
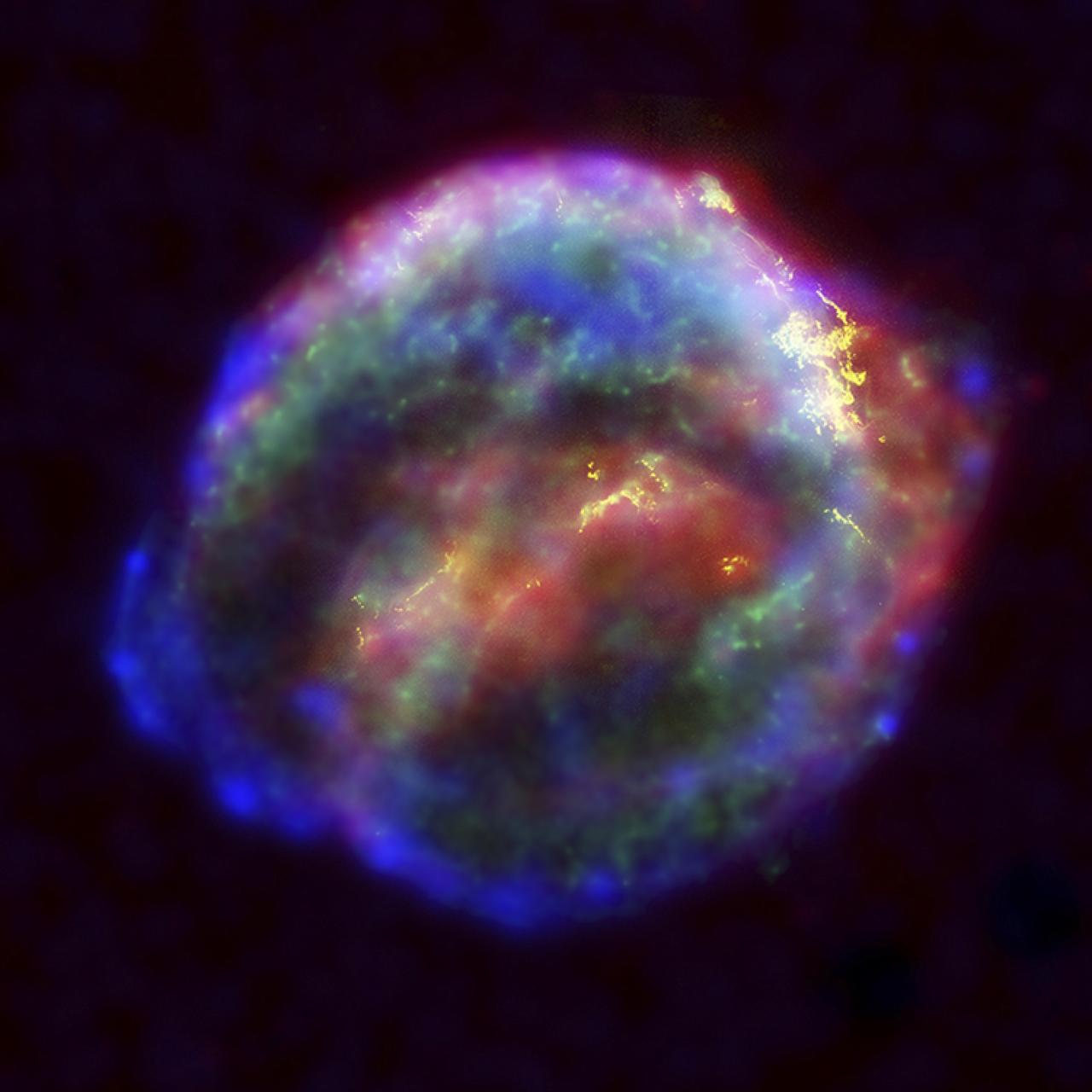
Image release September 2, 2010 ABOUT THIS IMAGE: This image shows the entire region around supernova 1987A. The most prominent feature in the image is a ring with dozens of bright spots. A shock wave of material unleashed by the stellar blast is slamming into regions along the ring's inner regions, heating them up, and causing them to glow. The ring, about a light-year across, was probably shed by the star about 20,000 years before it exploded. An international team of astronomers using the Hubble Space Telescope reports a significant brightening of the emissions from Supernova 1987A. The results, which appear in this week's Science magazine, are consistent with theoretical predictions about how supernovae interact with their immediate galactic environment. The team observed the supernova remnant in optical, ultraviolet, and near-infrared light. They studied the interaction between the ejecta from the stellar explosion and a glowing 6-trillion-mile-diameter ring of gas encircling the supernova remnant. The gas ring was probably shed some 20,000 years before the supernova exploded. Shock waves resulting from the impact of the ejecta onto the ring have brightened 30 to 40 pearl-like "hot spots" in the ring. These blobs likely will grow and merge together in the coming years to form a continuous, glowing circle. "We are seeing the effect a supernova can have in the surrounding galaxy, including how the energy deposited by these stellar explosions changes the dynamics and chemistry of the environment," said University of Colorado at Boulder Research Associate Kevin France of the Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy. "We can use these new data to understand how supernova processes regulate the evolution of galaxies." Discovered in 1987, Supernova 1987A is the closest exploding star to Earth to be detected since 1604 and it resides in the nearby Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy adjacent to our own Milky Way Galaxy. Credit: NASA, ESA, K. France (University of Colorado, Boulder), and P. Challis and R. Kirshner (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
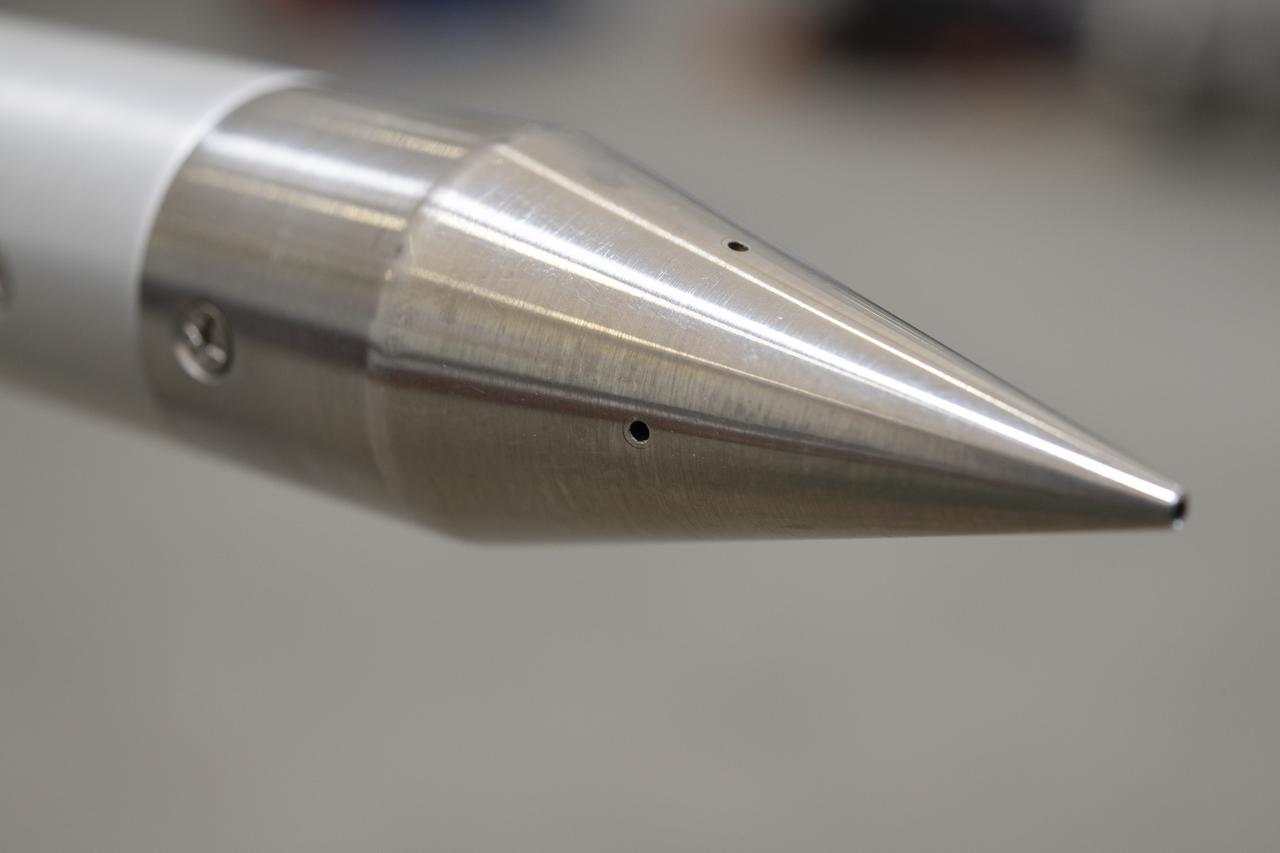

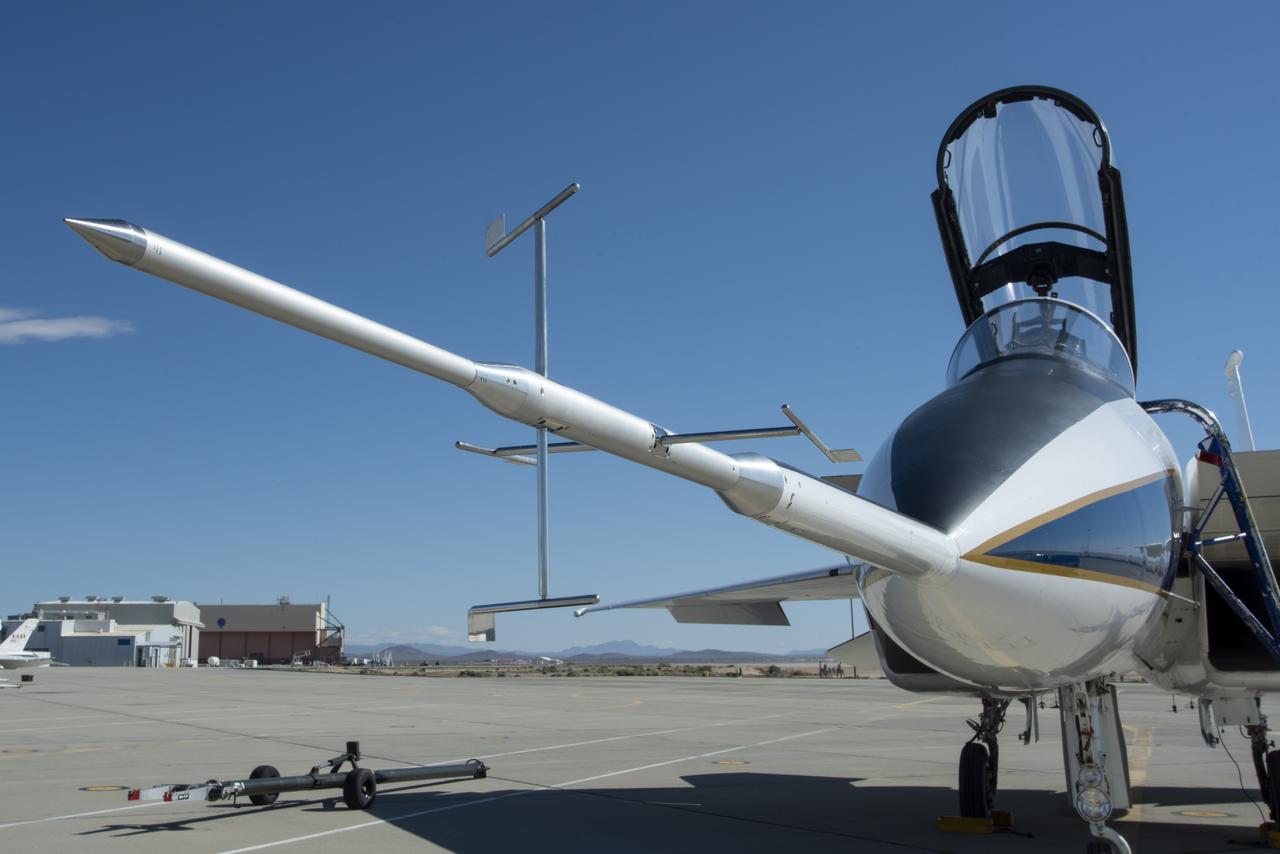
A close-up of NASA’s shock-sensing probe highlights its pressure ports, designed to measure air pressure changes during supersonic flight. The probe will be mounted on NASA’s F-15B Aeronautics Research Test Bed for calibration flights, validating its ability to measure shock waves generated by the X-59 as part of NASA's Quesst mission.
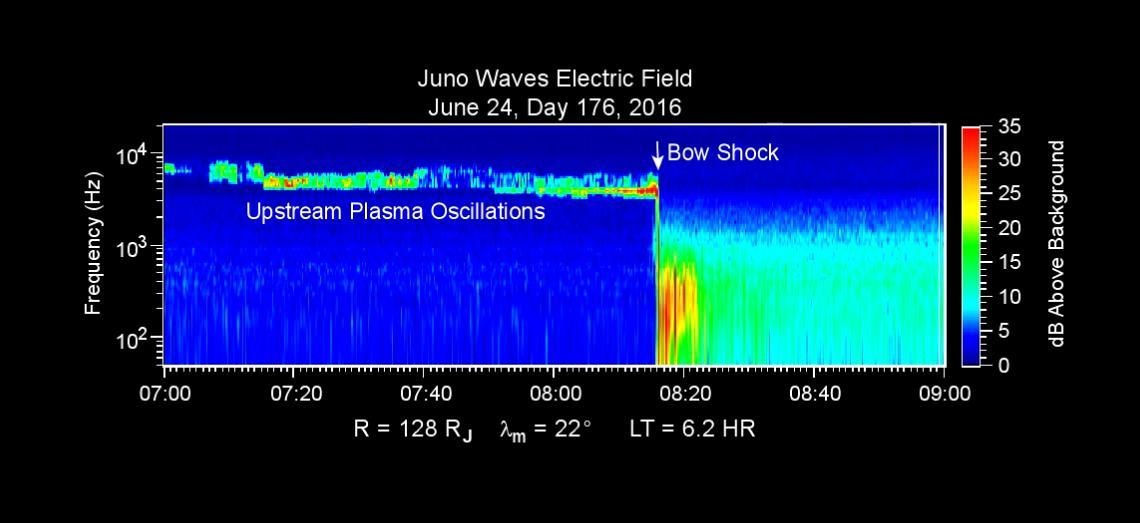
This chart presents data that the Waves investigation on NASA's Juno spacecraft recorded as the spacecraft crossed the bow shock just outside of Jupiter's magnetosphere on June 24, 2016, while approaching Jupiter. Audio accompanies the animation, with volume and pitch correlated to the amplitude and frequency of the recorded waves. The graph is a frequency-time spectrogram with color coding to indicate wave amplitudes as a function of wave frequency (vertical axis, in hertz) and time (horizontal axis, with a total elapsed time of two hours). During the hour before Juno reached the bow shock, the Waves instrument was detecting mainly plasma oscillations just below 10,000 hertz (10 kilohertz). The frequency of these oscillations is related to the local density of electrons; the data yield an estimate of approximately one electron per cubic centimeter (about 16 per cubic inch) in this region just outside Jupiter's bow shock. The broadband burst of noise marked "Bow Shock" is the region of turbulence where the supersonic solar wind is heated and slowed by encountering the Jovian magnetosphere. The shock is analogous to a sonic boom generated in Earth's atmosphere by a supersonic aircraft. The region after the shock is called the magnetosheath. The vertical bar to the right of the chart indicates the color coding of wave amplitude, in decibels (dB) above the background level detected by the Waves instrument. Each step of 10 decibels marks a tenfold increase in wave power. When Juno collected these data, the distance from the spacecraft to Jupiter was about 5.56 million miles (8.95 million kilometers), indicated on the chart as 128 times the radius of Jupiter. Jupiter's magnetic field is tilted about 10 degrees from the planet's axis of rotation. The note of 22 degrees on the chart indicates that at the time these data were recorded, the spacecraft was 22 degrees north of the magnetic-field equator. The "LT" notation is local time on Jupiter at the longitude of the planet directly below the spacecraft, with a value of 6.2 indicating approximately dawn. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20753
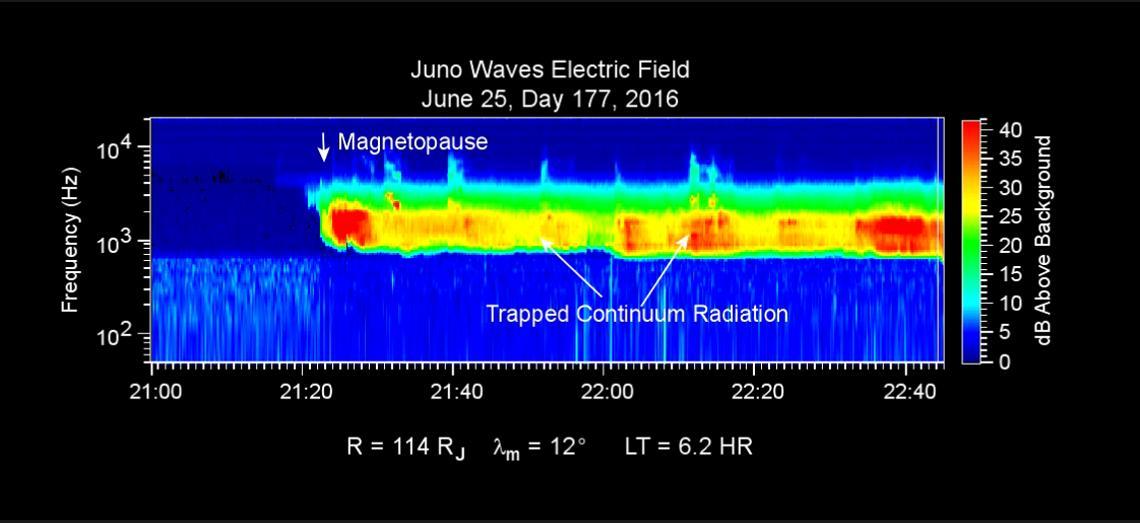
This chart presents data that the Waves investigation on NASA's Juno spacecraft recorded as the spacecraft crossed the bow shock just outside of Jupiter's magnetosphere on June 24, 2016, while approaching Jupiter. Audio accompanies the animation, with volume and pitch correlated to the amplitude and frequency of the recorded waves. The graph is a frequency-time spectrogram with color coding to indicate wave amplitudes as a function of wave frequency (vertical axis, in hertz) and time (horizontal axis, with a total elapsed time of two hours). During the hour before Juno reached the bow shock, the Waves instrument was detecting mainly plasma oscillations just below 10,000 hertz (10 kilohertz). The frequency of these oscillations is related to the local density of electrons; the data yield an estimate of approximately one electron per cubic centimeter (about 16 per cubic inch) in this region just outside Jupiter's bow shock. The broadband burst of noise marked "Bow Shock" is the region of turbulence where the supersonic solar wind is heated and slowed by encountering the Jovian magnetosphere. The shock is analogous to a sonic boom generated in Earth's atmosphere by a supersonic aircraft. The region after the shock is called the magnetosheath. The vertical bar to the right of the chart indicates the color coding of wave amplitude, in decibels (dB) above the background level detected by the Waves instrument. Each step of 10 decibels marks a tenfold increase in wave power. When Juno collected these data, the distance from the spacecraft to Jupiter was about 5.56 million miles (8.95 million kilometers), indicated on the chart as 128 times the radius of Jupiter. Jupiter's magnetic field is tilted about 10 degrees from the planet's axis of rotation. The note of 22 degrees on the chart indicates that at the time these data were recorded, the spacecraft was 22 degrees north of the magnetic-field equator. The "LT" notation is local time on Jupiter at the longitude of the planet directly below the spacecraft, with a value of 6.2 indicating approximately dawn. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20753
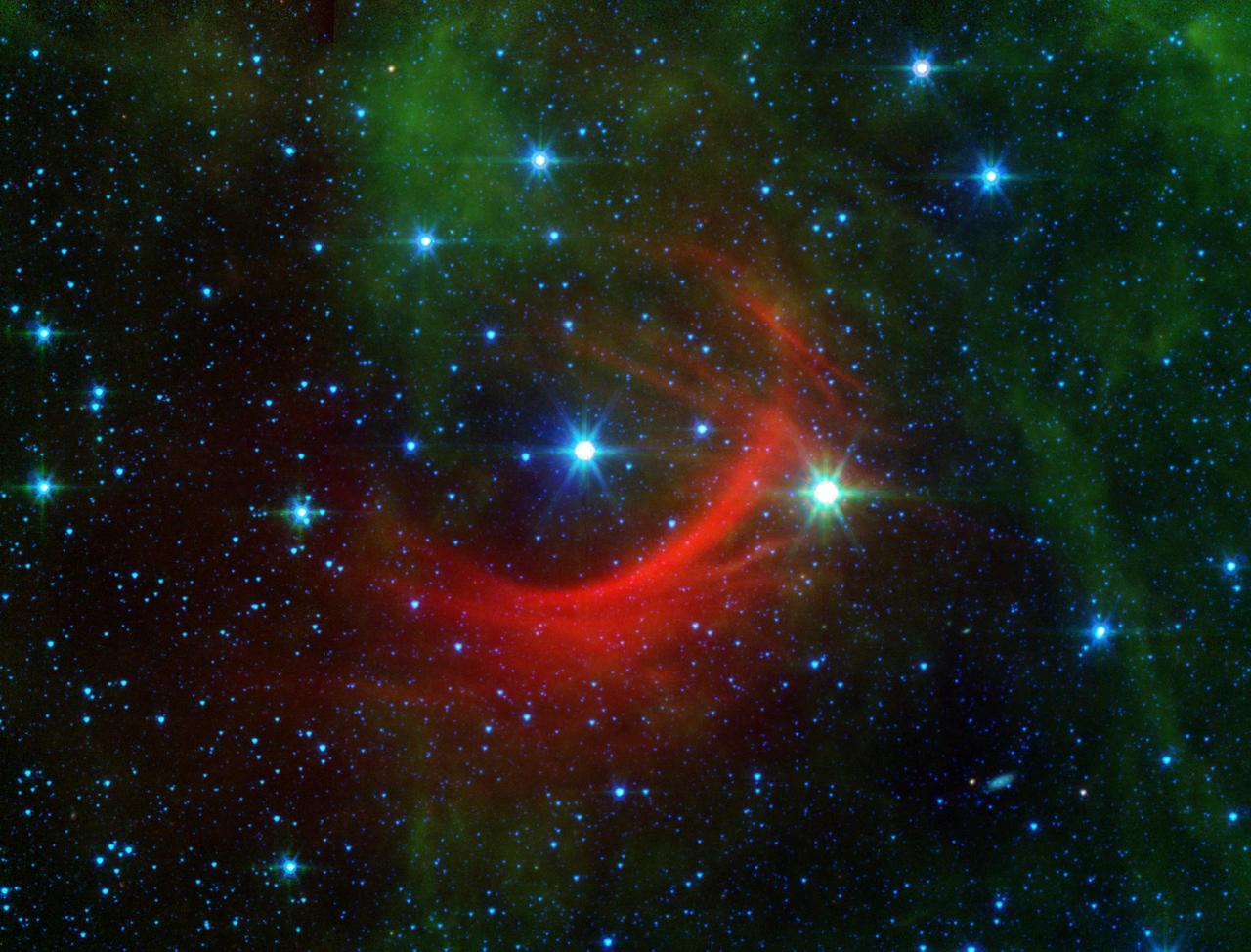

The red arc in this infrared image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope is a giant shock wave, created by a speeding star known as Kappa Cassiopeiae.
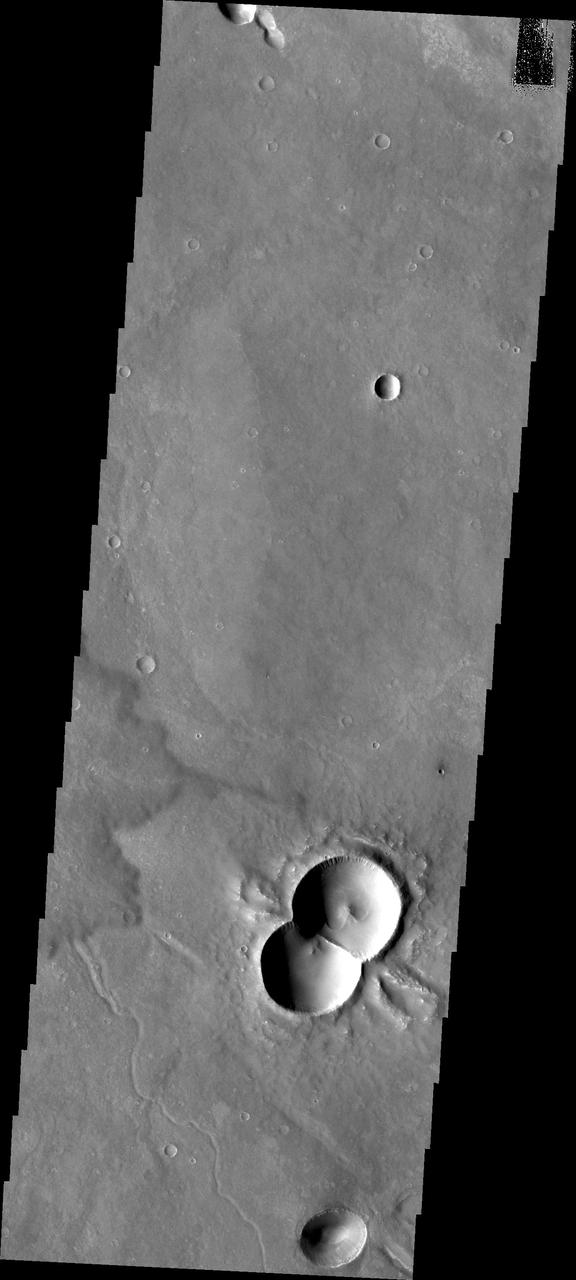

This doublet crater was formed when two meteorites impacted at the same time. The shock waves interact to form the straight central rim and the wings of ejecta on the outside of the rims. This image is from NASA Mars Odyssey.
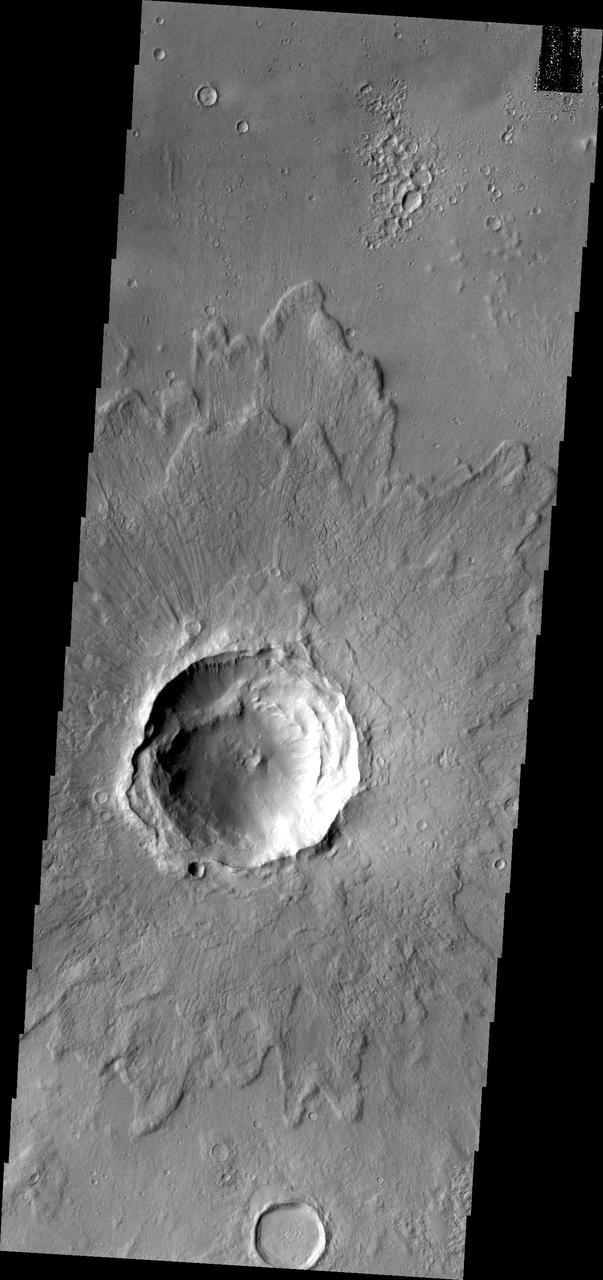

This image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft contains a relatively young crater and its ejecta. Layering in the ejecta is visible and relates to the shock waves from the impact. This unnamed crater is located in Arabia Terra.
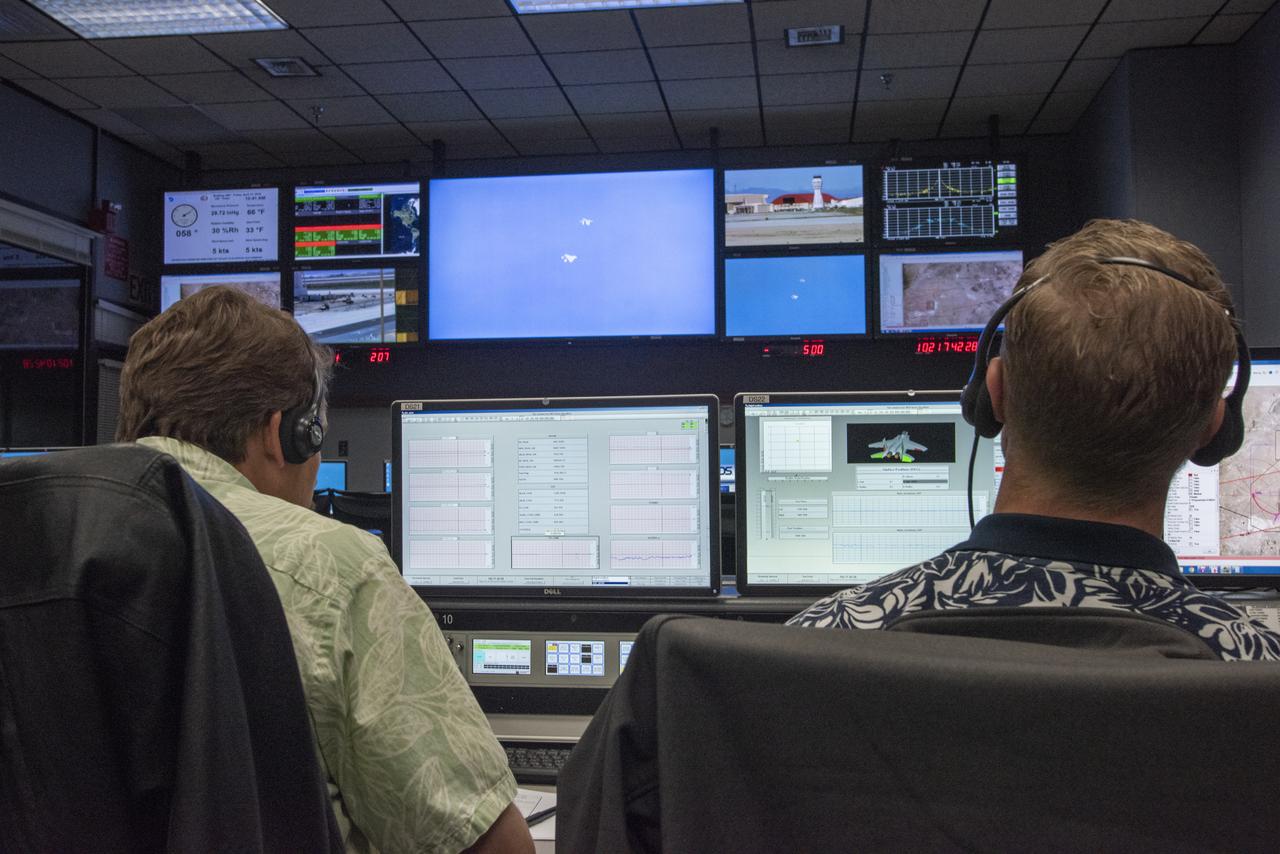

NASA engineers monitor an F-15 and an F/A-18 during a flight in support of the Shock Sensing Probe flight series, from the mission control room at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The flight series included the use of a technique commonly used by NASA's predecessor, the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics - combining two instruments onto the nose of an aircraft to measure the pressure of shock waves from another aircraft.

NASA recently completed flight testing a state-of-the-art instrument designed to capture high-quality measurements of shock waves created by supersonic aircraft in flight. It's called the Shock Sensing Probe. The probe's performance was tested in flight at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, using an innovative technique originated by NASA's predecessor, the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics.

NASA recently completed flight testing a state-of-the-art instrument designed to capture high-quality measurements of shock waves created by supersonic aircraft in flight. It’s called the Shock Sensing Probe. The probe’s performance was tested in flight at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, using an innovative technique originated by NASA’s predecessor, the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics.
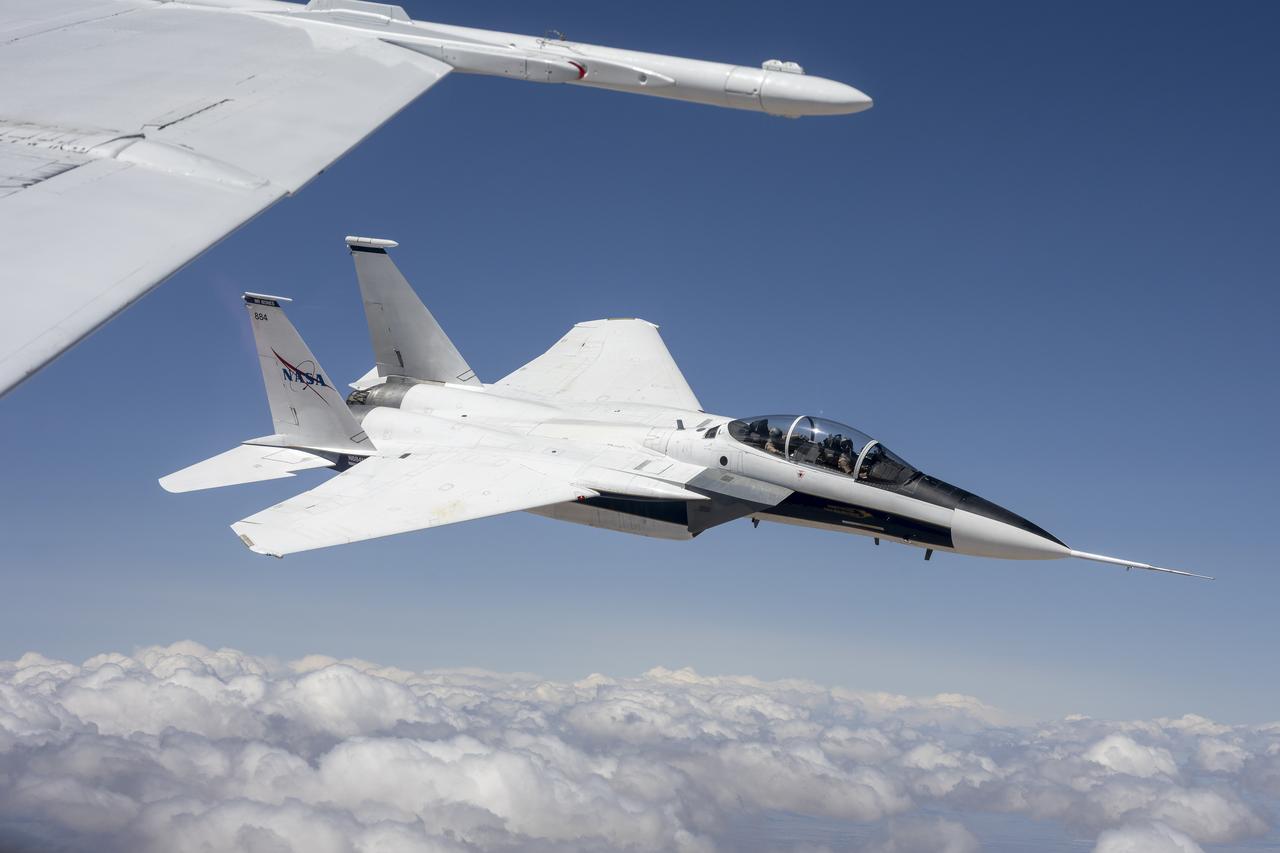

NASA's F-15D research aircraft conducts a calibration flight of a shock-sensing probe near NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The shock-sensing probe is designed to measure the signature and strength of shock waves in flight. The probe was validated during dual F-15 flights and will be flown behind NASA’s X-59 to measure small pressure changes caused by shock waves in support of the agency's Quesst mission.

NASA's F-15B Aeronautics Research Test Bed performs a calibration flight of the shock-sensing probe over Edwards, California, on Aug. 6, 2024. The probe will measure shock waves from NASA's X-59.

NASA's F-15B Aeronautics Research Test Bed performs a calibration flight of the shock-sensing probe over Edwards, California, on Aug. 6, 2024. The probe will measure shock waves from NASA's X-59.

NASA's F-15B Aeronautics Research Test Bed performs a calibration flight of the shock-sensing probe over Edwards, California, on Aug. 6, 2024. The probe will measure shock waves from NASA's X-59.

NASA's F-15B Aeronautics Research Test Bed performs a calibration flight of the shock-sensing probe over Edwards, California, on Aug. 6, 2024. The probe will measure shock waves from NASA's X-59.
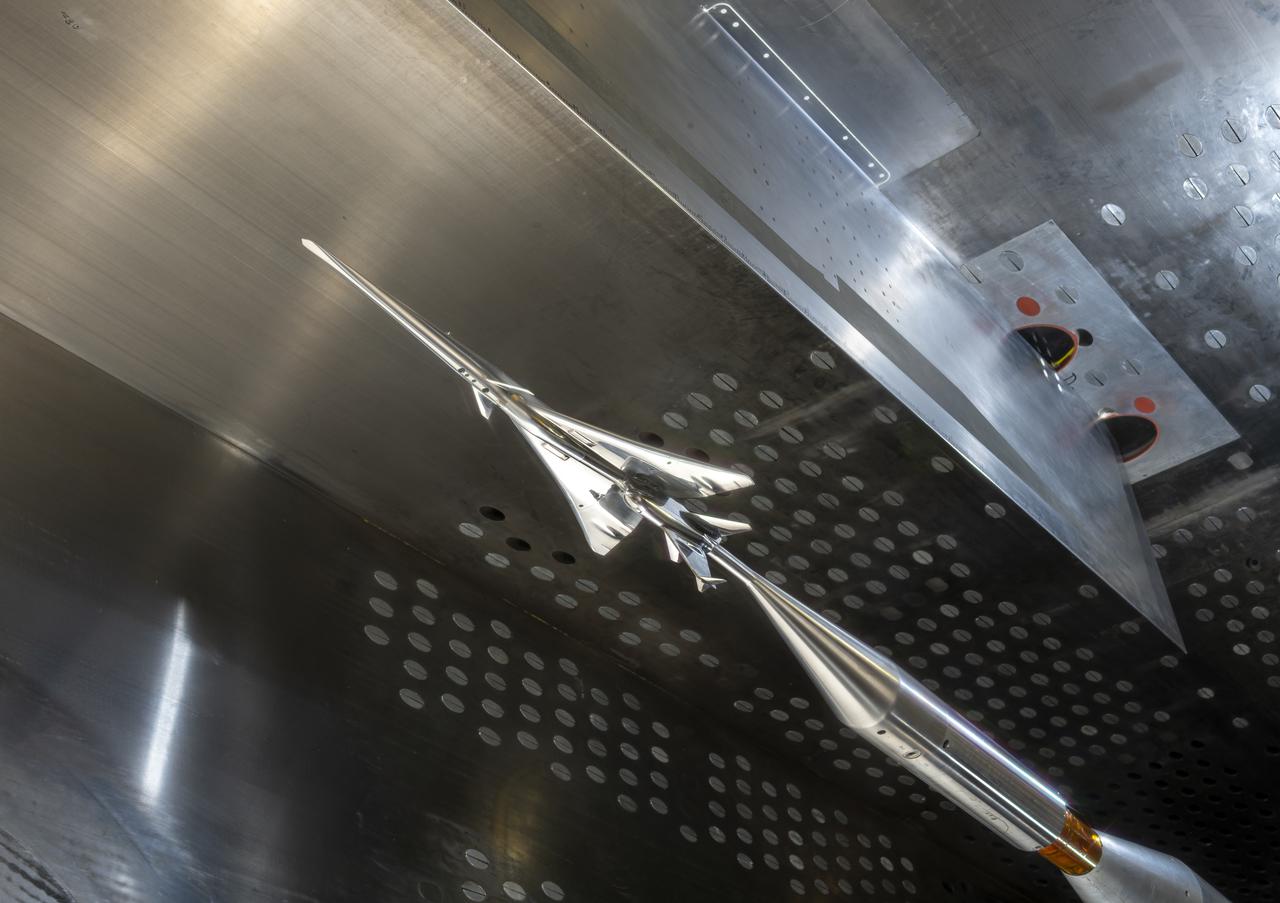

The X-59 Commercial Supersonic Transport model is installed upside down in the test section of the GRC 8x6 Supersonic wind tunnel. The blade hanging from the top of the tunnel will be measuring the shock waves coming from the bottom of the model during testing. The shock waves coming from the bottom of the model represent the sonic boom reaching the ground during flight. The shape of the model is designed so as to greatly reduce the shock waves to prevent the typical boom coming from a supersonic aircraft. Commercial Supersonic Transport, CST Project, X-59 Sonic Boom Test Model, in the 8x6-foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel, SWT
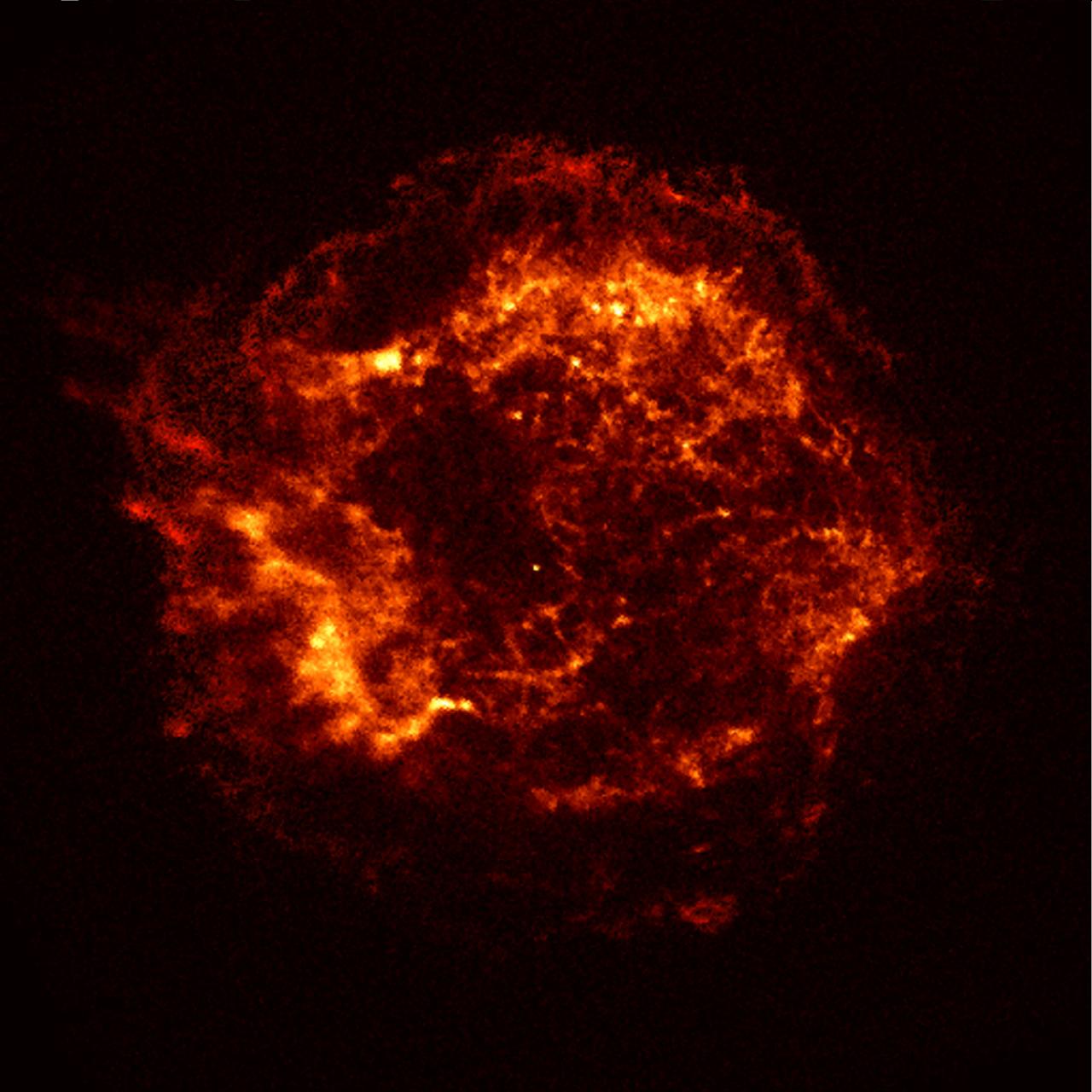
This x-ray image of the Cassiopeia A (CAS A) supernova remnant is the official first light image of the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO). The 5,000-second image was made with the Advanced Charged Coupled Device (CCD) Image Spectrometer (ACIS). Two shock waves are visible: A fast outer shock and a slower irner shock. The inner shock wave is believed to be due to the collision of ejecta from the supernova explosion with a circumstellar shell of material, heating it to a temperature of 10 million-degrees Celsius. The outer shock wave is analogous to an awesome sonic boom resulting from this collision The x-rays reveal a bright object near the center, which may be the long-sought neutron star or black hole remnant of the explosion that produced Cassiopeia A. Cassiopeia A is the 320-year-old remnant of a massive star that exploded. Located in the constellation Cassiopeia, it is 10 light-years across and 10,000 light-years from Earth. A supernova occurs when a massive star has used up its nuclear fuel and the pressure drops in the central core of the star. The matter in the core is crushed by gravity to higher and higher densities, and temperatures reach billions of degrees. Under these extreme conditions, nuclear reactions occur violently and catastrophically, reversing the collapse. A thermonuclear shock wave races through the now expanding stellar debris, fusing lighter elements into heavier ones and producing a brilliant visual outburst.
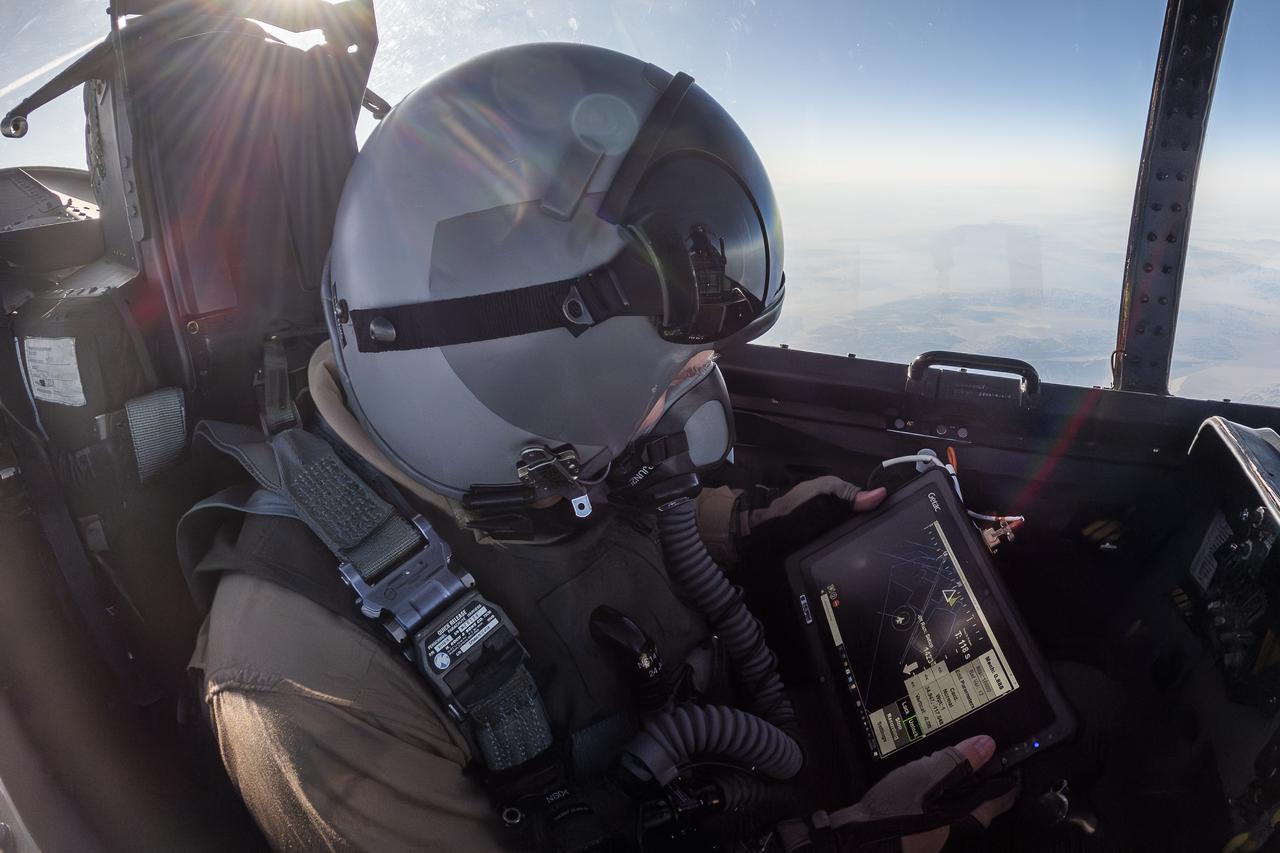

NASA photographer James Ross monitors the Airborne Location Integrating Geospatial Navigation System (ALIGNS) from the backseat of an F-15 near NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The ALIGNS provides real-time positioning guidance between aircraft for shock wave probing and schlieren imagery capture.

NASA test pilot Nils Larson inspects the agency’s F-15D research aircraft at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, ahead of a calibration flight for a newly installed near-field shock-sensing probe. Mounted on the F-15D, the probe is designed to measure shock waves generated by the X-59 quiet supersonic aircraft during flight. The data will help researchers better understand how shock waves behave in close proximity to the aircraft, supporting NASA’s Quesst mission to enable quiet supersonic flight over land.
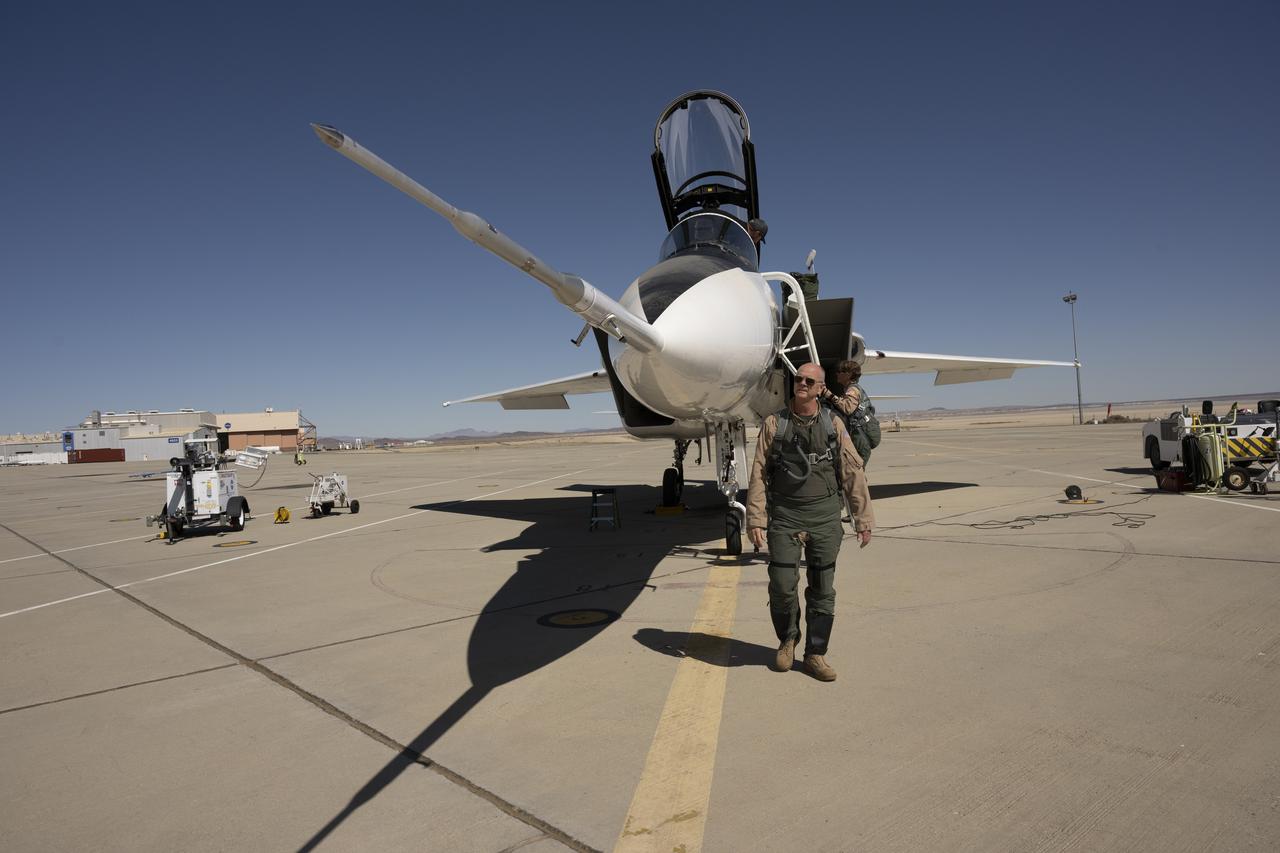

NASA test pilot Nils Larson inspects the agency’s F-15D research aircraft at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, ahead of a calibration flight for a newly installed near-field shock-sensing probe. Mounted on the F-15D, the probe is designed to measure shock waves generated by the X-59 quiet supersonic aircraft during flight. The data will help researchers better understand how shock waves behave in close proximity to the aircraft, supporting NASA’s Quesst mission to enable quiet supersonic flight over land.
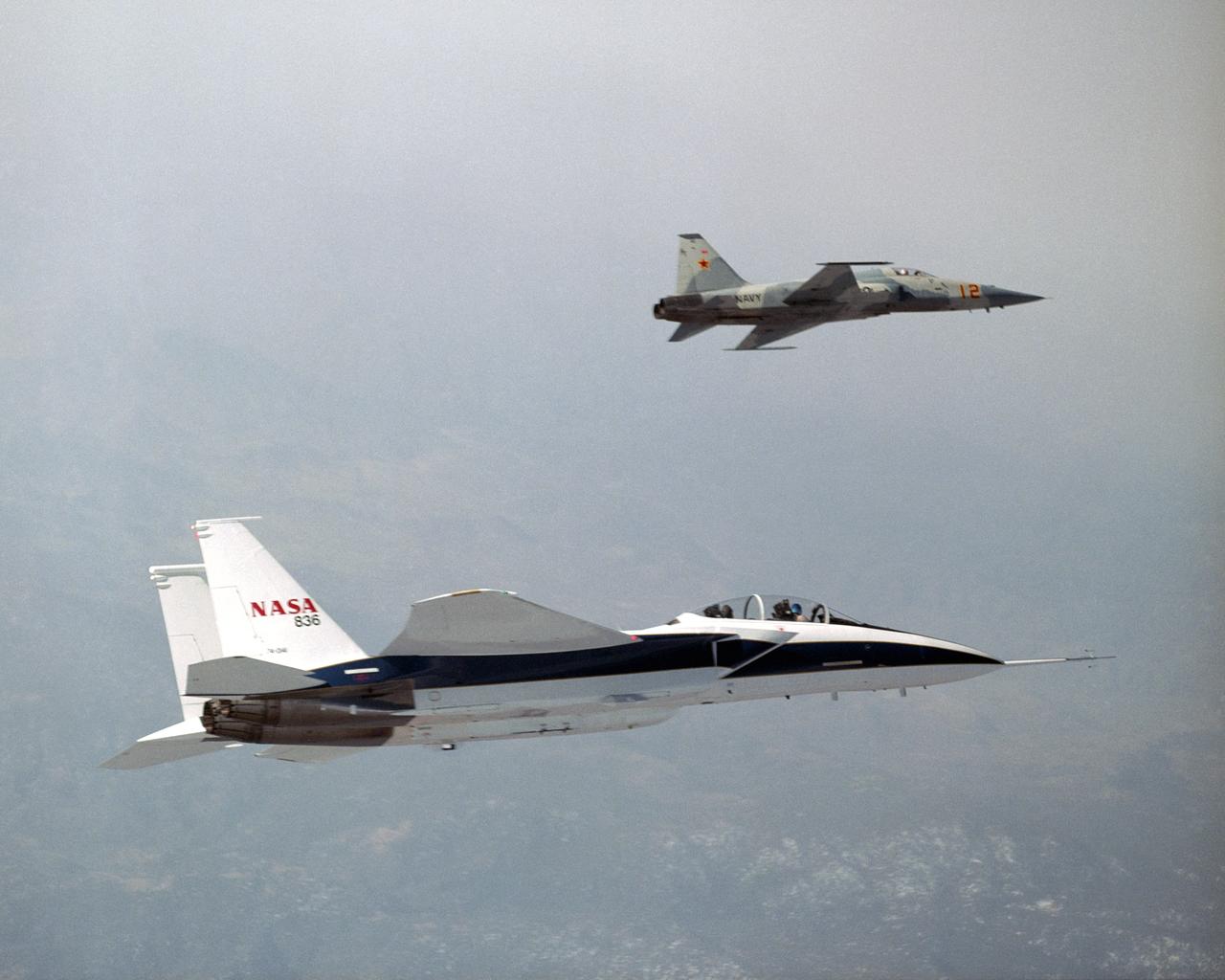

NASA's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft recently flew in the supersonic shock wave of a U.S. Navy F-5E in support of the F-5 Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency's (DARPA) Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. The flights originated from the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. Four flights were flown in order to measure the F-5E's near-field (close-up) sonic boom signature at Mach 1.4, during which more than 50 shockwave patterns were measured at distances as close as 100 feet below the F-5E.
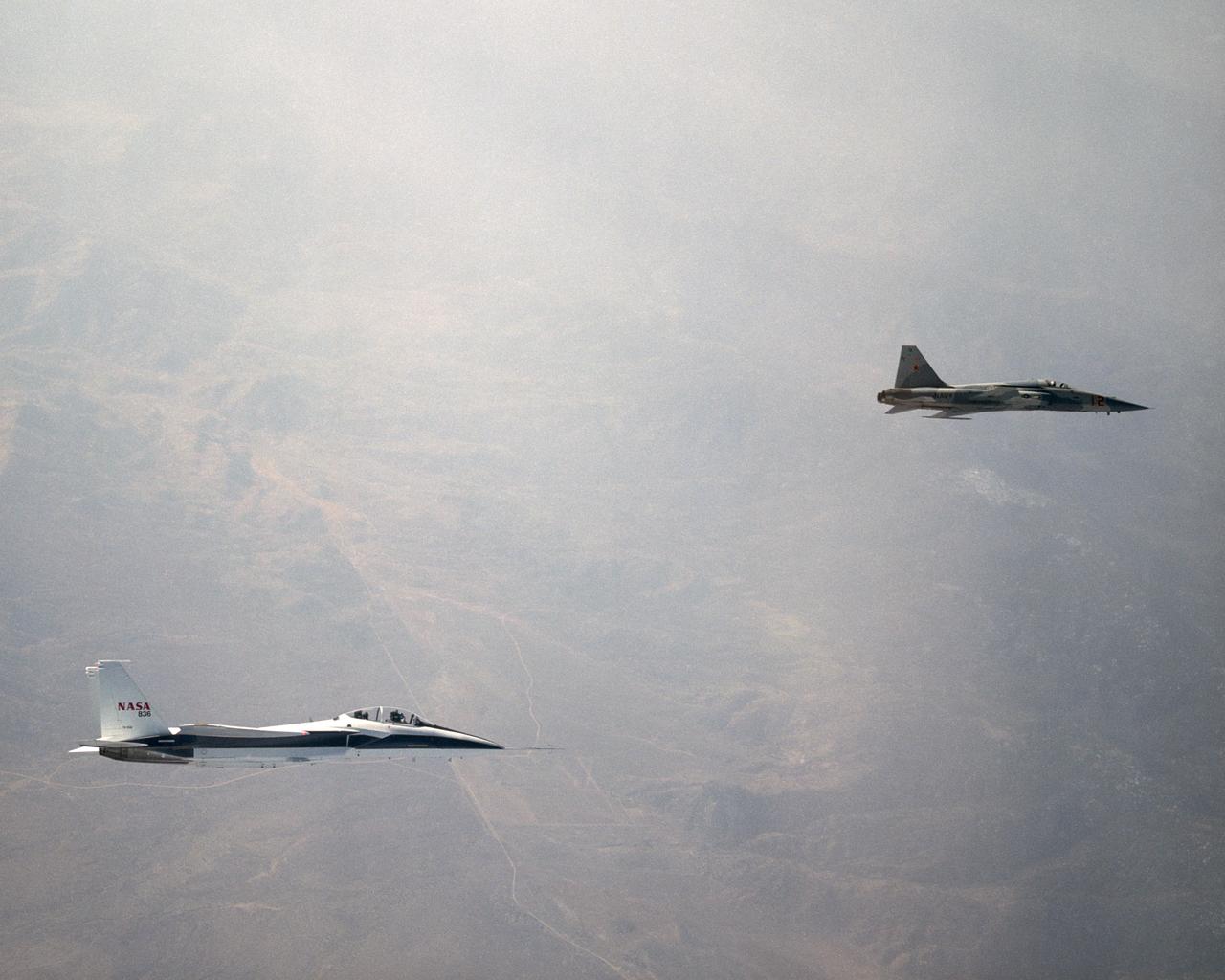

NASA's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft recently flew in the supersonic shock wave of a U.S. Navy F-5E in support of the F-5 Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency's (DARPA) Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. The flights originated from the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. Four flights were flown in order to measure the F-5E's near-field (close-up) sonic boom signature at Mach 1.4, during which more than 50 shockwave patterns were measured at distances as close as 100 feet below the F-5E.
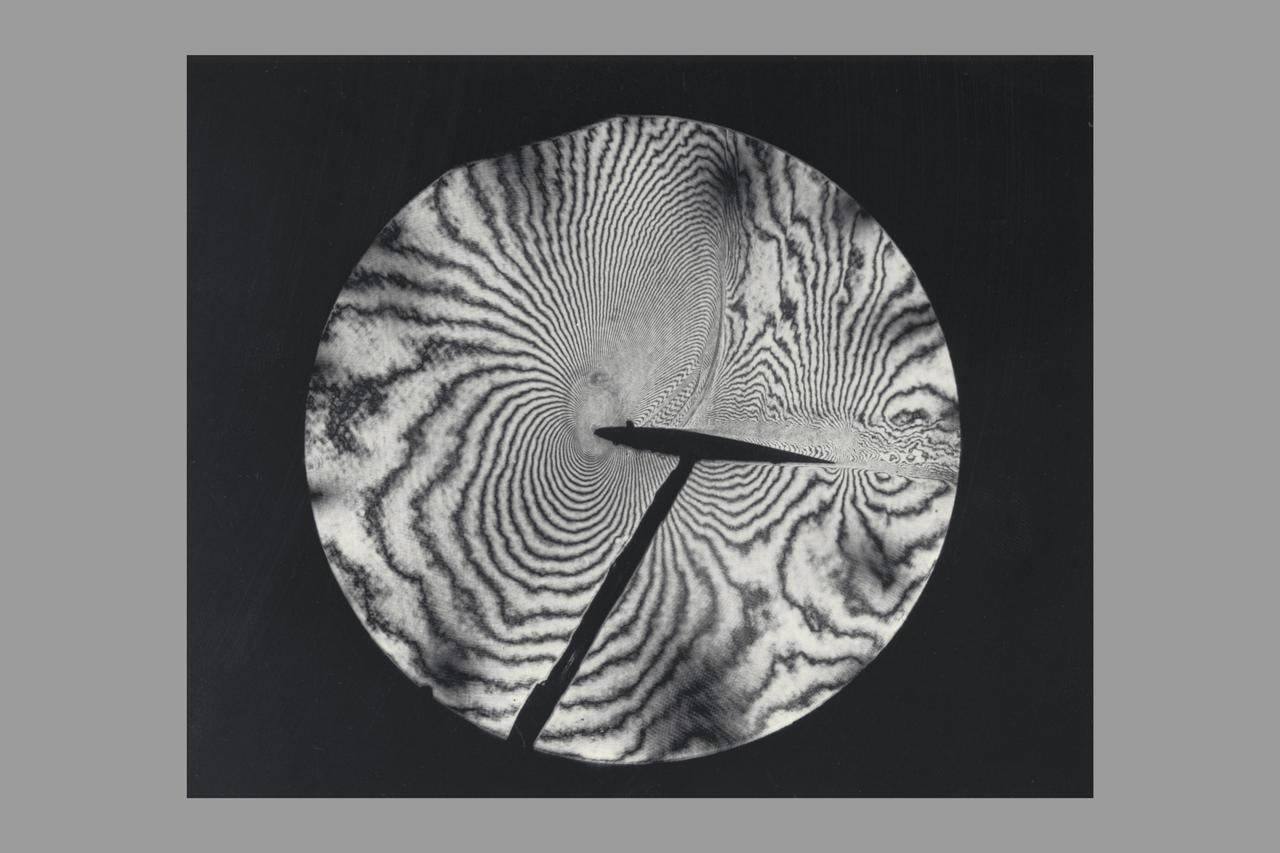

Interferogram of Transonic flow field - reconstructed laser hologram as an infinite-fringe interferogram shows shock-wave shape, location and separaton of the airfoil boundry layer
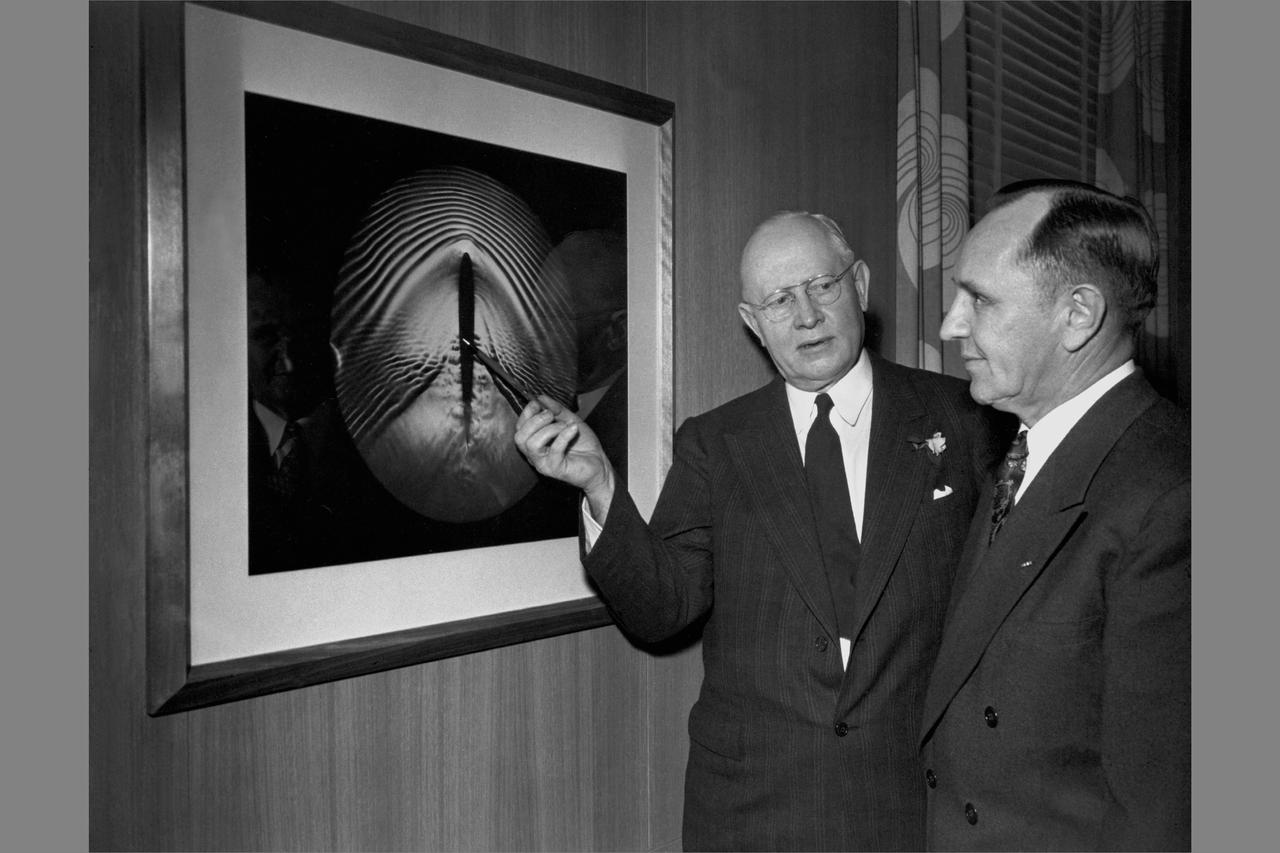

Ames Aeronautica Laboratory Dedication ceremonies; Dr. Lewis and Smity DeFrance, Director, Ames Research Center standing in front of shock-wave picture.
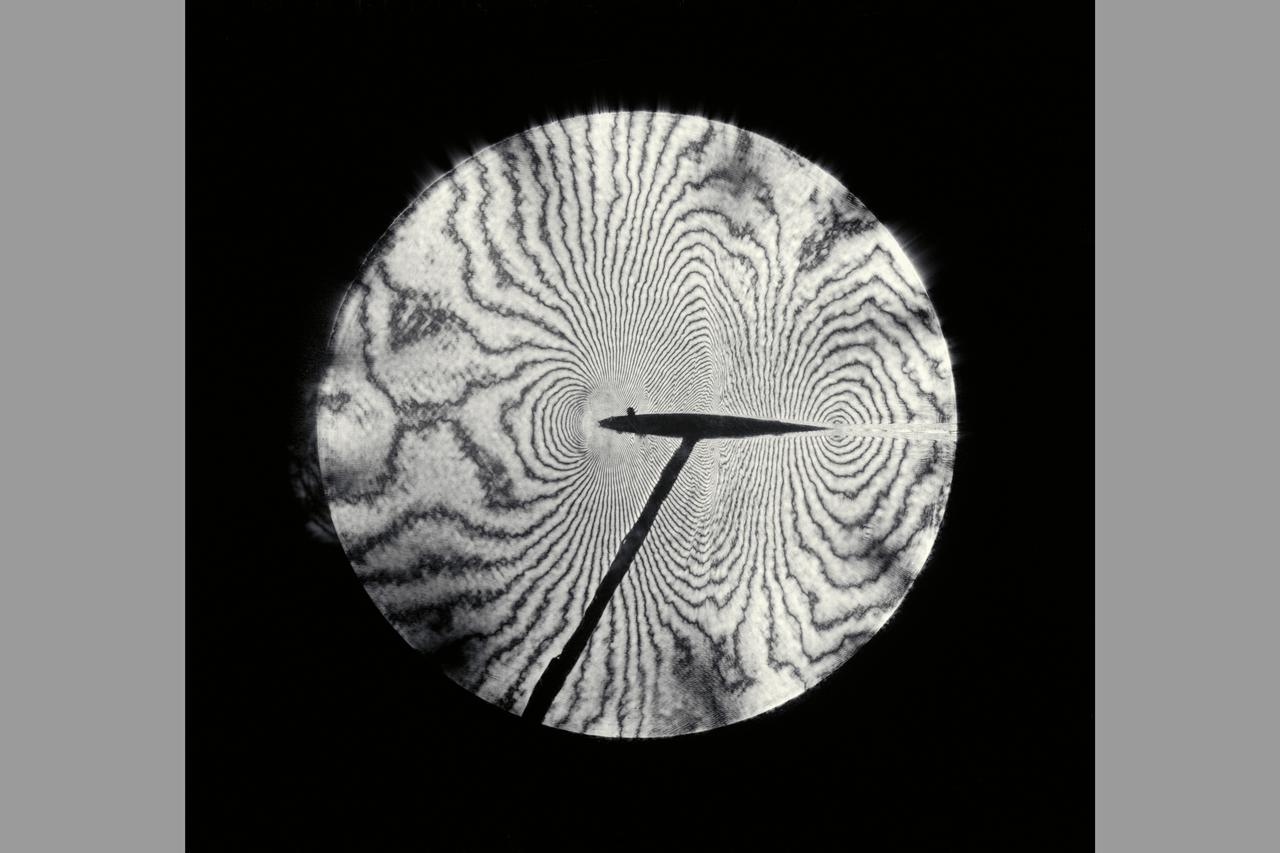

Interferogram of Transonic flow field - reconstructed laser hologram as an infinite-fringe interferogram shows shock-wave shape, location and separaton of the airfoil boundry layer
NASA's three Great Observatories -- the Hubble Space Telescope, the SpitzerSpace Telescope, and the Chandra X-ray Observatory -- joined forces to probe theexpanding remains of a supernova, called Kepler's supernova remnant, first seen 400 years ago by sky watchers, including astronomer Johannes Kepler. The combined image unveils a bubble-shaped shroud of gas and dust that is 14light-years wide and is expanding at 4 million miles per hour (2,000 kilometersper second). Observations from each telescope highlight distinct features of thesupernova remnant, a fast-moving shell of iron-rich material from the explodedstar, surrounded by an expanding shock wave that is sweeping up interstellar gasand dust. Each color in this image represents a different region of the electromagneticspectrum, from X-rays to infrared light. These diverse colors are shown in thepanel of photographs below the composite image. The X-ray and infrared datacannot be seen with the human eye. By color-coding those data and combining themwith Hubble's visible-light view, astronomers are presenting a more completepicture of the supernova remnant. Visible-light images from the Hubble telescope (colored yellow) reveal where the supernova shock wave is slamming into the densest regions of surrounding gas.The bright glowing knots are dense clumps from instabilities that form behindthe shock wave. The Hubble data also show thin filaments of gas that look likerippled sheets seen edge-on. These filaments reveal where the shock wave isencountering lower-density, more uniform interstellar material. The Spitzer telescope shows microscopic dust particles (colored red) that havebeen heated by the supernova shock wave. The dust re-radiates the shock wave'senergy as infrared light. The Spitzer data are brightest in the regionssurrounding those seen in detail by the Hubble telescope. The Chandra X-ray data show regions of very hot gas, and extremely high-energyparticles. The hottest gas (higher-energy X-rays, colored blue) is locatedprimarily in the regions directly behind the shock front. These regions alsoshow up in the Hubble observations, and also align with the faint rim of glowingmaterial seen in the Spitzer data. The X-rays from the region on the lower left(colored blue) may be dominated by extremely high-energy electrons that wereproduced by the shock wave and are radiating at radio through X-ray wavelengthsas they spiral in the intensified magnetic field behind the shock front. CoolerX-ray gas (lower-energy X-rays, colored green) resides in a thick interior shelland marks the location of heated material expelled from the exploded star. Kepler's supernova, the last such object seen to explode in our Milky Waygalaxy, resides about 13,000 light-years away in the constellation Ophiuchus. The Chandra observations were taken in June 2000, the Hubble in August 2003;and the Spitzer in August 2004. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06907

NACA Photographer/Graphic Supersonic Research: Schlieren photograph of the flow around airplane models showing effect of Sweptback on Shock Waves - M =1.2 (composite of shadowgraph samples on sweptback and straight wings
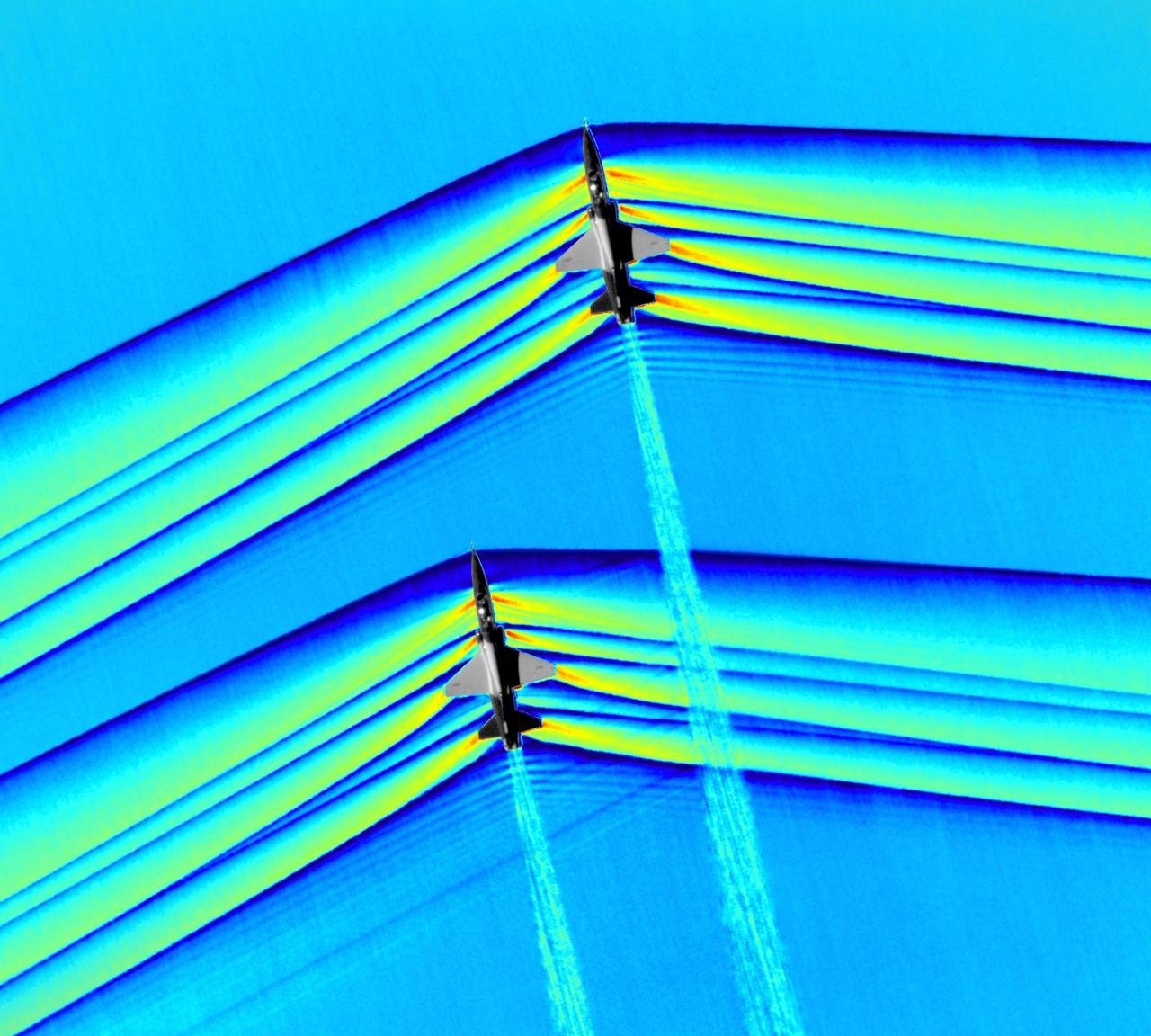
Composite image of Background Oriented Schlieren (BOS) data (contour) with a cut-out images of the T-38’s during a Mach Number 1.01 pass. This data is the first time shockwave interactions between two full scale aircraft traveling faster than the speed of sound have been imaged and shown with schlieren visualization. Original recording of the pass taken in the Black Mountain Supersonic Corridor at near Edwards AFB in December of 2018. Image acquired by JT Heineck, schlieren data processed by Neal Smith

Composite image of Background Oriented Schlieren (BOS) data (contour) with a cut-out images of the T-38’s during a Mach Number 1.01 pass. This data is the first time shockwave interactions between two full scale aircraft traveling faster than the speed of sound have been imaged and shown with schlieren visualization. Original recording of the pass taken in the Black Mountain Supersonic Corridor at near Edwards AFB in December of 2018. Image acquired by JT Heineck, schlieren data processed by Neal Smith

Composite image of Background Oriented Schlieren (BOS) data (contour) with a cut-out images of the T-38’s during a Mach Number 1.02 pass. The interaction of the shockwave of the trailing aircraft with the exhaust plume of the lead aircraft shows a shockwave reflection. Original recording of the pass taken in the Black Mountain Supersonic Corridor at near Edwards AFB in December of 2018. Image acquired by JT Heineck, schlieren data processed by Neal Smith.

Composite image of Background Oriented Schlieren (BOS) data (contour) with a cut-out images of the T-38’s during a Mach Number 1.02 pass. The interaction of the shockwave of the trailing aircraft with the exhaust plume of the lead aircraft shows a shockwave reflection. Original recording of the pass taken in the Black Mountain Supersonic Corridor at near Edwards AFB in December of 2018. Image acquired by JT Heineck, schlieren data processed by Neal Smith.
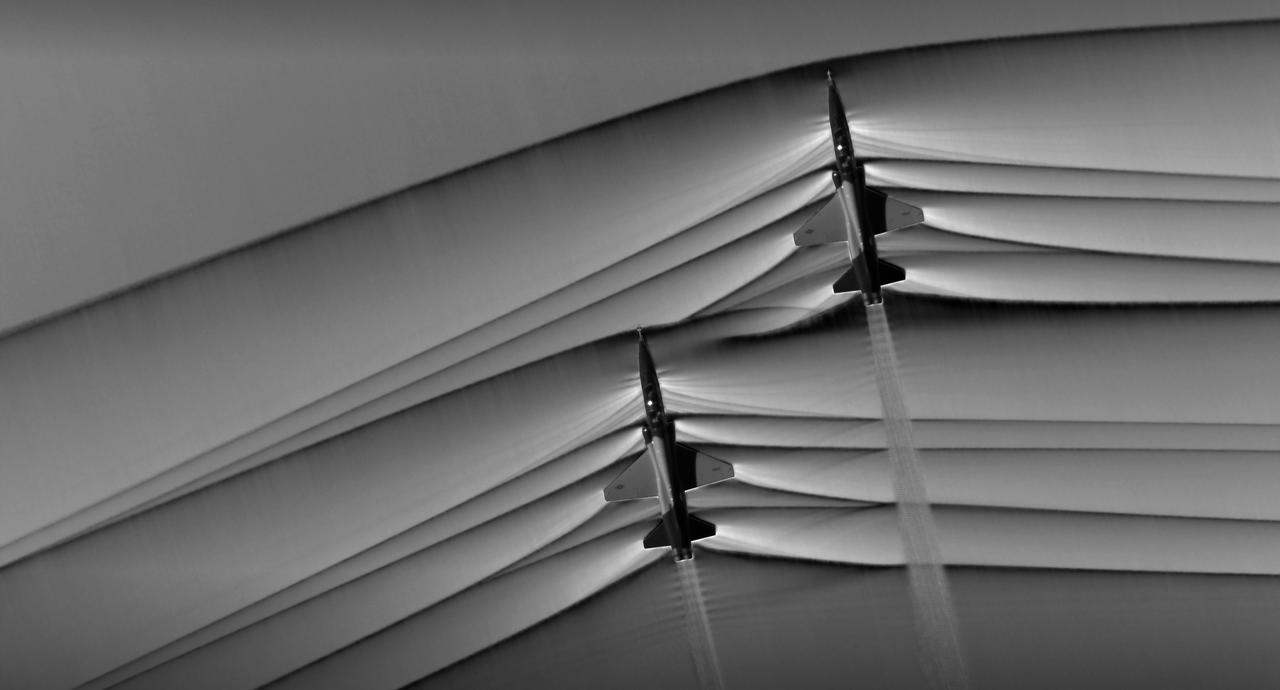
Composite image of Background Oriented Schlieren (BOS) data (contour) with a cut-out images of the T-38’s during a Mach Number 1.01 pass. This data is the first time shockwave interactions between two full scale aircraft traveling faster than the speed of sound have been imaged and shown with schlieren visualization. Original recording of the pass taken in the Black Mountain Supersonic Corridor at near Edwards AFB in December of 2018. Image acquired by JT Heineck, schlieren data processed by Neal Smith.
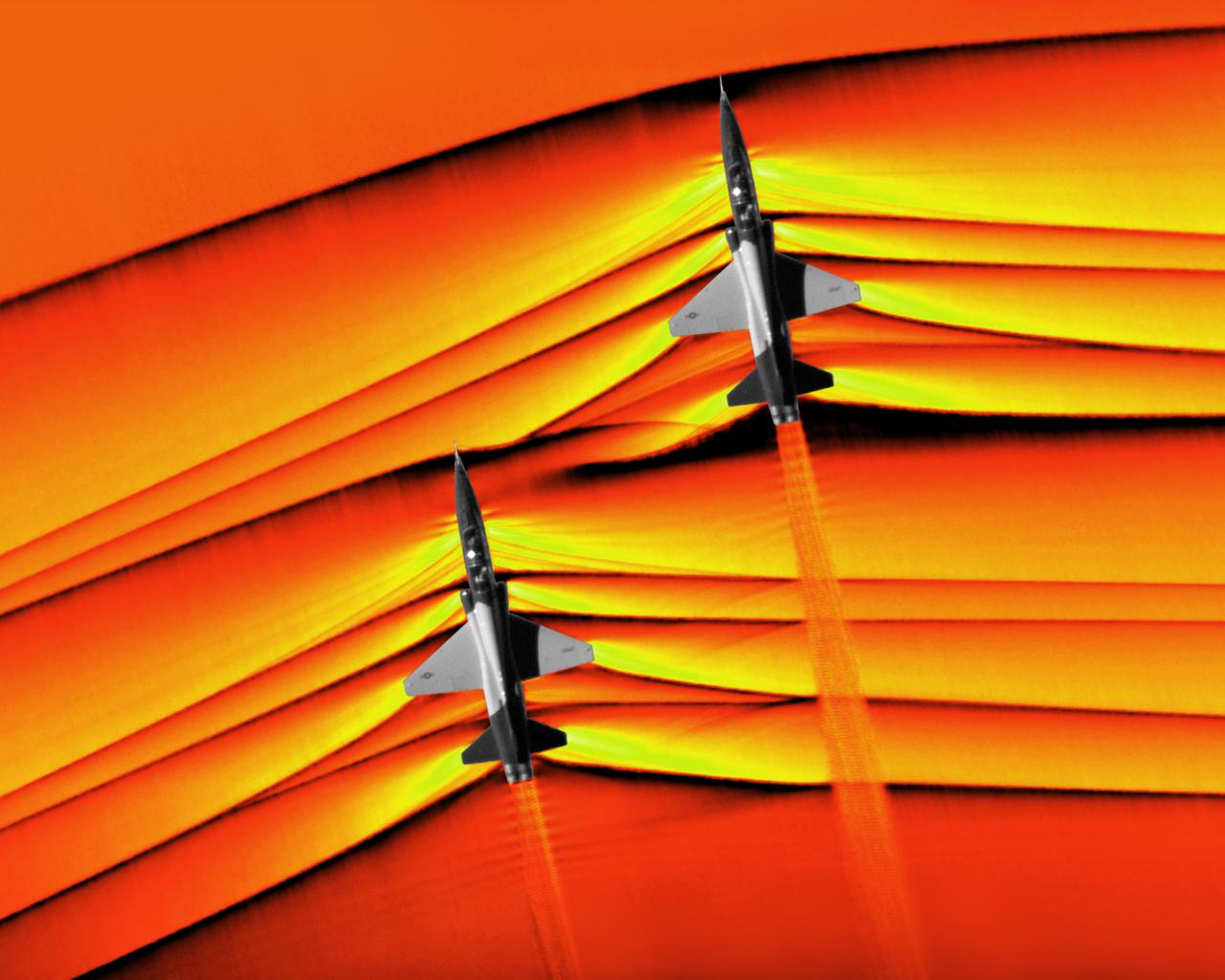
Composite image of Background Oriented Schlieren (BOS) data (contour) with a cut-out images of the T-38’s during a Mach Number 1.02 pass. The interaction of the shockwave of the trailing aircraft with the exhaust plume of the lead aircraft shows a shockwave reflection. Original recording of the pass taken in the Black Mountain Supersonic Corridor at near Edwards AFB in December of 2018. Image acquired by JT Heineck, schlieren data processed by Neal Smith.
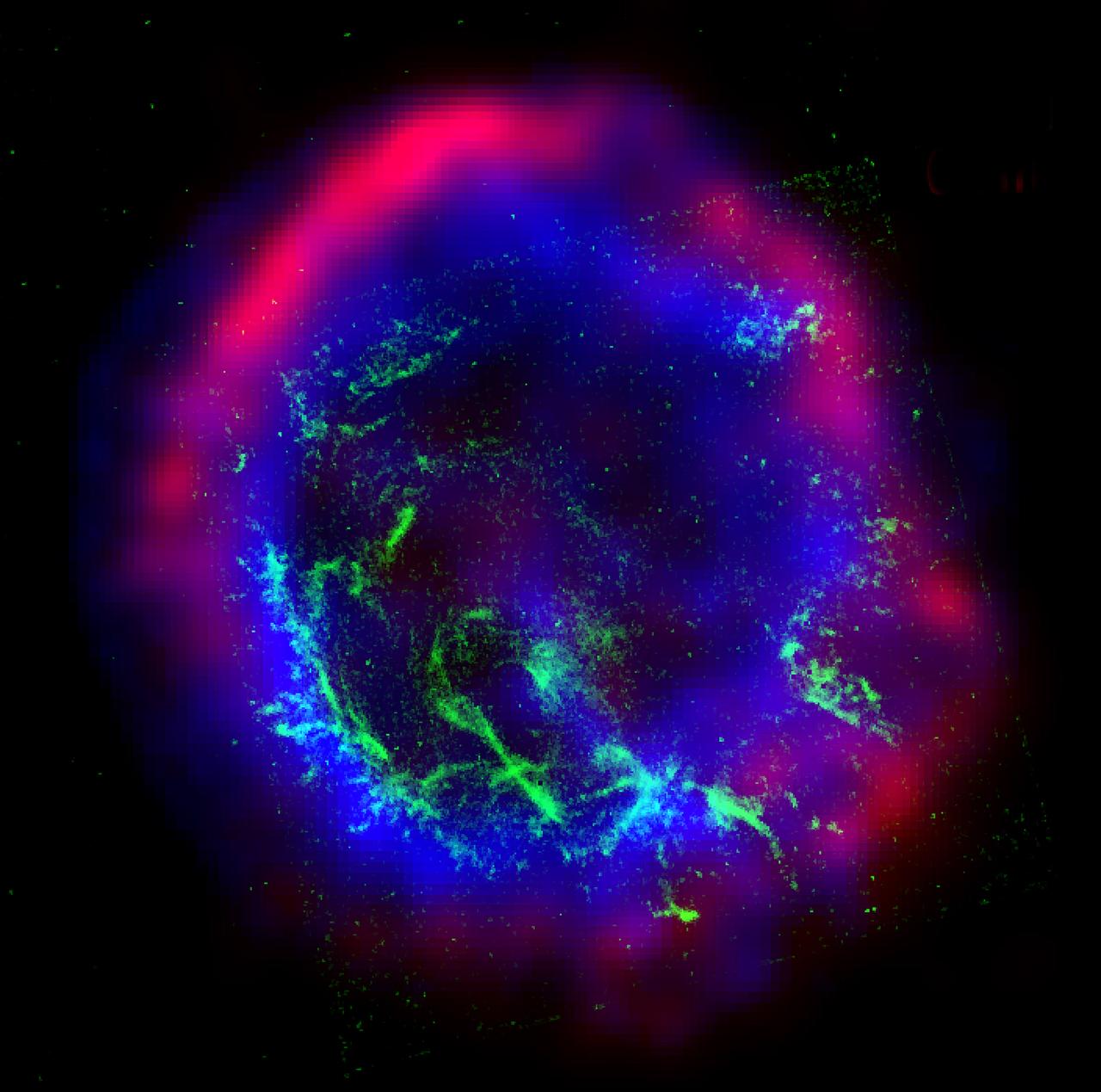
This image is a color composite of the supernova remnant E0102-72: x-ray (blue), optical (green), and radio (red). E0102-72 is the remnant of a star that exploded in a nearby galaxy known as the Small Magellanic Cloud. The star exploded outward at speeds in excess of 20 million kilometers per hour (12 million mph) and collided with surrounding gas. This collision produced two shock waves, or cosmic sonic booms, one traveling outward, and the other rebounding back into the material ejected by the explosion. The radio image, shown in red, was made using the Australia Telescope Compact Array. The radio waves are due to extremely high-energy electrons spiraling around magnetic field lines in the gas and trace the outward moving shock wave. The Chandra X-ray Observatory image, shown in blue, shows gas that has been heated to millions of degrees by the rebounding, or reverse shock wave. The x-ray data show that this gas is rich in oxygen and neon. These elements were created by nuclear reactions inside the star and hurled into space by the supernova. The Hubble Space Telescope optical image, shown in green, shows dense clumps of oxygen gas that have "cooled" to about 30,000 degrees. Photo Credit: X-ray (NASA/CXC/SAO); optical (NASA/HST): radio: (ACTA)
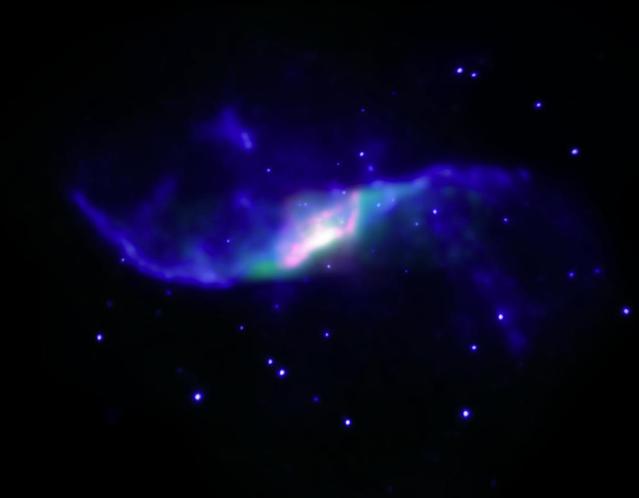

A composite image of the spiral galaxy NGC 4258 showing X-ray emission observed with NASA Chandra X-ray Observatory blue and infrared emission observed with NASA Spitzer Space Telescope red and green.
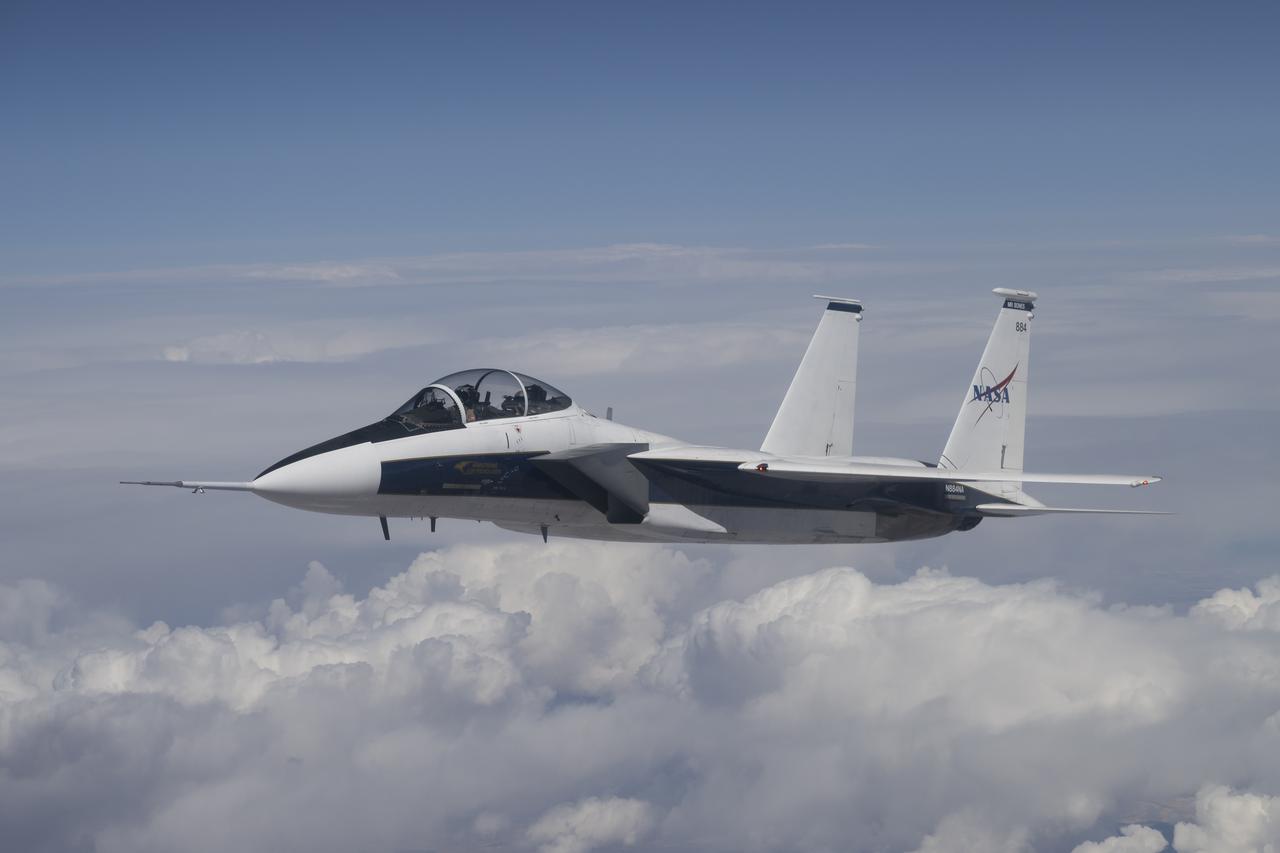

NASA’s F-15D research aircraft conducts a test flight near Edwards, California, with a newly installed near-field shock-sensing probe. Identical to a previously flown version that was intended as the backup, this new probe will capture shock wave data near the X-59 as it flies faster than the speed of sound, supporting NASA’s Quesst mission.

In-flight photo of the NASA F-15B used in tests of the X-33 Thermal Protection System (TPS) materials. Flying at subsonic speeds, the F-15B tests measured the air loads on the proposed X-33 protective materials. In contrast, shock loads testing investigated the local impact of the supersonic shock wave itself on the TPS materials. Similar tests had been done in 1985 for the space shuttle tiles, using an F-104 aircraft.

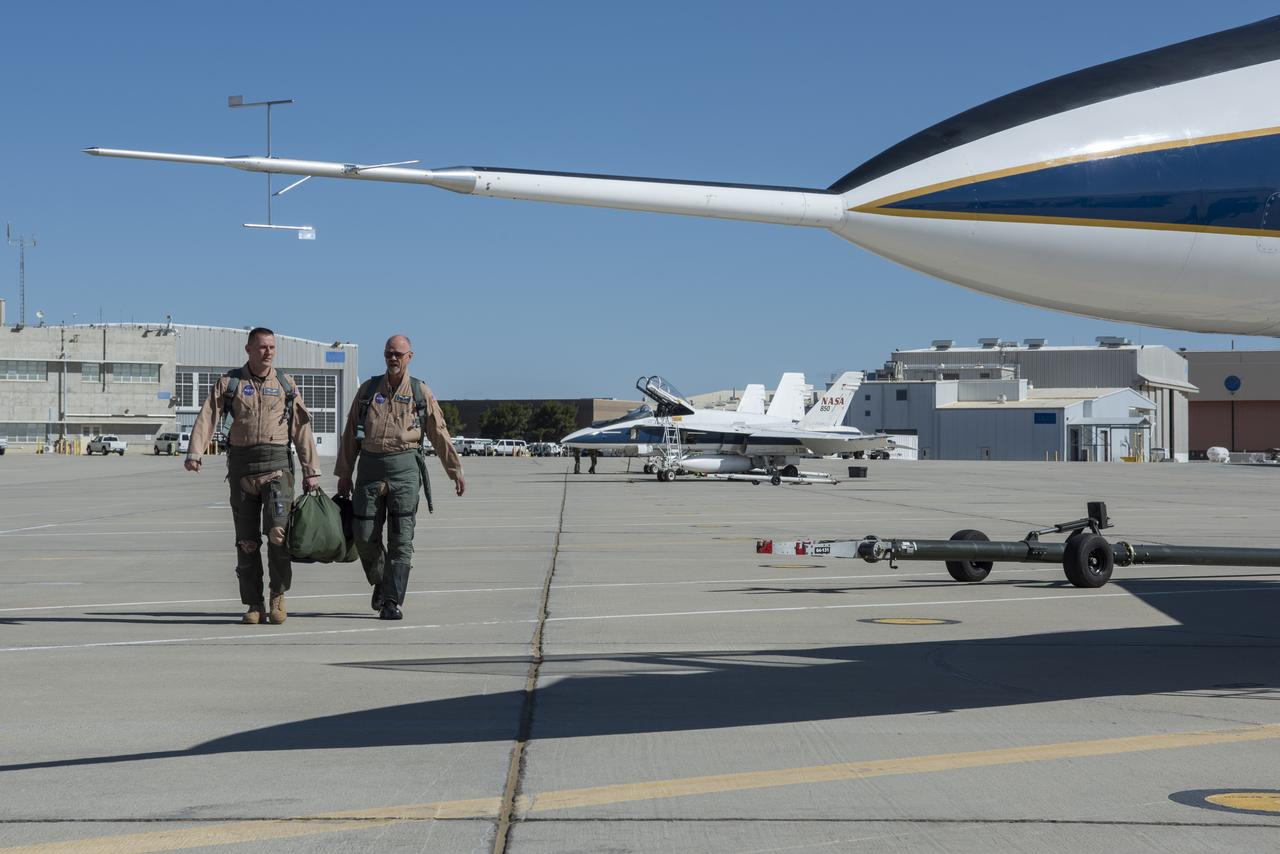
Two NASA F-15 aircraft sit on the ramp at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Edwards, California, ahead of dual F-15 flights that validated the integration of three tools – the Airborne Schlieren Photography System (ASPS), the Airborne Location Integrating Geospatial Navigation System (ALIGNS), and shock-sensing probe. Together these tools will measure and visualize the shock waves generated by NASA's X-59.
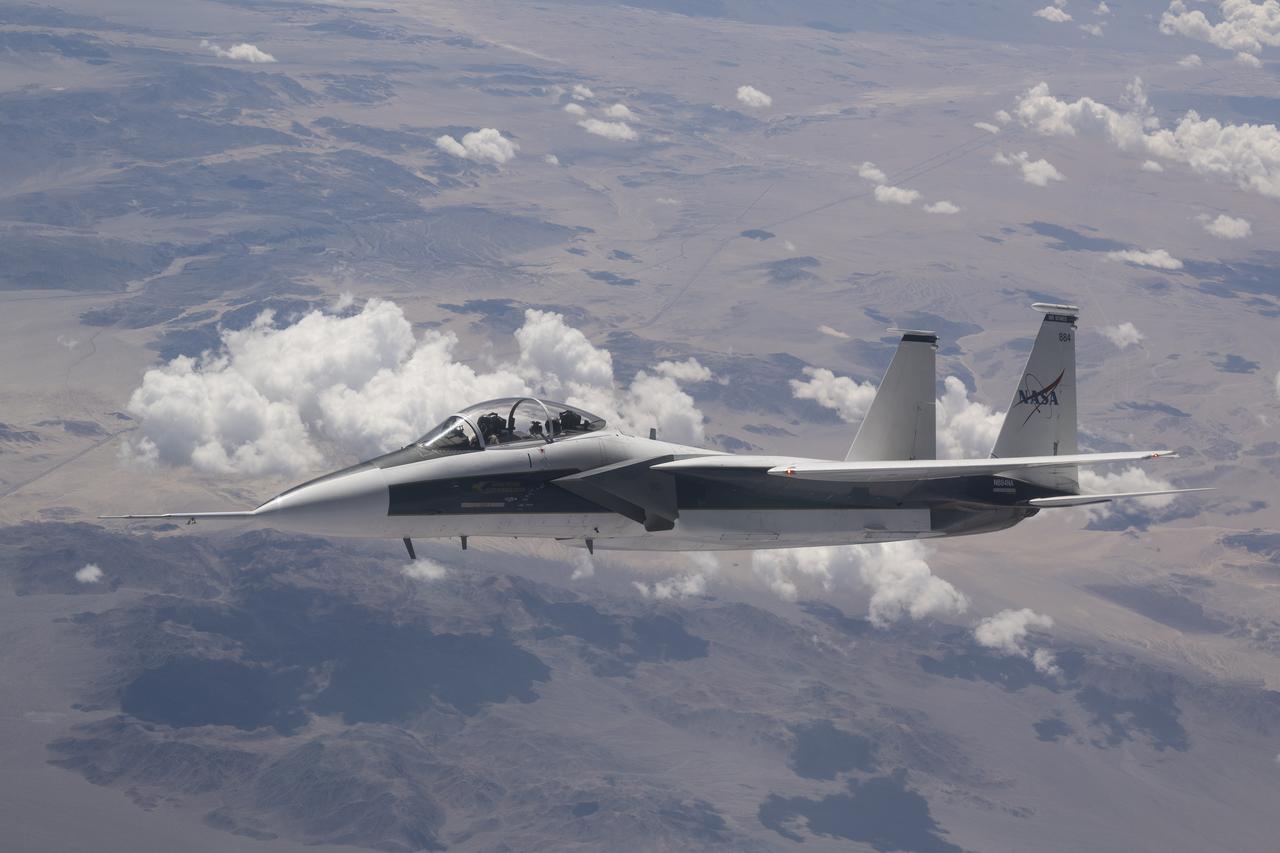

NASA’s F-15D research aircraft conducts a test flight near Edwards, California, with a newly installed near-field shock-sensing probe. Identical to a previously flown version that was intended as the backup, this new probe will capture shock wave data near the X-59 as it flies faster than the speed of sound, supporting NASA’s Quesst mission.
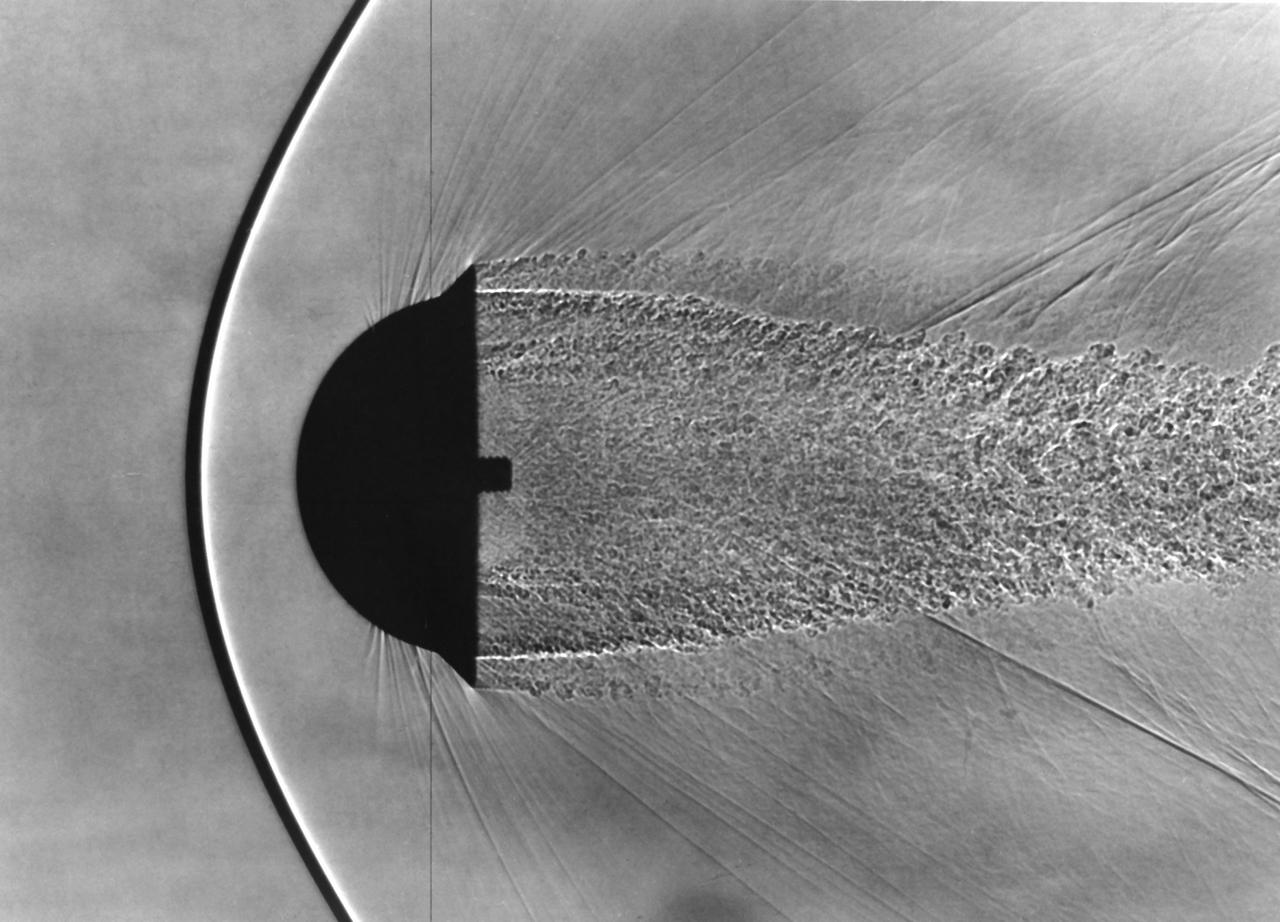
Shadowgraph of Finned Hemispherical model in free-flight show shock waves produced by blunt bodies (H. Julian Allen blunt nose theory) (Used in NASA/AMES publication 'Adventures in Research' A history of Ames Research Center 1940 - 1965 by Edwin P. Hartman - SP-4302)

This VIS image shows a double impact - two meteors hitting simultaneously. The two meteors would have started as a single object, at some point prior to impact the object separated into parts. The two parts followed the same path to the surface, hitting at the same time in close proximity. The linear feature at the center is where the shock waves intersect, its straightness showing the impacts were simultaneous (and nearly equal in size). The ejecta created from the impact tends to be focused to the sides of the doublet, often forming a butterfly-like ejecta blanket. The butterfly pattern is most common at oblique angle impacts, but can also form by the interaction of the impact shock waves. These craters are located in Utopia Planitia. Orbit Number: 72448 Latitude: 27.1977 Longitude: 95.4916 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2018-04-14 13:36 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22606
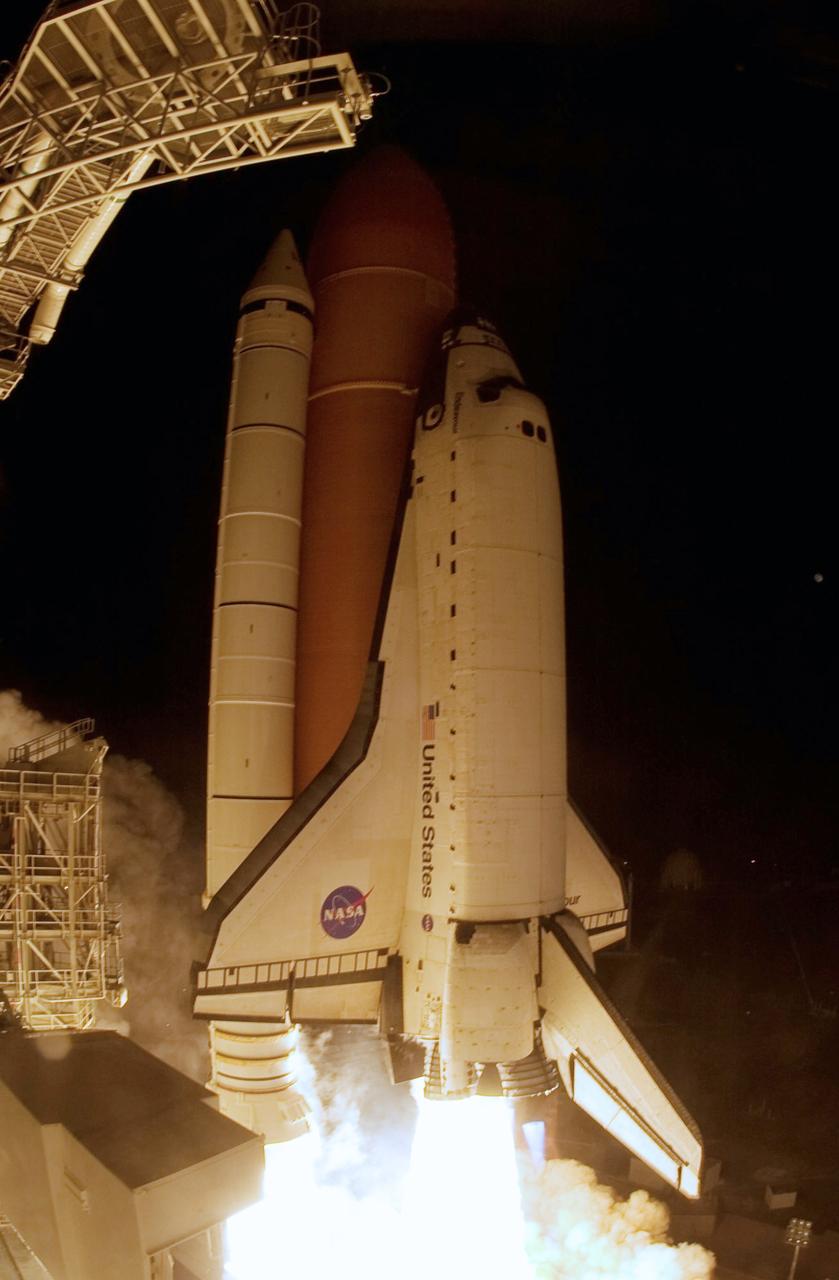

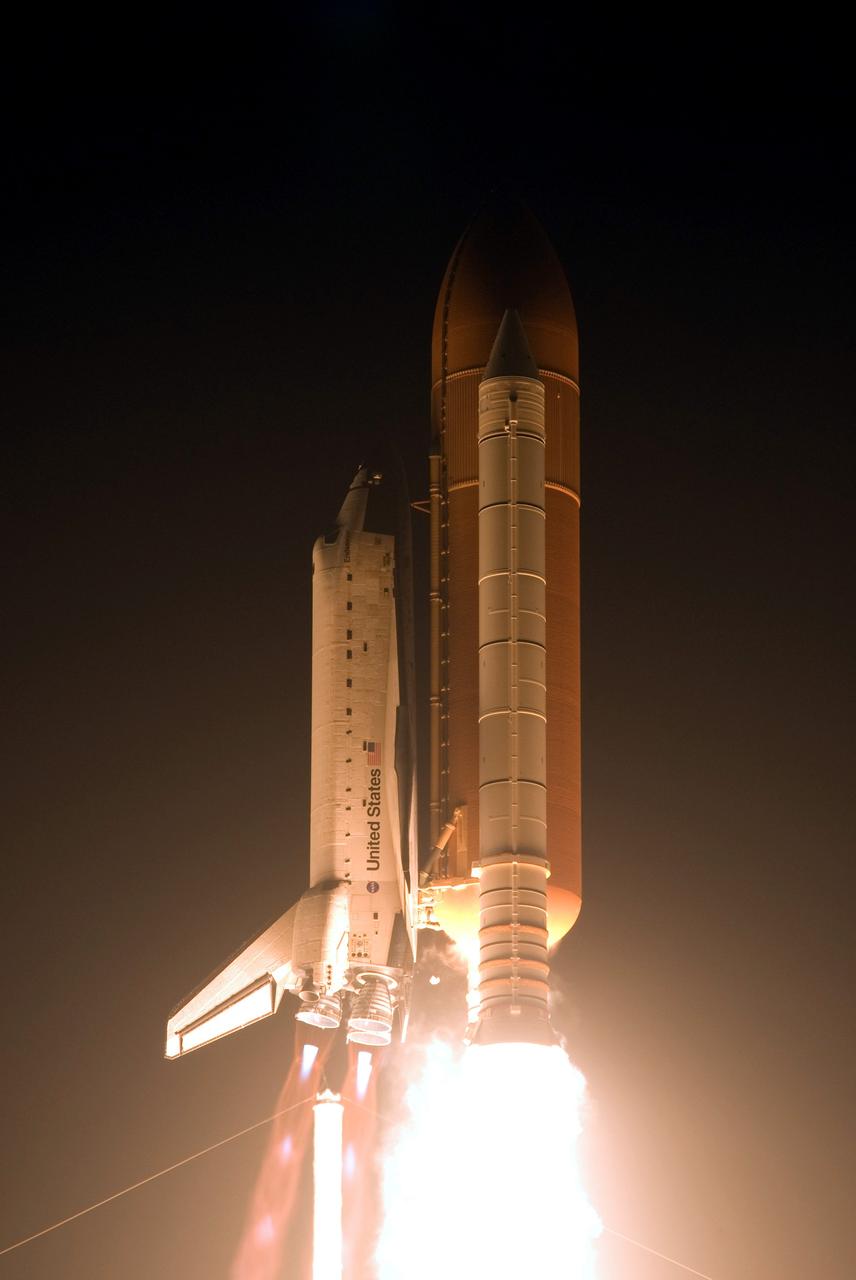
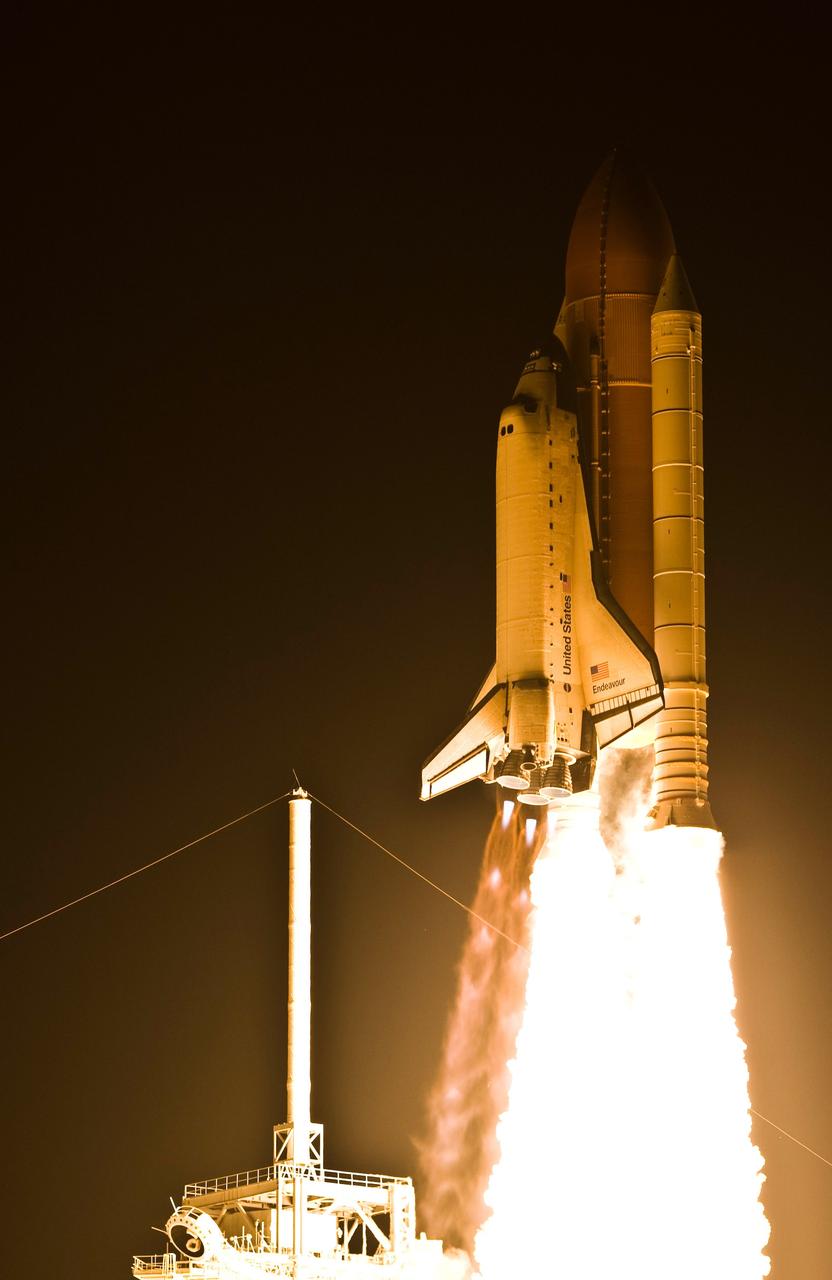
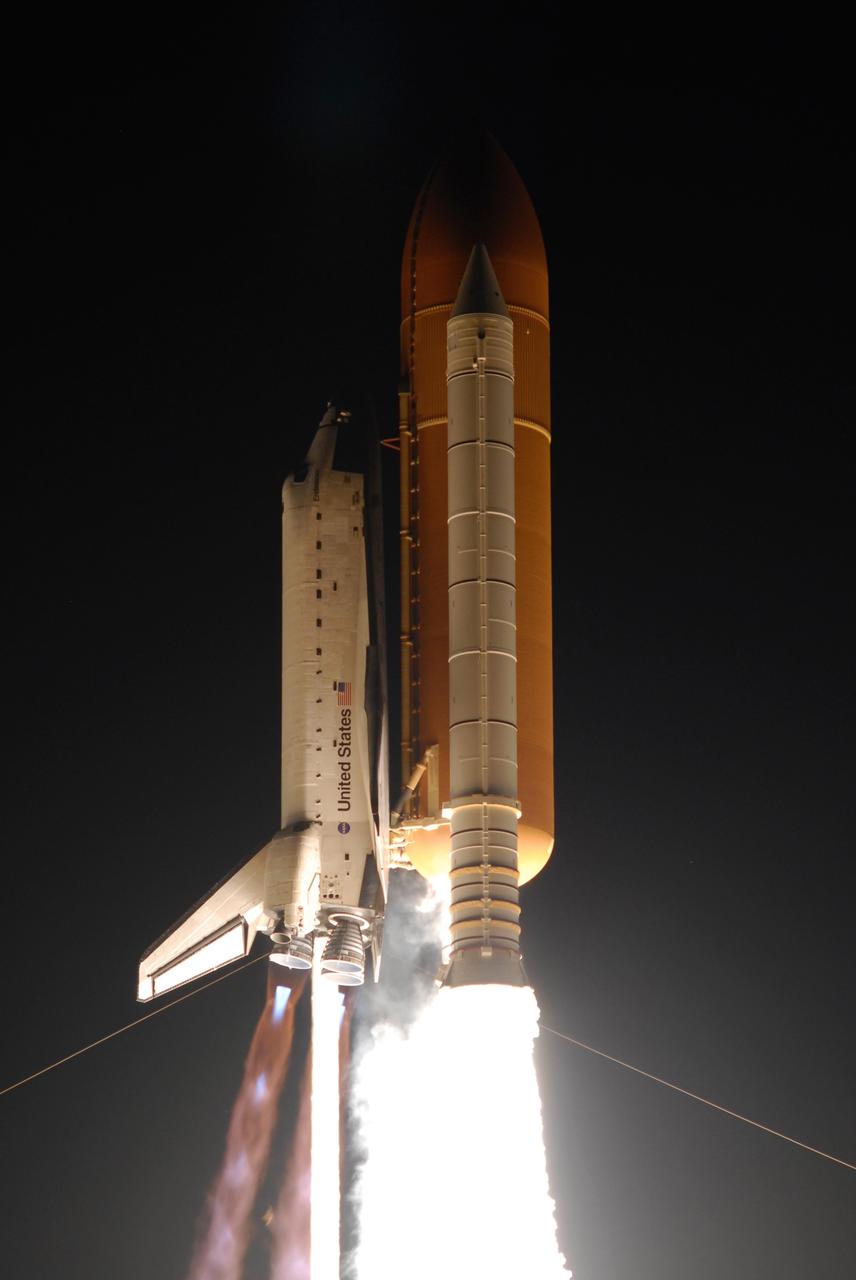
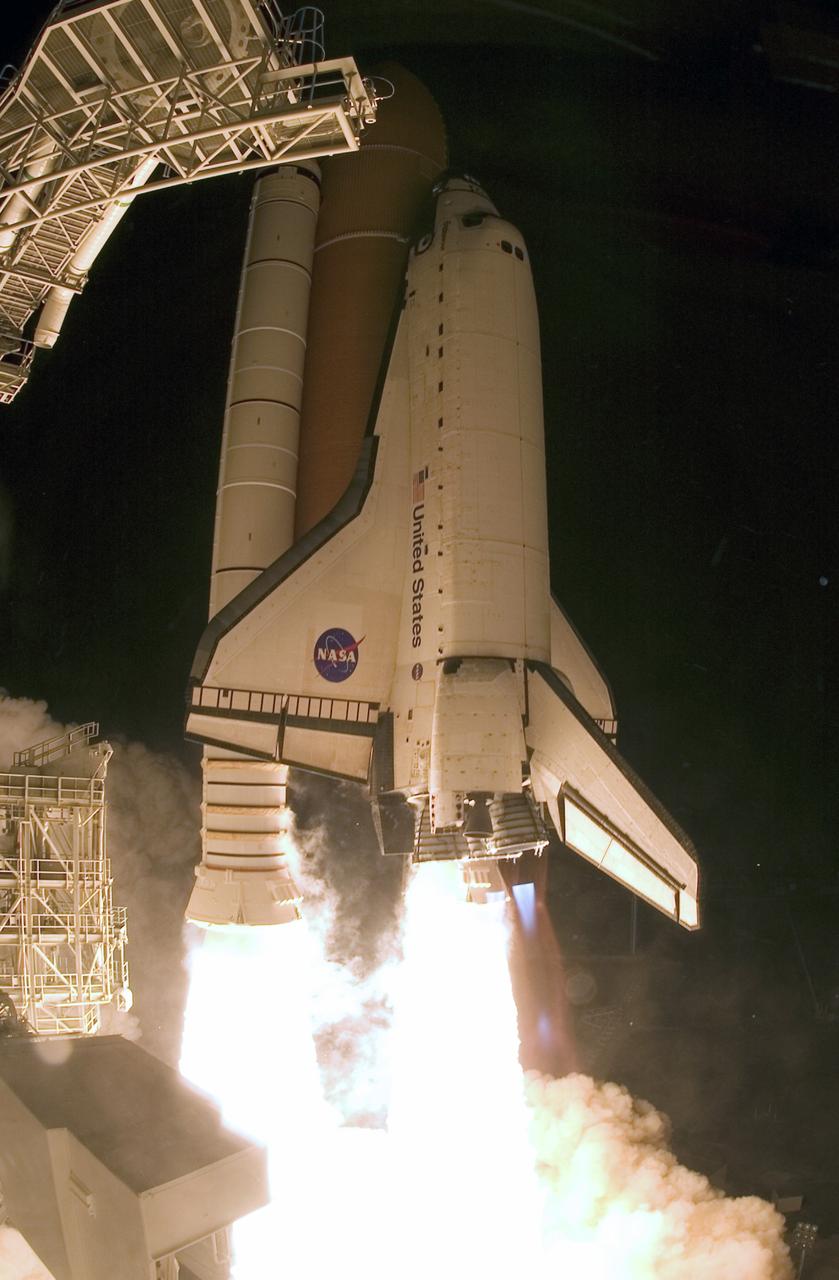
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Endeavour roars into the night sky on the STS-126 mission. Blue cones of light, the shock or mach diamonds that are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system can be seen beneath the nozzles of the main engines. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph-Kevin O'Connell
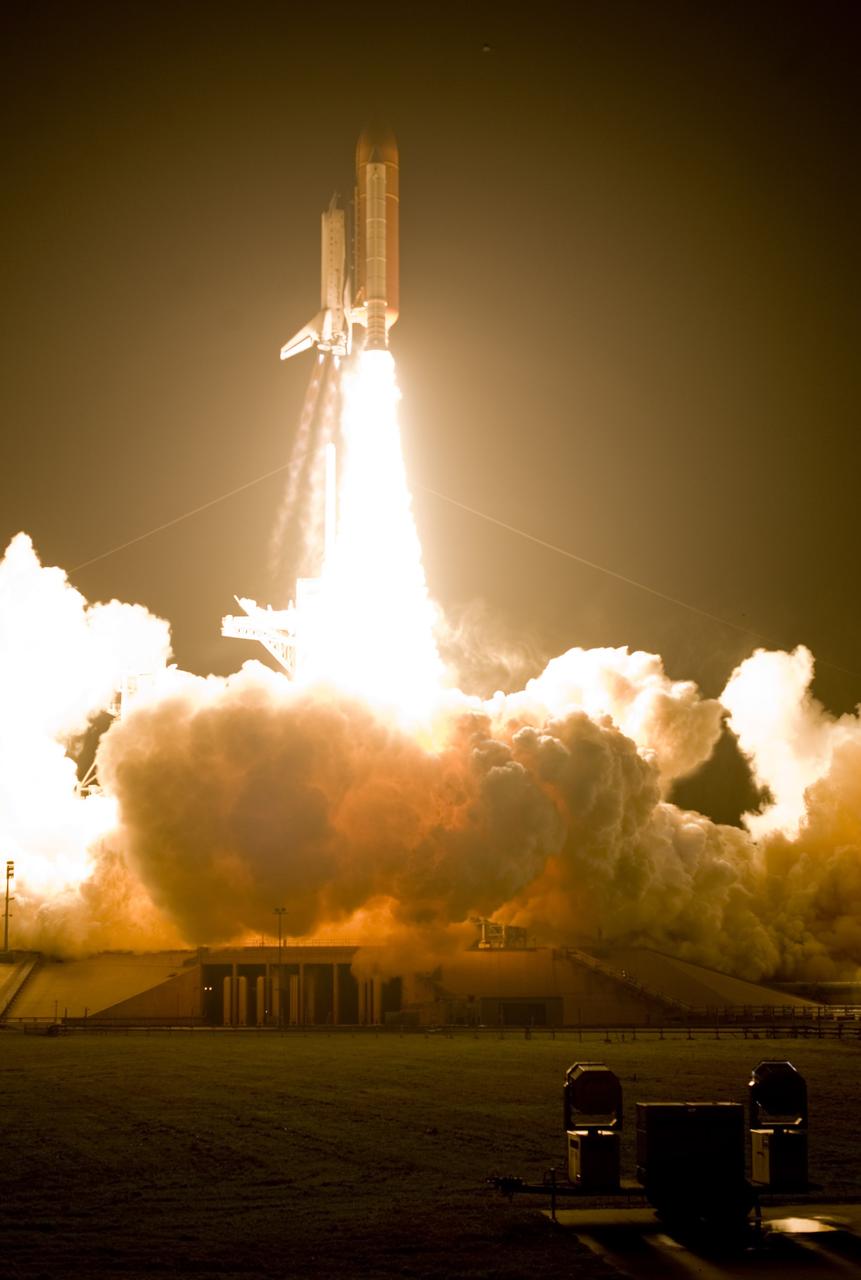

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Endeavour erupts from the smoke and steam as it roars into the night sky on the STS-126 mission. Blue cones of light, the shock or mach diamonds that are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system, can be seen beneath the nozzles of the main engines. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews
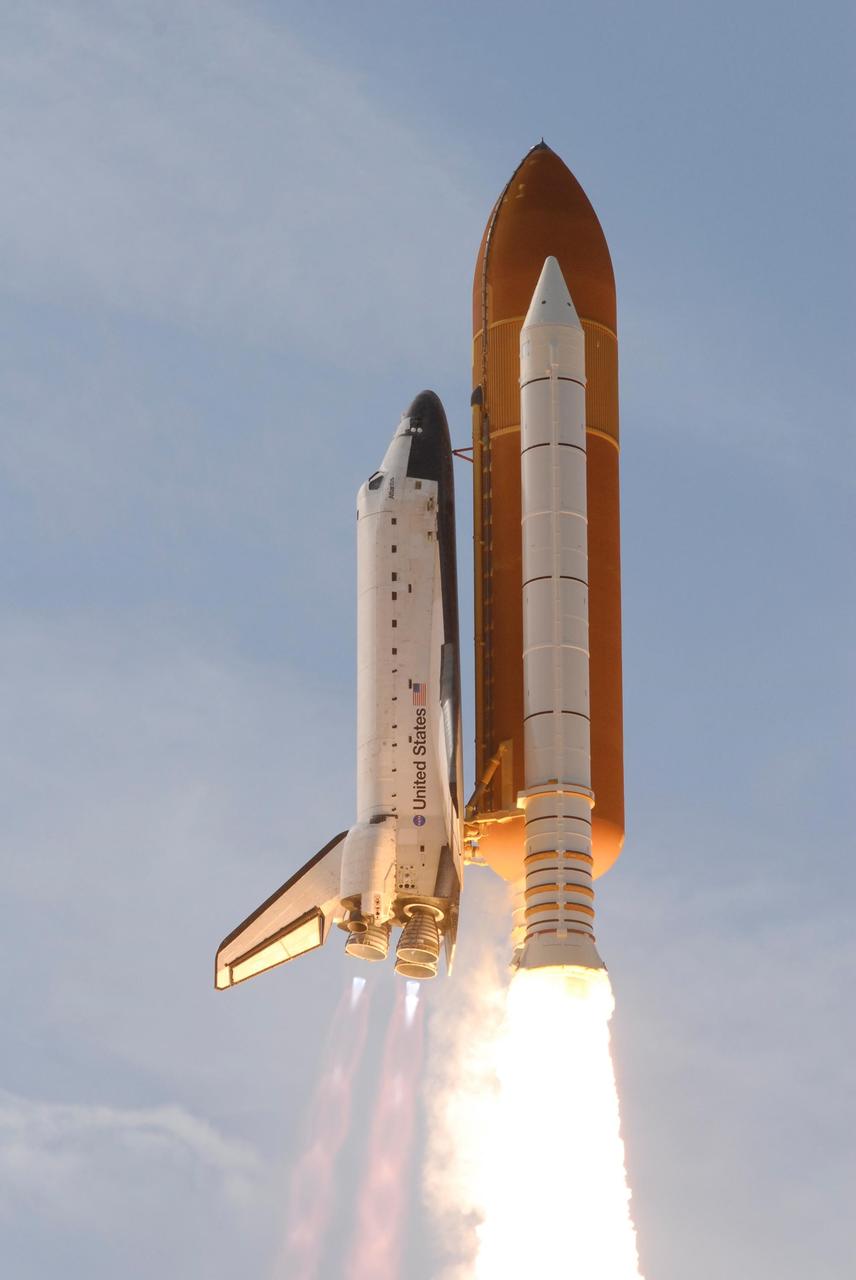

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The blue Florida sky helps silhouette space shuttle Atlantis as it hurtles into space on mission STS-122 to the International Space Station. Liftoff was on time at 2:45 p.m. EST. Below the nozzles of the main engines are the blue cones of light, known as shock or mach diamonds. They are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. The launch is the third attempt for Atlantis since December 2007 to carry the European Space Agency's Columbus laboratory to the International Space Station. During the 11-day mission, the crew's prime objective is to attach the laboratory to the Harmony module, adding to the station's size and capabilities. Photo credit: NASA/Jerry Cannon, Rusty Backer
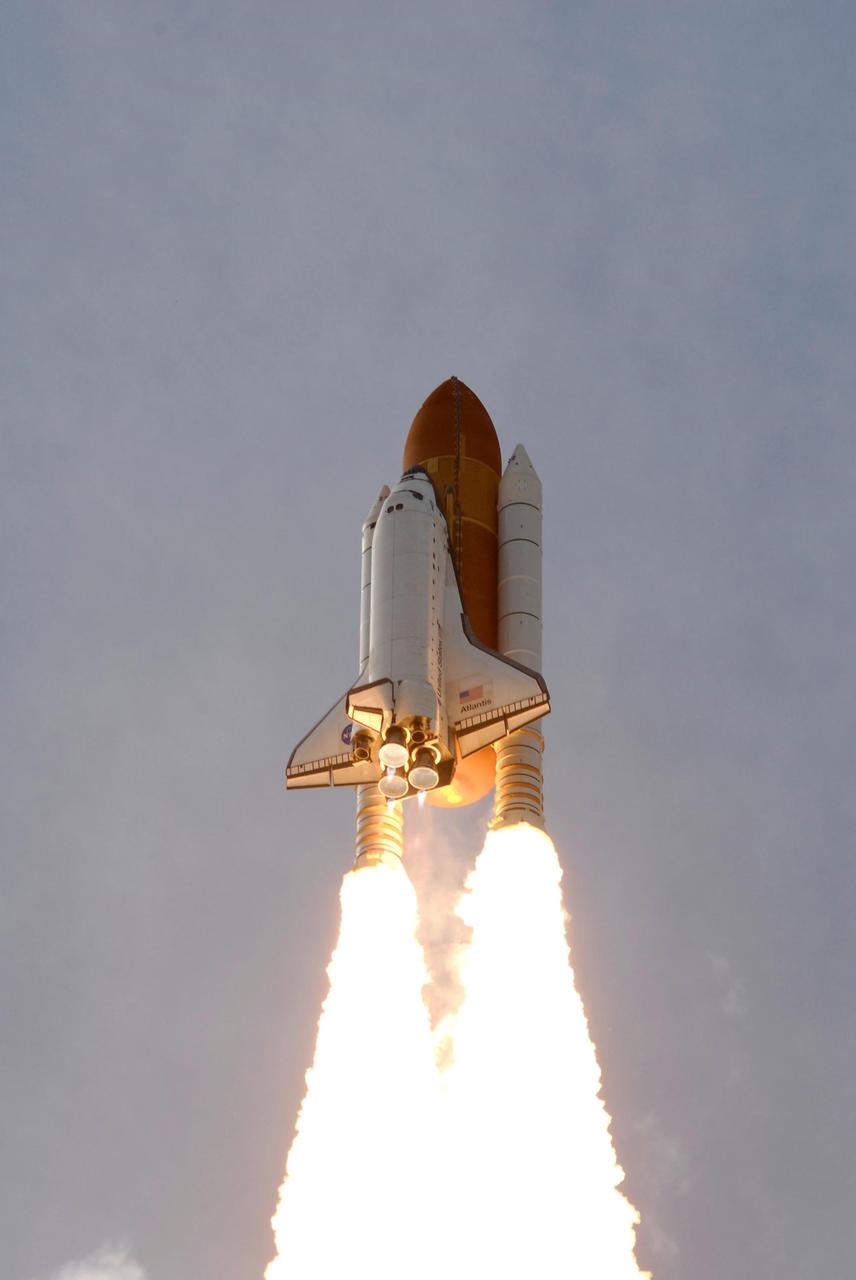

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Twin columns of fire help propel space shuttle Atlantis into space on mission STS-122 to the International Space Station. Liftoff was on time at 2:45 p.m. EST. Below the nozzles of the main engines are the blue cones of light, known as shock or mach diamonds. They are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. The launch is the third attempt for Atlantis since December 2007 to carry the European Space Agency's Columbus laboratory to the International Space Station. During the 11-day mission, the crew's prime objective is to attach the laboratory to the Harmony module, adding to the station's size and capabilities. Photo credit: NASA/Jerry Cannon, Rusty Backer

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Endeavour roars into the night sky on the STS-126 mission. Blue cones of light, the shock or mach diamonds that are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system can be seen beneath the nozzles of the main engines. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo credit: NASA/Rusty Backer-George Roberts

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Towers of flame propel space shuttle Endeavour into the dark sky past the lightning mast on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center on the launch of the STS-123 mission. Beneath the main engines are blue cones of light, the shock or mach diamonds that are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. Liftoff was on time at 2:28 a.m. EDT. Endeavour's crew will make a record-breaking 16-day mission to the International Space Station and deliver the first section of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory and the Canadian Space Agency's two-armed robotic system, Dextre. Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. --Racing into the night sky atop columns of fire, space shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-123 shows blue cones of light beneath its engines. The shock or mach diamonds are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. Liftoff was on time at 2:28 a.m. EDT. The crew will make a record-breaking 16-day mission to the International Space Station and deliver the first section of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory and the Canadian Space Agency's two-armed robotic system, Dextre. Photo credit: NASA/Jerry Cannon, Rusty Backer

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Endeavour roars into the night sky on the STS-126 mission. Blue cones of light, the shock or mach diamonds that are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system can be seen beneath the nozzles of the main engines. Liftoff was on time at 7:55 p.m. EST. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long-duration missions. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph-Kevin O'Connell
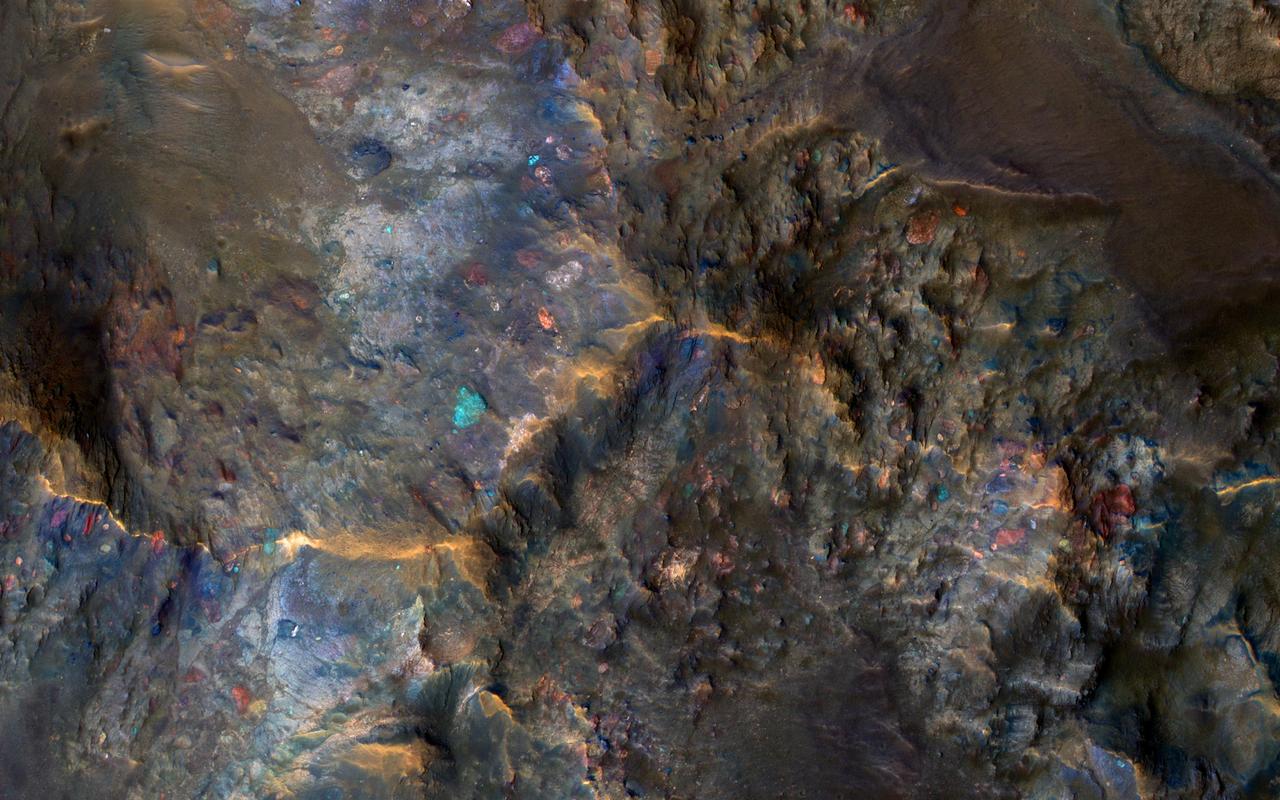
Large impact craters have central hills or mountains, because the tremendous shock waves from the impact first compresses the ground, then causes a rebound when it becomes uncompressed. This effectively raises bedrock that was once deeply buried to the surface. Furthermore, some of the most interesting bedrock on Mars is amongst the oldest and deeply buried. Thus, these crater central uplifts act as windows into ancient Mars, and enable us to peer into a time when certain geologic processes were more active than today. The enhanced colors in this image reflect different bedrock compositions. Some of the large blocks are broken up and jumbled by this impact event or were resampled from previous large impacts. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA15149
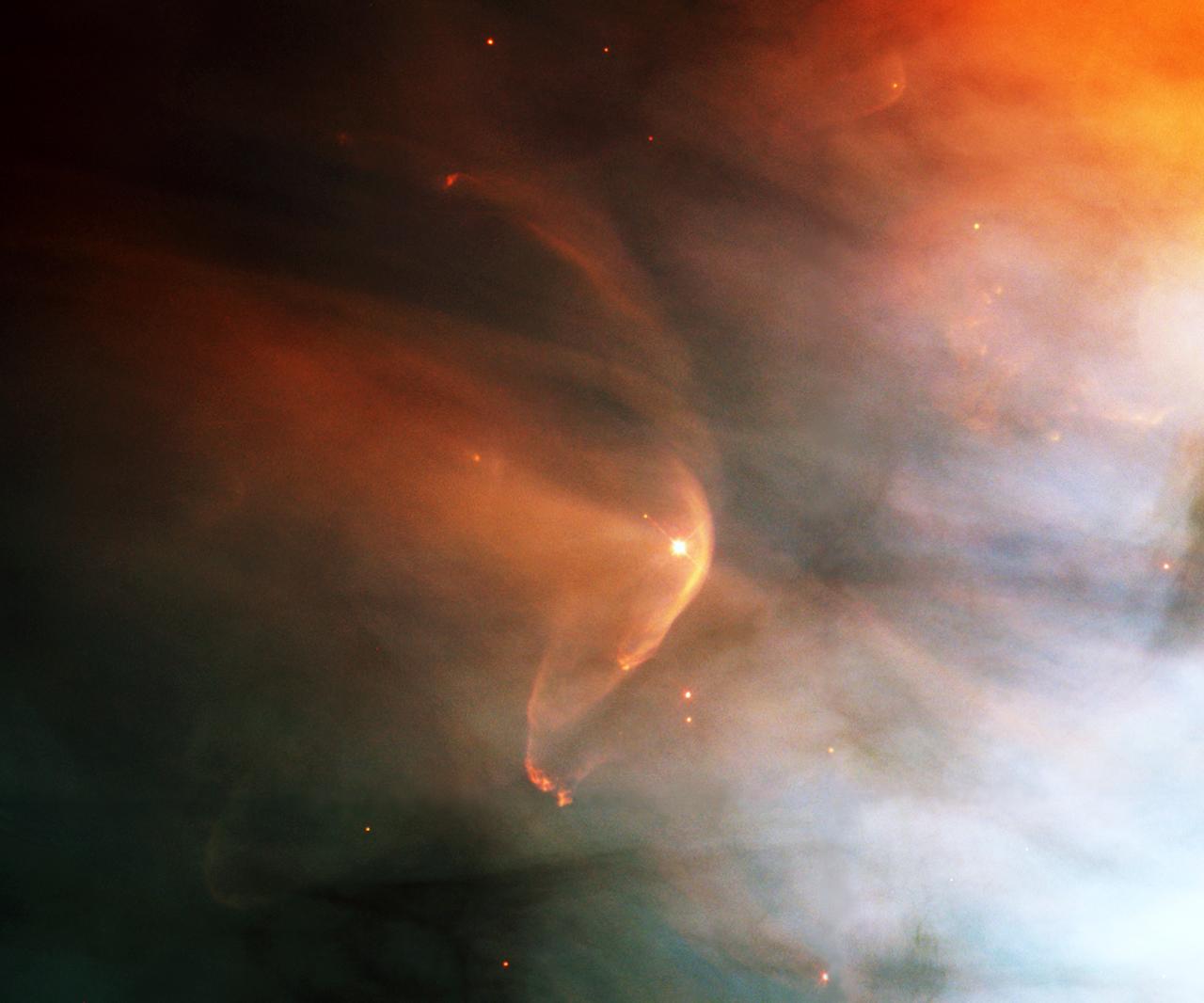

The nearby intense star-forming region known as the Great Nebula in the Orion constellation reveals a bow shock around a very young star as seen by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Named for the crescent-shaped wave made by a ship as it moves through the water, a bow shock can be created in space where two streams of gas collide. LL Ori emits a vigorous solar wind, a stream of charged particles moving rapidly outward from the star. Our own sun has a less energetic version of this wind. The material in the fast wind from LL Ori collides with slow moving gas evaporating away form the center of the Orion Nebula, which is located in the lower right of this image, producing the crescent shaped bow shock seen in the image. Astronomers have identified numerous shock fronts in this complex star-forming region and are using this data to understand the many complex phenomena associated with the birth of stars. A close visitor in our Milky Way Galaxy, the nebula is only 1,500 light years away from Earth. The filters used in this color composite represent oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen emissions.

An aerospace research engineer and technicians inspect the X-59 Commercial Supersonic Transport model’s installation and alignment before testing. The blade hanging from the top of the tunnel will be measuring the shock waves coming from the model during testing. The intent is to develop a supersonic aircraft with less sonic boom. Commercial Supersonic Transport, CST Project, X-59 Sonic Boom Test Model, in the 8x6-foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel, SWT
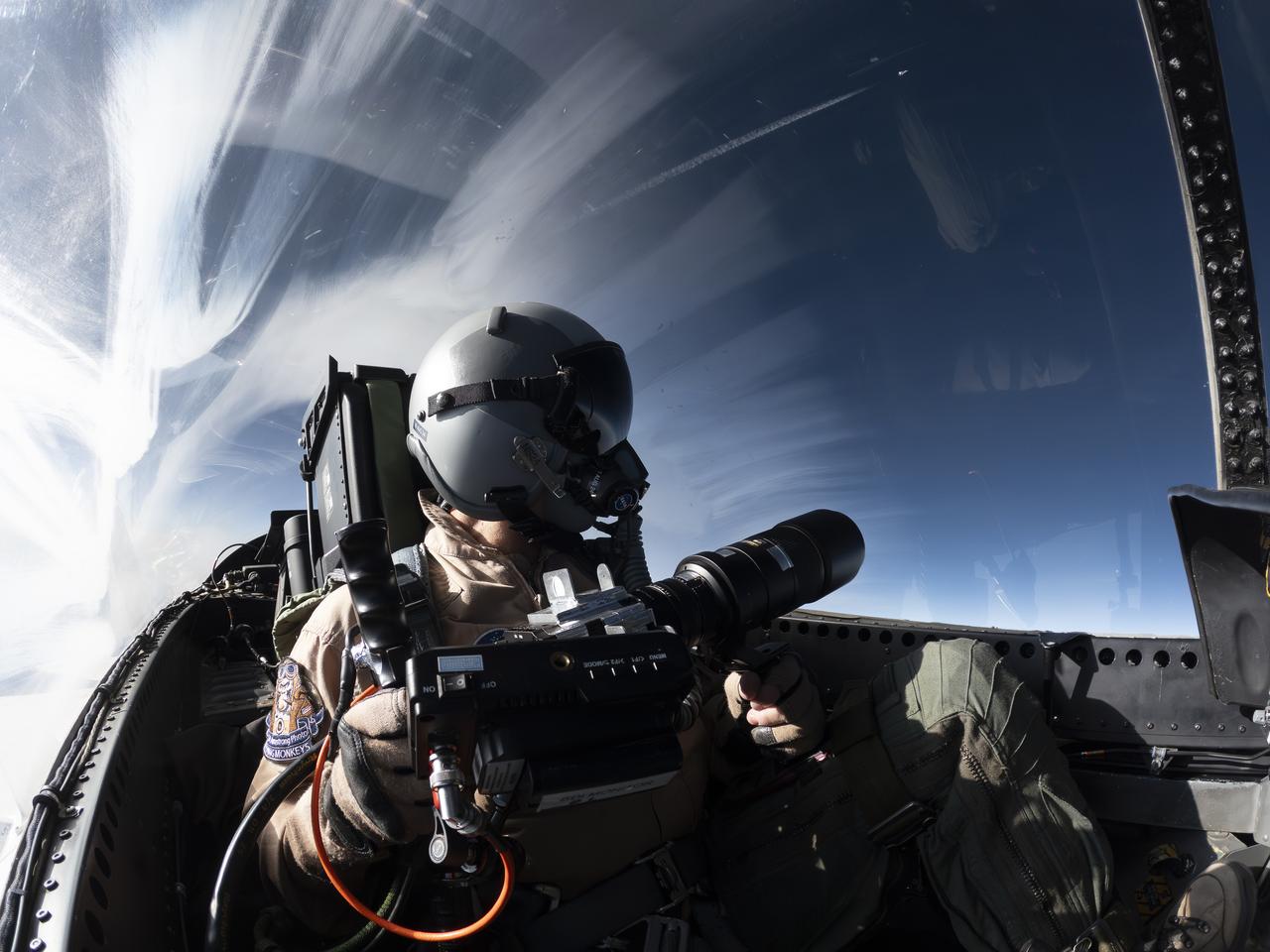

NASA Photographer Carla Thomas holds the Airborne Schlieren Photography System (ASPS), aiming it out the window in flight. The ASPS uses a photographic method called schlieren imaging, capable of visualizing changes in air density and revealing shock waves and air flow patterns around moving objects. The system is one of several tools validated during recent dual F-15 flights at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, in support of NASA’s Quesst mission, ahead of the X-59’s first flight.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This view of the shock wave condensation collars backlit by the sun occurred during the launch of Atlantis on STS-106 and was captured on an engineering 35mm motion picture film. One frame was digitized to make this still image. Although the primary effect is created by the Orbiter forward fuselage, secondary effects can be seen on the SRB forward skirt, Orbiter vertical stabilizer and wing trailing edges (behind SSME's).

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This view of the shock wave condensation collars backlit by the sun occurred during the launch of Atlantis on STS-106 and was captured on an engineering 35mm motion picture film. One frame was digitized to make this still image. Although the primary effect is created by the Orbiter forward fuselage, secondary effects can be seen on the SRB forward skirt, Orbiter vertical stabilizer and wing trailing edges (behind SSME's).

Columbia, which opened the era of the Space Transportation System with four orbital flight tests, is featured in re-entry in the emblem designed by the STS-61C crew representing the seven team members who manned the vehicle for its seventh STS mission. Gold lettering against black background honors the astronaut crewmembers on the delta pattern surrounding colorful re-entry shock waves, and the payload specialists are honored similarly below the sphere
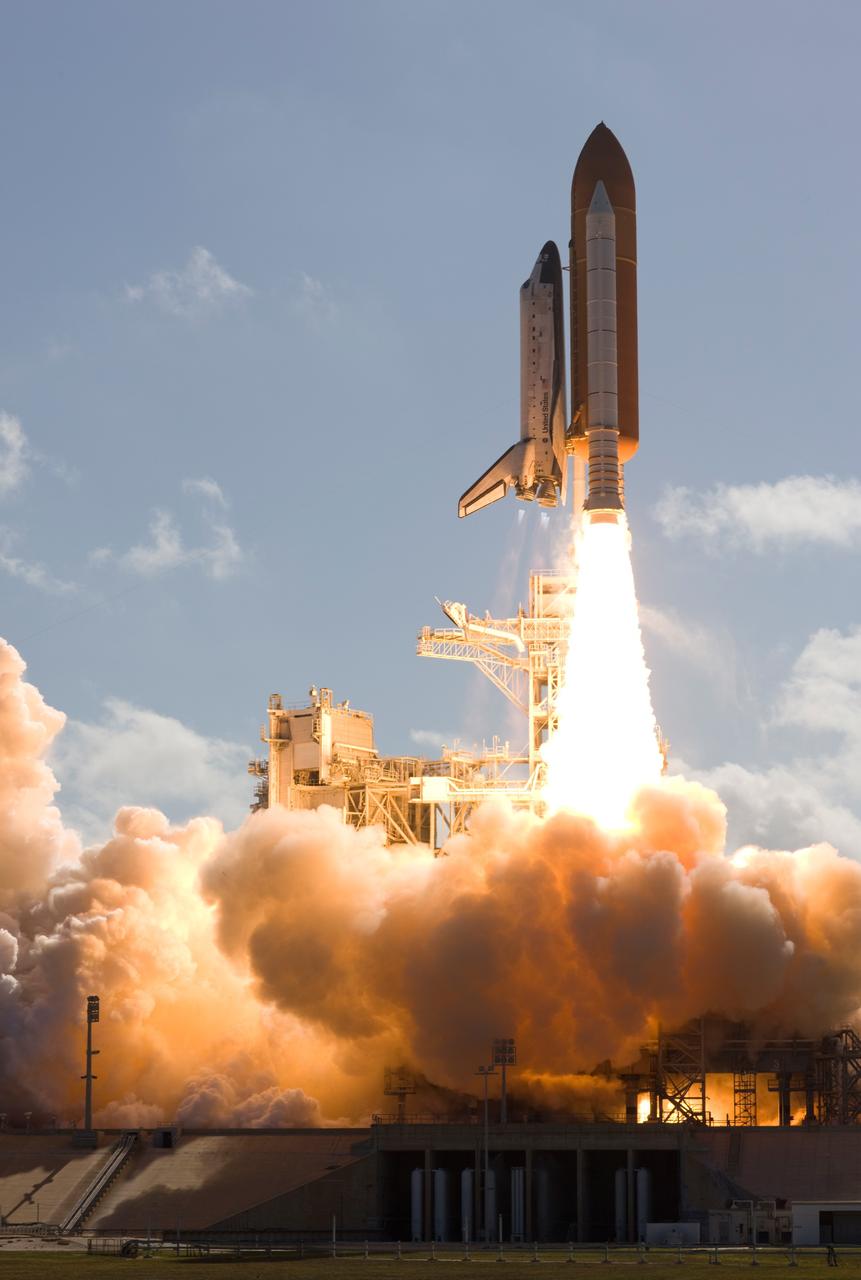

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center, smoke and steam billow across Launch Pad 39A as space shuttle Discovery races toward space atop twin towers of flame. Launch was on time at 5:02 p.m. EDT. Just visible beneath Discovery's main engine nozzles are blue cones of light, the shock or mach diamonds that are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. Discovery is making its 35th flight. The STS-124 mission is the 26th in the assembly of the space station. It is the second of three flights launching components to complete the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory. The shuttle crew will install Kibo's large Japanese Pressurized Module and its remote manipulator system, or RMS. The 14-day flight includes three spacewalks. Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis rockets into the blue sky above Launch Pad 39A after liftoff. Beneath Atlantis' main engines are blue cones of light, known as shock or mach diamonds. They are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. Liftoff of Atlantis on mission STS-117 to the International Space Station was on time at 7:38:04 p.m. EDT. The shuttle is delivering a new segment to the starboard side of the International Space Station's backbone, known as the truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install the S3/S4 truss segment, deploy a set of solar arrays and prepare them for operation. STS-117 is the 118th space shuttle flight, the 21st flight to the station, the 28th flight for Atlantis and the first of four flights planned for 2007. Photo Credit: NASA/Tony Gray & Don Kight

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Discovery is silhouetted against the clear blue Florida sky as it hurtles toward space on its STS-124 mission to the International Space Station. Beneath the main engine nozzles can be seen the blue cones of light, the shock or mach diamonds that are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. Liftoff was on time at 5:02 p.m. EDT. Discovery is making its 35th flight. The STS-124 mission is the 26th in the assembly of the space station. It is the second of three flights launching components to complete the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory. The shuttle crew will install Kibo's large Japanese Pressurized Module and its remote manipulator system, or RMS. The 14-day flight includes three spacewalks. Photo credit: NASA/Jerry Cannon, George Roberts

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Spewing twin columns of fire from the solid rocket boosters, space shuttle Discovery roars into the blue Florida sky toward space on mission STS-120 to the International Space Station. Below the three main engines are the blue cones of light, known as shock or mach diamonds. They are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. Liftoff of Discovery was on time at 11:38:19 a.m. EDT. The mission is the 23rd assembly flight to the space station and the 34th flight for Discovery. The STS-120 payload is the Italian-built U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. During the 14-day mission, the crew will install Harmony and move the P6 solar arrays to their permanent position and deploy them. Discovery is expected to complete its mission and return home at 4:50 a.m. EST on Nov. 6. Photo credit: NASA/Jerry Cannon, Mike Kerley, Don Kight

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space shuttle Discovery roars between the clouds into the blue Florida sky toward space on mission STS-120 to the International Space Station. Below the three main engines are the blue cones of light, known as shock or mach diamonds. They are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. Liftoff of Discovery was on time at 11:38:19 a.m. EDT. The mission is the 23rd assembly flight to the space station and the 34th flight for Discovery. The STS-120 payload is the Italian-built U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. During the 14-day mission, the crew will install Harmony and move the P6 solar arrays to their permanent position and deploy them. Discovery is expected to complete its mission and return home at 4:50 a.m. EST on Nov. 6. Photo credit: NASA/Tom Farrar, Scott Haun, Raphael Hernandez
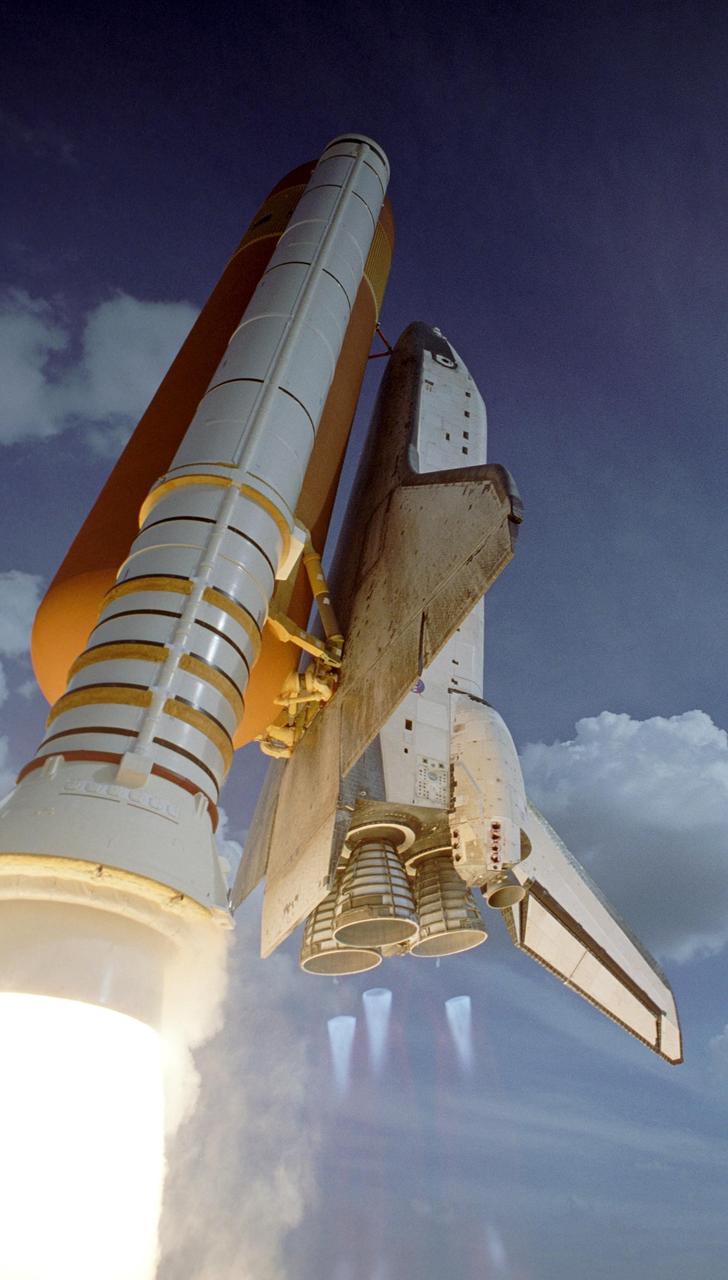

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space shuttle Atlantis soars into the cloudy sky after liftoff on mission STS-122, which occurred on time at 2:45 p.m. EST, from Launch Pad 39A. Below the main engine nozzles can be seen the blue cones of light, known as shock or mach diamonds. They are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. This is the third launch attempt for Atlantis since December 2007 to carry the European Space Agency's Columbus laboratory to the International Space Station. During the 11-day mission, the crew's prime objective is to attach the laboratory to the Harmony module, adding to the station's size and capabilities. Photo credit: NASA/Scott Haun, Richard Prickett
This full resolution mosaiced image covers an area of approximately 100 kilometers by 120 kilometers (62 by 74 miles) and is located in the Lakshmi region of Venus at 47 degrees north latitude and 334 east longitude. Due to the dense Venusian atmosphere, primary impact craters of less than a 3 kilometer (2 mile) diameter are nonexistent. The dark circular region and associated central bright feature in this image are thought to be the remnants of a meteoroid smaller than the size necessary to create an impact crater entering the atmosphere at a low velocity (approximately 350 meters/second.) The central bright feature appears to be a cluster of small secondary impacts, ejecta and debris from the original meteor that broke up in the atmosphere. Even though most of the meteorite did not hit the surface, the atmospheric shock wave could be great enough to modify the surrounding region. One explanation for this radar dark circular formation, called dark margins, could be that the shock wave was energetic enough to pulverize the surface (smooth surfaces generally appear radar dark.) Another explanation is that the surface could be blanketed by a fine material that was formed by the original meteor's breakup through the atmosphere. More than half of the impact craters on Venus have associated dark margins, and most of these are prominently located left of center of the crater. This is another effect which could be caused by the dense atmosphere of Venus. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00477
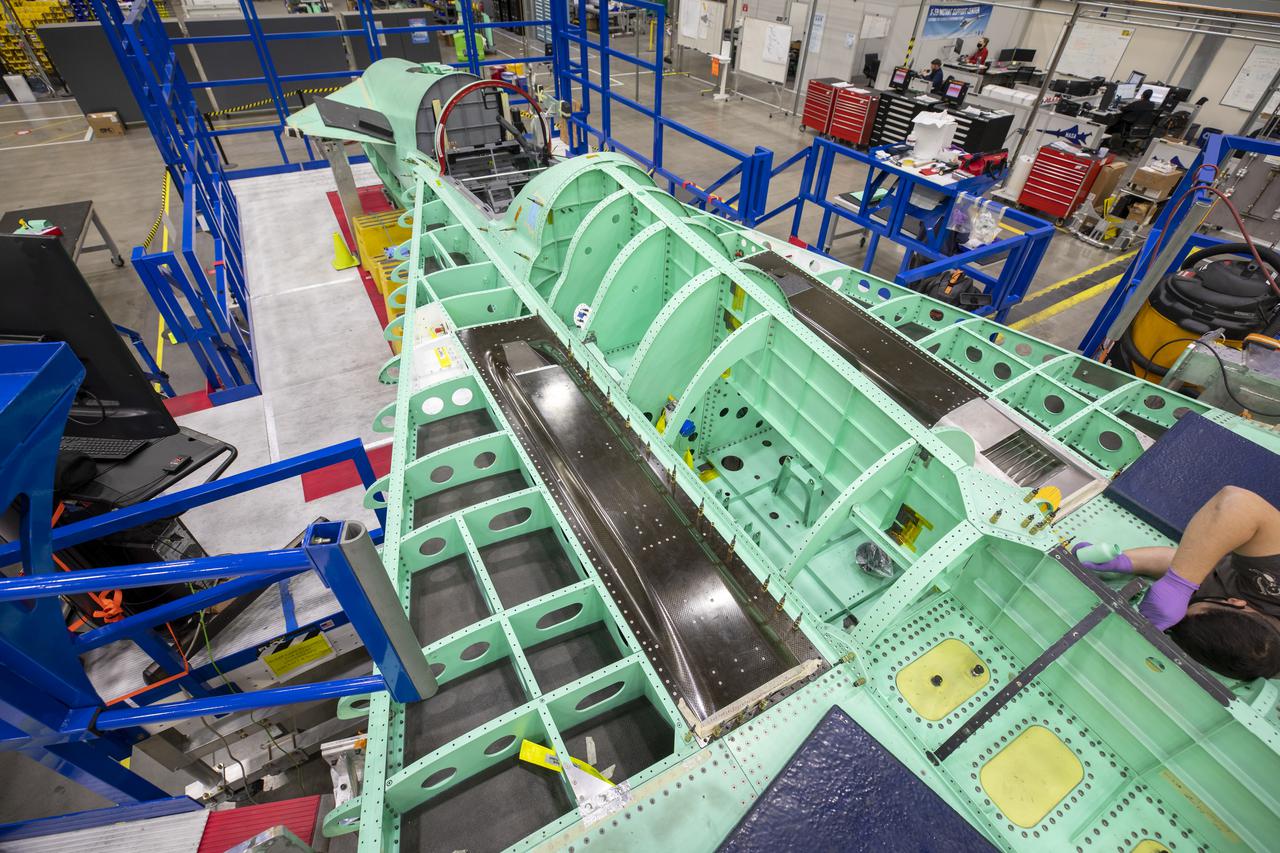
NASA is targeting 2022 for the first flight of the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology (QueSST) research aircraft. Its mission – fly over communities to collect data that could cut passenger travel time in half without disturbing people on the ground. NASA’s X-59 is equipped with supersonic technologies that aid in lowering the sound of the sonic boom. In this picture, the black rectangle panels are the air intakes for the environmental control system (ECS) that regulates the temperature, cabin pressure, and air distribution. The silver grate located at the rear of one of the ECS panels is the exhaust — both of these sections are traditionally housed on the underside of the plane. By placing these features on top of the X-59 wing, the wing blocks and prevents the ECS exhaust from interacting with the shock waves on the bottom of the aircraft. This unique design approach to re-shaping the shock wave pattern substantially reduces the sonic boom to more of a sonic “thump” when it reaches the ground. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 210 Forebody Date: 1/19/2021 Additional Info:
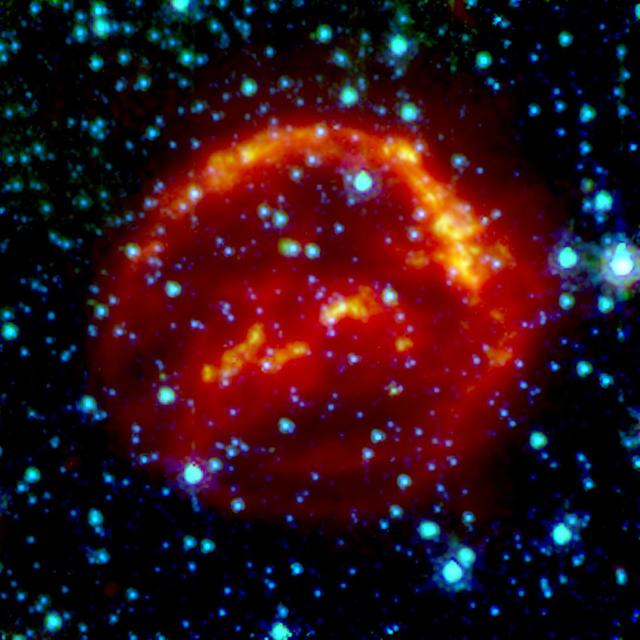

This Spitzer false-color image is a composite of data from the 24 micron channel of Spitzer's multiband imaging photometer (red), and three channels of its infrared array camera: 8 micron (yellow), 5.6 micron (blue), and 4.8 micron (green). Stars are most prominent in the two shorter wavelengths, causing them to show up as turquoise. The supernova remnant is most prominent at 24 microns, arising from dust that has been heated by the supernova shock wave, and re-radiated in the infrared. The 8 micron data shows infrared emission from regions closely associated with the optically emitting regions. These are the densest regions being encountered by the shock wave, and probably arose from condensations in the surrounding material that was lost by the supernova star before it exploded. The composite above (PIA06908, PIA06909, and PIA06910) represent views of Kepler's supernova remnant taken in X-rays, visible light, and infrared radiation. Each top panel in the composite above shows the entire remnant. Each color in the composite represents a different region of the electromagnetic spectrum, from X-rays to infrared light. The X-ray and infrared data cannot be seen with the human eye. Astronomers have color-coded those data so they can be seen in these images. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06910
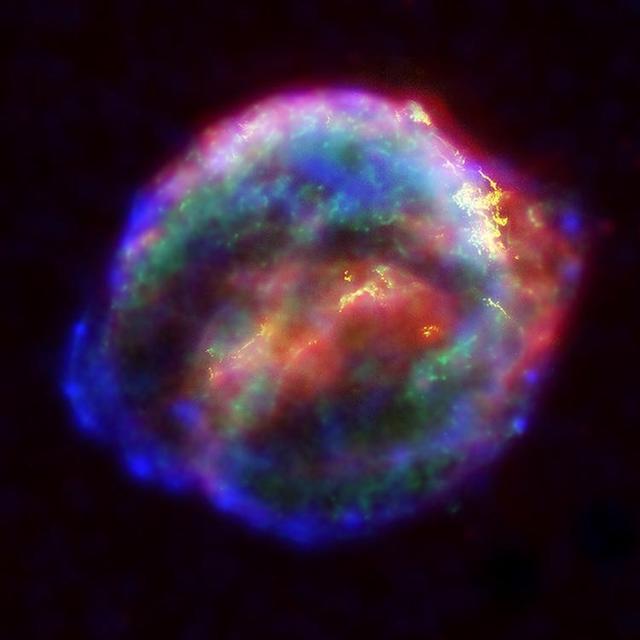
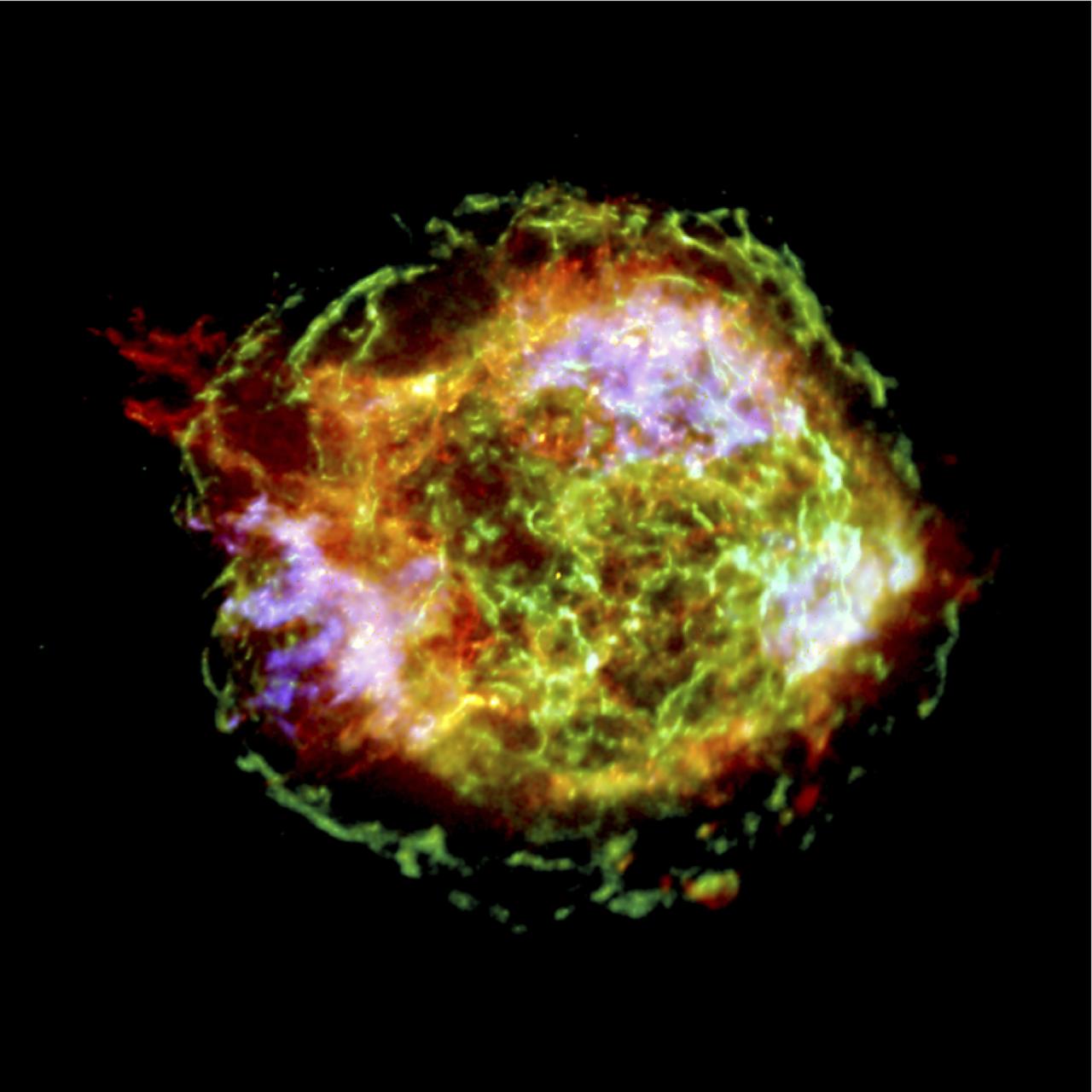
This Chandra image reveals, in detail, the turbulent debris created by a supernova explosion that was observed by the Danish Astronomer Tycho Brahe in the year 1572. The colors show different x-ray energies, with red, green, and blue representing low, medium, and high energies, respectively. Most likely caused by the destruction of a white dwarf star, a shock wave produced by the expanding debris is outlined by the sharp blue circular arcs of 20 million degree Celsius gas seen on the outer rim. The stellar debris, visible only by x-ray, has a temperature of about 10 million degrees, and shows up as mottled yellow, green, and red fingers of gas.
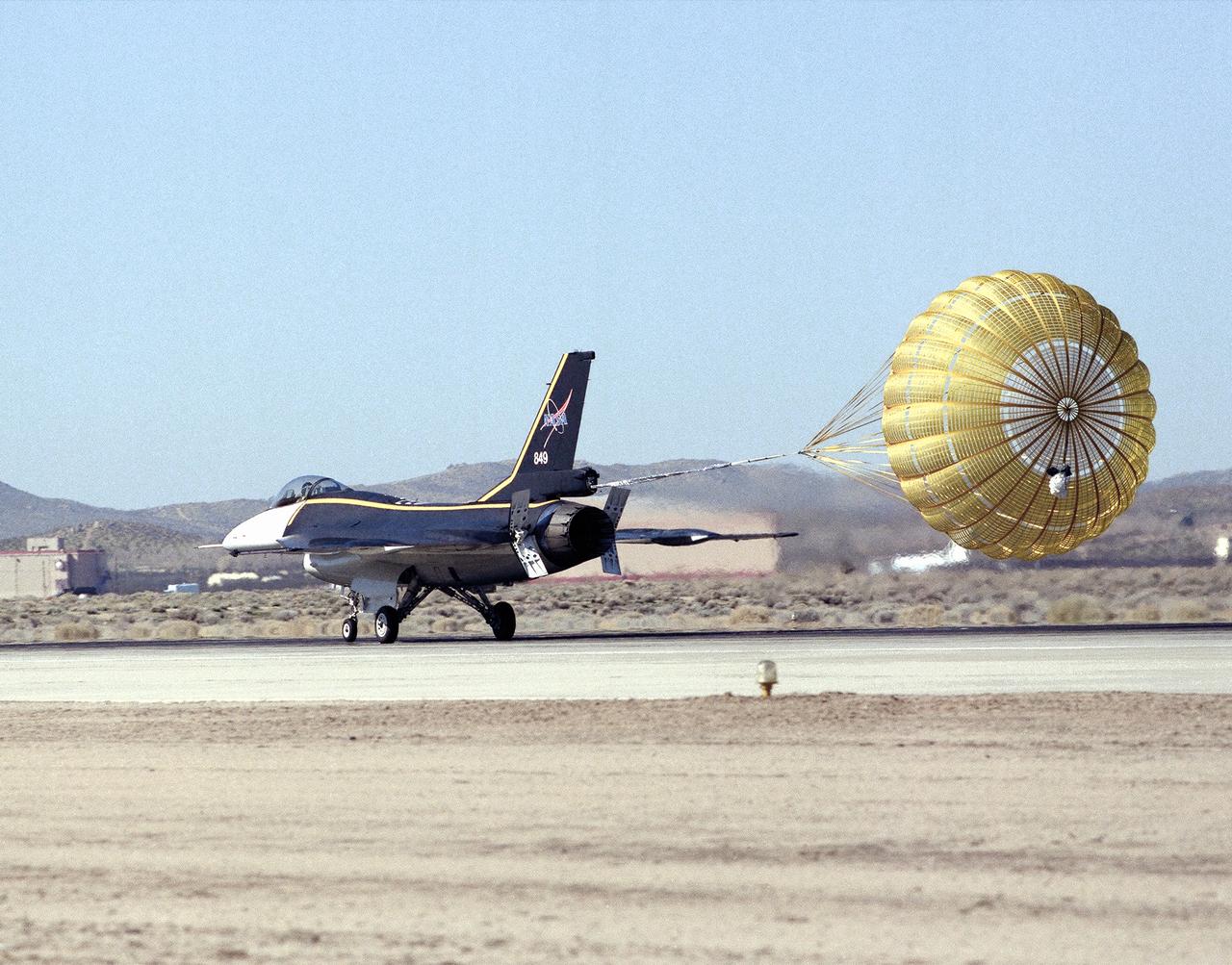

NASA's single-seat F-16XL makes a drag chute landing on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base in California's Mojave Desert. The aircraft was most recently used in the Cranked-Arrow Wing Aerodynamics Project (CAWAP) to test boundary layer pressures and distribution. Previously it had been used in a program to investigate the characteristics of sonic booms for NASA's High Speed Research Program. Data from the program will be used in the development of a high speed civilian transport. During the series of sonic boom research flights, the F-16XL was used to probe the shock waves being generated by a NASA SR-71 and record their shape and intensity.
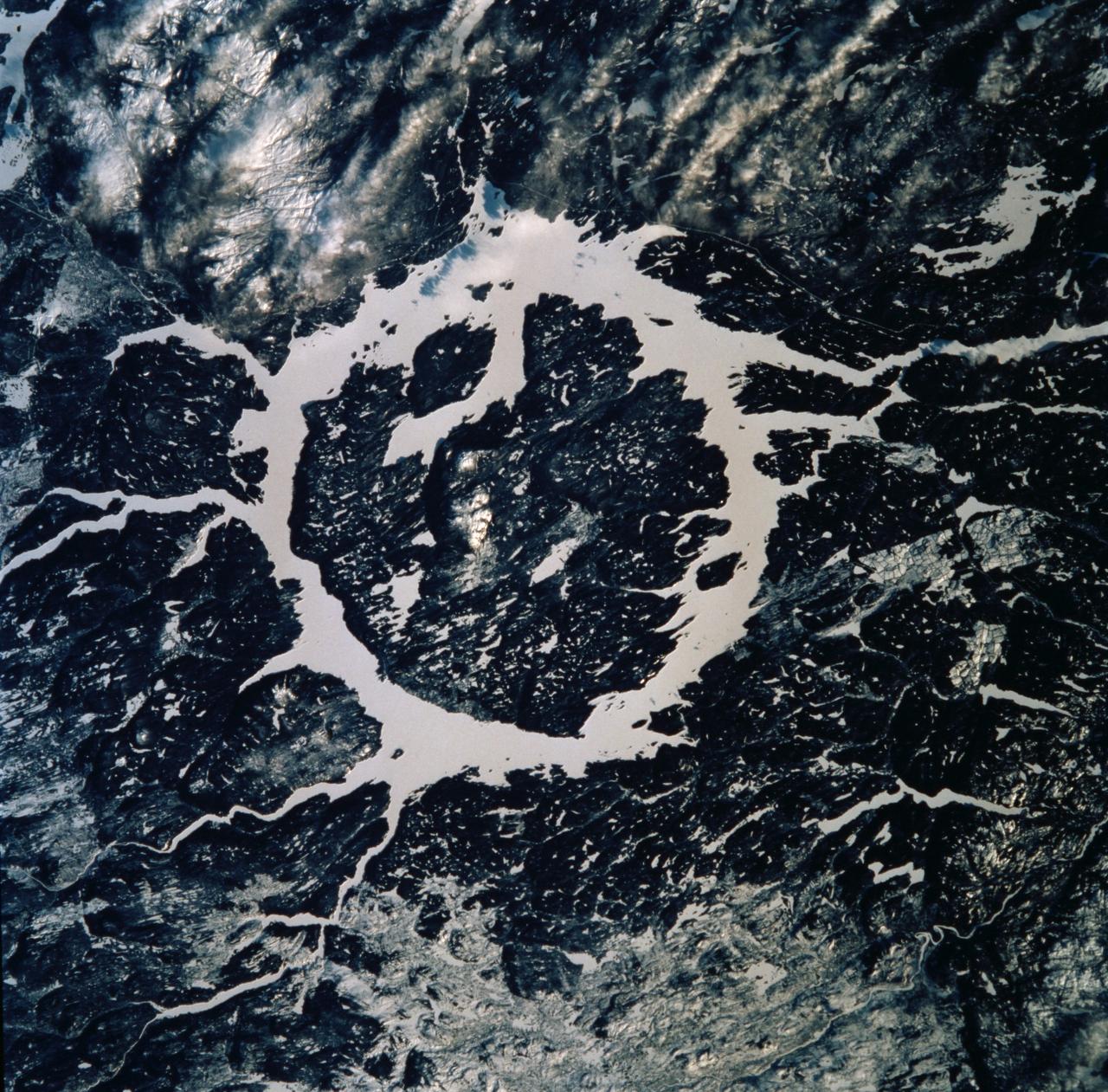
STS099-749-063 (11-22 February 2000) ---One of the astronauts aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour for the STS-99 mission recorded this 70mm image of Manicouagan, one of the largest and most famous craters in Canada. Lake Manicouagan and Lake Mushalagan, frozen in this image, surround the central uplift of the crater. The original crater diameter was 100 kilometers and the age has been dated at 214 million years. Shattercones, striated features found in rocks deformed by the passage of shock waves, and shattered and brecciated rocks found in the central uplift confirm the crater's impact origin, according the NASA scientists studying the STS-99 photo collection.
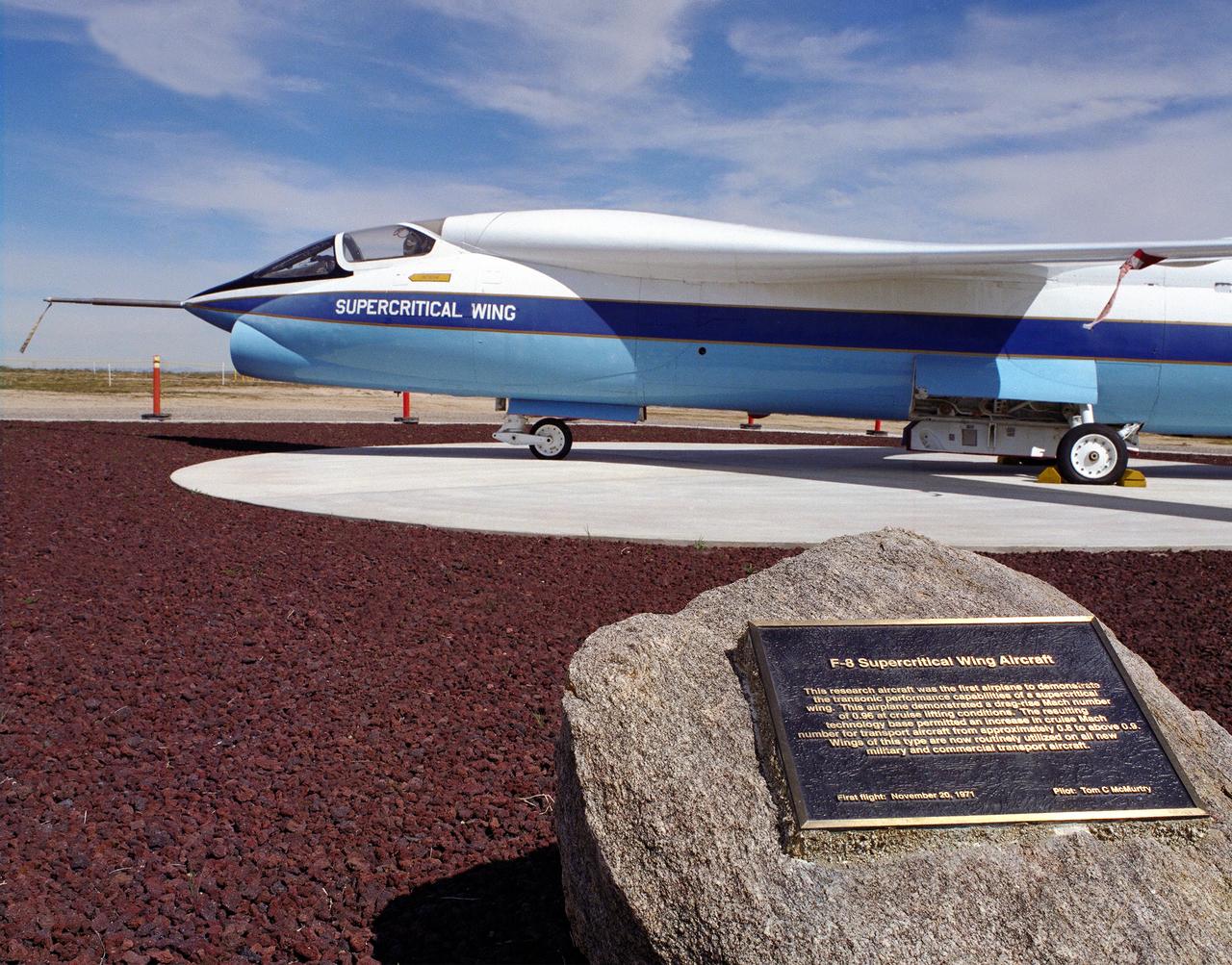

A Vought F-8A Crusader was selected by NASA as the testbed aircraft (designated TF-8A) to install an experimental Supercritical Wing (SCW) in place of the conventional wing. The unique design of the Supercritical Wing reduces the effect of shock waves on the upper surface near Mach 1, which in turn reduces drag. In the photograph the TF-8A Crusader with the Supercritical Wing is shown on static display in front of the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The F-8 SCW aircraft, along with the F-8 Digital Fly-By-Wire aircraft were placed on display on May 27, 1992, at a conference marking the 20th anniversary of the start of the two programs.
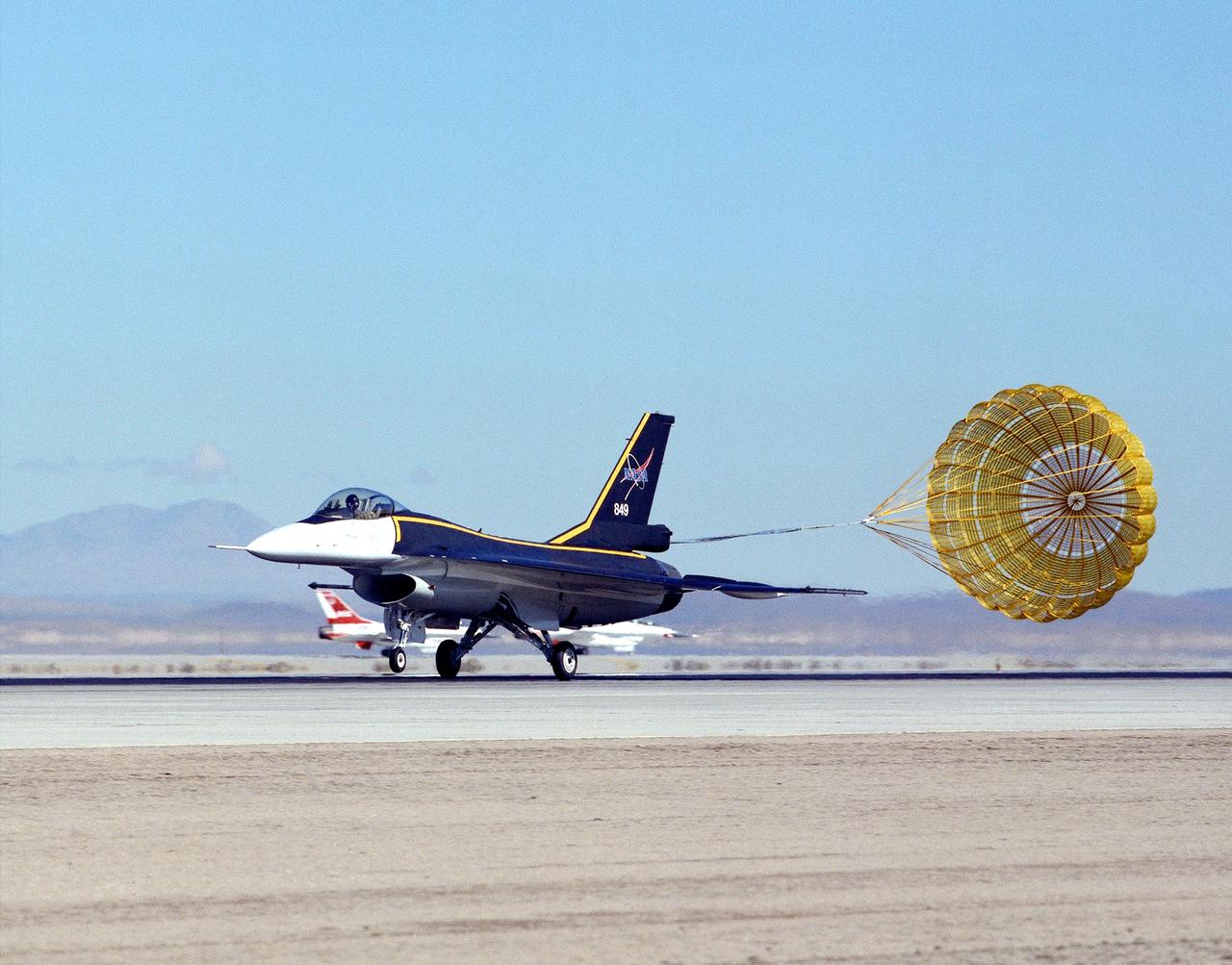

NASA's single-seat F-16XL makes a drag chute landing at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The aircraft was most recently used in the Cranked-Arrow Wing Aerodynamics Project (CAWAP) to test boundary layer pressures and distribution. Previously it had been used in a program to investigate the characteristics of sonic booms for NASA's High Speed Research Program. Data from the program will be used in the development of a high speed civilian transport. During the series of sonic boom research flights, the F-16XL was used to probe the shock waves being generated by a NASA SR-71 and record their shape and intensity.

Huge waves are sculpted in this two-lobed nebula called the Red Spider Nebula, located some 3,000 light-years away in the constellation of Sagittarius. This warm planetary nebula harbors one of the hottest stars known and its powerful stellar winds generate waves 100 billion kilometers (62.4 billion miles) high. The waves are caused by supersonic shocks, formed when the local gas is compressed and heated in front of the rapidly expanding lobes. The atoms caught in the shock emit the spectacular radiation seen in this image. Image credit: ESA/Garrelt Mellema (Leiden University, the Netherlands) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The blue cones of light, known as shock or mach diamonds, beneath Space Shuttle Discovery's main engines confirm its rapid rise into the night sky after liftoff on mission STS-116. Mach diamonds are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. Liftoff occurred on time at 8:47 p.m. EST. This was the second launch attempt for mission STS-116. The first launch attempt on Dec. 7 was postponed due a low cloud ceiling over Kennedy Space Center. This is Discovery's 33rd mission and the first night launch since 2003. The 20th shuttle mission to the International Space Station, STS-116 carries another truss segment, P5. It will serve as a spacer, mated to the P4 truss that was attached in September. After installing the P5, the crew will reconfigure and redistribute the power generated by two pairs of U.S. solar arrays. Landing is expected Dec. 21 at KSC. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray & Don Kight
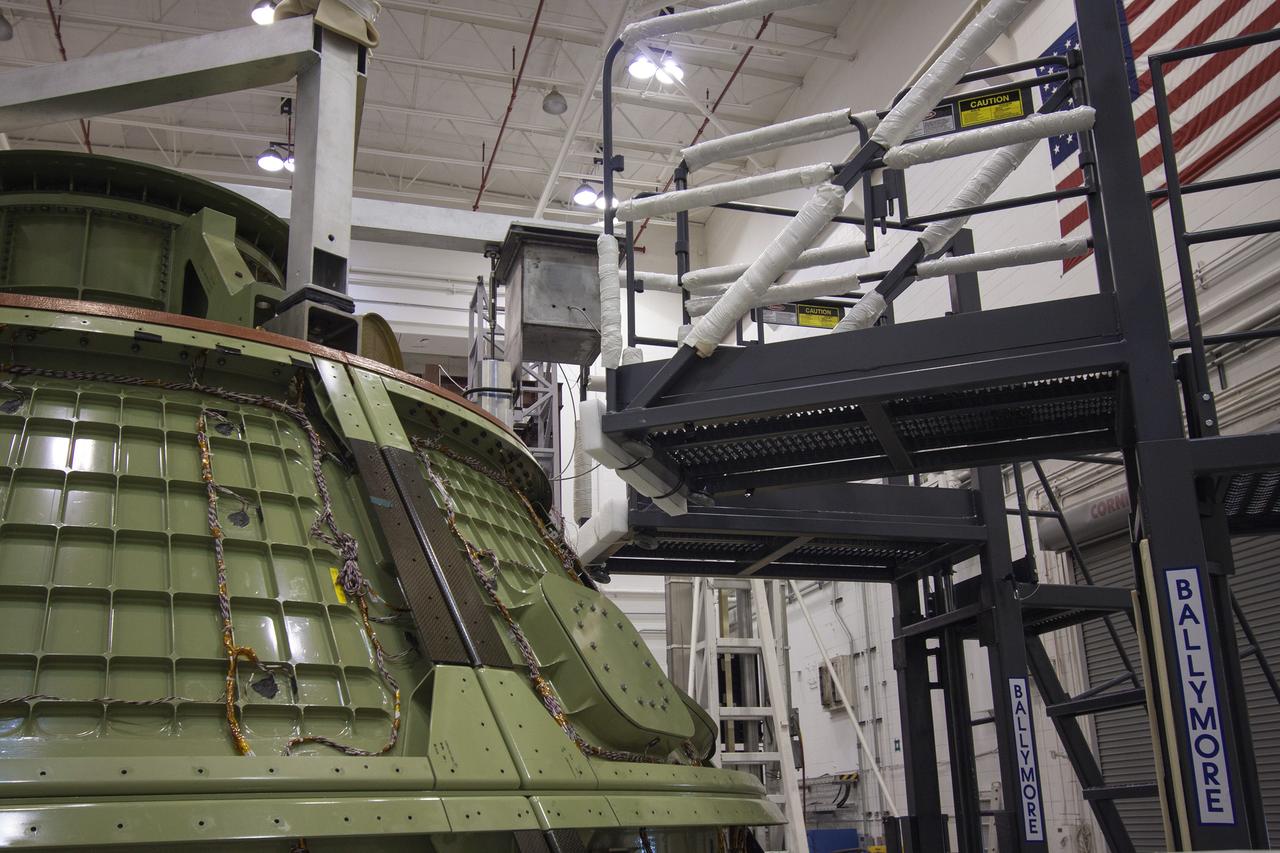

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space in Florida, a second firing of the escape hold down post has occurred during a pyrotechnic bolt test on the Orion ground test vehicle. Lockheed Martin performed tests over a series of days on the explosive bolts that separate Orion from the launch abort system. Data was collected on the effect of shock waves on Orion during the explosive bolt separation. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – As space shuttle Discovery roars toward space after launch from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, mach diamonds can be seen beneath the engine nozzles. Blue cones of light, the mach diamonds are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. Launch was on time at 7:43 p.m. EDT. The STS-119 mission is the 28th to the International Space Station and the 125th space shuttle flight. Discovery will deliver the final pair of power-generating solar array wings and the S6 truss segment. Installation of S6 will signal the station's readiness to house a six-member crew for conducting increased science. Photo credit: NASA/Rusty Backer, George Roberts
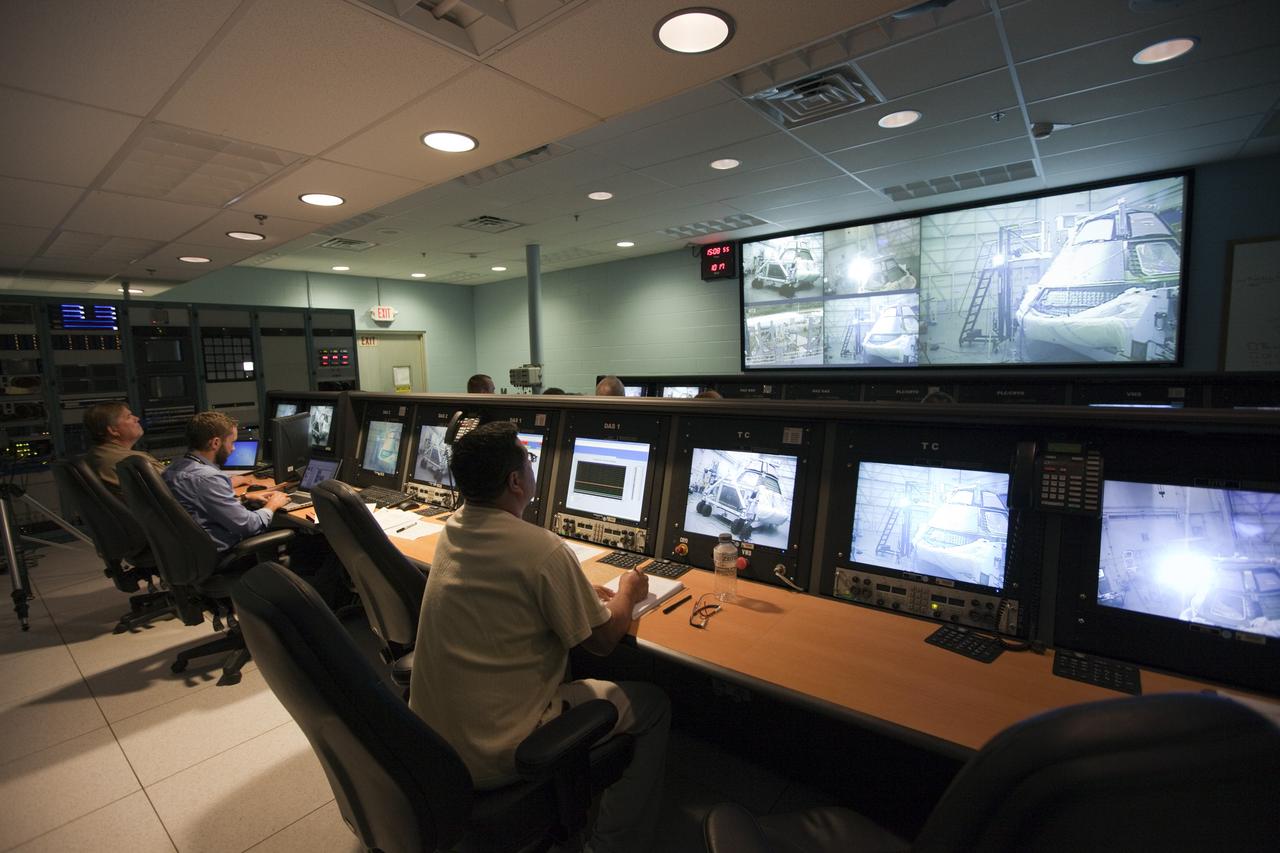

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- Inside the control room at the Launch Equipment Test Facility, or LETF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin engineers monitor the pyrotechnic bolt test on the Orion ground test vehicle at the LETF. Lockheed Martin performed tests over a series of days on the explosive bolts that separate Orion from the launch abort system. Data was collected on the effect of shock waves on Orion during the explosive bolt separation. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
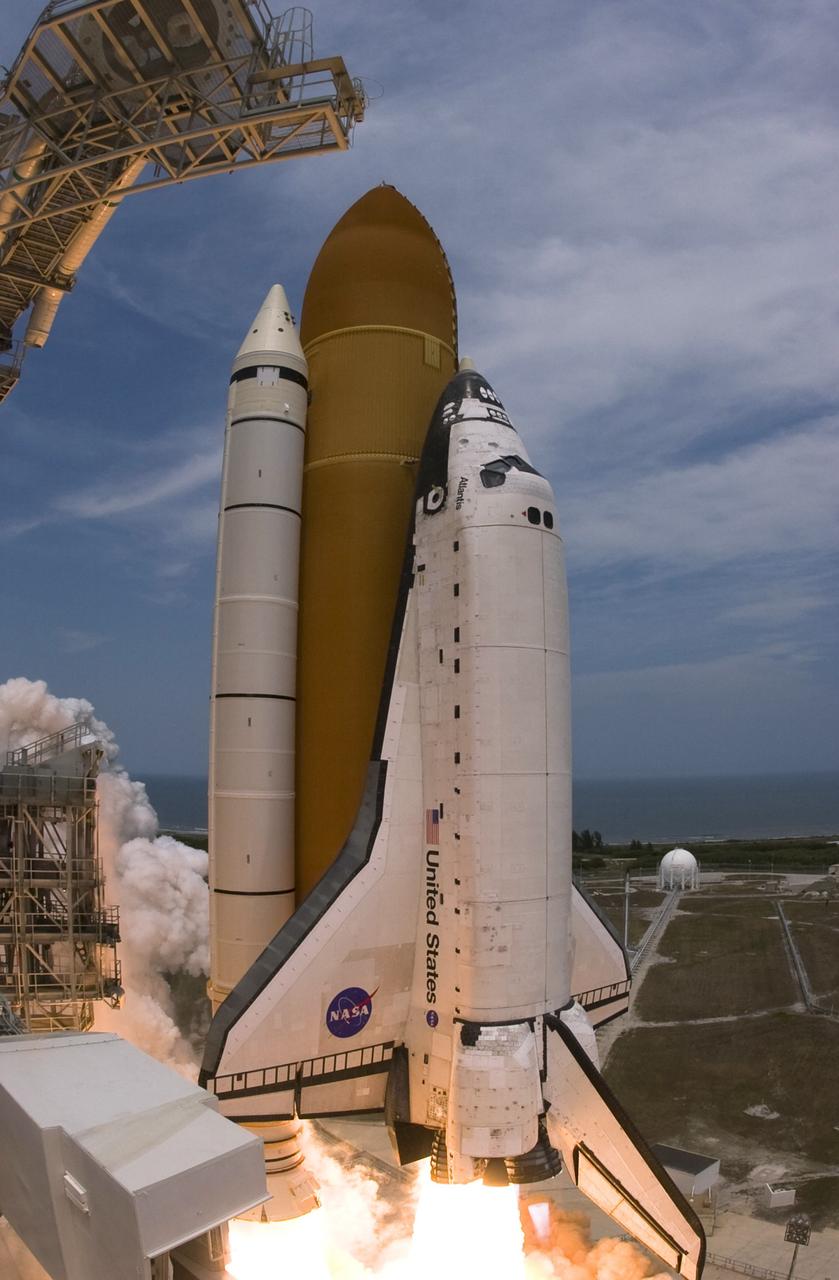

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A fish-eye view shows space shuttle Atlantis lifting off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At left in the foreground is the White Room, which provides access into the shuttle. On the horizon is the Atlantic Ocean. A blue mach diamond appears below the engine nozzle at right. The mach diamonds are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. Atlantis will rendezvous with NASA's Hubble Space Telescope on the STS-125 mission. Liftoff was on time at 2:01 p.m. EDT. Atlantis' 11-day flight will include five spacewalks to refurbish and upgrade the telescope with state-of-the-art science instruments that will expand Hubble's capabilities and extend its operational lifespan through at least 2014. The payload includes a Wide Field Camera 3, fine guidance sensor and the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph-Kevin O'Connell
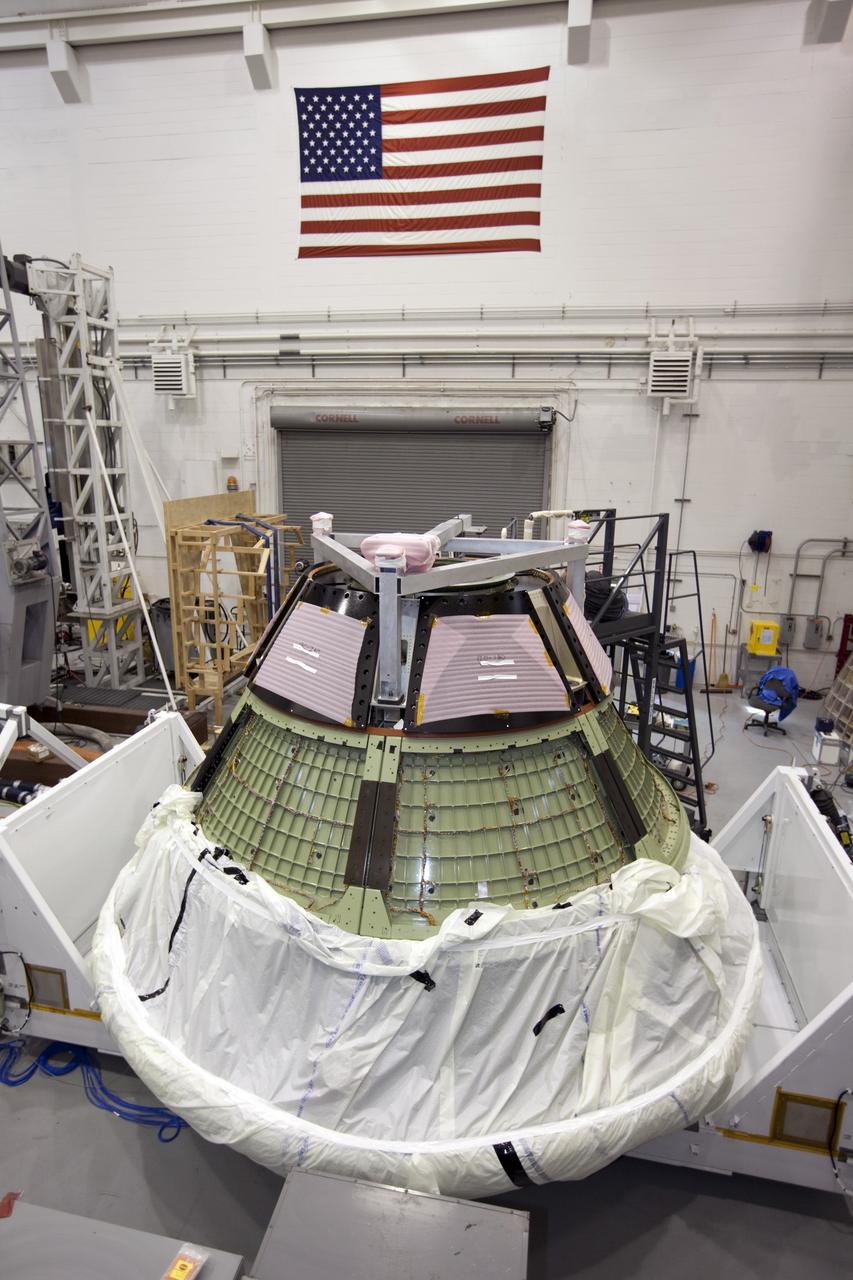

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space in Florida, the Orion ground test vehicle has been transferred to a test stand and prepared for a pyrotechnic bolt test. Lockheed Martin performed tests over a series of days on the explosive bolts that separate Orion from the launch abort system. Data was collected on the effect of shock waves on Orion during the explosive bolt separation. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
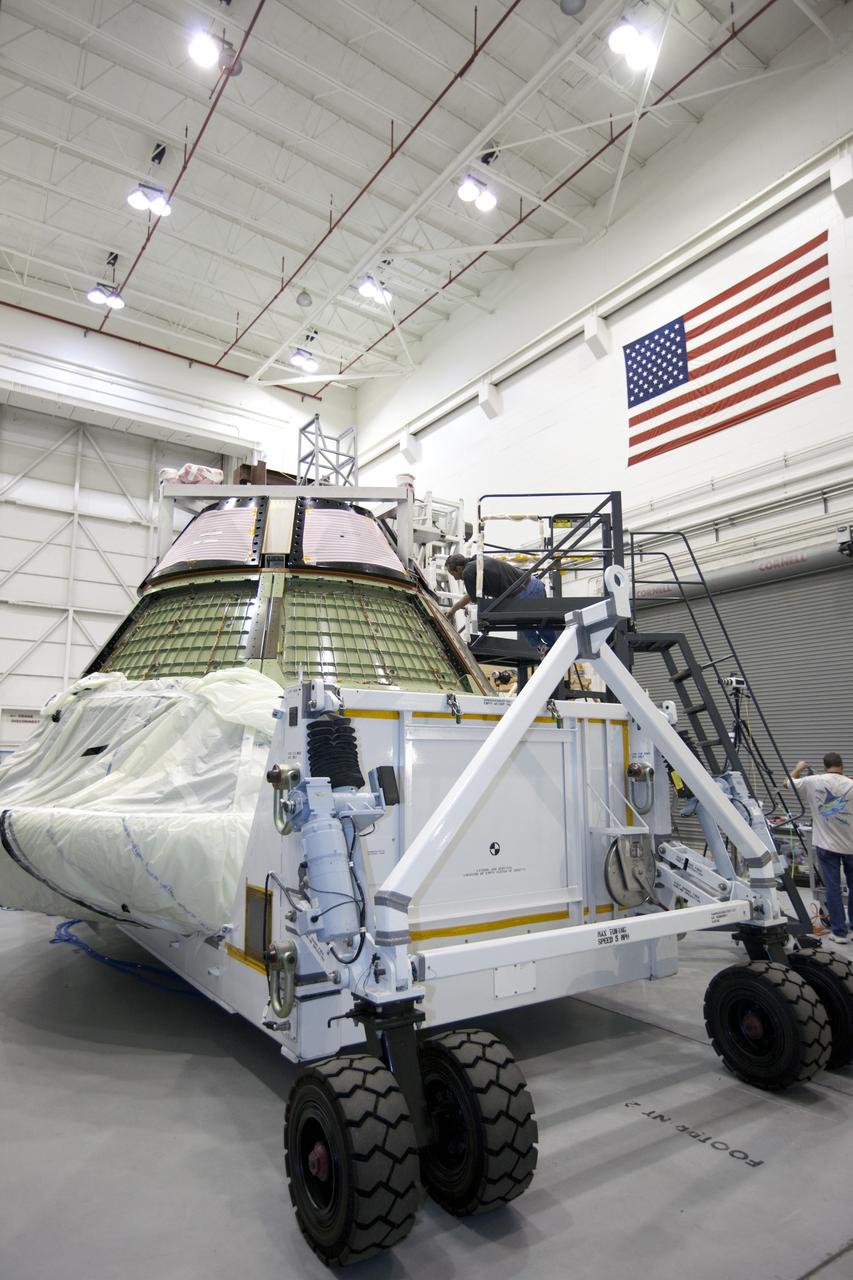

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- The Orion ground test vehicle sits on a test stand in the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida while engineers and technicians prepare it for a pyrotechnic bolt test. Lockheed Martin performed tests over a series of days on the explosive bolts that separate Orion from the launch abort system. Data was collected on the effect of shock waves on Orion during the explosive bolt separation. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
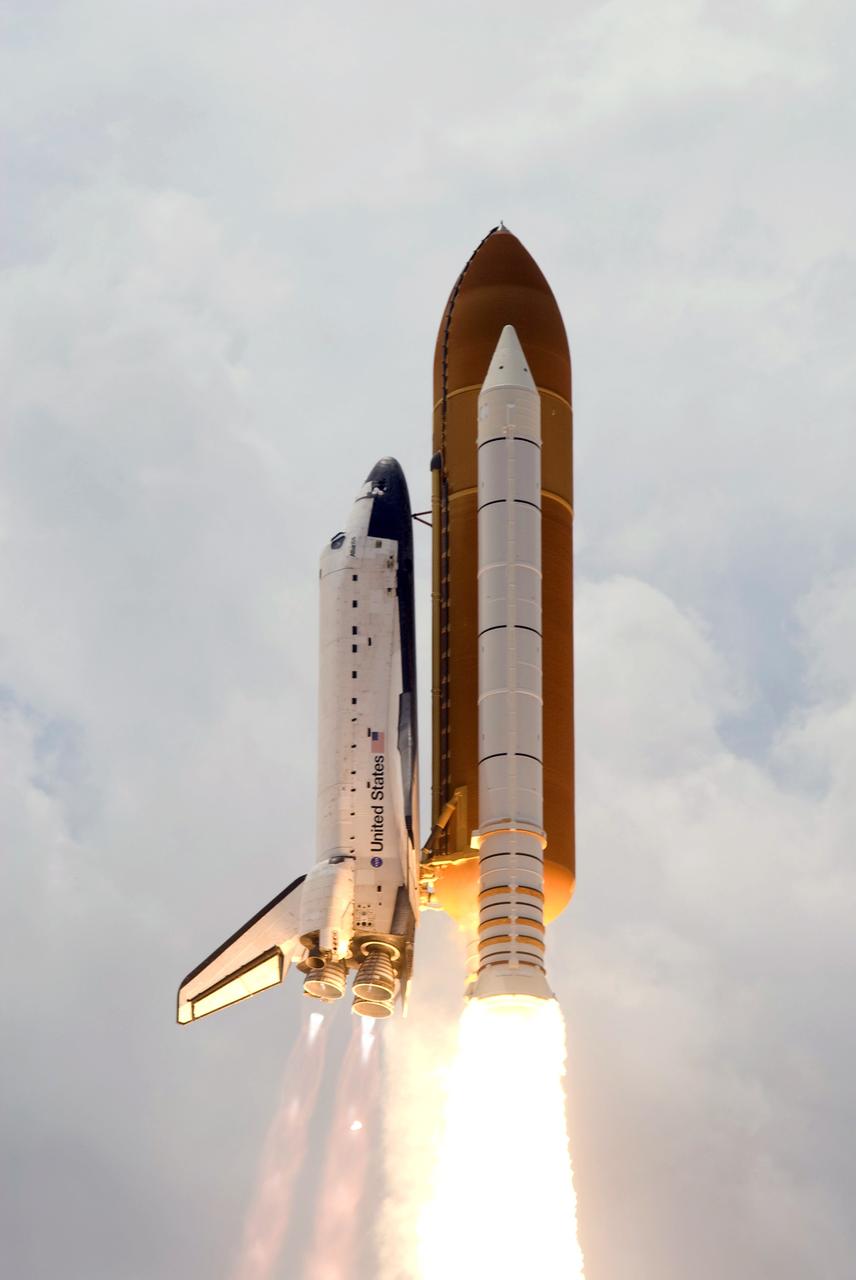

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Space shuttle Atlantis roars into the cloudy sky above Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on the STS-125 mission. Blue cones of light, mach diamonds, can be seen beneath the engine nozzles. The mach diamonds are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. Atlantis will rendezvous with NASA's Hubble Space Telescope on the STS-125 mission. Liftoff was on time at 2:01 p.m. EDT. Atlantis' 11-day flight will include five spacewalks to refurbish and upgrade the telescope with state-of-the-art science instruments that will expand Hubble's capabilities and extend its operational lifespan through at least 2014. The payload includes a Wide Field Camera 3, fine guidance sensor and the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. Photo credit: NASA/Michael Gayle-Rusty Backer
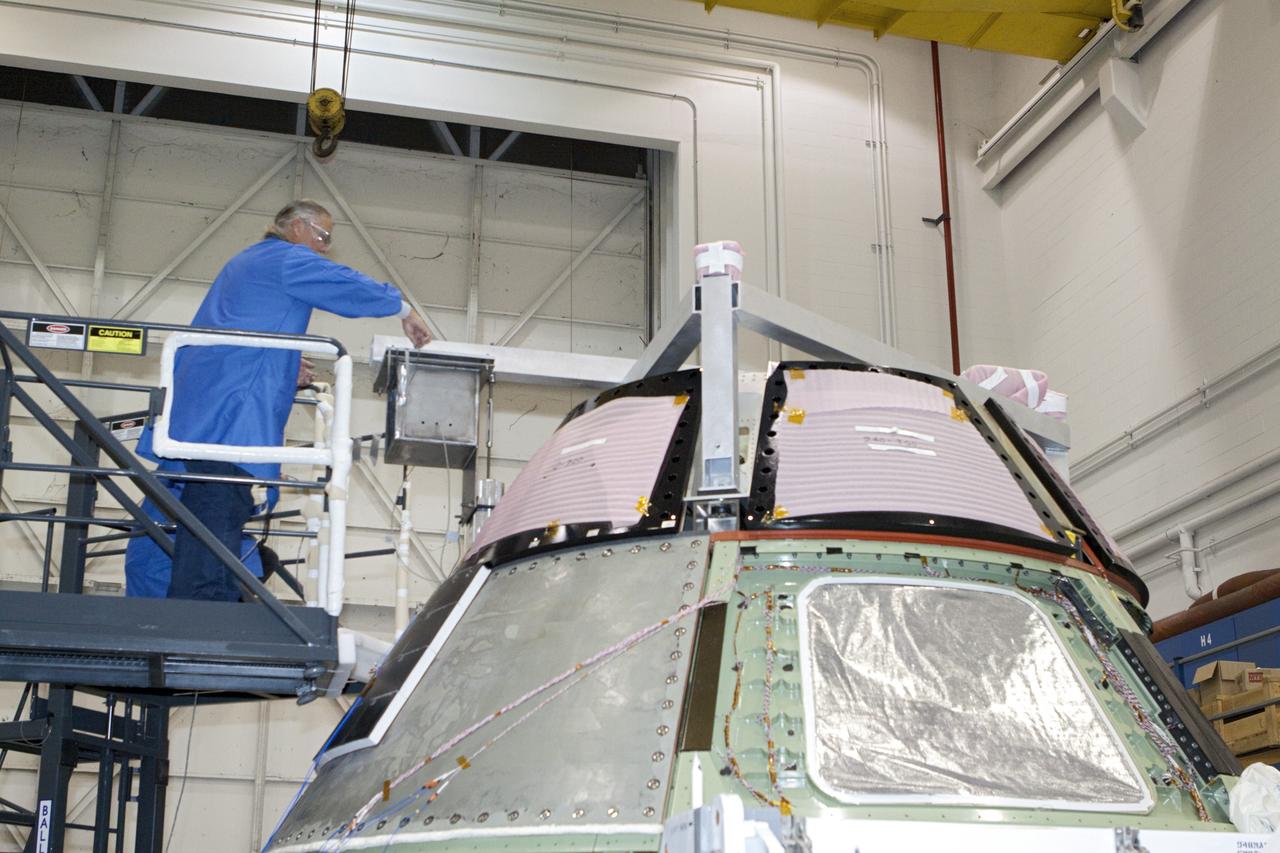

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space in Florida, a Lockheed Martin technician prepares the Orion ground test vehicle for a pyrotechnic bolt test. Lockheed Martin performed tests over a series of days on the explosive bolts that separate Orion from the launch abort system. Data was collected on the effect of shock waves on Orion during the explosive bolt separation. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

STS106-S-013 (8 September 2000)--- This view of shock-wave condensation collars backlit by the Sun occurred during the launch of the Space Shuttle Atlantis on September 8, 2000. The scene was captured on 35mm motion picture film. One frame was digitized to make this still image. Although the primary effect is created by the forward fuselage of the Atlantis, secondary effects can be seen on the solid rocket booster (SRB) forward skirt, shuttle vertical stabilizer and wing trailing edge, behind the Space Shuttle Main Engines (SSME). The perfect on-time launch took place at 8:45:47 a.m. (EDT), September 8, 2000. Onboard the shuttle were astronauts Terrence W. Wilcutt, Scott D. Altman, Edward T. Lu, Richard A. Mastracchio and Daniel C. Burbank, along with cosmonauts Yuri I. Malenchenko and Boris V. Morukov who represent the Russian Aviation and Space Agency.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Space shuttle Atlantis roars into the cloudy sky above Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on the STS-125 mission. Blue cones of light, mach diamonds, can be seen beneath the engine nozzles. The mach diamonds are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. Atlantis will rendezvous with NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. Liftoff was on time at 2:01 p.m. EDT. Atlantis' 11-day flight will include five spacewalks to refurbish and upgrade the telescope with state-of-the-art science instruments that will expand Hubble's capabilities and extend its operational lifespan through at least 2014. The payload includes a Wide Field Camera 3, fine guidance sensor and the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray-Tom Farrar

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Mach diamonds appear beneath Space Shuttle Discovery's main engines as the vehicle roars into the night sky after liftoff on mission STS-116. Mach diamonds are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. Liftoff occurred on time at 8:47 p.m. EST. This was the second launch attempt for mission STS-116. The first launch attempt on Dec. 7 was postponed due a low cloud ceiling over Kennedy Space Center. This is Discovery's 33rd mission and the first night launch since 2002. The 20th shuttle mission to the International Space Station, STS-116 carries another truss segment, P5. It will serve as a spacer, mated to the P4 truss that was attached in September. After installing the P5, the crew will reconfigure and redistribute the power generated by two pairs of U.S. solar arrays. Landing is expected Dec. 21 at KSC. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray & Don Kight

This x-ray photograph of the Supernova remnant Cassiopeia A, taken with the High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO) 2/Einstein Observatory, shows that the regions with fast moving knots of material in the expanding shell are bright and clear. A faint x-ray halo, just outside the bright shell, is interpreted as a shock wave moving ahead of the expanding debris. The HEAO-2, the first imaging and largest x-ray telescope built to date, was capable of producing actual photographs of x-ray objects. Shortly after launch, the HEAO-2 was nicknamed the Einstein Observatory by its scientific experimenters in honor of the centernial of the birth of Albert Einstein, whose concepts of relativity and gravitation have influenced much of modern astrophysics, particularly x-ray astronomy. The HEAO-2, designed and developed by TRW, Inc. under the project management of the Marshall Space Flight Center, was launched aboard an Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle on November 13, 1978.

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space in Florida, sensors have been placed on the Orion ground test vehicle and cameras placed nearby in order to monitor pyrotechnic bolt tests. Lockheed Martin performed tests over a series of days on the explosive bolts that separate Orion from the launch abort system. Data was collected on the effect of shock waves on Orion during the explosive bolt separation. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Orion ground test vehicle sits on a test stand in the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida while engineers and technicians prepare it for a pyrotechnic bolt test. Lockheed Martin performed tests over a series of days on the explosive bolts that separate Orion from the launch abort system. Data was collected on the effect of shock waves on Orion during the explosive bolt separation. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Space shuttle Atlantis roars into the cloudy sky above Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on the STS-125 mission. Blue cones of light, mach diamonds, can be seen beneath the engine nozzles. The mach diamonds are a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. Atlantis will rendezvous with NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. Liftoff was on time at 2:01 p.m. EDT. Atlantis' 11-day flight will include five spacewalks to refurbish and upgrade the telescope with state-of-the-art science instruments that will expand Hubble's capabilities and extend its operational lifespan through at least 2014. The payload includes a Wide Field Camera 3, fine guidance sensor and the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray-Tom Farrar
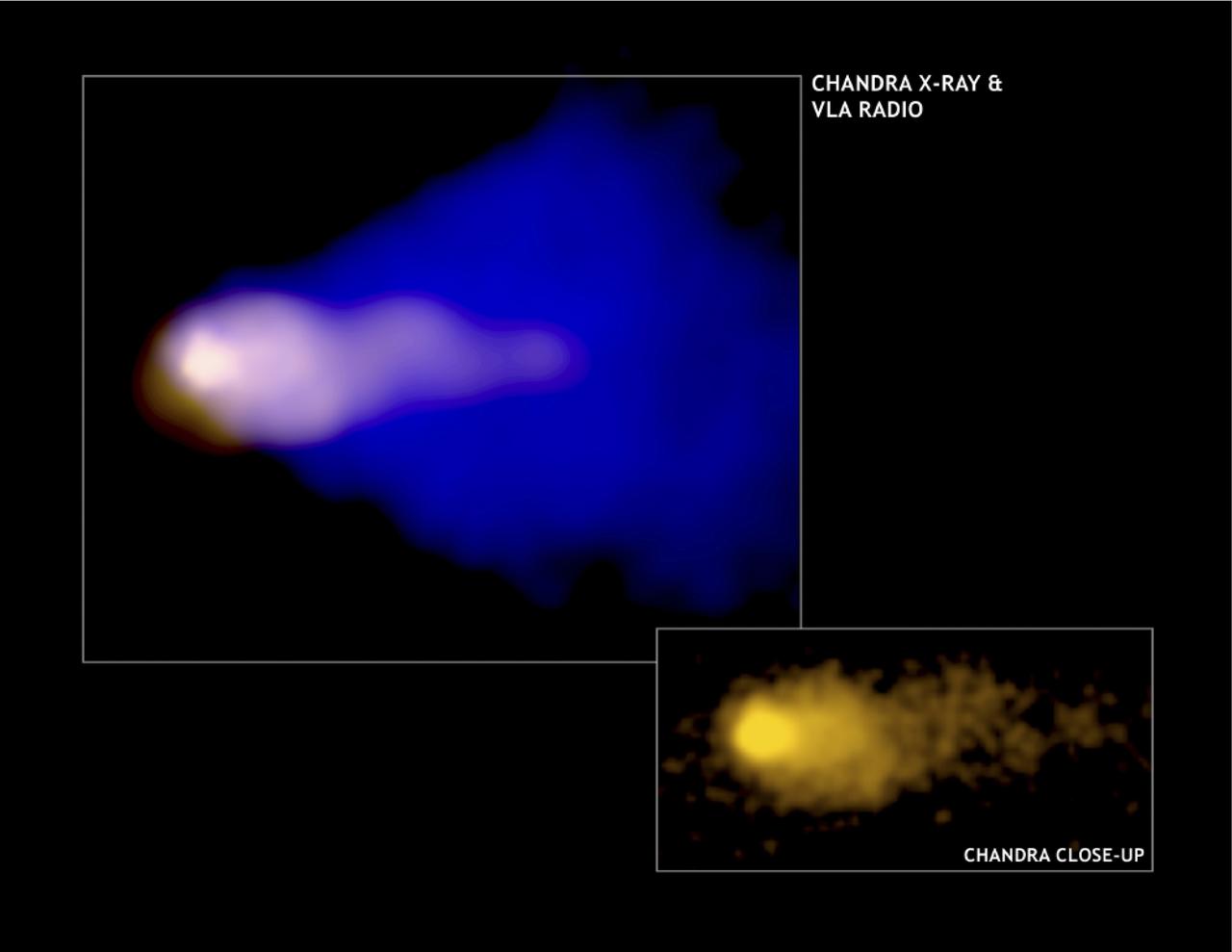

Astronomers have used an x-ray image to make the first detailed study of the behavior of high-energy particles around a fast moving pulsar. This image, from NASA's Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), shows the shock wave created as a pulsar plows supersonically through interstellar space. These results will provide insight into theories for the production of powerful winds of matter and antimatter by pulsars. Chandra's image of the glowing cloud, known as the Mouse, shows a stubby bright column of high-energy particles, about four light years in length, swept back by the pulsar's interaction with interstellar gas. The intense source at the head of the X-ray column is the pulsar, estimated to be moving through space at about 1.3 million miles per hour. A cone-shaped cloud of radio-wave-emitting particles envelopes the x-ray column. The Mouse, a.k.a. G359.23-0.82, was discovered in 1987 by radio astronomers using the National Science Foundation's Very Large Array in New Mexico. G359.23-0.82 gets its name from its appearance in radio images that show a compact snout, a bulbous body, and a remarkable long, narrow, tail that extends for about 55 light years. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama manages the Chandler program.
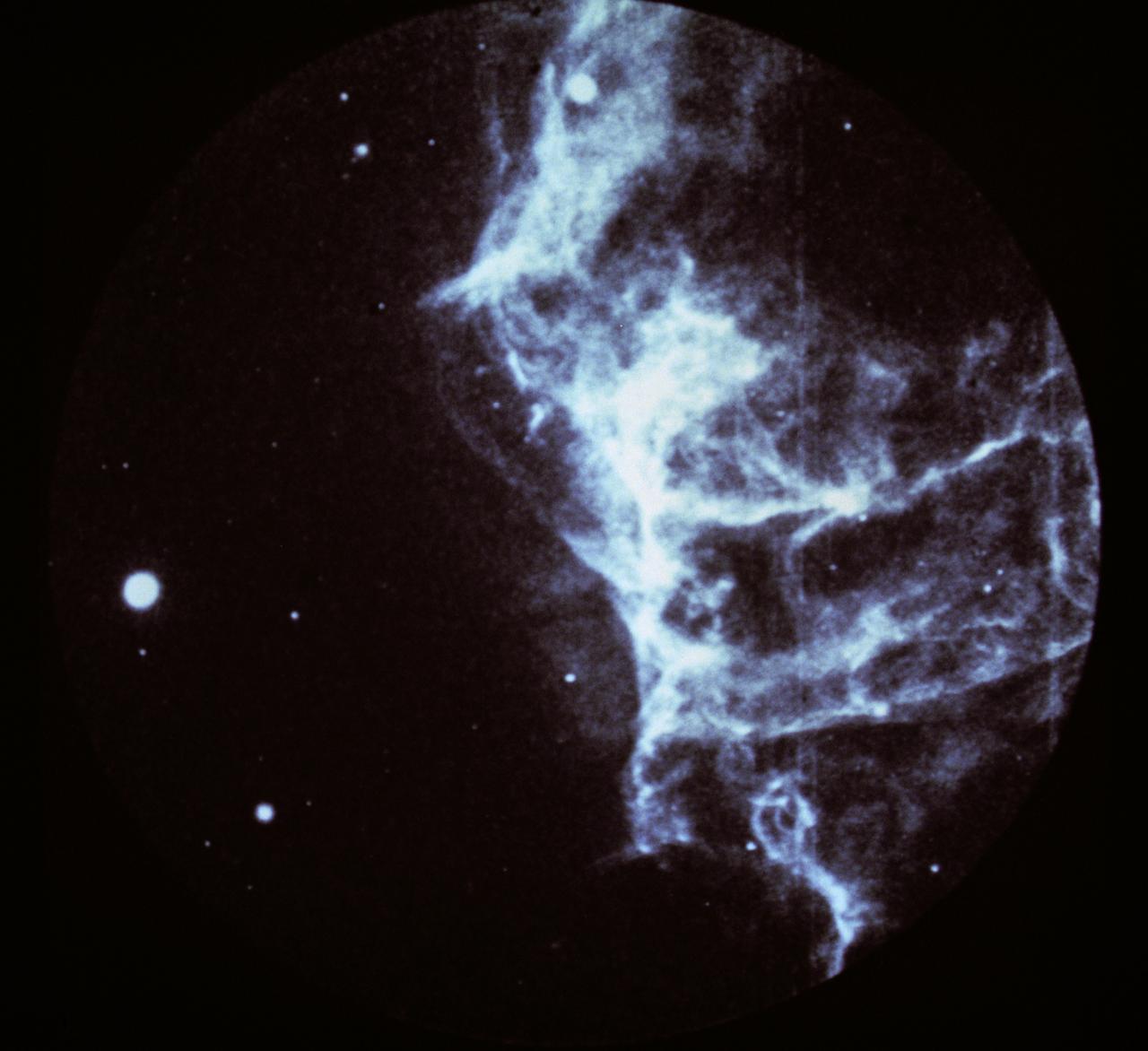
This image shows a part of the Cygnus loop supernova remnant, taken by the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT) on the Astro Observatory during the Astro-1 mission (STS-35) on December 5, 1990. Pictured is a portion of the huge Cygnus loop, an array of interstellar gas clouds that have been blasted by a 900,000 mile per hour shock wave from a prehistoric stellar explosion, which occurred about 20,000 years ago, known as supernova. With ultraviolet and x-rays, astronomers can see emissions from extremely hot gases, intense magnetic fields, and other high-energy phenomena that more faintly appear in visible and infrared light or in radio waves that are crucial to deepening the understanding of the universe. The Astro Observatory was designed to explore the universe by observing and measuring the ultraviolet radiation from celestial objects. Three instruments make up the Astro Observatory: The Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT), the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT), and the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimetry Experiment (WUPPE). The Marshall Space Flight Center had managment responsibilities for the Astro-1 mission. The Astro-1 Observatory was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-35) on December 2, 1990.

The Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO) has made a sturning, high-energy panorama of the central regions of our Milky Way galaxy. The findings are an important step toward understanding the most active area of the Milky Way as well as other galaxies throughout the universe. This 400 by 900-light-year mosaic of several CXO images reveals hundreds of white dwarf stars, neutron stars, and black holes bathed in an incandescent fog of miltimillion-degree gas. The diffuse x-ray emission seems to be related to the turmoil and density of matter in the inner Milky Way. Stars are forming there at a much more rapid rate than in the galactic "suburbs." Many of the most massive stars in the galaxy are located in the galactic center and are furiously boiling off their outer layers in searing stellar winds. Supernova explosions are far more common in the region and send shock waves booming through the inner galaxy. The super massive black hole at the center of the galaxy is located inside the bright white patch in the center of the image. The colors indicate x-ray energy bands-red (low), green (medial), and blue (high). A supernova occurs when a massive star has used up its nuclear fuel and the pressure drops in the central core of the star. The matter in the core is crushed by gravity to higher and higher densities, and temperatures reach billions of degrees. Under these extreme conditions, nuclear reactions occur violently and catastrophically reversing the collapse. A thermonuclear shock wave races through the now expanding stellar debris, fusing lighter elements into heavier ones and producing a brilliant visual outburst. (Photo credit: NASA/UMass/D. Wang et al)
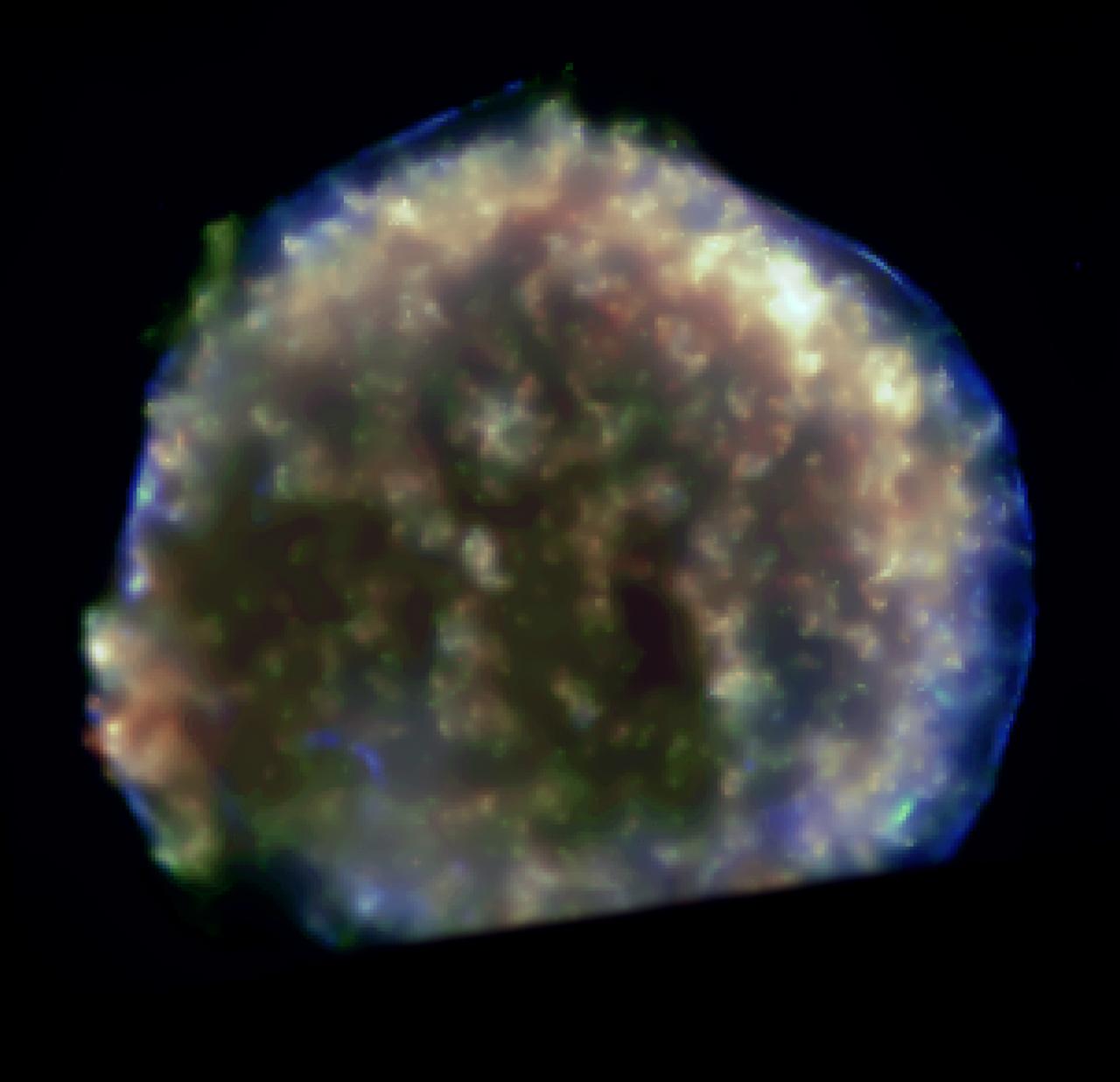
This spectacular Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO) image of the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A is the most detailed image ever made of the remains of an exploded star. The one-million-second image shows a bright outer ring (green) 10 light years in diameter that marks the location of a shock wave generated by the supernova explosion. In the upper left corner is a large jet-like structure that protrudes beyond the shock wave, and a counter-jet can be seen on the lower right. The x-ray spectra show that the jets are rich in silicon atoms, and relatively poor in iron atoms. This indicates that the jets formed soon after the initial explosion of the star, otherwise, the jets should have contained large quantities of iron from the star’s central regions. The bright blue areas are composed almost purely of iron gas, which was produced in the central, hottest regions of the star and somehow ejected in a direction almost perpendicular to the jets. The bright source at the center of the image is presumed to be a neutron star created during the supernova. Unlike most others, this neutron star is quiet, faint, and so far shows no evidence of pulsed radiation. A working hypothesis is that the explosion that created Cassiopeia A produced high speed jets similar to, but less energetic than, the hyper nova jets thought to produce gamma-ray bursts. During the explosion, the star may have developed an extremely strong magnetic filed that helped to accelerate the jets and later stifled any pulsar wind activity. CXO project management is the responsibility of NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama.
Four hundred years ago, sky watchers, including the famous astronomer Johannes Kepler, best known as the discoverer of the laws of planetary motion, were startled by the sudden appearance of a new star in the western sky, rivaling the brilliance of the nearby planets. Modern astronomers, using NASA's three orbiting Great Observatories, are unraveling the mysteries of the expanding remains of Kepler's supernova, the last such object seen to explode in our Milky Way galaxy. When a new star appeared Oct. 9, 1604, observers could use only their eyes to study it. The telescope would not be invented for another four years. A team of modern astronomers has the combined abilities of NASA's Great Observatories, the Spritzer Space Telescope (SST), Hubble Space Telescope (HST), and Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), to analyze the remains in infrared radiation, visible light, and X-rays. Visible-light images from Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys reveal where the supernova shock wave is slamming into the densest regions of surrounding gas. The astronomers used the SST to probe for material that radiates in infrared light, which shows heated microscopic dust particles that have been swept up by the supernova shock wave. The CXO data show regions of very hot gas. The combined image unveils a bubble-shaped shroud of gas and dust, 14 light-years wide and expanding at 4 million mph. There have been six known supernovas in our Milky Way over the past 1,000 years. Kepler's is the only one in which astronomers do not know what type of star exploded. By combining information from all three Great Observatories, astronomers may find the clues they need. Project management for both the HST and CXO programs is the responsibility of NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama.
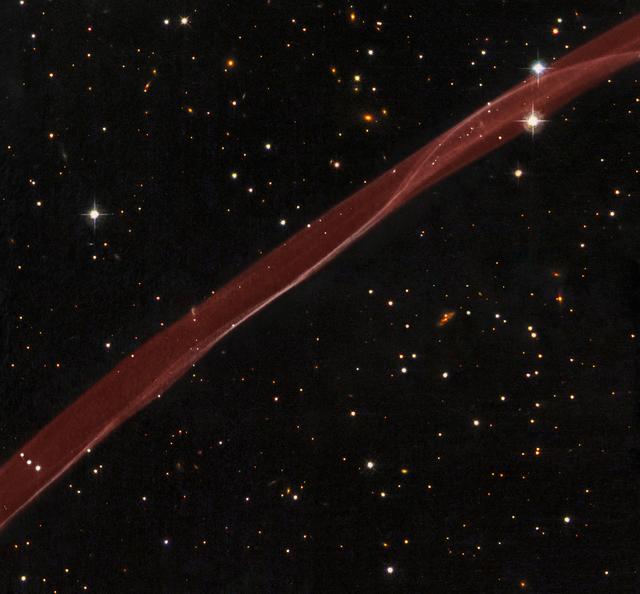

Release date: July 1, 2008 SN 1006 Supernova Remnant (Hubble) A delicate ribbon of gas floats eerily in our galaxy. A contrail from an alien spaceship? A jet from a black-hole? Actually this image, taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, is a very thin section of a supernova remnant caused by a stellar explosion that occurred more than 1,000 years ago. On or around May 1, 1006 A.D., observers from Africa to Europe to the Far East witnessed and recorded the arrival of light from what is now called SN 1006, a tremendous supernova explosion caused by the final death throes of a white dwarf star nearly 7,000 light-years away. The supernova was probably the brightest star ever seen by humans, and surpassed Venus as the brightest object in the night time sky, only to be surpassed by the moon. It was visible even during the day for weeks, and remained visible to the naked eye for at least two and a half years before fading away. It wasn't until the mid-1960s that radio astronomers first detected a nearly circular ring of material at the recorded position of the supernova. The ring was almost 30 arcminutes across, the same angular diameter as the full moon. The size of the remnant implied that the blast wave from the supernova had expanded at nearly 20 million miles per hour over the nearly 1,000 years since the explosion occurred. In 1976, the first detection of exceedingly faint optical emission of the supernova remnant was reported, but only for a filament located on the northwest edge of the radio ring. A tiny portion of this filament is revealed in detail by the Hubble observation. The twisting ribbon of light seen by Hubble corresponds to locations where the expanding blast wave from the supernova is now sweeping into very tenuous surrounding gas. The hydrogen gas heated by this fast shock wave emits radiation in visible light. Hence, the optical emission provides astronomers with a detailed "snapshot" of the actual position and geometry of the shock front at any given time. Bright edges within the ribbon correspond to places where the shock wave is seen exactly edge on to our line of sight. Today we know that SN 1006 has a diameter of nearly 60 light-years, and it is still expanding at roughly 6 million miles per hour. Even at this tremendous speed, however, it takes observations typically separated by years to see significant outward motion of the shock wave against the grid of background stars. In the Hubble image as displayed, the supernova would have occurred far off the lower right corner of the image, and the motion would be toward the upper left. SN 1006 resides within our Milky Way Galaxy. Located more than 14 degrees off the plane of the galaxy's disk, there is relatively little confusion with other foreground and background objects in the field when trying to study this object. In the Hubble image, many background galaxies (orange extended objects) far off in the distant universe can be seen dotting the image. Most of the white dots are foreground or background stars in our Milky Way galaxy. This image is a composite of hydrogen-light observations taken with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys in February 2006 and Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 observations in blue, yellow-green, and near-infrared light taken in April 2008. The supernova remnant, visible only in the hydrogen-light filter was assigned a red hue in the Heritage color image. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: W. Blair (Johns Hopkins University) To learn more about the Hubble Space Telescope go here: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This Chandra X-Ray Observatory image of the mysterious superstar Eta Carinae reveals a surprising hot irner core, creating more questions than answers for astronomers. The image shows three distinct structures: An outer, horseshoe shaped ring about 2 light-years in diameter, a hot inner core about 3 light-months in diameter, and a hot central source less than a light-month in diameter which may contain the superstar. In 1 month, light travels a distance of approximately 489 billion miles (about 788 billion kilometers). All three structures are thought to represent shock waves produced by matter rushing away from the superstar at supersonic speeds. The temperature of the shock-heated gas ranges from 60 million degrees Kelvin in the central regions to 7 million degrees Kelvin on the outer structure. Eta Carinae is one of the most enigmatic and intriguing objects in our galaxy. Between 1837 and 1856, it increased dramatically in brightness to become the most prominent star in the sky except for Sirius, even through it is 7,500 light-years away, more than 80 times the distance to Sirius. This "Great Eruption," as it is called, had an energy comparable to a supernova, yet did not destroy the star, which faded to become a dim star, invisible to the naked eye. Since 1940, Eta Carinae has begun to brighten again, becoming visible to the naked eye. Photo credit: NASA/CXC/SAO

This image was compiled using data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope using the Infrared Array Camera (IRAC) and the Multiband Imaging Photometer (MIPS) during Spitzer's "cold" mission, before the spacecraft's liquid helium coolant ran out in 2009. The colors correspond with IRAC wavelengths of 3.6 microns (blue), 4.5 microns (cyan) and 8 microns (green), and 24 microns (red) from the MIPS instrument. The green-and-orange delta filling most of this image is a nebula, or a cloud of gas and dust. This region formed from a much larger cloud of gas and dust that has been carved away by radiation from stars. The bright region at the tip of the nebula is dust that has been heated by the stars' radiation, which creates the surrounding red glow. The white color is the combination of four colors (blue, green, orange and red), each representing a different wavelength of infrared light, which is invisible to human eyes. The massive stars illuminating this region belong to a star cluster that extends above the white spot. On the left side of this image, a dark filament runs horizontally through the green cloud. A smattering of baby stars (the red and yellow dots) appear inside it. Known as Cepheus C, the area is a particularly dense concentration of gas and dust where infant stars form. This region is called Cepheus C because it lies in the constellation Cepheus, which can be found near the constellation Cassiopeia. Cepheus-C is about 6 light-years long, and lies about 40 light-years from the bright spot at the tip of the nebula. The small, red hourglass shape just below Cepheus C is V374 Ceph. Astronomers studying this massive star have speculated that it might be surrounded by a nearly edge-on disk of dark, dusty material. The dark cones extending to the right and left of the star are a shadow of that disk. The smaller nebula on the right side of the image includes a blue star crowned by a small, red arc of light. This "runaway star" is plowing through the gas and dust at a rapid clip, creating a shock wave or "bow shock" in front of itself. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23126
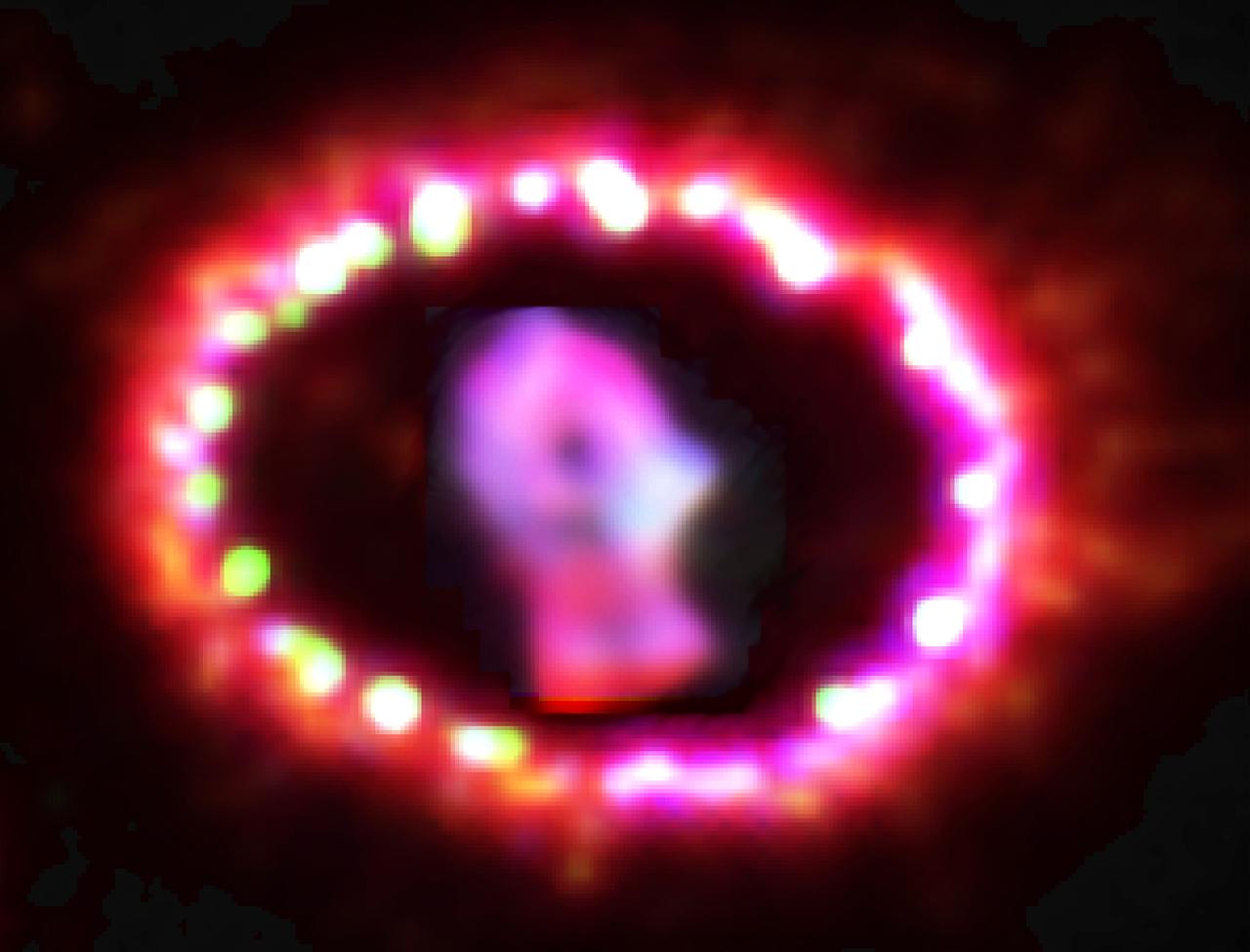
NASA image release June 10, 2011 Astronomers using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope are witnessing the unprecedented transition of a supernova to a supernova remnant, where light from an exploding star in a neighboring galaxy, the Large Magellanic Cloud, reached Earth in February 1987. Named Supernova 1987A, it was the closest supernova explosion witnessed in almost 400 years. The supernova's close proximity to Earth has allowed astronomers to study it in detail as it evolves. Now, the supernova debris, which has faded over the years, is brightening. This means that a different power source has begun to light the debris. The debris of SN 1987A is beginning to impact the surrounding ring, creating powerful shock waves that generate X-rays observed with NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. Those X-rays are illuminating the supernova debris and shock heating is making it glow in visible light. The results are being reported in the June 9, 2011, issue of the journal Nature by a team including Robert Kirshner of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA), who leads a long-term study of SN 1987A with Hubble. Since its launch in 1990, the Hubble telescope has provided a continuous record of the changes in SN 1987A. Credit: NASA, ESA, and P. Challis (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Fiery columns propel space shuttle Endeavour into space from NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A on the STS-127 mission. Liftoff was on-time at 6:03 p.m. EDT. Below the main engine nozzles are the blue mach diamonds, a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system. This was the sixth launch attempt for the STS-127 mission. The launch was scrubbed on June 13 and June 17 when a hydrogen gas leak occurred during tanking due to a misaligned Ground Umbilical Carrier Plate. The mission was postponed July 11, 12 and 13 due to weather conditions near the Shuttle Landing Facility at Kennedy that violated rules for launching, and lightning issues. Endeavour will deliver the Japanese Experiment Module's Exposed Facility and the Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section in the final of three flights dedicated to the assembly of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory complex on the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Mike Gayle, Rusty Backer

Screwjacks located on the exterior of the second throat section in the 10- by 10-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The 10- by 10 tunnel was the most powerful propulsion wind tunnel in the country when it began operating in 1956. The facility can generate wind speeds from Mach 3 to 3.5. A flexible wall nozzle located just upstream from the test section can be adjusted using screw jacks to produce the desired air flow. The 61-foot long second throat, seen here from the outside, was located just beyond the test section. It slows the supersonic air flow down to prevent shock waves. The second throat’s side walls can be adjusted up to three inches on each side using these electrically-driven screwjacks. The air and the 1.25-inch thick walls are cooled by water injection. During the 1960s the 10- by 10-foot tunnel supported the development of virtually all US launch vehicle systems. It was used for Atlas-Centaur, Saturn rockets, and Atlas-Agena testing.

S85-25870 (August 1985) --- The crew emblem for STS-51I is based on a strong patriotic theme with the basic colors of red, white and blue suggesting the American flag and a dominant American bald eagle in aggressive flight. The 19 stars signify the numerical sequence of the flight. The shock wave represents that formed by the orbiter during the entry phase of the flight. Surnames of crew members surround the top part of the circular design. The five-member crew composed of astronauts Joe H. Engle, commander; Richard O. Covey, pilot; John Michael (Mike) Lounge, William F. Fisher and James D. van Hoften, all mission specialists. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Discovery hurtles toward space on the STS-128 mission. Below the main engine nozzles are the blue mach diamonds, a formation of shock waves in the exhaust plume of an aerospace propulsion system Liftoff from Launch Pad 39A was on time at 11:59 p.m. EDT. The first launch attempt on Aug. 24 was postponed due to unfavorable weather conditions. The second attempt on Aug. 25 also was postponed due to an issue with a valve in space shuttle Discovery's main propulsion system. The STS-128 mission is the 30th International Space Station assembly flight and the 128th space shuttle flight. The 13-day mission will deliver more than 7 tons of supplies, science racks and equipment, as well as additional environmental hardware to sustain six crew members on the International Space Station. The equipment includes a freezer to store research samples, a new sleeping compartment and the COLBERT treadmill. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray-Tom Farrar