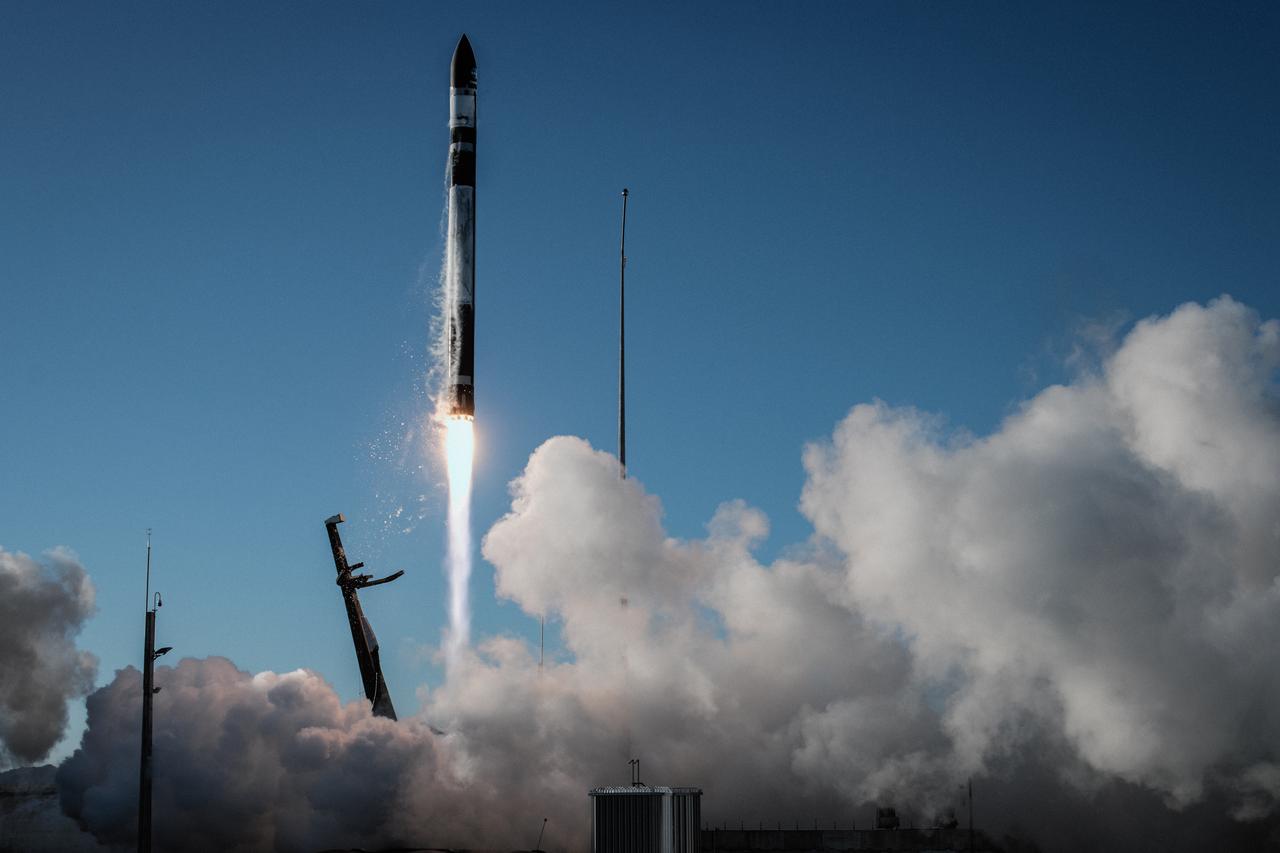

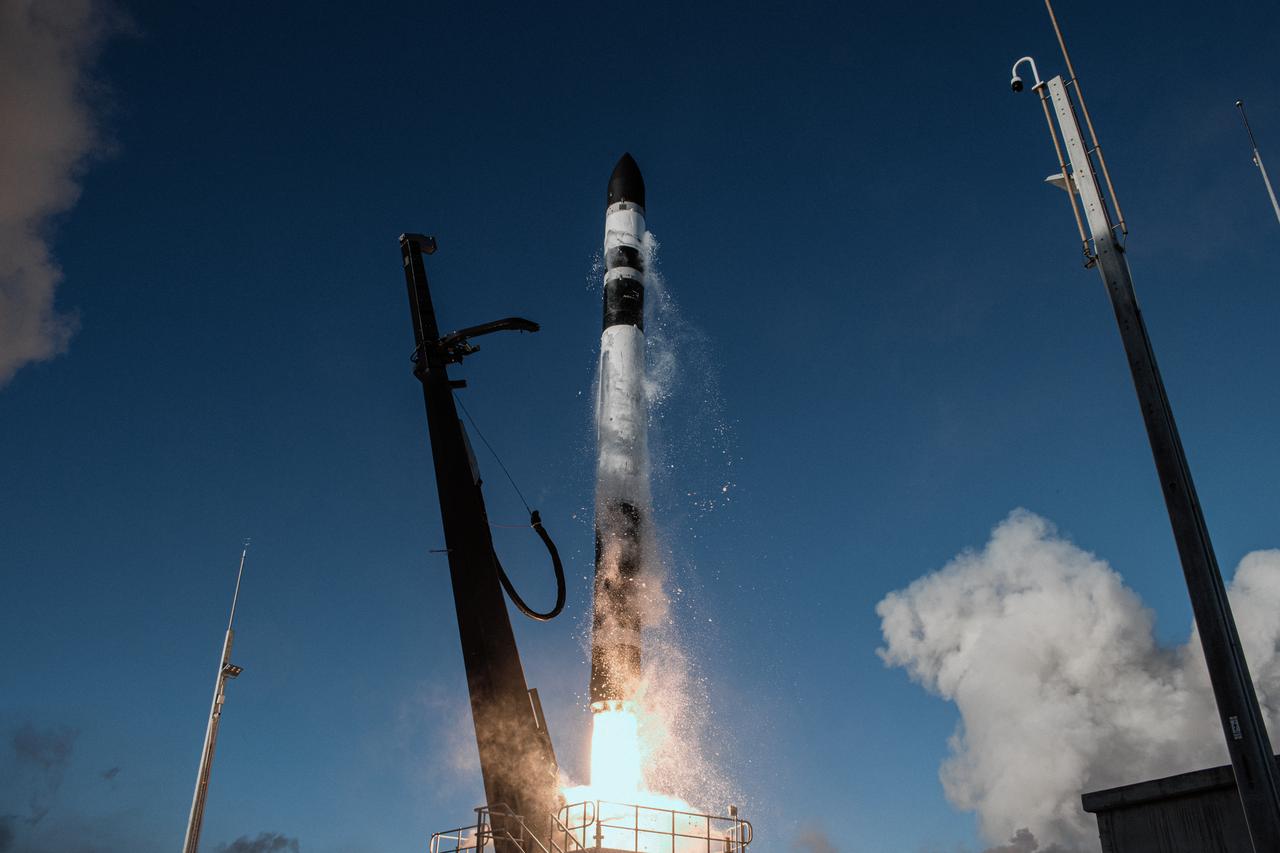
A Rocket Lab Electron rocket soars upward after liftoff from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket is poised for launch atop Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand. Launch time is May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT). The Electron rocket is carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

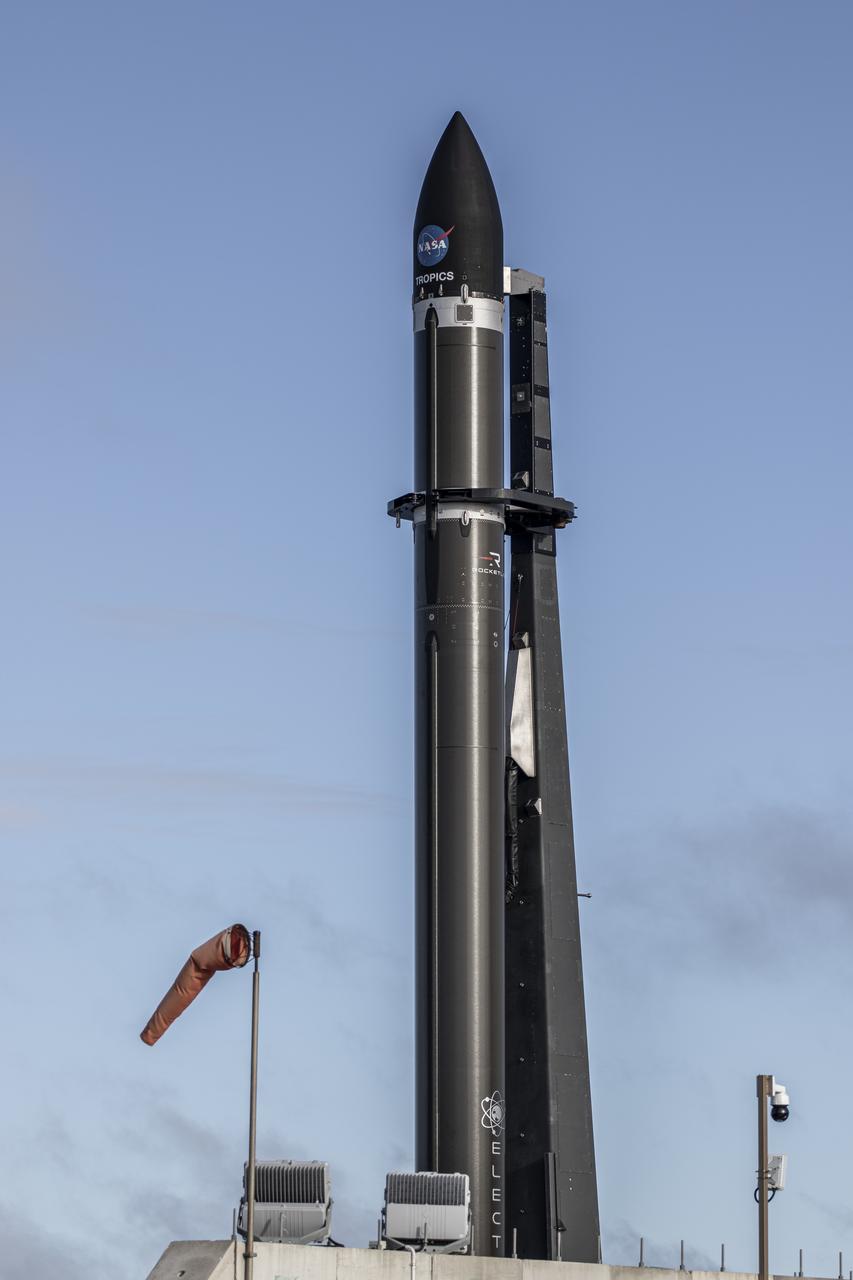
A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
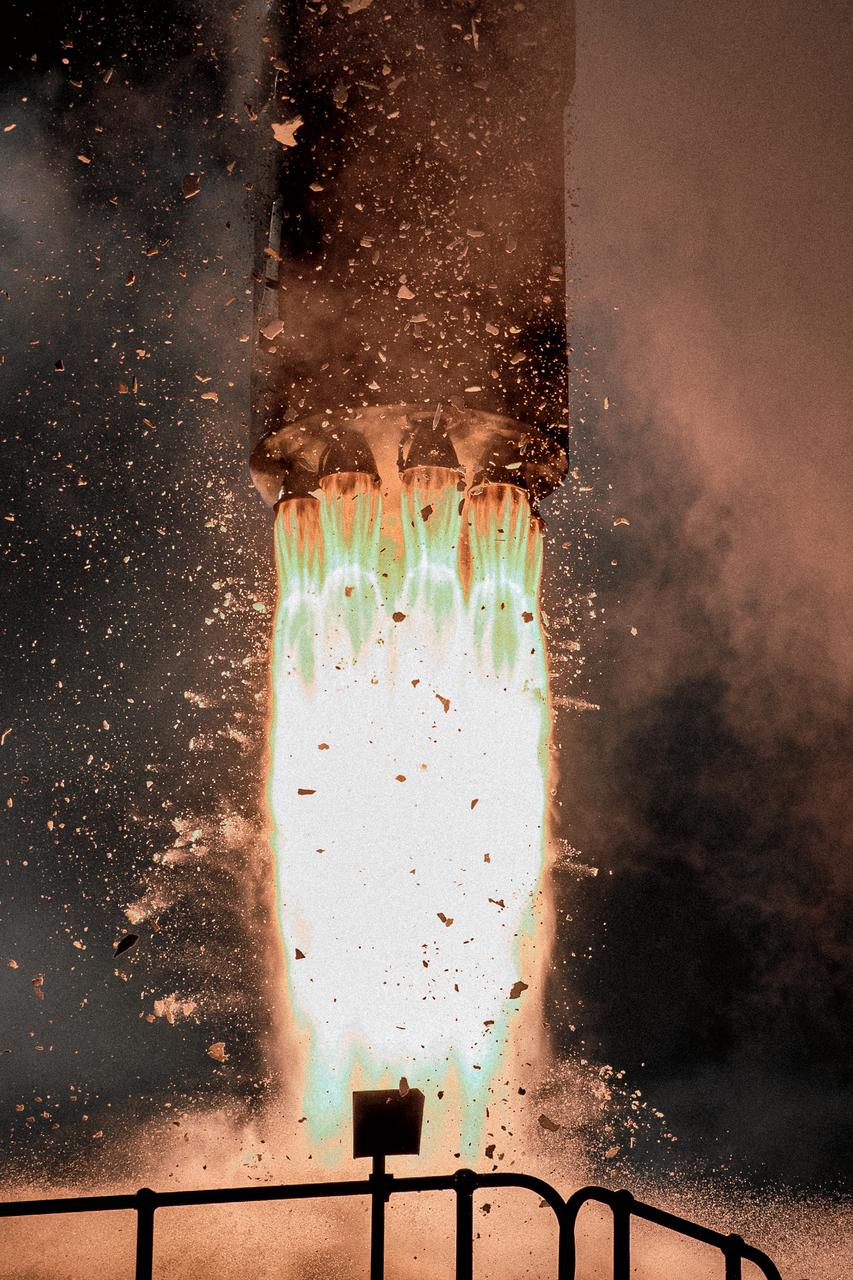

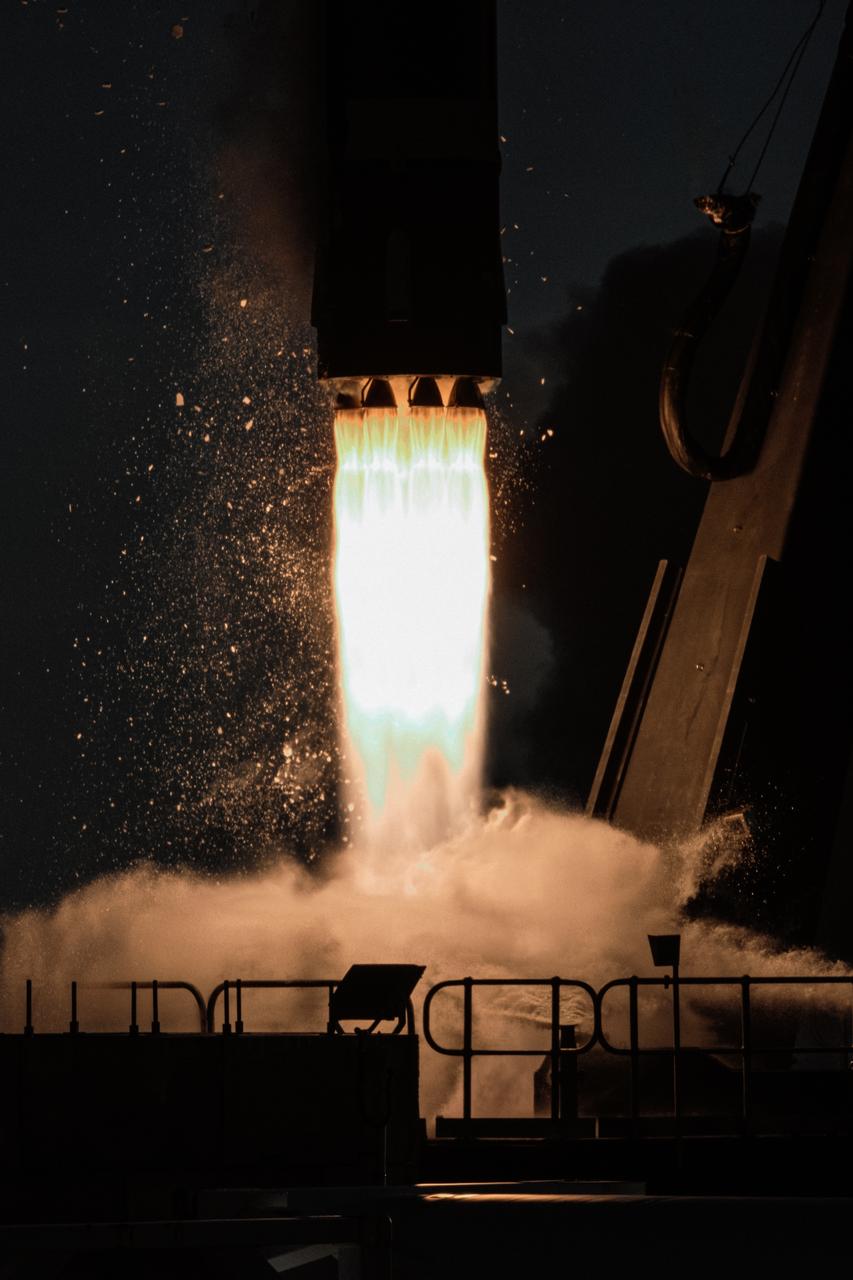
The engines of the first stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket ignite as the rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

The engines of the first stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket ignite as the rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
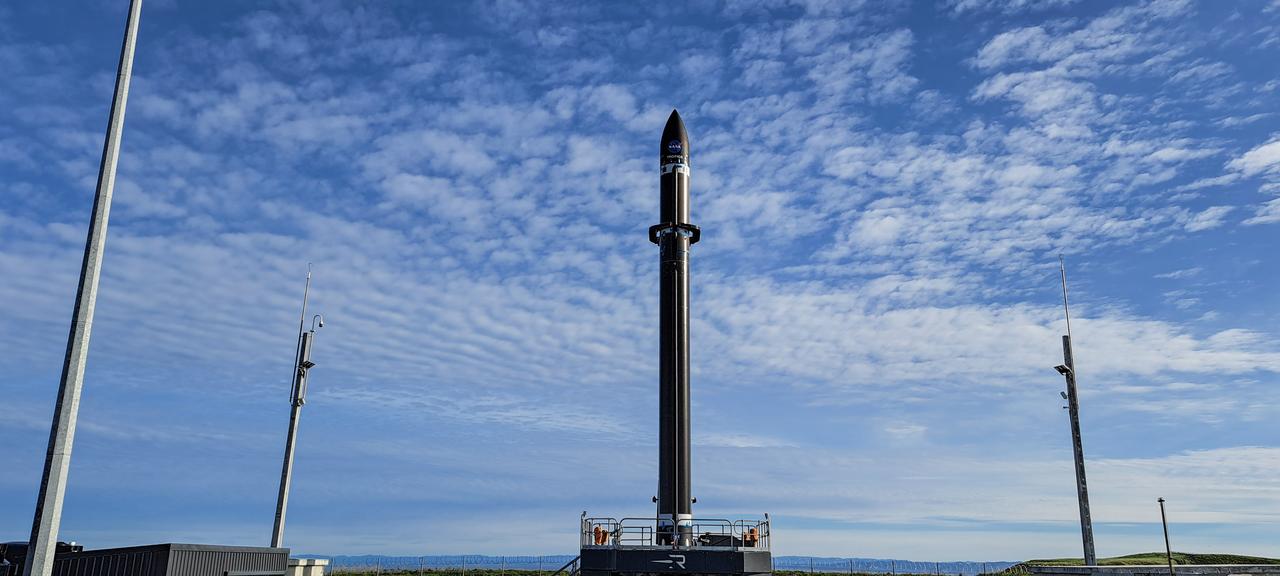

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, during a May 18, 2023, wet dress rehearsal for NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), to launch the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.

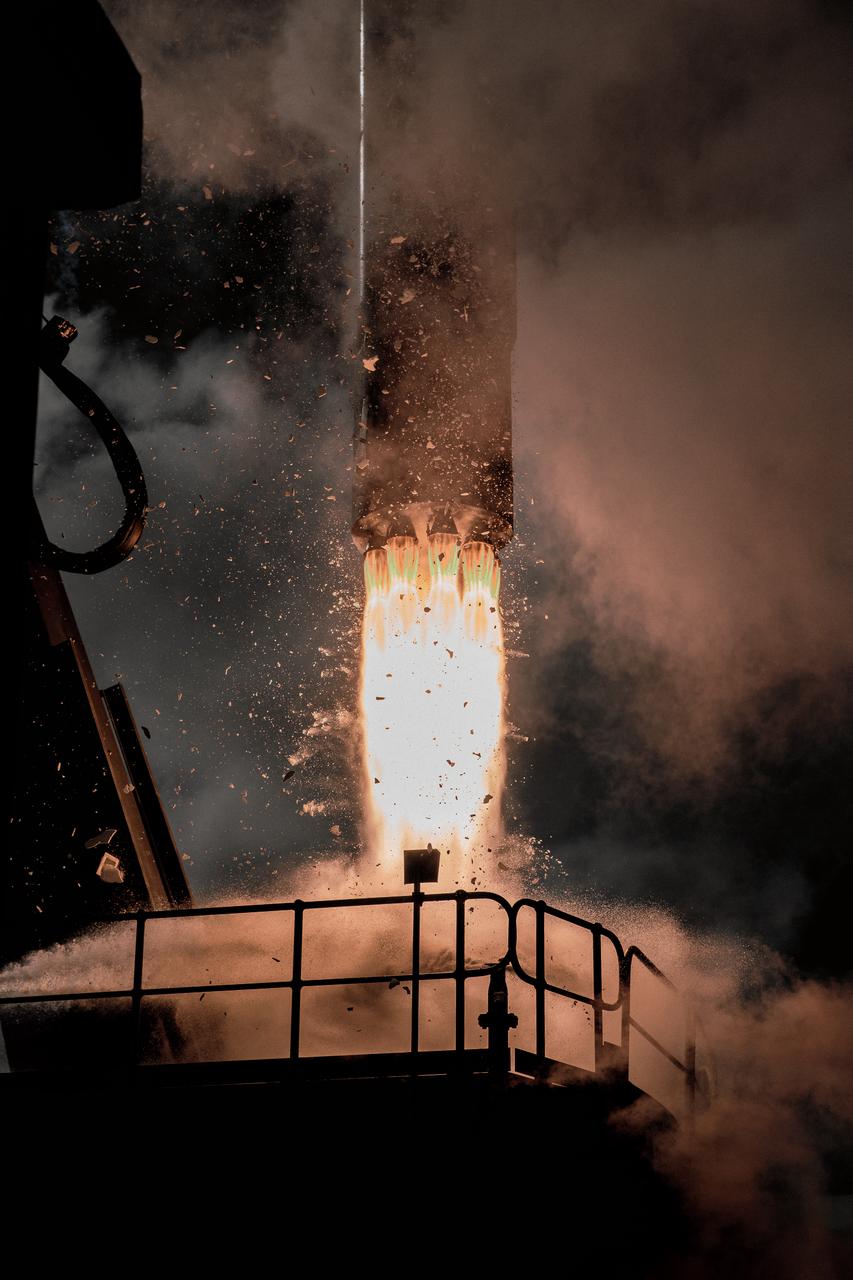
The first stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket ignites at liftoff from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
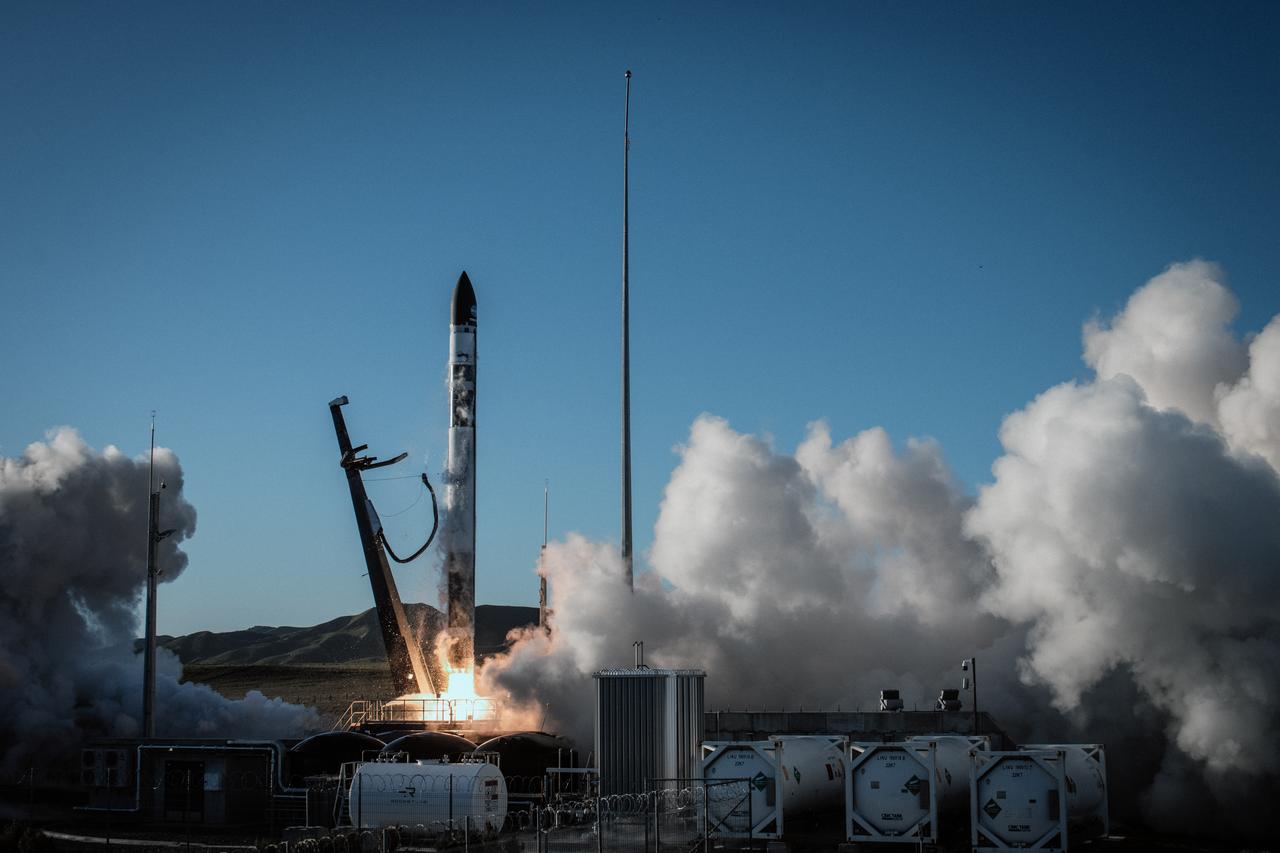

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
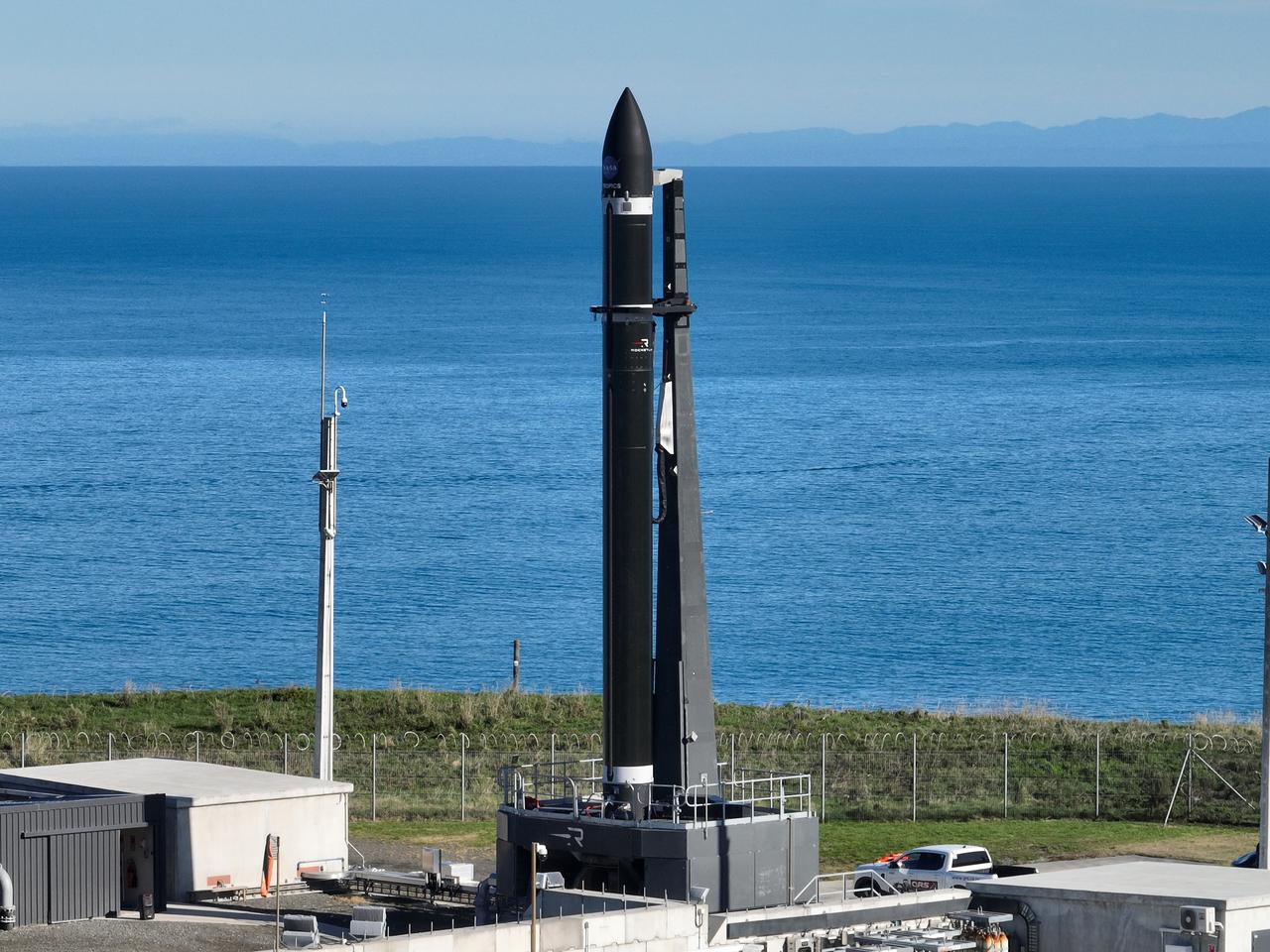

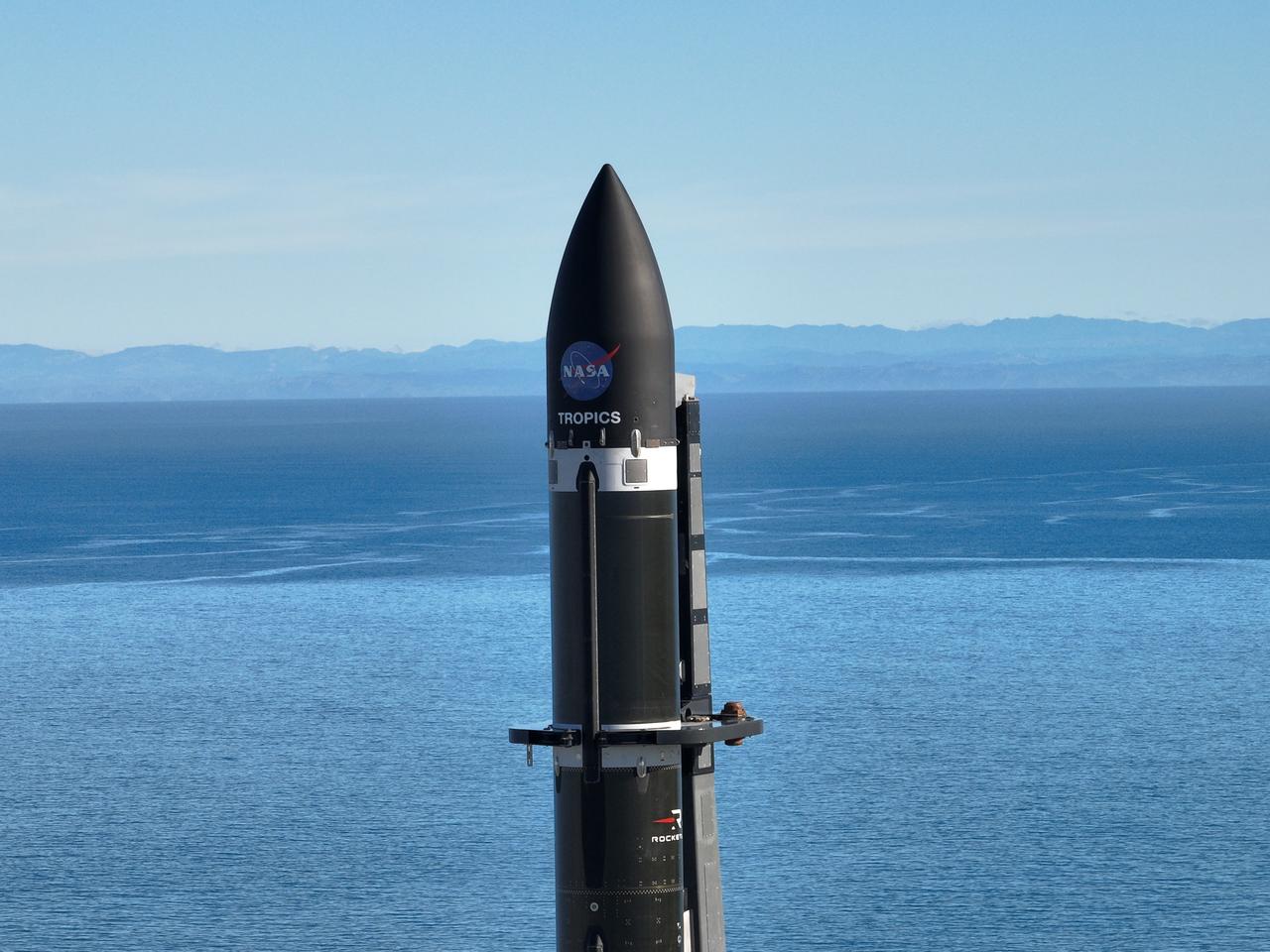
A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
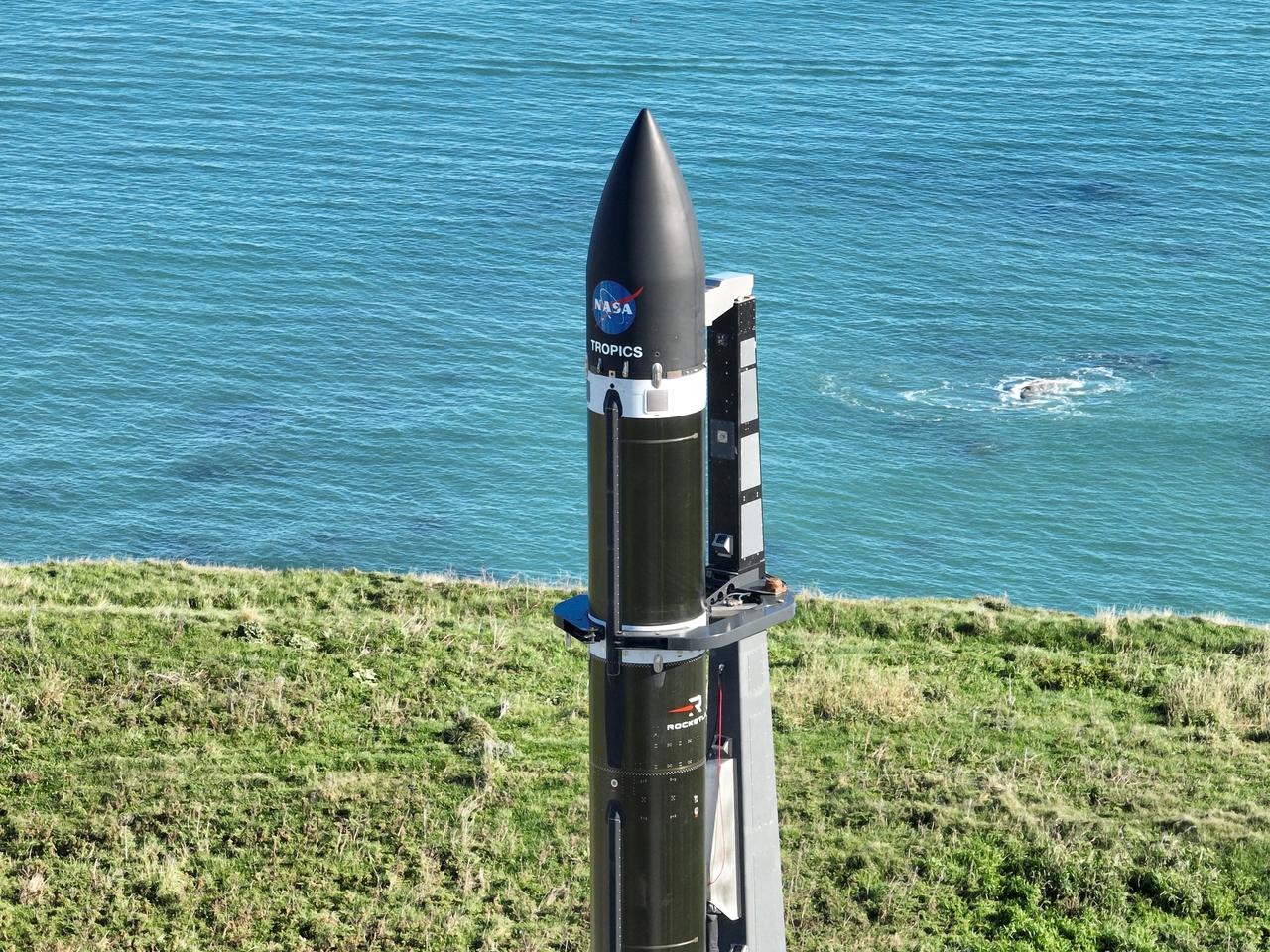

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
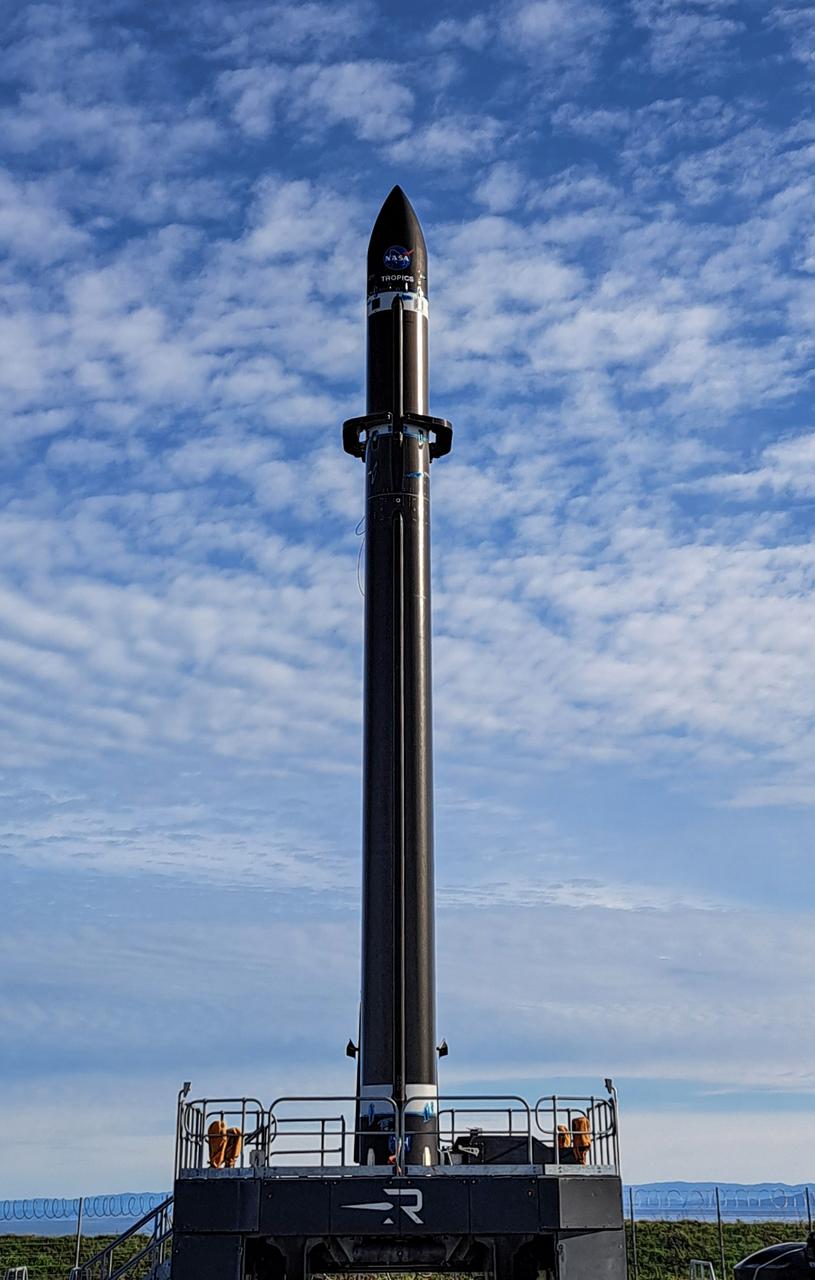

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, during a May 18, 2023, wet dress rehearsal for NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), to launch the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
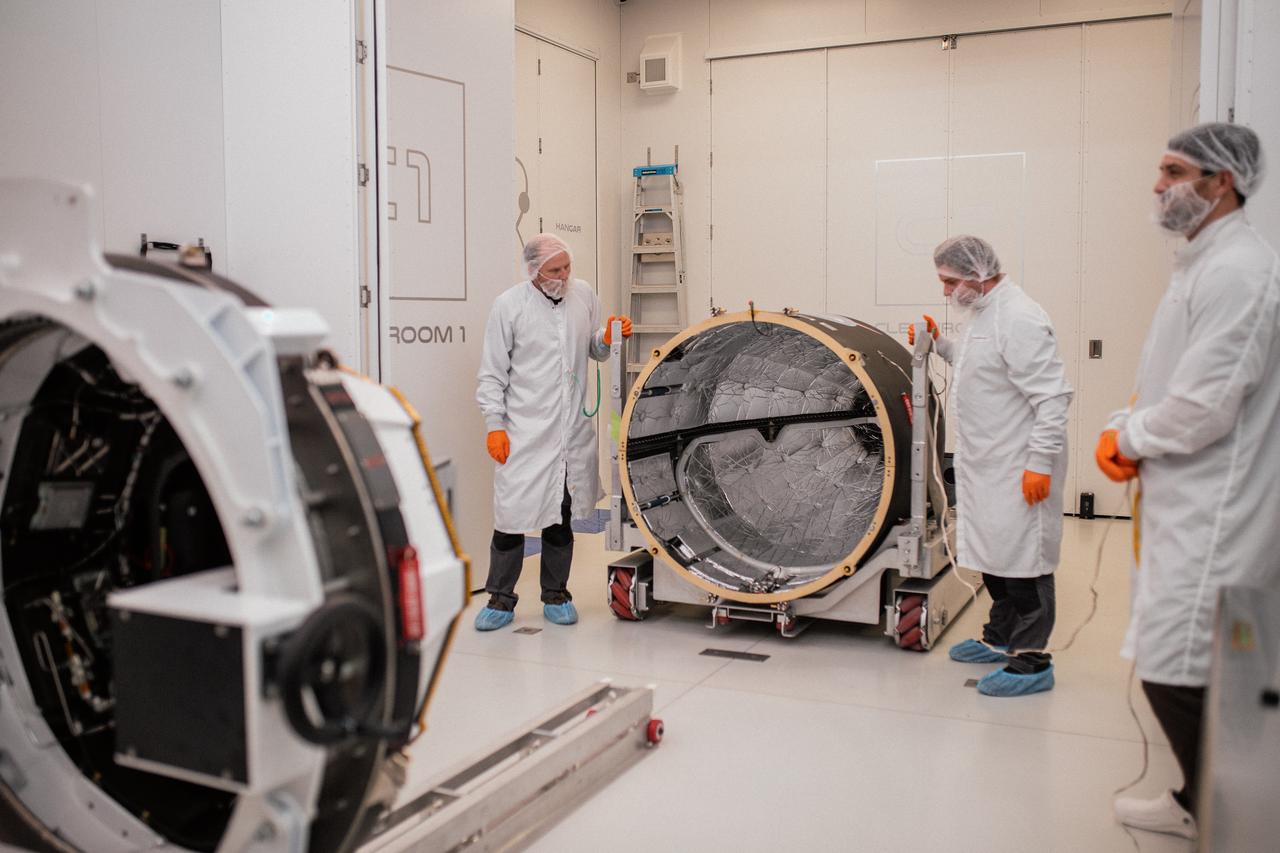

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
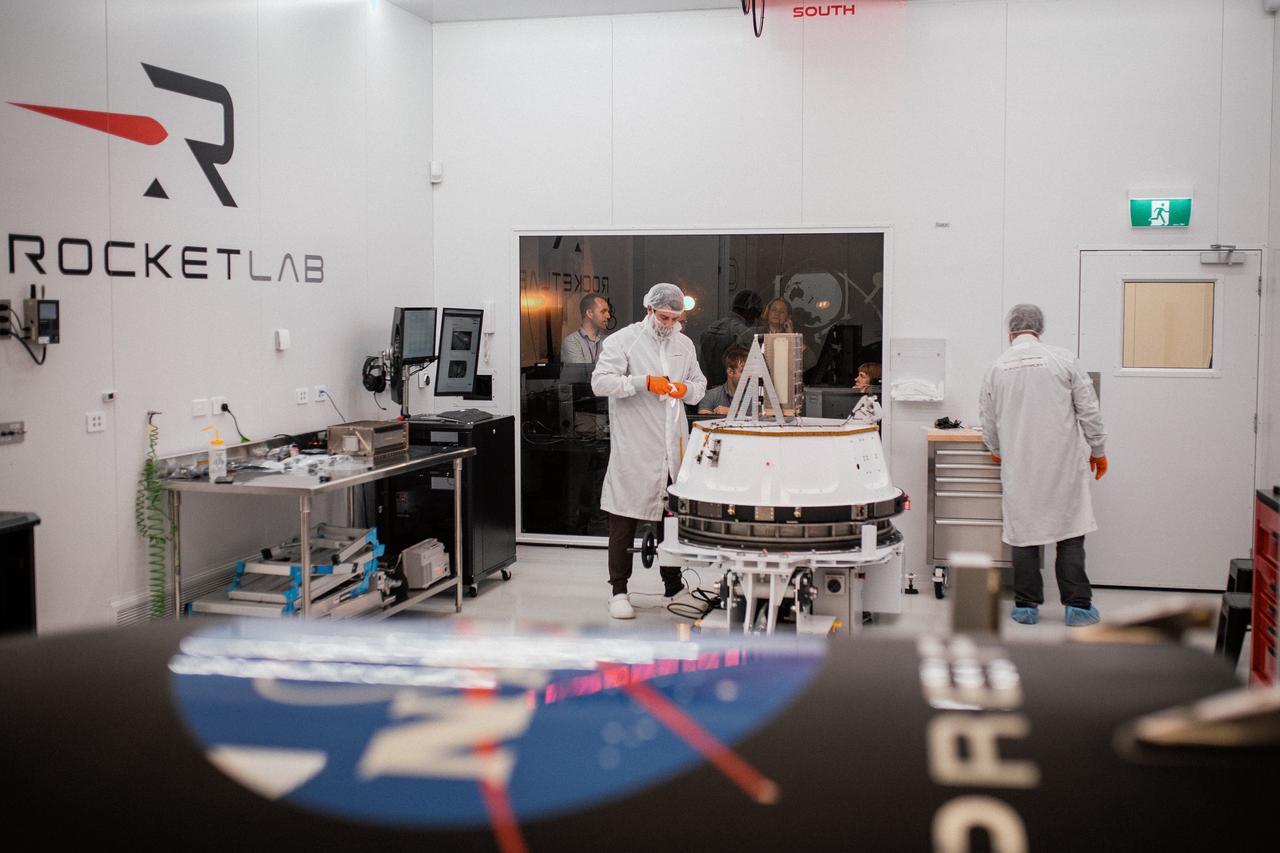

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
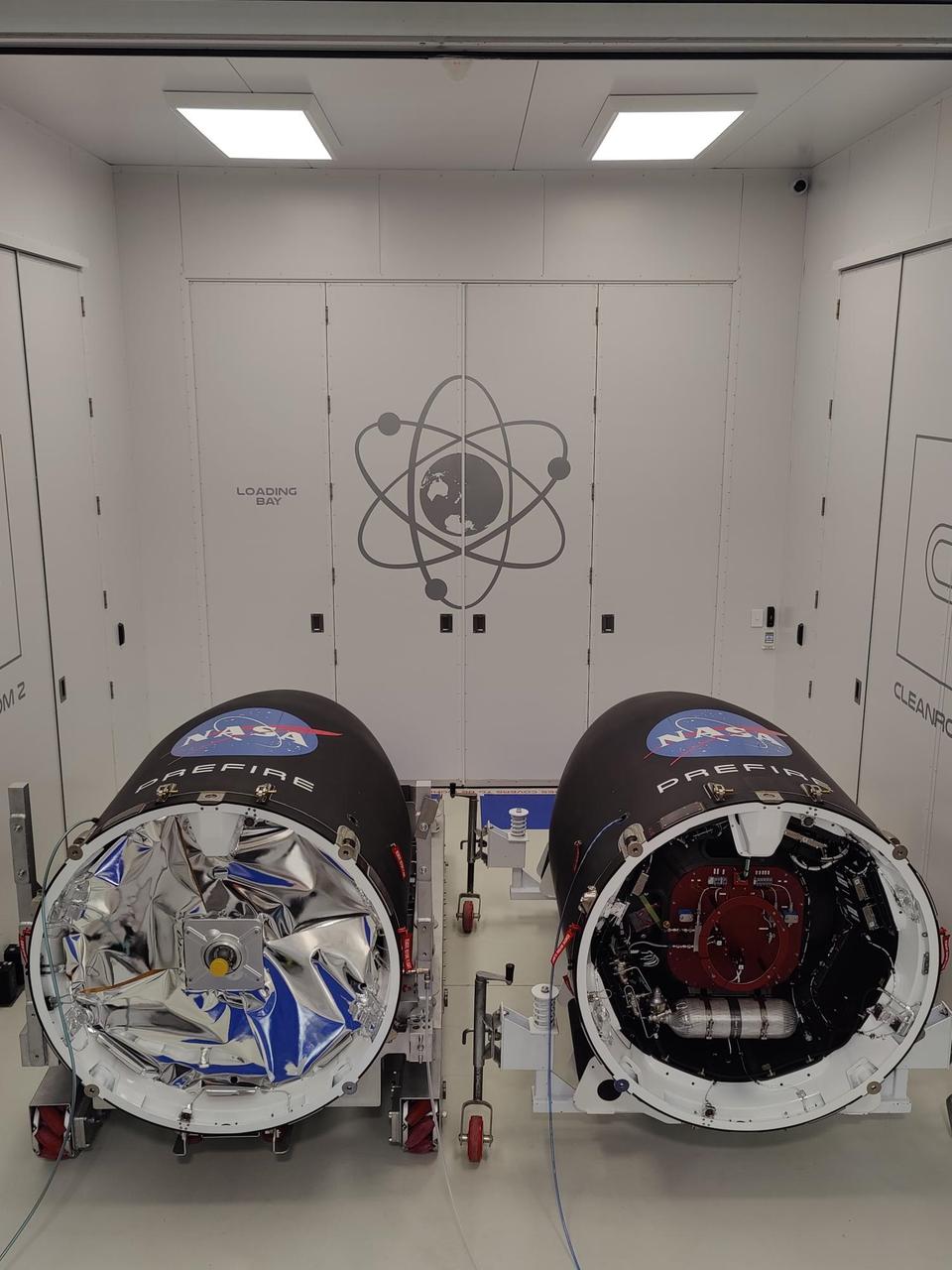

NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) CubeSats are encapsulated inside Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairings on Tuesday, May 21, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
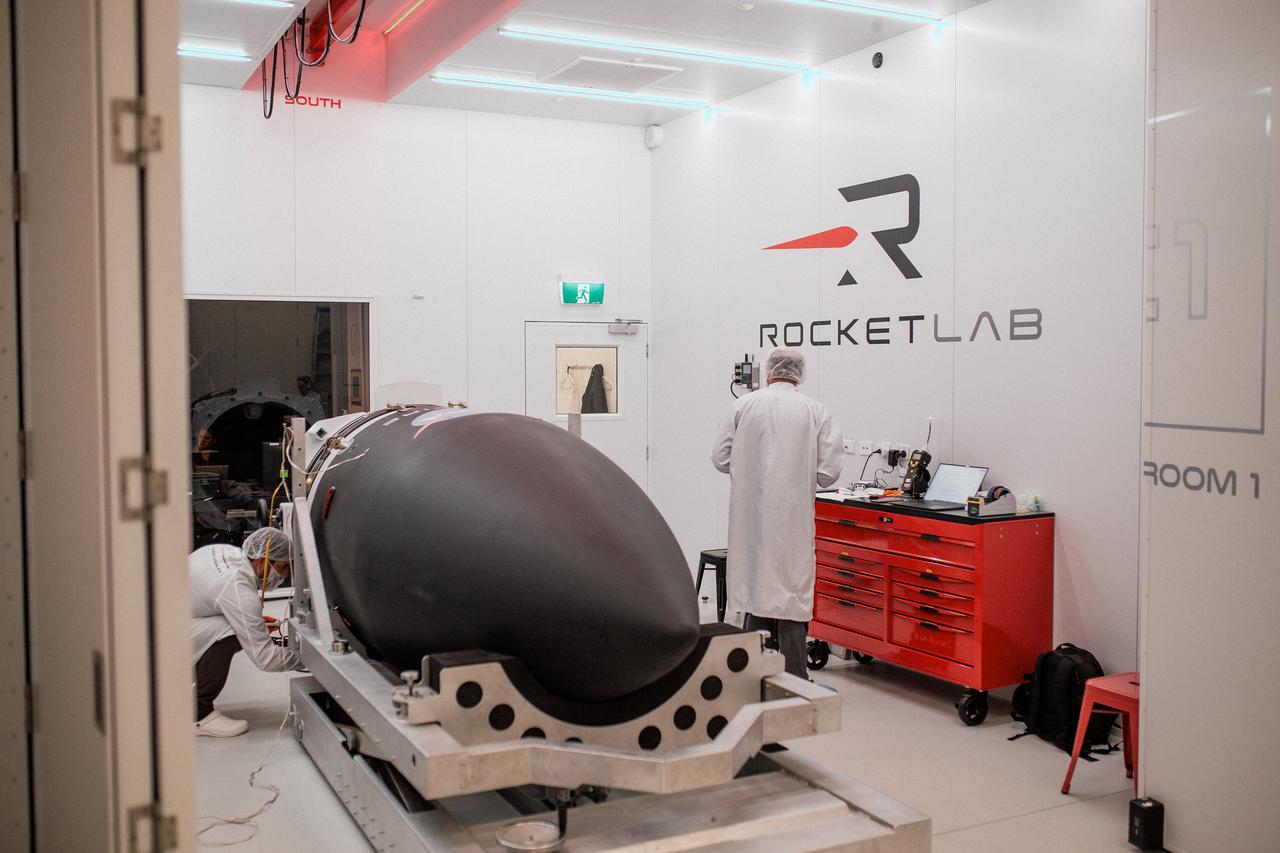

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
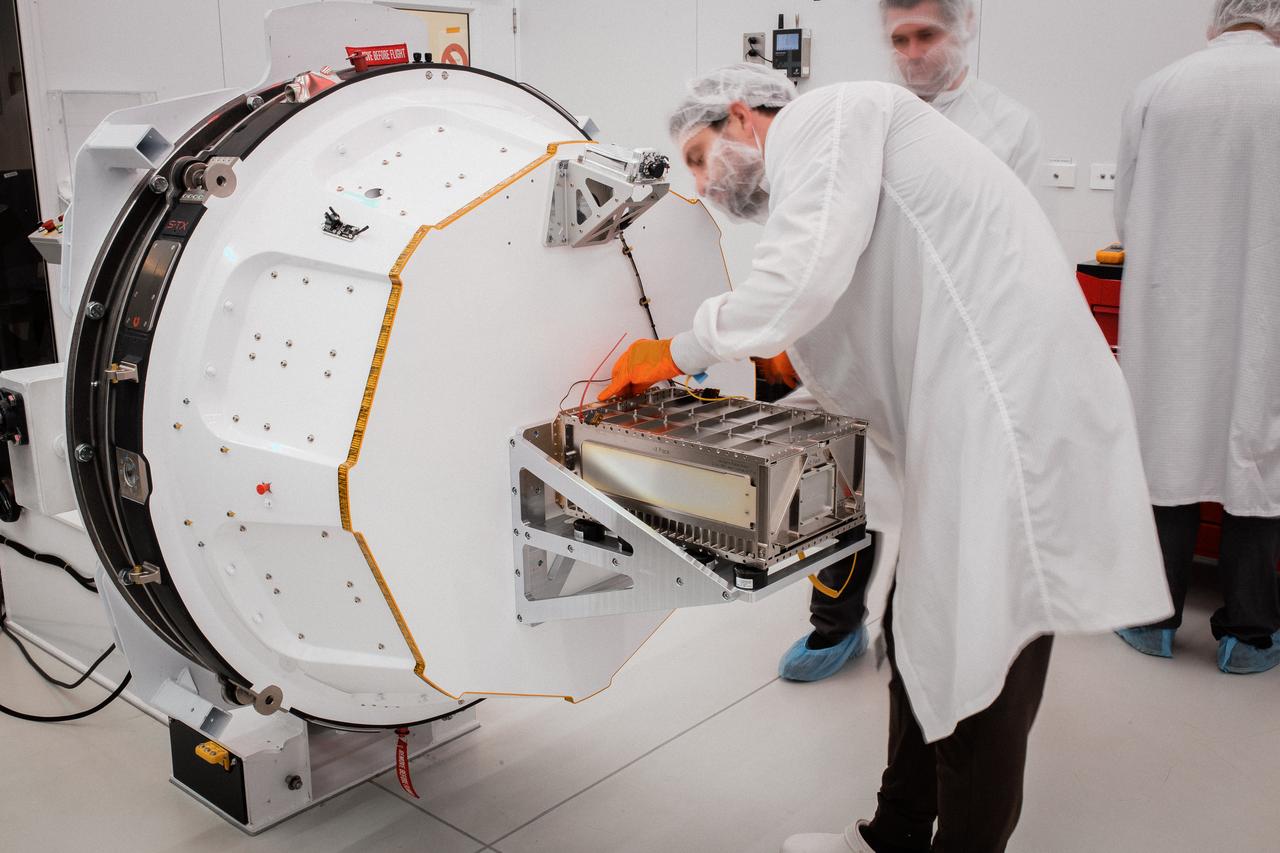

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
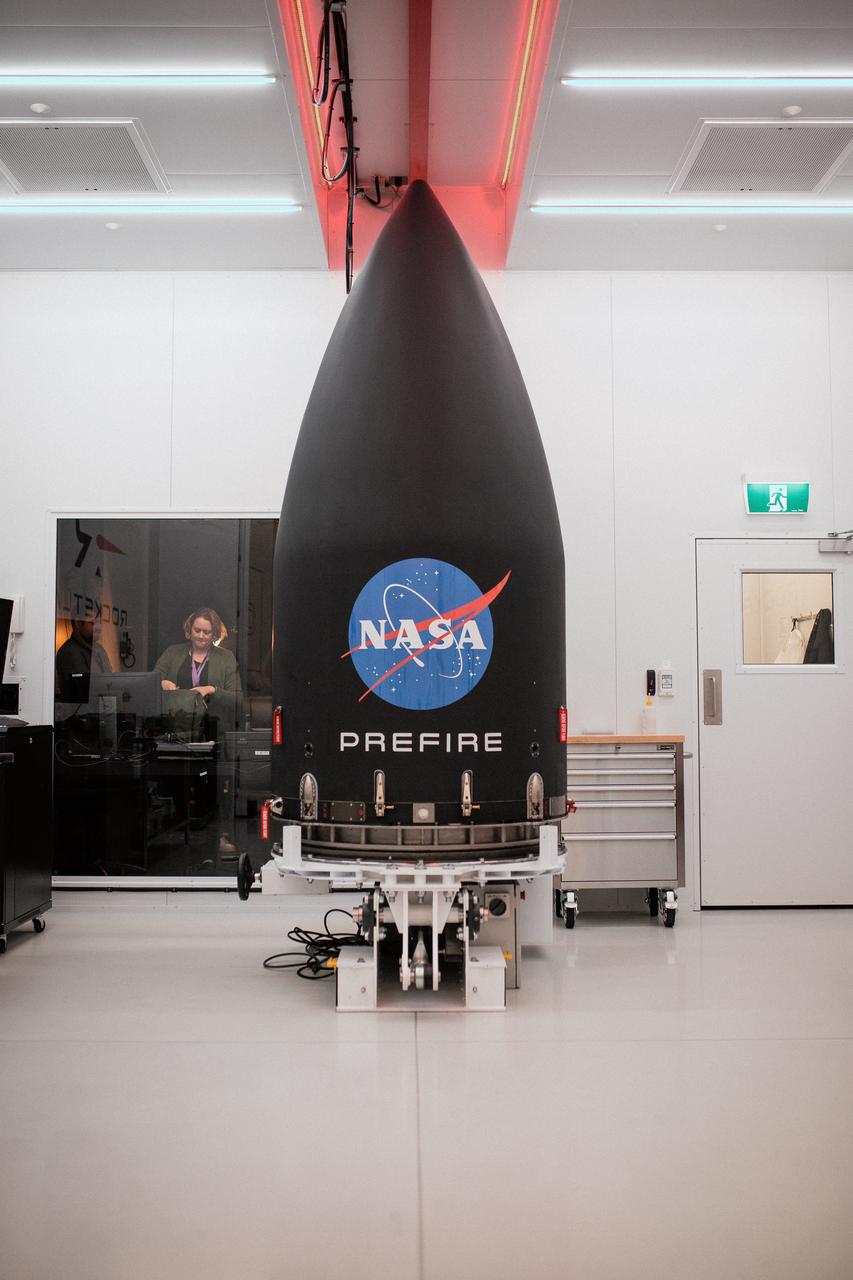

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
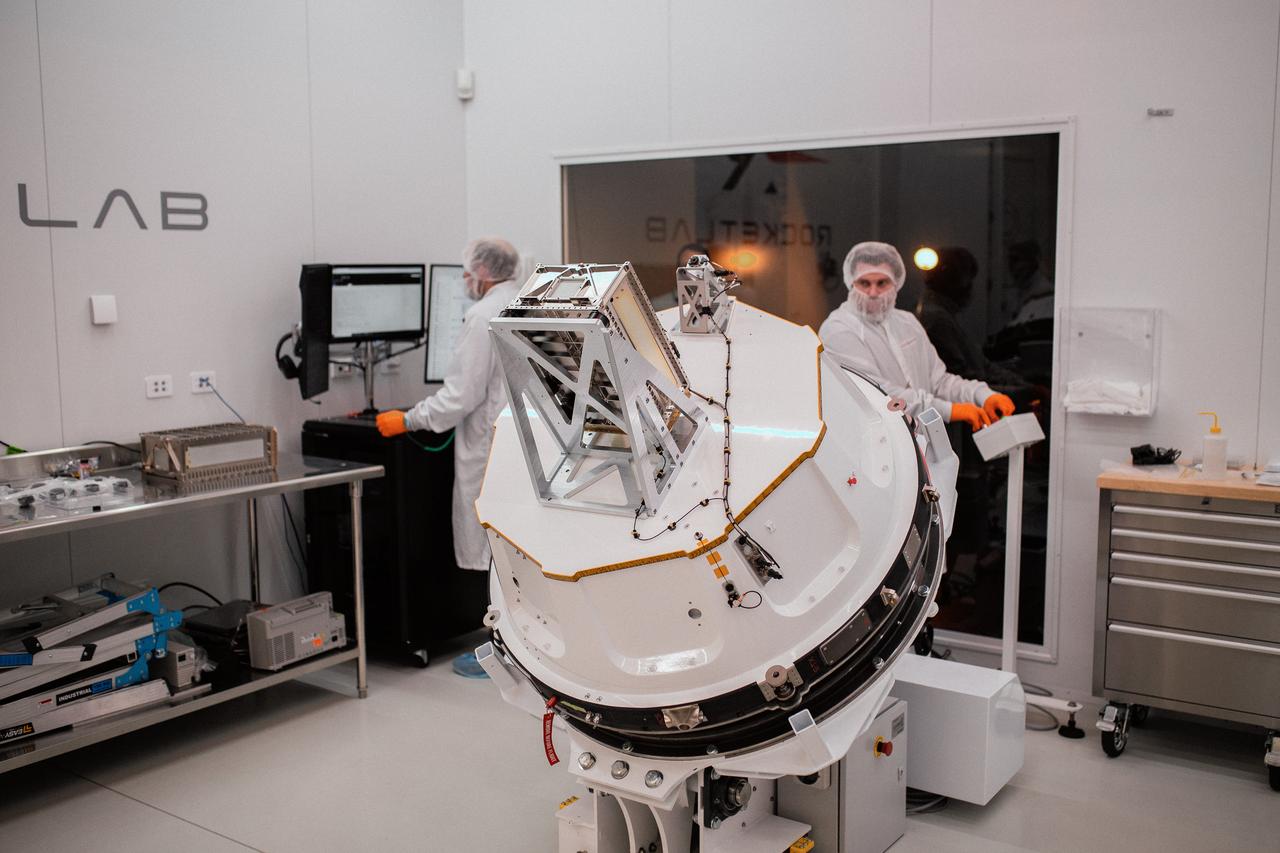

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
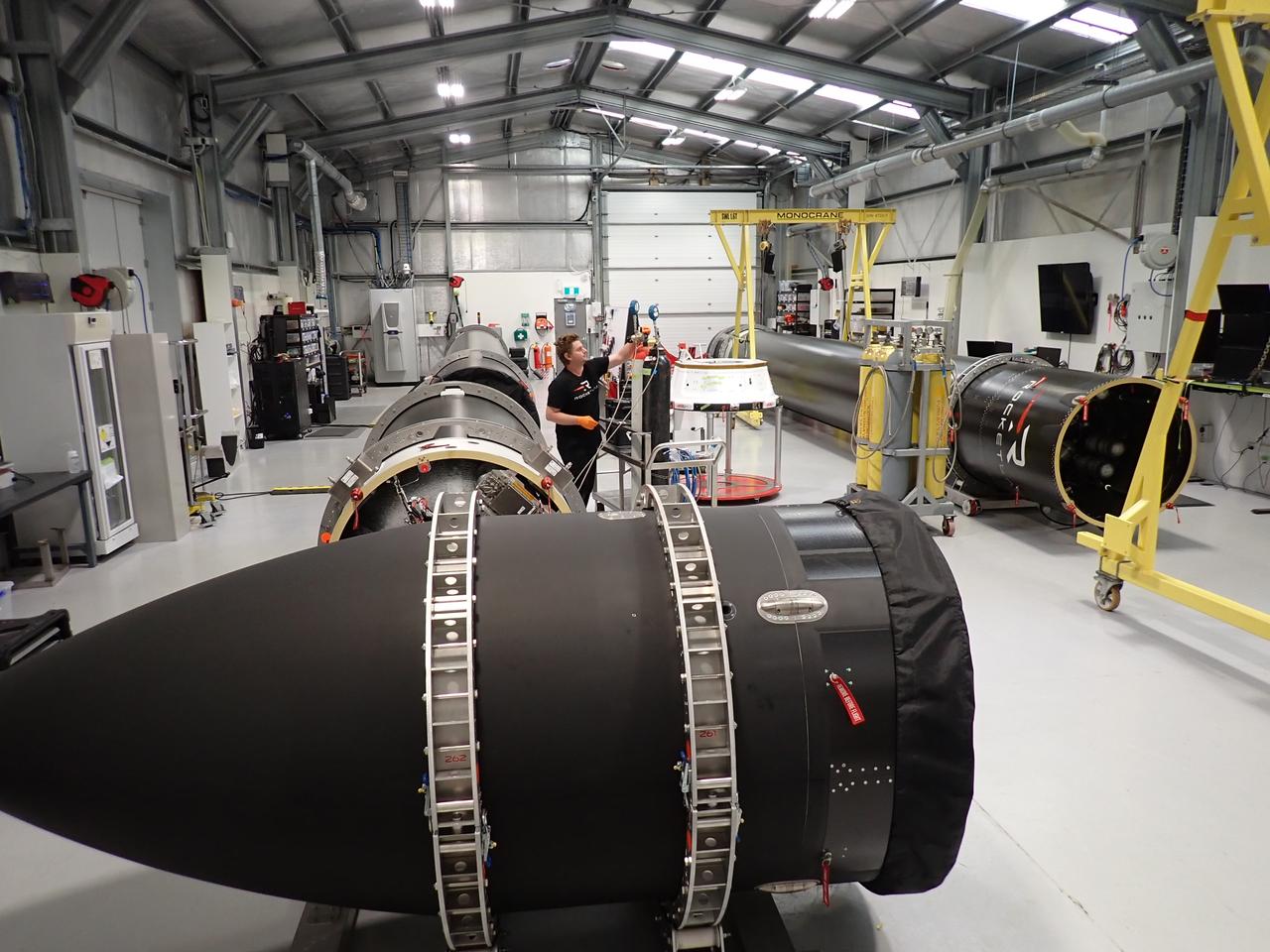

Technicians process NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) ahead of integration with a Rocket Lab Electron rocket on Thursday, May 2, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
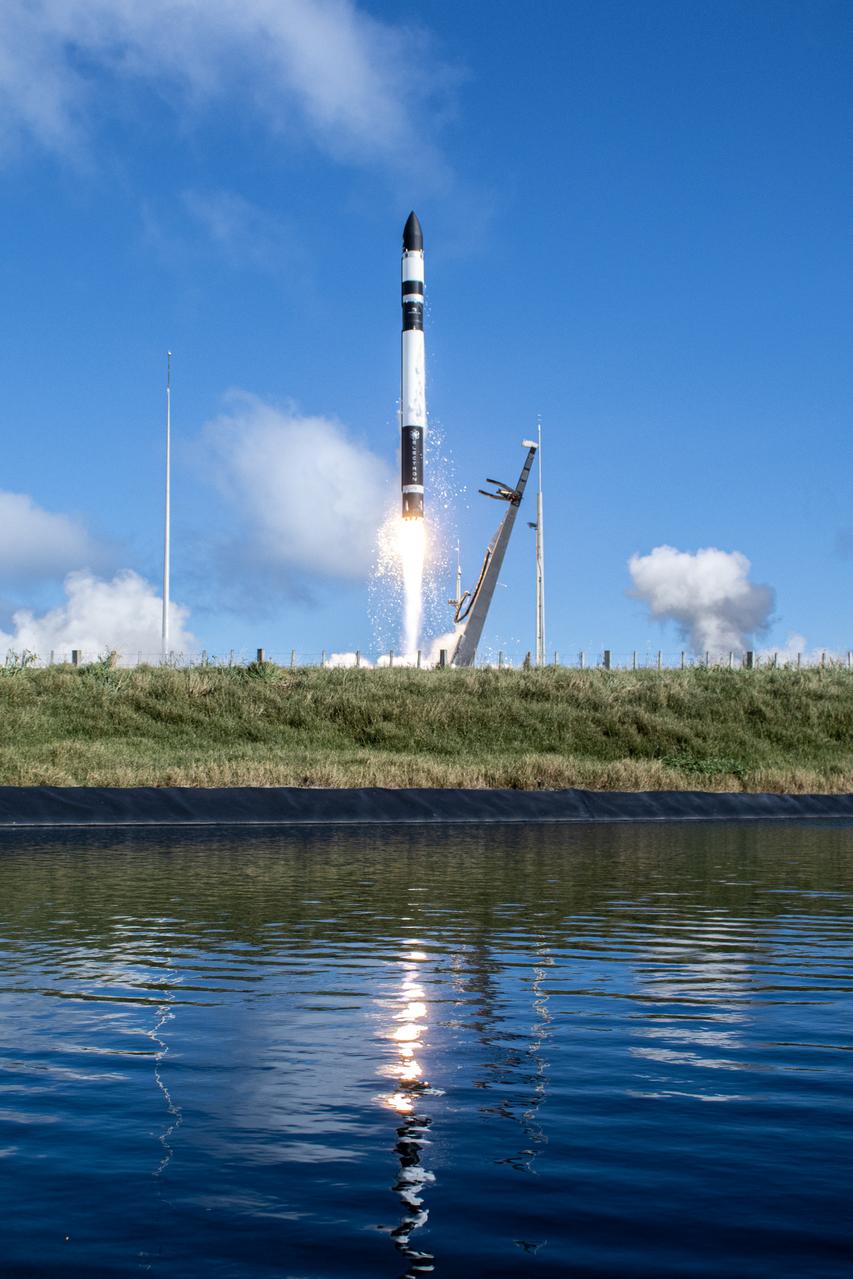

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
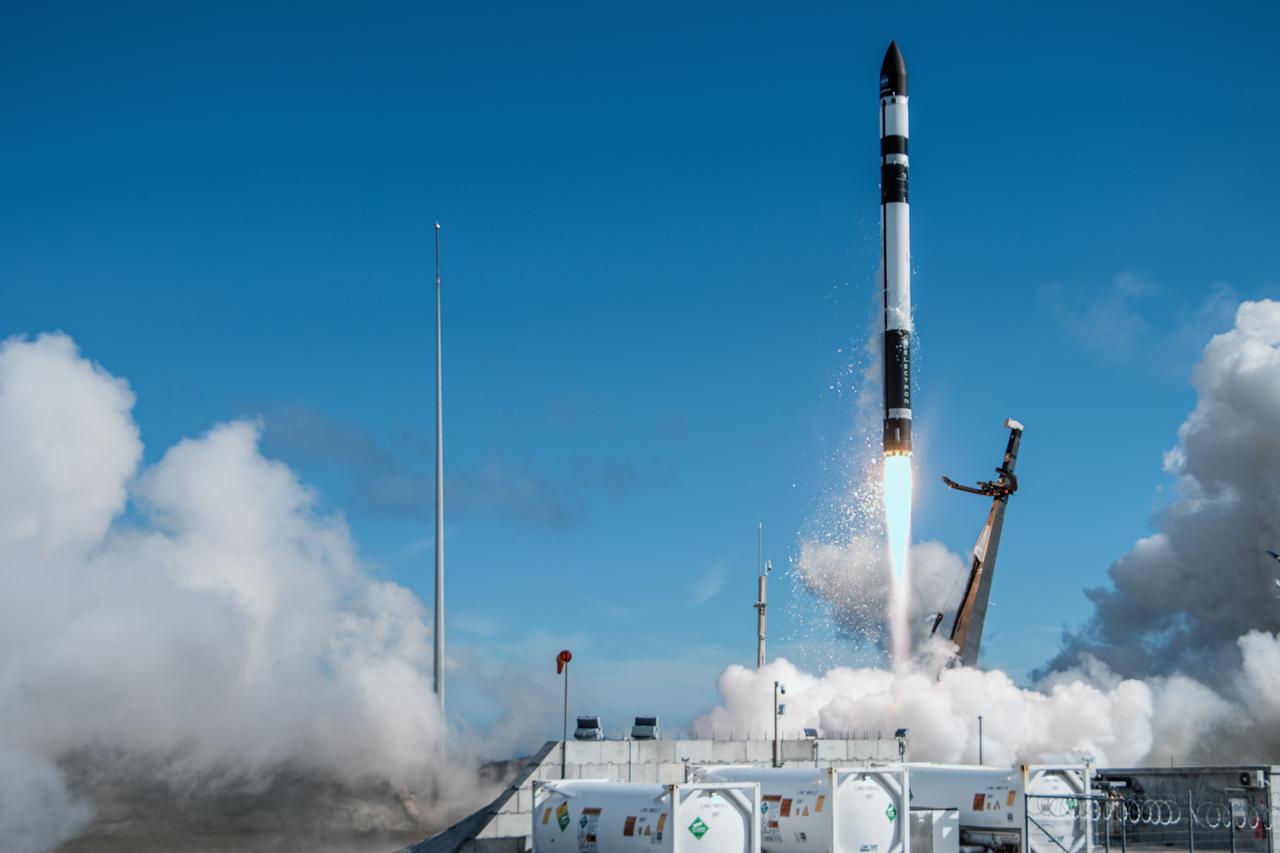

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
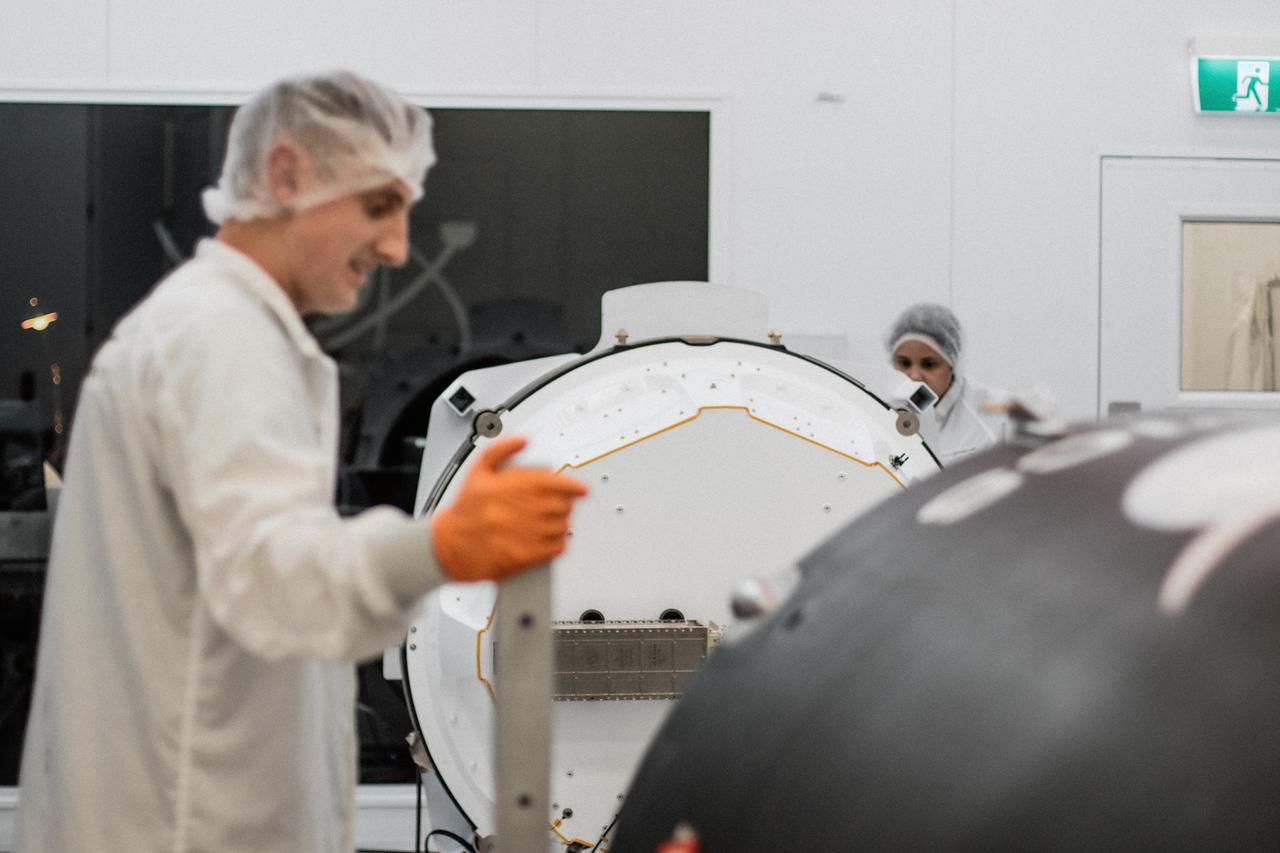

Two CubeSats are encapsulated at the Rocket Lab facility in Mahia, New Zealand, on April 24, 2023, in preparation for NASA’s second TROPICS (Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), for liftoff of the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
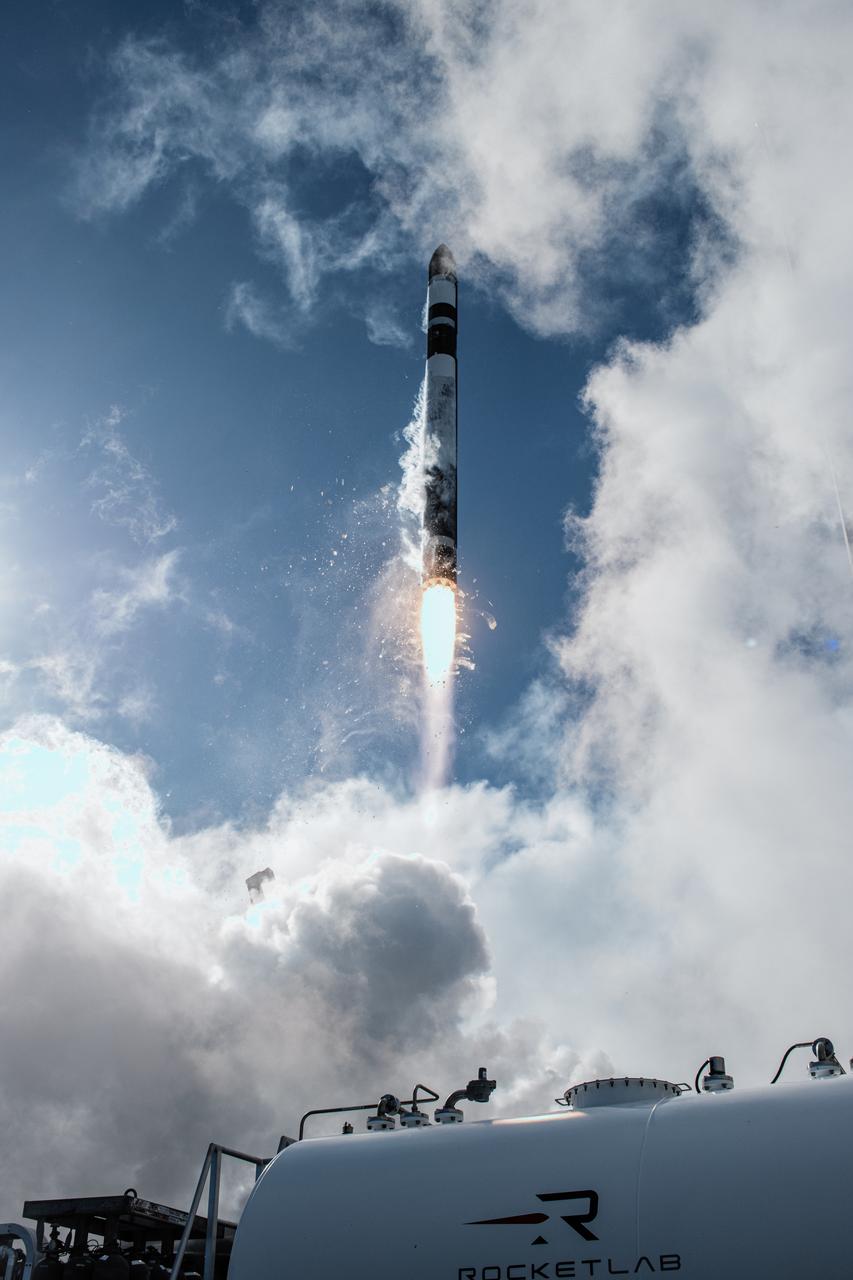

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket soars upward after liftoff from Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
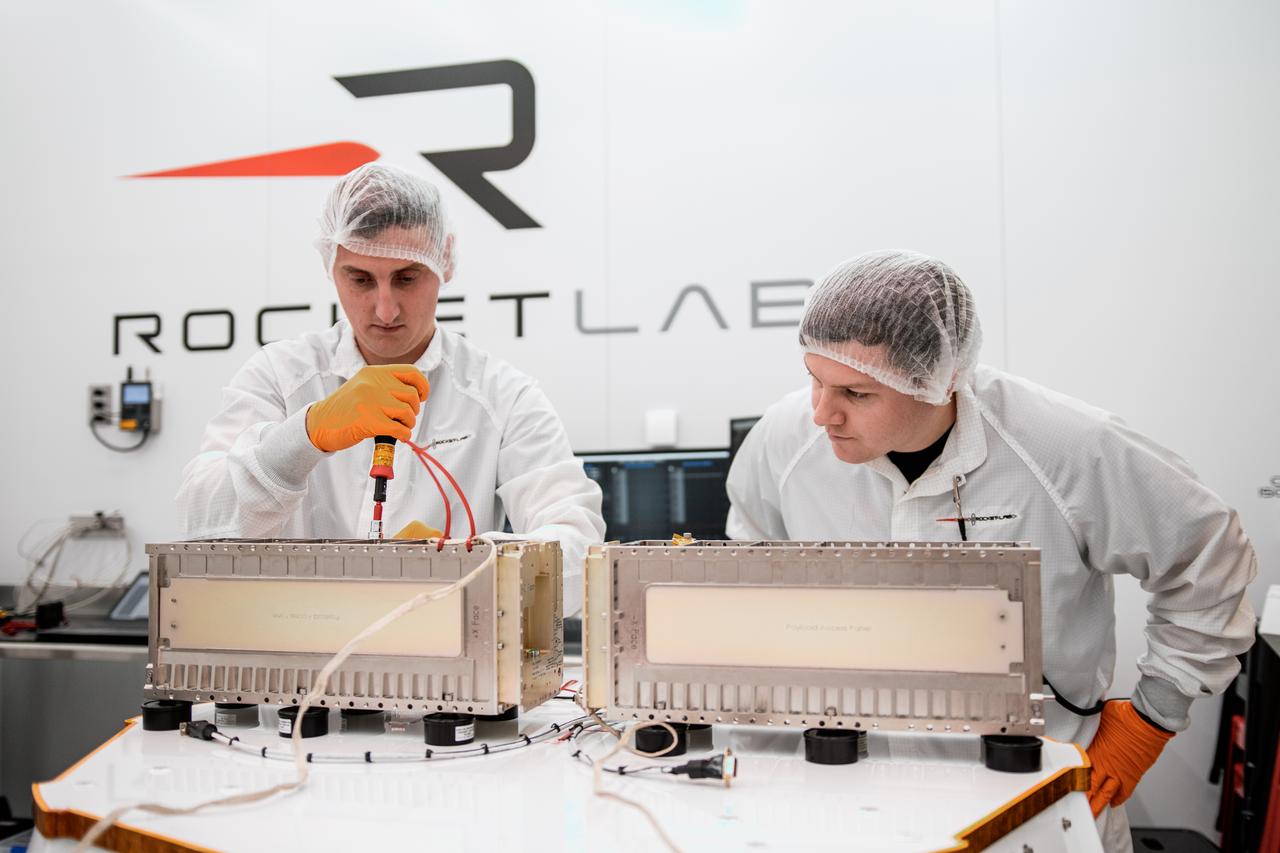

Two CubeSats are encapsulated at the Rocket Lab facility in Mahia, New Zealand, on April 24, 2023, in preparation for NASA’s second TROPICS (Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), for liftoff of the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.

Two CubeSats are encapsulated at the Rocket Lab facility in Mahia, New Zealand, on April 24, 2023, in preparation for NASA’s second TROPICS (Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), for liftoff of the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
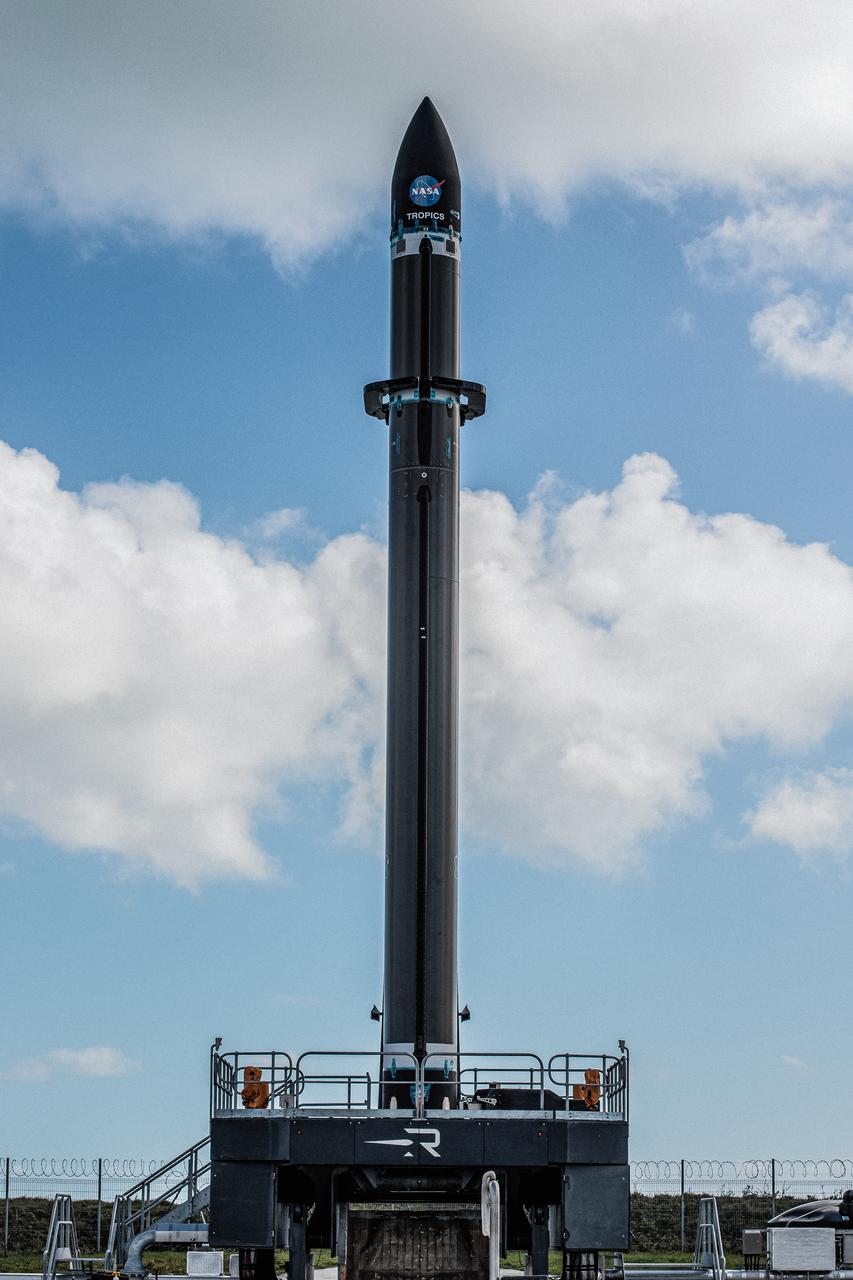

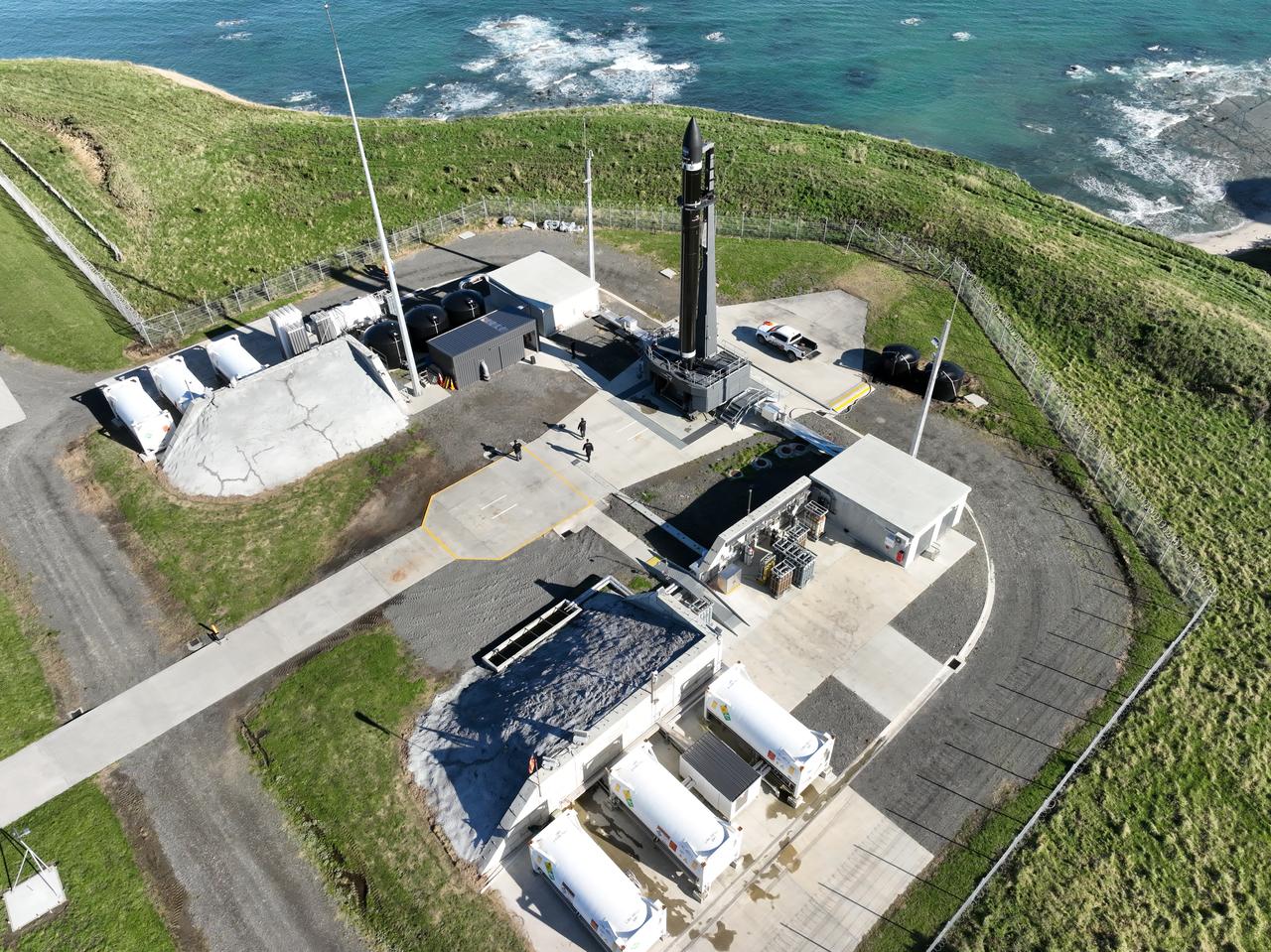
Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
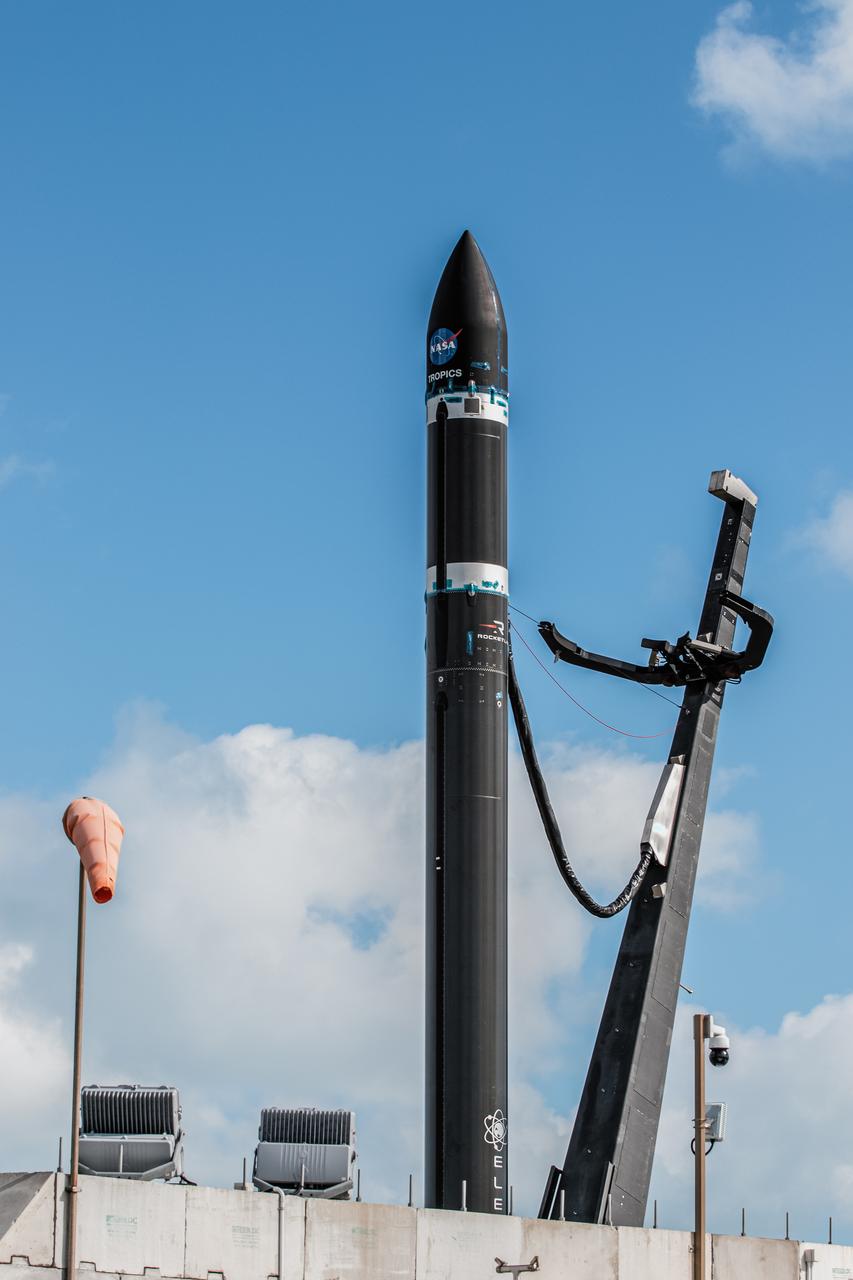

With the umbilical tower in view, Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
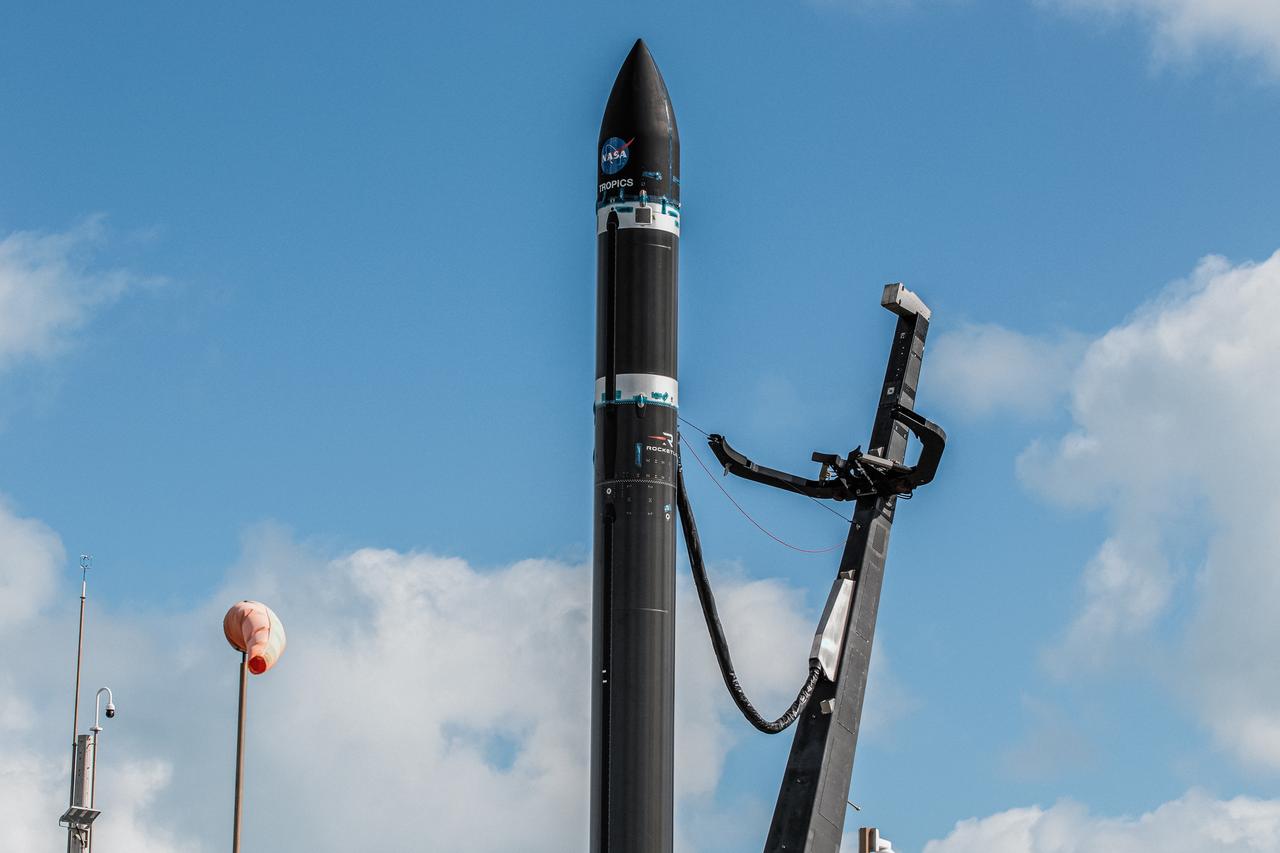

With the umbilical tower in view, Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad Saturday, May 25, 2024, at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the first of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the first CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” occurred at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT).
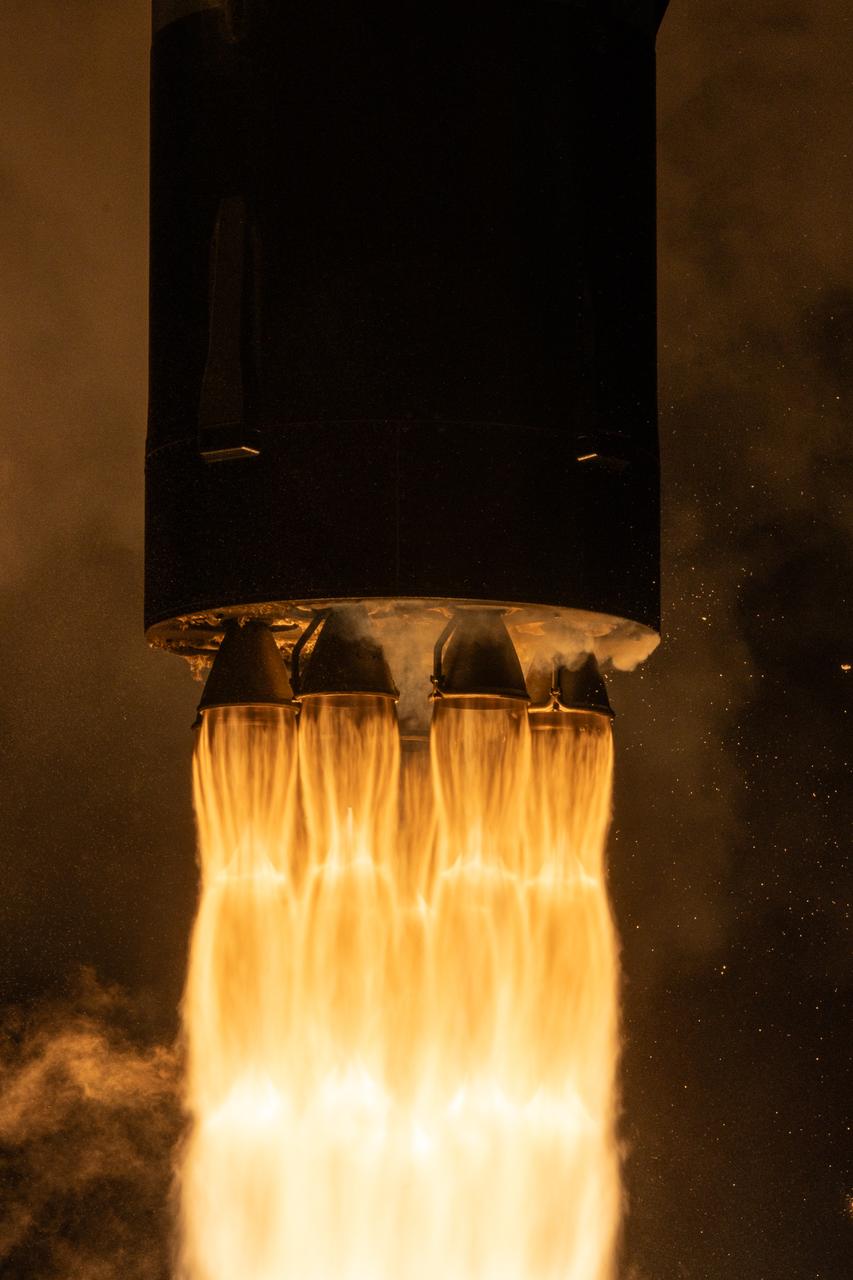

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off from Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT) Saturday, May 25, 2024, on the first of two launches which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission. The PREFIRE mission, expected to last at least 10 months, consists of sending two CubeSats to asynchronous, near-polar orbits, to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
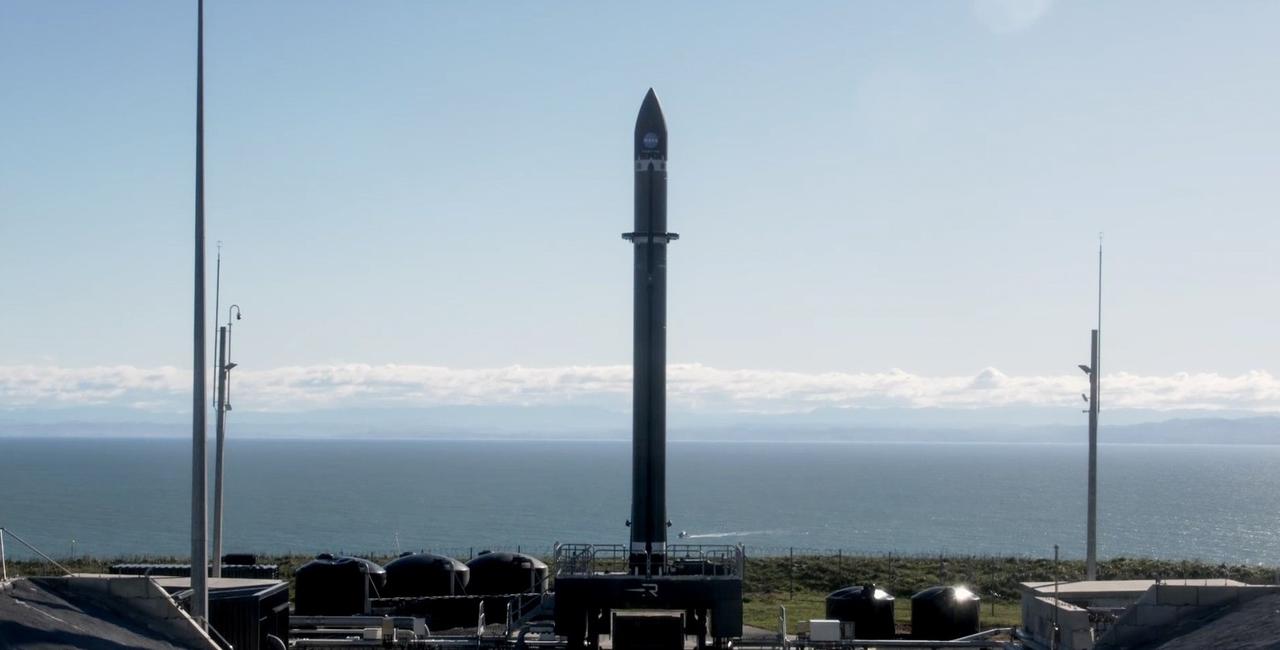

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad Saturday, May 25, 2024, at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the first of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the first CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” occurred at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT).
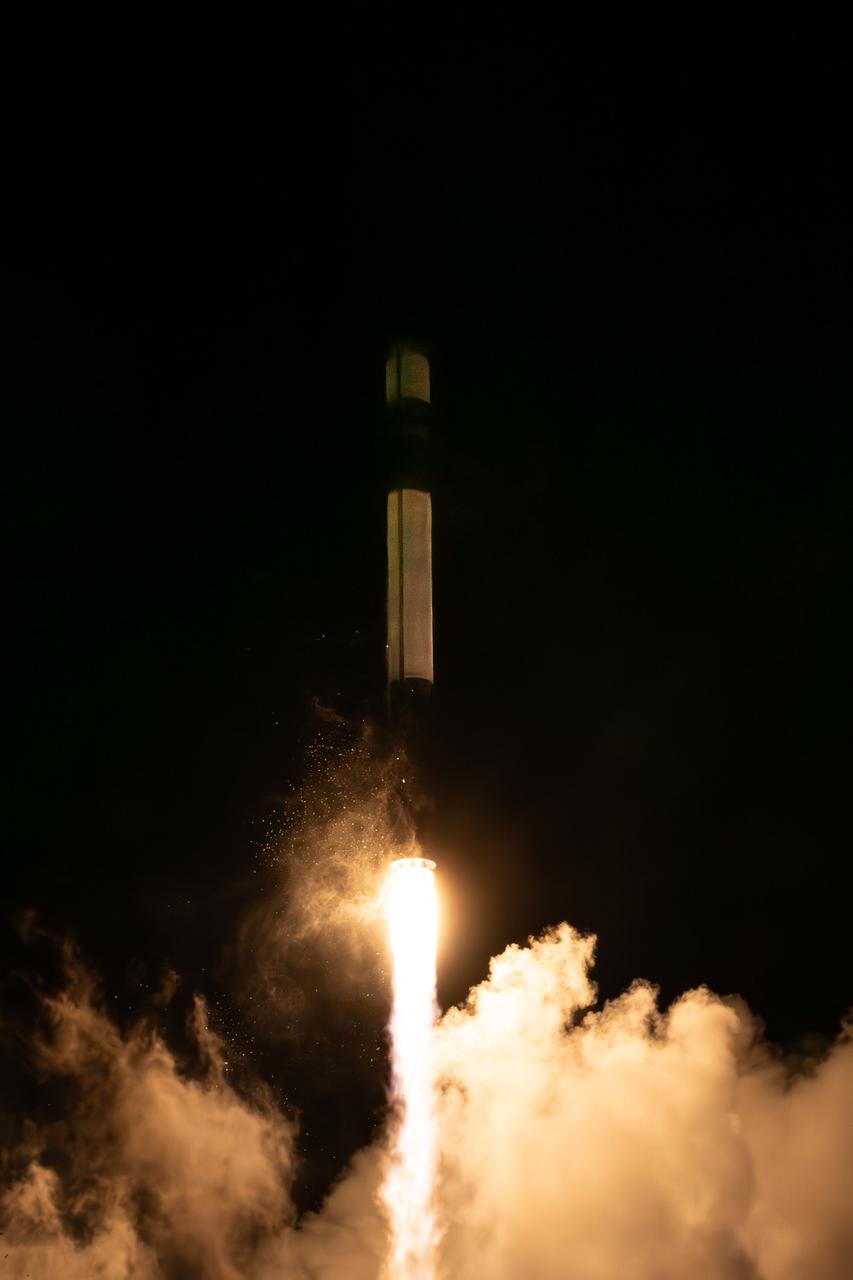

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off from Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT) Saturday, May 25, 2024, on the first of two launches which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission. The PREFIRE mission, expected to last at least 10 months, consists of sending two CubeSats to asynchronous, near-polar orbits, to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.

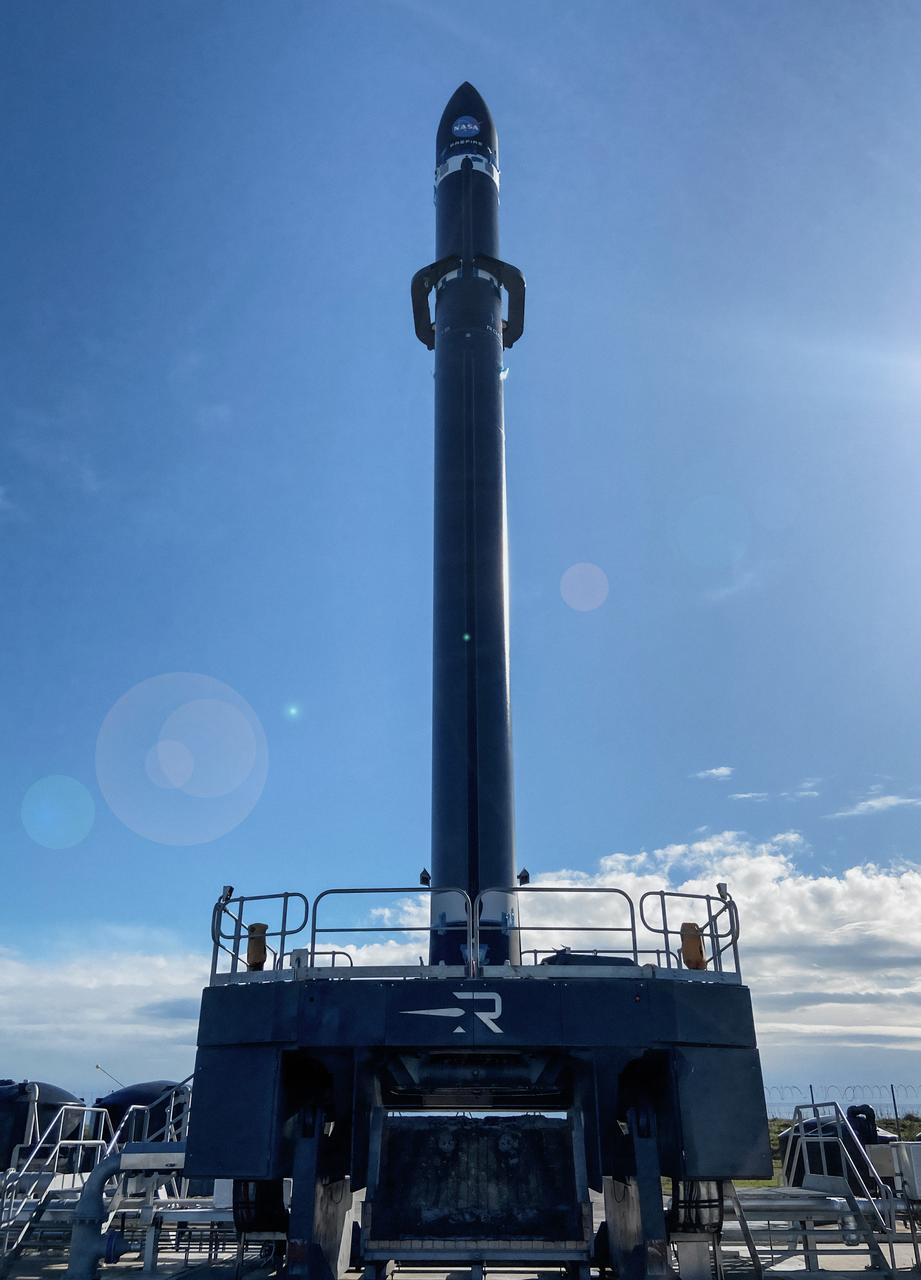
Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad Saturday, May 25, 2024, at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the first of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the first CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” occurred at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT).

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad Saturday, May 25, 2024, at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the first of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the first CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” occurred at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT).
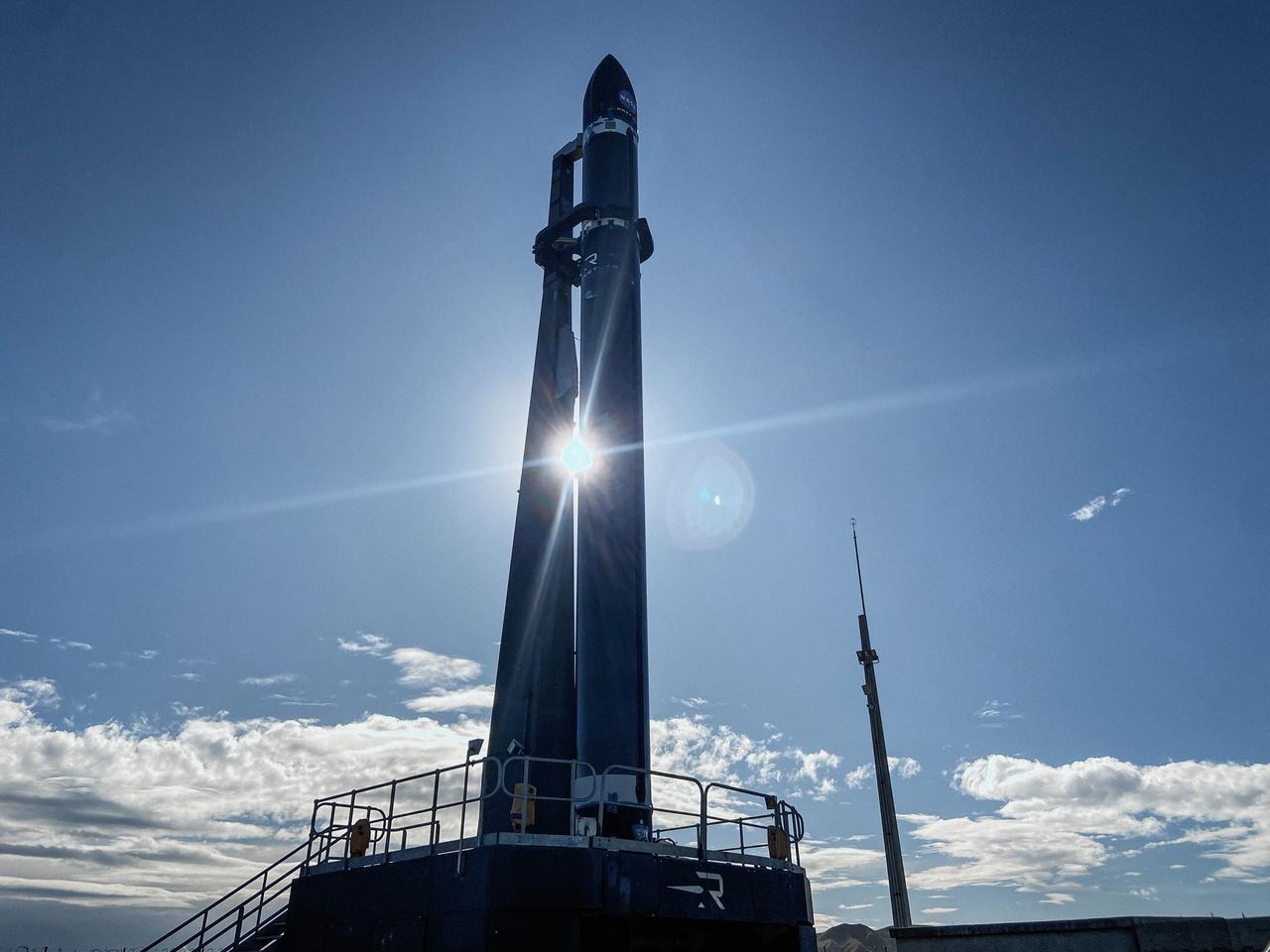

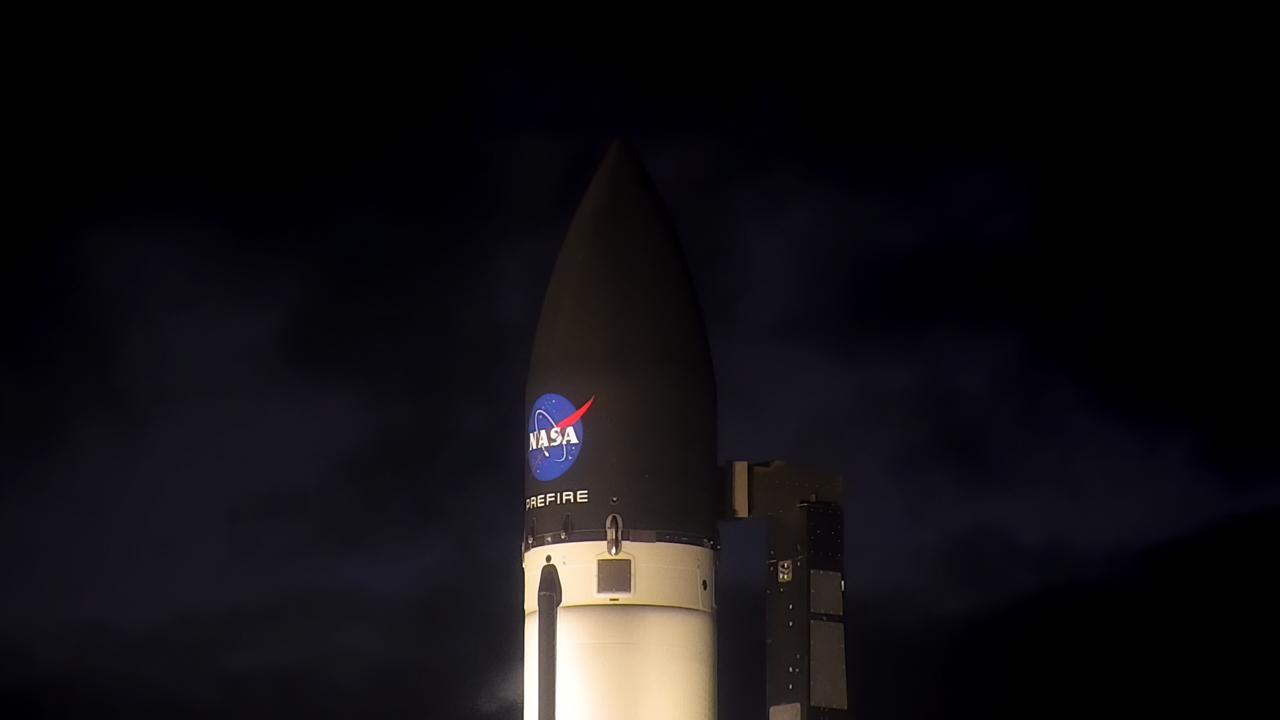
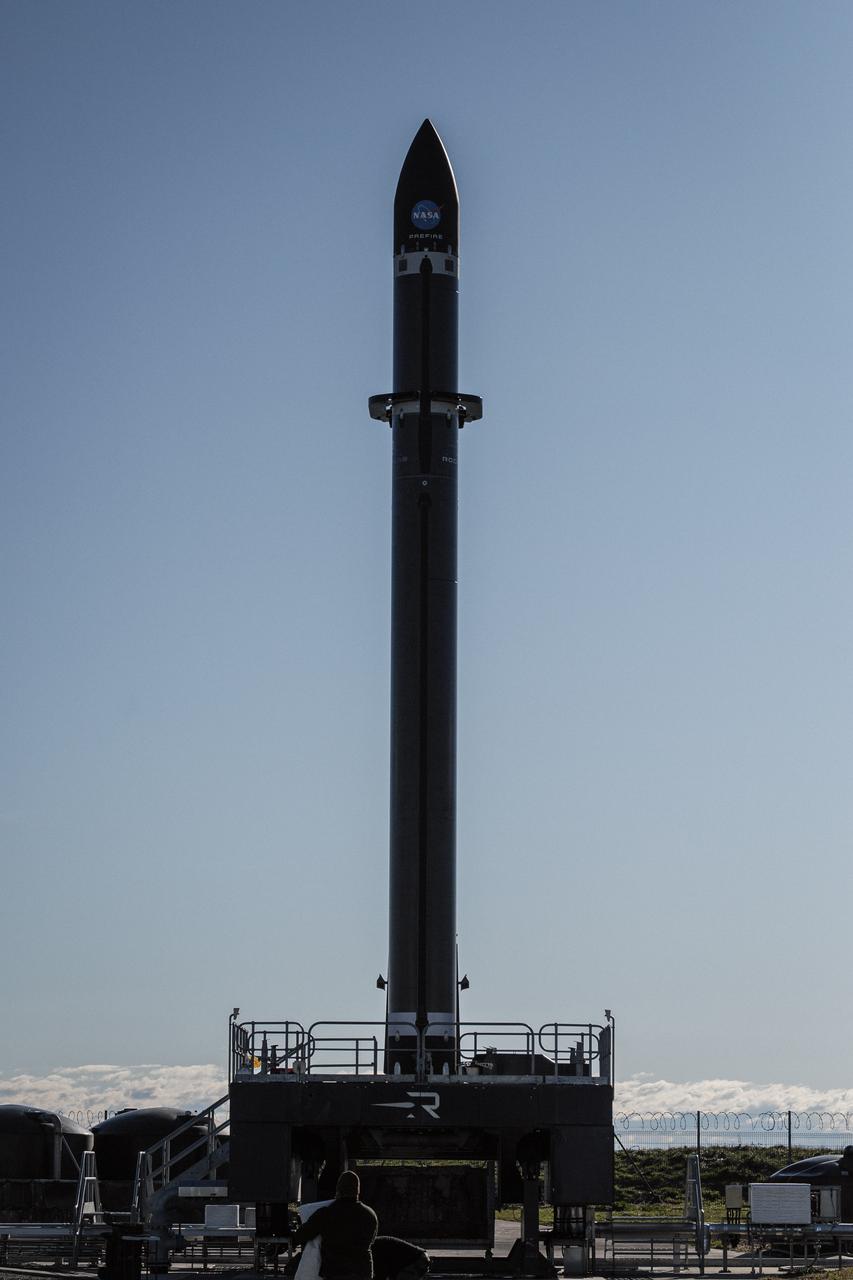
Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the second of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the second CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “PREFIRE and Ice” was targeted for Saturday, June 1, 2024, but was scrubbed for the day.

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the second of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the second CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “PREFIRE and Ice” was targeted for Saturday, June 1, 2024, but was scrubbed for the day.
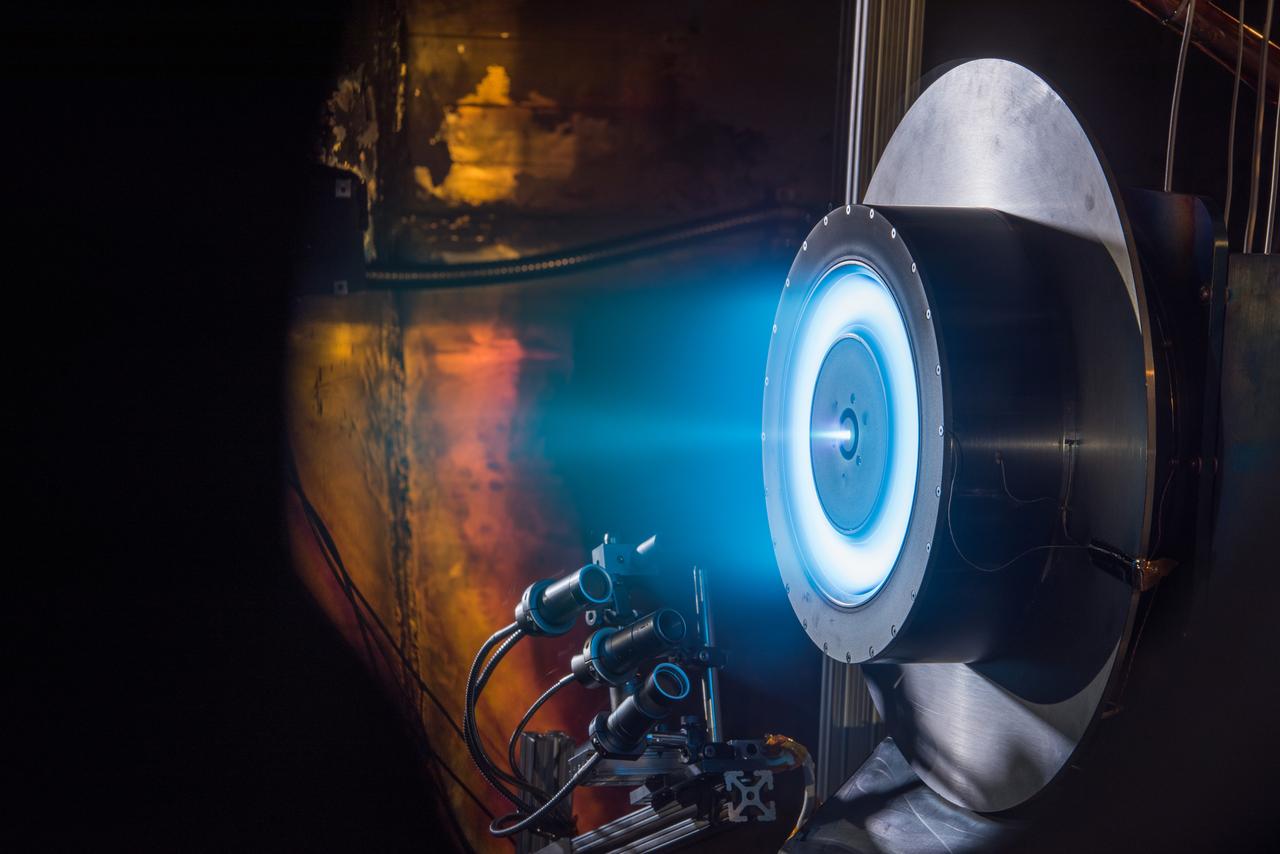
Hall Effect Rocket with Magnetic Shielding Technology Development Unit 1 with Large Radiator working in conjunction with High Power 300 volt Silicon Carbide Power Processing Unit

HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS FROM NORTH ALABAMA GATHER AT THE U.S. SPACE AND ROCKET CENTER'S DAVIDSON CENTER FOR THE "ROBOTS TO ROCKET CITY" EVENT SHOWCASING THEIR INDIVIDUAL ROBOTS PRIOR TO LATER COMPETITIONS.

HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS FROM NORTH ALABAMA GATHER AT THE U.S. SPACE AND ROCKET CENTER'S DAVIDSON CENTER FOR THE "ROBOTS TO ROCKET CITY" EVENT SHOWCASING THEIR INDIVIDUAL ROBOTS PRIOR TO LATER COMPETITIONS.

HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS FROM NORTH ALABAMA GATHER AT THE U.S. SPACE AND ROCKET CENTER'S DAVIDSON CENTER FOR THE "ROBOTS TO ROCKET CITY" EVENT SHOWCASING THEIR INDIVIDUAL ROBOTS PRIOR TO LATER COMPETITIONS.
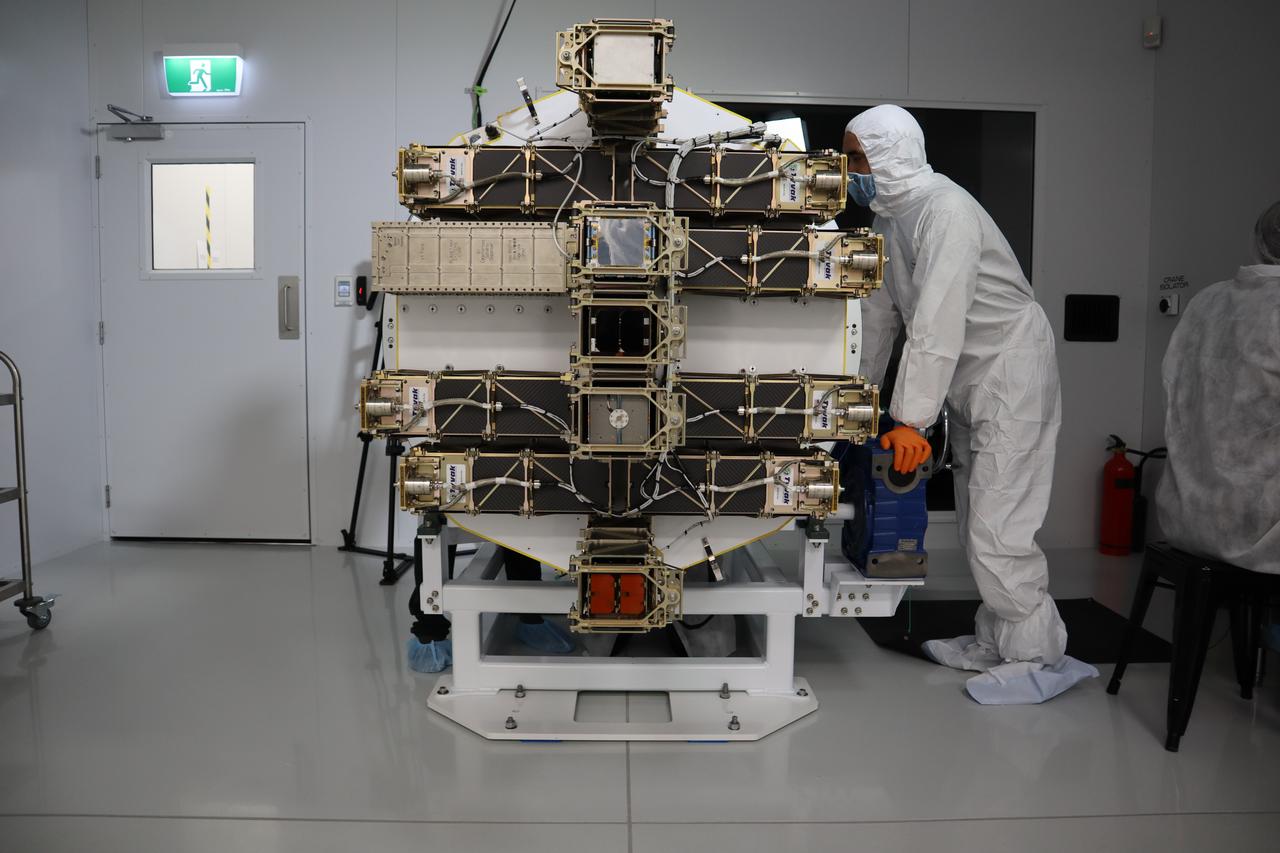

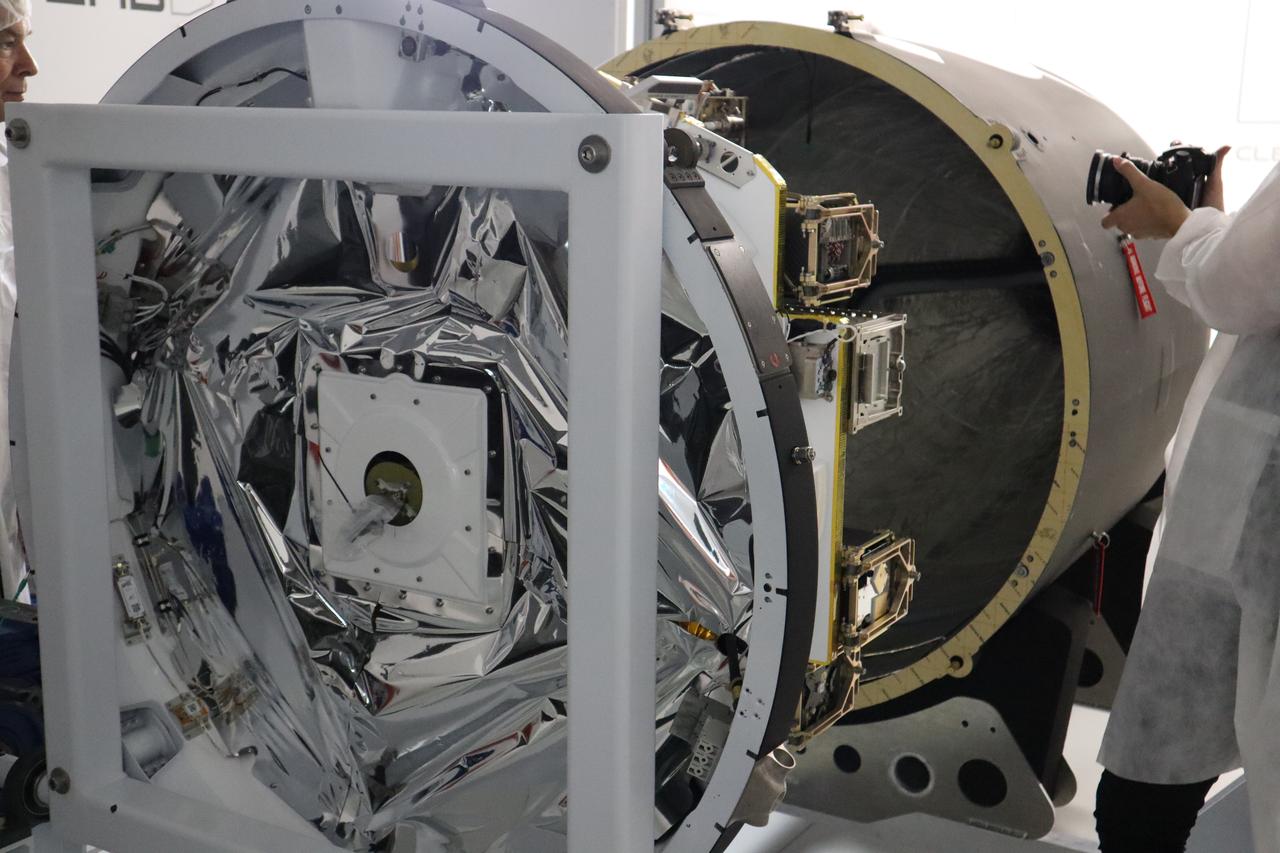
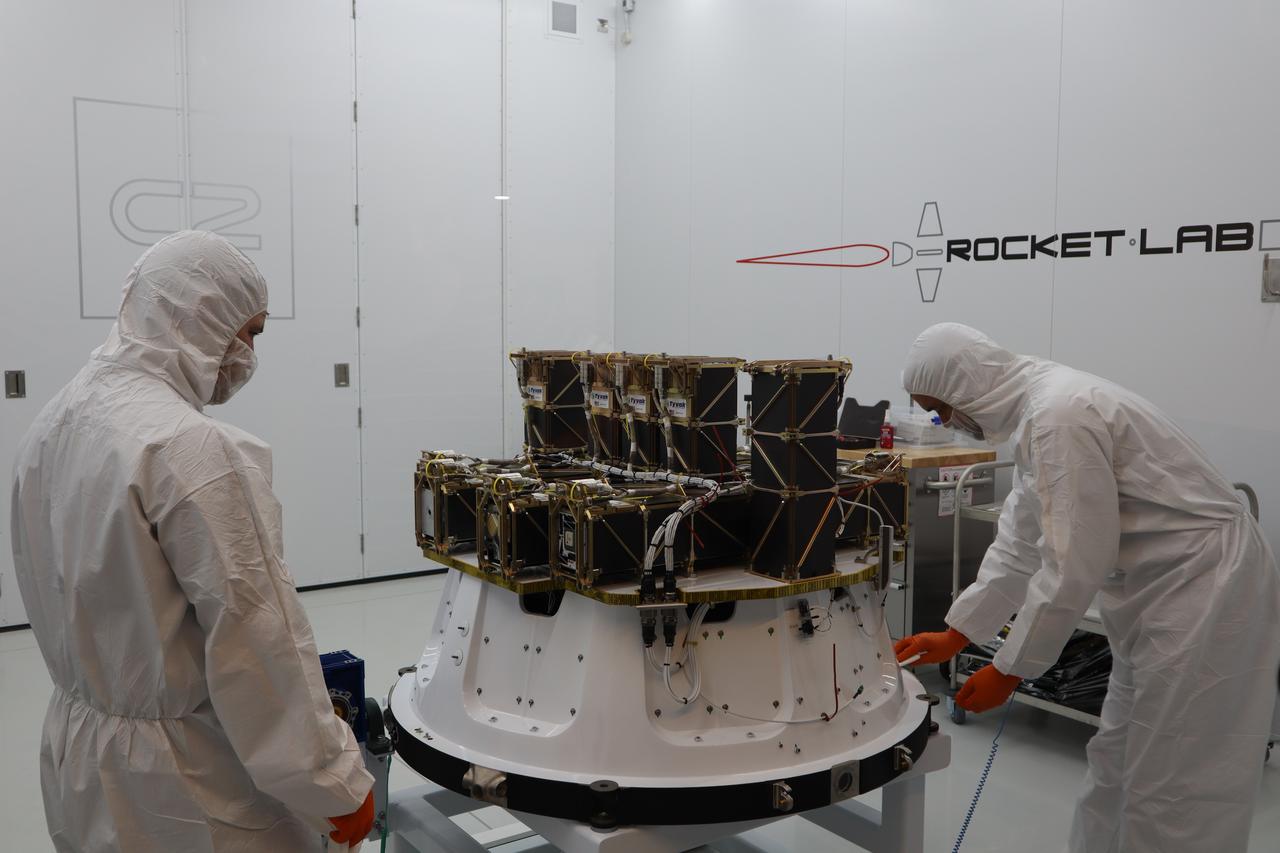
The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload has been encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
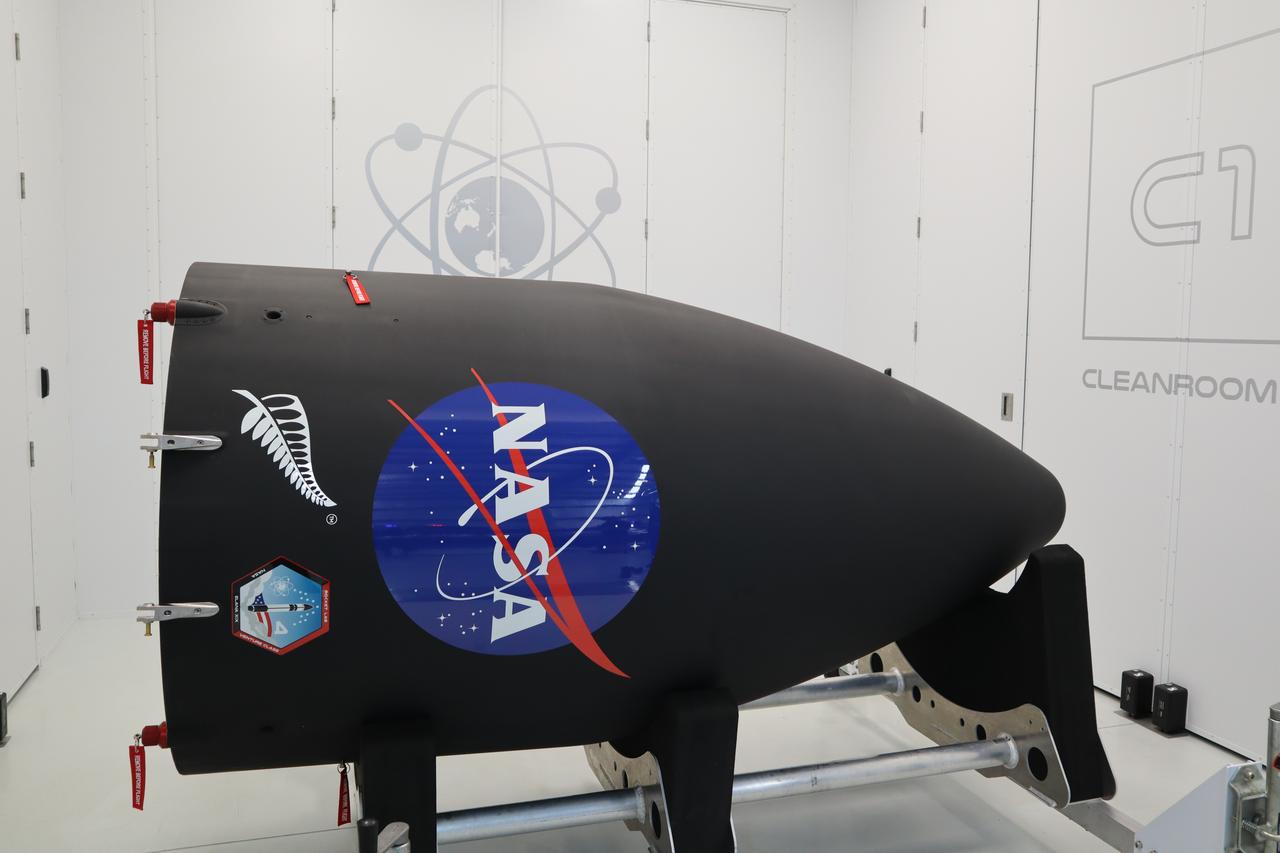
The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload has been encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

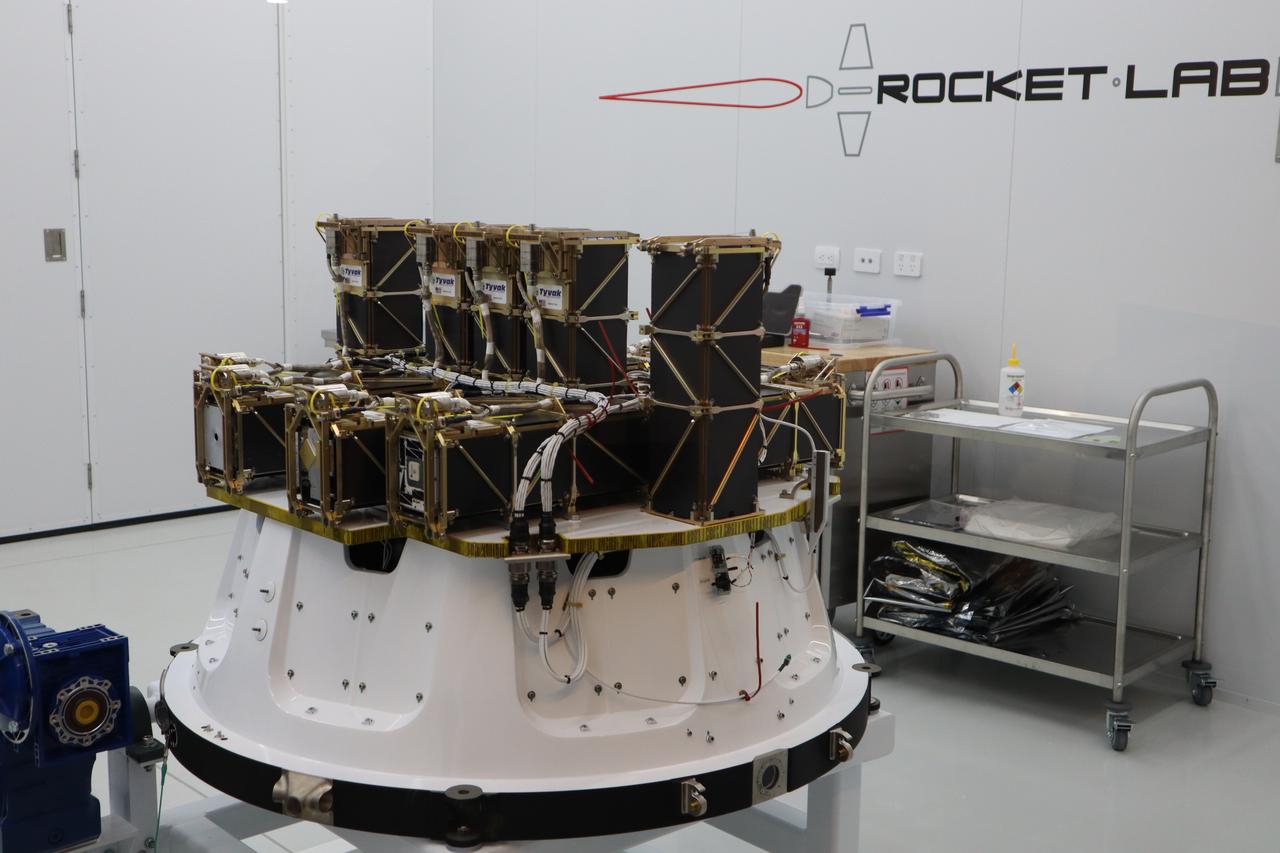
The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is prepared to be encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
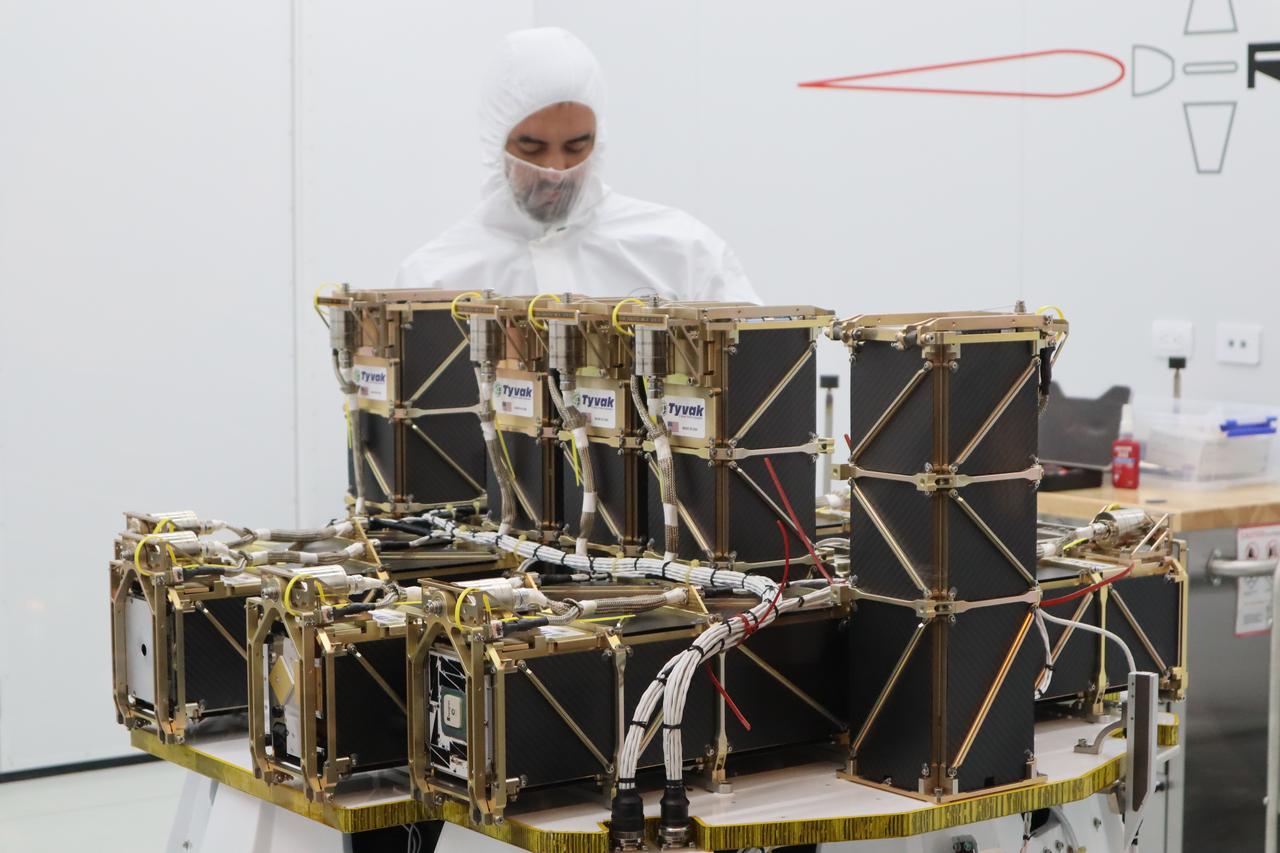

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is prepared to be encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
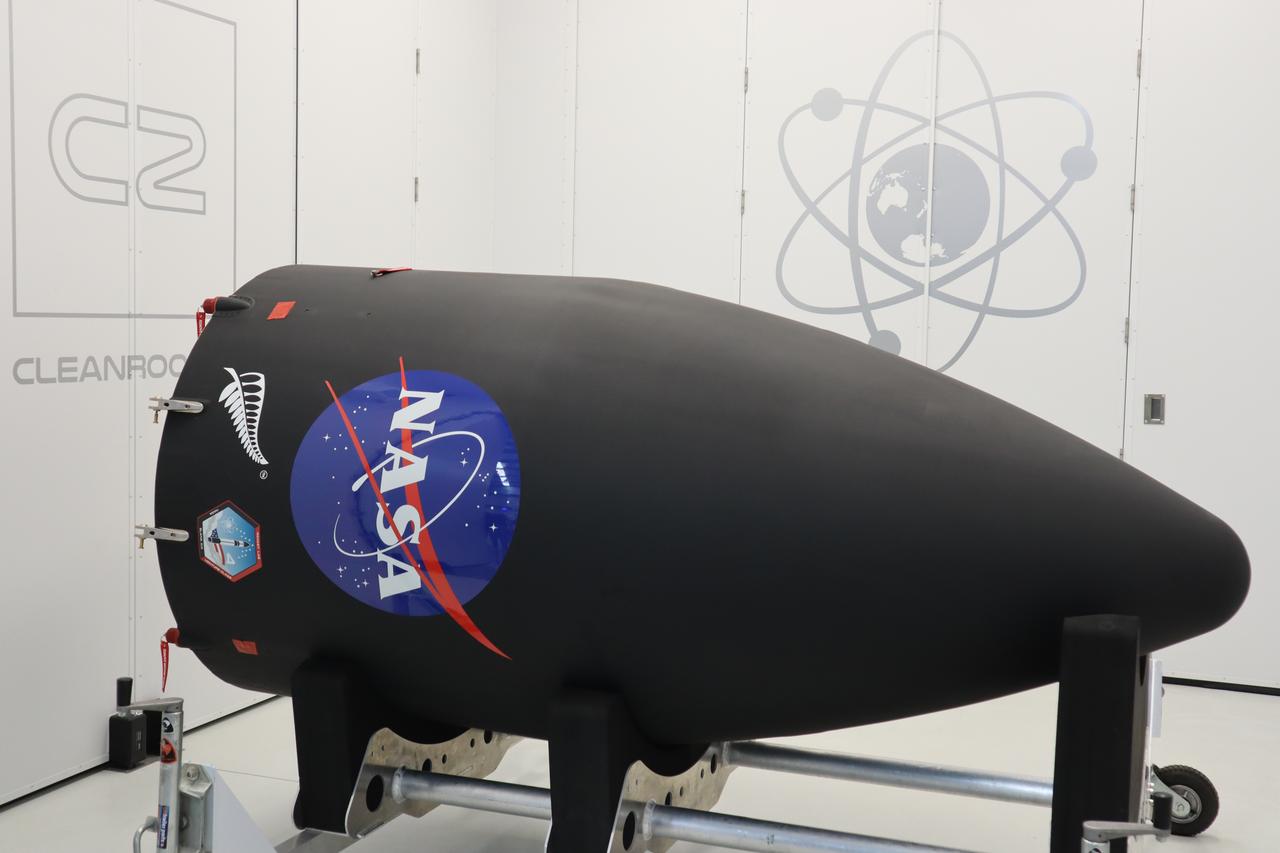
The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
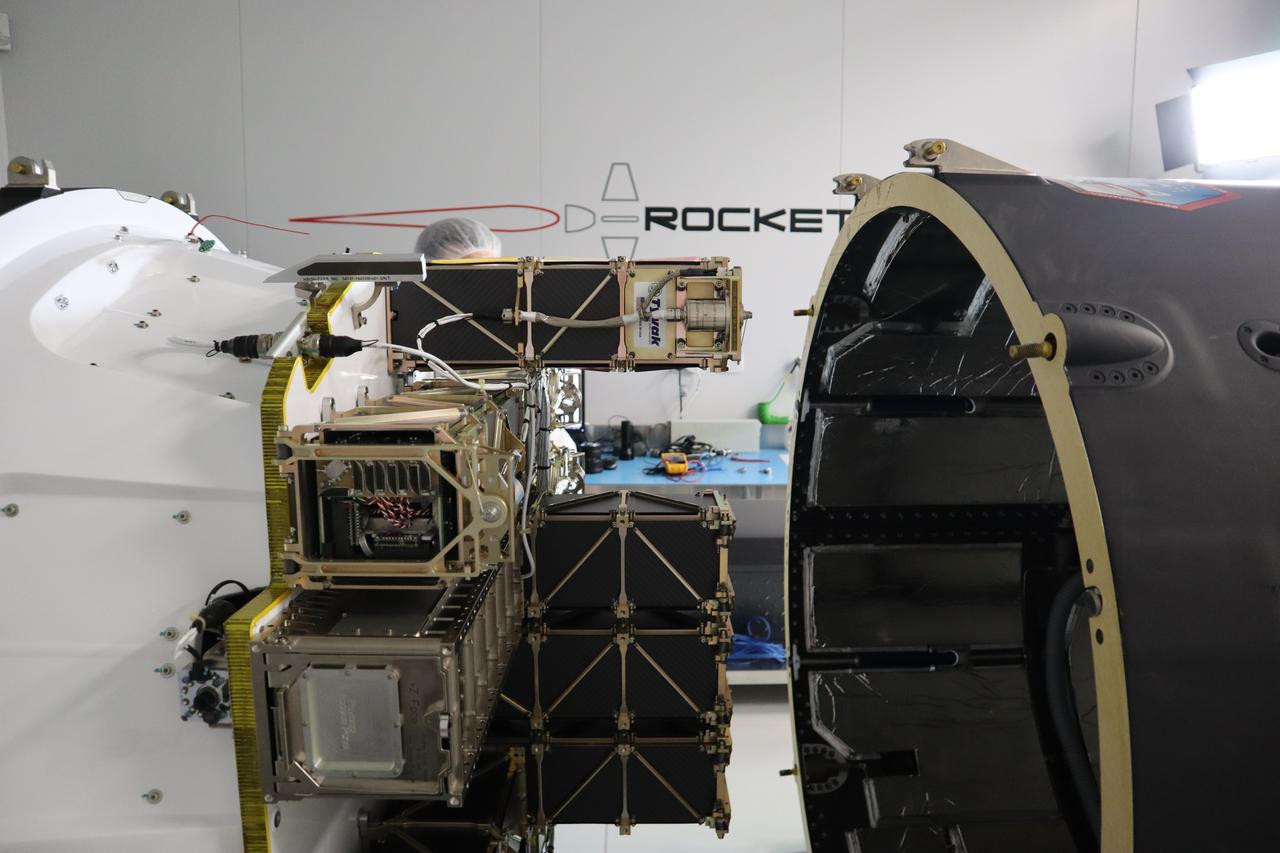

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
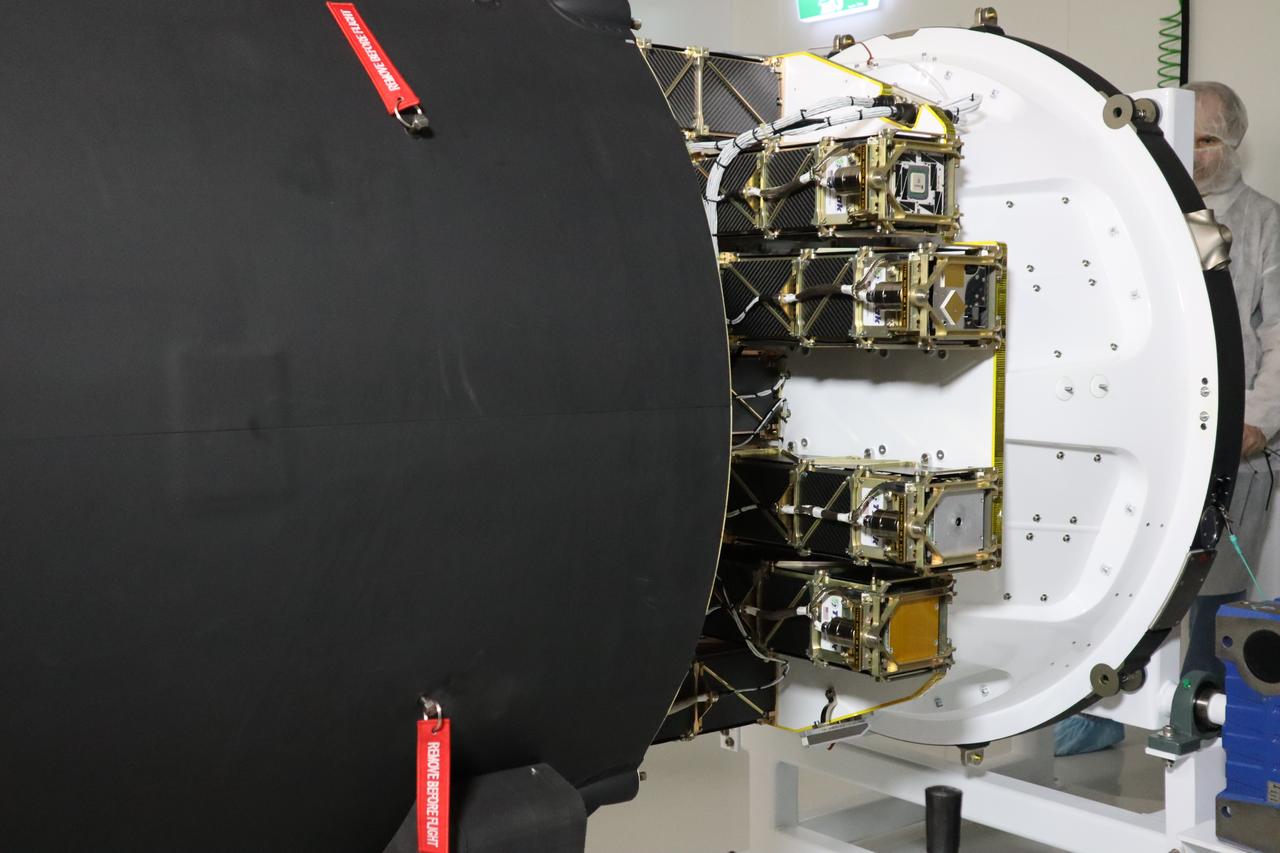

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
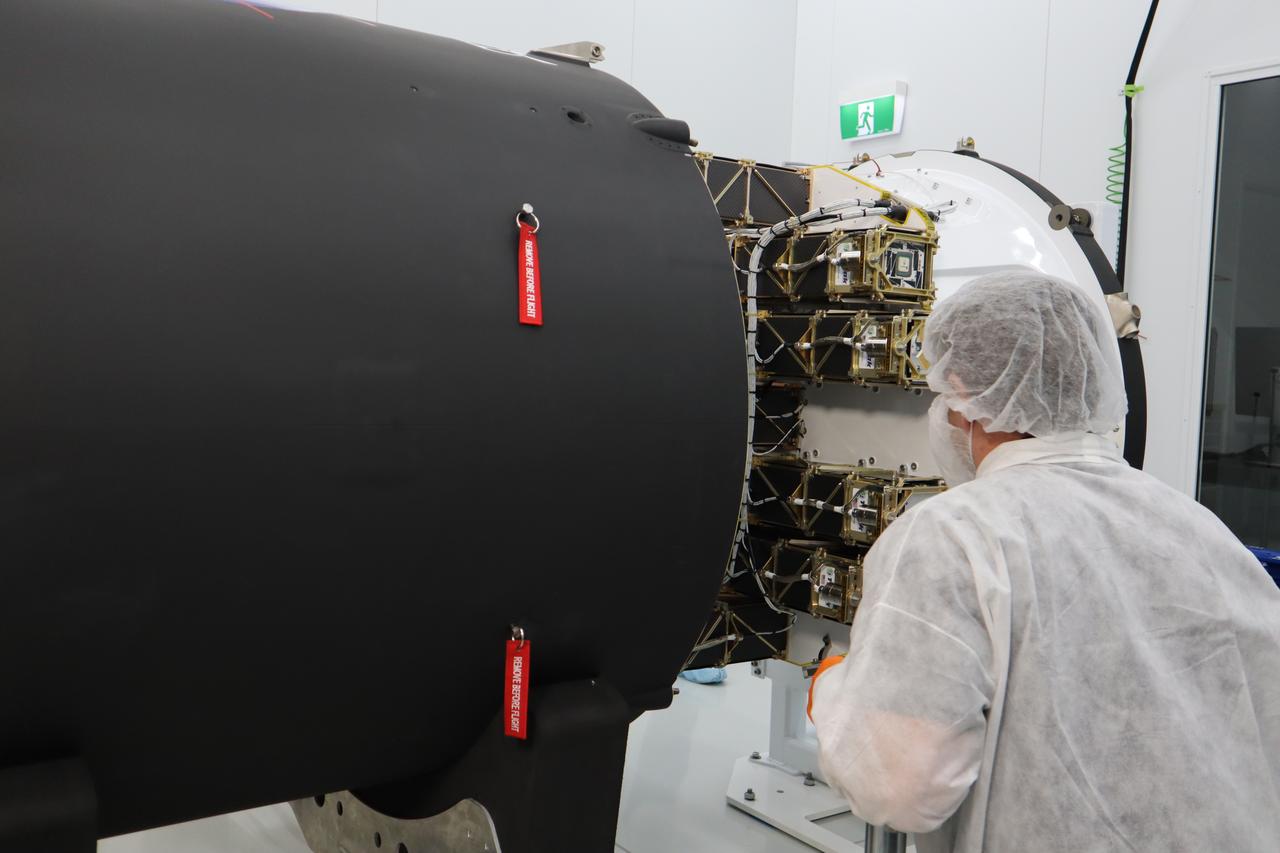
The Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing is prepared for the encapsulation of the Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
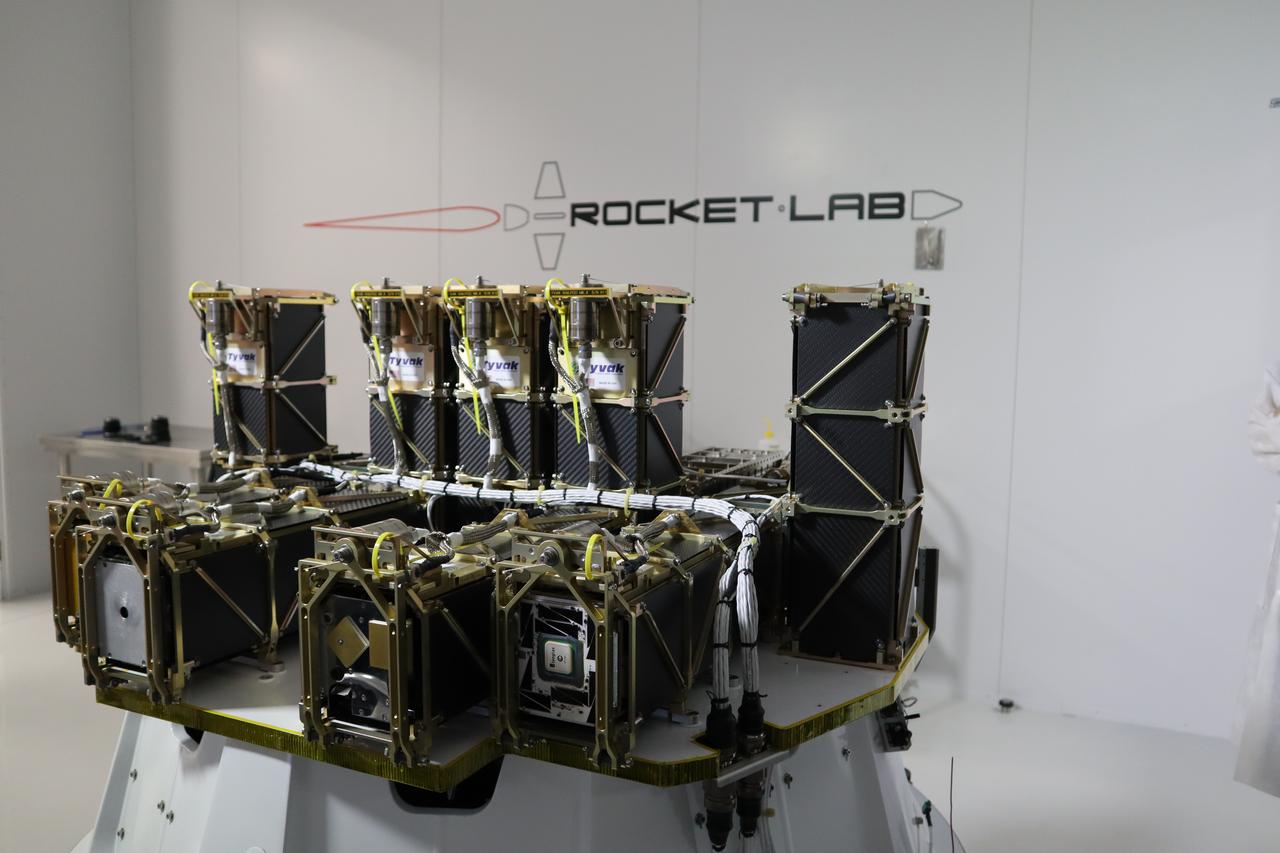

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload has been encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload has been encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is prepared to be encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is prepared to be encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is prepared to be encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
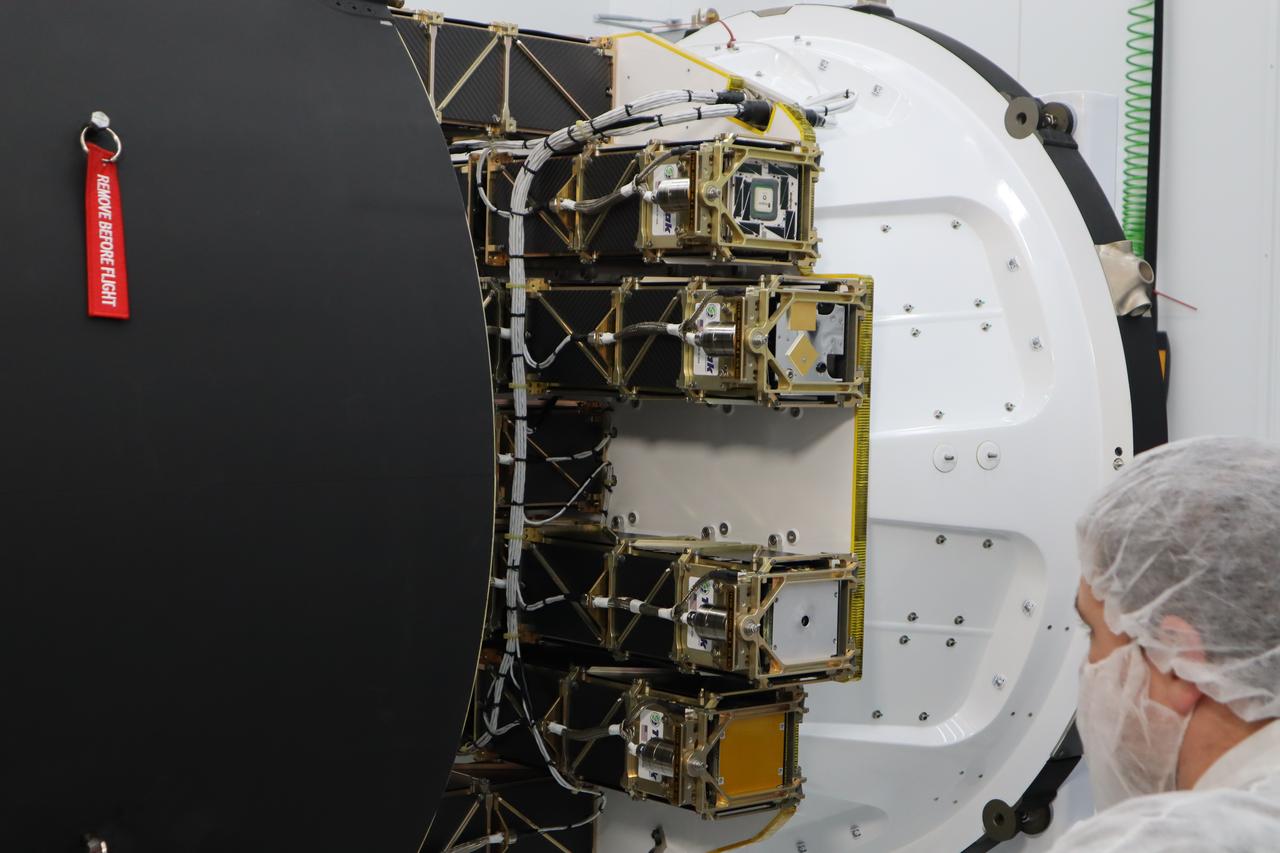
The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
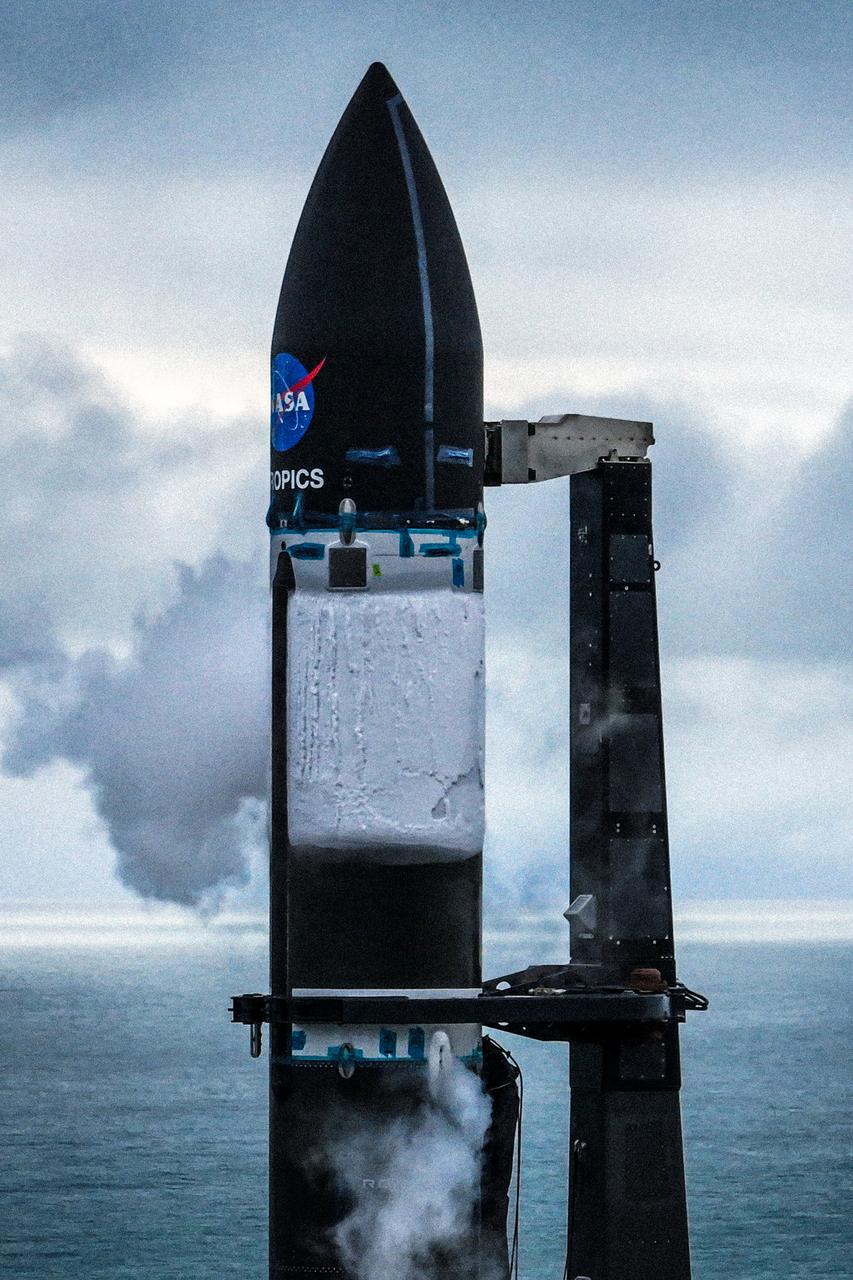

A wet dress rehearsal is underway for Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand on April 28, 2023. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
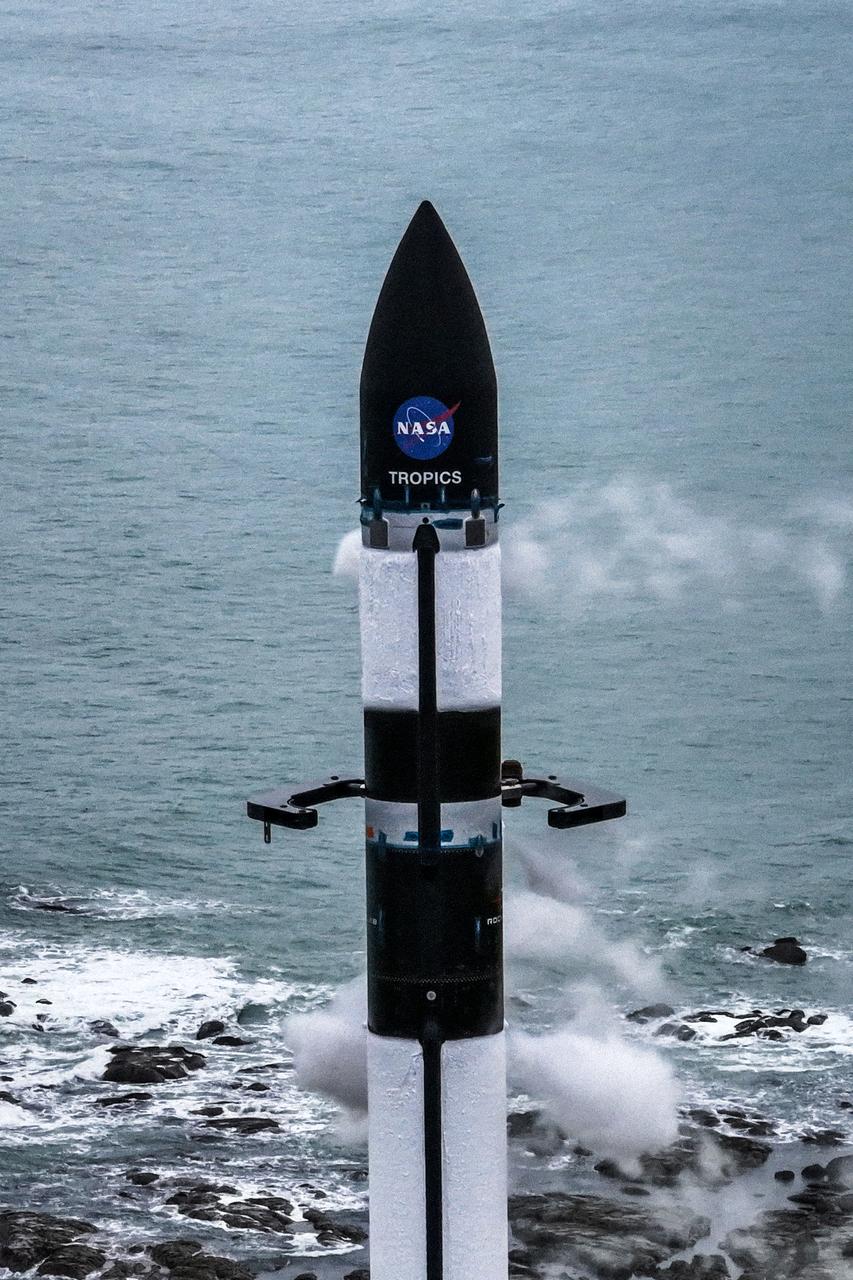

A wet dress rehearsal is underway for Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand on April 28, 2023. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
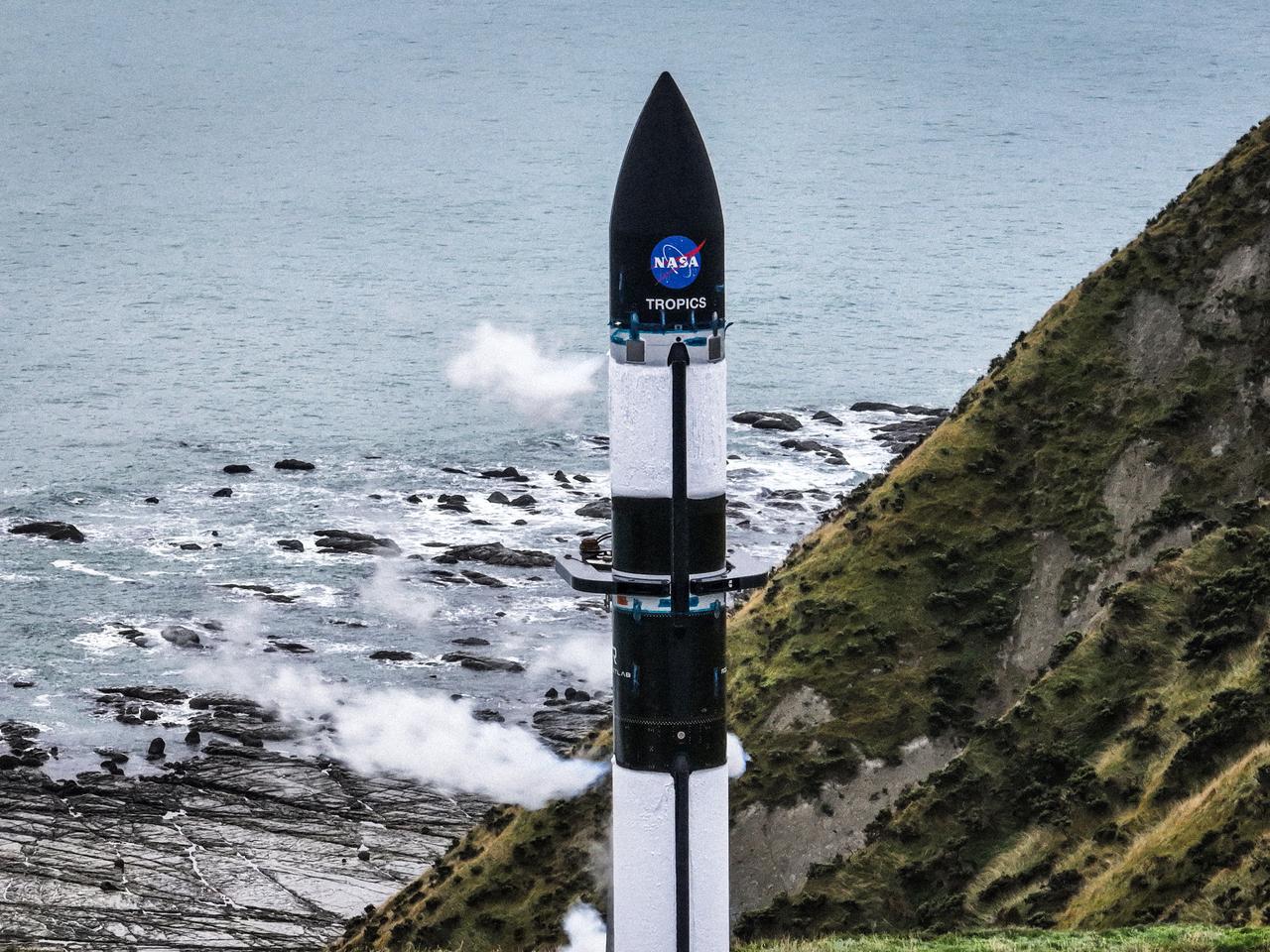

A wet dress rehearsal is underway for Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand on April 28, 2023. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
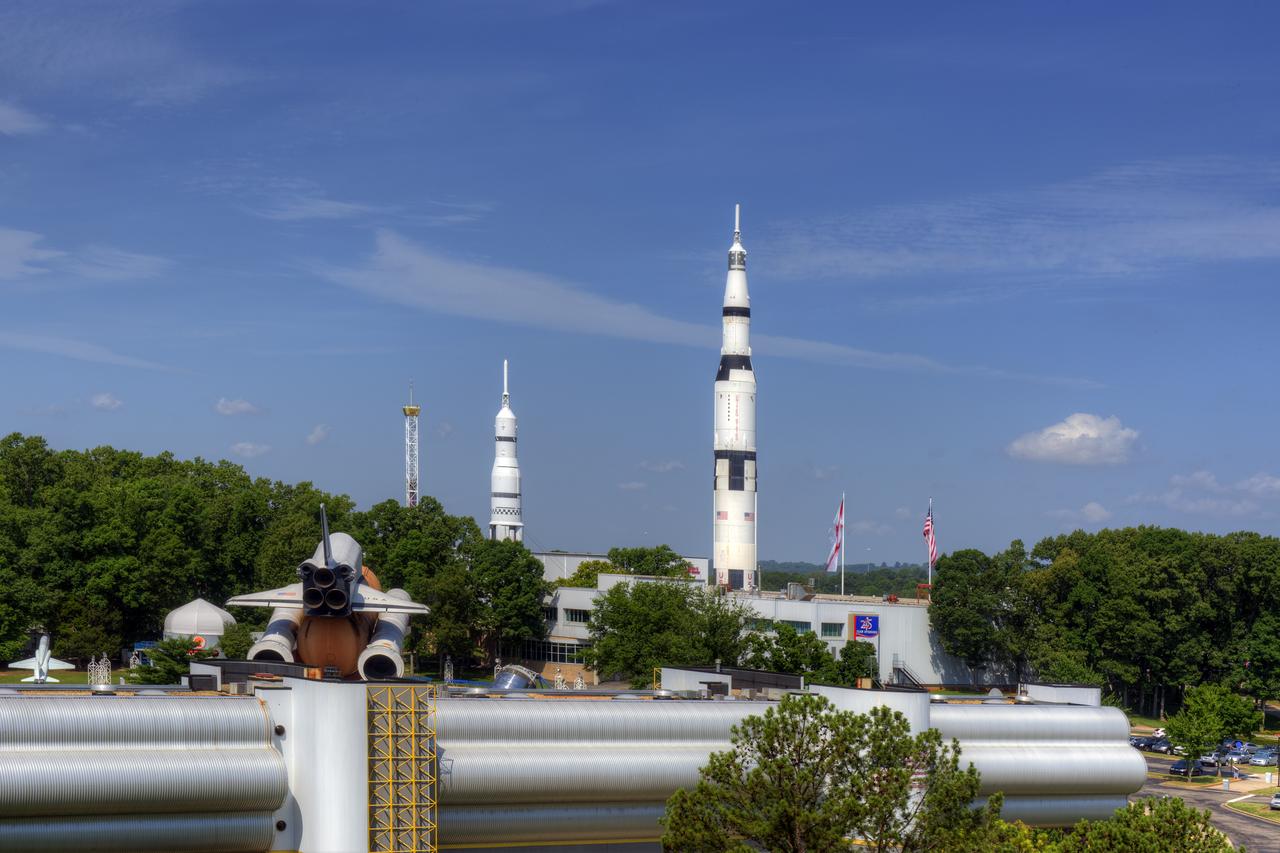

VIEW OF THE U.S. SPACE AND ROCKET CENTER, LOOKING WEST, FROM THE ROOF OF THE MARRIOTT HOTEL.
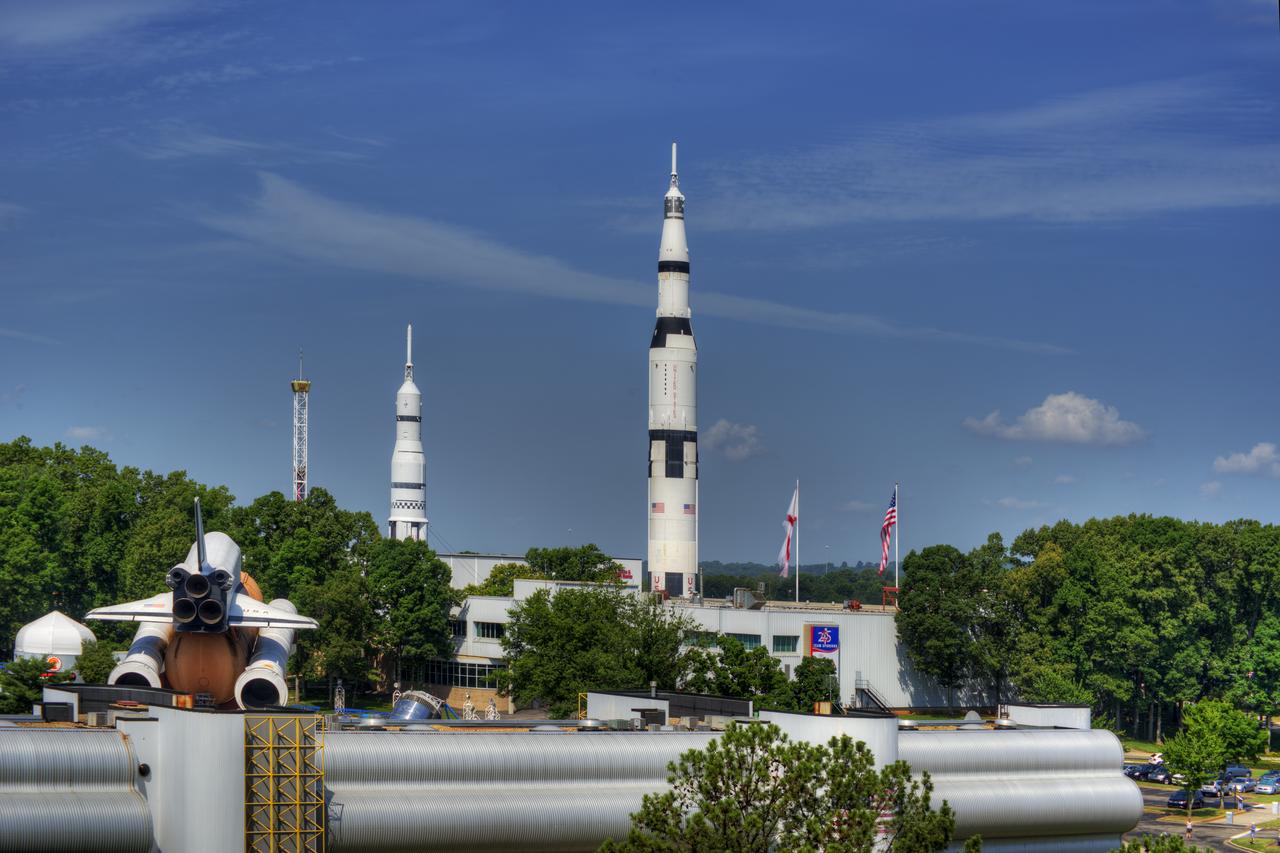

VIEW OF THE U.S. SPACE AND ROCKET CENTER, LOOKING WEST, FROM THE ROOF OF THE MARRIOTT HOTEL

By 1870, American and British inventors had found other ways to use rockets. For example, the Congreve rocket was capable of carrying a line over 1,000 feet to a stranded ship. In 1914, an estimated 1,000 lives were saved by this technique.
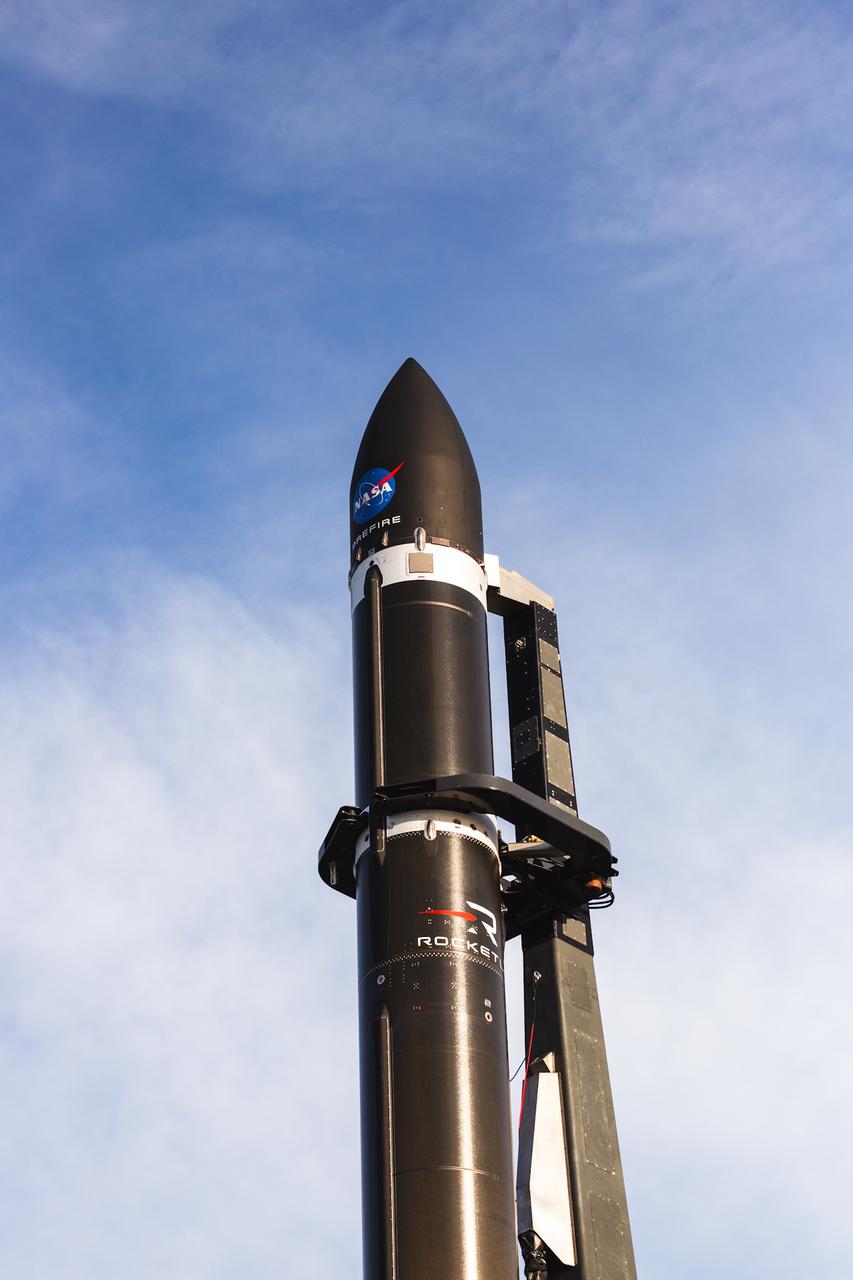

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket called “PREFIRE and Ice,” is vertical on the pad awaiting liftoff at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, ahead of NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission Wednesday, June 5, 2024. The mission, the second of two launches for NASA’S PREFIRE, features two identical 6U CubeSats in asynchronous, near-polar orbits, will study how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
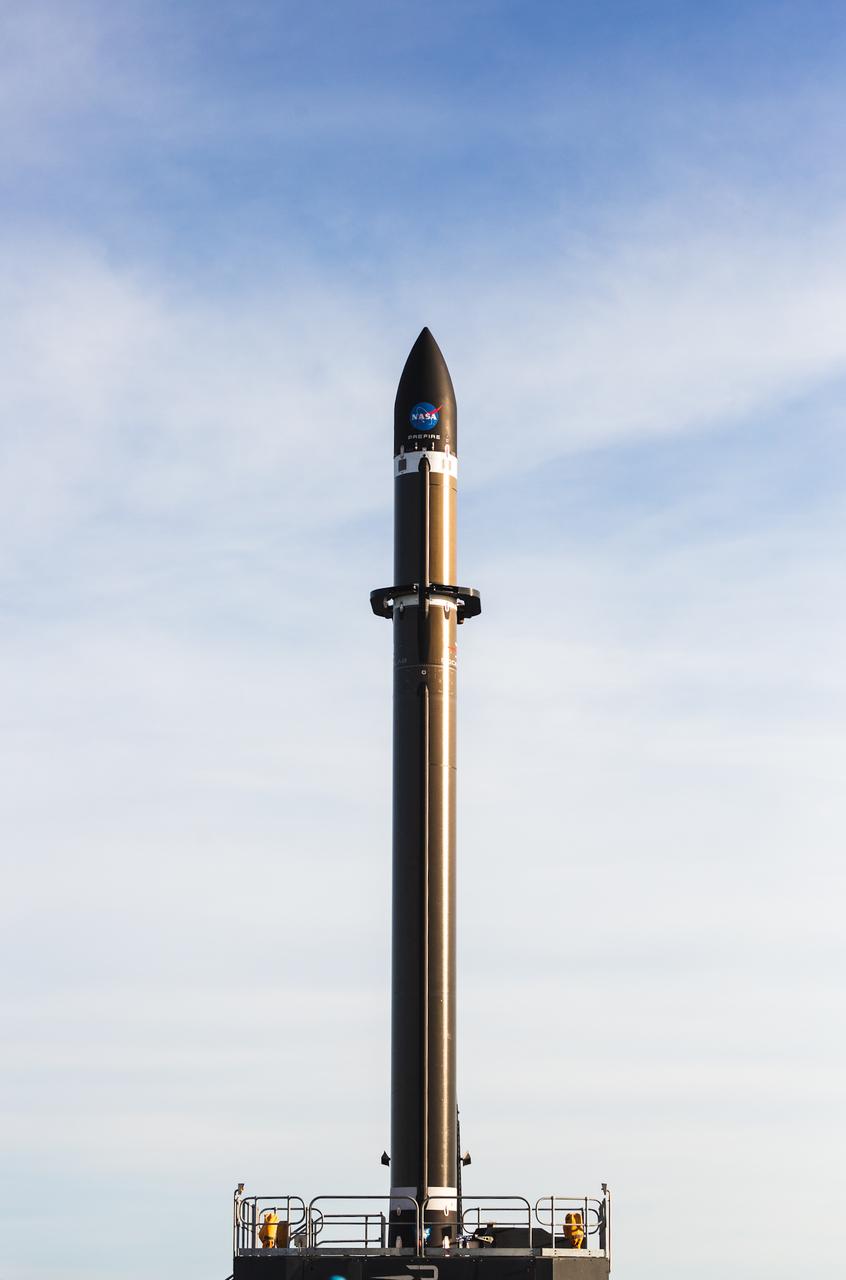

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket called “PREFIRE and Ice,” is vertical on the pad awaiting liftoff at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, ahead of NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission Wednesday, June 5, 2024. The mission, the second of two launches for NASA’S PREFIRE, features two identical 6U CubeSats in asynchronous, near-polar orbits, will study how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
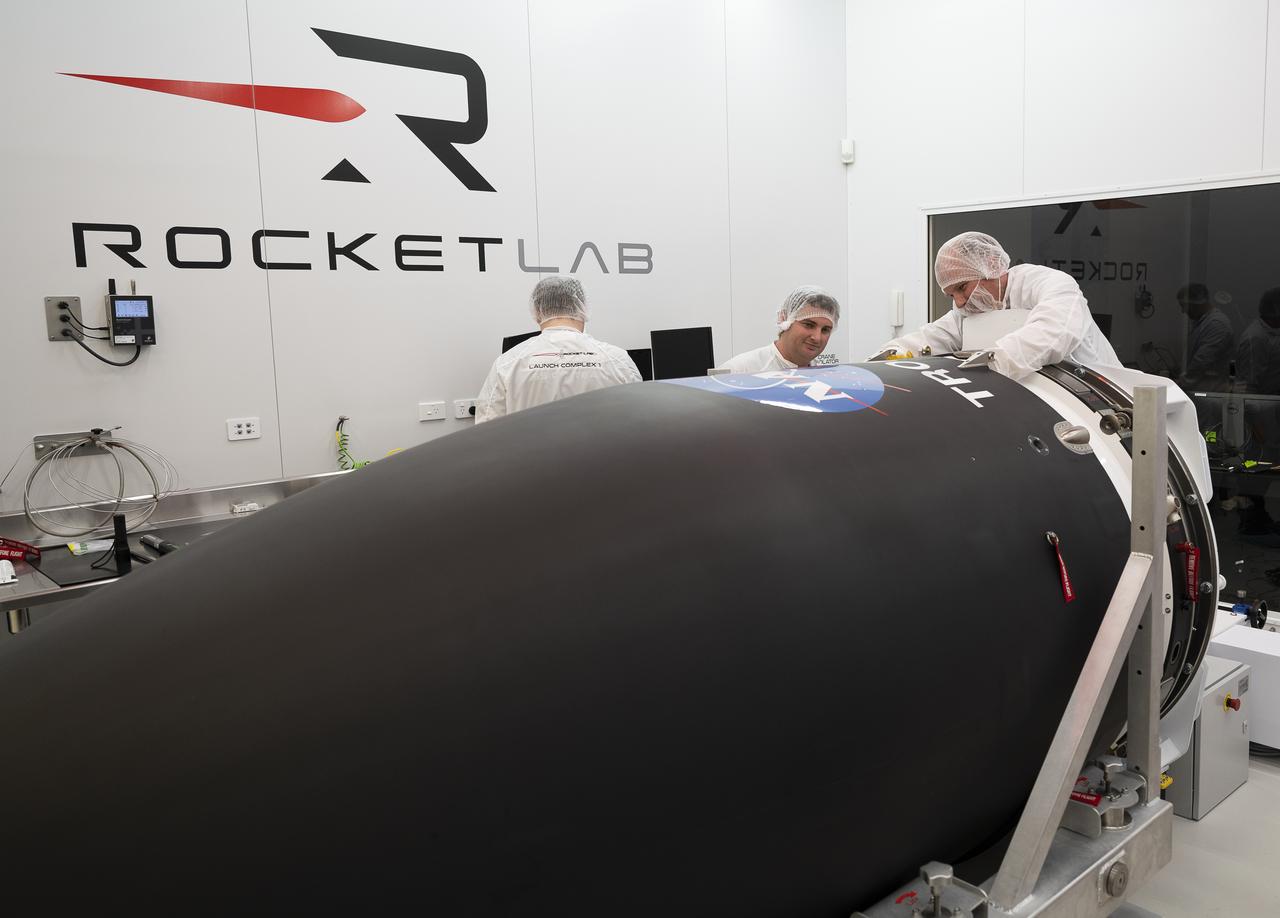

NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are encapsulated inside Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing in a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Technicians prepare NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats for encapsulation in Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing in a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
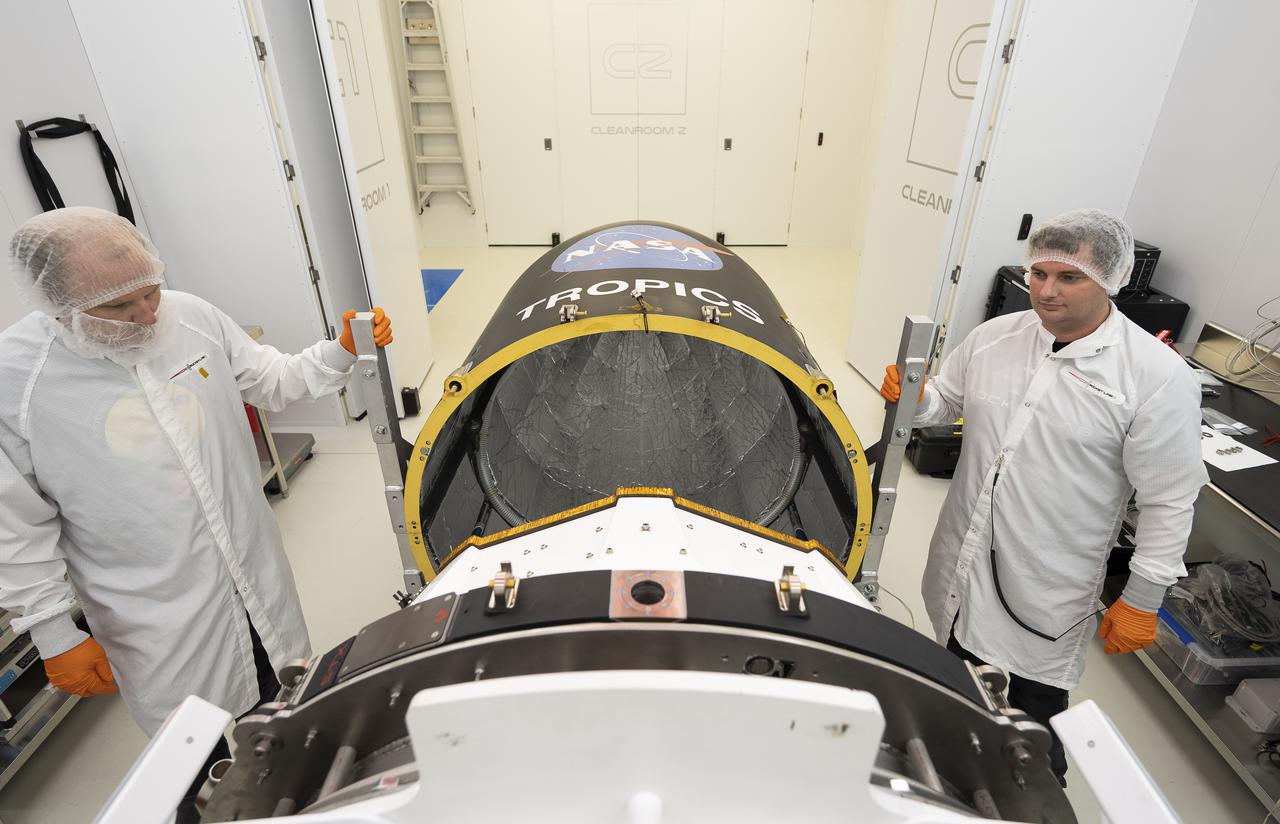

Technicians place NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats in Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing in a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

They sounded more like fireworks than rockets but the Chinese used rockets in battle.
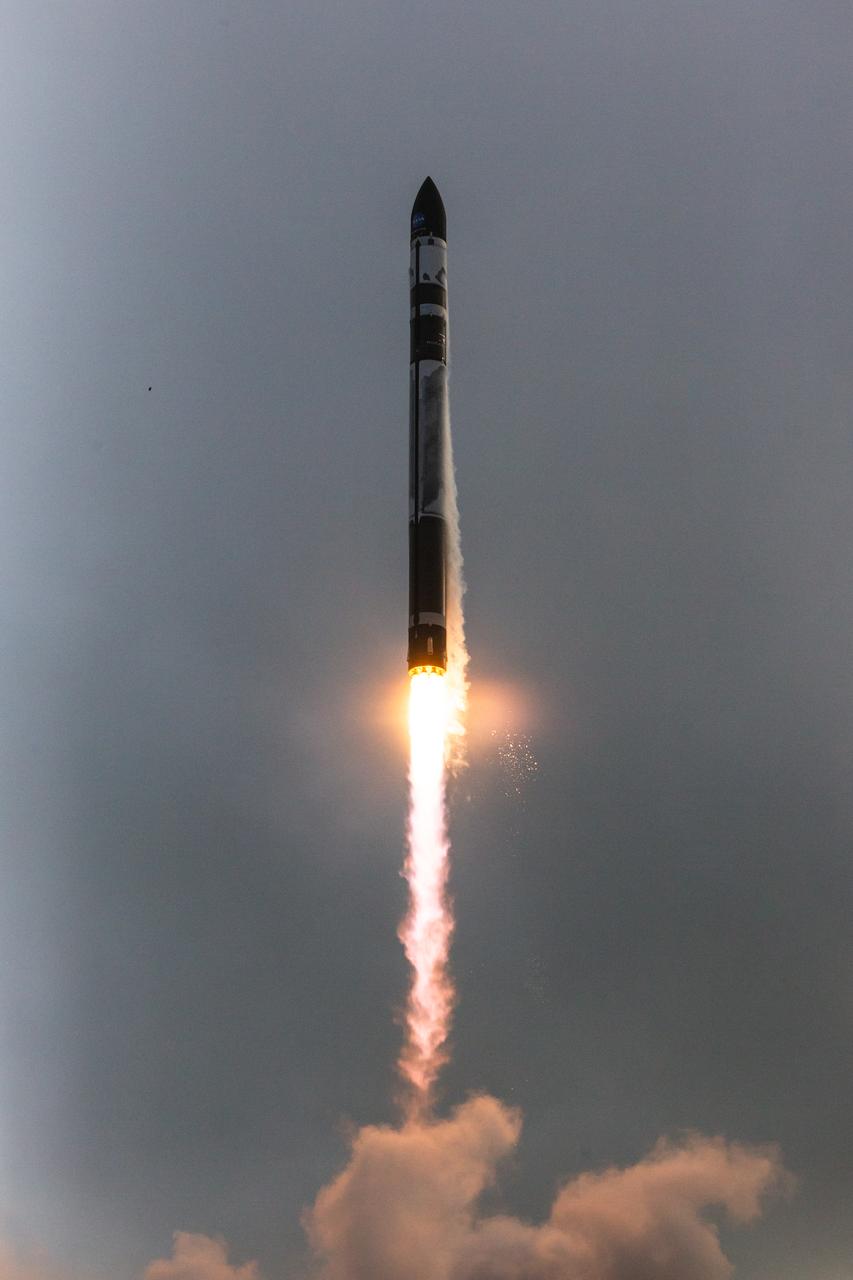

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket called “PREFIRE and Ice,” lifts off from Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand at 3:15 p.m. NZST Wednesday, June 5, 2024 (11:15 p.m. EDT, Tuesday, June 4), on the second of two launches for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment). The PREFIRE mission, expected to last at least 10 months, consists of sending two CubeSats to asynchronous, near-polar orbits, to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
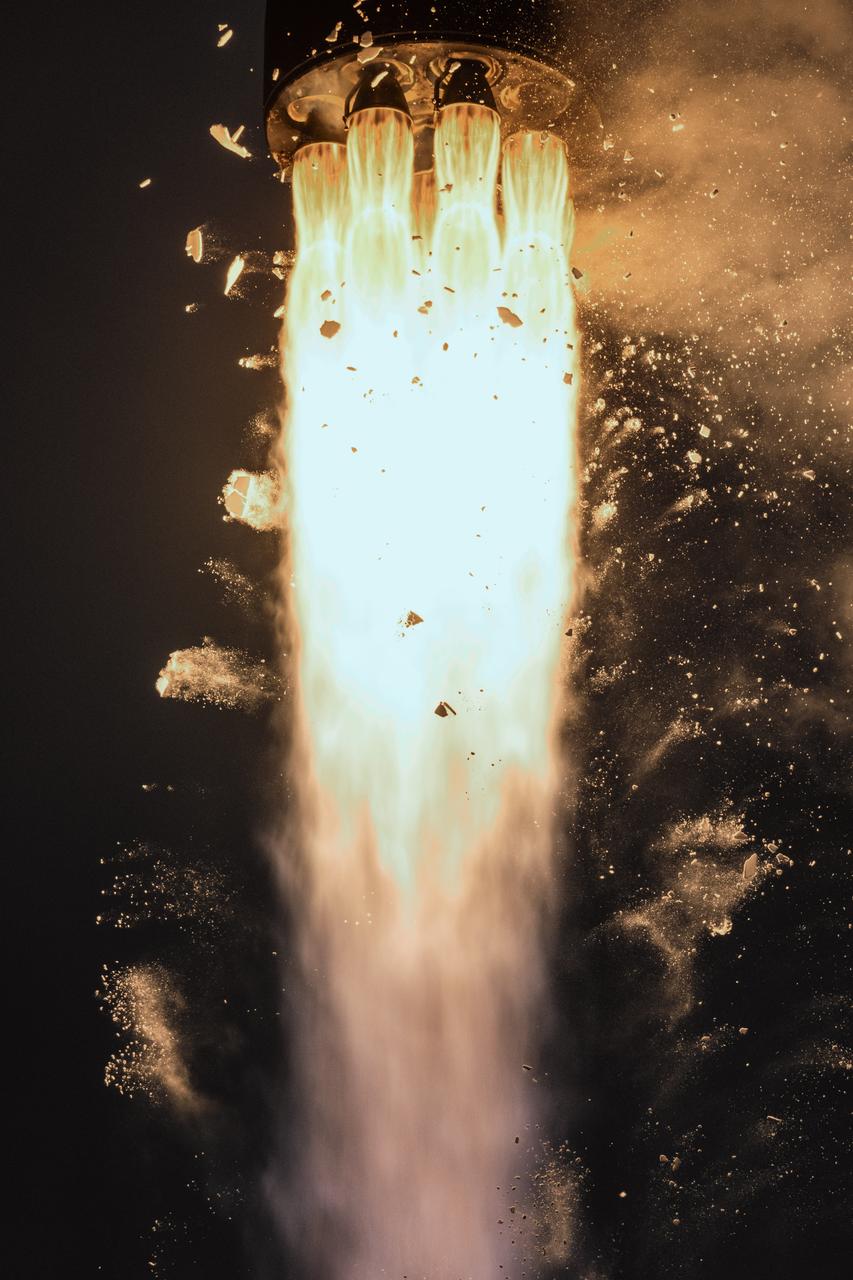

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket called “PREFIRE and Ice,” lifts off from Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand at 3:15 p.m. NZST Wednesday, June 5, 2024 (11:15 p.m. EDT, Tuesday, June 4), on the second of two launches for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment). The PREFIRE mission, expected to last at least 10 months, consists of sending two CubeSats to asynchronous, near-polar orbits, to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
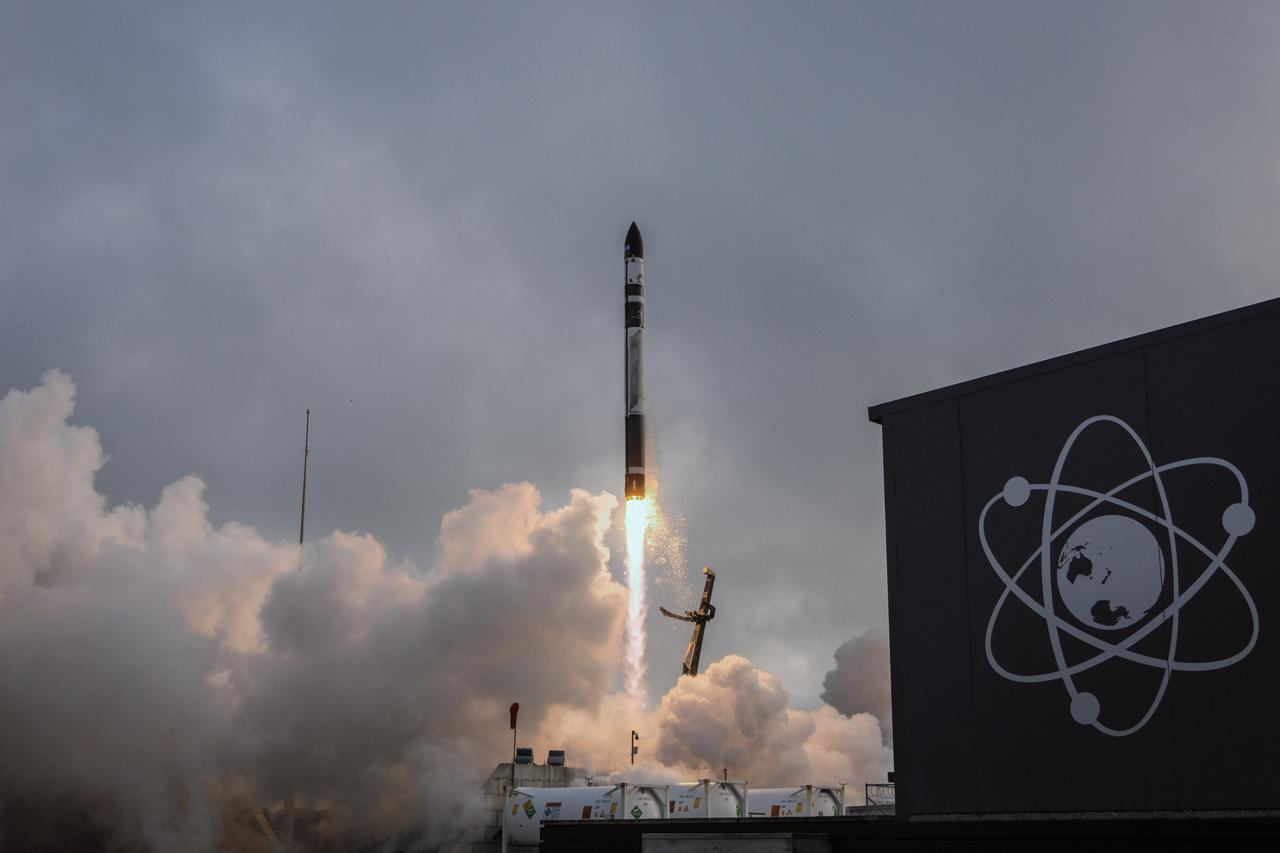

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket called “PREFIRE and Ice,” lifts off from Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand at 3:15 p.m. NZST Wednesday, June 5, 2024 (11:15 p.m. EDT, Tuesday, June 4), on the second of two launches for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment). The PREFIRE mission, expected to last at least 10 months, consists of sending two CubeSats to asynchronous, near-polar orbits, to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.

Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing is in view inside a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats have been encapsulated inside the payload fairing. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Technicians check Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing inside a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats have been encapsulated inside the payload fairing. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing is in view inside a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats have been encapsulated inside the payload fairing. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
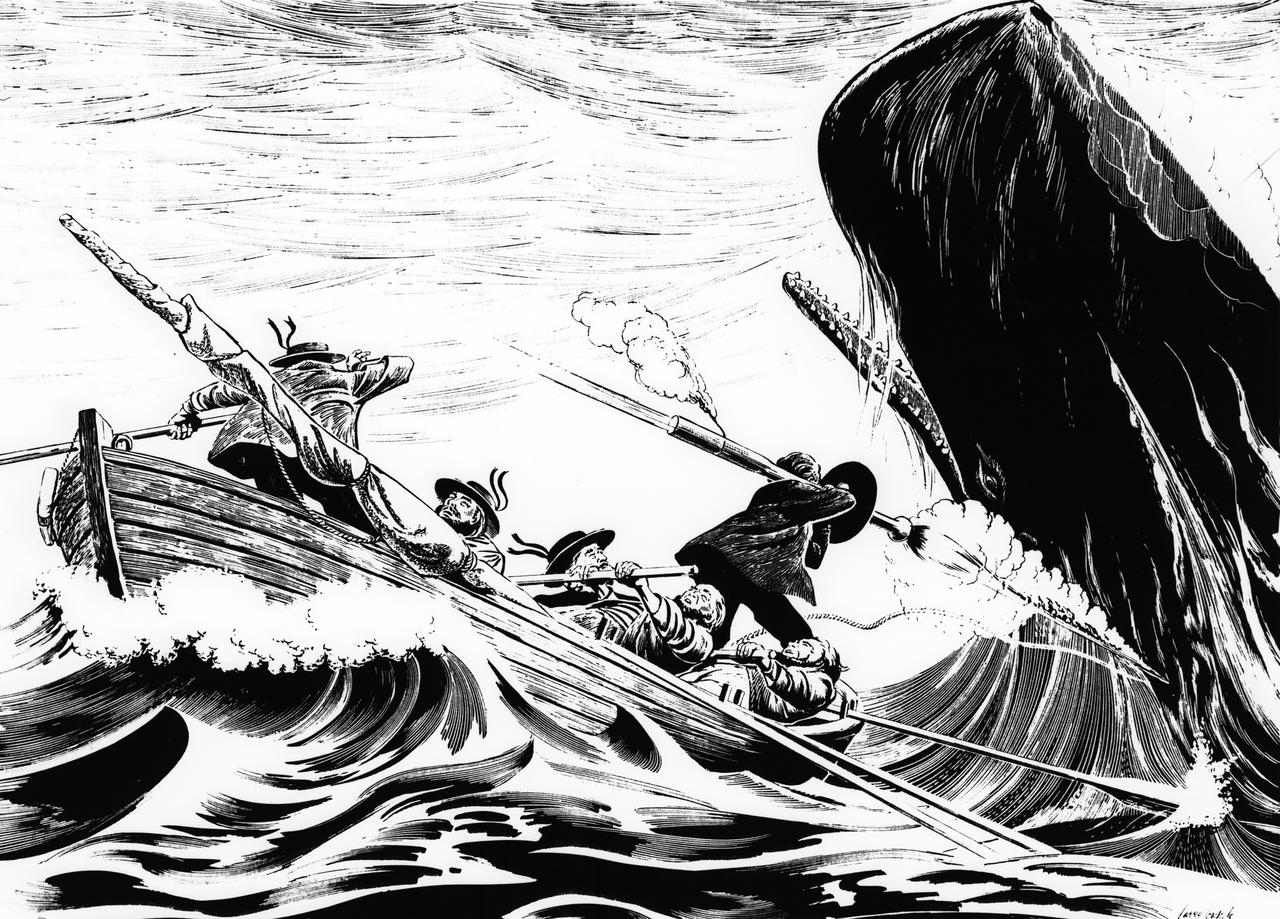

As far back as 1821, sailors hunted whales using rocket-propelled harpoons. These rocket harpoons were launched from a shoulder-held tube equipped with a circular black shield.
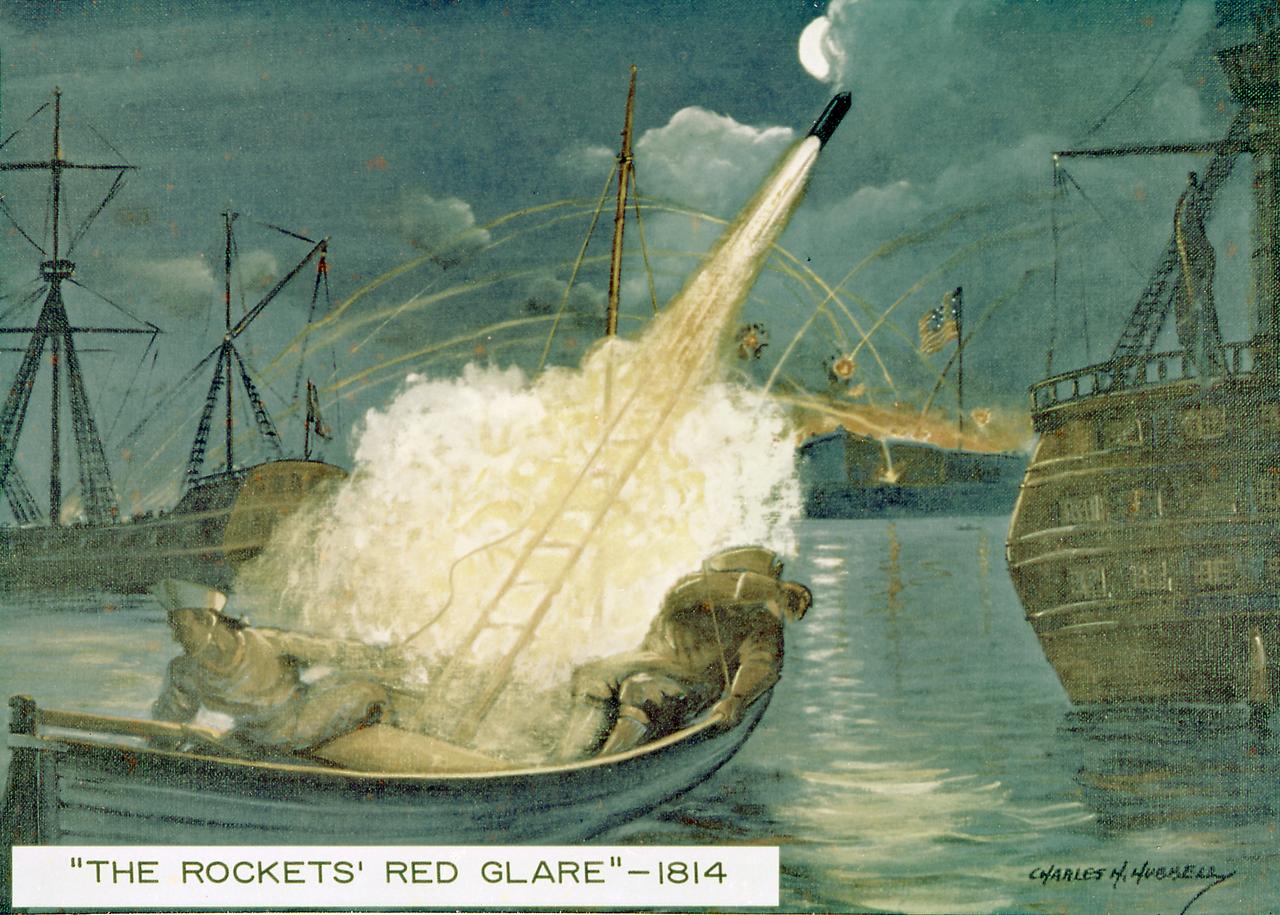

The British fired Congreve rockets against the United States in the War of 1812. As a result Francis Scott Key coined the phrase the "rocket's red glare." Congreve had used a 16-foot guide stick to help stabilize his rocket. William Hale, another British inventor, invented the stickless rocket in 1846. The U.S. Army used the Hale rocket more than 100 years ago in the war with Mexico. Rockets were also used to a limited extent by both sides in the American Civil War.

Early Chinese rockets were used in warfare and celebrations. In fact, the origin of the rocket is shown simply in these Chinese characters. They stand for both "rocket" and "fire arrow."
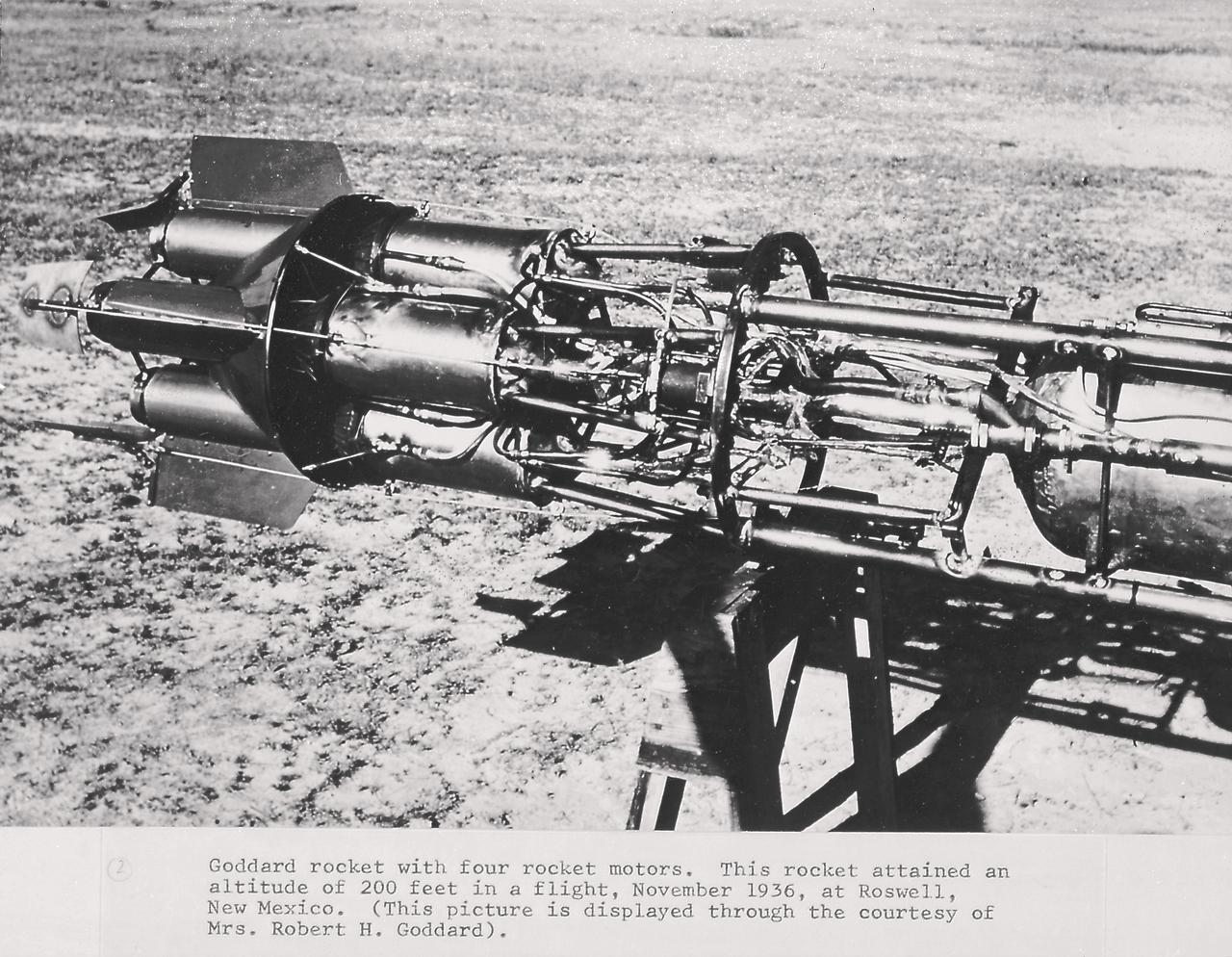
Goddard rocket with four rocket motors. This rocket attained an altitude of 200 feet in a flight, November 1936, at Roswell, New Mexico. From 1930 to 1941, Dr. Goddard made substantial progress in the development of progressively larger rockets which attained altitudes of 2400 meters, and refined his equipment for guidance and control, his techniques of welding, and his insulation, pumps, and other associated equipment. In many respects, Dr. Goddard laid the essential foundations of practical rocket technology
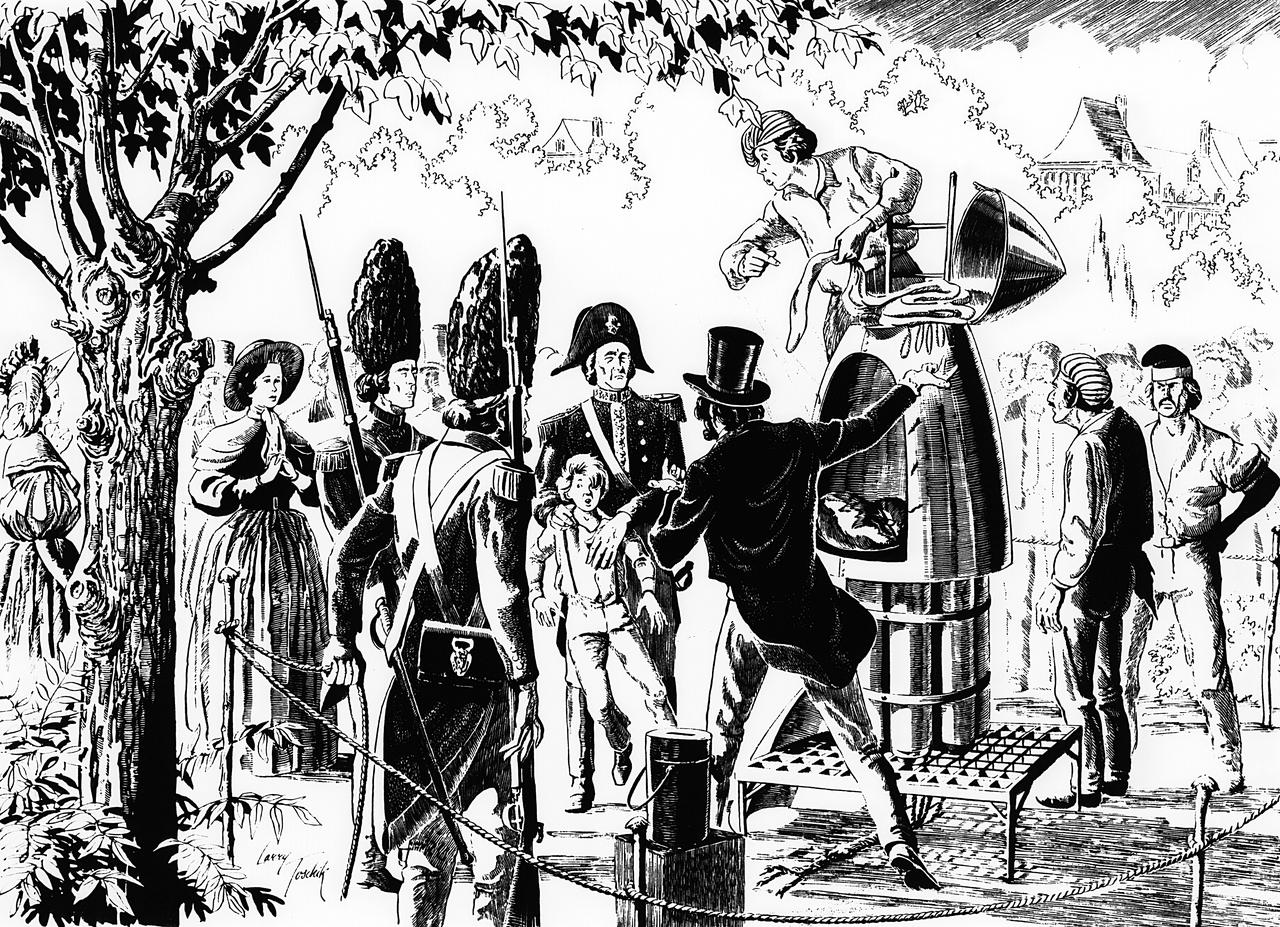

During the 19th century, rocket enthusiasts and inventors began to appear in almost every country. Some people thought these early rocket pioneers were geniuses, and others thought they were crazy. Claude Ruggieri, an Italian living in Paris, apparently rocketed small animals into space as early as 1806. The payloads were recovered by parachute. As depicted here by artist Larry Toschik, French authorities were not always impressed with rocket research. They halted Ruggieri's plans to launch a small boy using a rocket cluster. (Reproduced from a drawing by Larry Toschik and presented here courtesy of the artist and Motorola Inc.)
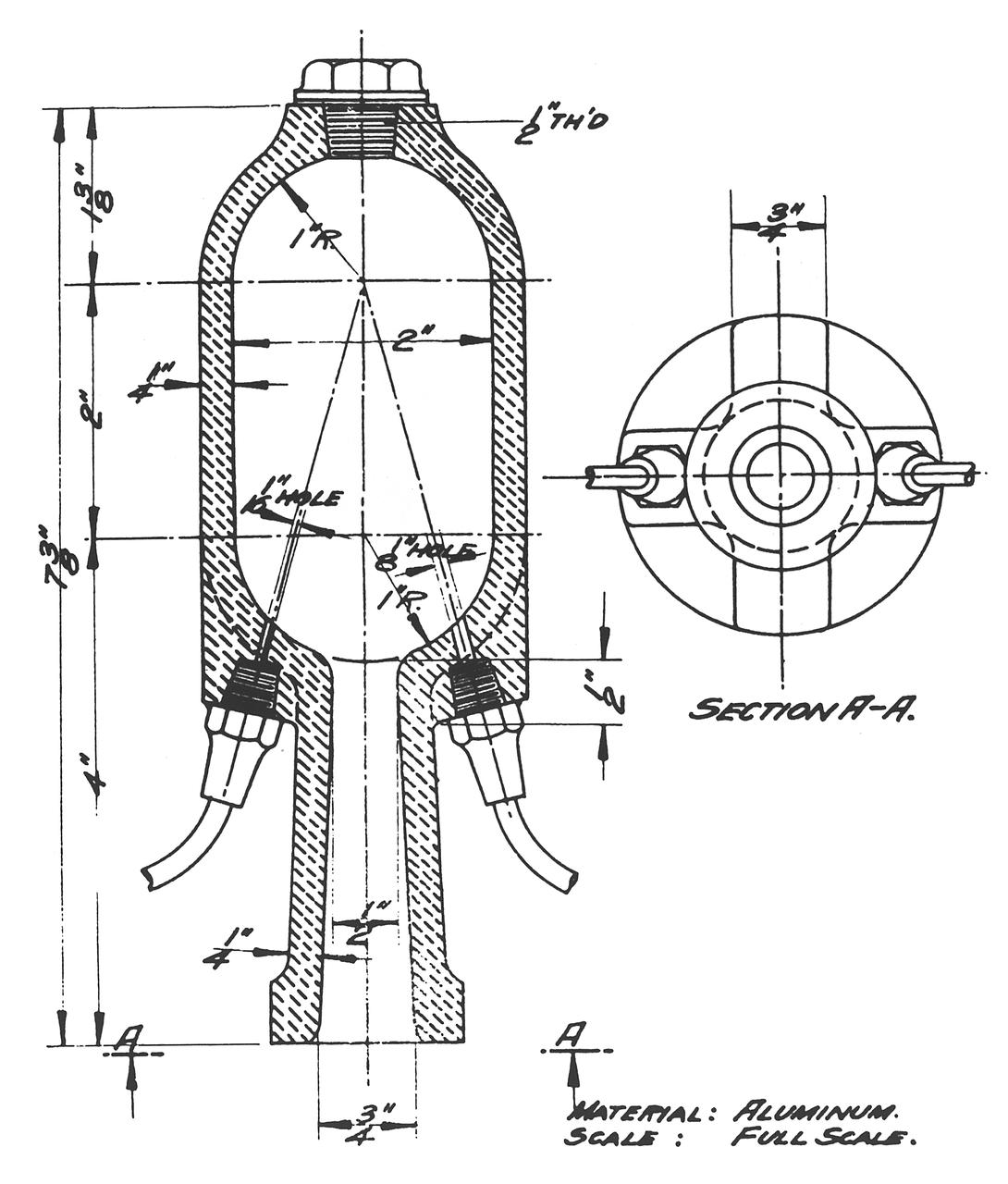
In addition to Dr. Robert Goddard's pioneering work, American experimentation in rocketry prior to World War II grew, primarily in technical societies. This is an early rocket motor designed and developed by the American Rocket Society in 1932.
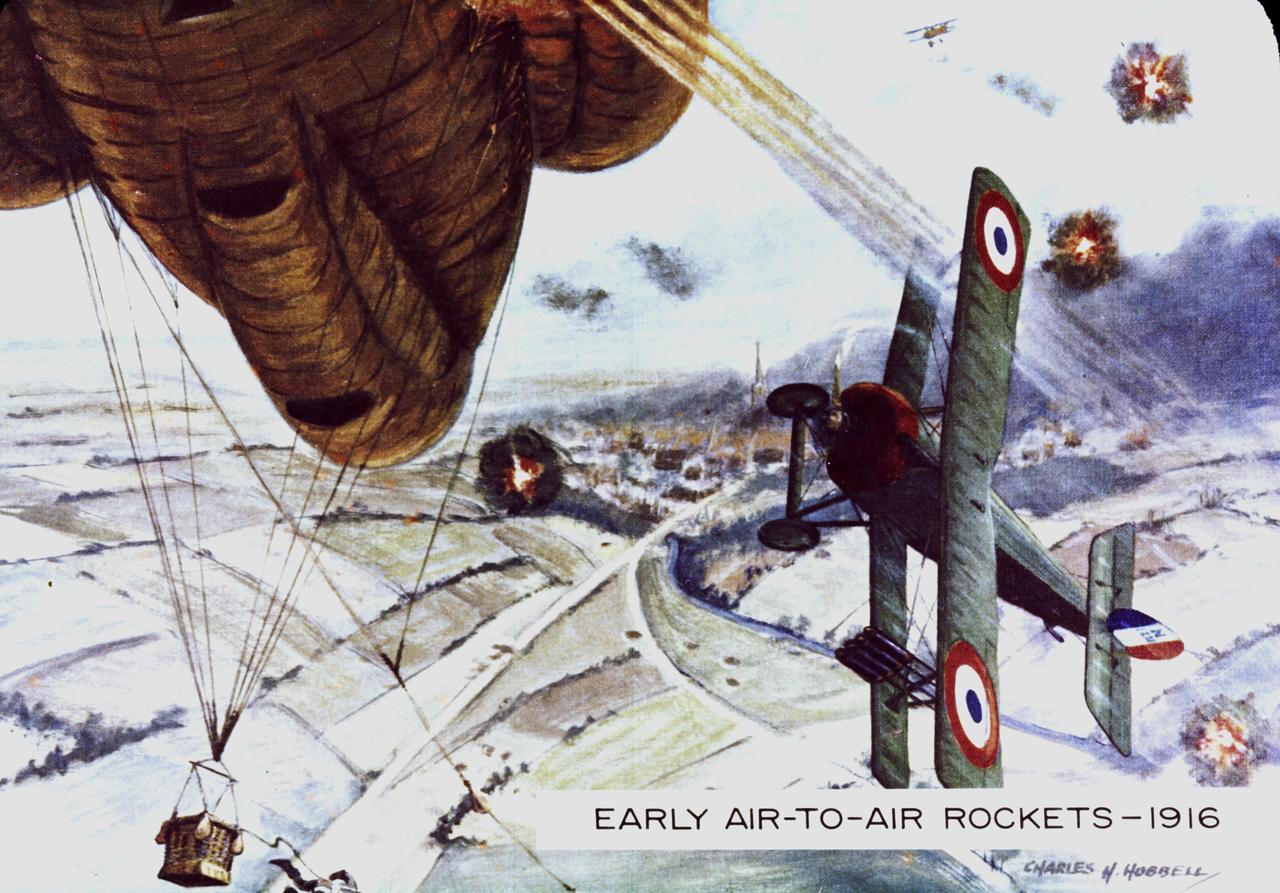

World War I enlisted rockets once again for military purposes. French pilots rigged rockets to the wing struts of their airplanes and aimed them at enemy observation balloons filled with highly inflammable hydrogen.
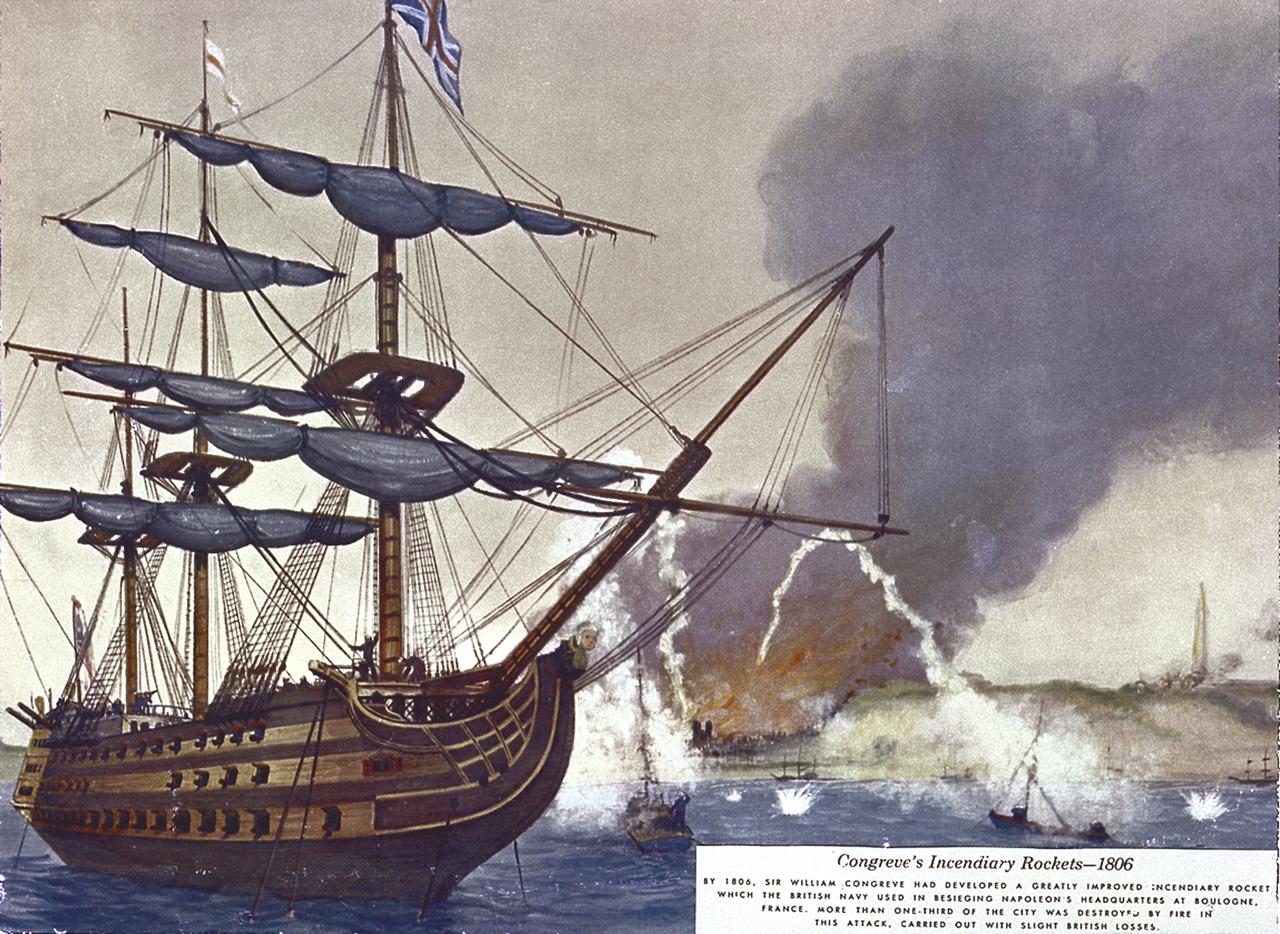
Sir William Congreve developed a rocket with a range of about 9,000 feet. The incendiary rocket used black powder, an iron case, and a 16-foot guide stick. In 1806, British used Congreve rockets to attack Napoleon's headquarters in France. In 1807, Congreve directed a rocket attack against Copenhagen.
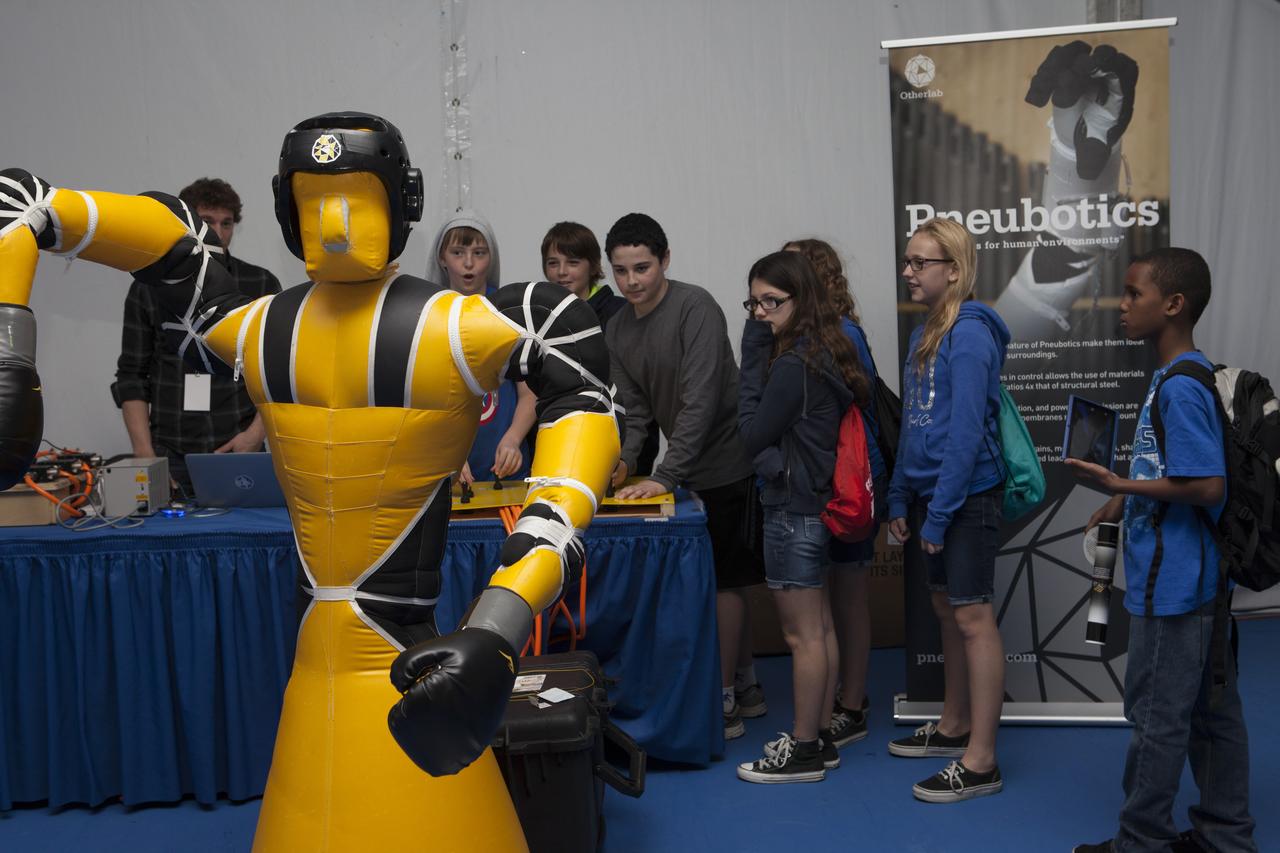

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Students observe as Otherlab shows off a life-size, inflatable robot from its "" program. The demonstration was one of several provided during the Robot Rocket Rally. The three-day event at Florida's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex is highlighted by exhibits, games and demonstrations of a variety of robots, with exhibitors ranging from school robotics clubs to veteran NASA scientists and engineers. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
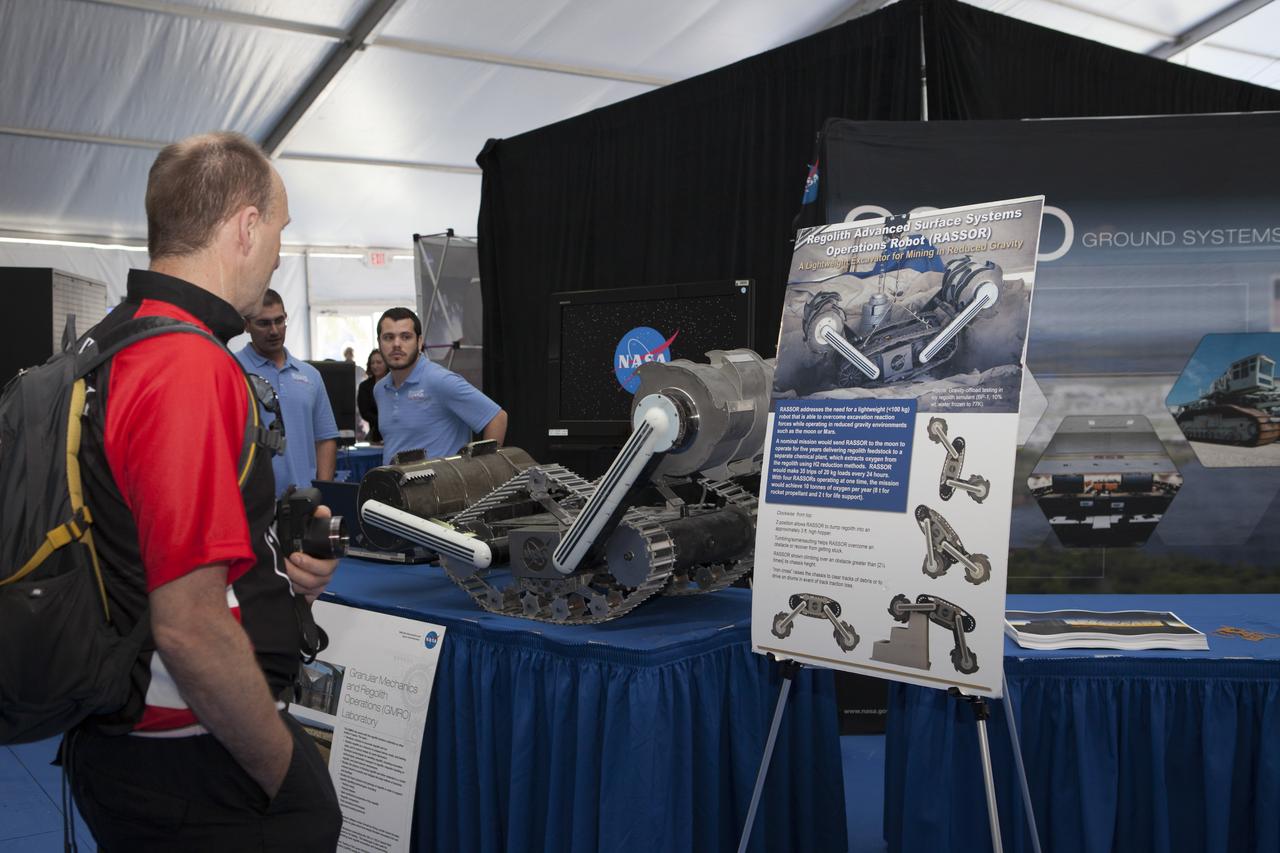

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A visitor to the Robot Rocket Rally takes an up-close look at RASSOR, a robotic miner developed by NASA Kennedy Space Center's Swamp Works. The three-day event at Florida's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex is highlighted by exhibits, games and demonstrations of a variety of robots, with exhibitors ranging from school robotics clubs to veteran NASA scientists and engineers. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
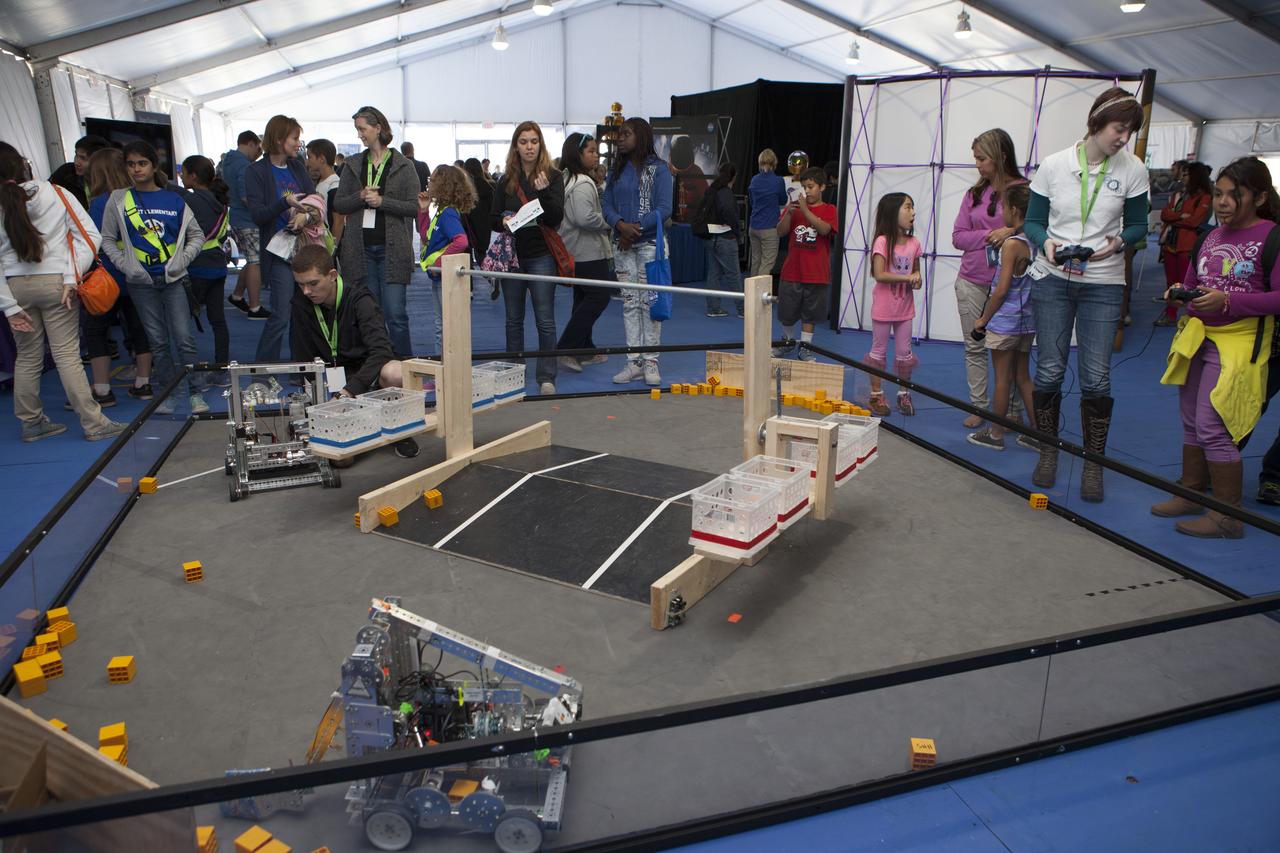
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Students from Hagerty High School in Oviedo, Fla., participants in FIRST Robotics, show off their robots' capabilities at the Robot Rocket Rally. The three-day event at Florida's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex is highlighted by exhibits, games and demonstrations of a variety of robots, with exhibitors ranging from school robotics clubs to veteran NASA scientists and engineers. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
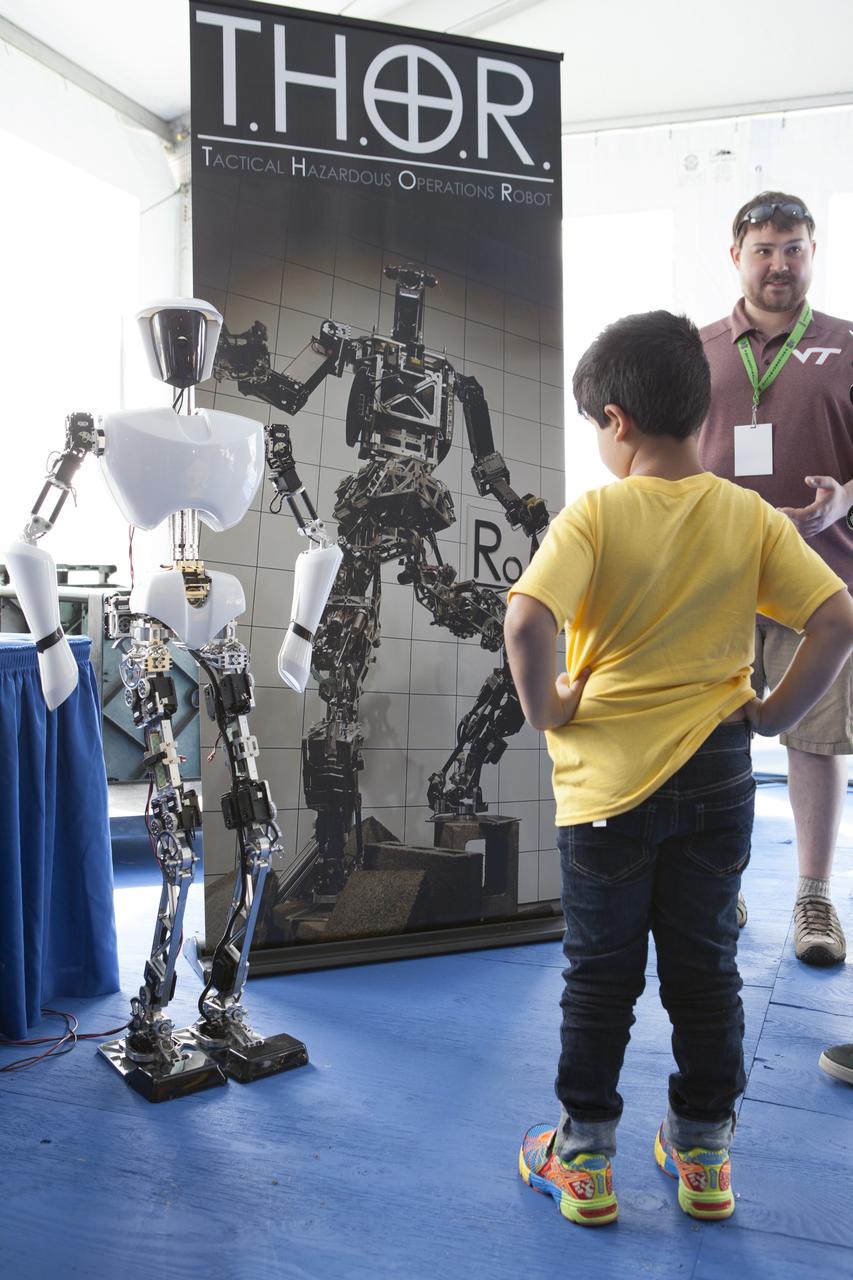

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A child gets an up-close look at Charli, an autonomous walking robot developed by Virginia Tech Robotics, during the Robot Rocket Rally. The three-day event at Florida's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex is highlighted by exhibits, games and demonstrations of a variety of robots, with exhibitors ranging from school robotics clubs to veteran NASA scientists and engineers. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

In the 19th Century, experiments in America, Europe, and elsewhere attempted to build postal rockets to deliver mail from one location to another. The idea was more novel than successful. Many stamps used in these early postal rockets have become collector's items.

In 1696, Robert Anderson, an Englishman, published a two-part treatise on how to make rocket molds, prepare propellants, and perform the calculations.
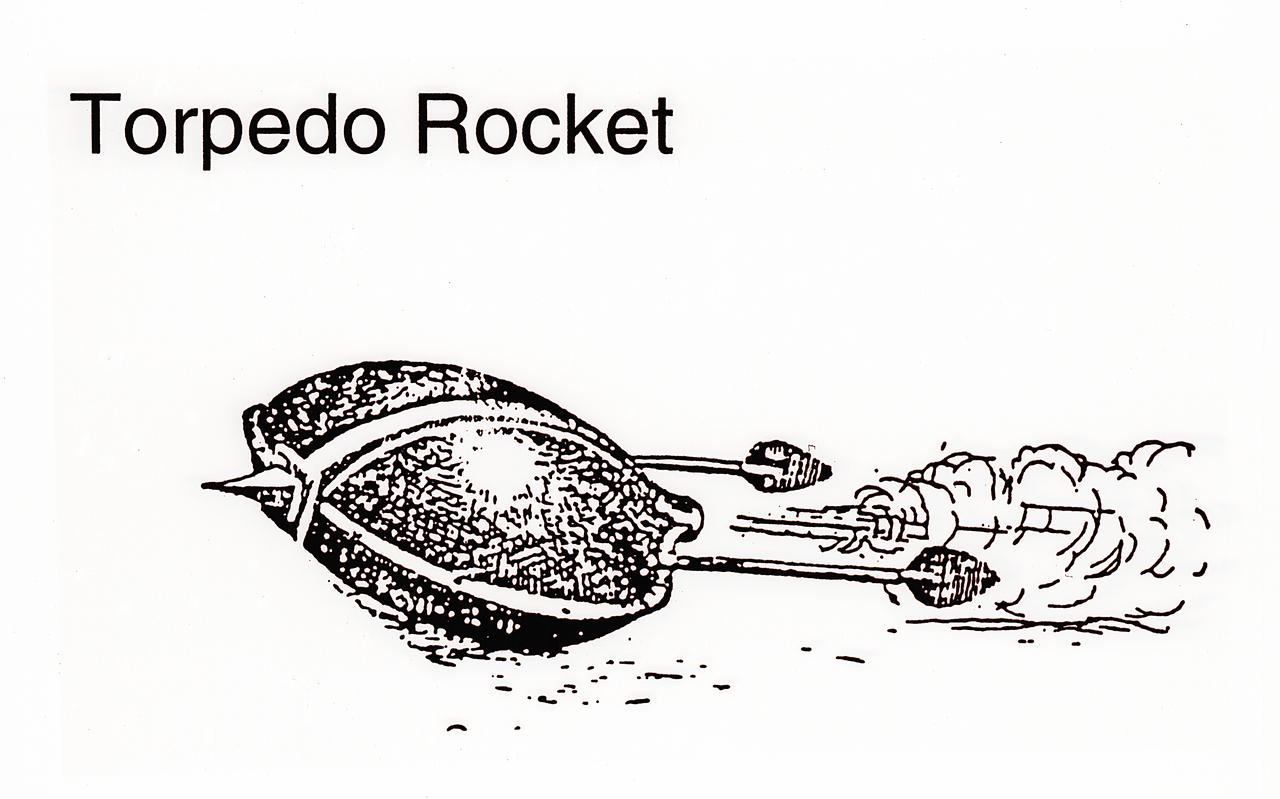
All through the 13th to the 15th Centuries there were reports of many rocket experiments. For example, Joanes de Fontana of Italy designed a surface-rurning, rocket-powered torpedo for setting enemy ships on fire
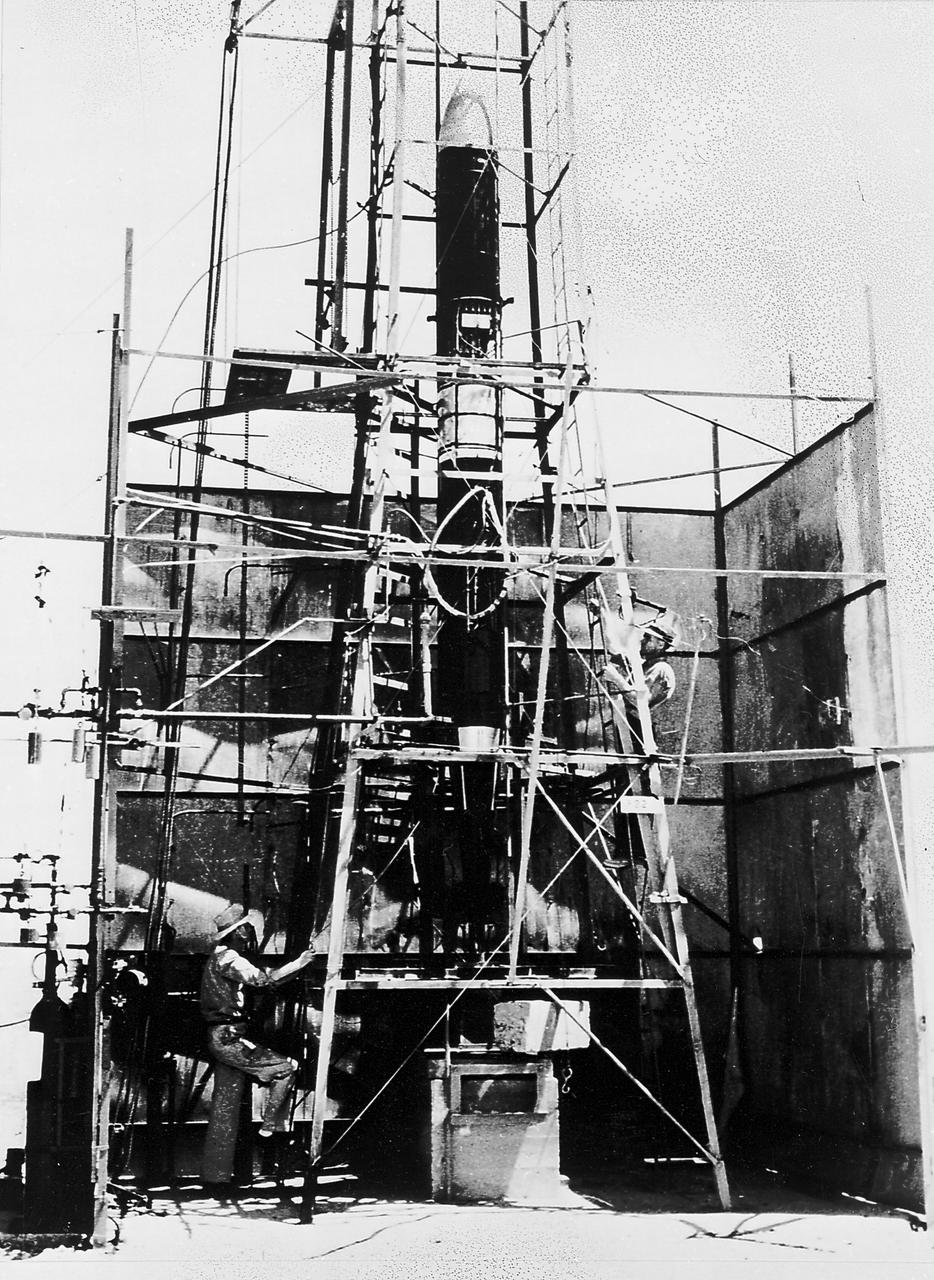
Goddard rocket in launching tower at Roswell, New Mexico, March 21, 1940. Fuel was injected by pumps from the fueling platform at left. From 1930 to 1941, Dr. Goddard made substantial progress in the development of progressively larger rockets, which attained altitudes of 2400 meters, and refined his equipment for guidance and control, his techniques of welding, and his insulation, pumps, and other associated equipment. In many respects, Dr. Goddard laid the essential foundations of practical rocket technology

During the early introduction of rockets to Europe, they were used only as weapons. Enemy troops in India repulsed the British with rockets. Later, in Britain, Sir William Congreve developed a rocket that could fire to about 9,000 feet. The British fired Congreve rockets against the United States in the War of 1812.
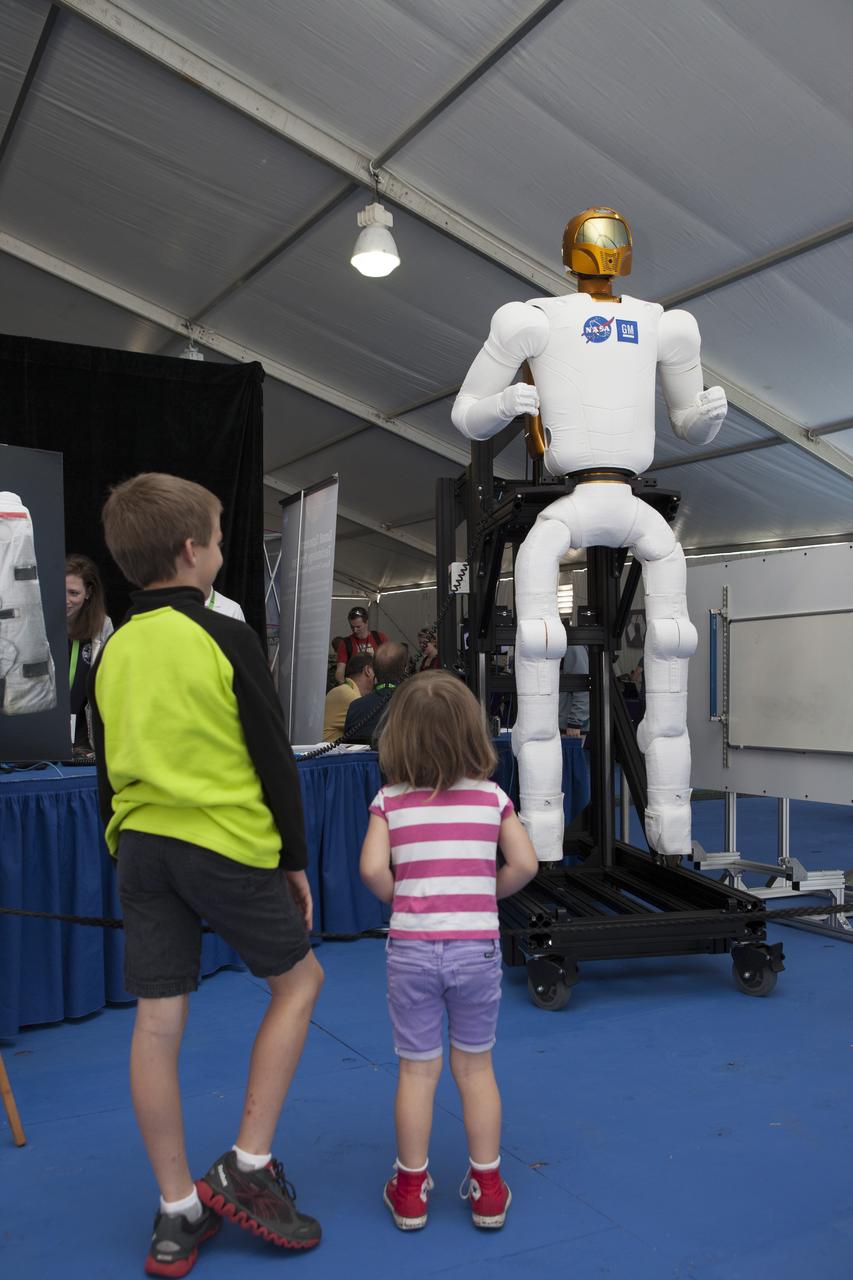

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Two young visitors get an up-close look at an engineering model of Robonaut 2, complete with a set of legs, during the Robot Rocket Rally. The three-day event at Florida's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex is highlighted by exhibits, games and demonstrations of a variety of robots, with exhibitors ranging from school robotics clubs to veteran NASA scientists and engineers. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
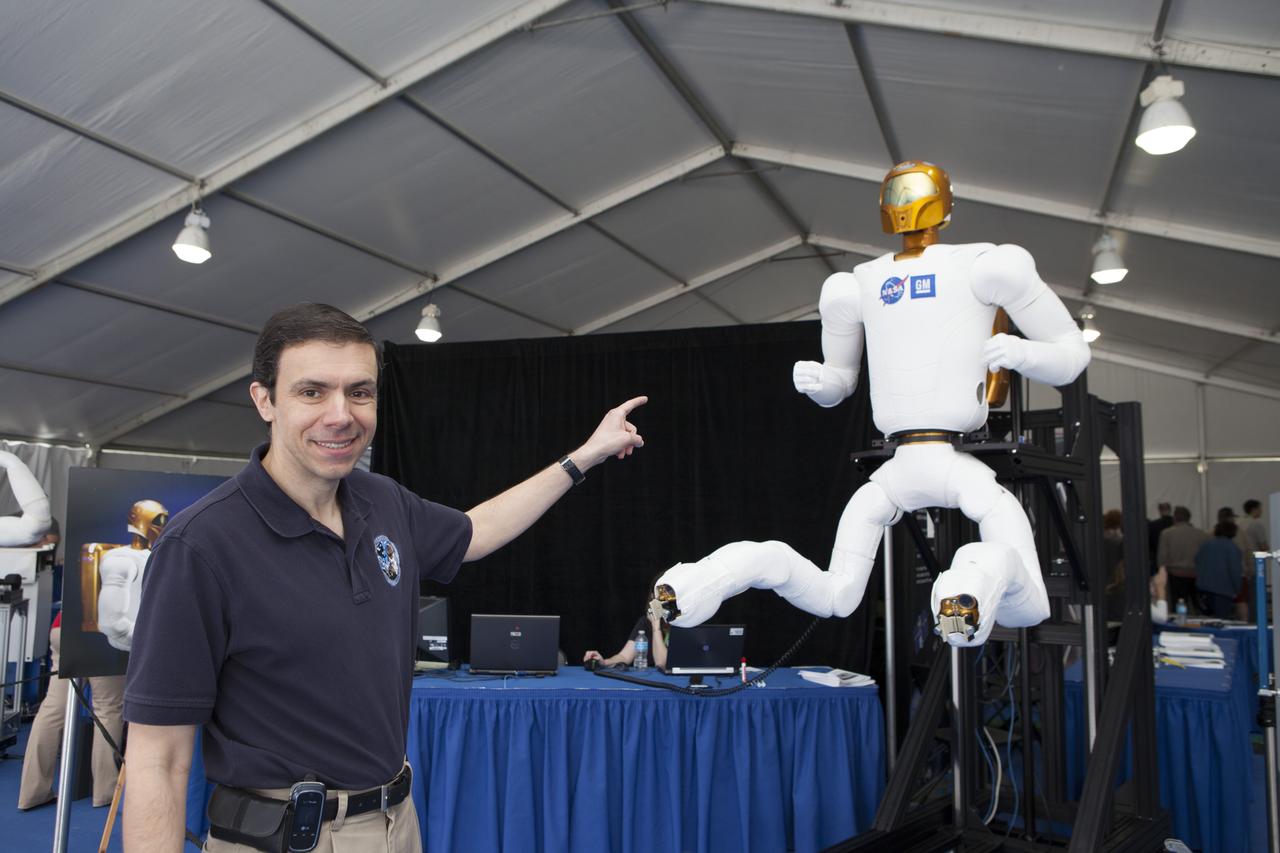

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Ron Diftler of NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston demonstrates the leg movements of Robonaut 2 during the Robot Rocket Rally. The three-day event at Florida's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex is highlighted by exhibits, games and demonstrations of a variety of robots, with exhibitors ranging from school robotics clubs to veteran NASA scientists and engineers. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
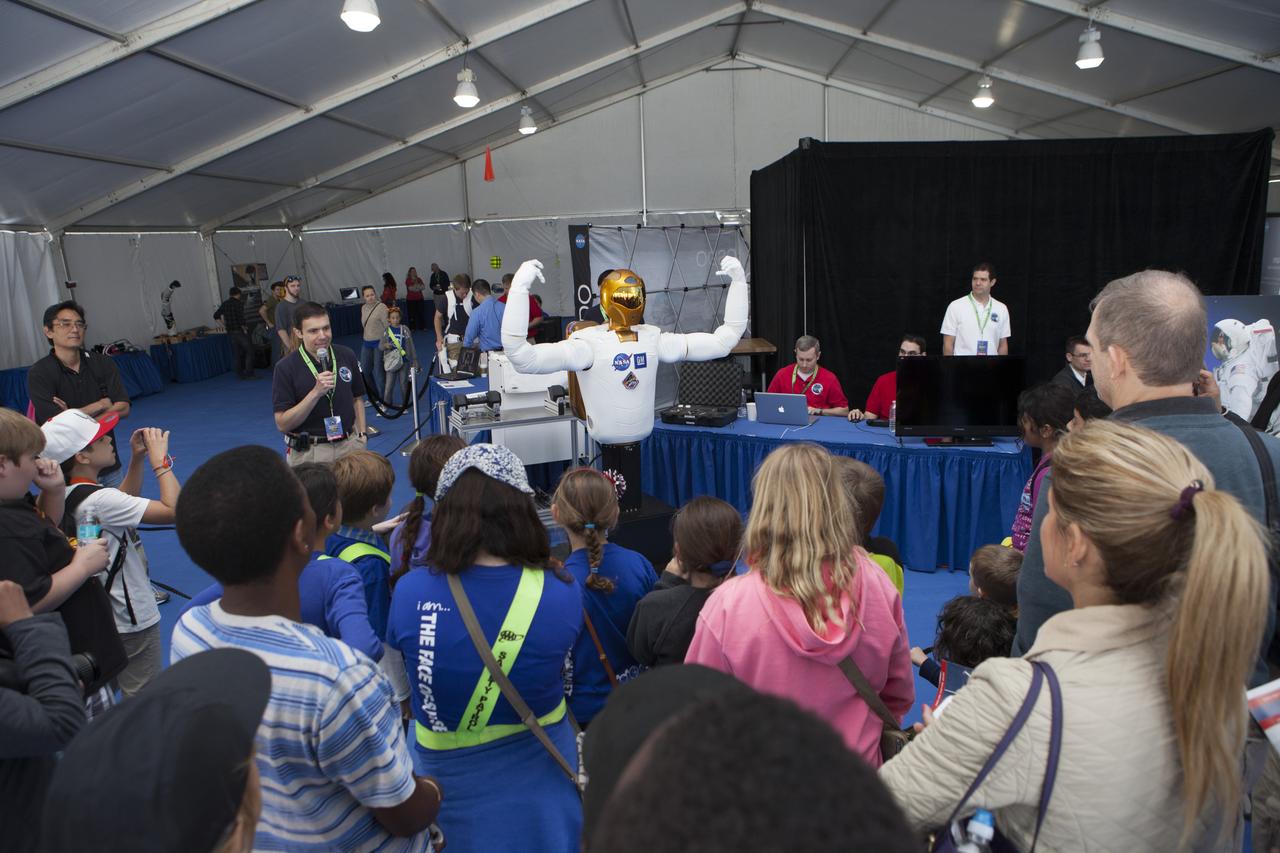

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A torso model of Robonaut 2, identical to R2 already on the International Space Station, is introduced to a crowd of onlookers by Ron Diftler of NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. The demonstration was one of several provided during the Robot Rocket Rally. The three-day event at Florida's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex is highlighted by exhibits, games and demonstrations of a variety of robots, with exhibitors ranging from school robotics clubs to veteran NASA scientists and engineers. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
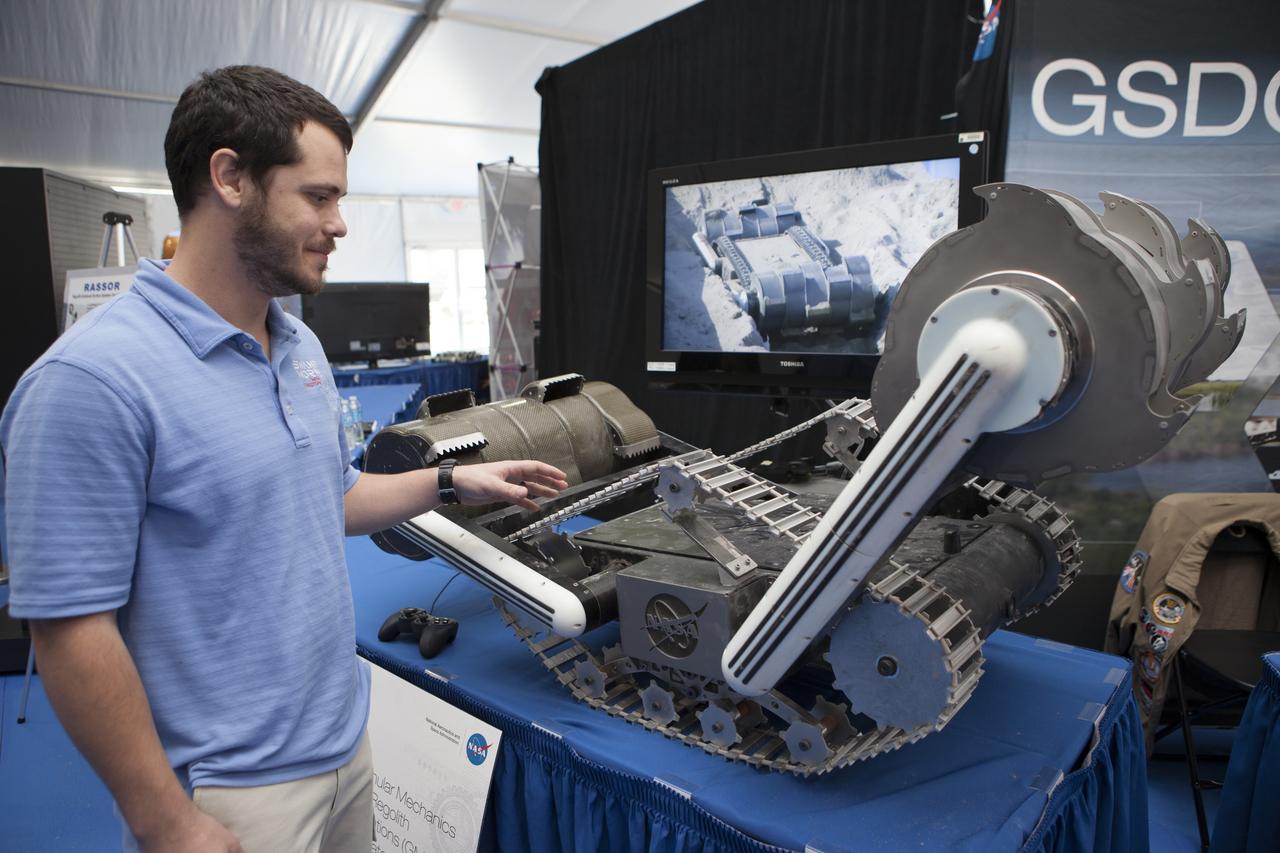

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Andrew Nick of Kennedy Space Center's Swamp Works shows off RASSOR, a robotic miner, at the Robot Rocket Rally. The three-day event at Florida's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex is highlighted by exhibits, games and demonstrations of a variety of robots, with exhibitors ranging from school robotics clubs to veteran NASA scientists and engineers. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
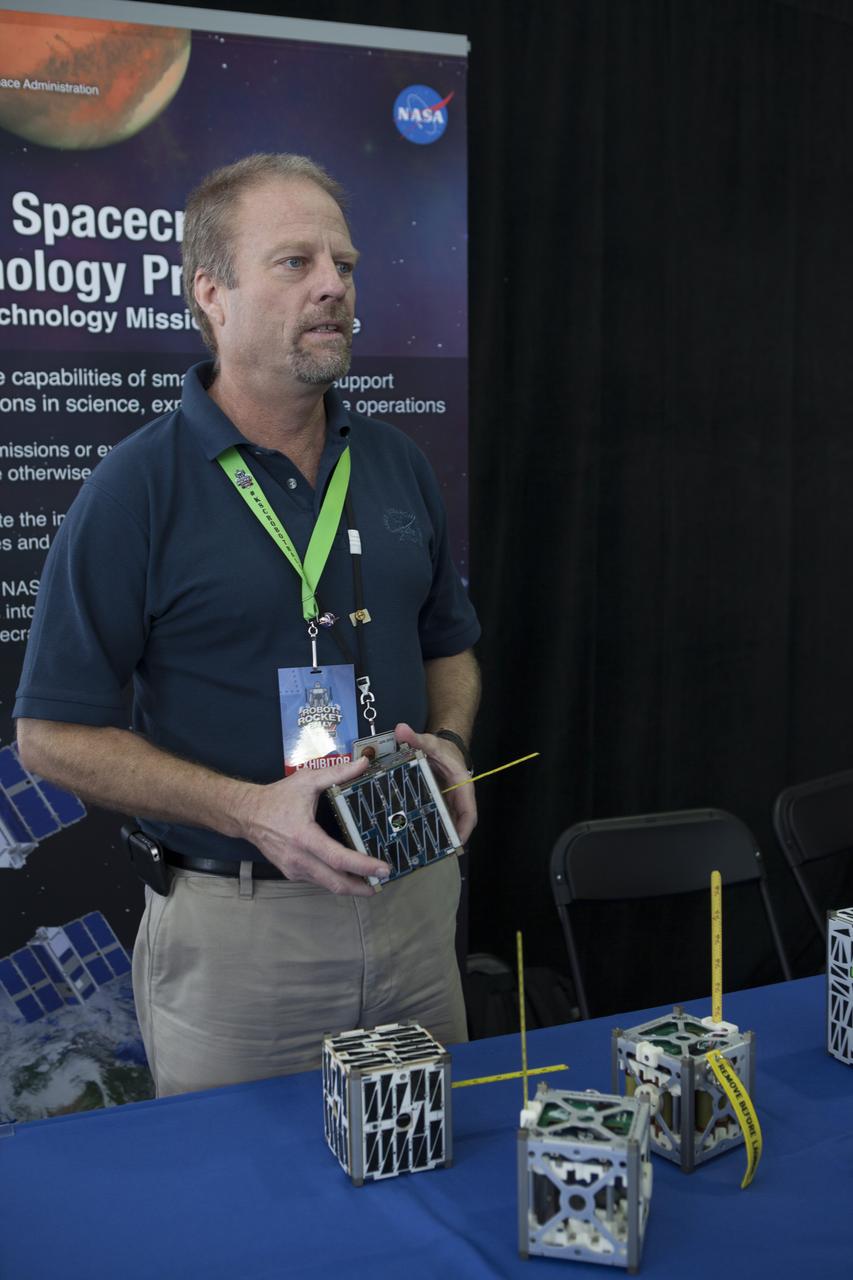

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Bruce Yost of NASA's Ames Research Center discusses a small satellite, known as PhoneSat, during the Robot Rocket Rally. The three-day event at Florida's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex is highlighted by exhibits, games and demonstrations of a variety of robots, with exhibitors ranging from school robotics clubs to veteran NASA scientists and engineers. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett