
Art and Science
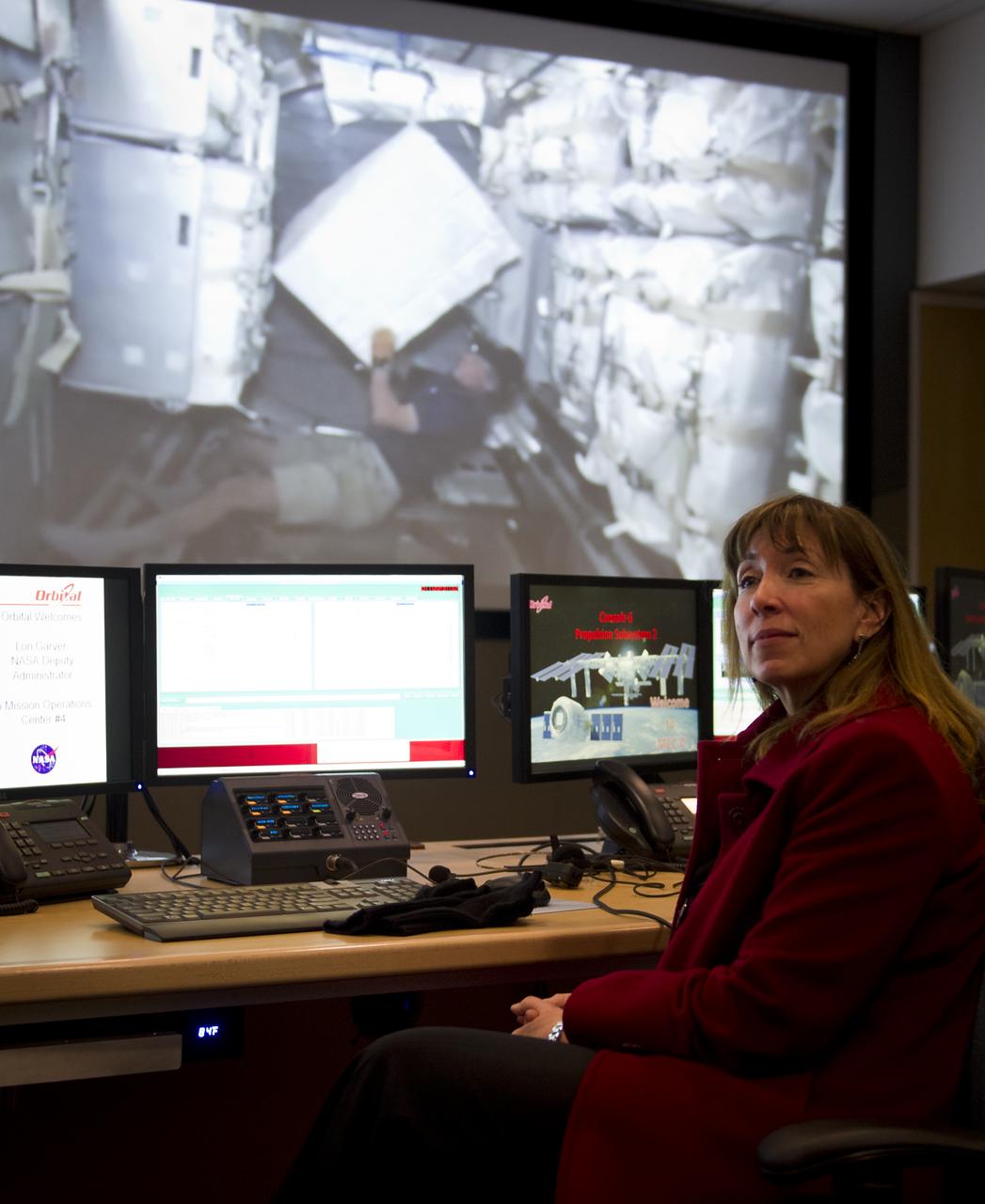

NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver, listens during a tour of the Orbital Sciences Corporation, Mission Operations Center, Tuesday, Jan. 11, 2011 in Dulles, VA. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
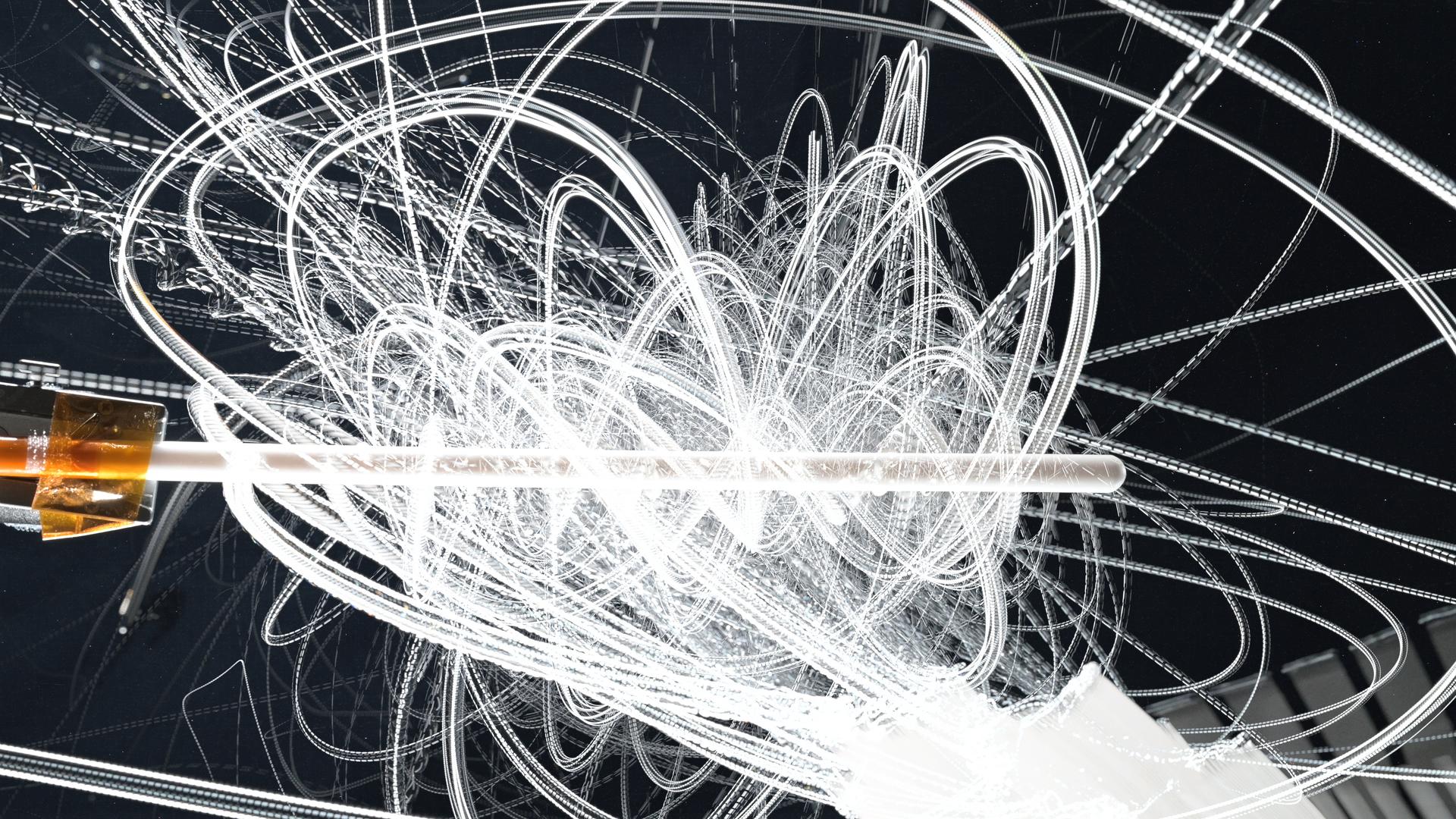

(February 19, 2025) -- NASA astronaut Don Pettit demonstrates electrostatic forces using charged water droplets and a knitting needle made of Teflon. This series of overlapping frames displays the unique attraction-repulsion properties of Teflon and charged droplets, similar to how charged particles from the Sun behave when they come in contact with Earth’s magnetic field. Highly energetic particles from space that collide with atoms and molecules in the atmosphere create the aurora borealis.
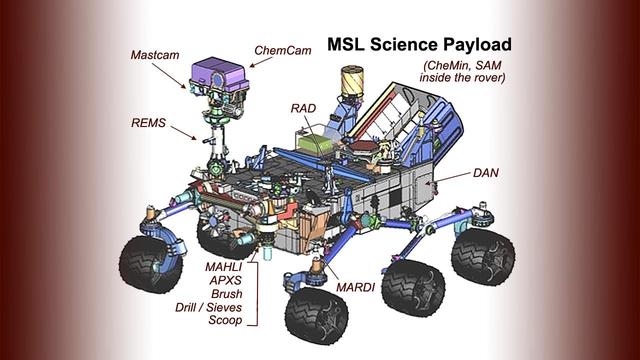
This drawing of the Mars Science Laboratory mission rover, Curiosity, indicates the location of science instruments and some other tools on the car-size rover.

Science at the Shadow Boundary

This illustration shows a conceptual design of a Mars Science Helicopter, a proposed follow-on to NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter. Researchers are considering how helicopters could be used in future missions. In addition to scouting, such a helicopter could carry science instruments to study terrain rovers can't reach. The proposed design is the product of collaboration between NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, NASA's Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley, and AeroVironment, Inc. A helicopter with this particular design could carry 4.5 to 11 pounds (2-5 kilograms) of science payload. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24729
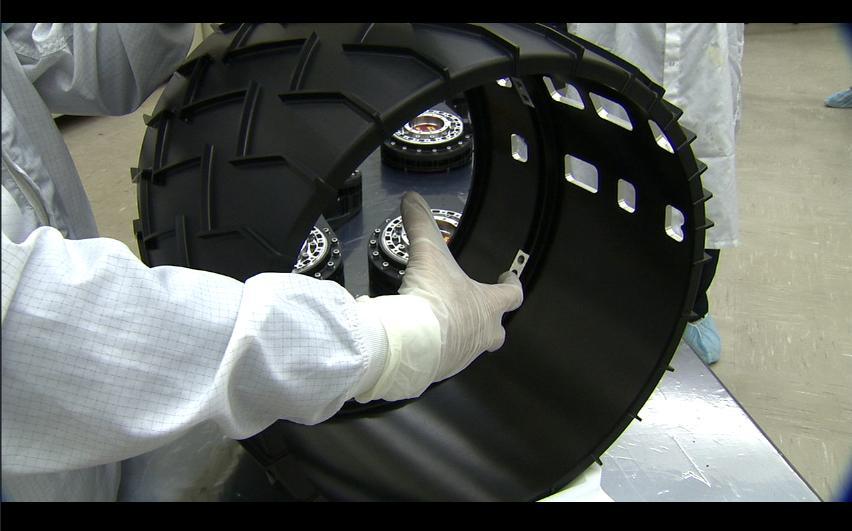

Each of the six wheels for NASA Mars Science Laboratory rover is about half a meter 20 inches in diameter.

This illustration of Moon to Mars multidisciplinary science shows astronauts collecting and analyzing lunar regolith. NASA’s Moon to Mars Objectives establish an objectives-based approach to the agency's human deep space exploration efforts; NASA’s Moon to Mars Architecture approach distills the objectives into operational capabilities and elements.

A model of NASA's Mars Science Helicopter concept is shown in this photo. This helicopter concept is a more capable proposed follow-on to NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter, which arrived at the Red Planet in the belly of the agency's Perseverance rover in February 2021. The six-rotor Mars Science Helicopter could be used during future Mars missions to serve as an aerial scout, carrying between 4.5 and 11 pounds (2 to 5 kilograms) of payload, including science instruments, and studying terrain that rovers can't reach. It remains in early conceptual and design stages. The proposed design is the product of collaboration between JPL, NASA's Ames Research Center in California's Silicon Valley, and AeroVironment Inc. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25661
Science Magazine Cover Image
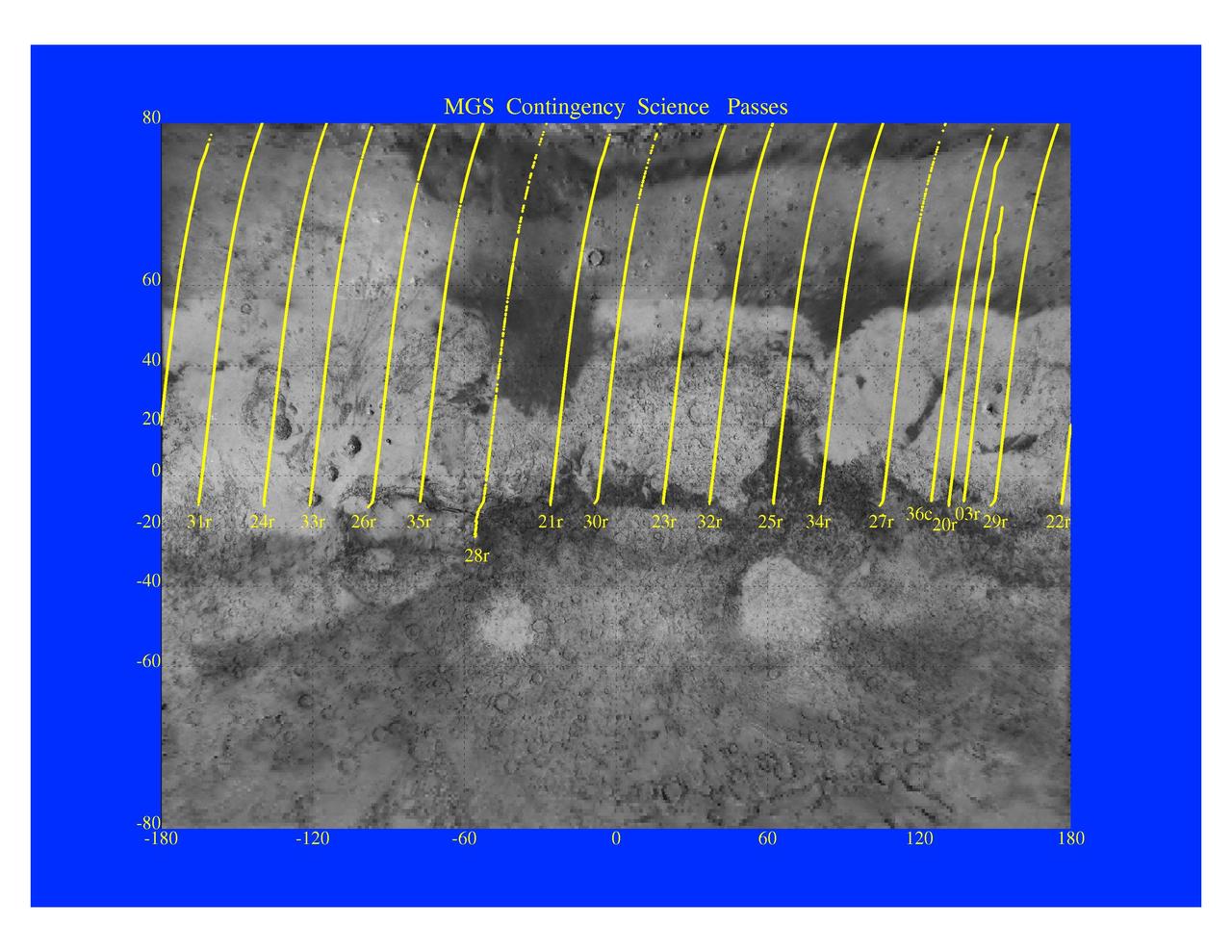
MGS Contingency Science Passes
The Blending of Art and Science
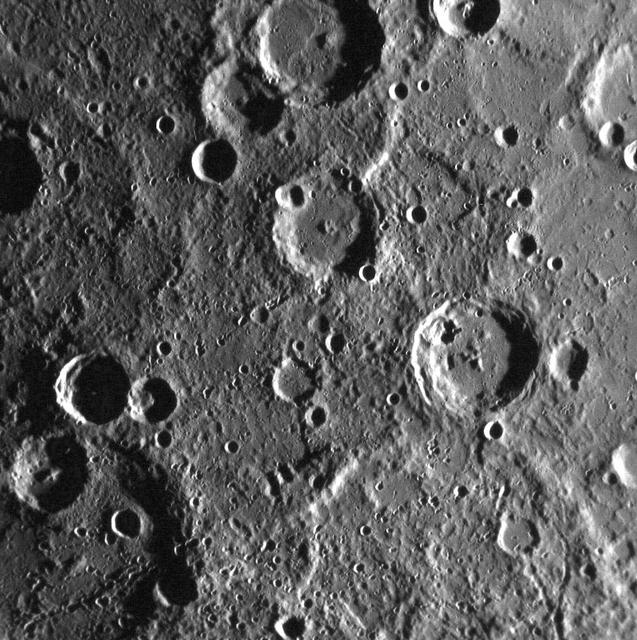

Let the Science Phase Begin!
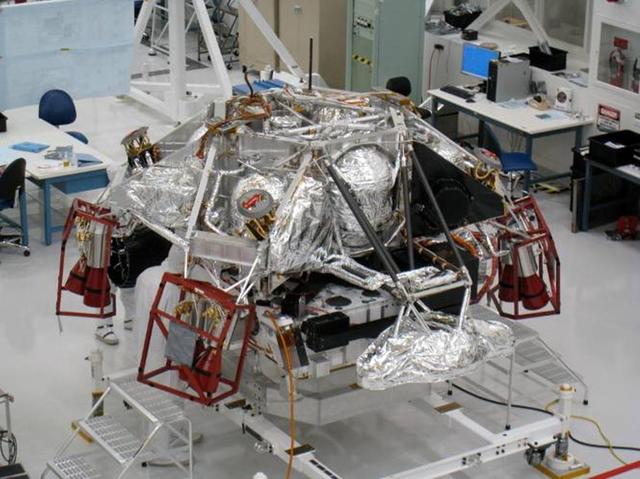

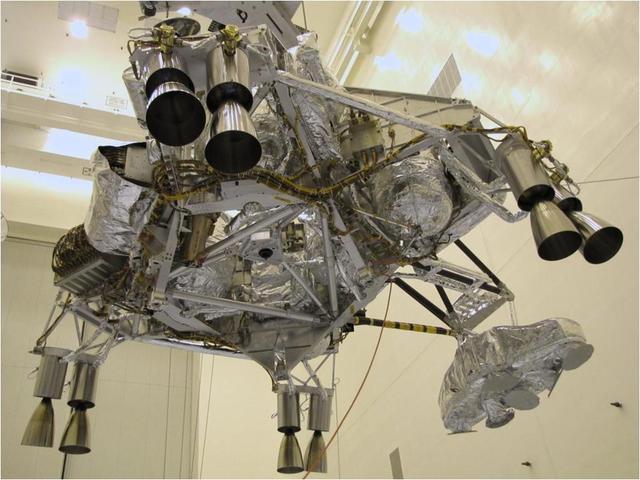
This portion of NASA Mars Science Laboratory, called the descent stage, does its main work during the final few minutes before touchdown on Mars.
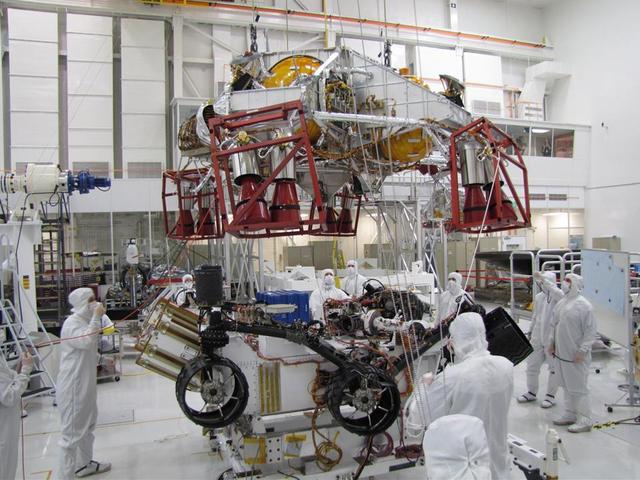

Spacecraft specialists test the descent stage and rover of the Mars Science Laboratory in this scene from the Spacecraft Assembly Facility at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
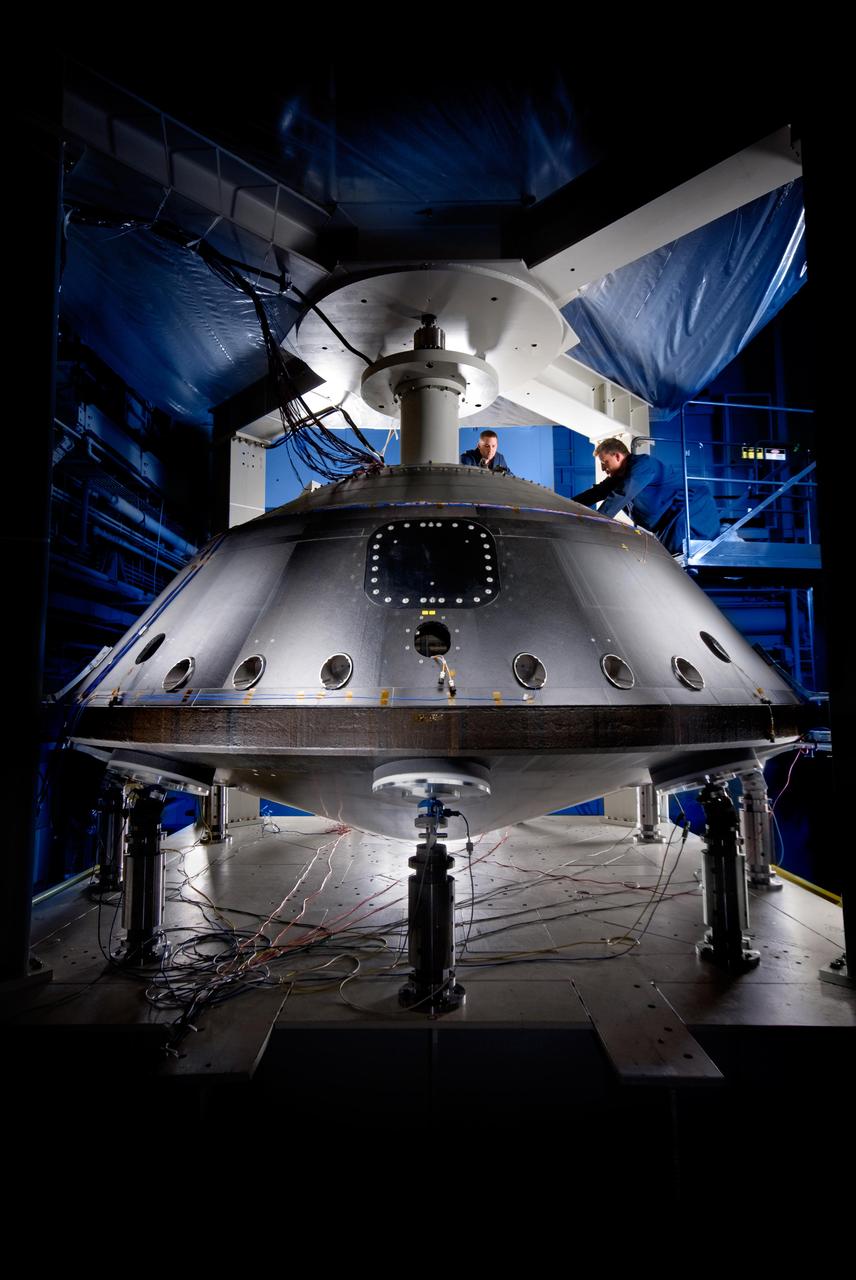

This image from July 2008 shows the aeroshell for NASA Mars Science Laboratory while it was being worked on by spacecraft technicians at Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company near Denver.
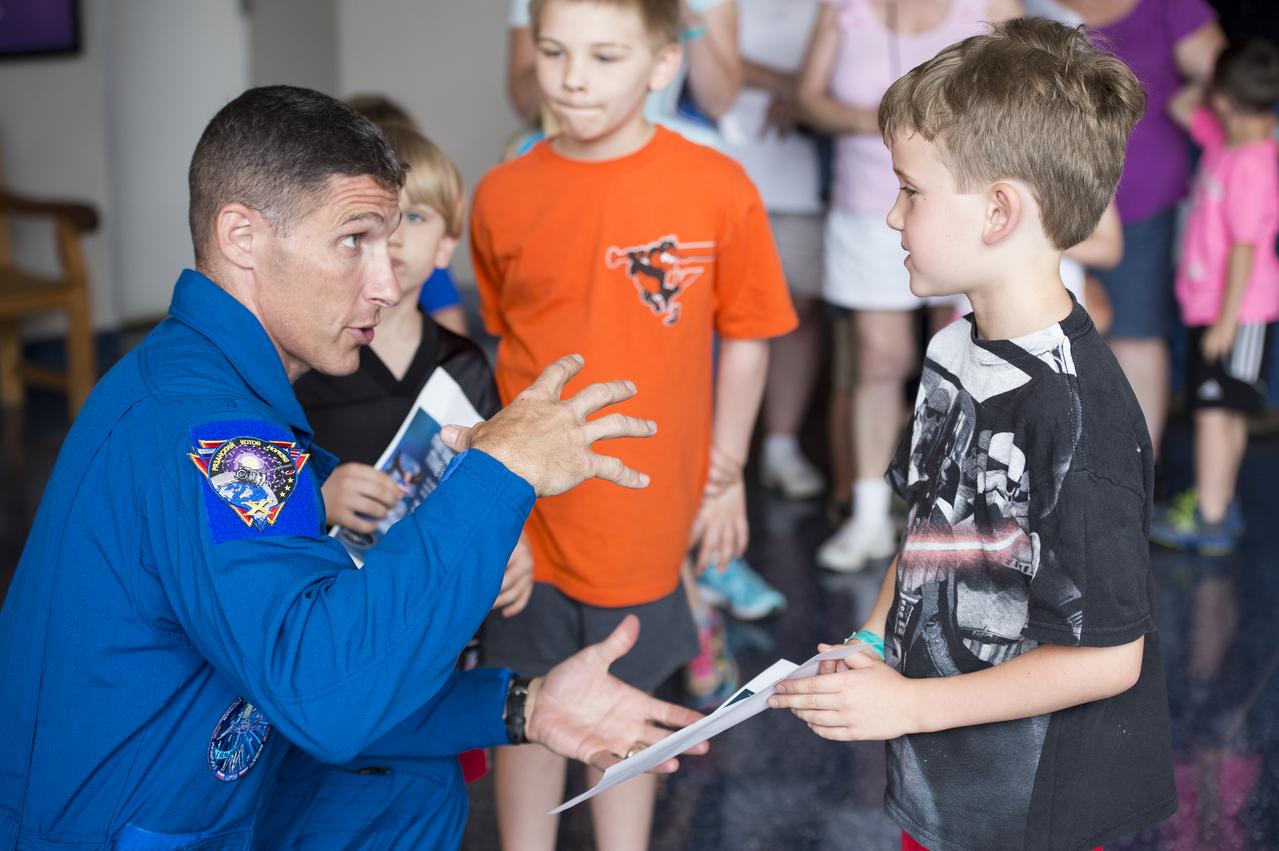

NASA Astronaut Mike Hopkins explains what it was like to live on the International Space Station for 6 months to visitors at the Maryland Science Center in Baltimore, MD on Monday, June 9, 2014. Hopkins served on Expeditions 37 and 38 with Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kotov and Sergey Ryazanskiy and returned home in March, 2014. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Astronaut Mike Hopkins explains what it was like to live on the International Space Station for 6 months to visitors at the Maryland Science Center in Baltimore, MD on Monday, June 9, 2014. Hopkins served on Expeditions 37 and 38 with Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kotov and Sergey Ryazanskiy and returned home in March, 2014. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Astronaut Mike Hopkins explains what it was like to live on the International Space Station for 6 months to visitors at the Maryland Science Center in Baltimore, MD on Monday, June 9, 2014. Hopkins served on Expeditions 37 and 38 with Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kotov and Sergey Ryazanskiy and returned home in March, 2014. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Astronaut Mike Hopkins explains what it was like to live on the International Space Station for 6 months to visitors at the Maryland Science Center in Baltimore, MD on Monday, June 9, 2014. Hopkins served on Expeditions 37 and 38 with Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kotov and Sergey Ryazanskiy and returned home in March, 2014. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Astronaut Mike Hopkins explains what it was like to live on the International Space Station for 6 months to visitors at the Maryland Science Center in Baltimore, MD on Monday, June 9, 2014. Hopkins served on Expeditions 37 and 38 with Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kotov and Sergey Ryazanskiy and returned home in March, 2014. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

The Mars Science Laboratory mission powered descent vehicle is the integrated combination of the spacecraft descent stage and the rover Curiosity.
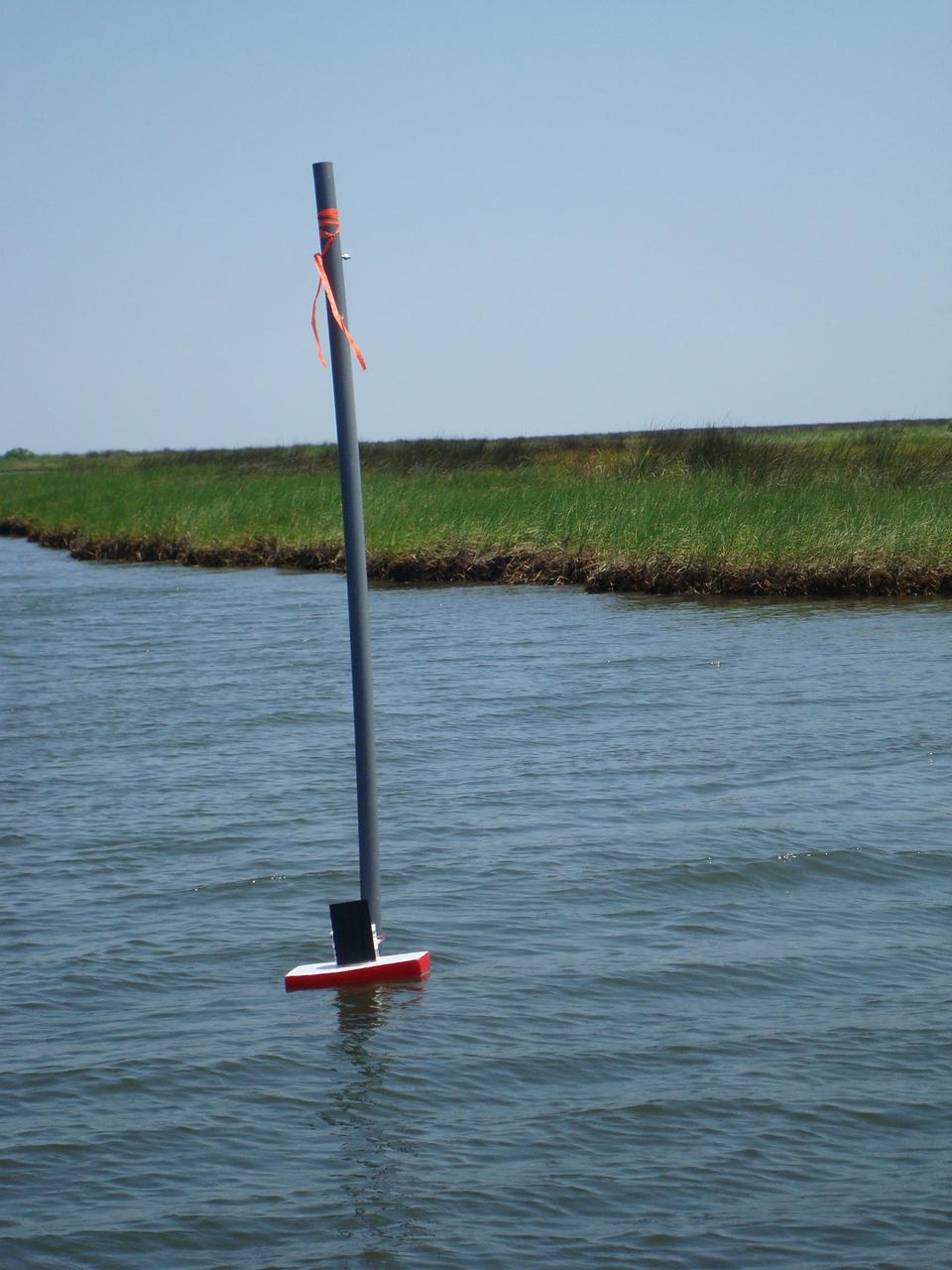

Once tethered in place in Gulf Coast waters, a DRIFTER sensor device is able to transmit valuable information about water temperature and conductivity. The Applied Science and Technology Project Office at Stennis Space Center designed the DRIFTER as an inexpensive device that can be used for science projects in local schools. Two of the devices, deployed in coastal waters, survived Hurricane Isaac, continuing to transmit valuable data regarding the storm.
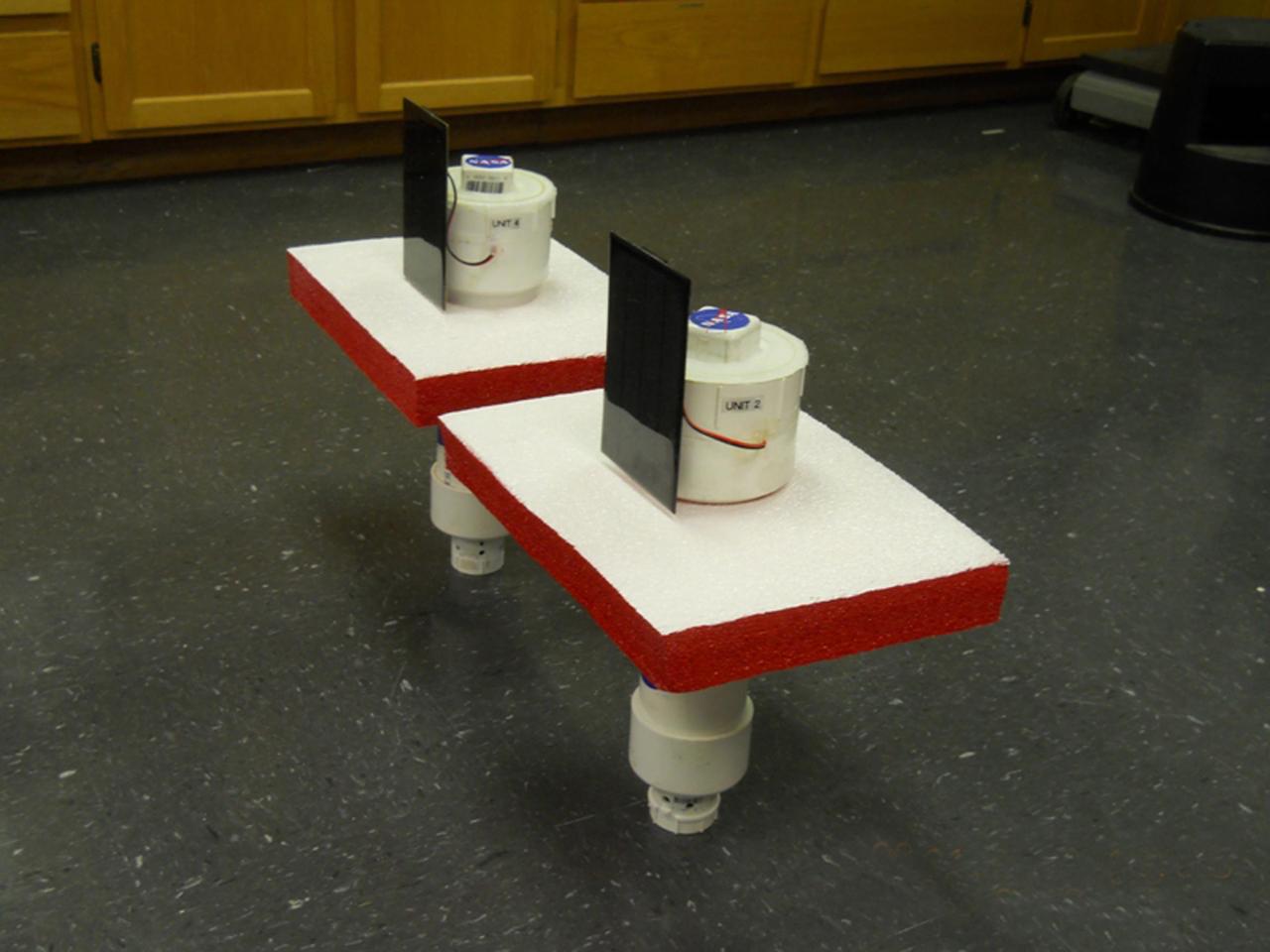

DRIFTER sensor devices were designed by the Applied Science and Technology Project Office as inexpensive tools that can be used for science projects in local schools. The devices transmit information about water temperature and conductivity for use by Gulf Coast researchers. The DRIFTER project began as an effort to help Gulf Coast oyster fishermen dealing with the effects of fresh water intrusion.
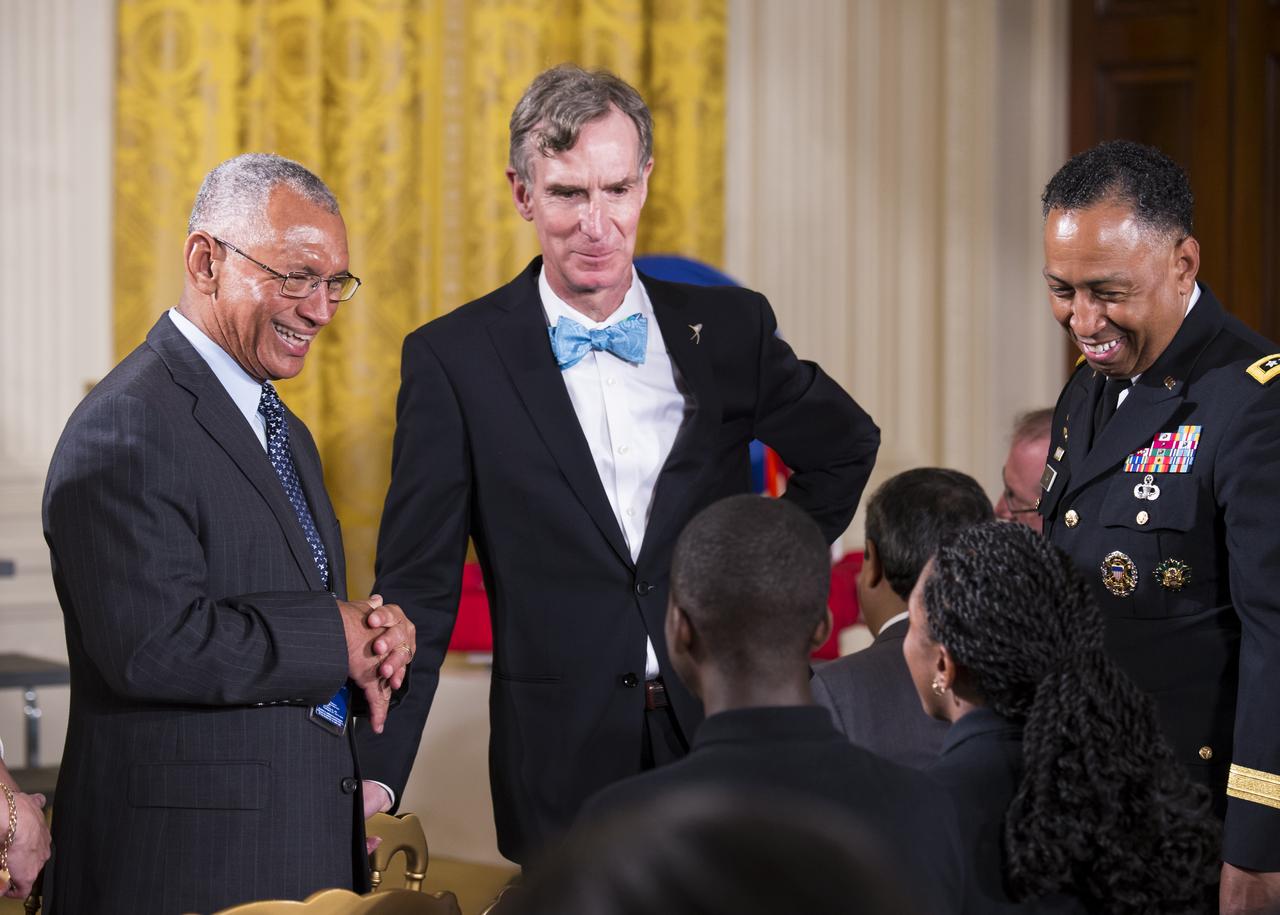

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden (left) and Bill Nye, The Science Guy, speak with some students that participated in the White House Science Fair. The fourth White House Science Fair was held at the White House on May 27, 2014 and included 100 students from more than 30 different states who competed in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) competitions. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
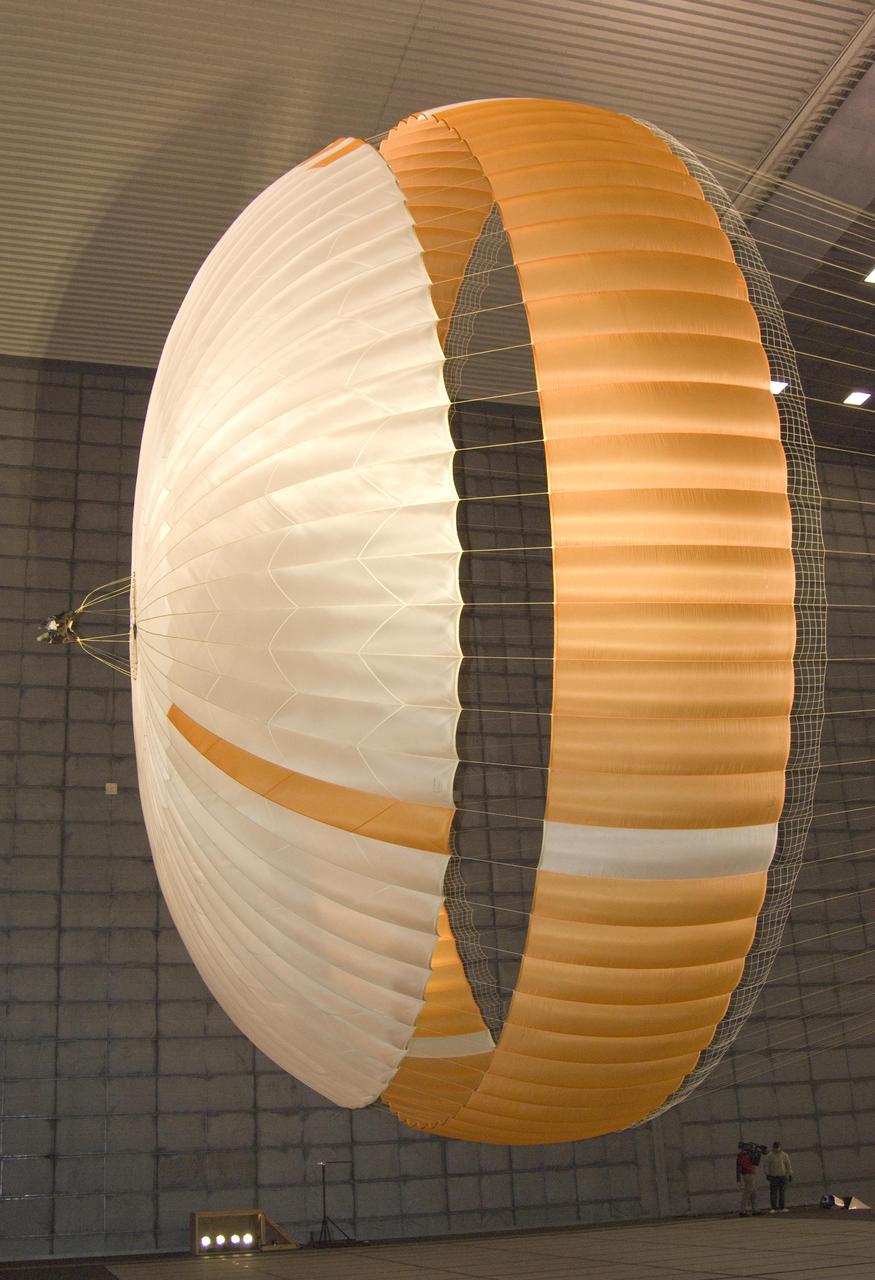

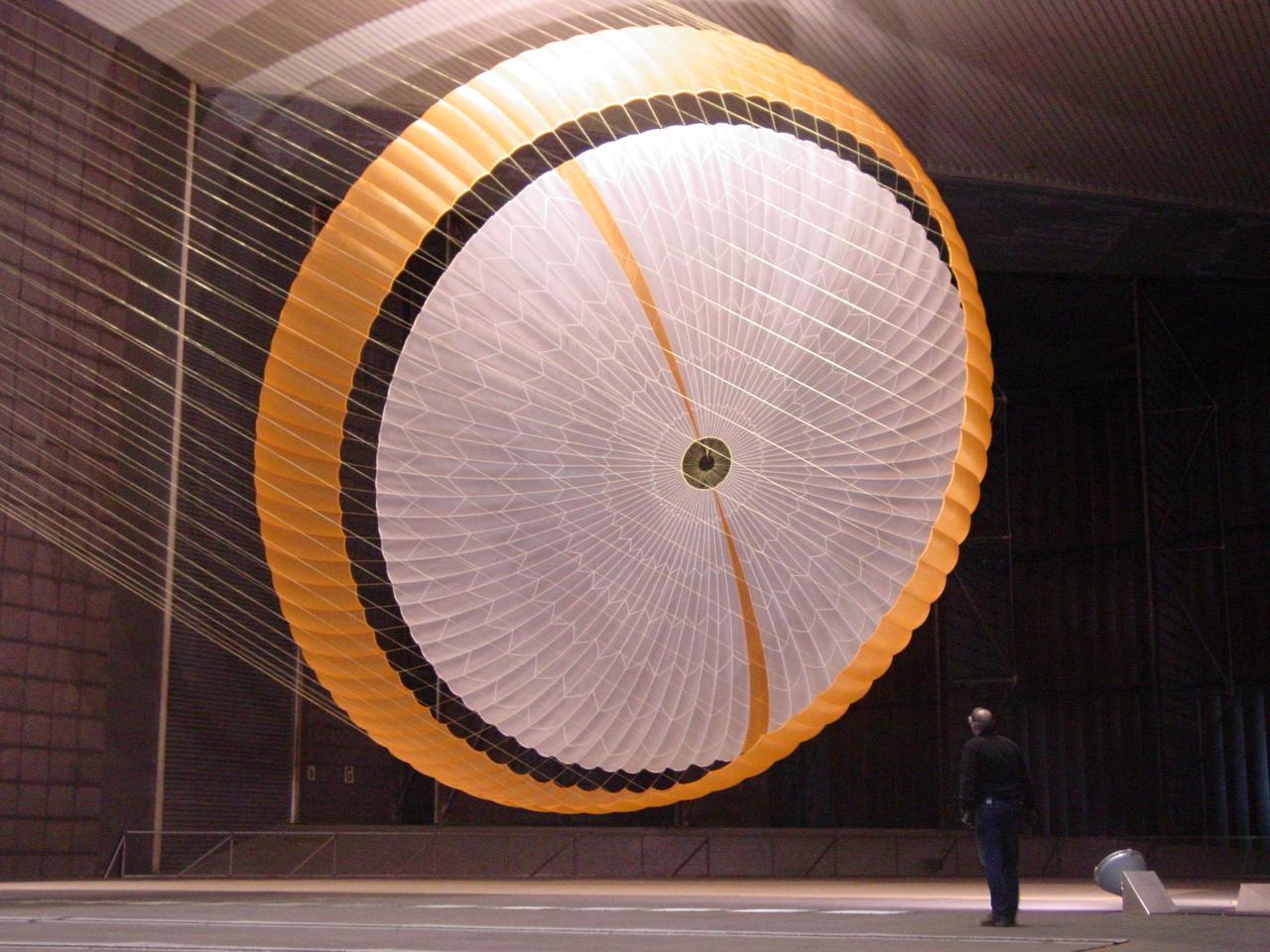
The parachute for NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission opens to a diameter of nearly 16 meters 51 feet. This image shows a duplicate qualification-test parachute inside the world's largest wind tunnel, at NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. The Mars Science Laboratory will be launched in 2011 for a landing on Mars in 2012. Its parachute is the largest ever built to fly on an extraterrestrial mission. The parachute uses a configuration called disk-gap-band, with 80 suspension lines. Most of the orange and white fabric is nylon, though a small disk of heavier polyester is used near the vent in the apex of the canopy due to higher stresses there. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11994
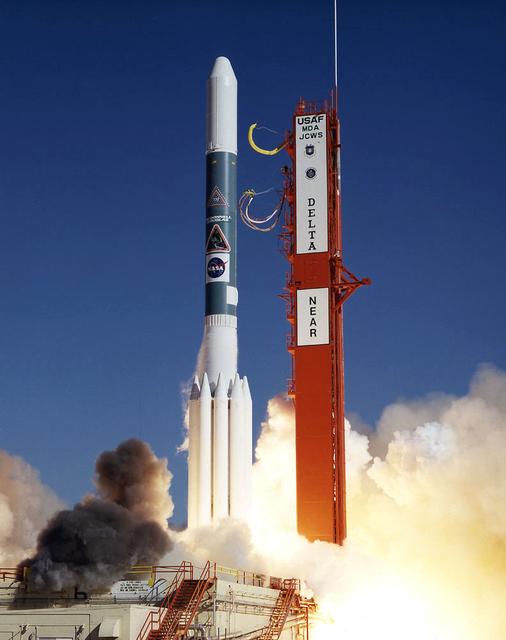

The Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous (NEAR) spacecraft embarks on a journey that will culminate in a close encounter with an asteroid. The launch of NEAR inaugurates NASA's irnovative Discovery program of small-scale planetary missions with rapid, lower-cost development cycles and focused science objectives. NEAR will rendezvous in 1999 with the asteroid 433 Eros to begin the first long-term, close-up look at an asteroid's surface composition and physical properties. NEAR's science payload includes an x-ray/gamma ray spectrometer, an near-infrared spectrograph, a laser rangefinder, a magnetometer, a radio science experiment and a multi-spectral imager.

This image, taken April 9, 2010, shows the test radar affixed to a gimbal mounting at the front of a helicopter, carrying an engineering test model of the landing radar for NASA Mars Science Laboratory.

The descent stage of NASA Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft is being lifted during assembly of the spacecraft in this photograph taken inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA Kennedy Space Center, Fla.

The team developing the landing system for NASA Mars Science Laboratory tested the deployment of an early parachute design in mid-October 2007 inside the world largest wind tunnel, at NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California.
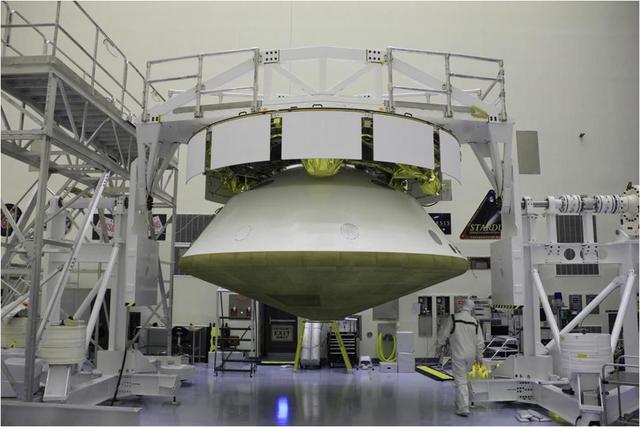

NASA Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft has been fully stacked for flight in this photograph from inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA Kennedy Space Center, Fla., in October 2011.
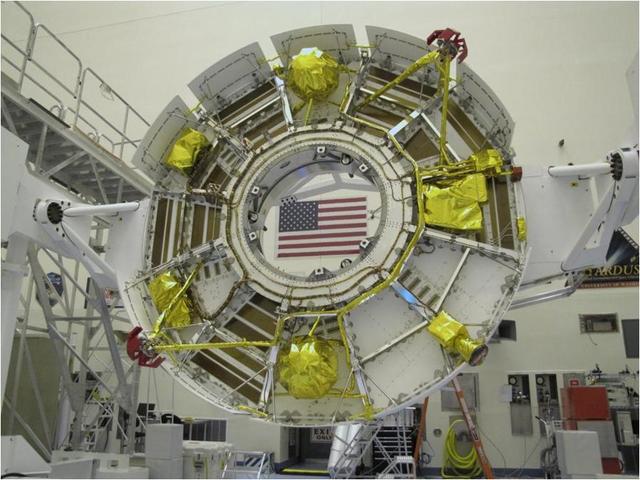

The cruise stage of NASA Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft is being prepared for final stacking of the spacecraft in this photograph from inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA Kennedy Space Center, Fla.
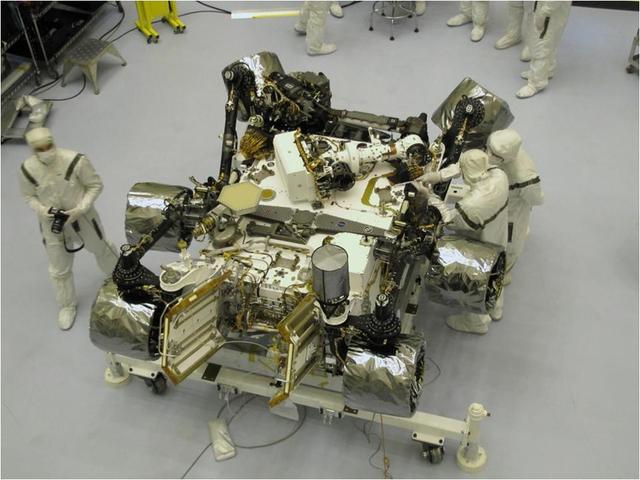

The Mars Science Laboratory mission rover, Curiosity, is prepared for final integration into the complete NASA spacecraft in this photograph taken inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA Kennedy Space Center, Fla.
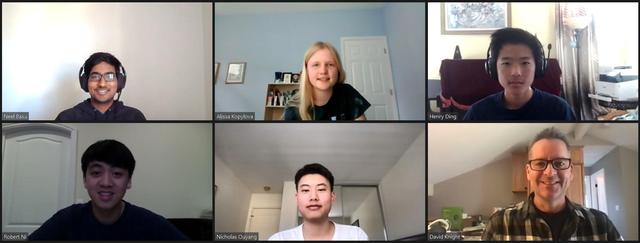
For the fourth consecutive year, Irvine's University High School won the Southern California regional round of the National Science Bowl, hosted by JPL. The team, including coach David Knight (lower right), paused for a group shot after their victory on March 20, 2021. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23730
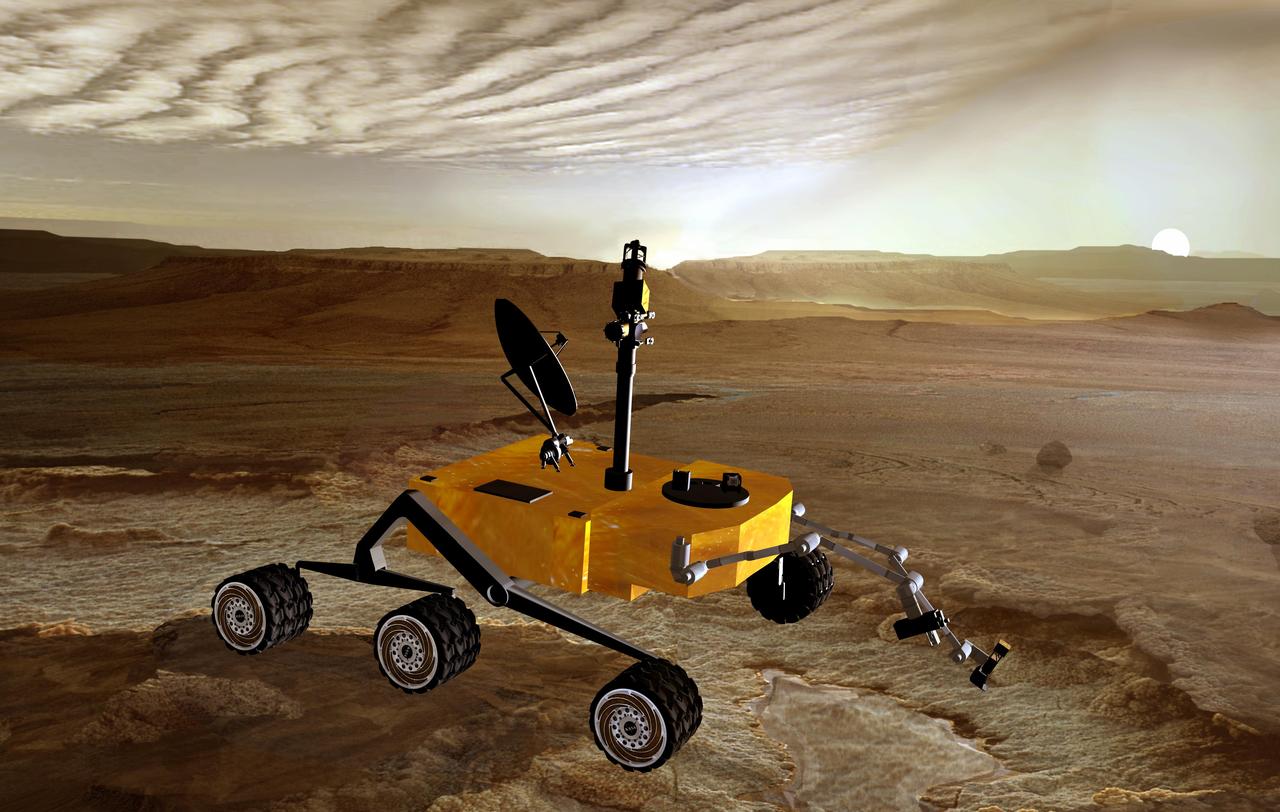

Sunset on Mars catches NASA Mars Science Laboratory in the foreground in this artist concept. The mission is under development for launch in 2009 and a precision landing on Mars in 2010.
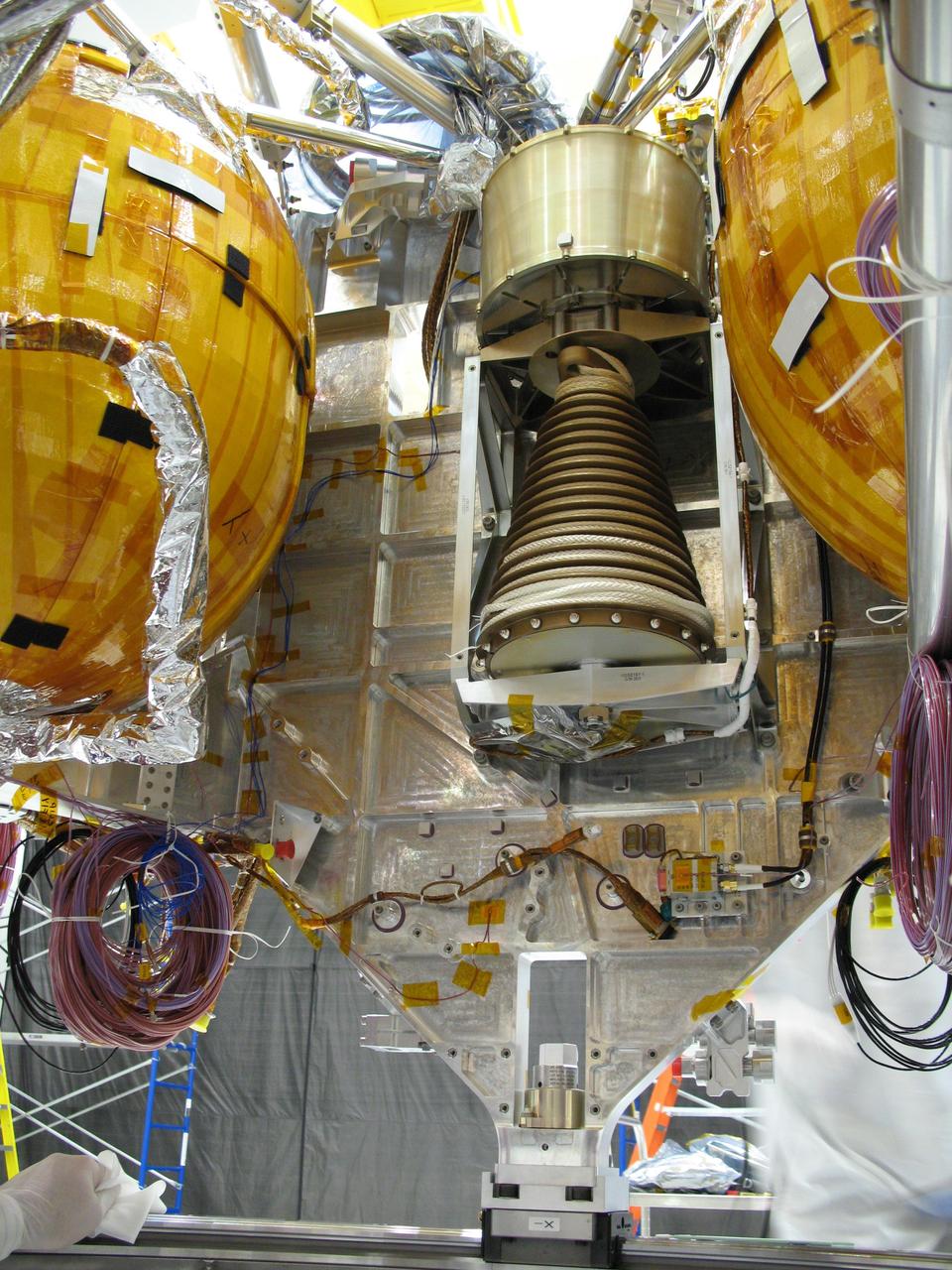

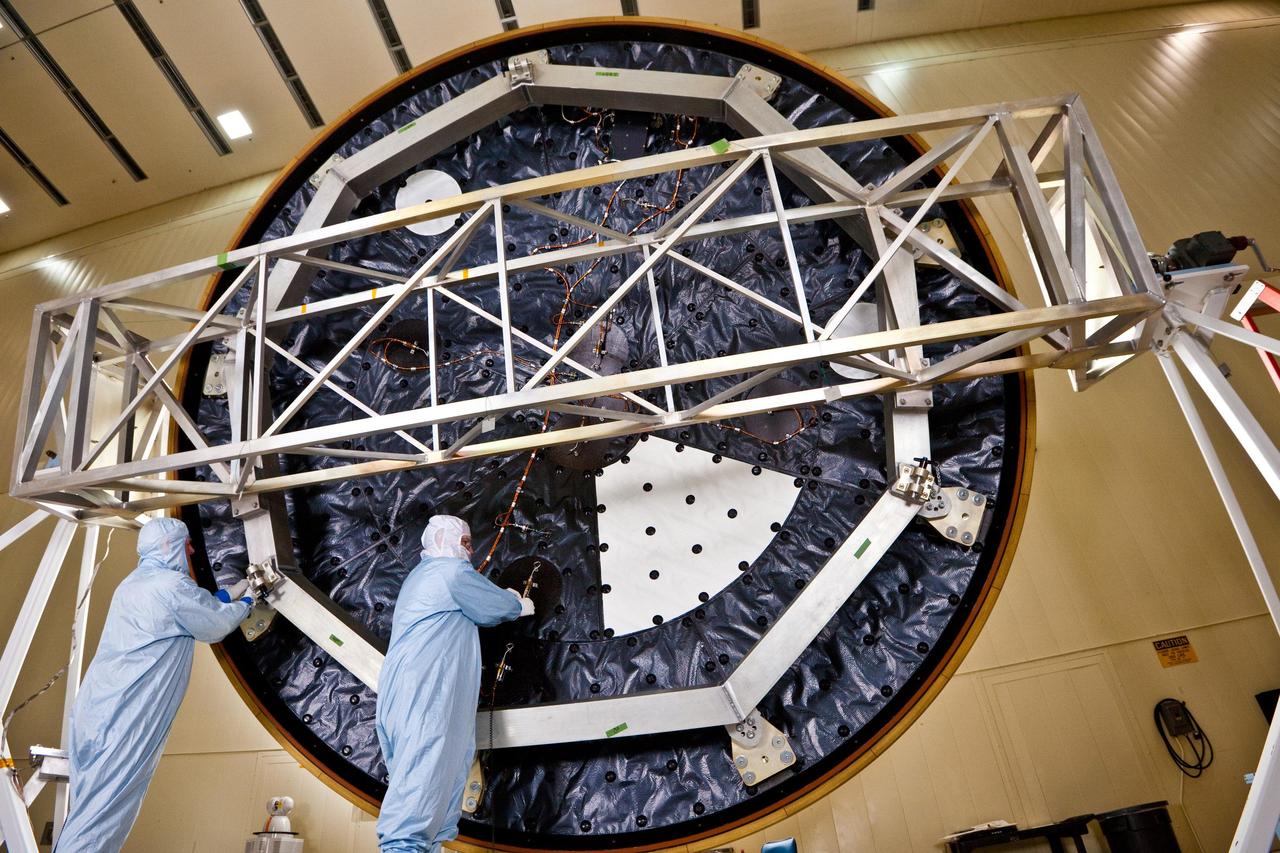
This view of a portion of the descent stage of NASA Mars Science Laboratory shows two of the stage three spherical fuel tanks flanking the bridle device assembly.
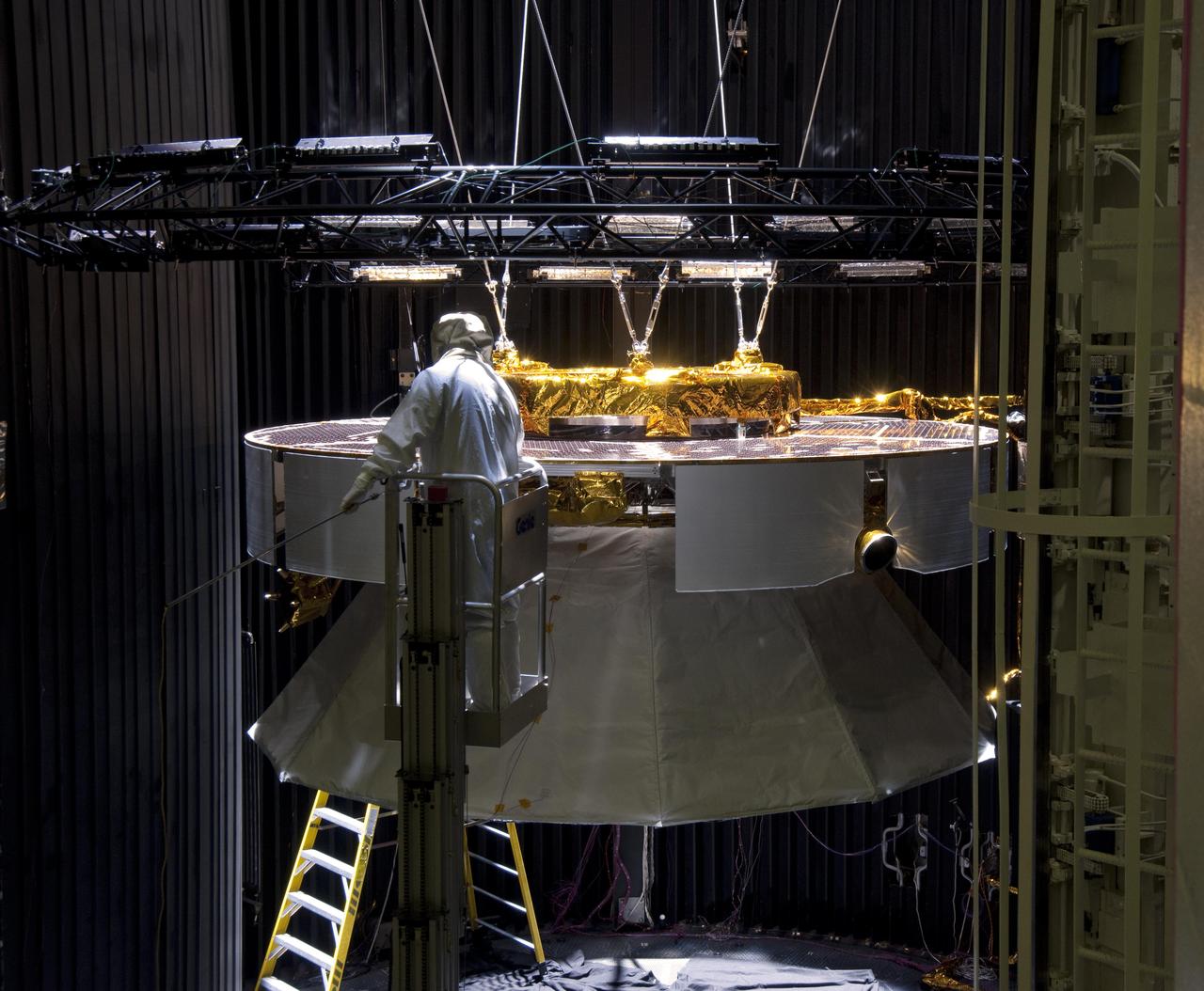

Testing of the cruise stage for NASA Mars Science Laboratory in August 2010 included a session in a facility that simulates the environment found in interplanetary space.
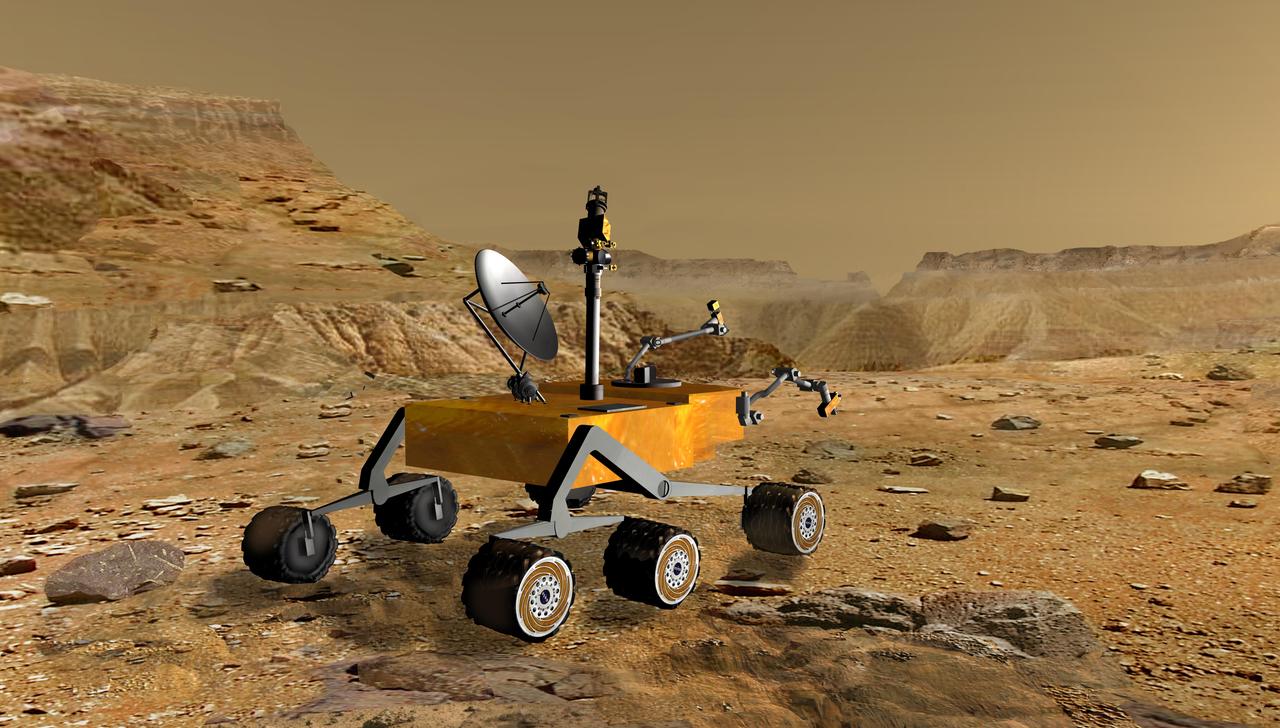

NASA Mars Science Laboratory travels near a canyon on Mars in this artist concept. The mission is under development for launch in 2009 and a precision landing on Mars in 2010.
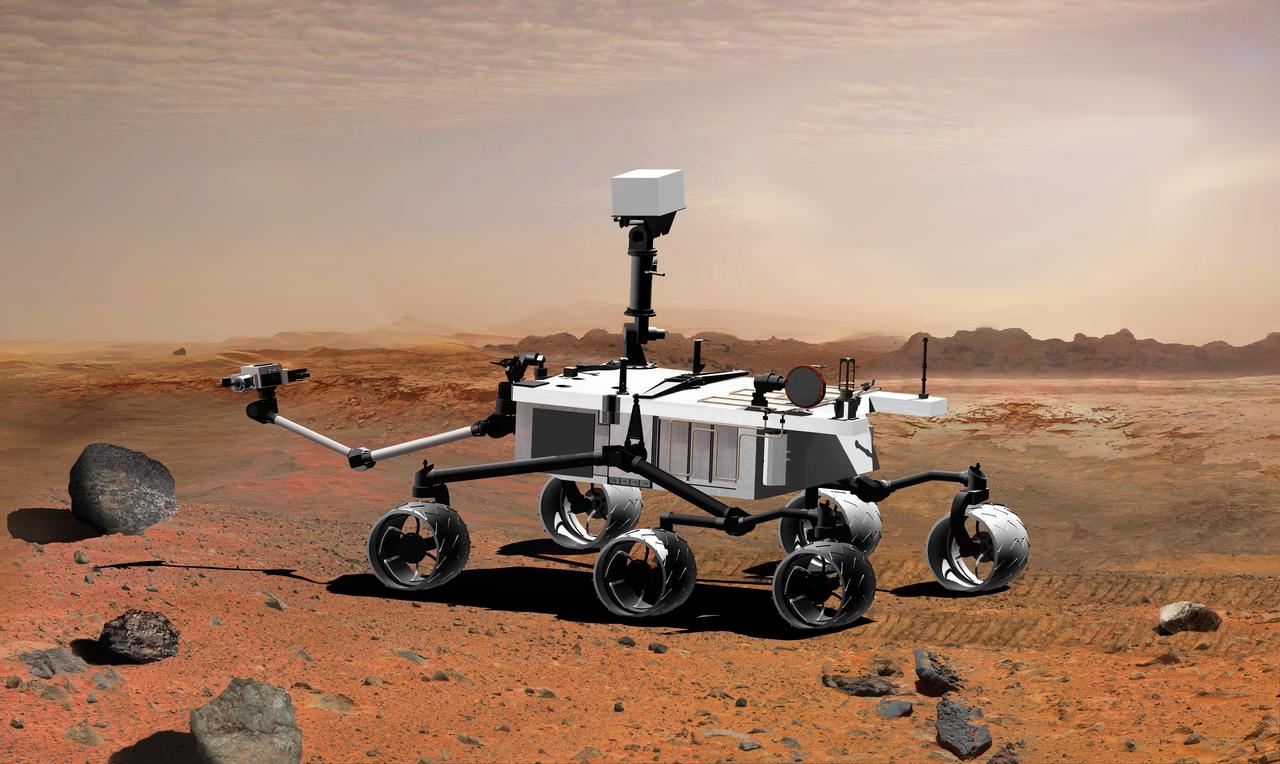

NASA Mars Science Laboratory, a mobile robot for investigating Mars past or present ability to sustain microbial life, is in development for a launch opportunity in 2011 previously 2009.

This is hardware for controlling the final lowering of NASA Mars Science Laboratory rover to the surface of Mars from the spacecraft hovering, rocket-powered descent stage.
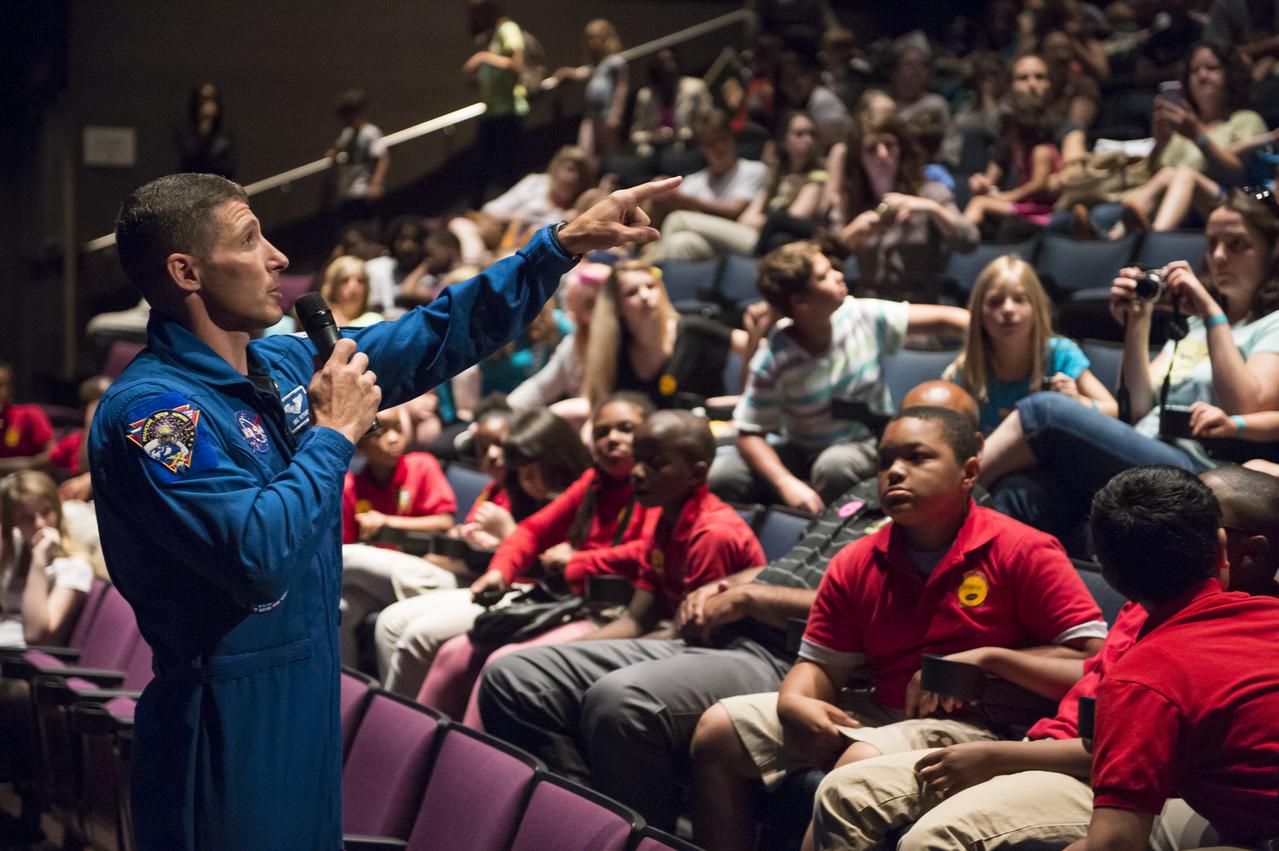

NASA Astronaut Mike Hopkins explains what it was like to live on the International Space Station for 6 months to seventh graders from Clear Spring Middle School at the Maryland Science Center in Baltimore, MD on Monday, June 9, 2014. Hopkins served on Expeditions 37 and 38 with Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kotov and Sergey Ryazanskiy and returned home in March, 2014. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
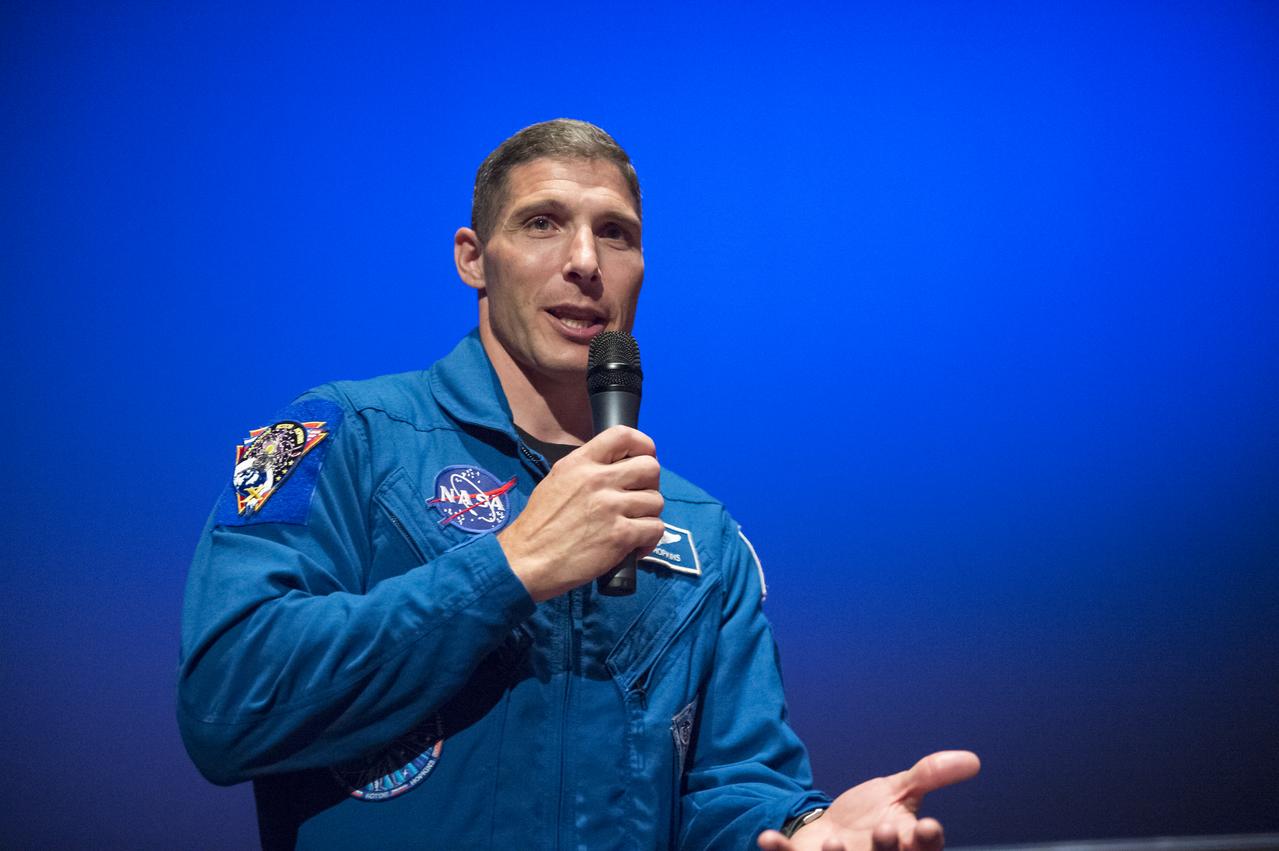

NASA Astronaut Mike Hopkins explains what it was like to live on the International Space Station for 6 months to seventh graders from Clear Spring Middle School at the Maryland Science Center in Baltimore, MD on Monday, June 9, 2014. Hopkins served on Expeditions 37 and 38 with Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kotov and Sergey Ryazanskiy and returned home in March, 2014. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
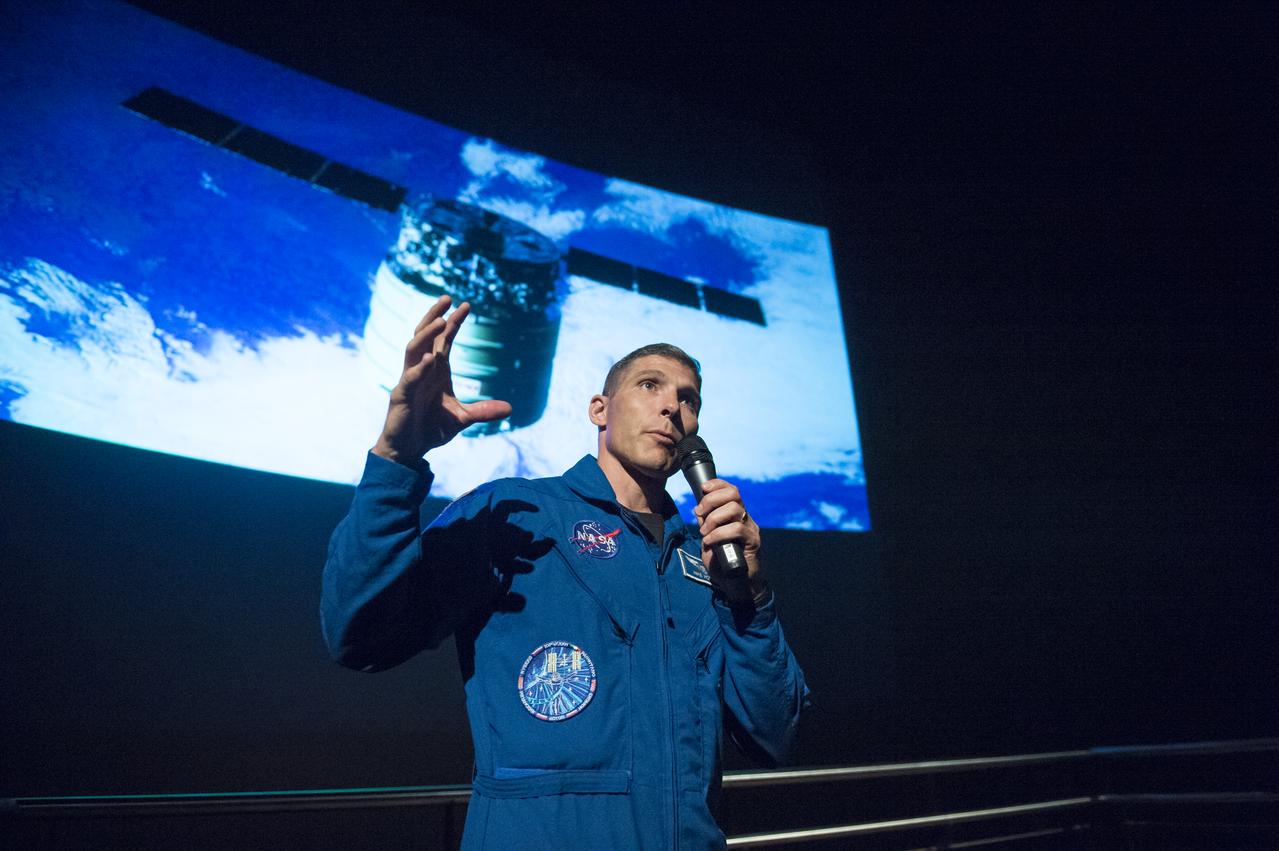

NASA Astronaut Mike Hopkins explains what it was like to live on the International Space Station for 6 months to seventh graders from Clear Spring Middle School at the Maryland Science Center in Baltimore, MD on Monday, June 9, 2014. Hopkins served on Expeditions 37 and 38 with Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kotov and Sergey Ryazanskiy and returned home in March, 2014. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
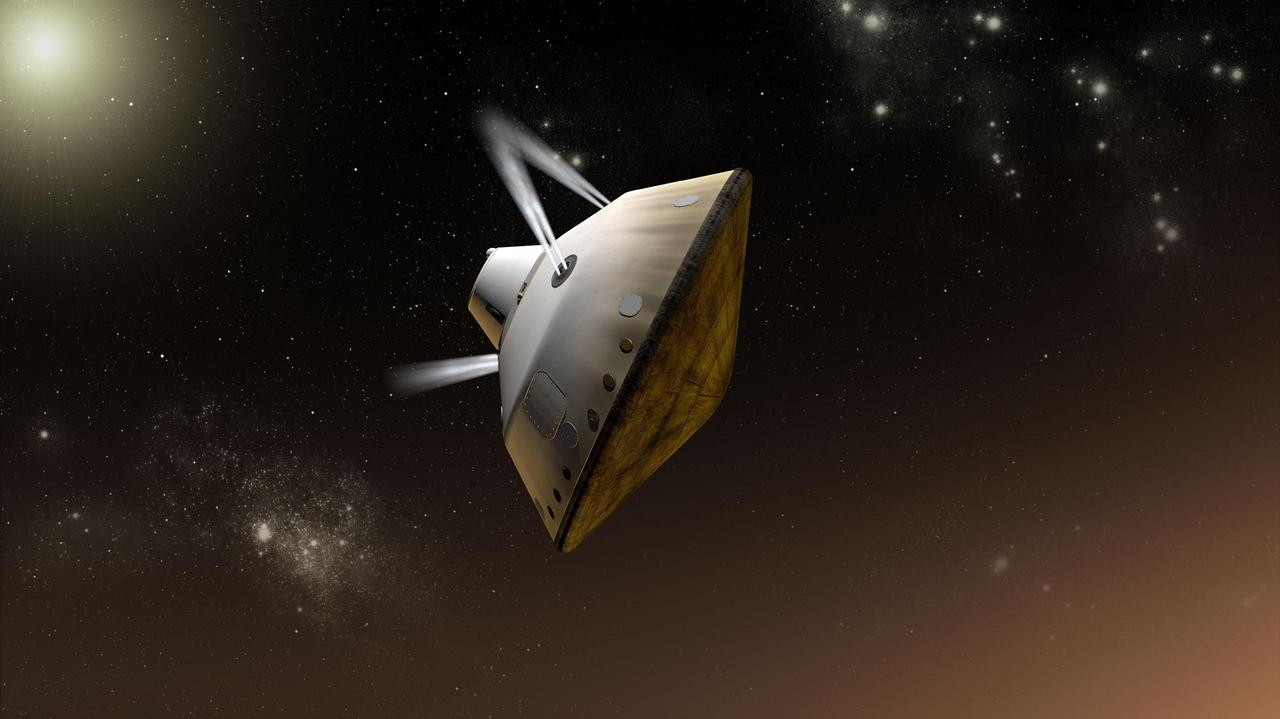

This artist concept shows thrusters firing during the entry, descent and landing phase for NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission to Mars.
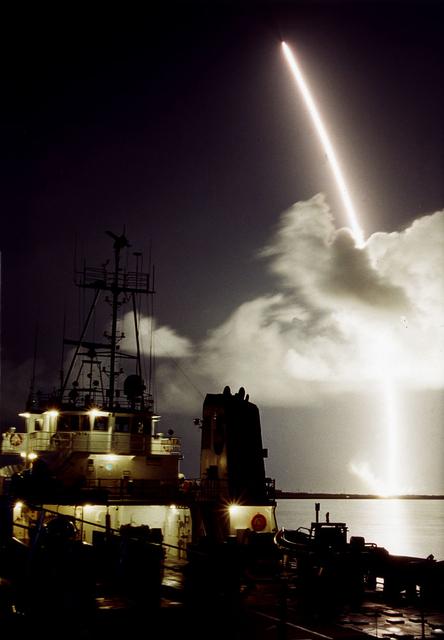

The 7-year journey to Saturn began with the liftoff of a Titan IVB/ Centaur carrying the Cassini orbiter and its attached Huygens probe. After a 2.2-billion mile journey that included two swingbys of Venus and one of the Earth to gain additional velocity, the two-story tall spacecraft will arrive at Saturn in July 2004. The orbiter will circle the planet for 4 years, its compliment of 12 scientific instruments gathering data about Saturn's atmosphere, rings and magnetosphere and conducting close-up observations of Saturnian moons. Huygens, with a separate suite of 6 science instruments, will separate from Cassini to fly on a ballistic trajectory toward Titan, the only celestial body besides Earth to have an atmosphere rich in nitrogen. Scientists are eager to study further this chemical similarity in hopes of learning more about the origins of our own planet Earth. Huygens will provide the first direct sampling of Titan's atmospheric chemistry and the first detailed photographs of its surface. The Cassini mission is an International effort involving NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI).
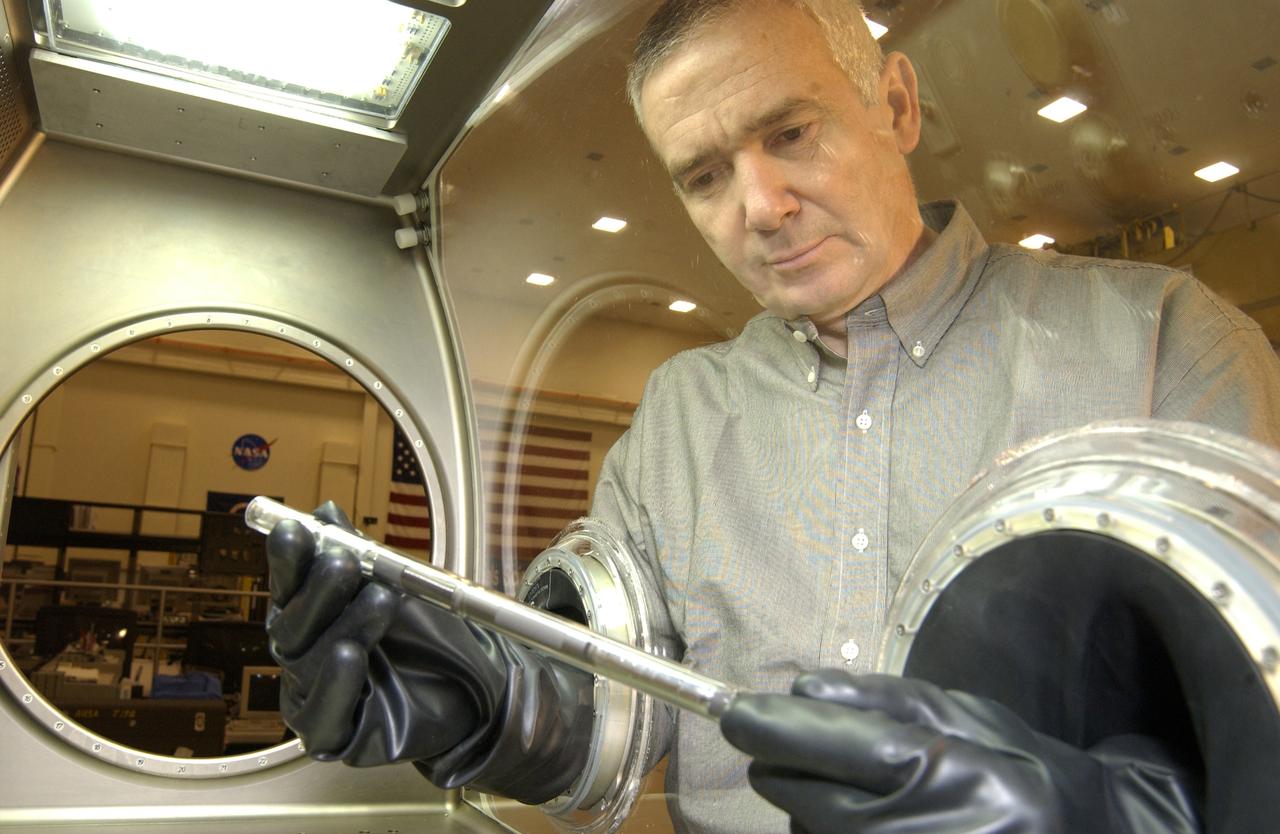

One of the first materials science experiments on the International Space Station -- the Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules (SUBSA) -- will be conducted during Expedition Five inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox. The glovebox is the first dedicated facility delivered to the Station for microgravity physical science research, and this experiment will be the first one operated inside the glovebox. The glovebox's sealed work environment makes it an ideal place for the furnace that will be used to melt semiconductor crystals. Astronauts can change out samples and manipulate the experiment by inserting their hands into a pair of gloves that reach inside the sealed box. Dr. Aleksandar Ostrogorsky, a materials scientist from the Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, N.Y., and the principal investigator for the SUBSA experiment, uses the gloves to examine an ampoule like the ones used for his experiment inside the glovebox's work area. The Microgravity Science Glovebox and the SUBSA experiment are managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala.
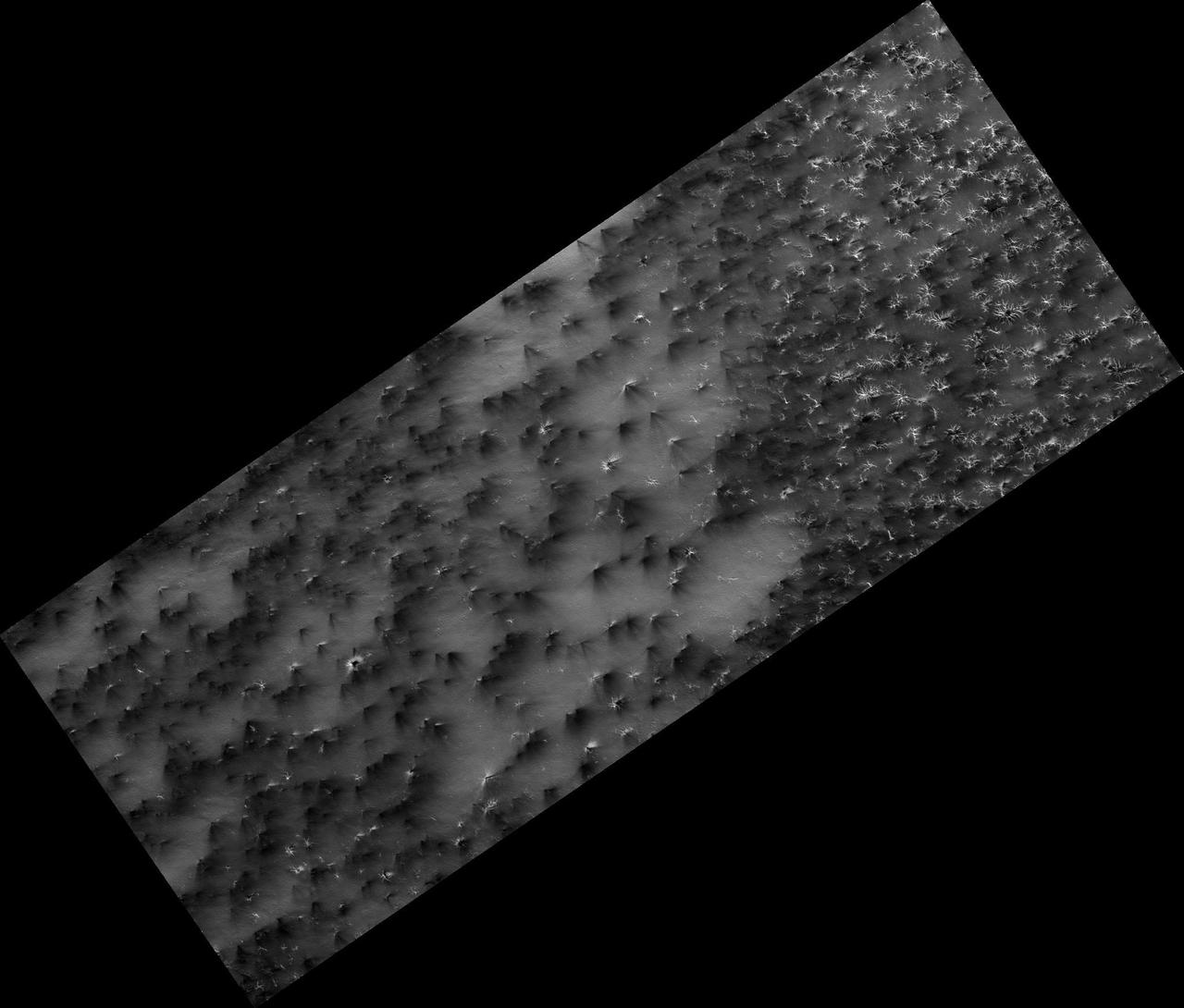
Science in Motion: Isolated Araneiform Topography
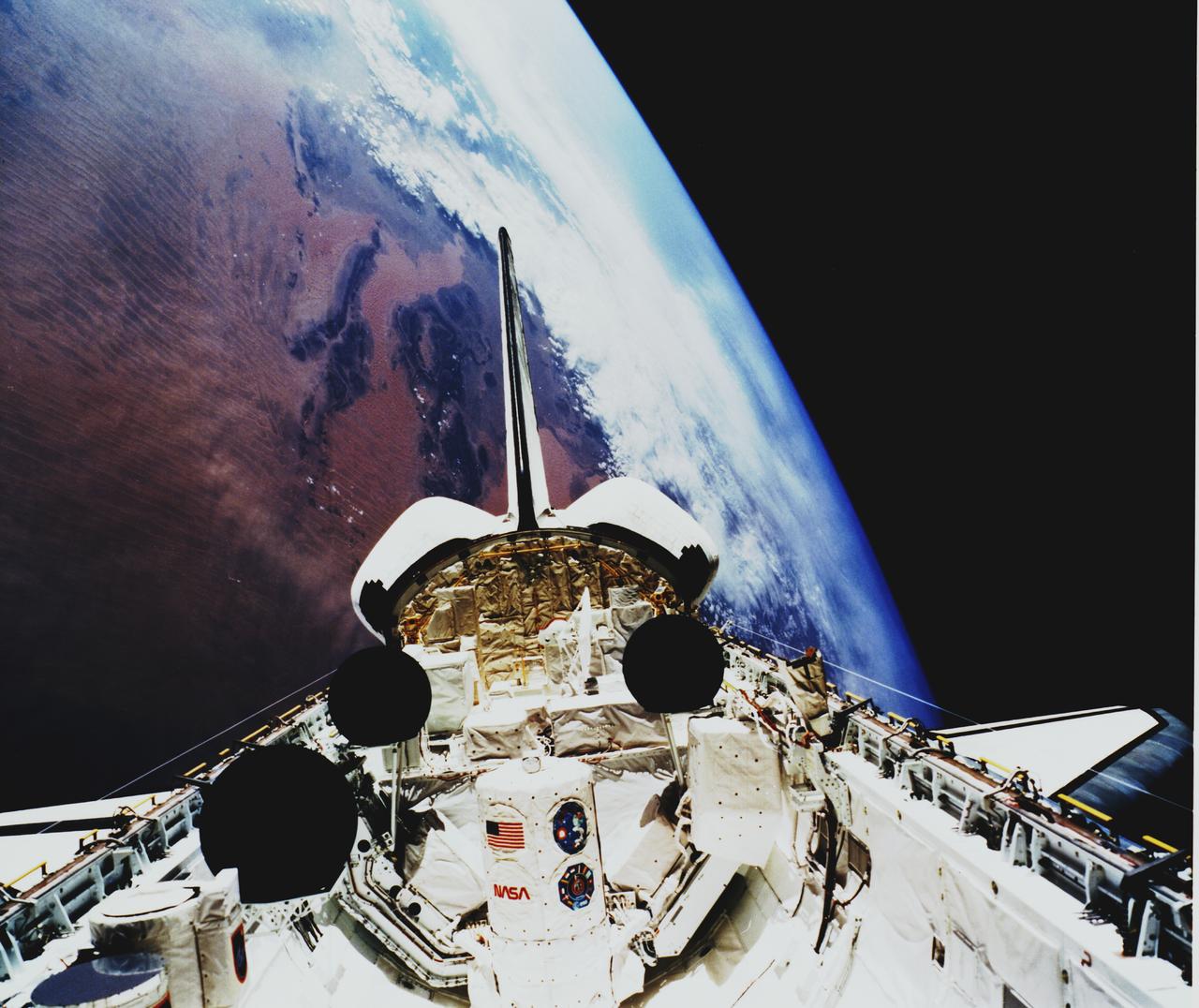

Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-45) onboard photo of Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (Atlas-1) module in open cargo bay. Atlas-1 pallets are back dropped against the Atlas Mountains. Taken over Mali in the western Sahara, shows dunes in the Iguidi Dune Sea.
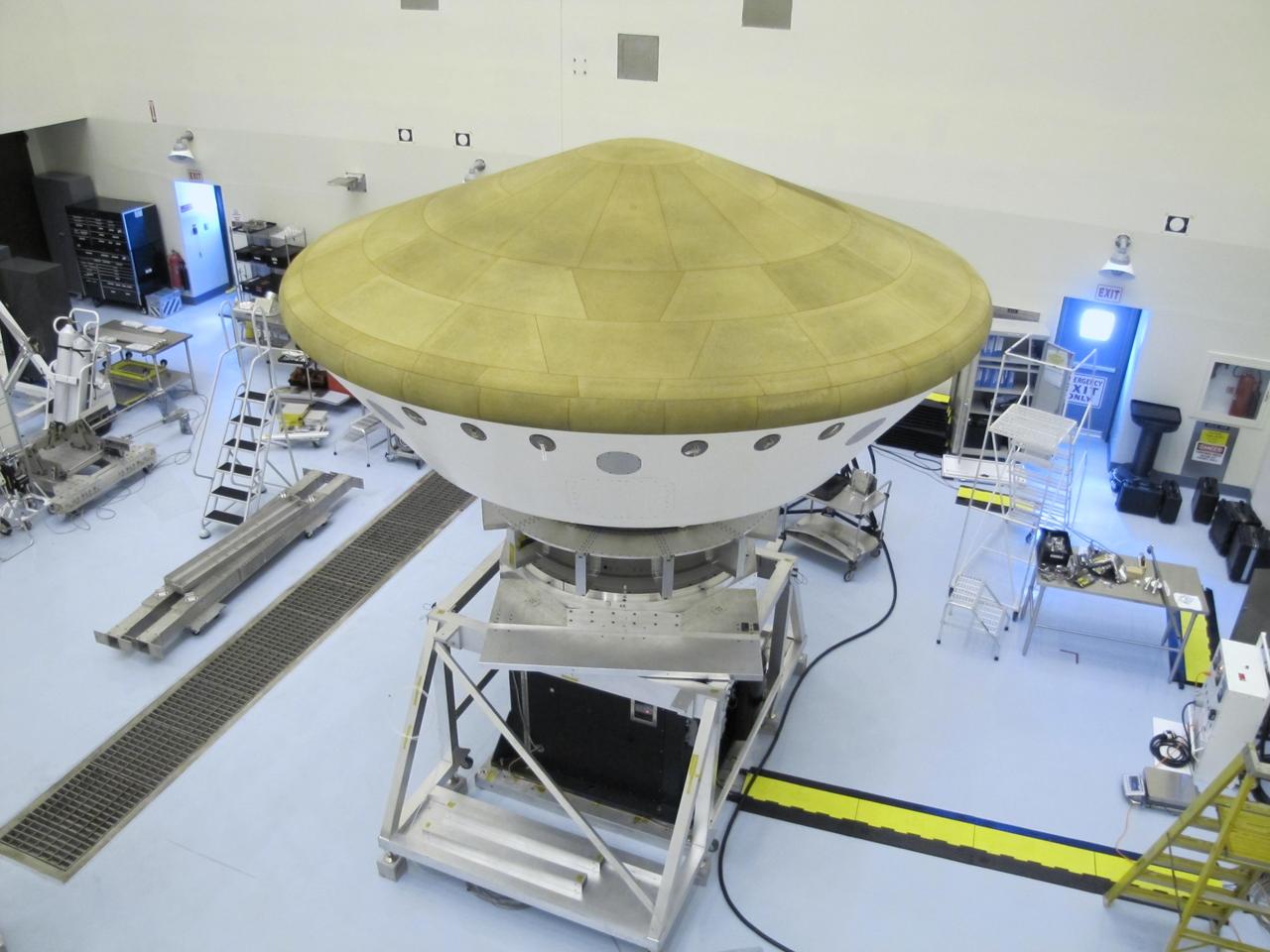

At the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Mars Science Laboratory rover, Curiosity, and the spacecraft descent stage have been enclosed inside the spacecraft aeroshell.
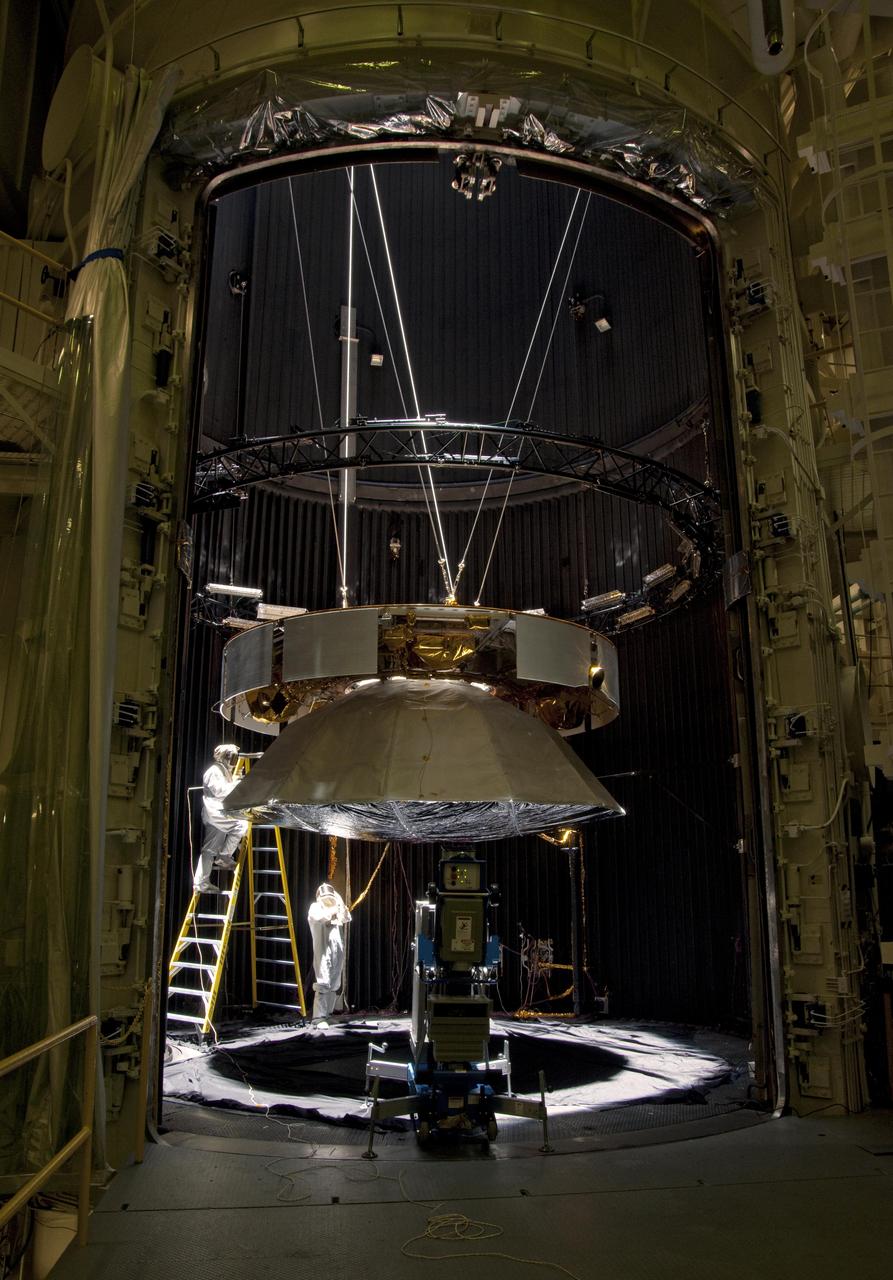

Testing of the cruise stage for NASA Mars Science Laboratory in August 2010 included a session in a facility that simulates the environment found in interplanetary space. Spacecraft technicians at JPL prepare a space-simulation test.

During final stacking of NASA Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft, the heat shield is positioned for integration with the rest of the spacecraft in this photograph from inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA Kennedy Space Center, Fla.
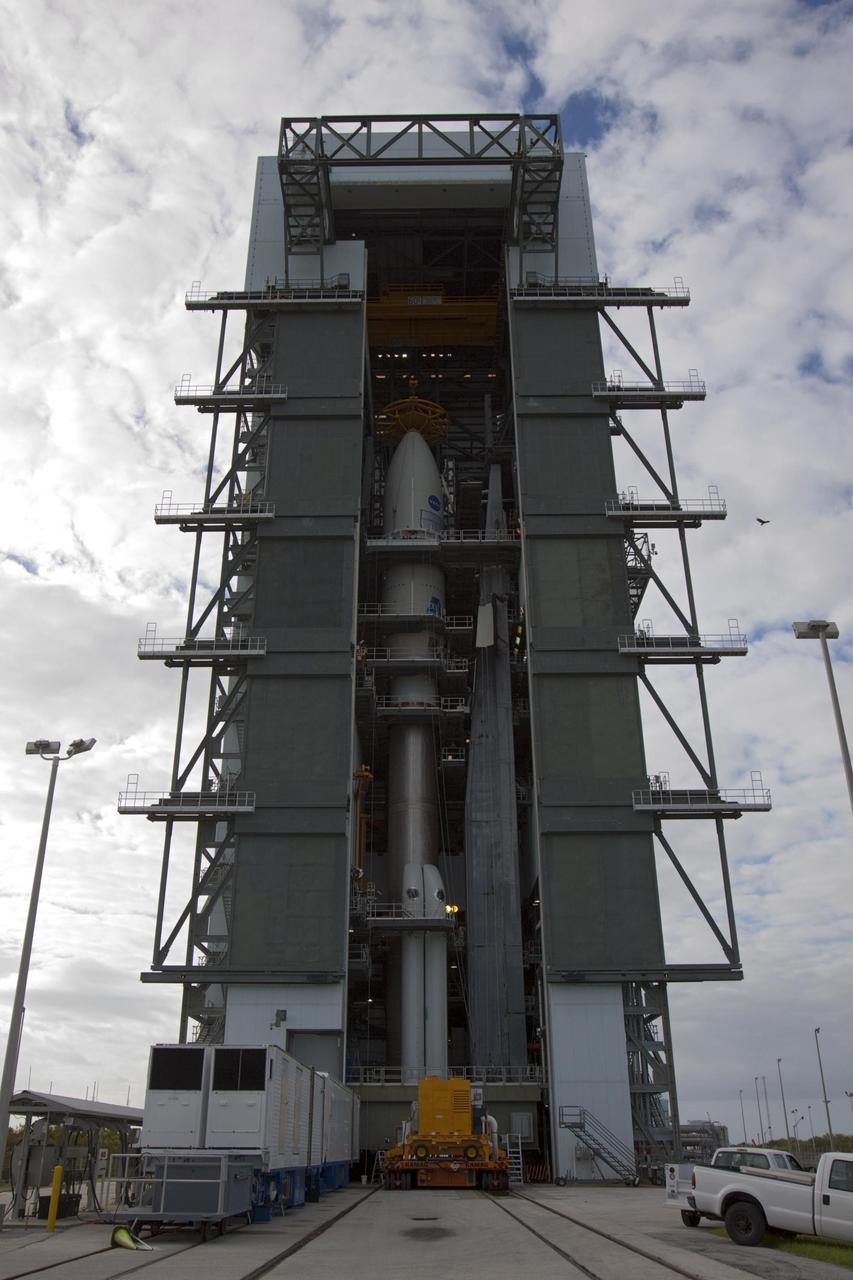

In the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41, the payload fairing containing NASA Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft was attached to its Atlas V rocket on Nov. 3, 2011.

Technicians at Lockheed Martin Space Systems, Denver, prepare the heat shield for NASA Mars Science Laboratory. With a diameter of 4.5 meters nearly 15 feet, this heat shield is the largest ever built for a planetary mission.
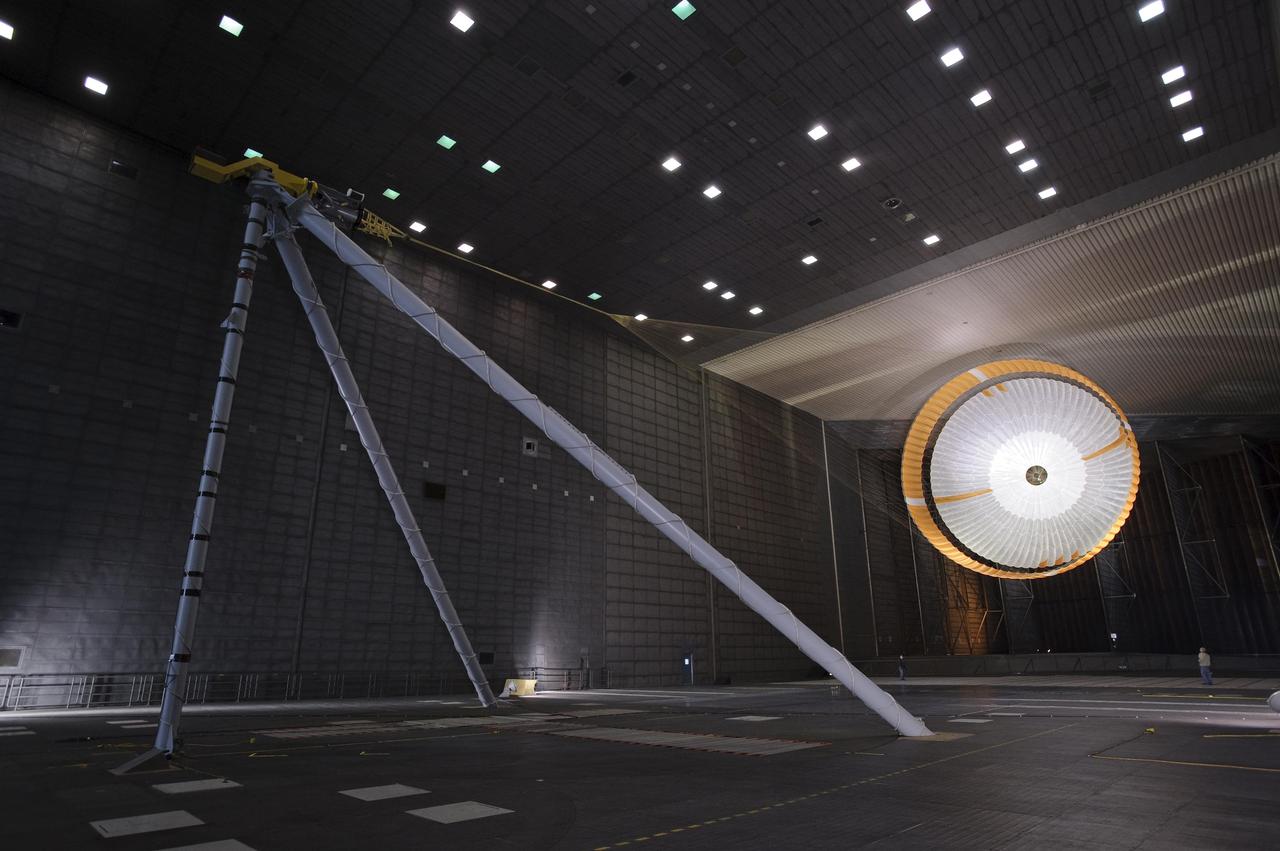

The parachute for NASA Mars Science Laboratory passed flight-qualification testing in March and April 2009 inside the world largest wind tunnel, at NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif.
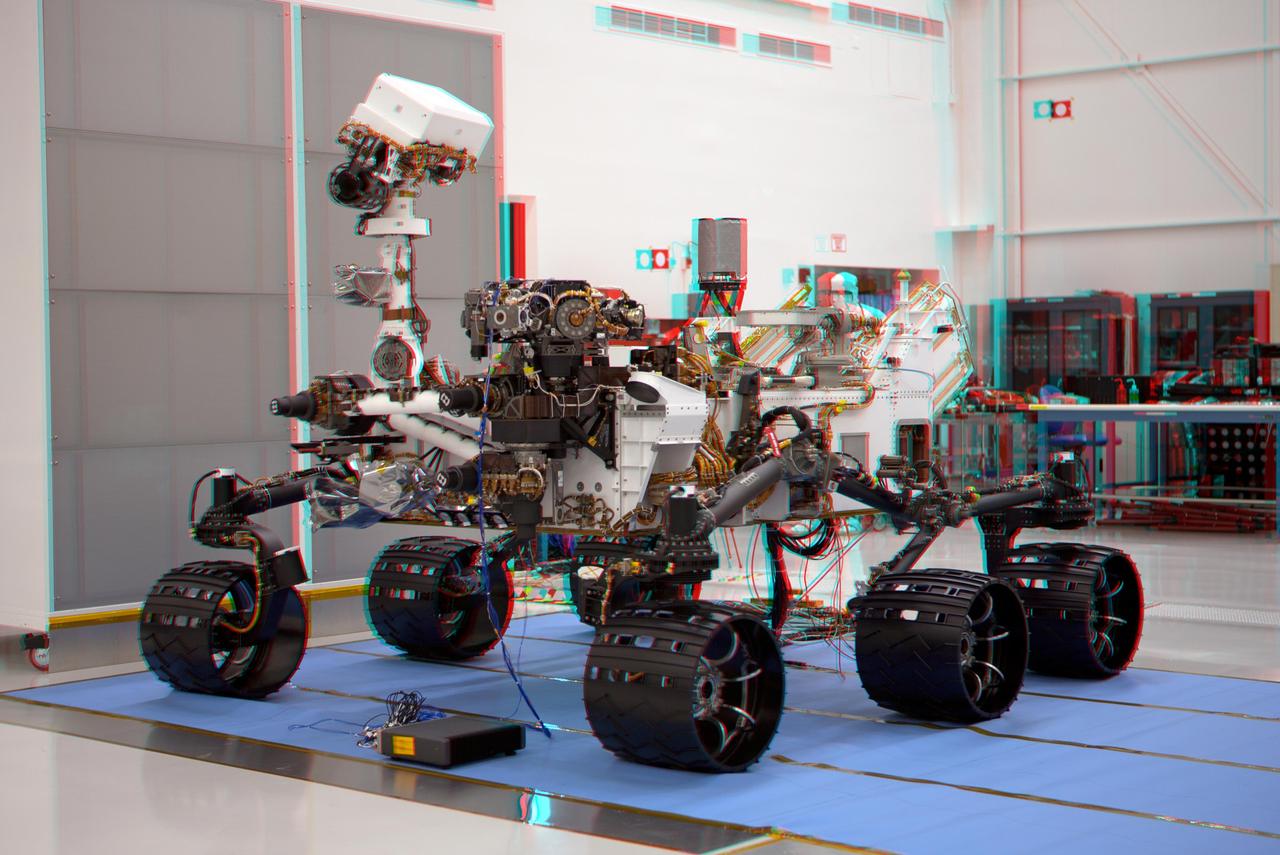
This stereo image of NASA Mars Science Laboratory Curiosity Rovert was taken May 26, 2011, in Spacecraft Assembly Facility at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
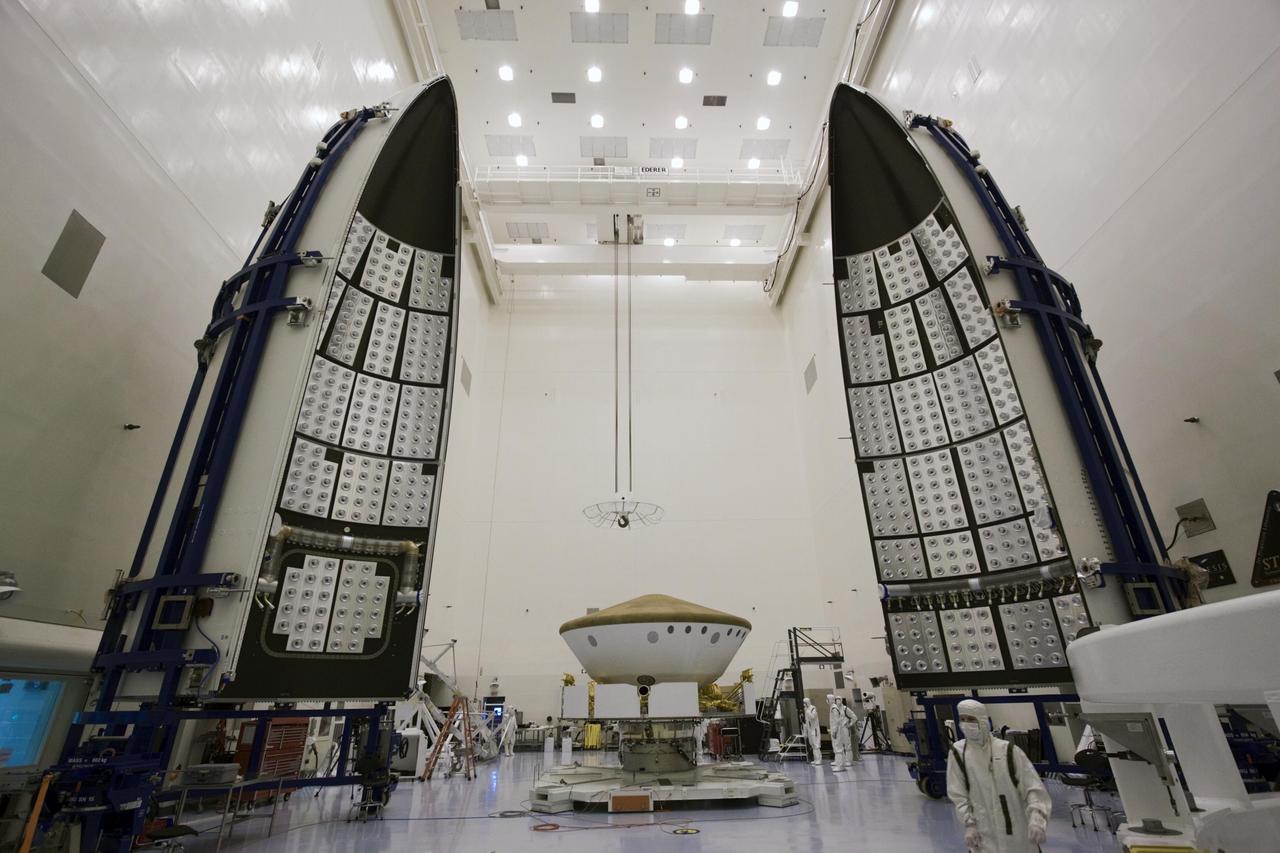

Preparations are under way to enclose NASA Mars Science Laboratory in an Atlas V rocket payload fairing. The fairing protects the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent.
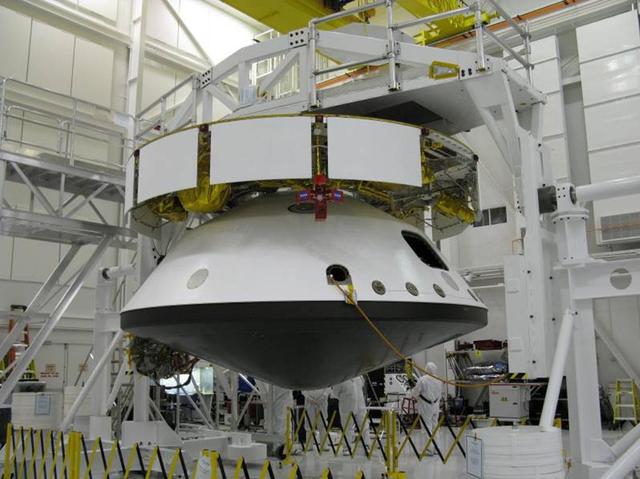

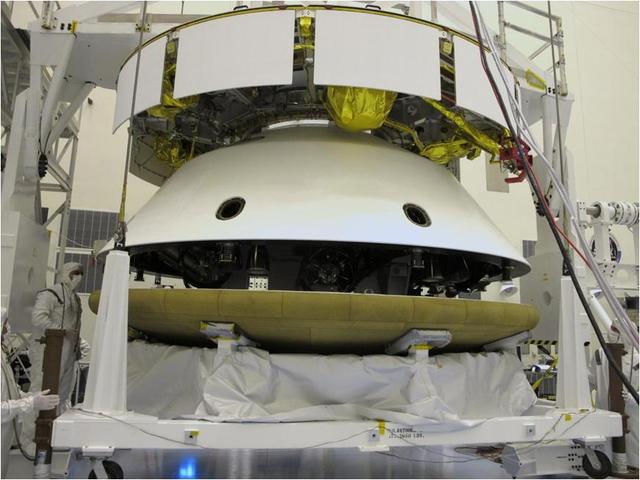
The major components of NASA Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft -- cruise stage atop the aeroshell, which has the descent stage and rover inside -- were connected together in October 2008 for several weeks of system testing.
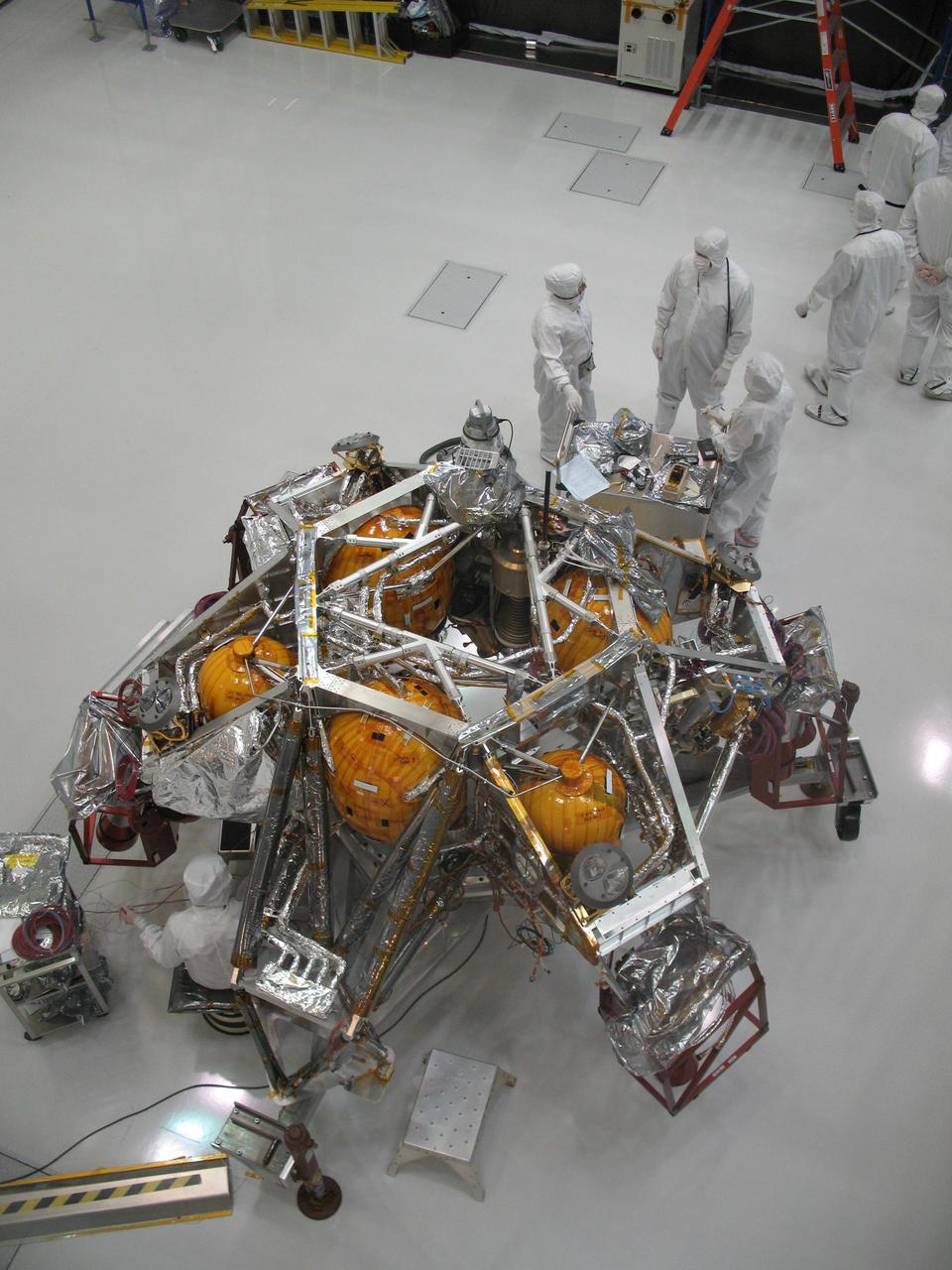

This image from early October 2008 shows personnel working on the descent stage of NASA Mars Science Laboratory inside the Spacecraft Assembly Facility at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
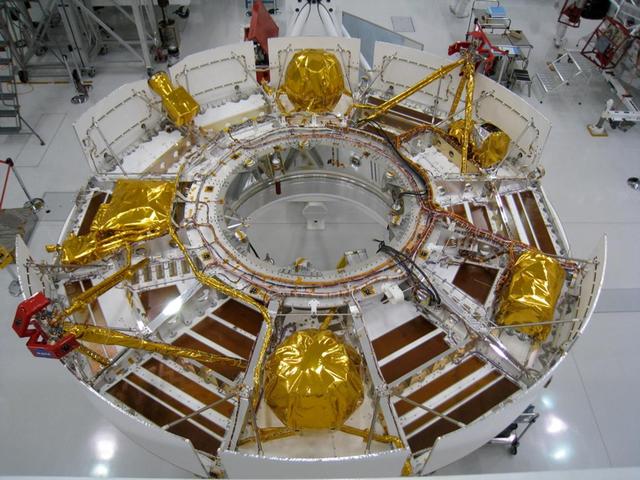

This portion of NASA Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft, called the cruise stage, will do its work during the flight between Earth and Mars after launch in the fall of 2011.
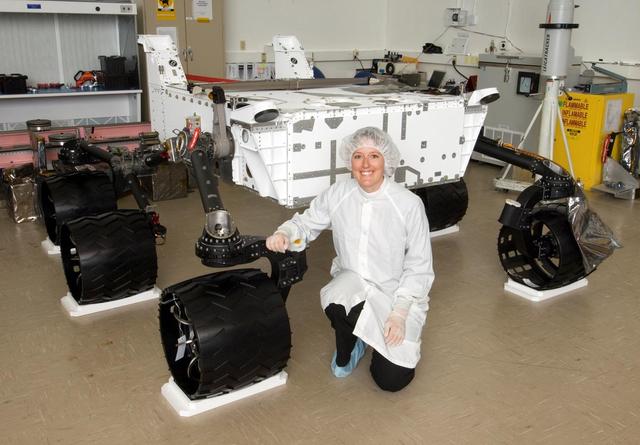

This image from August 2008 shows NASA Mars Science Laboratory rover in the course of its assembly, before additions of its arm, mast, laboratory instruments and other equipment.
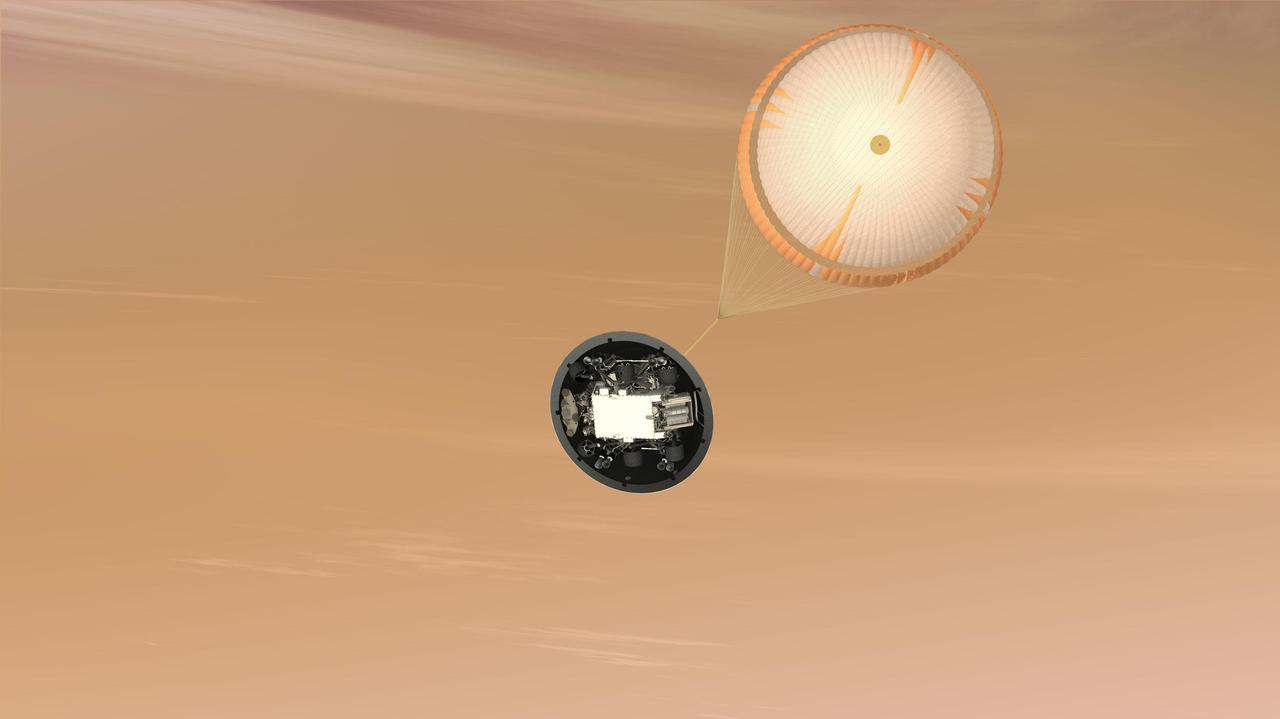
This artist concept is of NASA Mars Science Laboratory MSL Curiosity rover parachute system; the largest parachute ever built to fly on a planetary mission. The parachute is attached to the top of the backshell portion of the spacecraft aeroshell.
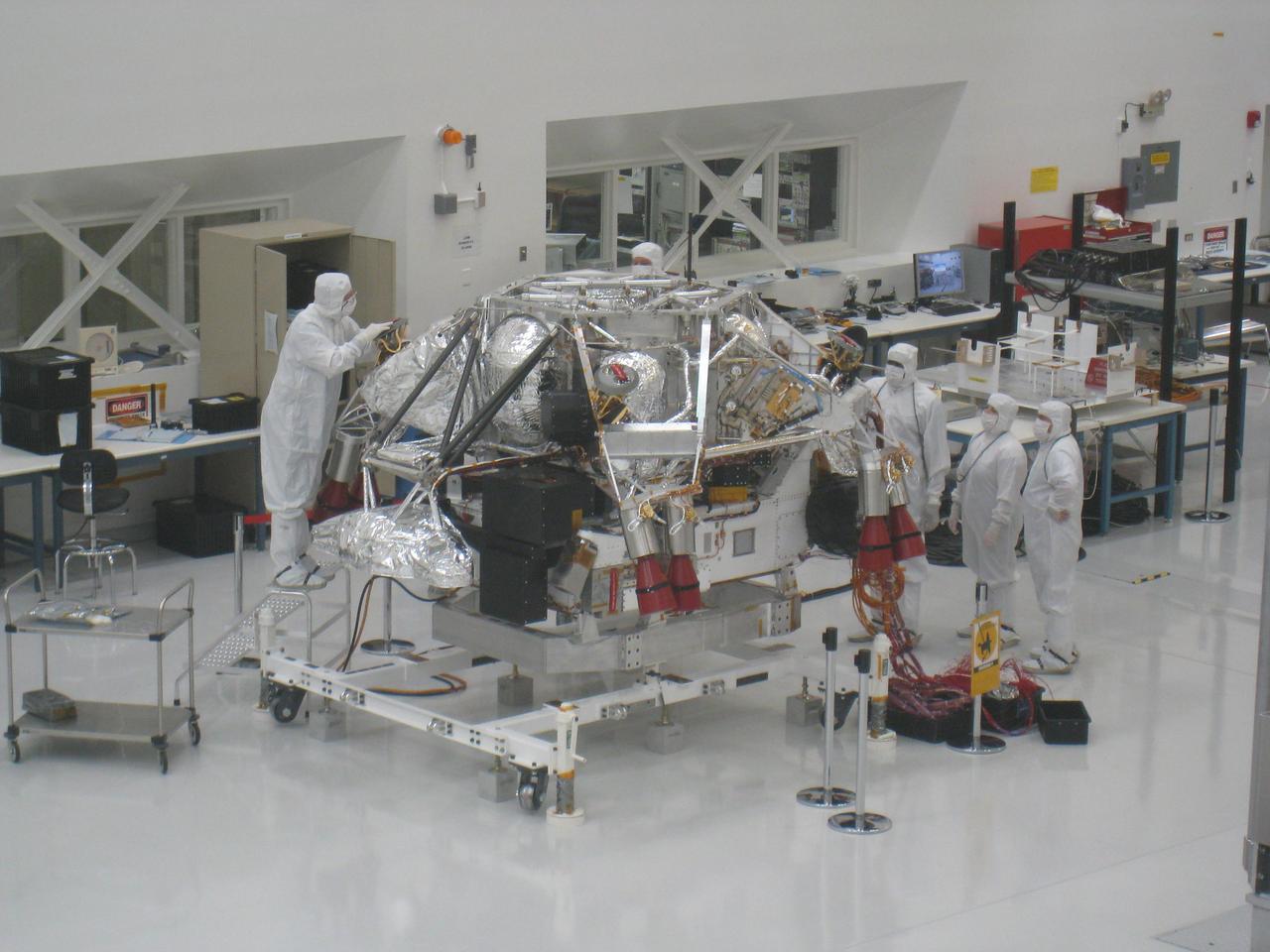

In this February 17, 2009, image, NASA Mars Science Laboratory rover is attached to the spacecraft descent stage. The image was taken inside the Spacecraft Assembly Facility at NASA JPL, Pasadena, Calif.
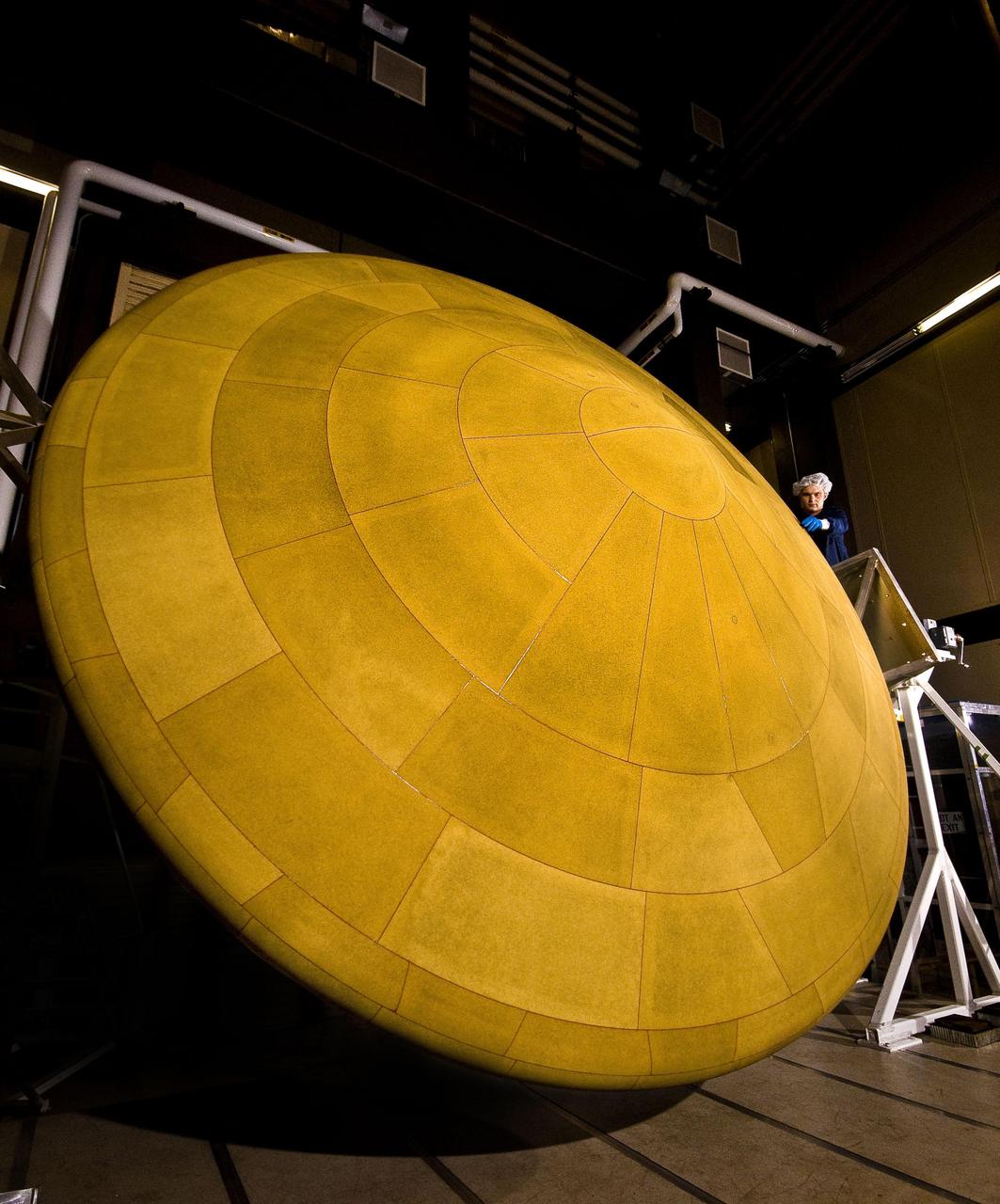
This image shows NASA Mars Science Laboratory heat shield, and a spacecraft worker at Lockheed Martin Space Systems, Denver. It is the largest heat shield ever built for descending through the atmosphere of any planet.
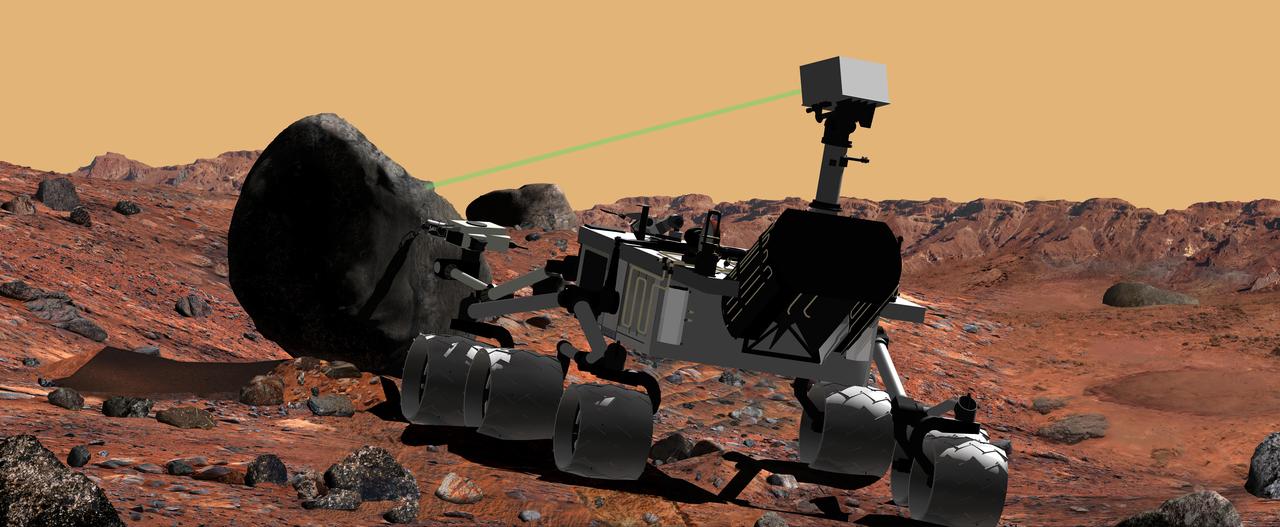
This artist conception of NASA Mars Science Laboratory portrays use of the rover ChemCam instrument to identify the chemical composition of a rock sample on the surface of Mars.
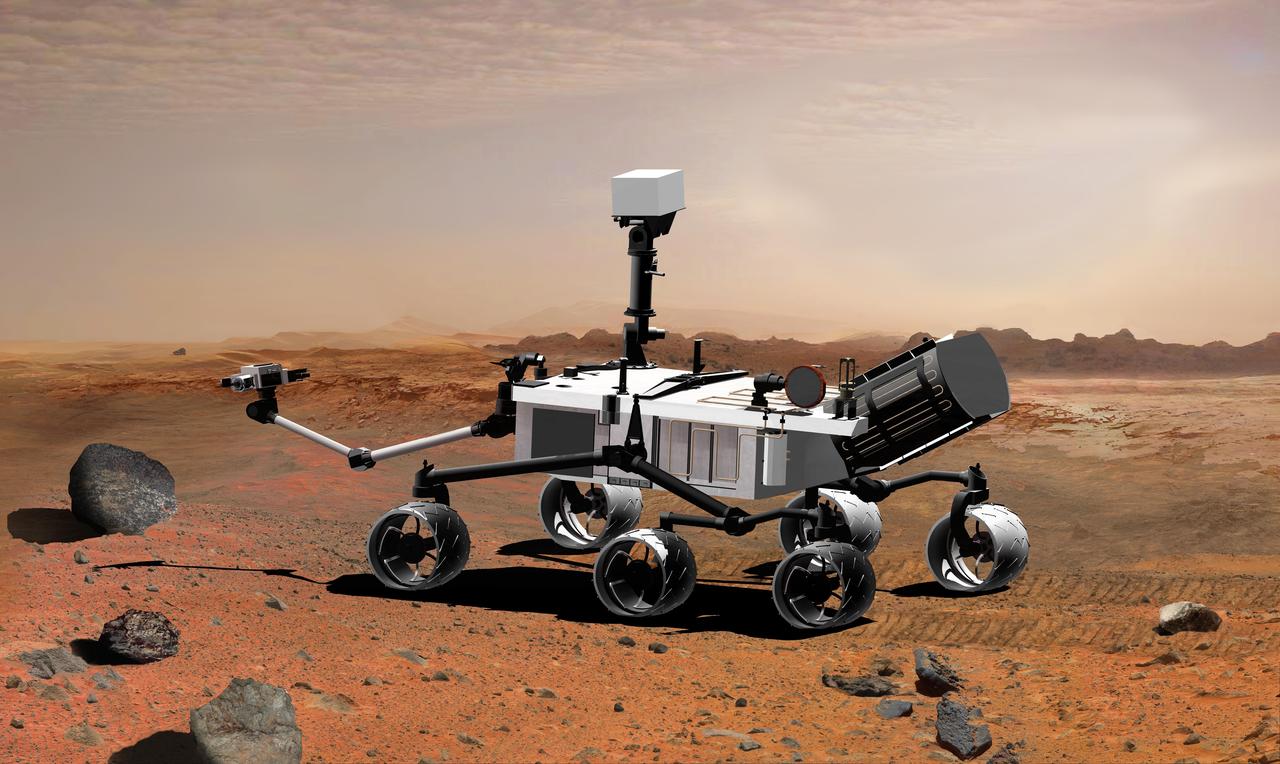

NASA Mars Science Laboratory, a mobile robot for investigating Mars past or present ability to sustain microbial life, is in development for a launch opportunity in 2011 previously 2009.
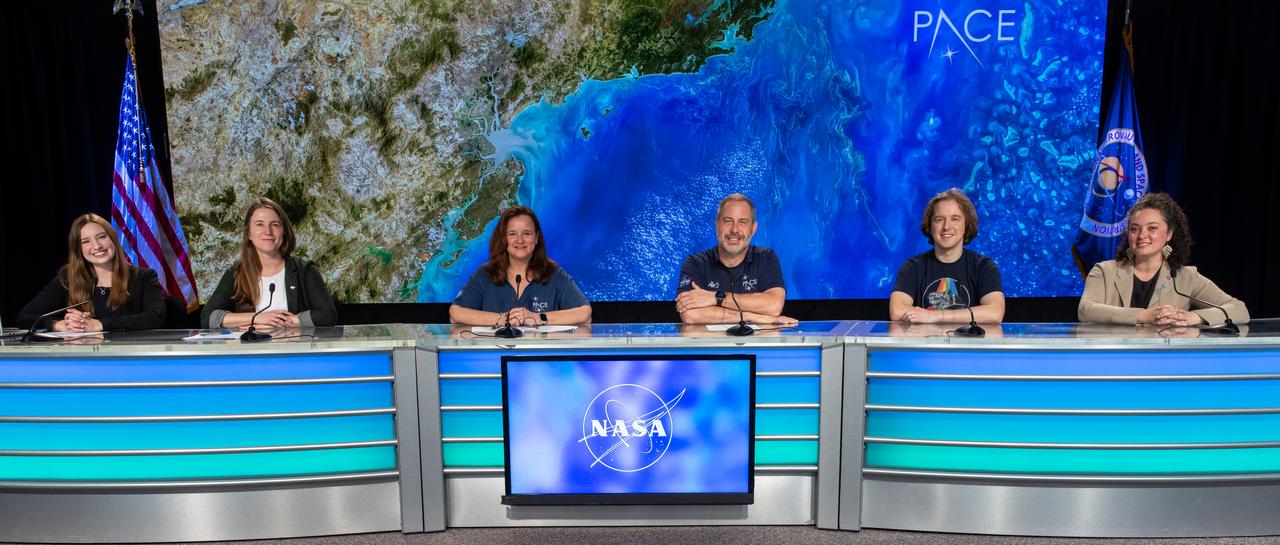

A PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) mission and science briefing takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, Feb. 4, 2024. Participants, from left to right are: Katherine Rohloff, NASA Communications; Kate Calvin, Chief Scientist, and Senior Climate advisor, NASA Headquarters; Karen St. Germain, Earth Science Division director, NASA Headquarters; Jeremy Werdell, PACE project scientist, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center; Andy Sayer, PACE Atmospheric Scientist, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center; and Natasha Sadoff, Satellite Needs Program Manager, NASA Headquarters. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton, as well new data on clouds and aerosols. Liftoff aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida is set for no earlier than 1:33 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Feb 6, 2024.
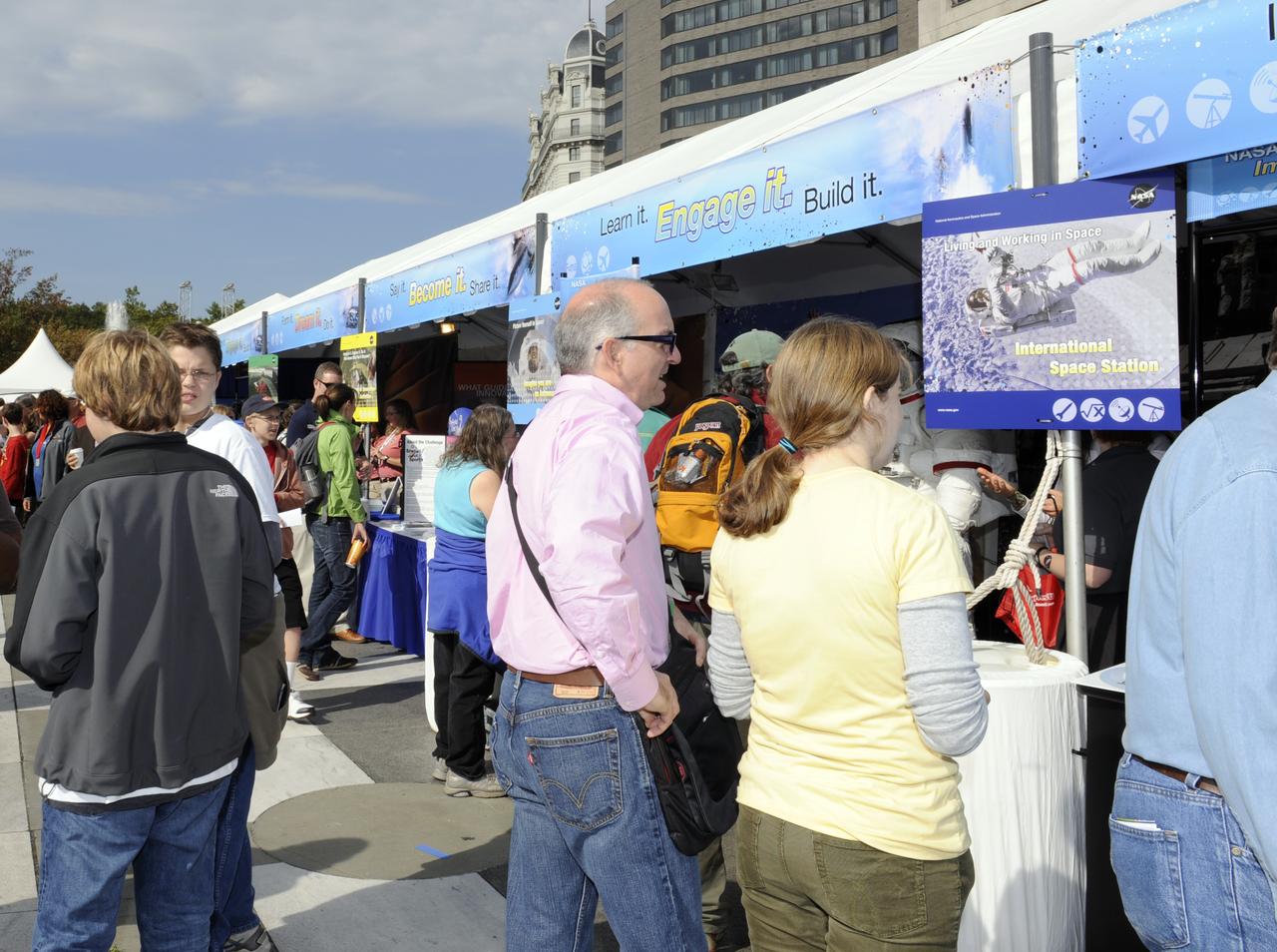

Visitors to the USA Science and Engineering Festival look over the many exhibits, Saturday, Oct. 23, 2010, at Freedom Plaza in Washington. NASA, joined with more than 500 science organizations this weekend to inspire the next generation of scientists and engineers during the first national science and engineering festival held in the nation's capital. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
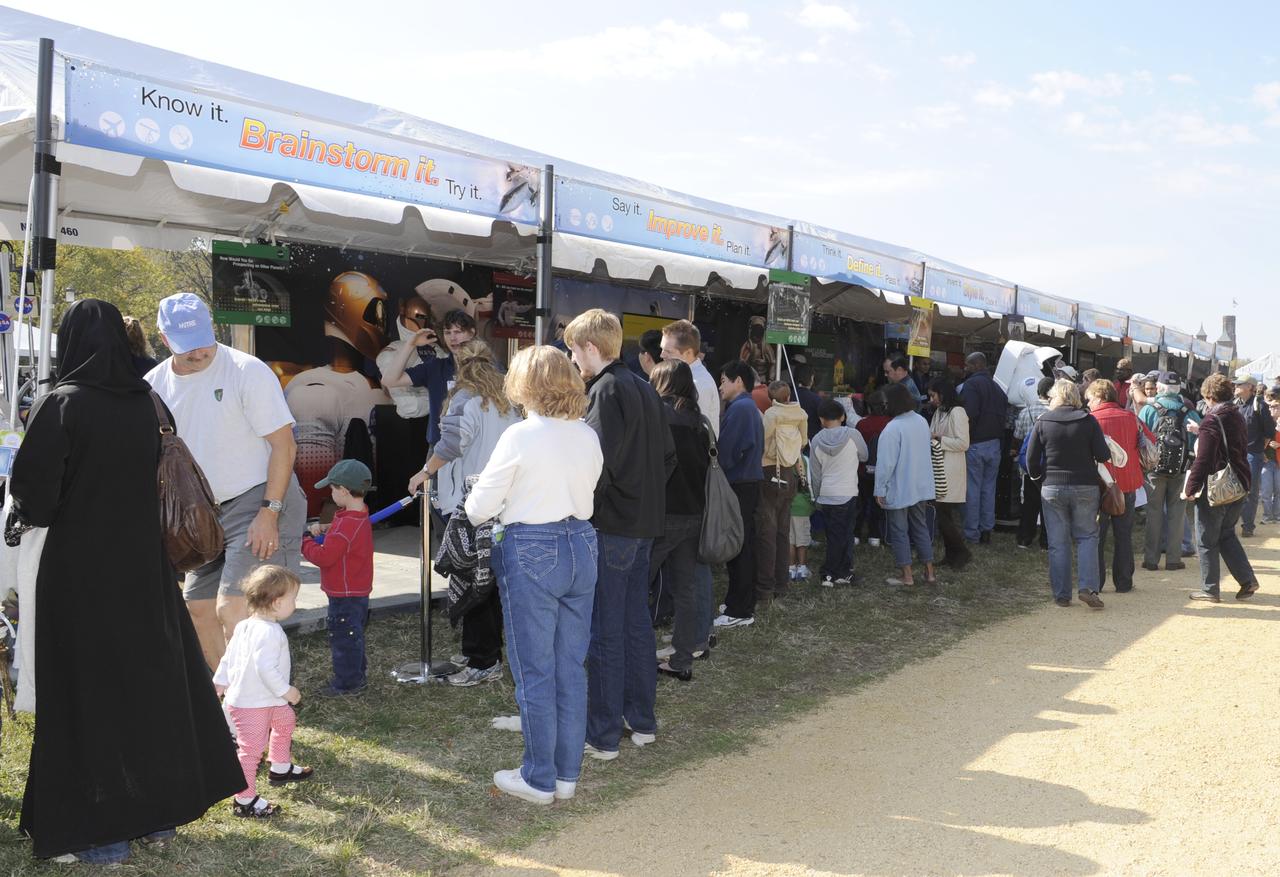

Visitors crowd the NASA exhibits during the USA Science and Engineering Festival, Saturday, Oct. 23, 2010, on the National Mall in Washington. NASA, joined with more than 500 science organizations this weekend to inspire the next generation of scientists and engineers during the first national science and engineering festival held in the nation's capital. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
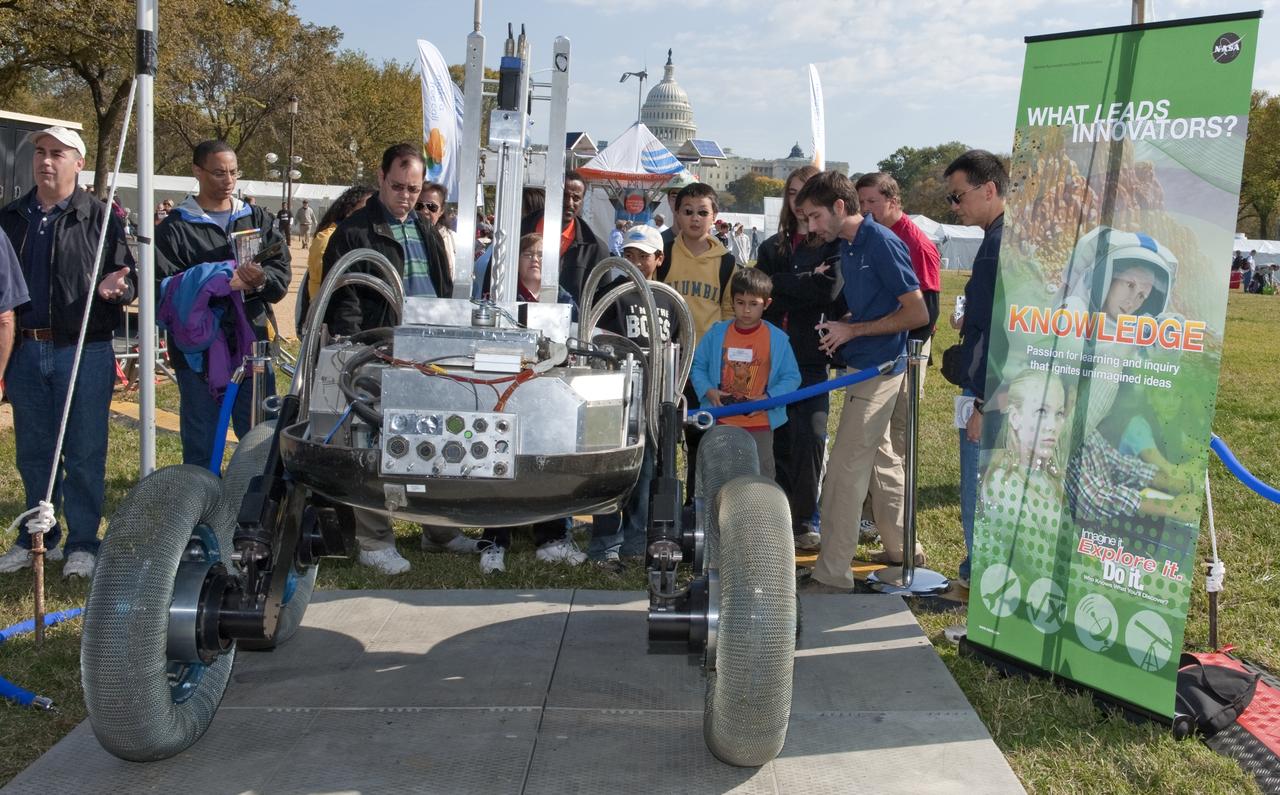

Visitors to the USA Science and Engineering Festival look on at one of the many exhibits, Saturday, Oct. 23, 2010, on the National Mall in Washington. NASA, joined with more than 500 science organizations this weekend to inspire the next generation of scientists and engineers during the first national science and engineering festival held in the nation's capital. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

NASA Marshall Space Flight Center’s Science and Technology Office held its 11th annual Science and Technology Jamboree Dec. 8 at Marshall Activities Building 4316. A poster session with around 60 poster presentations highlighted current science and technology topics and the innovative projects underway across the center. Here, Debra Needham, right, talks with coworker Sabrina Savage about one of the presentations. Both Needham and Savage are scientists in the Heliophysics & Planetary Science Branch of the Science Research and Projects Division.
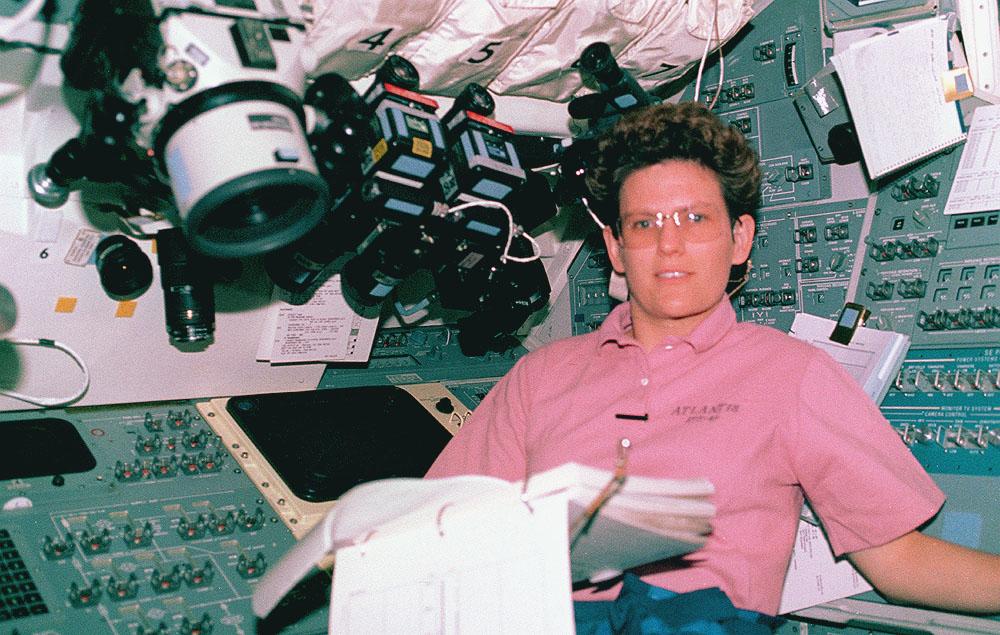
Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-45) onboard photo of Mission Specialist Kathryn Sullivan working in the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (Atlas-1) module. Atlas-1 flew in a series of Spacelab flights that measured long term variability in the total energy radiated by the Sun and determined the variability in the solar spectrum.
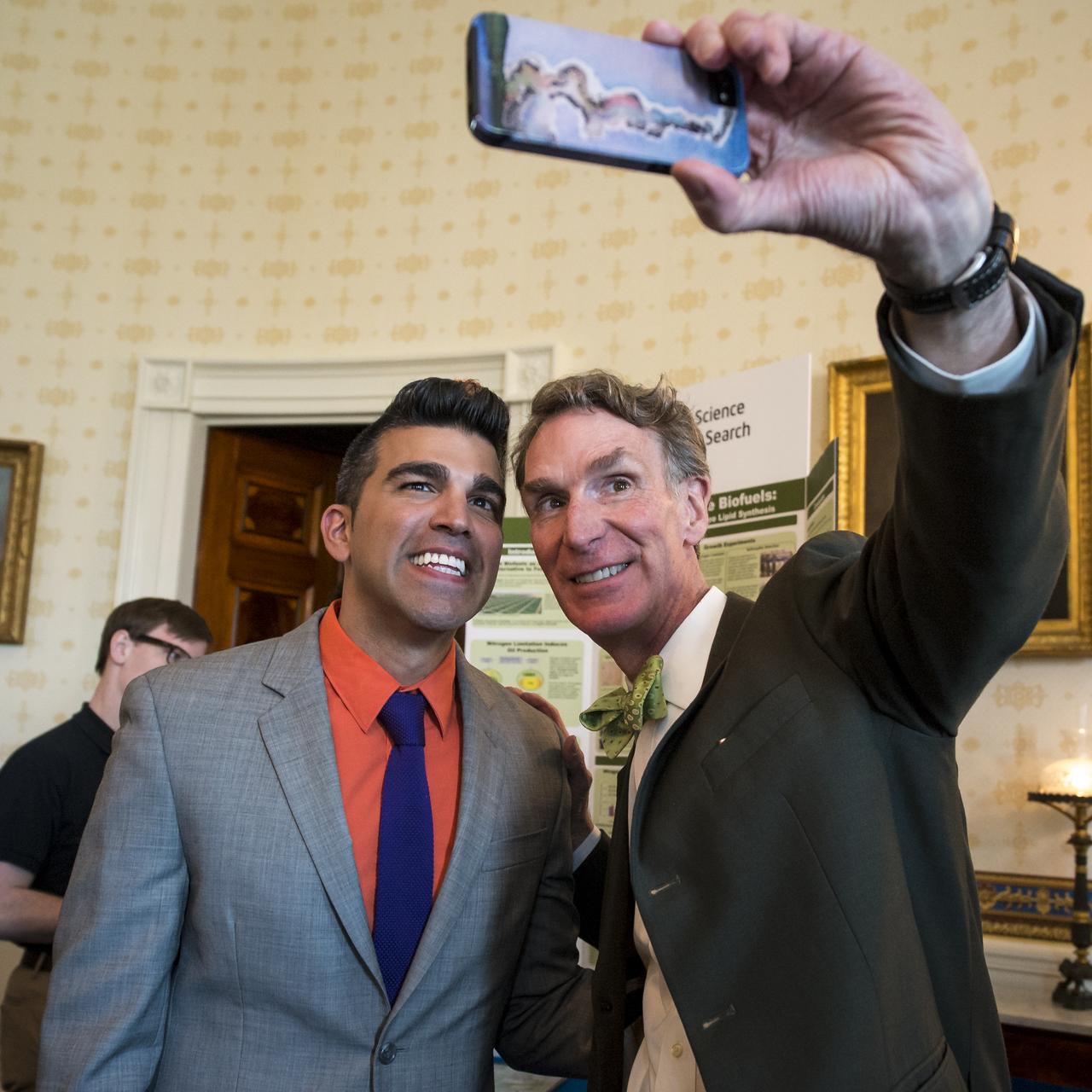

Planetary Society Executive Director and “Bill Nye the Science Guy” host Bill Nye, right, photographs himself with NASA Mars Curiosity Landing mission controller, Bobak "Mohawk Guy" Ferdowsi, during the White House Science Fair held at the White House, April 22, 2013. The science fair celebrated student winners of a broad range of science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) competitions from across the country. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
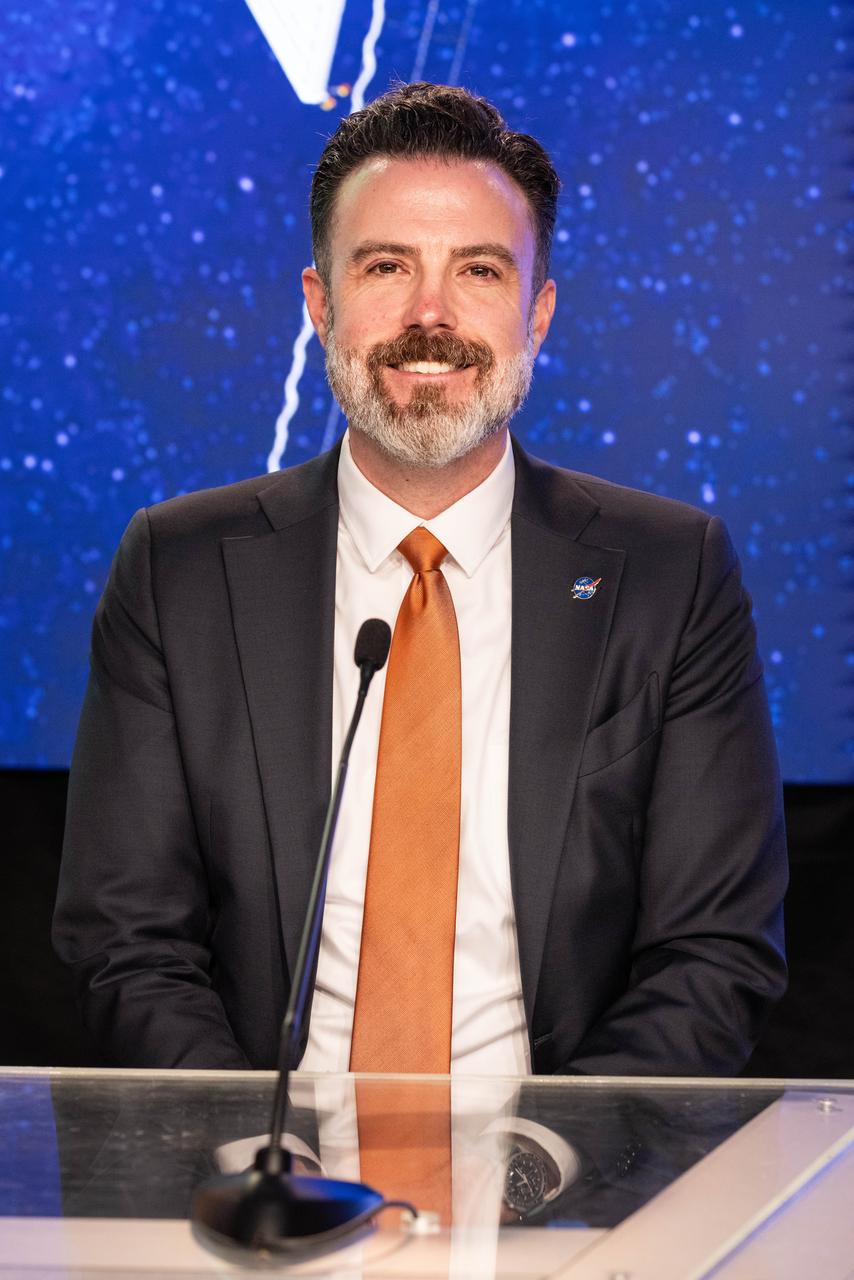

Jamie Favors, director, Space Weather Program, Heliophysics Division, NASA Headquarters in Washington, participates in a science briefing on NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission and its two rideshares – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, Sept. 21, 2025. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. The three missions will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth. Launch is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.

Joe Westlake, director, Heliophysics Division, NASA Headquarters in Washington, participates in a science briefing on NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission and its two rideshares – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, Sept. 21, 2025. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. The three missions will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth. Launch is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.

James Spann, senior scientist, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Office of Space Weather Observations, participates in a science briefing on NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission and its two rideshares – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and NOAA’s Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, Sept. 21, 2025. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. The three missions will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth. Launch is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
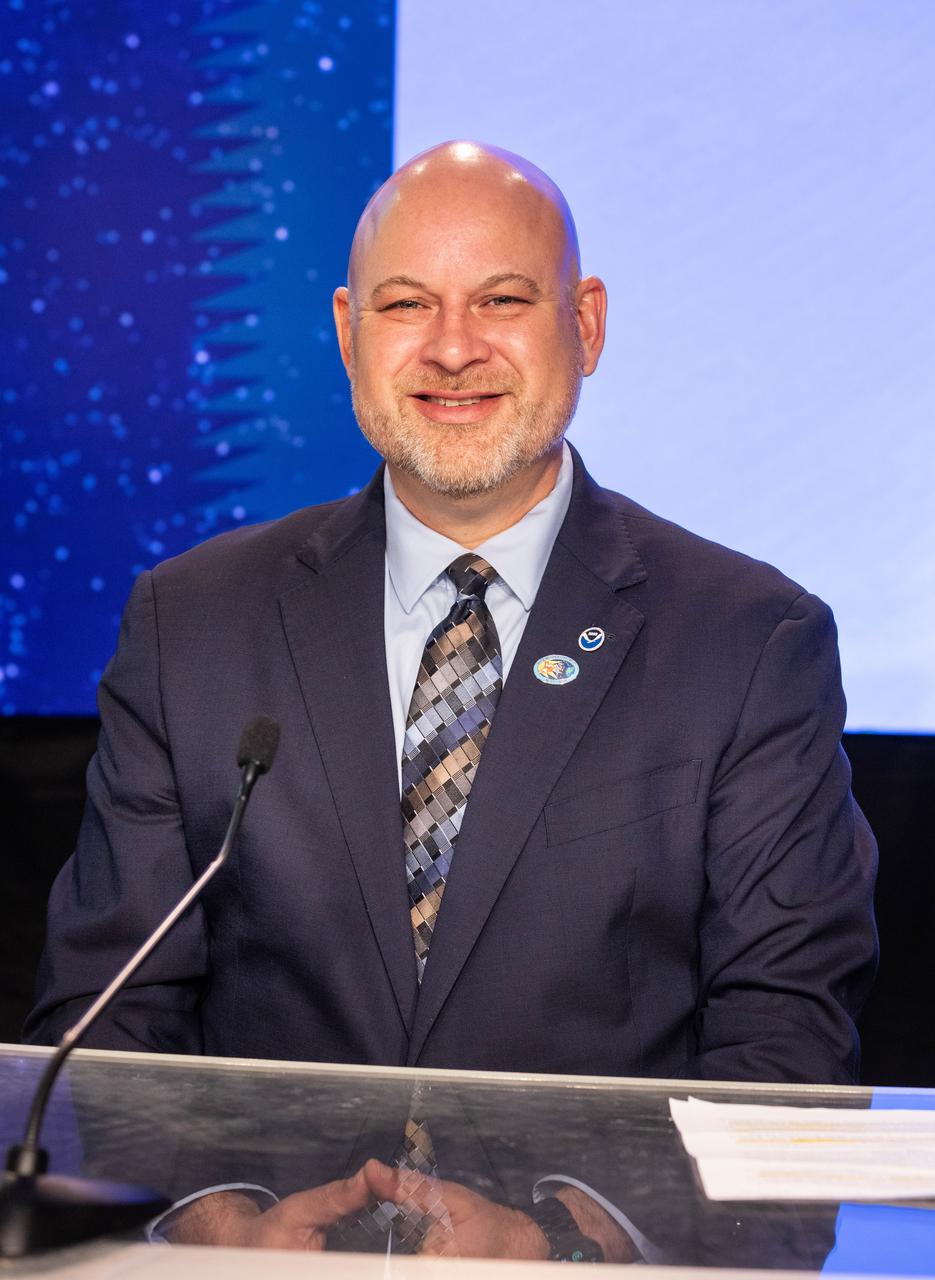

Clinton Wallace, director, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Space Weather Prediction Center, participates in a science briefing on NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission and its two rideshares – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and NOAA’s Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, Sept. 21, 2025. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. The three missions will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth. Launch is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
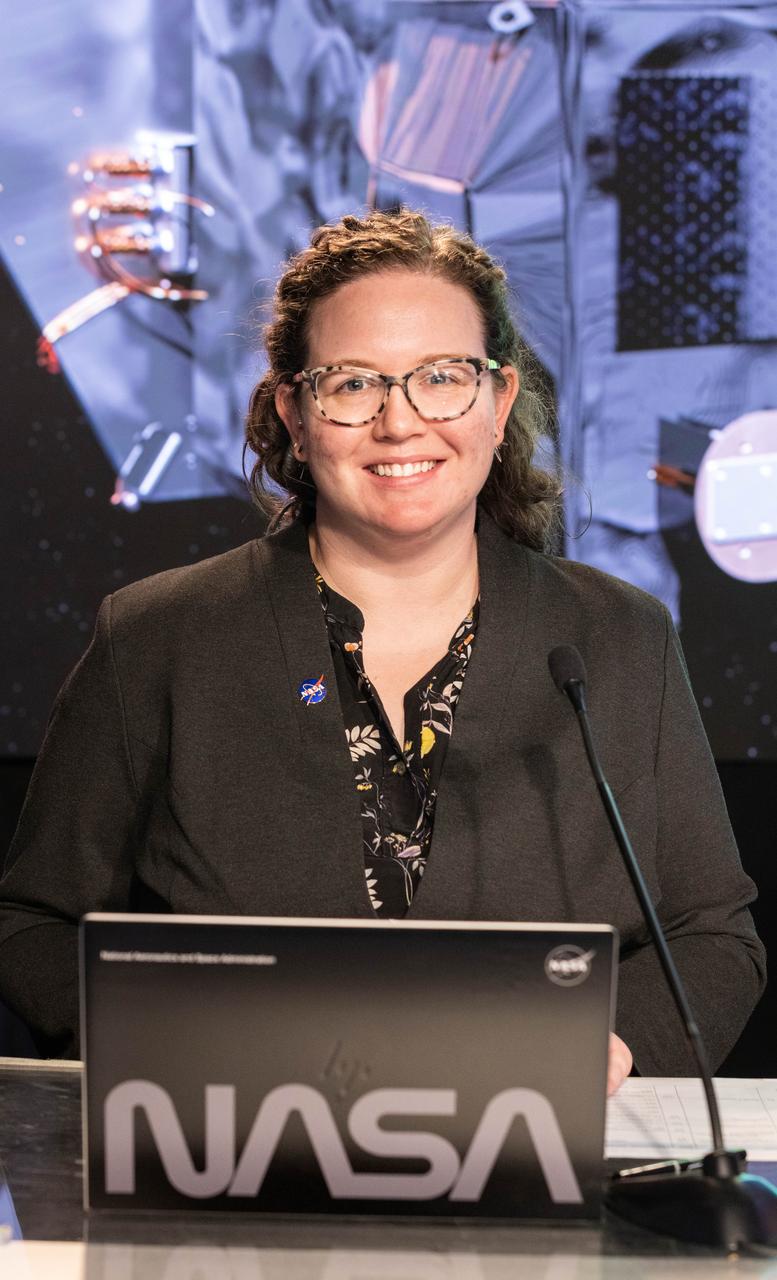

Sarah Frazier, NASA Communications, participates in a science briefing on NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission and its two rideshares – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, Sept. 21, 2025. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. The three missions will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth. Launch is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
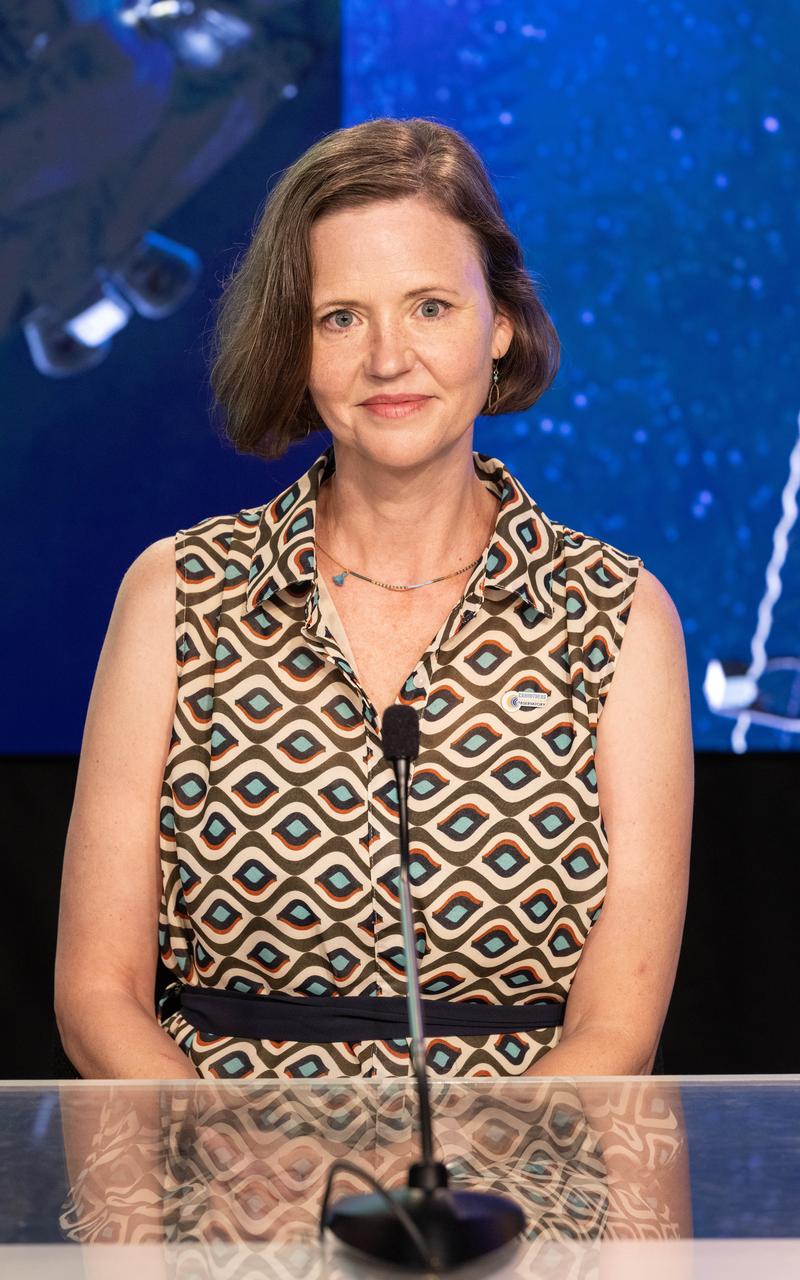

Lara Waldrop, Carruthers Geocorona Observatory principal investigator, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, participates in a science briefing on NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission and its two rideshares – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, Sept. 21, 2025. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. The three missions will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth. Launch is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
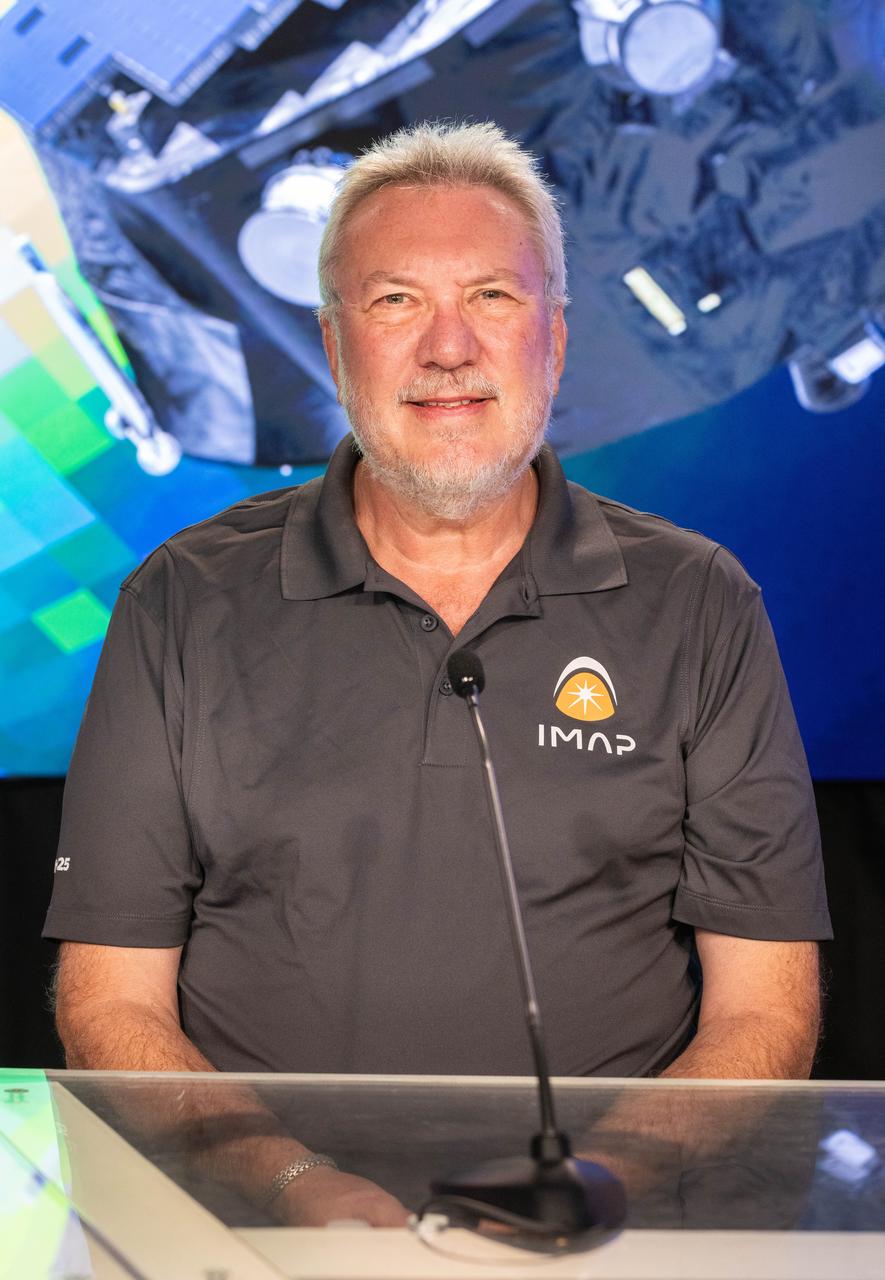

David McComas, IMAP principal investigator, Princeton University, participates in a science briefing on NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission and its two rideshares – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, Sept. 21, 2025. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. The three missions will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth. Launch is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
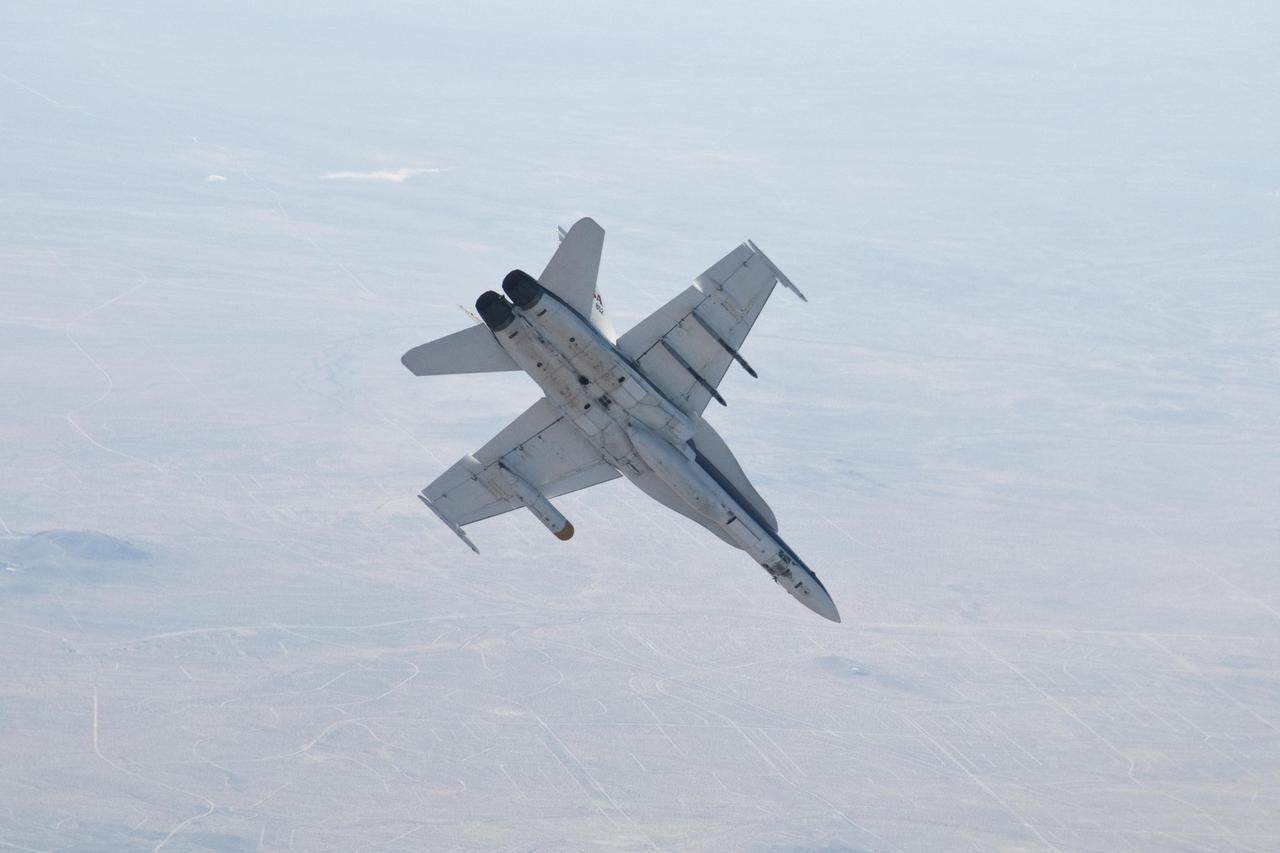

A NASA Dryden Flight Research Center F/A-18 852 aircraft performs a roll during June 2011 flight tests of a Mars landing radar. A test model of the landing radar for NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission is inside a pod under the aircraft left wing.
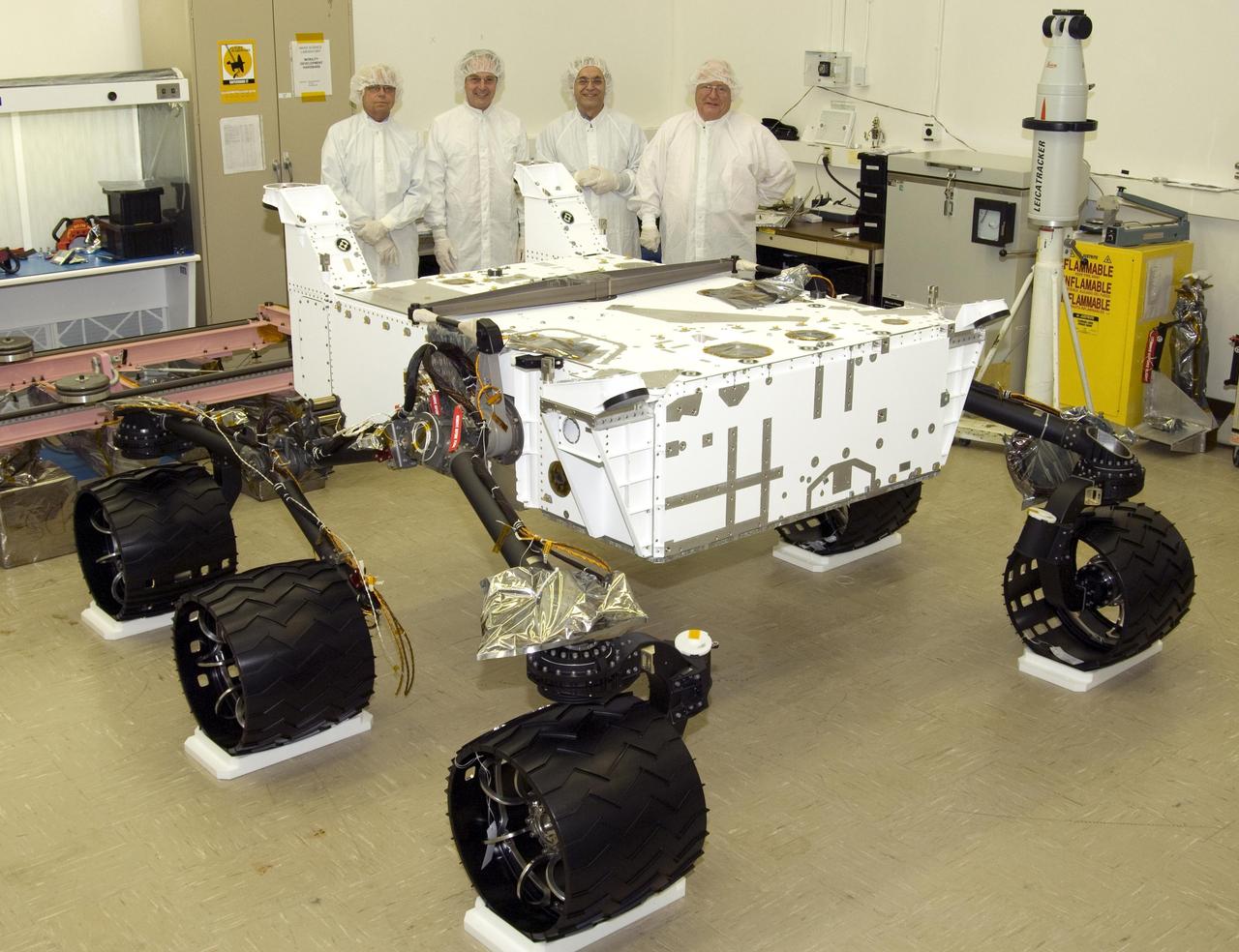

This image taken in August 2008 in a clean room at NASA JPL, Pasadena, Calif., shows NASA next Mars rover, the Mars Science Laboratory, in the course of its assembly, before additions of its arm, mast, laboratory instruments and other equipment.
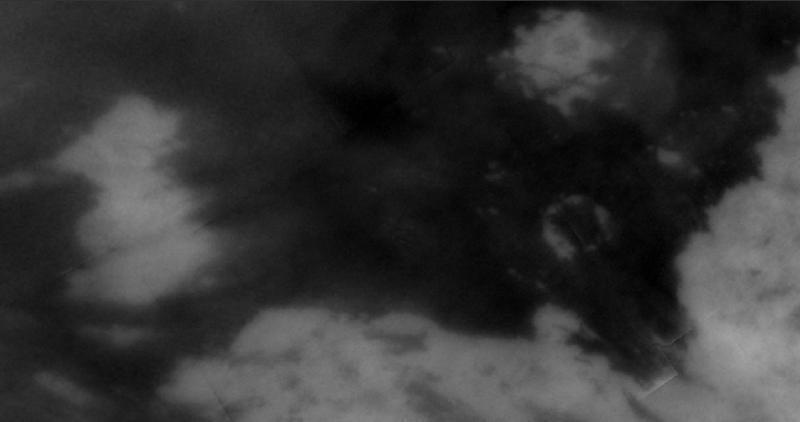

Comparing Notes on Titan -- Radar & Imaging Science Subsystem
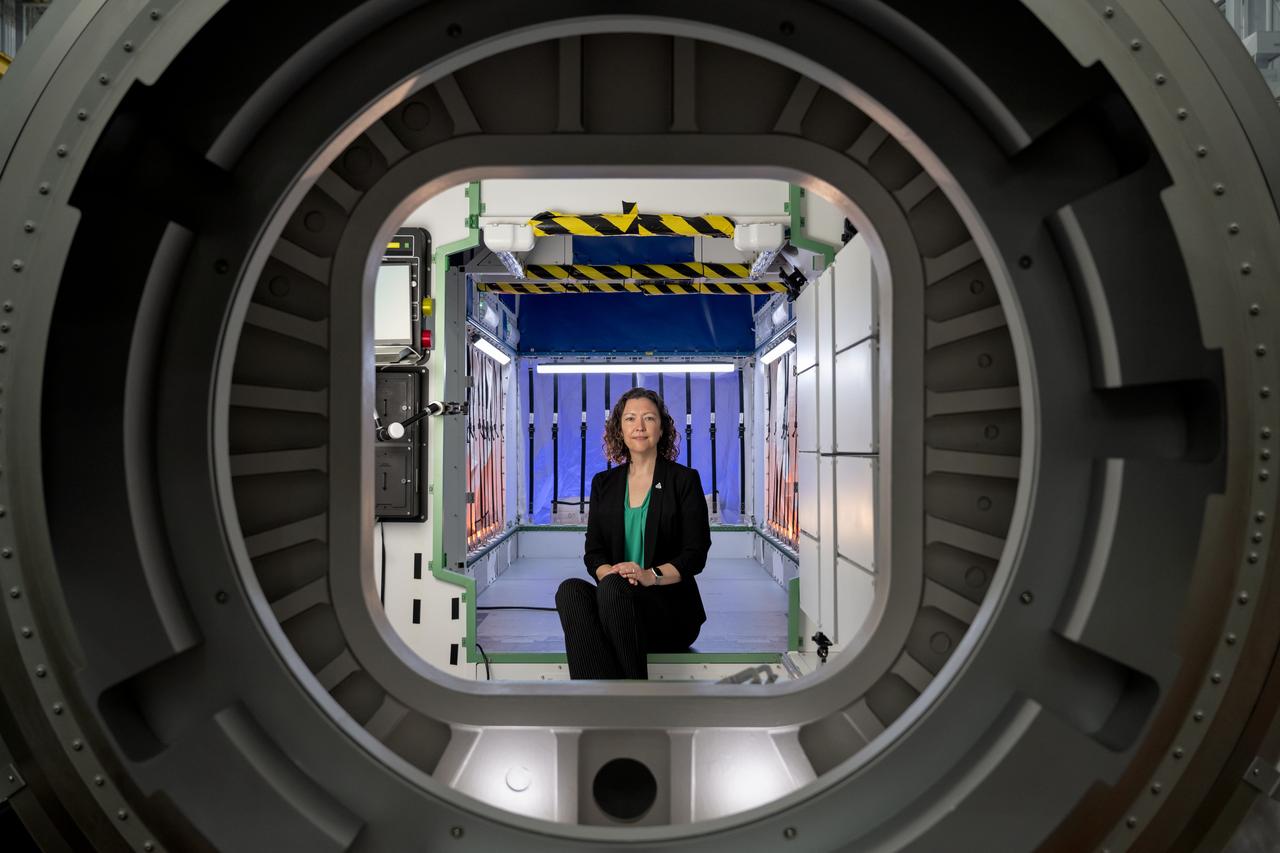

jsc2024e064820 -- Stephanie Dudley, Gateway’s mission integration and utilization manager, sits inside a high-fidelity HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) mockup at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. HALO is one four Gateway modules where astronauts will live, conduct science, and prepare for missions to investigate the lunar South Pole region. Dudley works with NASA’s partner space agencies and academia to identify science opportunities on Gateway.
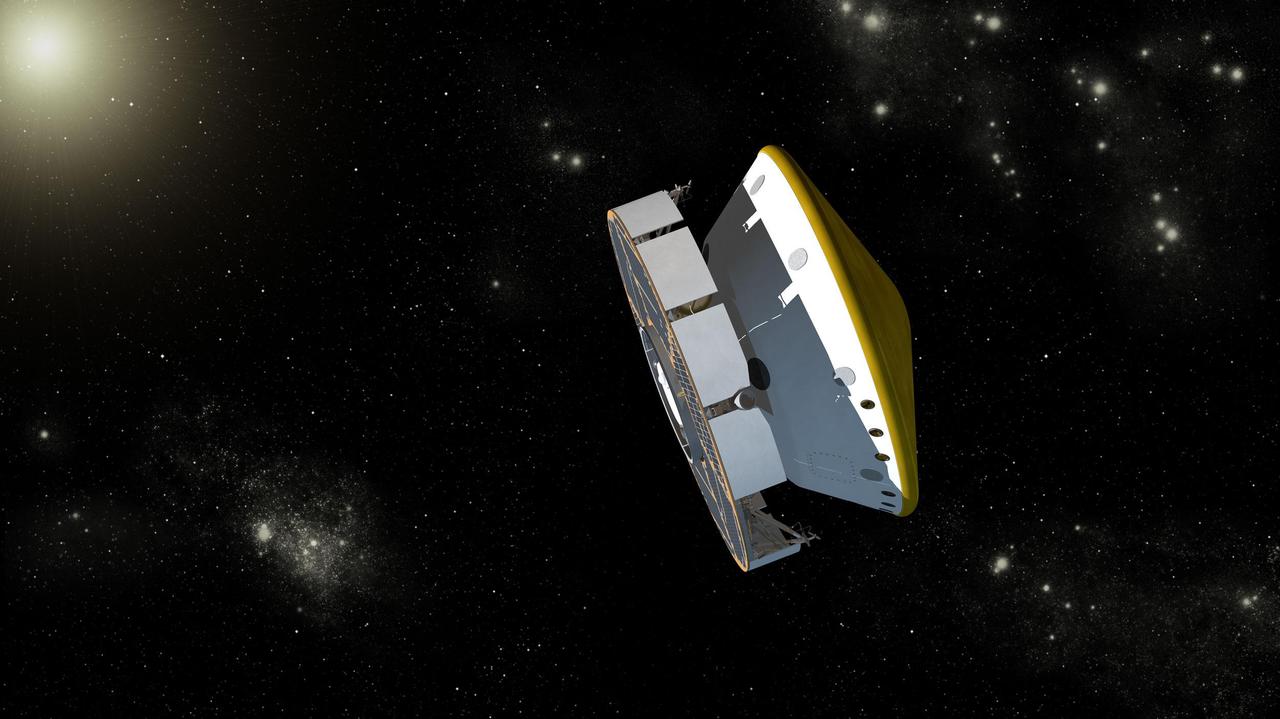

This is an artist concept of NASA Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft during its cruise phase between launch and final approach to Mars. The spacecraft includes a disc-shaped cruise stage on the left attached to the aeroshell.
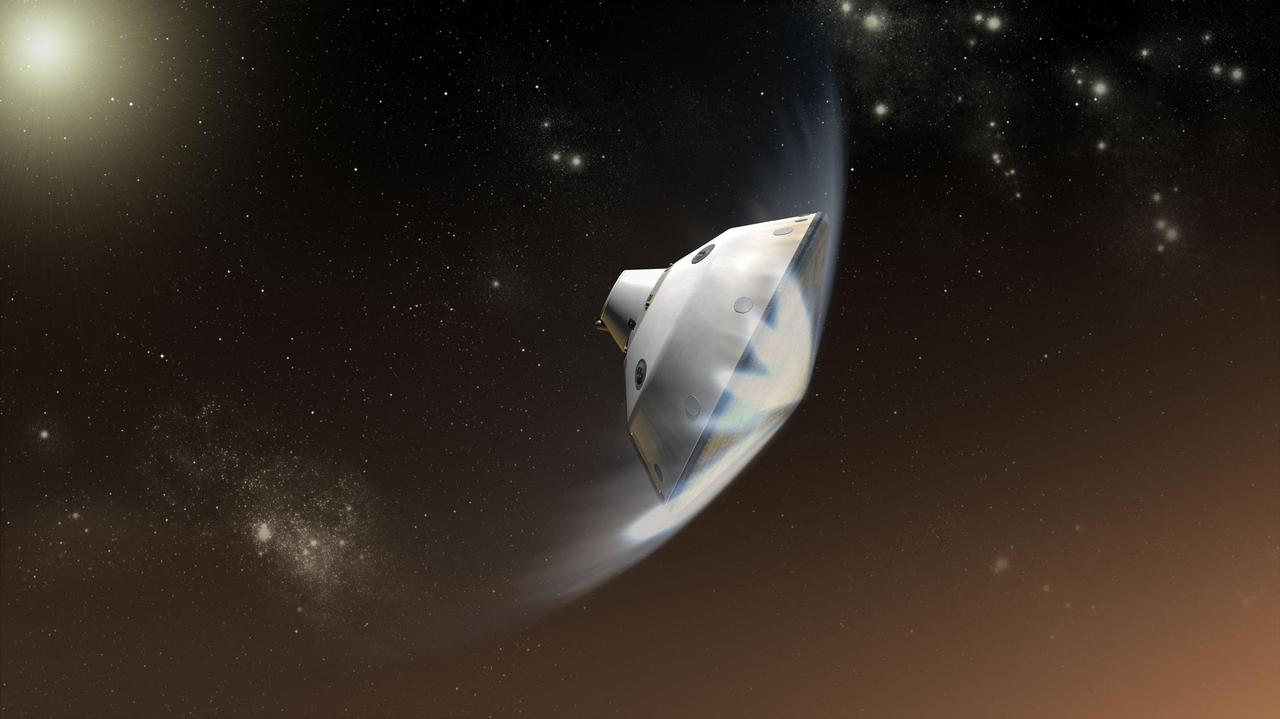

This artist concept depicts the interaction of NASA Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft with the upper atmosphere of Mars during the entry, descent and landing of the Curiosity rover onto the Martian surface.
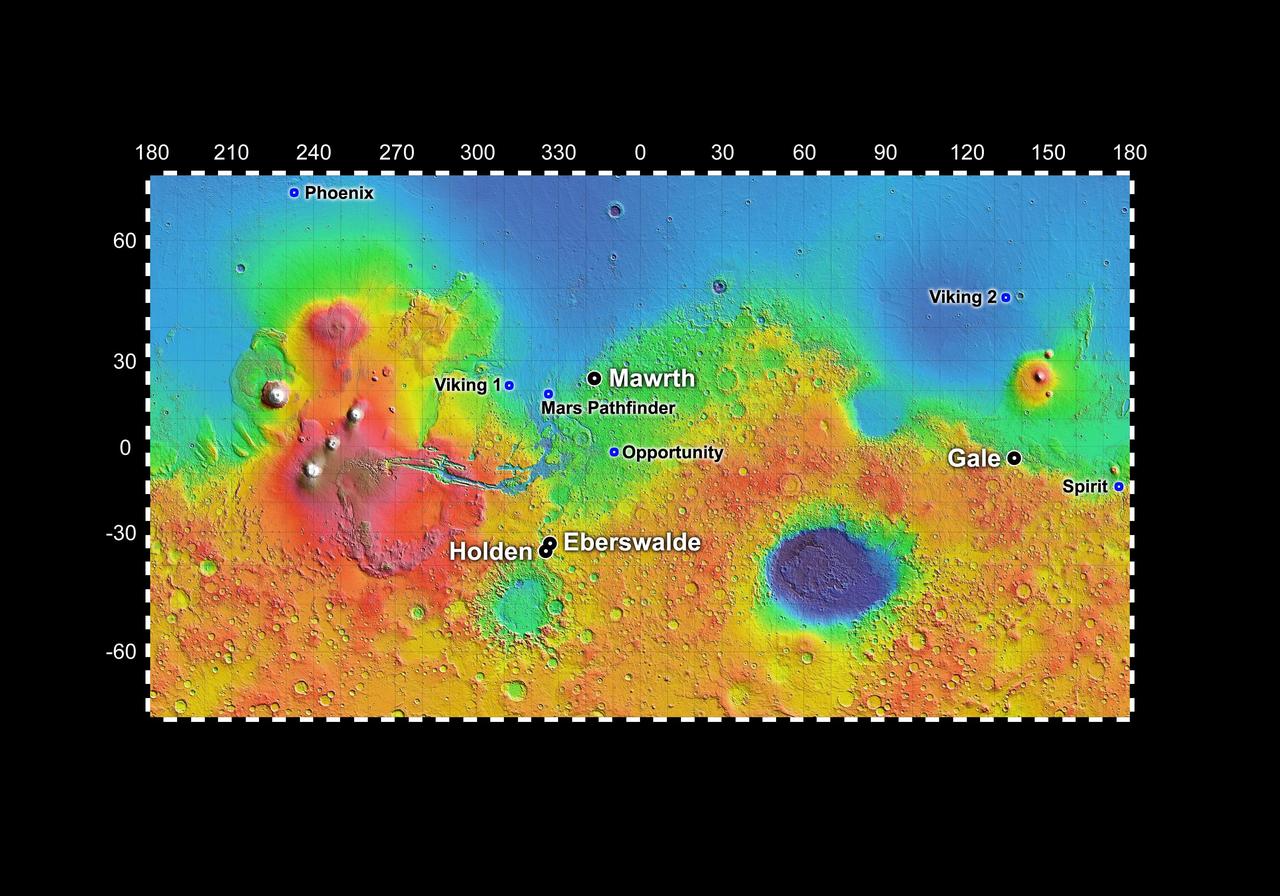
Out of more than 30 sites considered as possible landing targets for NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission, by November 2008 four of the most intriguing places on Mars rose to the final round of the site-selection process.
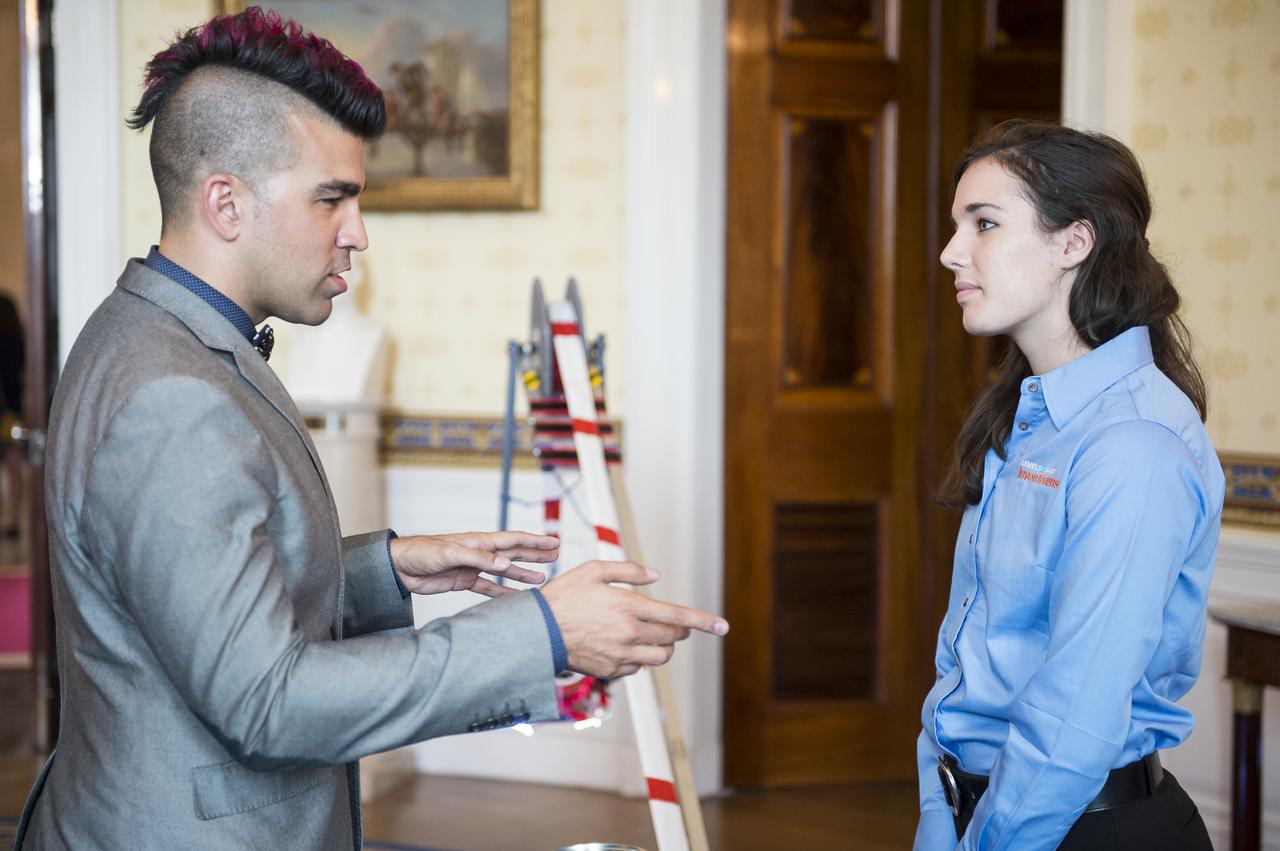

Bobak Ferdowsi, a system's engineer at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory who became widely known for his mohawk hairstyle during the broadcast of the Curiosity landing on Mars, is seen here discussing a project with a participant in the White House Science Fair. The fourth White House Science Fair was held at the White House and included 100 students from more than 30 different states who competed in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) competitions. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
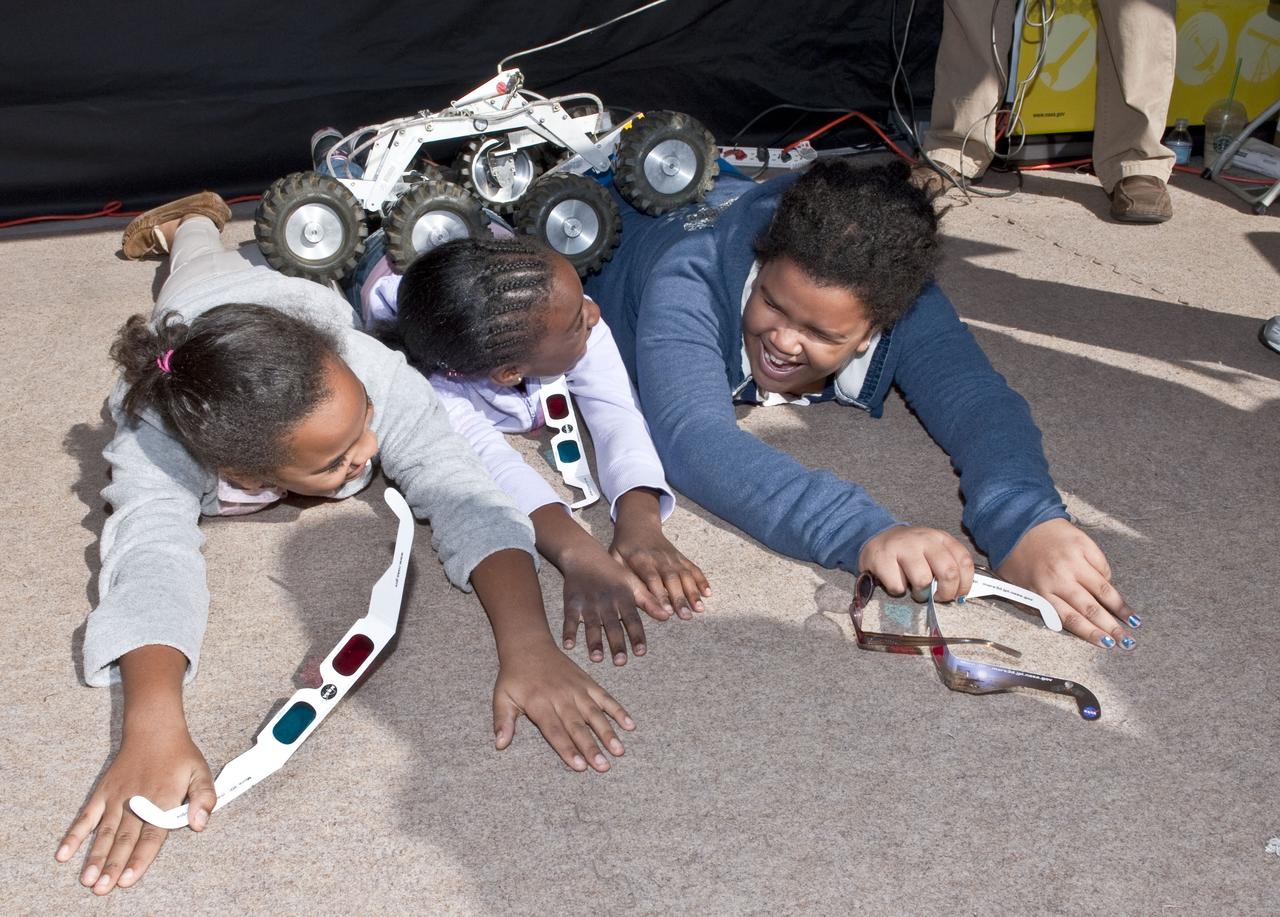

Children react as a tiny Mars Rover rolls over their backs at the USA Science and Engineering Festival, Saturday, Oct. 23, 2010, at Freedom Plaza in Washington. NASA, joined with more than 500 science organizations this weekend to inspire the next generation of scientists and engineers during the first national science and engineering festival held in the nation's capital. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
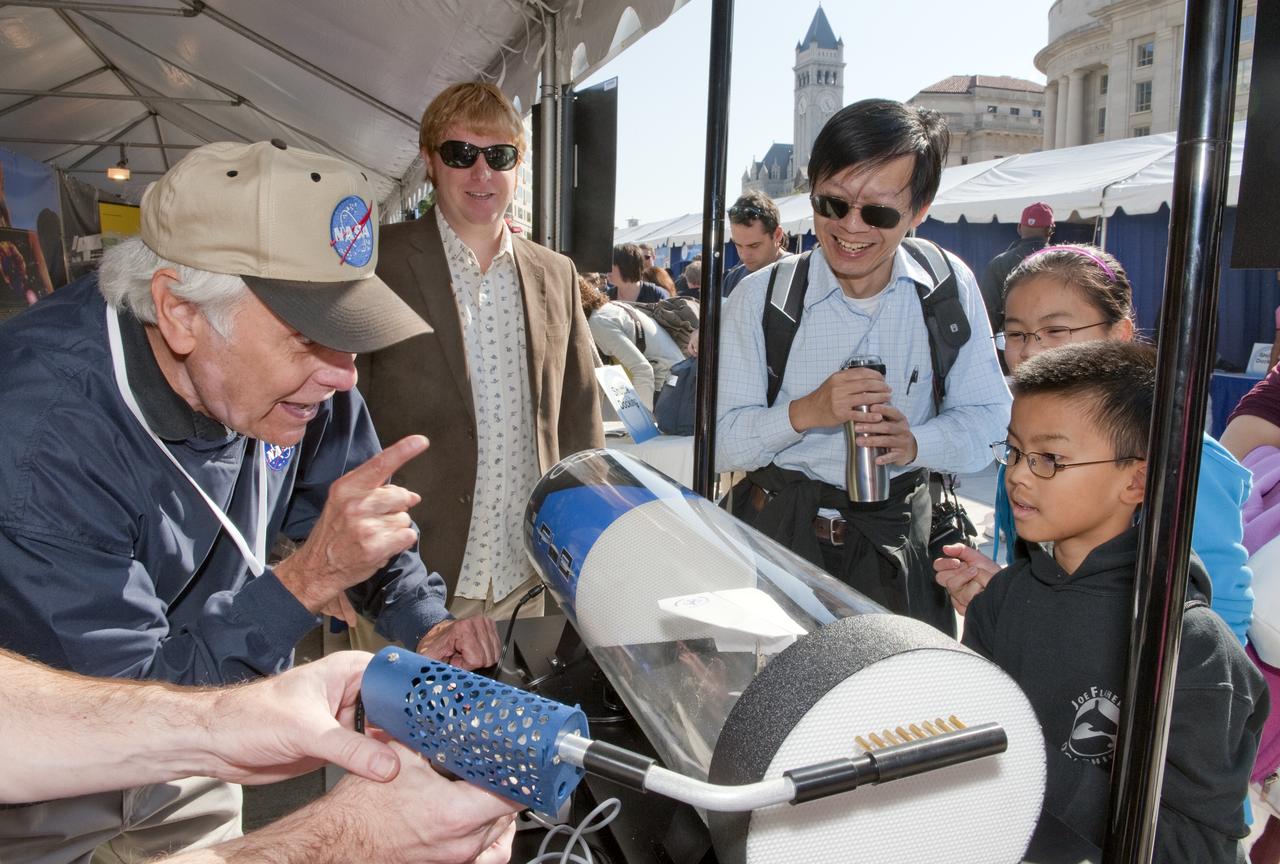

Priniciples of air flow are explained to visitors to the wind tunnel exhibit at the USA Science and Engineering Festival, Saturday, Oct. 23, 2010, at Freedom Plaza in Washington. NASA, joined with more than 500 science organizations this weekend to inspire the next generation of scientists and engineers during the first national science and engineering festival held in the nation's capital. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

Participants look through telescopes to observe the Sun during the USA Science and Engineering Festival, Saturday, Oct. 23, 2010, at Freedom Plaza in Washington. NASA, joined with more than 500 science organizations this weekend to inspire the next generation of scientists and engineers during the first national science and engineering festival held in the nation's capital. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
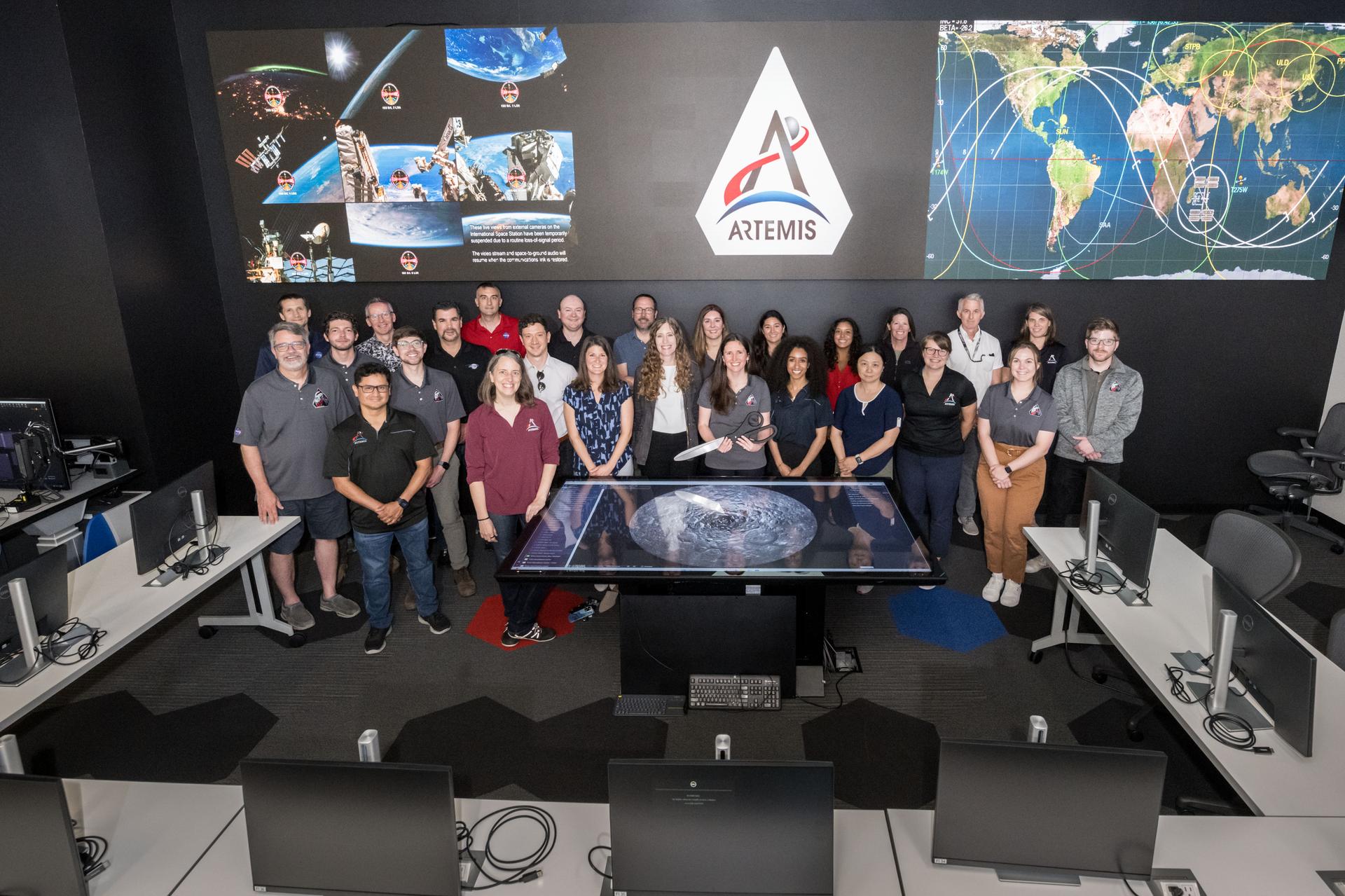

jsc2025e057255 --- NASA’s Artemis III lunar science team is pictured in the Science Evaluation Room (SER) at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Located in the Christopher C. Kraft Jr. Mission Control Center, the SER supports the mission’s main flight control room for lunar science and planetary observations. Built specifically for Artemis missions with these science priorities in mind, the SER is equipped to support rapid data interpretation, collaborative analysis, real-time decision making, and seamless coordination between the science and operations teams.
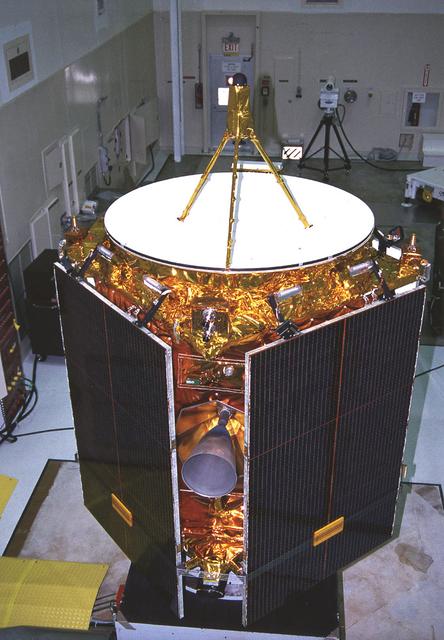

The Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous (NEAR) spacecraft undergoing preflight preparation in the Spacecraft Assembly Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2) at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). NEAR will perform two critical mission events - Mathilde flyby and the Deep-Space maneuver. NEAR will fly-by Mathilde, a 38-mile (61-km) diameter C-type asteroid, making use of its imaging system to obtain useful optical navigation images. The primary science instrument will be the camera, but measurements of magnetic fields and mass also will be made. The Deep-Space Maneuver (DSM) will be executed about a week after the Mathilde fly-by. The DSM represents the first of two major burns during the NEAR mission of the 100-pound bi-propellant (Hydrazine/nitrogen tetroxide) thruster. This maneuver is necessary to lower the perihelion distance of NEAR's trajectory. The DSM will be conducted in two segments to minimize the possibility of an overburn situation.

An artist concept of NASA Mars Science Laboratory left serves to compare it with Spirit, one of NASA twin Mars Exploration Rovers

NASA, NOAA, and mission leaders participate in a science briefing on NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission and its two rideshares – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, Sept. 21, 2025. From left are: Sarah Frazier, NASA Communications; Joe Westlake, director, Heliophysics Division, NASA Headquarters in Washington; David McComas, IMAP principal investigator, Princeton University; Lara Waldrop, Carruthers Geocorona Observatory principal investigator, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign; Jamie Favors, director, Space Weather Program, Heliophysics Division, NASA Headquarters; Clinton Wallace, director, NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center; James Spann, senior scientist, NOAA Office of Space Weather Observations. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. The missions will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth. Launch is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.

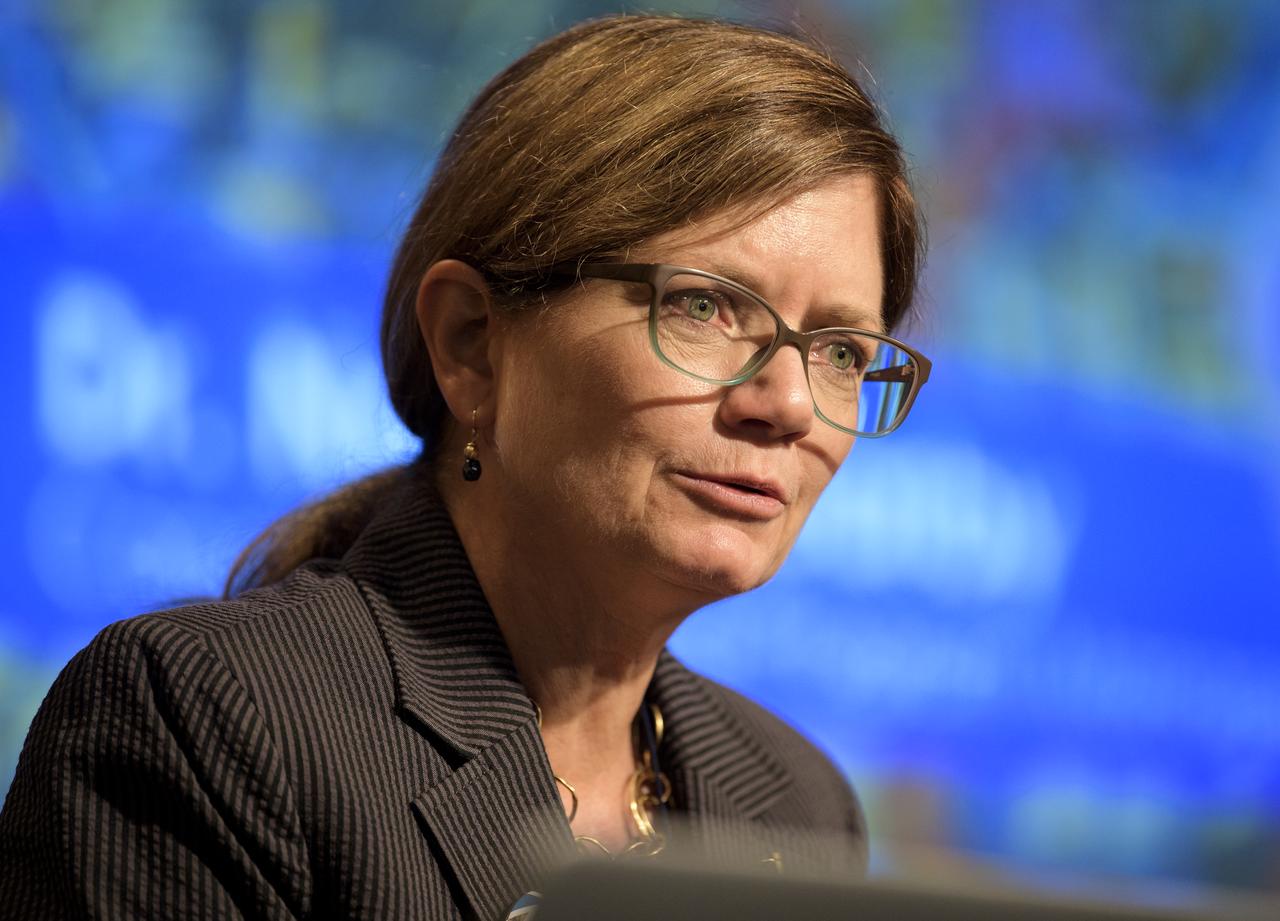
Sandra Cauffman, acting Director of the Earth Sciences Division of the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, speaks during the 2019 Annual Earth Science Applications Showcase, Thursday, Aug. 1, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters and present their research projects. DEVELOP is a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisers from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

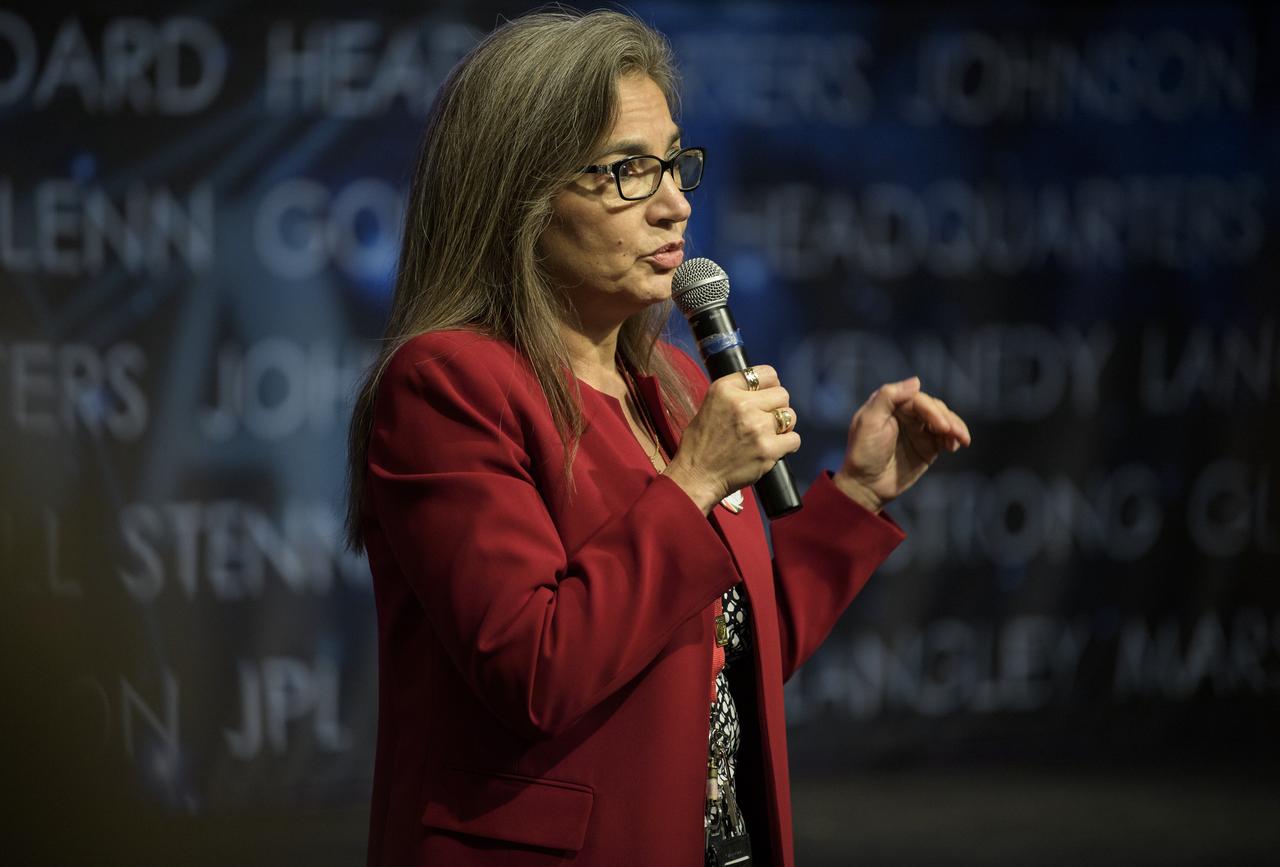
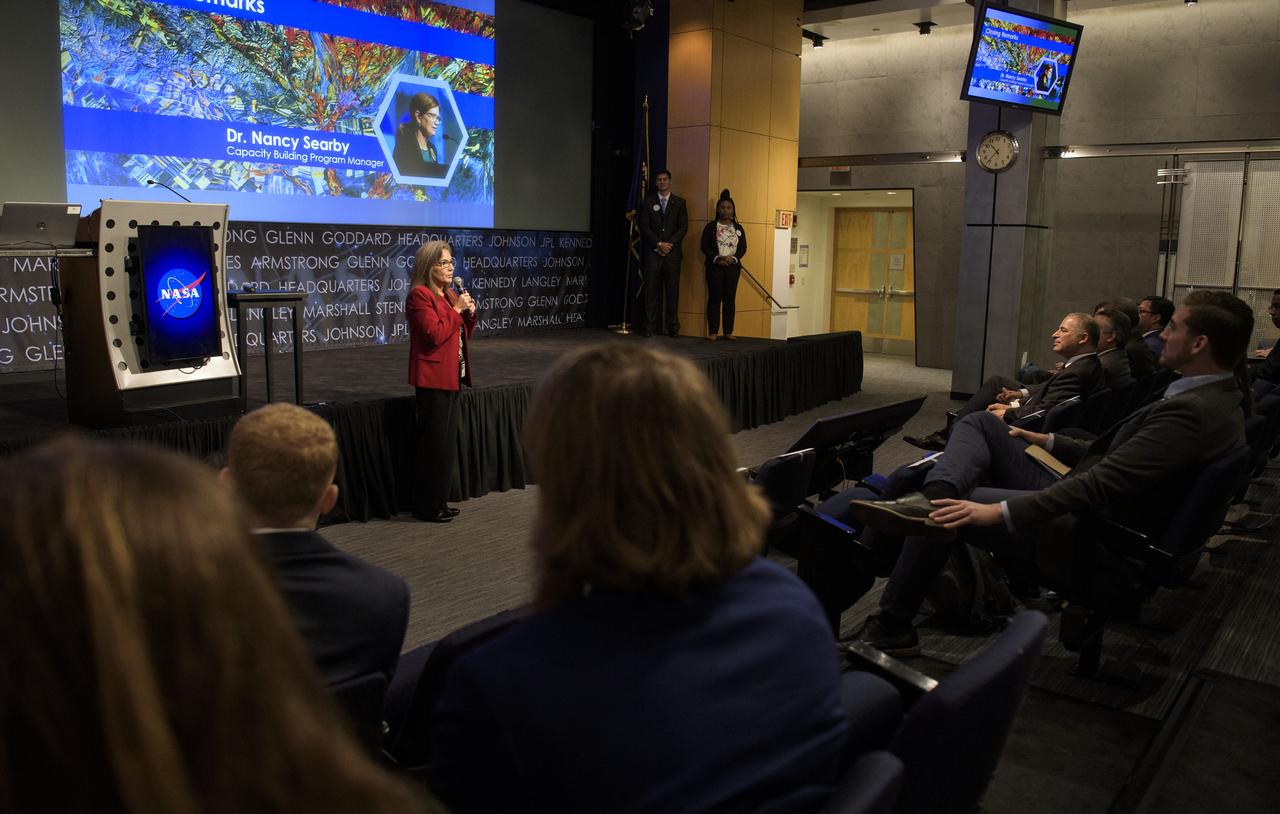
Capacity Building Program Manager for NASA's Applied Sciences Program (Earth Science Division) Nancy Searby speaks during the 2019 Annual Earth Science Applications Showcase, Thursday, Aug. 1, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters and present their research projects. DEVELOP is a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisers from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Sandra Cauffman, acting Director of the Earth Sciences Division of the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, speaks during the 2019 Annual Earth Science Applications Showcase, Thursday, Aug. 1, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters and present their research projects. DEVELOP is a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisers from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Sandra Cauffman, acting Director of the Earth Sciences Division of the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, speaks during the 2019 Annual Earth Science Applications Showcase, Thursday, Aug. 1, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters and present their research projects. DEVELOP is a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisers from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Kenton Ross, DEVELOP's National Science Advisor, speaks about SICA during the 2019 Annual Earth Science Applications Showcase, Thursday, Aug. 1, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters and present their research projects. DEVELOP is a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisers from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Cindy Schmidt, a research scientist in the Earth Science Division at NASA's Ames Research Center, speaks about the Indigenous Peoples Pilot and drought monitoring in the Navajo Nation during the 2019 Annual Earth Science Applications Showcase, Thursday, Aug. 1, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters and present their research projects. DEVELOP is a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisers from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)