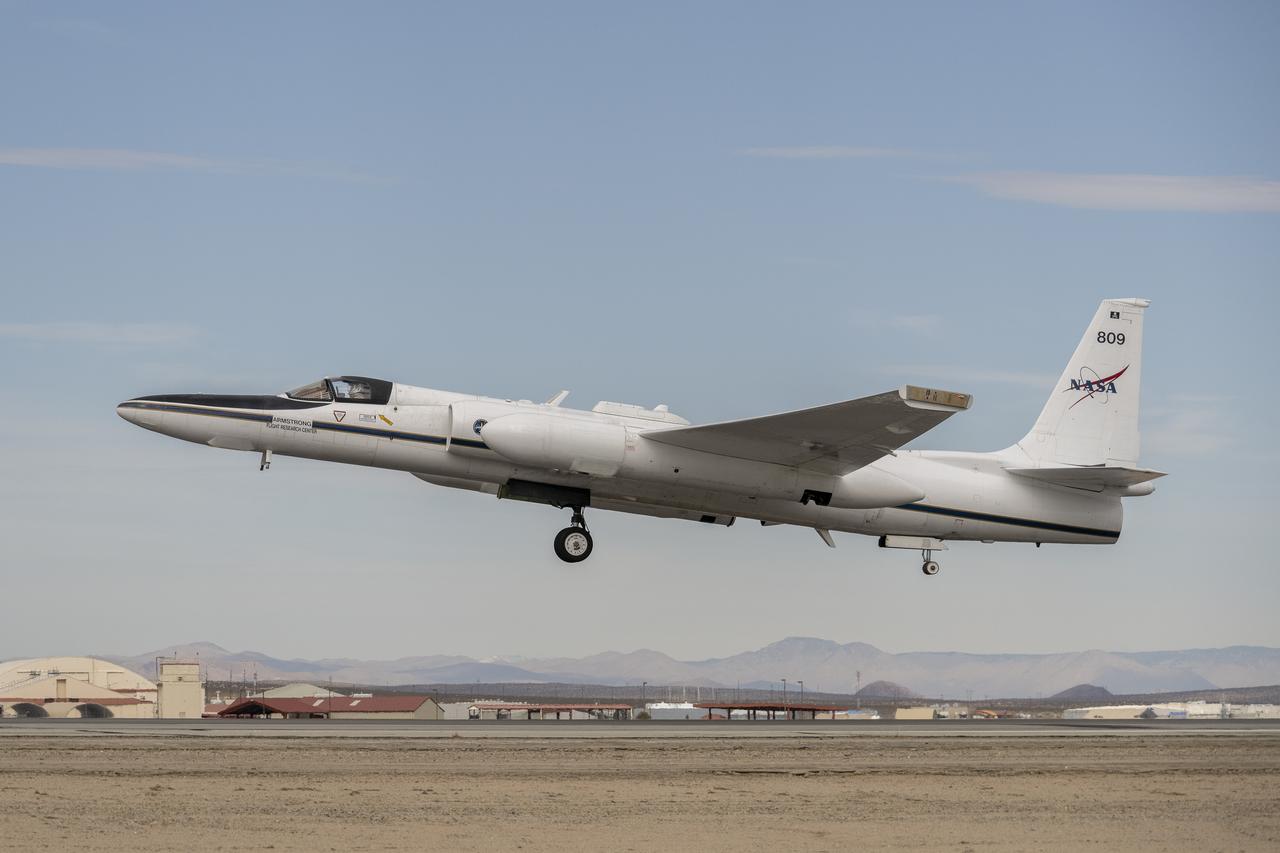

A team of experts wrap up science flights on the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California after the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Pilot Tim Williams ascends the ER-2 on the runway for one of the final science flights validating satellite-borne data. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
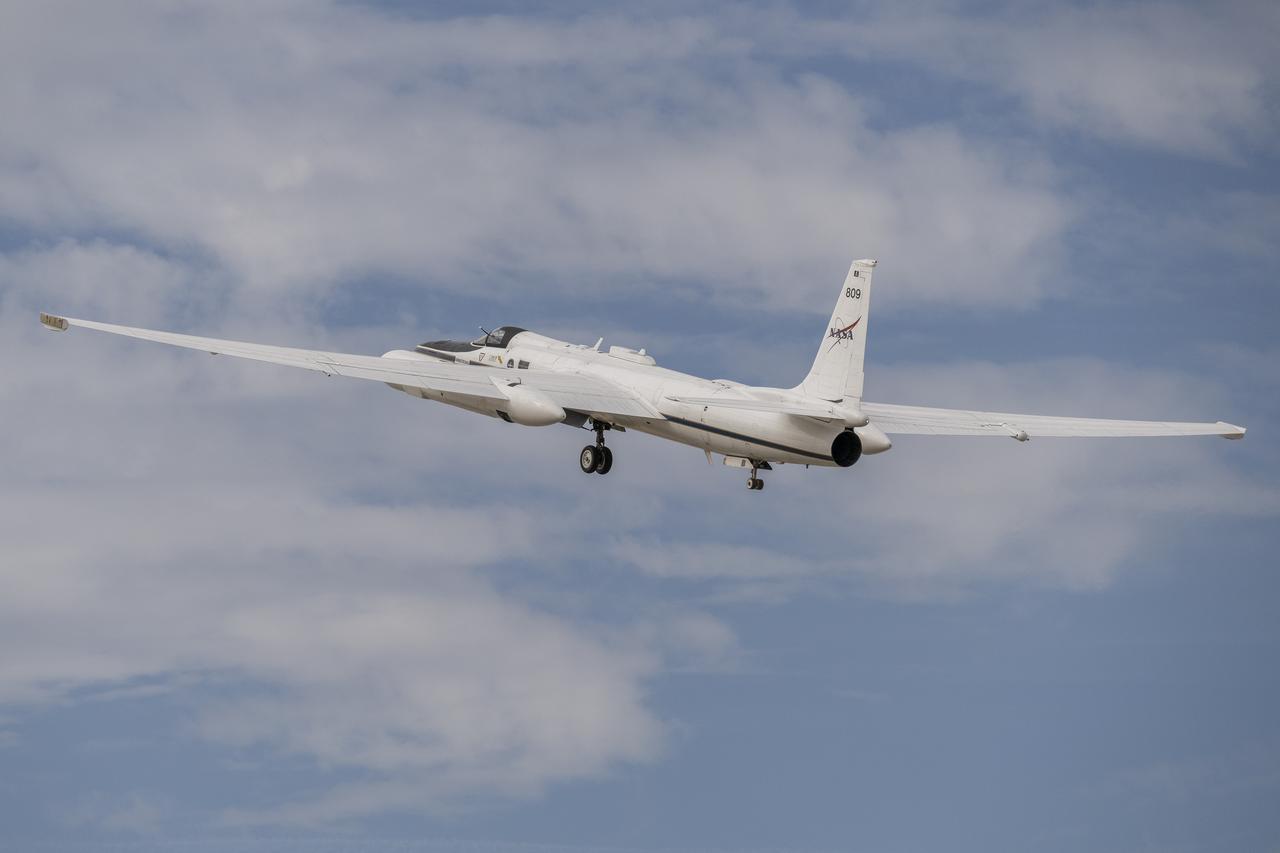

A team of experts wrap up science flights on the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California after the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Pilot Tim Williams ascends the ER-2 to higher skies for one of the final science flights validating satellite-borne data. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
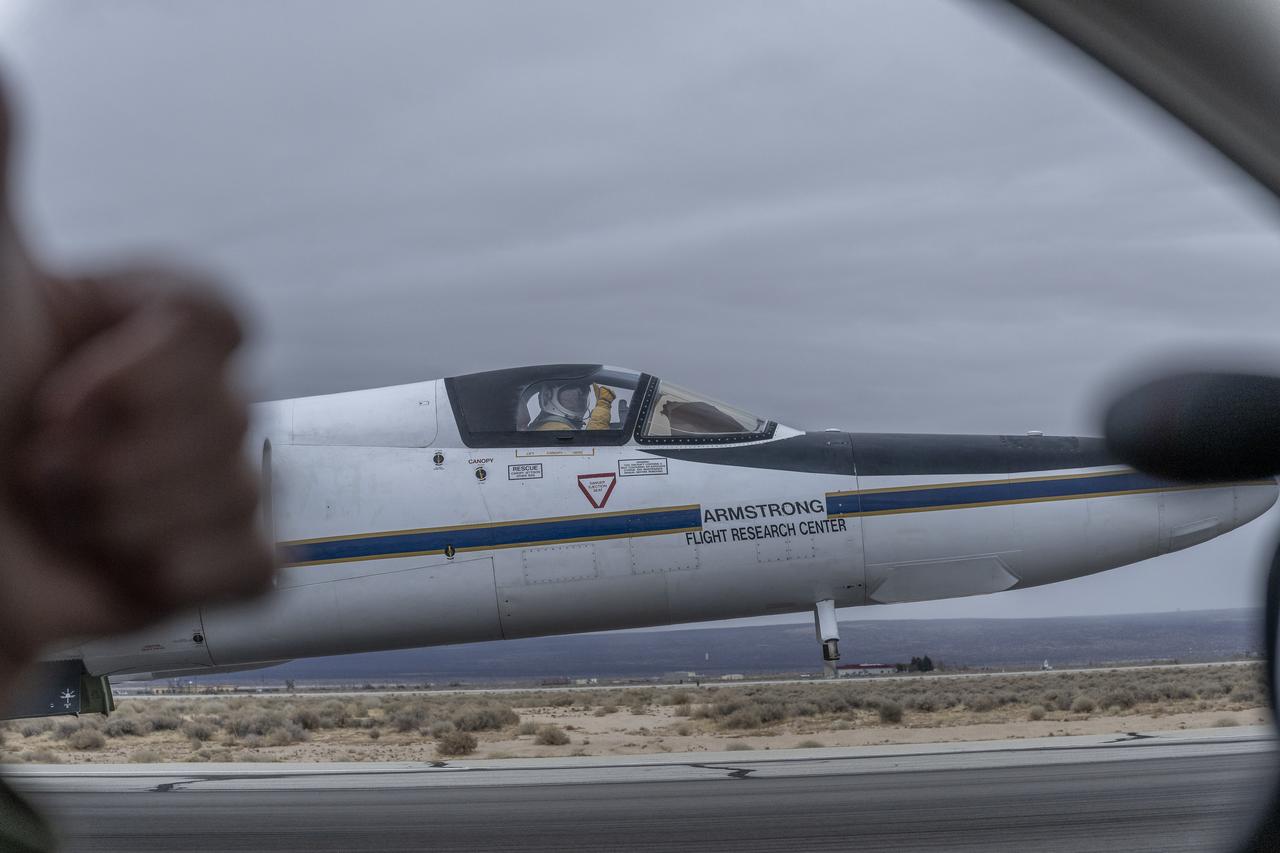

A team of experts wrap up science flights on the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California after the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Pilot Kirt Stallings ascends the ER-2 on the runway for one of the final science flights validating satellite-borne data. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
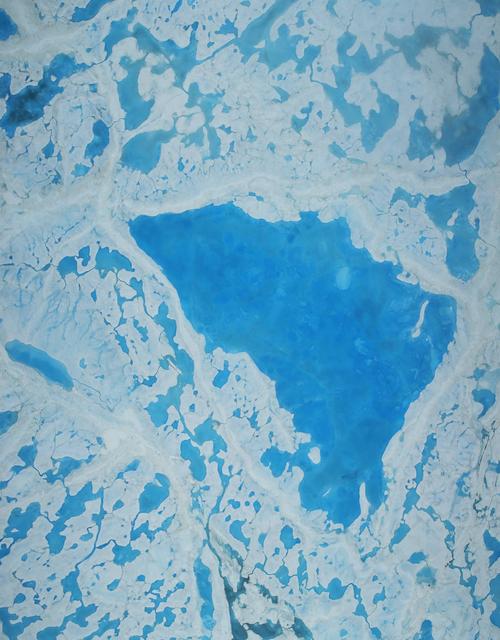

This summer, with sea ice across the Arctic Ocean shrinking to below-average levels, a NASA airborne survey of polar ice just completed its first flights. Its target: aquamarine pools of melt water on the ice surface that may be accelerating the overall sea ice retreat. NASA’s Operation IceBridge completed the first research flight of its new 2016 Arctic summer campaign on July 13. The science flights, which continue through July 25, are collecting data on sea ice in a year following a record-warm winter in the Arctic. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/29T6mxc" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/29T6mxc</a> Caption: A large pool of melt water over sea ice, as seen from an Operation IceBridge flight over the Beaufort Sea on July 14, 2016. During this summer campaign, IceBridge will map the extent, frequency and depth of melt ponds like these to help scientists forecast the Arctic sea ice yearly minimum extent in September. Credit: NASA/Operation IceBridge
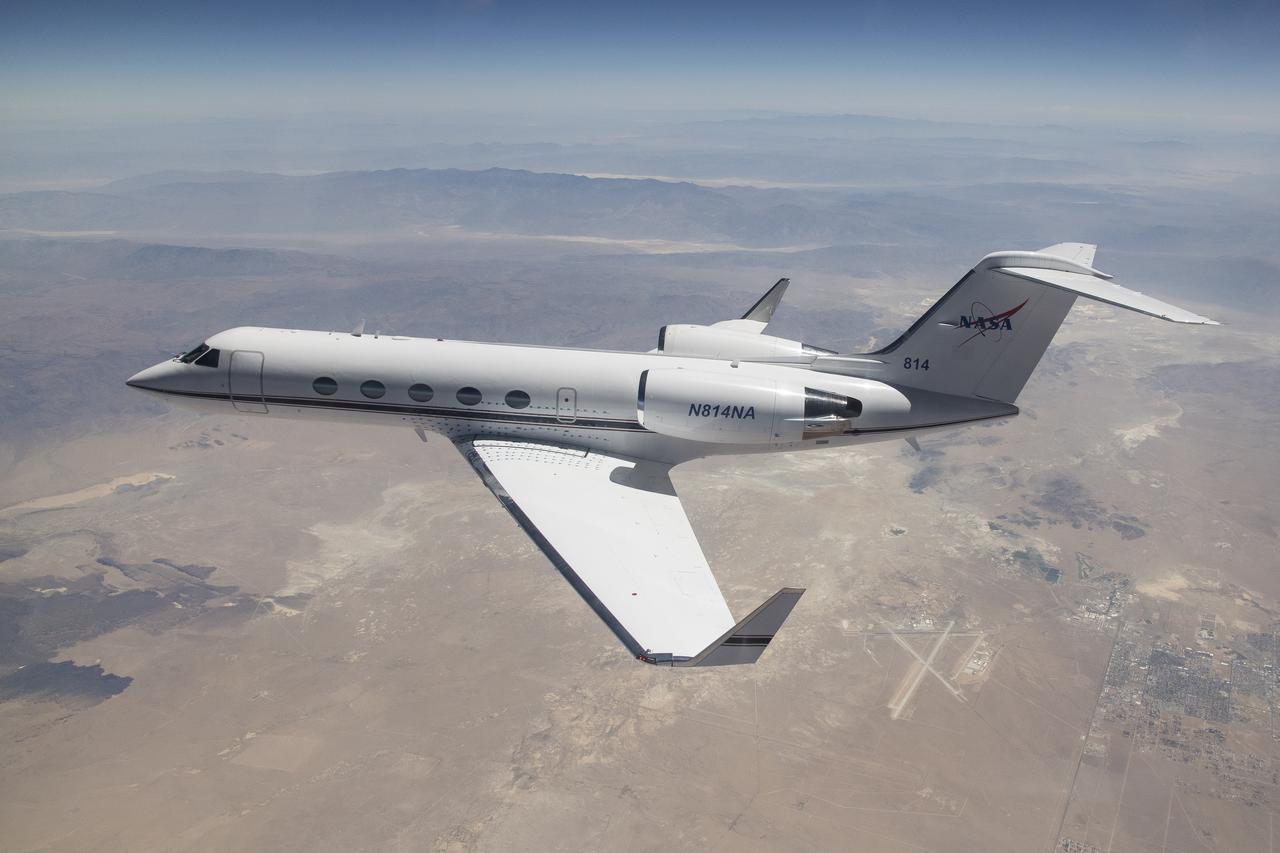

In a series of baseline flights beginning on June 24, 2024, the G-IV aircraft flew over the Antelope Valley to analyze aircraft performance. To accommodate a new radar instrument developed by JPL, NASA’s Airborne Science Program has selected the Gulfstream-IV aircraft to be modified and operated by Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California and will accommodate new instrumentation on board in support of the agency’s science mission directorate. Baseline flights began at NASA Armstrong in June 2024
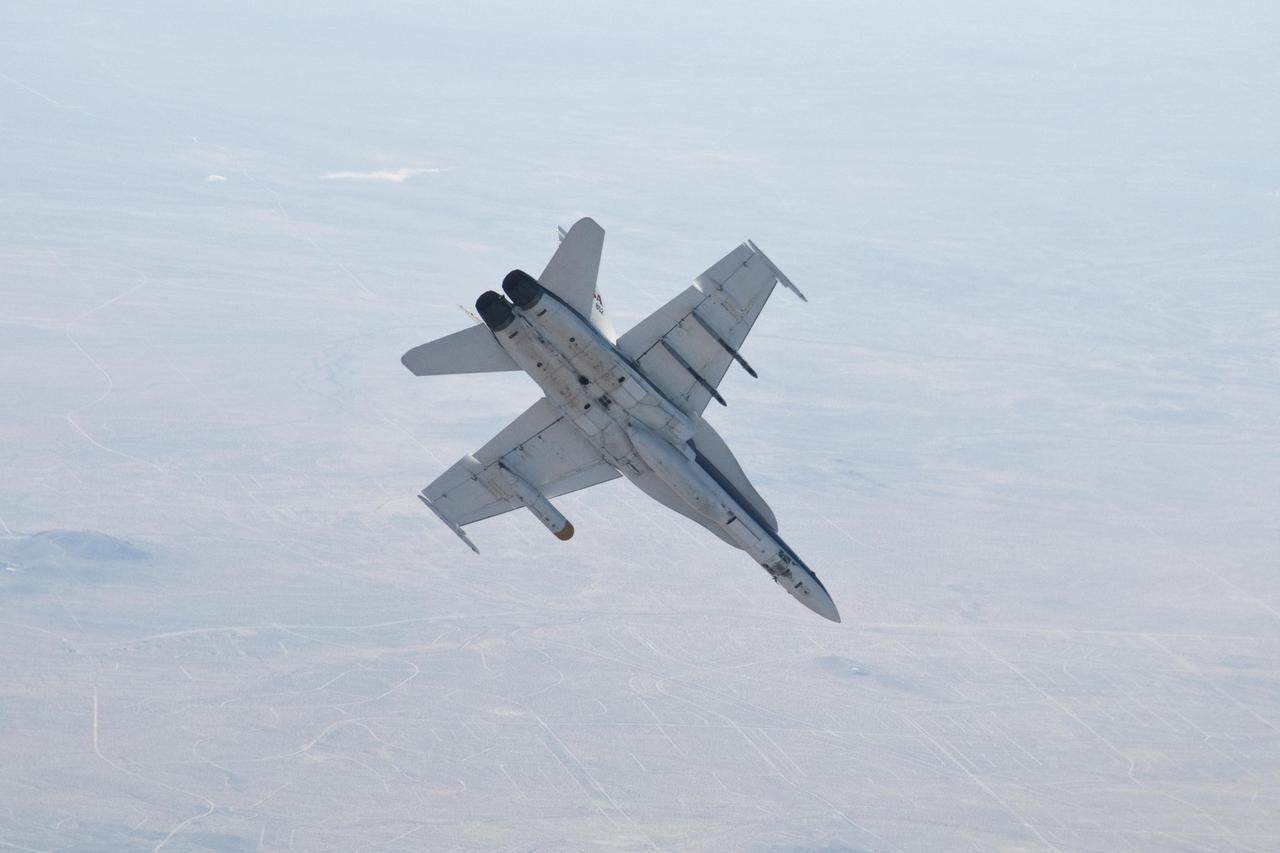

A NASA Dryden Flight Research Center F/A-18 852 aircraft performs a roll during June 2011 flight tests of a Mars landing radar. A test model of the landing radar for NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission is inside a pod under the aircraft left wing.

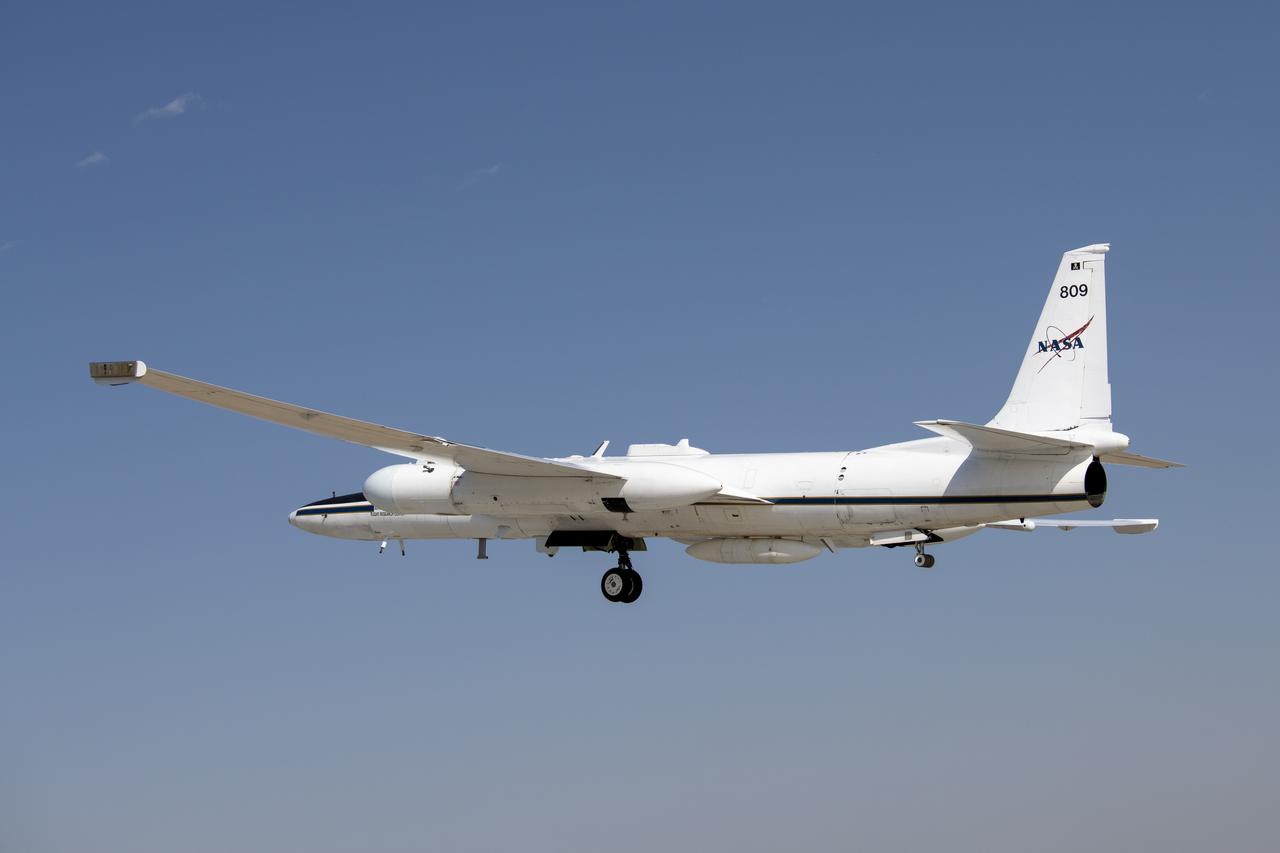
NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center ER-2 #809 high-altitude aircraft prepped for Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere (DCOTSS) science flights in Palmdale, CA.

NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center ER-2 pilot Gary Toroni and engineering technician Raul "Corky" Cortes preparing for Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere (DCOTSS) science flights in Palmdale, CA on June 17, 2021.

NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center operates ER-2 #809 high-altitude aircraft for Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere (DCOTSS) science flights on June 17, 2021.

NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center ER-2 #809 high-altitude aircraft prepared for Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere (DCOTSS) science flights in Palmdale, CA on June 17, 2021.
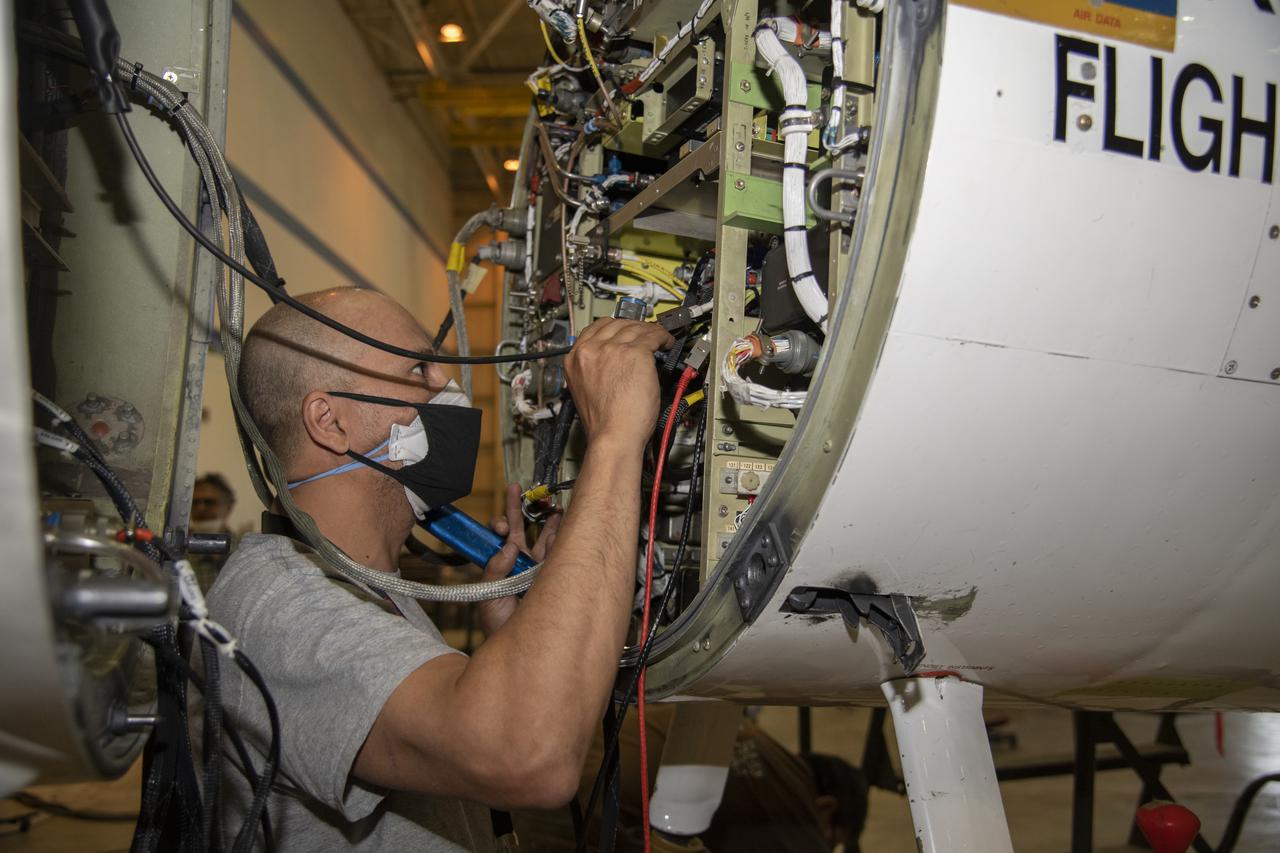

NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center ER-2 #809 high-altitude aircraft maintained by avionics technician Gregory Bantalin for Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere (DCOTSS) science flights.
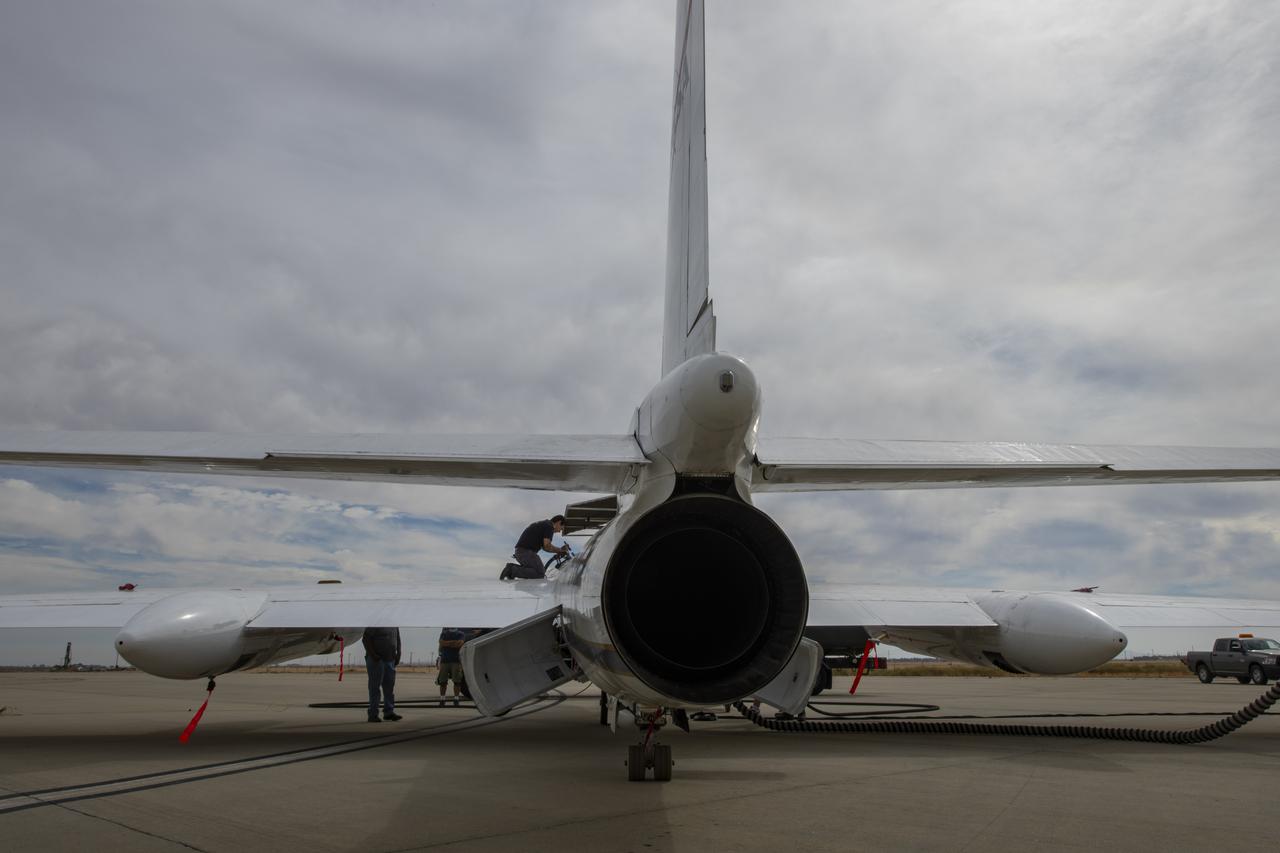

NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center ER-2 #809 high-altitude aircraft prepped for Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere (DCOTSS) science flights in Palmdale, CA.
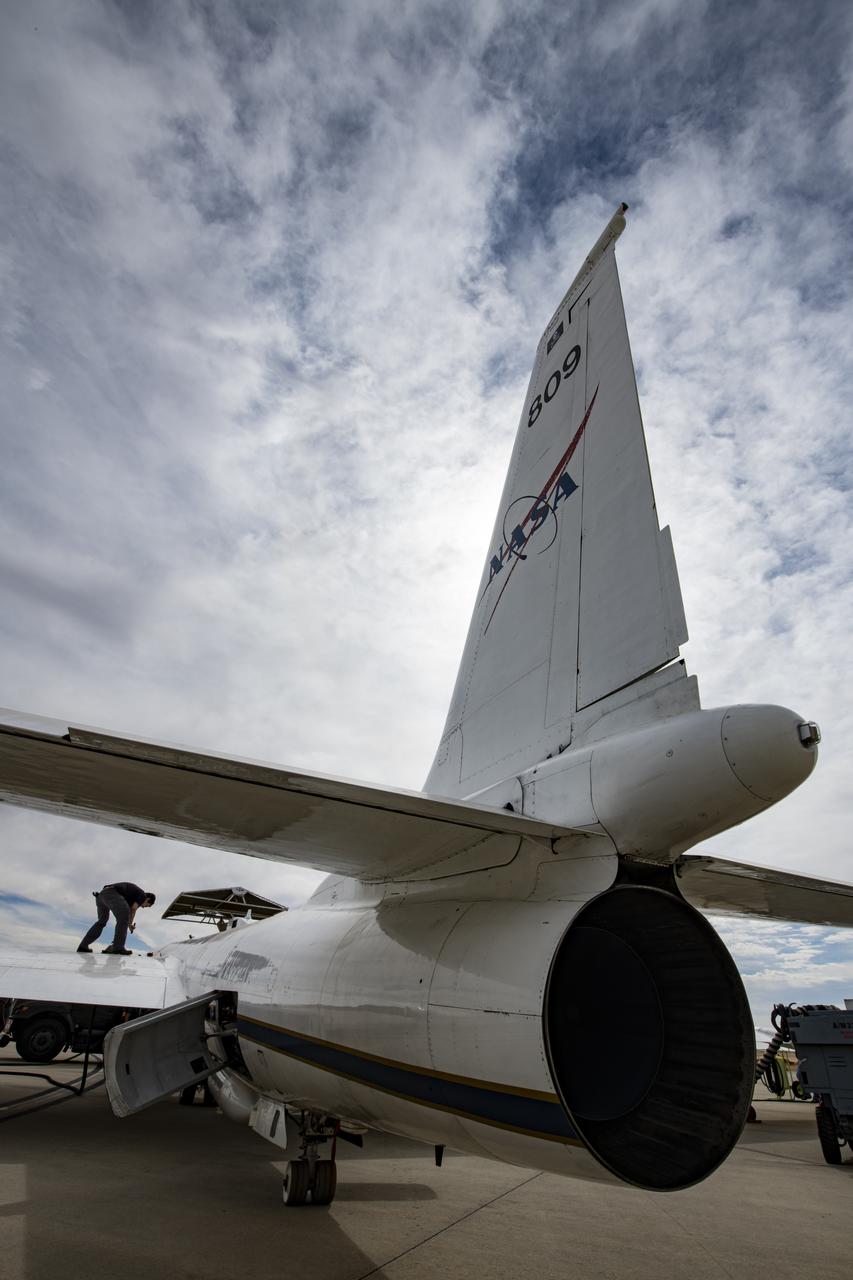

NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center ER-2 #809 high-altitude aircraft prepped for Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere (DCOTSS) science flights in Palmdale, CA.
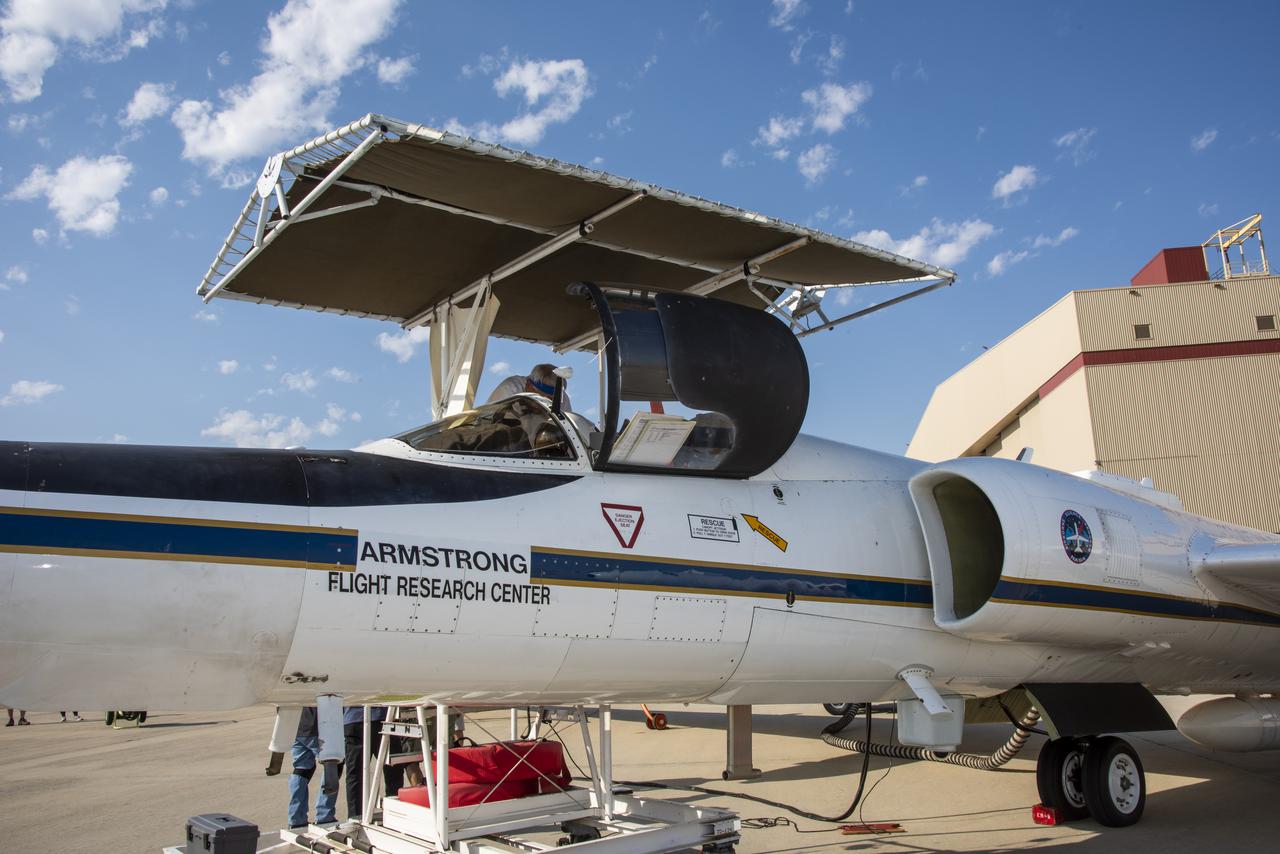

NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center ER-2 #809 high-altitude aircraft prepared for Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere (DCOTSS) science flights in Palmdale, CA on June 17, 2021
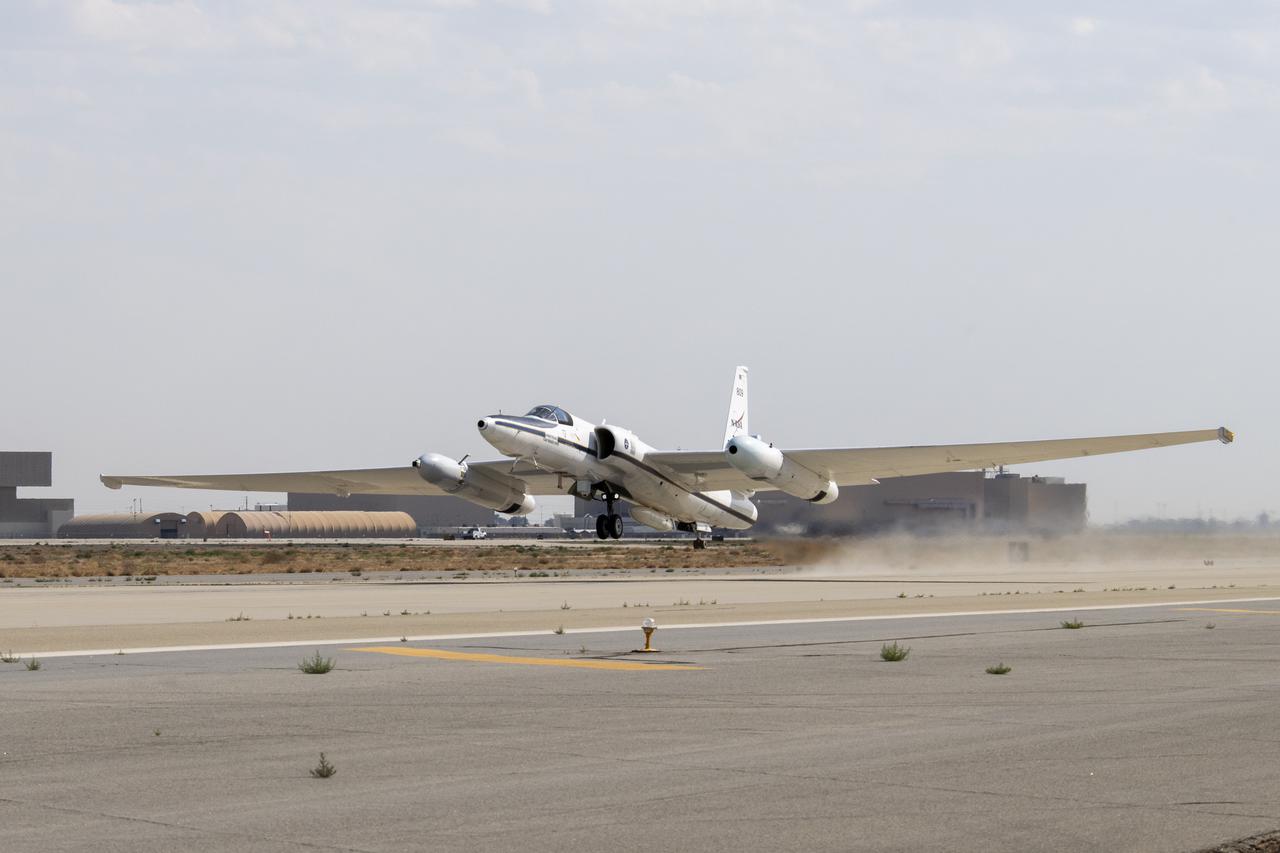

NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center ER-2 #809 high-altitude aircraft taking off for Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere (DCOTSS) science flights in Palmdale, CA on June 17, 2021.
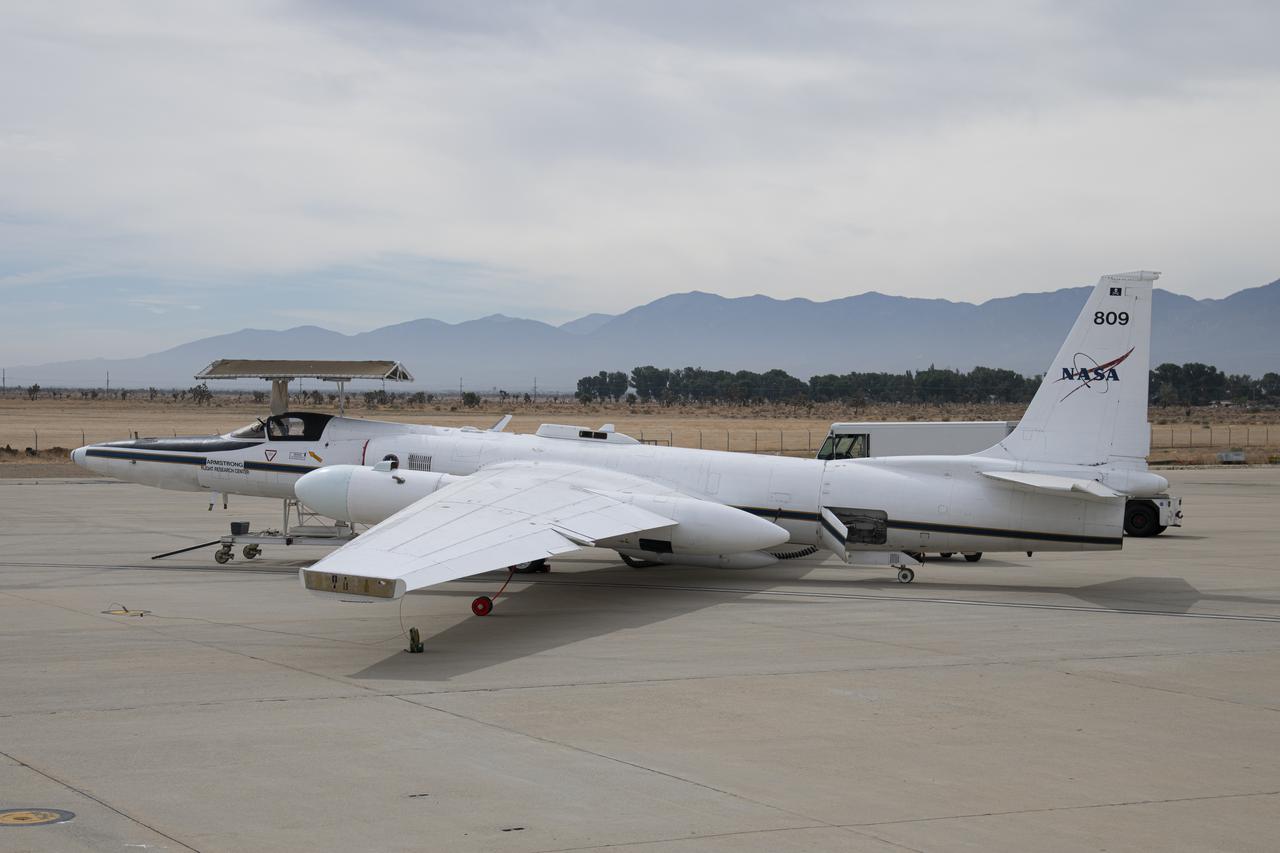

NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center ER-2 #809 high-altitude aircraft prepped for Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere (DCOTSS) science flights in Palmdale, CA.
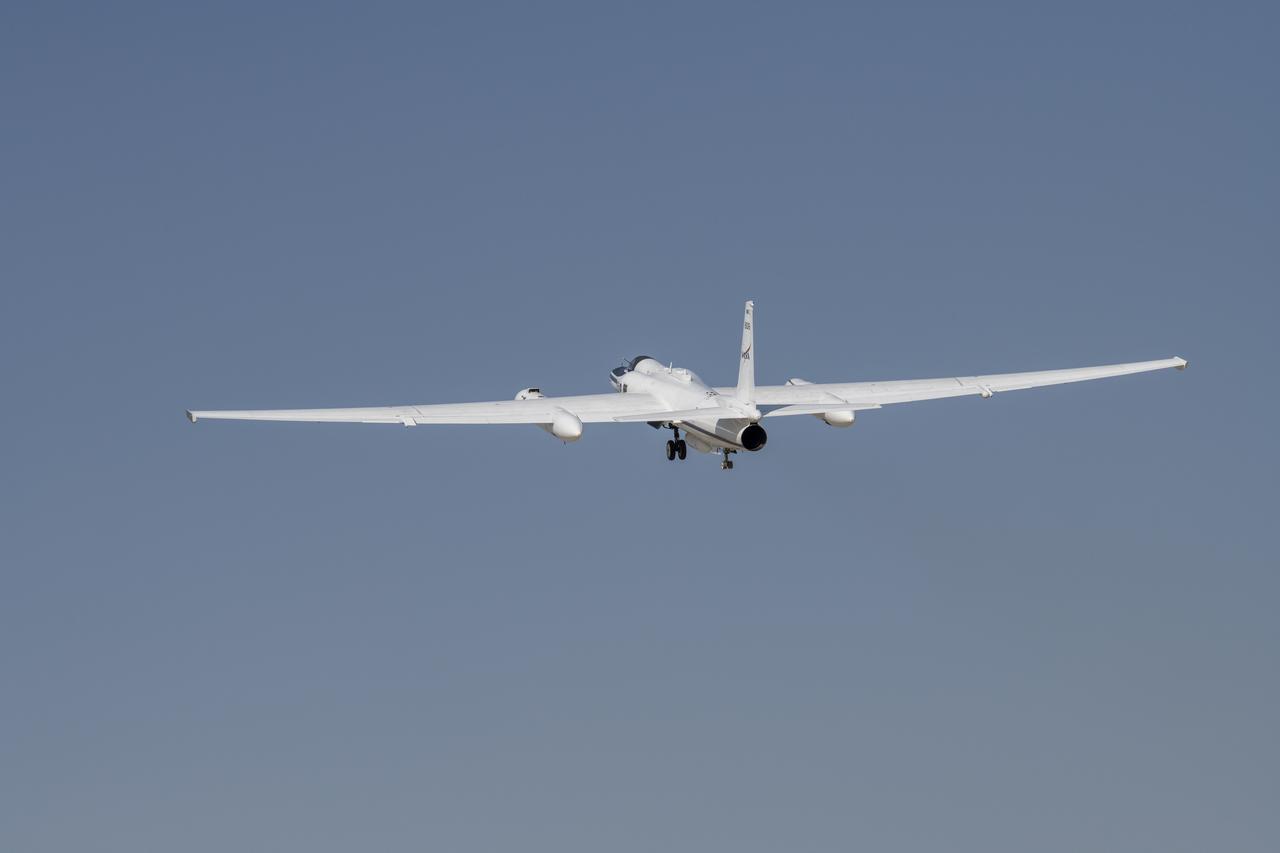

NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center operates ER-2 #809 high-altitude aircraft for Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere (DCOTSS) science flights on June 17, 2021.
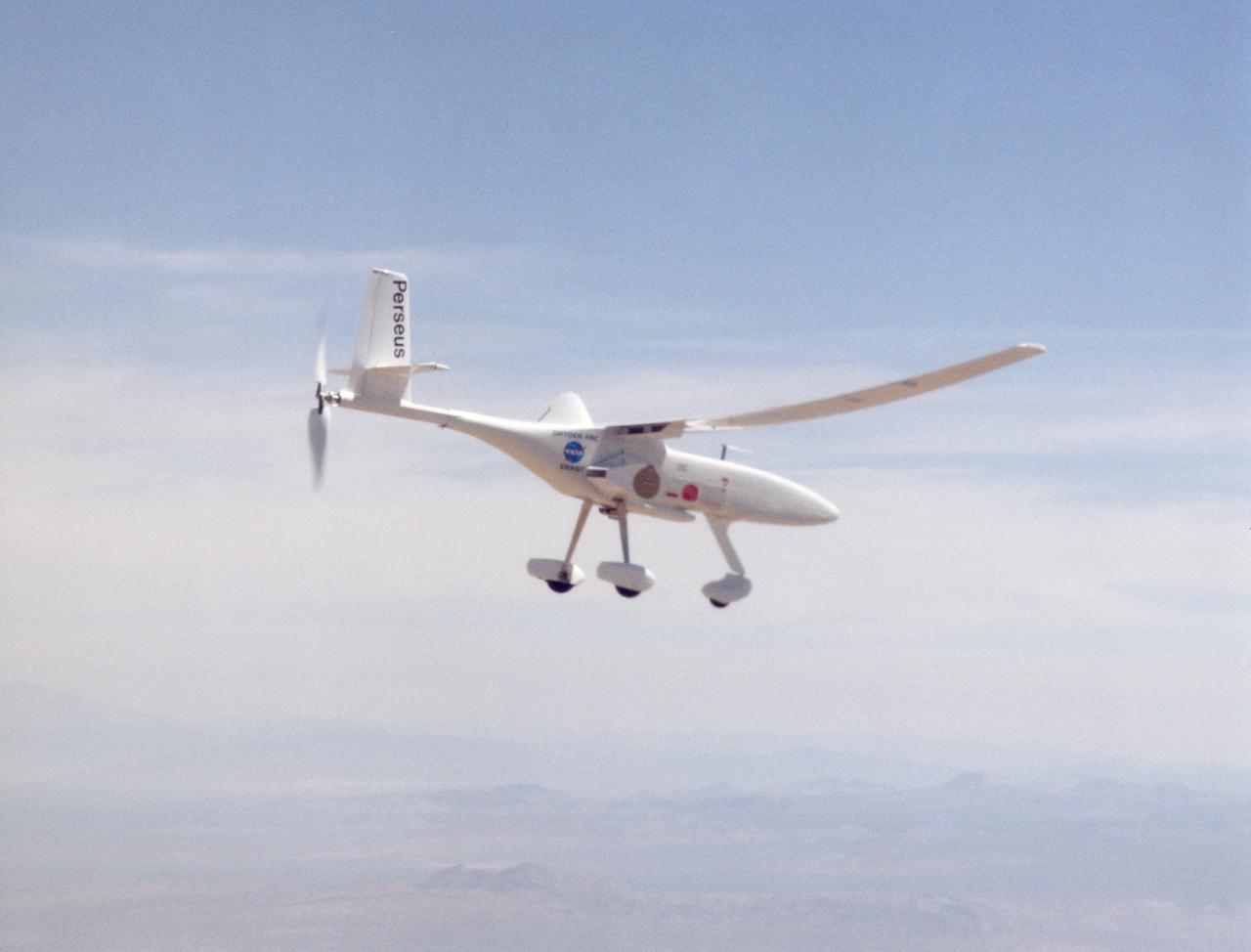

A long, slender wing and a pusher propeller at the rear characterize the Perseus B remotely piloted research aircraft, seen here during a test flight in June 1998.
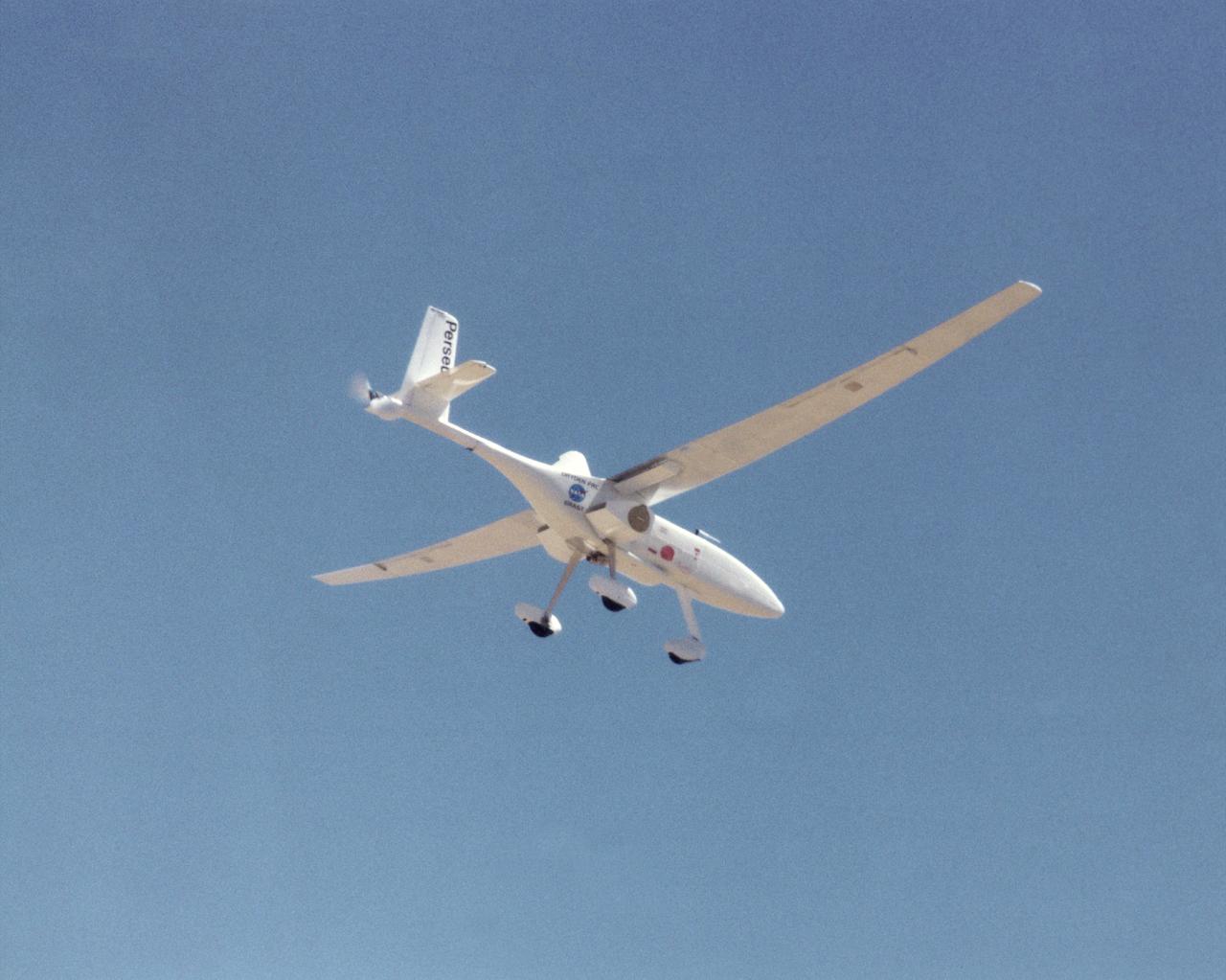

A long, slender wing and a pusher propeller at the rear characterize the Perseus B remotely piloted research aircraft, seen here during a test flight in June 1998.
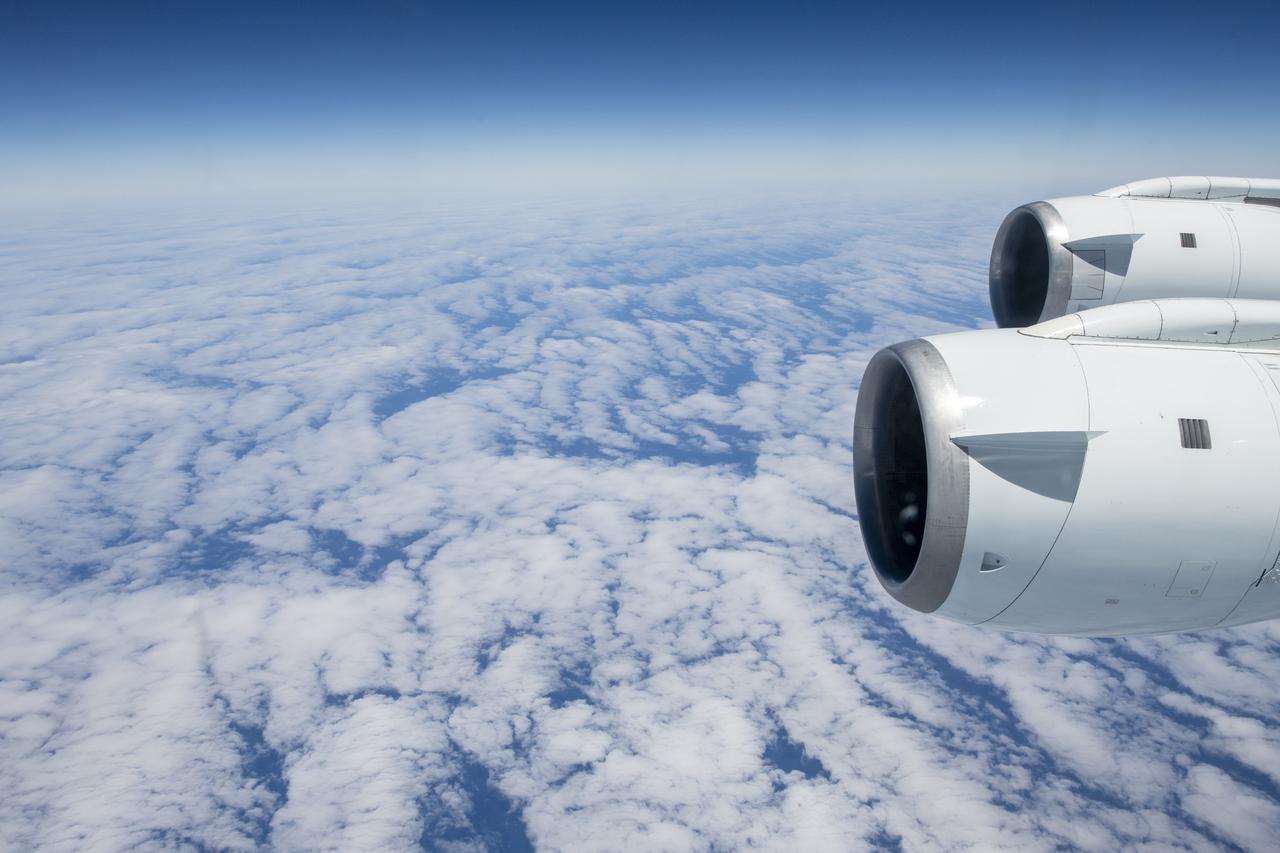

NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center flies the DC-8 airborne science laboratory in support of the Convective Processes Experiment - Aerosols and Winds campaign, CPEX-AW, on Aug 6, 2021.
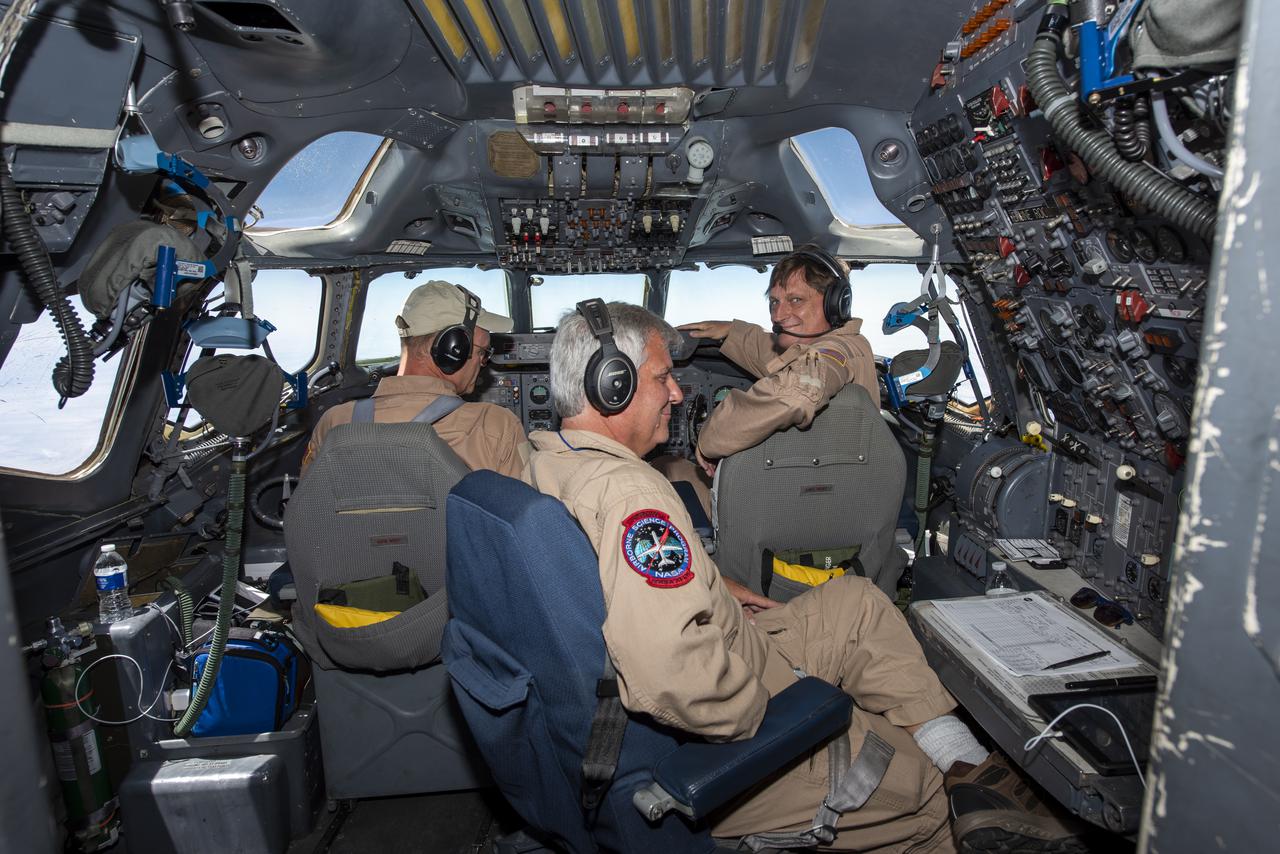

NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center flies the DC-8 airborne science laboratory in support of the Convective Processes Experiment - Aerosols and Winds campaign, CPEX-AW, on Aug 6, 2021. From left to right: Nils Larson, David Fedors and Mark Crane
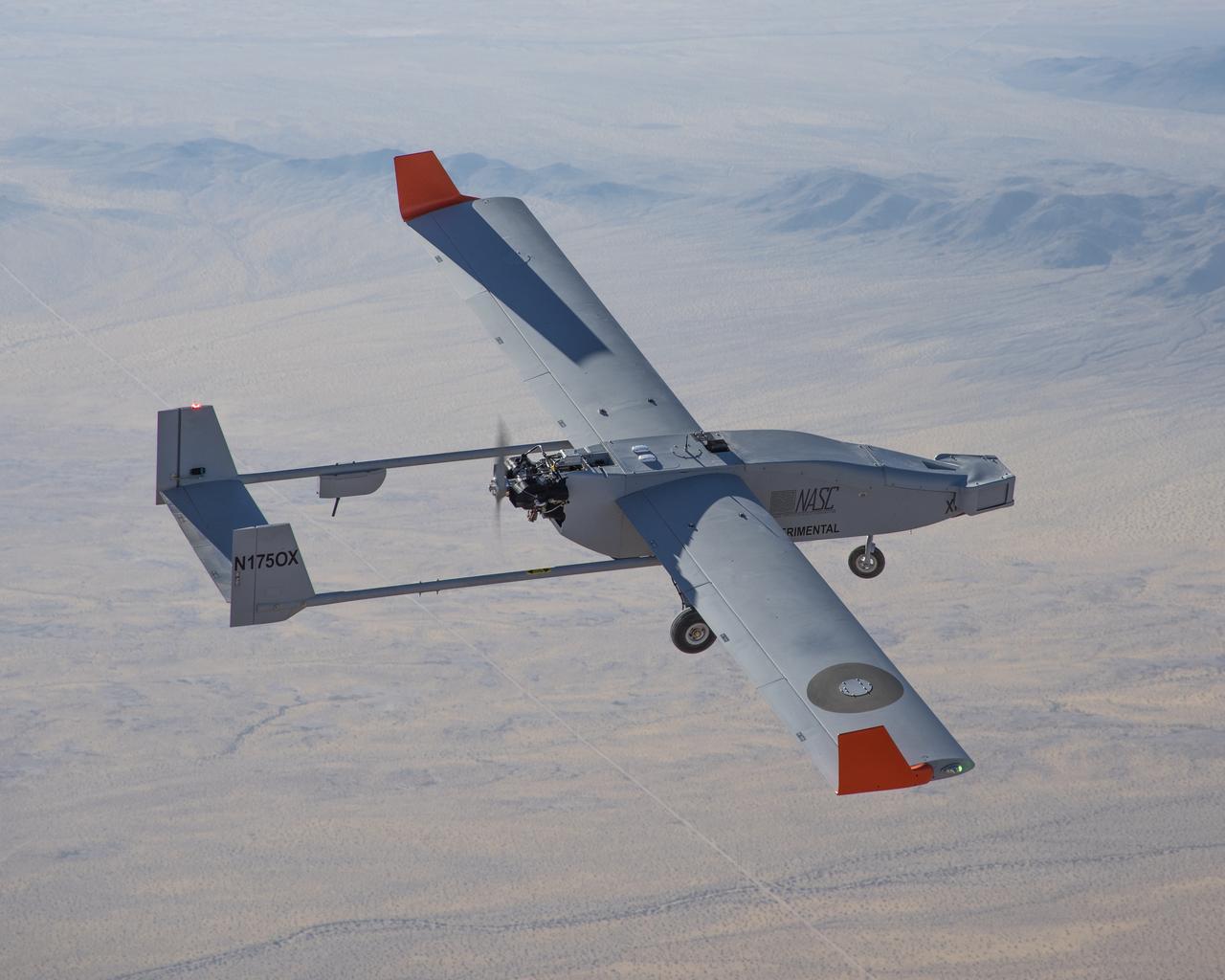

The NAVMAR Applied Sciences Corporation TigerShark, flew over Edwards Air Force Base on July 9, 2019 during a systems checkout flight for Flight Test Six.
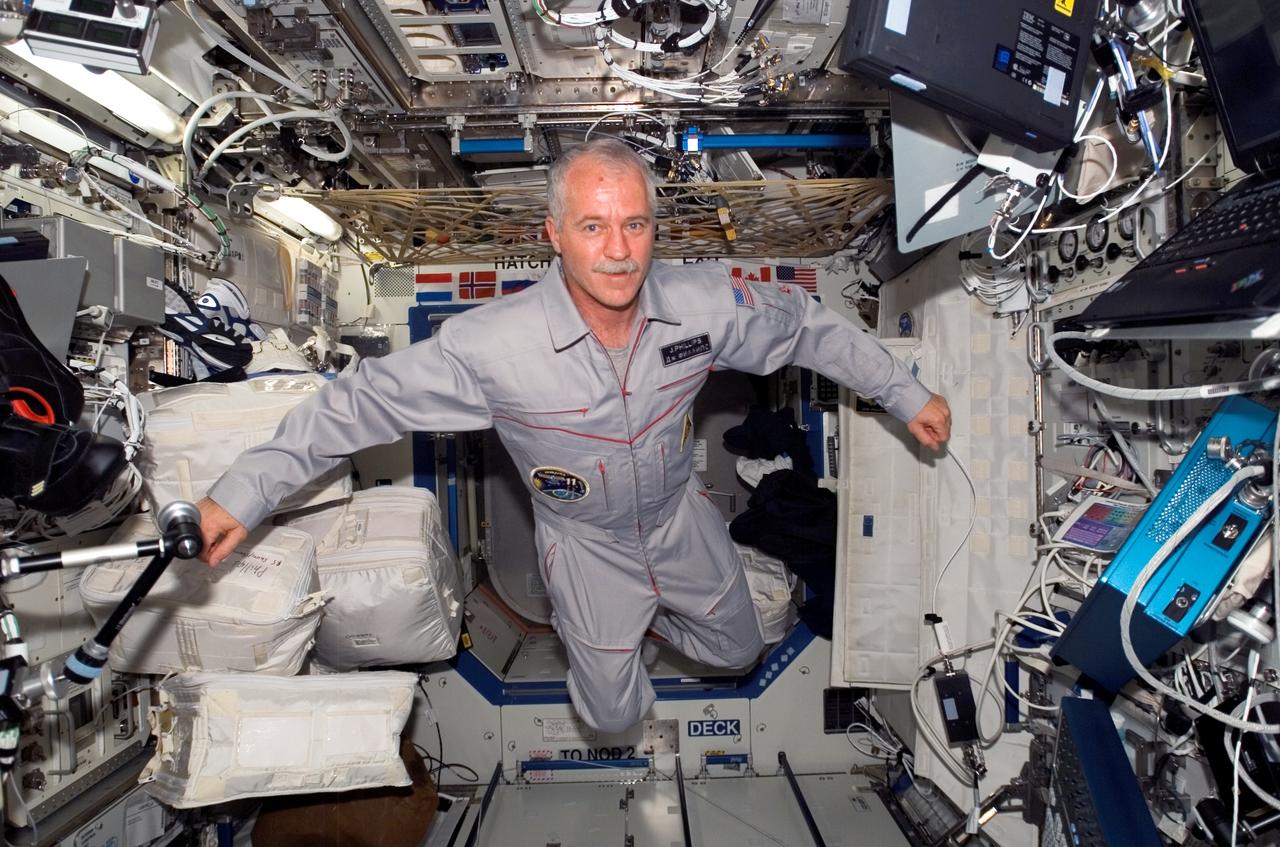

ISS011-E-05140 (17 April 2005) --- Astronaut John L. Phillips, Expedition 11 NASA science officer and flight engineer, floats in the Destiny laboratory of the international space station.
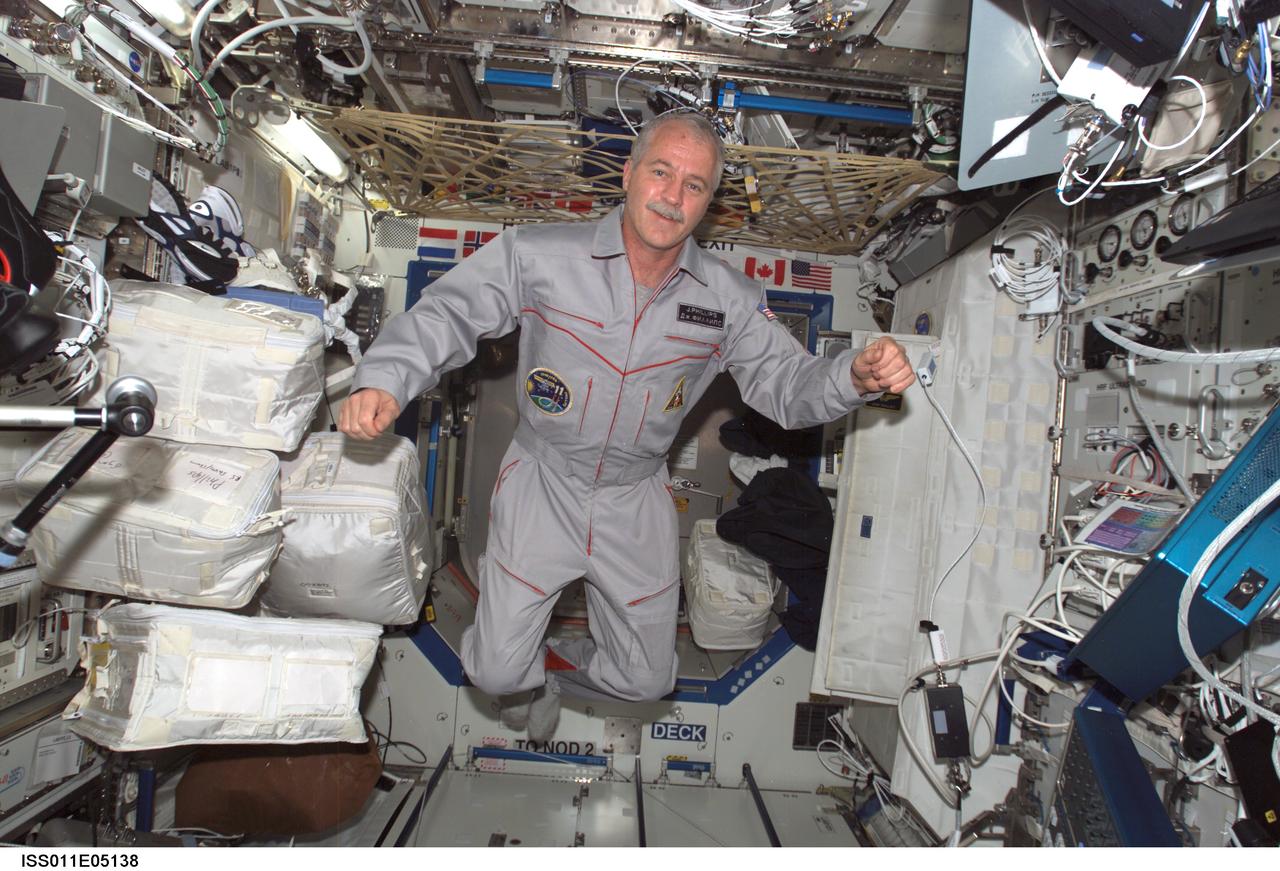

ISS011-E-05138 (17 April 2005) --- Astronaut John L. Phillips, Expedition 11 NASA ISS science officer and flight engineer, floats in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station (ISS).
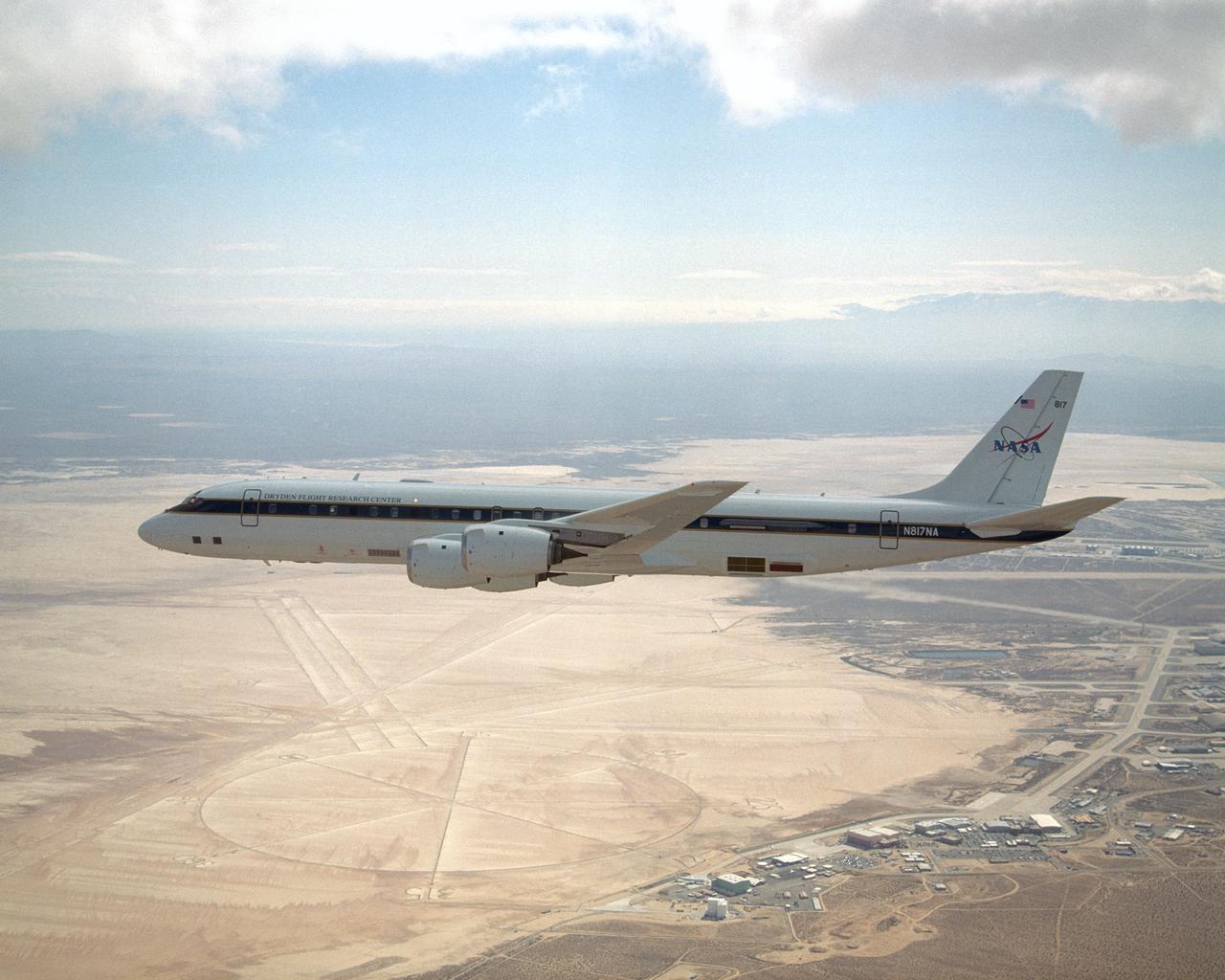

NASA's large Airborne Science research aircraft, a modified DC-8 airliner, displayed new colors in a check flight Feb. 24, 2004, over its home base, the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards AFB, California.
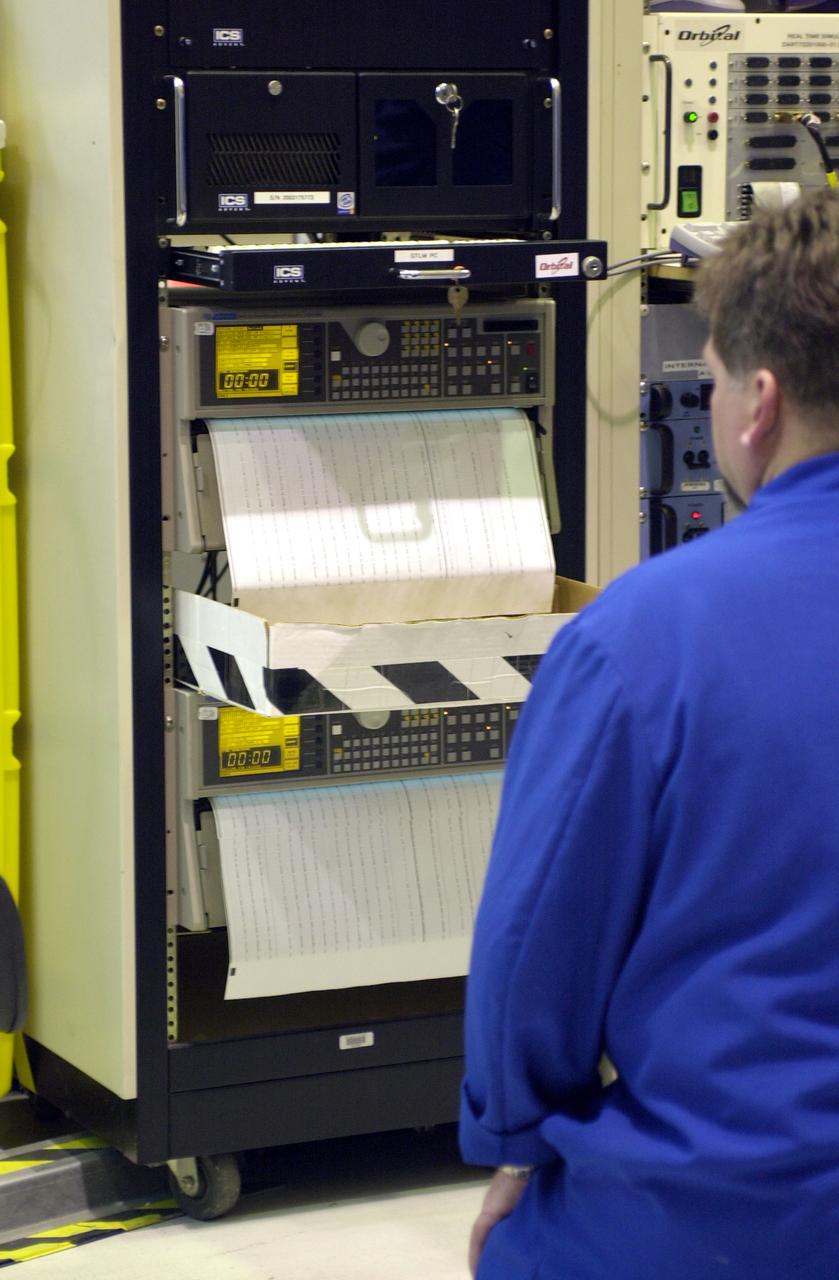

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a worker monitors the data produced by the second flight simulation of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket. The rocket is the launch vehicle for NASA's Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, or AIM, spacecraft. AIM is the seventh Small Explorers mission under NASA's Explorer Program. The program provides frequent flight opportunities for world-class scientific investigations from space within heliophysics and astrophysics. The AIM spacecraft will fly three instruments designed to study polar mesospheric clouds located at the edge of space, 50 miles above the Earth's surface in the coldest part of the planet's atmosphere. The mission's primary goal is to explain why these clouds form and what has caused them to become brighter and more numerous and appear at lower latitudes in recent years. AIM's results will provide the basis for the study of long-term variability in the mesospheric climate and its relationship to global climate change. AIM is scheduled to be mated to the Pegasus XL during the second week of April, after which final inspections will be conducted. Launch is scheduled for April 25.
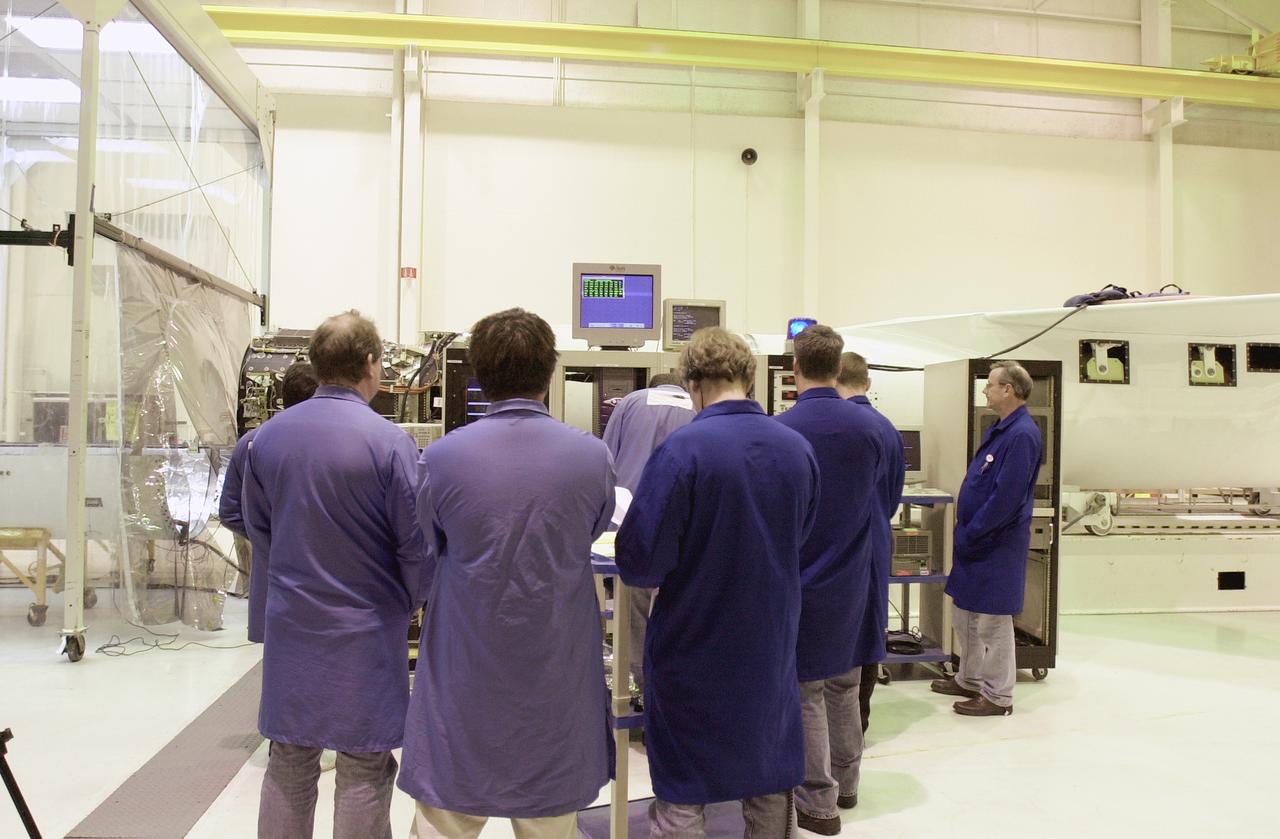

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers monitor the data produced by the second flight simulation of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket. The rocket is the launch vehicle for NASA's Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, or AIM, spacecraft. AIM is the seventh Small Explorers mission under NASA's Explorer Program. The program provides frequent flight opportunities for world-class scientific investigations from space within heliophysics and astrophysics. The AIM spacecraft will fly three instruments designed to study polar mesospheric clouds located at the edge of space, 50 miles above the Earth's surface in the coldest part of the planet's atmosphere. The mission's primary goal is to explain why these clouds form and what has caused them to become brighter and more numerous and appear at lower latitudes in recent years. AIM's results will provide the basis for the study of long-term variability in the mesospheric climate and its relationship to global climate change. AIM is scheduled to be mated to the Pegasus XL during the second week of April, after which final inspections will be conducted. Launch is scheduled for April 25.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket undergoes its second flight simulation. The rocket is the launch vehicle for NASA's Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, or AIM, spacecraft. AIM is the seventh Small Explorers mission under NASA's Explorer Program. The program provides frequent flight opportunities for world-class scientific investigations from space within heliophysics and astrophysics. The AIM spacecraft will fly three instruments designed to study polar mesospheric clouds located at the edge of space, 50 miles above the Earth's surface in the coldest part of the planet's atmosphere. The mission's primary goal is to explain why these clouds form and what has caused them to become brighter and more numerous and appear at lower latitudes in recent years. AIM's results will provide the basis for the study of long-term variability in the mesospheric climate and its relationship to global climate change. AIM is scheduled to be mated to the Pegasus XL during the second week of April, after which final inspections will be conducted. Launch is scheduled for April 25.
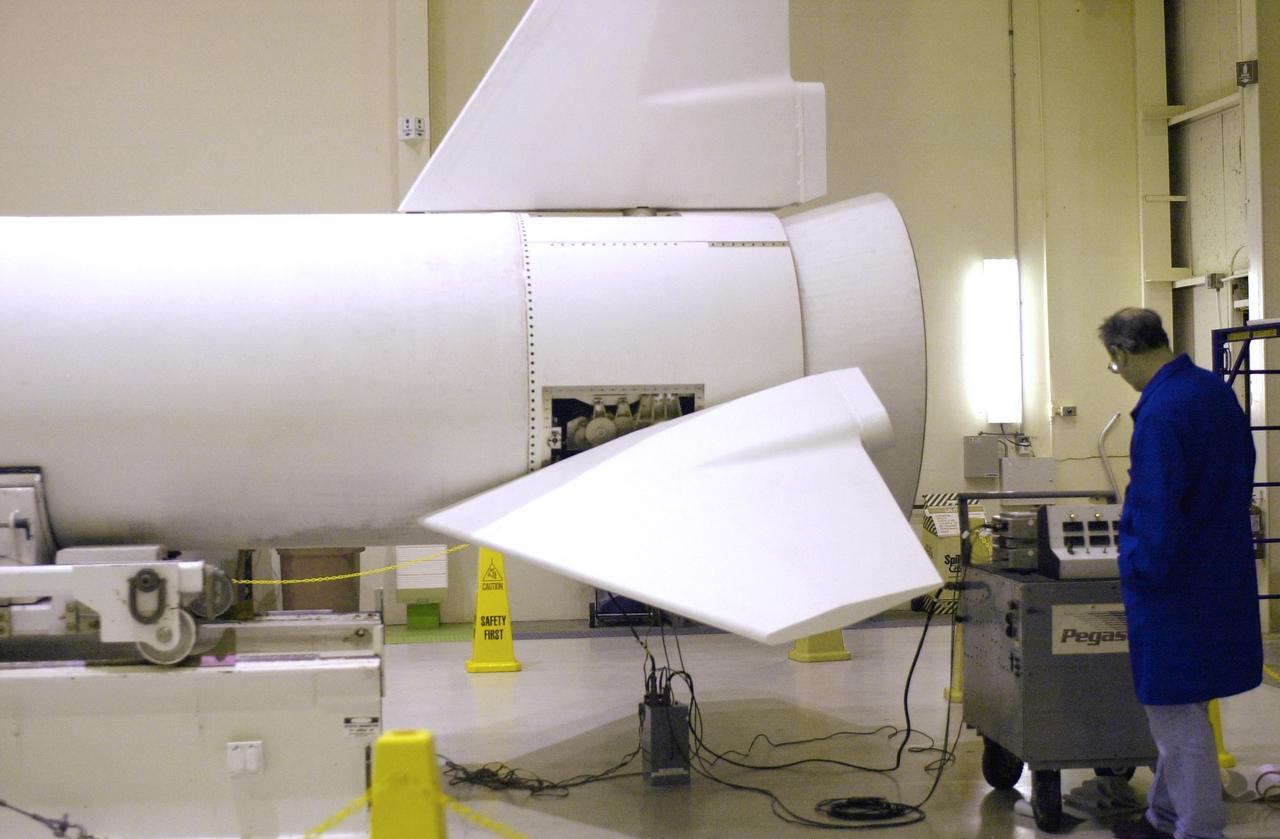
At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a worker monitors the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket after a second flight simulation. The rocket is the launch vehicle for NASA's Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, or AIM, spacecraft. AIM is the seventh Small Explorers mission under NASA's Explorer Program. The program provides frequent flight opportunities for world-class scientific investigations from space within heliophysics and astrophysics. The AIM spacecraft will fly three instruments designed to study polar mesospheric clouds located at the edge of space, 50 miles above the Earth's surface in the coldest part of the planet's atmosphere. The mission's primary goal is to explain why these clouds form and what has caused them to become brighter and more numerous and appear at lower latitudes in recent years. AIM's results will provide the basis for the study of long-term variability in the mesospheric climate and its relationship to global climate change. AIM is scheduled to be mated to the Pegasus XL during the second week of April, after which final inspections will be conducted. Launch is scheduled for April 25.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers monitor the data produced by the second flight simulation of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket. The rocket is the launch vehicle for NASA's Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, or AIM, spacecraft. AIM is the seventh Small Explorers mission under NASA's Explorer Program. The program provides frequent flight opportunities for world-class scientific investigations from space within heliophysics and astrophysics. The AIM spacecraft will fly three instruments designed to study polar mesospheric clouds located at the edge of space, 50 miles above the Earth's surface in the coldest part of the planet's atmosphere. The mission's primary goal is to explain why these clouds form and what has caused them to become brighter and more numerous and appear at lower latitudes in recent years. AIM's results will provide the basis for the study of long-term variability in the mesospheric climate and its relationship to global climate change. AIM is scheduled to be mated to the Pegasus XL during the second week of April, after which final inspections will be conducted. Launch is scheduled for April 25.
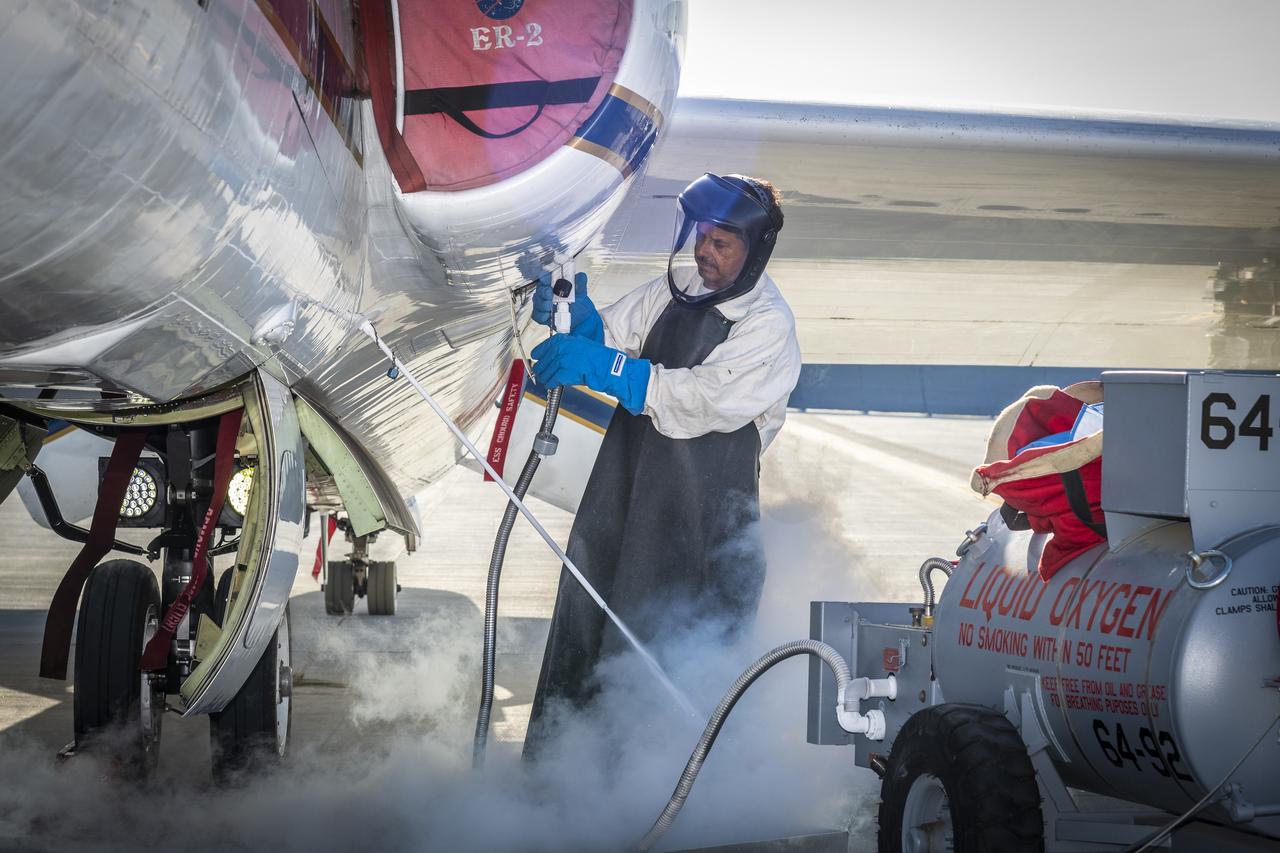

Francisco Rodriguez (aircraft mechanic) services liquid oxygen or LOX on the ER-2 during the Geological Earth Mapping Experiment (GEMx) research project. Experts like Rodriguez sustain a high standard of safety on airborne science aircraft like the ER-2 and science missions like GEMx. The ER-2 is based out of NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
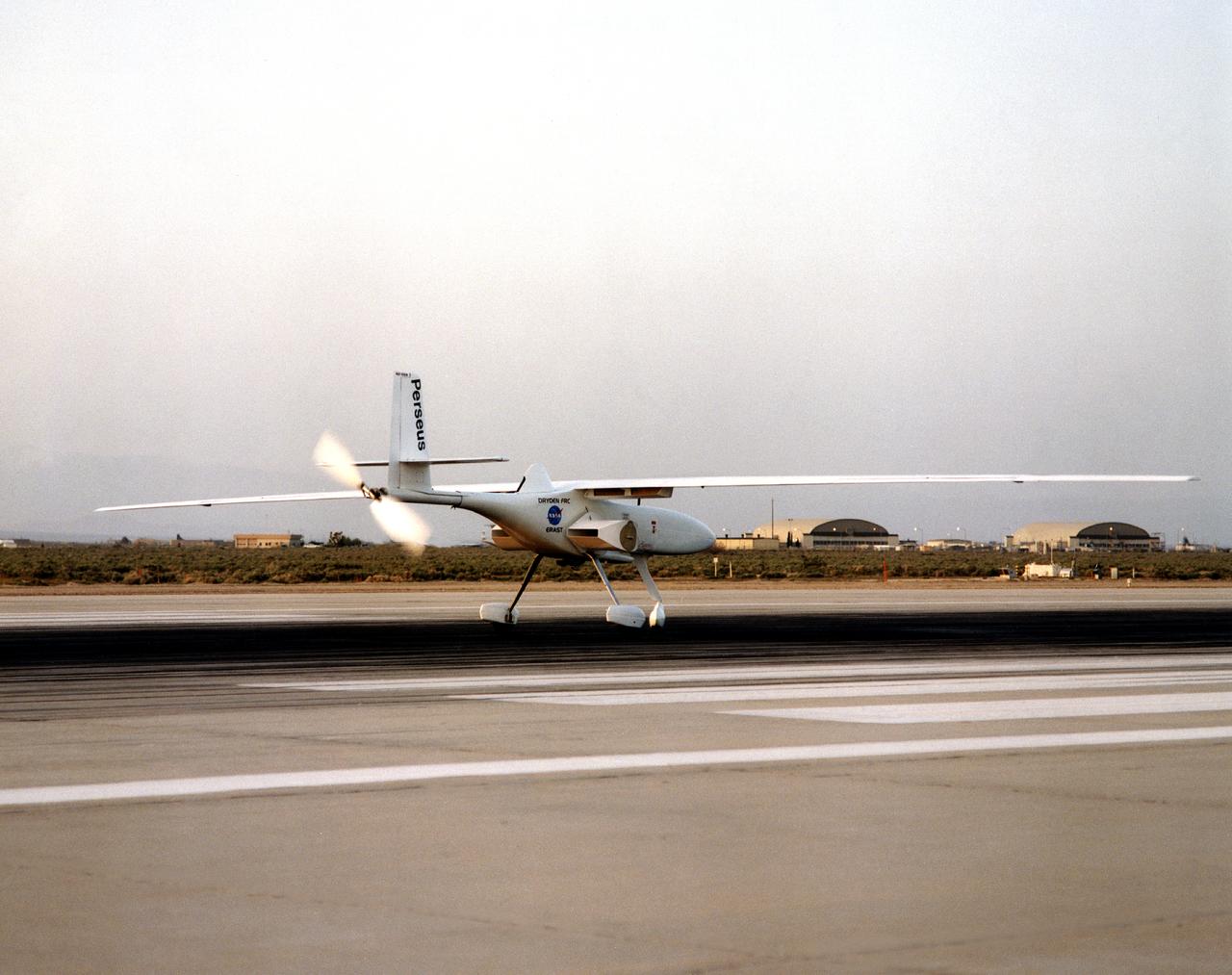

The Perseus B remotely piloted aircraft on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base, California at the conclusion of a development flight at NASA's Dryden flight Research Center. The Perseus B is the latest of three versions of the Perseus design developed by Aurora Flight Sciences under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program.
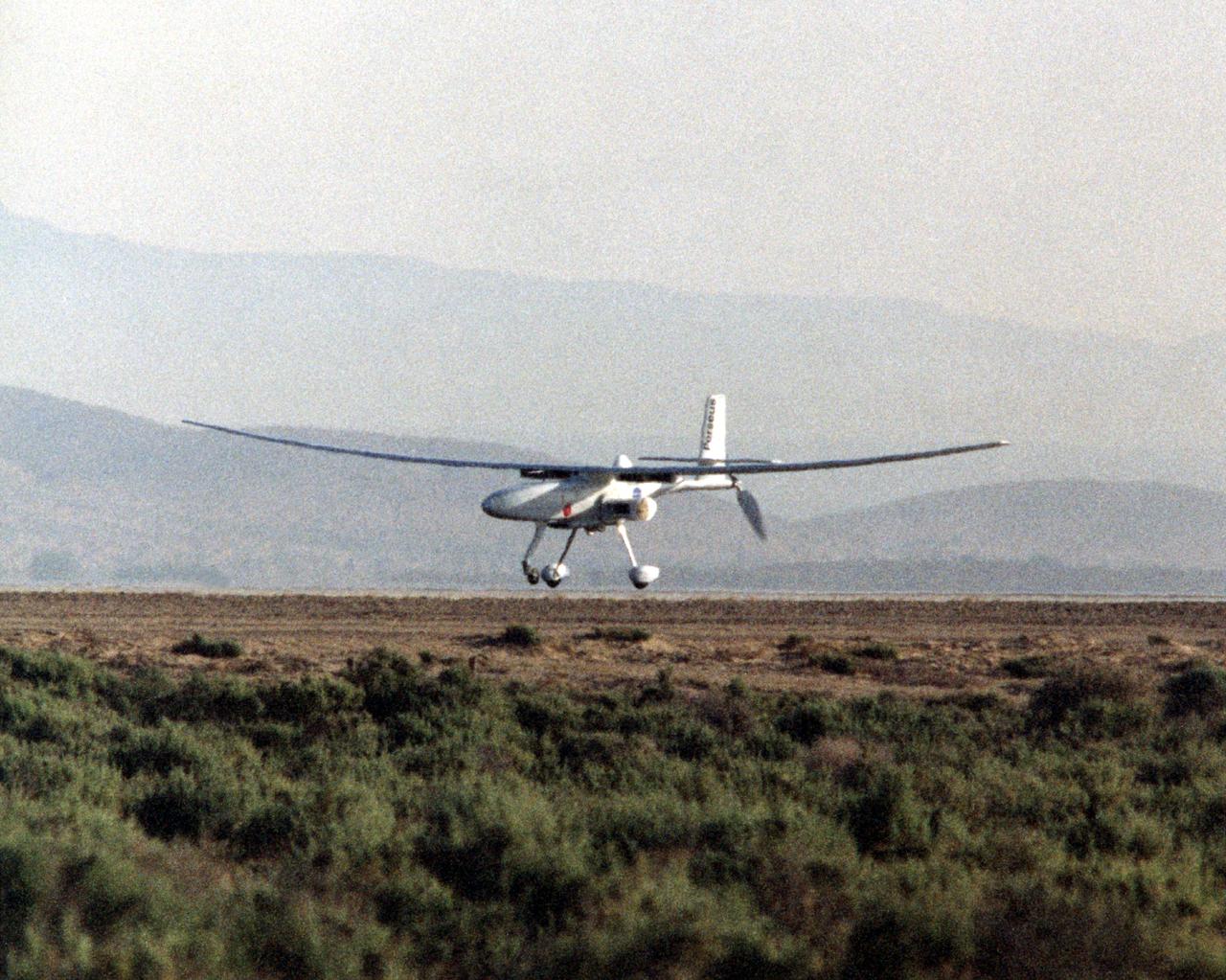

The Perseus B remotely piloted aircraft nears touchdown at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. at the conclusion of a development flight at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The Perseus B is the latest of three versions of the Perseus design developed by Aurora Flight Sciences under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program.
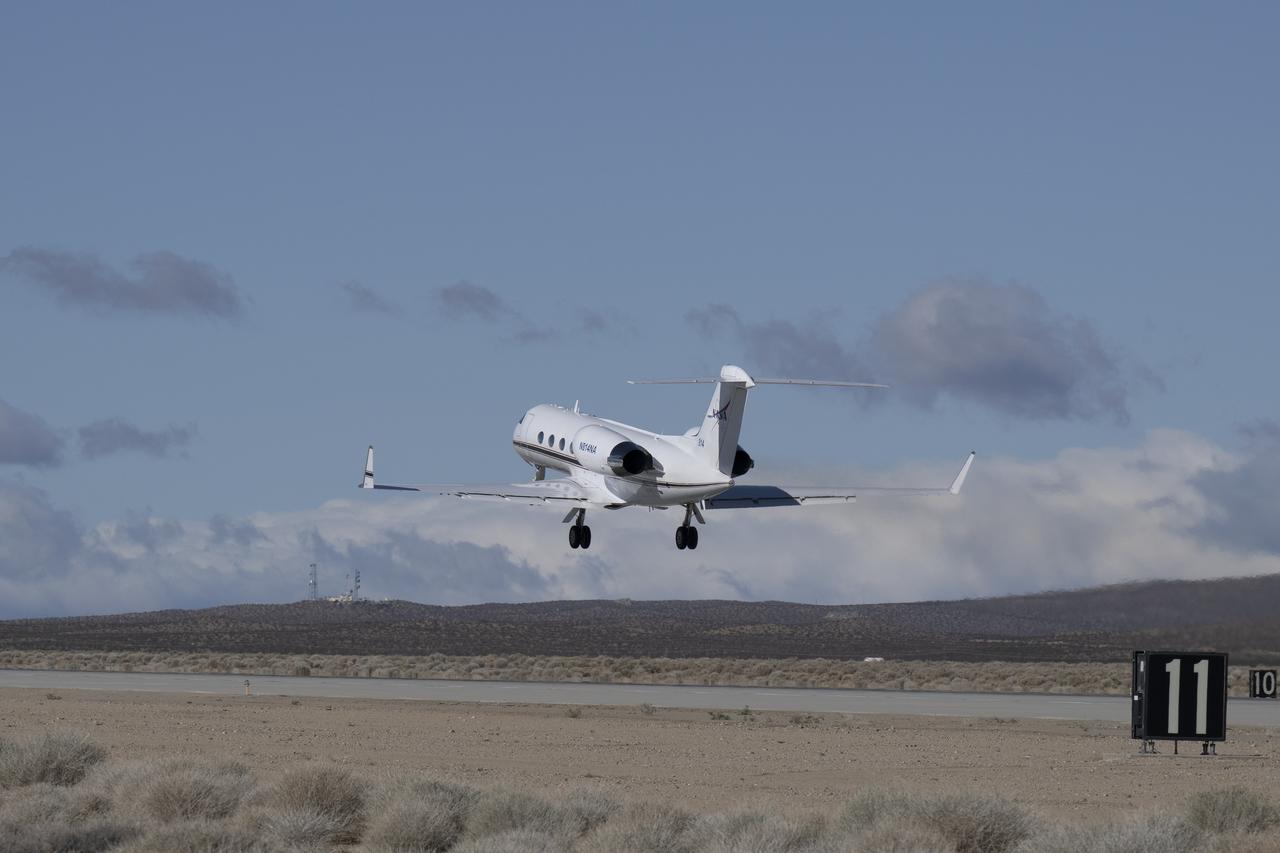

The G-IV aircraft lifts off from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, on March 18, 2025. As the newest member of NASA Armstrong’s airborne science fleet, the G-IV was sent to Avenger Aerospace Solutions in Cartersville, Georgia, for modifications that will optimize the G-IV’s performance as a research aircraft.
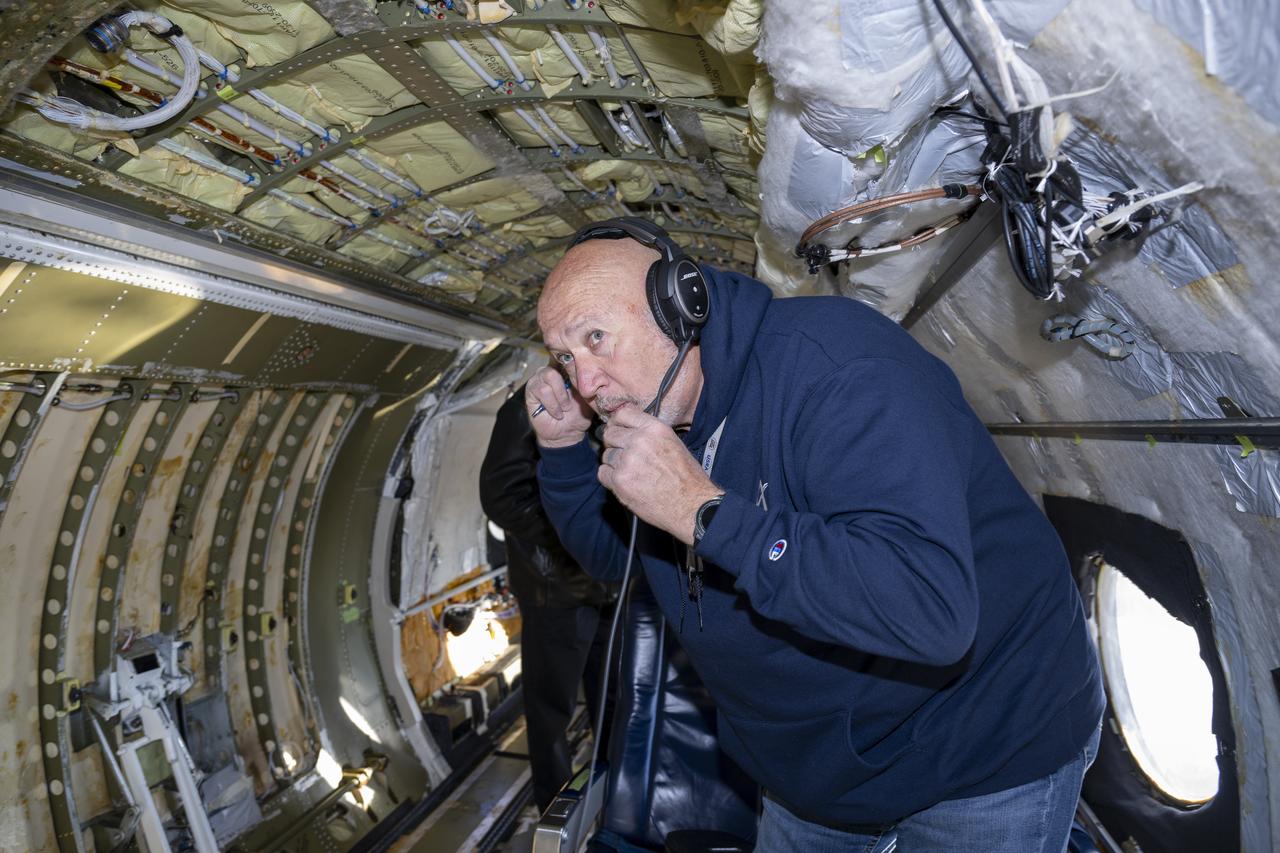

Martin Hench, flight systems engineer, checks the communications system onboard the G-IV aircraft as it prepares to depart NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, on March 18, 2025. As the newest member of NASA Armstrong’s airborne science fleet, the G-IV was sent to Avenger Aerospace Solutions in Cartersville, Georgia, for modifications that will optimize the G-IV’s performance as a research aircraft.
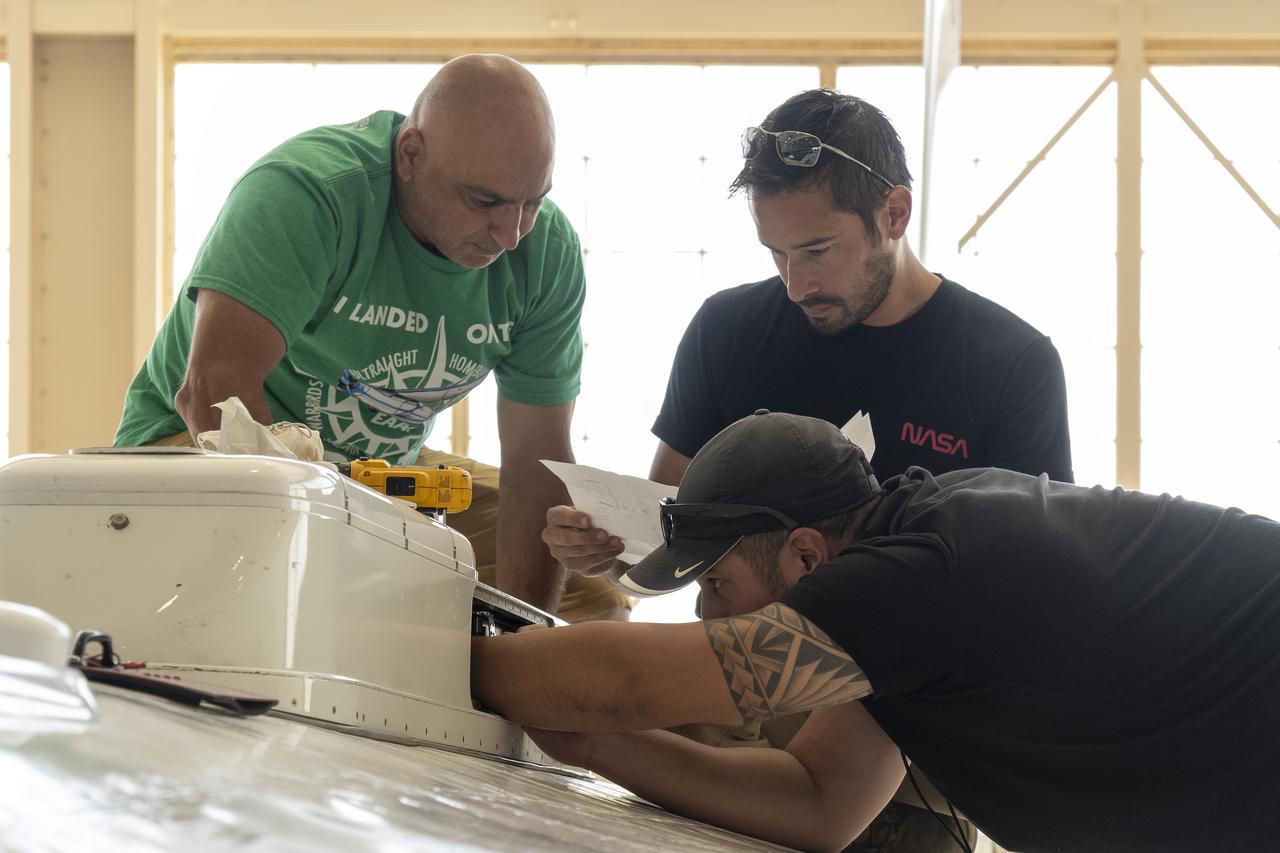

Sam Habbal (quality inspector), Darick Alvarez (aircraft mechanic), and Juan Alvarez (crew chief) work on the network “canoe” on top of the ER-2 aircraft, which provides network communication with the pilot onboard. Experts like these sustain a high standard of safety while outfitting instruments onboard science aircraft like the ER-2 and science missions like the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem Postlaunch Airborne eXperiment (PACE-PAX) mission. The ER-2 is based out of NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
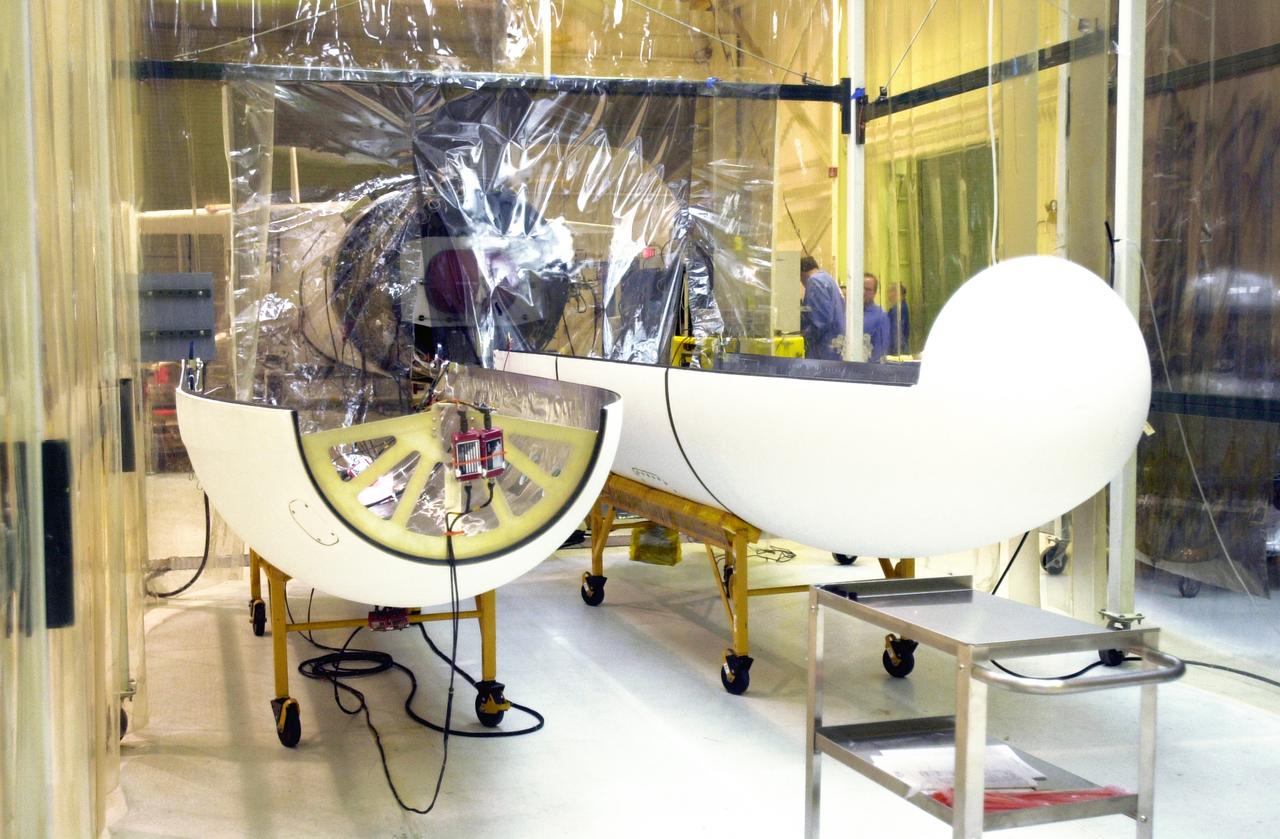
Seen at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California is the fairing (foreground) for the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket. In the background is the third stage, under the clean room tent. The rocket is the launch vehicle for NASA's Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, or AIM, spacecraft. AIM is the seventh Small Explorers mission under NASA's Explorer Program. The program provides frequent flight opportunities for world-class scientific investigations from space within heliophysics and astrophysics. The AIM spacecraft will fly three instruments designed to study polar mesospheric clouds located at the edge of space, 50 miles above the Earth's surface in the coldest part of the planet's atmosphere. The mission's primary goal is to explain why these clouds form and what has caused them to become brighter and more numerous and appear at lower latitudes in recent years. AIM's results will provide the basis for the study of long-term variability in the mesospheric climate and its relationship to global climate change. AIM is scheduled to be mated to the Pegasus XL during the second week of April, after which final inspections will be conducted. Launch is scheduled for April 25.
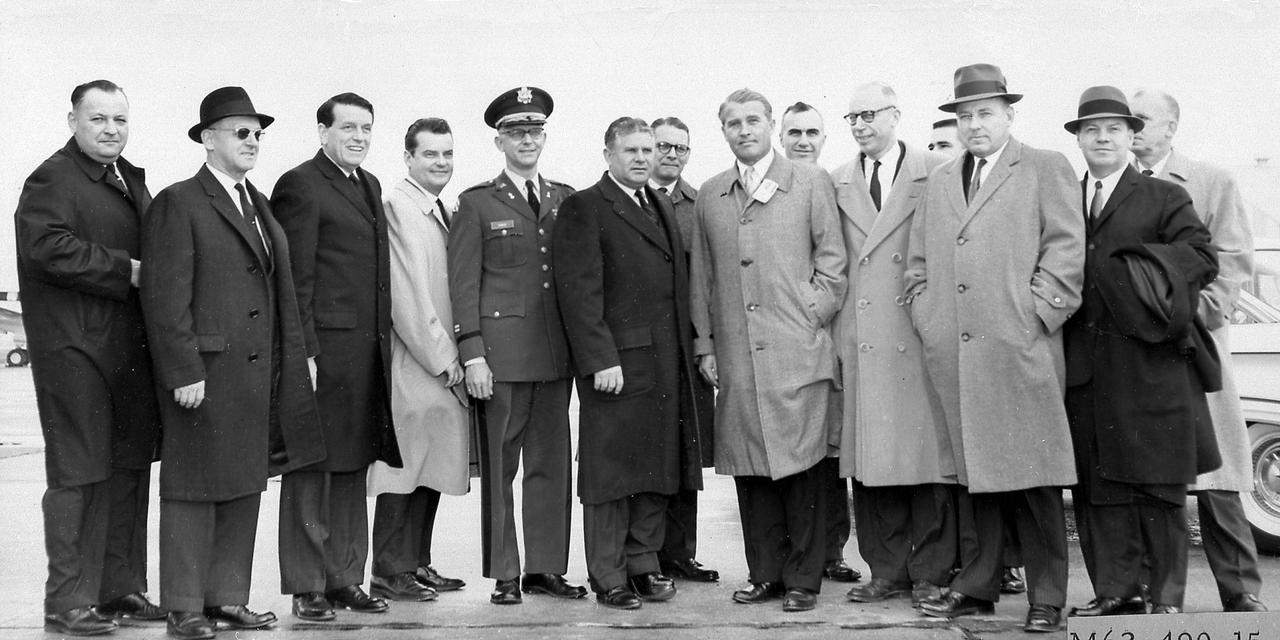

The members of the House Committee on Science and Astronautics visited the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) on March 9, 1962 to gather first-hand information of the nation's space exploration program. The congressional group was composed of members of the Subcommittee on Marned Space Flight. Headed by Representative Olin E. Teague of Texas, other members were James G. Fulton, Pennsylvania; Ken Heckler, West Virginia; R. Walter Riehlman, New York; Richard L. Roudebush,, Indiana; John W. Davis, Georgia; James C. Corman, California; Joseph Waggoner, Louisiana; J. Edgar Chenoweth, Colorado; and William G. Bray, Indiana.

The members of the House Committee on Science and Astronautics visited the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) on March 9, 1962 to gather first-hand information of the nation's space exploration program. The congressional group was composed of members of the Subcommittee on Marned Space Flight. Headed by Representative Olin E. Teague of Texas, other members were James G. Fulton, Pennsylvania; Ken Heckler, West Virginia; R. Walter Riehlman, New York; Richard L. Roudebush, Indiana; John W. Davis, Georgia; James C. Corman, California; Joseph Waggoner, Louisiana; J. Edgar Chenoweth, Colorado; and William G. Bray, Indiana.
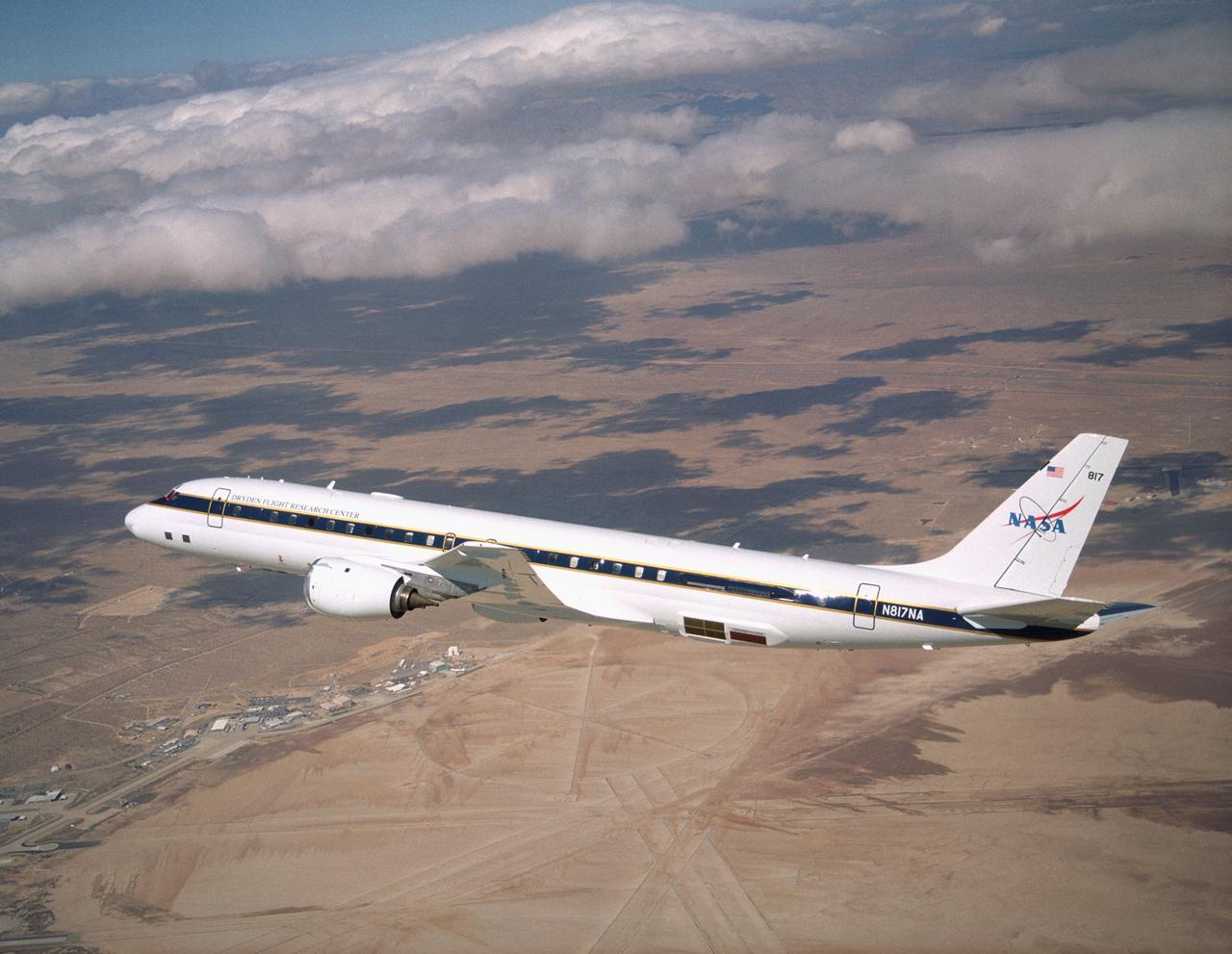

NASA's large Airborne Science research aircraft, a modified DC-8 airliner, displayed new colors in a check flight Feb. 24, 2004, over its home base, the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards AFB, California.
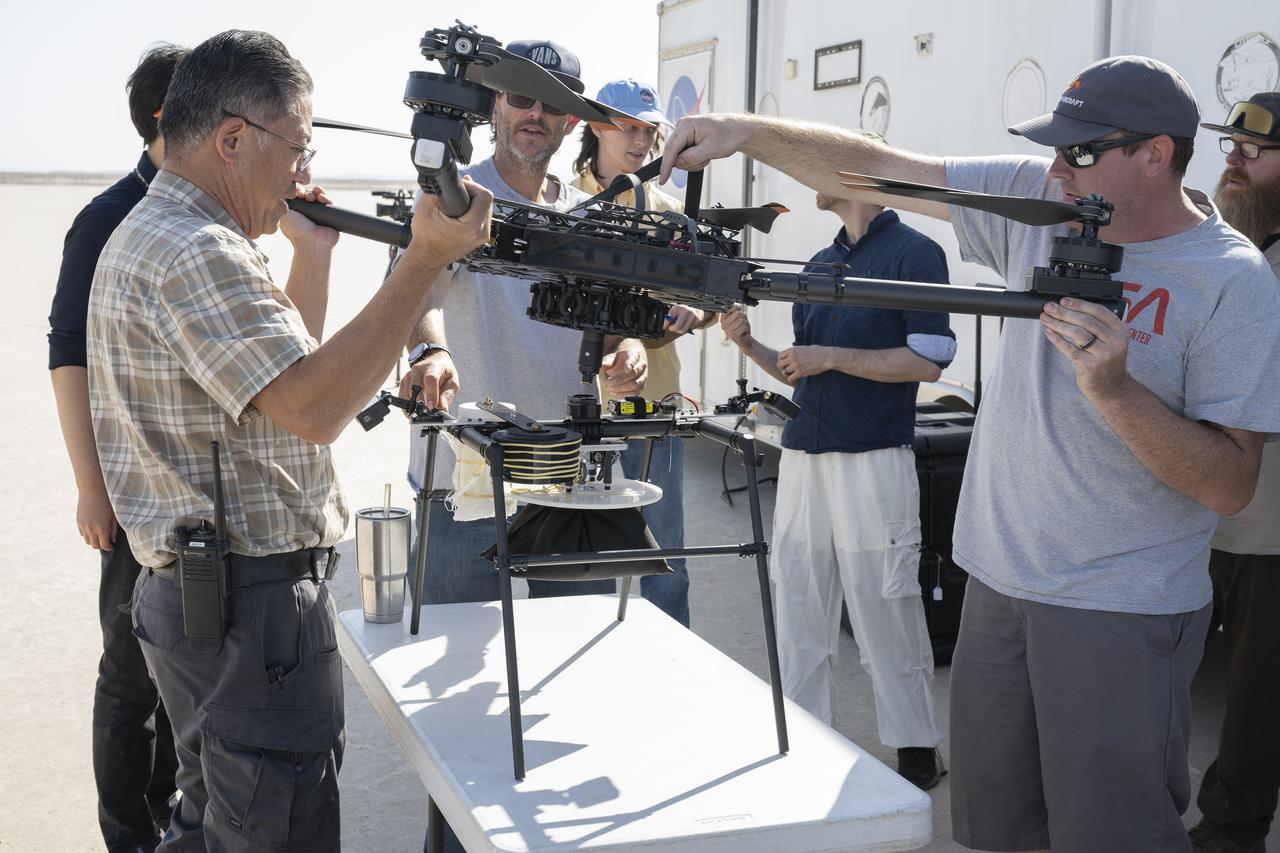

Derek Abramson, left, and Justin Link, right, attach an Alta X drone to the Enhancing Parachutes by Instrumenting the Canopy test experiment on June 4, 2025, at NASA’s Armstong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. Abramson is NASA chief engineer at the center’s Dale Reed Subscale Flight Research Laboratory, where Link also works as a pilot for small uncrewed aircraft systems. NASA researchers are developing technology to make supersonic parachutes safer and more reliable for delivering science instruments and payloads to Mars.
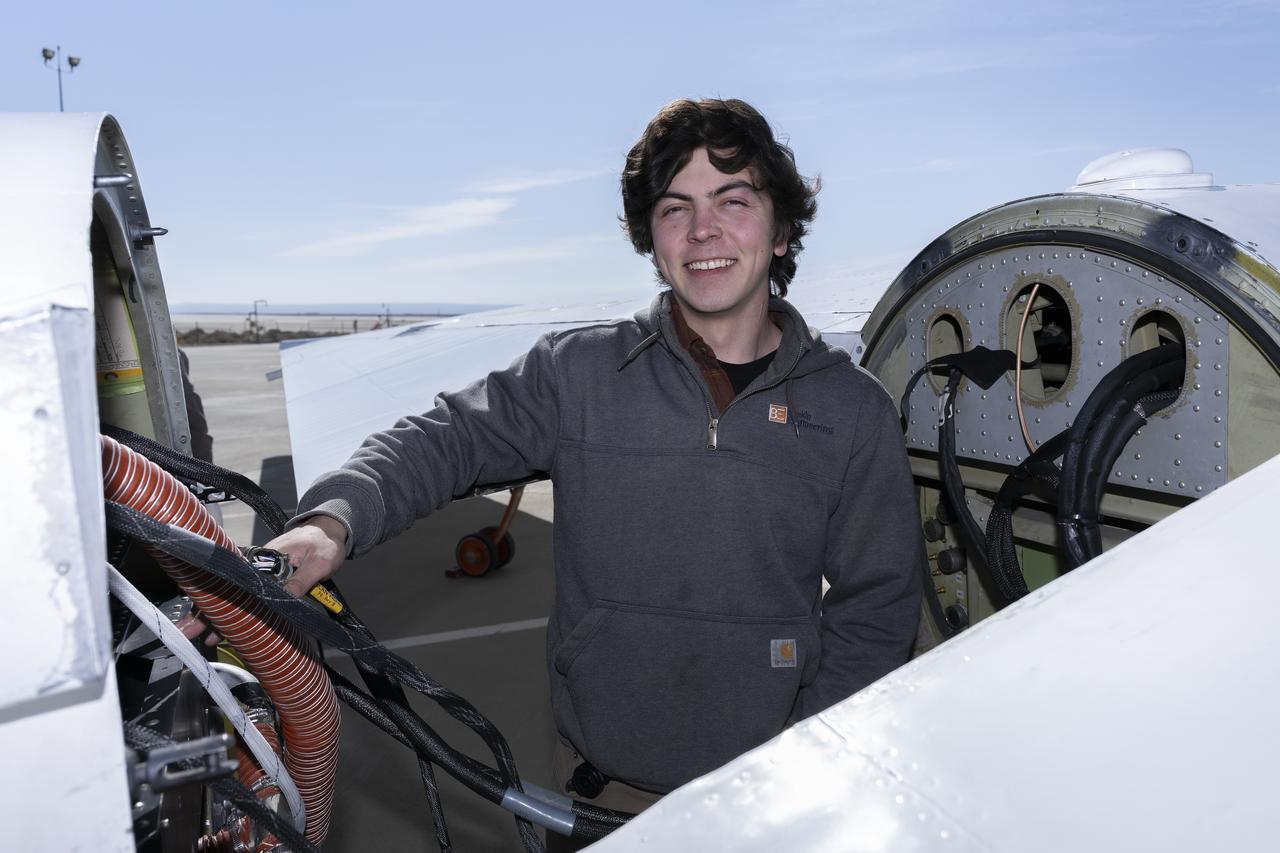

A team of experts wrap up science flights on the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California after the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Nikolas Gibson from NASA Ames Research Center integrates the enhanced MODIS Airbrone Simulator (eMAS) instrument onto the ER-2. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.

An ER-2 high-altitude Earth science aircraft banks away during a flight over the southern Sierra Nevada. NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center operates two of the Lockheed-built aircraft on a wide variety of environmental science, atmospheric sampling, and satellite data verification missions.
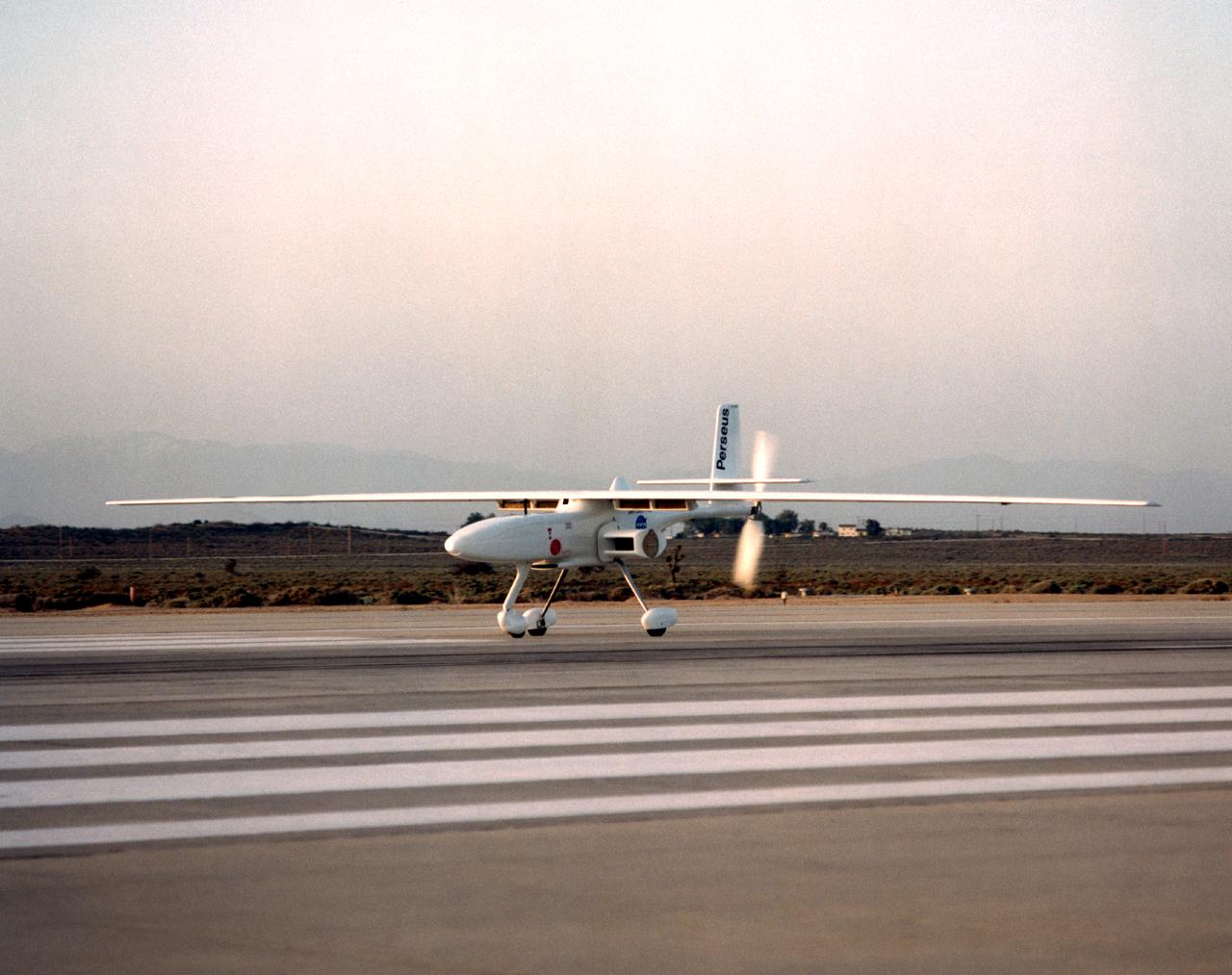

The Perseus B remotely piloted aircraft taxis on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base, California, before a series of development flights at NASA's Dryden flight Research Center. The Perseus B is the latest of three versions of the Perseus design developed by Aurora Flight Sciences under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program.
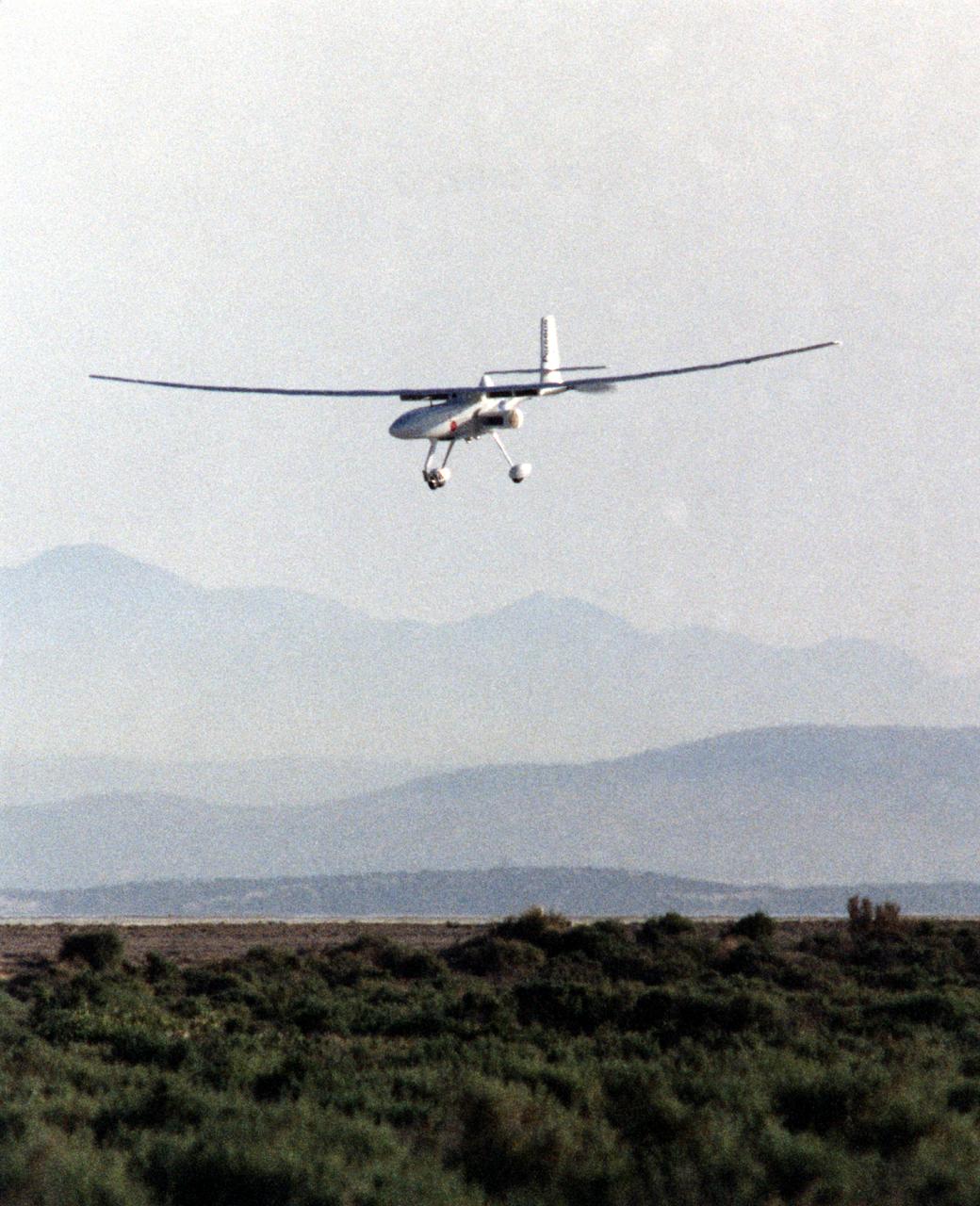

The Perseus B remotely piloted aircraft approaches the runway at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. at the conclusion of a development flight at NASA's Dryden flight Research Center in April 1998. The Perseus B is the latest of three versions of the Perseus design developed by Aurora Flight Sciences under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program.
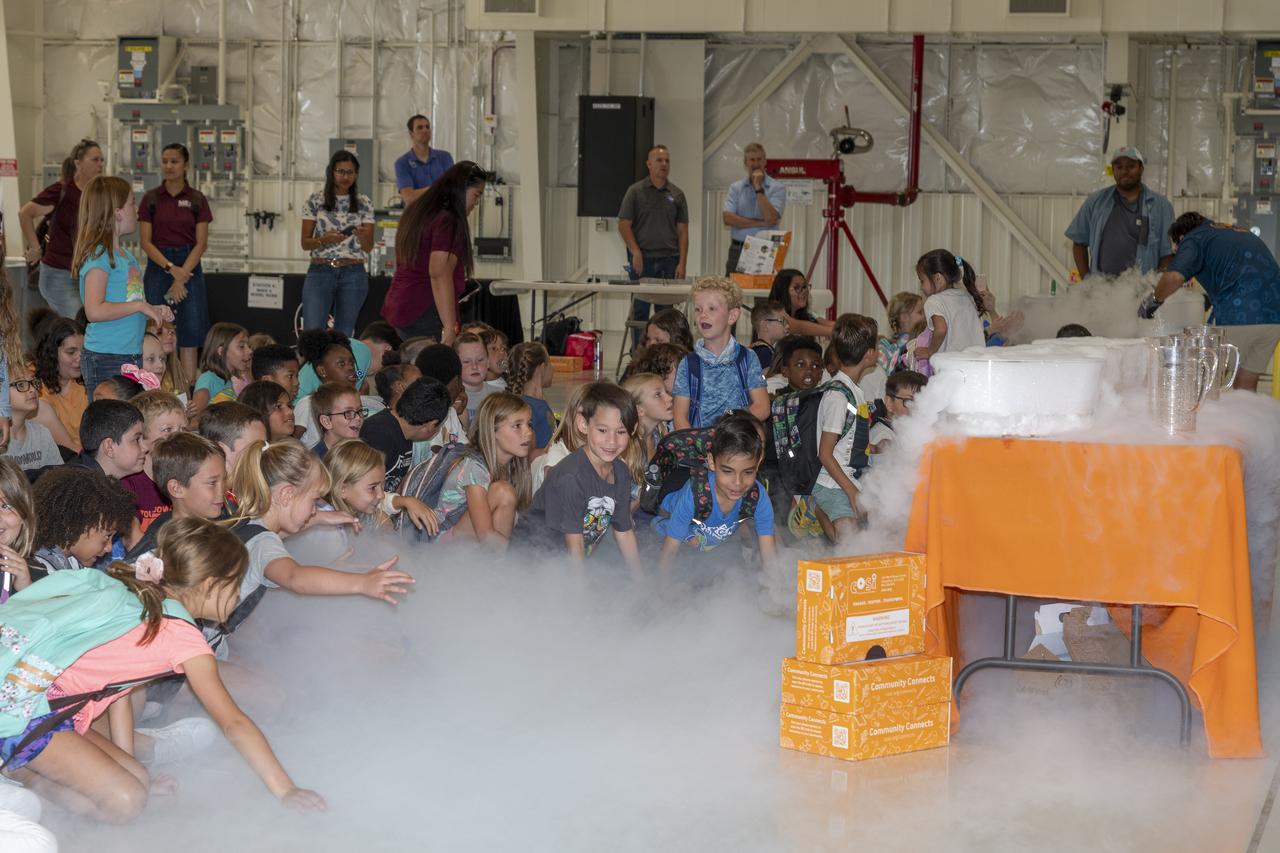

Students are wrapped in a cloud from a demonstration by NASA’s California Office of STEM Engagement event with Center of Science and Industry at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
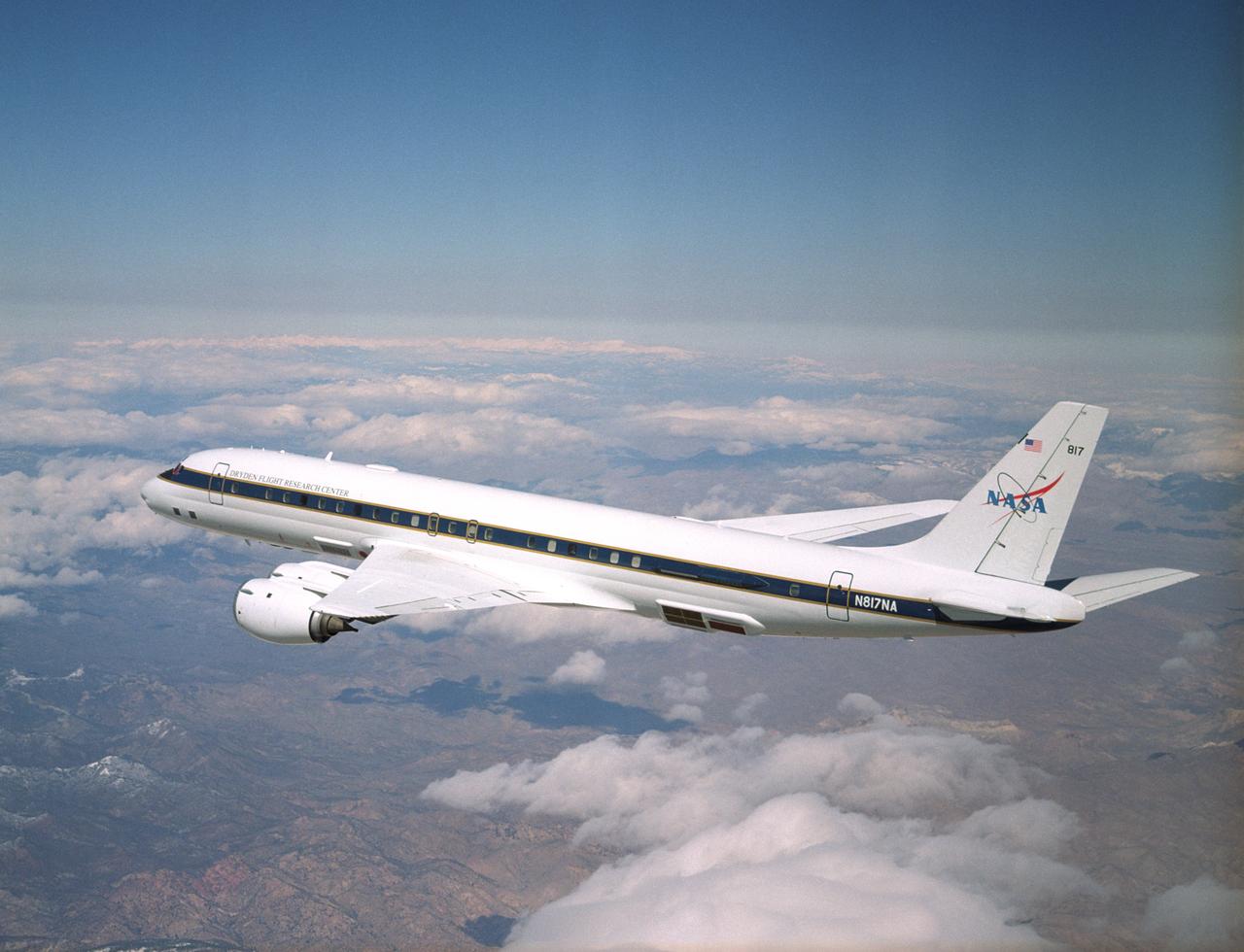

NASA's DC-8 Airborne Science research aircraft, in new colors and markings, in flight Feb. 24, 2004. Dark panels on lower fuselage are synthetic aperture radar antennas enabling sophisticated studies of Earth features.
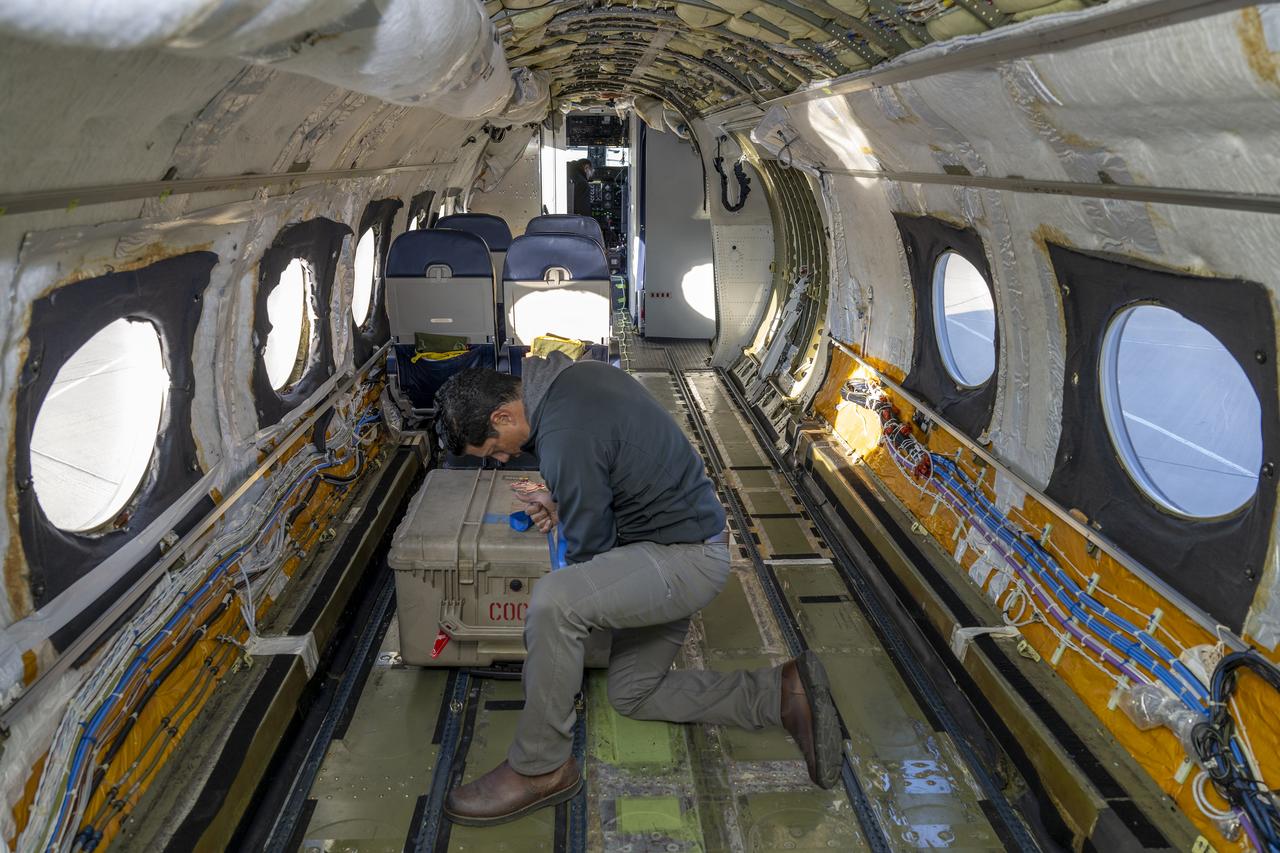

Jose “Manny” Rodriguez, technical engineer at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, secures a trunk onboard the G-IV aircraft on March 18, 2025. As the newest member of NASA Armstrong’s airborne science fleet, the G-IV was sent to Avenger Aerospace Solutions in Cartersville, Georgia, for modifications that will optimize the G-IV’s performance as a research aircraft.
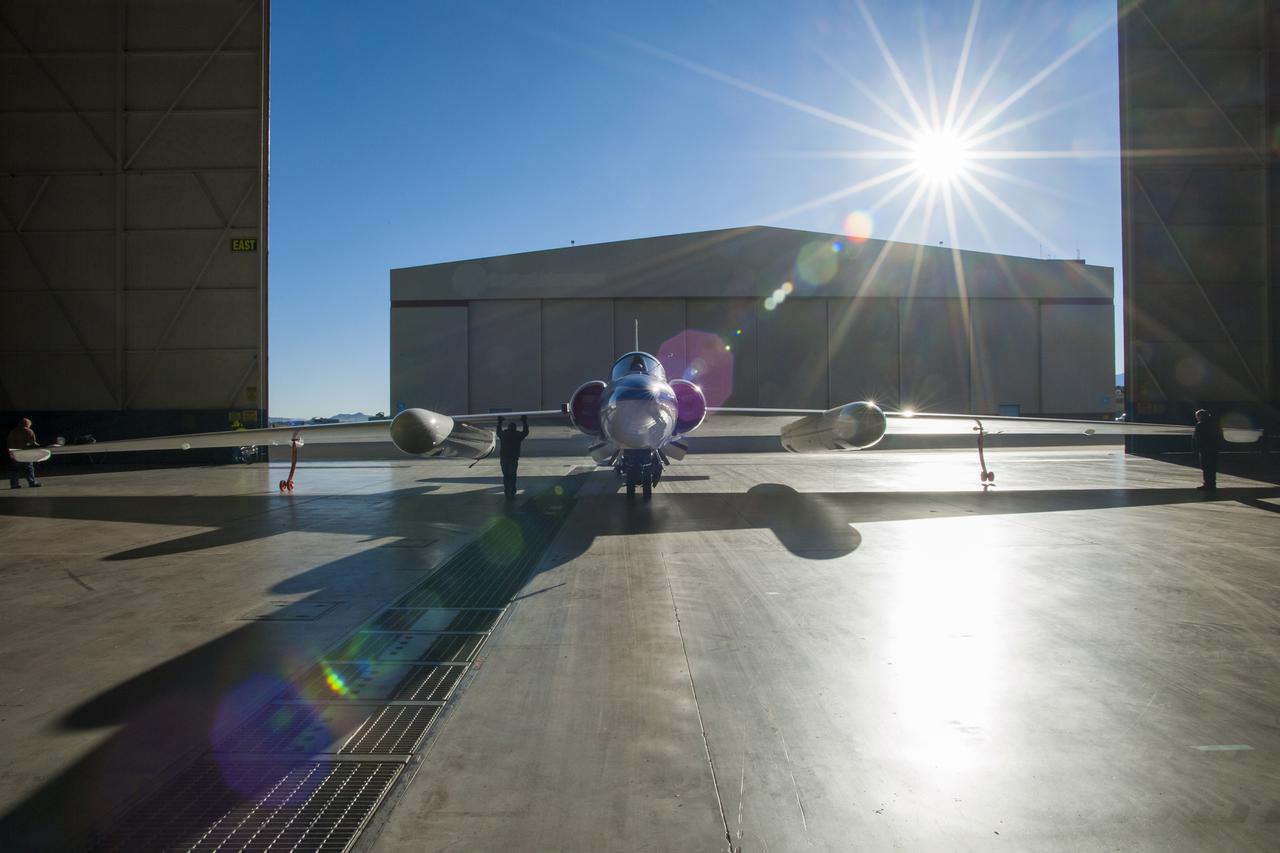

One of two NASA ER-2s (civilian U2-Rs) being backed out of the hangar at Building 703 in Palmdale. Capable of long duration flights at very high altitudes, the ER-2s have wing pods to accommodate science experiments and sensors, as well as a large volume bay behind the pilot. NASA first flew a U-2 for science—a first generation aircraft—in 1972.
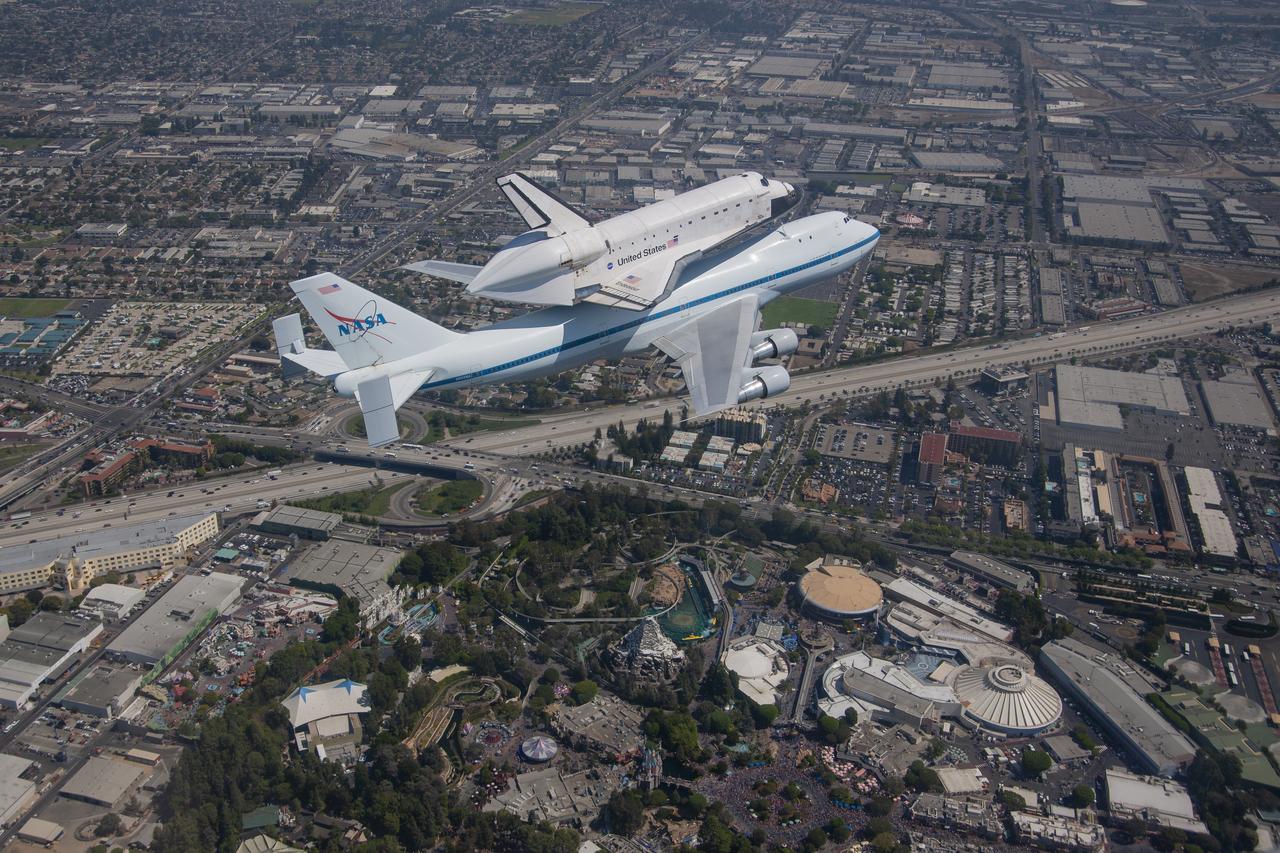

Space shuttle Endeavour and its host NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft fly over Disneyland in 2012 on its way to the Los Angeles International Airport, and an overland journey to the California Science Center. Californians gazed at the morning sky Sept. 21 looking to see Endeavour over their community. The final leg of Endeavour’s flight from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, Florida, offered many people an opportunity to witness the historic flight.
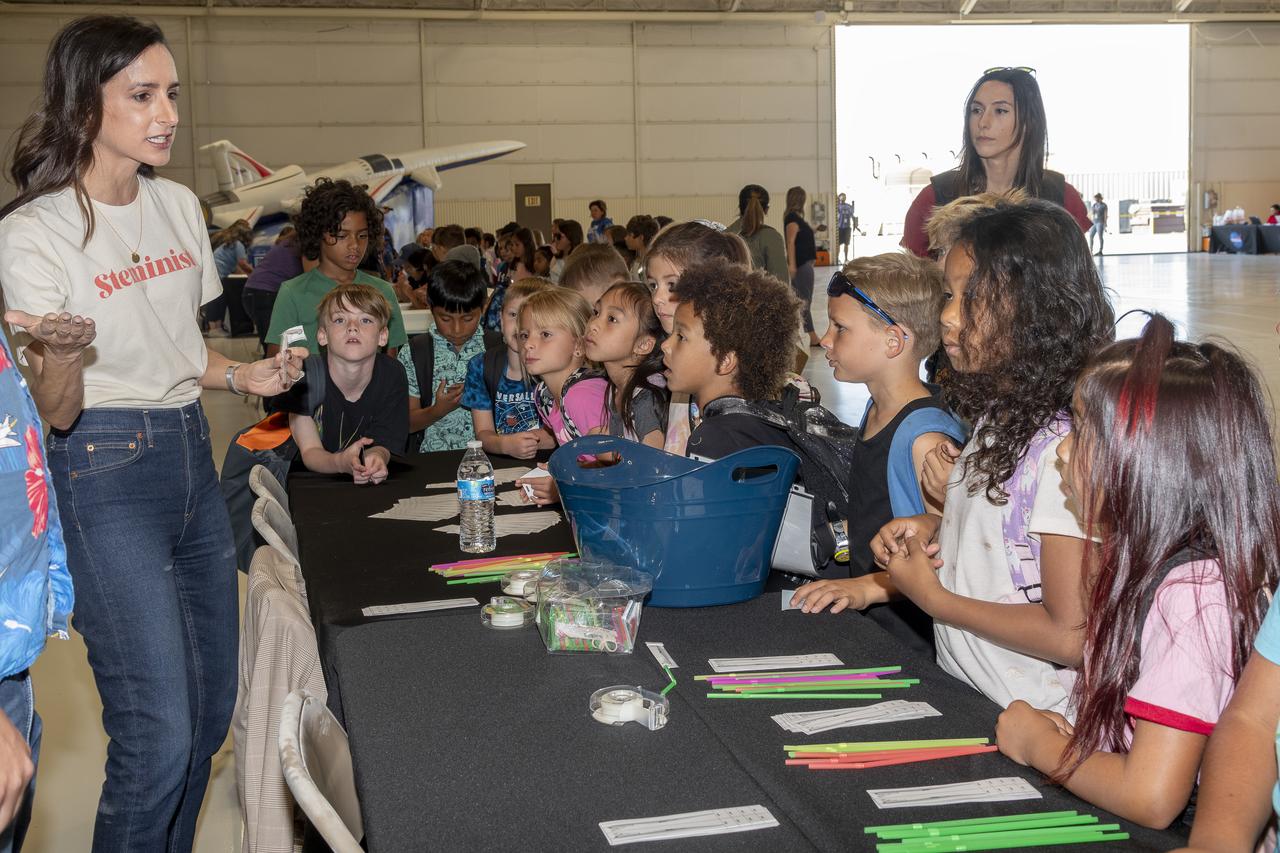

Kate M. McMurtry, deputy director of Integrated Aviation Systems Program shares with students how NASA is working to quiet the sonic boom with the development of the X-59 aircraft at NASA’s California Office of STEM Engagement event with Center of Science and Industry at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.

NASA astronaut Jonny Kim is seen in the audience as MSIT Minister Jong-Ho Lee delivers remarks prior to the singing of a joint statement between NASA and the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea, Tuesday, April 25, 2023, at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
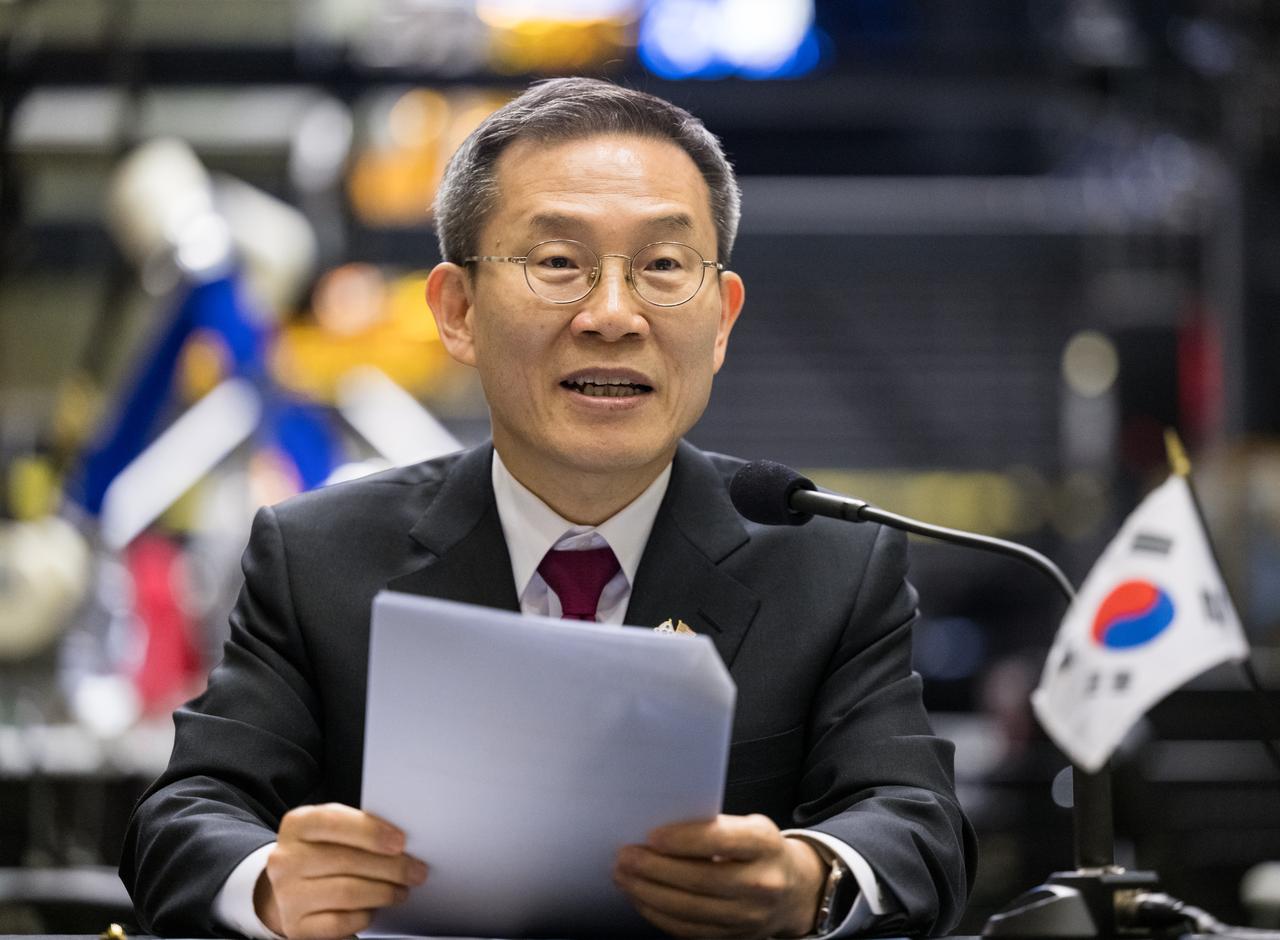

MSIT Minister Jong-Ho Lee delivers remarks prior to the signing of a joint statement between NASA and the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea, Tuesday, April 25, 2023, at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
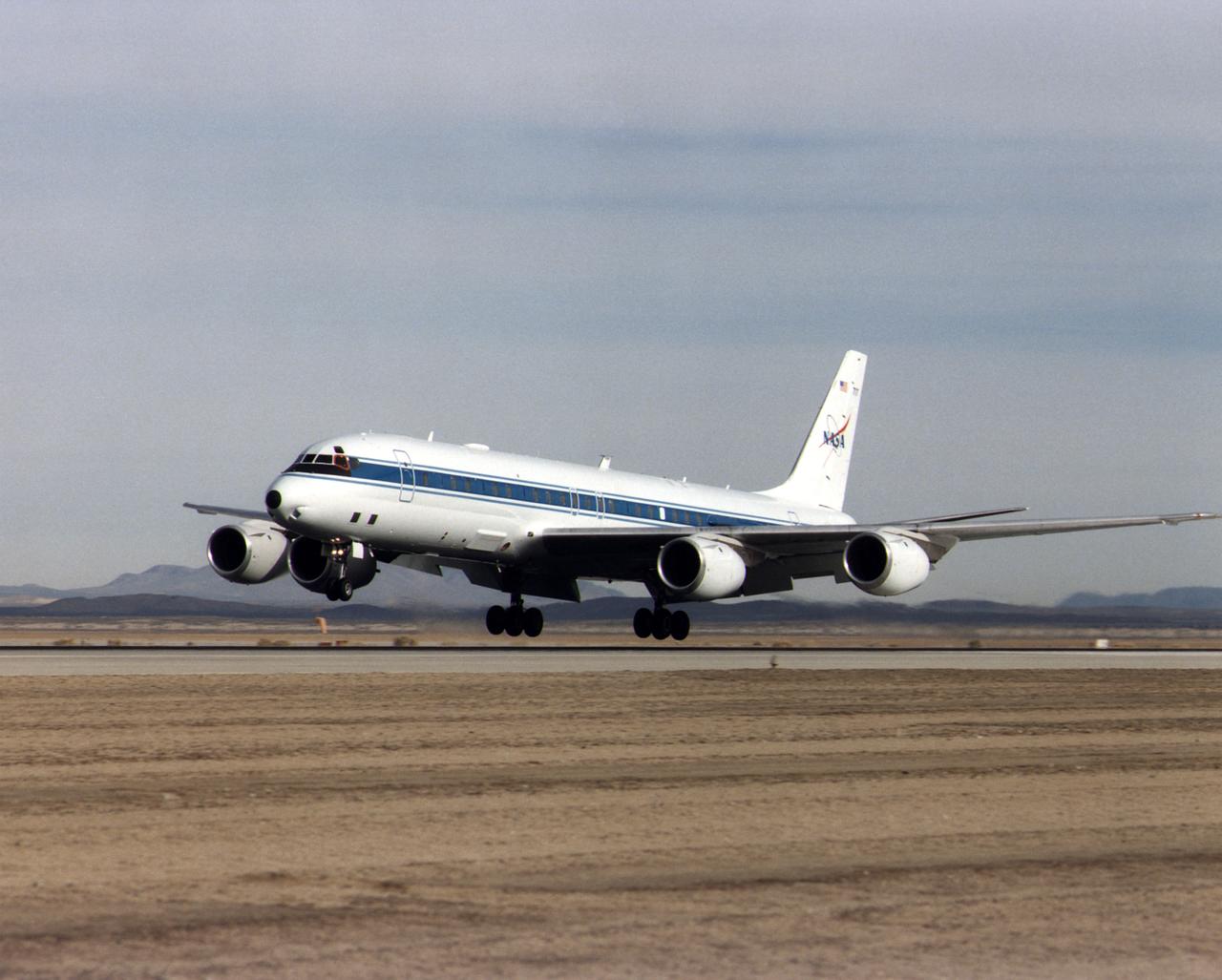

NASA's DC-8 Airborne Science platform landed at Edwards Air Force Base, California, to join the fleet of aircraft at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The white aircraft with a blue stripe running horizontally from the nose to the tail is shown with its main landing gear just above the runway. The former airliner is a "dash-72" model and has a range of 5,400 miles. The craft can stay airborne for 12 hours and has an operational speed range between 300 and 500 knots. The research flights are made at between 500 and 41,000 feet. The aircraft can carry up to 30,000 lbs of research/science payload equipment installed in 15 mission-definable spaces.
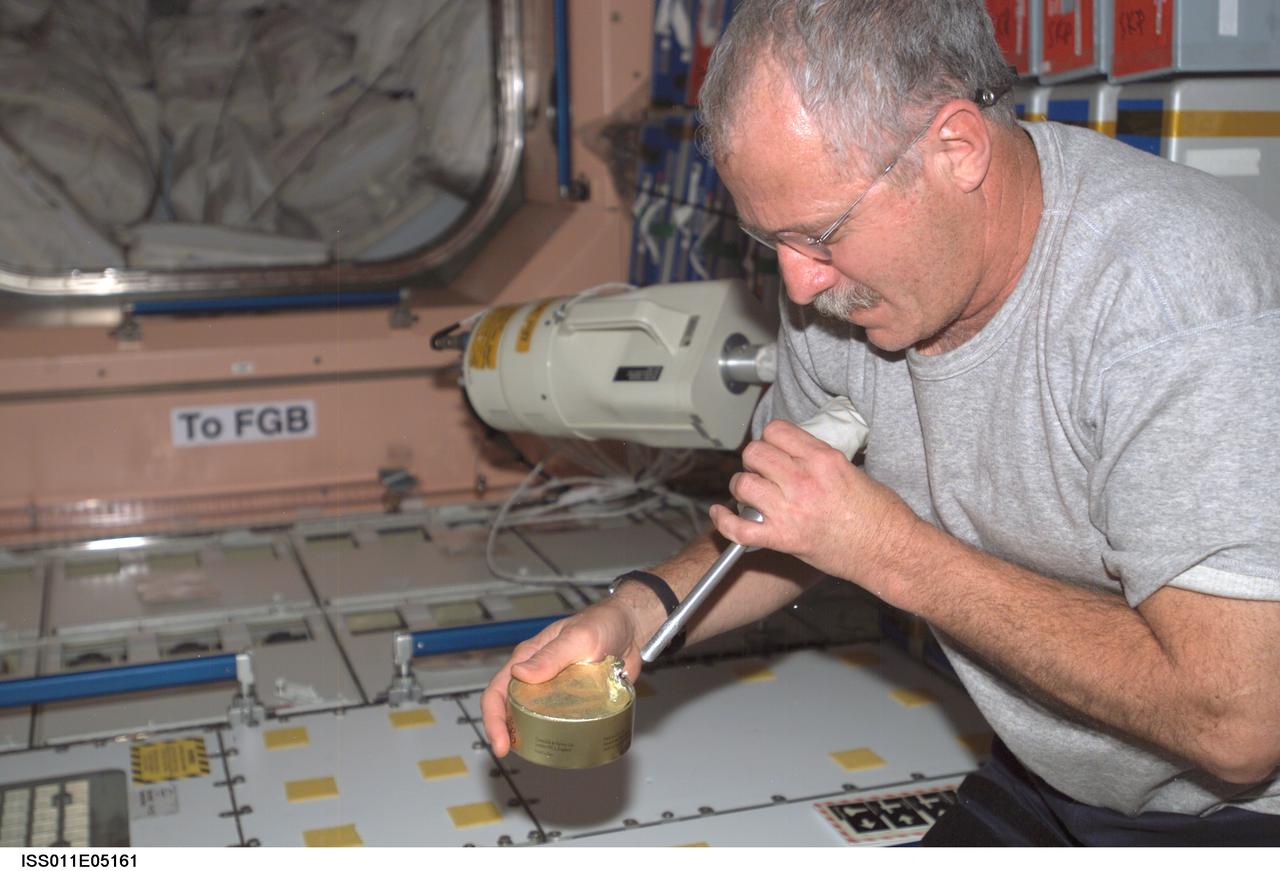

ISS011-E-05161 (17 April 2005) --- Astronaut John L. Phillips, Expedition 11 NASA ISS science officer and flight engineer, uses the ISS wet/dry vacuum cleaner assembly to catch floating debris from the top of a food can in the Unity node of the International Space Station (ISS).
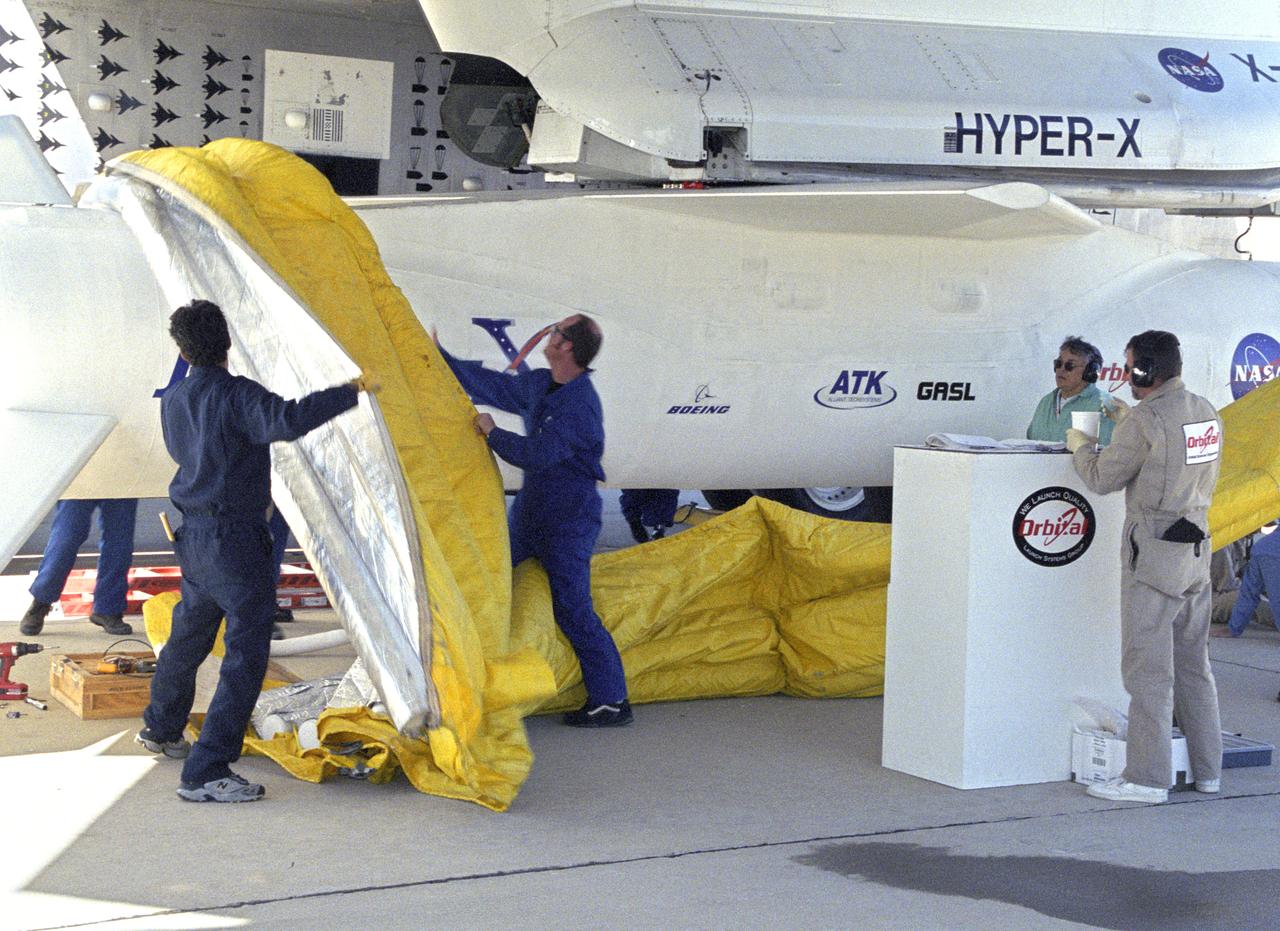

Orbital Sciences Corp. technicians remove protective shrouds from the modified Pegasus booster before takeoff on the X-43A's Mach 9.6 record scramjet flight.
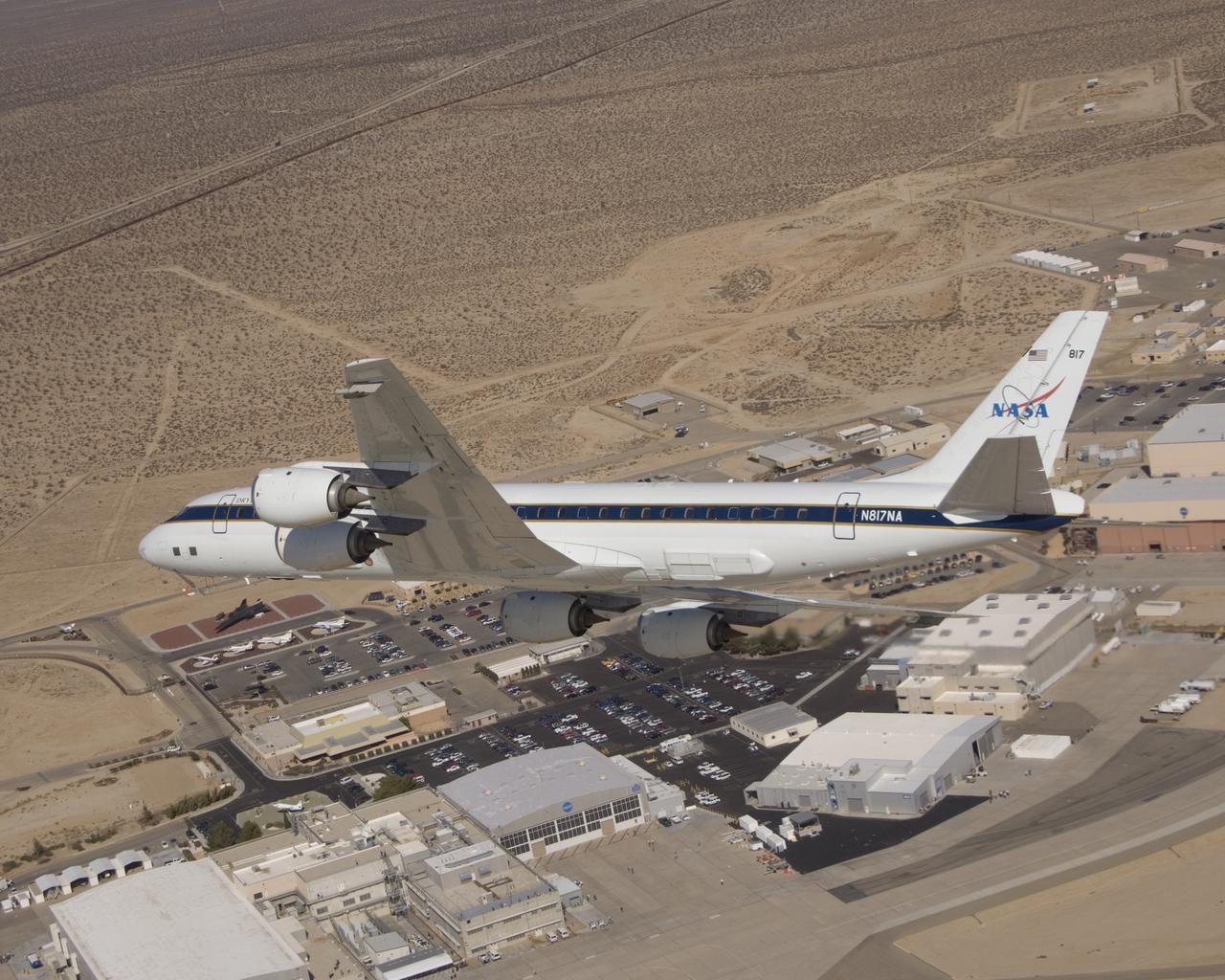

NASA's DC-8 airborne science laboratory soars over the Dryden Flight Research Center upon its return to the center on Nov. 8, 2007.
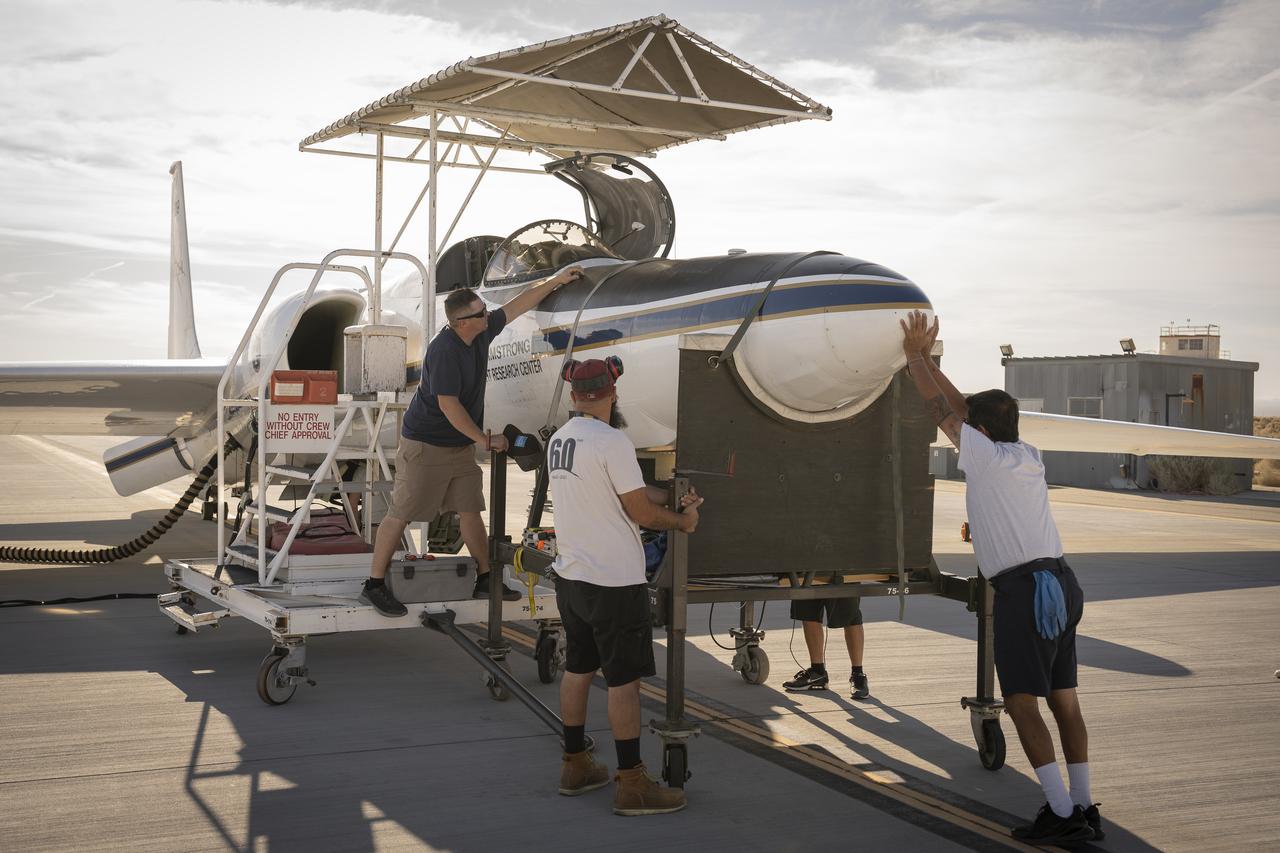

Crew members reattach the nose cone of NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft at Edwards, California, on Thursday, Aug. 21, 2025, ahead of a mission for the Geological Earth Mapping Experiment (GEMx). The aircraft’s nose houses key science instruments used to collect data during flight.
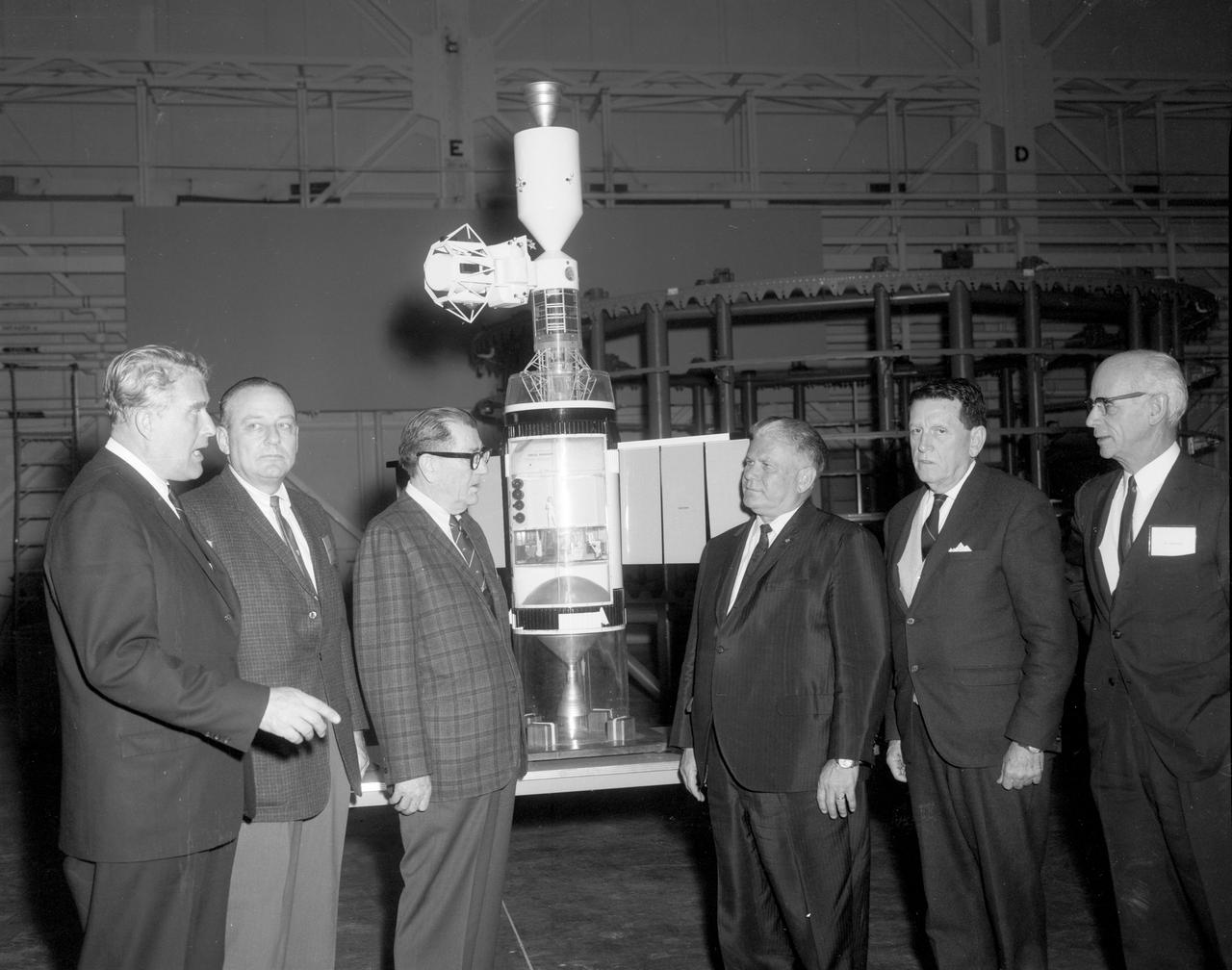

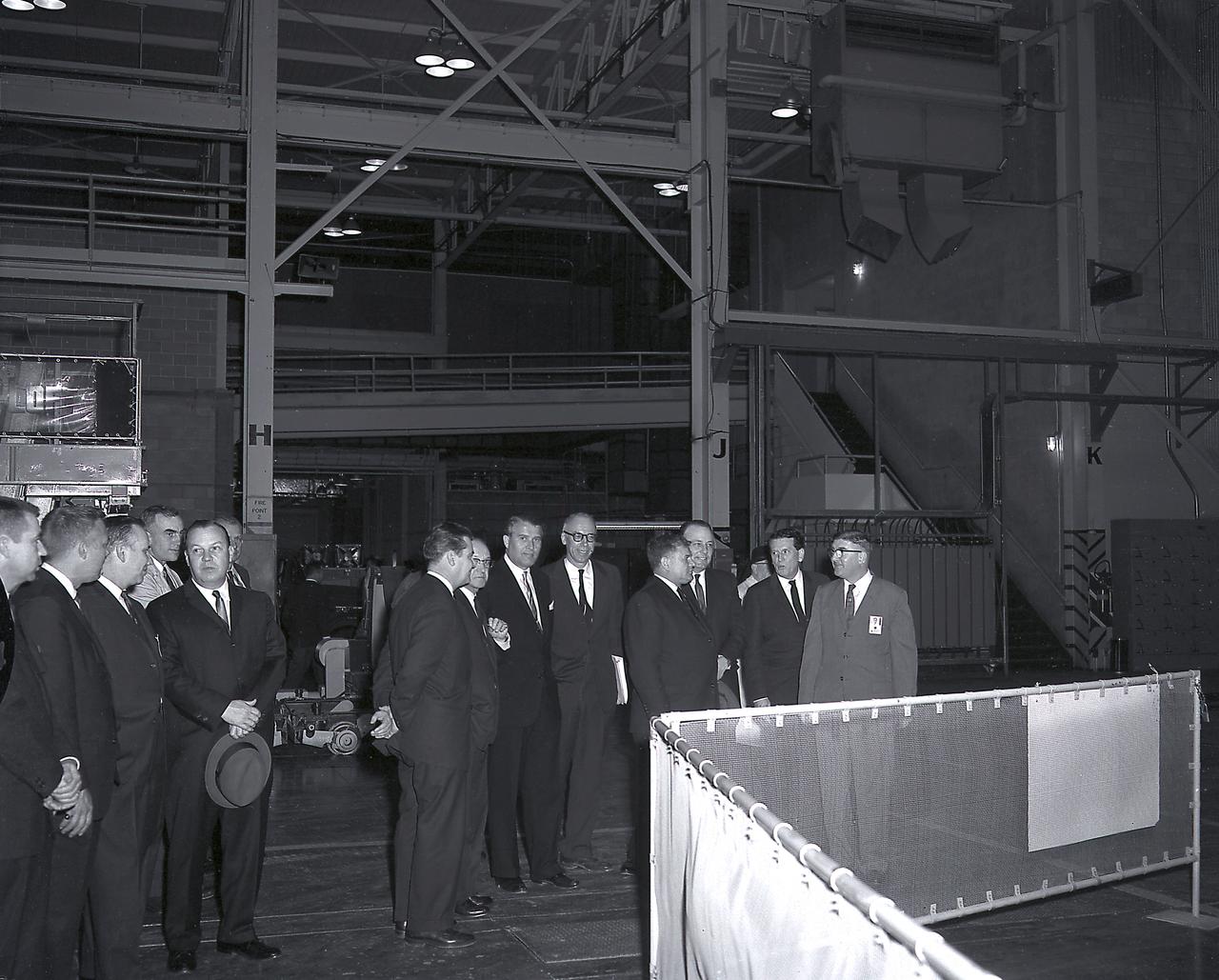
The members of the House Committee on Science and Astronautics visited the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) on March 9, 1962 to gather firsthand information of the nation’s space exploration program. The congressional group was composed of members of the Subcommittee on Manned Space Flight. Standing at the Apollo Applications Program Cluster Model in building 4745 are (left-to-right): Dr. Wernher von Braun, MSFC; Congressman Joe D. Waggoner, Democratic representative of Louisiana; Congressman Earle Cabell, Democratic representative of Texas; Subcommittee Chairman Olin E. Teague, Democratic representative of Texas; Congressman James G. Fulton, Republican representative of Pennsylvania; and Dr. Ernst Stuhlinger, associate MSFC director for science. The subcommittee was briefed on MSFC’s manned space efforts earlier in the day and then inspected mockups of the Saturn I Workshop and the Apollo Telescope Mount, two projects developed by MSFC for the post-Apollo program.
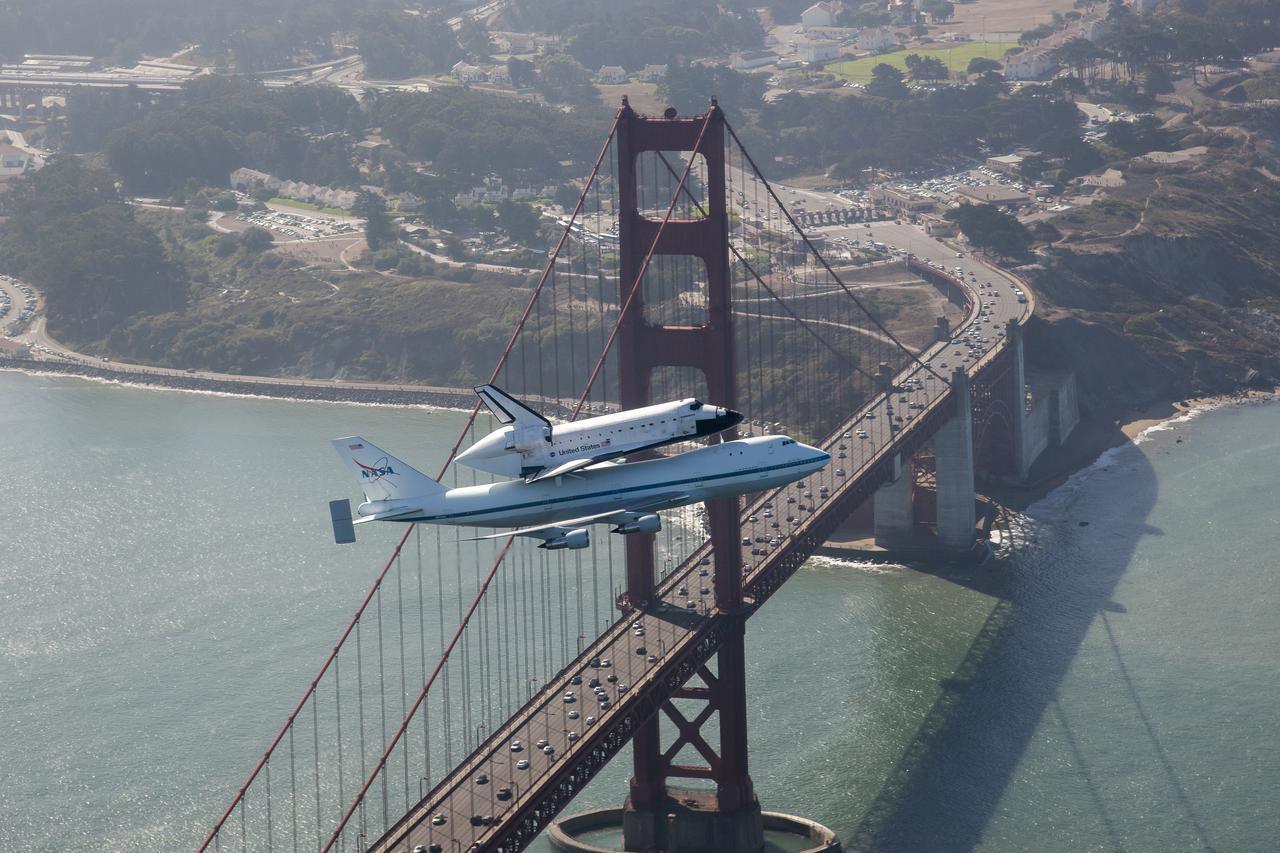

Space shuttle Endeavour and its host NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft fly by the Golden Gate Bridge in 2012 on its way to the Los Angeles International Airport and an overland journey to the California Science Center. Californians looked up at the morning sky Sept. 21 to catch a glimpse of Endeavour. The final leg of Endeavour’s flight from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, Florida, offered many people an opportunity to witness the historic flight. Space shuttle Endeavour and its host NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft fly by the Golden Gate Bridge in 2012 on its way to the Los Angeles International Airport and an overland journey to the California Science Center. Californians looked up at the morning sky Sept. 21 to catch a glimpse of Endeavour. The final leg of Endeavour’s flight from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, Florida, offered many people an opportunity to witness the historic flight.
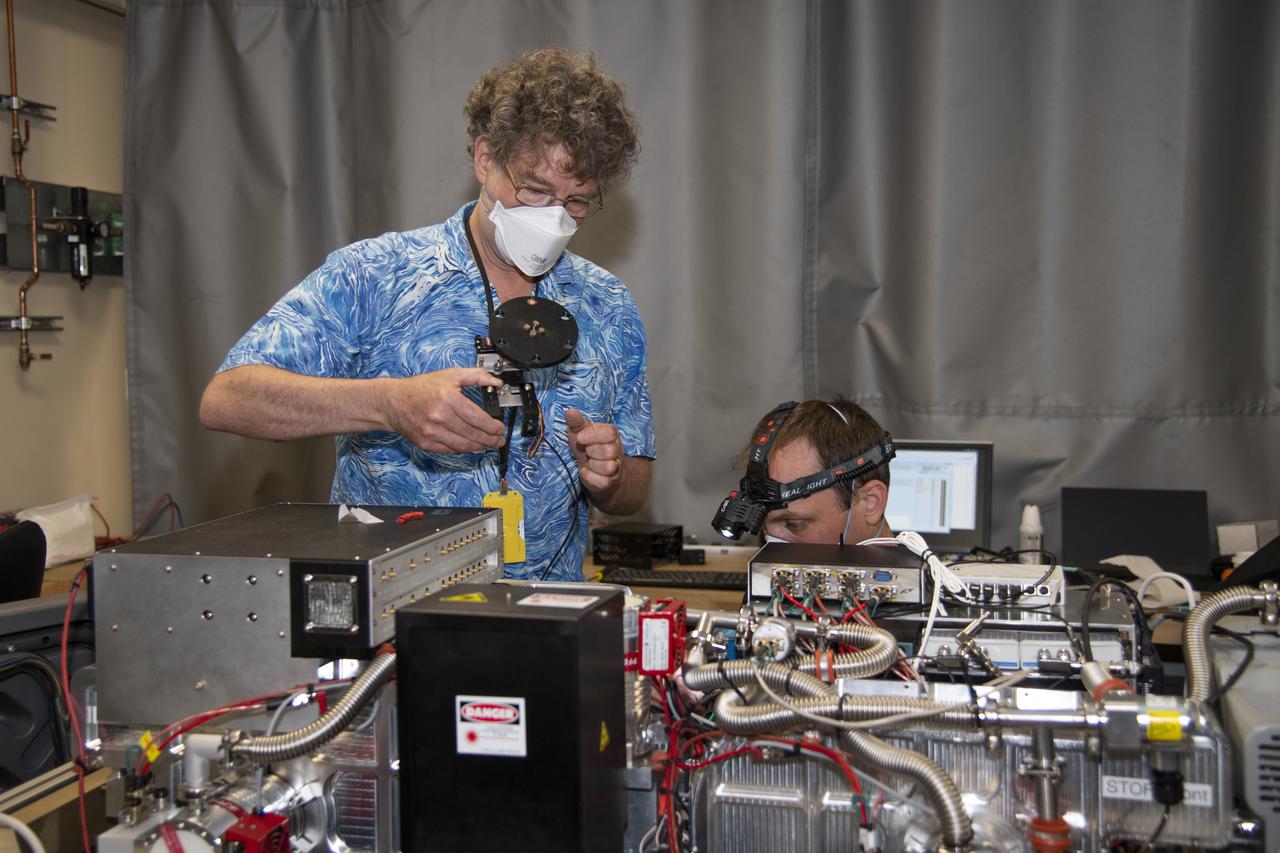

Particle Analysis by Laser Mass Spectrometry or PALMS instrument maintained by Dave Thomson and Justin Jacquot of Purdue University as part of NASA's Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere (DCOTSS) mission
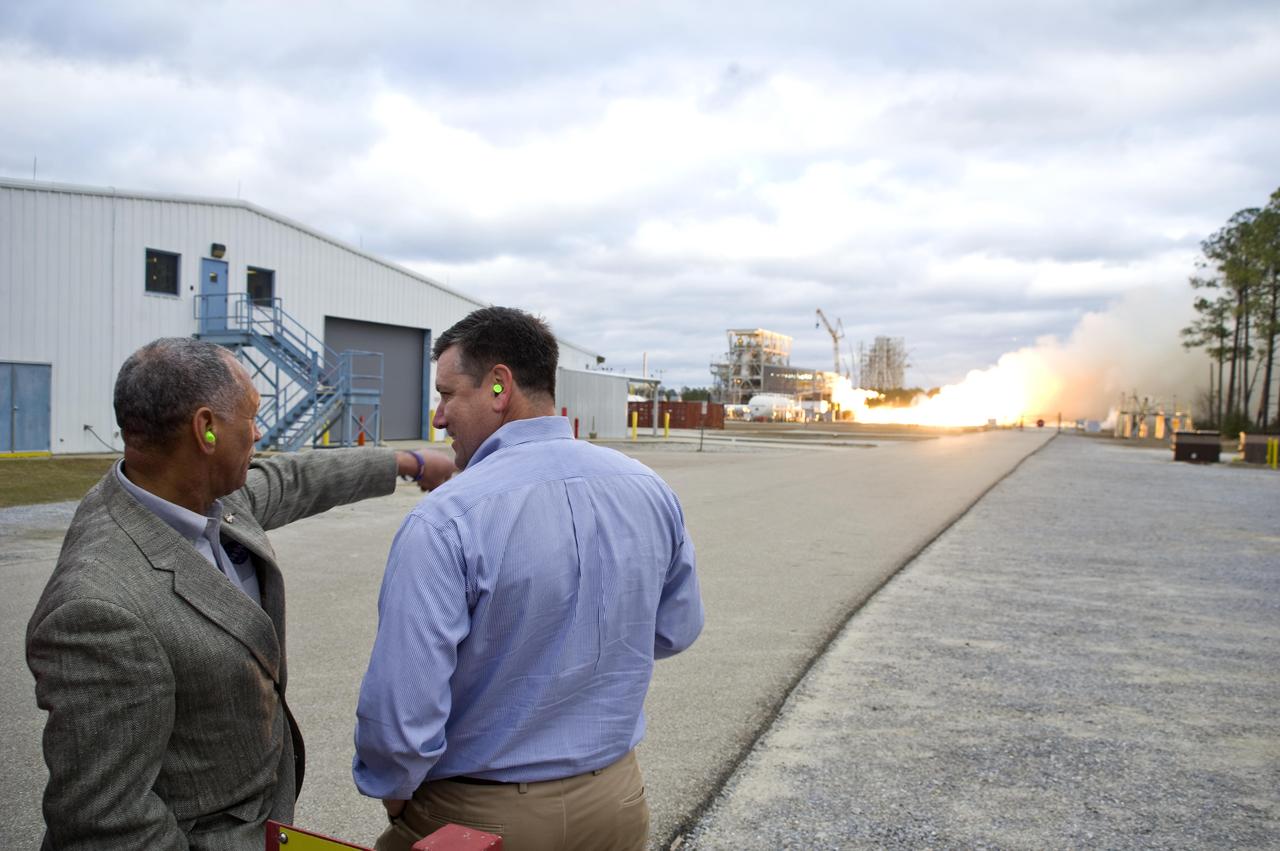

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden (l) and John C. Stennis Space Center Director Patrick Scheuermann watch the successful test of the first Aerojet AJ26 flight engine Feb. 7, 2011. The test was conducted on the E-1 Test Stand at Stennis. The engine now will be sent to Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where it will be used to power the first stage of Orbital Sciences Corporation's Taurus II space vehicle. The Feb. 7 test supports NASA's commitment to partner with companies to provide commercial cargo flights to the International Space Station. NASA has partnered with Orbital to carry out the first of eight cargo missions to the space station in early 2012.
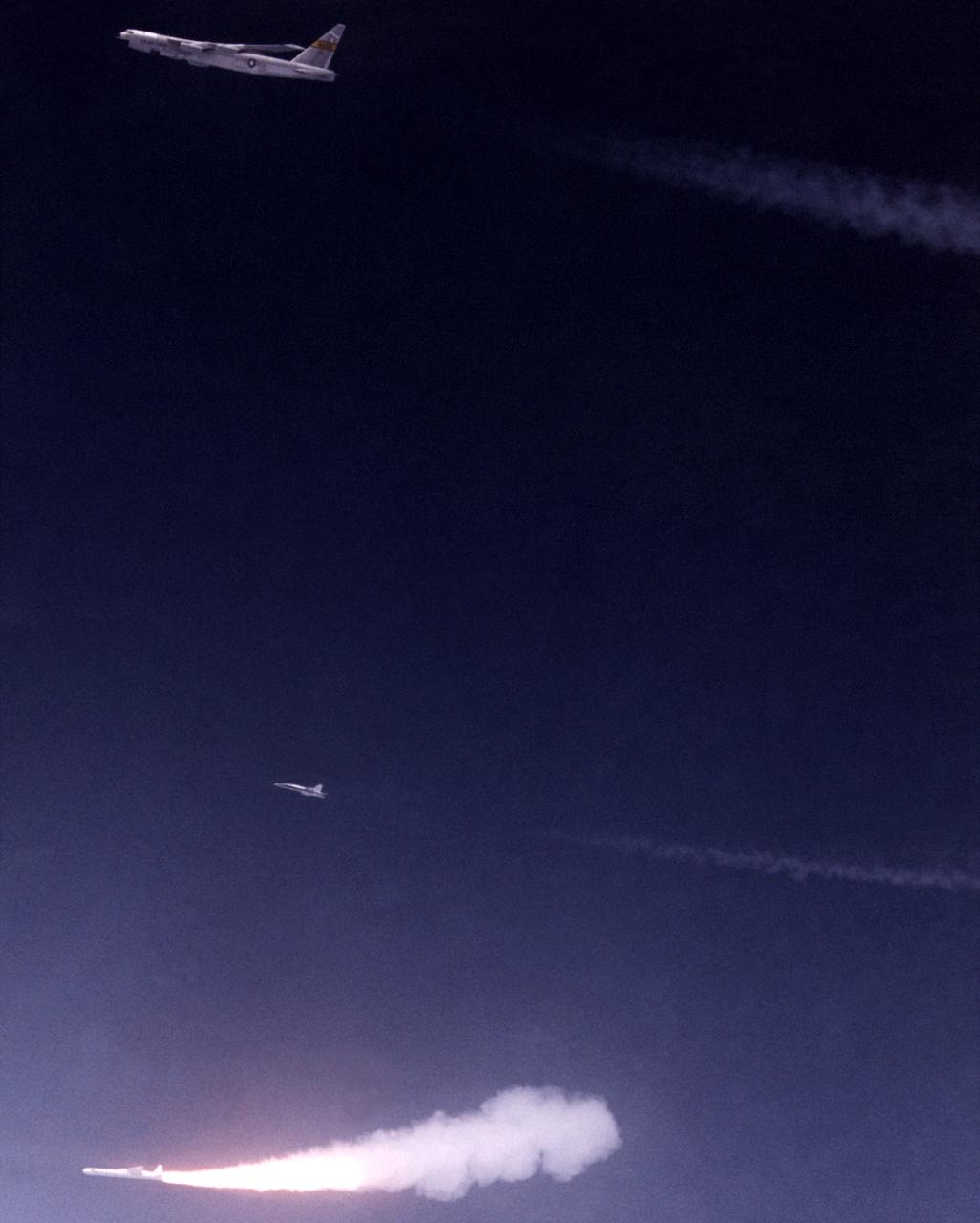

Against the midnight blue of a high-altitude sky, Orbital Sciences’ Pegasus winged rocket booster ignites after being dropped from NASA’s B-52 mothership on a July 1991 flight. A NASA chase plane for the flight is also visible above the rocket and below the B-52.
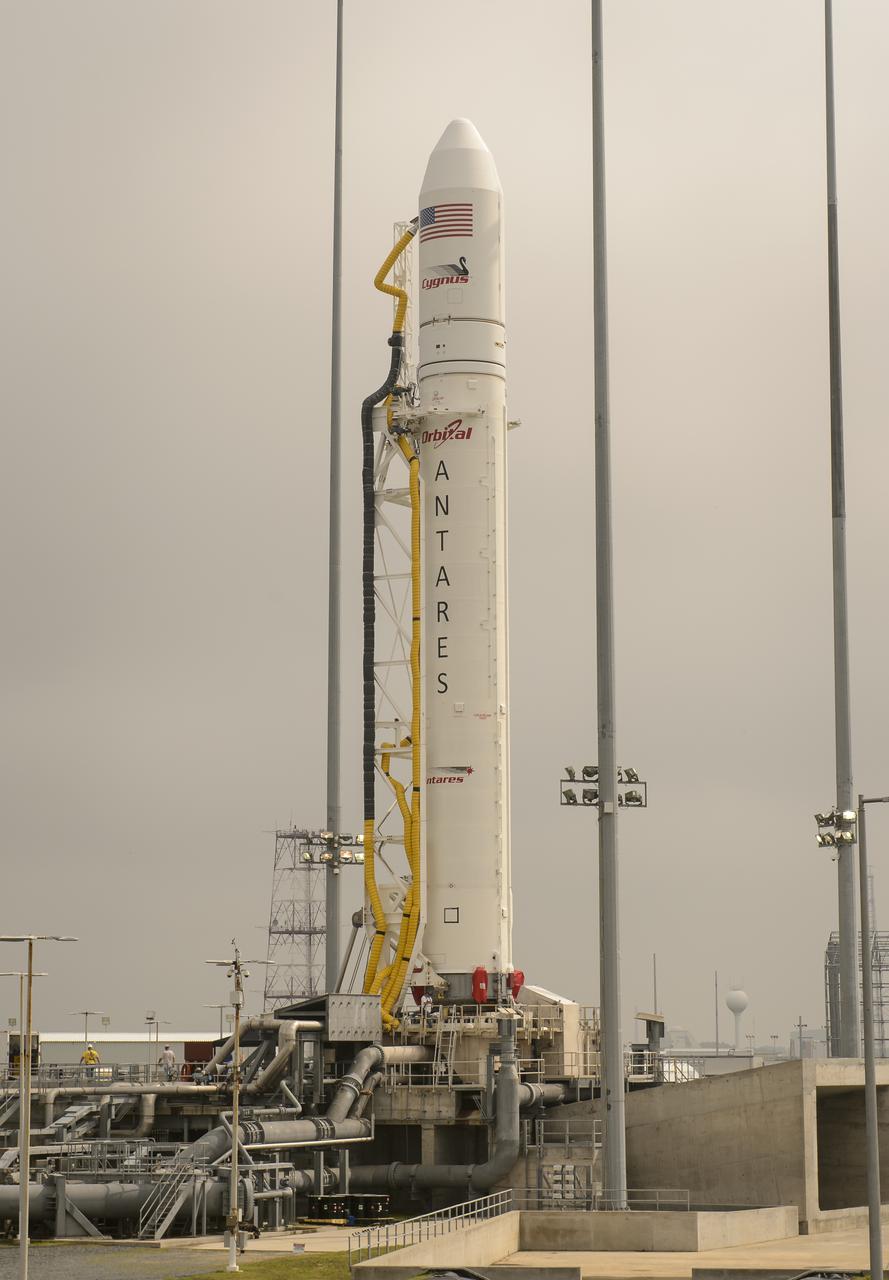

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket, with the Cygnus spacecraft onboard, is seen on launch Pad-0A, Friday, July 11, 2014, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. The Antares will launch with the Cygnus spacecraft filled with over 3,000 pounds of supplies for the International Space Station, including science experiments, experiment hardware, spare parts, and crew provisions. The Orbital-2 mission is Orbital Sciences' second contracted cargo delivery flight to the space station for NASA. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket, with the Cygnus spacecraft onboard, is seen, Saturday, July 12, 2014, at launch Pad-0A of NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. The Antares will launch with the Cygnus spacecraft filled with over 3,000 pounds of supplies for the International Space Station, including science experiments, experiment hardware, spare parts, and crew provisions. The Orbital-2 mission is Orbital Sciences' second contracted cargo delivery flight to the space station for NASA. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket, with the Cygnus spacecraft onboard, is seen, Saturday, July 12, 2014, at launch Pad-0A of NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. The Antares will launch with the Cygnus spacecraft filled with over 3,000 pounds of supplies for the International Space Station, including science experiments, experiment hardware, spare parts, and crew provisions. The Orbital-2 mission is Orbital Sciences' second contracted cargo delivery flight to the space station for NASA. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA’s B200 taking off for an eight-hour science flight on March 5. Located on the center of the aircraft’s fuselage is the DopplerScatt radar instrument, developed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California.
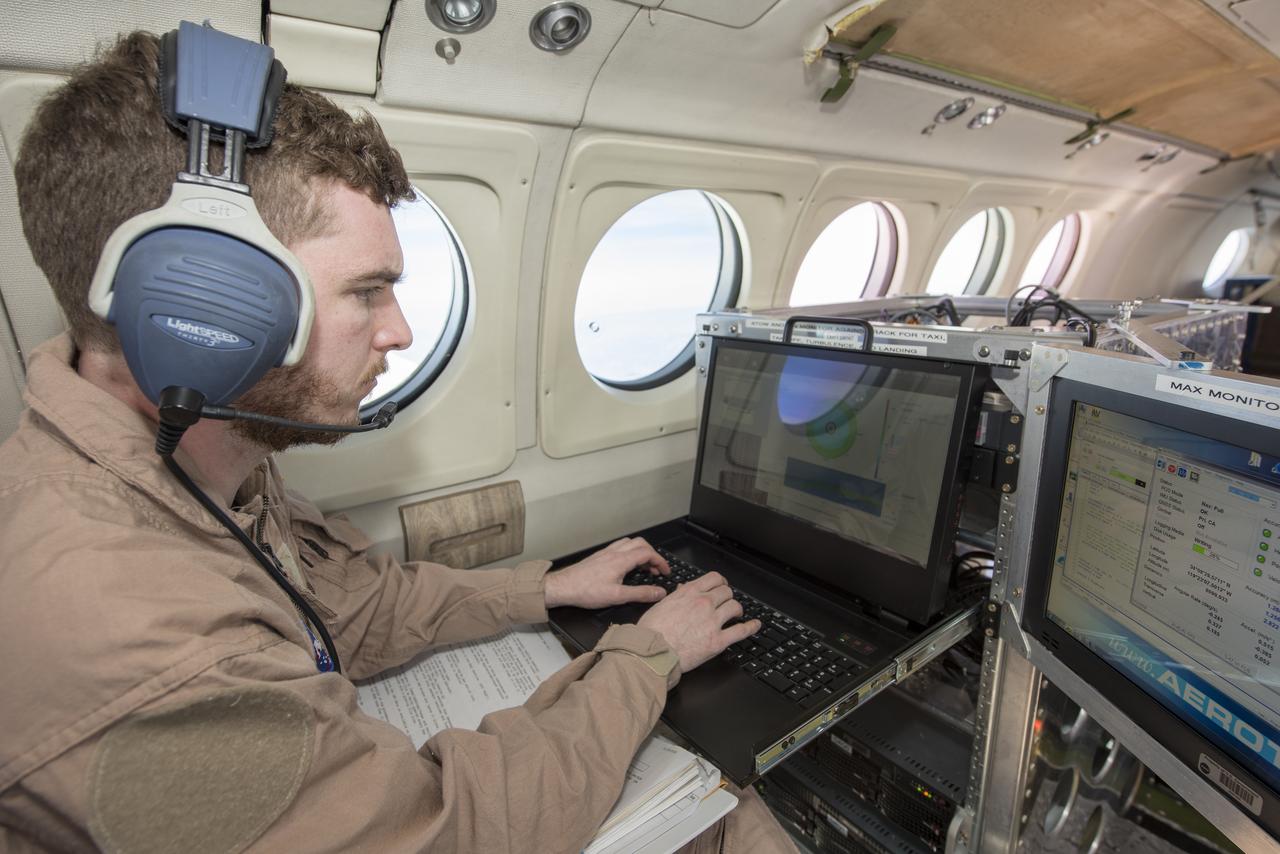

Radar operator Alexander Winteer monitors incoming wind data from the DopplerScatt radar instrument during a science flight off the California Coast on March 5, 2018.
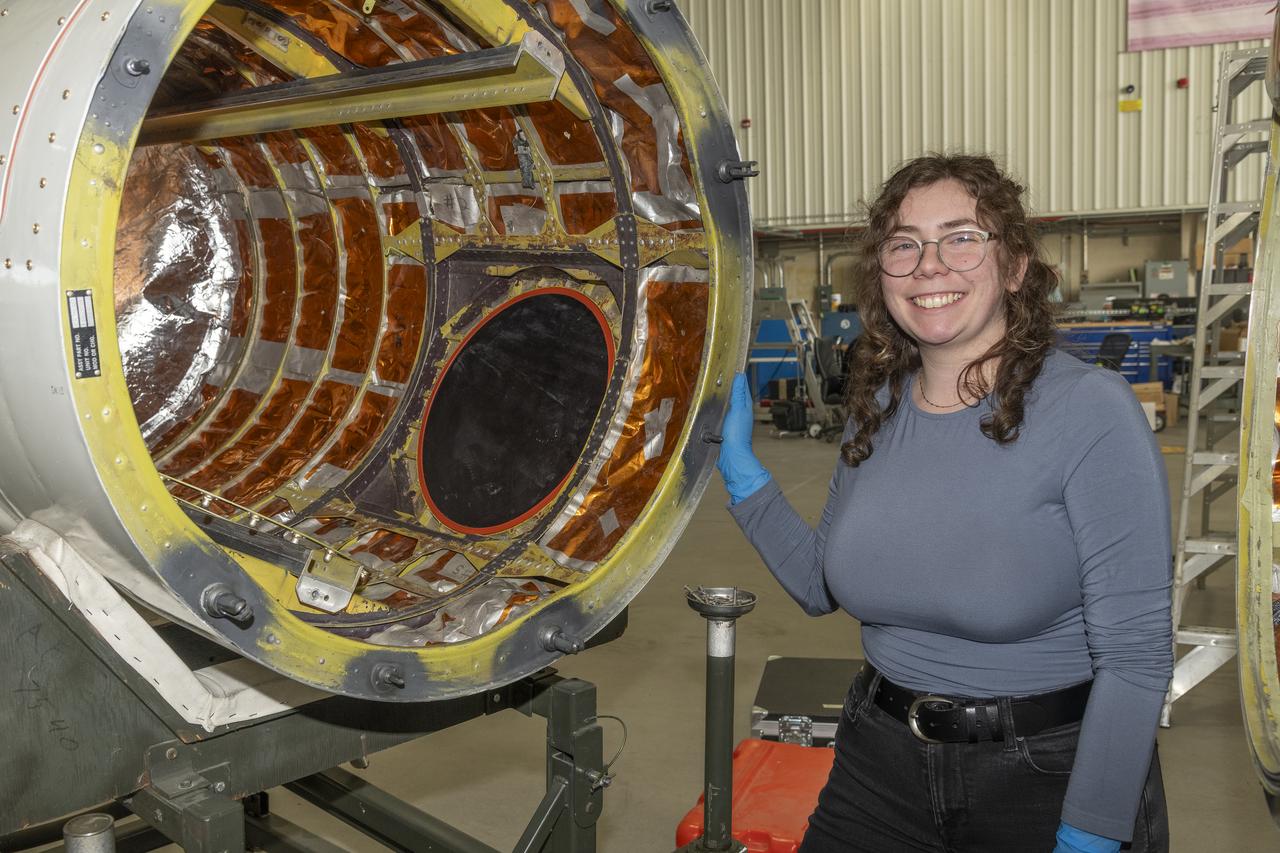

A team of experts prepares the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California for the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Researcher Jennifer Moore from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center smiles beside the ER-2 aircraft’s forebody pod where the Cloud Physics Lidar (CPL) instrument will be installed. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
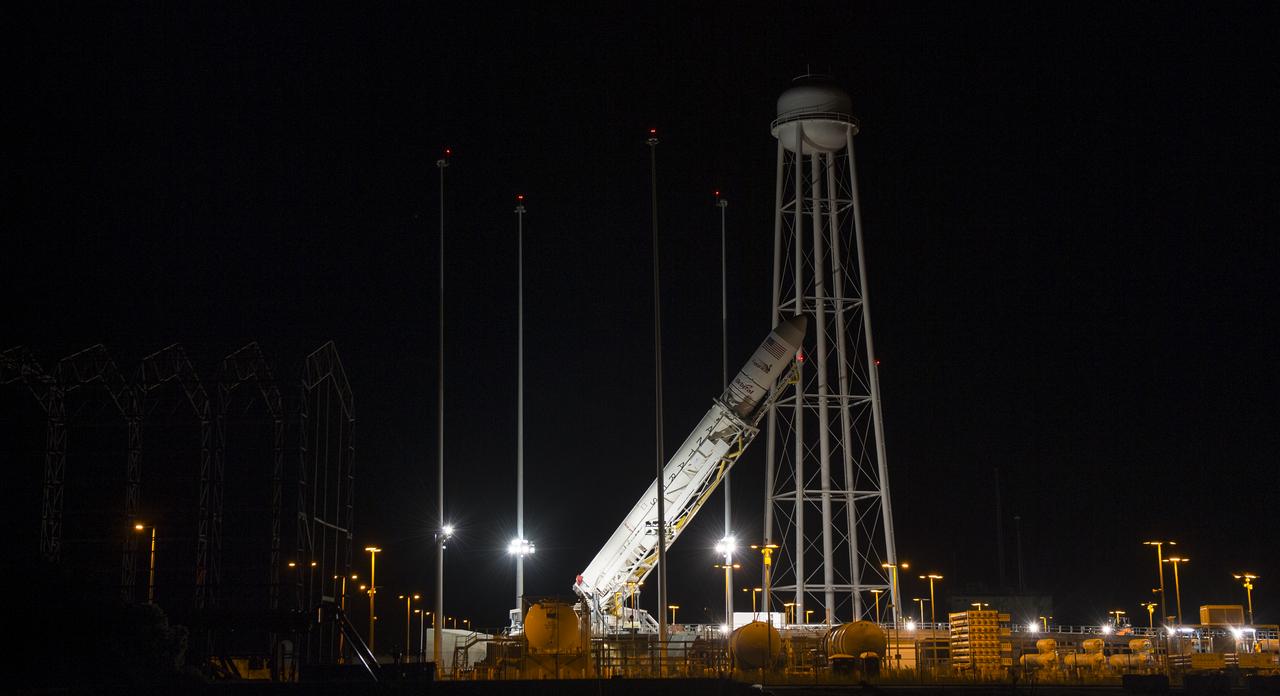

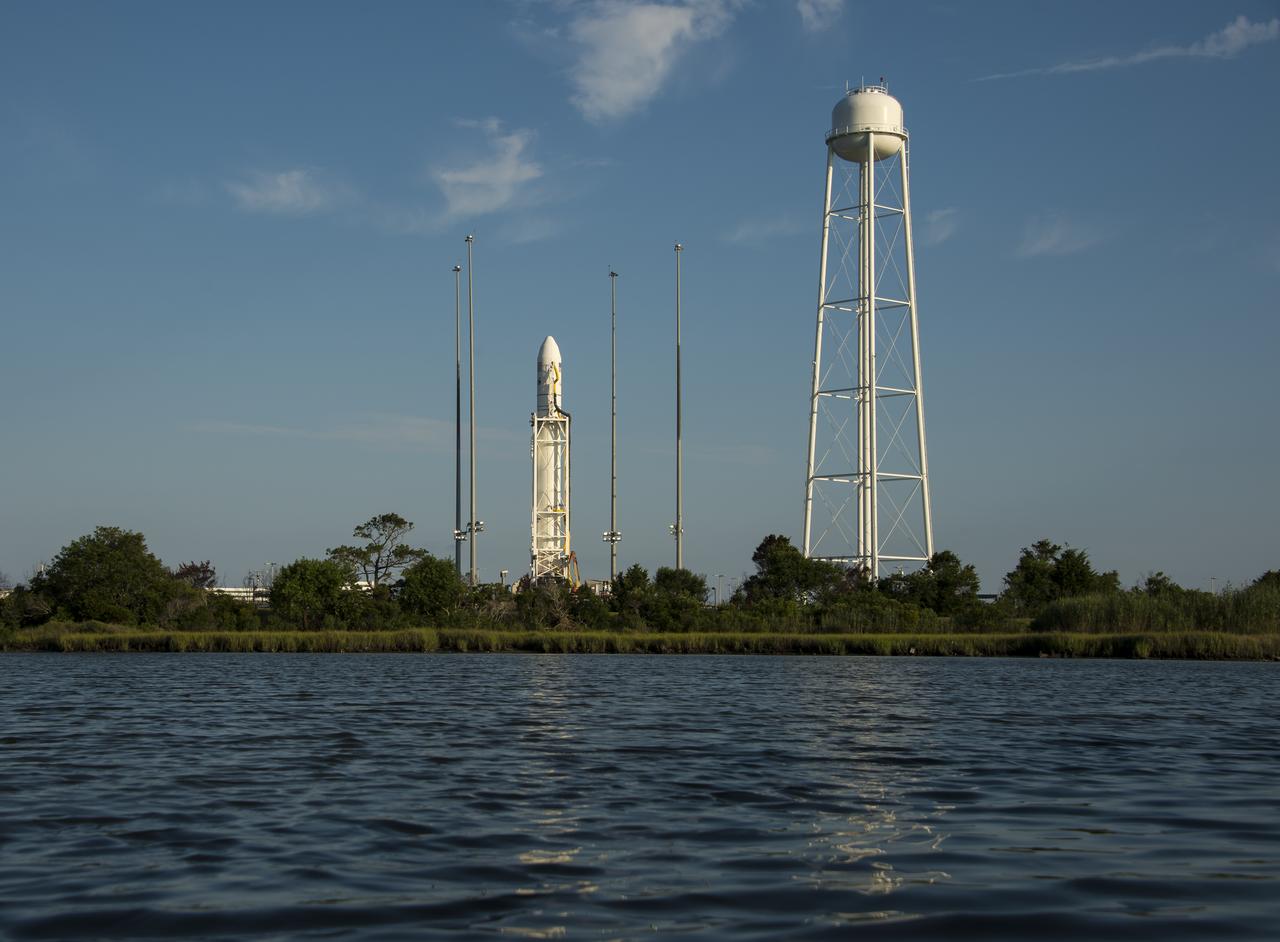
The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket, with the Cygnus spacecraft onboard, is raised at launch Pad-0A, Saturday, Oct. 25, 2014, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. The Antares will launch with the Cygnus spacecraft filled with over 5,000 pounds of supplies for the International Space Station, including science experiments, experiment hardware, spare parts, and crew provisions. The Orbital-3 mission is Orbital Sciences' third contracted cargo delivery flight to the space station for NASA. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
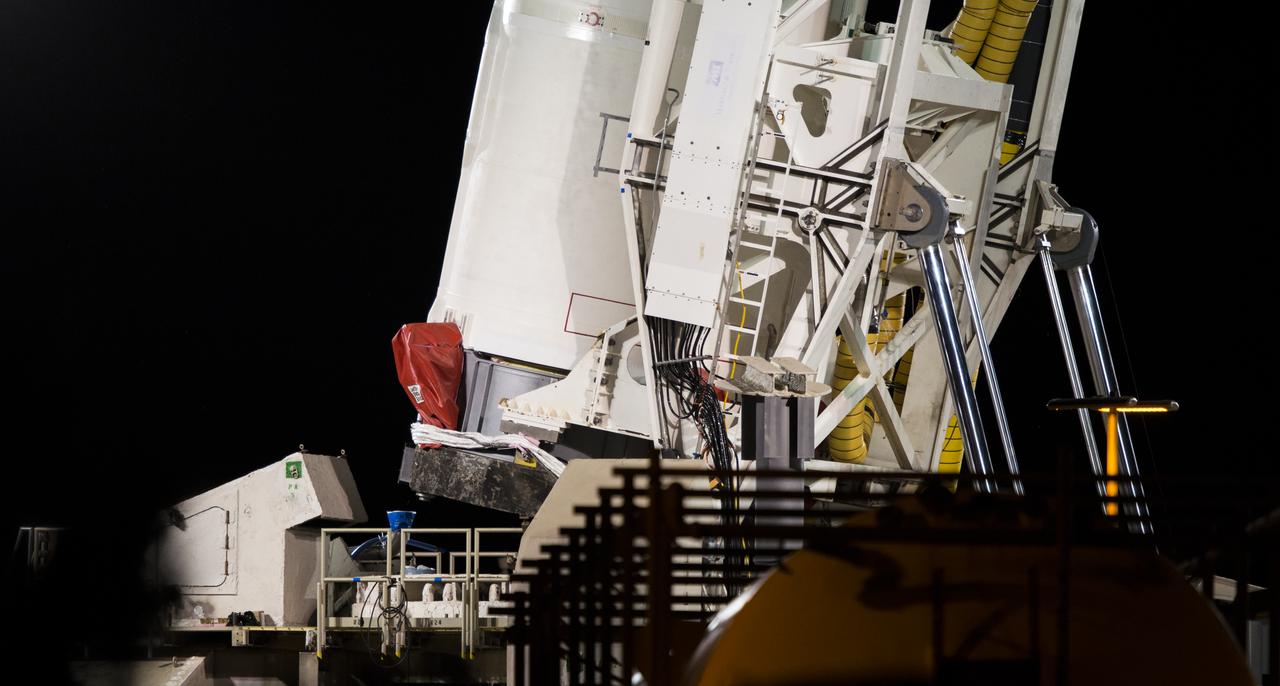

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket, with the Cygnus spacecraft onboard, is raised at launch Pad-0A, Saturday, Oct. 25, 2014, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. The Antares will launch with the Cygnus spacecraft filled with over 5,000 pounds of supplies for the International Space Station, including science experiments, experiment hardware, spare parts, and crew provisions. The Orbital-3 mission is Orbital Sciences' third contracted cargo delivery flight to the space station for NASA. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
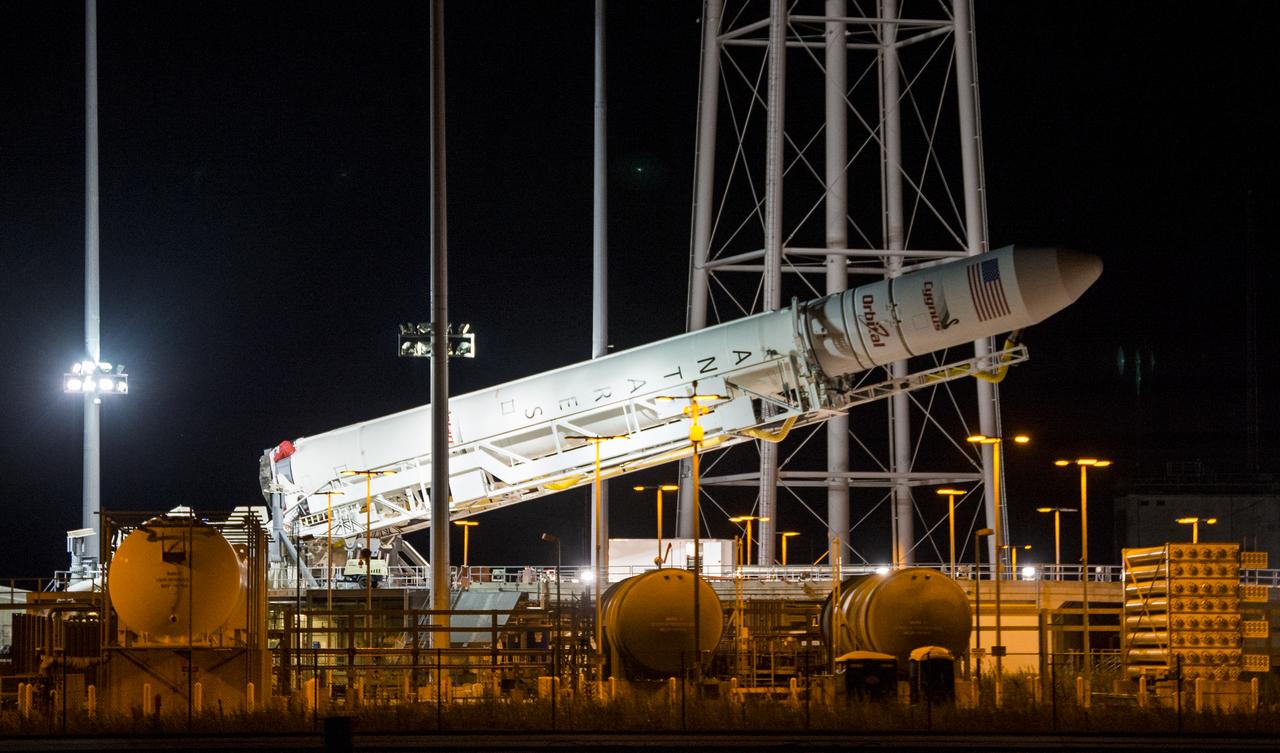

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket, with the Cygnus spacecraft onboard, is raised at launch Pad-0A, Saturday, Oct. 25, 2014, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. The Antares will launch with the Cygnus spacecraft filled with over 5,000 pounds of supplies for the International Space Station, including science experiments, experiment hardware, spare parts, and crew provisions. The Orbital-3 mission is Orbital Sciences' third contracted cargo delivery flight to the space station for NASA. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
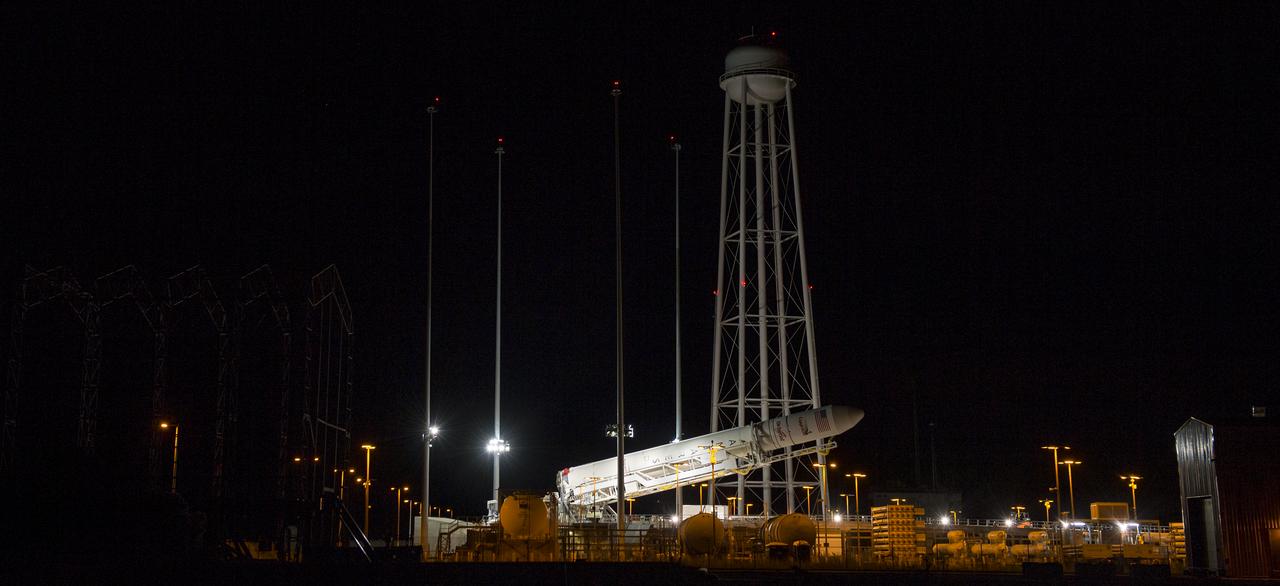

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket, with the Cygnus spacecraft onboard, is raised at launch Pad-0A, Saturday, Oct. 25, 2014, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. The Antares will launch with the Cygnus spacecraft filled with over 5,000 pounds of supplies for the International Space Station, including science experiments, experiment hardware, spare parts, and crew provisions. The Orbital-3 mission is Orbital Sciences' third contracted cargo delivery flight to the space station for NASA. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Workers are seen as they prepare the Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket, with the Cygnus spacecraft onboard, to be raised at launch Pad-0A, Friday, Oct. 24, 2014, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. The Antares will launch with the Cygnus spacecraft filled with over 5,000 pounds of supplies for the International Space Station, including science experiments, experiment hardware, spare parts, and crew provisions. The Orbital-3 mission is Orbital Sciences' third contracted cargo delivery flight to the space station for NASA. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
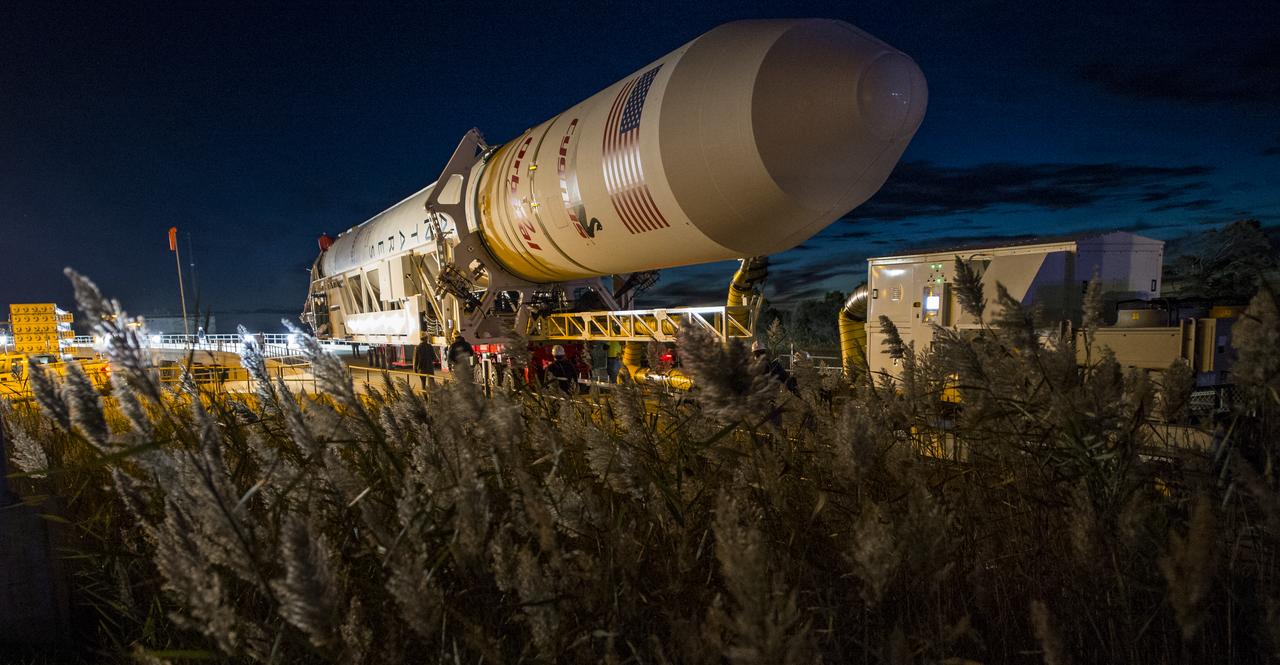

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket, with the Cygnus spacecraft onboard, arrives at launch Pad-0A, Friday, Oct. 24, 2014, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. The Antares will launch with the Cygnus spacecraft filled with over 5,000 pounds of supplies for the International Space Station, including science experiments, experiment hardware, spare parts, and crew provisions. The Orbital-3 mission is Orbital Sciences' third contracted cargo delivery flight to the space station for NASA. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
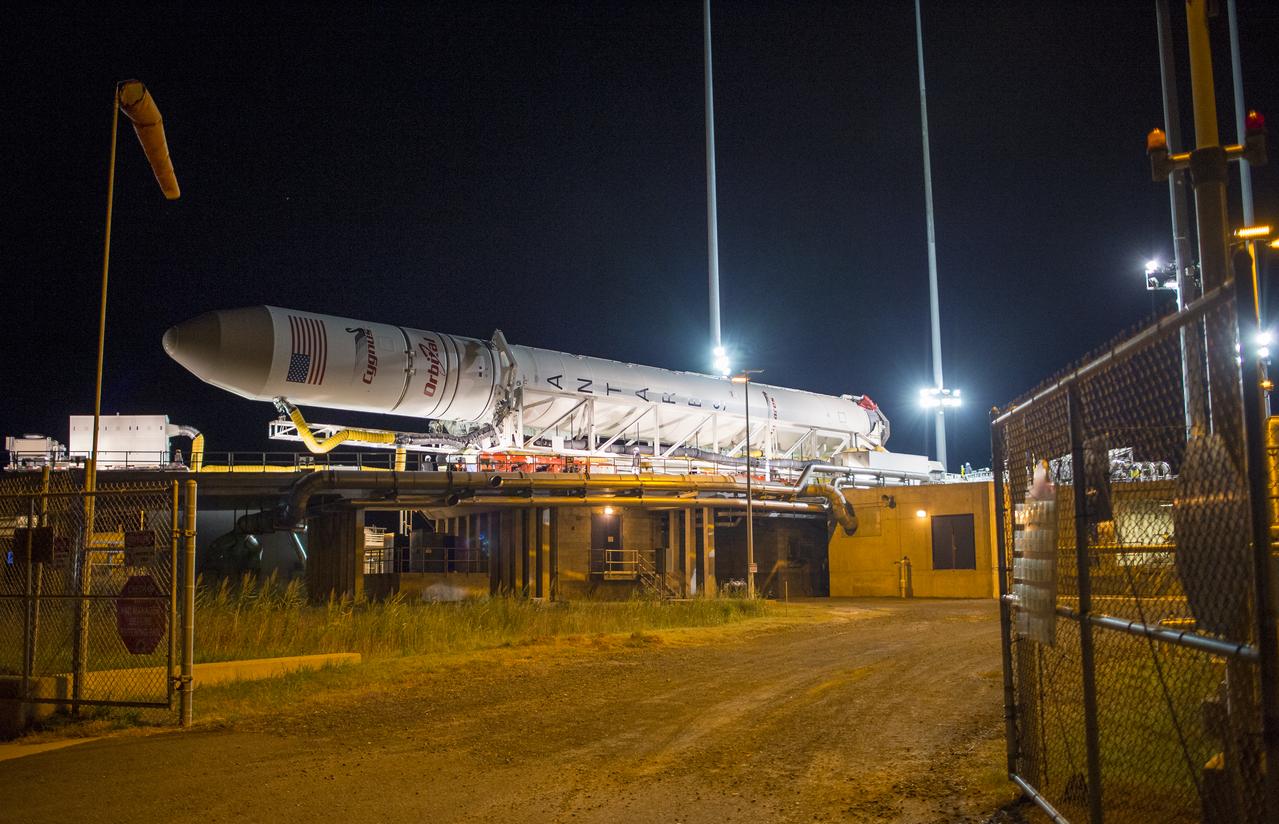

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket, with the Cygnus spacecraft onboard, arrives at launch Pad-0A, Friday, Oct. 24, 2014, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. The Antares will launch with the Cygnus spacecraft filled with over 5,000 pounds of supplies for the International Space Station, including science experiments, experiment hardware, spare parts, and crew provisions. The Orbital-3 mission is Orbital Sciences' third contracted cargo delivery flight to the space station for NASA. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
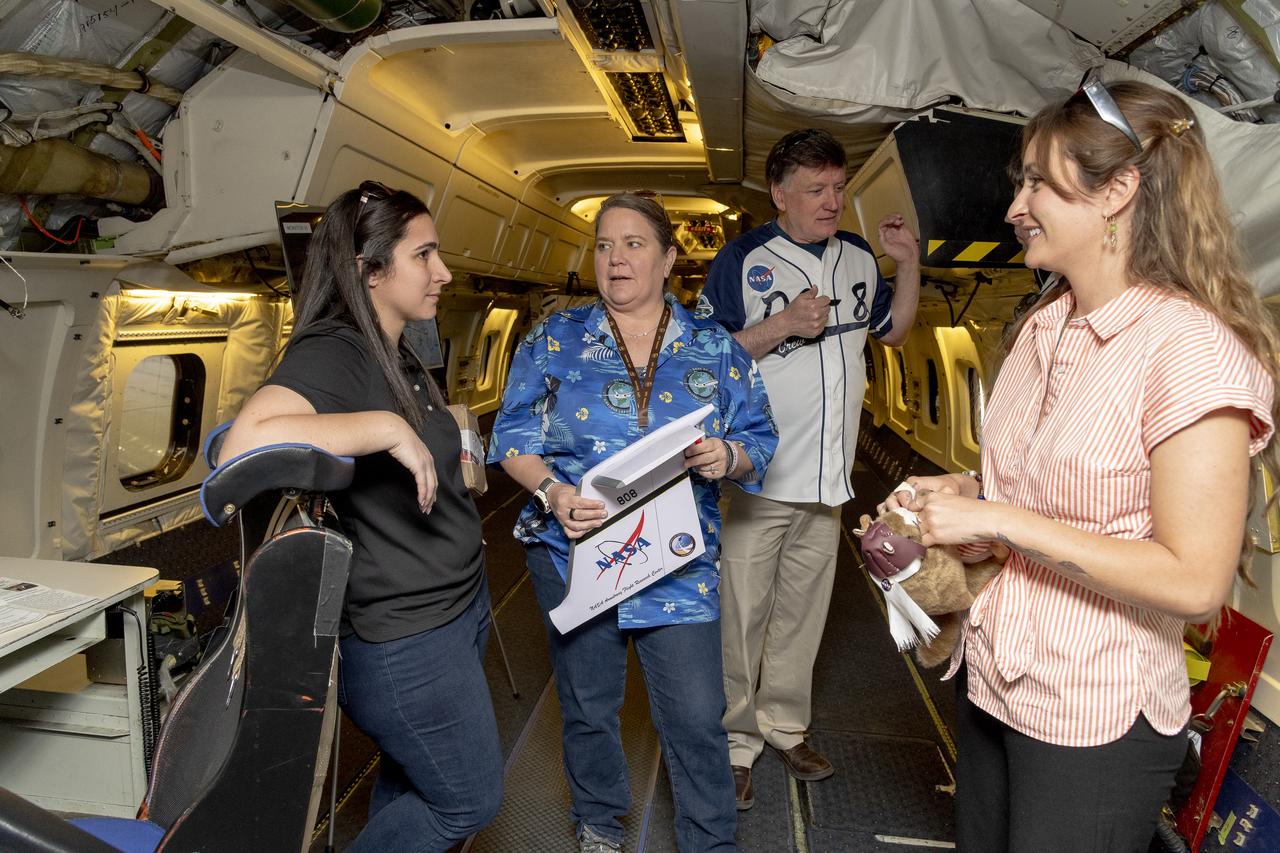

Members of the DC-8 program team tour an empty aircraft and recall past missions. Usually the DC-8 has between 15 and 30 instrument racks installed for a given science mission. The aircraft was spacious by comparison on May 2, 2024, when NASA personnel, friends, and family gathered at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California to celebrate the DC-8 staff, aircraft, and science campaigns. Conversing here are DC-8 aircraft deputy manager Kirsten Boogaard, left, with NASA Armstrong pilot Carrie Worth, Mike Zimmerman, and NASA Armstrong public affairs specialist for airborne science, Erica Heim.
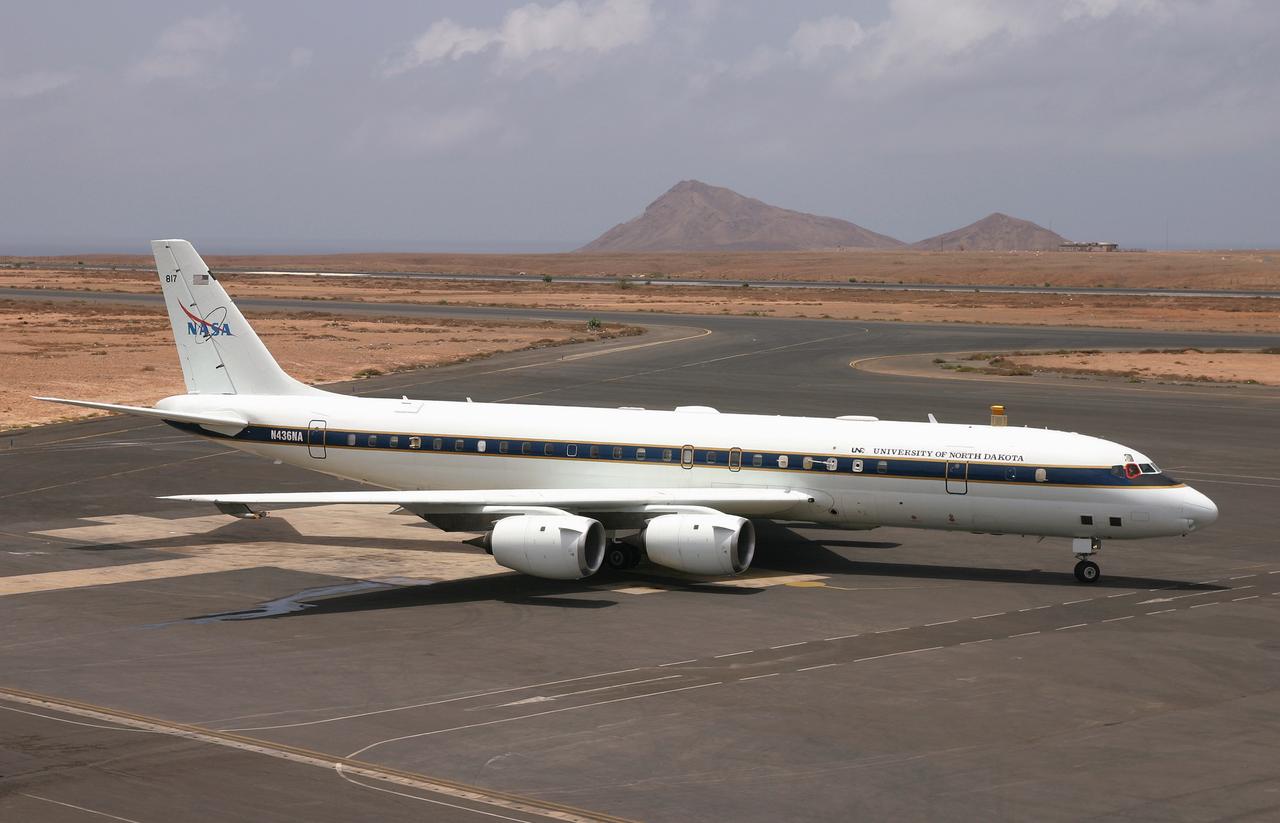

NASA's DC-8 Flying Laboratory taxis up to the ramp at Sal Island's Amilcar Cabral International Airport after a science flight for the NAMMA mission. (Ames photo # ACD06-0135-035)
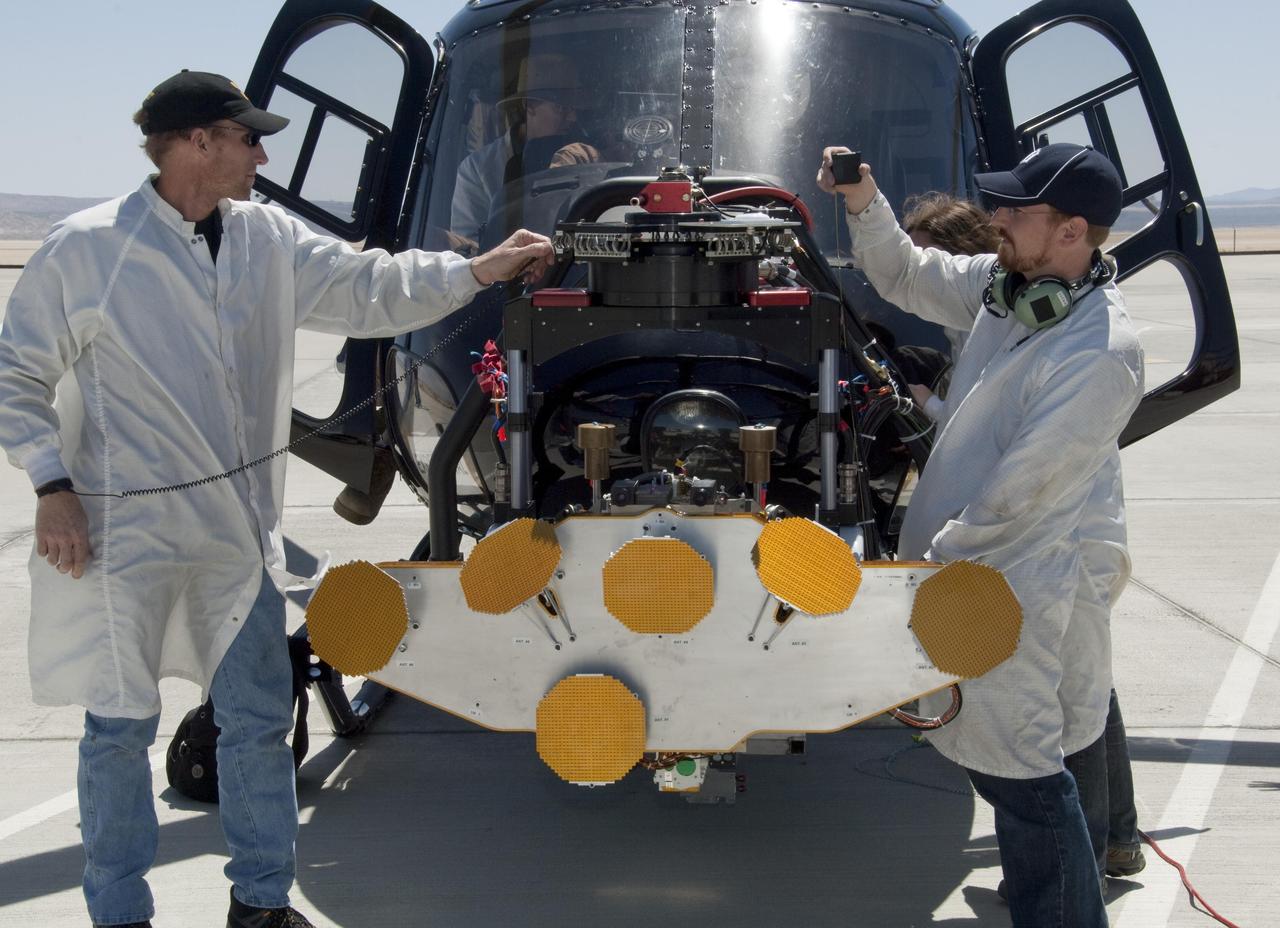

In advance of a testing flight at NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, members of the test team prepare the engineering model of the Mars Science Laboratory descent radar on the nose gimbal of a helicopter. The yellow disks are the radar antennae.
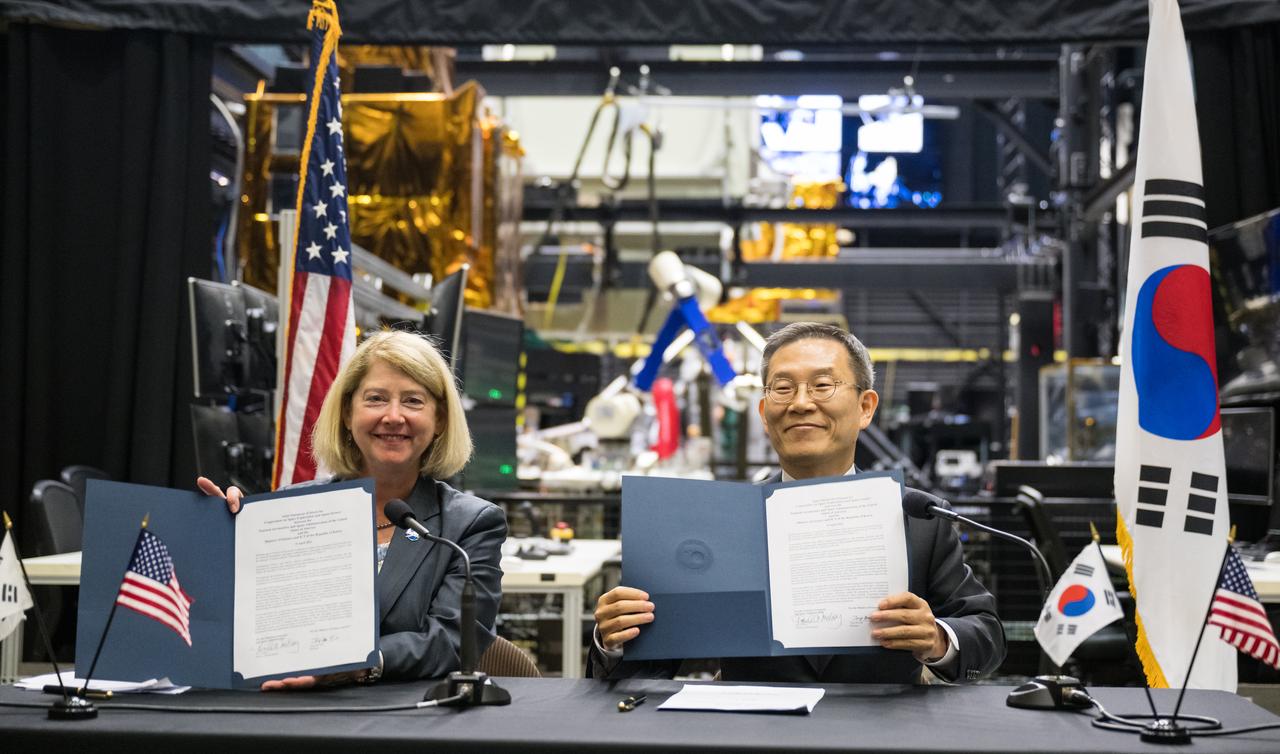
NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy and MSIT Minister Jong-Ho Lee display the Joint Statement of Intent to advance cooperation in exploration and science between NASA and the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea after signing them, Tuesday, April 25, 2023, at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
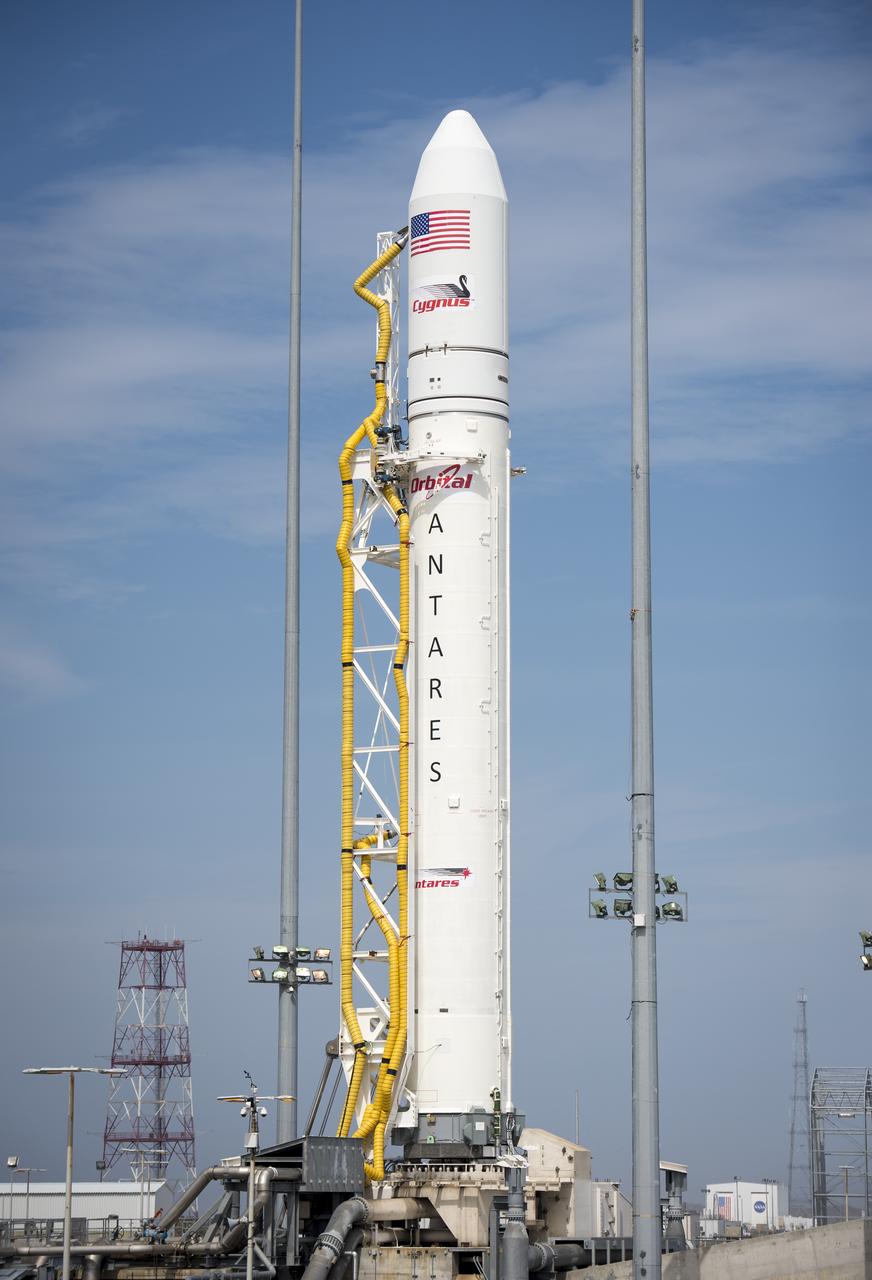

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket is seen on the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) Pad-0A at the NASA Wallops Flight Facility, Friday, April 19, 2013 in Virginia. NASA's commercial space partner, Orbital Sciences Corporation, is scheduled to test launch its first Antares on Saturday, April 20, 2013. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
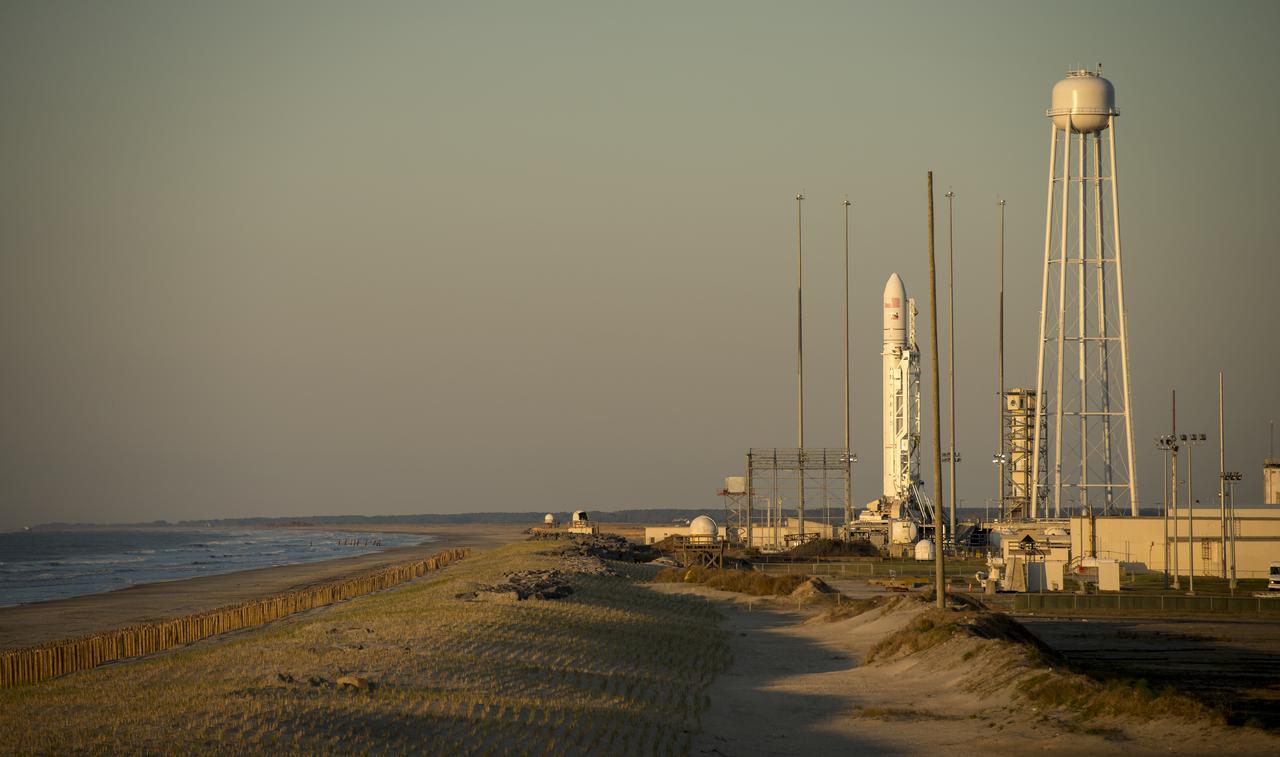

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket is seen during sunrise on the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) Pad-0A at the NASA Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, Sunday, April 21, 2013. NASA's commercial space partner, Orbital Sciences Corporation, is scheduled to test launch its first Antares later in the day. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
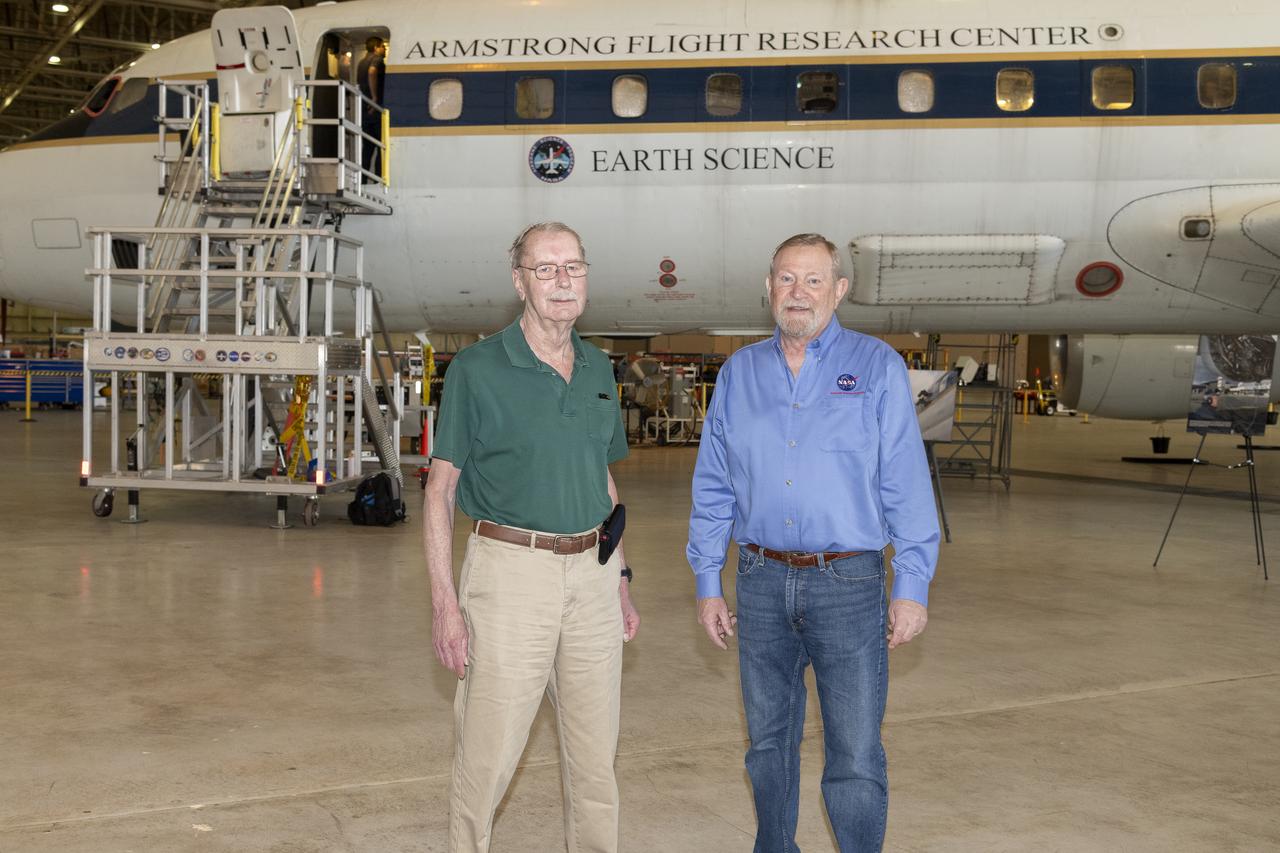

Retired NASA mission manager Chris Jennison and Randy Albertson, right, who retired in 2019 as NASA’s Airborne Science Program deputy director, stand in front of the DC-8 aircraft at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California. On May 2, 2024, NASA personnel, friends, and family celebrated the DC-8 staff, aircraft, and science campaigns.
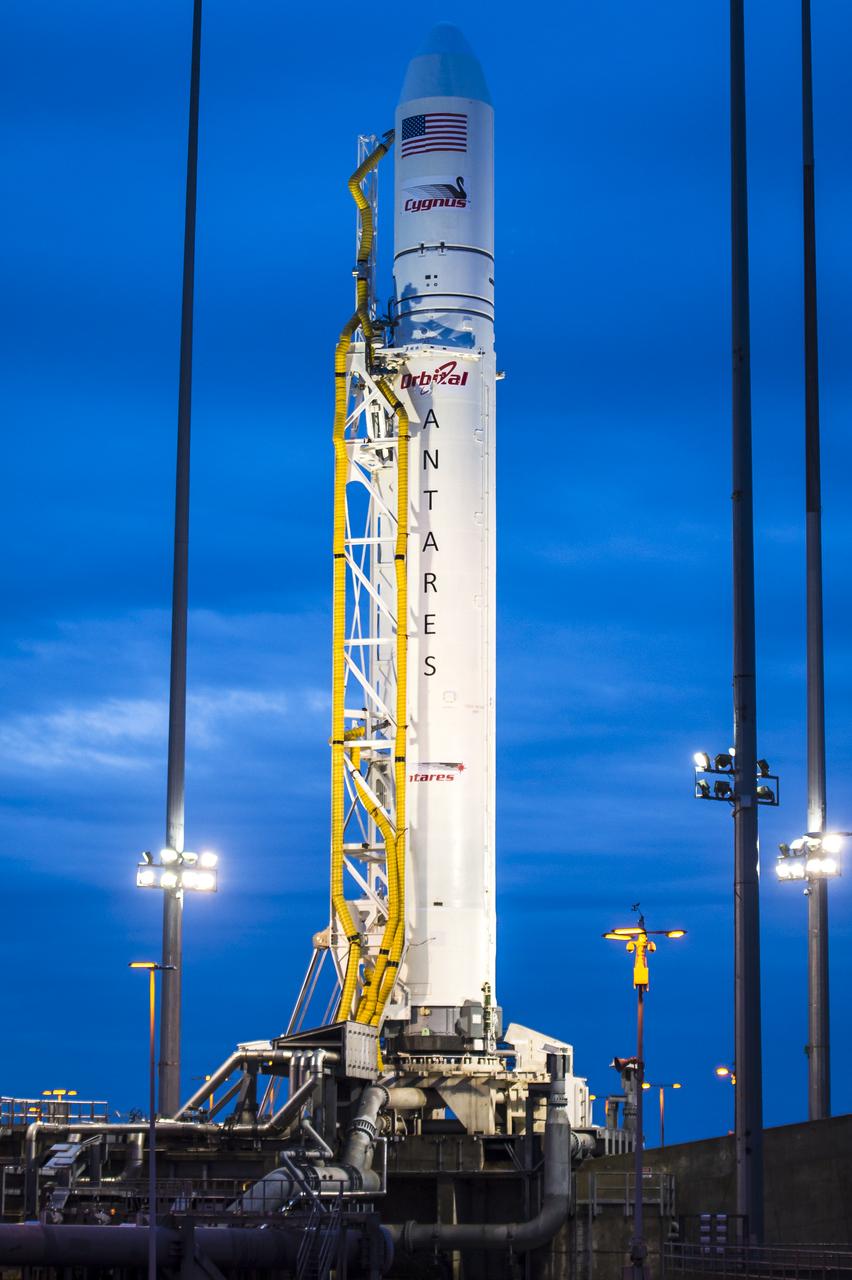

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket is seen on the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) Pad-0A at the NASA Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, Saturday, April 20, 2013. NASA's commercial space partner, Orbital Sciences Corporation, is scheduled to test launch its first Antares later in the day. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
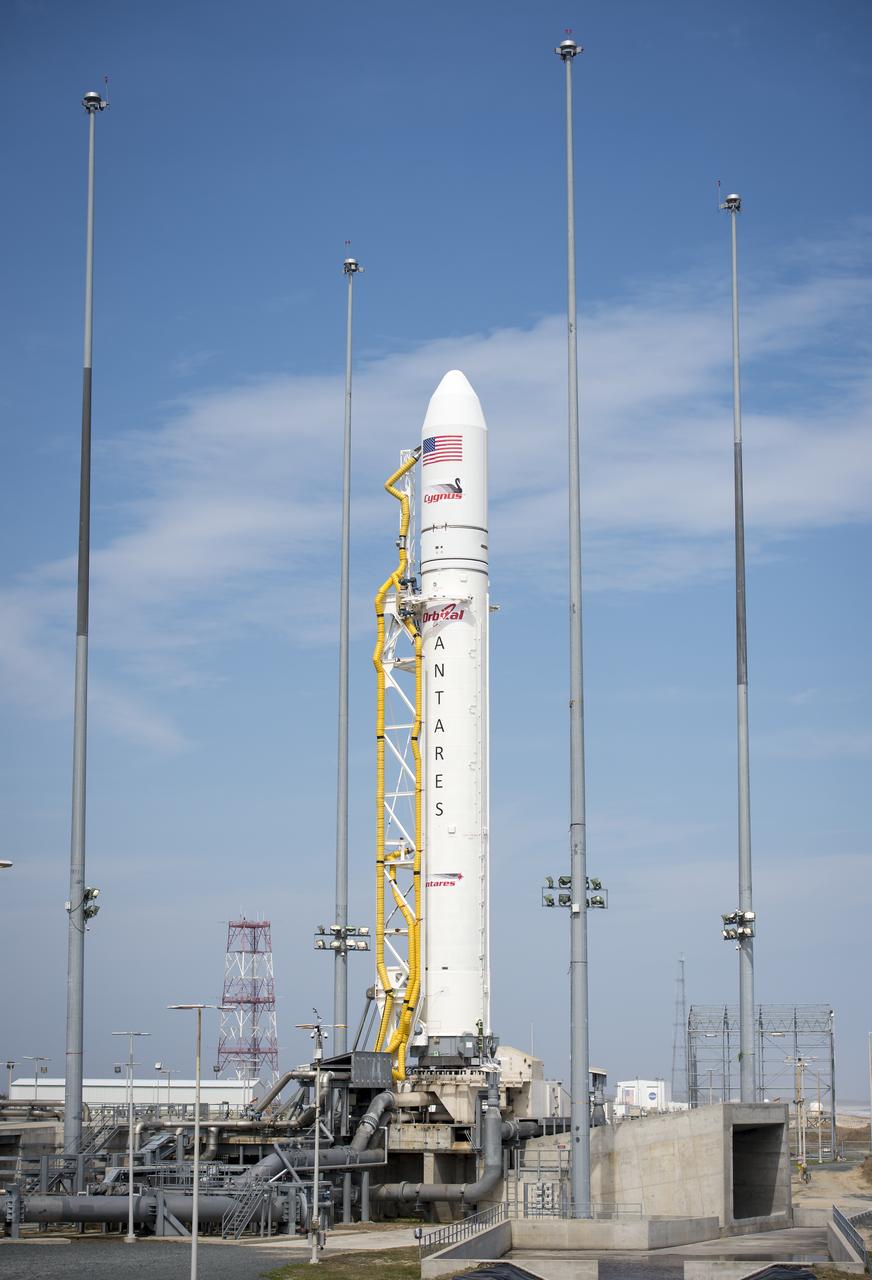

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket is seen on the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) Pad-0A at the NASA Wallops Flight Facility, Friday, April 19, 2013 in Virginia. NASA's commercial space partner, Orbital Sciences Corporation, is scheduled to test launch its first Antares on Saturday, April 20, 2013. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
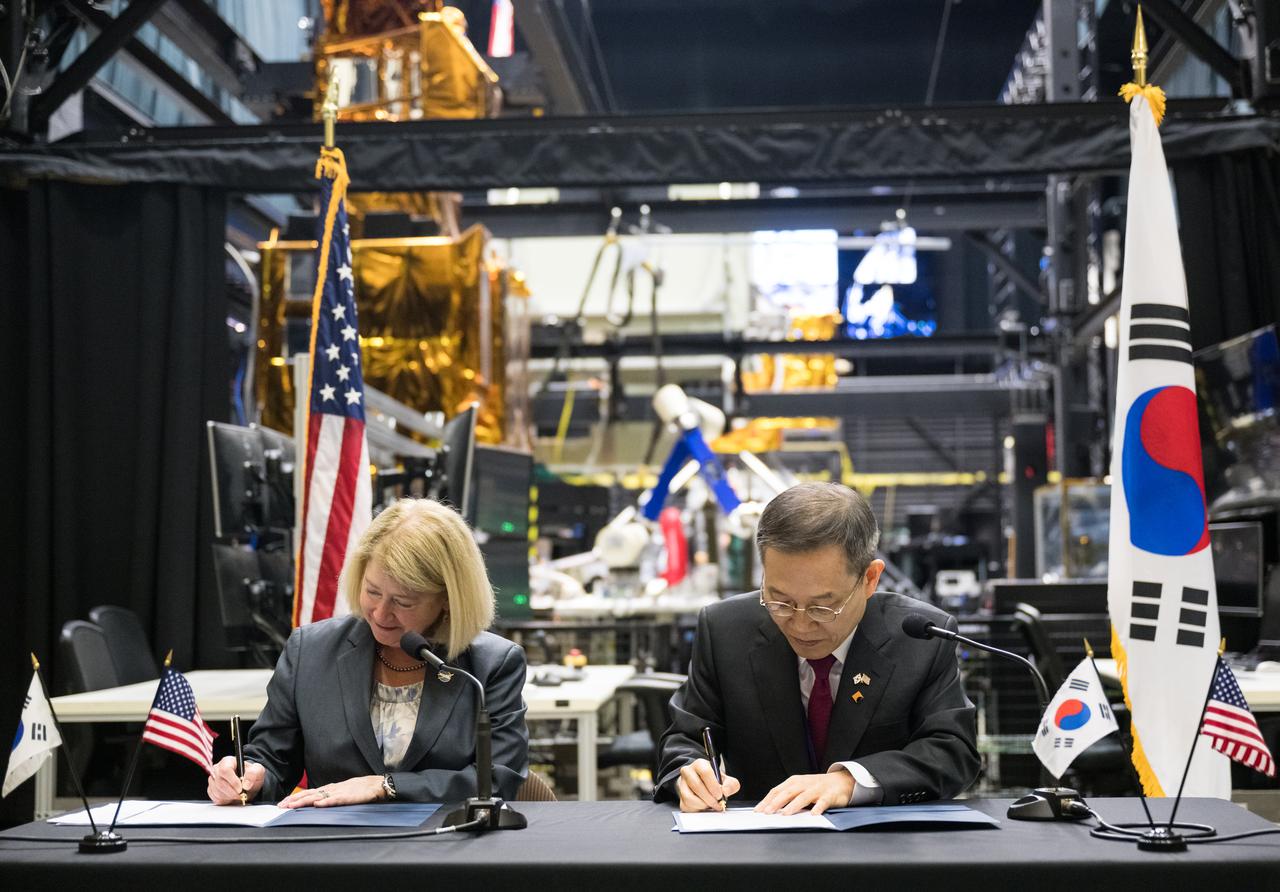

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy and MSIT Minister Jong-Ho Lee sign a Joint Statement of Intent to advance cooperation in exploration and science between NASA and the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea, Tuesday, April 25, 2023, at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy and MSIT Minister Jong-Ho Lee shake hands after signing a Joint Statement of Intent to advance cooperation in exploration and science between NASA and the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea, Tuesday, April 25, 2023, at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
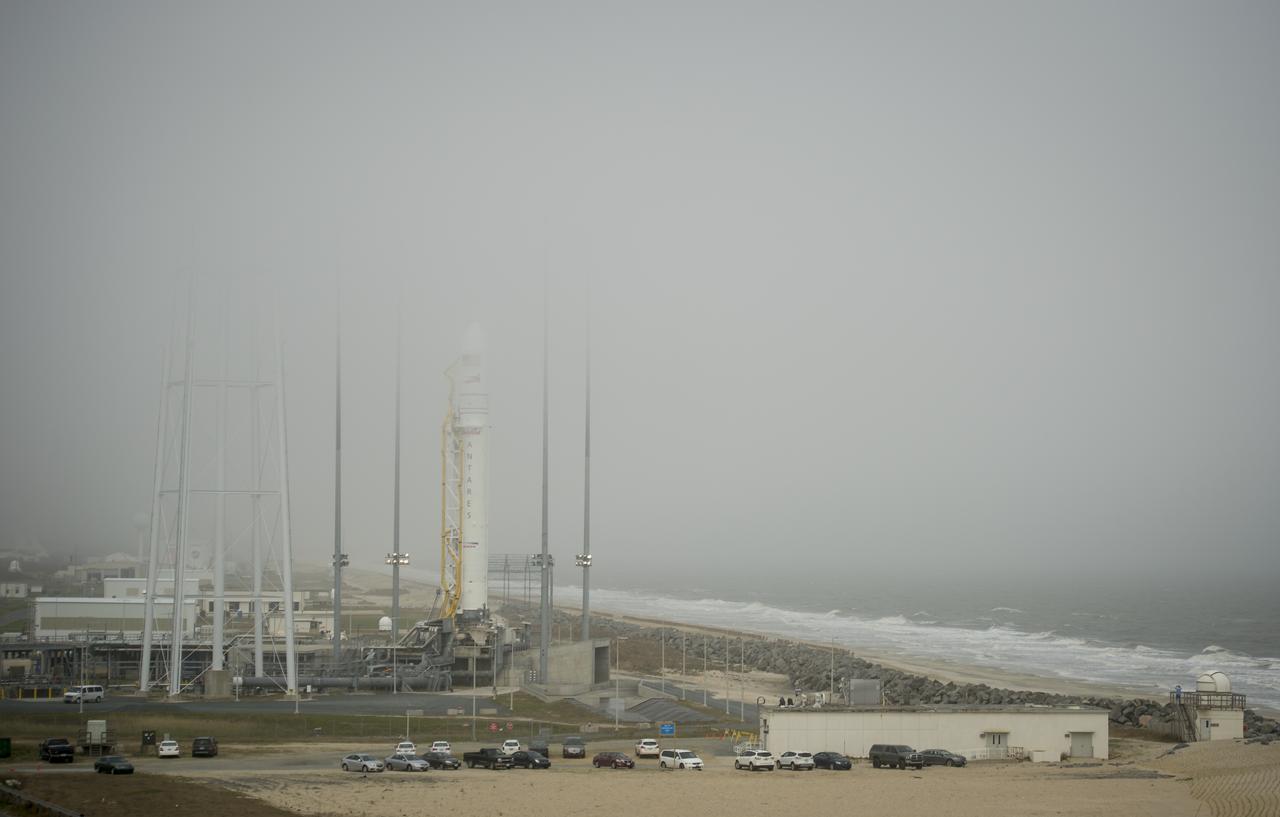

Fog rolls in as the Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket is seen on the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) Pad-0A at the NASA Wallops Flight Facility, Friday, April 19, 2013 in Virginia. NASA's commercial space partner, Orbital Sciences Corporation, is scheduled to test launch its first Antares on Saturday, April 20, 2013. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket is seen on the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) Pad-0A at the NASA Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, Saturday, April 20, 2013. NASA's commercial space partner, Orbital Sciences Corporation, is scheduled to test launch its first Antares later in the day. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
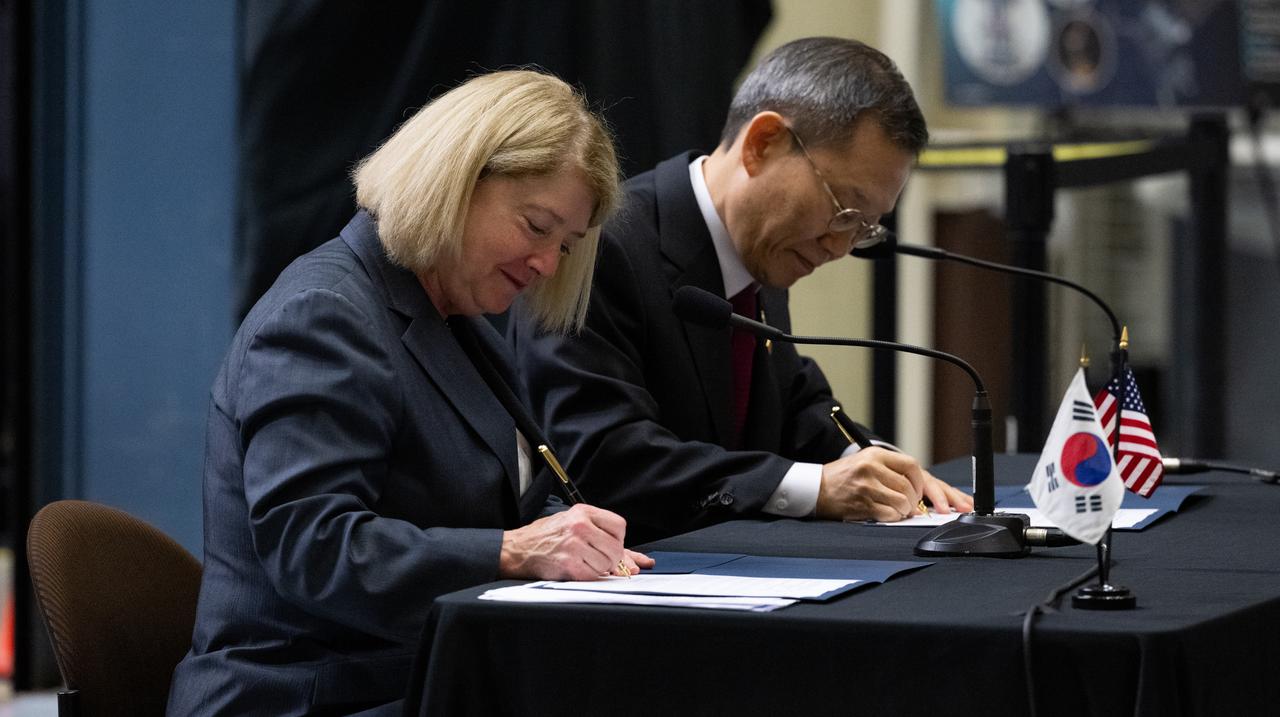

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, left, and MSIT Minister Jong-Ho Lee sign a Joint Statement of Intent to advance cooperation in exploration and science between NASA and the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea, Tuesday, April 25, 2023, at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket is seen on the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) Pad-0A at the NASA Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, Saturday, April 20, 2013. NASA's commercial space partner, Orbital Sciences Corporation, is scheduled to test launch its first Antares later in the day. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket is seen during sunrise on the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) Pad-0A at the NASA Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, Sunday, April 21, 2013. NASA's commercial space partner, Orbital Sciences Corporation, is scheduled to test launch its first Antares later in the day. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
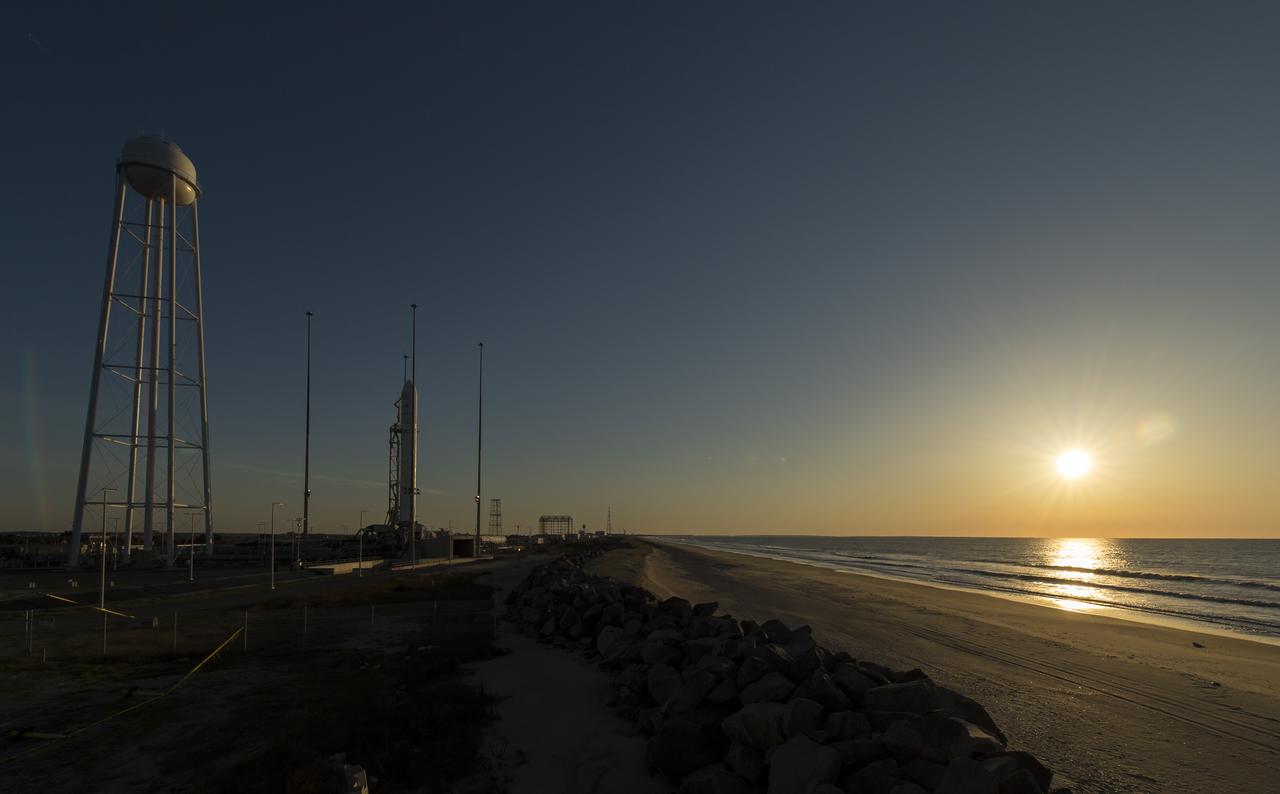

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket is seen during sunrise on the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) Pad-0A at the NASA Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, Sunday, April 21, 2013. NASA's commercial space partner, Orbital Sciences Corporation, is scheduled to test launch its first Antares later in the day. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
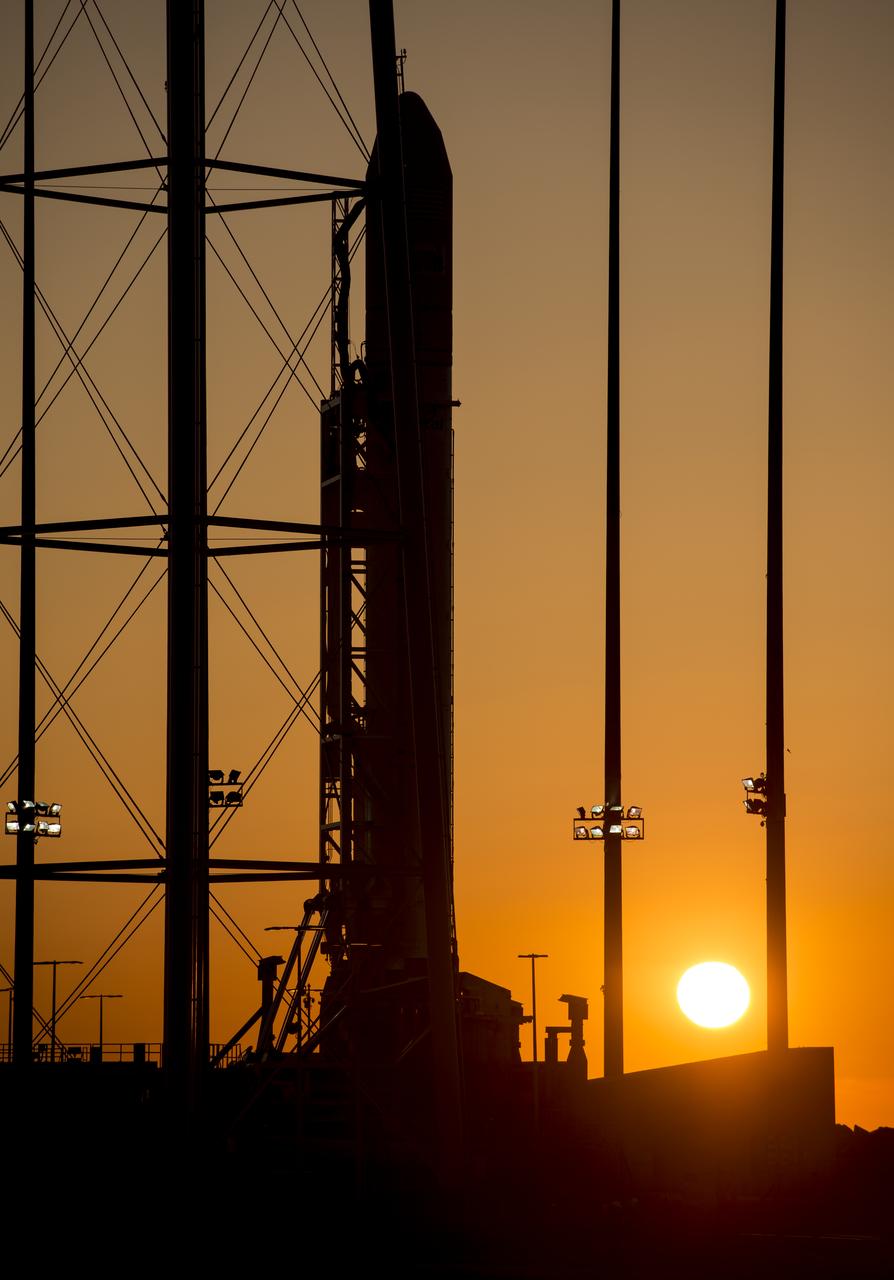

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket is seen during sunrise on the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) Pad-0A at the NASA Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, Sunday, April 21, 2013. NASA's commercial space partner, Orbital Sciences Corporation, is scheduled to test launch its first Antares later in the day. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
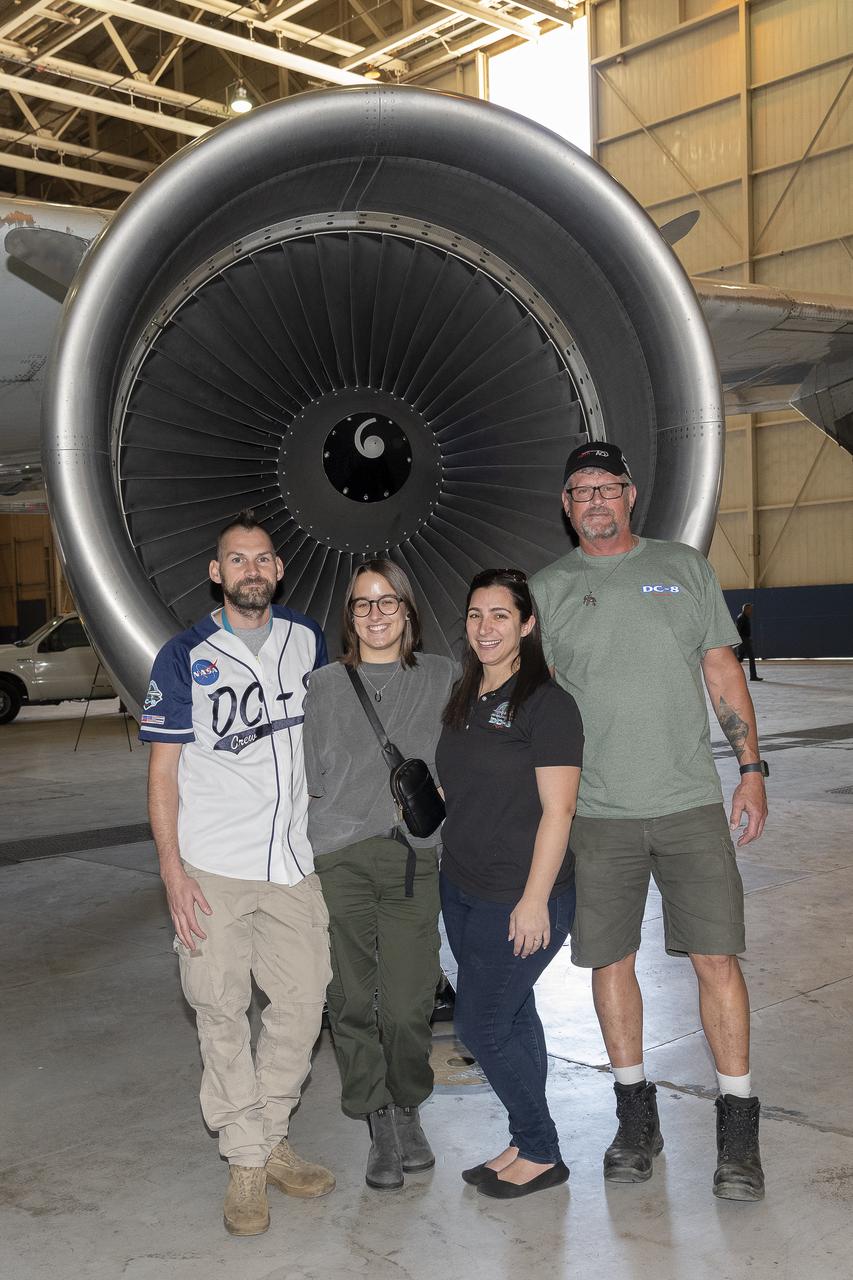

Members of past science missions pose together in front of the DC-8 aircraft’s left engine turbine at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California. From left are avionics lead Kelly Jellison, chemical scientist Katherine Ball, DC-8 Deputy Program Manager Kirsten Boogaard, and DC-8 safety engineer Garry Moors. On May 2, 2024, NASA personnel, friends, and family celebrated the DC-8 staff, aircraft, and science campaigns.
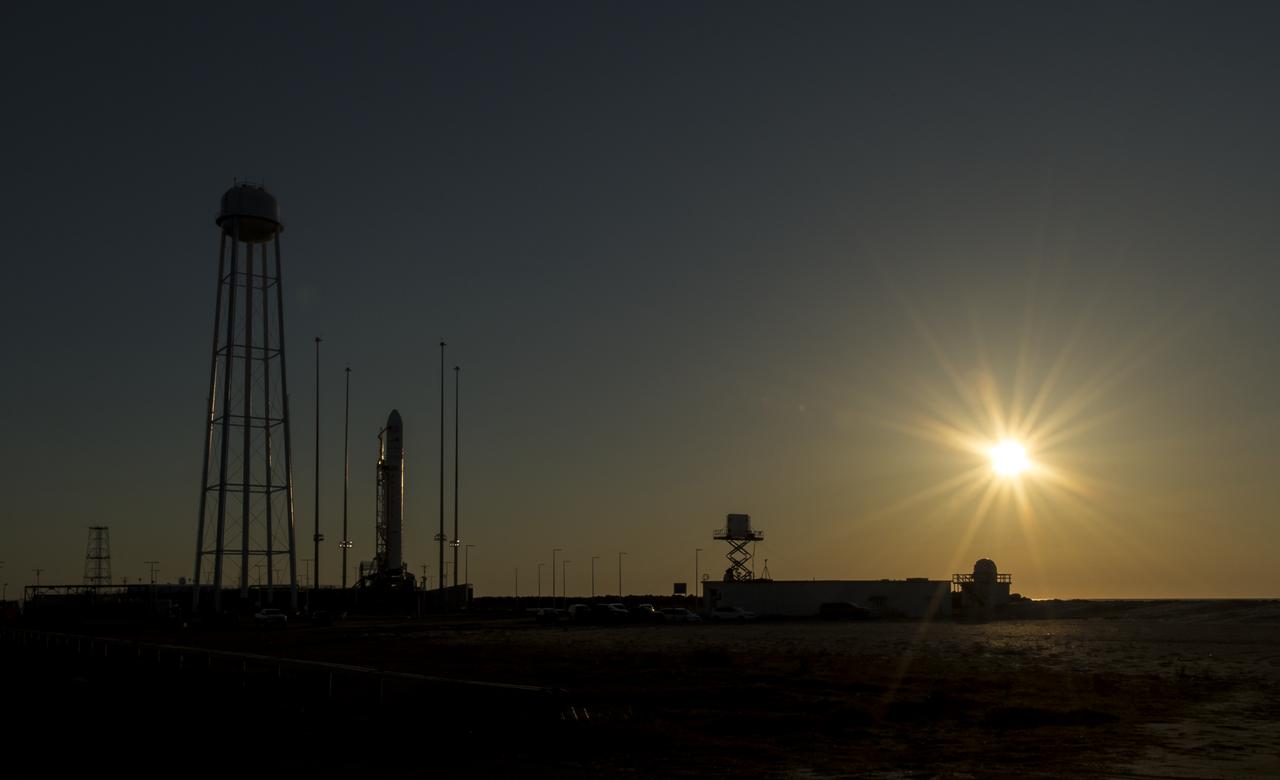

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket is seen during sunrise on the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) Pad-0A at the NASA Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, Sunday, April 21, 2013. NASA's commercial space partner, Orbital Sciences Corporation, is scheduled to test launch its first Antares later in the day. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy and MSIT Minister Jong-Ho Lee pose for a photo after signing a Joint Statement of Intent to advance cooperation in exploration and science between NASA and the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea, Tuesday, April 25, 2023, at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy and MSIT Minister Jong-Ho Lee sign a Joint Statement of Intent to advance cooperation in exploration and science between NASA and the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea, Tuesday, April 25, 2023, at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
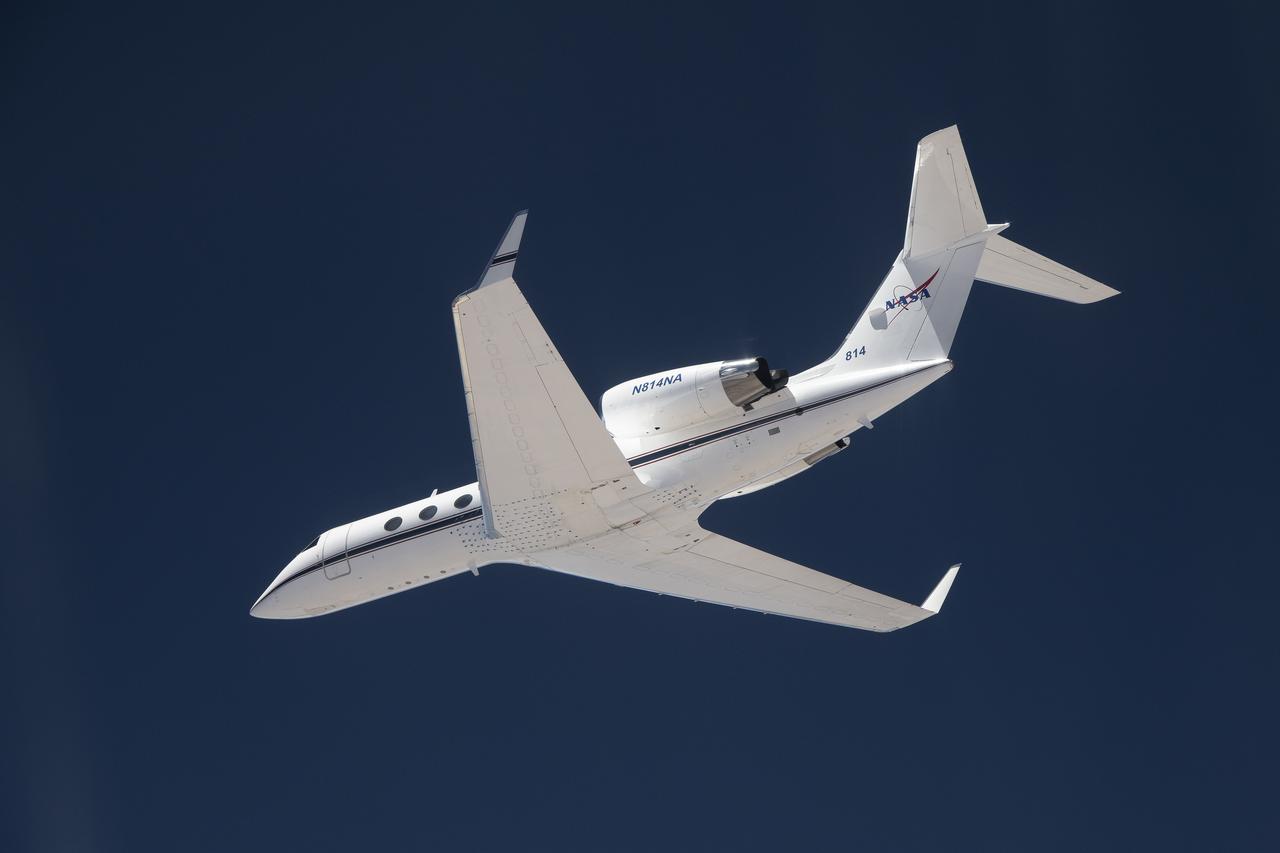

The G-IV aircraft flies overhead in the Mojave Desert near NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. Baseline flights like this one occurred in June 2024, and future flights in service of science research will benefit from the installment of the Soxnav navigational system, developed in collaboration with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California and the Bay Area Environmental Research Institute in California’s Silicon Valley. This navigational system provides precise, economical aircraft guidance for a variety of aircraft types moving at high speeds.
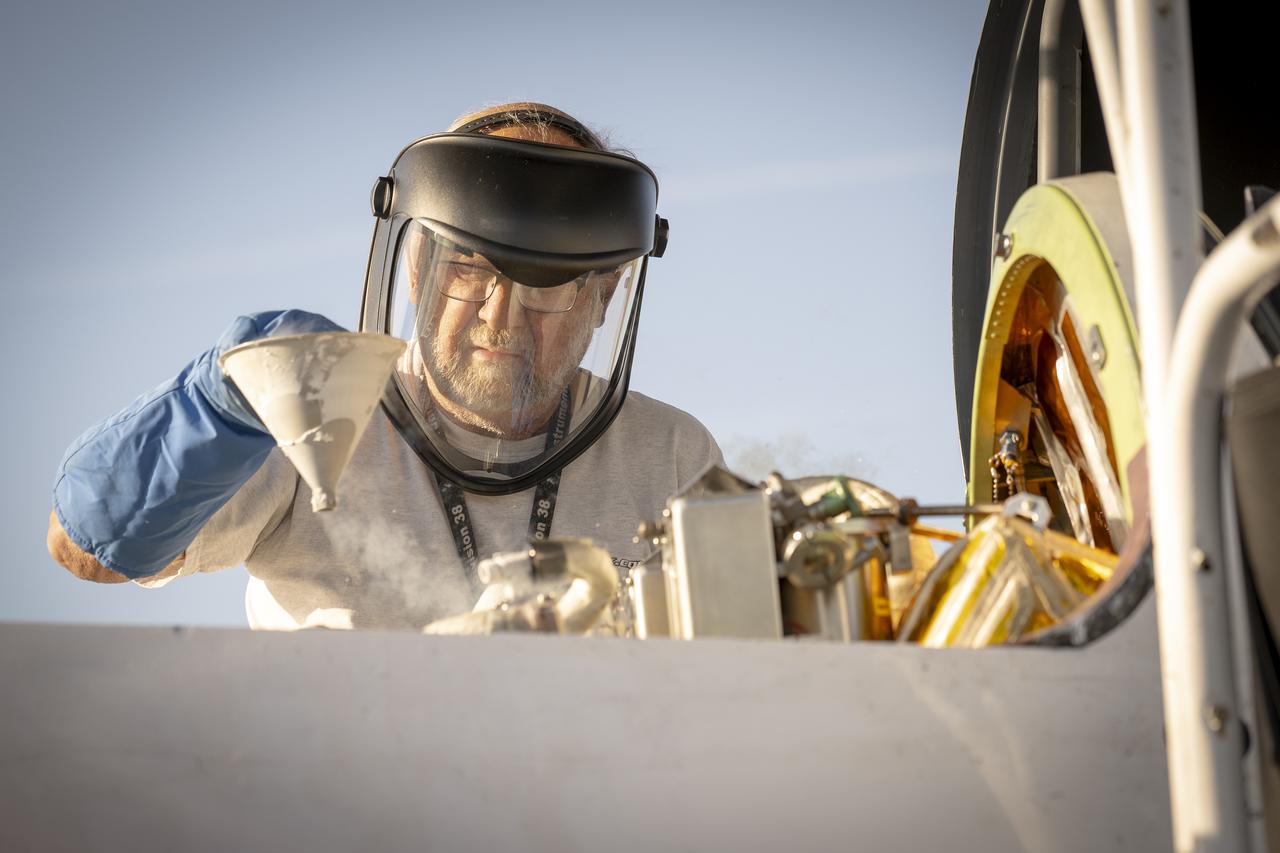

A crew member handles liquid nitrogen servicing for NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft at Edwards, California, on Thursday, Aug. 21, 2025. Liquid nitrogen is used to support key science instruments for extended flight durations in critical research missions, such as the Geological Earth Mapping Experiment (GEMx), which requires flights of up to eight hours at approximately 65,000 feet altitude.