
A banner signing event was held April 22, 2019, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, to mark the accomplishments of the Kennedy engineering team that supported the Ground Support Equipment (GSE) Subsystem Software development. This team includes the software leads, local developers, remote developers, modelers, project engineers, software quality assurance, build team members, integrators, system engineers, a chief engineer and some software managers. There are 60 unique instances of GSE Subsystem Software code. As of today, 58 of those 60 instances have completed software Level 5 Verification (L5V) and are in the process of completing Subsystem Verification & Validation.

A banner signing event was held April 22, 2019, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, to mark the accomplishments of the Kennedy engineering team that supported the Ground Support Equipment (GSE) Subsystem Software development. This team includes the software leads, local developers, remote developers, modelers, project engineers, software quality assurance, build team members, integrators, system engineers, a chief engineer and some software managers. There are 60 unique instances of GSE Subsystem Software code. As of today, 58 of those 60 instances have completed software Level 5 Verification (L5V) and are in the process of completing Subsystem Verification & Validation.

A banner signing event was held April 22, 2019, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, to mark the accomplishments of the Kennedy engineering team that supported the Ground Support Equipment (GSE) Subsystem Software development. This team includes the software leads, local developers, remote developers, modelers, project engineers, software quality assurance, build team members, integrators, system engineers, a chief engineer and some software managers. There are 60 unique instances of GSE Subsystem Software code. As of today, 58 of those 60 instances have completed software Level 5 Verification (L5V) and are in the process of completing Subsystem Verification & Validation.

A banner signing event was held April 22, 2019, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, to mark the accomplishments of the Kennedy engineering team that supported the Ground Support Equipment (GSE) Subsystem Software development. This team includes the software leads, local developers, remote developers, modelers, project engineers, software quality assurance, build team members, integrators, system engineers, a chief engineer and some software managers. There are 60 unique instances of GSE Subsystem Software code. As of today, 58 of those 60 instances have completed software Level 5 Verification (L5V) and are in the process of completing Subsystem Verification & Validation.

A banner signing event was held April 22, 2019, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, to mark the accomplishments of the Kennedy engineering team that supported the Ground Support Equipment (GSE) Subsystem Software development. This team includes the software leads, local developers, remote developers, modelers, project engineers, software quality assurance, build team members, integrators, system engineers, a chief engineer and some software managers. There are 60 unique instances of GSE Subsystem Software code. As of today, 58 of those 60 instances have completed software Level 5 Verification (L5V) and are in the process of completing Subsystem Verification & Validation.
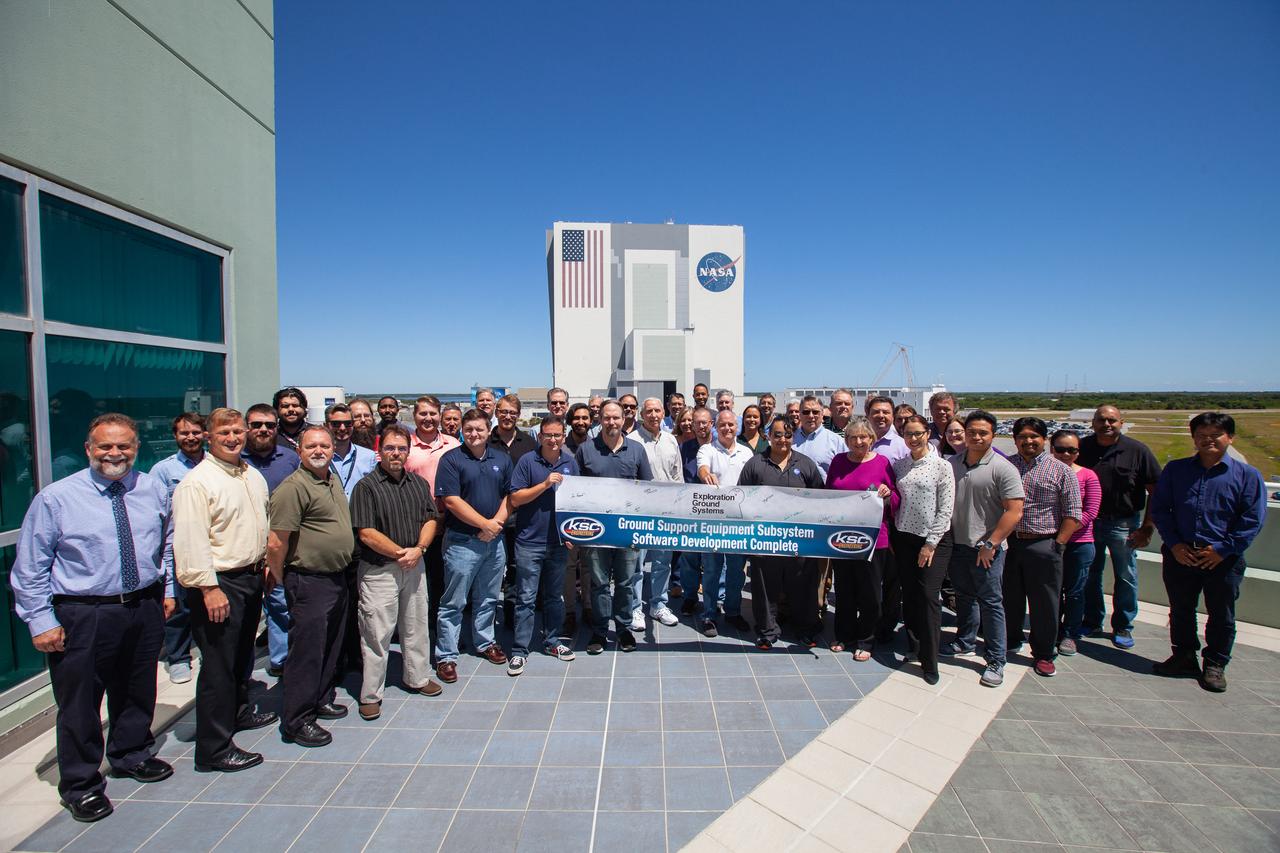

A banner signing event was held April 22, 2019, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, to mark the accomplishments of the Kennedy engineering team that supported the Ground Support Equipment (GSE) Subsystem Software development. The team gathered in the observation area of the Operations Support Building II with a view of the Vehicle Assembly Building behind them. This team includes the software leads, local developers, remote developers, modelers, project engineers, software quality assurance, build team members, integrators, system engineers, a chief engineer and some software managers. There are 60 unique instances of GSE Subsystem Software code. As of today, 58 of those 60 instances have completed software Level 5 Verification (L5V) and are in the process of completing Subsystem Verification & Validation.
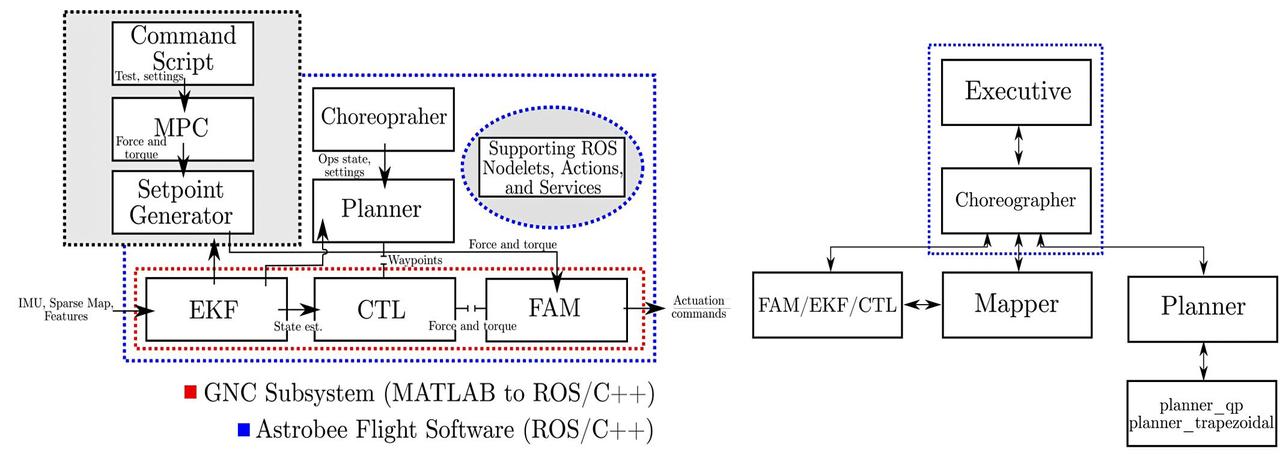
jsc2025e032820 (3/20/2025) --- Left: Astrobee’s guidance, navigation and control (GNC) subsystem. Components shown in black (Matlab/ROS/C++/Python) indicate a replacement pipeline overriding Astrobee’s default GNC subsystem, outlined in red. Right: software interface between GNC components and Astrobee’s finite state machines (FSMs). The FSM-based nodelets are outlined in blue. Image courtesy of Hector Gutierrez.
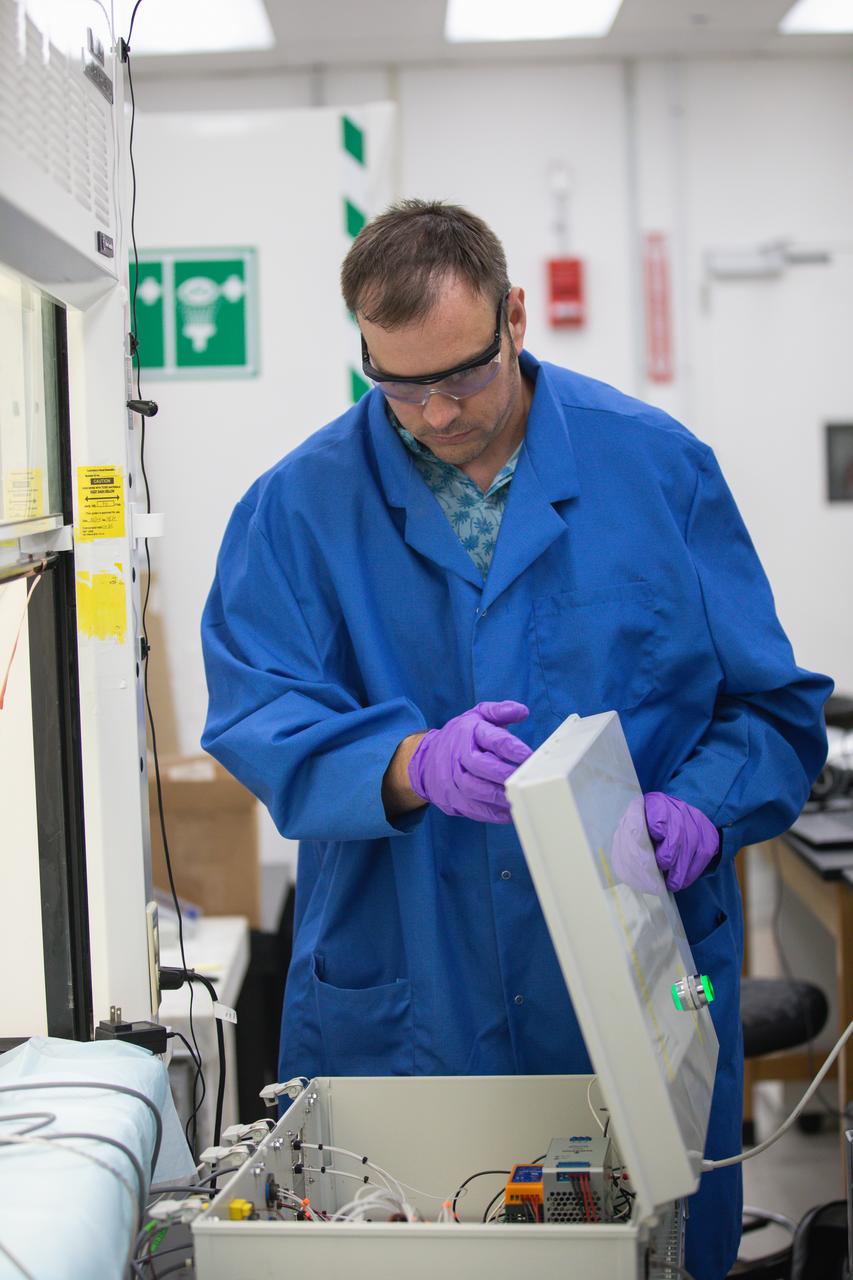

Beau Peacock, software engineer, conducts testing of the Volatile Monitoring Oxygen Measurement Subsystem (VMOMS) for Molten Regolith Electrolysis (MRE) inside a laboratory in the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 19, 2024. The high-temperature electrolytic process aims to extract oxygen from simulated lunar regolith which will be critical to the agency’s Artemis campaign. Oxygen extracted from the Moon can be utilized for propellent to NASA’s lunar landers, breathable oxygen for astronauts, and a variety of other industrial and scientific applications for NASA’s future missions to the Moon.
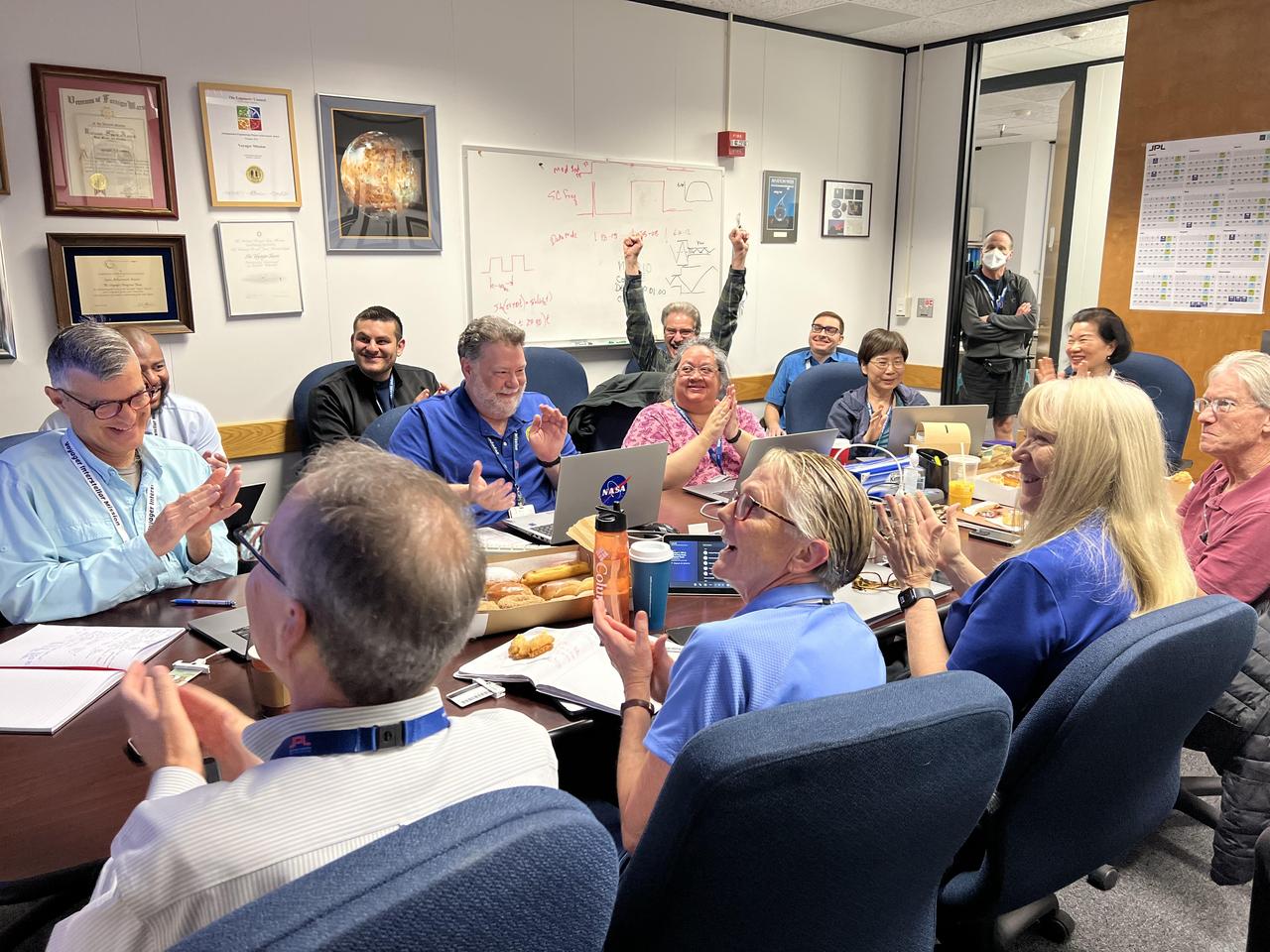

In a conference room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, members of the Voyager mission team gathered April 20, 2024, to find out if an issue on Voyager 1 had been partially resolved. Just after 6:40 a.m., a cheer went up around the room as the group heard back from the spacecraft: It was returning engineering data for the first time since November 2023. Nearly two full days earlier, the team had sent a series of commands to move a section of software code used by the flight data subsystem (FDS) computer to a new location. The physical location where the code was previously stored has been damaged, causing the mission to go five months without receiving science or engineering data. But the commands were a success, and the team received data about the health and status of the spacecraft, prompting celebration. The commands were sent on April 18, 2024. Due to Voyager 1's distance from Earth – over 15 billion miles or 24 billion kilometers – a radio signal takes about 22 ½ hours to travel to the spacecraft, and 22 ½ hours to return to Earth. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26275