
Suomi NPP capture this true-color image of the storms over the Midwest and US South on April 30, 2017. This images comes from the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument on @NASA.NPP Credit: NASA/NOAA/NPP/VIIRS <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an ominous thunderstorm cloud hovers over the Vehicle Assembly Building in the Launch Complex 39 area. Severe storms associated with a frontal system are moving through Central Florida, producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
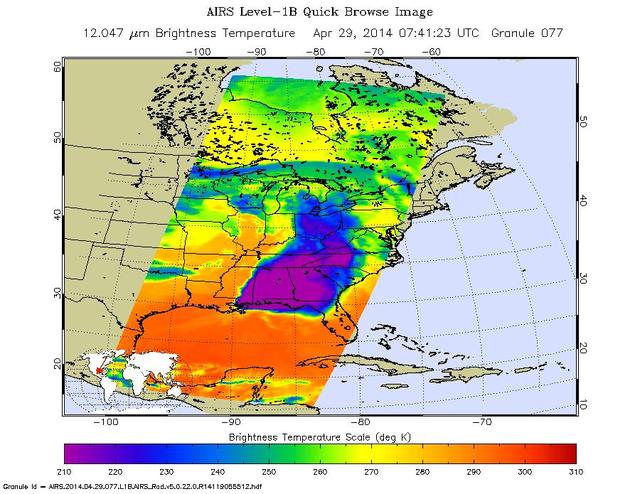
NASA Aqua spacecraft passed over central and southern United States on April 27-29, 2014 capturing this false-color infrared image of the slow-moving low-pressure system that spawned the strong supercell thunderstorms.
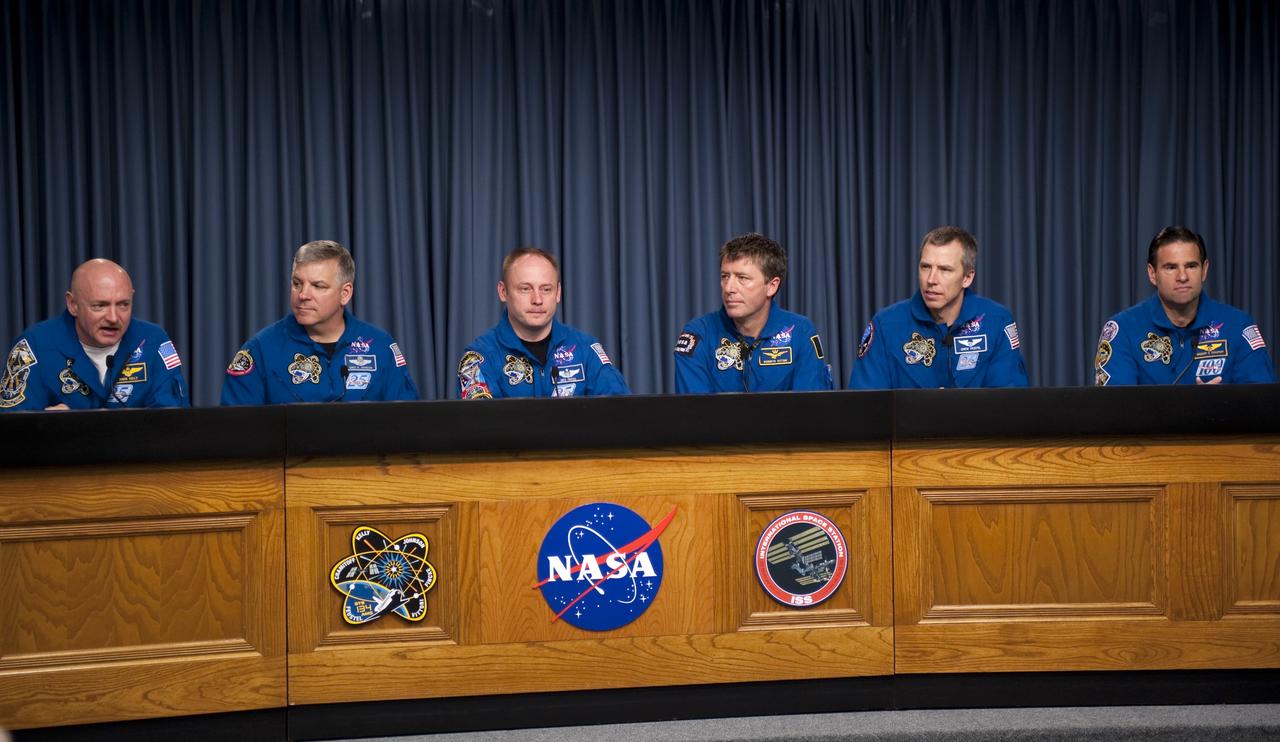

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The STS-134 crew answers media questions in the Press Site TV auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left, are Commander Mark Kelly, Pilot Greg H. Johnson, and Mission Specialists Michael Fincke, European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, Andrew Feustel, and Greg Chamitoff. The crew was scheduled to answer questions at Launch Pad 39A, where space shuttle Endeavour is awaiting liftoff, but severe storms associated with a frontal system passing over Central Florida brought the media event indoors. Endeavour's six crew members are at Kennedy for the launch countdown dress rehearsal called the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) and related training. Targeted to launch April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT, they will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
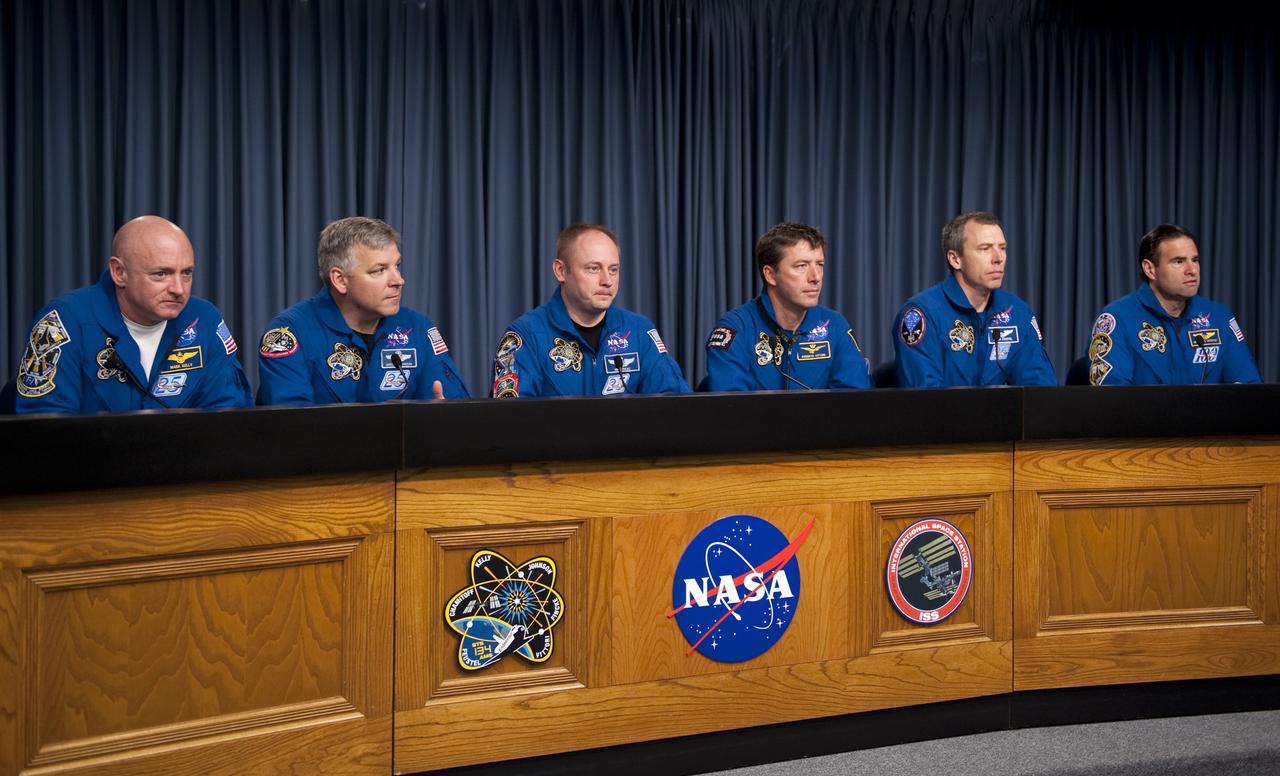

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The STS-134 crew answers media questions in the Press Site TV auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left, are Commander Mark Kelly, Pilot Greg H. Johnson, and Mission Specialists Michael Fincke, European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, Andrew Feustel, and Greg Chamitoff. The crew was scheduled to answer questions at Launch Pad 39A, where space shuttle Endeavour is awaiting liftoff, but severe storms associated with a frontal system passing over Central Florida brought the media event indoors. Endeavour's six crew members are at Kennedy for the launch countdown dress rehearsal called the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) and related training. Targeted to launch April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT, they will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
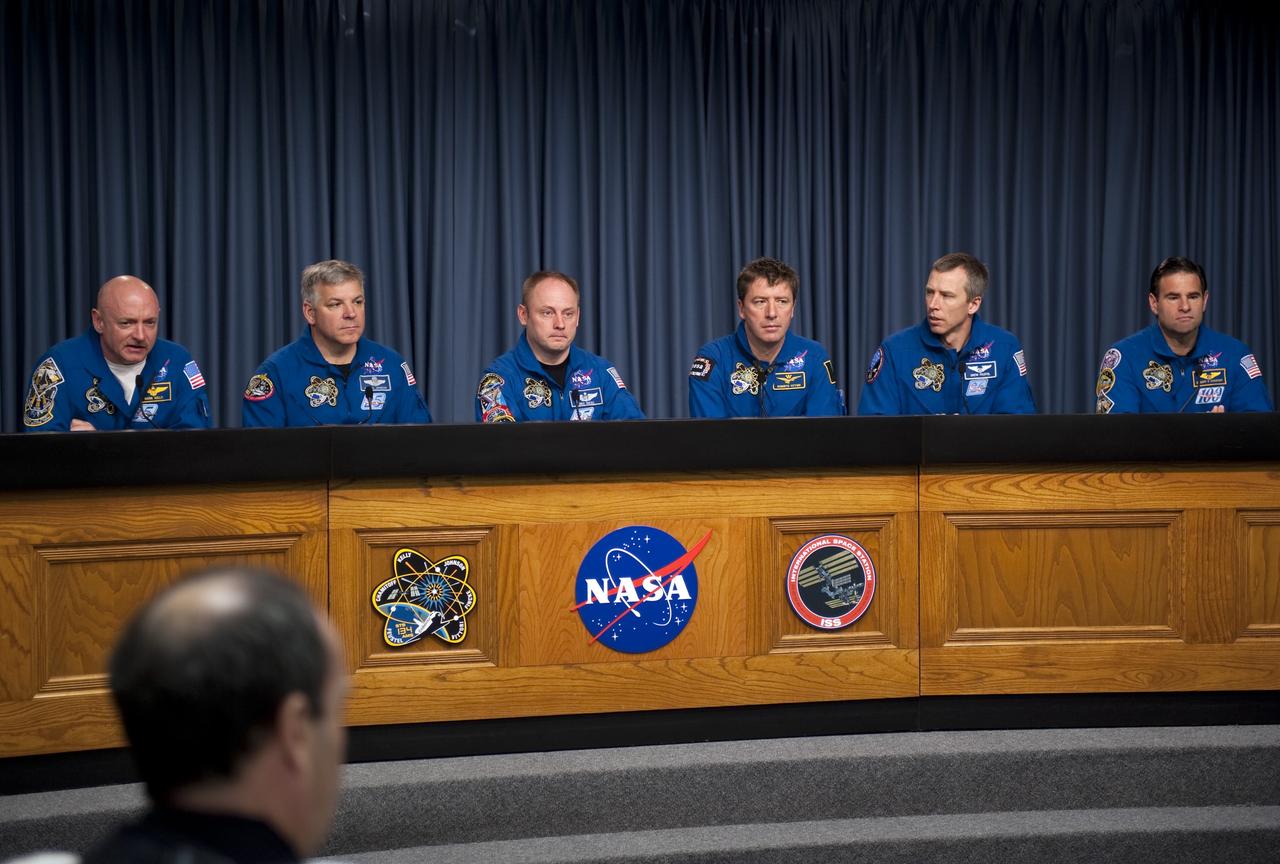

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The STS-134 crew answers media questions in the Press Site TV auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left, are Commander Mark Kelly, Pilot Greg H. Johnson, and Mission Specialists Michael Fincke, European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, Andrew Feustel, and Greg Chamitoff. The crew was scheduled to answer questions at Launch Pad 39A, where space shuttle Endeavour is awaiting liftoff, but severe storms associated with a frontal system passing over Central Florida brought the media event indoors. Endeavour's six crew members are at Kennedy for the launch countdown dress rehearsal called the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) and related training. Targeted to launch April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT, they will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
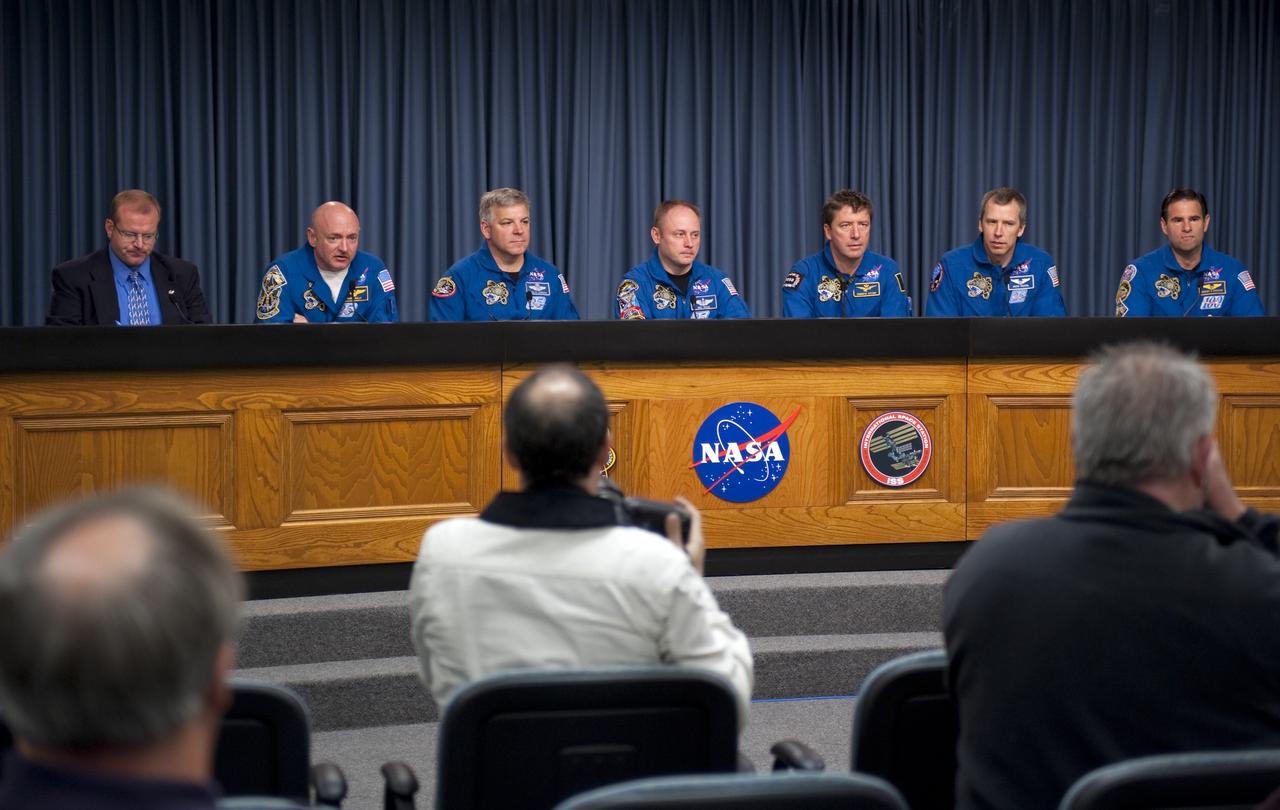

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The STS-134 crew answers media questions in the Press Site TV auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left, are Kennedy's News Chief Allard Beutel, Commander Mark Kelly, Pilot Greg H. Johnson, and Mission Specialists Michael Fincke, European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, Andrew Feustel, and Greg Chamitoff. The crew was scheduled to answer questions at Launch Pad 39A, where space shuttle Endeavour is awaiting liftoff, but severe storms associated with a frontal system passing over Central Florida brought the media event indoors. Endeavour's six crew members are at Kennedy for the launch countdown dress rehearsal called the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) and related training. Targeted to launch April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT, they will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
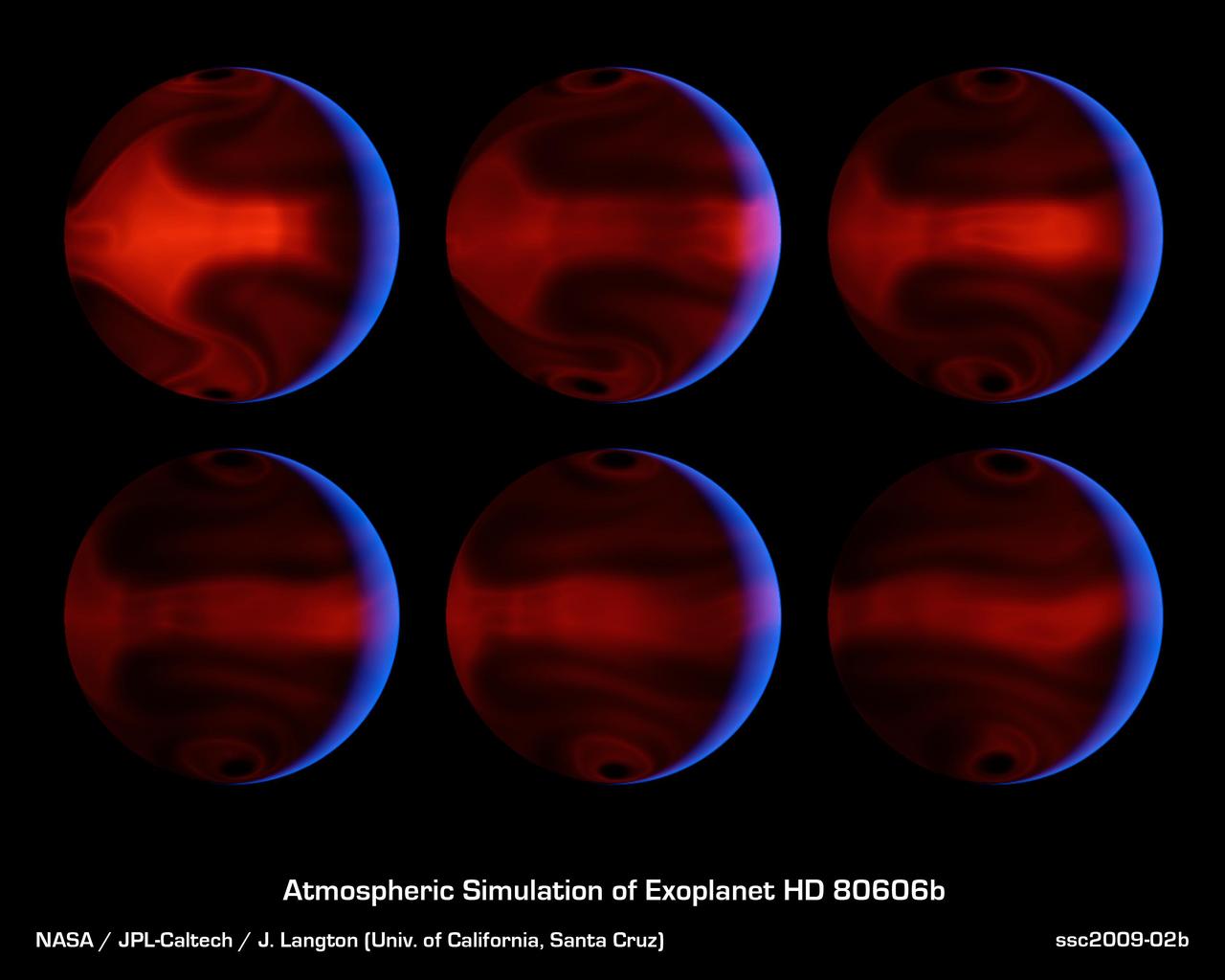
These computer-generated images from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope chart the development of severe weather patterns on the highly eccentric exoplanet HD 80606b during the days after its closest approach to its parent star.
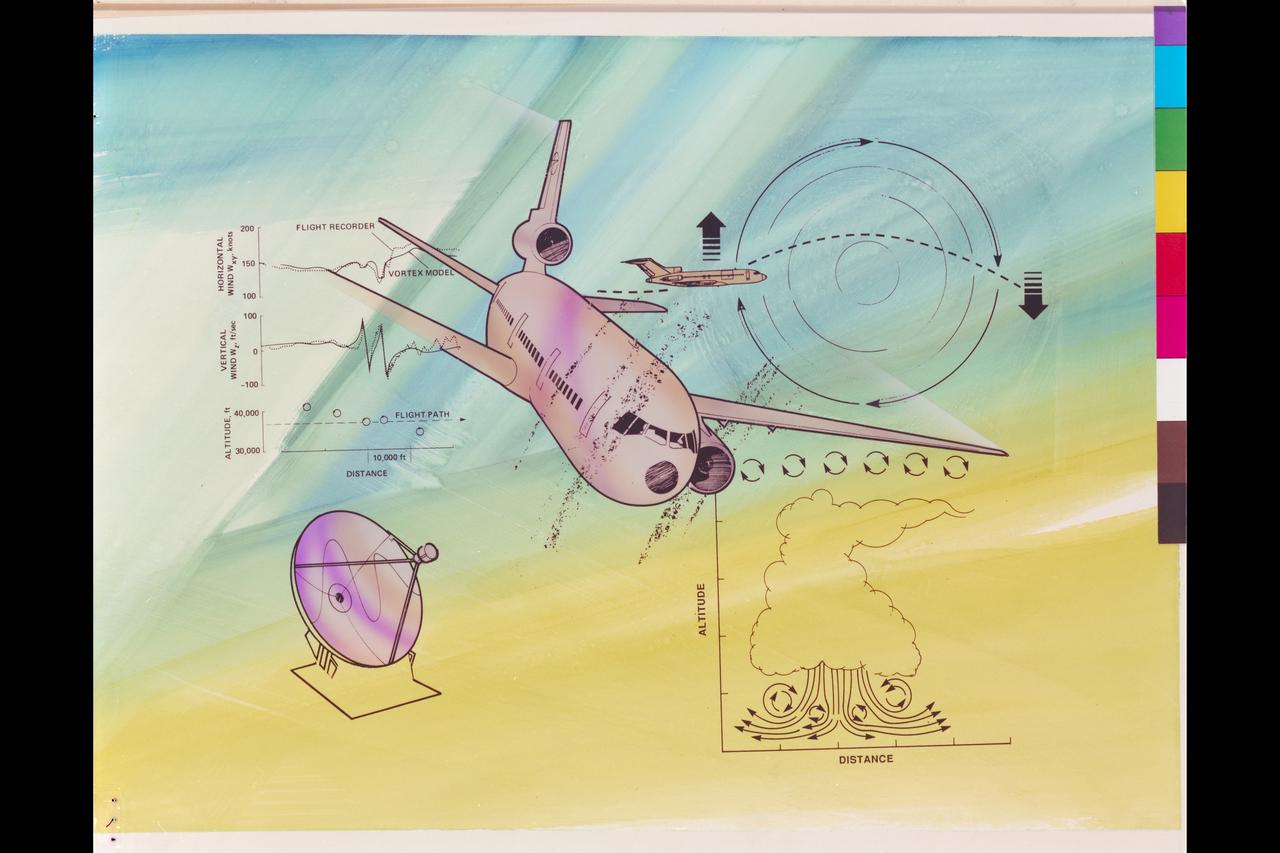
Research Automation - ATC (Air Traffic Control) Sever weather flight (Artwork)

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians and engineers will perform a walk down and detailed inspections of space shuttle Endeavour following severe storms over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The frontal system moved through Central Florida producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. During the inspections, teams found only minor damage to Endeavour's external fuel tank foam insulation and evaluations indicate there was no damage to the spacecraft. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew are targeted to launch April 29 at 3:47 p.m. EDT. They will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A worker performs a walk down of space shuttle Endeavour following severe storms over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The frontal system moved through Central Florida producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. During detailed inspections, technicians and engineers found only minor damage to Endeavour's external fuel tank foam insulation and evaluations indicate there was no damage to the spacecraft. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew are targeted to launch April 29 at 3:47 p.m. EDT. They will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians and engineers will perform a walk down and detailed inspections of space shuttle Endeavour following severe storms over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The frontal system moved through Central Florida producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. During the inspections, teams found only minor damage to Endeavour's external fuel tank foam insulation and evaluations indicate there was no damage to the spacecraft. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew are targeted to launch April 29 at 3:47 p.m. EDT. They will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
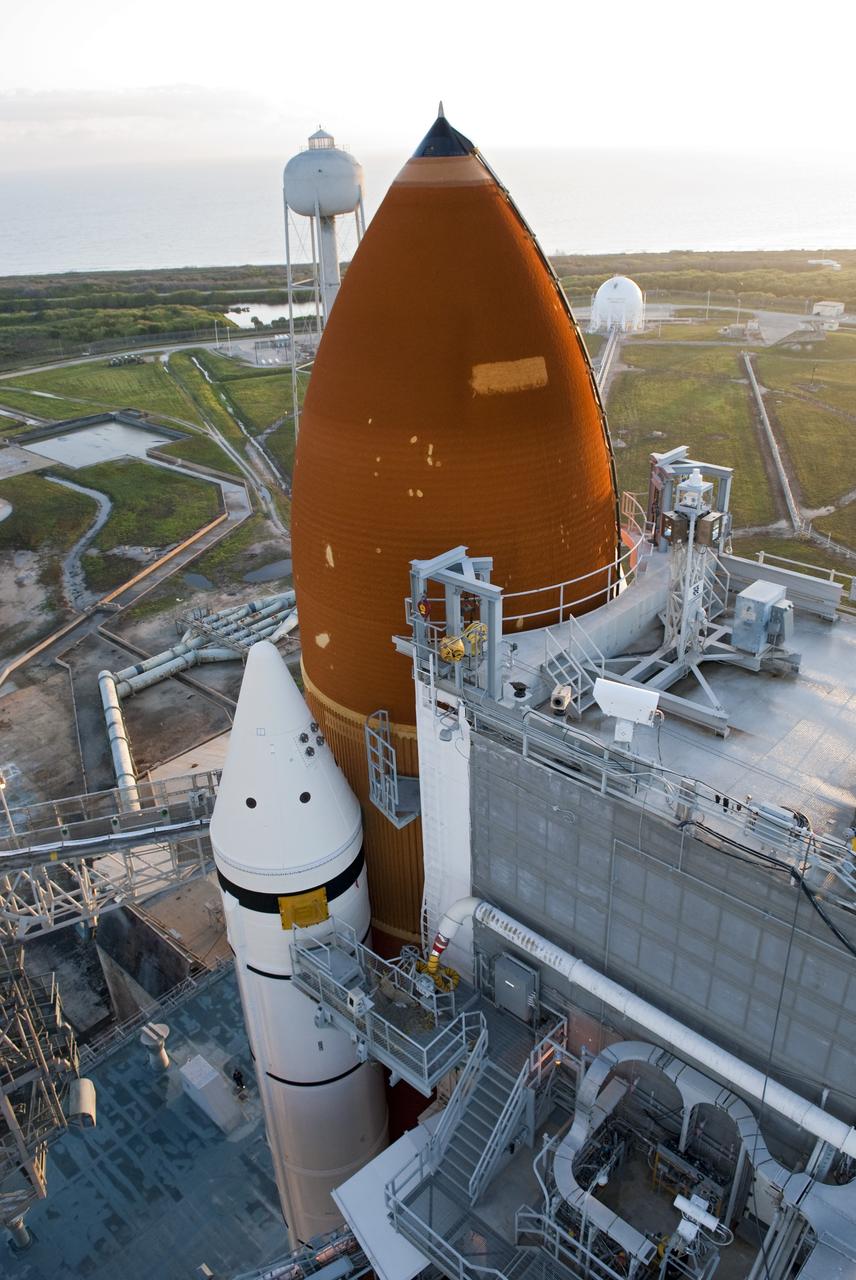

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians and engineers will perform a walk down and detailed inspections of space shuttle Endeavour following severe storms over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The frontal system moved through Central Florida producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. During the inspections, teams found only minor damage to Endeavour's external fuel tank foam insulation and evaluations indicate there was no damage to the spacecraft. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew are targeted to launch April 29 at 3:47 p.m. EDT. They will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
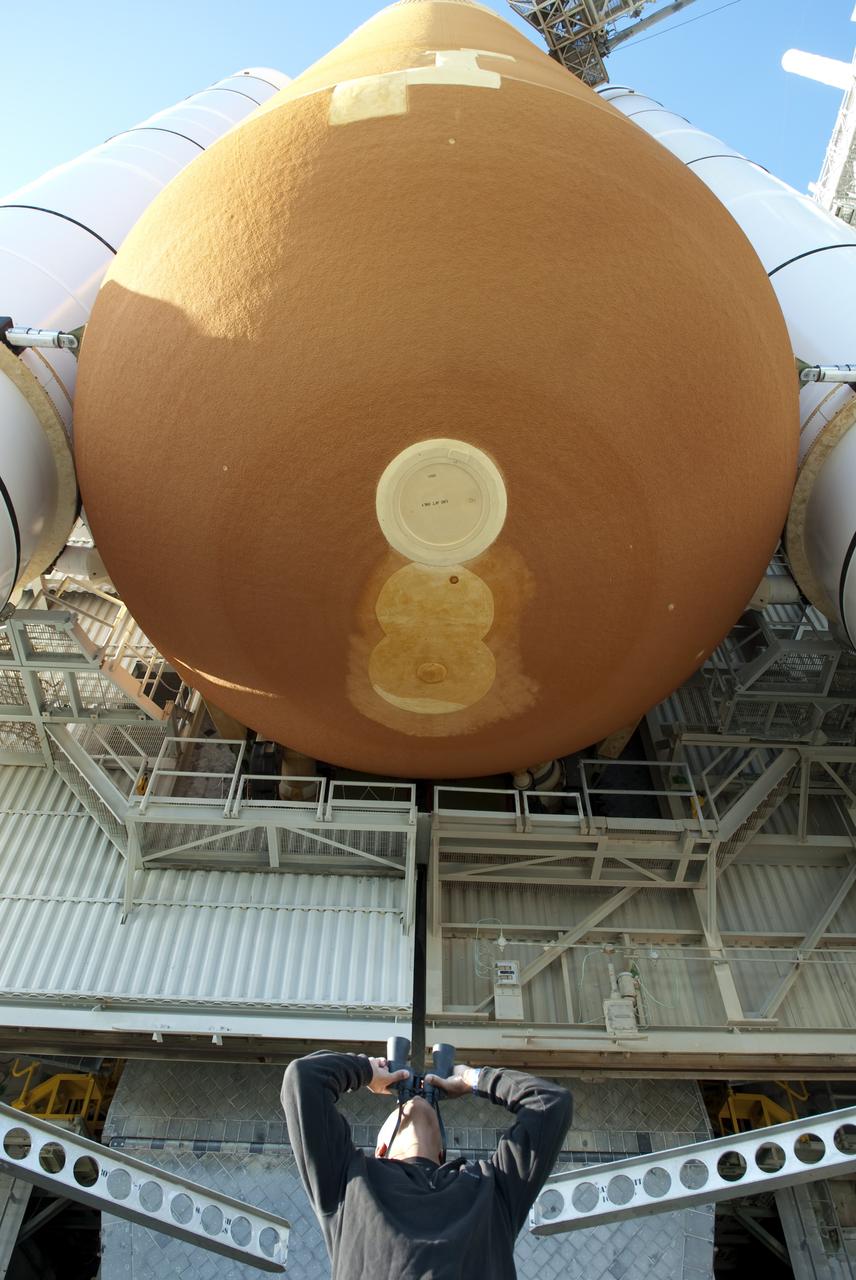

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A worker performs a walk down of space shuttle Endeavour following severe storms over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The frontal system moved through Central Florida producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. During detailed inspections, technicians and engineers found only minor damage to Endeavour's external fuel tank foam insulation and evaluations indicate there was no damage to the spacecraft. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew are targeted to launch April 29 at 3:47 p.m. EDT. They will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
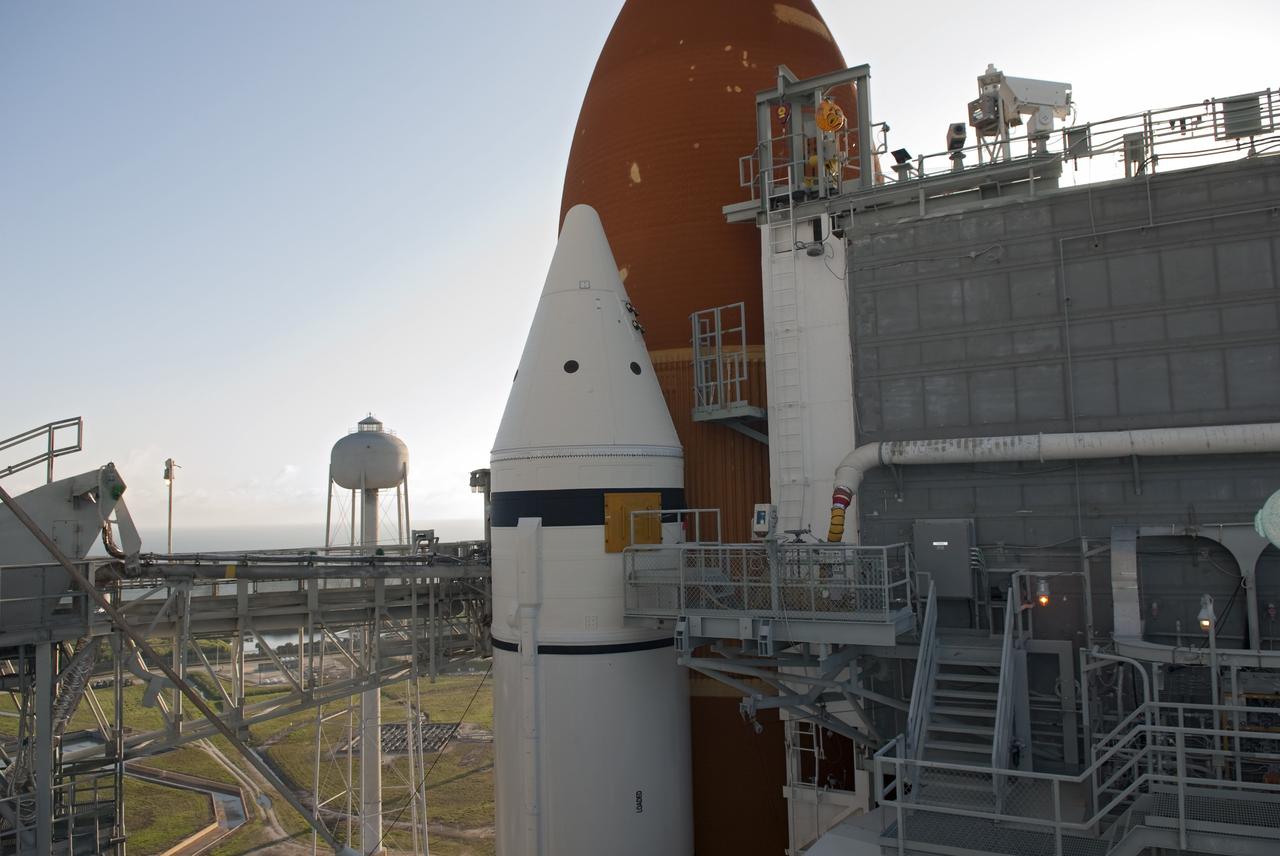

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians and engineers will perform a walk down and detailed inspections of space shuttle Endeavour following severe storms over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The frontal system moved through Central Florida producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. During the inspections, teams found only minor damage to Endeavour's external fuel tank foam insulation and evaluations indicate there was no damage to the spacecraft. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew are targeted to launch April 29 at 3:47 p.m. EDT. They will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
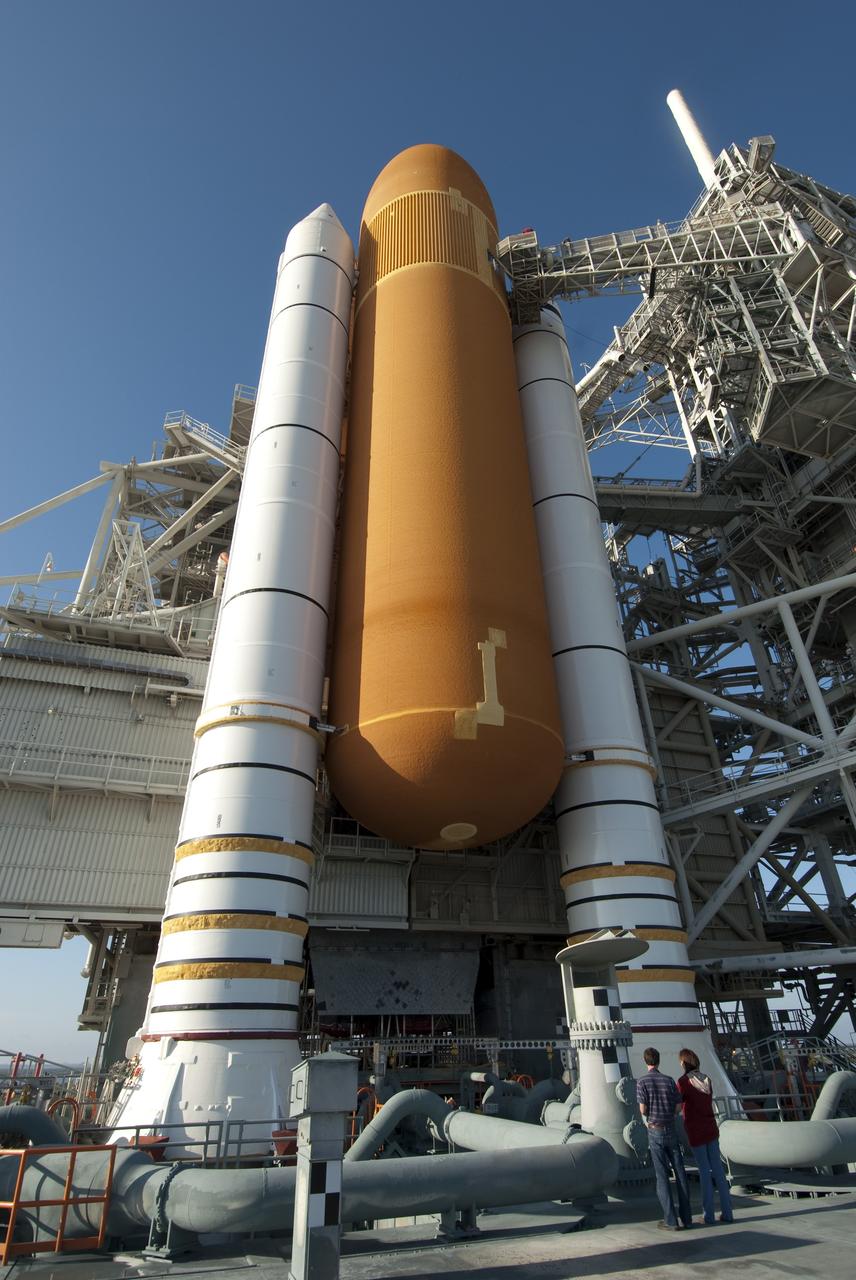

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers perform a walk down of space shuttle Endeavour following severe storms over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The frontal system moved through Central Florida producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. During detailed inspections, technicians and engineers found only minor damage to Endeavour's external fuel tank foam insulation and evaluations indicate there was no damage to the spacecraft. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew are targeted to launch April 29 at 3:47 p.m. EDT. They will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A walk down and detailed inspections of space shuttle Endeavour indicate that the external fuel tank foam insulation sustained only minor damage during severe storms over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Seen here, the ET-122 logo is emblazoned on Endeavour's external tank. The frontal system moved through Central Florida producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. Evaluations by technicians and engineers indicate there was no damage to the spacecraft. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew are targeted to launch April 29 at 3:47 p.m. EDT. They will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
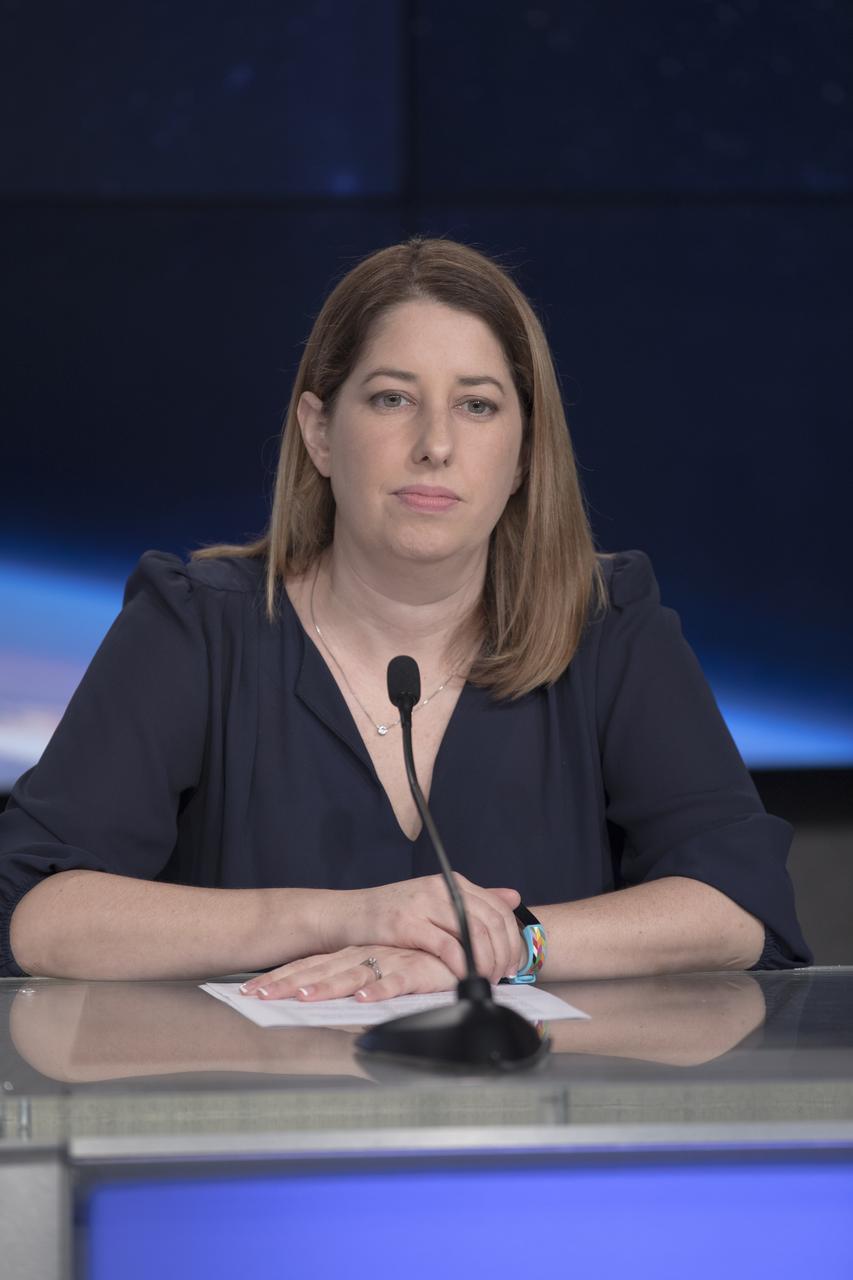

In the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium, Kristin Calhoun, a research scientist with NOAA's National Severe Storms Laboratory, speaks to members of the media at a mission briefing on National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's, or NOAA's, Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S. The spacecraft is the second satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA weather satellites. It will launch to a geostationary position over the U.S. to provide images of storms and help predict weather forecasts, severe weather outlooks, watches, warnings, lightning conditions and longer-term forecasting. GOES-S is slated to lift off at 5:02 p.m. EST on March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
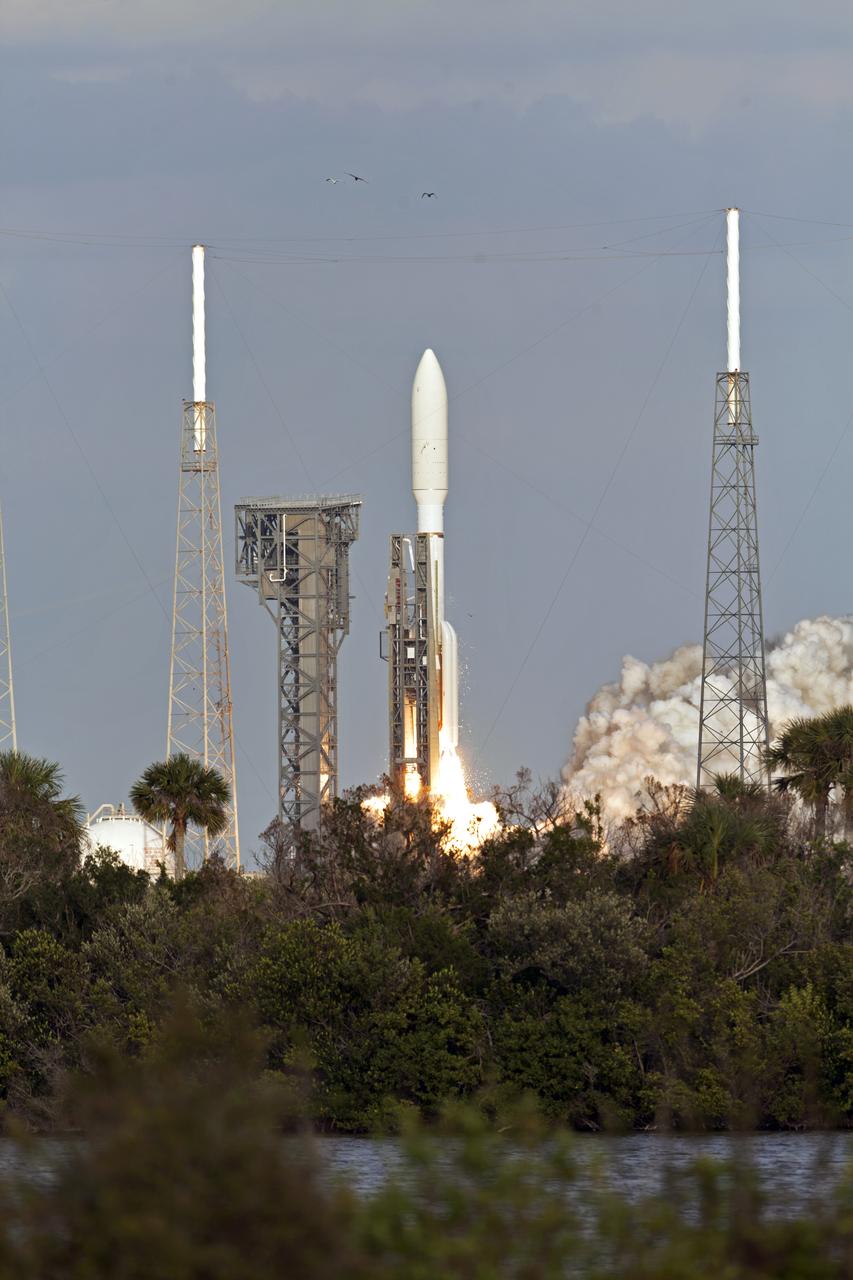

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying the NOAA Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S. Liftoff was at 5:02 p.m. EST. GOES-S is the second satellite in a series of next-generation weather satellites. It will launch to a geostationary position over the U.S. to provide images of storms and help predict weather forecasts, severe weather outlooks, watches, warnings, lightning conditions and longer-term forecasting.
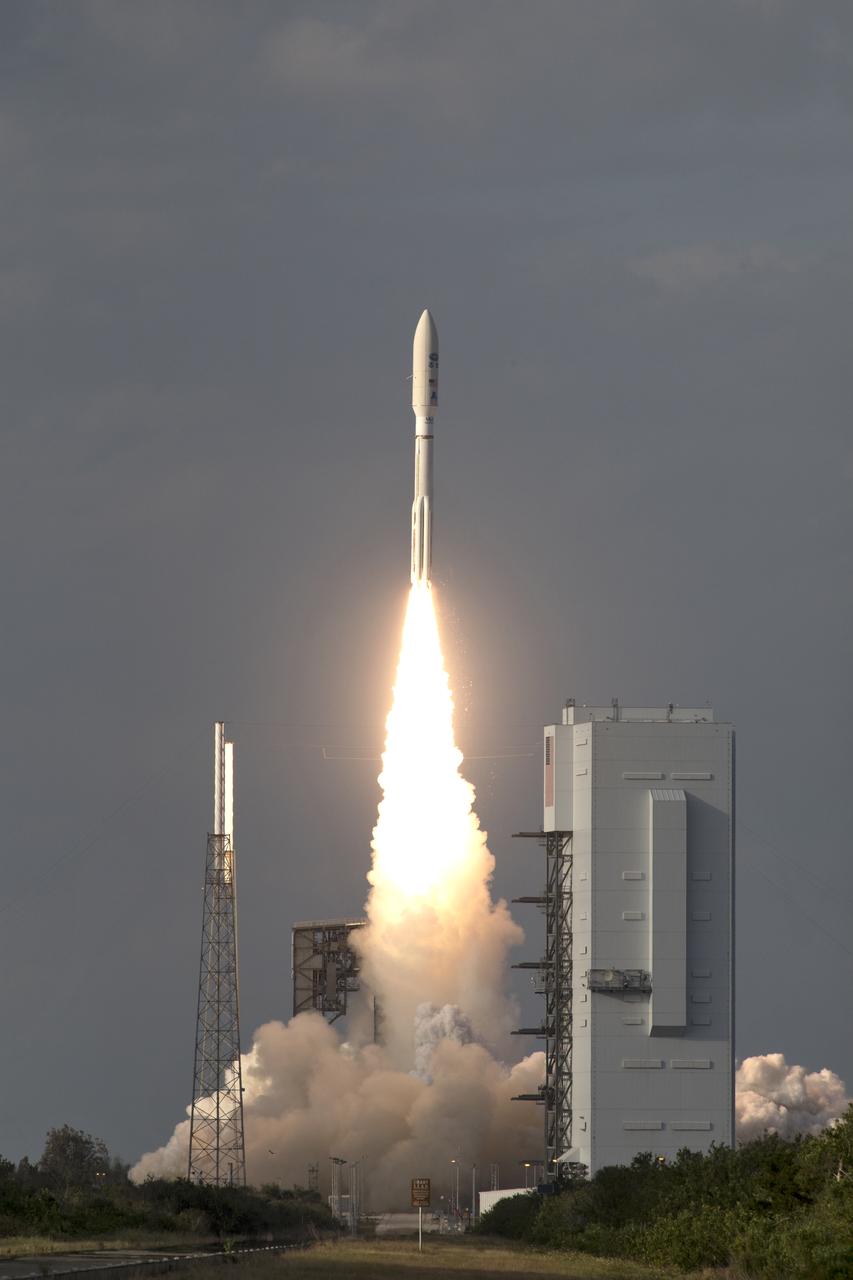

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying the NOAA Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S. Liftoff was at 5:02 p.m. EST. GOES-S is the second satellite in a series of next-generation weather satellites. It will launch to a geostationary position over the U.S. to provide images of storms and help predict weather forecasts, severe weather outlooks, watches, warnings, lightning conditions and longer-term forecasting.
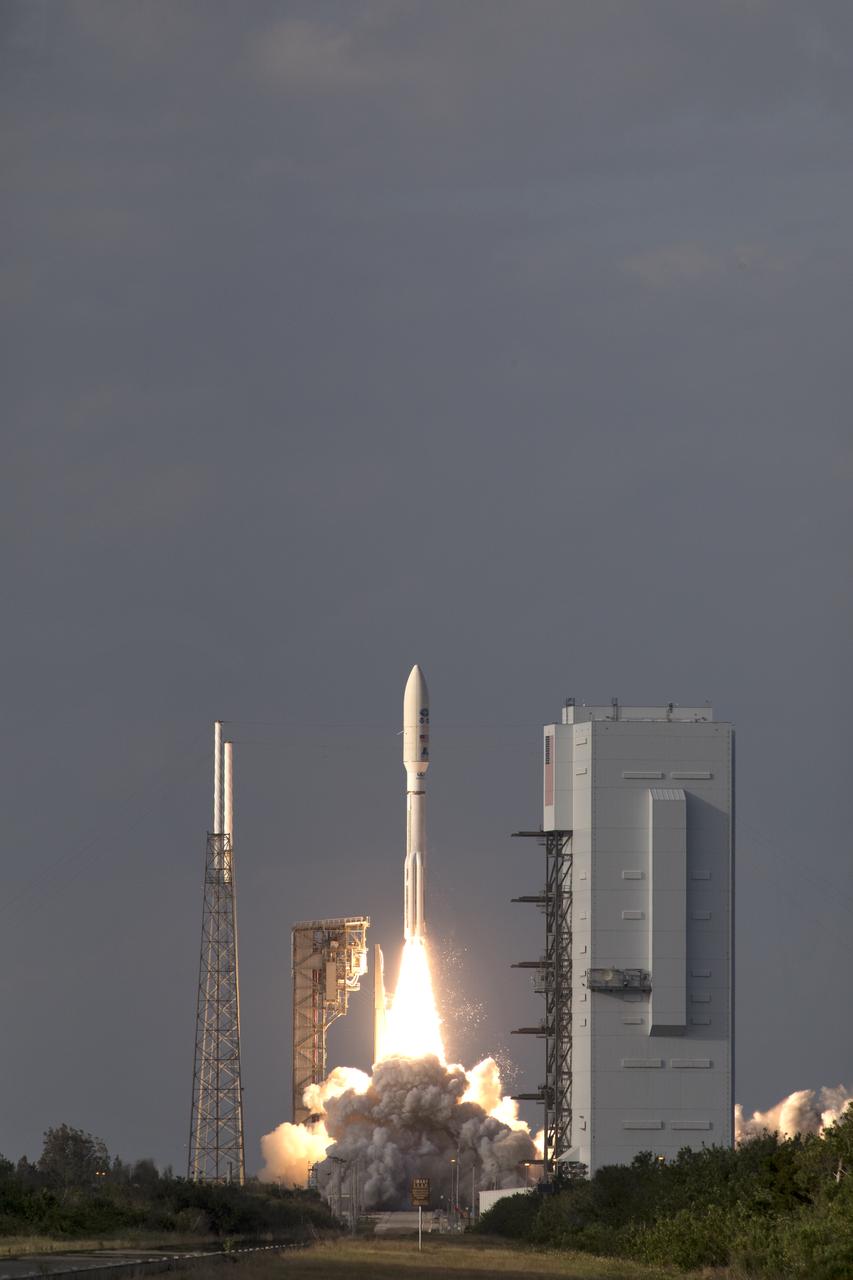

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying the NOAA Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S. Liftoff was at 5:02 p.m. EST. GOES-S is the second satellite in a series of next-generation weather satellites. It will launch to a geostationary position over the U.S. to provide images of storms and help predict weather forecasts, severe weather outlooks, watches, warnings, lightning conditions and longer-term forecasting.
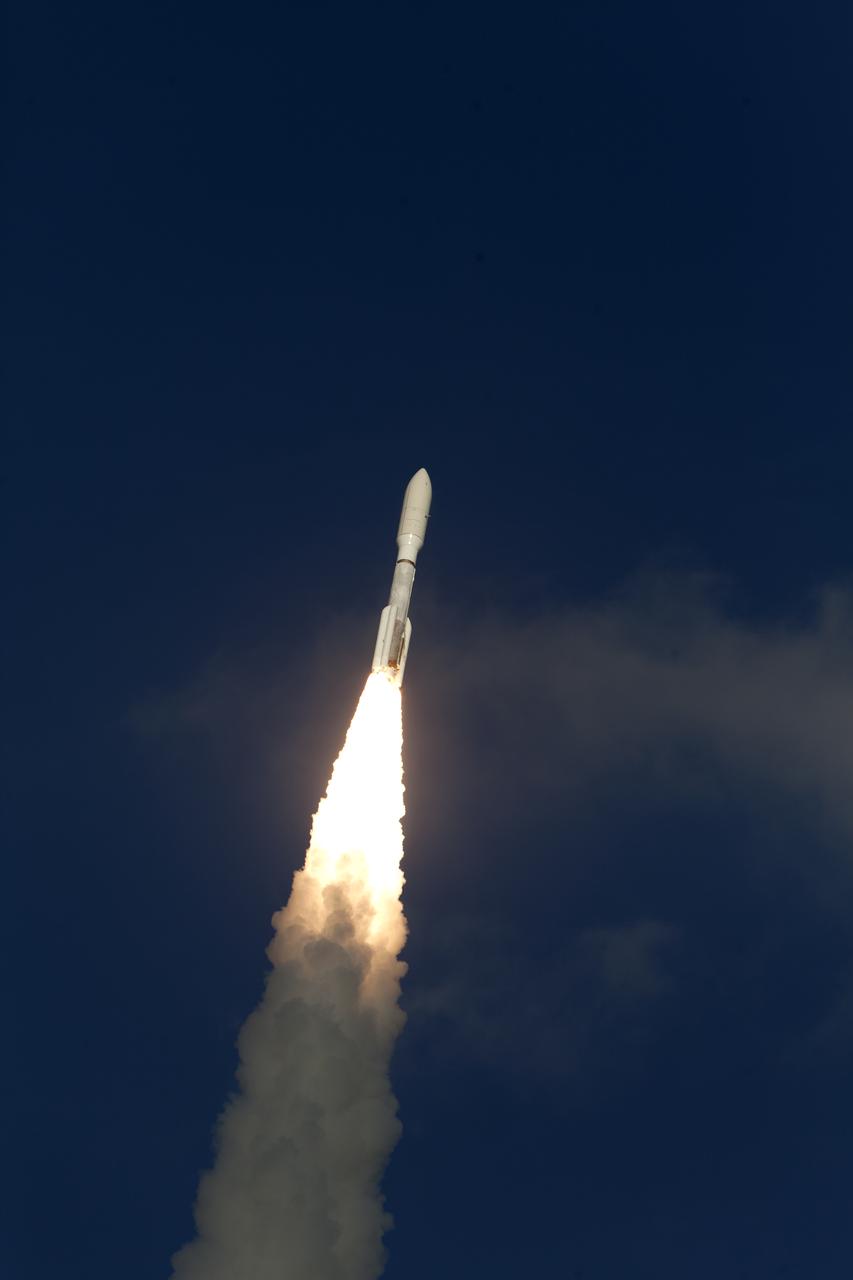

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying the NOAA Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S. Liftoff was at 5:02 p.m. EST. GOES-S is the second satellite in a series of next-generation weather satellites. It will launch to a geostationary position over the U.S. to provide images of storms and help predict weather forecasts, severe weather outlooks, watches, warnings, lightning conditions and longer-term forecasting.
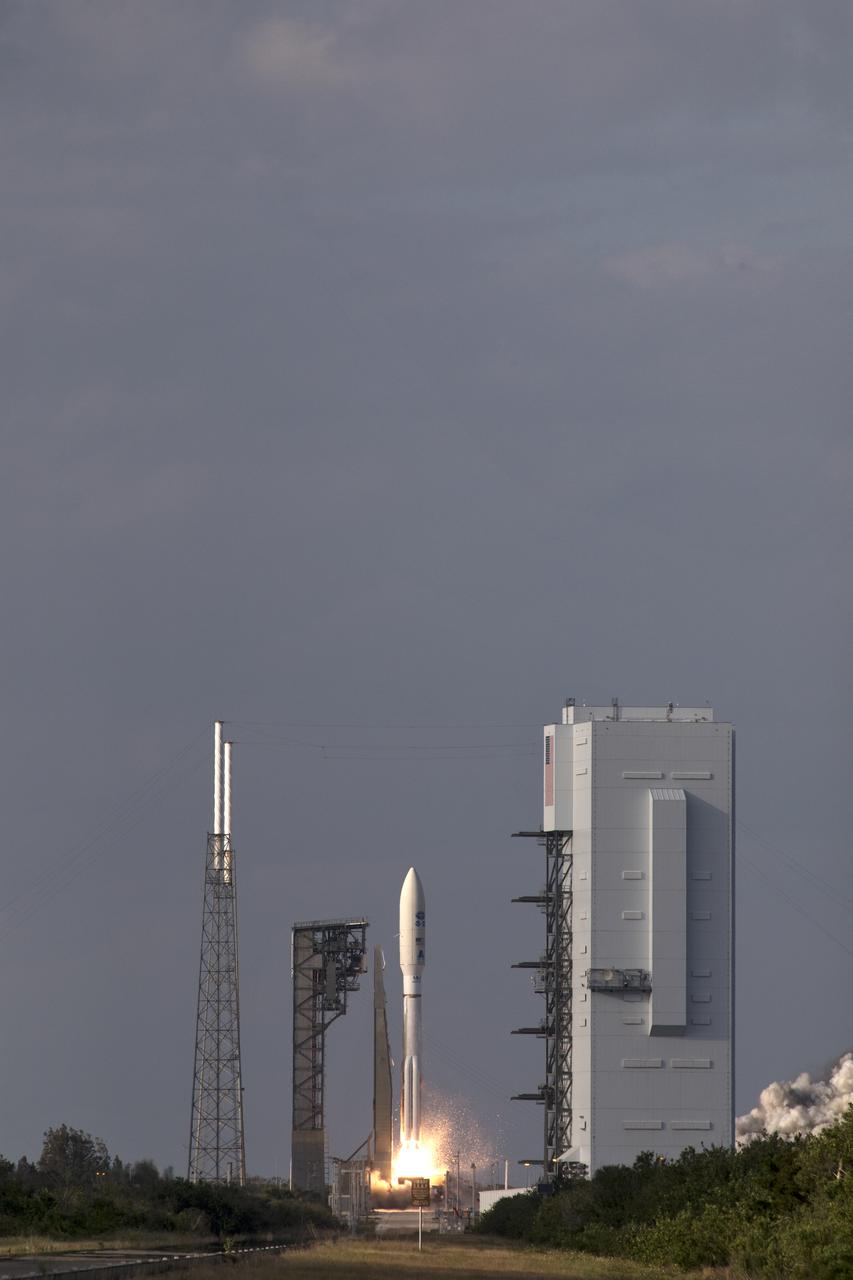

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying the NOAA Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S. Liftoff was at 5:02 p.m. EST. GOES-S is the second satellite in a series of next-generation weather satellites. It will launch to a geostationary position over the U.S. to provide images of storms and help predict weather forecasts, severe weather outlooks, watches, warnings, lightning conditions and longer-term forecasting.

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying the NOAA Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S. Liftoff was at 5:02 p.m. EST. GOES-S is the second satellite in a series of next-generation weather satellites. It will launch to a geostationary position over the U.S. to provide images of storms and help predict weather forecasts, severe weather outlooks, watches, warnings, lightning conditions and longer-term forecasting.
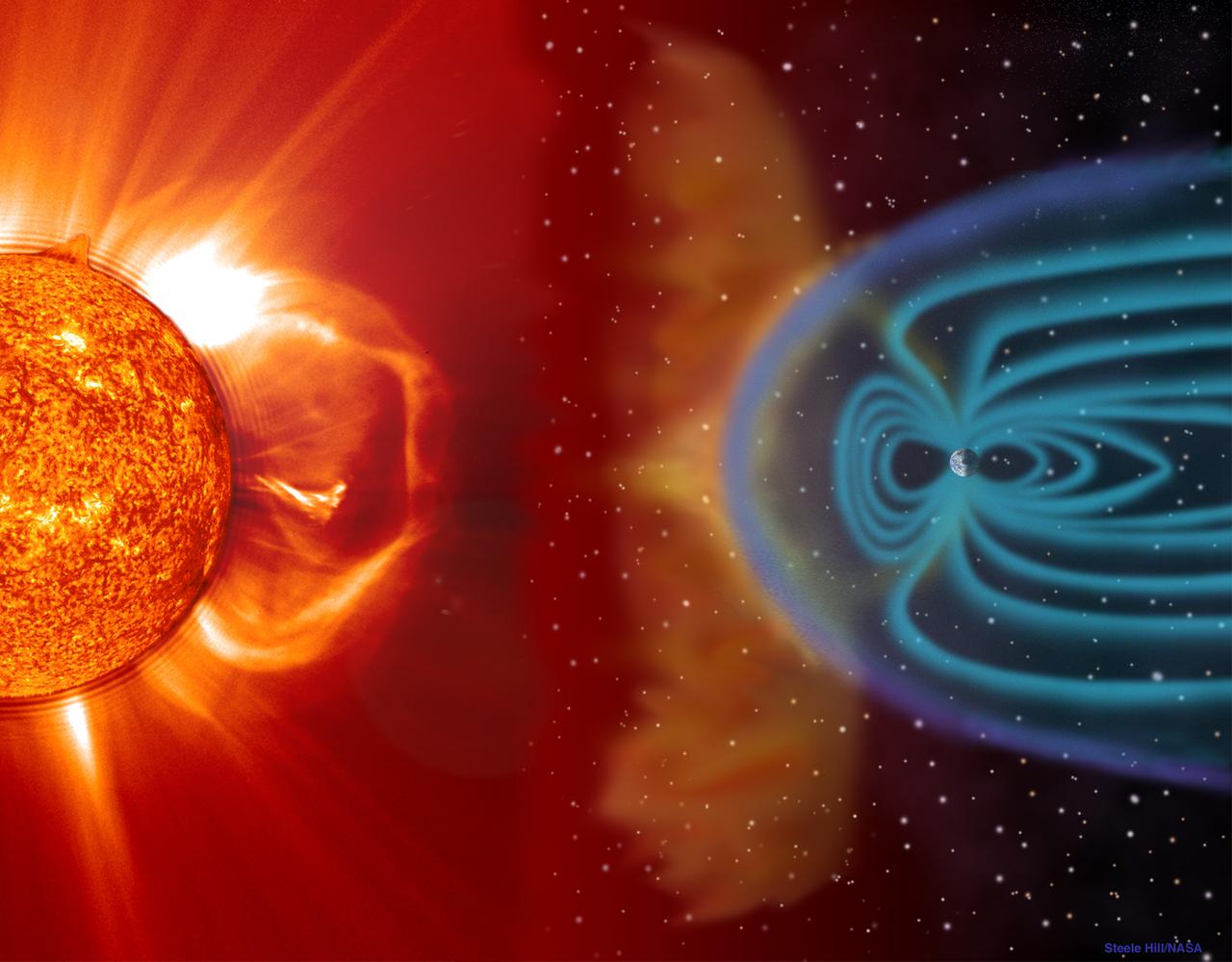
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and university scientists from the National Space Science and Technology Center (NSSTC) in Huntsville, Alabama, are watching the Sun in an effort to better predict space weather - blasts of particles and magnetic fields from the Sun that impact the magnetosphere, the magnetic bubble around the Earth. Filled by charged particles trapped in the Earth's magnetic field, the spherical comet-shaped magnetosphere extends out 40,000 miles from Earth's surface in the sunward direction and more in other directions. This image illustrates the Sun-Earth cornection. When massive solar explosions, known as coronal mass ejections, blast through the Sun's outer atmosphere and plow toward Earth at speeds of thousands of miles per second, the resulting effects can be harmful to communication satellites and astronauts outside the Earth's magnetosphere. Like severe weather on Earth, severe space weather can be costly. On the ground, magnetic storms wrought by these solar particles can knock out electric power. By using the Solar Vector Magnetograph, a solar observation facility at MSFC, scientists are learning what signs to look for as indicators of potential severe space weather.
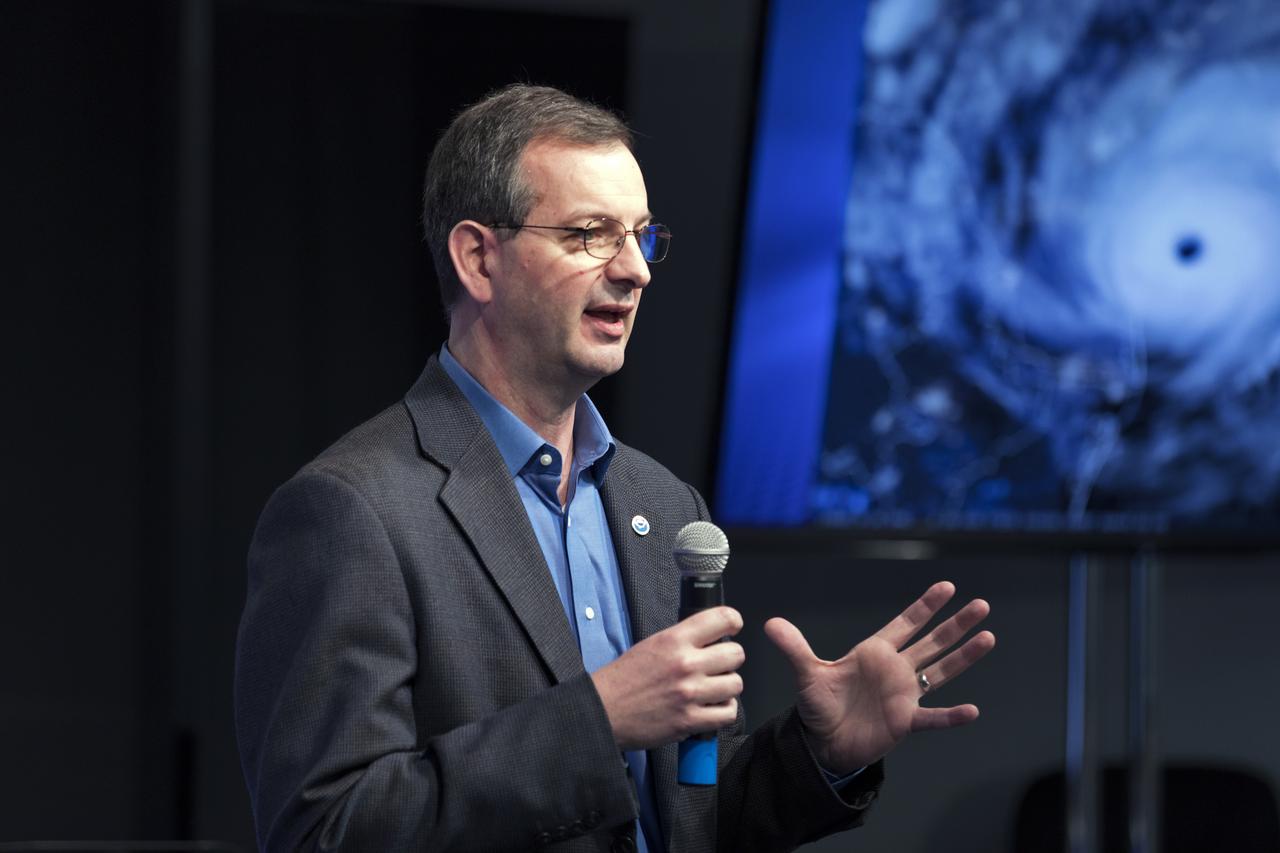

Joe Pica, director of the Office of Observations for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's, or NOAA’s, National Weather Service, speaks to members of social media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S, the second spacecraft in a series of next-generation NOAA weather satellites. It will launch to a geostationary position over the U.S. to provide images of storms and help predict weather forecasts, severe weather outlooks, watches, warnings, lightning conditions and longer-term forecasting. GOES-S is slated to lift off at 5:02 p.m. EST on March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
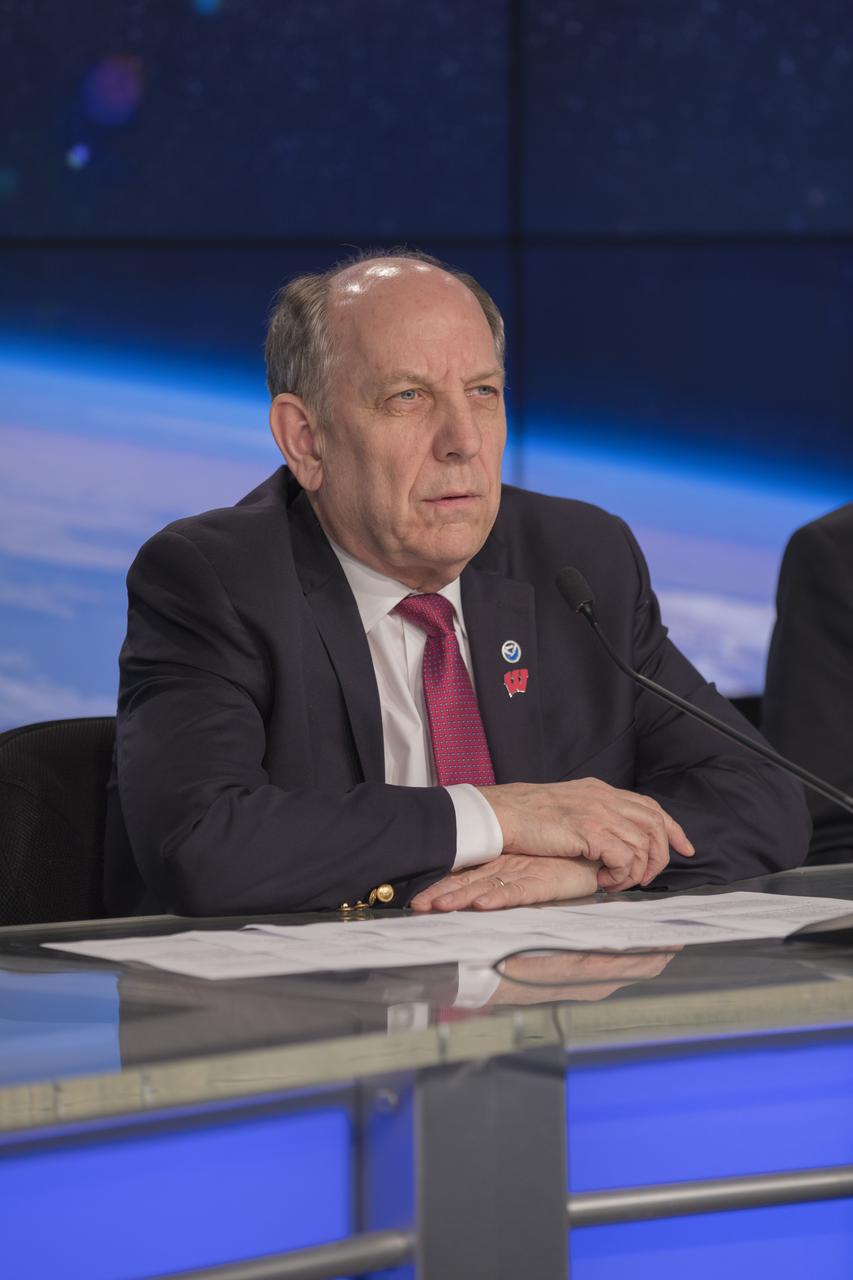

In the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium, Louis Uccellini, director of the National Weather Service for NOAA, speaks to members of the media at a mission briefing on National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's, or NOAA's, Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S. The spacecraft is the second satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA weather satellites. It will launch to a geostationary position over the U.S. to provide images of storms and help predict weather forecasts, severe weather outlooks, watches, warnings, lightning conditions and longer-term forecasting. GOES-S is slated to lift off at 5:02 p.m. EST on March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket
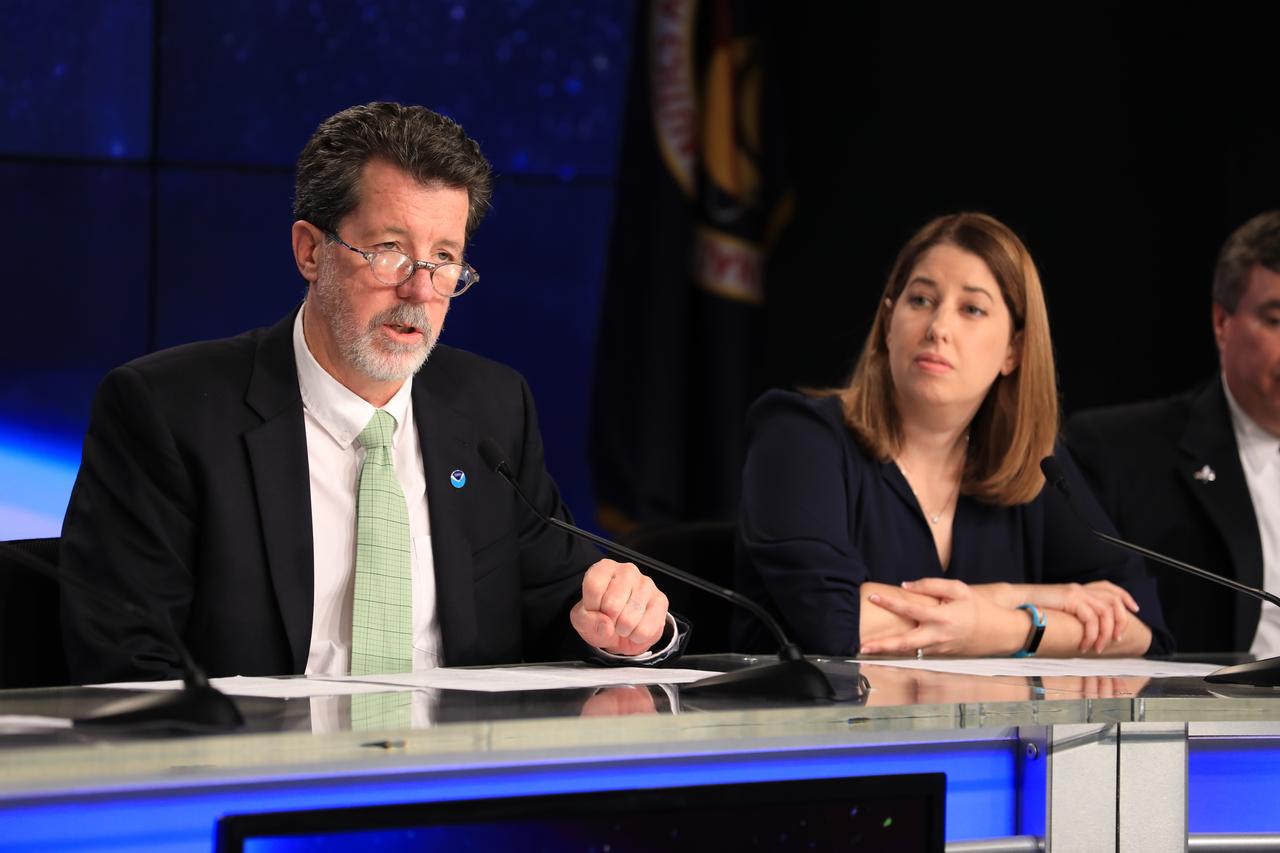

In the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium, Jim Roberts, a scientist with the Earth System Research Laboratory's Office of Atmospheric Research for NOAA, left, and Kristin Calhoun, a research scientist with NOAA's National Severe Storms Laboratory, speak to members of the media at a mission briefing on National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's, or NOAA's, Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S. The spacecraft is the second satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA weather satellites. It will launch to a geostationary position over the U.S. to provide images of storms and help predict weather forecasts, severe weather outlooks, watches, warnings, lightning conditions and longer-term forecasting. GOES-S is slated to lift off at 5:02 p.m. EST on March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
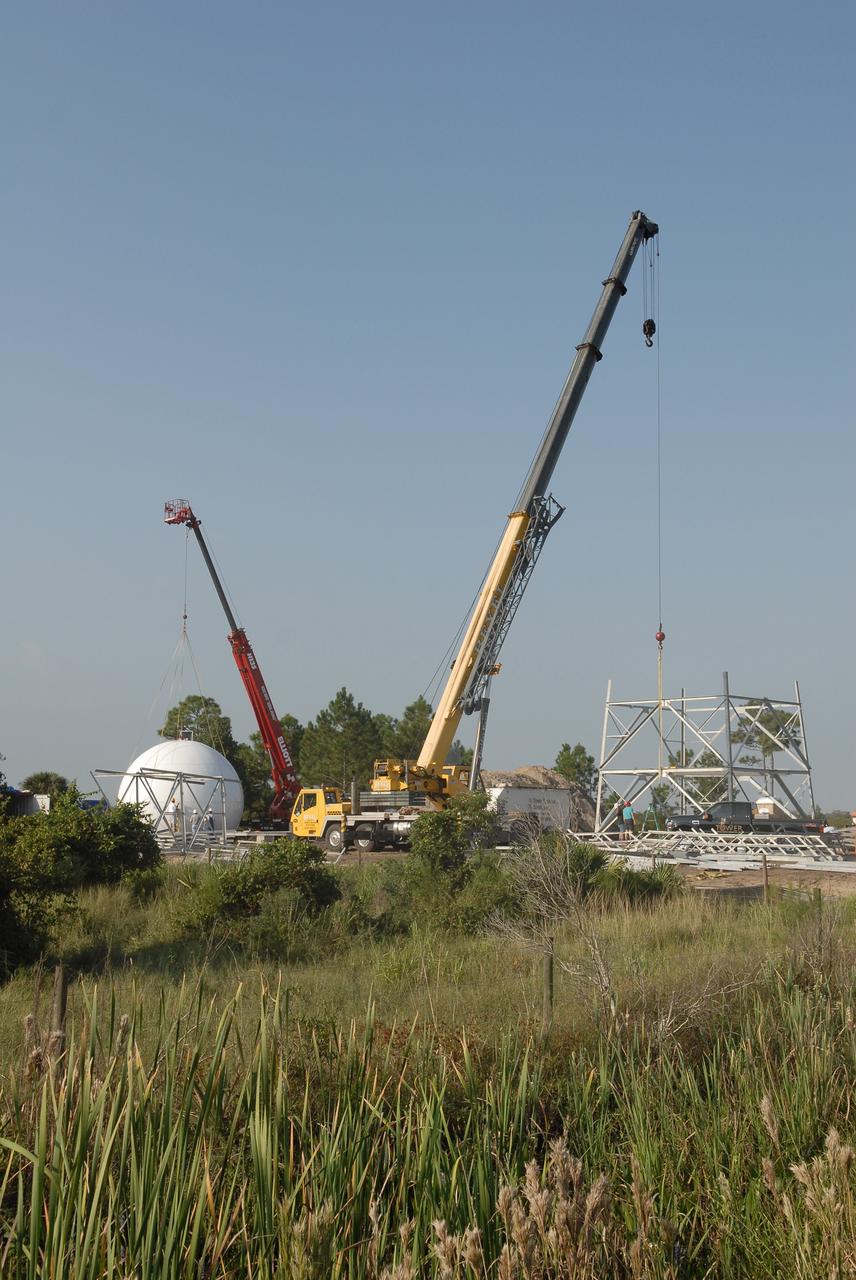

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Construction continues on the Doppler weather radar facility for the 45th Weather Squadron being built in an area near S.R. 520 in Orange County, Florida. The new site will replace one at Patrick Air Force Base and will be used by NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the 45th Space Wing and their customers. The site will be able to monitor weather conditions directly above the launch pads at Kennedy. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria. The new radar, replacing what was installed 25 years ago at Patrick Air Force Base, includes Doppler capability to detect winds and identify the type, size and number of precipitation particles. The site is ideally distant from the launch pads and has unobstructed views of Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and Kennedy. The radar will be used by forecasters at the USAF 45th Weather Squadron. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

One of several Environmental Continuous Air Monitors, or ECAMS, is located in the Space Coast area on July 27, 2020, in preparation for launch of NASA’s Mars 2020 mission on July 30. The ECAMS are updated versions of those that were used for the launch of Curiosity. The Data Collection and Assessment Center uses information from the network of remote monitoring devises, including several that are located in areas for specific weather forecasting reported back to the operations center.
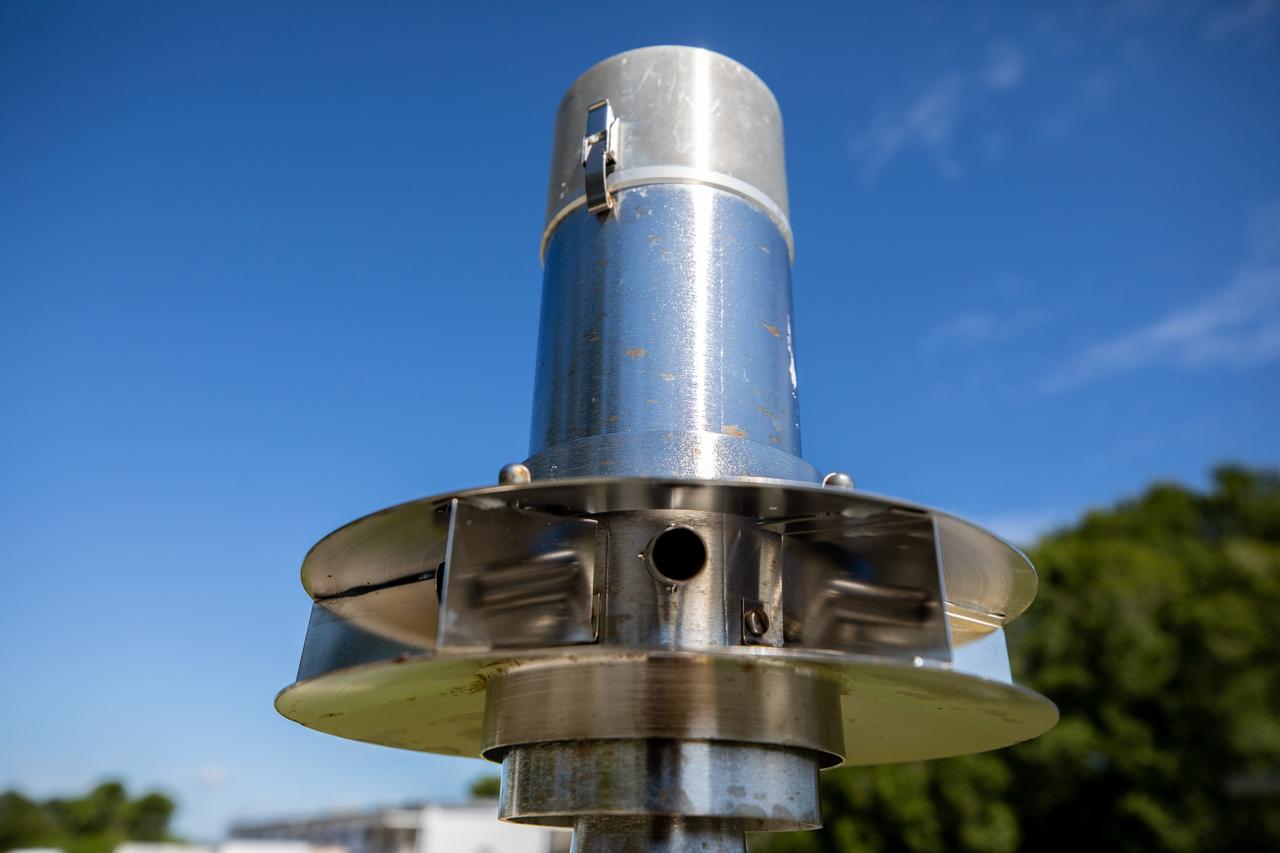

A close-up view of one of several Environmental Continuous Air Monitors, or ECAMS, located in the Space Coast area on July 27, 2020, in preparation for launch of NASA’s Mars 2020 mission on July 30. The ECAMS are updated versions of those that were used for the launch of Curiosity. The Data Collection and Assessment Center uses information from the network of remote monitoring devises, including several that are located in areas for specific weather forecasting reported back to the operations center.
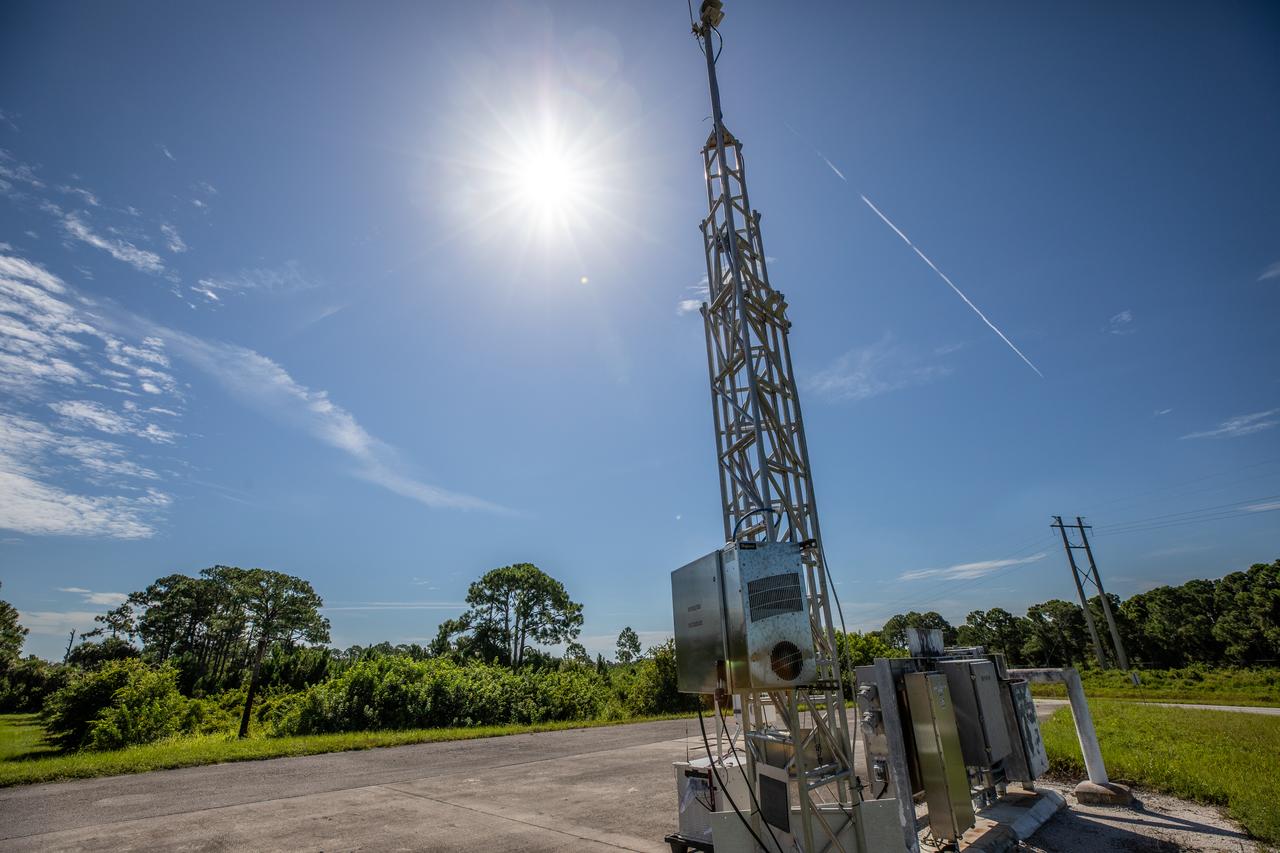

One of several Environmental Continuous Air Monitors, or ECAMS, is located in the Space Coast area on July 27, 2020, in preparation for launch of NASA’s Mars 2020 mission on July 30. The ECAMS are updated versions of those that were used for the launch of Curiosity. The Data Collection and Assessment Center uses information from the network of remote monitoring devises, including several that are located in areas for specific weather forecasting reported back to the operations center.
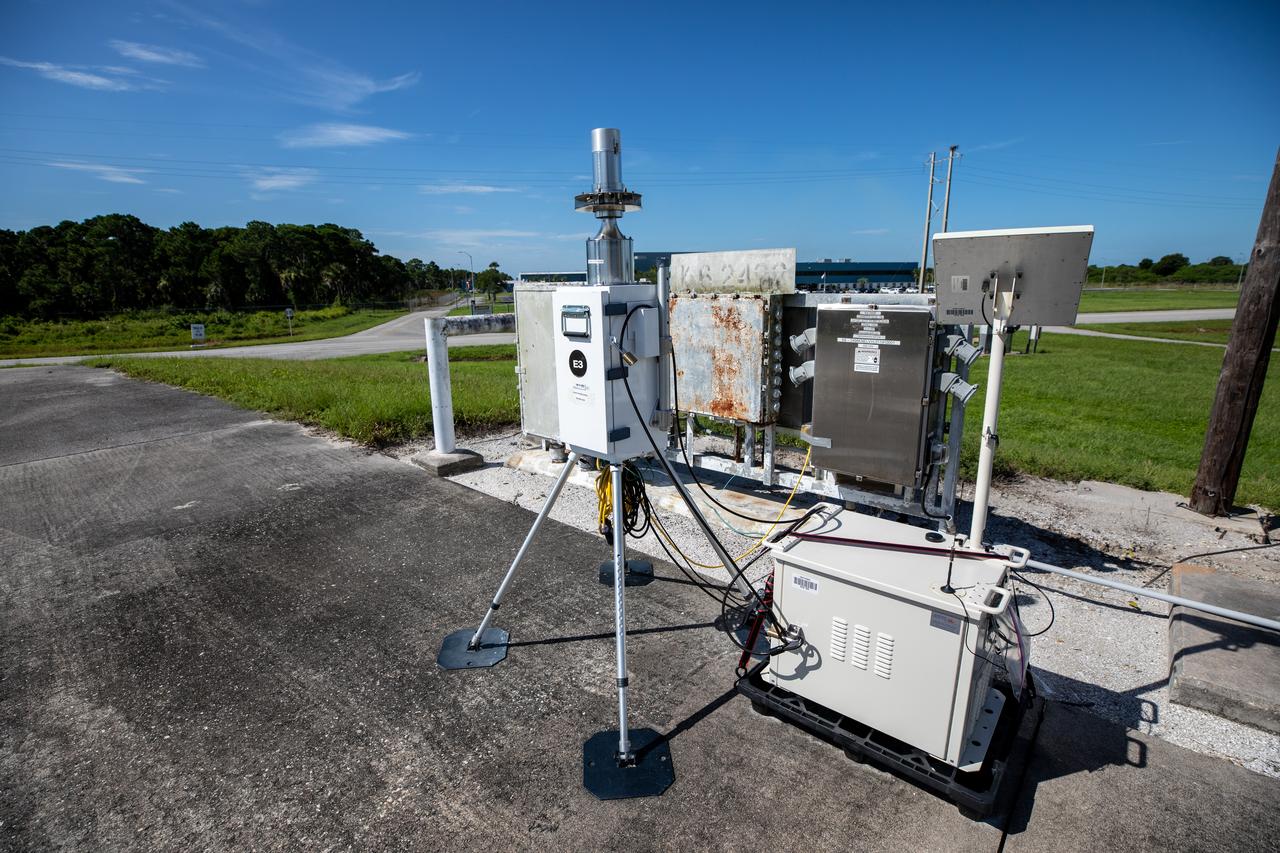

A close-up view of one of several Environmental Continuous Air Monitors, or ECAMS, located in the Space Coast area on July 27, 2020, in preparation for launch of NASA’s Mars 2020 mission on July 30. The ECAMS are updated versions of those that were used for the launch of Curiosity. The Data Collection and Assessment Center uses information from the network of remote monitoring devises, including several that are located in areas for specific weather forecasting reported back to the operations center.
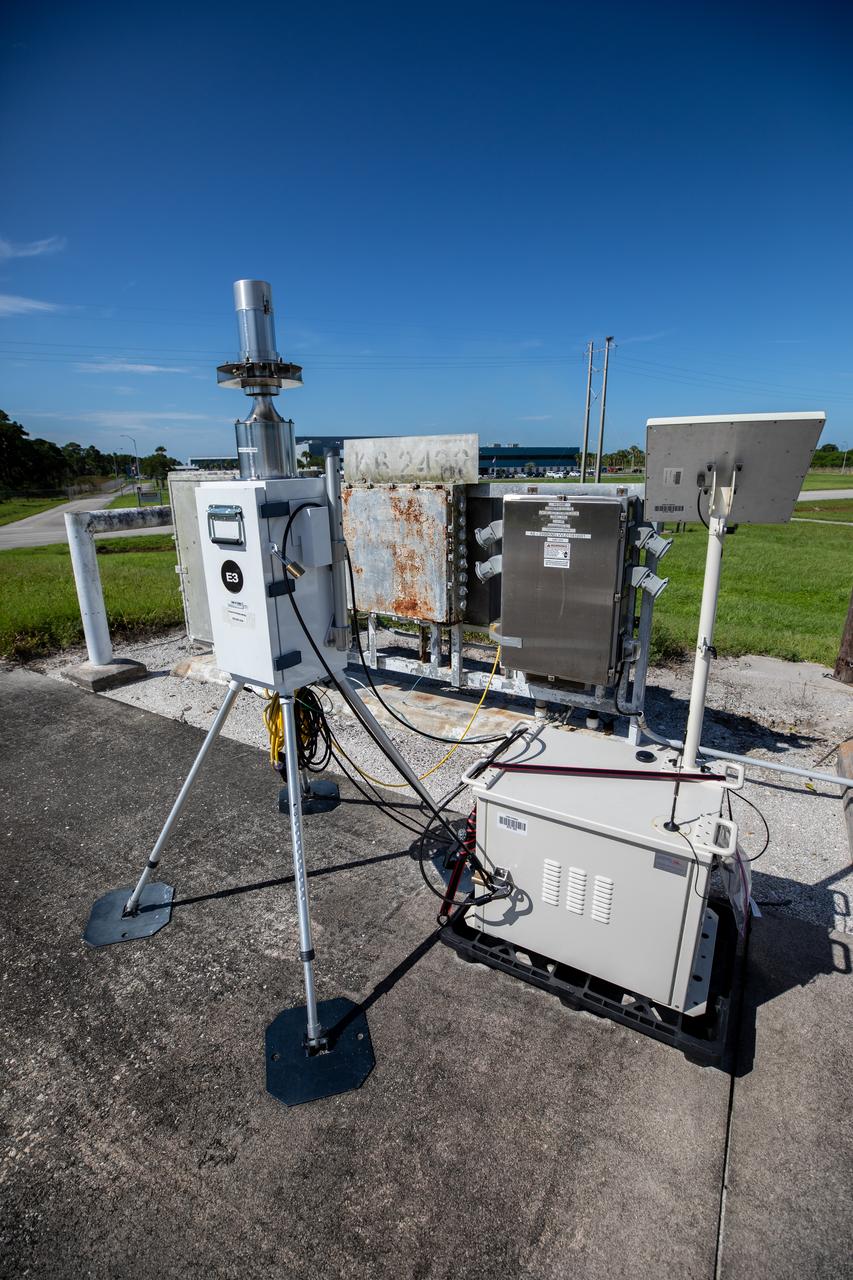

A close-up view of one of several Environmental Continuous Air Monitors, or ECAMS, located in the Space Coast area on July 27, 2020, in preparation for launch of NASA’s Mars 2020 mission on July 30. The ECAMS are updated versions of those that were used for the launch of Curiosity. The Data Collection and Assessment Center uses information from the network of remote monitoring devises, including several that are located in areas for specific weather forecasting reported back to the operations center.
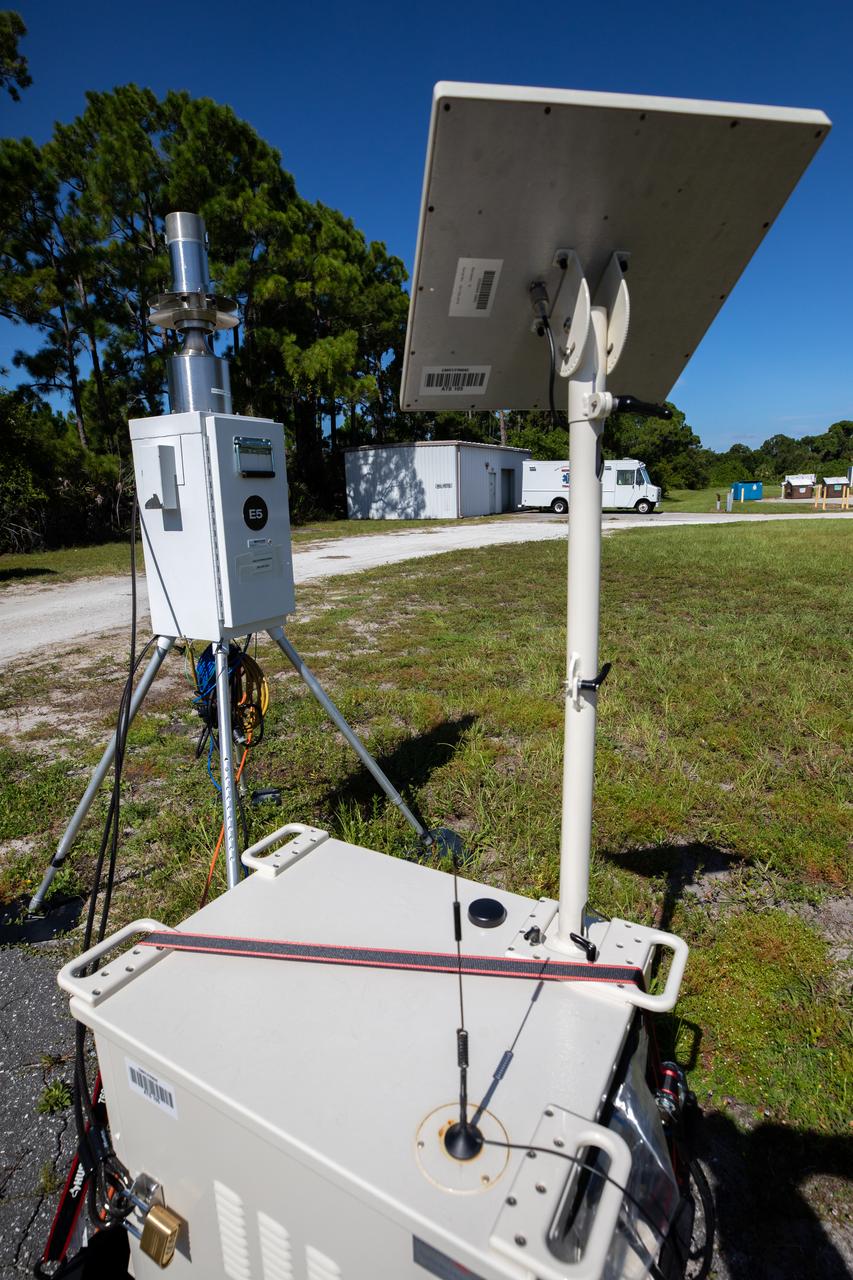

A close-up view of one of several Environmental Continuous Air Monitors, or ECAMS, located in the Space Coast area on July 27, 2020, in preparation for launch of NASA’s Mars 2020 mission on July 30. The ECAMS are updated versions of those that were used for the launch of Curiosity. The Data Collection and Assessment Center uses information from the network of remote monitoring devises, including several that are located in areas for specific weather forecasting reported back to the operations center.

One of several Environmental Continuous Air Monitors, or ECAMS, is located in the Space Coast area on July 27, 2020, in preparation for launch of NASA’s Mars 2020 mission on July 30. The ECAMS are updated versions of those that were used for the launch of Curiosity. The Data Collection and Assessment Center uses information from the network of remote monitoring devises, including several that are located in areas for specific weather forecasting reported back to the operations center.
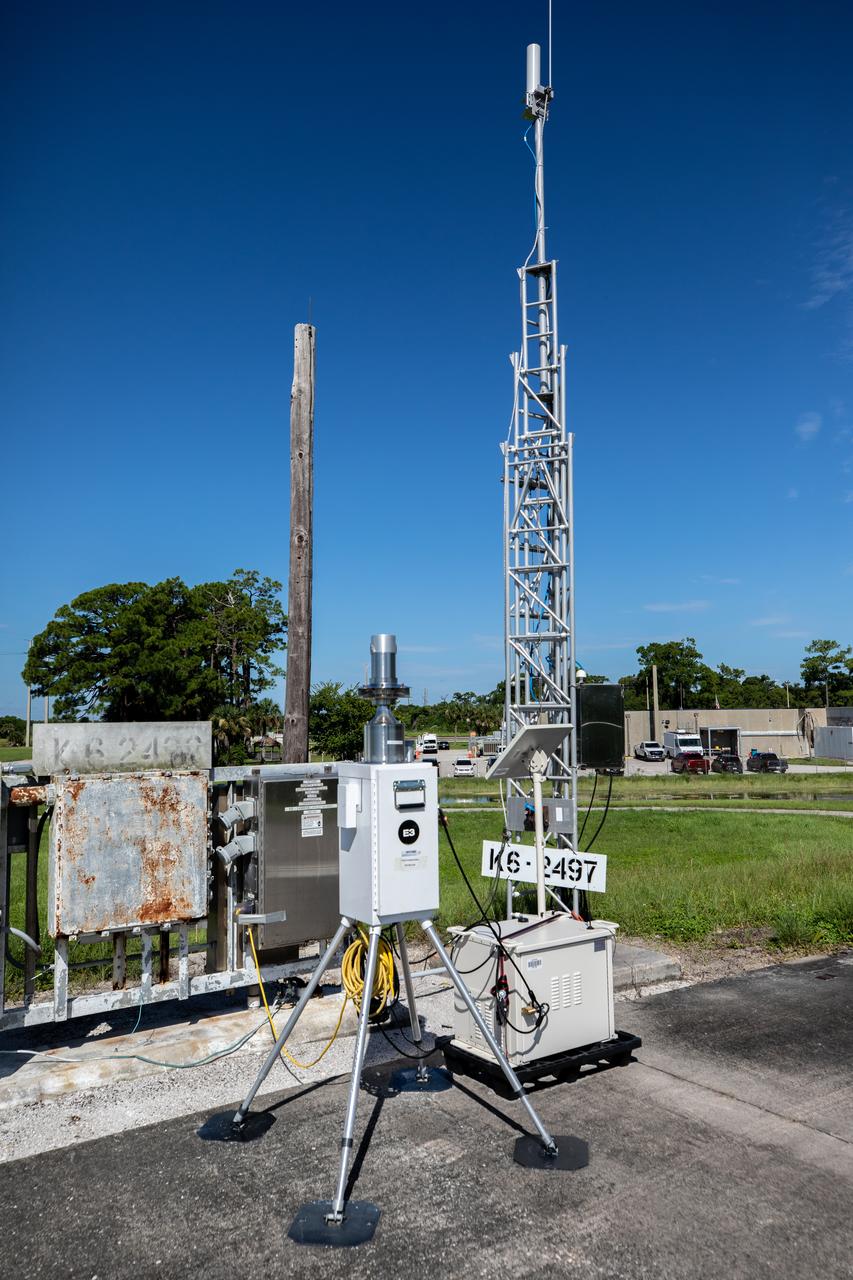

A close-up view of one of several Environmental Continuous Air Monitors, or ECAMS, located in the Space Coast area on July 27, 2020, in preparation for launch of NASA’s Mars 2020 mission on July 30. The ECAMS are updated versions of those that were used for the launch of Curiosity. The Data Collection and Assessment Center uses information from the network of remote monitoring devises, including several that are located in areas for specific weather forecasting reported back to the operations center.
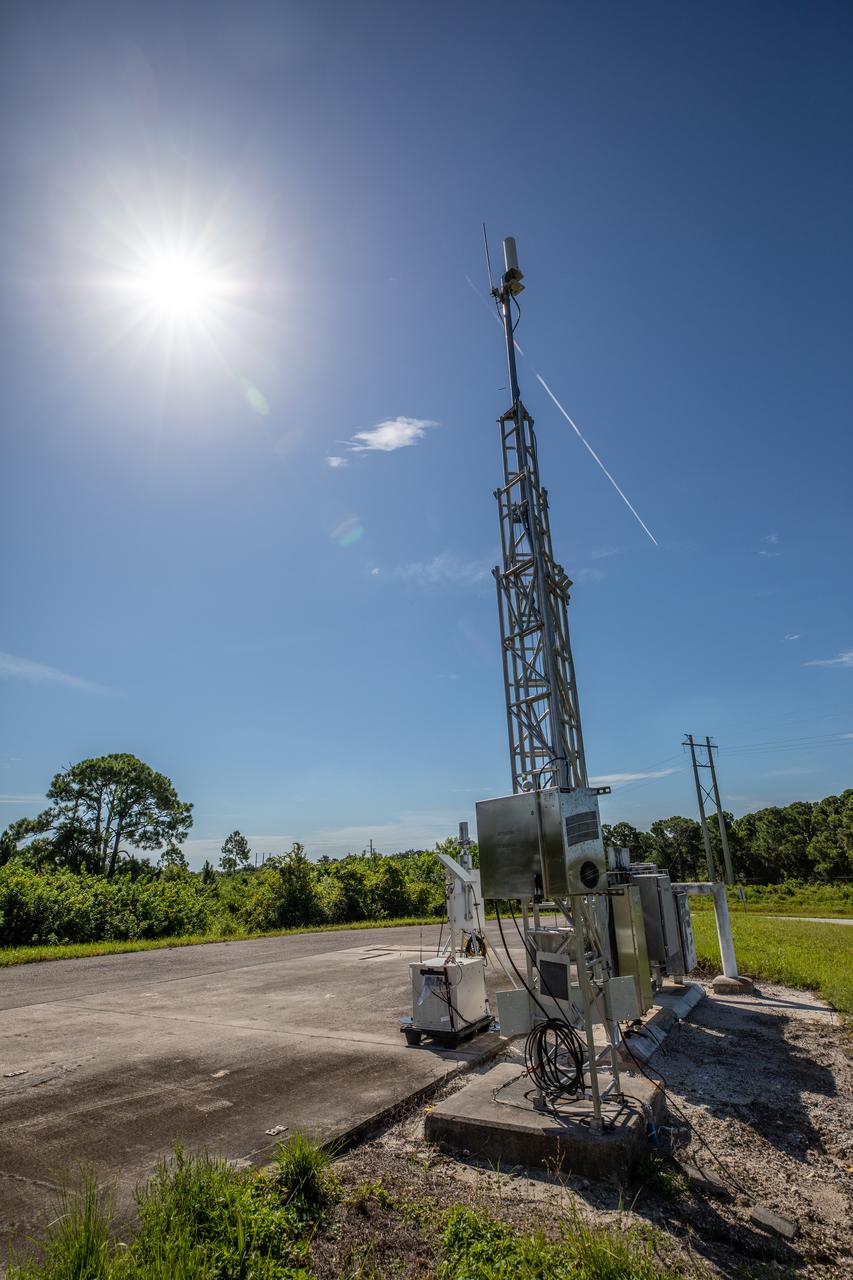

One of several Environmental Continuous Air Monitors, or ECAMS, is located in the Space Coast area on July 27, 2020, in preparation for launch of NASA’s Mars 2020 mission on July 30. The ECAMS are updated versions of those that were used for the launch of Curiosity. The Data Collection and Assessment Center uses information from the network of remote monitoring devises, including several that are located in areas for specific weather forecasting reported back to the operations center.
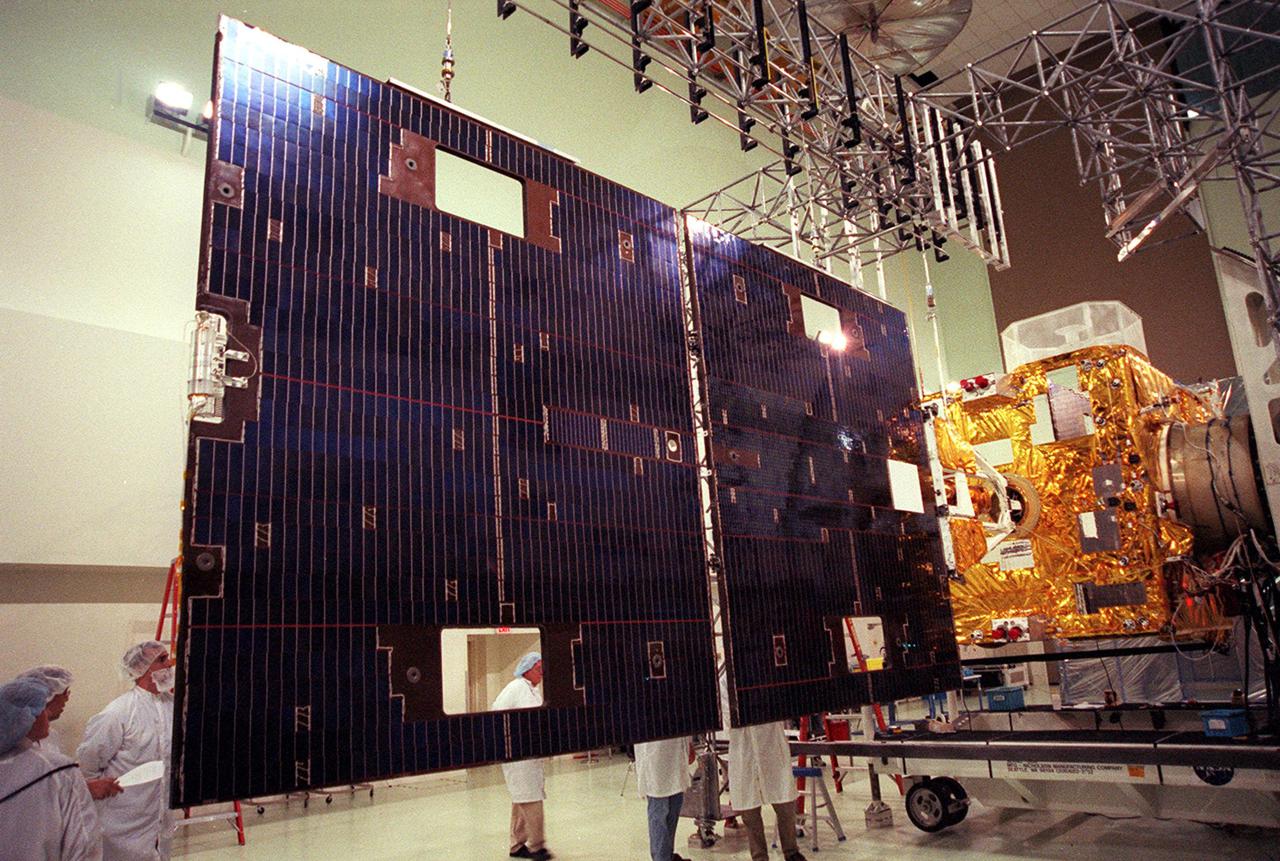

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., take a close look at the solar panel on the GOES-M satellite. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
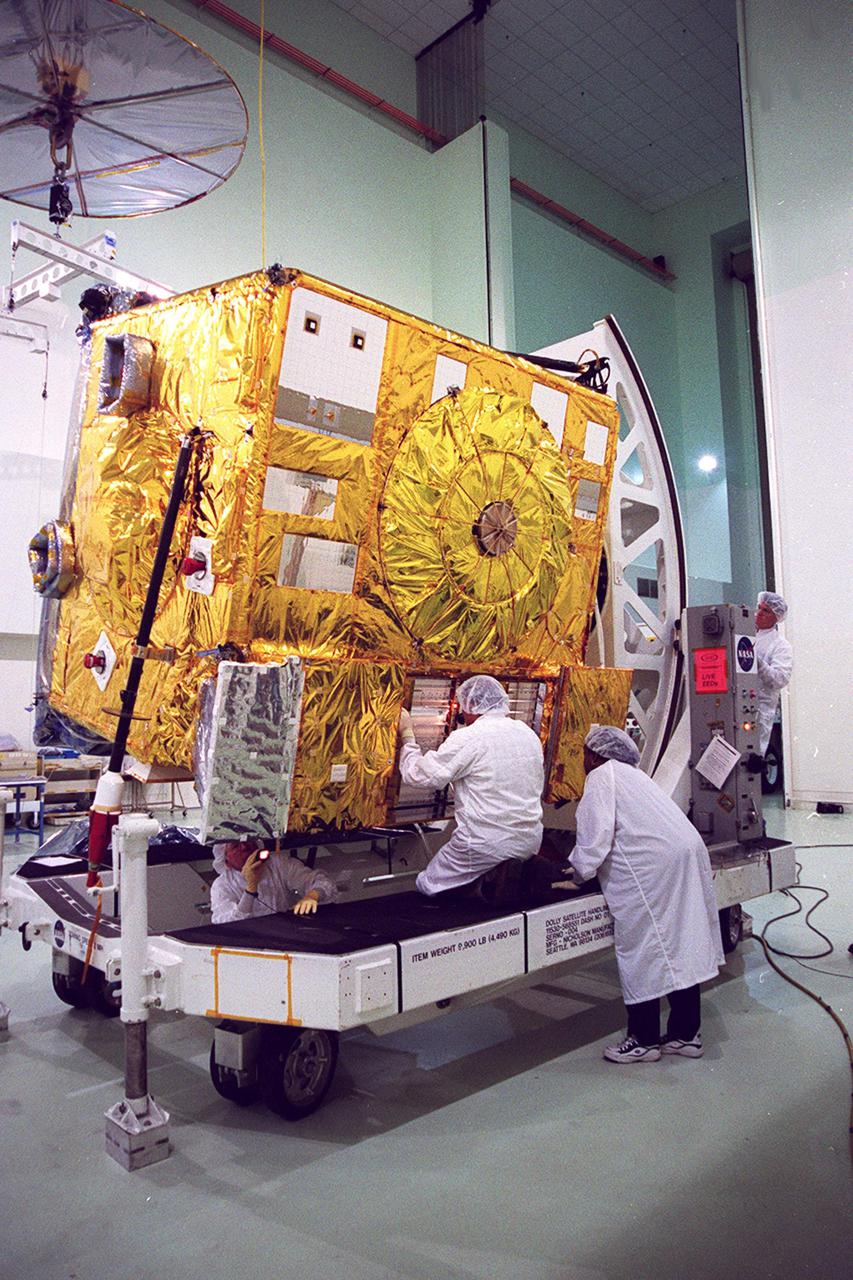

With the GOES-M satellite tilted on a workstand at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla, workers check out a part of the underside. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
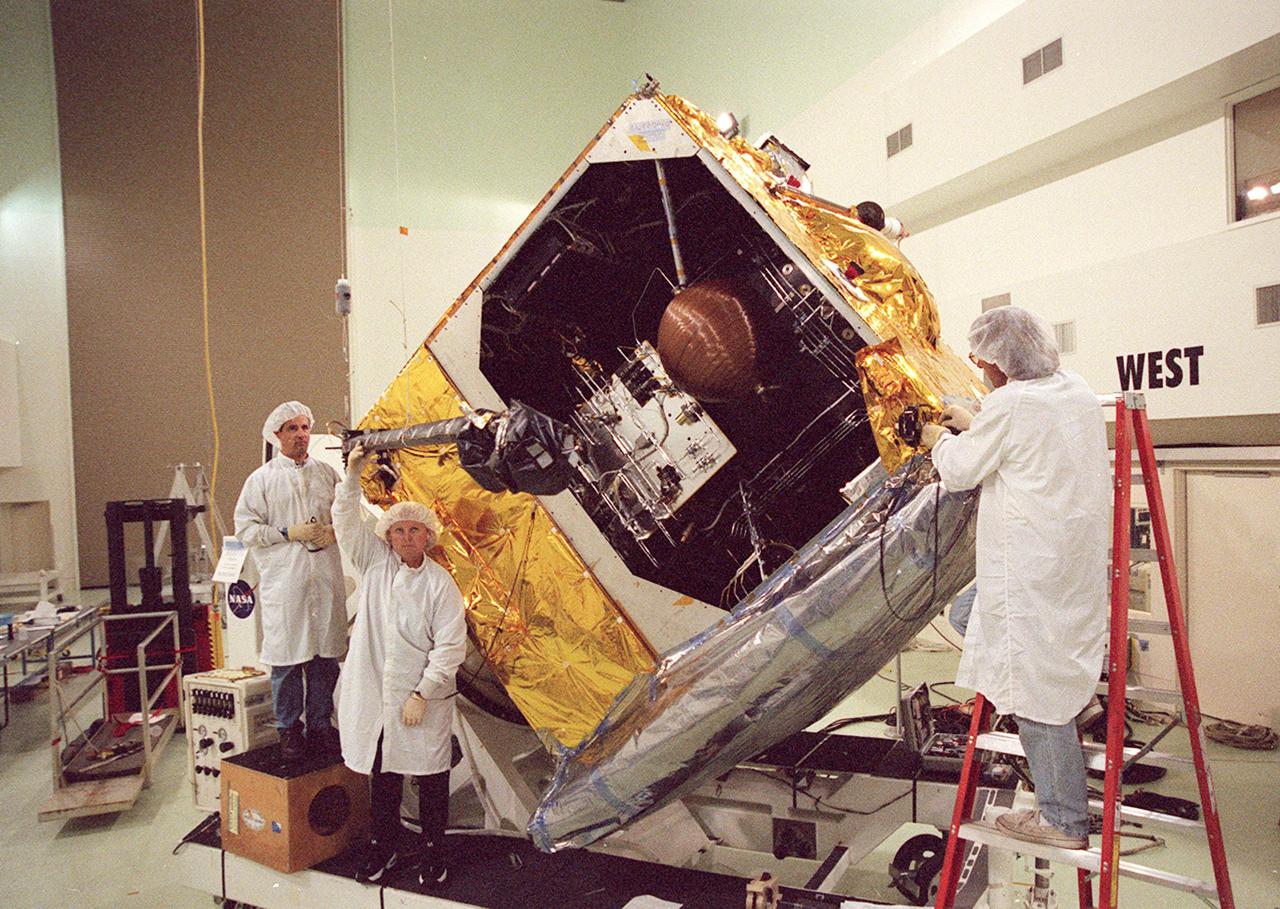

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., begin deploying the magnetometer boom on the GOES-M satellite. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
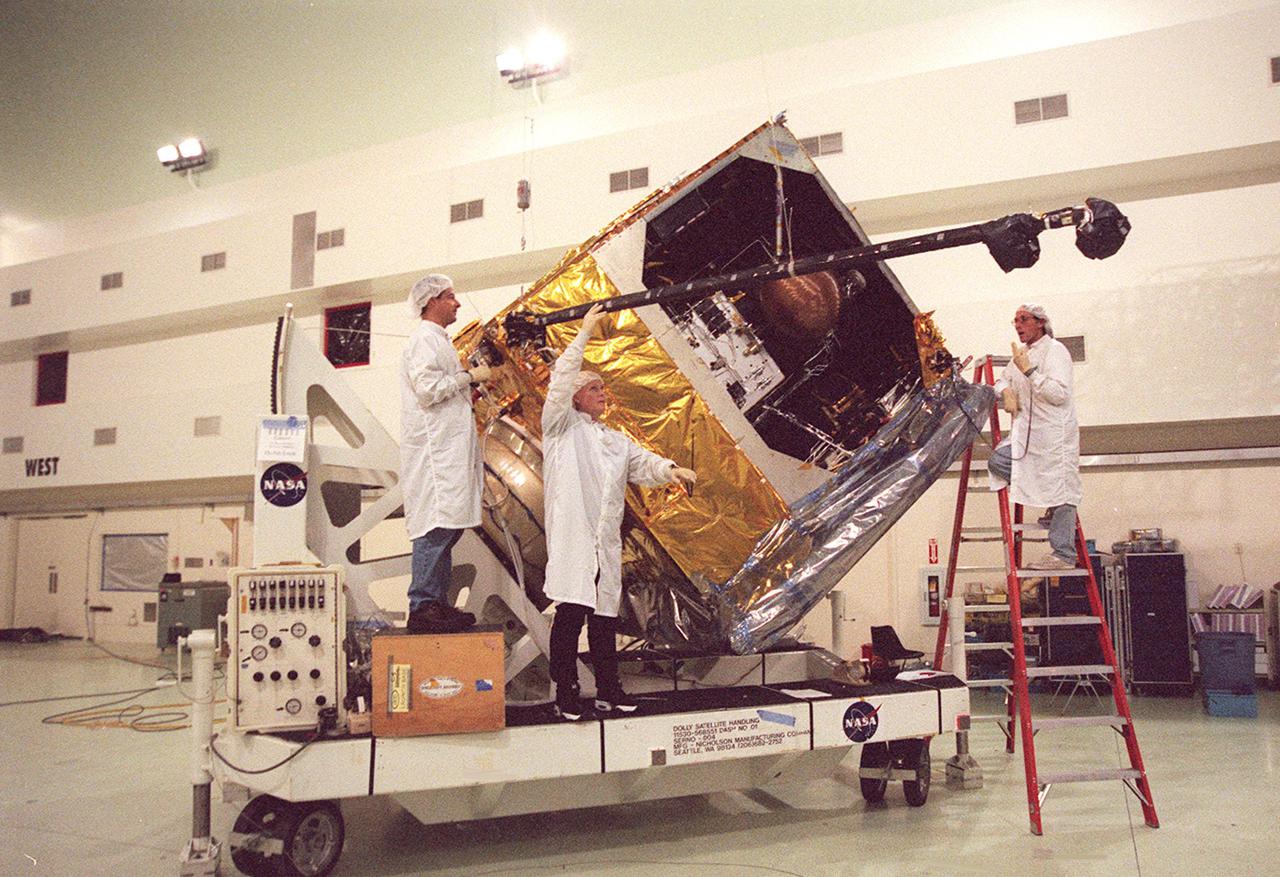

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., deploy the magnetometer boom on the GOES-M satellite. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station

At Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., an overhead crane lifts the GOES-M (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite) from the transporter. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite will undergo testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
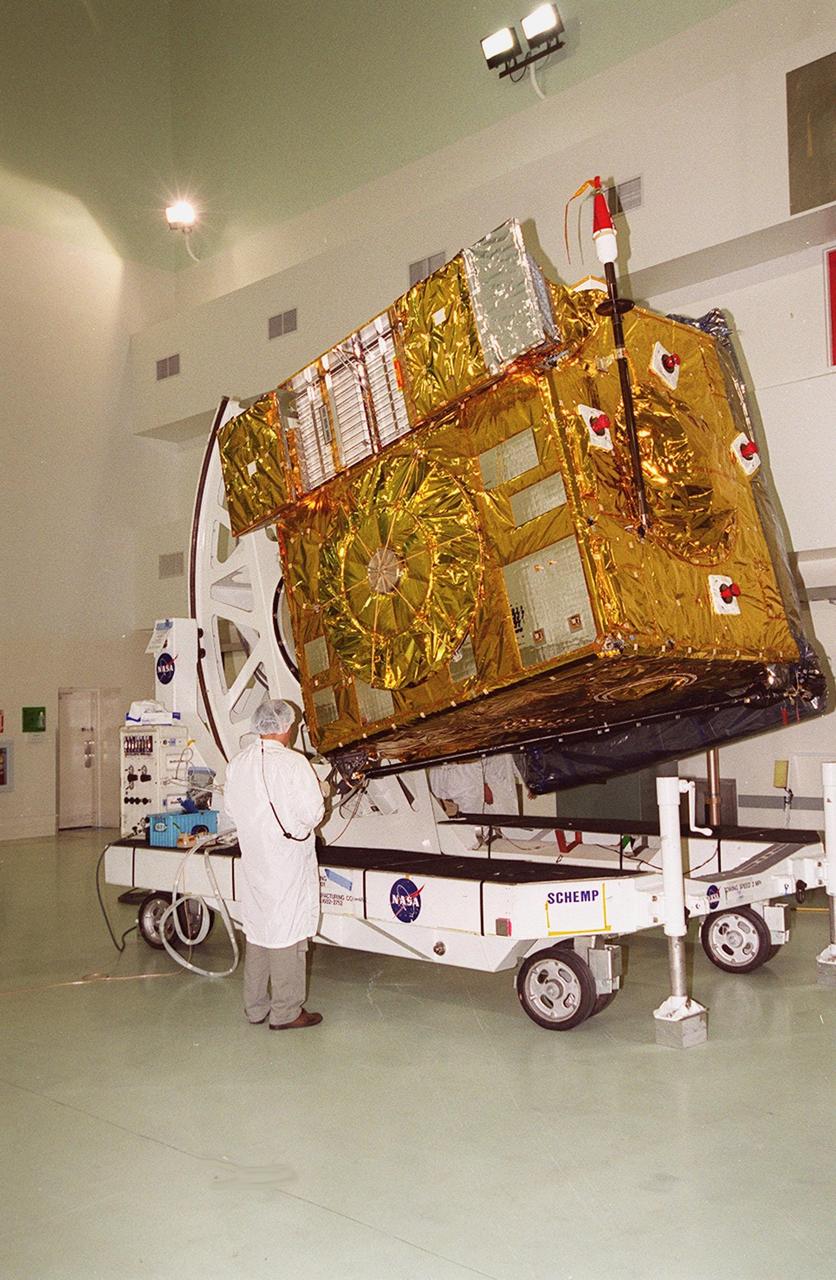

At Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., the GOES-M satellite is lifted at an angle on a workstand. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
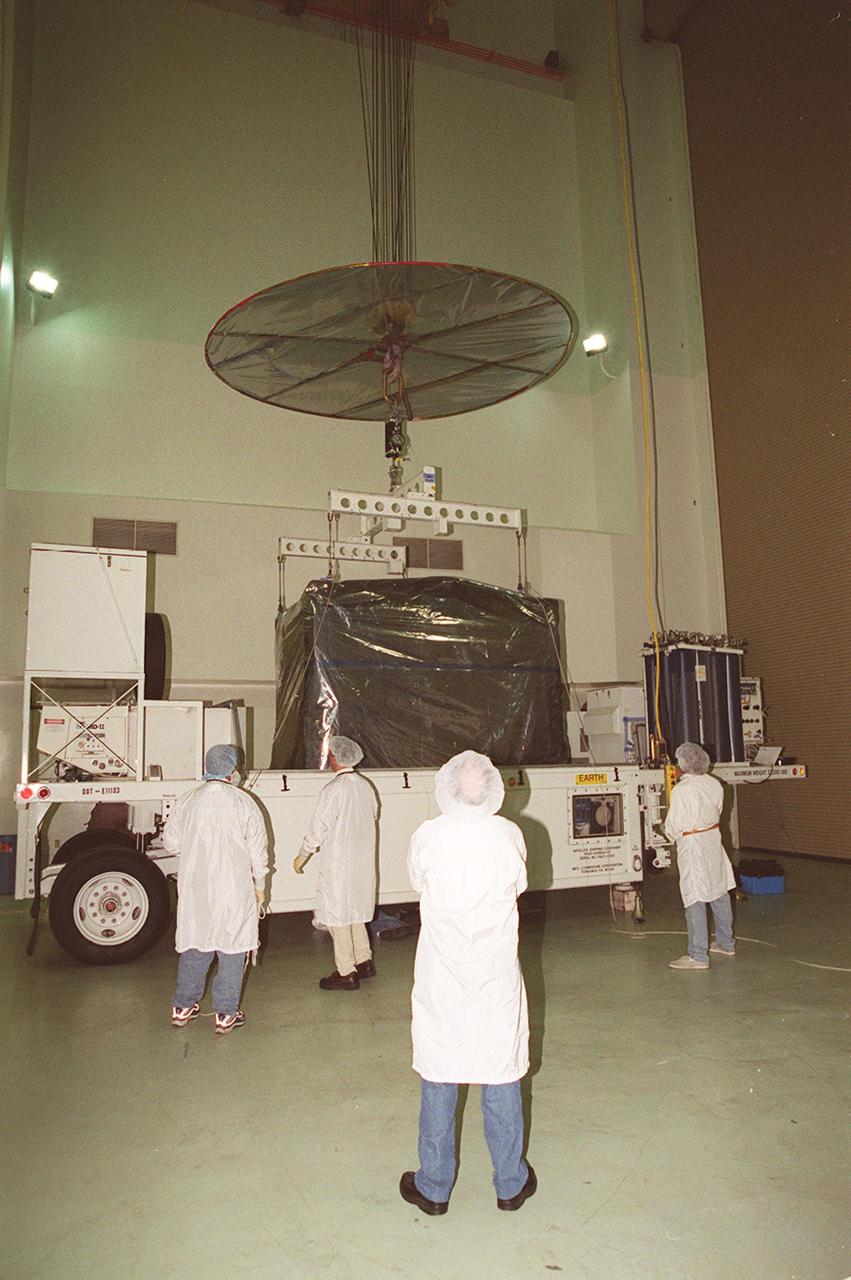

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After arrival at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., the GOES-M (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite) is attached to an overhead crane. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite will undergo testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
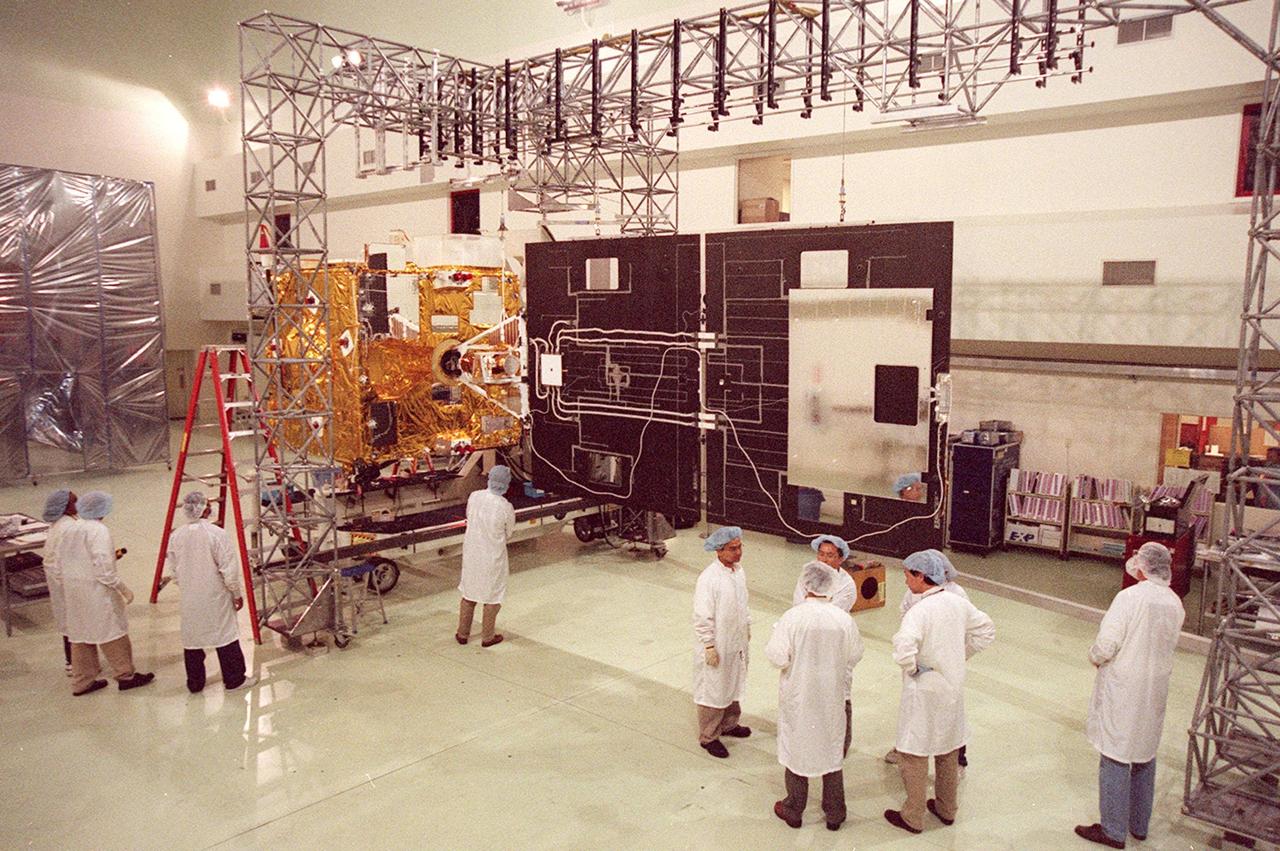
Workers (at left) at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., observe the inside of the solar panel on the GOES-M satellite. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
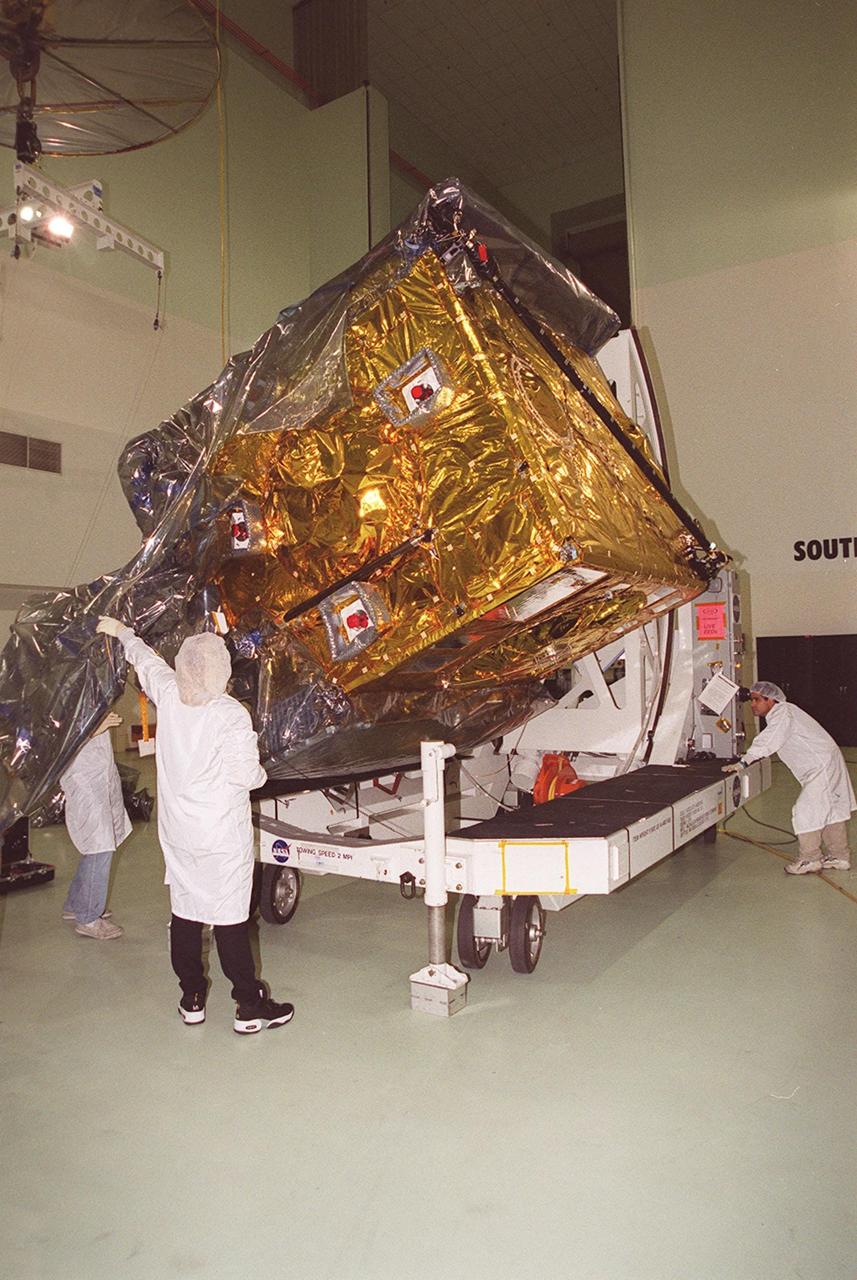

At Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., the GOES-M (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite) satellite is tilted on a workstand so that workers can remove the rest of the protective cover. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite will undergo testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
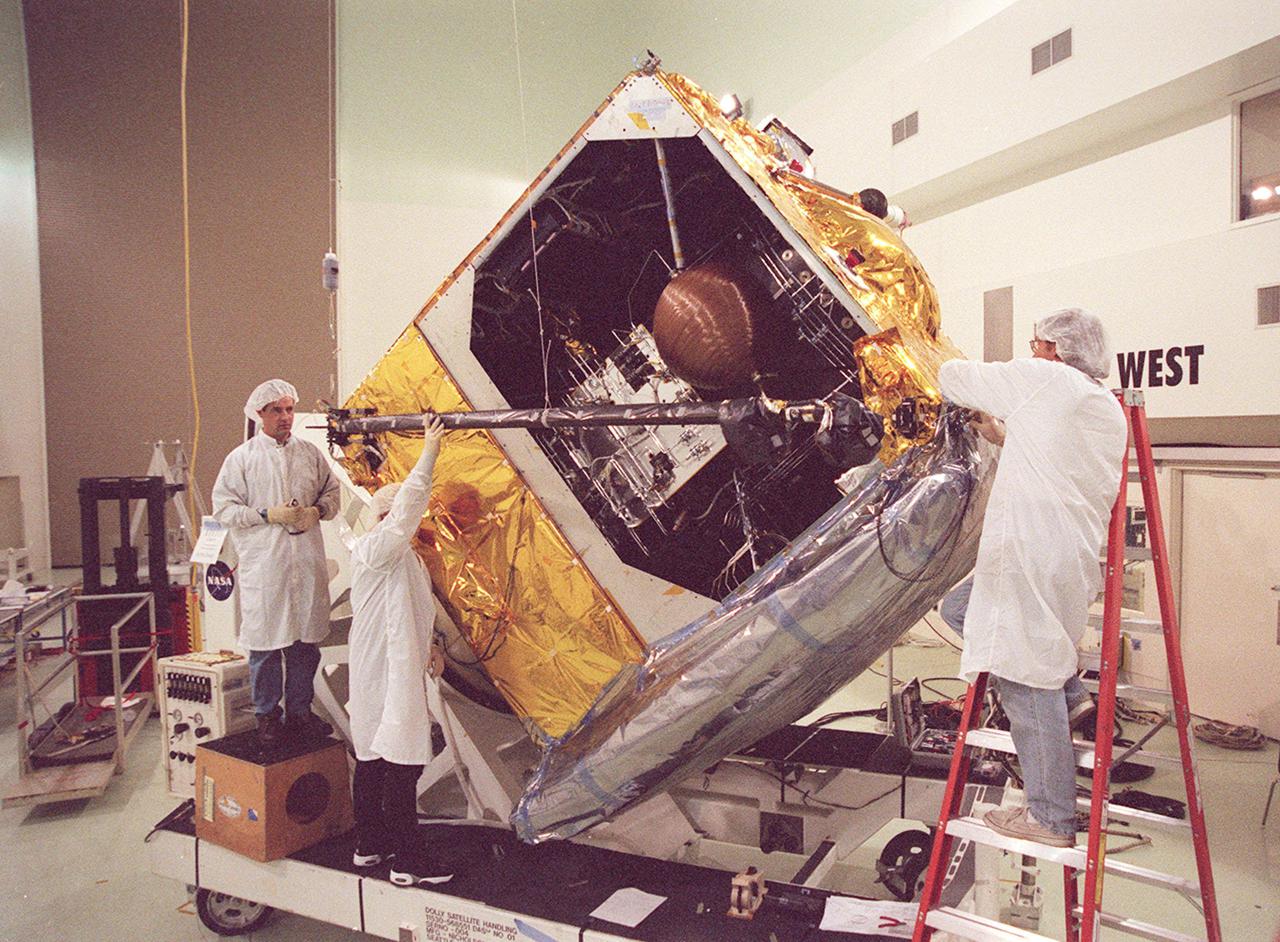

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., begin deploying the magnetometer boom on the GOES-M satellite. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
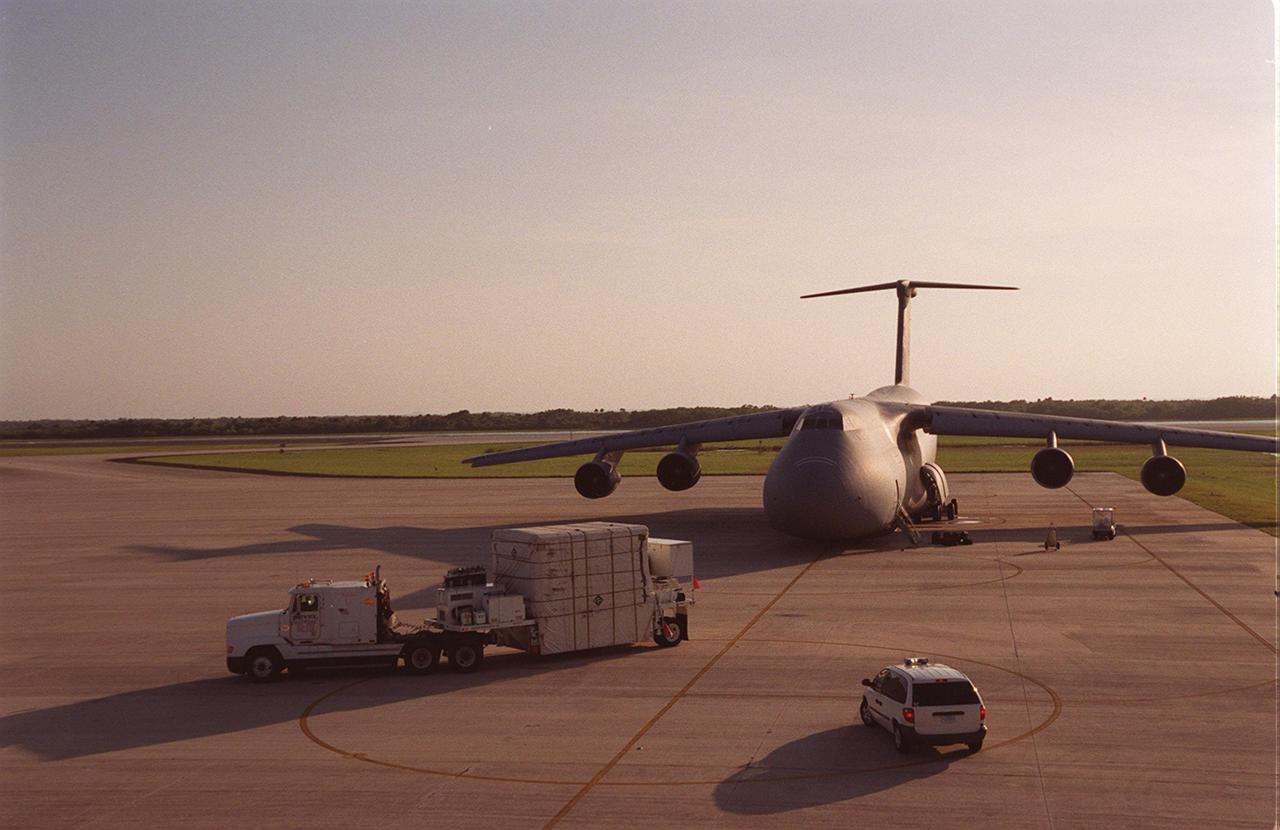

At the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility, the GOES-M satellite, encased in a container, begins its trek to Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., where it will undergo final testing. The GOES-M (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, I-M Series) provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking, and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to be launched on an Atlas-IIA booster, with a Centaur upper stage, July 12 from Launch Pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
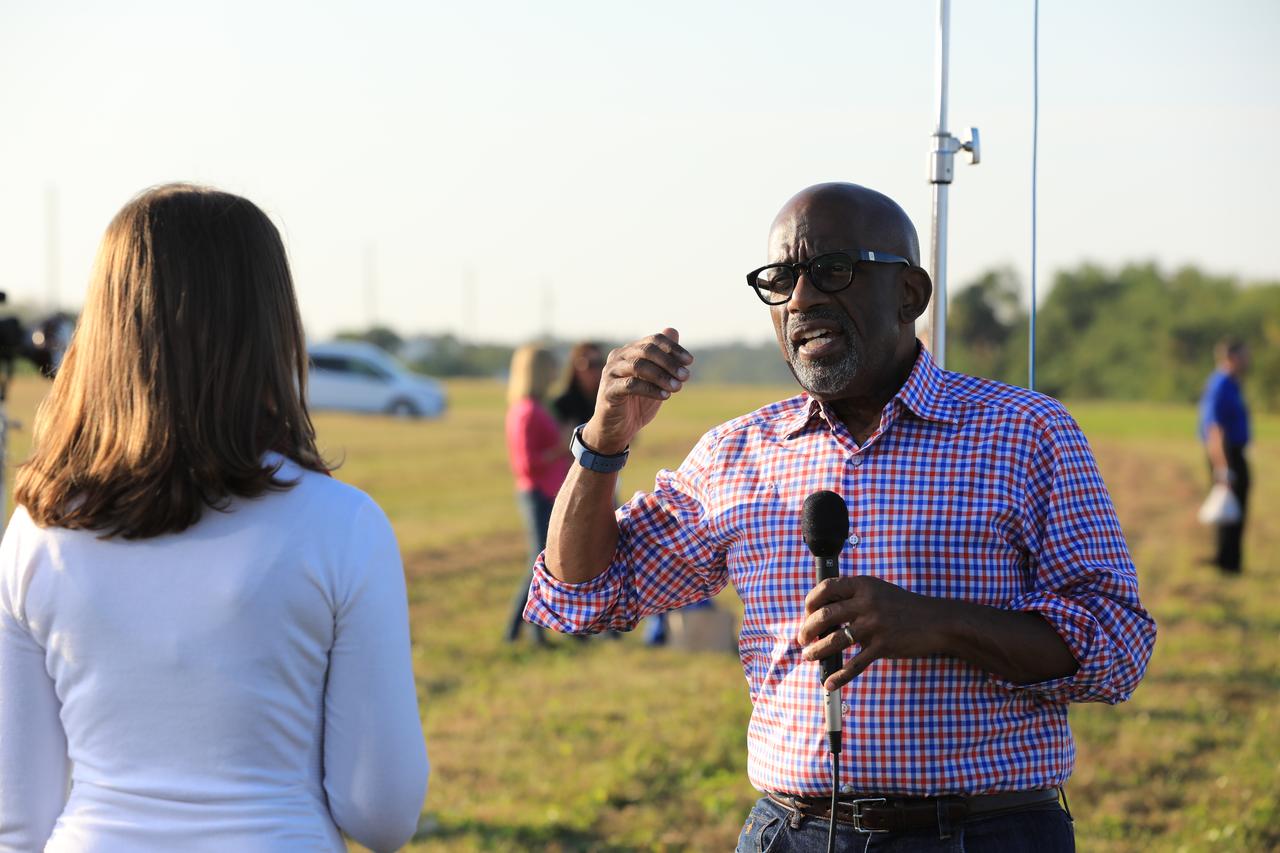

During the countdown for the launch of NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-R, Stephanie Martin of NASA Communications, left, interviews Al Roker, weather forecaster on NBC's "Today Show." GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation GOES satellites for NOAA, the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration. It will launch to a geostationary orbit over the western hemisphere to provide images of storms and help meteorologists predict severe weather conditionals and develop long-range forecasts.
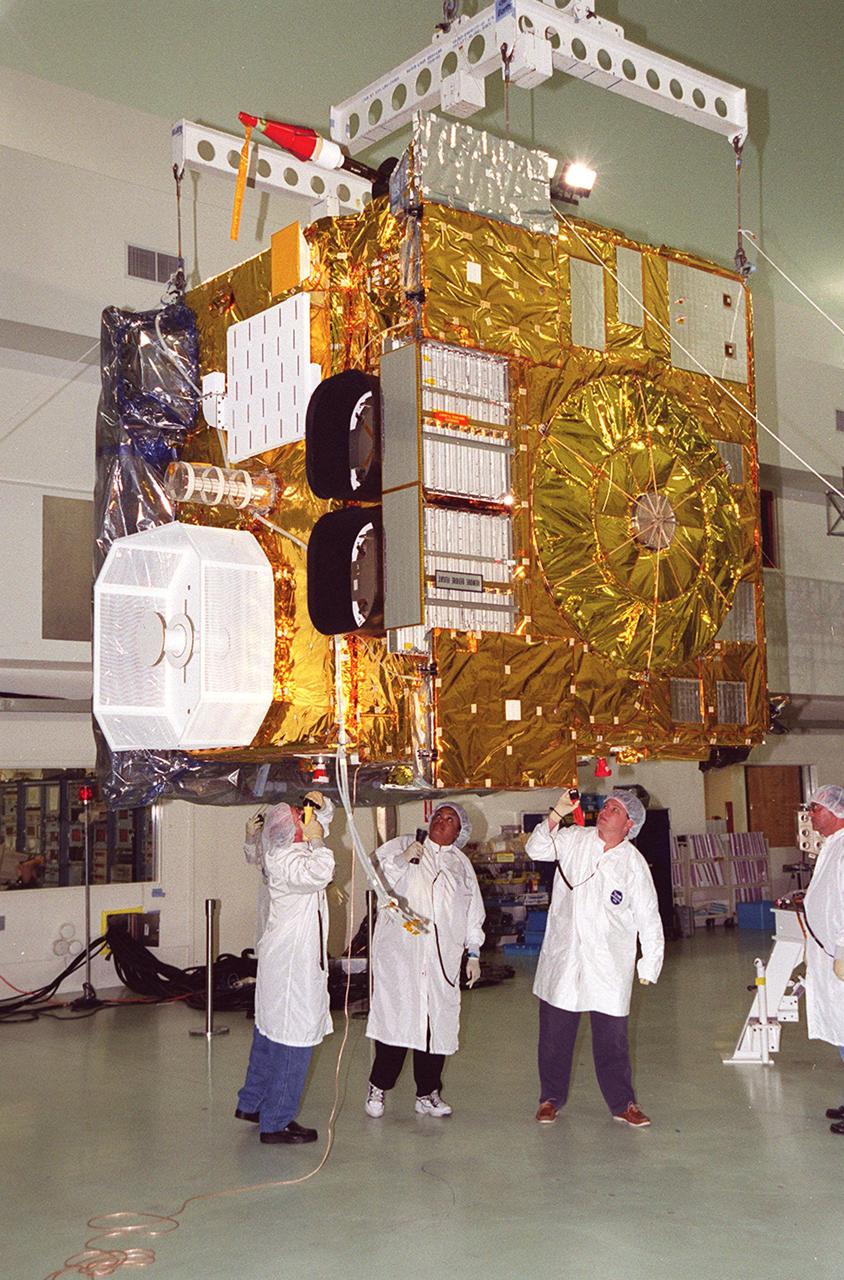

While an overhead crane lifts the GOES-M satellite at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., workers check the underside. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After arrival at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., the GOES-M (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite) is attached to an overhead crane. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite will undergo testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
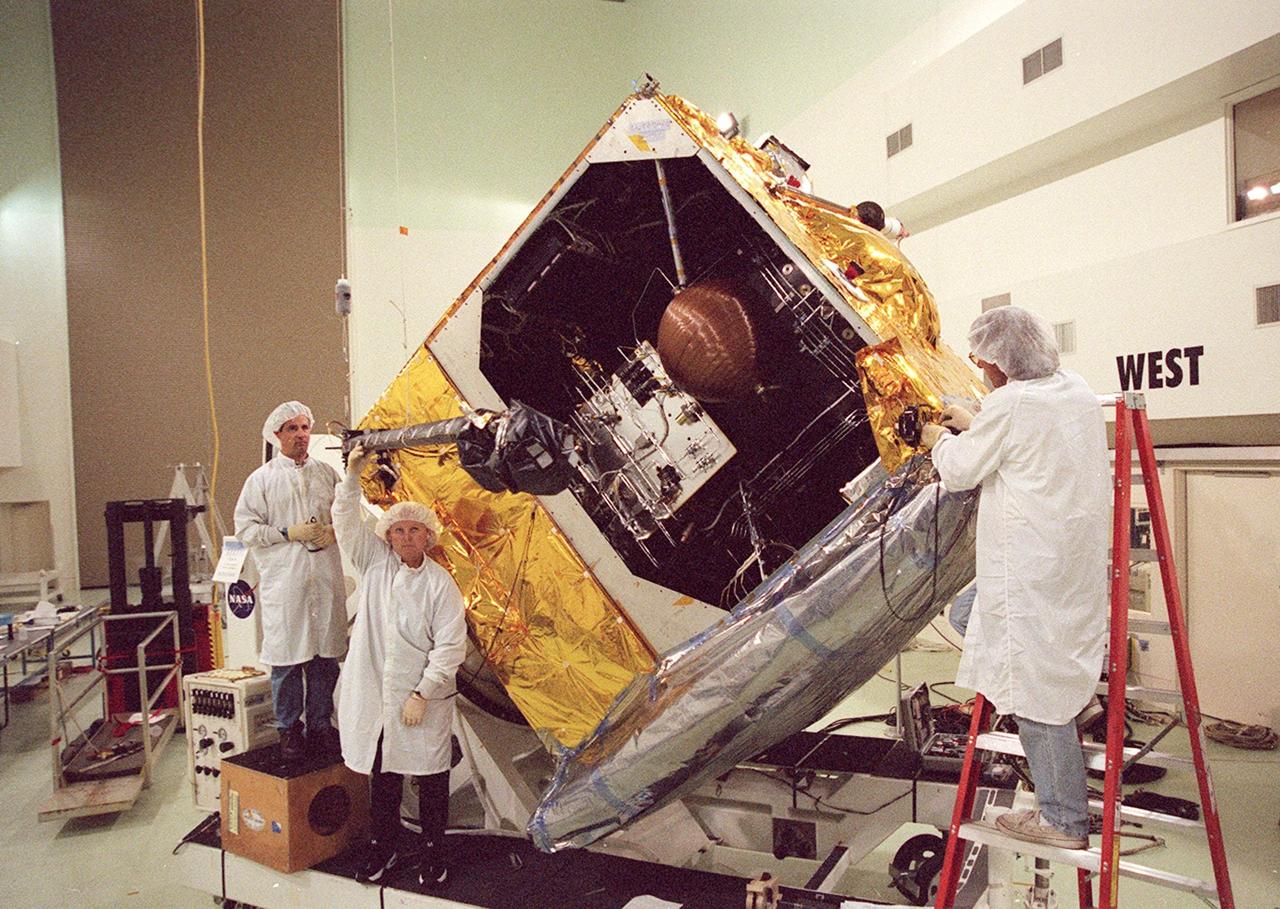

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., begin deploying the magnetometer boom on the GOES-M satellite. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station

At Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., an overhead crane lifts the GOES-M (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite) from the transporter. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite will undergo testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
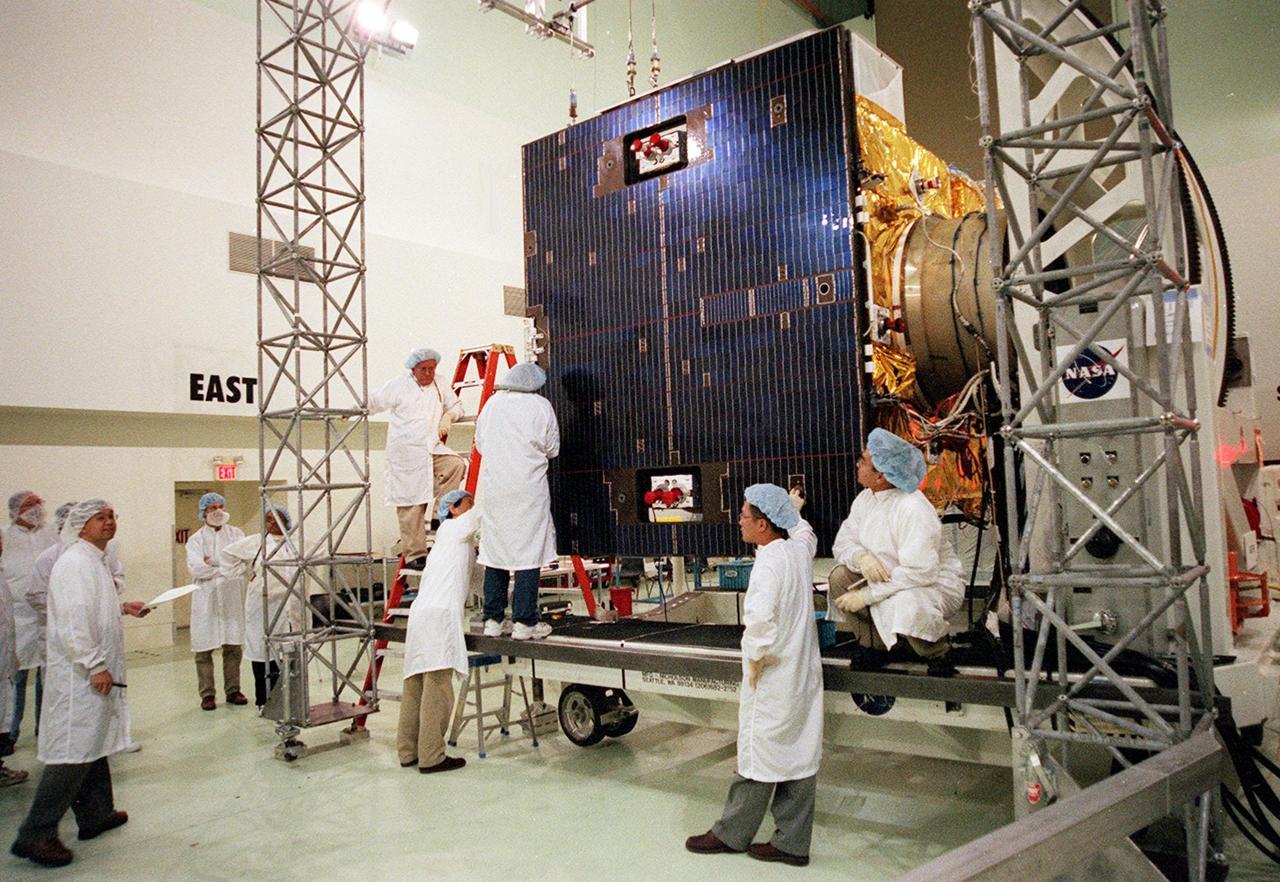

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., check the solar panel on the GOES-M satellite. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
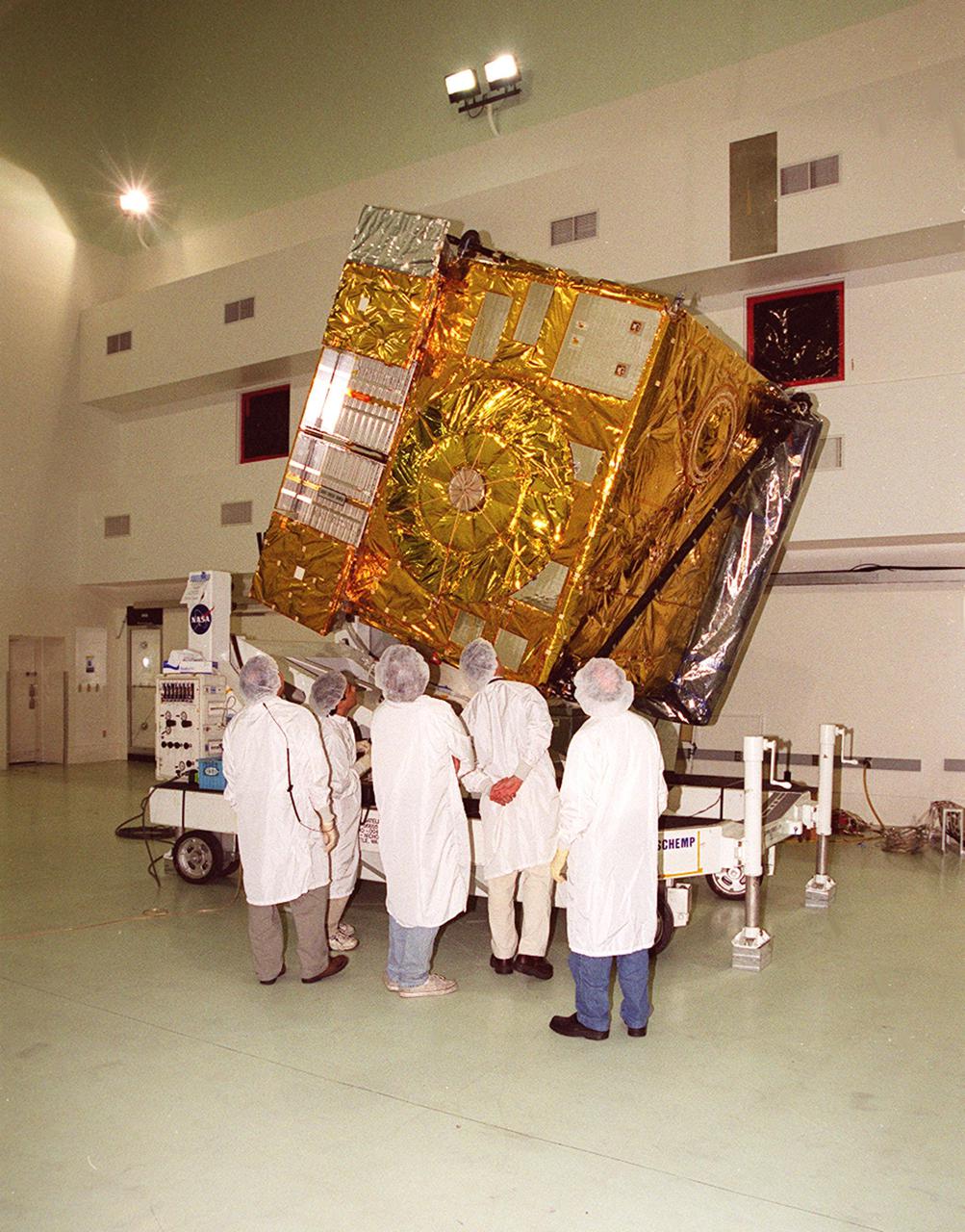

At Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., workers look over the GOES-M satellite after removal of its protective cover. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite will undergo testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
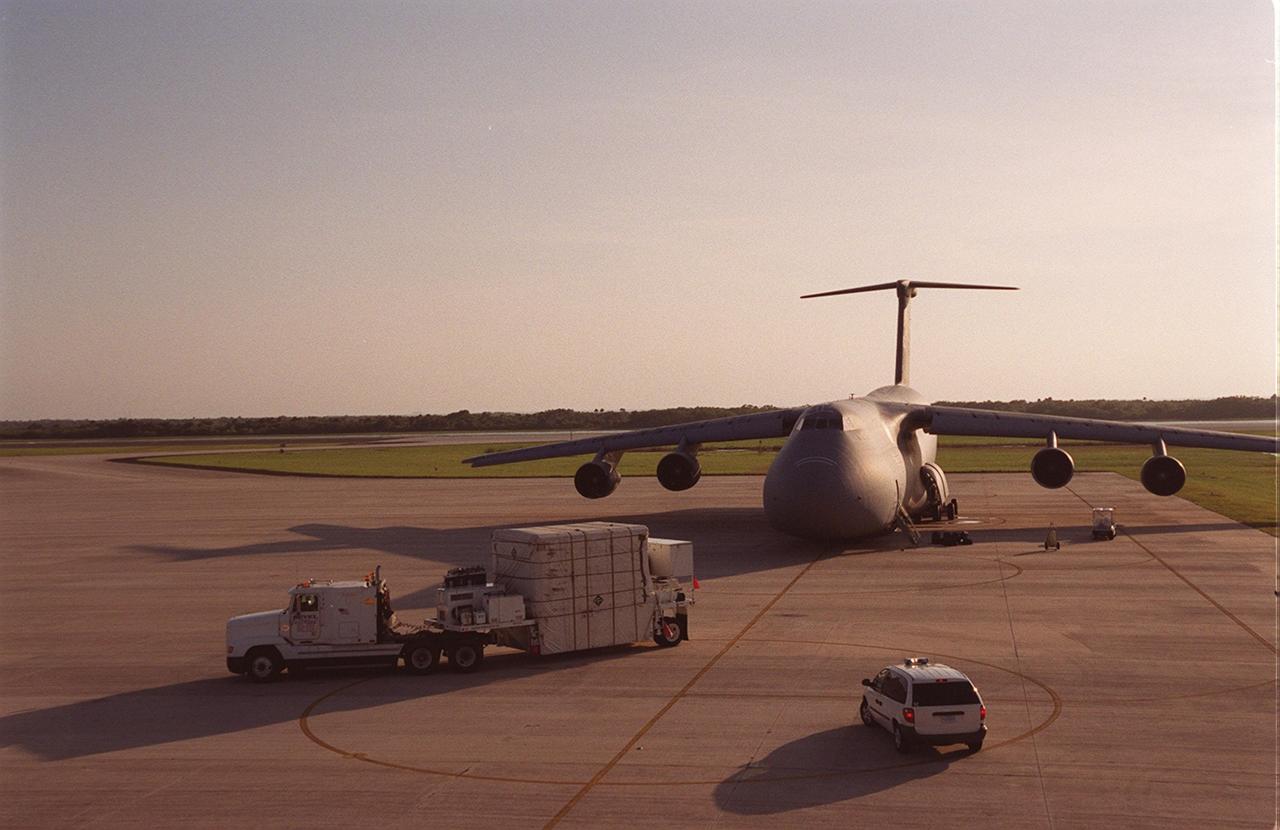

At the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility, the GOES-M satellite, encased in a container, begins its trek to Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., where it will undergo final testing. The GOES-M (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, I-M Series) provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking, and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to be launched on an Atlas-IIA booster, with a Centaur upper stage, July 12 from Launch Pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., confer about their findings after opening the solar panel on the GOES-M satellite. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
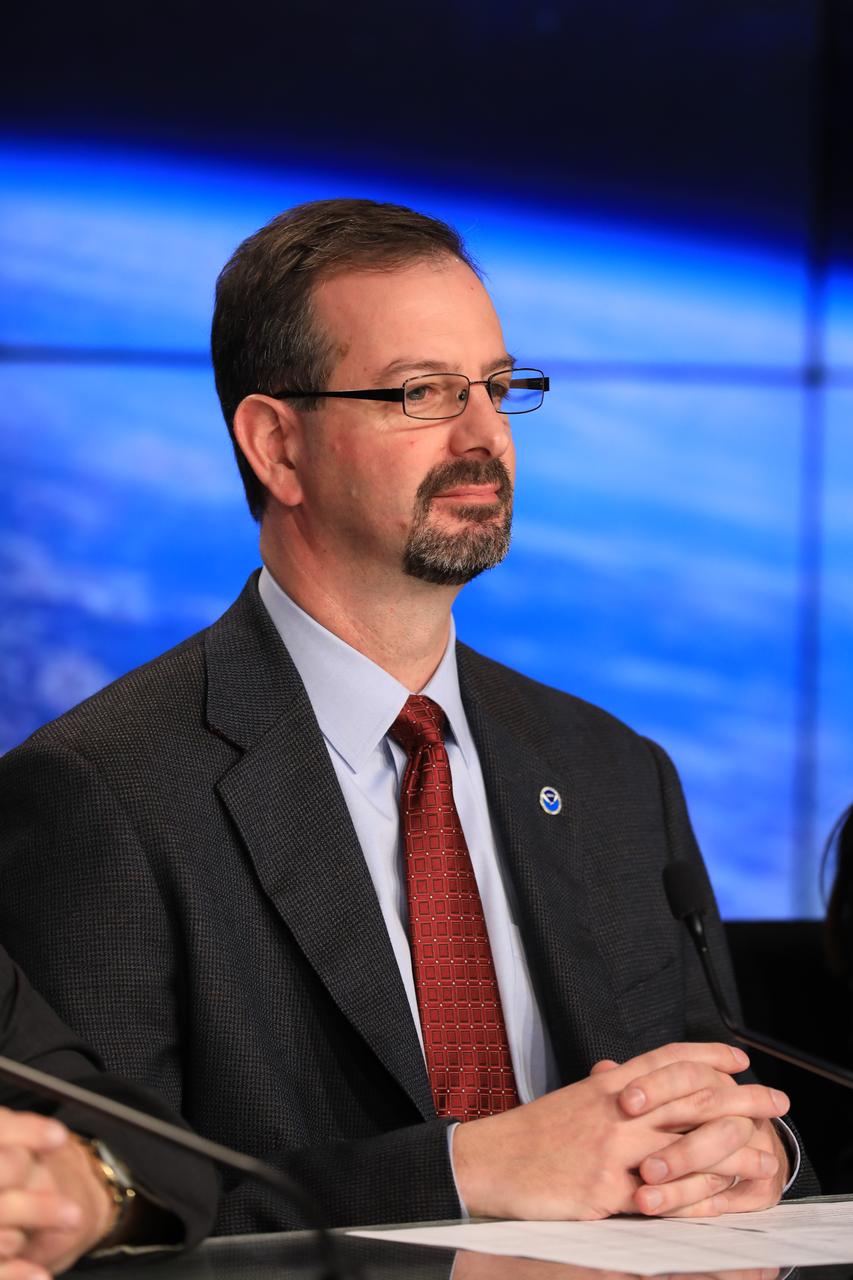

In the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium, Joseph A. Pica, director of the National Weather Service Office of Observations, speaks to the media during a mission briefing on the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R). GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation GOES satellites for NOAA, the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration. It will launch to a geostationary orbit over the western hemisphere to provide images of storms and help meteorologists predict severe weather conditionals and develop long-range forecasts.
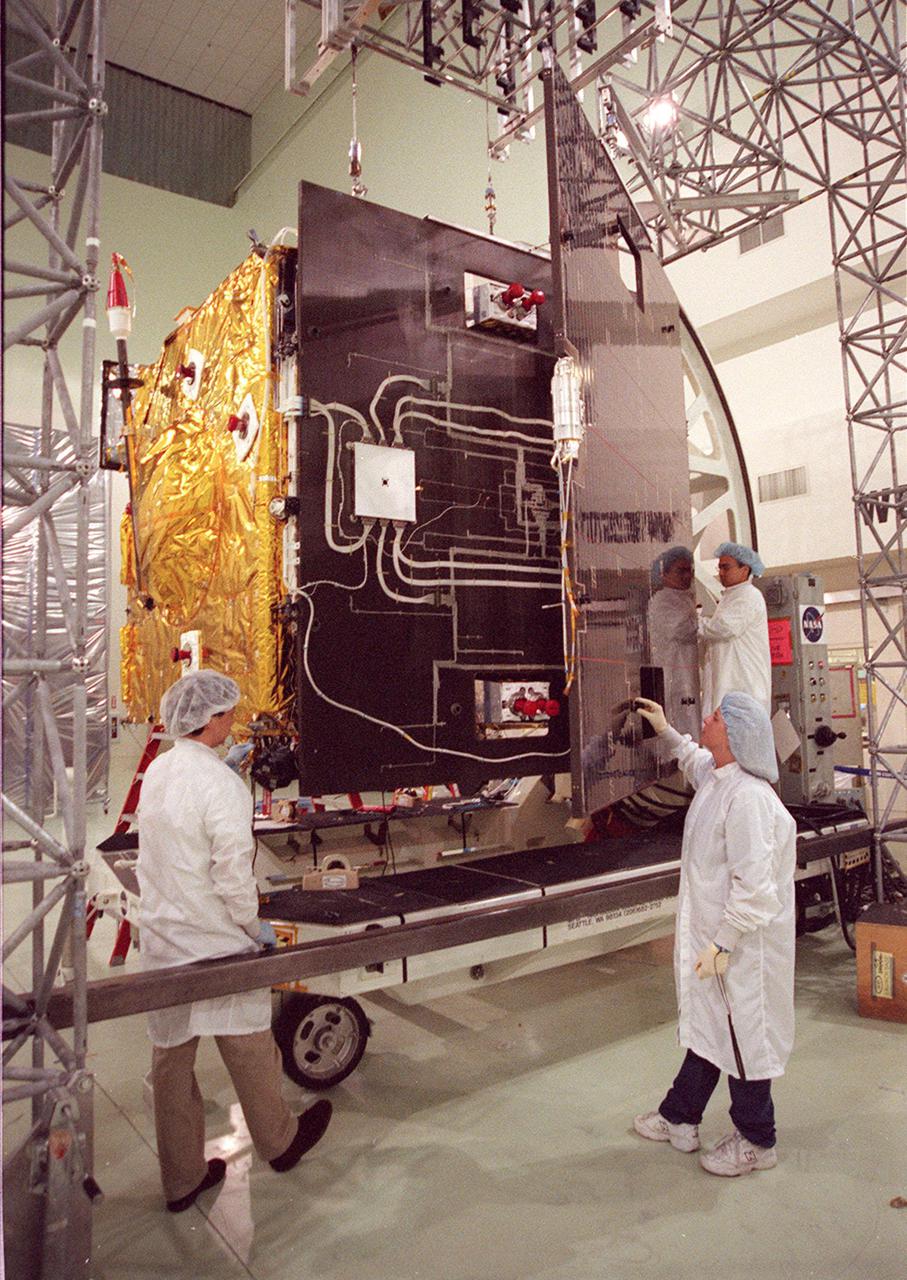

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., open the solar panel on the GOES-M satellite. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
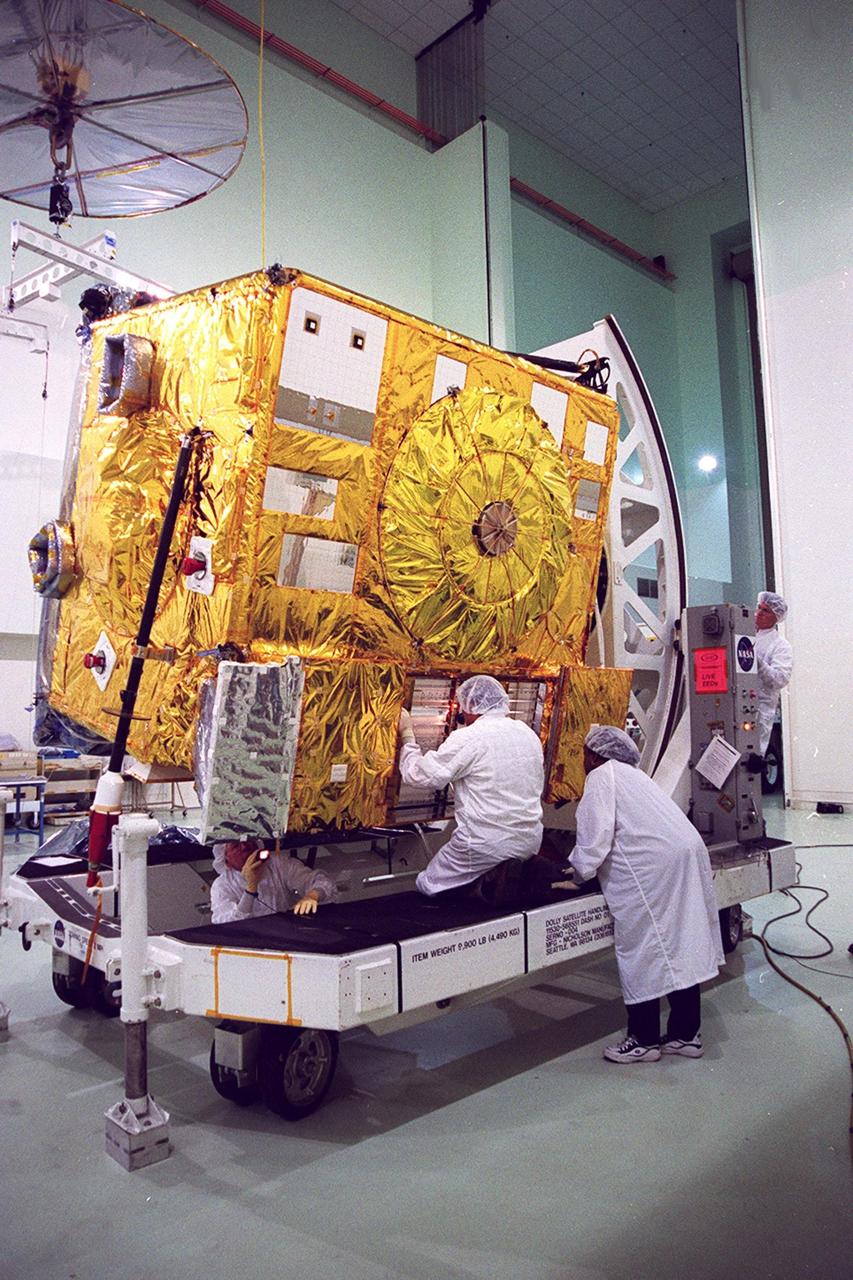

With the GOES-M satellite tilted on a workstand at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla, workers check out a part of the underside. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
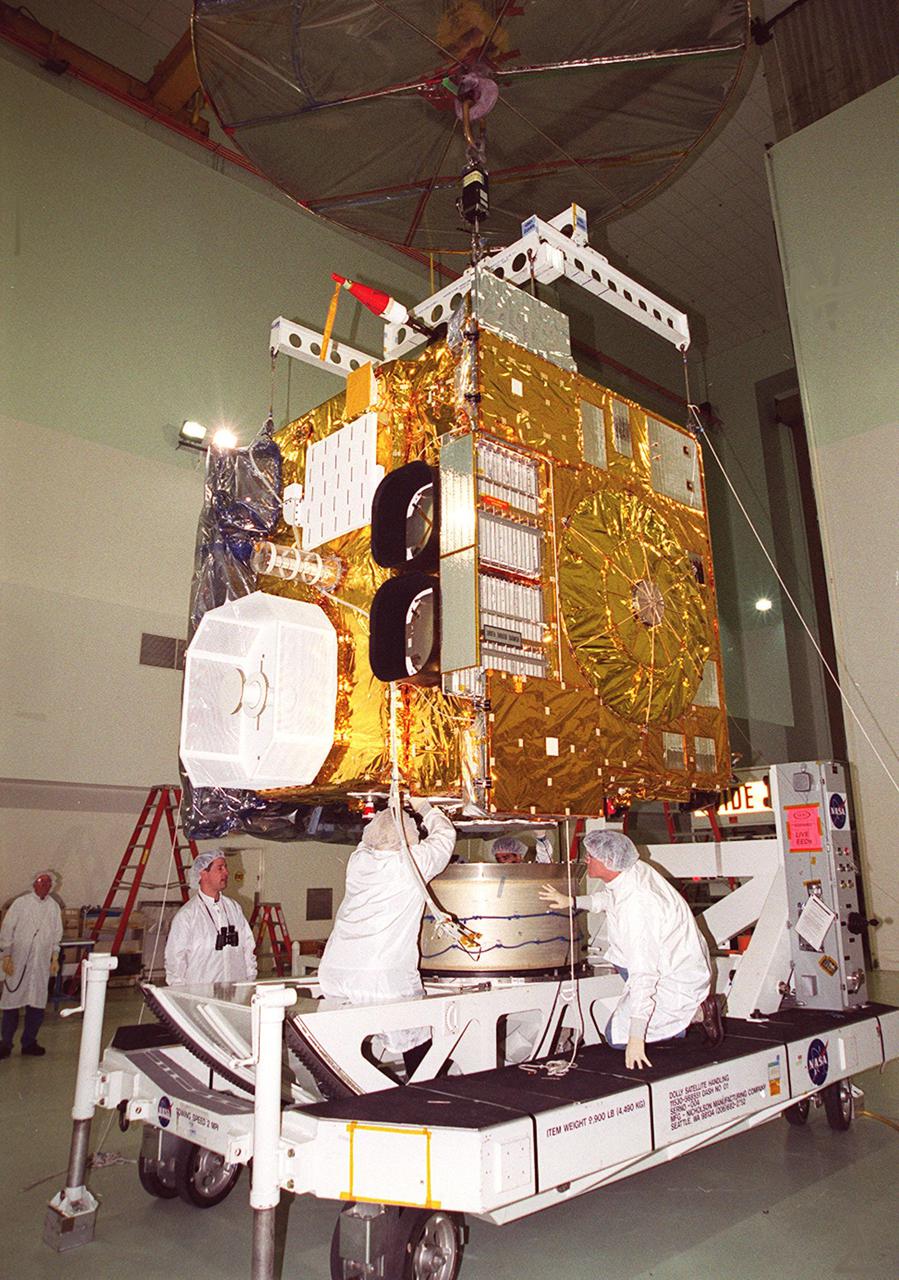

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., work on the GOES-M satellite. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
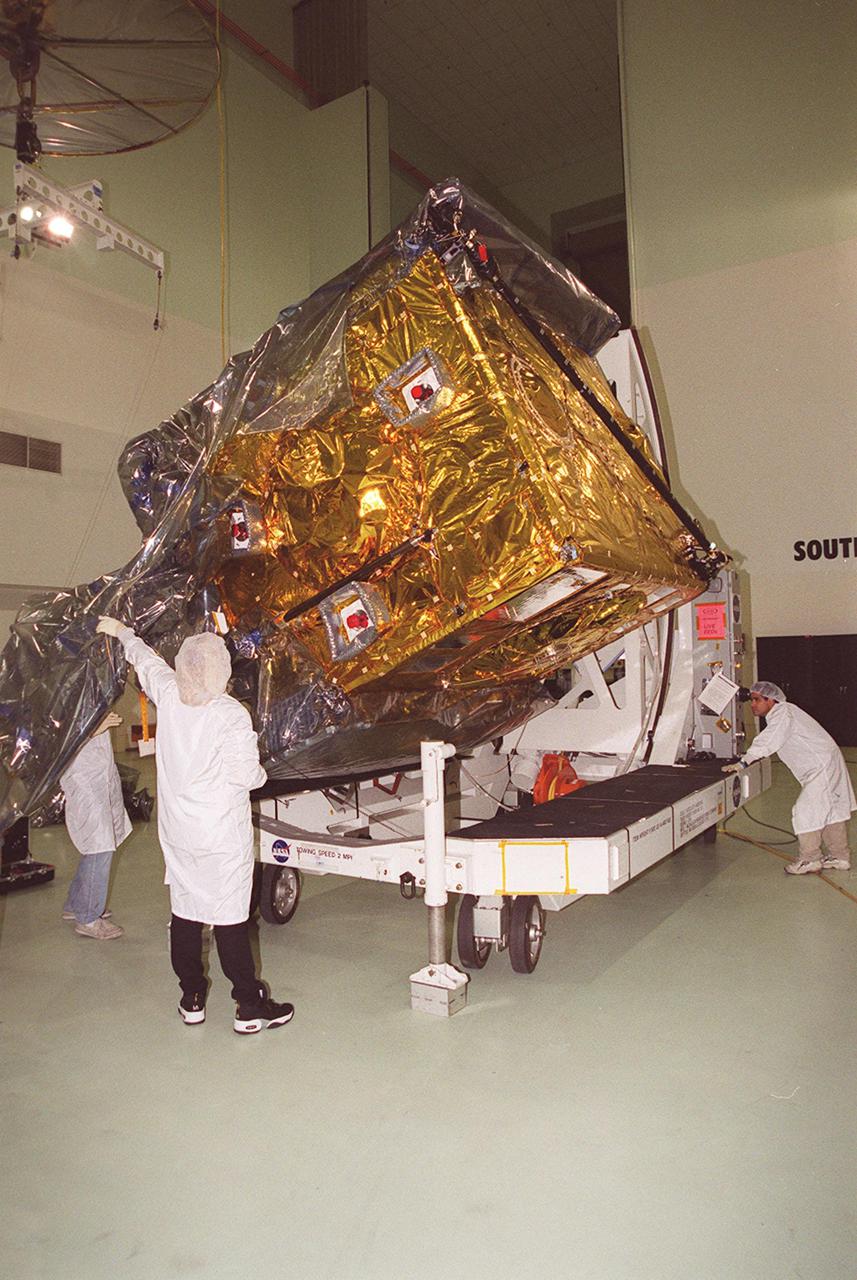

At Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., the GOES-M (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite) satellite is tilted on a workstand so that workers can remove the rest of the protective cover. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite will undergo testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
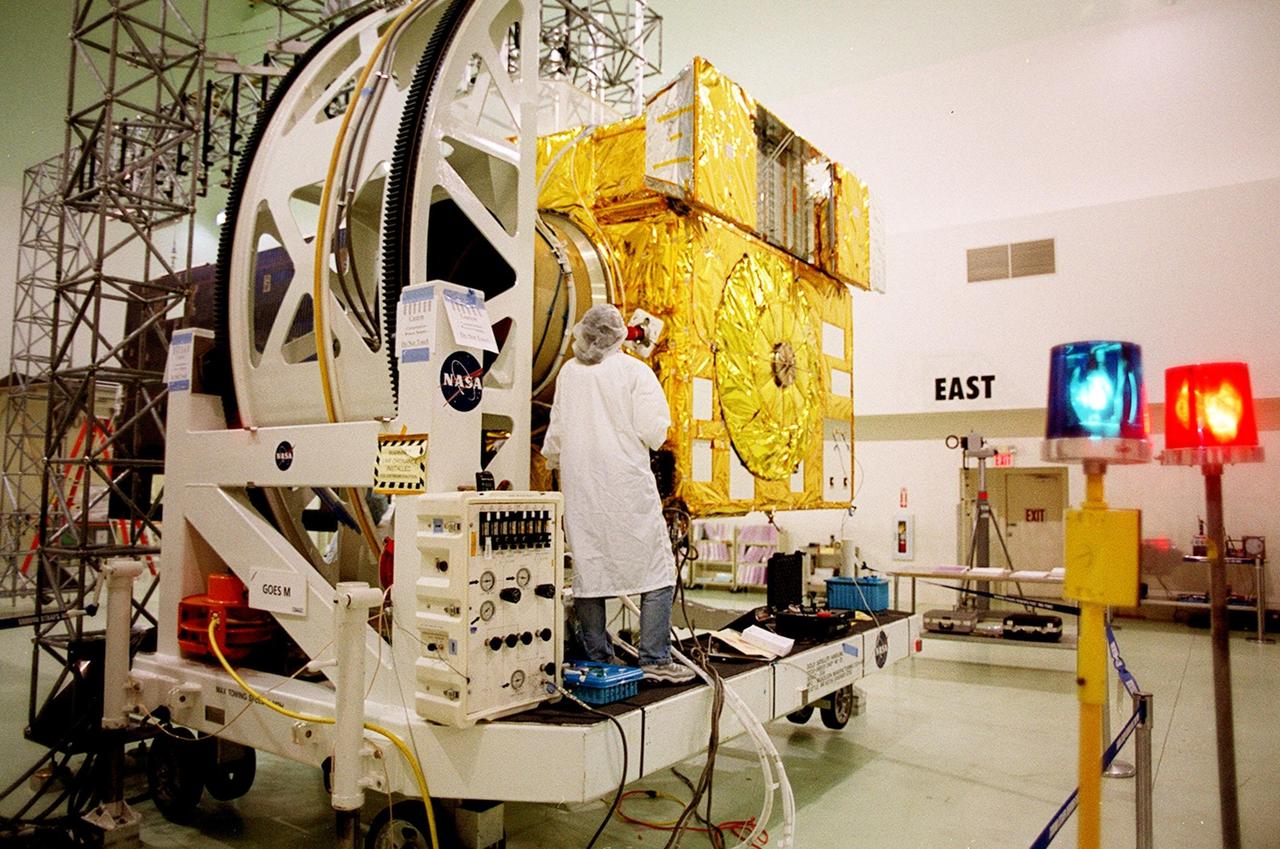

At Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., a worker checks components of the GOES-M satellite. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
At Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., a worker (right) turns the GOES-M satellite, bringing its side into view. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
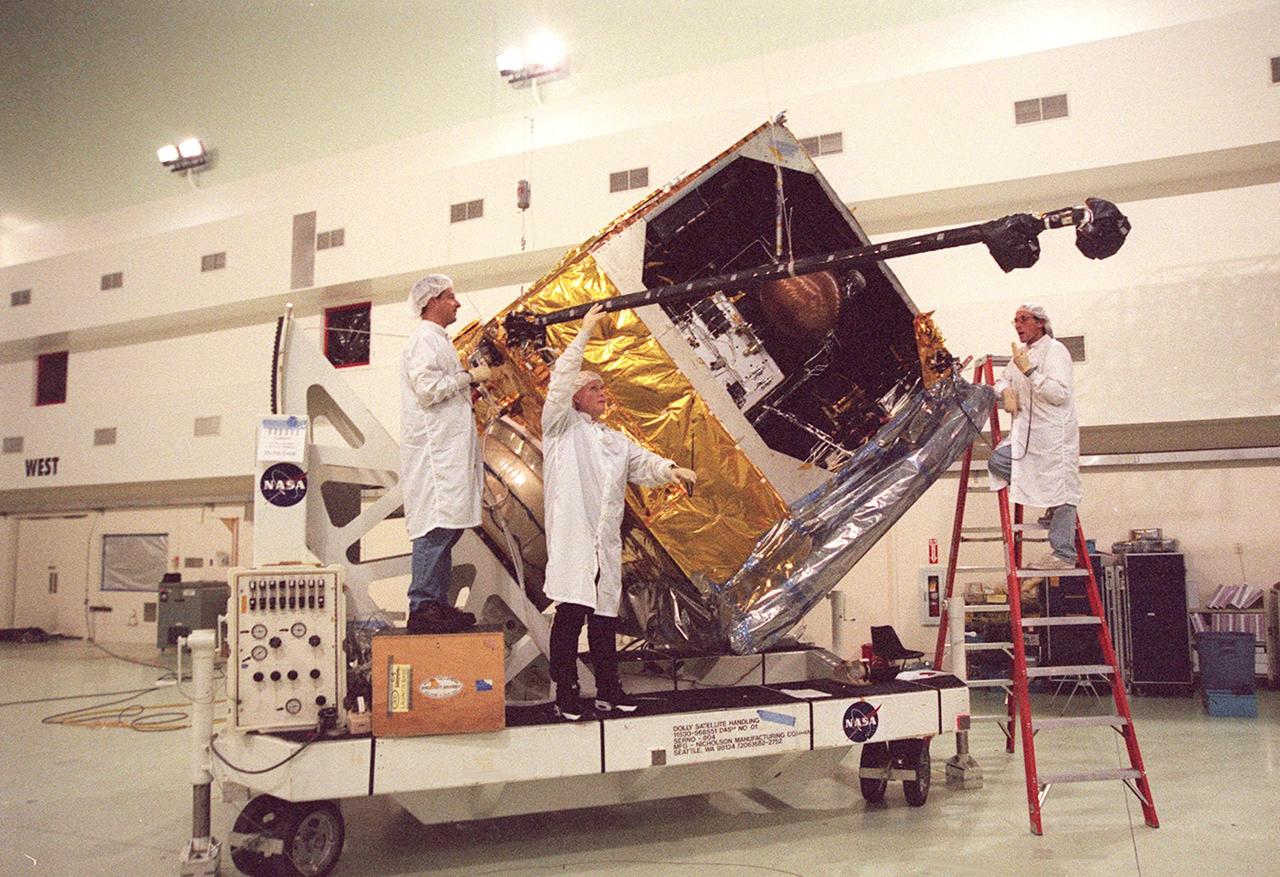

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., deploy the magnetometer boom on the GOES-M satellite. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
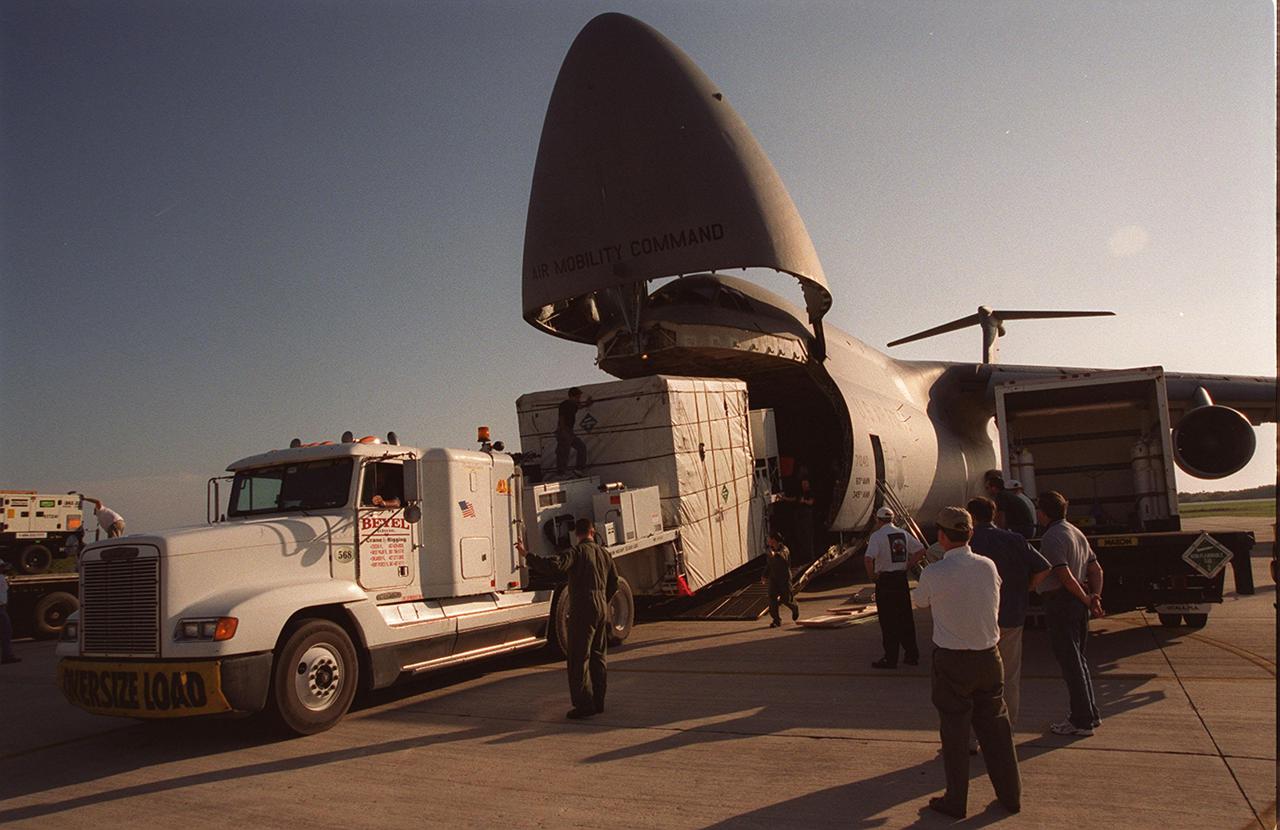

At the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility, the GOES-M satellite is offloaded from the yawning mouth of the C-5 aircraft. It will be transferred to Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., for final testing. The GOES-M (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, I-M Series) provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking, and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to be launched on an Atlas-IIA booster, with a Centaur upper stage, July 12 from Launch Pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
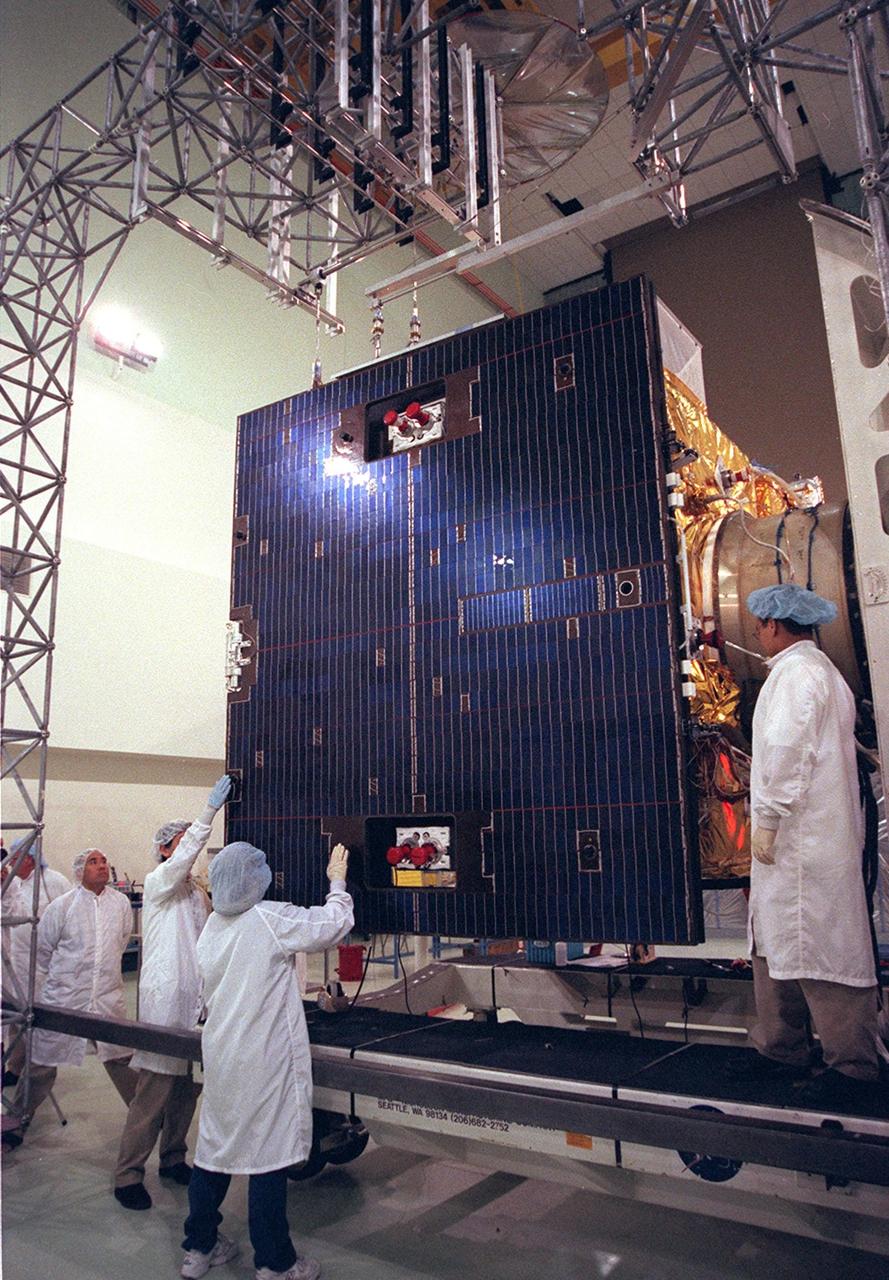

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., prepare to open the solar panel on the GOES-M satellite. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
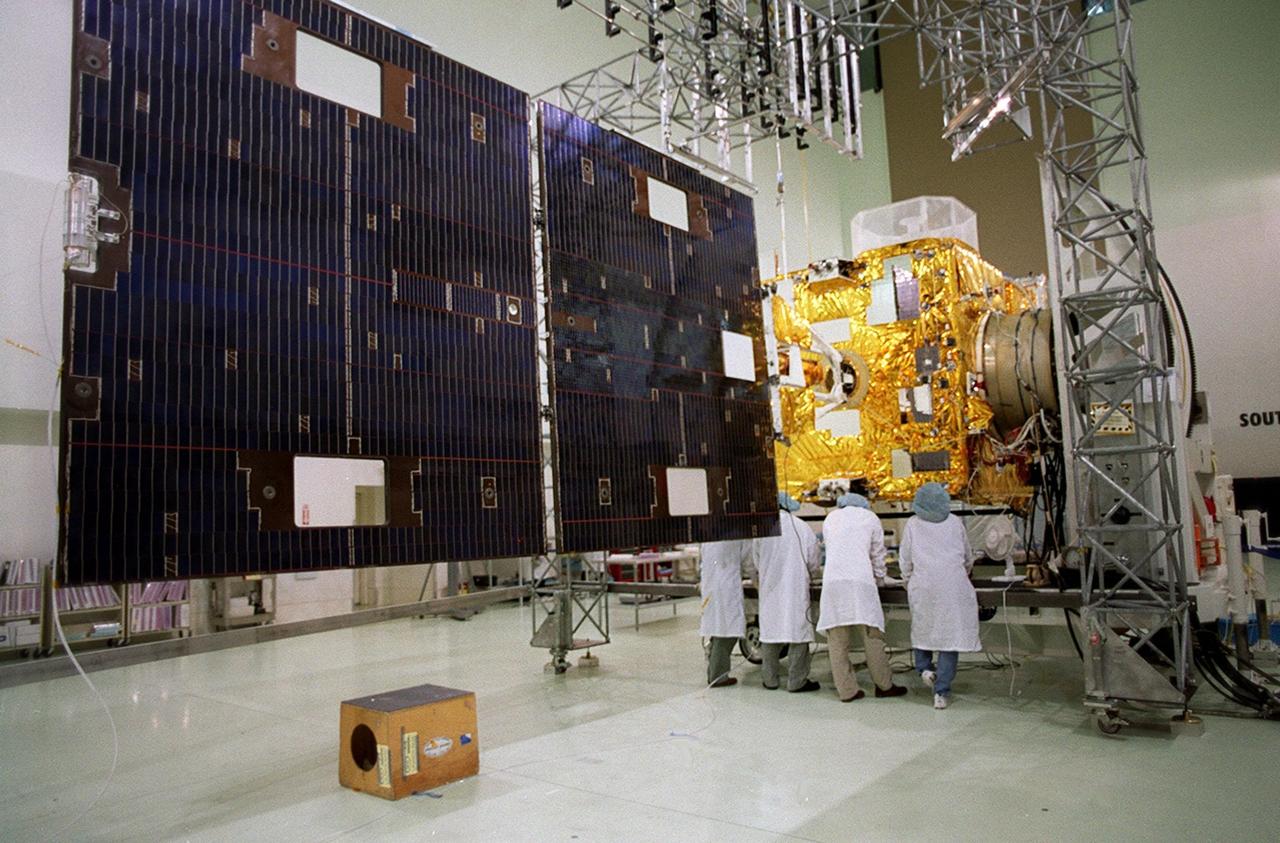

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., look at components on the GOES-M satellite after opening the solar panel. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
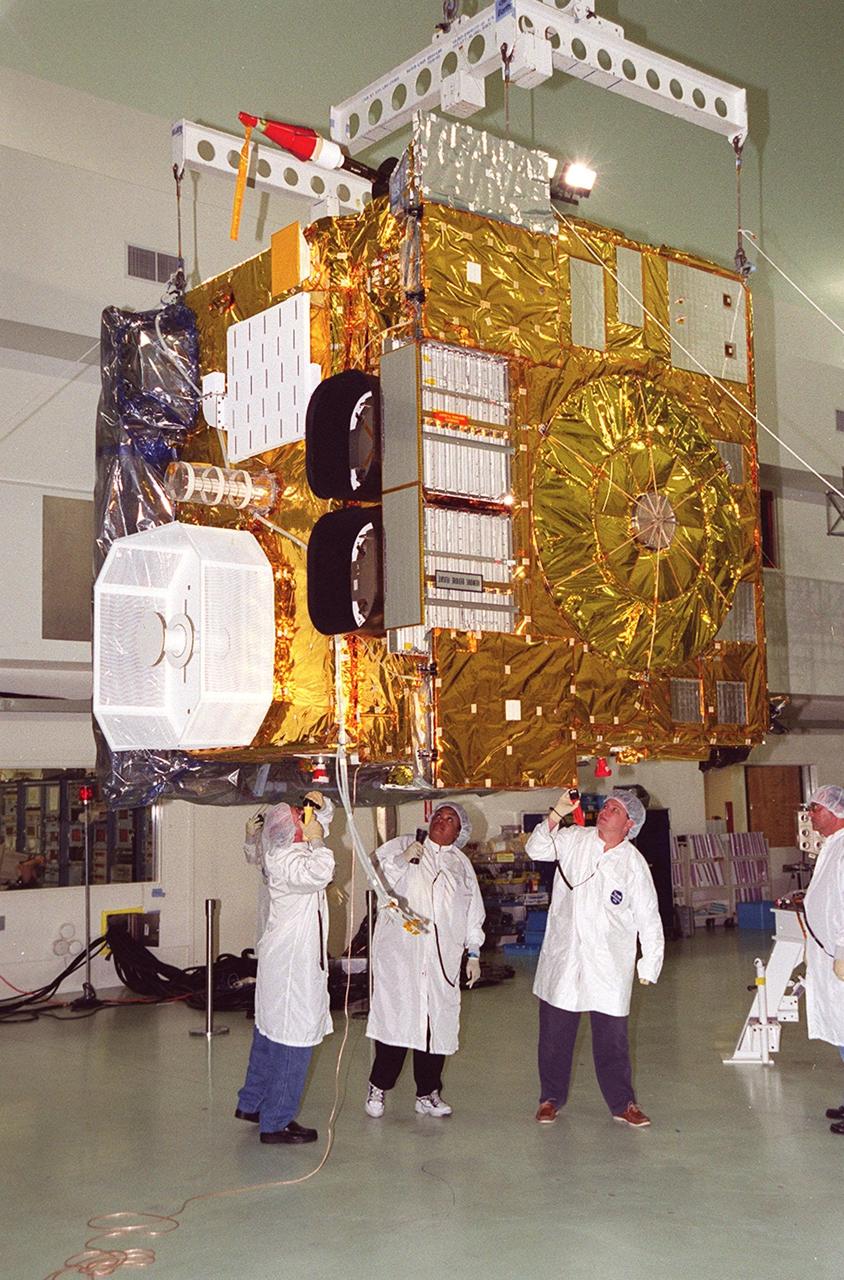

While an overhead crane lifts the GOES-M satellite at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., workers check the underside. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
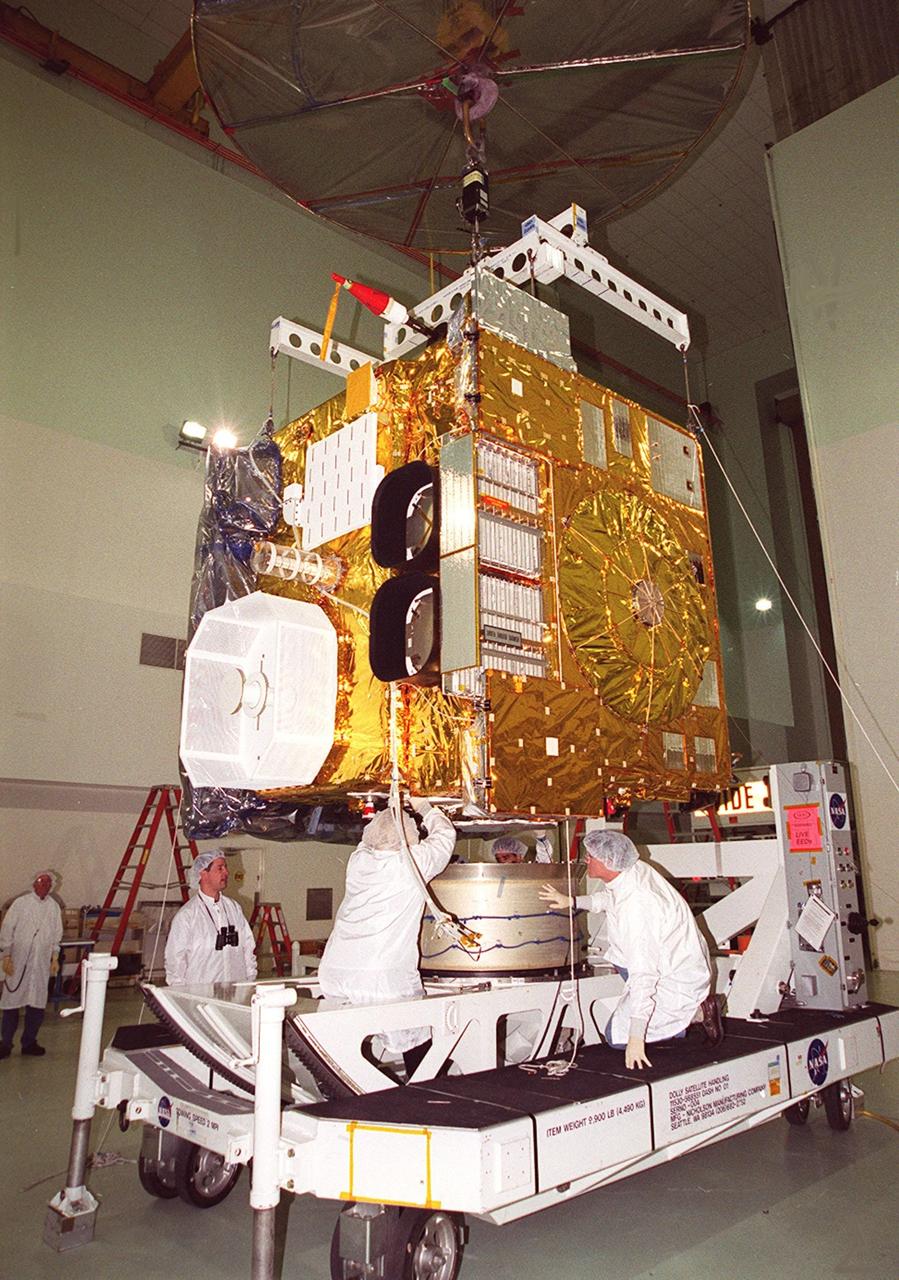

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., work on the GOES-M satellite. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
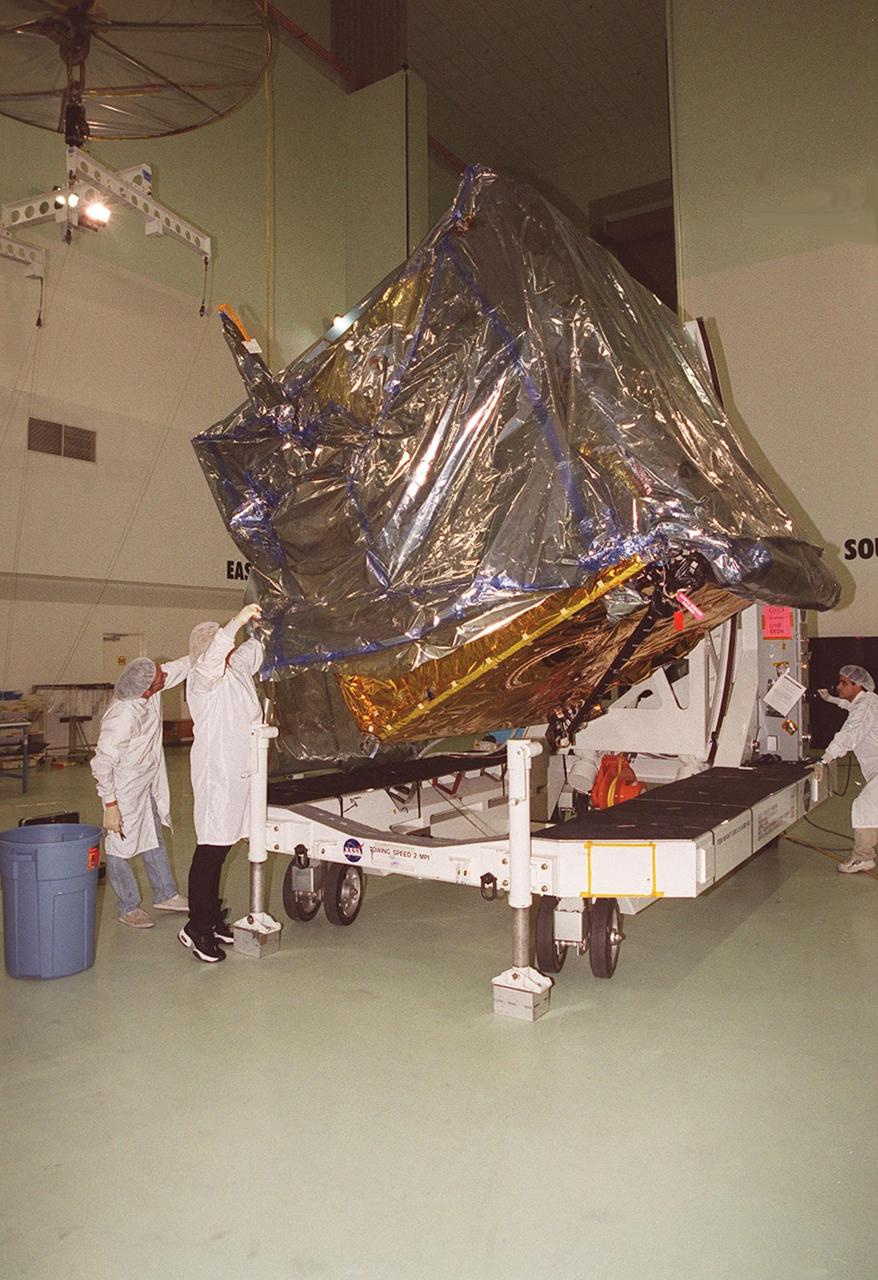

At Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., the GOES-M (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite) satellite is tilted on a workstand so that workers can remove part of the protective cover. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite will undergo testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
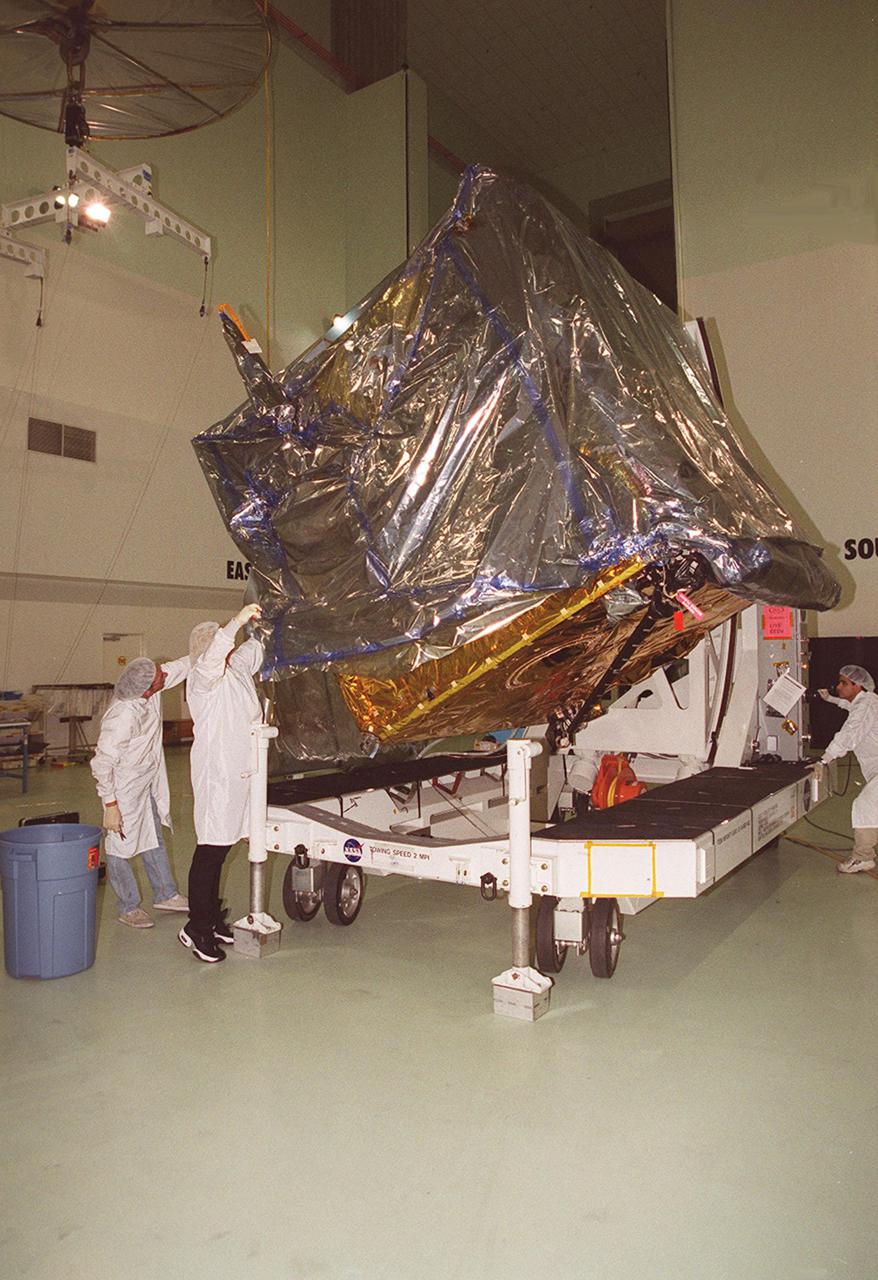

At Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., the GOES-M (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite) satellite is tilted on a workstand so that workers can remove part of the protective cover. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite will undergo testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
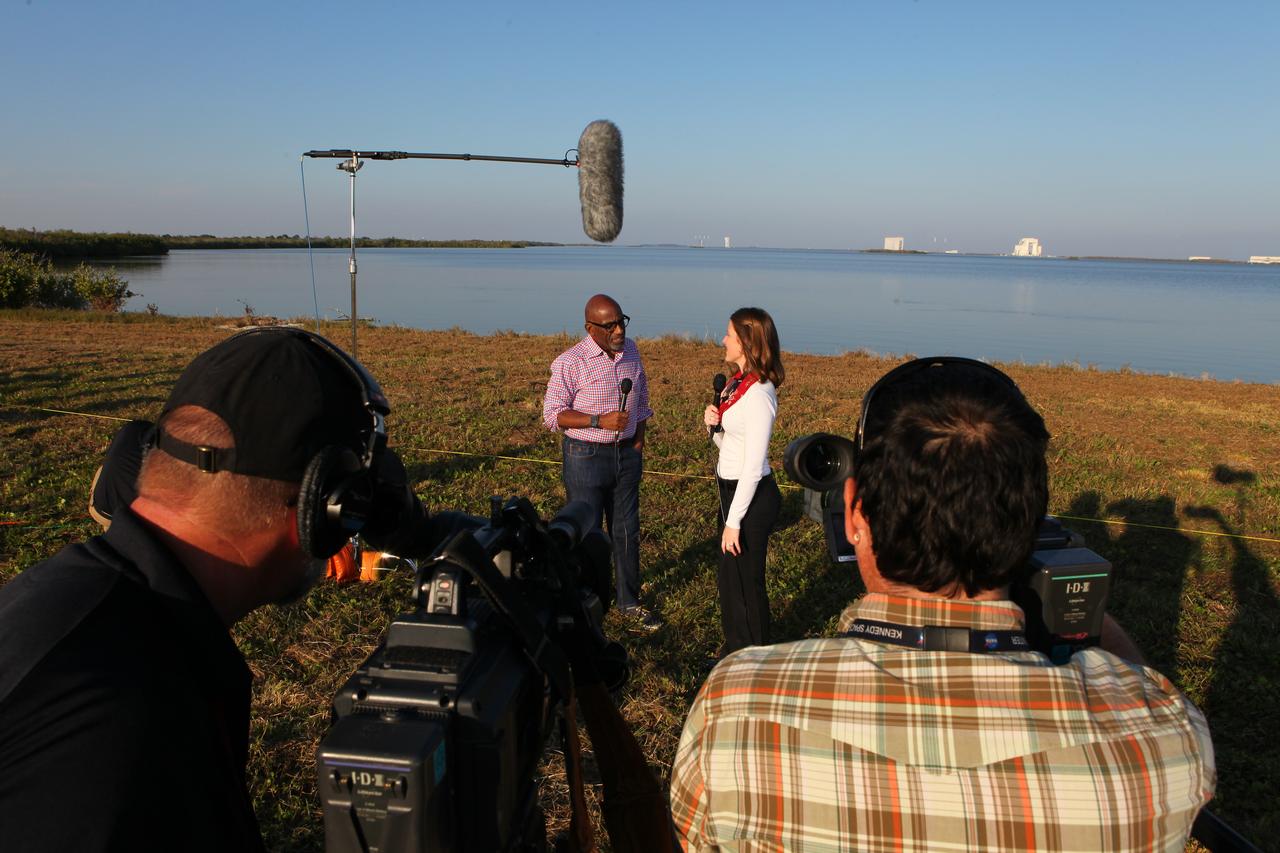

During the countdown for the launch of NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-R, Stephanie Martin of NASA Communications, right, interviews Al Roker, weather forecaster on NBC's "Today Show." GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation GOES satellites for NOAA, the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration. It will launch to a geostationary orbit over the western hemisphere to provide images of storms and help meteorologists predict severe weather conditionals and develop long-range forecasts.

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., observe the solar panel on the GOES-M satellite as they open it. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
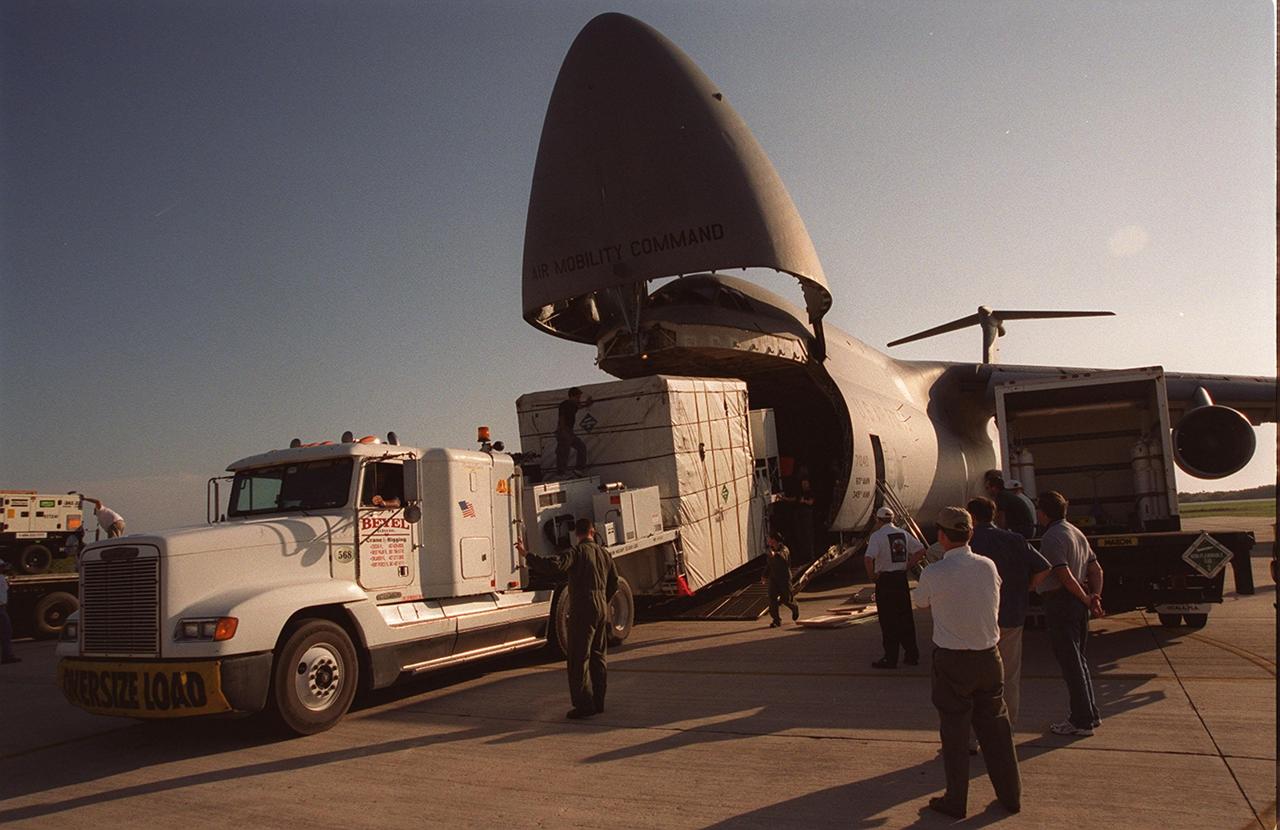

At the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility, the GOES-M satellite is offloaded from the yawning mouth of the C-5 aircraft. It will be transferred to Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., for final testing. The GOES-M (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, I-M Series) provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking, and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to be launched on an Atlas-IIA booster, with a Centaur upper stage, July 12 from Launch Pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
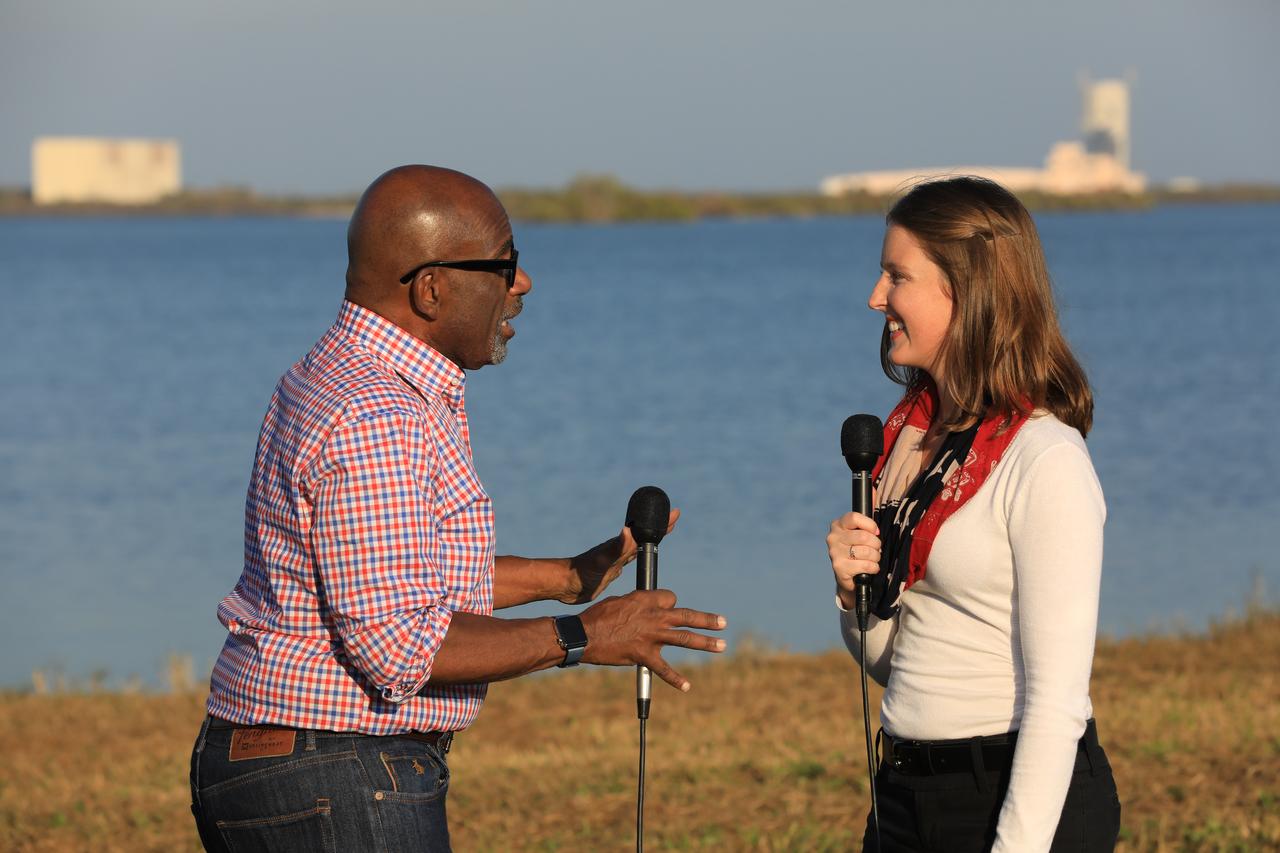

During the countdown for the launch of NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-R, Stephanie Martin of NASA Communications, right, interviews Al Roker, weather forecaster on NBC's "Today Show." GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation GOES satellites for NOAA, the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration. It will launch to a geostationary orbit over the western hemisphere to provide images of storms and help meteorologists predict severe weather conditionals and develop long-range forecasts.
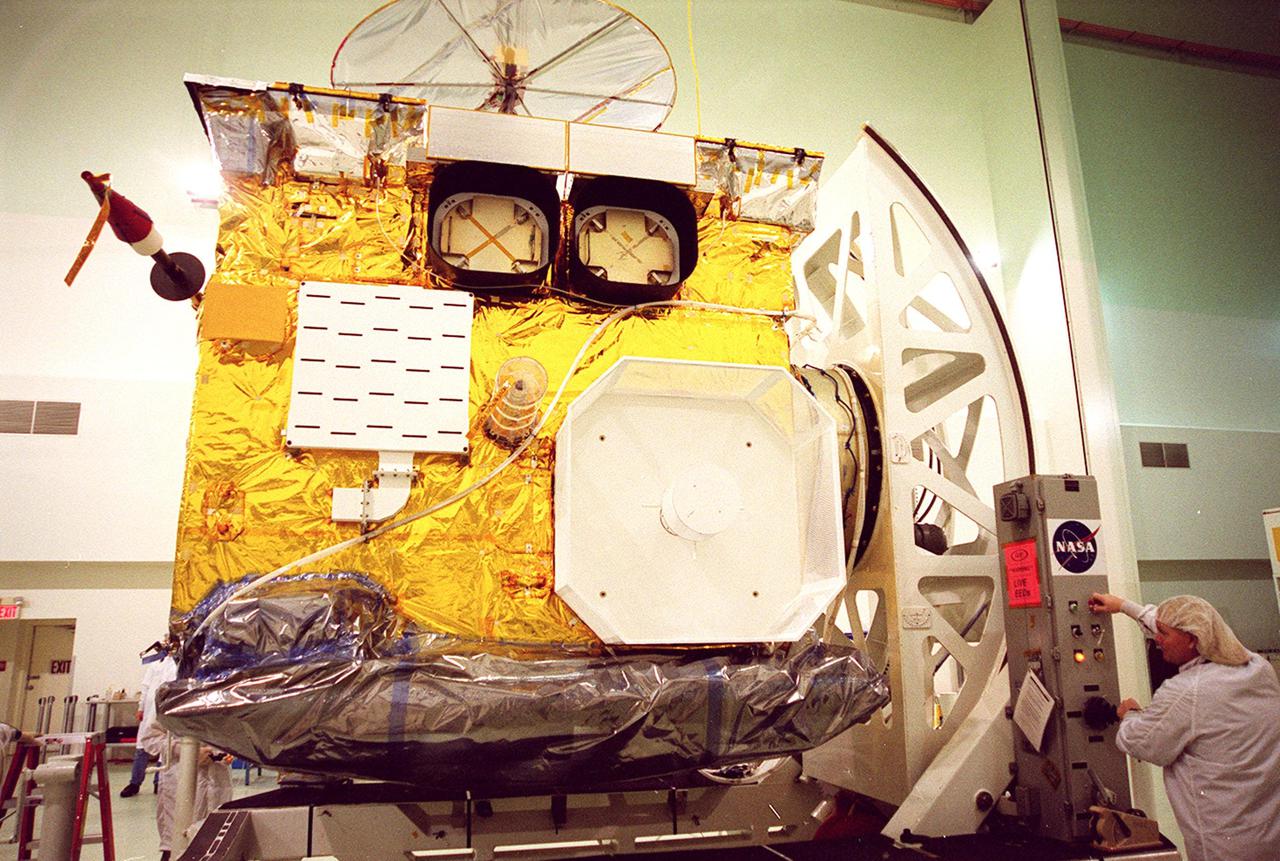
At Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., a worker (right) turns the GOES-M satellite, bringing its side into view. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
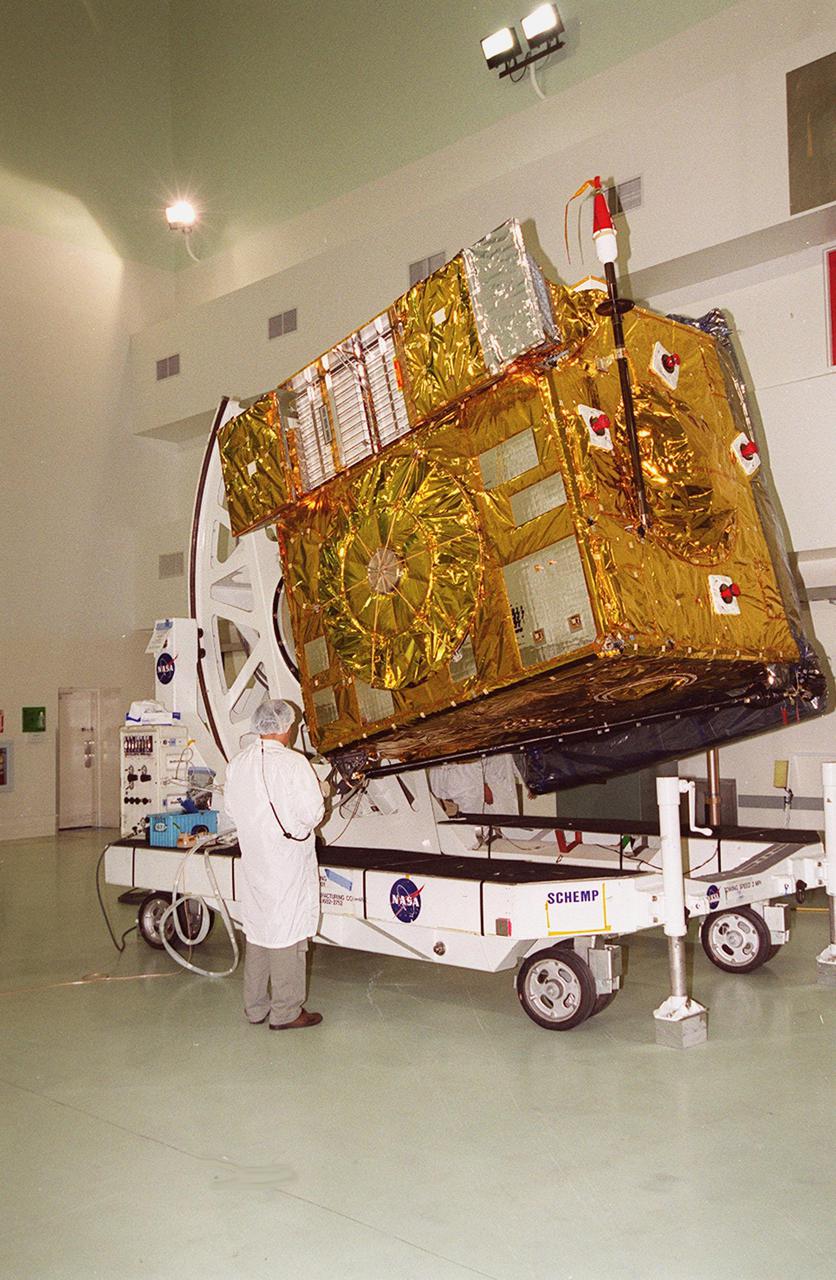

At Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., the GOES-M satellite is lifted at an angle on a workstand. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
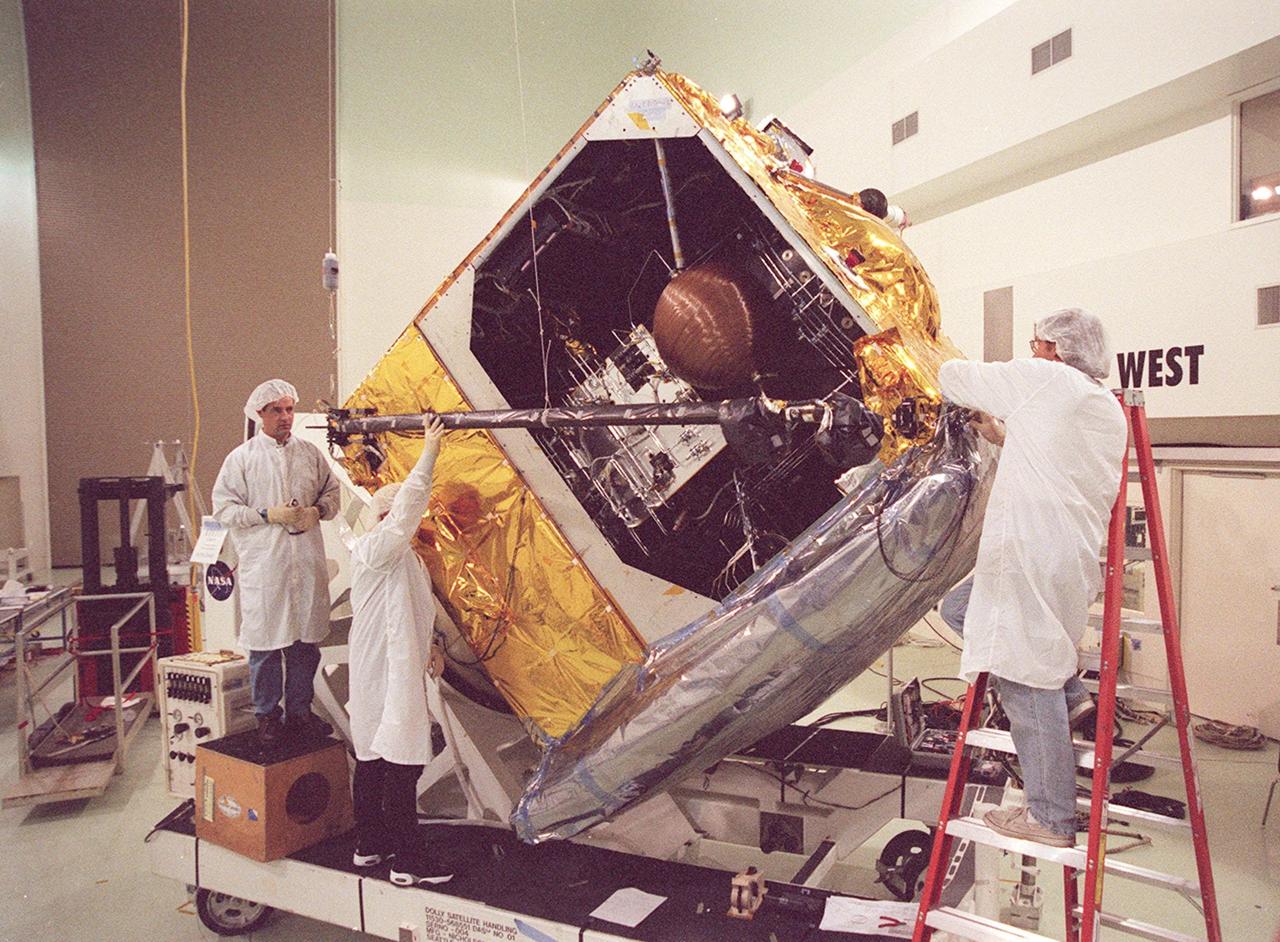

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., begin deploying the magnetometer boom on the GOES-M satellite. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
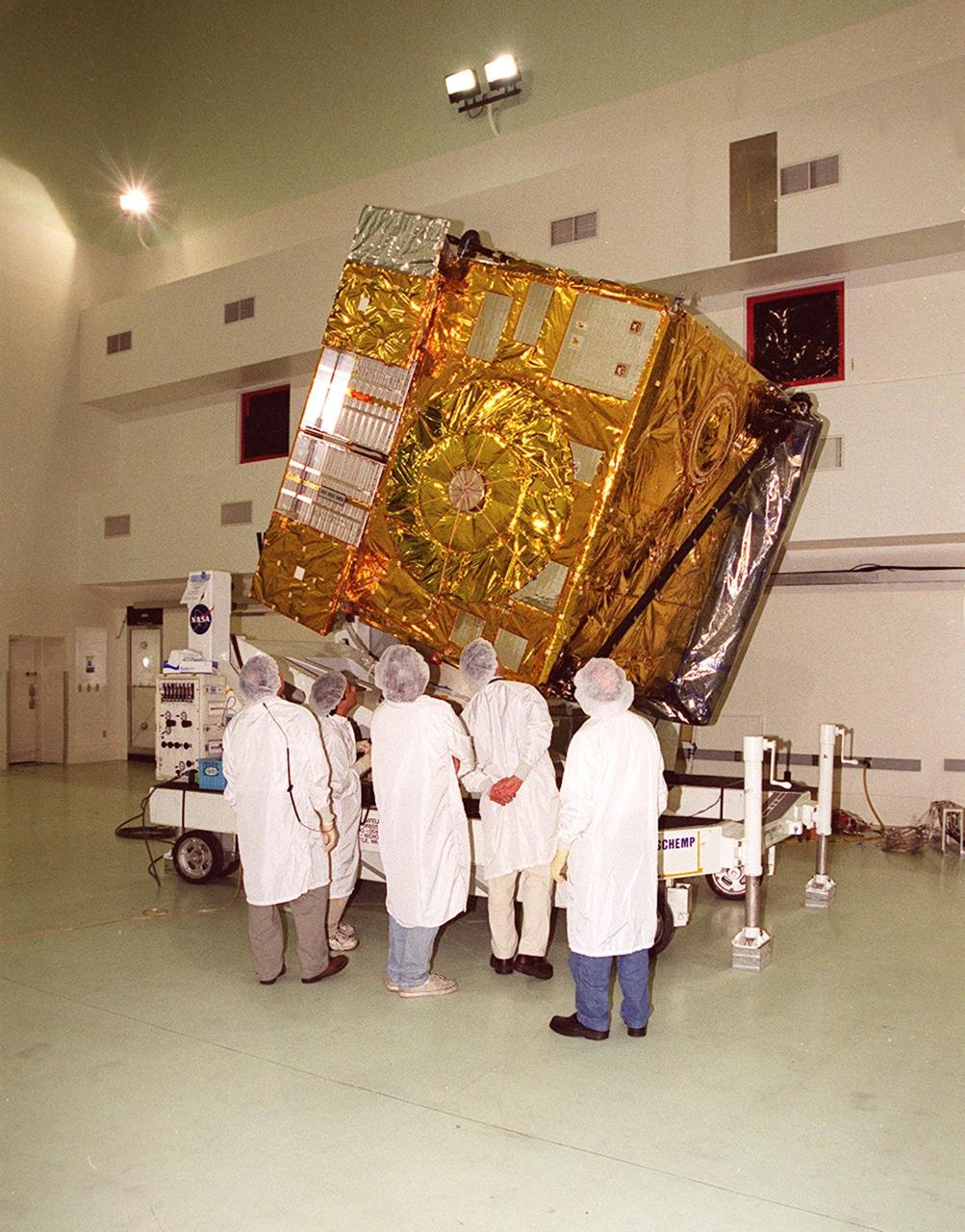

At Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., workers look over the GOES-M satellite after removal of its protective cover. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite will undergo testing at Astrotech before its scheduled launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
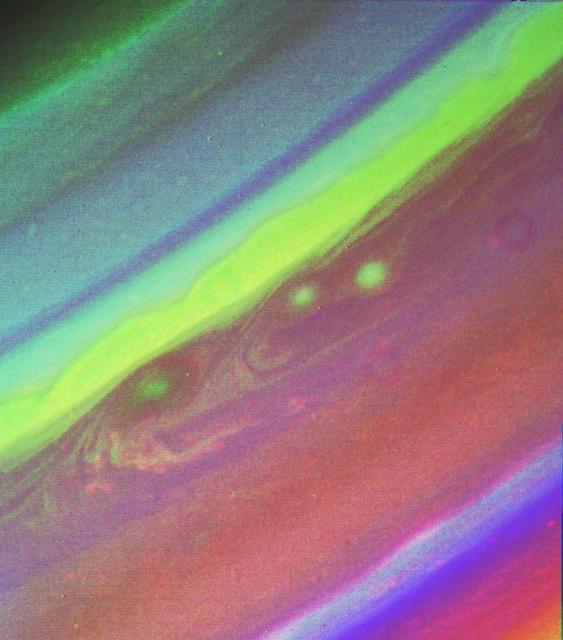
This false color picture of Saturn’s northern hemisphere was assembled from ultraviolet, violet and green images obtained Aug. 19 by Voyager 2 from a range of 7.1 million kilometers (4.4 million miles). The several weather patterns evident include three spots flowing westward at about 15 meters-per-second (33 mph). Although the cloud system associated with the western-most spot is part of this flow, the spot itself moves eastward at about 30 meters-per-second (65 mph). Their joint flow shows the anti-cyclonic rotation of the spot, which is about 3,000 km. (1,900 mi.) in diameter. The ribbon- like feature to the north marks a high-speed jet where wind speeds approach 150 meters-per-second (330 mph). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01365
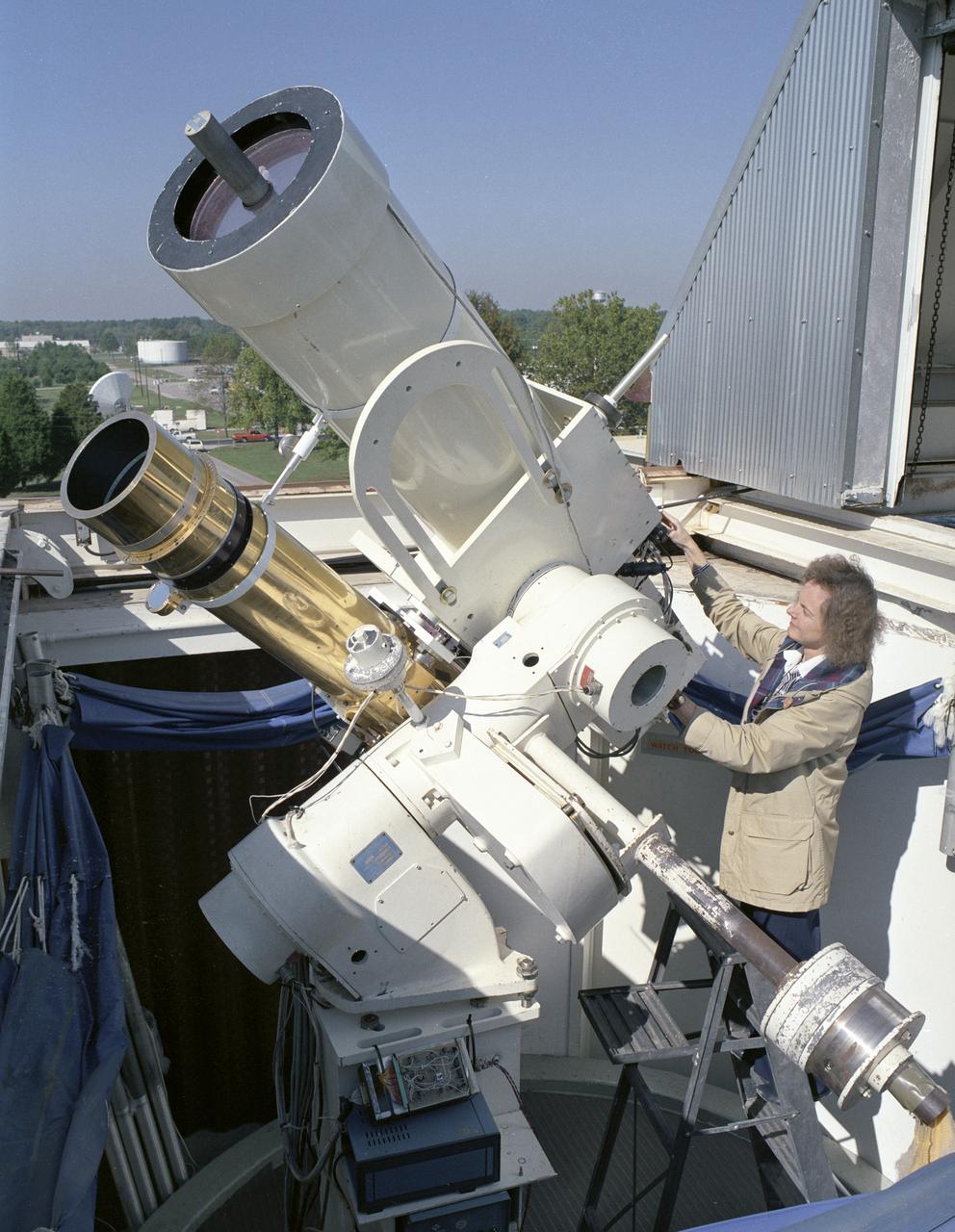

Using the Solar Vector Magnetograph, a solar observation facility at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), scientists from the National Space Science and Technology Center (NSSTC) in Huntsville, Alabama, are monitoring the explosive potential of magnetic areas of the Sun. This effort could someday lead to better prediction of severe space weather, a phenomenon that occurs when blasts of particles and magnetic fields from the Sun impact the magnetosphere, the magnetic bubble around the Earth. When massive solar explosions, known as coronal mass ejections, blast through the Sun's outer atmosphere and plow toward Earth at speeds of thousands of miles per second, the resulting effects can be harmful to communication satellites and astronauts outside the Earth's magnetosphere. Like severe weather on Earth, severe space weather can be costly. On the ground, the magnetic storm wrought by these solar particles can knock out electric power. The researchers from MSFC and NSSTC's solar physics group develop instruments for measuring magnetic fields on the Sun. With these instruments, the group studies the origin, structure, and evolution of the solar magnetic field and the impact it has on Earth's space environment. This photograph shows the Solar Vector Magnetograph and Dr. Mona Hagyard of MSFC, the director of the observatory who leads the development, operation and research program of the Solar Vector Magnetograph.
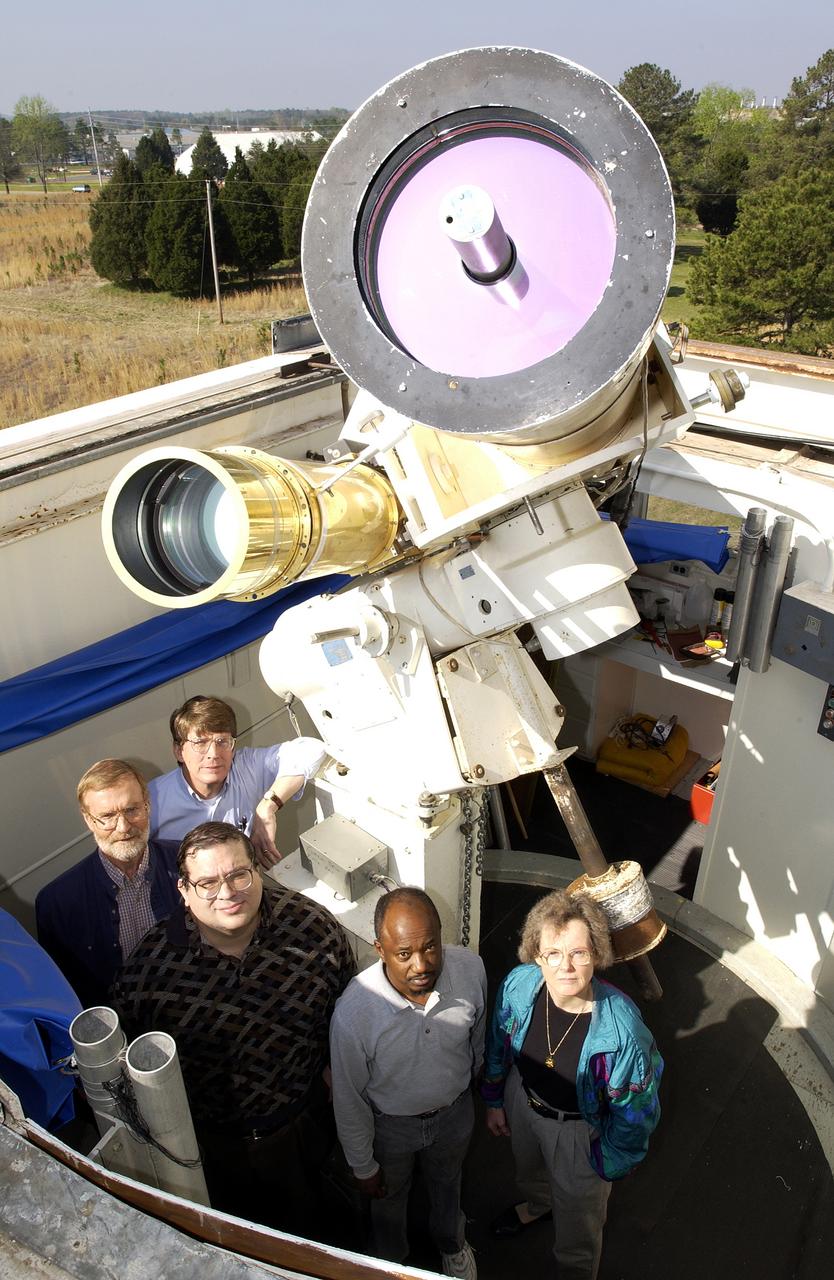

Using the Solar Vector Magnetograph, a solar observation facility at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), scientists from the National Space Science and Technology Center (NSSTC) in Huntsville, Alabama, are monitoring the explosive potential of magnetic areas of the Sun. This effort could someday lead to better prediction of severe space weather, a phenomenon that occurs when blasts of particles and magnetic fields from the Sun impact the magnetosphere, the magnetic bubble around the Earth. When massive solar explosions, known as coronal mass ejections, blast through the Sun's outer atmosphere and plow toward Earth at speeds of thousands of miles per second, the resulting effects can be harmful to communication satellites and astronauts outside the Earth's magnetosphere. Like severe weather on Earth, severe space weather can be costly. On the ground, magnetic storms wrought by these solar particles can knock out electric power. Photographed are a group of contributing researchers in front of the Solar Vector Magnetograph at MSFC. The researchers are part of NSSTC's solar physics group, which develops instruments for measuring magnetic fields on the Sun. With these instruments, the group studies the origin, structure, and evolution of the solar magnetic fields and the impact they have on Earth's space environment.
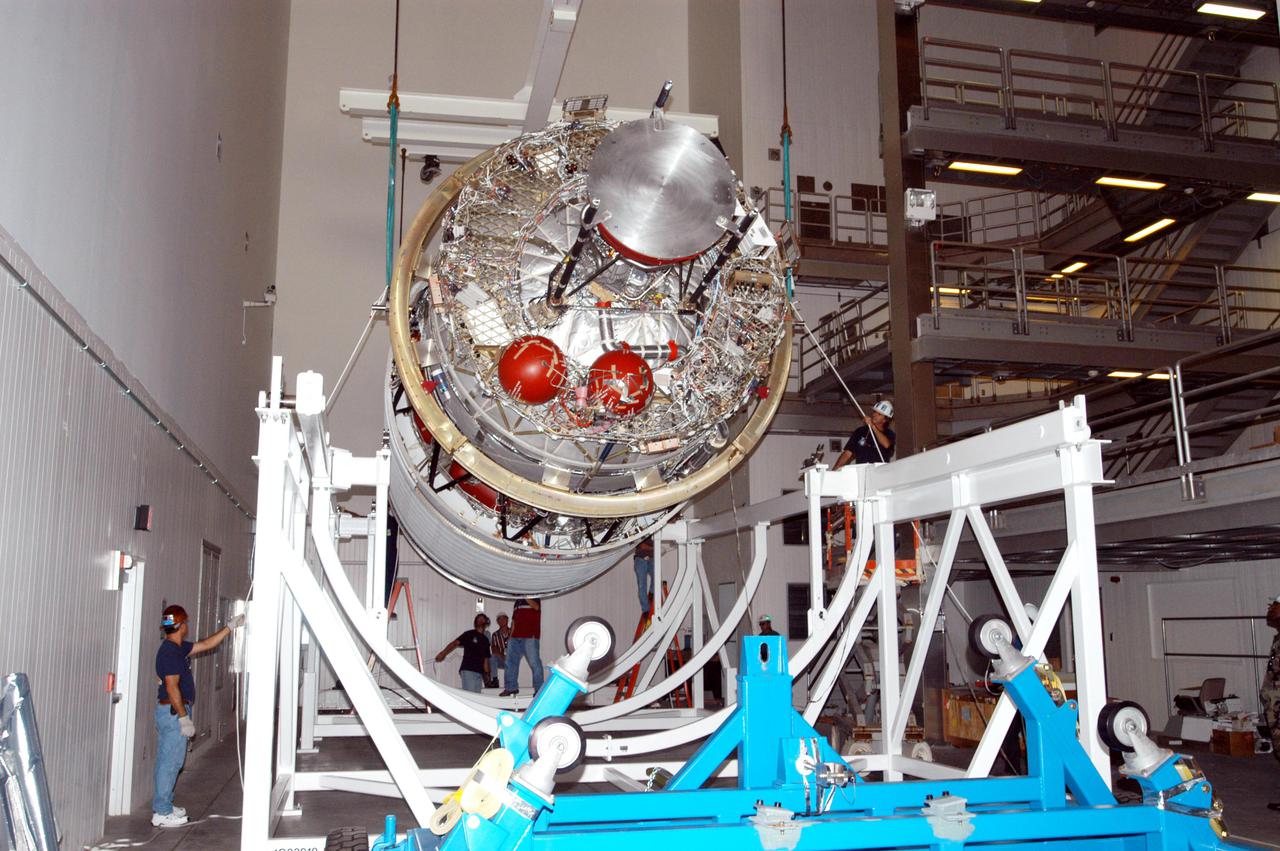
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Boeing Delta Operations Center, the second stage of a Boeing Delta IV launch vehicle is lowered onto a work stand. The Delta IV rocket will be used for the 2005 launching of the GOES-N weather satellite for NASA and NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). The first in a series of three advanced weather satellites including GOES-O and GOES-P, the GOES-N will provide continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. It will provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric “triggers” of severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. When these conditions develop, GOES-N will be able to monitor storm development and track their movements.
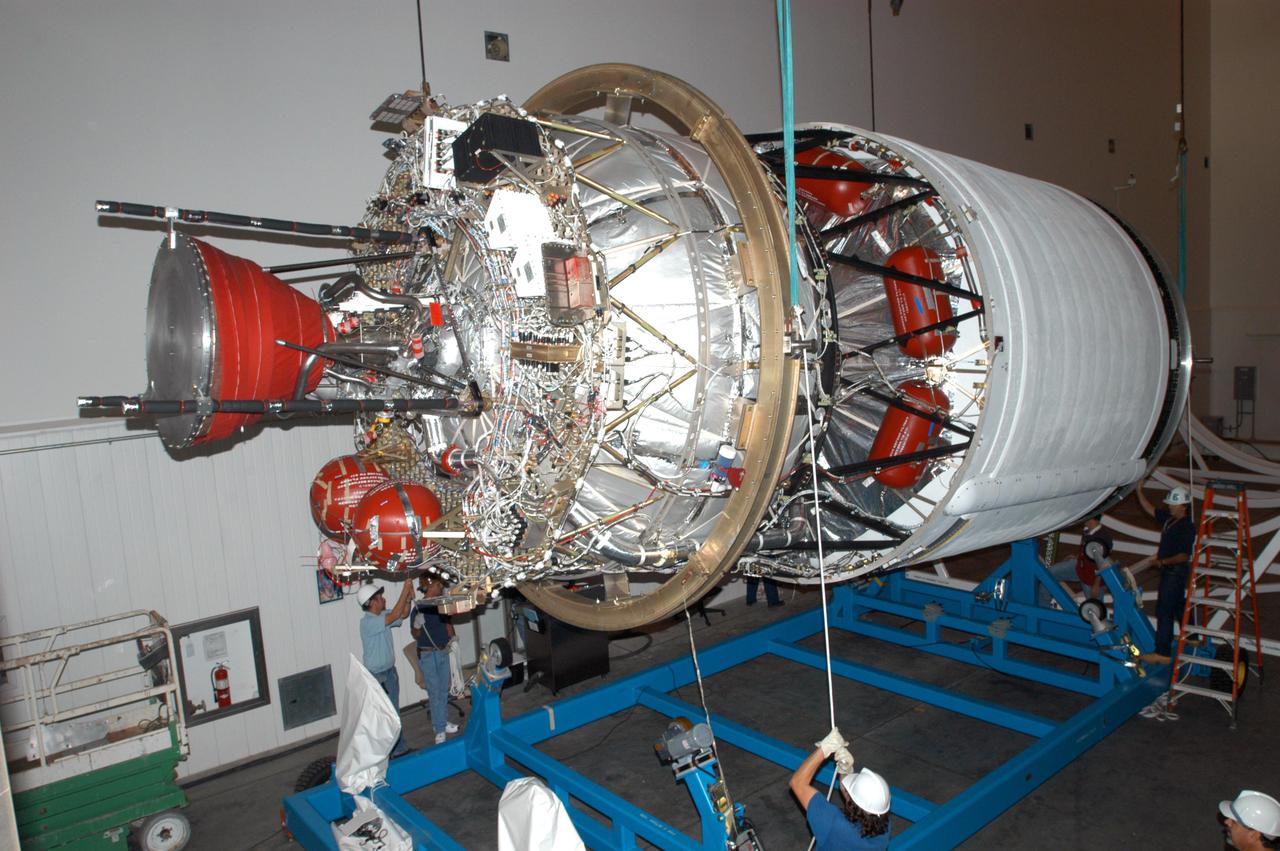

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Boeing Delta Operations Center, the second stage of a Boeing Delta IV launch vehicle is lifted off its transporter for transfer to a work stand. The Delta IV rocket will be used for the 2005 launching of the GOES-N weather satellite for NASA and NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). The first in a series of three advanced weather satellites including GOES-O and GOES-P, the GOES-N will provide continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. It will provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric “triggers” of severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. When these conditions develop, GOES-N will be able to monitor storm development and track their movements.
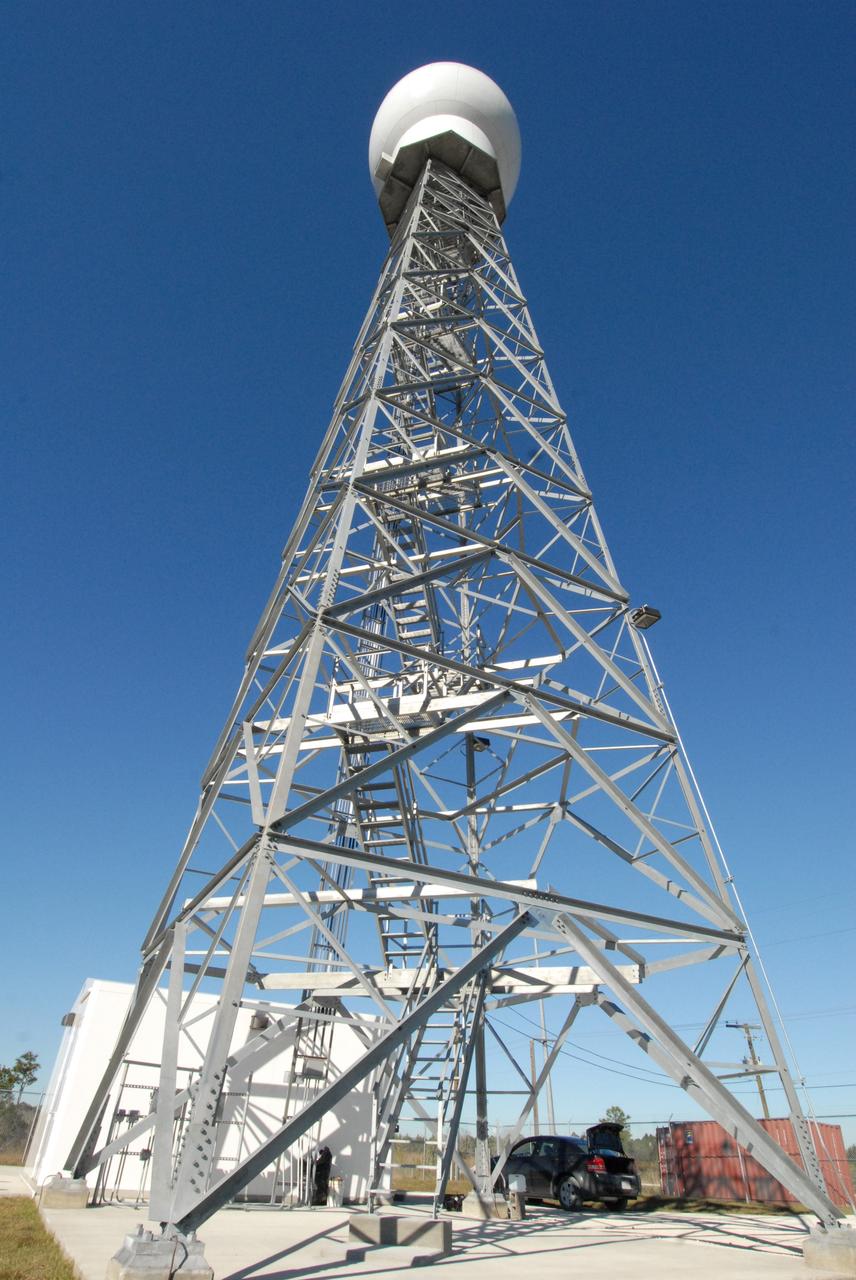

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A replacement weather Doppler radar has been installed in the radome on top of this tower in a remote field located west of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The dome houses the rotating antenna and pedestal and protects them from the elements. The tower is 100 feet high; the radome is 22 feet in diameter, the antenna 14 feet in diameter. It rotates at 6 rpm. The structure can withstand 130 mph winds. It is undergoing initial testing and expected to become operational in the summer. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria for space shuttle and rocket launches. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
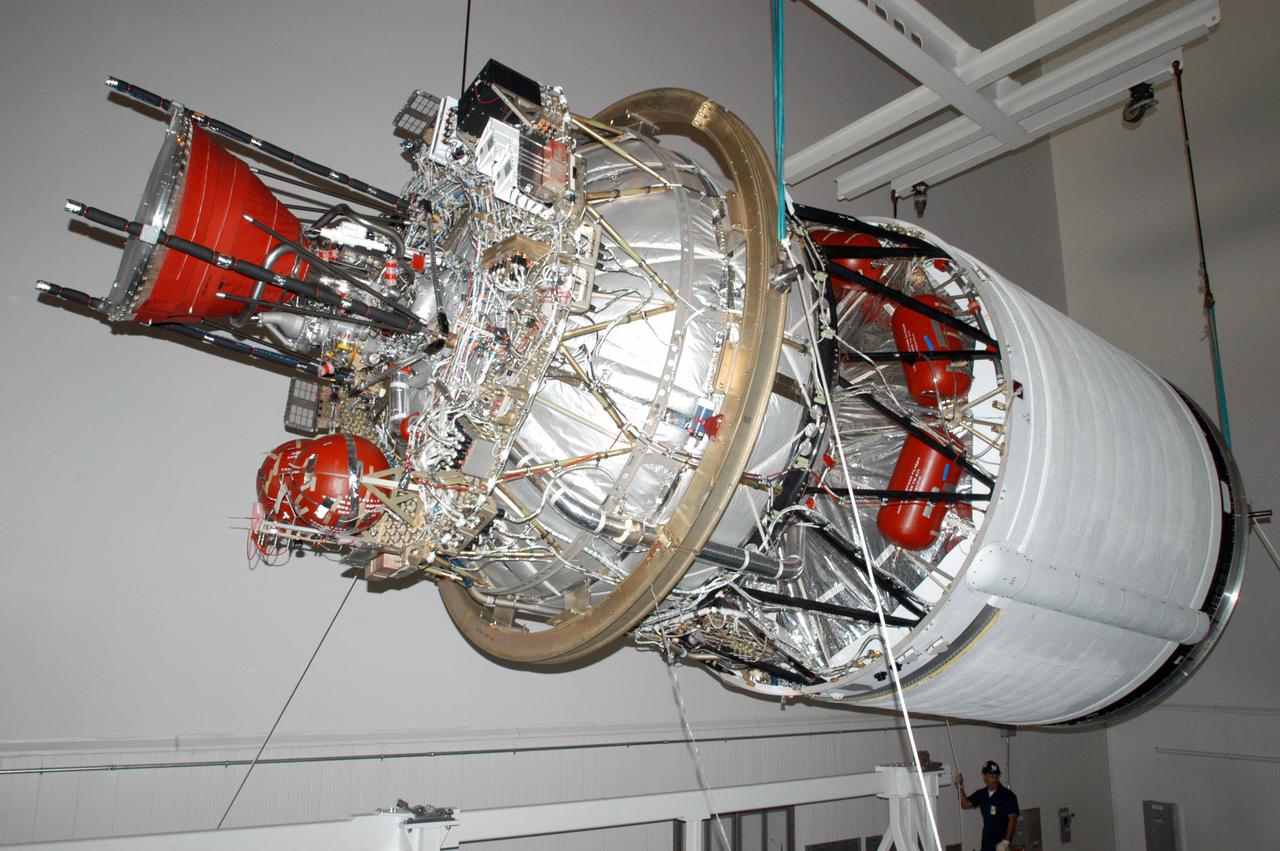
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Boeing Delta Operations Center, the suspended second stage of a Boeing Delta IV launch vehicle is moved toward a work stand. The Delta IV rocket will be used for the 2005 launching of the GOES-N weather satellite for NASA and NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). The first in a series of three advanced weather satellites including GOES-O and GOES-P, the GOES-N will provide continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. It will provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric “triggers” of severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. When these conditions develop, GOES-N will be able to monitor storm development and track their movements.
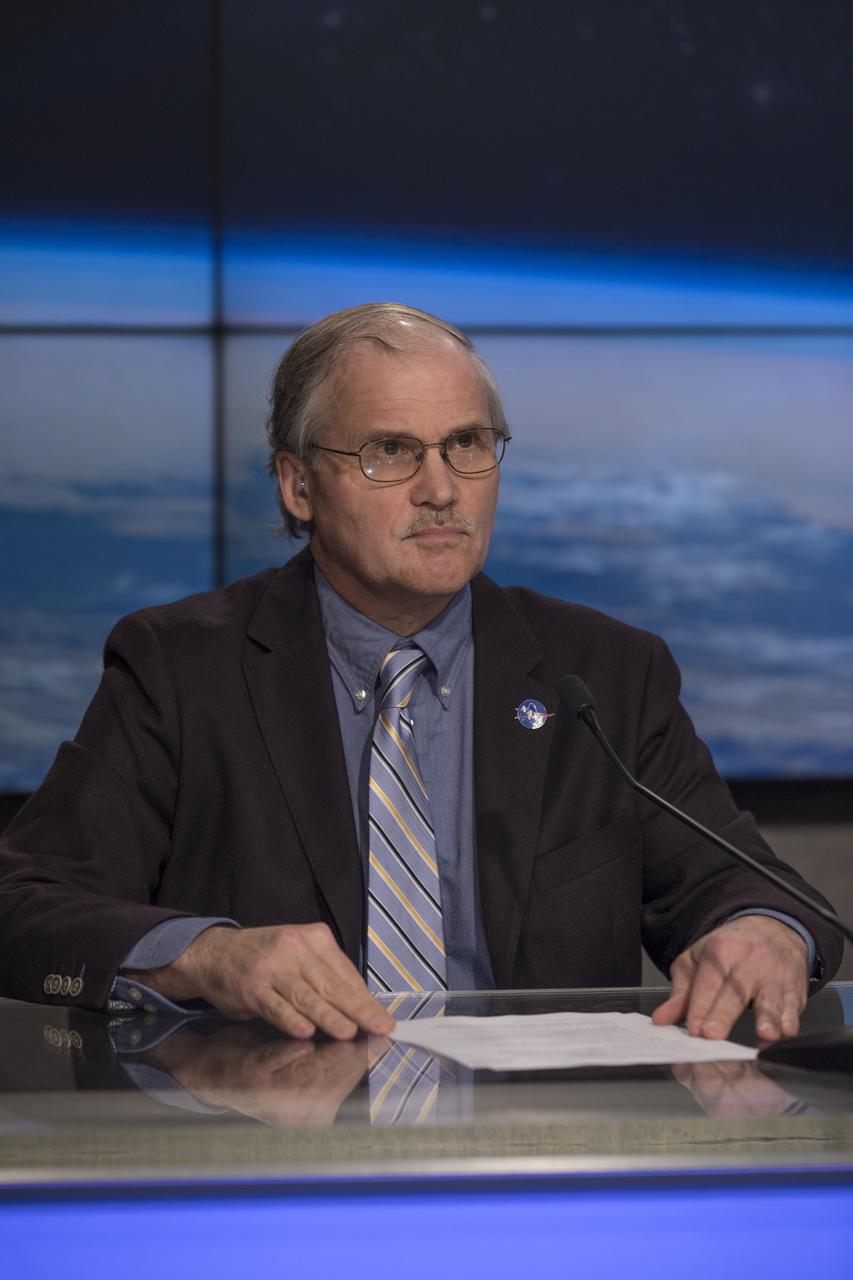

In the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium, Steve Cole of NASA Communications speaks to members of the media at a mission briefing on National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's, or NOAA's, Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S. The spacecraft is the second satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA weather satellites. It will launch to a geostationary position over the U.S. to provide images of storms and help predict weather forecasts, severe weather outlooks, watches, warnings, lightning conditions and longer-term forecasting. GOES-S is slated to lift off at 5:02 p.m. EST on March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.

Tim Walsh, GOES-R System Program director for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA, speaks to members of social media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S, the second spacecraft in a series of next-generation NOAA weather satellites. It will launch to a geostationary position over the U.S. to provide images of storms and help predict weather forecasts, severe weather outlooks, watches, warnings, lightning conditions and longer-term forecasting. GOES-S is slated to lift off at 5:02 p.m. EST on March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
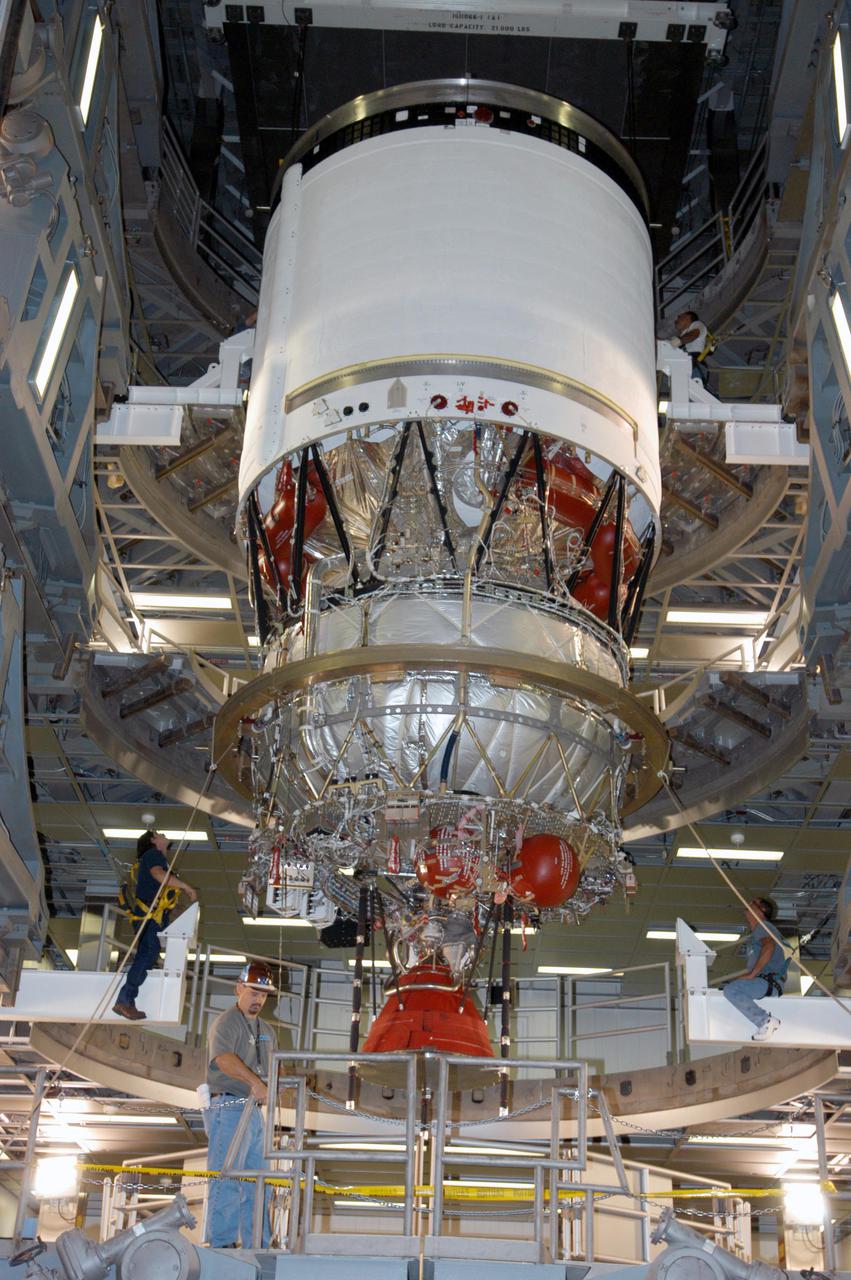

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Boeing Delta Operations Center, the Delta IV second stage is lowered onto a test stand. Nozzles will be installed and a deployment test will follow. The Delta IV rocket will be used for the 2005 launching of the GOES-N weather satellite for NASA and NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). The first in a series of three advanced weather satellites including GOES-O and GOES-P, the GOES-N will provide continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. It will provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric “triggers” of severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. When these conditions develop, GOES-N will be able to monitor storm development and track their movements.
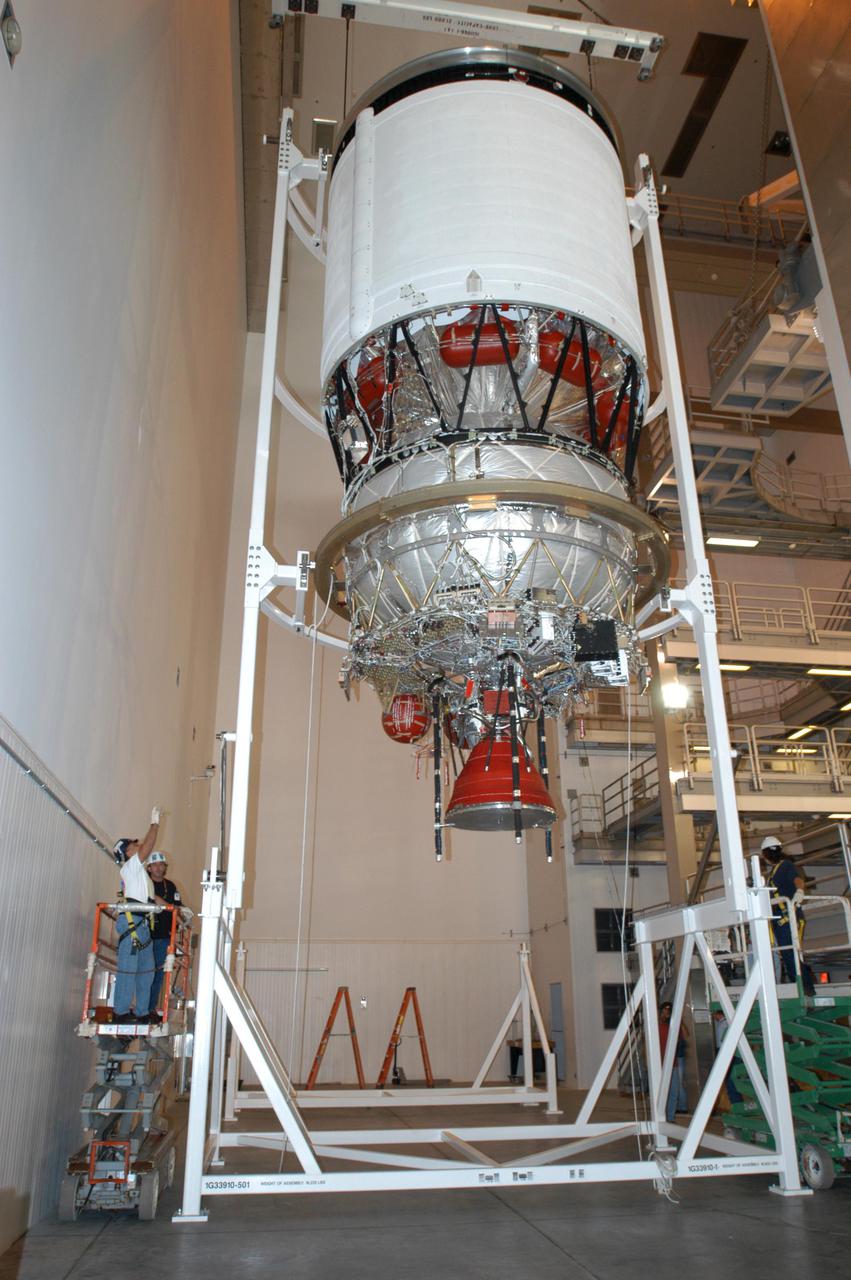

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Boeing Delta Operations Center, the Delta IV second stage is rotated to a vertical position so that the nozzles can be installed. A deployment test will follow. The Delta IV rocket will be used for the 2005 launching of the GOES-N weather satellite for NASA and NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). The first in a series of three advanced weather satellites including GOES-O and GOES-P, the GOES-N will provide continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. It will provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric “triggers” of severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. When these conditions develop, GOES-N will be able to monitor storm development and track their movements.
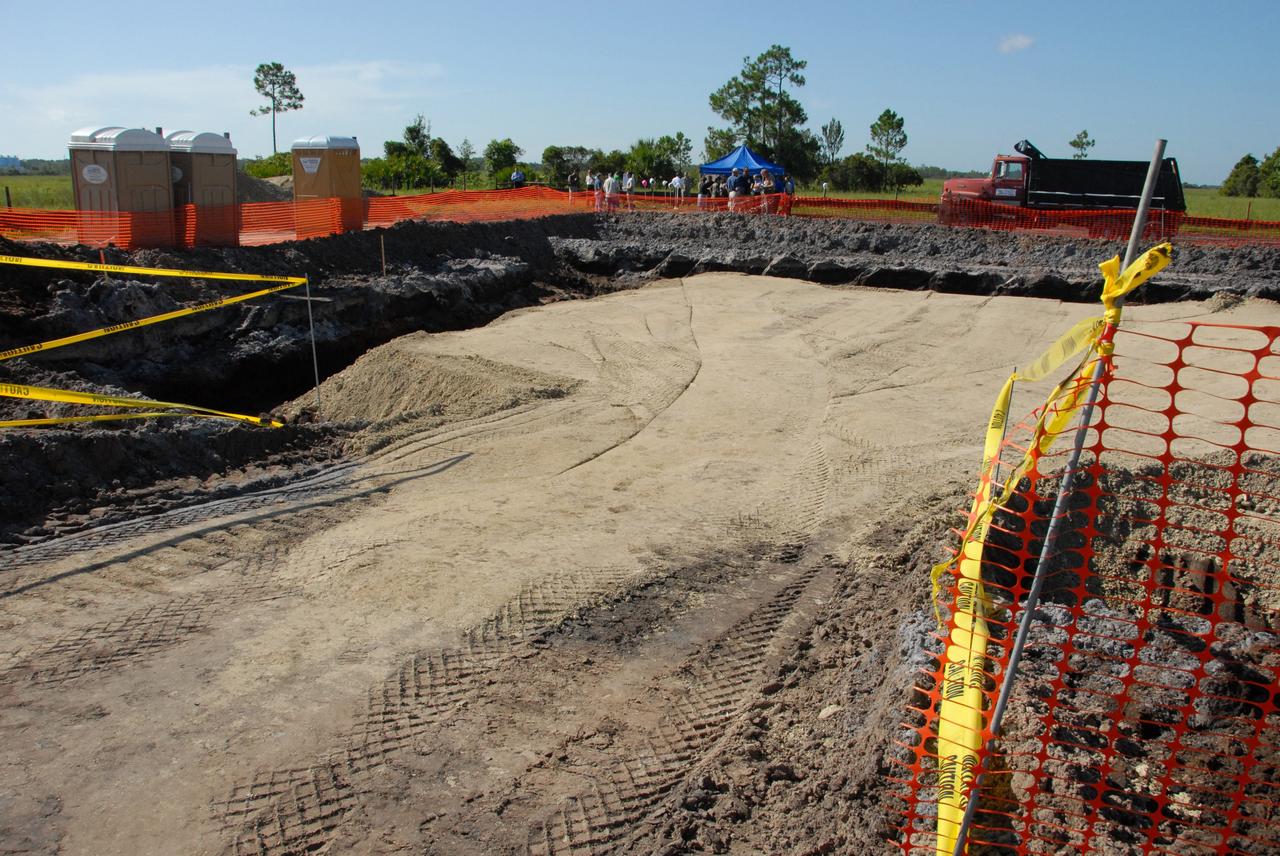

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The construction site is leveled for a new weather radar to be used by NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the 45th Space Wing and their customers. In the background is the location where a mock ground-breaking ceremony was held. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria. The new radar, replacing what was installed 25 years ago, includes Doppler capability to detect winds and identify the type, size and number of precipitation particles. The site is ideally distant from the launch pads and has unobstructed views of Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
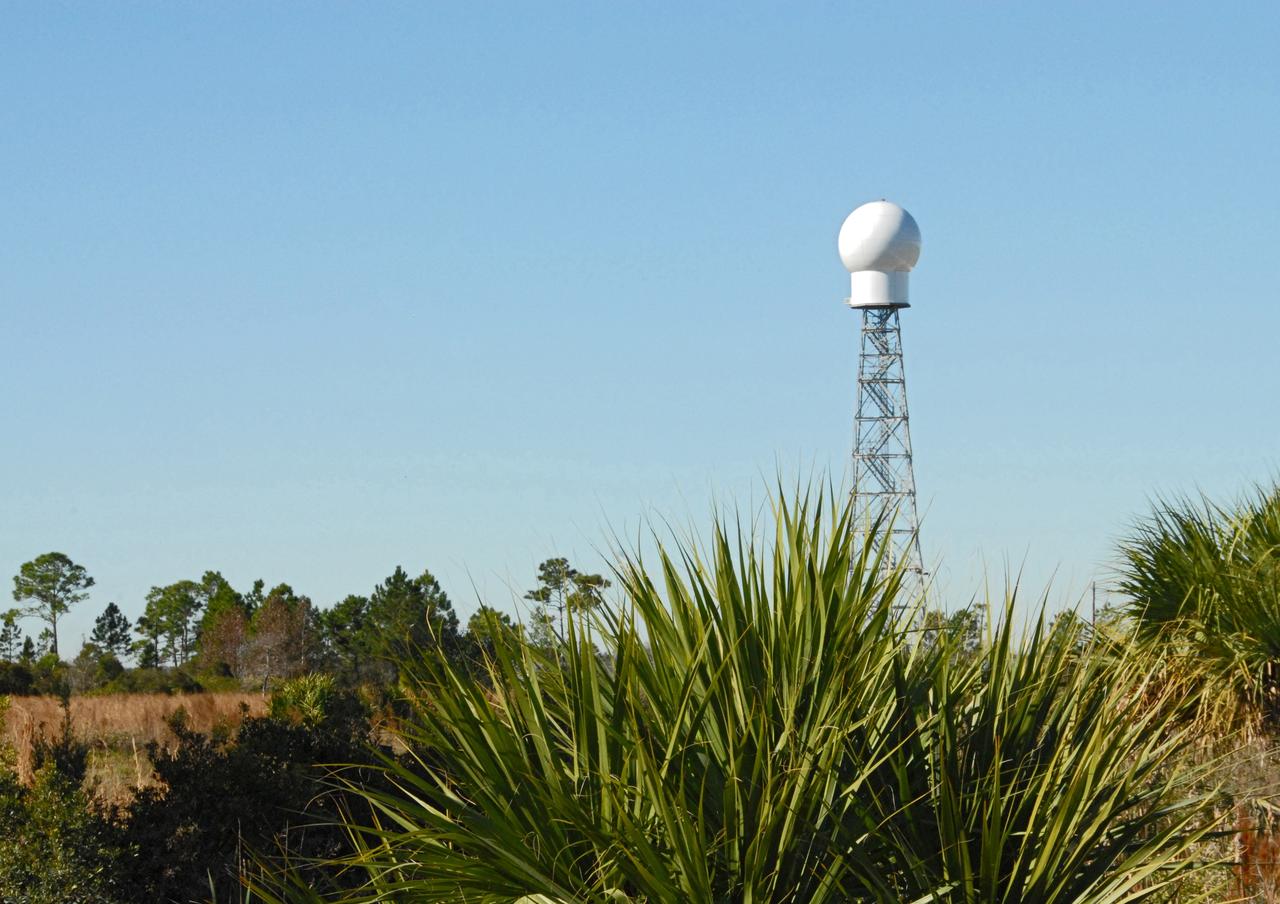

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A replacement weather Doppler radar has been installed on top of this tower in a remote field located west of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The radome houses the rotating antenna and pedestal and protects them from the elements. The tower is 100 feet high; the radome is 22 feet in diameter, the antenna 14 feet in diameter. It rotates at 6 rpm. The structure can withstand 130 mph winds. It is undergoing initial testing and expected to become operational in the summer. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria for space shuttle and rocket launches. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
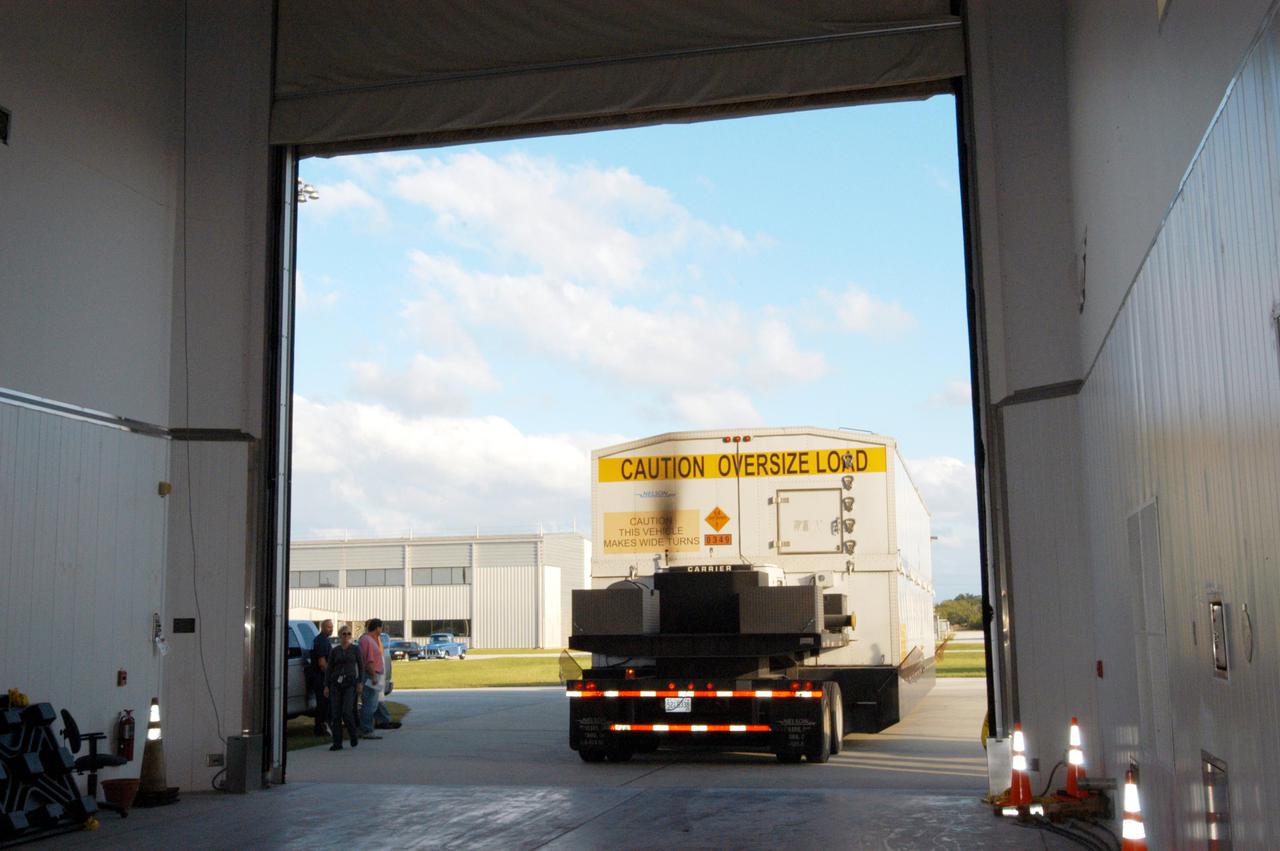

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A truck carrying the second stage of a Boeing Delta IV launch vehicle arrives at the Boeing Delta Operations Center. The Delta IV rocket will be used for the 2005 launching of the GOES-N weather satellite for NASA and NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). The first in a series of three advanced weather satellites including GOES-O and GOES-P, the GOES-N will provide continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. It will provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric “triggers” of severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. When these conditions develop, GOES-N will be able to monitor storm development and track their movements.
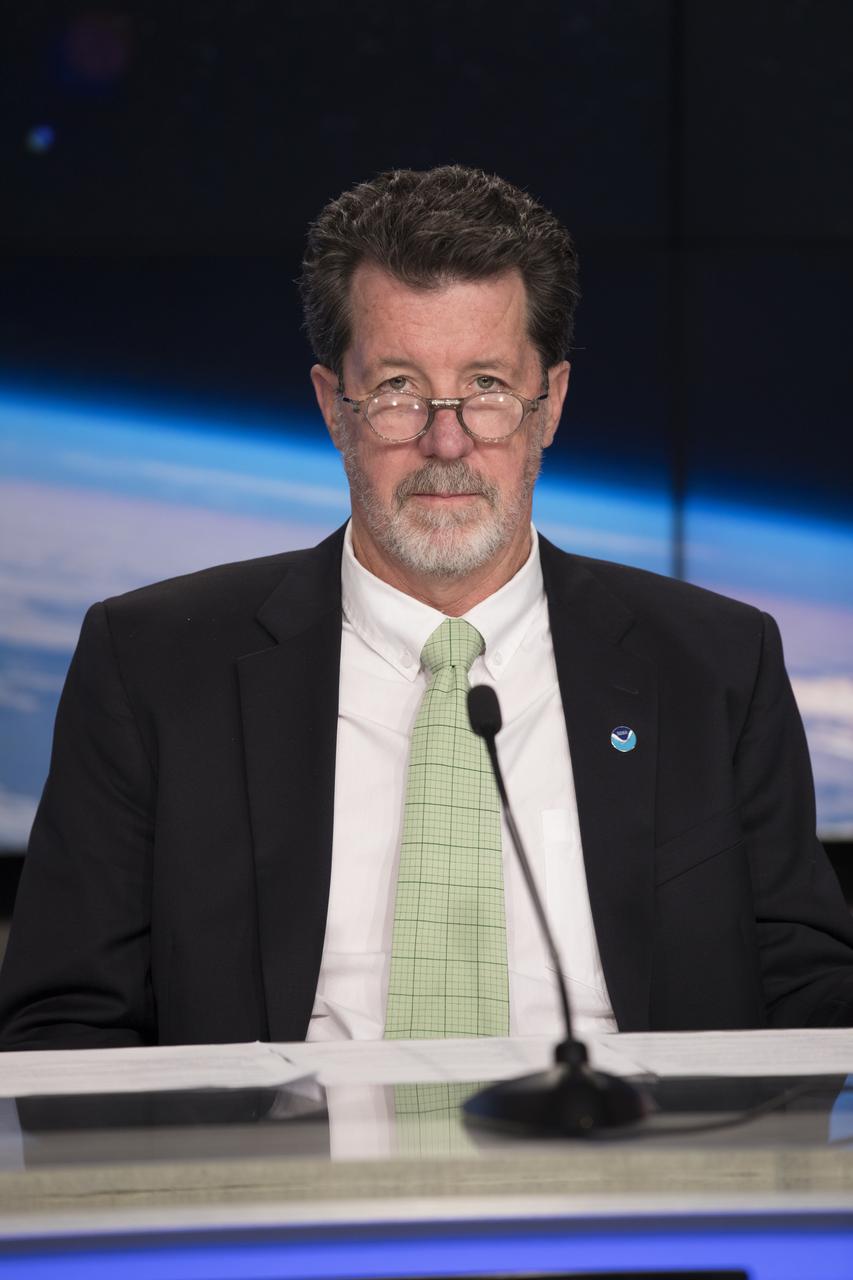

In the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium, Jim Roberts, a scientist with the Earth System Research Laboratory's Office of Atmospheric Research for NOAA, speaks to members of the media at a mission briefing on National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's, or NOAA's, Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S. The spacecraft is the second satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA weather satellites. It will launch to a geostationary position over the U.S. to provide images of storms and help predict weather forecasts, severe weather outlooks, watches, warnings, lightning conditions and longer-term forecasting. GOES-S is slated to lift off at 5:02 p.m. EST on March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
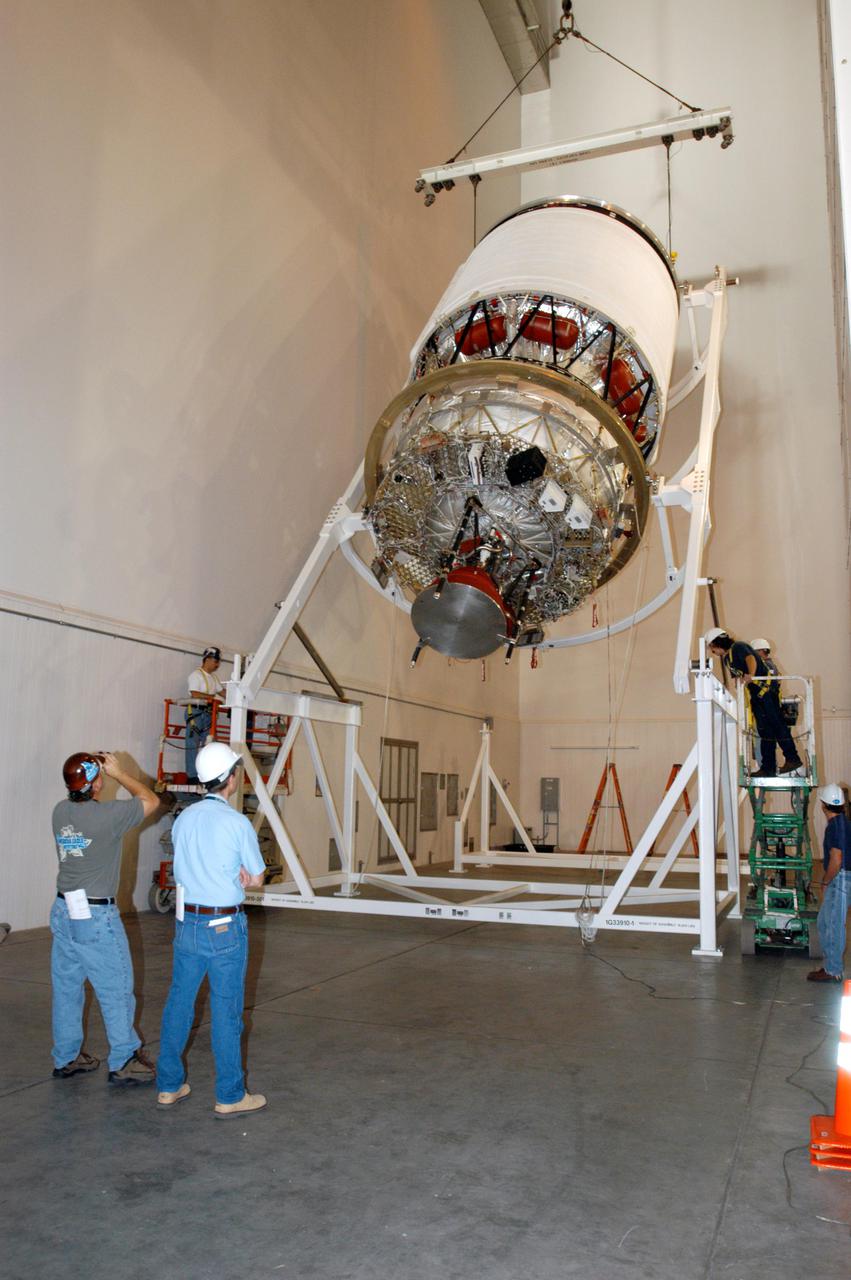

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Boeing Delta Operations Center, the Delta IV second stage is rotated to a vertical position so that the nozzles can be installed. A deployment test will follow. The Delta IV rocket will be used for the 2005 launching of the GOES-N weather satellite for NASA and NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). The first in a series of three advanced weather satellites including GOES-O and GOES-P, the GOES-N will provide continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. It will provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric “triggers” of severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. When these conditions develop, GOES-N will be able to monitor storm development and track their movements.
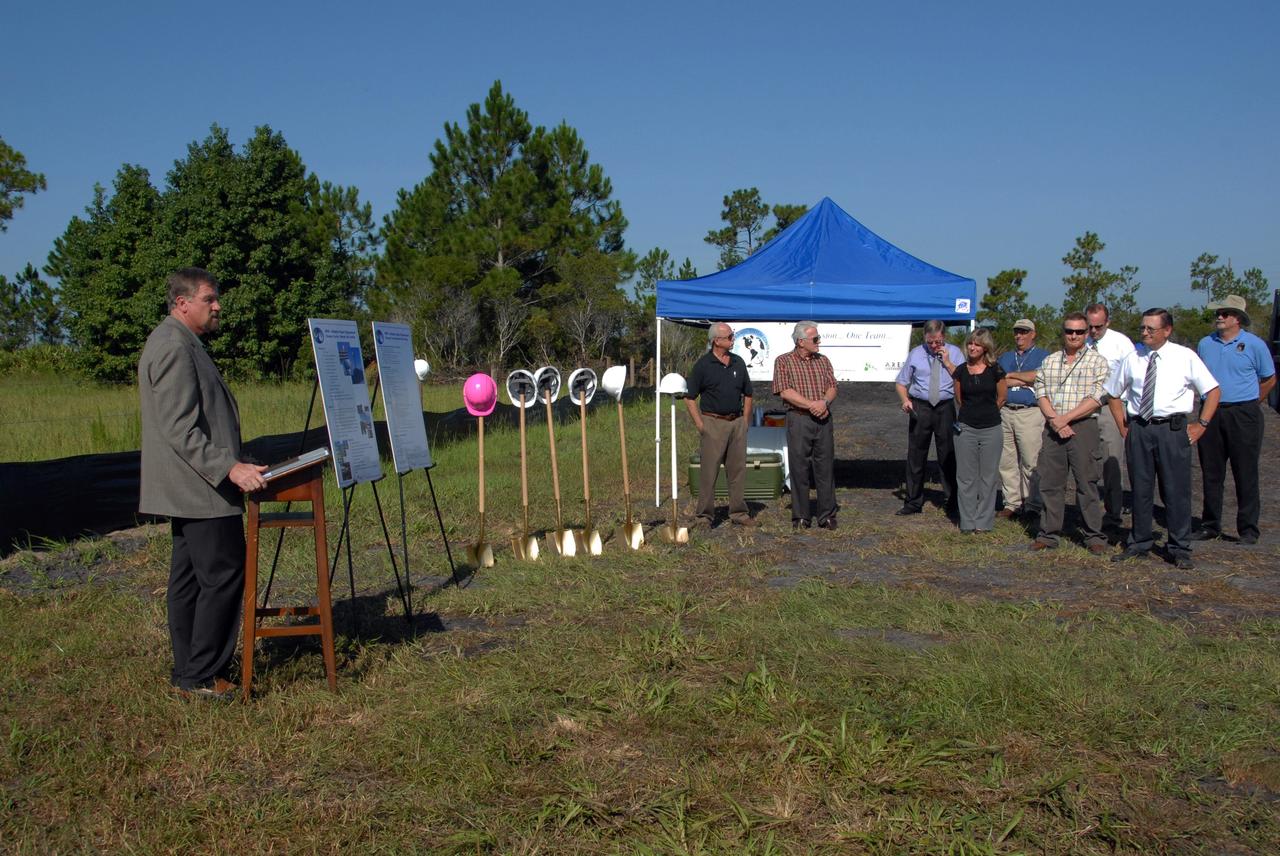

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A new weather radar site is dedicated with a mock ground-breaking ceremony. At the podium is Pat Carr, SLRSC program director with ITT. The site will be used by NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the 45th Space Wing and their customers. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria. The new radar, replacing what was installed 25 years ago, includes Doppler capability to detect winds and identify the type, size and number of precipitation particles. The site is ideally distant from the launch pads and has unobstructed views of Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
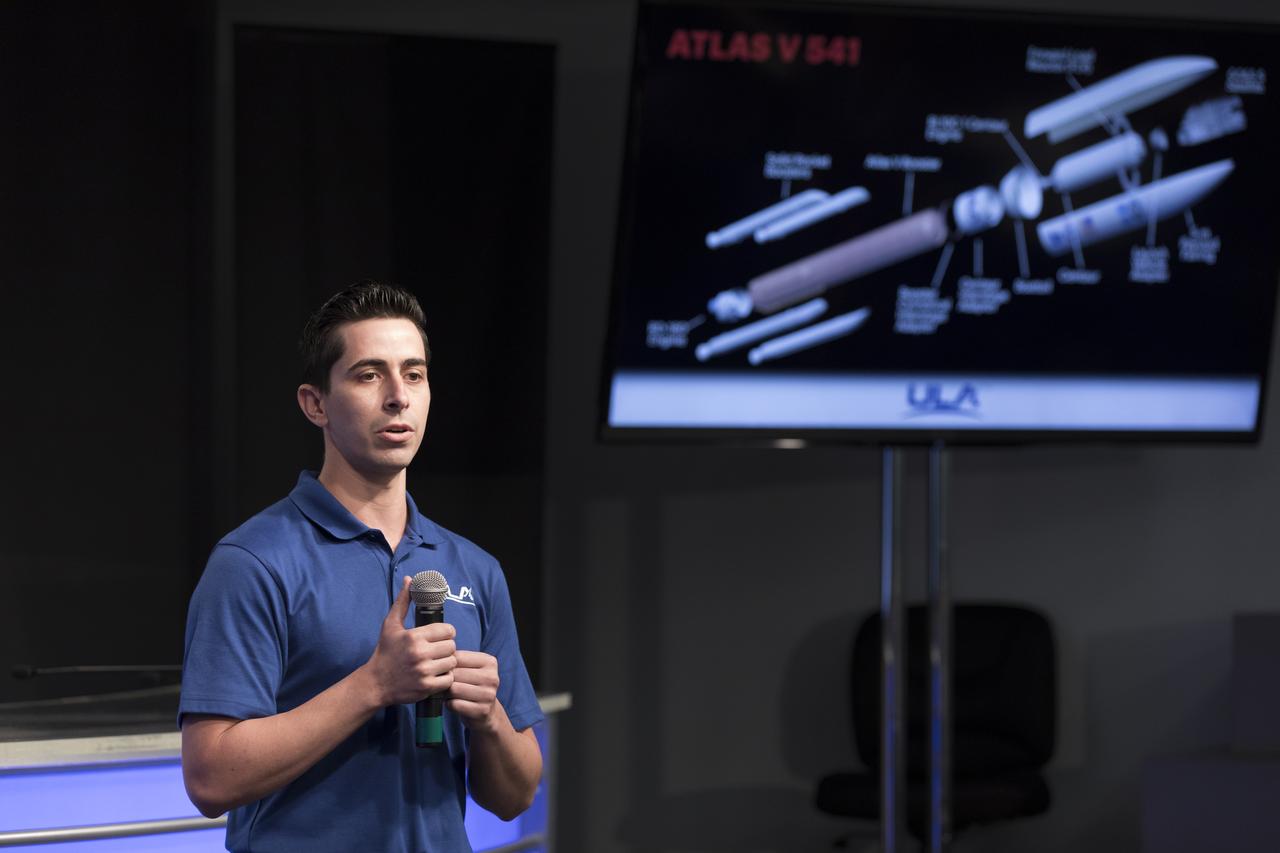

Gabriel Rodriguez-Mena, a United Launch Alliance systems test engineer, speaks to members of social media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's, or NOAA's, Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S. The spacecraft is the second satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA weather satellites. It will launch to a geostationary position over the U.S. to provide images of storms and help predict weather forecasts, severe weather outlooks, watches, warnings, lightning conditions and longer-term forecasting. GOES-S is slated to lift off at 5:02 p.m. EST on March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.

In the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium, George Morrow, deputy director of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, speaks to members of the media at a mission briefing on National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's, or NOAA's, Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S. The spacecraft is the second satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA weather satellites. It will launch to a geostationary position over the U.S. to provide images of storms and help predict weather forecasts, severe weather outlooks, watches, warnings, lightning conditions and longer-term forecasting. GOES-S is slated to lift off at 5:02 p.m. EST on March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.