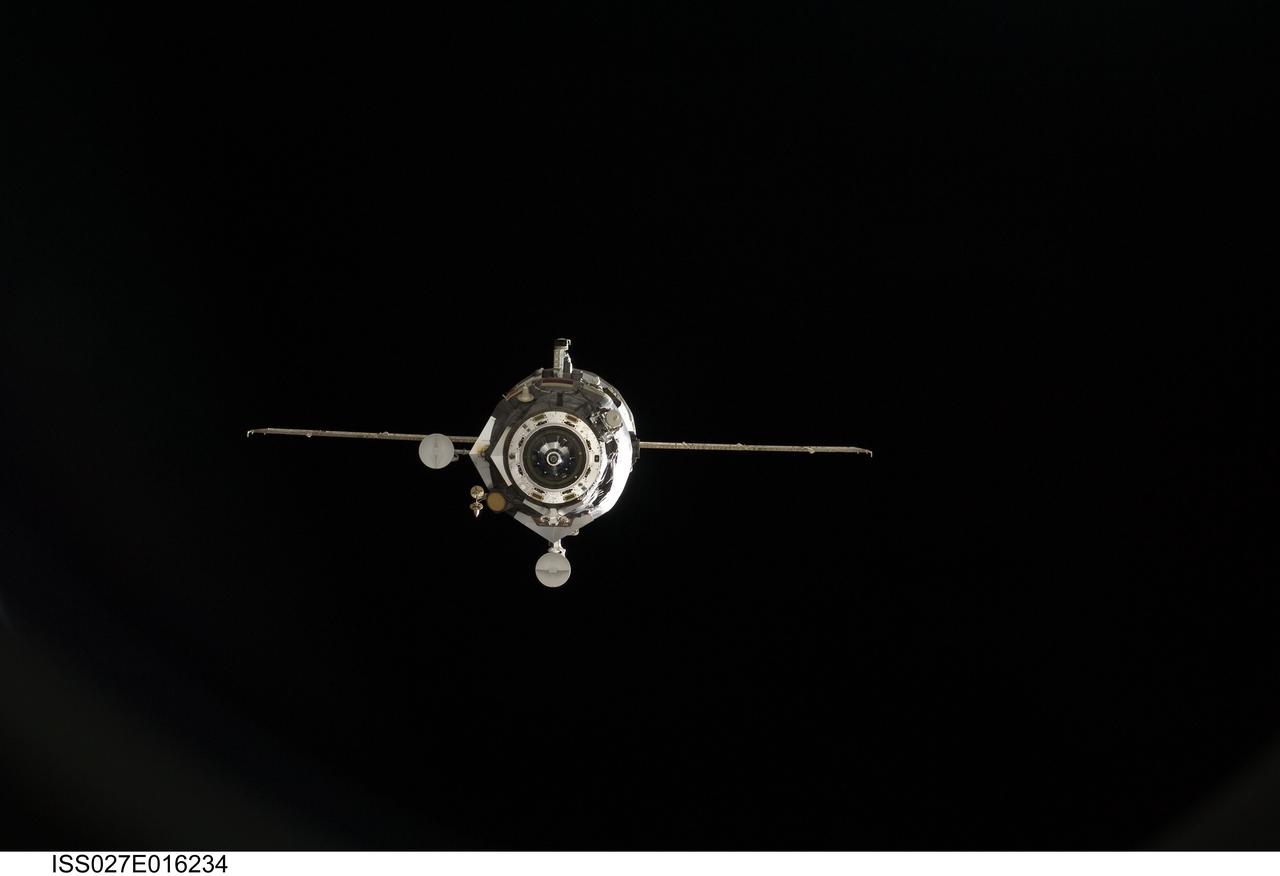

ISS027-E-016234 (22 April 2011) --- The unpiloted ISS Progress 41 supply vehicle departs from the International Space Station at 7:41 a.m. (EDT) on April 22, 2011. Filled with trash and discarded items, Progress 41 will remain in orbit a safe distance from the station for engineering tests before being commanded by flight controllers to descend to a destructive re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean. The departure of Progress 41 clears the way for the next unpiloted supply ship, ISS Progress 42, which is set to launch April 27 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, delivering three tons of food, fuel and supplies for the Expedition 27 crew.
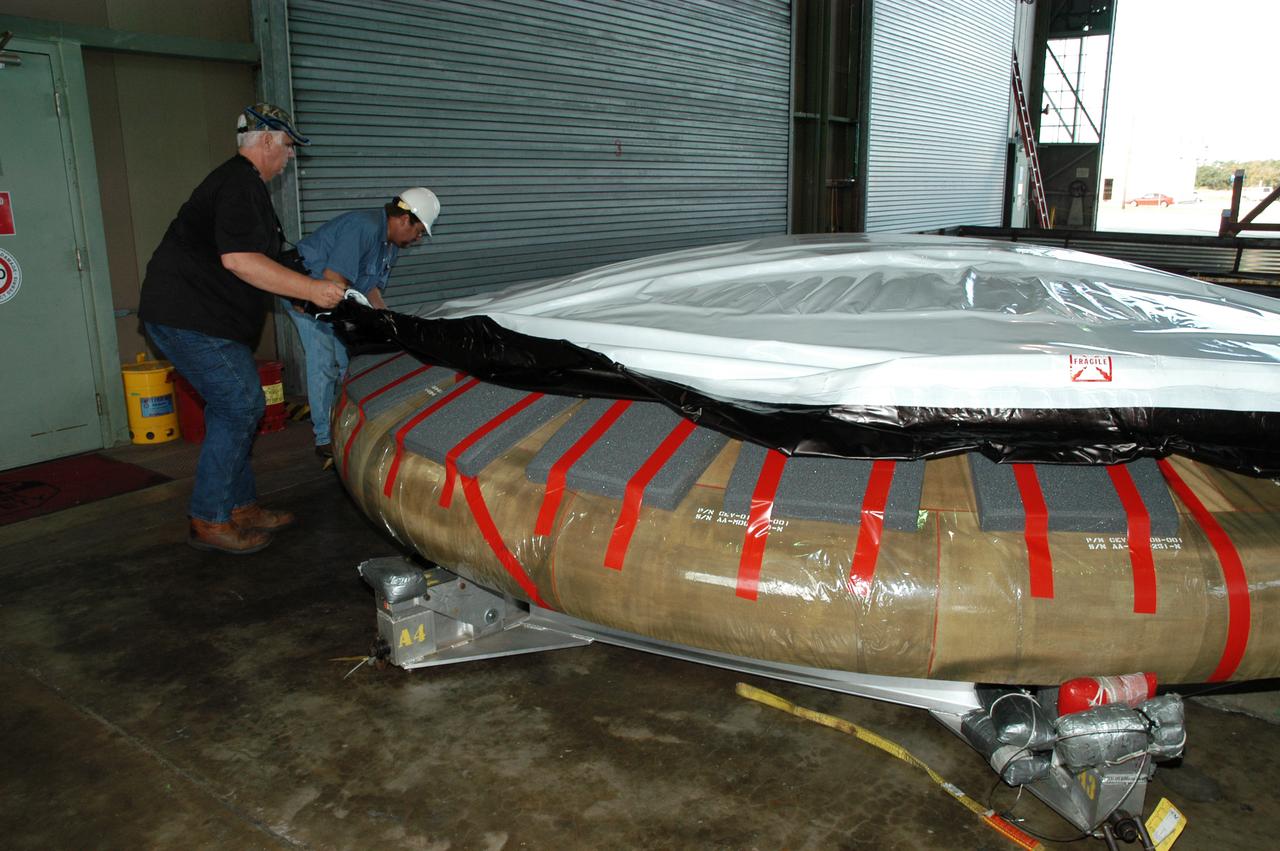

In Hangar N at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a heat shield for the Constellation crew exploration vehicle, or CEV, is being prepared for a demonstration. A developmental heat shield for the Orion spacecraft is being tested and evaluated at Kennedy. The shield was designed and assembled by the Boeing Company in Huntington Beach, Calif., for NASA's Constellation Program. The thermal protection system manufacturing demonstration unit is designed to protect astronauts from extreme heat during re-entry to Earth's atmosphere from low Earth orbit and lunar missions. The CEV will be used to dock and gain access to the International Space Station, travel to the moon in the 2018 timeframe and play a crucial role in exploring Mars.
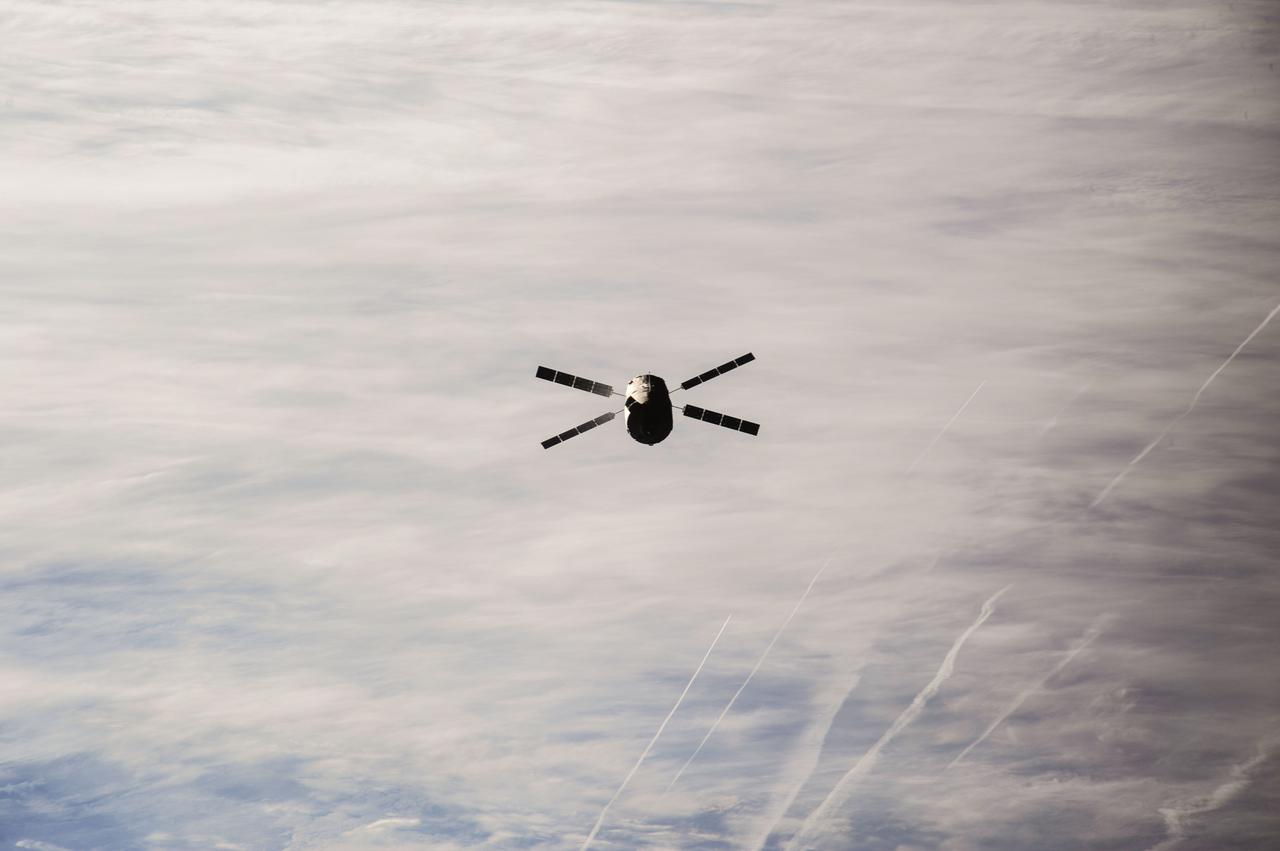

ISS037-E-021215 (28 Oct. 2013) --- The European Space Agency’s fourth Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV-4), also known as the “Albert Einstein,” begins its relative separation from the International Space Station during the Expedition 37 mission. The ATV-4 undocked from the aft port of the Zvezda Service Module at 4:55 a.m. (EDT) Oct. 28, 2013. The ATV, filled with trash and unneeded items, is scheduled to be sent into Earth’s atmosphere for a planned destructive re-entry over an uninhabited area of the south Pacific Ocean on Nov. 2.

At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the news media tour the spaceport's Vehicle Assembly Building. They were briefed on progress to upgrade and modify crawler-transporter CT 2 to support the Space Launch System. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch Dec. 4, 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket, and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
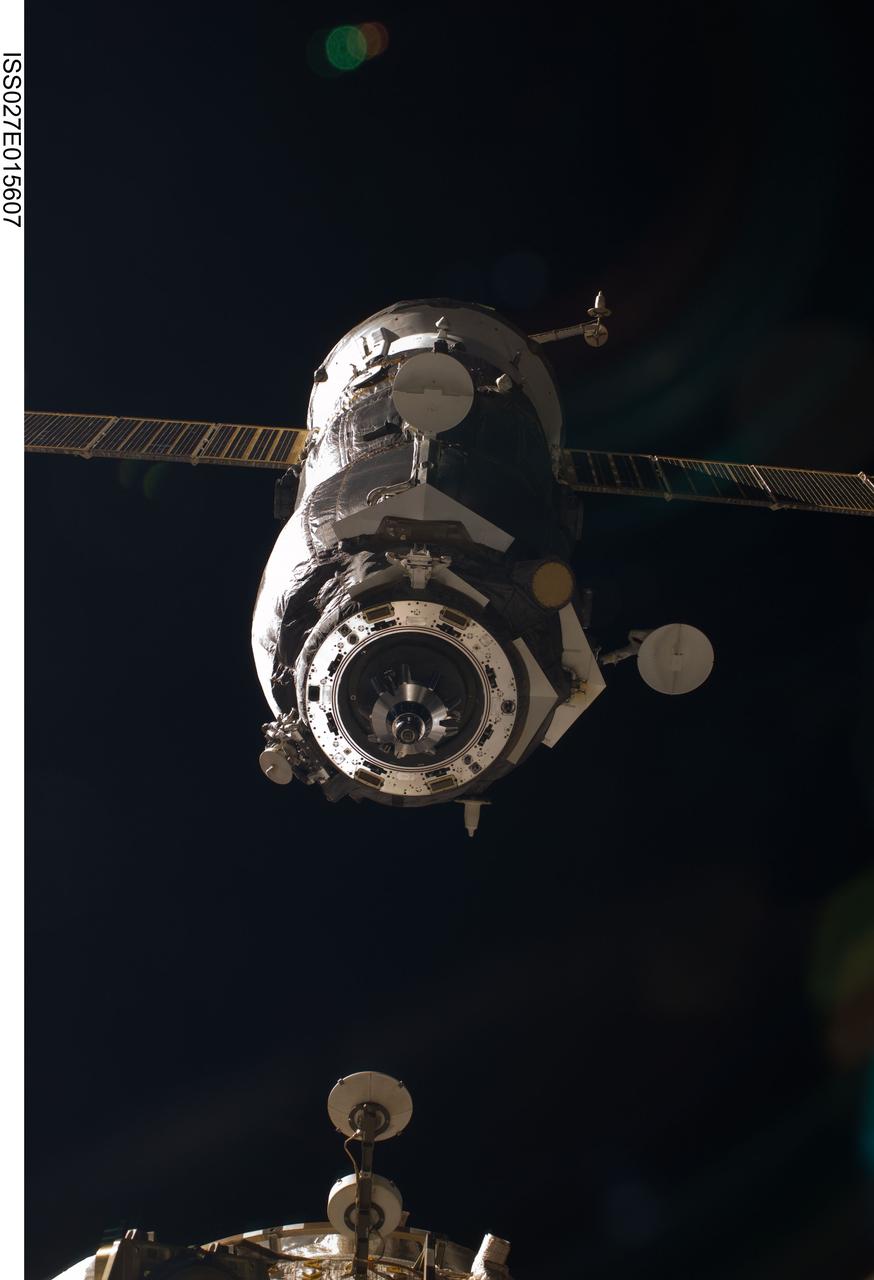

ISS027-E-015607 (22 April 2011) --- The unpiloted ISS Progress 41 supply vehicle departs from the International Space Station at 7:41 a.m. (EDT) on April 22, 2011. Filled with trash and discarded items, Progress 41 will remain in orbit a safe distance from the station for engineering tests before being commanded by flight controllers to descend to a destructive re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean. The departure of Progress 41 clears the way for the next unpiloted supply ship, ISS Progress 42, which is set to launch April 27 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, delivering three tons of food, fuel and supplies for the Expedition 27 crew.
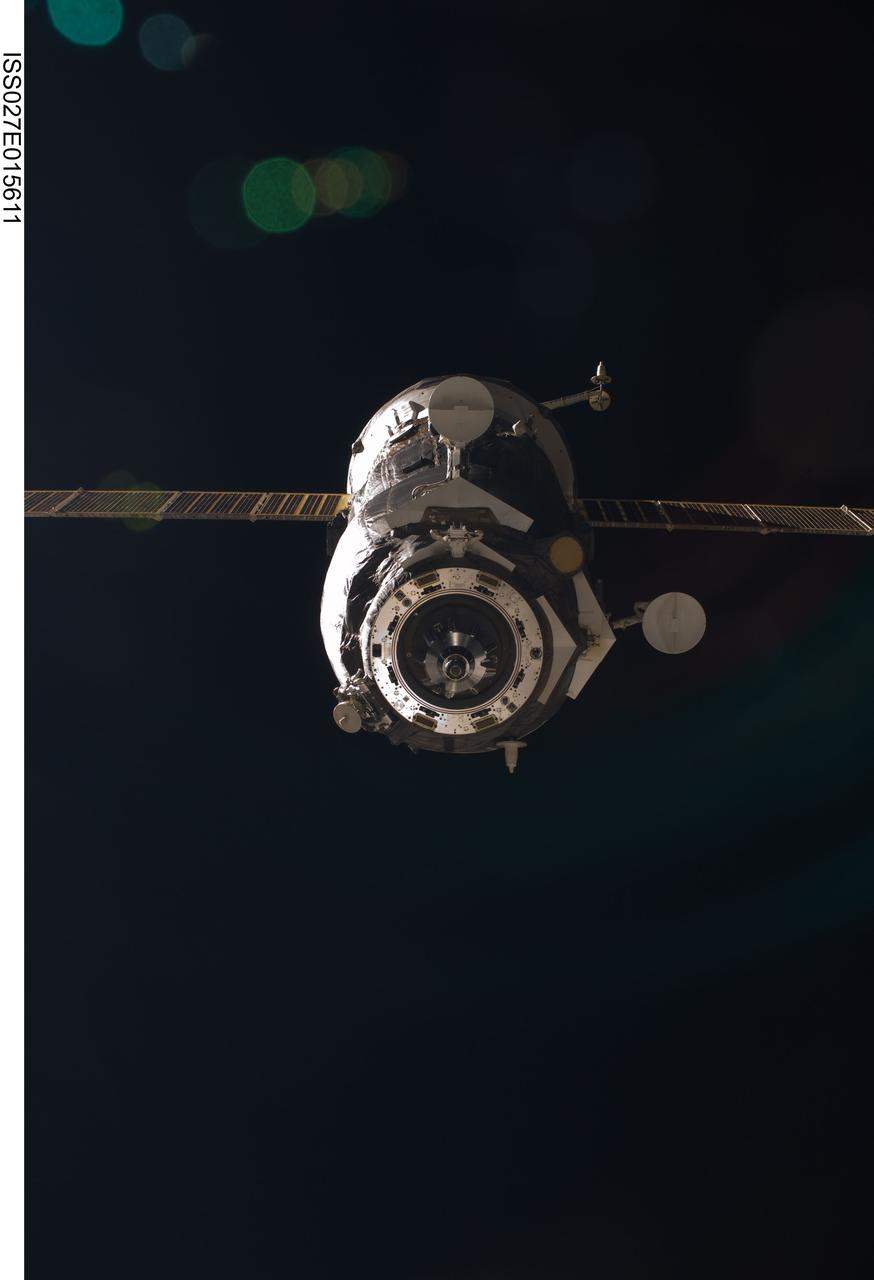

ISS027-E-015611 (22 April 2011) --- The unpiloted ISS Progress 41 supply vehicle departs from the International Space Station at 7:41 a.m. (EDT) on April 22, 2011. Filled with trash and discarded items, Progress 41 will remain in orbit a safe distance from the station for engineering tests before being commanded by flight controllers to descend to a destructive re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean. The departure of Progress 41 clears the way for the next unpiloted supply ship, ISS Progress 42, which is set to launch April 27 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, delivering three tons of food, fuel and supplies for the Expedition 27 crew.
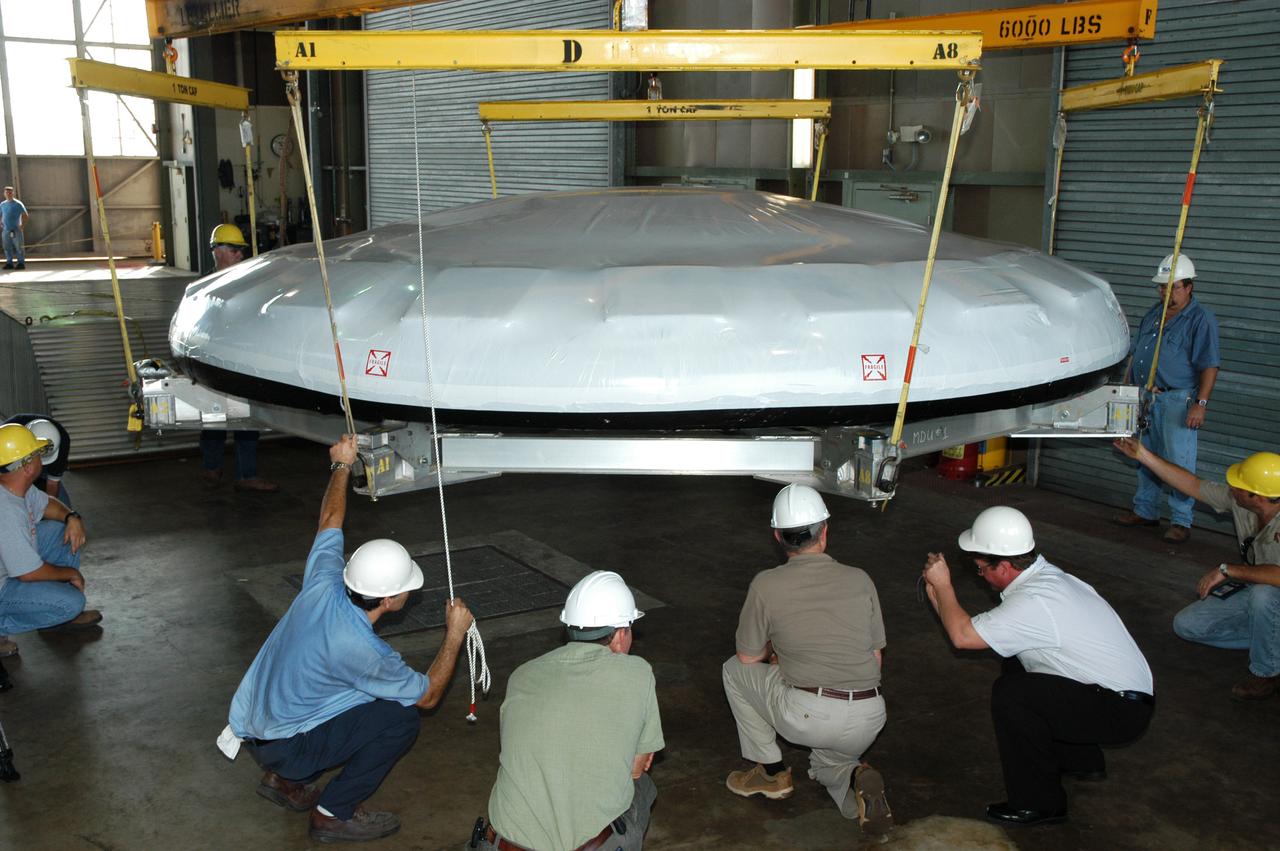

In Hangar N at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a heat shield for the Constellation crew exploration vehicle, or CEV, is being prepared for a demonstration. A developmental heat shield for the Orion spacecraft is being tested and evaluated at Kennedy. The shield was designed and assembled by the Boeing Company in Huntington Beach, Calif., for NASA's Constellation Program. The thermal protection system manufacturing demonstration unit is designed to protect astronauts from extreme heat during re-entry to Earth's atmosphere from low Earth orbit and lunar missions. The CEV will be used to dock and gain access to the International Space Station, travel to the moon in the 2018 timeframe and play a crucial role in exploring Mars.
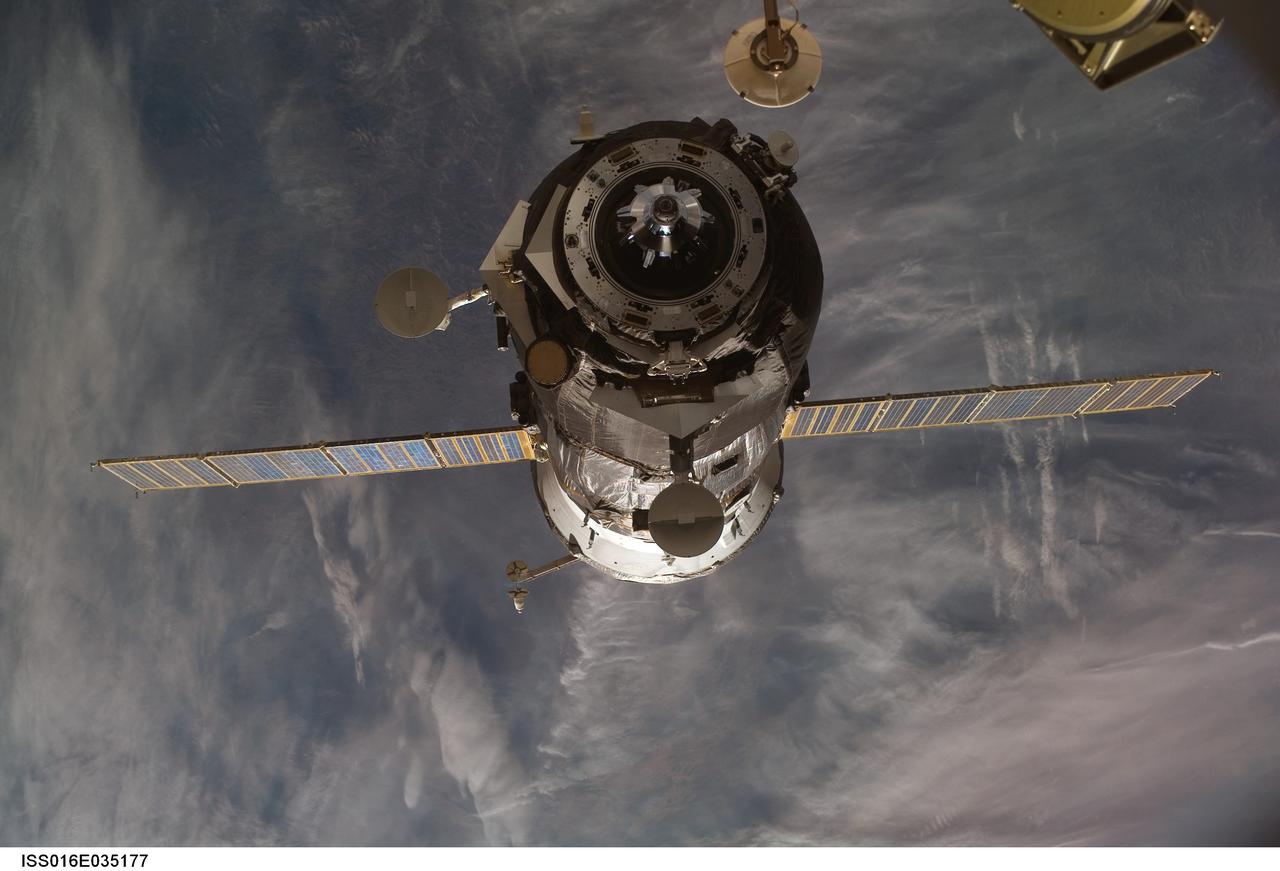

ISS016-E-035177 (7 April 2008) --- An unpiloted Progress 28 resupply vehicle departs from the Pirs Docking Compartment of the International Space Station at 4:50 a.m. (EDT) on Monday, April 7, 2008, and headed into its deorbit and destructive re-entry into Earth's atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean. The Progress, which has been attached to the station since February, had been loaded with trash and discards before its departure. The undocking clears the way for the arrival Thursday of the Soyuz TMA-12 spacecraft carrying the Expedition 17 crew and a South Korean spaceflight participant.
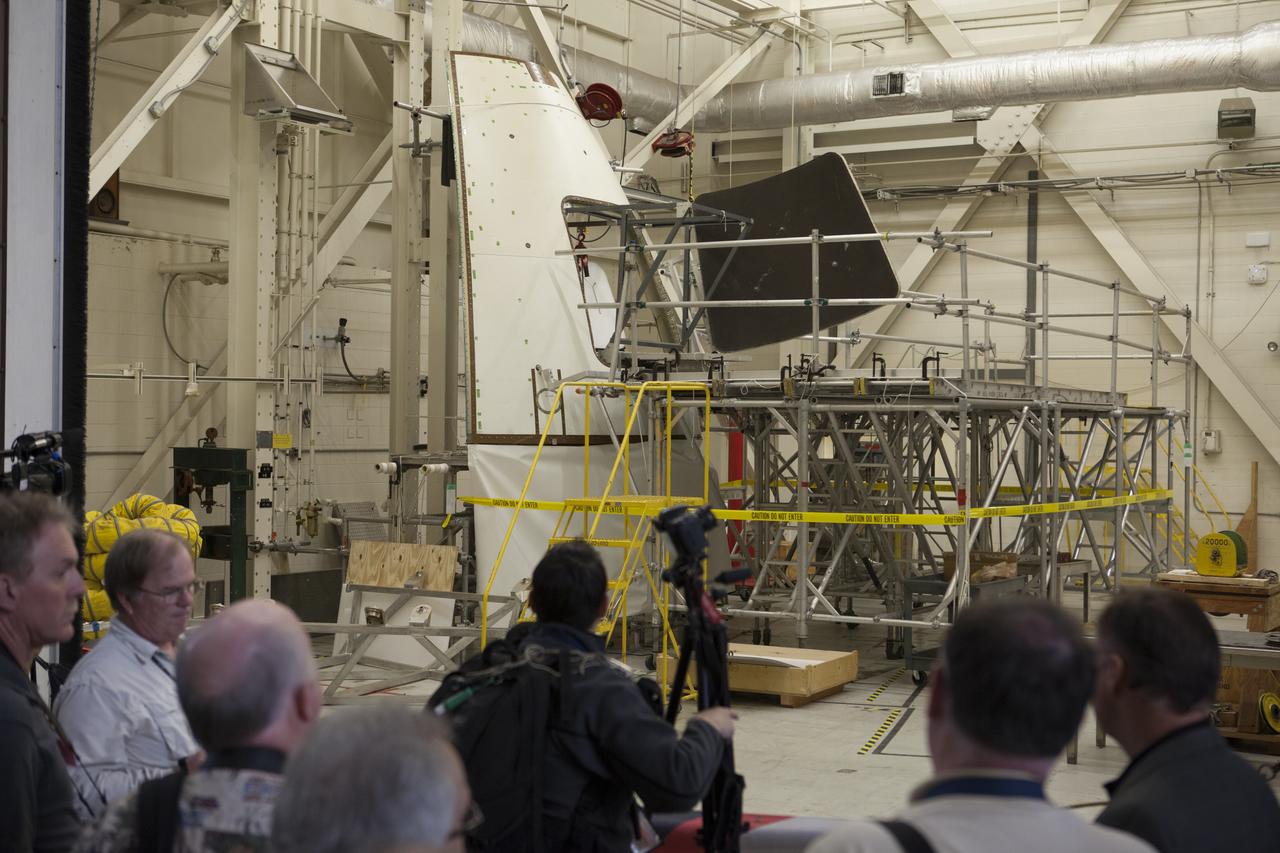

At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the news media tour the spaceport's Vehicle Assembly Building. They were shown an ogive panel which, together with others, cover the Orion spacecraft during launch. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch Dec. 4, 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket, and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
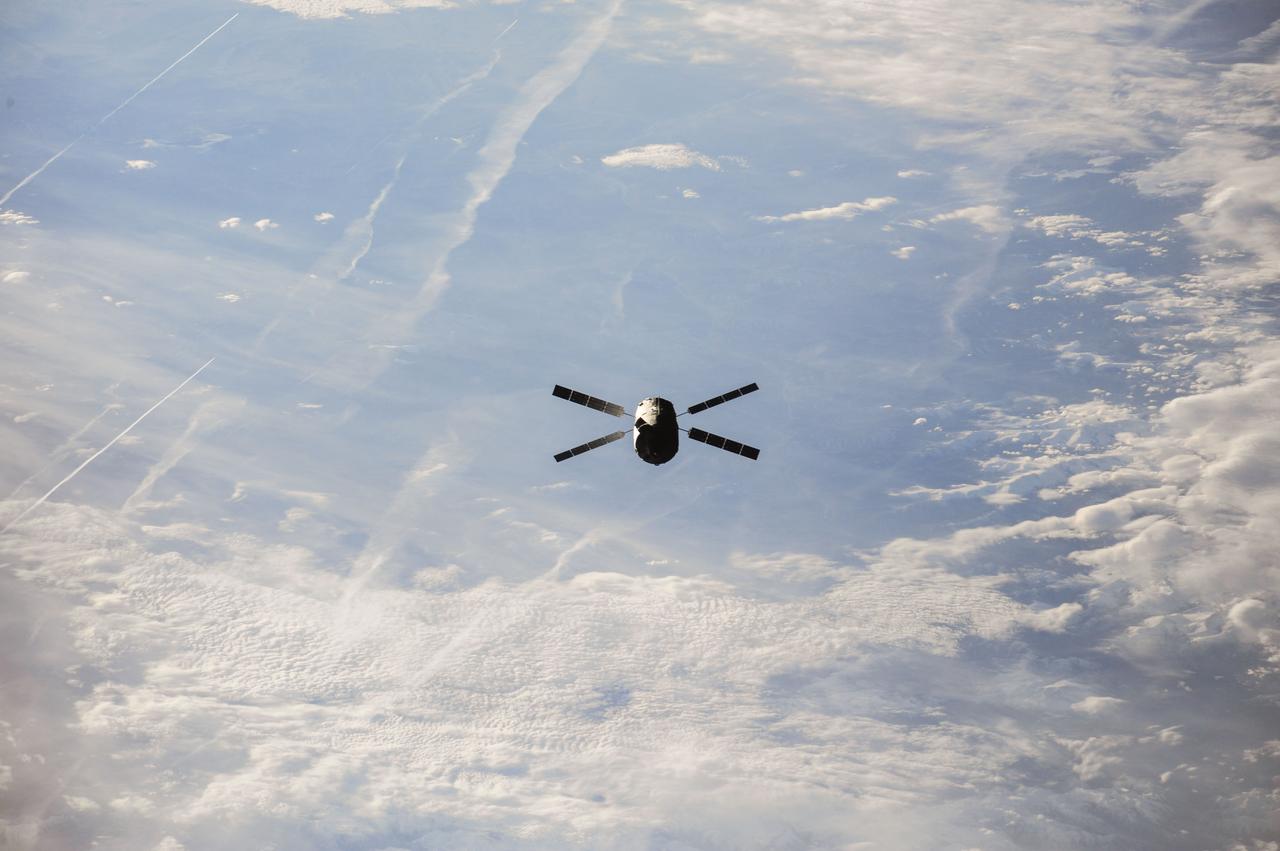

ISS037-E-021218 (28 Oct. 2013) --- The European Space Agency’s fourth Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV-4), also known as the “Albert Einstein,” begins its relative separation from the International Space Station during the Expedition 37 mission. The ATV-4 undocked from the aft port of the Zvezda Service Module at 4:55 a.m. (EDT) Oct. 28, 2013. The ATV, filled with trash and unneeded items, is scheduled to be sent into Earth’s atmosphere for a planned destructive re-entry over an uninhabited area of the south Pacific Ocean on Nov. 2.
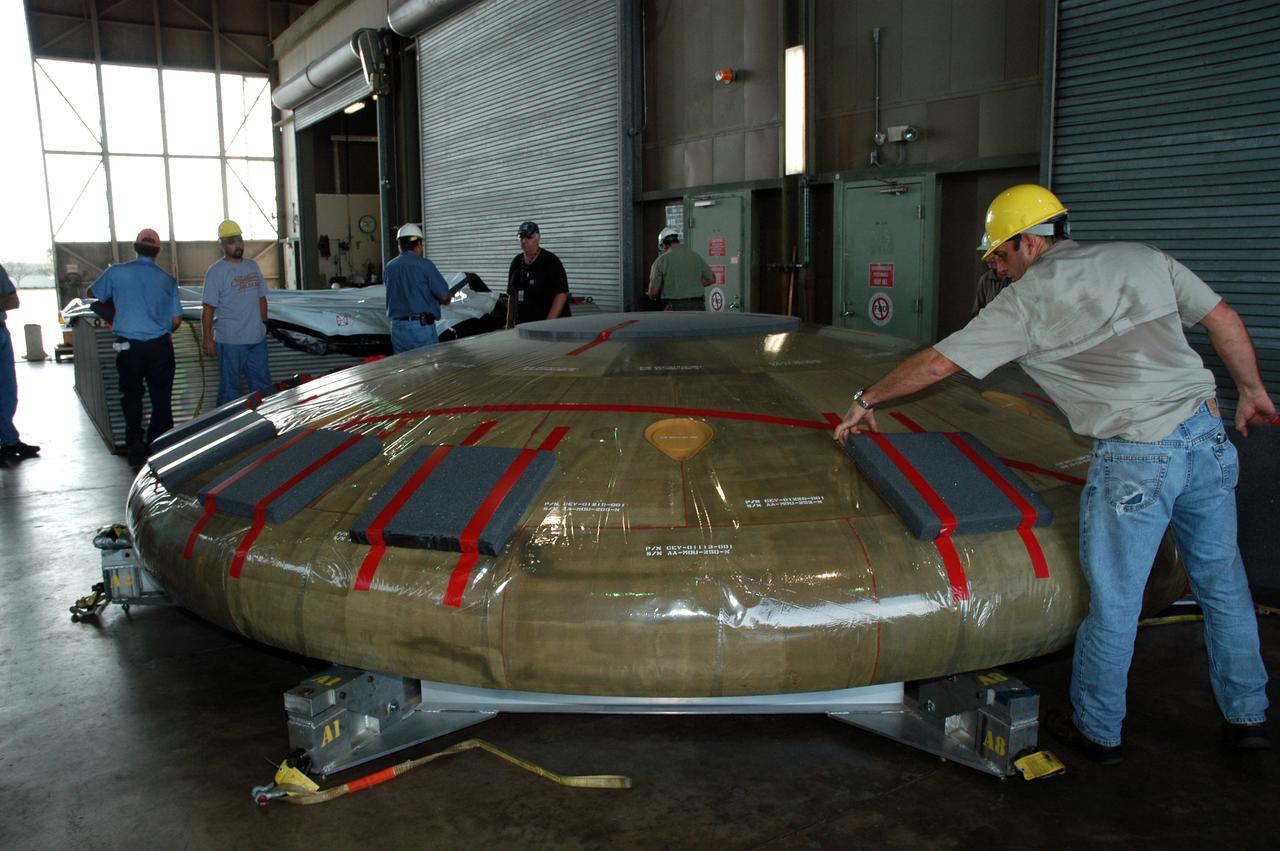

In Hangar N at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a heat shield for the Constellation crew exploration vehicle, or CEV, is being prepared for a demonstration. A developmental heat shield for the Orion spacecraft is being tested and evaluated at Kennedy. The shield was designed and assembled by the Boeing Company in Huntington Beach, Calif., for NASA's Constellation Program. The thermal protection system manufacturing demonstration unit is designed to protect astronauts from extreme heat during re-entry to Earth's atmosphere from low Earth orbit and lunar missions. The CEV will be used to dock and gain access to the International Space Station, travel to the moon in the 2018 timeframe and play a crucial role in exploring Mars.
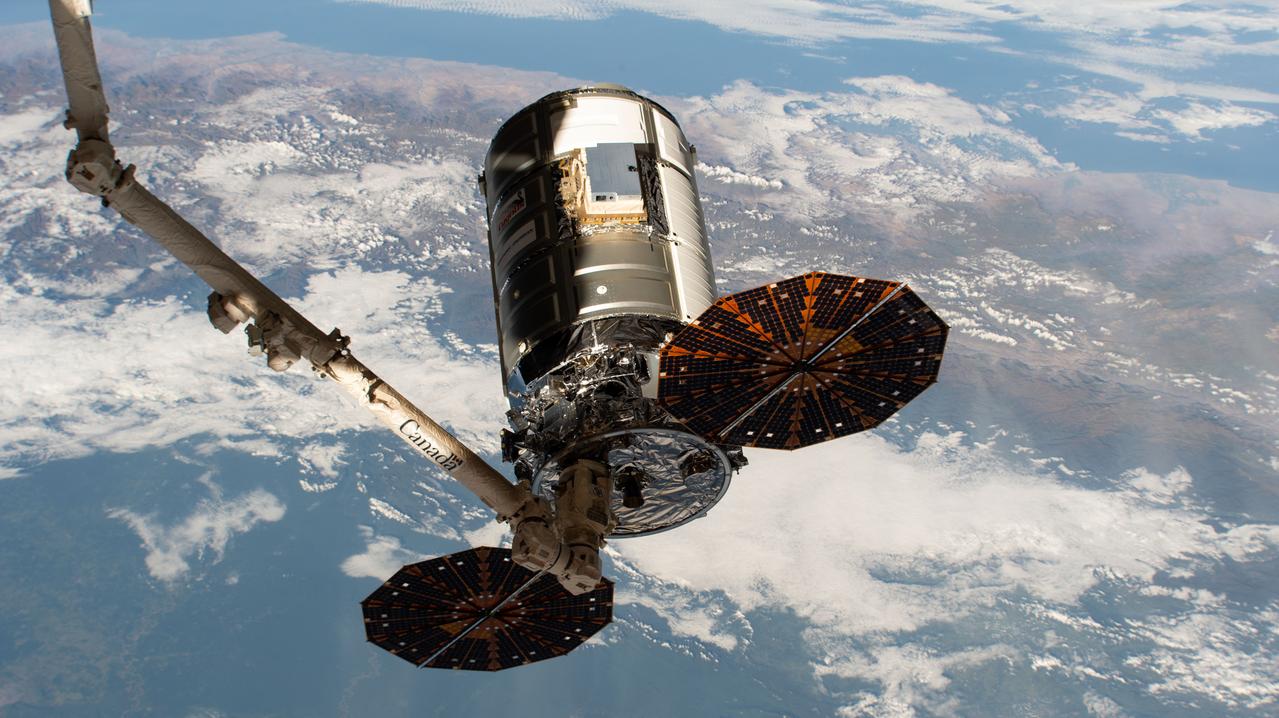

iss063e010583 (May 11, 2020) --- The Northrop Grumman (NG)-13 Cygnus vehicle (S.S. Robert Henry Lawrence Jr.) cargo craft is pictured in the grips of the Canadarm2 robotic arm shortly before its departure from the International Space Station (ISS) for a destructive re-entry over the South Pacific Ocean. Seen in the view is the High Definition Earth Viewing (HDEV) payload attached to the Cygnus. The HDEV experiment, deployed and activated in April 2014, placed four commercially available HD cameras on the exterior of the space station and used them to stream live video of Earth for viewing online. Almost 350 million viewers visited the site over HDEV’s life span.
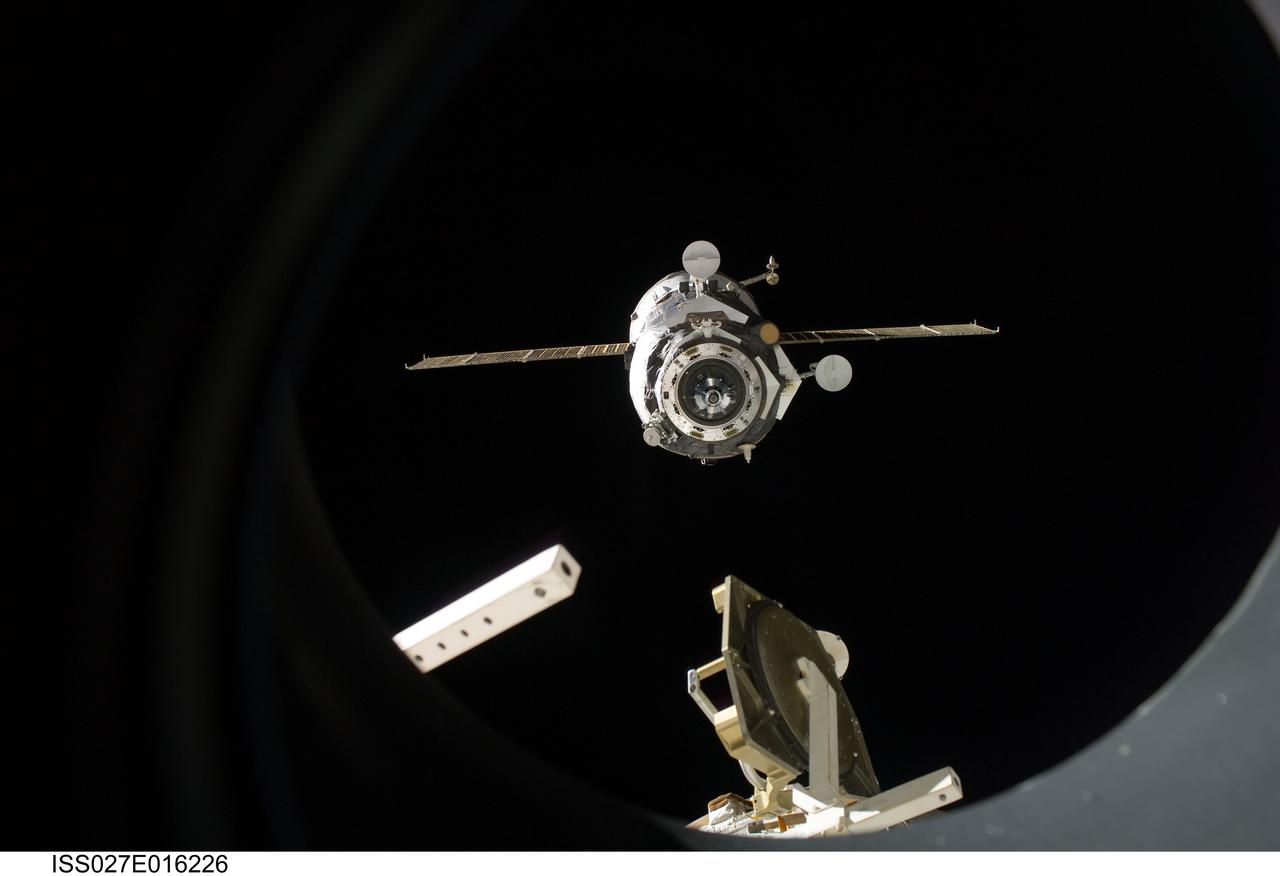

ISS027-E-016226 (22 April 2011) --- The unpiloted ISS Progress 41 supply vehicle departs from the International Space Station at 7:41 a.m. (EDT) on April 22, 2011. Filled with trash and discarded items, Progress 41 will remain in orbit a safe distance from the station for engineering tests before being commanded by flight controllers to descend to a destructive re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean. The departure of Progress 41 clears the way for the next unpiloted supply ship, ISS Progress 42, which is set to launch April 27 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, delivering three tons of food, fuel and supplies for the Expedition 27 crew.