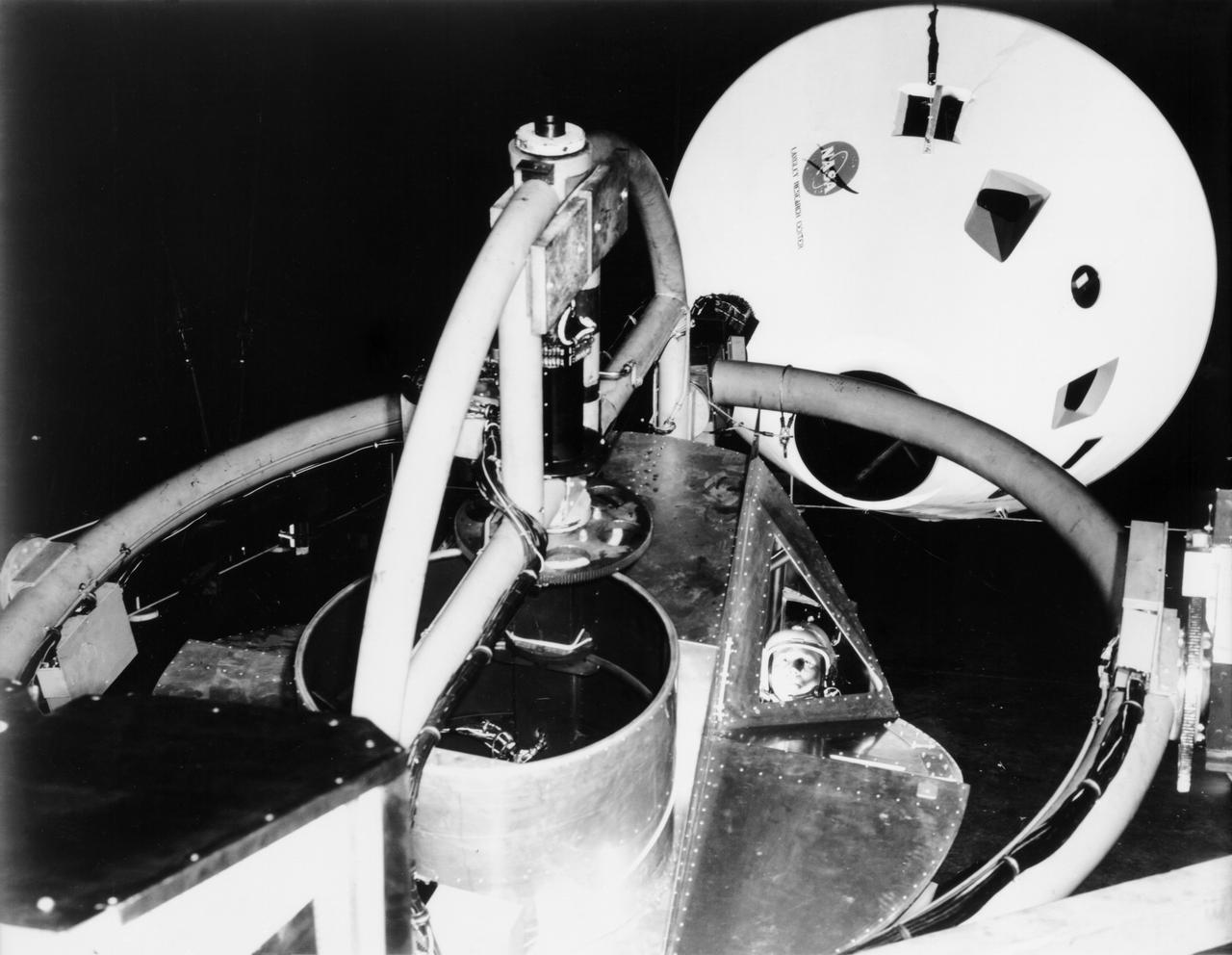

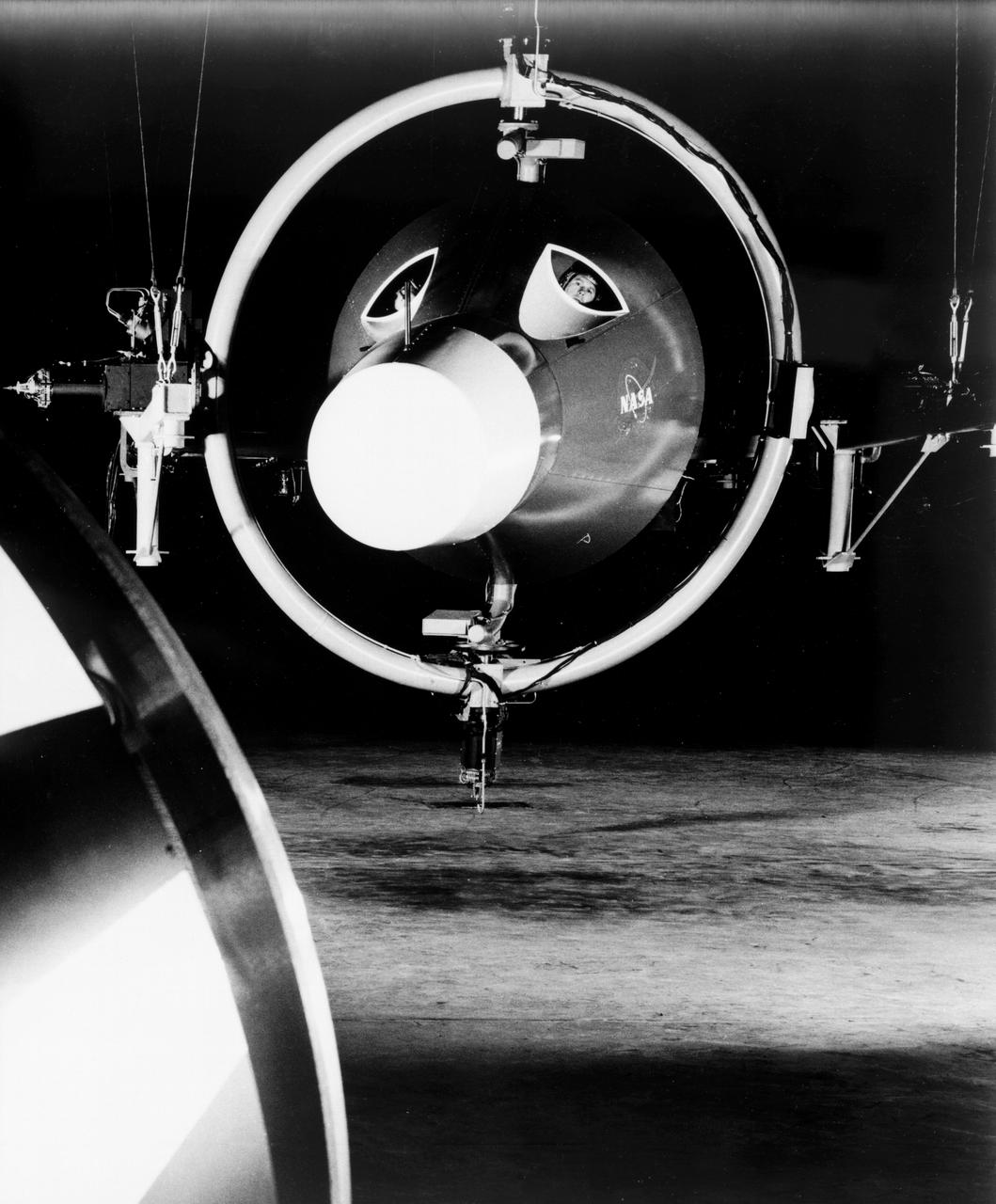
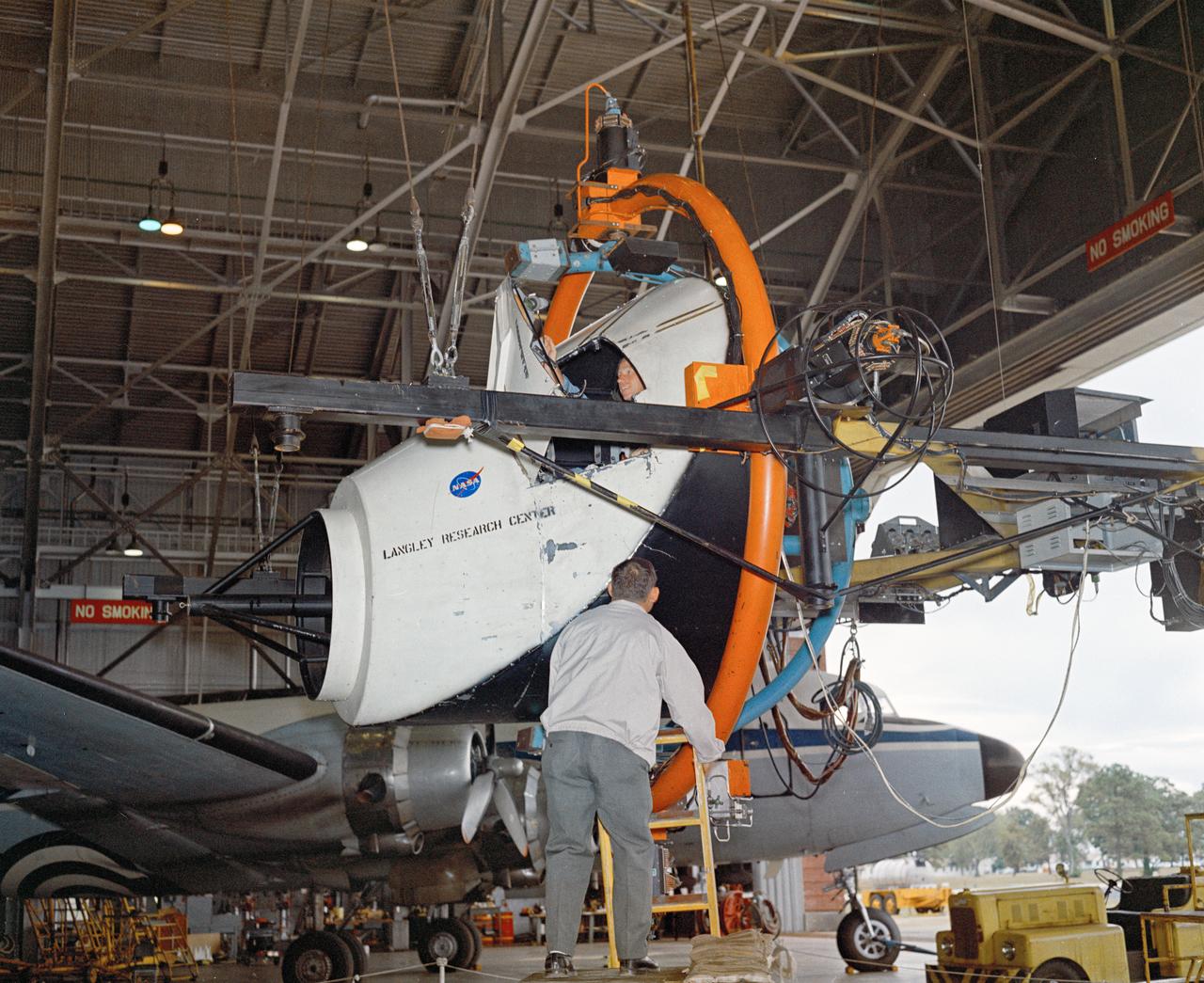
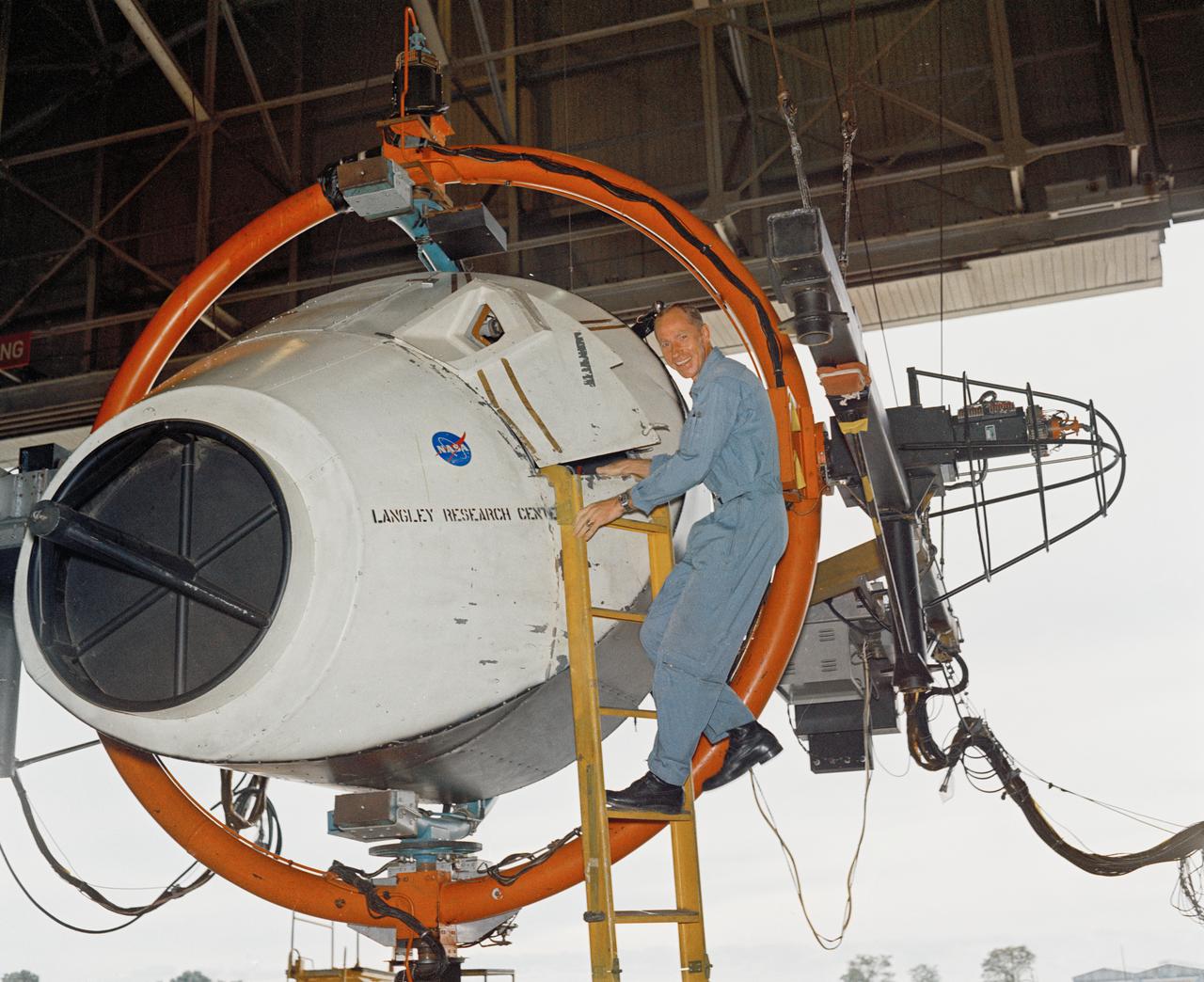
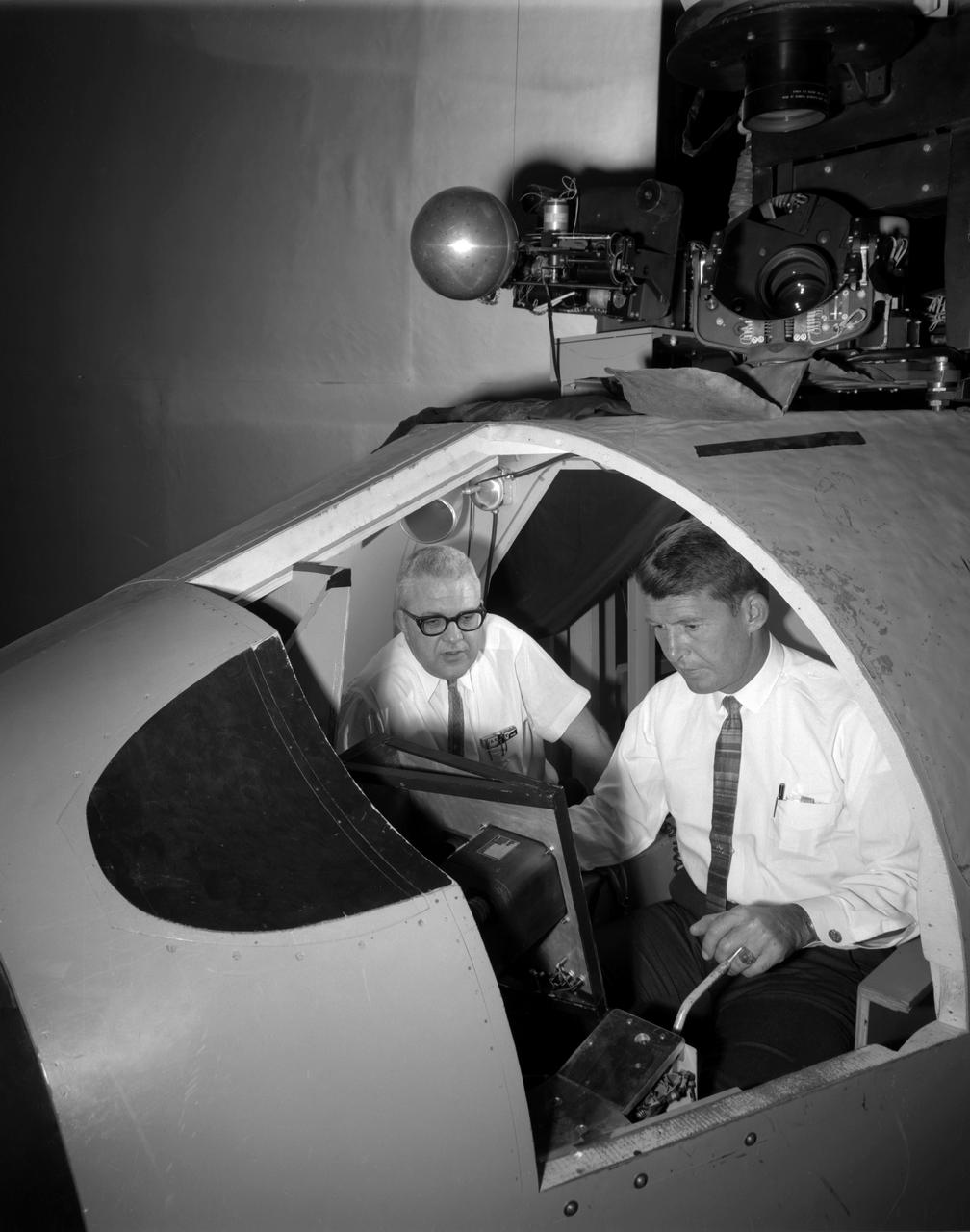
Originally the Rendezvous was used by the astronauts preparing for Gemini missions. The Rendezvous Docking Simulator was then modified and used to develop docking techniques for the Apollo program. "The LEM pilot's compartment, with overhead window and the docking ring (idealized since the pilot cannot see it during the maneuvers), is shown docked with the full-scale Apollo Command Module." A.W. Vogeley described the simulator as follows: "The Rendezvous Docking Simulator and also the Lunar Landing Research Facility are both rather large moving-base simulators. It should be noted, however, that neither was built primarily because of its motion characteristics. The main reason they were built was to provide a realistic visual scene. A secondary reason was that they would provide correct angular motion cues (important in control of vehicle short-period motions) even though the linear acceleration cues would be incorrect." -- Published in A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27 - December 1, 1966;
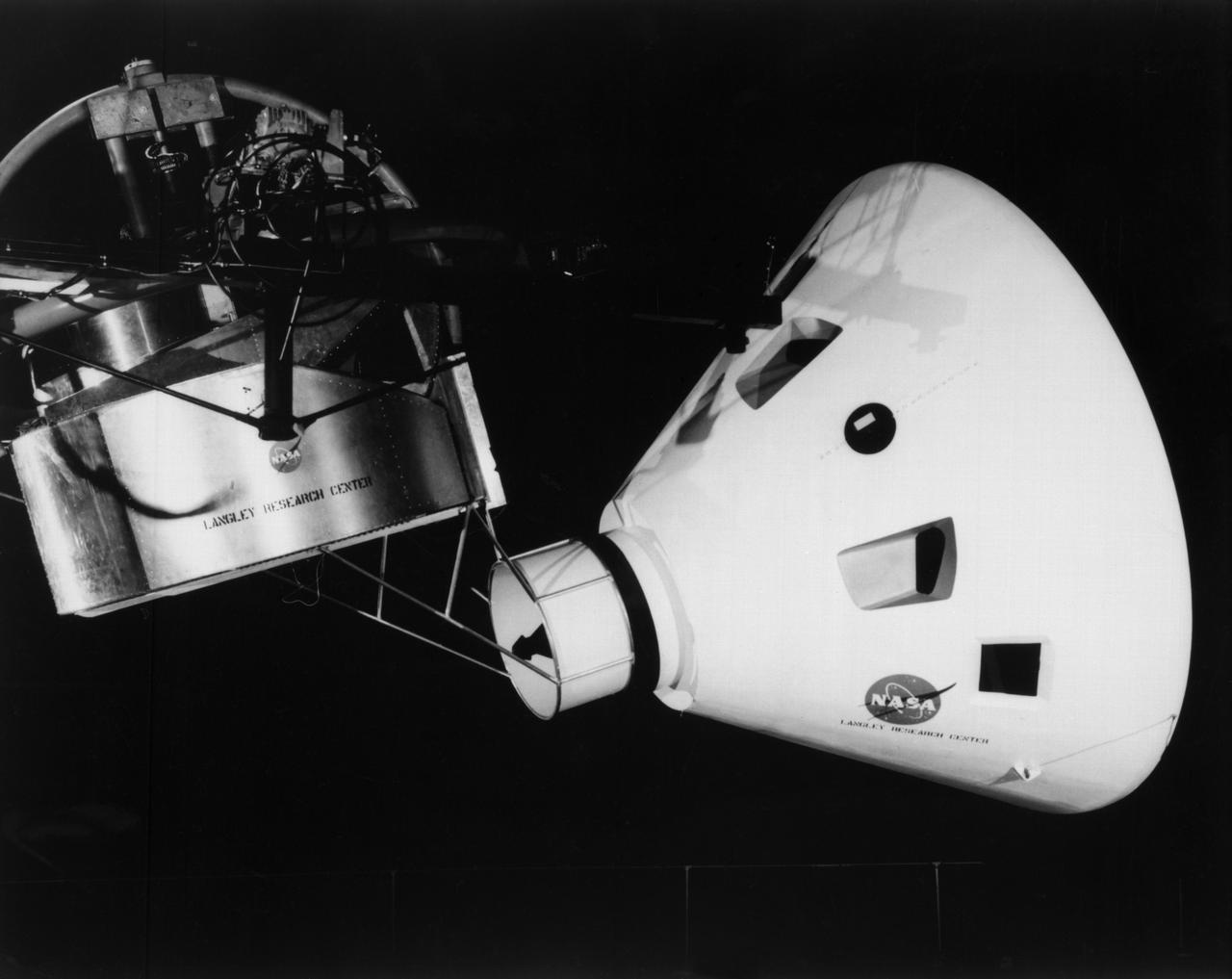
Originally the Rendezvous was used by the astronauts preparing for Gemini missions. The Rendezvous Docking Simulator was then modified and used to develop docking techniques for the Apollo program. "The LEM pilot's compartment, with overhead window and the docking ring (idealized since the pilot cannot see it during the maneuvers), is shown docked with the full-scale Apollo Command Module." A.W. Vogeley described the simulator as follows: "The Rendezvous Docking Simulator and also the Lunar Landing Research Facility are both rather large moving-base simulators. It should be noted, however, that neither was built primarily because of its motion characteristics. The main reason they were built was to provide a realistic visual scene. A secondary reason was that they would provide correct angular motion cues (important in control of vehicle short-period motions) even though the linear acceleration cues would be incorrect." -- Published in A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27 - December 1, 1966;
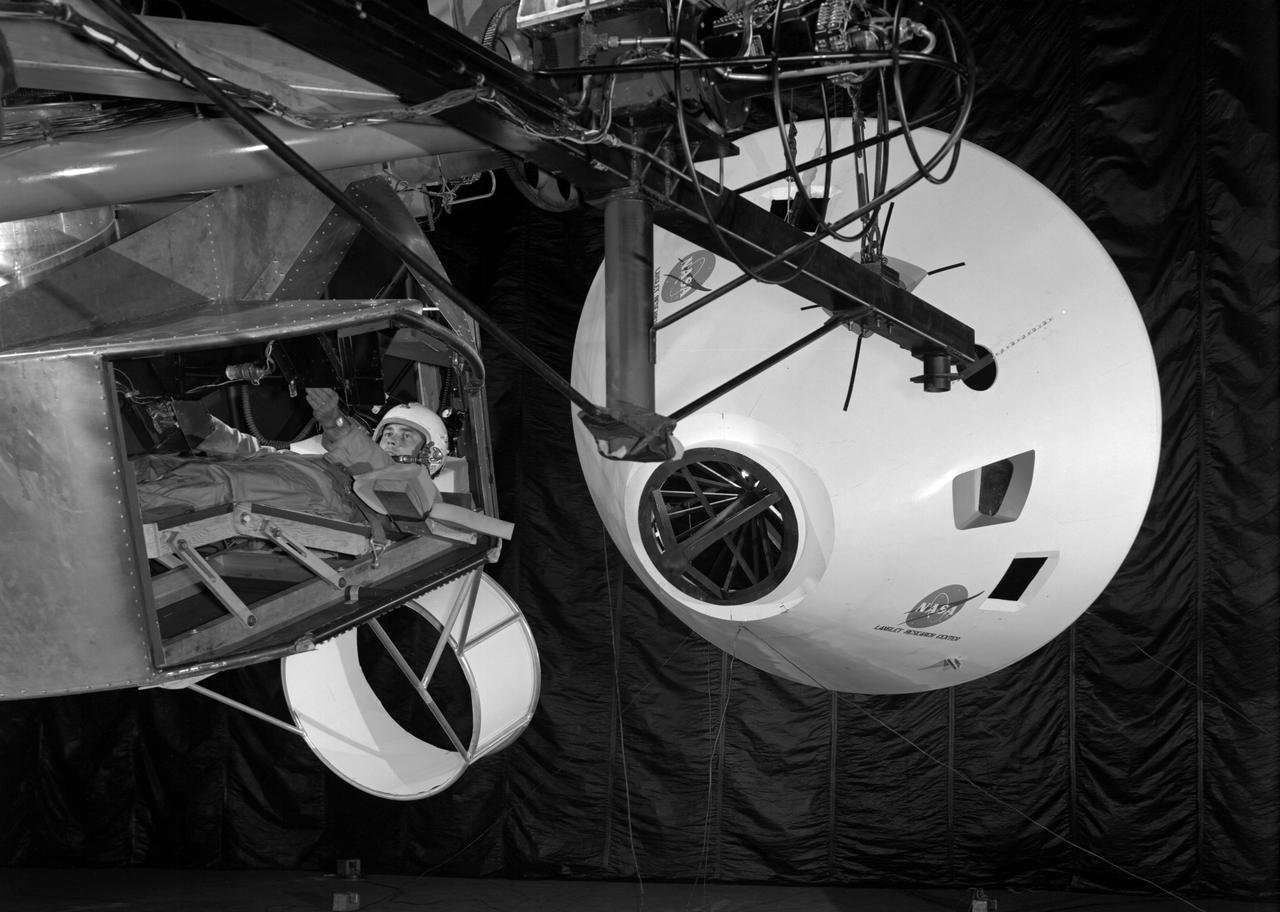

Originally the Rendezvous was used by the astronauts preparing for Gemini missions. The Rendezvous Docking Simulator was then modified and used to develop docking techniques for the Apollo program. The pilot is shown maneuvering the LEM into position for docking with a full-scale Apollo Command Module. From A.W. Vogeley, Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center, Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27 - December 1, 1966. The Rendezvous Docking Simulator and also the Lunar Landing Research Facility are both rather large moving-base simulators. It should be noted, however, that neither was built primarily because of its motion characteristics. The main reason they were built was to provide a realistic visual scene. A secondary reason was that they would provide correct angular motion cues (important in control of vehicle short-period motions) even though the linear acceleration cues would be incorrect. Apollo Rendezvous Docking Simulator: Langley s Rendezvous Docking Simulator was developed by NASA scientists to study the complex task of docking the Lunar Excursion Module with the Command Module in Lunar orbit.
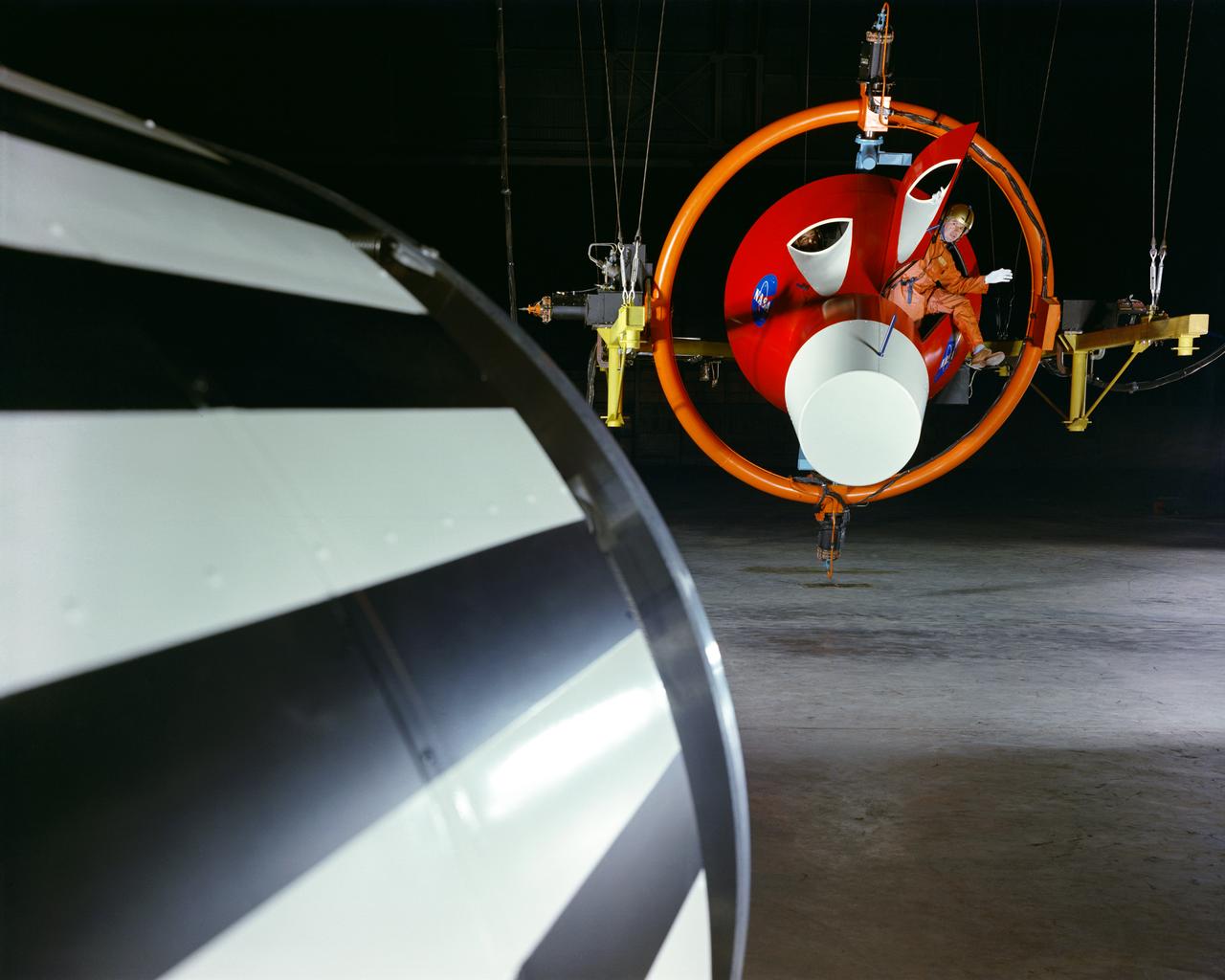

Practicing with a full-scale model of the Gemini Capsule in Langley's Rendezvous Docking Simulator. -- Caption and photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, (page 89), by James Schultz.
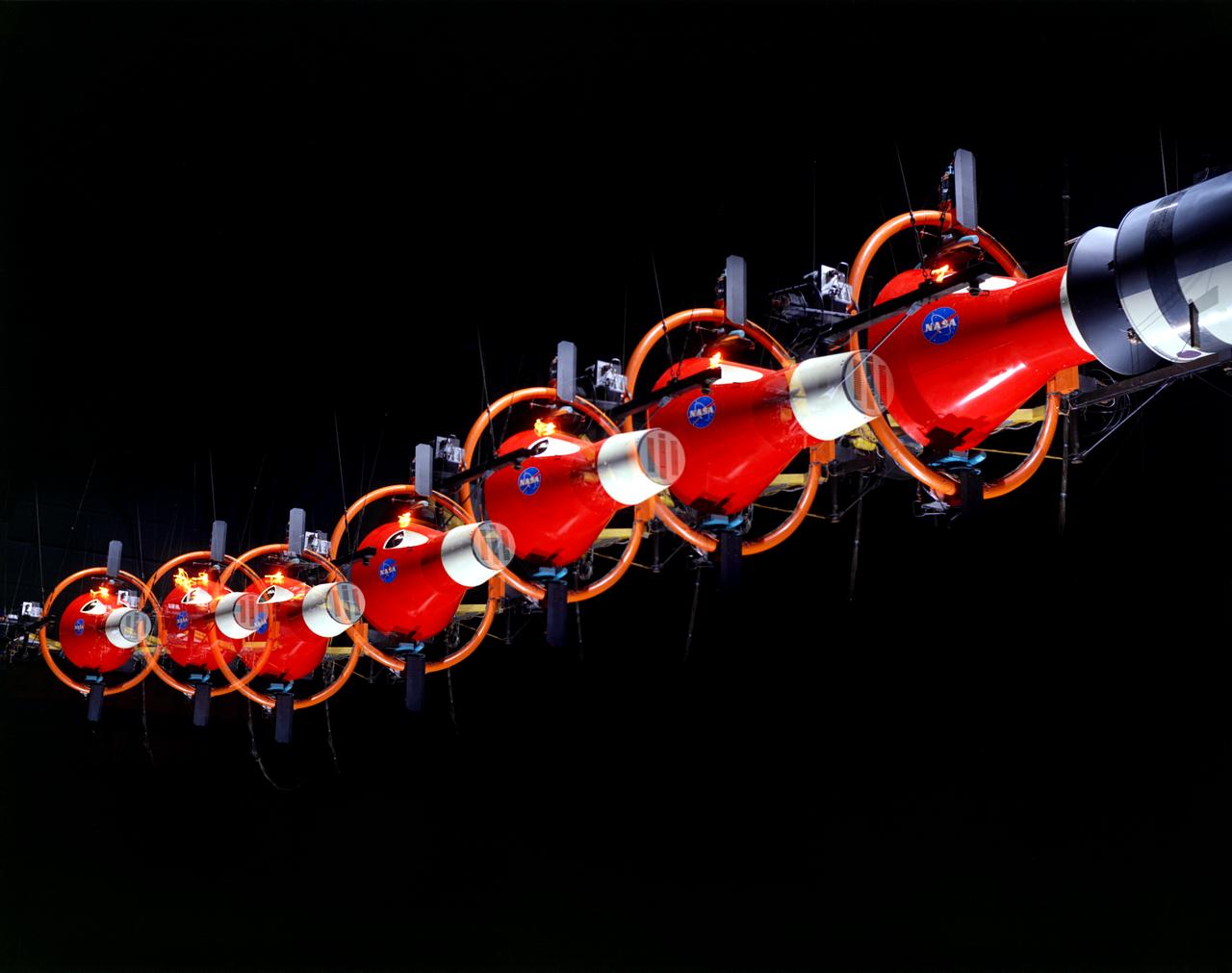
![Multiple exposure of Gemini rendezvous docking simulator. Francis B. Smith wrote in his paper "Simulators for Manned Space Research," "The rendezvous and docking operation of the Gemini spacecraft with the Agena and of the Apollo Command Module with the Lunar Excursion Module have been the subject of simulator studies for several years. [This figure] illustrates the Gemini-Agena rendezvous docking simulator at Langley. The Gemini spacecraft was supported in a gimbal system by an overhead crane and gantry arrangement which provided 6 degrees of freedom - roll, pitch, yaw, and translation in any direction - all controllable by the astronaut in the spacecraft. Here again the controls fed into a computer which in turn provided an input to the servos driving the spacecraft so that it responded to control motions in a manner which accurately simulated the Gemini spacecraft." A.W. Vogeley further described the simulator in his paper "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," "Docking operations are considered to start when the pilot first can discern vehicle target size and aspect and terminate, of course, when soft contact is made. ... This facility enables simulation of the docking operation from a distance of 200 feet to actual contact with the target. A full-scale mock-up of the target vehicle is suspended near one end of the track. ... On [the Agena target] we have mounted the actual Agena docking mechanism and also various types of visual aids. We have been able to devise visual aids which have made it possible to accomplish nighttime docking with as much success as daytime docking." -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203; Francis B. Smith, "Simulators for Manned Space Research," Paper presented at the 1966 IEEE International convention, March 21-25, 1966; A.W. Vogeley, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," Paper presented at the Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, August 17-21, 1964.](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/LRC-1963-B701_P-08973/LRC-1963-B701_P-08973~medium.jpg)
Multiple exposure of Gemini rendezvous docking simulator. Francis B. Smith wrote in his paper "Simulators for Manned Space Research," "The rendezvous and docking operation of the Gemini spacecraft with the Agena and of the Apollo Command Module with the Lunar Excursion Module have been the subject of simulator studies for several years. [This figure] illustrates the Gemini-Agena rendezvous docking simulator at Langley. The Gemini spacecraft was supported in a gimbal system by an overhead crane and gantry arrangement which provided 6 degrees of freedom - roll, pitch, yaw, and translation in any direction - all controllable by the astronaut in the spacecraft. Here again the controls fed into a computer which in turn provided an input to the servos driving the spacecraft so that it responded to control motions in a manner which accurately simulated the Gemini spacecraft." A.W. Vogeley further described the simulator in his paper "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," "Docking operations are considered to start when the pilot first can discern vehicle target size and aspect and terminate, of course, when soft contact is made. ... This facility enables simulation of the docking operation from a distance of 200 feet to actual contact with the target. A full-scale mock-up of the target vehicle is suspended near one end of the track. ... On [the Agena target] we have mounted the actual Agena docking mechanism and also various types of visual aids. We have been able to devise visual aids which have made it possible to accomplish nighttime docking with as much success as daytime docking." -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203; Francis B. Smith, "Simulators for Manned Space Research," Paper presented at the 1966 IEEE International convention, March 21-25, 1966; A.W. Vogeley, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," Paper presented at the Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, August 17-21, 1964.
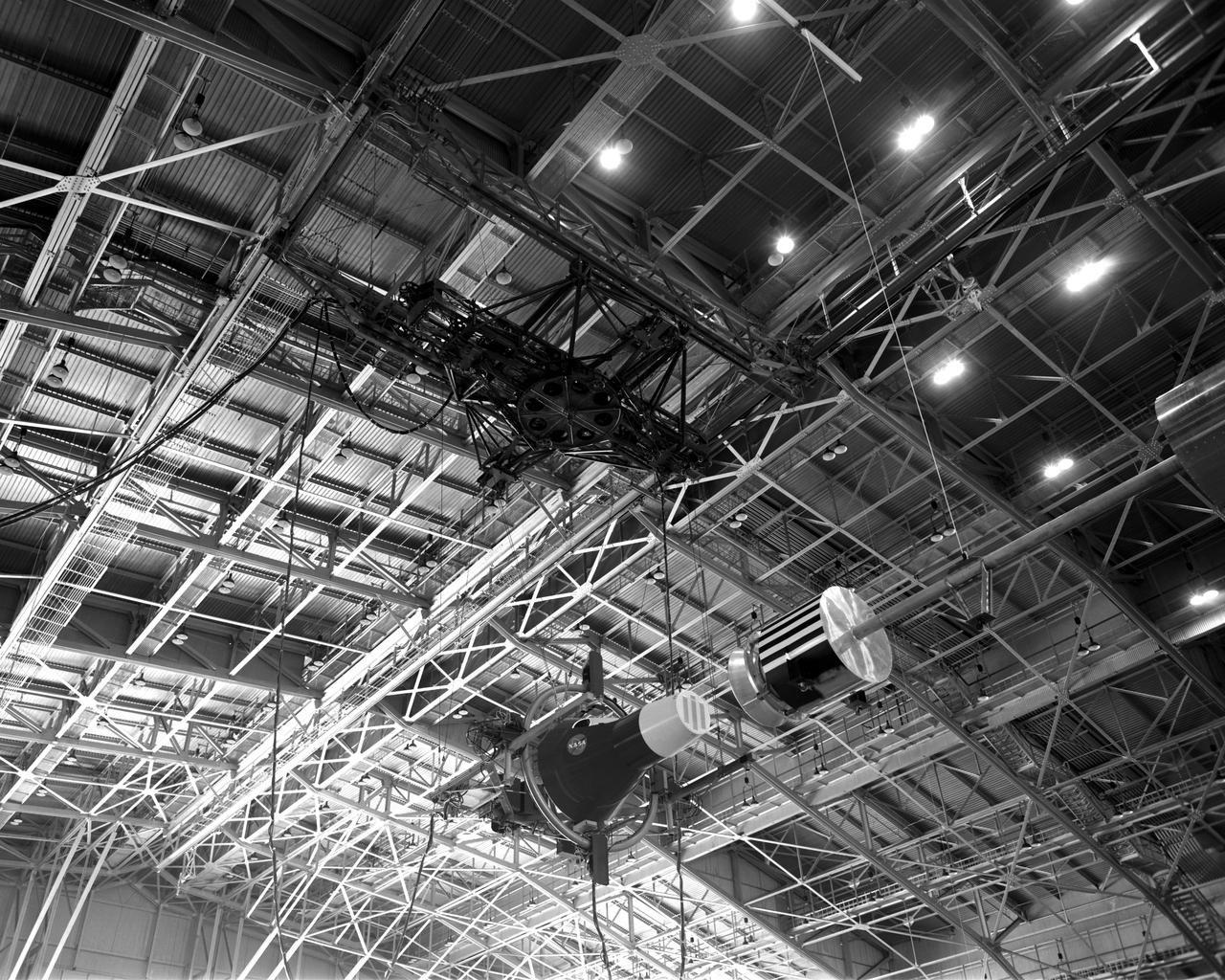

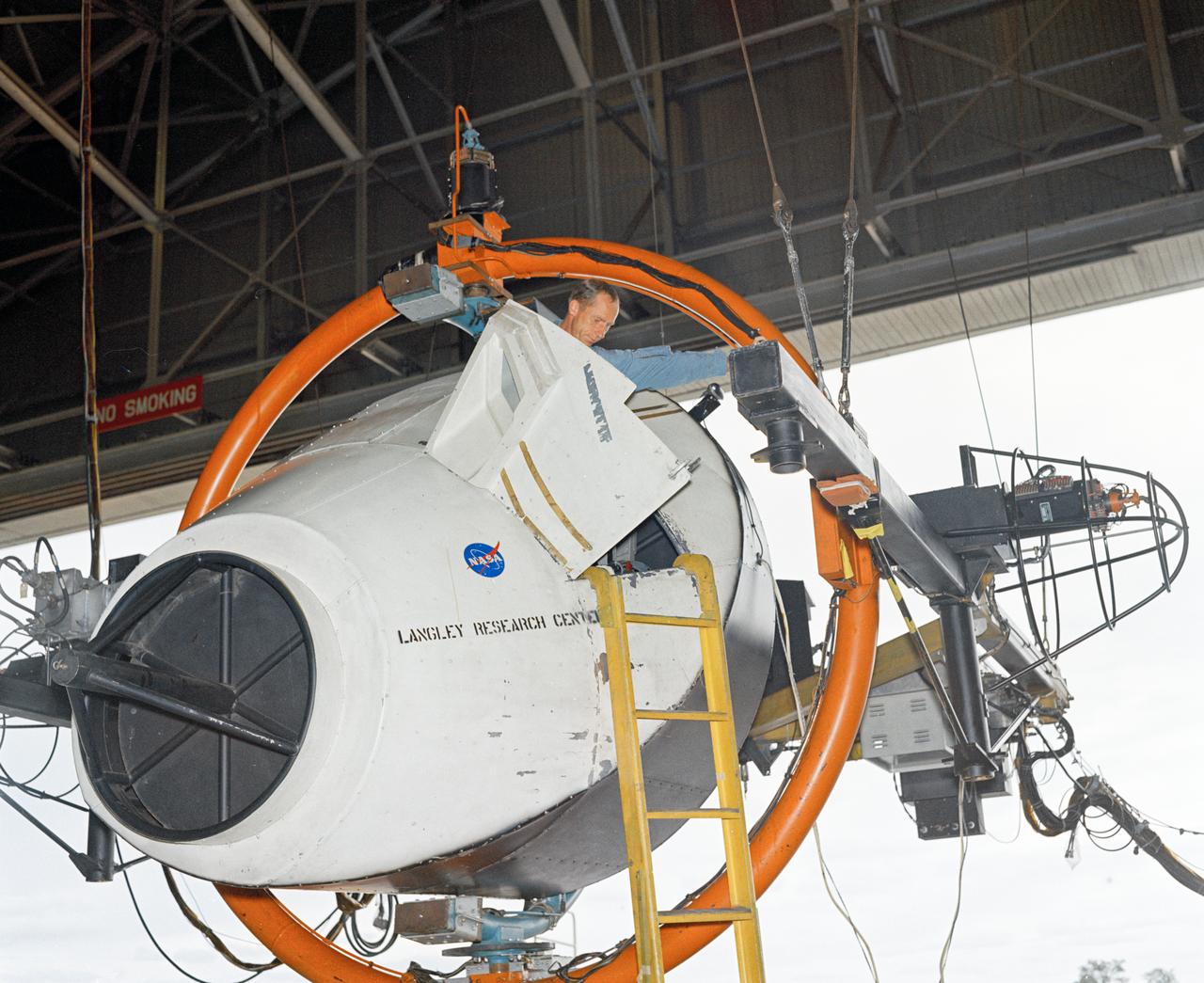
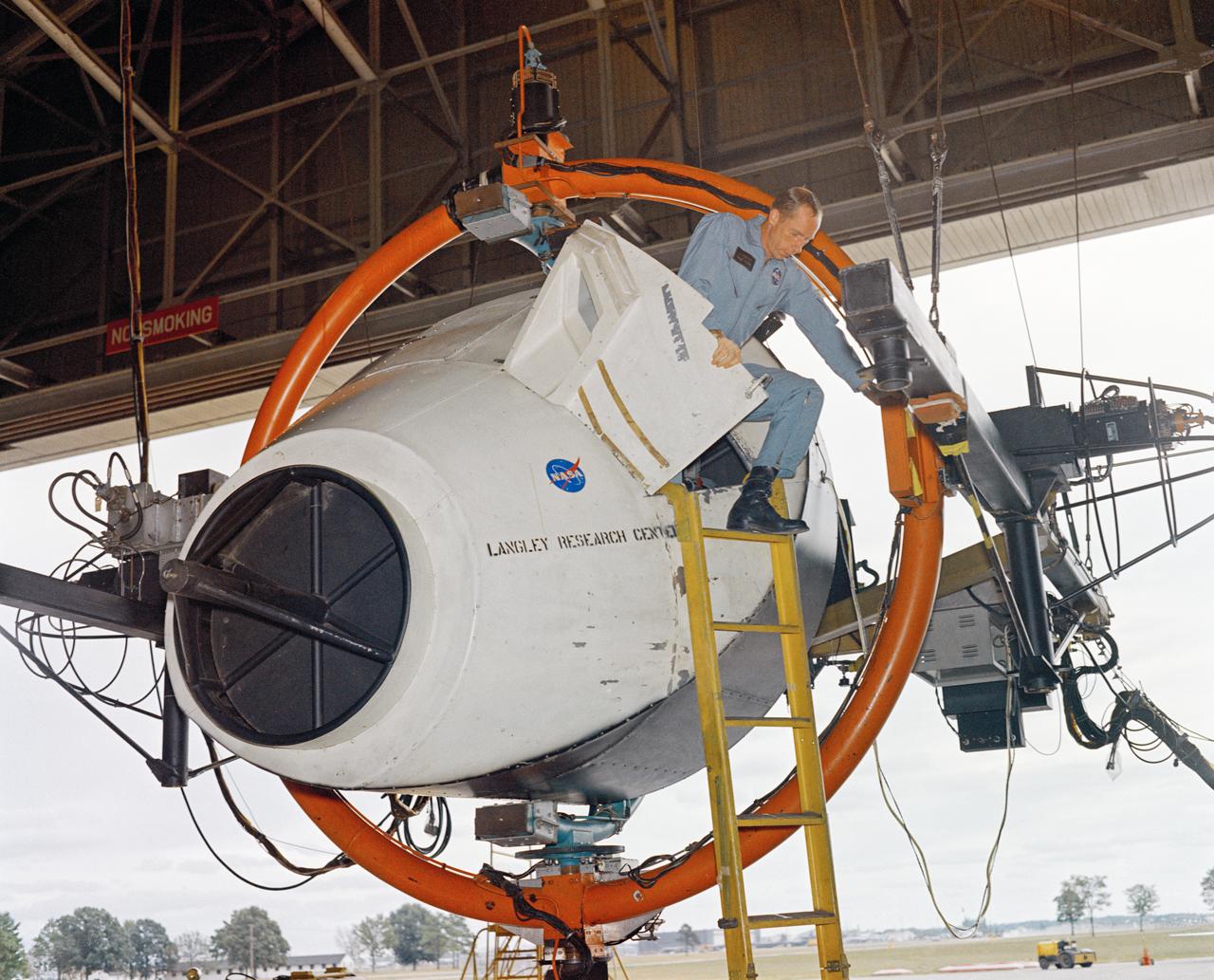
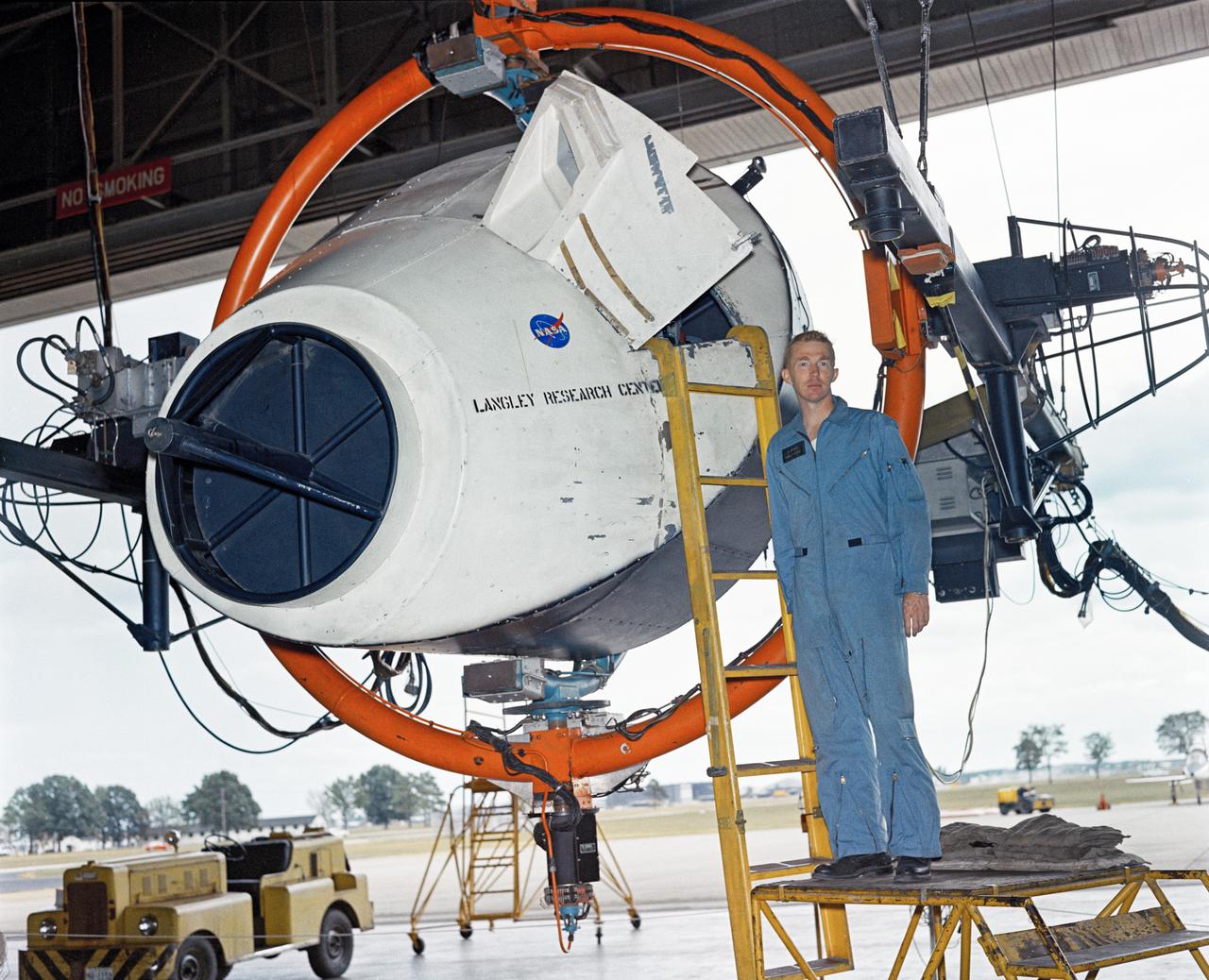
Rendezvous Docking Simulator Suspended From the Roof of the West Area Hangar Image 1963-L-05016 on page 372 of Spaceflight Revolution NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo
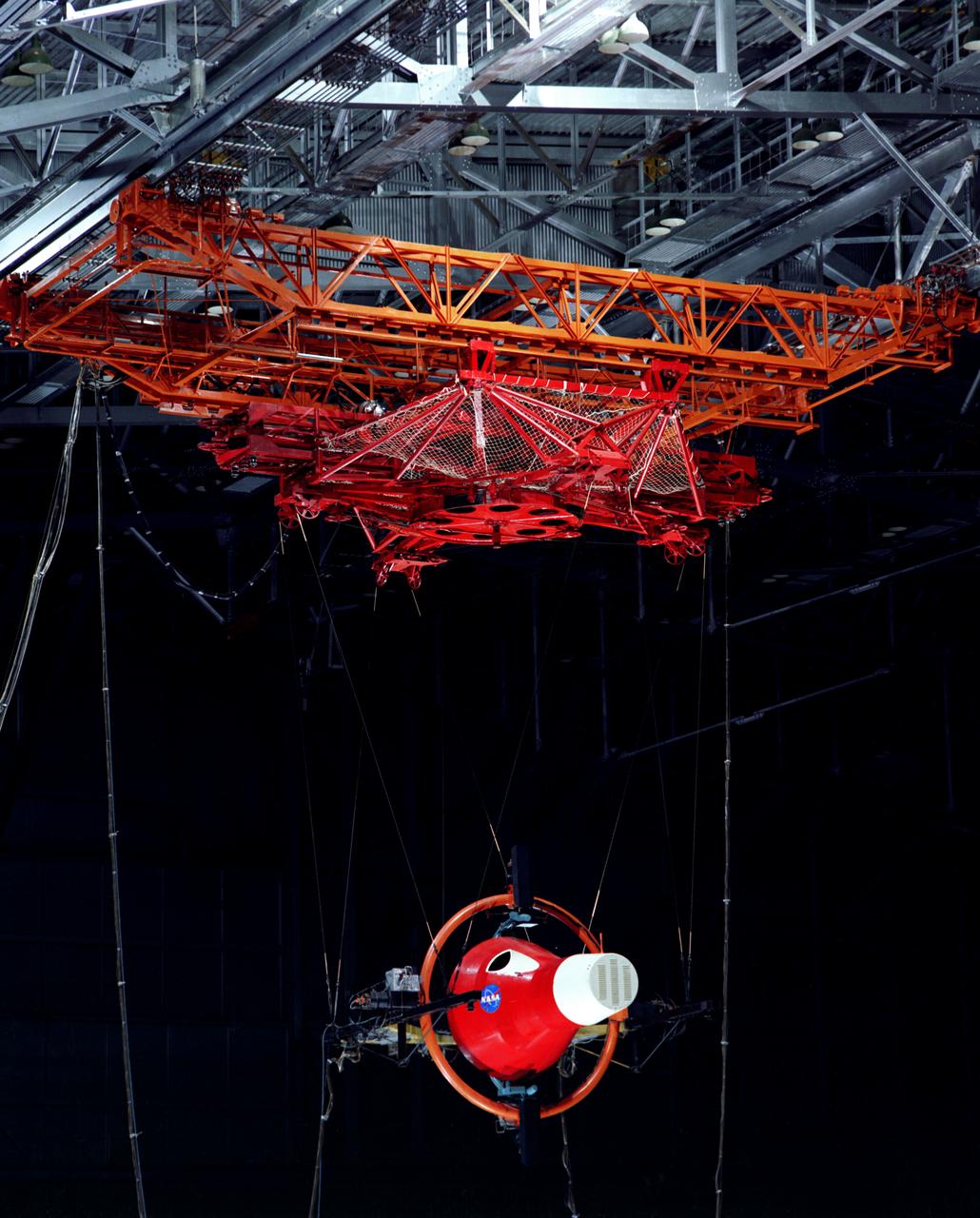

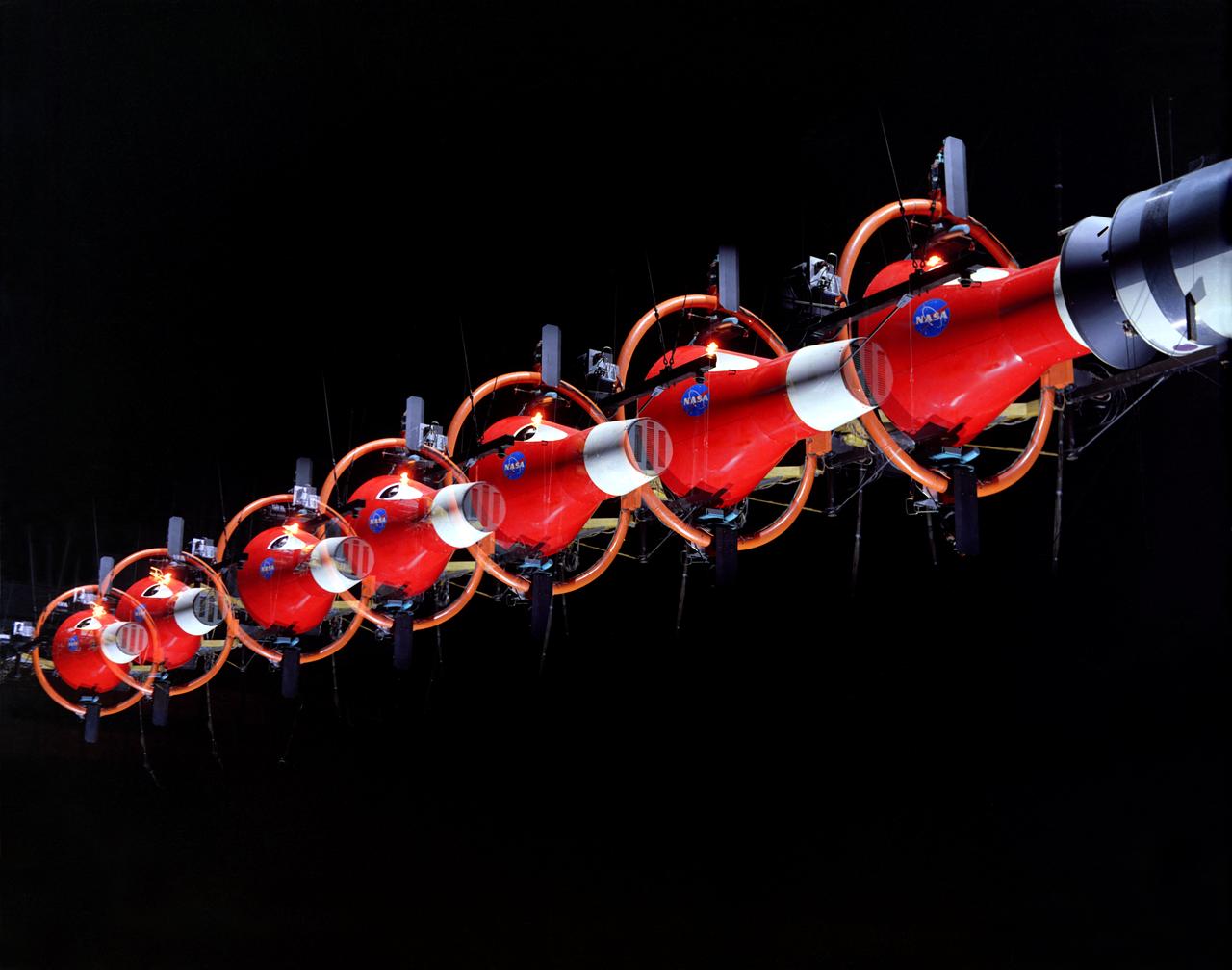
Gemini Rendezvous Docking Simulator suspended from the roof of the Langley Research Center s aircraft hangar. Francis B. Smith wrote: The rendezvous and docking operation of the Gemini spacecraft with the Agena and of the Apollo Command Module with the Lunar Excursion Module have been the subject of simulator studies for several years. This figure illustrates the Gemini-Agena rendezvous docking simulator at Langley. The Gemini spacecraft was supported in a gimbal system by an overhead crane and gantry arrangement which provided 6 degrees of freedom - roll, pitch, yaw, and translation in any direction - all controllable by the astronaut in the spacecraft. Here again the controls fed into a computer which in turn provided an input to the servos driving the spacecraft so that it responded to control motions in a manner which accurately simulated the Gemini spacecraft. -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203 Francis B. Smith, Simulators for Manned Space Research, Paper presented at the 1966 IEEE International convention, March 21-25, 1966.
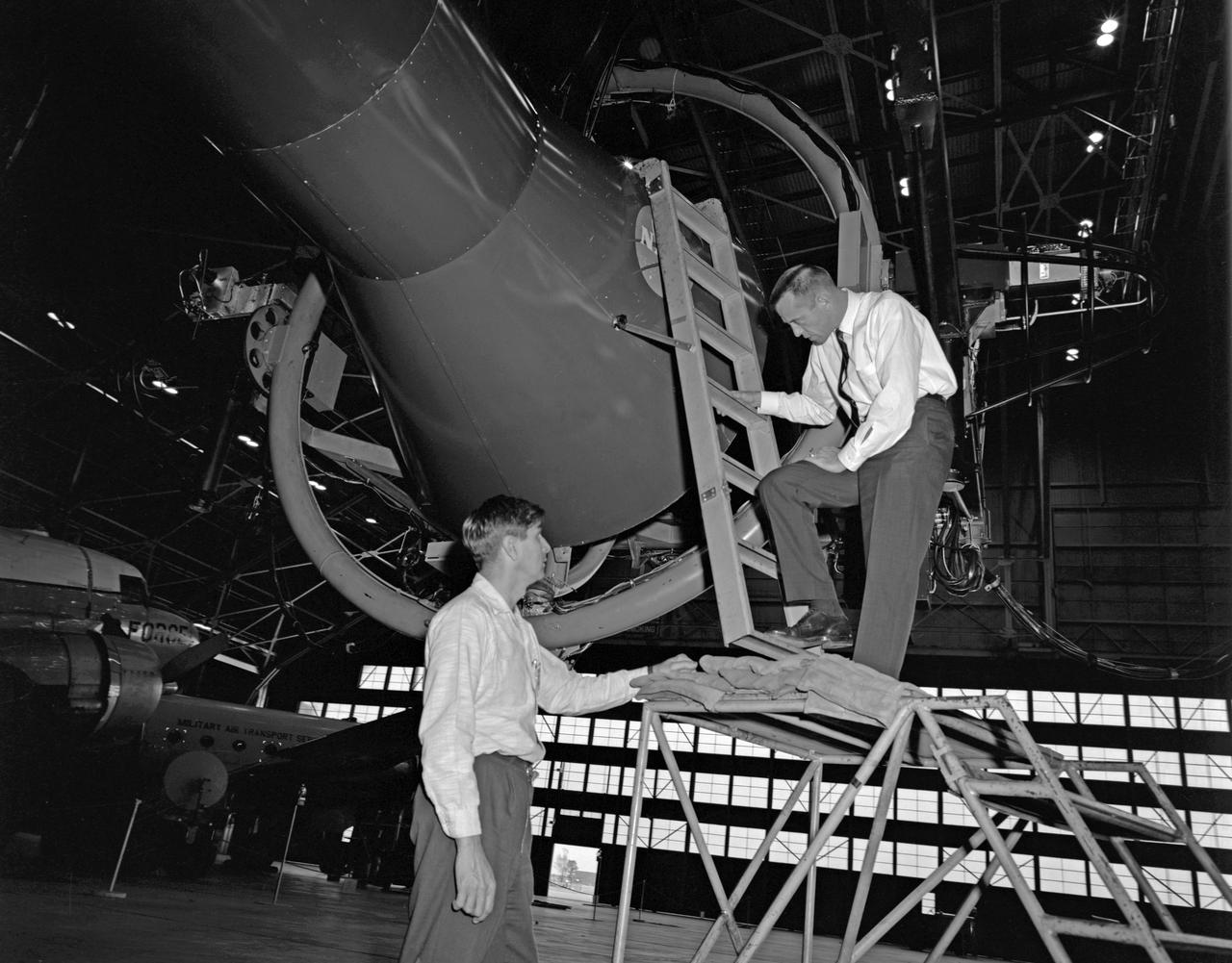

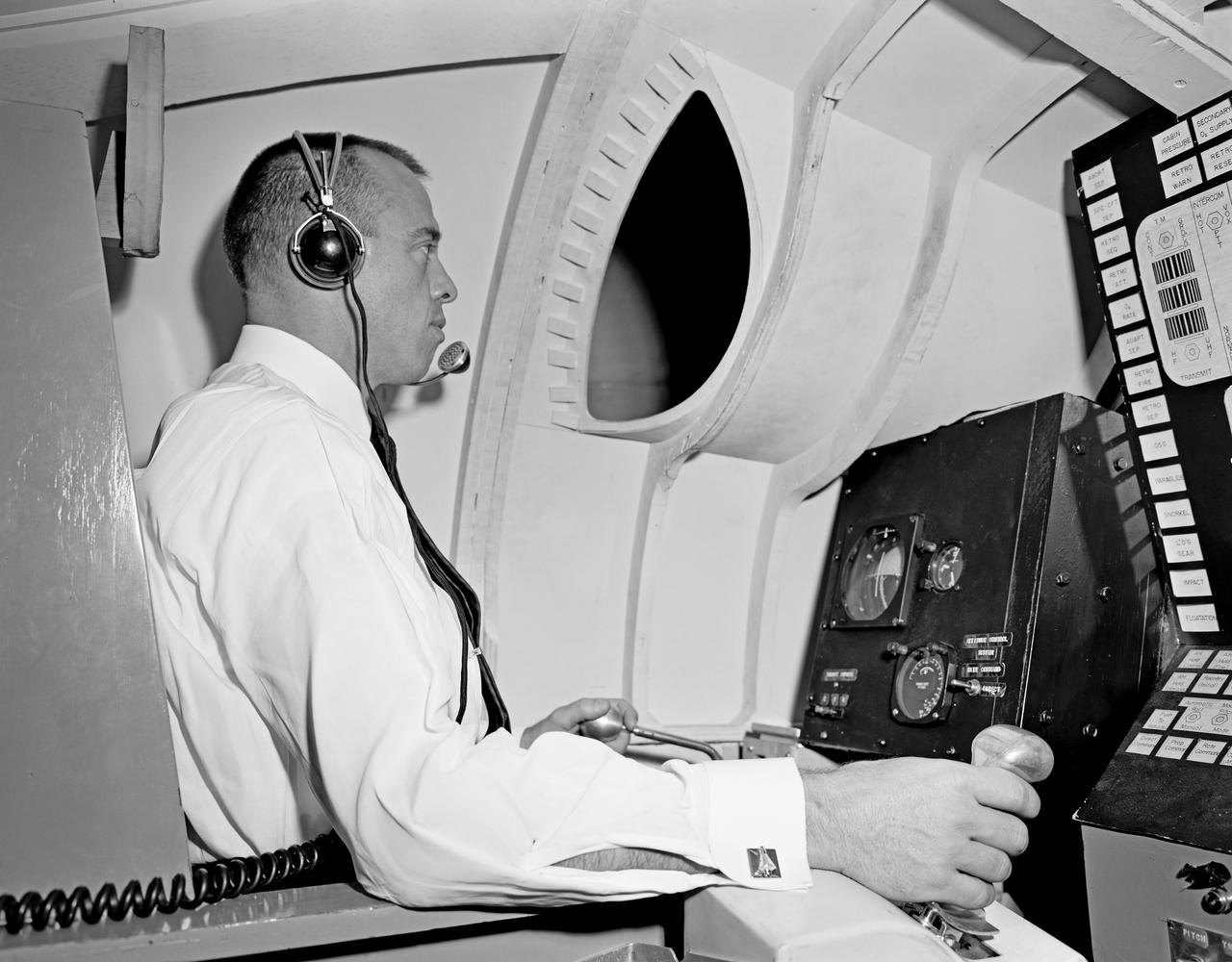
Astronaut Alan Shepard (right) was one of 14 astronauts, 8 NASA test pilots, and 2 McDonnell test pilots who took part in simulator studies. Shepard flew the simulator on November 14, 1963. A.W. Vogeley wrote: "Many of the astronauts have flown this simulator in support of the Gemini studies and they, without exception, appreciated the realism of the visual scene. The simulator has also been used in the development of pilot techniques to handle certain jet malfunctions in order that aborts could be avoided. In these situations large attitude changes are sometimes necessary and the false motion cues that were generated due to earth gravity were somewhat objectionable; however, the pilots were readily able to overlook these false motion cues in favor of the visual realism." Roy F. Brissenden noted that: "The basic Gemini control studies developed the necessary techniques and demonstrated the ability of human pilots to perform final space docking with the specified Gemini-Agena systems using only visual references. ... Results... showed that trained astronauts can effect the docking with direct acceleration control and even with jet malfunctions as long as good visual conditions exist.... Probably more important than data results was the early confidence that the astronauts themselves gained in their ability to perform the maneuver in the ultimate flight mission." Shepard commented: "I had the feeling tonight - a couple of times - that I was actually doing the space mission instead of the simulation. As I said before, I think it is a very good simulation." Shepard also commented on piloting techniques. Most astronauts arrived at this same preferred technique: Shepard: "I believe I have developed the preferred technique for these conditions and the technique appeared to me to be best was to come in slightly above the target so that I was able to use the longitudinal marks on the body of the target as a reference, particularly for a lateral translation and, of course, I used the foreshortening effect for a vertical translation, and this appeared to give me the best results. By that I mean the least number of control motions and the lowest fuel usage and the best end techniques, or the best end conditions, I should say." Engineer: "When you started to run you didn't start thrusting immediately I don't believe. It looked like you started working on your attitudes, then started closing in." Shepard: "That is correct. I did that because I felt that I wanted to get the X-axis translation in the most effective vector and for minimum fuel usage that wouldn't introduce any other lateral or vertical offsets that did not already exist." -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203; A.W. Vogeley, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," Paper presented at the Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, August 17-21, 1964; Roy F. Brissenden, "Initial Operations with Langley's Rendezvous Docking Facility," Langley Working Paper, LWP-21, 1964.

Astronaut Alan Shepard (right) was one of 14 astronauts, 8 NASA test pilots, and 2 McDonnell test pilots who took part in simulator studies. Shepard flew the simulator on November 14, 1963. A.W. Vogeley wrote: "Many of the astronauts have flown this simulator in support of the Gemini studies and they, without exception, appreciated the realism of the visual scene. The simulator has also been used in the development of pilot techniques to handle certain jet malfunctions in order that aborts could be avoided. In these situations large attitude changes are sometimes necessary and the false motion cues that were generated due to earth gravity were somewhat objectionable; however, the pilots were readily able to overlook these false motion cues in favor of the visual realism." Roy F. Brissenden noted that: "The basic Gemini control studies developed the necessary techniques and demonstrated the ability of human pilots to perform final space docking with the specified Gemini-Agena systems using only visual references. ... Results... showed that trained astronauts can effect the docking with direct acceleration control and even with jet malfunctions as long as good visual conditions exist.... Probably more important than data results was the early confidence that the astronauts themselves gained in their ability to perform the maneuver in the ultimate flight mission." Shepard commented: "I had the feeling tonight - a couple of times - that I was actually doing the space mission instead of the simulation. As I said before, I think it is a very good simulation." Shepard also commented on piloting techniques. Most astronauts arrived at this same preferred technique: Shepard: "I believe I have developed the preferred technique for these conditions and the technique appeared to me to be best was to come in slightly above the target so that I was able to use the longitudinal marks on the body of the target as a reference, particularly for a lateral translation and, of course, I used the foreshortening effect for a vertical translation, and this appeared to give me the best results. By that I mean the least number of control motions and the lowest fuel usage and the best end techniques, or the best end conditions, I should say." Engineer: "When you started to run you didn't start thrusting immediately I don't believe. It looked like you started working on your attitudes, then started closing in." Shepard: "That is correct. I did that because I felt that I wanted to get the X-axis translation in the most effective vector and for minimum fuel usage that wouldn't introduce any other lateral or vertical offsets that did not already exist." -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203; A.W. Vogeley, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," Paper presented at the Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, August 17-21, 1964; Roy F. Brissenden, "Initial Operations with Langley's Rendezvous Docking Facility," Langley Working Paper, LWP-21, 1964.

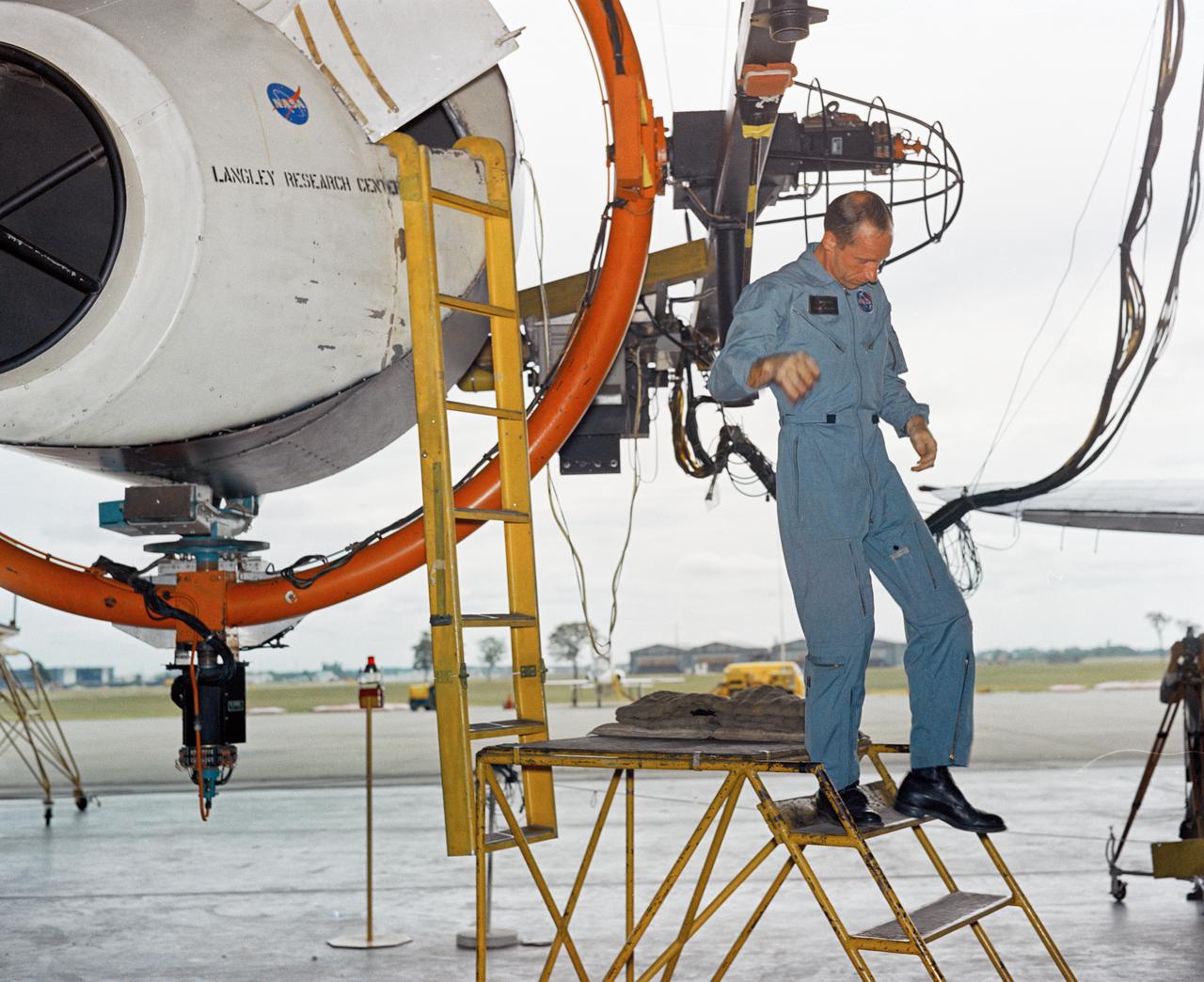
Unidentified Pilot eyeballs his way to a docking by peering through the portal in his capsule. Photo published in Spaceflight Revolution, NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo. By James R. Hansen. NASA SP-4308, 1995, p. 372.

Multiple exposure of Rendezvous Docking Simulator. Francis B. Smith, described the simulator as follows: The rendezvous and docking operation of the Gemini spacecraft with the Agena and of the Apollo Command Module with the Lunar Excursion Module have been the subject of simulator studies for several years. This figure illustrates the Gemini-Agena rendezvous docking simulator at Langley. The Gemini spacecraft was supported in a gimbal system by an overhead crane and gantry arrangement which provided 6 degrees of freedom - roll, pitch, yaw, and translation in any direction - all controllable by the astronaut in the spacecraft. Here again the controls fed into a computer which in turn provided an input to the servos driving the spacecraft so that it responded to control motions in a manner which accurately simulated the Gemini spacecraft. -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203 Francis B. Smith, Simulators for Manned Space Research, Paper presented at the 1966 IEEE International convention, March 21-25, 1966.

Multiple exposure of Rendezvous Docking Simulator. Francis B. Smith, described the simulator as follows: The rendezvous and docking operation of the Gemini spacecraft with the Agena and of the Apollo Command Module with the Lunar Excursion Module have been the subject of simulator studies for several years. This figure illustrates the Gemini-Agena rendezvous docking simulator at Langley. The Gemini spacecraft was supported in a gimbal system by an overhead crane and gantry arrangement which provided 6 degrees of freedom - roll, pitch, yaw, and translation in any direction - all controllable by the astronaut in the spacecraft. Here again the controls fed into a computer which in turn provided an input to the servos driving the spacecraft so that it responded to control motions in a manner which accurately simulated the Gemini spacecraft. -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203 Francis B. Smith, Simulators for Manned Space Research, Paper presented at the 1966 IEEE International convention, March 21-25, 1966.

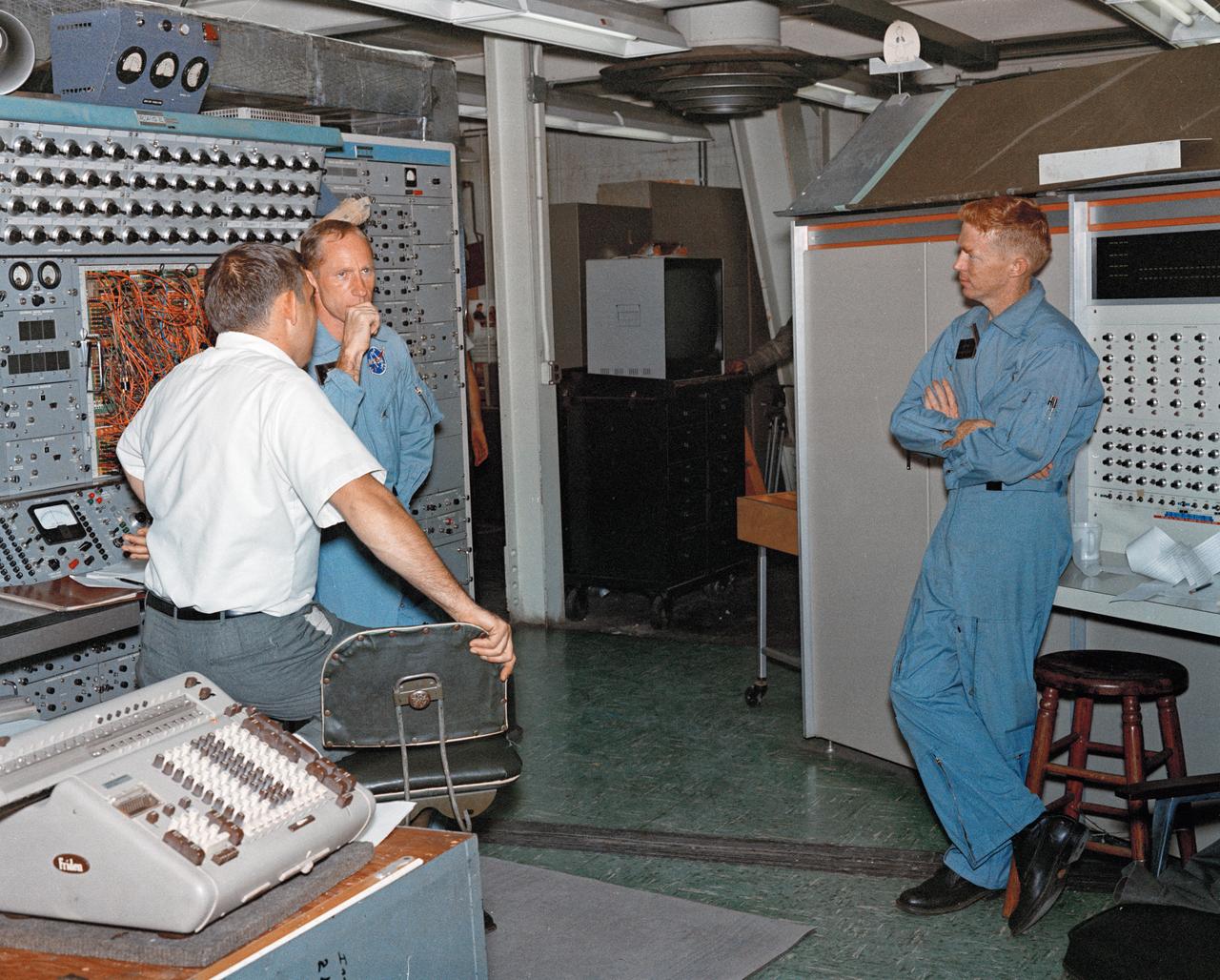
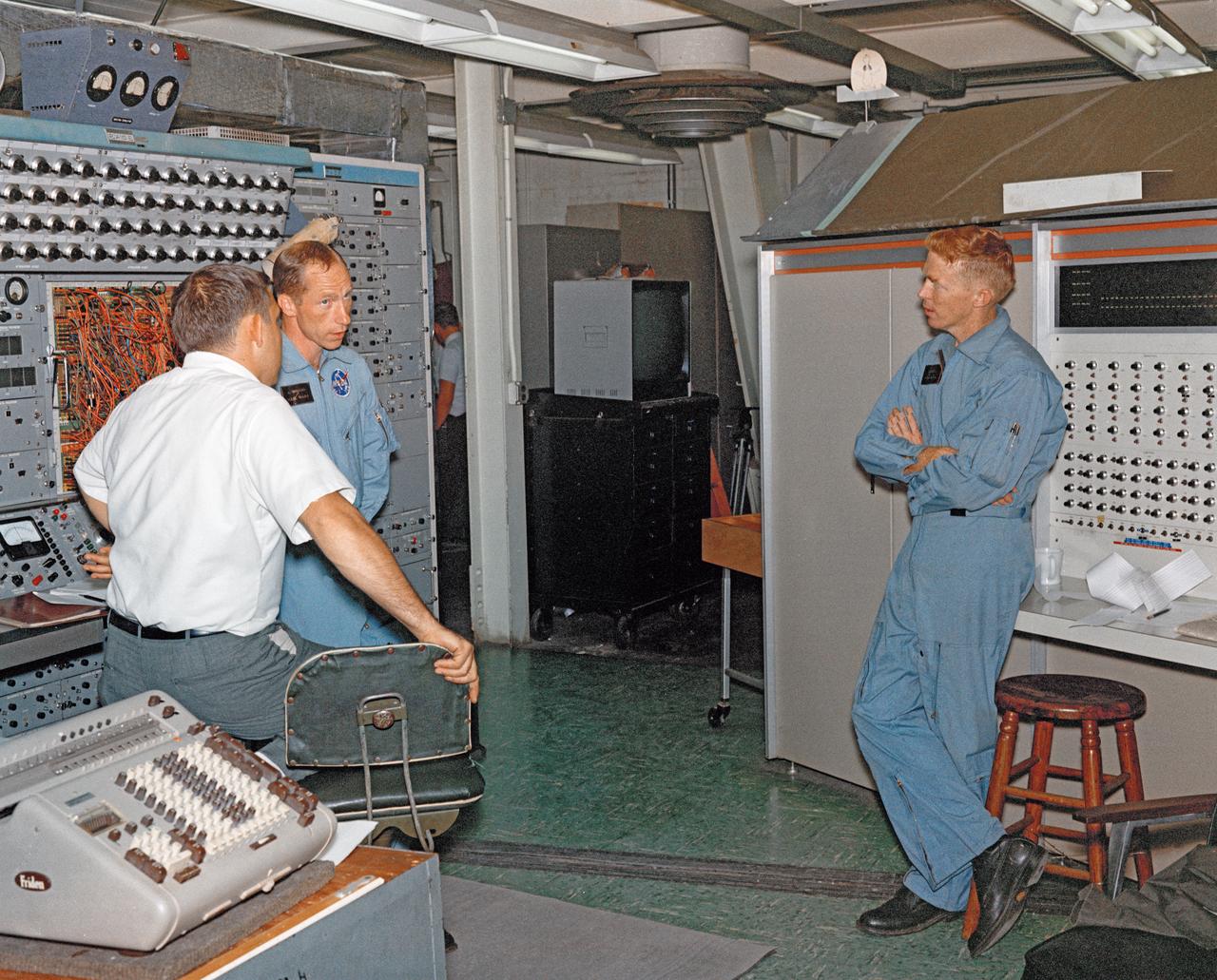
Alan Shepard and engineer looking at equipment, alone in Visual Docking Simulator, with engineers in Visual Docking Simulator.
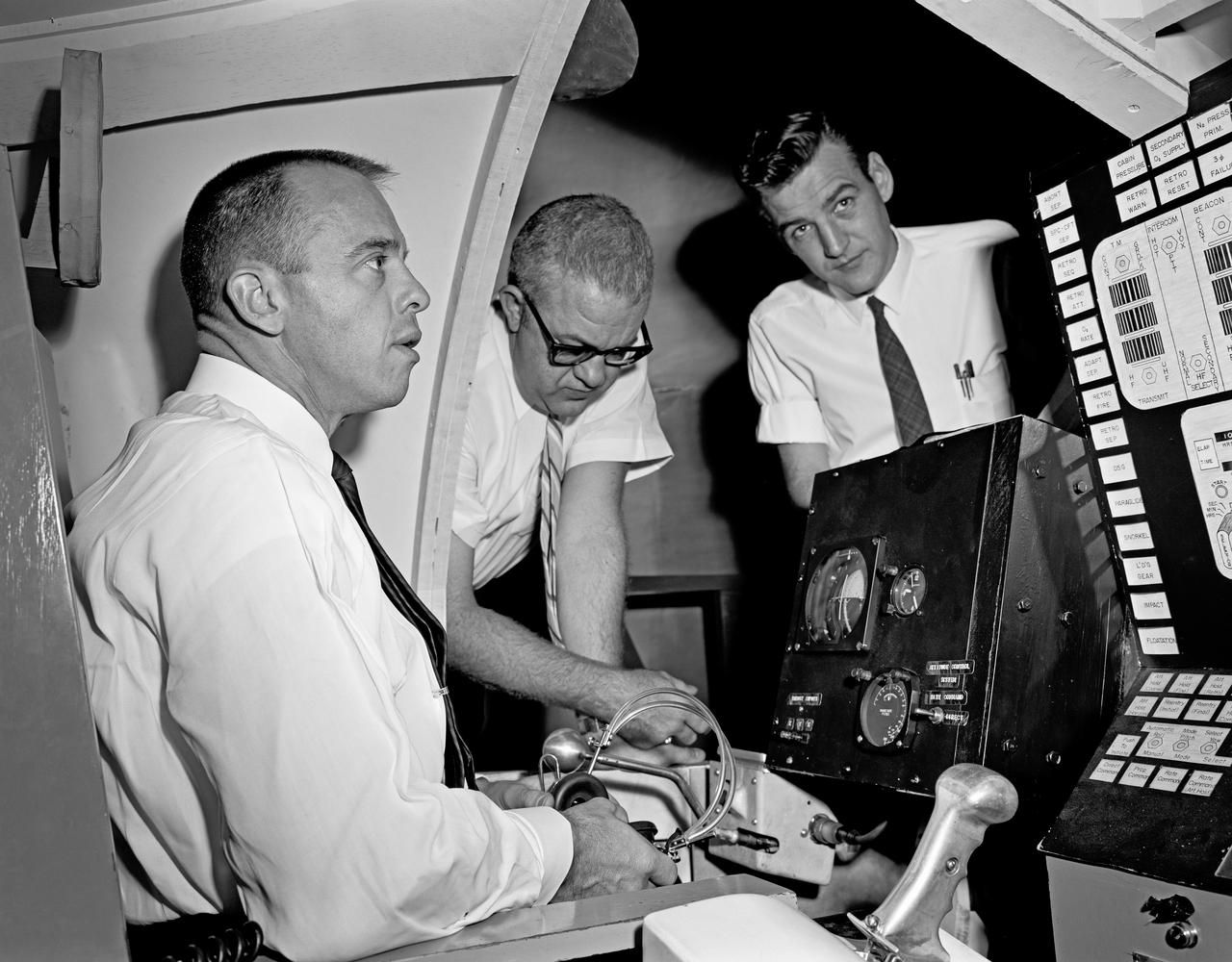

Alan Shepard and engineer looking at equipment, alone in Visual Docking Simulator, with engineers in Visual Docking Simulator.
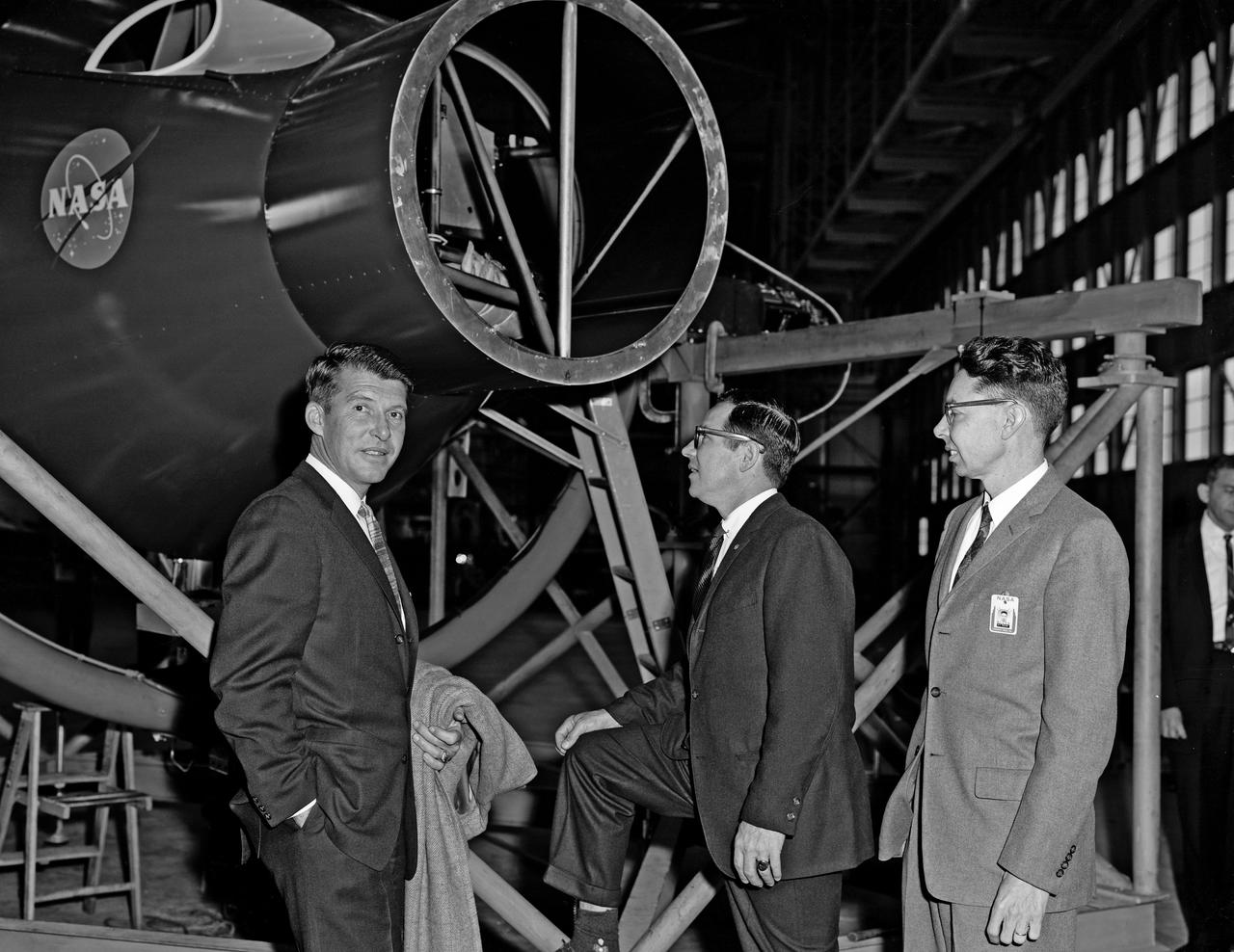

Walter (Wally) M. Schirra Visit to Langley Research Center to the Rendezvous Docking Simulator.

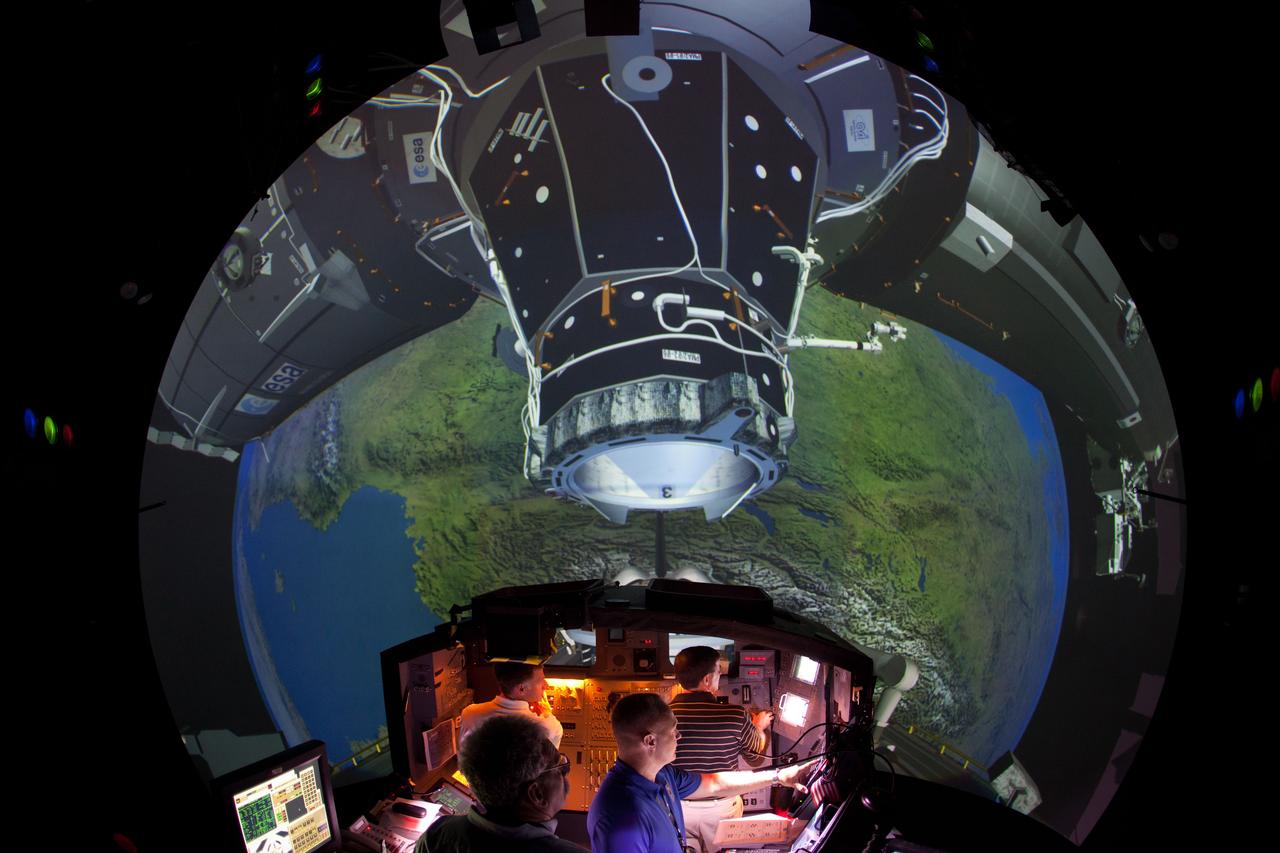
Boeing CST-100 Starliner flight directors Bob Dempsey and Edward Van Cise operate a simulated Orbital Flight Test-2 rendezvous and docking with the International Space Station from inside the Mission Control Center at NASA’s Johnson Space Center on Friday, April 23, 2021. As part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on Boeing’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
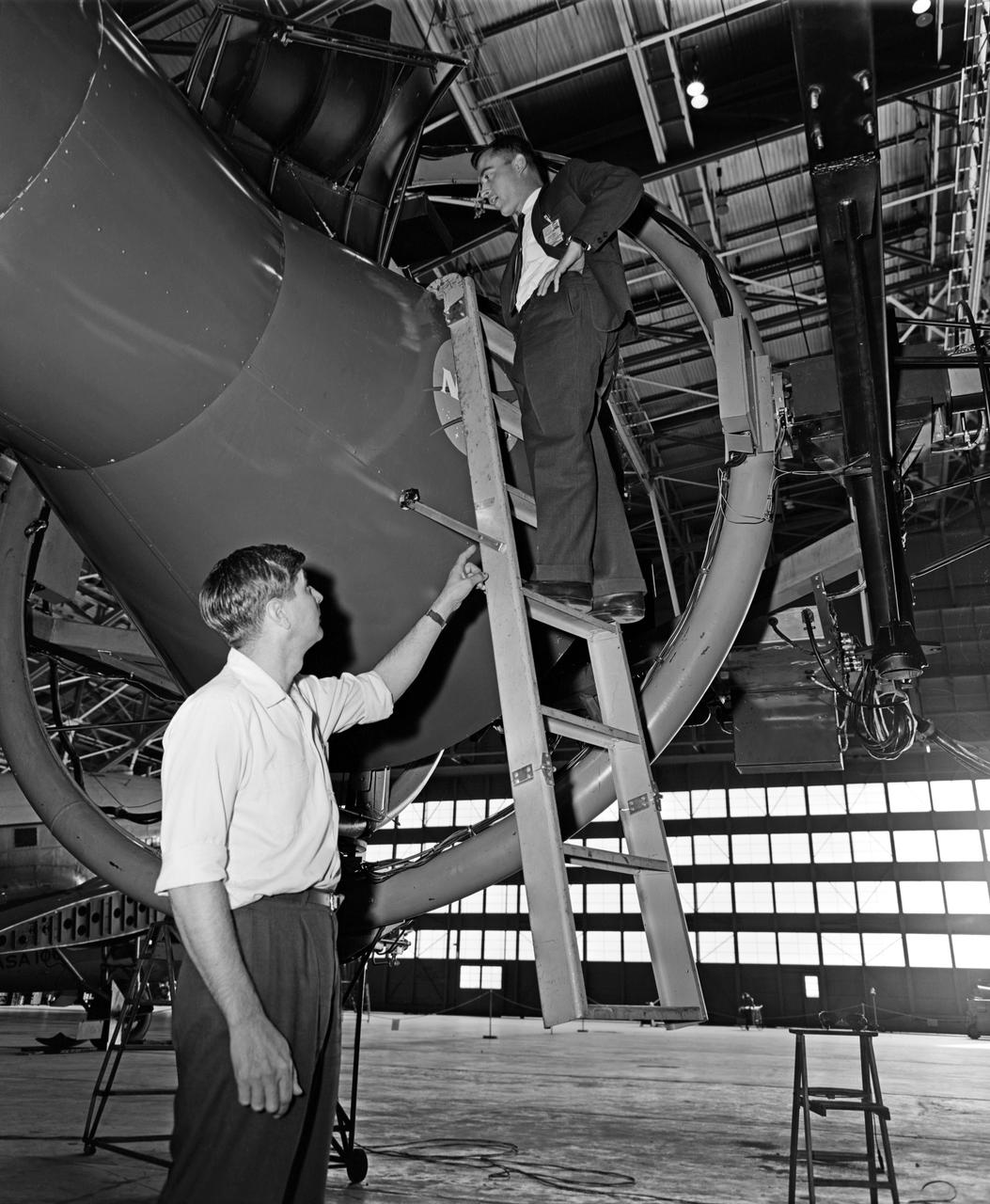

Astronaut John Young (above) was one of 14 astronauts, 8 NASA test pilots, and 2 McDonnell test pilots who took part in simulator studies. Young piloted the simulator on November 12, 1963 Arthur Vogeley wrote: "Many of the astronauts have flown this simulator in support of the Gemini studies and they, without exception, appreciated the realism of the visual scene. The simulator has also been used in the development of pilot techniques to handle certain jet malfunctions in order that aborts could be avoided. In these situations large attitude changes are sometimes necessary and the false motion cues that were generated due to earth gravity were somewhat objectionable; however, the pilots were readily able to overlook these false motion cues in favor of the visual realism." Roy F. Brissenden wrote: "The basic Gemini control studies developed the necessary techniques and demonstrated the ability of human pilots to perform final space docking with the specified Gemini-Agena systems using only visual references. ... Results... showed that trained astronauts can effect the docking with direct acceleration control and even with jet malfunctions as long as good visual conditions exist.... Probably more important than data results was the early confidence that the astronauts themselves gained in their ability to perform the maneuver in the ultimate flight mission." -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203; A.W. Vogeley, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," Paper presented at the Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, August 17-21, 1964; Roy F. Brissenden, "Initial Operations with Langley's Rendezvous Docking Facility," Langley Working Paper, LWP-21, 1964.
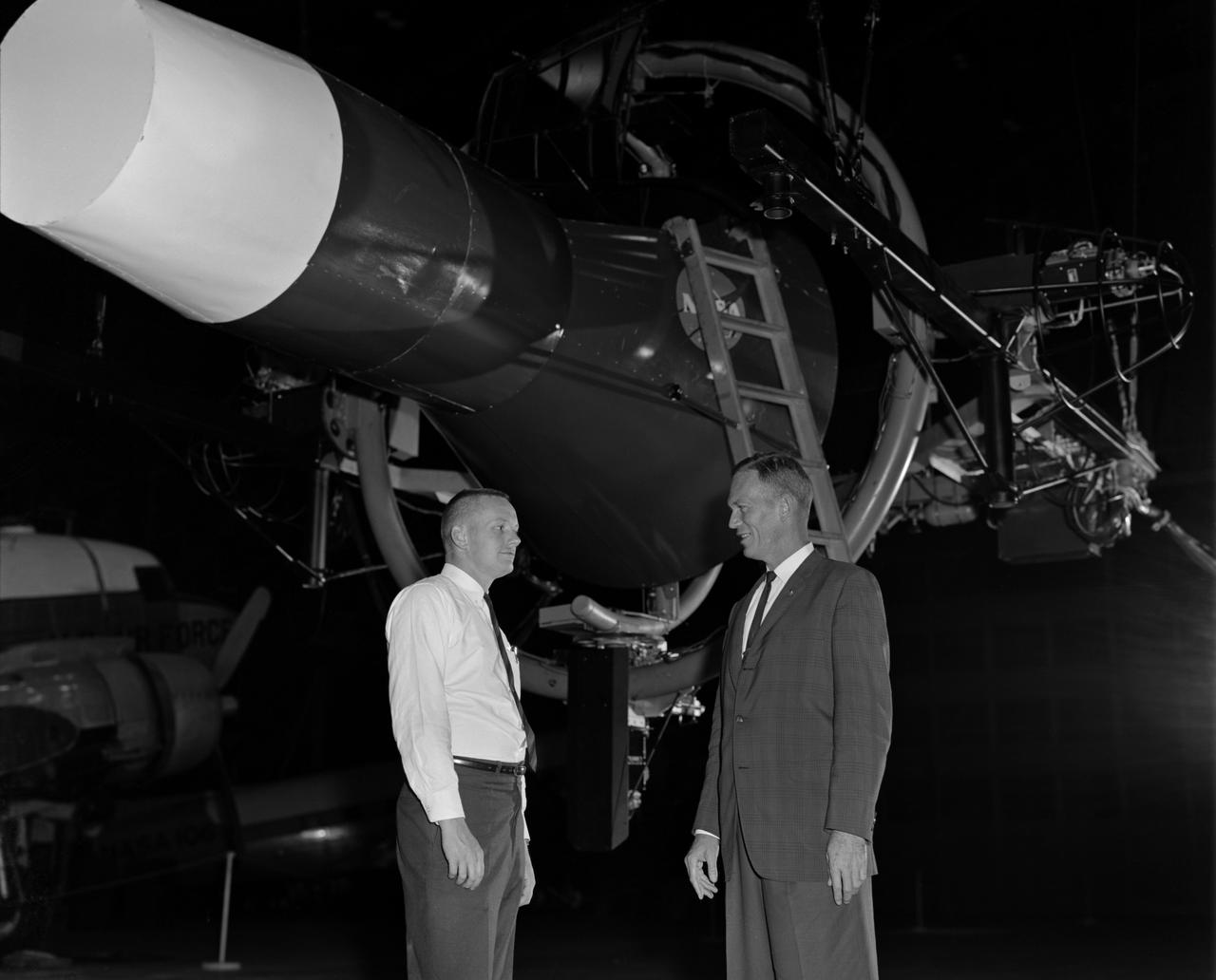

Astronaut Neil Armstrong (left) was one of 14 astronauts, 8 NASA test pilots, and 2 McDonnell test pilots who took part in simulator studies. Armstrong was the first astronaut to participate (November 6, 1963). A.W. Vogeley described the simulator in his paper "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," "Many of the astronauts have flown this simulator in support of the Gemini studies and they, without exception, appreciated the realism of the visual scene. The simulator has also been used in the development of pilot techniques to handle certain jet malfunctions in order that aborts could be avoided. In these situations large attitude changes are sometimes necessary and the false motion cues that were generated due to earth gravity were somewhat objectionable; however, the pilots were readily able to overlook these false motion cues in favor of the visual realism." Roy F. Brissenden, noted in his paper "Initial Operations with Langley's Rendezvous Docking Facility," "The basic Gemini control studies developed the necessary techniques and demonstrated the ability of human pilots to perform final space docking with the specified Gemini-Agena systems using only visual references. ... Results... showed that trained astronauts can effect the docking with direct acceleration control and even with jet malfunctions as long as good visual conditions exist.... Probably more important than data results was the early confidence that the astronauts themselves gained in their ability to perform the maneuver in the ultimate flight mission." Francis B. Smith, noted in his paper "Simulators for Manned Space Research," "Some major areas of interest in these flights were fuel requirements, docking accuracies, the development of visual aids to assist alignment of the vehicles, and investigation of alternate control techniques with partial failure modes. However, the familiarization and confidence developed by the astronaut through flying and safely docking the simulator during these tests was one of the major contributions. For example, it was found that fuel used in docking from 200 feet typically dropped from about 20 pounds to 7 pounds after an astronaut had made a few training flights." -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203; A.W. Vogeley, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," Paper presented at the Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, August 17-21, 1964; Roy F. Brissenden, "Initial Operations with Langley's Rendezvous Docking Facility," Langley Working Paper, LWP-21, 1964; Francis B. Smith, "Simulators for Manned Space Research," Paper presented at the 1966 IEEE International convention, March 21-25, 1966.
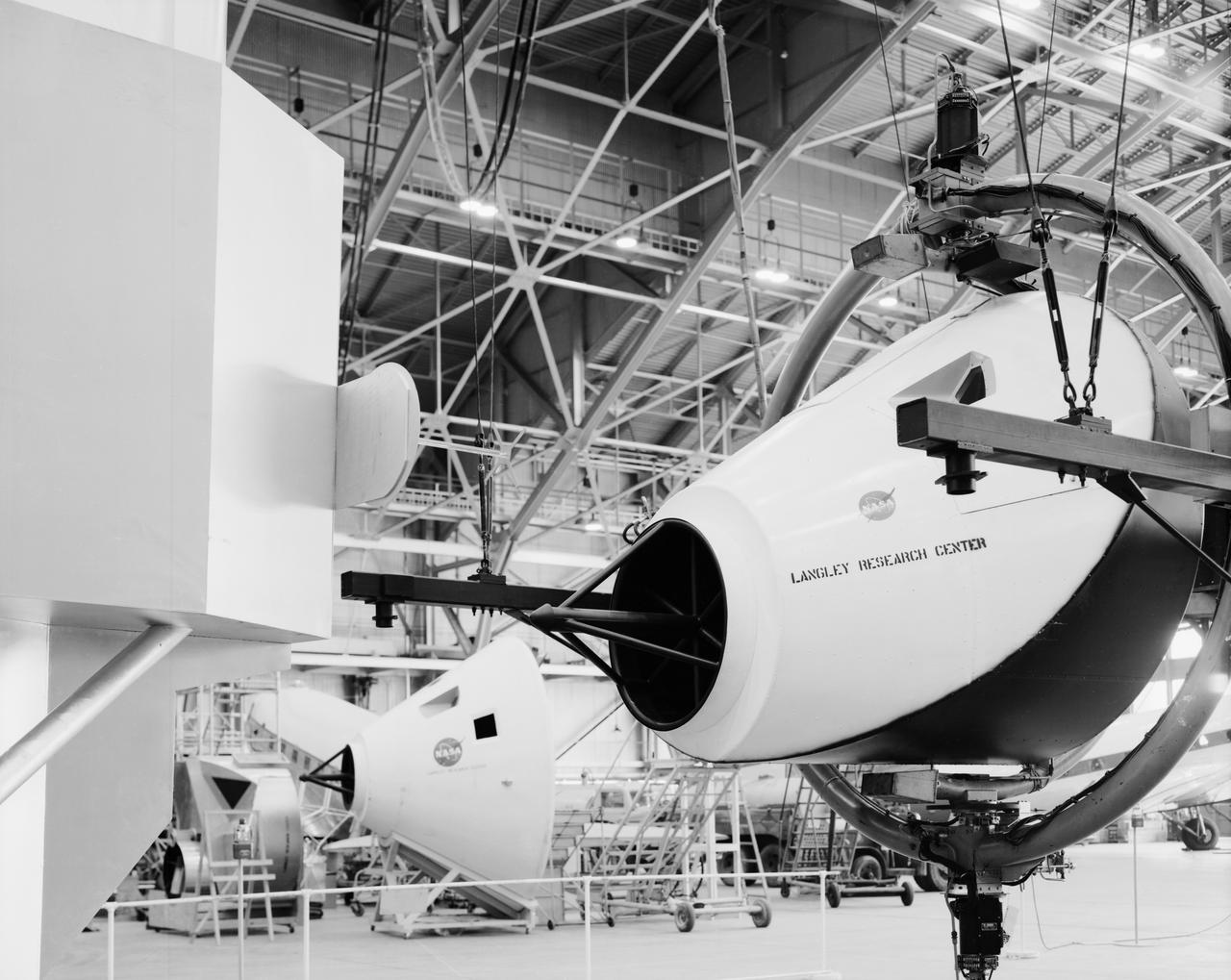

Originally the Rendezvous was used by the astronauts preparing for Gemini missions. The Rendezvous Docking Simulator was then modified and used to develop docking techniques for the Apollo program. This picture shows a later configuration of the Apollo docking with the LEM target. A.W. Vogeley described the simulator as follows: The Rendezvous Docking Simulator and also the Lunar Landing Research Facility are both rather large moving-base simulators. It should be noted, however, that neither was built primarily because of its motion characteristics. The main reason they were built was to provide a realistic visual scene. A secondary reason was that they would provide correct angular motion cues (important in control of vehicle short-period motions) even though the linear acceleration cues would be incorrect. -- Published in A.W. Vogeley, Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center, Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27 - December 1, 1966.

Marshall employees conduct tests on the simulated rendezvous docking mechanism (SRDM)as depicted in this photo of the flat floor area in building 4619.

20th Anniversary of the First Lunar Landing Colloquium held at Langley. William H. Michael Jr. (center) reviews the evolution of his parking orbit concept with Clinton E. Brown (right) head of the Lunar Exploration Working Group and Arthur Vogeley (left) mastermind of Langley's rendezvous and docking simulators of the 1960's.

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
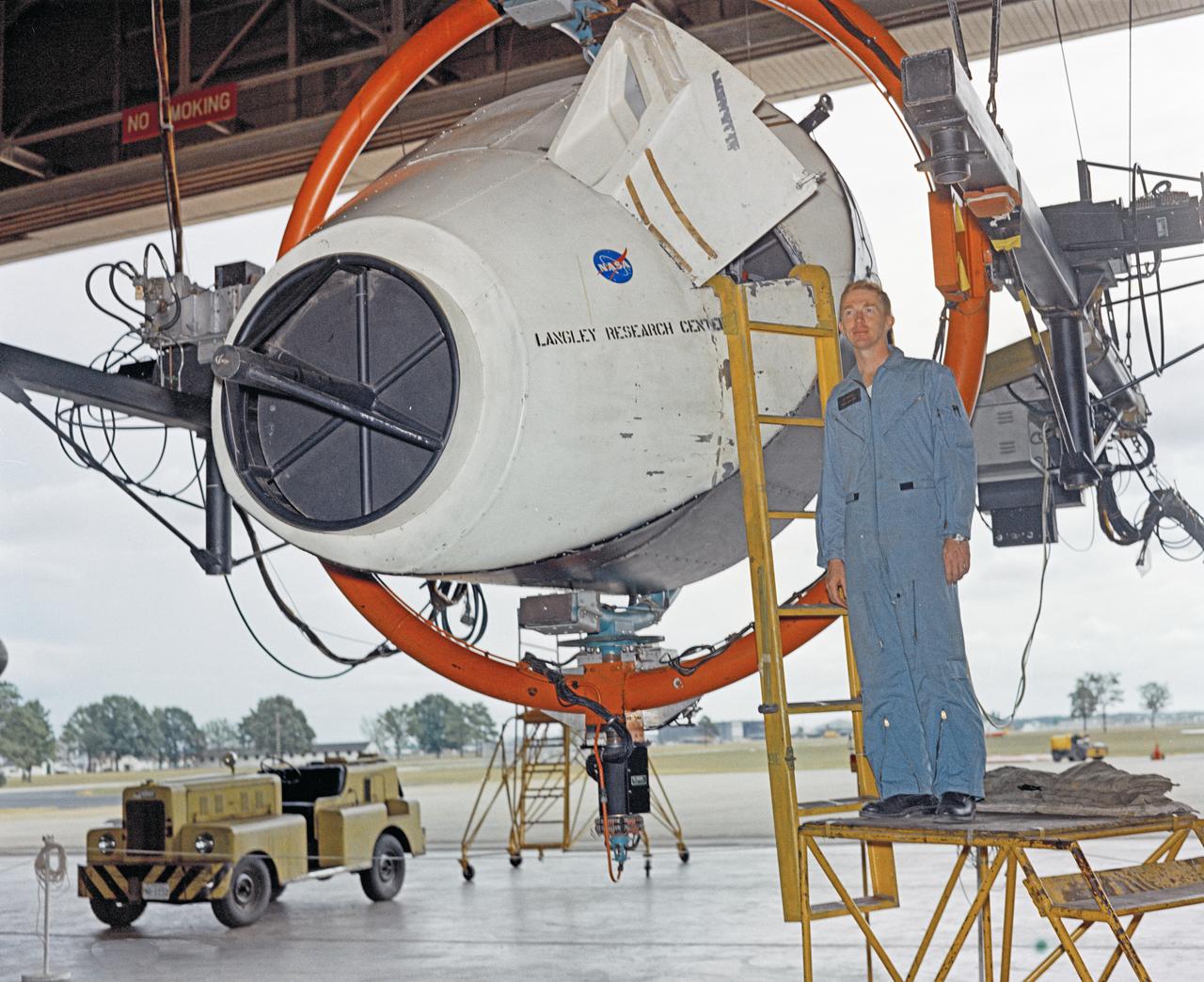

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.

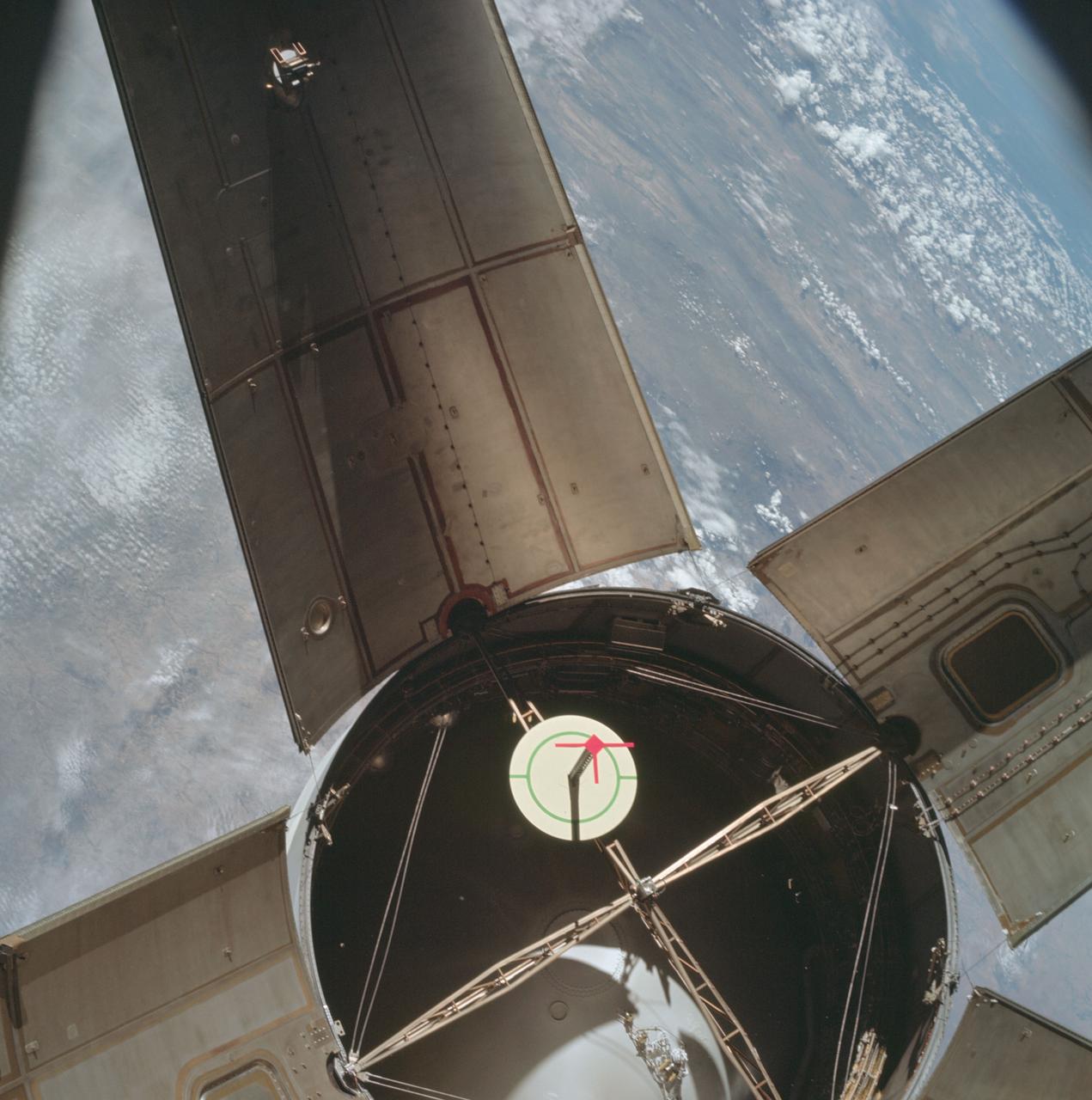
AS07-03-1538 (11 Oct. 1968) --- The expended Saturn IVB stage as photographed from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during transposition and docking maneuvers. This photograph was taken during Apollo 7's second revolution of Earth. Earth below has heavy cloud cover. The round, white disc inside the open panels of the Saturn IVB is a simulated docking target similar to that used on the lunar module for docking during lunar missions.

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
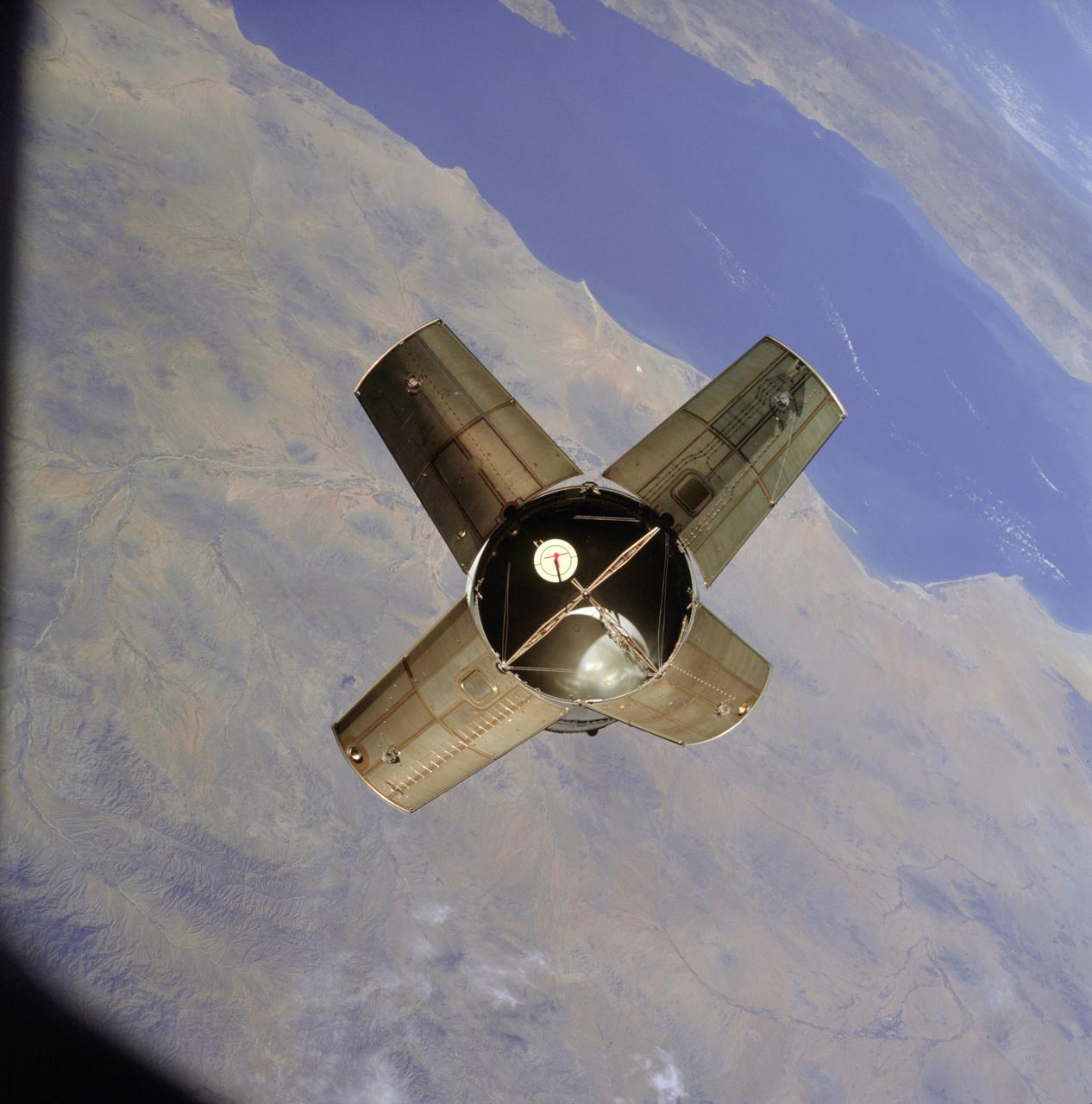

AS07-03-1531 (11 Oct. 1968) --- The expended Saturn IVB stage as photographed from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during transposition and docking maneuvers. This photograph was taken over Sonora, Mexico, during Apollo 7's second revolution of Earth. The round, white disc inside the open panels of the Saturn IVB is a simulated docking target similar to that used on the lunar module for docking during lunar missions.

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
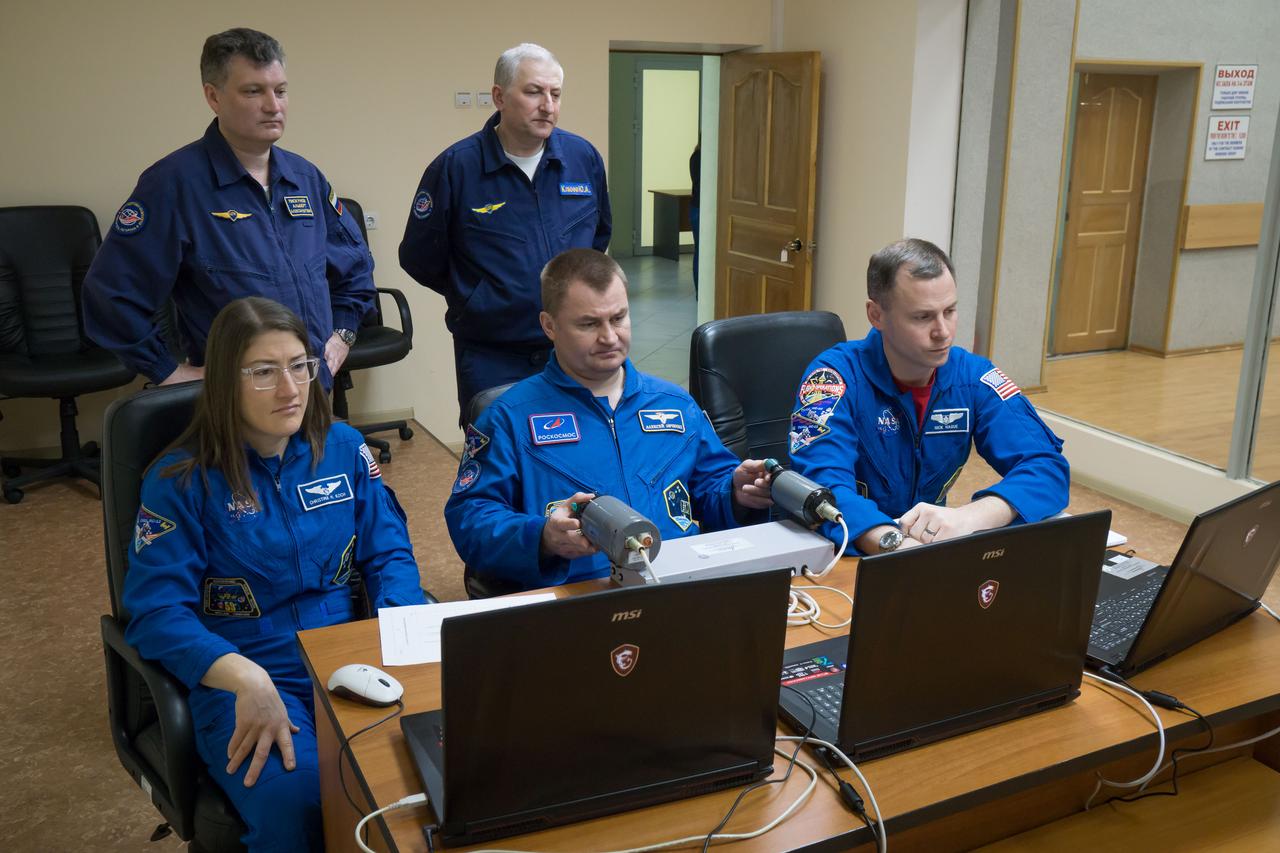

At their Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 59 crewmembers Christina Koch of NASA (left), Alexey Ovchinin of Roscosmos (center) and Nick Hague of NASA (right) rehearse rendezvous and docking techniques on a laptop computer simulator March 7 as they prepare for launch. They will launch March 14, U.S. time, on the Soyuz MS-12 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome for a six-and-a-half month mission on the International Space Station...NASA/Victor Zelentsov.
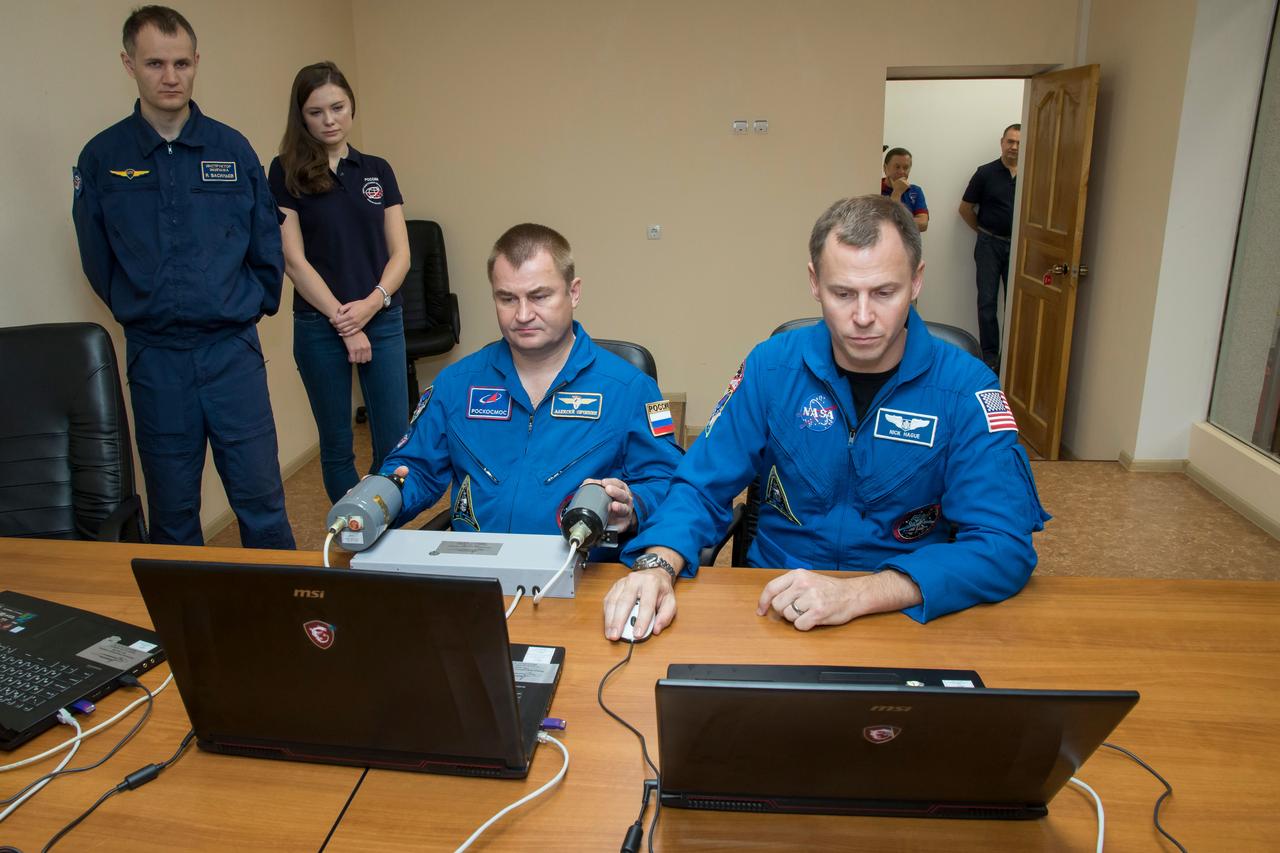

jsc2018e085891 (Oct. 3, 2018) --- Expedition 57 crew members Alexey Ovchinin of Roscosmos, left, and Nick Hague of NASA, right, conduct rendezvous and docking procedures on a laptop training simulator as part of their pre-launch preparations, Wednesday, Oct. 3, 2018 at the Cosmonaut Hotel in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Ovchinin and Hague are scheduled to launch on Oct. 11 onboard the Soyuz MS-10 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan for a six-month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Victor Zelentsov)
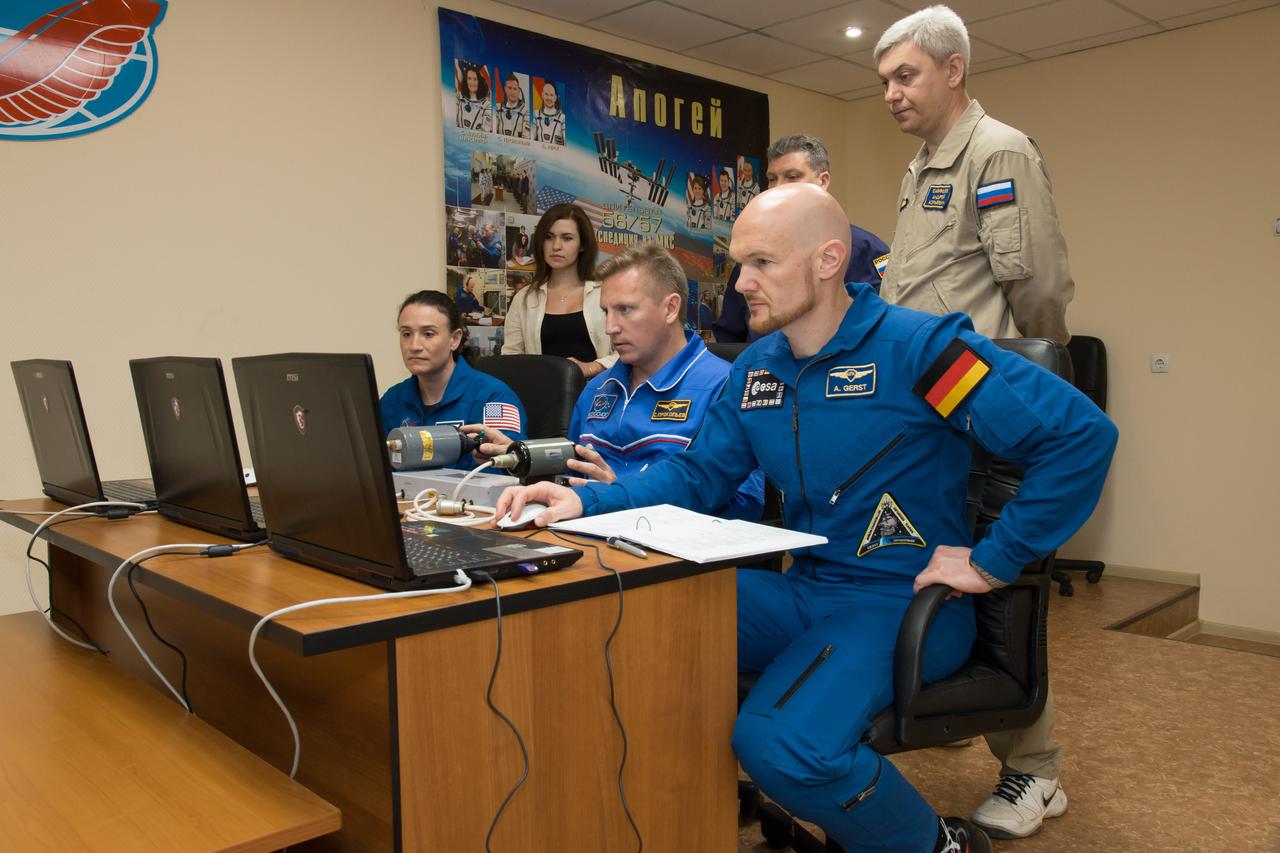

jsc2018e050821 - At the Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 56 crewmembers Serena Aunon-Chancellor of NASA (left), Sergey Prokopyev of Roscosmos (center) and Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency (right) conduct rendezvous and docking procedures on a laptop training simulator May 29 as part of their pre-launch preparations. Aunon-Chancellor, Prokopyev and Gerst will launch June 6 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on the Soyuz MS-09 spacecraft for a six-month mission on the International Space Station...NASA/Victor Zelentsov.
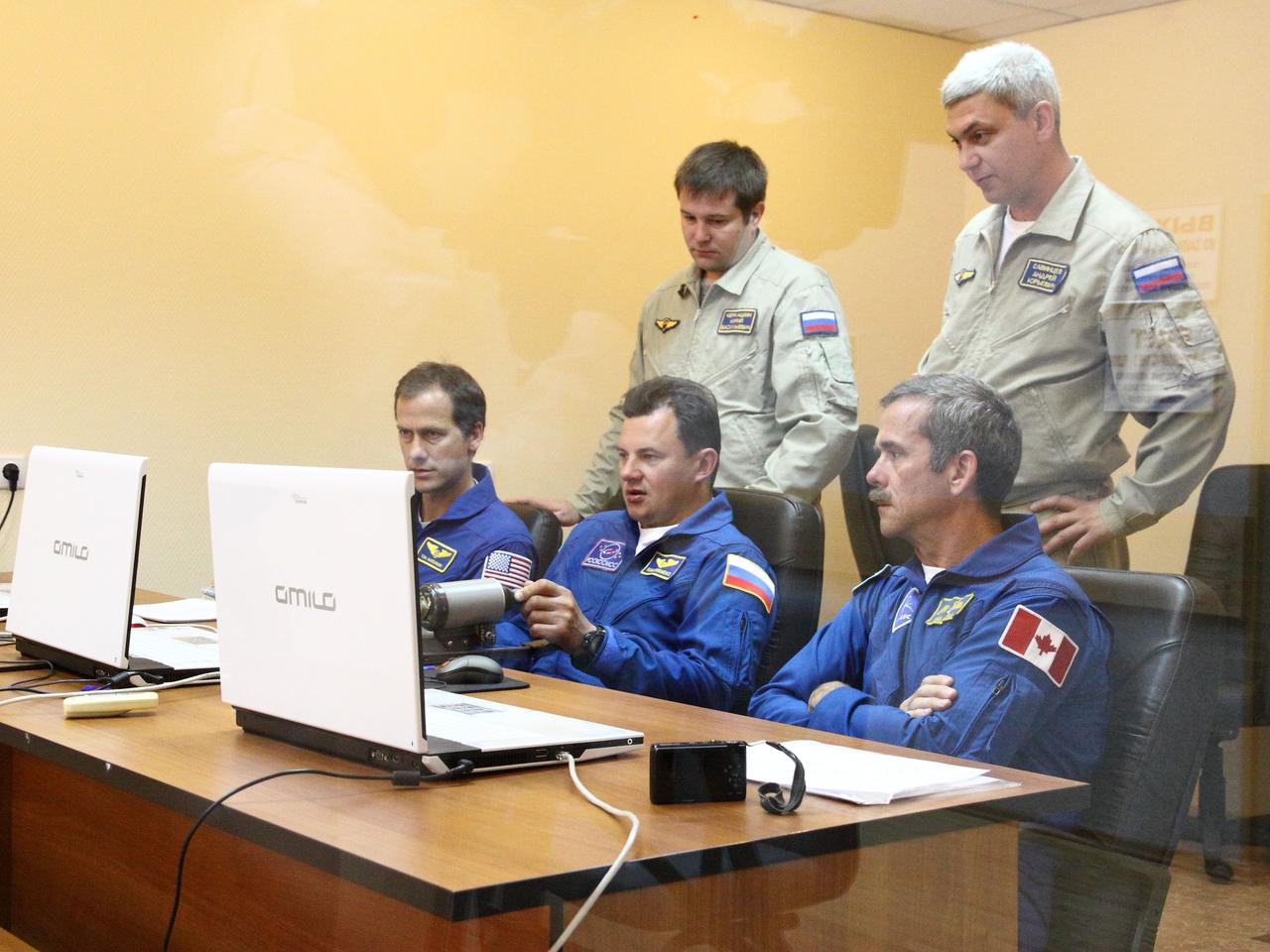

At their Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, the Expedition 32/33 backup crew members participate in a rendezvous and docking practice session using laptop computer simulators July 9, 2012 as they train for support of the prime crew’s launch July 15 to the International Space Station in the Soyuz TMA-05M spacecraft. From left to right with their instructors are backup Flight Engineer Tom Marshburn of NASA, backup Soyuz Commander Roman Romanenko and backup Flight Engineer Chris Hadfield of the Canadian Space Agency. NASA/Victor Zelentsov
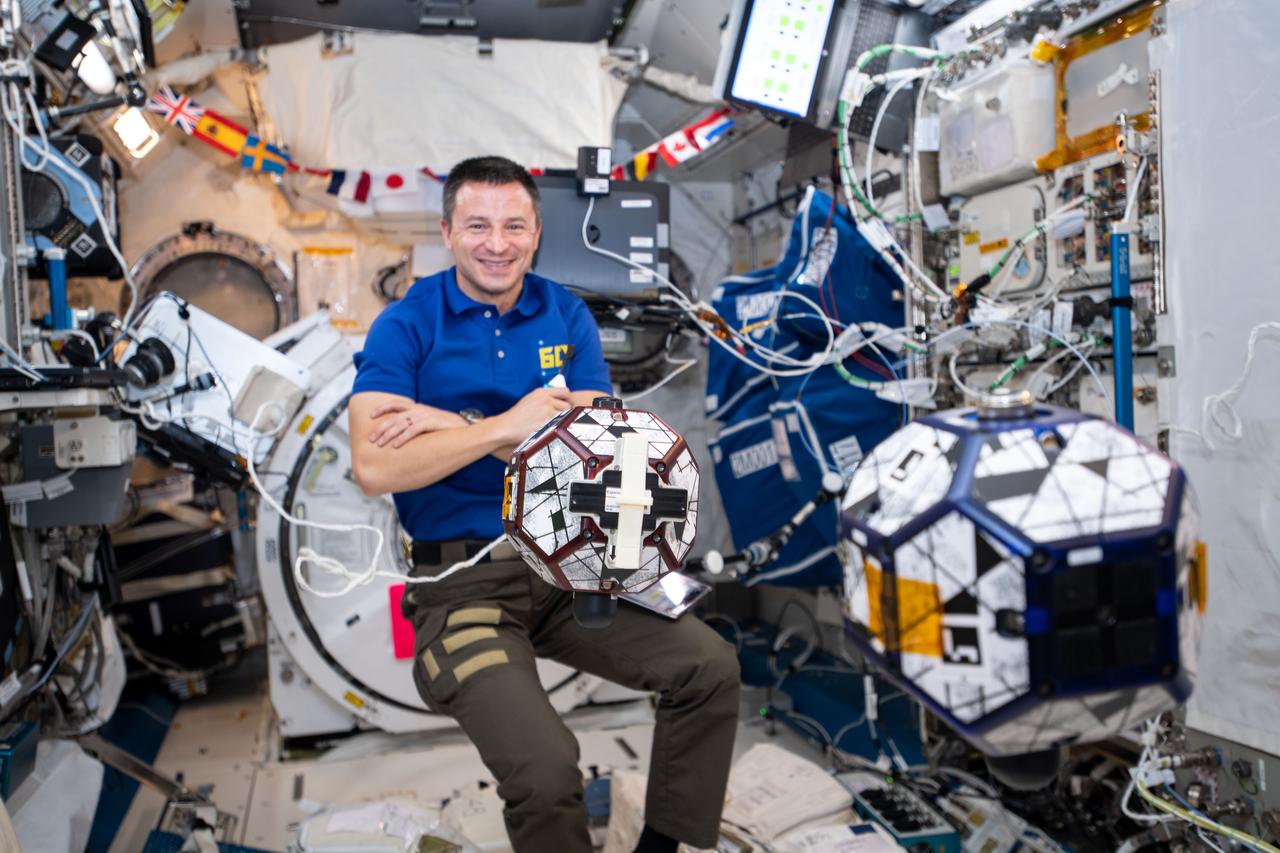

iss060e033147 (Aug. 9, 2019) --- Expedition 60 Flight Engineer Andrew Morgan of NASA monitors a pair of tiny, free-floating satellites known as SPHERES, or Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites. Middle and high school students compete to design algorithms that autonomously control the basketball-sized SPHERES satellites aboard the station. The student-written software tests rendezvous and docking maneuvers that simulate scenarios such as retrieving an inoperable satellite.
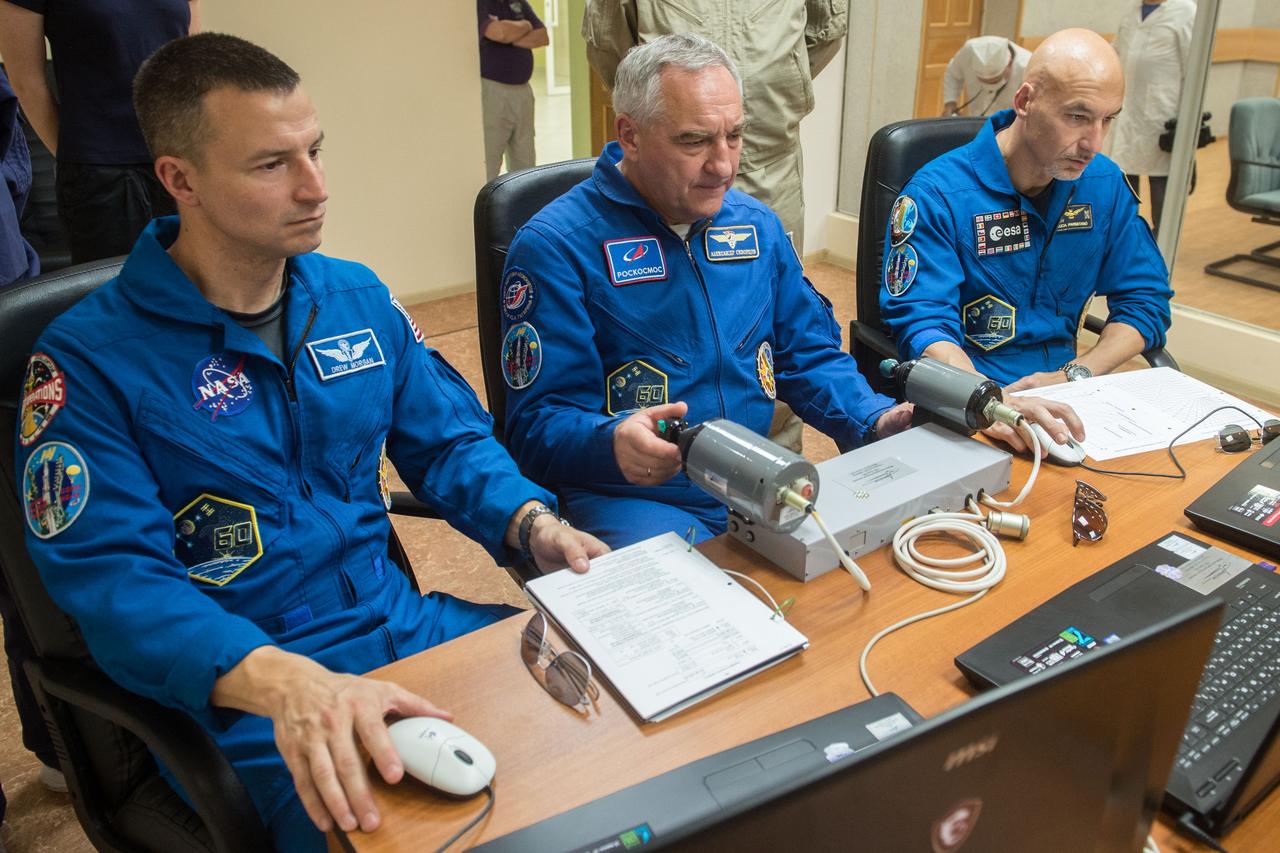

jsc2019e039265 - At the Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 60 crewmembers Drew Morgan of NASA (left), Alexander Skvortsov of Roscosmos (center) and Luca Parmitano of the European Space Agency (right) practice rendezvous and docking techniques on a laptop computer simulator July 12 as part of pre-launch activities. They will launch July 20 on the Soyuz MS-13 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on a mission to the International Space Station...Andrey Shelepin/GCTC.
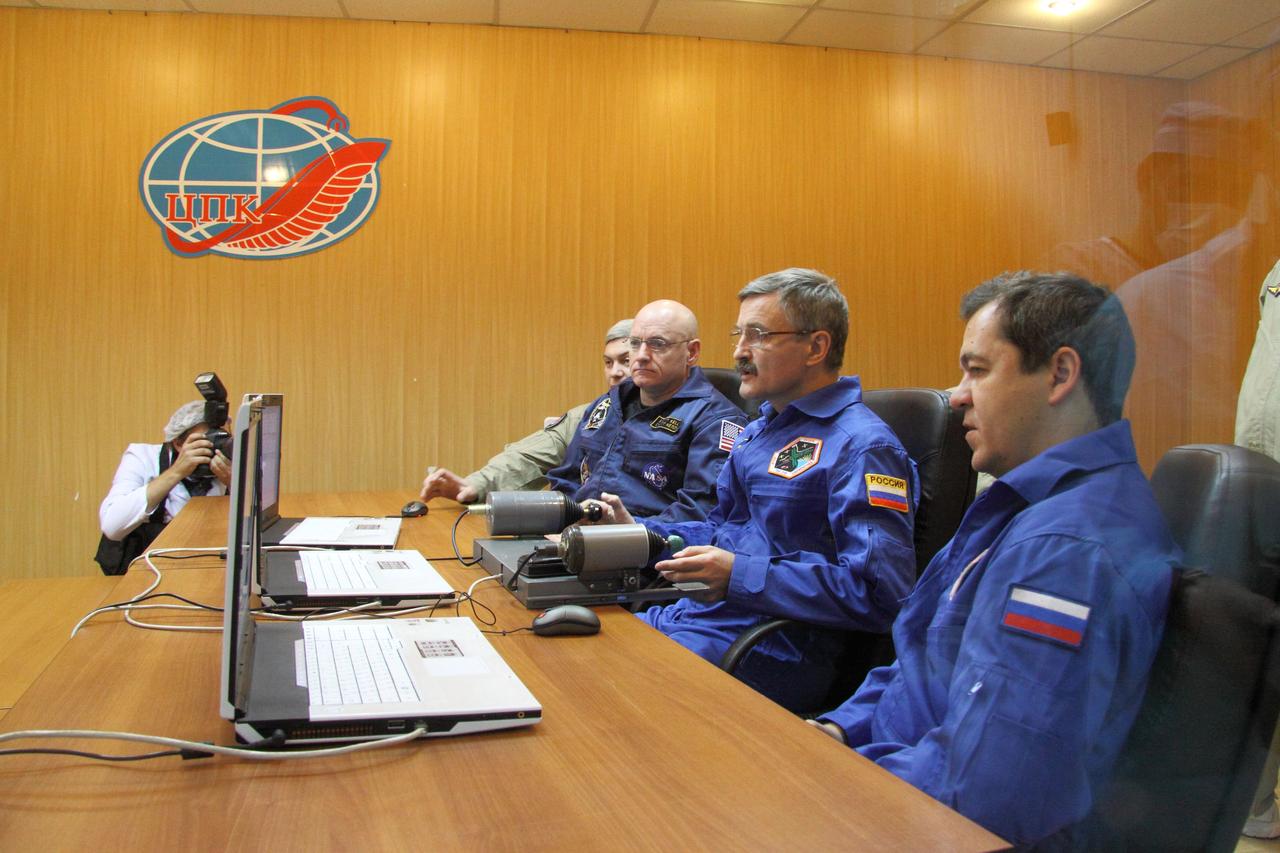

At their crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 25 Flight Engineers Scott Kelly of NASA (left), Alexander Kaleri (center) and Oleg Skripochka review rendezvous and docking programs on a laptop simulator October 2, 2010 as they prepare for their launch October 8 in the Soyuz TMA-01M spacecraft to the International Space Station. Credit: NASA/Victor Zelentsov
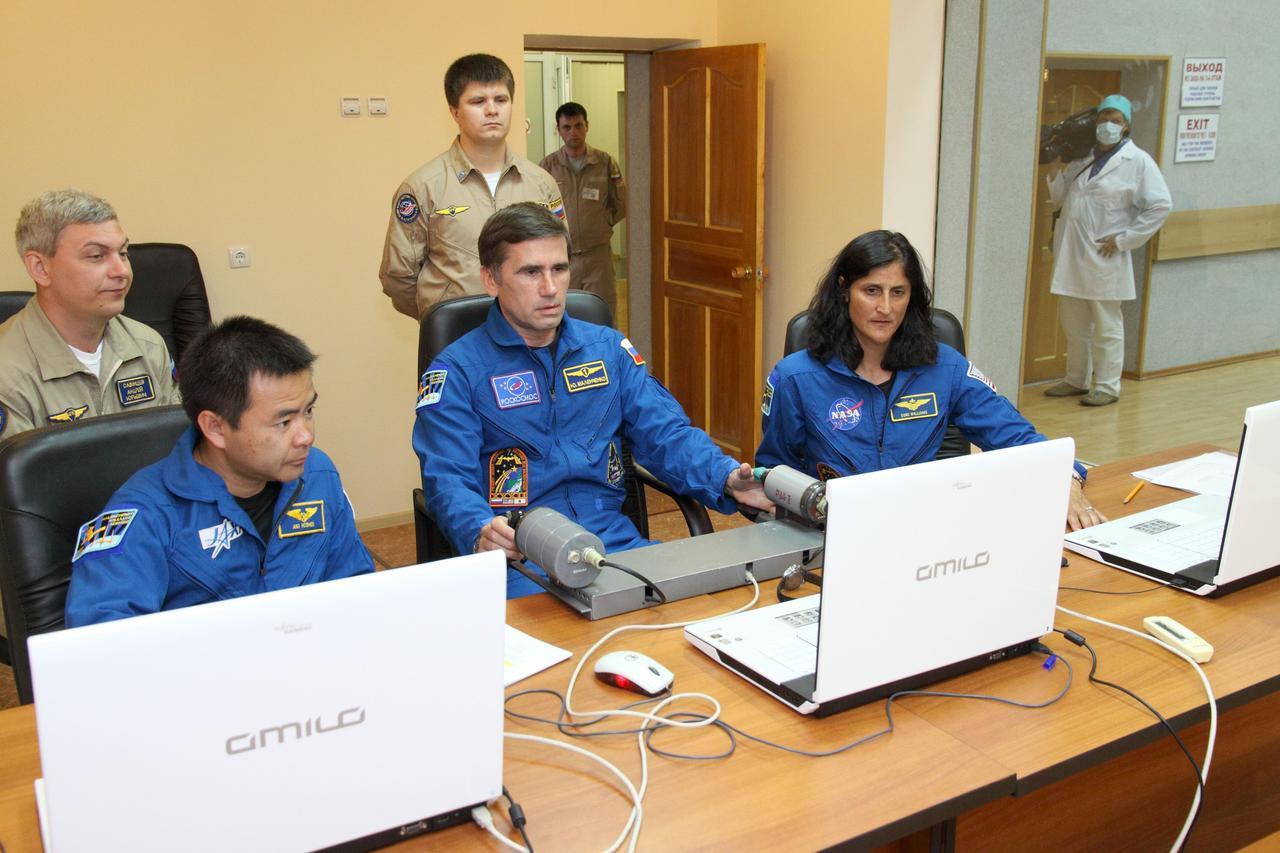

At their Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, the Expedition 32/33 prime crew members participate in a rendezvous and docking practice session using laptop computer simulators July 9, 2012 as they prepare for their launch July 15 to the International Space Station in their Soyuz TMA-05M spacecraft. From left to right with their instructors are Flight Engineer Aki Hoshide of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, Soyuz Commander Yuri Malenchenko and NASA Flight Engineer Sunita Williams. NASA/Victor Zelentsov

At their Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 50-51 crewmembers Peggy Whitson of NASA (left), Oleg Novitskiy of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos, center) and Thomas Pesquet of the European Space Agency (right) practice rendezvous and docking procedures on a laptop simulator computer Nov. 10 as part of their preflight training. They will launch Nov. 18, Baikonur time, on the Soyuz MS-03 spacecraft for a six-month mission on the International Space Station. NASA/Alexander Vysotsky
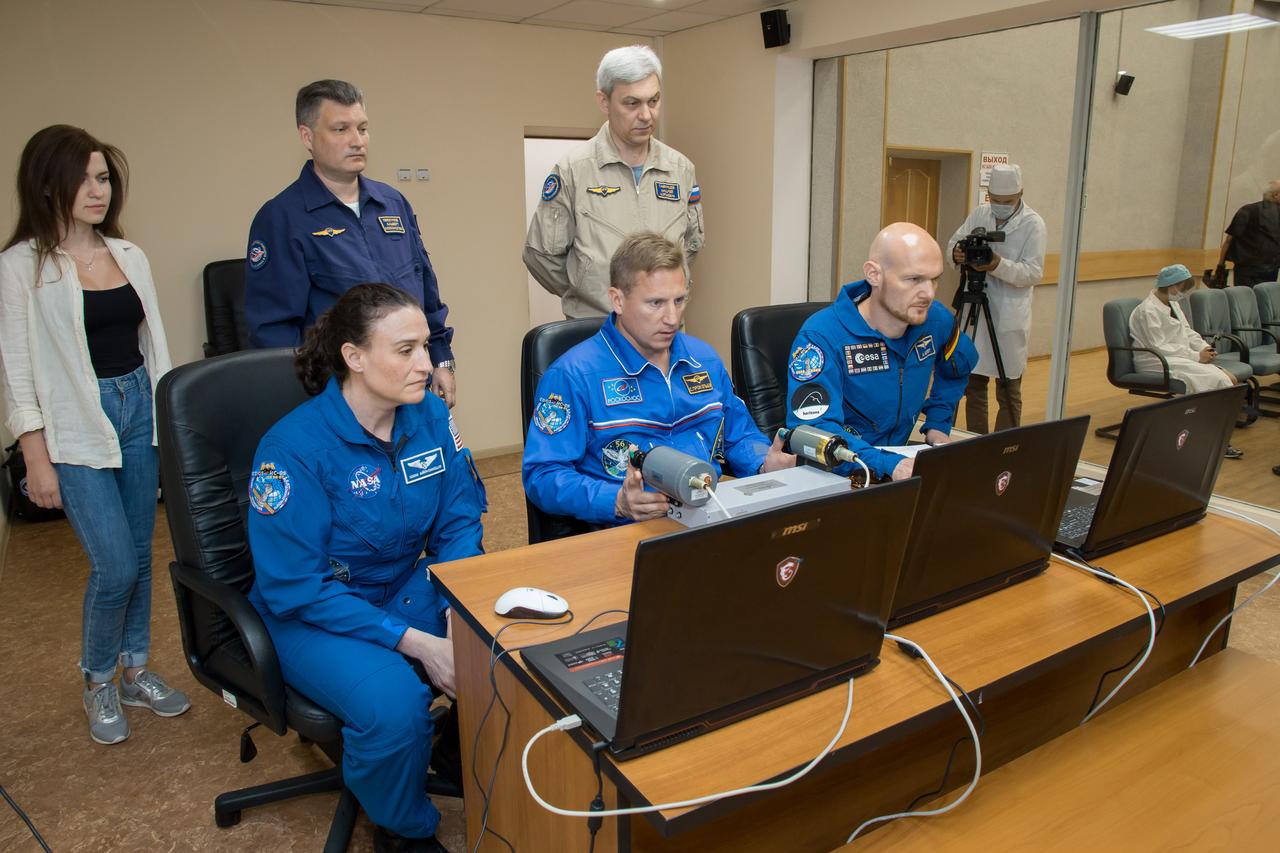

jsc2018e050820 - At the Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 56 crewmembers Serena Aunon-Chancellor of NASA (left), Sergey Prokopyev of Roscosmos (center) and Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency (right) conduct rendezvous and docking procedures on a laptop training simulator May 29 as part of their pre-launch preparations. Aunon-Chancellor, Prokopyev and Gerst will launch June 6 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on the Soyuz MS-09 spacecraft for a six-month mission on the International Space Station...NASA/Victor Zelentsov.
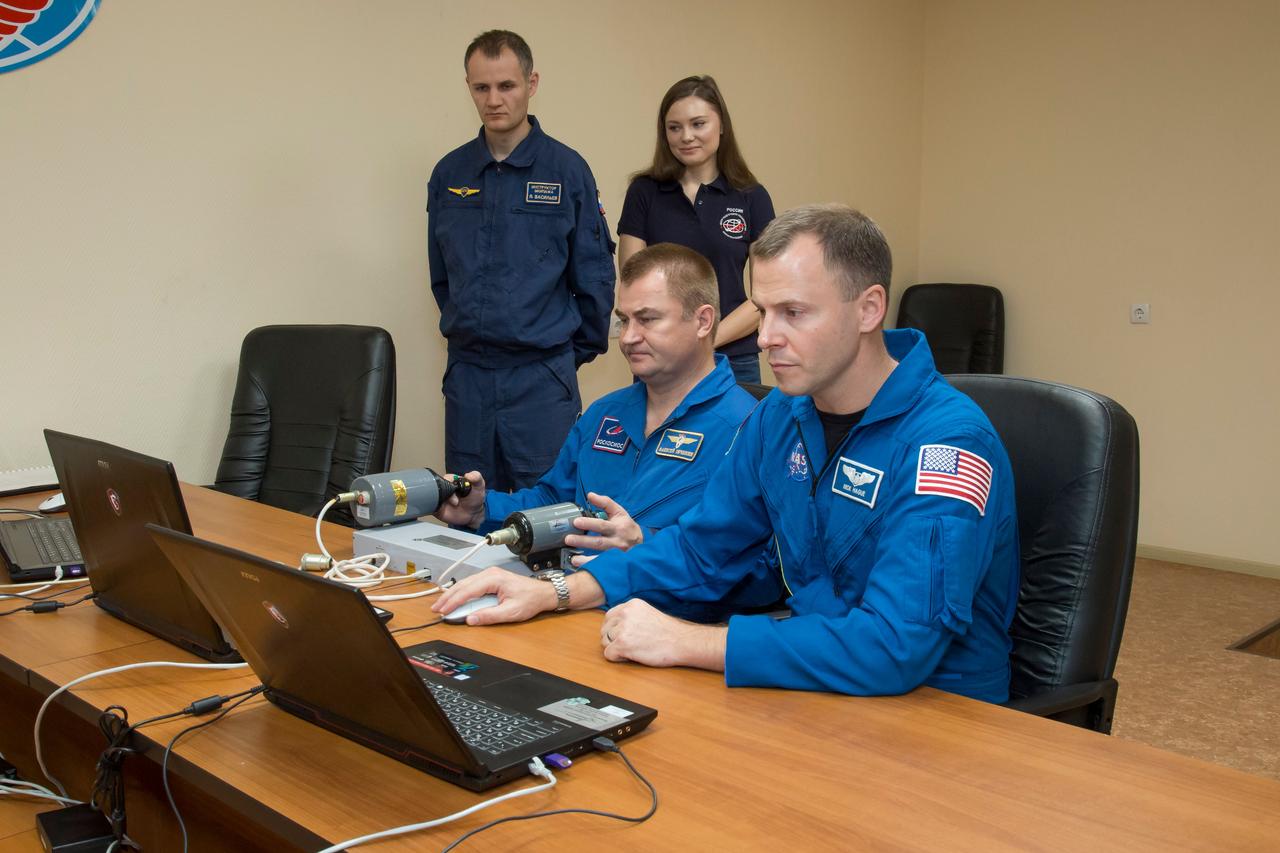

jsc2018e085890 (Oct. 3, 2018) --- Expedition 57 crew members Alexey Ovchinin of Roscosmos, left, and Nick Hague of NASA, right, conduct rendezvous and docking procedures on a laptop training simulator as part of their pre-launch preparations, Wednesday, Oct. 3, 2018 at the Cosmonaut Hotel in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Ovchinin and Hague are scheduled to launch on Oct. 11 onboard the Soyuz MS-10 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan for a six-month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Victor Zelentsov)

JSC2004-E-45159 (13 October 2004) --- Flight Director Paul Hill and Jennifer L. Hagin, lead Shuttle Data Processing Systems (DPS) officer, discuss the progress of the STS-114 fully-integrated simulations in the shuttle flight control room (WFCR) in Johnson Space Center’s (JSC) Mission Control Center (MCC). The seven member crew was in a JSC-based simulator during the sims. The dress rehearsal of Discovery's rendezvous and docking with the International Space Station (ISS) was the first flight-specific training for the Space Shuttle's return to flight.
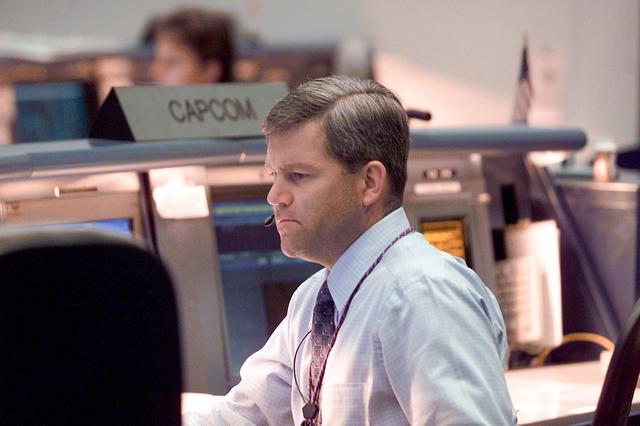

JSC2004-E-45138 (13 October 2004) --- Astronaut Stephen N. Frick monitors communications at the spacecraft communicator (CAPCOM) console in the Shuttle Flight Control Room (WFCR) in Johnson Space Center’s (JSC) Mission Control Center (MCC) with the STS-114 crewmembers during a fully-integrated simulation on October 13. The seven member crew was in a JSC-based simulator during the sims. The dress rehearsal of Discovery's rendezvous and docking with the International Space Station (ISS) was the first flight-specific training for the Space Shuttle's return to flight.

At their Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 59 backup crewmembers Drew Morgan of NASA (left), Alexander Skvortsov of Roscosmos (center) and Luca Parmitano of the European Space Agency (right) rehearse rendezvous and docking techniques on a laptop computer simulator March 7 as they conduct pre-launch preparations. They are the backups to the prime crewmembers, Christina Koch of NASA, Alexey Ovchinin of Roscosmos and Nick Hague of NASA, who will launch March 14, U.S. time, on the Soyuz MS-12 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome for a six-and-a-half month mission on the International Space Station...NASA/Victor Zelentsov.

jsc2017e137340 - At their Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 54-55 backup crewmembers Jeanette Epps of NASA (left), Sergey Prokopyev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos, center) and Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency (right) conduct rendezvous and docking runs on a laptop computer simulator Dec. 11. They are serving as backups to Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos and Scott Tingle of NASA who will launch Dec. 17 on the Soyuz MS-07 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome for a five month mission on the International Space Station...Andrey Shelepin / Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center.
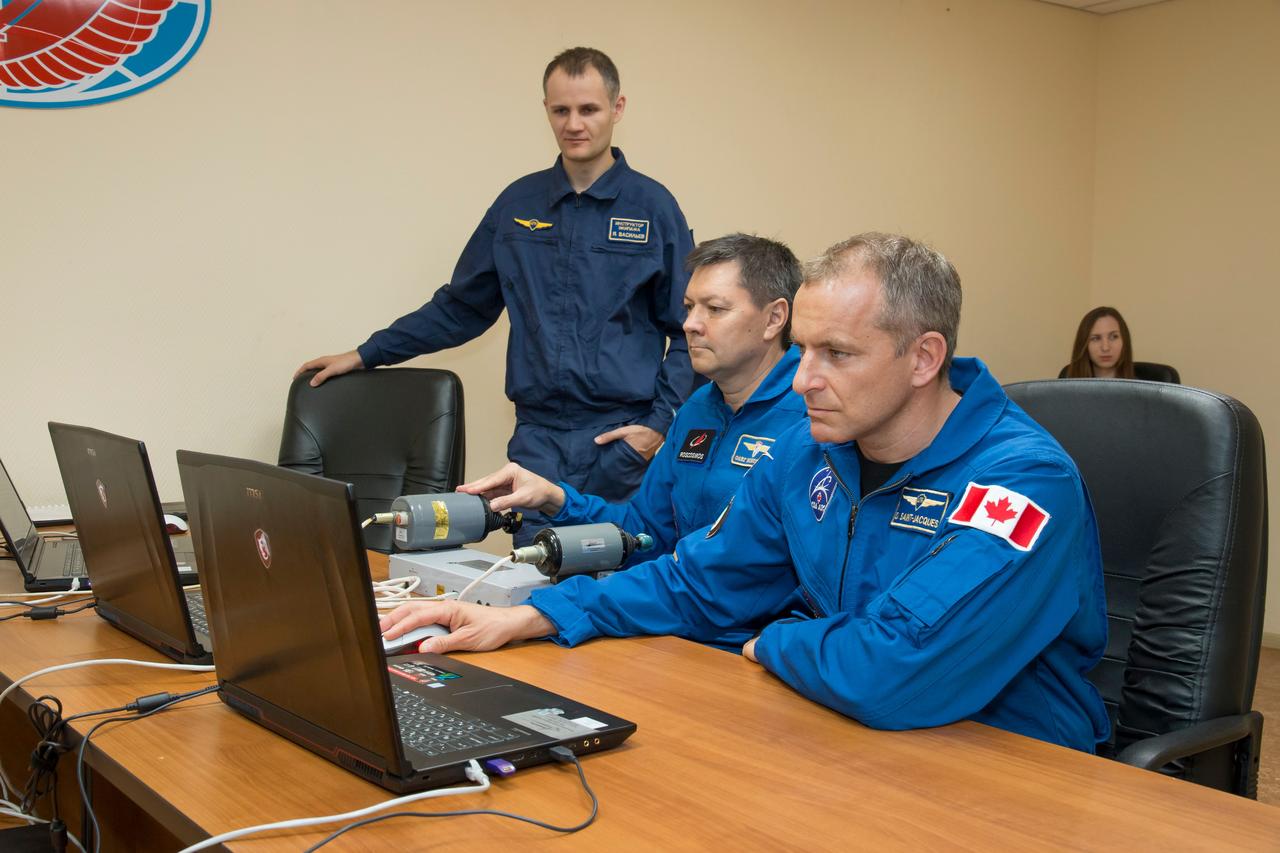

jsc2018e085894 (Oct. 3, 2018) --- Expedition 57 backup crew members Oleg Kononenko of Roscosmos, left, and David Saint-Jacques of the Canadian Space Agency, right, practice rendezvous and docking procedures on a laptop training simulator as part of their pre-launch preparations, Wednesday, Oct. 3, 2018 at the Cosmonaut Hotel in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Alexey Ovchinin of Roscosmos and Nick Hague of NASA are scheduled to launch on Oct. 11 onboard the Soyuz MS-10 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan for a six-month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Victor Zelentsov)
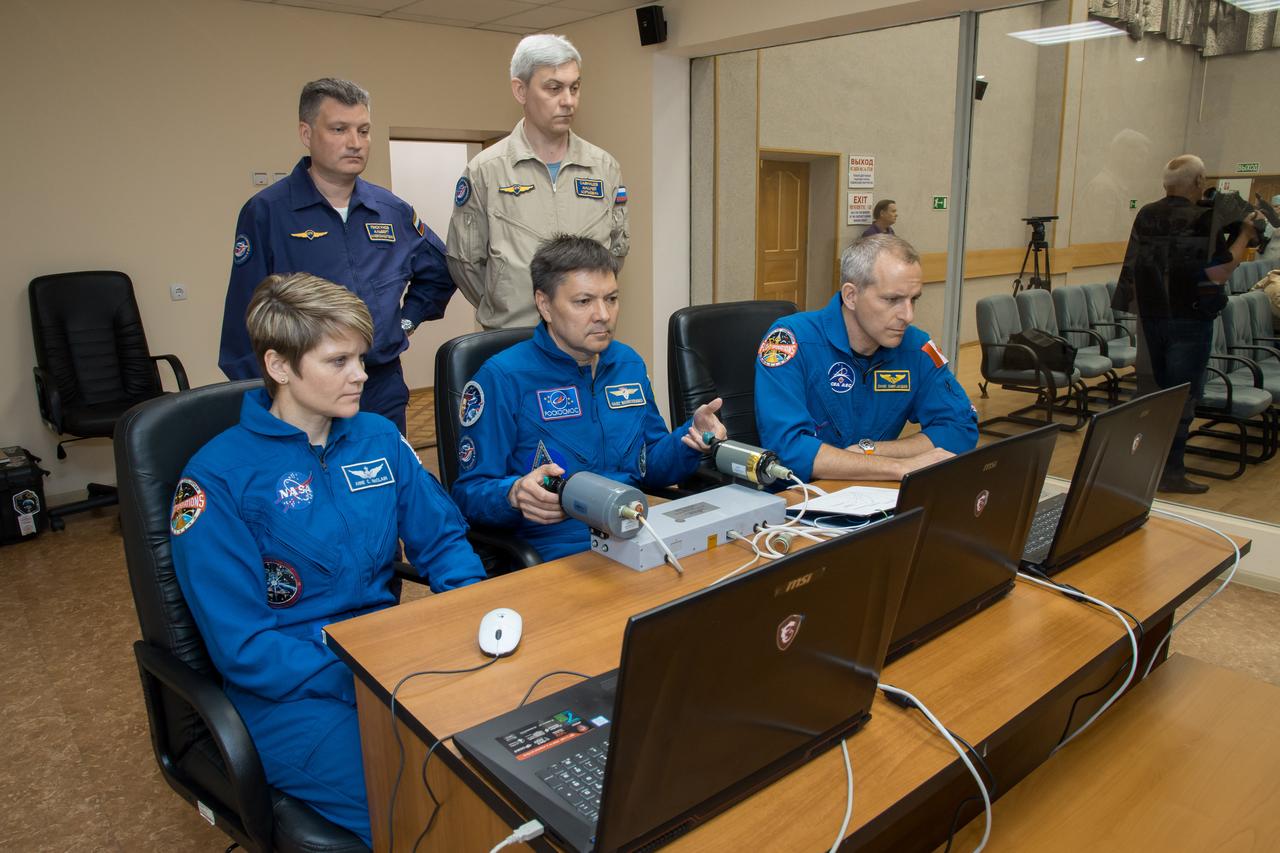

jsc2018e050822 - At the Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 56 backup crewmembers Anne McClain of NASA (left), Oleg Kononenko of Roscosmos (center) and David Saint-Jacques of the Canadian Space Agency (right) conduct rendezvous and docking procedures on a laptop training simulator May 29 as part of their pre-launch preparations. They are serving as backups to the prime crew, Serena Aunon-Chancellor of NASA, Sergey Prokopyev of Roscosmos and Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency, who will launch June 6 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on the Soyuz MS-09 spacecraft for a six-month mission on the International Space Station..NASA/Victor Zelentsov
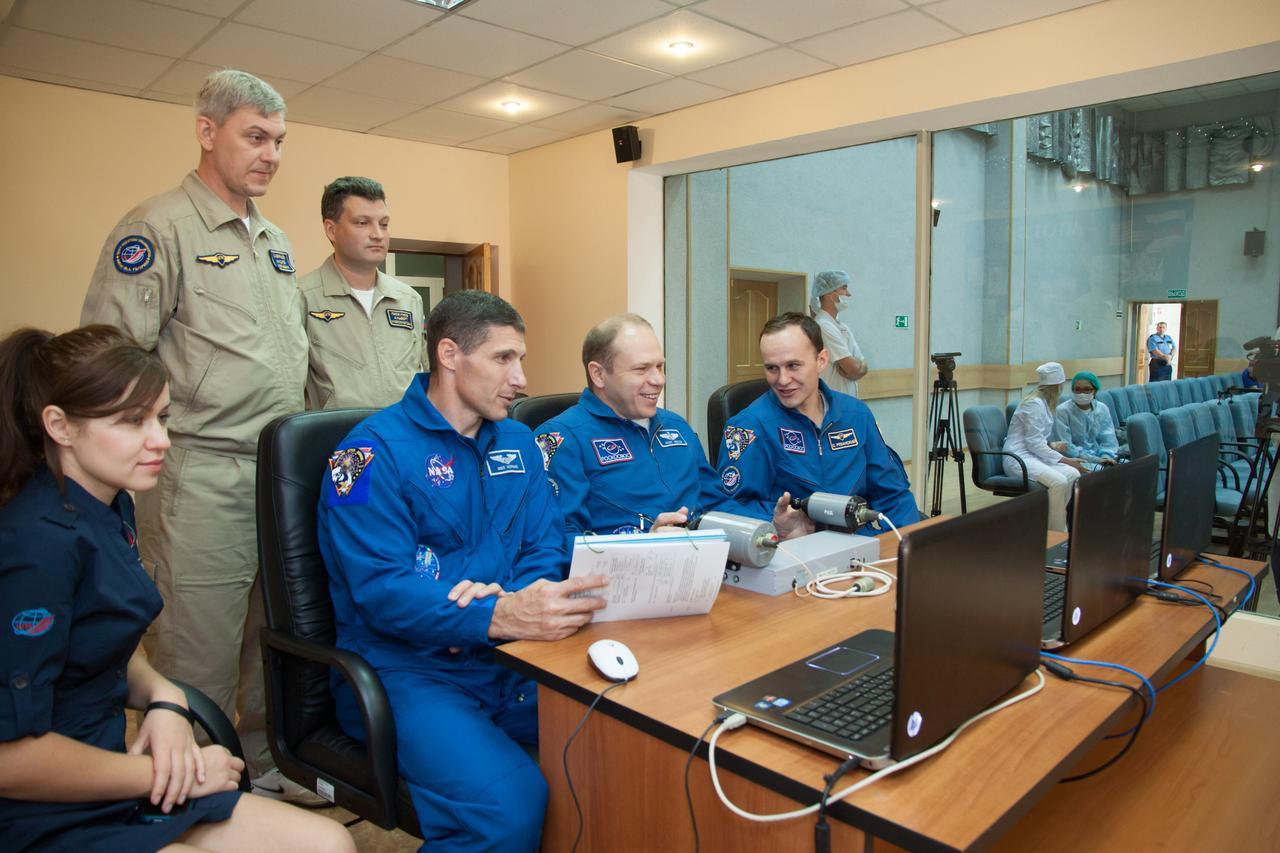

At their Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 37/38 Flight Engineer Michael Hopkins of NASA (left), Soyuz Commander Oleg Kotov (center) and Flight Engineer Sergey Ryazanskiy come under the watchful eye of training instructors Sept. 18 as they practice rendezvous and docking techniques on a laptop computer simulator. Hopkins, Kotov and Ryazanskiy are set to launch Sept. 26, Kazakh time, from the Baikonur Cosmodrome on their Soyuz TMA-10M spacecraft for a five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. NASA/Victor Zelentsov
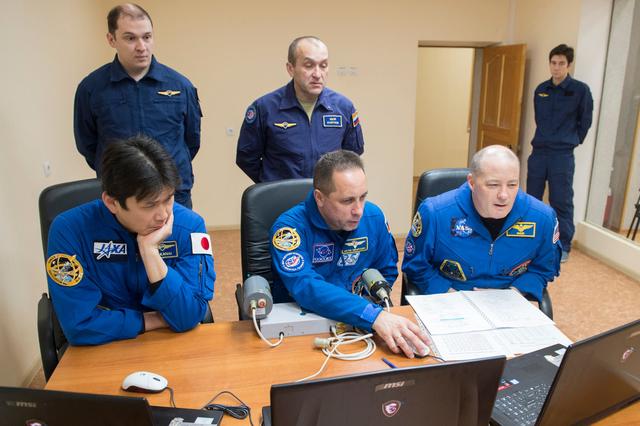

jsc2017e137334 - At their Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 54-55 prime crewmembers Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA, left), Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos, center) and Scott Tingle of NASA (right) practice rendezvous and docking techniques on a laptop computer simulator Dec. 11 as part of their pre-launch training. They will launch Dec. 17 on the Soyuz MS-07 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome for a five month mission on the International Space Station...Andrey Shelepin / Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center.

JSC2011-E-060127 (28 June 2011) --- The STS-135 crew practices rendezvous and docking with the International Space Station in the Systems Engineering Simulator at NASA?s Johnson Space Center in Houston June 28, 2011. NASA astronaut Chris Ferguson, commander, is at back left, and astronaut Rex Walheim, mission specialist, is at back right; and astronaut Doug Hurley, pilot, is at center. The session marked the crew's final scheduled training in the "Dome" in preparation for the final mission of the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA photo/Houston Chronicle, Smiley N. Pool
![Astronaut James Lovell at the controls of the Visual Docking Simulator. From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27-December 1, 1966. "This facility was [later known as the Visual-Optical Simulator.] It presents to the pilot an out-the-window view of his target in correct 6 degrees of freedom motion. The scene is obtained by a television camera pick-up viewing a small-scale gimbaled model of the target." "For docking studies, the docking target picture was projected onto the surface of a 20-foot-diameter sphere and the pilot could, effectively, maneuver into contract. this facility was used in a comparison study with the Rendezvous Docking Simulator - one of the few comparison experiments in which conditions were carefully controlled and a reasonable sample of pilots used. All pilots preferred the more realistic RDS visual scene. The pilots generally liked the RDS angular motion cues although some objected to the false gravity cues that these motions introduced. Training time was shorter on the RDS, but final performance on both simulators was essentially equal. " "For station-keeping studies, since close approach is not required, the target was presented to the pilot through a virtual-image system which projects his view to infinity, providing a more realistic effect. In addition to the target, the system also projects a star and horizon background. "](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/LRC-1963-B701_P-09093/LRC-1963-B701_P-09093~medium.jpg)
Astronaut James Lovell at the controls of the Visual Docking Simulator. From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27-December 1, 1966. "This facility was [later known as the Visual-Optical Simulator.] It presents to the pilot an out-the-window view of his target in correct 6 degrees of freedom motion. The scene is obtained by a television camera pick-up viewing a small-scale gimbaled model of the target." "For docking studies, the docking target picture was projected onto the surface of a 20-foot-diameter sphere and the pilot could, effectively, maneuver into contract. this facility was used in a comparison study with the Rendezvous Docking Simulator - one of the few comparison experiments in which conditions were carefully controlled and a reasonable sample of pilots used. All pilots preferred the more realistic RDS visual scene. The pilots generally liked the RDS angular motion cues although some objected to the false gravity cues that these motions introduced. Training time was shorter on the RDS, but final performance on both simulators was essentially equal. " "For station-keeping studies, since close approach is not required, the target was presented to the pilot through a virtual-image system which projects his view to infinity, providing a more realistic effect. In addition to the target, the system also projects a star and horizon background. "

Walter (Wally) M. Schirra in Visual Docking Simulator From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27-December 1, 1966. "This facility was [later known as the Visual-Optical Simulator. It presents to the pilot an out-the-window view of his target in correct 6 degrees of freedom motion. The scene is obtained by a television camera pick-up viewing a small-scale gimbaled model of the target. "For docking studies, the docking target picture was projected onto the surface of a 20-foot-diameter sphere and the pilot could, effectively, maneuver into contract. this facility was used in a comparison study with the Rendezvous Docking Simulator - one of the few comparison experiments in which conditions were carefully controlled and a reasonable sample of pilots used. All pilots preferred the more realistic RDS visual scene. The pilots generally liked the RDS angular motion cues although some objected to the false gravity cues that these motions introduced. Training time was shorter on the RDS, but final performance on both simulators was essentially equal. " "For station-keeping studies, since close approach is not required, the target was presented to the pilot through a virtual-image system which projects his view to infinity, providing a more realistic effect. In addition to the target, the system also projects a star and horizon background. "
![Astronaut Virgil "Gus" Grissom at the controls of the Visual Docking Simulator. From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27-December 1, 1966. "This facility was [later known as the Visual-Optical Simulator.] It presents to the pilot an out-the-window view of his target in correct 6 degrees of freedom motion. The scene is obtained by a television camera pick-up viewing a small-scale gimbaled model of the target." "For docking studies, the docking target picture was projected onto the surface of a 20-foot-diameter sphere and the pilot could, effectively, maneuver into contract. this facility was used in a comparison study with the Rendezvous Docking Simulator - one of the few comparison experiments in which conditions were carefully controlled and a reasonable sample of pilots used. All pilots preferred the more realistic RDS visual scene. The pilots generally liked the RDS angular motion cues although some objected to the false gravity cues that these motions introduced. Training time was shorter on the RDS, but final performance on both simulators was essentially equal. " "For station-keeping studies, since close approach is not required, the target was presented to the pilot through a virtual-image system which projects his view to infinity, providing a more realistic effect. In addition to the target, the system also projects a star and horizon background. "](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/LRC-1963-B701_P-01515/LRC-1963-B701_P-01515~medium.jpg)
Astronaut Virgil "Gus" Grissom at the controls of the Visual Docking Simulator. From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27-December 1, 1966. "This facility was [later known as the Visual-Optical Simulator.] It presents to the pilot an out-the-window view of his target in correct 6 degrees of freedom motion. The scene is obtained by a television camera pick-up viewing a small-scale gimbaled model of the target." "For docking studies, the docking target picture was projected onto the surface of a 20-foot-diameter sphere and the pilot could, effectively, maneuver into contract. this facility was used in a comparison study with the Rendezvous Docking Simulator - one of the few comparison experiments in which conditions were carefully controlled and a reasonable sample of pilots used. All pilots preferred the more realistic RDS visual scene. The pilots generally liked the RDS angular motion cues although some objected to the false gravity cues that these motions introduced. Training time was shorter on the RDS, but final performance on both simulators was essentially equal. " "For station-keeping studies, since close approach is not required, the target was presented to the pilot through a virtual-image system which projects his view to infinity, providing a more realistic effect. In addition to the target, the system also projects a star and horizon background. "
![Astronaut Virgil "Gus" Grissom at the controls of the Visual Docking Simulator. From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27-December 1, 1966. "This facility was [later known as the Visual-Optical Simulator.] It presents to the pilot an out-the-window view of his target in correct 6 degrees of freedom motion. The scene is obtained by a television camera pick-up viewing a small-scale gimbaled model of the target." "For docking studies, the docking target picture was projected onto the surface of a 20-foot-diameter sphere and the pilot could, effectively, maneuver into contract. this facility was used in a comparison study with the Rendezvous Docking Simulator - one of the few comparison experiments in which conditions were carefully controlled and a reasonable sample of pilots used. All pilots preferred the more realistic RDS visual scene. The pilots generally liked the RDS angular motion cues although some objected to the false gravity cues that these motions introduced. Training time was shorter on the RDS, but final performance on both simulators was essentially equal. " "For station-keeping studies, since close approach is not required, the target was presented to the pilot through a virtual-image system which projects his view to infinity, providing a more realistic effect. In addition to the target, the system also projects a star and horizon background. "](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/LRC-1963-B701_P-01516/LRC-1963-B701_P-01516~medium.jpg)
Astronaut Virgil "Gus" Grissom at the controls of the Visual Docking Simulator. From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27-December 1, 1966. "This facility was [later known as the Visual-Optical Simulator.] It presents to the pilot an out-the-window view of his target in correct 6 degrees of freedom motion. The scene is obtained by a television camera pick-up viewing a small-scale gimbaled model of the target." "For docking studies, the docking target picture was projected onto the surface of a 20-foot-diameter sphere and the pilot could, effectively, maneuver into contract. this facility was used in a comparison study with the Rendezvous Docking Simulator - one of the few comparison experiments in which conditions were carefully controlled and a reasonable sample of pilots used. All pilots preferred the more realistic RDS visual scene. The pilots generally liked the RDS angular motion cues although some objected to the false gravity cues that these motions introduced. Training time was shorter on the RDS, but final performance on both simulators was essentially equal. " "For station-keeping studies, since close approach is not required, the target was presented to the pilot through a virtual-image system which projects his view to infinity, providing a more realistic effect. In addition to the target, the system also projects a star and horizon background. "
![Astronaut Frank Borman at the controls of the Visual Docking Simulator. From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27-December 1, 1966. "This facility was [later known as the Visual-Optical Simulator.] It presents to the pilot an out-the-window view of his target in correct 6 degrees of freedom motion. The scene is obtained by a television camera pick-up viewing a small-scale gimbaled model of the target." "For docking studies, the docking target picture was projected onto the surface of a 20-foot-diameter sphere and the pilot could, effectively, maneuver into contract. this facility was used in a comparison study with the Rendezvous Docking Simulator - one of the few comparison experiments in which conditions were carefully controlled and a reasonable sample of pilots used. All pilots preferred the more realistic RDS visual scene. The pilots generally liked the RDS angular motion cues although some objected to the false gravity cues that these motions introduced. Training time was shorter on the RDS, but final performance on both simulators was essentially equal. " "For station-keeping studies, since close approach is not required, the target was presented to the pilot through a virtual-image system which projects his view to infinity, providing a more realistic effect. In addition to the target, the system also projects a star and horizon background. "](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/LRC-1963-B701_P-09368/LRC-1963-B701_P-09368~medium.jpg)
Astronaut Frank Borman at the controls of the Visual Docking Simulator. From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27-December 1, 1966. "This facility was [later known as the Visual-Optical Simulator.] It presents to the pilot an out-the-window view of his target in correct 6 degrees of freedom motion. The scene is obtained by a television camera pick-up viewing a small-scale gimbaled model of the target." "For docking studies, the docking target picture was projected onto the surface of a 20-foot-diameter sphere and the pilot could, effectively, maneuver into contract. this facility was used in a comparison study with the Rendezvous Docking Simulator - one of the few comparison experiments in which conditions were carefully controlled and a reasonable sample of pilots used. All pilots preferred the more realistic RDS visual scene. The pilots generally liked the RDS angular motion cues although some objected to the false gravity cues that these motions introduced. Training time was shorter on the RDS, but final performance on both simulators was essentially equal. " "For station-keeping studies, since close approach is not required, the target was presented to the pilot through a virtual-image system which projects his view to infinity, providing a more realistic effect. In addition to the target, the system also projects a star and horizon background. "
![Astronaut Charles Conrad at the controls of the Visual Docking Simulator. From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27-December 1, 1966. "This facility was [later known as the Visual-Optical Simulator.] It presents to the pilot an out-the-window view of his target in correct 6 degrees of freedom motion. The scene is obtained by a television camera pick-up viewing a small-scale gimbaled model of the target." "For docking studies, the docking target picture was projected onto the surface of a 20-foot-diameter sphere and the pilot could, effectively, maneuver into contract. this facility was used in a comparison study with the Rendezvous Docking Simulator - one of the few comparison experiments in which conditions were carefully controlled and a reasonable sample of pilots used. All pilots preferred the more realistic RDS visual scene. The pilots generally liked the RDS angular motion cues although some objected to the false gravity cues that these motions introduced. Training time was shorter on the RDS, but final performance on both simulators was essentially equal. " "For station-keeping studies, since close approach is not required, the target was presented to the pilot through a virtual-image system which projects his view to infinity, providing a more realistic effect. In addition to the target, the system also projects a star and horizon background. "](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/LRC-1963-B701_P-09519/LRC-1963-B701_P-09519~medium.jpg)
Astronaut Charles Conrad at the controls of the Visual Docking Simulator. From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27-December 1, 1966. "This facility was [later known as the Visual-Optical Simulator.] It presents to the pilot an out-the-window view of his target in correct 6 degrees of freedom motion. The scene is obtained by a television camera pick-up viewing a small-scale gimbaled model of the target." "For docking studies, the docking target picture was projected onto the surface of a 20-foot-diameter sphere and the pilot could, effectively, maneuver into contract. this facility was used in a comparison study with the Rendezvous Docking Simulator - one of the few comparison experiments in which conditions were carefully controlled and a reasonable sample of pilots used. All pilots preferred the more realistic RDS visual scene. The pilots generally liked the RDS angular motion cues although some objected to the false gravity cues that these motions introduced. Training time was shorter on the RDS, but final performance on both simulators was essentially equal. " "For station-keeping studies, since close approach is not required, the target was presented to the pilot through a virtual-image system which projects his view to infinity, providing a more realistic effect. In addition to the target, the system also projects a star and horizon background. "
![Astronaut James Lovell at the controls of the Visual Docking Simulator. From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27-December 1, 1966. "This facility was [later known as the Visual-Optical Simulator.] It presents to the pilot an out-the-window view of his target in correct 6 degrees of freedom motion. The scene is obtained by a television camera pick-up viewing a small-scale gimbaled model of the target." "For docking studies, the docking target picture was projected onto the surface of a 20-foot-diameter sphere and the pilot could, effectively, maneuver into contract. this facility was used in a comparison study with the Rendezvous Docking Simulator - one of the few comparison experiments in which conditions were carefully controlled and a reasonable sample of pilots used. All pilots preferred the more realistic RDS visual scene. The pilots generally liked the RDS angular motion cues although some objected to the false gravity cues that these motions introduced. Training time was shorter on the RDS, but final performance on both simulators was essentially equal. " "For station-keeping studies, since close approach is not required, the target was presented to the pilot through a virtual-image system which projects his view to infinity, providing a more realistic effect. In addition to the target, the system also projects a star and horizon background. "](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/LRC-1963-B701_P-09094/LRC-1963-B701_P-09094~medium.jpg)
Astronaut James Lovell at the controls of the Visual Docking Simulator. From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27-December 1, 1966. "This facility was [later known as the Visual-Optical Simulator.] It presents to the pilot an out-the-window view of his target in correct 6 degrees of freedom motion. The scene is obtained by a television camera pick-up viewing a small-scale gimbaled model of the target." "For docking studies, the docking target picture was projected onto the surface of a 20-foot-diameter sphere and the pilot could, effectively, maneuver into contract. this facility was used in a comparison study with the Rendezvous Docking Simulator - one of the few comparison experiments in which conditions were carefully controlled and a reasonable sample of pilots used. All pilots preferred the more realistic RDS visual scene. The pilots generally liked the RDS angular motion cues although some objected to the false gravity cues that these motions introduced. Training time was shorter on the RDS, but final performance on both simulators was essentially equal. " "For station-keeping studies, since close approach is not required, the target was presented to the pilot through a virtual-image system which projects his view to infinity, providing a more realistic effect. In addition to the target, the system also projects a star and horizon background. "
![Astronauts Charles Conrad (left) and John W. Young (right) at the controls of the Visual Docking Simulator. From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27-December 1, 1966. "This facility was [later known as the Visual-Optical Simulator.] It presents to the pilot an out-the-window view of his target in correct 6 degrees of freedom motion. The scene is obtained by a television camera pick-up viewing a small-scale gimbaled model of the target." "For docking studies, the docking target picture was projected onto the surface of a 20-foot-diameter sphere and the pilot could, effectively, maneuver into contract. this facility was used in a comparison study with the Rendezvous Docking Simulator - one of the few comparison experiments in which conditions were carefully controlled and a reasonable sample of pilots used. All pilots preferred the more realistic RDS visual scene. The pilots generally liked the RDS angular motion cues although some objected to the false gravity cues that these motions introduced. Training time was shorter on the RDS, but final performance on both simulators was essentially equal. " "For station-keeping studies, since close approach is not required, the target was presented to the pilot through a virtual-image system which projects his view to infinity, providing a more realistic effect. In addition to the target, the system also projects a star and horizon background. "](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/LRC-1963-B701_P-09520/LRC-1963-B701_P-09520~medium.jpg)
Astronauts Charles Conrad (left) and John W. Young (right) at the controls of the Visual Docking Simulator. From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27-December 1, 1966. "This facility was [later known as the Visual-Optical Simulator.] It presents to the pilot an out-the-window view of his target in correct 6 degrees of freedom motion. The scene is obtained by a television camera pick-up viewing a small-scale gimbaled model of the target." "For docking studies, the docking target picture was projected onto the surface of a 20-foot-diameter sphere and the pilot could, effectively, maneuver into contract. this facility was used in a comparison study with the Rendezvous Docking Simulator - one of the few comparison experiments in which conditions were carefully controlled and a reasonable sample of pilots used. All pilots preferred the more realistic RDS visual scene. The pilots generally liked the RDS angular motion cues although some objected to the false gravity cues that these motions introduced. Training time was shorter on the RDS, but final performance on both simulators was essentially equal. " "For station-keeping studies, since close approach is not required, the target was presented to the pilot through a virtual-image system which projects his view to infinity, providing a more realistic effect. In addition to the target, the system also projects a star and horizon background. "

AS07-03-1535 (11 Oct. 1968) --- The expended Saturn IVB stage as photographed from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during transposition and docking maneuvers at an altitude of 126 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of three hours, 11 minutes. The round, white disc inside the open panels of the Saturn IVB is a simulated docking target similar to that used on the lunar module for docking during lunar missions. The spacecraft is directly over Odessa-Midland, Texas. The view between the two panels (area of large puffy clouds) extends southwest across Texas into the Mexican State of Chihuahua. The distance between the Apollo 7 spacecraft and the S-IVB is approximately 50 feet.
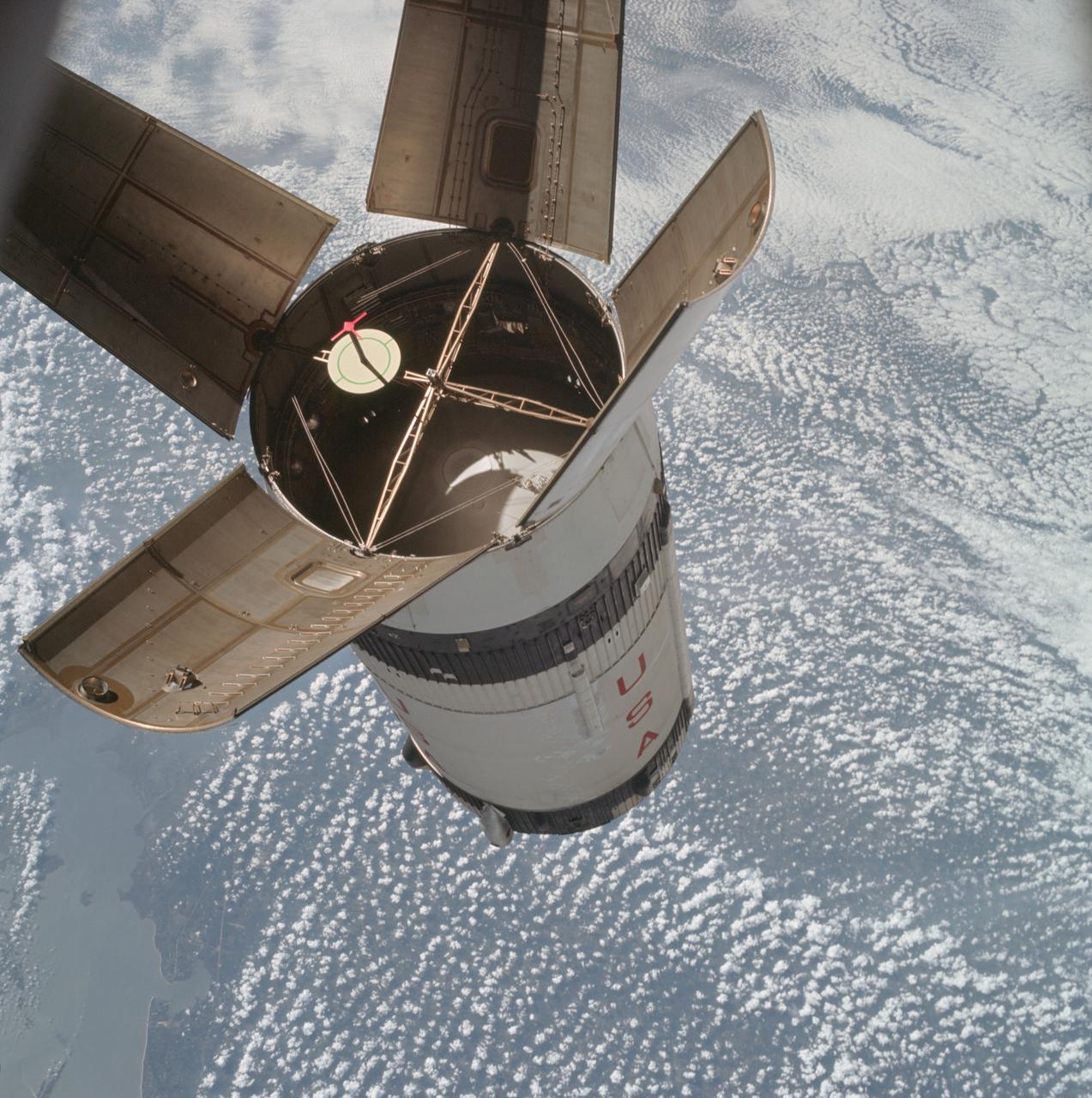

AS07-03-1541 (11 Oct. 1968) --- The expended Saturn IVB stage as photographed from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during transposition and docking maneuvers. St. Louis Bay and Lake Borgne area just east of New Orleans is seen below. The round, white disc inside the open panels of the Saturn IVB is a simulated docking target similar to that used on the lunar module for docking during lunar missions.
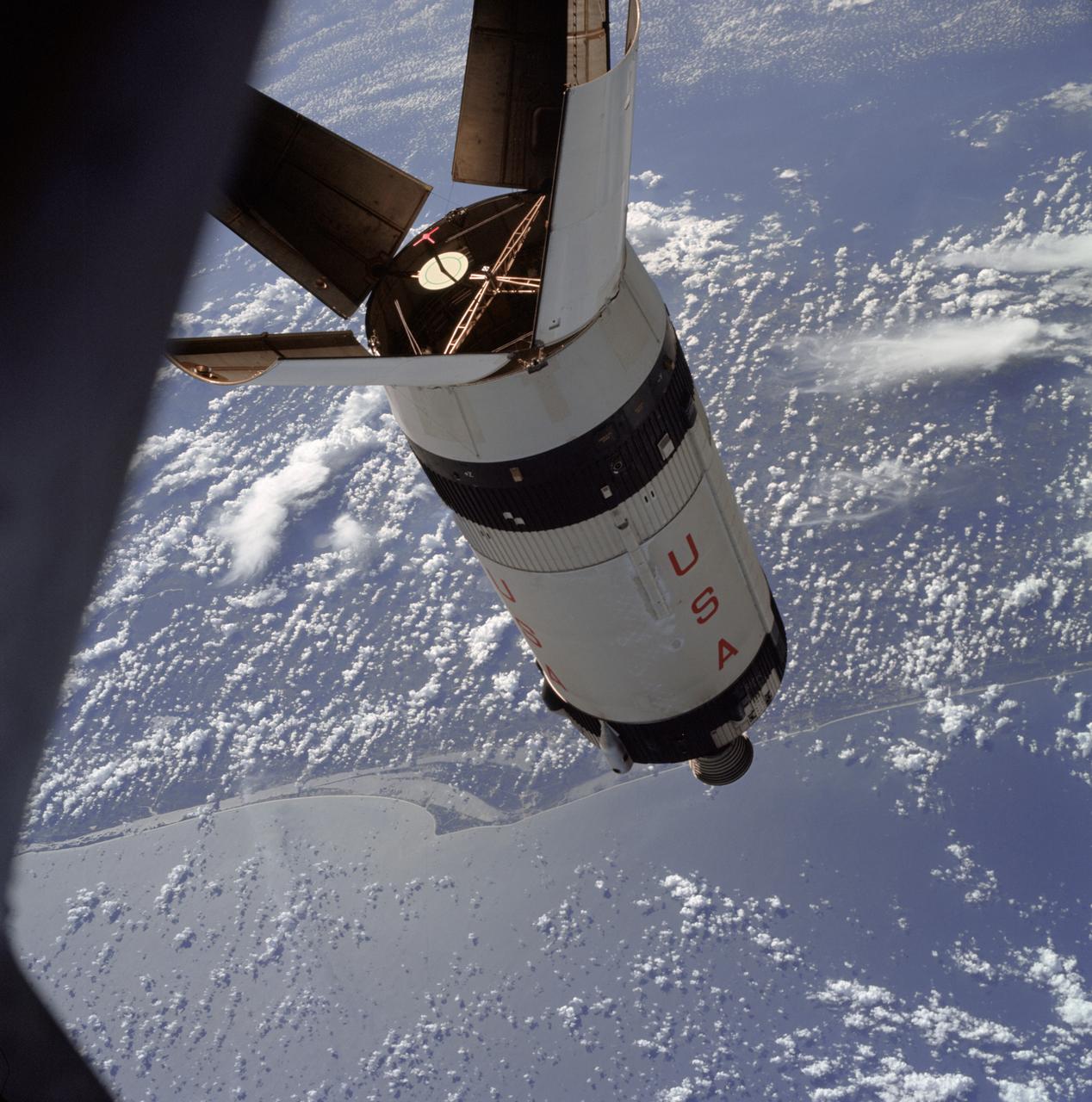

AS07-03-1545 (11 Oct. 1968) --- The expended Saturn S-IVB stage as photographed from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during transposition and docking maneuvers at an approximate altitude of 125 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of three hours and 16 minutes (beginning of third revolution). This view is over the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Cape Kennedy, Florida. The Florida coastline from Flagler Beach southward to Vero Beach is clearly visible in picture. Much of the Florida peninsula can be seen. Behind the open panels is the Gulf of Mexico. Distance between the Apollo 7 spacecraft and the S-IVB is approximately 100 feet. The round, white disc inside the open panels of the S-IVB is a simulated docking target similar to that used on the Lunar Module (LM) for docking during lunar missions.
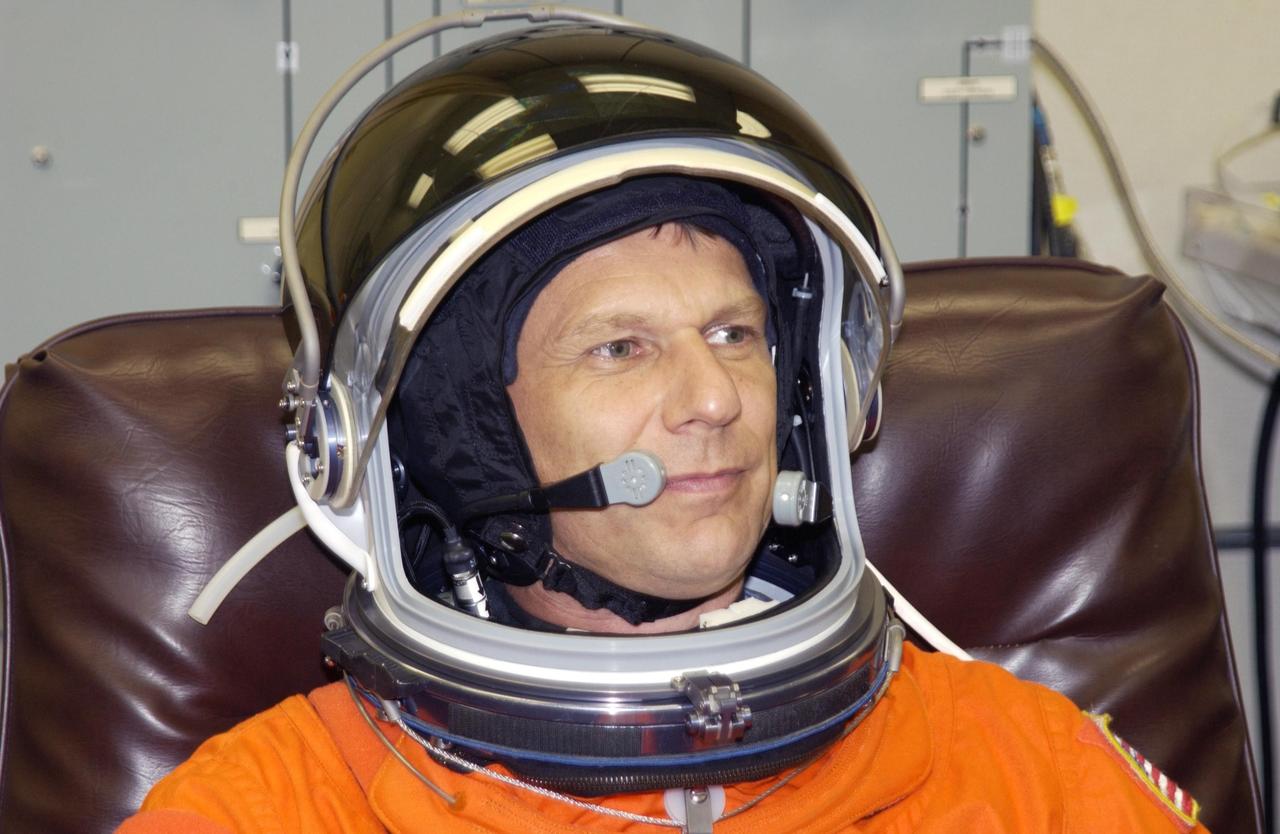

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - STS-112 Mission Specialist Piers Sellers tries out his helmet during suit check, part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. The TCDT also includes emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 2, between 2 and 6 p.m. EDT. STS-112 is the 15th assembly mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis will be carrying the S1 Integrated Truss Structure, the first starboard truss segment. The S1 will be attached to the central truss segment, S0, during the 11-day mission. Sellers will be undertaking three spacewalks during the mission. In addition, he will be in charge of on-board computers and rendezvous tools during Atlantis' approach for docking and the undocking and flyaround. STS-112 is Sellers first Shuttle flight.

17-11-28-20-2: (17 Sept. 2014) --- At the Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 41/42 backup crewmembers Scott Kelly of NASA (left), Mikhail Kornienko of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), center, and Gennady Padalka of Roscosmos brush up on rendezvous and docking skills Sept. 17 on a laptop computer simulator. The three are backups to Flight Engineer Barry Wilmore of NASA, Soyuz Commander Alexander Samokutyaev of Roscosmos and Flight Engineer Elena Serova of Roscosmos who are scheduled to launch from the Baikonur Cosmodrome Sept. 26, Kazakh time, in the Soyuz TMA-14M spacecraft for a 5 ½ month mission on the International Space Station. Serova will become the fourth Russian woman to fly in space and the first Russian woman to live and work on the station. Kelly and Kornienko will launch in March 2015 to spend a full year on the station. Photo credit: NASA/Victor Zelentsov
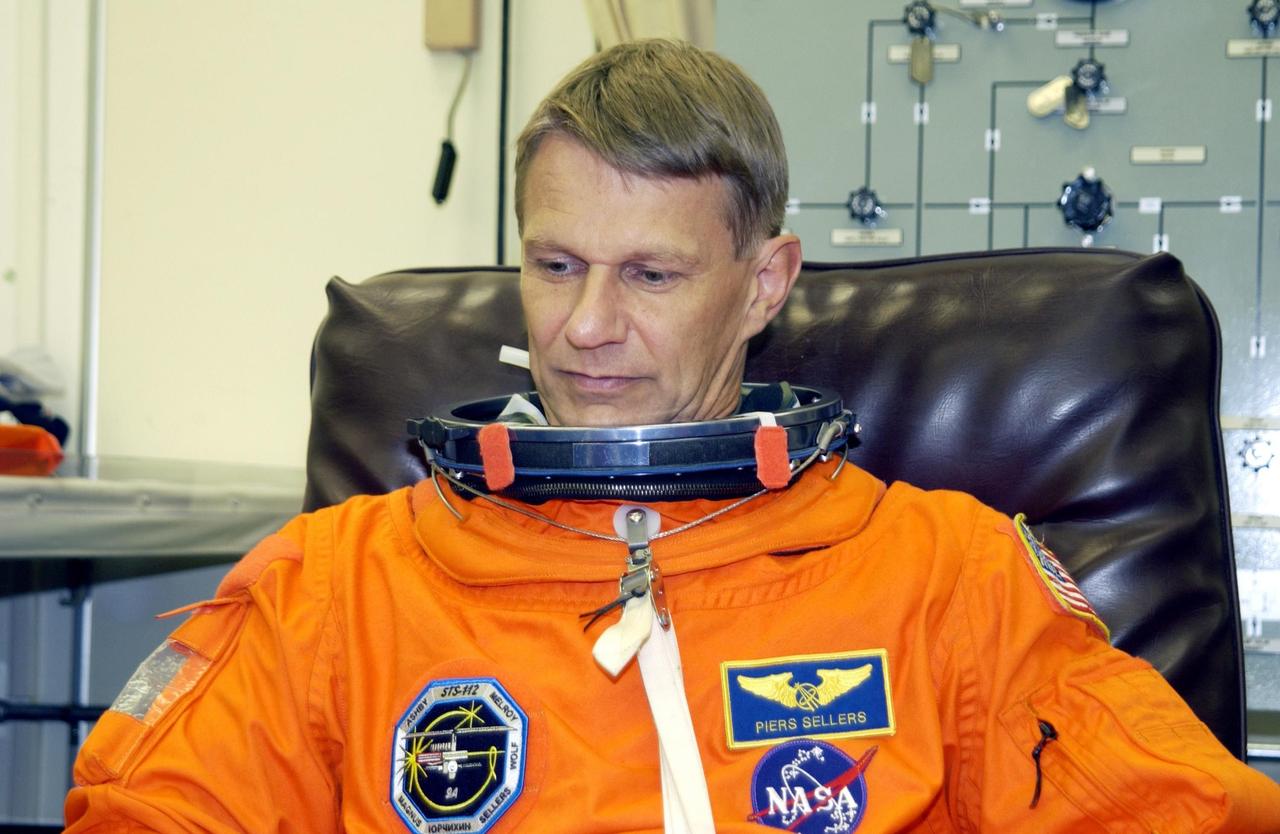

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - STS-112 Mission Specialist Piers Sellers undergoes suit check, part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. The TCDT also includes emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 2, between 2 and 6 p.m. EDT. STS-112 is the 15th assembly mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis will be carrying the S1 Integrated Truss Structure, the first starboard truss segment. The S1 will be attached to the central truss segment, S0, during the 11-day mission. Sellers will be undertaking three spacewalks during the mission. In addition, he will be in charge of on-board computers and rendezvous tools during Atlantis' approach for docking and the undocking and flyaround. STS-112 is Sellers first Shuttle flight.
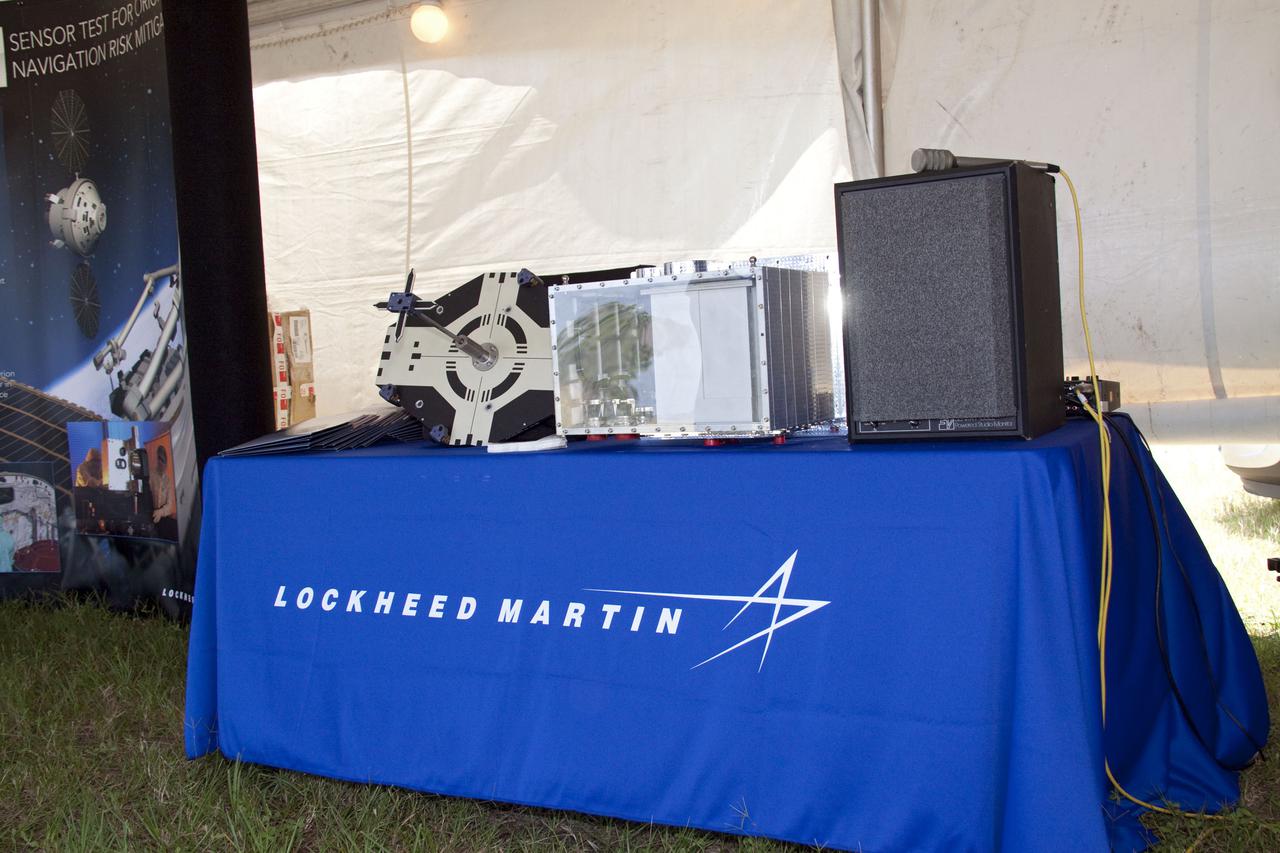

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A model of the Sensor Test for Orion Relnav Risk Mitigation, or STORRM, is displayed at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Seen here, is the International Space Station docking target and STORMM sensor enclosure assembly. A flight test of STORRM will be performed on STS-134 on the last on-orbit day of the mission, when space shuttle Endeavour will fly a dedicated maneuver to simulate an Orion rendezvous trajectory. Throughout the maneuver, two Orion sensors will collect visual- and laser-based relative navigation data. This will provide an unprecedented in-flight test opportunity for America's next-generation exploration spacecraft. STS-134 also will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour was scheduled to launch at 3:47 p.m. on April 29, but that attempt was scrubbed for at least 72 hours while engineers assess an issue associated with the shuttle's Auxiliary Power Unit 1. STS-134 will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts134_index.html. Photo credit: NASA_Jack Pfaller
![Test subject wearing jet-shoe apparatus and resting in sling support. The cables are not attached. From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27 - December 1, 1966. "As mentioned previously, Langley is conducting in-house and contract studies of extra-vehicular activities wherein zero gravity is simulated by the water-immersion technique. ... Water immersion is a very useful technique where motions are slow. When more rapid motion is required, as in studying one-man propulsion systems, other approaches are required. For these studies Langley has been using the RDS [Rendezvous Docking Simulator] in a manner similar to the LLRF [Lunar Landing Research Facility] technique. The test subjects are suspended in a sling support from a single RDS cable. As they translate about, the RDS tracks them, keeping the cable vertical. The test subjects operate in an effectively zero g environment in the horizontal plane. Tracking was originally done visually using closed-circuit TV, but recently a fast-response servo system using cable angle sensors has provided better operation. Some results of tests where subjects moved about merely by jumping and also where propulsion in the form of simple "jet-shoes" was provided are given in reference 20. Both methods, within limits, appear feasible. Full six-degree-of-freedom equipment for studies of more sophisticated one-man propulsion systems is now being procured. Called OMPRA (One-Man Propulsion Research Apparatus), the device will provide a gimbal system for rotational freedom, a quick response vertical servo for this translational freedom that is not now feasible with the RDS, and a versatile maneuvering unit."](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/LRC-1967-B701_P-01373/LRC-1967-B701_P-01373~medium.jpg)
Test subject wearing jet-shoe apparatus and resting in sling support. The cables are not attached. From A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27 - December 1, 1966. "As mentioned previously, Langley is conducting in-house and contract studies of extra-vehicular activities wherein zero gravity is simulated by the water-immersion technique. ... Water immersion is a very useful technique where motions are slow. When more rapid motion is required, as in studying one-man propulsion systems, other approaches are required. For these studies Langley has been using the RDS [Rendezvous Docking Simulator] in a manner similar to the LLRF [Lunar Landing Research Facility] technique. The test subjects are suspended in a sling support from a single RDS cable. As they translate about, the RDS tracks them, keeping the cable vertical. The test subjects operate in an effectively zero g environment in the horizontal plane. Tracking was originally done visually using closed-circuit TV, but recently a fast-response servo system using cable angle sensors has provided better operation. Some results of tests where subjects moved about merely by jumping and also where propulsion in the form of simple "jet-shoes" was provided are given in reference 20. Both methods, within limits, appear feasible. Full six-degree-of-freedom equipment for studies of more sophisticated one-man propulsion systems is now being procured. Called OMPRA (One-Man Propulsion Research Apparatus), the device will provide a gimbal system for rotational freedom, a quick response vertical servo for this translational freedom that is not now feasible with the RDS, and a versatile maneuvering unit."
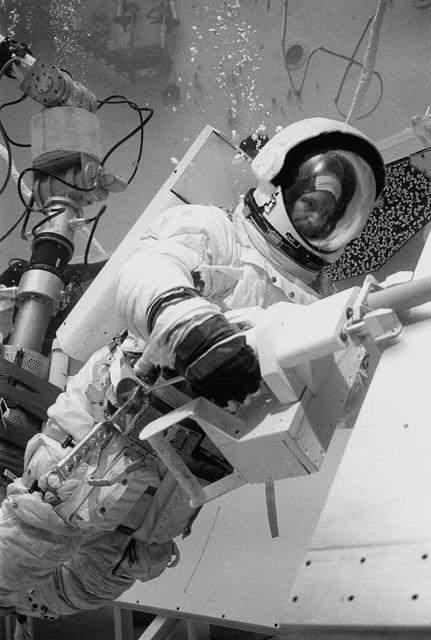

In February 1980, a satellite called Solar Maximum Mission Spacecraft, or Solar Max, was launched into Earth's orbit. Its primary objective was to provide a detailed study of solar flares, active regions on the Sun's surface, sunspots, and other solar activities. Additionally, it was to measure the total output of radiation from the Sun. Not much was known about solar activity at that time except for a slight knowledge of solar flares. After its launch, Solar Max fulfilled everyone's expectations. However, after a year in orbit, Solar Max's Altitude Control System malfunctioned, preventing the precise pointing of instruments at the Sun. NASA scientists were disappointed at the lost data, but not altogether dismayed because Solar Max had been designed for Space Shuttle retrievability enabling repair of the satellite. On April 6, 1984, Space Shuttle Challenger (STS-41C), Commanded by astronaut Robert L. Crippen and piloted by Francis R. Scobee, launched on a historic voyage. This voyage initiated a series of firsts for NASA; the first satellite retrieval, the first service use of a new space system called the Marned Maneuvering Unit (MMU), the first in-orbit repair, the first use of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), and the Space Shuttle Challenger's first space flight. The mission was successful in retrieving Solar Max. Mission Specialist Dr. George D. Nelson, using the MMU, left the orbiter's cargo bay and rendezvoused with Solar Max. After attaching himself to the satellite, he awaited the orbiter to maneuver itself nearby. Using the RMS, Solar Max was captured and docked in the cargo bay while Dr. Nelson replaced the altitude control system and the coronagraph/polarimeter electronics box. After the repairs were completed, Solar Max was redeposited in orbit with the assistance of the RMS. Prior to the April 1984 launch, countless man-hours were spent preparing for this mission. The crew of Challenger spent months at Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) practicing retrieval maneuvers, piloting the MMU, and training on equipment so they could make the needed repairs to Solar Max. Pictured is Dr. Nelson performing a replacement task on the Solar Max mock-up in the NBS.
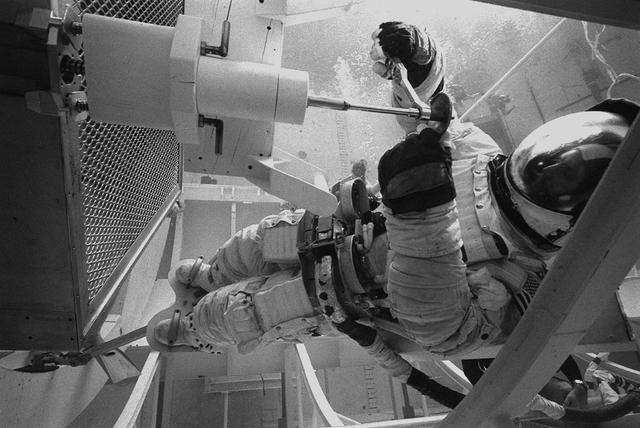

In February 1980, a satellite called Solar Maximum Mission Spacecraft, or Solar Max, was launched into Earth's orbit. Its primary objective was to provide a detailed study of solar flares,active regions on the Sun's surface, sunspots, and other solar activities. Additionally, it was to measure the total output of radiation from the Sun. Not much was known about solar activity at that time except for a slight knowledge of solar flares. After its launch, Solar Max fulfilled everyone's expectations. However, after a year in orbit, Solar Max's Altitude Control System malfunctioned, preventing the precise pointing of instruments at the Sun. NASA scientists were disappointed at the lost data, but not altogether dismayed because Solar Max had been designed for Space Shuttle retrievability enabling the repair of the satellite. On April 6, 1984, Space Shuttle Challenger (STS-41C), Commanded by astronaut Robert L. Crippen and piloted by Francis R. Scobee, launched on a historic voyage. This voyage initiated a series of firsts for NASA; the first satellite retrieval, the first service use of a new space system called the Marned Maneuvering Unit (MMU), the first in-orbit repair, the first use of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), and the Space Shuttle Challenger's first space flight. The mission was successful in retrieving Solar Max. Mission Specialist Dr. George D. Nelson, using the MMU, left the orbiter's cargo bay and rendezvoused with Solar Max. After attaching himself to the satellite, he awaited the orbiter to maneuver itself nearby. Using the RMS, Solar Max was captured and docked in the cargo bay while Dr. Nelson replaced the altitude control system and the coronagraph/polarimeter electronics box. After the repairs were completed, Solar Max was redeposited in orbit with the assistance of the RMS. Prior to the April 1984 launch, countless man-hours were spent preparing for this mission. The crew of Challenger spent months at Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) practicing retrieval maneuvers, piloting the MMU, and training on equipment so they could make the needed repairs to Solar Max. Pictured is Dr. Nelson performing a replacement task on the Solar Max mock-up in the NBS.
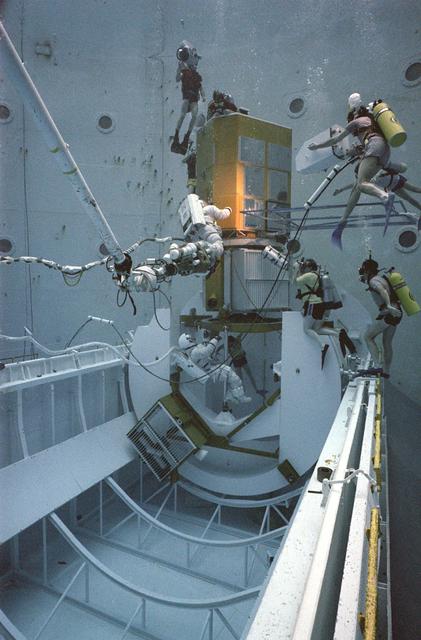

In February 1980, a satellite called Solar Maximum Mission Spacecraft, or Solar Max, was launched into Earth's orbit. Its primary objective was to provide a detailed study of solar flares, active regions on the Sun's surface, sunspots, and other solar activities. Additionally, it was to measure the total output of radiation from the Sun. Not much was known about solar activity at that time except for a slight knowledge of solar flares. After its launch, Solar Max fulfilled everyone's expectations. However, after a year in orbit, Solar Max's Altitude Control System malfunctioned, preventing the precise pointing of instruments at the Sun. NASA scientists were disappointed at the lost data, but not altogether dismayed because Solar Max had been designed for Space Shuttle retrievability enabling the repair of the satellite. On April 6, 1984, Space Shuttle Challenger (STS-41C), Commanded by astronaut Robert L. Crippen and piloted by Francis R. Scobee, launched on a historic voyage. This voyage initiated a series of firsts for NASA; the first satellite retrieval, the first service use of a new space system called the Marned Maneuvering Unit (MMU), the first in-orbit repair, the first use of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), and the Space Shuttle Challenger's first space flight. The mission was successful in retrieving Solar Max. Mission Specialist Dr. George D. Nelson, using the MMU, left the orbiter's cargo bay and rendezvoused with Solar Max. After attaching himself to the satellite, he awaited the orbiter to maneuver itself nearby. Using the RMS, Solar Max was captured and docked in the cargo bay while Dr. Nelson replaced the altitude control system and the coronagraph/polarimeter electronics box. After the repairs were completed, Solar Max was redeposited in orbit with the assistance of the RMS. Prior to the April 1984 launch, countless man-hours were spent preparing for this mission. The crew of Challenger spent months at Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) practicing retrieval maneuvers, piloting the MMU, and training on equipment so they could make the needed repairs to Solar Max. Pictured are crew members training for repair tasks.
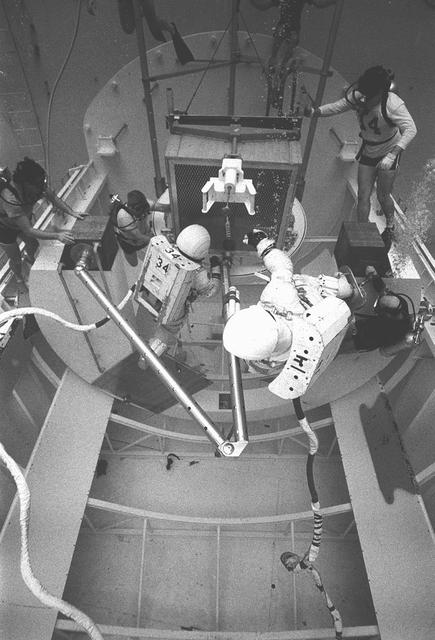

In February 1980, a satellite called Solar Maximum Mission Spacecraft, or Solar Max, was launched into Earth's orbit. Its primary objective was to provide a detailed study of solar flares, active regions on the Sun's surface, sunspots, and other solar activities. Additionally, it was to measure the total output of radiation from the Sun. Not much was known about solar activity at that time except for a slight knowledge of solar flares. After its launch, Solar Max fulfilled everyone's expectations. However, after a year in orbit, Solar Max's Altitude Control System malfunctioned, preventing the precise pointing of instruments at the Sun. NASA scientists were disappointed at the lost data, but not altogether dismayed because Solar Max had been designed for Space Shuttle retrievability enabling the repair of the satellite. On April 6, 1984, Space Shuttle Challenger (STS-41C), Commanded by astronaut Robert L. Crippen and piloted by Francis R. Scobee, launched on a historic voyage. This voyage initiated a series of firsts for NASA; the first satellite retrieval, the first service use of a new space system called the Marned Maneuvering Unit (MMU), the first in-orbit repair, the first use of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), and the Space Shuttle Challenger's first space flight. The mission was successful in retrieving Solar Max. Mission Specialist Dr. George D. Nelson, using the MMU, left the orbiter's cargo bay and rendezvoused with Solar Max. After attaching himself to the satellite, he awaited the orbiter to maneuver itself nearby. Using the RMS, Solar Max was captured and docked in the cargo bay while Dr. Nelson replaced the altitude control system and the coronagraph/polarimeter electronics box. After the repairs were completed, Solar Max was redeposited in orbit with the assistance of the RMS. Prior to the April 1984 launch, countless man-hours were spent preparing for this mission. The crew of Challenger spent months at Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) practicing retrieval maneuvers, piloting the MMU, and training on equipment so they could make the needed repairs to Solar Max. Pictured are crew members training on repair tasks.
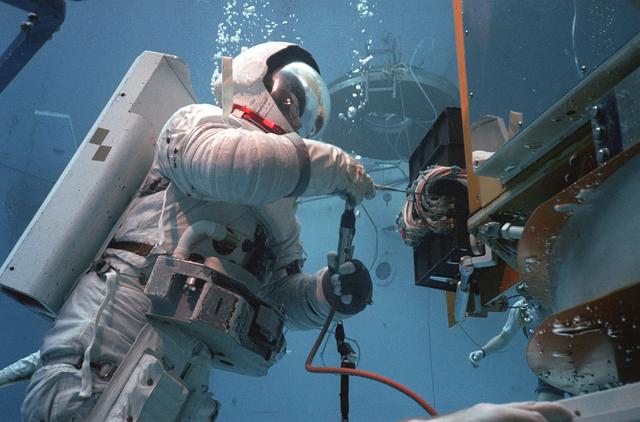

In February 1980, a satellite called Solar Maximum Mission Spacecraft, or Solar Max, was launched into Earth's orbit. Its primary objective was to provide a detailed study of solar flares, active regions on the Sun's surface, sunspots, and other solar activities. Additionally, it was to measure the total output of radiation from the Sun. Not much was known about solar activity at that time except for a slight knowledge of solar flares. After its launch, Solar Max fulfilled everyone's expectations. However, after a year in orbit, Solar Max's Altitude Control System malfunctioned, preventing the precise pointing of instruments at the Sun. NASA scientists were disappointed at the lost data, but not altogether dismayed because Solar Max had been designed for Space Shuttle retrievability enabling the repair of the satellite. On April 6, 1984, Space Shuttle Challenger (STS-41C), Commanded by astronaut Robert L. Crippen and piloted by Francis R. Scobee, launched on a historic voyage. This voyage initiated a series of firsts for NASA; the first satellite retrieval, the first service use of a new space system called the Marned Maneuvering Unit (MMU), the first in-orbit repair, the first use of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), and the Space Shuttle Challenger's first space flight. The mission was successful in retrieving Solar Max. Mission Specialist Dr. George D. Nelson, using the MMU, left the orbiter's cargo bay and rendezvoused with Solar Max. After attaching himself to the satellite, he awaited the orbiter to maneuver itself nearby. Using the RMS, Solar Max was captured and docked in the cargo bay while Dr. Nelson replaced the altitude control system and the coronagraph/polarimeter electronics box. After the repairs were completed, Solar Max was redeposited in orbit with the assistance of the RMS. Prior to the April 1984 launch, countless man-hours were spent preparing for this mission. The crew of Challenger spent months at Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) practicing retrieval maneuvers, piloting the MMU, and training on equipment so they could make the needed repairs to Solar Max. Pictured is Dr. Nelson performing a replacement task on the Solar Max mock-up in the NBS.
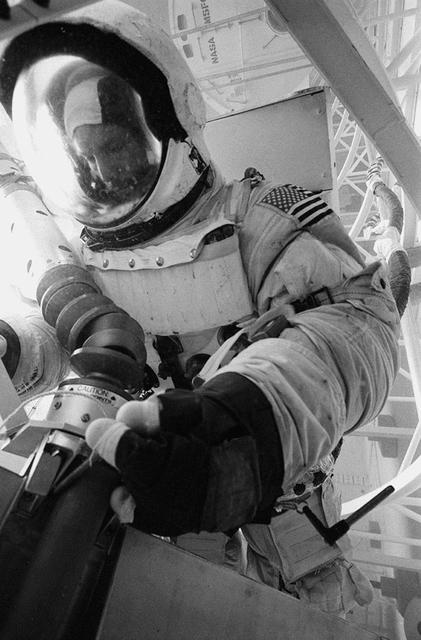

In February 1980, a satellite called Solar Maximum Mission Spacecraft, or Solar Max, was launched into Earth's orbit. Its primary objective was to provide a detailed study of solar flares,active regions on the Sun's surface, sunspots, and other solar activities. Additionally, it was to measure the total output of radiation from the Sun. Not much was known about solar activity at that time except for a slight knowledge of solar flares. After its launch, Solar Max fulfilled everyone's expectations. However, after a year in orbit, Solar Max's Altitude Control System malfunctioned, preventing the precise pointing of instruments at the Sun. NASA scientists were disappointed at the lost data, but not altogether dismayed because Solar Max had been designed for Space Shuttle retrievability, enabling repair to the satellite. On April 6, 1984, Space Shuttle Challenger (STS-41C), Commanded by astronaut Robert L. Crippen and piloted by Francis R. Scobee, launched on a historic voyage. This voyage initiated a series of firsts for NASA; the first satellite retrieval, the first service use of a new space system called the Marned Maneuvering Unit (MMU), the first in-orbit repair, the first use of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), and the Space Shuttle Challenger's first space flight. The mission was successful in retrieving Solar Max. Mission Specialist Dr. George D. Nelson, using the MMU, left the orbiter's cargo bay and rendezvoused with Solar Max. After attaching himself to the satellite, he awaited the orbiter to maneuver itself nearby. Using the RMS, Solar Max was captured and docked in the cargo bay while Dr. Nelson replaced the altitude control system and the coronagraph/polarimeter electronics box. After the repairs were completed, Solar Max was redeposited in orbit with the assistance of the RMS. Prior to the April 1984 launch, countless man-hours were spent preparing for this mission. The crew of Challenger spent months at Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) practicing retrieval maneuvers, piloting the MMU, and training on equipment so they could make the needed repairs to Solar Max. Pictured is Dr. Nelson performing a replacement task on the Solar Max mock-up in the NBS.