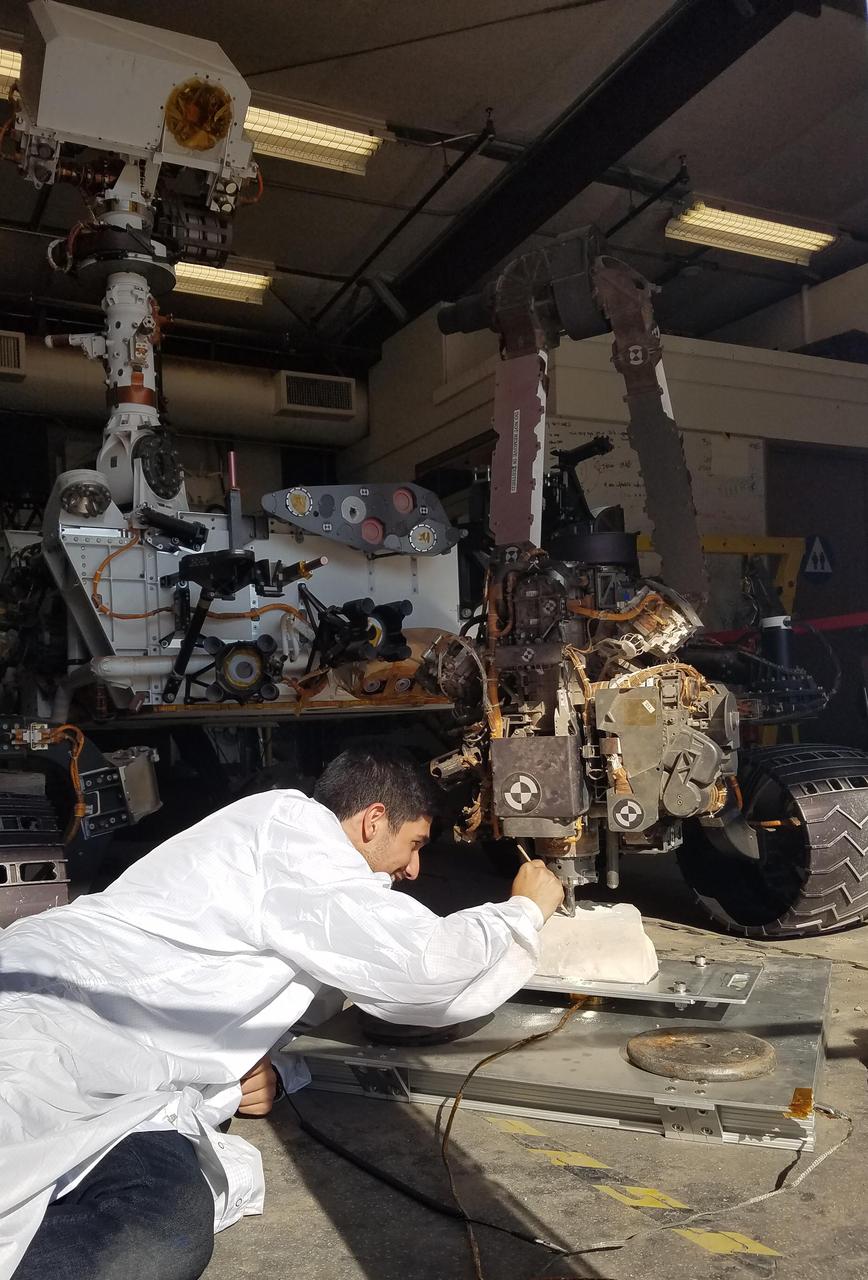

In the summer and fall of 2017, the team operating NASA's Curiosity Mars rover conducted tests in the "Mars Yard" at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to develop techniques that Curiosity might be able to use to resume drilling into rocks on Mars. JPL robotics engineer Vladimir Arutyunov, in this June 29, 2017, photo, checks the test rover's drill bit at its contact point with a rock. Note that the stabilizer post visible to the right of the bit is not in contact with the rock, unlike the positioning used and photographed by Curiosity when drilling into rocks on Mars in 2013 to 2016. In late 2016, after Curiosity's drill had collected sample material from 15 Martian rocks, the drill's feed mechanism ceased working reliably. That motorized mechanism moved the bit forward or back with relation to the stabilizer posts on either side of the bit. In normal drilling by Curiosity, the stabilizers were positioned on the target rock first, and then the feed mechanism extended the rotation-percussion bit into the rock. In the alternative technique seen here, called "feed-extended drilling," the test rover's stabilizers are not used to touch the rock. The bit is advanced into the rock by motion of the robotic arm rather than the drill's feed mechanism. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22061
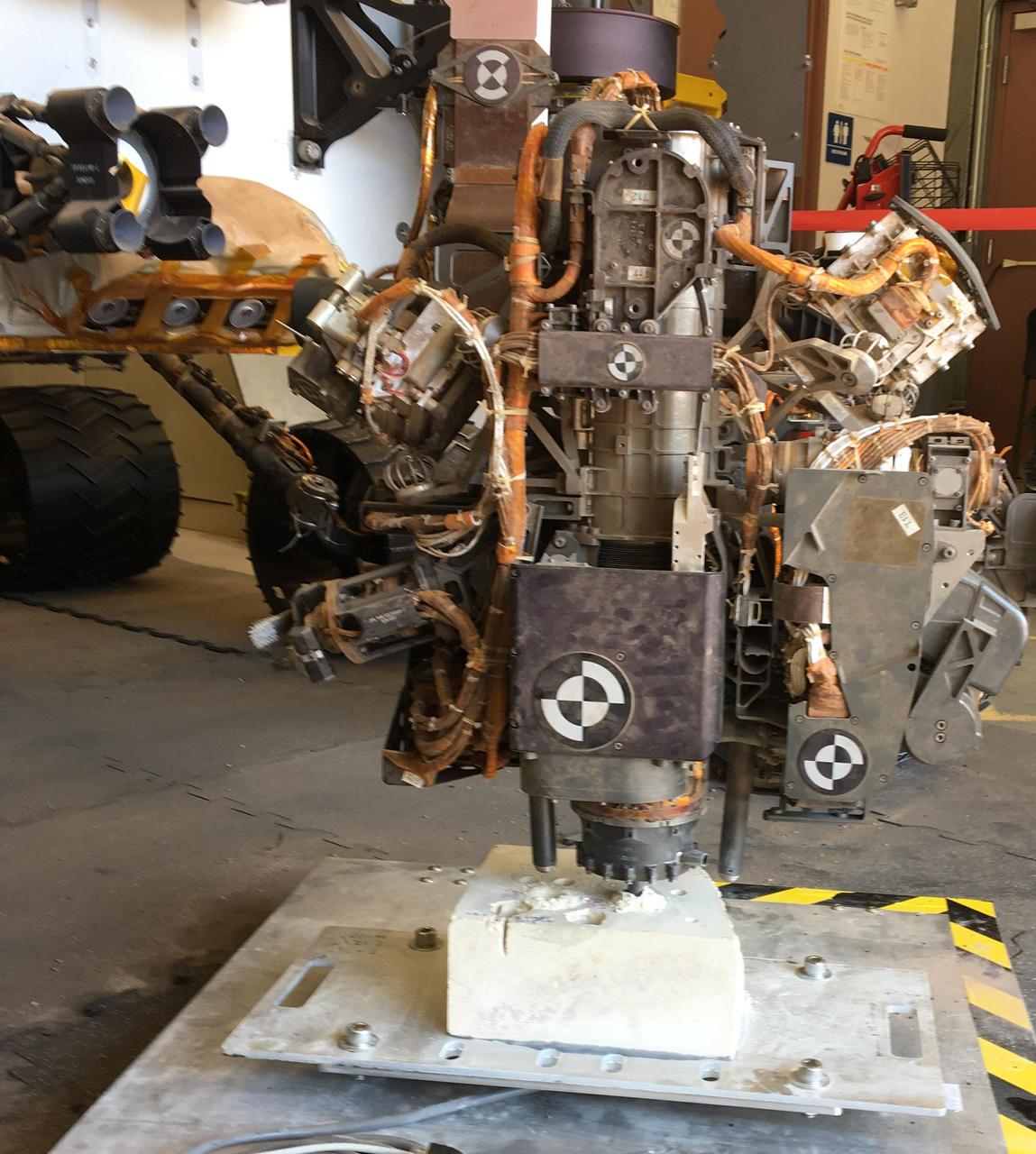

This photo taken in the "Mars Yard" at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, on Aug. 1, 2017, shows a step in development of possible alternative techniques that NASA's Curiosity Mars rover might be able to use to resume drilling into rocks on Mars. In late 2016, after Curiosity's drill had collected sample material from 15 Martian rocks in four years, the drill's feed mechanism ceased working reliably. That motorized mechanism moved the bit forward or back with relation to stabilizer posts on either side of the bit. In normal drilling by Curiosity, the stabilizers were positioned on the target rock first, and then the feed mechanism extended the rotation-percussion bit into the rock. In the alternative technique seen here, called "feed-extended drilling," the test rover's stabilizers are not used to touch the rock. The bit is advanced into the rock by motion of the robotic arm rather than the drill's feed mechanism. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22062
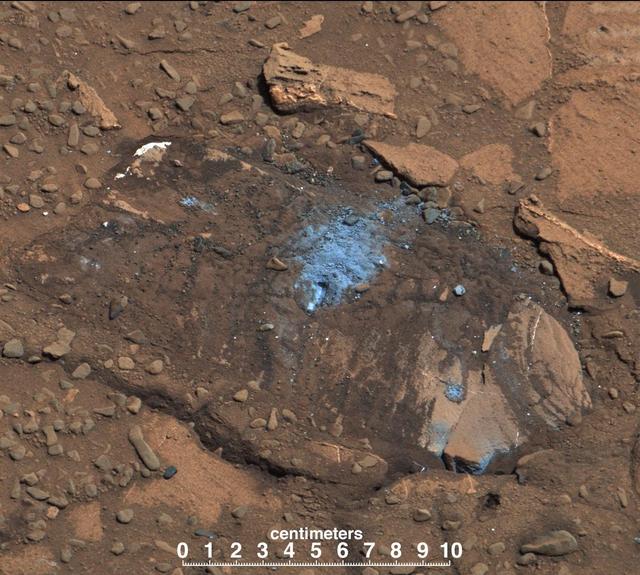

The Bonanza King rock on Mars, pictured here, was tapped by the drill belonging to NASA Mars rover Curiosity. The tapping resulted in sand piling up on the rock after drilling, showing the rock was not firmly in place.
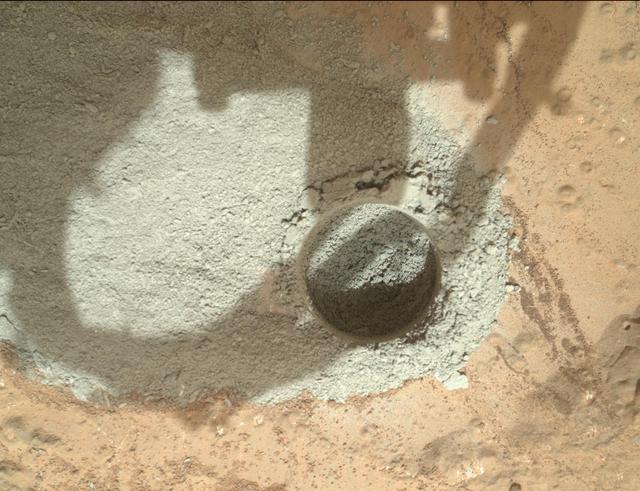

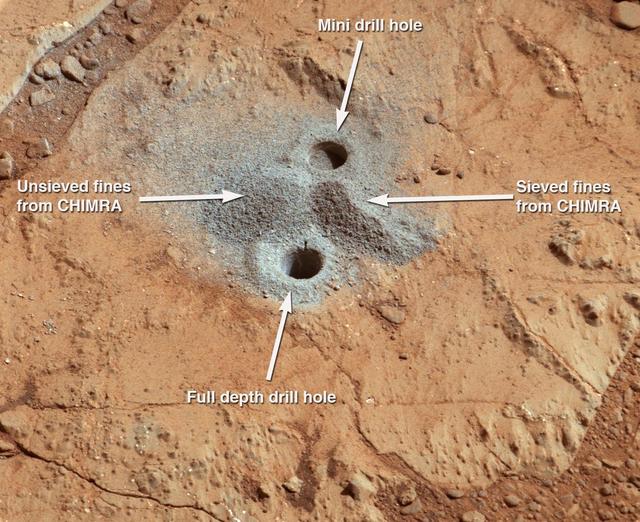
In an activity called the mini drill test, NASA Mars rover Curiosity used its drill to generate this ring of powdered rock for inspection in advance of the rover first full drilling.
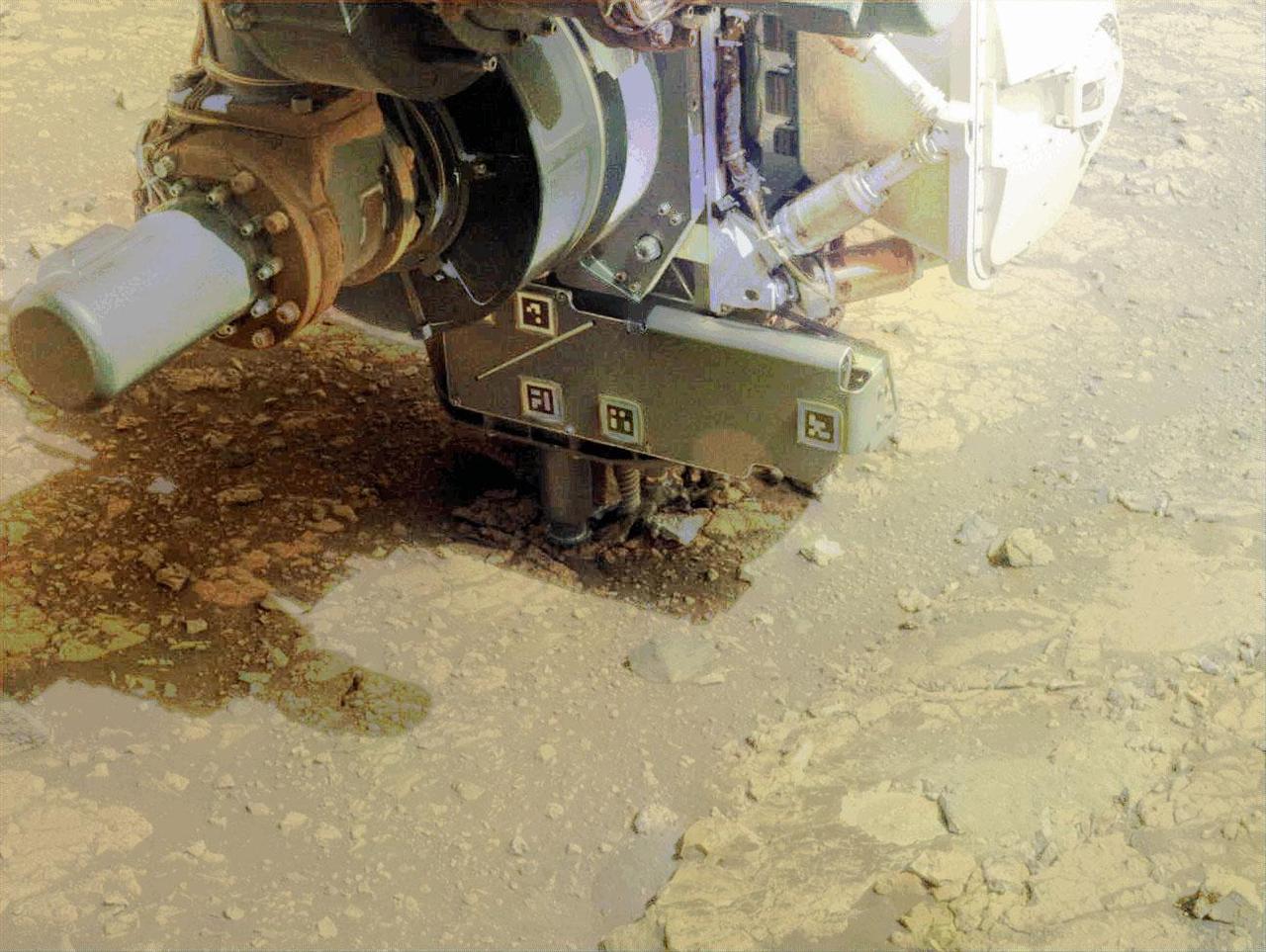

In this video, the robotic arm on NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover uses its percussive drill on a rocky outcrop near the rim of Jezero Crater that the science team calls “Kenmore” on June 10, 2025, the 1,531st Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Before drilling, the team abraded the rock to determine it was worthy of drilling. The eight images that make up this GIF were taken approximately one minute apart by one of the rover's front hazard-avoidance cameras. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26575
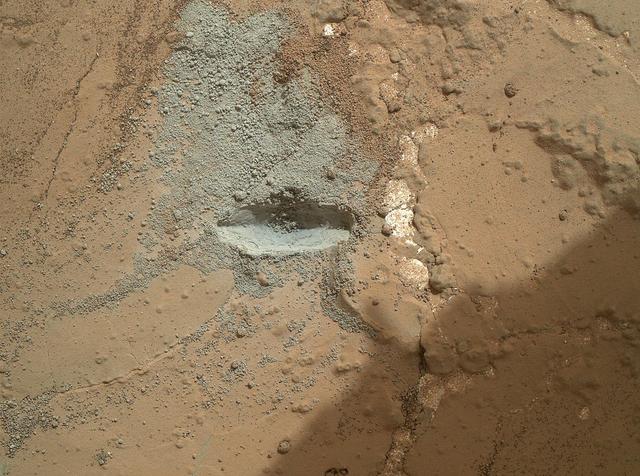

The bit in the rotary-percussion drill of NASA Mars rover Curiosity left its mark in a target patch of rock called John Klein during a test on Feb. 2, 2013, in preparation for the first drilling of a rock by the rover.

This frame from an animation from NASA Mars rover Curiosity shows the rover drilling into rock target Cumberland. The drilling was performed during the 279th Martian day, or sol, of the Curiosity work on Mars May 19, 2013.

This frame from a video clip shows moments during a demonstration of drilling into a rock at NASA JPL, Pasadena, Calif., with a test double of the Mars rover Curiosity. The drill combines hammering and rotation motions of the bit.
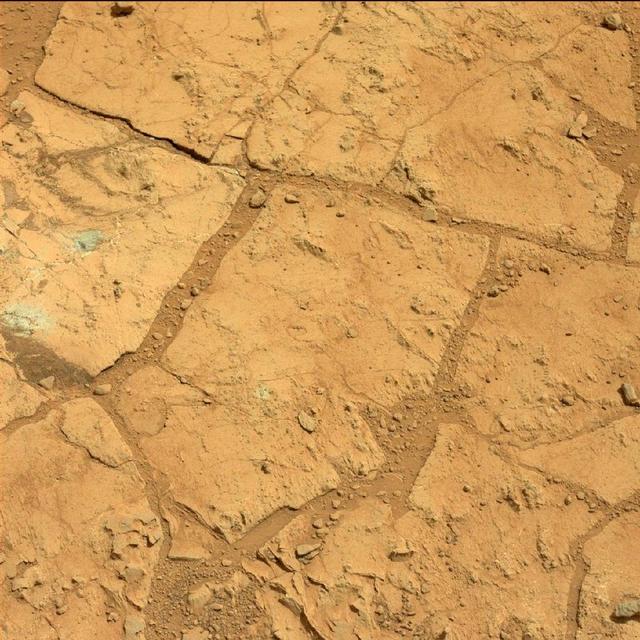

A blink pair of images taken before and after NASA Curiosity performed a mini drill test on a Martian rock shows changes resulting from that activity.

Engineers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory performed tests on rocks such as this one to understand why the first attempt by the agency's Perseverance rover resulted in a powderized sample. A duplicate of the rover's drill attempted to create cores from crumbly rocks. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25049
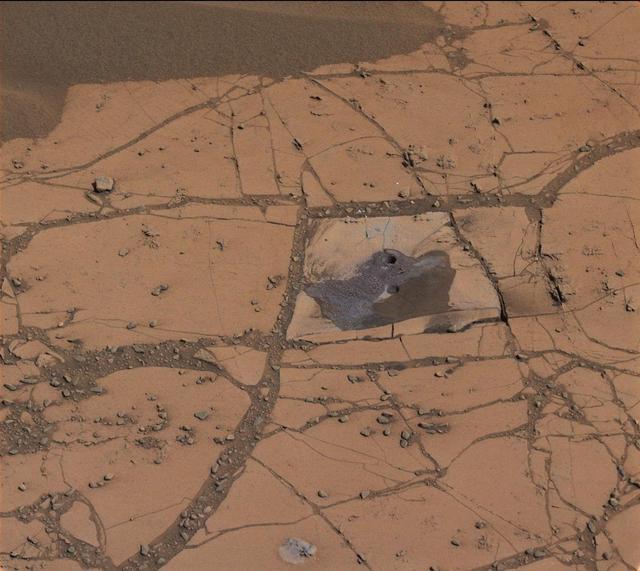

This image shows the first holes drilled by NASA Mars rover Curiosity at Mount Sharp. The loose material near the drill holes is drill tailings and an accumulation of dust that slid down the rock during drilling.

A day after NASA Mars rover Curiosity drilled the first sample-collection hole into a rock on Mars, the rover Chemistry and Camera ChemCam instrument shot laser pulses into the fresh rock powder that the drilling generated.
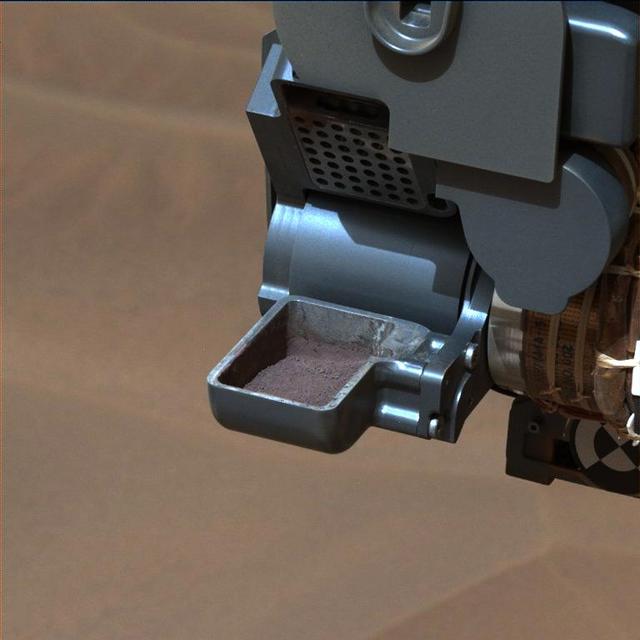
This image from NASA Curiosity rover shows a sample of powdered rock extracted by the rover drill from the Confidence Hills target -- the first rock drilled after Curiosity reached the base of Mount Sharp in September 2014.

This image shows the first holes into rock drilled by NASA Mars rover Curiosity, with drill tailings around the holes plus piles of powdered rock collected from the deeper hole and later discarded.

This view NASA Curiosity Mars Rover shows the rover drill in position for a mini-drill test to assess whether a rock target called Mojave is appropriate for full-depth drilling to collect a sample. It was taken on Jan. 13, 2015.
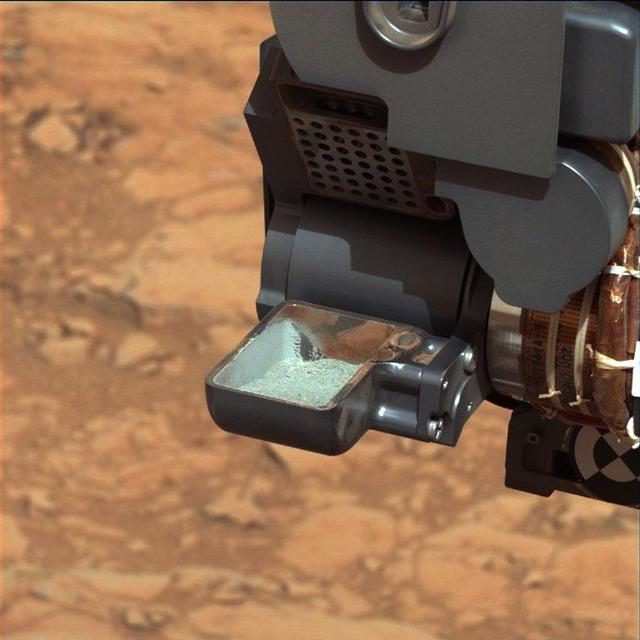

NASA Curiosity rover shows the first sample of powdered rock extracted by the rover drill. The image was taken after the sample was transferred from the drill to the rover scoop.

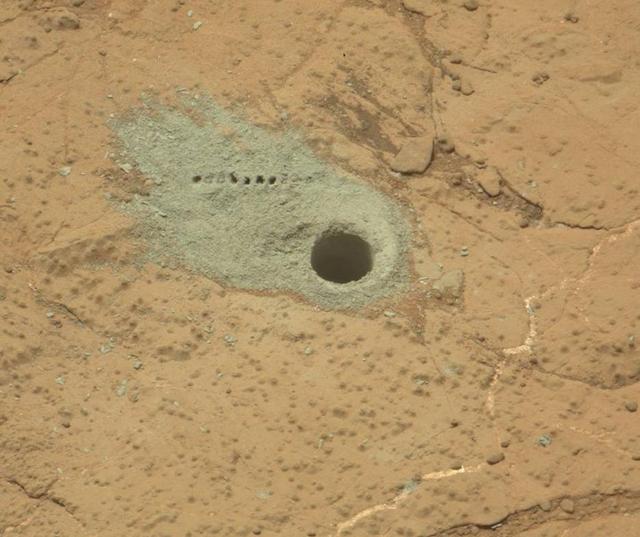
The hole that NASA Curiosity Mars rover drilled into target rock John Klein provided a view into the interior of the rock, as well as obtaining a sample of powdered material from the rock.
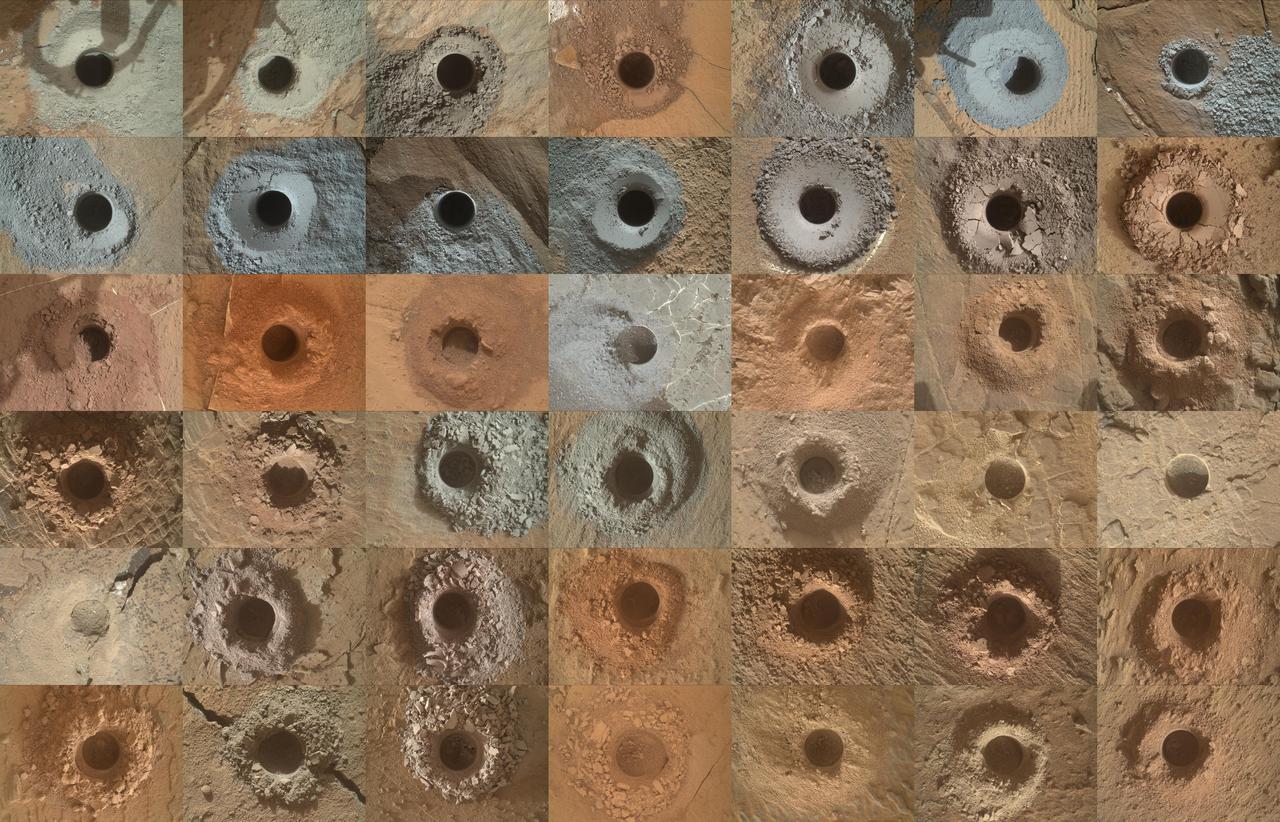

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover has collected 42 powderized rock samples with the drill on the end of its robotic arm. This grid shows all 42 holes made by the drill when collecting the samples, from "John Klein" (drilled on Feb. 9, 2013, the 182nd Martian day, or sol, of the mission) in the upper left, to "Kings Canyon" (drilled on Aug. 3, 2024, the 4,263rd Martian day, or sol, of the mission) in the lower right. Each hole is a little over a half-inch (16 millimeters) wide. The images were captured by the Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI), a camera on the end of the rover's arm. After drilling a sample, the powderized rock is trickled into instruments inside of Curiosity's belly that can analyze the composition of the rocks. Those instruments include Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) and Chemistry & Mineralogy (CheMin). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26403
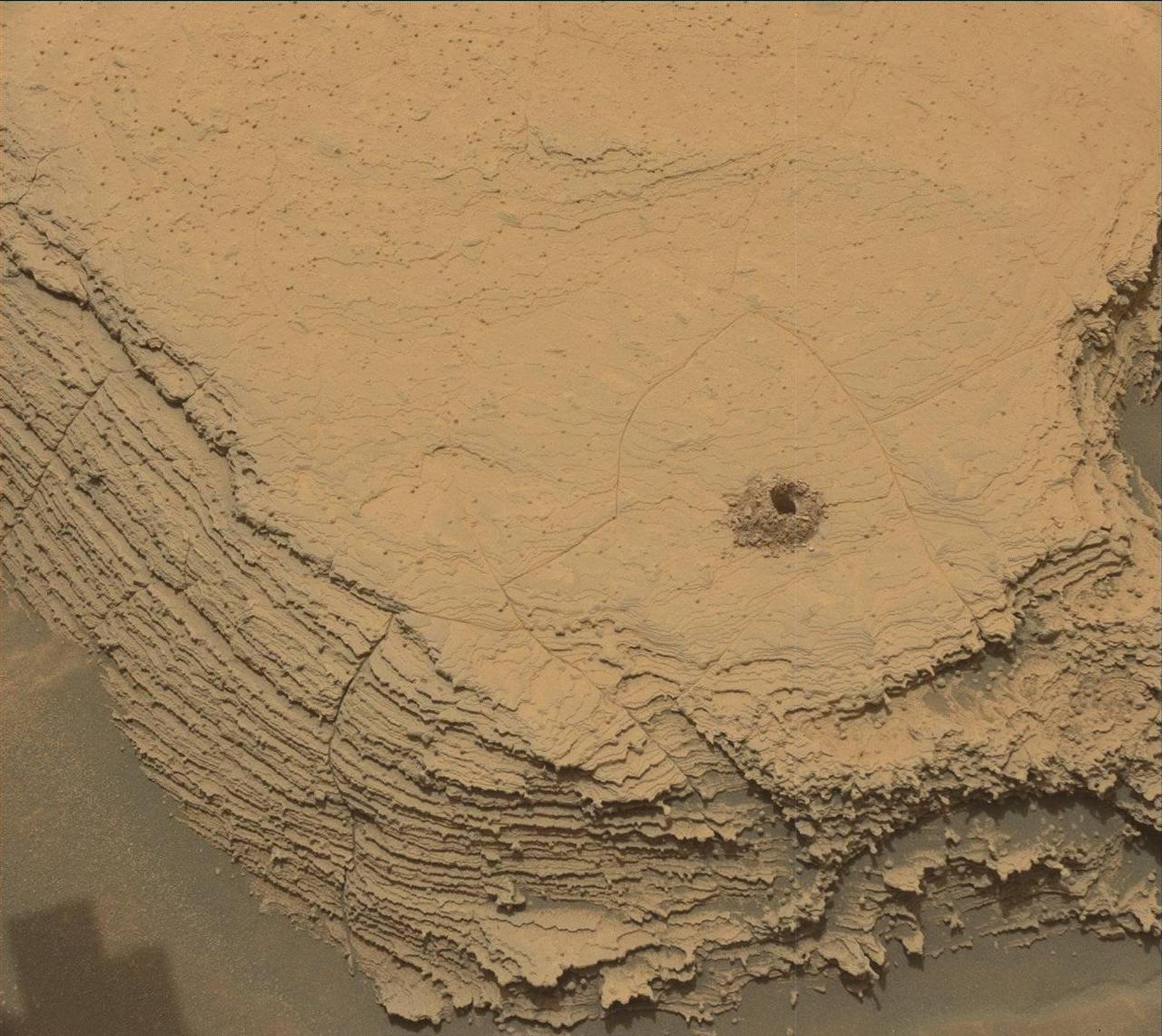

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover used its Mast Camera, or Mastcam, to capture this image of its 36th successful drill hole on Mount Sharp, at a rock called "Canaima." The pulverized sample of this rock was drilled on Oct. 3, 2022, the 3,612th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25418
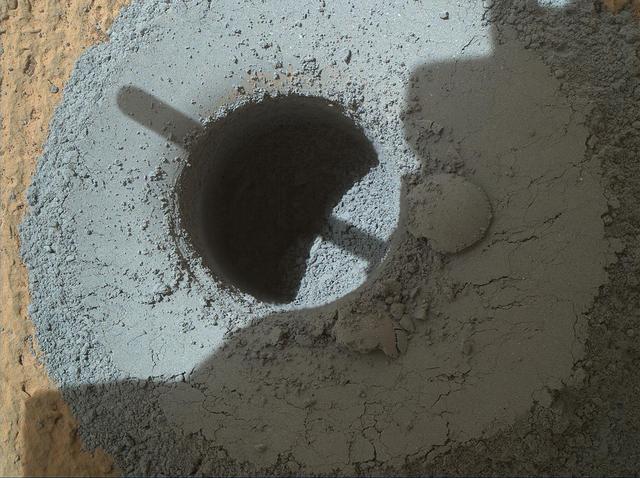

This hole, with a diameter slightly smaller than a U.S. dime, was drilled by NASA Curiosity Mars rover into a rock target called Telegraph Peak. The rock is located within the basal layer of Mount Sharp. The hole was drilled on Feb. 24, 2015.

This image demonstrates how engineers place the drill carried by NASA Mars rover Curiosity onto rock targets. They first set down the drill two stabilizing prongs near the target, as shown by the dashed line.
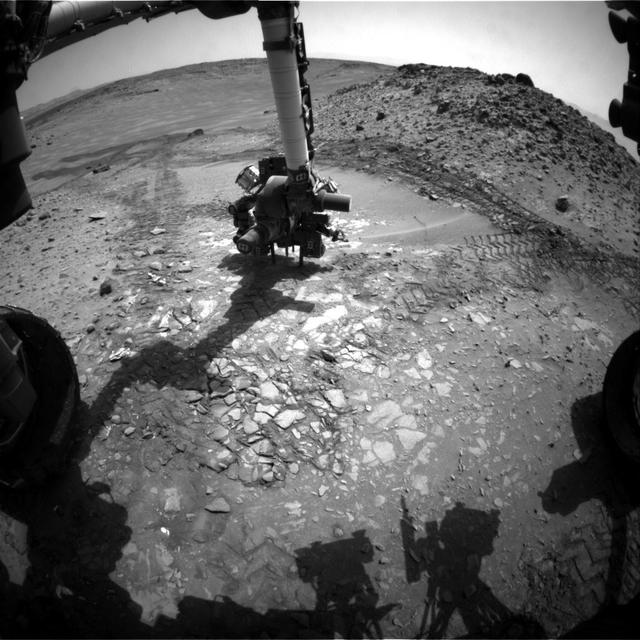

This image from the front Hazcam on NASA Curiosity Mars rover shows the rover drill in place during a test of whether the rock beneath it, Bonanza King, would be an acceptable target for drilling to collect a sample.
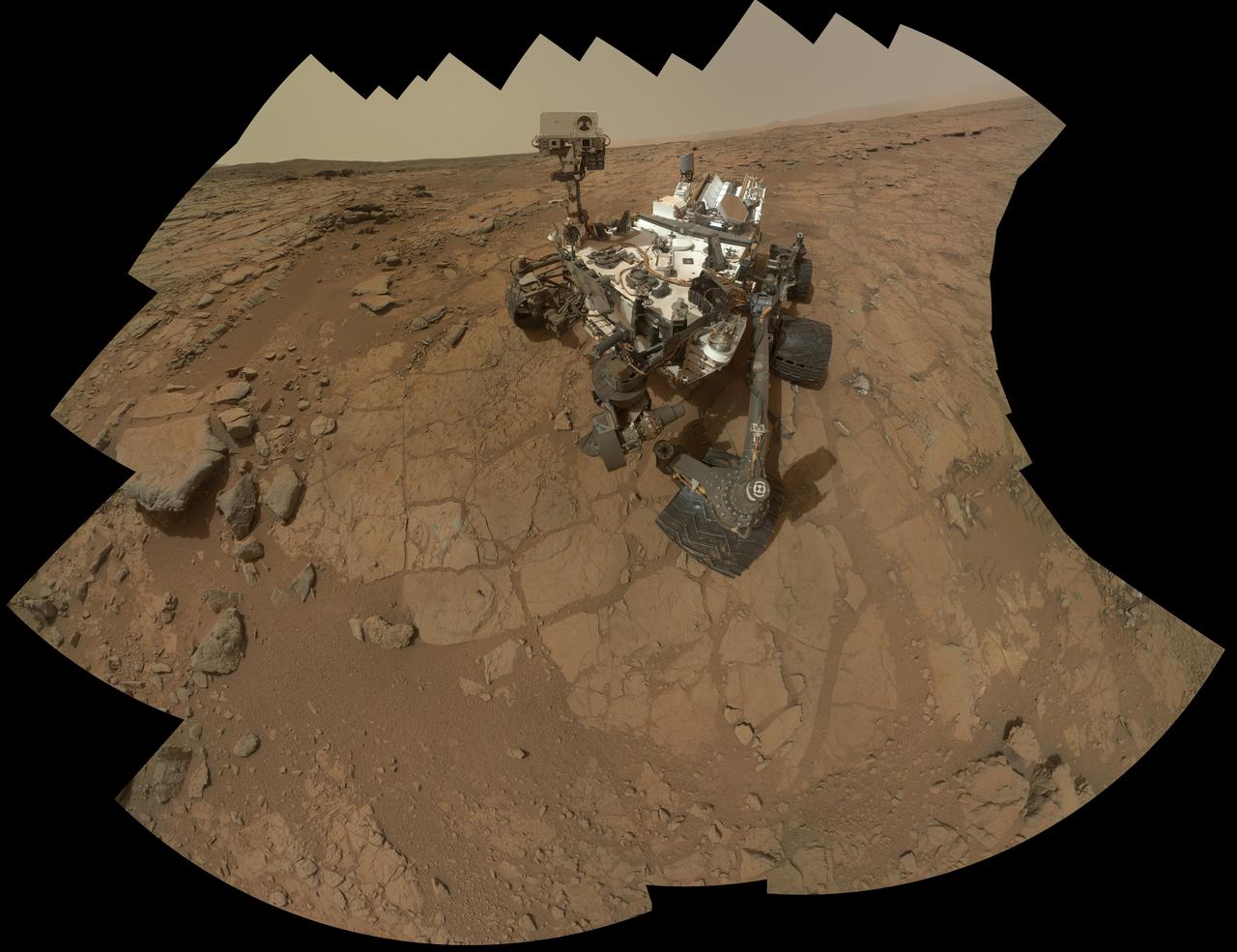

The rover is positioned at a patch of flat outcrop called John Klein, which was selected as the site for the first rock-drilling activities by NASA Curiosity. This self-portrait was acquired to document the drilling site.
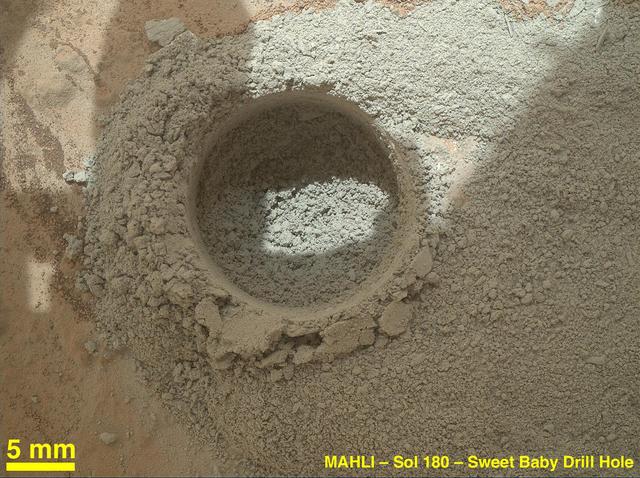

After an activity called the mini drill test by NASA Mars rover Curiosity, the rover MAHLI camera recorded this view of the results. The test generated a ring of powdered rock for inspection in advance of the rover first full drilling.
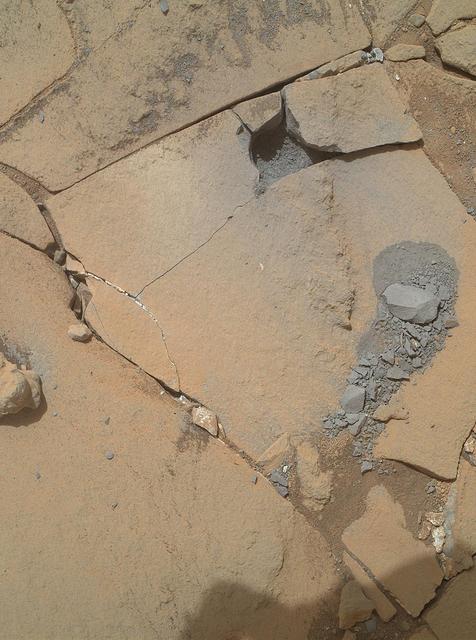

This Jan. 13, 2015, view from NASA Curiosity Mars rover shows outcomes of a mini-drill test to assess whether the Mojave rock is appropriate for full-depth drilling to collect a sample.
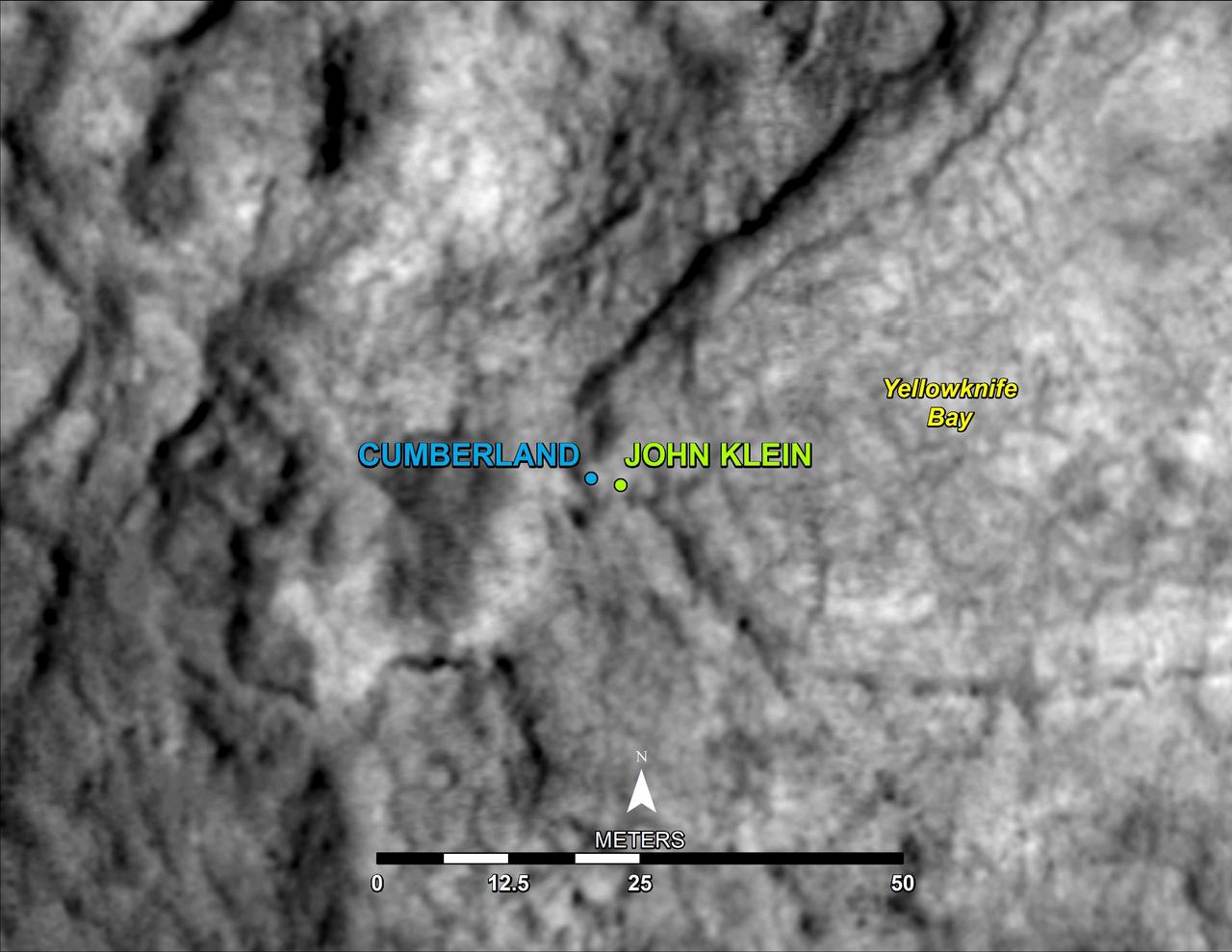

This map shows the location of Cumberland, the second rock-drilling target for NASA Mars rover Curiosity, in relation to the rover first drilling target, John Klein, within the southwestern lobe of a shallow depression called Yellowknife Bay.
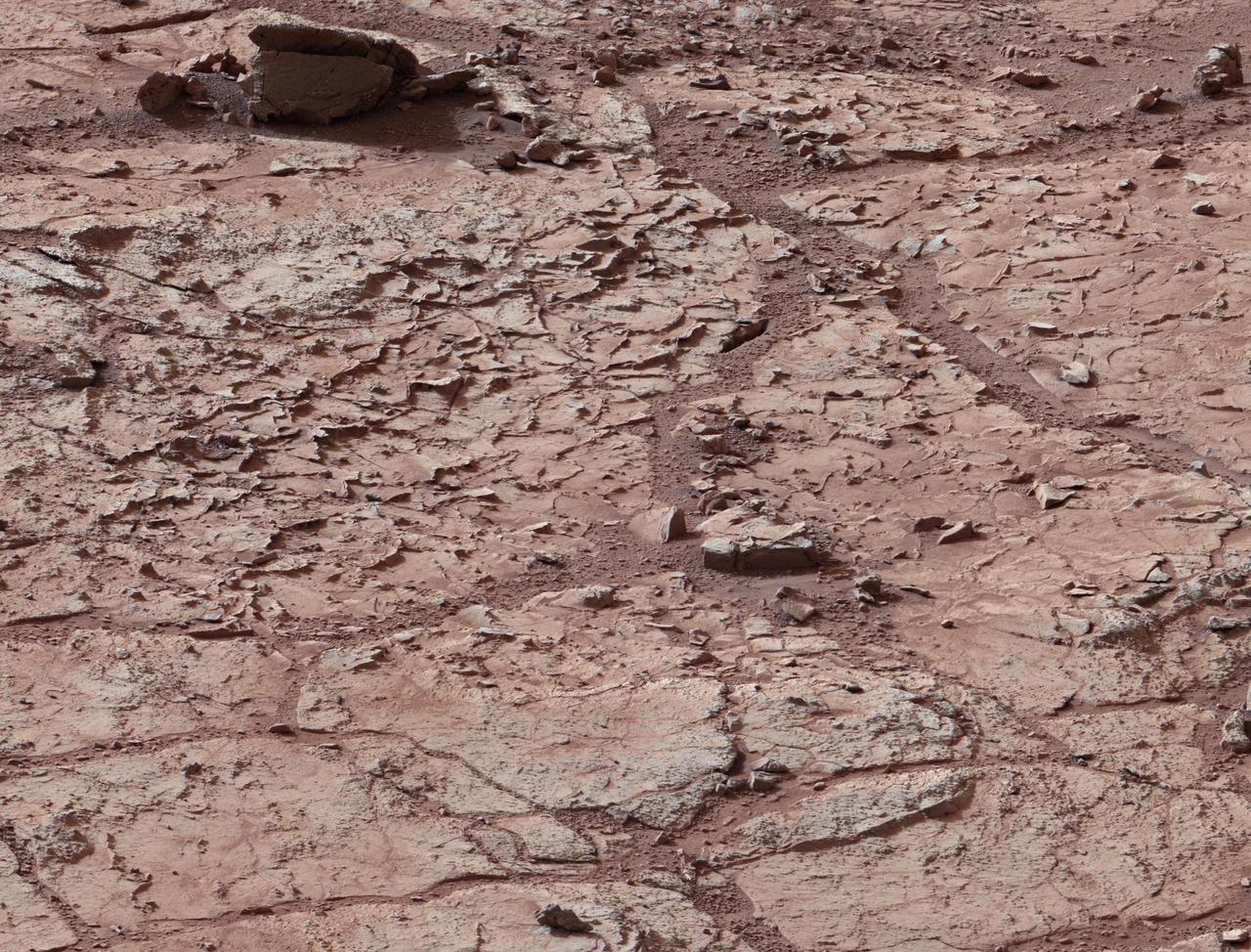

This view shows the patch of veined, flat-lying rock selected as the first drilling site for NASA Mars rover Curiosity.
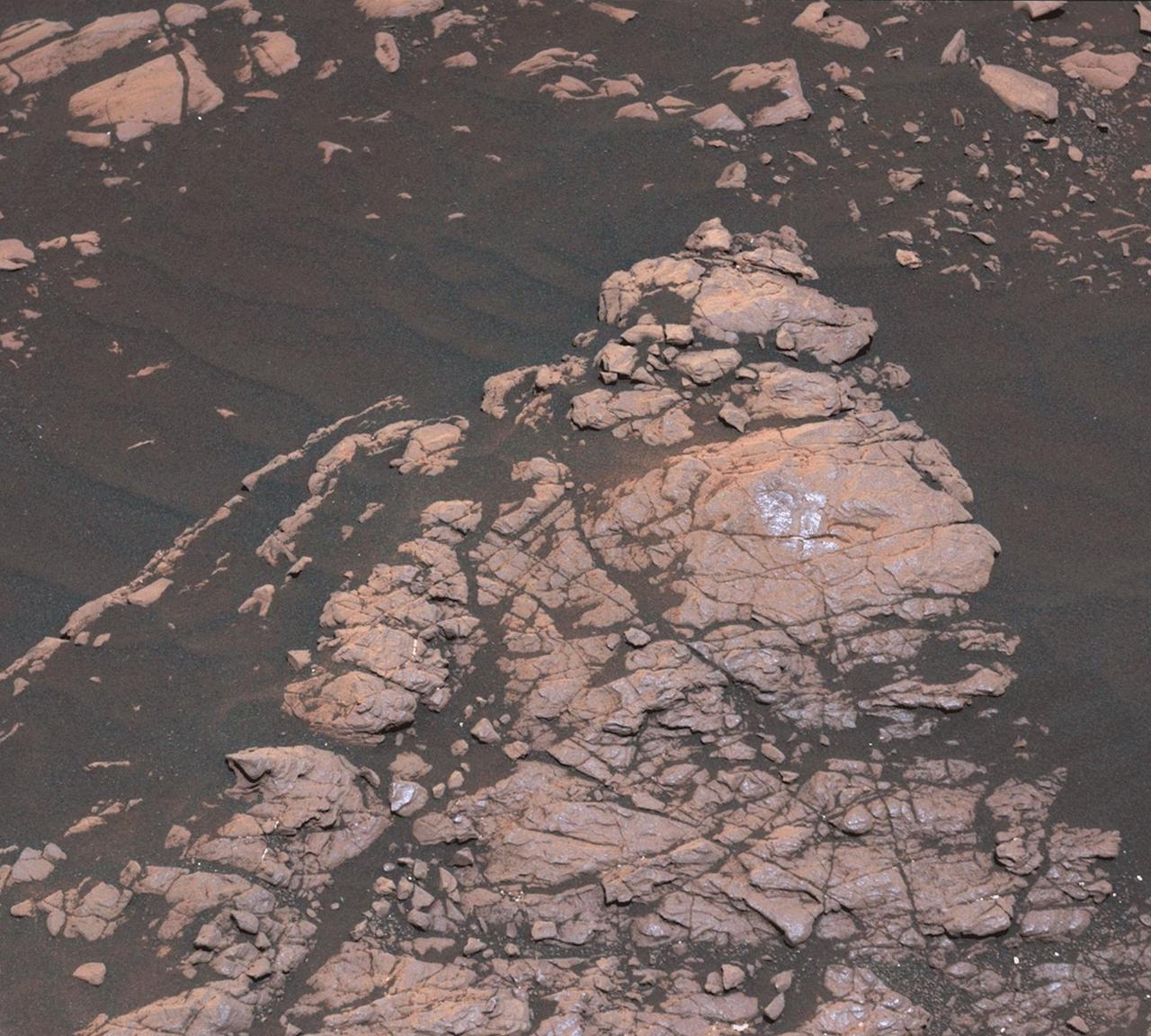

The Mast Camera, or Mastcam, on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover captured this set of images before and after it drilled a rock nicknamed "Aberlady," on Saturday, April 6, 2019 (the 2,370th Martian day, or sol, of the mission). The rock and others nearby appear to have moved when the drill was retracted. This was the first time Curiosity has drilled in the long-awaited "clay-bearing unit." The scene is presented with a color adjustment that approximates white balancing to resemble how the rocks and sand would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23138
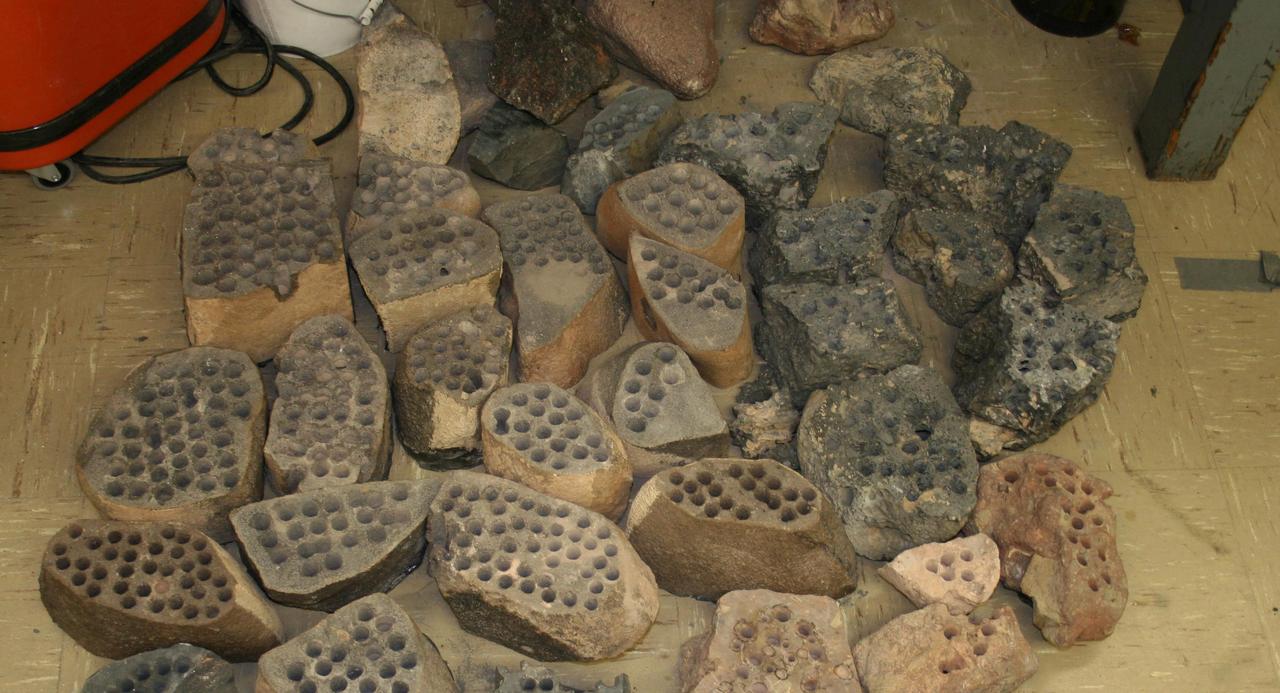

The development of the Mars rover Curiosity capabilities for drilling into a rock on Mars required years of development work. Seen here are some of the rocks used in bit development testing and lifespan testing at JPL in 2007.

This Aug. 12, 2012, image from the Mastcam on NASA Curiosity Mars rover shows an outcrop that includes the Bonanza King rock under consideration as a drilling target. Raised ridges on the flat rocks are visible at right.
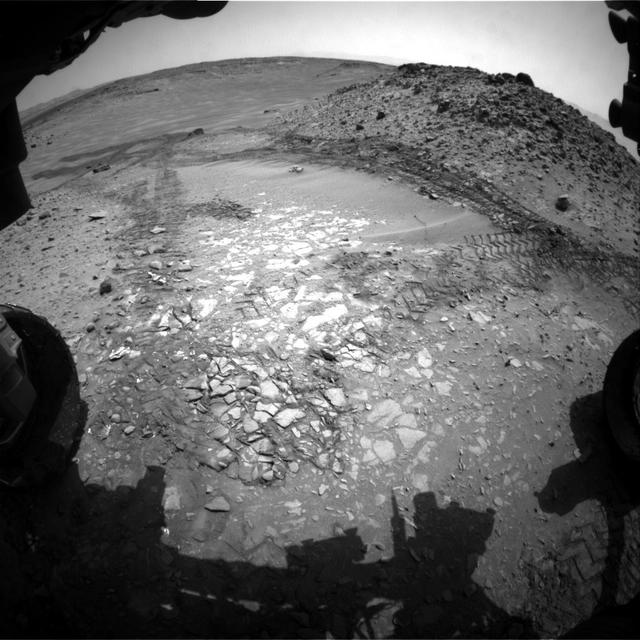

The pale rocks in the foreground of this Aug. 14, 2014, image from NASA Curiosity Mars rover include the Bonanza King target under consideration to become the fourth rock drilled by the rover.
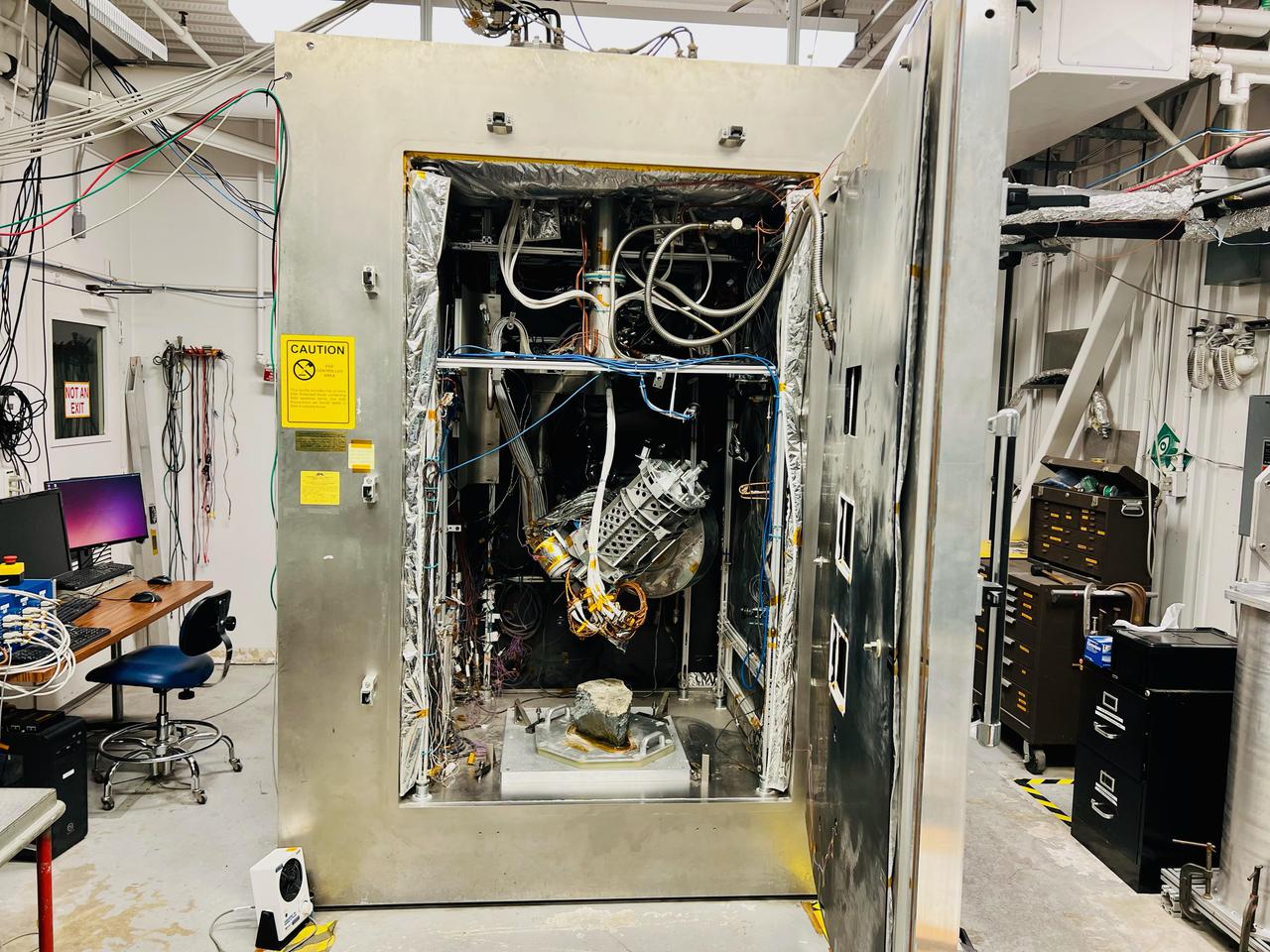

Engineers working with NASA's Perseverance Mars rover set up this test area at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in late 2021 to practice drilling into crumbly rocks using a duplicate of the rover's rock-coring drill. Perseverance's drill was designed to provide solid rock cores roughly the size of a piece of chalk; however, the rover's first sample, nicknamed "Roubion," collapsed into powder, prompting a test campaign. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25048
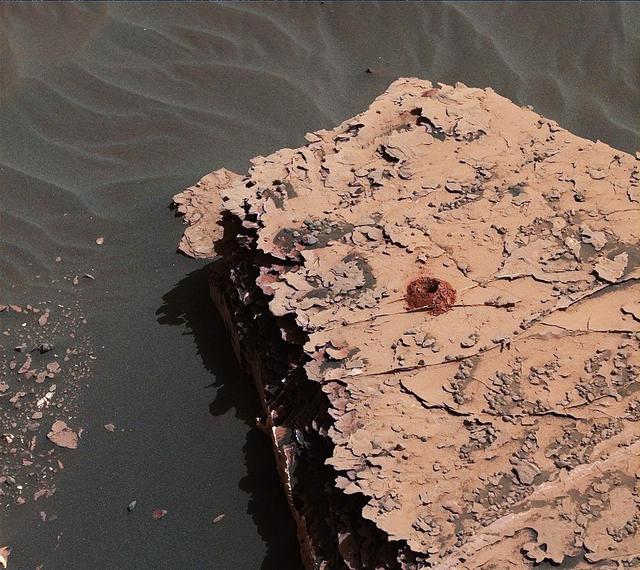

NASA's Curiosity rover successfully drilled a hole 2 inches (5.1 centimeters) deep in a target called "Duluth" on May 20, 2018. The hole is about .6 inches (1.6 centimeters) across. It was the first rock sample captured by the drill since October 2016. A mechanical issue took the drill offline in December 2016. Engineers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, had to innovate a new way for the rover to drill in order to restore this ability. The new technique, called Feed Extended Drilling (FED) keeps the drill's bit extended out past two stabilizer posts that were originally used to steady the drill against Martian rocks. It lets Curiosity drill using the force of its robotic arm, a little more like a human would while drilling into a wall at home. This image was taken by Curiosity's Mast Camera (Mastcam) on Sol 2057. It has been white balanced and contrast-enhanced. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22325
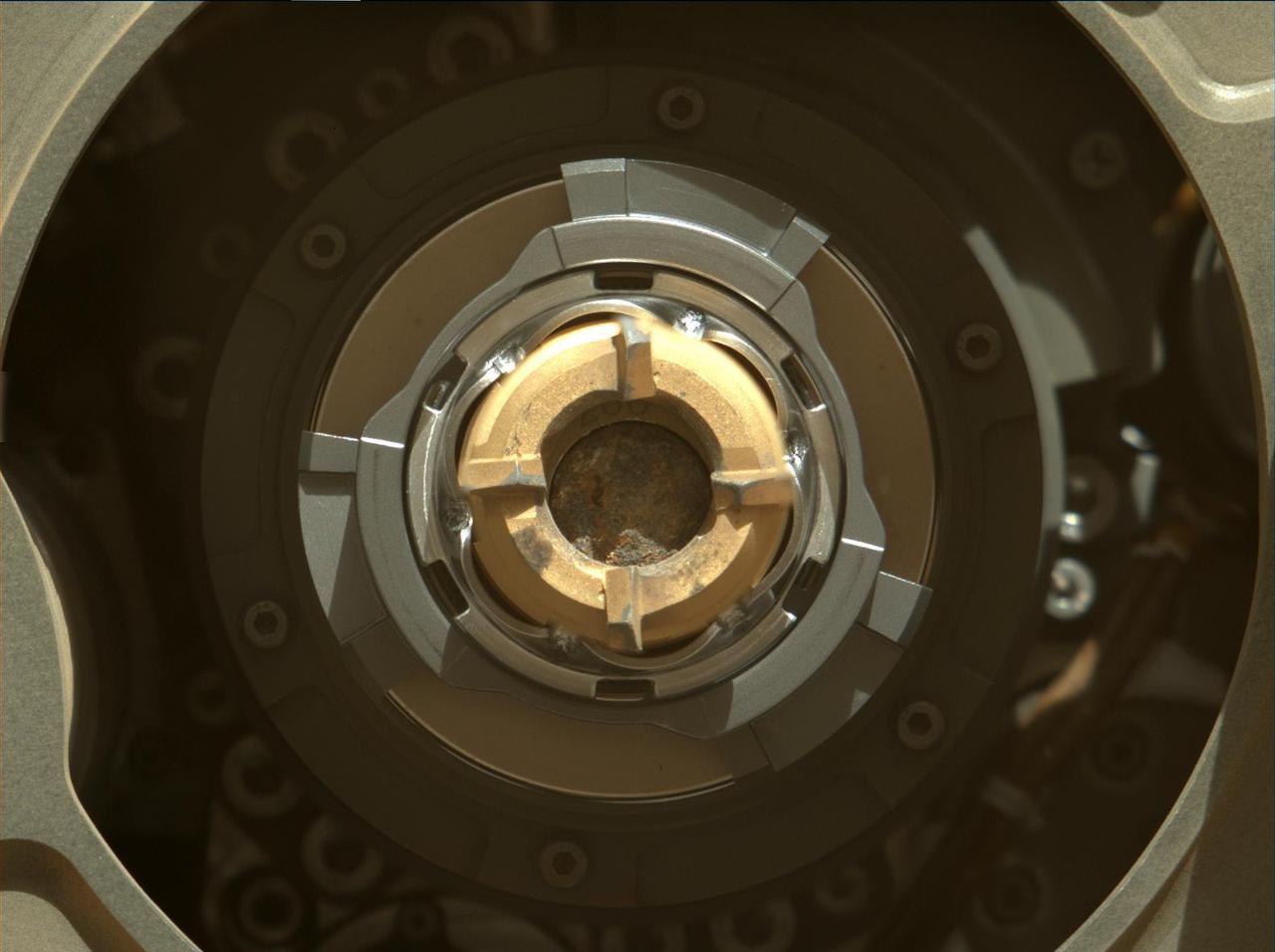
This Mastcam-Z image shows a sample of Mars rock inside the sample tube on Sept. 1, 2021 (the 190th sol, or Martian day, of the mission), shortly after the coring operation. The image was taken after coring concluded but prior to an operation that vibrates the drill bit and tube to clear the tube's lip of any residual material. The bronze-colored outer-ring is the coring bit. The lighter-colored inner-ring is the open end of the sample tube, and inside is a rock core sample slightly thicker than a pencil. A portion of the tube's serial number – 266 – can be seen on the top side of tube's wall. Arizona State University in Tempe leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24804
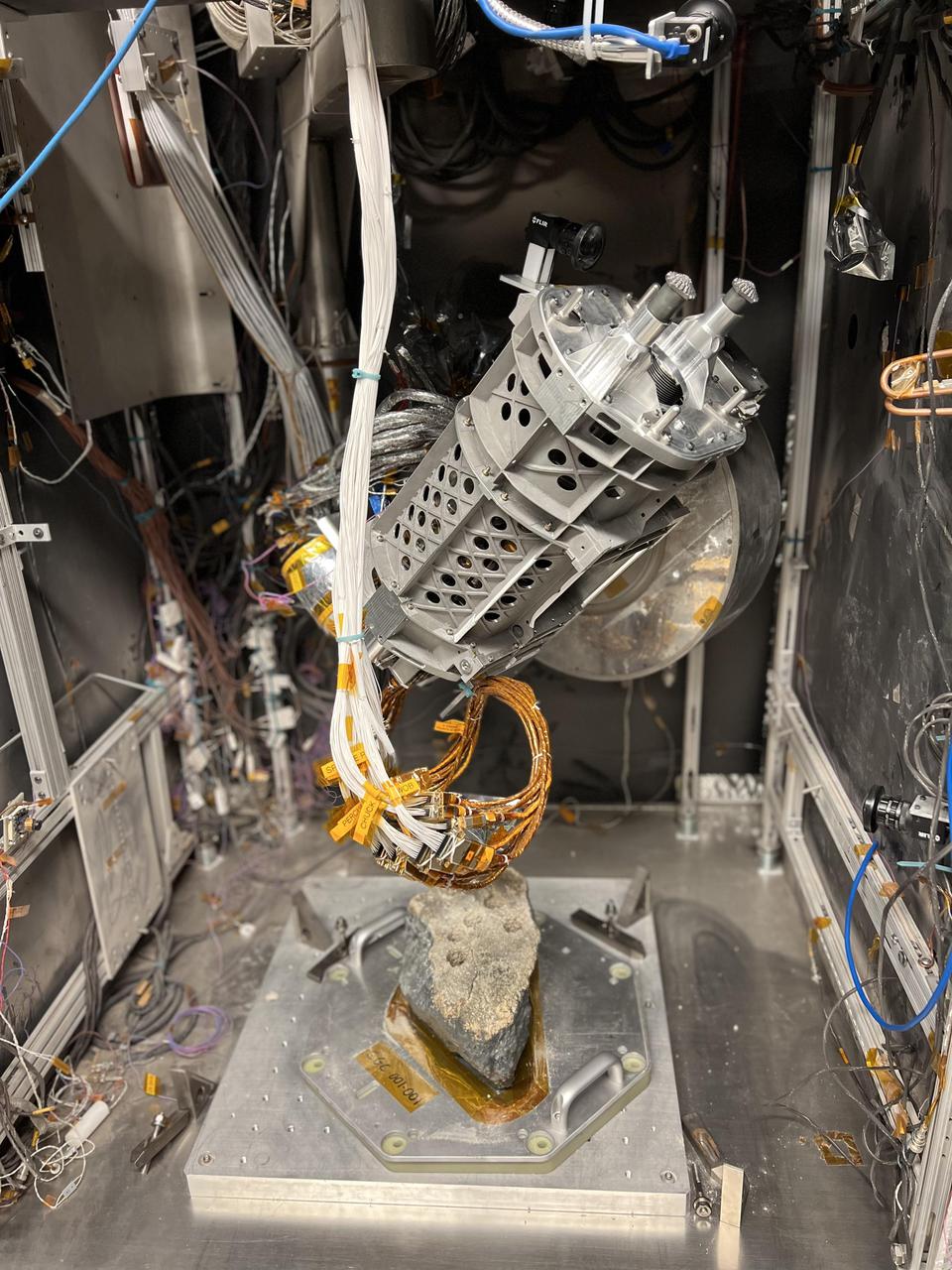

This drill is a duplicate of the one aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. It was used in a test campaign at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California to learn how crumbly rocks respond to the drill. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25050
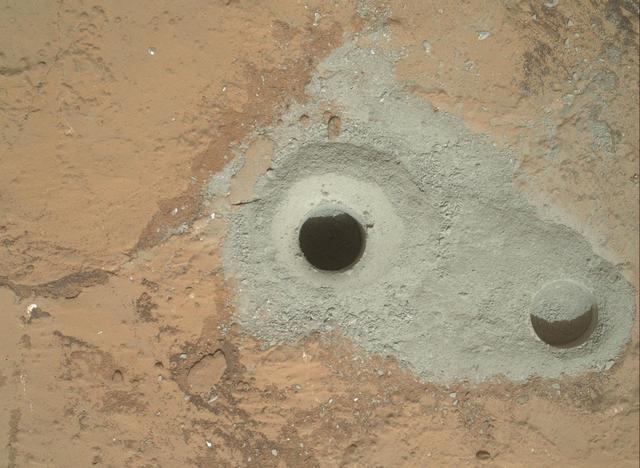

At the center of this image from NASA Curiosity rover is the hole in a rock called John Klein where the rover conducted its first sample drilling on Mars.

This wide view of the John Klein location selected for the first rock drilling by NASA Mars rover Curiosity is a mosaic taken by Curiosity right Mast Camera Mastcam.
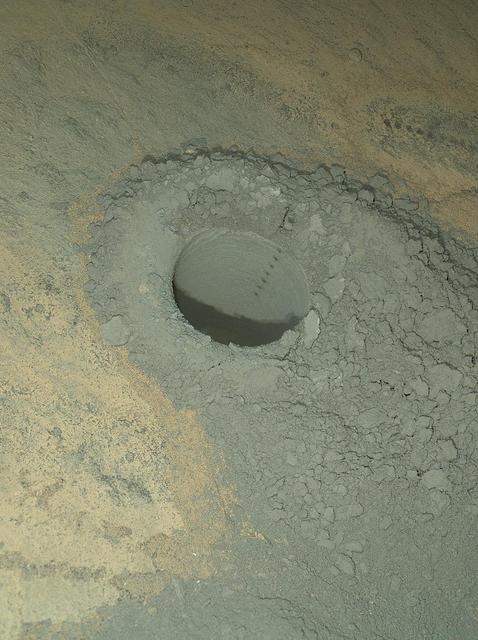

NASA Curiosity Mars rover provided this nighttime view of a hole produced by the rover drill and, inside the hole, a line of scars produced by the rover rock-zapping laser.
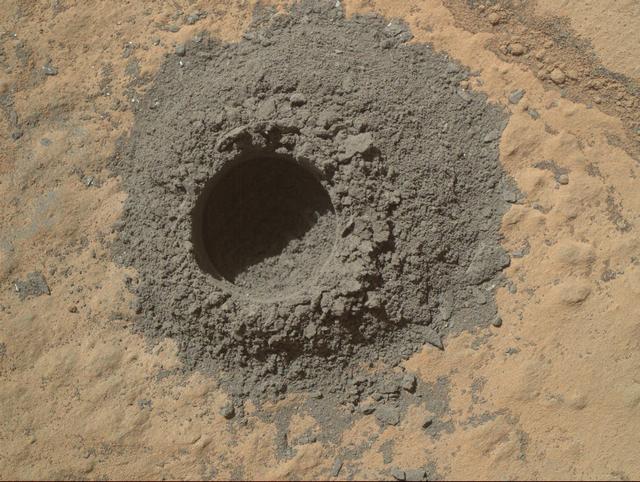

NASA Curiosity Mars rover completed a shallow mini drill test April 29, 2014, in preparation for full-depth drilling at a rock target called Windjana. The hole results from the test is 0.63 inch across and about 0.8 inch deep.

In this illustration, NASA's Mars 2020 rover uses its drill to core a rock sample on Mars. Scheduled to launch in July 2020, the Mars 2020 rover represents the first leg of humanity's first round trip to another planet. The rover will collect and store rock and soil samples on the planet's surface that future missions will retrieve and return to Earth. NASA and the European Space Agency are solidifying concepts for a Mars sample return mission. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23491
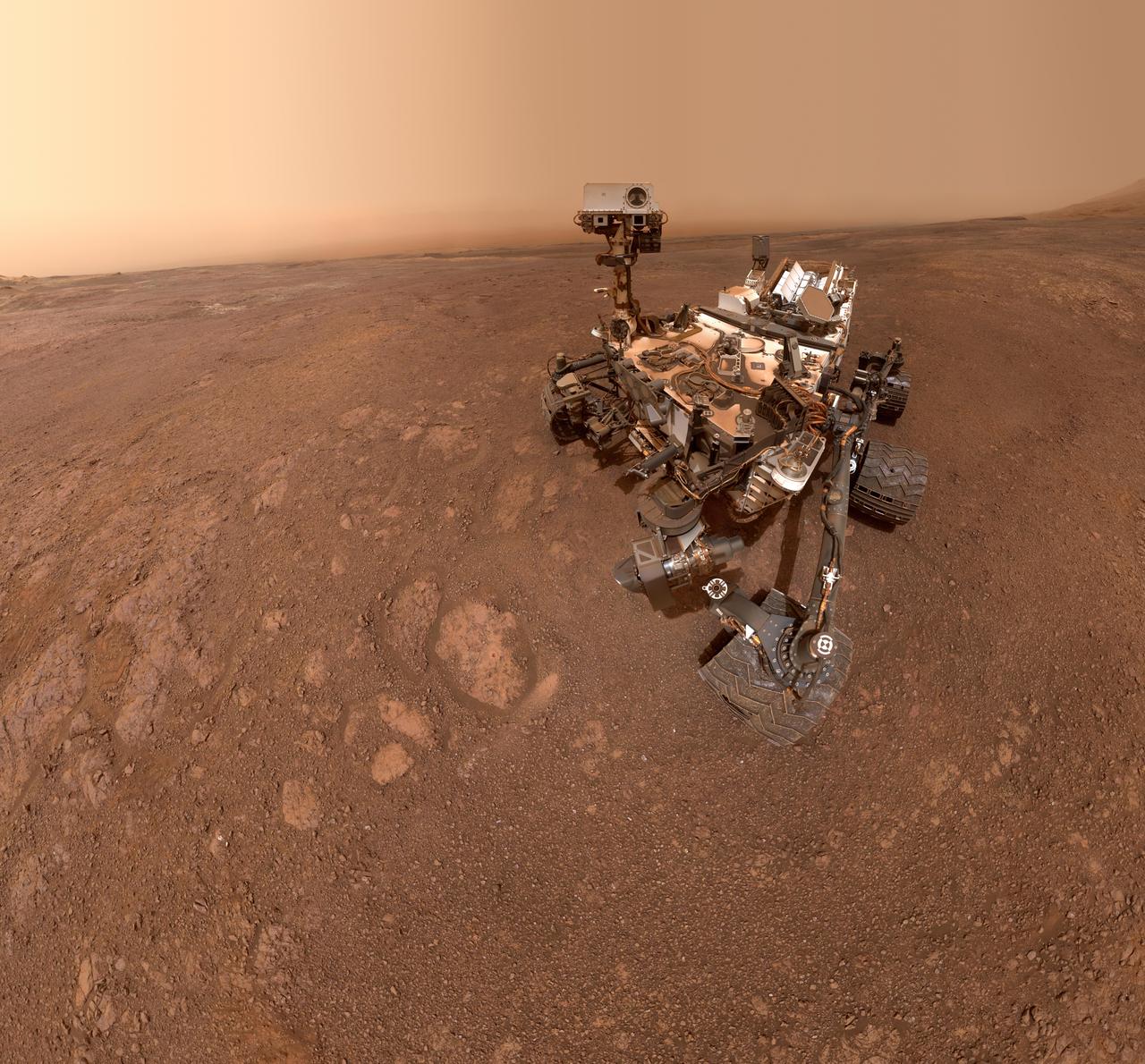

A selfie taken by NASA's Curiosity Mars rover on Sol 2291 (January 15) at the "Rock Hall" drill site, located on Vera Rubin Ridge. This was Curiosity's 19th drill site. The drill hole is visible to the rover's lower-left; the entire scene is slightly dustier than usual due to a regional dust storm affecting the area. The selfie is composed of 57 individual images taken by the rover's Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI), a camera on the end of the rover's robotic arm. The images are then stitched together into a panorama. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22960
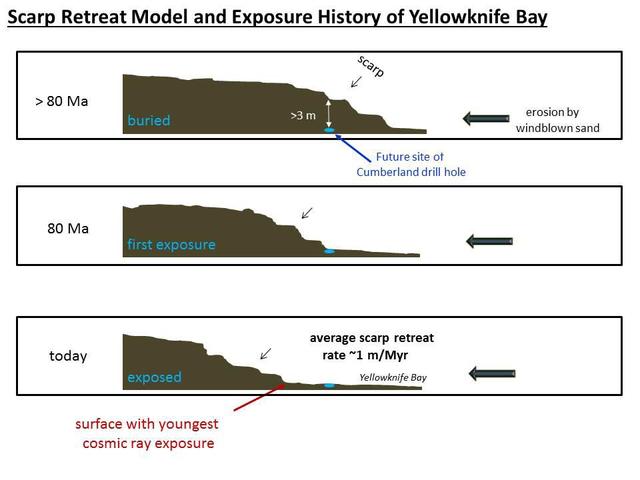
NASA Curiosity Mars rover has made measurements indicating that the Cumberland rock target the rover drilled in May 2013 has been exposed at the surface for about 80 million years.

This frame from an animation of NASA Curiosity rover shows the complicated suite of operations involved in conducting the rover first rock sample drilling on Mars and transferring the sample to the rover scoop for inspection.
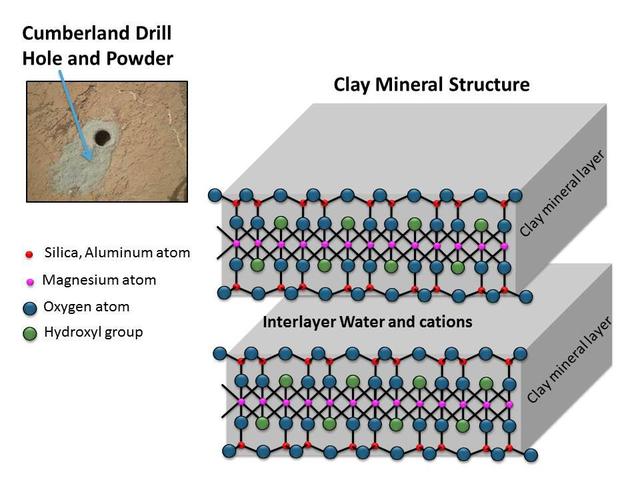
This schematic shows the atomic structure of the smallest units that make up the layers and interlayer region of clay minerals. This structure is similar to the clay mineral in drilled rock powder collected by NASA Curiosity Mars rover.
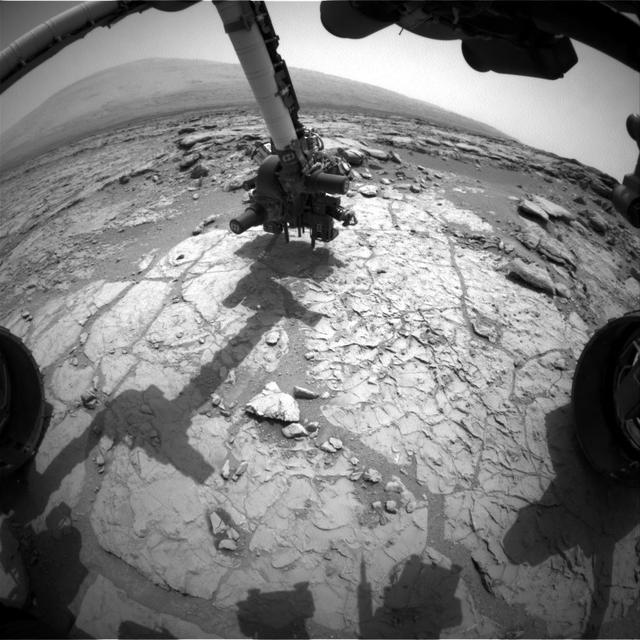

The percussion drill in the turret of tools at the end of the robotic arm of NASA Mars rover Curiosity has been positioned in contact with the rock surface in this image from the rover front Hazard-Avoidance Camera Hazcam.
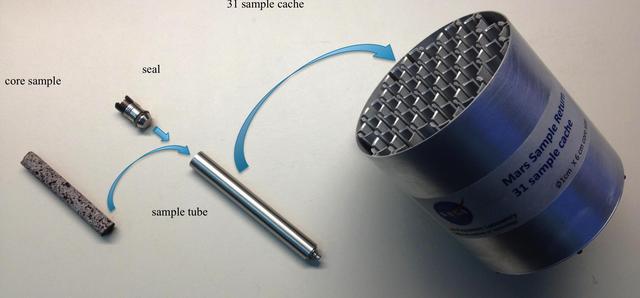
This picture shows one prototype for hardware to cache samples of cores drilled from Martian rocks for possible future return to Earth; a major objective for NASA Mars 2020 rover.
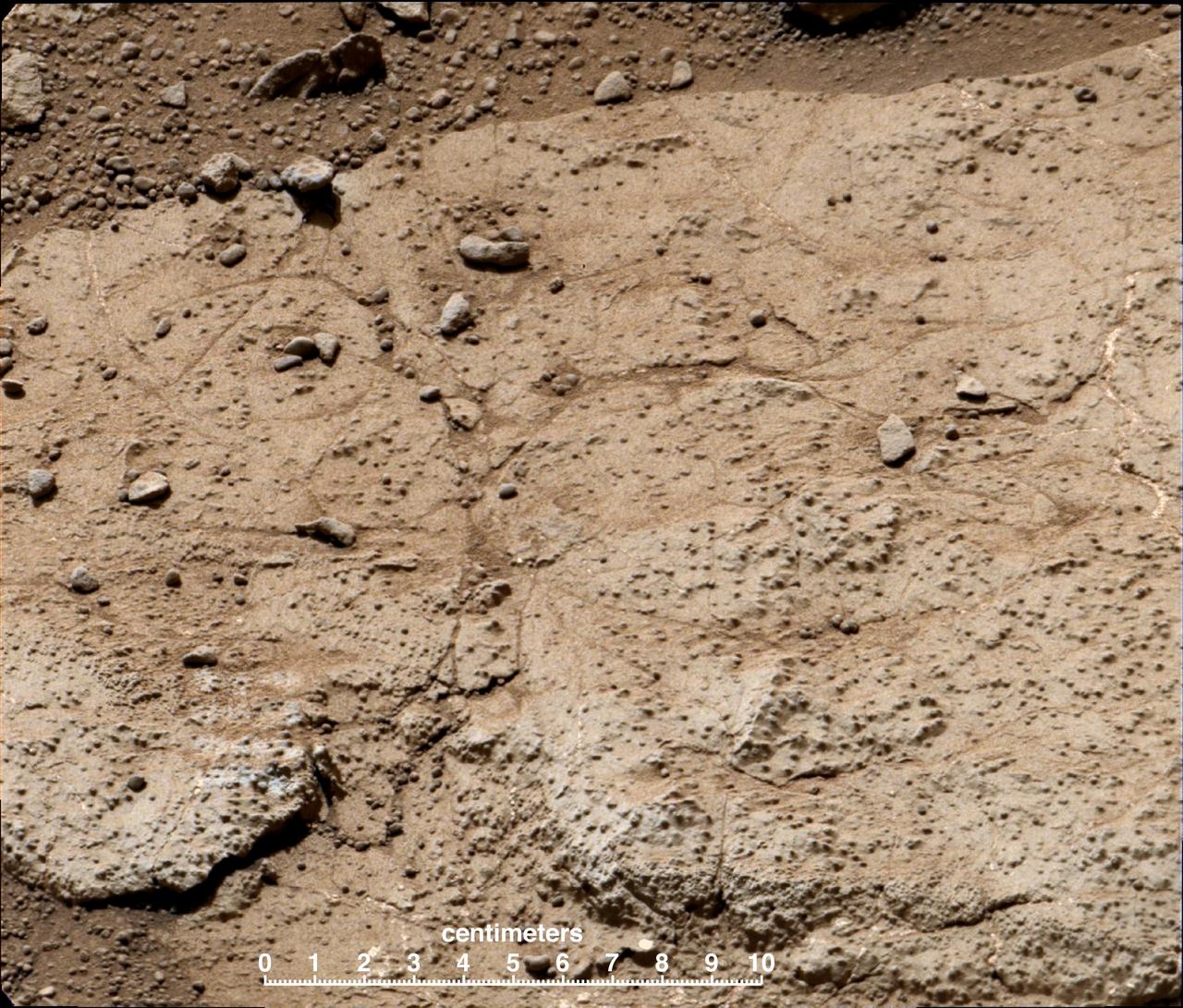

Cumberland has been selected as the second target for drilling by NASA Mars rover Curiosity. The rover has the capability to collect powdered material from inside the target rock and analyze that powder with laboratory instruments.
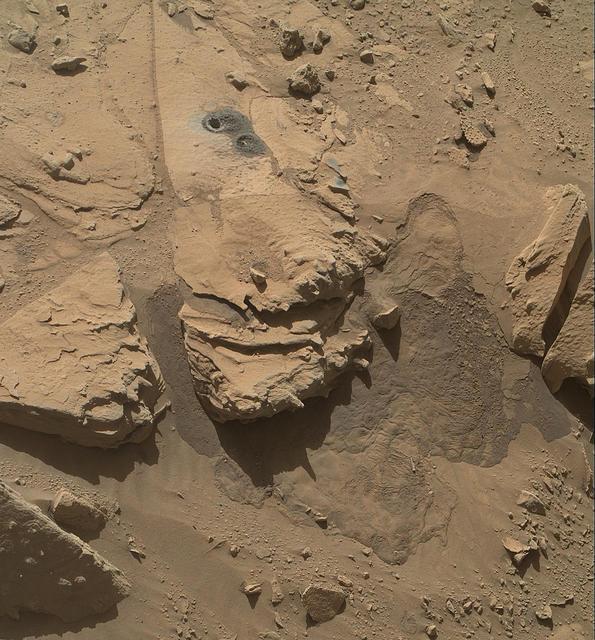

This May 12, 2014, view from NASA Curiosity Mars Rover shows the rock target Windjana and its immediate surroundings after inspection of the site by the rover by drilling and other activities.

This set of images shows the results from the rock abrasion tool from NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity left and the drill from NASA Curiosity rover right.
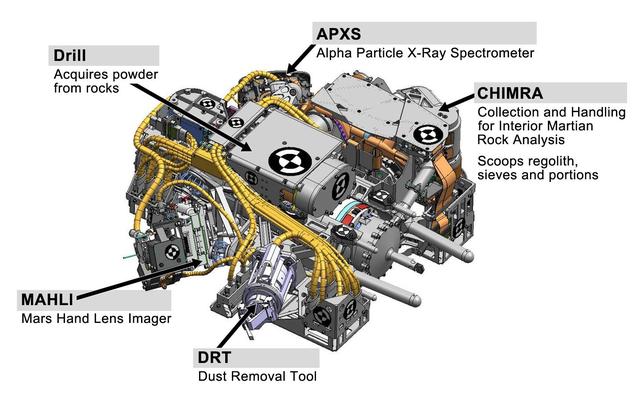
This engineering drawing shows the five devices that make up the turret at the end of the arm on NASA Curiosity rover. These include: the drill for acquiring powdered samples from interiors of rocks.
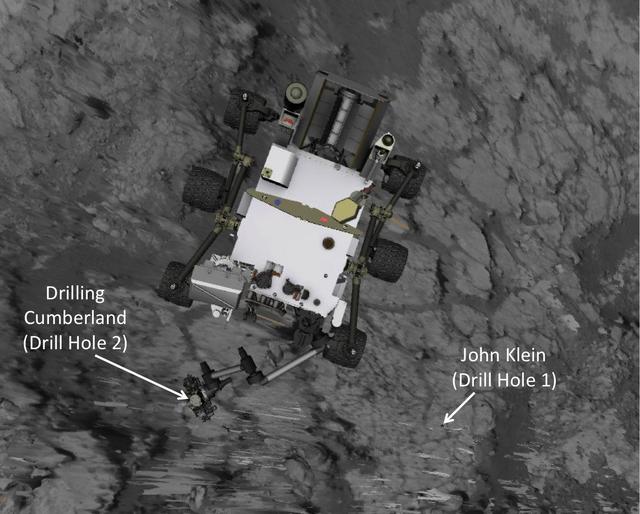

This image produced from software used for planning drives of NASA Mars rover Curiosity depicts the location and size of the rover when it was driven into position for drilling into rock target Cumberland.
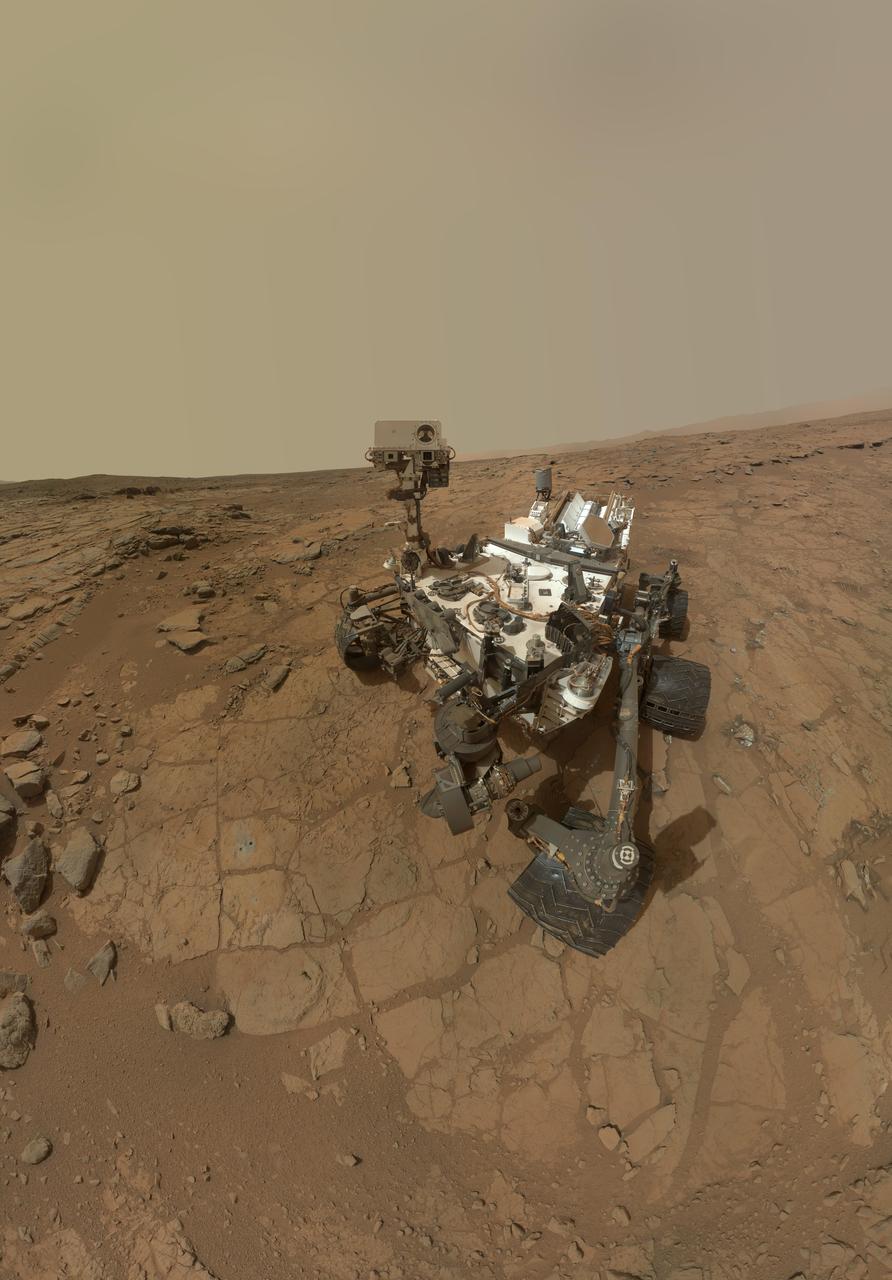

This self-portrait of NASA Mars rover Curiosity combines dozens of exposures to show gray-powder and two holes where Curiosity used its drill on the rock target John Klein.
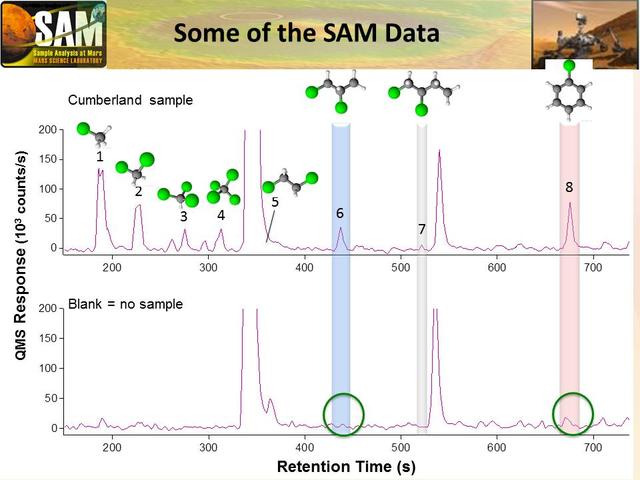
Data graphed here are examples from the Sample Analysis at Mars SAM laboratory detection of Martian organics in a sample of powder that the drill on NASA Curiosity Mars rover collected from a rock target called Cumberland.

The Chemistry and Camera ChemCam instrument on NASA Mars rover Curiosity was used to check the composition of gray tailings from the hole in rock target Cumberland that the rover drilled on May 19, 2013.
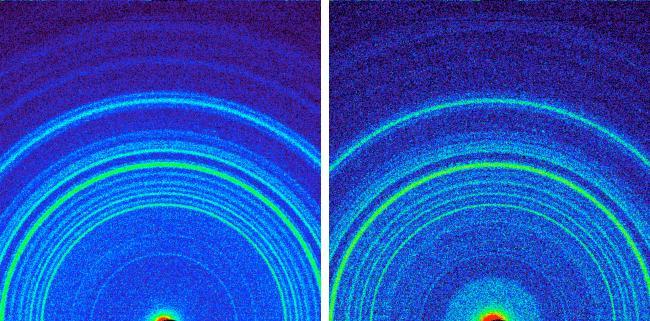
These images, made from data obtained by Curiosity CheMin, show the patterns obtained from a drift of windblown dust and sand called Rocknest and from a powdered rock sample drilled from the John Klein bedrock.
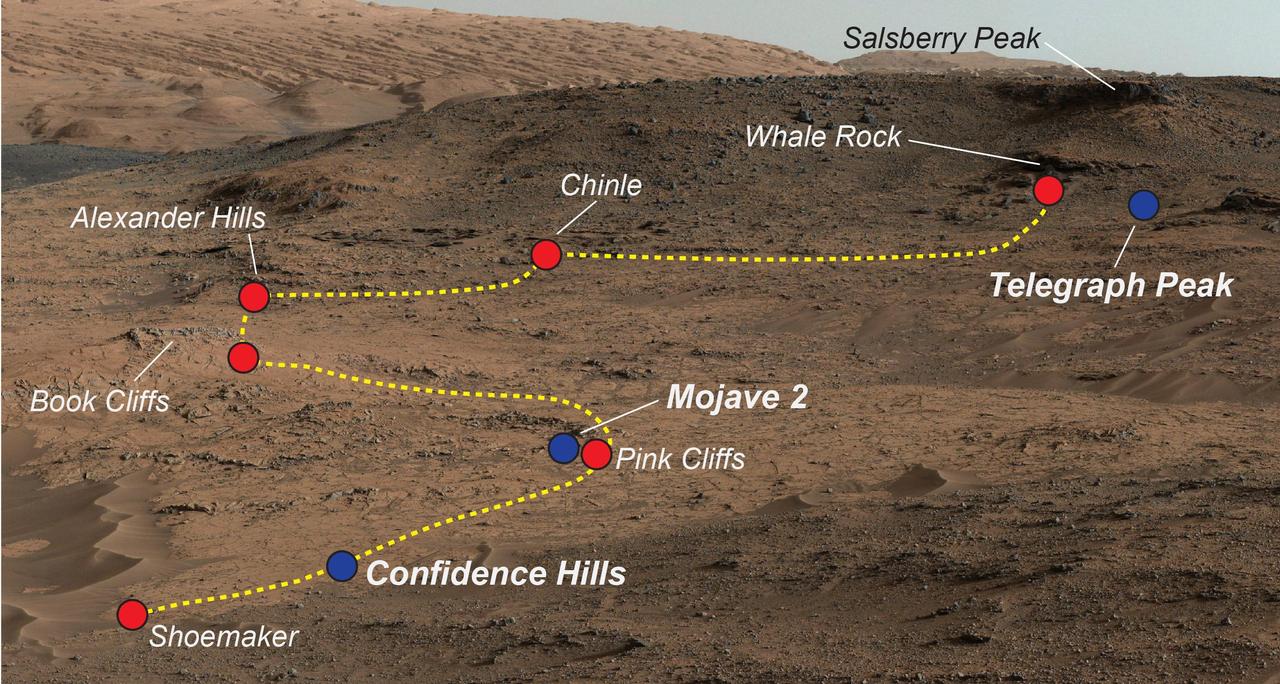
NASA's Curiosity Mars rover examined a mudstone outcrop area called "Pahrump Hills" on lower Mount Sharp, in 2014 and 2015. This view shows locations of some targets the rover studied there. The blue dots indicate where drilled samples of powdered rock were collected for analysis. The rover drilled a sample of rock powder at "Confidence Hills" in September 2014 and analyzed it with internal laboratory instruments. Then the mission conducted a walkabout survey up the slope, along the route indicated in yellow, stopping for close inspection at the red-dot locations. Observations from the walkabout were used to choose where to take additional drilled samples for analysis during a second pass up the slope. The "Mojave 2" sample was collected in January 2015 and the "Telegraph Peak" one in February 2015. This view of the outcrop and other portions of Mount Sharp beyond is a mosaic of images taken by the rover's Mast Camera (Mastcam) in September 2014. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21709
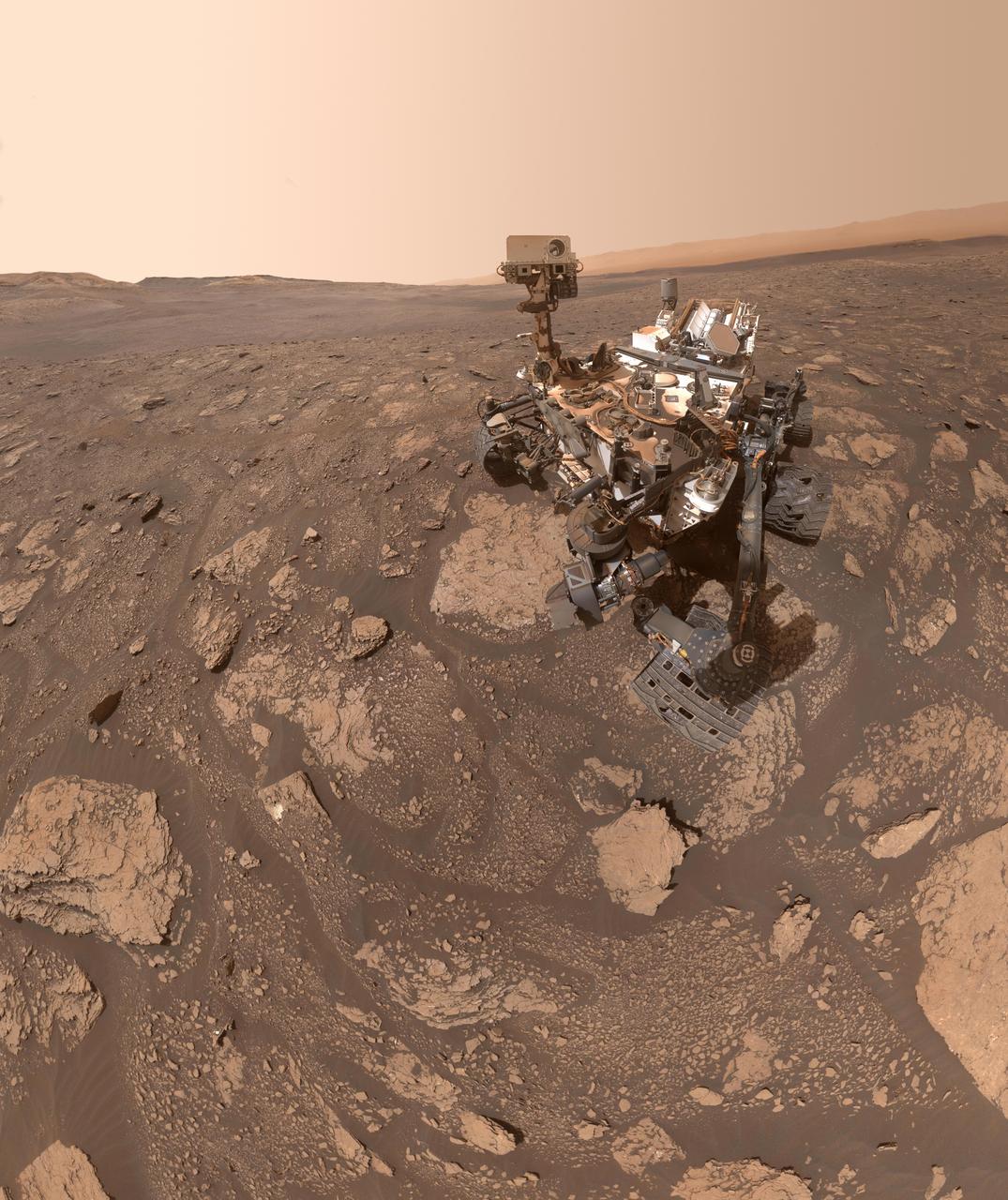

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover took this selfie at a location nicknamed "Mary Anning" after a 19th century English paleontologist. Curiosity snagged three samples of drilled rock at this site on its way out of the Glen Torridon region, which scientists believe was a site where ancient conditions would have been favorable to supporting life, if it ever was present. Curiosity took the selfie using a camera called the Mars Hand Lens Imager located on the end of its robotic arm (videos explaining how Curiosity's selfies are taken can be found here). A close-up detail from within the selfie shows the three holes that a rock drill, also found on the end of Curiosity's arm, added to the surface. The three drill holes are named "Mary Anning," "Mary Anning 3" and "Groken," the last name coming from a site of geological interest in the Scottish countryside. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24173
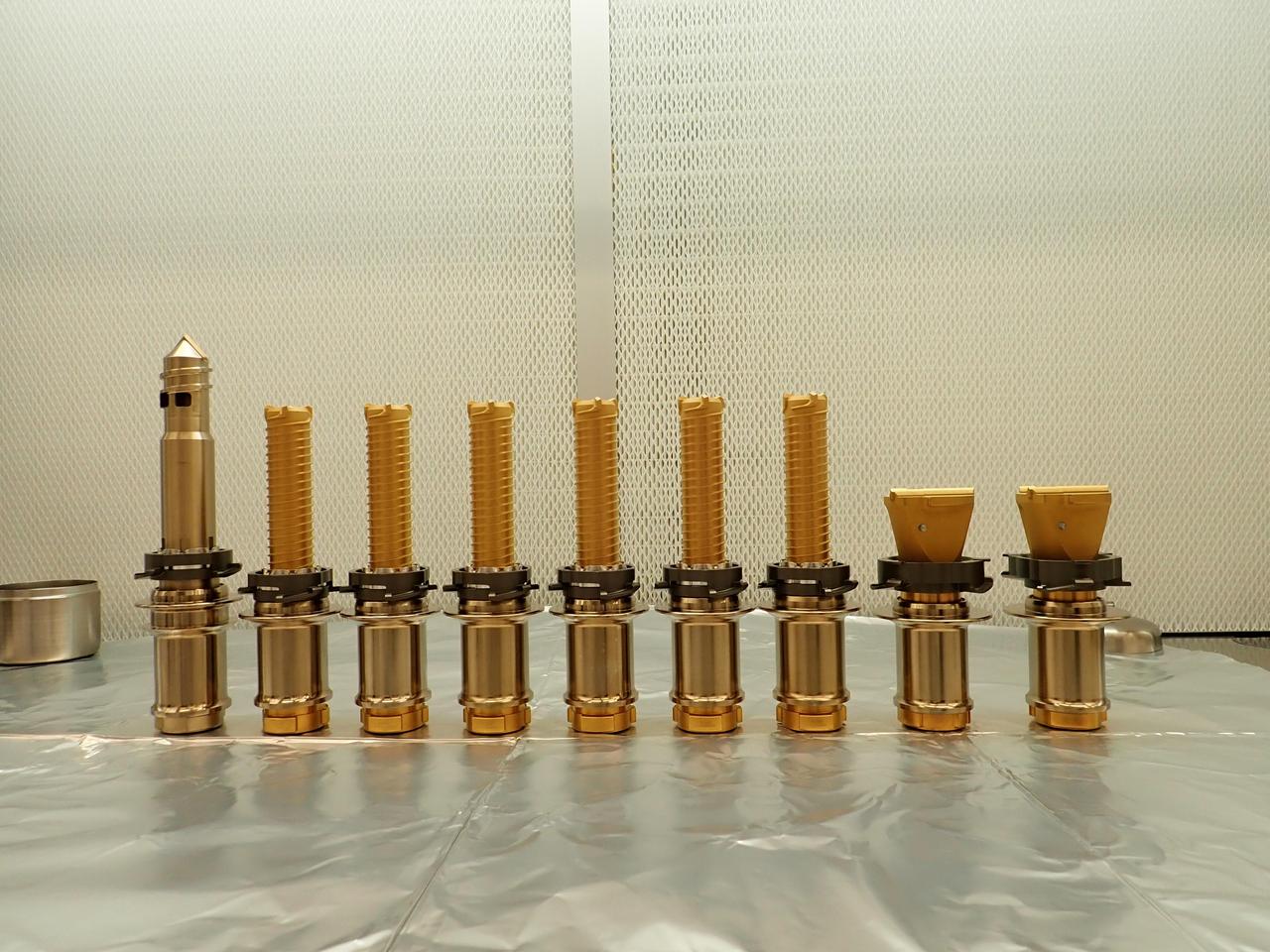

The drill bits used by NASA's Perseverance Mars rover are seen before being installed prior to launch. The regolith bit is on the left, followed by six bits used for drilling rock cores. On the right are two abrasion bits that are used to remove the dust-covered outer layer of a rock so that the rover can take accurate data of its composition. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25590
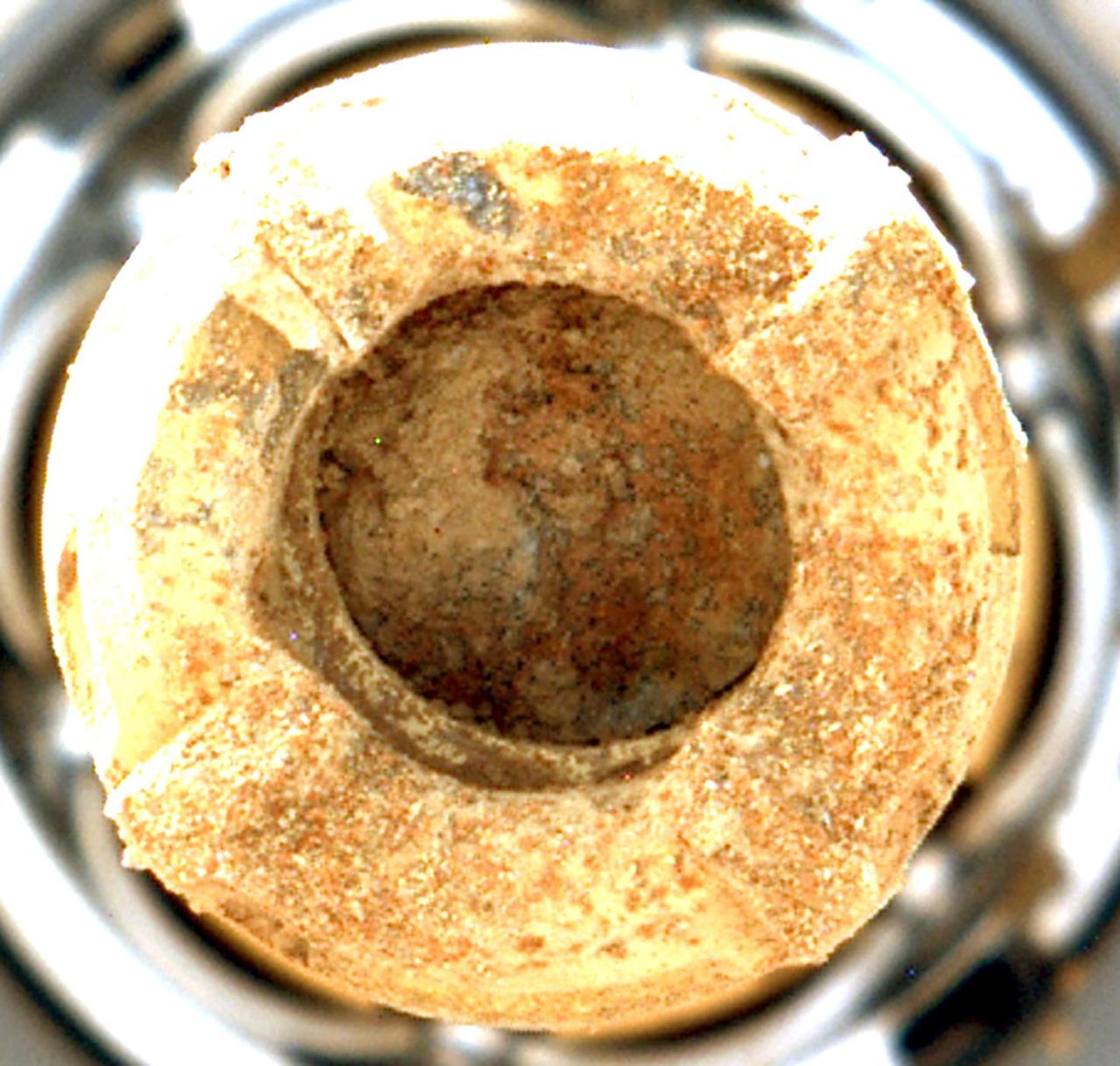

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z instrument to capture this view of the "Cheyava Falls" rock sample within the rover's drill bit on July 21, 2024, the 1,215th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Markings akin to leopard spots can be seen in the rock – fascinating traits that may bear on the question of whether the Red Planet was home to microscopic life in the distant past. The spots seen in the rock are small, irregularly shaped light patches surrounded by a thin rim of dark minerals. These spots indicate chemical conditions during formation or alteration of this rock billions of years ago that could have provided energy for microbial life, if it was ever present at this location on Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26370
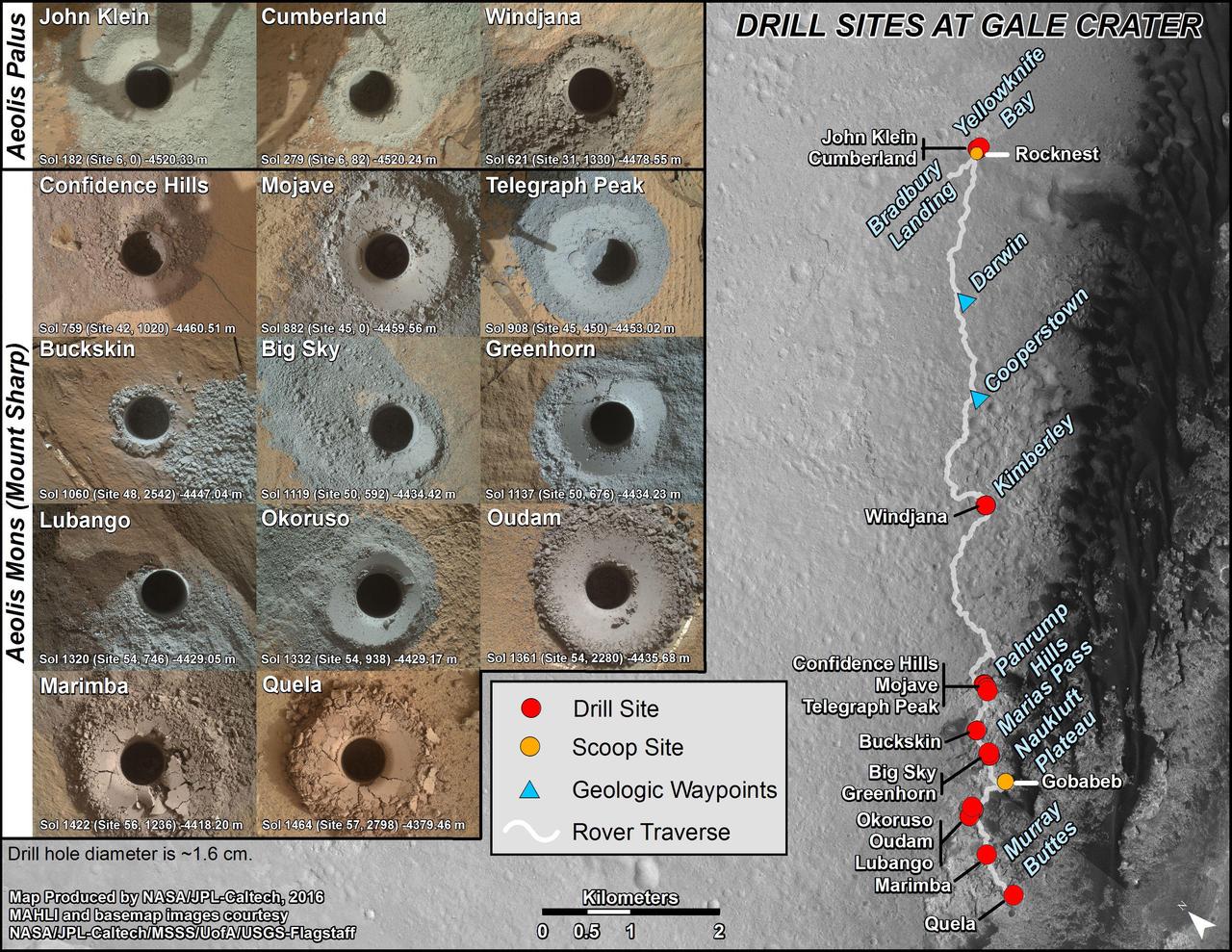
This graphic maps locations of the sites where NASA's Curiosity Mars rover collected its first 18 rock or soil samples for analysis by laboratory instruments inside the vehicle. It also presents images of the drilled holes where 14 rock-powder samples were acquired. Curiosity scooped two soil samples at each of the other two sites: Rocknest and Gobabeb. The diameter of each drill hole is about 0.6 inch (1.6 centimeters), slightly smaller than a U.S. dime. The images used here are raw color, as recorded by the rover's Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera. Notice the differences in color of the material at different drilling sites. For the map, north is toward upper left corner. The scale bar represents 2 kilometers (1.2 miles). The base map is from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The latest sample site included is "Quela,"where Curiosity drilled into bedrock of the Murray formation on Sept. 18, 2016, during the 1,464th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Curiosity landed in August 2012 on the plain (named Aeolis Palus) near Mount Sharp (or Aeolis Mons). More drilling samples collected by MSL are available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20845
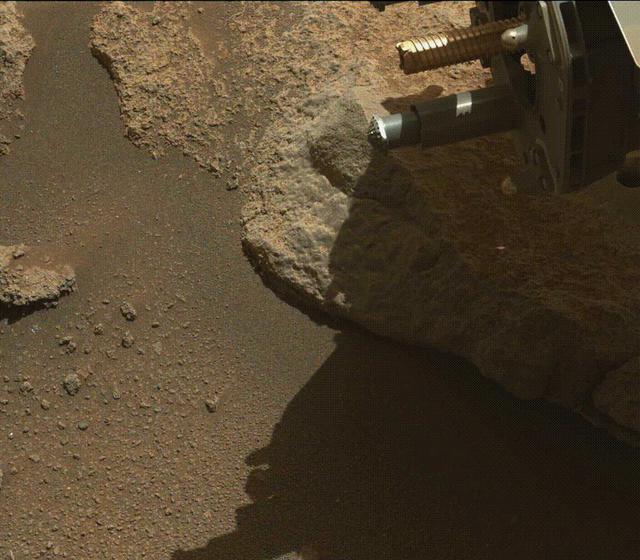

A portion of a cored-rock sample is ejected from the rotary percussive drill on NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. The imagery was collected by the rover's Mastcam-Z instrument on Jan. 15, 2022, the 322nd Martian day, or sol, of the mission, during an experiment that oriented the drill and sample tube (unseen here) around 9 degrees below horizontal and then rotated and extended the drill's spindle. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25072

These 26 holes represent each of the rock samples NASA's Curiosity Mars rover has collected as of early July 2020. A map in the upper left shows where the holes were drilled along the rover's route, along with where it scooped six samples of soil. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23977
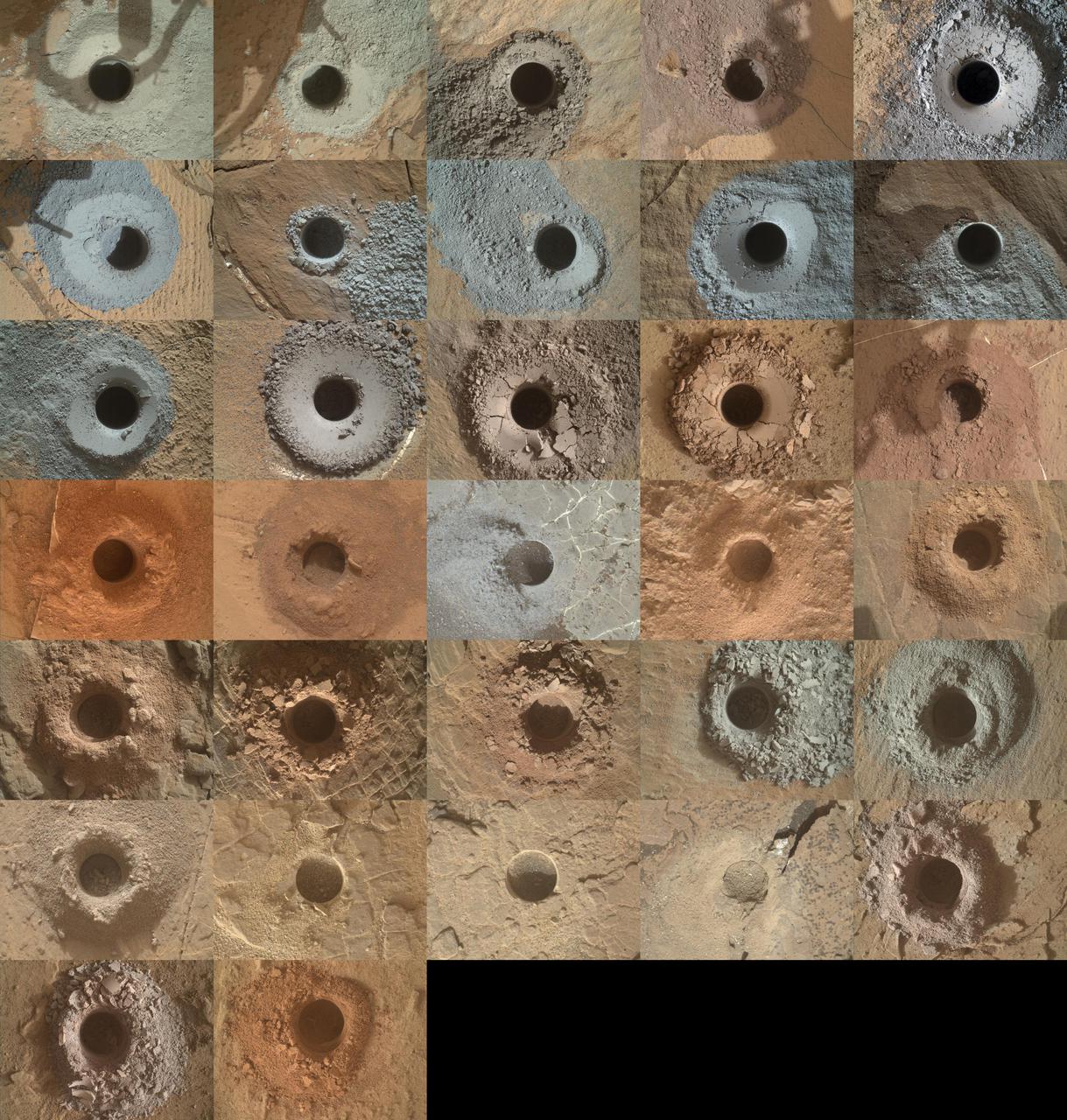

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover has used the drill on its robotic arm to take 32 rock samples to date. The Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI), a camera on the end of the robotic arm, provided the images in this mosaic. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24764

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover conducted a test on Oct. 17, 2017, as part of the rover team's development of a new way to use the rover's drill. This image from Curiosity's front Hazard Avoidance Camera (Hazcam) shows the drill's bit touching the ground during an assessment of measurements by a sensor on the rover's robotic arm. Curiosity used its drill to acquire sample material from Martian rocks 15 times from 2013 to 2016. In December 2016, the drill's feed mechanism stopped working reliably. During the test shown in this image, the rover touched the drill bit to the ground for the first time in 10 months. The image has been adjusted to brighten shaded areas so that the bit is more evident. The date was the 1,848th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars In drill use prior to December 2016, two contact posts -- the stabilizers on either side of the bit -- were placed on the target rock while the bit was in a withdrawn position. Then the motorized feed mechanism within the drill extended the bit forward, and the bit's rotation and percussion actions penetrated the rock. A promising alternative now under development and testing -- called feed-extended drilling -- uses motion of the robotic arm to directly advance the extended bit into a rock. In this image, the bit is touching the ground but the stabilizers are not. In the Sol 1848 activity, Curiosity pressed the drill bit downward, and then applied smaller sideways forces while taking measurements with a force/torque sensor on the arm. The objective was to gain understanding about how readings from the sensor can be used during drilling to adjust for any sideways pressure that might risk the bit becoming stuck in a rock. While rover-team engineers are working on an alternative drilling method, the mission continues to examine sites on Mount Sharp, Mars, with other tools. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22063

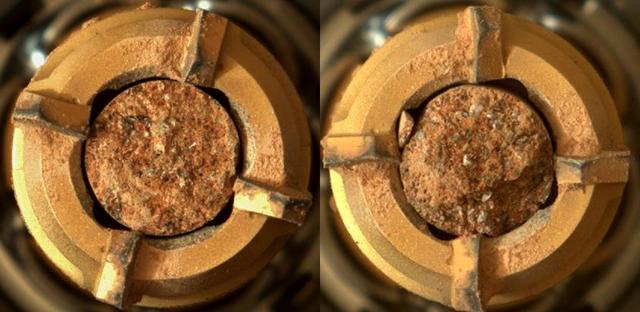
These abrasion targets, nicknamed "Guilliamus" (left) and "Bellegarde" (right), are from the first and second rocks drilled by NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. These images were taken by the rover's Mastcam-Z camera system. The rover abrades rocks using a tool on its robotic arm before drilling them in order to clear away dust and weathering rinds, allowing other instruments to study the rocks and determine if scientists want to grab a sample of them. Arizona State University in Tempe leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24769
This image taken by the Mastcam-Z camera aboard NASA's Perseverance rover on Sept. 4, 2021, confirmed that the rover had retained a rock core in the sample tube held in the drill at the end of its robotic arm. After Perseverance drilled the hole called "Montdenier" in the rock nicknamed "Rochette" on Sept. 1 and acquired the rock core, which is slightly thicker than a pencil, the rover vibrated it to clear any material stuck between the coring bit and the sample tube within the bit. The rover then conducted additional imaging to double-check that it retained the rock. This image has been processed to enhance contrast. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24832

This animation depicts NASA Mars rover Curiosity drilling a hole to collect a rock-powder sample at a target site called John
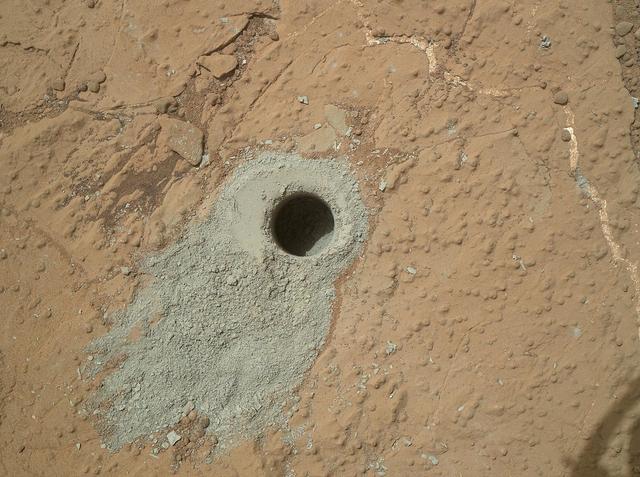

NASA Mars rover Curiosity drilled into this rock target, Cumberland, during the 279th Martian day, or sol, of the rover work on Mars May 19, 2013 and collected a powdered sample of material from the rock interior.
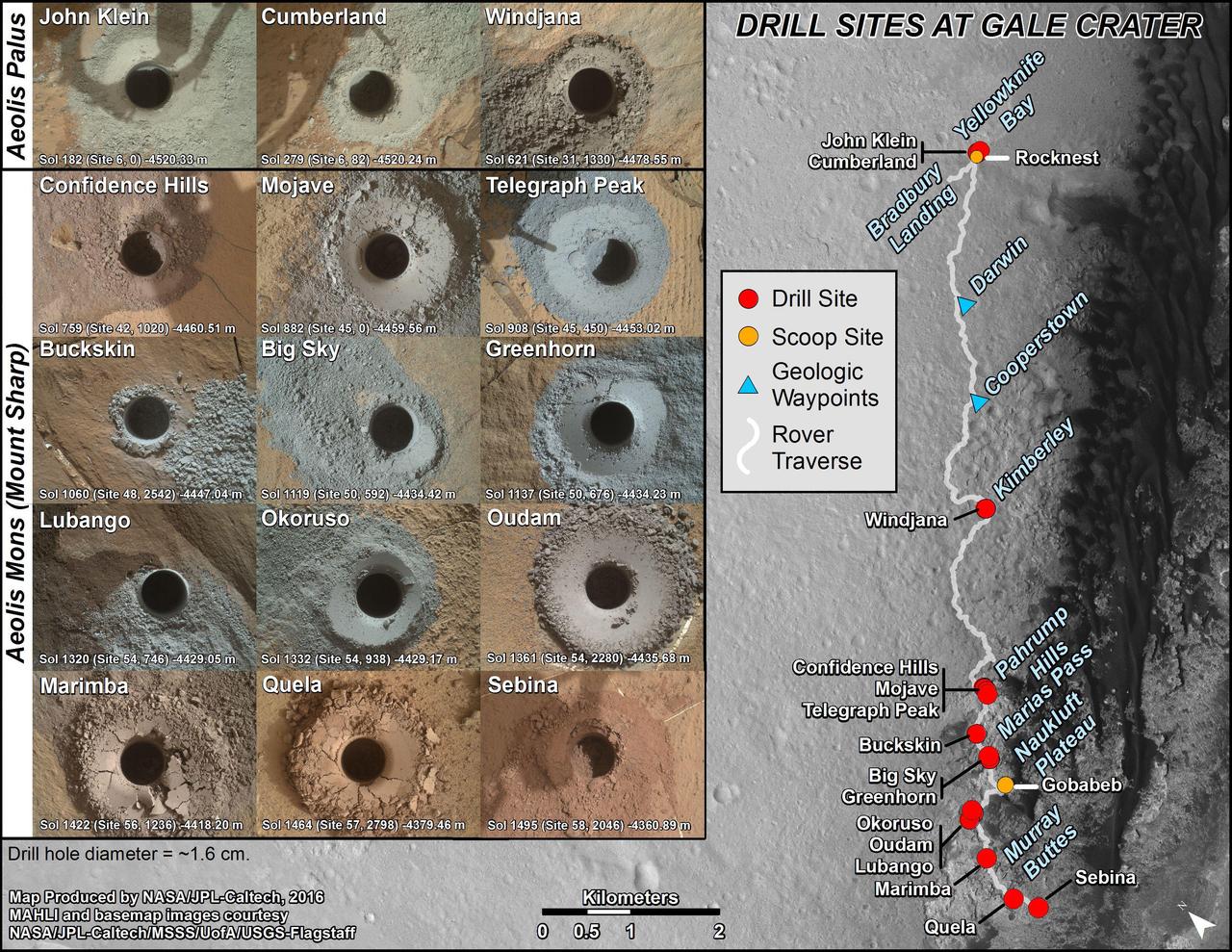
nal Caption Released with Image: This graphic maps locations of the sites where NASA's Curiosity Mars rover collected its first 19 rock or soil samples for analysis by laboratory instruments inside the vehicle. It also presents images of the drilled holes where 15 rock-powder samples were acquired. Curiosity scooped two soil samples at each of the other two sites: Rocknest and Gobabeb. The diameter of each drill hole is about 0.6 inch (1.6 centimeters), slightly smaller than a U.S. dime. The images used here are raw color, as recorded by the rover's Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera. Notice the differences in color of the material at different drilling sites. For the map, north is toward the upper left corner. The scale bar represents 2 kilometers (1.2 miles). The base map is from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The latest sample site included is "Sebina,"where Curiosity drilled into bedrock of the Murray formation on Oct. 20, 2016, during the 1,495th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Curiosity landed in August 2012 on the plain (named Aeolis Palus) near Mount Sharp (or Aeolis Mons). The drilling dates for the first 13 rock samples collected are, by location: "John Klein" on Feb. 8, 2013 (Sol 182); "Cumberland" on May 19, 2013 (Sol 279); "Windjana" on May 5, 2014 (Sol 621); "Confidence Hills" on Sept. 24, 2014 (Sol 759); "Mojave" on Jan. 29, 2015 (Sol 882); "Telegraph Peak" on Feb. 24, 2015 (Sol 908); "Buckskin" on July 30, 2015 (Sol 1060); "Big Sky" on Sept. 29, 2015 (Sol 1119); "Greenhorn" on Oct. 18, 2015 (Sol 1137); "Lubango" on April 23, 2016 (Sol 1320); "Okoruso" on May 5, 2016 (Sol 1332); "Oudam" on June 4, 2016 (Sol 1361); "Quela" on Sept. 18, 2016 (Sol 1464). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21254
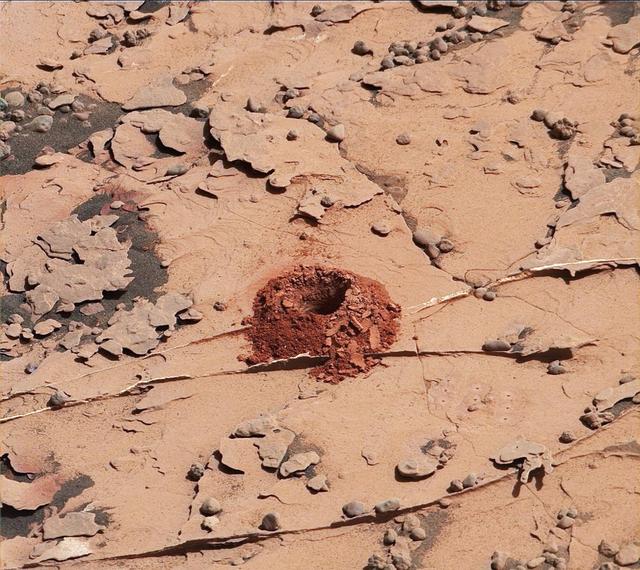

A close-up image of a 2-inch-deep hole produced using a new drilling technique for NASA's Curiosity rover. The hole is about 0.6 inches (1.6 centimeters) in diameter. This image was taken by Curiosity's Mast Camera (Mastcam) on Sol 2057. It has been white balanced and contrast-enhanced. Curiosity drilled this hole in a target called "Duluth" on May 20, 2018. It was the first rock sample captured by the drill since October 2016. A mechanical issue took the drill offline in December 2016. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22326
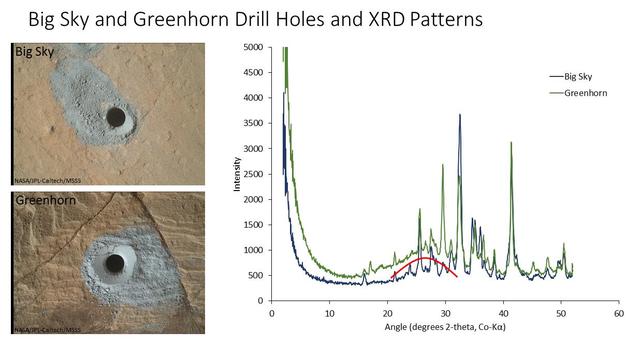
The graph at right presents information from the NASA Curiosity Mars rover's onboard analysis of rock powder drilled from the "Big Sky" and "Greenhorn" target locations, shown at left. X-ray diffraction analysis of the Greenhorn sample inside the rover's Chemistry and Mineralogy (CheMin) instrument revealed an abundance of silica in the form of noncrystalline opal. The broad hump in the background of the X-ray diffraction pattern for Greenhorn, compared to Big Sky, is diagnostic of opal. The image of Big Sky at upper left was taken by the rover's Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera the day the hole was drilled, Sept. 29, 2015, during the mission's 1,119th Martian day, or sol. The Greenhorn hole was drilled, and the MAHLI image at lower left was taken, on Oct. 18, 2015 (Sol 1137). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20272
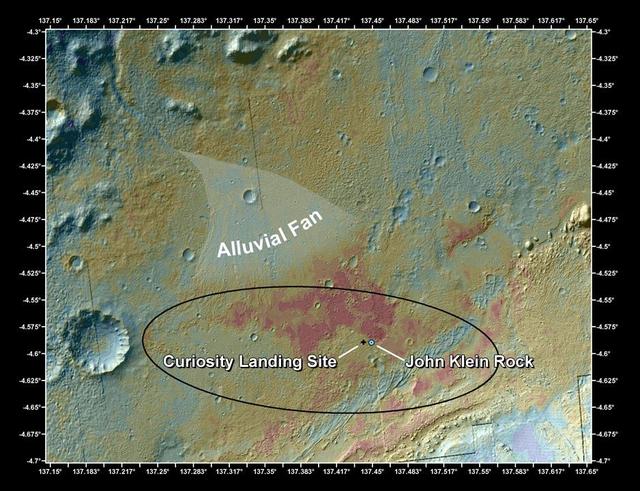
This false-color map shows the area within Gale Crater on Mars, where NASA Curiosity rover landed on Aug. 5, 2012 PDT Aug. 6, 2012 EDT and the location where Curiosity collected its first drilled sample at the John Klein rock.
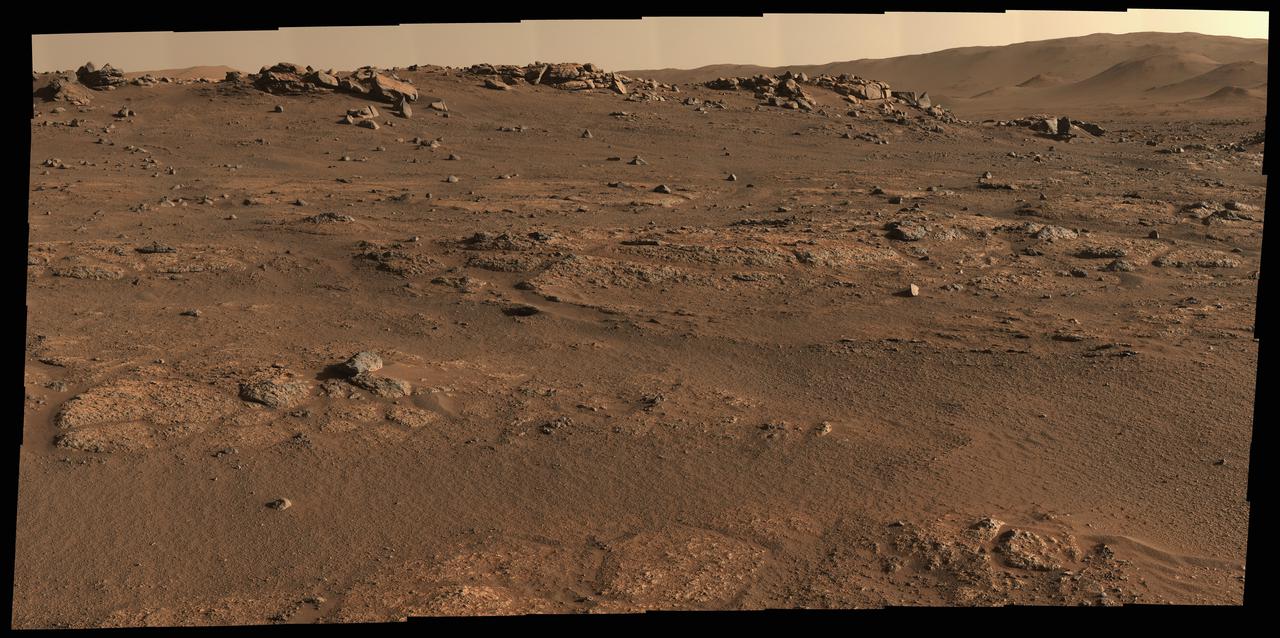

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z camera system to create this panorama of its first drill site. Scientists will be looking for a rock to drill somewhere in this. Perseverance's team has nicknamed this region the "Crater Floor Fractured Rough" unit. The flat, light-colored stones are informally referred to as "paver rocks" and will be the first type from which Perseverance will collect a sample for planned return to Earth by subsequent missions. Small hills to the south of the rover and the sloping inner walls of the Jezero Crater rim fill the distant background of this view. The panorama is stitched together from 70 individual images taken on July 28, 2021, the 155th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This panorama is seen here in natural color. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24765
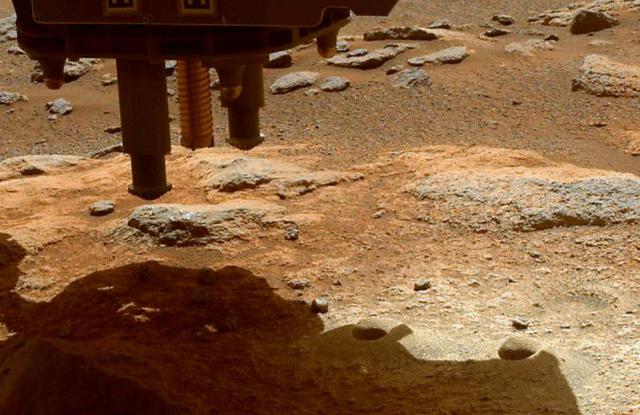

The robotic arm on NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its percussive drill to eject fragments of cored rock from a sample tube on Jan. 15, 2022, the 322nd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. One of the rover's hazard cameras (hazcam) obtained same-day, before-and-after images of the surface below the rover to help better understand the results of this operation. There are two versions of the image: Animation frame 1 shows the ground below Perseverance prior to the use of the rover's percussive drill on Jan. 15. Animation frame 2 shows the same ground later that same day, after the percussive drill was employed. In this second image, at least eight new pieces of rock fragments can be seen. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25070
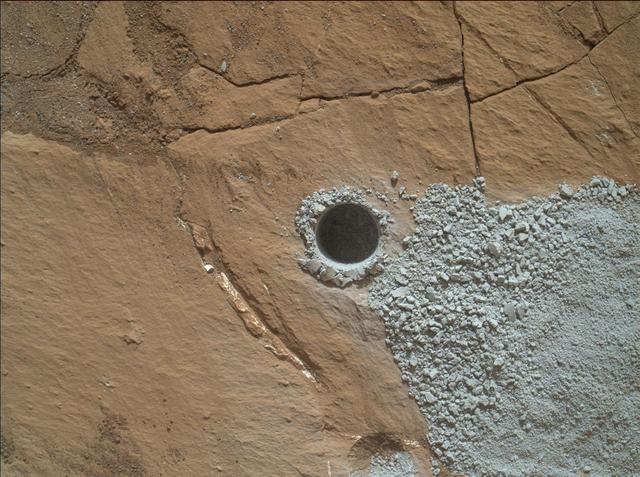

NASA's Curiosity Mars Rover drilled this hole to collect sample material from a rock target called "Buckskin" on July 30, 2015, during the 1060th Martian day, or sol, of the rover's work on Mars. The diameter is slightly smaller than a U.S. dime. Curiosity landed on Mars on Aug. 6, 2012, Universal Time (evening of Aug. 5, PDT). The rover took this image with the Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera, which is mounted on the same robotic arm as the sample-collecting drill. Rock powder from the collected sample was subsequently delivered to a laboratory inside the rover for analysis. The rover's drill did not experience any sign during this sample collection of an intermittent short-circuiting issue that was detected earlier in 2015. The Buckskin target is in an area near "Marias Pass" on lower Mount Sharp where Curiosity had detected unusually high levels of silica and hydrogen. MAHLI was built by Malin Space Science Systems, San Diego. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Science Laboratory Project for the NASA Science Mission Directorate, Washington. JPL designed and built the project's Curiosity rover. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19804
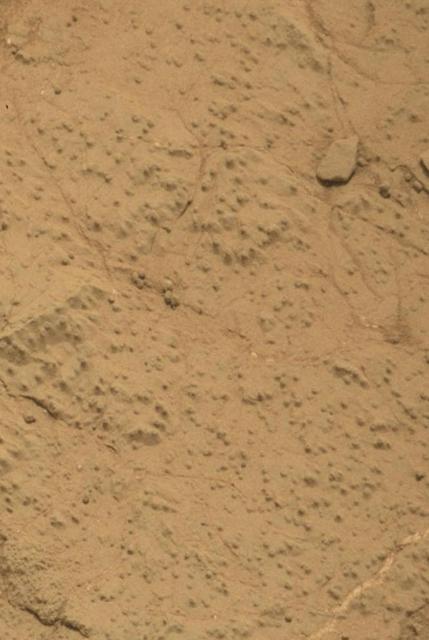

This image from the Mars Hand Lens Imager MAHLI on NASA Mars rover Curiosity shows the rock target Cumberland before and after Curiosity drilled into it to collect a sample for analysis.
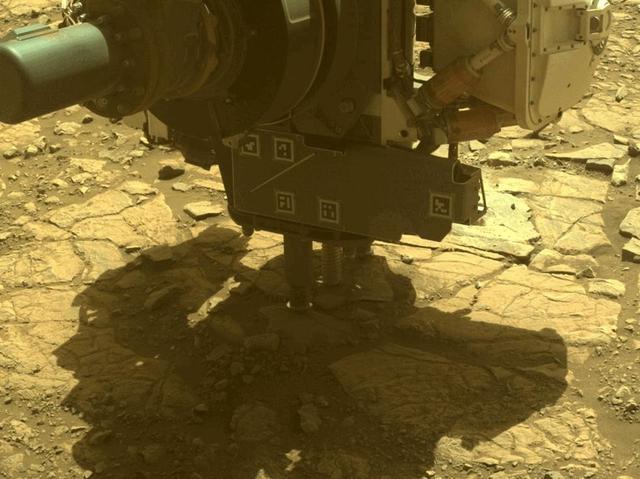

The robotic arm on NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its percussive drill to core and collect the "Main River" rock sample on March 10, 2025, the 1,441st Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The time-lapse movie, taken by one of the rover's hazard cameras, is made up of 35 images taken over the course of 34 minutes. The sample was taken from a rock the rover science team named "Broom Point" at a location near the rim of Jezero Crater called "Witch Hazel Hill." A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program (MEP) portfolio and the agency's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26571

This image taken by the front left hazard camera (hazcam) aboard NASA's Mars Perseverance rover shows the cored-rock sample remaining in the sample tube after the drill bit was extracted from the bit carousel on Jan. 7, 2022. The sample was collected from a rock in the "South Séítah" region of Jezero Crater on Dec. 29, 2021. This image has been processed to enhance contrast. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25067
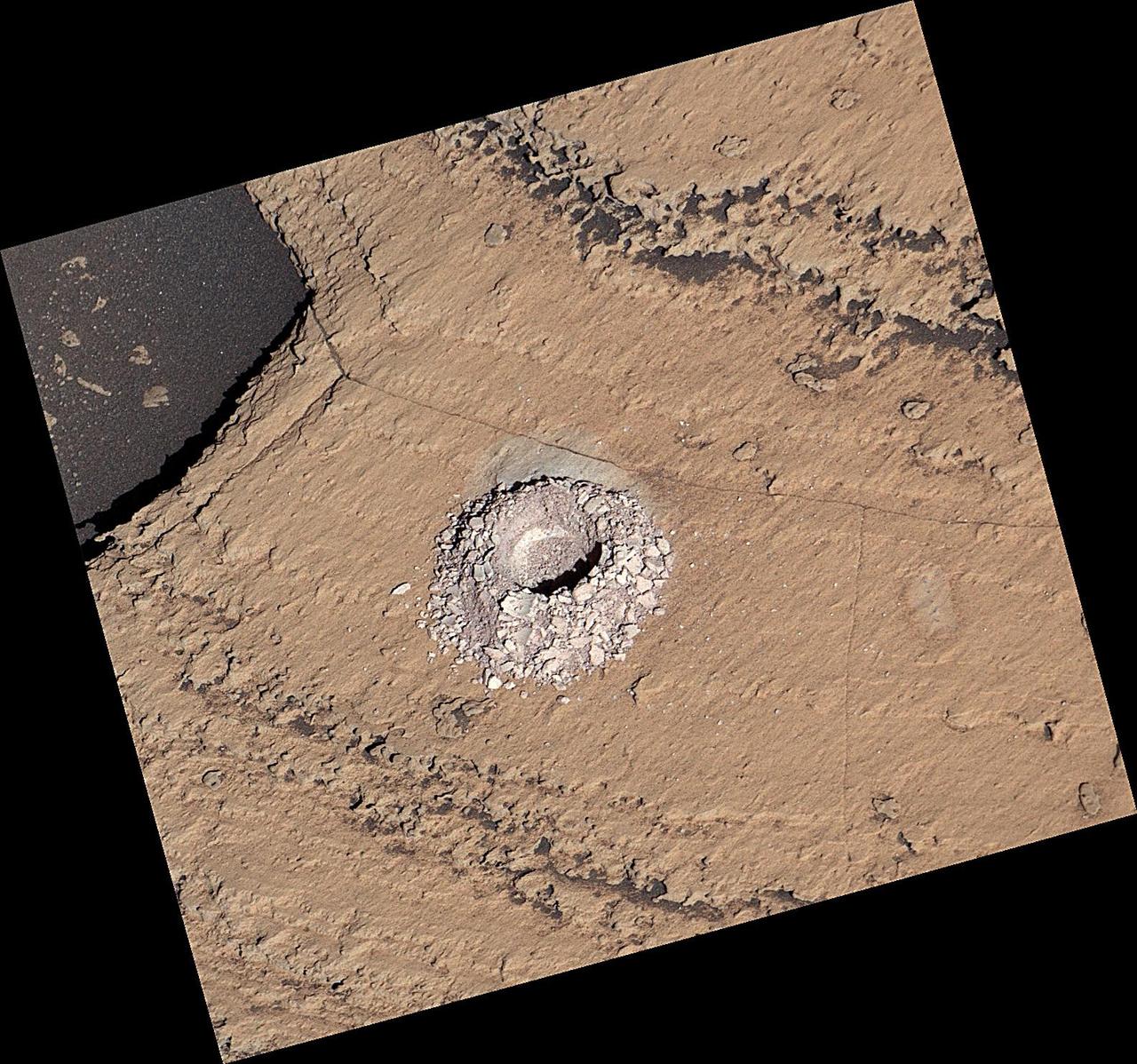

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover used the drill on the end of its robotic arm to collect a sample from a rock nicknamed "Sequoia" on Oct. 17, 2023, the 3,980th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The mission was naming science targets after locations in California's Sierra Nevada mountain range at the time this sample was collected. This image was captured by the rover's Mast Camera, or Mastcam. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26048

This self-portrait of NASA's Curiosity Mars rover shows the vehicle at a drilled sample site called "Okoruso," on the "Naukluft Plateau" of lower Mount Sharp. The scene combines multiple images taken with the rover's Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) on May 11, 2016, during the 1,338th Martian day, or sol, of the rover's work on Mars. In front of the rover is the hole, surrounded by grayish drill cuttings, created by using Curiosity's drill to collect sample rock powder at Okoruo, plus a patch of powder dumped onto the ground after delivery of a portion to the rover's internal Chemistry and Mineralogy (CheMin) laboratory instrument. The rover team compared the rock powder from drilling at Okoruso to material from the nearby "Lubango" drilling site, which is visible behind the rover, just to the left of the mast. The Lubango site was selected within a pale zone, or "halo," beside a fracture in the area's sandstone bedrock. Okoruso is in less-altered bedrock farther from any fractures. Note that the Okoruso drill cuttings appear darker than the Lubango drill cuttings. The Lubango sample was found to be enriched in silica and sulfates, relative to Okoruso. To the left of the rover, in this scene, several broken rocks reveal grayish interiors. Here, Curiosity was driven over the rocks in a fracture-associated halo, so that freshly exposed surfaces could be examined with MAHLI, Mast Camera (Mastcam) and Chemistry and Camera (ChemCam) instruments. An upper portion of Mount Sharp is prominent on the horizon. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20602
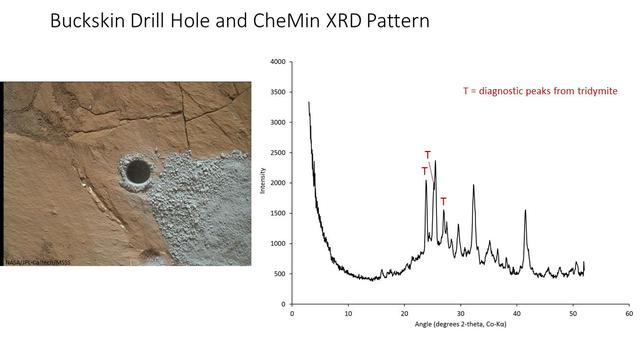
The graph at right presents information from the NASA Curiosity Mars rover's onboard analysis of rock powder drilled from the "Buckskin" target location, shown at left. X-ray diffraction analysis of the Buckskin sample inside the rover's Chemistry and Mineralogy (CheMin) instrument revealed the presence of a silica-containing mineral named tridymite. This is the first detection of tridymite on Mars. Peaks in the X-ray diffraction pattern are from minerals in the sample, and every mineral has a diagnostic set of peaks that allows identification. The image of Buckskin at left was taken by the rover's Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera on July 30, 2015, and is also available at PIA19804. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20271
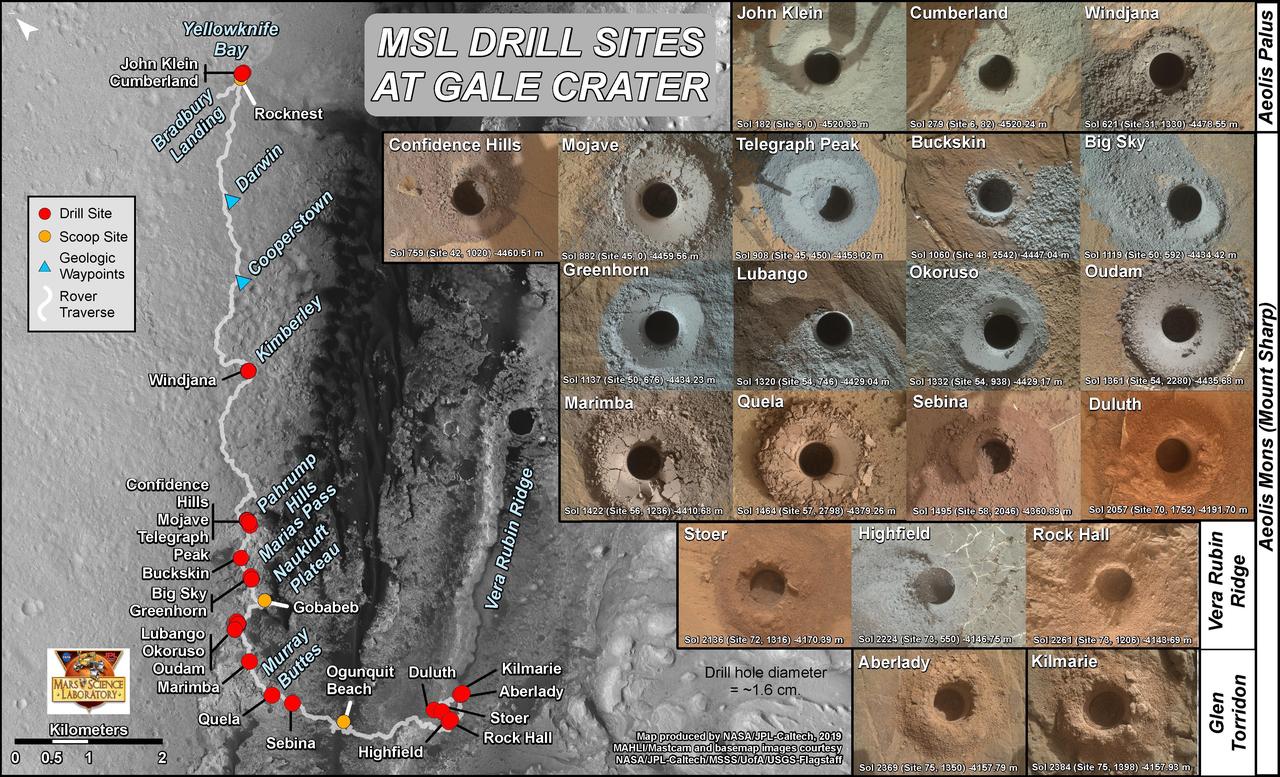

This graphic maps locations of the sites where NASA's Curiosity Mars rover collected its rock and soil samples for analysis by laboratory instruments inside the vehicle. It also presents images of the drilled holes where 21 rock-powder samples were acquired. The diameter of each drill hole is about 0.6 inch (1.6 centimeters), slightly smaller than a U.S. dime. The images used here are raw color, as recorded by the rover's Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera. Notice the differences in color of the material at different drilling sites. For the map, north is toward upper left corner. The scale bar represents 2 kilometers (1.2 miles). The base map is from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23413
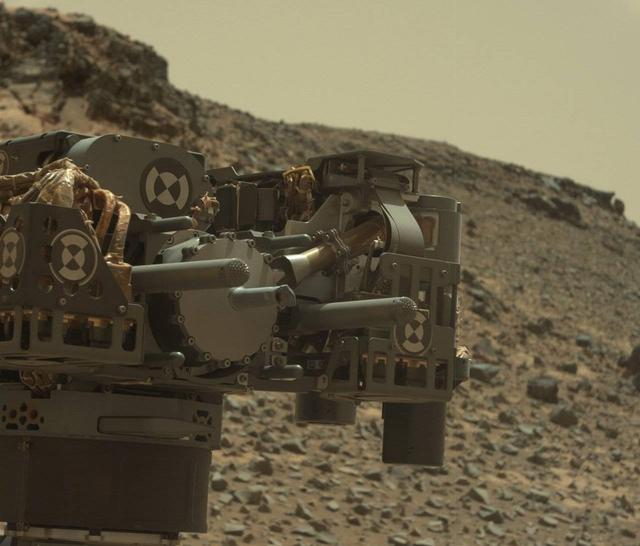

This view from the Mast Camera (Mastcam) on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover shows the rover's drill just after finishing a drilling operation at a target rock called "Telegraph Peak" on Feb. 24, 2015, the 908th Martian day, or sol, of the rover's work on Mars. Three sols later, a fault-protection action by the rover halted a process of transferring sample powder that was collected during this drilling. The image is in raw color, as recorded directly by the camera, and has not been white-balanced. The fault-protection event, triggered by an irregularity in electrical current, led to engineering tests in subsequent days to diagnose the underlying cause. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19145
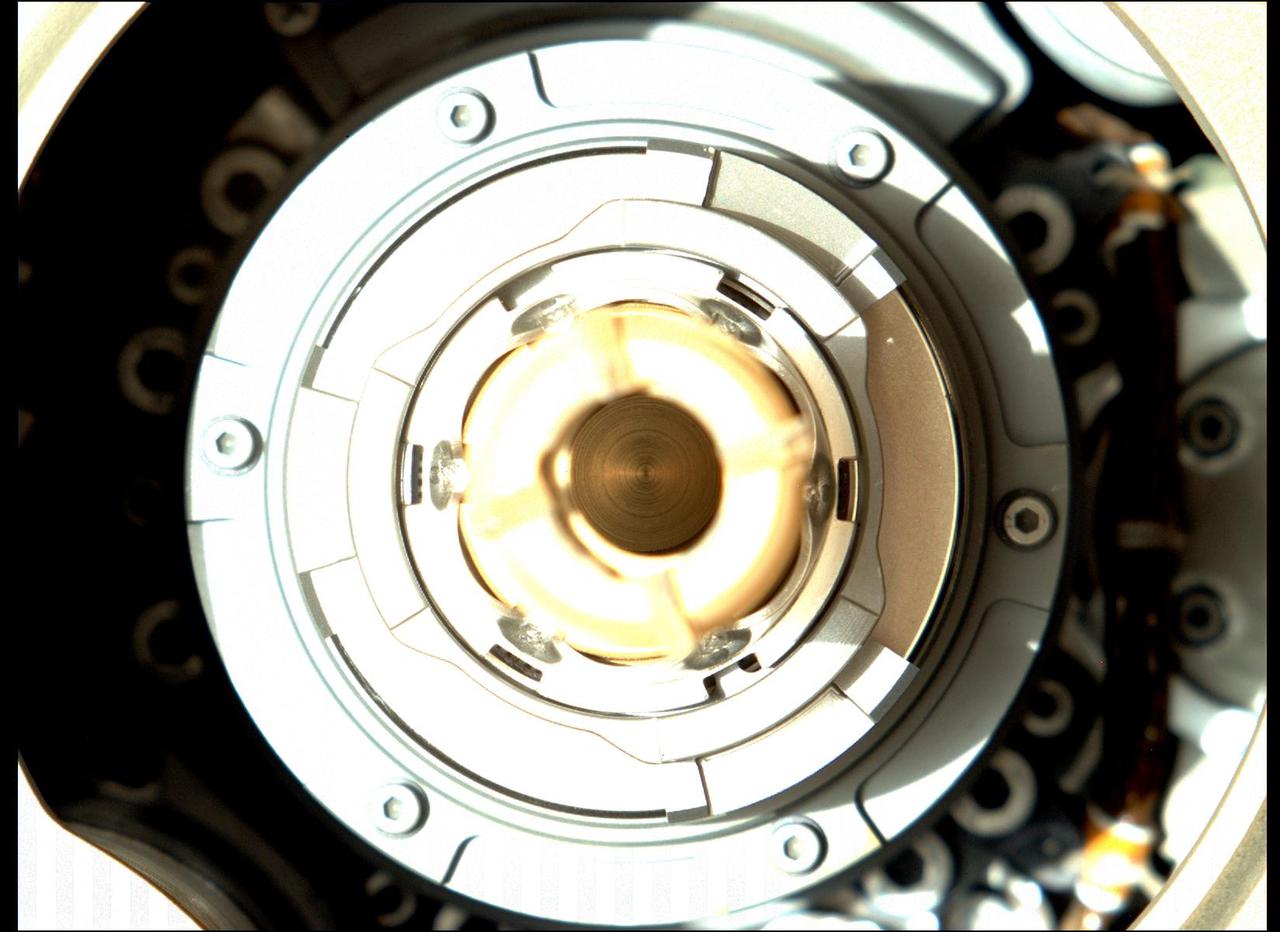
This image taken by the Mastcam-Z camera aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover on Jan. 20, 2022, shows that the rover successfully expelled the remaining large fragments of cored rock from a sample tube held in the drill at the end of its robotic arm. The sample was originally collected by the rover on Dec. 29, 2021, from a rock the team calls "Issole." This image has been processed to enhance contrast. Arizona State University in Tempe leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25073

This pair of images shows two cylinders of rock the size of classroom chalk inside the drill of NASA's Perseverance rover from an outcrop called "Wildcat Ridge" in Mars' Jezero Crater. The image of the rock core on the left, called "Hazeltop," was taken by Perseverance's Mastcam-Z instrument on July 25, 2022, the 509th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The image on the right, of the rock core called "Bearwallow," was taken on Aug. 2, 2022, the 516th sol. Each core is about 0.5 inches, or 13 millimeters, in diameter and 2.4 inches, or 60 millimeters, long. They were taken from an ancient river delta in Jezero Crater, a fan-shaped area where, billions of years ago, a river once flowed into a lake and deposited rocks and sediment. Scientists interpret these rocks to be fine-grained sedimentary rocks. They appear to have formed under saltwater conditions, possibly as water from the crater's ancient lake was evaporating. These rock cores have been sealed in ultra-clean sample tubes and stored in Perseverance's Sampling and Caching System as part of the mission's search for ancient signs of microbial life. The verification of ancient life on Mars carries an enormous burden of proof. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24929
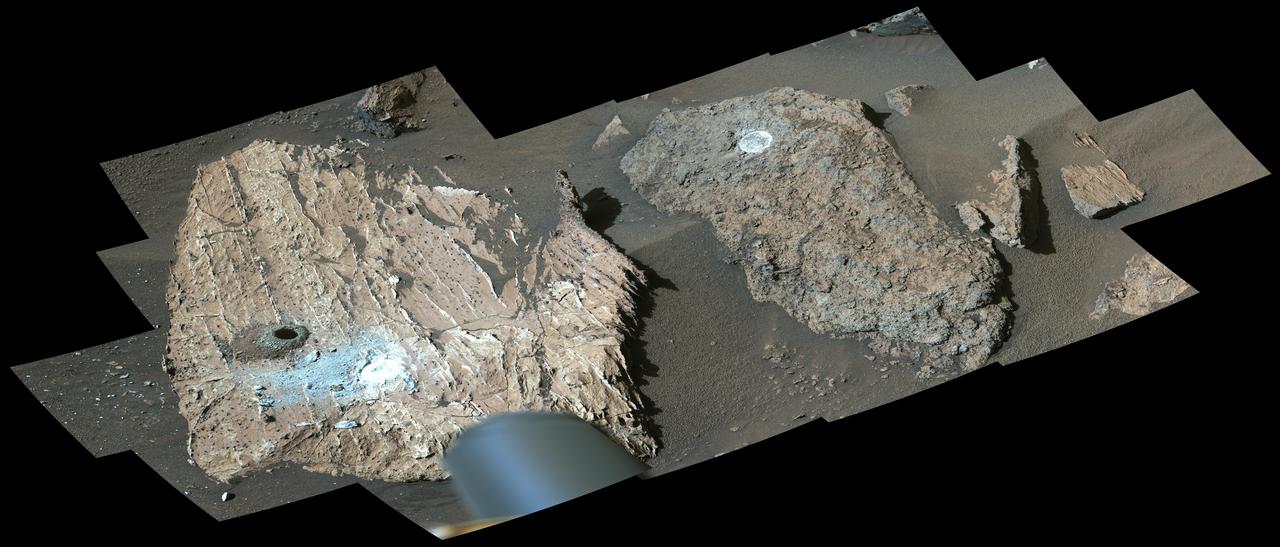

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z instrument to view this workspace around the sample collected from a rock nicknamed "Cheyava Falls." A drill hole is visible (far left) where a sample was collected on July 21, 2024. At right is a rock nicknamed "Steamboat Mountain." A circular white abrasion patch can be seen on each rock; these are where the rover used an abrasion tool to clear away the top surface, allowing instruments to study the rocks' composition. The images that make up this composite were taken by the rover's Mastcam-Z instrument on July 23, 2024, the 1217th day, or sol, of the mission. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26401

This video clip shows a test of a new percussive drilling technique at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. On May 19, NASA's Curiosity rover is scheduled to test percussive drilling on Mars for the first time since December 2016. The video clip was shot on March 28, 2018. It has been sped up by 50 times. Curiosity's drill was designed to pulverize rocks samples into powder, which can then be deposited into two chemistry laboratories carried inside of the rover. Curiosity's science team is eager to the rover using percussive drilling again; it will approach a clay-enriched area later this year that could shed new light on the history of water in Gale Crater. An animation is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22324
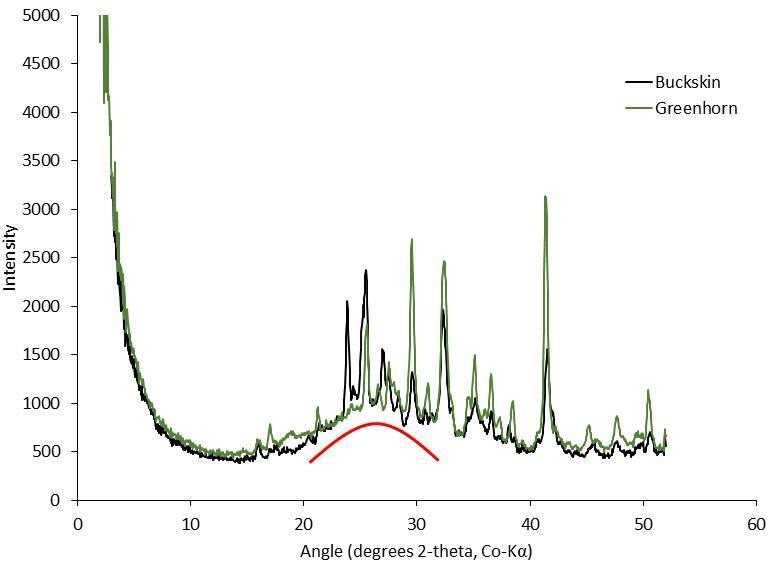
This graph presents information from the NASA Curiosity Mars rover's onboard analysis of rock powder drilled from the "Buckskin" and "Greenhorn" target locations on lower Mount Sharp. Buckskin, in the "Marias Pass" area, and Greenhorn, in the "Bridger Basin" area, both contain high concentrations of silica. X-ray diffraction analysis of powered samples inside Curiosity's Chemistry and Mineralogy (CheMin) instrument revealed that each of them contains silica in the form of noncrystalline opal. The broad hump in the two X-ray diffraction patterns is diagnostic of opaline silica. Some of the silica in Buckskin is in the form of tridymite. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20273
This pair of images shows two cylinders of rock the size of classroom chalk inside the drill of NASA's Perseverance rover from an outcrop called "Skinner Ridge" in Mars' Jezero Crater. The image of the rock core on the left, called "Swift Run," was taken by Perseverance's Mastcam-Z instrument on July 6, 2022, the 490th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The image on the right, of the rock core called "Skyland," was taken on July 11, 2022, the 495th sol of the mission. Each core is about 0.5 inches, or 13 millimeters, in diameter and 2.4 inches, or 60 millimeters, long. They were taken from an ancient river delta in Jezero Crater, a fan-shaped area where, billions of years ago, a river once flowed into a lake and deposited rocks and sediment. Scientists believe these rock samples contain materials transported by water from potentially hundreds of miles outside of Jezero Crater. These rock cores have been sealed in ultra-clean sample tubes and stored in Perseverance's Sampling and Caching System as part of the mission's search for signs of ancient microbial life. The verification of ancient life on Mars carries an enormous burden of proof. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24927
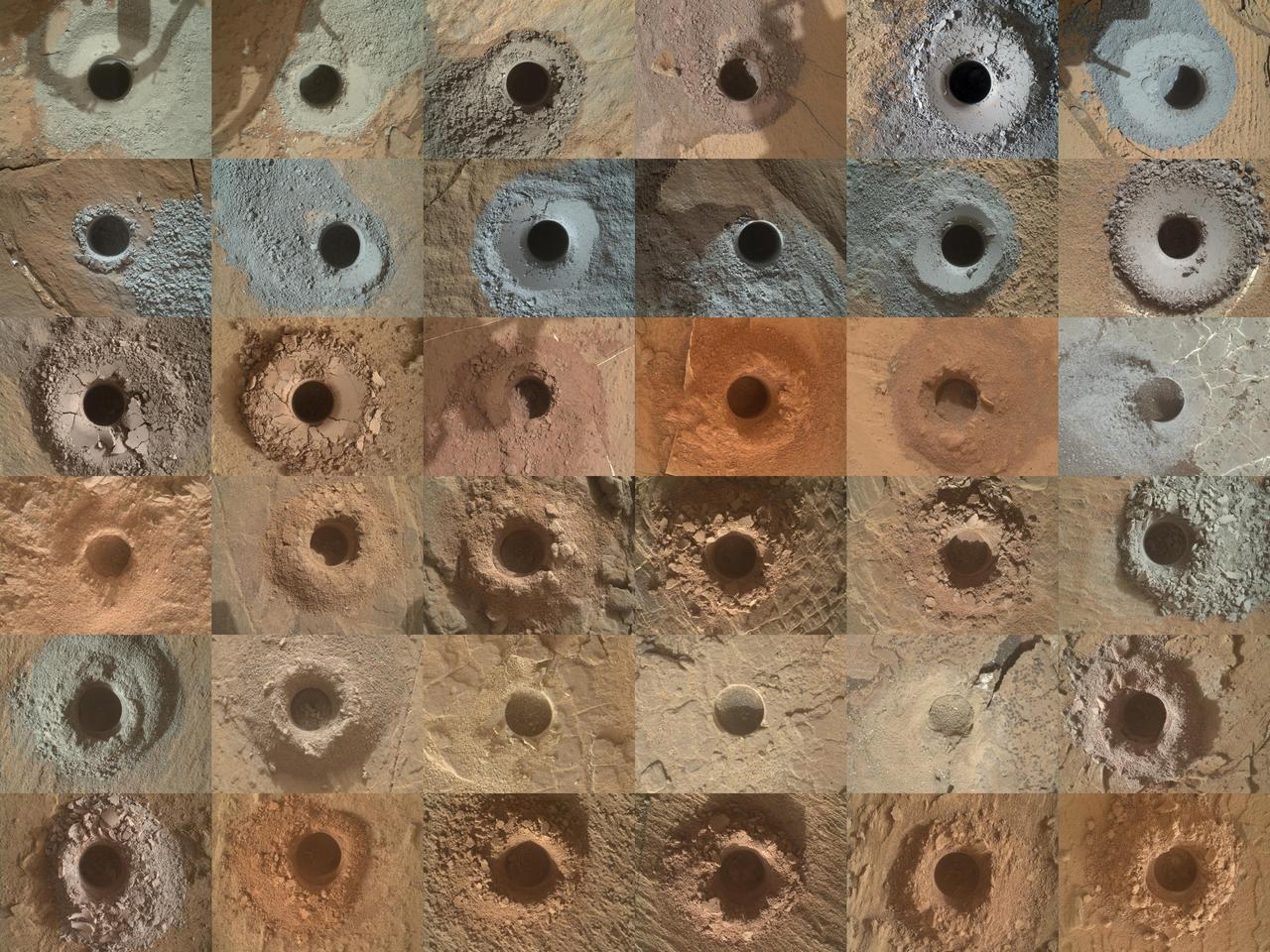

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover has collected 36 powderized rock samples with the drill on the end of its robotic arm. This grid shows all 36 holes to date. The images in the grid were captured by the Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) on the end of Curiosity's arm. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25416
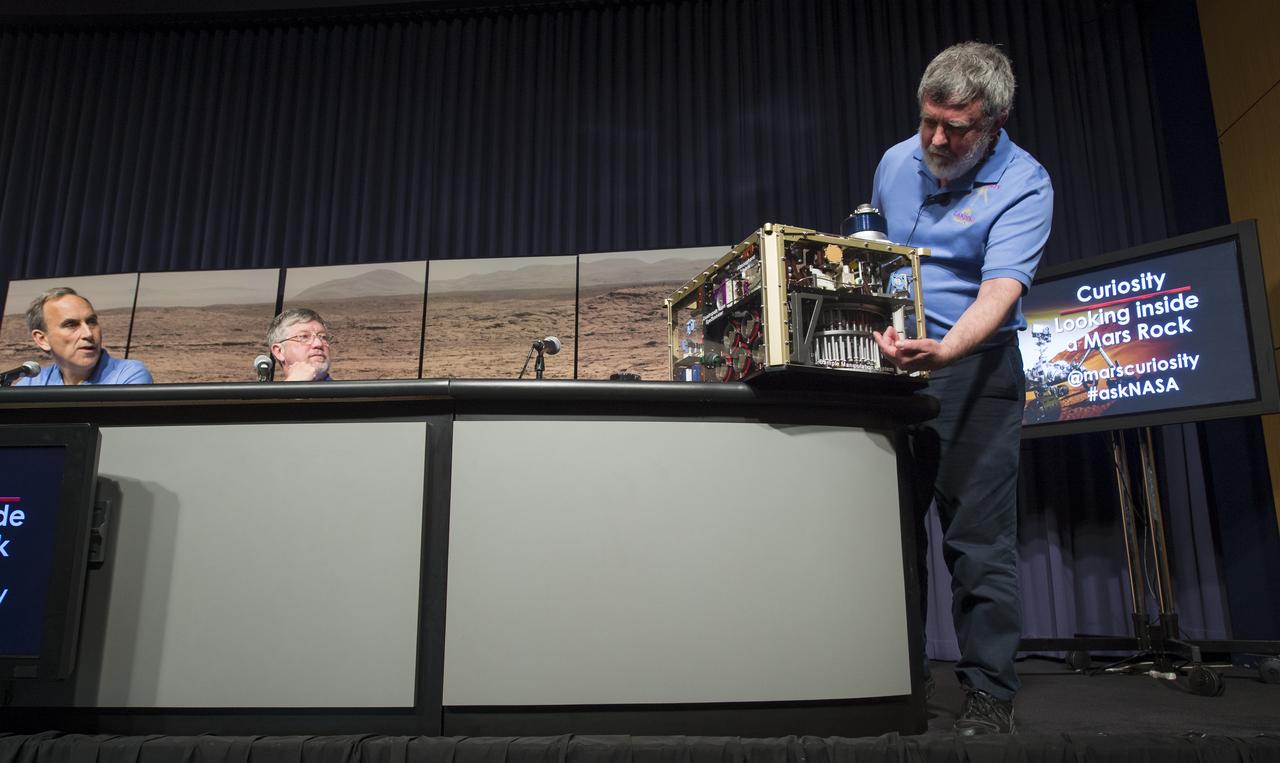

Paul Mahaffy (right), principal investigator for Curiosity's Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) investigation at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland, demonstrates how the SAM instrument drilled and captured rock samples on the surface of Mars at a news conference, Tuesday, March 12, 2013 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The analysis of the rock sample collected shows ancient Mars could have supported living microbes. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
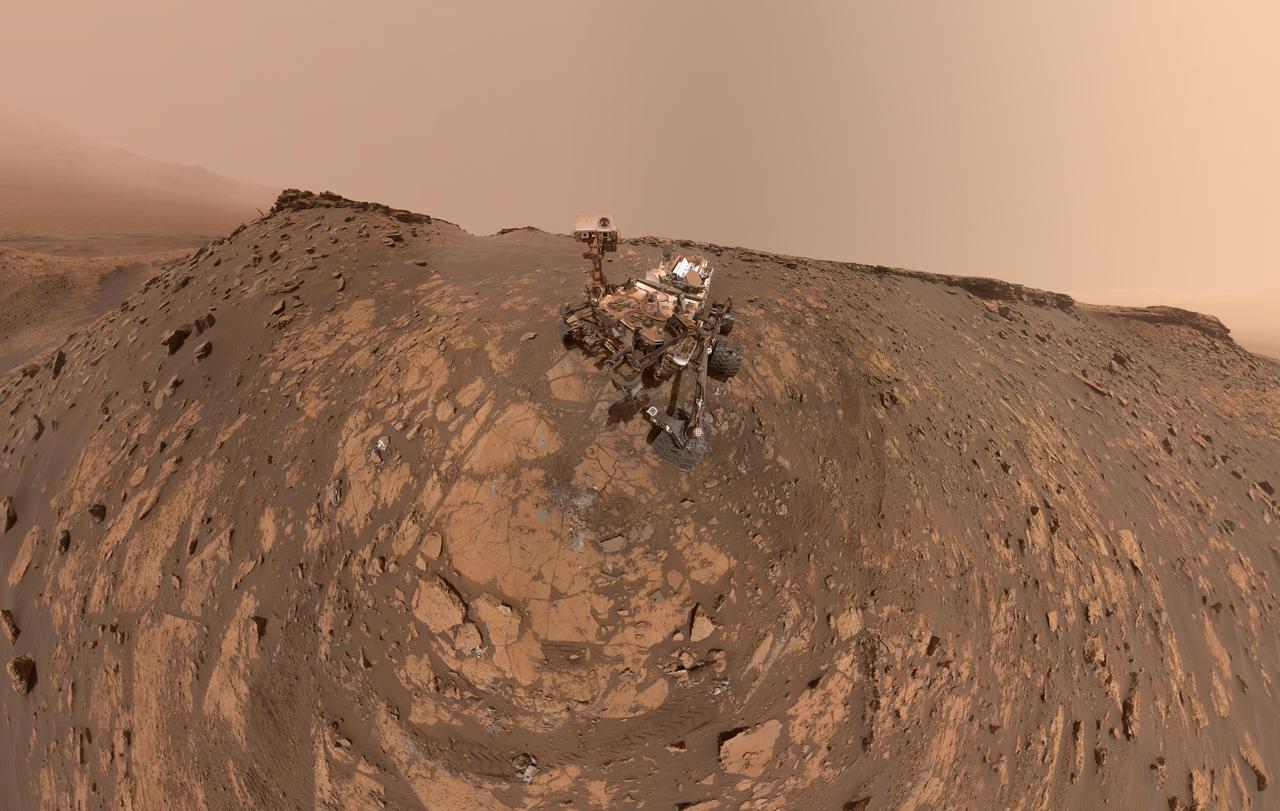

This selfie was taken by NASA's Curiosity Mars rover on Feb. 26, 2020 (the 2,687th Martian day, or sol, of the mission). The crumbling rock layer at the top of the image is the Greenheugh Pediment, which Curiosity climbed soon after taking the image. Directly to the left of Curiosity's foremost wheel is a hole the rover drilled at a rock feature called "Hutton." The selfie includes 86 individual images taken by the Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera on the end of Curiosity's robotic arm. The images were then stitched into a panorama. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23624
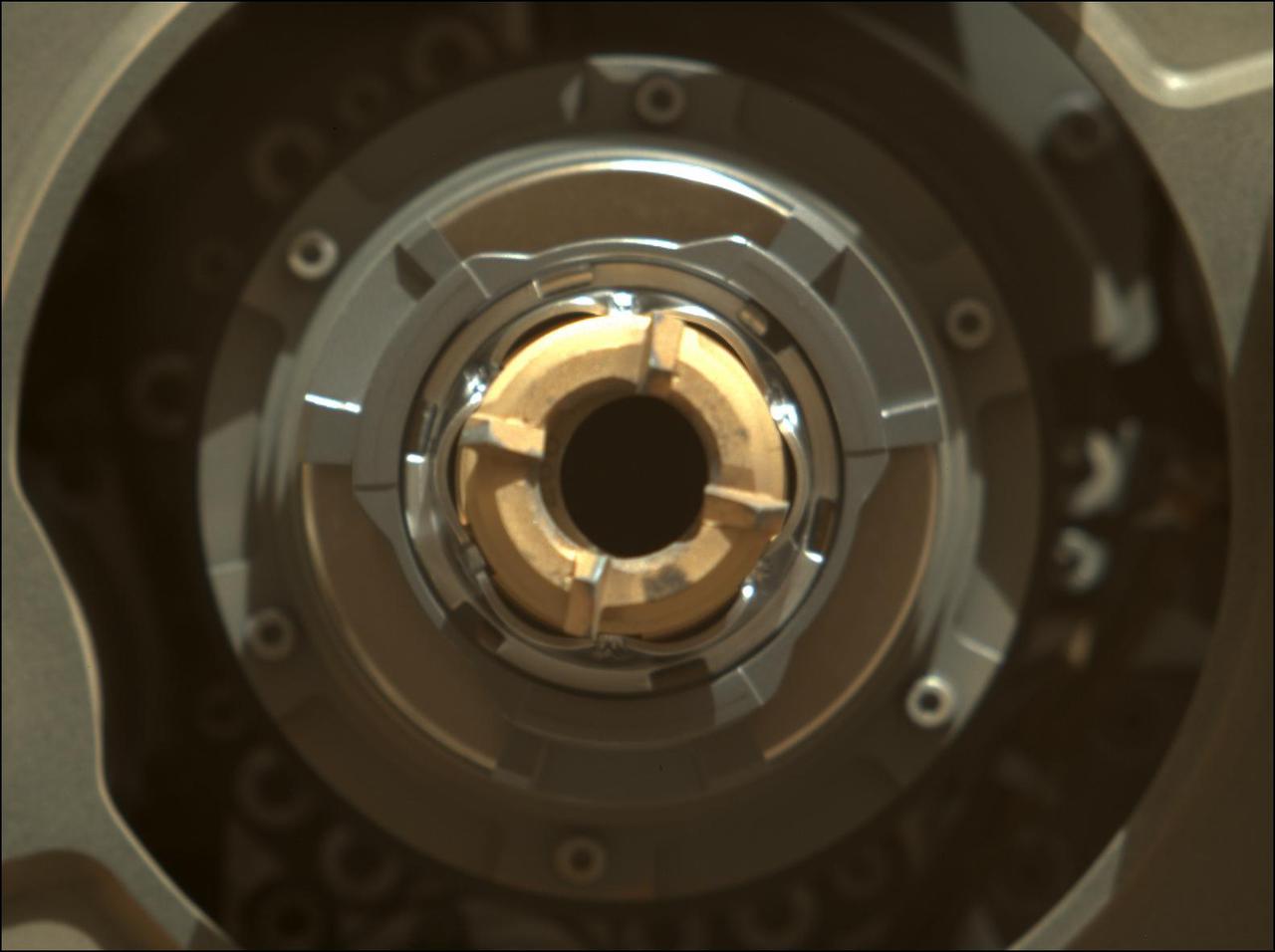
This Mastcam-Z image shows Perseverance's drill with no cored-rock sample evident in the sample tube. The image was taken on Sept. 1, 2021 (the 190th sol, or Martian day, of the mission), after coring – and after a cleaning operation was performed to clear the sample tube's lip of any residual material. The bronze-colored ring is the coring bit. The half-moon inside the bit is the open end of the sample tube. A portion of the tube's serial number – 266 – can be seen on the left side of tube's rim. Arizona State University in Tempe leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24803

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover used its Mast Camera, or Mastcam, to take this 360-degree panorama of at the "Avanavero" drill site. The panorama is made up of 127 individual images taken on June 20, 2022, the 3,509th Martian day, or sol, of the mission, and stitched together back on Earth. The color has been adjusted to match the lighting conditions as the human eye would perceive them on Earth. At this location, Curiosity used the drill on its robotic arm to collect a rock sample for analysis by laboratory instruments inside the vehicle. It has collected more than three dozen such samples in its decade on the Red Planet. In the center of the panorama is a gap between two hills – nicknamed "Paraitepuy Pass" – that Curiosity is currently driving through; beyond it is a layered sulfate-bearing region, which represents a drier, saltier era in the history of Mount Sharp, the 3-mile-tall (5-kilometer-tall) mountain the rover has been ascending since 2014. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25407
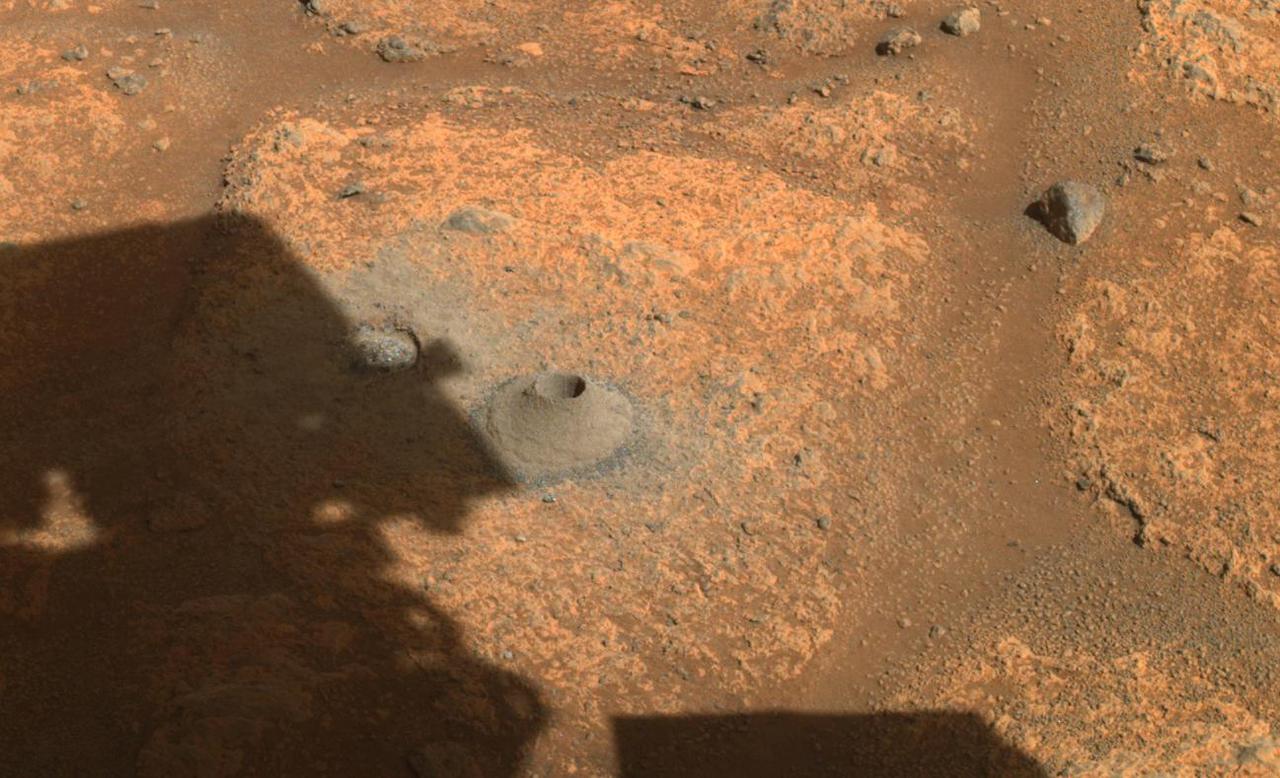

This image taken by NASA's Perseverance rover on August 6, 2021, shows the hole drilled in a Martian rock in preparation for the rover's first attempt to collect a sample. It was taken by one of the rover's hazard cameras in what the rover's science team has nicknamed a "paver rock" in the "Crater Floor Fractured Rough" area of Jezero Crater. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24795
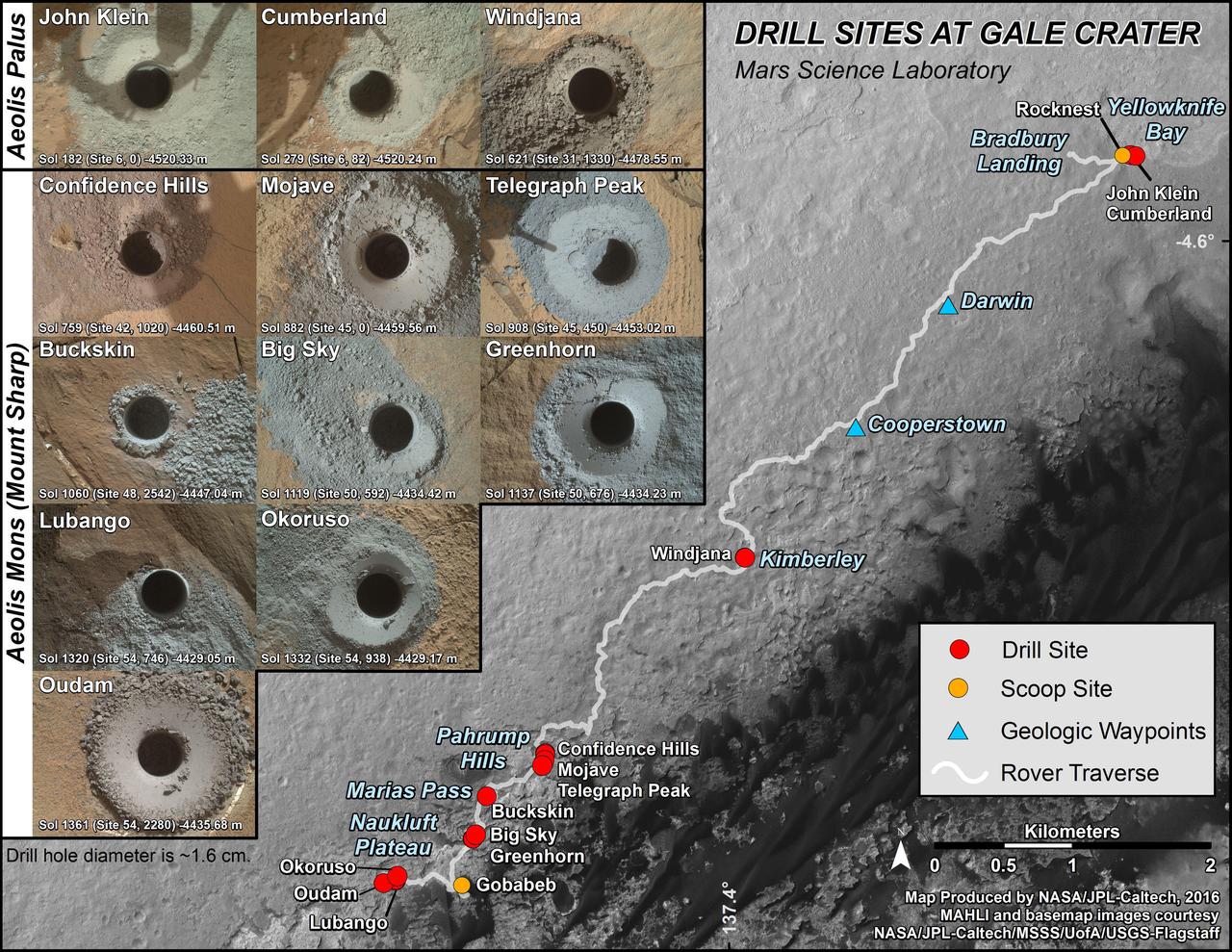
This graphic maps locations of the first 14 sites where NASA's Curiosity Mars rover collected rock or soil samples for analysis by laboratory instruments inside the vehicle. It also presents images of the drilled holes where 12 rock-powder samples were acquired. At the other two sites -- Rocknest and Gobabeb -- Curiosity scooped soil samples. The diameter of each drill hole is about 0.6 inch (1.6 centimeters), slightly smaller than a U.S. dime. The images used here are raw color, as recorded by the rover's Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera. Notice the differences in color of the material at different drilling sites. The latest sample site included is "Oudam," where Curiosity drilled into mudstone of the "Murray formation" on June 4, during the 1,361th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Curiosity landed in August 2012 on the plain (named Aeolis Palus) near Mount Sharp (or Aeolis Mons). Dates when the first 11 drilled-rock samples were collected are: "John Klein" on Feb. 8, 2013 (Sol 182); "Cumberland" on May 19, 2013 (Sol 279); "Windjana" on May 5, 2014 (Sol 621); "Confidence Hills" on Sept. 24, 2014 (Sol 759); "Mojave" on Jan. 29, 2015 (Sol 882); "Telegraph Peak" on Feb. 24, 2015 (Sol 908); "Buckskin" on July 30, 2015 (Sol 1060); "Big Sky" on Sept. 29, 2015 (Sol 1119); "Greenhorn" on Oct. 18, 2015 (Sol 1137); "Lubango" on April 23, 2016 (Sol 1320); and "Okoruso" on May 5, 2016 (Sol 1332). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20748
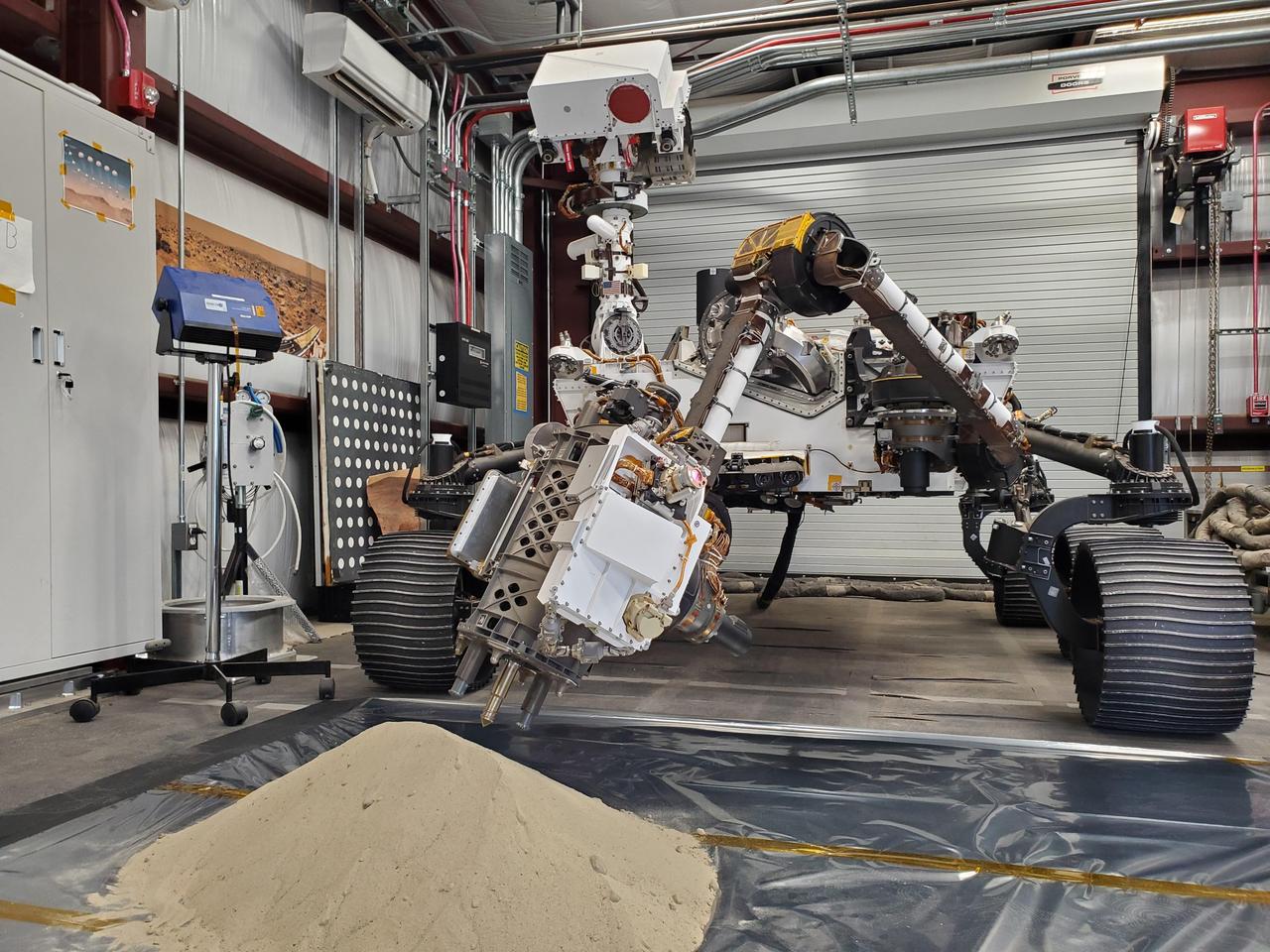

Optimism, a full-scale replica of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover, tests a model of Perseverance's regolith bit in a pile of simulated regolith – broken rock and dust – at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. As with rock cores, Perseverance uses a drill on the end of its robotic arm to collect regolith samples. But to gather the loose material of Martian regolith the rover employs a different drill bit that looks like a spike with small holes on its end. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25651
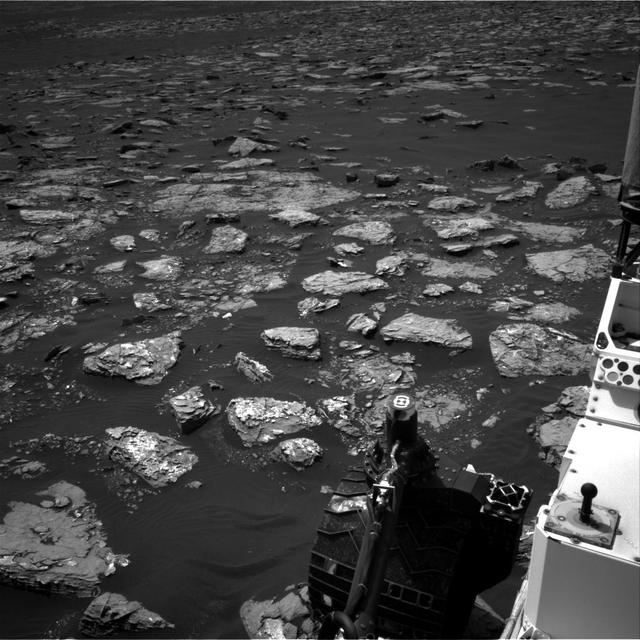

This view from the Navigation Camera (Navcam) on the mast of NASA's Curiosity Mars rover shows rocky ground within view while the rover was working at an intended drilling site called "Precipice" on lower Mount Sharp. The right-eye camera of the stereo Navcam took this image on Dec. 2, 2016, during the 1,537th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars. On the previous sol, an attempt to collect a rock-powder sample with the rover's drill ended before drilling began. This led to several days of diagnostic work while the rover remained in place, during which it continued to use cameras and a spectrometer on its mast, plus environmental monitoring instruments. In this view, hardware visible at lower right includes the sundial-theme calibration target for Curiosity's Mast Camera. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21140
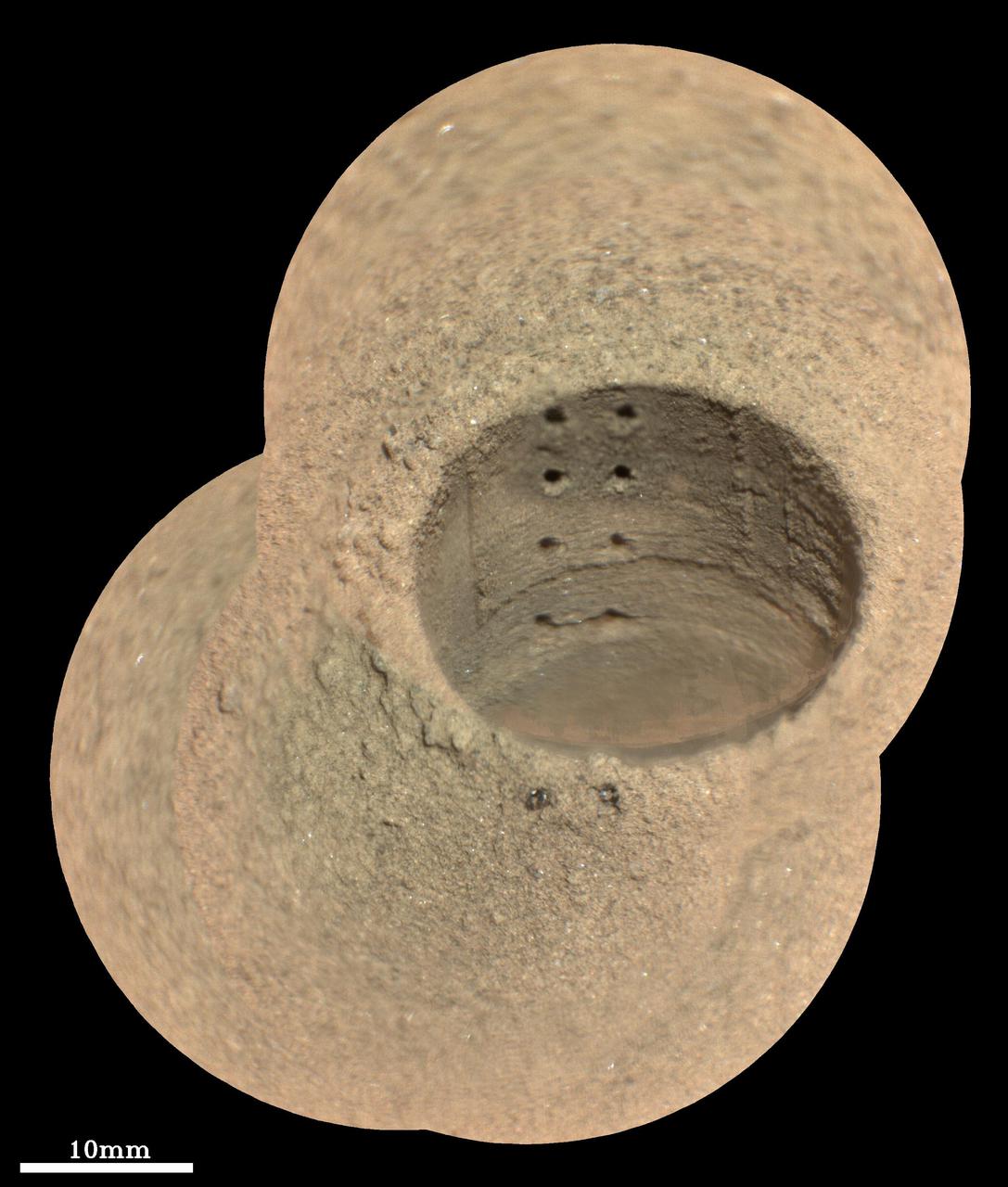

This composite image, made from four taken by the SuperCam instrument aboard NASA's Perseverance rover on August 8, 2021, shows the hole in a Martian rock where the rover attempted to collect its first sample; the small pits within it were created by laser zaps from SuperCam during subsequent efforts to analyze the rock's composition. The rover science team has nicknamed the drill hole "Roubion." The team believes that because of this rock's unusual composition, the process of extracting a core created a significant pile of tailings (or cuttings) around the coring hole. Eight pits produced by 30 laser shots each are seen in two columns inside the drill hole. The SuperCam team's analysis suggests that the top six pits penetrated the compacted mound of tailings around the hole, while the bottom two pits in the hole interrogated material below the rock surface. Two additional laser pits can be seen in the tailings at the near side of the hole. Two vertical ridges inside the hole – one on each side of the laser pits – were produced as the drill was removed, prior to laser analysis. Some bright mineral grains can be seen as glints in the tailings and in the drill hole. A few clumps or larger pieces of material are seen at the top of the tailings pile just to the left of the hole. The SuperCam images were taken from a distance of 7.32 feet (2.23 meters). A scale bar is included in this image. Perseverance landed in Mars' Jezero Crater on February 18, 2021, and has been exploring the floor of the crater since. At the time these images were taken, Perseverance was in an area nicknamed the "Crater Floor Fractured Rough" area. SuperCam is led by Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico, where the instrument's Body Unit was developed. That part of the instrument includes several spectrometers as well as control electronics and software. The Mast Unit, including the Remote Microscopic Imager used for these images, was developed and built by several laboratories of the CNRS (the French research center) and French universities under the contracting authority of Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES, the French space agency). A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24749
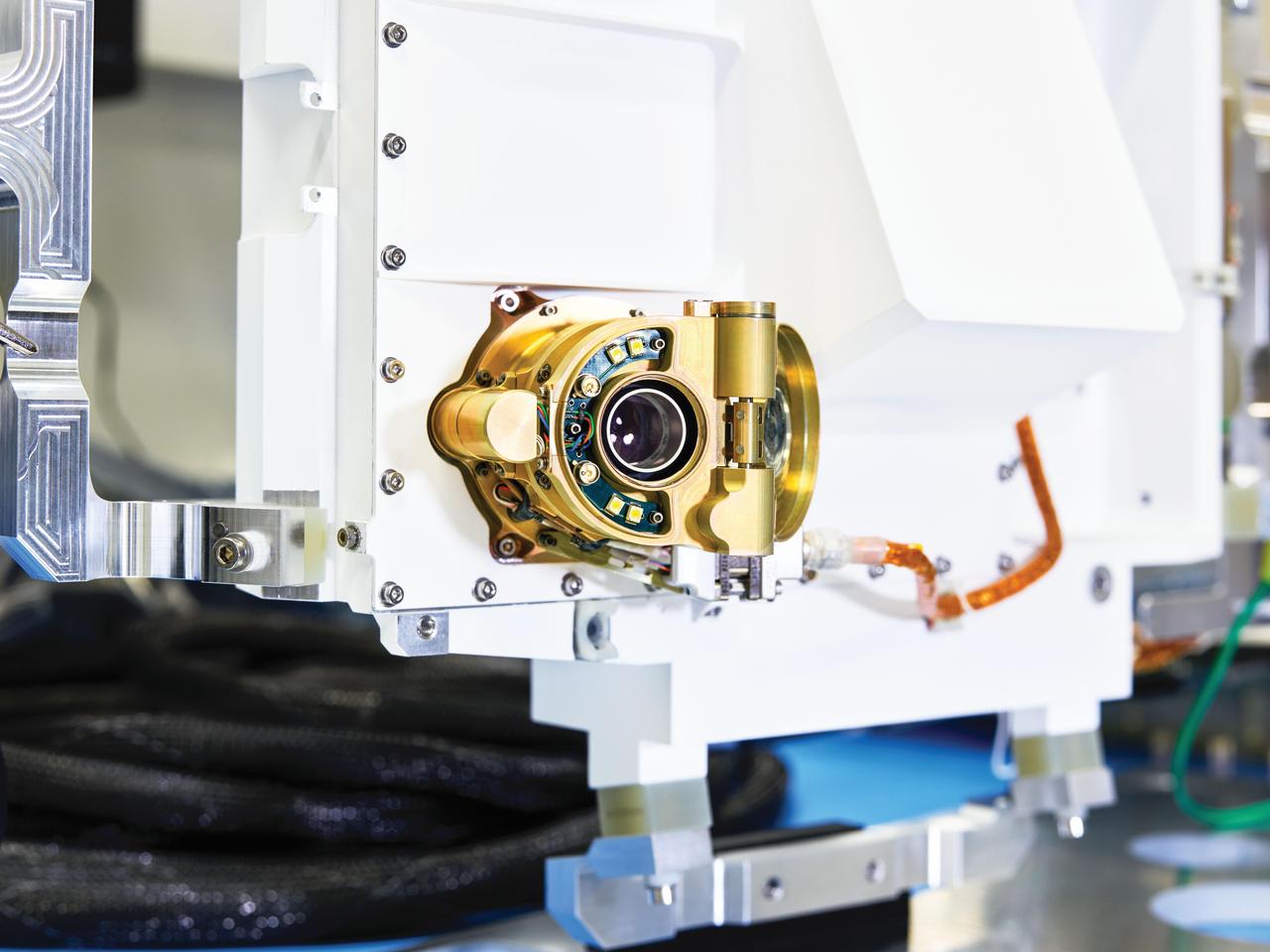

A close-up view of an engineering model of SHERLOC (Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals), one the instruments aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. Located on the end of the rover's robotic arm, this instrument features an auto-focusing camera (pictured) that shoots black-and-white images used by SHERLOC's color camera, called WATSON (Wide Angle Topographic Sensor for Operations and eNgineering), to zero in on rock textures. SHERLOC also has a laser, which aims for the dead center of rock surfaces depicted in WATSON's images. The laser uses a technique called Raman spectroscopy to detect minerals in microscopic rock features; that data is then superimposed on WATSON's images. These mineral maps help scientists determine which rock samples Perseverance should drill so that they can be sealed in metal tubes and left on the Martian surface for a future mission to return to Earth. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23894