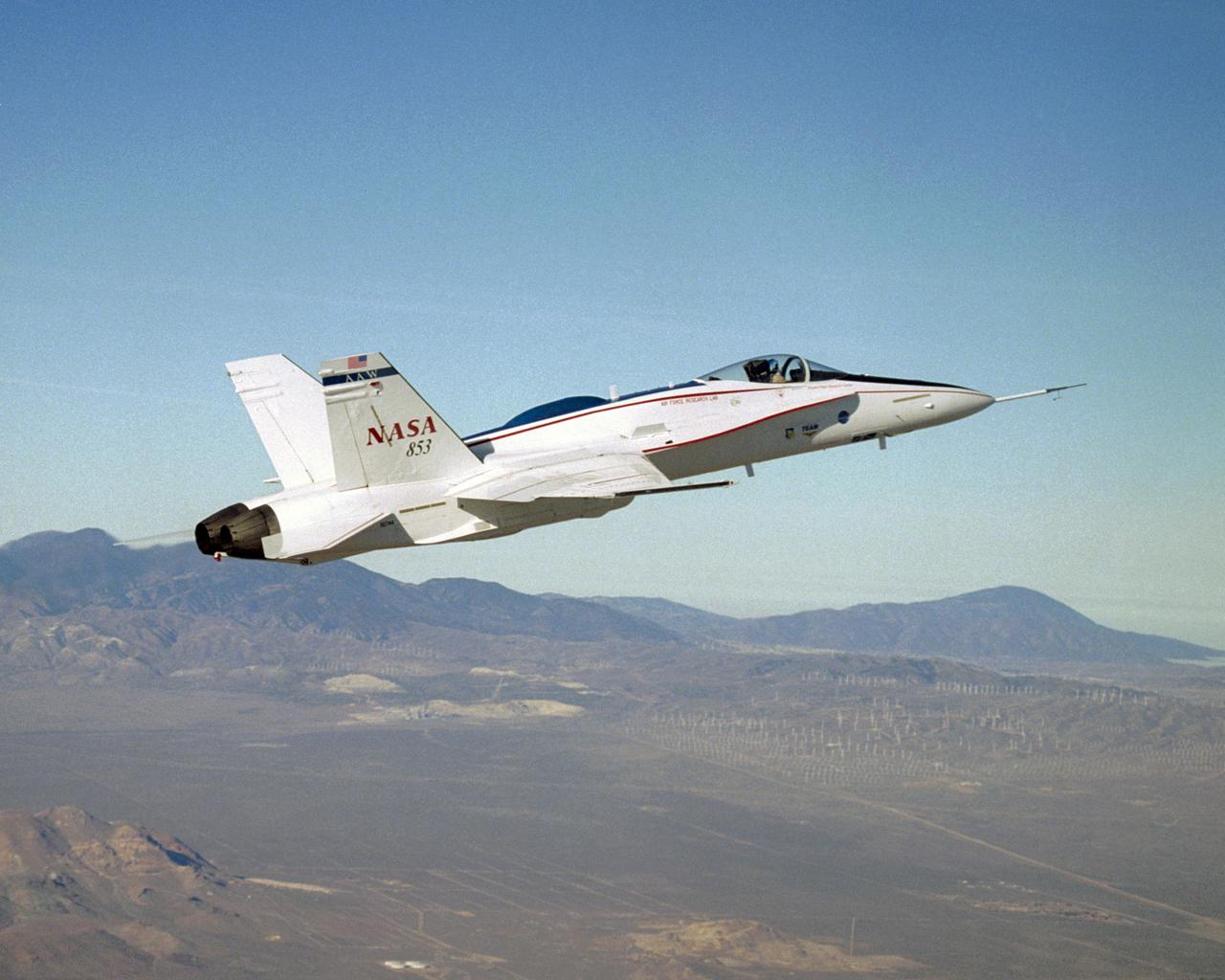

NASA's Active Aeroelastic Wing F/A-18 resumed flight tests in the second phase of the program at the Dryden Flight Research Center in early December 2004.

An Amphitech OASys Ka-band radar was the primary sensor installed on Scaled Composites' Proteus for the second phase of NASA-sponsored unmanned aerial vehicle Detect, See and Avoid flight tests.
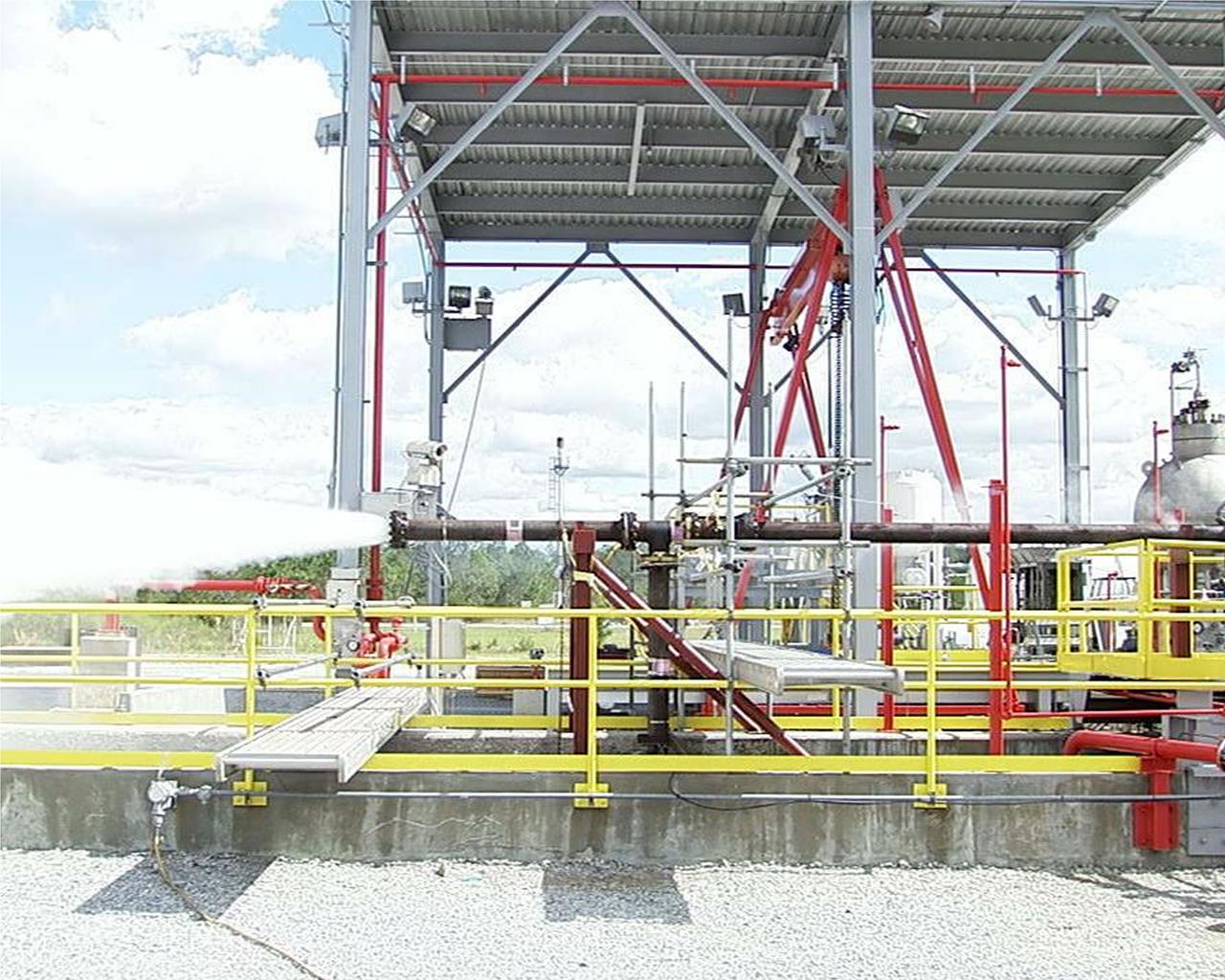

Phase 2 of the A-3 Test Facility Subscale Diffuser Risk Mitigation Project at Stennis Space Center reached a milestone Oct. 25 when the E-3 Test Facility produced superheated (500+ degrees) steam for approximately 3 seconds at more than 400 psi. The test team, led by Barry Robinson of NASA's Test Projects Office, followed that success with further tests to lengthen the duration of steam production. On Nov. 1, they were able to maintain a consistent pressure and temperature of steam for 60 seconds. In December, the team began Phase 3 of the testing, providing data for the design and procurement to build the full-scale version of the steam diffuser for SSC's A-3 Test Stand.
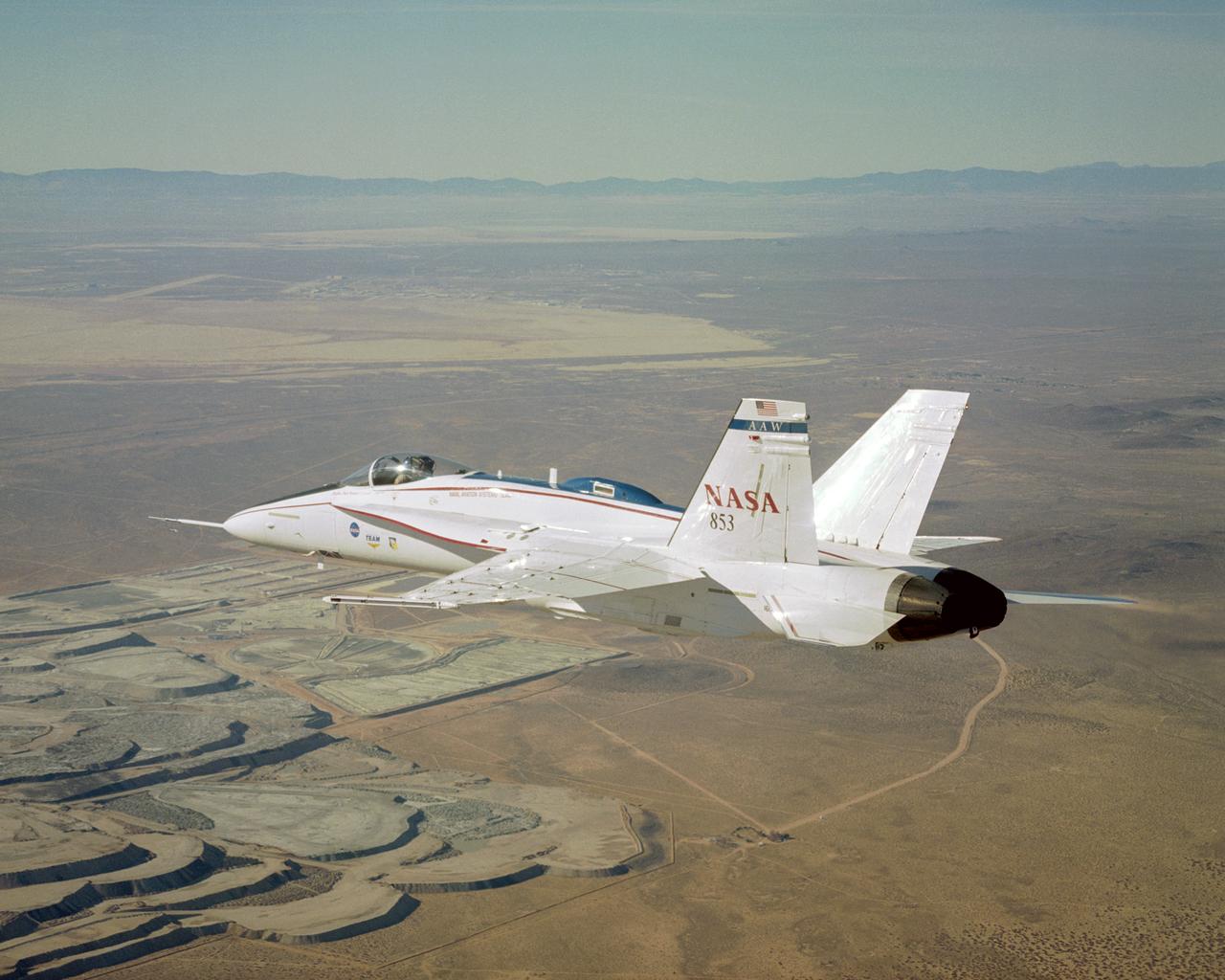

NASA's modified Active Aeroelastic Wing F/A-18 skims over portions of the U.S. Borax mine during a recent mission from the Dryden Flight Research Center.
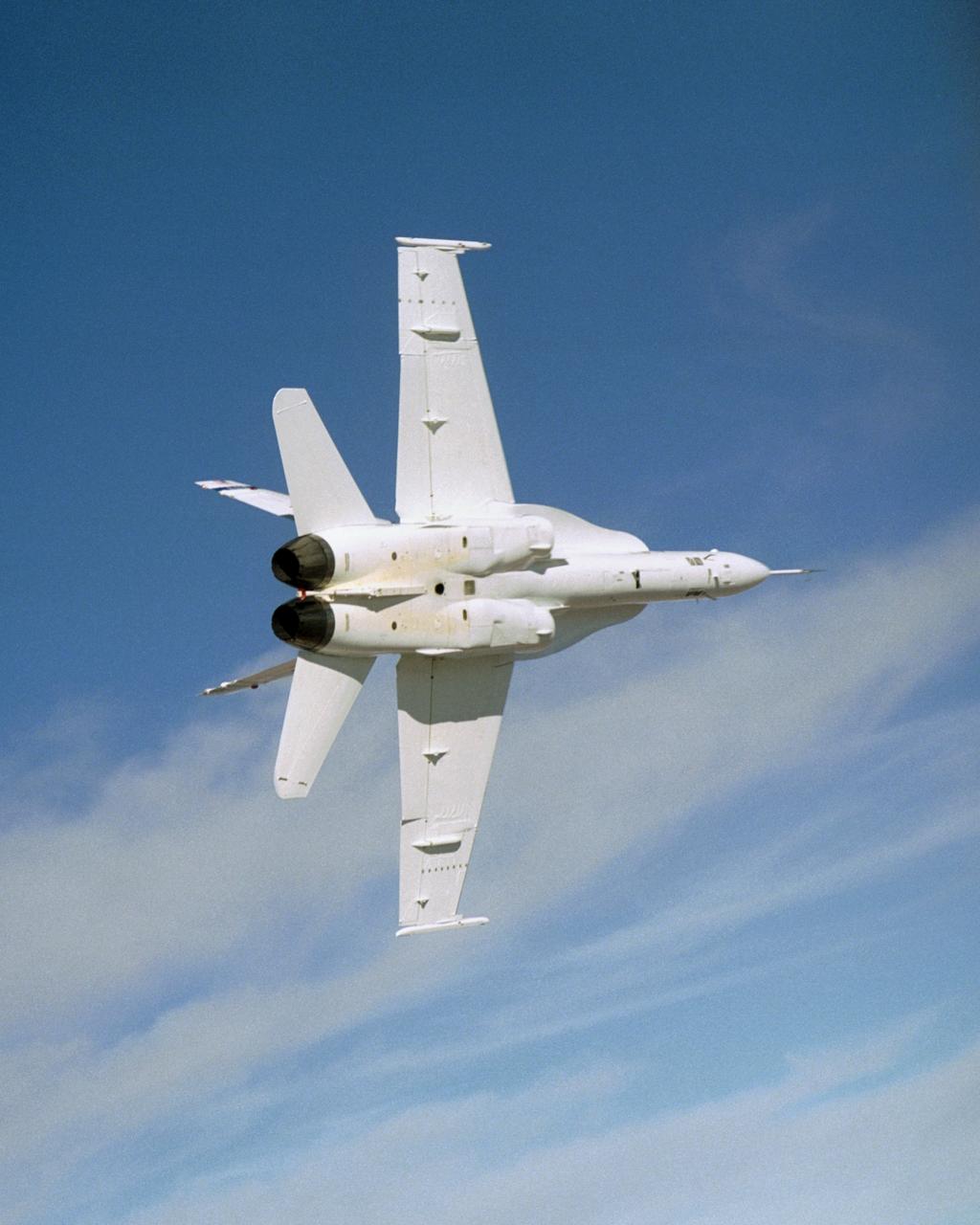

NASA's Active Aeroelastic Wing F/A-18 rolls into a hard left turn during a research flight in early December 2004 from the Dryden Flight Research Center.

The U.S. Air Force Thunderbirds fly over NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, during the second phase of its winter training in February 2025 to prepare for the upcoming air show season. The Thunderbirds perform all over the world in F-16 Fighting Falcons, a multi-role fighter jet.
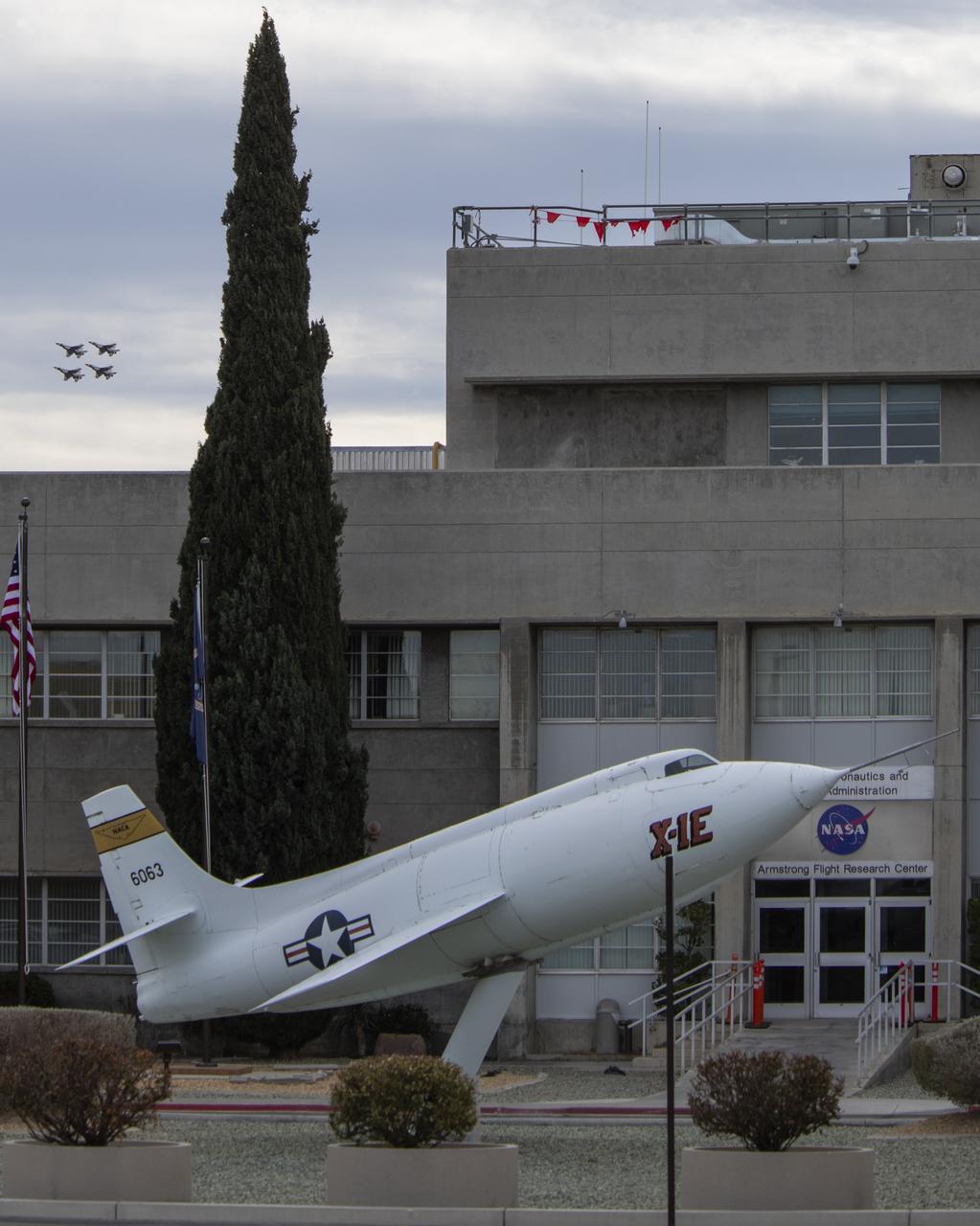

The U.S. Air Force Thunderbirds fly over NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, during the second phase of its winter training in February 2025 to prepare for the upcoming air show season. The Thunderbirds perform all over the world in F-16 Fighting Falcons, a multi-role fighter jet.

The U.S. Air Force Thunderbirds fly over NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, during the second phase of its winter training in February 2025 to prepare for the upcoming air show season. The Thunderbirds perform all over the world in F-16 Fighting Falcons, a multi-role fighter jet.
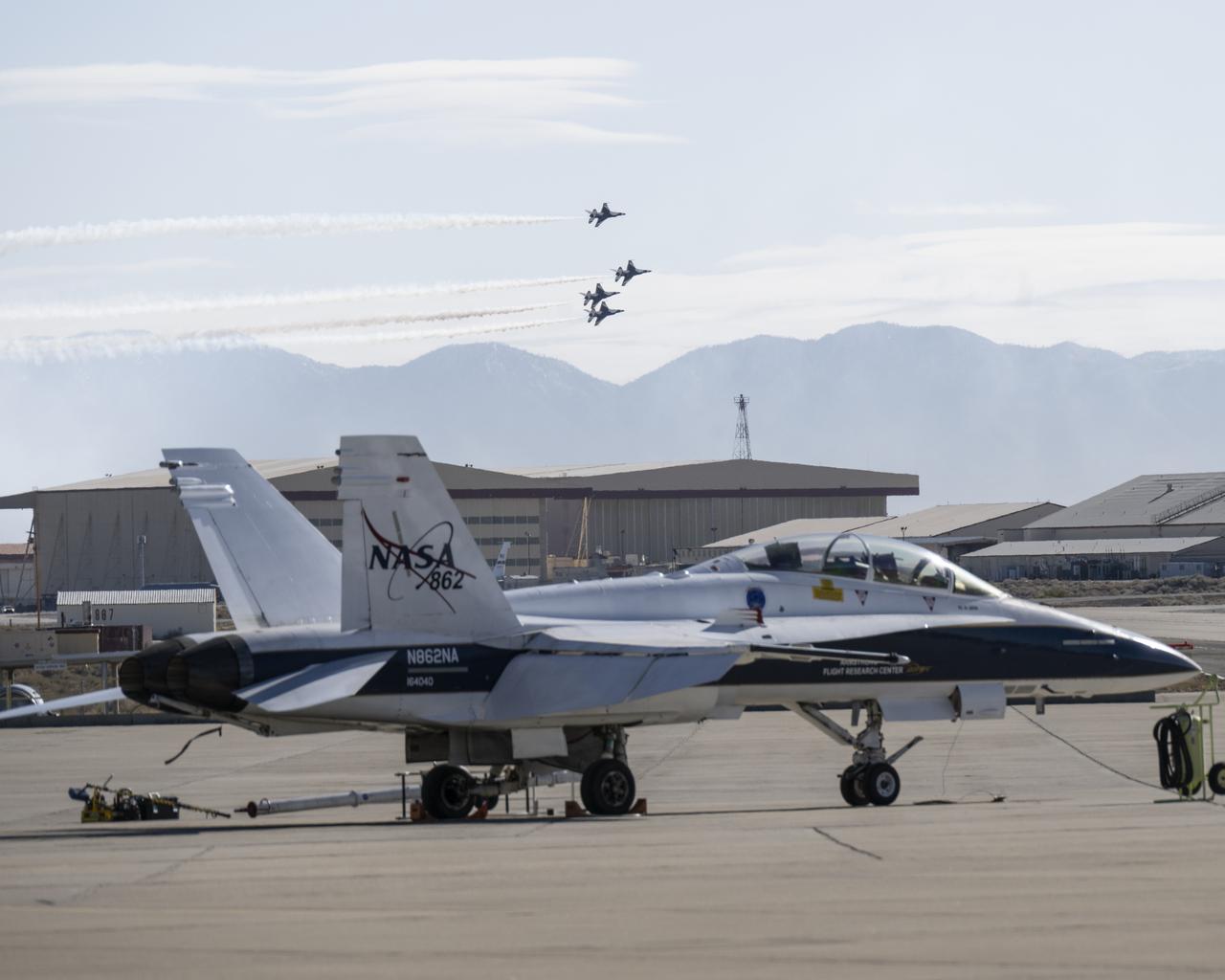

The U.S. Air Force Thunderbirds fly over NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, during the second phase of its winter training in February 2025 to prepare for the upcoming air show season. The Thunderbirds perform all over the world in F-16 Fighting Falcons, a multi-role fighter jet.
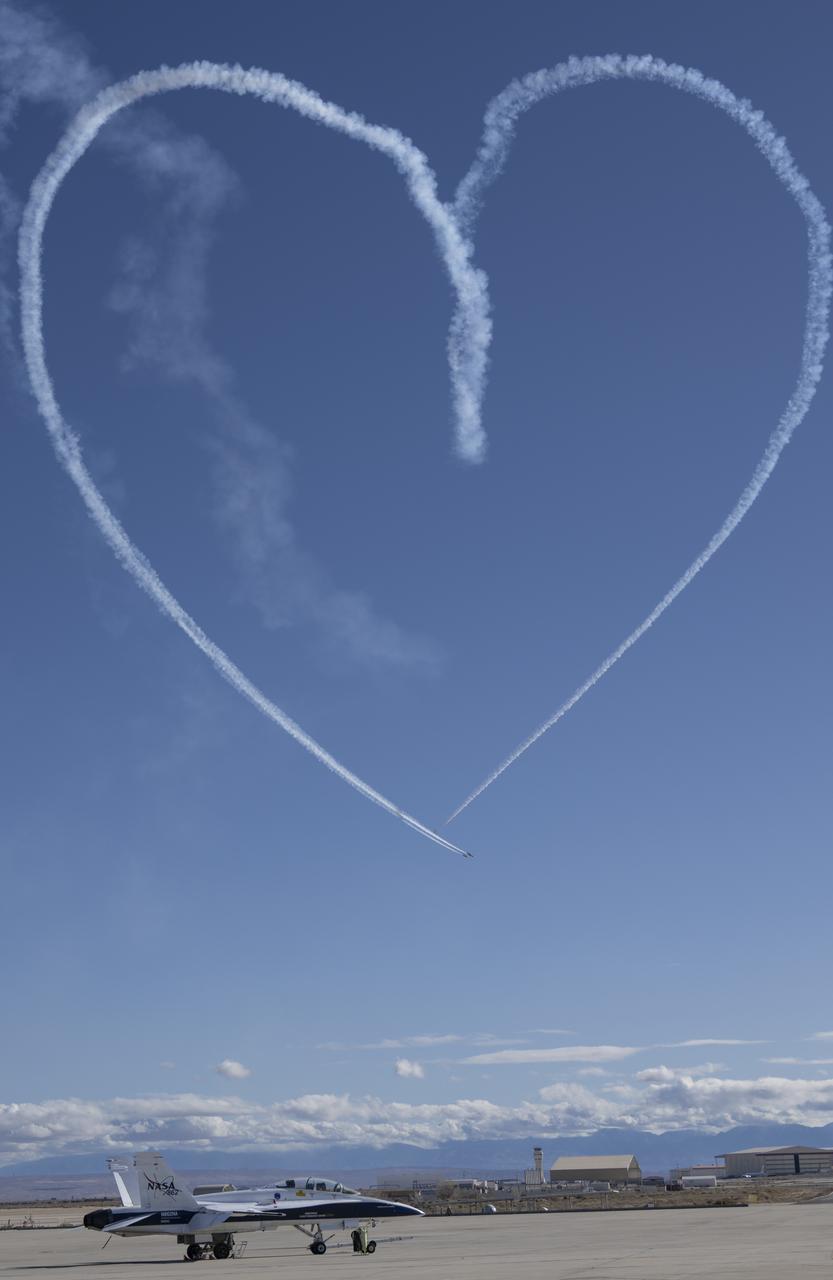

The U.S. Air Force Thunderbirds fly over NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, during the second phase of its winter training in February 2025 to prepare for the upcoming air show season. The Thunderbirds perform all over the world in F-16 Fighting Falcons, a multi-role fighter jet.
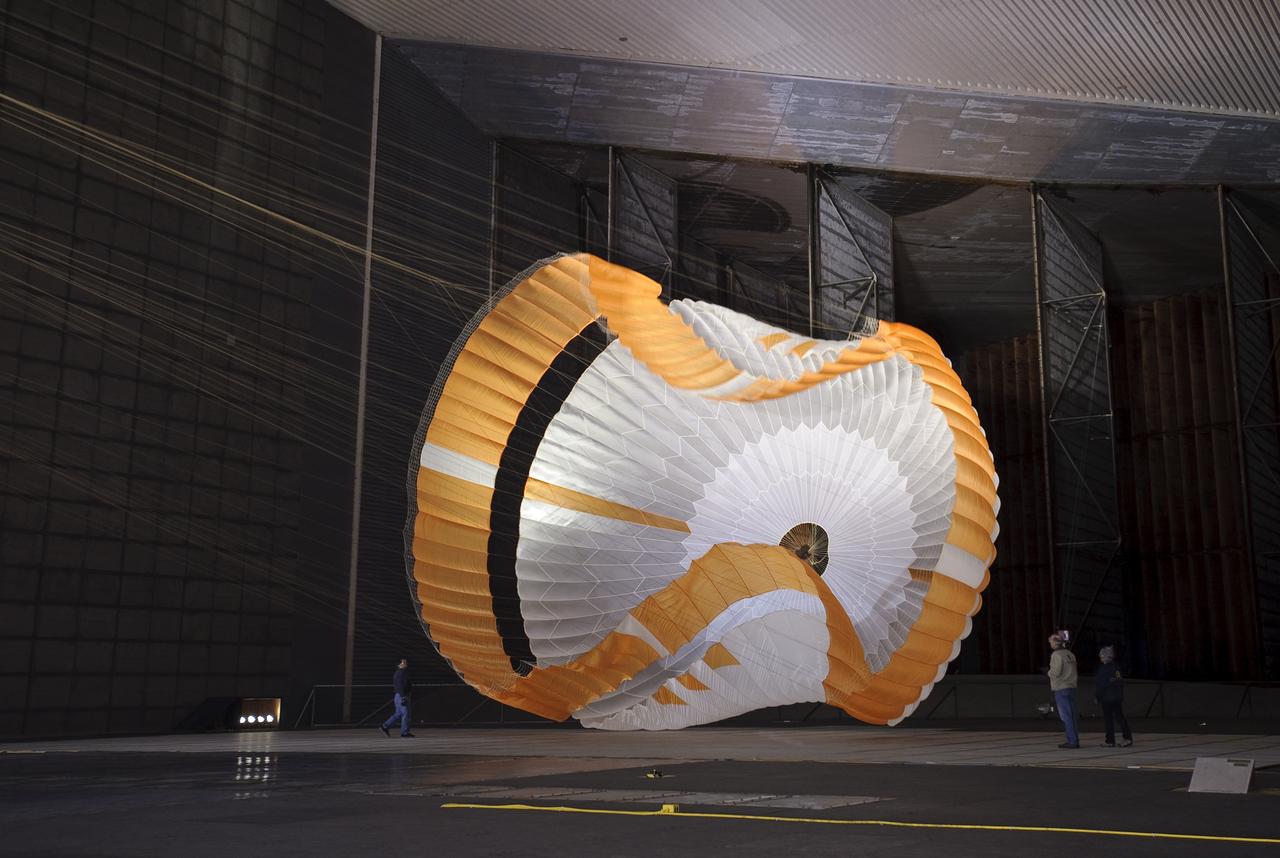

Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) parachuste test in the NASA Ames 80x120ft Subsonic Wind Tunnel at Moffett Field, Calif. (TR #22 - Phase 6) is the largest ever built to fly on an extraterrestrail mission. This image shows the qualification-test parachute beginning to open a few seconds after it was launched from a mortar into an 80-mile-per-hour (36-meter-per-second) wind.
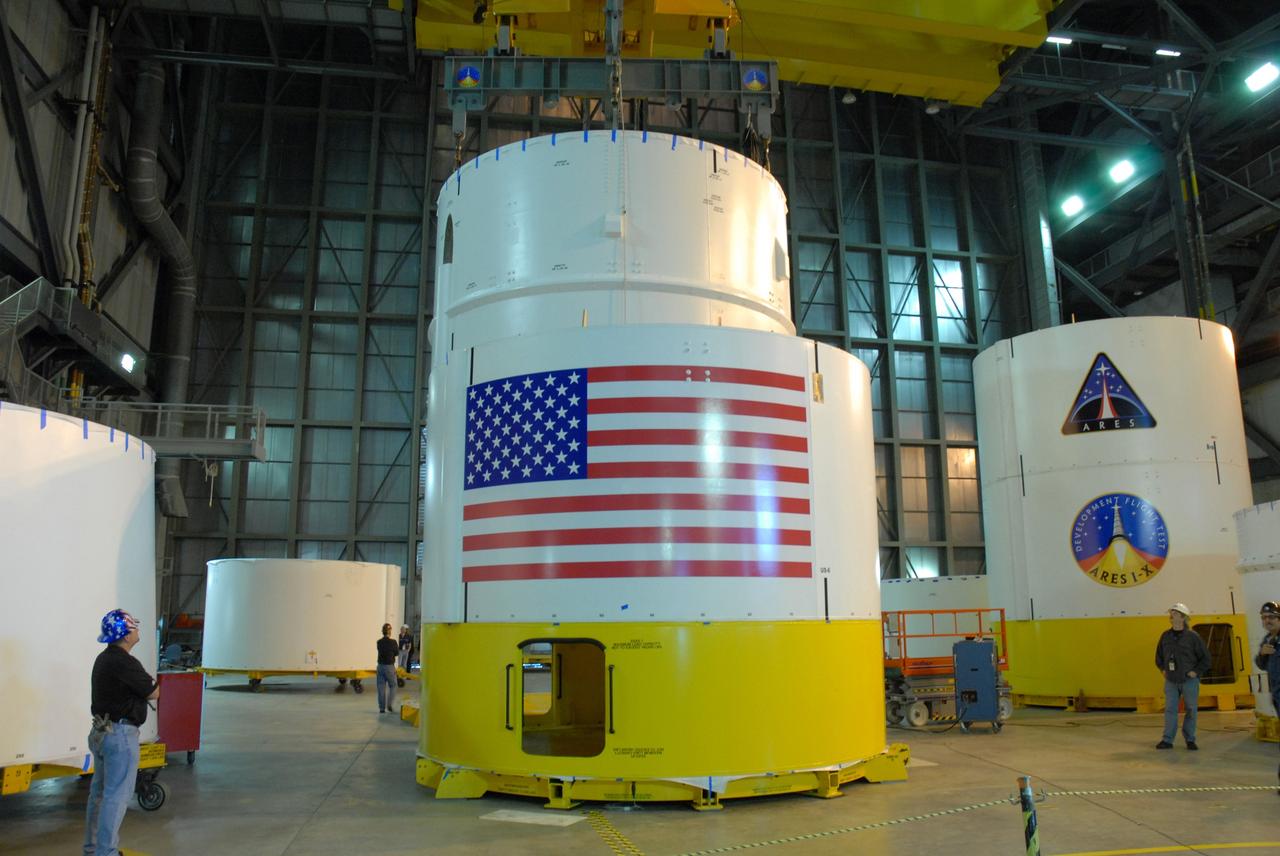
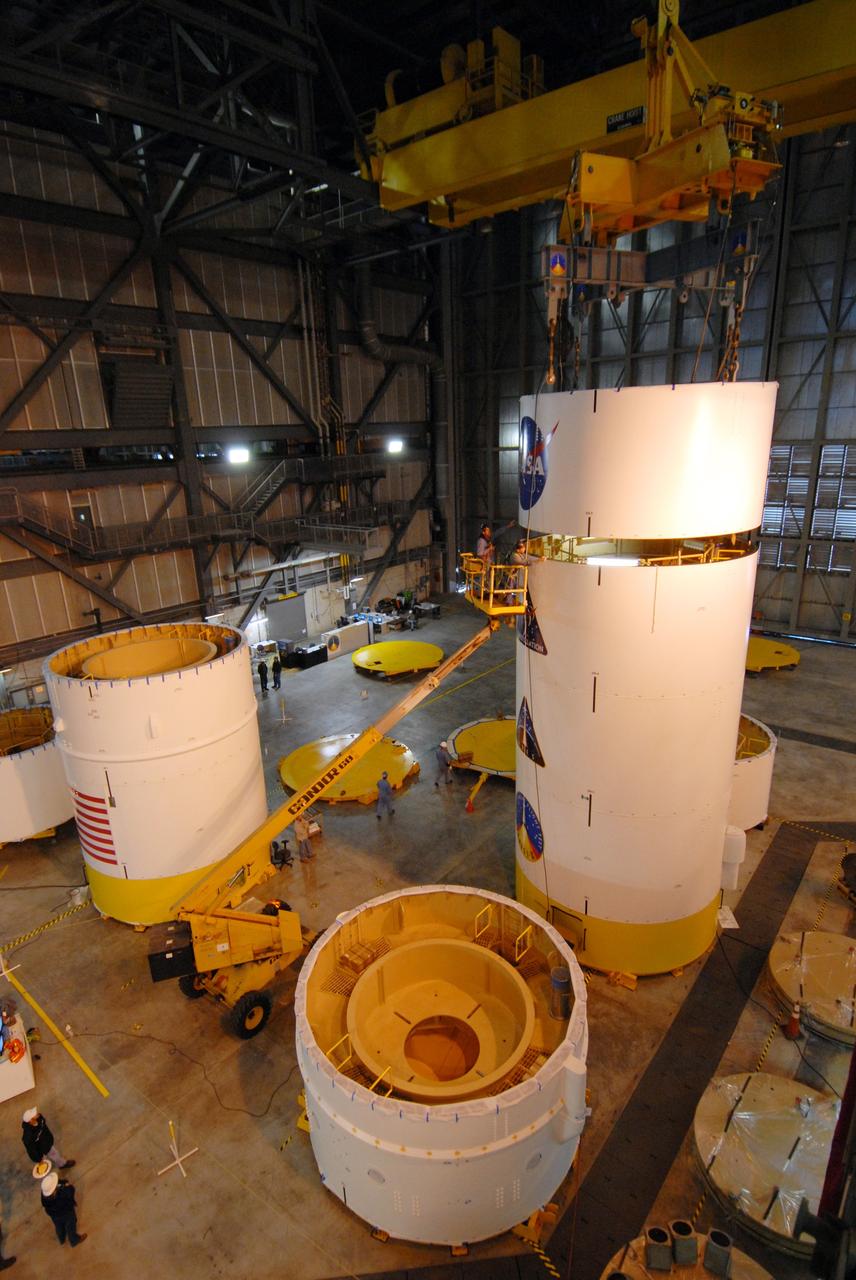
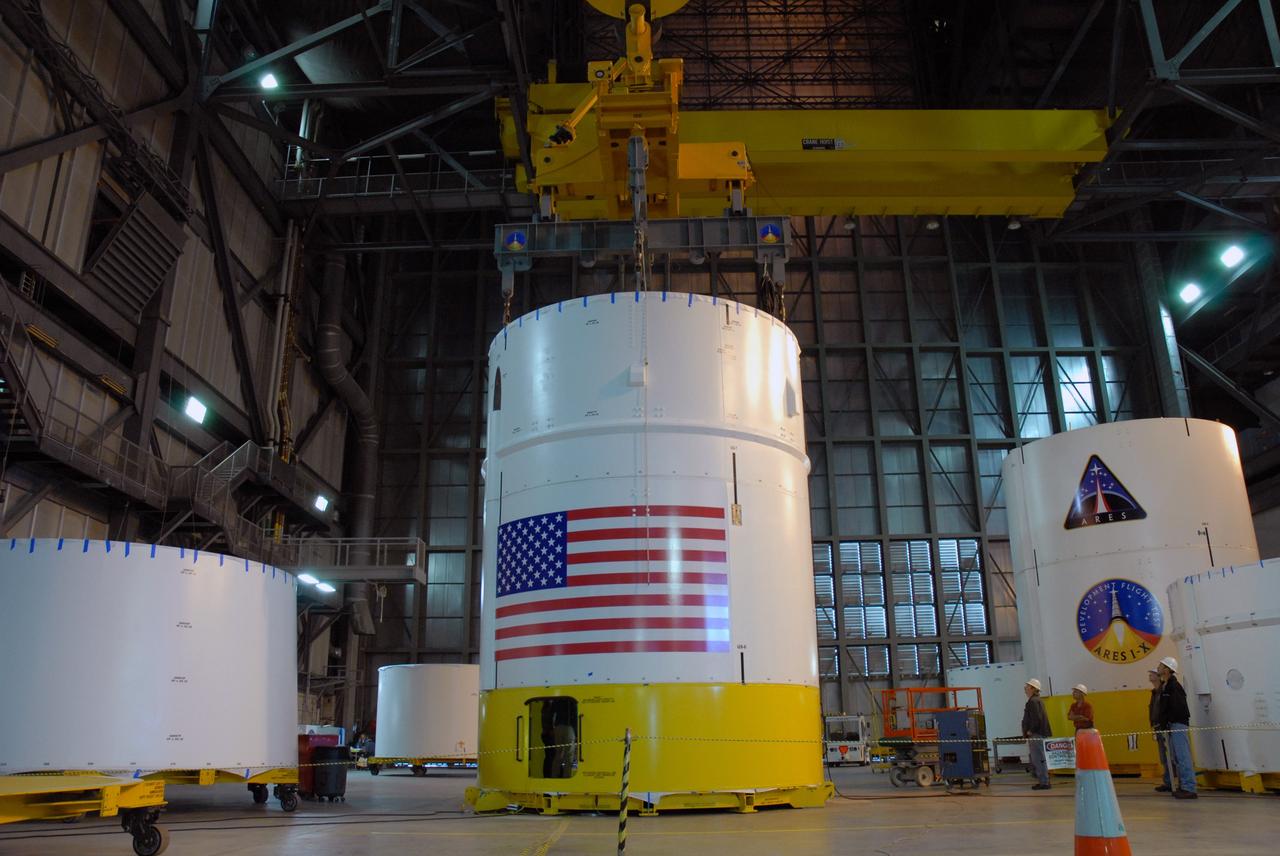
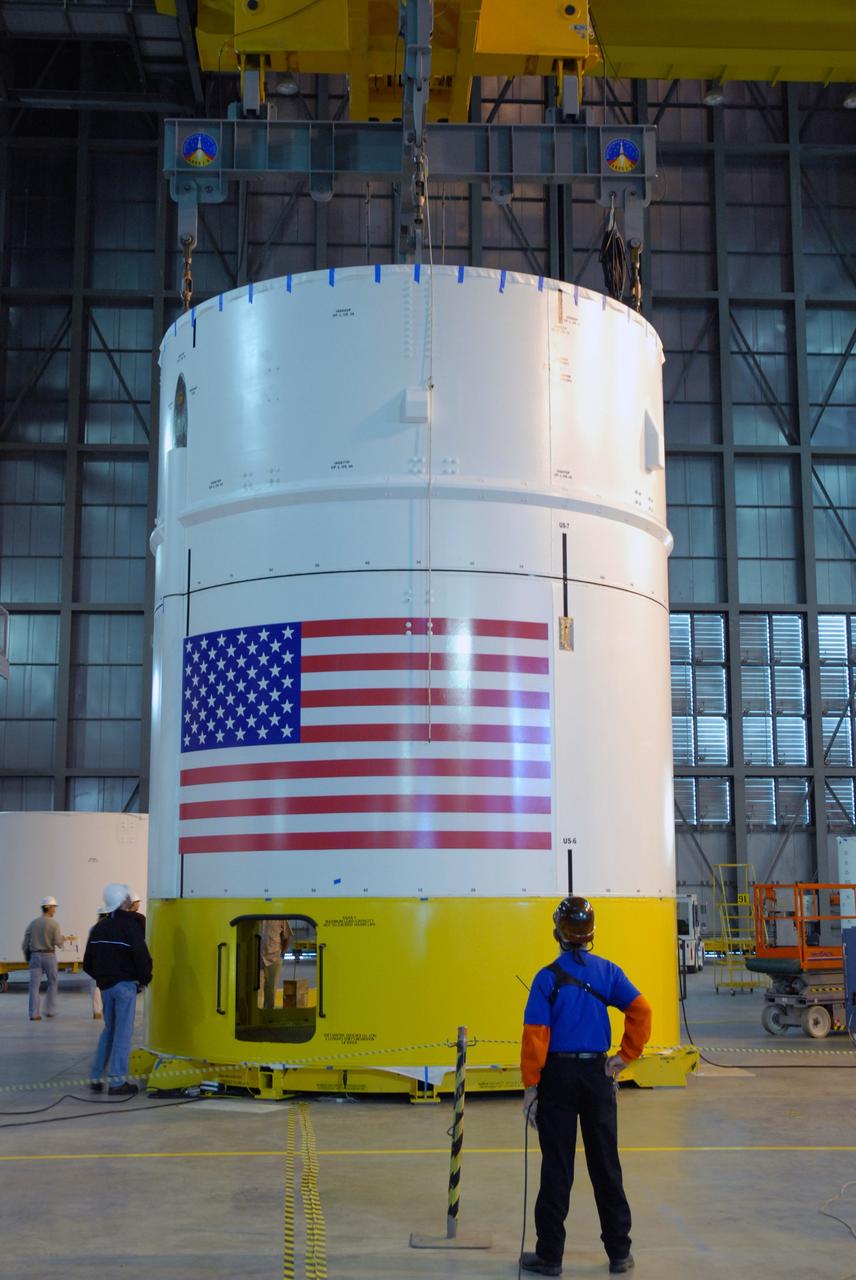
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane moves the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segment 7 toward segment 6 (in front, with U.S. flag decal). The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight identified as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
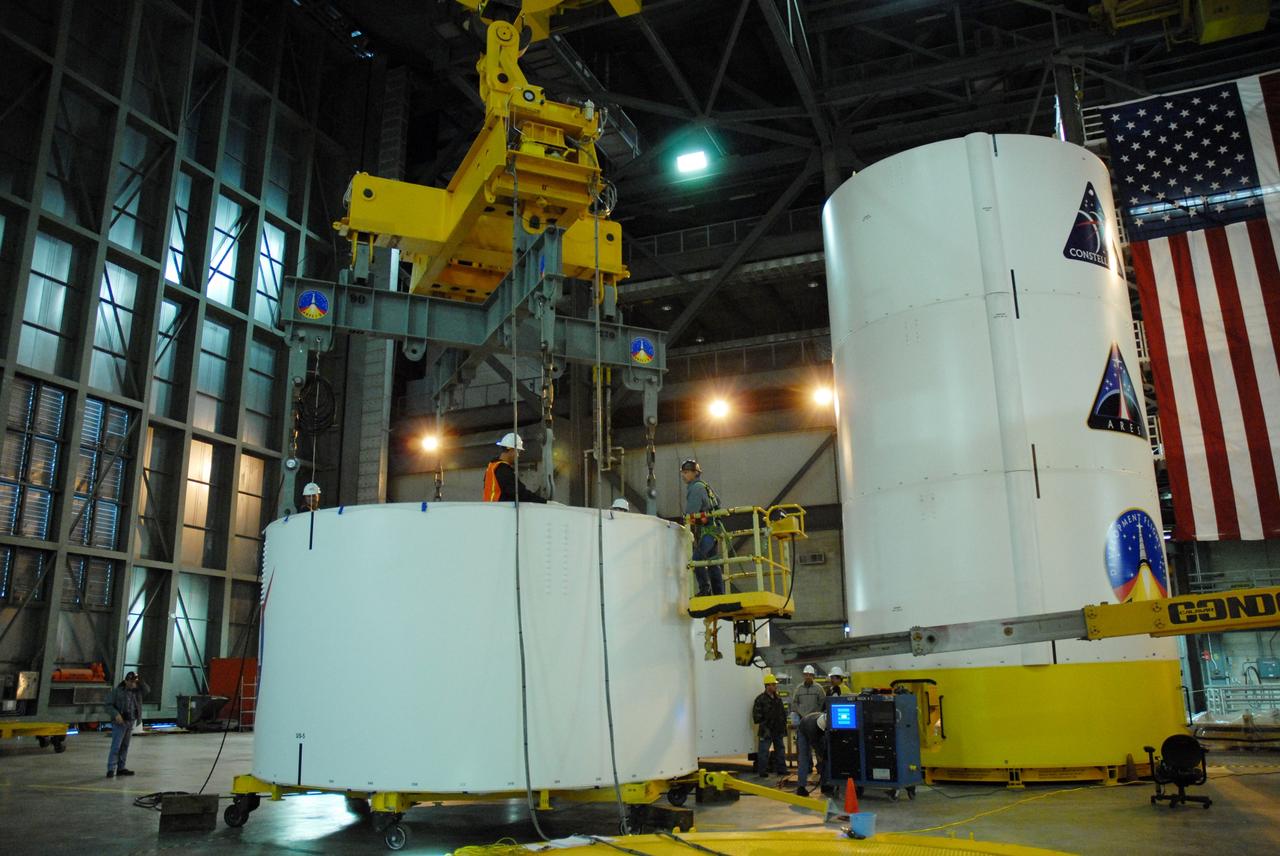

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is attached to segment 5 of the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segments to lift it. Segment 5 will be stacked on to segment 4, at the top of the tall stack at right.The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight known as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

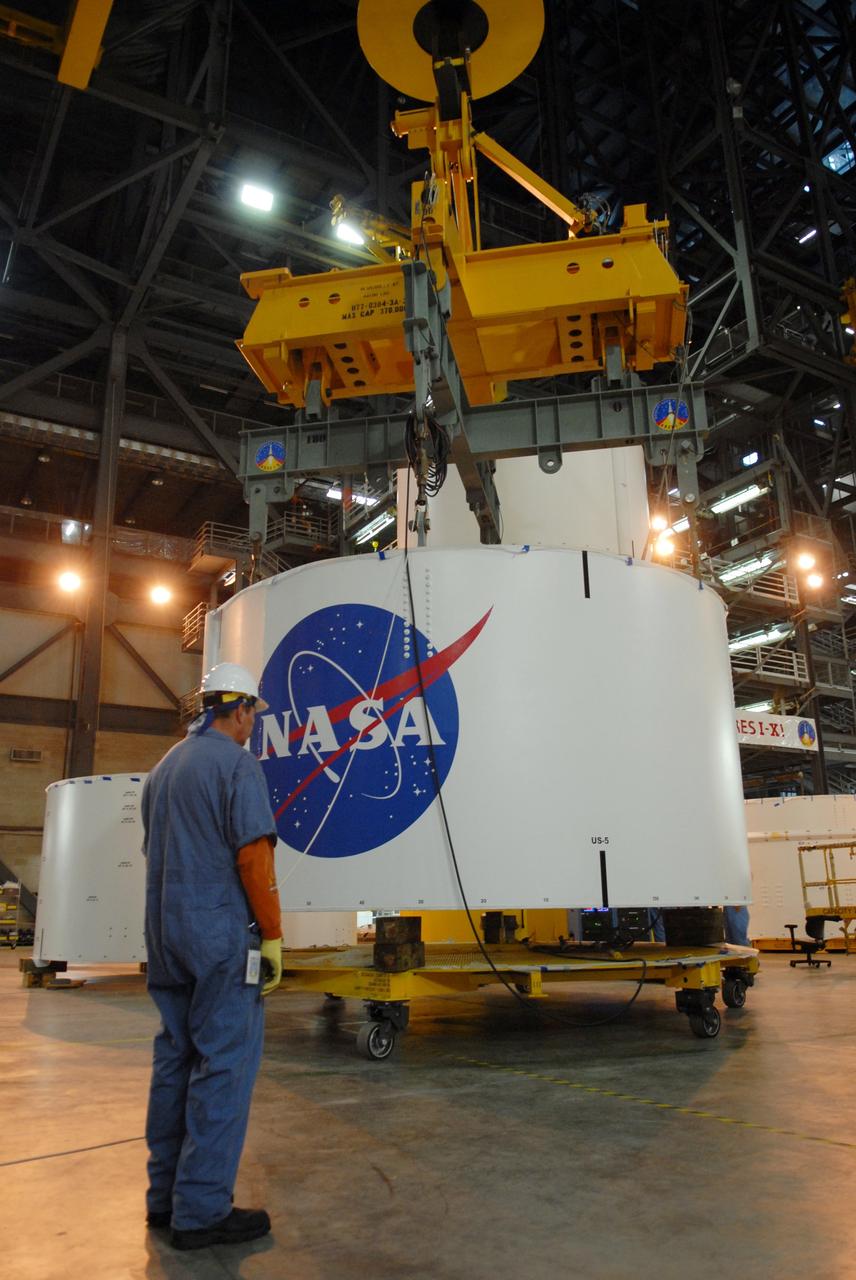
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers segment 5 of the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segments onto segment 4, at top of the tall stack below. The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight known as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

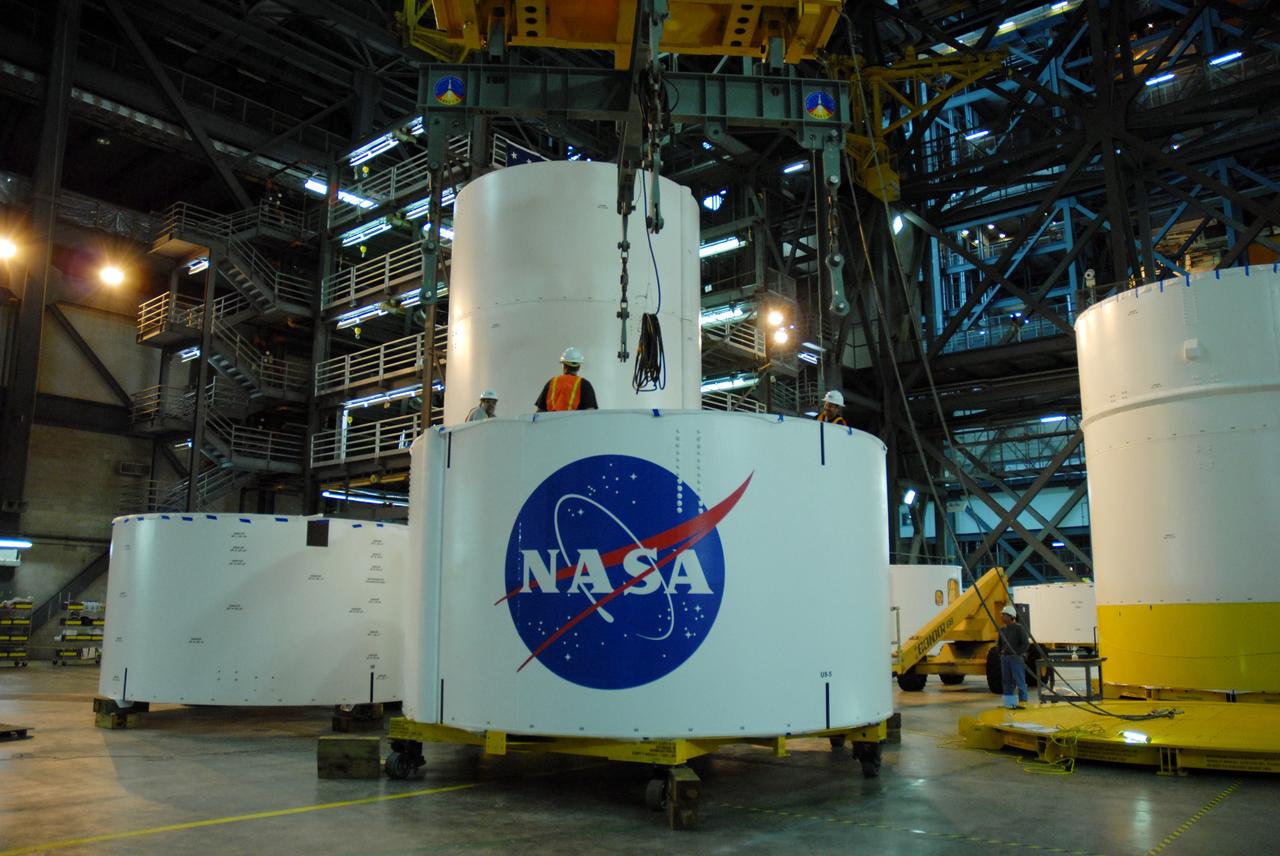
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segment 7 is stacked onto segment 6. The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight identified as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, work is under way to stack the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segment 5 to segment 4. The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight known as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts segment 5 of the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segments. It will be placed on segment 4, at top of the tall stack behind it.The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight known as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
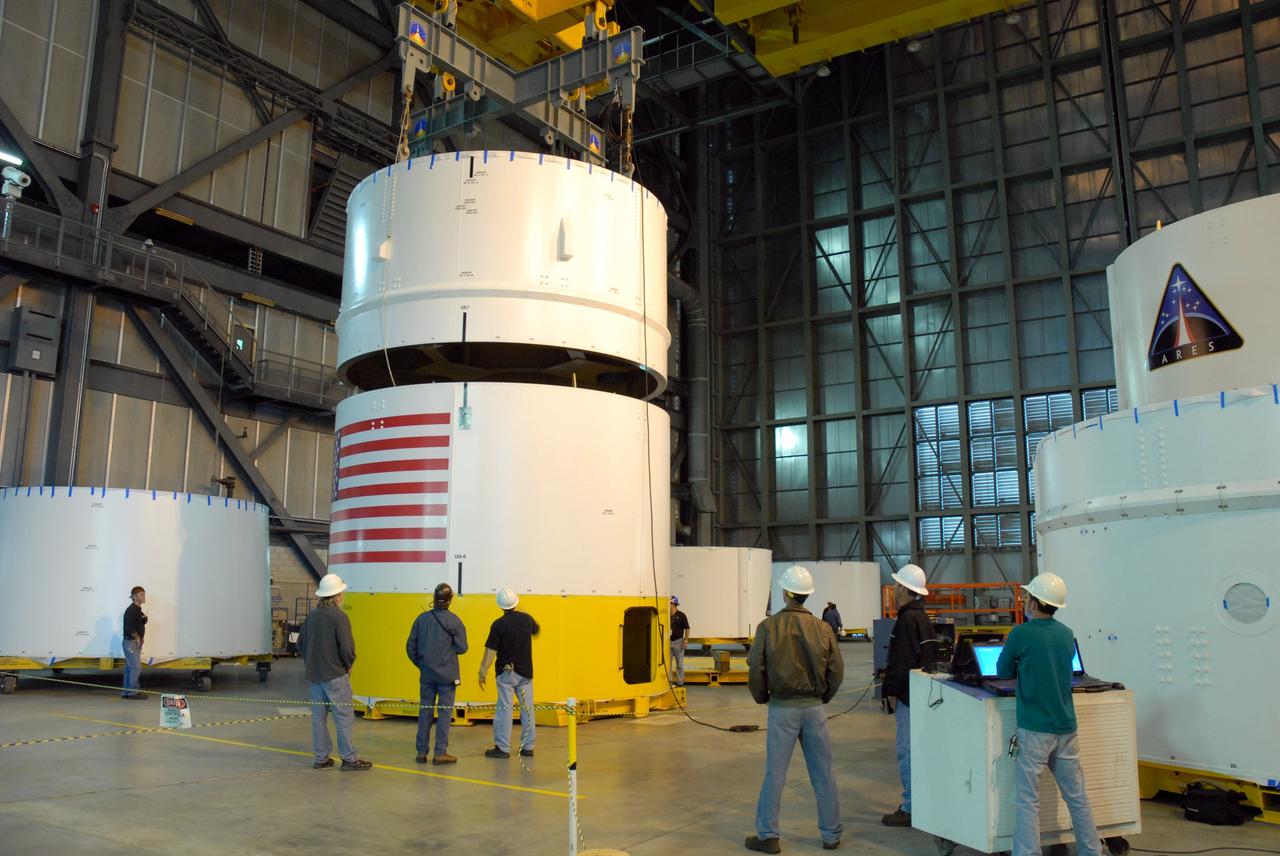

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segment 7 toward segment 6. The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight identified as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
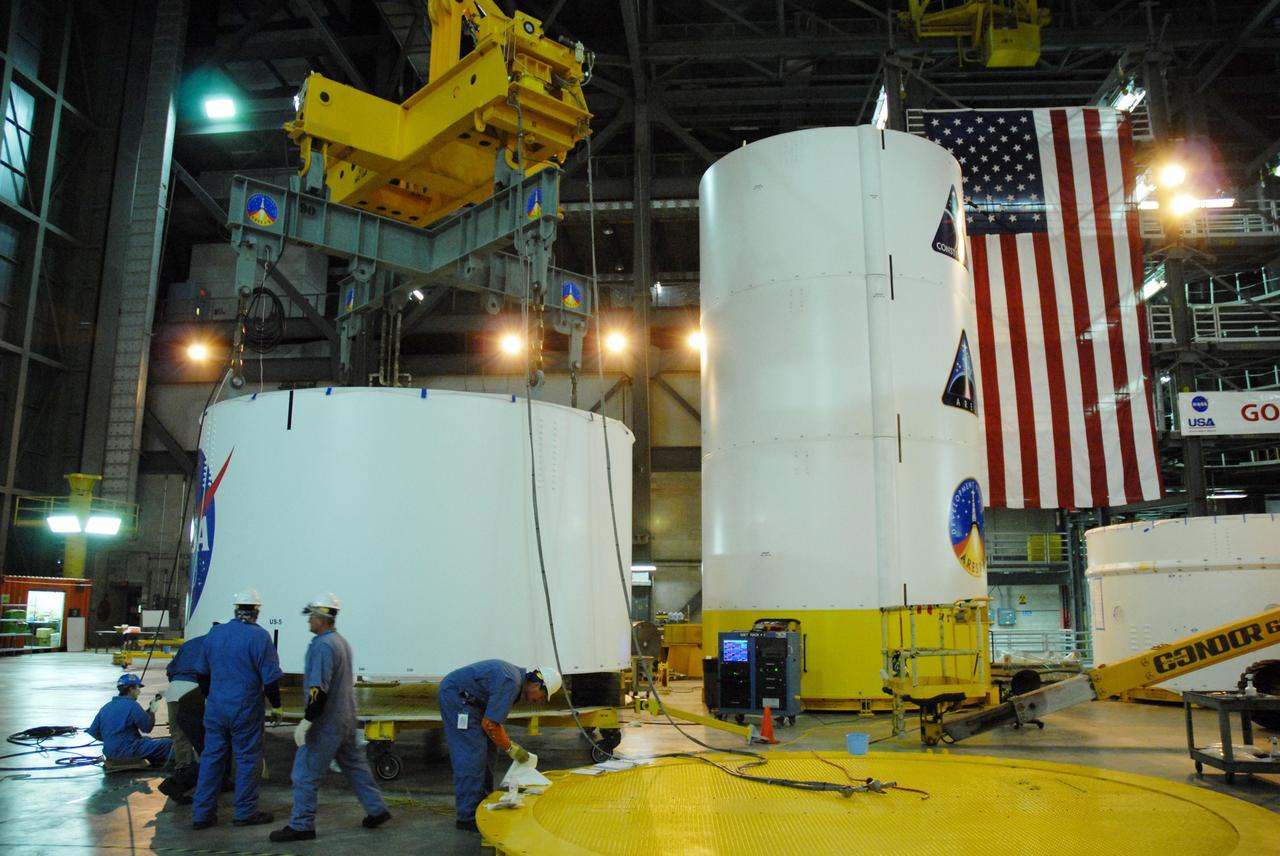

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is attached to segment 5 of the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segments to lift it. Segment 5 will be stacked on to segment 4, at the top of the tall stack at right. The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight known as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
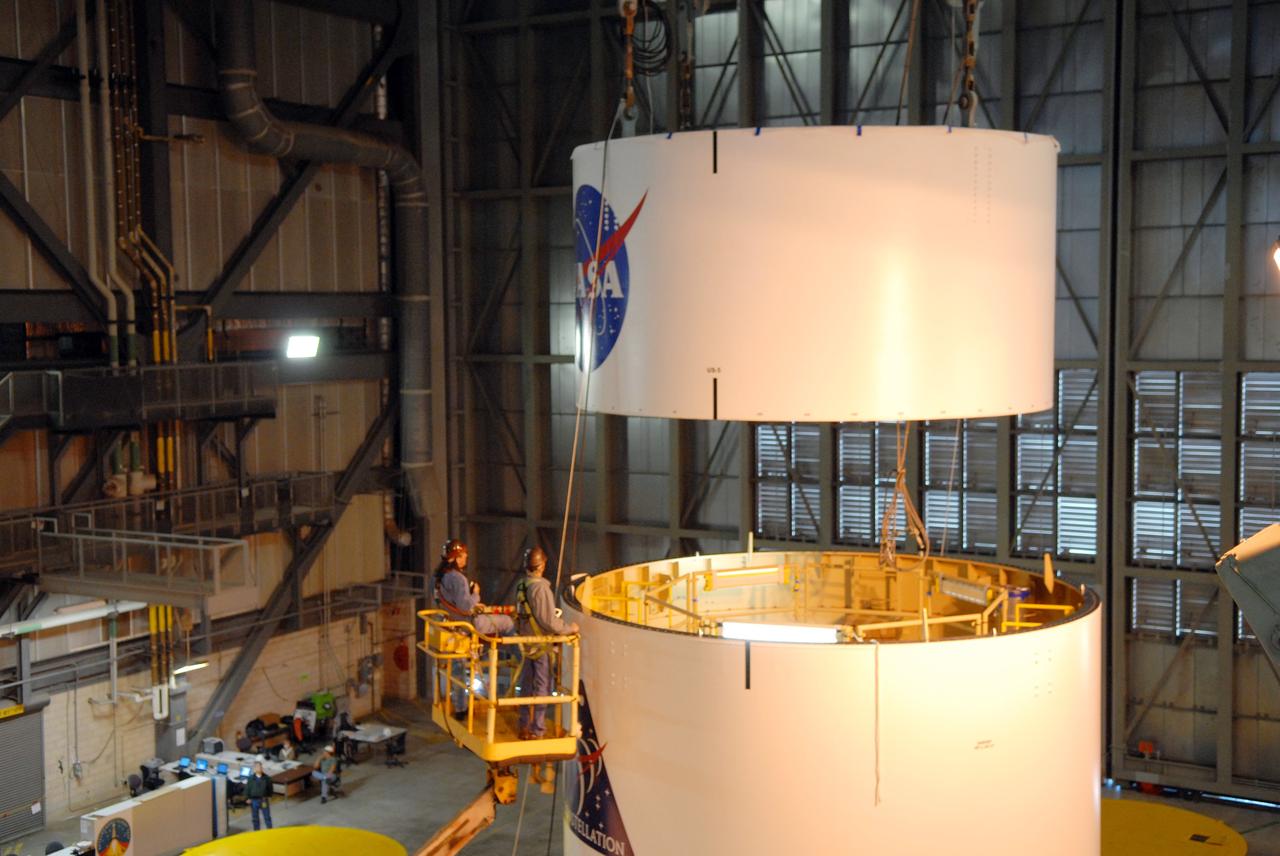

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers segment 5 of the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segments toward segment 4, at top of the tall stack below. The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight known as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is ready to lift the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segment 7. The segment will be stacked onto segment 6. The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight identified as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
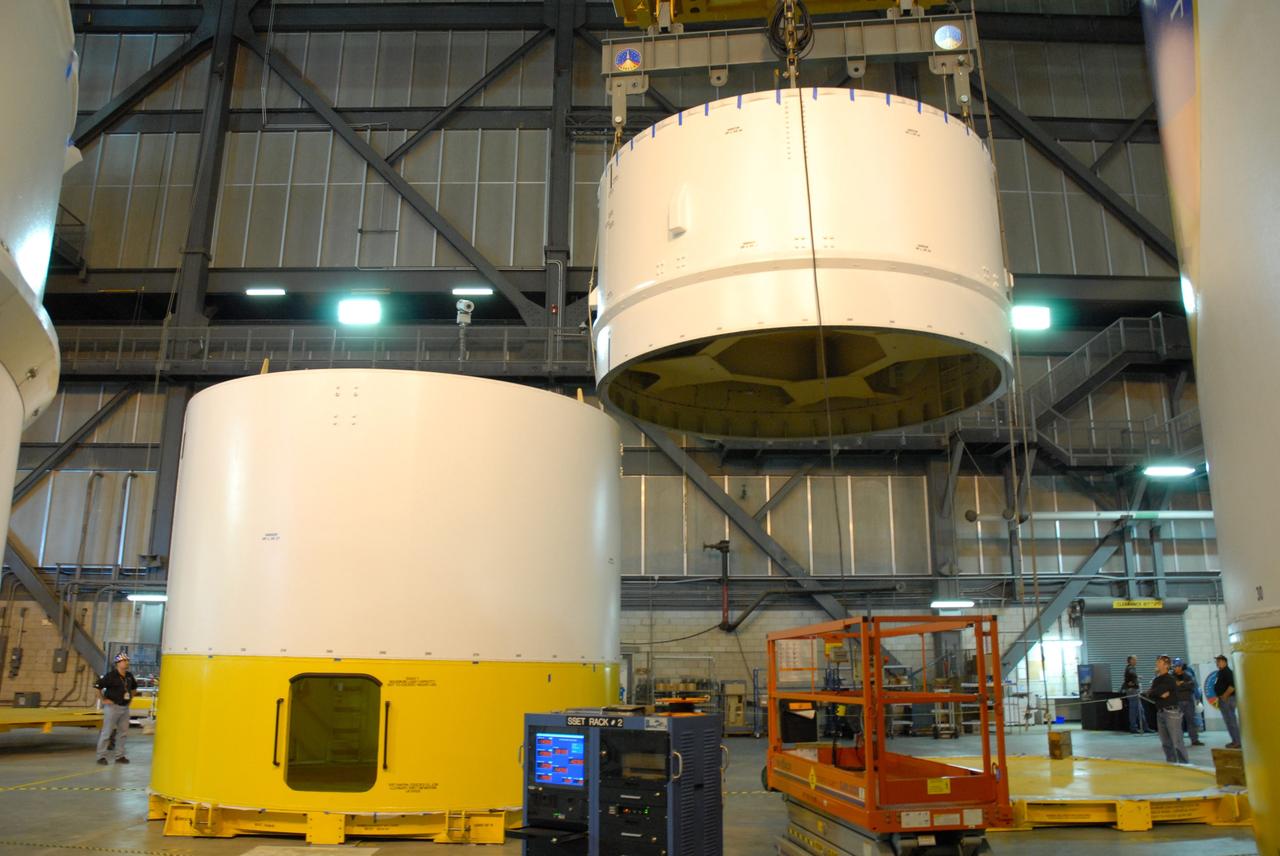

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segment 7. The segment will be stacked onto segment 6. The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight identified as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
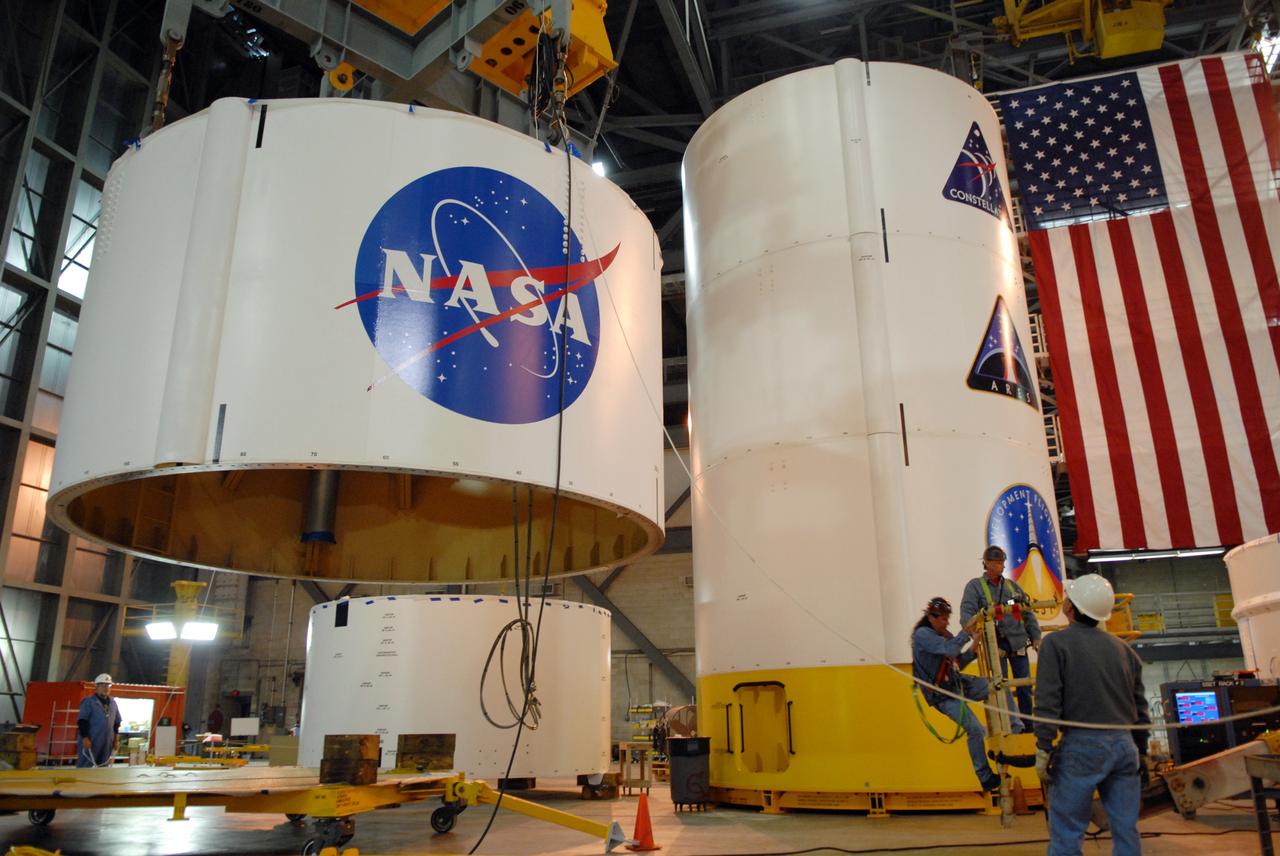

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts segment 5 of the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segments. It will be placed on segment 4, at top of the tall stack behind it. The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight known as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segment 7 onto segment 6. The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight identified as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
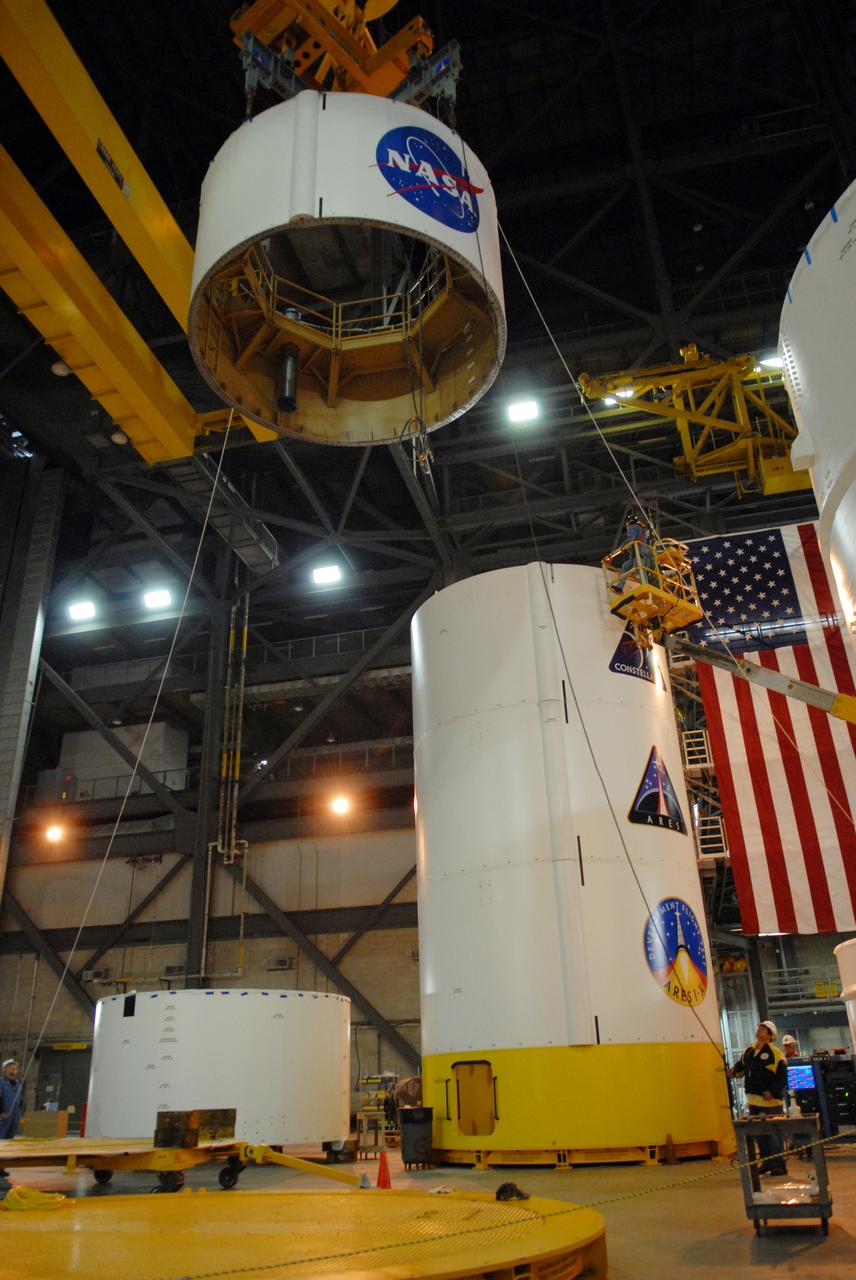

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane moves segment 5 of the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segments toward the tall stack behind it. Segment 5 will be placed on segment 4, at top of the tall stack. The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight known as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
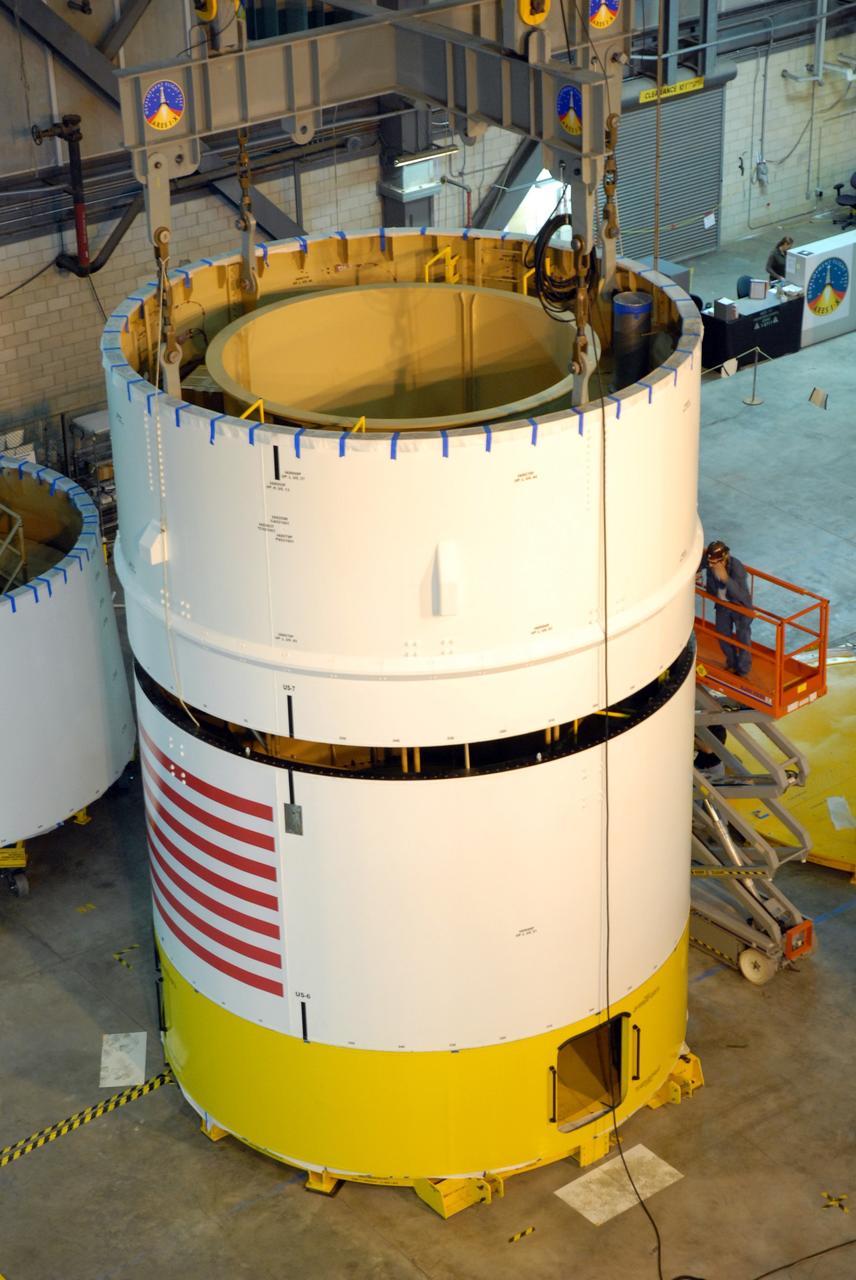

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segment 7 onto segment 6. The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight identified as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
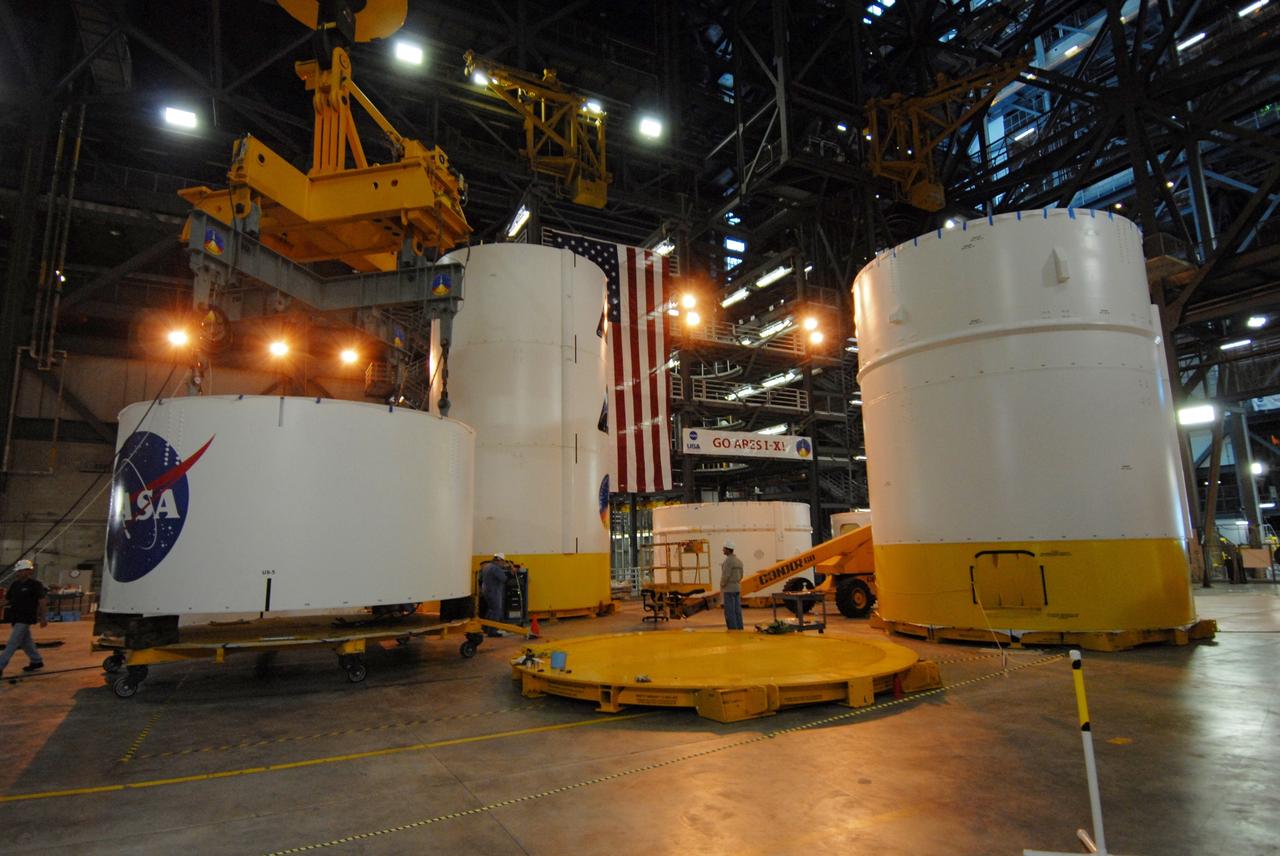

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts segment 5 of the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segments. It will be placed on segment 4, at top of the tall stack behind it. The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight known as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
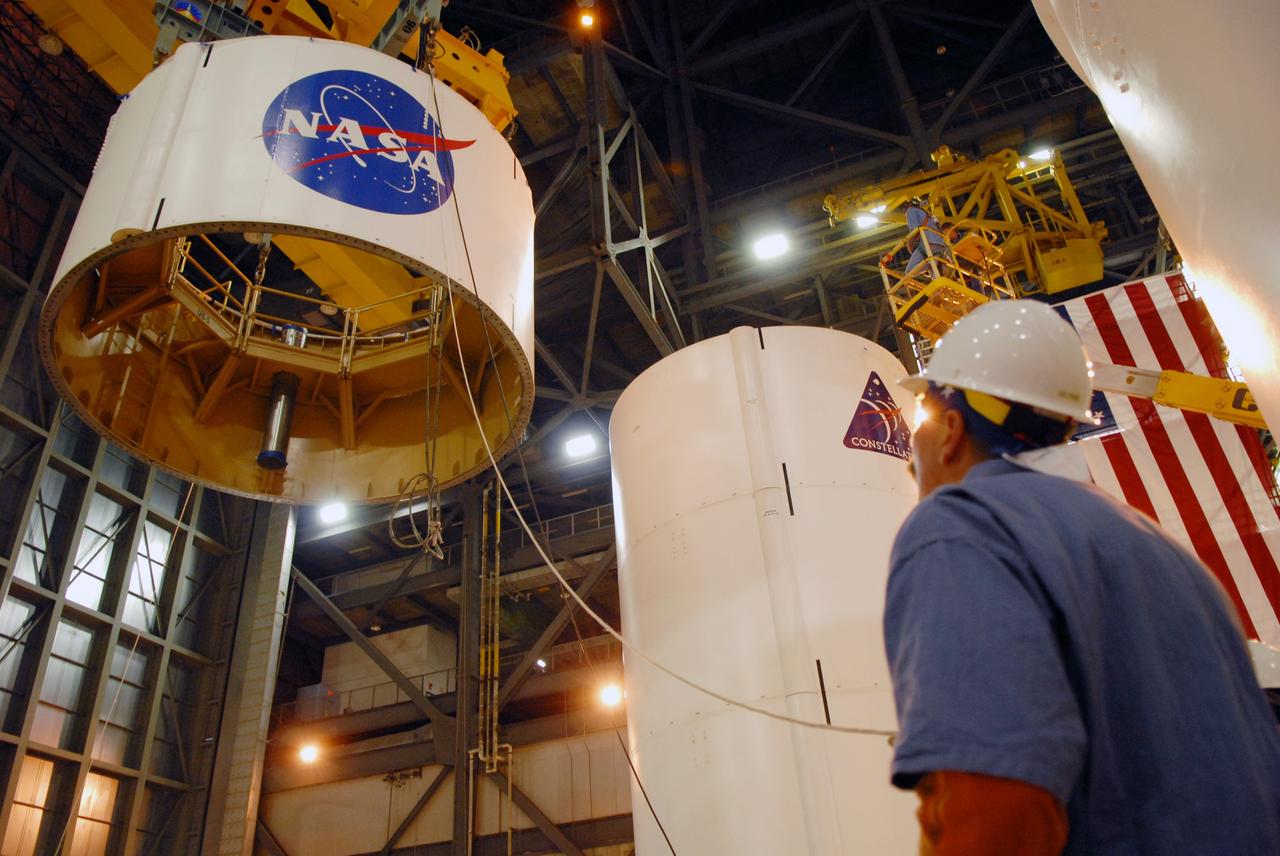

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts segment 5 of the Ares I-X upper stage simulator segments toward the tall stack behind it. Segment 5 will be placed on segment 4, at top of the tall stack. The upper stage simulator comprises 11 segments, each approximately 18 feet in diameter, that will be used in the test flight known as Ares I-X in 2009. The simulator segments will simulate the mass and the outer mold line. The upper stage accounts for nearly one-quarter of the total height of the Ares I. It will take the Ares I on the second phase of its journey from Earth, providing the guidance, navigation and control needed for the second phase of the Ares I ascent flight. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
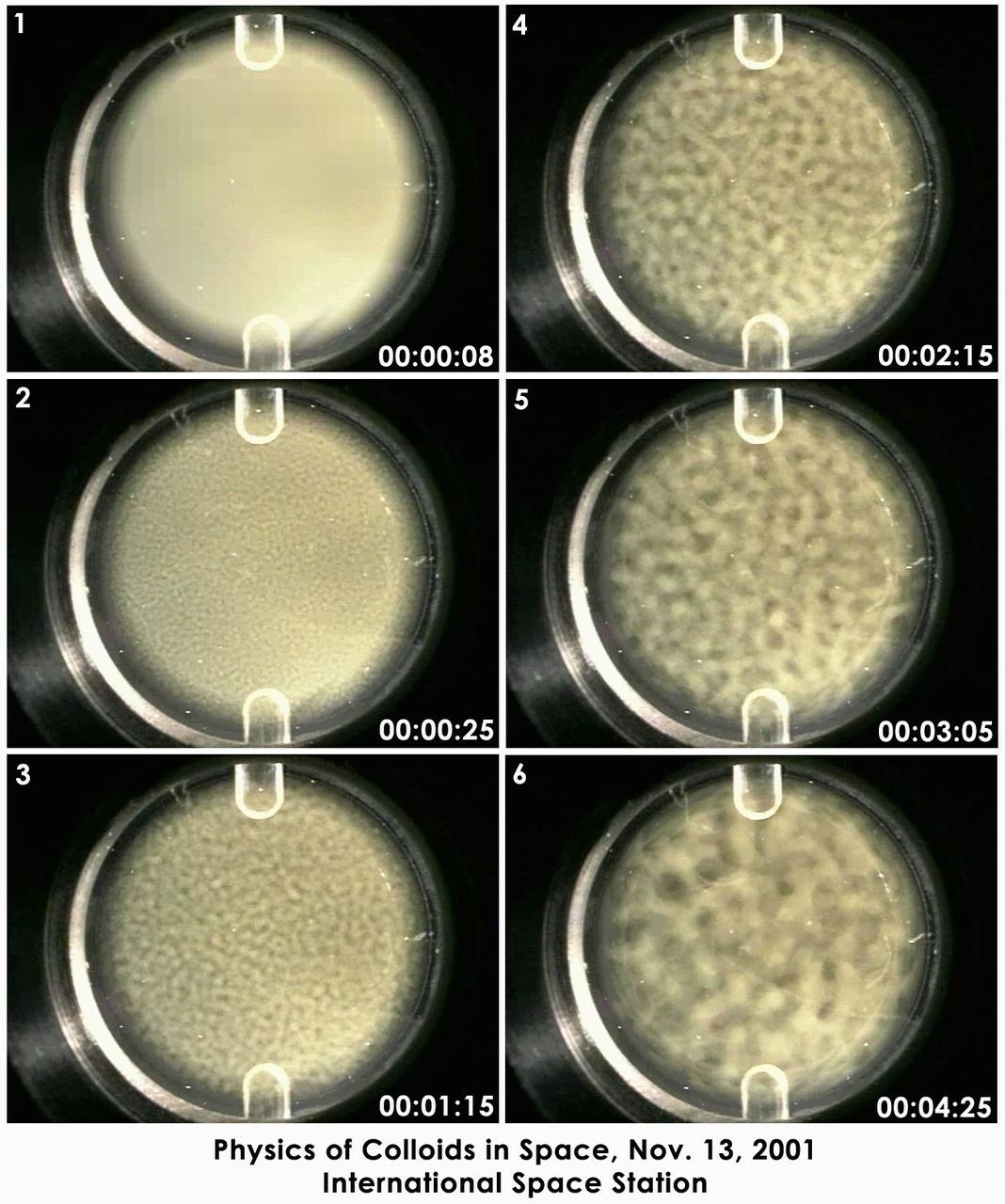
Still photographs taken over 16 hours on Nov. 13, 2001, on the International Space Station have been condensed into a few seconds to show the de-mixing -- or phase separation -- process studied by the Experiment on Physics of Colloids in Space. Commanded from the ground, dozens of similar tests have been conducted since the experiment arrived on ISS in 2000. The sample is a mix of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA or acrylic) colloids, polystyrene polymers and solvents. The circular area is 2 cm (0.8 in.) in diameter. The phase separation process occurs spontaneously after the sample is mechanically mixed. The evolving lighter regions are rich in colloid and have the structure of a liquid. The dark regions are poor in colloids and have the structure of a gas. This behavior carnot be observed on Earth because gravity causes the particles to fall out of solution faster than the phase separation can occur. While similar to a gas-liquid phase transition, the growth rate observed in this test is different from any atomic gas-liquid or liquid-liquid phase transition ever measured experimentally. Ultimately, the sample separates into colloid-poor and colloid-rich areas, just as oil and vinegar separate. The fundamental science of de-mixing in this colloid-polymer sample is the same found in the annealing of metal alloys and plastic polymer blends. Improving the understanding of this process may lead to improving processing of these materials on Earth.
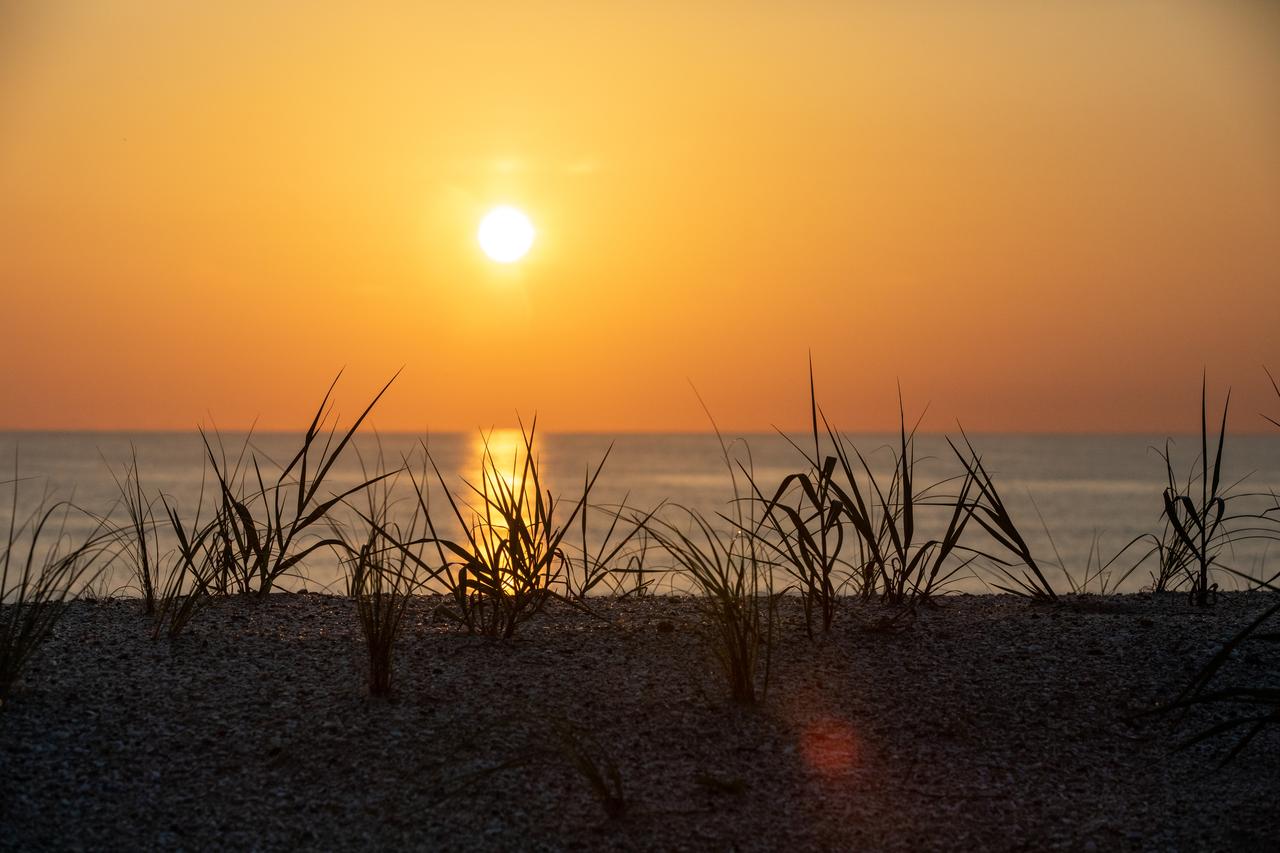

A beautiful sunrise is captured over sand dunes at the beach at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 15, 2020. Teams at Kennedy are working on dune restoration efforts, which has included bringing about 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand in to Kennedy’s beaches to build up dunes that have been affected by beach erosion and storm surges. Once the dunes were built up, native coastal vegetation was replanted to help stabilize the dunes and provide a habitat for wildlife at the Florida spaceport. The first phase of dune restoration efforts are now complete, and the second phase is scheduled to be completed by March 2021.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Kelvin Manning, associate director of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, welcomes participants to an industry conference inside the Television Auditorium at Kennedy. The conference was held following the program's request for proposals from commercial companies for a development and certification contract called the Commercial Crew Transportation Capability CCtCap. The contract will provide a finish line for the agency following more than four years of development work by CCP and American aerospace companies. CCtCap is the second phase of a two-phase certification plan for privately built and operated integrated crew transportation systems. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Kathy Lueders, acting program manager of the Commercial Crew Program, welcomes participants to an industry conference inside the Television Auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The conference was held following the program's request for proposals from commercial companies for a development and certification contract called the Commercial Crew Transportation Capability CCtCap. The contract will provide a finish line for the agency following more than four years of development work by CCP and American aerospace companies. CCtCap is the second phase of a two-phase certification plan for privately built and operated integrated crew transportation systems. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Phil McAlister, NASA's director of Commercial Spaceflight Development, welcomes participants to an industry conference inside the Television Auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The conference was held following the program's request for proposals from commercial companies for a development and certification contract called the Commercial Crew Transportation Capability CCtCap. The contract will provide a finish line for the agency following more than four years of development work by CCP and American aerospace companies. CCtCap is the second phase of a two-phase certification plan for privately built and operated integrated crew transportation systems. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Lee Pagel of NASA's Commercial Crew Program is seen before the start of an industry conference inside the Television Auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The conference was held following the program's request for proposals from commercial companies for a development and certification contract called the Commercial Crew Transportation Capability CCtCap. The contract will provide a finish line for the agency following more than four years of development work by CCP and American aerospace companies. CCtCap is the second phase of a two-phase certification plan for privately built and operated integrated crew transportation systems.. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
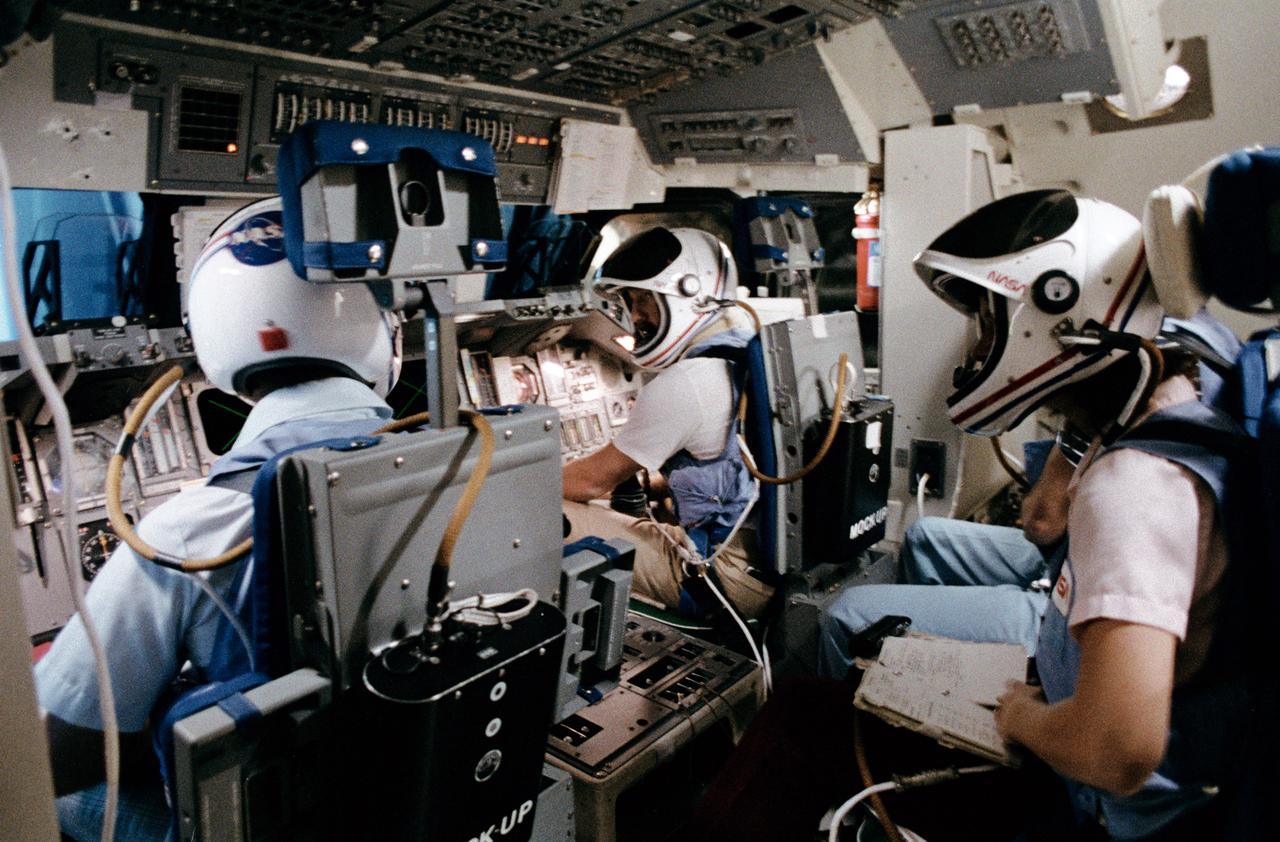

S83-32723 (23 May 1983) --- This scene in the Shuttle Mission Simulator (SMS) previews next month?s STS-7 flight in the space shuttle Challenger. Taken during a simulation session, the photo illustrates the seating arrangement for launch and landing phases of the Challenger?s second spaceflight and its first with five crew members. Pictured, left to right, are astronauts Robert L. Crippen, commander; Frederick H. Hauck, pilot; Sally K. Ride and John M. Fabian (almost totally obscured), mission specialists. Dr. Norman E. Thagard, a third mission specialist, will be seated in the middeck for launch and landing phases. Photo credit: NASA/Otis Imboden/National Geographic Society.
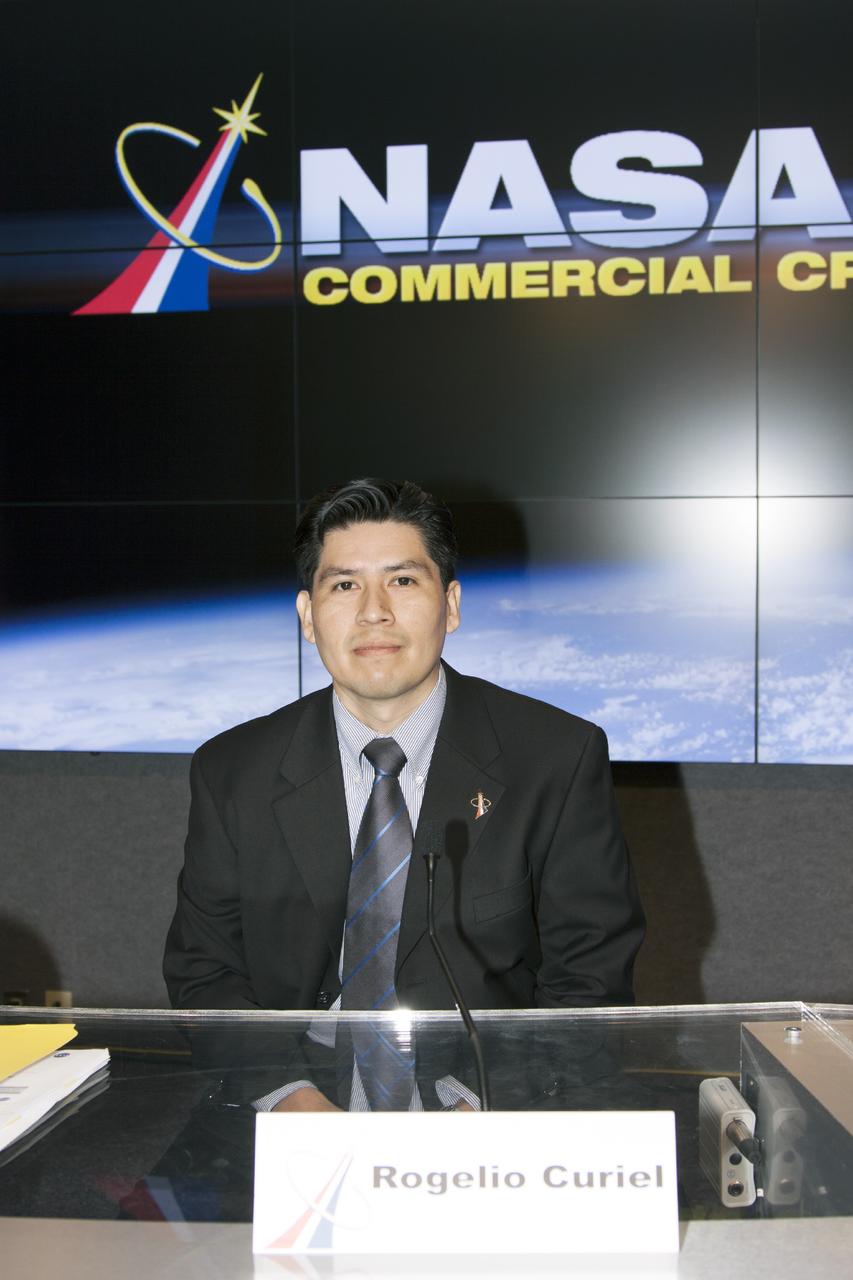

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Rogelio Curiel of NASA's Commercial Crew Program is seen before the start of an industry conference inside the Television Auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The conference was held following the program's request for proposals from commercial companies for a development and certification contract called the Commercial Crew Transportation Capability CCtCap. The contract will provide a finish line for the agency following more than four years of development work by CCP and American aerospace companies. CCtCap is the second phase of a two-phase certification plan for privately built and operated integrated crew transportation systems. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
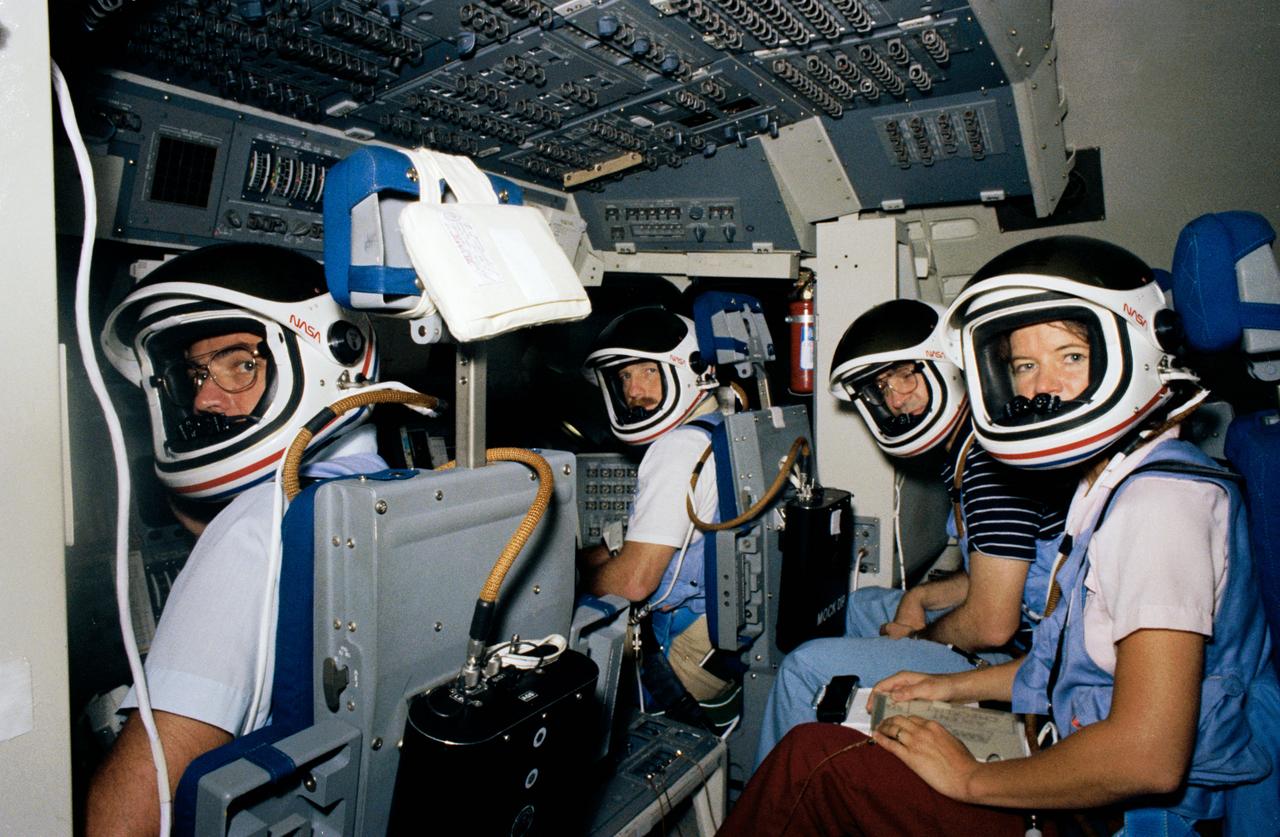

S83-32569 (23 May 1983) --- A preview of NASA?s next spaceflight is provided by this scene in the Johnson Space Center?s Shuttle mission simulator (SMS) with four-fifths of the crew in the same stations they will be in for launch and landing phases of the Challenger?s second space mission. They are (left-right) Astronauts Robert L. Crippen, crew commander; Frederick H. Hauck, pilot; John M. Fabian and Dr. Sally K. Ride, mission specialists. Dr. Norman E. Thagard, a third mission specialist, is to be seated in the mid-deck area below the flight deck for launch and landing phases. Launch is now scheduled for June 18.
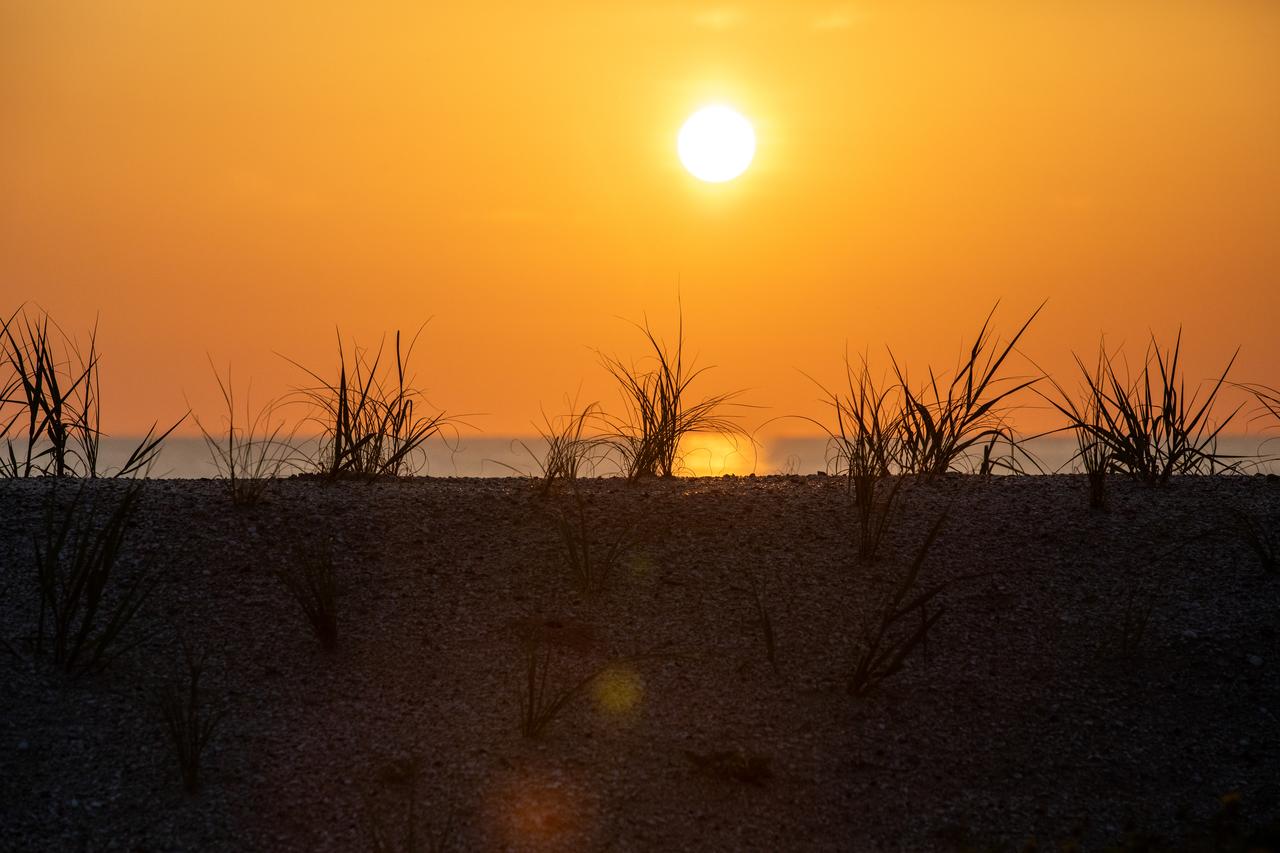

A beautiful sunrise is captured over sand dunes at the beach at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 15, 2020. Teams at Kennedy are working on dune restoration efforts, which has included bringing about 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand in to Kennedy’s beaches to build up dunes that have been affected by beach erosion and storm surges. Once the dunes were built up, native coastal vegetation was replanted to help stabilize the dunes and provide a habitat for wildlife at the Florida spaceport. The first phase of dune restoration efforts are now complete, and the second phase is scheduled to be completed by March 2021.
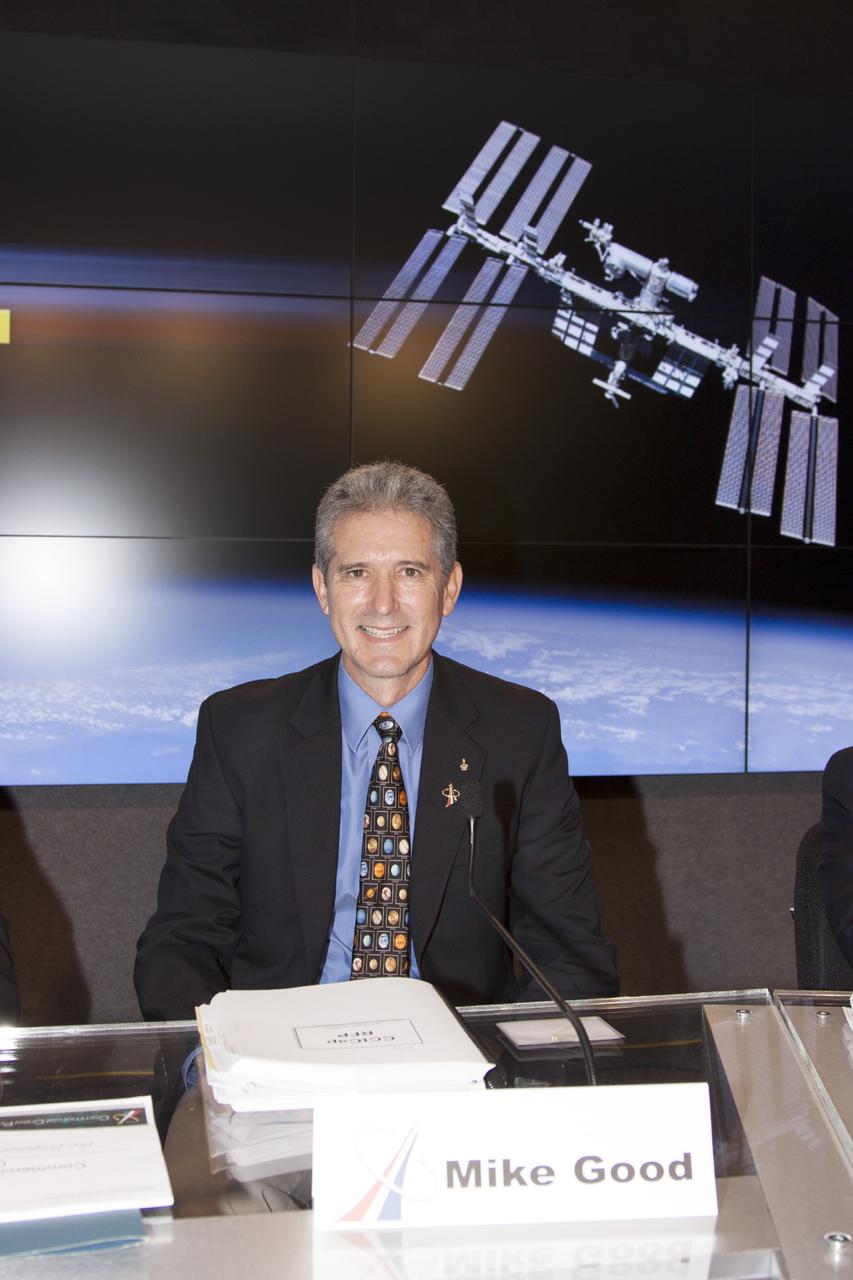

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Astronaut Mike Good of NASA's Commercial Crew Program is seen before the start of an industry conference inside the Television Auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The conference was held following the program's request for proposals from commercial companies for a development and certification contract called the Commercial Crew Transportation Capability CCtCap. The contract will provide a finish line for the agency following more than four years of development work by CCP and American aerospace companies. CCtCap is the second phase of a two-phase certification plan for privately built and operated integrated crew transportation systems. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
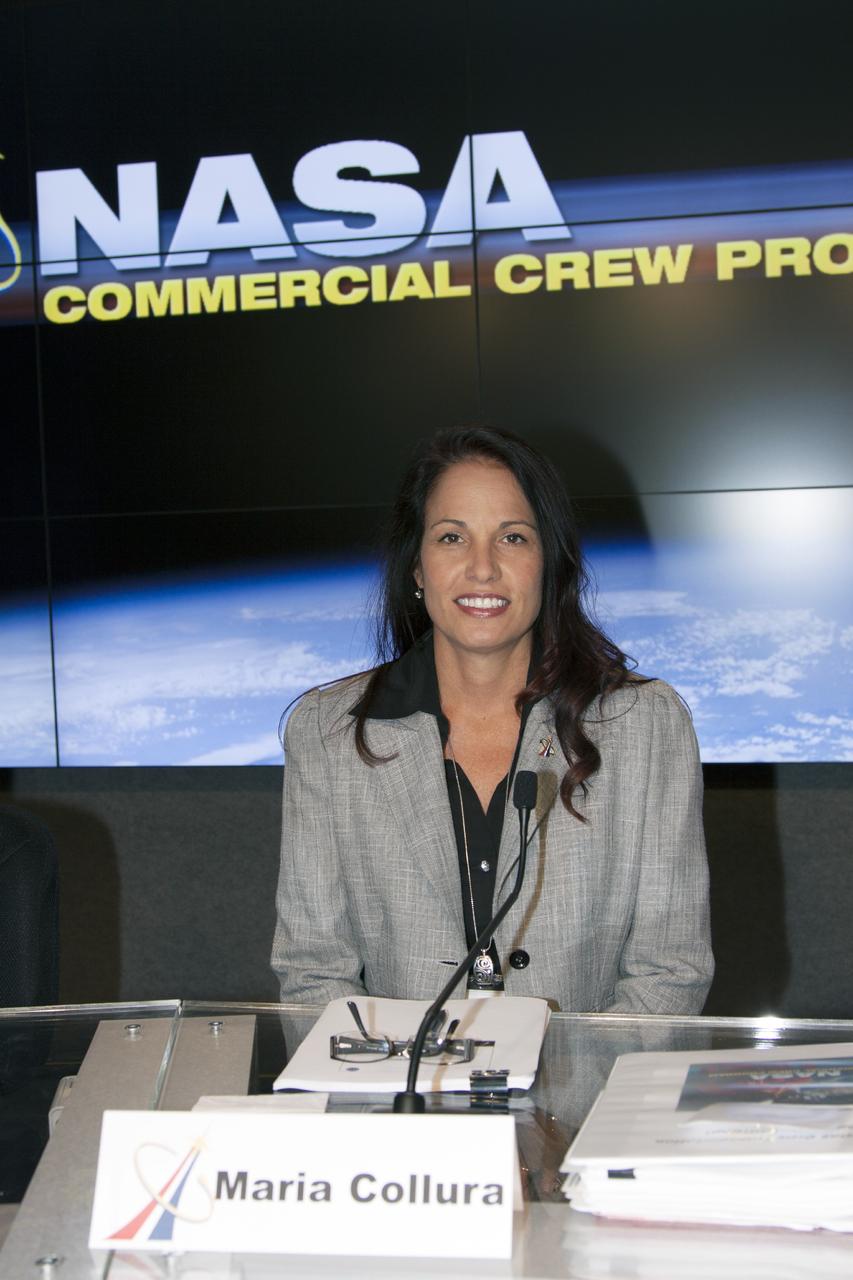

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Maria Collura of NASA's Commercial Crew Program is seen before the start of an industry conference inside the Television Auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The conference was held following the program's request for proposals from commercial companies for a development and certification contract called the Commercial Crew Transportation Capability CCtCap. The contract will provide a finish line for the agency following more than four years of development work by CCP and American aerospace companies. CCtCap is the second phase of a two-phase certification plan for privately built and operated integrated crew transportation systems. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
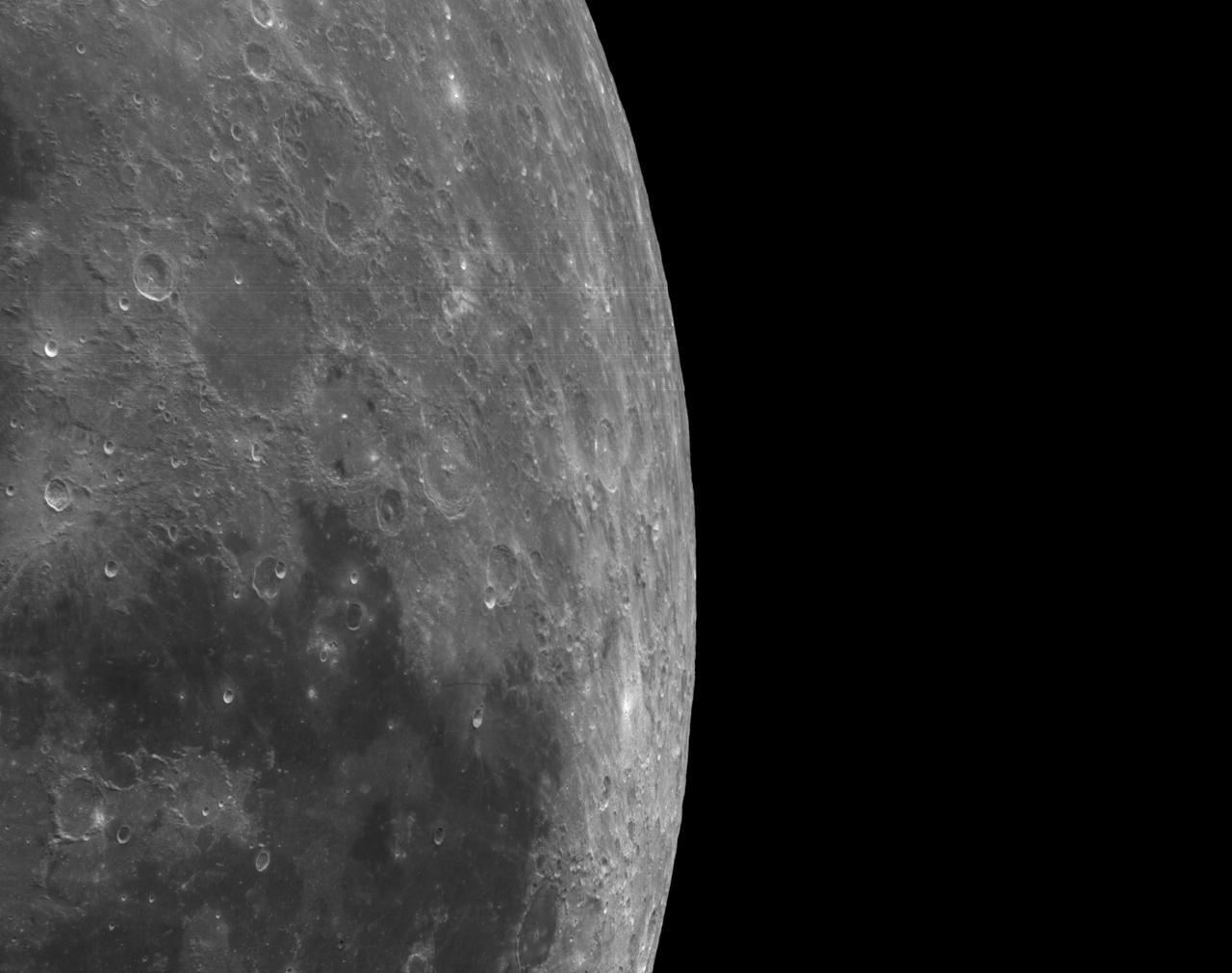

art001e002581 (Dec. 5, 2022): The optical navigation camera mounted on the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
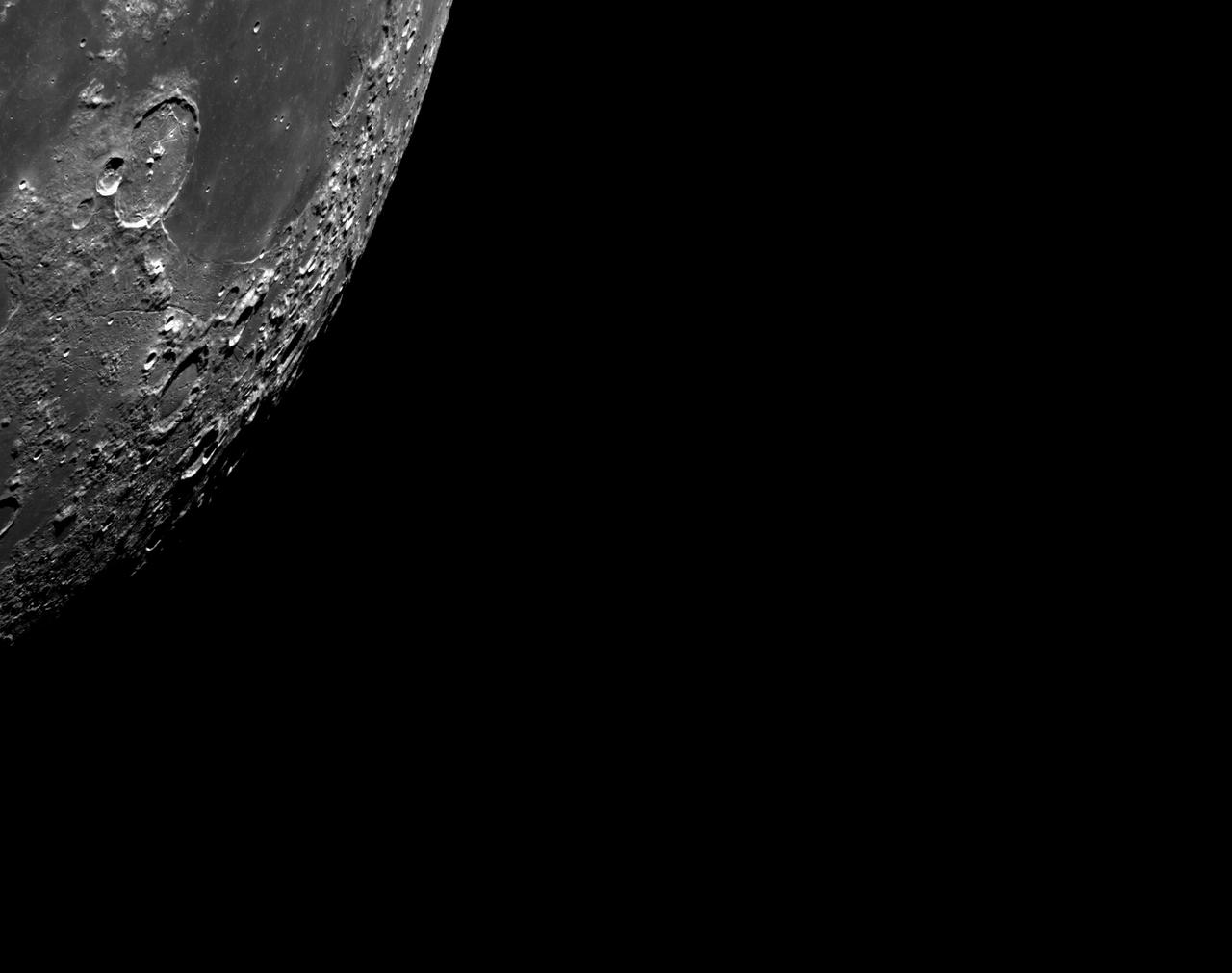

art001e002592 (Dec. 5, 2022): The optical navigation camera mounted on the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
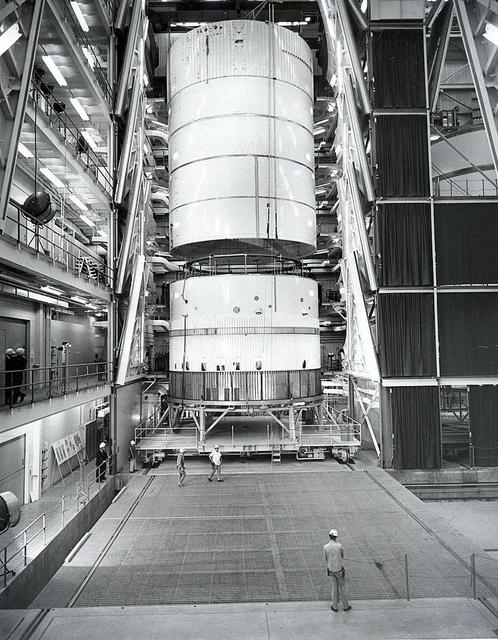
The hydrogen-powered second stage is being lowered into place during the final phase of fabrication of the Saturn V moon rocket at North American's Seal Beach, California facility. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
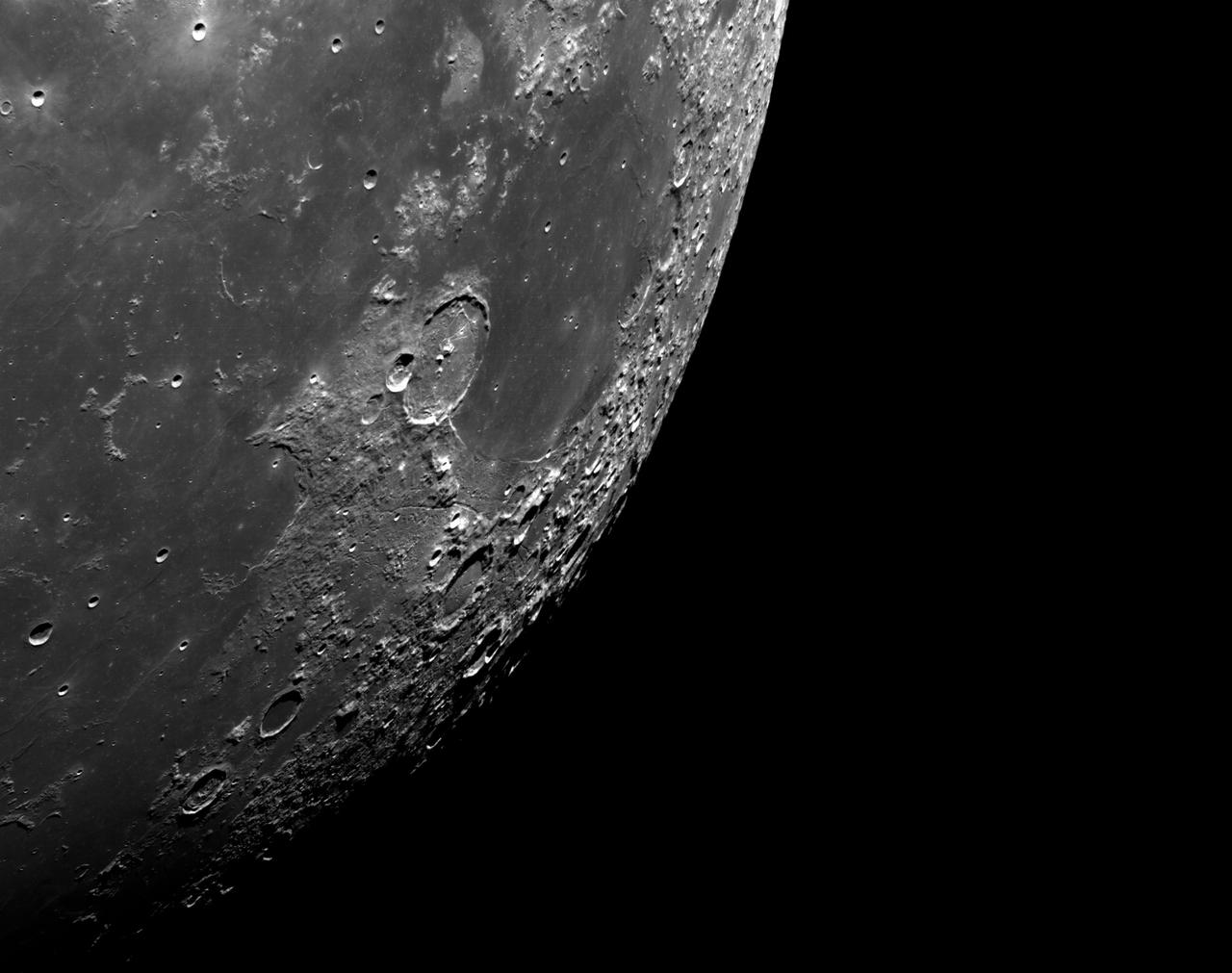

art001e002593 (Dec. 5, 2022): The optical navigation camera mounted on the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
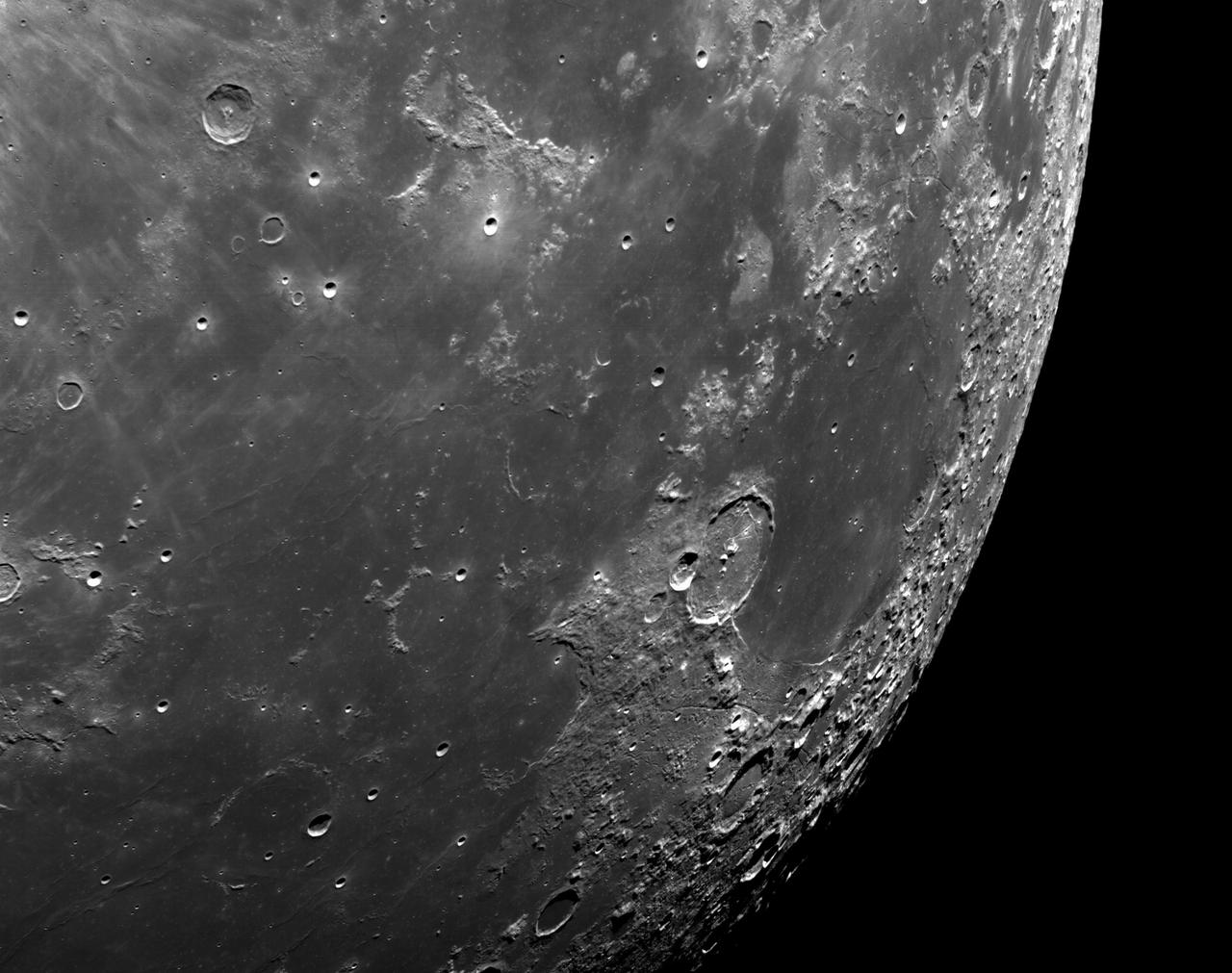

art001e002594 (Dec. 5, 2022): The optical navigation camera mounted on the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
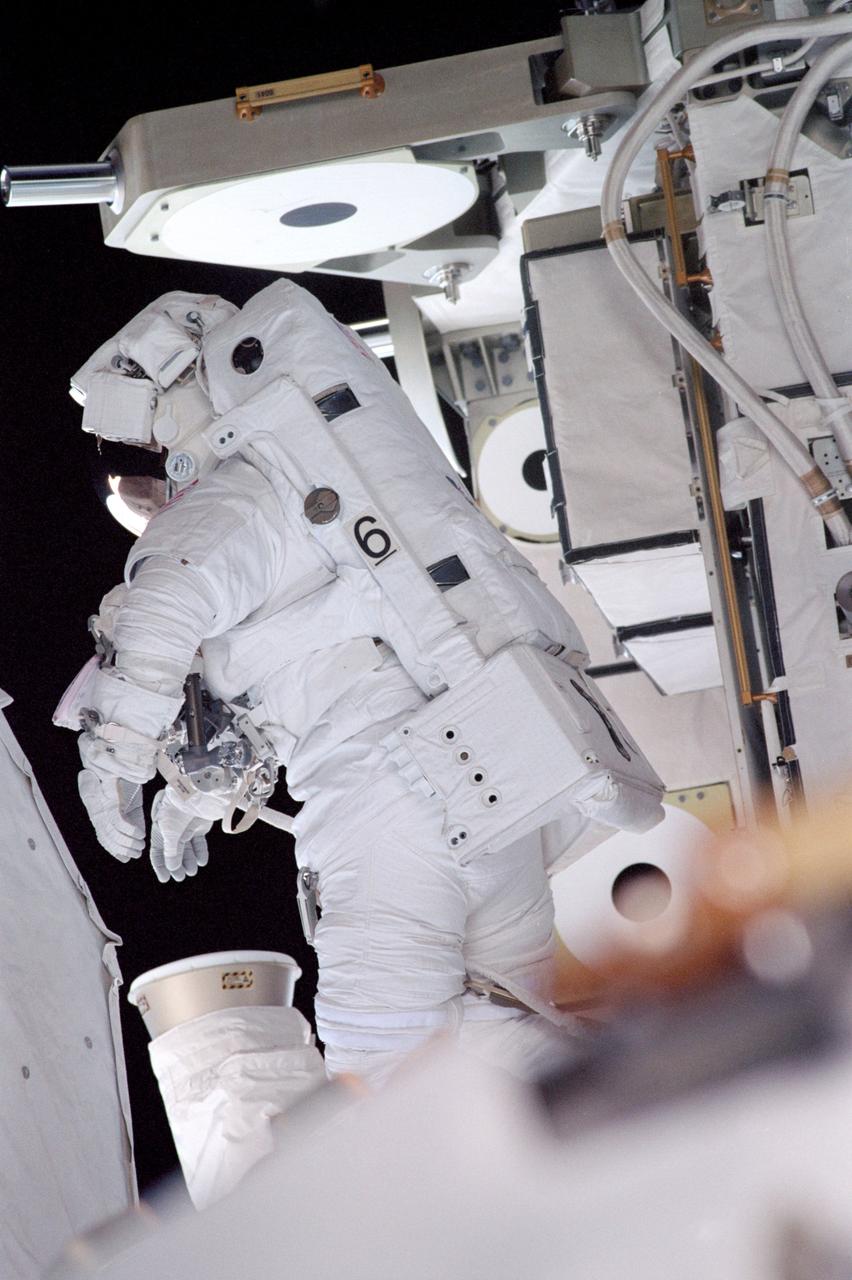

STS104-315-007 (12-24 July 2001) --- Astronaut James F. Reilly, STS-104 mission specialist, participates in one of three space walks aimed toward wrapping up the completion of work on the second phase of the International Space Station (ISS). Reilly was joined on the extravehicular activity (EVA) by astronaut Michael L. Gernhardt.
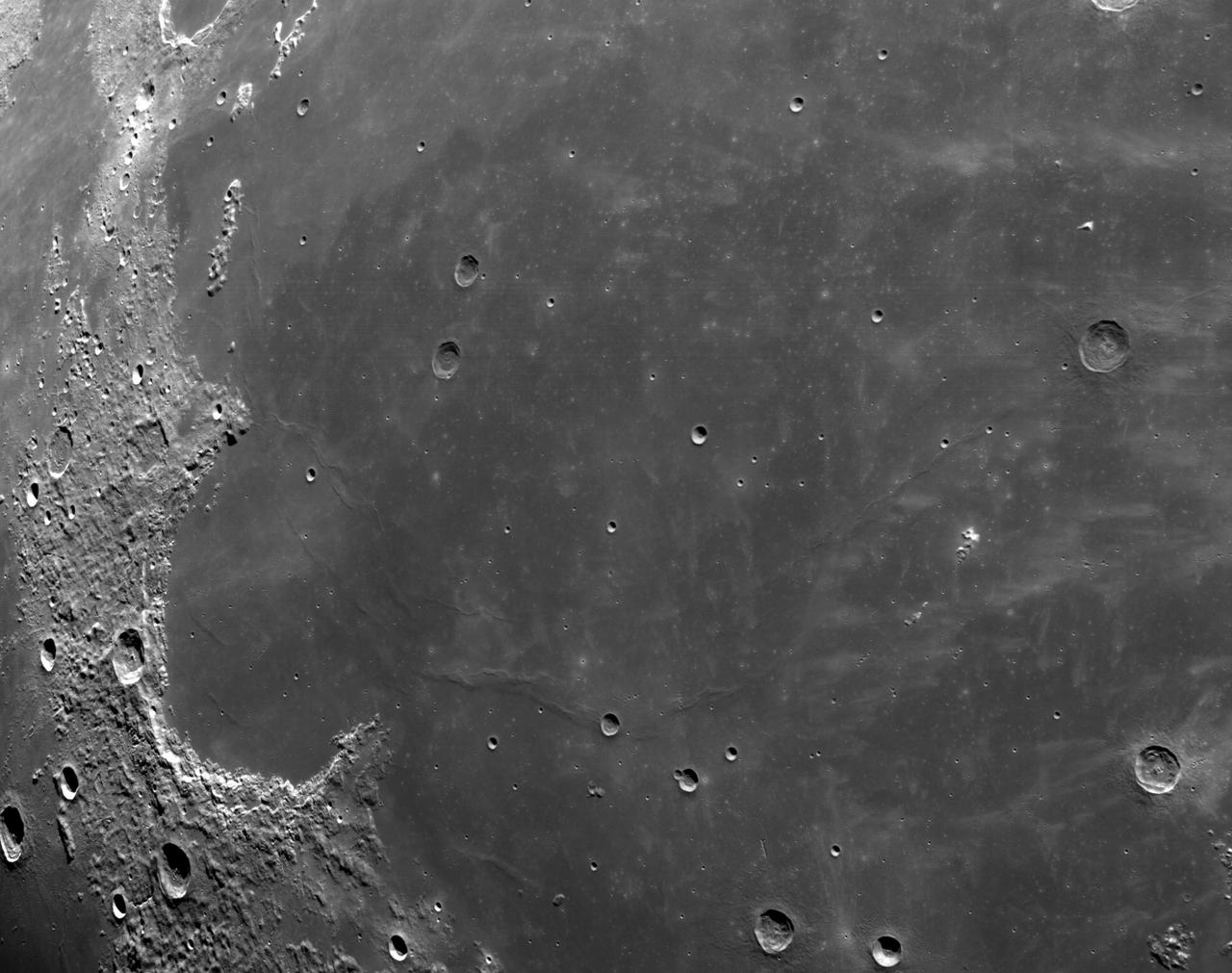

art001e002610 (Dec. 5, 2022): The optical navigation camera mounted on the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
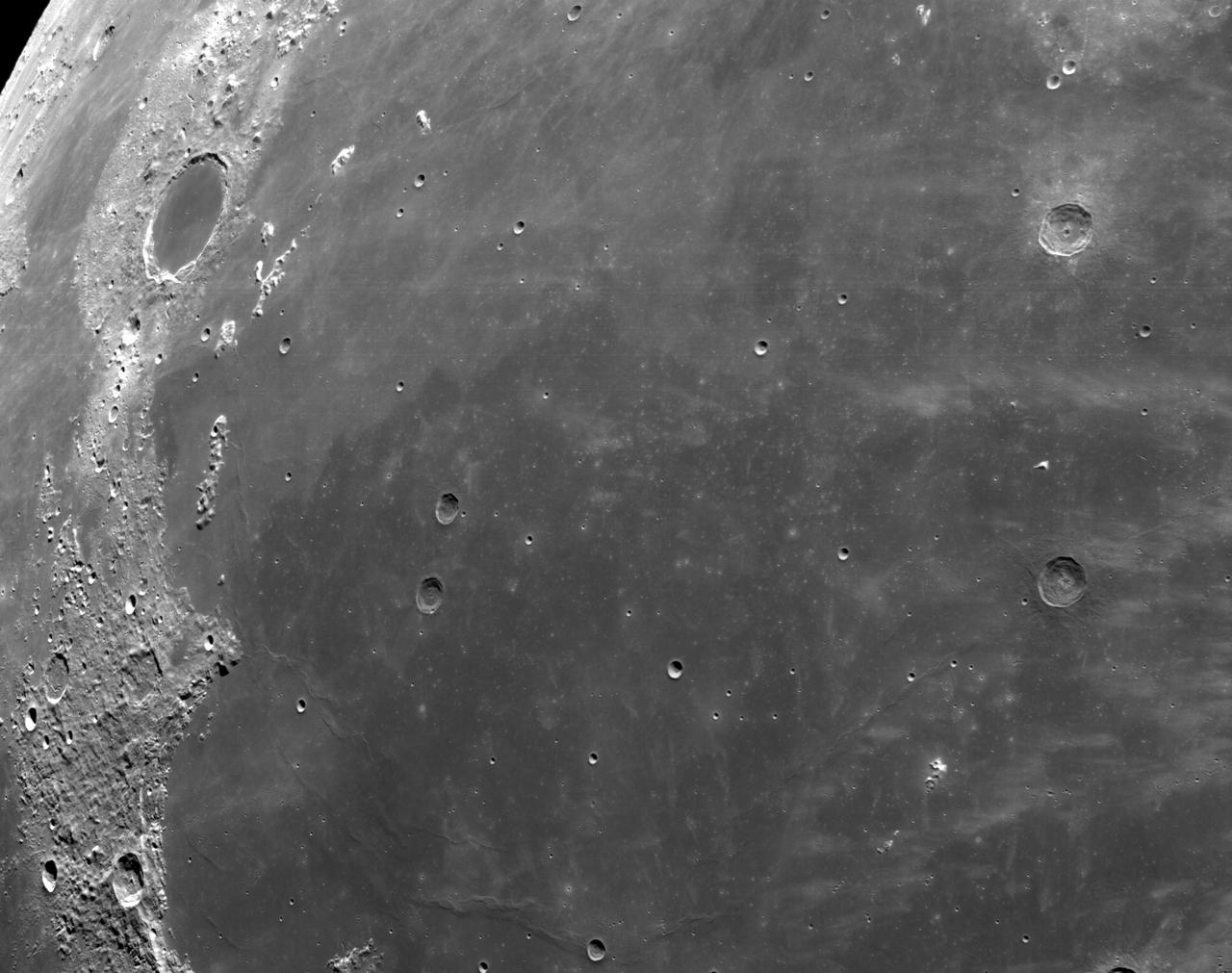

art001e002604 (Dec. 5, 2022): The optical navigation camera mounted on the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
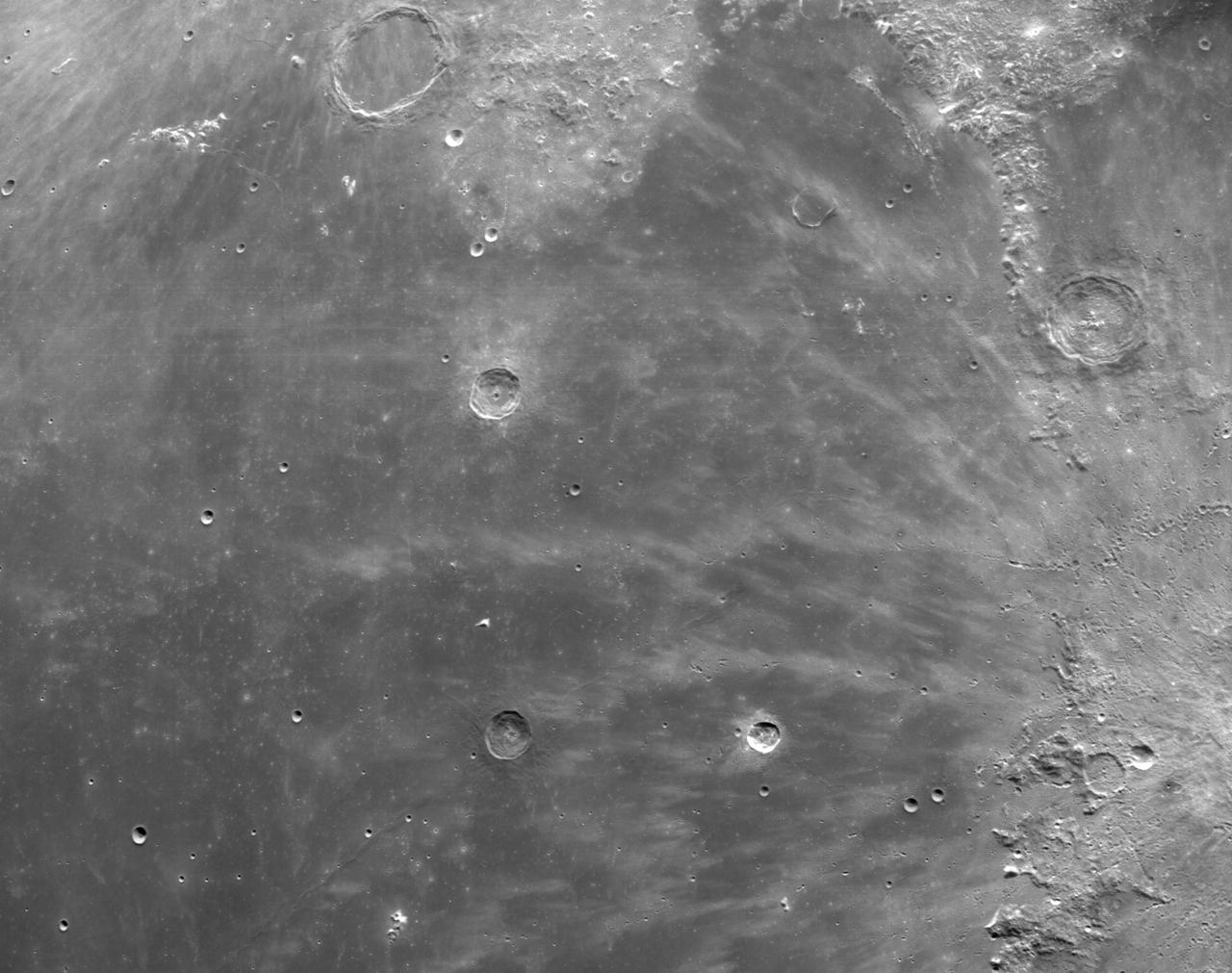

art001e002599 (Dec. 5, 2022): The optical navigation camera mounted on the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
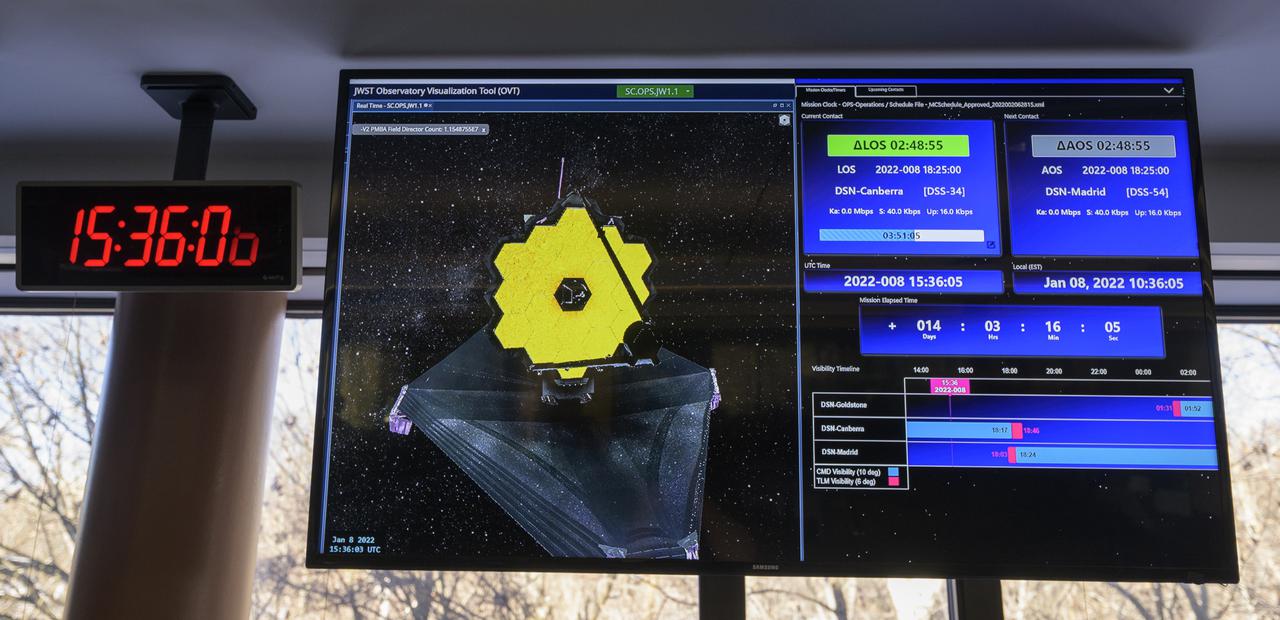
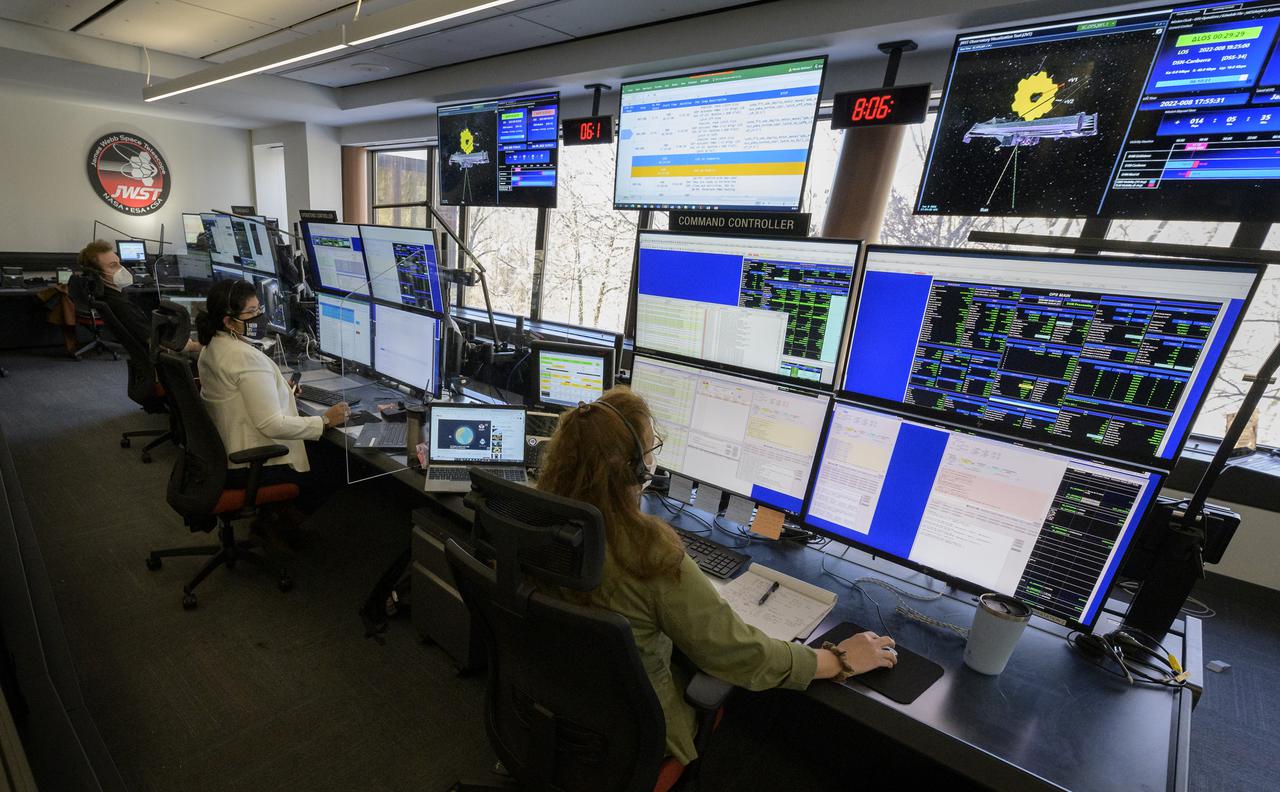
A monitor in the NASA James Webb Space Telescope flight control room of the Space Telescope Science Institute shows the progress of the second primary mirror wing latching on the Webb observatory, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, in Baltimore. When fully latched, the infrared observatory will have completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
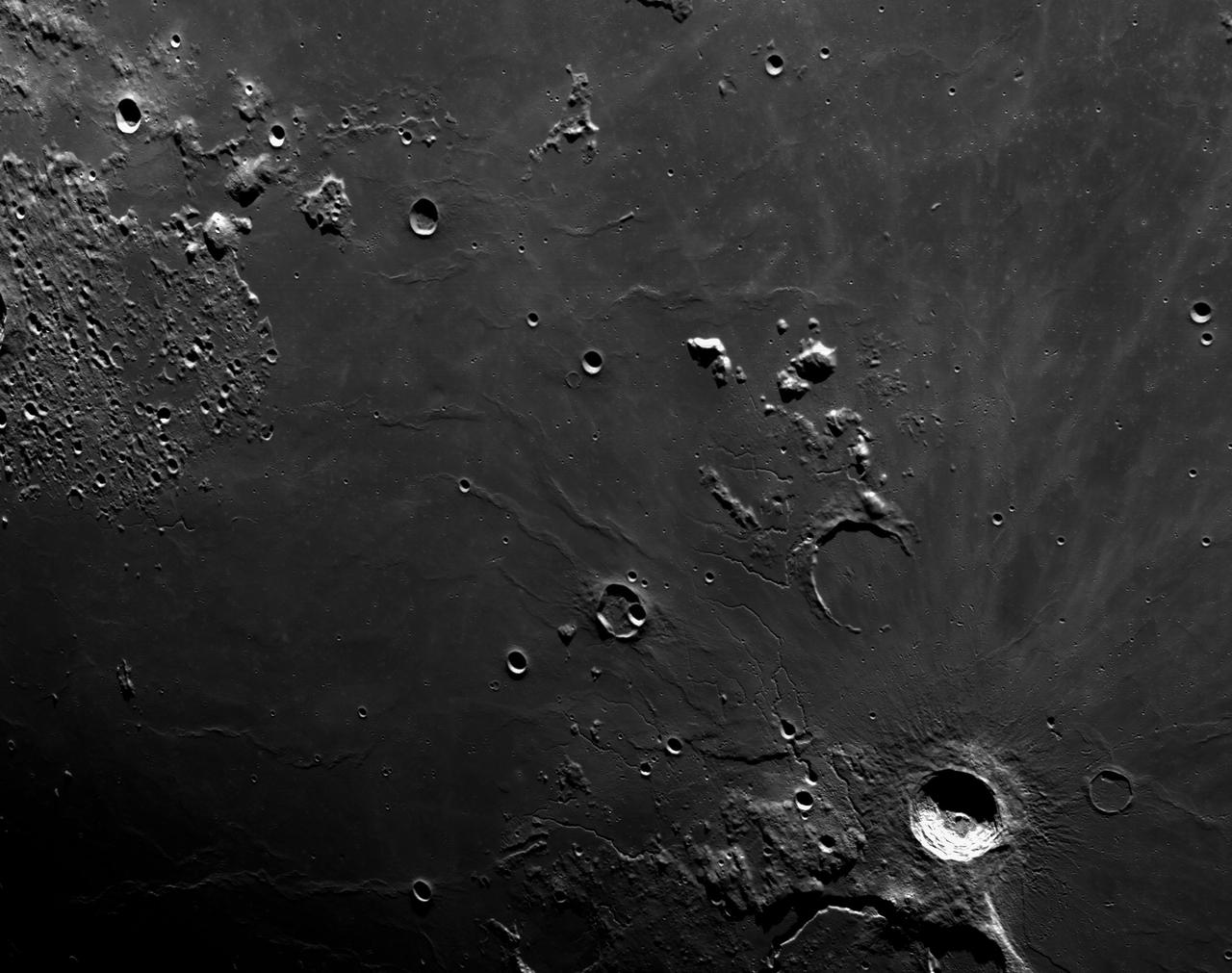

art001e002647 (Dec. 5, 2022): The optical navigation camera mounted on the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
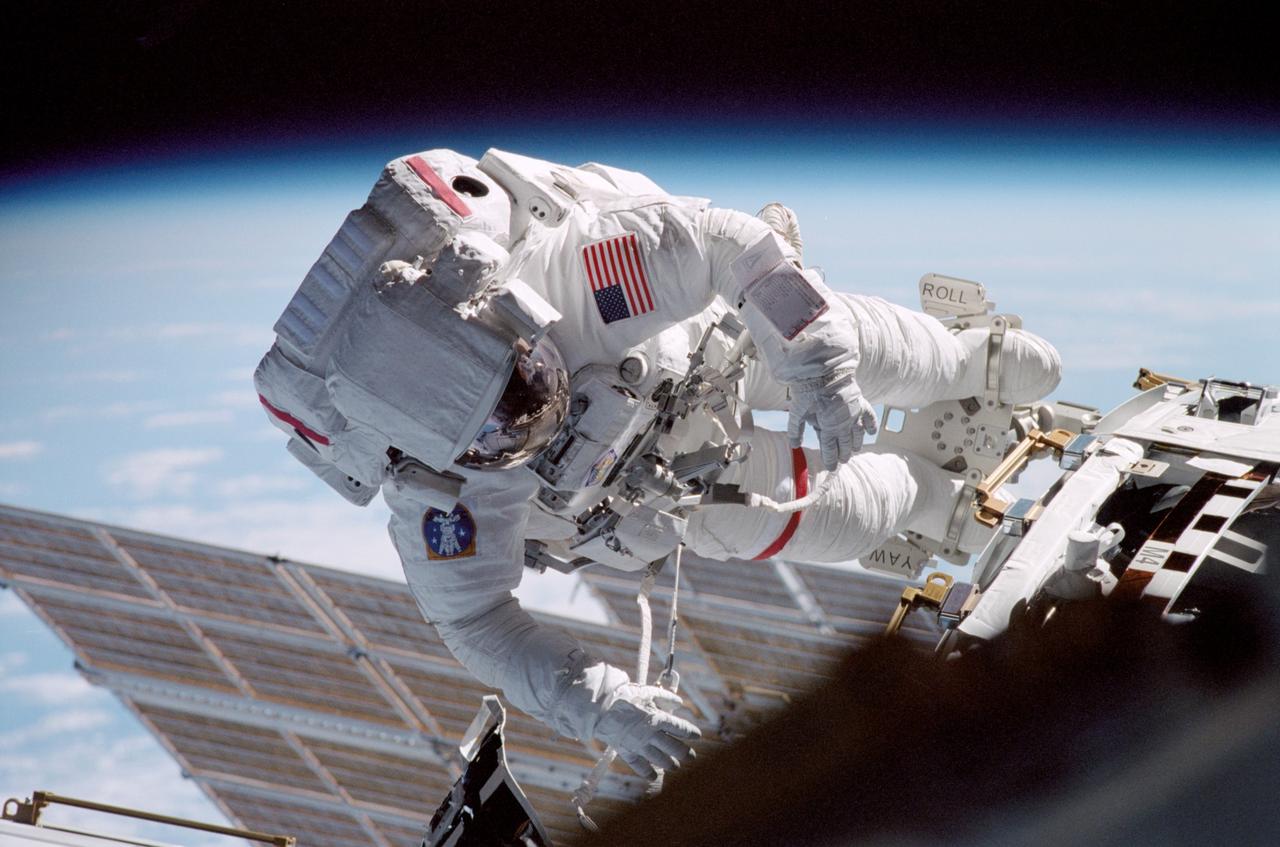

STS104-315-005 (12-24 July 2001) --- With Earth's horizon in the background, astronaut Michael L. Gernhardt, STS-104 mission specialist, participates in one of three space walks aimed toward wrapping up the completion of work on the second phase of the International Space Station (ISS). Gernhardt was joined on the extravehicular activity (EVA) by astronaut James F. Reilly.
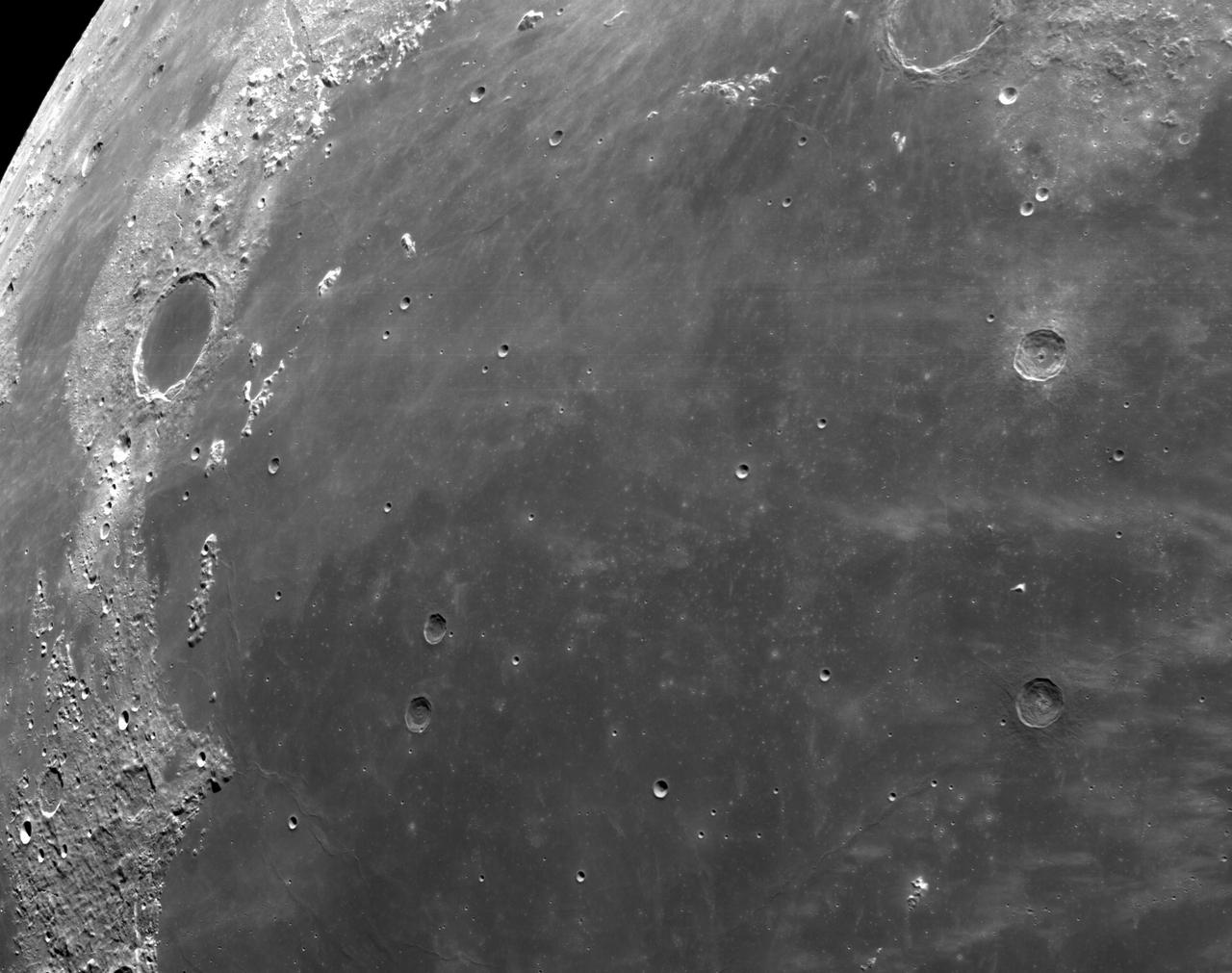

art001e002602 (Dec. 5, 2022): The optical navigation camera mounted on the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
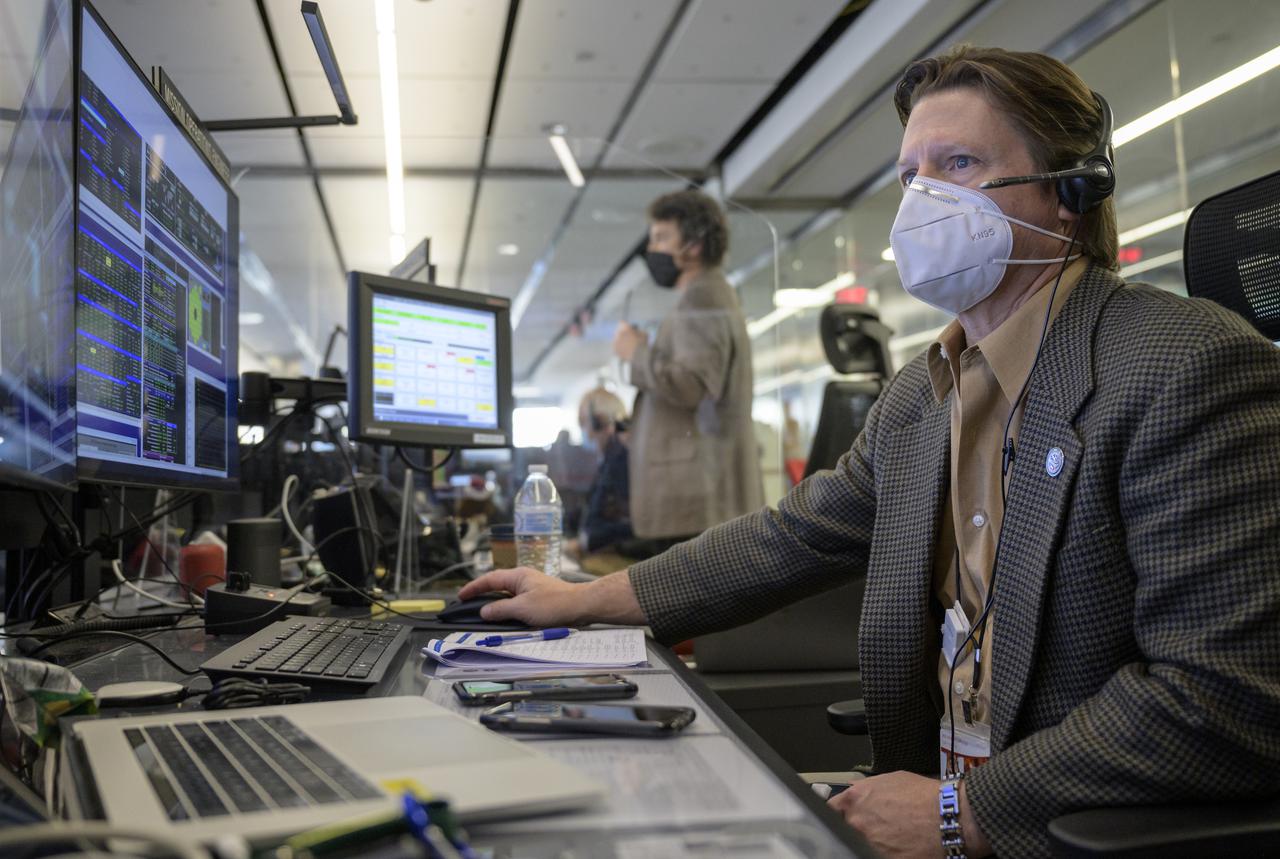

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Engineer Kenny McKenzie monitors the progress of Webb’s second primary mirror wing latching, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, in Baltimore. When fully latched, the infrared observatory will have completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Flight Research Inc.’s Bell OH-58C Kiowa helicopter lands on a helipad at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California in March 2021 at the completion of an urban air mobility scenario. The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project conducted a second phase of research called build II. This helicopter was used as a surrogate urban air mobility vehicle to study aspects of a future air taxi mission.
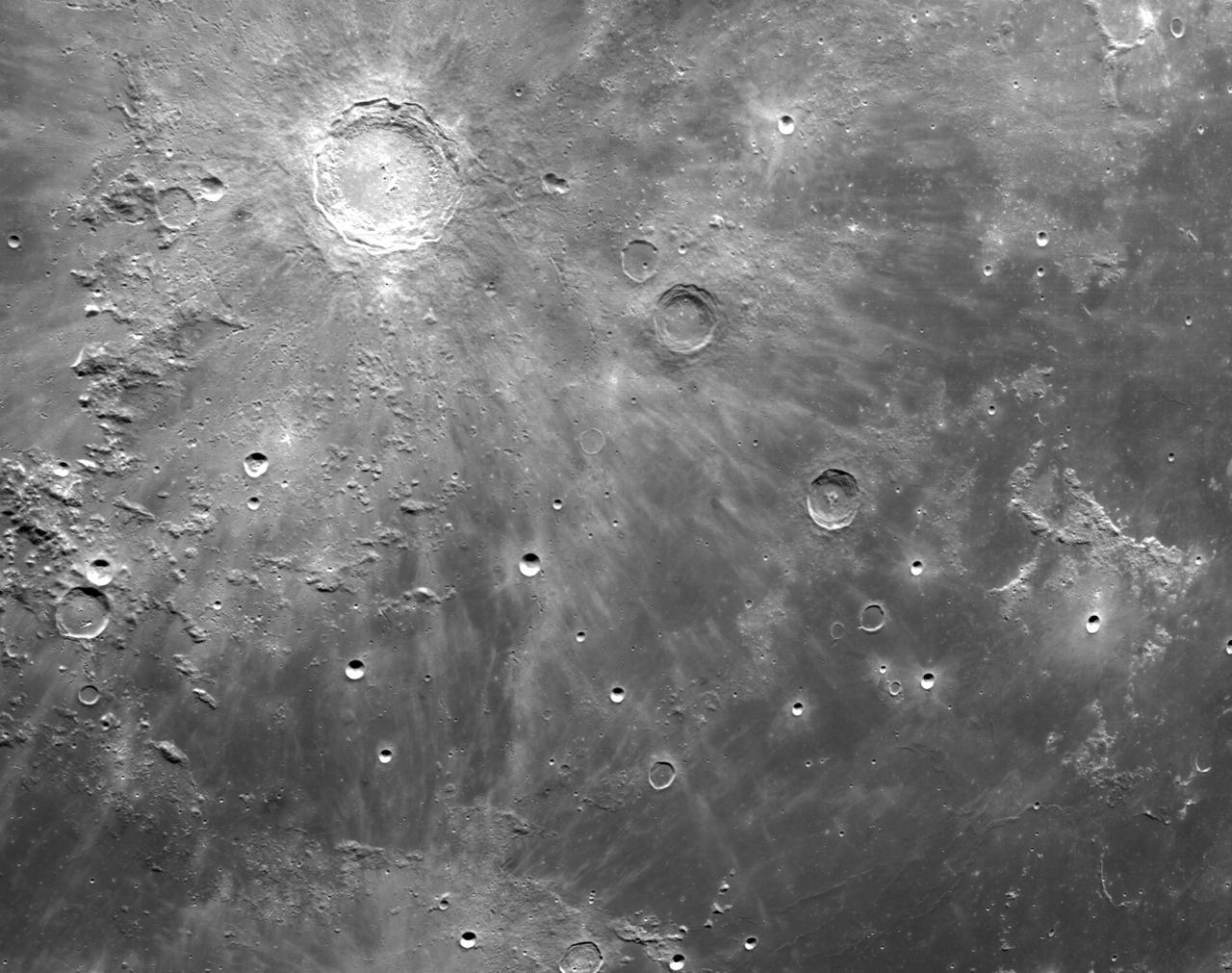

art001e002596 (Dec. 5, 2022): The optical navigation camera mounted on the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
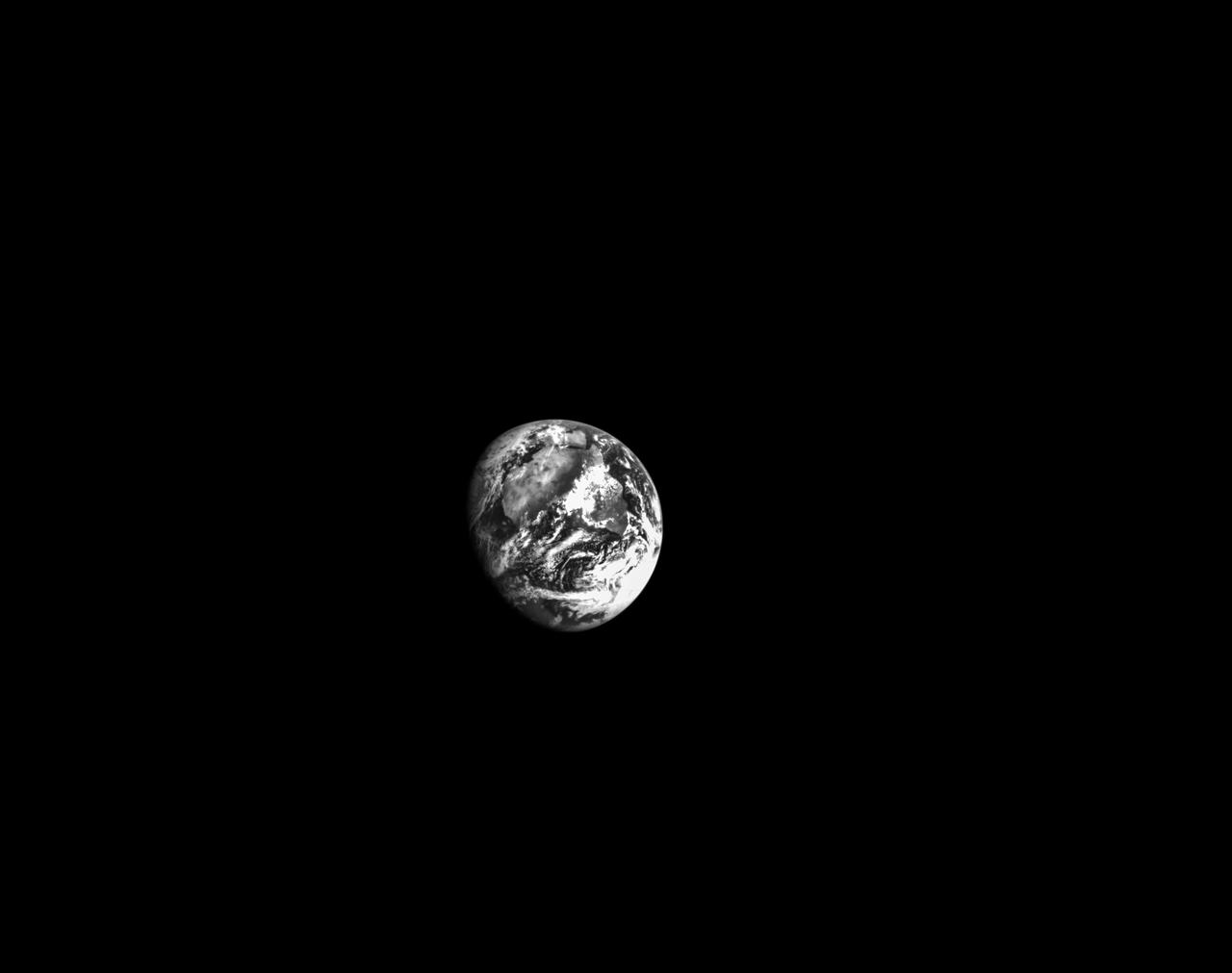

On the second day of the 25.5-day Artemis I mission, Orion used its optical navigation camera to snap black and white photos of planet Earth. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness as a method for determining its position in space for future missions under differing lighting conditions.

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Mission team members monitor the progress of Webb’s second primary mirror wing latching, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, in Baltimore. When fully latched, the infrared observatory will have completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

art001e002655 (Dec. 5, 2022): The optical navigation camera mounted on the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
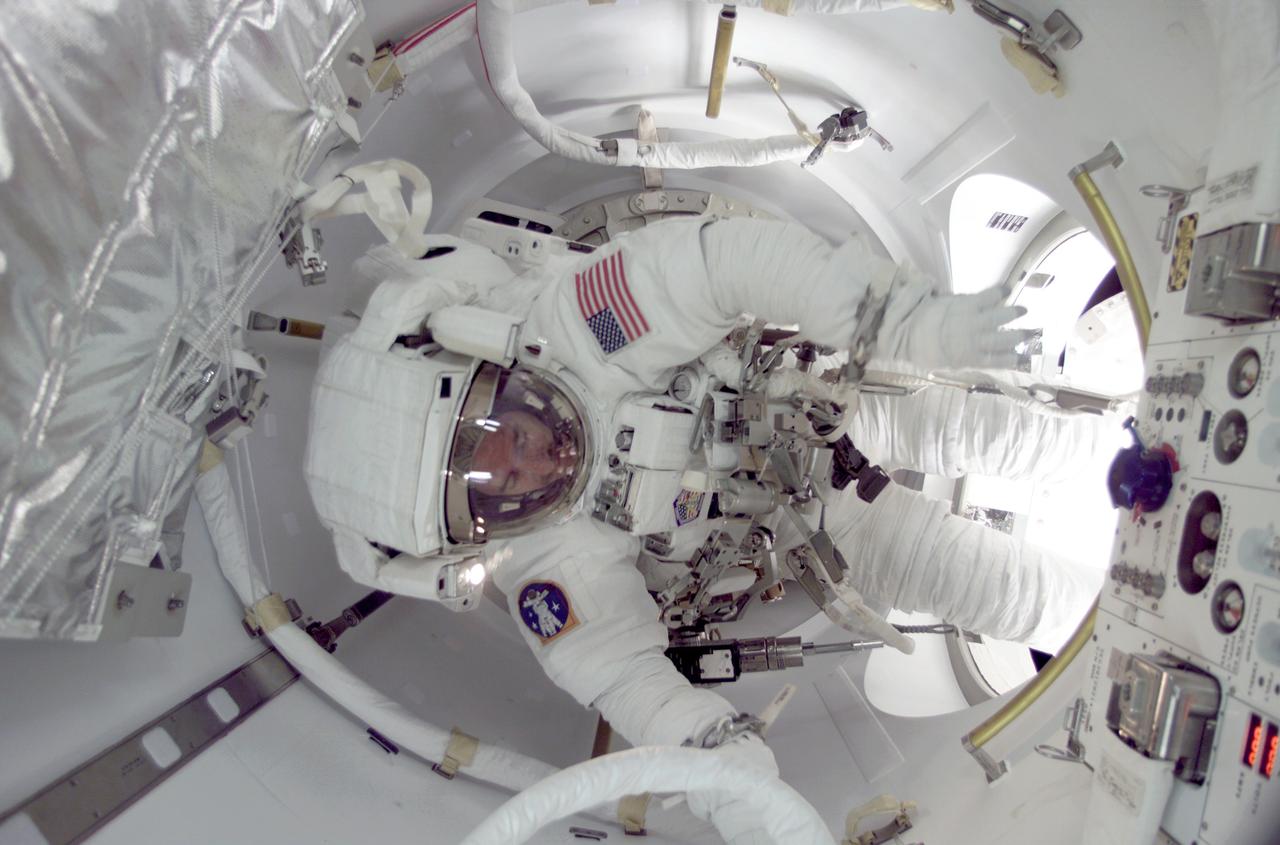

Astronaut James F. Reilly, STS-104 mission specialist, participates in space history as he joins fellow astronaut and mission specialist Michael L. Gernhardt (out of frame) in utilizing the new Quest Airlock for the first ever space walk to egress from the International Space Station (ISS). The major objective of the mission was to install and activate the airlock, which completed the second phase of construction on the ISS. The airlock accommodates both United States and Russian space suits and was designed and built at the Marshall Space Flight Center by the Boeing Company.
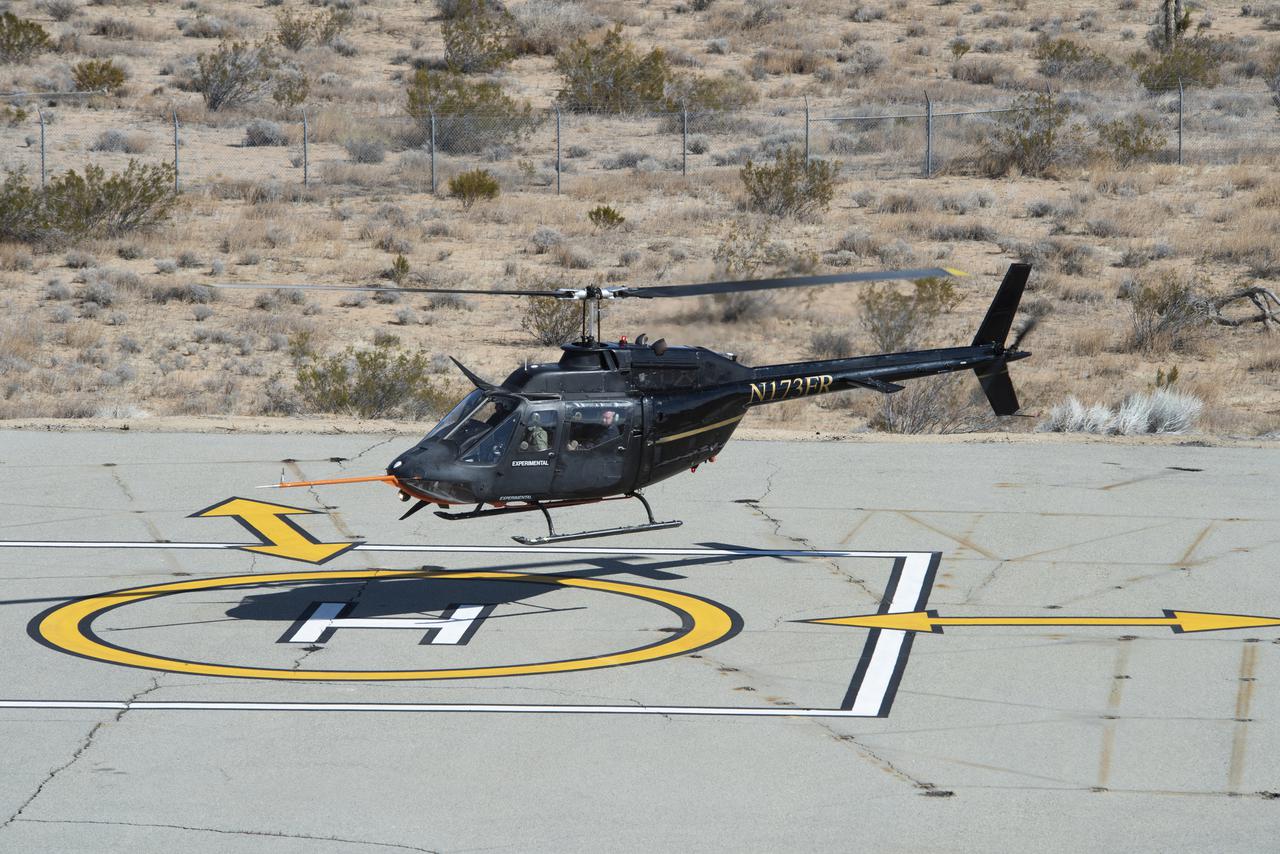

Flight Research Inc.’s Bell OH-58C Kiowa helicopter hovers over a helipad after completing an urban air mobility approach at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California in March 2021. The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign studied the viability of various urban air mobility approach options during a second phase called build II. This helicopter was used as a surrogate urban air mobility or air taxi vehicle.
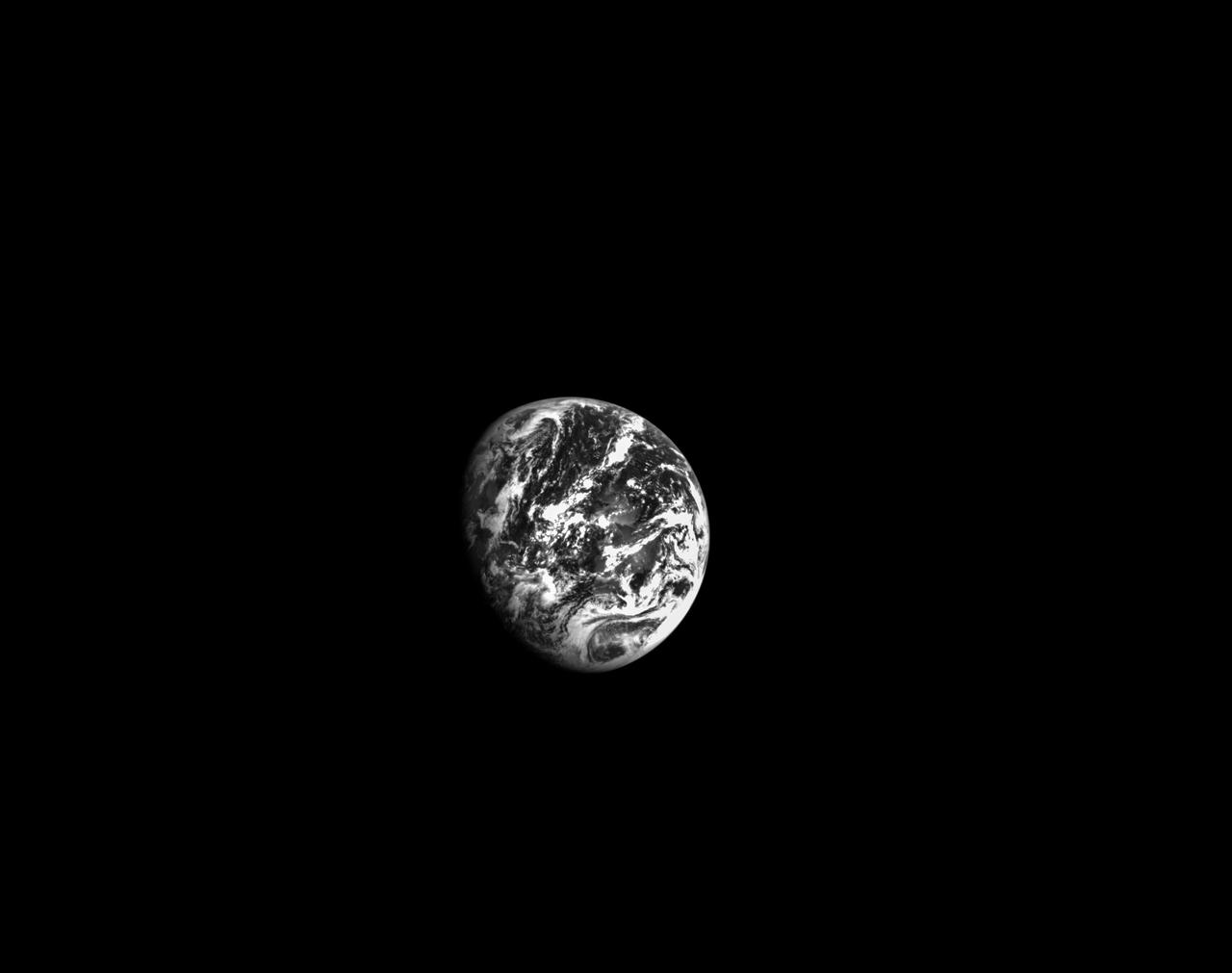

On the second day of the 25.5-day Artemis I mission, Orion used its optical navigation camera to snap black and white photos of planet Earth. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness as a method for determining its position in space for future missions under differing lighting conditions.
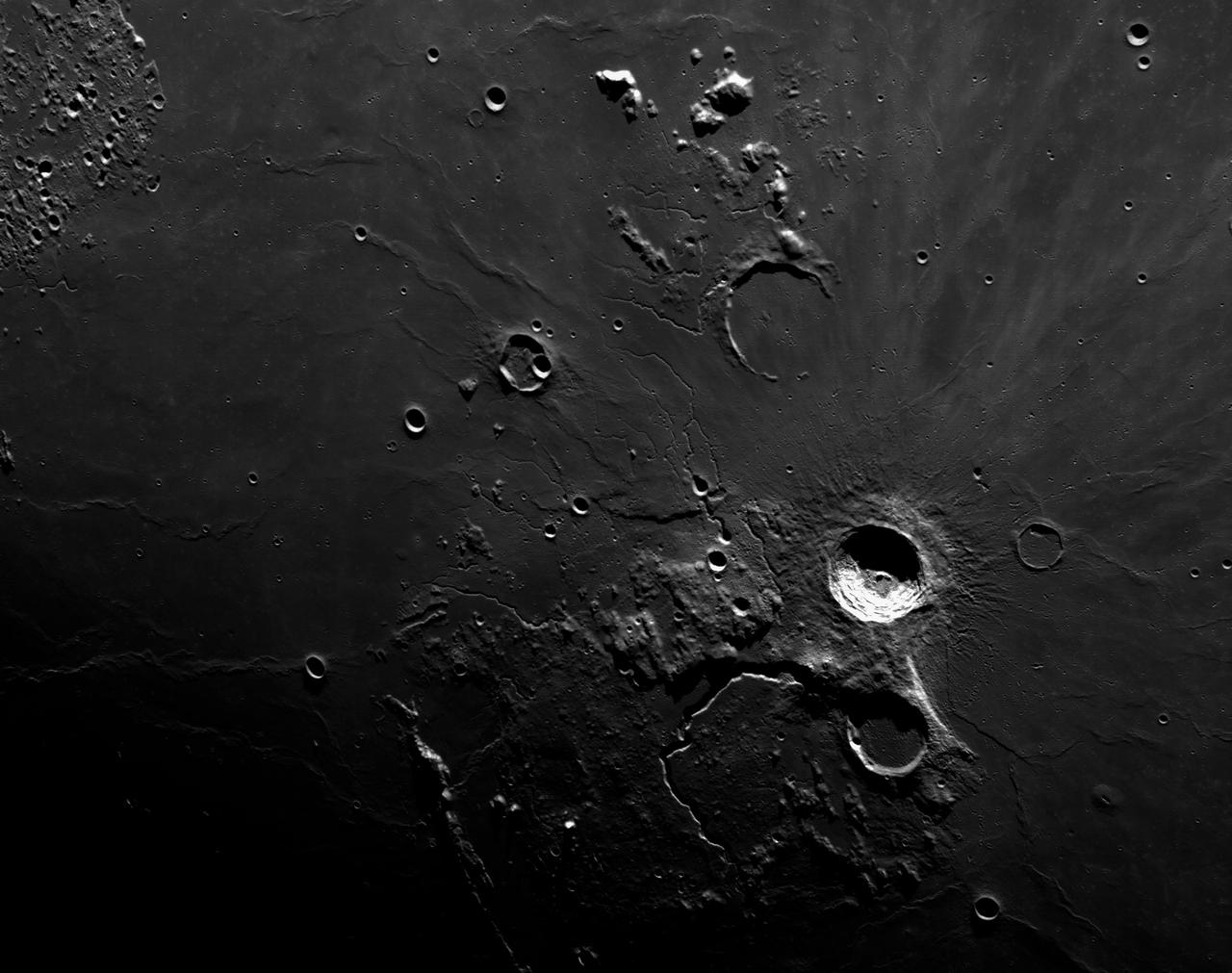

art001e002652 (Dec. 5, 2022): The optical navigation camera mounted on the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
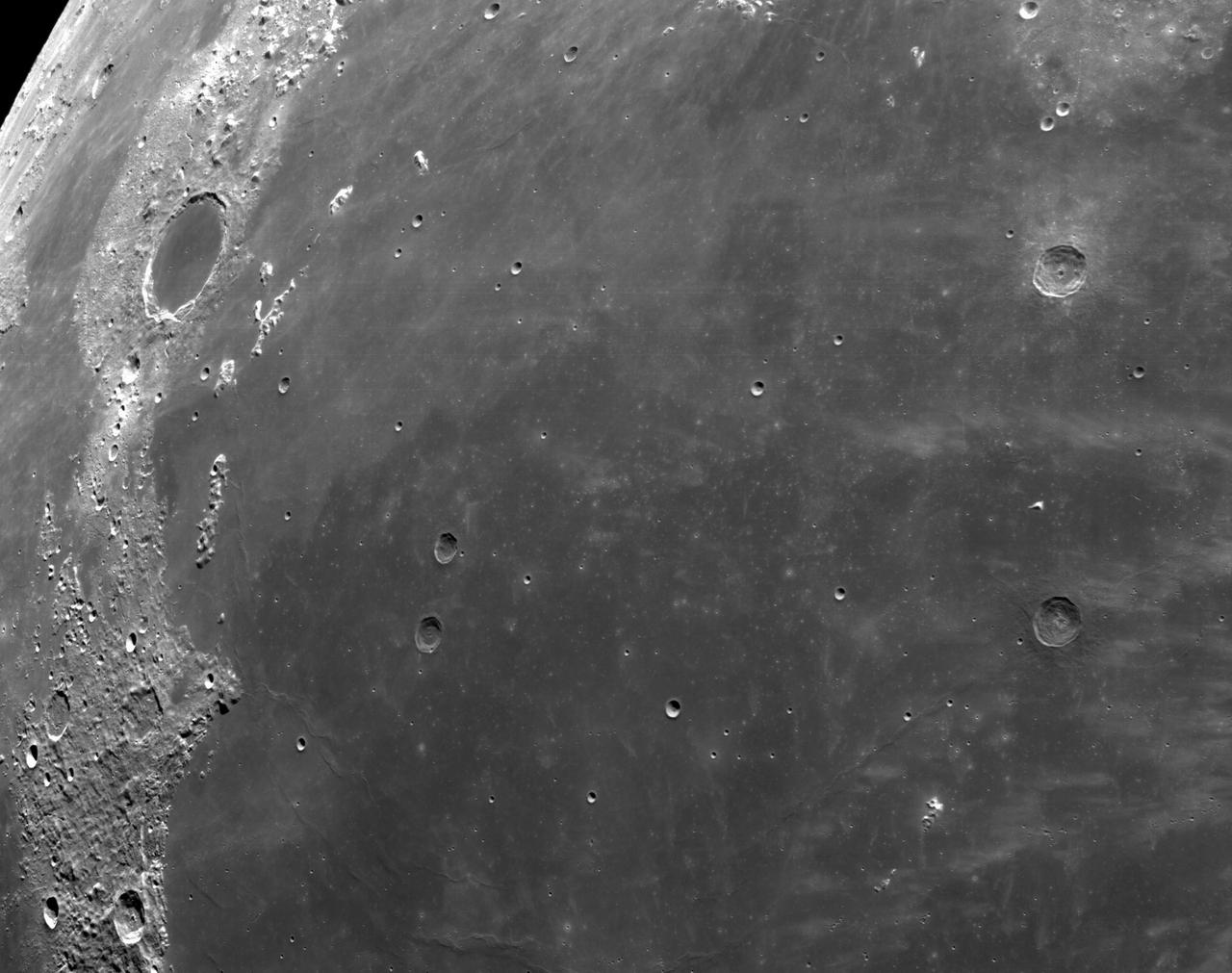

art001e002603 (Dec. 5, 2022): The optical navigation camera mounted on the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
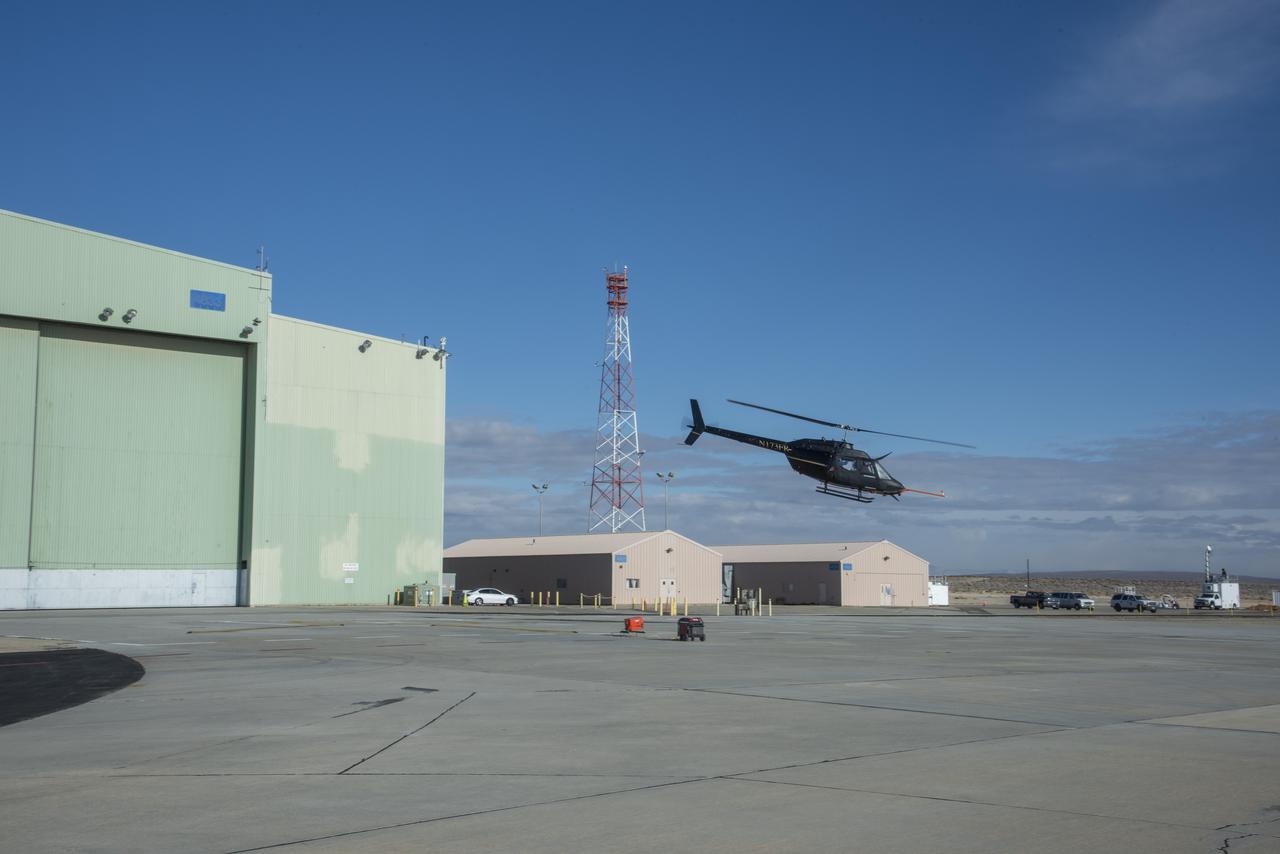

Flight Research Inc.'s Bell OH-58C Kiowa helicopter departs the leeward heliport at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California in March 2021. The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project studied wind and structure interactions as part of a second phase of testing called build II. This helicopter was used as a surrogate urban air mobility or air taxi vehicle.

art001e002595 (Dec. 5, 2022): The optical navigation camera mounted on the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.

art001e002630 (Dec. 5, 2022): The optical navigation camera mounted on the Orion spacecraft captured these views of the Moon’s surface. On flight day 20 of the Artemis I mission, the spacecraft made its second and final close approach to the Moon before its returned powered flyby burn. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
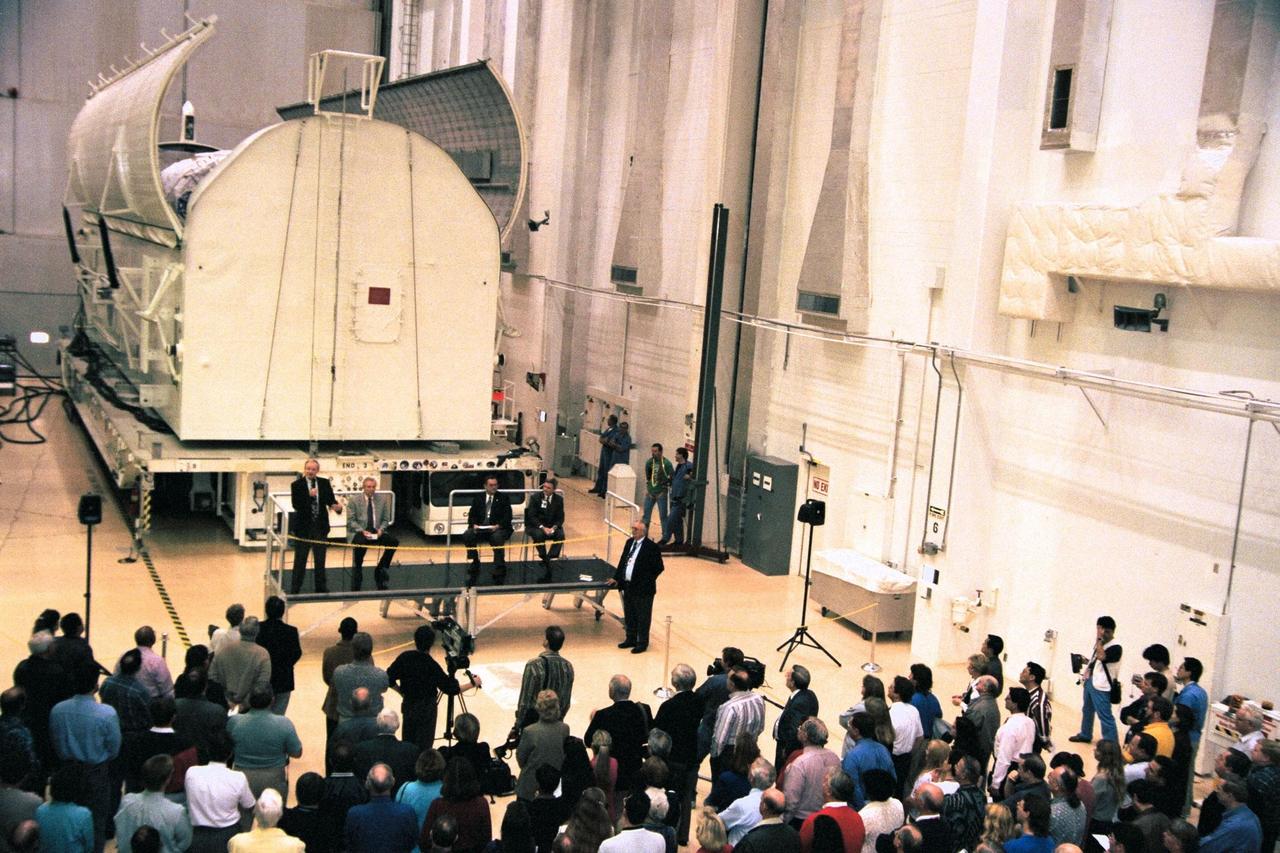

The STS-90 Neurolab payload is honored with a ceremony after being lowered into its payload canister in KSC's Operations and Checkout Building for the last time. This phase of the Shuttle program is winding down as the second phase of the International Space Station (ISS) program gets under way. Microgravity and life science research that formerly was conducted in Spacelab modules, such as Neurolab, will eventually be conducted inside the completed ISS. Investigations during the Neurolab mission will focus on the effects of microgravity on the nervous system. The crew of STS-90, slated for launch in April, will include Commander Richard Searfoss, Pilot Scott Altman, Mission Specialists Richard Linnehan, Dafydd (Dave) Williams, M.D., and Kathryn (Kay) Hire, and Payload Specialists Jay Buckey, M.D., and James Pawelczyk, Ph.D
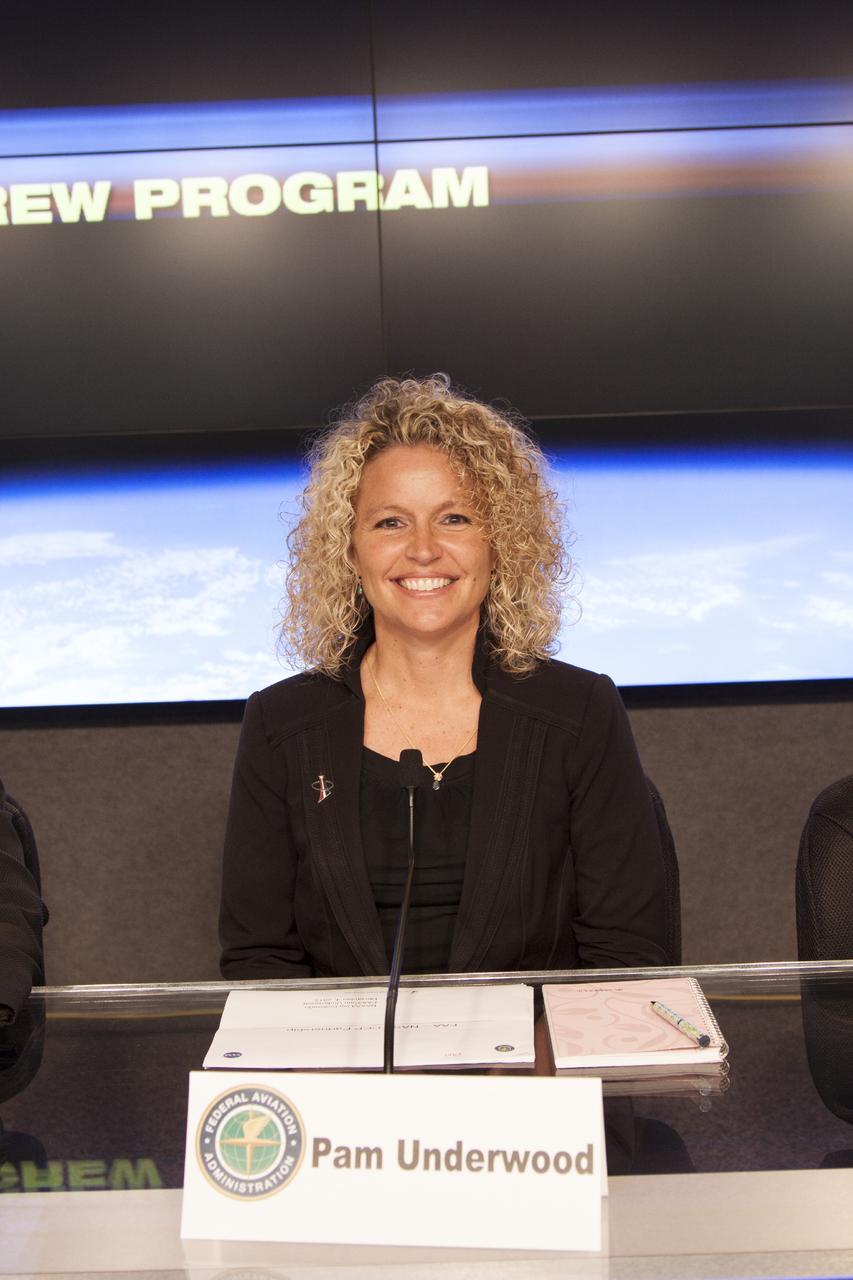

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Pam Underwood of the Federal Aviation Administration's Office of Commercial Transportation and a panelist of the Commercial Crew Transportation Capability, or CCtCap, Pre-Proposal Conference, is seen before the start of an industry conference inside the Television Auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The conference was held following the Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, request for proposals from commercial companies for a development and certification contract under CCtCap. The contract will provide a finish line for the agency following more than four years of development work by CCP and American aerospace companies. CCtCap is the second phase of a two-phase certification plan for privately built and operated integrated crew transportation systems. CCP’s goal is to aid in the development of commercial capabilities for crew transportation and rescue services to and from the International Space Station and other low-Earth orbit destinations by the end of 2017. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Lisa Colloredo, associate program manager of NASA's Commercial Crew Program and a panelist of the Commercial Crew Transportation Capability, or CCtCap, Pre-Proposal Conference, is seen before the start of an industry conference inside the Television Auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The conference was held following the Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, request for proposals from commercial companies for a development and certification contract under CCtCap. The contract will provide a finish line for the agency following more than four years of development work by CCP and American aerospace companies. CCtCap is the second phase of a two-phase certification plan for privately built and operated integrated crew transportation systems. CCP’s goal is to aid in the development of commercial capabilities for crew transportation and rescue services to and from the International Space Station and other low-Earth orbit destinations by the end of 2017. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
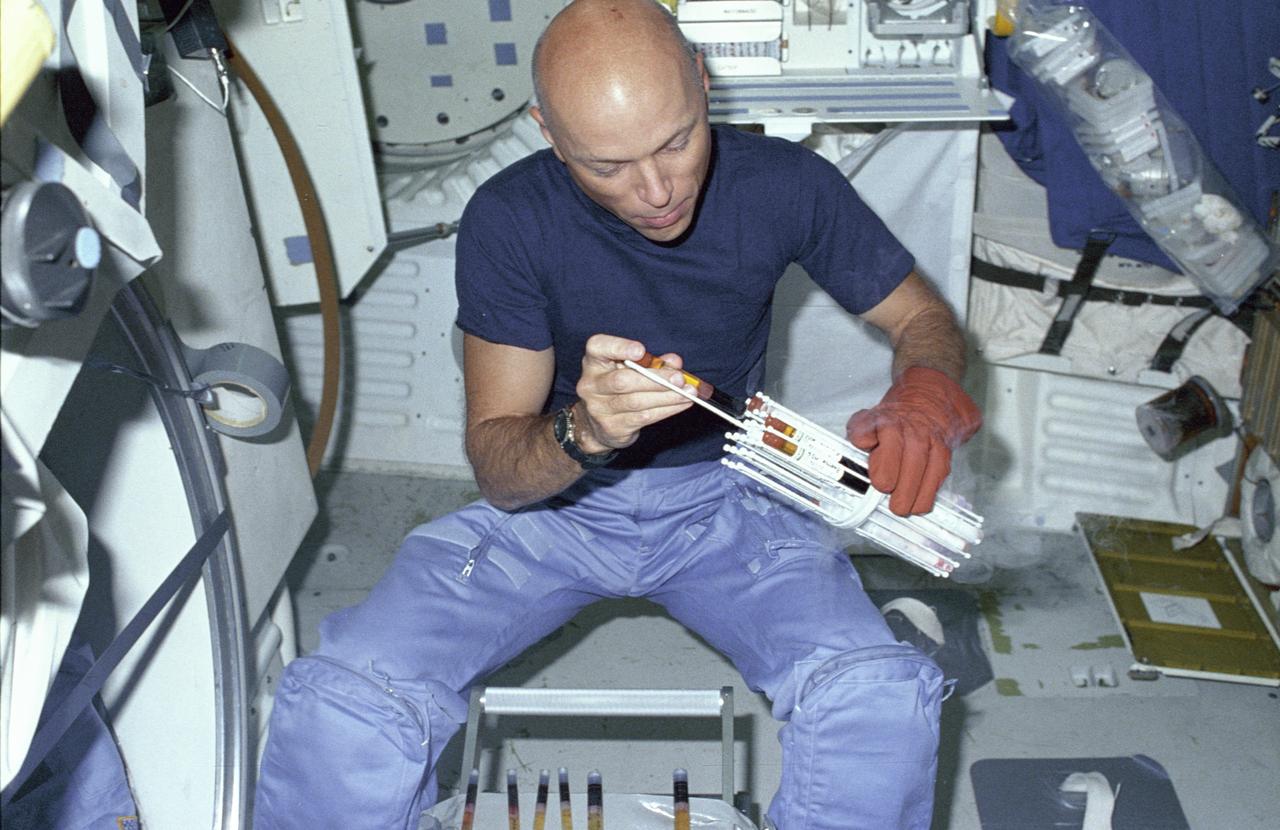

While instruments on the pallets in the payload bay observed the universe, biological experiments were performed in the middeck of the Shuttle Orbiter Challenger. Studying life processes in a microgravity environment can shed new light on the functioning of biological systems on Earth. These investigations can also help us understand how living organisms react to prolonged weightlessness. One such experiment was the vitamin D metabolites and bone demineralization experiment. This investigation measured the vitamin D metabolite levels of crew members to gain information on the cause of bone demineralization and mineral imbalance that occur during prolonged spaceflight as well as on Earth. Research into the biochemical nature of vitamin D has shown that the D-metabolites play a major role in regulating the body's calcium and phosphorus levels. One major function of the most biologically active vitamin D metabolite is to regulate the amount of calcium absorbed from the diet and taken out of bones. This investigation had two phases. The first was the developmental phase, which included extensive testing before flight, and the second, or final phase, involved the postflight analysis of the crew's blood samples. This photograph shows astronaut Story Musgrave in the middeck of the Shuttle Orbiter Challenger, attending to the blood samples he collected from crew members for the experiment.
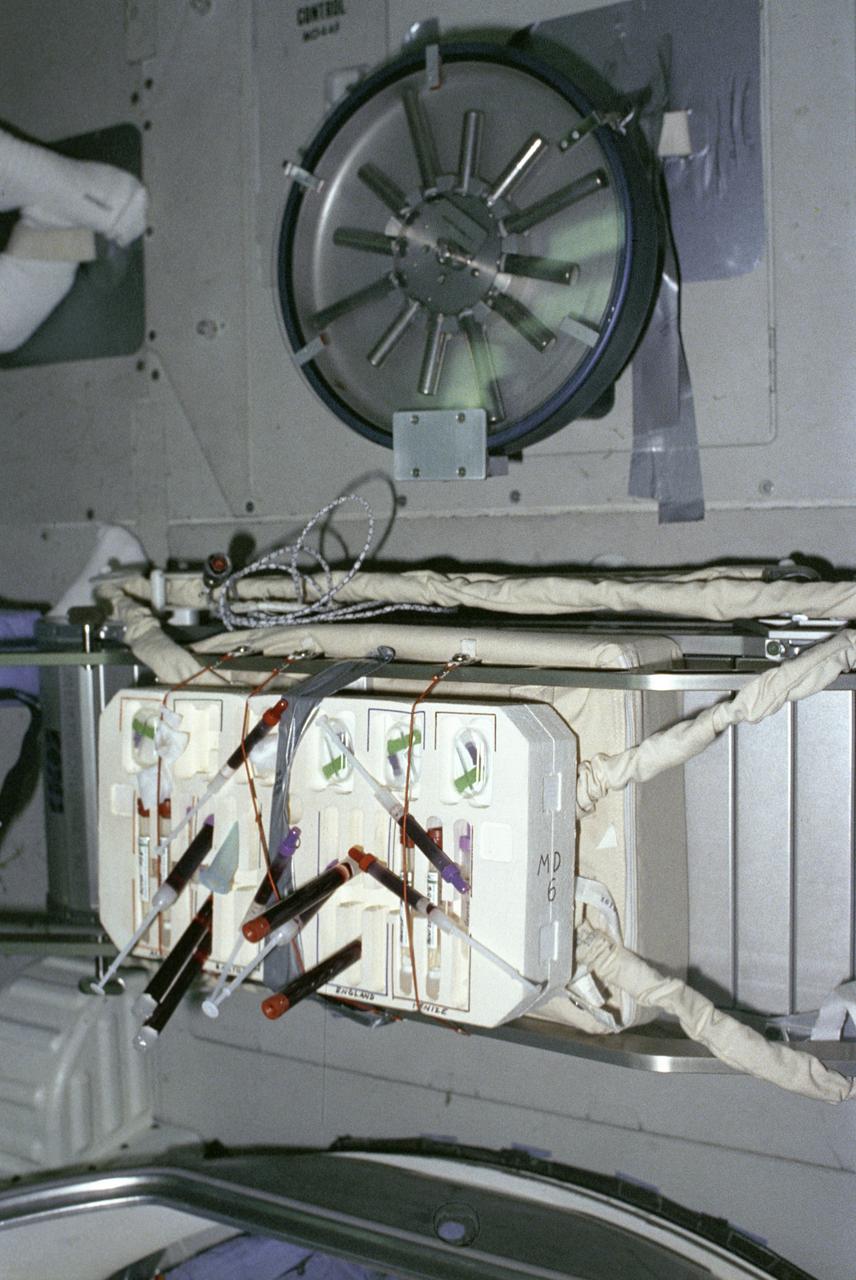
While instruments on the pallets in the payload bay observed the universe, biological experiments were performed in the middeck of the Shuttle Orbiter Challenger. Studying life processes in a microgravity environment can shed new light on the functioning of biological systems on Earth. These investigations can also help us understand how living organisms react to prolonged weightlessness. One such experiment was the vitamin D metabolites and bone demineralization experiment. This investigation measured the vitamin d metabolite levels of crew members to gain information on the cause of bone demineralization and mineral imbalance that occur during prolonged spaceflight as well as on Earth. Research into the biochemical nature of vitamin D has shown that the D-metabolites play a major role in regulating the body's calcium and phosphorus levels. One major function of the most biologically active vitamin D metabolite is to regulate the amount of calcium absorbed from the diet and taken out of bones. This investigation had two phases. The first was the developmental phase, which included extensive testing before flight, and the second, or final phase, involved the postflight analysis of the crew's blood samples. This photograph shows a blood draw test kit and centrifuge used for the experiment aboard the Spacelab-2. Marshall Space Flight Center had management responsibilities of all Spacelab missions.
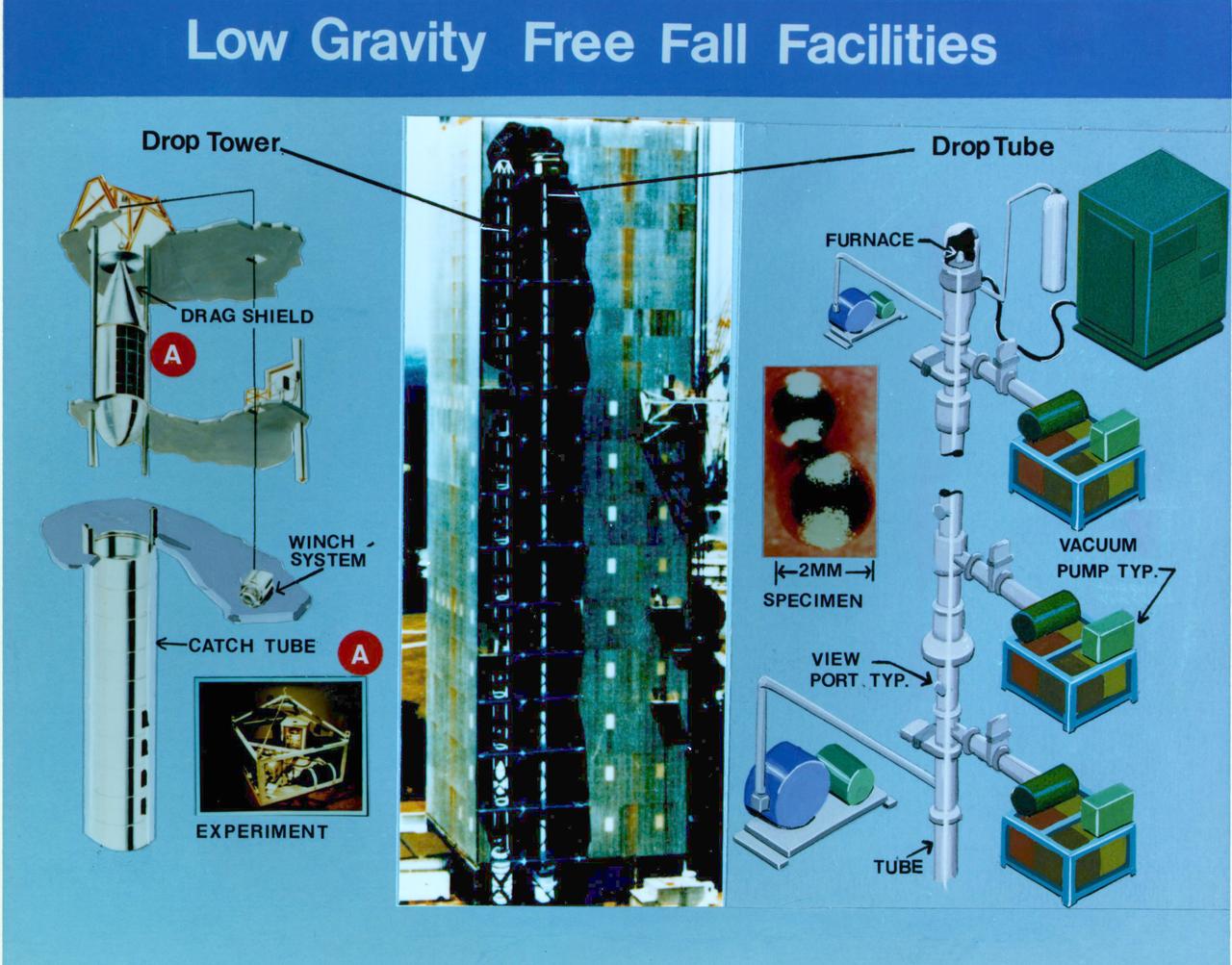
Composite of Marshall Space Flight Center's Low-Gravity Free Fall Facilities.These facilities include a 100-meter drop tower and a 100-meter drop tube. The drop tower simulates in-flight microgravity conditions for up to 4.2 seconds for containerless processing experiments, immiscible fluids and materials research, pre-flight hardware design test and flight experiment simulation. The drop tube simulates in-flight microgravity conditions for up to 4.6 seconds and is used extensively for ground-based microgravity convection research in which extremely small samples are studied. The facility can provide deep undercooling for containerless processing experiments that require materials to remain in a liquid phase when cooled below the normal solidification temperature.
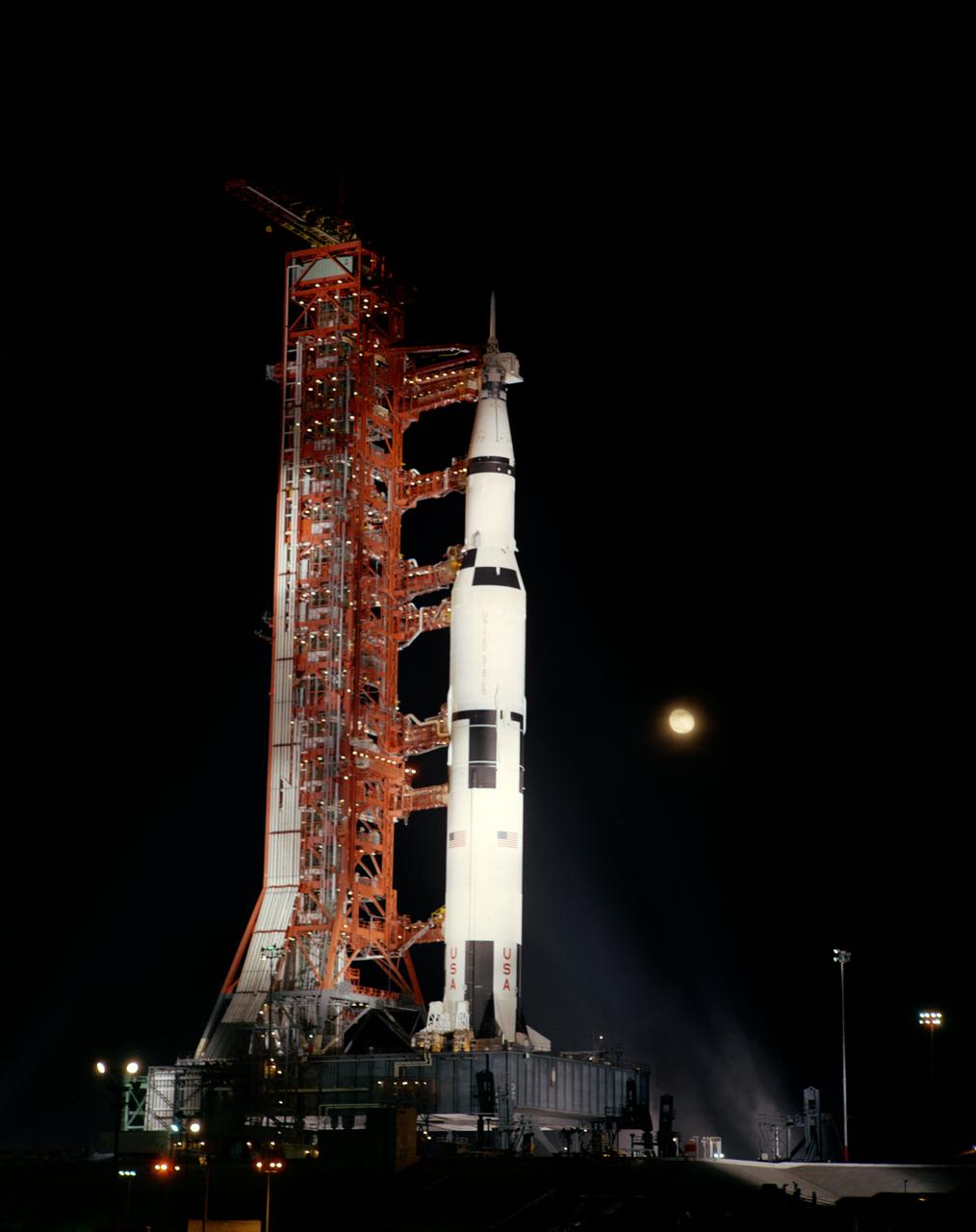

S69-56596 (28 Oct. 1969) --- A nighttime, ground-level view of Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC) showing the Apollo 12 (Spacecraft 108/Lunar Module 6/Saturn 507) space vehicle, during the terminal phase of a Countdown Demonstration Test (CDDT). The crew of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) second lunar landing mission will be astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander; Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot; and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 12 launch has been scheduled for 11:22 a.m. (EST) on Nov. 14, 1969.
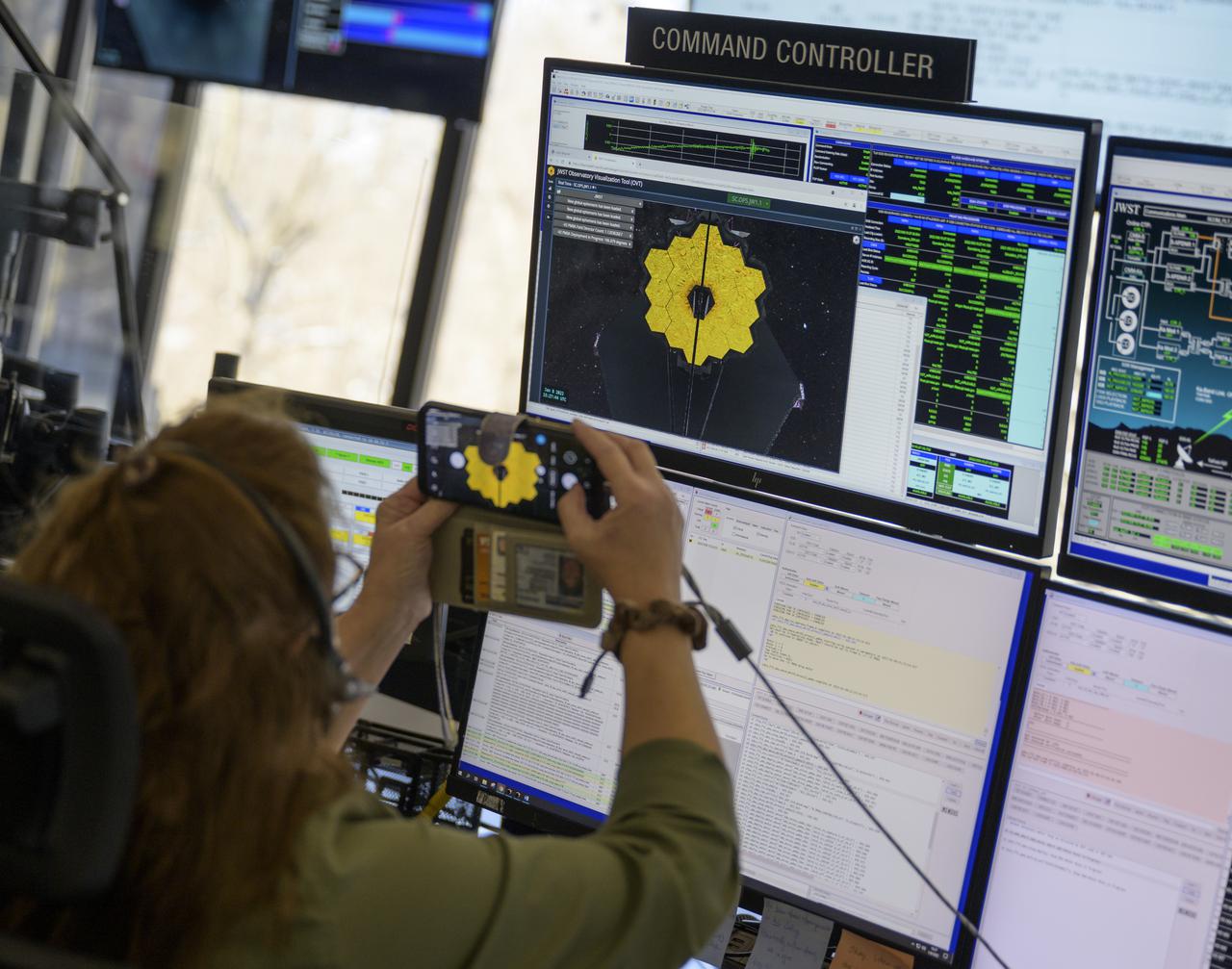

Engineering teams at NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore monitor progress as the observatory’s second primary mirror wing rotates into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
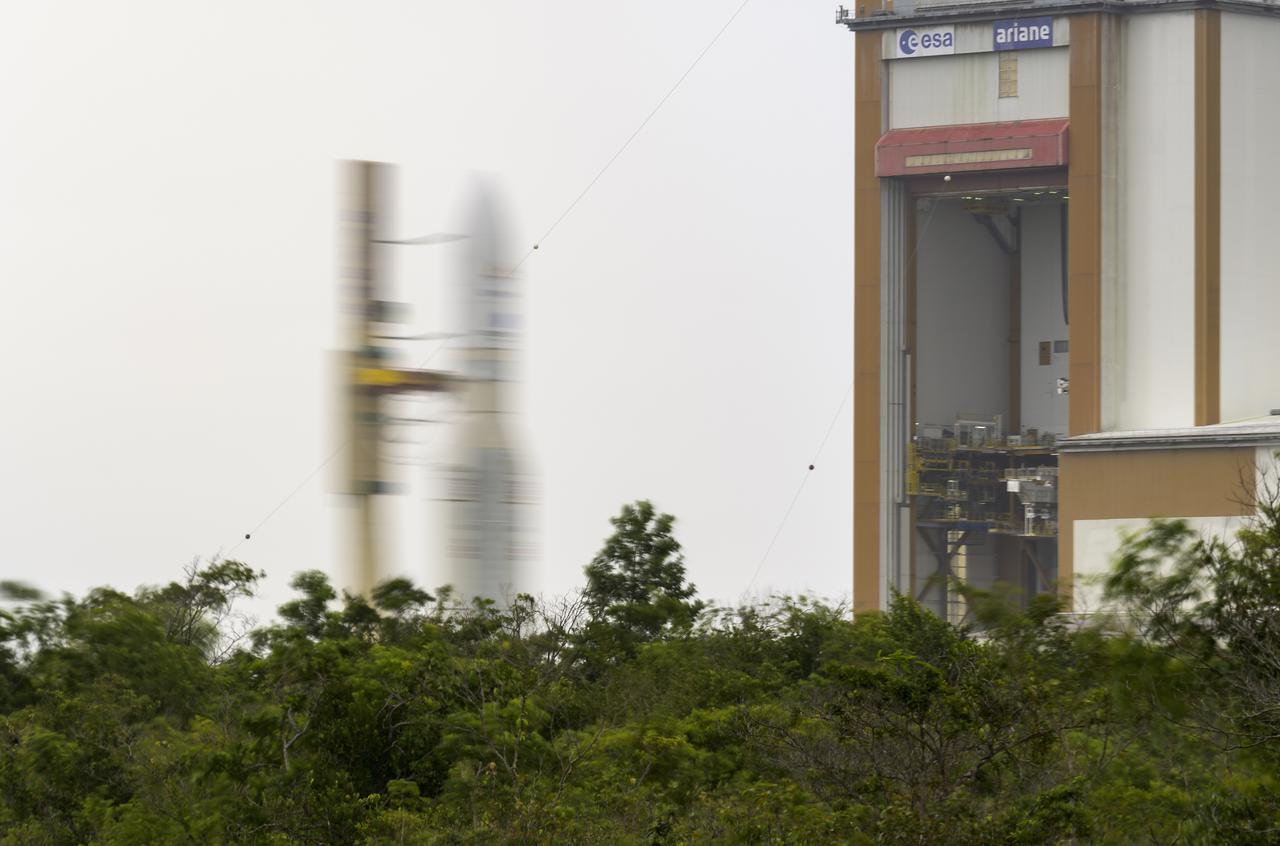

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen in this 30 second exposure, as it is rolled out to the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
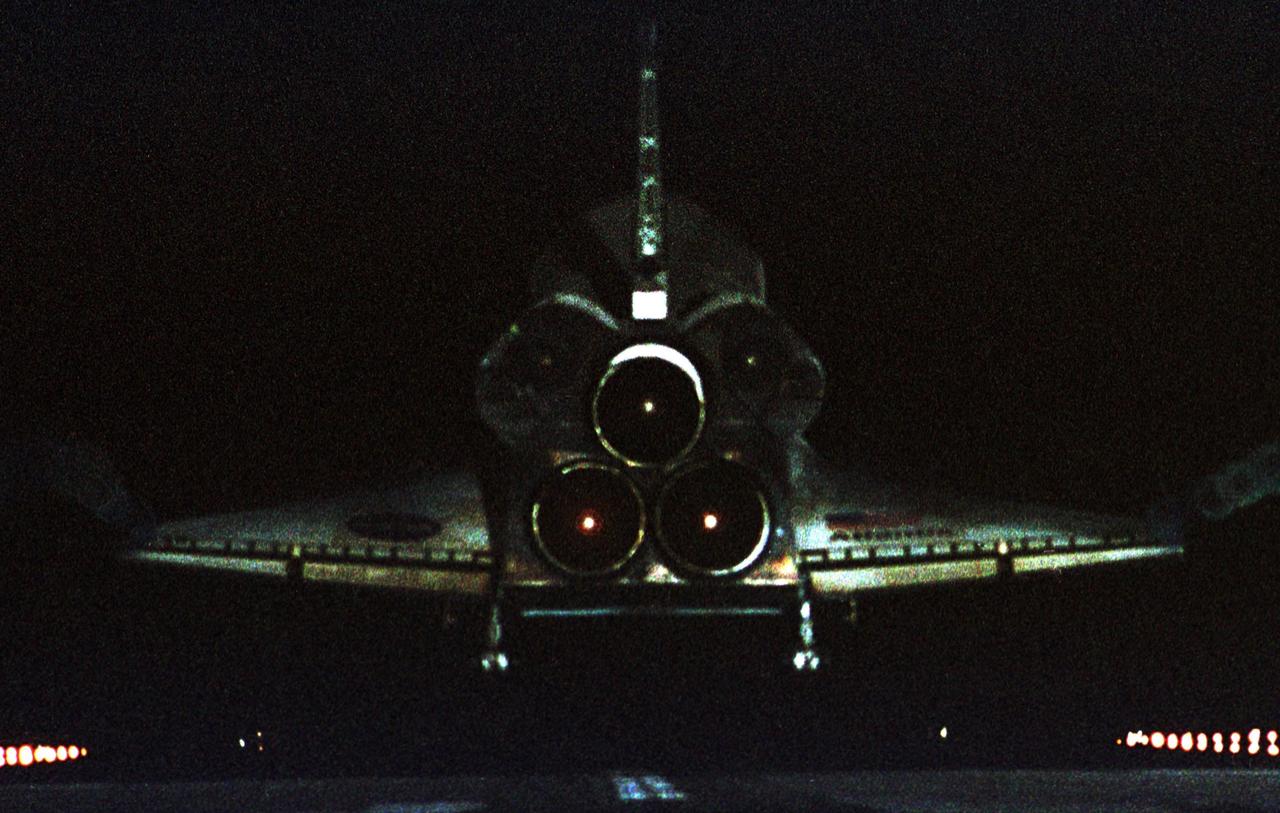
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Atlantis prepares to land on Runway 15 at the Shuttle Landing Facility to complete a 12-day, 18-hour, 34-minute-long STS-104 mission. Main gear touchdown occurred at 11:38:55 p.m. EDT. At the controls is Commander Steven W. Lindsey. Other crew members on board are Pilot Charles Hobaugh and Mission Specialists Michael Gernhardt, Janet Lynn Kavandi and James F. Reilly. This is the 18th nighttime landing for a Space Shuttle, the 13th at Kennedy Space Center. The mission delivered the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station, completing the second phase of the assembly of the Space Station

Engineering teams at NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore monitor progress as the observatory’s second primary mirror wing rotates into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
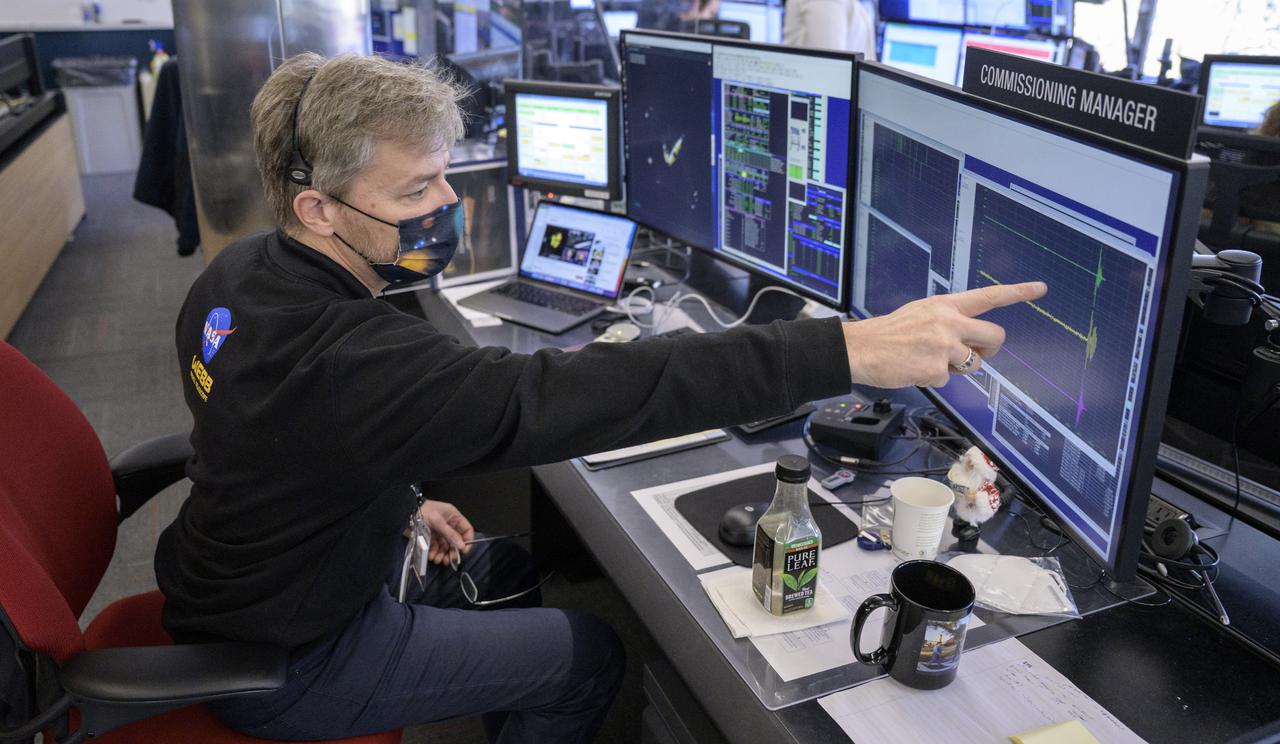

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Commissioning Manager John Durning monitors the progress of the Webb observatory as it’s second primary mirror wing is prepared to rotate into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
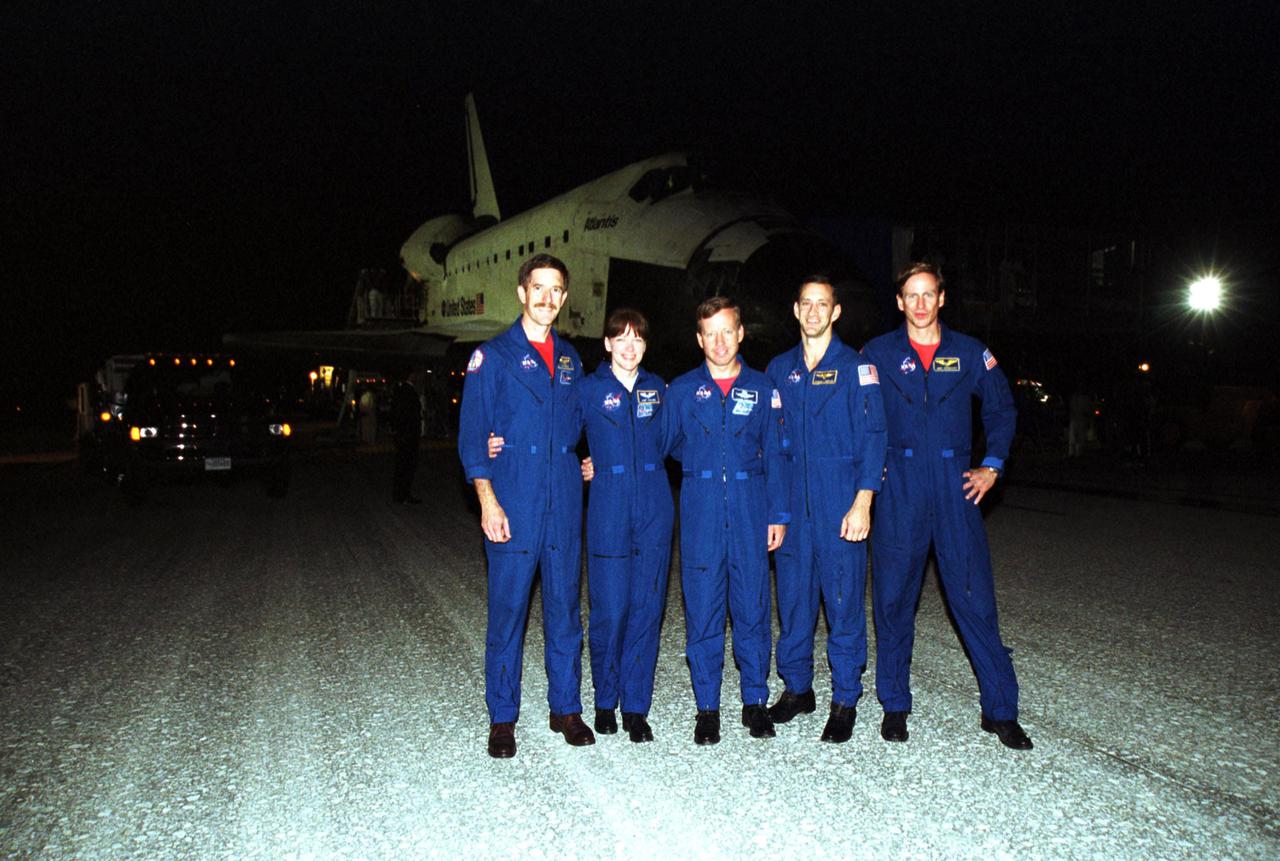

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- After a perfect landing at the Shuttle Landing Facility, the STS-104 crew poses for a photo. Standing in front of Atlantis are Mission Specialists James Reilly and Janet Lynn Kavandi, Commander Steven Lindsey, Pilot Charles Hobaugh and Mission Specialist Michael Gernhardt. Atlantis touched down at 11:38:55 p.m. EDT July 24, 2001, completing a 12-day, 18-hour, 34-minute-long mission to the International Space Station. The mission delivered the Joint Airlock Module to the Space Station, completing the second phase of the assembly of the Space Station. This is the 18th nighttime landing for a Space Shuttle, the 13th at Kennedy Space Center

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., workers place the second row of segments of the transportation canister around the Space Tracking and Surveillance System – Demonstrators, or STSS Demo, spacecraft. The STSS Demo is a space-based sensor component of a layered Ballistic Missile Defense System designed for the overall mission of detecting, tracking and discriminating ballistic missiles. STSS is capable of tracking objects after boost phase and provides trajectory information to other sensors. It will be launched by NASA for the Missile Defense Agency between 8 and 8:58 a.m. EDT Sept. 18. Approved for Public Release 09-MDA-04886 (10 SEPT 09) Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
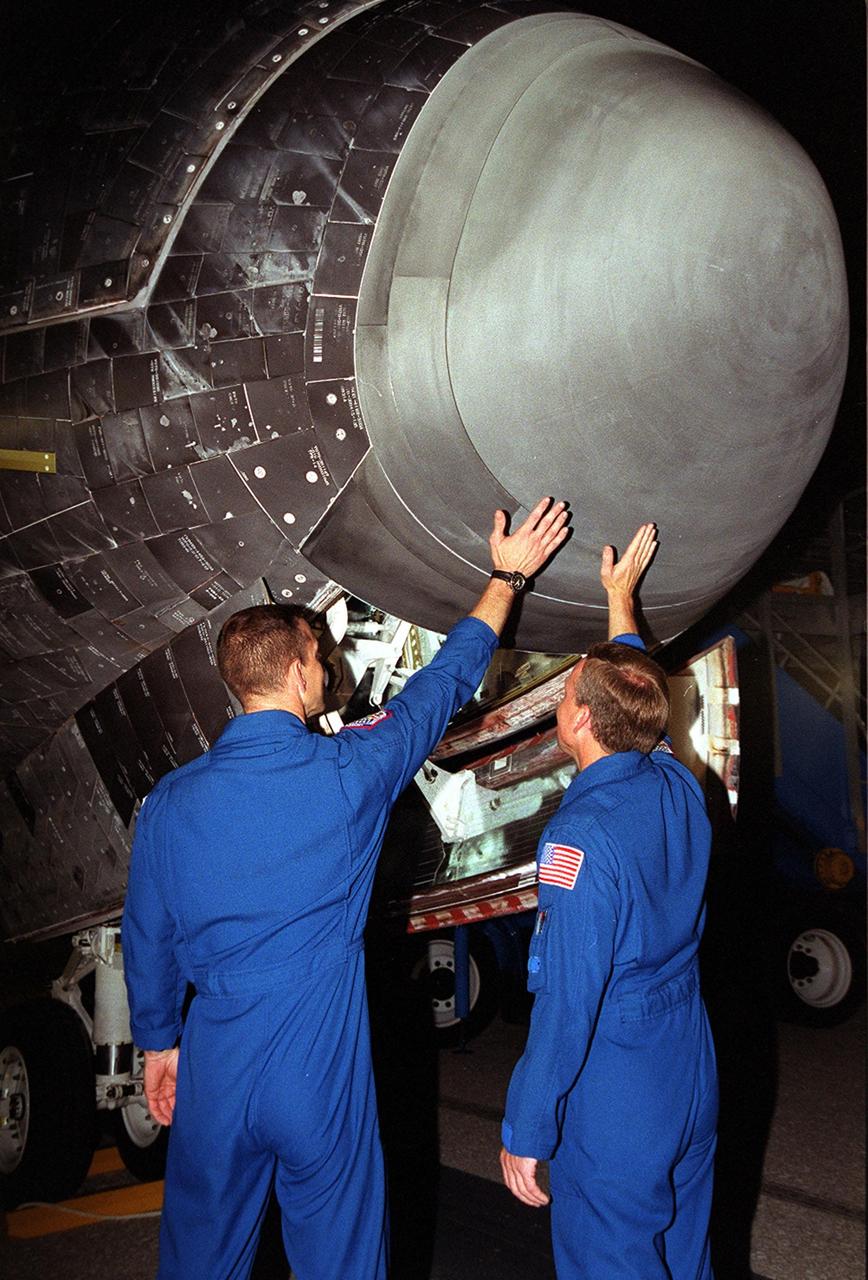

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- During their post-landing walkaround under orbiter Atlantis, Pilot Charles Hobaugh (left) and Commander Steven Lindsey feel the heat from the nose of the orbiter. Atlantis touched down at 11:38:55 p.m. EDT July 24, 2001, completing a 12-day, 18-hour, 34-minute-long mission to the International Space Station. The mission delivered the Joint Airlock Module to the Space Station, completing the second phase of the assembly of the Space Station. This is the 18th nighttime landing for a Space Shuttle, the 13th at Kennedy Space Center
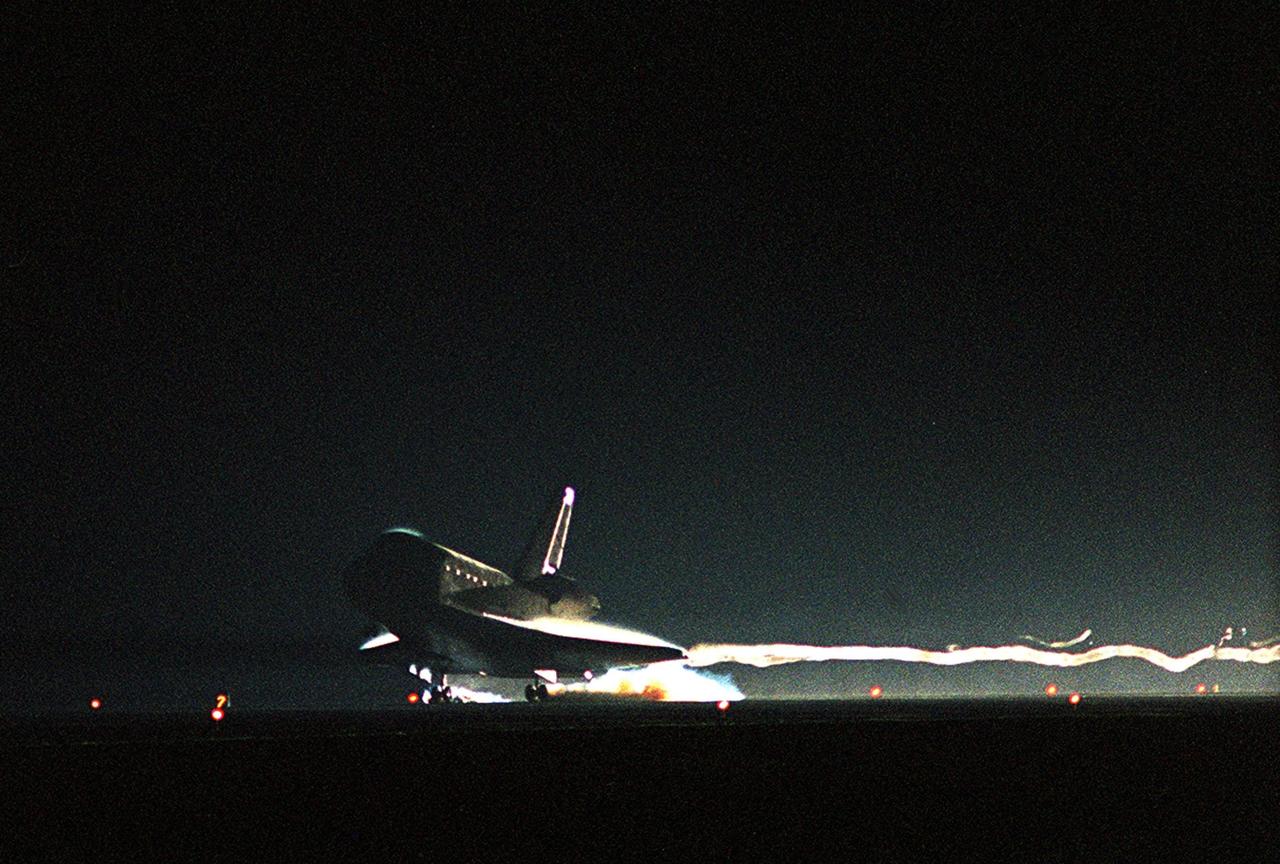

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Air waves stream behind Atlantis as it touches down on Runway 15 at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown occurred at 11:38:55 p.m. EDT, completing complete a 12-day, 18-hour, 34-minute-long STS-104 mission. At the controls is Commander Steven W. Lindsey. Other crew members on board are Pilot Charles Hobaugh and Mission Specialists Michael Gernhardt, Janet Lynn Kavandi and James F. Reilly. This is the 18th nighttime landing for a Space Shuttle, the 13th at Kennedy Space Center. The mission delivered the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station, completing the second phase of the assembly of the Space Station
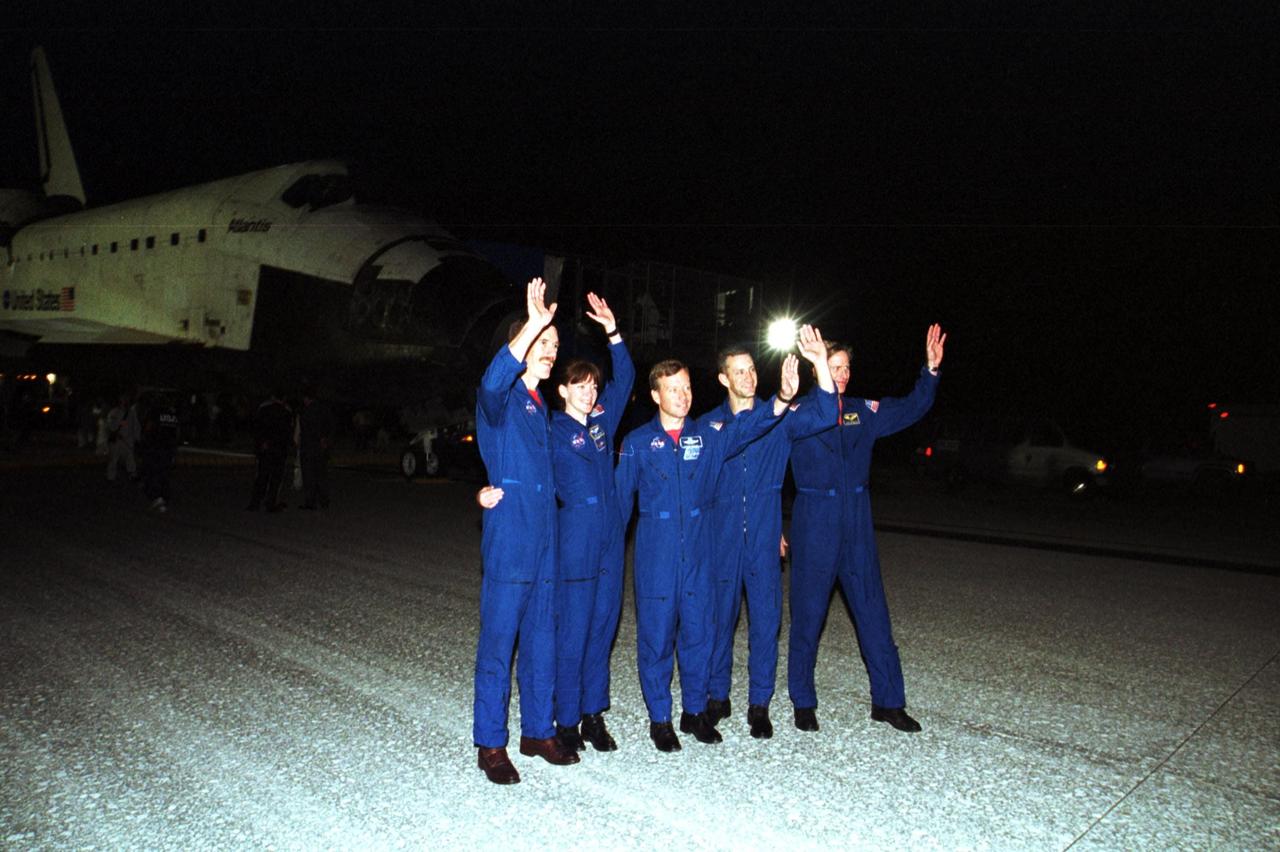

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-104 crew wave at onlookers who welcomed them home from their almost 13-day mission to the International Space Station. From left are Mission Specialists James Reilly and Janet Lynn Kavandi, Commander Steven Lindsey, Pilot Charles Hobaugh and Mission Specialist Michael Gernhardt. Atlantis touched down at 11:38:55 p.m. EDT July 24, 2001. The mission delivered the Joint Airlock Module to the Space Station, completing the second phase of the assembly of the Space Station. This is the 18th nighttime landing for a Space Shuttle, the 13th at Kennedy Space Center

Engineering teams celebrate at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore as the second primary mirror wing of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope unfolds, before beginning the process of latching the mirror wing into place, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022. When fully latched, the infrared observatory will have completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
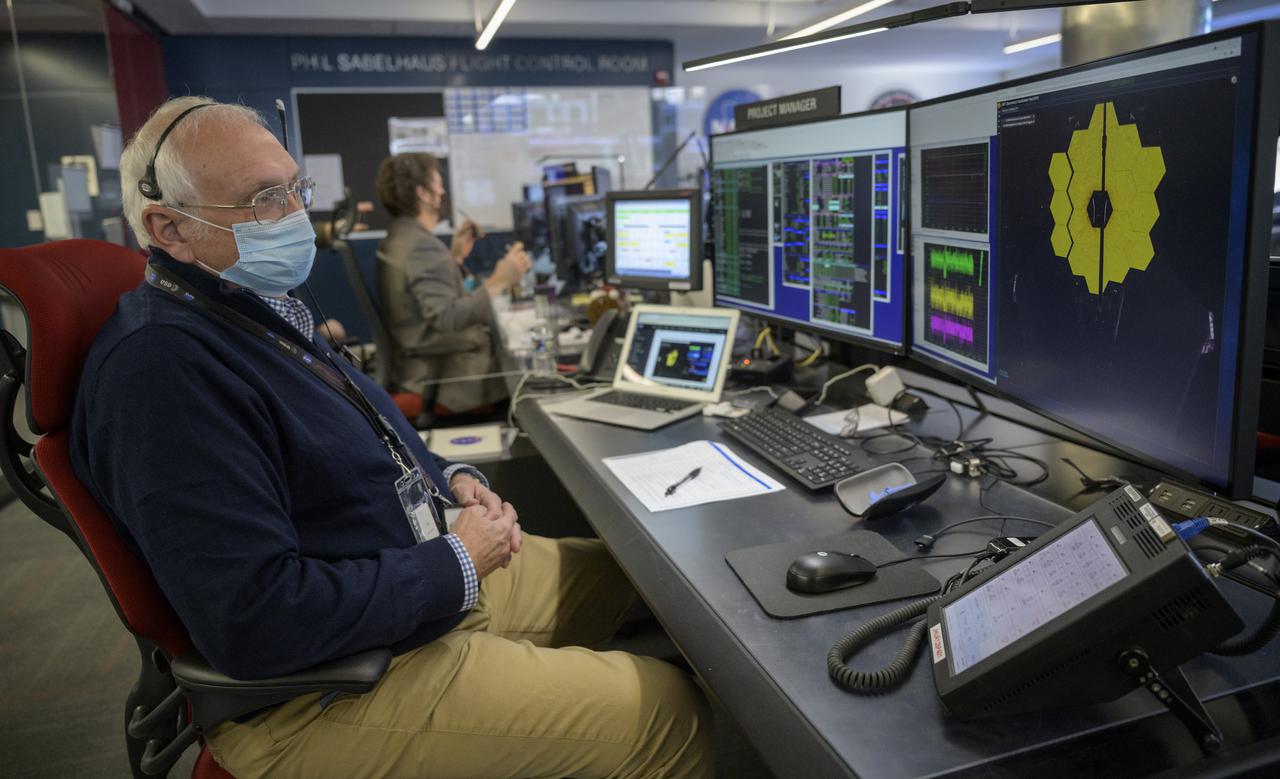

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Project Manager Bill Ochs monitors the progress of the observatory’s second primary mirror wing as it rotates into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
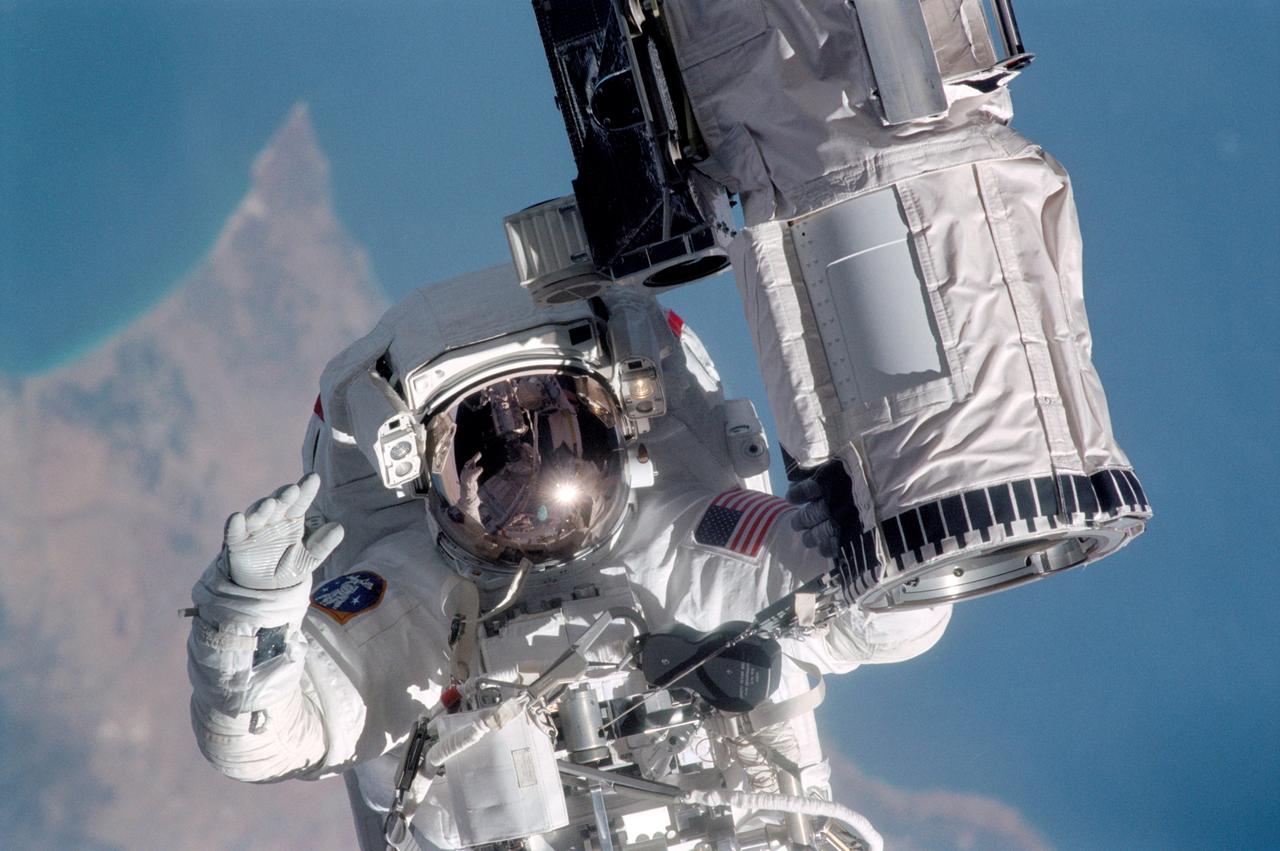

Astronaut Michael L. Gernhardt, STS-104 mission specialist, participates in one of three STS-104 space walks while holding on to the end effector of the Canadarm on the Space Shuttle Atlantis. Gernhardt was joined on the extravehicular activity (EVA) by astronaut James F. Reilly (out of frame). The major objective of the mission was to install and activate the Joint Airlock, which completed the second phase of construction on the International Space Station (ISS). The airlock accommodates both United States and Russian space suits and was designed and built at the Marshall Space Flight Center by the Boeing Company.
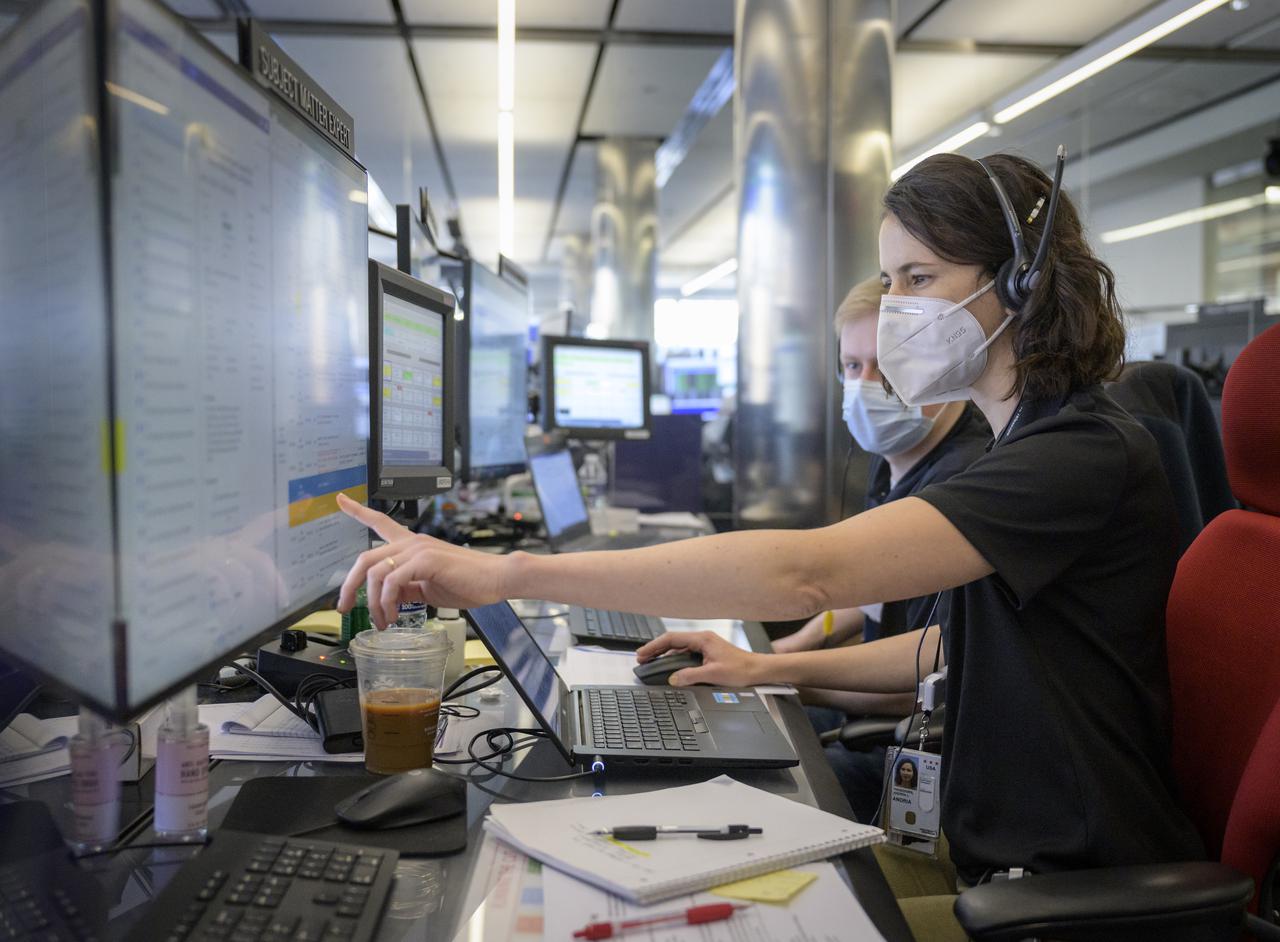

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Timeline Coordinator Andria Hagedorn monitors the progress of the Webb observatory’s second primary mirror wing as it rotates into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
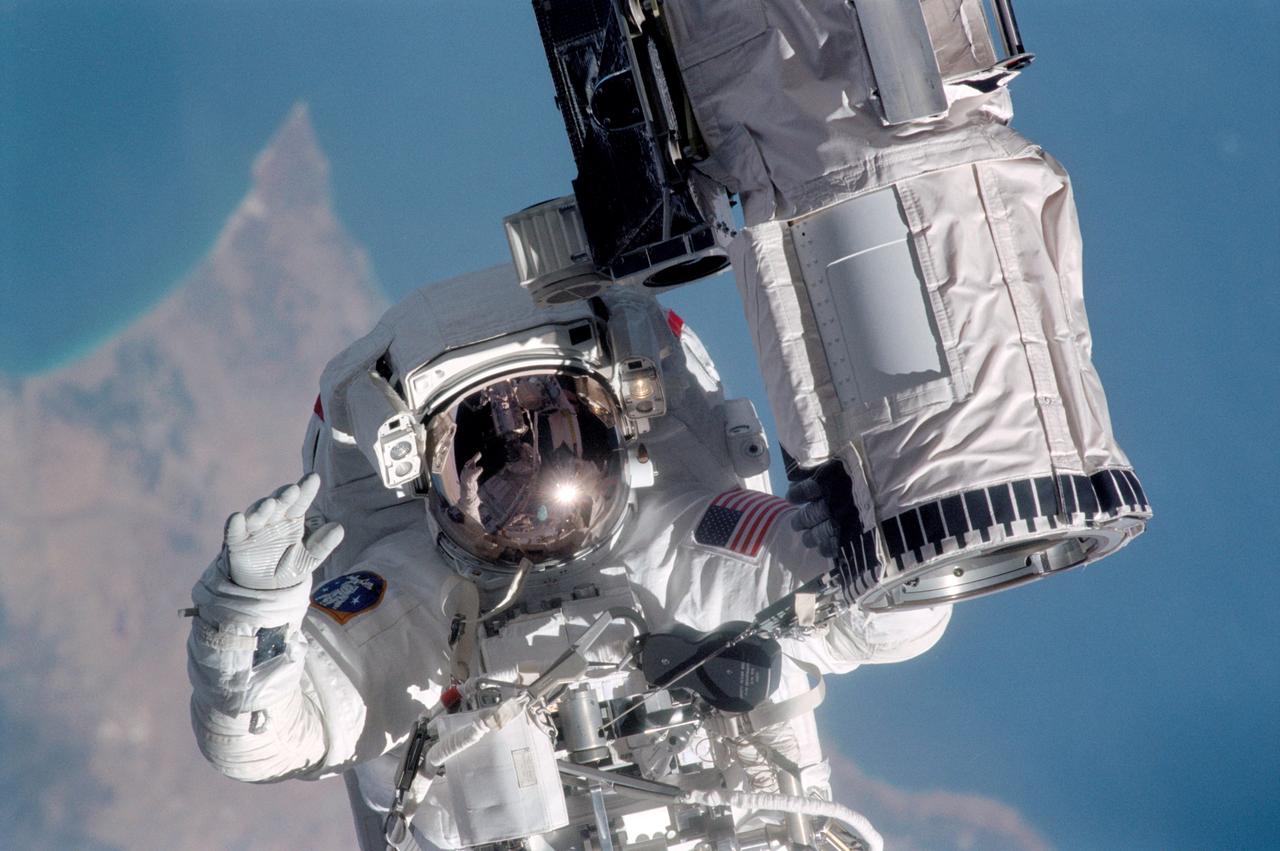

STS104-315-013 (12-24 July 2001) --- Holding onto the end effector of the Canadarm on the Space Shuttle Atlantis, astronaut Michael L. Gernhardt, STS-104 mission specialist, participates in one of three STS-104 space walks. The extravehicular activity (EVA) was designed to help wrap up the completion of work on the second phase of the International Space Station (ISS). Gernhardt was joined on the extravehicular activity (EVA) by astronaut James F. Reilly. The jutting peninsula in the background is Cape Kormakiti on the north central coast of Cyprus and the water body to the left of the cape is Morphu Bay.
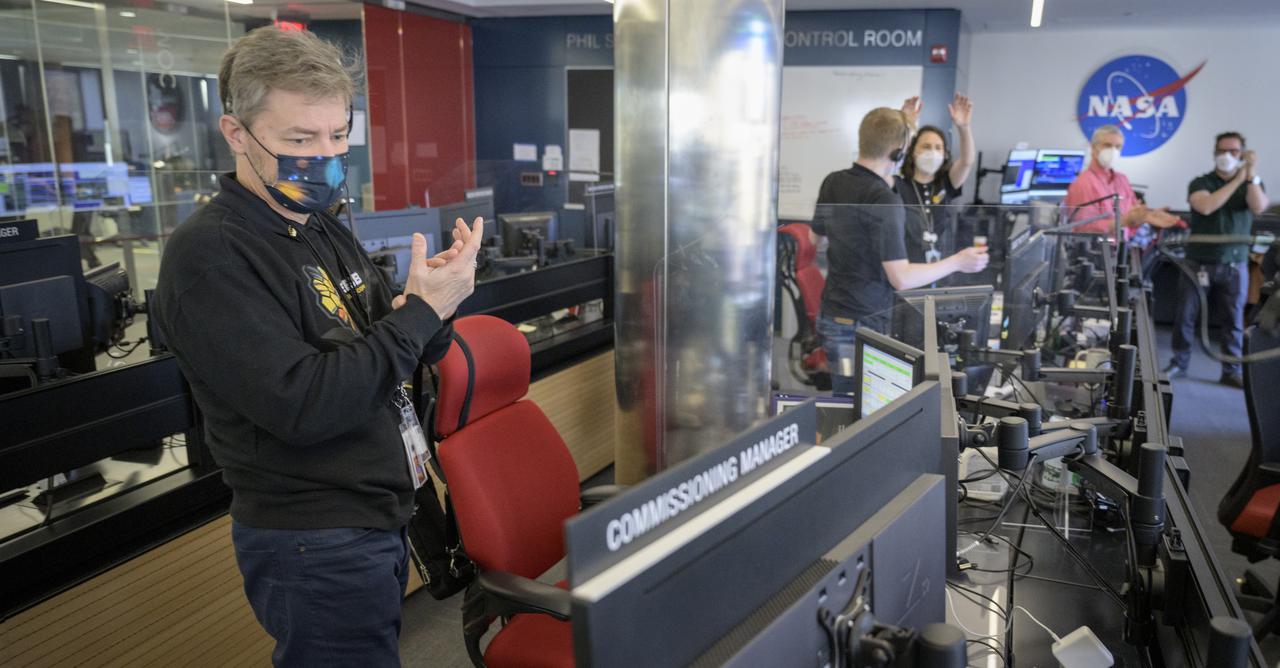

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Commissioning Manager John Durning, left, and engineering teams celebrate at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore as the second primary mirror wing of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope unfolds, before beginning the process of latching the mirror wing into place, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022. When fully latched, the infrared observatory will have completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
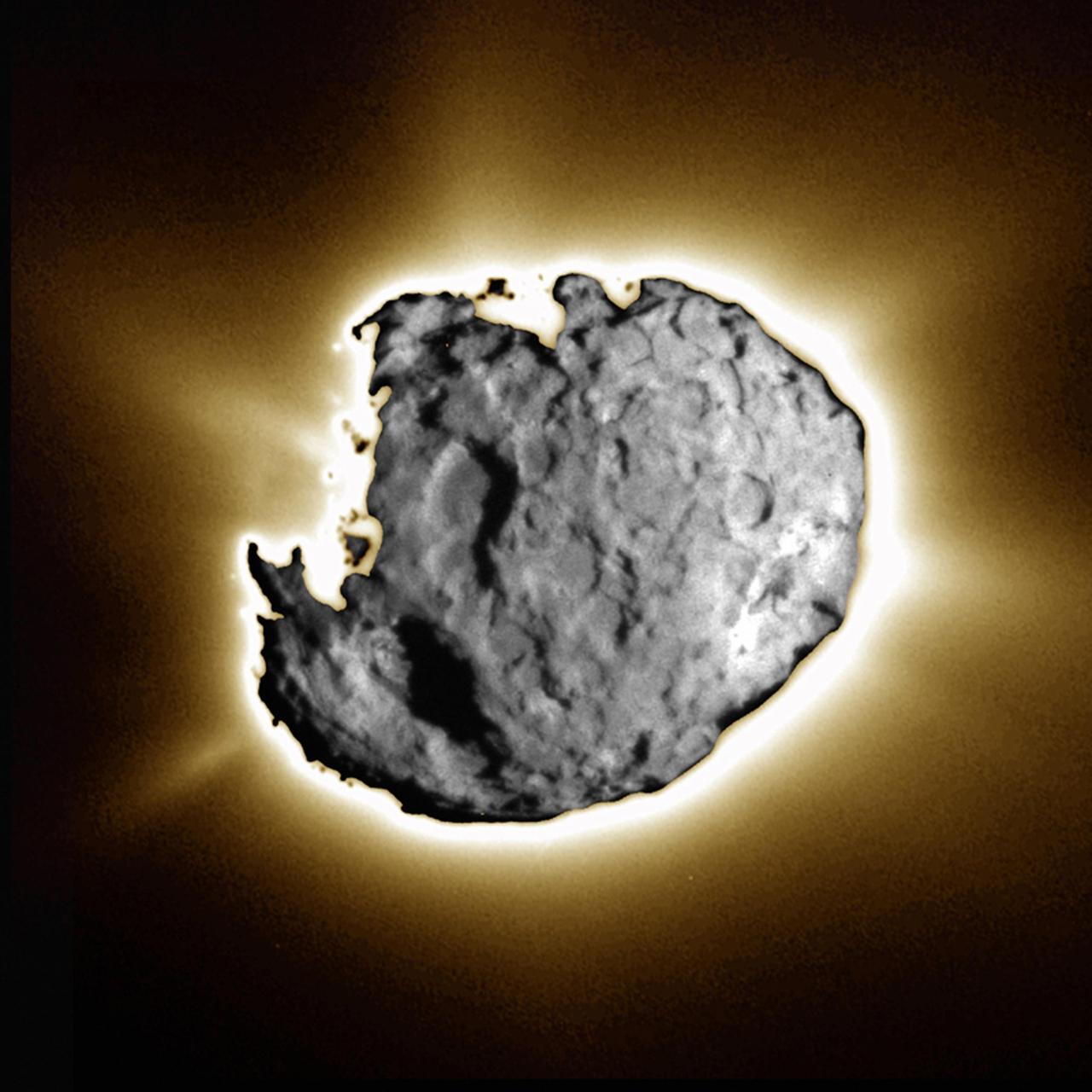
This composite image was taken by the navigation camera during the close approach phase of Stardust's Jan 2, 2004 flyby of comet Wild 2. Several large depressed regions can be seen. Comet Wild 2 is about five kilometers (3.1 miles) in diameter. To create this image, a short exposure image showing tremendous surface detail was overlain on a long exposure image taken just 10 seconds later showing jets. Together, the images show an intensely active surface, jetting dust and gas streams into space and leaving a trail millions of kilometers long. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05578
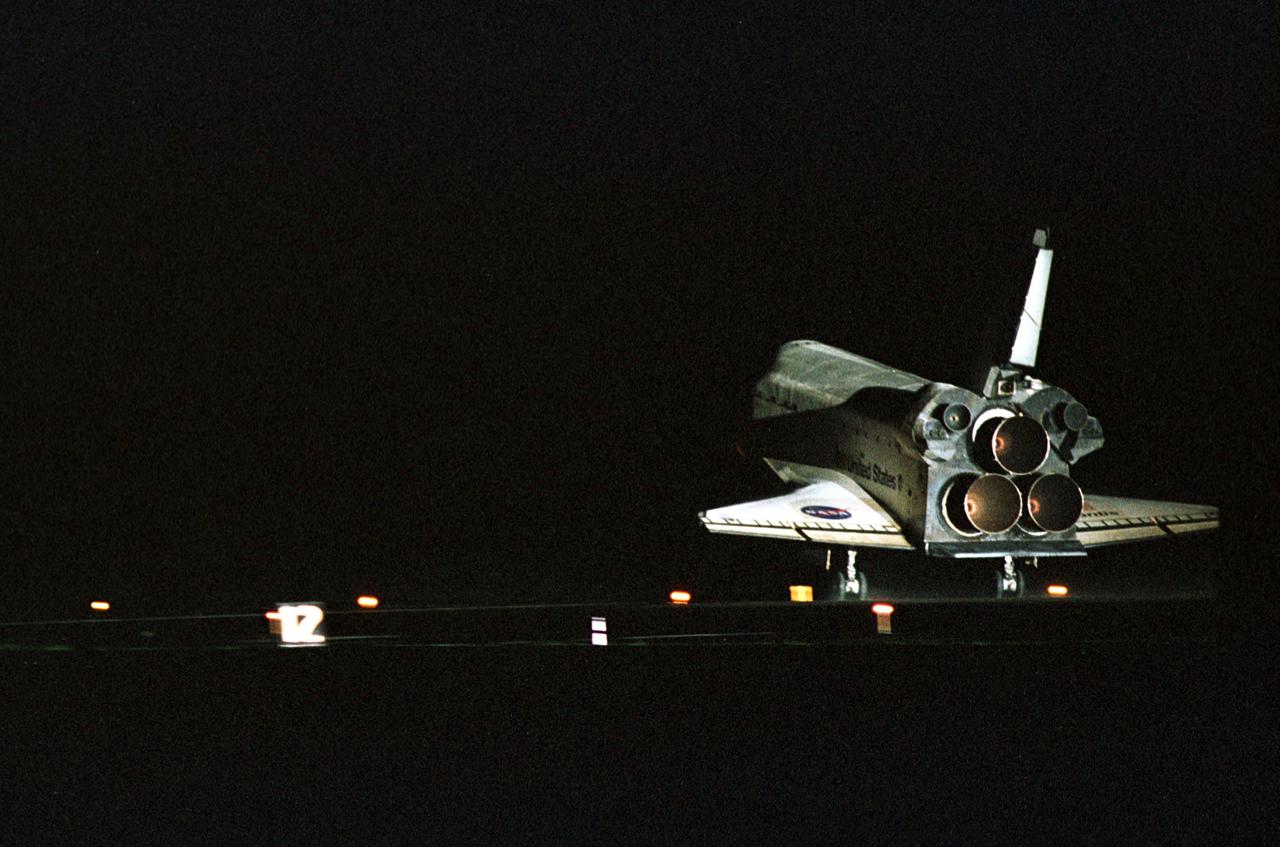

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Atlantis touches down on KSC’s Runway 15 as Atlantis completes a 12-day, 18-hour, 34-minute-long STS-104 mission. Main gear touchdown occurred at 11:38:55 p.m. EDT. At the controls is Commander Steven W. Lindsey. Other crew members on board are Pilot Charles Hobaugh and Mission Specialists Michael Gernhardt, Janet Lynn Kavandi and James F. Reilly. This is the 18th nighttime landing for a Space Shuttle, the 13th at Kennedy Space Center. The mission delivered the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station, which was subsequently attached to the Unity Node, completing the second phase of the assembly of the Space Station
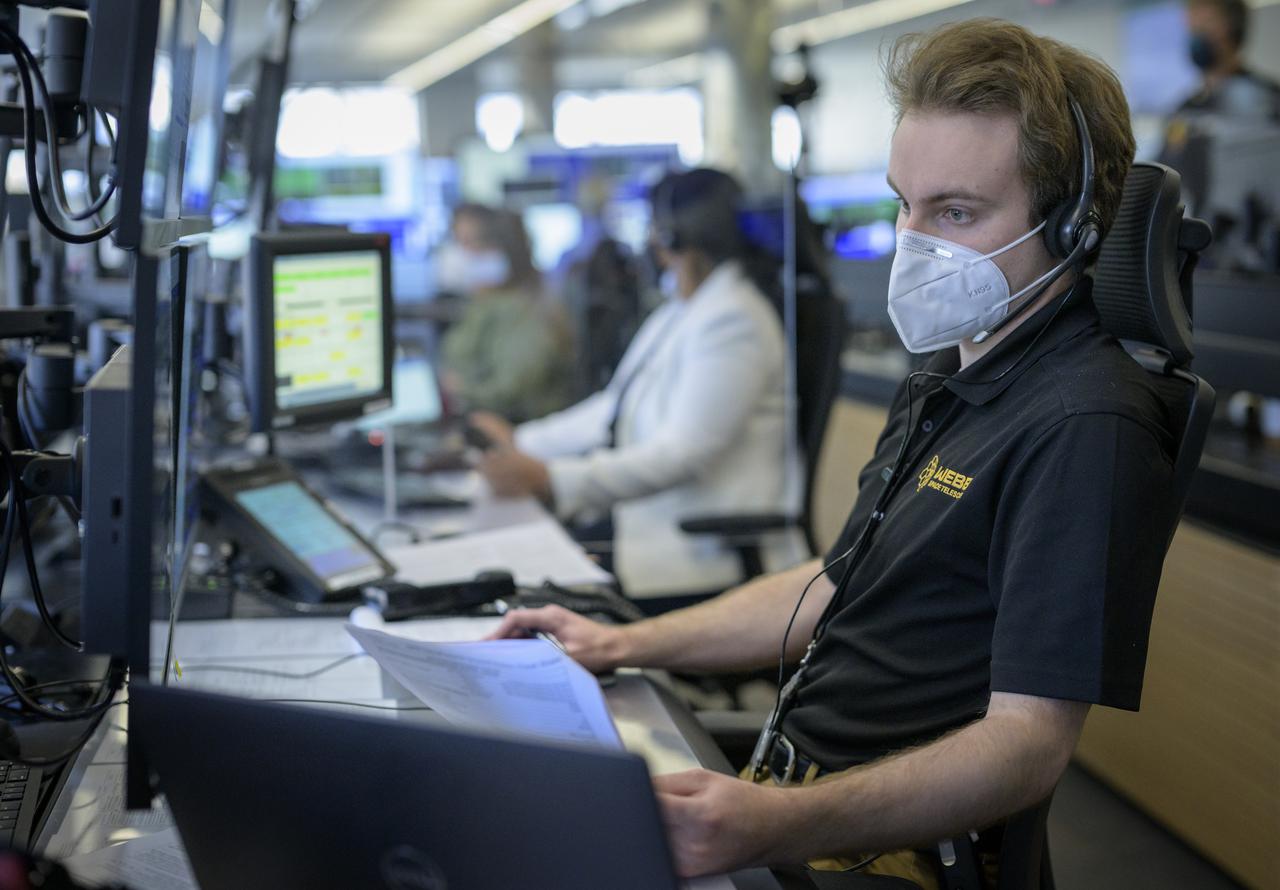

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Ground Engineer Evan Adams monitors the progress of the Webb observatory as it’s second primary mirror wing is prepared to rotate into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
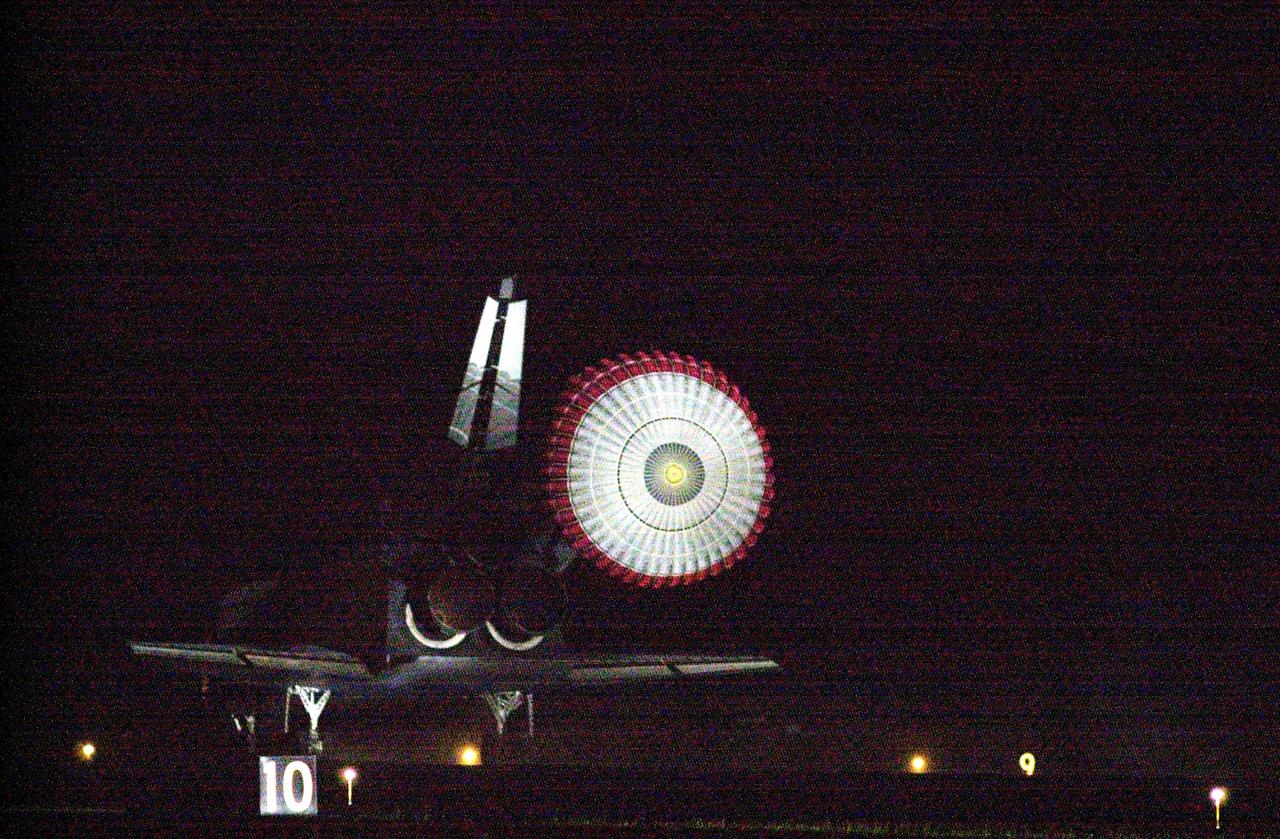

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- With the drag chute slowing its speed, Atlantis prepares to land on Runway 15 at the Shuttle Landing Facility to complete a 12-day, 18-hour, 34-minute-long STS-104 mission. Main gear touchdown occurred at 11:38:55 p.m. EDT. At the controls is Commander Steven W. Lindsey. Other crew members on board are Pilot Charles Hobaugh and Mission Specialists Michael Gernhardt, Janet Lynn Kavandi and James F. Reilly. This is the 18th nighttime landing for a Space Shuttle, the 13th at Kennedy Space Center. The mission delivered the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station, completing the second phase of the assembly of the Space Station
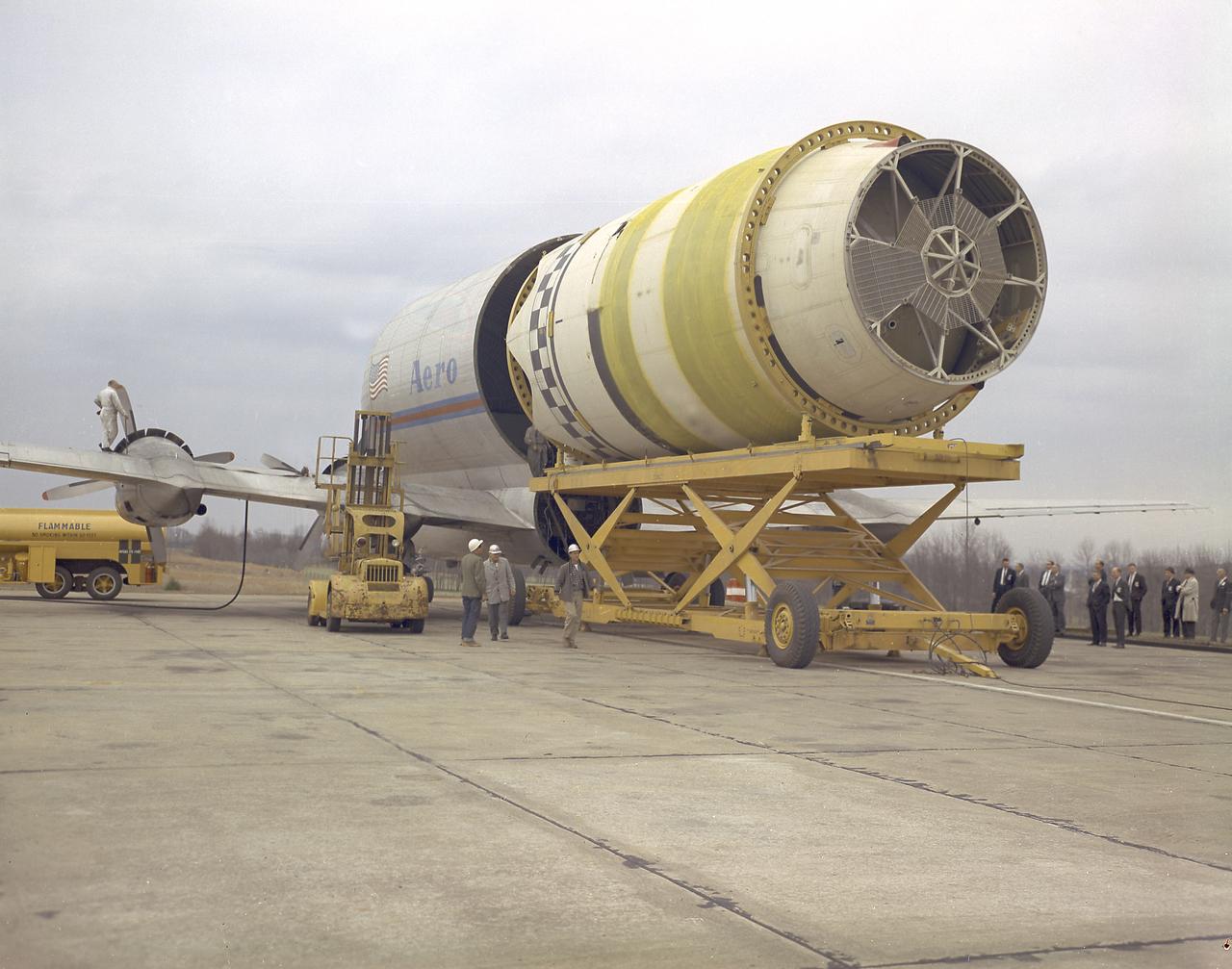

The photograph shows the loading operation of the Saturn I S-IV stage (second stage) into the Pregnant Guppy at the Redstone Airfield, Huntsville, Alabama. The Pregnant Guppy was a Boeing B-377 Stratocruiser modified to transport various stages of Saturn launch vehicles. The modification project called for lengthening the fuselage to accommodate the S-IV stage. After the flight test of that modification, phase two called for the enlargement of the plane's cabin section to approximately double its normal volume. The fuselage separated just aft of the wing's trailing edge to load and unload the S-IV and other cargoes.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- With the drag chute slowing its speed, Atlantis prepares to land on Runway 15 at the Shuttle Landing Facility to complete a 12-day, 18-hour, 34-minute-long STS-104 mission. Main gear touchdown occurred at 11:38:55 p.m. EDT. At the controls is Commander Steven W. Lindsey. Other crew members on board are Pilot Charles Hobaugh and Mission Specialists Michael Gernhardt, Janet Lynn Kavandi and James F. Reilly. This is the 18th nighttime landing for a Space Shuttle, the 13th at Kennedy Space Center. The mission delivered the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station, completing the second phase of the assembly of the Space Station
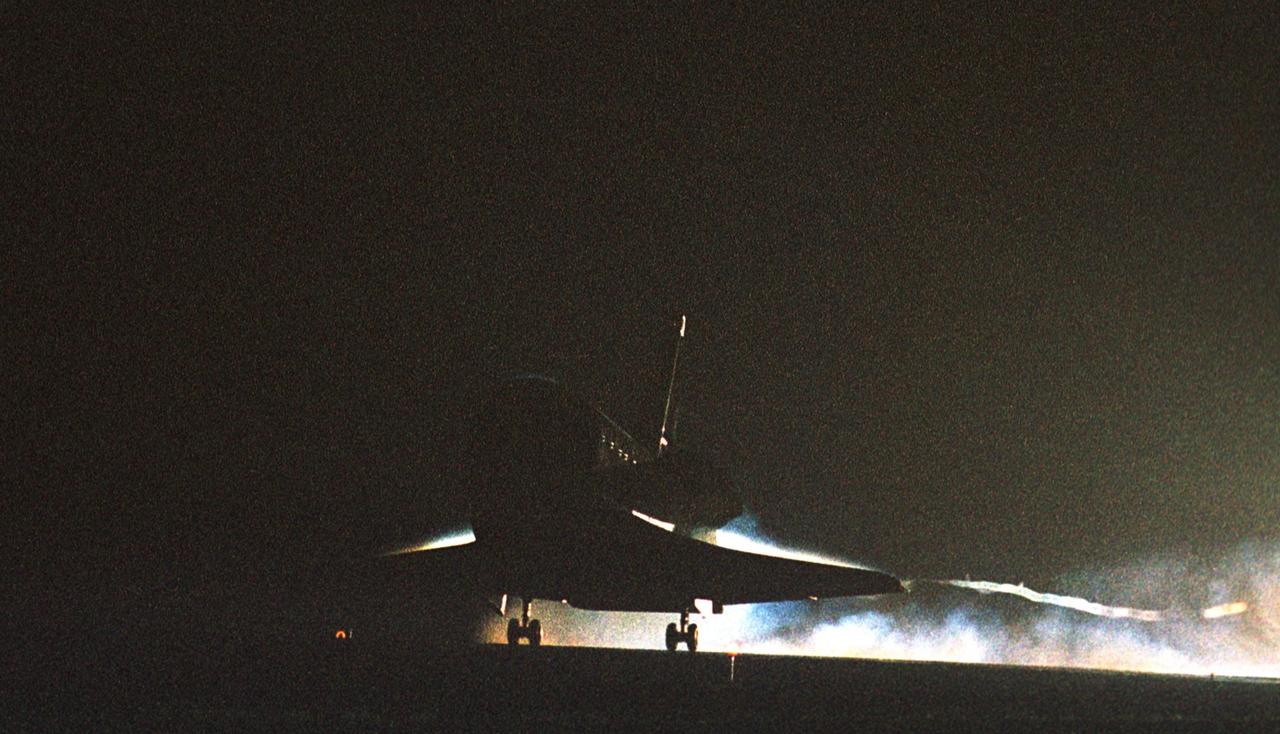

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Atlantis touches down on Runway 15 at the Shuttle Landing Facility to complete a 12-day, 18-hour, 34-minute-long STS-104 mission. Main gear touchdown occurred at 11:38:55 p.m. EDT. At the controls is Commander Steven W. Lindsey. Other crew members on board are Pilot Charles Hobaugh and Mission Specialists Michael Gernhardt, Janet Lynn Kavandi and James F. Reilly. This is the 18th nighttime landing for a Space Shuttle, the 13th at Kennedy Space Center. The mission delivered the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station, completing the second phase of the assembly of the Space Station
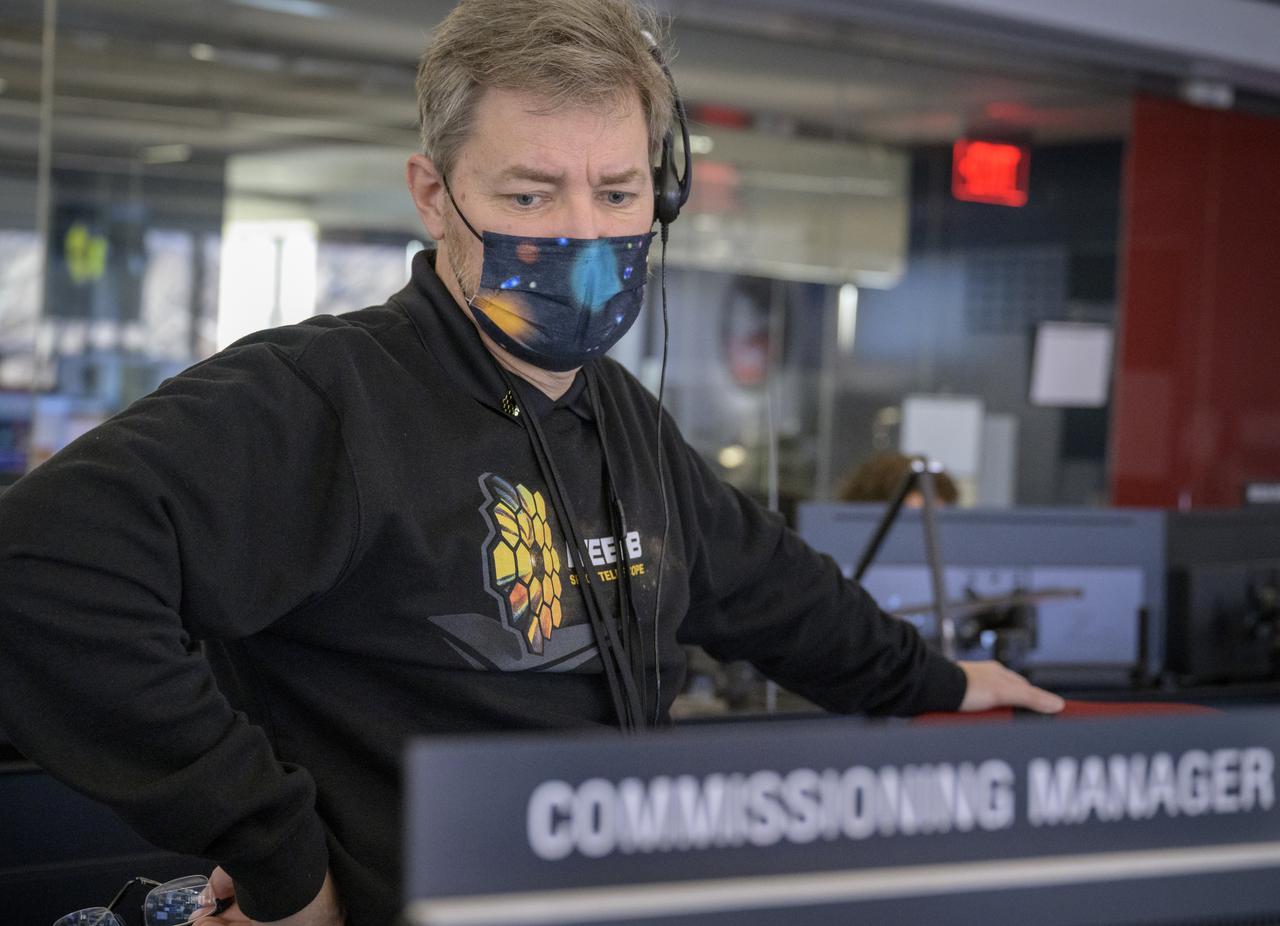

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Commissioning Manager John Durning monitors the progress of the Webb observatory as it’s second primary mirror wing is rotated into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
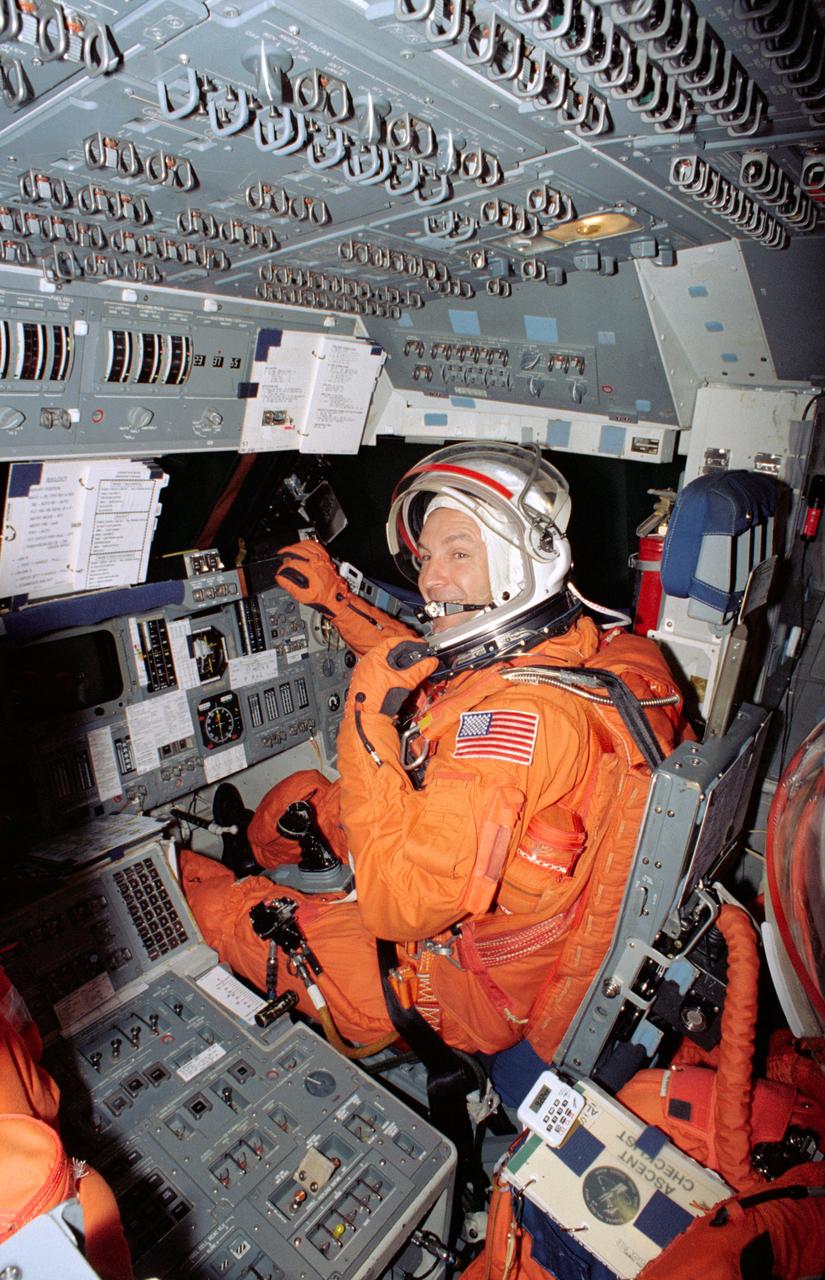

S94-40091 (23 June 1994) --- Astronaut Curtis L. Brown mans the pilot's station of a Shuttle trainer during a rehearsal of procedures to be followed during launch and entry phases of the scheduled November flight of STS-66. This rehearsal, held in the Crew Compartment Trainer (CCT) of the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Shuttle Mockup and Integration Laboratory, was followed by a training session on emergency egress procedures. Making his second flight in space, Brown will join four other NASA astronauts and a European mission specialist for a week and a half aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis in Earth-orbit in support of the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS-3).
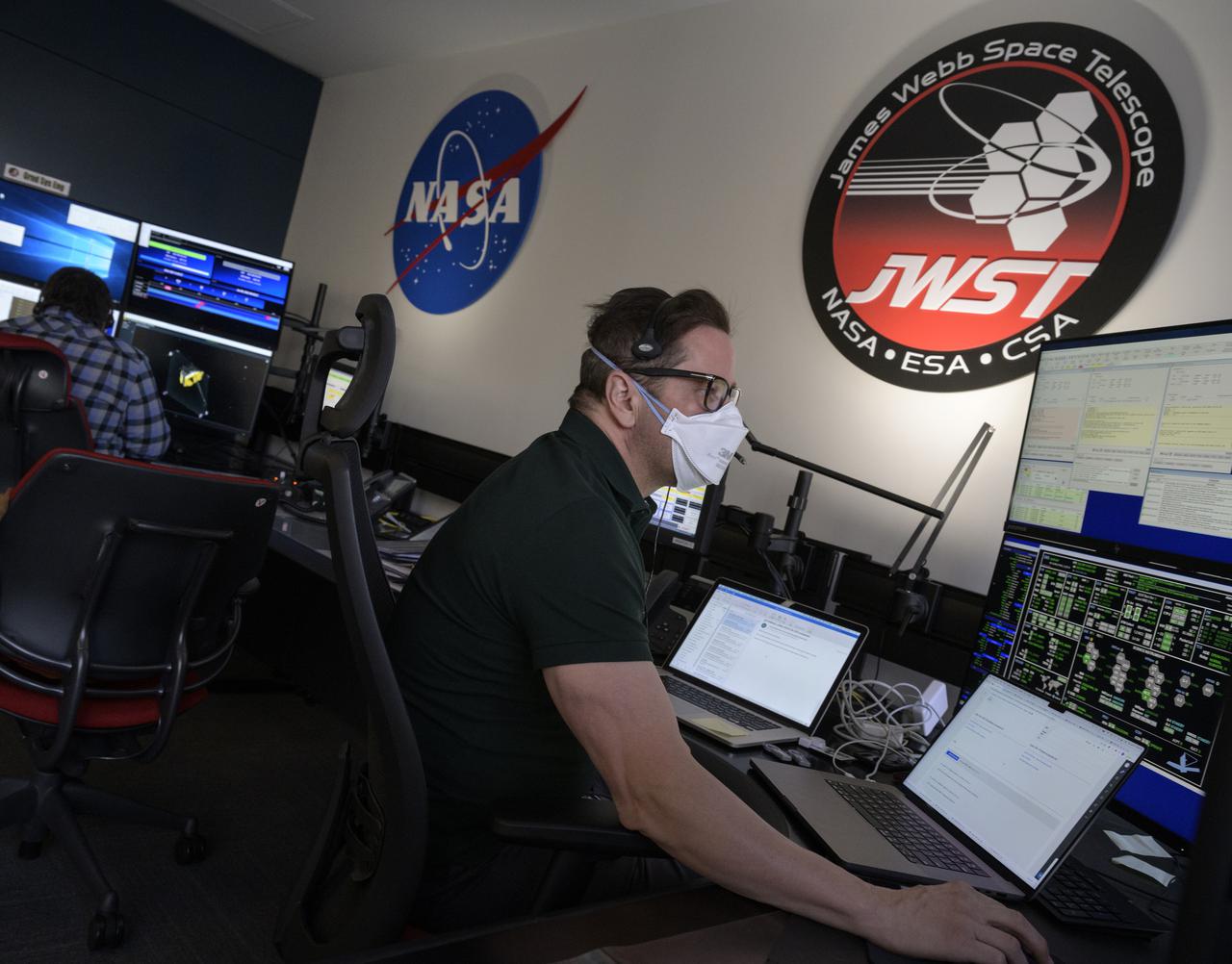

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Ground Systems Engineer Carl Reis at NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore monitors the progress as the observatory’s second primary mirror wing rotates into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)