
Mark Pestana is a research pilot and project manager at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif. He is a pilot for the Beech B200 King Air, the T-34C and the Predator B. He flies the F-18 Hornet as a co-pilot and flight test engineer. Pestana has accumulated more than 4,000 hours of military and civilian flight experience. He was also a flight engineer on the NASA DC-8 flying laboratory. Pestana was the project manager and pilot for the Hi–rate Wireless Airborne Network Demonstration flown on the NASA B200 research aircraft. He flew B200 research missions for the X-38 Space Integrated Inertial Navigation Global Positioning System experiment. Pestana also participated in several deployments of the DC-8, including Earth science expeditions ranging from hurricane research over the Caribbean Sea to ozone studies over the North Pole, atmospheric chemistry over the South Pacific, rain forest health in Central America, Rocky Mountain ice pack assessment, and volcanic and tectonic activity around the Pacific Rim. He came to Dryden as a DC-8 mission manager in June 1998 from NASA Johnson Space Center, Houston, where he served as the Earth and Space Science discipline manager for the International Space Station Program at Johnson. Pestana also served as a flight crew operations engineer in the Astronaut Office, developing the controls, displays, tools, crew accommodations and procedures for on-orbit assembly, test, and checkout of the International Space Station. He led the analysis and technical negotiations for modification of the Russian Soyuz spacecraft as an emergency crew return vehicle for space station crews. He joined the U.S. Air Force Reserve in 1991 and held various positions as a research and development engineer, intelligence analyst, and Delta II launch vehicle systems engineer. He retired from the U.S. Air Force Reserve with the rank of colonel in 2005. Prior to 1990, Pestana was on active duty with the U.S. Air Force as the director of mi
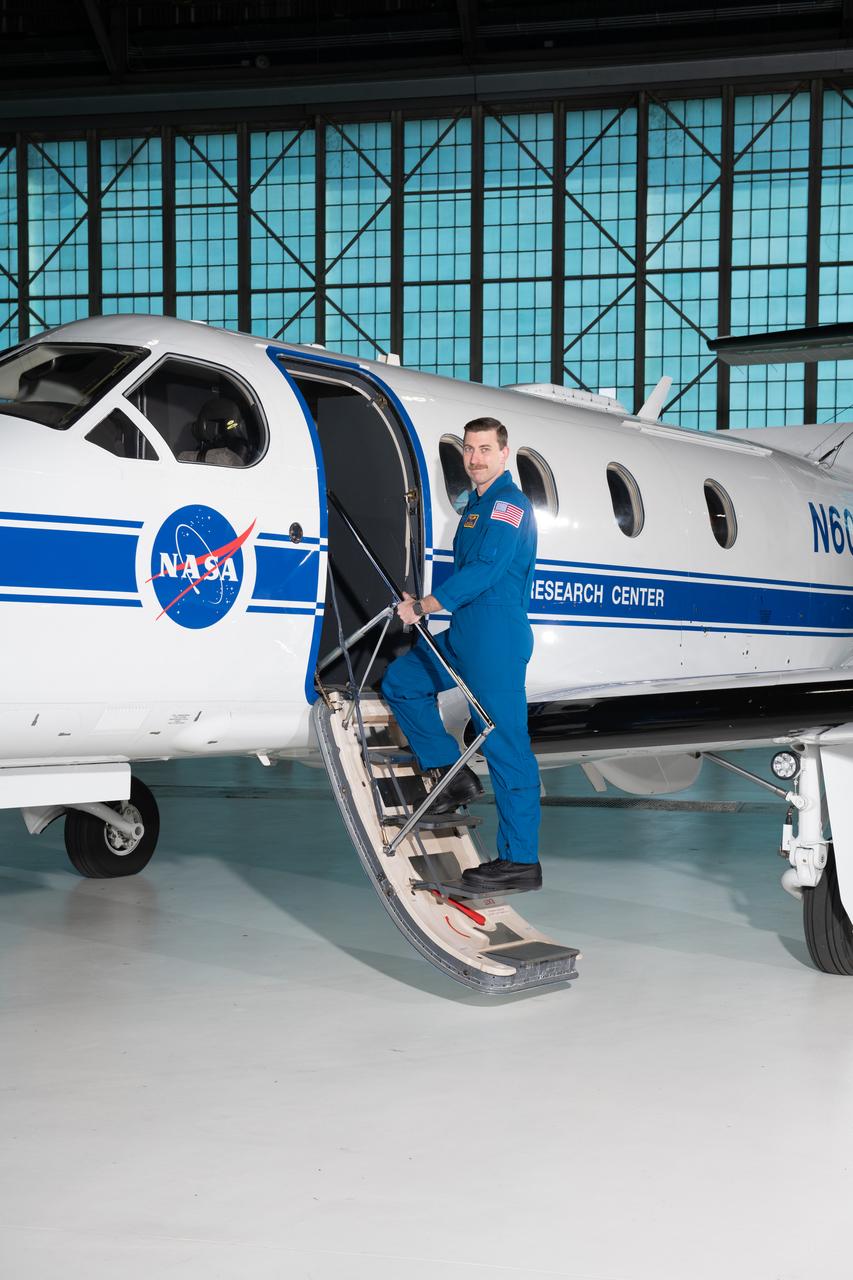

Jeremy Johnson, a research pilot and aviation safety officer, poses in front of a PC-12 aircraft inside the hangar at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland on Thursday, April 17, 2025. Johnson flies NASA planes to support important scientific research and testing, working with researchers to plan and carry out flights that will get them the data they need while ensuring safety.
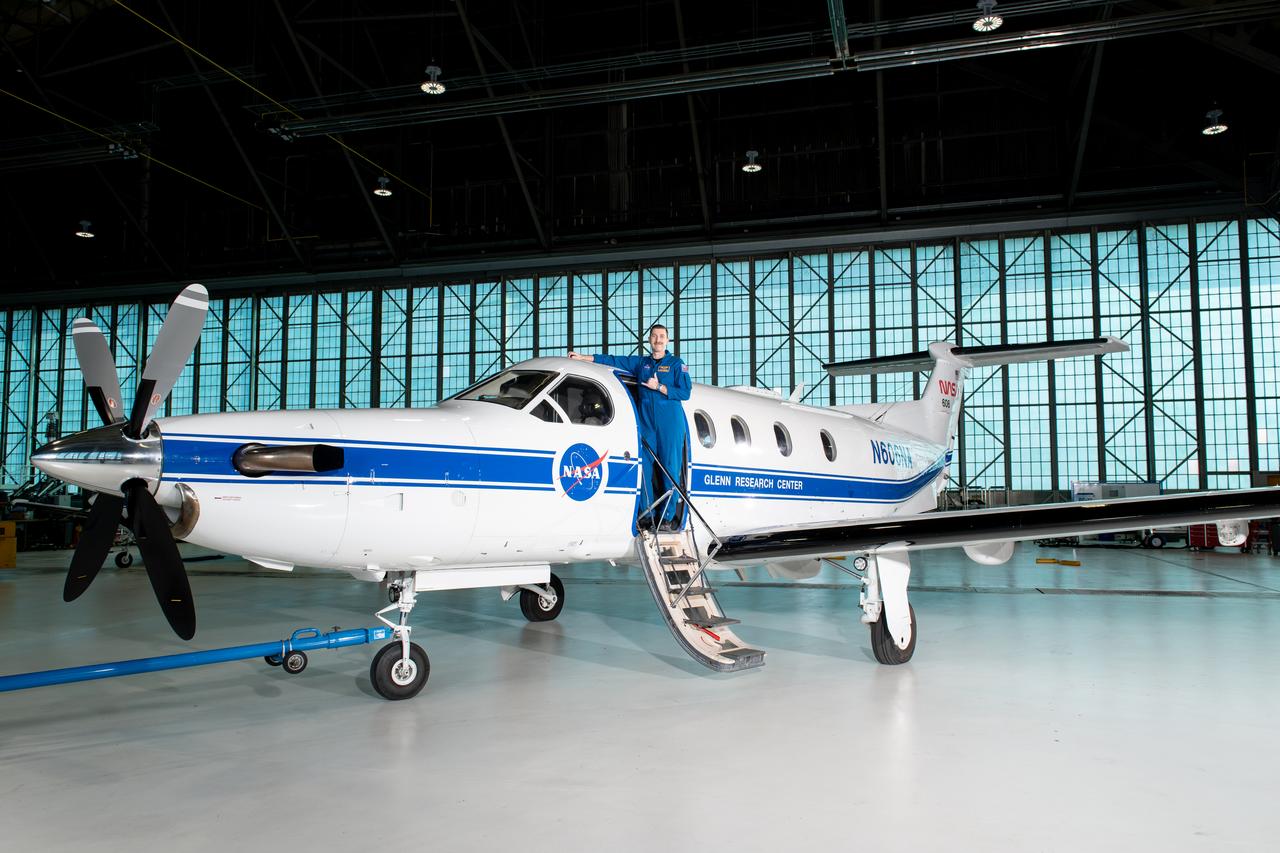

Jeremy Johnson, a research pilot and aviation safety officer, poses in front of a PC-12 aircraft inside the hangar at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland on Thursday, April 17, 2025. Johnson flies NASA planes to support important scientific research and testing, working with researchers to plan and carry out flights that will get them the data they need while ensuring safety.
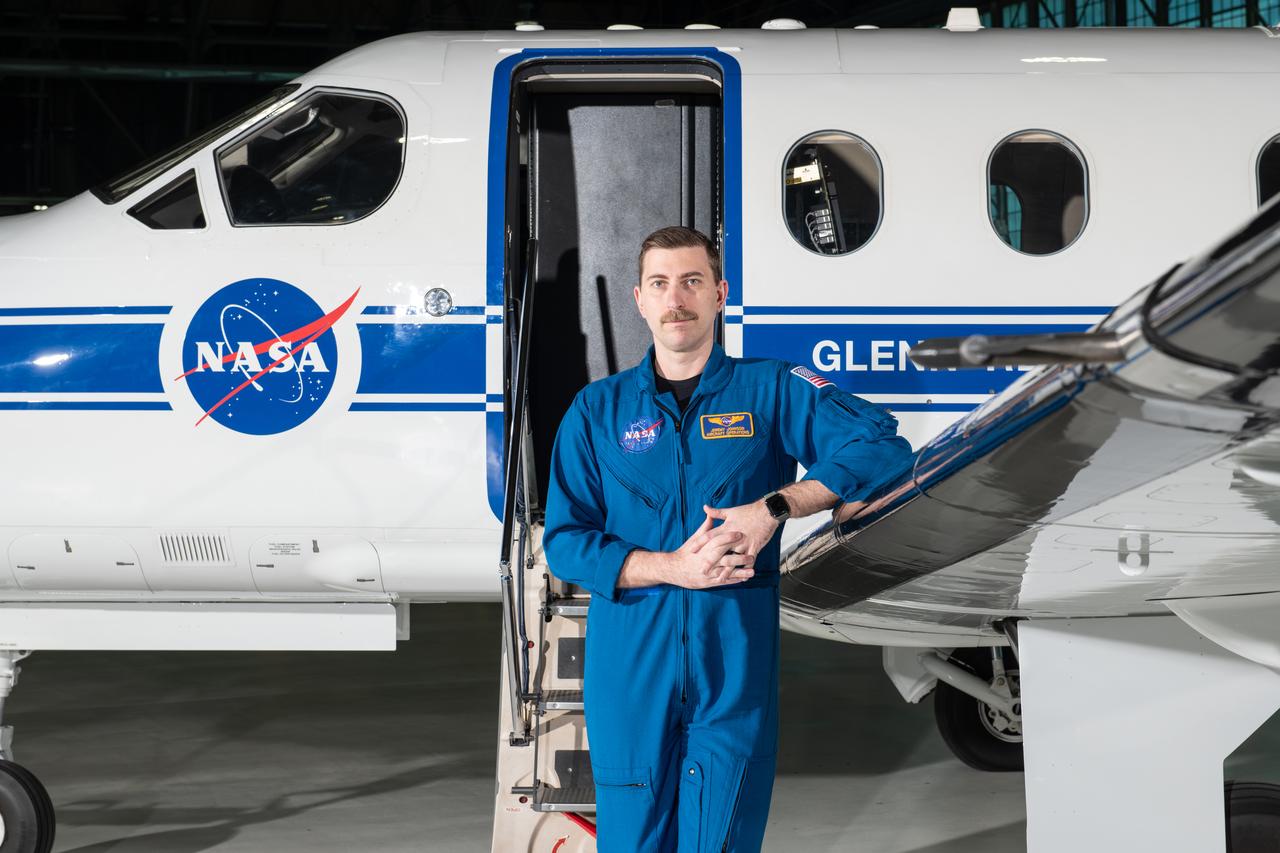

Jeremy Johnson, a research pilot and aviation safety officer, poses in front of a PC-12 aircraft inside the hangar at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland on Thursday, April 17, 2025. Johnson flies NASA planes to support important scientific research and testing, working with researchers to plan and carry out flights that will get them the data they need while ensuring safety.
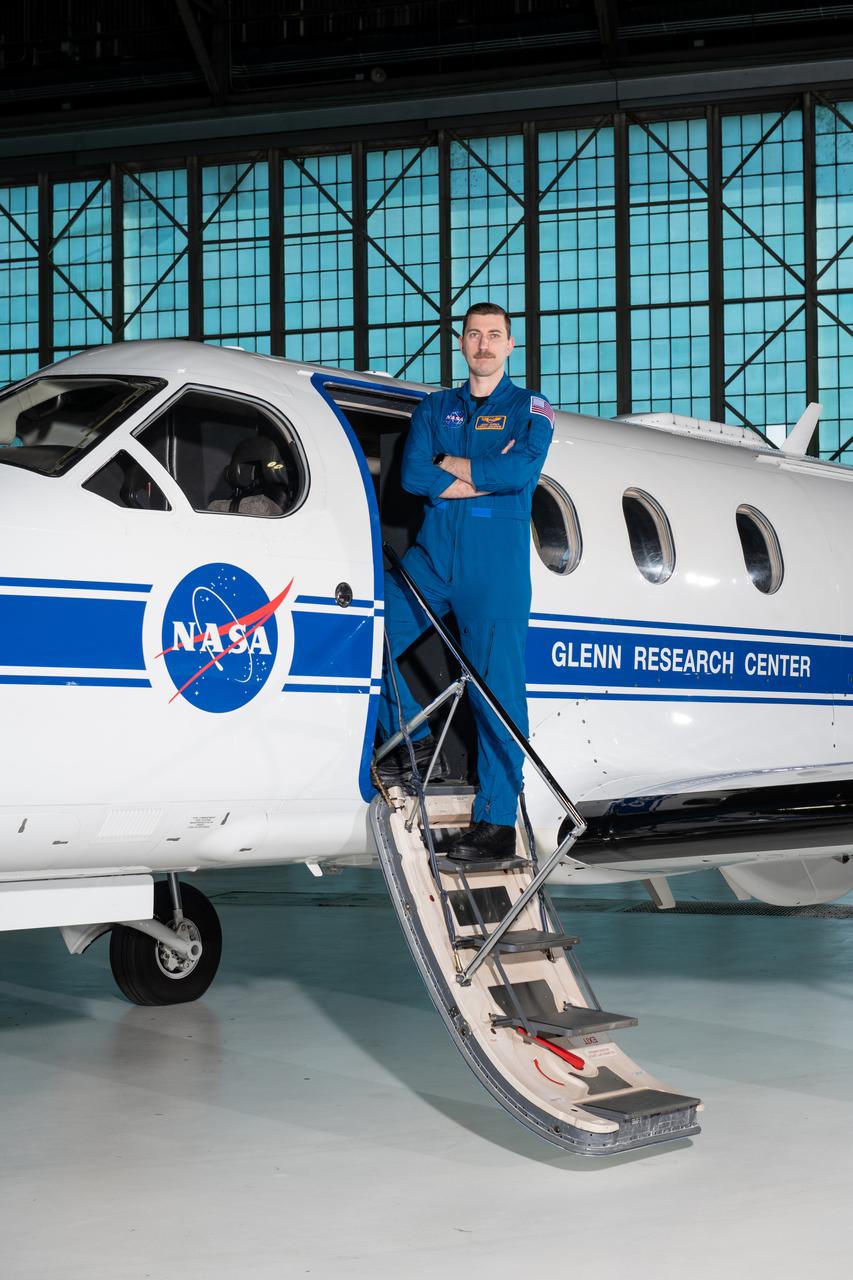

Jeremy Johnson, a research pilot and aviation safety officer, poses in front of a PC-12 aircraft inside the hangar at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland on Thursday, April 17, 2025. Johnson flies NASA planes to support important scientific research and testing, working with researchers to plan and carry out flights that will get them the data they need while ensuring safety.

Jeremy Johnson, a research pilot and aviation safety officer, poses in front of a PC-12 aircraft inside the hangar at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland on Thursday, April 17, 2025. Johnson flies NASA planes to support important scientific research and testing, working with researchers to plan and carry out flights that will get them the data they need while ensuring safety.
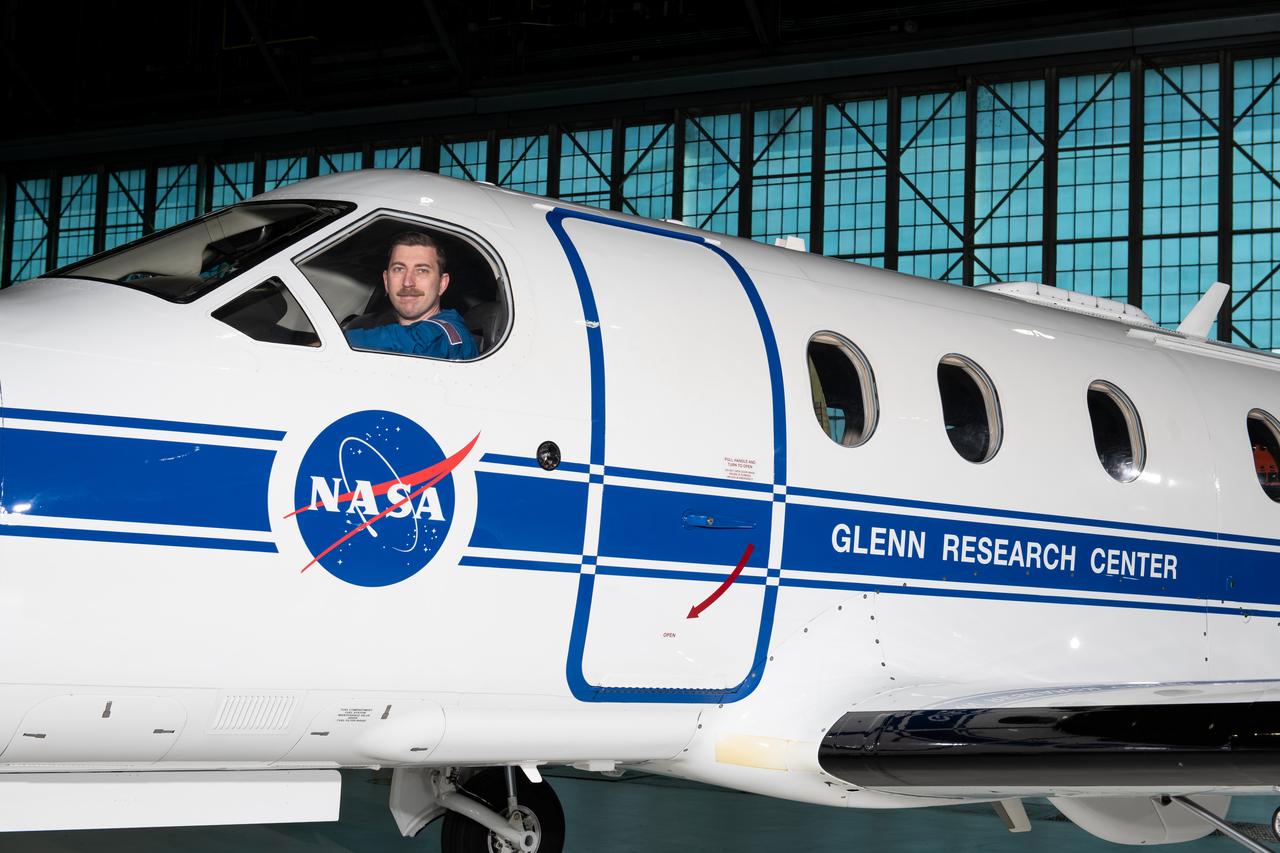

Jeremy Johnson, a research pilot and aviation safety officer, poses in the PC-12 aircraft inside the hangar at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland on Thursday, April 17, 2025. Johnson flies NASA planes to support important scientific research and testing, working with researchers to plan and carry out flights that will get them the data they need while ensuring safety.
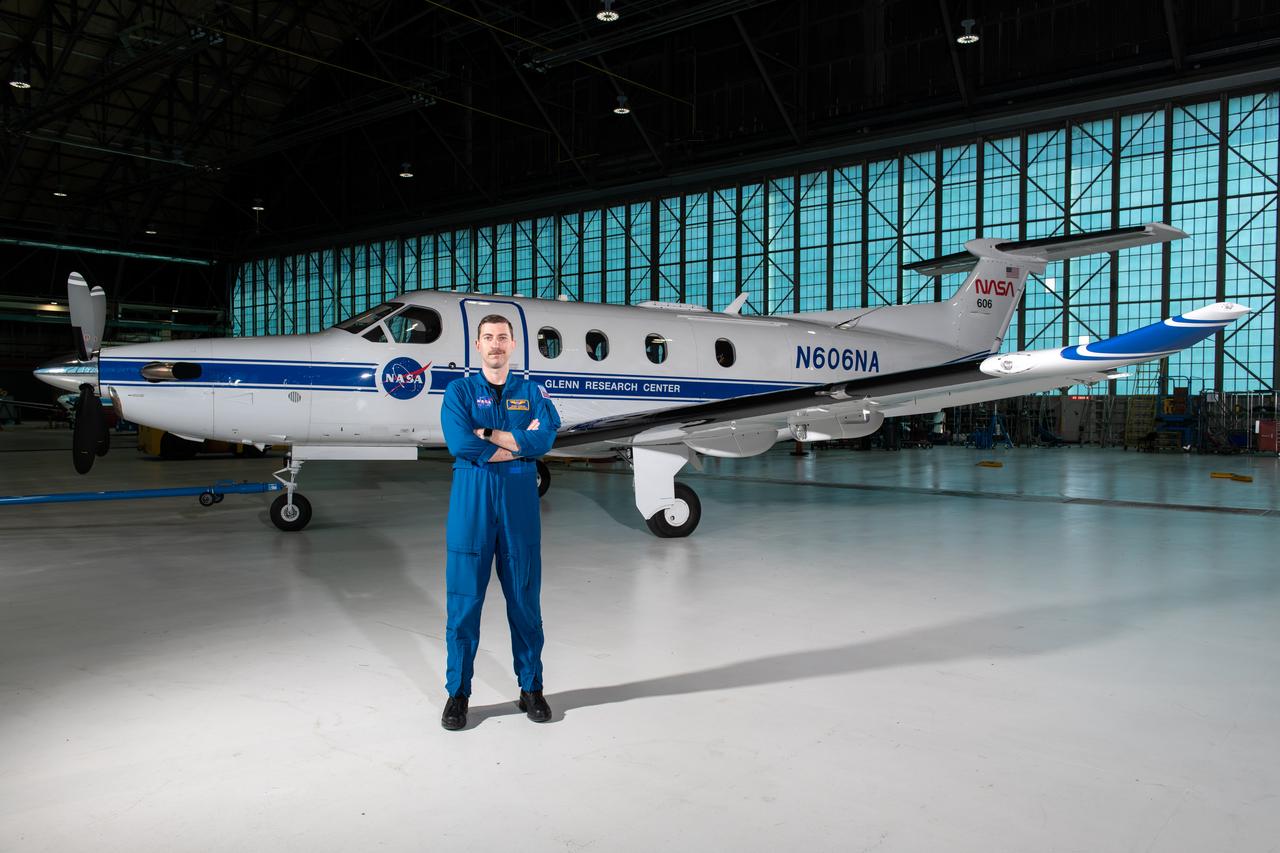

Jeremy Johnson, a research pilot and aviation safety officer, poses in front of a PC-12 aircraft inside the hangar at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland on Thursday, April 17, 2025. Johnson flies NASA planes to support important scientific research and testing, working with researchers to plan and carry out flights that will get them the data they need while ensuring safety.
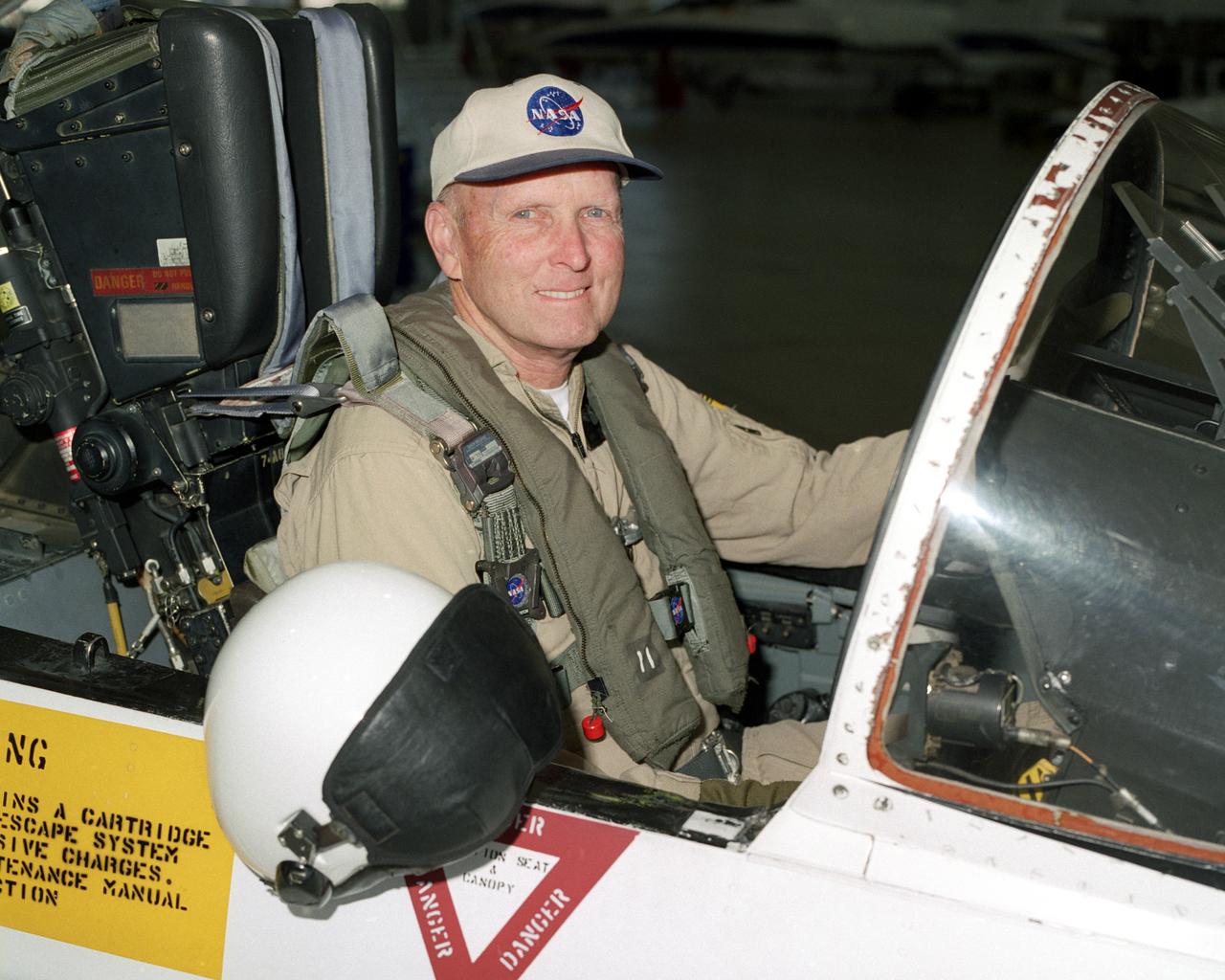

Former NASA astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton, seated in the cockpit of an F/A-18, is a research pilot at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif. Since transferring to Dryden in 1986, his assignments have included a variety of flight research and support activities piloting NASA's B-52 launch aircraft, the 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA), and other multi-engine and high performance aircraft. He flew a series of development air launches of the X-38 prototype Crew Return Vehicle and in the launches for the X-43A Hyper-X project. Fullerton also flies Dryden's DC-8 Airborne Science aircraft in support a variety of atmospheric physics, ground mapping and meteorology studies. Fullerton also was project pilot on the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft program, during which he successfully landed both a modified F-15 and an MD-11 transport with all control surfaces neutralized, using only engine thrust modulation for control. Fullerton also evaluated the flying qualities of the Russian Tu-144 supersonic transport during two flights in 1998, one of only two non-Russian pilots to fly that aircraft. With more than 15,000 hours of flying time, Fullerton has piloted 135 different types of aircraft in his career. As an astronaut, Fullerton served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16, and 17 lunar missions. In 1977, Fullerton was on one of the two flight crews that piloted the Space Shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test Program at Dryden. Fullerton was the pilot on the STS-3 Space Shuttle orbital flight test mission in 1982, and commanded the STS-51F Spacelab 2 mission in 1985. He has logged 382 hours in space flight. In July 1988, he completed a 30-year career with the U.S. Air Force and retired as a colonel.
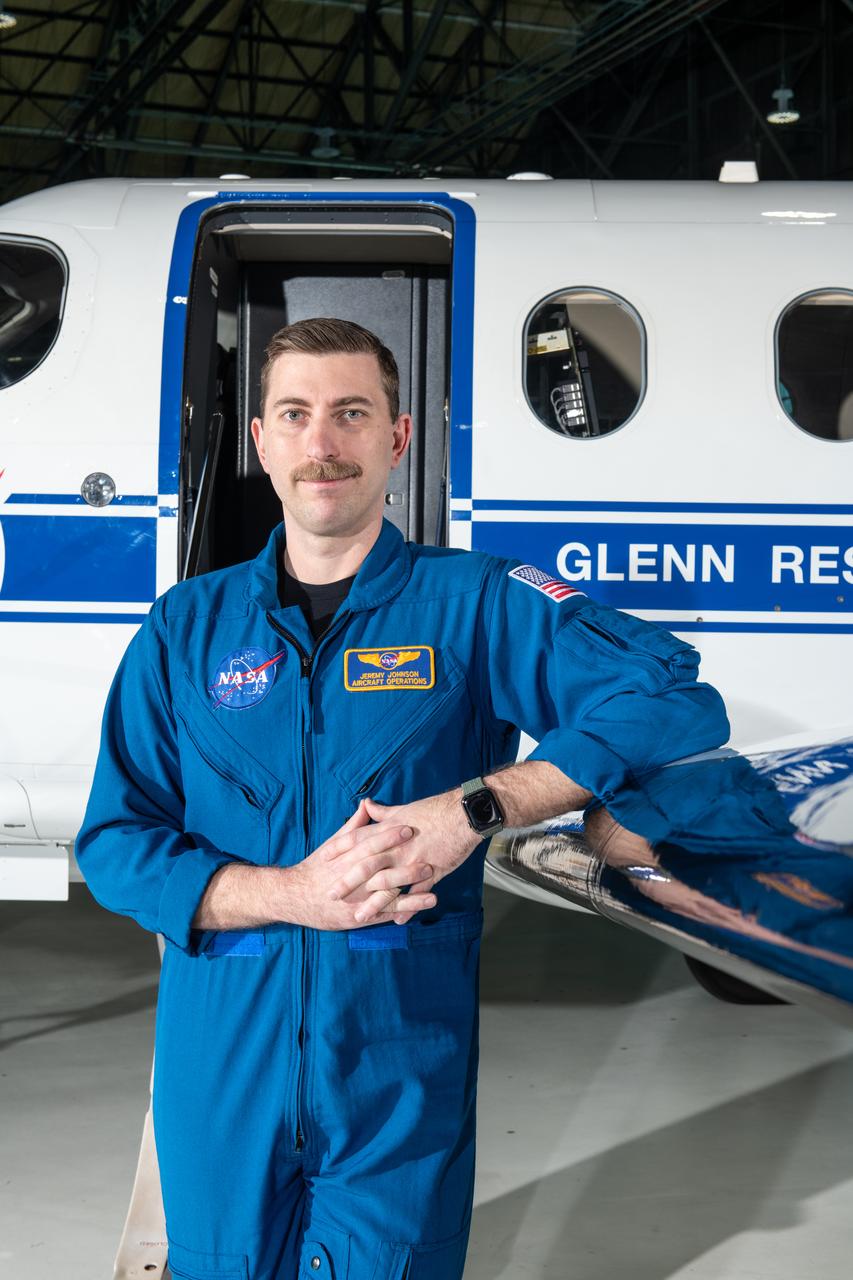

Jeremy Johnson, a research pilot and aviation safety officer, poses in front of a PC-12 aircraft inside the hangar at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland on Thursday, April 17, 2025. Johnson flies NASA planes to support important scientific research and testing, working with researchers to plan and carry out flights that will get them the data they need while ensuring safety.
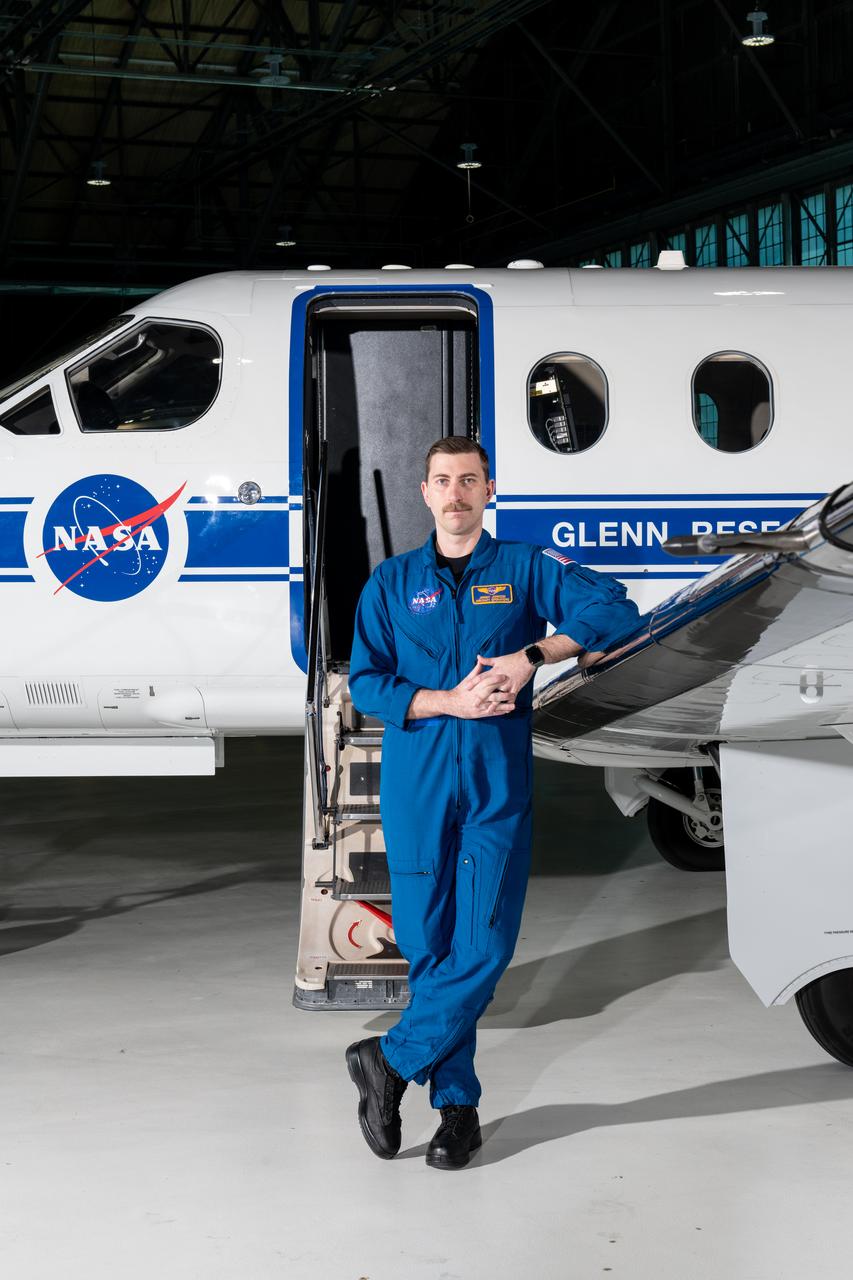

Jeremy Johnson, a research pilot and aviation safety officer, poses in front of a PC-12 aircraft inside the hangar at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland on Thursday, April 17, 2025. Johnson flies NASA planes to support important scientific research and testing, working with researchers to plan and carry out flights that will get them the data they need while ensuring safety.
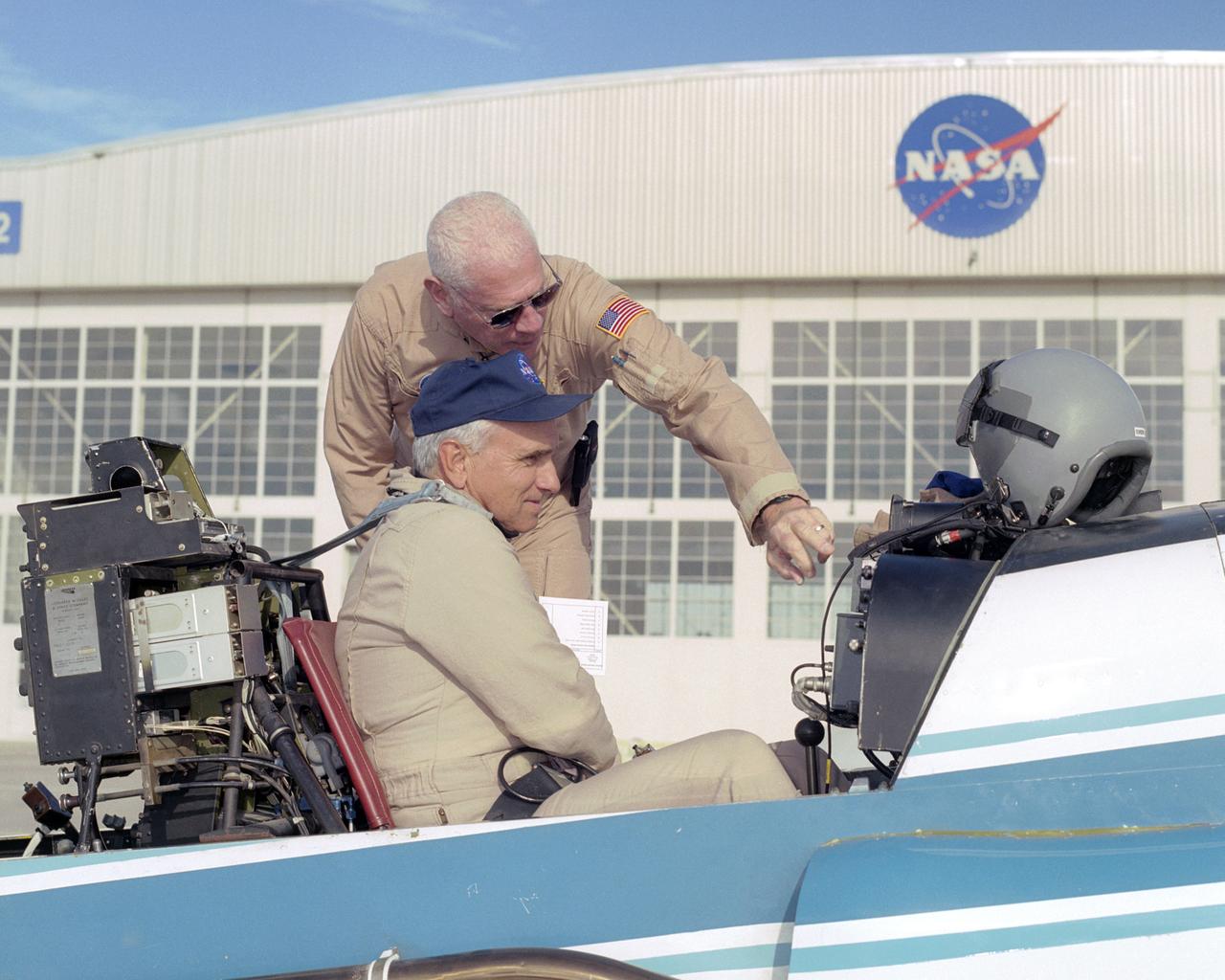

NASA pilot Ed Lewis (rear) briefs NASA test pilot Dick Ewers on the flight instruments of NASA's YO-3A acoustics research aircraft prior to a checkout flight.
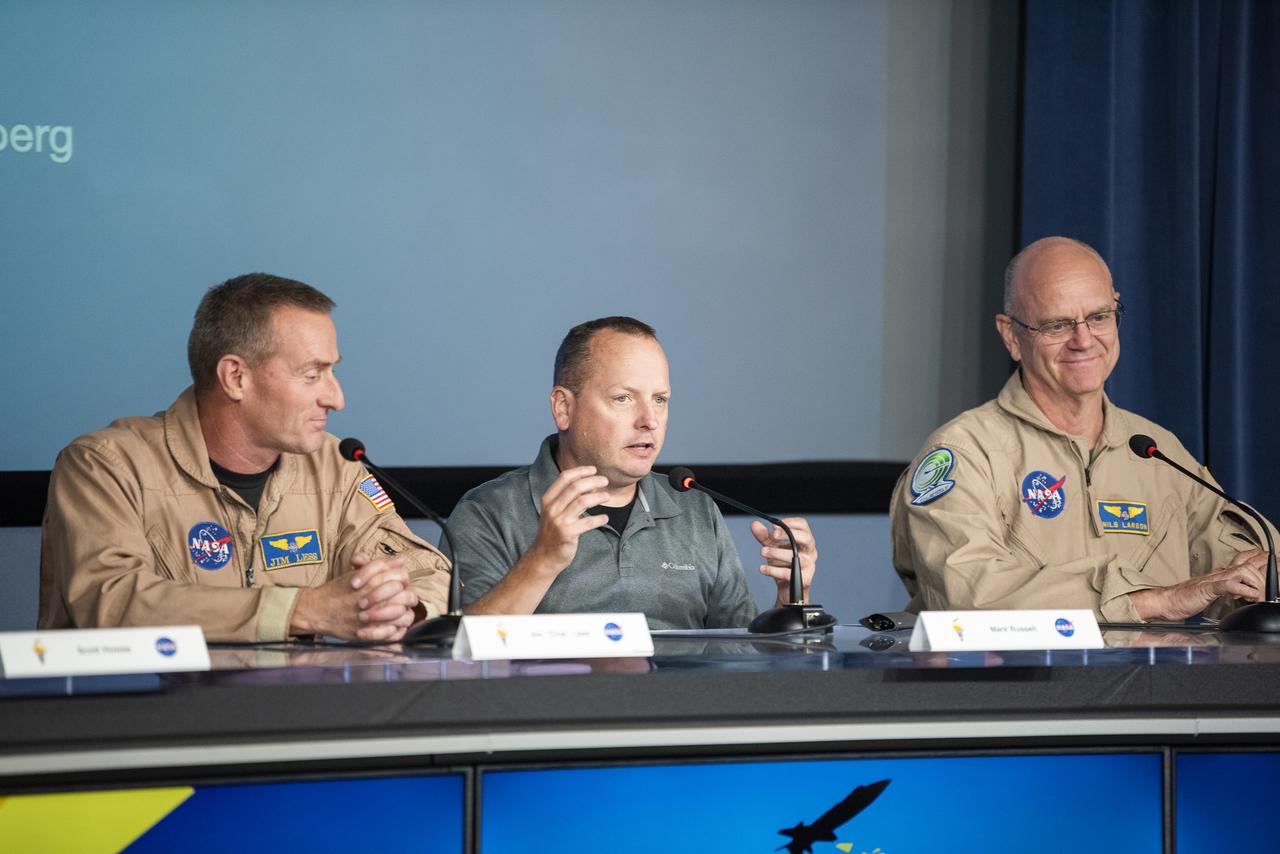

Mark Russell, center, a research pilot at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, explains the differences in flight environments at different NASA centers. Jim Less, a NASA pilot at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, left, Russell, and Nils Larson, NASA Armstrong chief X-59 aircraft pilot and senior advisor on flight research, provided perspective on flight research at the Ideas to Flight Workshop on Sept. 18 at NASA Armstrong.
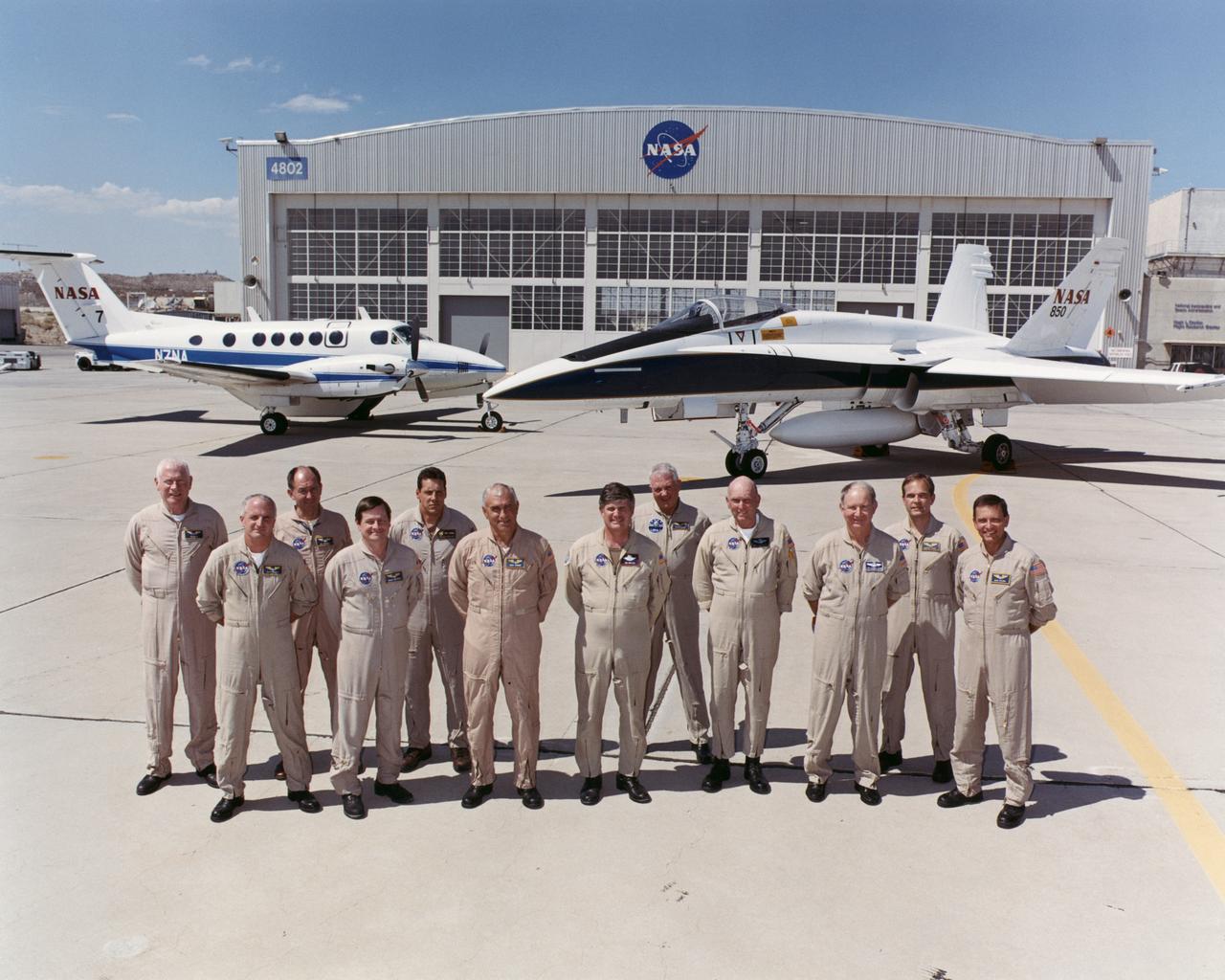

2004 NASA Dryden Research Pilots. Left to Right: Edwin W. Lewis, Jr., David A. Wright (Director of Flight Operations), William Frederick Brockett, Frank Batteas, Craig R. Bomben, Richard G. Ewers, James W. Smolka, Douglas H. Baker, C. Gordon Fullerton (Chief Pilot), James Barrilleaux, Martin J. Trout, and Mark Pestana. (not pictured: Dana Purifoy)
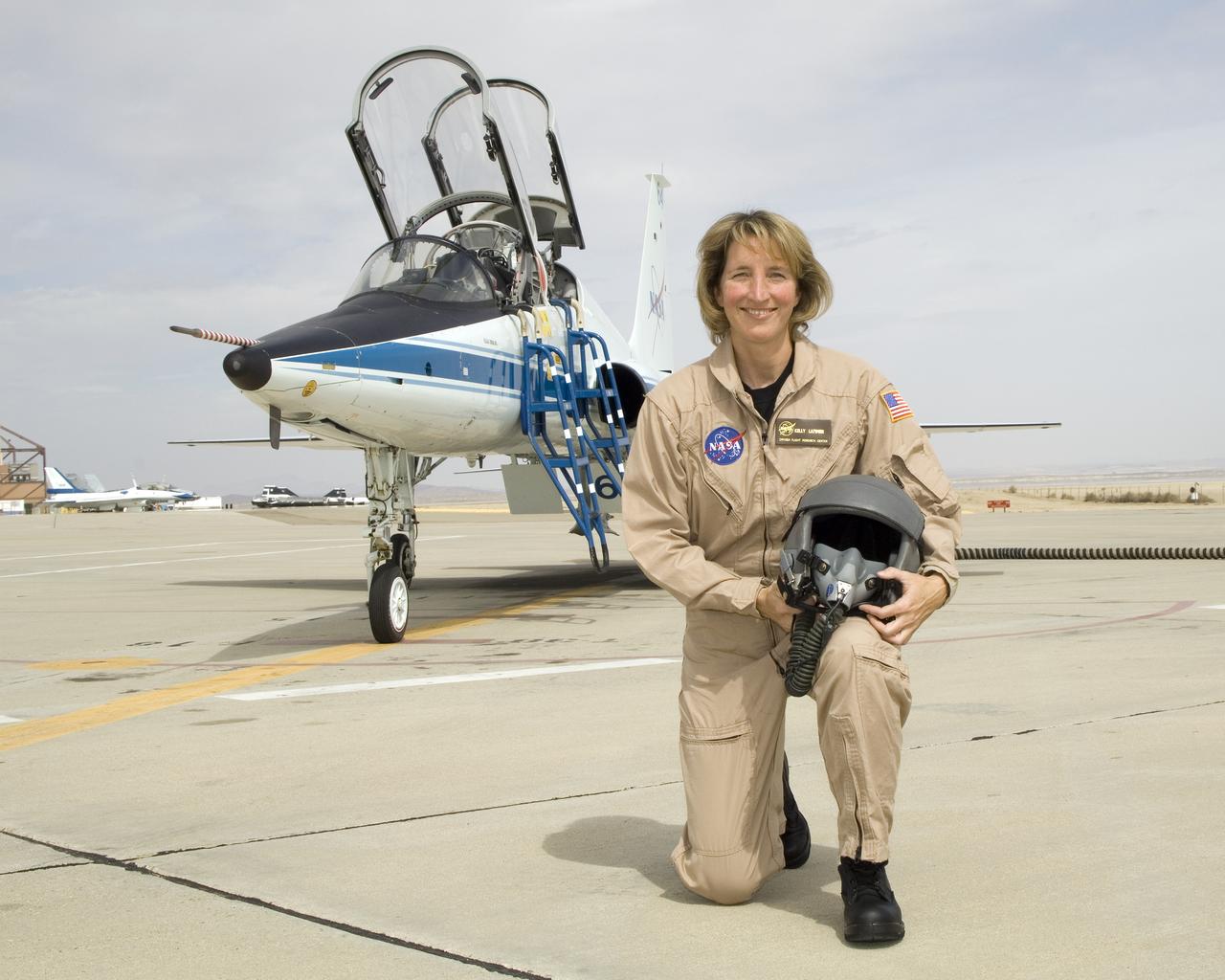

Kelly Latimer is a research pilot in the Flight Crew Branch of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif. Latimer joined NASA in March 2007 and will fly the T38, T-34, G-III, C-17 and the "Ikhana" Predator B. Latimer is Dryden's first female research test pilot. Prior to joining NASA, Latimer was on active duty with the U.S. Air Force. She has accumulated more than 5,000 hours of military and civilian flight experience in 30 aircraft. Latimer's first association with NASA was while attending graduate school at George Washington University, Washington, D.C. Her studies included work with the Joint Institute for the Advancement of Flight Sciences at NASA's Langley Research Center, Hampton, Va. She flew an Air Force C-17 during a 2005 NASA study to reduce aircraft noise. A team of California Polytechnic State University students and Northrop Grumman personnel were stationed on Rogers Dry Lake located at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., to record the noise footprint of the aircraft as it made various landing approaches to Edwards' runway. Latimer completed undergraduate pilot training at Reese Air Force Base, Texas, in 1990. She remained at Reese as a T-38 instructor pilot until 1993. She was assigned as a C-141 aircraft commander at McCord Air Force Base, Tacoma, Wash., until 1996. Latimer graduated from the U.S. Air Force Test Pilot School at Edwards in Class 96B. She served as a C-17 and C-141 experimental test pilot at Edwards until 2000. She then became the chief of the Performance Branch and a T-38 instructor pilot at The Air Force Test Pilot School. She returned to McCord in 2002, where she was a C-17 aircraft commander and the operations officer for the 62nd Operations Support Squadron. In 2004, Latimer became the commander of Edwards' 418th Flight Test Squadron and director of the Global Reach Combined Test Force. Following that assignment, she deployed to Iraq as an advisor to the Iraqi Air Force. Her last active duty tour was as an instructor a
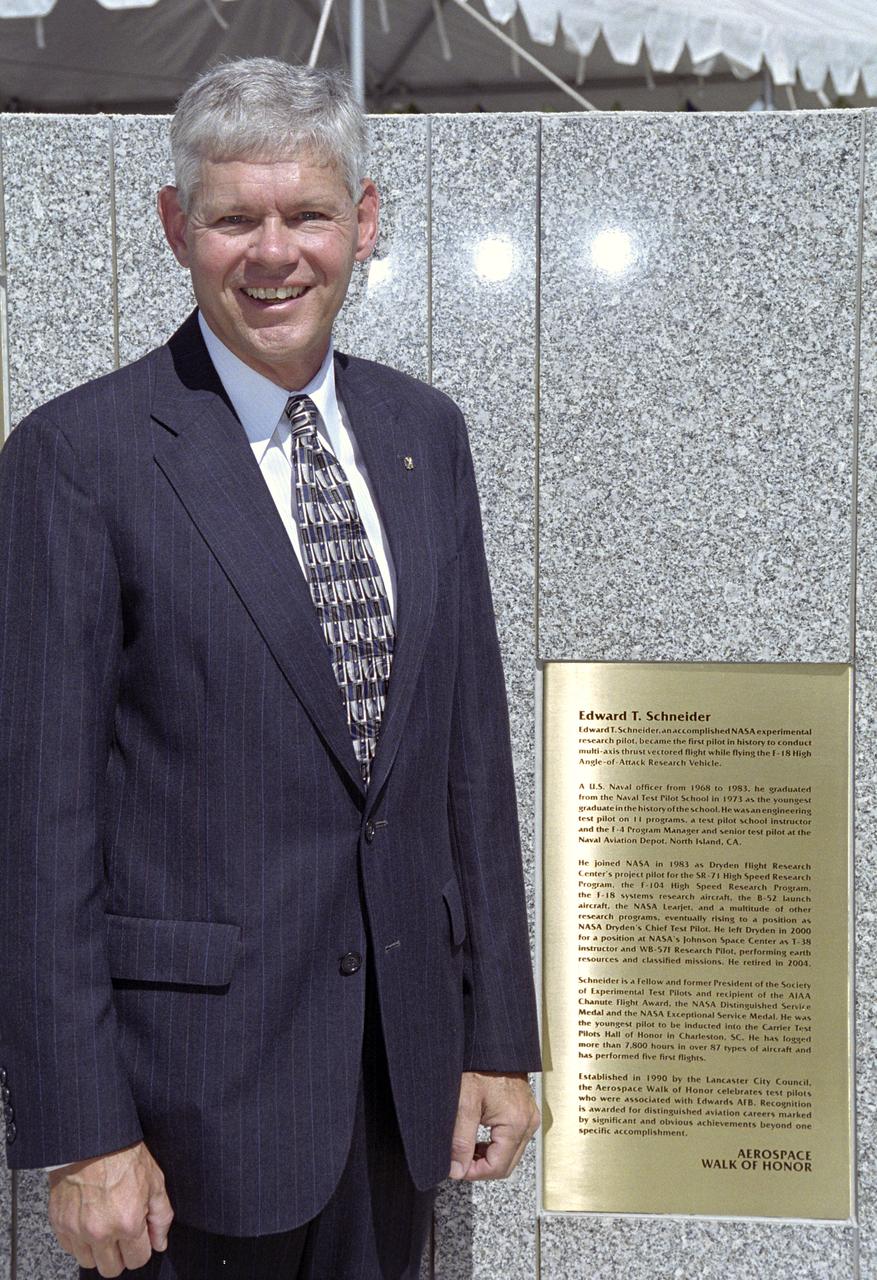

Former NASA research pilot Eddie Schneider was on hand when a brass plaque summarizing his career was unveiled during the 2005 Aerospace Walk of Honor ceremonies in Lancaster, California.
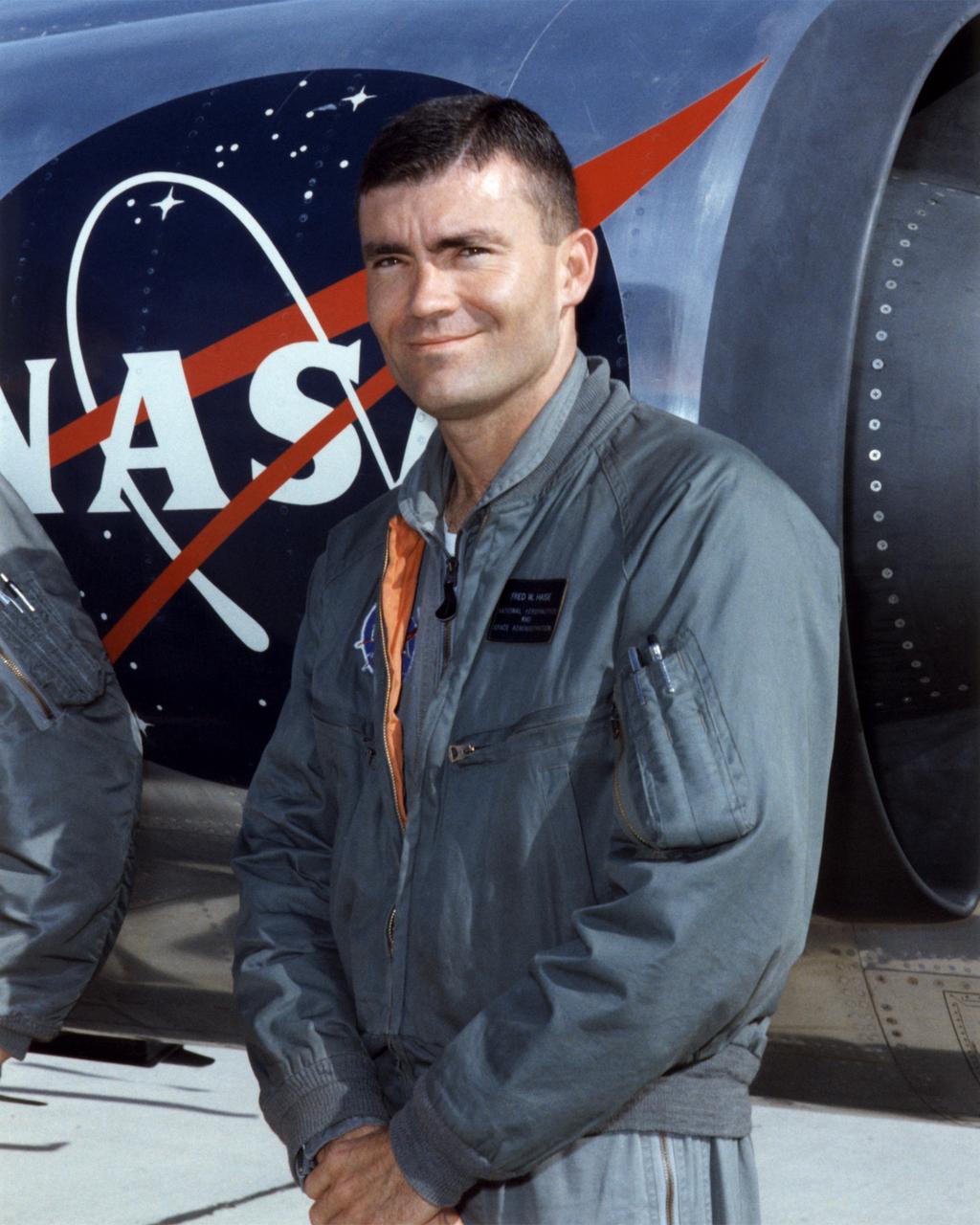

Fred W. Haise Jr. was a research pilot and an astronaut for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration from 1959 to 1979. He began flying at the Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio (today the Glenn Research Center), in 1959. He became a research pilot at the NASA Flight Research Center (FRC), Edwards, Calif., in 1963, serving NASA in that position for three years until being selected to be an astronaut in 1966 His best-known assignment at the FRC (later redesignated the Dryden Flight Research Center) was as a lifting body pilot. Shortly after flying the M2-F1 on a car tow to about 25 feet on April 22, 1966, he was assigned as an astronaut to the Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. While at the FRC he had also flown a variety of other research and support aircraft, including the variable-stability T-33A to simulate the M2-F2 heavyweight lifting body, some light aircraft including the Piper PA-30 to evaluate their handling qualities, the Apache helicopter, the Aero Commander, the Cessna 310, the Douglas F5D, the Lockheed F-104 and T-33, the Cessna T-37, and the Douglas C-47. After becoming an astronaut, Haise served as a backup crewmember for the Apollo 8, 11, and 16 missions. He flew on the aborted Apollo 13 lunar mission in 1970, spending 142 hours and 54 minutes in space before returning safely to Earth. In 1977, he was the commander of three free flights of the Space Shuttle prototype Enterprise when it flew its Approach and Landing Tests at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. Meanwhile, from April 1973 to January 1976, Haise served as the Technical Assistant to the Manager of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Project. In 1979, he left NASA to become the Vice President for Space Programs with the Grumman Aerospace Corporation. He then served as President of Grumman Technical Services, an operating division of Northrop Grumman Corporation, from January 1992 until his retirement. Haise was born in Biloxi, Miss., on November 14, 1933. He underwent flight traini
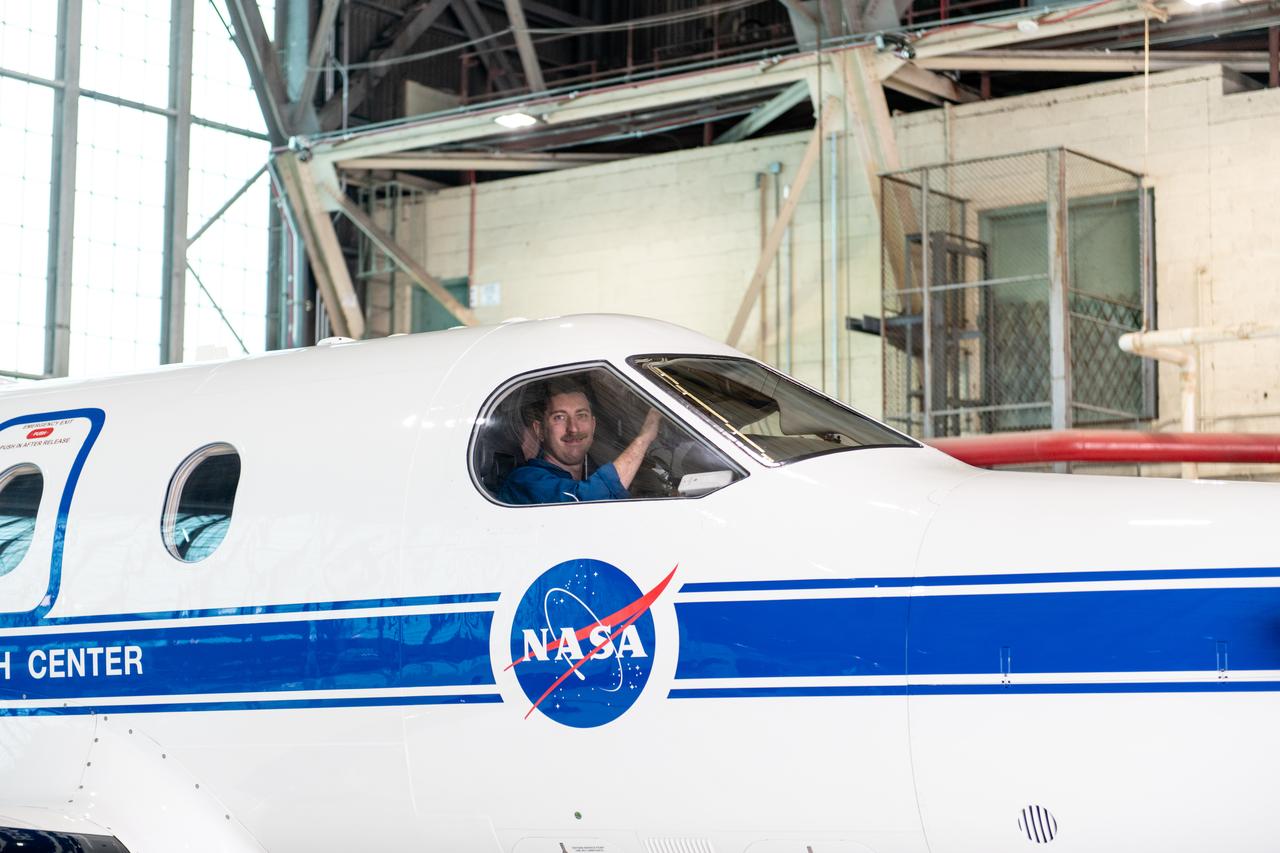

Jeremy Johnson leaving the hangar for a test flight in NASA Glenn Research Center’s PC-12 aircraft on Wednesday, April 16, 2025.
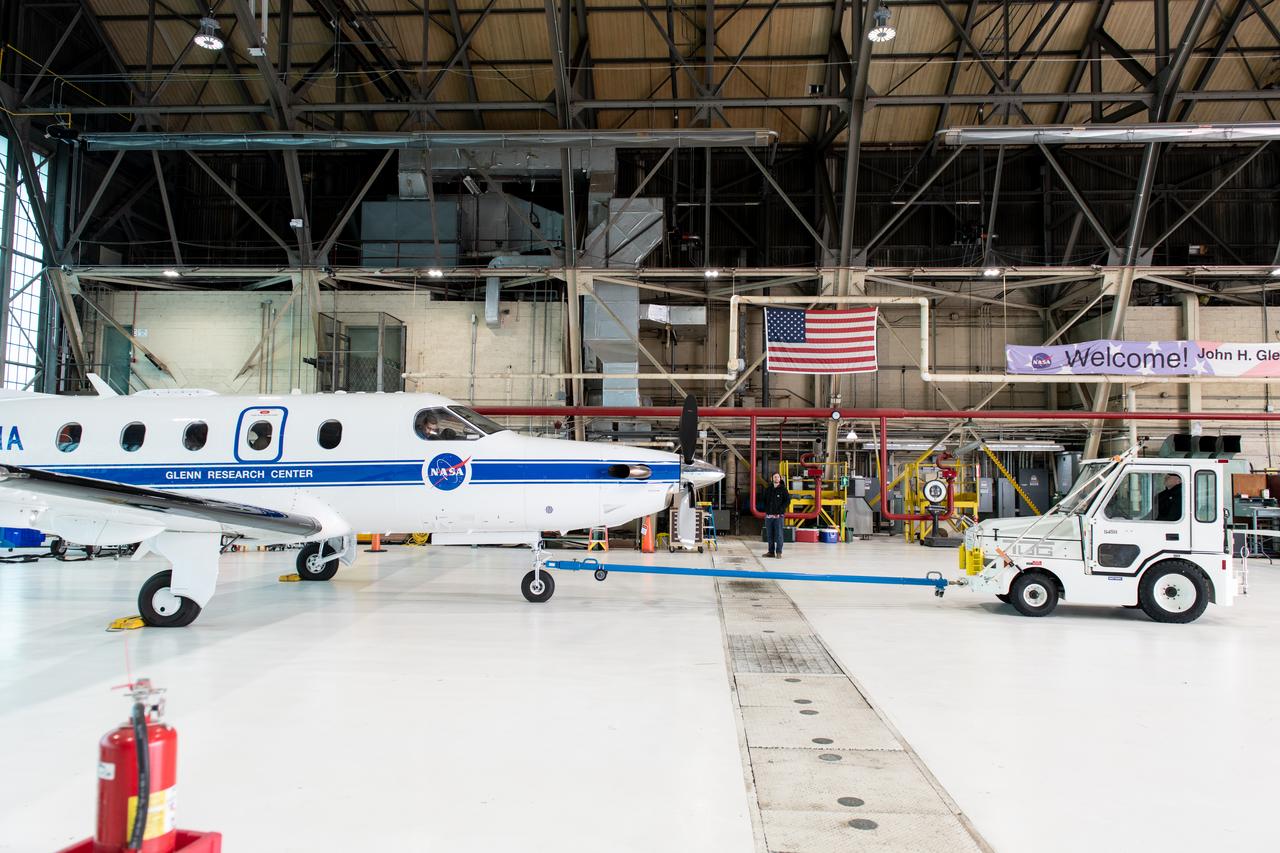

Jeremy Johnson leaving the hangar for a test flight in NASA Glenn Research Center’s PC-12 aircraft on Wednesday, April 16, 2025.
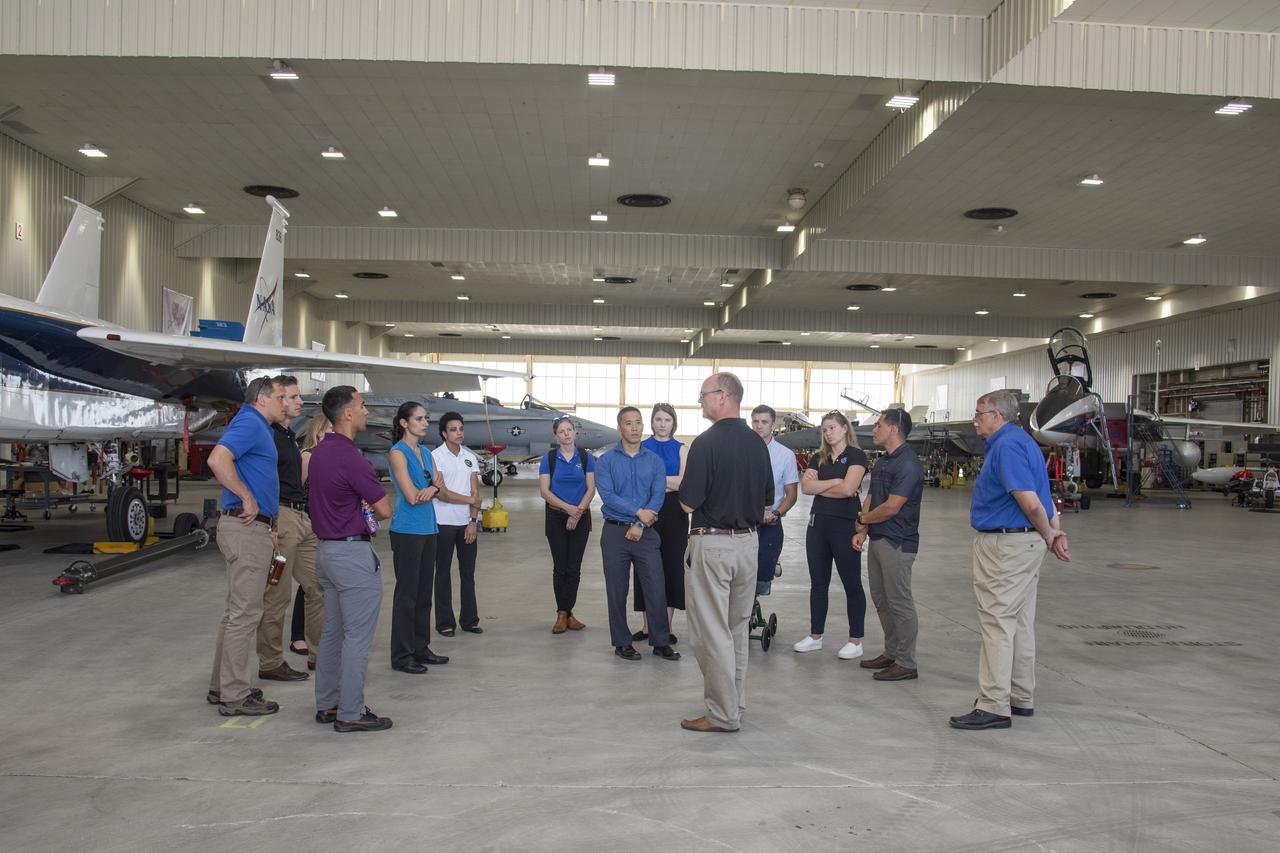

NASA's 2017 astronaut candidates toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California. On the right, NASA's, X-59 pilot Nils Larsen, briefs the astronauts as they look at Armstrong's fleet of supersonic research support aircraft, including the F-15, which will fly in tandem with the X-59 QueSST during early flight test stages, and the F-18, which is conducting supersonic research in support of the overall mission.
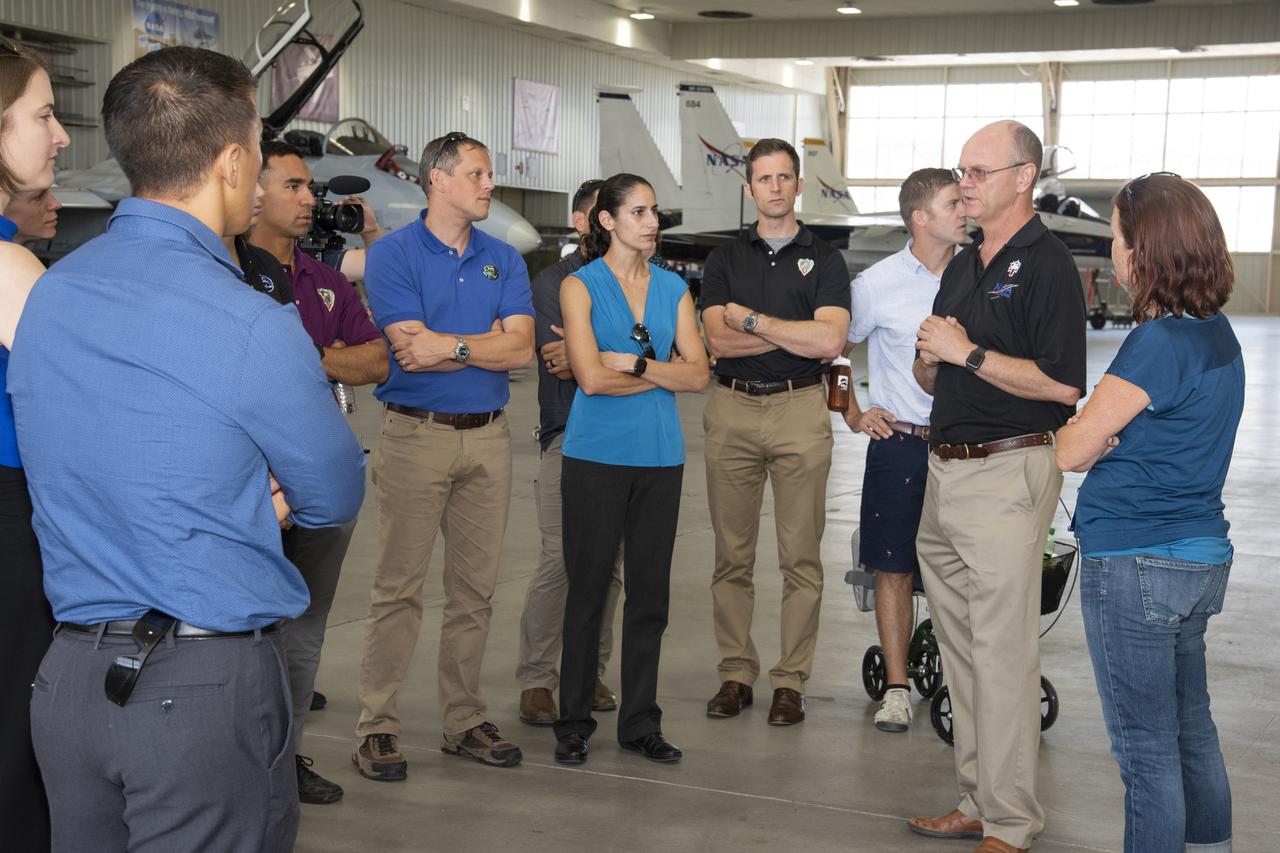

NASA’s 2017 astronaut candidates toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California. On the right, NASA’s, X-59 pilot Nils Larsen, briefs the astronauts as they look at Armstrong’s fleet of supersonic research support aircraft, including the F-15, which will fly in tandem with the X-59 QueSST during early flight test stages, and the F-18, which is conducting supersonic research in support of the overall mission.
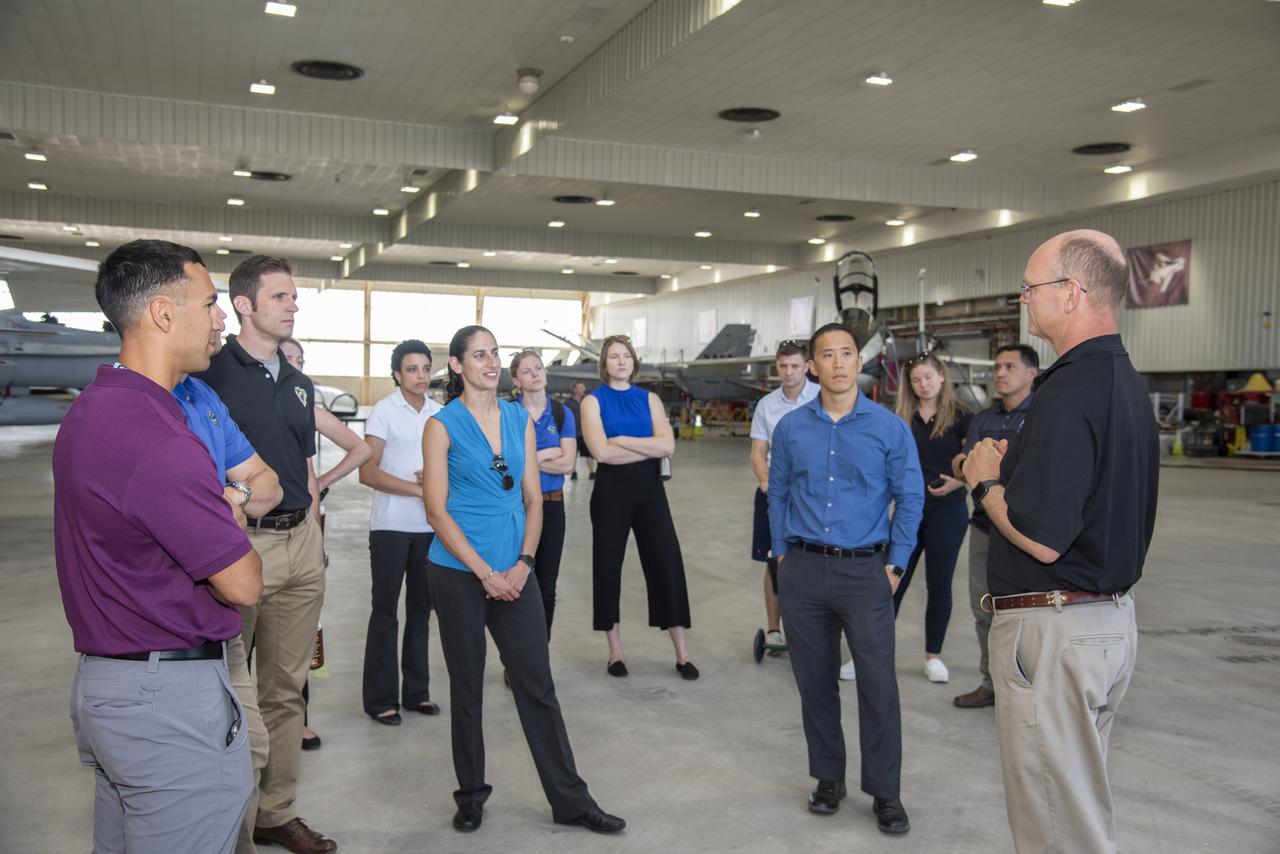

NASA's 2017 astronaut candidates toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California. On the right, NASA's, X-59 pilot Nils Larsen, briefs the astronauts as they look at Armstrong's fleet of supersonic research support aircraft, including the F-15, which will fly in tandem with the X-59 QueSST during early flight test stages, and the F-18, which is conducting supersonic research in support of the overall mission.
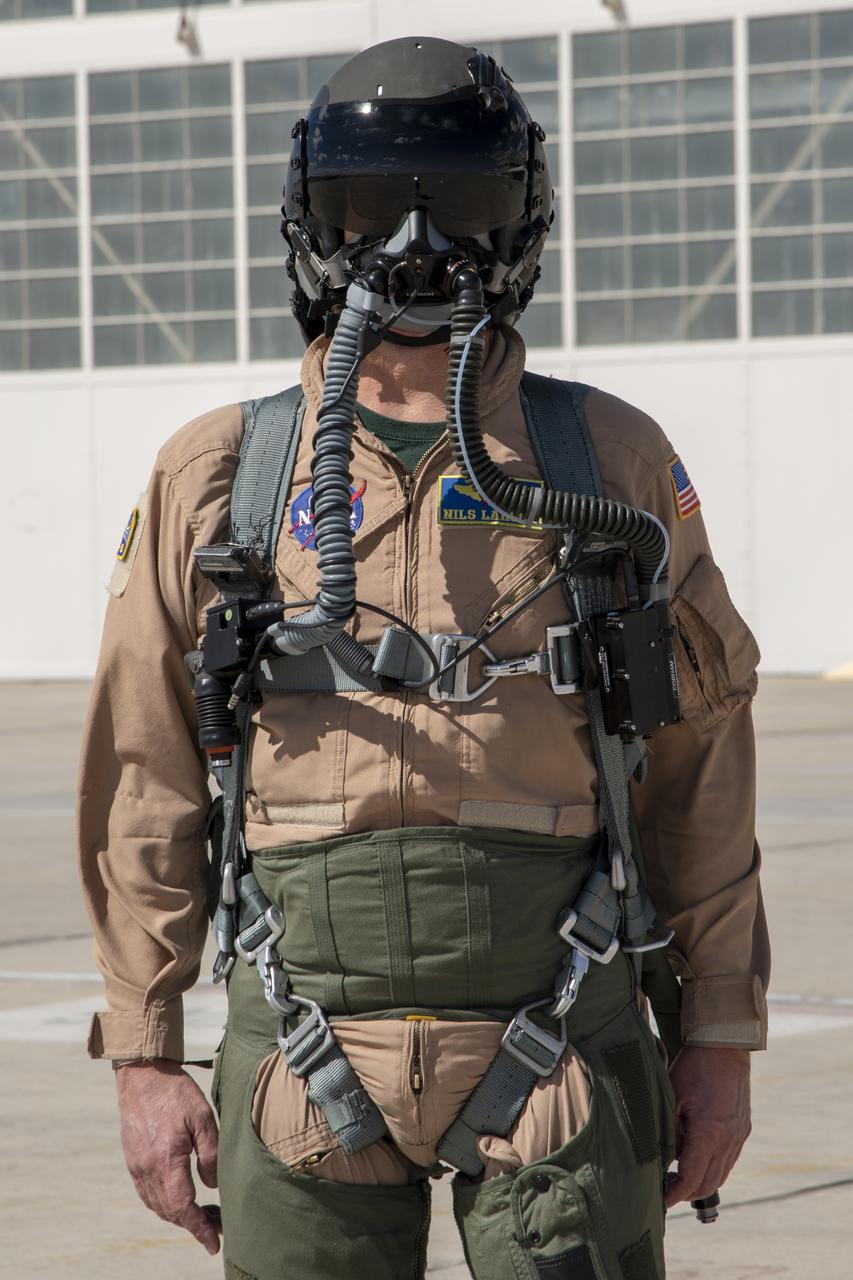

NASA Pilot Nils Larson wears a U.S. Air Force harness configuration with a helmet and an oxygen mask that is being used in the Pilot Breathing Assessment program at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California.
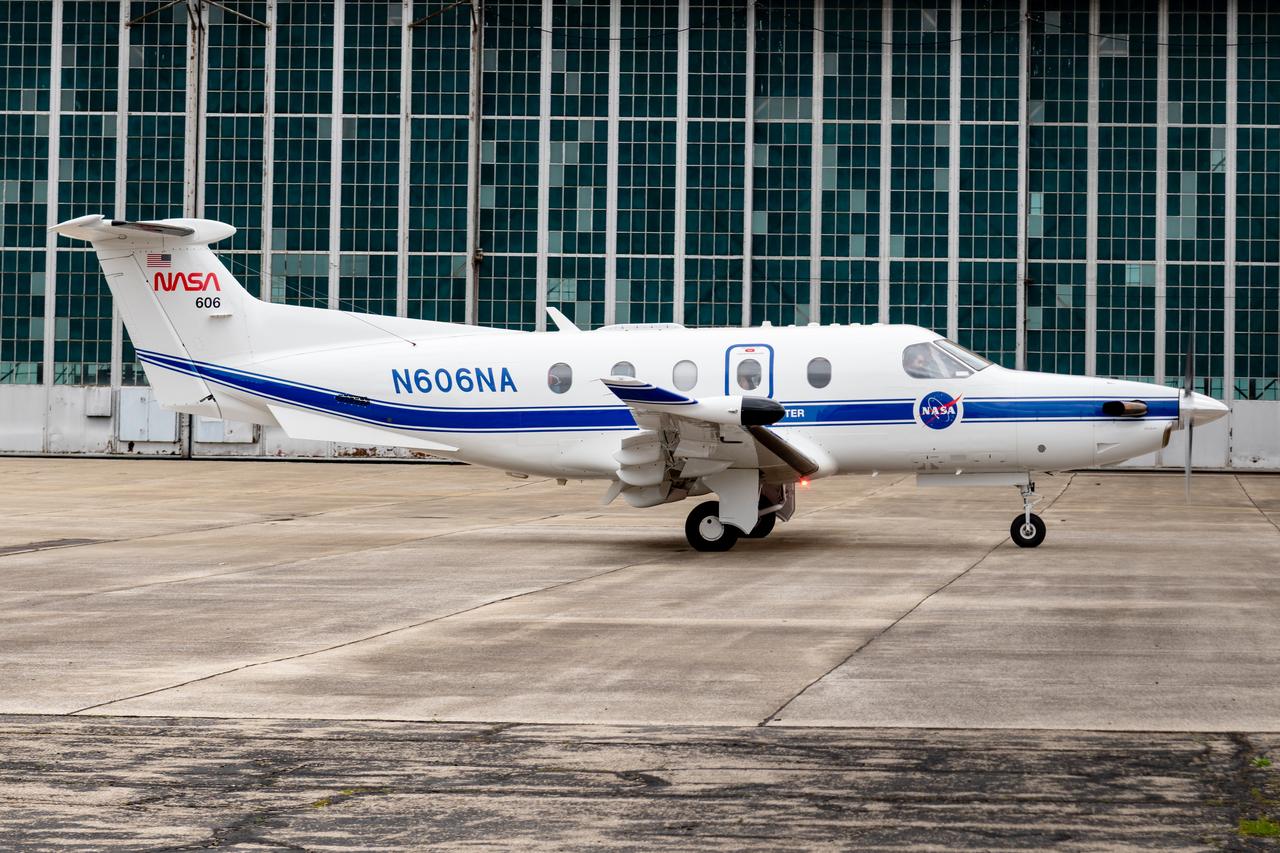

Jeremy Johnson leaving the hangar for a test flight in NASA Glenn Research Center’s PC-12 aircraft on Wednesday, April 16, 2025.

Jeremy Johnson leaving the hangar for a test flight in NASA Glenn Research Center’s PC-12 aircraft on Wednesday, April 16, 2025.
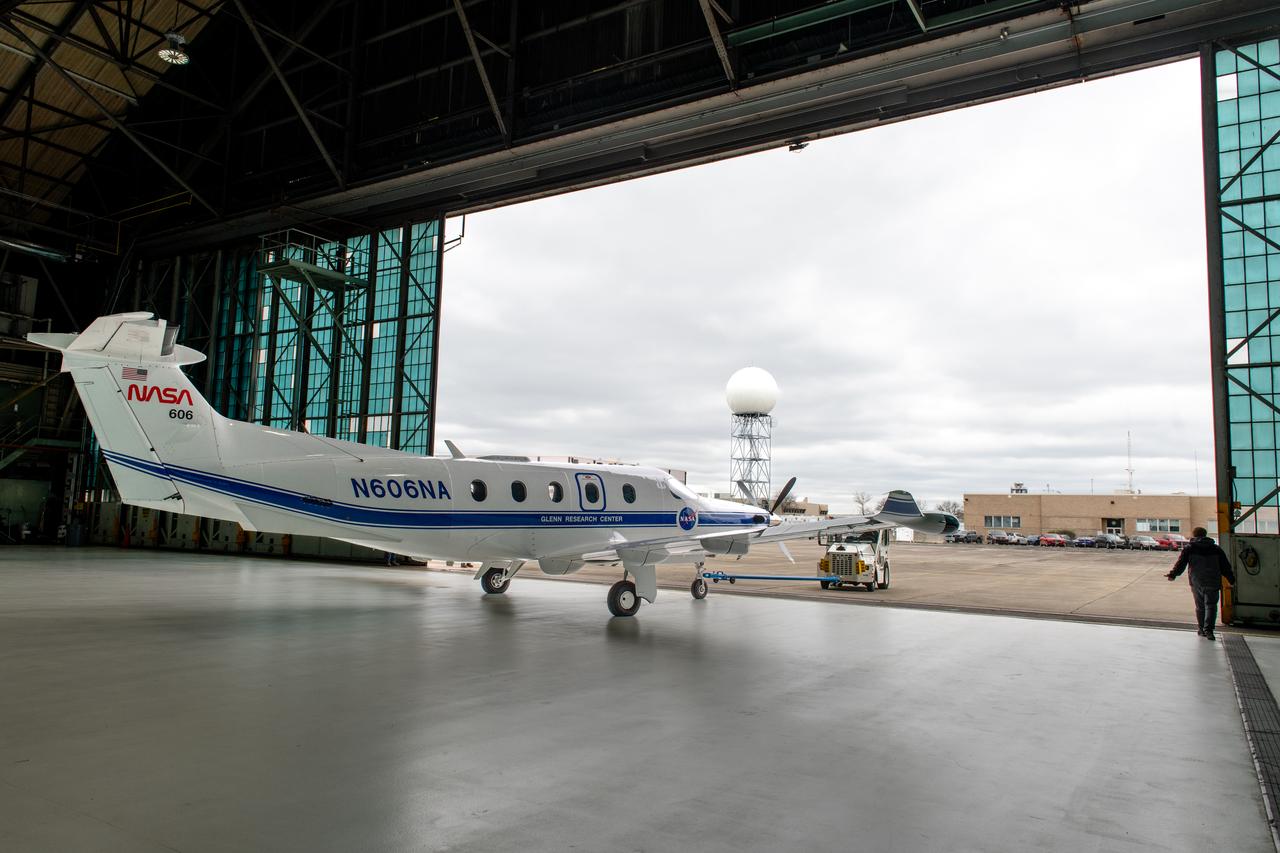

Jeremy Johnson leaving the hangar for a test flight in NASA Glenn Research Center’s PC-12 aircraft on Wednesday, April 16, 2025.
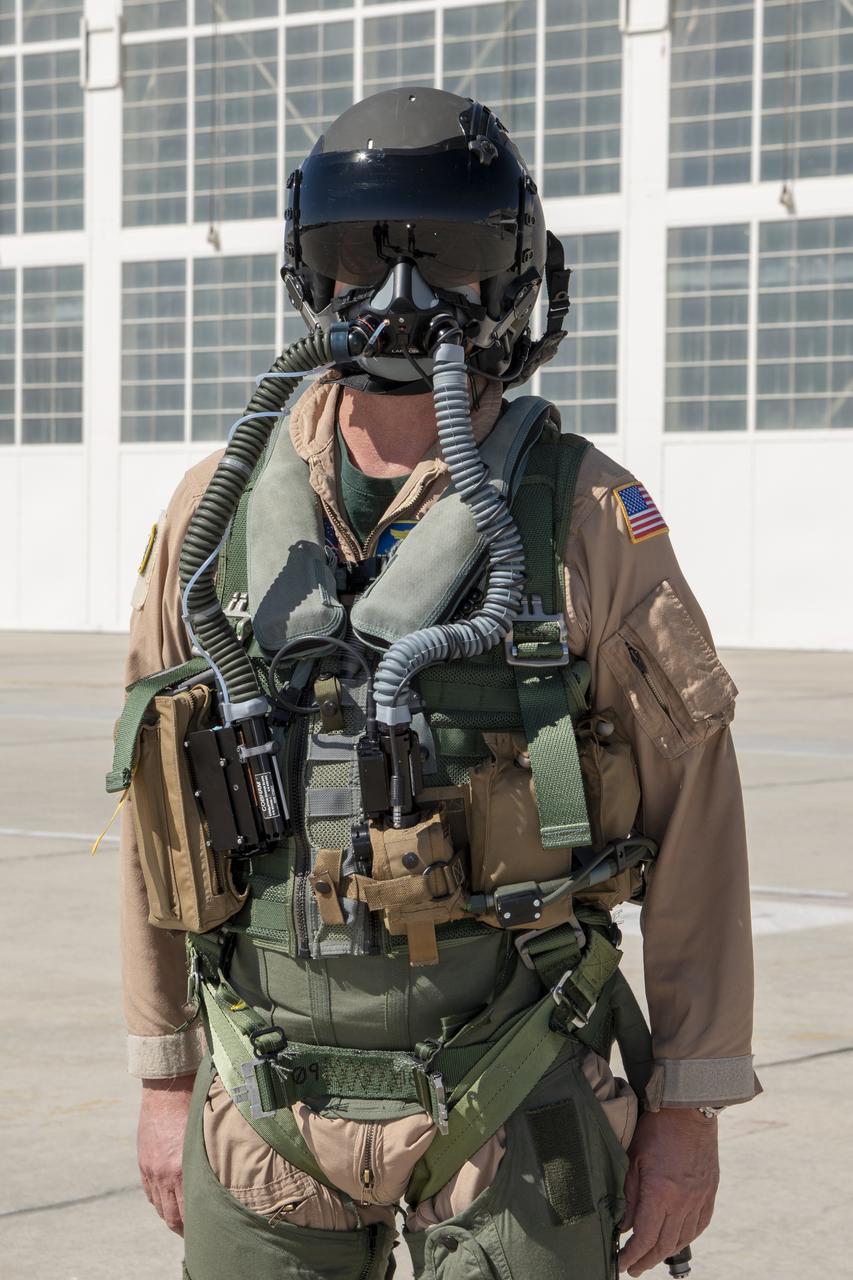

NASA Pilot Nils Larson wears a U.S. Navy harness configuration to show the integrated parachute harness and the built-in survival vest. The Navy configuration is bulkier and weighs more than the U.S. Air Force harness. Both configurations are being used in the Pilot Breathing Assessment program at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California.
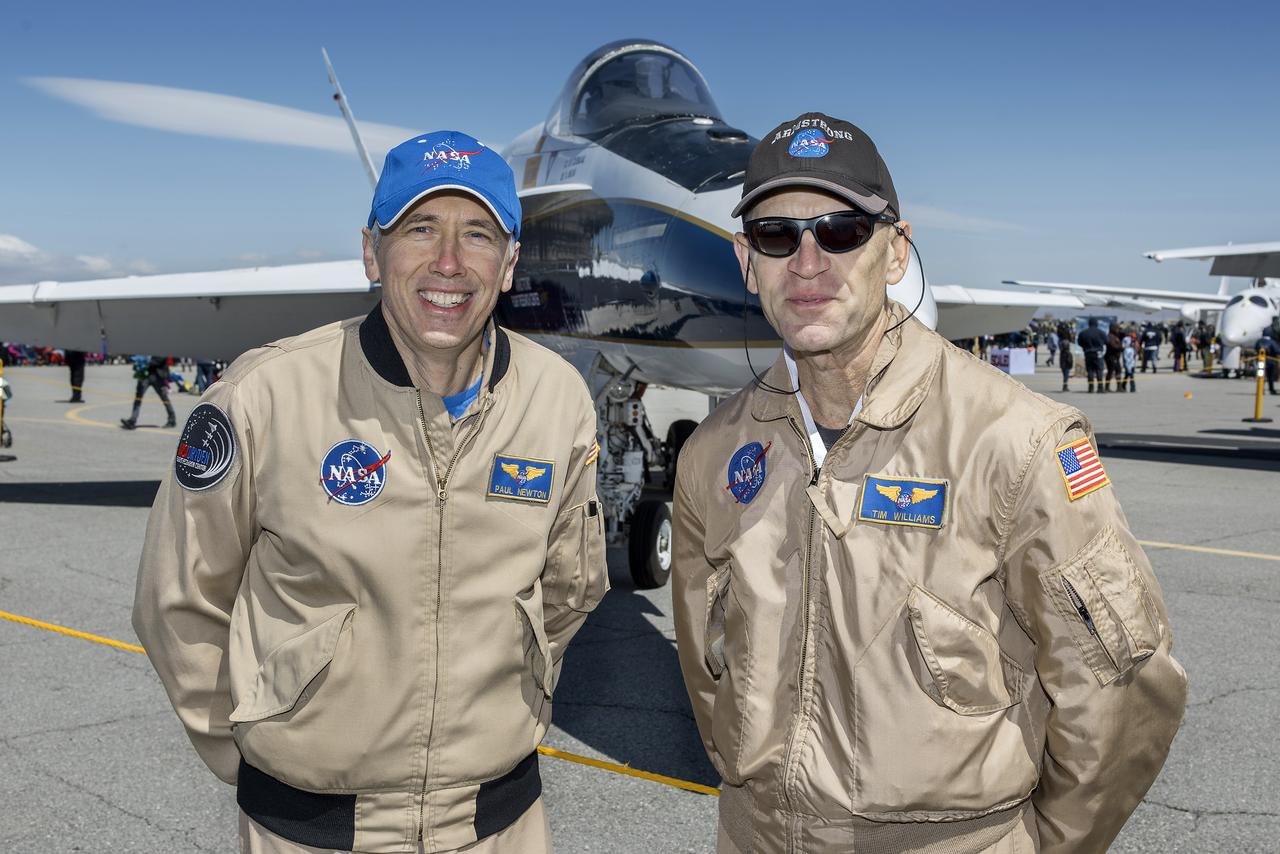

NASA Armstrong Research Center pilots Paul Newton and Tim Williams stand by the center’s F/A-18 research aircraft.
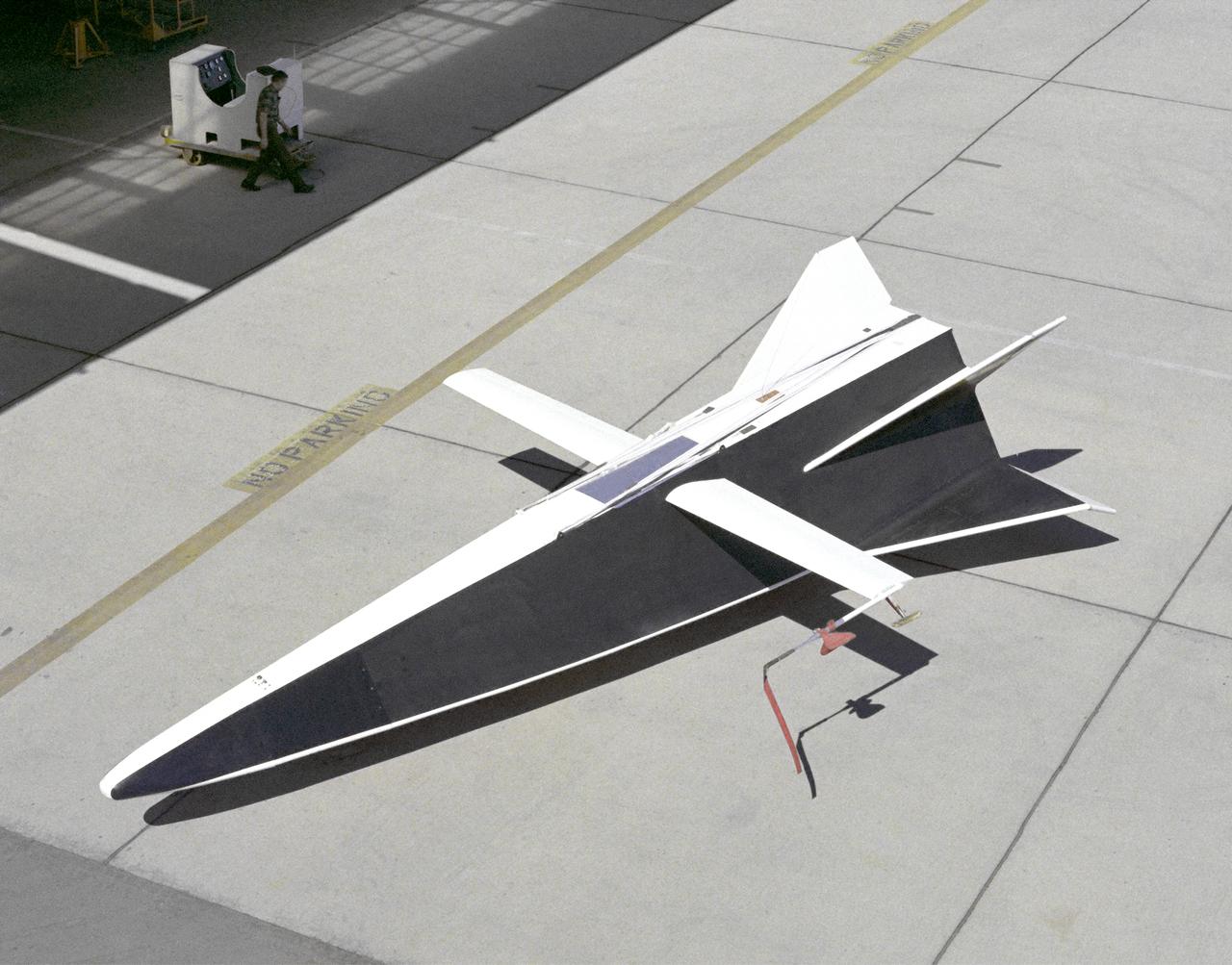
The Hyper III was a full-scale lifting-body remotely piloted research vehicle (RPRV) built at what was then the NASA Flight Research Center located at Edwards Air Force Base in Southern California.
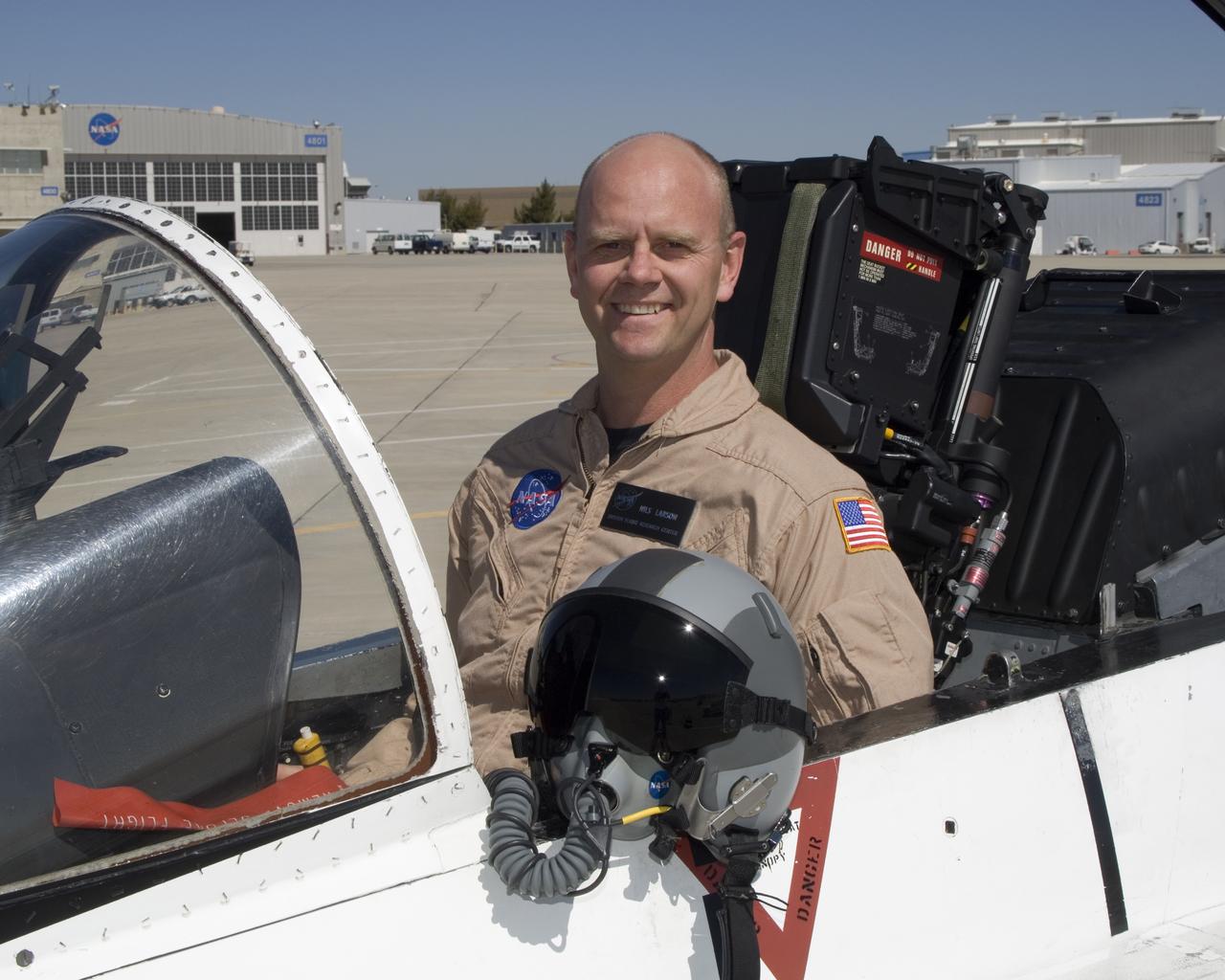

Nils Larson is a research pilot in the Flight Crew Branch of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif. Larson joined NASA in February 2007 and will fly the F-15, F-18, T-38 and ER-2. Prior to joining NASA, Larson was on active duty with the U.S. Air Force. He has accumulated more that 4,900 hours of military and civilian flight experience in more than 70 fixed and rotary winged aircraft. Larson completed undergraduate pilot training at Williams Air Force Base, Chandler, Ariz., in 1987. He remained at Williams as a T-37 instructor pilot. In 1991, Larson was assigned to Beale Air Force Base, Calif., as a U-2 pilot. He flew 88 operational missions from Korea, Saudi Arabia, the United Kingdom, Panama and other locations. Larson graduated from the U.S. Air Force Test Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., in Class 95A. He became a flight commander and assistant operations officer for the 445th squadron at Edwards. He flew the radar, avionics integration and engine tests in F-15 A-D, the early flights of the glass cockpit T-38C and airworthiness flights of the Coast Guard RU-38. He was selected to serve as an Air Force exchange instructor at the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School, Patuxent River, Md. He taught systems and fixed-wing flight test and flew as an instructor pilot in the F-18, T-2, U-6A Beaver and X-26 Schweizer sailplane. Larson commanded U-2 operations for Warner Robins Air Logistics Center's Detachment 2 located in Palmdale, Calif. In addition to flying the U-2, Larson supervised the aircraft's depot maintenance and flight test. He was the deputy group commander for the 412th Operations Group at Edwards before retiring from active duty in 2007 with the rank of lieutenant colonel. His first experience with NASA was at the Glenn Research Center, Cleveland, where he served a college summer internship working on arcjet engines. Larson is a native of Bethany, W.Va,, and received his commission from the U.S. Air Force Academy in 1986 with a
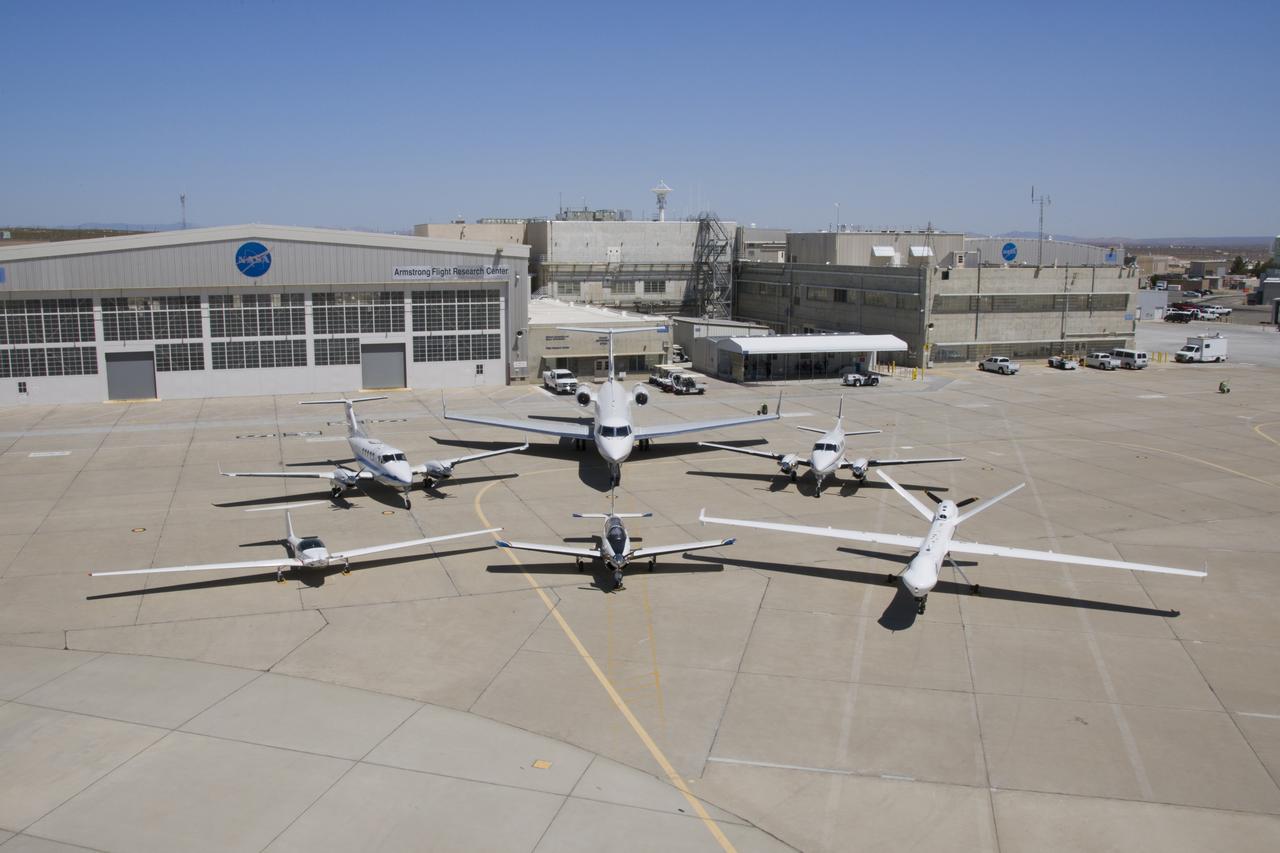

NASA’s Ikhana remotely piloted aircraft (front-right) is situated near NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s Hangar 4802 after an Unmanned Aircraft Systems Integration into the National Airspace System Flight Test Series 4 flight, along with five flight “intruders.” These intruders, which include NASA’s TG-14 (front-left), T-34C (front-center), B-200 King Air (back-left), Gulfstream-III (back-center) and a Honeywell C-90 King Air (back-right), fly within a pre-determined distance to Ikhana to test Detect-and-Avoid technology during research flights.
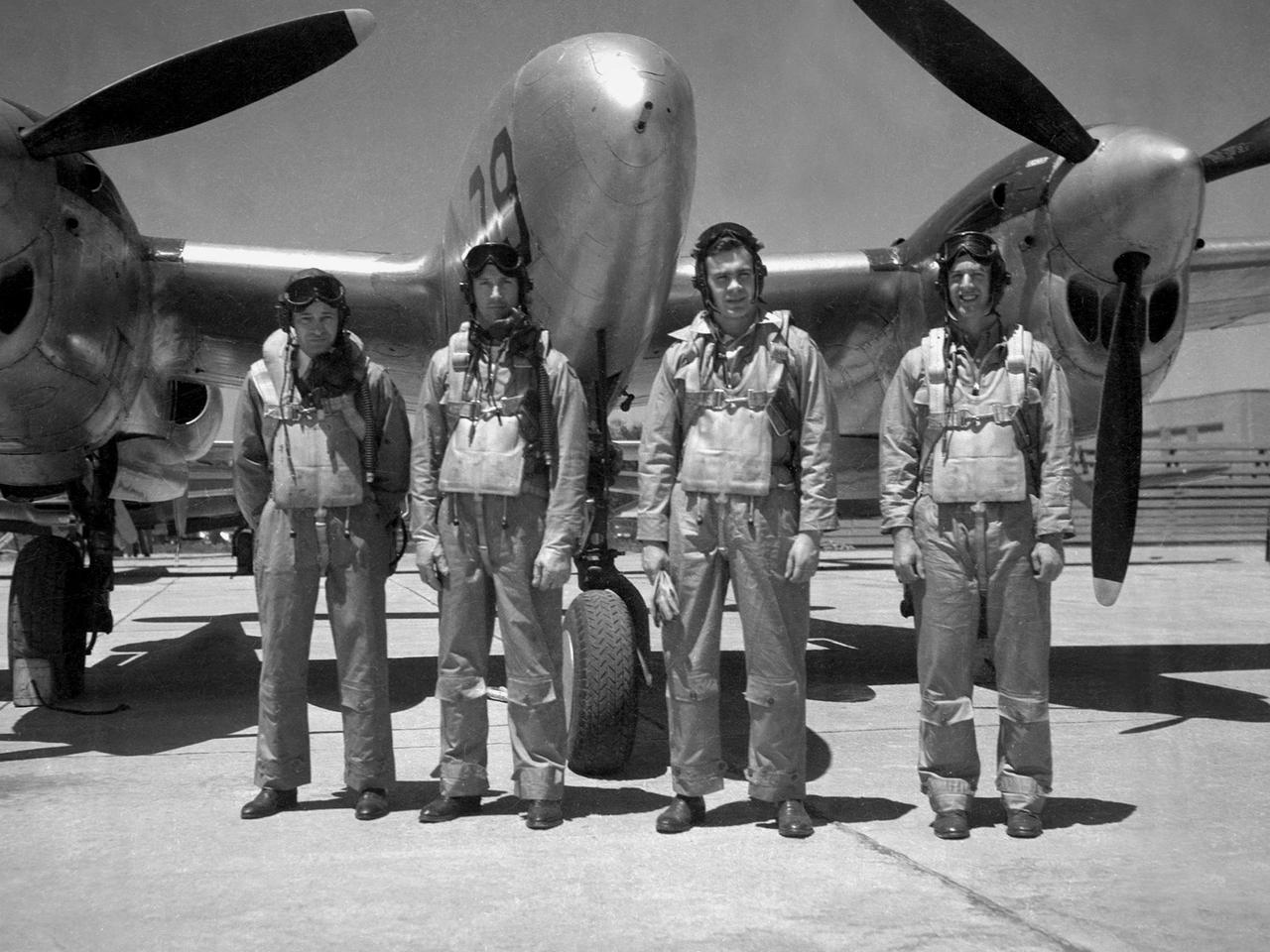

The Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory’s pilot corps during the final days of World War II: from left to right, Joseph Vensel, Howard Lilly, William Swann, and Joseph Walker. William “Eb” Gough joined the group months after this photograph. These men were responsible for flying the various National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) aircraft to test new engine modifications, study ice buildup, and determine fuel performance. Vensel, a veteran pilot from Langley, was the Chief of Flight Operations and a voice of reason at the laboratory. In April 1947 Vensel was transferred to lead the new Muroc Flight Tests Unit in California until 1966. Lilly was a young pilot with recent Navy experience. Lilly also flew in the 1946 National Air Races. He followed Vensel to Muroc in July 1947 where he became the first NACA pilot to penetrate the sound barrier. On May 3, 1948, Lilly became the first NACA pilot to die in the line of duty. Swann was a young civilian pilot when he joined the NACA. He spent his entire career at the Cleveland laboratory, and led the flight operations group from the early 1960s until 1979. Two World War II veterans joined the crew after the war. Walker was a 24-year-old P–38 reconnaissance pilot. He joined the NACA as a physicist in early 1945 but soon worked his way into the cadre of pilots. Walker later gained fame as an X-plane pilot at Muroc and was killed in a June 1966 fatal crash. Gough survived being shot down twice during the war and was decorated for flying rescue missions in occupied areas.
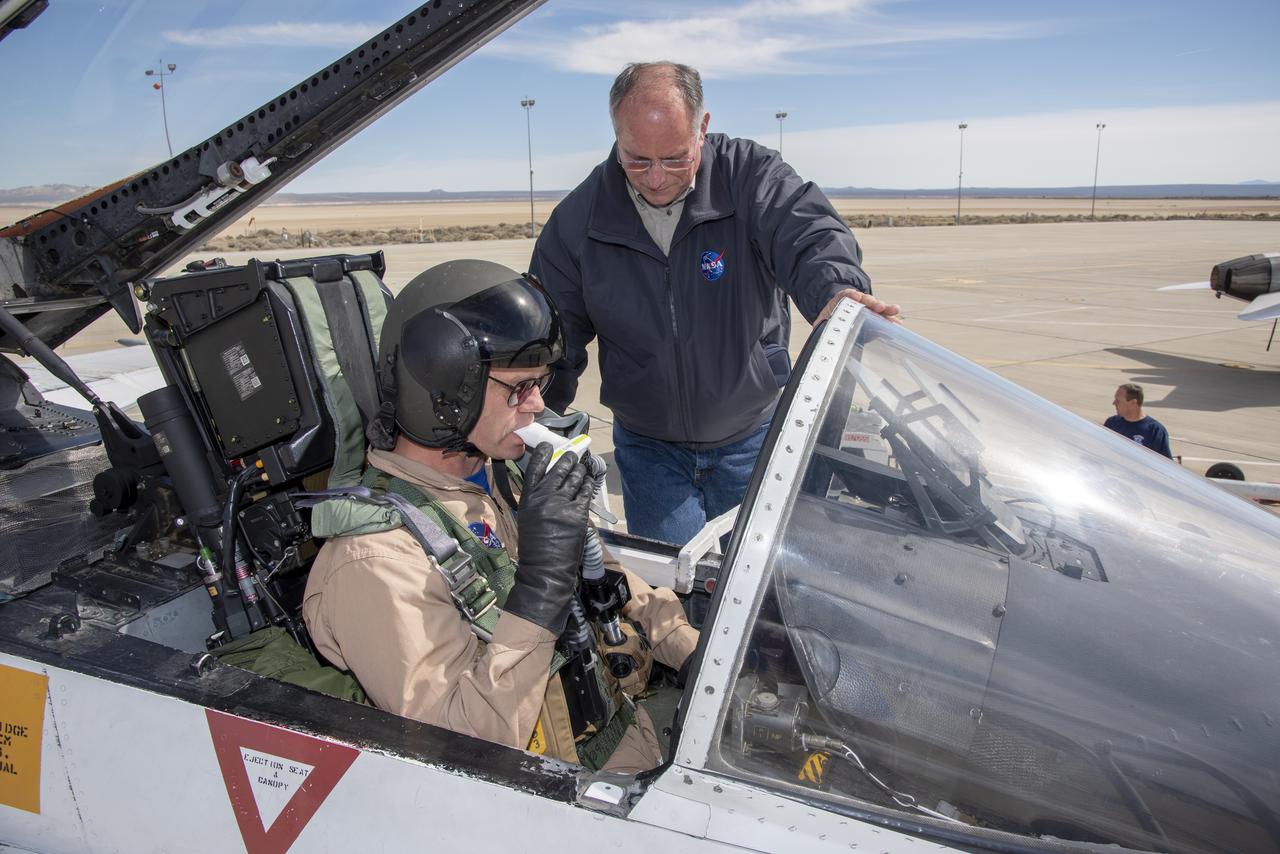

Phillip Wellner from Life Support conducts a spirometry test on NASA Pilot Nils Larson before a Pilot Breathing Assessment flight at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California.Â

NASA's 2017 astronaut candidates (L to R) Jenni Sidey-Gibbons, Jessica Watkins and Joshua Kutryk practice flying in an F-18 aircraft cockpit simulator at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California. The F-18's are flown for research support and pilot proficiency. Currently, the F-18 is conducting supersonic research in support of the X-59 QueSST overall mission.
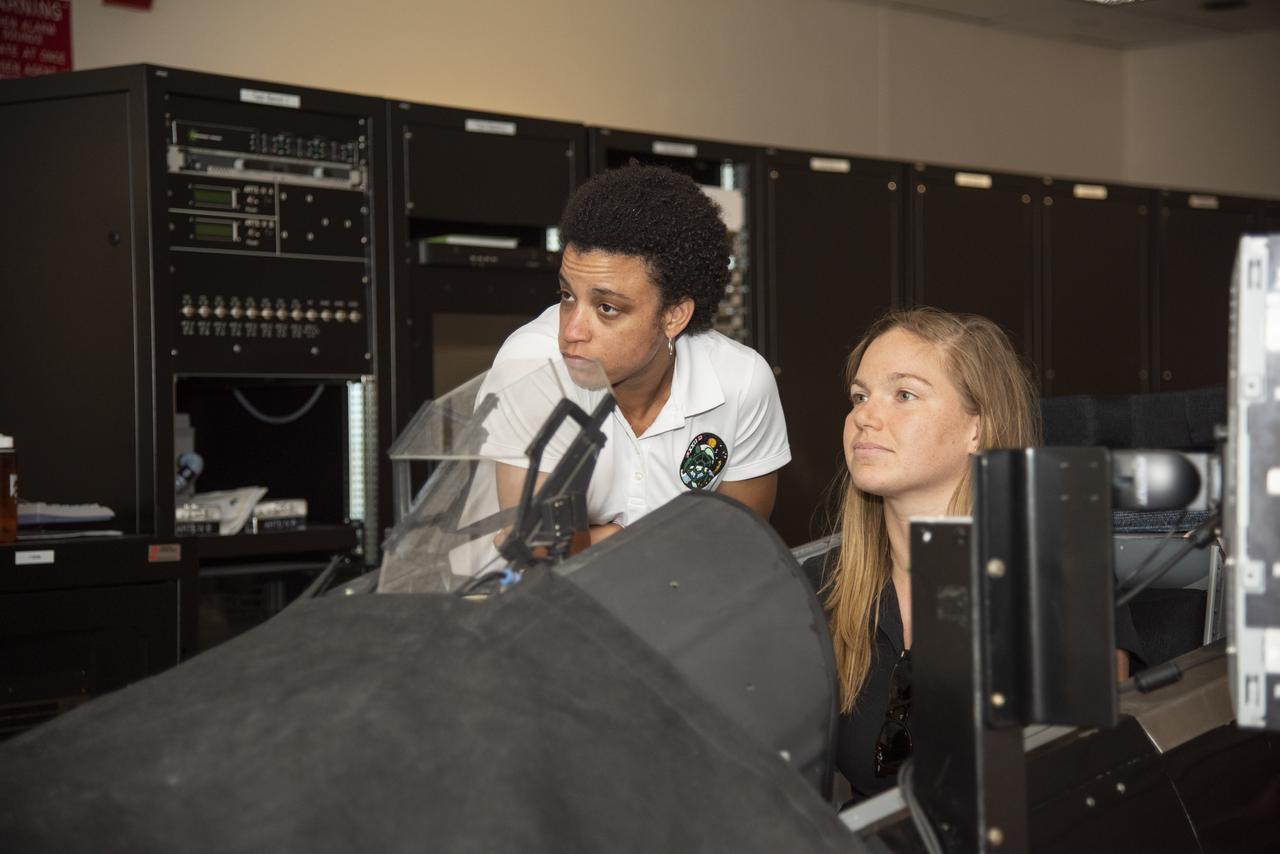

NASA's 2017 astronaut candidates (L to R) Jessica Watkins and Jenni Sidey-Gibbons practice flying in an F-18 aircraft cockpit simulator at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California. The F-18's are flown for research support and pilot proficiency. Currently, the F-18's are being used to conduct supersonic research in support of the X-59 QueSST overall mission.

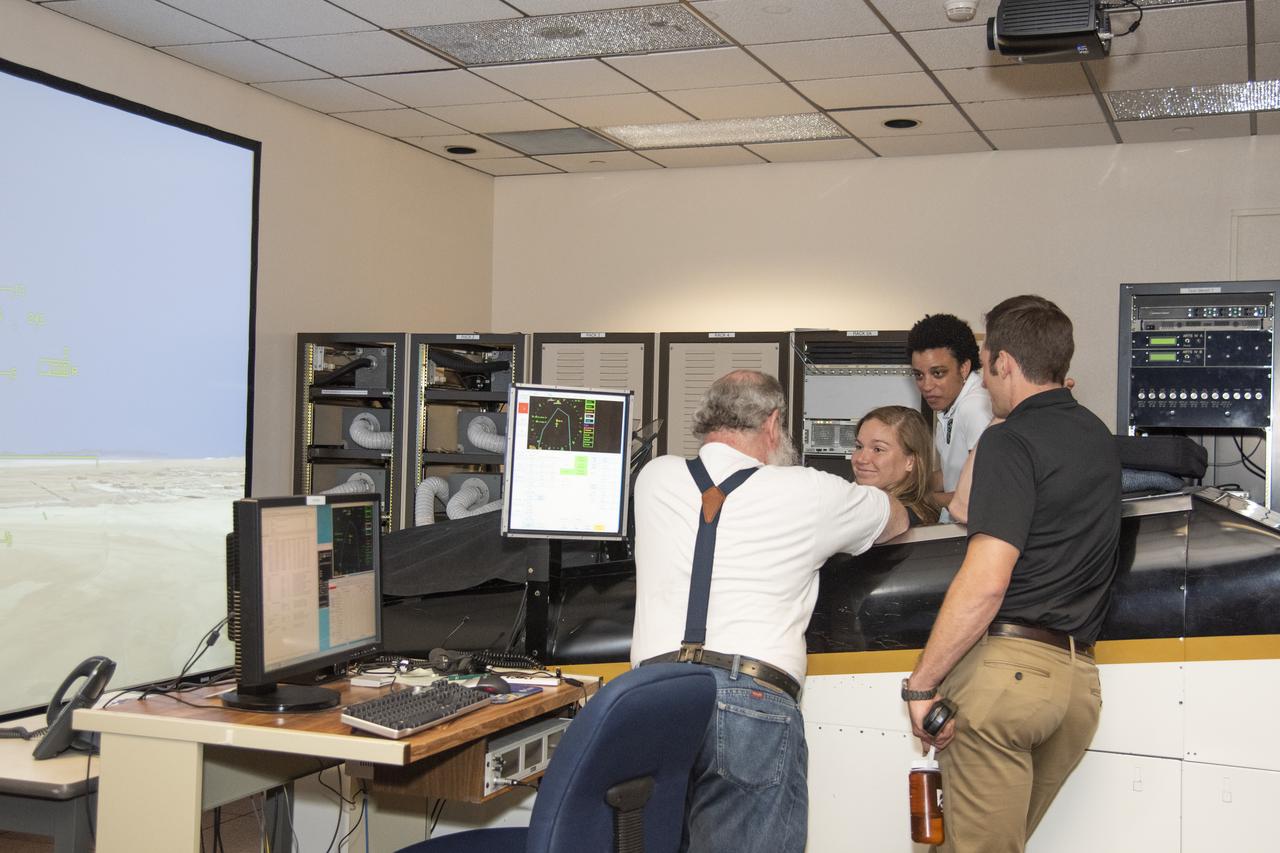
NASA’s 2017 astronaut candidates (L to R) Jessica Watkins, Jenni Sidey-Gibbons, Joshua Kutryk, and Jasmin Moghbeli practice flying in an F-18 aircraft cockpit simulator at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California. The F-18’s are flown for research support and pilot proficiency. Currently, the F-18’s are being used to conduct supersonic research in support of the X-59 QueSST overall mission.

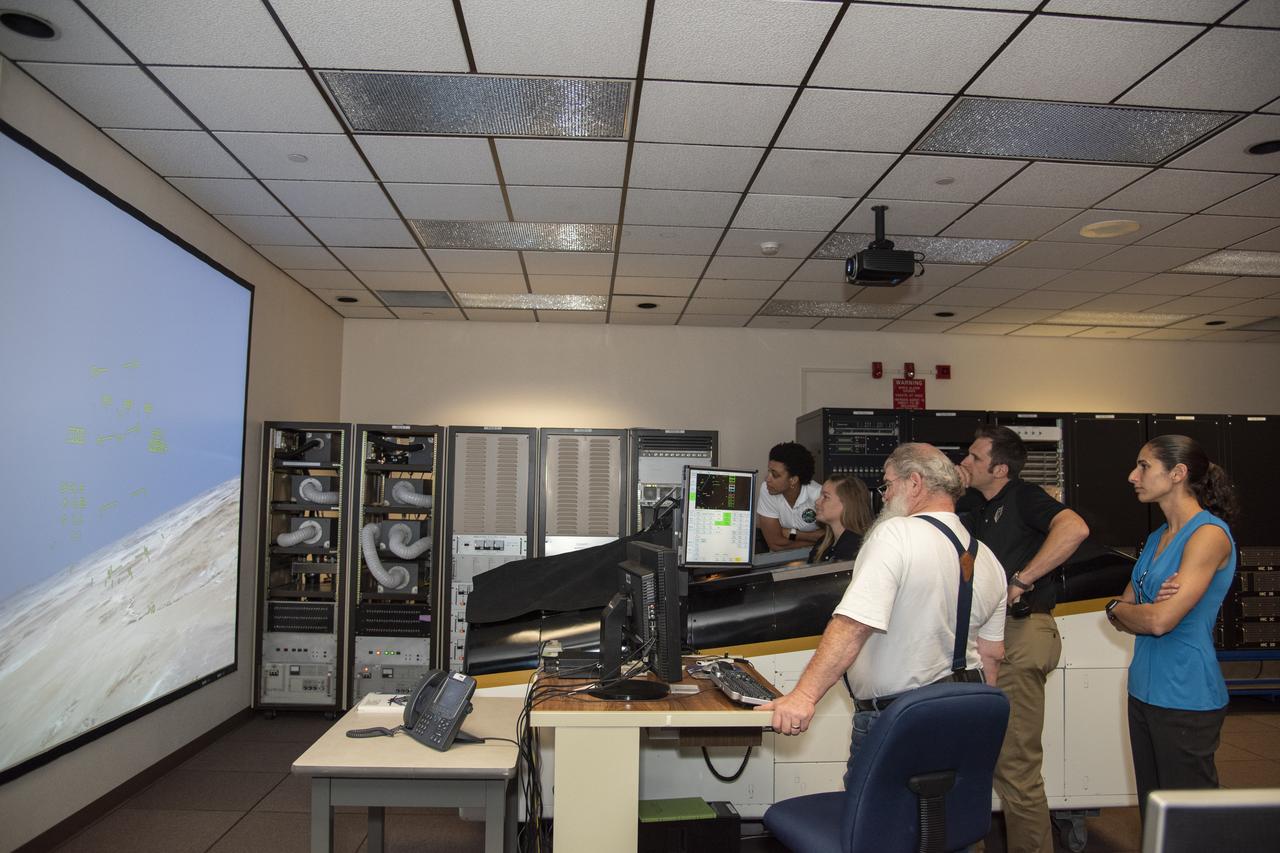
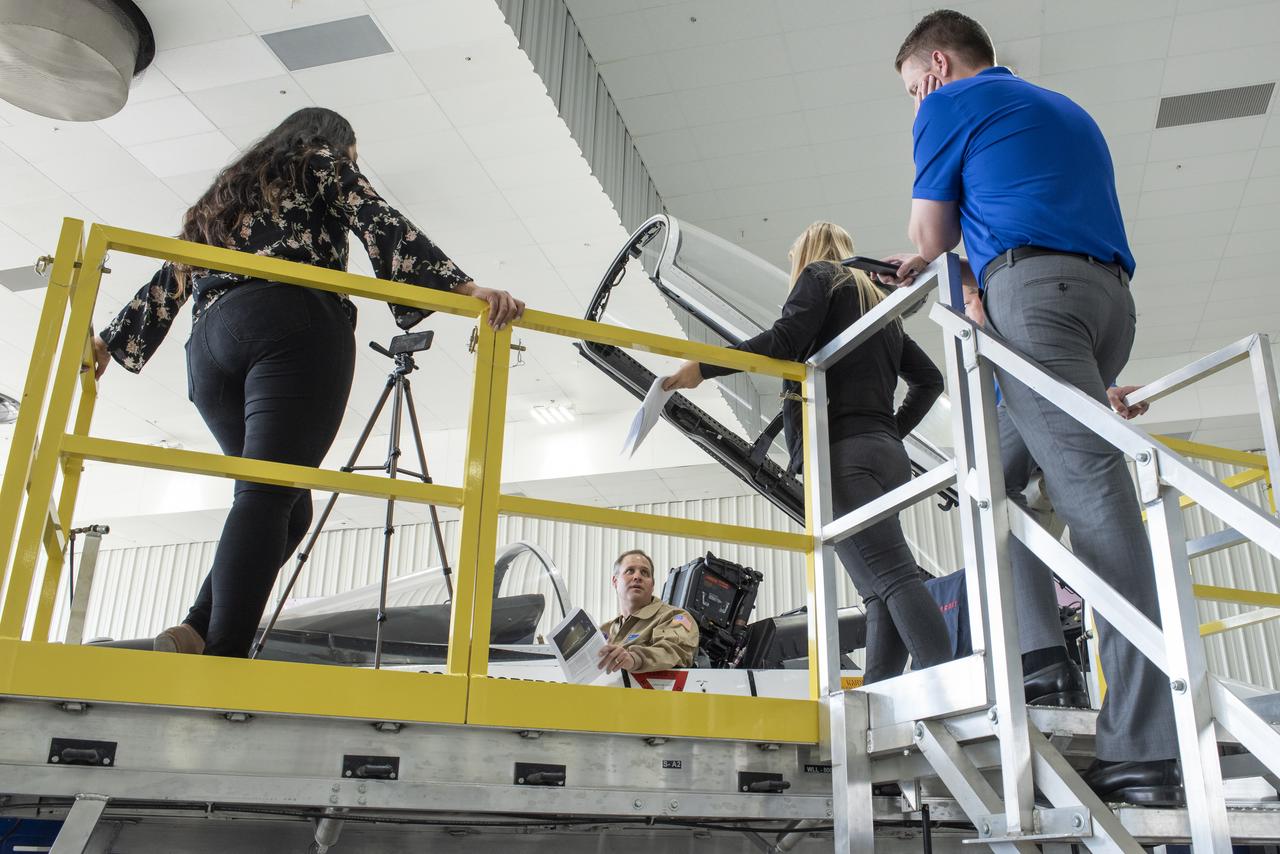
NASA Administrator Bridenstine learns about the many uses for mission control rooms for flight research projects such as monitoring the flights for safety, gathering data and talking to the pilot and project researcher.
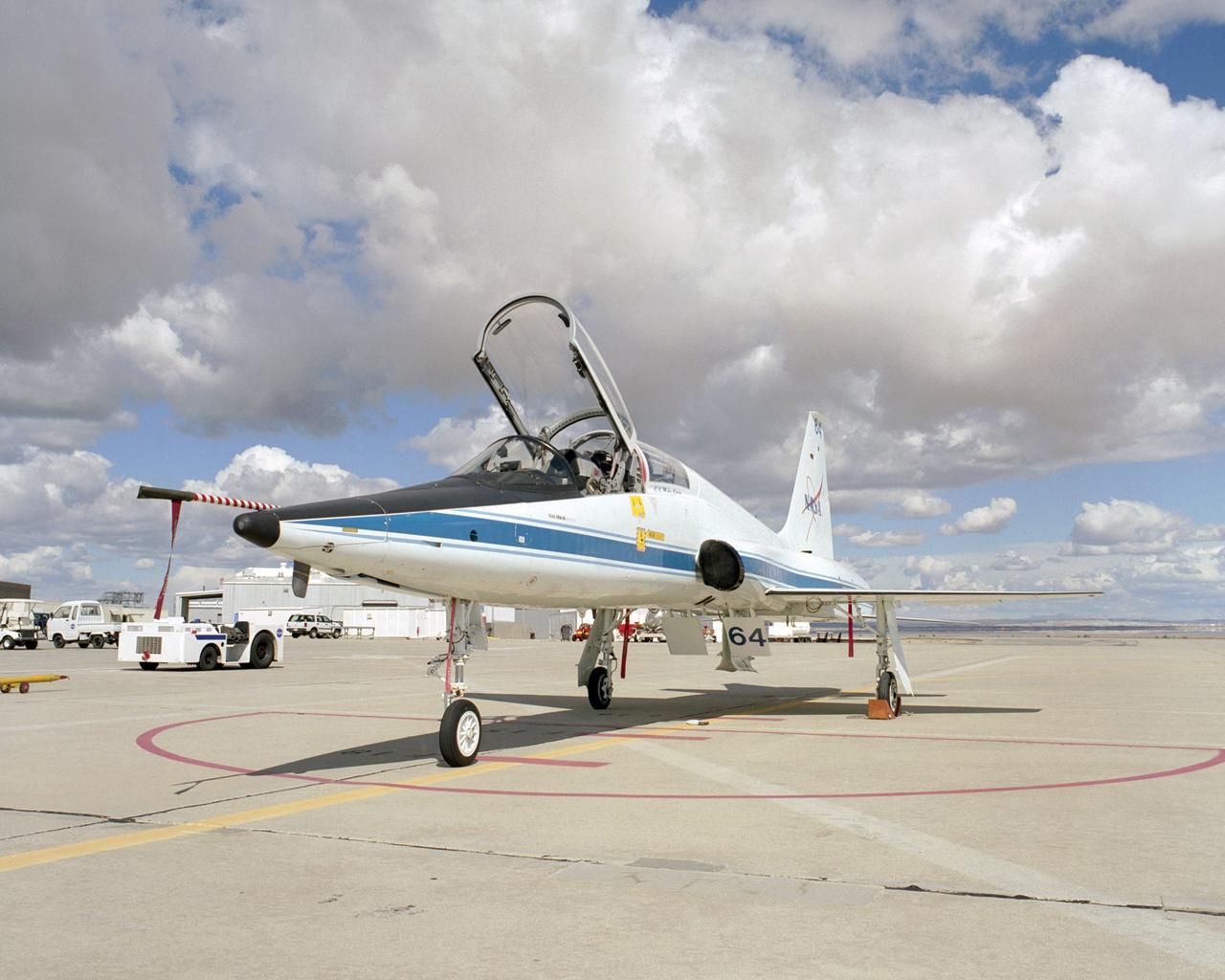

Formerly at NASA's Langley Research Center, this Northrop T-38 Talon is now used for mission support and pilot proficiency at the Dryden Flight Research Center.

NASA's ultra-quiet YO-3A acoustics research aircraft taxis out from the ramp at the Dryden Flight Research Center before a pilot checkout flight.

NASA Administrator Bridenstine, former navy pilot, sits comfortably back in F-18 jet cockpit at Armstrong Flight Research Center.
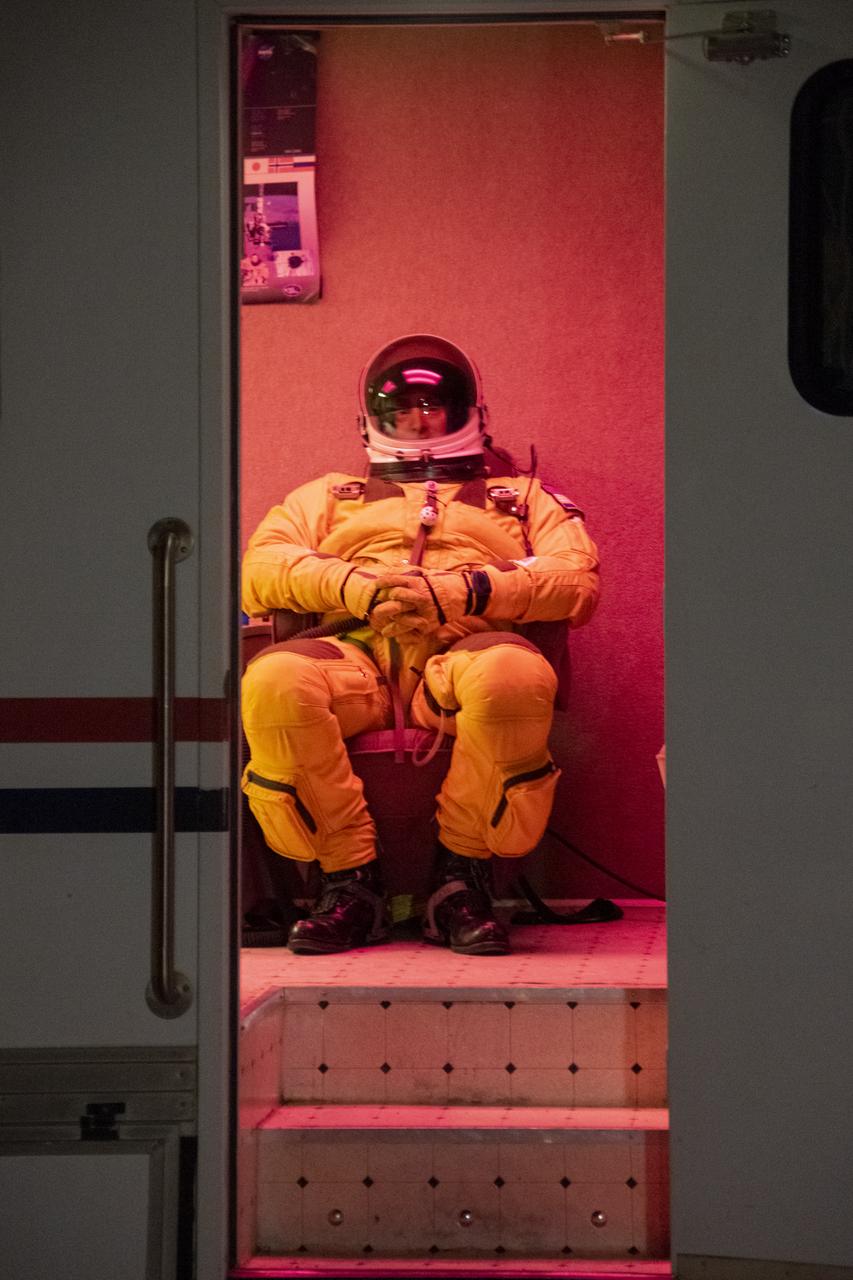

Pilot Stu Broce is pre-breathing 100% oxygen prior to take off for an Air-LUSI flight at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center.
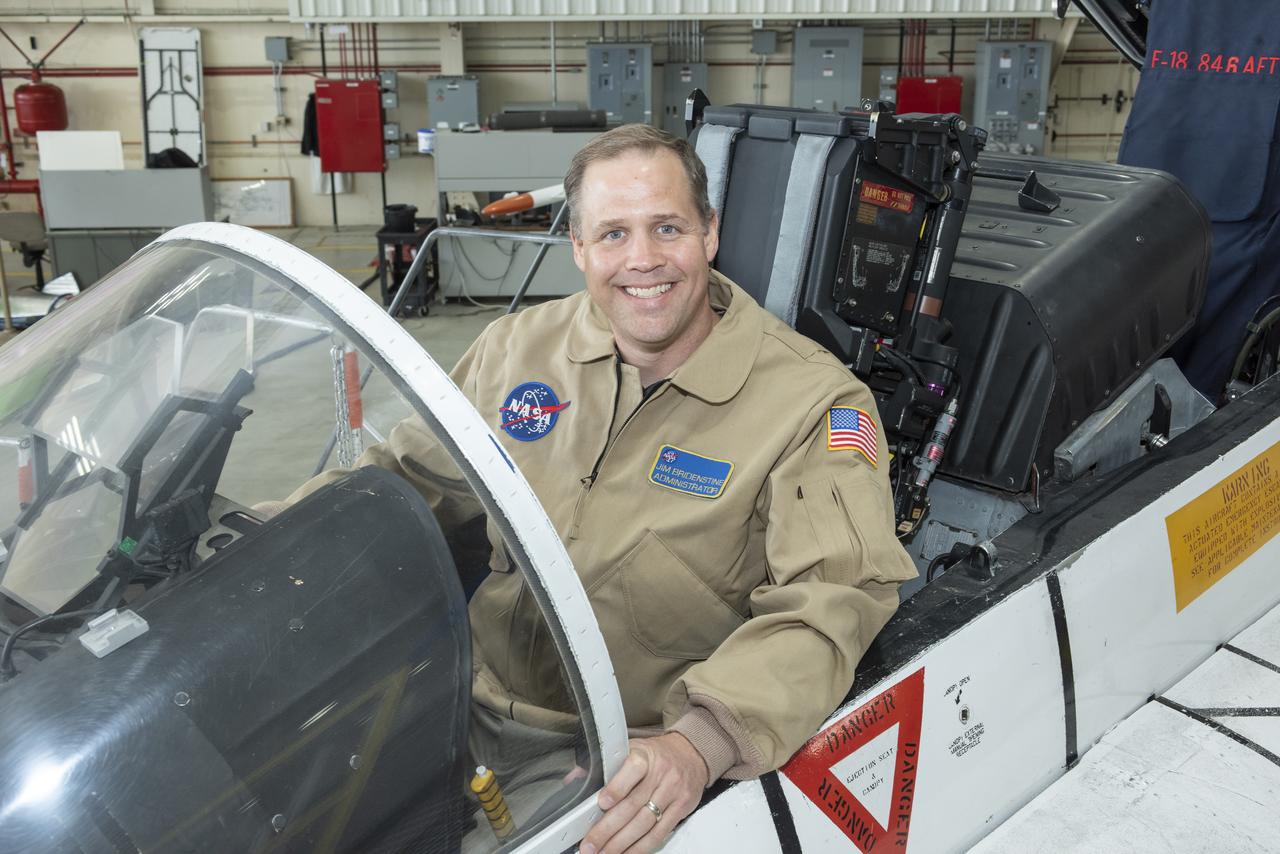

NASA Administrator Bridenstine, former navy pilot, sits comfortably back in F-18 jet cockpit at Armstrong Flight Research Center.
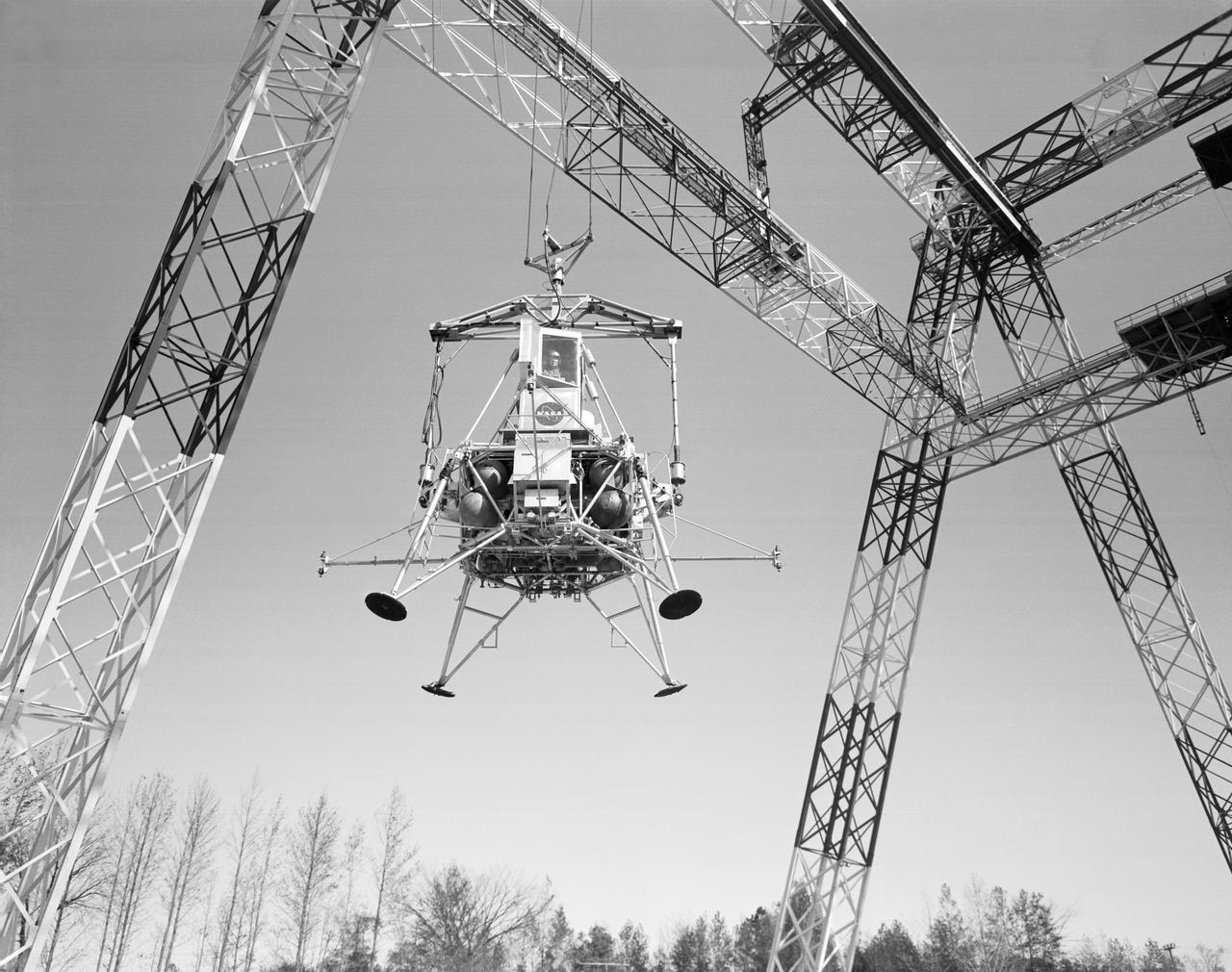

Lunar landing test of LEM at LLRF Lunar Landing Research Facility: A NASA Langley research pilot flies a lunar lander in a test conducted in the Lunar Landing Research Facility.
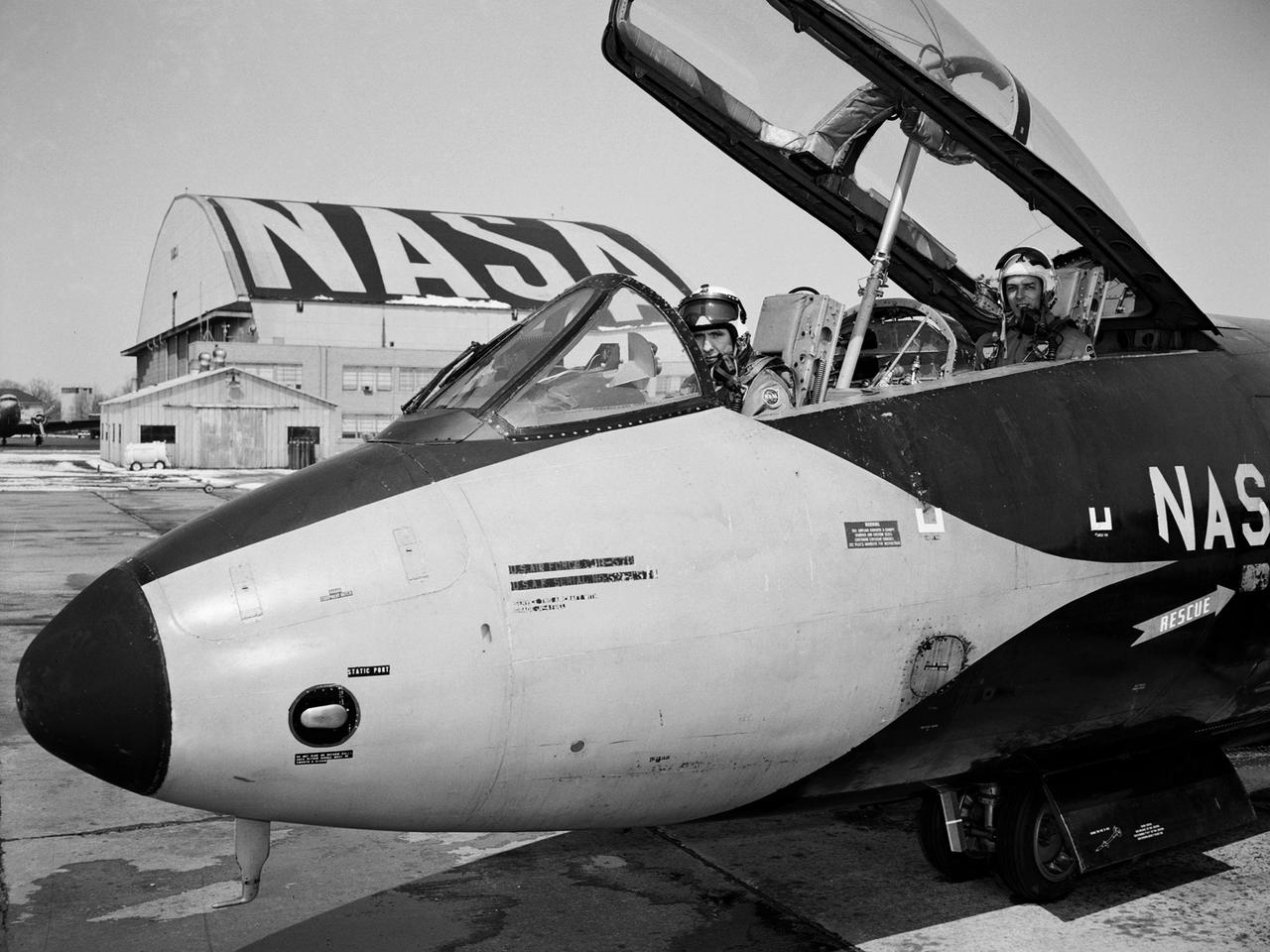

Pilot Earle Boyer and researcher Henry Brandhorst prepare for a solar cell calibration flight in a Martin B-57B Canberra at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Lewis was in the early stages of decades-long energy conversion and space power research effort. Brandhorst, a member of the Chemistry and Energy Conversion Division, led a team of Lewis researchers in a quest to develop new power sources to sustain spacecraft in orbit. Solar cells proved to be an important source of energy, but researchers discovered that their behavior varied at different atmospheric levels. Their standardization and calibration were critical. Brandhorst initiated a standardized way to calibrate solar cells in the early 1960s using the B-57B aircraft. The pilots would take the aircraft up into the troposphere and open the solar cell to the sunlight. The aircraft would steadily descend while instruments recorded how much energy was being captured by the solar cell. From this data, Brandhorst could determine the estimated power for a particular solar cell at any altitude. Pilot Earle Boyer joined NASA Lewis in October 1962. He had flown Convair F-102 Delta Dagger fighters in the Air Force and served briefly in the National Guard before joining the Langley Research Center. Boyer was only at Langley a few months before he transferred to Cleveland. He flew the B-57B, a Convair F-106 Delta Dart, Gulfstream G-1 with an experimental turboprop, Learjet and many other aircraft over the next 32 years at Lewis.
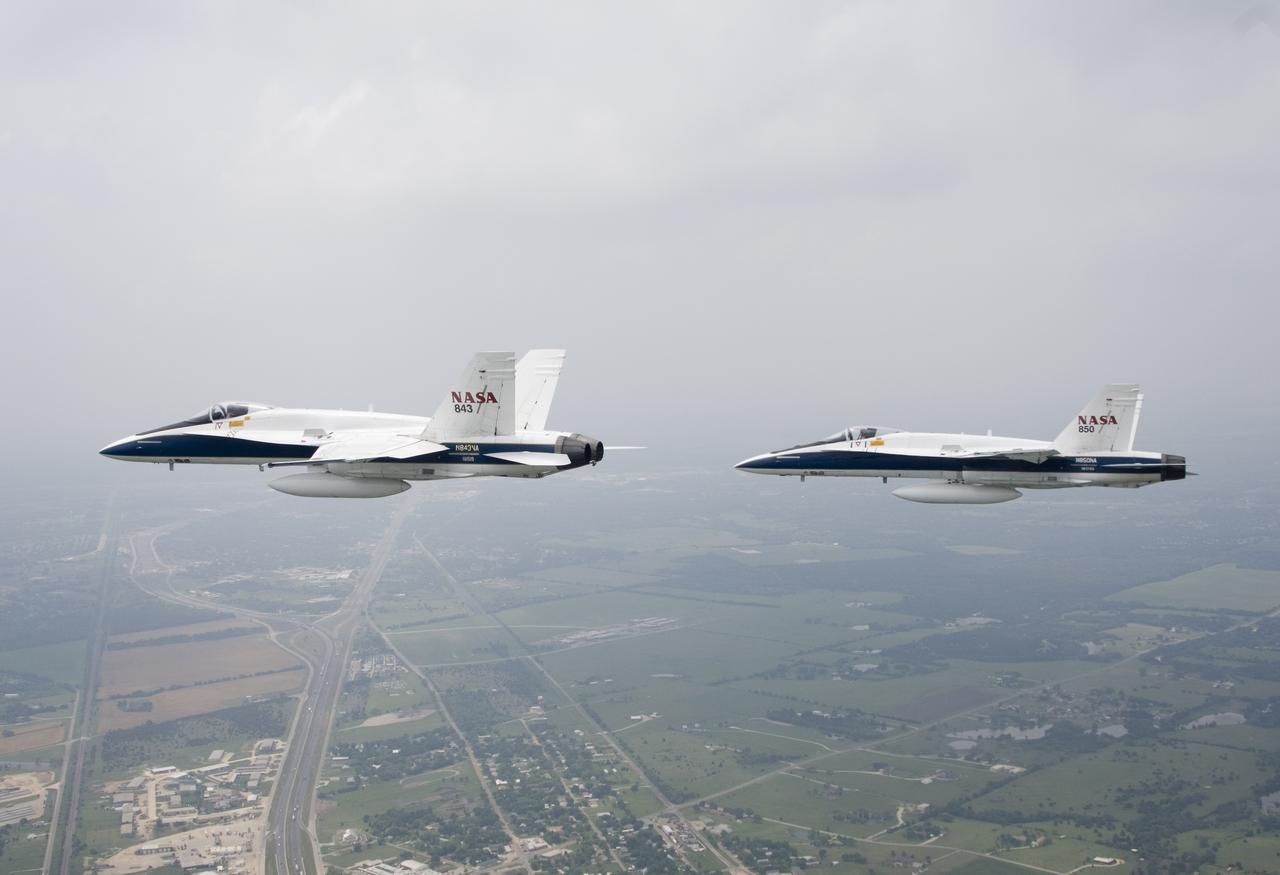

Two NASA F/A-18s flown by NASA Dryden research pilots Jim Smolka and Nils Larson cruise over the Texas landscape after supporting a SOFIA check flight in May 2007.
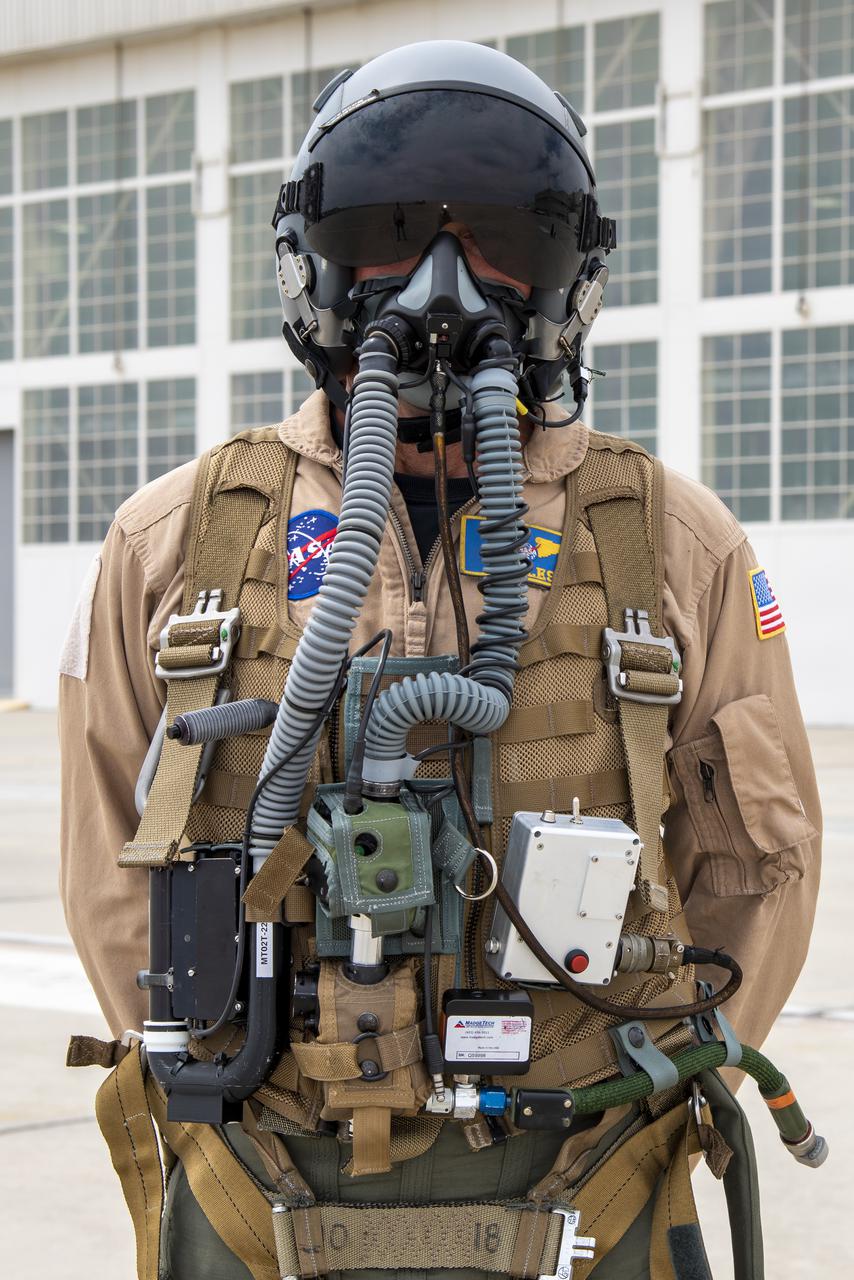

NASA research pilot Jim Less wears a U.S. Navy harness configuration with the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California prototype mask, which uses laser sensors to determine levels of carbon dioxide and water exhaled inside the mask. This prototype was tested in conjunction with the current VigilOX system, which measures the pilot’s oxygen concentration, breathing pressures and flow rates. This and the U.S. Air Force configuration was used in the Pilot Breathing Assessment program at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California.

This turboprop-powered Beech T-34C is flown by NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center for mission support and pilot proficiency.
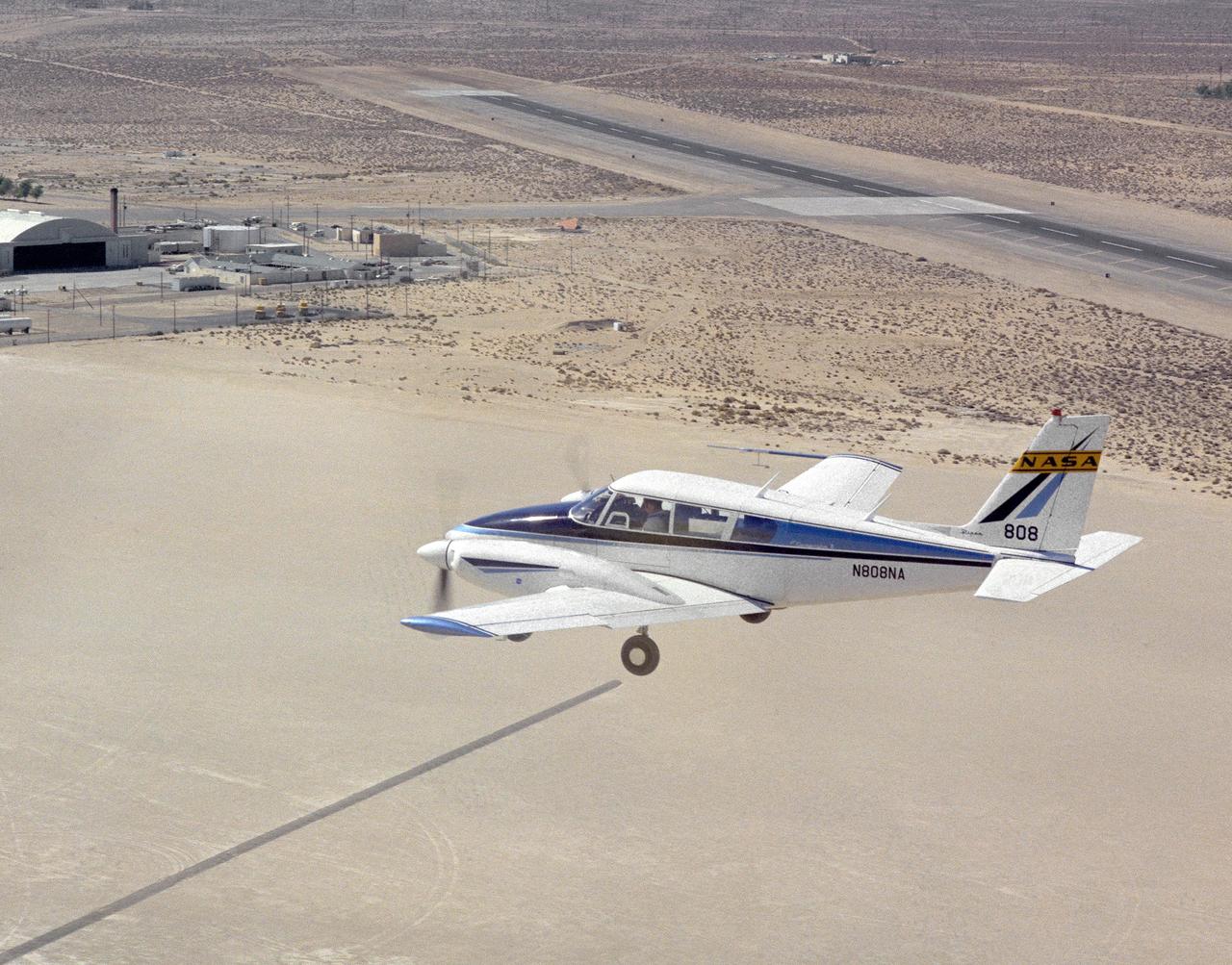

Dryden Flight Research Center's Piper PA-30 Twin Commanche, which helped validate the RPRV concept, descends to a remotely controlled landing on Rogers Dry Lake, unassisted by the onboard pilot. A Piper PA-30 Twin Commanche, known as NASA 808, was used at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center as a rugged workhorse in a variety of research projects associated with both general aviation and military projects. In the early 1970s, the PA-30, serial number 301498, was used to test a flight technique used to fly Remotely Piloted Research Vehicles (RPRV's). The technique was first tested with the cockpit windows of the light aircraft blacked out while the pilot flew the aircraft utilizing a television monitor which gave him a "pilot's eye" view ahead of the aircraft. Later pilots flew the aircraft from a ground cockpit, a procedure used with all RPRV's. TV and two-way telemetry allow the pilot to be in constant control of the aircraft. The apparatus mounted over the cockpit is a special fish eye lens camera, used to obtain images that are transmitted to the ground based cockpit. This project paved the way for sophisticated, highly successful research programs involving high risk spin, stall, and flight control conditions, such as the HiMAT and the subscale F-15 remotely piloted vehicles. Over the years, NASA 808 has also been used for spin and stall research related to general aviation aircraft and also research to alleviate wake vortices behind large jetliners.
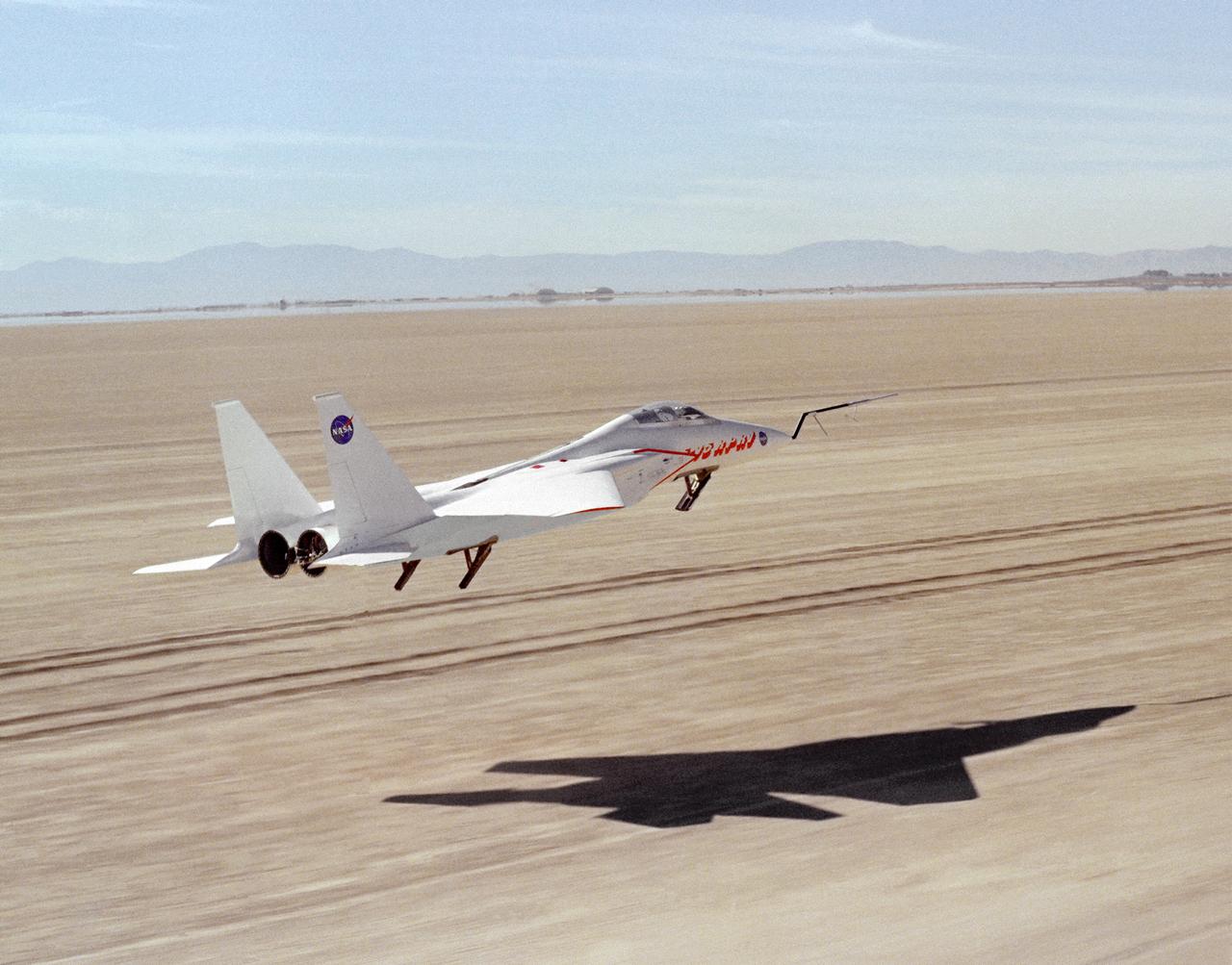

This photograph shows NASA's 3/8th-scale remotely piloted research vehicle landing on Rogers Dry Lakebed at Edwards Air Force Base, California, in 1975.
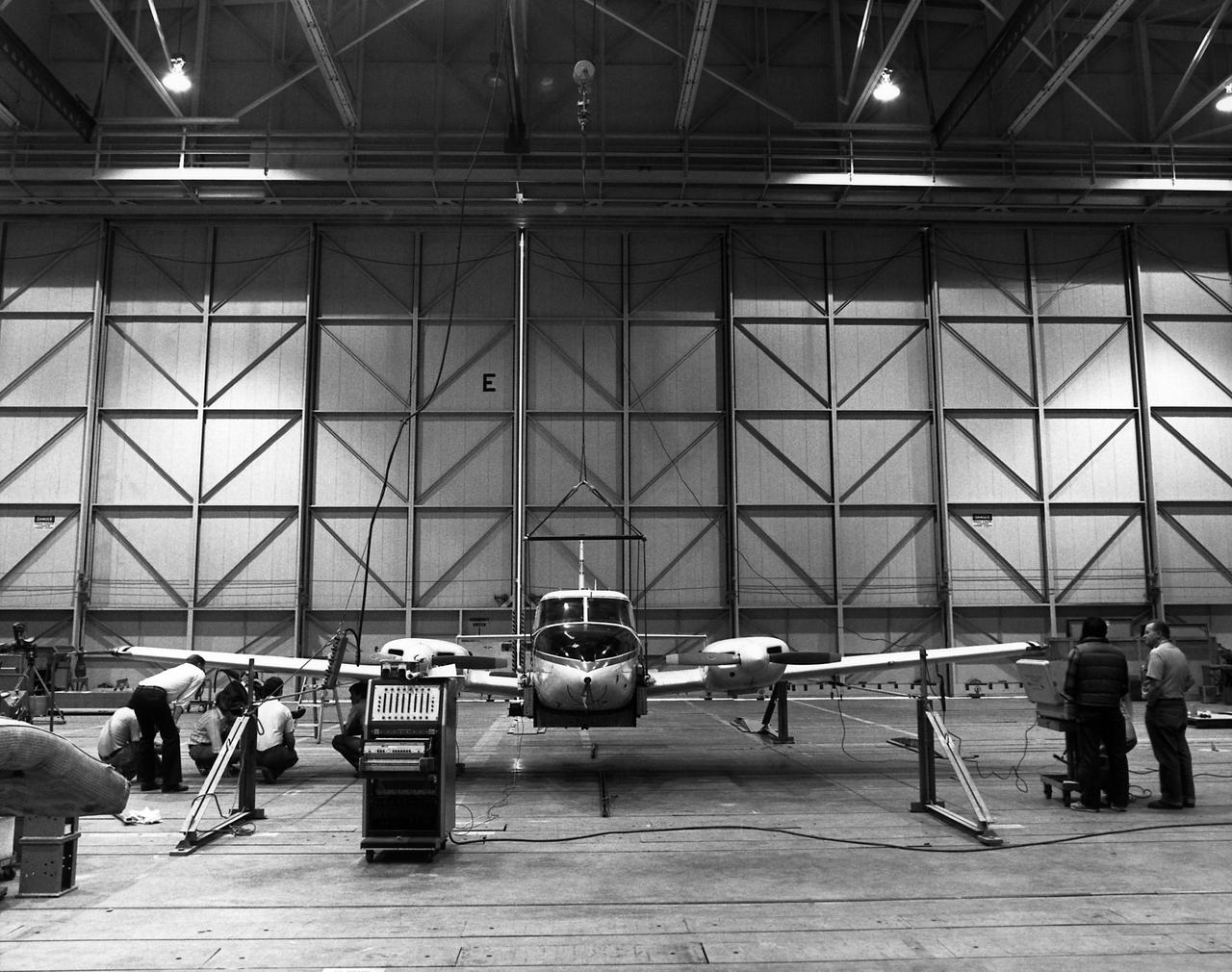

Technicians check instrumentation and systems on NASA 808, a PA-30 aircraft, prior to a research flight. The aircraft was used as the testbed in development of control systems for remotely piloted vehicles that were "flown" from the ground. The concept led to highly successful programs such as the HiMAT and the subscale F-15 remotely piloted vehicles. Over the years, NASA 808 has also been used for spin and stall research related to general aviation aircraft and also research to alleviate wake vortices behind large jetliners. This 1980 photograph taken inside a hangar shows technicians measuring moment of inertia.
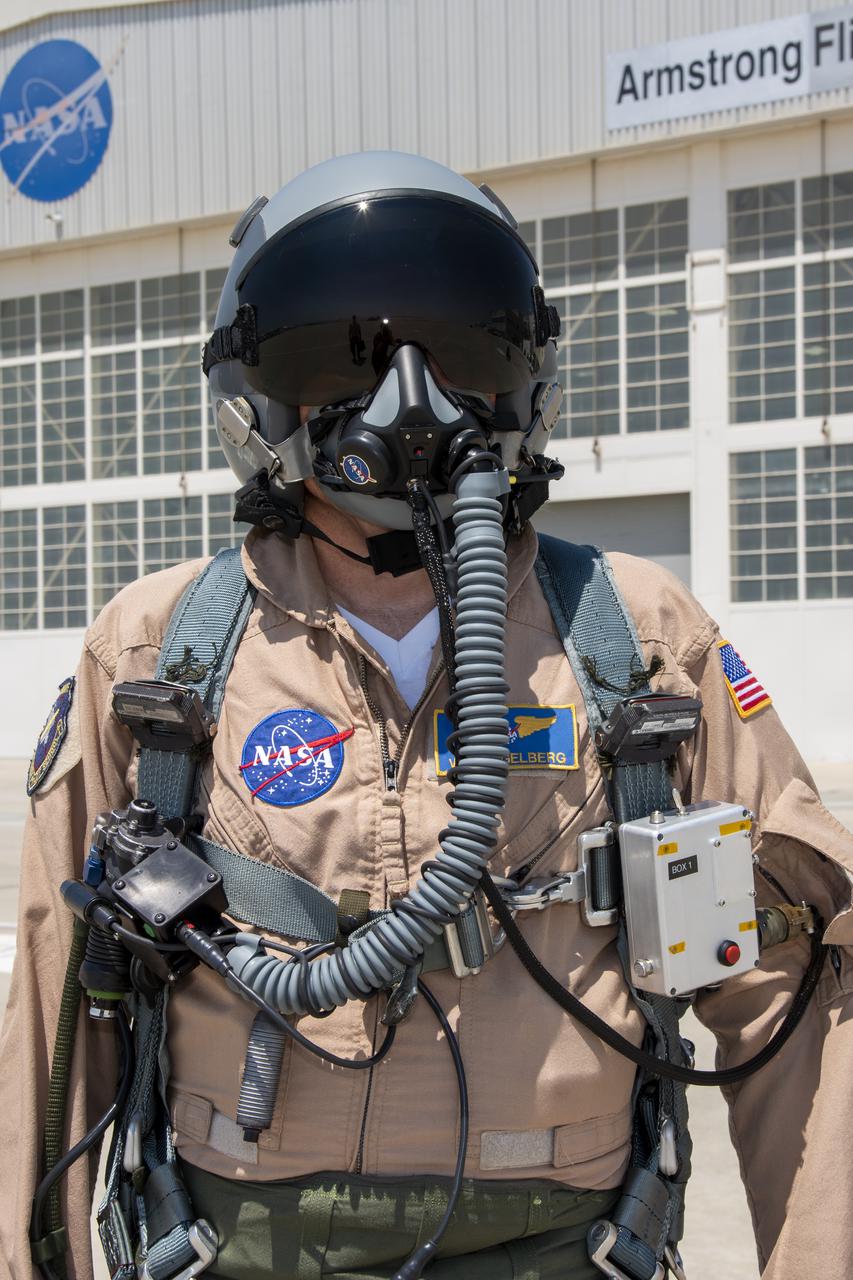

NASA research pilot Wayne Ringelberg wears a U.S. Air Force configuration of the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California prototype mask, which uses laser sensors to determine levels of carbon dioxide and water exhaled inside the mask. This prototype was tested in conjunction with the current VigilOX system, which measures the pilot’s oxygen concentration, breathing pressures and flow rates. This and the U.S. Navy configuration was used in the Pilot Breathing Assessment program at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California.
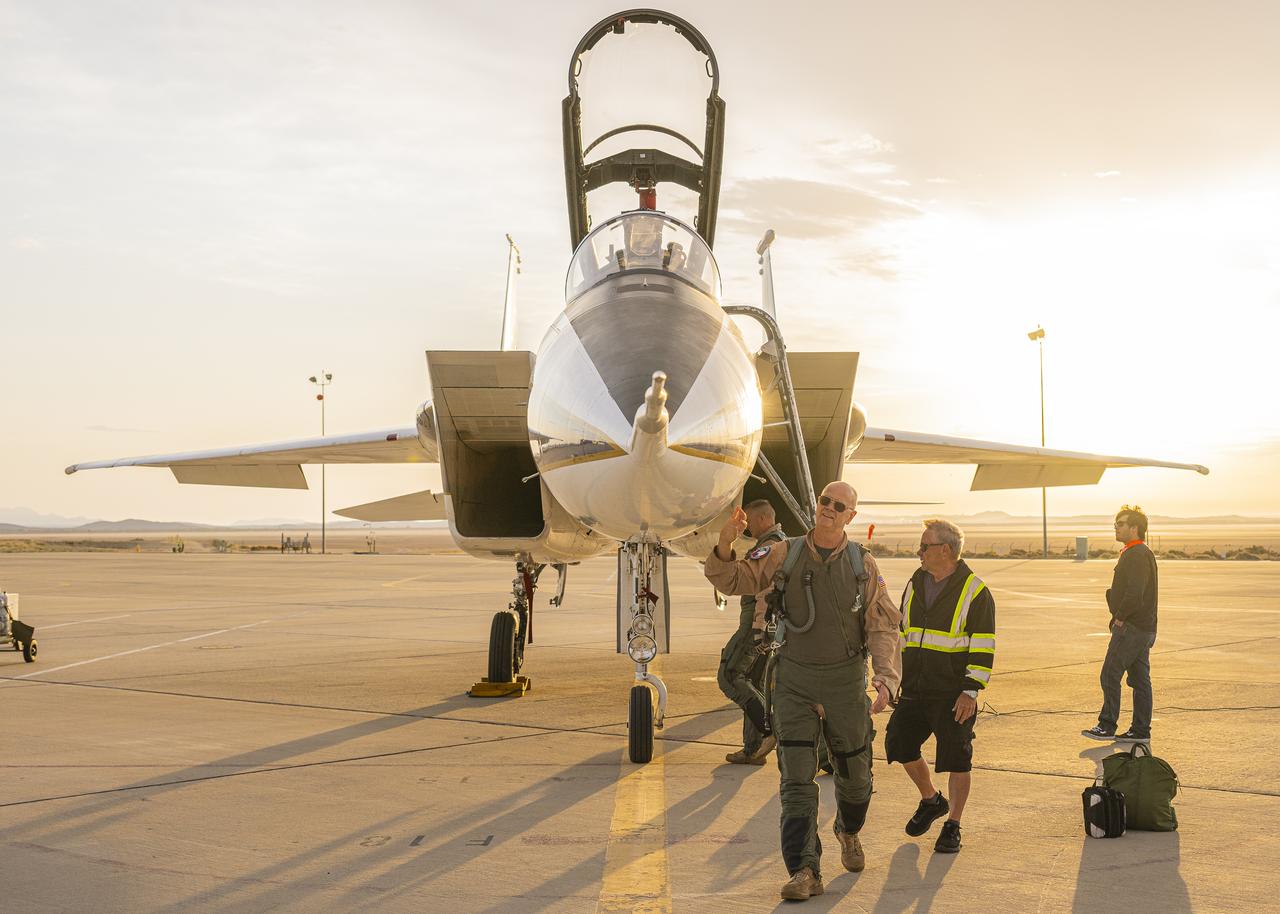

NASA test pilot Nils Larson walks around an F-15B research aircraft for a rehearsal flight supporting the agency’s Quesst mission at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The flight was part of a full-scale dress rehearsal for Phase 2 of the mission, which will eventually measure quiet sonic thumps generated by the X-59. The flight series helped NASA teams refine procedures and practice data collection ahead of future X-59 flights.
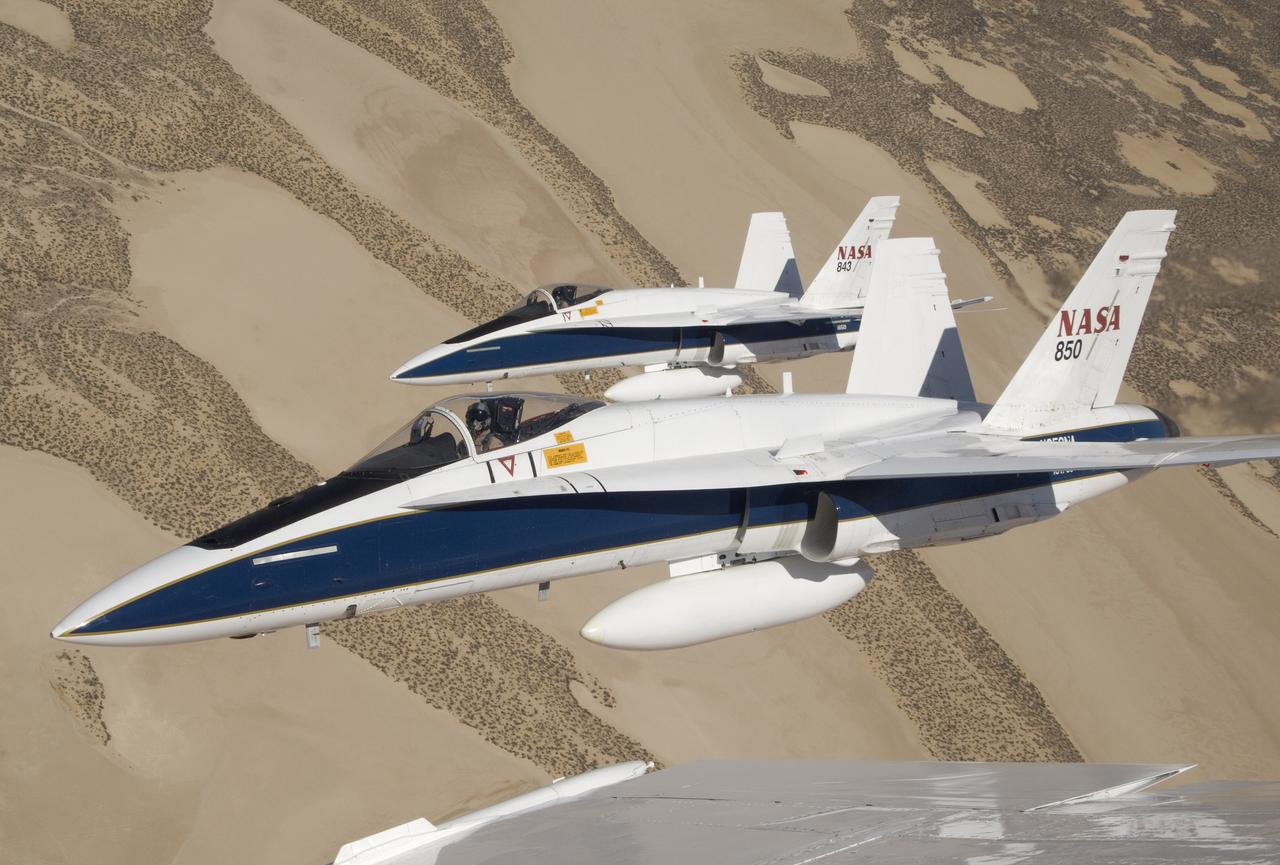

Two NASA Dryden F/A-18s flown by research pilots Frank Batteas and Nils Larson were captured by photographer Lori Losey from a third F/A-18 flown by Dick Ewers as they flew in tight formation over the desert at Edwards Air Force Base.
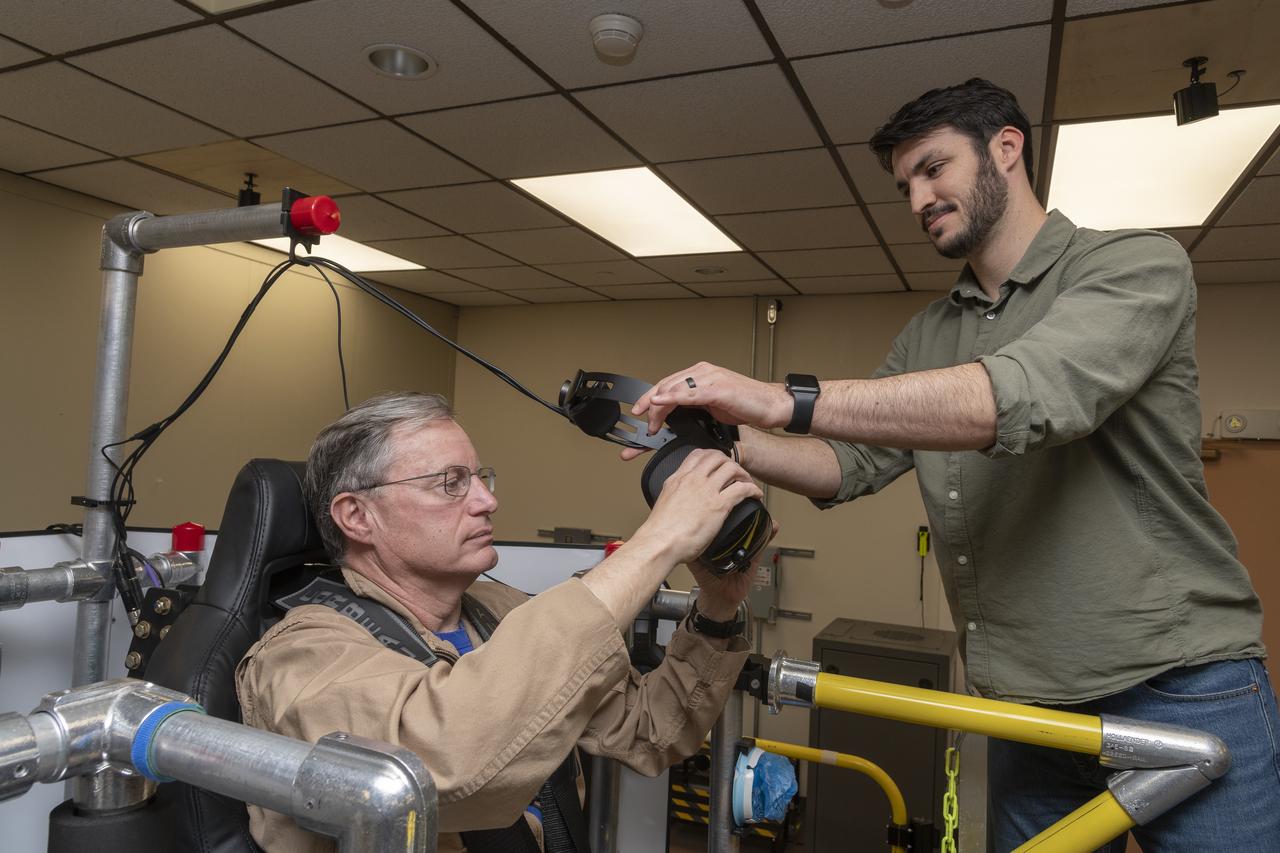

NASA test pilot Wayne Ringelberg and NASA researcher Kyle Barnes prepare for Ringelberg’s ride in the air taxi virtual reality flight simulator during a test at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in March 2024.
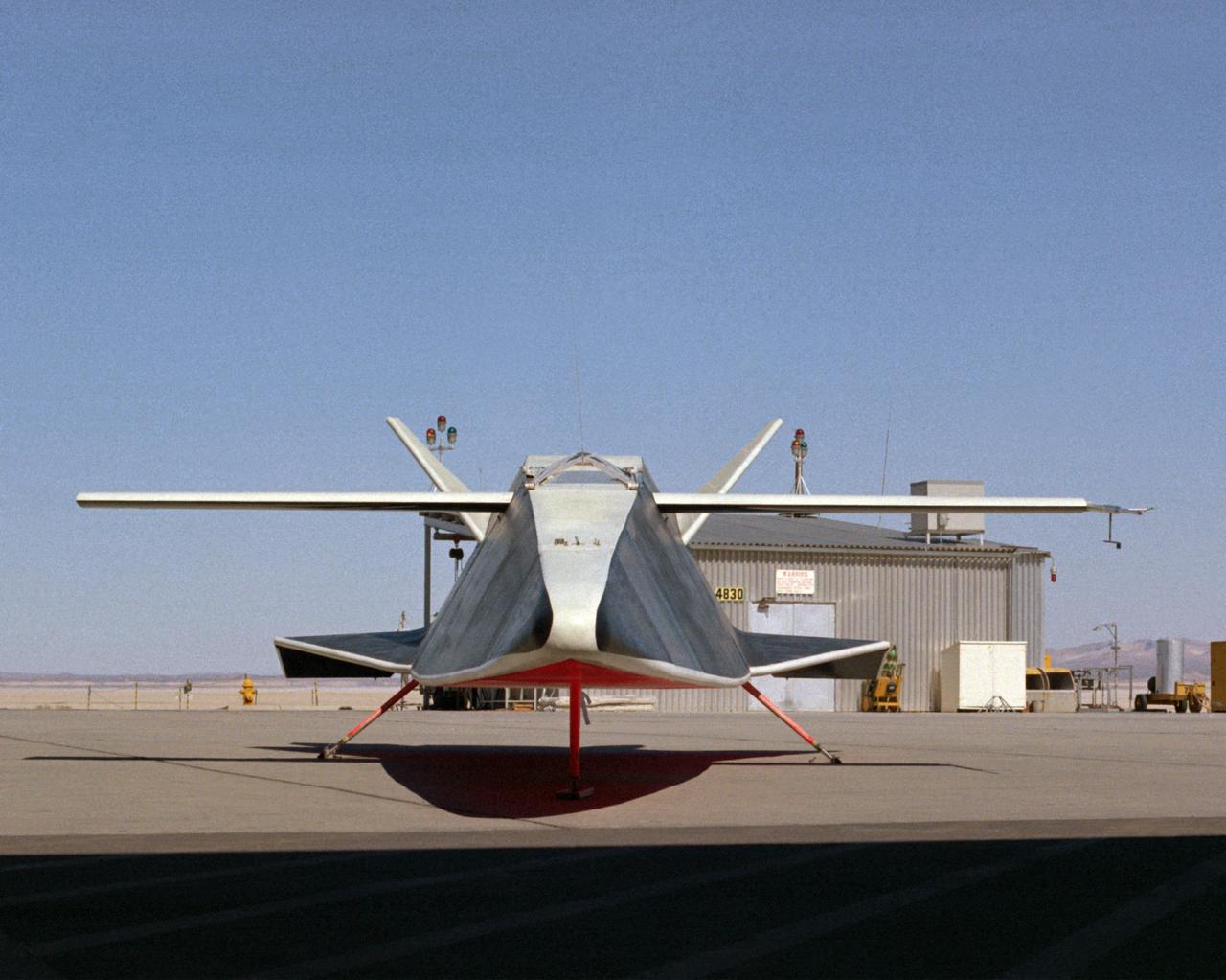

The Hyper III was a low-cost test vehicle for an advanced lifting-body shape. Like the earlier M2-F1, it was a "homebuilt" research aircraft, i.e., built at the Flight Research Center (FRC), later redesignated the Dryden Flight Research Center. It had a steel-tube frame covered with Dacron, a fiberglass nose, sheet aluminum fins, and a wing from an HP-11 sailplane. Construction was by volunteers at the FRC. Although the Hyper III was to be flown remotely in its initial tests, it was fitted with a cockpit for a pilot. On the Hyper III's only flight, it was towed aloft attached to a Navy SH-3 helicopter by a 400-foot cable. NASA research pilot Bruce Peterson flew the SH-3. After he released the Hyper III from the cable, NASA research pilot Milt Thompson flew the vehicle by radio control until the final approach when Dick Fischer took over control using a model-airplane radio-control box. The Hyper III flared, then landed and slid to a stop on Rogers Dry Lakebed.
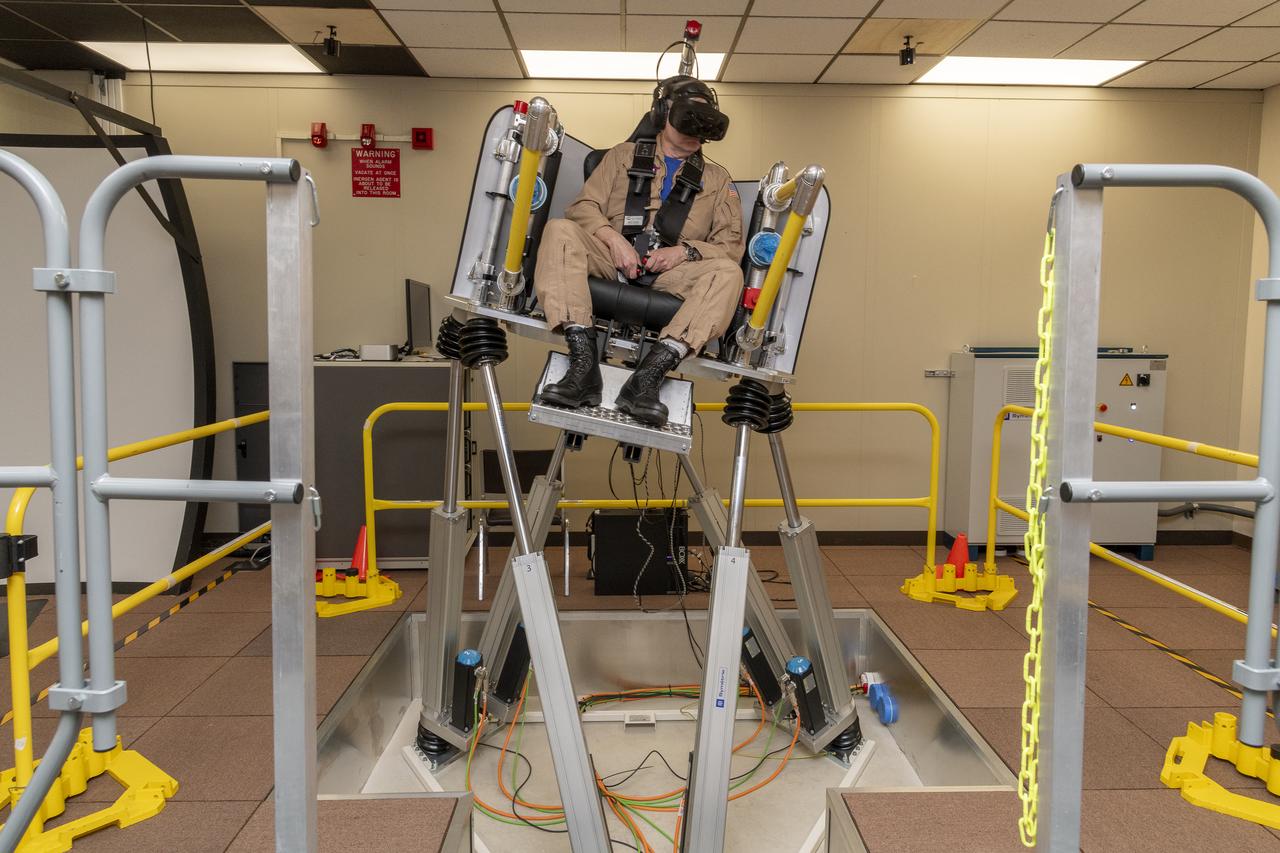

NASA test pilot Wayne Ringelberg sits in the air taxi virtual reality flight simulator during a test at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in March 2024.
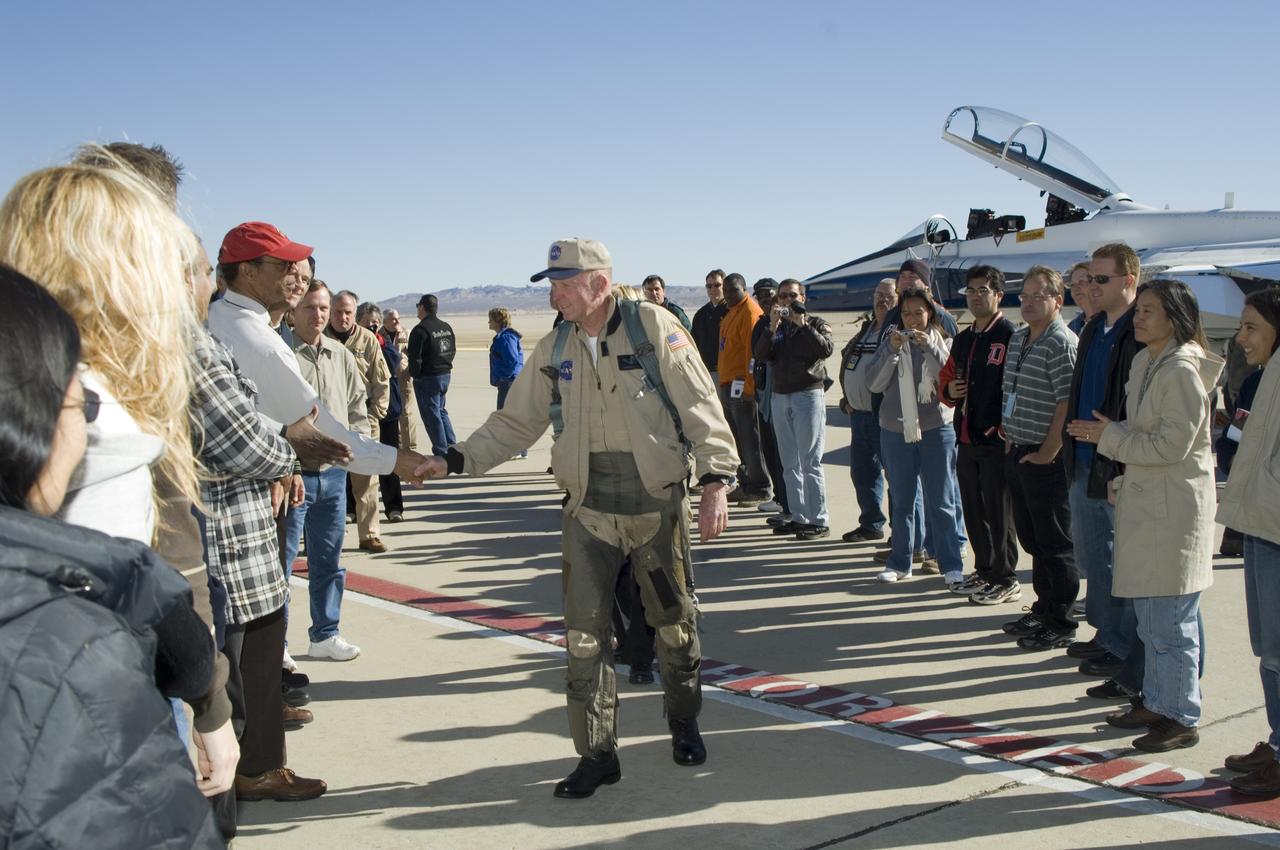

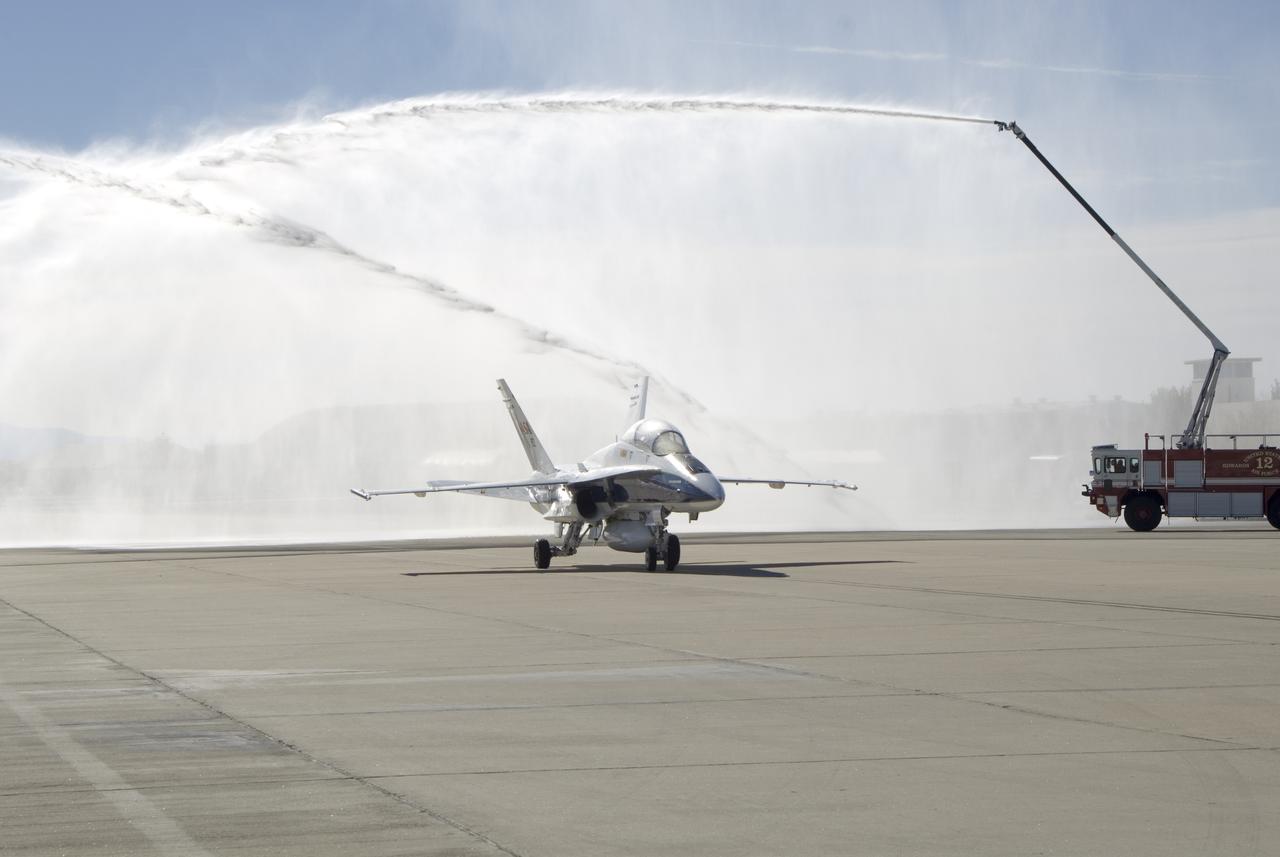
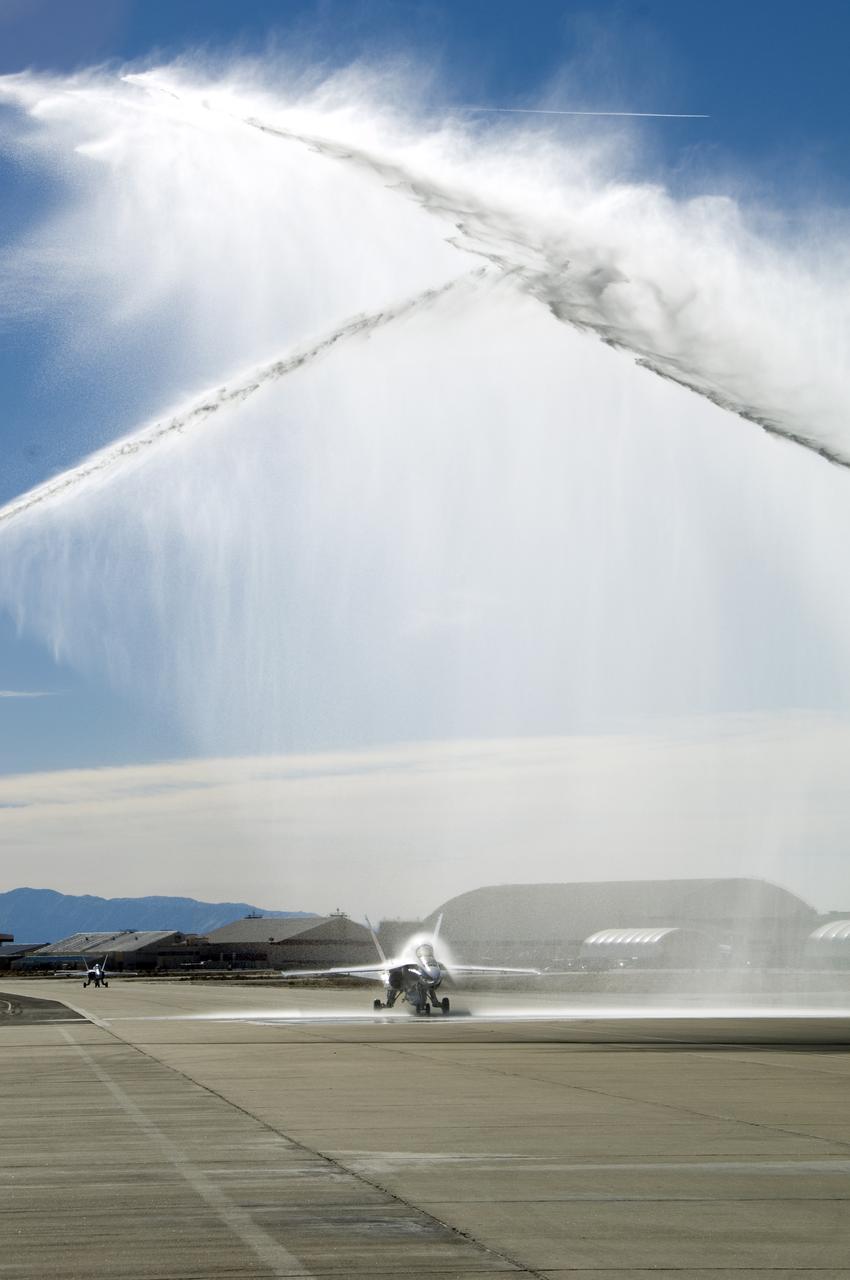
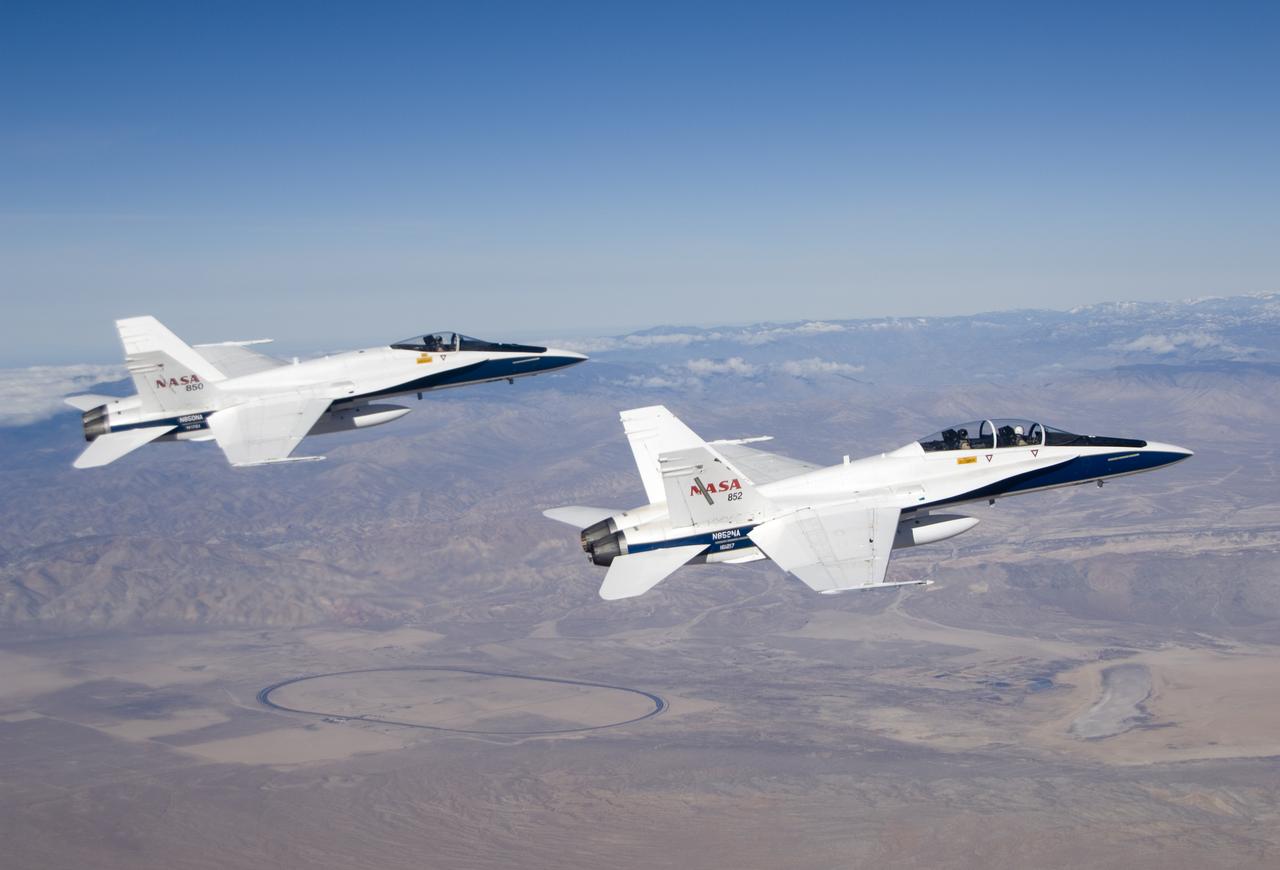
Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of sp
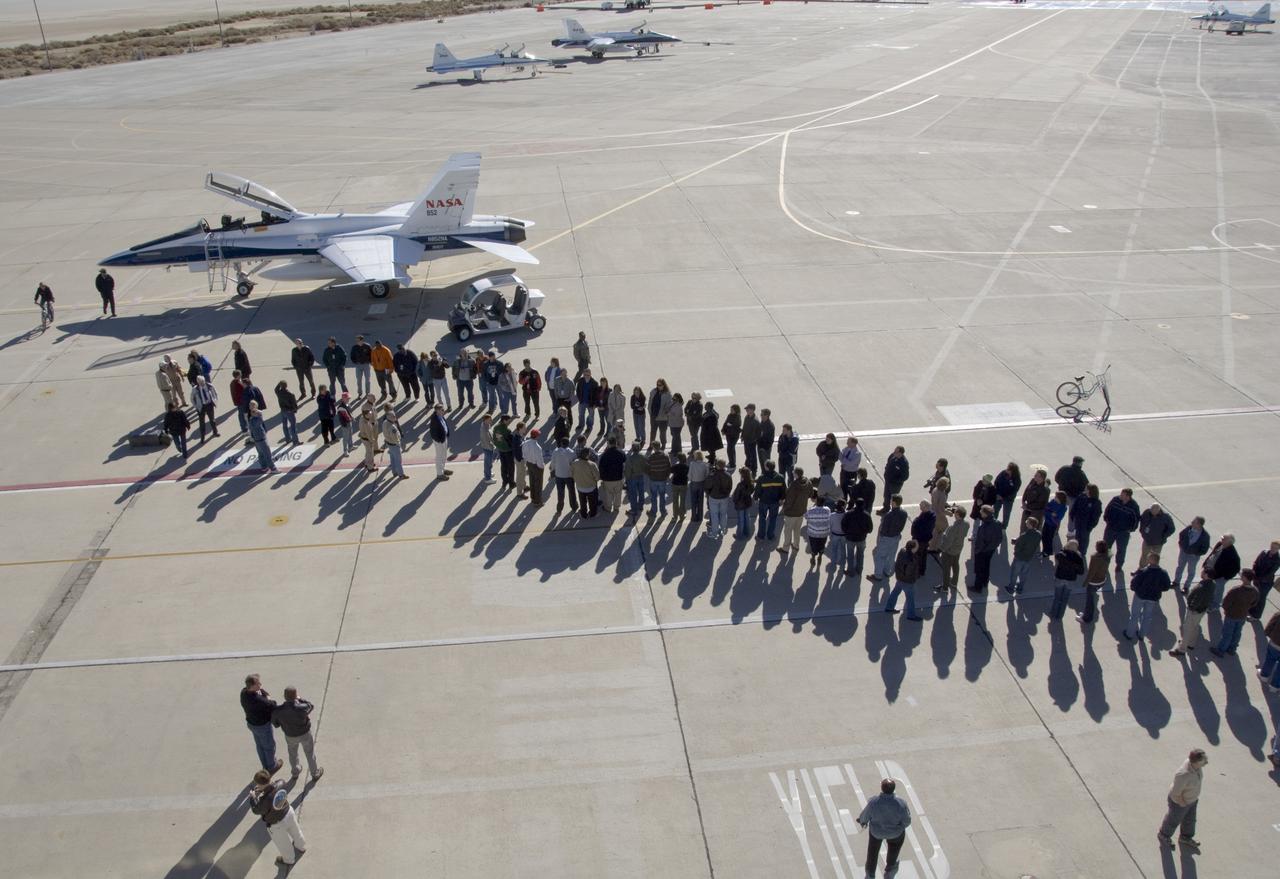

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of
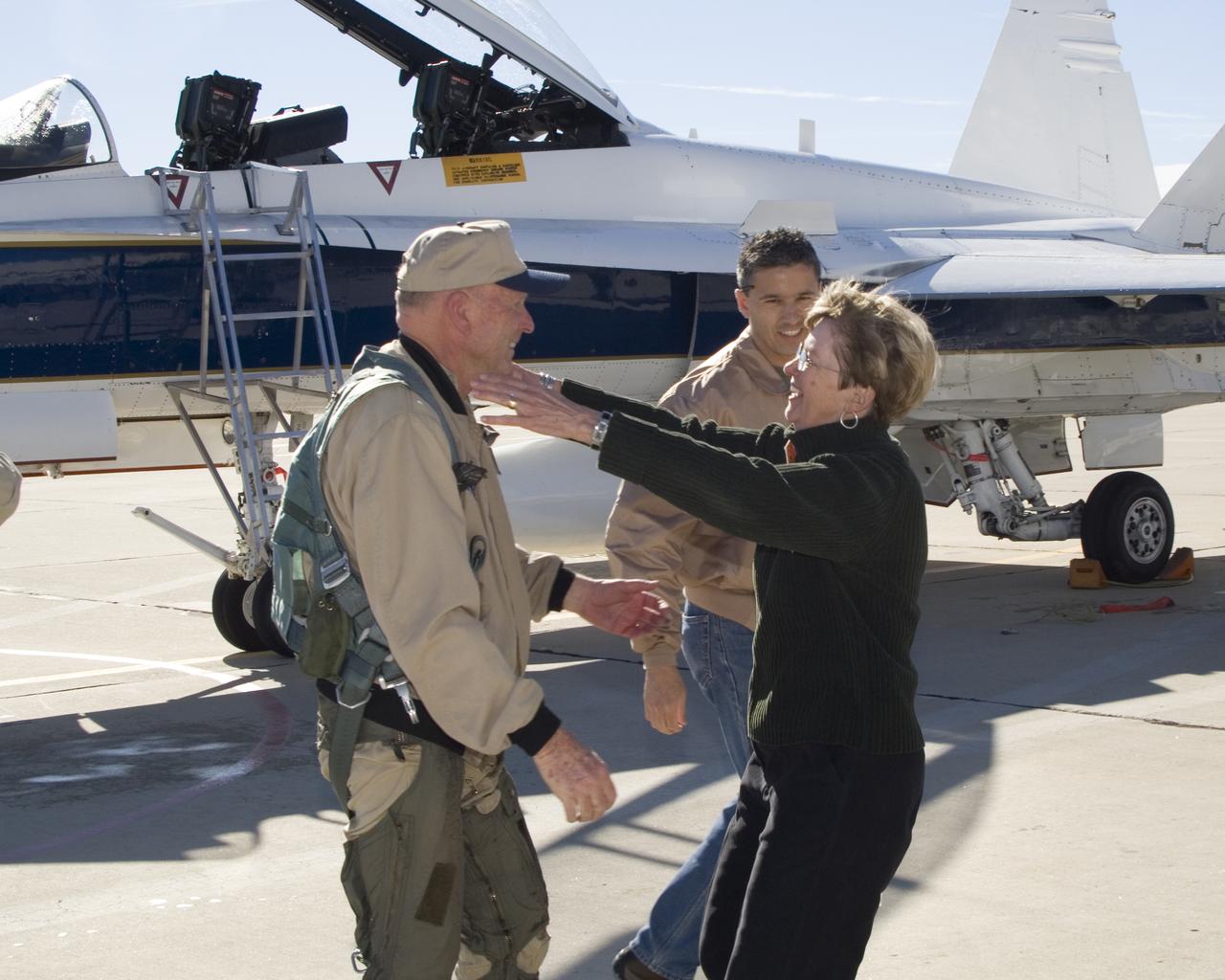

NASA Dryden research pilot Gordon Fullerton is greeted by his wife Marie on the Dryden ramp after his final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007.
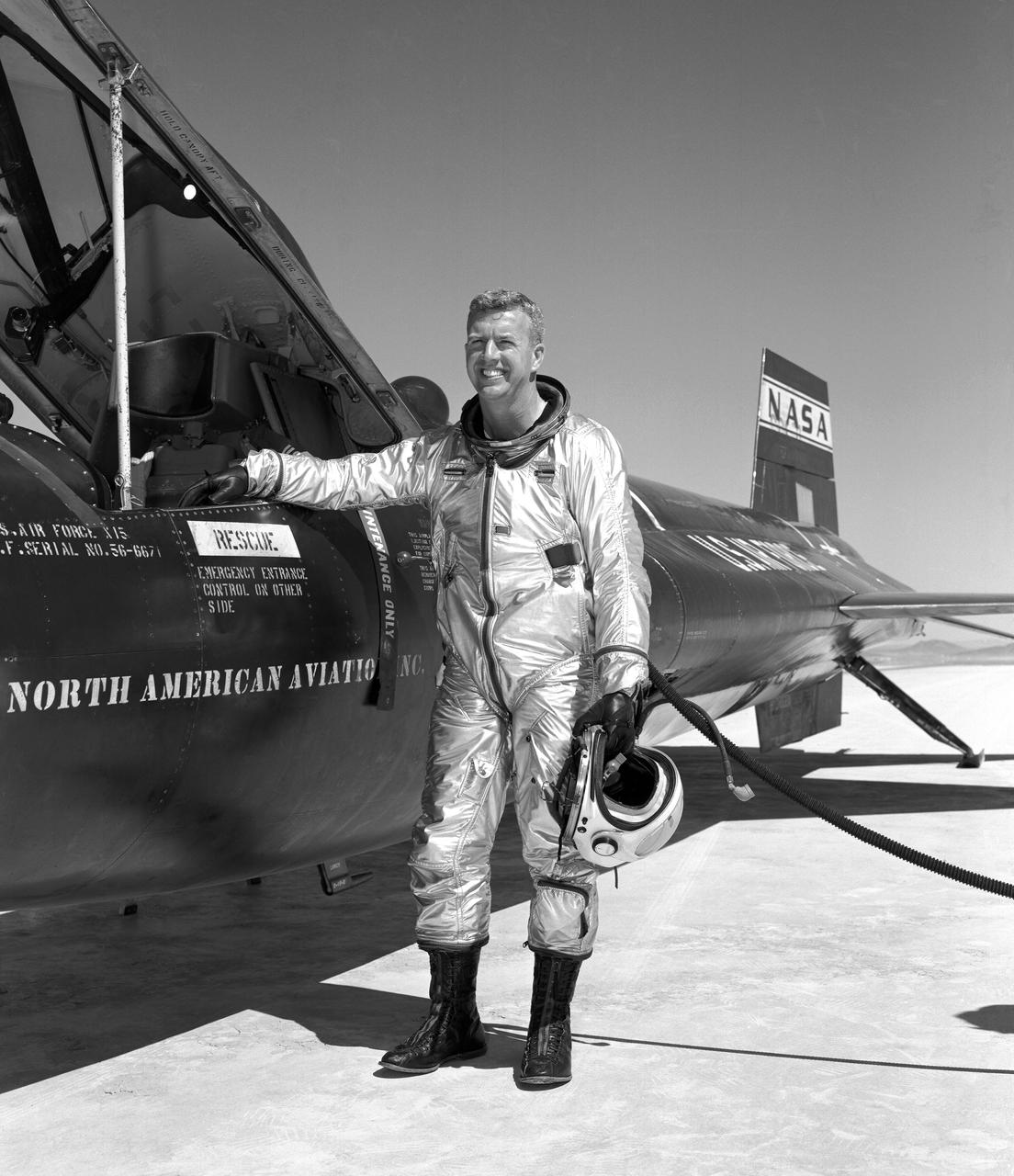

Walker made the first NASA-piloted X-15 flight March 25, 1960, and flew the aircraft 24 times, achieving its highest altitude (354,300 ft.) Aug. 22, 1963. He died piloting a F-104 that was caught up in a vortex of the XB-70.
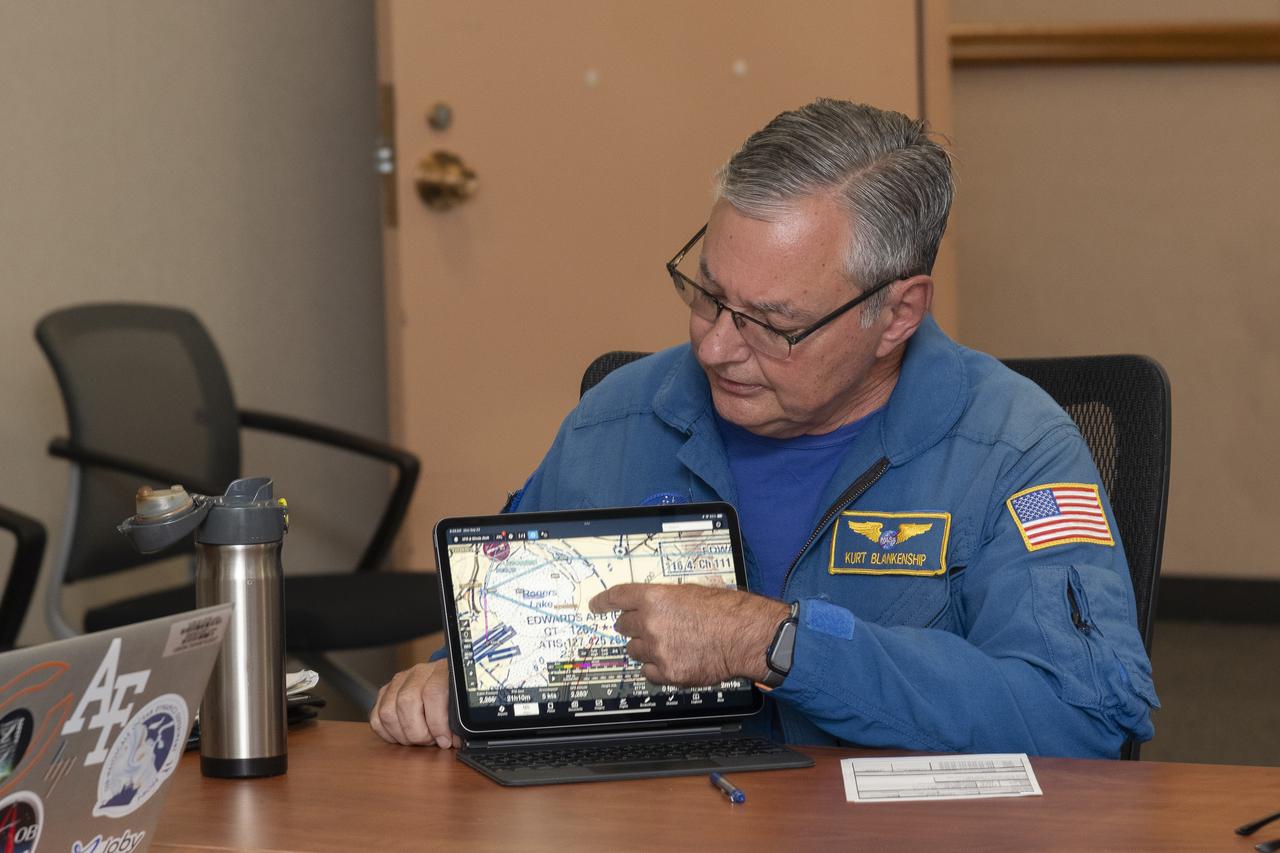

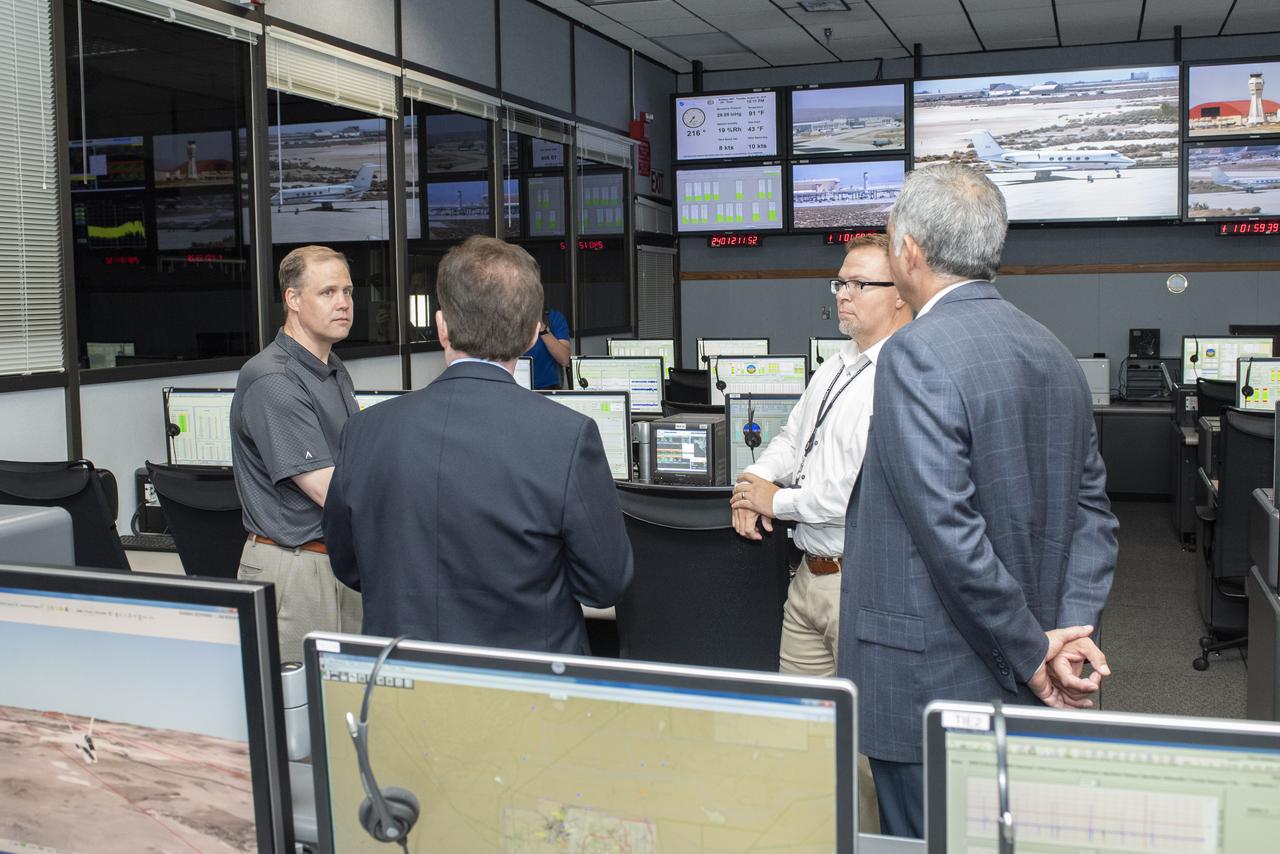
NASA pilot Kurt Blankenship maps out flight plans during a pre-flight brief. Pilots, crew, and researchers from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California and NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland are briefed on the flight plan to gather Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast signal data between the aircraft and ping-Stations on the ground at NASA Armstrong. These flights are the first cross-center research activity with the Pilatus-PC-12 at NASA Armstrong.
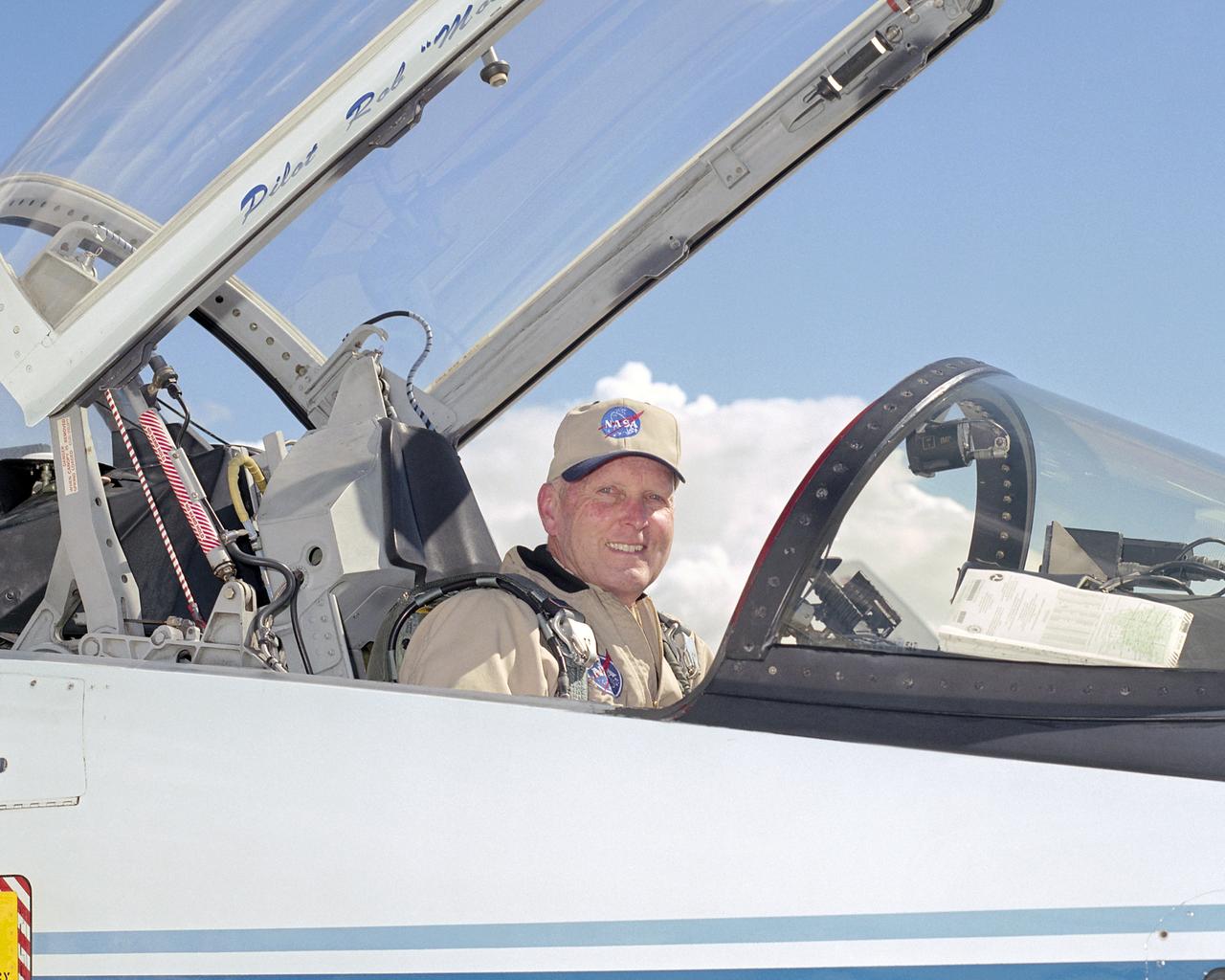

NASA Dryden Flight Research Center's chief pilot Gordon Fullerton in the cockpit of the center's T-38 Talon mission support aircraft.
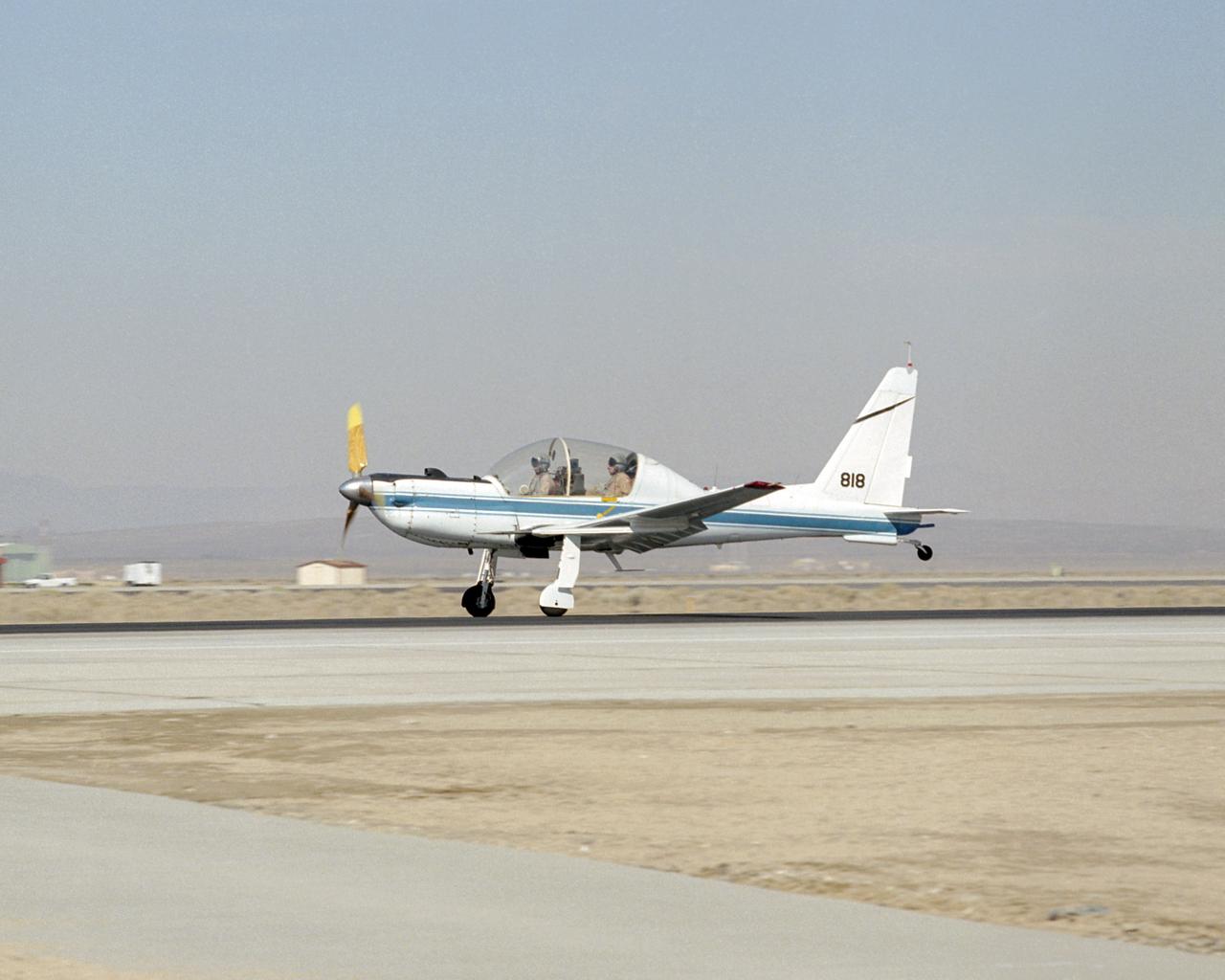

NASA's converted YO-3A observation plane, now used for acoustics research, touches down at Edwards Air Force Base following a pilot checkout flight.
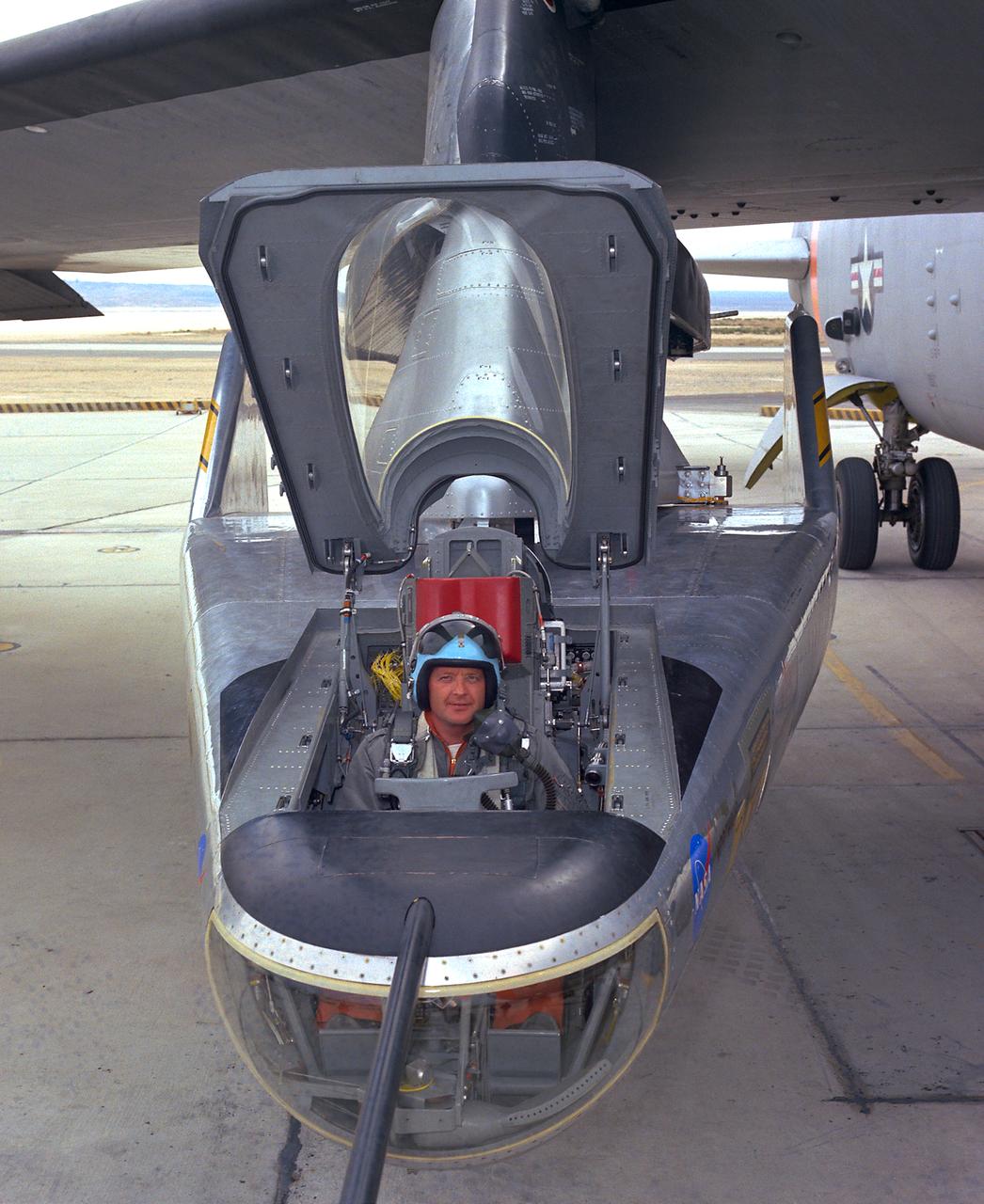

NASA research pilot Milt Thompson sits in the M2-F2 "heavyweight" lifting body research vehicle before a 1966 test flight. The M2-F2 and the other lifting-body designs were all attached to a wing pylon on NASA’s B-52 mothership and carried aloft. The vehicles were then drop-launched and, at the end of their flights, glided back to wheeled landings on the dry lake or runway at Edwards AFB. The lifting body designs influenced the design of the Space Shuttle and were also reincarnated in the design of the X-38 in the 1990s.
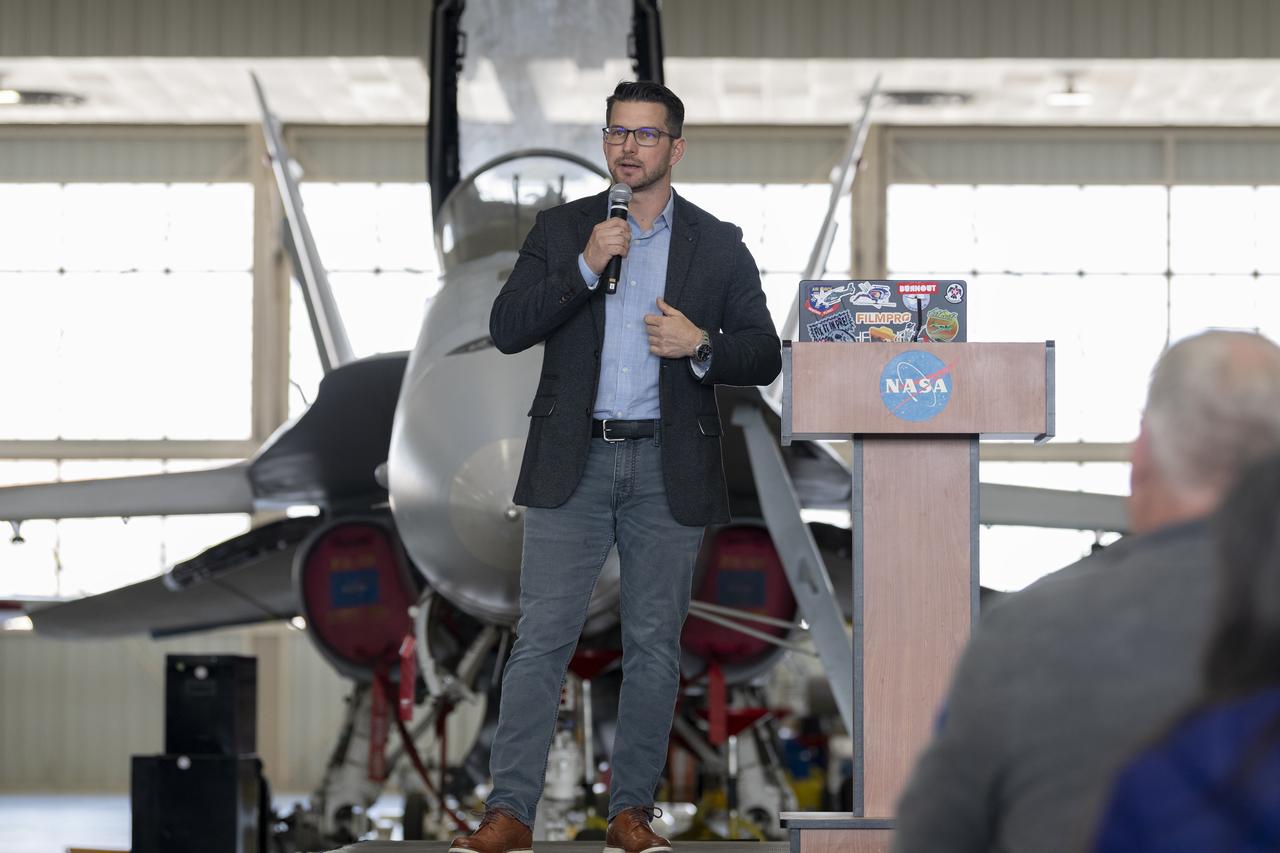

Aerial coordinator and test pilot Kevin LaRosa II describes what it takes to safely plan and document breathtaking footage of aircraft at a presentation at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. He has a long list of film credits, including “Ironman”; “Avengers”; “Transformer 5”; “Top Gun: Maverick”; and “Devotion”.
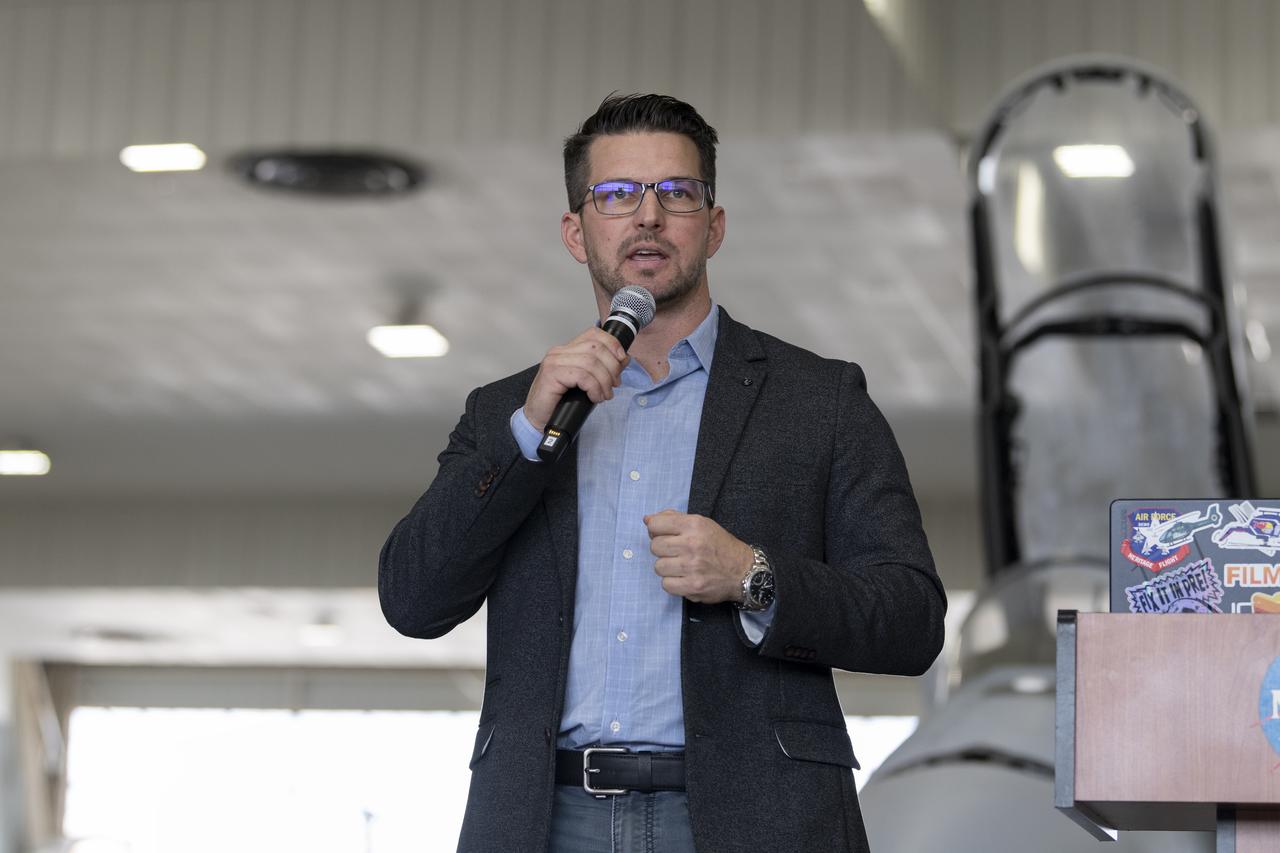

Aerial coordinator and test pilot Kevin LaRosa II describes what it takes to safely plan and document breathtaking footage of aircraft at a presentation at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. He has a long list of film credits, including “Ironman”; “Avengers”; “Transformer 5”; “Top Gun: Maverick”; and “Devotion”.
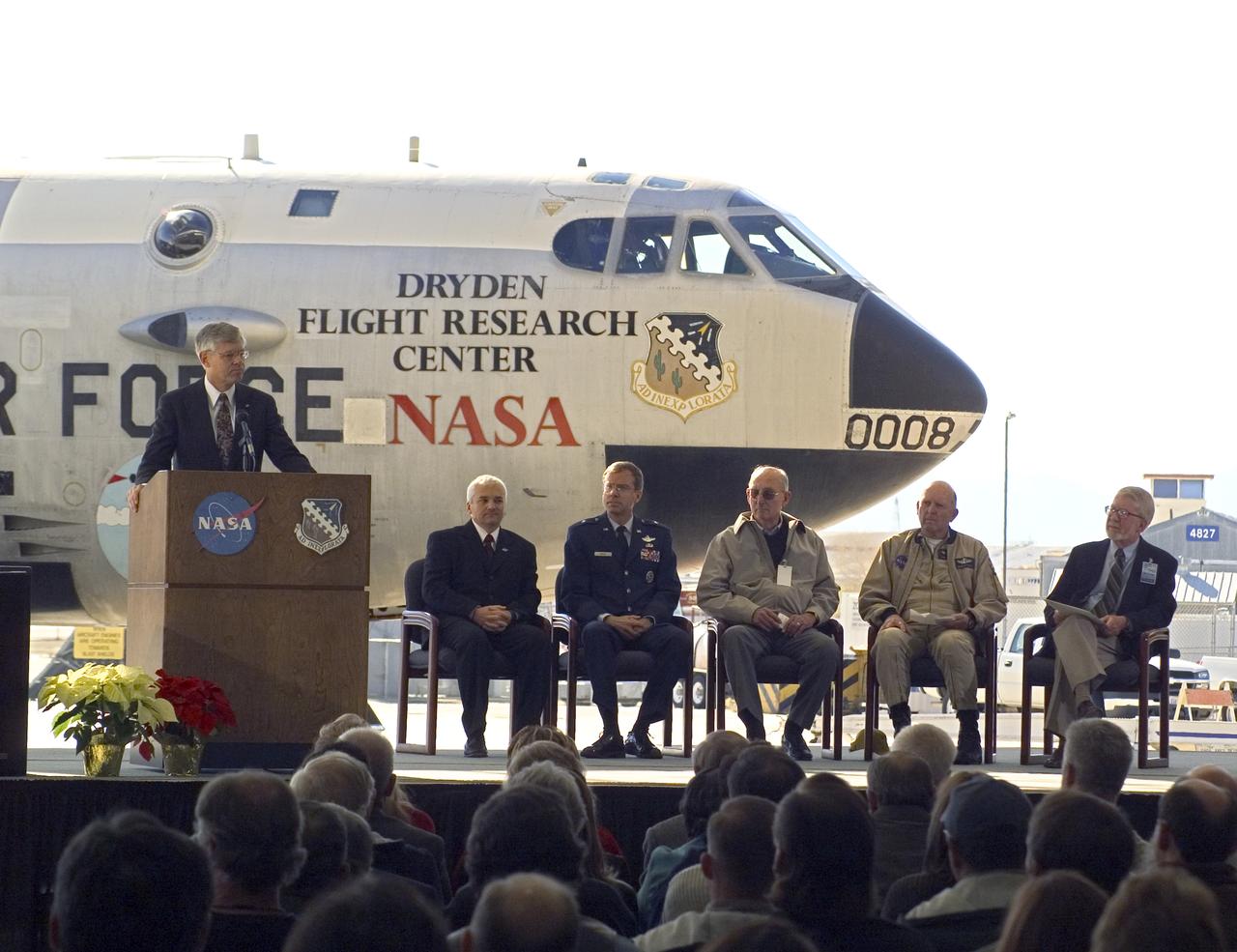

Retired NASA Dryden research pilot Ed Schneider served as master of ceremonies at the retirement ceremony for NASA's B-52B, on Dec. 17, 2004.
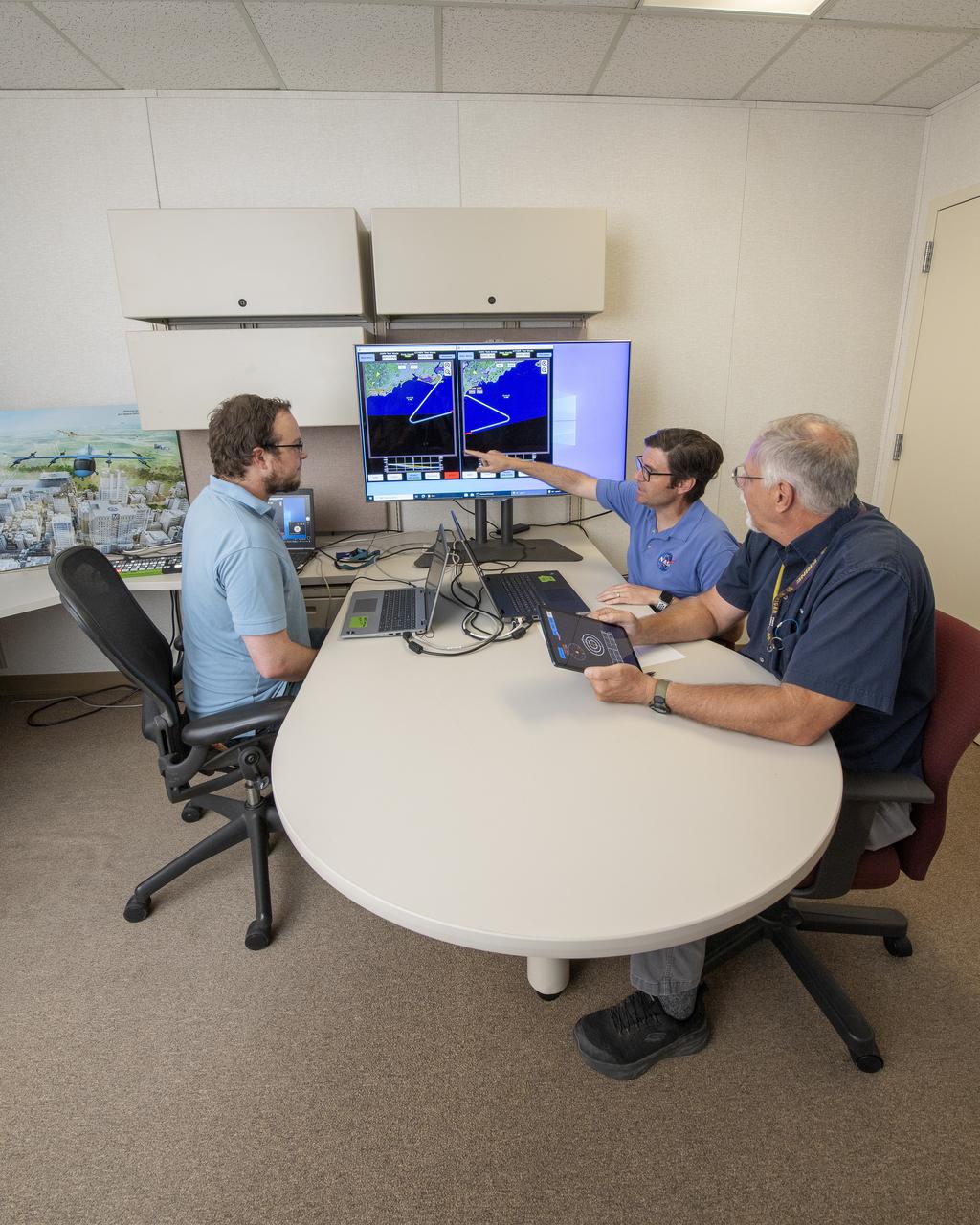

NASA software developer, Ethan Williams, left, pilot Scott Howe, and operations test consultant Jan Scofield run a flight path management software simulation at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in May 2023. This simulation research supports the integration of automated systems for the advanced air mobility mission.
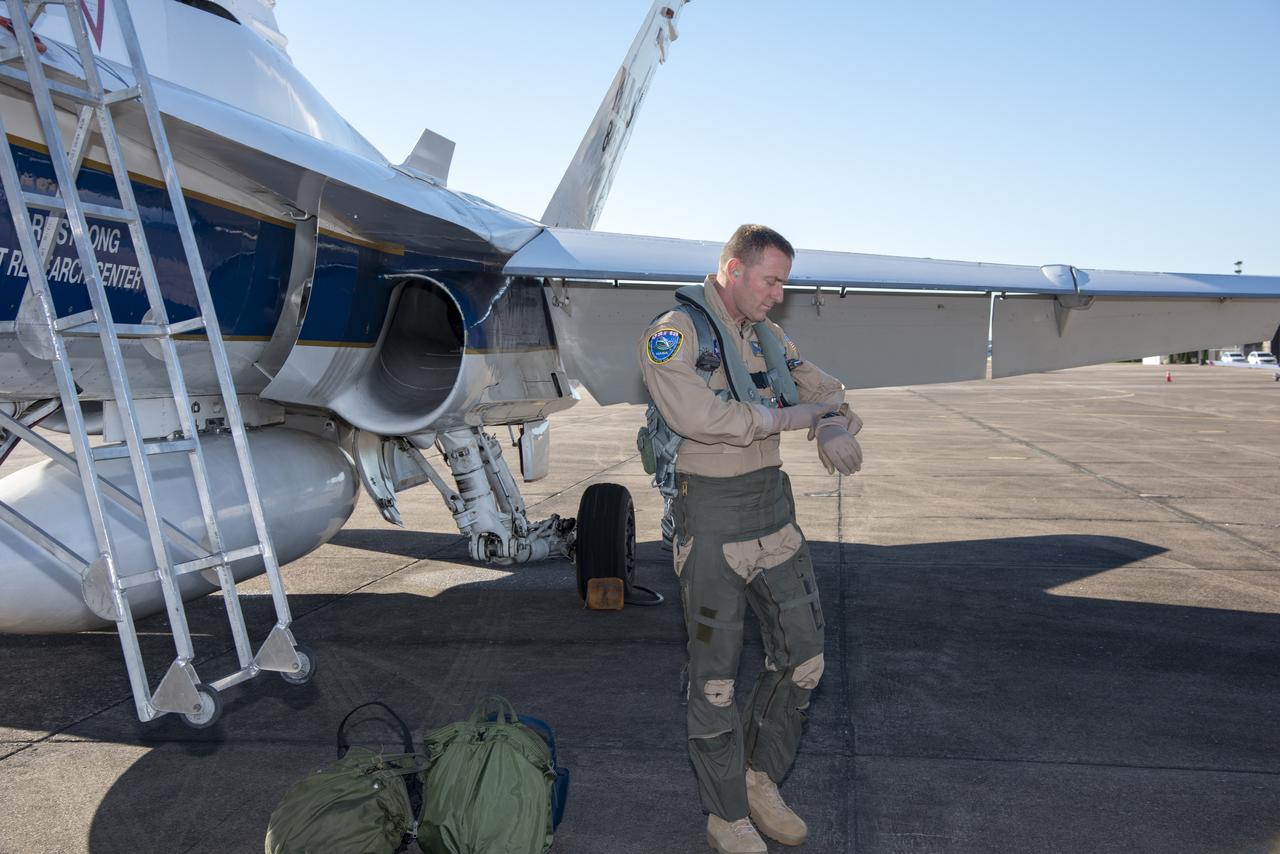

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
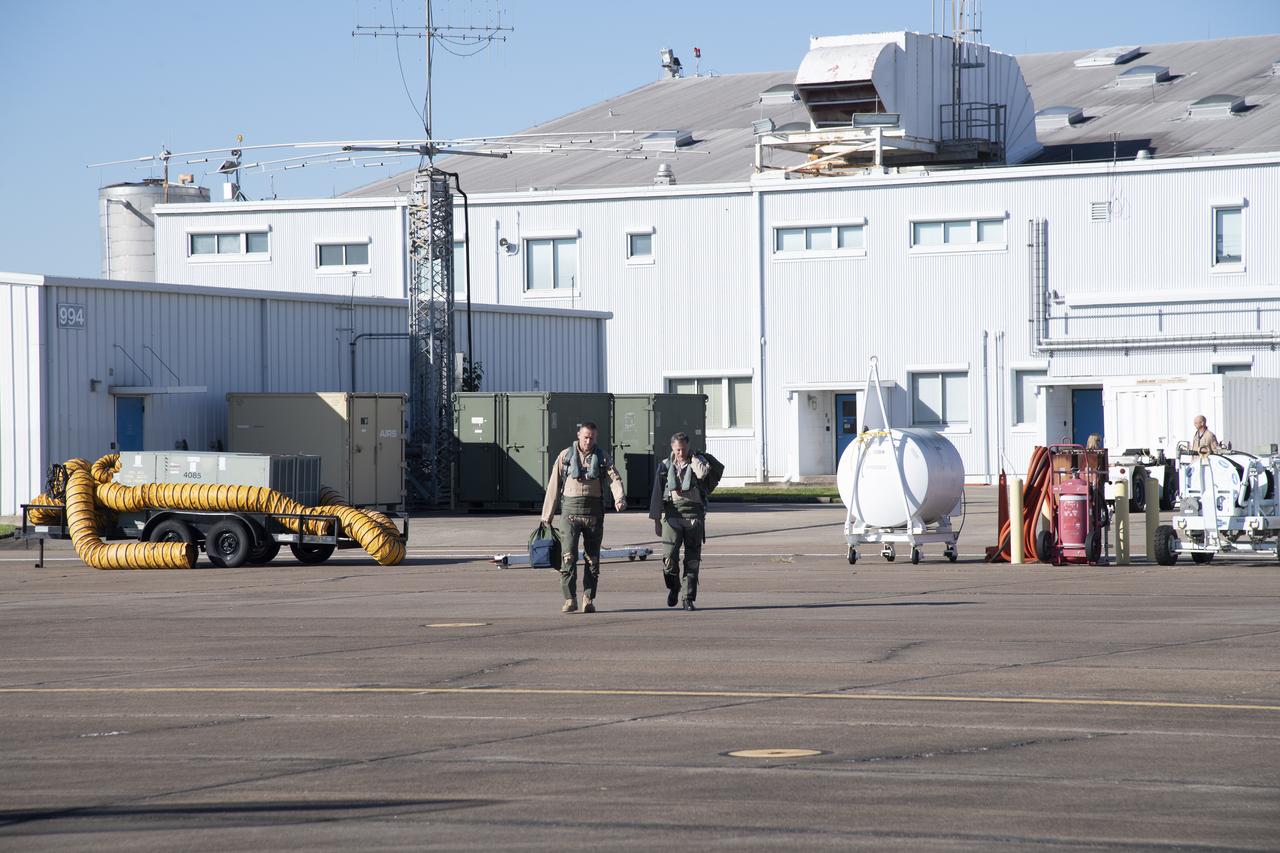

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
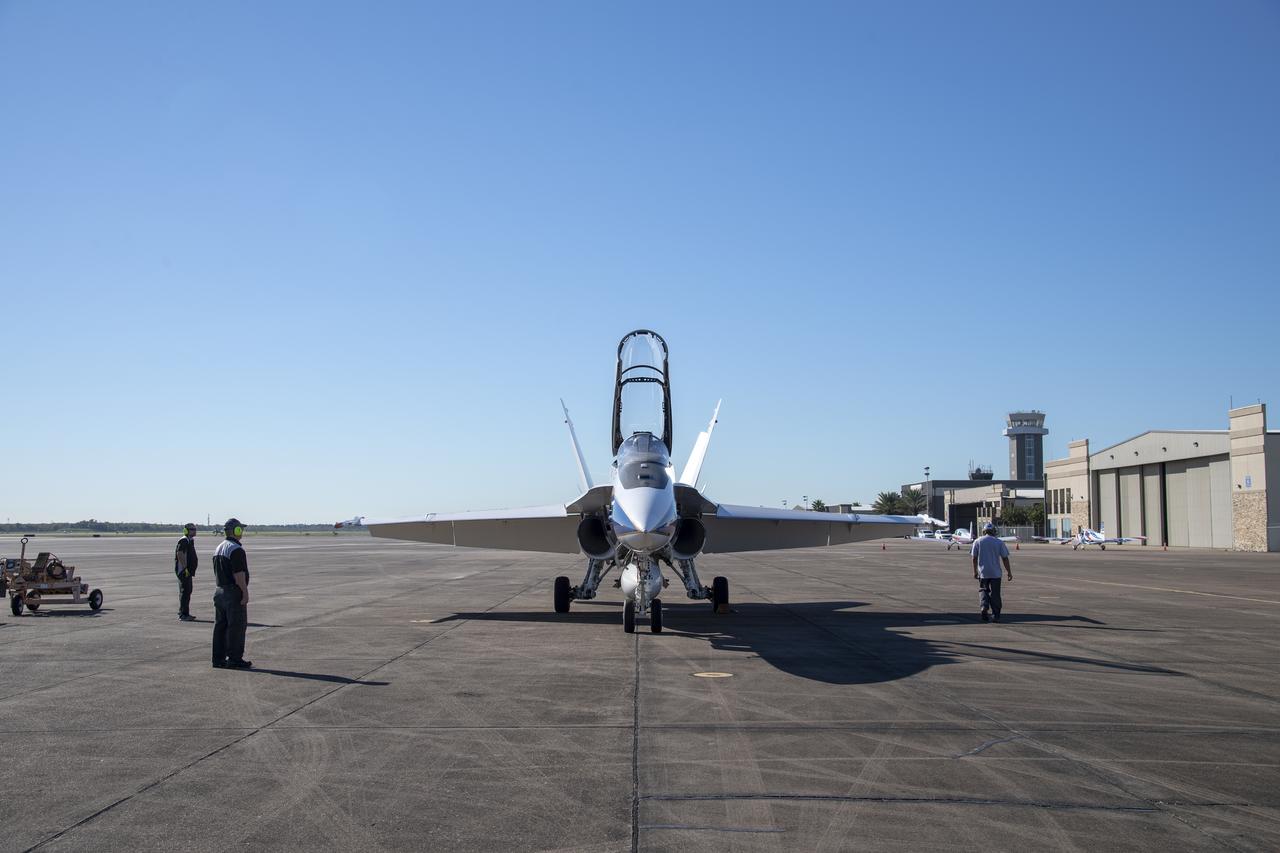

NASA test pilots Jim "Clue" Less and Wayne "Ringo" Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
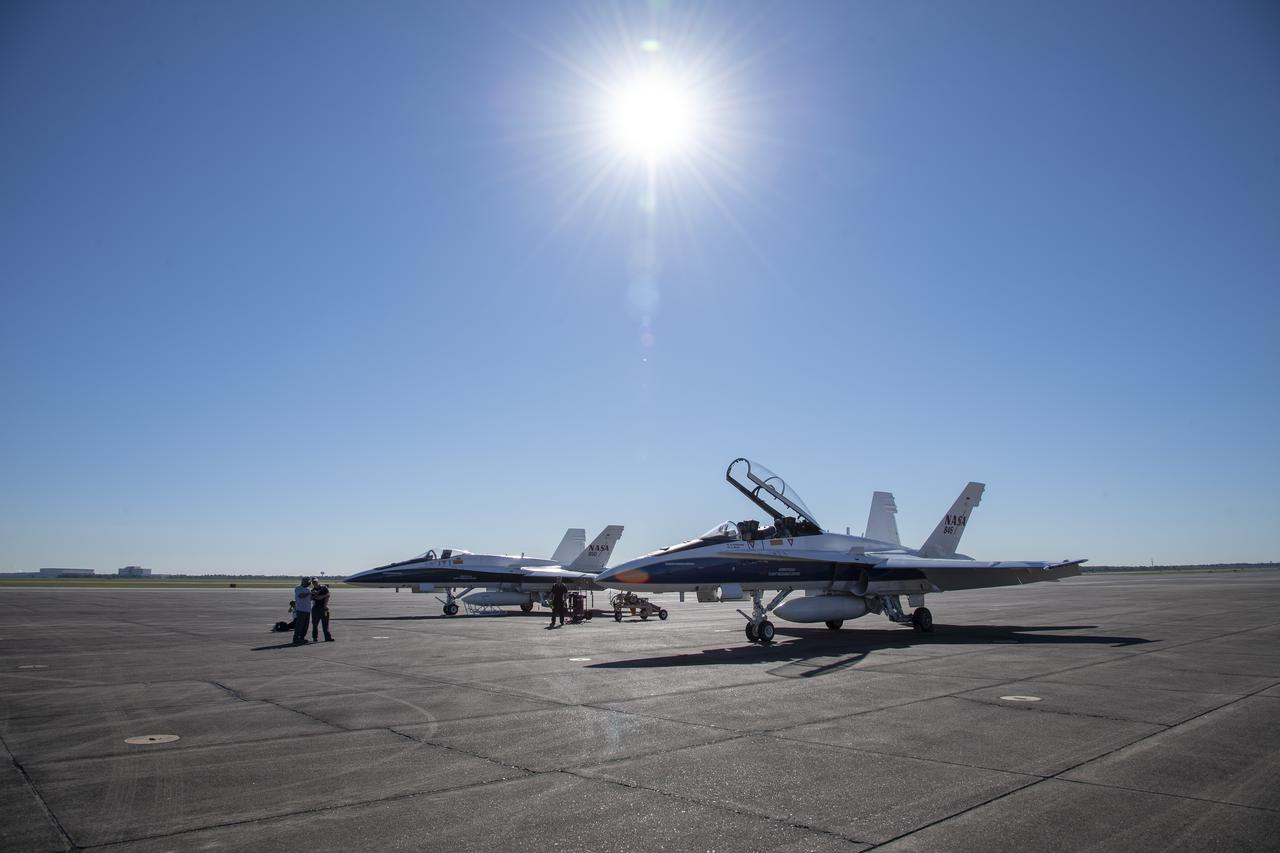

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
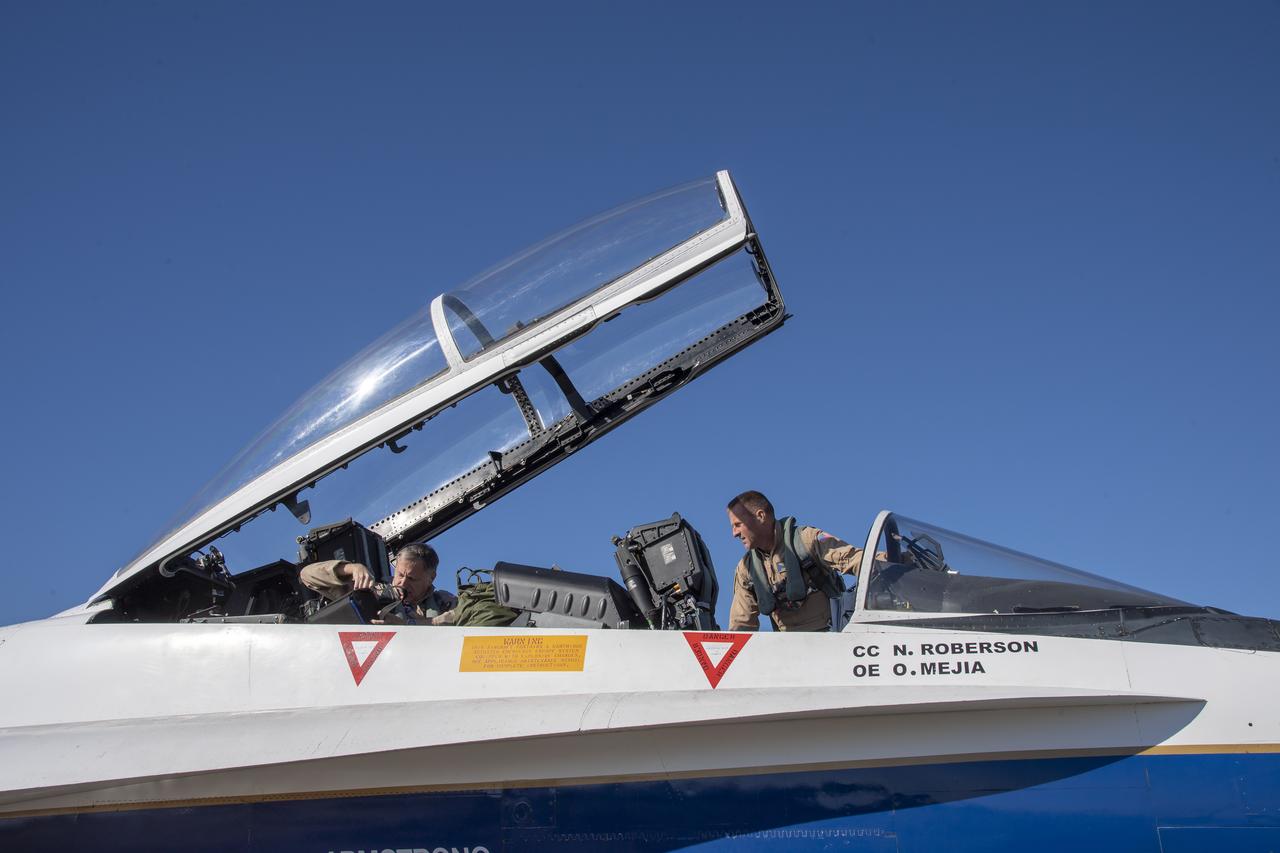

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
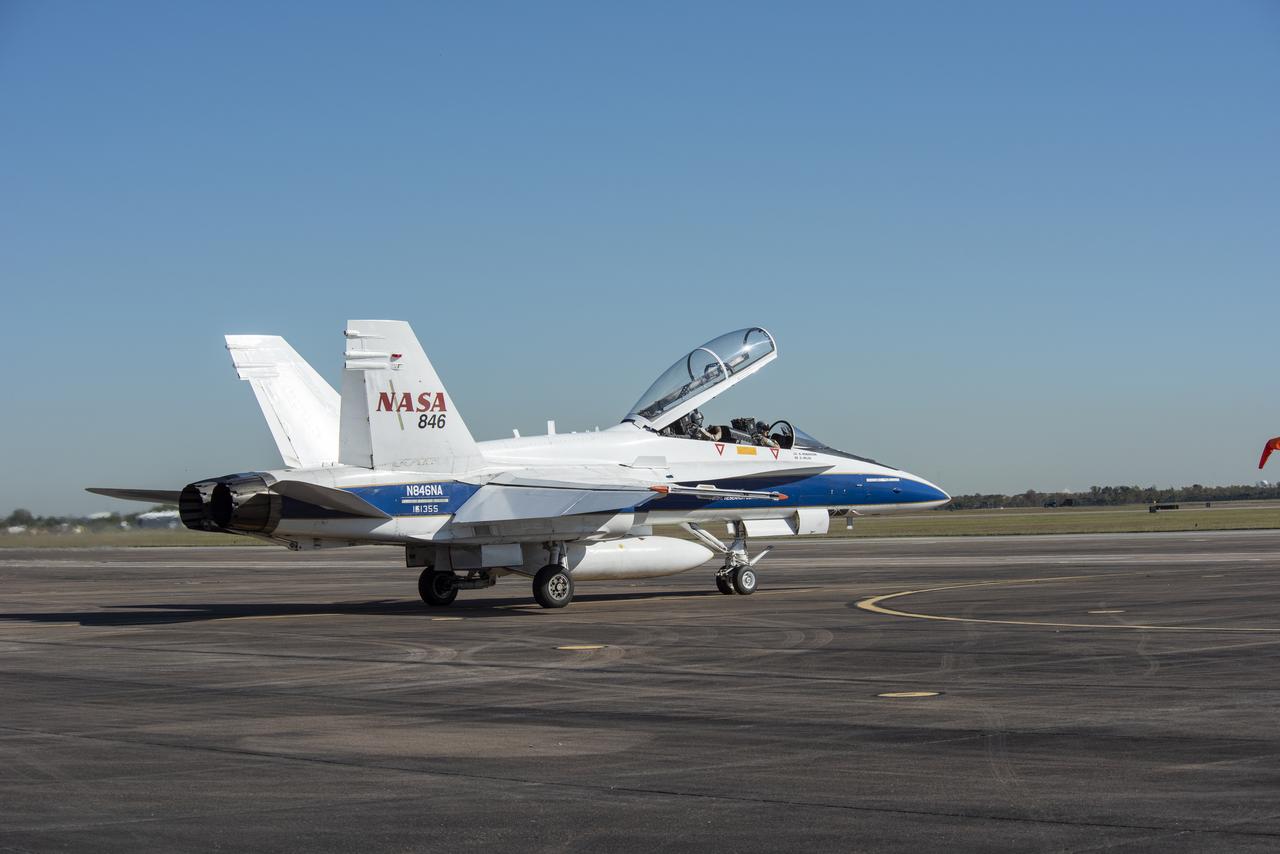

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
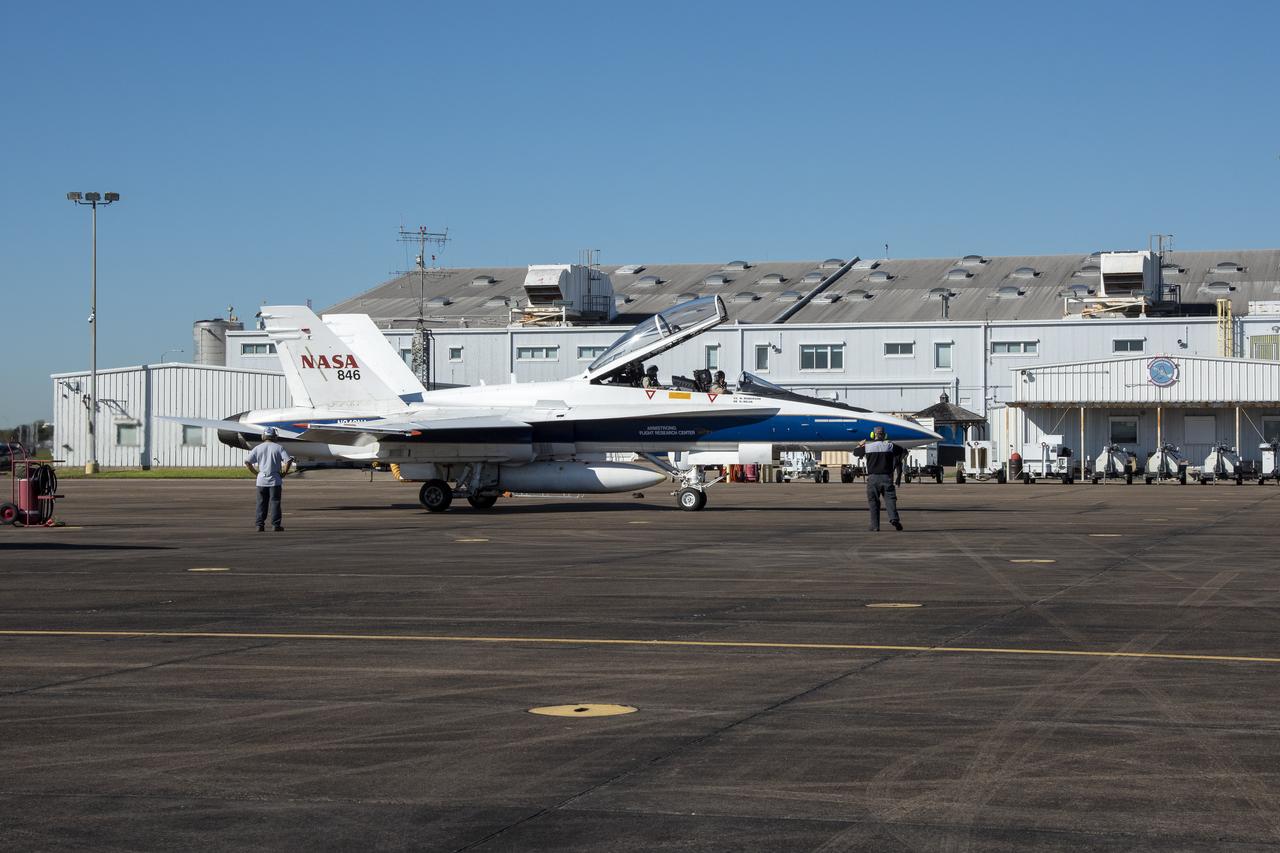

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
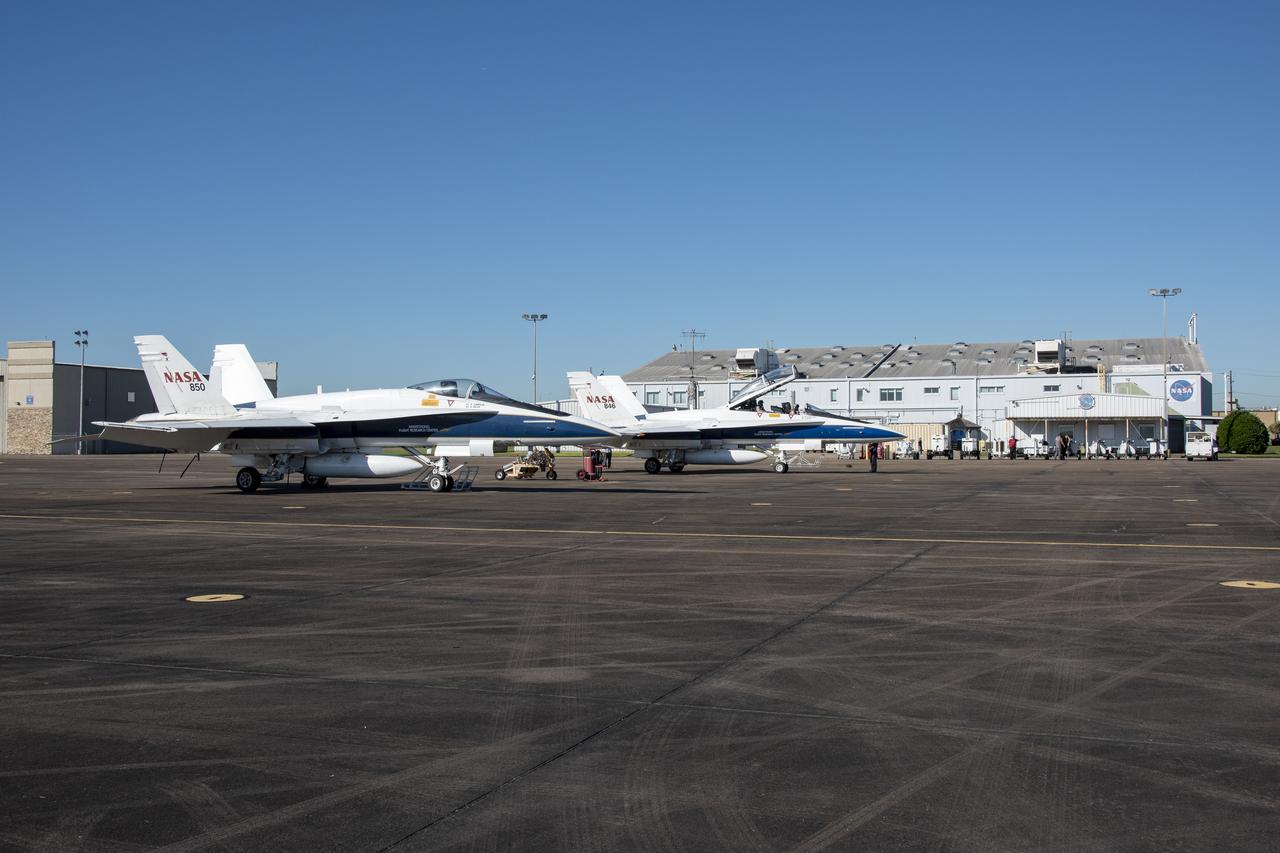

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
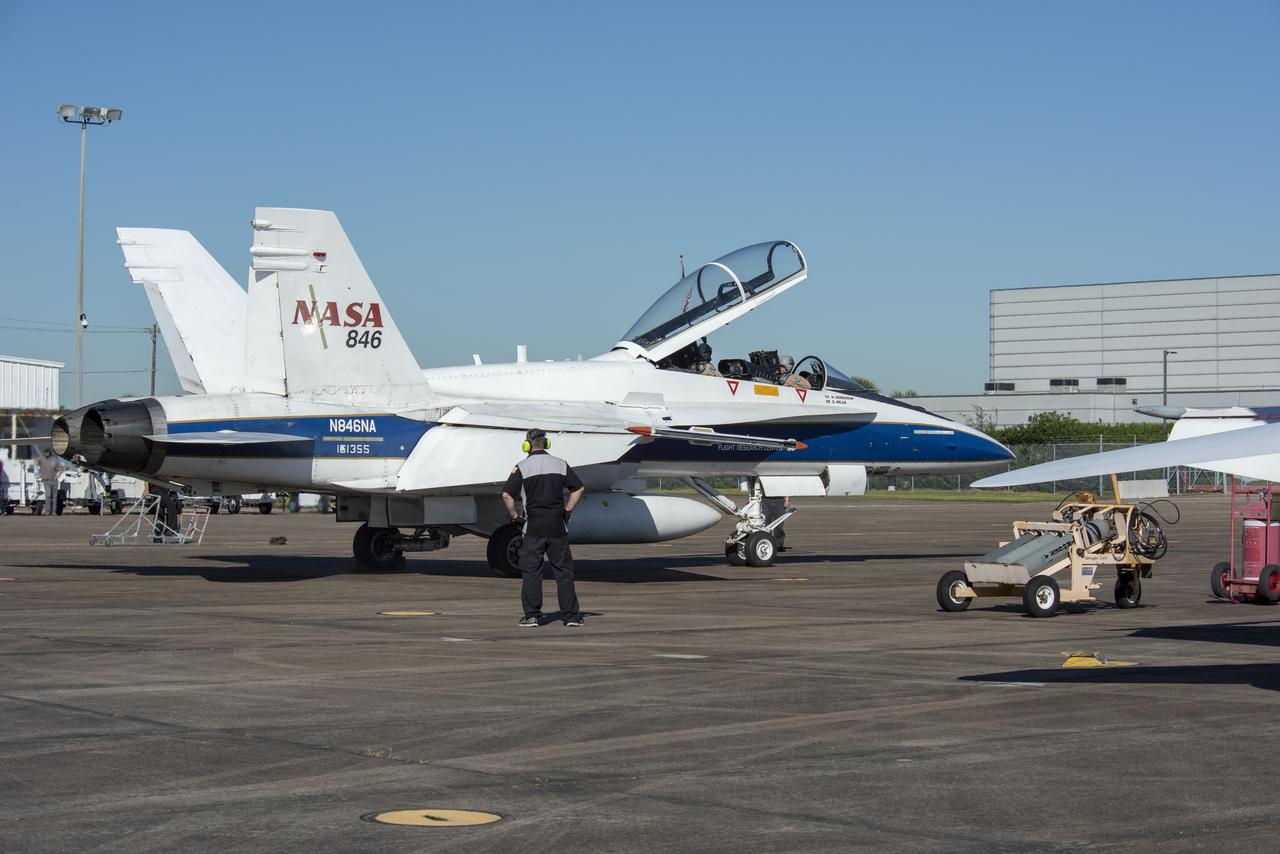

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
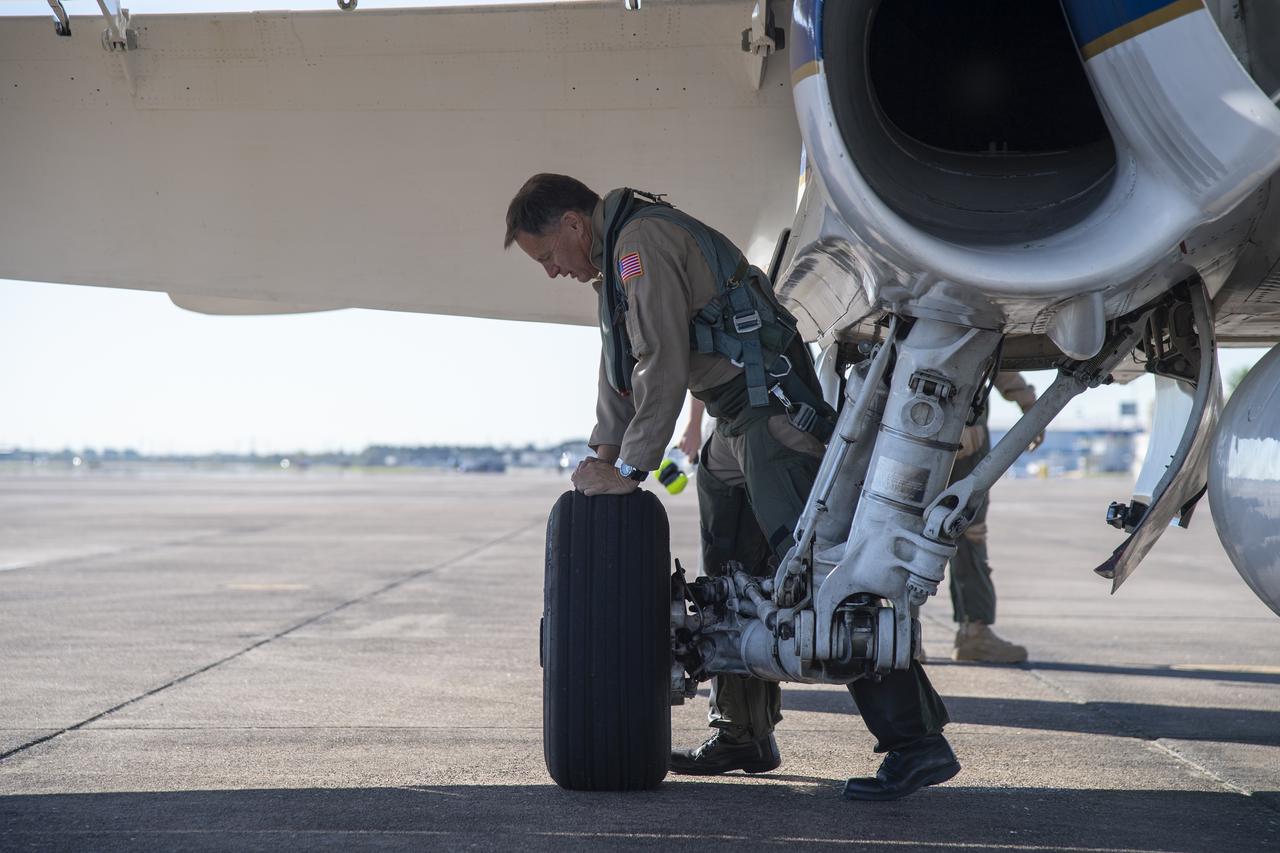

NASA test pilots Jim "Clue" Less and Wayne "Ringo" Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
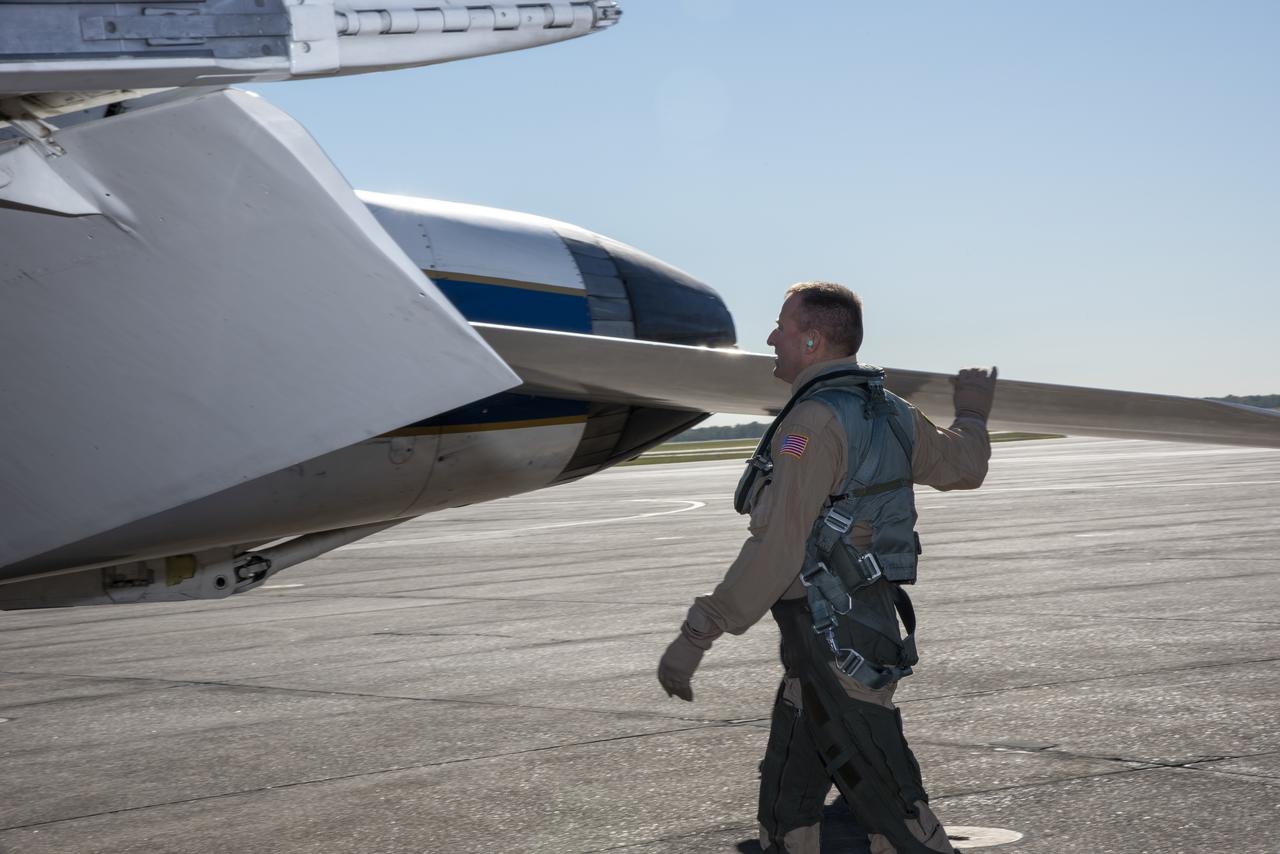

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
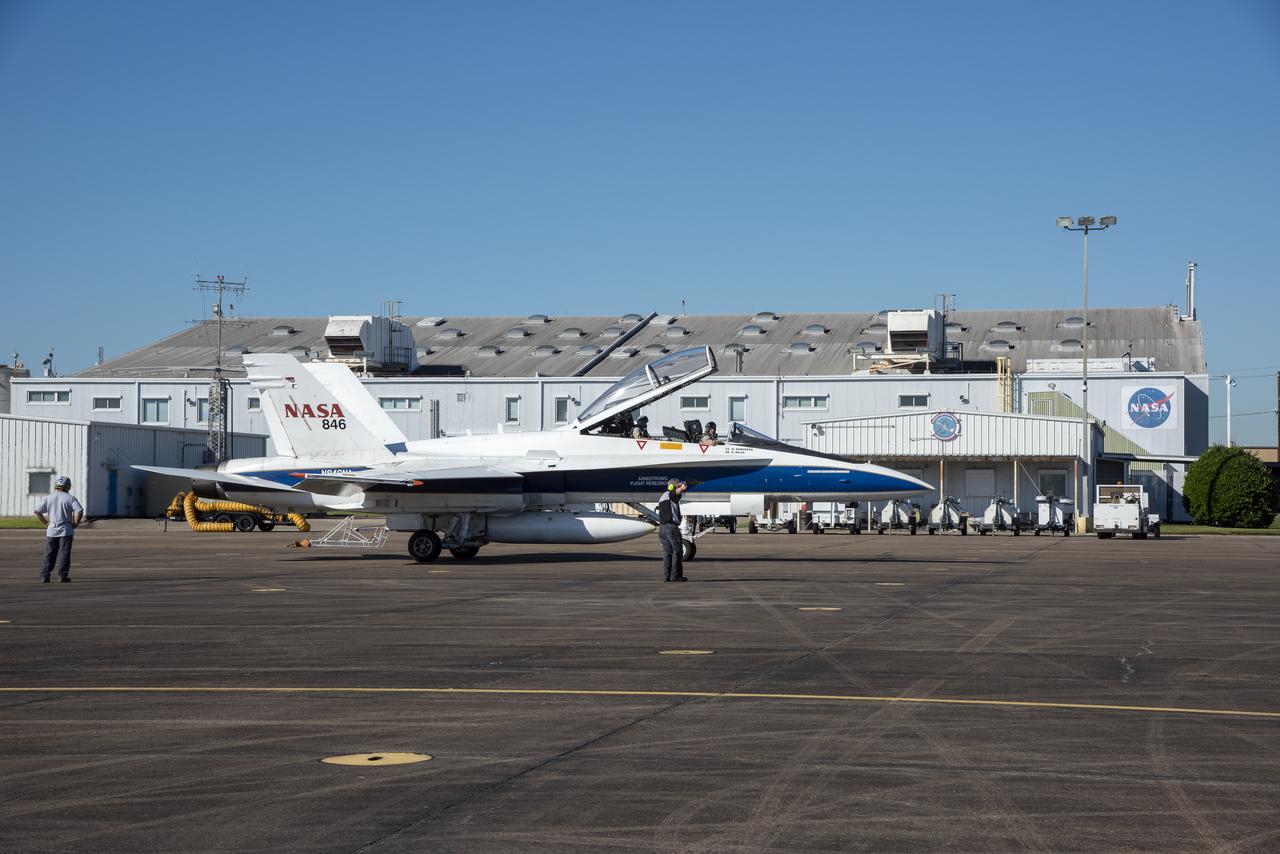

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
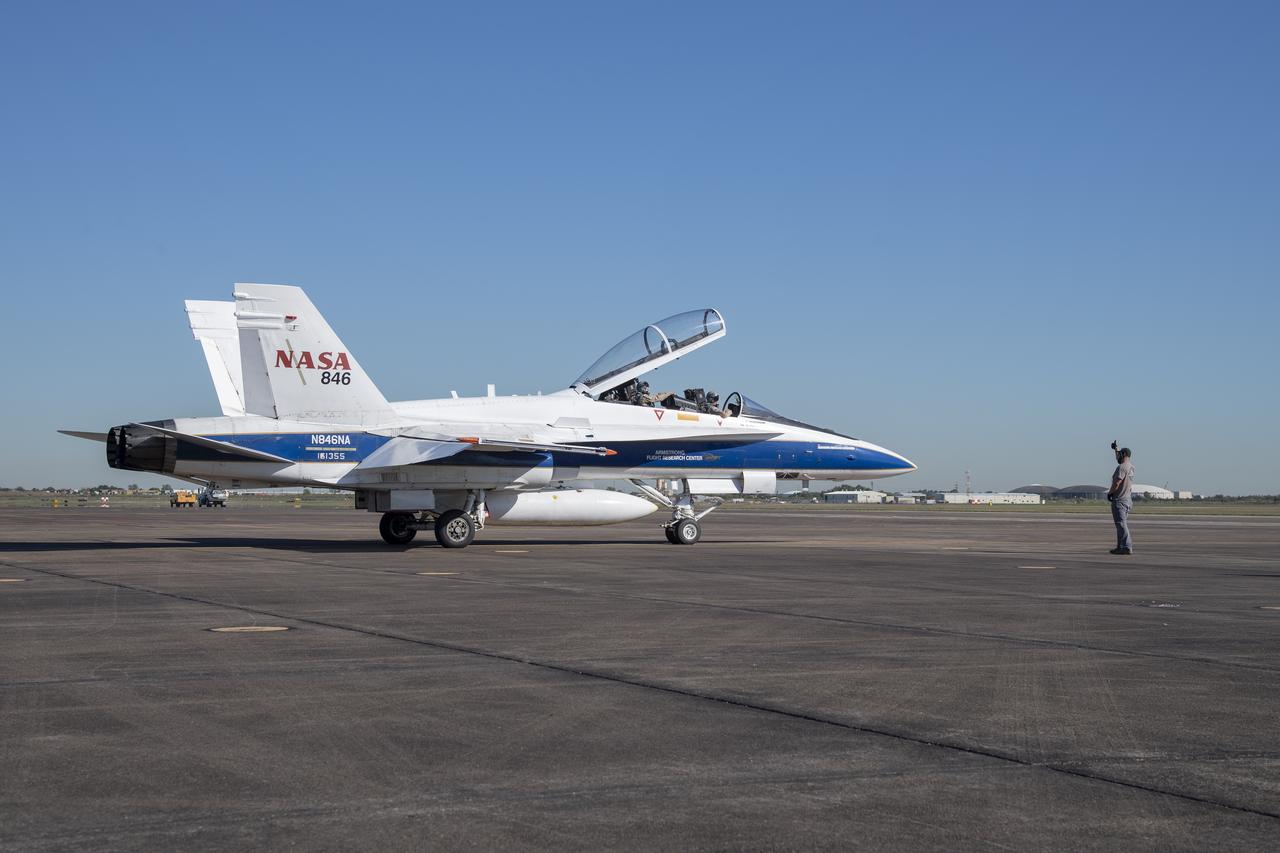

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
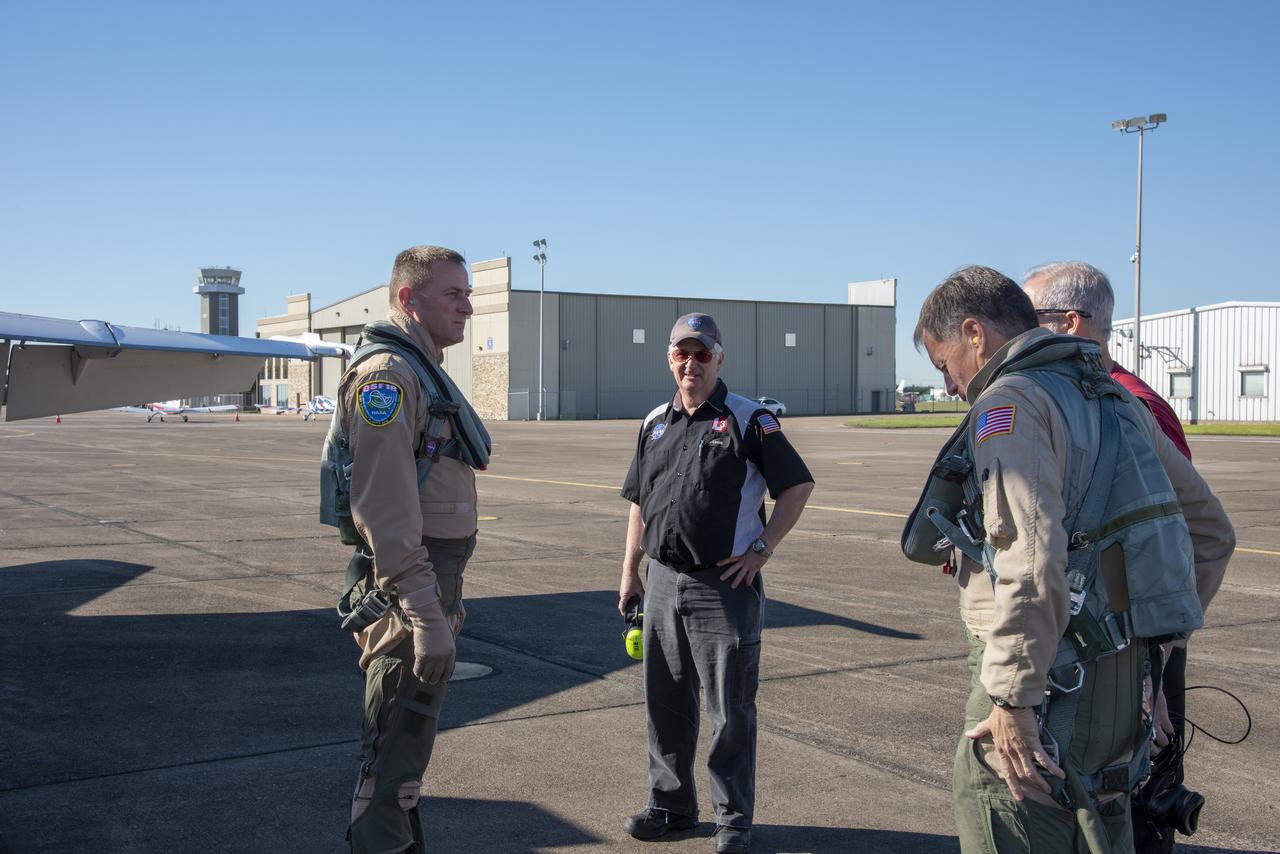

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
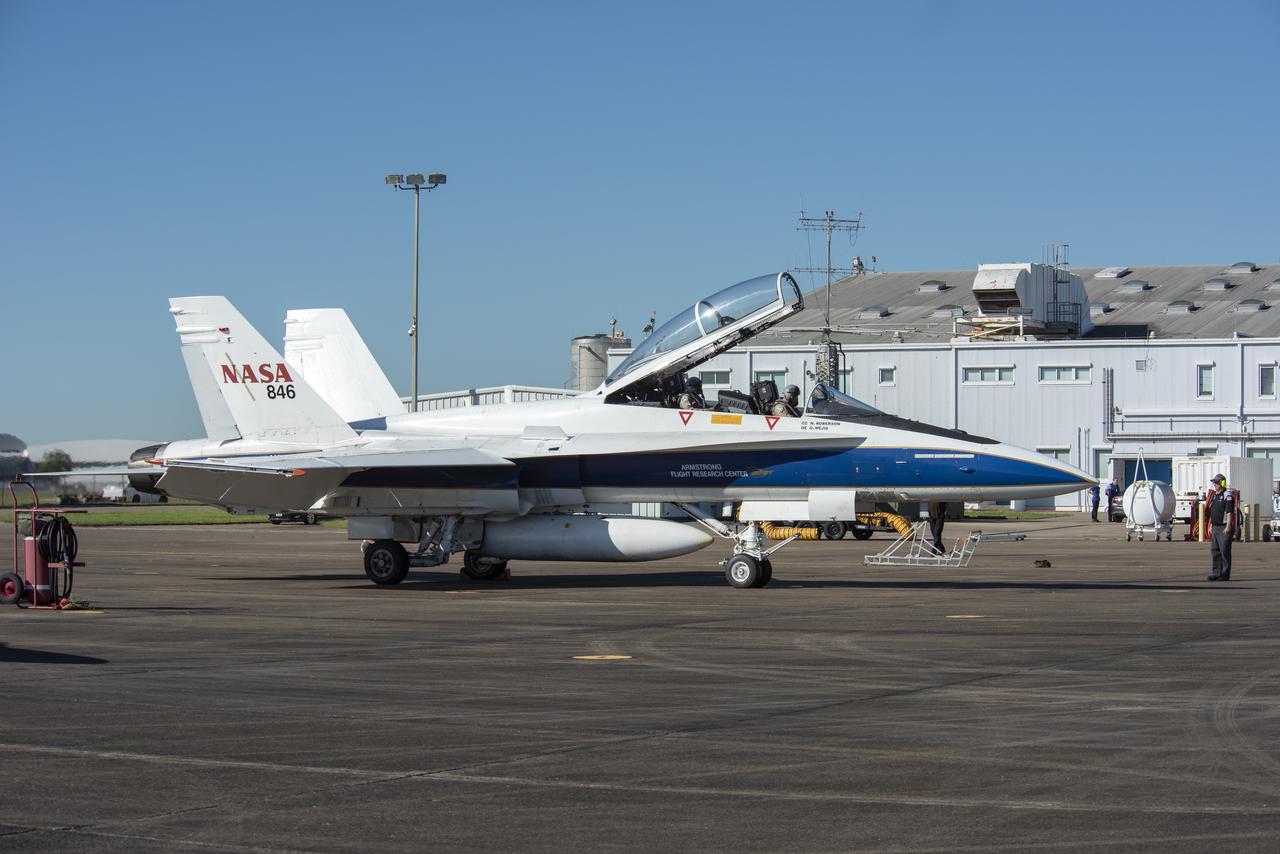

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
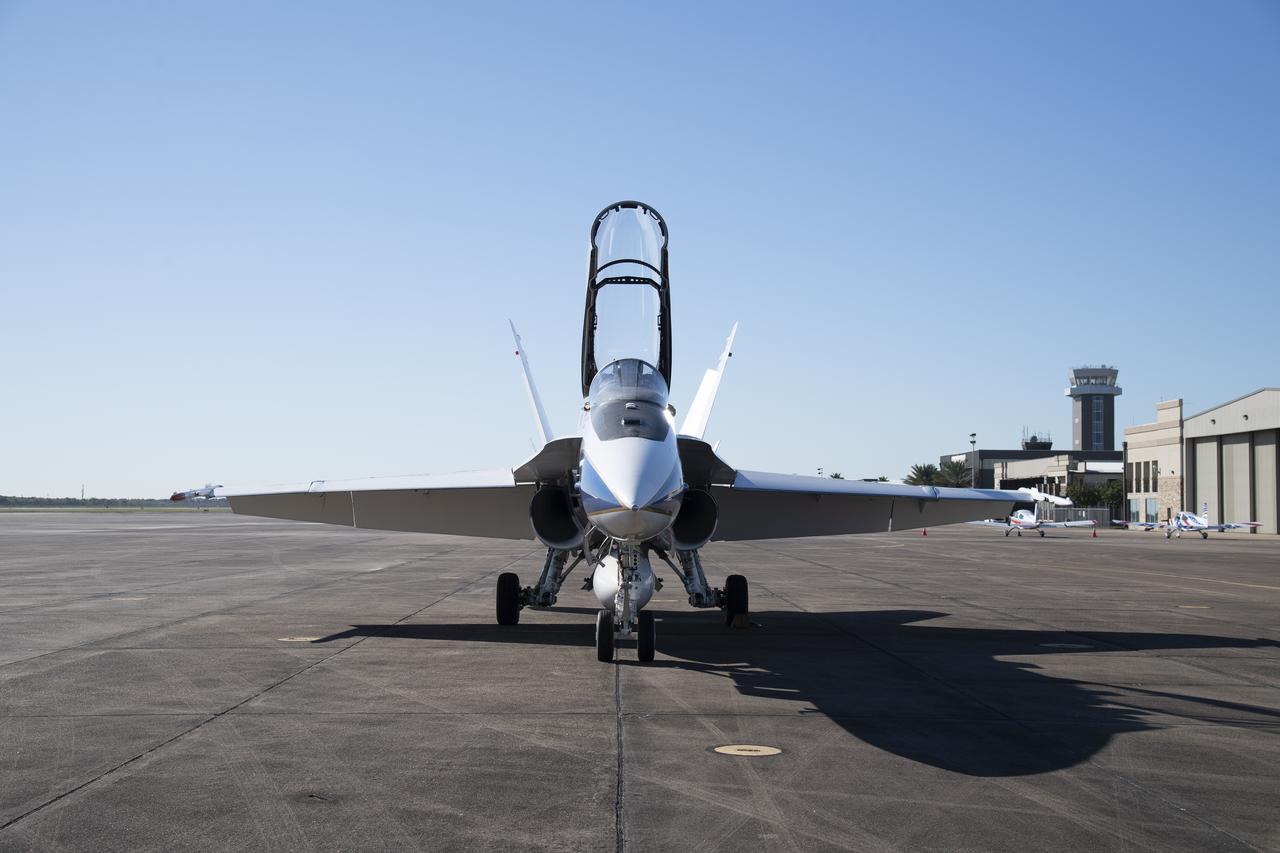

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
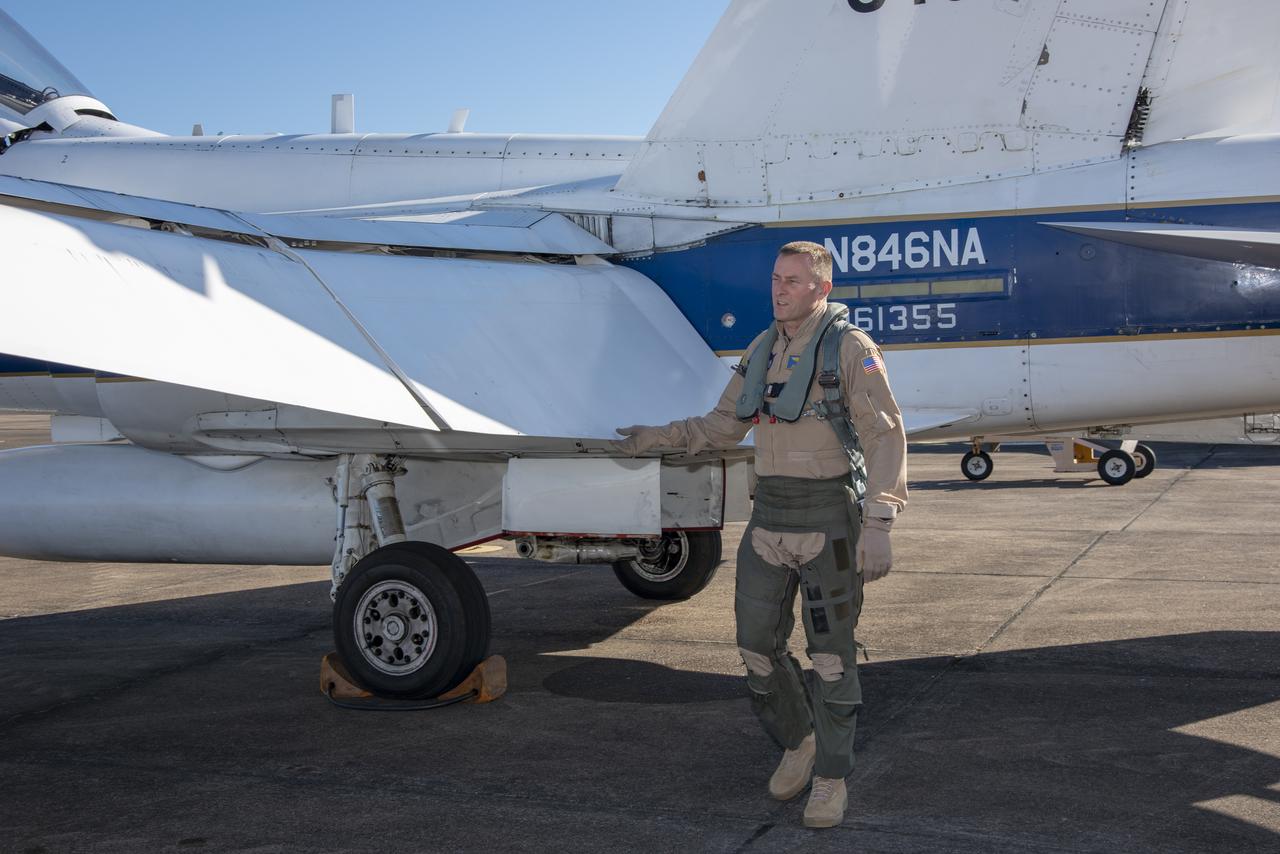

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
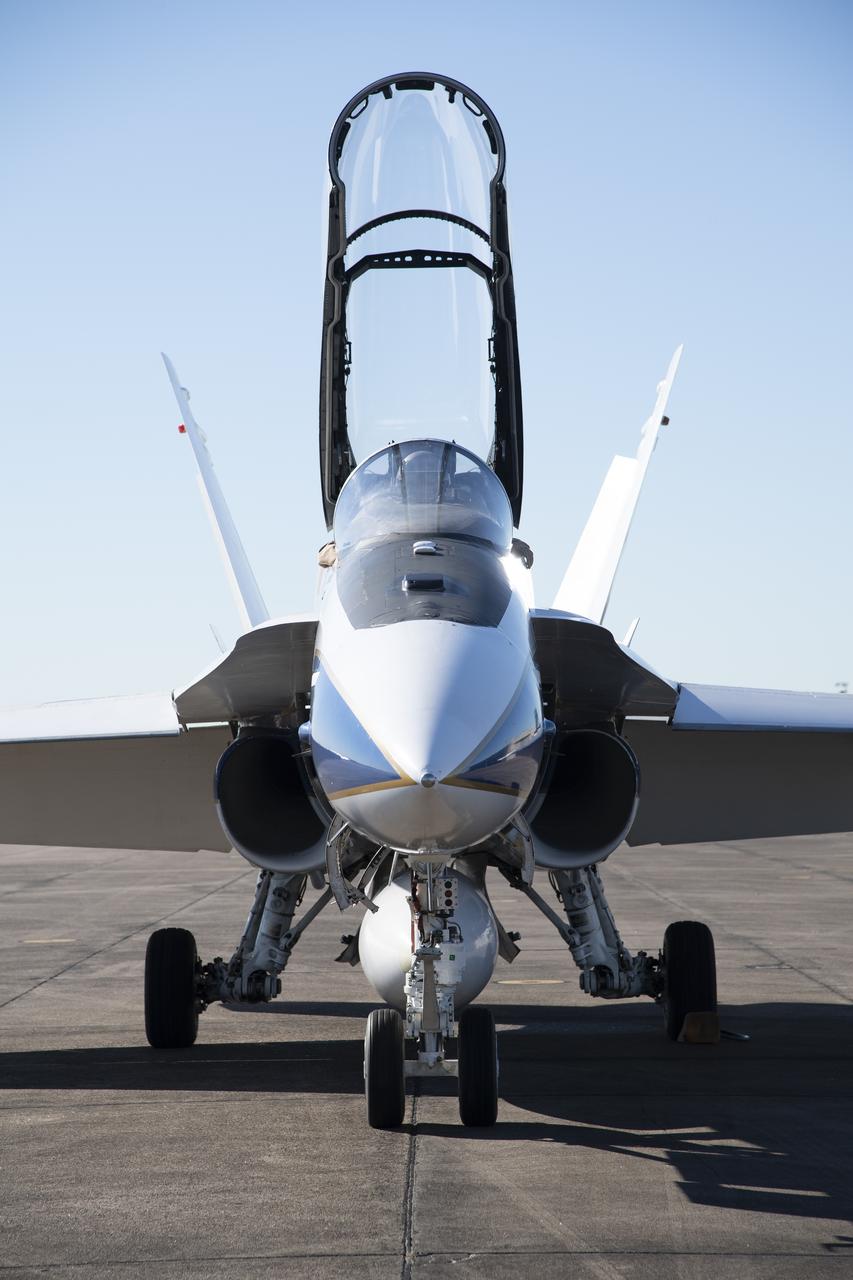

NASA test pilots Jim "Clue" Less and Wayne "Ringo"Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.

NASA test pilots Jim "Clue" Less and Wayne "Ringo" Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
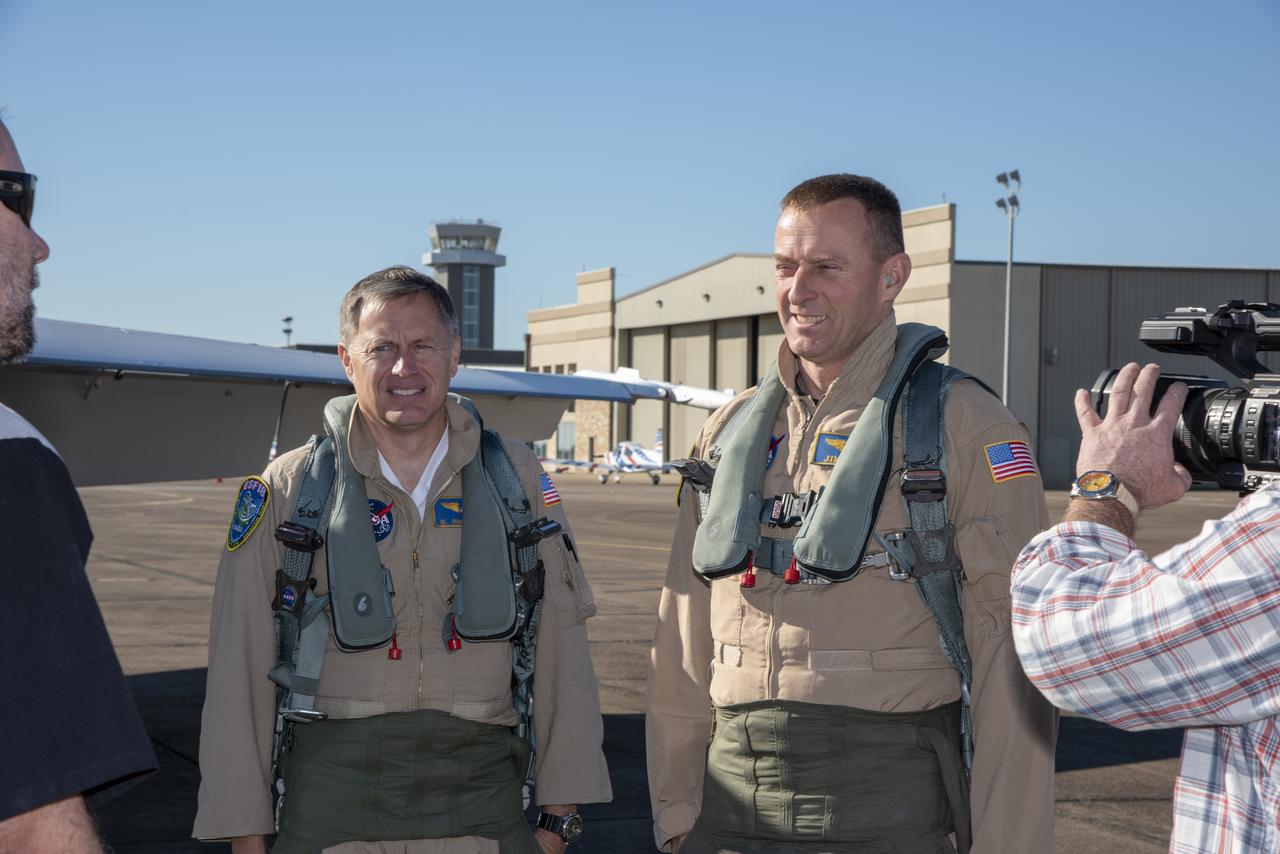

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
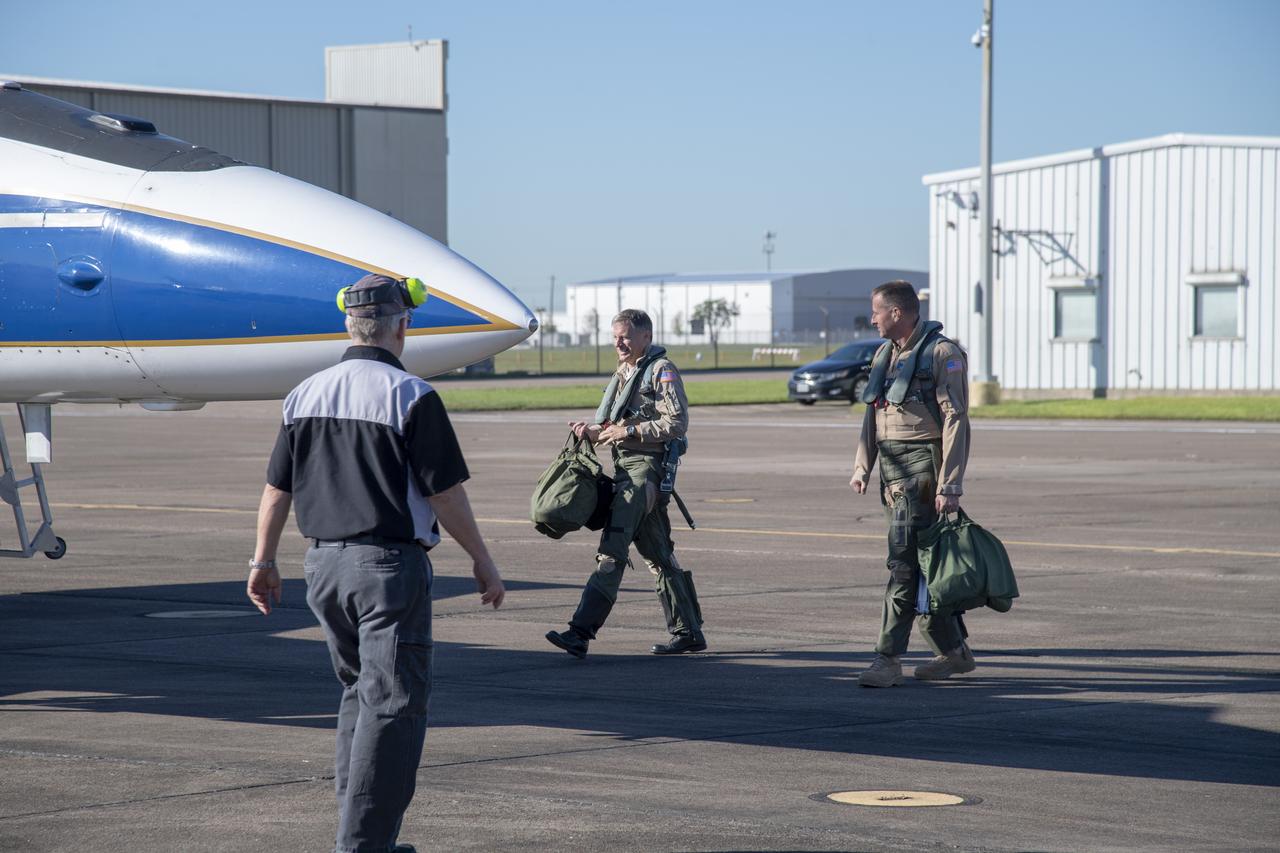

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
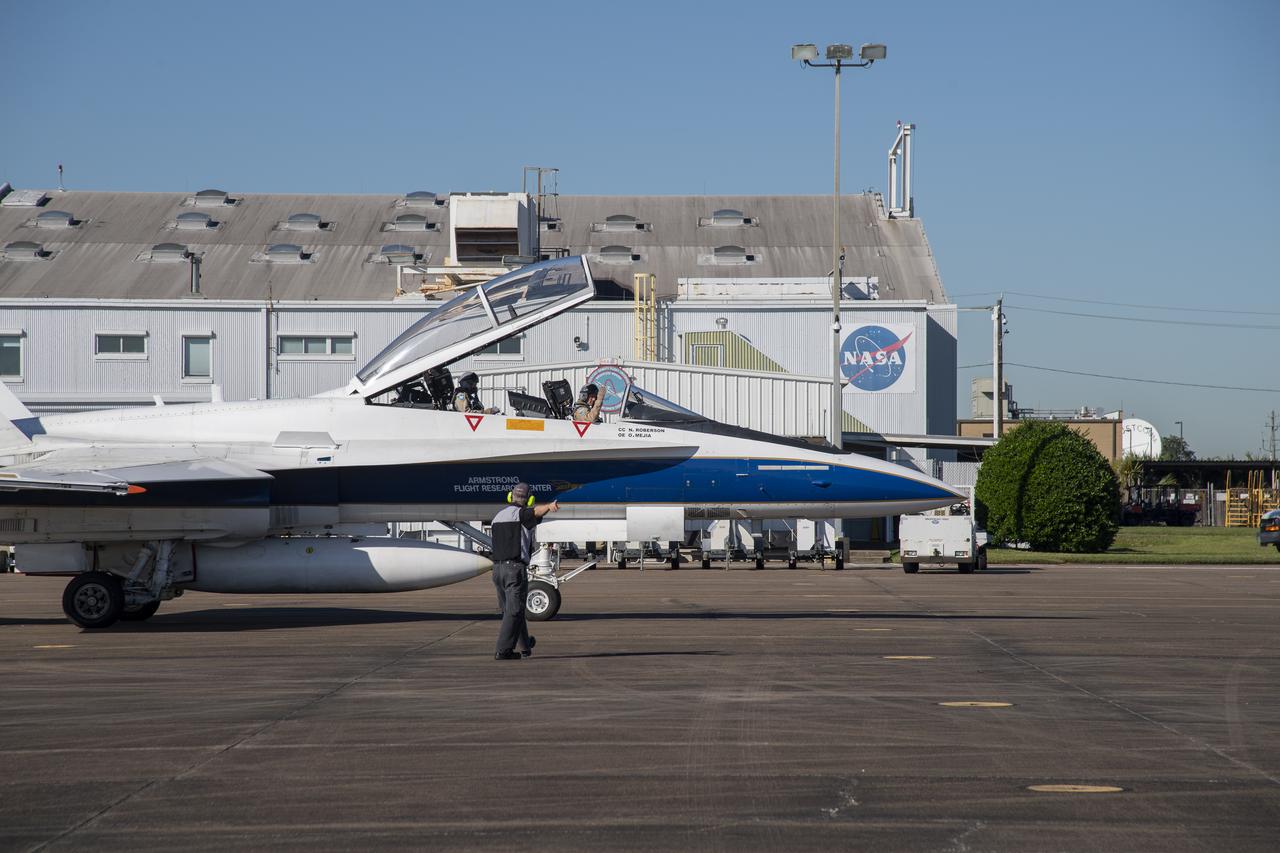

NASA test pilots Jim "Clue" Less and Wayne "Ringo" Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
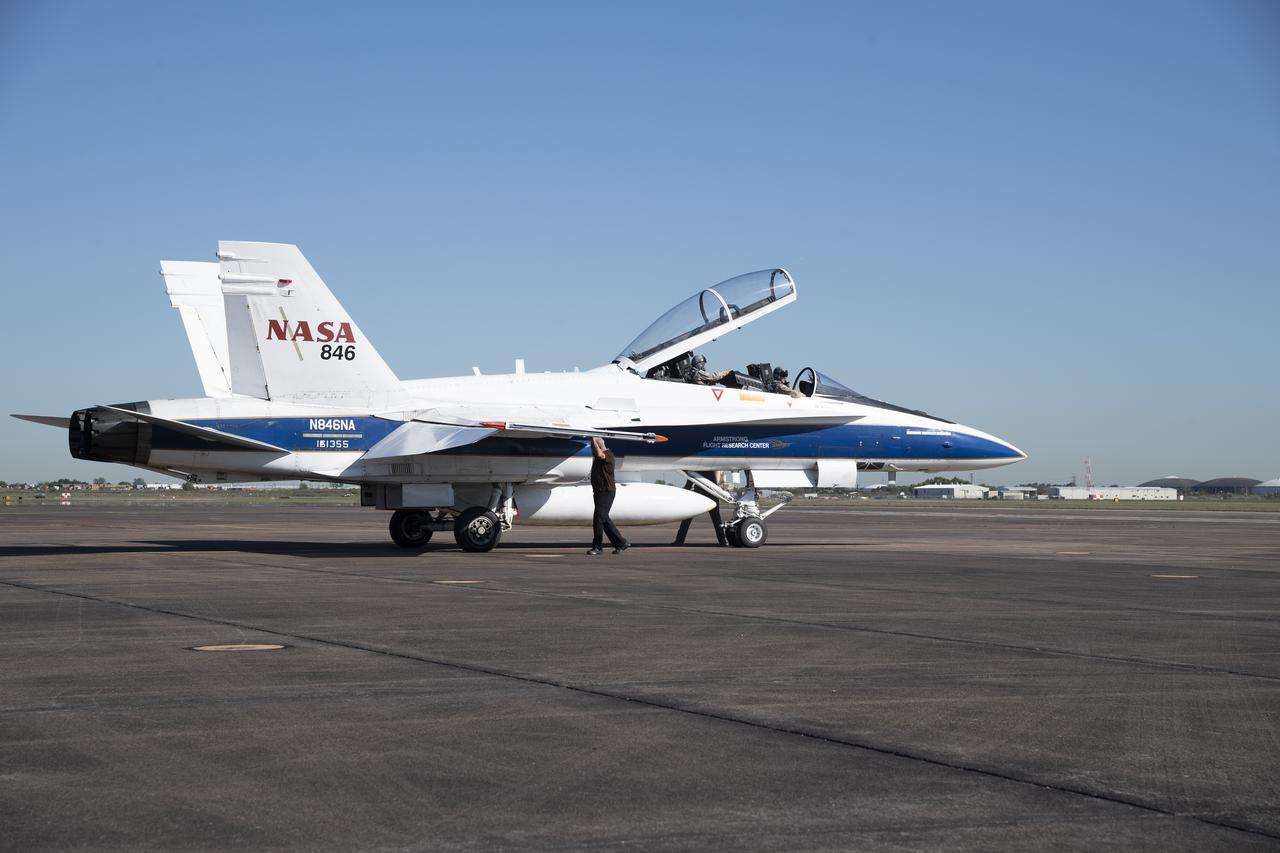

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
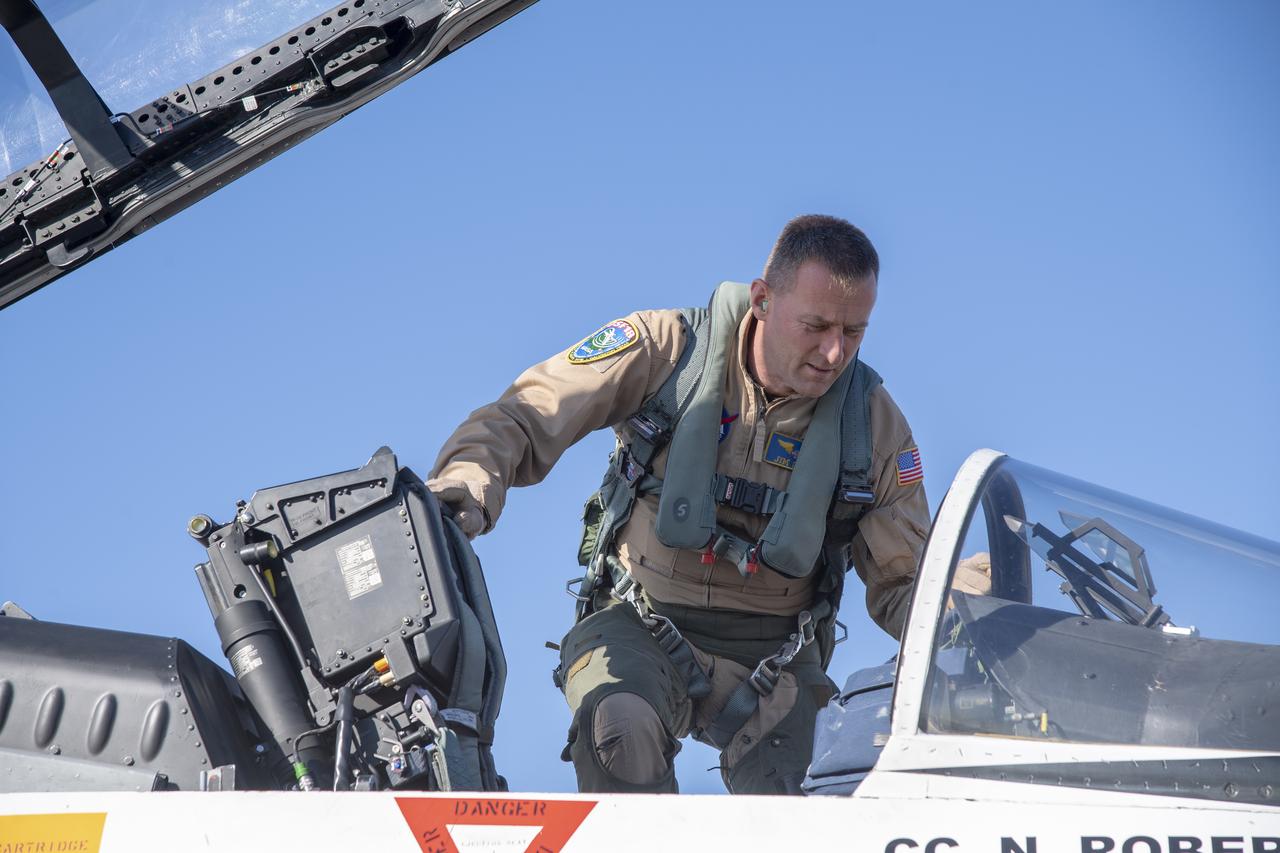

NASA test pilots Jim "Clue" Less and Wayne "Ringo" Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
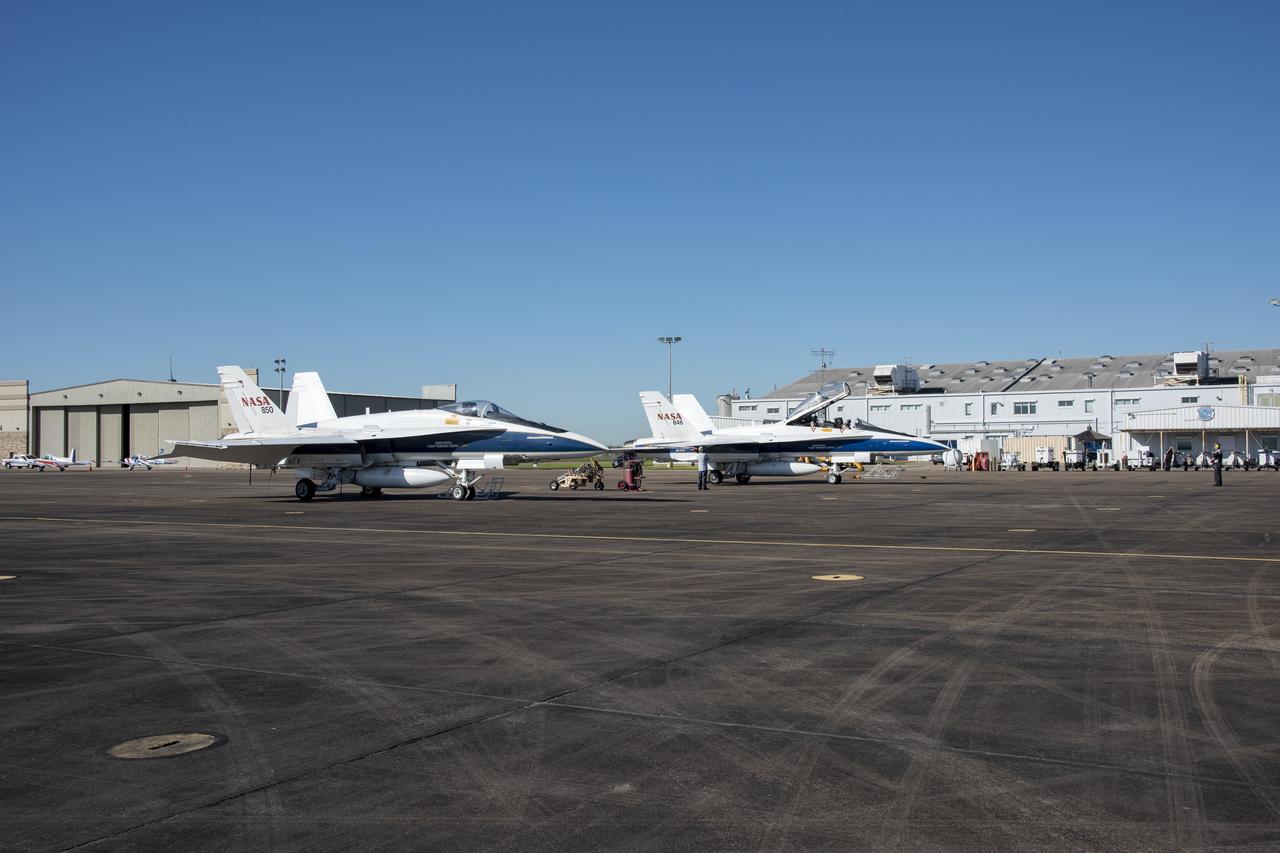

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
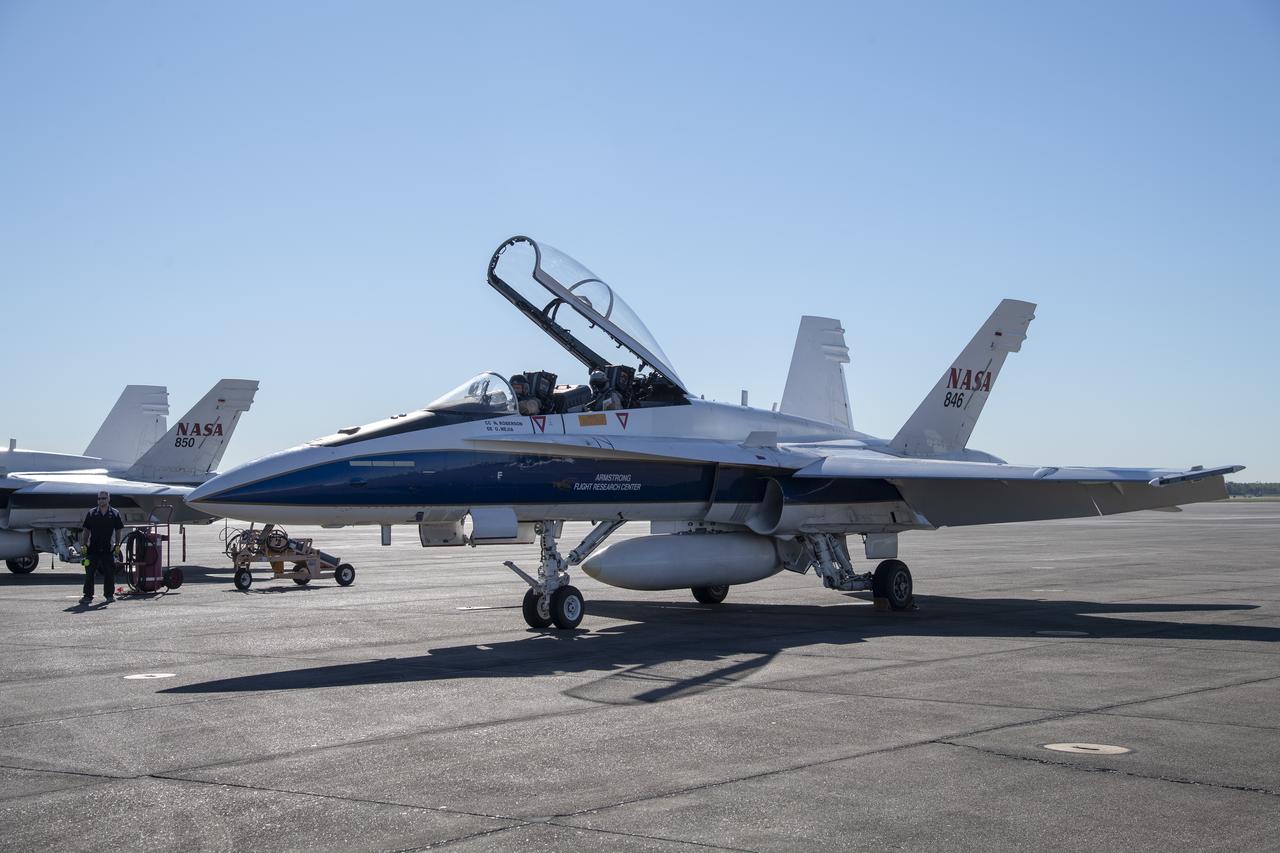

NASA test pilots Jim "Clue" Less and Wayne "Ringo" Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
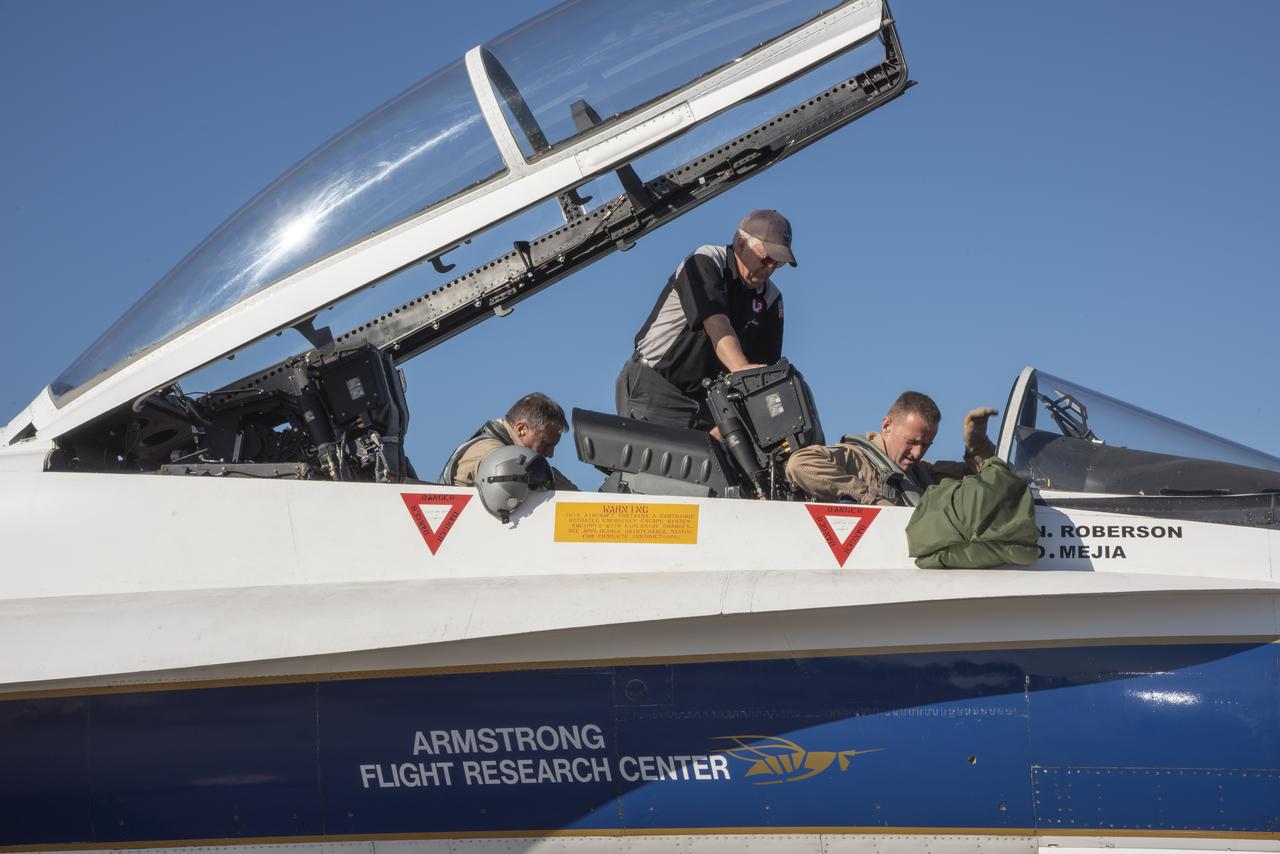

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
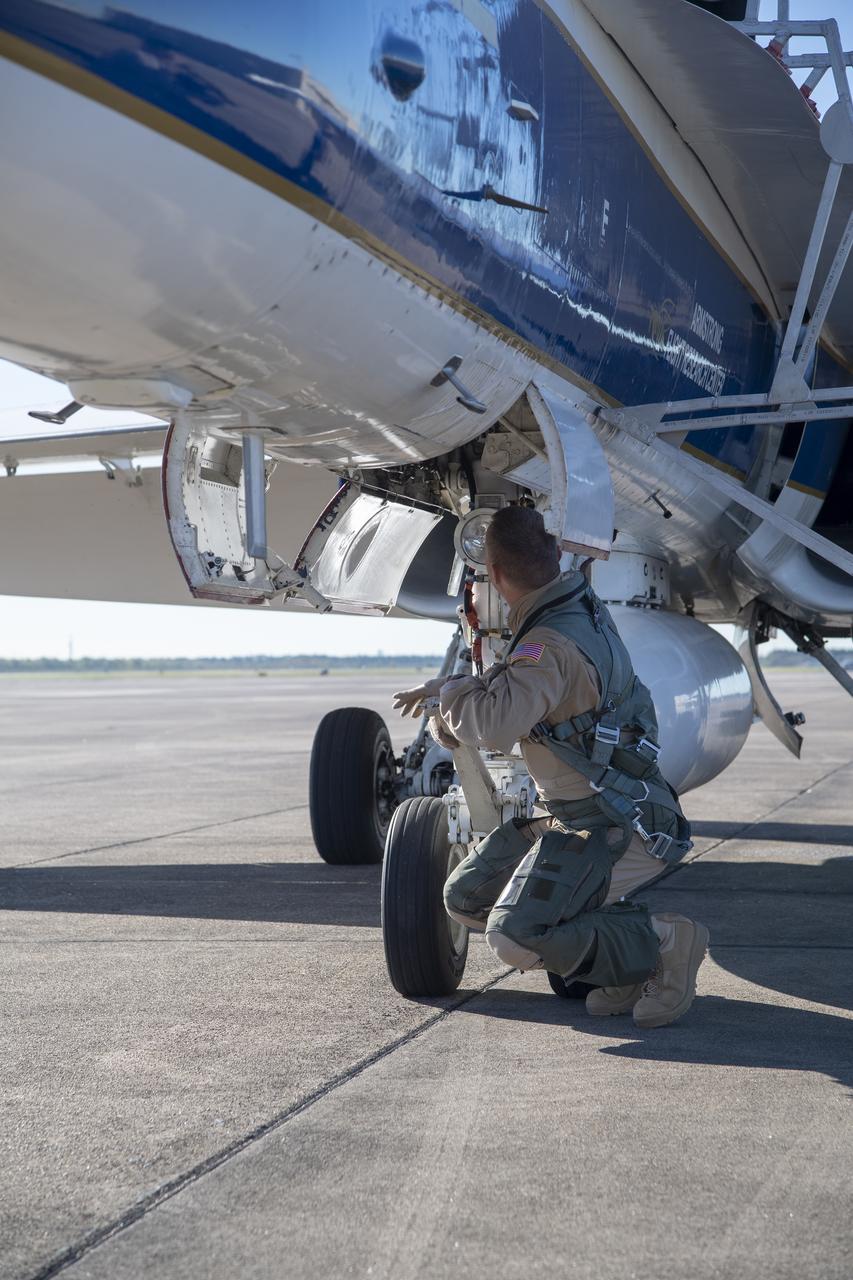

NASA test pilots Jim "Clue"Less and Wayne "Ringo" Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
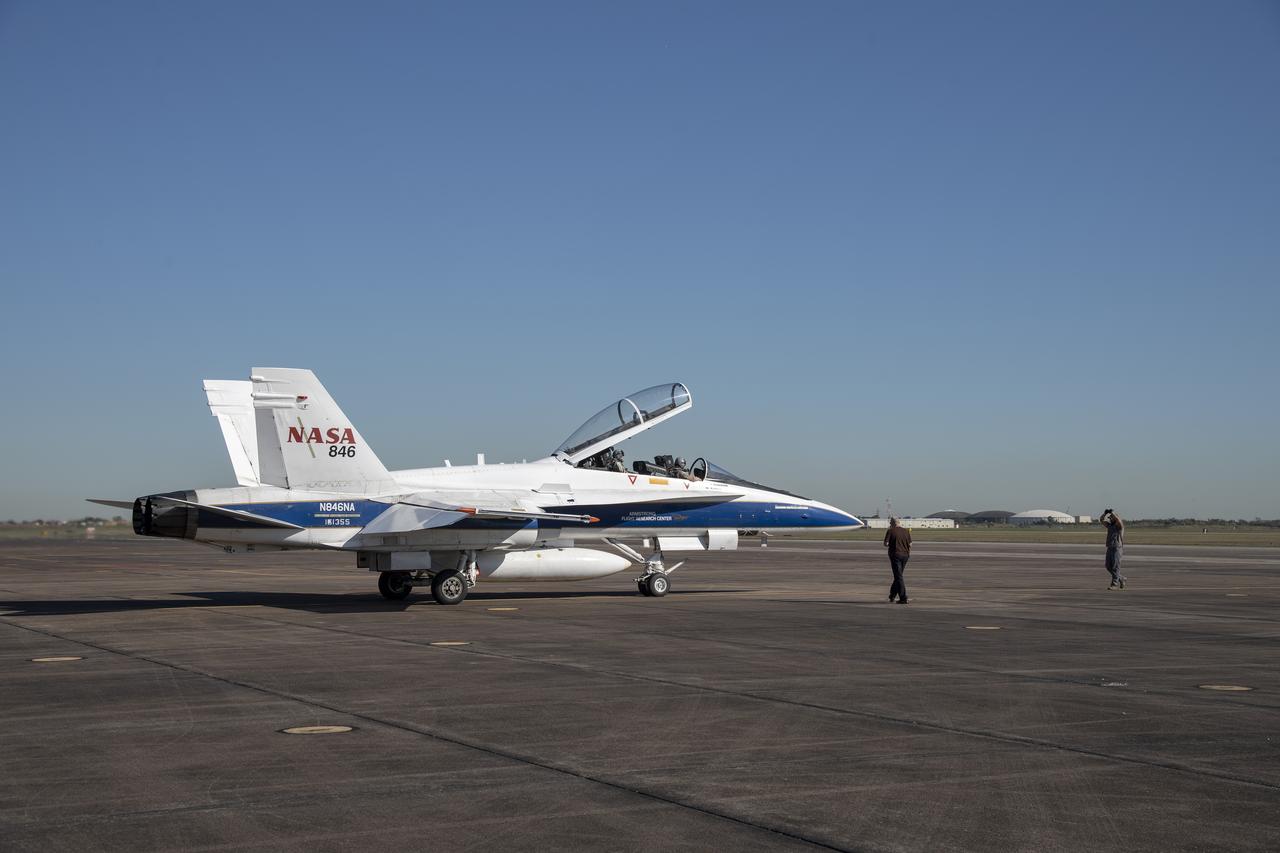

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.