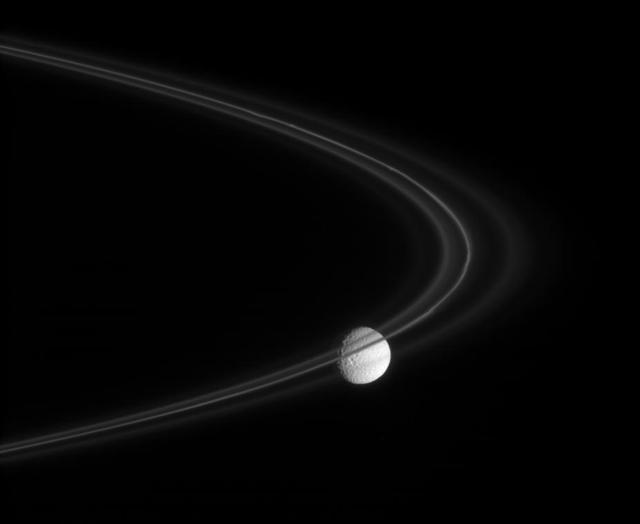

A Wisp of Smoke
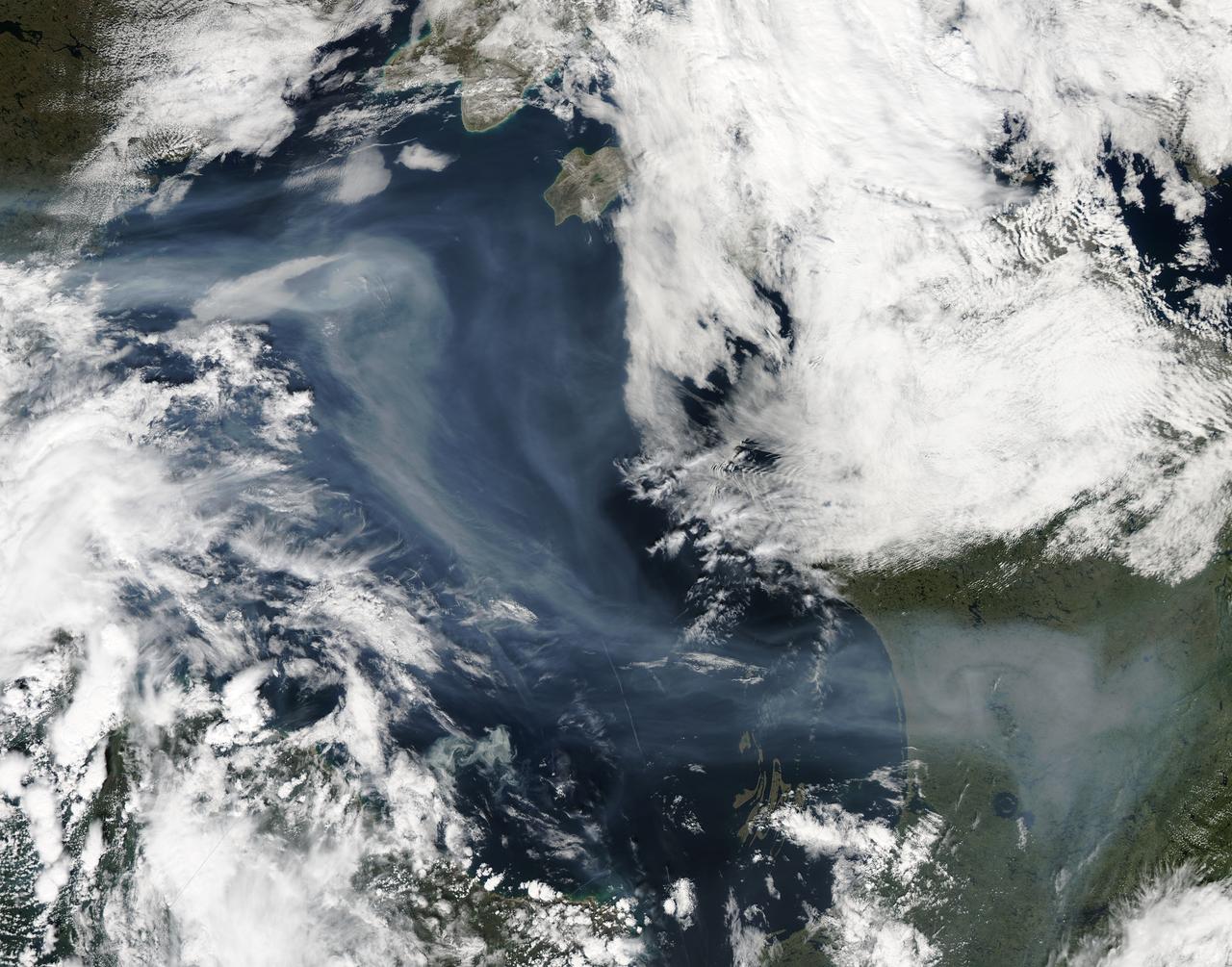

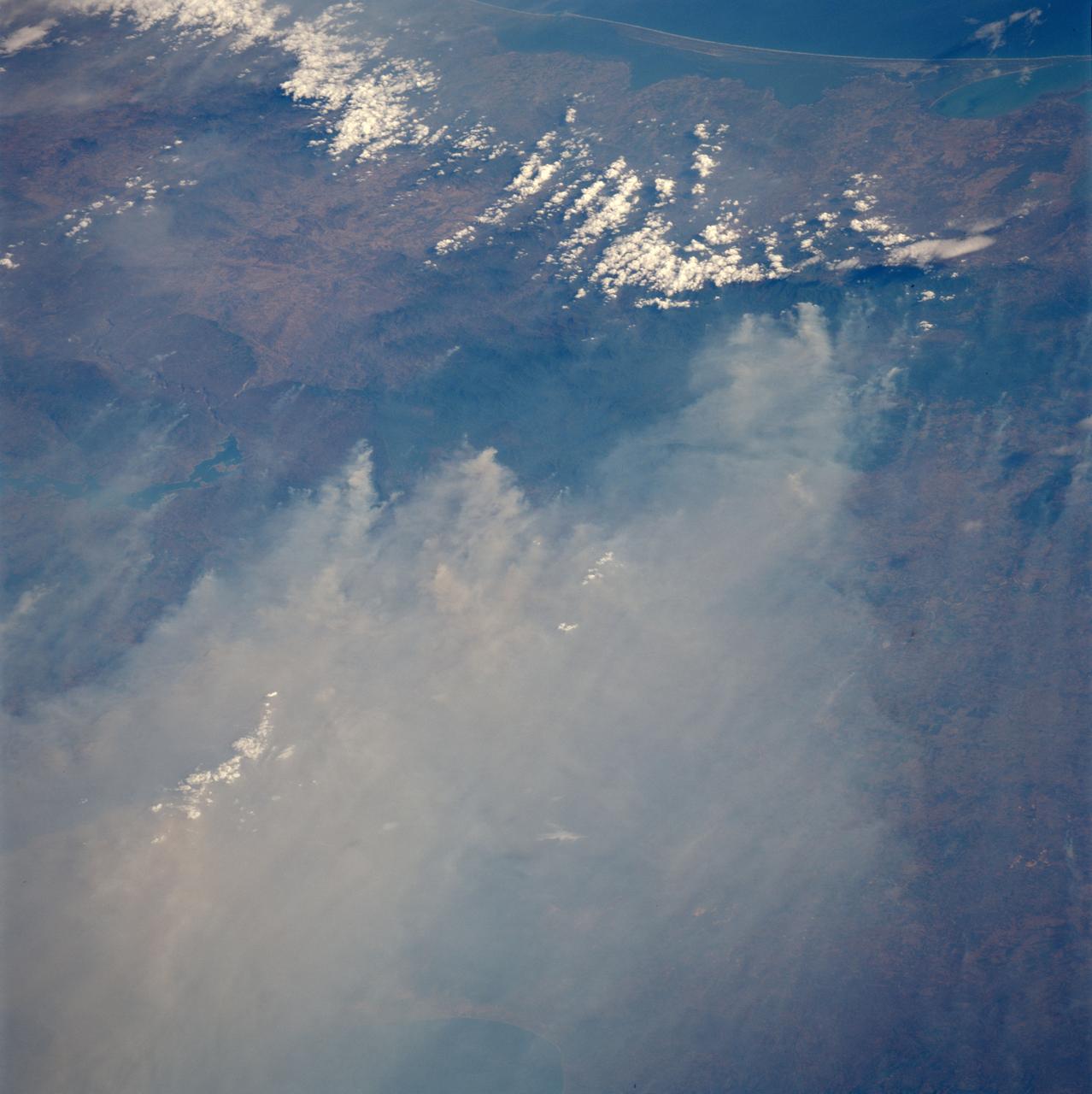
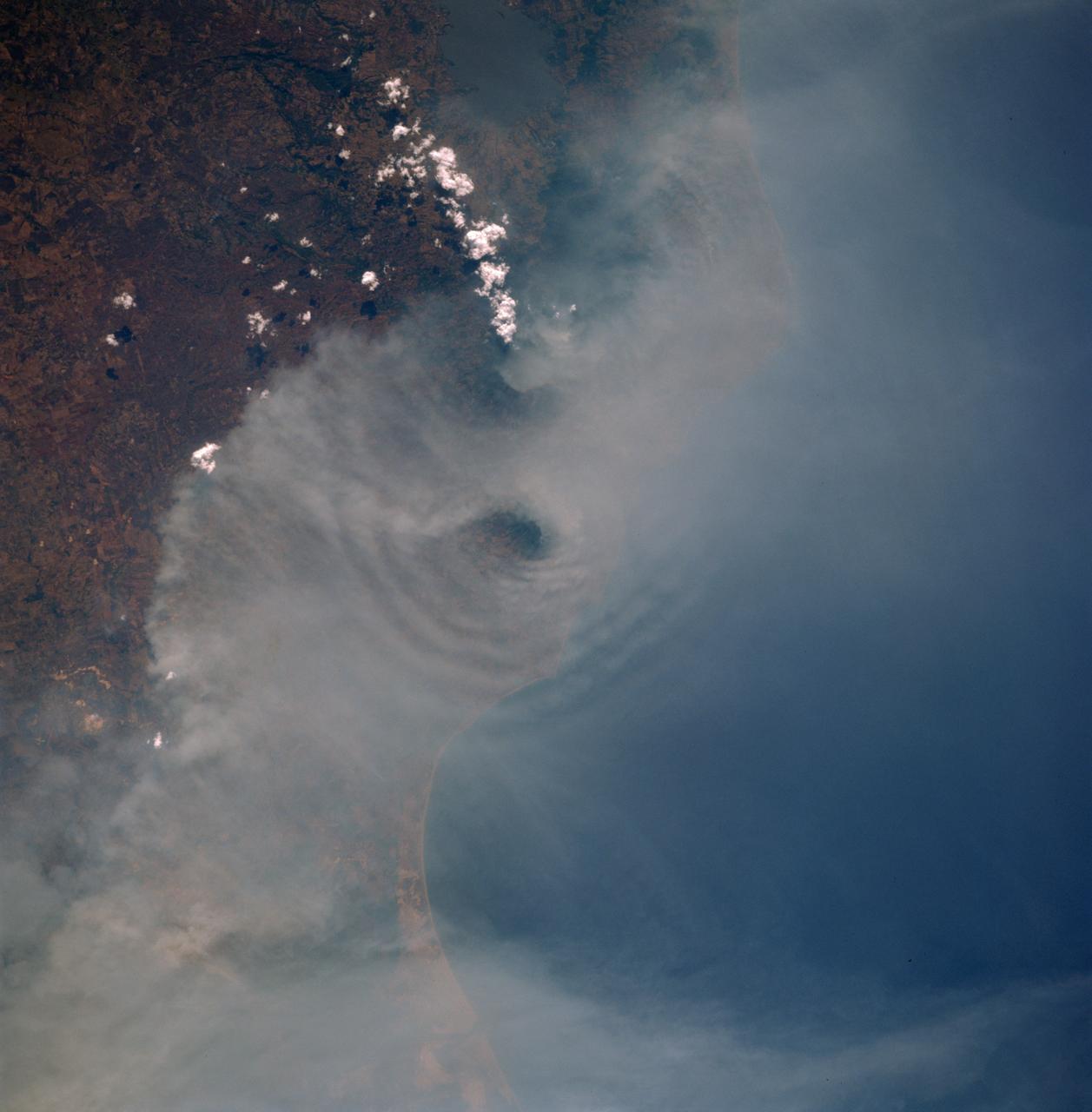
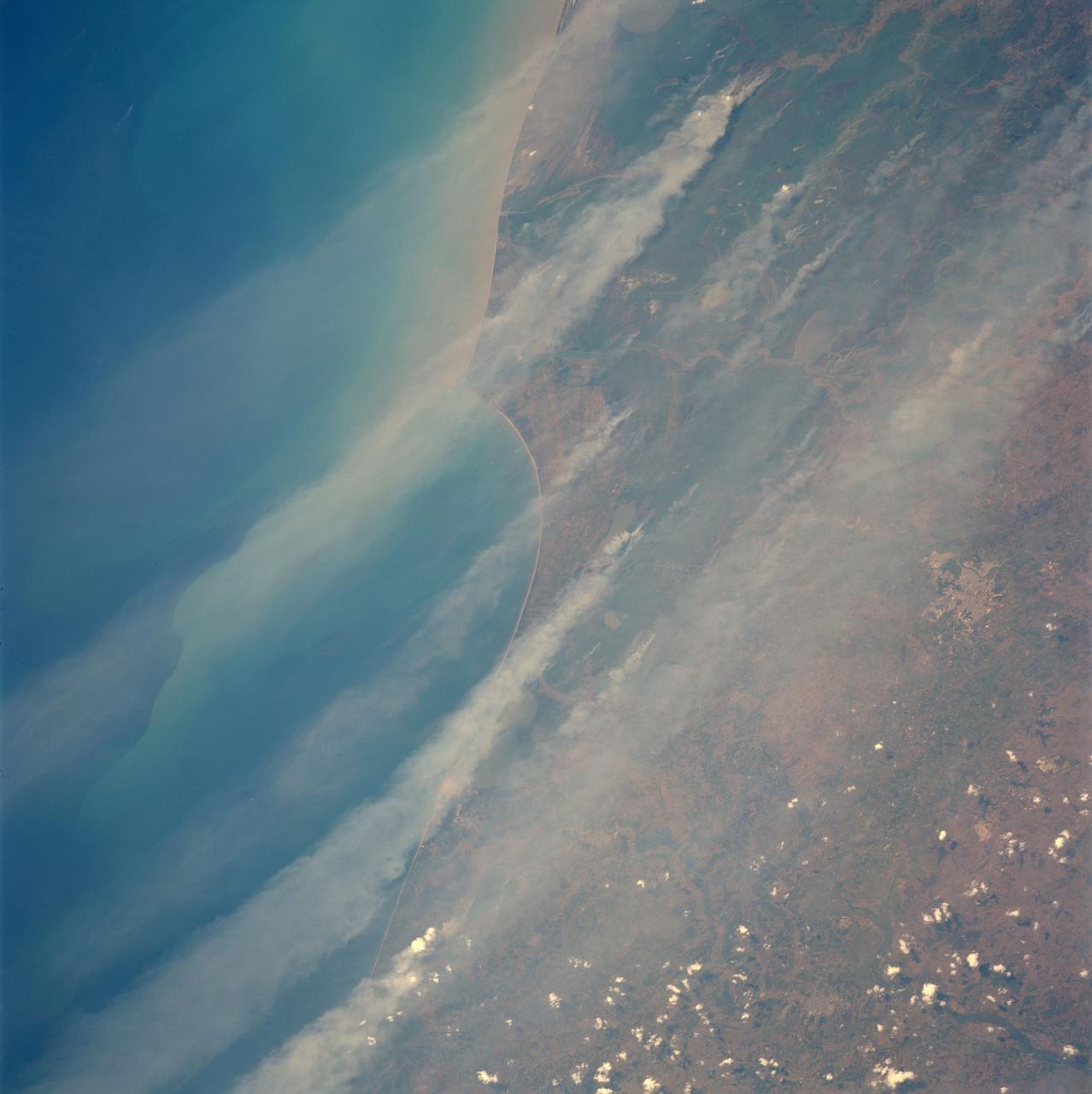
A vigorous summer fire season continued through July, 2013 as many large wildfires continued to burn in the forests of northern Canada. The high fire activity not only laid waste to thousands of hectares of boreal forest, but sent thick smoke billowing high into the atmosphere, where it was carried far across the Atlantic Ocean. On July 30, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite captured this true-color image of a river of smoke spreading south across the Hudson Bay. The blue background is formed by the waters of Hudson Bay. In the southeast the green, forest-covered land of Quebec province peeks from under a large cloud bank. Another large bank of white cloud covers the water in the southwest, and a smaller cloud bank covers the territory of Nunavut in the northwest. A bit of Baffin Island can be seen near the top center of the image. Looking closely at the image, it appears that the gray smoke mixes with whiter cloud in the south, suggesting they may be at the same level in the atmosphere. In the northeast corner of the image, a ribbon of smoke appears to blow over a bank of popcorn clouds as well as over a few lower-lying clouds, causing some of the clouds to appear gray beneath the smoky veil. Where cloud meets smoke in the northeast, however, the line of the cloud bank remains sharp, while the smoke appears to continue traveling under the edge. Although these interpretations are somewhat subjective in this true-color image, the false-color image of the same scene (not shown here) lends strength to the interpretation. Data from other NASA instruments, designed to measure cloud height and characteristics, agree that clouds vary in height, and that smoke mingles with cloud in the south. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
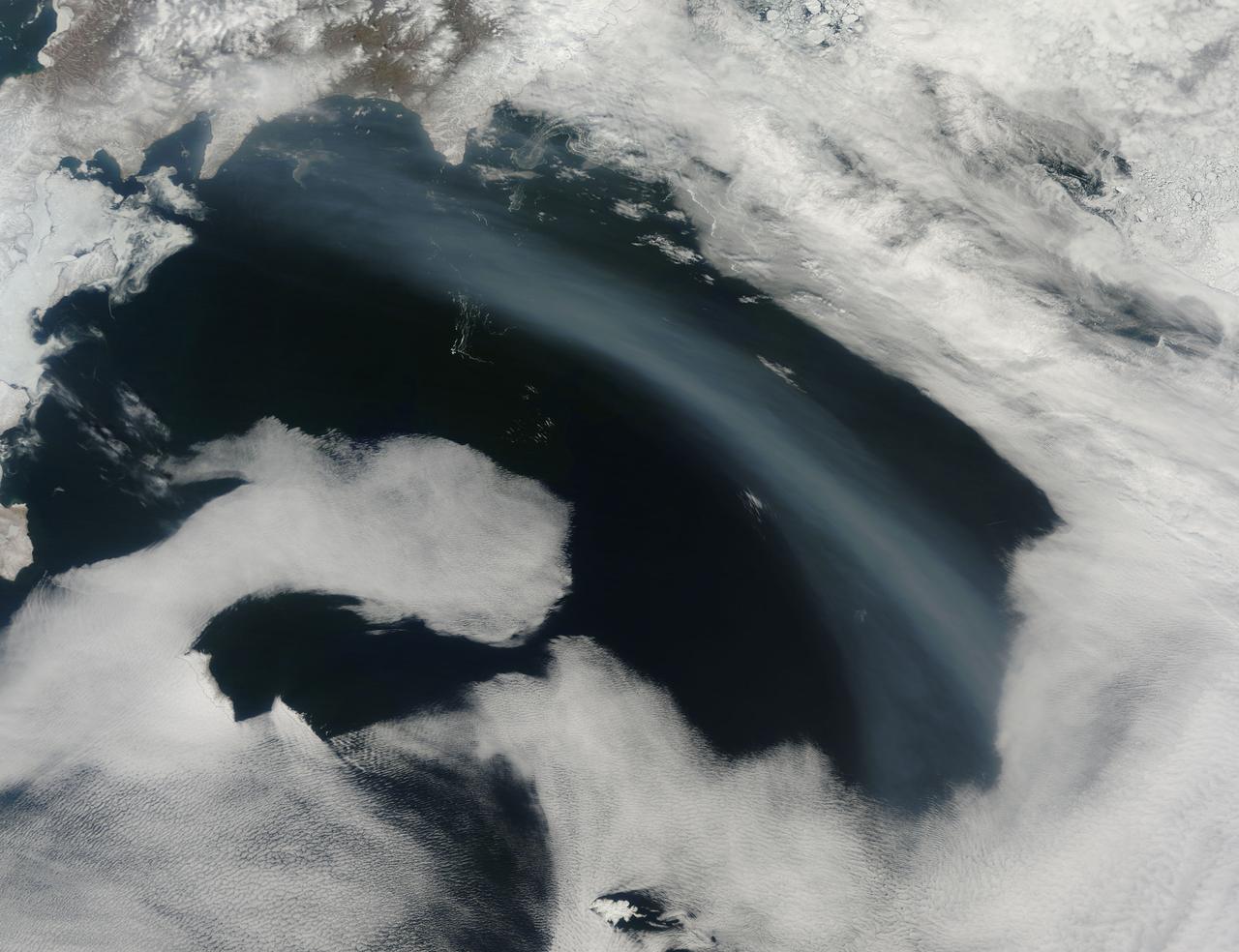

Smoke from Far Eastern Russia’s spring wildfires reached the Bering Sea by May 11, 2012. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer aboard NASA’s Terra satellite passed over the region at 23:30 UTC on that same day and acquired this true-color image of a broad band of smoke stretching across the blue waters. In this image, the plume of smoke appears light gray while banks of cloud are bright white. Snow covers much of Kamchatka the land mass in the west. Karaginsky Island, just off Kamchatka’s eastern shore, is surrounded by sea ice. Clouds stream off the southwest shores of Beringa and Medny Islands. To the east, Attu Station, Alaska, is surrounded by cloud. In early May, numerous wildfires burned near Lake Baikal, in Siberia. These fires billowed heavy smoke across eastern Mongolia, China and Russia’s Far East. An image of the smoke and fires was captured on May 8 and appeared as the MODIS image of the day on May 11. That image can be viewed here: <a href="http://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/individual.php?db_date=2012-05-11" rel="nofollow">modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/individual.php?db_date=2012-0...</a>. According to a model by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), it is possible that smoke from the Lake Baikal region could take just a few days to reach the Bering Sea. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
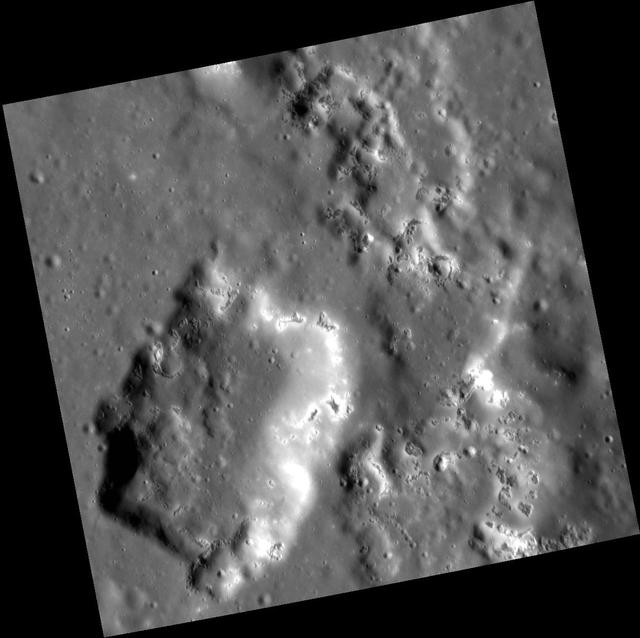

Hole-y Smokes!

Canada has already had its share of wildfires this season, and the smoke from these wildfires is slowly drifting south over the United States' Midwest. The drifting smoke can be seen in this Terra satellite image over Lake Michigan, as well as parts of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Indiana and Ohio. The smoke released by any type of fire (forest, brush, crop, structure, tires, waste or wood burning) is a mixture of particles and chemicals produced by incomplete burning of carbon-containing materials. All smoke contains carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and particulate matter (PM or soot). Smoke can contain many different chemicals, including aldehydes, acid gases, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), benzene, toluene, styrene, metals and dioxins. The type and amount of particles and chemicals in smoke varies depending on what is burning, how much oxygen is available, and the burn temperature. Exposure to any type of smoke should be avoided if possible, but especially by those with respiratory issues, the elderly, and children. This natural-color satellite image was collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Terra satellite on June 09, 2015. Credit: NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
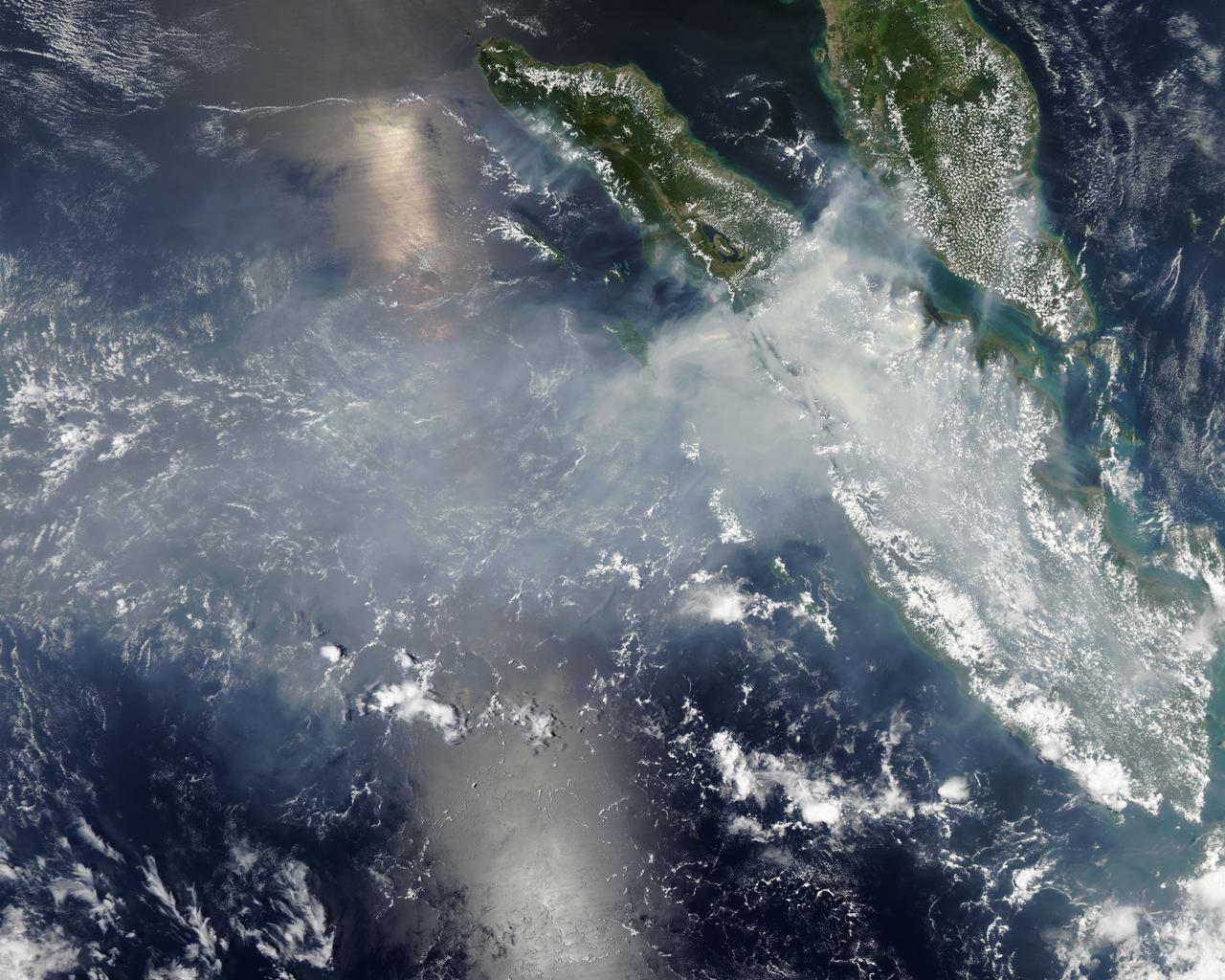

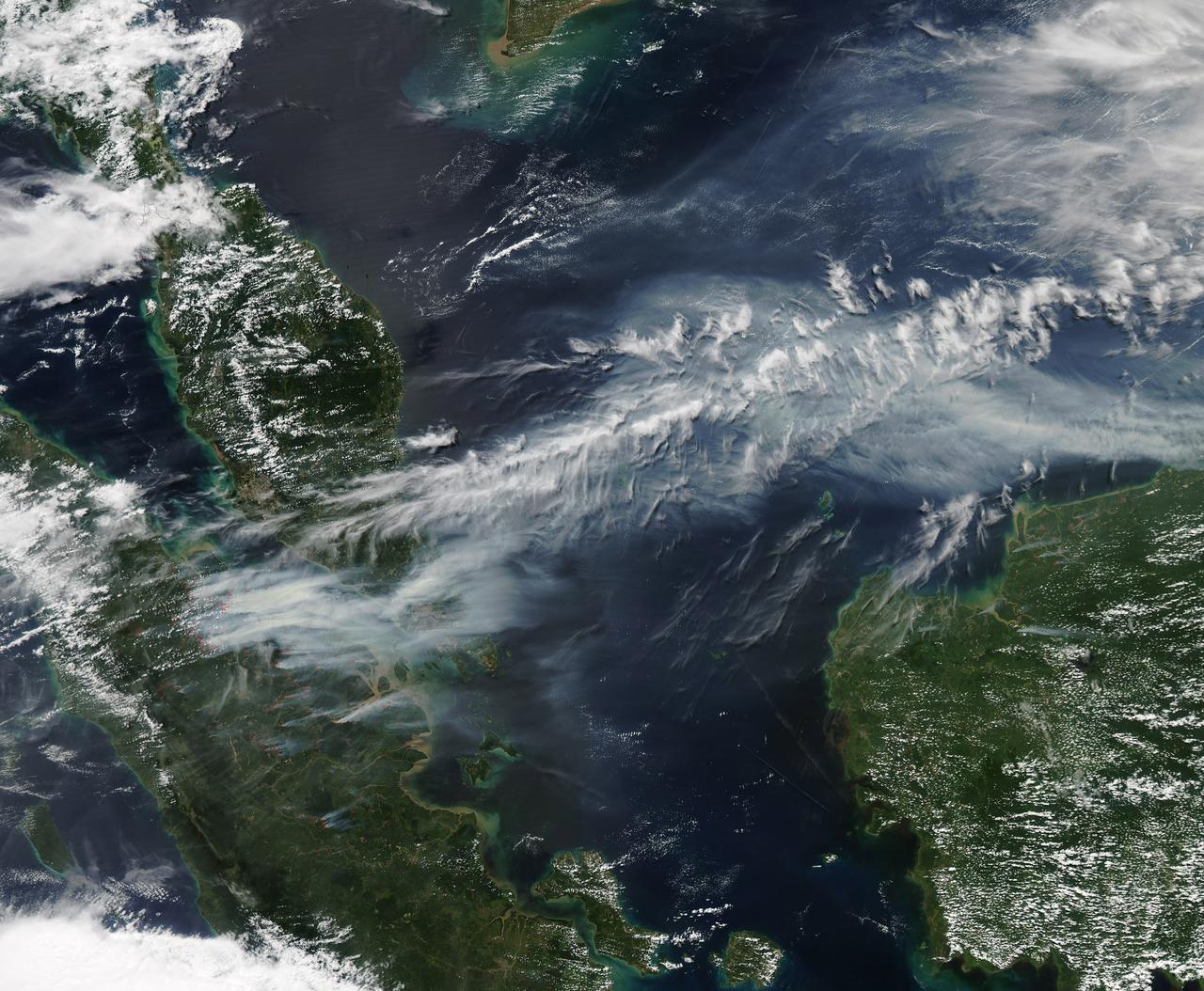
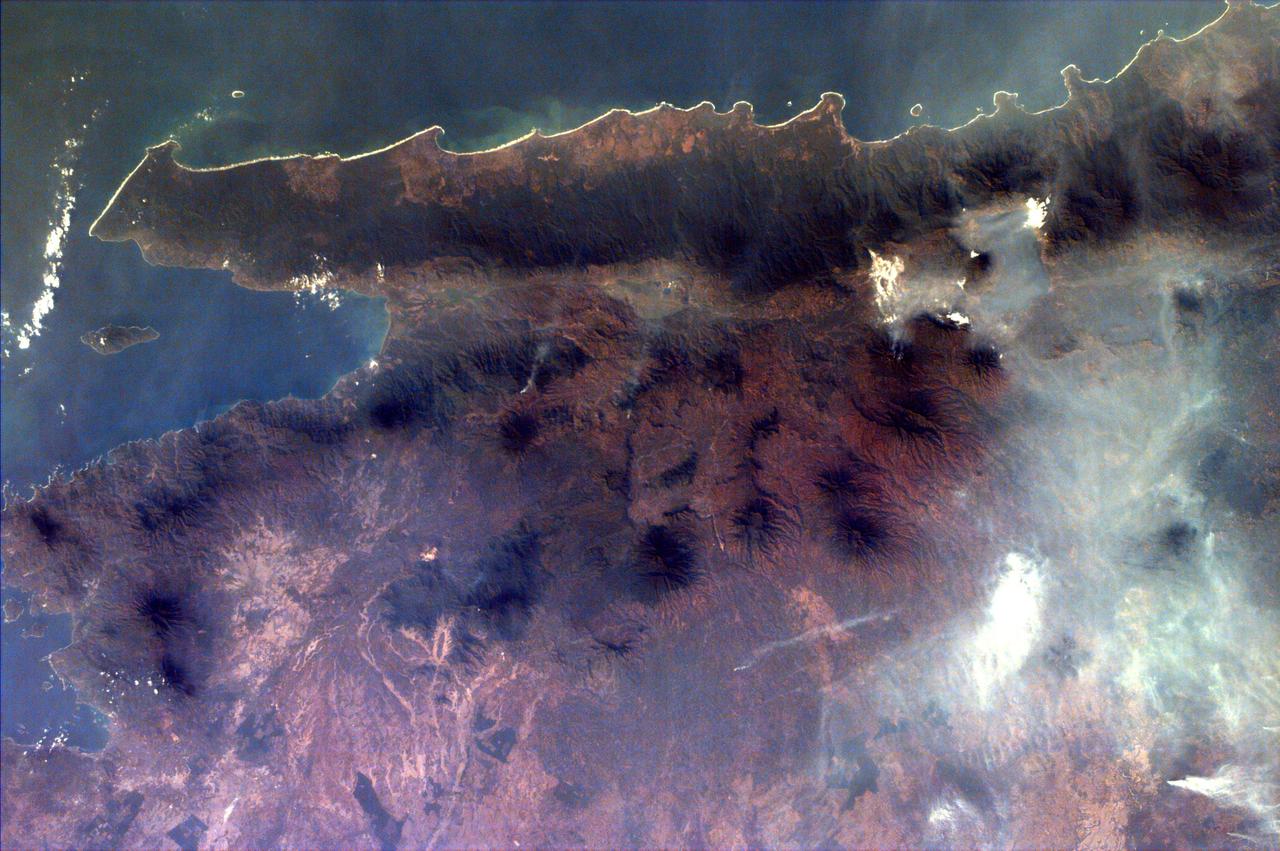
Fires burning in Sumatra continued to pour smoke over the region in mid-March, 2014, bringing air quality to dangerous levels. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite captured this true-color image of the smoke and haze across the region on March 12. According to the Jakarta Post, on March 12 the Sumatra Environmental Laboratory reported that 10 of 12 spots in Riau had an air quality of index above 300 on the Pollutant Standards Index (PSI), which is considered hazardous. Hazardous air quality had been recorded in some of the locations for 11 consecutive days. The province of Riau is located in the central eastern coast of Sumatra and, in this image, is hidden under thick bands of light gray smoke. Intense fires, reported as deliberately set to clear land, were burning in the Giam Siak Kecil-Bukit Batu biosphere reserve. This reserve contains over 700,000 hectares of sensitive peat forest that sustains a wide range of plant and animal species, including the Sumatra tiger, elephant, tapir and sun bear. With visibility as low as 500 m (1640 ft), 58 flights were cancelled in Pekanbaru, the capital of Riau province, on March 11. Schools were closed across the region, with 43,000 students affected in Payakumbuh, West Sumatra. On March 14, Selangor, Malaysia closed 203 schools, affecting 211,700 pupils, until the air quality improved. On that same day, according to Riau Health Agency, more than 55,000 residents in the province were suffering from haze-related illnesses, including acute respiratory infections, pneumonia and skin and eye irritation. Poor air quality not only affected transportation, human health and the ecosystem, but has had significant economic impacts. On March 17, Reuters reported that the poor air quality had forced Chevron, the country’s biggest oil producer, to close hundreds of its wells. As a result, Indonesia’s crude oil output dropped to 790,000 barrels per day (bpd) – significantly lower than the 870,000 bpd target. Although slash-and-burn techniques, which use fire to clear land, is illegal in Indonesia, the practice is still widespread, with approximately 99% of fires in Sumatra considered to be intentionally set. This year’s early agricultural fires began in February in Riau Province, home to palm-oil and pulpwood plantations. The emergency has prompted strong government response, including a shoot-on-sight order for any suspects involved in land burning activities that resisted arrest. According to the Jakarta Post, police have named as many as 60 suspected-fire starters in Riau. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
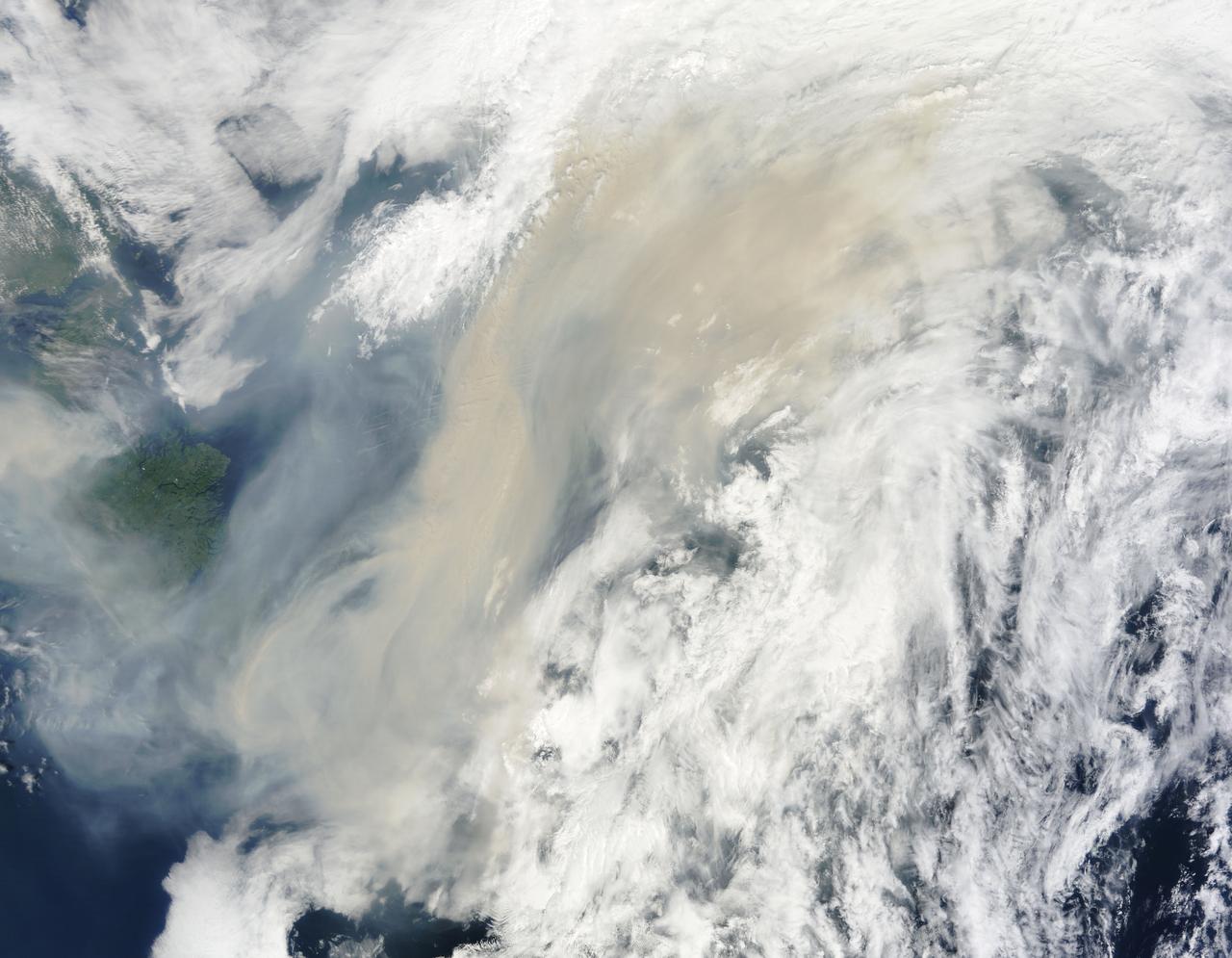

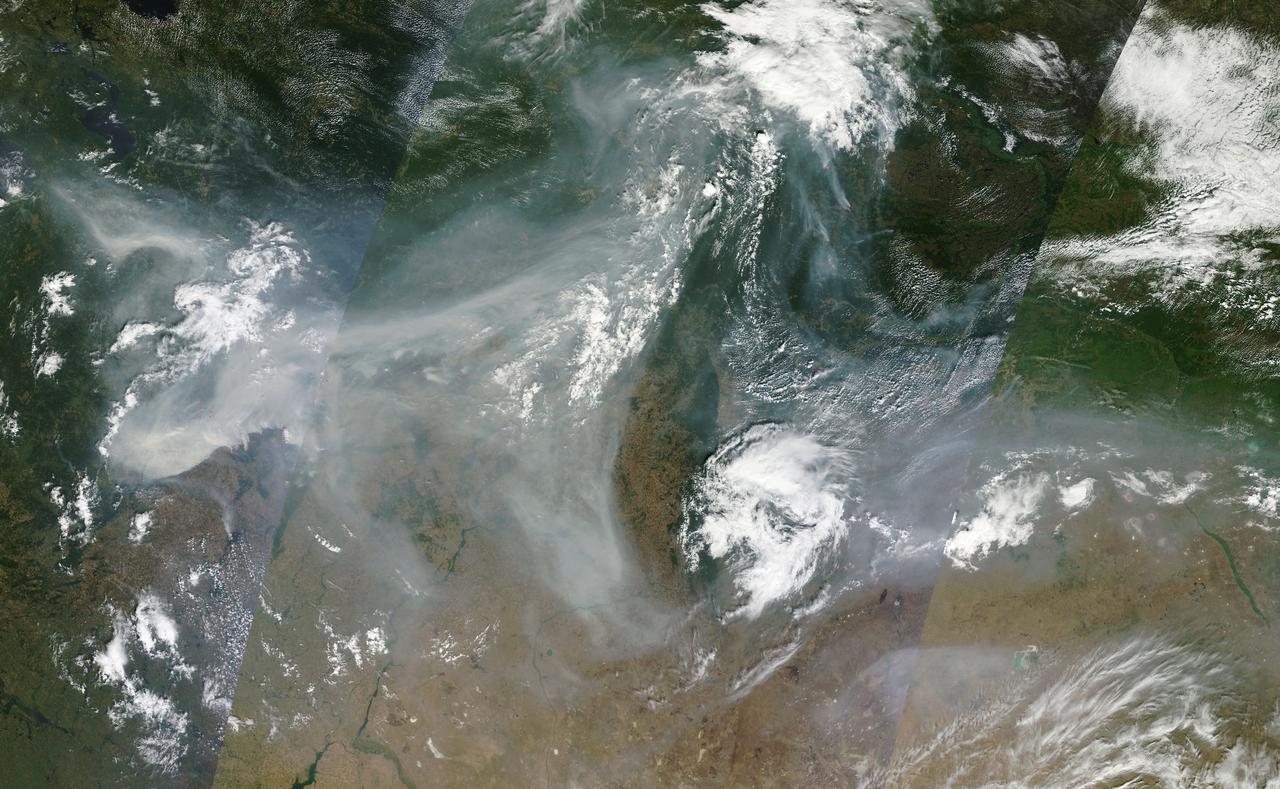
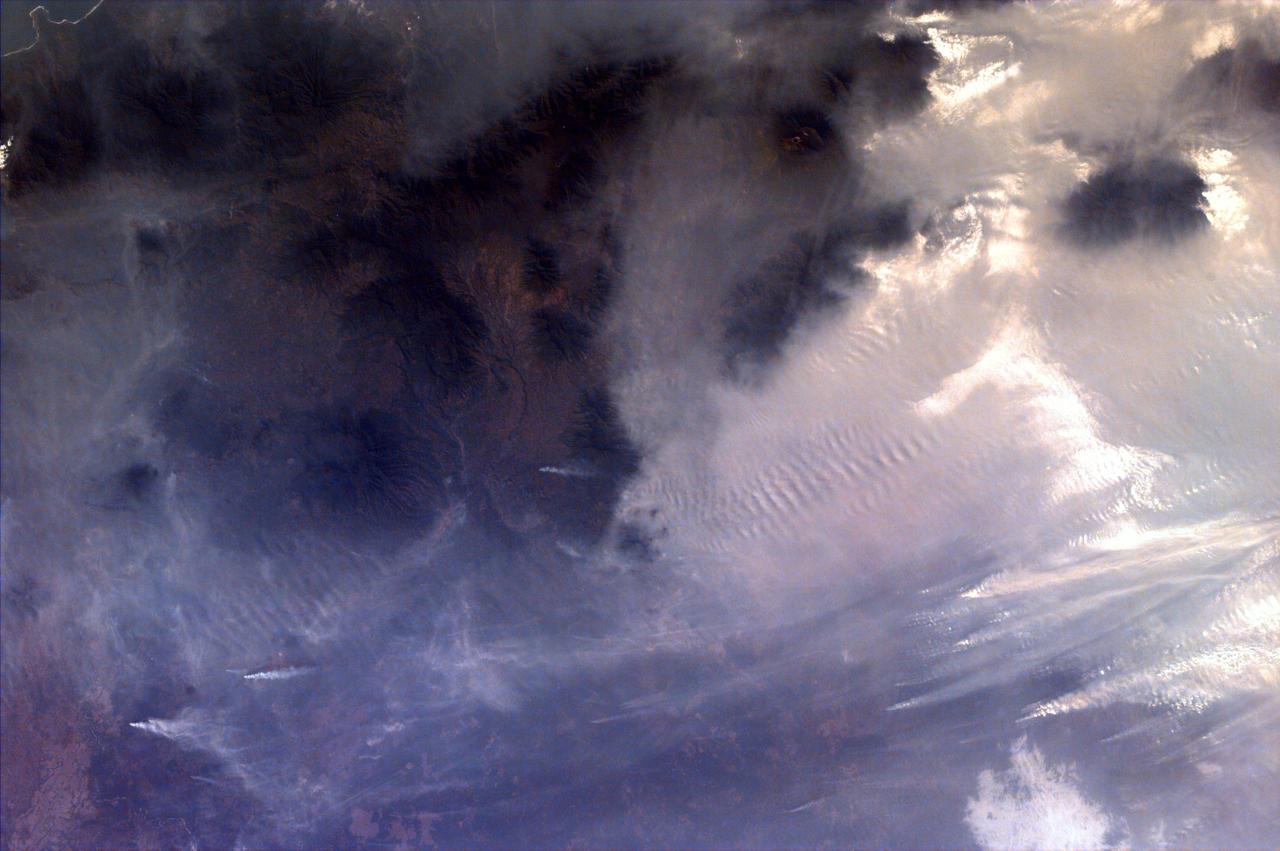
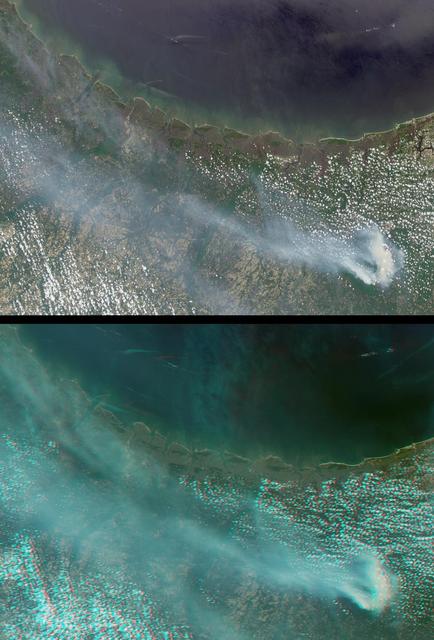
Generally the old saying “where there is smoke, there is fire” rings true, but when thick, hot smoke rises high aloft into the atmosphere it may travel hundreds, sometimes thousands of kilometers away from the source. This was the case on July 6, 2013 when the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument flying on NASA’s Terra satellite captured this true-color image of a thick river of smoke curling across the Atlantic Ocean. In the west of the image, the green land of Canada can be seen, most of which is covered by a thin gray haze. A thick veil of smoke obscures much of southern Canada, and this tan-gray veil blows to the east, then to the northeast. The color of the smoke appears both tan and gray, and is stretched into brush-stroke like curves across the ocean, which disappears from view under the smoke. The smoke filled plume is so high that it even hides the bright white clouds from view as it travels over them. Fires have been burning across Canada since early June, especially in Manitoba and Quebec. Rain in Quebec on July 5 helped diminish the fires in that location, although a severe fire was ignited when a freight train carrying oil derailed in the small, picturesque town of Lac-Megantic. This accident, which occurred on July 6, the same day this image was captured, killed at least 35 people and poured thick smoke into the skies. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

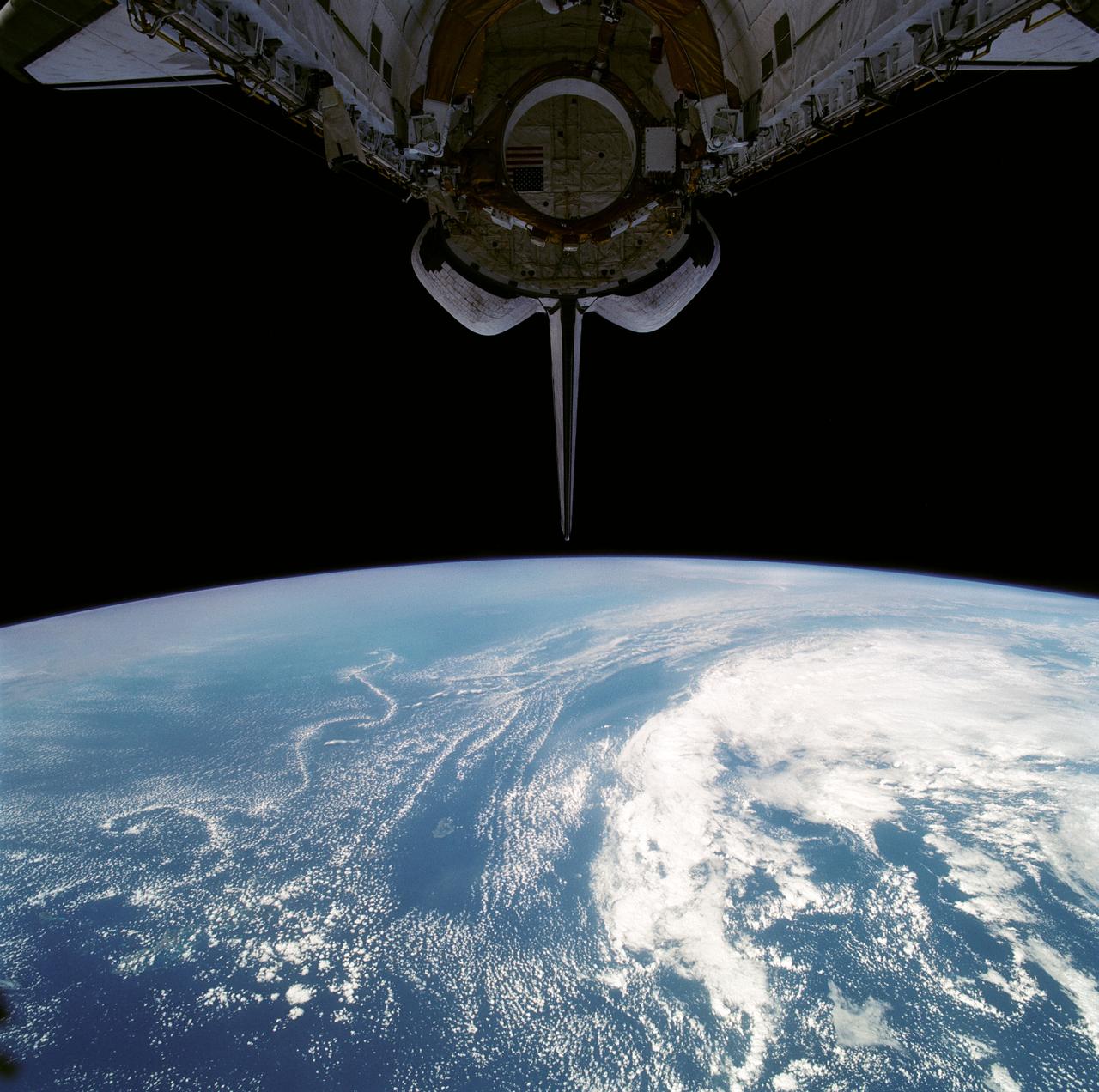
iss071e439719 (Aug. 6, 2024) --- A wildfire in Canada and its smoke spreading in the atmosphere are pictured from the Intenational Space Station as it orbited 263 miles above North Dakota.

NASA image acquired August 4, 2010 Intense fires continued to rage in western Russia on August 4, 2010. Burning in dry peat bogs and forests, the fires produced a dense plume of smoke that reached across hundreds of kilometers. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) captured this view of the fires and smoke in three consecutive overpasses on NASA’s Terra satellite. The smooth gray-brown smoke hangs over the Russian landscape, completely obscuring the ground in places. The top image provides a close view of the fires immediately southeast of Moscow, while the lower image shows the full extent of the smoke plume. To read more about this image go to: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=45046" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=45046</a> To view the high res go here: NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team at NASA GSFC. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a><b></b></b>
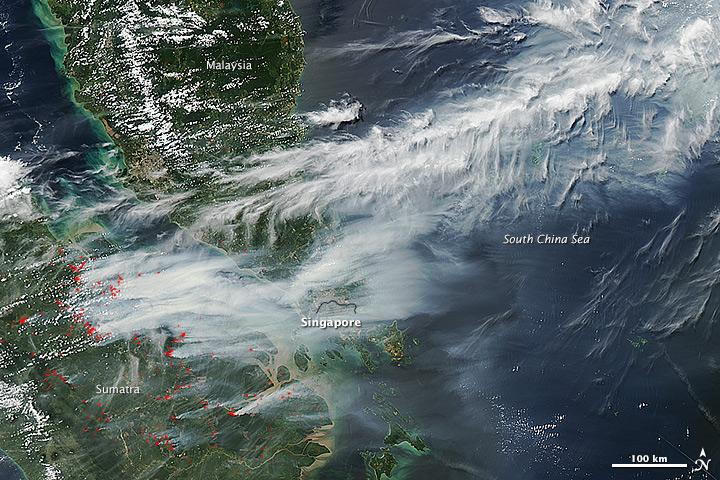

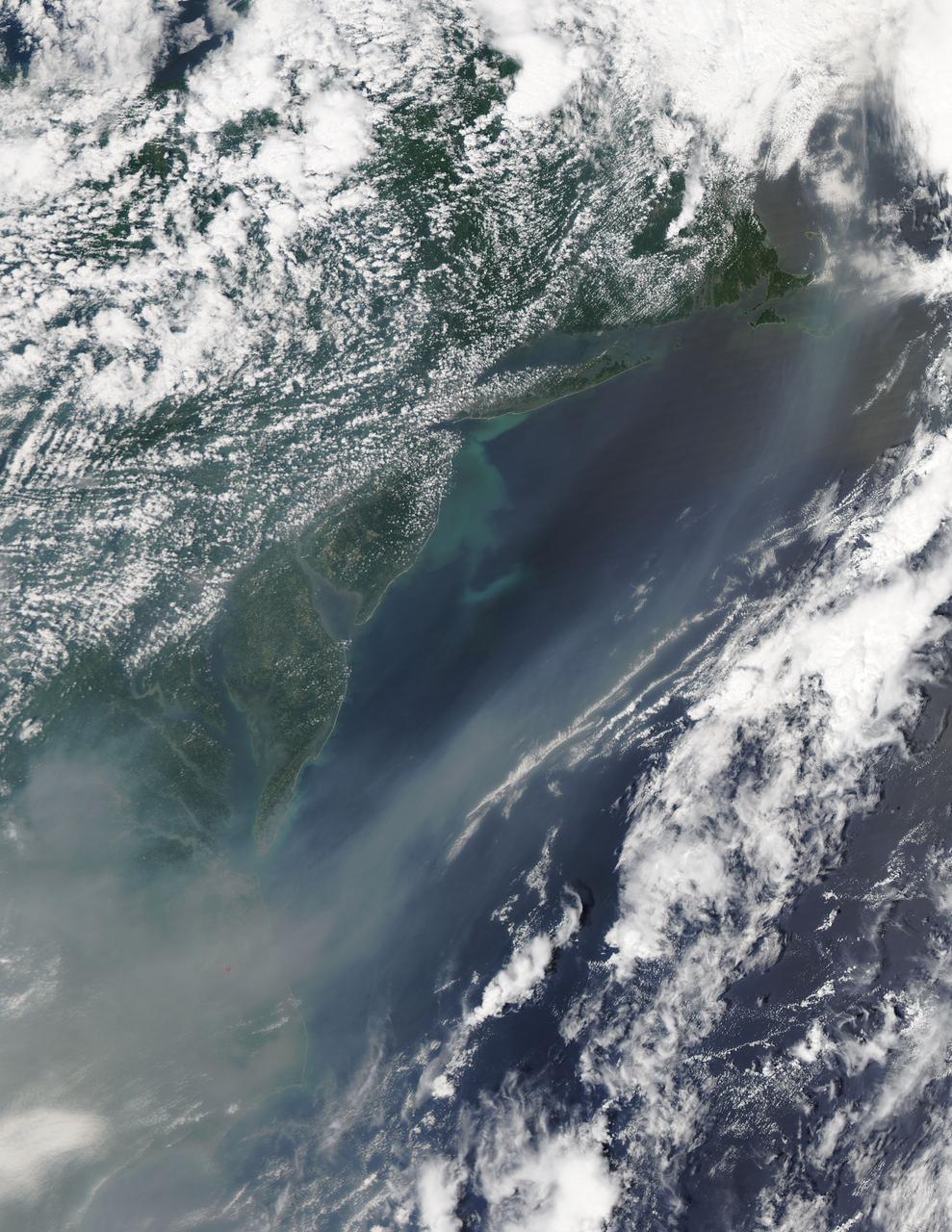
On June 19, 2013, NASA’s Aqua satellite captured a striking image of smoke billowing from illegal wildfires on the Indonesian island of Sumatra. The smoke blew east toward southern Malaysia and Singapore, and news media reported that thick clouds of haze had descended on Singapore, pushing pollution levels to record levels. Singapore’s primary measure of pollution, the Pollutant Standards Index (PSI)—a uniform measure of key pollutants similar to the Air Quality Index (AQI) used by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency—spiked to 371 on the afternoon of June 20, 2013, the highest level ever recorded. The previous record occurred in 1997, when the index hit 226. Health experts consider any level above 300 to be “hazardous” to human health. Levels above 200 are considered “very unhealthy.” The image above was captured by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), an instrument that observes the entire surface of Earth’s every 1 to 2 days. The image was captured during the afternoon at 6:30 UTC (2:30 p.m. local time). Though local laws prohibit it, farmers in Sumatra often burn forests during the dry season to prepare soil for new crops. The BBC reported that Singapore’s Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong warned that the haze could “easily last for several weeks and quite possibly longer until the dry season ends in Sumatra.” NASA image by Jeff Schmaltz, LANCE/EOSDIS Rapid Response. Caption by Adam Voiland. Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> Instrument: Aqua - MODIS <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA's Aqua satellite captured this image of the clouds over Canada. Entwined within the clouds is the smoke billowing up from the wildfires that are currently burning across a large expanse of the country. The smoke has become entrained within the clouds causing it to twist within the circular motion of the clouds and wind. This image was taken by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument on the Aqua satellite on May 9, 2016. Image Credit: NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz LANCE/EOSDIS MODIS Rapid Response Team, GSFC <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
On June 19, 2013, NASA’s Aqua satellite captured a striking image of smoke billowing from illegal wildfires on the Indonesian island of Sumatra. The smoke blew east toward southern Malaysia and Singapore, and news media reported that thick clouds of haze had descended on Singapore, pushing pollution levels to record levels. Singapore’s primary measure of pollution, the Pollutant Standards Index (PSI)—a uniform measure of key pollutants similar to the Air Quality Index (AQI) used by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency—spiked to 371 on the afternoon of June 20, 2013, the highest level ever recorded. The previous record occurred in 1997, when the index hit 226. Health experts consider any level above 300 to be “hazardous” to human health. Levels above 200 are considered “very unhealthy.” The image above was captured by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), an instrument that observes the entire surface of Earth’s every 1 to 2 days. The image was captured during the afternoon at 6:30 UTC (2:30 p.m. local time). Though local laws prohibit it, farmers in Sumatra often burn forests during the dry season to prepare soil for new crops. The BBC reported that Singapore’s Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong warned that the haze could “easily last for several weeks and quite possibly longer until the dry season ends in Sumatra.” NASA image by Jeff Schmaltz, LANCE/EOSDIS Rapid Response. Caption by Adam Voiland. Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> Instrument: Aqua - MODIS <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
These images acquired in 2002 from NASA Terra satellite show smoke over Rondonia, Brazil.

NASA image acquired August 4, 2010 Intense fires continued to rage in western Russia on August 4, 2010. Burning in dry peat bogs and forests, the fires produced a dense plume of smoke that reached across hundreds of kilometers. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) captured this view of the fires and smoke in three consecutive overpasses on NASA’s Terra satellite. The smooth gray-brown smoke hangs over the Russian landscape, completely obscuring the ground in places. The top image provides a close view of the fires immediately southeast of Moscow, while the lower image shows the full extent of the smoke plume. To read more about this image go to: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=45046" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=45046</a> NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team at NASA GSFC. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a><b></b></b>

On May 2, 2002, numerous fires in southern Mexico sent smoke drifting northward over the Gulf of Mexico. These views from NASA Terra satellite illustrate the smoke extent over parts of the Gulf and the southern Mexican states of Tabasco, Campeche and Ch

The InciWeb Incident Information System is following 18 fires in Alaska that are contributing, along with 49 uncontrolled fires under surveillance by the Canadian Wildland Fire Information System, to vast areas of visible smoke throughout Canadian provinces and stretching into northern U.S. states. This image from the Suomi NPP satellite's VIIRS instrument was taken from NOAA View on June 28, 2015. The smoke from these fires can also be seen in NOAA View as Aerosol Optical Thickness, a measure of how aerosols, such as smoke from wildfires, scatter and absorb sunlight. <b><a href="http://goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">Credit: NOAA/NASA GOES Project</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

The smoke from the Canadian wildfires that was in the middle of the U.S. on June 30 has drifted its way to the East Coast obscuring parts of the coast from New Jersey to North Carolina. Images taken on June 30 showed the smoke covering states from Minnesota to Tennessee. The jet stream has pushed the smoke along so that by July 1 it reached the U.S. East Coast. Residents of the area will get a preview of July 4th fireworks with redder than usual sunrises and sunsets due to particulates in the air. This natural-color satellite image was collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Aqua satellite on July 1, 2015. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
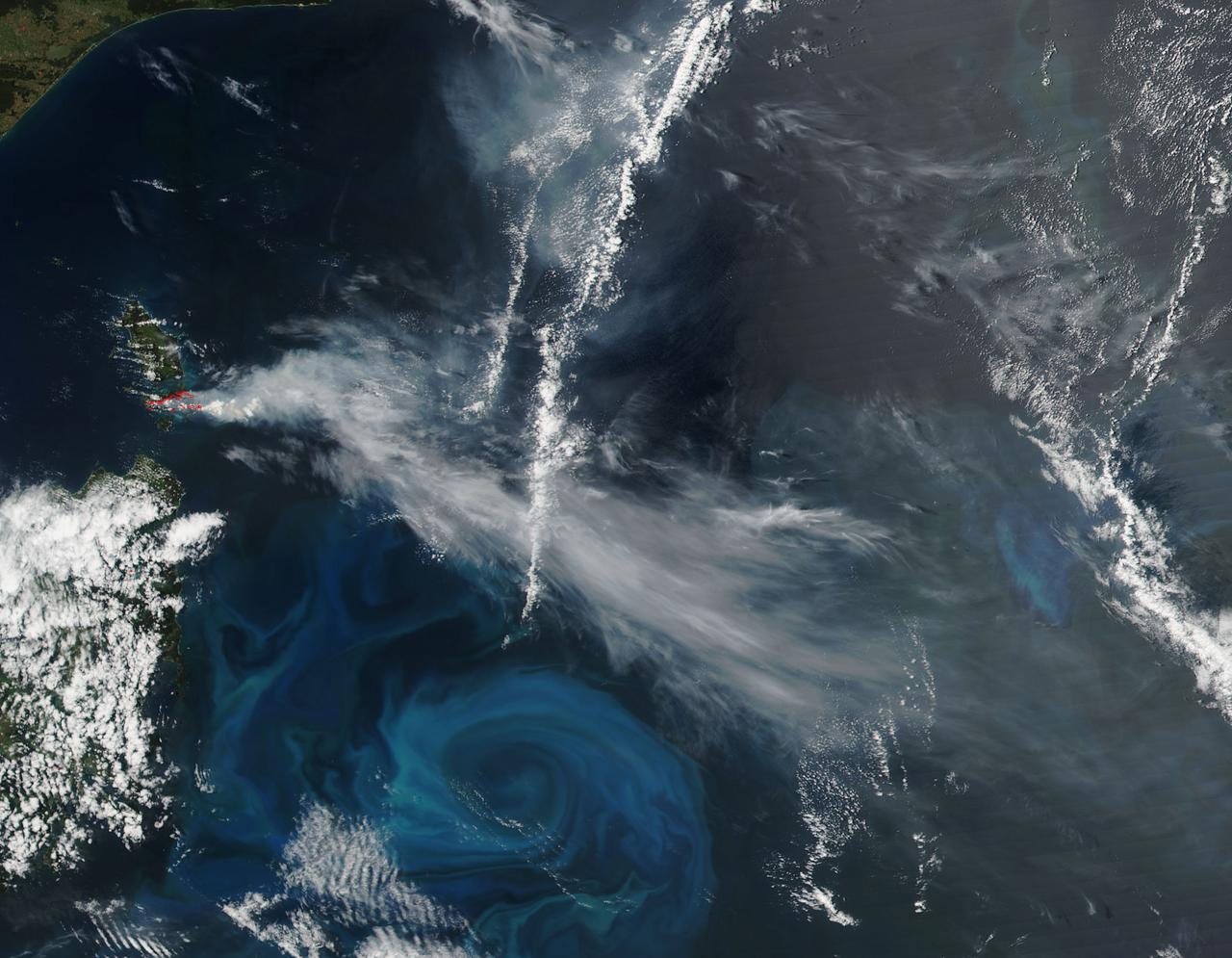
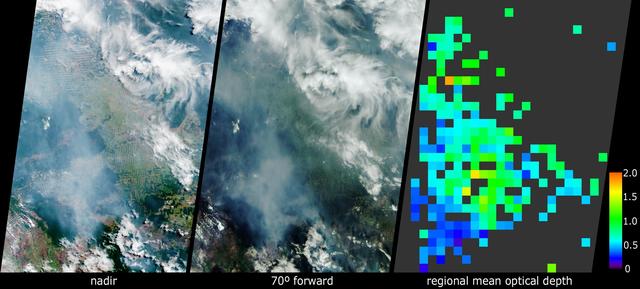
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Australia's Cape Barren Island and captured an image of phytoplankton and smoke from fires that resembled an eye and eyebrow. The Tasmanian Fire Service reported that a vegetation fire near Thunder and Lightning Bay, Cape Barren Island started on December 4 and was still blazing on December 8. Cape Barren Island is one of a trail of islands in the Bass Strait of the South Pacific Ocean, between southeastern Australia and Tasmania. This natural-color satellite image from Dec. 7 was collected by the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite. The red dots in the image represent heat signatures from the fires as detected by VIIRS. A light grey stream of smoke was blowing to the southeast in what could be seen as the "eyebrow" to the "eye" or swirl of blue and green phytoplankton below it. Phytoplankton are tiny microscopic plant-like organisms that form the base of the marine food chain. Like land plants, phytoplankton contain chlorophyll which is used in photosynthesis to turn sunlight into chemical energy. The chlorophyll gives the phytoplankton their green color, which is visible from space when large numbers of the organism group together. NASA image courtesy MODIS Rapid Response Team #nasagoddard #earth #smoke #Phytoplankton #science b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
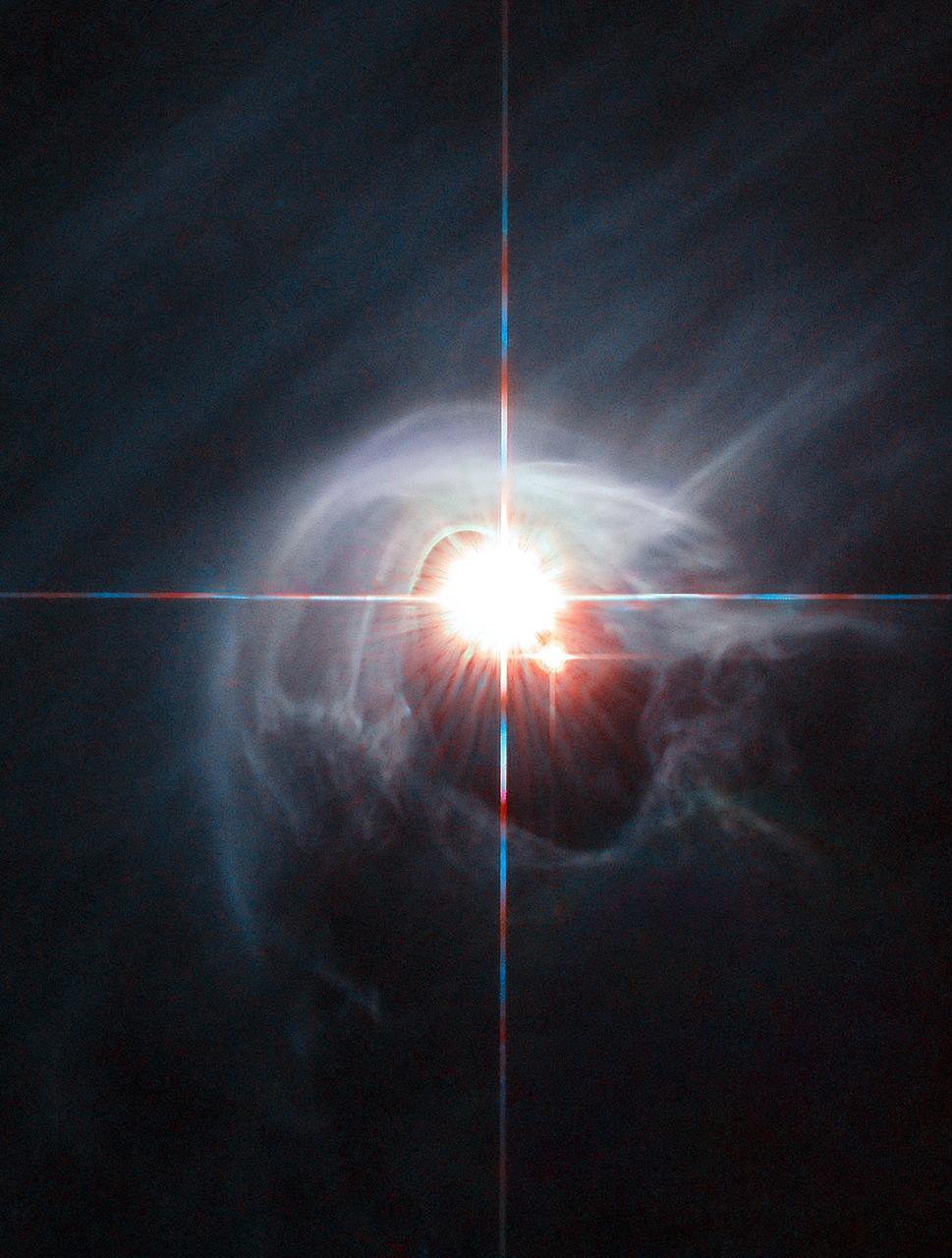

Two stars shine through the centre of a ring of cascading dust in this image taken by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. The star system is named DI Cha, and while only two stars are apparent, it is actually a quadruple system containing two sets of binary stars. As this is a relatively young star system it is surrounded by dust. The young stars are moulding the dust into a wispy wrap. The host of this alluring interaction between dust and star is the Chamaeleon I dark cloud — one of three such clouds that comprise a large star-forming region known as the Chamaeleon Complex. DI Cha's juvenility is not remarkable within this region. In fact, the entire system is among not only the youngest but also the closest collections of newly formed stars to be found and so provides an ideal target for studies of star formation.
A look at smoke from the Chisholm forest fire, which ignited on May 23, 2001 about 160 kilometers north of Edmonton in Alberta, Canada, as seen by NASA Terra spacecraft.
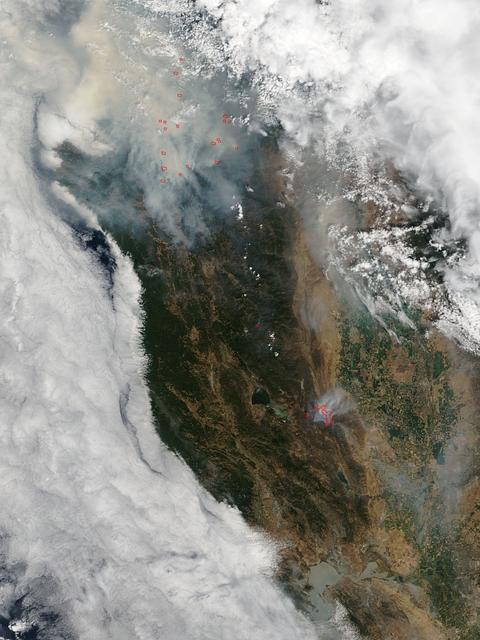

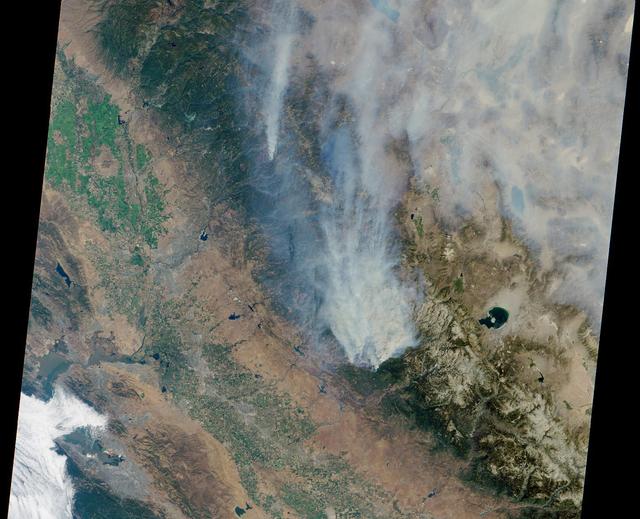
This satellite image shows smoke from several fires in Oregon and California on Aug. 2, 2015. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image of smoke from these fires Aug. 2 at 21:05 UTC (5:05 p.m. EDT). The multiple red pixels are heat signatures detected by MODIS. The smoke appears to be a light brown color. InciWeb is an interagency all-risk incident information management system that coordinates with federal, state and local agencies to manage wildfires. In Oregon smoke from the Cable Crossing Fire, the Stouts Fire and the Potter Mountain Complex Fire commingle. The Cable Crossing Fire was reported burning on forestlands protected by the Douglas Forest Protective Association (DFPA) at approximately 3:25 p.m. on Tuesday, July 28, 2015, near Oregon Highway 138 East, near Mile Post 23, east of Glide. South of the Cable Crossing Fire is the Stouts Fire also in forestlands of the DFPA. This fire was reported on Thursday, July 30, 2015, burning approximately 11 miles east of Canyonville near the community of Milo. East of the other fires is the Potter Mountain Complex Fire. These fires are located in the Deschutes Forest consists of eight fires. According to Inciweb they were started by dry lightning on Saturday, Aug. 2, at approximately 5:30 p.m. about five miles north of Toketee Lake. In northern California, smoke from the River Complex Fire, the Fork Complex Fire and the Shf July Lightning Fire was visible in the MODIS image. The River Complex currently consists of seven reported and observed fires on the Six Rivers and Shasta Trinity National Forests. Originally identified as 18 fires, some have burned together. Inciweb noted that in the Six Rivers National Forest there are fires in the Trinity Alps Wilderness. Those fires include the Groves Fire and the Elk Fire. In the Shasta-Trinity National Forest the fires include the Happy Fire at 2,256 acres, Daily Fire at 16 acres, the Look Fire at 7 acres, Onion Fire at 136 acres and Smokey Fire at 1 acre. In the same forest, south of the River Complex is the Fork Complex fire. Inciweb reported that the Fork Complex consists of (at current count) over 40 fires, all of which were ignited by lightning between July 29 and 31, 2015. To the southwest of this complex is the Mad River Complex. This is a series of seven lightning fires that started on July 30, 2015 after a lightning storm moved through Northern California. To the east of this and the other fires, burns another near Redding, California, called the Shf July Lightning Fire. This is also under the Shasta-Trinity National Forest management. At 8 p.m. PDT on Aug. 2, Inciweb reported that approximately 15 lightning strikes occurred within 24 hours throughout the Shasta Trinity National Forest and resulted in two new fires. The Caves fire, east of Mt. Shasta, is approximately one-tenth of an acre. The Bluejay fire, east of Shasta Lake, is approximately four acres. Image credit: NASA Goddard's MODIS Rapid Response Team, Jeff Schmaltz <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
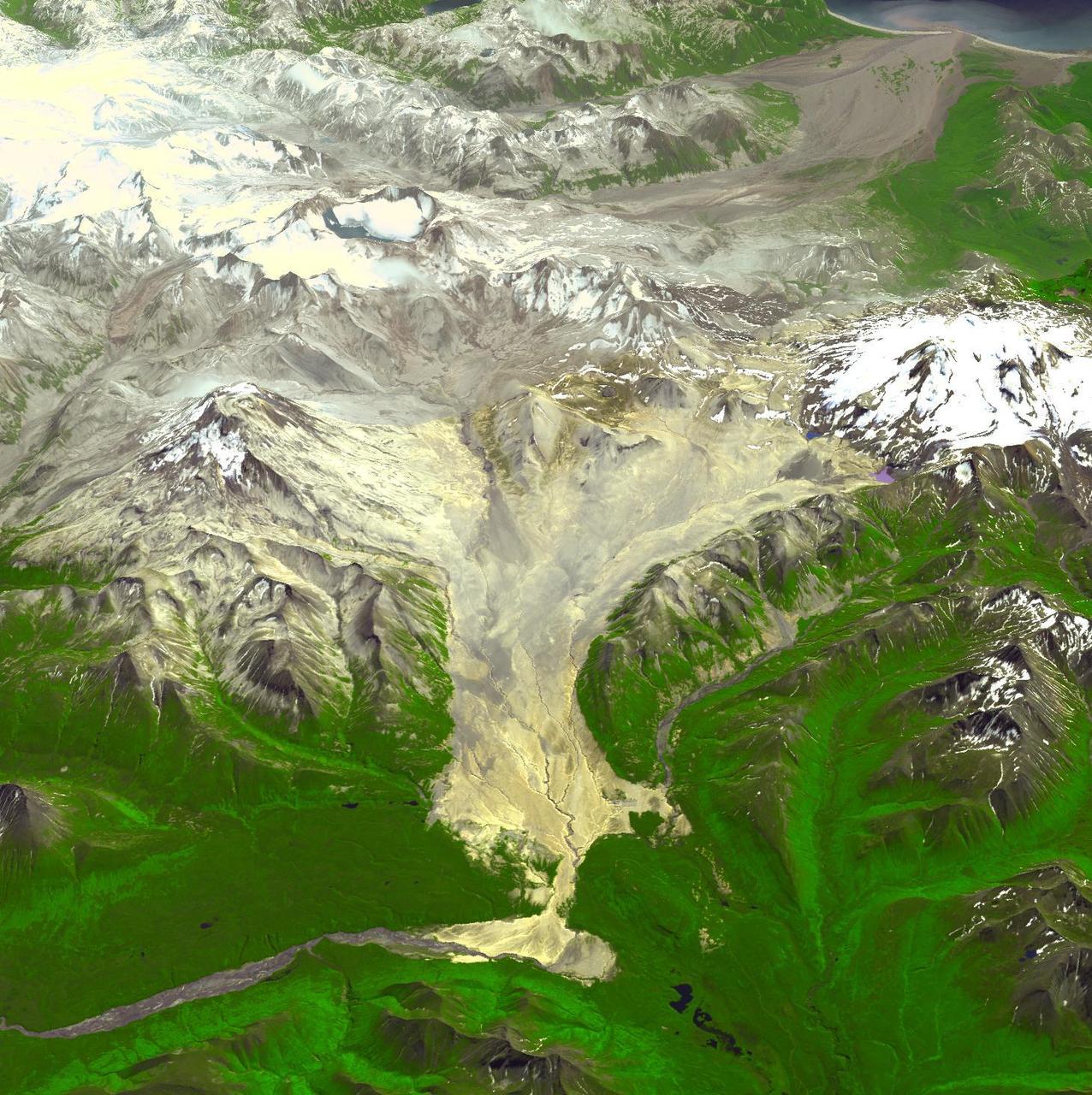
This image acquired by NASA Terra spacecraft is of the Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes. Located in Katmai National Park, Alaska, the park is filled with ash flows from the 1912 eruption of Novarupta.

As the Space Shuttle Atlantis flew over the Indonesian archipelago on Saturday, Sept. 27, 1997, middle school students across the country used NASA Kidsat camera to photograph the fires and smoke that blanket the island of Sumatra.
These images and data products from NASA Terra spacecraft documented extensive smoke from fires burning throughout Nigeria and north central Africa on January 31, 2003.

Two stars shine through the center of a ring of cascading dust in this image taken by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. The star system is named DI Cha, and while only two stars are apparent, it is actually a quadruple system containing two sets of binary stars. As this is a relatively young star system it is surrounded by dust. The young stars are molding the dust into a wispy wrap. The host of this alluring interaction between dust and star is the Chamaeleon I dark cloud — one of three such clouds that comprise a large star-forming region known as the Chamaeleon Complex. DI Cha's juvenility is not remarkable within this region. In fact, the entire system is among not only the youngest but also the closest collections of newly formed stars to be found and so provides an ideal target for studies of star formation. Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

L1-422 Nike Smoke Rocket and Launcher in Firing Position. Image taken at Wallops Island.
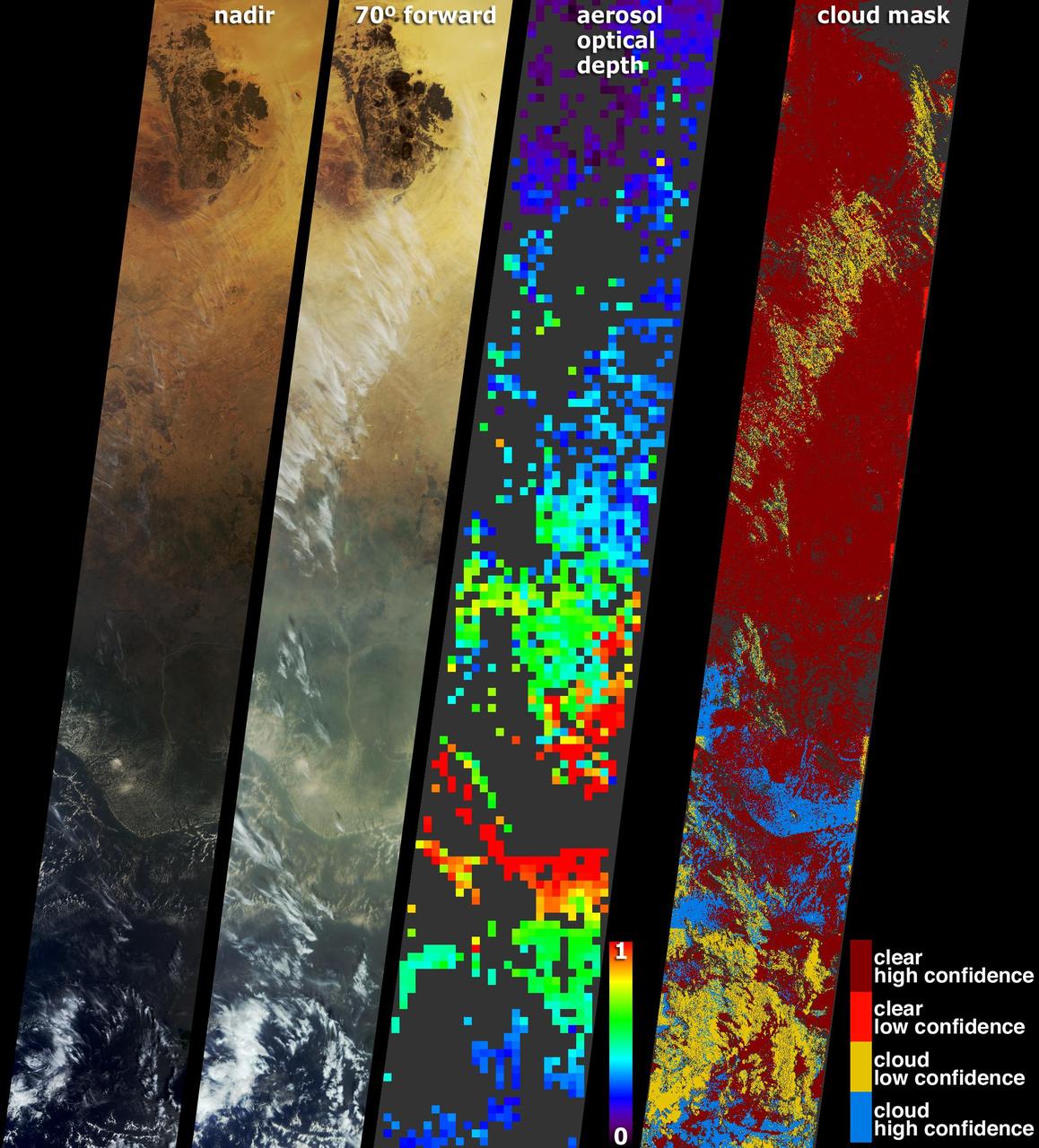
These data products from NASA Terra satellite document the presence of airborne particulates on March 13, 2002, during Terra orbit 11880. At least once a year for a period lasting from a week to several months, northern Sumatra is obscured by smoke and

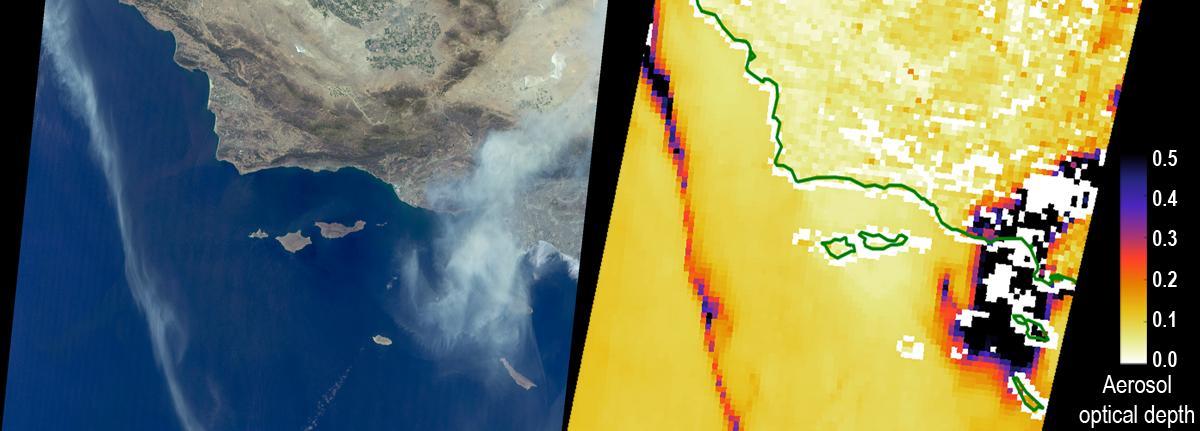
This observation shows the burn area and smoke plume created by the Apple fire in Southern California on Aug. 1, 2020. The observation was made possible by NASA's Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station (ECOSTRESS). Data gathered by the mission can be further refined to measure the temperature of the wildfire, smoke plume and surrounding landscape. ECOSTRESS collected this data when the space station passed over the region at about 1:15 p.m. PST on Saturday, Aug. 1, 2020, when the burn area was approximately 4,000 acres in size. As of Aug. 3, it was more than 26,000 acres. Black smoke can be seen drifting east and over Joshua Tree National Park in the Mojave Desert. With a resolution of about 77 by 77 yards (70 by 70 meters), the image enables surface-temperature conditions down to the size of a football field to be studied. Tasked with detecting plant water use and stress, ECOSTRESS measures the temperature of plants as they heat up when they run out of water. But it can also measure and track heat-related phenomena like fires, heat waves, and volcanoes. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23799

NASA’s Aqua satellite captured a large area of smoke from the Long Valley Wildfire that was affecting Yosemite National Park. This natural-color satellite image was collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer instrument that flies aboard the Aqua satellite. The image, taken July 20, showed actively burning areas in red, as detected by MODIS’s thermal bands. According to Inciweb, an interagency all-risk incident information management system that coordinates with federal, state and local agencies to manage wildfires, the fire started on Tuesday July 11, 2017. It is located about two miles north of Doyle, California and about 50 miles north of Reno, Nevada. As of July 21 the fire covered 83,733 acres and was 91 percent contained. NASA image courtesy NASA MODIS Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
Smoke from multiple wildfires burning in Southern California in October, 2007, can be seen in this false-color image from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder AIRS on NASA Aqua satellite.
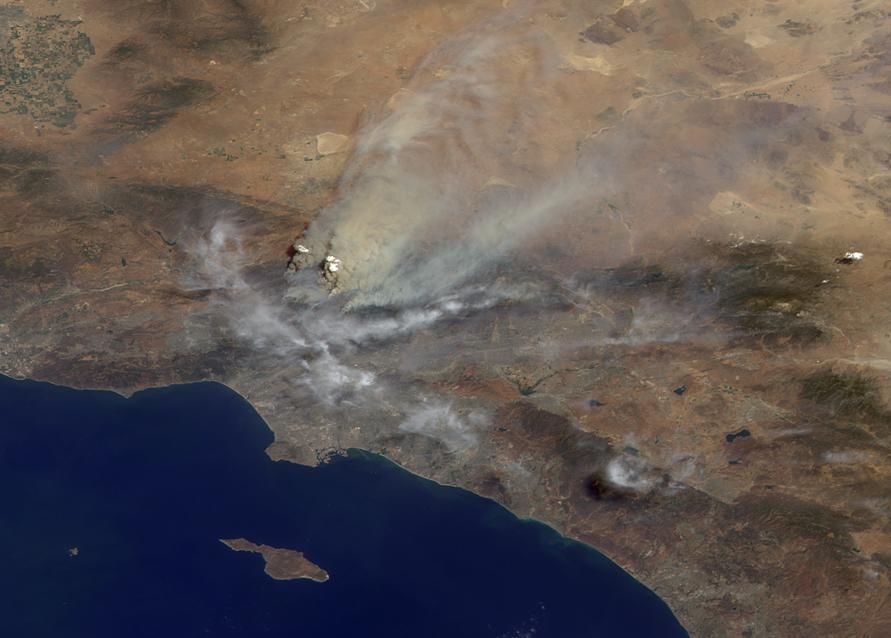

The Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer MISR instrument on NASA Terra satellite captured this Aug. 30 image of smoke plumes from the Station and other wildfires burning throughout Southern California.
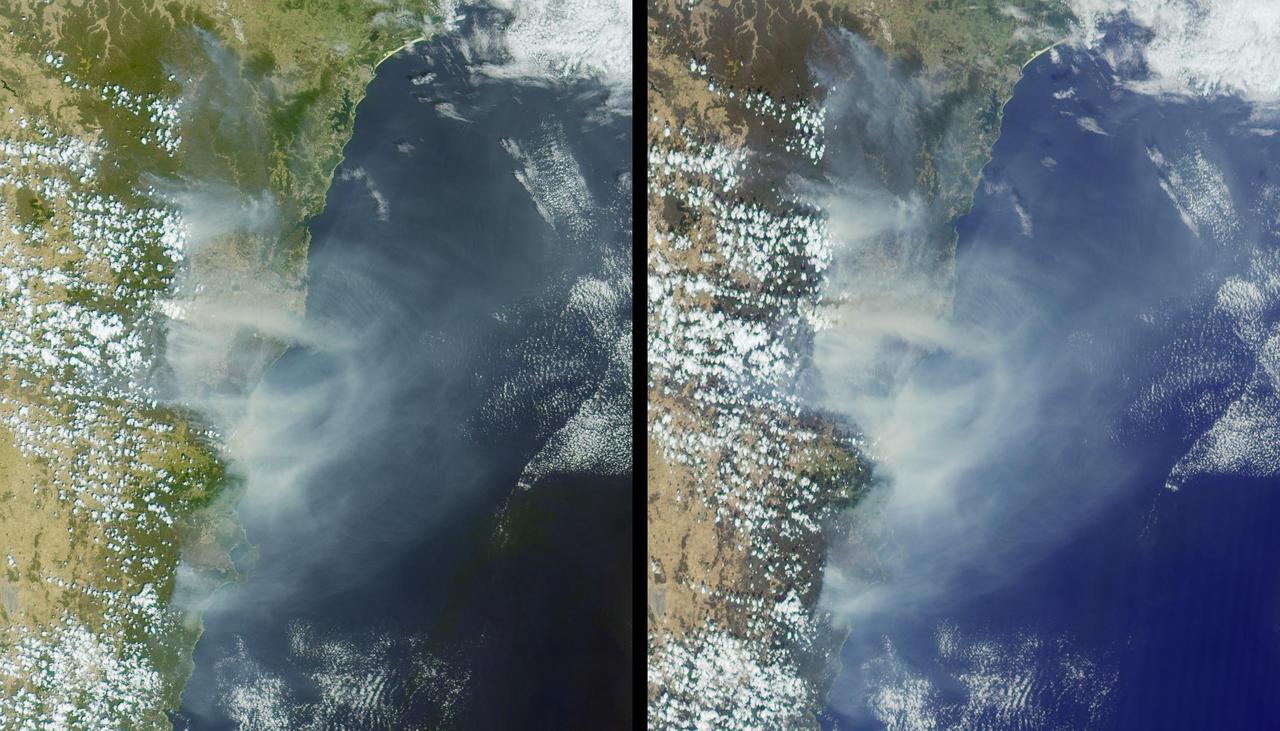

Australia largest city of Sydney was clouded with smoke when more than 70 wildfires raged across the state of New South Wales when NASA Terra satellite captured this image the morning of December 30, 2001.
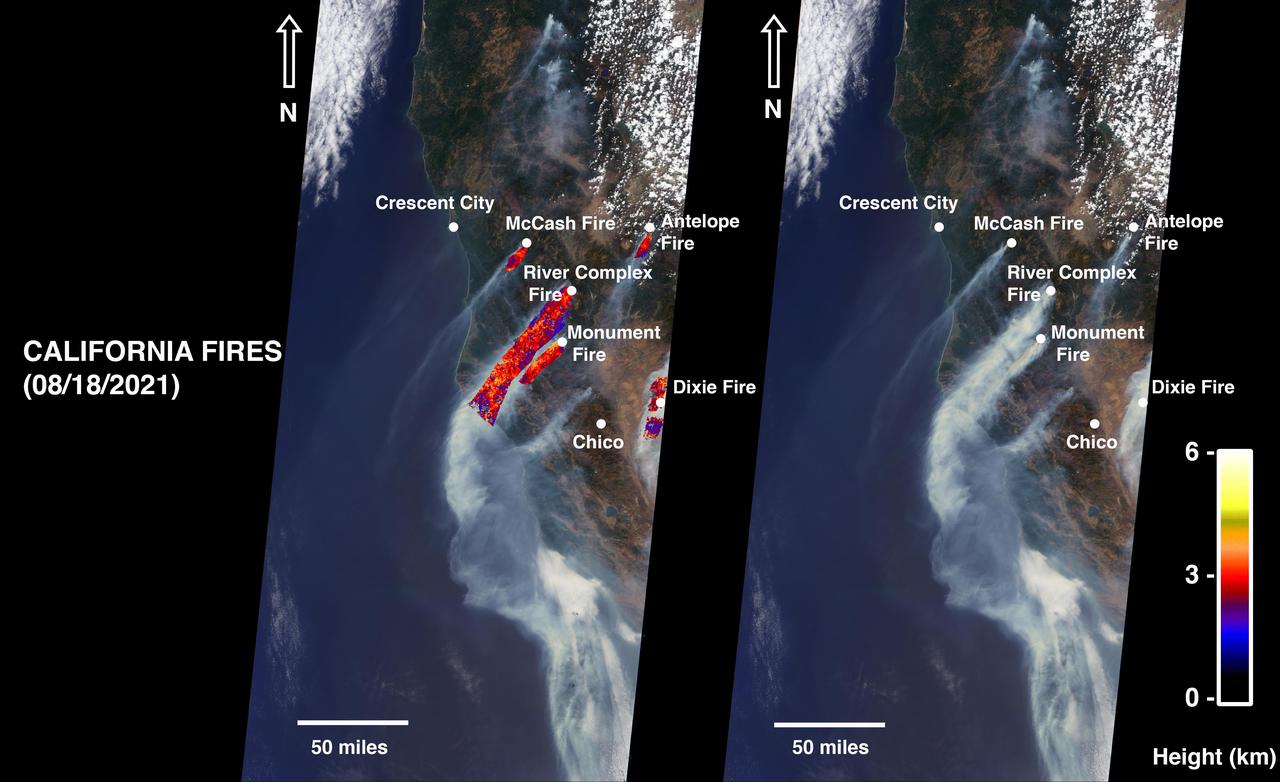
On August 18, 2021, at 12:10 p.m. local time, the Multi-angle Imaging Spectroradiometer (MISR) instrument captured imagery of the McCash, Antelope, River Complex, Monument, and Dixie fires as it passed overhead aboard NASA's Terra satellite. Combined, the fires had burned over 1 million acres as of August 24, 2021. MISR has nine cameras that view Earth at different angles. The right side of the image shows smoke from the five fires as observed by MISR's nadir (downward-pointing) camera. The multi-angular information from MISR's images is used to calculate the height of the smoke plumes. The results of those calculations are shown on the left side of the image. Smoke from areas in red reached an altitude of at least 9,842 feet (3,000 meters). The highest plume top near the active fires reached approximately 19,685 feet (6,000 meters). In general, higher-altitude plumes like this one transport smoke greater distances from the source, impacting communities downwind. In recent weeks, smoke from fires in the Western U.S. and Canada has impacted much of the East Coast. This data was acquired during Terra orbit 115254. The smoke plume height calculation was performed using the publicly available MISR INteractive eXplorer (MINX)software tool. The MISR Plume Height Project maintains a database of global smoke plume heights. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23698
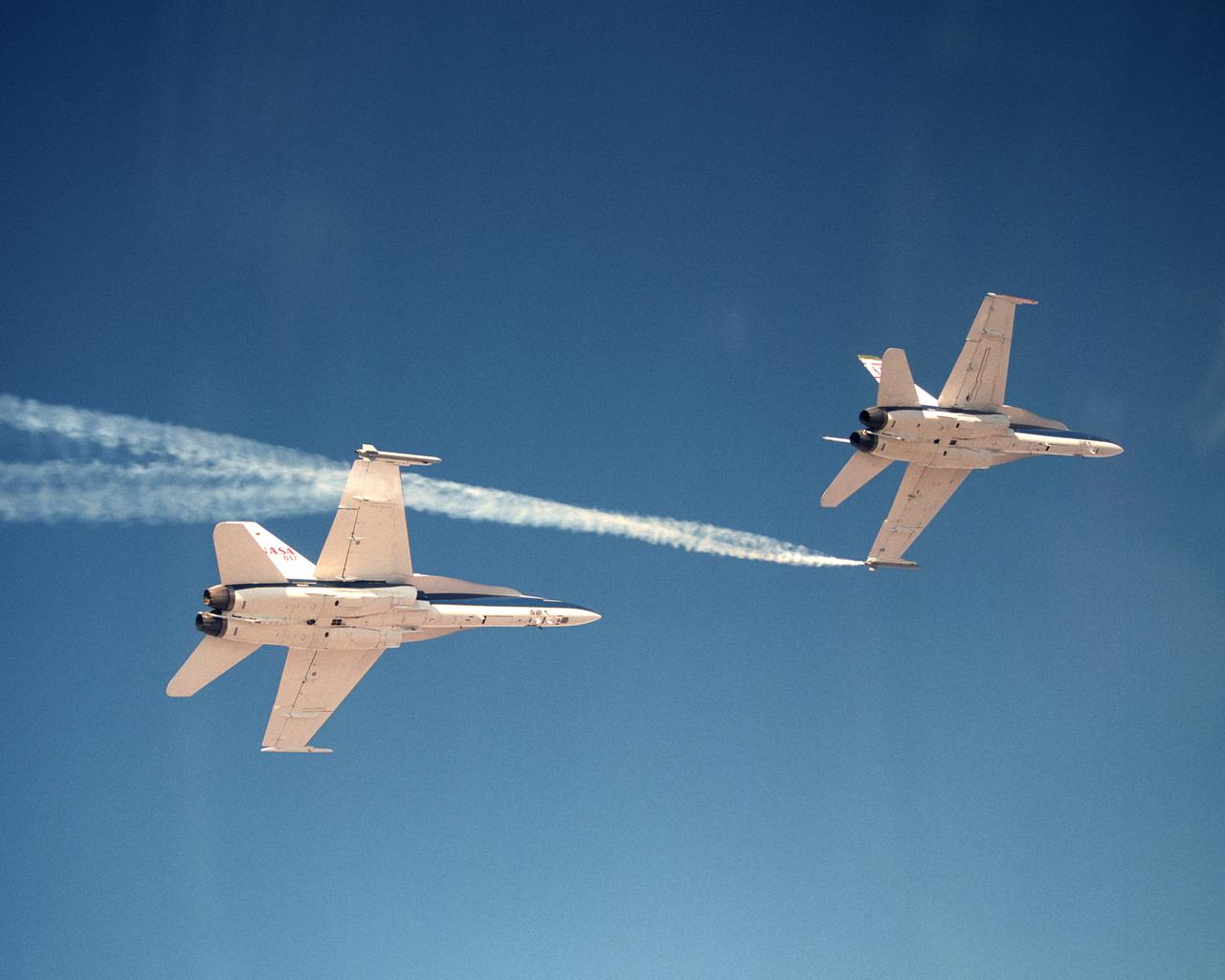

Smoke generators show the twisting paths of wingtip vortices behind two NASA Dryden F/A-18 jets used in the Autonomous Formation Flight (AFF) program
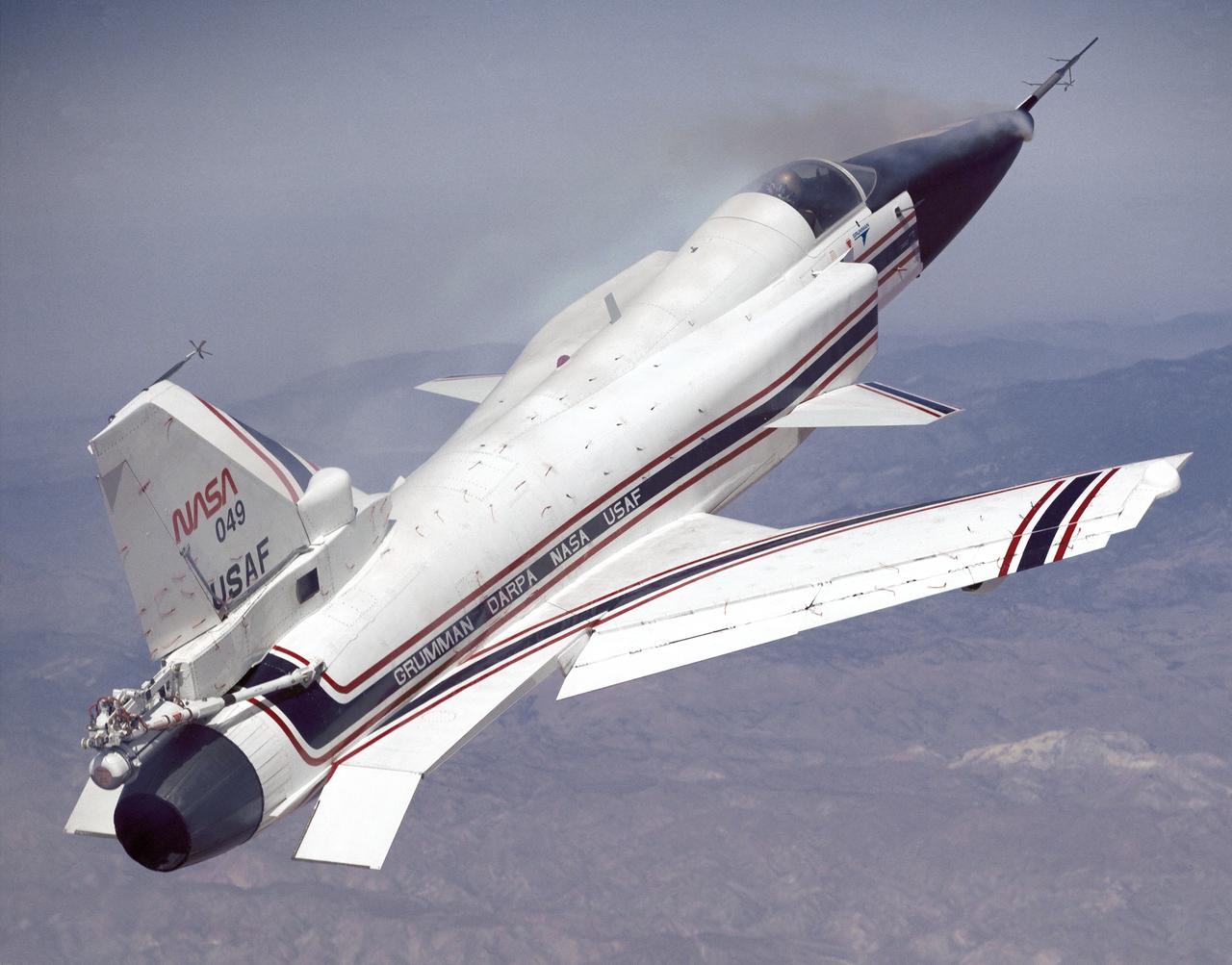

This photo shows the X-29 during a 1991 research flight. Smoke generators in the nose of the aircraft were used to help researchers see the behavior of the air flowing over the aircraft. The smoke here is demonstrating forebody vortex flow. This mission was flown September 10, 1991, by NASA research pilot Rogers Smith.

STS039-72-060 (28 April-6 May 1991) --- This view from the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Discovery shows the smoke from burning oil well fires, aftermath of Iraqi occupation. Oil wells to the north of the Bay of Kuwait and just south of Kuwait City, on the south shore, can be seen burning out of control. Compared with pictures of the same area shot during STS-37 (April 1991), this frame shows a complete shift of winds, with much of the smoke blowing eastward over the Gulf. The STS-37 scenes showed lengthy southward-blowing sheets of smoke toward Saudi Arabia. In this view, the Gulf island Faylakah Awhah is barely visible through the smoke.
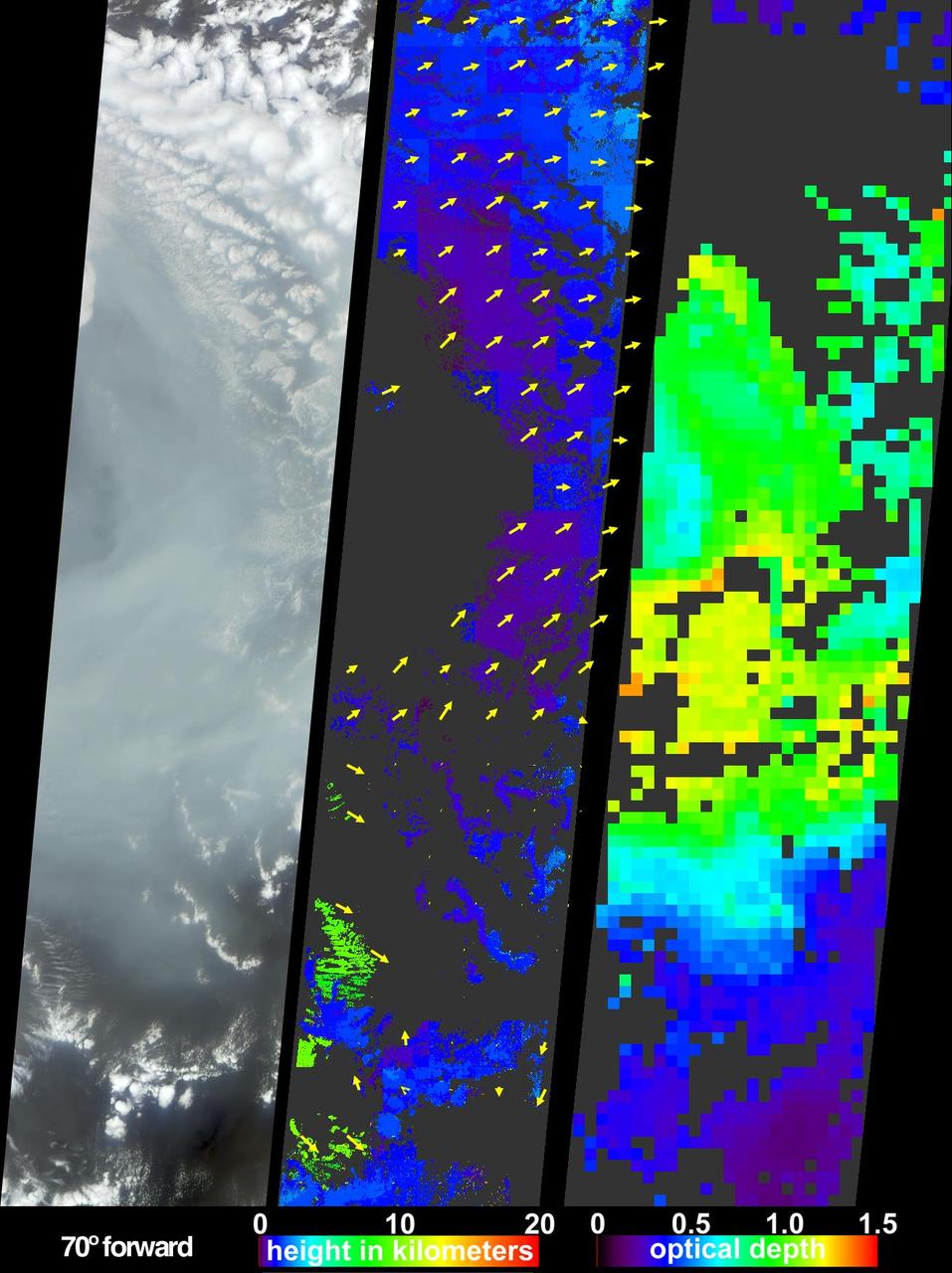
During the first two weeks of April, 2003, numerous fires occurred in eastern Russia and northeast China, and produced a large amount of smoke that rose to form a thick layer of tiny atmospheric particles, or aerosols seen here by NASA Terra spacecraft.
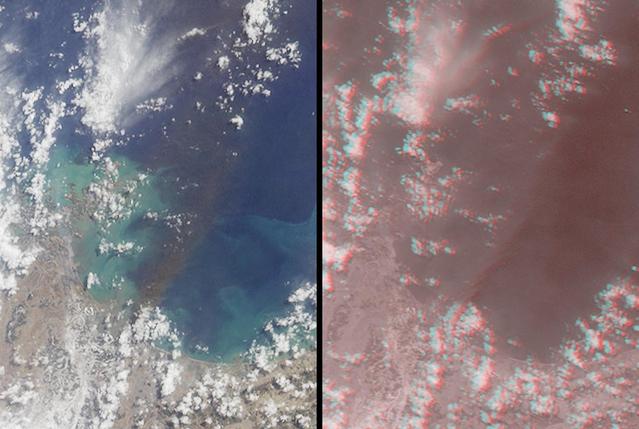
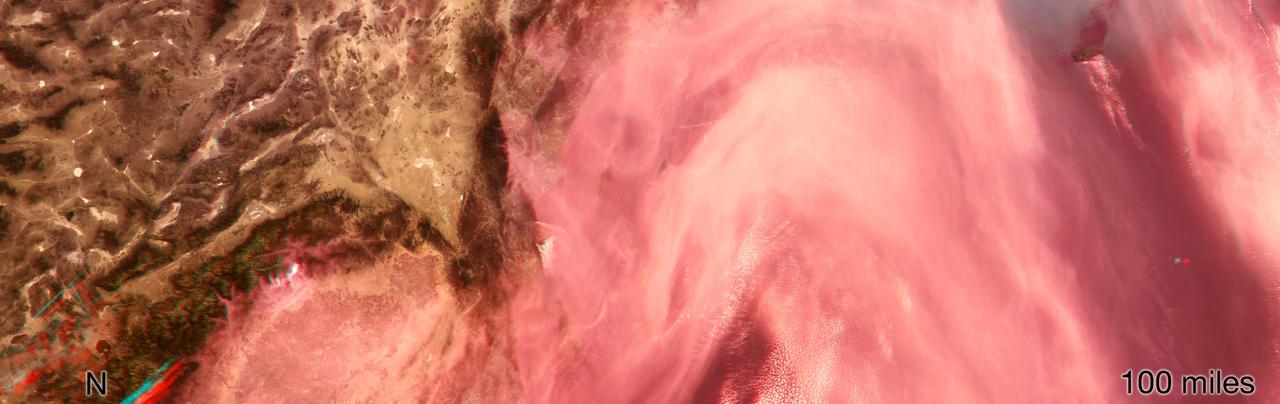
This images, acquired on March 12, 2011 by NASA Terra spacecraft, shows a large smoke plume that appears to be associated either with the Shiogama incident or Sendai port fires. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
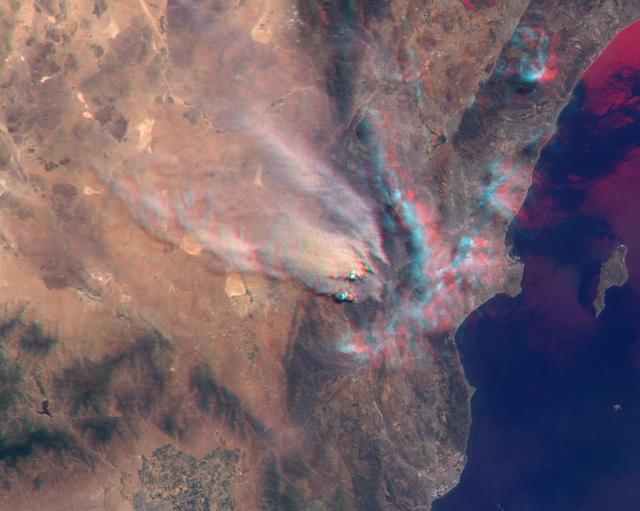

NASA Terra satellite took this anaglyph of several pyrocumulus clouds, created by the Station Fire, visible above the smoke plumes rising from the San Gabriel Mountains north of Los Angeles. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
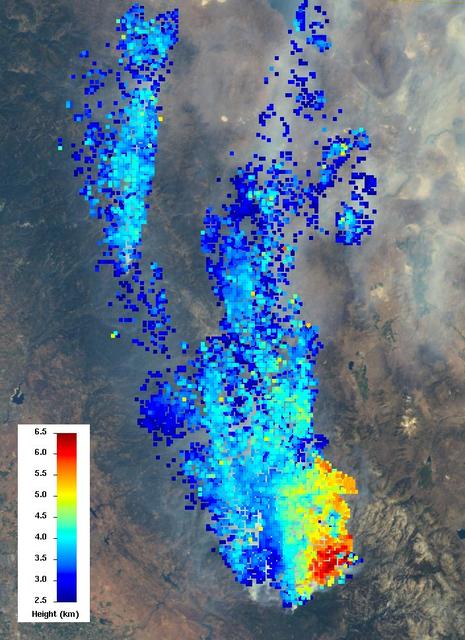
This image from the MISR instrument onboard NASA Terra spacecraft shows a 121-by-165-mile 194-by-266 kilometer portion of California Rim fire where the smoke is the thickest.
The extent, height, and amount of smoke originating from the B&B Complex Fires in central Oregon are captured in these September 4, 2003 views from NASA Terra spacecraft.
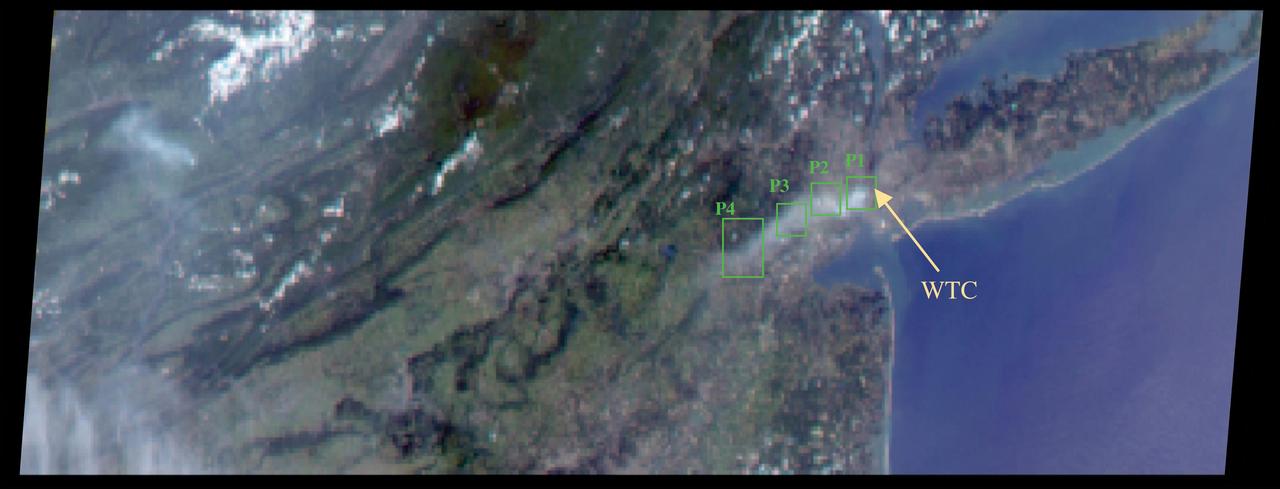

The collapse of the World Trade Center on September 11, 2001, and the fires that followed produced a noxious smoke plume, a complex mixture of tiny airborne particles and gases as seen by NASA Terra spacecraft.
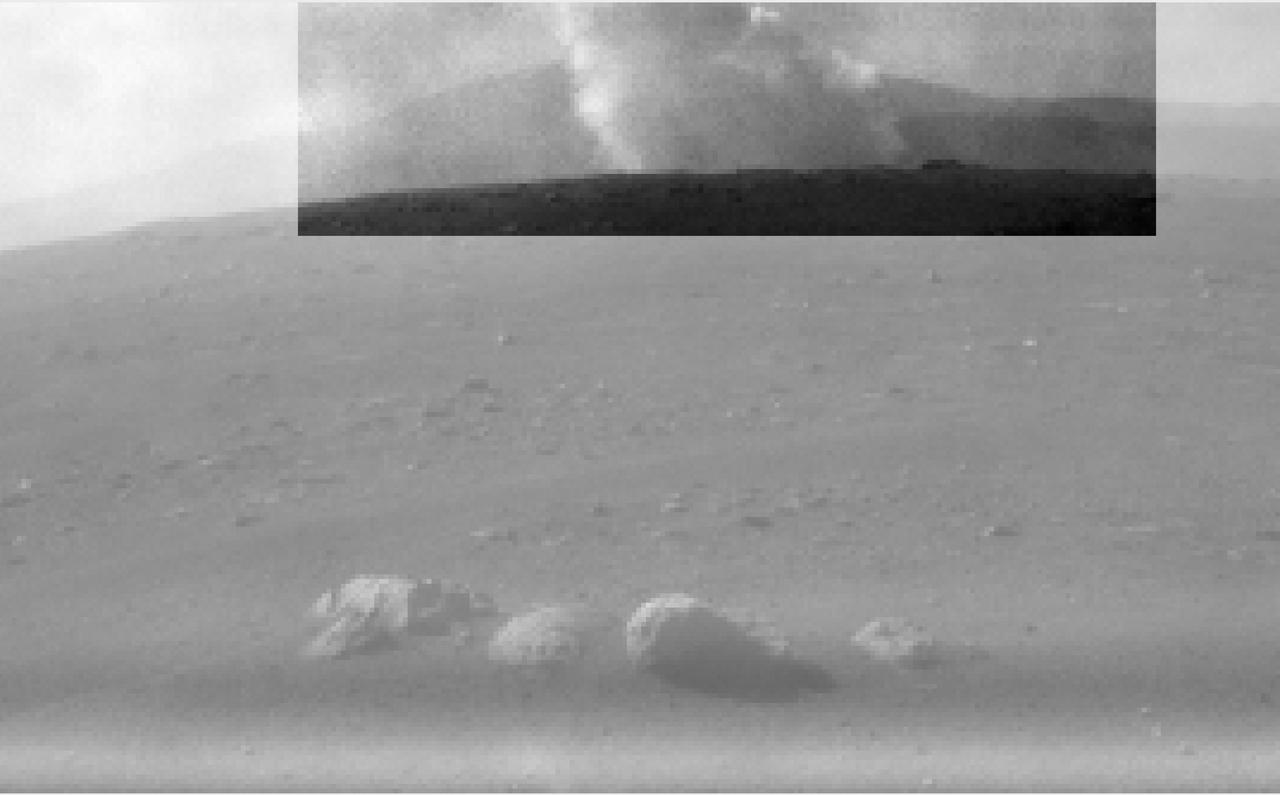

This image from one of the rear Hazard Cameras, or Hazcams, aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover, shows a smoke plume from the crashed descent stage that lowered the rover to the Martian surface. This image was taken within a minute or two after the rover landed on February 18, 2021. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24425
Smoke Flow Investigation XF7C-1 (Cowling Exhaust J.1 Type)
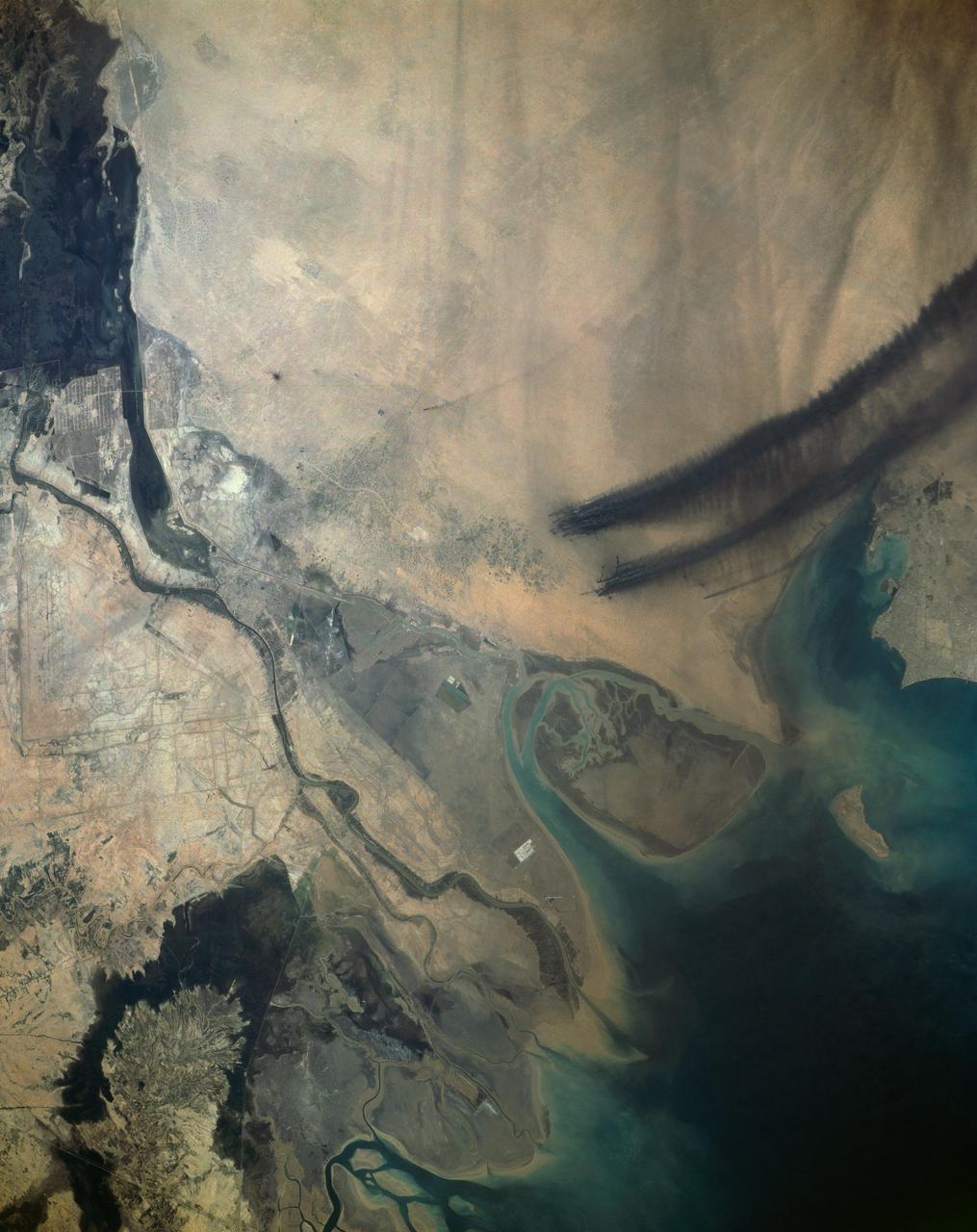

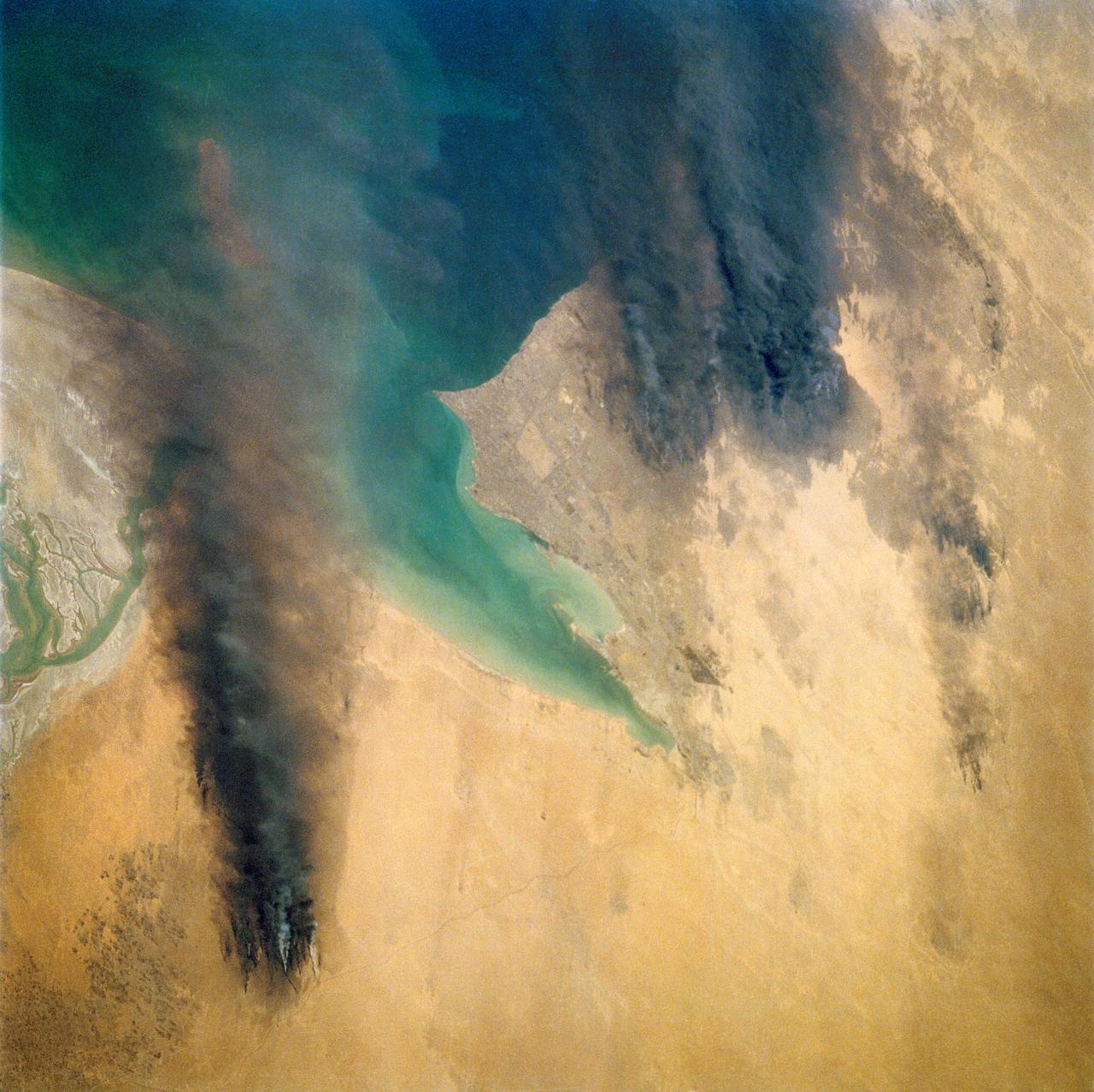
Smoke from the burning oil fields to the north of Kuwait City, seen on the south shore of Kuwayt Bay, almost totally obscures the view of the tiny, but oil rich, nation of Kuwait (30.0N, 48.0E). During the brief war between Iraq and the Allied forces, many of the oil wells in Kuwait were destroyed and set afire. For several months, those fires burned out of control, spewing wind borne smoke and ash for hundreds of miles.
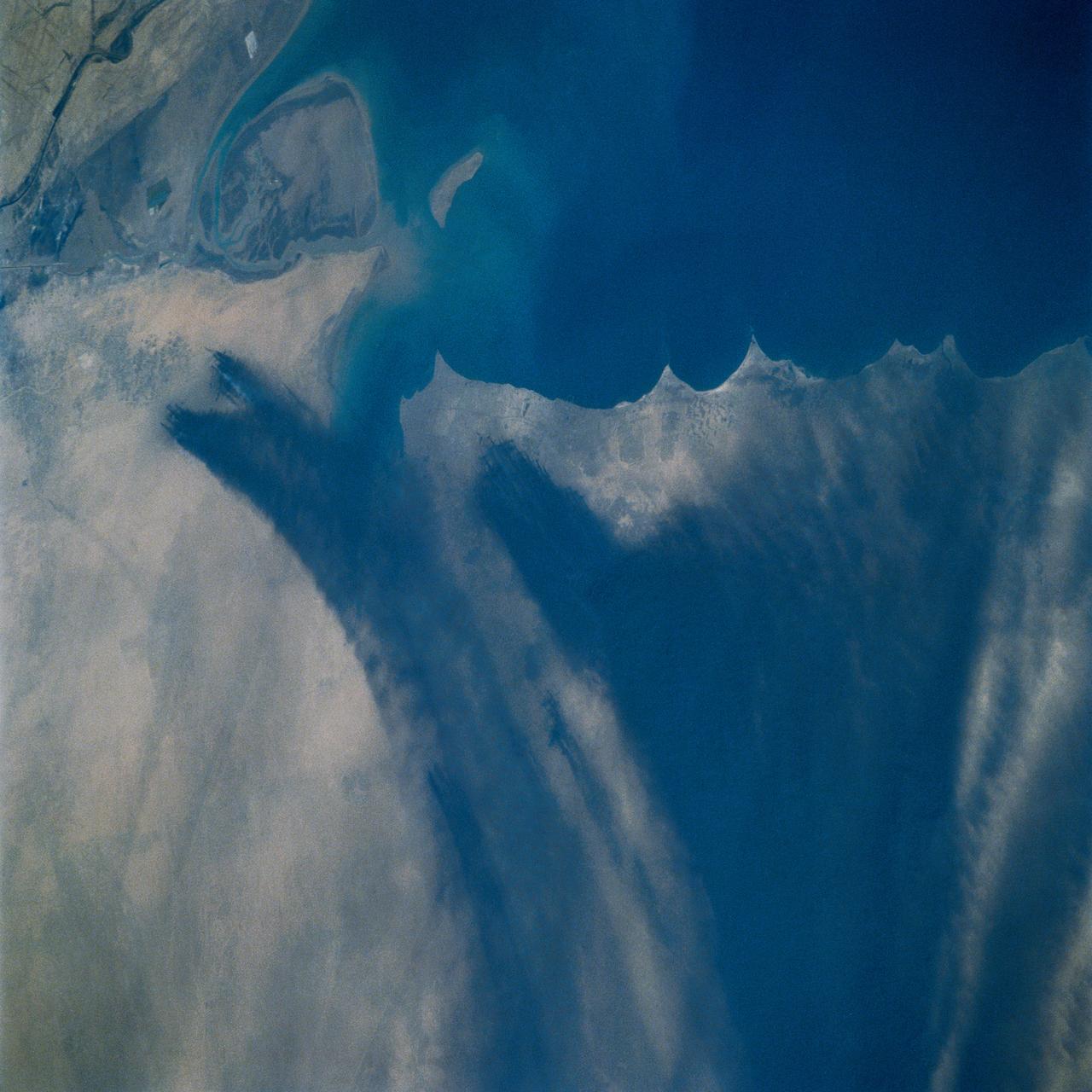

Smoke from the burning oil fields to the north and south of Kuwait City, seen on the south shore of Kuwayt Bay almost totally obscures the view of the tiny, but oil rich, nation of Kuwait (29.0N, 48.0E). During the brief war between Iraq and the Allied forces, many of the oil wells in Kuwait were destroyed and set afire. For several months, those fires burned out of control, spewing wind borne smoke and ash for hundreds of miles.

This visible image of California Rim Fire was acquired Aug. 23, 2013 by the Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer MISR instrument on NASA Terra spacecraft, showing extensive, brownish smoke.
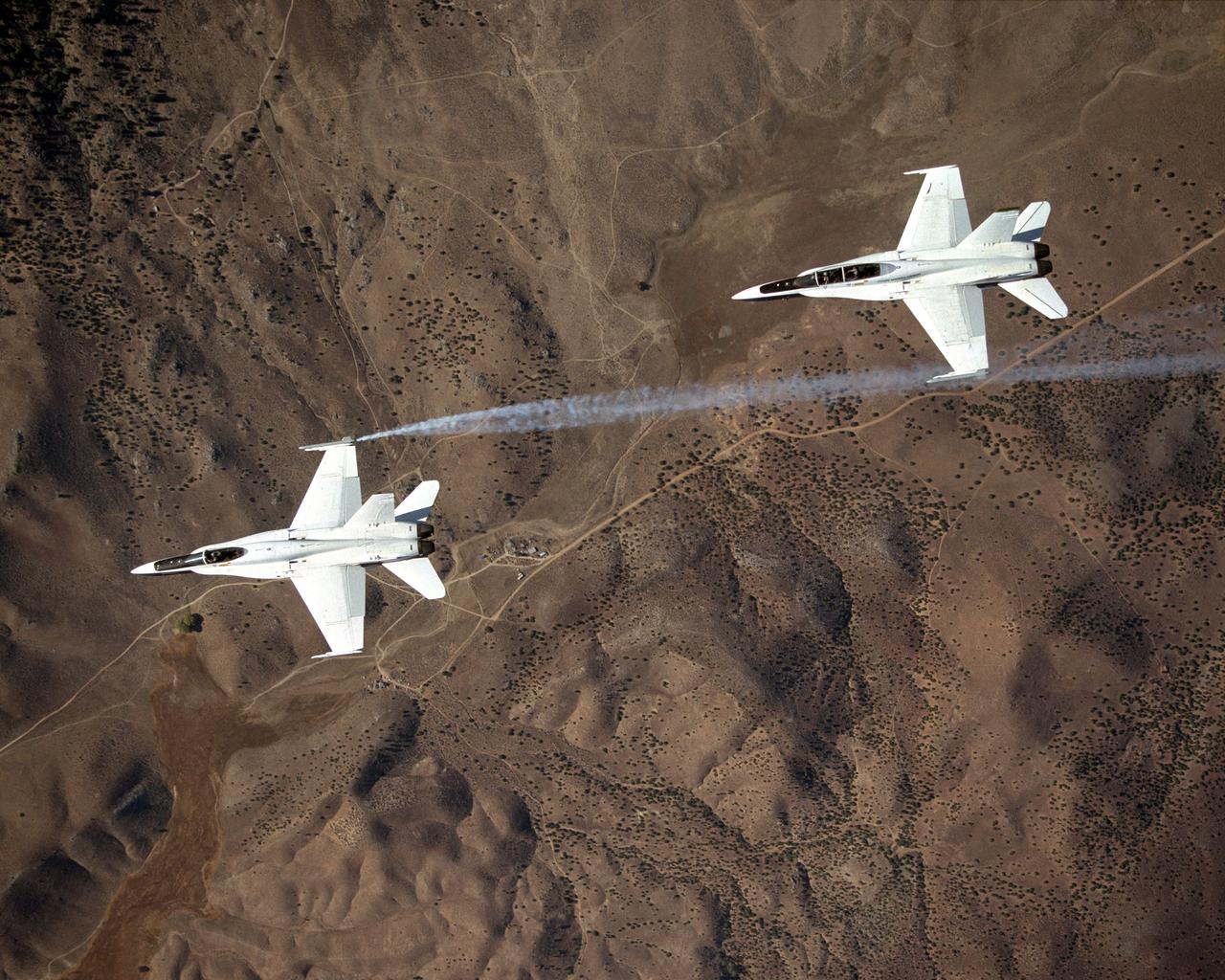

Smoke generators show the twisting paths of wingtip vortices behind two NASA Dryden F/A-18's used in the Autonomous Formation Flight (AFF) program during flight #743.
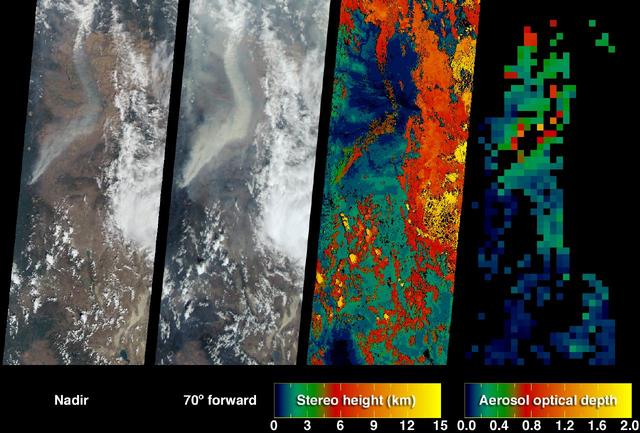
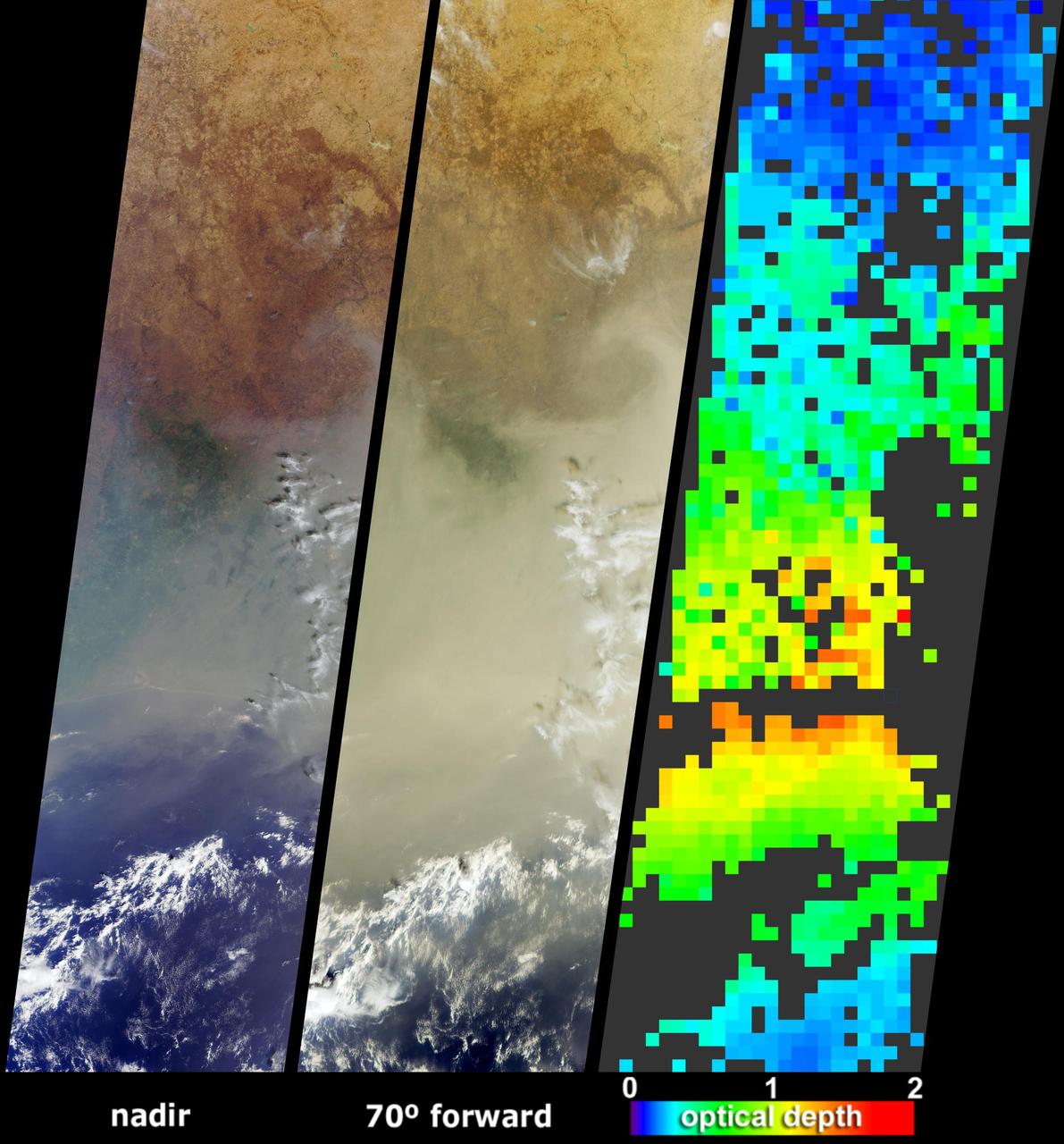
The Sand Fire in the Santa Clarita Valley area of Southern California erupted on Friday, July 22, 2016, and rapidly grew to more than 37,000 acres (58 square miles, or 150 square kilometers) over the weekend. As of Tuesday, July 26, hundreds of residents still remain under evacuation orders, and the fire claimed the life of a local resident. The fire is currently 25 percent contained. The Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite passed over the region on July 23 around 11:50 a.m. PDT. At left is an image acquired by MISR's 60-degree forward-viewing camera. The oblique view angle makes the smoke more apparent than it would be in a more conventional vertical view. Smoke from the Sand Fire is visible on the right-hand side of the image, and a long streamer of smoke from the Soberanes Fire near Big Sur in Central California is visible over the ocean near the left-hand side of the image. Like the Sand Fire, the Soberanes Fire also broke out on July 22, and quickly grew to more than 19,000 acres (30 square miles, or 77 square kilometers), causing the evacuation of hundreds of people and closure of several state parks. The Soberanes Fire is currently only 10 percent contained. The swath width of the MISR image is 257 miles (414 kilometers). At right is a map of aerosol optical depth, a quantitative measure of the smoke abundance in the atmosphere, derived from the images acquired by MISR's nine differently angled cameras. The thick smoke from both fires is apparent. Individual squares making up this map measure 2.7 miles (4.4 kilometers) on a side. The product shown here is a prototype of a new version of the MISR aerosol product to be publicly released in the near future, and increases the spatial resolution of the aerosol information by a factor of 16 compared to the currently available product, making it possible to discern finer details in the distribution of the smoke. These data were captured during Terra orbit 88284. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20720

39,000 acres (60 square miles, or 160 square kilometers). Thousands of residents were evacuated, and the fire claimed the life of one person. The Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite passed over the region on July 23 around 11:50 a.m. PDT. At left is an image acquired by MISR's 60-degree forward-viewing camera. The oblique view angle makes the smoke more apparent than it would be in a more conventional vertical view. This cropped image is about 185 miles (300 kilometers) wide. Smoke from the Sand Fire is visible on the right-hand side of the image. Stereoscopic analysis of MISR's multiple camera angles is used to compute the height of the smoke plume from the Sand Fire. In the right-hand image, these heights are superimposed on the underlying image. The color scale shows that the plume extends up to about 4 miles (6 kilometers) above its source in Santa Clarita, but rapidly diminishes in height as winds push it to the southwest. The data compare well with a pilot report issued at Los Angeles International Airport on the evening of July 22, which reported smoke at 15,000-18,000 feet altitude (4.5 to 5.5 kilometers). Air quality warnings were issued for the San Fernando Valley and the western portion of Los Angeles due to this low-hanging smoke. However, data from air quality monitoring instruments seem to indicate that the smoke did not actually reach the ground. These data were captured during Terra orbit 88284. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20724
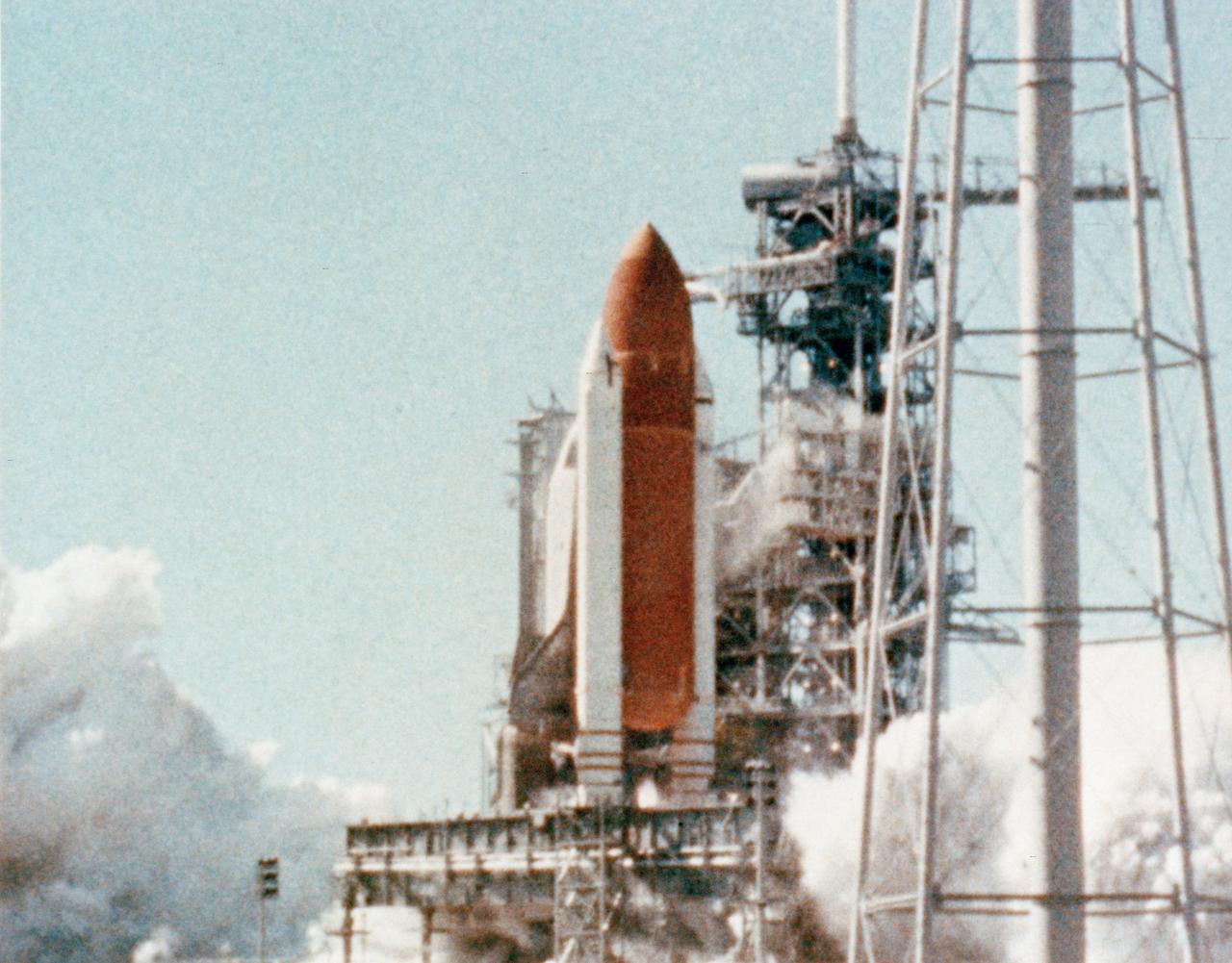
51L-10096 (12 Feb 1986) --- Time as of 0.445, first evidence of black smoke right hand (RH) solid rocket booster (SRB) near field joint, 39B-1/11. (Item E-60) (FC).

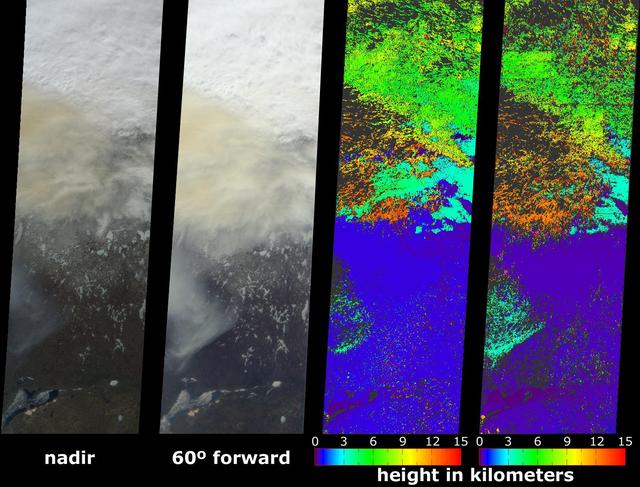
Data from the Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite was used to produce this stereo anaglyph of the Woolsey Fire in southern California on Nov. 11, 2018. It shows a three-dimensional view of the smoke plume -- visible through red-blue 3D glasses. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22817

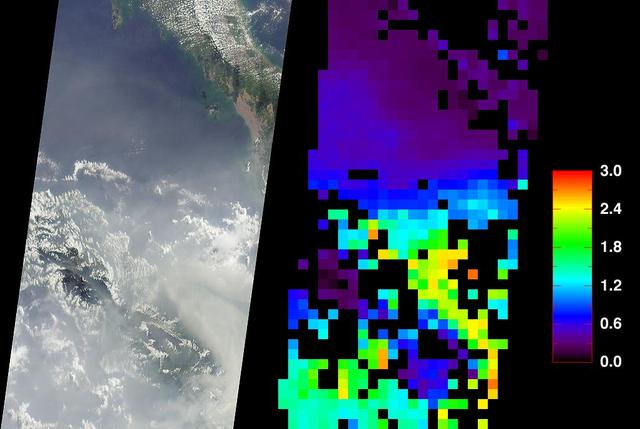
Stable, south flowing air over the western Pacific Ocean (26.0N, 131.0E) is disturbed by islands south of Korea, resulting in sinuous clouds known as von Karman vortices. The smoke plume from Japan's Mount Unzen Volcano on Kyushu, is visible just west of the large cloud mass and extending southward. A very large, purple tinged dust pall, originating in Mongolia, can be seen on the Earth's Limb, covering eastern China and extending into the East China Sea.
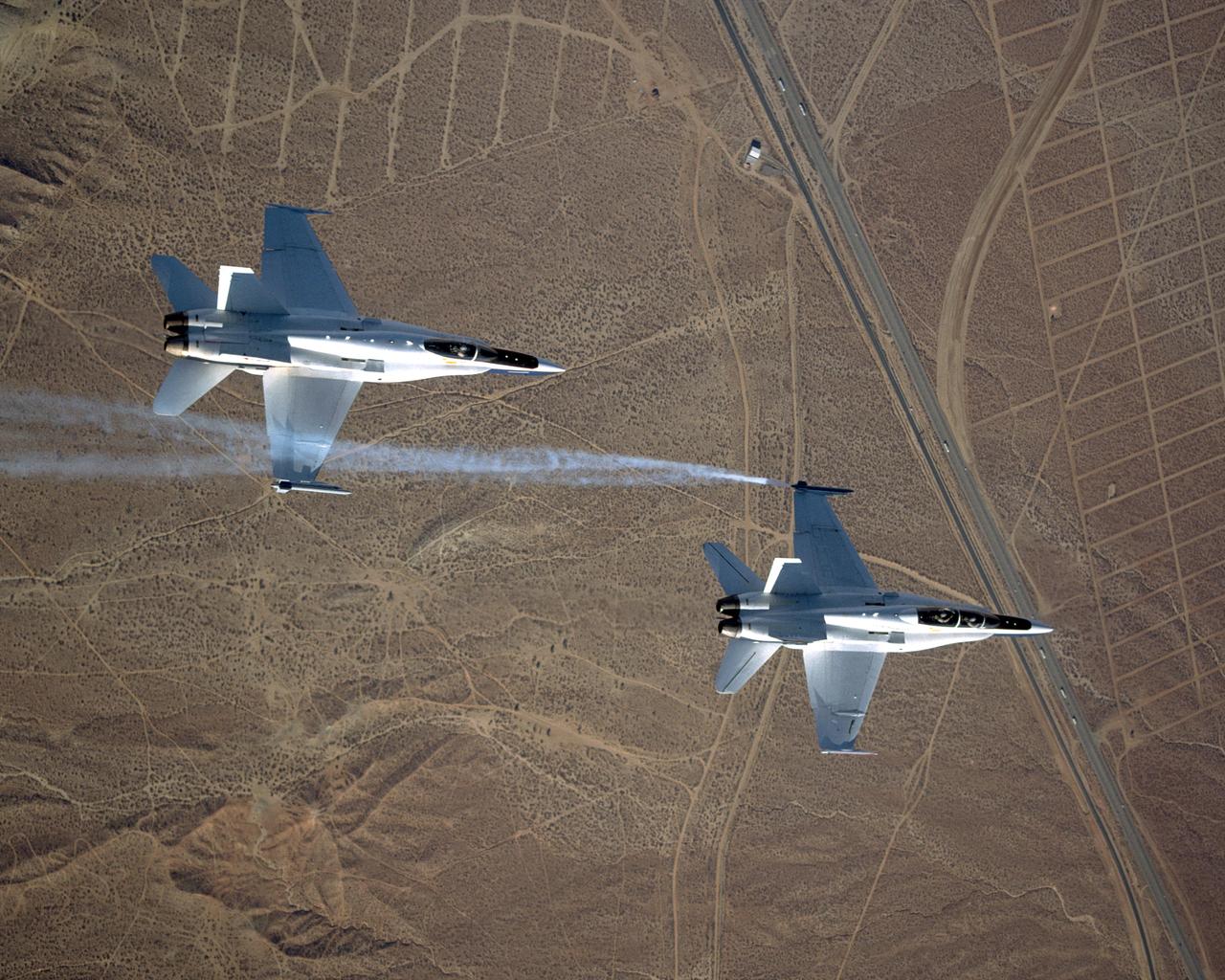

Smoke generators show the twisting paths of wingtip vortices behind two NASA Dryden F/A-18's used in the Autonomous Formation Flight (AFF) program during flight #743.
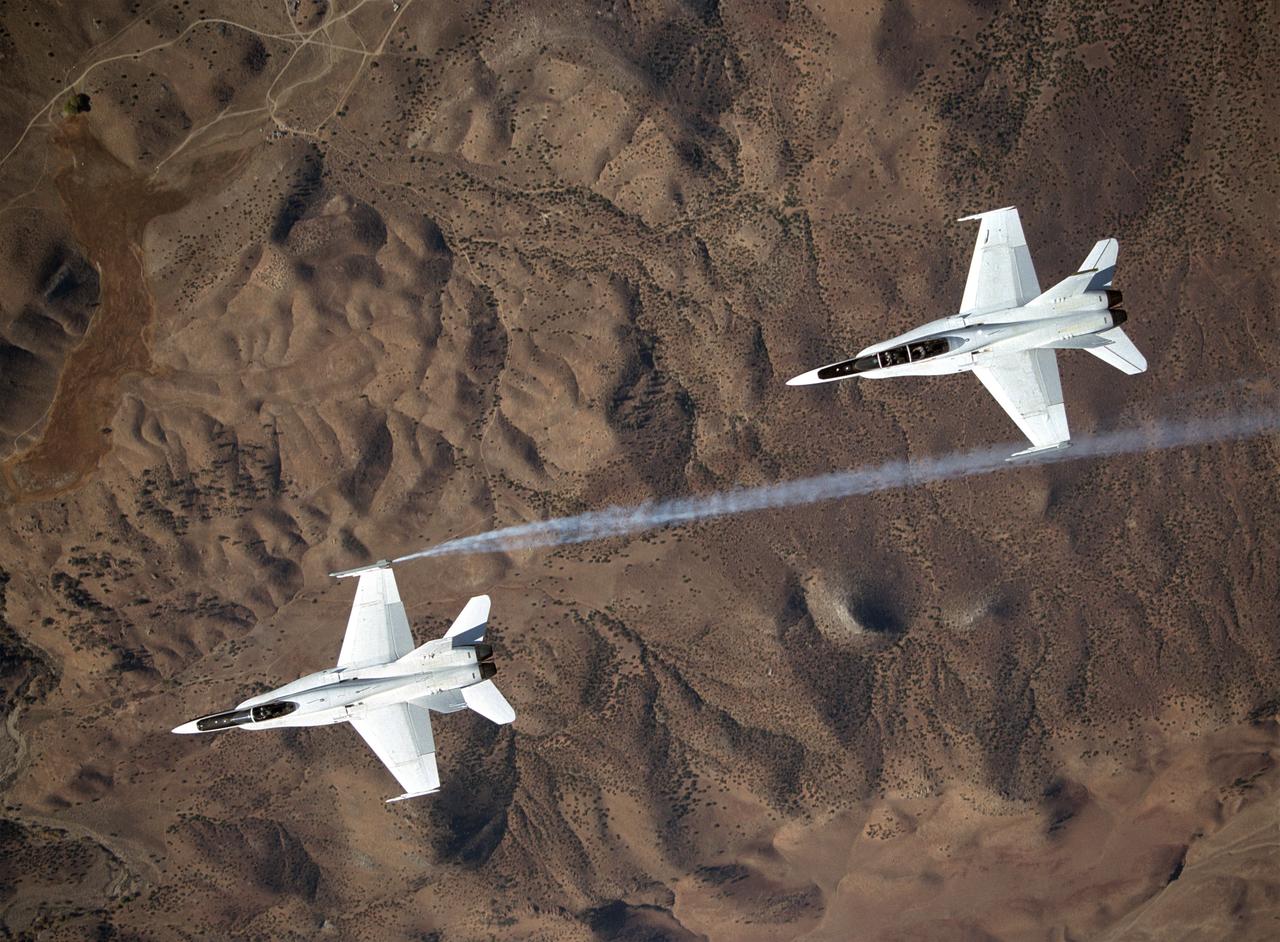

Smoke generators show the twisting paths of wingtip vortices behind two NASA Dryden F/A-18's used in the Autonomous Formation Flight (AFF) program during flight #743.
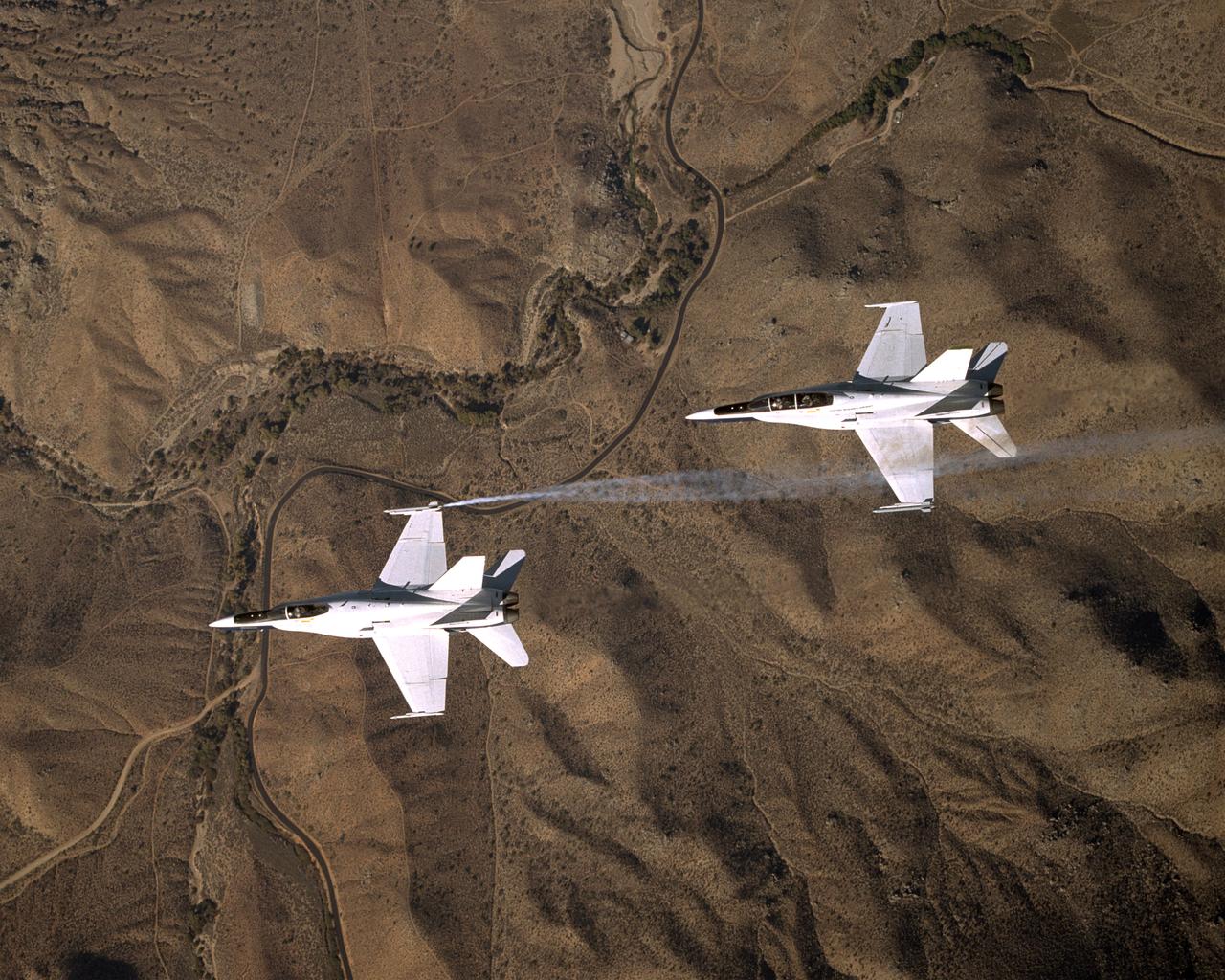

Smoke generators show the twisting paths of wingtip vortices behind two NASA Dryden F/A-18's used in the Autonomous Formation Flight (AFF) program during flight #743.

In this image, the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has captured the smoking gun of a newborn star, the Herbig–Haro objects numbered 7 to 11 (HH 7–11). These five objects, visible in blue in the top center of the image, lie within NGC 1333, a reflection nebula full of gas and dust found about a thousand light-years away from Earth. Bright patches of nebulosity near newborn stars, Herbig-Haro objects like HH 7–11 are transient phenomena. Traveling away from the star that created them at a speed of up to about 150,000 miles per hour, they disappear into nothingness within a few tens of thousands of years. The young star that is the source of HH 7–11 is called SVS 13, and all five objects are moving away from SVS 13 toward the upper left. The current distance between HH 7 and SVS 13 is about 20,000 times the distance between Earth and the Sun. Herbig–Haro objects are formed when jets of ionized gas ejected by a young star collide with nearby clouds of gas and dust at high speeds. The Herbig-Haro objects visible in this image are no exception to this and were formed when the jets from the newborn star SVS 13 collided with the surrounding clouds. These collisions created the five brilliant clumps of light within the reflection nebula.

Middle school students across the country photographed the fires and smoke over southern Sumatra from a camera aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis September 27, 1997.
Middle school students across the country photographed the fires and smoke over southern Sumatra from a camera aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis September 27, 1997.

Middle school students across the country photographed the fires and smoke over southern Sumatra from a camera aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis September 27, 1997.

Middle school students across the country photographed the fires and smoke over southern Sumatra from a camera aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis September 27, 1997.
NASA Terra spacecraft saw a pall of smoke and dust largely obscured the nations of Cote dIvoire, Ghana, Burkina Faso and southern Mali on January 12, 2004.
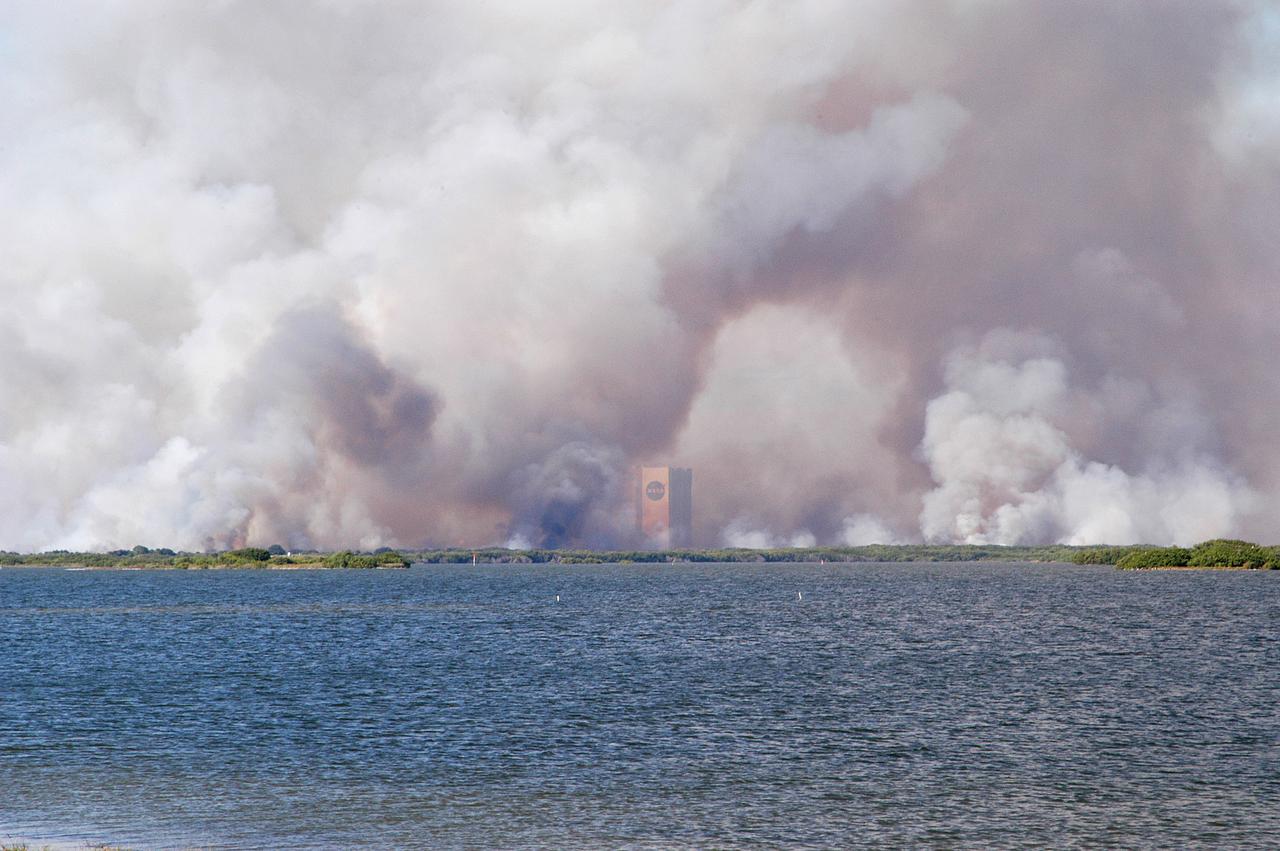

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Smoke from a successful controlled burn near KSC’s Launch Complex 39 surrounds the Vehicle Assembly Building and spreads across the horizon. The water in the foreground is the Banana River.
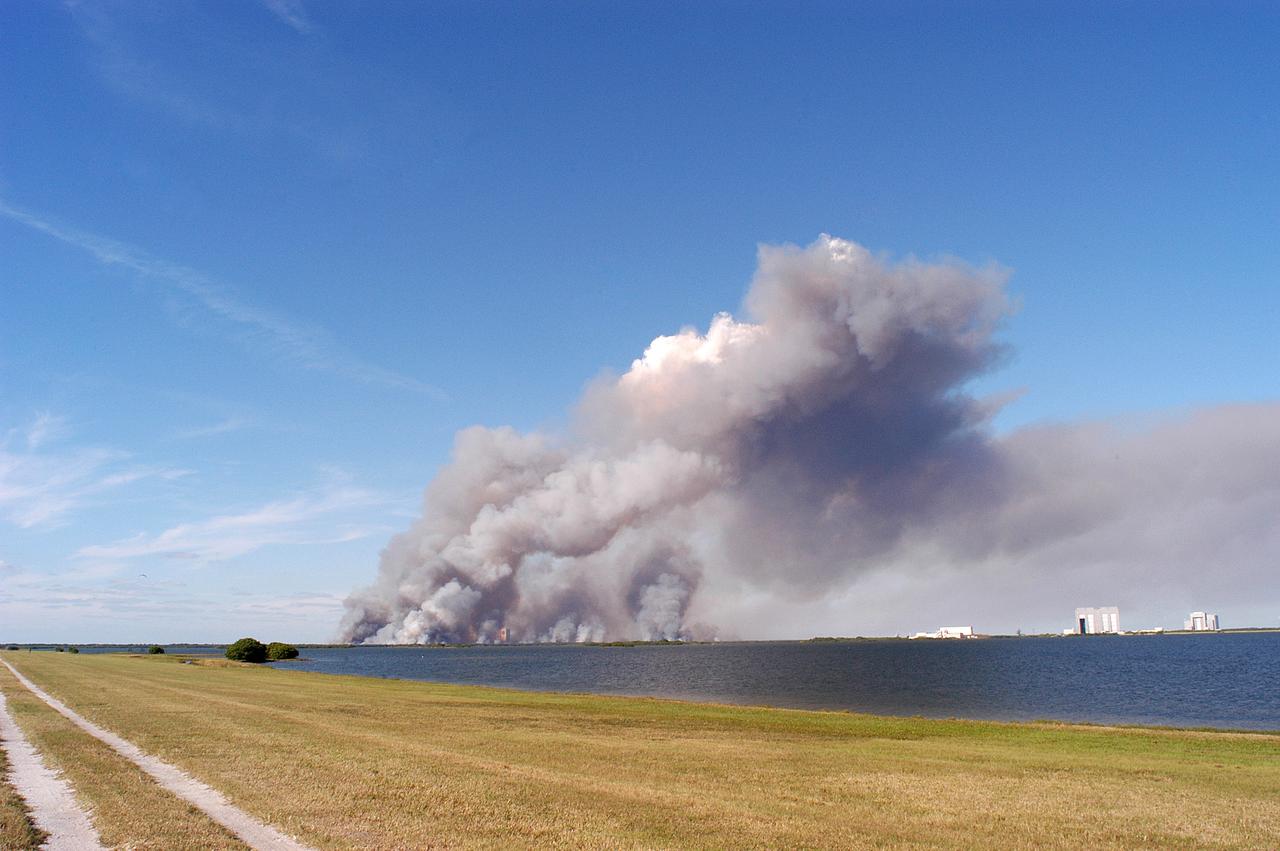

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A successful controlled burn near KSC’s Launch Complex 39 area creates clouds of smoke in a clear blue sky. The water seen is the Banana River.

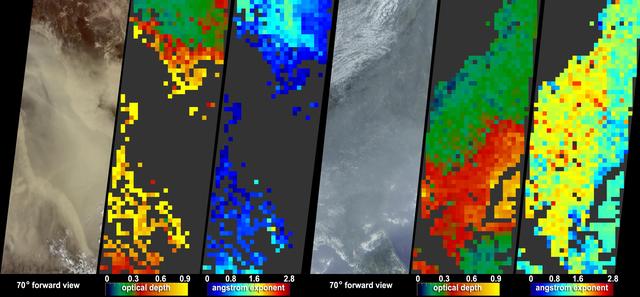
On Aug. 16, 2016, at around 10:30 a.m., a brush fire ignited in the Cajon Pass east of Los Angeles, just to the west of Interstate 15. Within a matter of hours, extreme temperatures, high winds and low humidity allowed the fire to spread rapidly, burning through brush left tinder-dry by years of drought. Firefighters quickly responded, ordering the evacuation of about 83,000 people in and around the Cajon Pass, Wrightwood, Lytle Creek, Oak Hills and surrounding areas. An as-yet uncounted number of homes and structures have burned, and Interstate 15 remains closed to downed power lines and barrier damage. By Aug. 17, the fire had expanded to more than 30,000 acres and remains zero percent contained as some 1,300 firefighters continue to battle to save homes and evacuate residents. The Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite passed over the region on Aug. 17 around 11:50 a.m. PDT and captured this natural-color image from MISR's 70-degree forward-viewing camera, which covers an areas about 257 miles (414 kilometers) wide. The oblique view angle makes the smoke more apparent than it would be in a more conventional vertical view. The Los Angeles metropolitan area is the large gray area on the coast in the center of the image. Three plumes from the Blue Cut Fire are clearly visible in the mountains to the north. This oblique view also shows an enormous cloud of smoke spreading northeastward over a significant portion of eastern California and Nevada. This smoke probably originated from the fire as it consumed almost 20,000 acres on the evening of the 16th and traveled north overnight. Also visible from this oblique view is considerable haziness filling California's Central Valley, to the northwest of the Blue Cut Fire. This haziness is most likely due to smoke from several other fires burning in California, including the Soberanes Fire near Monterey, the Clayton Fire that has destroyed 175 structures north of San Francisco, the Chimney Fire and the Cedar Fire, which is visible in the image in the southern Sierra Nevada. The total number of acres burned in California this year has tripled in just the past week. The 3D stereo anaglyph is made by combining data from MISR's 60-degree and 70-degree forward-viewing cameras. You will need red-blue glasses to view the 3D effect (ensure the red lens is over your left eye). In order to enable stereo viewing, the image has been rotated so north is to the left. These data were acquired during Terra orbit 88648. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20888
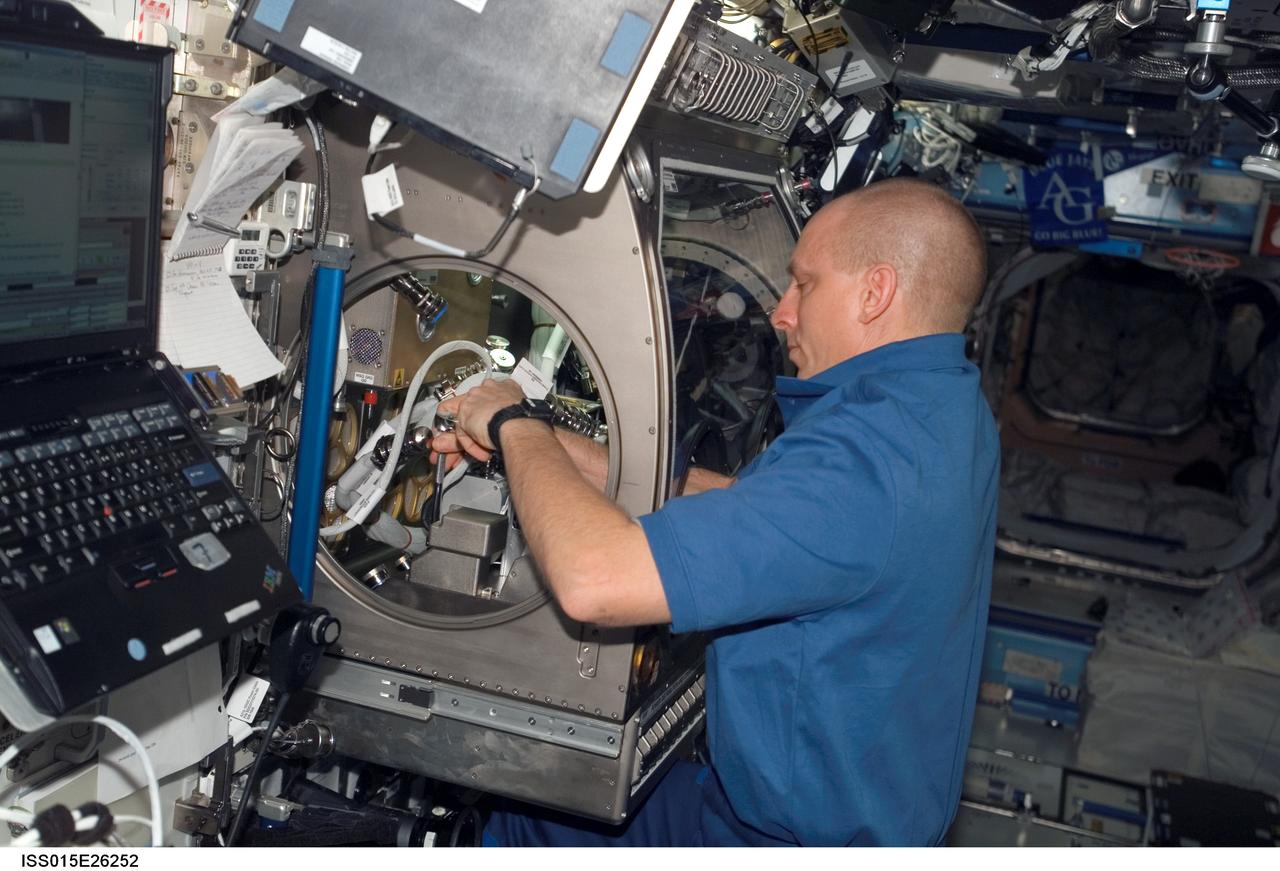

ISS015-E-26252 (1 Sept. 2007) --- Astronaut Clay Anderson, Expedition 15 flight engineer, works on the Smoke and Aerosol Measurement Experiment (SAME) hardware setup located in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. SAME will measure the smoke properties, or particle size distribution, of typical particles that are produced from different materials that can be found onboard station and other spacecrafts. SAME aims to test the performance of ionization smoke detectors and evaluate the performance of the photoelectric smoke detectors. The data will be used to develop a model that can predict smoke droplet growth that will be used to evaluate future smoke detection devices.
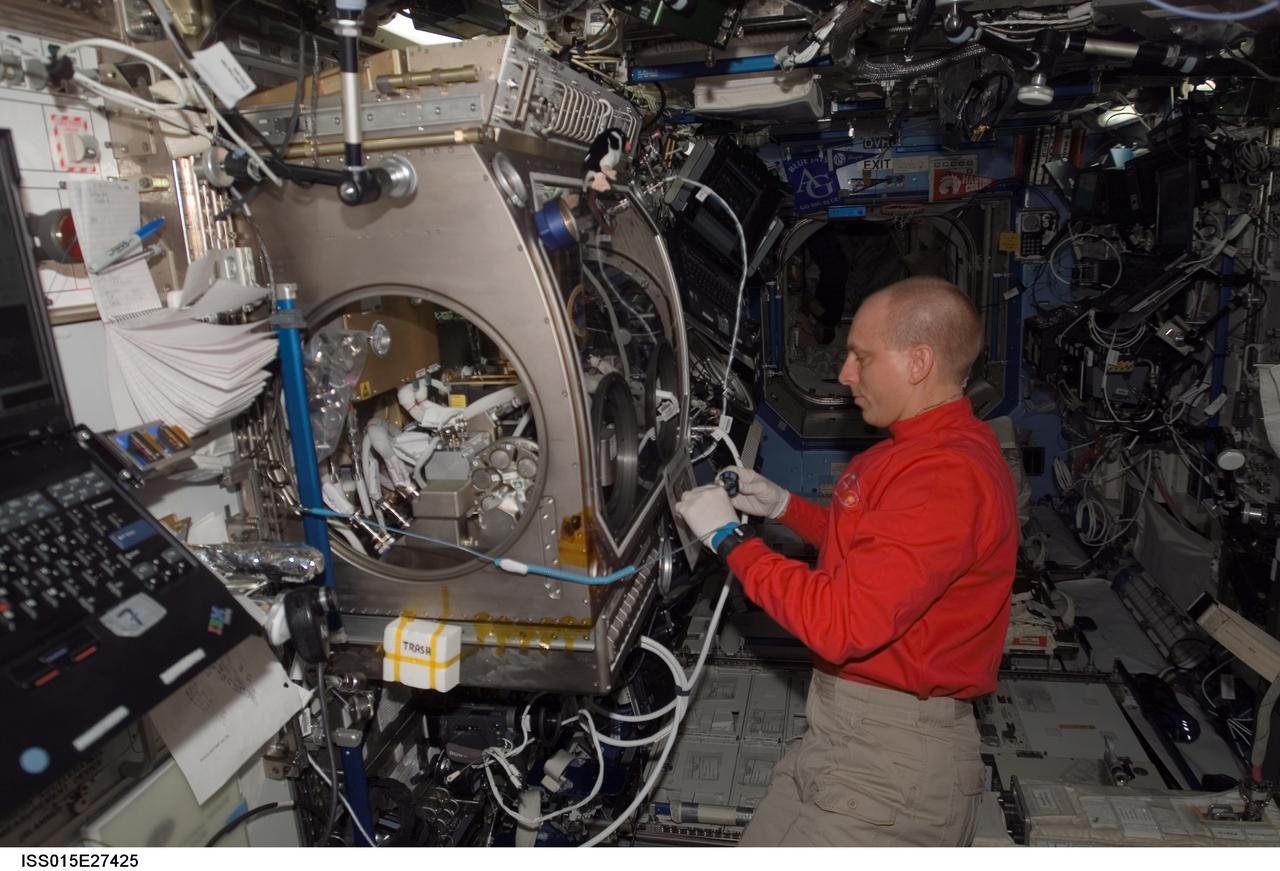

ISS015-E-27425 (8 Sept. 2007) --- NASA astronaut Clay Anderson, Expedition 15 flight engineer, works on the Smoke and Aerosol Measurement Experiment (SAME) hardware located in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. SAME will measure the smoke properties, or particle size distribution, of typical particles that are produced from different materials that can be found onboard station and other spacecrafts. SAME aims to test the performance of ionization smoke detectors and evaluate the performance of the photoelectric smoke detectors. The data will be used to develop a model that can predict smoke droplet growth that will be used to evaluate future smoke detection devices.
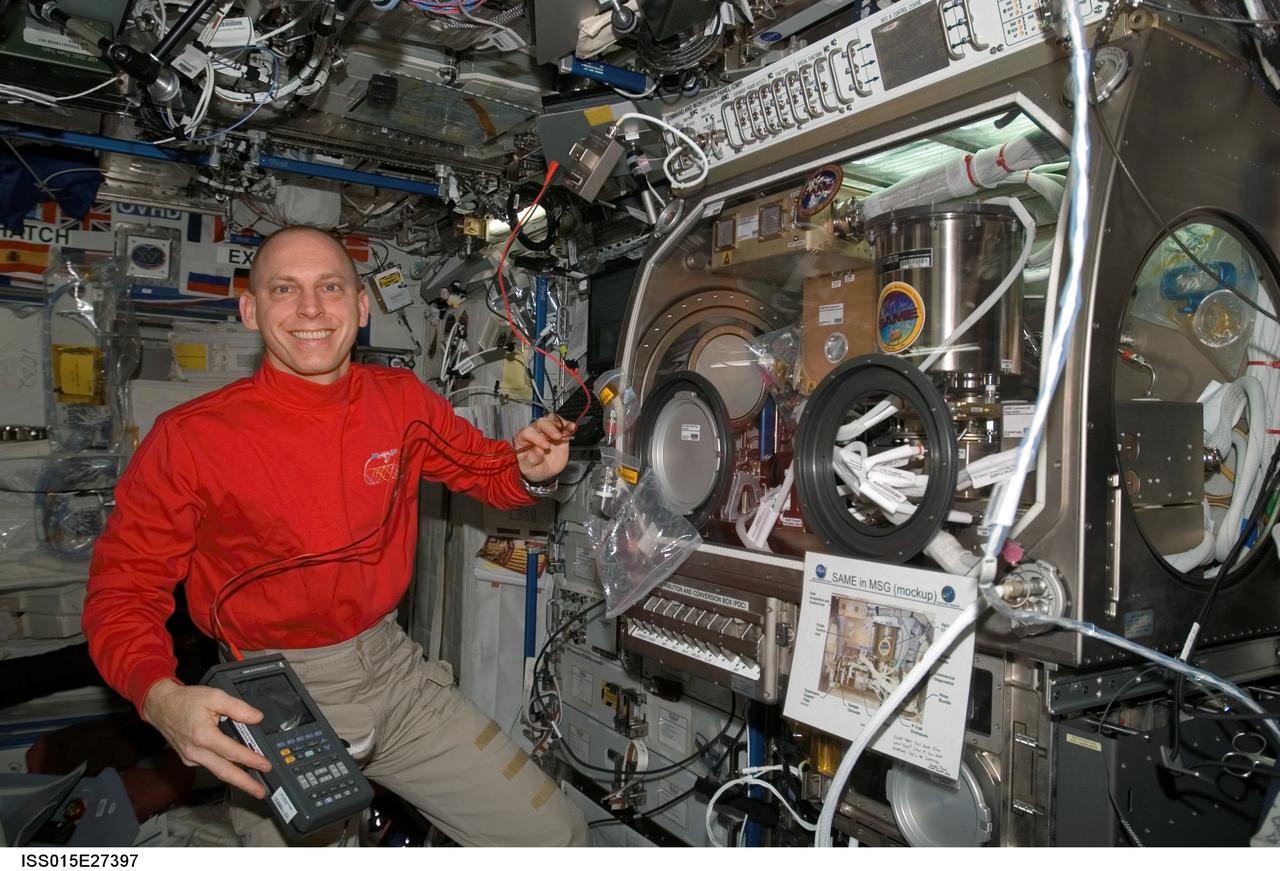

ISS015-E-27397 (8 Sept. 2007) --- NASA astronaut Clay Anderson, Expedition 15 flight engineer, pauses for a photo while working on the Smoke and Aerosol Measurement Experiment (SAME) hardware located in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. SAME will measure the smoke properties, or particle size distribution, of typical particles that are produced from different materials that can be found onboard station and other spacecrafts. SAME aims to test the performance of ionization smoke detectors and evaluate the performance of the photoelectric smoke detectors. The data will be used to develop a model that can predict smoke droplet growth that will be used to evaluate future smoke detection devices.
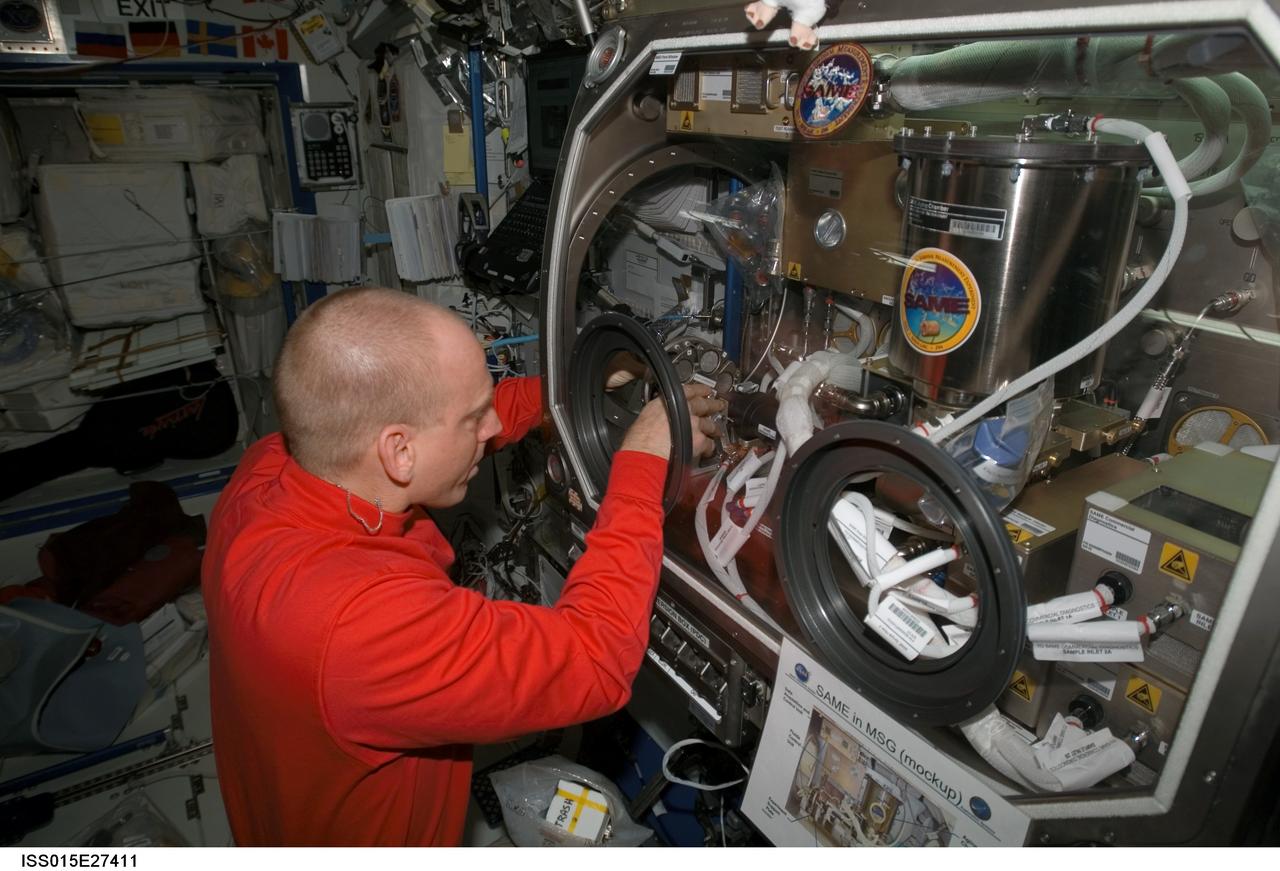

ISS015-E-27411 (8 Sept. 2007) --- NASA astronaut Clay Anderson, Expedition 15 flight engineer, works on the Smoke and Aerosol Measurement Experiment (SAME) hardware located in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. SAME will measure the smoke properties, or particle size distribution, of typical particles that are produced from different materials that can be found onboard station and other spacecrafts. SAME aims to test the performance of ionization smoke detectors and evaluate the performance of the photoelectric smoke detectors. The data will be used to develop a model that can predict smoke droplet growth that will be used to evaluate future smoke detection devices.

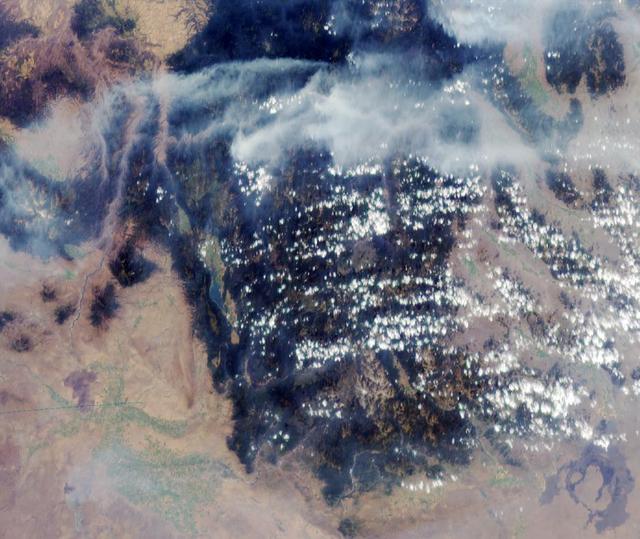
Lightning strikes have sparked more than a thousand fires in northern California. Cape Mendocino is at the center of the image and Mt. Shasta is near the upper right.
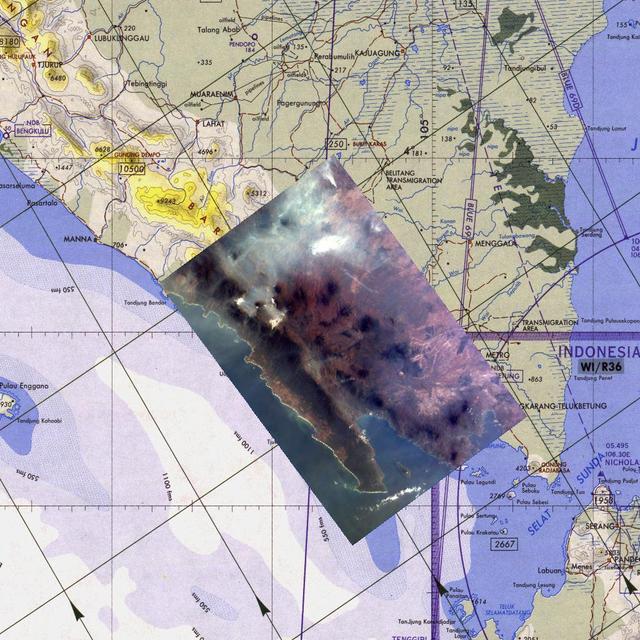
How precisely do the size of the aerosol particles comprising the dust that obscured the Red Sea on July 26, 2005? This image is from NASA Terra spacecraft.
The Hayman fire, situated about 65 kilometers southwest of Denver, Colorado, is the largest fire ever recorded in that state. The images were captured on June 9, 2002 by NASA Terra satellite.
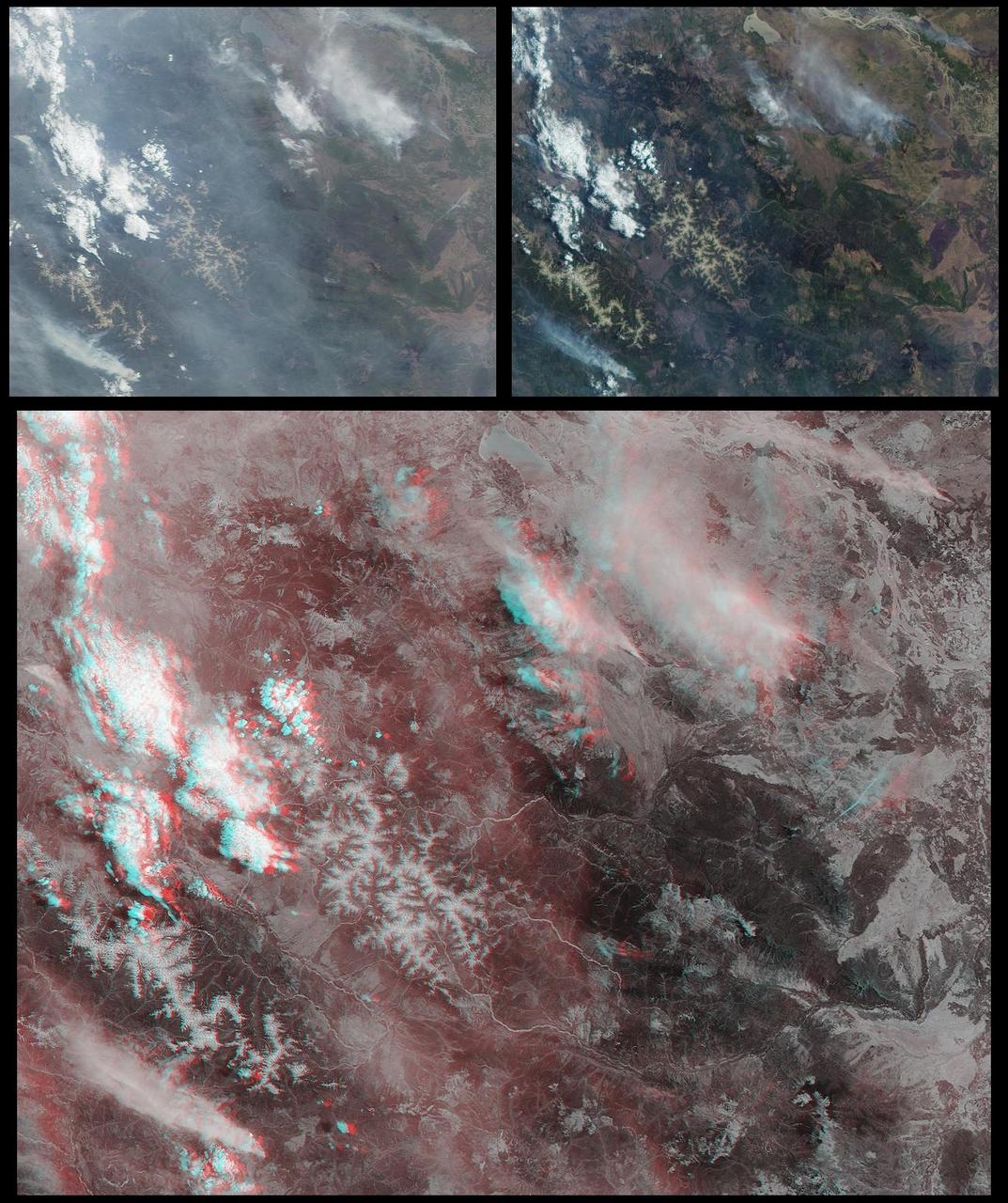
Several mountain ranges and a portion of the Amur River are visible in this set of stereo images of Russia far east Khabarovsk region taken by the MISR instrument aboard NASA Terra spacecraft. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
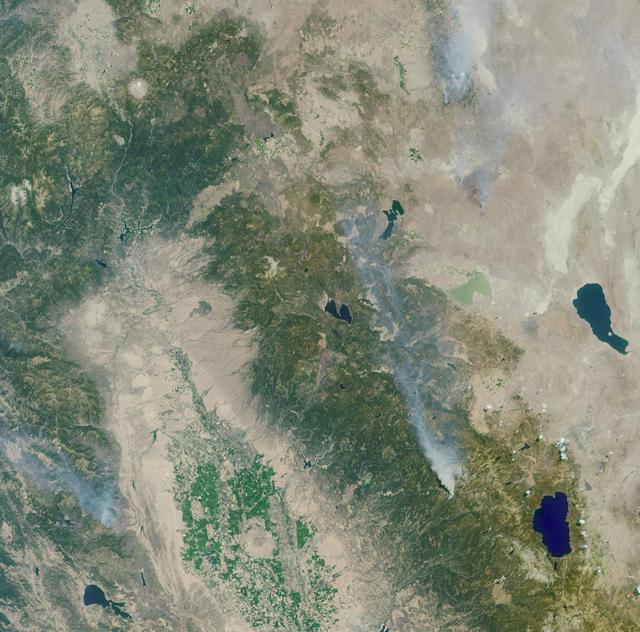

These images from NASA Terra satellite are of the Central Valley and the Sierra Nevada Mountains showing several smoke plumes from wildfires burning throughout Northern California on August 13, 2001.

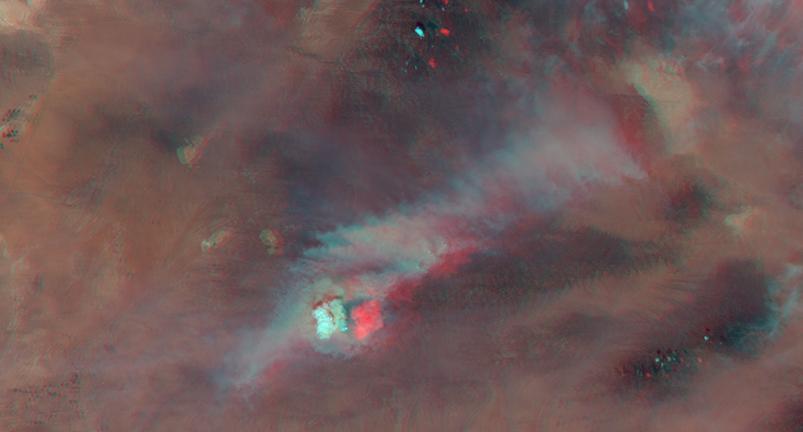
Large smoke plumes were produced by the Blackjack complex fire in southeastern Georgia Okefenokee Swamp as seen by the MISR instrument aboard NASA Terra spacecraft May 8, 2002. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
The height and extent of billowing smoke plumes from bushfires near Canberra, the Australian capital, are illustrated by these views from NASA Terra spacecraft acquired on January 18, 2003.

NASA Terra satellite passed over the Silver Fire in New Mexico June 12, 2013. By combining information from different MISR cameras, scientists have produced a 3D image of the smoke plume associated with the Silver Fire.

These images from NASA Terra satellite are of smoke plumes from devastating wildfires in the northwestern U.S. This view of the Clearwater and Salmon River Mountains in Idaho was acquired on August 5, 2000 Terra orbit 3370.
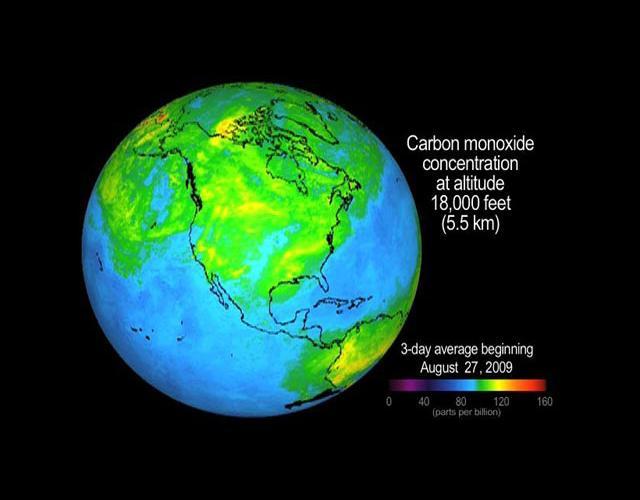
Carbon monoxide in the smoke from the Station fire was lofted high into the atmosphere, where it was observed by JPL Atmospheric Infrared Sounder instrument onboard NASA Aqua satellite. Animation available at the Photojournal.

Large plumes of smoke rising from devastating wildfires burning near Los Angeles and San Diego on Sunday, October 26, 2003, are highlighted in this set of images from NASA Terra spacecraft.
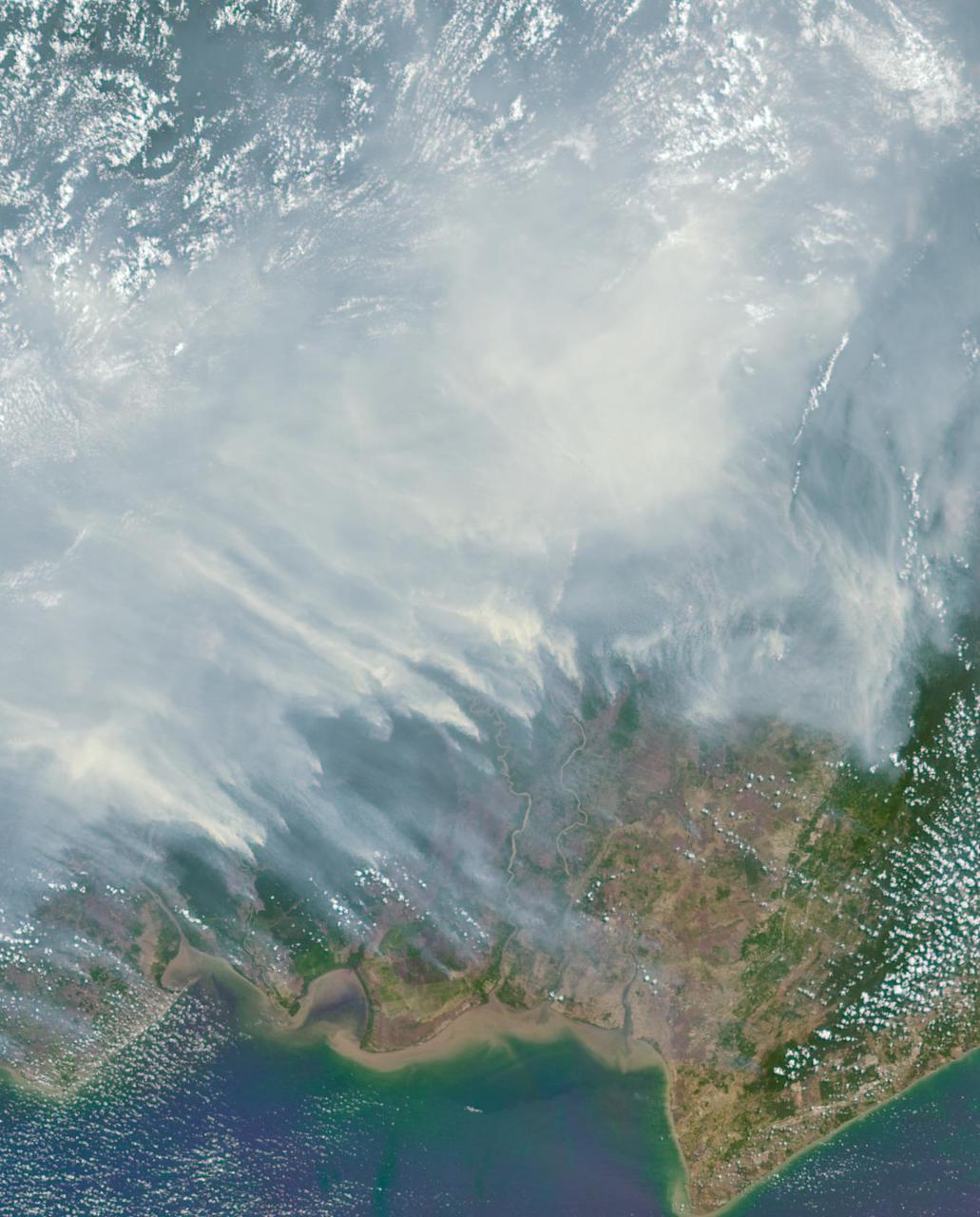
The worst forest fires in nearly two decades are burning out of control on Borneo, creating the thick blanket of smoke in this Oct. 14, 2015 image from NASA Terra spacecraft.

This false-color image, obtained by NASA Terra spacecraft on May 17, 2020, indicates the former location of the drilling platform red symbol and pointing to a plume of smoke white arrow.
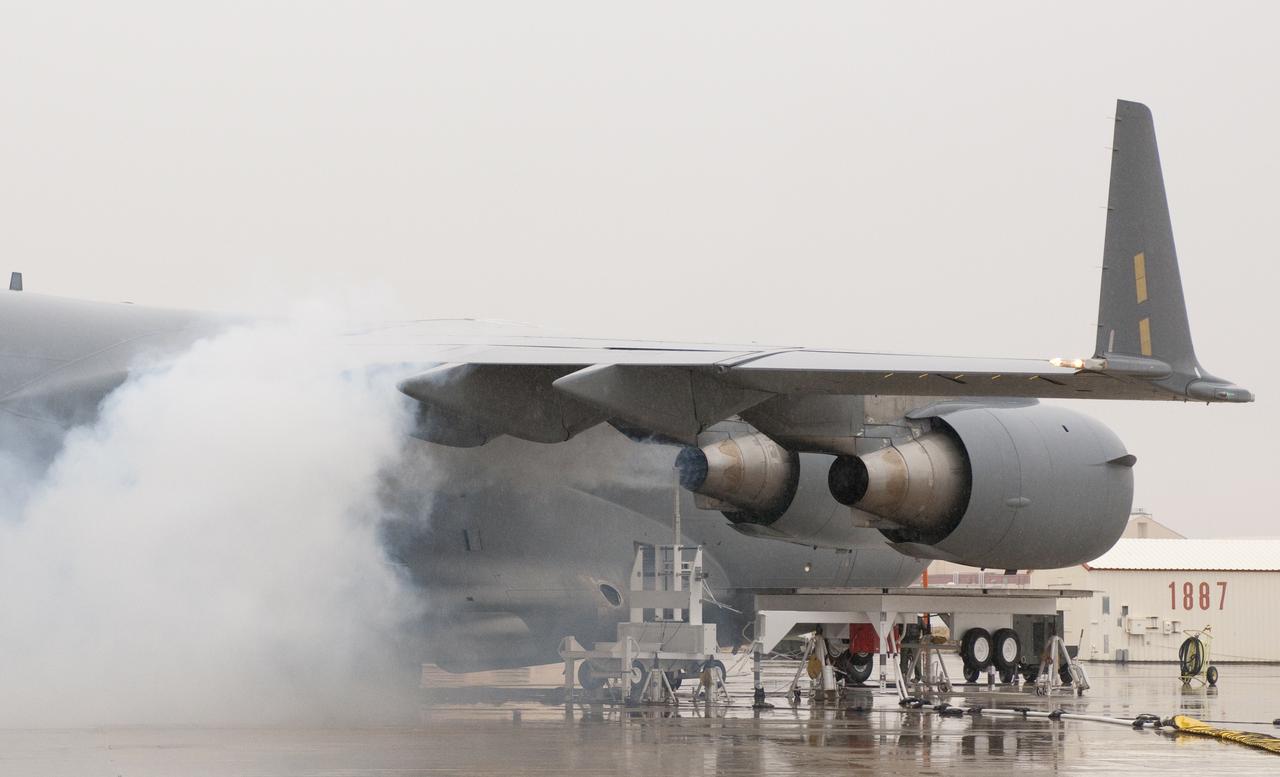

Oil smoke billows from the right inboard engine of the C-17 while a probe collects emissions data during 2011 VIPR engine health monitoring tests.

This infrared image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope shows a galaxy that appears to be sizzling hot, with huge plumes of smoke swirling around it. The galaxy is known as Messier 82 or the Cigar galaxy.

These ASTER images cover an area of 11 x 14 km on the north rim of the Grand Canyon, Arizona, and were acquired May 12, 2000. The left image displays bands 3,2,1 in RGB, displaying vegetation as red. The large dark area is burned forest, and small smoke plumes can be seen at the edges where active fires are burning. The right display substitutes SWIR band 8 for band 3. The bright red spots are the active fires, visible because the SWIR wavelength region has the capability to penetrate through the smoke. This image is located at 35.9 degrees north latitude and 113.4 degrees west longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11092

STS091-701-075 (2-12 June 1998) --- Fires across Mexico and Central America which created heavy smoke plumes for a few weeks in May and June, 1998, were recorded on 70mm film by the crewmembers of STS-91. The smoke circulated around a high pressure system over the Gulf of Mexico and brought thick smoke and soot to the south central United States. Scientists are looking at burning regions like this around the world to study the smokes affect on the albedo or the reflectance of the sun's rays and how it may influence the world's climate. This view captures the area from the Gulf of Tehuantepec, on the south side, to the Bay of Campeche to the north in early June 1998.

STS091-725-088 (2-12 June 1998)--- In this 70mm picture photographed during one of Discovery's passes over Mexico, waves generated by the volcanic peaks are seen as the wind carrying the smoke moves by the peaks. Along the coast of the Bay of Campeche, the fires burn around the peak of the Cerro San Martin (5,577 feet), which is west and higher than the peak with the waves around it. Lago Catemaco is on the west, center edge of the photo. Fires across Mexico and Central America created heavy smoke plumes for a few weeks in May and June, 1998. The smoke circulated around a high pressure system over the Gulf of Mexico and brought thick smoke and soot to the south central United States. Scientists are looking at burning regions like this around the world to study the smokes affect on the albedo or the reflectance of the suns rays and how it may influence our world's climate.

STS091-713-024 (2-12 June 1998) --- A 70mm view, taken from Discovery, showing heavy Smoke in Mexico along the coast of the Bay of Campeche. Fires across Mexico and Central America created heavy smoke plumes for a few weeks in May and June, 1998. The smoke circulated around a high pressure system over the Gulf of Mexico and brought thick smoke and soot to the south central United States. Scientists are looking at burning regions like this around the world to study the smokes affect on the albedo or the reflectance of the suns rays and how it may influence our world's climate. The fires in this view are north of the city of Villahermosa, in the lower center or south edge of the photo. The smaller city of Cardenas is to the west of Villahermosa. The point along the coast is the Rio Grijalva river delta. Laguna de Terminos is to the east of this delta.

On July 24, 2022, the Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured data on a smoke plume from the Oak Fire burning near Yosemite National Park in California. As of July 26, the Oak Fire had scorched more than 18,000 acres (7,284 hectares) and was 26% contained, with thousands of residents under evacuation orders. Hot, dry air, along with vegetation parched from years of drought, fueled the fire's rapid spread. The MISR instrument contains nine cameras that view Earth at different angles. The left panel in the image above shows an image captured by MISR's nadir (downward-pointing) camera of a smoke plume from the fire. Although the fire was burning near Yosemite at the time, it wasn't a threat to the national park. The panel on the right indicates the height of various parts of the plume as measured by several of MISR's cameras. Yellow areas are higher than the red and blue regions in the smoke plume. The height of the plume top near the active fire was about 17,060 feet (5,200 meters), or roughly 3 miles (nearly 5 kilometers). In general, higher-altitude plumes transport smoke greater distances from the source, impacting communities downwind. On the day the images were captured, unhealthy-to-hazardous air quality was reported in the area around Lake Tahoe and Truckee, about 125 miles (200 kilometers) north of the fire. MISR researchers calculate smoke plume height using the publicly available MISR INteractive eXplorer (MINX) software tool. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24907
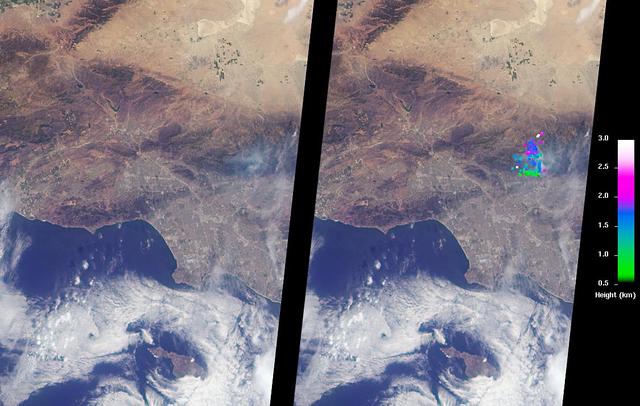
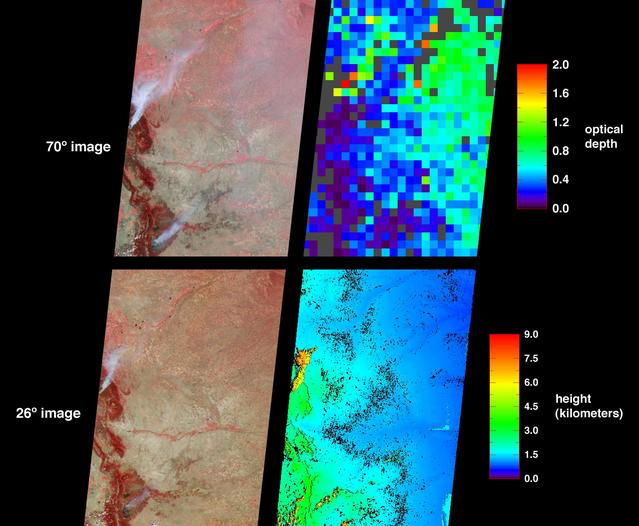
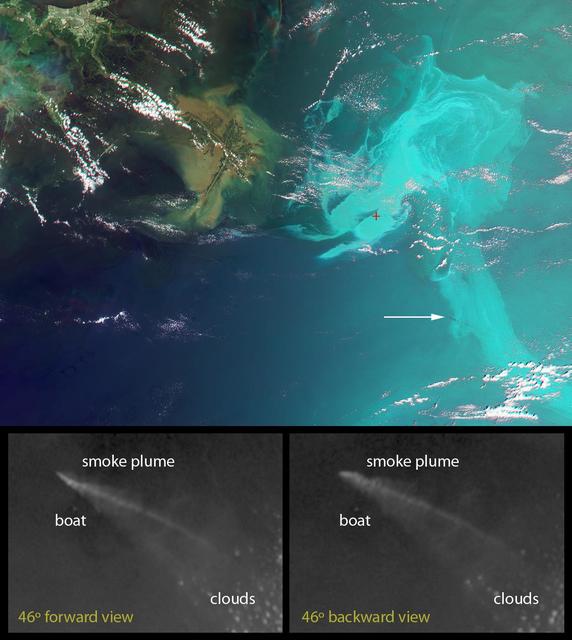
The Los Angeles area is currently suffering the effects of three major wildfires that are blanketing the area with smoke. Over the past few days, Southern California has experienced record-breaking temperatures, topping 110 degrees Fahrenheit in some cities. The heat, in combination with offshore winds, helped to stoke the Sherpa Fire west of Santa Barbara, which has been burning since June 15, 2016. Over the weekend of June 18-19, this fire rapidly expanded in size, forcing freeway closures and evacuations of campgrounds and state beaches. On Monday, June 20, two new fires ignited in the San Gabriel Mountains north of Azusa and Duarte, together dubbed the San Gabriel Complex Fire. They have burned more than 4,900 acres since June 20, sending up plumes of smoke visible to many in the Los Angeles basin and triggering air quality warnings. More than 1,400 personnel have been battling the blazes in the scorching heat, and evacuations were ordered for neighborhoods in the foothills. On June 21, the Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured this view of the San Gabriel Mountains and Los Angeles Basin from its 46-degree forward-viewing camera, which enhances the visibility of the smoke compared to the more conventional nadir (vertical) view. The width of this image is about 75 miles (120 kilometers) across. Smoke from the San Gabriel Complex Fire is visible at the very right of the image. Stereoscopic analysis of MISR's multiple camera angles is used to compute the height of the smoke plume from the San Gabriel Complex Fire. In the right-hand image, these heights are superimposed on the underlying image. The color scale shows that the plume is not much higher than the surrounding mountains. As a result, much of the smoke is confined to the local area. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20718
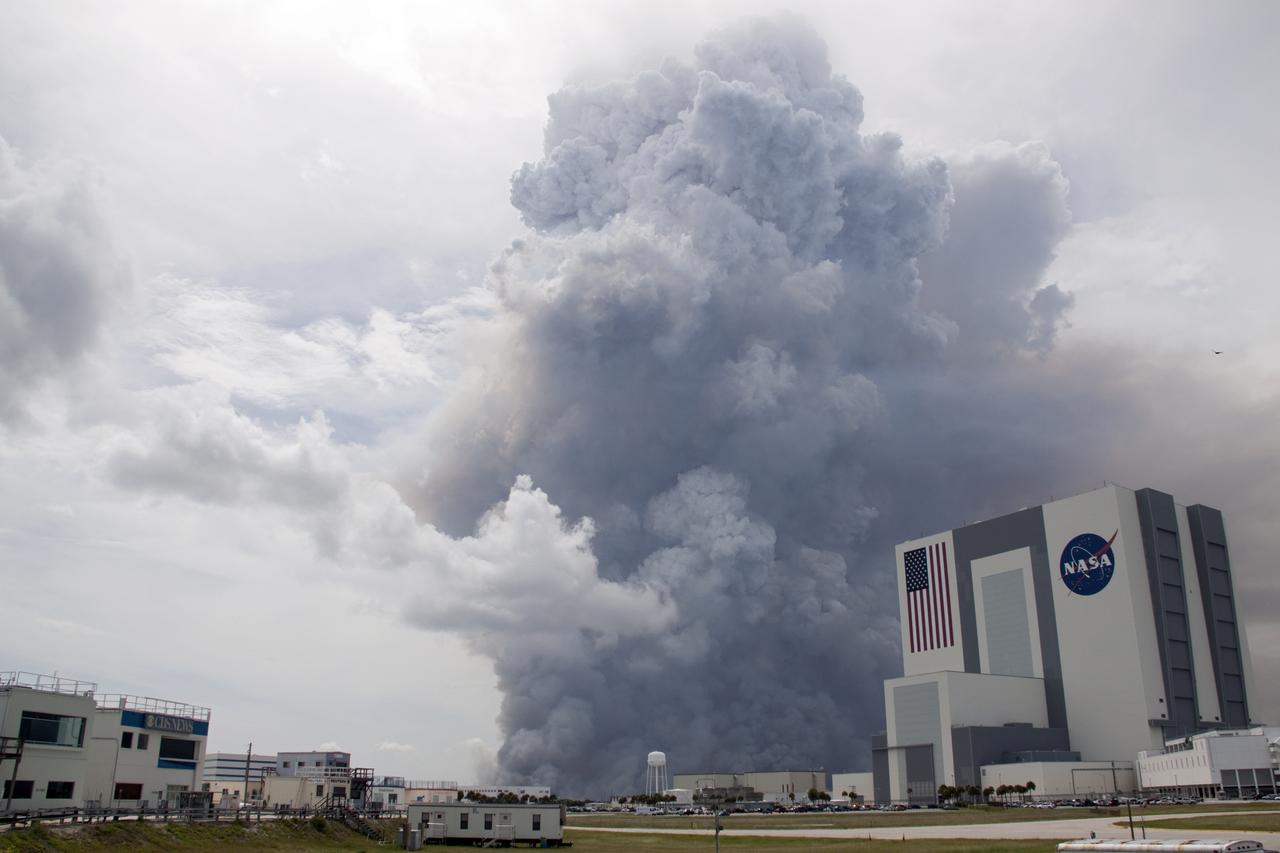

SMOKE NEAR VAB FROM CONTROLLED BURN
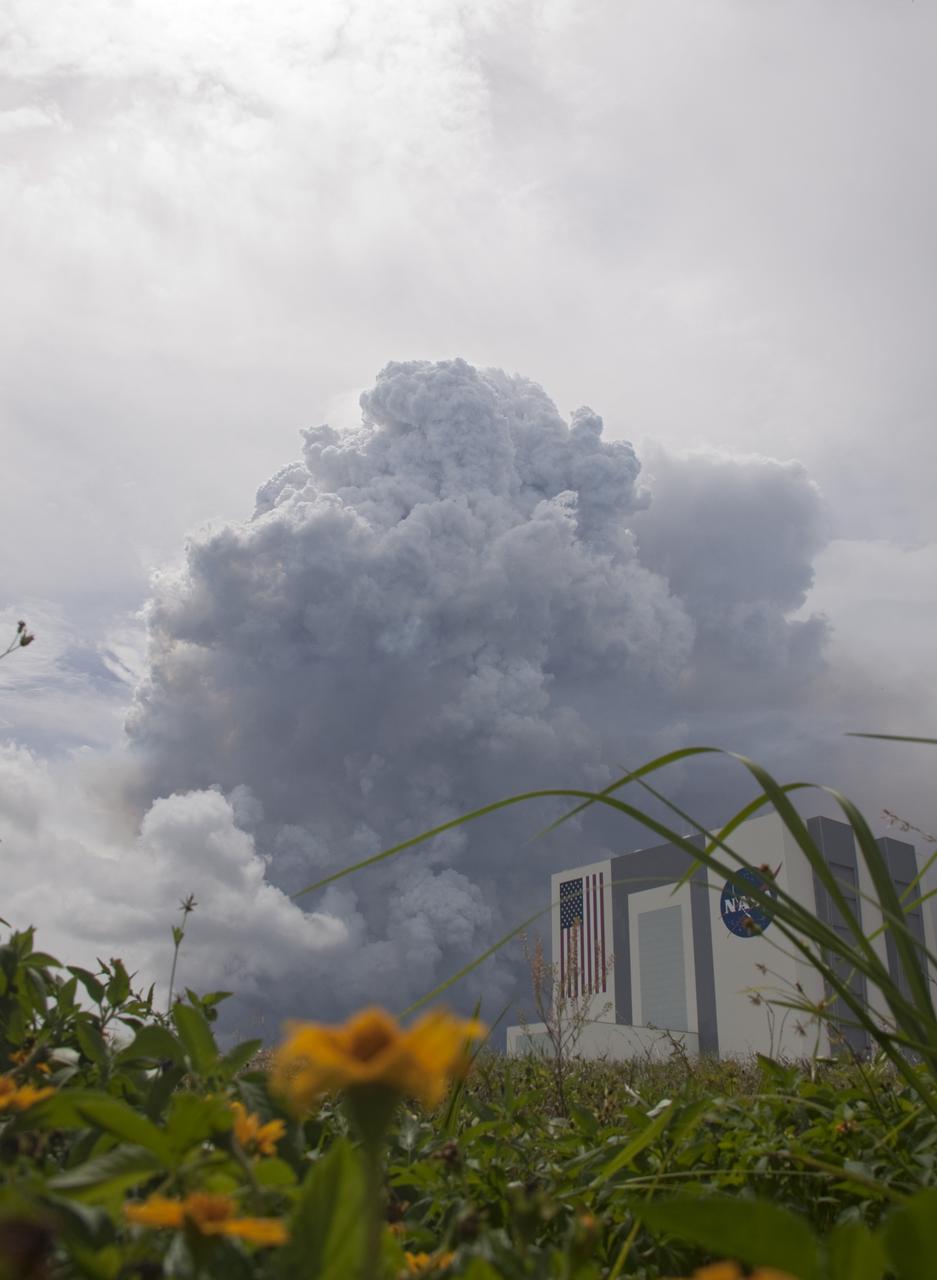

SMOKE NEAR VAB FROM CONTROLLED BURN
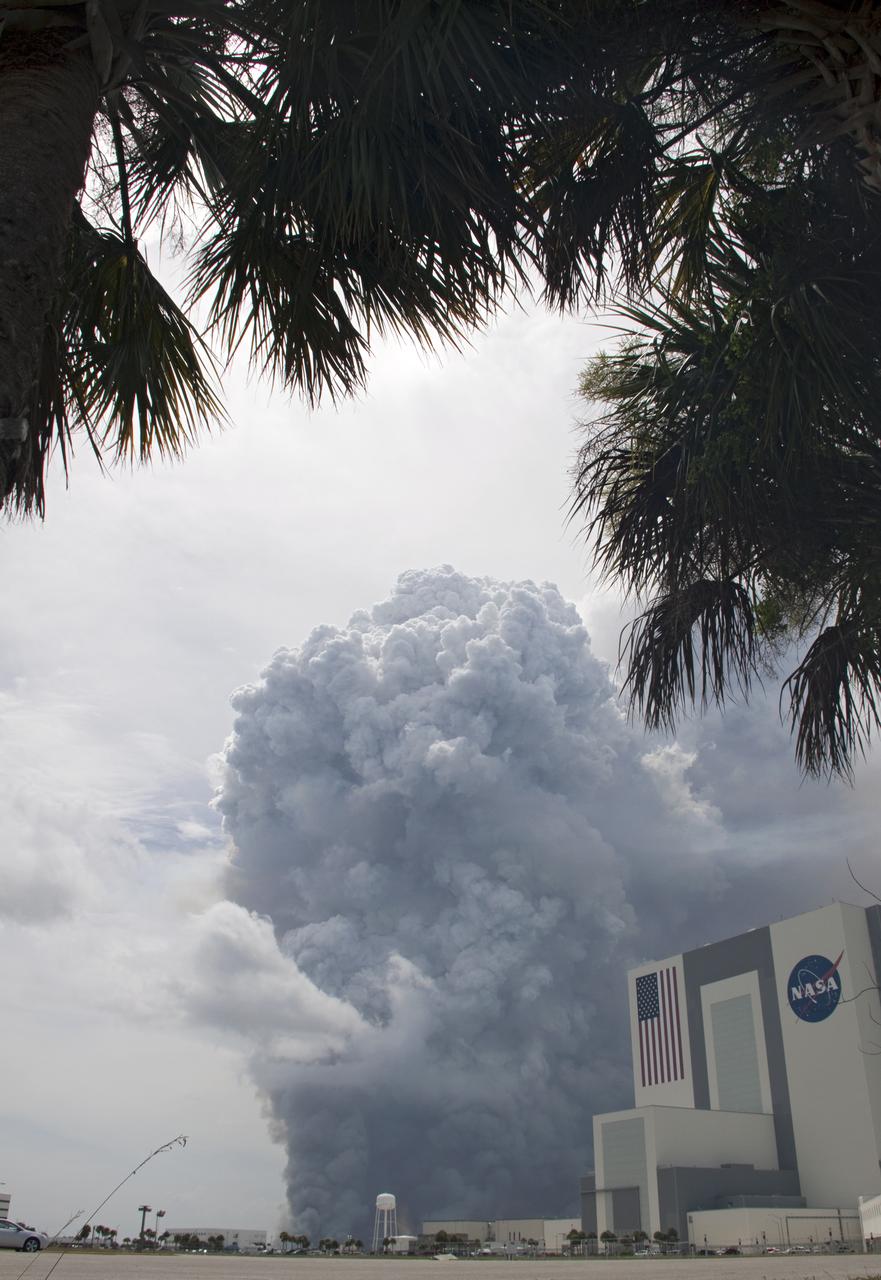

SMOKE NEAR VAB FROM CONTROLLED BURN
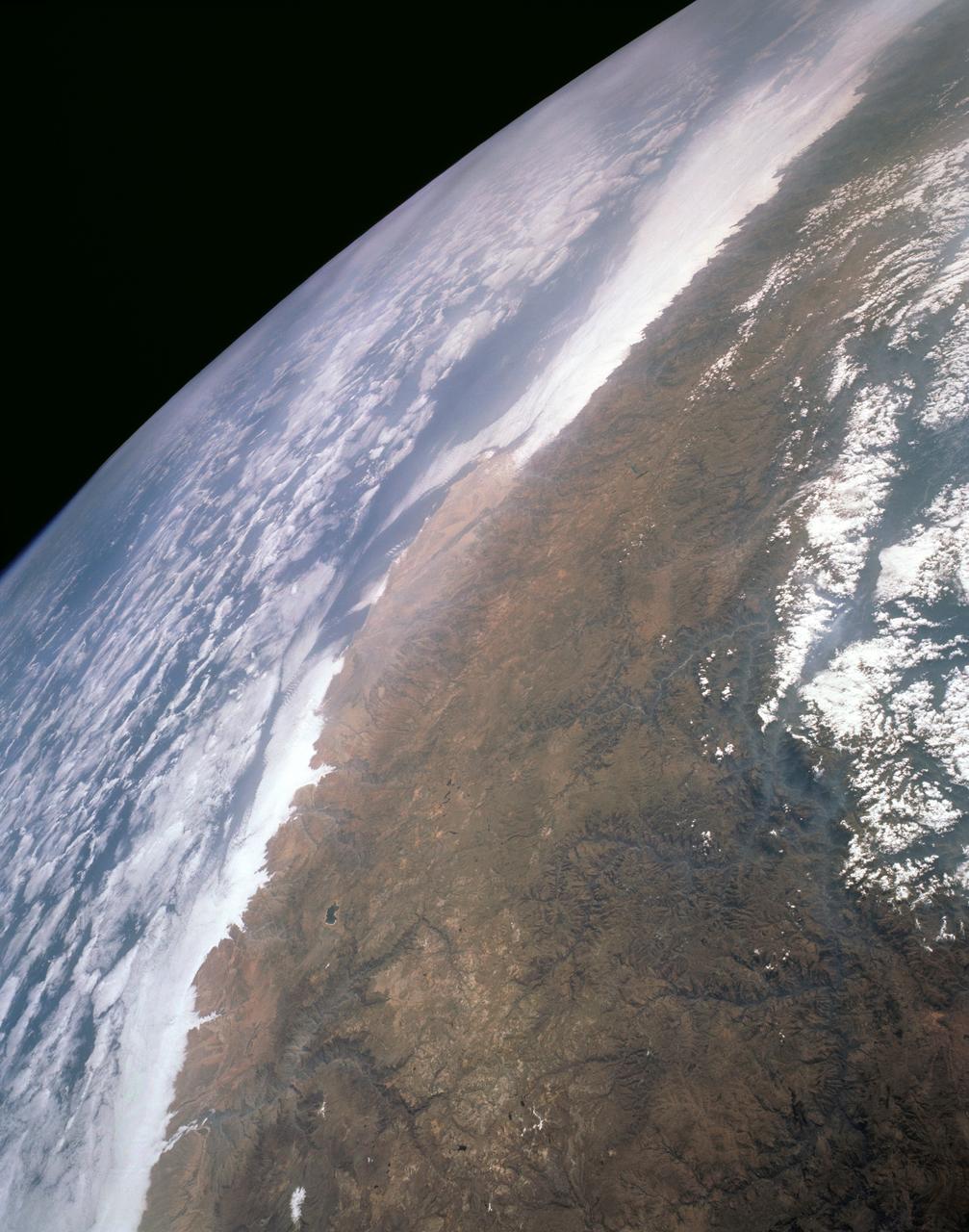

STS043-151-159 (2-11 August 1991) --- This photograph looks westward over the high plateau of the southern Peruvian Andes west and north of Lake Titicaca (not in field of view). Lima, Peru lies under the clouds just north of the clear coastal area. Because the high Andes have been uplifted 10,000 to 13,000 feet during the past 20 million years, the rivers which cut down to the Pacific Ocean have gorges almost that deep, such as the Rio Ocona at the bottom of the photograph. The eastern slopes of the Andes are heavily forested, forming the headwaters of the Amazon system. Smoke from burning in the Amazon basin fills river valleys on the right side of the photograph. A Linhof camera was used to take this view.
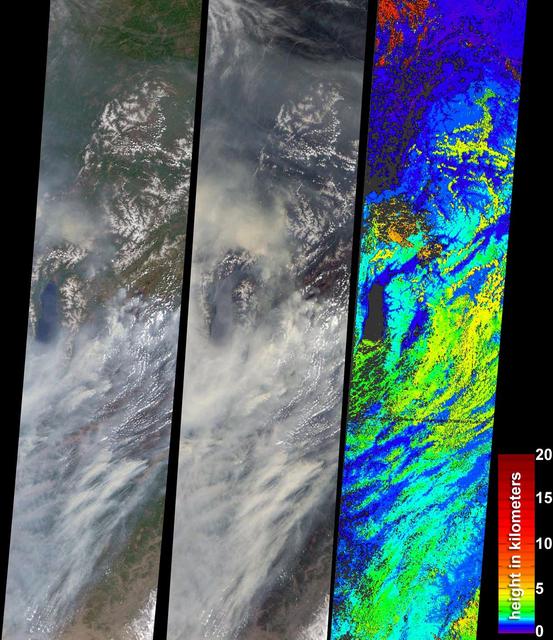
During the 2003 fire season, blazes in the taiga forests of Eastern Siberia were part of a vast network of fires across Siberia and the Russian Far East, northeast China and northern Mongolia seen here by NASA Terra spacecraft.
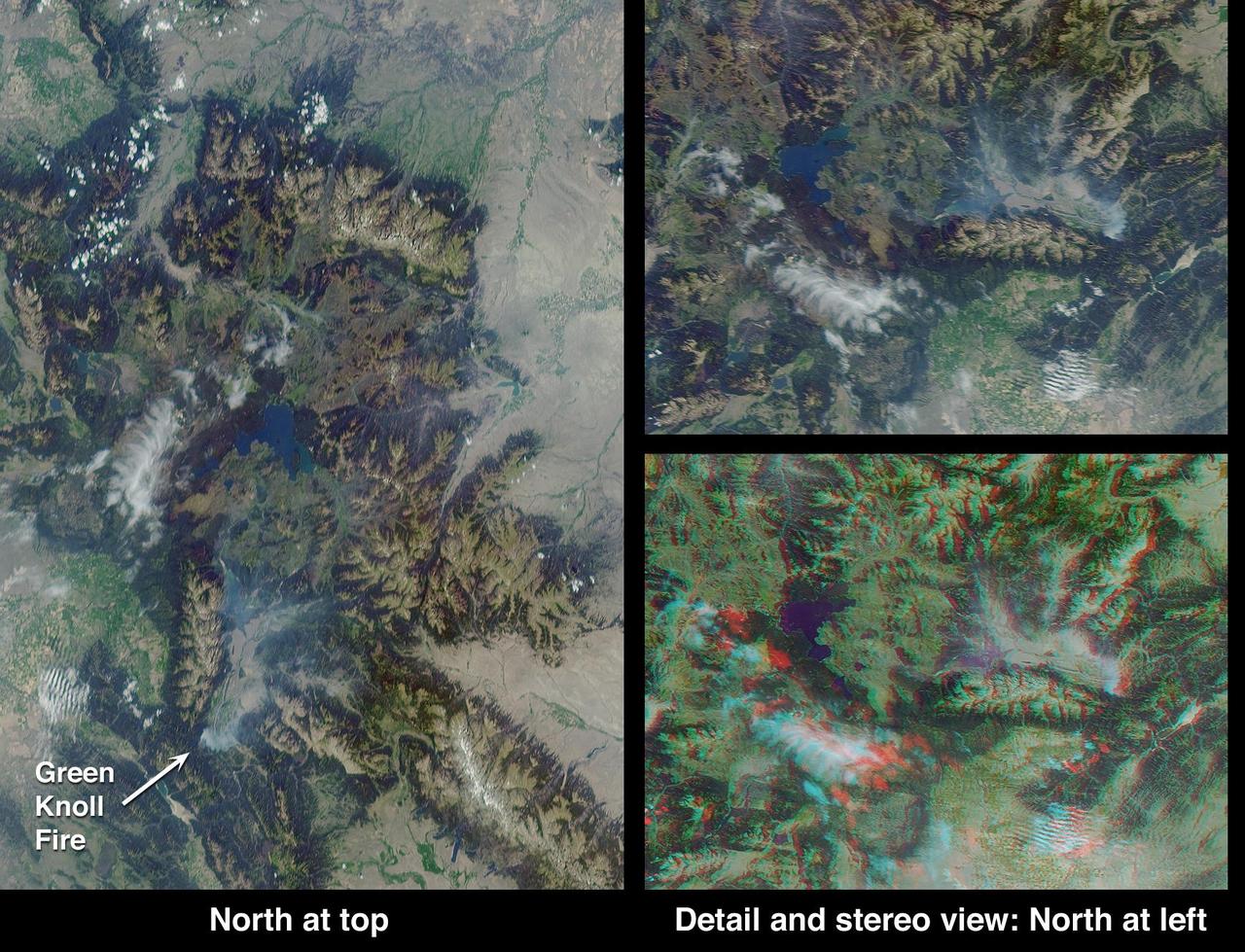

This anaglyph from the MISR instrument aboard NASA Terra spacecraft shows the area around Jackson Hole, Wyoming, where the Green Knoll forest fire raged for many days in July, 2001. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
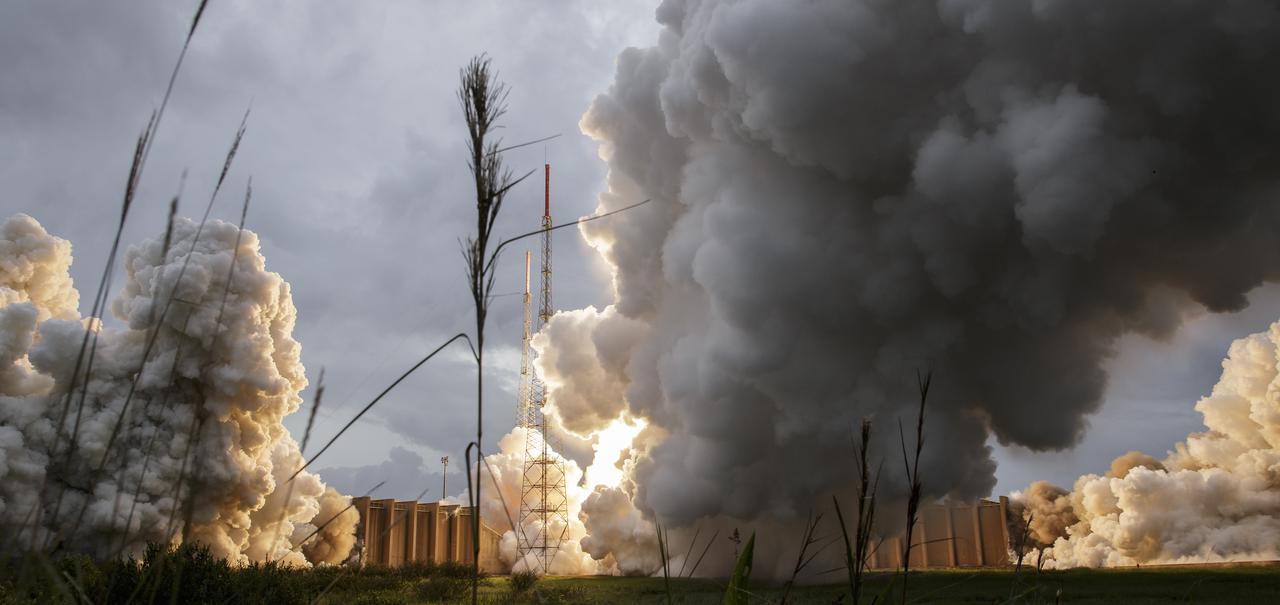

Steam and smoke from Arianespace's Ariane 5 Vulcain engine, center, and two solid rocket boosters, is seen as it launches with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, from the ELA-3 Launch Zone of Europe’s Spaceport at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Terra spacecraft acquired this image of the Wallow fire in Arizona on June 21, 2011; vegetation appears in red, bare ground in shades of tan, burned areas in black and very-dark red; and smoke from the active fire front appears gray.
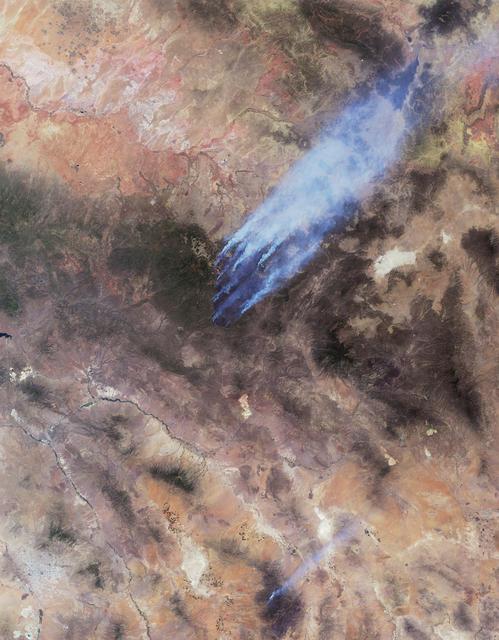

This image from NASA Terra spacecraft shows the Wallow and Horseshoe 2 Fires burning in Arizona. The data were acquired mid-morning on June 7, 2011. Nearly 10 distinct bluish-colored smoke plumes can be seen blowing toward the upper right northeast.
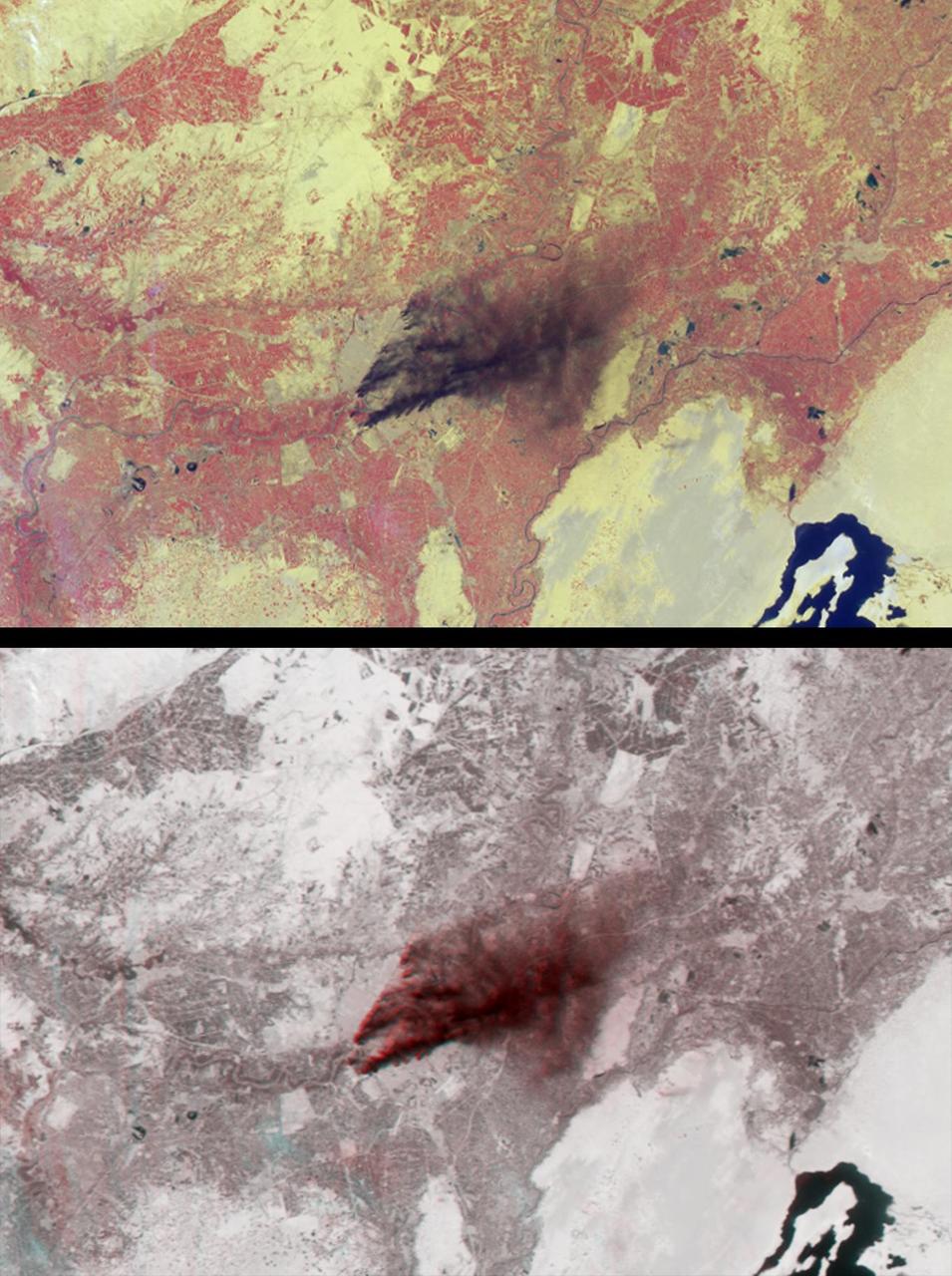

Dark smoke from oil fires extend for about 60 kilometers south of Iraq capital city of Baghdad in this anaglyph acquired by the MISR instrument aboard NASA Terra spacecraft on April 2, 2003. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.