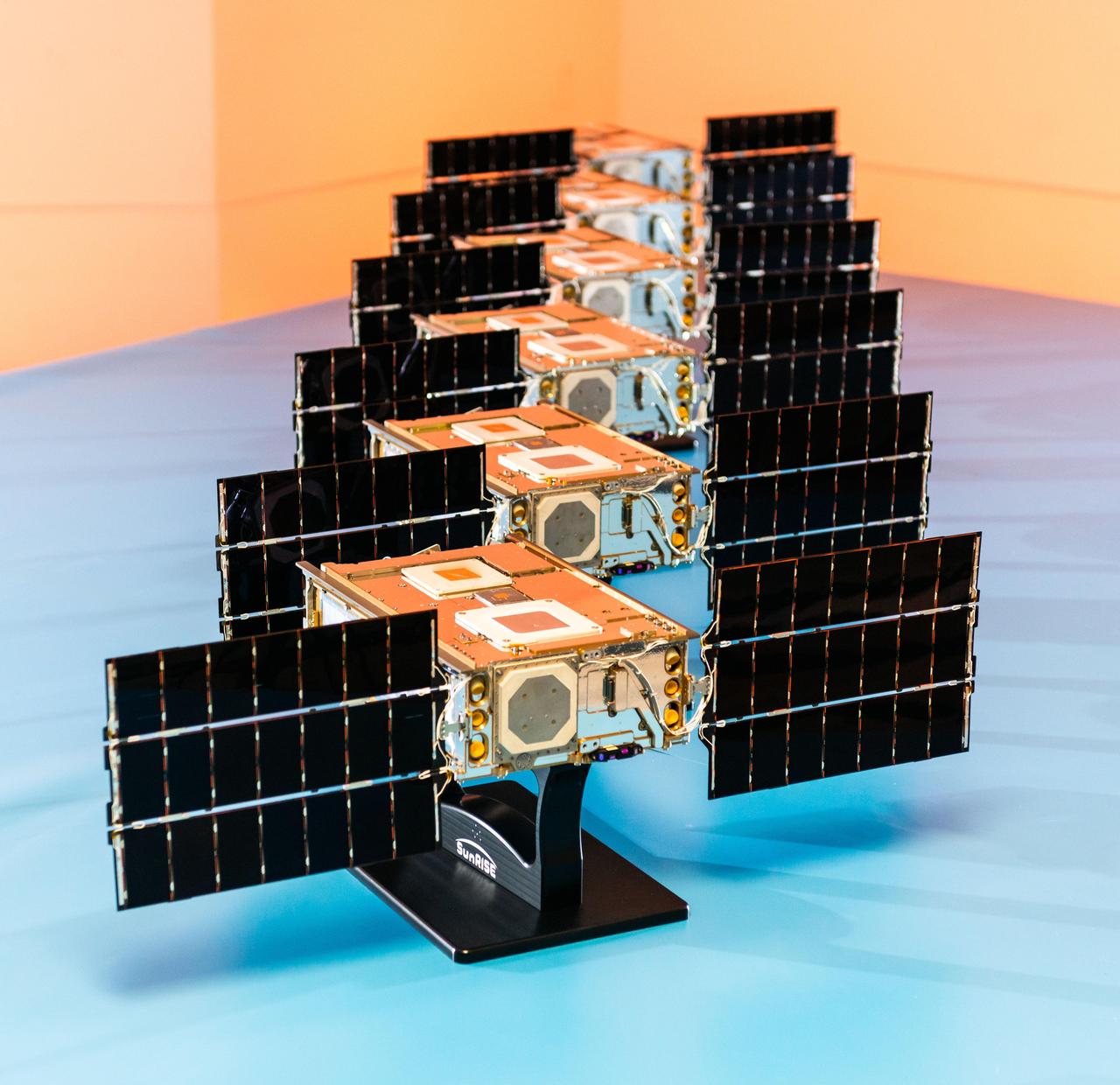
Shown here at Utah State University's Space Dynamics Laboratory in Logan, Utah, in November, 2023, the six satellites that make up NASA's Sun Radio Interferometer Space Experiment (SunRISE) mission are each only about the size of a cereal box, flanked by small solar panels. Once in space, the six SmallSats fly about 6 miles (10 kilometers) apart and each deploy four radio antennas that extend 10 feet (2.5 meters). Using a technique called interferometry, the six satellites will effectively act like one big radio receiver and detect solar radio bursts, or eruptions of radio waves in the outer atmosphere of the Sun. In the places where these radio bursts arise, scientists also see eruptions of accelerated particles, which can damage spacecraft electronics, including on communications satellites in Earth orbit, and pose a health threat to astronauts. Keeping track of solar radio bursts and pinpointing their location could help warn humans of approaching accelerated particles. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25789

CAPE-2: Cajun Advanced Picosatellite Experiment – ELaNa IV CAPE-2 was developed by students from the University of Louisiana Lafayette to engage, inspire and educate K-12 students to encourage them to pursue STEM careers. The secondary focus is the technology demonstration of deployed solar panels to support the following payloads: text to speech, voice repeater, tweeting, email, file transfer and data collection from buoys. Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative on the ELaNa IV mission as an auxiliary payload aboard the U.S. Air Force-led Operationally Responsive Space (ORS-3) Mission on November 19, 2013.
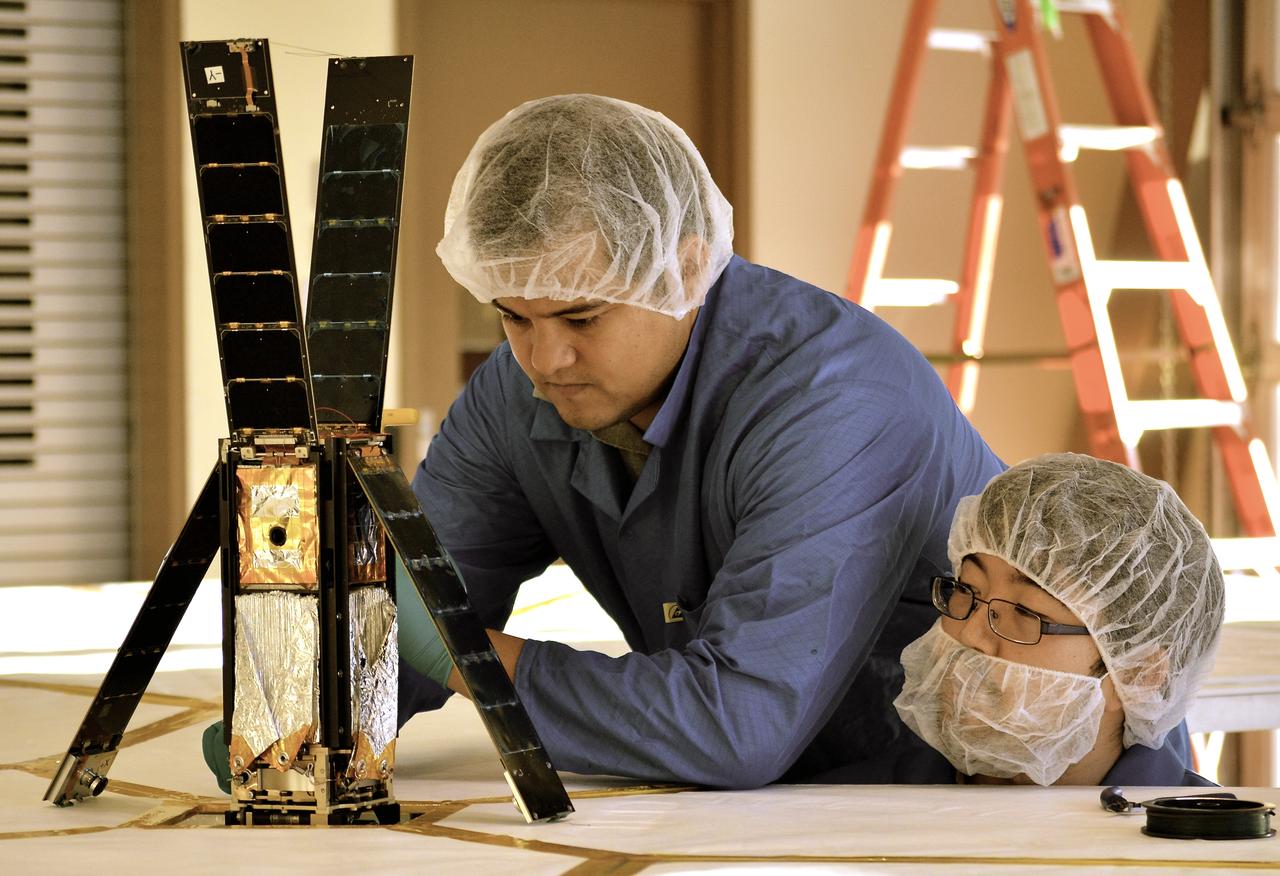

Students Alex Diaz and Riki Munakata of California Polytechnic State University testing the LightSail CubeSat. LightSail is a citizen-funded technology demonstration mission sponsored by the Planetary Society using solar propulsion for CubeSats. The spacecraft is designed to “sail” on the energy of solar photons striking the thin, reflective sail material. The first LightSail mission is designed to test the spacecraft’s critical systems, including the sequence to autonomously deploy a Mylar solar sail with an area of 32 square meters (344 square feet). The Planetary Society is planning a second, full solar sailing demonstration flight for 2016. Light is made of packets of energy called photons. While photons have no mass, they have energy and momentum. Solar sails use this momentum as a method of propulsion, creating flight by light. LightSail’s solar sail is packaged into a three-unit CubeSat about the size of a loaf of bread. Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative on the ELaNa XI mission as an auxiliary payload aboard the U.S. Air Force X-37B space plane mission on May 20, 2015.

The Close Orbiting Propellant Plume Elemental Recognition (COPPER) was developed by students from St. Louis University as a technology demonstration mission whose objective is to test the suitability of a commercially-available compact uncooled microbolometer (tiny infrared camera) array for scientific imagery of Earth in the long-wave infrared range (LWIR, 7-13 microns). Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative on the ELaNa IV mission as an auxiliary payload aboard the U.S. Air Force-led Operationally Responsive Space (ORS-3) Mission on November 19, 2013.
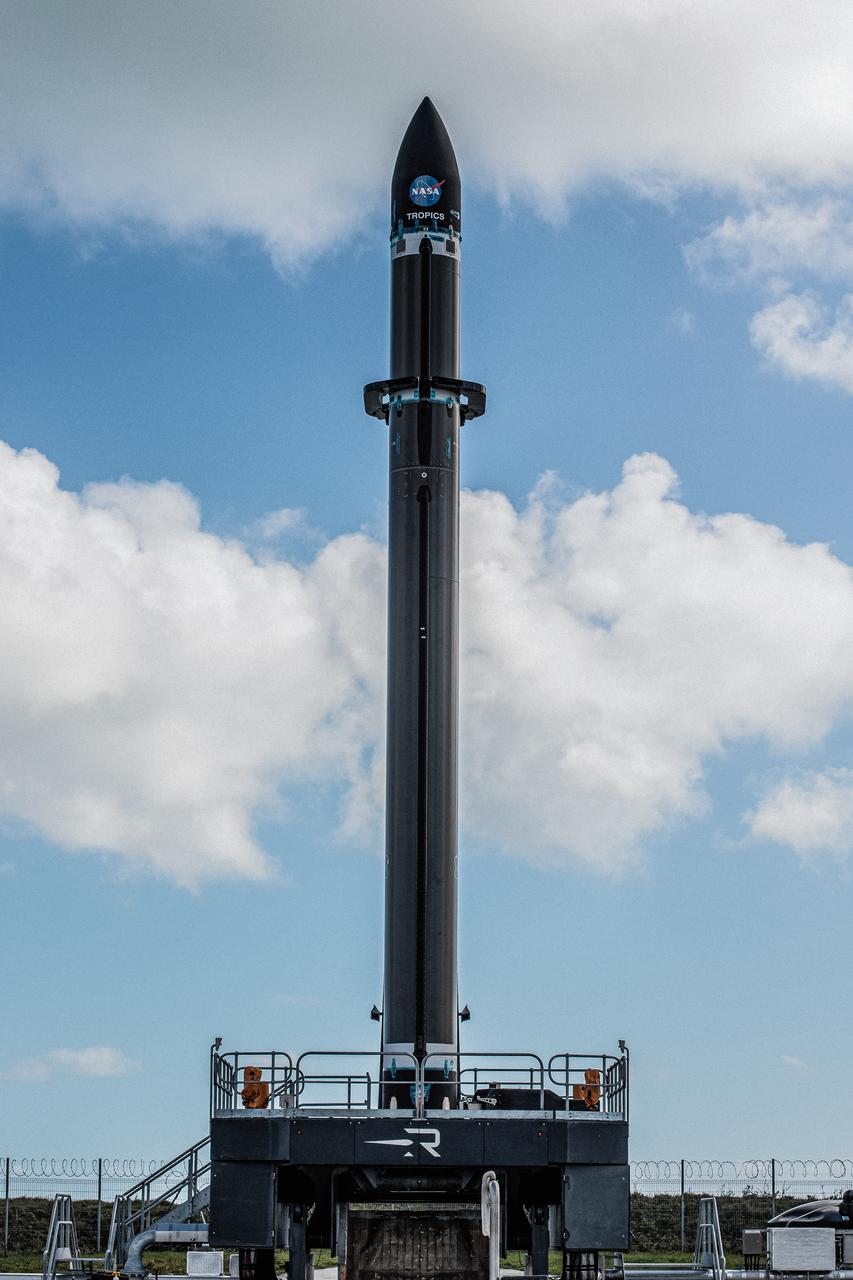

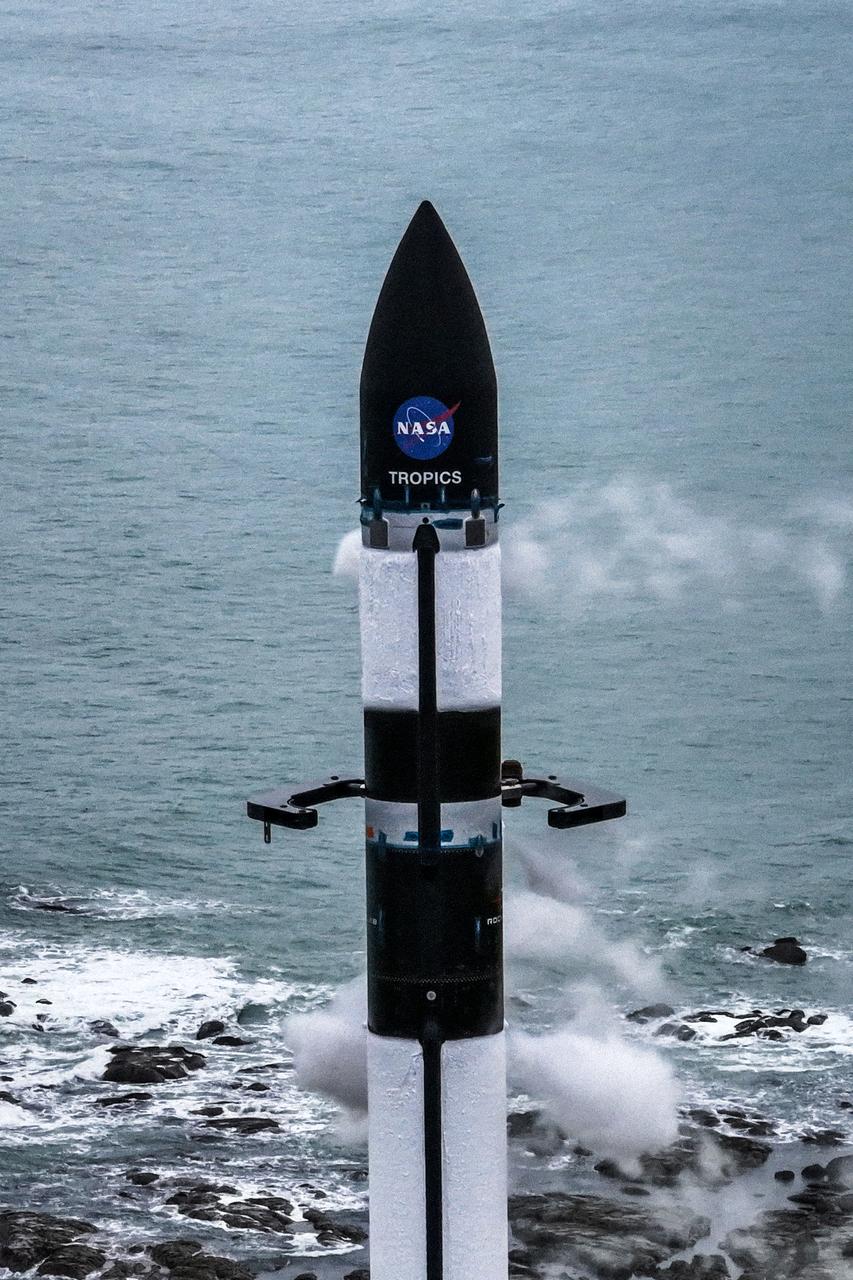
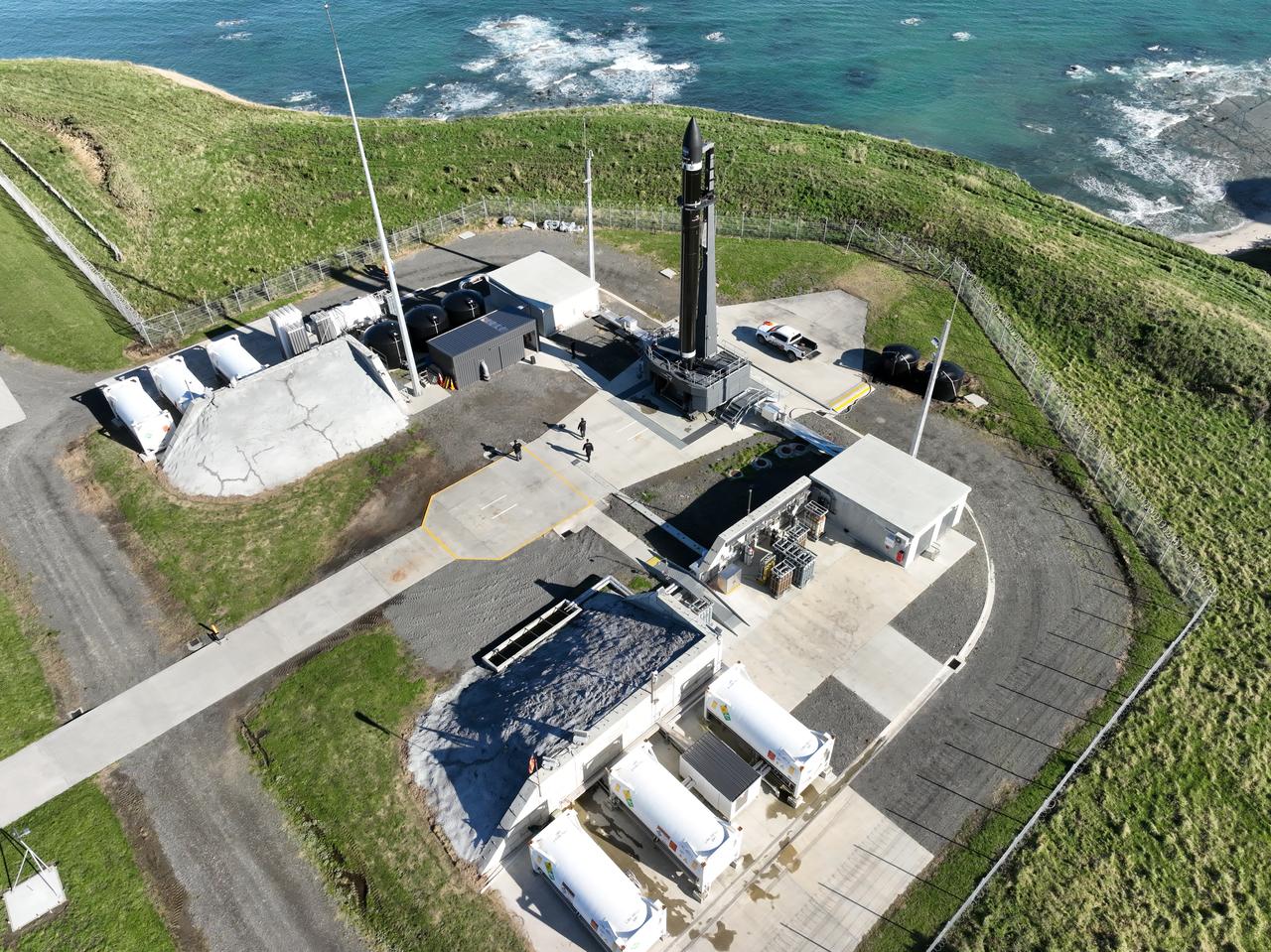
Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
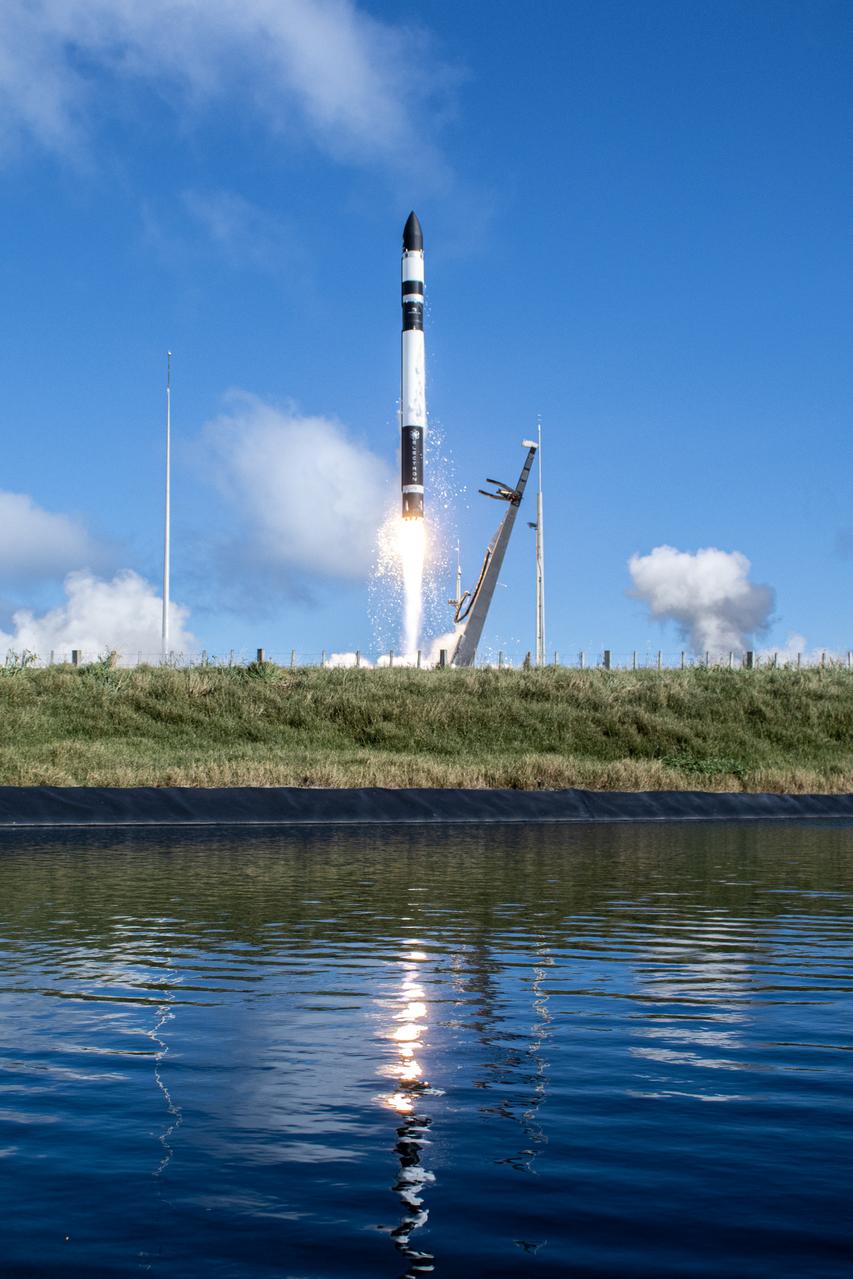

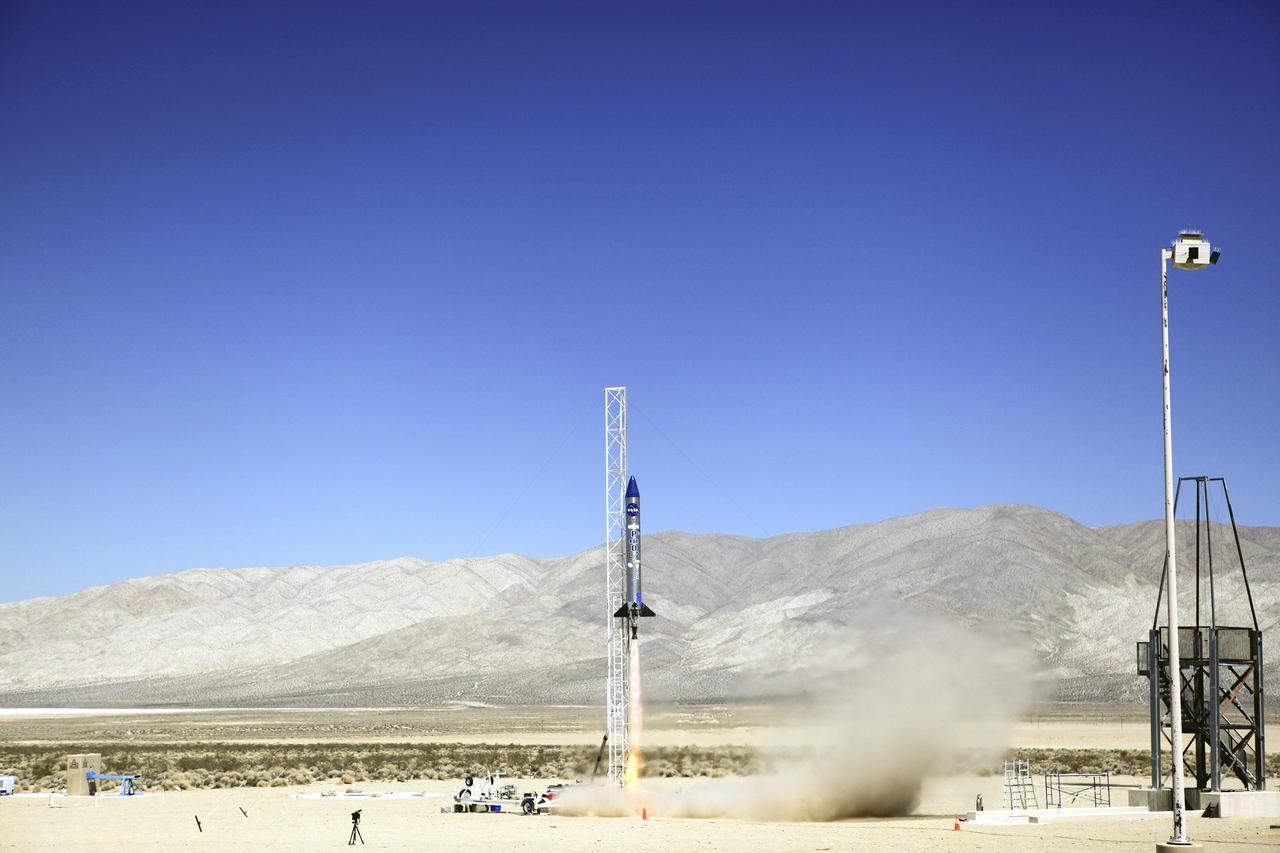
A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
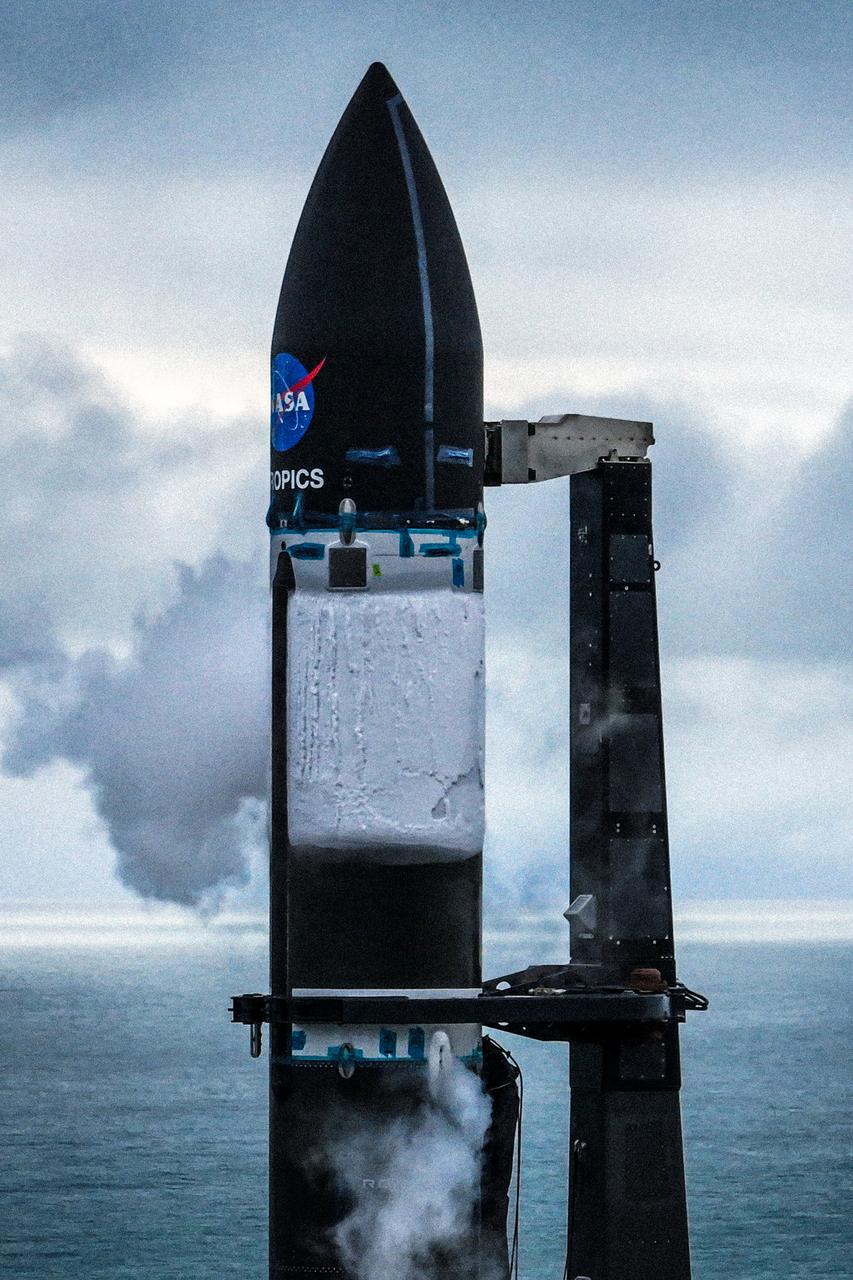

A wet dress rehearsal is underway for Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand on April 28, 2023. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
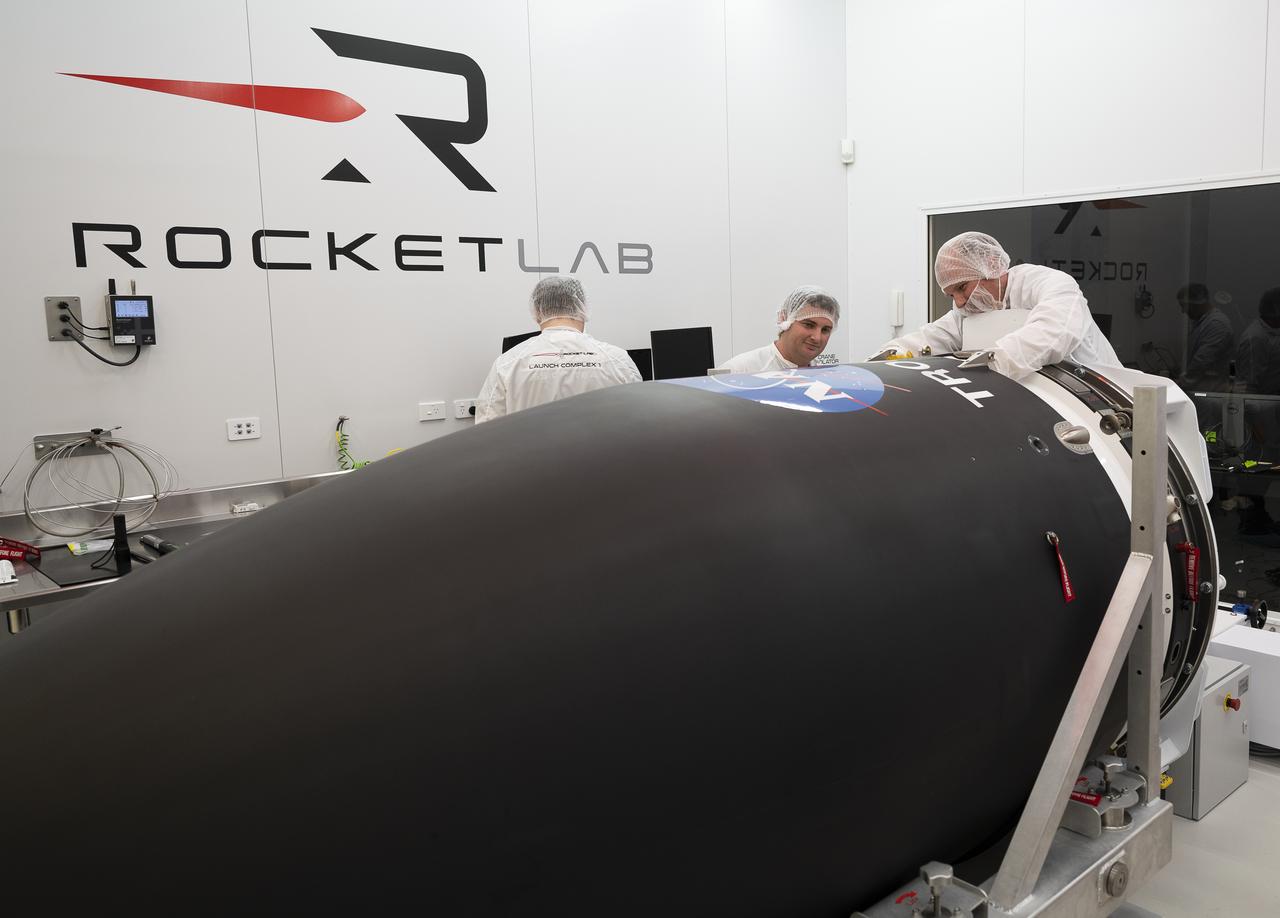

NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are encapsulated inside Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing in a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
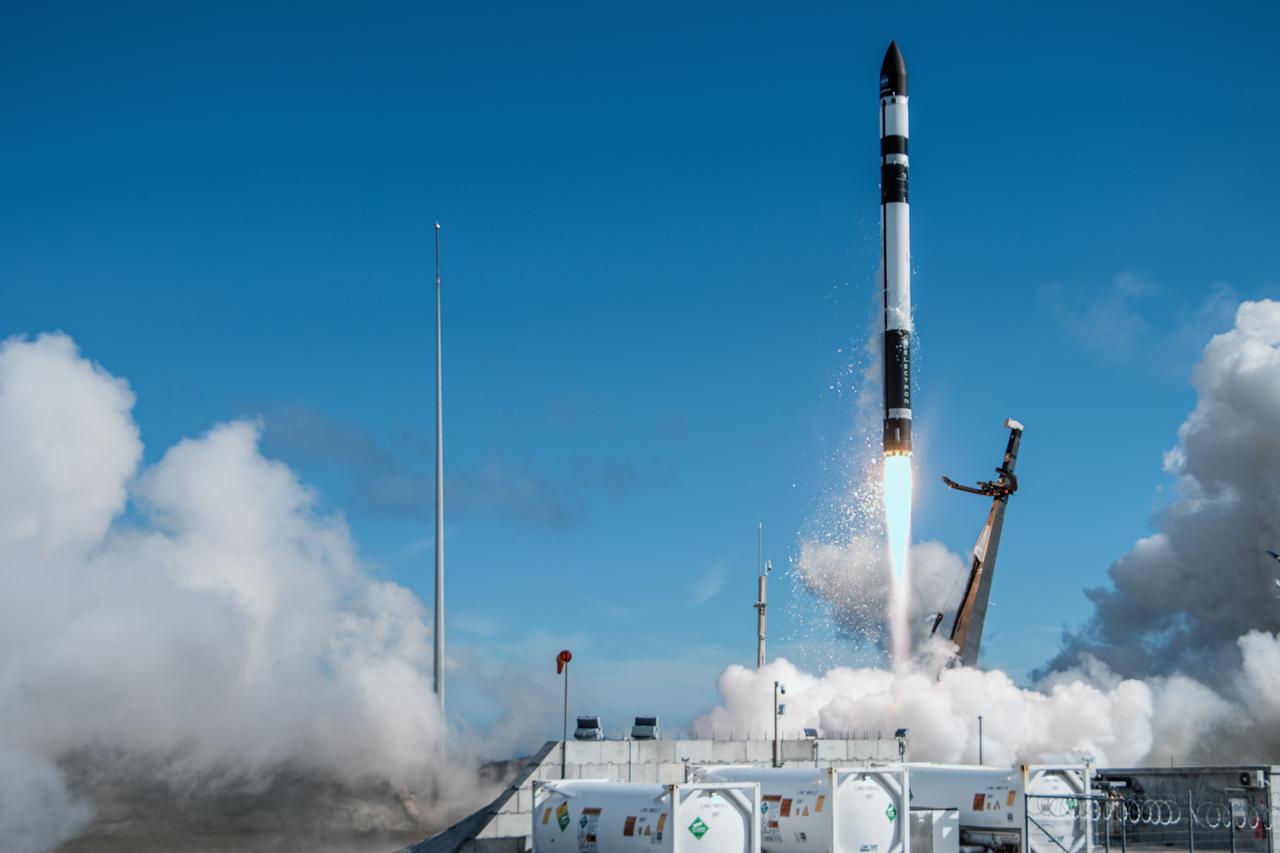

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Technicians prepare NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats for encapsulation in Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing in a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

A wet dress rehearsal is underway for Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand on April 28, 2023. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Scott Higginbotham, NASA mission manager for Educational Launch of Nanosatellites, or ELaNa-X, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, participates in a news conference at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, following NASA's successful launch of the Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite, or SMAP, on its mission to study the Earth's soil moisture. To learn more about ELaNa, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
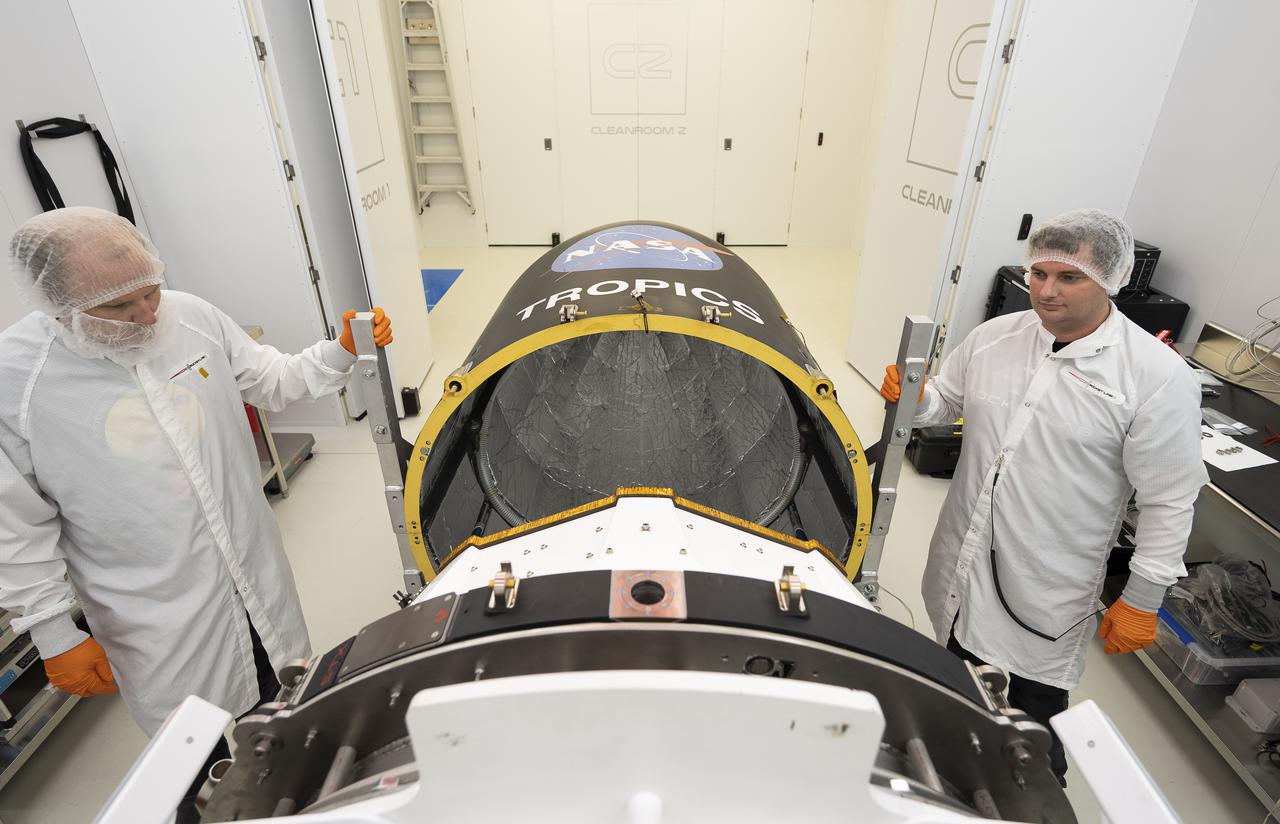

Technicians place NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats in Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing in a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
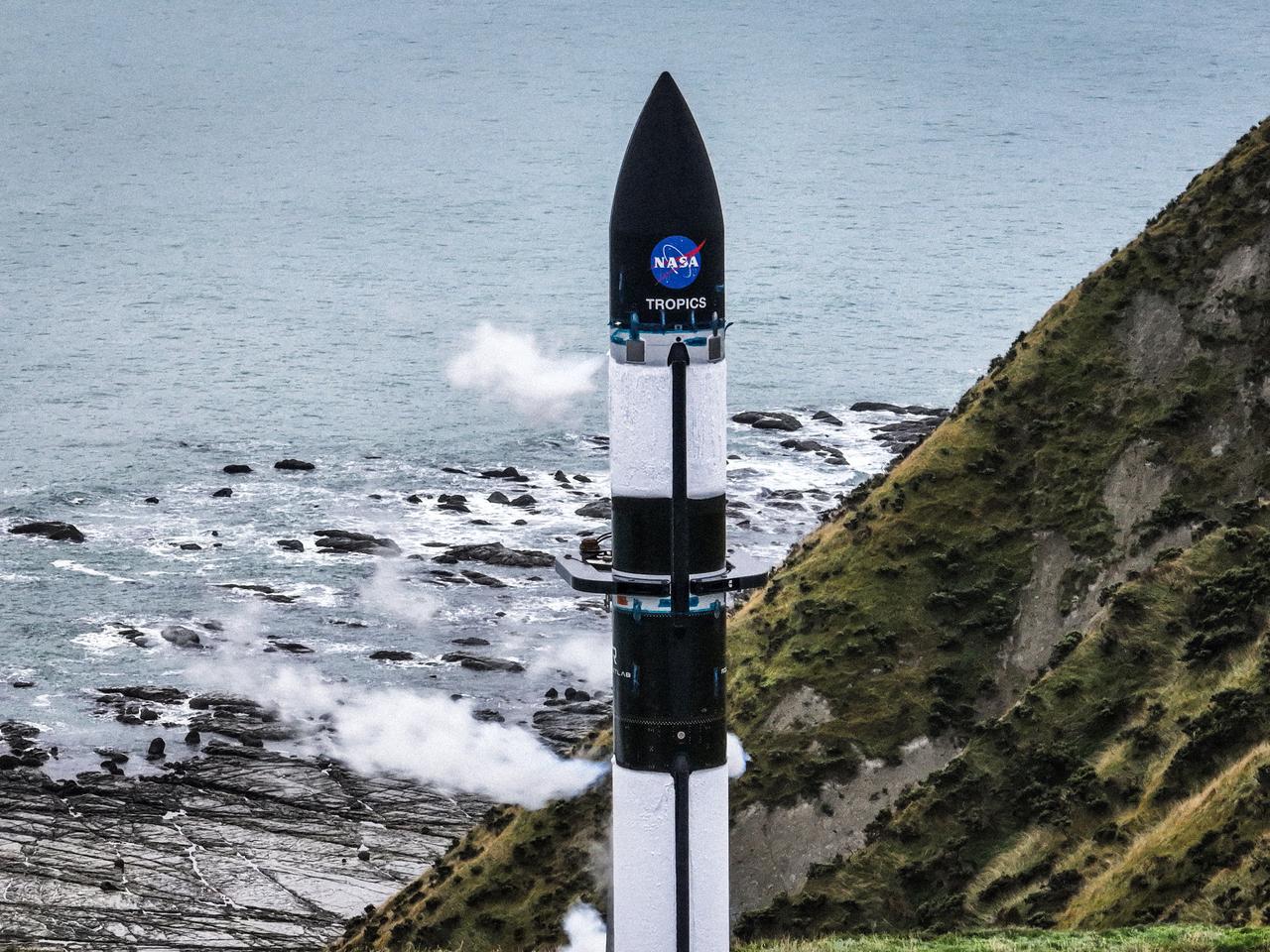

A wet dress rehearsal is underway for Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand on April 28, 2023. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing is in view inside a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats have been encapsulated inside the payload fairing. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
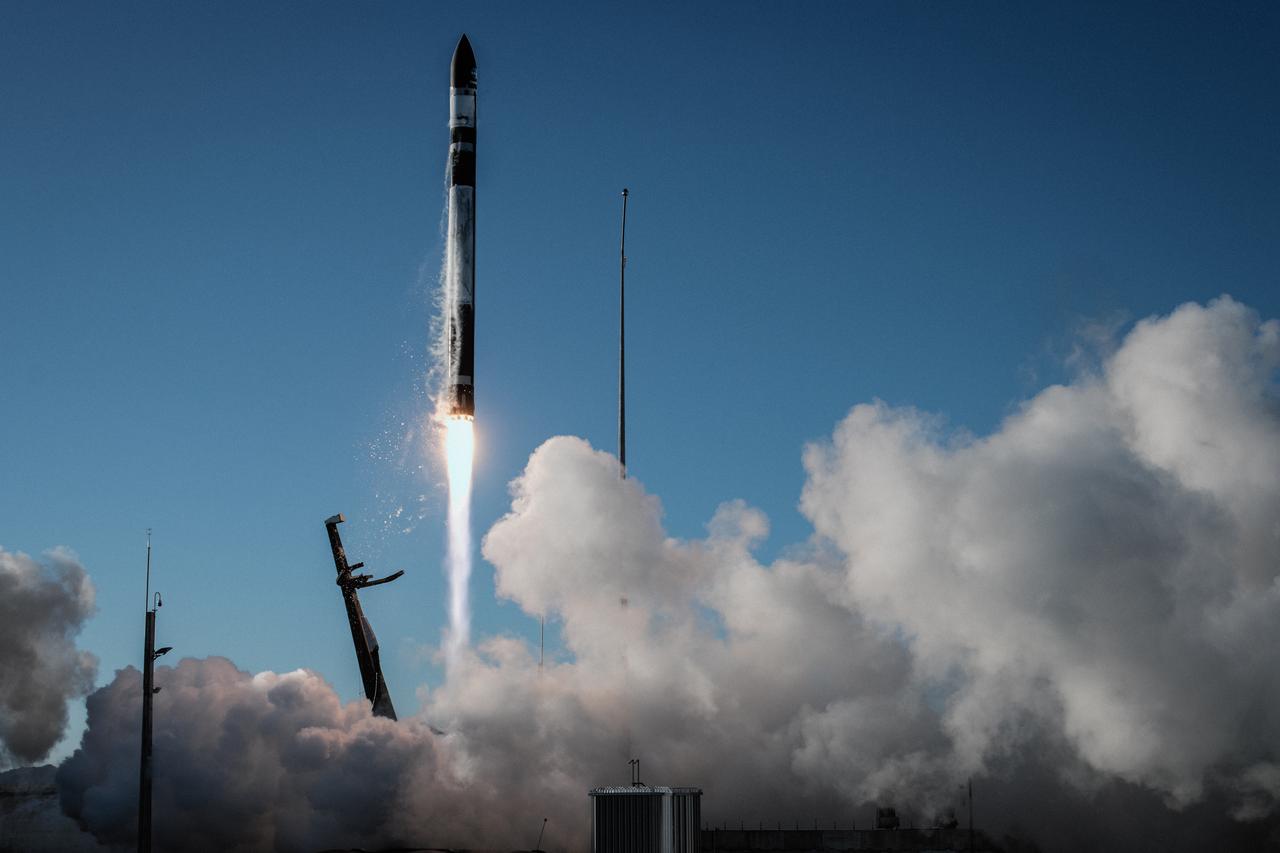

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket soars upward after liftoff from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Technicians check Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing inside a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats have been encapsulated inside the payload fairing. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
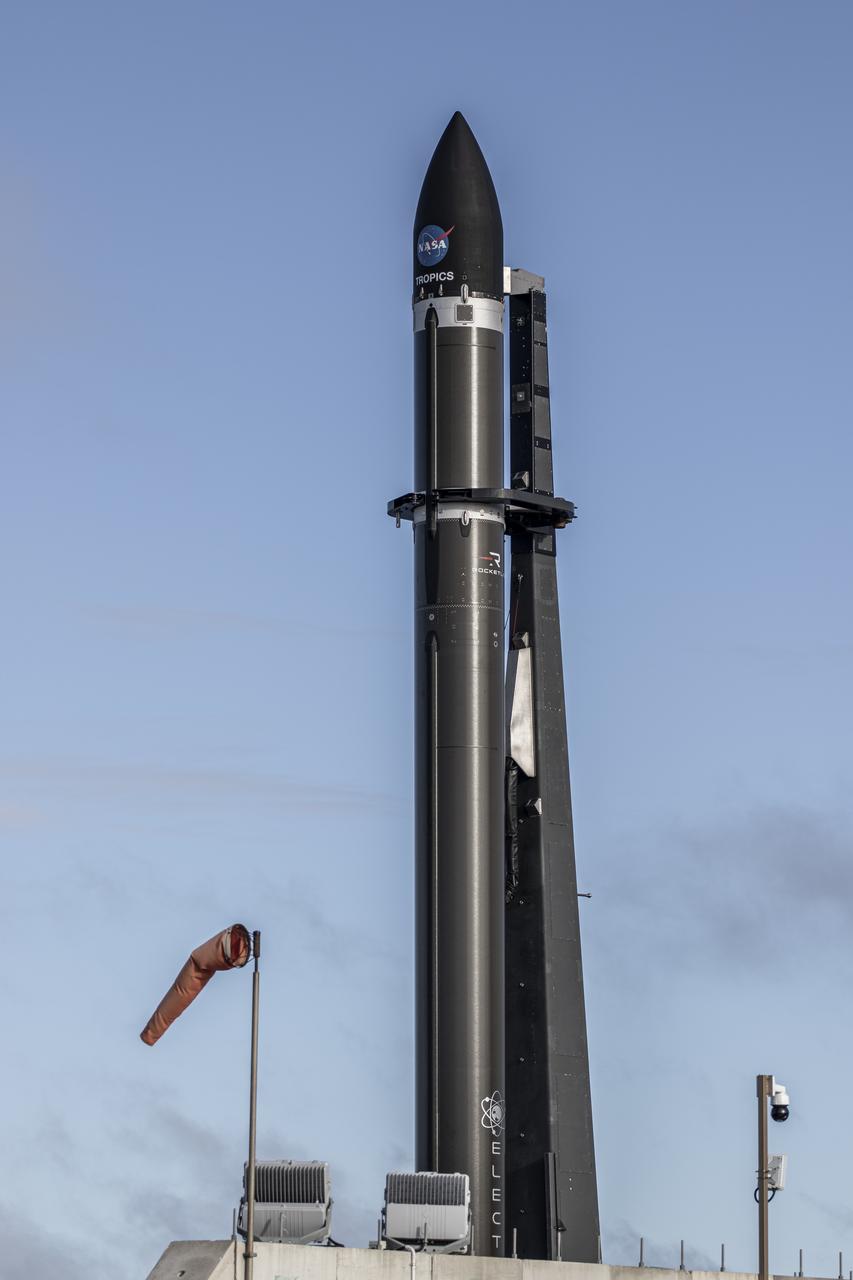

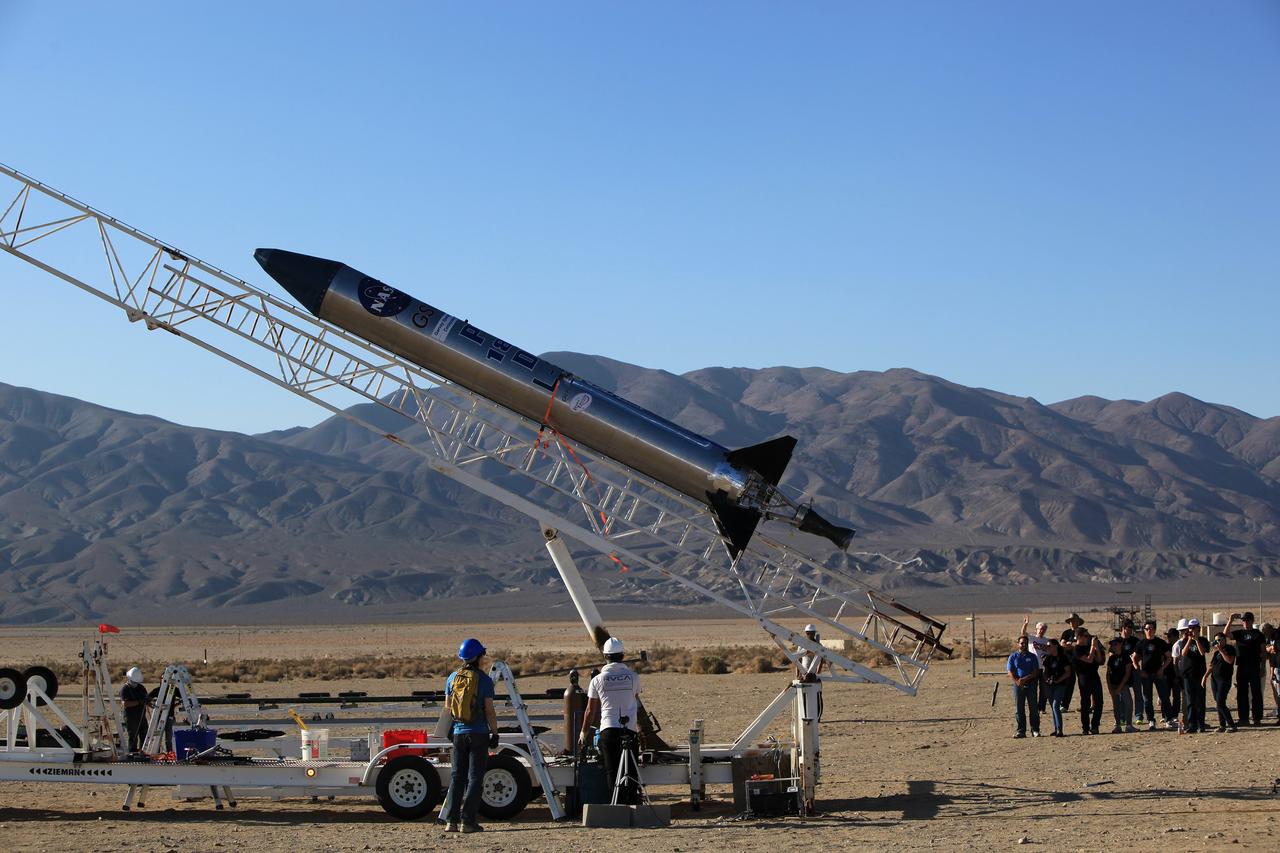
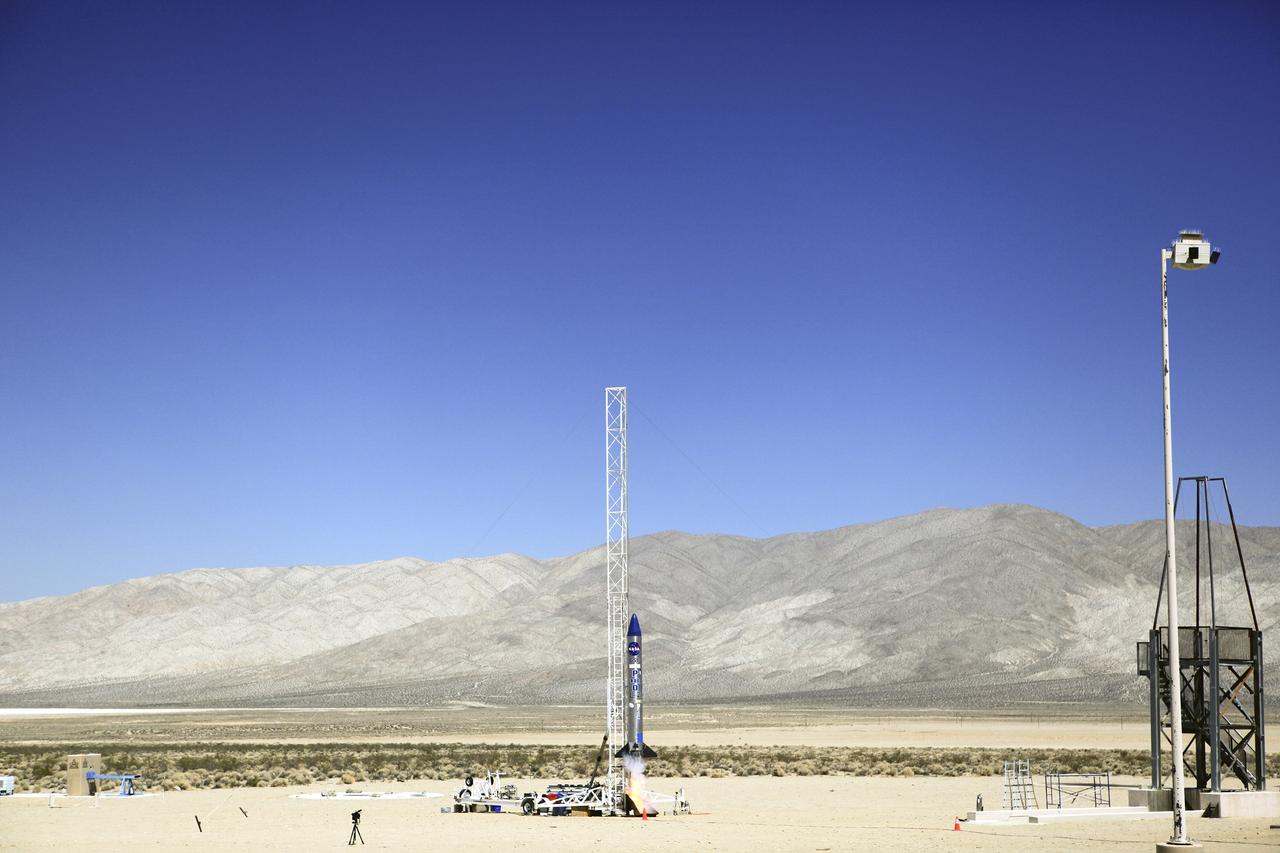
A Rocket Lab Electron rocket is poised for launch atop Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand. Launch time is May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT). The Electron rocket is carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
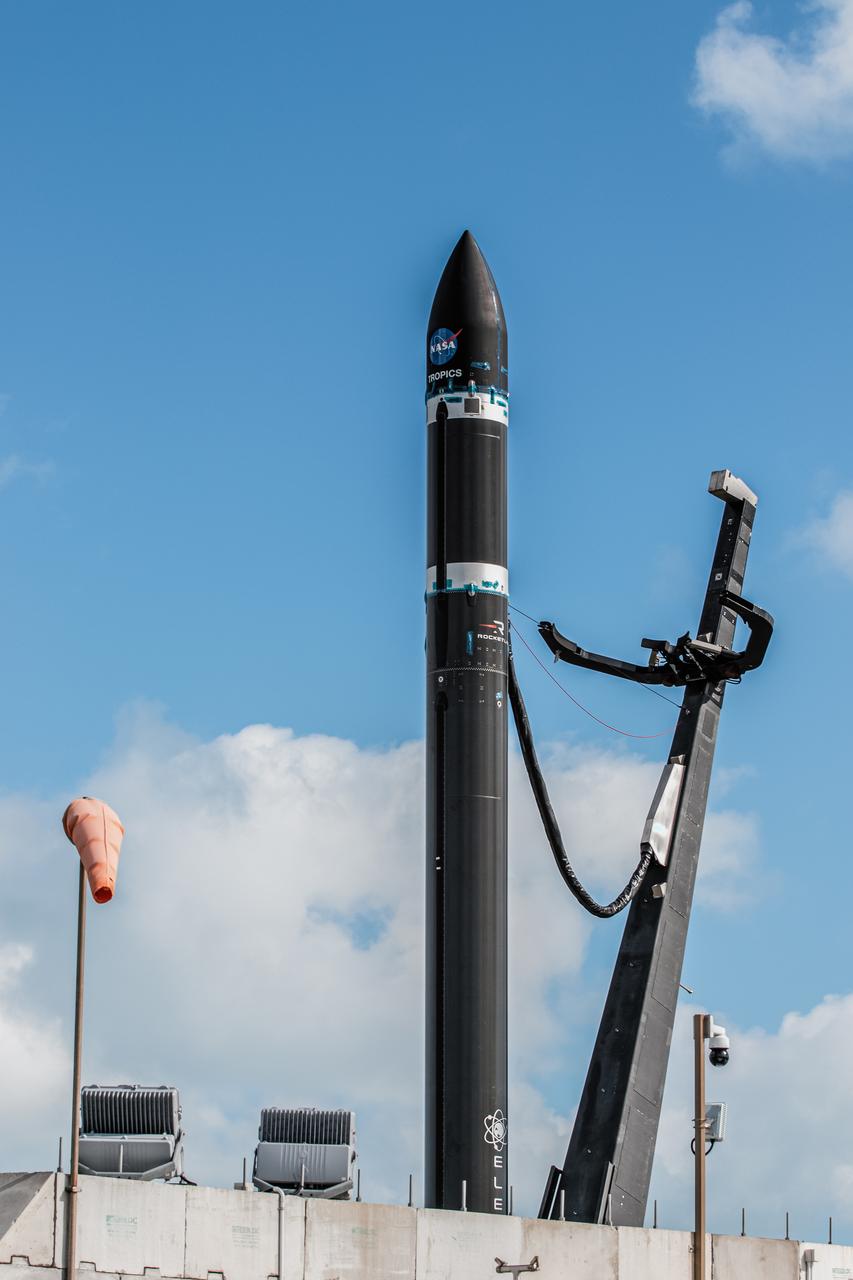

With the umbilical tower in view, Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
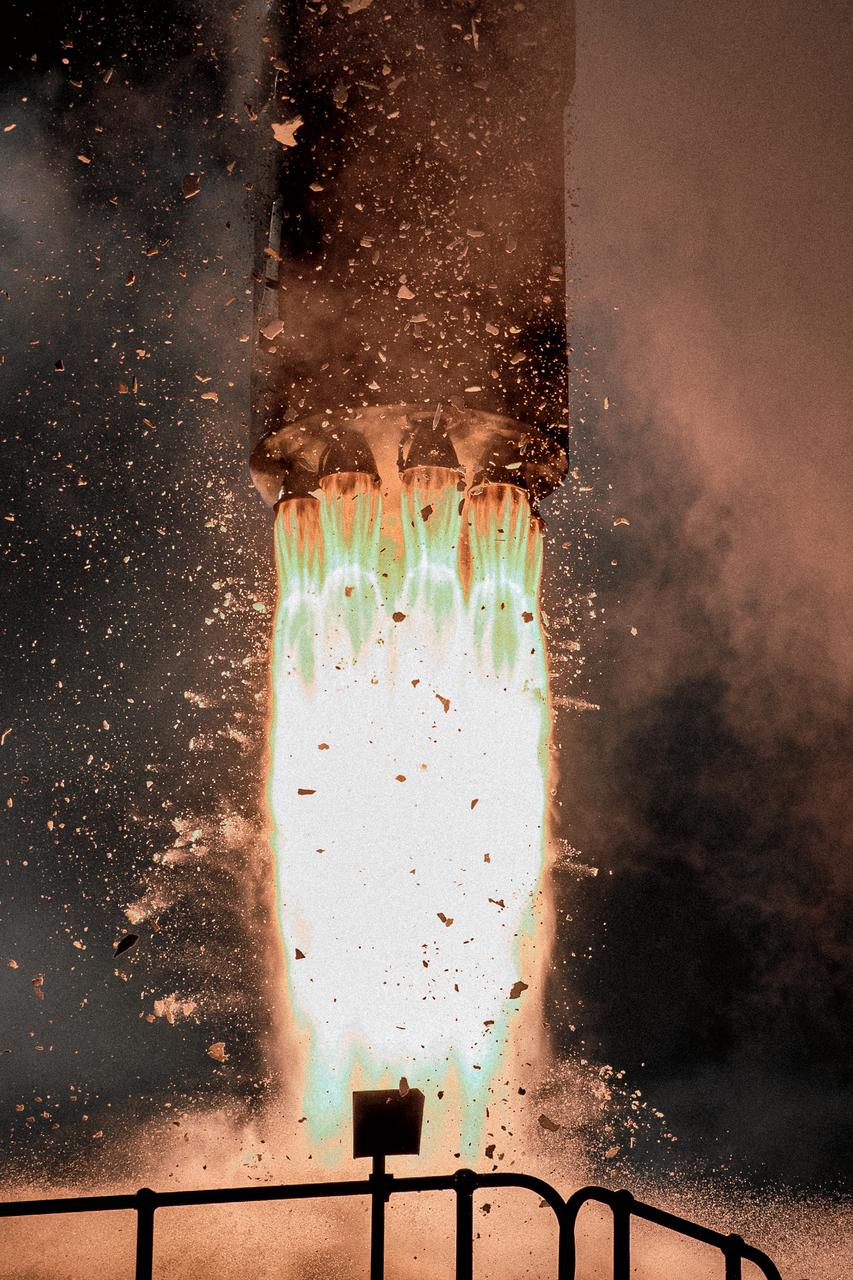

The engines of the first stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket ignite as the rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
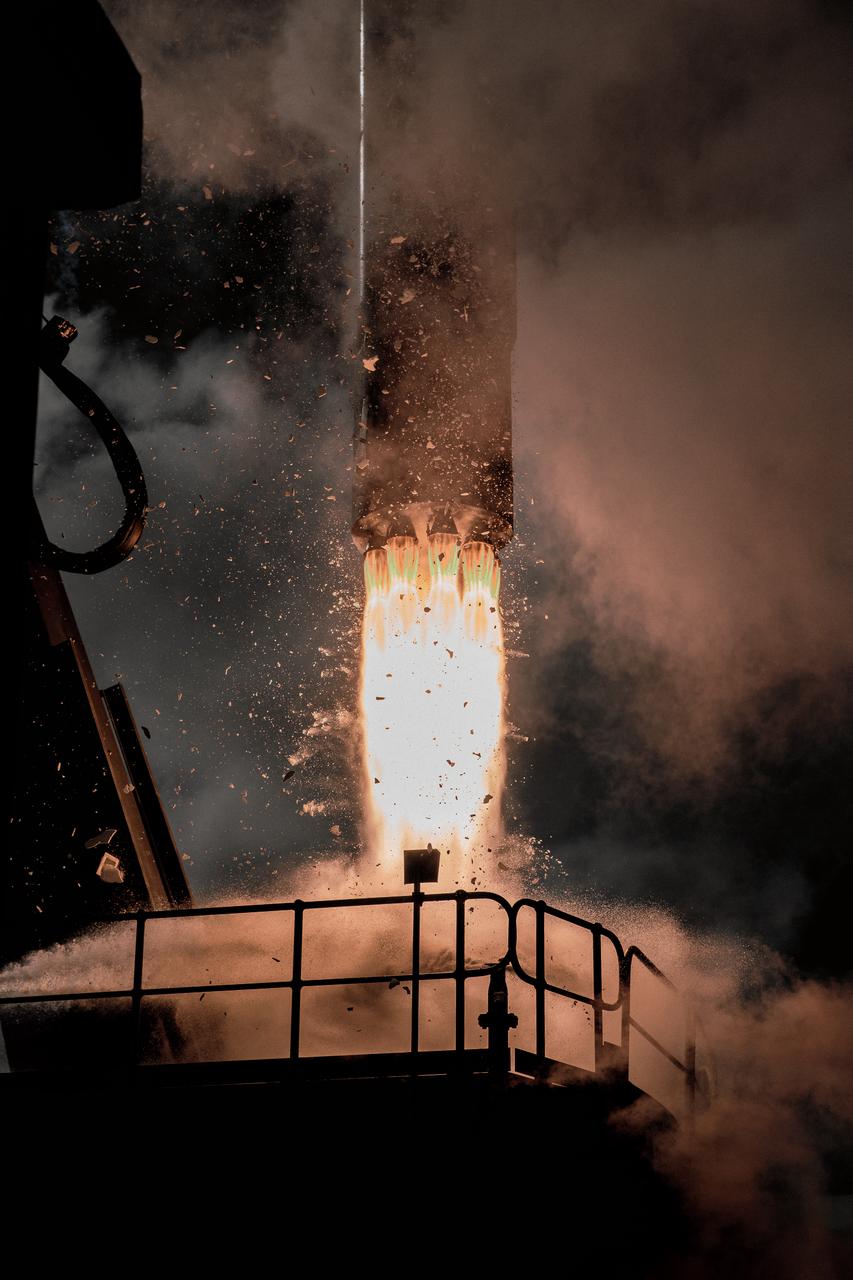

The engines of the first stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket ignite as the rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
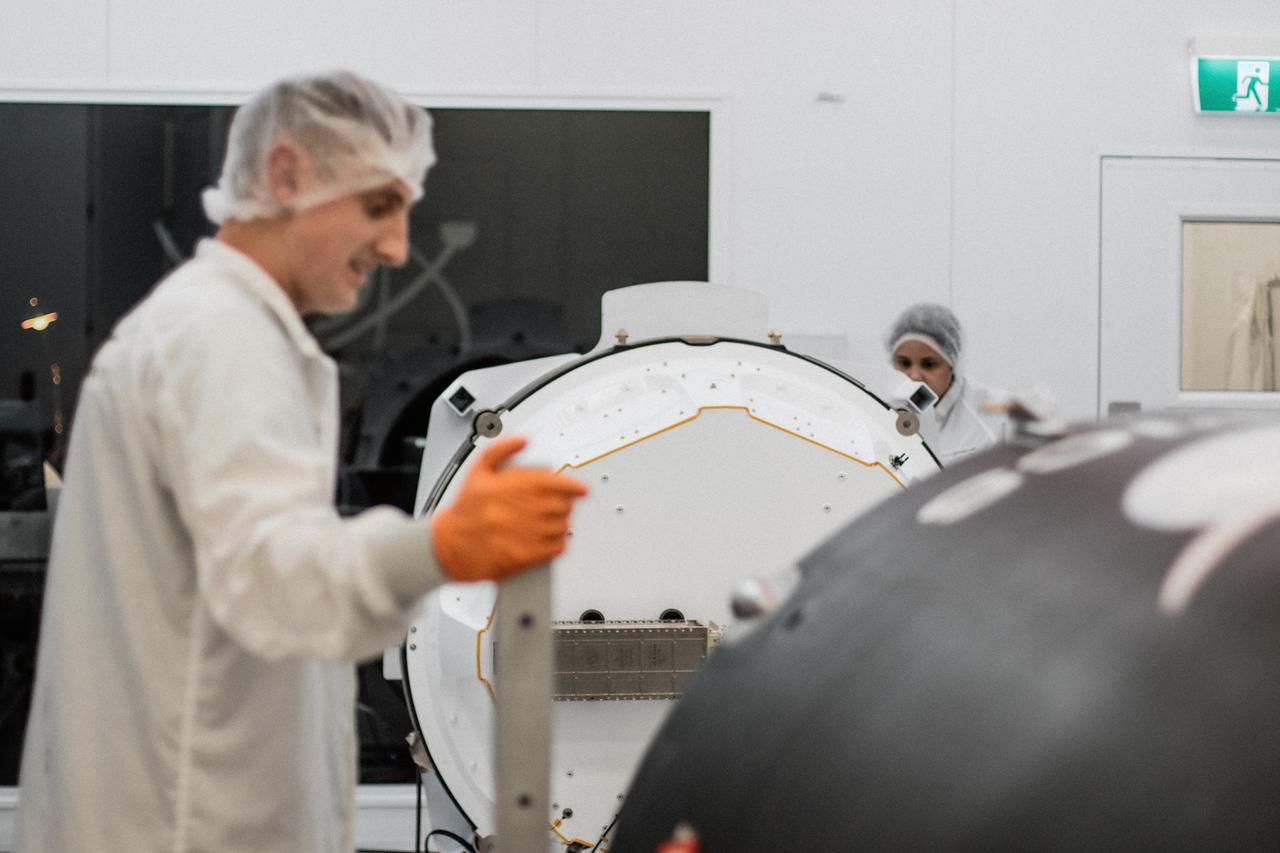

Two CubeSats are encapsulated at the Rocket Lab facility in Mahia, New Zealand, on April 24, 2023, in preparation for NASA’s second TROPICS (Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), for liftoff of the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
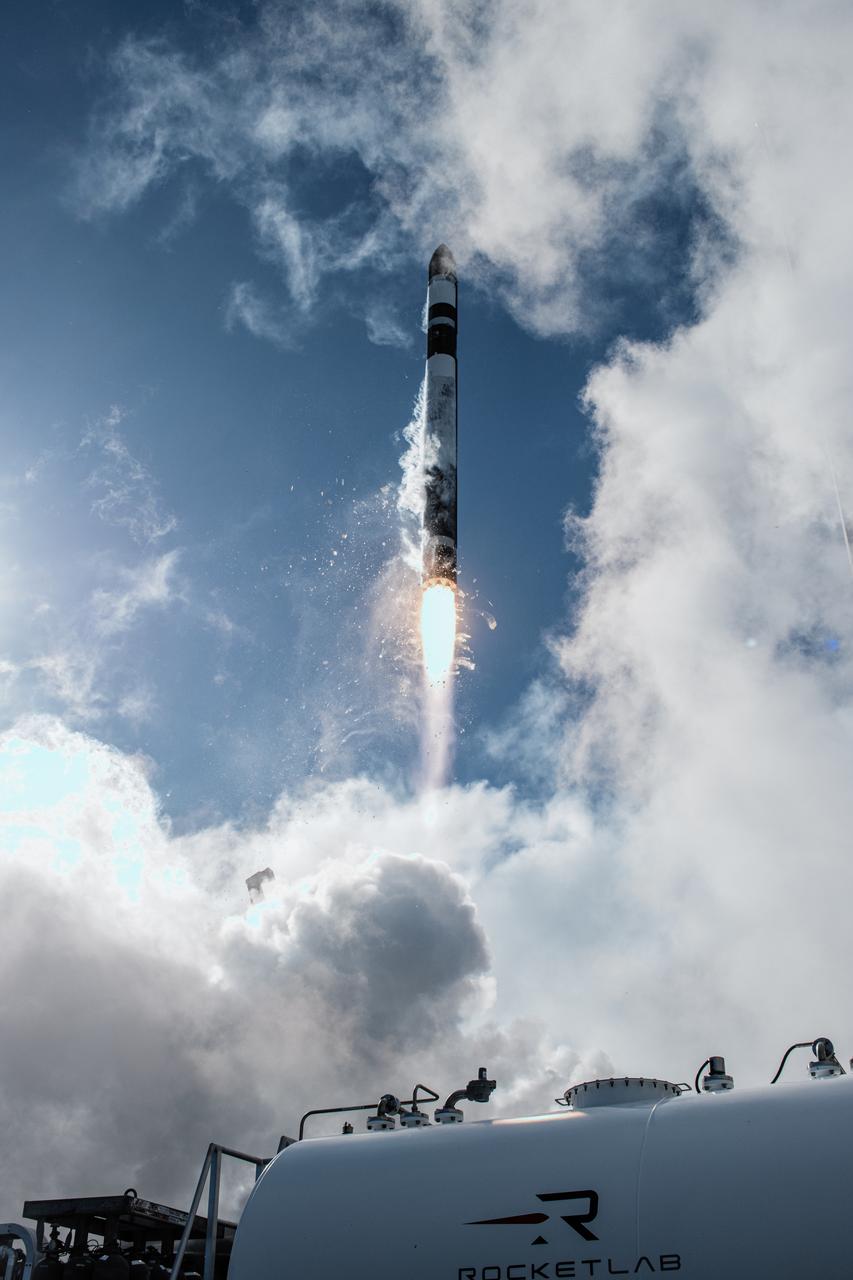

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket soars upward after liftoff from Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Two CubeSats are encapsulated at the Rocket Lab facility in Mahia, New Zealand, on April 24, 2023, in preparation for NASA’s second TROPICS (Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), for liftoff of the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
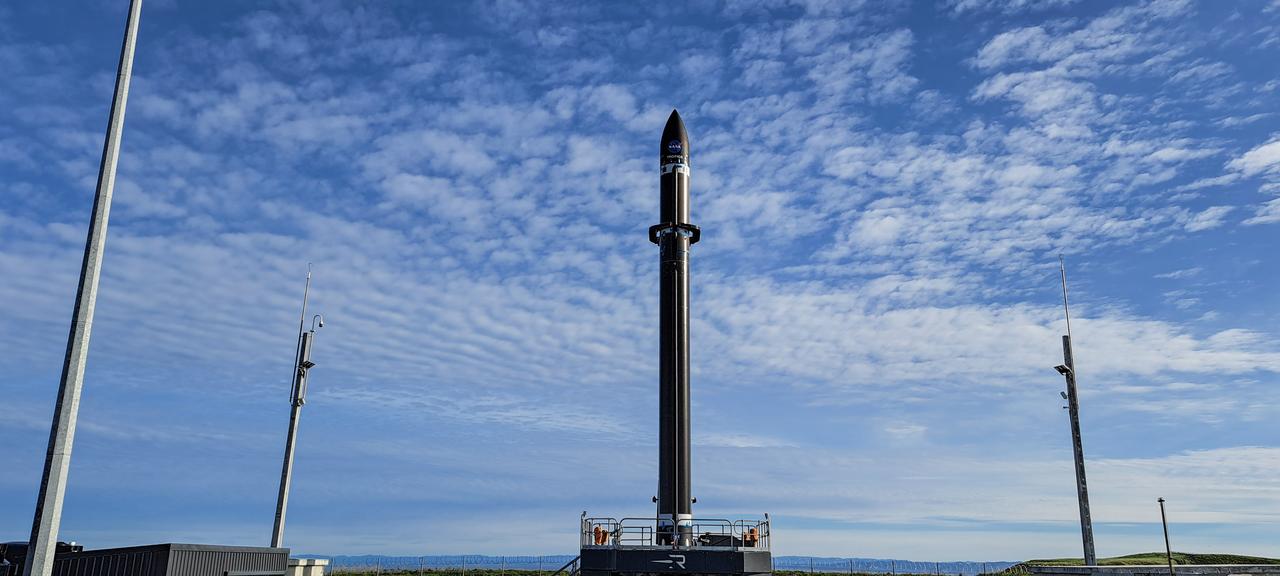

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, during a May 18, 2023, wet dress rehearsal for NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), to launch the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
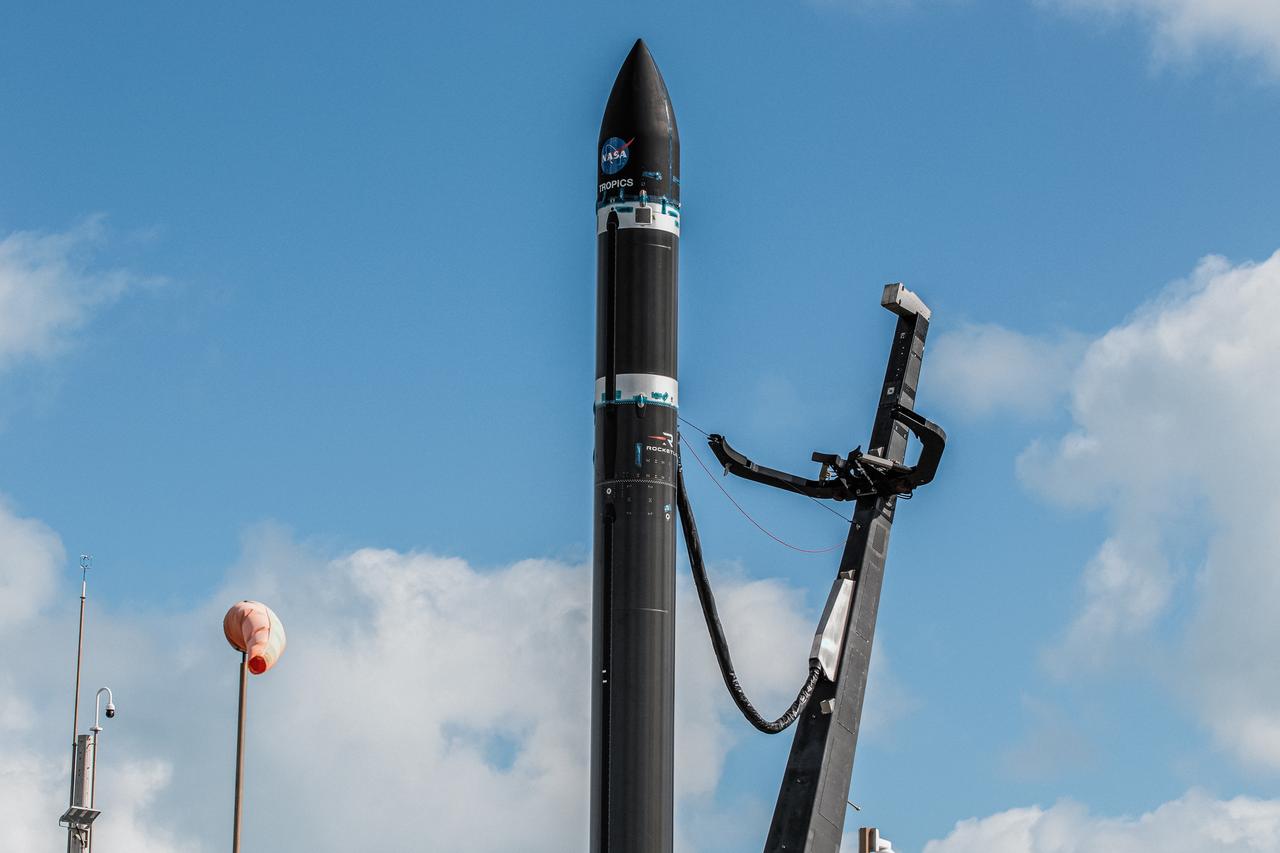

With the umbilical tower in view, Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Two CubeSats are encapsulated at the Rocket Lab facility in Mahia, New Zealand, on April 24, 2023, in preparation for NASA’s second TROPICS (Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), for liftoff of the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
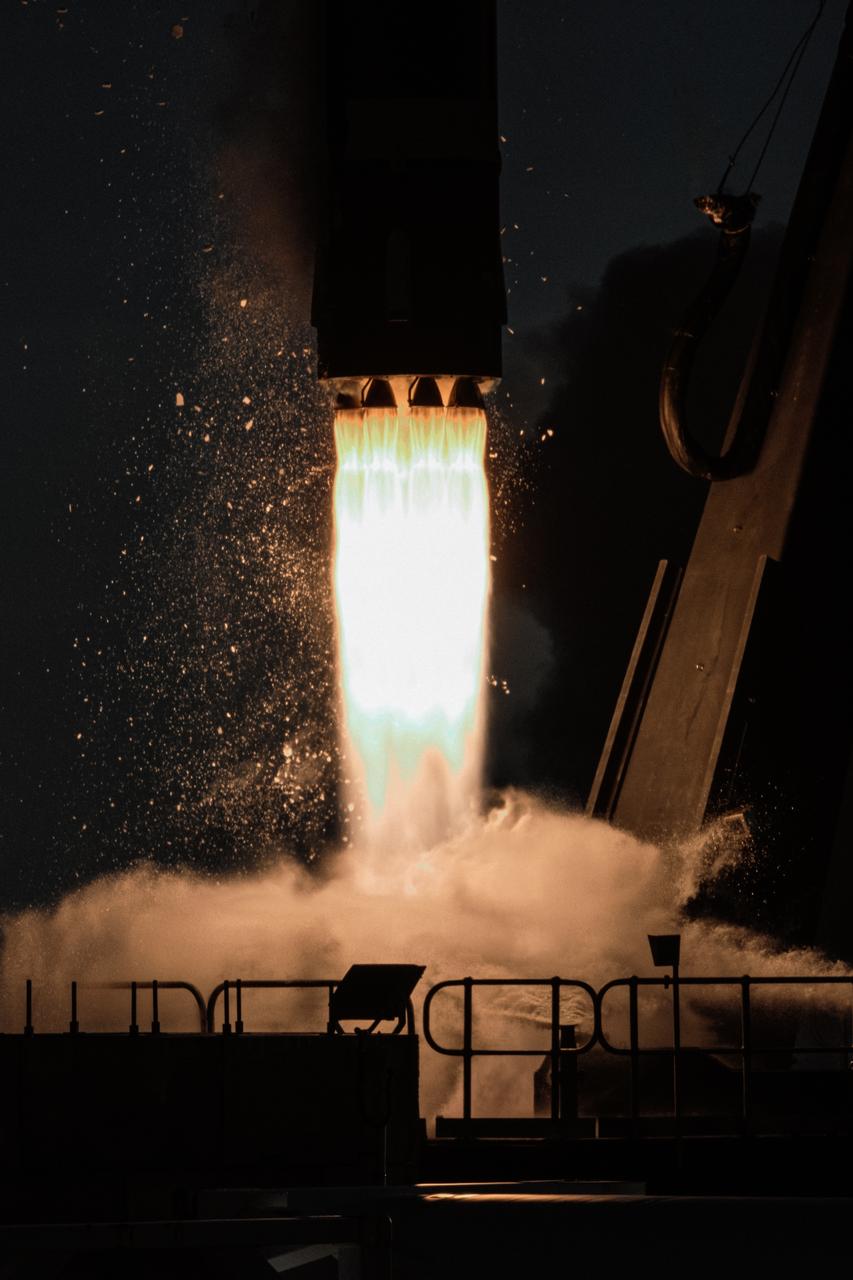

The first stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket ignites at liftoff from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
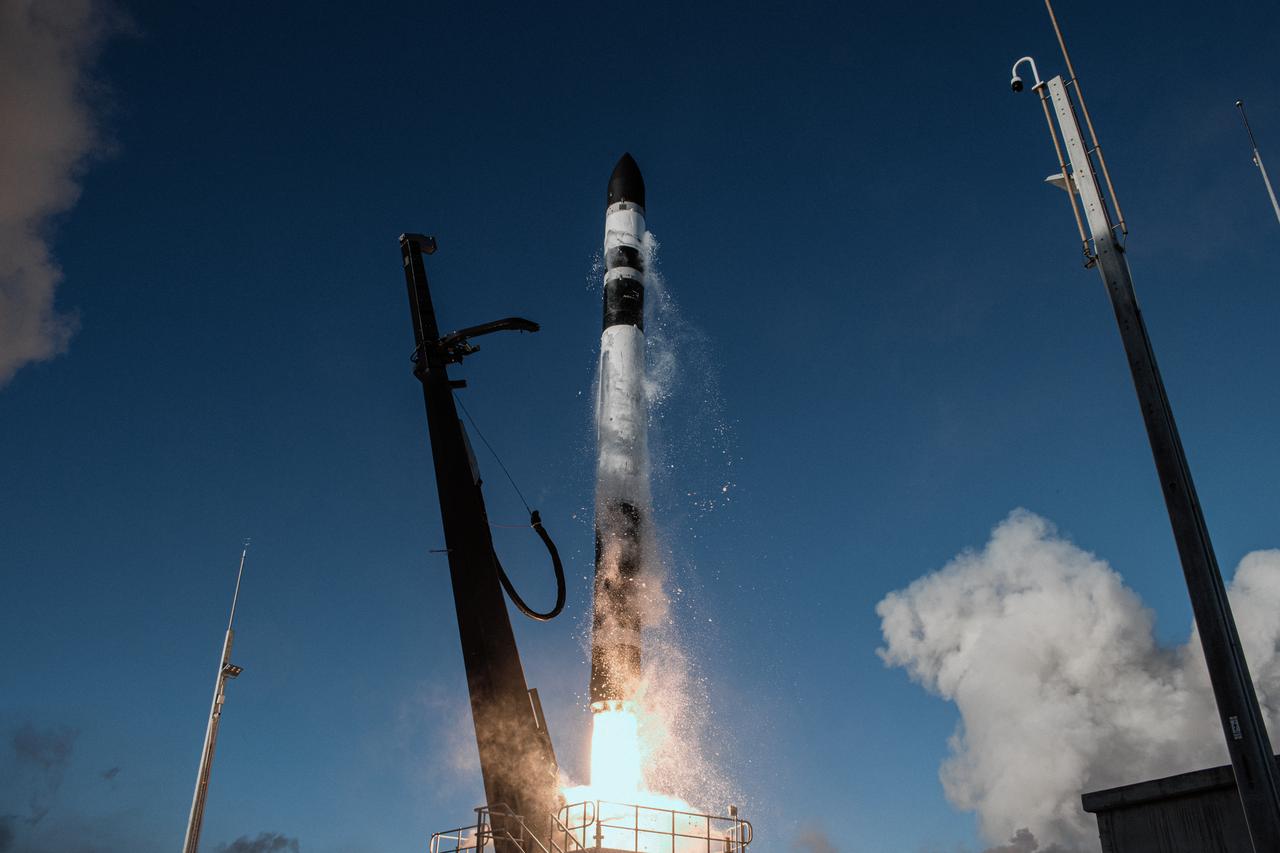

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
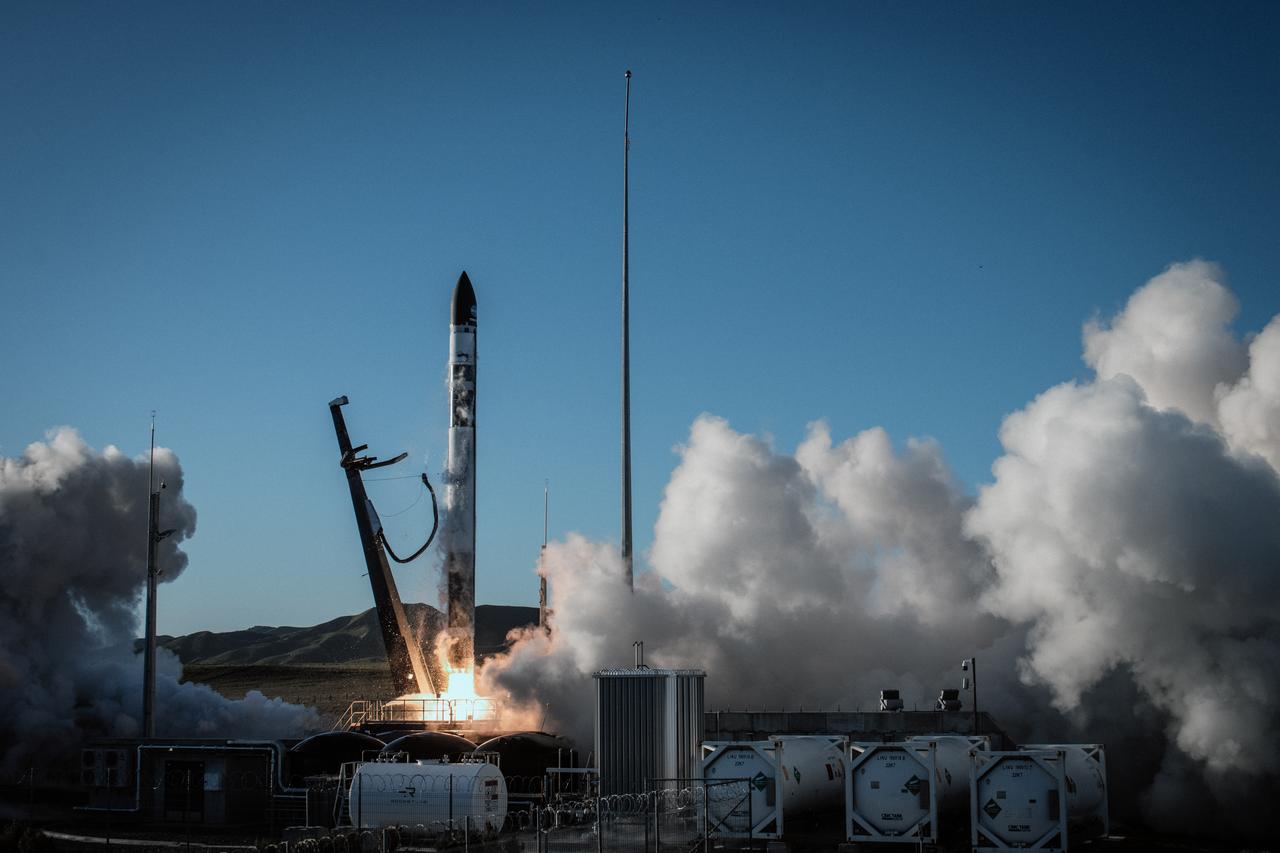

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
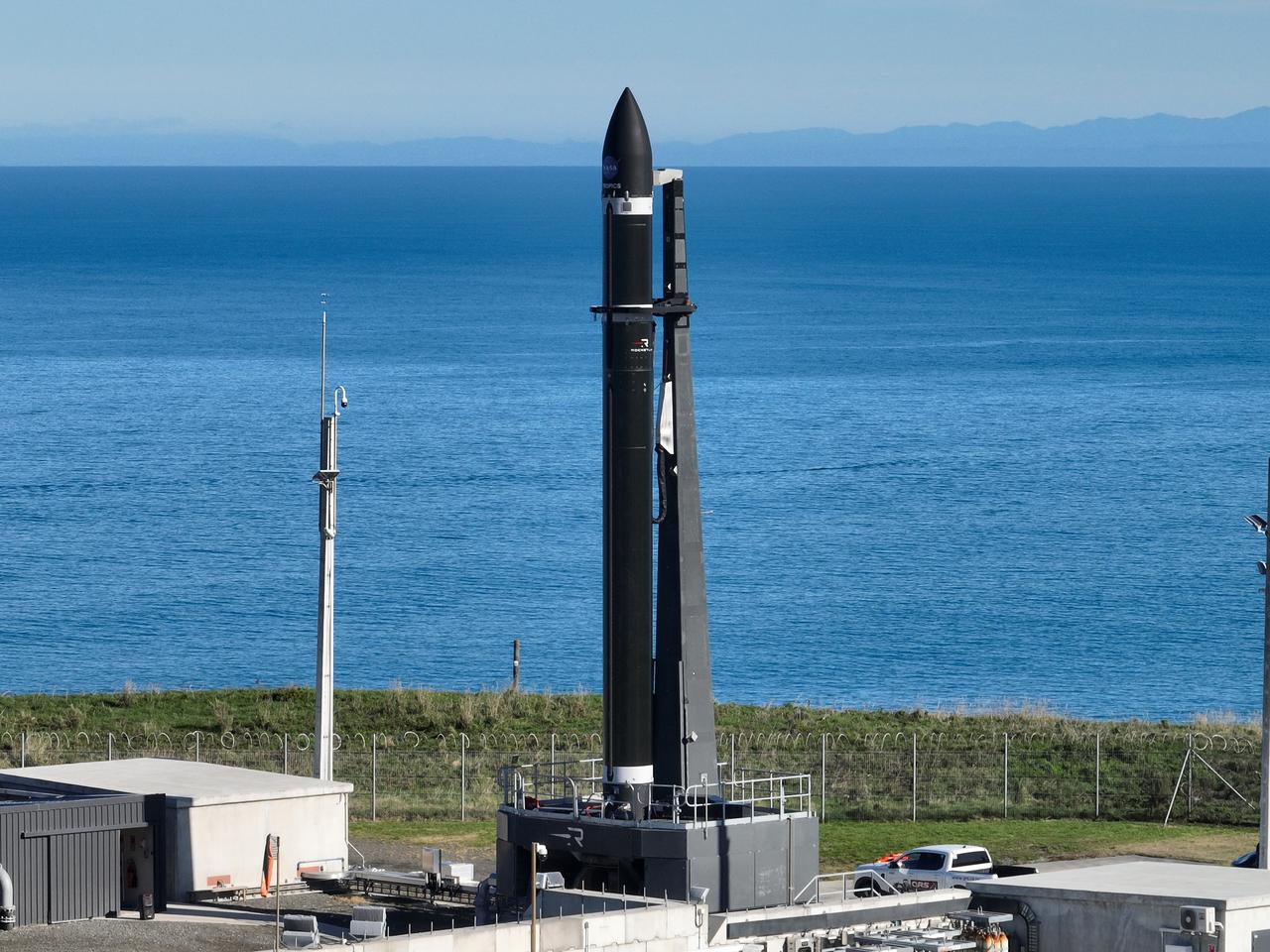

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
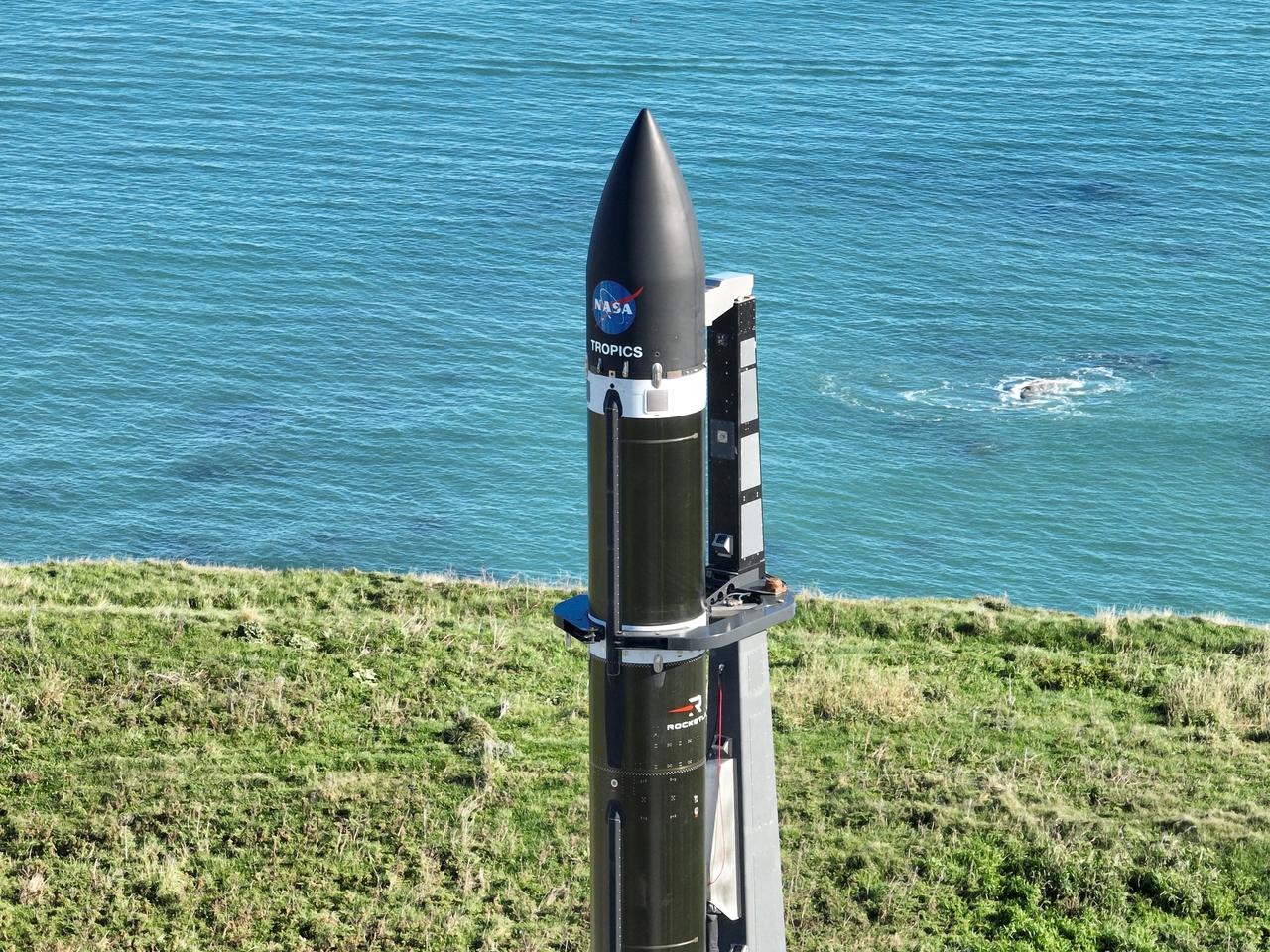

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing is in view inside a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats have been encapsulated inside the payload fairing. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
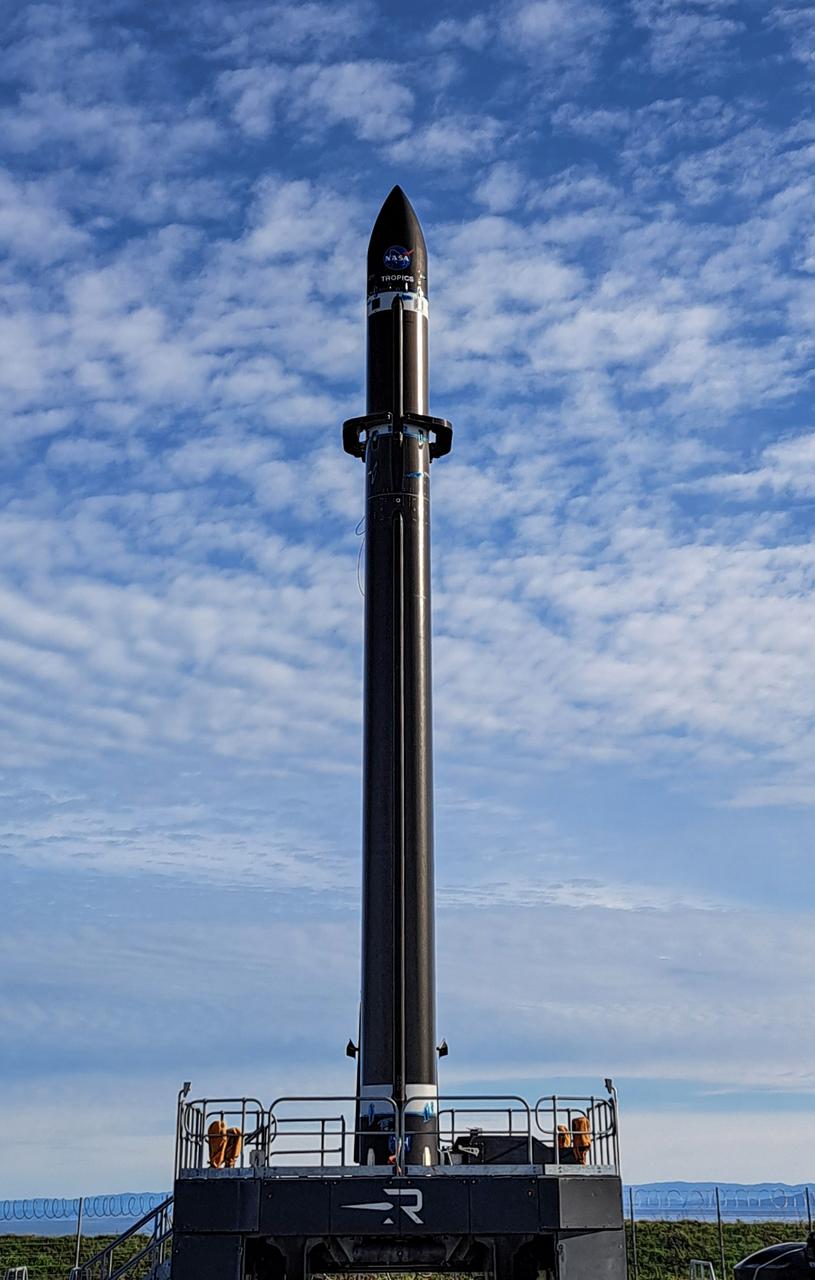

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, during a May 18, 2023, wet dress rehearsal for NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), to launch the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
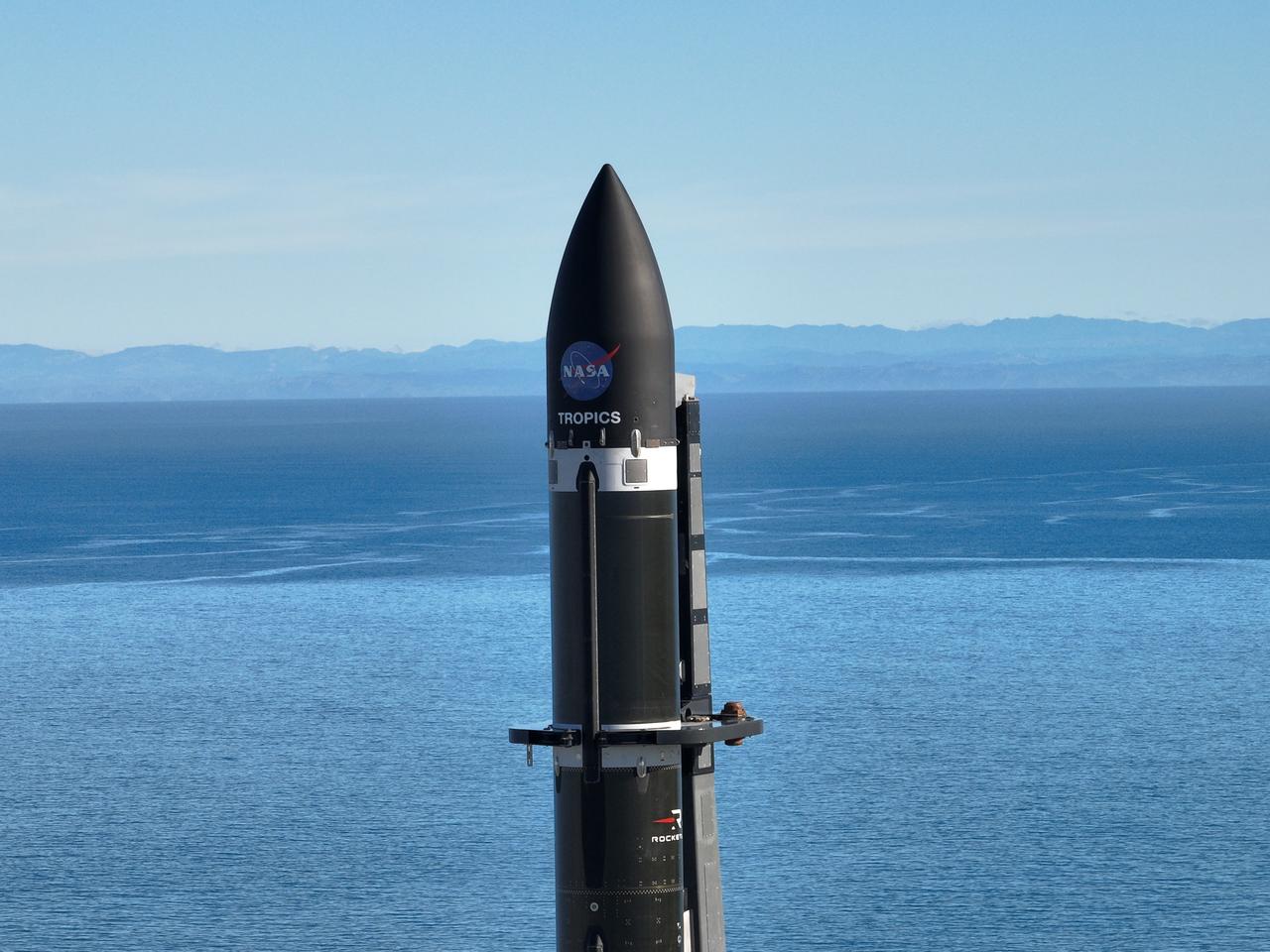

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
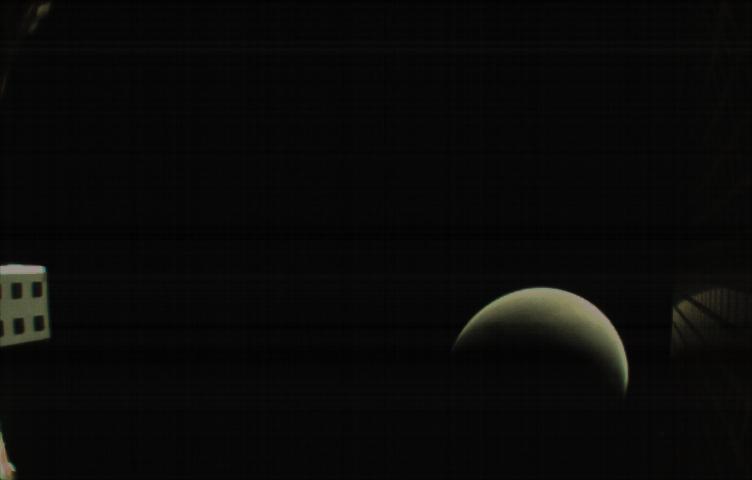

MarCO-B, one of the experimental Mars Cube One (MarCO) CubeSats, took this image of Mars from about 10,900 miles (17,500 kilometers) away just after NASA’s InSight spacecraft landed on Mars on Nov. 26, 2018. MarCO-B flew by Mars with its twin, MarCO-A, to serve as communications relays for InSight as it touched down on the Red Planet around noon PST (3 p.m. EST). This image was taken at 1 p.m. PST (4 p.m. EST). A crescent Mars with its south pole in the 4 o’clock position is visible in this picture. MarCO-B’s antenna reflector mirrors a portion of the illuminated part of Mars on the bottom right. The antenna feed (white rectangle with gold squares) is visible on the left. This image was taken about 50 minutes after PIA22833 and 10 seconds after PIA22832. The MarCO and InSight projects are managed for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, by JPL, a division of Caltech, Pasadena. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
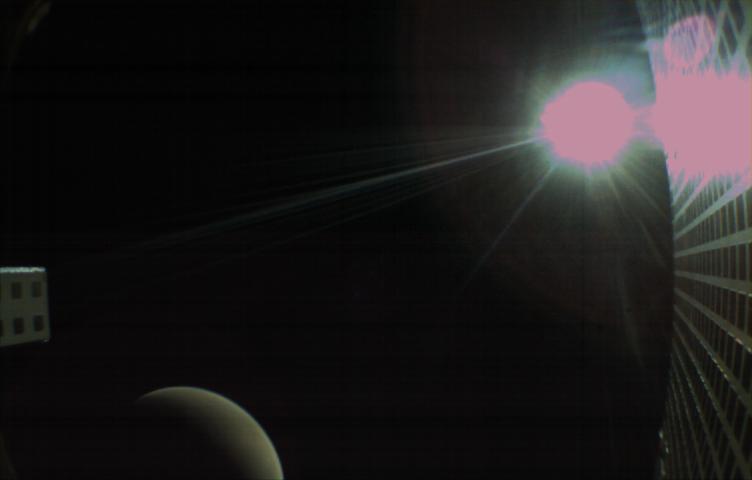

MarCO-B, one of the experimental Mars Cube One (MarCO) CubeSats, took this image of Mars from about 10,900 miles (17,500 kilometers) away just after NASA’s InSight spacecraft landed on Mars on Nov. 26, 2018. MarCO-B flew by Mars with its twin, MarCO-A, to serve as communications relays for InSight as it touched down on the Red Planet around noon PST (3 p.m. EST). This image was taken at 1 p.m. PST (4 p.m. EST). Mars’ south pole is facing the viewer in this image. MarCO-B’s antenna reflector is on the right and antenna feed (white rectangle with gold square) is on the left. The Sun at upper right overexposed part of the image. This image was taken after PIA22833 and shortly before PIA22834. The MarCO and InSight projects are managed for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, by JPL, a division of Caltech, Pasadena. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
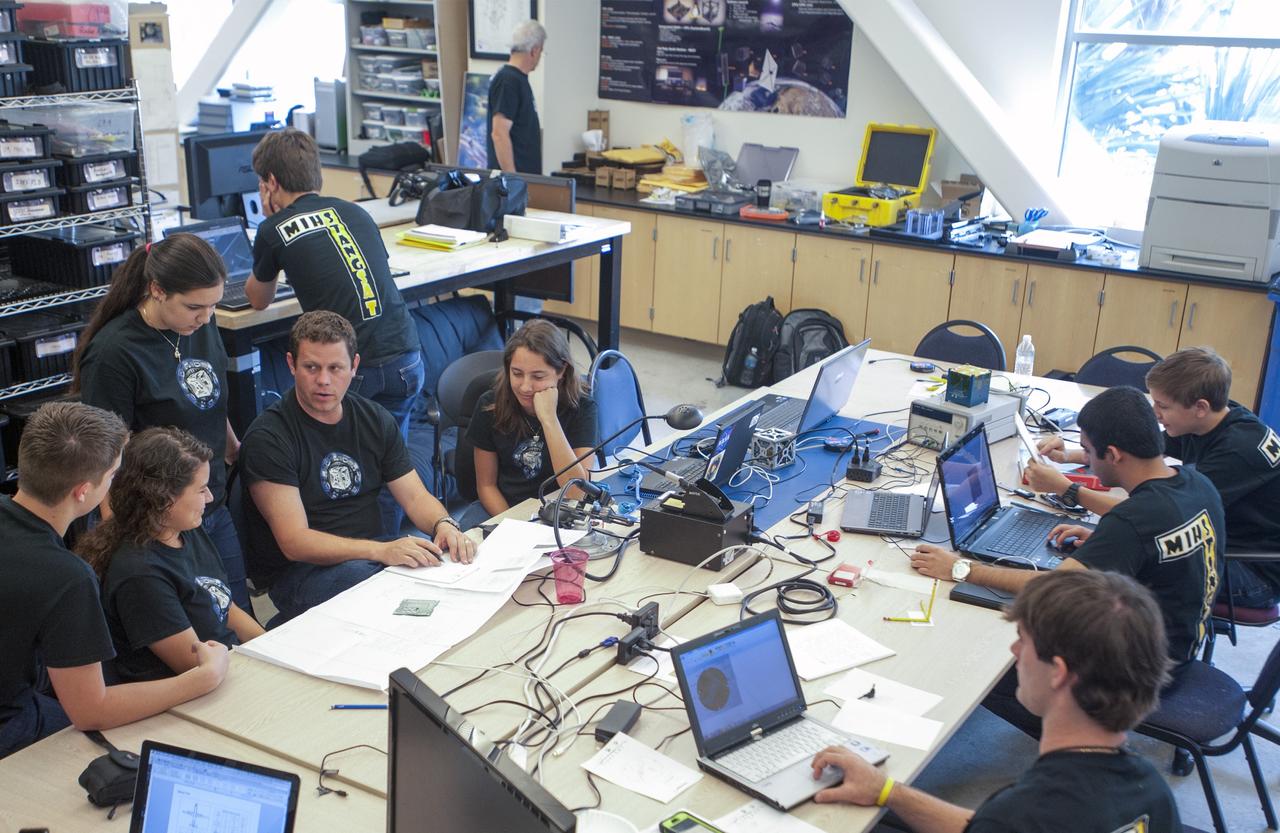

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – NASA mentors and the student launch team for the StangSat and Polysat go through final checks in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payloads, which include sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cubes, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi PeoplesCollectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
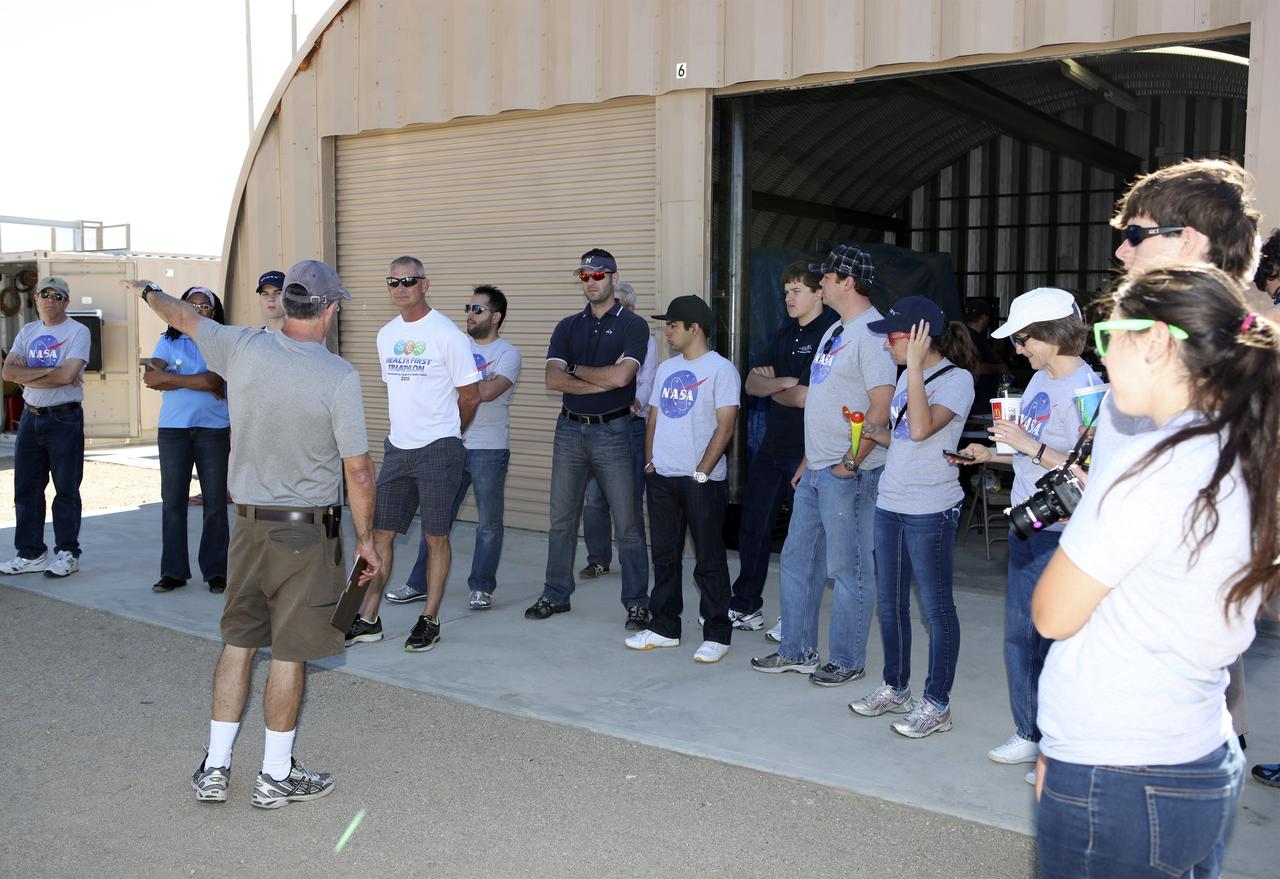

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers participate in a pre-task briefing as preparations continue for the June 15 launch of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation Prospector P-18D rocket on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube section. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
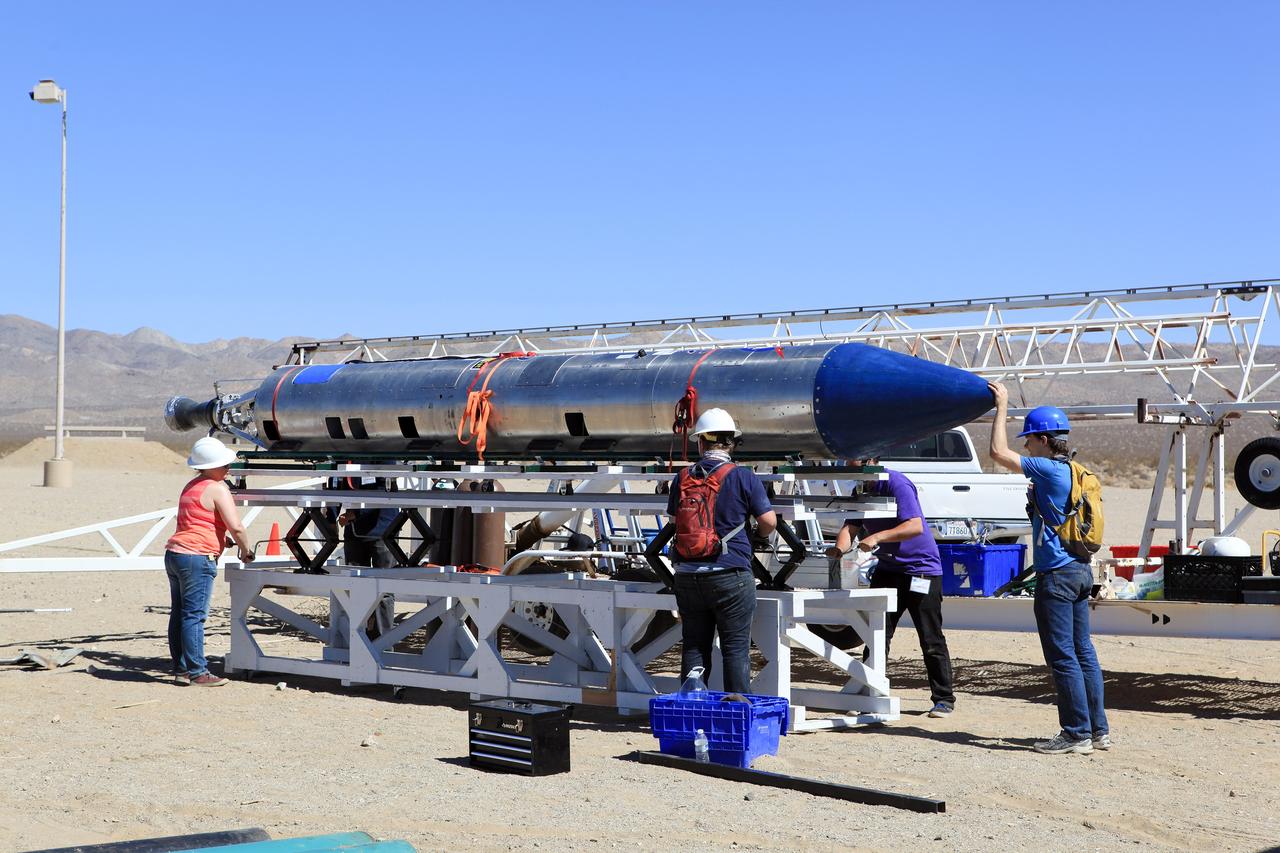

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers checkout the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket at the Friends of Amateur Rocketry launch site. The rocket is scheduled for launch June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital mission. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – NASA mentors and the student launch team for the StangSat and Polysat go through final checks in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payloads, which include sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cubes, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers assist as the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket is lifted into position for its scheduled launch on June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – As the sun rises in the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket is positioned for launch with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers checkout the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket. The rocket is scheduled for launch June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
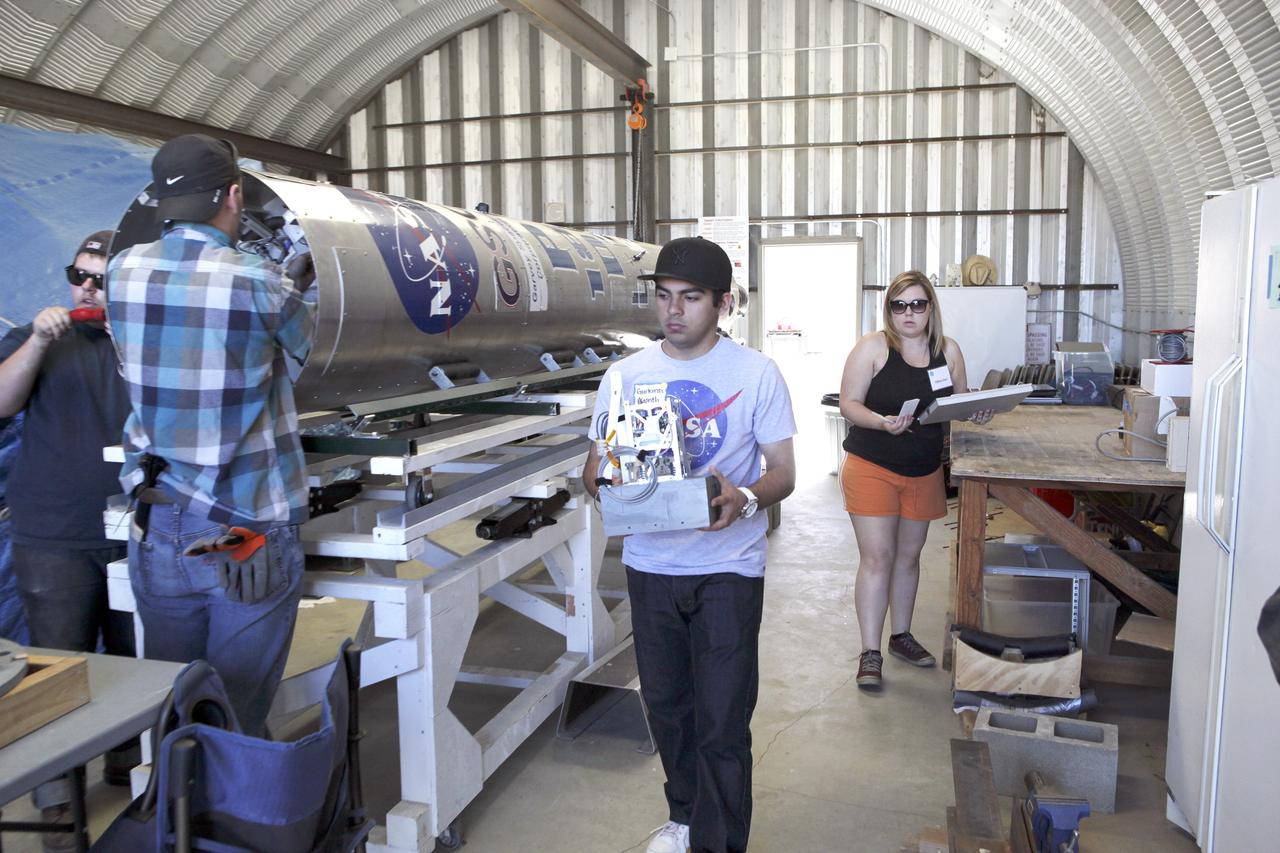

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers prepare to load the RUBICS-1 payload into the body of the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket for launch June 15 on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The flight will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube section. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
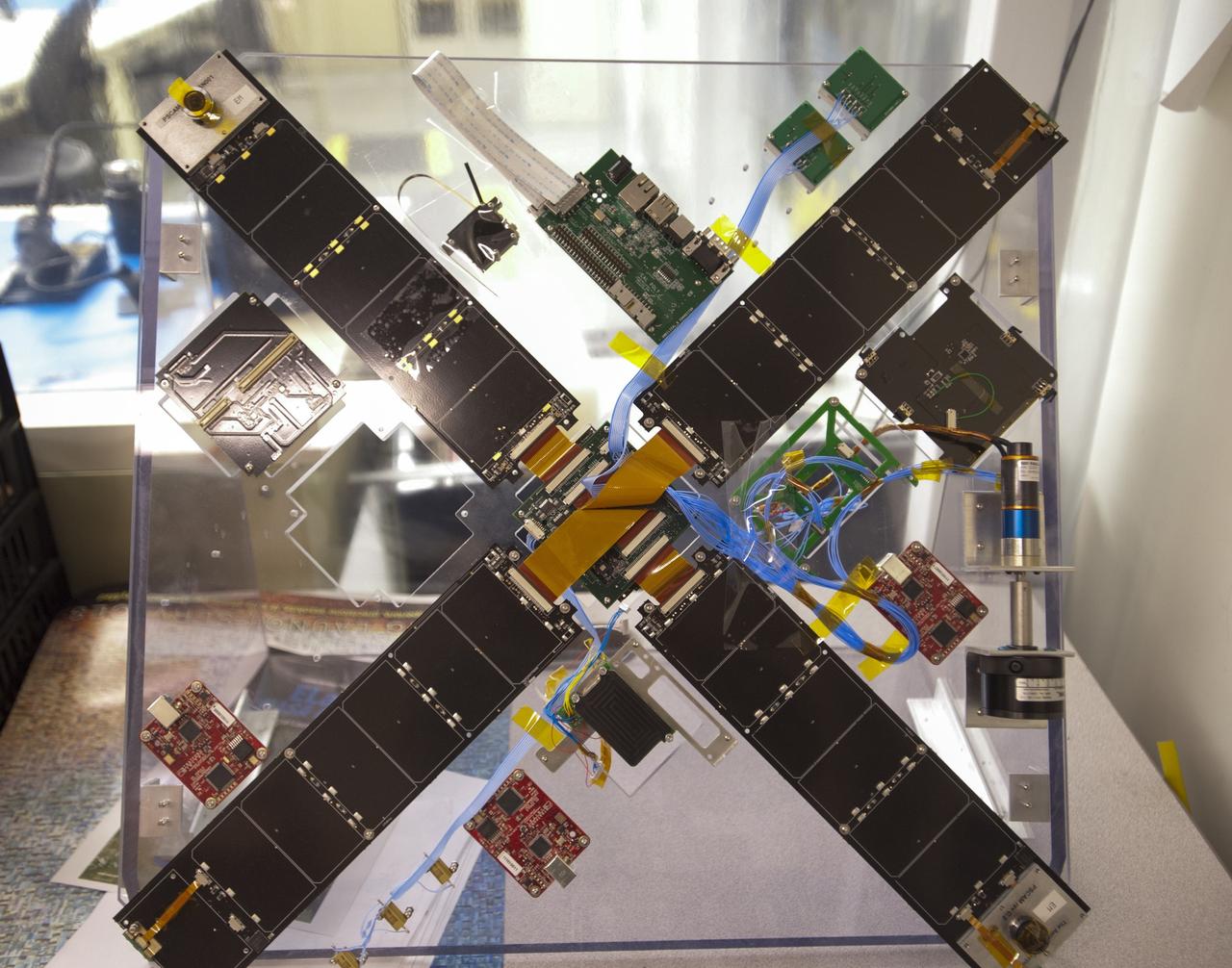
SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – Some of the componentry for the Polysat in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payload, which includes sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cube sections, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Known as a CubeSat, the satellite will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. It will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
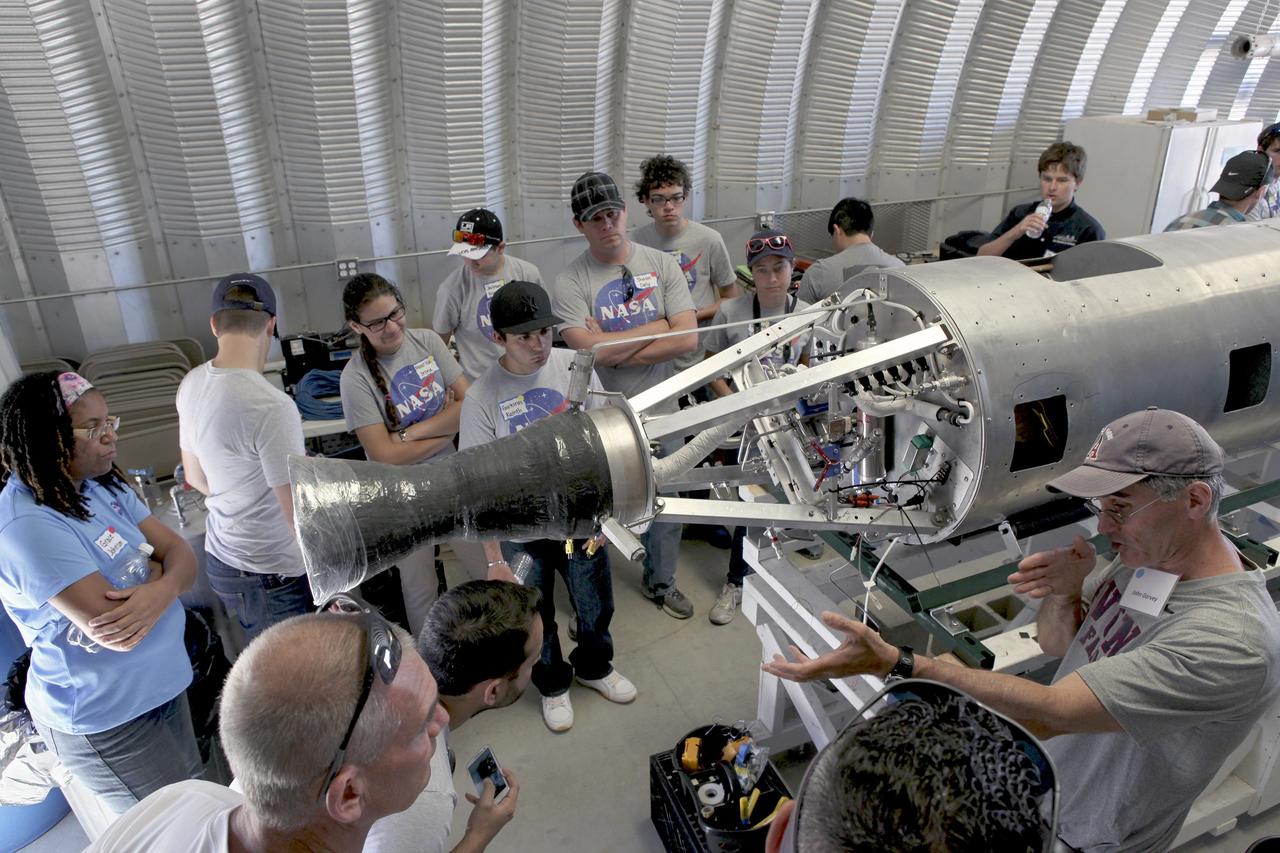

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, John Garvey, far right, describes his company's Prospector-18 rocket. Long Beach, Calif.-based Garvey Spacecraft Corp. built the rocket and its engine. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
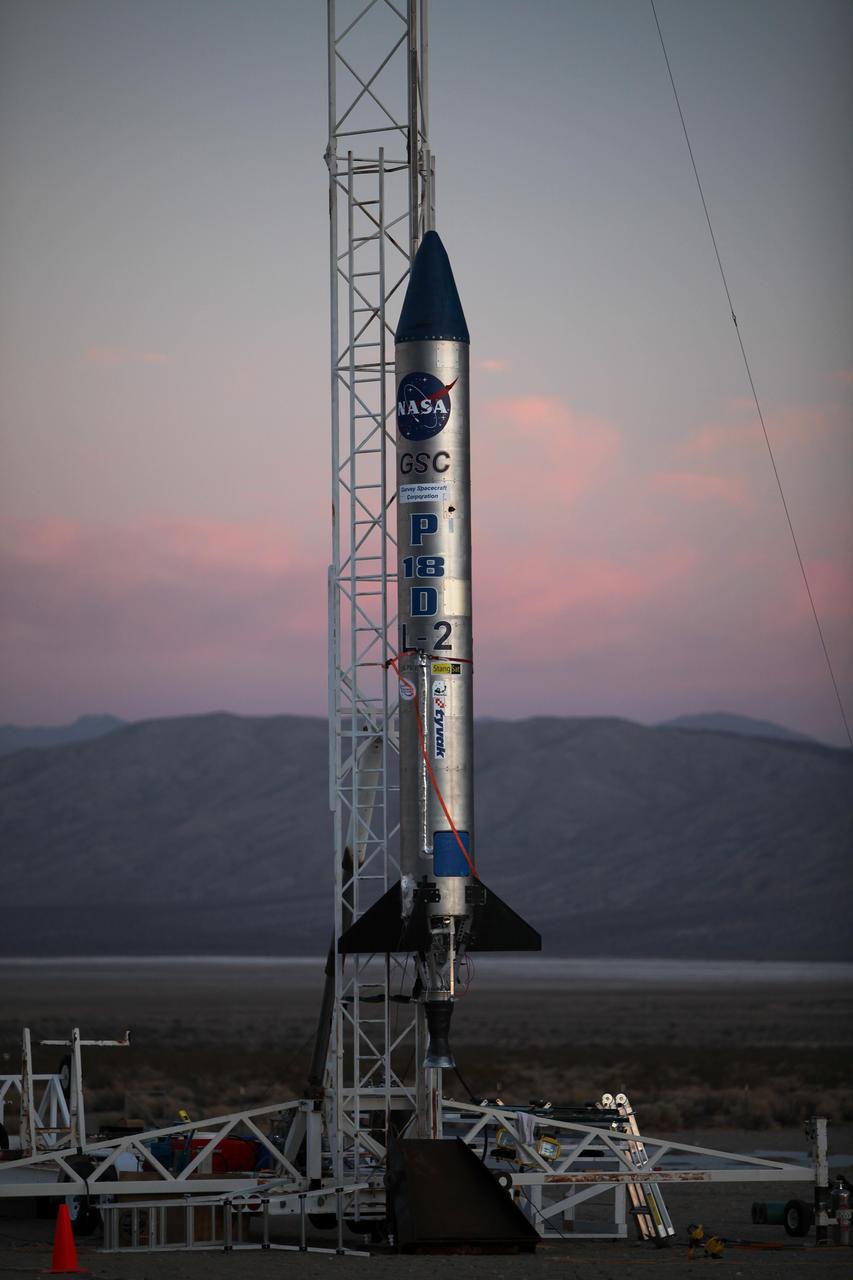

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – As the sun rises in the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket is positioned for launch with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
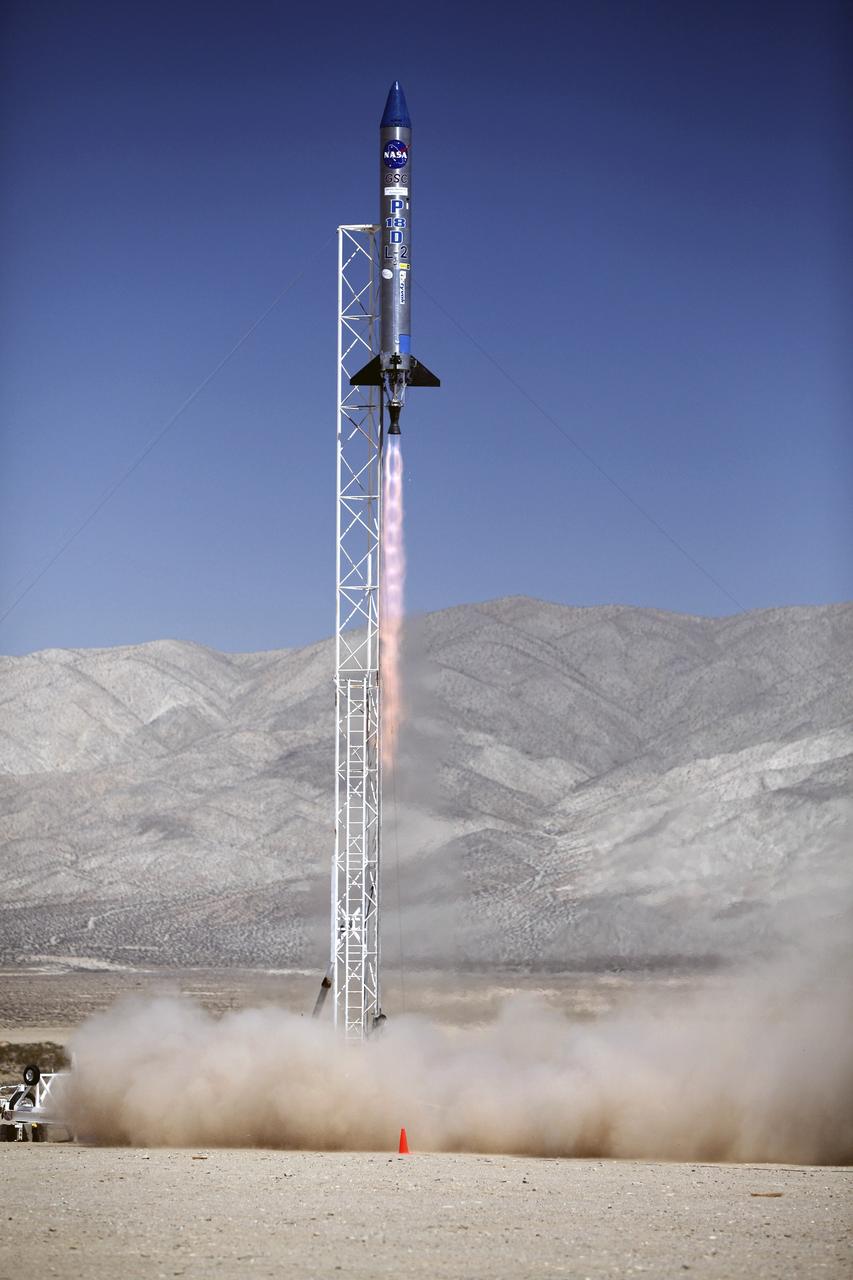

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket lifts off at 10:52 a.m. PDT carrying the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket carried four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
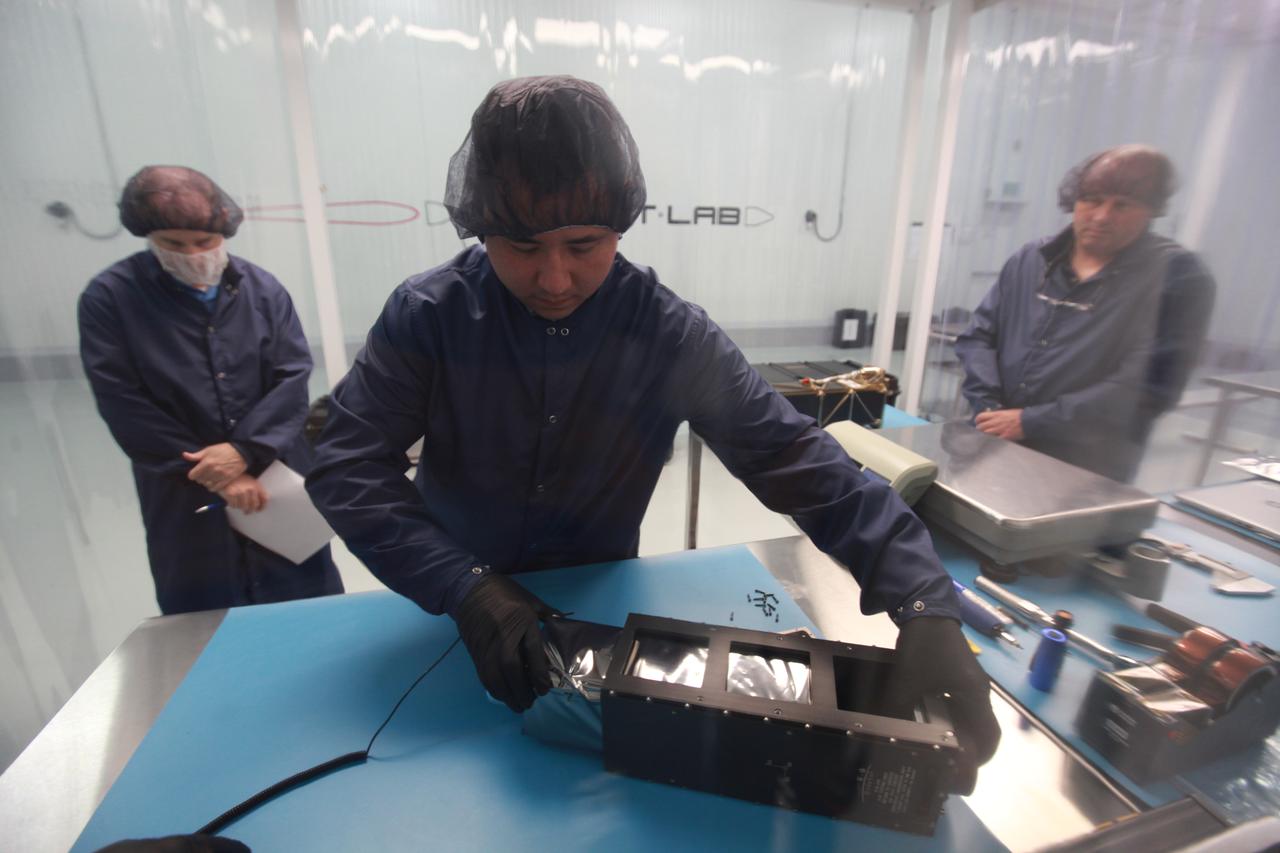

The NASA Langley Research Center (LaRC) Shields-1 CubeSat will demonstrate a research payload with materials durability experiments on emerging radiation shielding technologies. Shields-1 incorporates eight mdosimeters for radiation shielding experiments: one in the atomic number (Z)-grade radiation shielding vault, three behind experimental Z-grade radiation shielding samples developed at NASA LaRC, three behind baseline aluminum shielding samples, and one deep inside the research payload. The Z-grade is defined as an atomic number gradient of shielding materials using a low atomic number metal, such as aluminum, with a high atomic number material, like tantalum. The metals are fabricated into the vault structure. Also, Shields-1 measures a charge dissipation film resistance for technology development. The Shields-1 mission contributes to the SmallSat community with the development of technologies to increase the lifetimes of CubeSat missions from months to years in multiple radiation environments and increase the return on investment for scientific and commercial spacecraft.
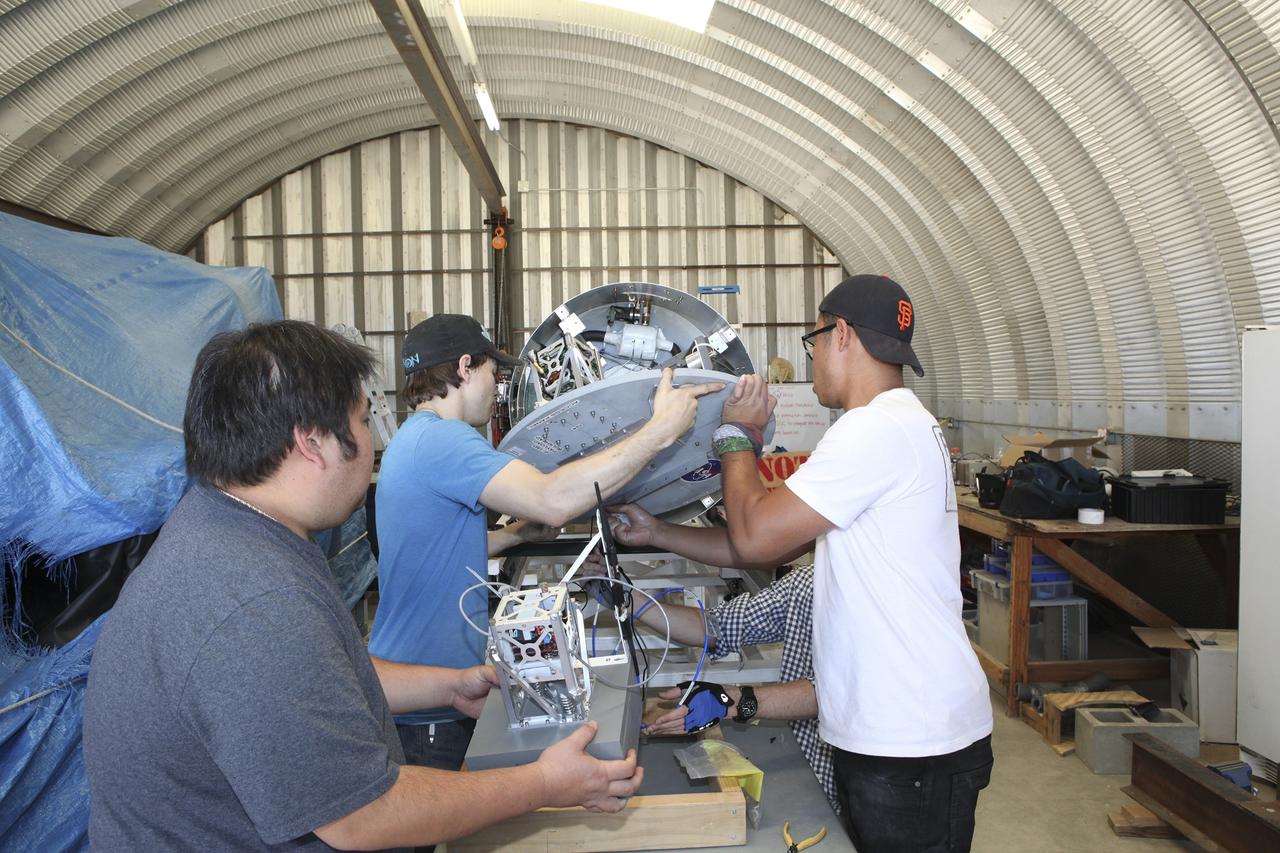

In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers checkout the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket engine. The rocket is scheduled for launch June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube section. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
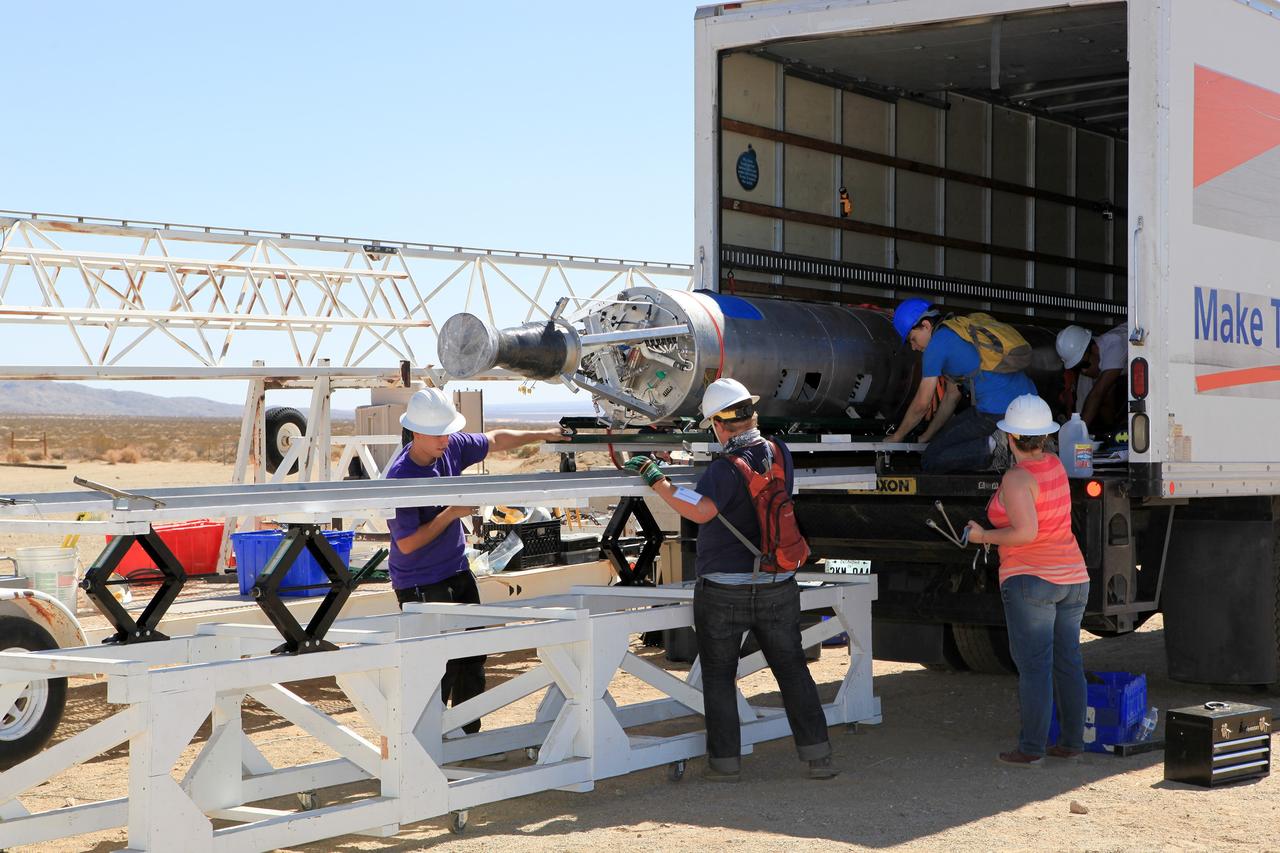

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers unload the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket from a truck at the launch site. The rocket is scheduled for launch June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
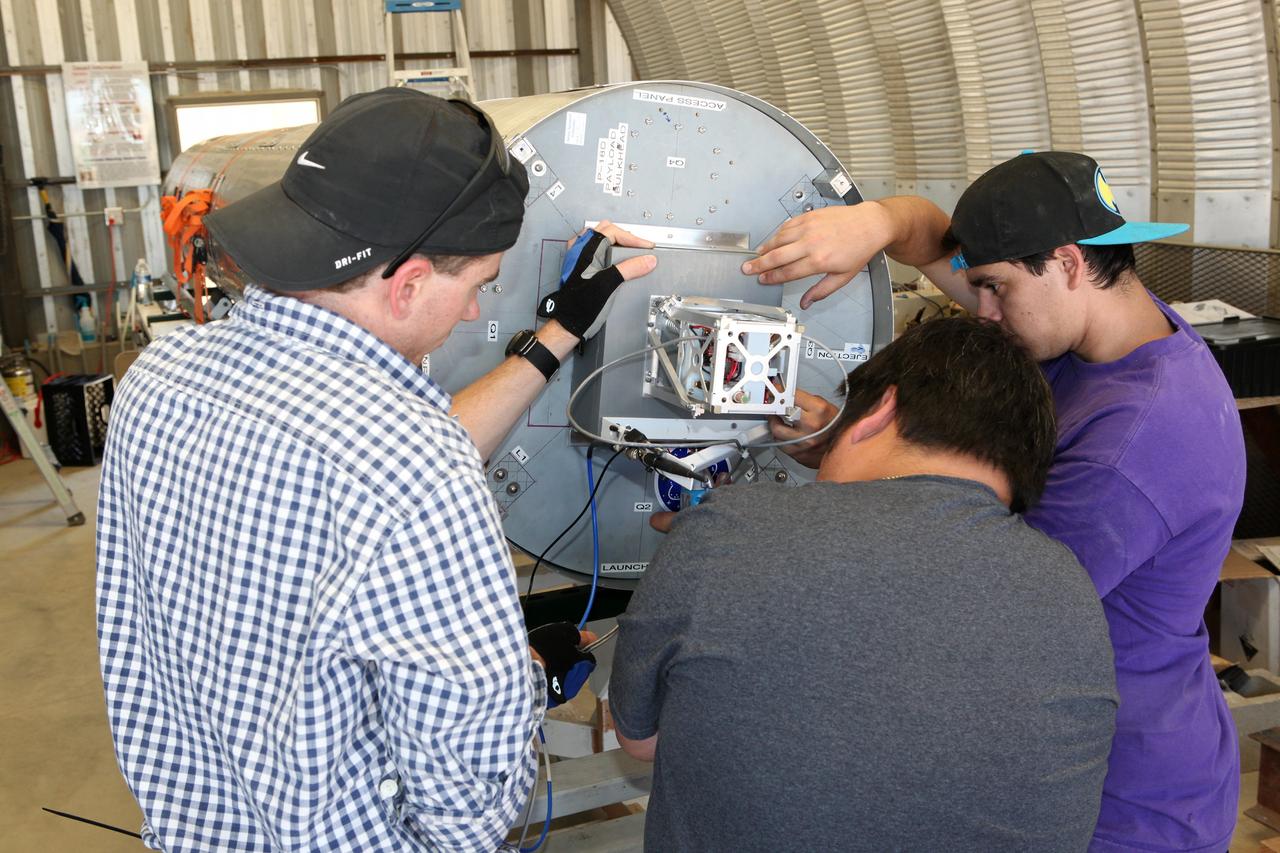

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers checkout the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket. The rocket is scheduled for launch June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
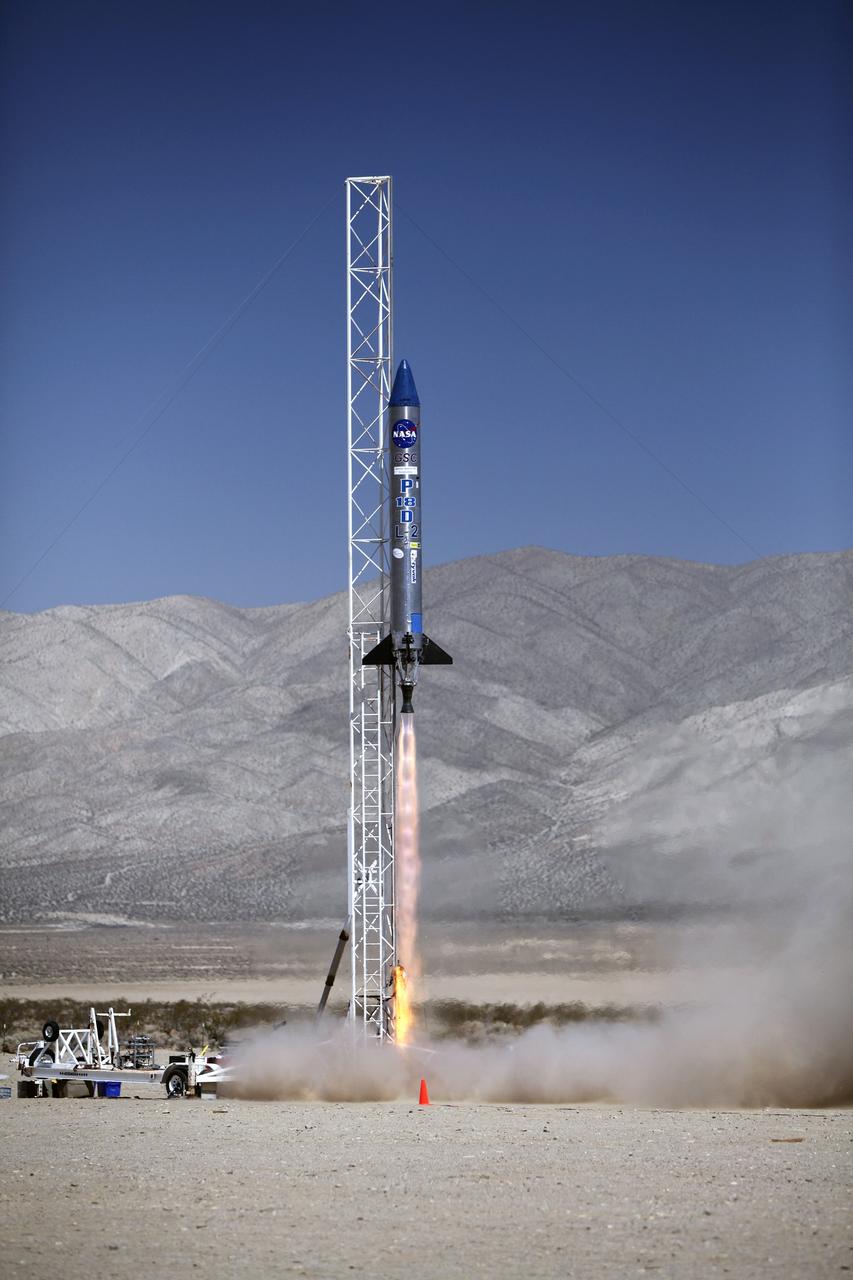

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket lifts off at 10:52 a.m. PDT carrying the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket carried four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
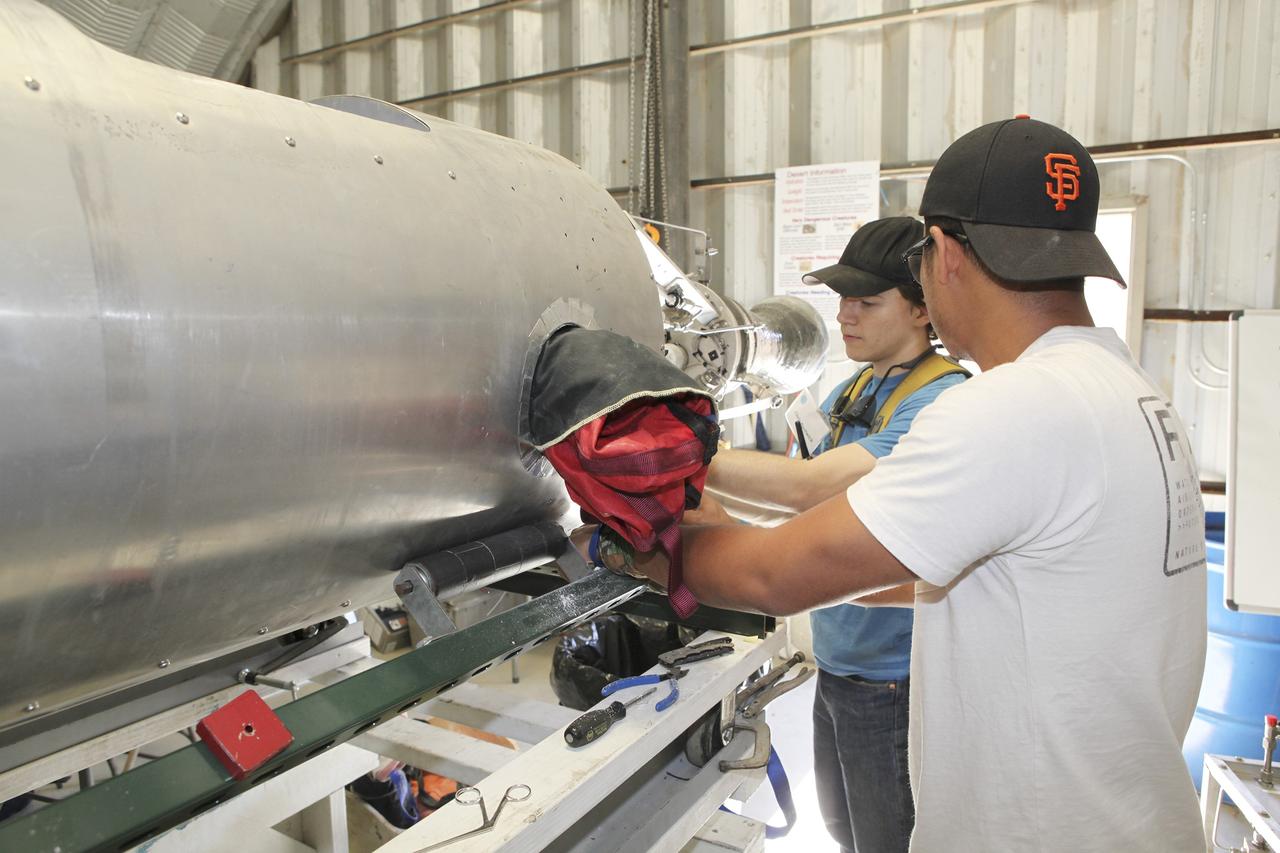

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers pack the parachute in the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket. The work is in preparation for the June 15 launch of a on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube section. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

This illustration shows NASA's Lunar Flashlight carrying out a trajectory correction maneuver with the Moon and Earth in the background. Powered by the small satellite's four thrusters, the maneuver is needed to reach lunar orbit. Lunar Flashlight launched Nov. 30, 2022, and will take about four months to reach its science orbit to seek out surface water ice in the darkest craters of the Moon's South Pole. A technology demonstration, the small satellite, or SmallSat, will use a reflectometer equipped with four lasers that emit near-infrared light in wavelengths readily absorbed by surface water ice. To achieve the mission's goals with the satellite's limited amount of propellent, Lunar Flashlight will employ an energy-efficient near-rectilinear halo orbit, taking it within 9 miles (15 kilometers) of the lunar South Pole and 43,000 miles (70,000 kilometers) away at its farthest point. Only one other spacecraft has employed this type of orbit: NASA's Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment (CAPSTONE) mission, which launched in June 2022. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25258
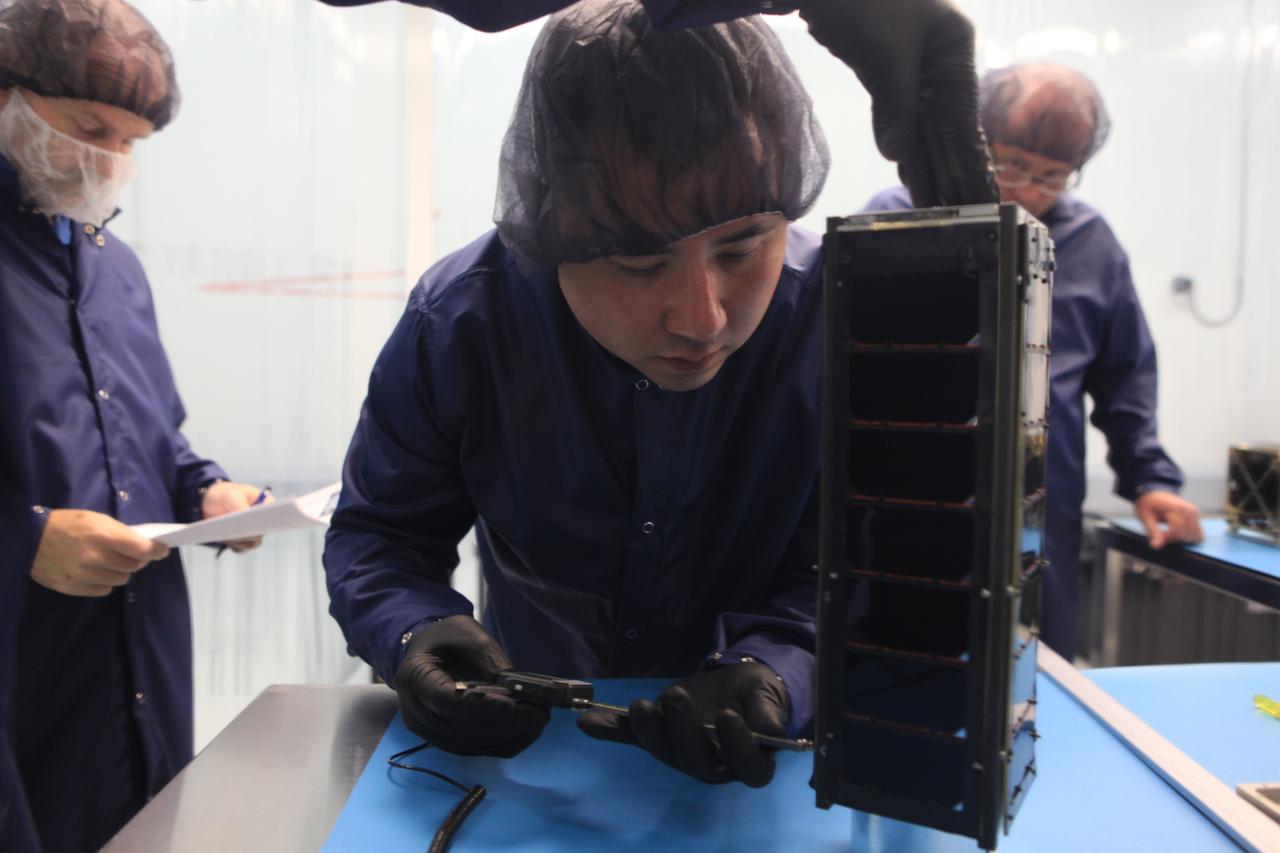

The NASA Langley Research Center (LaRC) Shields-1 CubeSat will demonstrate a research payload with materials durability experiments on emerging radiation shielding technologies. Shields-1 incorporates eight mdosimeters for radiation shielding experiments: one in the atomic number (Z)-grade radiation shielding vault, three behind experimental Z-grade radiation shielding samples developed at NASA LaRC, three behind baseline aluminum shielding samples, and one deep inside the research payload. The Z-grade is defined as an atomic number gradient of shielding materials using a low atomic number metal, such as aluminum, with a high atomic number material, like tantalum. The metals are fabricated into the vault structure. Also, Shields-1 measures a charge dissipation film resistance for technology development. The Shields-1 mission contributes to the SmallSat community with the development of technologies to increase the lifetimes of CubeSat missions from months to years in multiple radiation environments and increase the return on investment for scientific and commercial spacecraft.
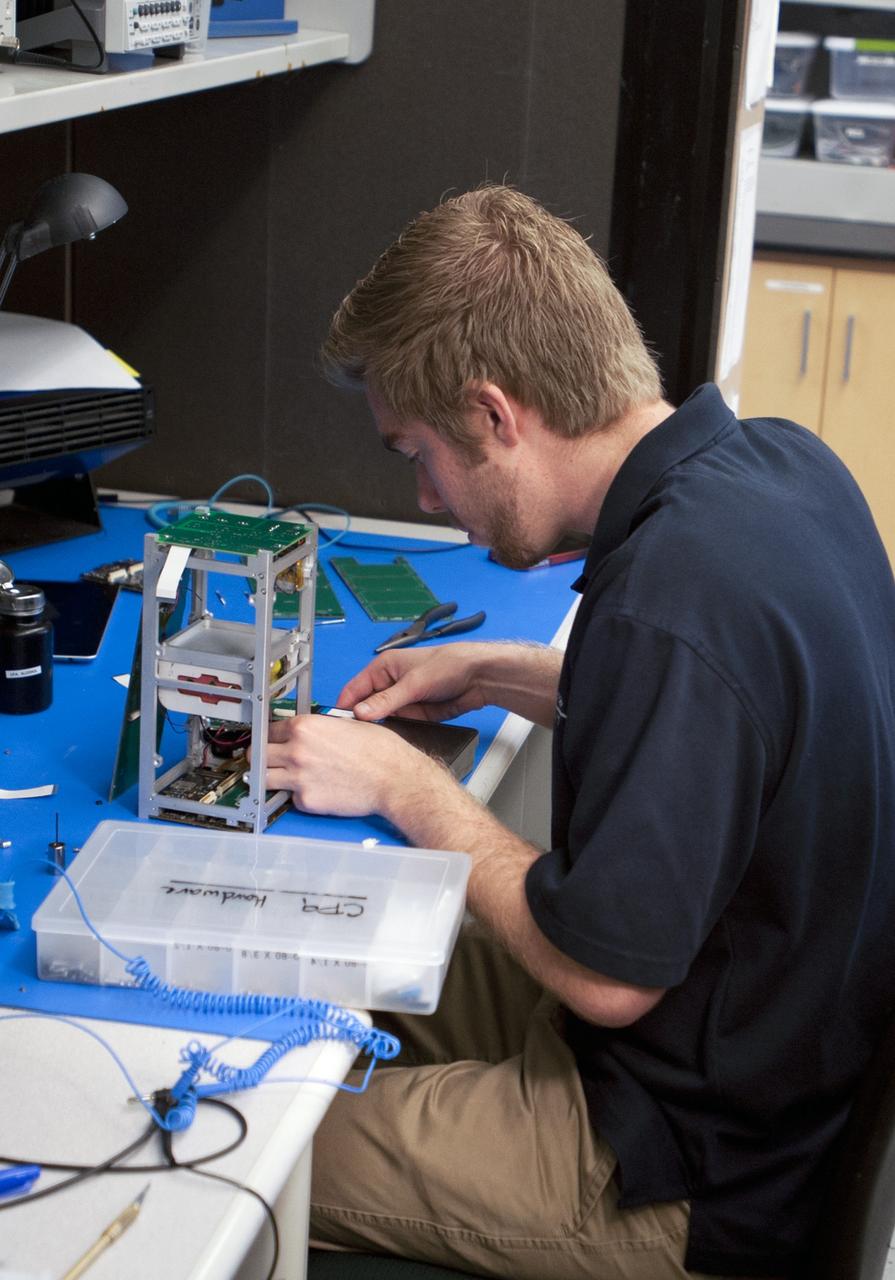

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – A member of the student launch team for the Polysat works through final checks in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payloads, which include sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cubes, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
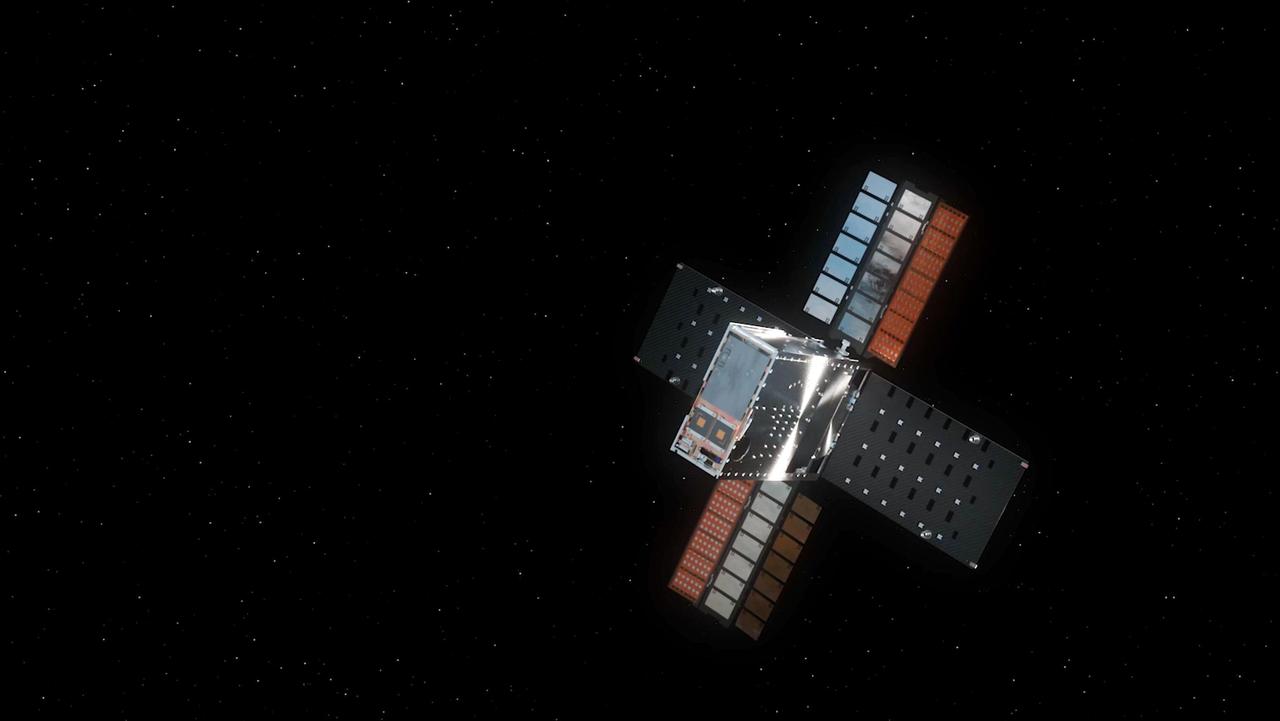

This illustration shows NASA's Lunar Flashlight, with its four solar arrays deployed, shortly after launch. The small satellite, or SmallSat, launched Nov. 30, 2022, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket as a rideshare with ispace's HAKUTO-R Mission 1. It will take about three months to reach its science orbit to seek out surface water ice in the darkest craters of the Moon's South Pole. A technology demonstration, Lunar Flashlight will use a reflectometer equipped with four lasers that emit near-infrared light in wavelengths readily absorbed by surface water ice. This is the first time that multiple colored lasers will be used to seek out ice inside these dark regions on the Moon, which haven't seen sunlight in billions of years. Should the lasers hit bare rock or regolith (broken rock and dust), the light will reflect back to the spacecraft. But if the target absorbs the light, that would indicate the presence of water ice. The greater the absorption, the more ice there may be. The science data collected by the mission will be compared with observations made by other lunar missions to help reveal the distribution of surface water ice on the Moon for potential use by future astronauts. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25626
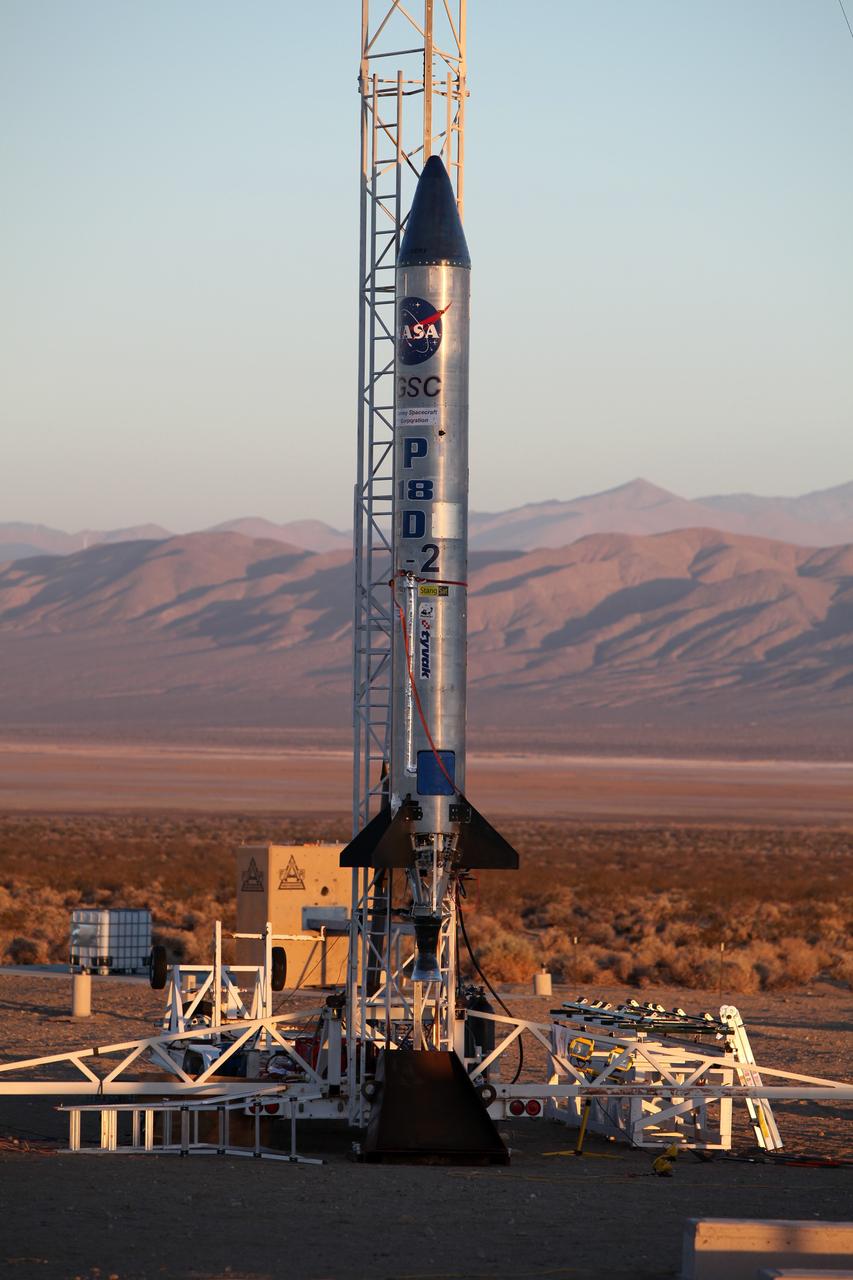

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – As the sun rises in the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket is positioned for launch with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
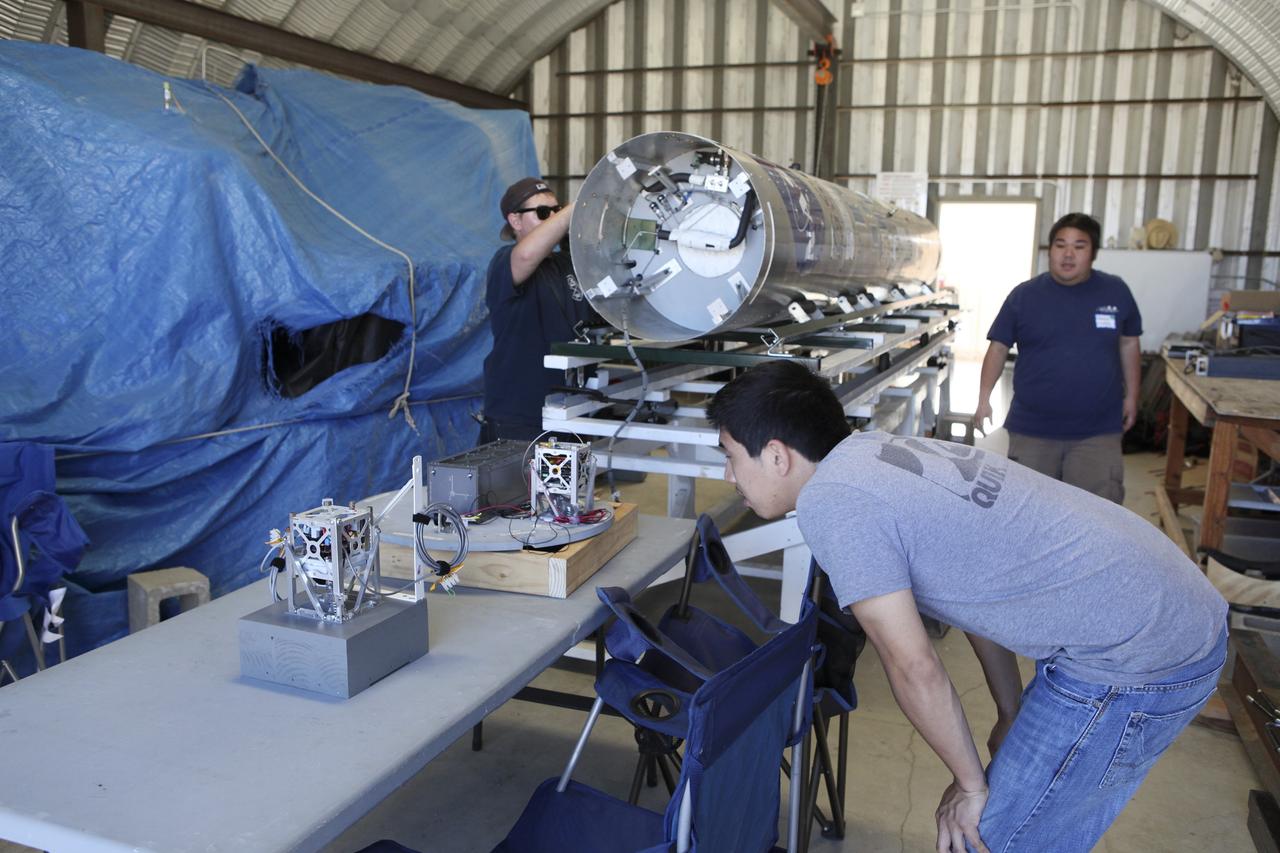

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers checkout the RUBICS-1 payload which will be placed into the body of the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket for launch June 15 on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The flight will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube section. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
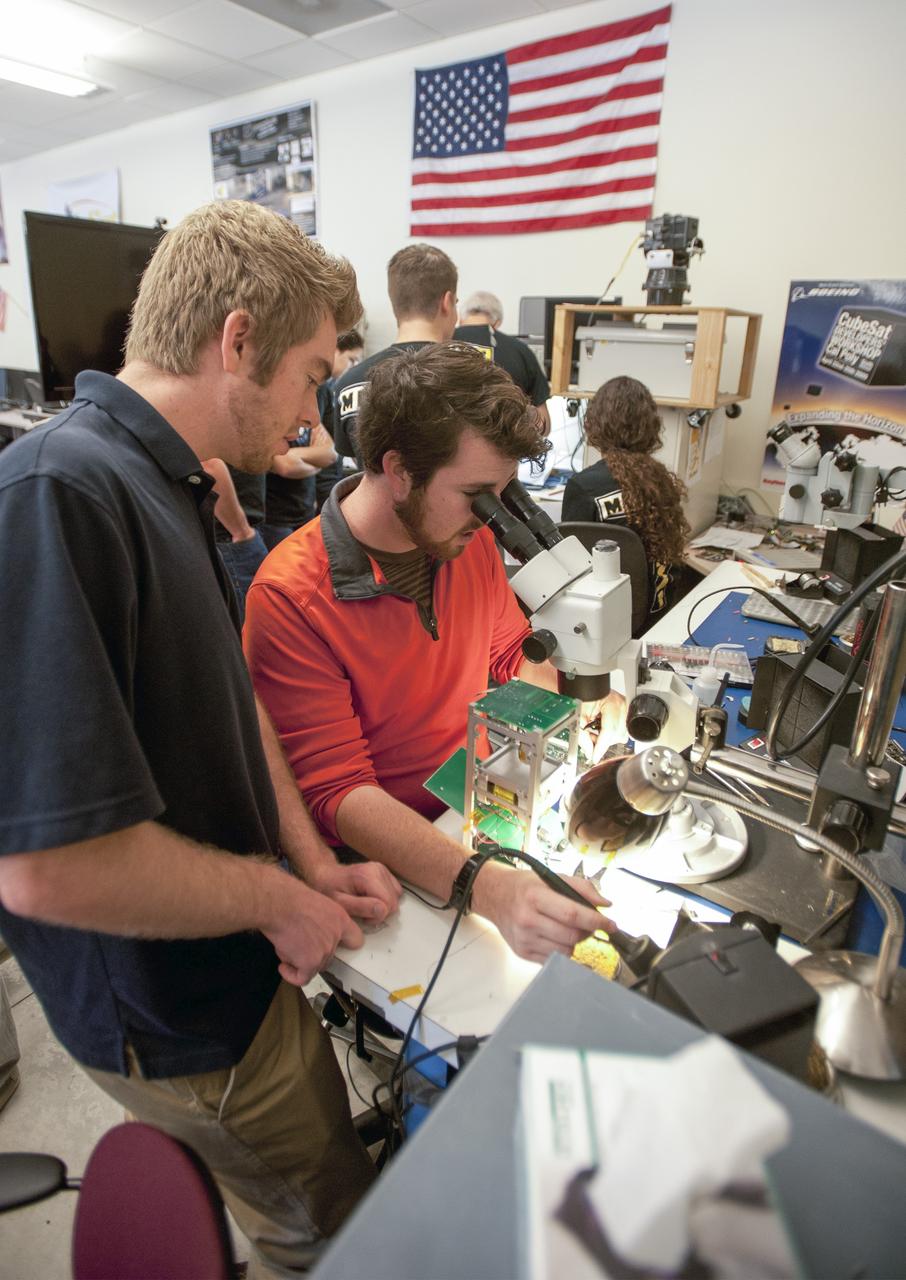

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – Members of the student launch team for the Polysat works through final checks in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payload, which includes sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cube sections, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Known as a CubeSat, the satellite will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. It will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
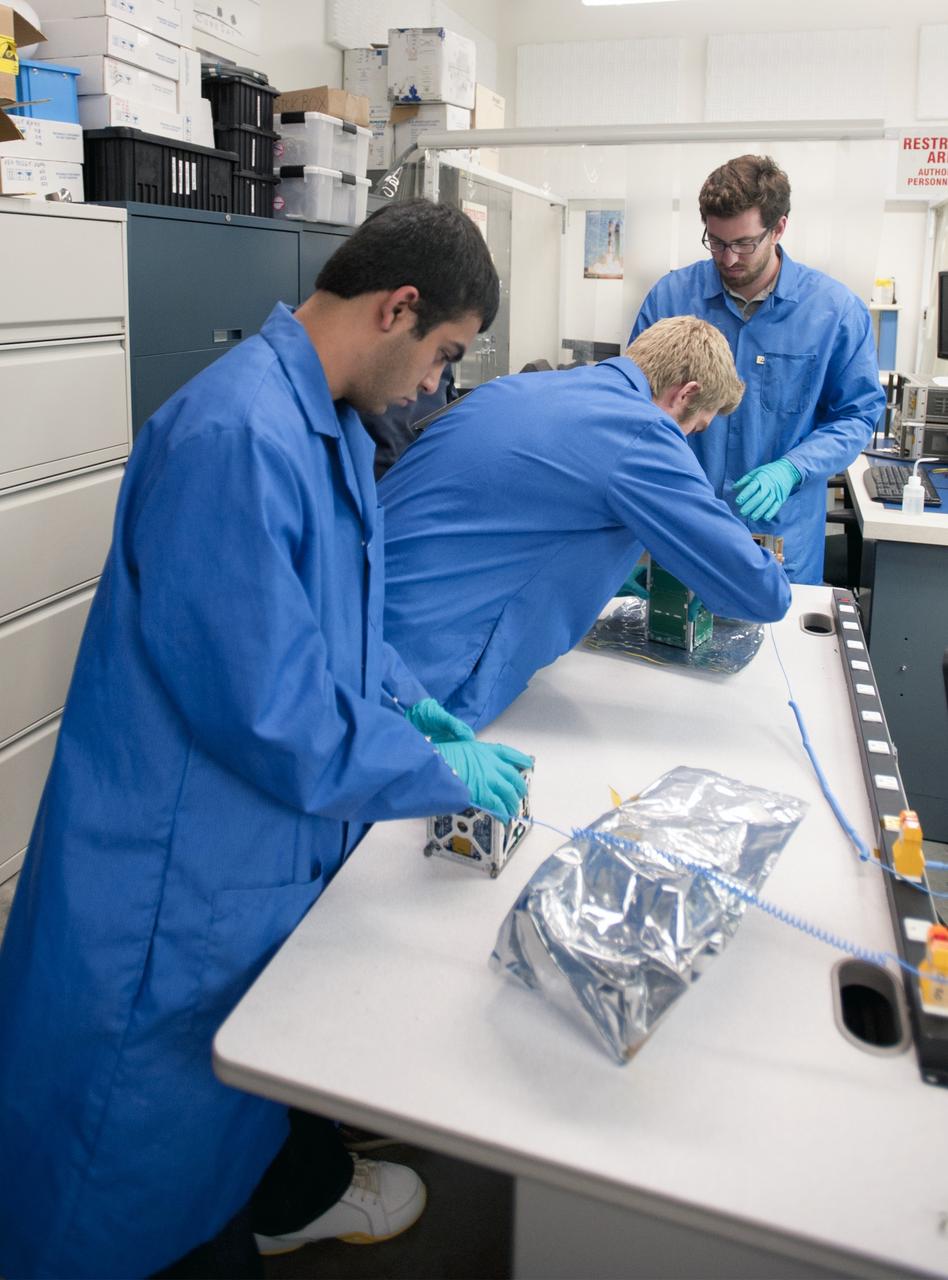

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. –Members of the student launch team for the Polysat works through final checks in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payload, which includes sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cube sections, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Known as a CubeSat, the satellite will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. It will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers watch as the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket is lifted into position for its scheduled launch on June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket lifts off at 10:52 a.m. PDT carrying the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket carried four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket lifts off at 10:52 a.m. PDT carrying the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket carried four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, final checkouts are completed on the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket positioned for launch with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

The NASA Langley Research Center (LaRC) Shields-1 CubeSat will demonstrate a research payload with materials durability experiments on emerging radiation shielding technologies. Shields-1 incorporates eight mdosimeters for radiation shielding experiments: one in the atomic number (Z)-grade radiation shielding vault, three behind experimental Z-grade radiation shielding samples developed at NASA LaRC, three behind baseline aluminum shielding samples, and one deep inside the research payload. The Z-grade is defined as an atomic number gradient of shielding materials using a low atomic number metal, such as aluminum, with a high atomic number material, like tantalum. The metals are fabricated into the vault structure. Also, Shields-1 measures a charge dissipation film resistance for technology development. The Shields-1 mission contributes to the SmallSat community with the development of technologies to increase the lifetimes of CubeSat missions from months to years in multiple radiation environments and increase the return on investment for scientific and commercial spacecraft.
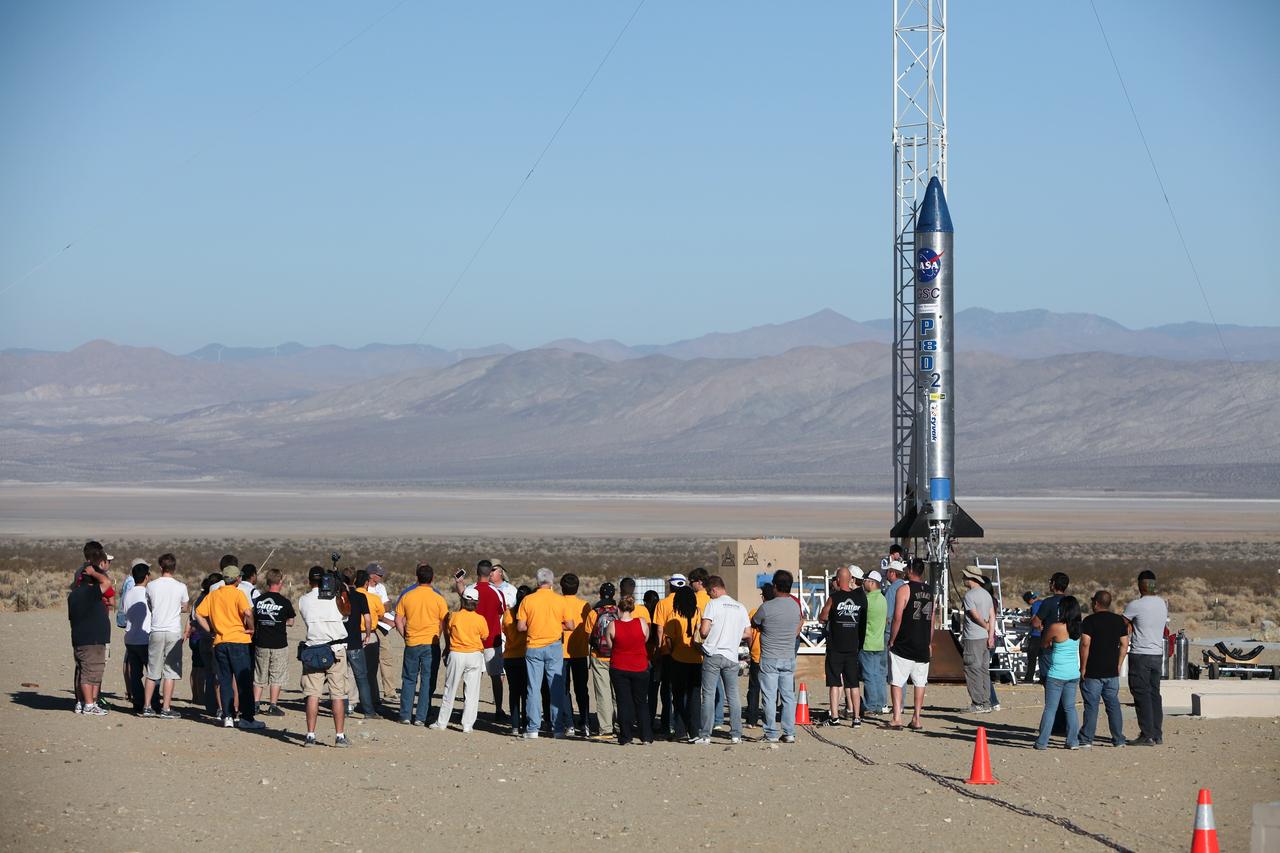

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers participate in a pre-launch briefing before the lift off of the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket. The rocket is scheduled to launch the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
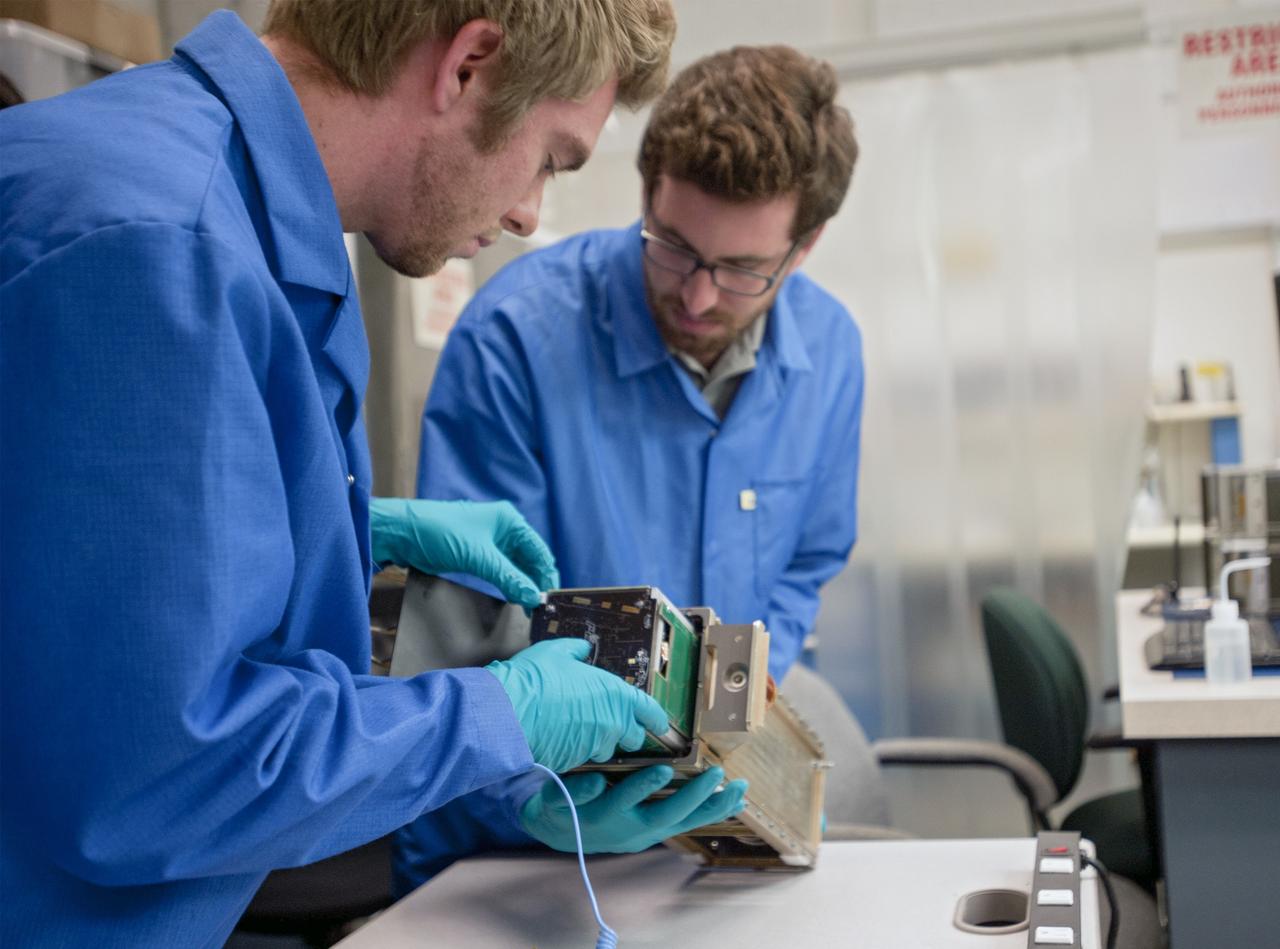

KSC-2013-2721 – SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. –Members of the student launch team load a payload into a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Dispensor, or P-Pod nanolauncher/carrier in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payload, which includes sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cube sections, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Known as a CubeSat, the satellite will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. It will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Also, a new launcher/carrier of a lightweight design also is being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
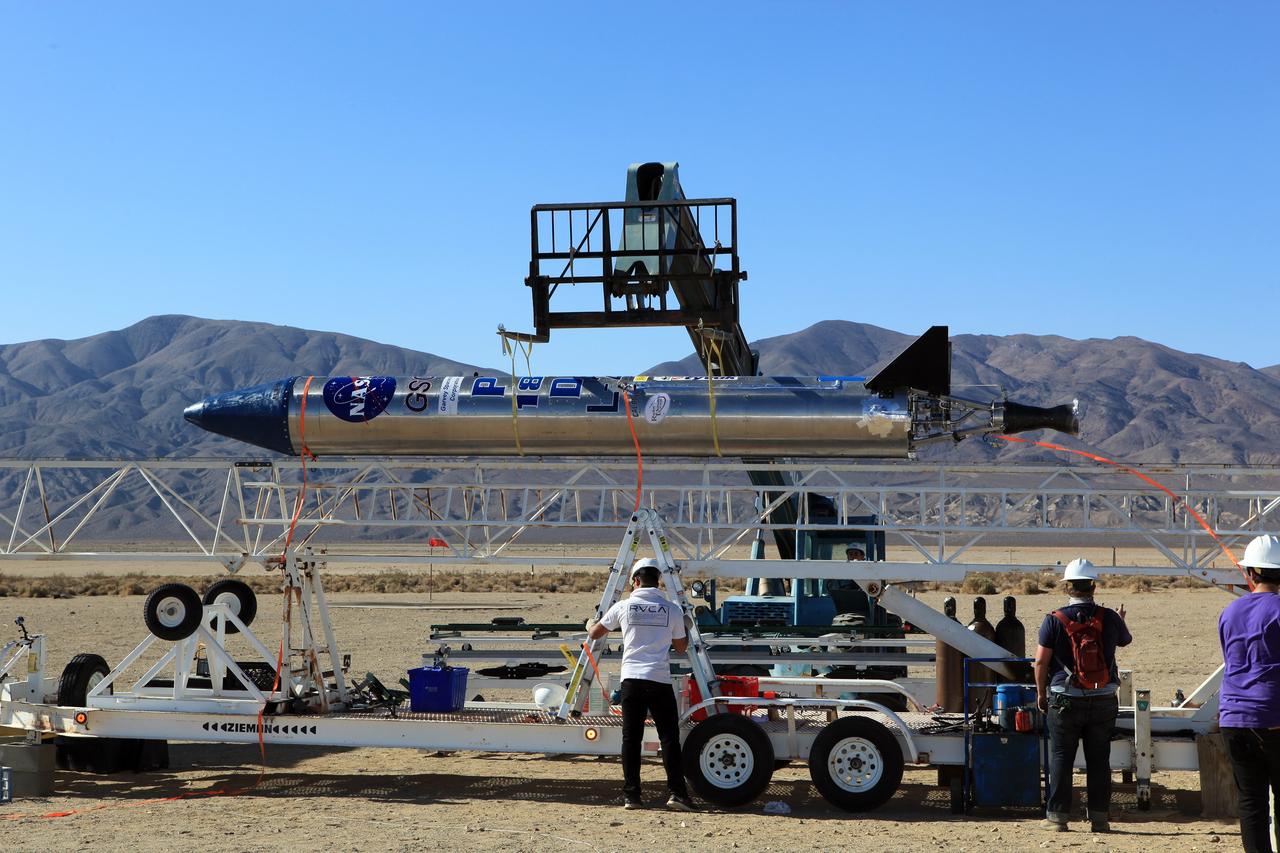

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers assist as the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket is lifted into position for its scheduled launch on June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
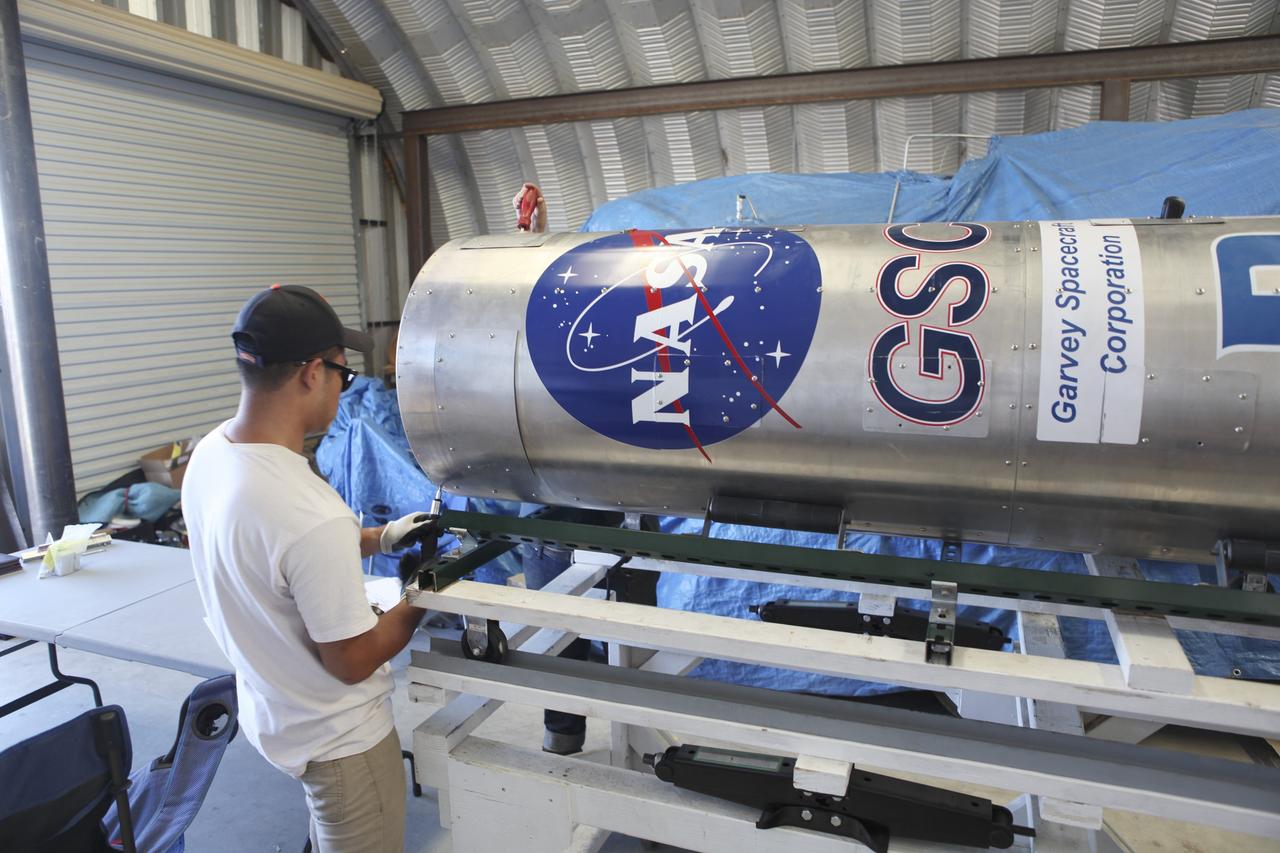

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, a student checks out the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket scheduled for launch June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube section. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
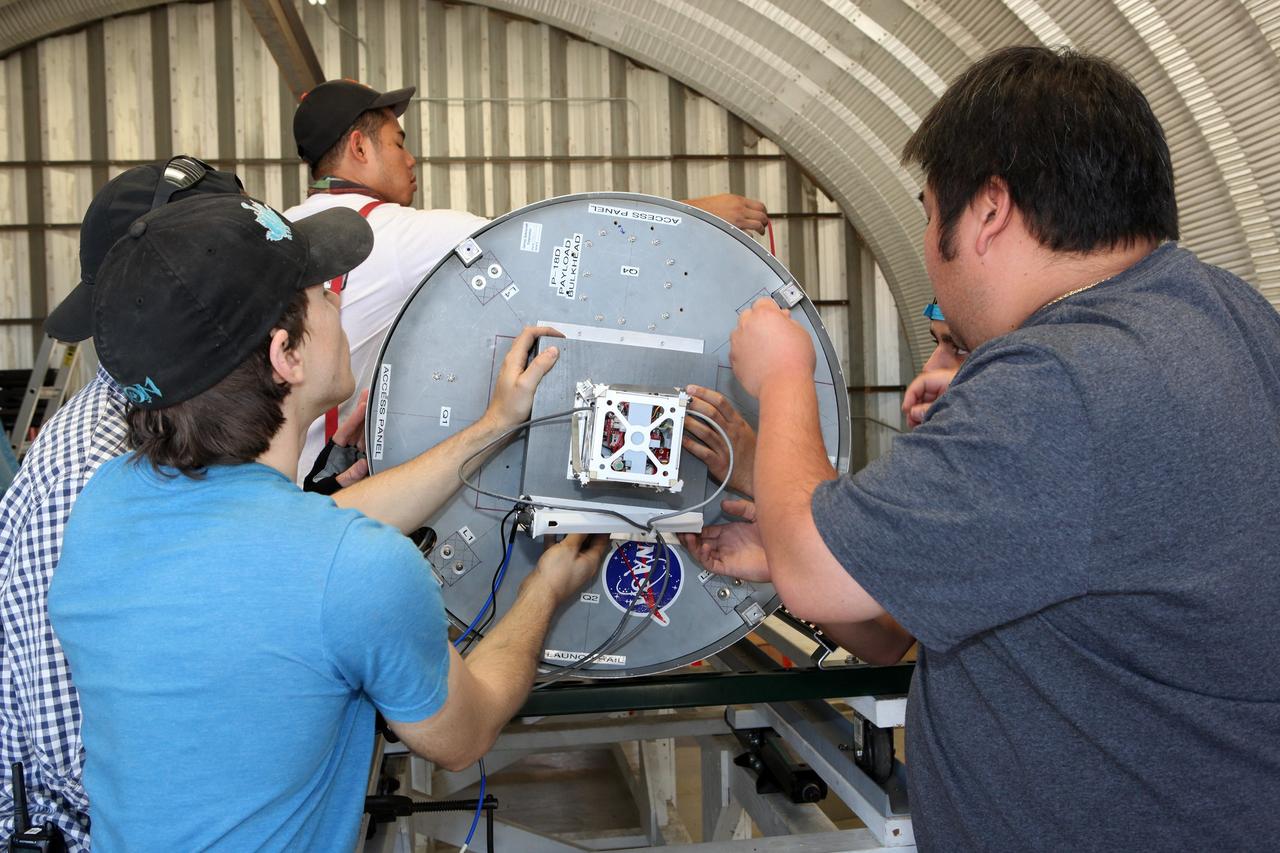

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers checkout the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket. The rocket is scheduled for launch June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
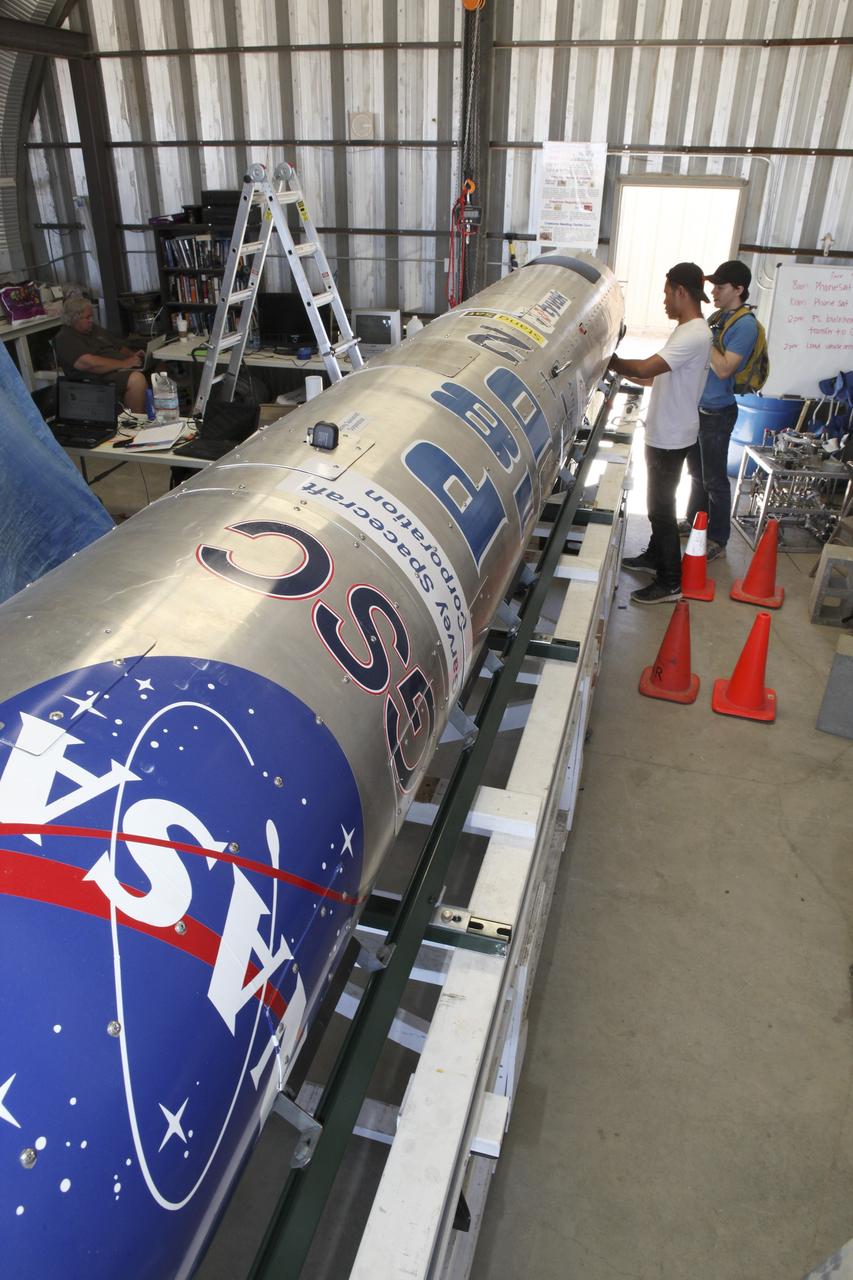

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers pack the parachute in the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket. The work is in preparation for the June 15 launch of a on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube section. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
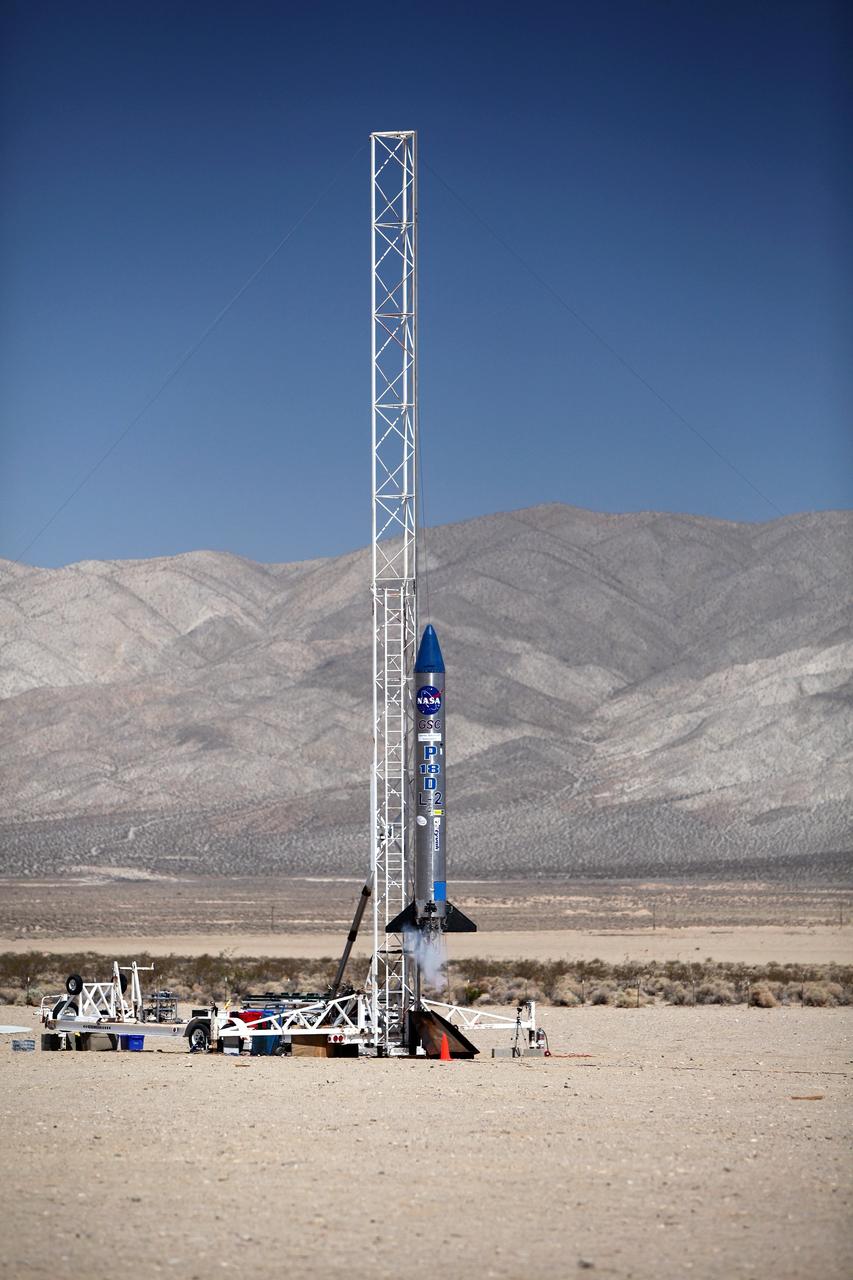

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, the ignition sequence begins on the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket. The vehicle is carrying the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket carried four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
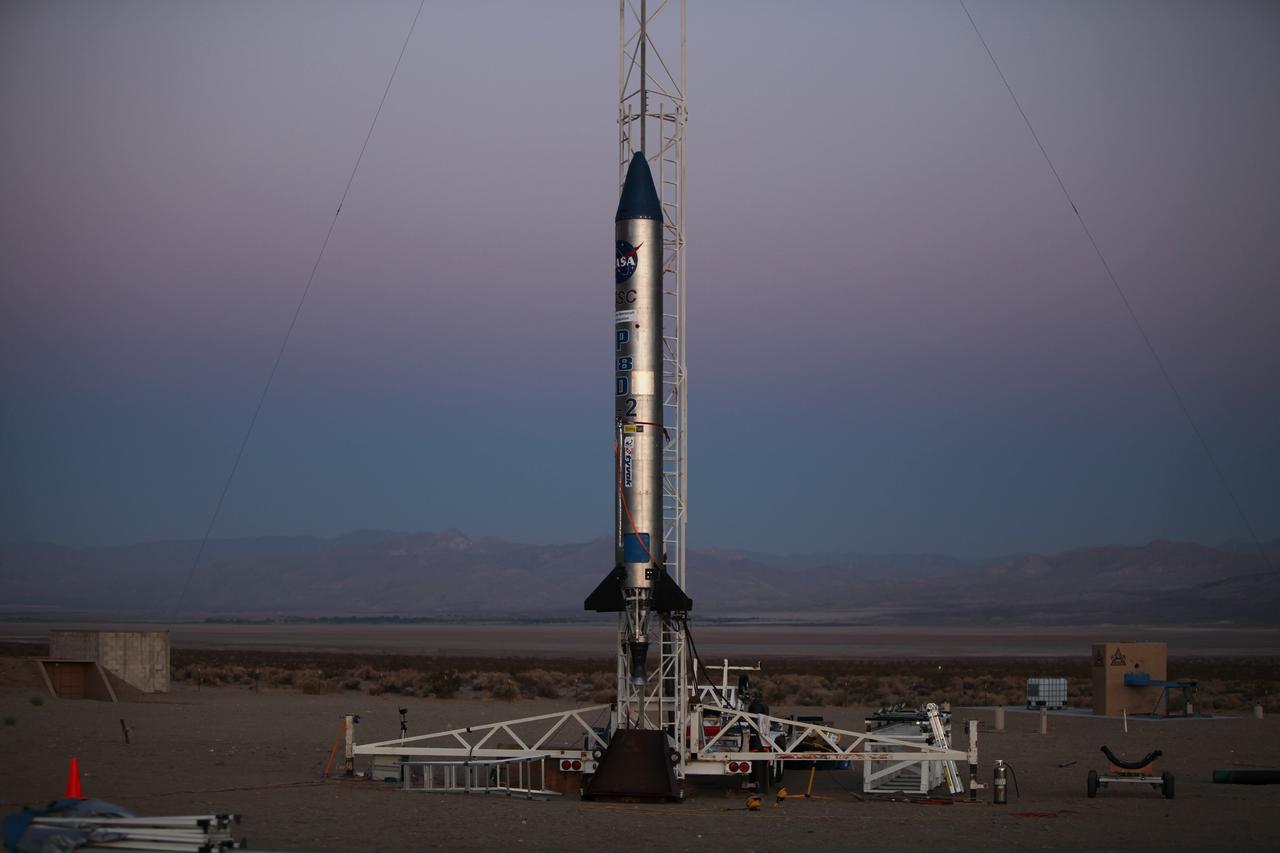

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – As the sun rises in the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket is positioned for launch with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
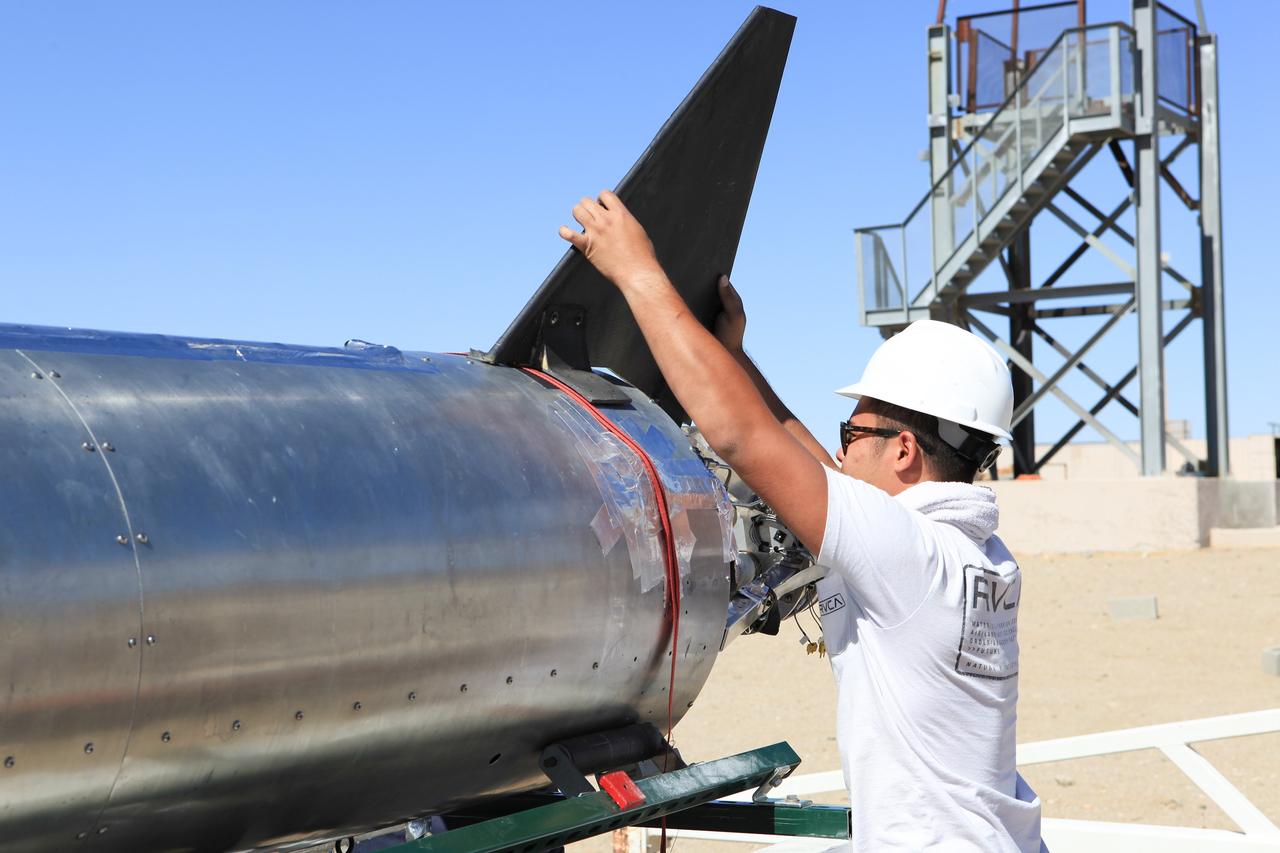

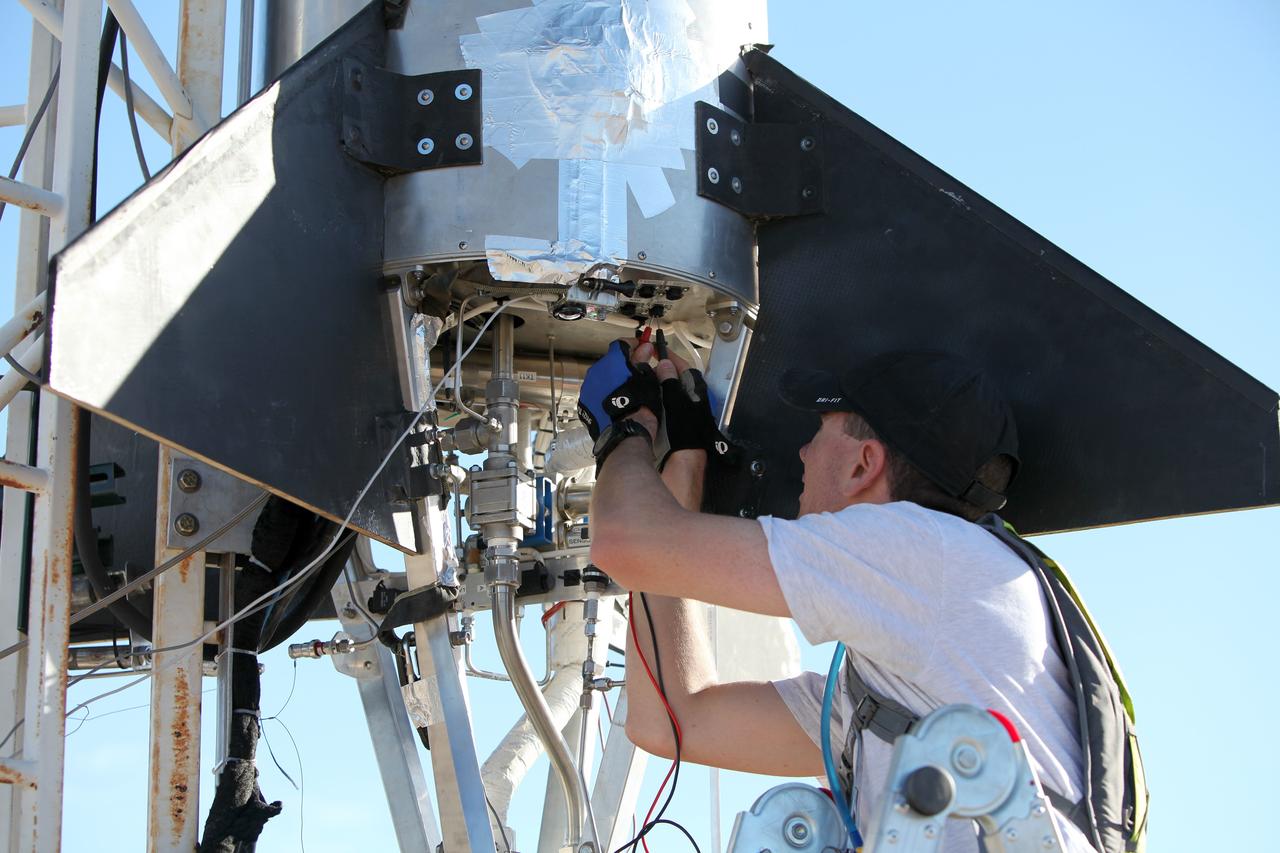
MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, a student attaches a tail fin to the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket at the Friends of Amateur Rocketry launch site. The rocket is scheduled for flight June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
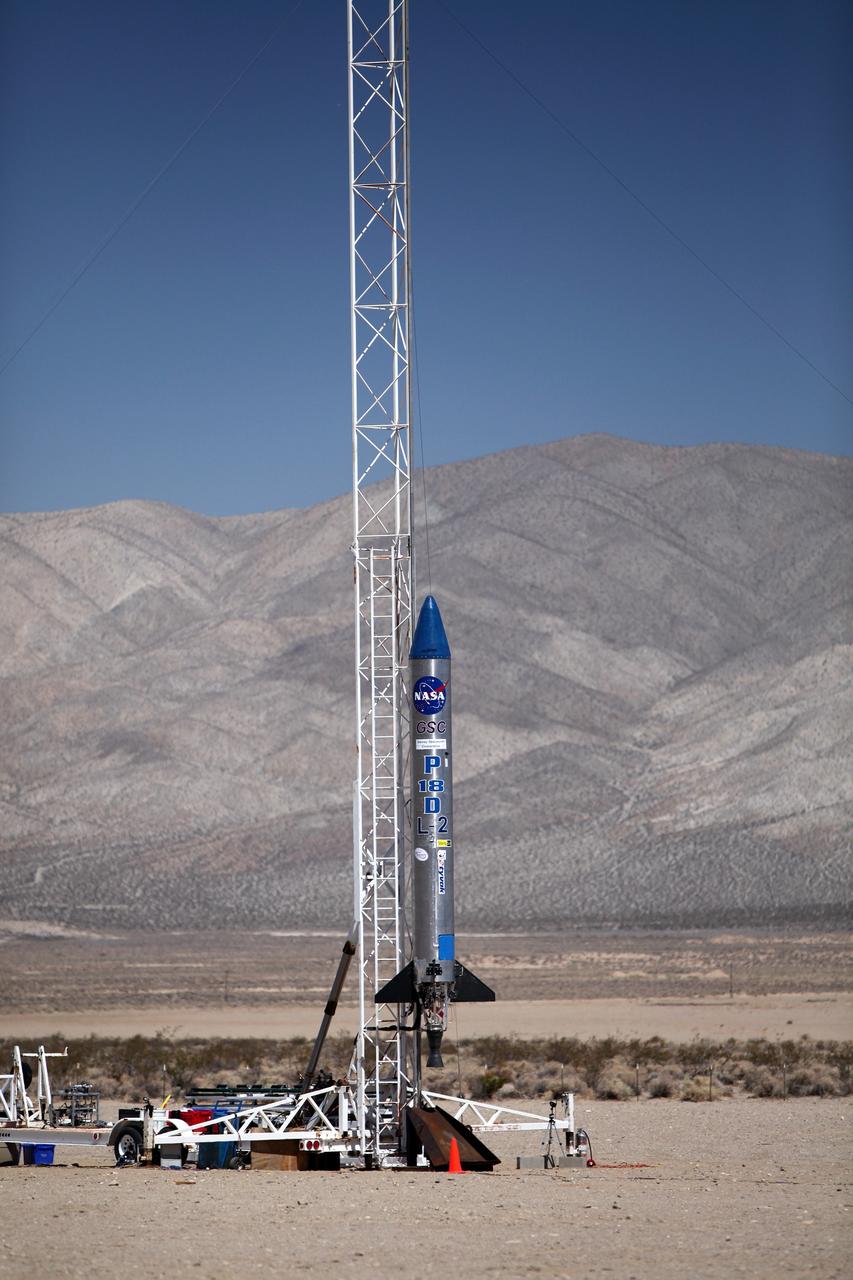

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket is positioned for launch with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket lifts off at 10:52 a.m. PDT carrying the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket carried four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
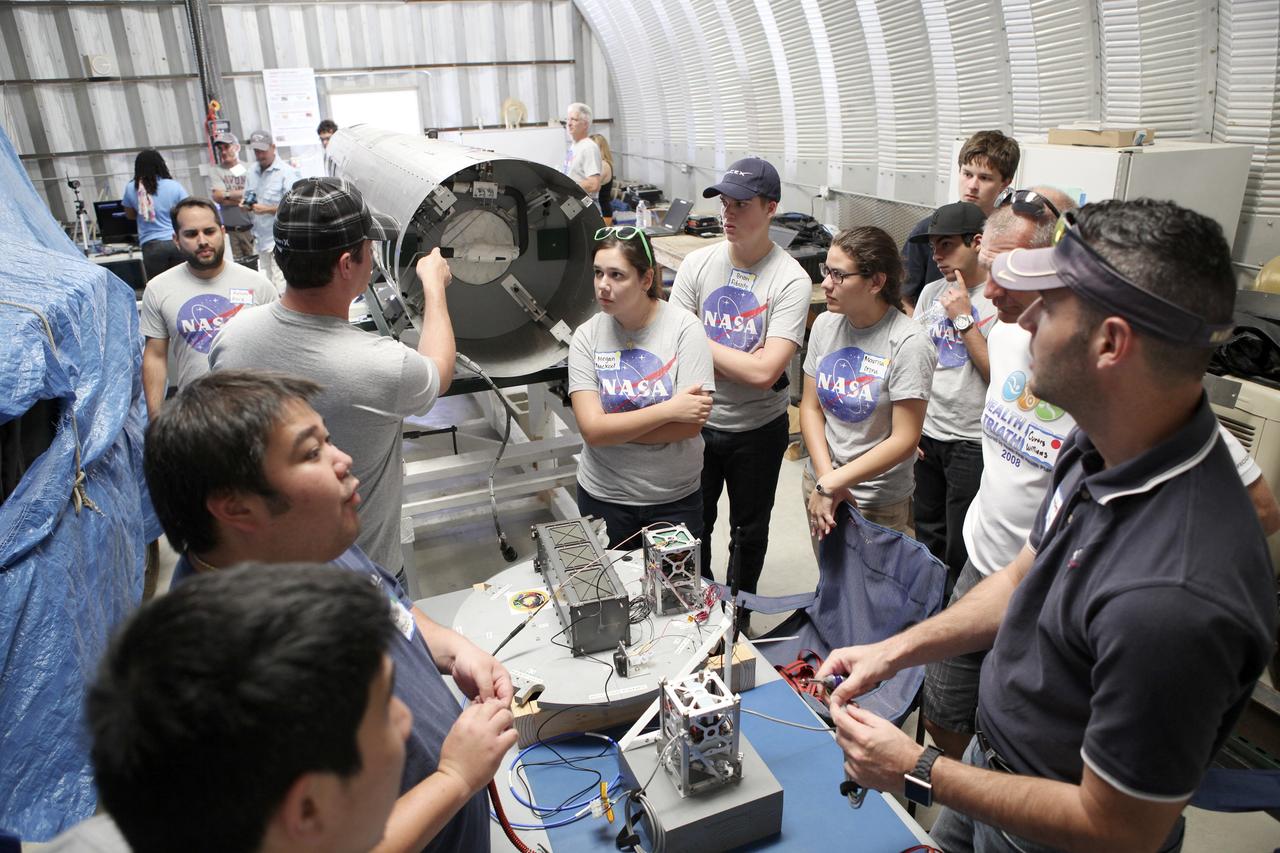

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers checkout the RUBICS-1 payload into the body of the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket for launch June 15 on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The flight will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube section. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
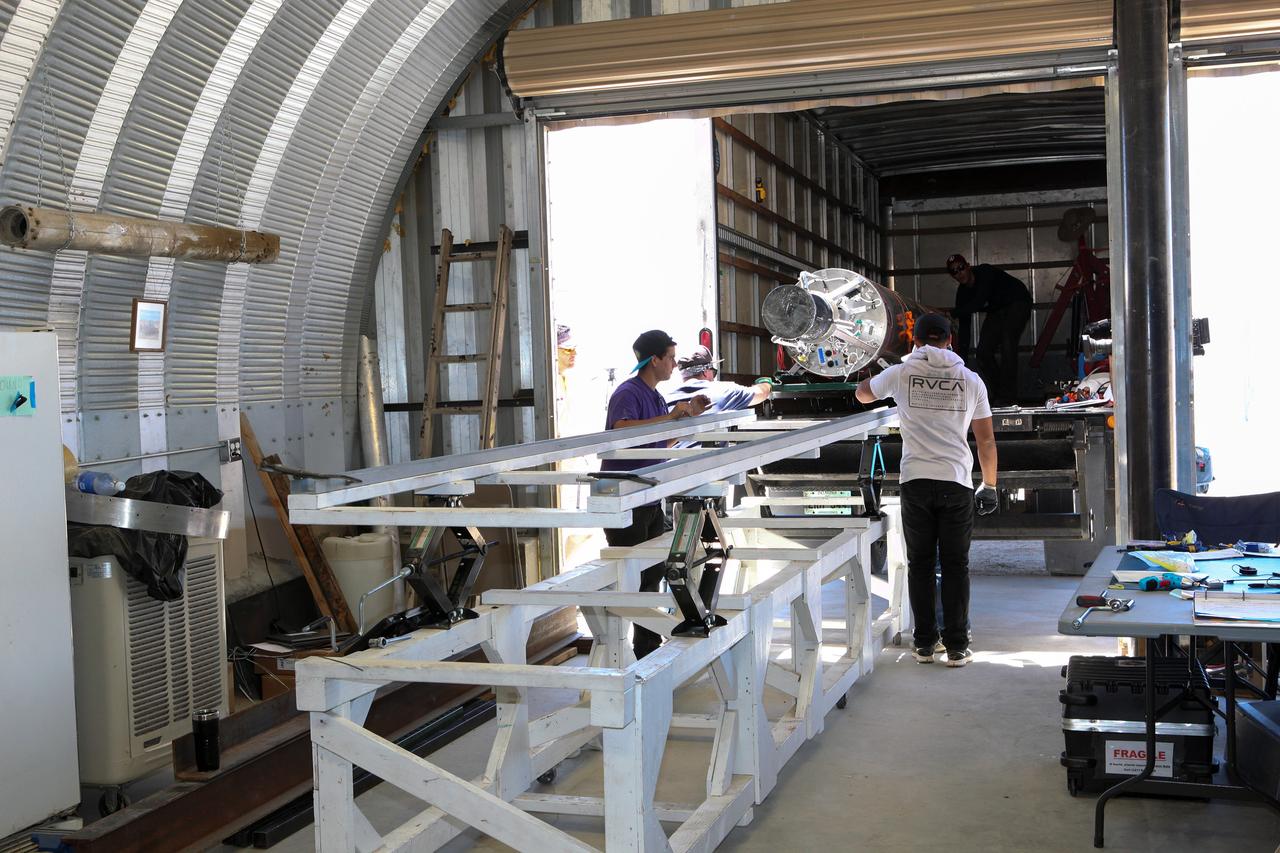

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers load the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket onto a truck for transportation to the launch site. The rocket is scheduled for launch June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
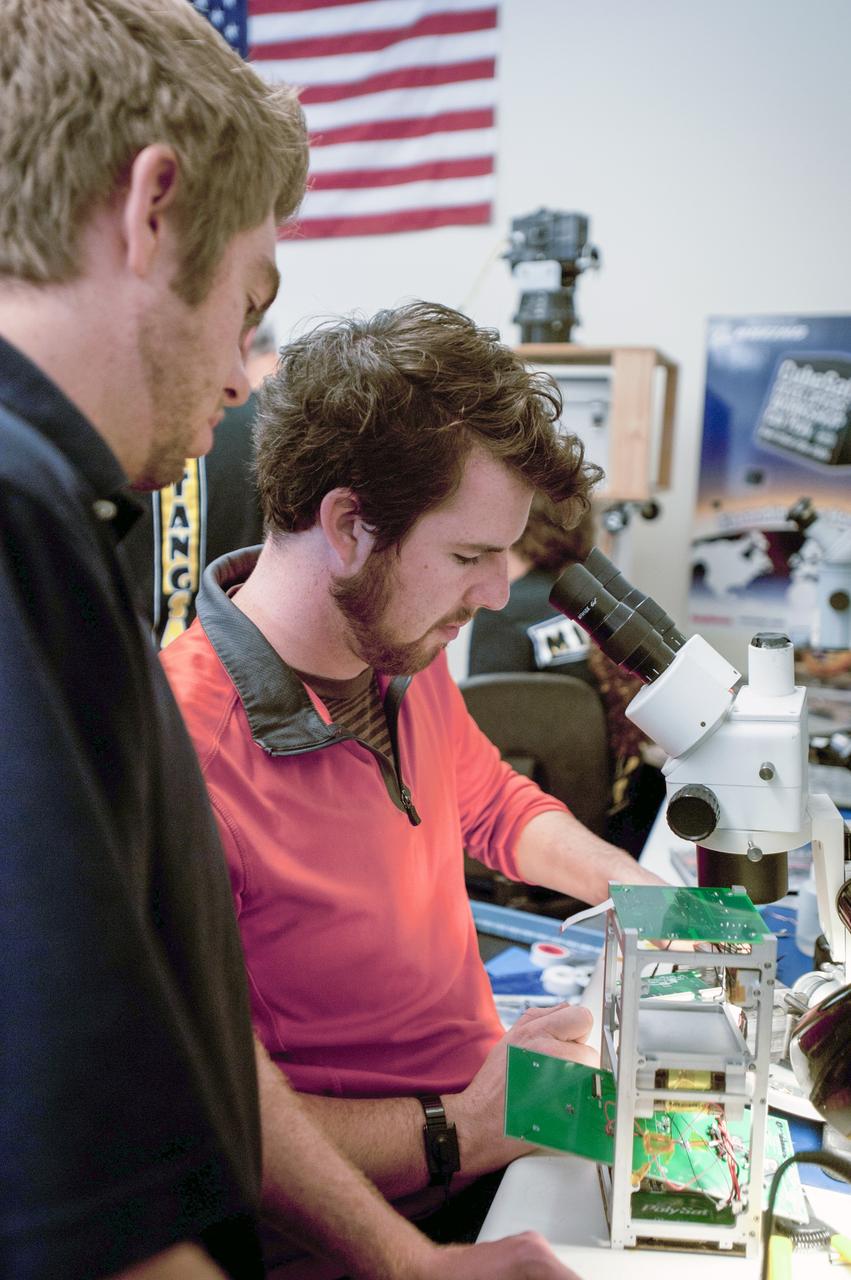

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – Members of the student launch team for the Polysat works through final checks in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payload, which includes sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cube sections, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Known as a CubeSat, the satellite will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. It will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – Members of the student launch team for the StangSat go through final checks in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payloads, which include sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cubes, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
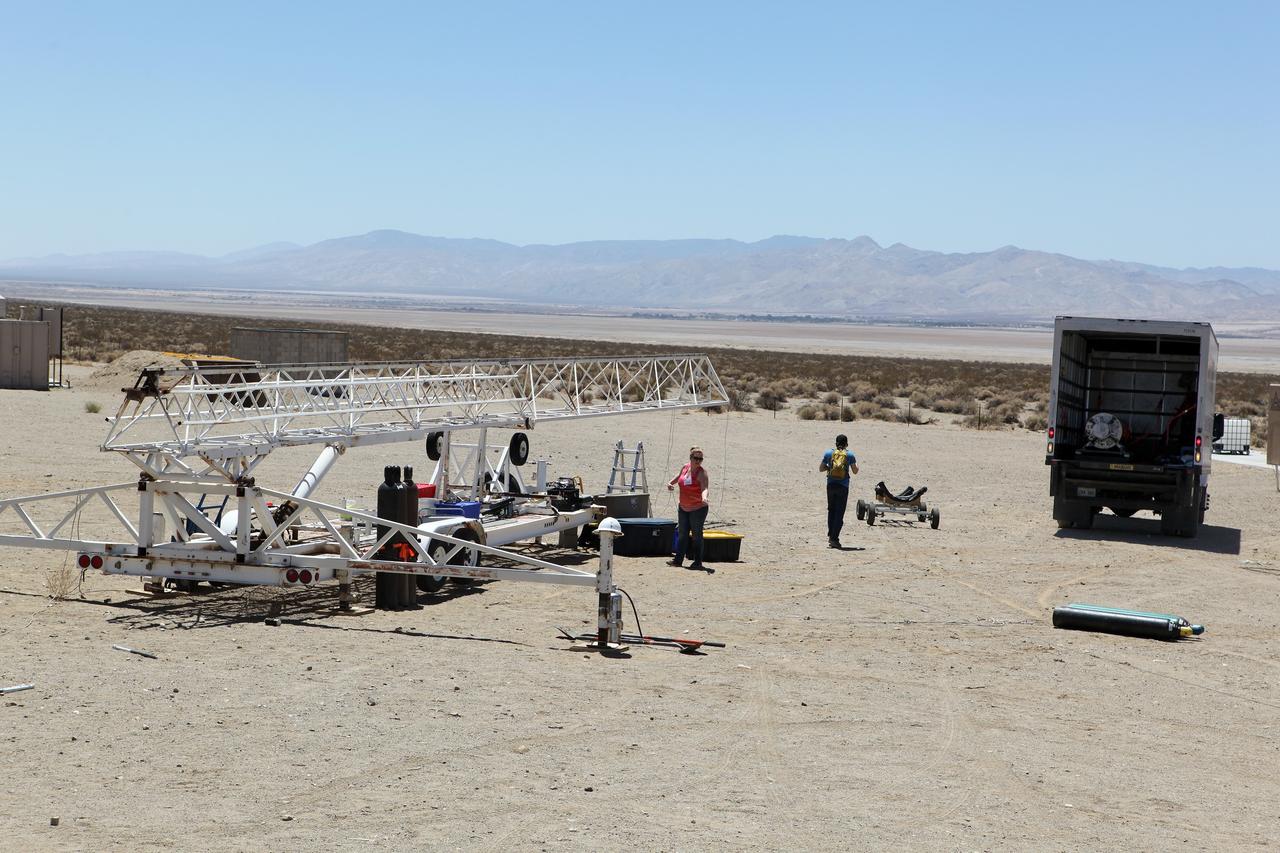

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers prepare the launch stand for the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket. The rocket is scheduled for launch June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
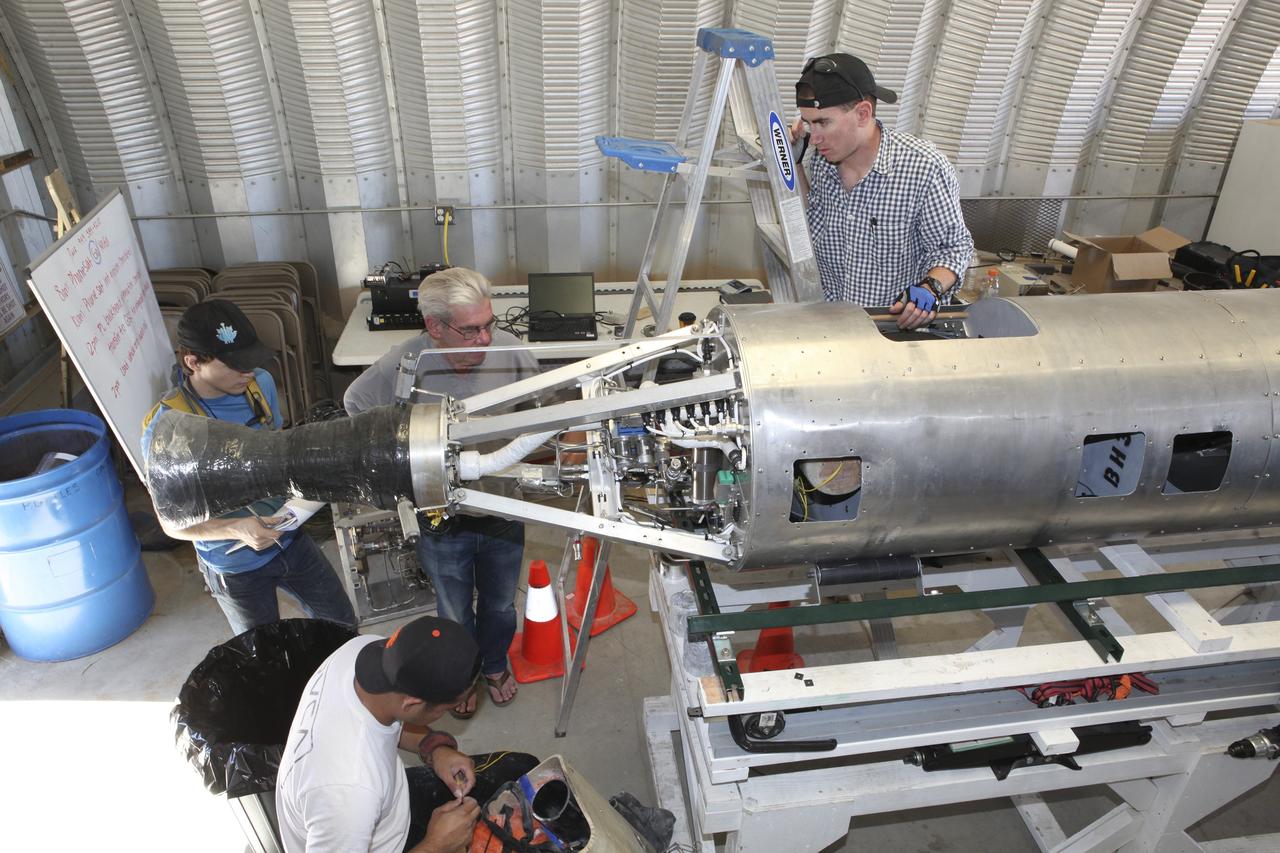

In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers checkout the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket engine. The rocket is scheduled for launch June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube section. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – A member of the student launch team for the Polysat works through final checks in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payloads, which include sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cubes, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
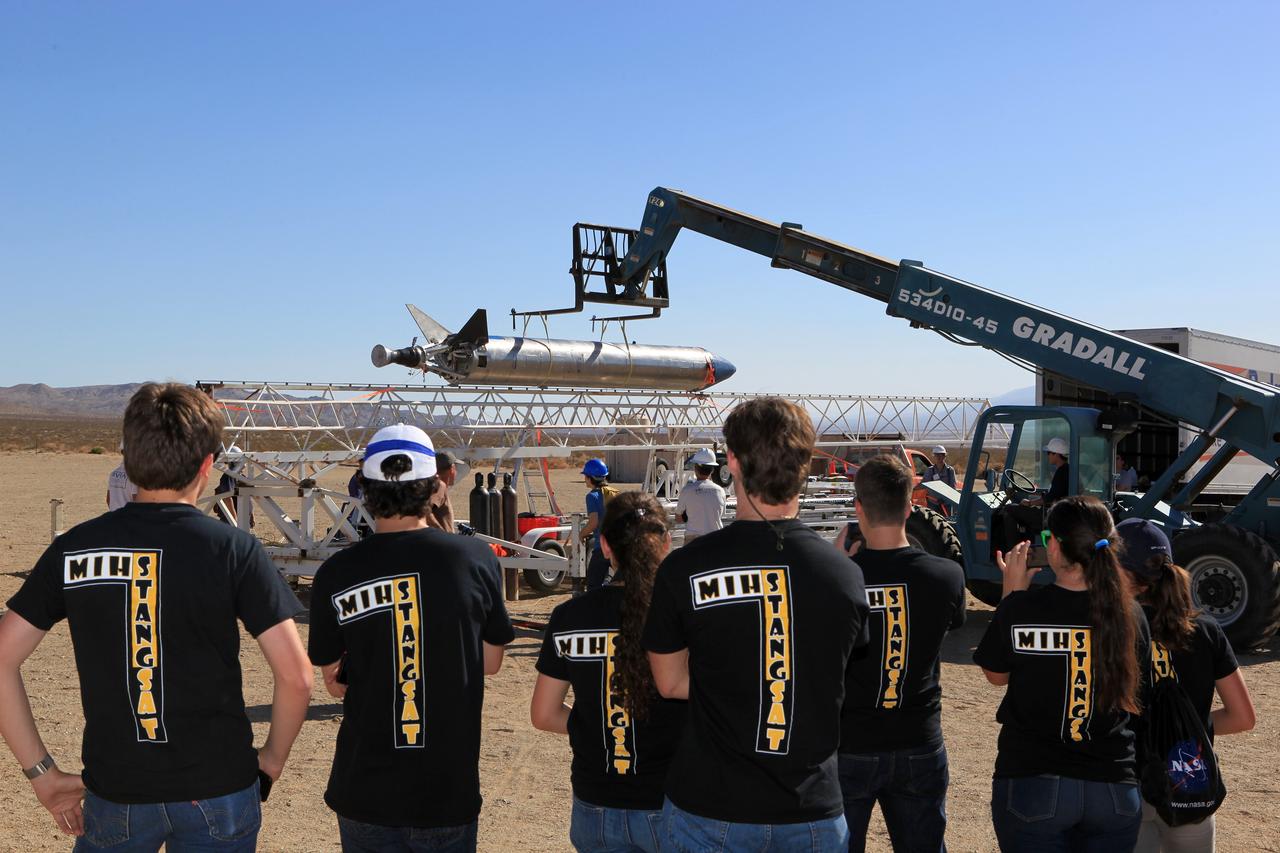

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students from Merritt Island High School in Florida watch as the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket is lifted into position for its scheduled launch on June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections, one developed by students from the school that is located near the Kennedy Space Center. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
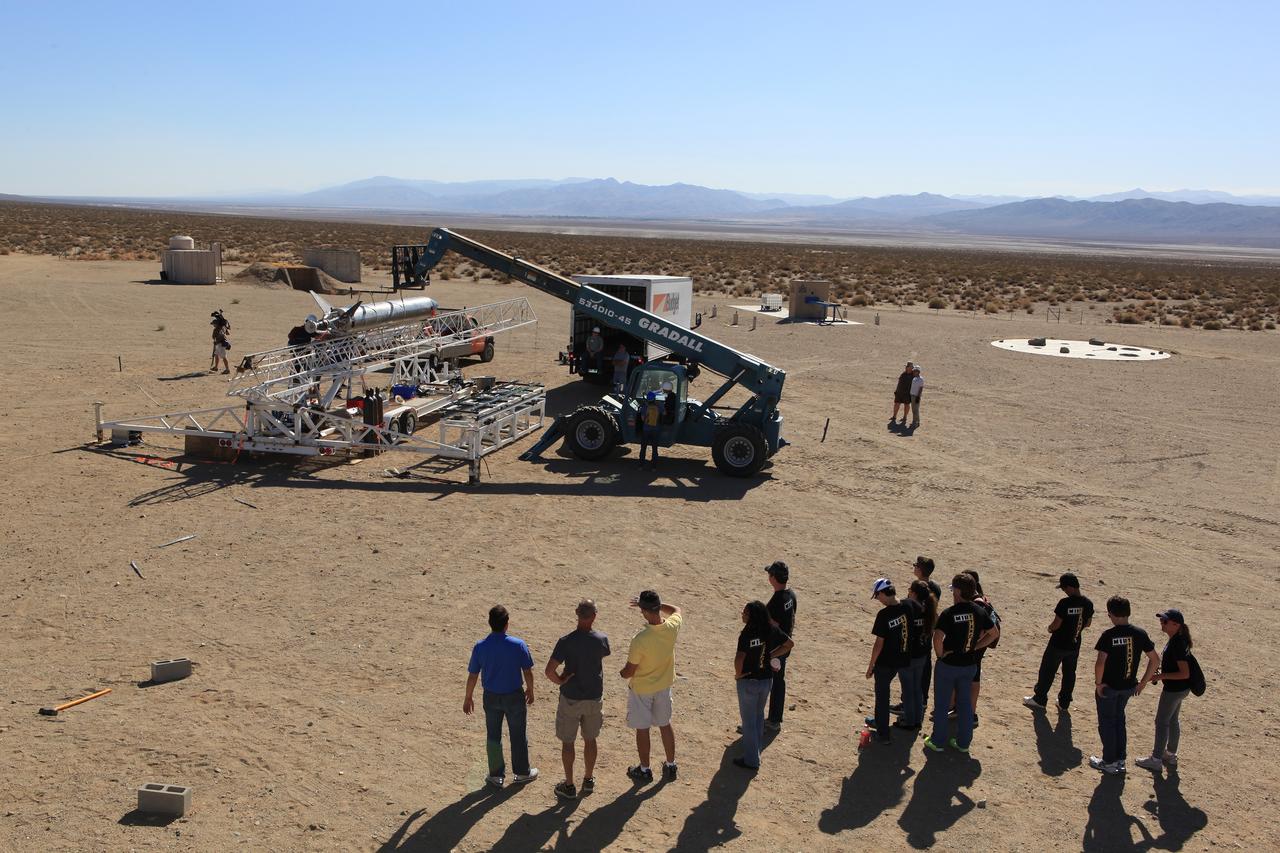

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students from Merritt Island High School in Florida watch as the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket is lifted into position for its scheduled launch on June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube section, one developed by students from the school that is located near the Kennedy Space Center. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
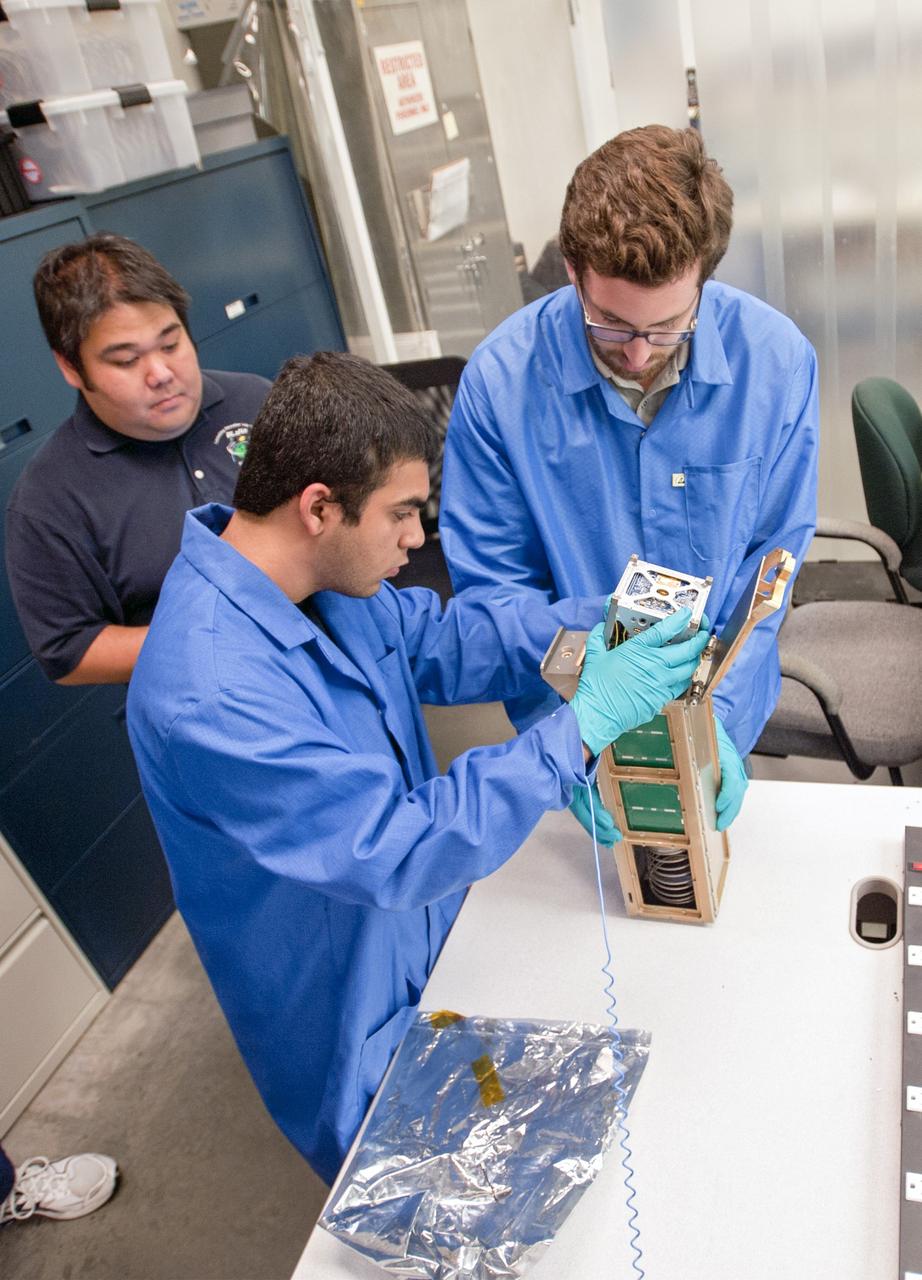

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – Roland Coelho, third from left, CalPoly program lead, and members of the student launch team load a payload into a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Dispensor, or P-Pod nanolauncher/carrier in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payload, which includes sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cube sections, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Known as a CubeSat, the satellite will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. It will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Also, a new launcher/carrier of a lightweight design also is being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
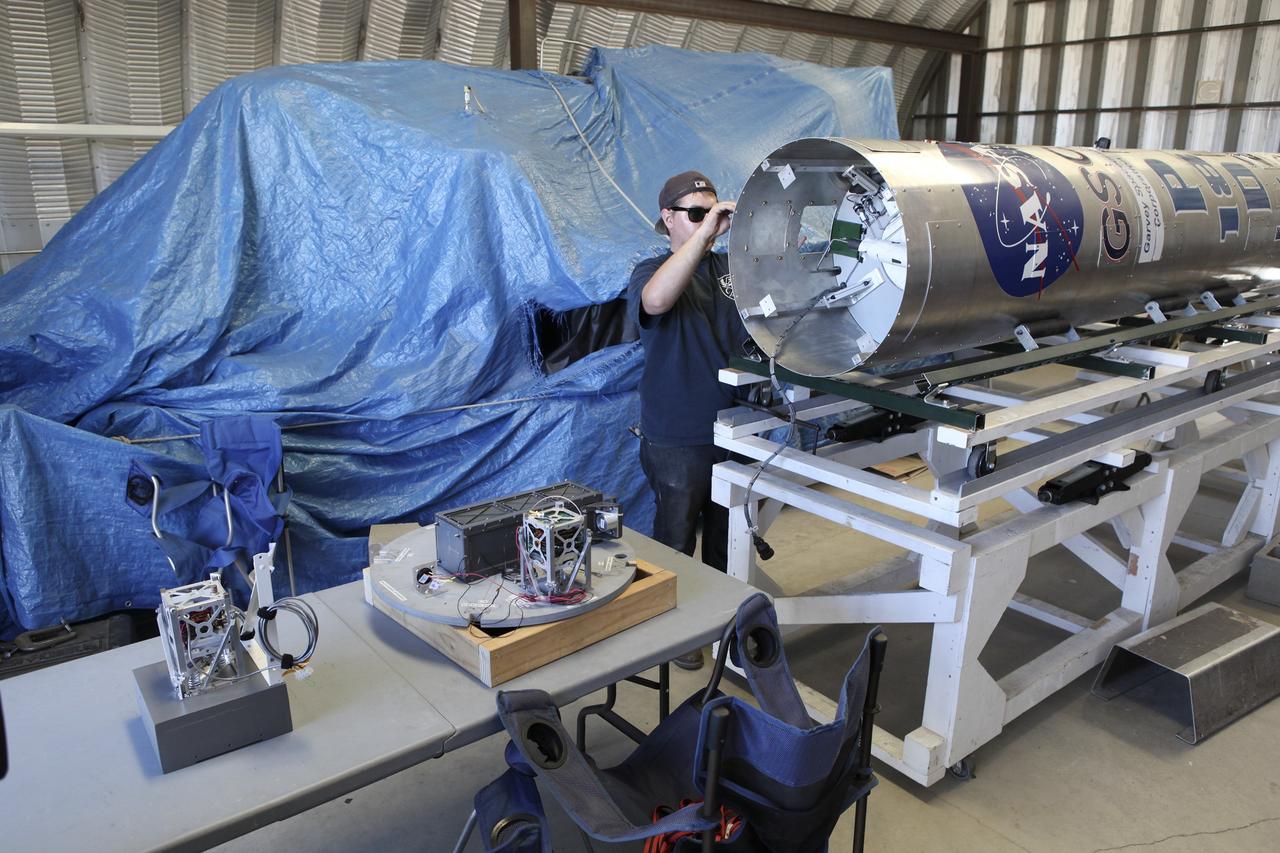

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, a student checks out the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket scheduled for launch June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube section. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
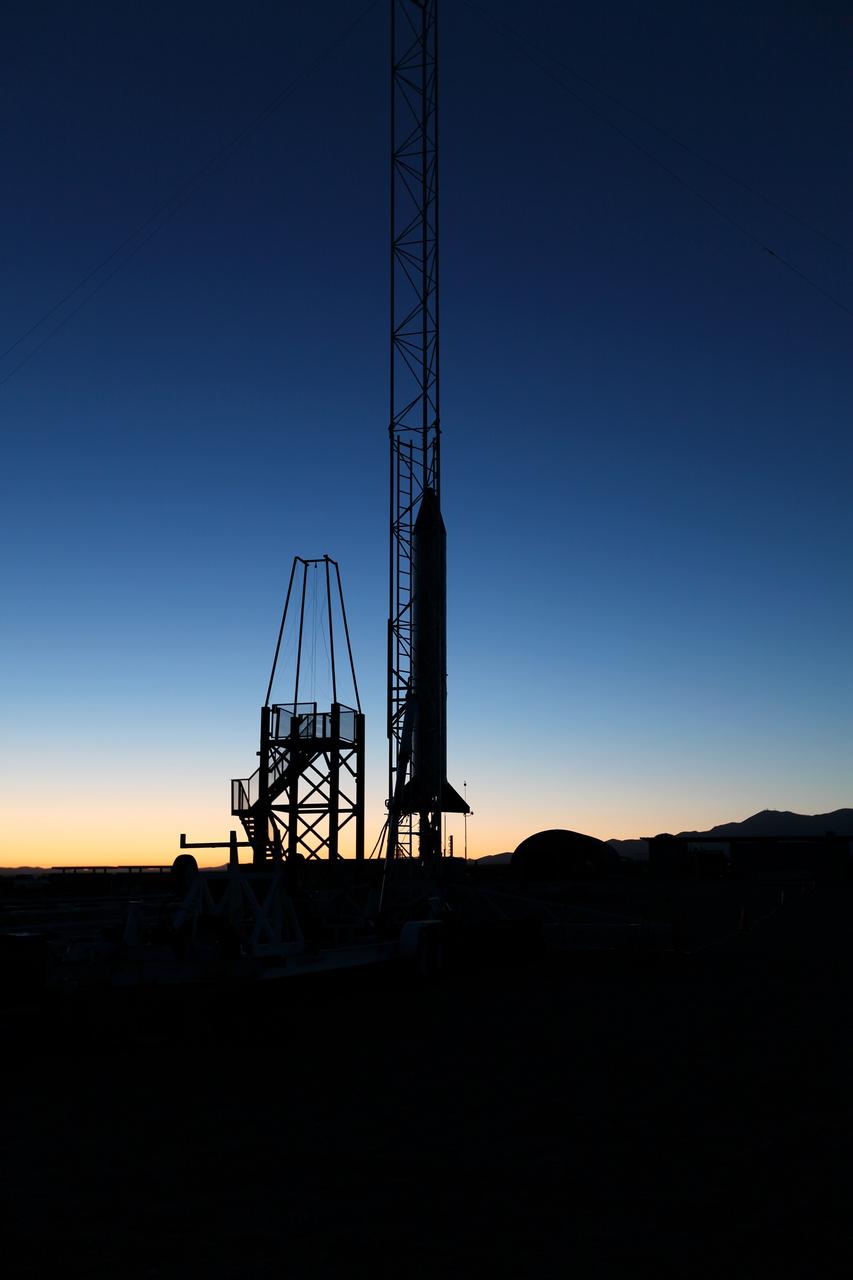

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – As the sun rises in the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket is positioned for launch with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
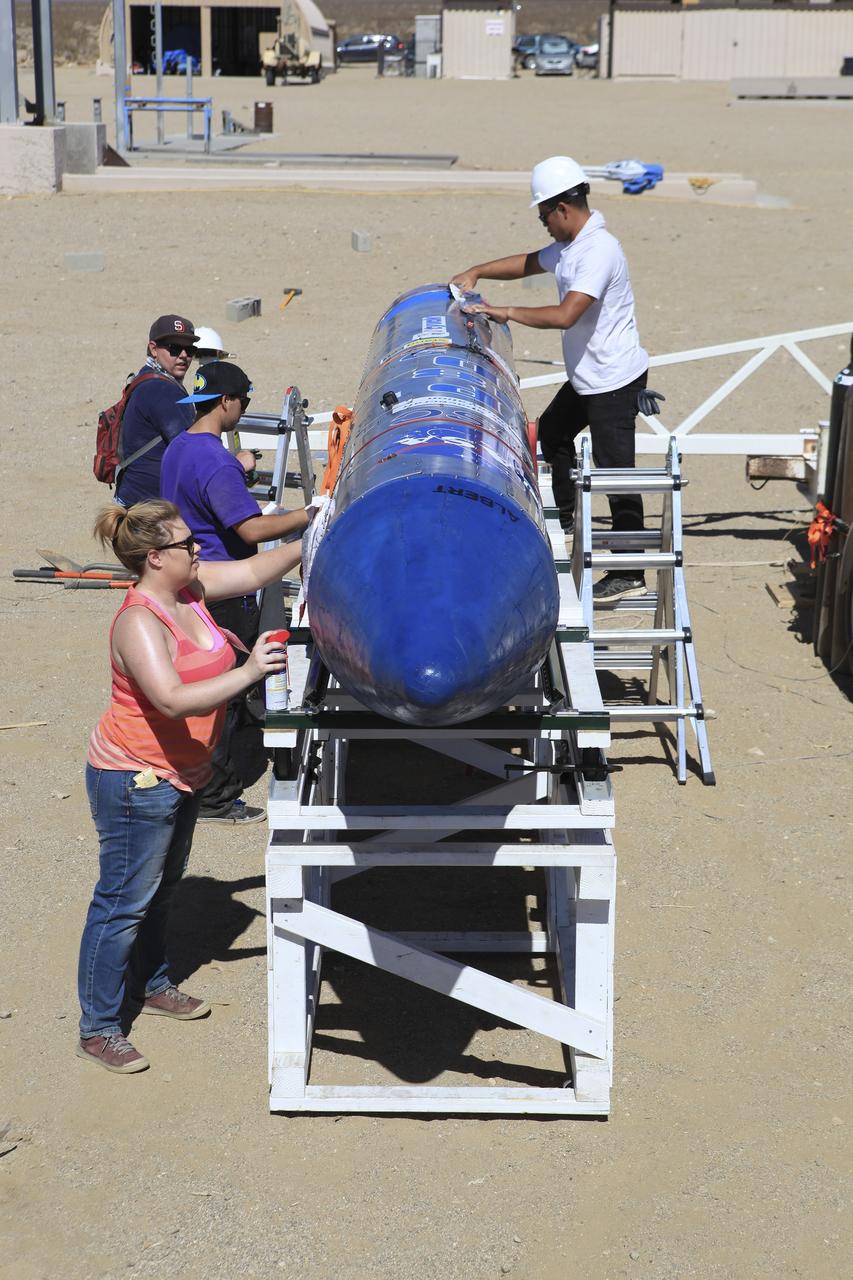

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers checkout the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket at the Friends of Amateur Rocketry launch site. The rocket is scheduled for flight June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
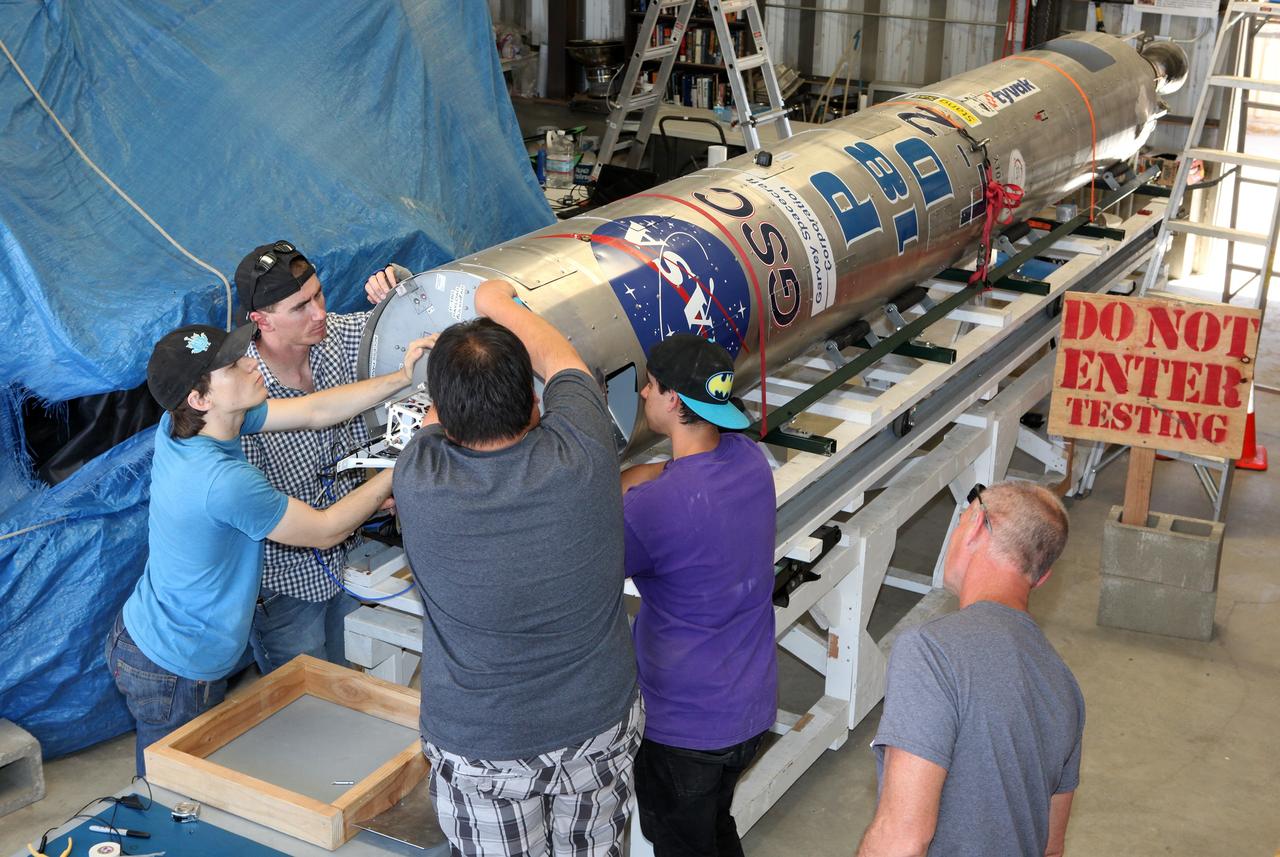

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers checkout the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket. The rocket is scheduled for launch June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
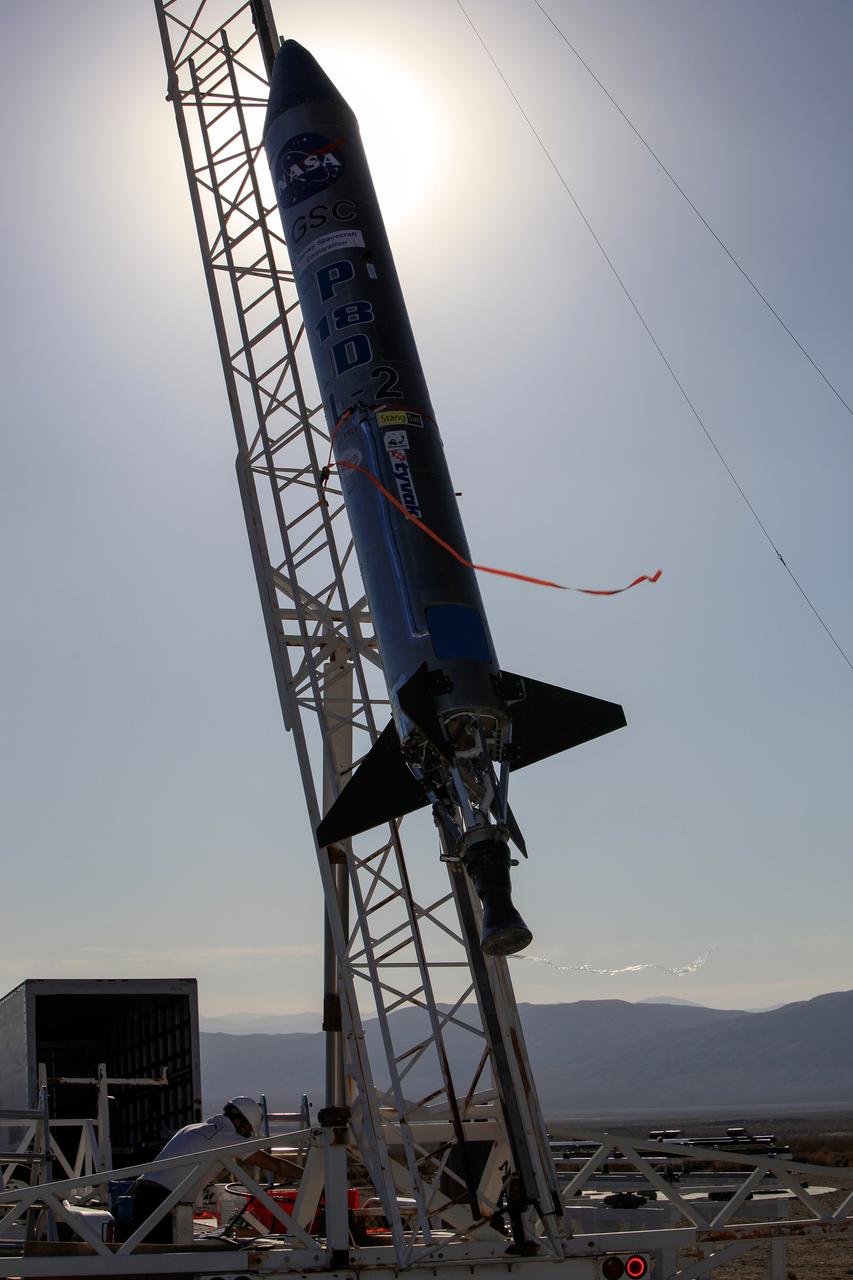

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket is lifted into position for its scheduled launch on June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
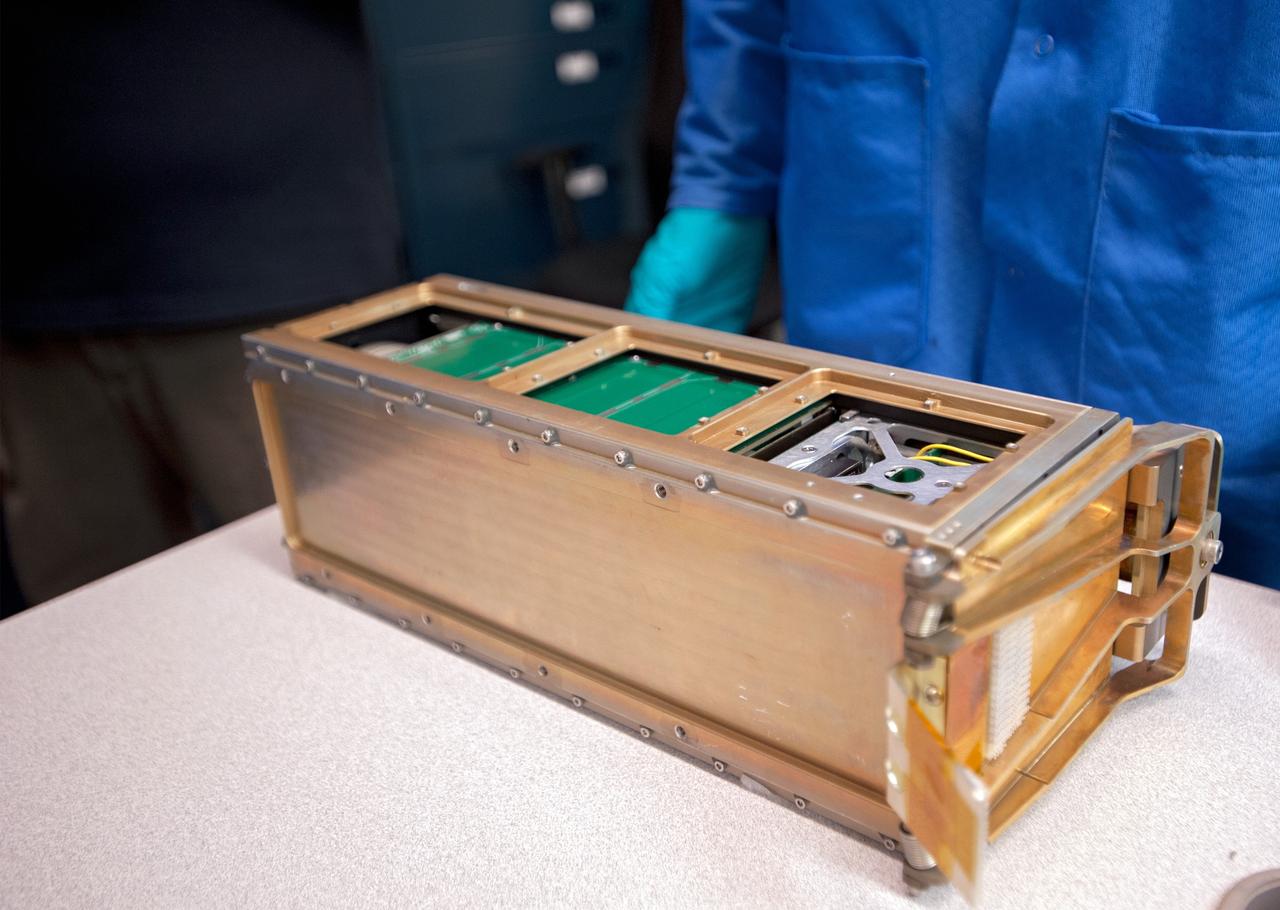

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – A Poly Picosatellite Orbital Dispensor, or P-Pod nanolauncher/carrier in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payload, which includes sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cube sections, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Known as a CubeSat, the satellite will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. It will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
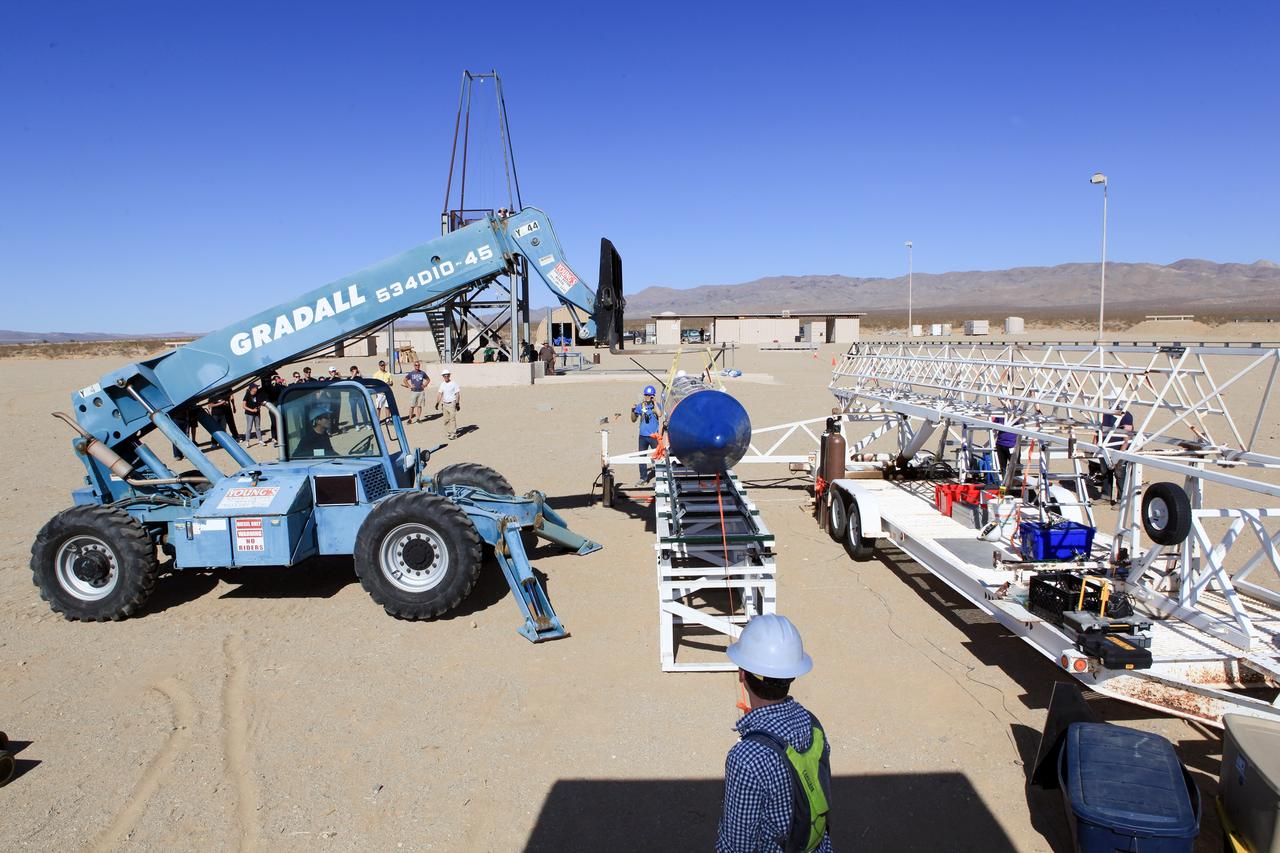

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers assist as the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket is lifted into position for its scheduled launch on June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
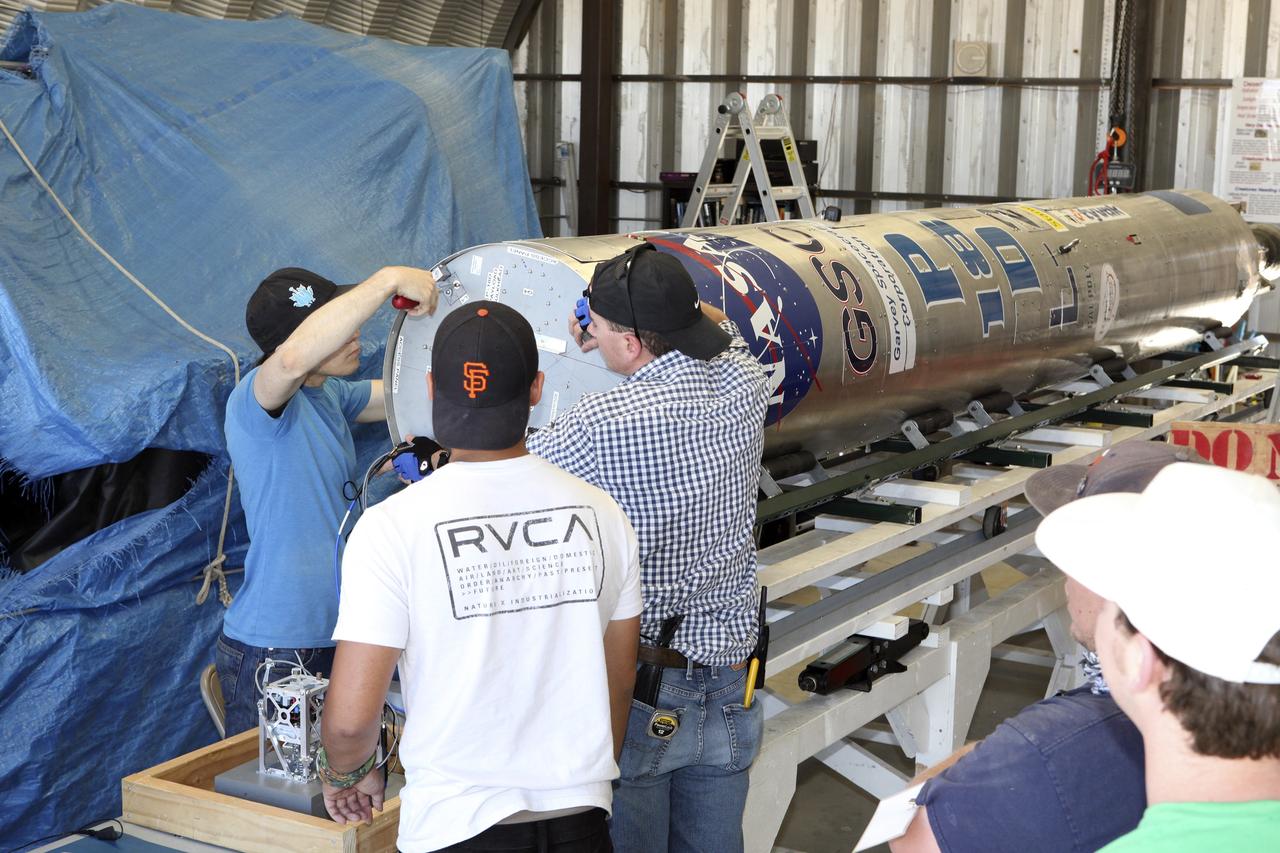

In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers checkout the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket engine. The rocket is scheduled for launch June 15 with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube section. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
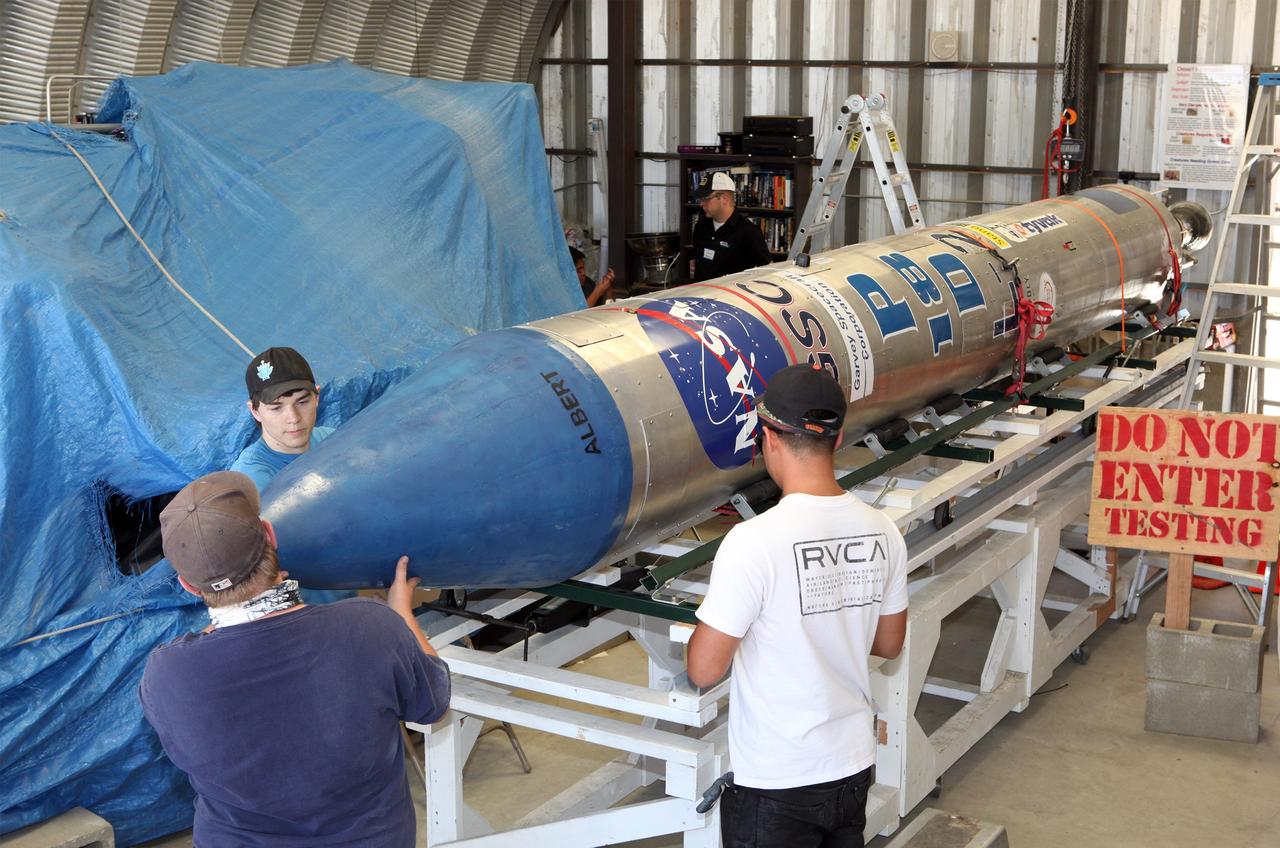

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students install the nose cone on the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket. The work is in preparation for the June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis