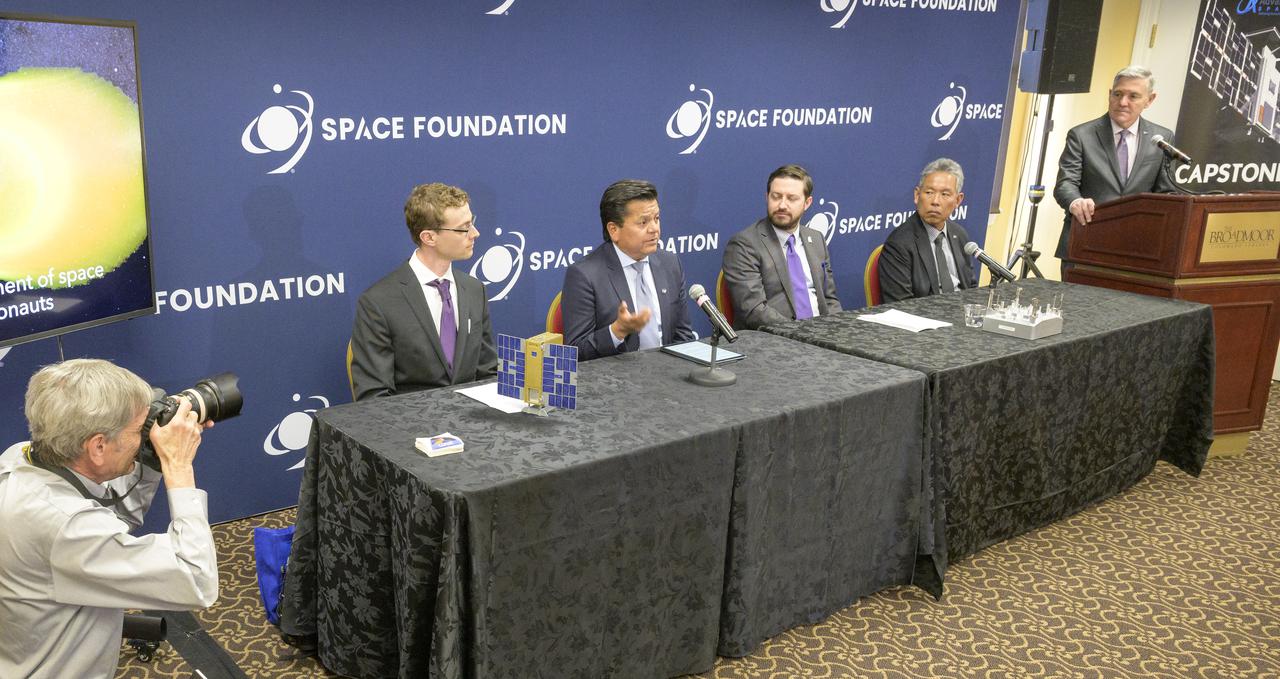

NASA Associate Administrator Bob Cabana, right, moderates a news conference, “Small Satellites, Big Missions: Pathfinding CubeSats Exploring the Moon and Beyond,” during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. The panel included, from left: Joe Shoer, Lockheed Martin; Andres Martinez, program executive for small spacecraft in NASA’s Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate; Bradley Cheetham (CEO) Advanced Space; and Elwood Agasid, deputy program manager for Small Spacecraft Technology at Ames Research Center and Space Technology Hall of Fame inductee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
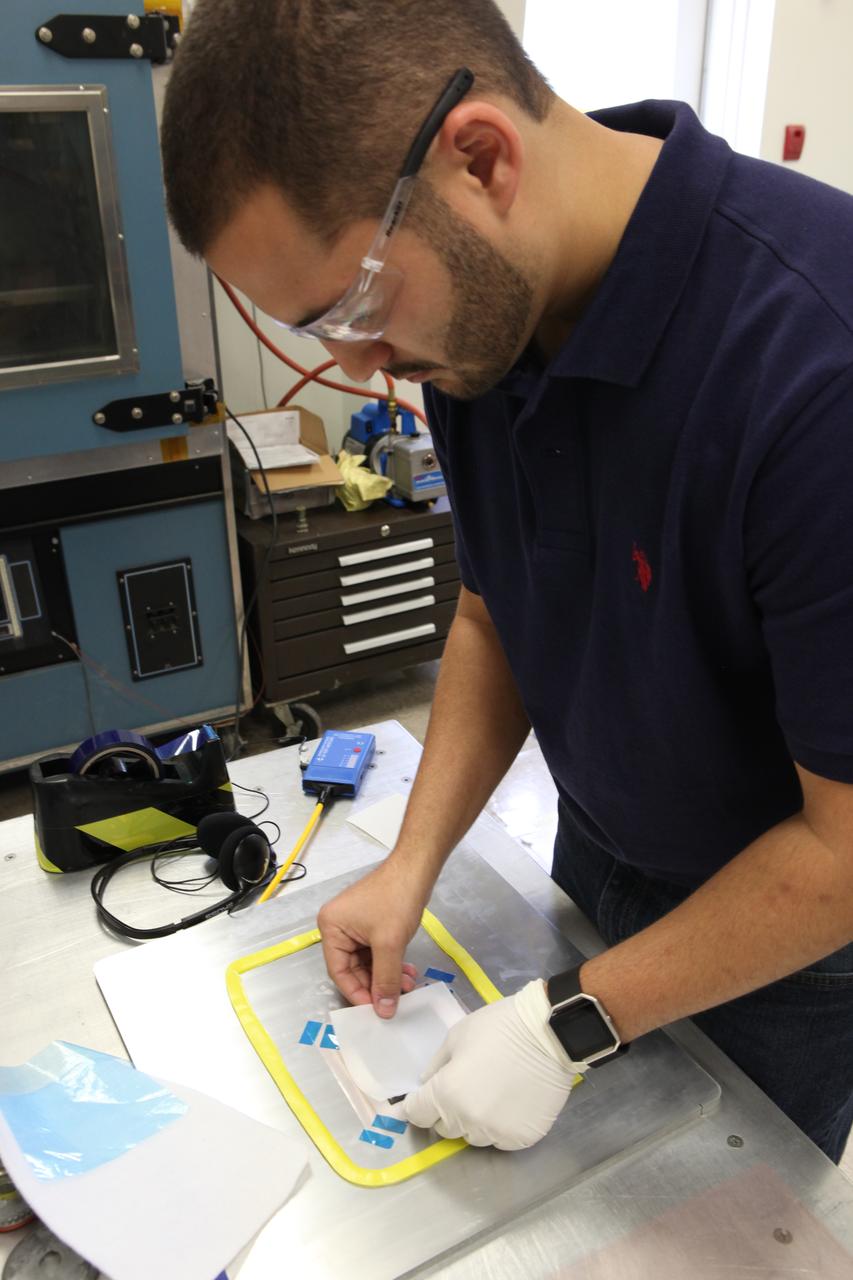

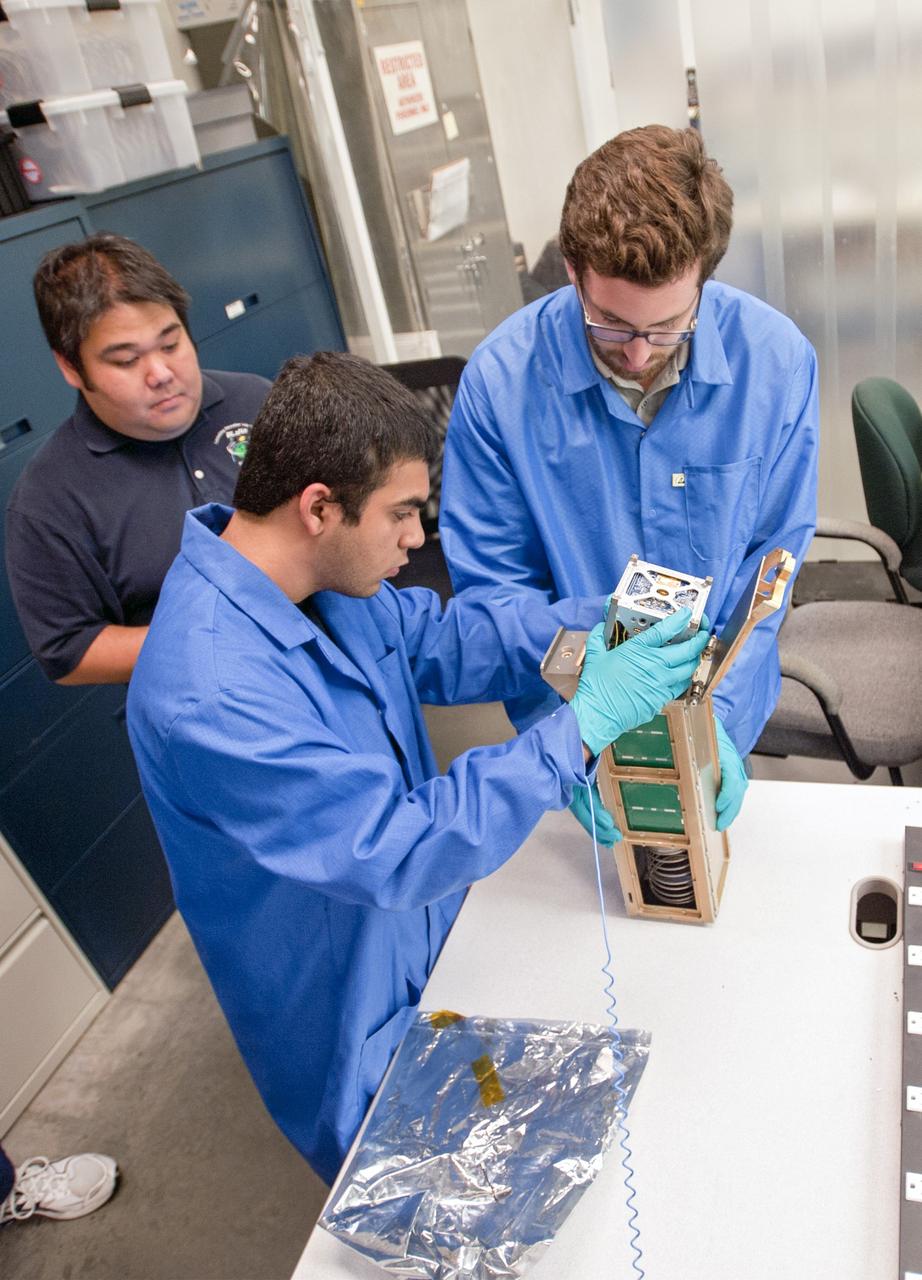
Daniel Perez, Ph.D., a graduate student from the University of Miami, prepares layers of the prototype structure for a new solid-state battery in the Prototype Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The size of the battery is so small that it could be a prime candidate for use in microsatellites, including CubeSats. Researchers at Kennedy are collaborating with experts at the University of Miami. The university partnership is funded through the Small Spacecraft Technology Program, in NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate.
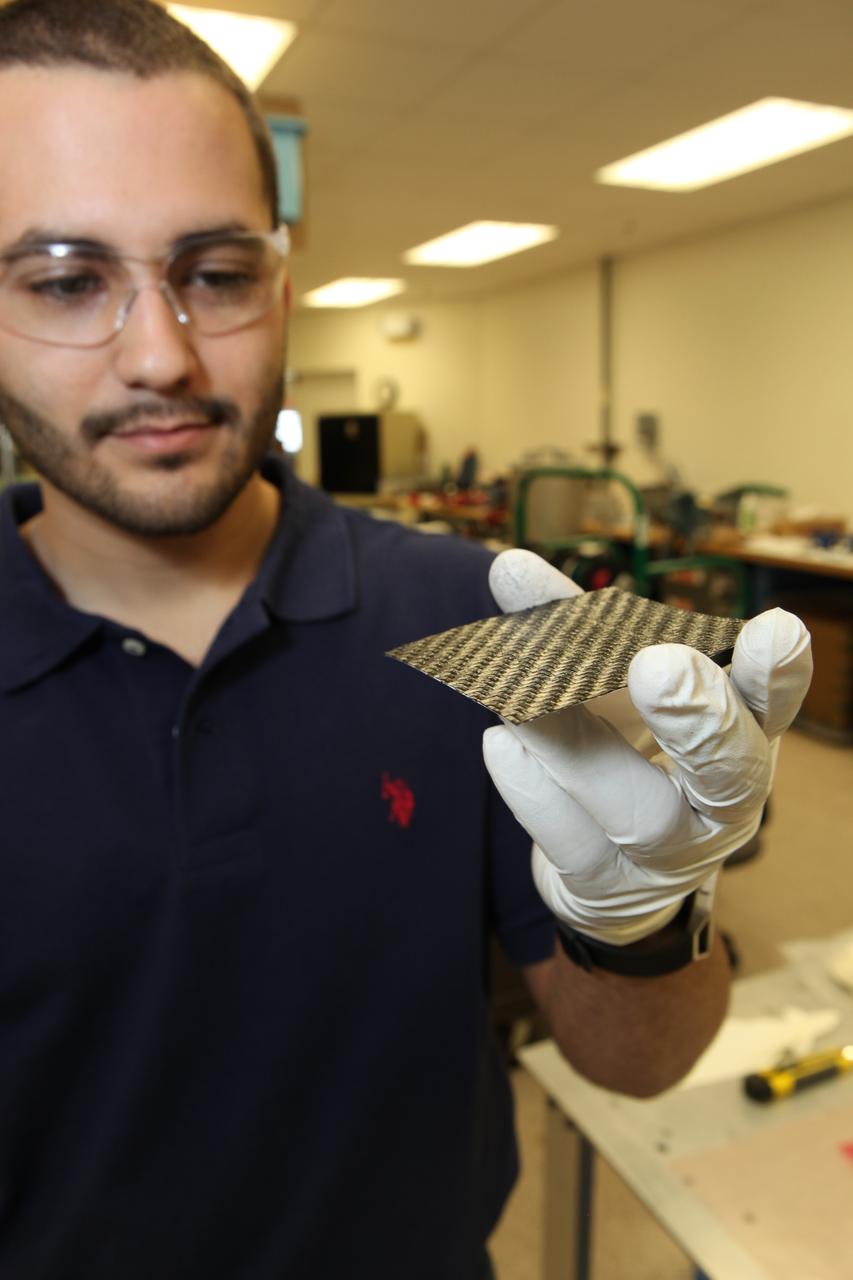

Daniel Perez, Ph.D., a graduate student from the University of Miami, displays a piece of the prototype structure for a new solid-state battery in the Prototype Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The size of the battery is so small that it could be a prime candidate for use in microsatellites, including CubeSats. Researchers at Kennedy are collaborating with experts at the University of Miami. The university partnership is funded through the Small Spacecraft Technology Program, in NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate.
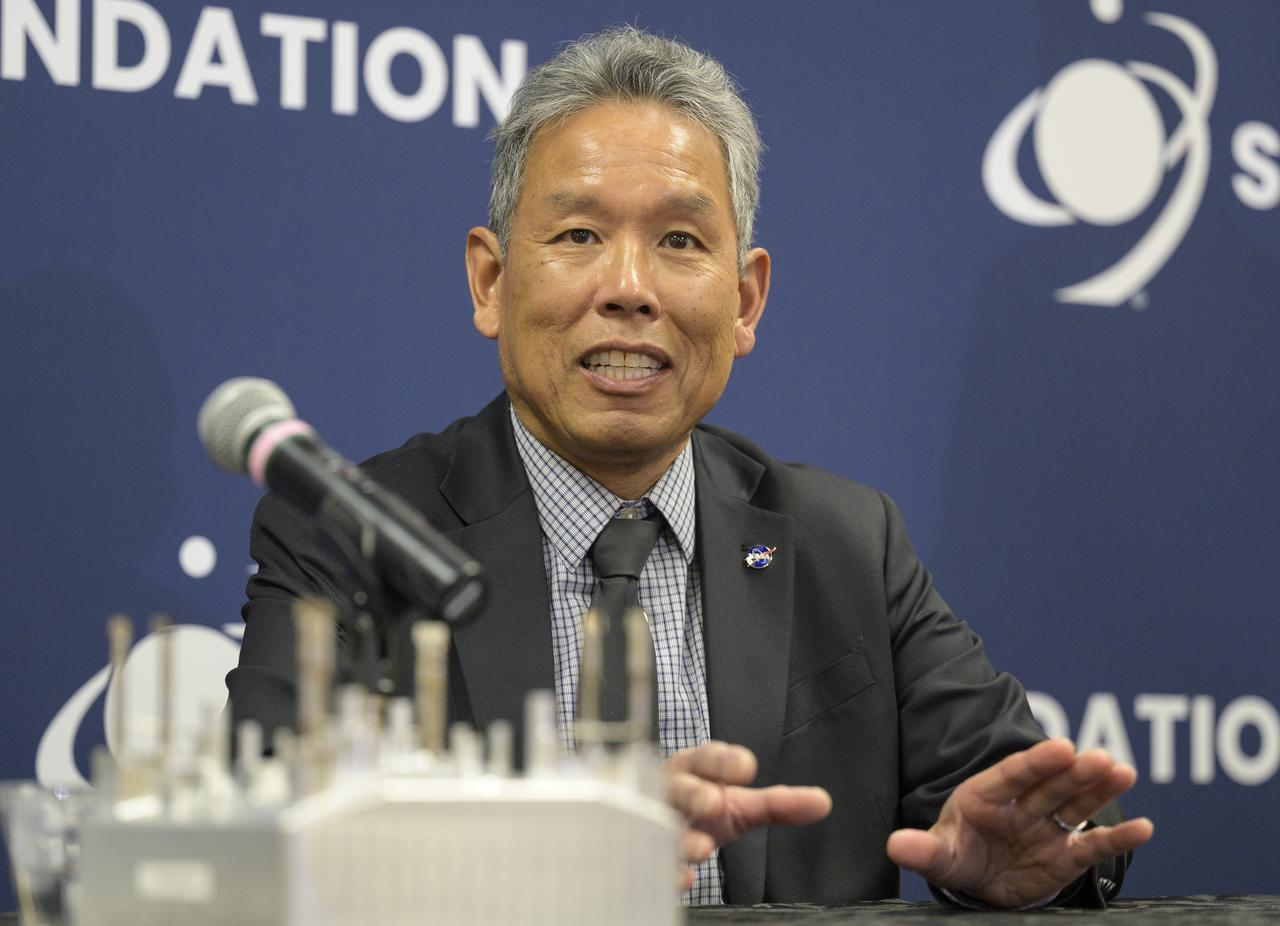

Elwood Agasid, deputy program manager for Small Spacecraft Technology at Ames Research Center and Space Technology Hall of Fame inductee speaks at “Small Satellites, Big Missions: Pathfinding CubeSats Exploring the Moon and Beyond,” a news conference during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
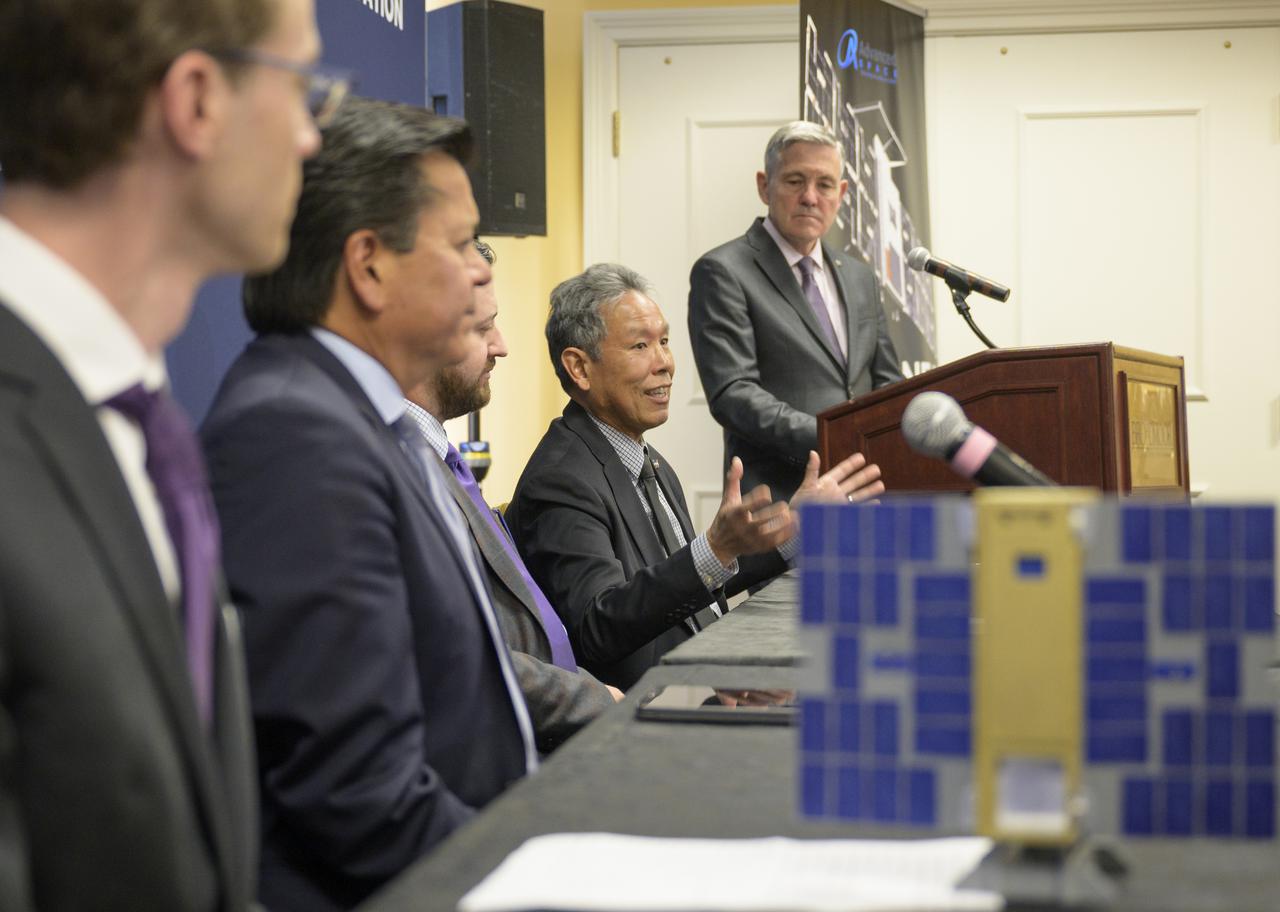

Elwood Agasid, deputy program manager for Small Spacecraft Technology at Ames Research Center and Space Technology Hall of Fame inductee speaks at “Small Satellites, Big Missions: Pathfinding CubeSats Exploring the Moon and Beyond,” a news conference during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
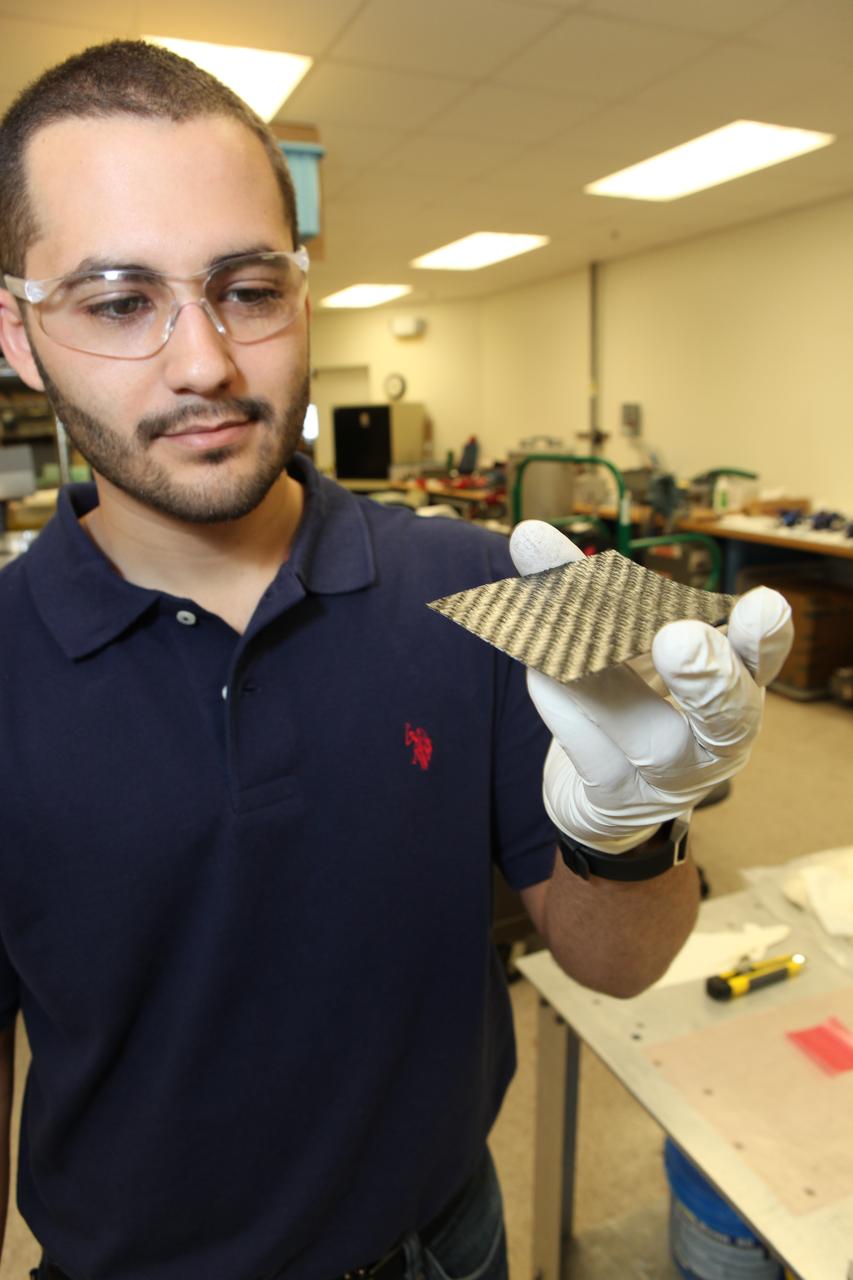

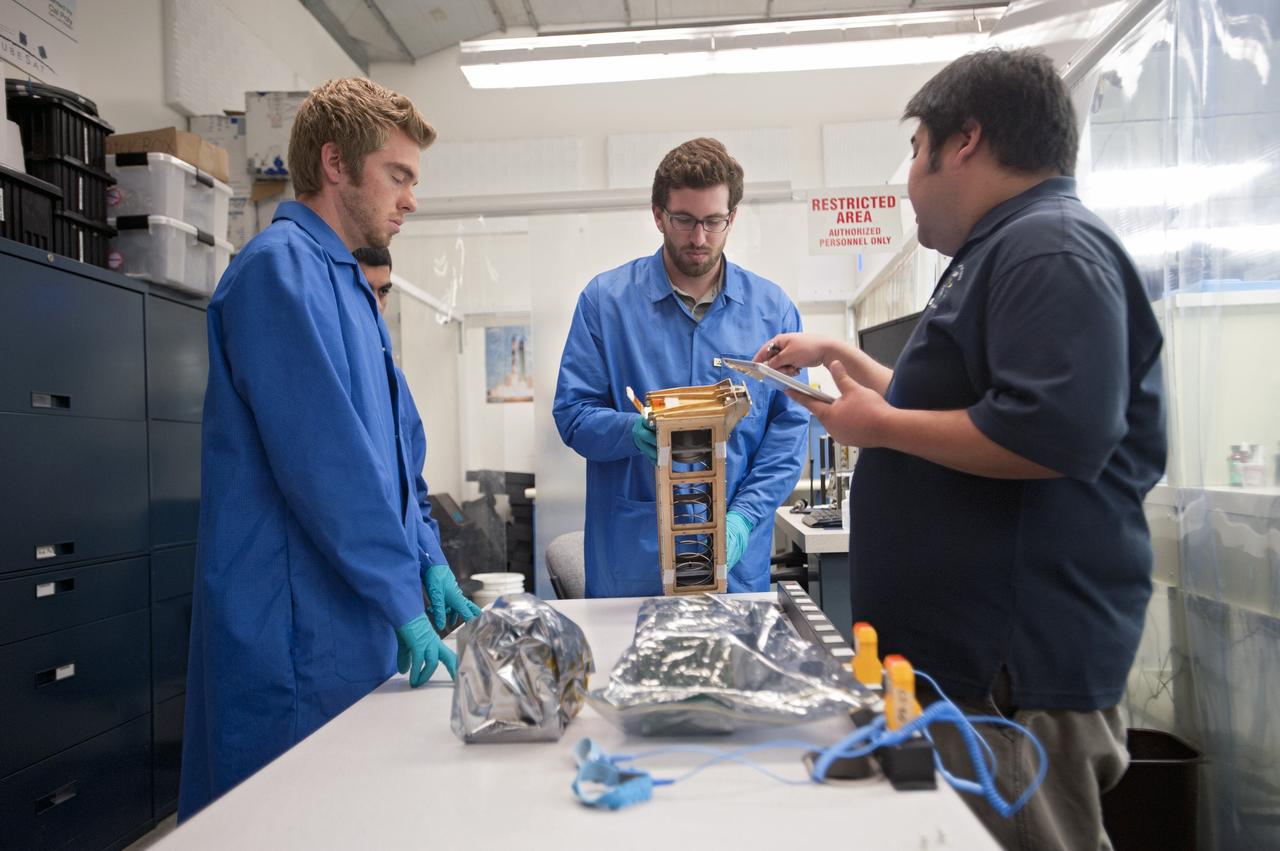
Daniel Perez, Ph.D., a graduate student from the University of Miami, displays a piece of the prototype structure for a new solid-state battery in the Prototype Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The size of the battery is so small that it could be a prime candidate for use in microsatellites, including CubeSats. Researchers at Kennedy are collaborating with experts at the University of Miami. The university partnership is funded through the Small Spacecraft Technology Program, in NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate.
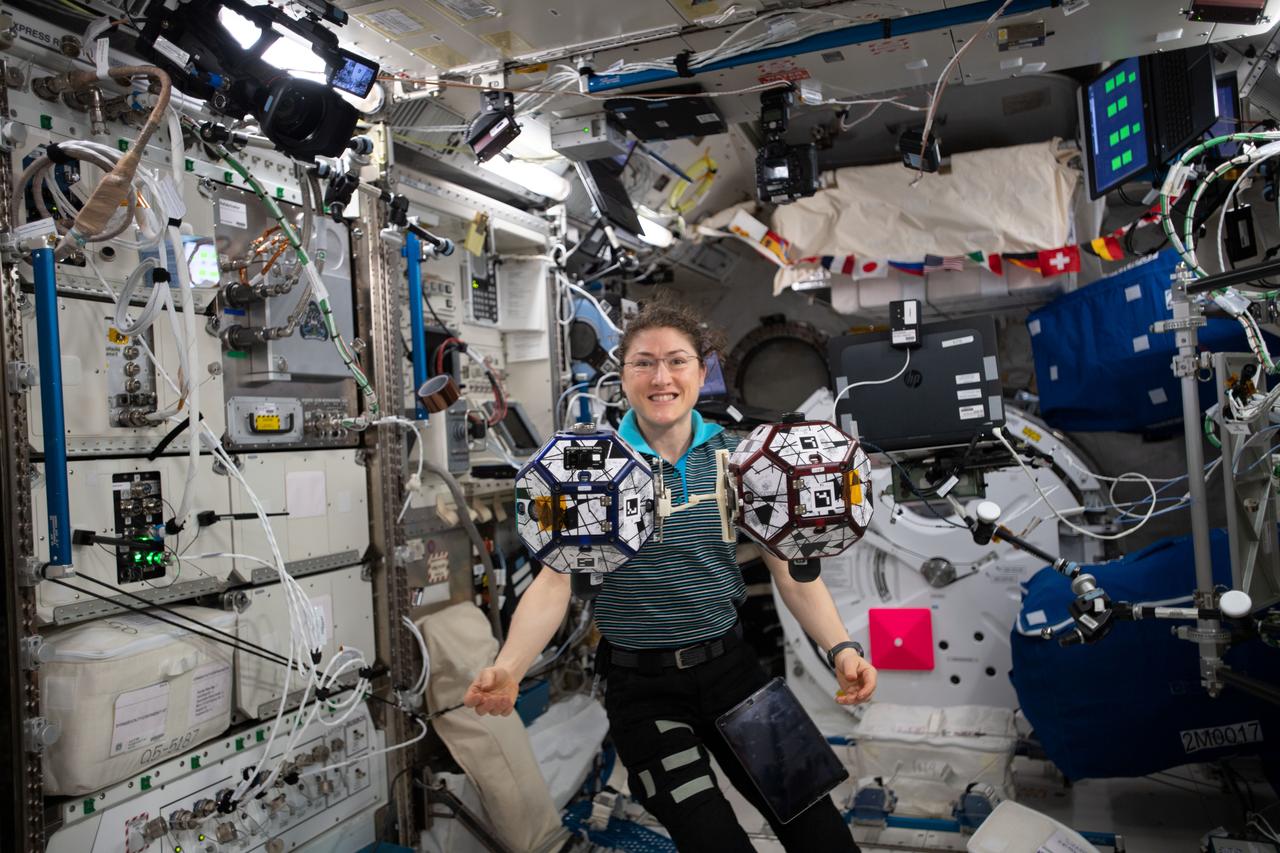

iss060e020172 (July 29, 2019) --- With advances in propulsion, swarms of small spacecraft are expected to become feasible in the near future. Expedition 60 Flight Engineer Christina Koch of NASA can be seen here floating with the SPHERES robots which are putting some of these technologies to the test. The crew was preparing to run code from participants of the SPHERES Zero Robotics (ZR) 2019 Middle School Summer Program. The SPHERES team tests algorithms developed by students and selects the best designs for the competition to operate the robots on board the space station.
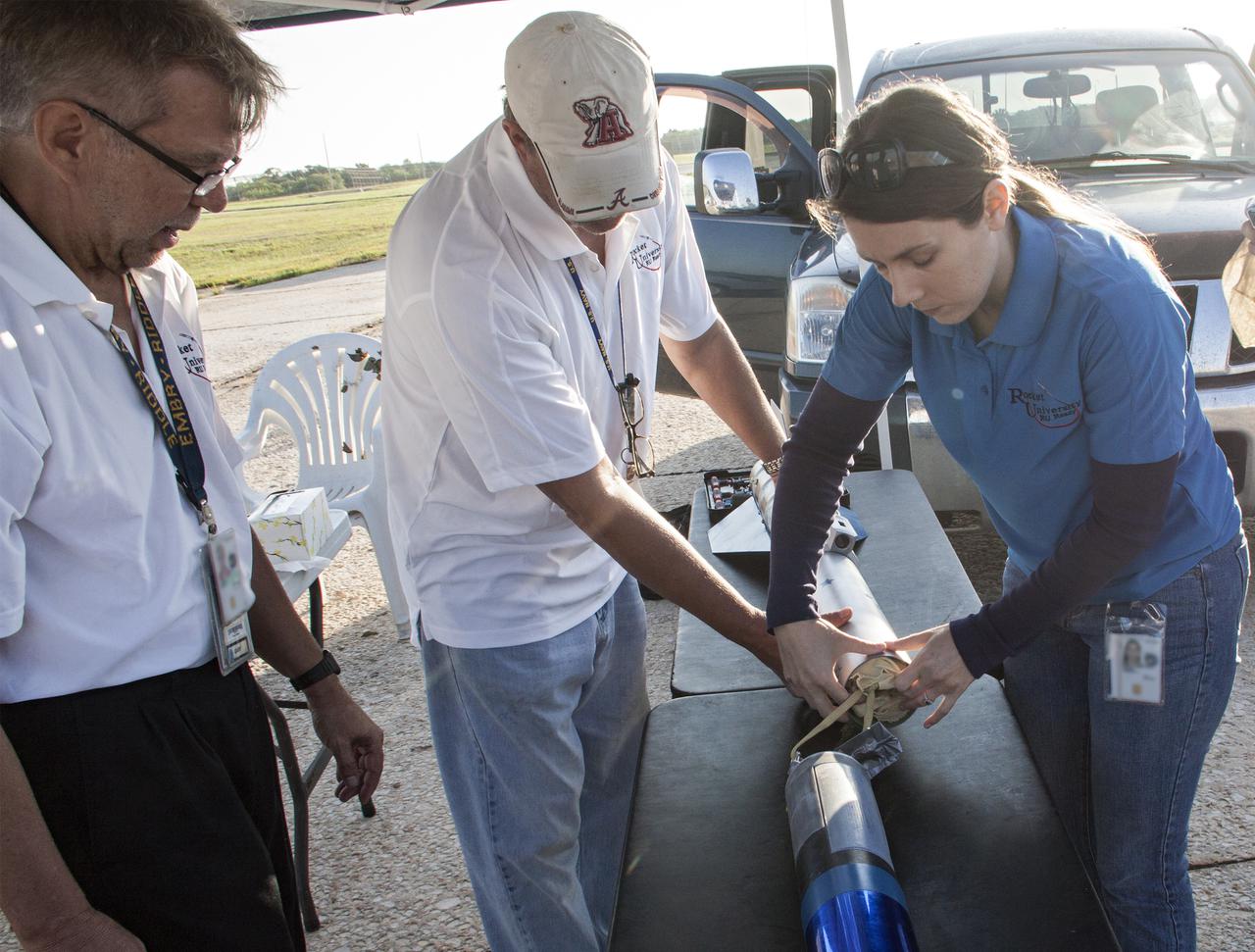

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, from the left, Gary Dahlke of Engineering and Technology, George Mizell of Quality Assurance and Kim Simpson of Fluids, Mechanical and Structural Systems make final adjustments to a small rocket prior to launch as part of Rocket University. The goal was to test its systems and to verify that it performed as designed. As part of Rocket University, the engineers are given an opportunity to work a fast-track project to develop skills in developing spacecraft systems of the future. As NASA plans for future spaceflight programs to low-Earth orbit and beyond, teams of engineers at Kennedy are gaining experience in designing and flying launch vehicle systems on a small scale. Four teams of five to eight members from Kennedy are designing rockets complete with avionics and recovery systems. Launch operations require coordination with federal agencies, just as they would with rockets launched in support of a NASA mission. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
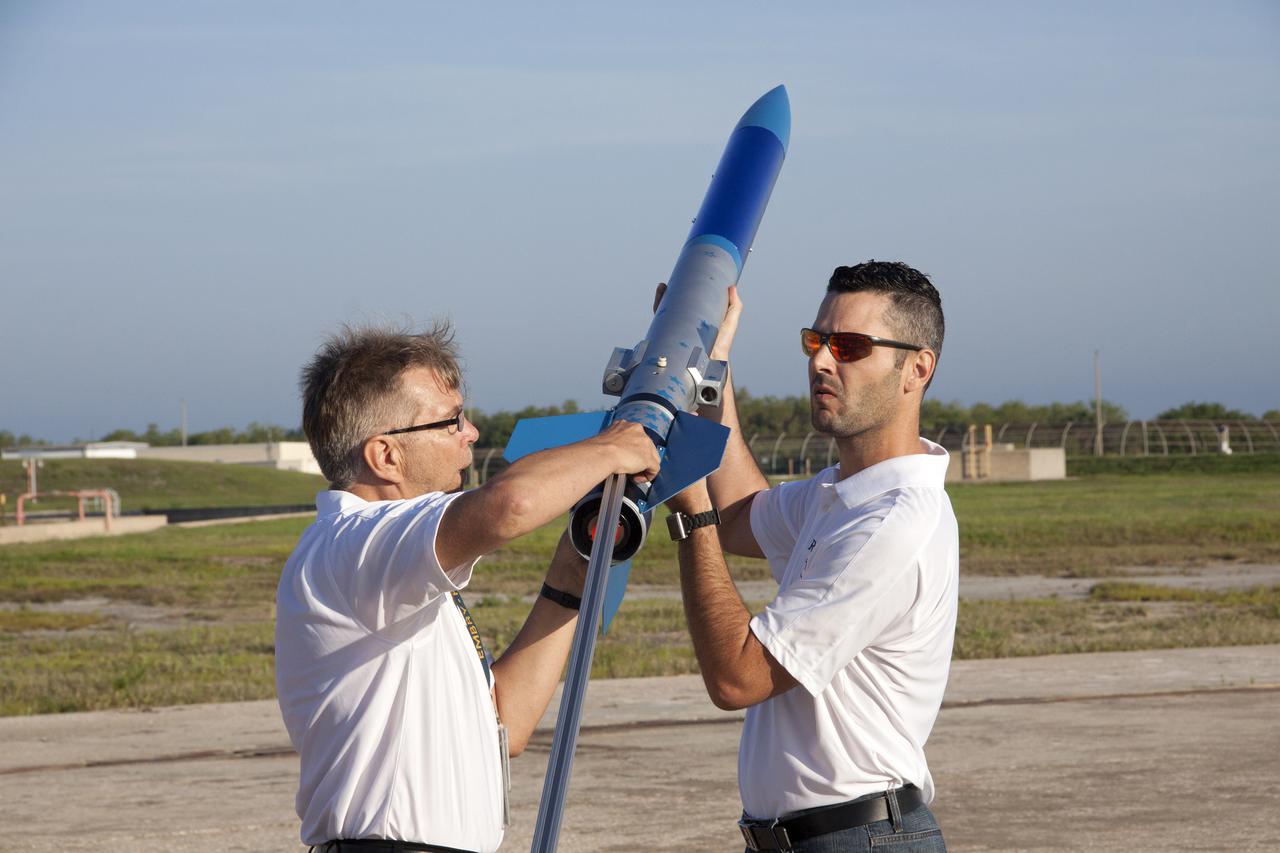

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Gary Dahlke of Engineering and Technology, left, and Leandro James of Systems Hardware Engineering attach a small rocket prior to its launch stand as part of Rocket University. The goal was to test its systems and to verify that it performed as designed. As part of Rocket University, the engineers are given an opportunity to work a fast-track project to develop skills in developing spacecraft systems of the future. As NASA plans for future spaceflight programs to low-Earth orbit and beyond, teams of engineers at Kennedy are gaining experience in designing and flying launch vehicle systems on a small scale. Four teams of five to eight members from Kennedy are designing rockets complete with avionics and recovery systems. Launch operations require coordination with federal agencies, just as they would with rockets launched in support of a NASA mission. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
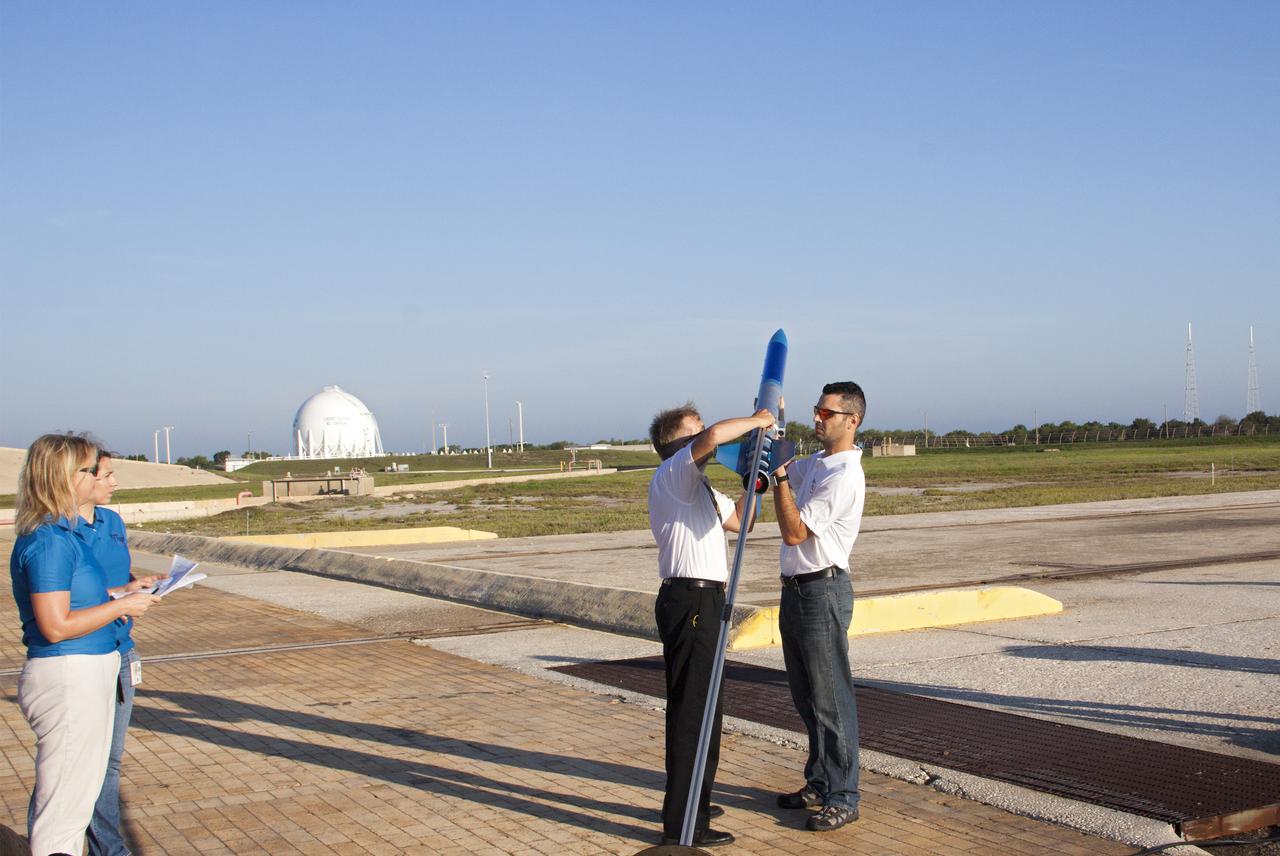

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as Susan Danley of Flight Structures and Kim Simpson of Fluids, Mechanical and Structural Systems look on, Gary Dahlke of Engineering and Technology, left, and Leandro James of Systems Hardware Engineering attach a small rocket prior to its launch stand as part of Rocket University. The goal was to test its systems and to verify that it performed as designed. As part of Rocket University, the engineers are given an opportunity to work a fast-track project to develop skills in developing spacecraft systems of the future. As NASA plans for future spaceflight programs to low-Earth orbit and beyond, teams of engineers at Kennedy are gaining experience in designing and flying launch vehicle systems on a small scale. Four teams of five to eight members from Kennedy are designing rockets complete with avionics and recovery systems. Launch operations require coordination with federal agencies, just as they would with rockets launched in support of a NASA mission. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
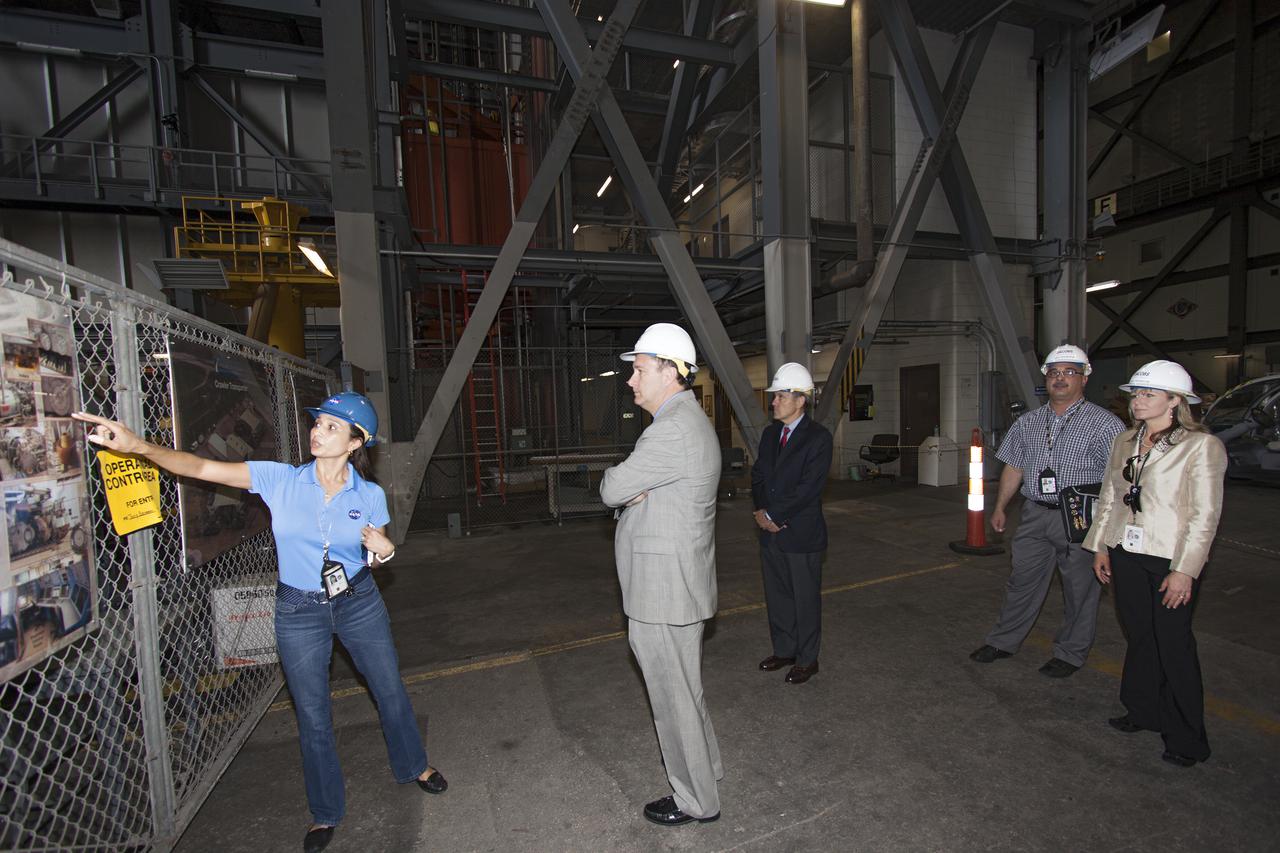

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA Associate Administrator Robert Lightfoot, center, tours the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, during a visit to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Here, he receives a briefing from Mary Hanna, crawler-transporter project manager. Behind him, from left, are Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, Jose Lopez, VAB project manager, and Joy Burkey, program specialist. The VAB is being readied to support NASA's new Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System heavy-lift rocket, the SLS. NASA's FY2014 budget proposal includes a plan to robotically capture a small near-Earth asteroid and redirect it safely to a stable orbit in the Earth-moon system where astronauts can visit and explore it. Performing these elements for the proposed asteroid initiative integrates the best of NASA's science, technology and human exploration capabilities and draws on the innovation of America's brightest scientists and engineers. It uses current and developing capabilities to find both large asteroids that pose a hazard to Earth and small asteroids that could be candidates for the initiative, accelerates our technology development activities in high-powered solar electric propulsion and takes advantage of our hard work on the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft, helping to keep NASA on target to reach the President's goal of sending humans to Mars in the 2030s. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
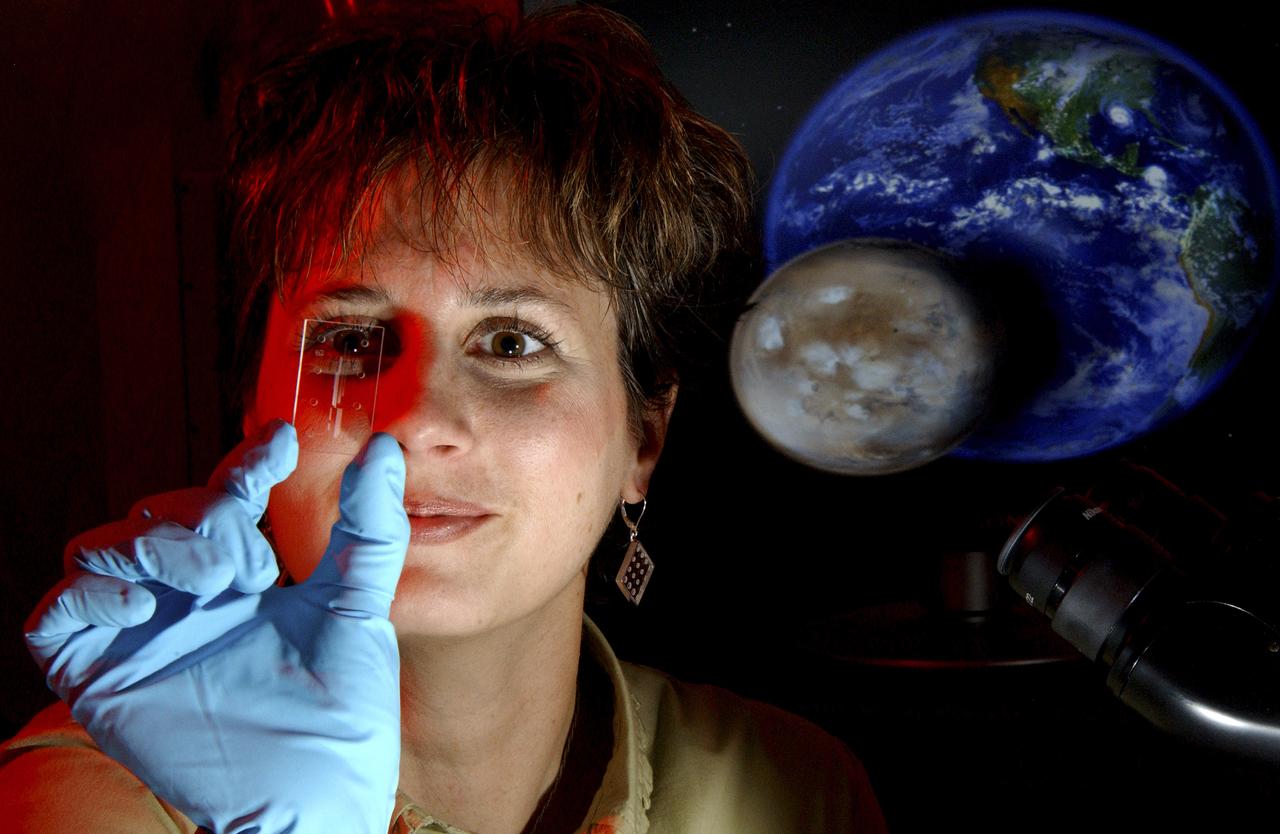

Dr. Lisa Monaco, Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC’s) project scientist for the Lab-on-a-Chip Applications Development (LOCAD) program, examines a lab on a chip. The small dots are actually ports where fluids and chemicals can be mixed or samples can be collected for testing. Tiny channels, only clearly visible under a microscope, form pathways between the ports. Many chemical and biological processes, previously conducted on large pieces of laboratory equipment, can now be performed on these small glass or plastic plates. Monaco and other researchers at MSFC in Huntsville, Alabama, are customizing the chips to be used for many space applications, such as monitoring microbes inside spacecraft and detecting life on other planets. The portable, handheld Lab-on-a Chip Application Development Portable Test System (LOCAD-PTS) made its debut flight aboard Discovery during the STS-116 mission launched December 9, 2006. The system allowed crew members to monitor their environment for problematic contaminants such as yeast, mold, and even E.coli, and salmonella. Once LOCAD-PTS reached the International Space Station (ISS), the Marshall team continued to manage the experiment, monitoring the study from a console in the Payload Operations Center at MSFC. The results of these studies will help NASA researchers refine the technology for future Moon and Mars missions. (NASA/MSFC/D.Stoffer)
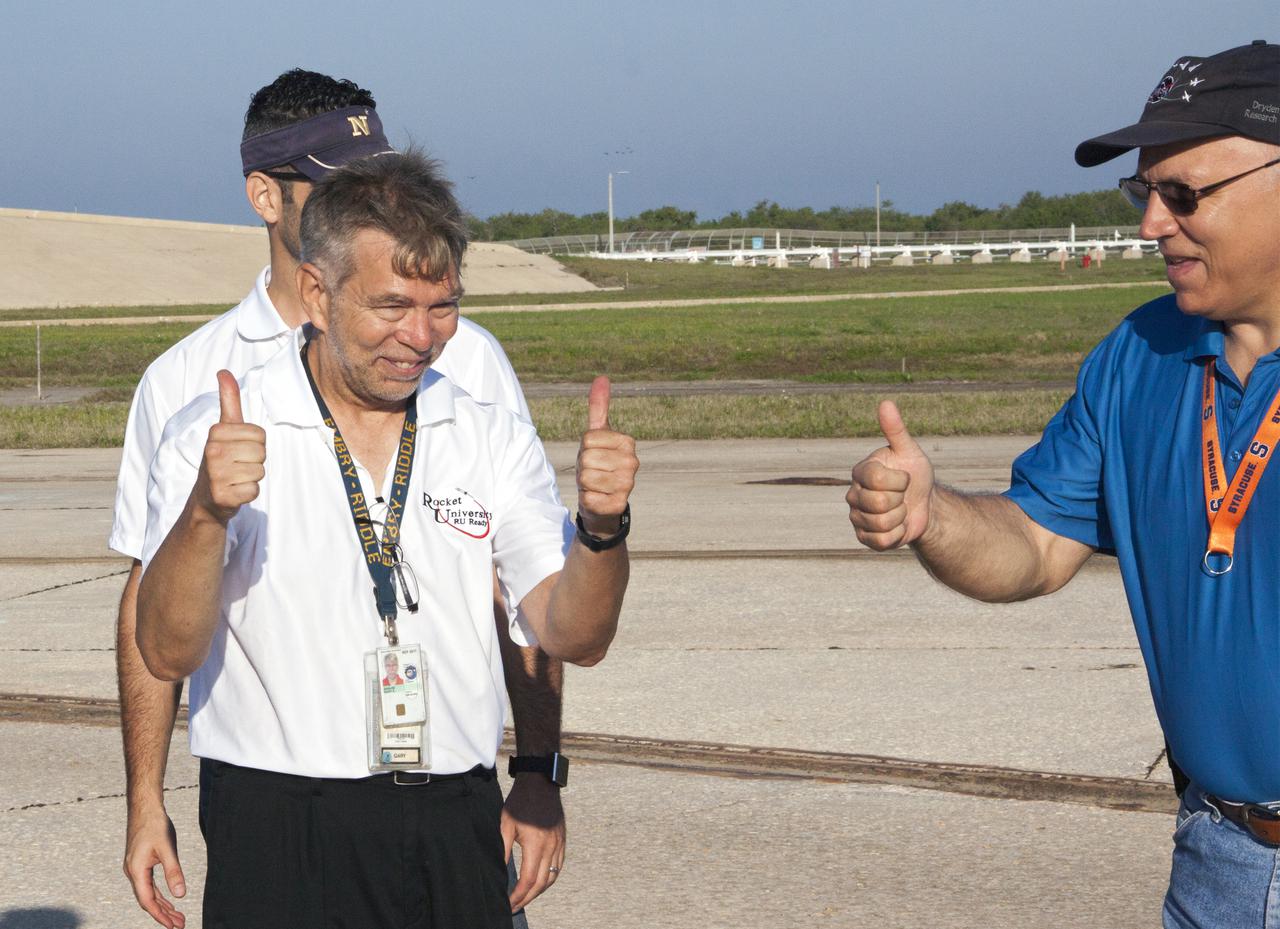

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Gary Dahlke of Engineering and Technology, left and Peter Checklick of Safety and Mission Assurance give 'thumbs up' after the successful launch of a small rocket at Launch Pad 39A as part of Rocket University. Leandro James of Systems Hardware Engineering is partially obscured by Dahlke. The goal was to test its systems and to verify that it performed as designed. As part of Rocket University, the engineers are given an opportunity to work a fast-track project to develop skills in developing spacecraft systems of the future. As NASA plans for future spaceflight programs to low-Earth orbit and beyond, teams of engineers at Kennedy are gaining experience in designing and flying launch vehicle systems on a small scale. Four teams of five to eight members from Kennedy are designing rockets complete with avionics and recovery systems. Launch operations require coordination with federal agencies, just as they would with rockets launched in support of a NASA mission. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
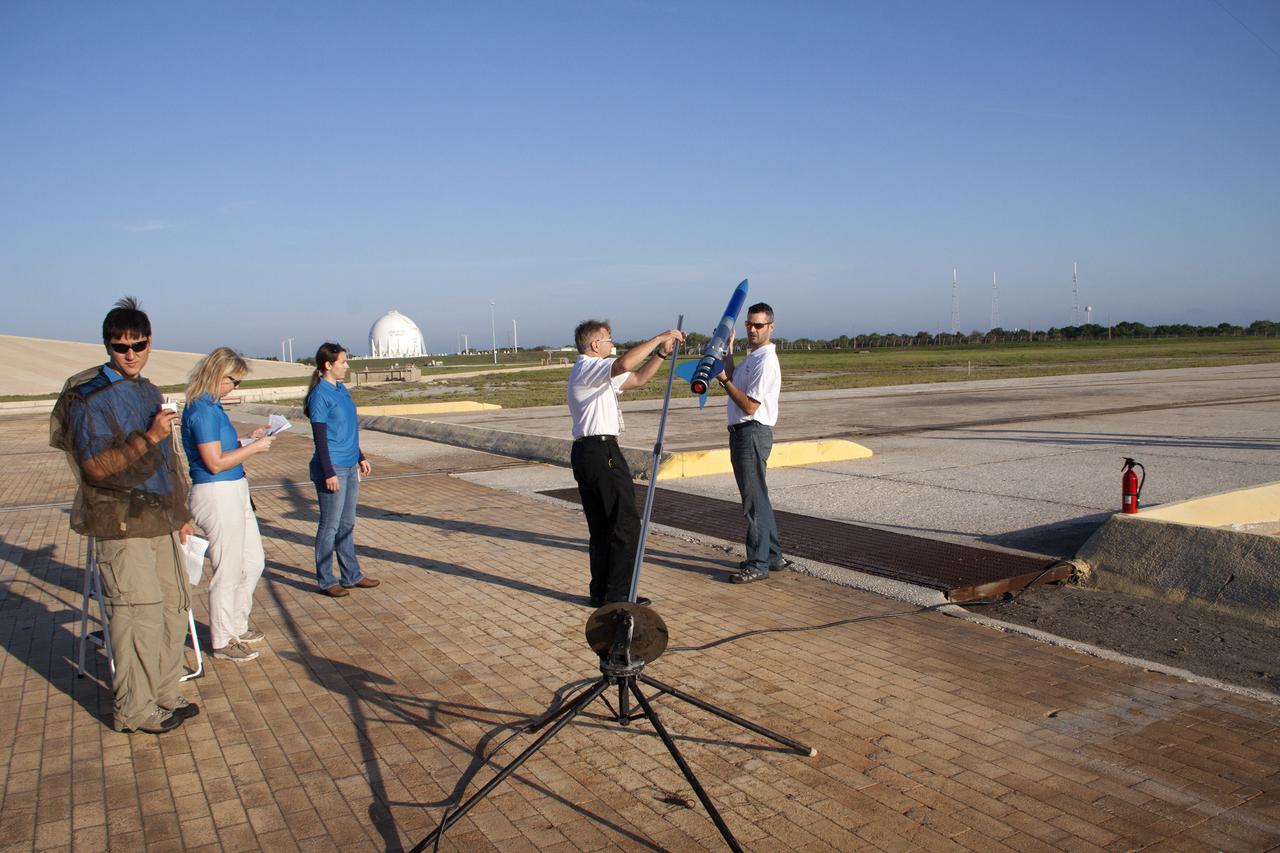

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as Morgan Simpson of Flight Hardware Processing, Susan Danley of Flight Structures and Kim Simpson of Fluids, Mechanical and Structural Systems look on, Gary Dahlke of Engineering and Technology, left, and Leandro James of Systems Hardware Engineering attach a small rocket prior to its launch stand as part of Rocket University. The goal was to test its systems and to verify that it performed as designed. As part of Rocket University, the engineers are given an opportunity to work a fast-track project to develop skills in developing spacecraft systems of the future. As NASA plans for future spaceflight programs to low-Earth orbit and beyond, teams of engineers at Kennedy are gaining experience in designing and flying launch vehicle systems on a small scale. Four teams of five to eight members from Kennedy are designing rockets complete with avionics and recovery systems. Launch operations require coordination with federal agencies, just as they would with rockets launched in support of a NASA mission. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
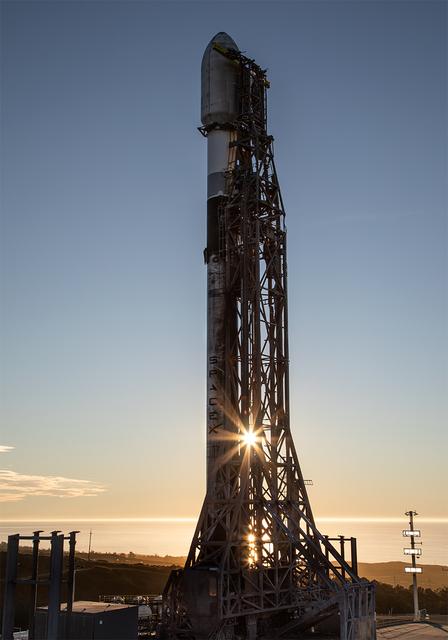

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission stands vertical on the launch pad of Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Nov. 27, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
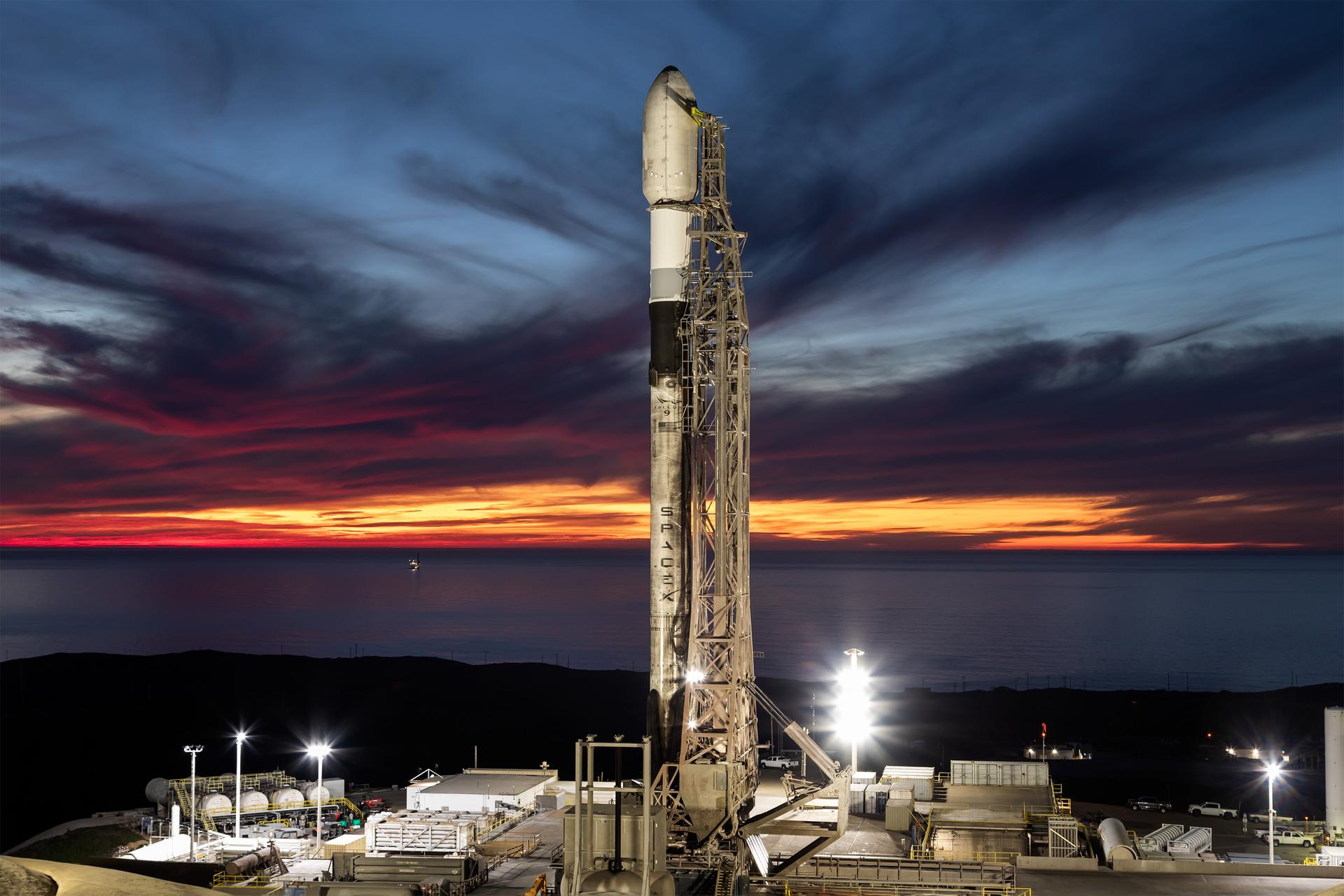

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission stands vertical on the launch pad of Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Nov. 27, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
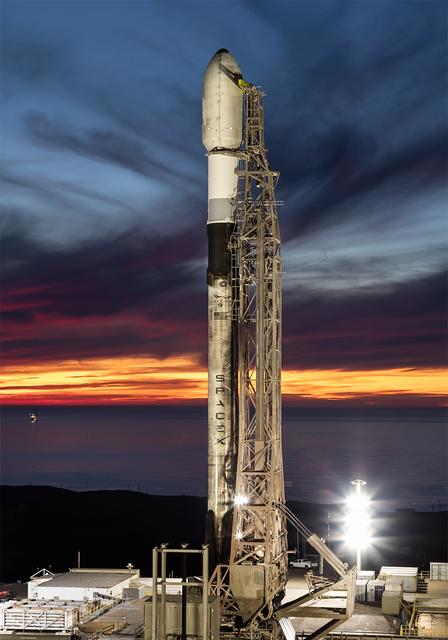

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission stands vertical on the launch pad of Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Nov. 27, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
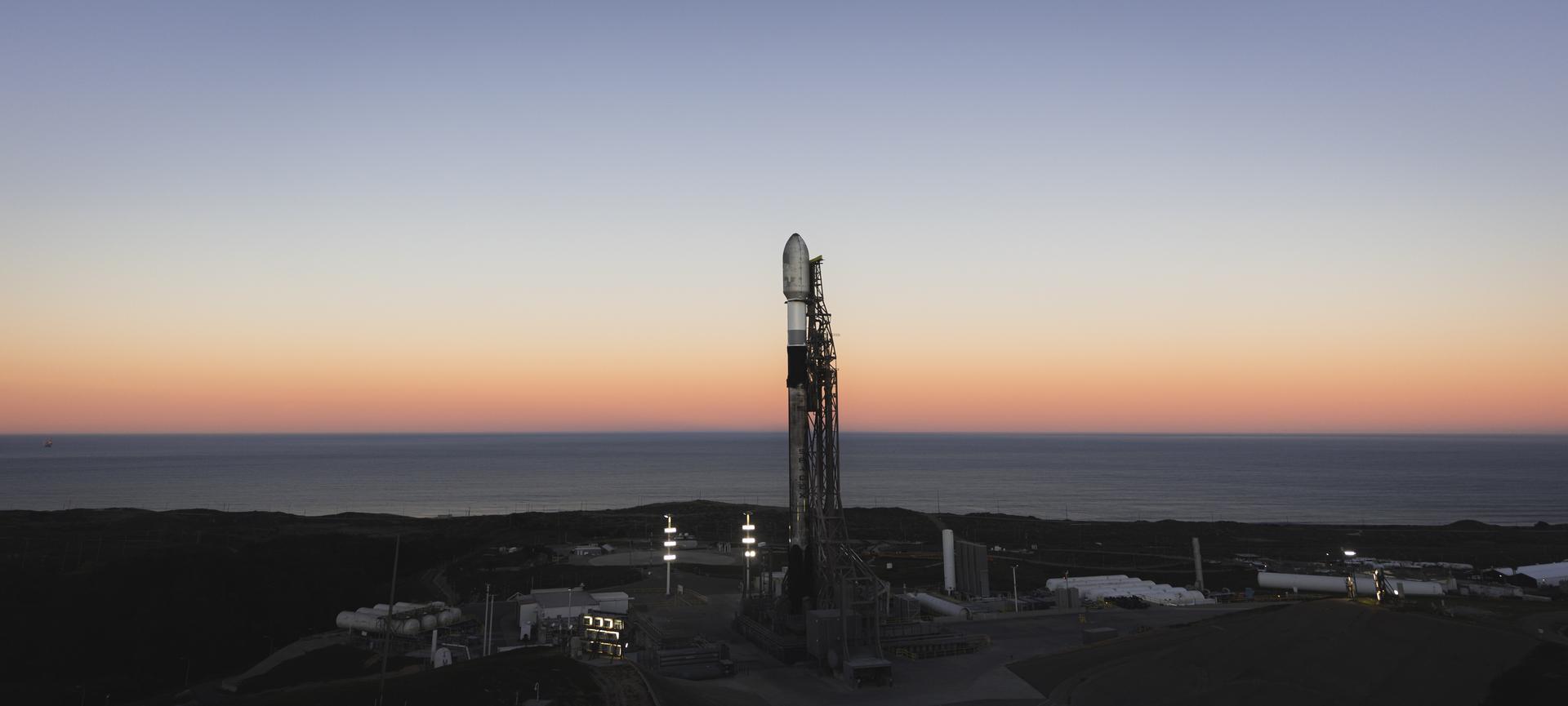

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission stands vertical on the launch pad of Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Nov. 26, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
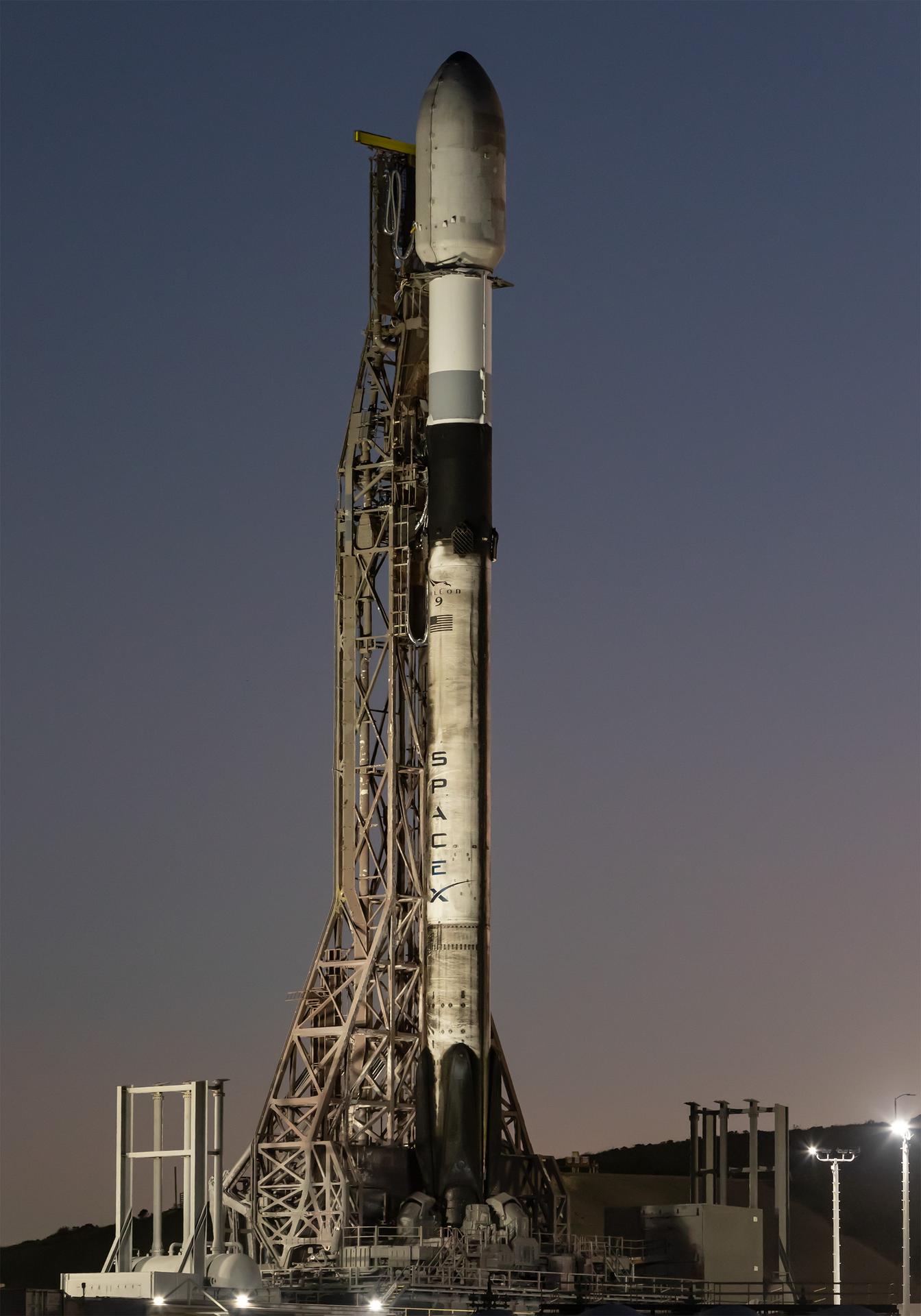

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission stands vertical on the launch pad of Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Nov. 26, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
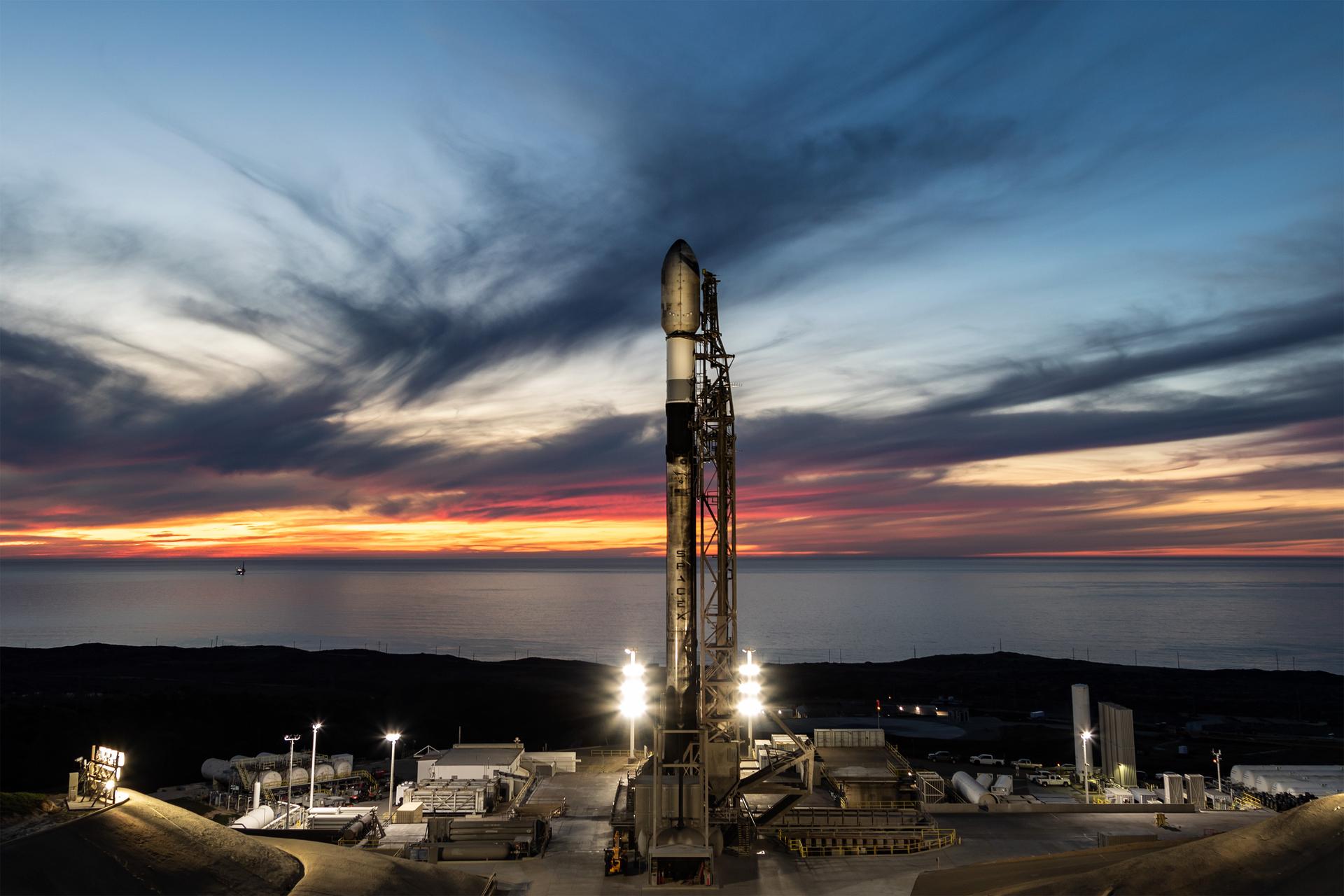

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission stands vertical on the launch pad of Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Nov. 27, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
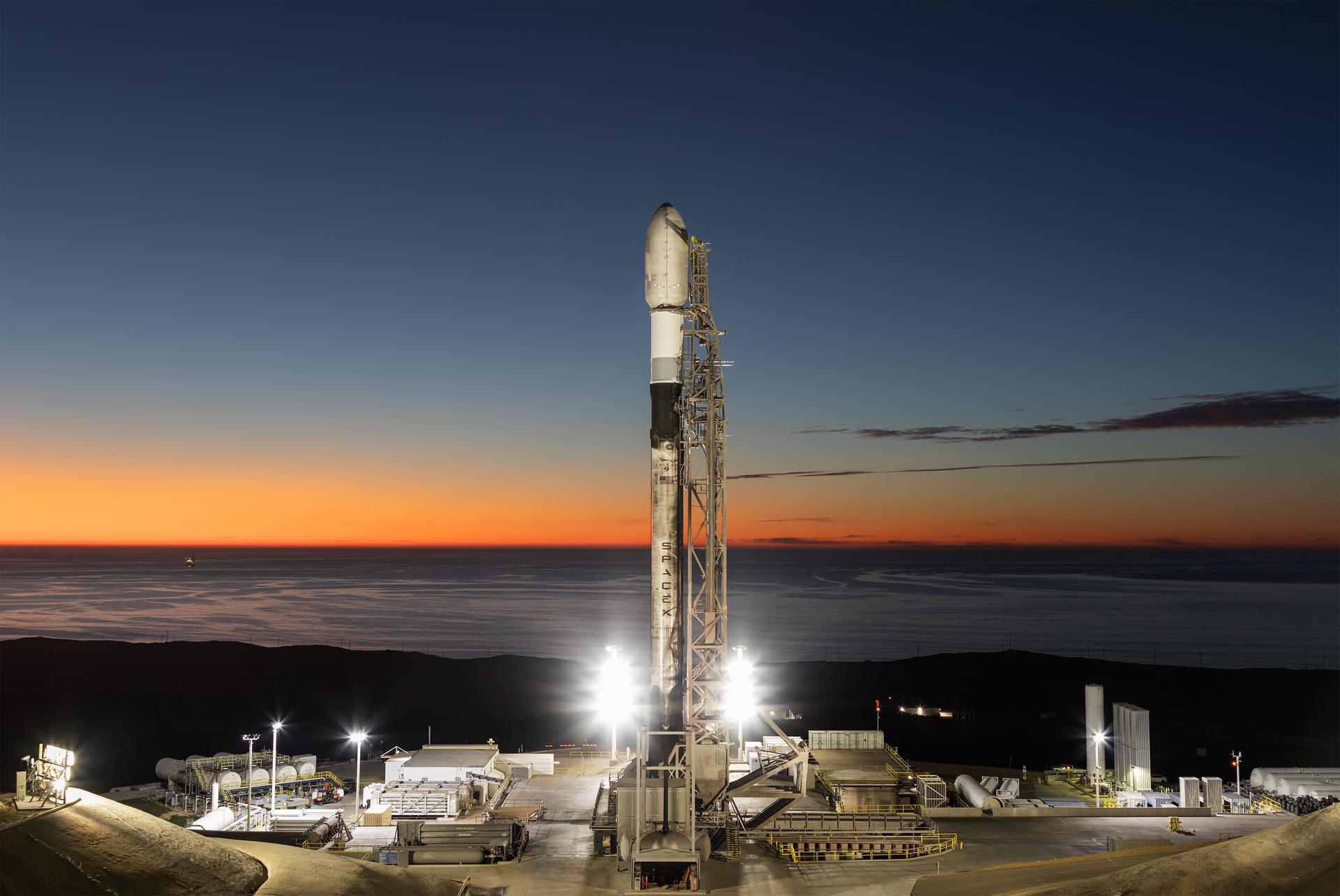

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission stands vertical on the launch pad of Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Nov. 27, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
![Teams encapsulate NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat inside a SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing along with several other satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at [TIME, DAY, DATE], as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users. Launch of SpaceX’s Transporter-15 mission, carrying R5-S7, is scheduled for 10:18 a.m. PST Wednesday, Nov. 26, 2025, from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 East.](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC-20251126-PH-SPX01_0001/KSC-20251126-PH-SPX01_0001~large.jpg)
Teams encapsulate NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat inside a SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing along with several other satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at [TIME, DAY, DATE], as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users. Launch of SpaceX’s Transporter-15 mission, carrying R5-S7, is scheduled for 10:18 a.m. PST Wednesday, Nov. 26, 2025, from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 East.
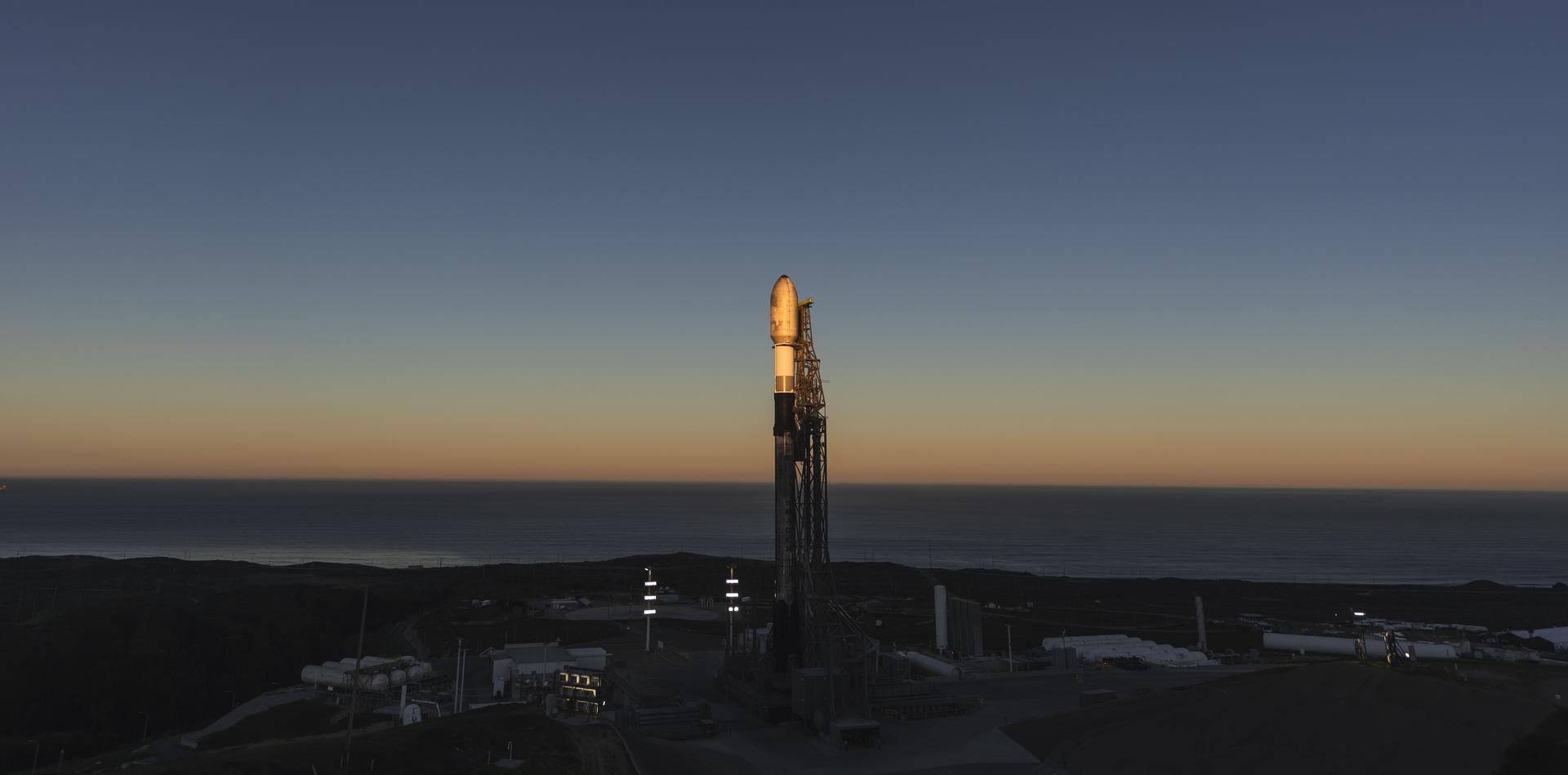

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission stands vertical on the launch pad of Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Nov. 26, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
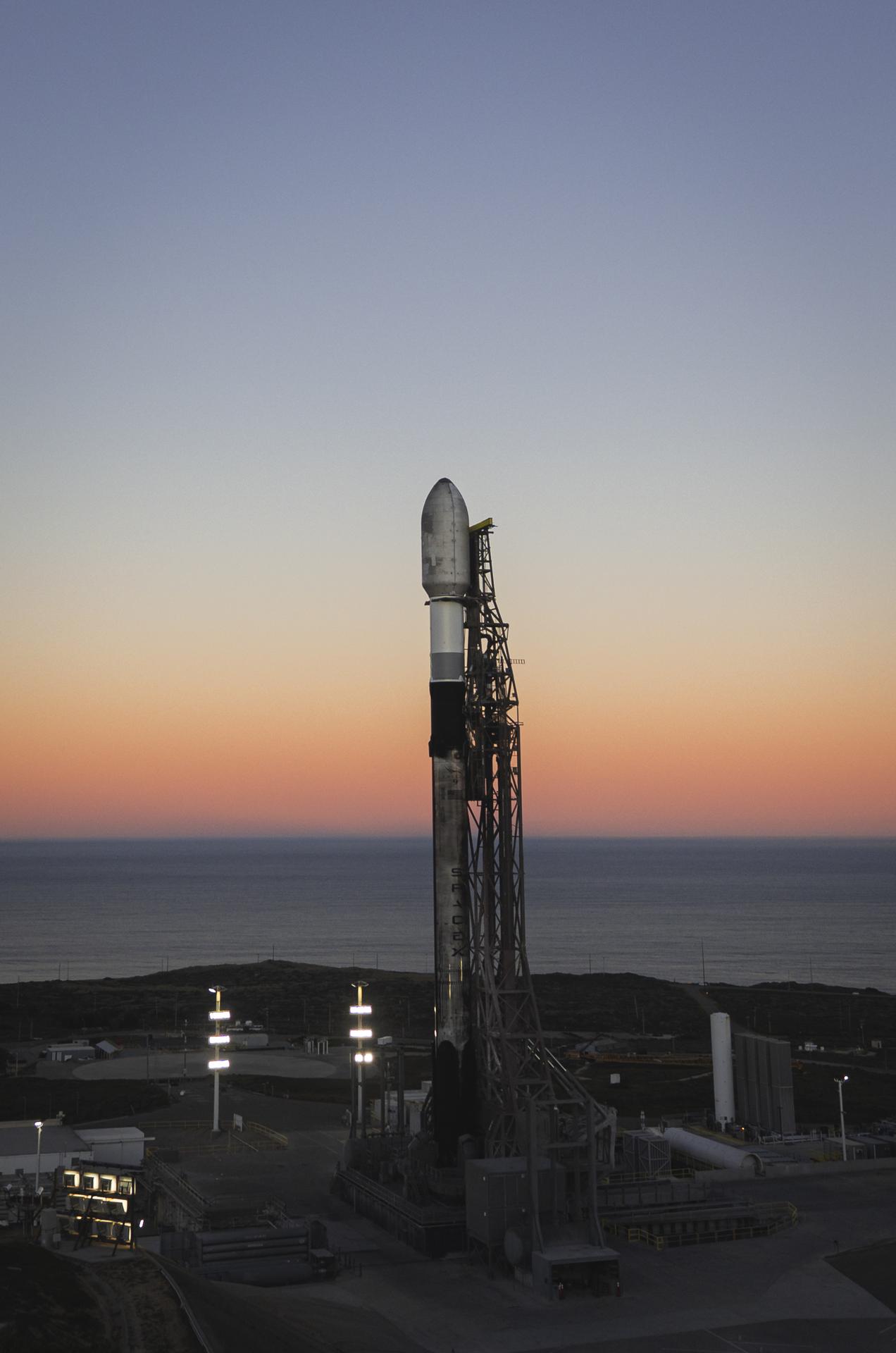

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission stands vertical on the launch pad of Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Nov. 26, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
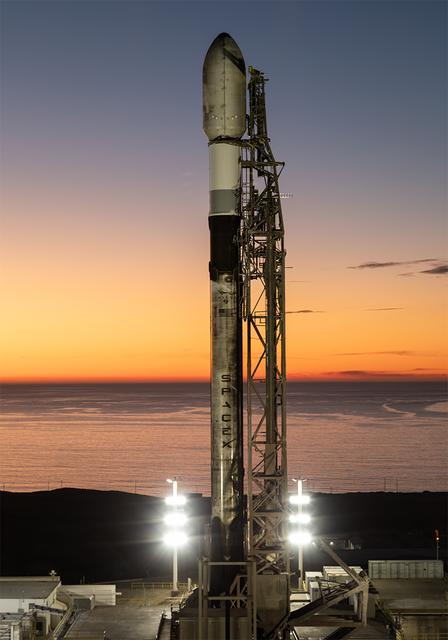

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission stands vertical on the launch pad of Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Nov. 27, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
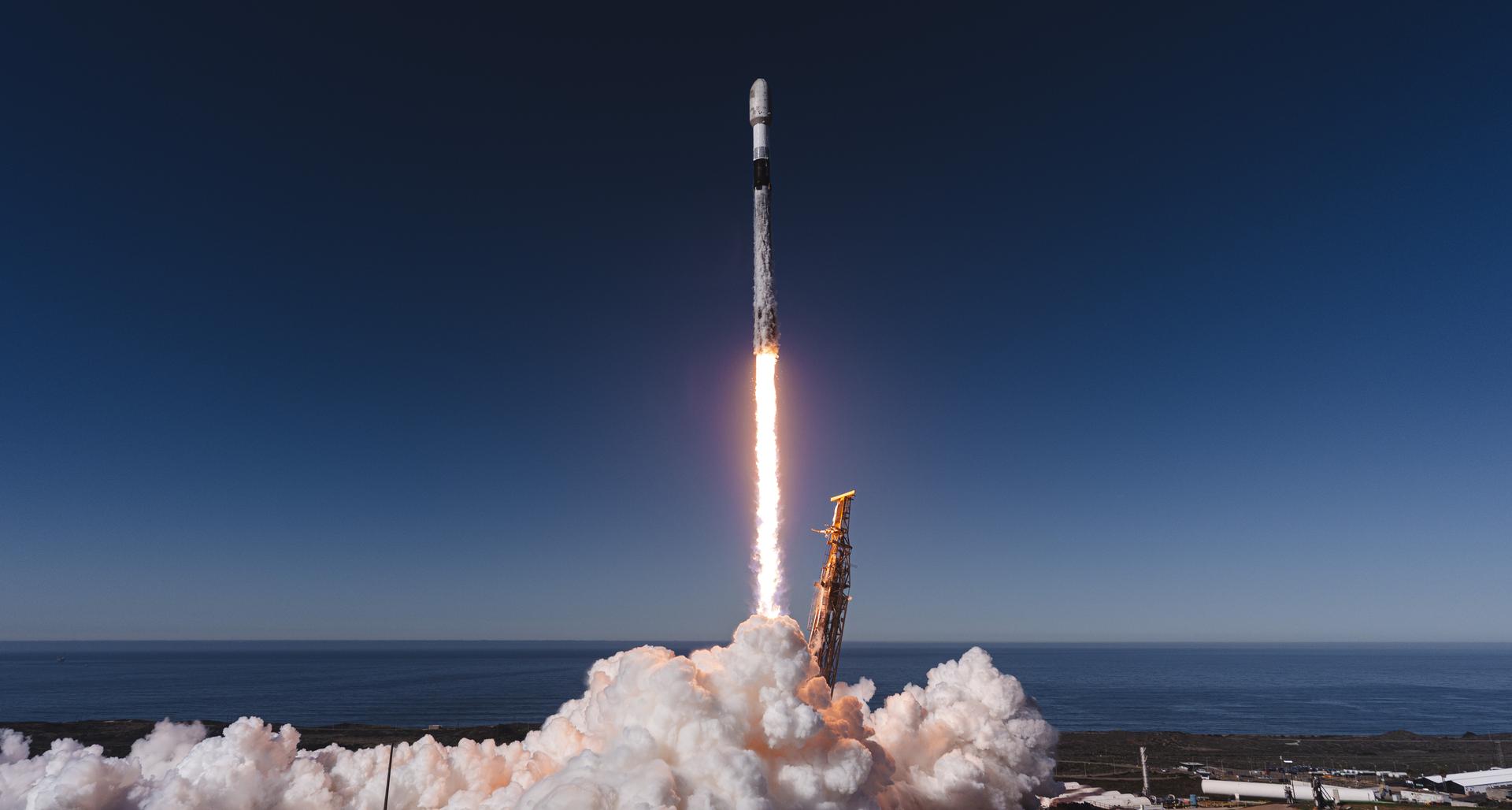

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 10:44 a.m. PST Friday, Nov. 28, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
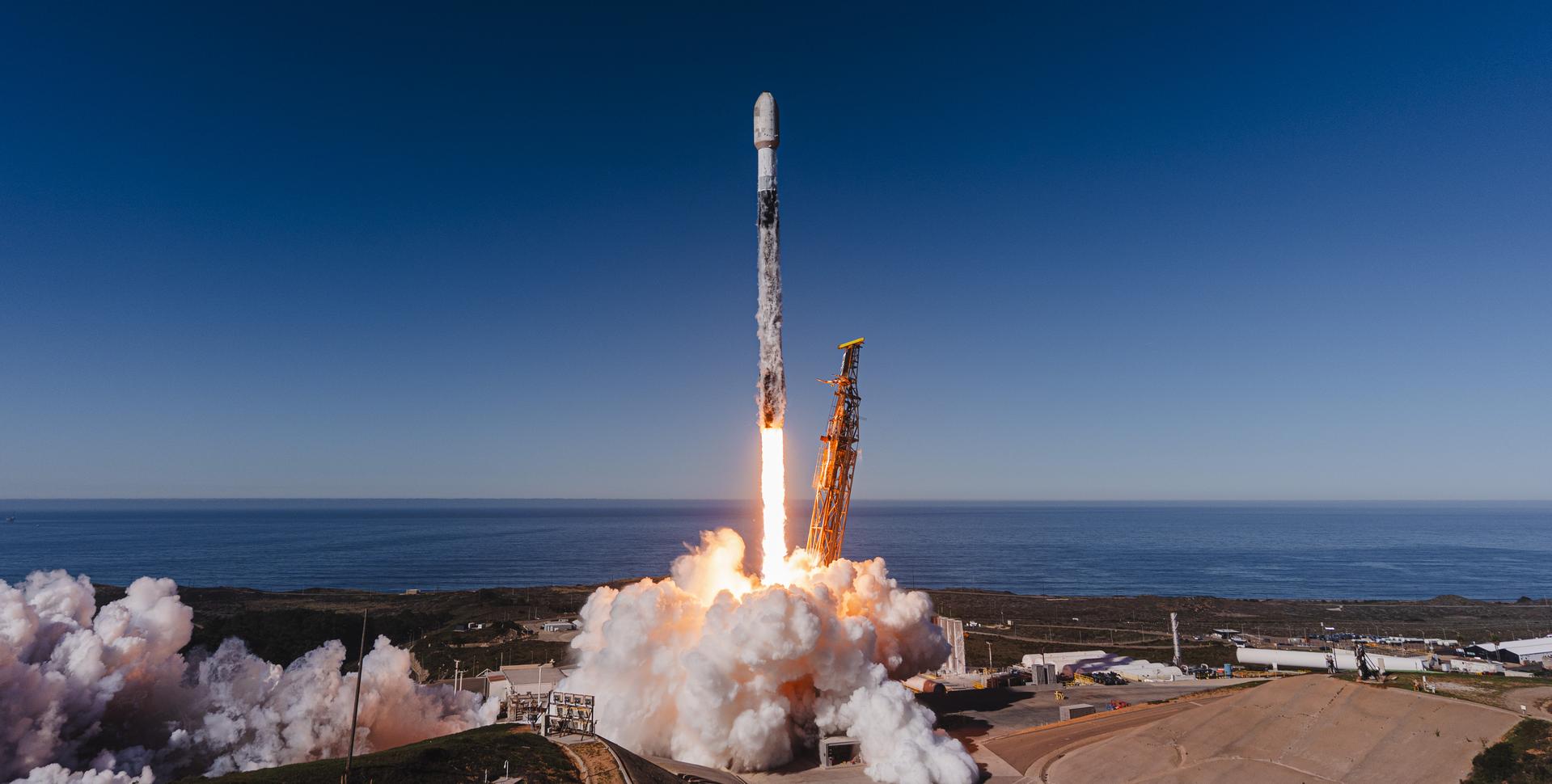

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 10:44 a.m. PST Friday, Nov. 28, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
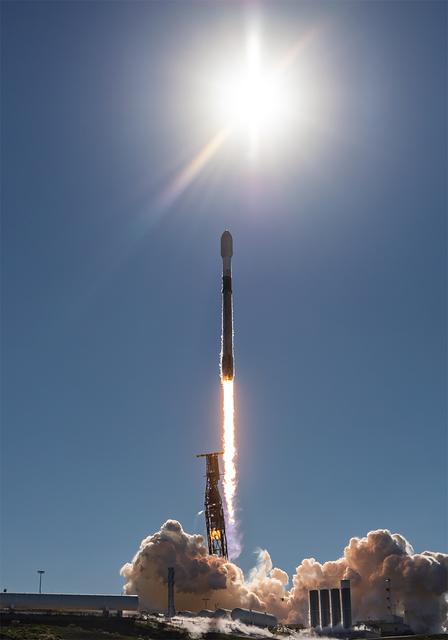

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 10:44 a.m. PST Friday, Nov. 28, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
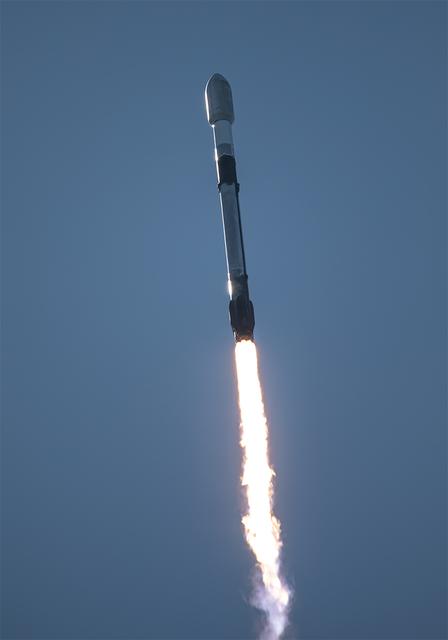

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 10:44 a.m. PST Friday, Nov. 28, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
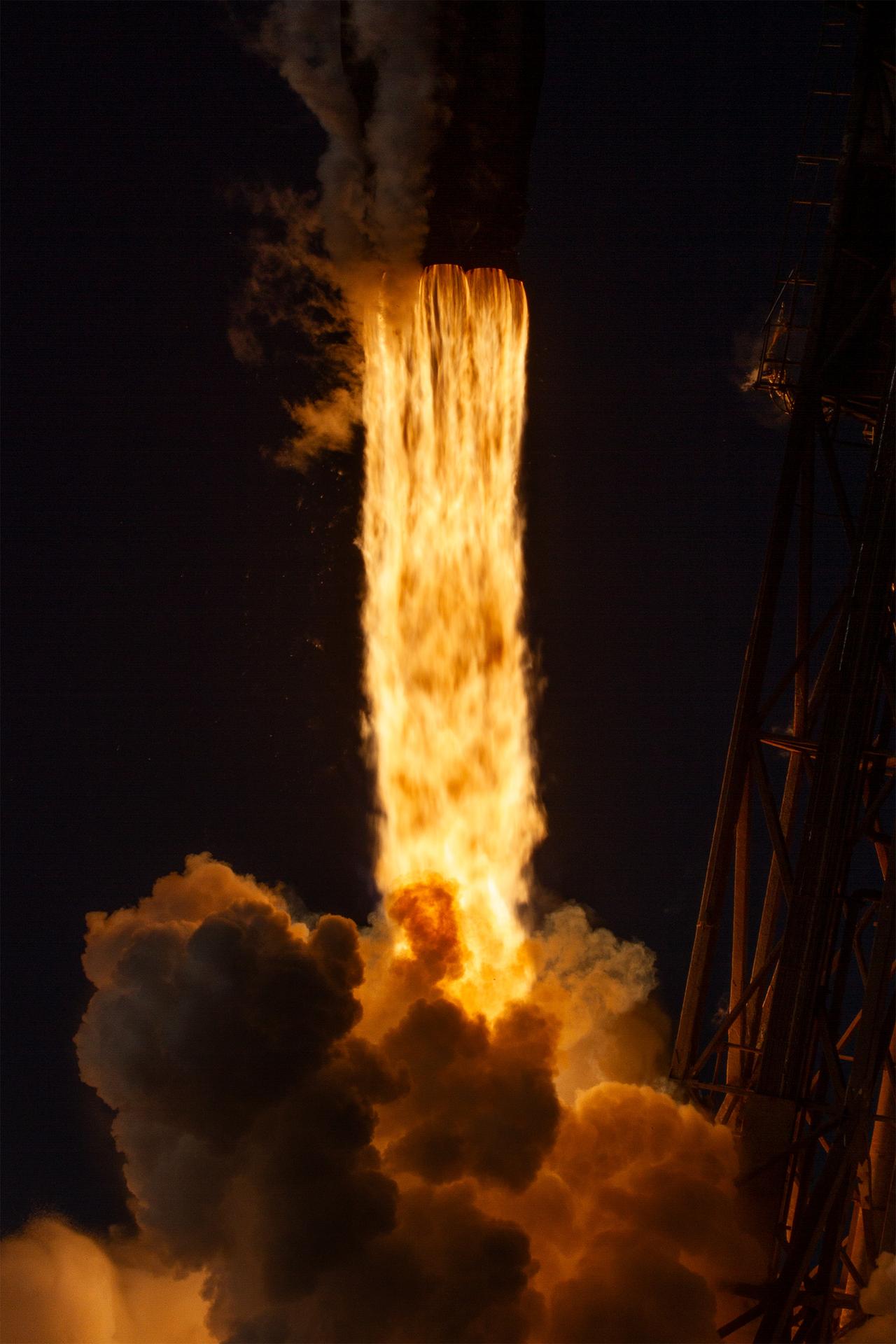

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 10:44 a.m. PST Friday, Nov. 28, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 10:44 a.m. PST Friday, Nov. 28, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
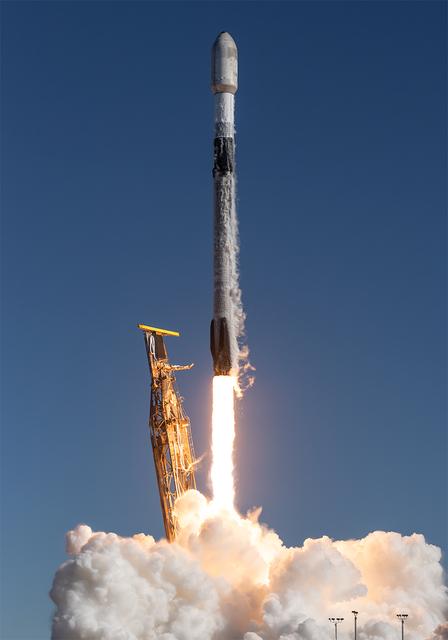

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 10:44 a.m. PST Friday, Nov. 28, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
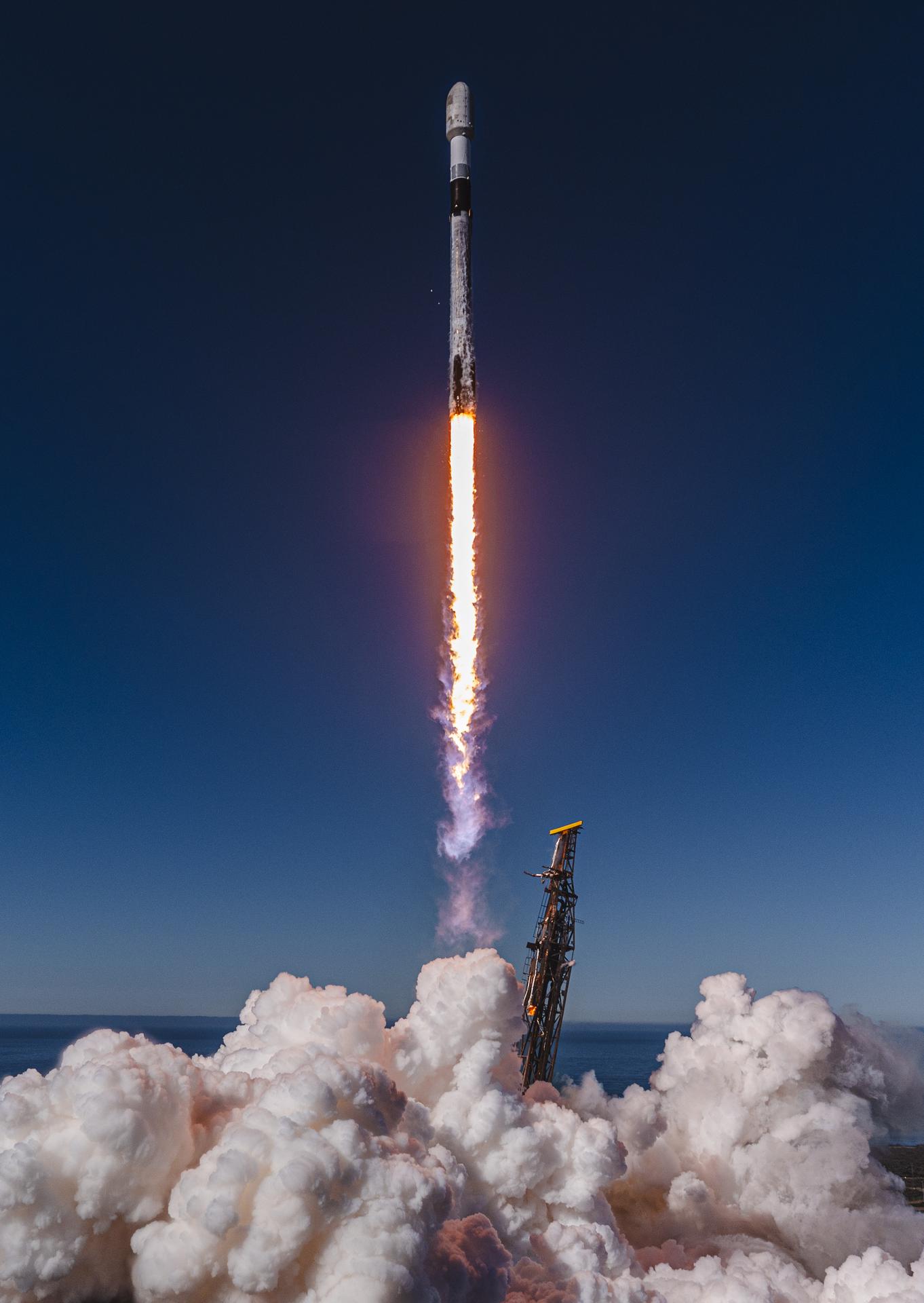

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 10:44 a.m. PST Friday, Nov. 28, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 10:44 a.m. PST Friday, Nov. 28, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
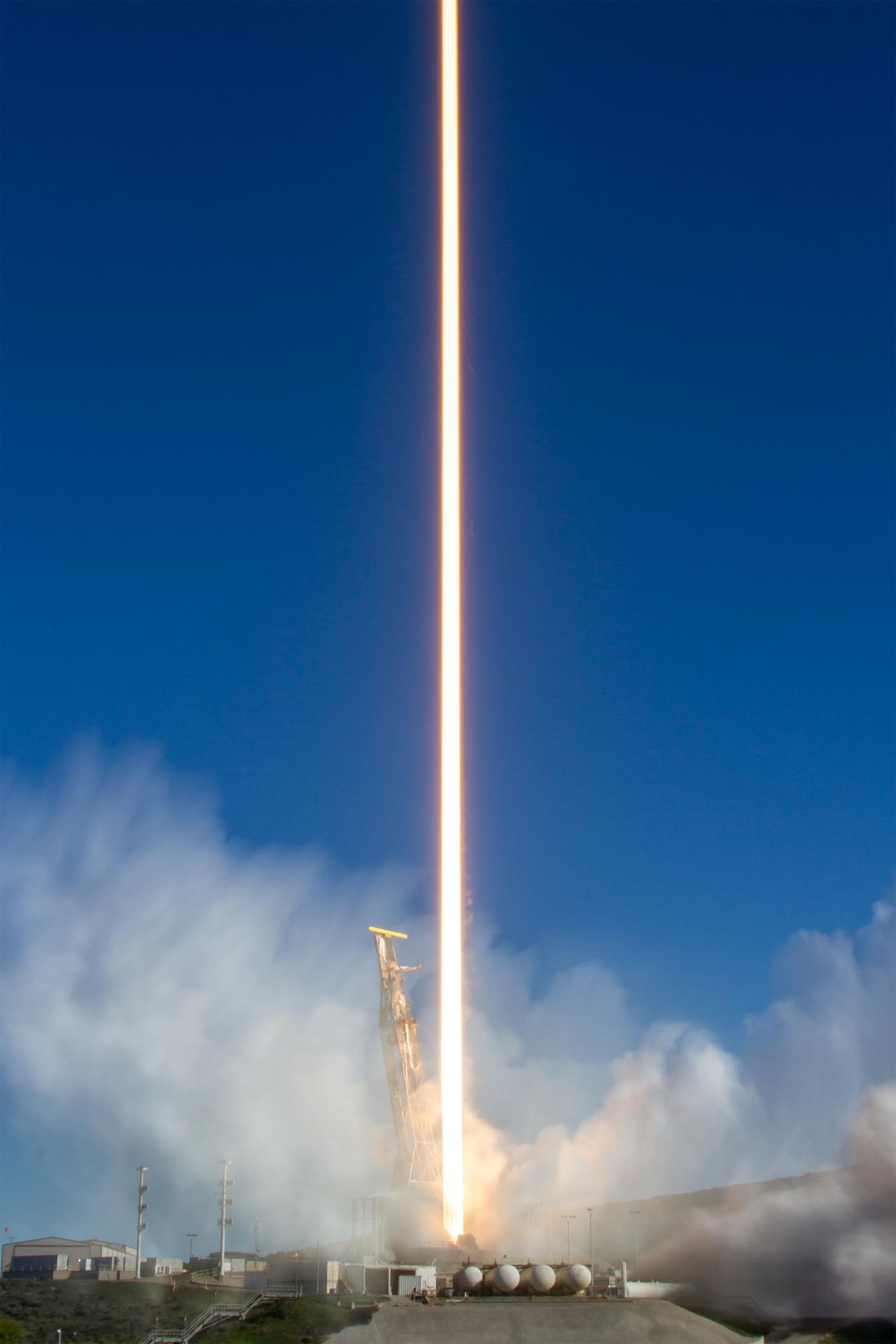

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 10:44 a.m. PST Friday, Nov. 28, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
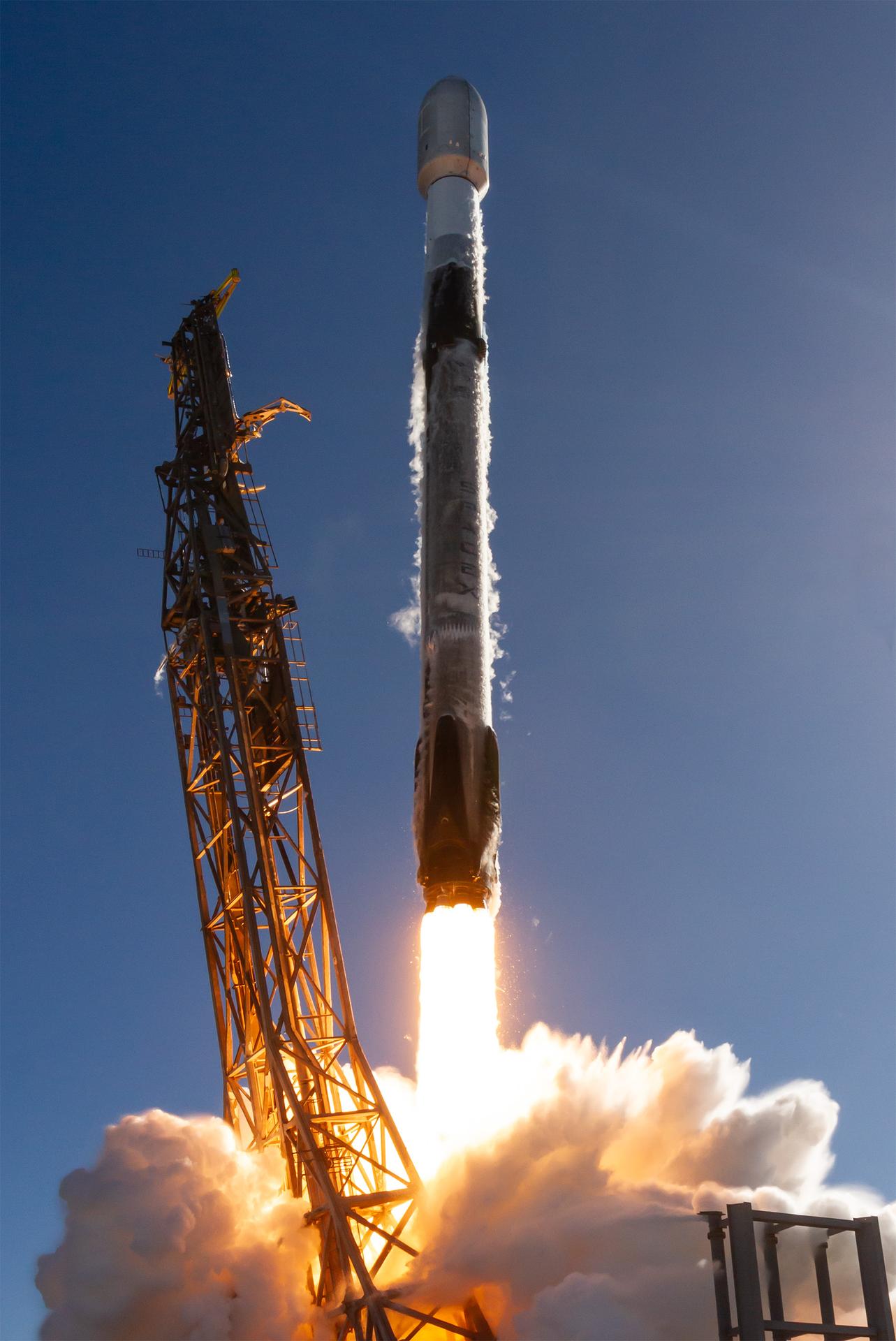

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 10:44 a.m. PST Friday, Nov. 28, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
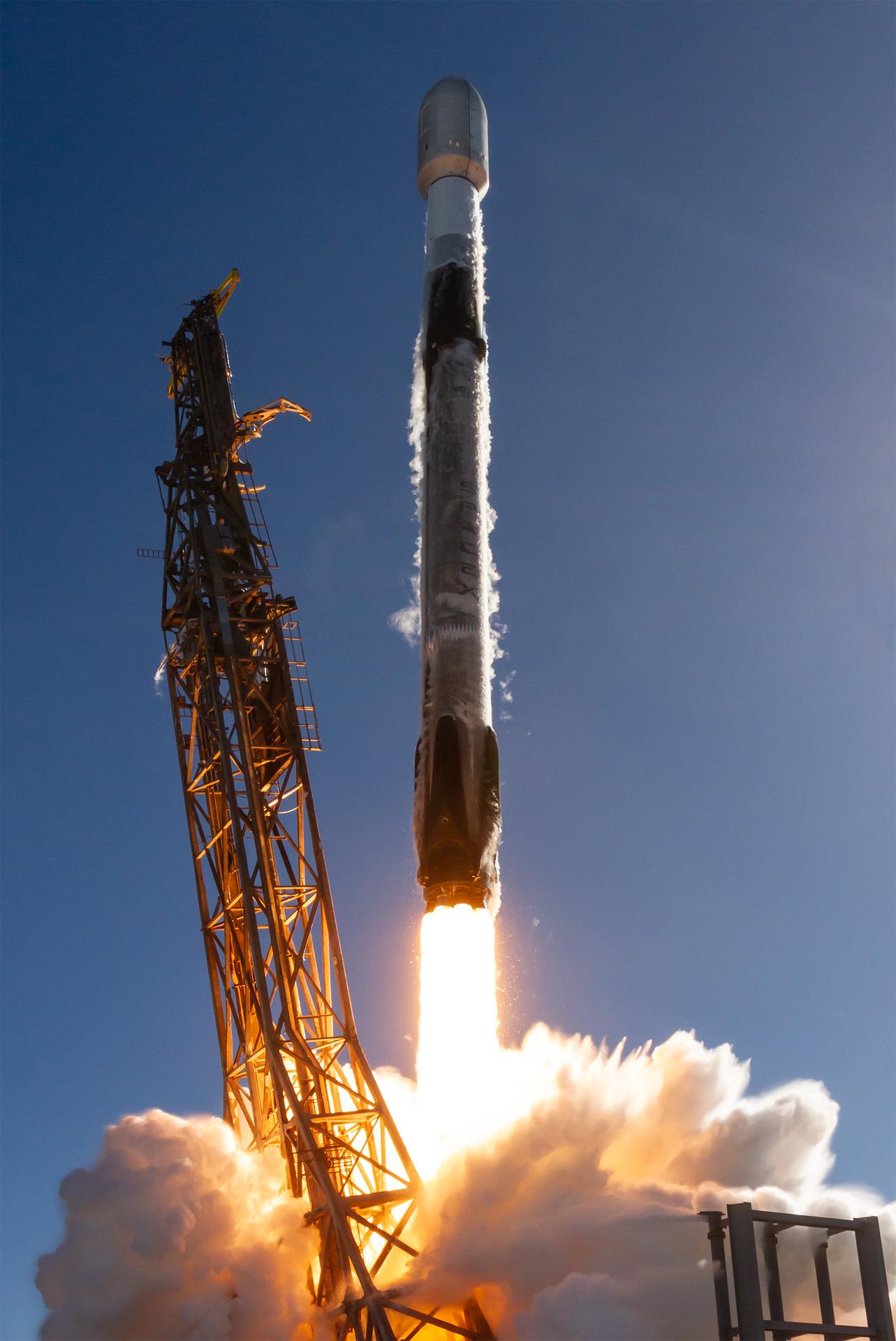

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 10:44 a.m. PST Friday, Nov. 28, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
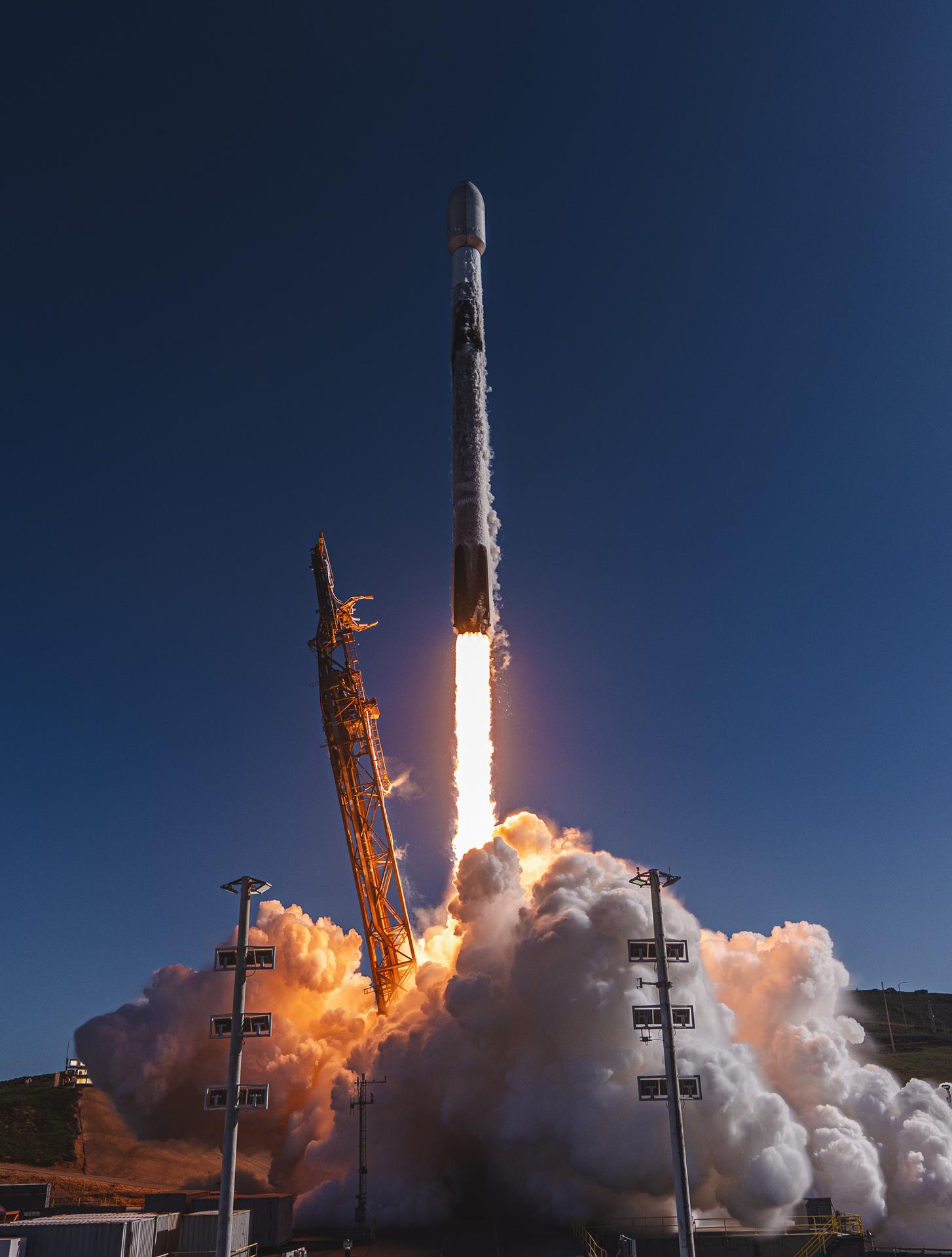

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 10:44 a.m. PST Friday, Nov. 28, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
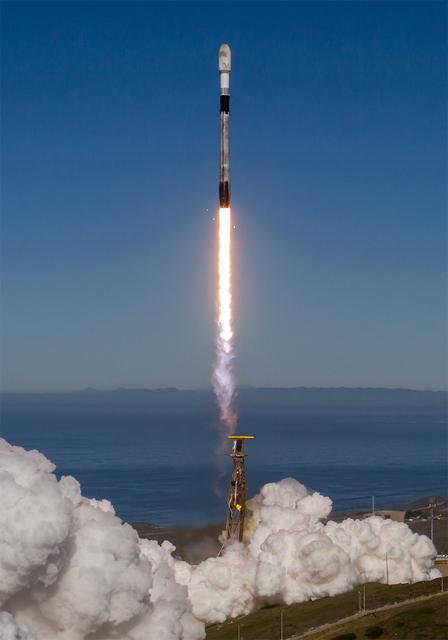

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 10:44 a.m. PST Friday, Nov. 28, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.
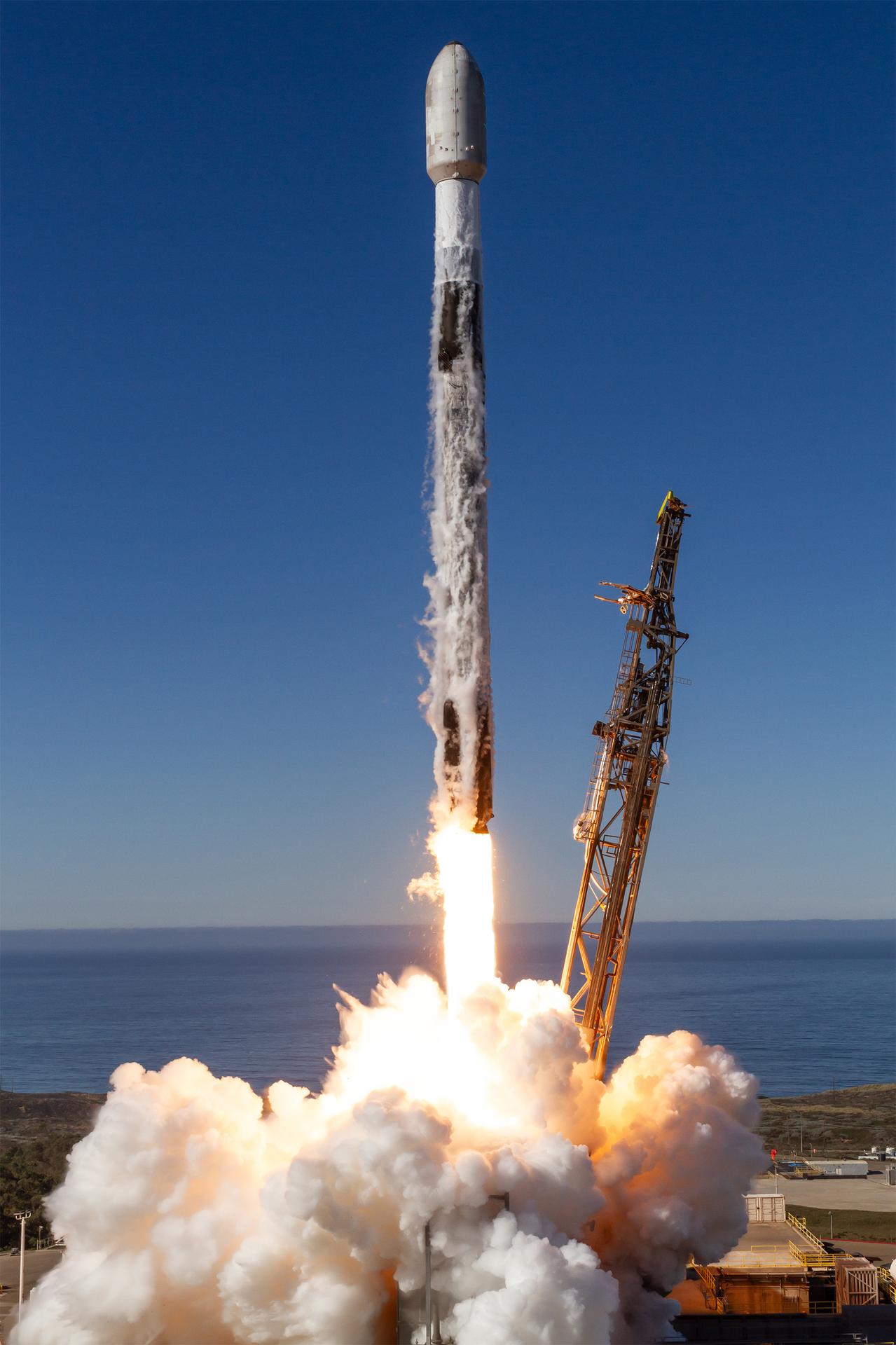

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s R5-S7 (Realizing Rapid, Reduced-cost high-Risk Research project Spacecraft 7) CubeSat along with several other satellites as part of the company’s Transporter-15 mission lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 10:44 a.m. PST Friday, Nov. 28, 2025. The latest in a series of spacecraft, R5-S7 will explore ways to get multiple technology prototypes into low Earth orbit rapidly and at a low cost, accelerating the demonstration of these technologies in orbit and allowing engineers and scientists to more quickly prove them and make them available to NASA missions and other users.

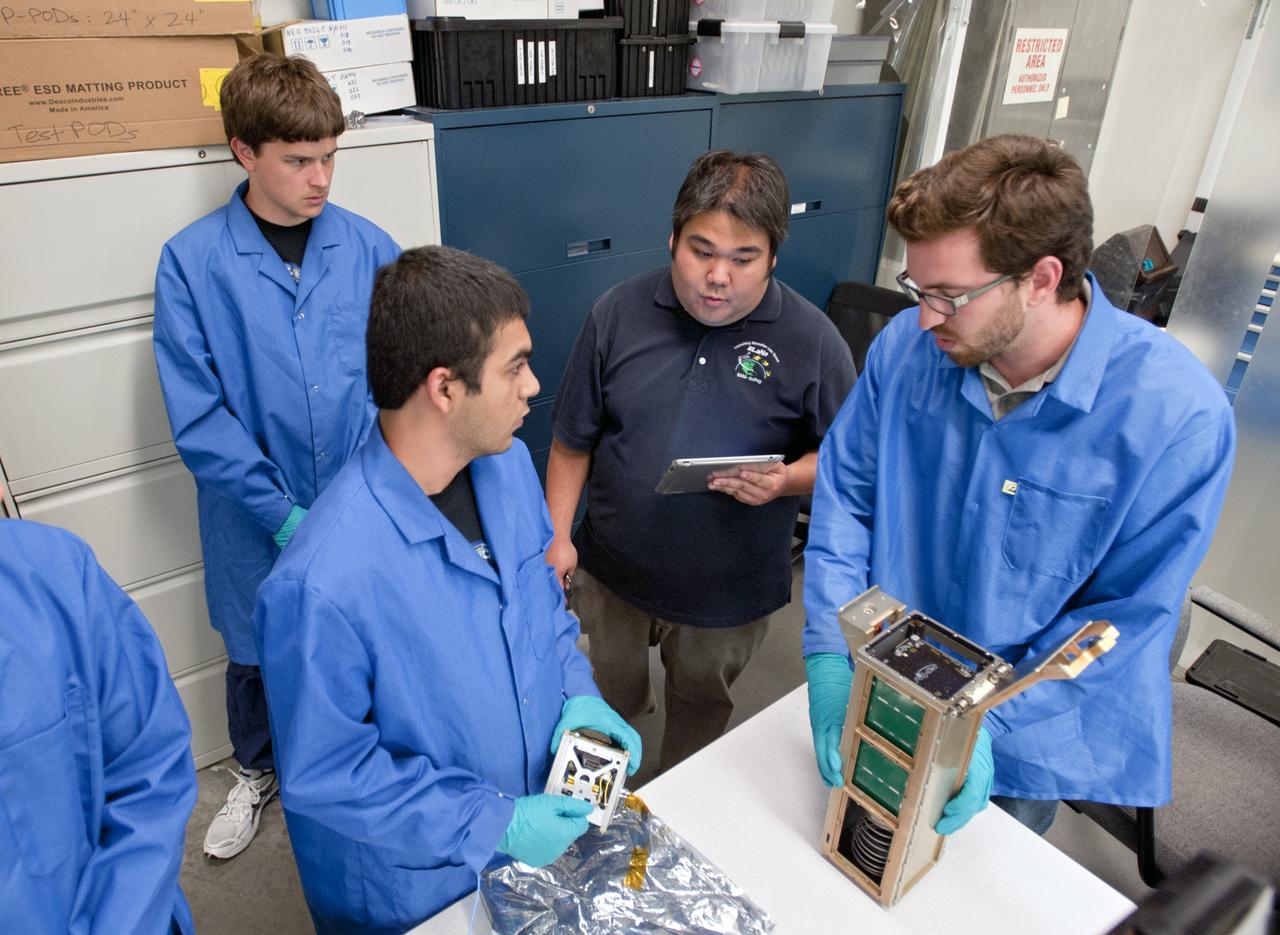
SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – Roland Coelho, third from left, CalPoly program lead, and members of the student launch team load a payload into a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Dispensor, or P-Pod nanolauncher/carrier in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payload, which includes sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cube sections, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Known as a CubeSat, the satellite will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. It will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Also, a new launcher/carrier of a lightweight design also is being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – Roland Coelho, right, CalPoly program lead, and members of the student launch team for the Polysat works through final checks in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payload, which includes sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cube sections, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Known as a CubeSat, the satellite will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. It will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, twin communications-relay CubeSats, called Mars Cube One (MarCO) are prepared for installation on an Atlas V rocket. MarCO constitutes a technology demonstration being built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena in California. They will launch in on the same United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket as NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft to land on Mars. CubeSats are a class of spacecraft based on a standardized small size and modular use of off-the-shelf technologies. Many have been made by university students, and dozens have been launched into Earth orbit using extra payload mass available on launches of larger spacecraft. InSight is the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. InSight will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, manages the InSight mission for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate. InSight is part of NASA's Discovery Program, managed by its Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The spacecraft, including cruise stage and lander, was built and tested by Lockheed Martin Space in Denver. Several European partners, including France's space agency, the Centre National d'Étude Spatiales, and the German Aerospace Center, are supporting the mission. United Launch Alliance of Centennial, Colorado, is providing the Atlas V launch service. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at its Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is responsible for laun
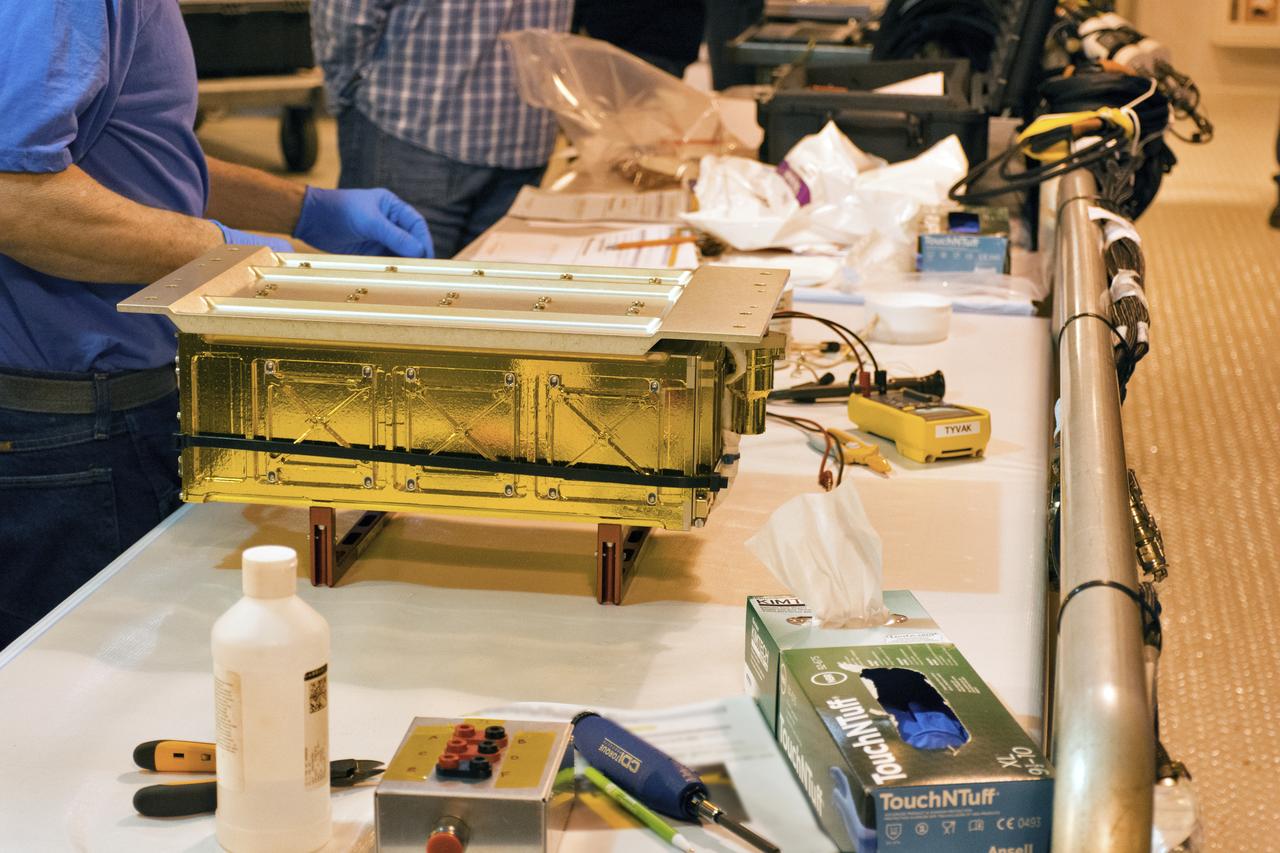

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, twin communications-relay CubeSats, called Mars Cube One (MarCO) are prepared for installation on an Atlas V rocket. MarCO constitutes a technology demonstration being built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena in California. They will launch in on the same United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket as NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft to land on Mars. CubeSats are a class of spacecraft based on a standardized small size and modular use of off-the-shelf technologies. Many have been made by university students, and dozens have been launched into Earth orbit using extra payload mass available on launches of larger spacecraft. InSight is the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. InSight will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, manages the InSight mission for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate. InSight is part of NASA's Discovery Program, managed by its Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The spacecraft, including cruise stage and lander, was built and tested by Lockheed Martin Space in Denver. Several European partners, including France's space agency, the Centre National d'Étude Spatiales, and the German Aerospace Center, are supporting the mission. United Launch Alliance of Centennial, Colorado, is providing the Atlas V launch service. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at its Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is responsible for laun
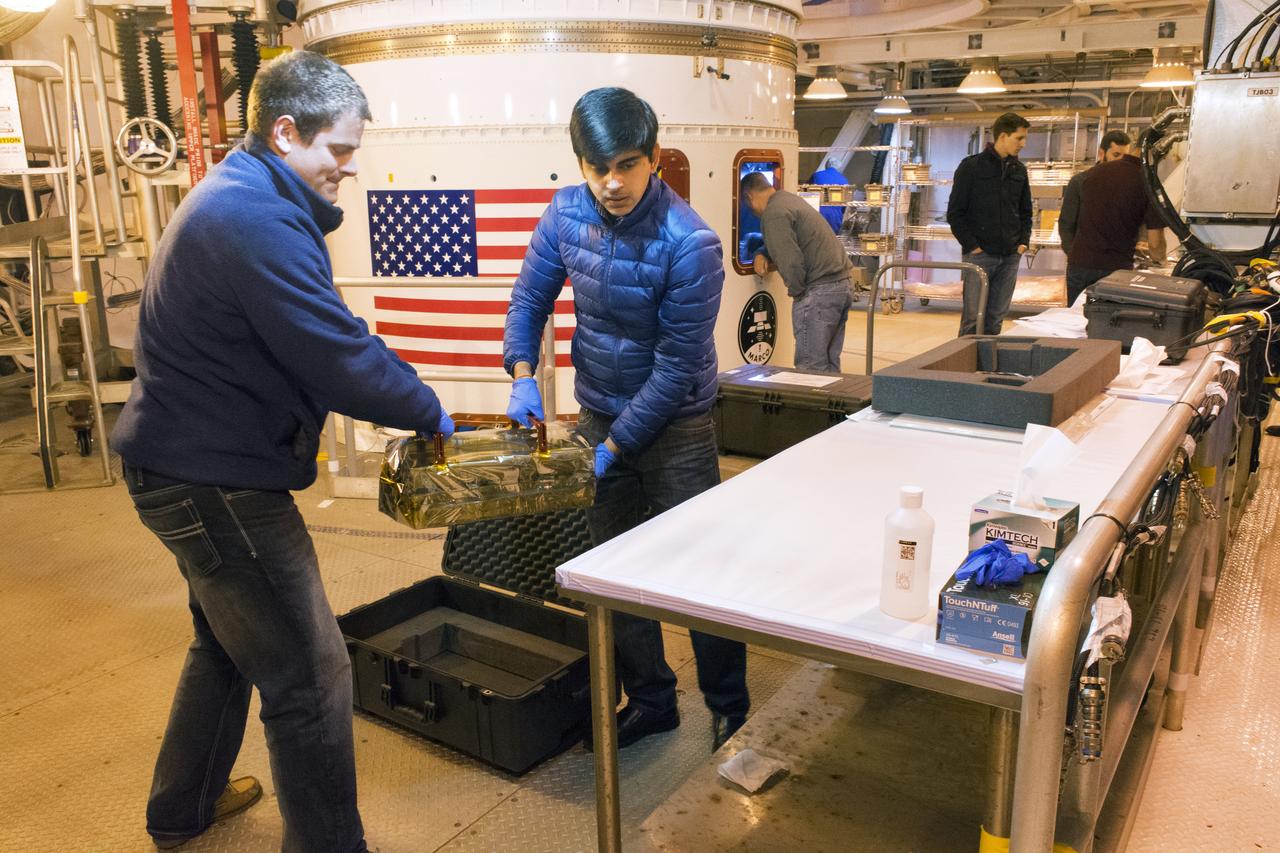

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, twin communications-relay CubeSats, called Mars Cube One (MarCO) are prepared for installation on an Atlas V rocket. MarCO constitutes a technology demonstration being built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena in California. They will launch in on the same United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket as NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft to land on Mars. CubeSats are a class of spacecraft based on a standardized small size and modular use of off-the-shelf technologies. Many have been made by university students, and dozens have been launched into Earth orbit using extra payload mass available on launches of larger spacecraft. InSight is the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. InSight will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, manages the InSight mission for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate. InSight is part of NASA's Discovery Program, managed by its Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The spacecraft, including cruise stage and lander, was built and tested by Lockheed Martin Space in Denver. Several European partners, including France's space agency, the Centre National d'Étude Spatiales, and the German Aerospace Center, are supporting the mission. United Launch Alliance of Centennial, Colorado, is providing the Atlas V launch service. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at its Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is responsible for laun
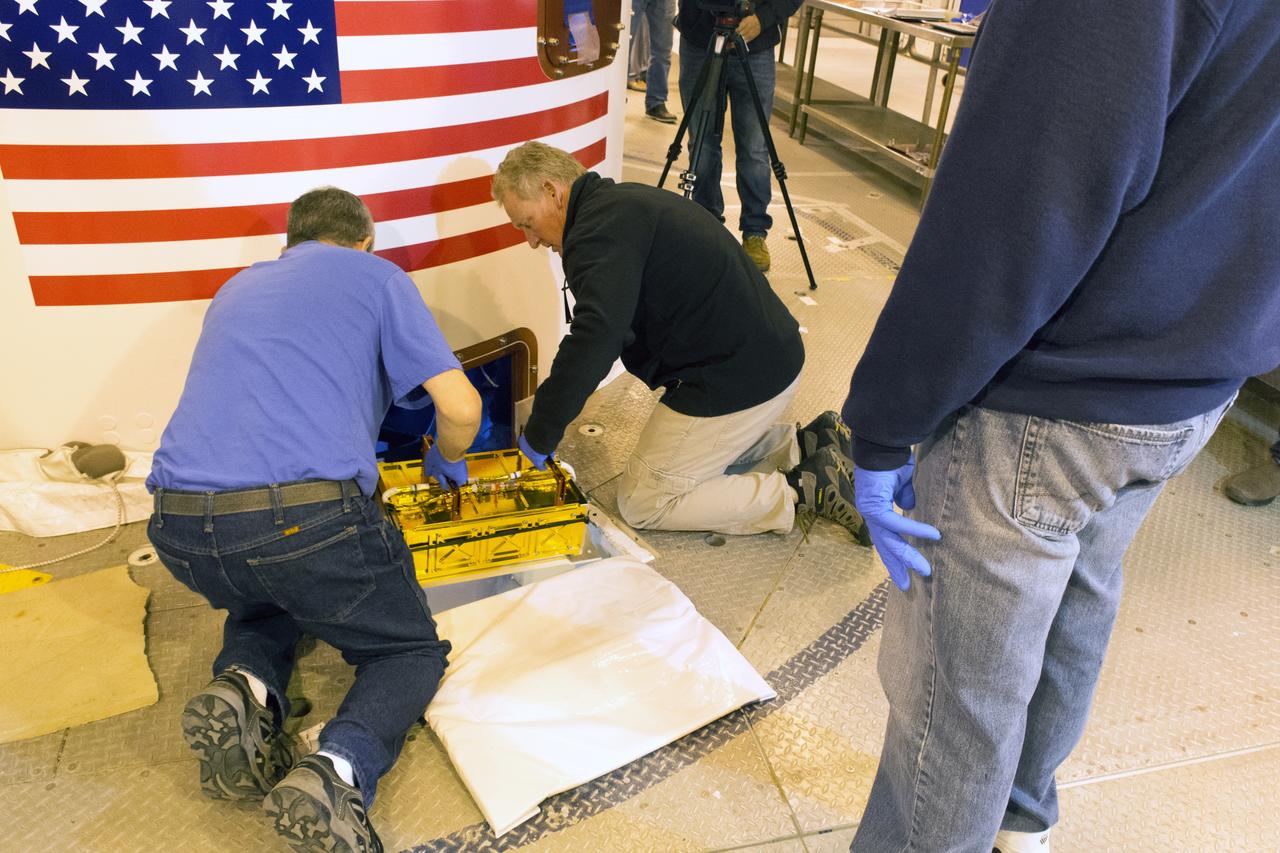

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, twin communications-relay CubeSats, called Mars Cube One (MarCO) are installed on an Atlas V rocket. MarCO constitutes a technology demonstration being built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena in California. They will launch in on the same United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket as NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft to land on Mars. CubeSats are a class of spacecraft based on a standardized small size and modular use of off-the-shelf technologies. Many have been made by university students, and dozens have been launched into Earth orbit using extra payload mass available on launches of larger spacecraft. InSight is the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. InSight will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, manages the InSight mission for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate. InSight is part of NASA's Discovery Program, managed by its Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The spacecraft, including cruise stage and lander, was built and tested by Lockheed Martin Space in Denver. Several European partners, including France's space agency, the Centre National d'Étude Spatiales, and the German Aerospace Center, are supporting the mission. United Launch Alliance of Centennial, Colorado, is providing the Atlas V launch service. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at its Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is responsible for launch management.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, twin communications-relay CubeSats, called Mars Cube One (MarCO) are prepared for installation on an Atlas V rocket. MarCO constitutes a technology demonstration being built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena in California. They will launch in on the same United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket as NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft to land on Mars. CubeSats are a class of spacecraft based on a standardized small size and modular use of off-the-shelf technologies. Many have been made by university students, and dozens have been launched into Earth orbit using extra payload mass available on launches of larger spacecraft. InSight is the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. InSight will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, manages the InSight mission for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate. InSight is part of NASA's Discovery Program, managed by its Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The spacecraft, including cruise stage and lander, was built and tested by Lockheed Martin Space in Denver. Several European partners, including France's space agency, the Centre National d'Étude Spatiales, and the German Aerospace Center, are supporting the mission. United Launch Alliance of Centennial, Colorado, is providing the Atlas V launch service. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at its Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is responsible for laun
At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, twin communications-relay CubeSats, called Mars Cube One (MarCO) are prepared for installation on an Atlas V rocket. MarCO constitutes a technology demonstration being built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena in California. They will launch in on the same United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket as NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft to land on Mars. CubeSats are a class of spacecraft based on a standardized small size and modular use of off-the-shelf technologies. Many have been made by university students, and dozens have been launched into Earth orbit using extra payload mass available on launches of larger spacecraft. InSight is the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. InSight will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, manages the InSight mission for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate. InSight is part of NASA's Discovery Program, managed by its Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The spacecraft, including cruise stage and lander, was built and tested by Lockheed Martin Space in Denver. Several European partners, including France's space agency, the Centre National d'Étude Spatiales, and the German Aerospace Center, are supporting the mission. United Launch Alliance of Centennial, Colorado, is providing the Atlas V launch service. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at its Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is responsible for laun
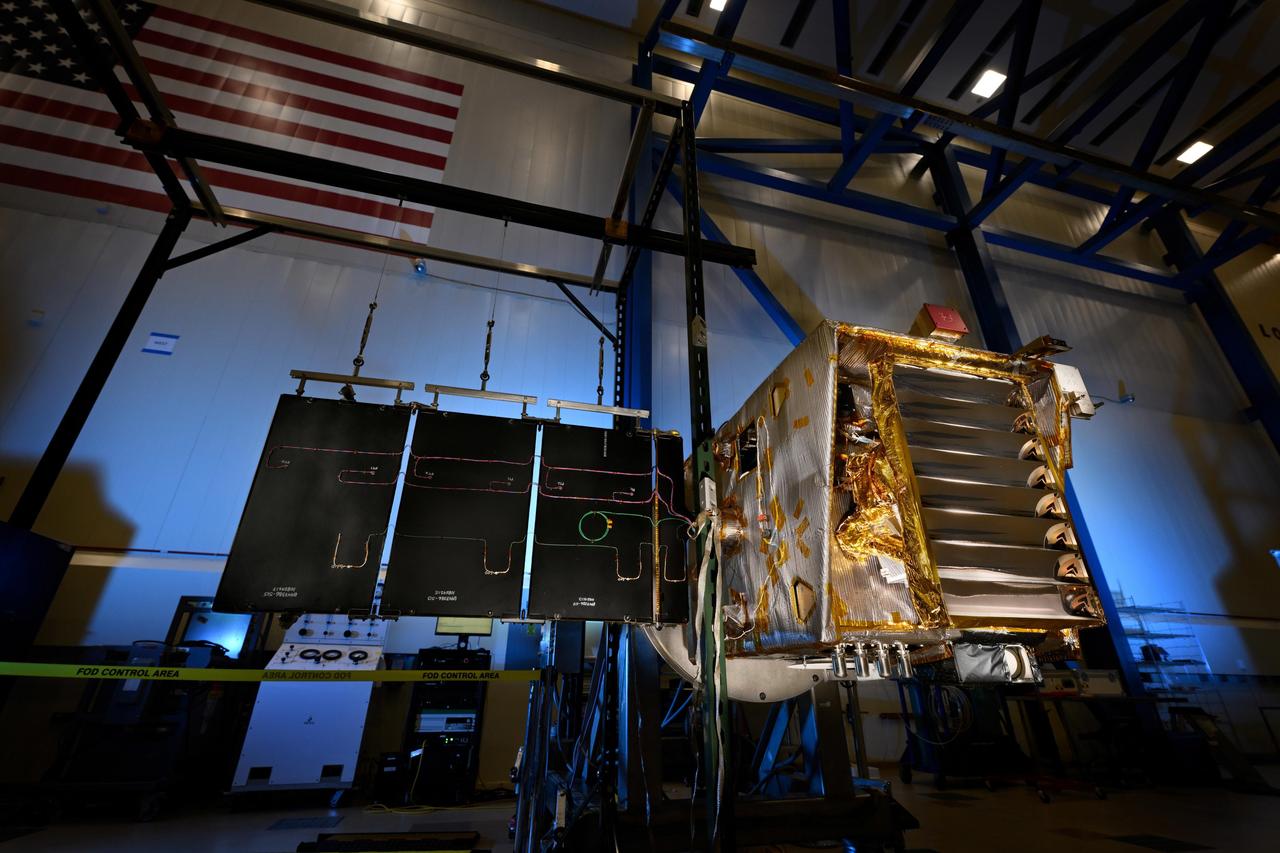

NASA's Lunar Trailblazer spacecraft sits in a clean room in August 2024 after undergoing environmental testing at Lockheed Martin Space in Littleton, Colorado. Now that those tests are done, the orbiter and its science instruments will go through flight system software tests that simulate key aspects of launch, maneuvers, and the science mission while in orbit around the Moon. This photo shows Lunar Trailblazer with a solar array deployed. The large silver grate attached to the spacecraft is the radiator for the High-resolution Volatiles and Minerals Moon Mapper (HVM³) instrument. HVM³ is one of two instruments that will be used by the mission to detect and map water on the Moon's surface to determine its abundance, location, form, and how it changes over time. This data will be key to our understanding of this crucial resource on the Moon for future exploration. The spacecraft is just 440 pounds (200 kilograms) and 11.5 feet (3.5 meters) wide with its solar panels fully deployed. The project is led by Principal Investigator Bethany Ehlmann of Caltech and managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, which is also providing systems engineering, navigation, and mission assurance. Caltech manages JPL for the agency. Lunar Trailblazer is part of NASA's Small Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration (SIMPLEx) program, which provides opportunities for low-cost, high-risk science missions that are responsive to requirements for flexibility. These lower-cost missions serve as an ideal platform for technical and architecture innovation, contributing to NASA's science research and technology development objectives. SIMPLEx mission investigations are managed by the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as part of the Discovery Program at NASA Headquarters in Washington. IPAC leads mission operations, including planning, scheduling, and sequencing all science and spacecraft activities. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26390
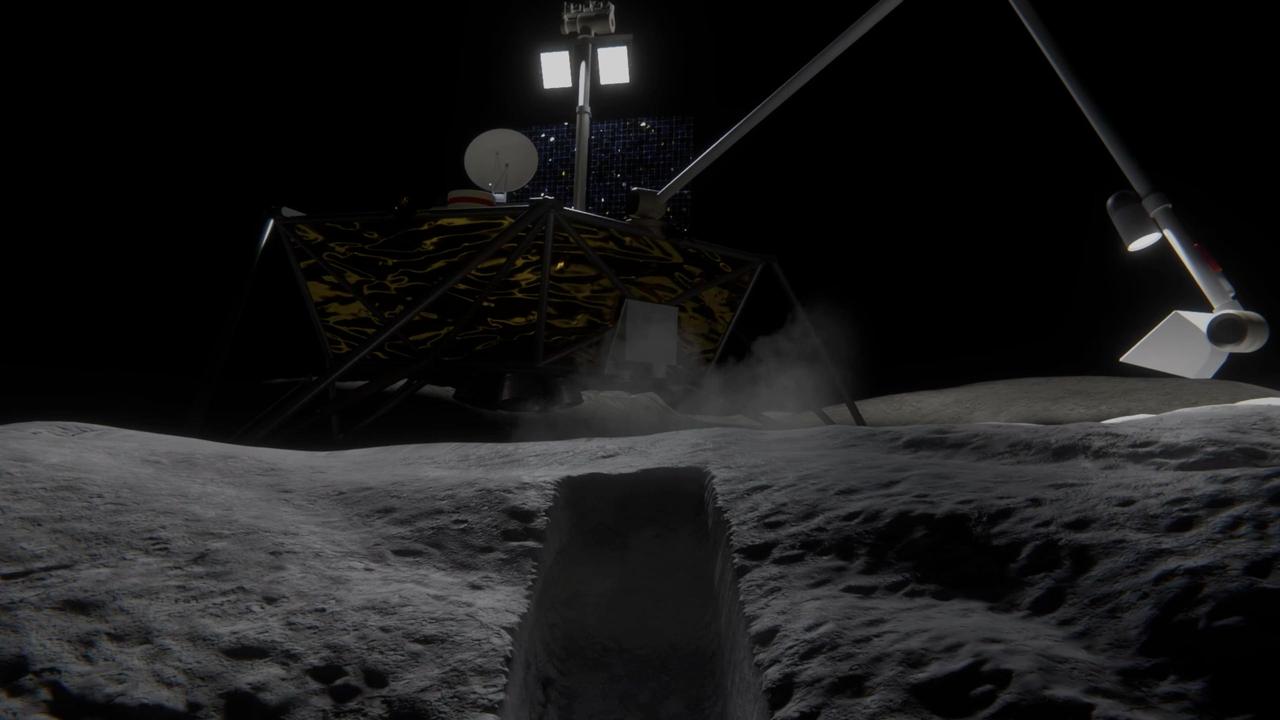

NASA's Cold Operable Lunar Deployable Arm (COLDArm) robotic arm system reaches out from a lander on the Moon and scoops up regolith (broken rock and dust). Managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, COLDArm is designed to operate during lunar night, a period that lasts about 14 Earth days. It can function in temperatures as cold as minus 280 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 173 degrees Celsius). Frigid temperatures during lunar night would stymie the arms on current spacecraft, which must rely on energy-consuming heaters to stay warm. To operate in the cold, the 6-foot-6-inch (2-meter) arm combines several key new technologies: gears made of bulk metallic glass that require no wet lubrication or heating, cold motor controllers that don't need to be kept warm in an electronics box near the core of the spacecraft, and a cryogenic six-axis force torque sensor that lets the arm "feel" what it's doing and make adjustments. A variety of attachments and small instruments could go on the end of the arm, such as a 3D-printed titanium scoop that could collect samples from a planet's surface, similar to what's depicted here. Like the arm on NASA's now-retired InSight Mars lander, COLDArm is also capable of deploying science instruments to the surface. The arm system could be attached to a stationary lander or to a rover. Motiv Space Systems, a partner on COLDArm, developed the cold motor controllers, and also built sections of the arm and assembled it from JPL-supplied parts at the company's Pasadena, California, facility. The COLDArm project is funded through the Lunar Surface Innovation Initiative and managed by the Game Changing Development program in NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26347

KSC-2013-2721 – SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. –Roland Coelho, third from left, CalPoly program lead, and members of the student launch team load a payload into a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Dispensor, or P-Pod nanolauncher/carrier in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payload, which includes sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cube sections, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Known as a CubeSat, the satellite will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. It will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Also, a new launcher/carrier of a lightweight design also is being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
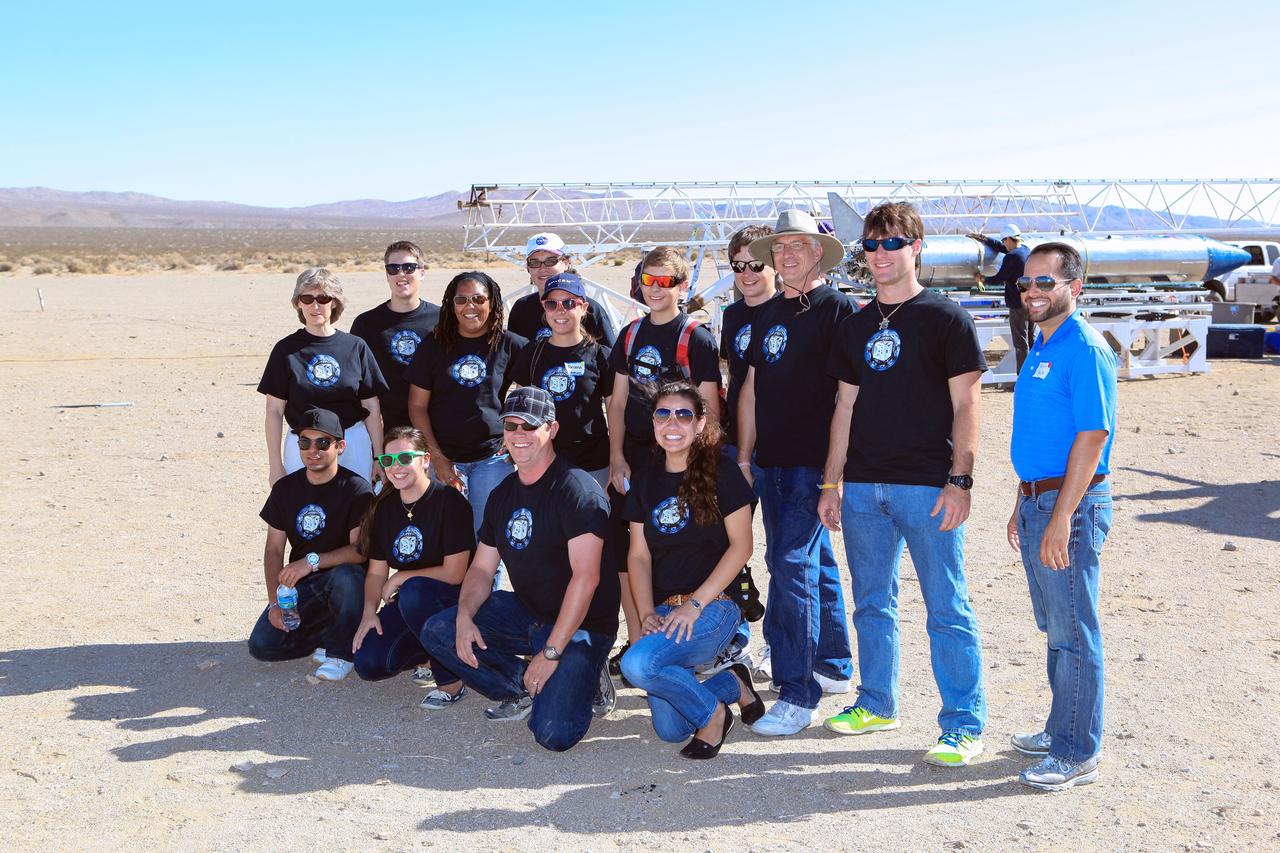

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, a student StangSat Team of students from Merritt Island High School in Florida posed for a pre-launch photograph as the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket, in the background, was being prepared for flight at the Friends of Amateur Rocketry launch site. Kneeling from left to right, are: Gurkirat Kainth, Megan Mackool, NASA mentor Shaun Daly and Maurisa Orona. Standing from left to right, are: teacher sponsor Tracey Beatovich, Brian Robusto, NASA Education program manager Grace Johnson, Nathan Stephens, Briana Luthman, Jackson Kinney, Steven Krygier, NASA mentor Jim Kinney, Joshua Zirkle and NASA mentor Kelvin Ruiz. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
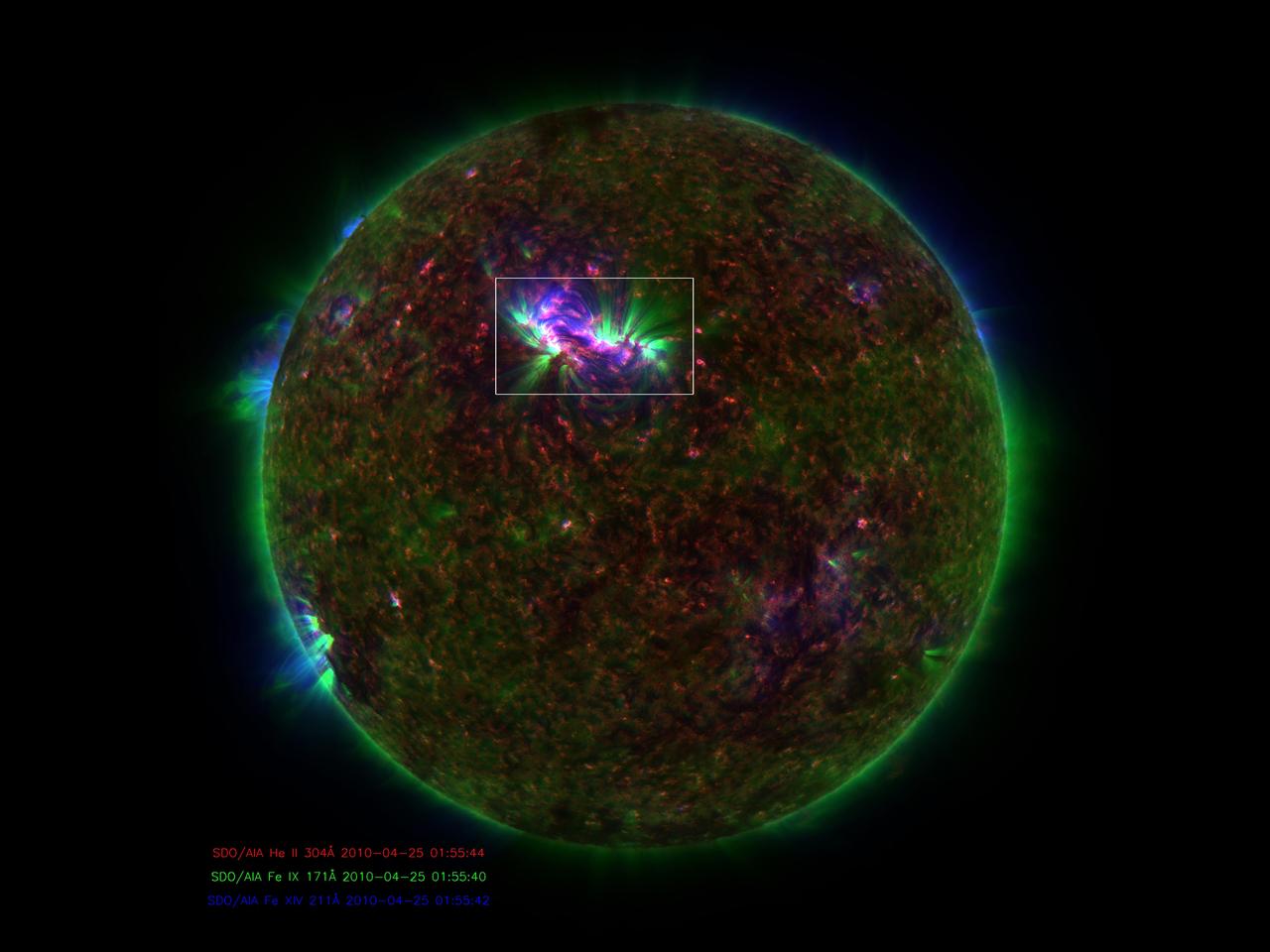
NASA image release January 6, 2010 Caption: Spicules on the sun, as observed by the Solar Dynamics Observatory. These bursts of gas jet off the surface of the sun at 150,000 miles per hour and contain gas that reaches temperatures over a million degrees. GREENBELT, Md. -- Observations from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and the Japanese satellite Hinode show that some gas in the giant, fountain-like jets in the sun's atmosphere known as spicules can reach temperatures of millions of degrees. The finding offers a possible new framework for how the sun's high atmosphere gets so much hotter than the surface of the sun. What makes the high atmosphere, or corona, so hot – over a million degrees, compared to the sun surface's 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit -- remains a poorly understood aspect of the sun's complicated space weather system. That weather system can reach Earth, causing auroral lights and, if strong enough, disrupting Earth's communications and power systems. Understanding such phenomena, therefore, is an important step towards better protecting our satellites and power grids. "The traditional view is that all the heating happens higher up in the corona," says Dean Pesnell, who is SDO's project scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "The suggestion in this paper is that cool gas is being ejected from the sun's surface in spicules and getting heated on its way to the corona." Spicules were first named in the 1940s, but were hard to study in detail until recently, says Bart De Pontieu of Lockheed Martin's Solar and Astrophysics Laboratory, Palo Alto, Calif. who is the lead author on a paper on this subject in the January 7, 2011 issue of Science magazine. In visible light, spicules can be seen to send large masses of so-called plasma – the electromagnetic gas that surrounds the sun – up through the lower solar atmosphere or photosphere. The amount of material sent up is stunning, some 100 times as much as streams away from the sun in the solar wind towards the edges of the solar system. But nobody knew if they contained hot gas. "Heating of spicules to the necessary hot temperatures has never been observed, so their role in coronal heating had been dismissed as unlikely," says De Pontieu. Now, De Pontieu's team -- which included researchers at Lockheed Martin, the High Altitude Observatory of the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) in Colorado and the University of Oslo, Norway -- was able to combine images from SDO and Hinode to produce a more complete picture of the gas inside these gigantic fountains. The scientists found that a large fraction of the gas is heated to a hundred thousand degrees, while a small fraction is heated to millions of degrees. Time-lapsed images show that this material spews up into the corona, with most falling back down towards the surface of the sun. However, the small fraction of the gas that is heated to millions of degrees does not immediately return to the surface. Given the large number of spicules on the Sun, and the amount of material in the spicules, the scientists believe that if even some of that super hot plasma stays aloft it would make a contribution to coronal heating. Astrophysicist Jonathan Cirtain, who is the U.S. project scientist for Hinode at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, Ala., says that incorporating such new information helps address an important question that reaches far beyond the sun. "This breakthrough in our understanding of the mechanisms which transfer energy from the solar photosphere to the corona addresses one of the most compelling questions in stellar astrophysics: How is the atmosphere of a star heated?" he says. "This is a fantastic discovery, and demonstrates the muscle of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, comprised of numerous instruments on multiple observatories." Hinode is the second mission in NASA's Solar Terrestrial Probes program, the goal of which is to improve understanding of fundamental solar and space physics processes. The mission is led by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ). The collaborative mission includes the U.S., the United Kingdom, Norway and Europe. NASA Marshall manages Hinode U.S. science operations and oversaw development of the scientific instrumentation provided for the mission by NASA, academia and industry. The Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center is the lead U.S. investigator for the Solar Optical Telescope on Hinode. SDO is the first mission in a NASA science program called Living With a Star, the goal of which is to develop the scientific understanding necessary to address those aspects of the sun-Earth system that directly affect our lives and society. NASA Goddard built, operates, and manages the SDO spacecraft for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. To learn more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sdo/news/news20110106-spicules.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sdo/news/news20110106-spicules...</a> Credit: NASA Goddard/SDO/AIA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>