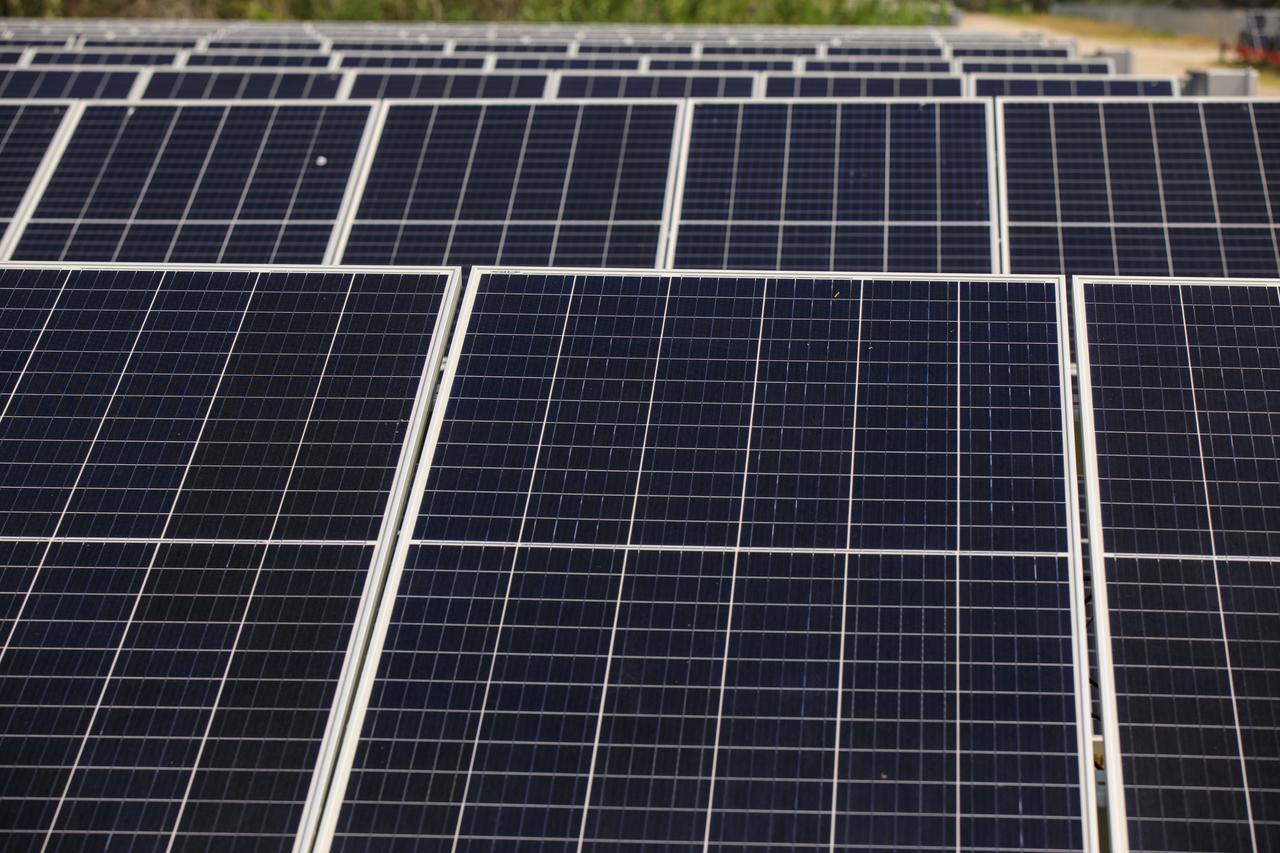

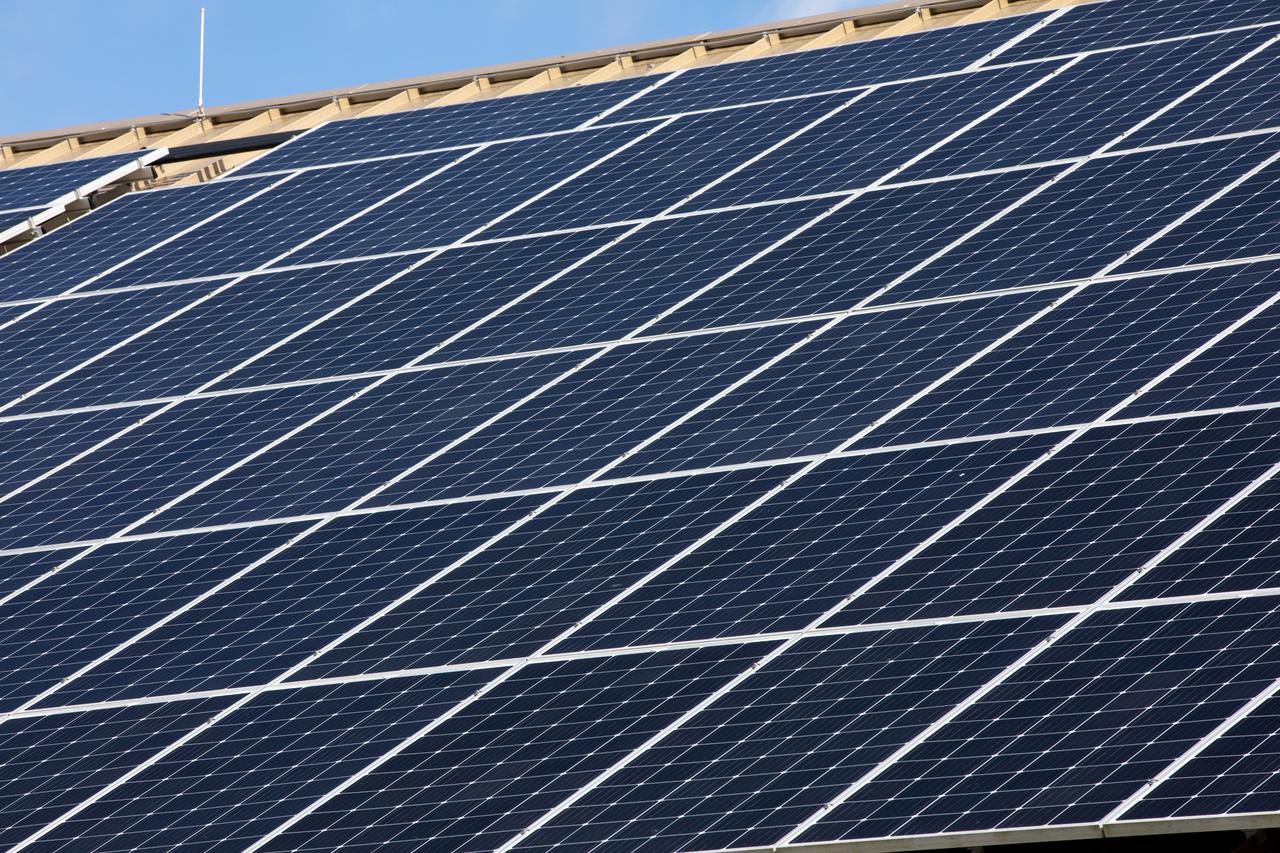
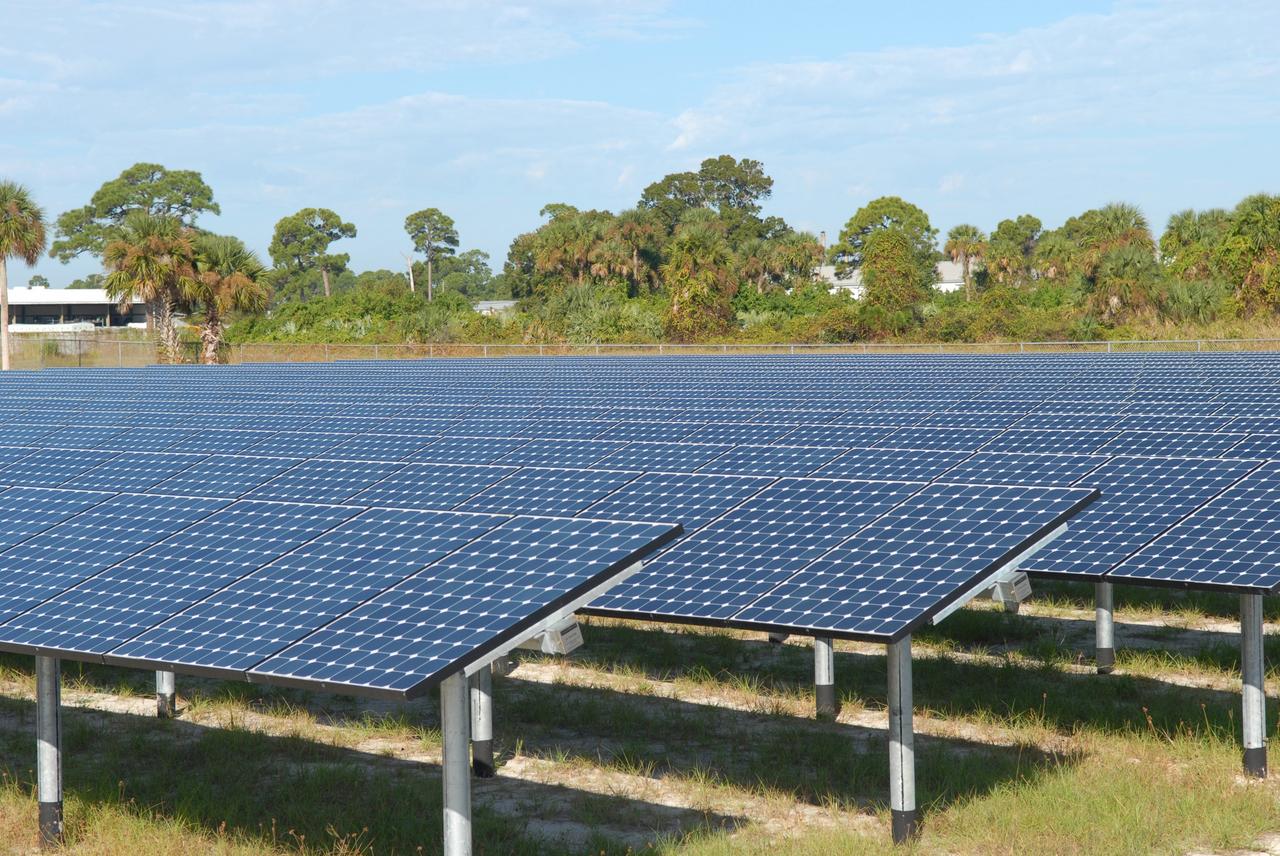
Seen here is an up-close view of solar panels that are part of Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) new Discovery Solar Energy Center – a 74.5-megawatt solar site, spanning 491 acres at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The site contains about 250,000 solar panels in total, producing enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels do not directly power anything at Kennedy, but rather, send energy directly to FPL's electricity grid for distribution to existing customers. Construction began in spring 2020, and the energy center became fully operational on May 30, 2021.

Seen here is an up-close view of solar panels that are part of Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) new Discovery Solar Energy Center – a 74.5-megawatt solar site, spanning 491 acres at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The site contains about 250,000 solar panels in total, producing enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels do not directly power anything at Kennedy, but rather, send energy directly to FPL's electricity grid for distribution to existing customers. Construction began in spring 2020, and the energy center became fully operational on May 30, 2021.

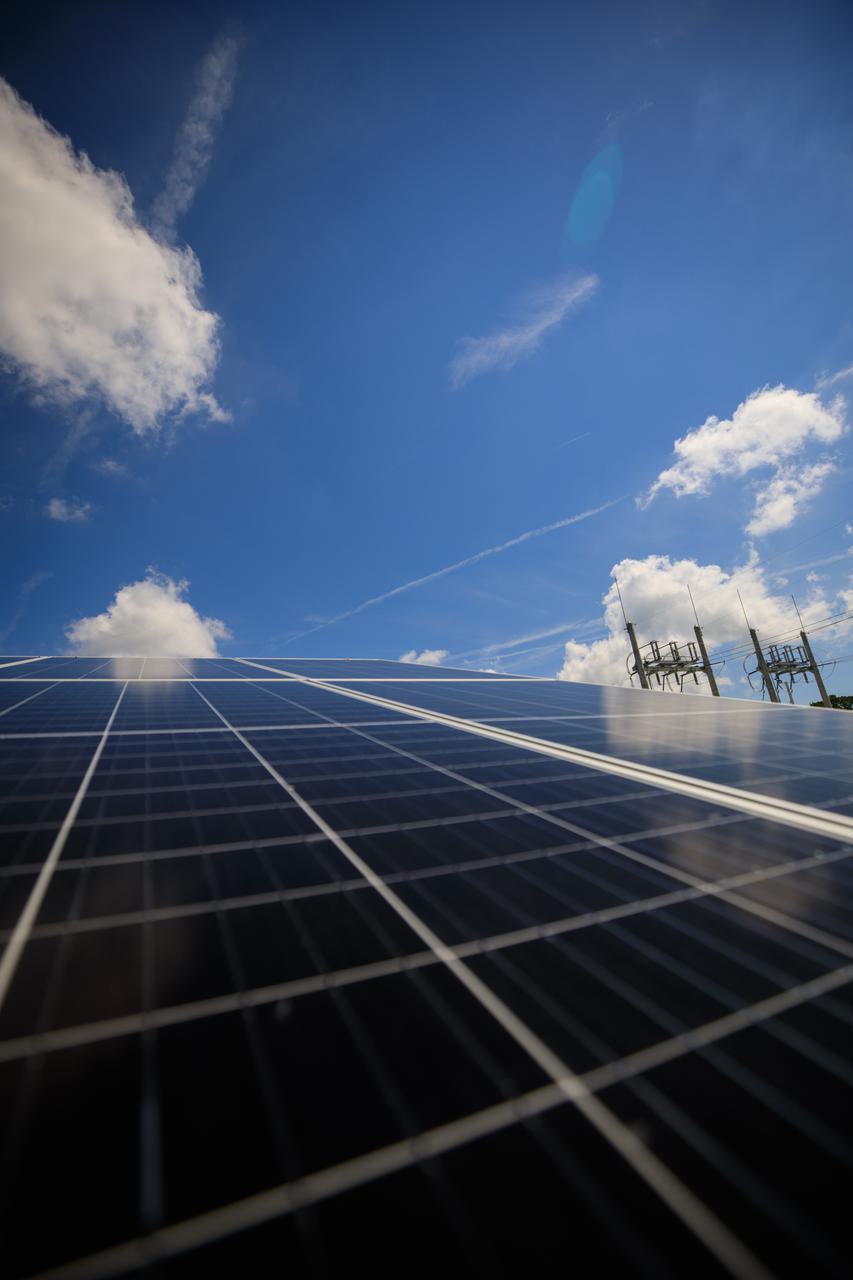
In this view are solar panels that are part of Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) new Discovery Solar Energy Center – a 74.5-megawatt solar site, spanning 491 acres at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The site contains about 250,000 solar panels in total, producing enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels do not directly power anything at Kennedy, but rather, send energy directly to FPL's electricity grid for distribution to existing customers. Construction began in spring 2020, and the energy center became fully operational on May 30, 2021.
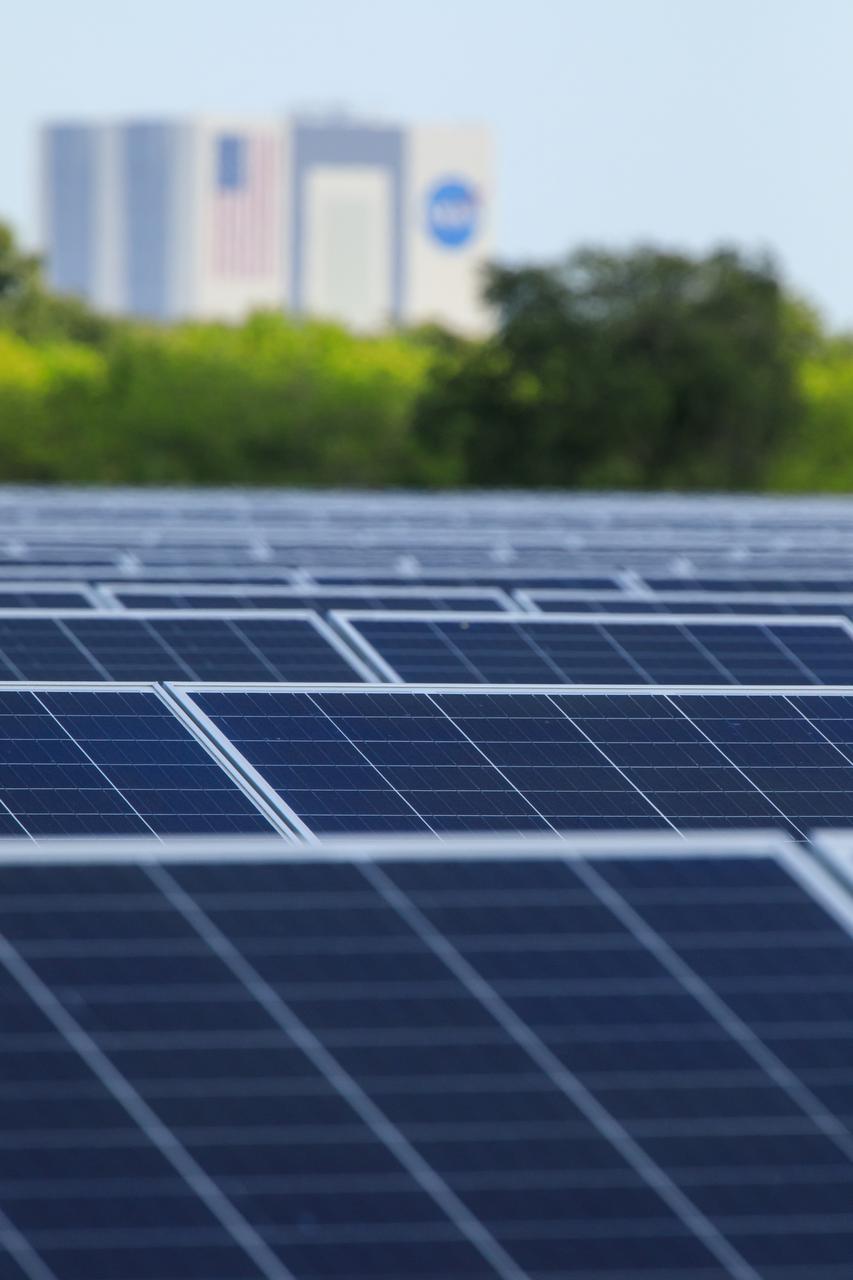

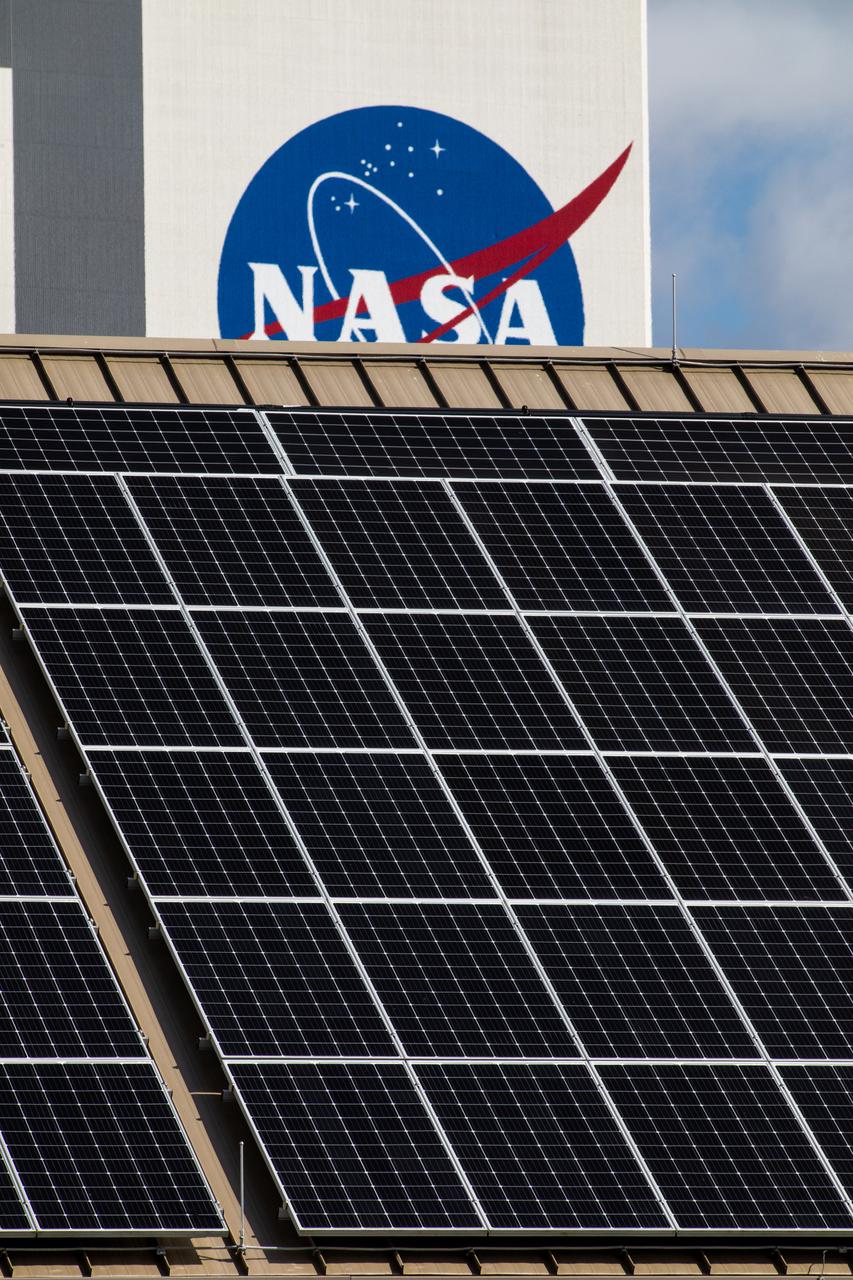
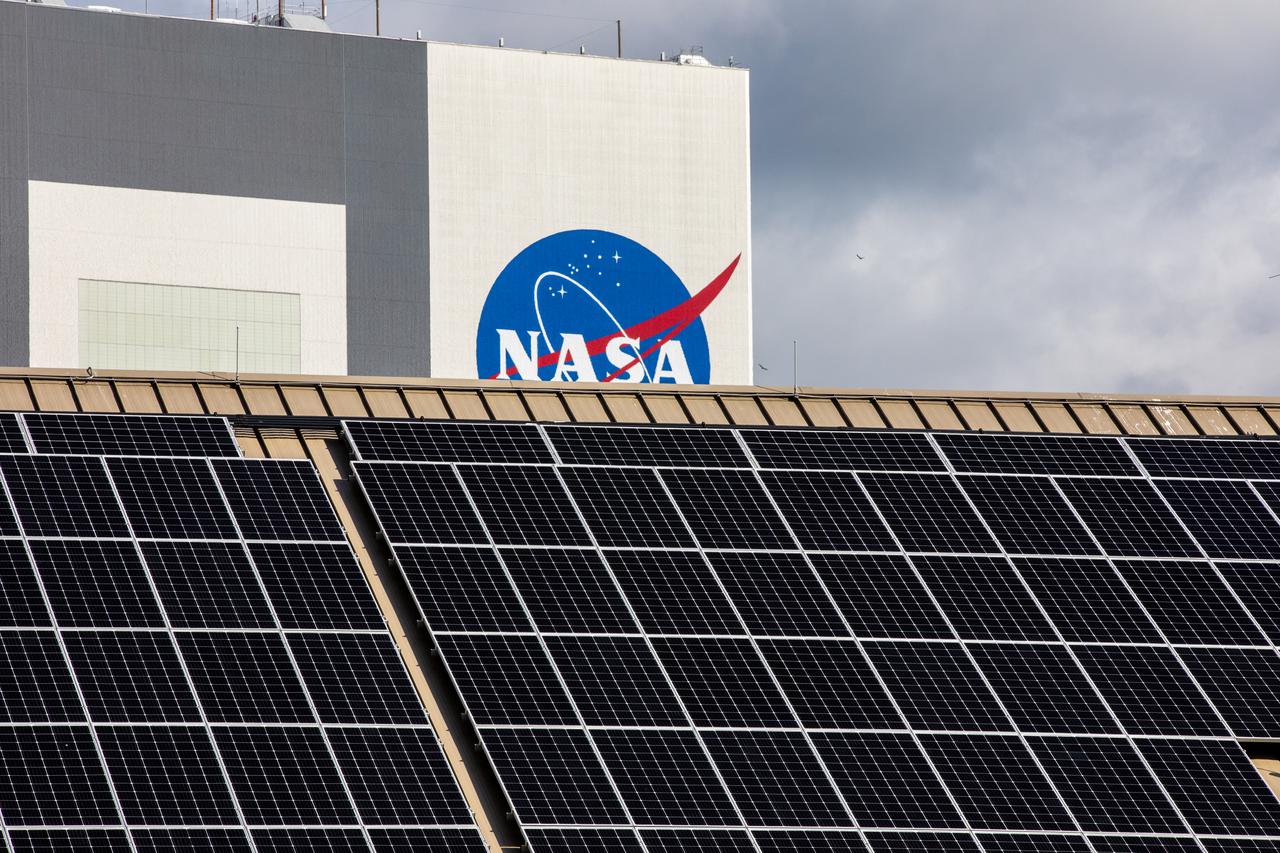
Seen here, with the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building in the background, is an up-close view of solar panels that are part of Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) new Discovery Solar Energy Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 74.5-megawatt solar site spans 491 acres at Kennedy and contains about 250,000 solar panels. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels produce enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. The panels do not directly power anything at Kennedy, and instead, send energy directly to FPL’s electricity grid for distribution to existing customers. Construction began in spring 2020, and the energy center became fully operational on May 30, 2021.
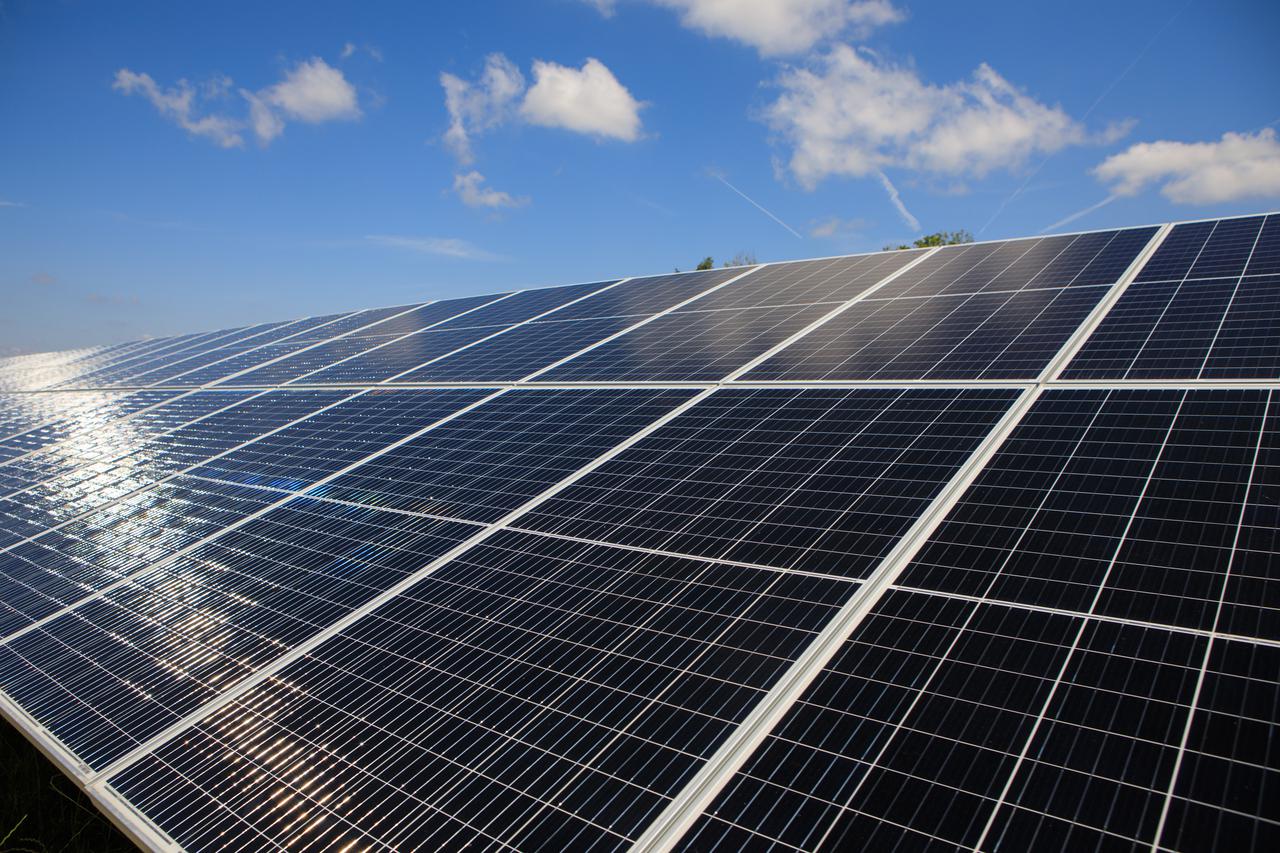

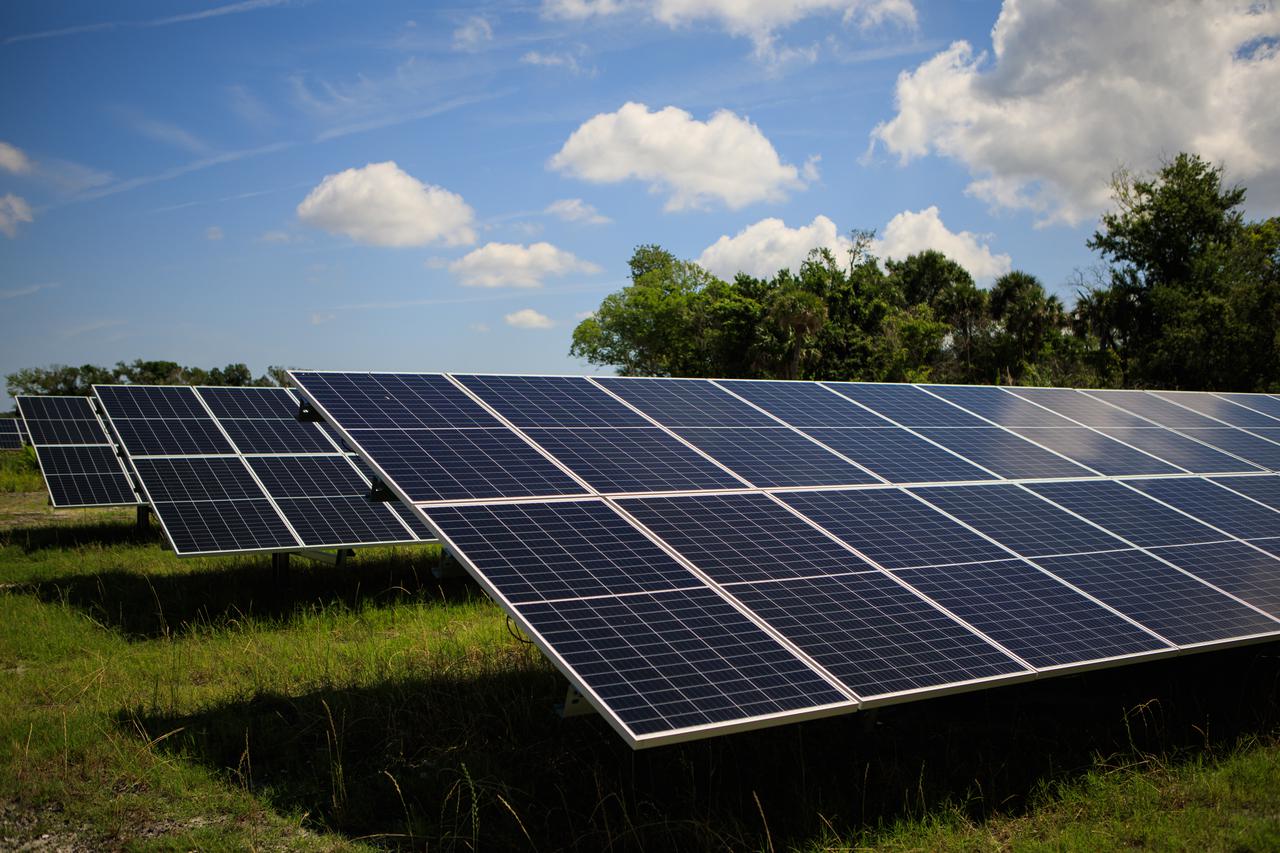
Seen here is an up-close view of solar panels that are part of Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) new Discovery Solar Energy Center – a 74.5-megawatt solar site, spanning 491 acres at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The site contains about 250,000 solar panels in total, producing enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels do not directly power anything at Kennedy, but rather, send energy directly to FPL's electricity grid for distribution to existing customers. Construction began in spring 2020, and the energy center became fully operational on May 30, 2021.
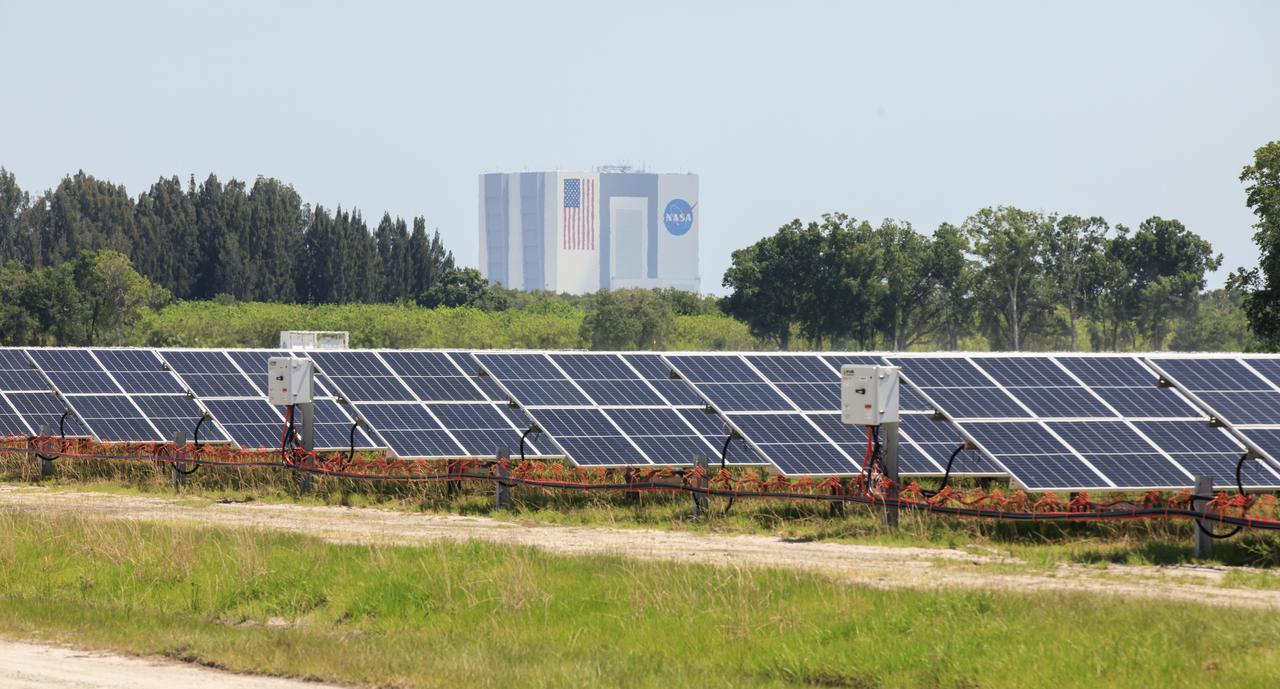

With the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building serving as the backdrop, a portion of the solar panels that make up Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) new Discovery Solar Energy Center is seen at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 74.5-megawatt solar site spans 491 acres at Kennedy and contains about 250,000 solar panels. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels produce enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. The panels do not directly power anything at Kennedy, and instead, send energy directly to FPL’s electricity grid for distribution to existing customers. Construction began in spring 2020, and the energy center became fully operational on May 30, 2021.

Guest speaker John Sherwin shares a presentation featuring residential solar and home energy-saving methods during a “lunch and learn” held Tuesday, Oct. 23, 2018, for employees at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Sherwin is the director of the Photovoltaic System Certification and Testing Program at the Florida Solar Energy Center in Cocoa. The event was one of two held during October in conjunction with Energy Awareness Month, which aims to recognize the importance of energy management for our national prosperity, security and environmental sustainability.
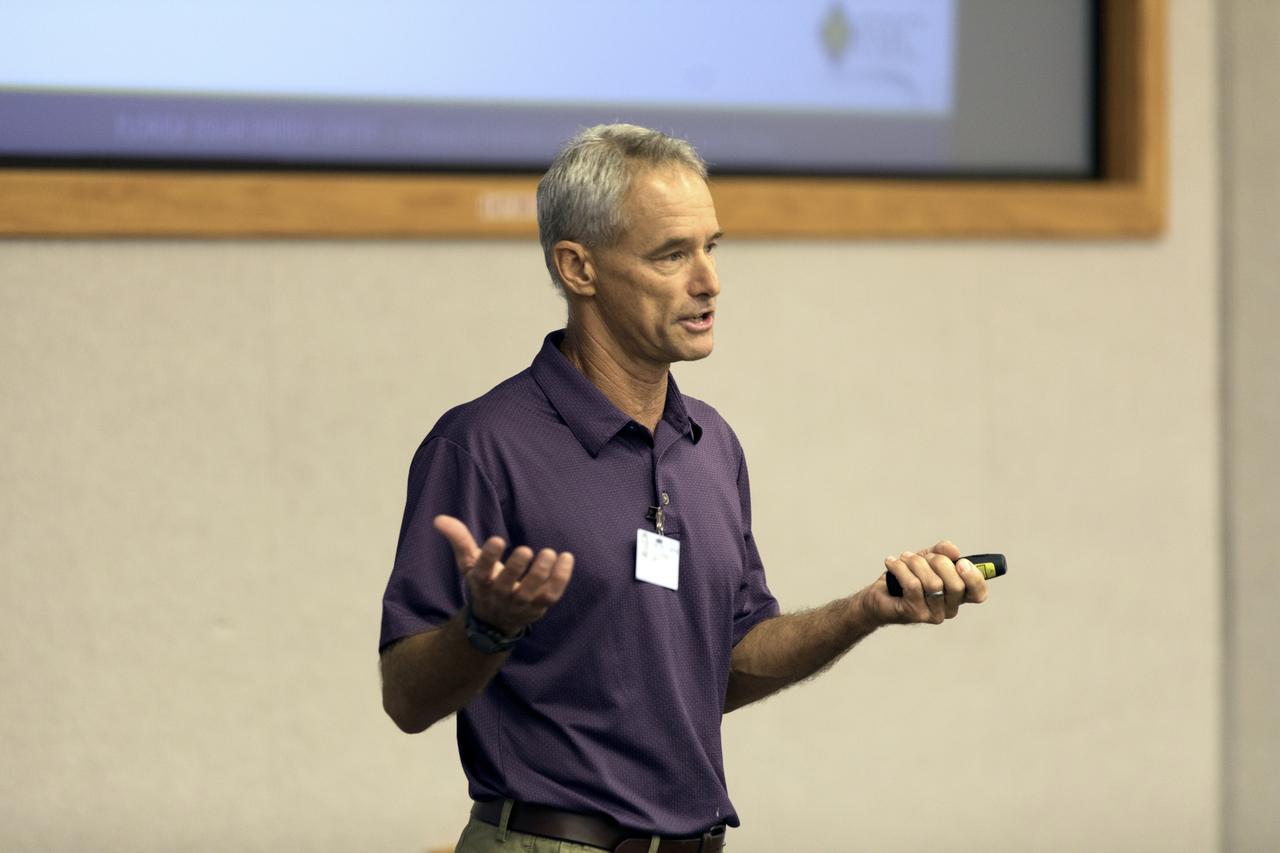

Guest speaker John Sherwin explains residential solar and home energy-saving methods during a “lunch and learn” held Tuesday, Oct. 23, 2018, for employees at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Sherwin is the director of the Photovoltaic System Certification and Testing Program at the Florida Solar Energy Center in Cocoa. The event was one of two held during October in conjunction with Energy Awareness Month, which aims to recognize the importance of energy management for our national prosperity, security and environmental sustainability.

NASA Kennedy Space Center's Sam Ball, third from left, speaks during the Energy Action Day employee event held in NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. Part of Energy Awareness Month, the event featured subject matter experts in the area of solar energy, its connections to the space program and options for residential solar power. From left to right are Nick Murdock, energy and water program manager at Kennedy; Chuck Tatro of NASA's Launch Services Program; Ball; Anuj Chokshi of FPL; Bill McMullen of Southern Power; John Sherwin of the Florida Solar Energy Center in Cocoa; and Lorraine Koss of the Brevard County Solar Co-op.
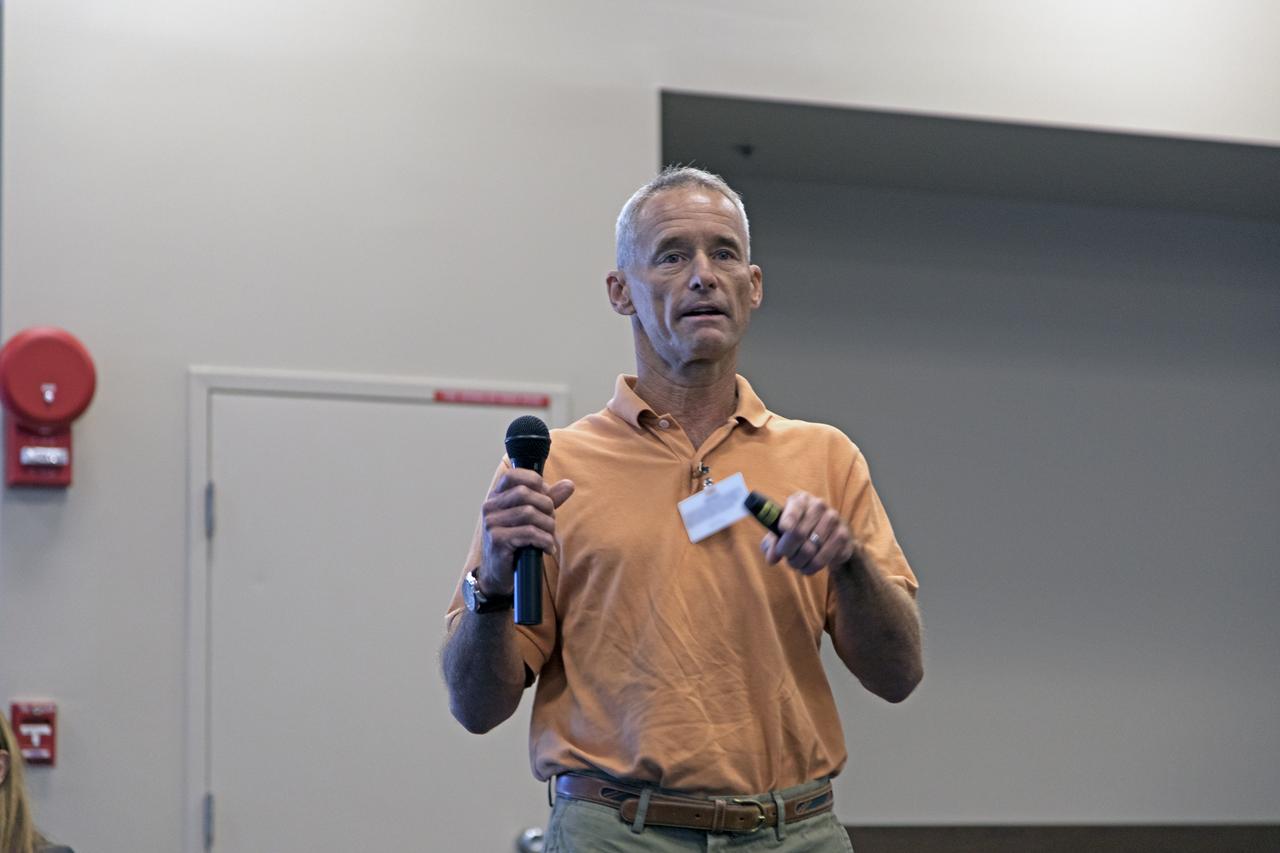

John Sherwin of the Florida Solar Energy Center in Cocoa speaks during the Energy Action Day employee event held in NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. Part of Energy Awareness Month, the event featured subject matter experts in the area of solar energy, its connections to the space program and options for residential solar power.
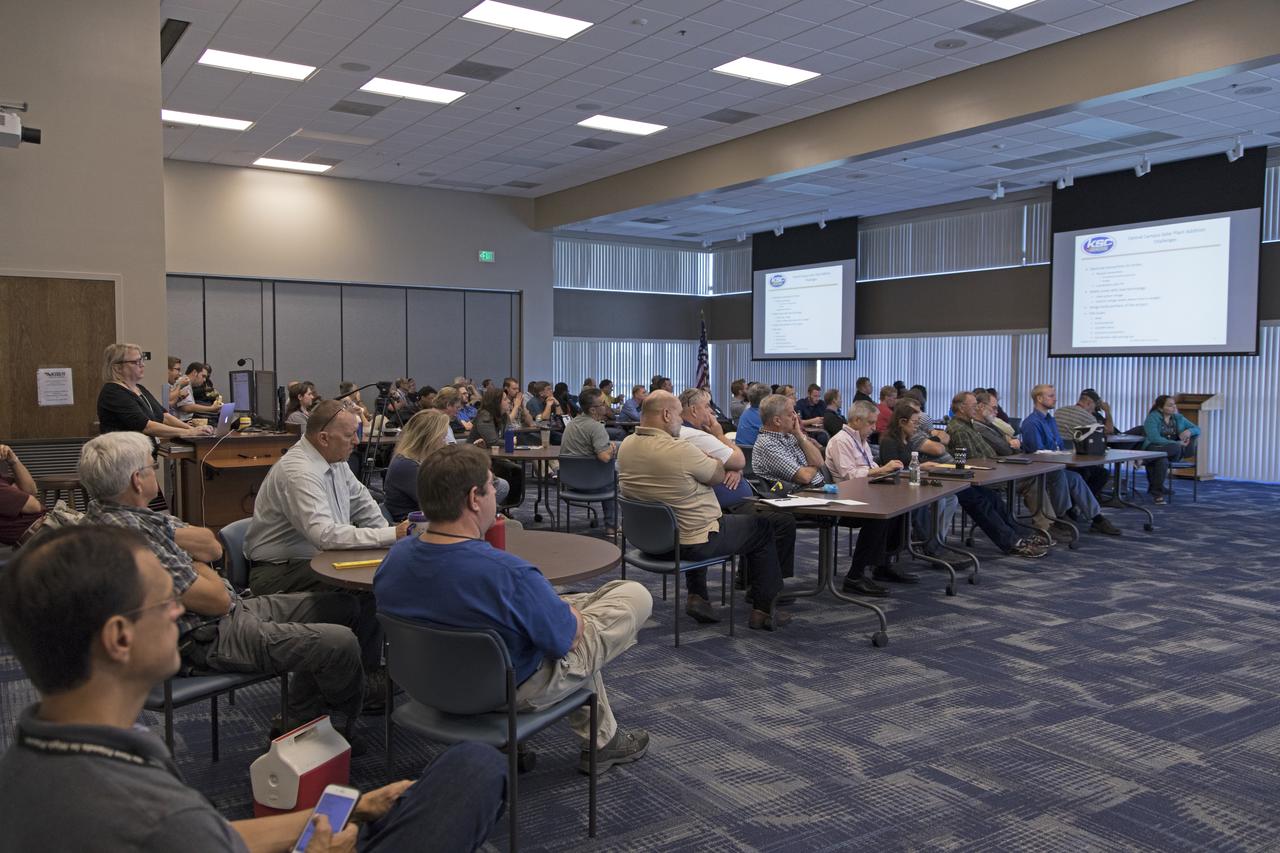

NASA Kennedy Space Center employees attend the Energy Action Day event held in the center's Space Station Processing Facility. Part of Energy Awareness Month, the event featured subject matter experts in the area of solar energy, its connections to the space program and options for residential solar power.
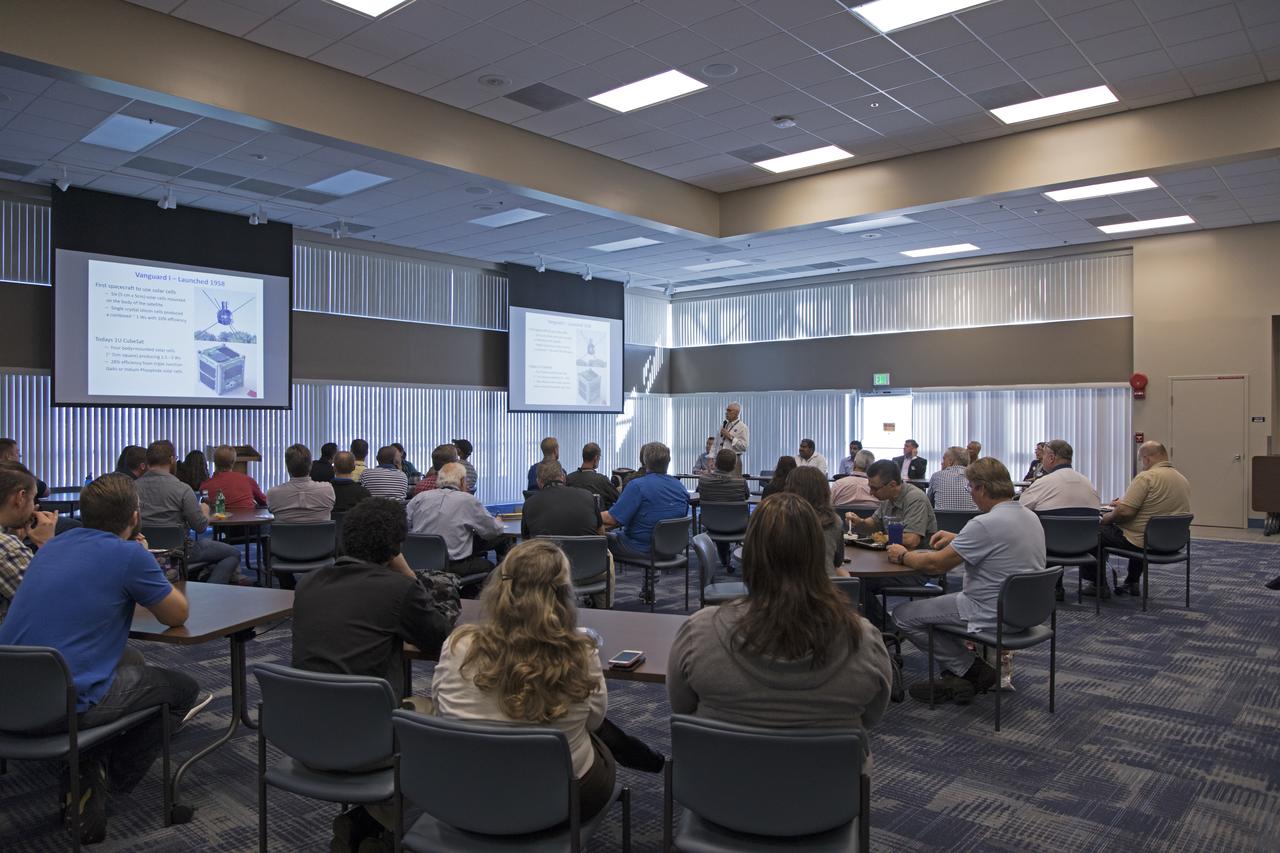

Chuck Tatro of NASA's Launch Services Program discusses the use of solar arrays on space science missions during the Energy Action Day employee event held in Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. Part of Energy Awareness Month, the event featured subject matter experts in the area of solar energy, its connections to the space program and options for residential solar power.
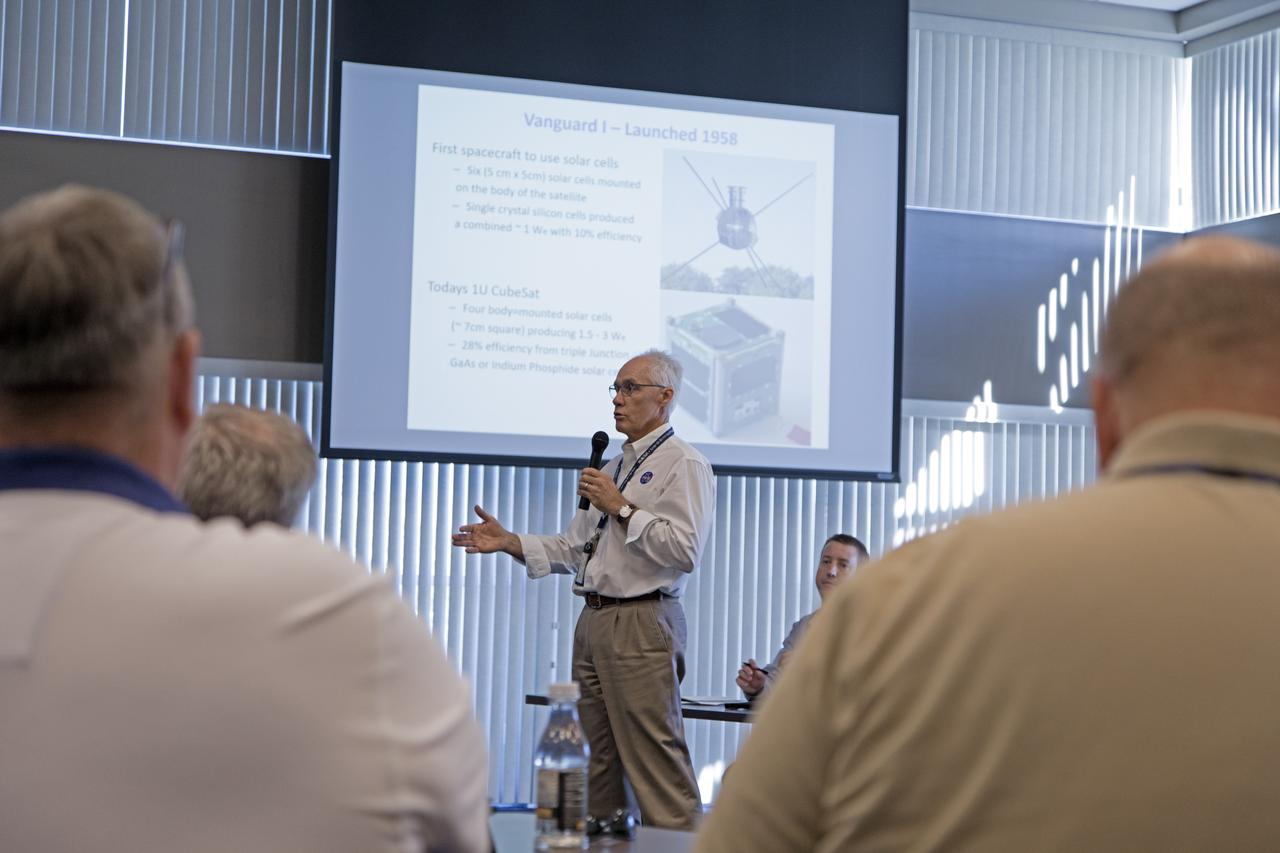

Chuck Tatro of NASA's Launch Services Program discusses the use of solar arrays on space science missions during the Energy Action Day employee event held in Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. Part of Energy Awareness Month, the event featured subject matter experts in the area of solar energy, its connections to the space program and options for residential solar power.
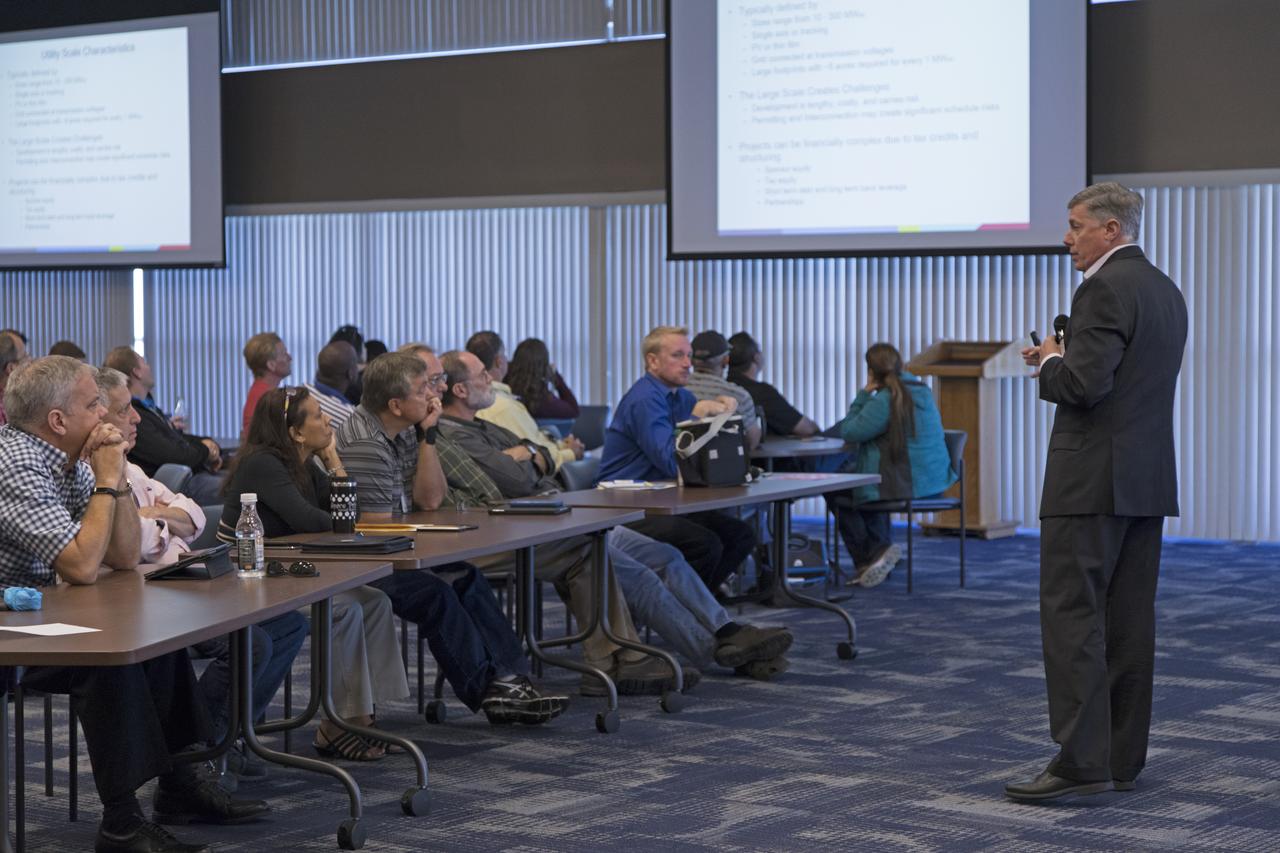

Bill McCullen of Southern Power speaks to NASA Kennedy Space Center employees during the Energy Action Day event held in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. Part of Energy Awareness Month, the event featured subject matter experts in the area of solar energy, its connections to the space program and options for residential solar power.
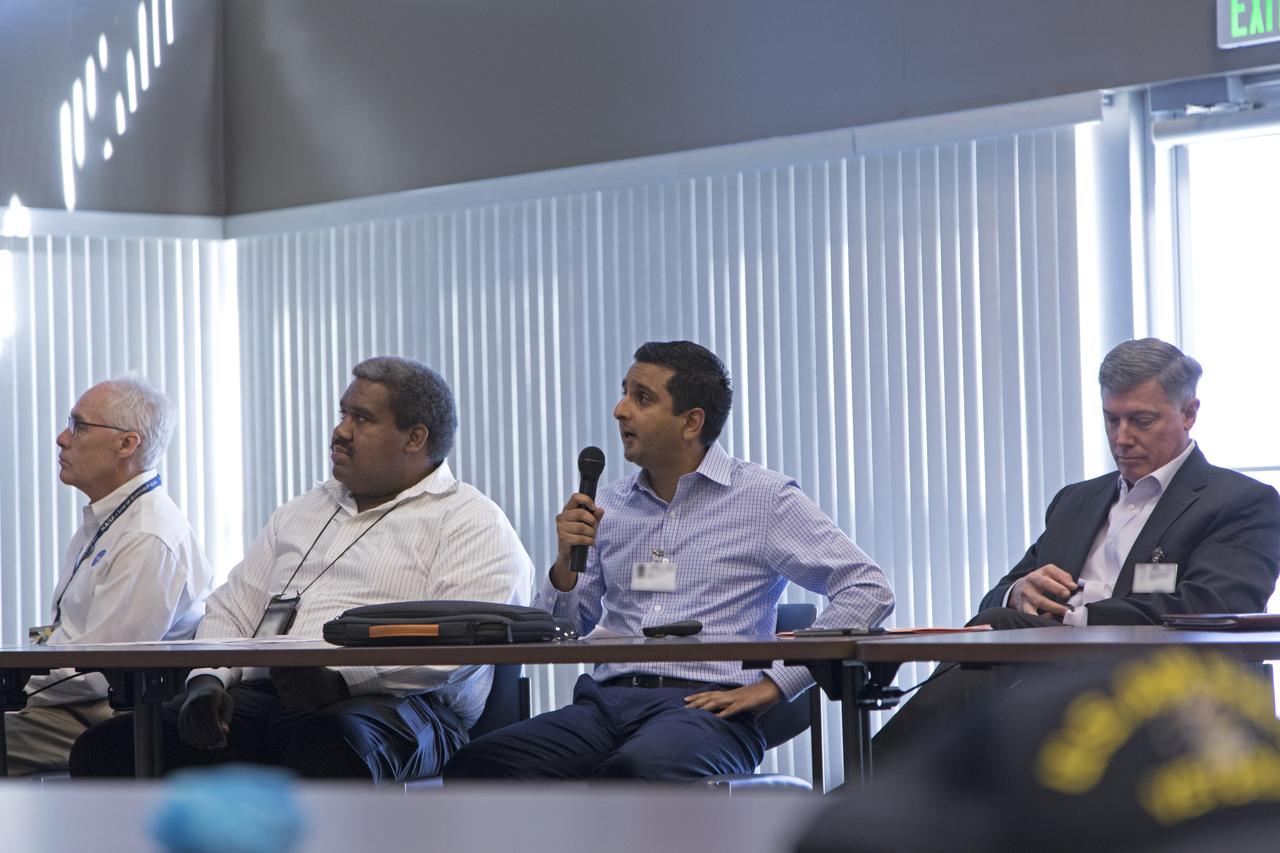

Anuj Chokshi of FPL, center, speaks during the Energy Action Day employee event held in NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. Part of Energy Awareness Month, the event featured subject matter experts in the area of solar energy, its connections to the space program and options for residential solar power. From left to right are Chuck Tatro of NASA's Launch Services Program; Sam Ball of NASA Kennedy's Engineering directorate; Chokshi; and Bill McMullen of Southern Power.
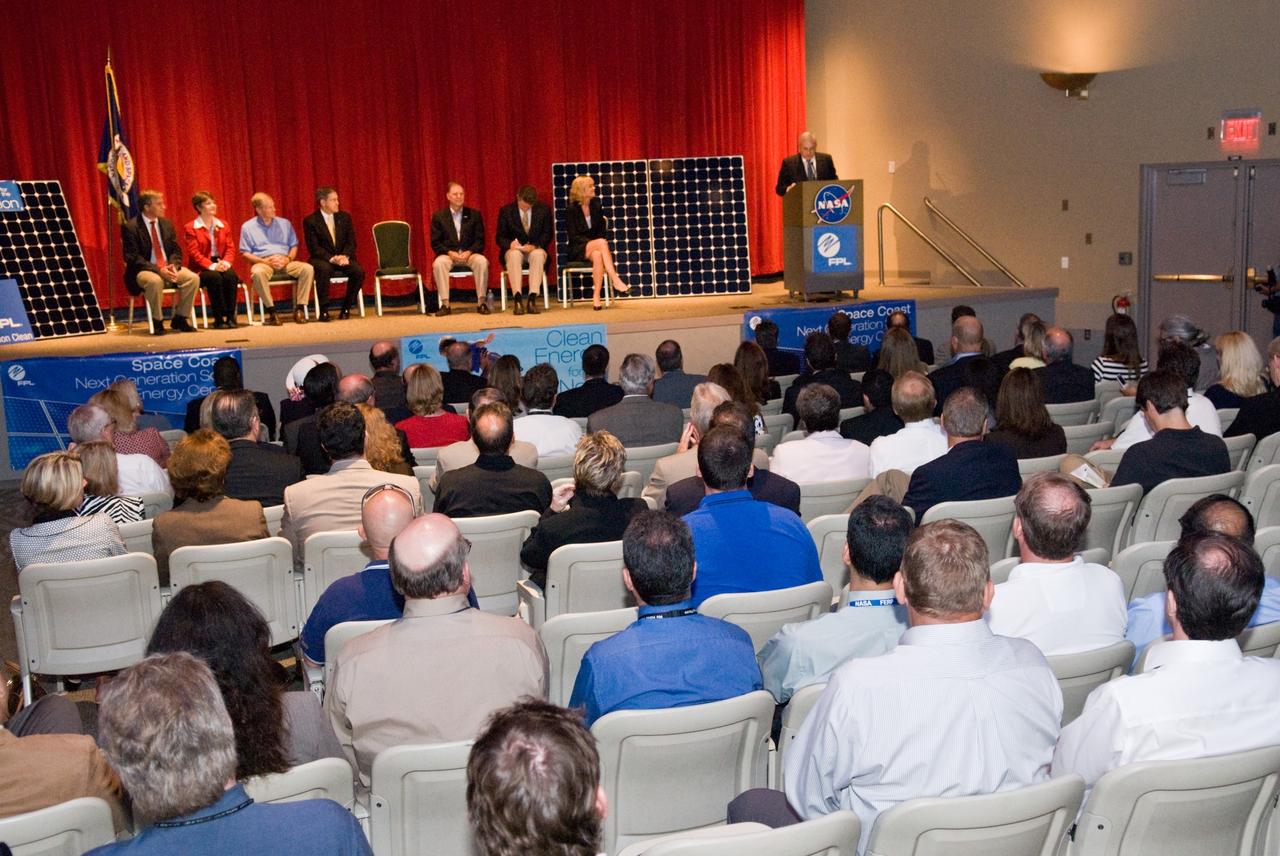

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Armando Olivera, president and CEO of Florida Power & Light, or FPL, speaks to guests at the groundbreaking ceremony for the joint NASA and FPL solar power project at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Others on the stage are, from left, Ed Smeloff with SunPower Corporation, Florida Rep. Suzanne Kosmas, Sen. Bill Nelson, Center Director Bob Cabana, Florida Rep. Bill Posey, Eric Draper, deputy director of Audubon of Florida, and Pam Rauch, vice president of External Affairs for FPL. FPL, Florida's largest electric utility, will build and maintain two solar photovoltaic power generation systems at Kennedy. One will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of emissions-free power for FPL customers, which is enough energy to serve roughly 1,100 homes. The second is a one-megawatt solar power facility that will provide renewable energy directly to Kennedy. The FPL facilities at NASA will help provide Florida residents and America's space program with new sources of clean energy that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The one megawatt facility also will help NASA meet its goal for use of power generated from renewable energy. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
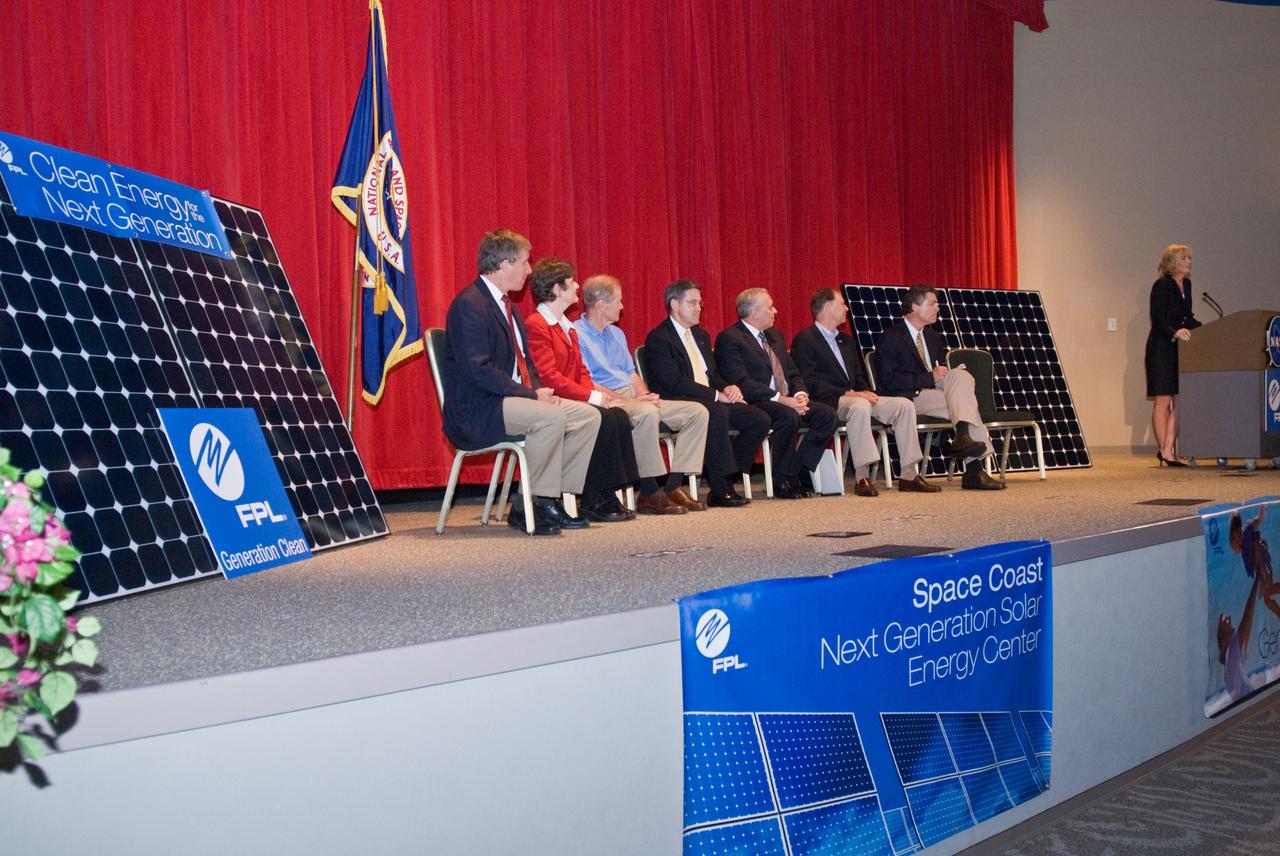

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Pam Rauch, vice president of External Affairs for Florida Power & Light, or FPL, speaks to guests at the groundbreaking ceremony for the joint NASA and FPL solar power project at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Others on the stage are Ed Smeloff with SunPower Corporation, Florida Rep. Suzanne Kosmas, Sen. Bill Nelson, Center Director Bob Cabana, Armando Olivera, president and CEO of FPL, Florida Rep. Bill Posey and Eric Draper, deputy director of Audubon of Florida. FPL, Florida's largest electric utility, will build and maintain two solar photovoltaic power generation systems at Kennedy. One will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of emissions-free power for FPL customers, which is enough energy to serve roughly 1,100 homes. The second is a one-megawatt solar power facility that will provide renewable energy directly to Kennedy. The FPL facilities at NASA will help provide Florida residents and America's space program with new sources of clean energy that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The one megawatt facility also will help NASA meet its goal for use of power generated from renewable energy. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
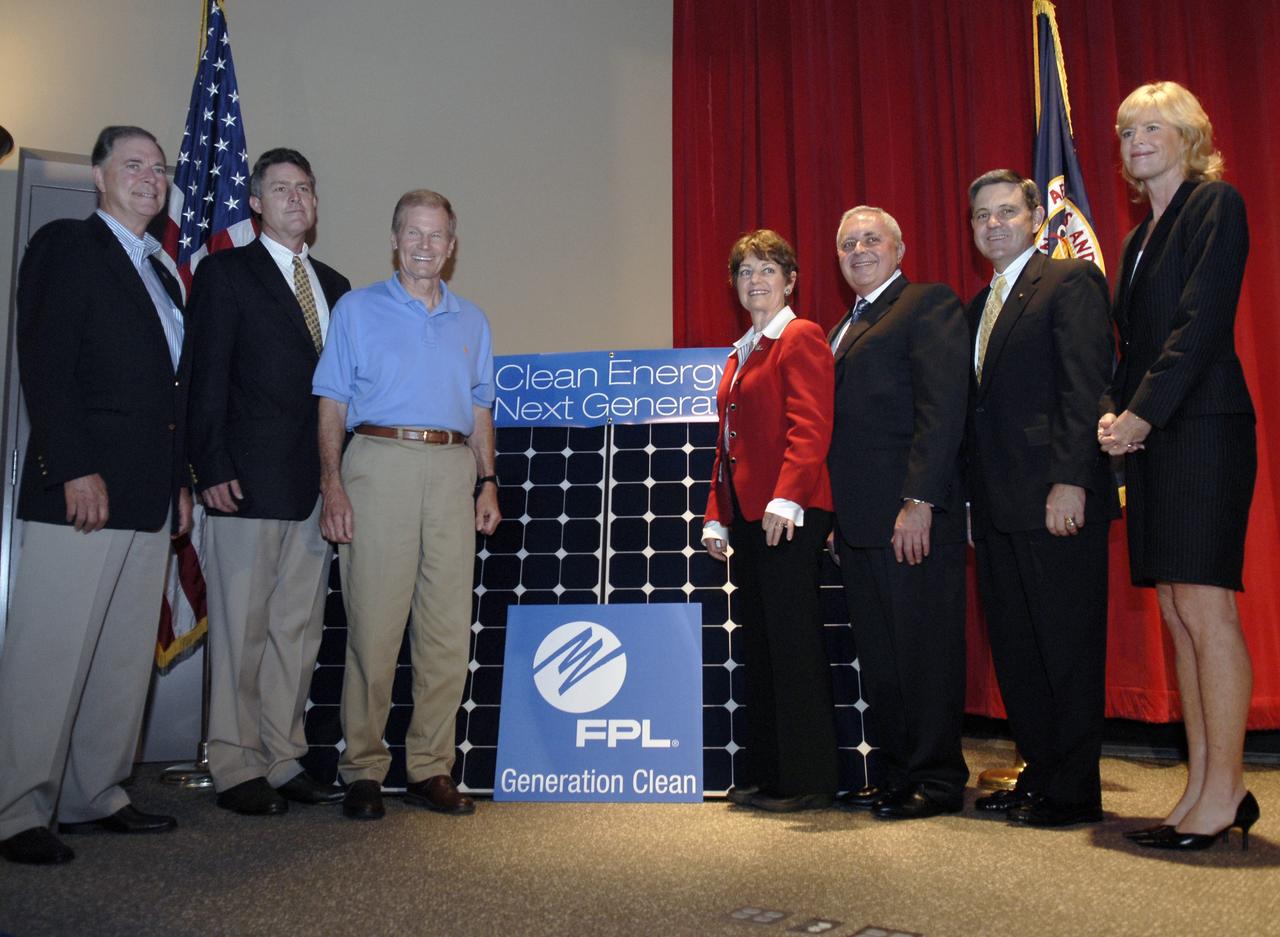

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Gathering on stage for the groundbreaking ceremony for the joint NASA and Florida Power & Light, or FPL, solar power project at NASA's Kennedy Space Center are Florida Rep. Bill Posey, Eric Draper, deputy director of Audubon of Florida, Sen. Bill Nelson, Florida Rep. Suzanne Kosmas, Armando Olivera, president and CEO of FPL, Center Director Bob Cabana and Pam Rauch, vice president of External Affairs for FPL. FPL, Florida's largest electric utility, will build and maintain two solar photovoltaic power generation systems at Kennedy. One will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of emissions-free power for FPL customers, which is enough energy to serve roughly 1,100 homes. The second is a one-megawatt solar power facility that will provide renewable energy directly to Kennedy. The FPL facilities at NASA will help provide Florida residents and America's space program with new sources of clean energy that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The one megawatt facility also will help NASA meet its goal for use of power generated from renewable energy. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
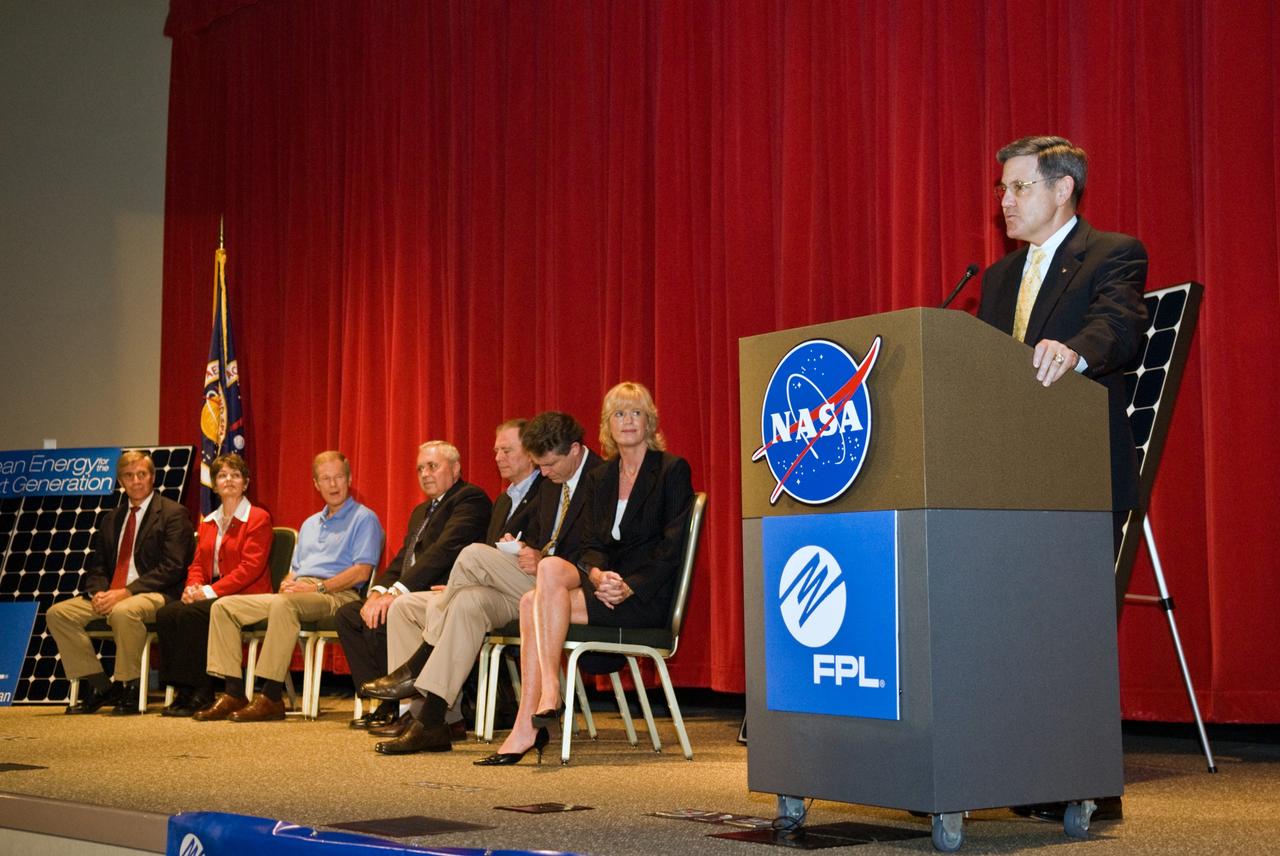

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Center Director of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Bob Cabana addresses guests at the groundbreaking ceremony for the joint NASA and Florida Power & Light, or FPL, solar power project at Kennedy. Others on the stage are (from left) Ed Smeloff with SunPower Corporation, Florida Rep. Suzanne Kosmas, Sen. Bill Nelson, Armando Olivera, president and CEO of FPL, Florida Rep. Bill Posey, Eric Draper, deputy director of Audubon of Florida, and Pam Rauch, vice president of External Affairs for FPL. FPL, Florida's largest electric utility, will build and maintain two solar photovoltaic power generation systems at Kennedy. One will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of emissions-free power for FPL customers, which is enough energy to serve roughly 1,100 homes. The second is a one-megawatt solar power facility that will provide renewable energy directly to Kennedy. The FPL facilities at NASA will help provide Florida residents and America's space program with new sources of clean energy that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The one megawatt facility also will help NASA meet its goal for use of power generated from renewable energy. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
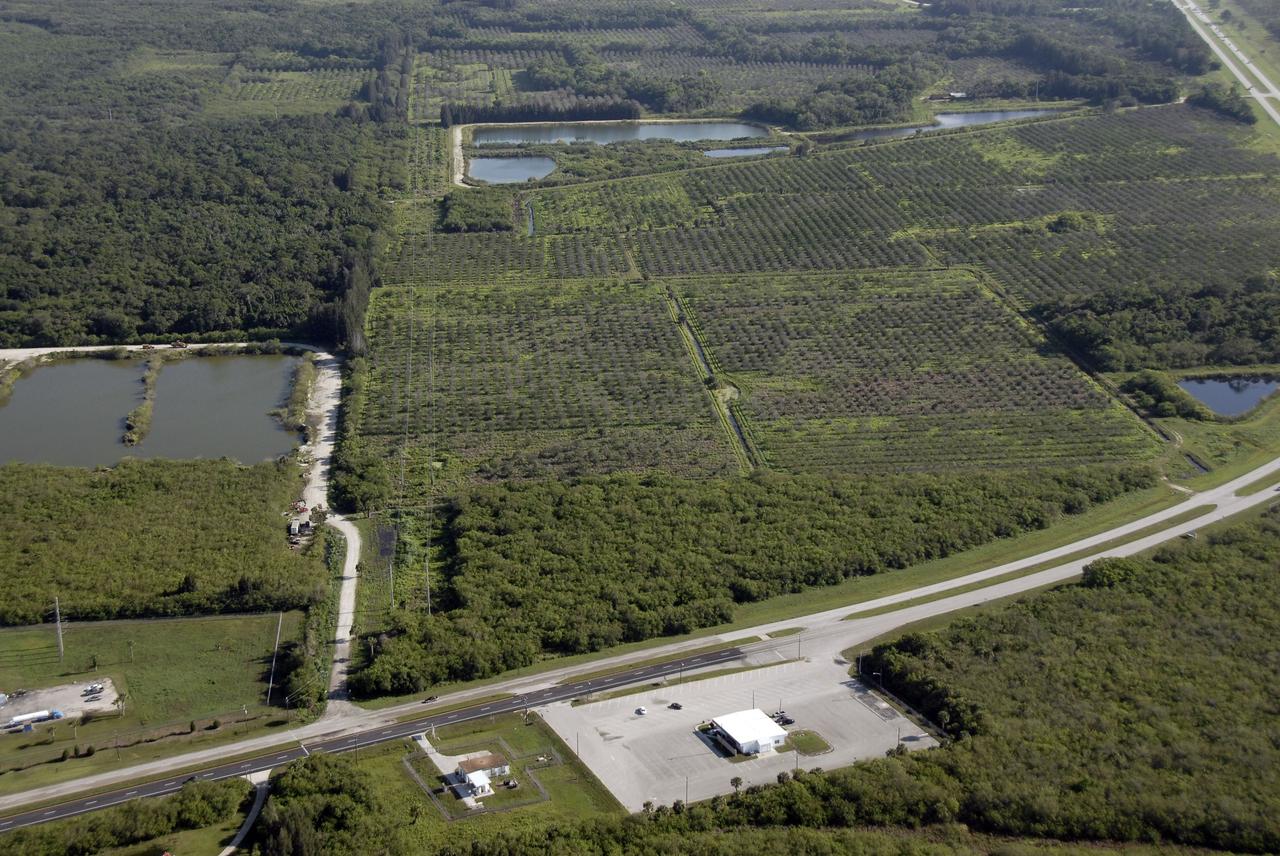

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of the site on S.R. 3 on NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida where a solar power system will be built. The solar power systems are being constructed by NASA and Florida Power & Light Company as part of a public-private partnership that promotes a clean-energy future. A groundbreaking ceremony took place on May 27 at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. FPL, Florida's largest electric utility, will build and maintain two solar photovoltaic power generation systems at Kennedy. One, which will be built on the pictured location, will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of emissions-free power for FPL customers, which is enough energy to serve roughly 1,100 homes. The second is a one-megawatt solar power facility that will provide renewable energy directly to Kennedy. The FPL facilities at NASA will help provide Florida residents and America's space program with new sources of clean energy that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The one megawatt facility also will help NASA meet its goal for use of power generated from renewable energy. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of the site in the Industrial Area of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida where a solar power system will be built. The solar power systems are being constructed by NASA and Florida Power & Light Company as part of a public-private partnership that promotes a clean-energy future. A groundbreaking ceremony took place on May 27 at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. FPL, Florida's largest electric utility, will build and maintain two solar photovoltaic power generation systems at Kennedy. One will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of emissions-free power for FPL customers, which is enough energy to serve roughly 1,100 homes. The second, which will be built on the pictured location, is a one-megawatt solar power facility that will provide renewable energy directly to Kennedy. The FPL facilities at NASA will help provide Florida residents and America's space program with new sources of clean energy that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The one megawatt facility also will help NASA meet its goal for use of power generated from renewable energy. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
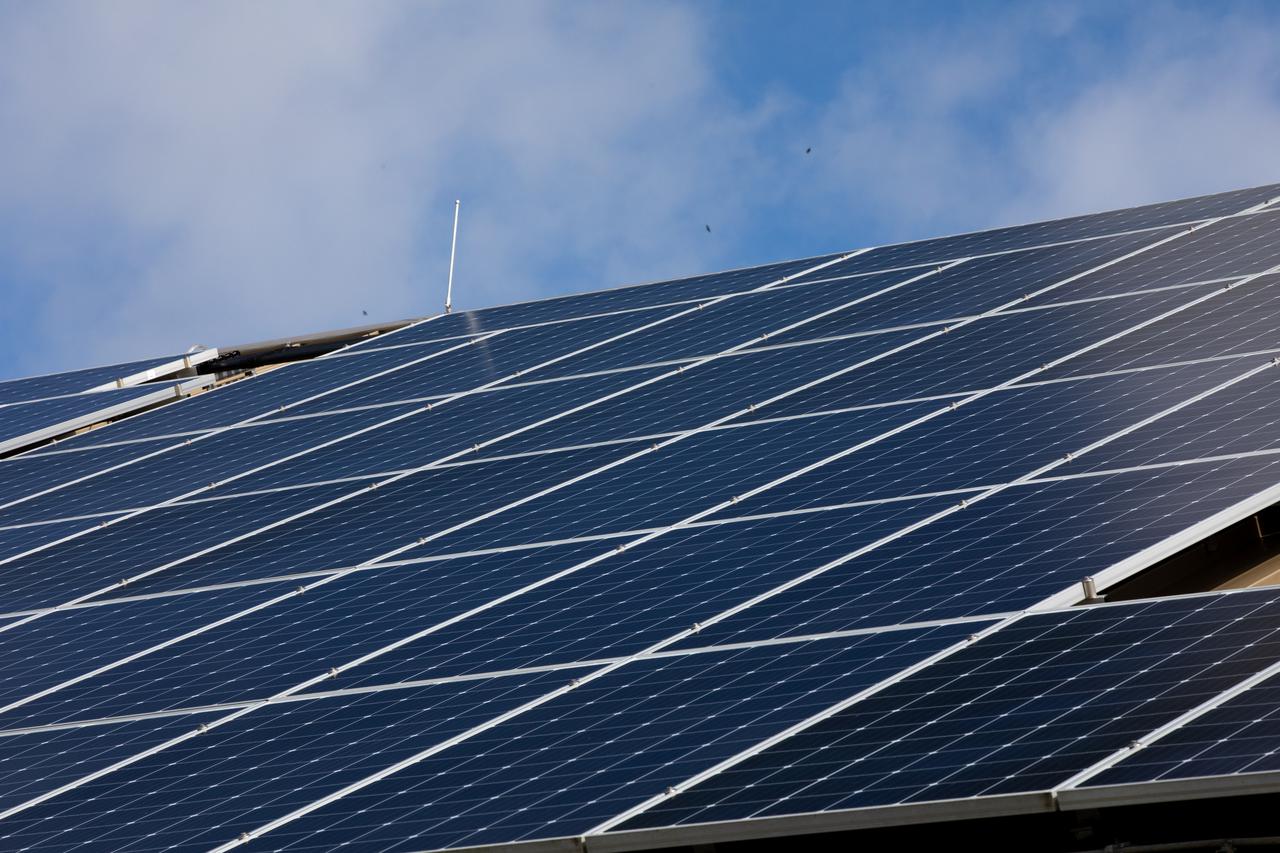

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
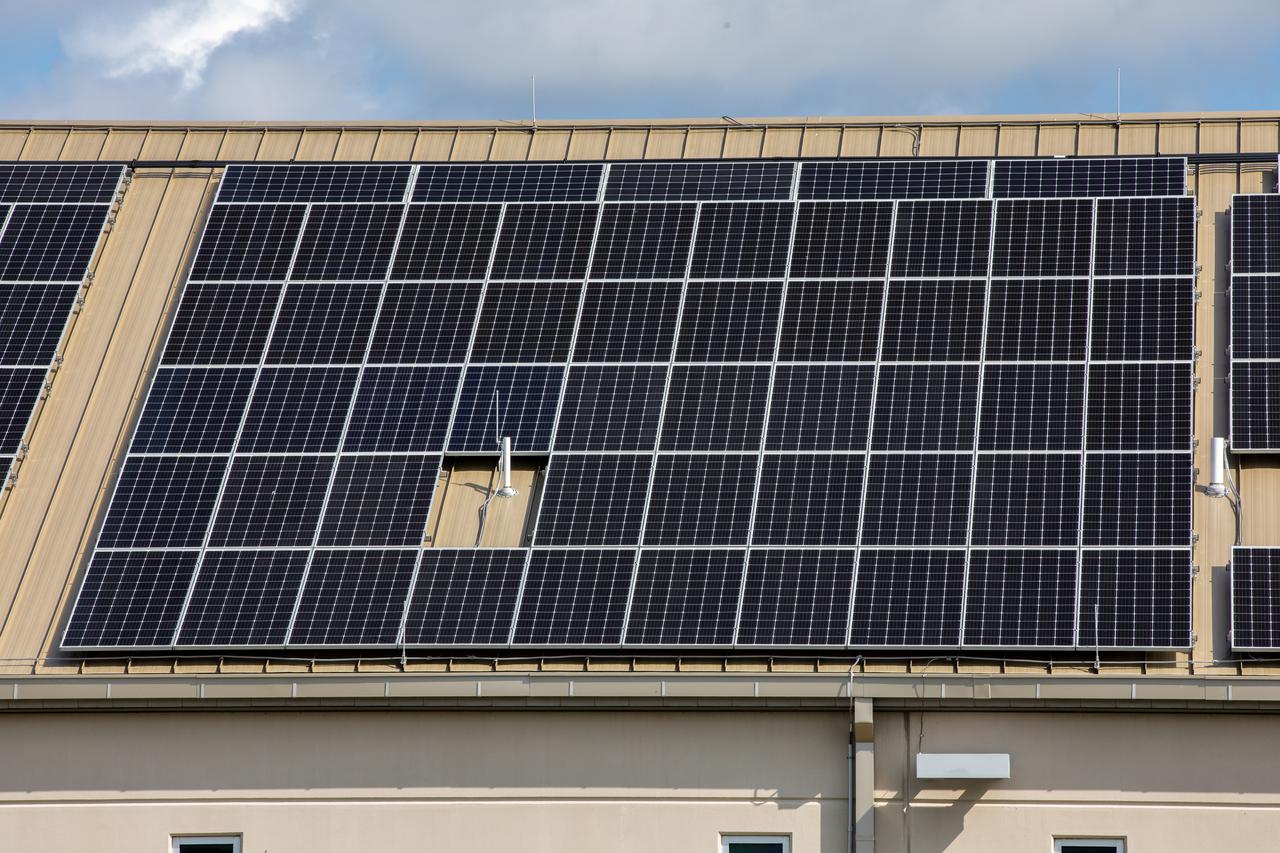

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
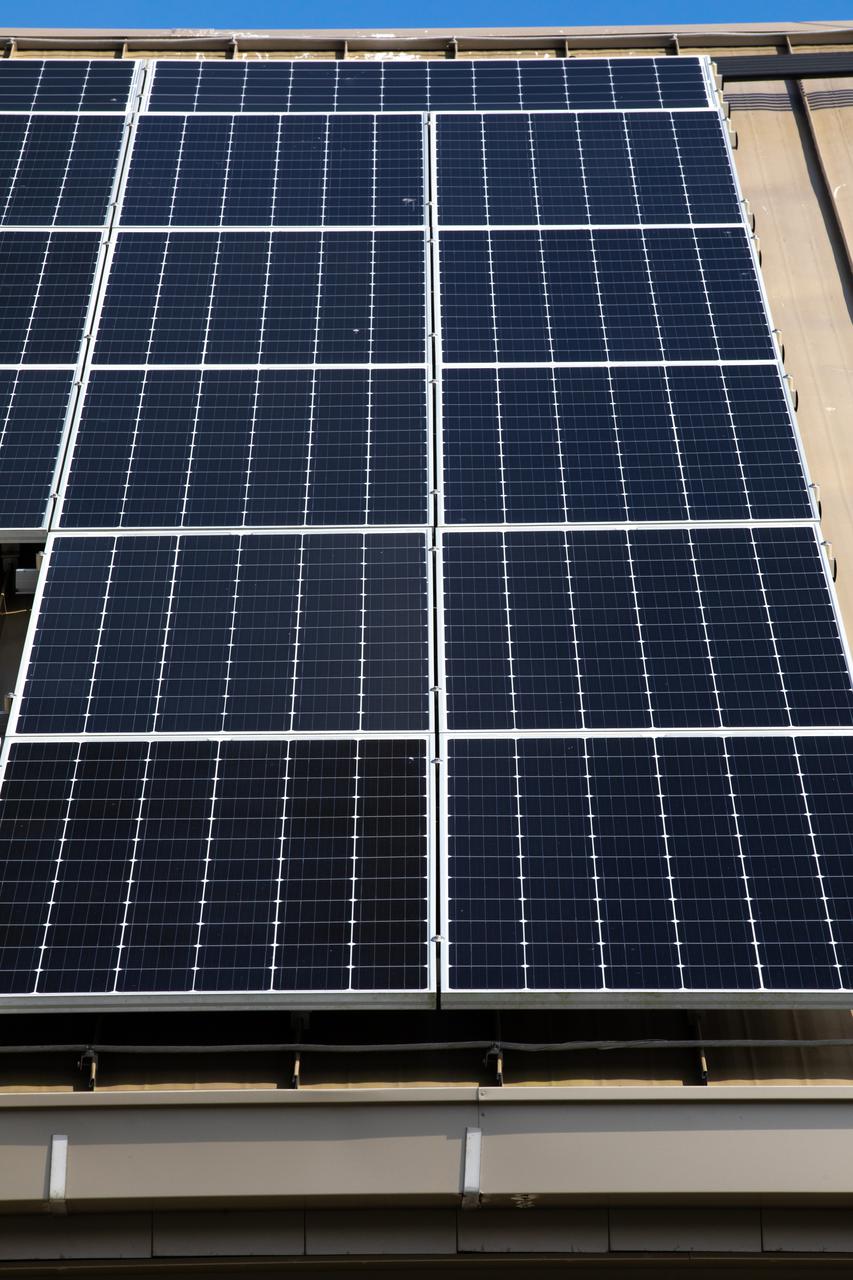

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
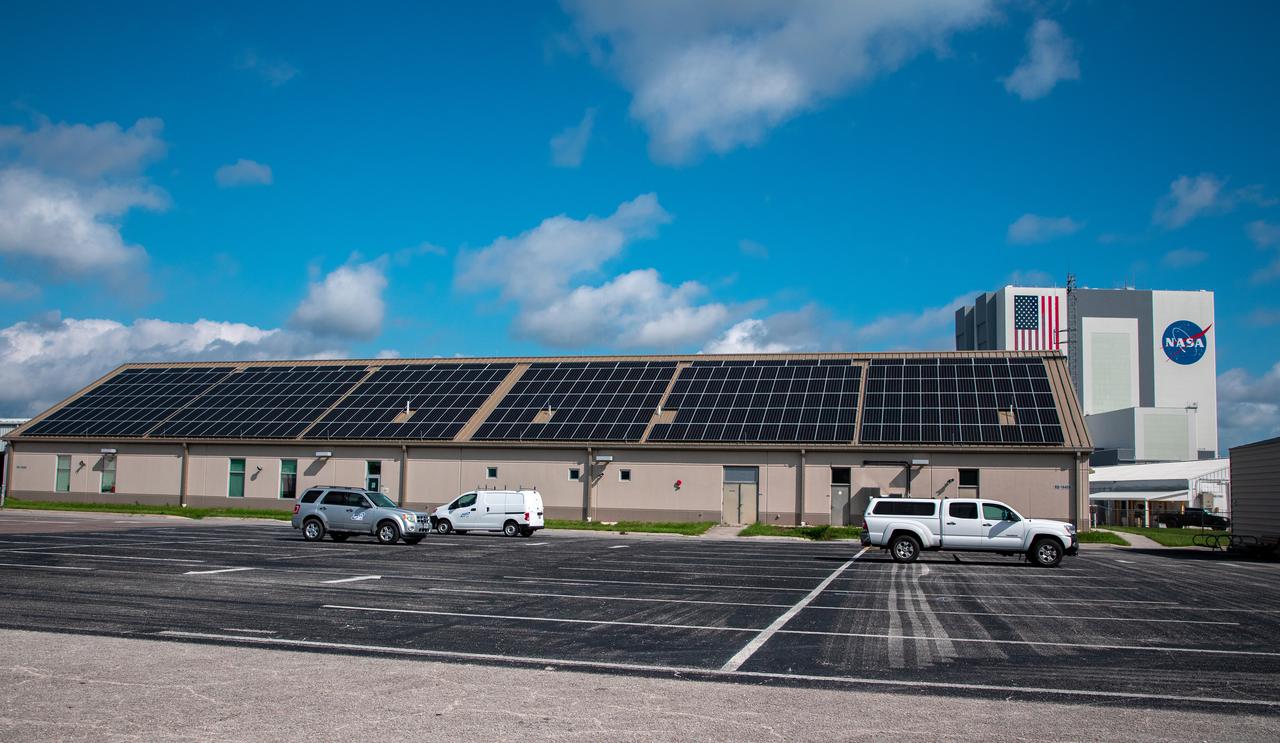

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
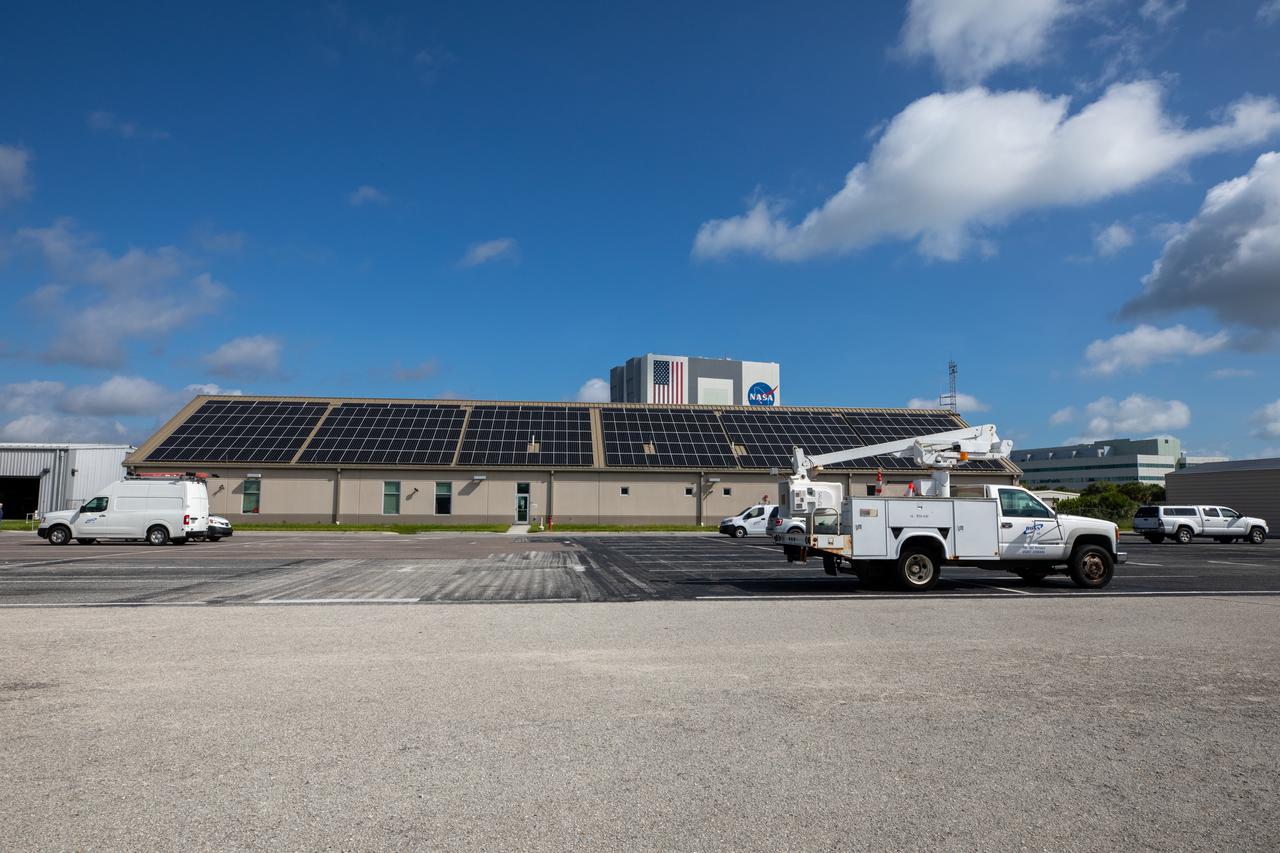

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
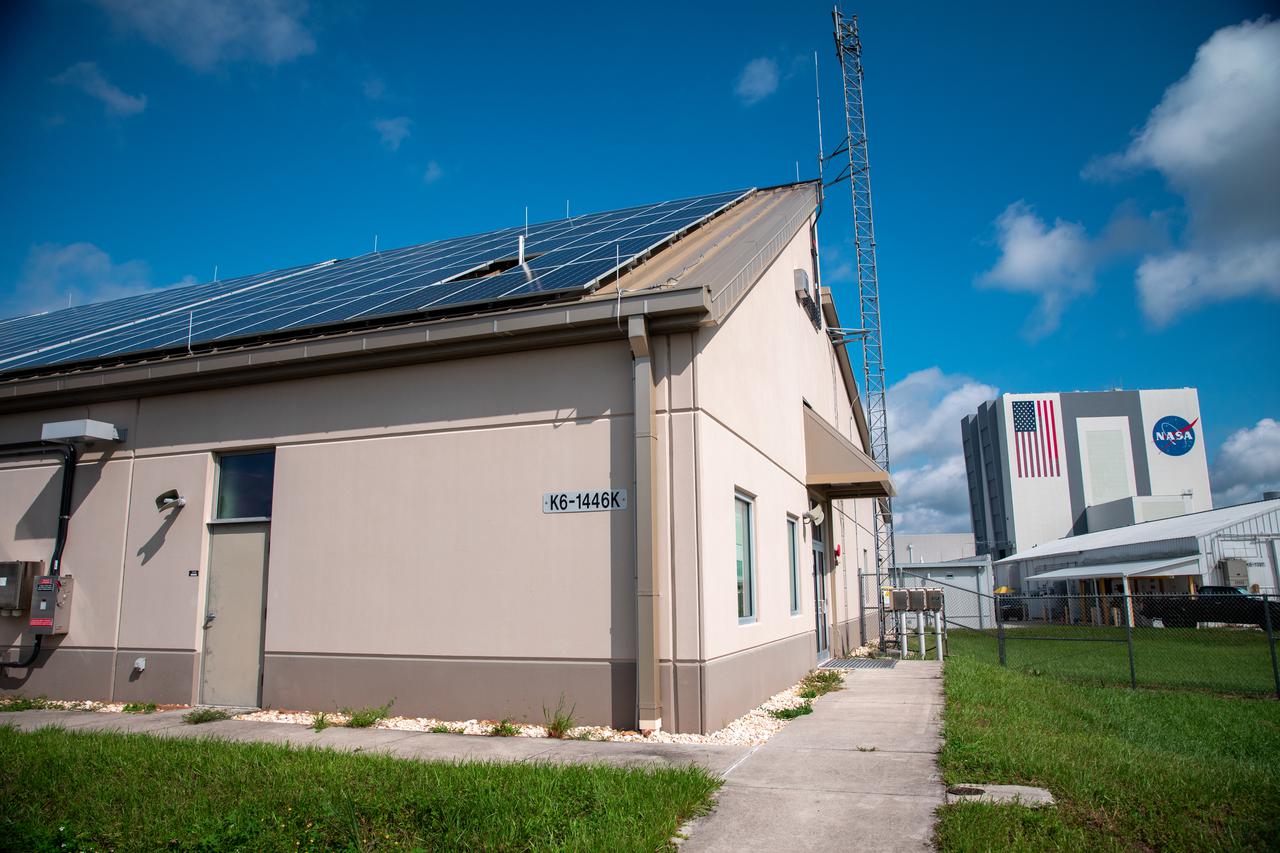

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
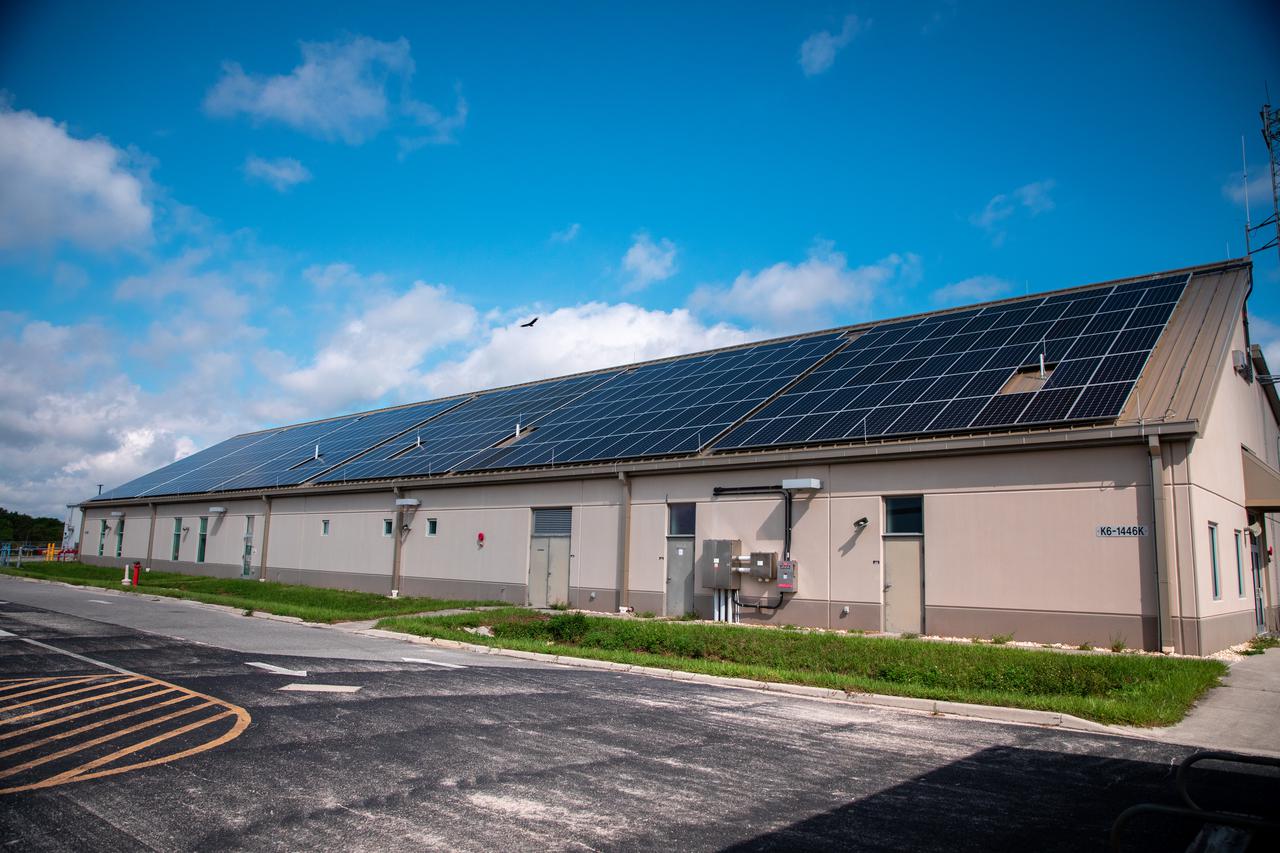

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
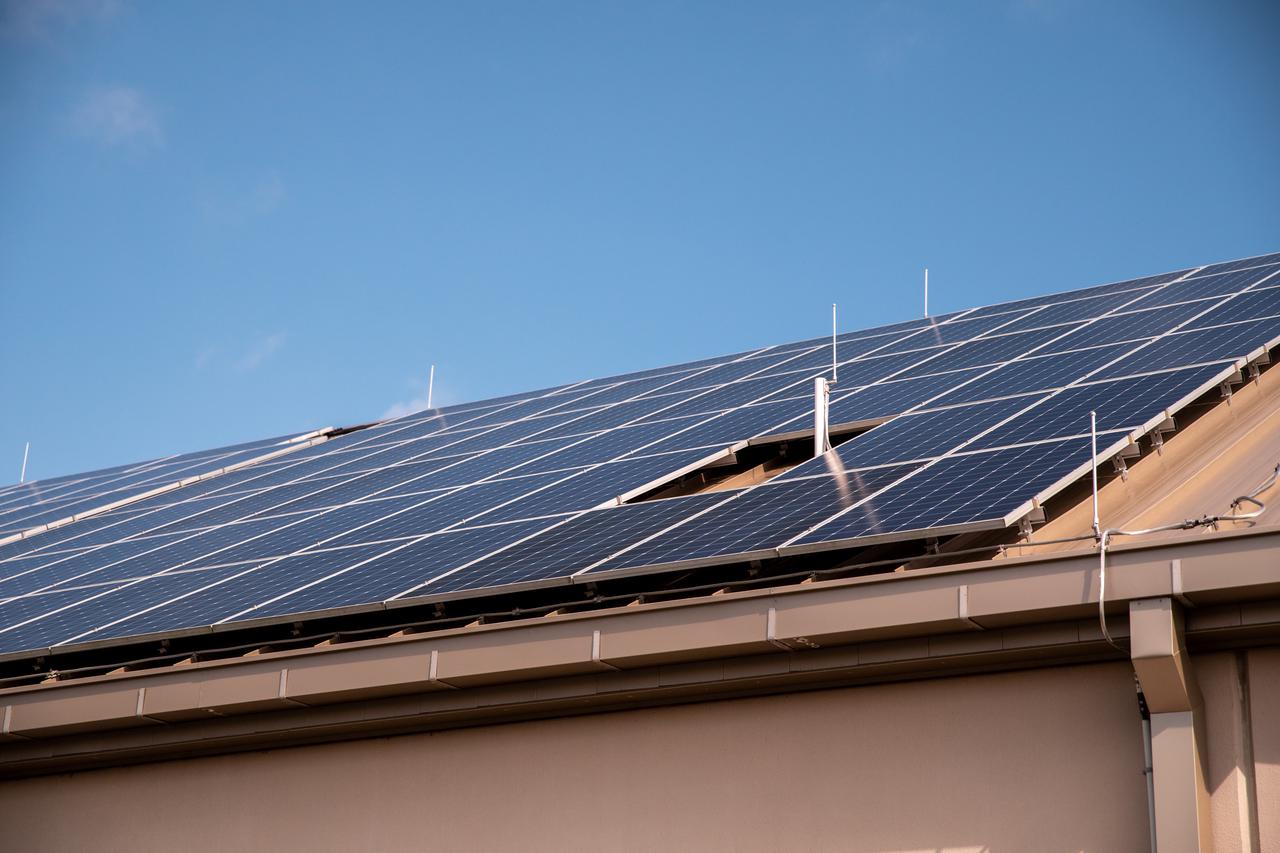

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
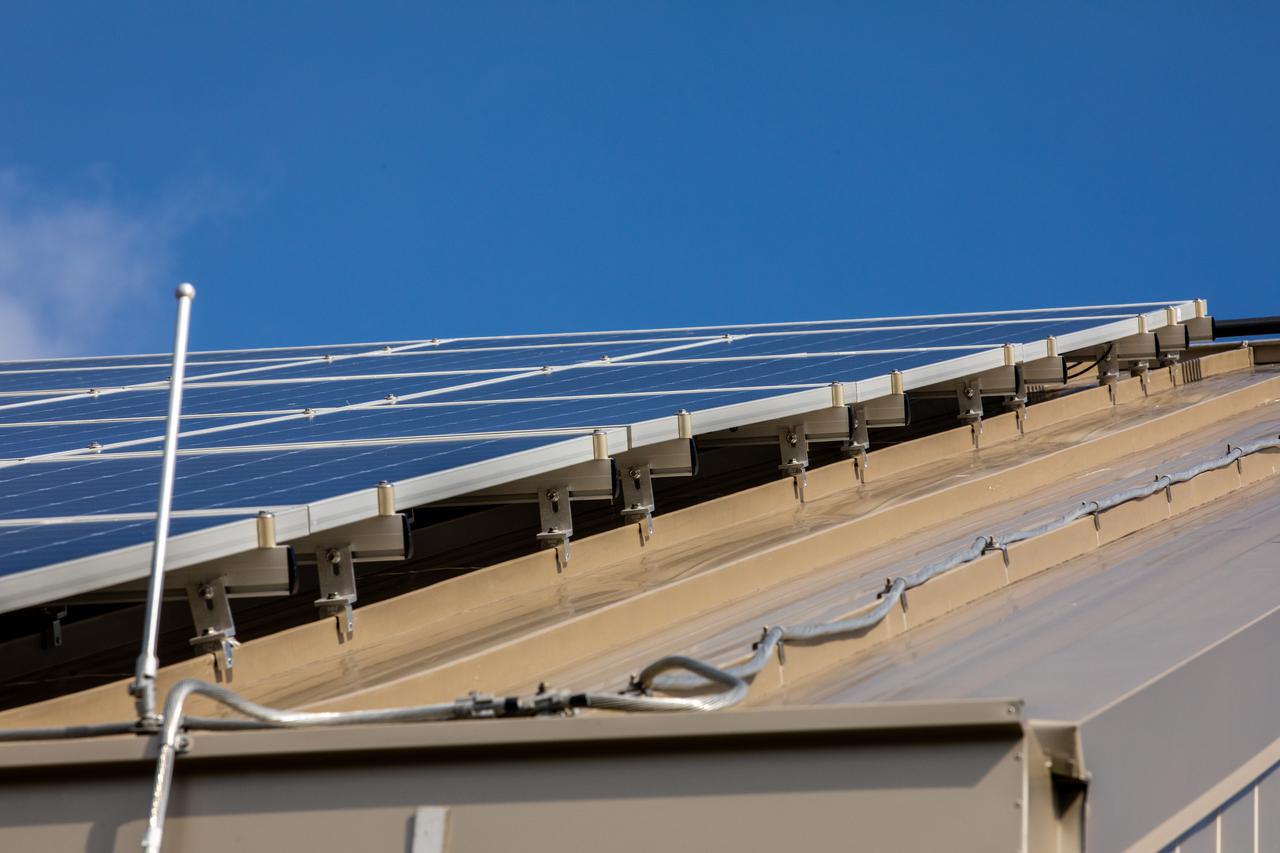

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
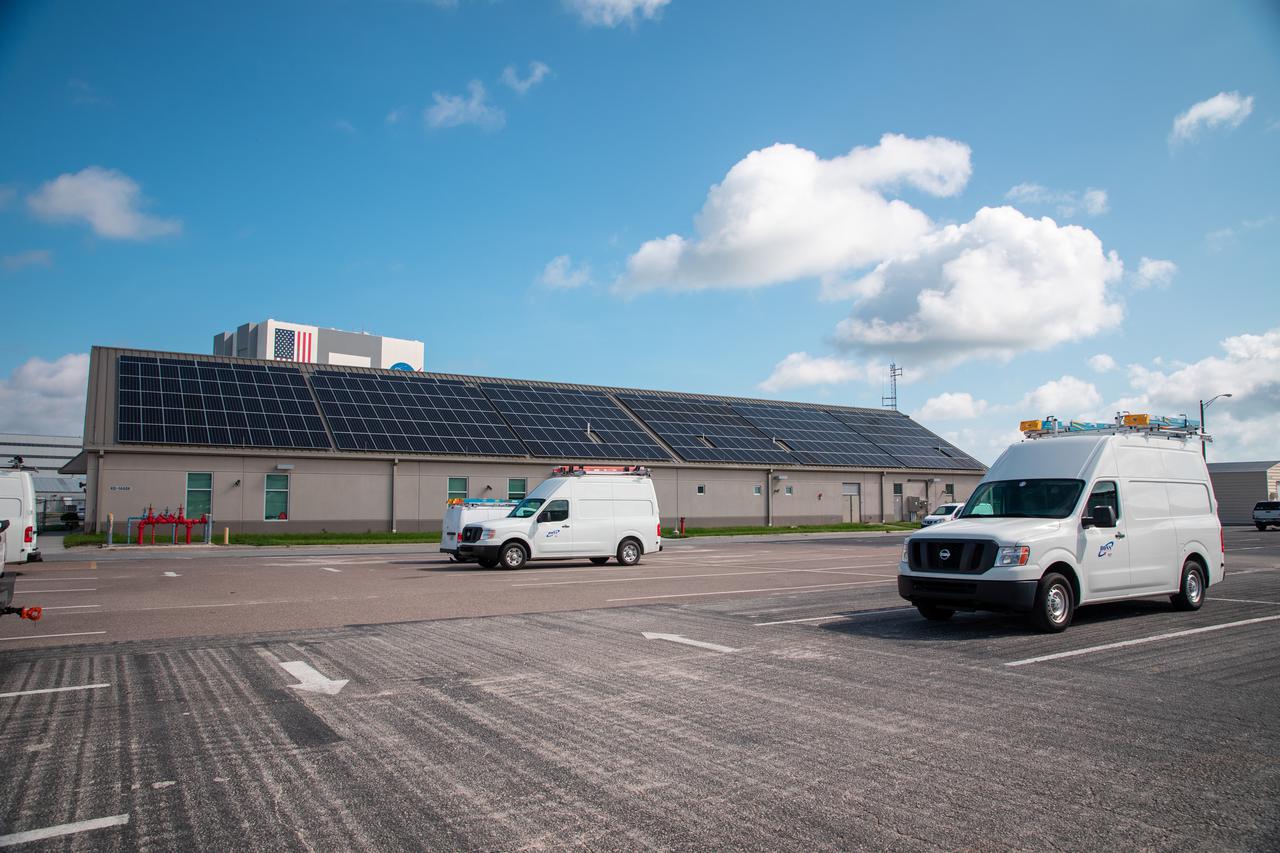

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
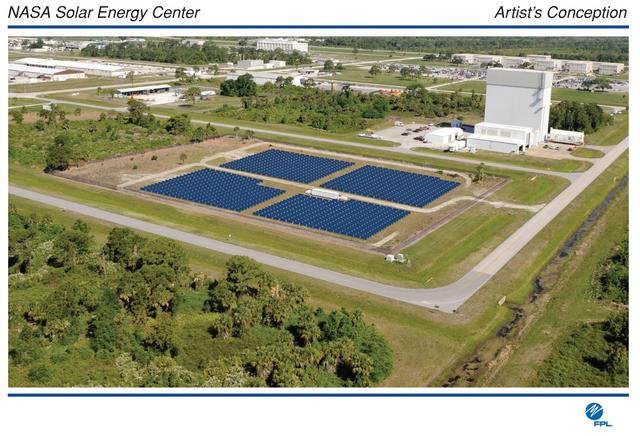

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This is a rendering of one of two proposed solar power systems that NASA and Florida Power & Light Company are beginning to construct on NASA's Kennedy Space Center as part of a public-private partnership that promotes a clean-energy future. A groundbreaking ceremony took place on May 27 at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. FPL, Florida's largest electric utility, will build and maintain two solar photovoltaic power generation systems at Kennedy. One will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of emissions-free power for FPL customers, which is enough energy to serve roughly 1,100 homes. The second is a one-megawatt solar power facility that will provide renewable energy directly to Kennedy. The FPL facilities at NASA will help provide Florida residents and America's space program with new sources of clean energy that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The one megawatt facility also will help NASA meet its goal for use of power generated from renewable energy. Photo courtesy of FPL
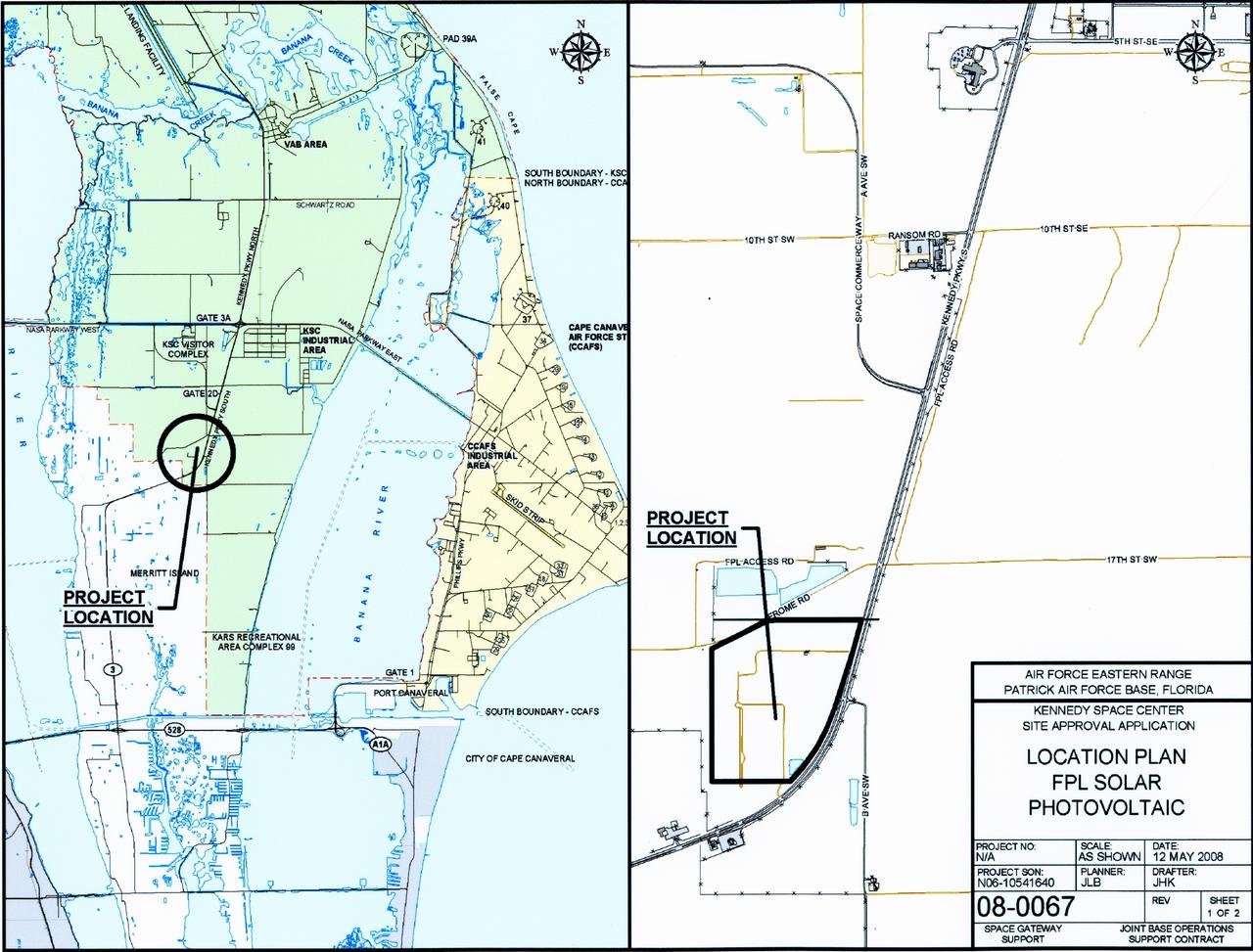
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – These maps show one of the locations of the proposed solar power systems that NASA and Florida Power & Light Company are beginning to construct on NASA's Kennedy Space Center as part of a public-private partnership that promotes a clean-energy future. A groundbreaking ceremony took place on May 27 at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. FPL, Florida's largest electric utility, will build and maintain two solar photovoltaic power generation systems at Kennedy. One will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of emissions-free power for FPL customers, which is enough energy to serve roughly 1,100 homes. The second is a one-megawatt solar power facility that will provide renewable energy directly to Kennedy. The FPL facilities at NASA will help provide Florida residents and America's space program with new sources of clean energy that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The one megawatt facility also will help NASA meet its goal for use of power generated from renewable energy. Photo courtesy of FPL
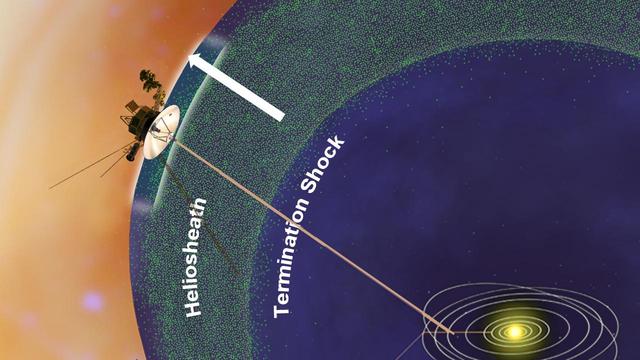
This artist concept shows NASA Voyager 1 spacecraft in a new region at the edge of our solar system where there are fewer low energy particles that originate from inside our solar system.
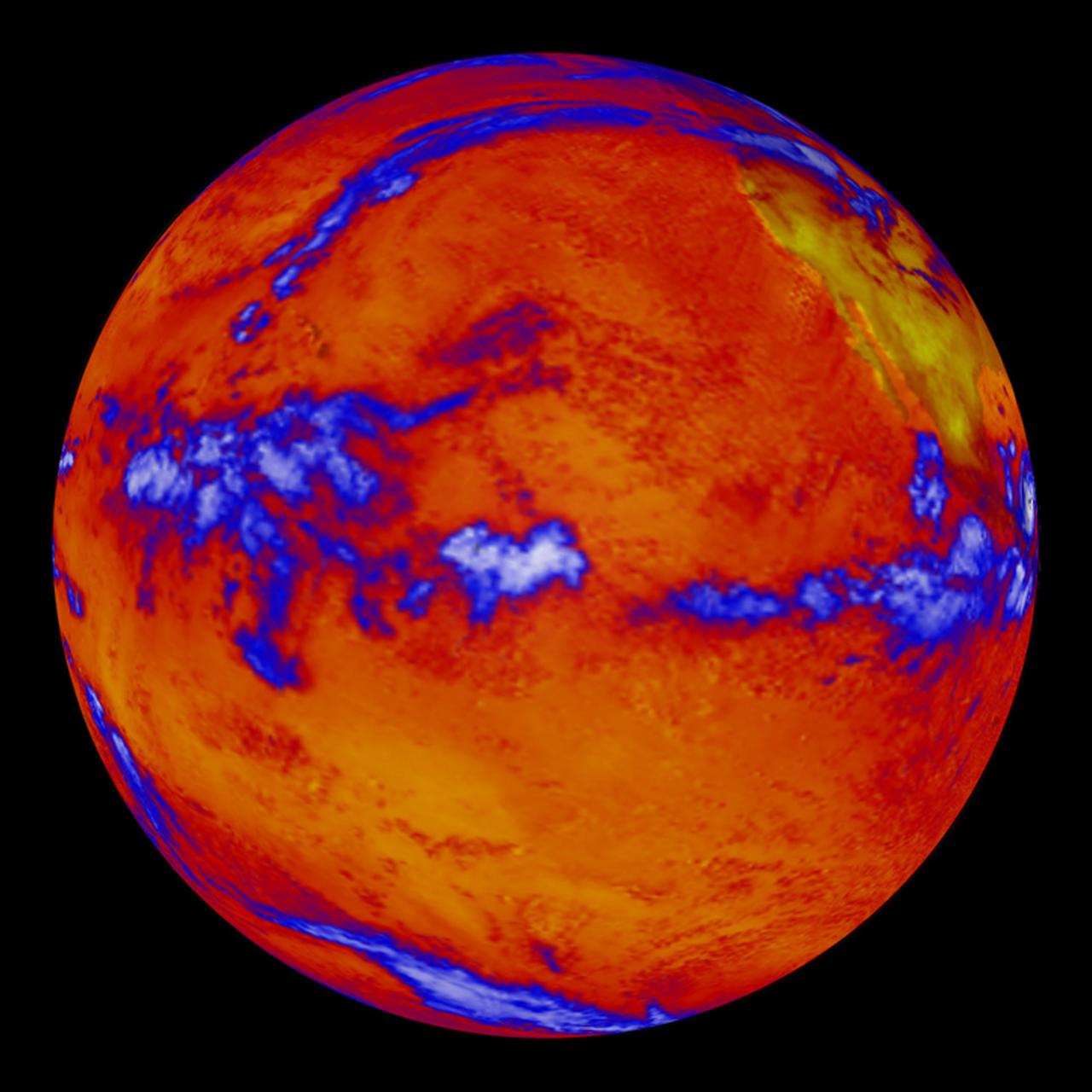
Absorption of solar energy heats up our planet's surface and atmosphere making life for us possible. But the energy carnot stay bound up in the Earth's environment forever. If it did, the Earth would be as hot as the sun. Instead, as the surface and atmosphere warm, they emit thermal long wave radiation, some of which escapes into space and allows the Earth to cool. This false color image of the Earth was produced by the Clouds and the Earth's Radiant Energy System (CERES) instrument flying aboard NASA's Terra spacecraft. The image shows where more or less heat, in the form of long-wave radiation, is emanating from the top of the Earth's atmosphere. As one can see in the image, the thermal radiation leaving the oceans is fairly uniform. The blue swaths represent thick clouds, the tops of which are so high they are among the coldest places on Earth. In the American Southwest, which can be seen in the upper right hand corner of the globe, there is often little cloud cover to block outgoing radiation and relatively little water to absorb solar energy making the amount of outgoing radiation in this area exceeding that of the oceans. Recently, NASA researchers discovered that incoming solar radiation and outgoing thermal radiation increased in the tropics from the 1980s to the 1990s. They believe the unexpected change has to do with apparent change in circulation patterns around the globe, which effectively reduce the amount of water vapor and cloud cover in the upper reaches of the atmosphere. Without the clouds, more sunlight was allowed to enter the tropical zones and more thermal energy was allowed to leave. The findings may have big implications for climate change and future global warming. (Image courtesy NASA Goddard)
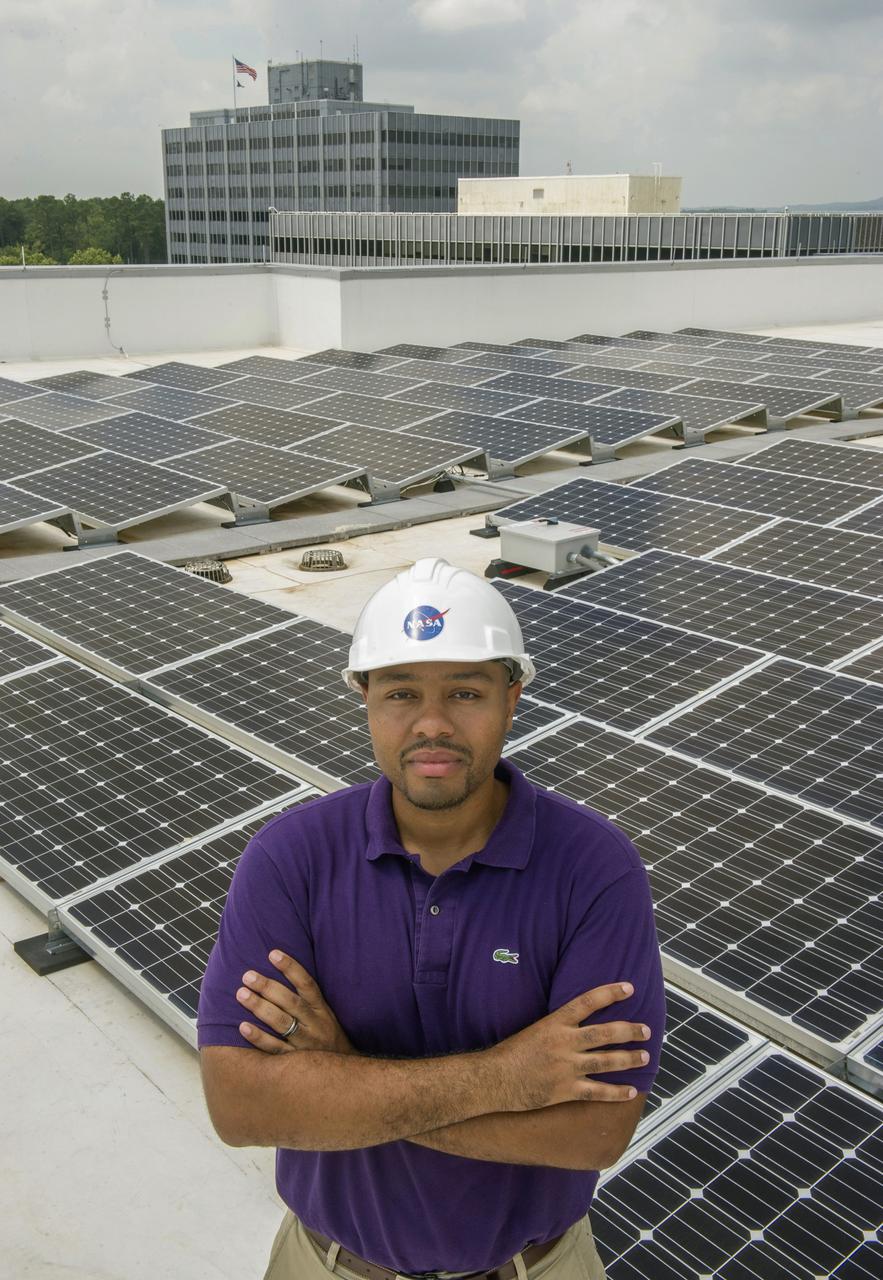

BYRON L. WILLIAMS, FACILITIES MECHANICAL ENGINEER, STANDING ON THE ROOF OF BUILDING 4220 IN FRONT OF THE SOLAR ENERGY PANELS.

Guest speaker Robin Thomas shares a presentation focusing on energy resilience and the Ascension Island wind turbine generator project during a “lunch and learn” held Tuesday, Oct. 23, 2018, for employees at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Thomas is a resource efficiency manager working with the U.S. Air Force 45th Space Wing’s Civil Engineering Squadron based at Patrick Air Force Base. The event was one of two held during October in conjunction with Energy Awareness Month, which aims to recognize the importance of energy management for our national prosperity, security and environmental sustainability.
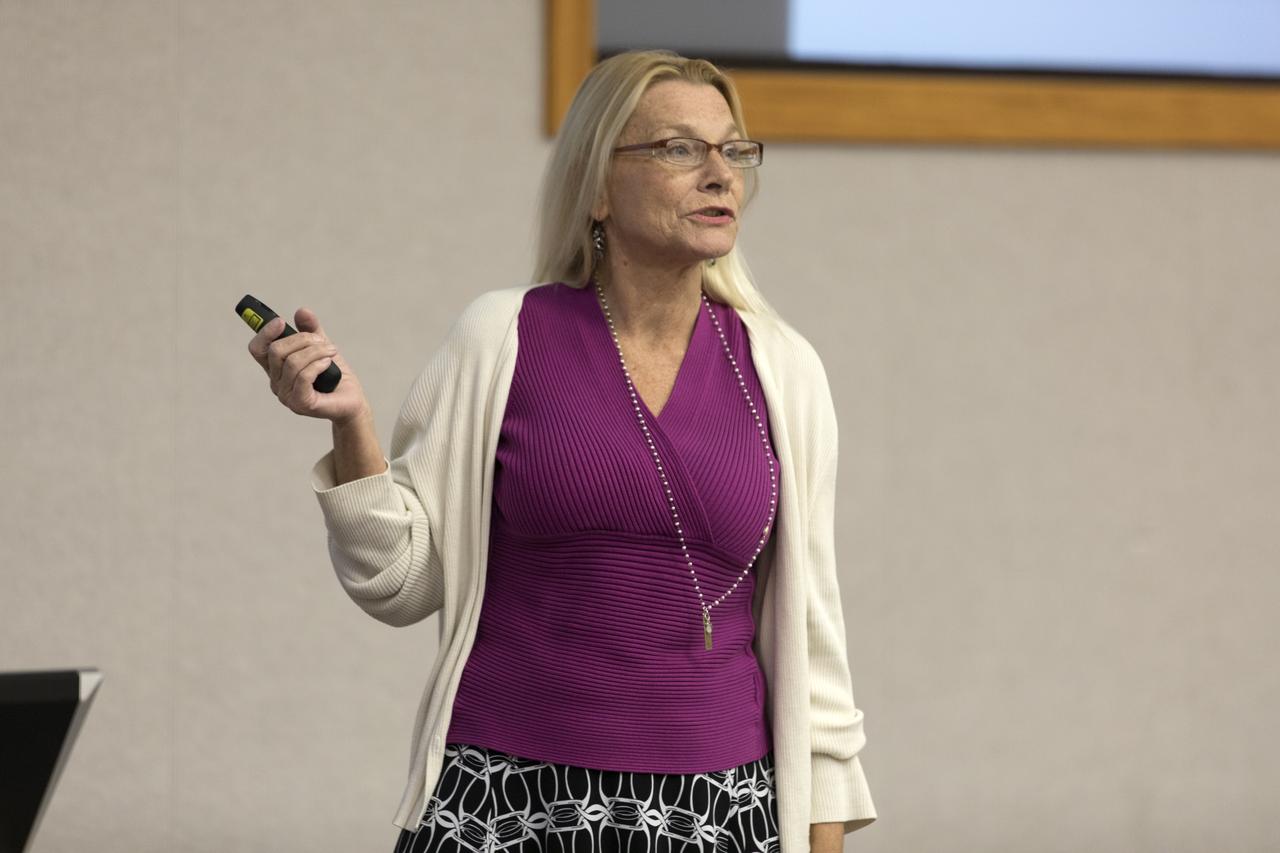

Guest speaker Robin Thomas discusses energy resilience and the Ascension Island wind turbine generator project during a “lunch and learn” held Tuesday, Oct. 23, 2018, for employees at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Thomas is a resource efficiency manager working with the U.S. Air Force 45th Space Wing’s Civil Engineering Squadron based at Patrick Air Force Base. The event was one of two held during October in conjunction with Energy Awareness Month, which aims to recognize the importance of energy management for our national prosperity, security and environmental sustainability.

Guest speaker Robin Thomas discusses energy resilience and the Ascension Island wind turbine generator project during a “lunch and learn” held Tuesday, Oct. 23, 2018, for employees at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Thomas is a resource efficiency manager working with the U.S. Air Force 45th Space Wing’s Civil Engineering Squadron based at Patrick Air Force Base. The event was one of two held during October in conjunction with Energy Awareness Month, which aims to recognize the importance of energy management for our national prosperity, security and environmental sustainability.
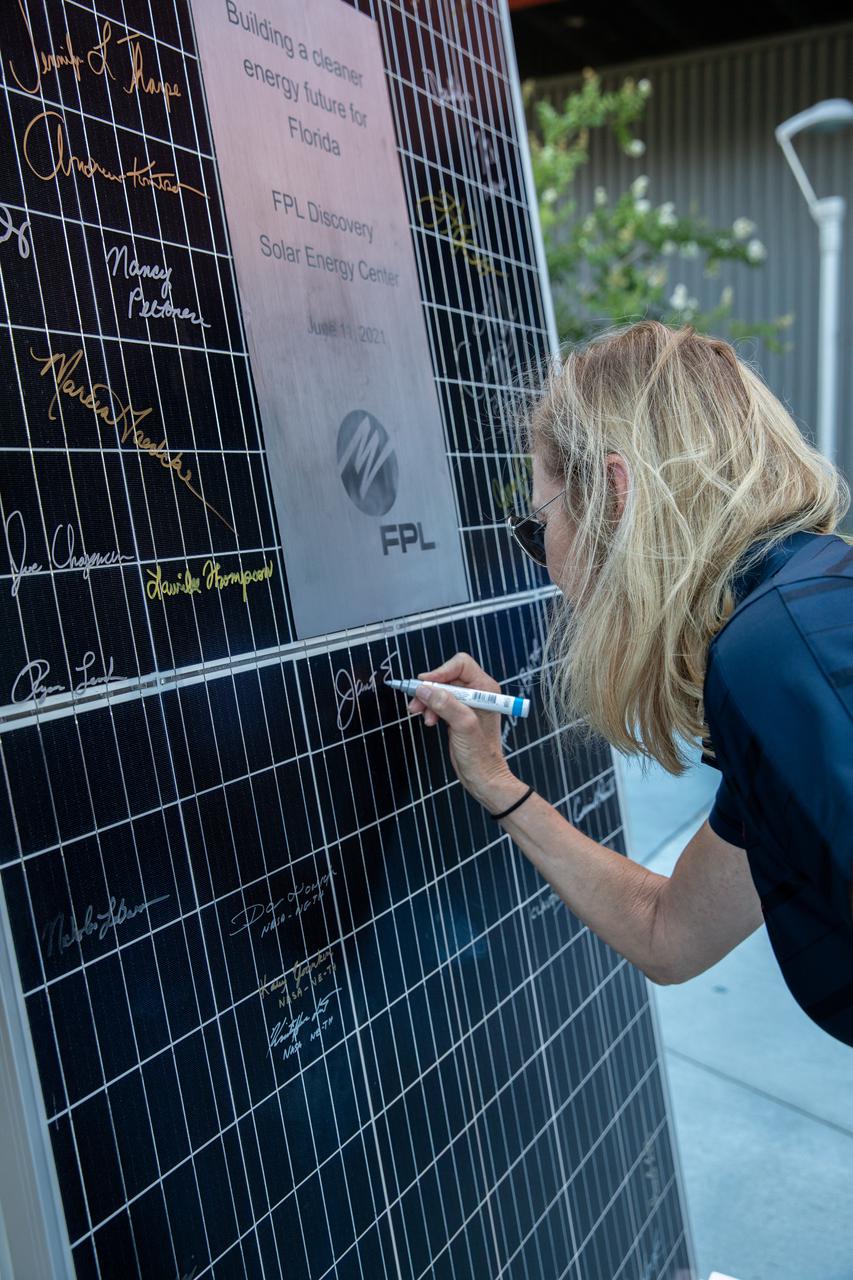

As part of a ribbon-cutting ceremony held on June 11, 2021, Janet Petro, acting director of NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, signs a solar panel which will be put on display at the Visitor Complex to commemorate the Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) Discovery Solar Energy Center becoming operational at the center. Discovery Solar Energy Center is a 74.5-megawatt solar site, spanning 491 acres at the spaceport. The site contains about 250,000 solar panels in total, producing enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels do not directly power anything at Kennedy, but rather, send energy directly to FPL's electricity grid for distribution to existing customers. Construction began in spring 2020, and the energy center became fully operational on May 30, 2021.
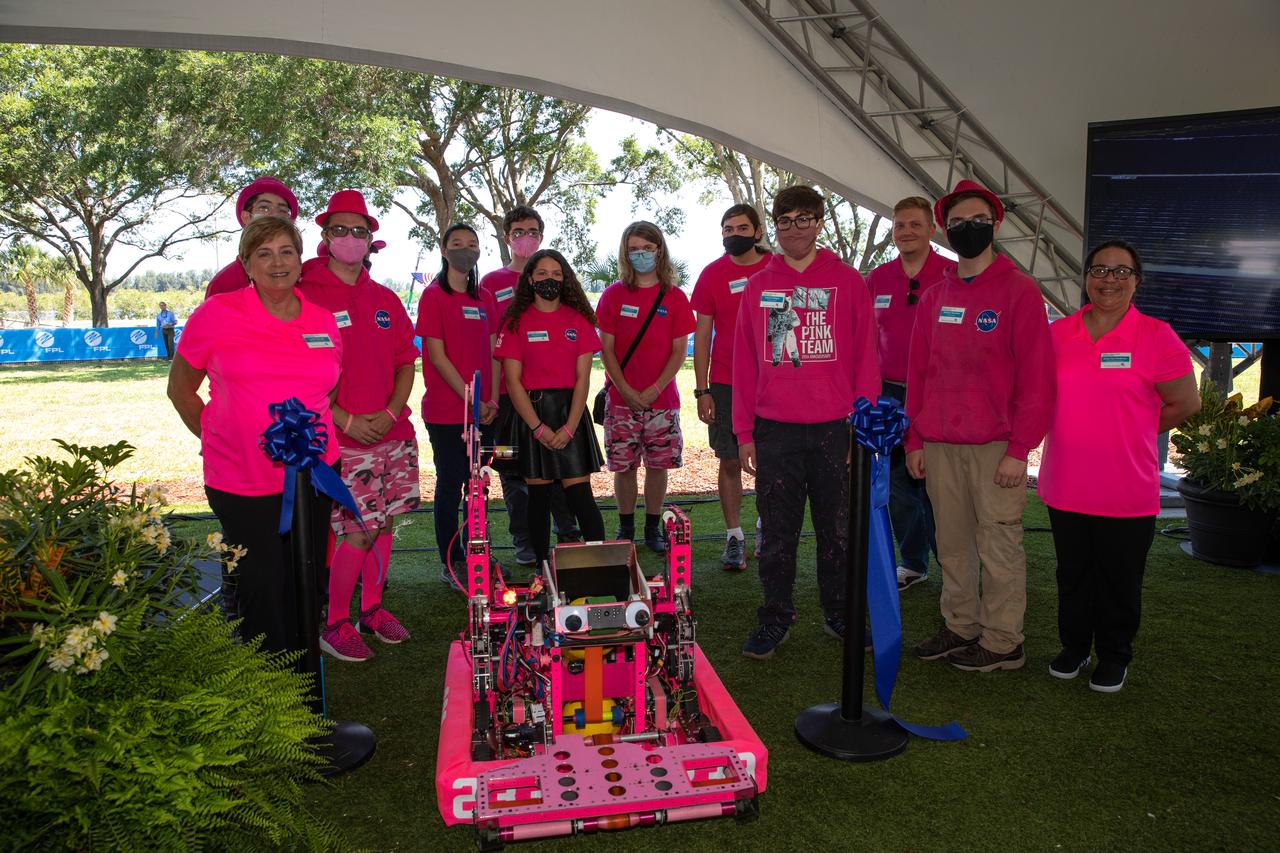

Students and faculty from Rockledge High School’s Pink Team, a robotics team mentored by NASA engineers, pose for a photo at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on June 11, 2021. Using the school’s 2021 competition robot – affectionately named “Pinky” – the Pink Team re-engineered their robot to carry a large pair of scissors to cut the ceremonial ribbon for the Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) Discovery Solar Energy Center becoming operational at the center. Discovery Solar Energy Center is a 74.5-megawatt solar site, spanning 491 acres at the spaceport. The site contains about 250,000 solar panels in total, producing enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels do not directly power anything at Kennedy, but rather, send energy directly to FPL's electricity grid for distribution to existing customers. Construction began in spring 2020, and the energy center became fully operational on May 30, 2021.
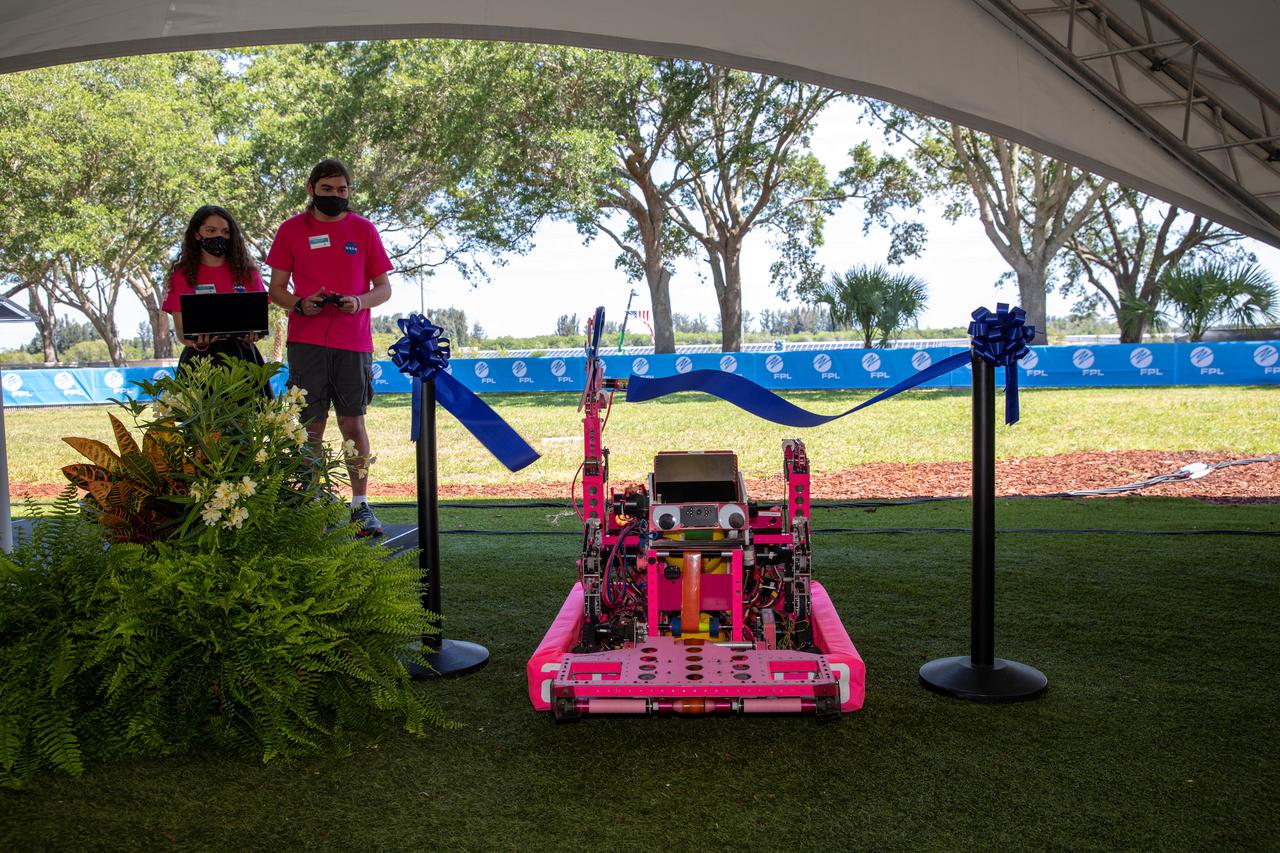

Students from Rockledge High School’s Pink Team, a robotics team mentored by NASA engineers, control the school’s 2021 competition robot – affectionately named “Pinky” – as it cuts the ceremonial ribbon to commemorate the Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) Discovery Solar Energy Center becoming operational at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 11, 2021. The Pink Team re-engineered their robot to carry a large pair of scissors specifically for the ceremony, which took place at the center’s Visitor Complex. Discovery Solar Energy Center is a 74.5-megawatt solar site, spanning 491 acres at the spaceport. The site contains about 250,000 solar panels in total, producing enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels do not directly power anything at Kennedy, but rather, send energy directly to FPL's electricity grid for distribution to existing customers. Construction began in spring 2020, and the energy center became fully operational on May 30, 2021.
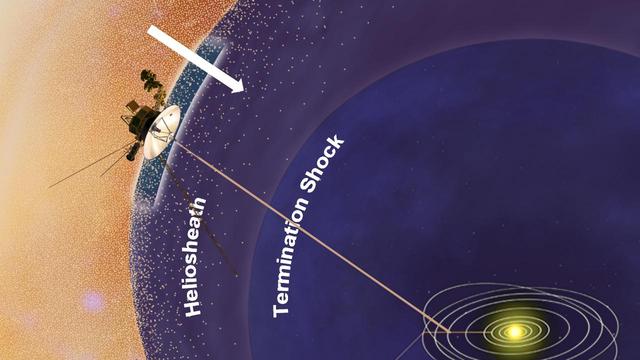
This artist concept shows NASA Voyager 1 spacecraft in a new region at the edge of our solar system where the amount of high-energy particles diffusing into our solar system from outside has increased.
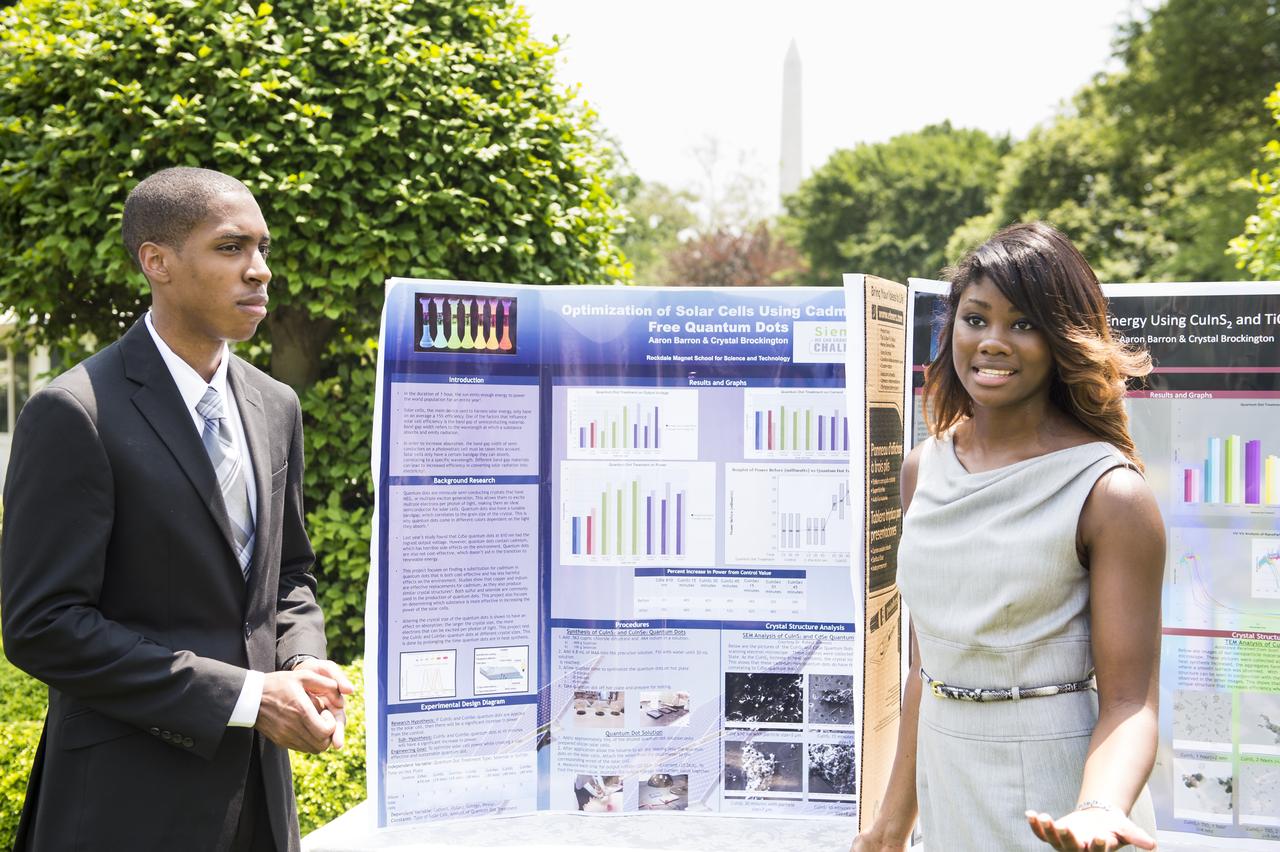

Crystal Brockington and Aaron Barron, both 18 years old, designed a more efficient and cost effective solar cell that harnesses energy without cadmium, which has been shown to be harmful to the environment. They were selected to participate in the White House Science Fair after they were awarded the High School Grand Prize at the Siemens We Can Change the World Challenge. The fourth White House Science Fair was held at the White House on May 27, 2014 and included 100 students from more than 30 different states who competed in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) competitions. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
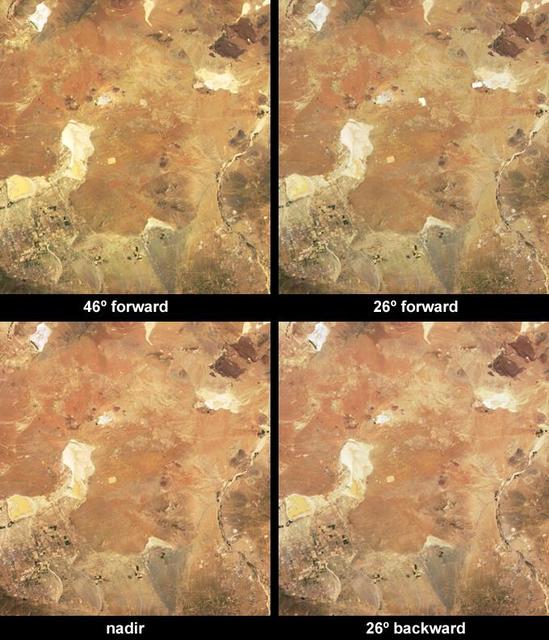

These images, from 8 April 2003 show that depending upon the position of the Sun, the solar power stations in California Mohave Desert can reflect solar energy from their large, mirror-like surfaces directly toward one of NASA Terra cameras.
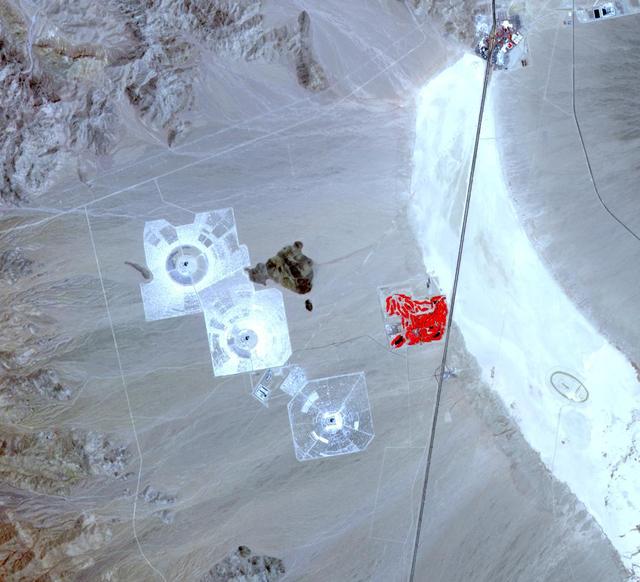

On May 30, 2013, NASA Terra spacecraft acquired this image of the largest solar plant of its kind in the world started producing power in southern California Mojave Desert near the Nevada border.
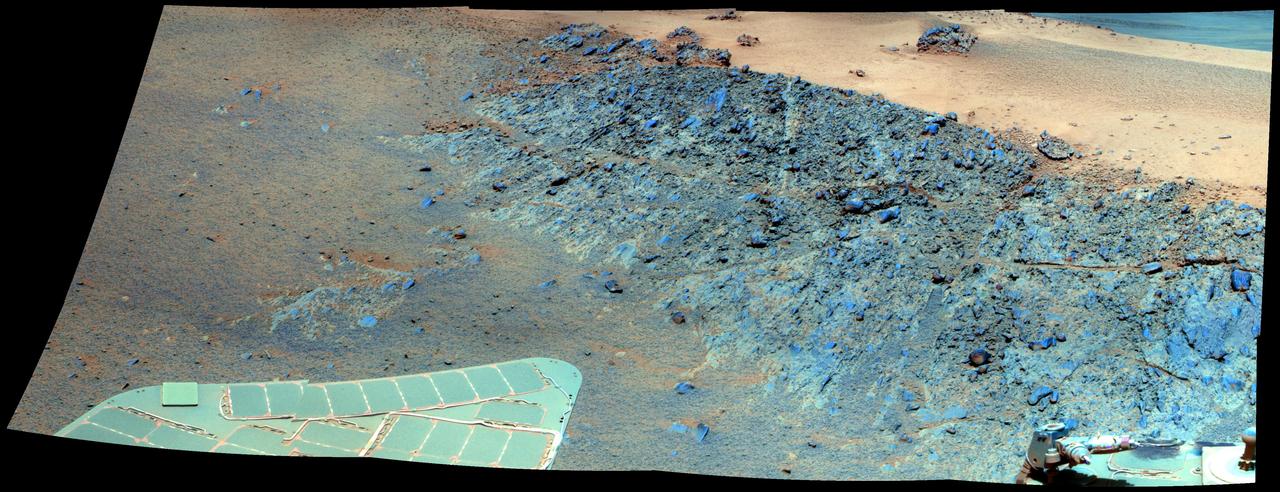

This false color mosaic from NASA rover Opportunity shows a north-facing outcrop, informally named Greeley Haven. This site optimizes Opportunity solar energy as winter approaches.
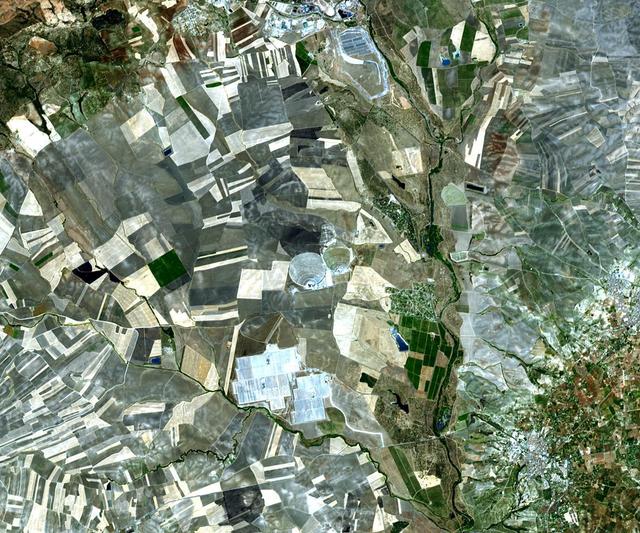

The world largest solar power tower recently began operating outside Seville, Spain -- and it marks a historic moment in the saga of renewable energy. This image was acquired by NASA Terra spacecraft.
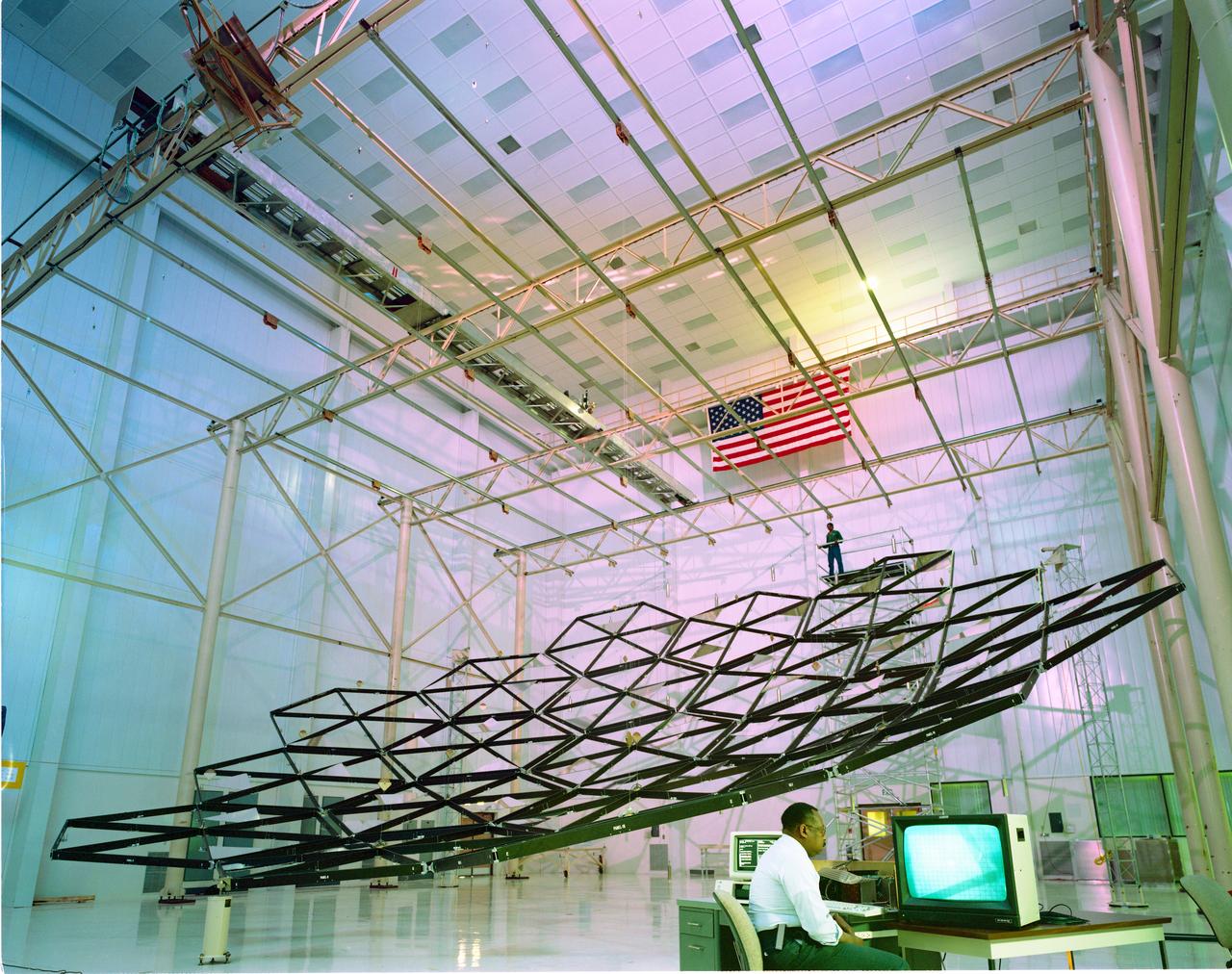

Testing of the Solar Dynamic Collector for Space Freedom. The solar dynamic power system includes a solar concentrator, which collects sunlight; a receiver, which accepts and stores the concentrated solar energy and transfers this energy to a gas; a Brayton turbine, alternator, and compressor unit, which generates electric power; and a radiator, which rejects waste heat.
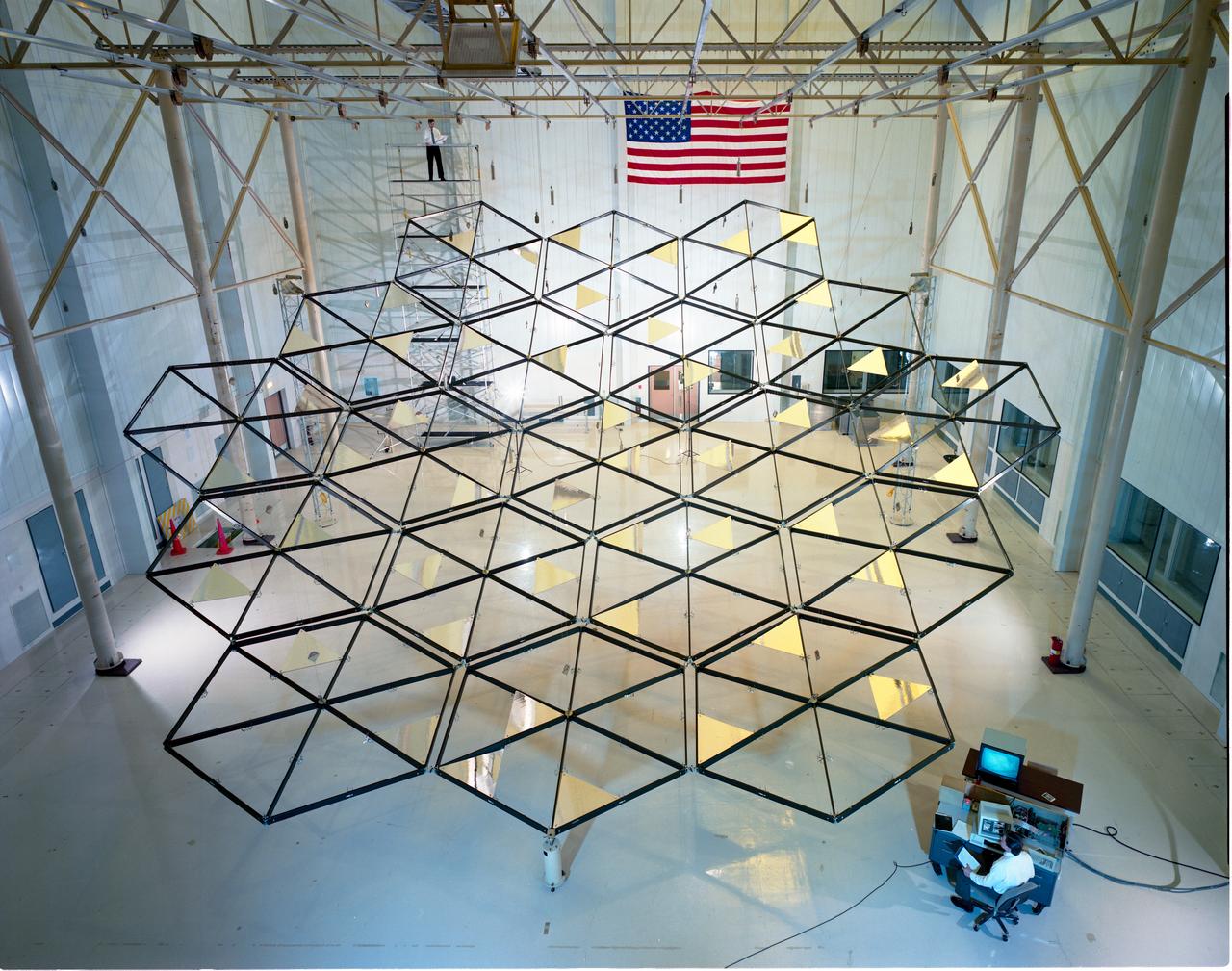
Testing of the Solar Dynamic Collector for Space Freedom. The solar dynamic power system includes a solar concentrator, which collects sunlight; a receiver, which accepts and stores the concentrated solar energy and transfers this energy to a gas; a Brayton turbine, alternator, and compressor unit, which generates electric power; and a radiator, which rejects waste heat.
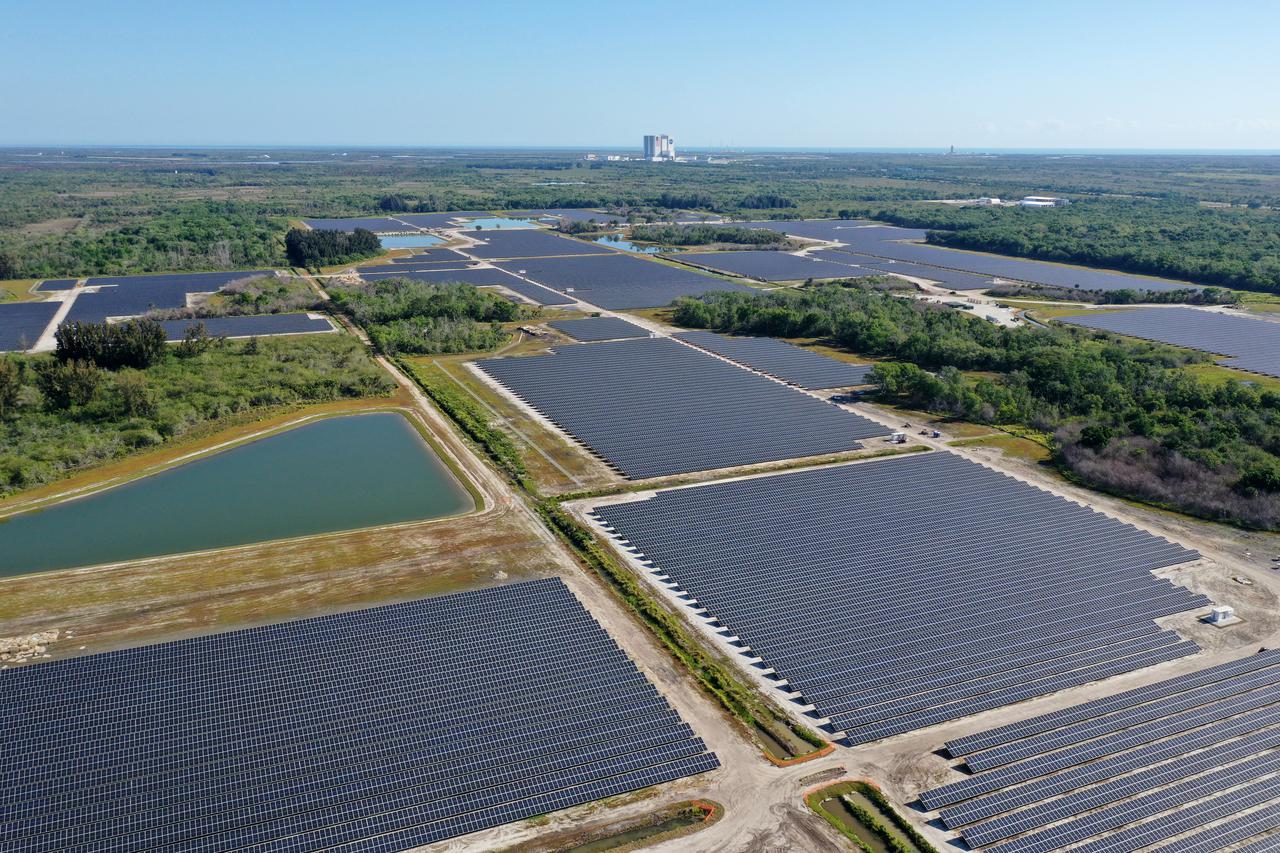

Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) new Discovery Solar Energy Center is a 74.5 megawatt solar site, spanning 491 acres at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The site contains about 250,000 solar panels, and once it’s operational, will produce enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. Construction began in spring 2020, and teams expect to have the solar site finished by May 2021. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels will not directly power anything at Kennedy, but rather, will send energy directly to FPL’s electricity grid for distribution to existing customers.
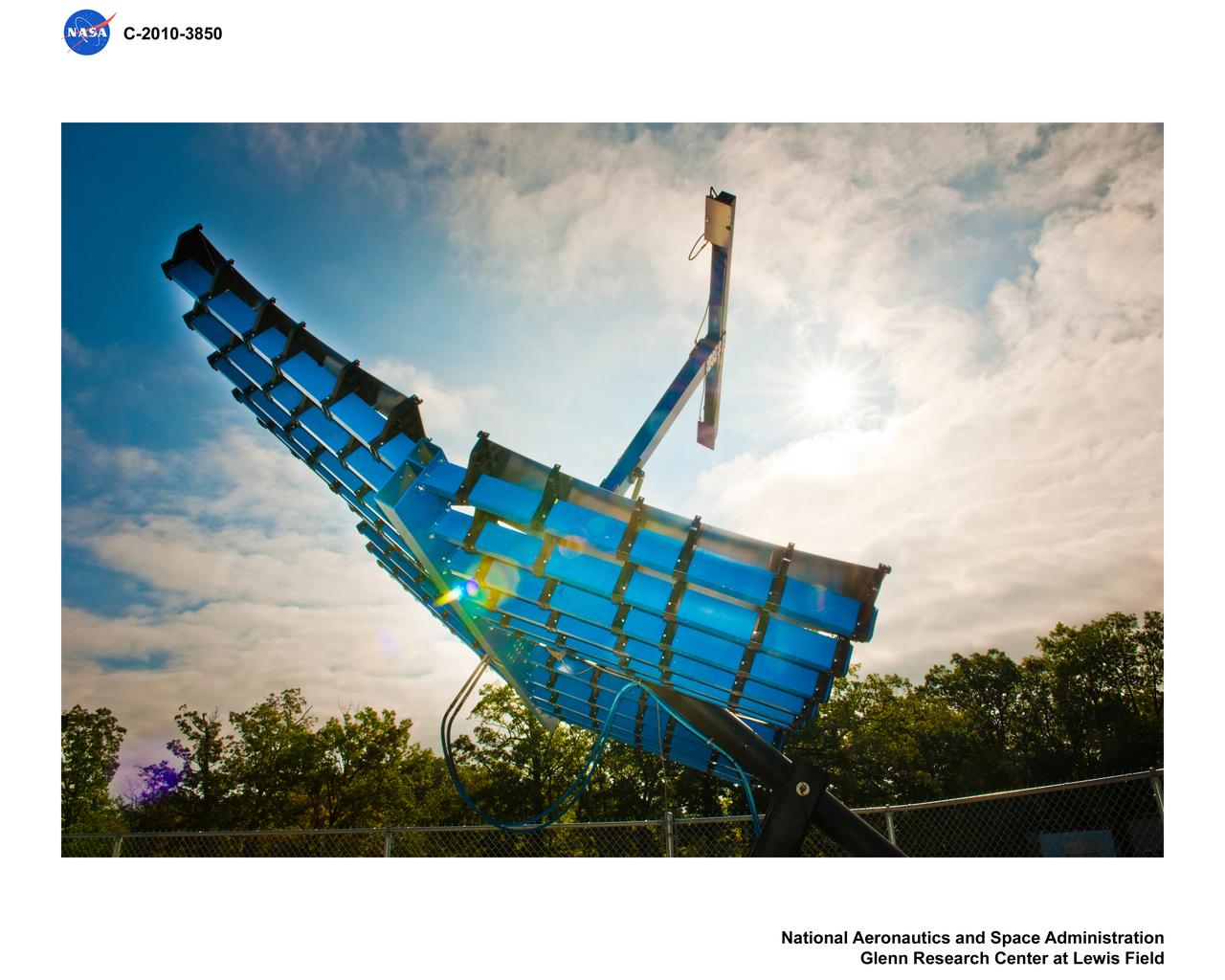

Power Energy Storage and Conversion - StarGen Inc. Solar Collector

The Direct Gain Solar Thermal Engine was designed with no moving parts. The concept of Solar Thermal Propulsion Research uses focused solar energy from an inflatable concentrator (a giant magnifying glass) to heat a propellant (hydrogen) and allows thermal expansion through the nozzle for low thrust without chemical combustion. Energy limitations and propellant weight associated with traditional combustion engines are non-existant with this concept. The Direct Gain Solar Thermal Engine would be used for moving from a lower orbit to an upper synchronous orbit.
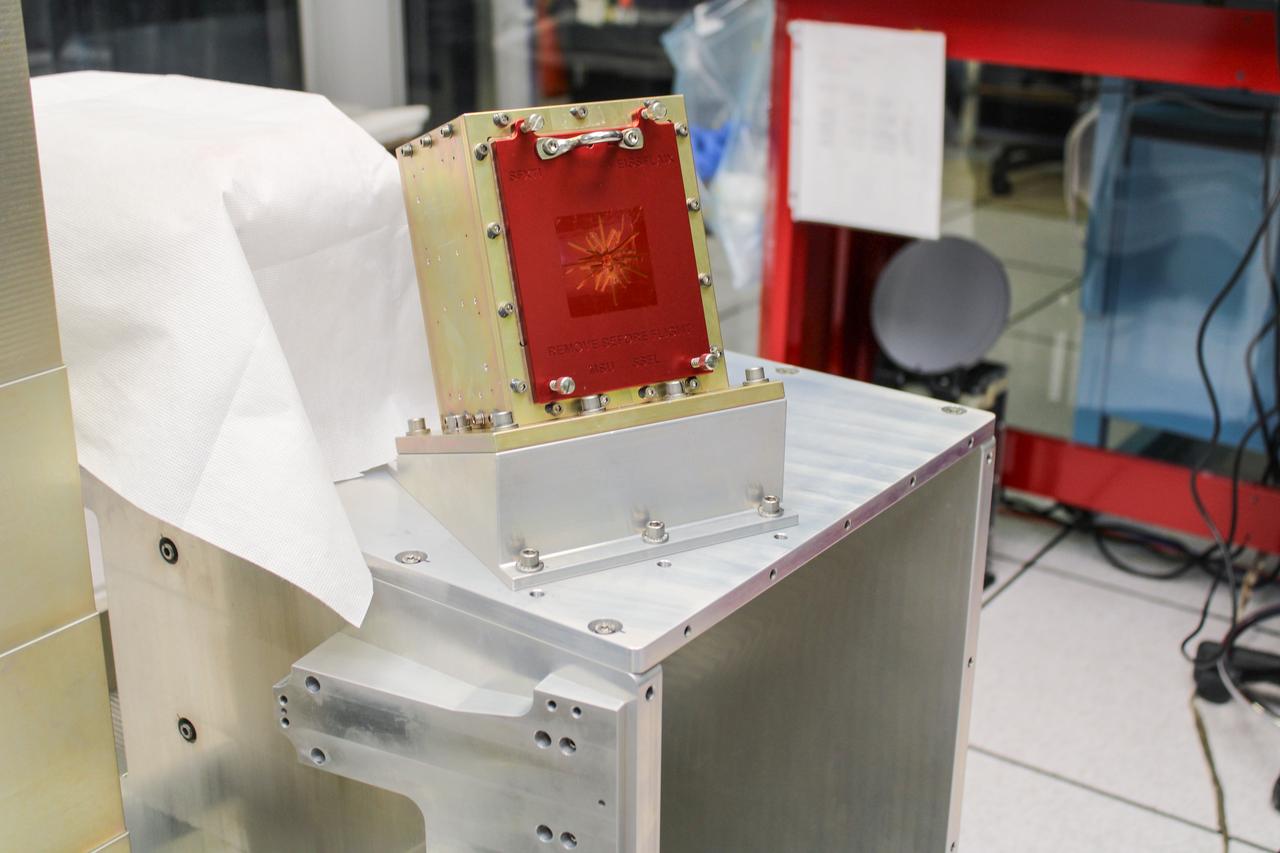
jsc2025e044726 (5/12/2025) --- Solar Flare X-Ray Timing Instrument (SFXTI) integrated on Space Test Program – Houston 10 (STP-H10). STP-H10-SFXTI measures solar hard X-ray energy spectra with high energy and time resolution. These measurements can only be made from space because solar X-rays do not penetrate Earth’s atmosphere. Image courtesy of Montana State University.

This artist’s concept shows the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System spacecraft sailing in space using the energy of the Sun.
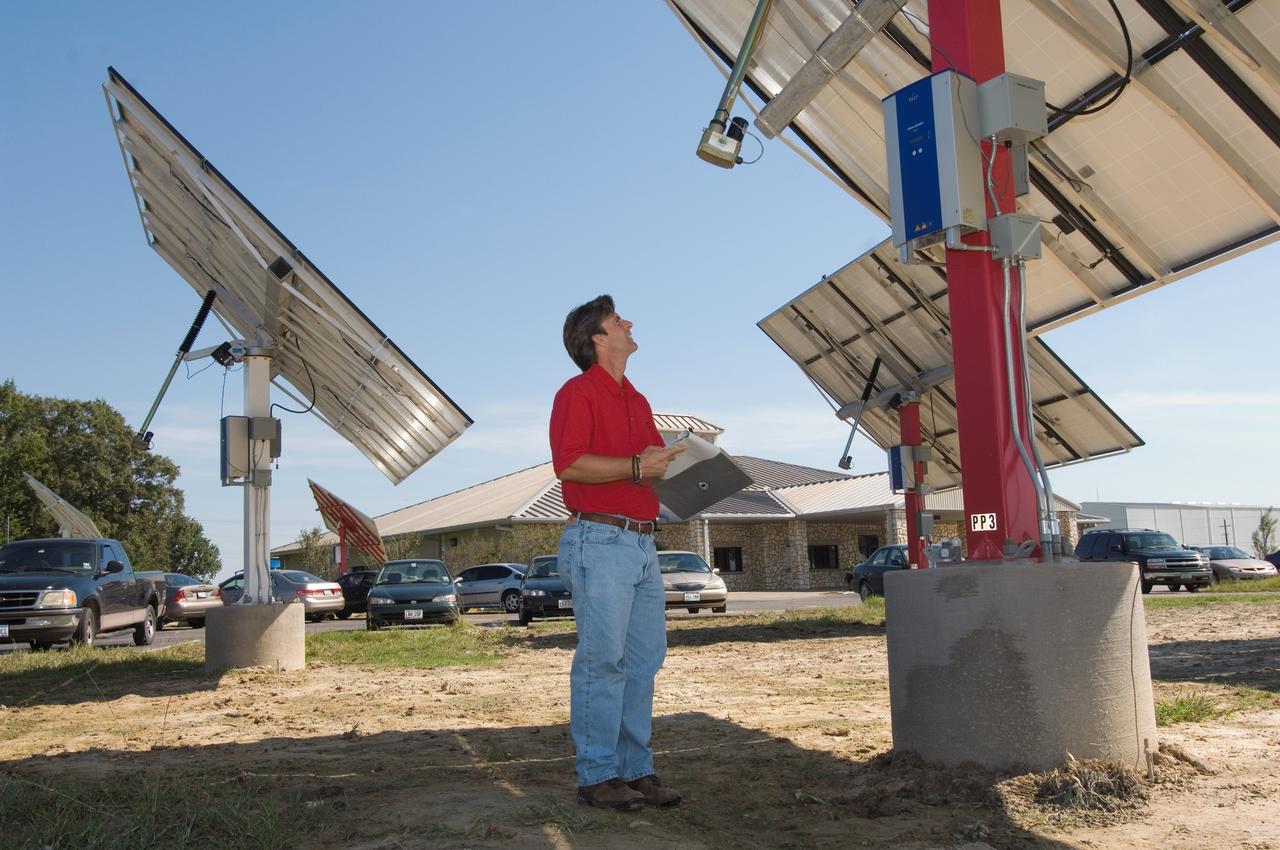

Solar panel and wind farm at the JSC Child Care Center. View of Jerry Rowlands, Energy Management and Control System manager for CSC.
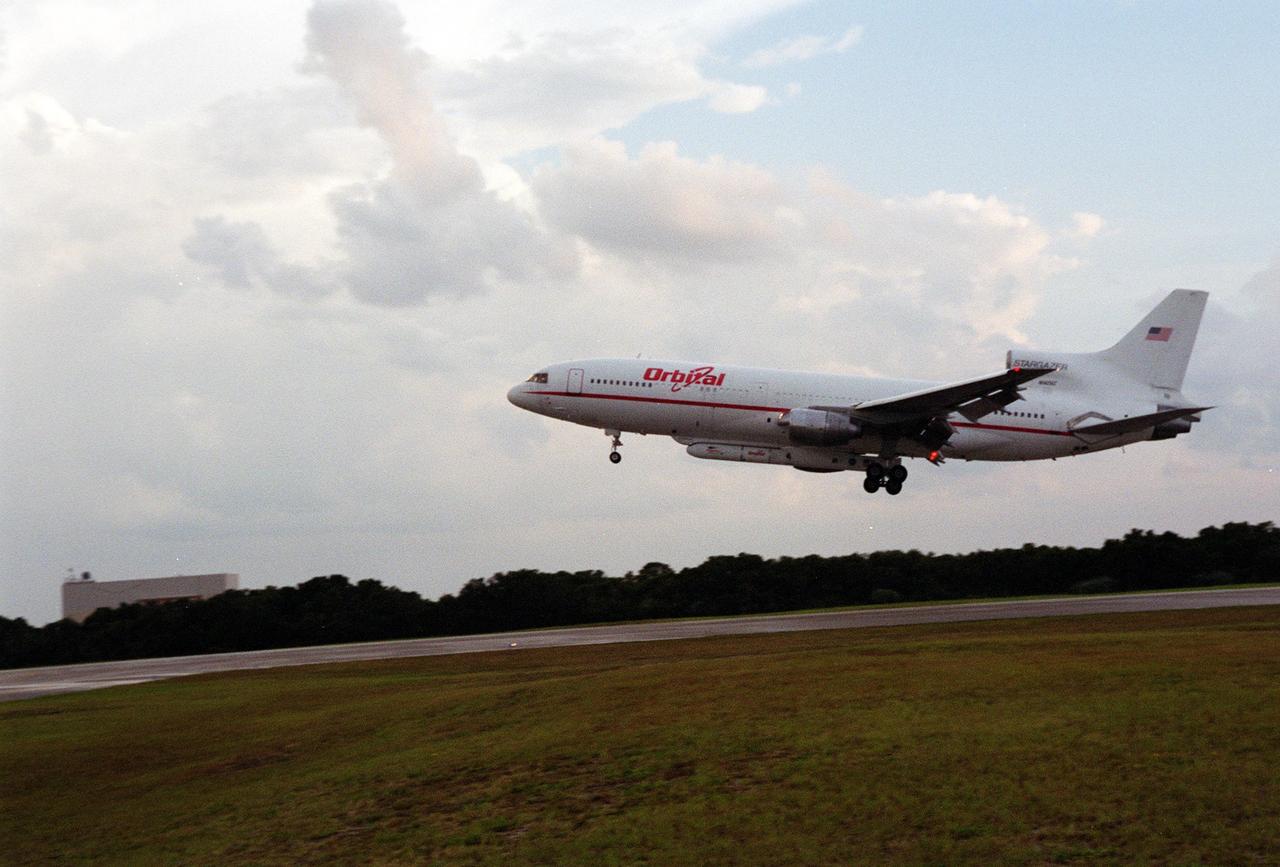

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- An L-1011 aircraft called the Stargazer gets ready to land at the Skid Strip, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Underneath its belly it carries the Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus XL launch vehicle with the High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (HESSI) attached. The Pegasus XL will launch the HESSI no earlier than June 12 from CCAFS. The primary mission of HESSI is to explore the basic physics of particle acceleration and energy release in solar flares
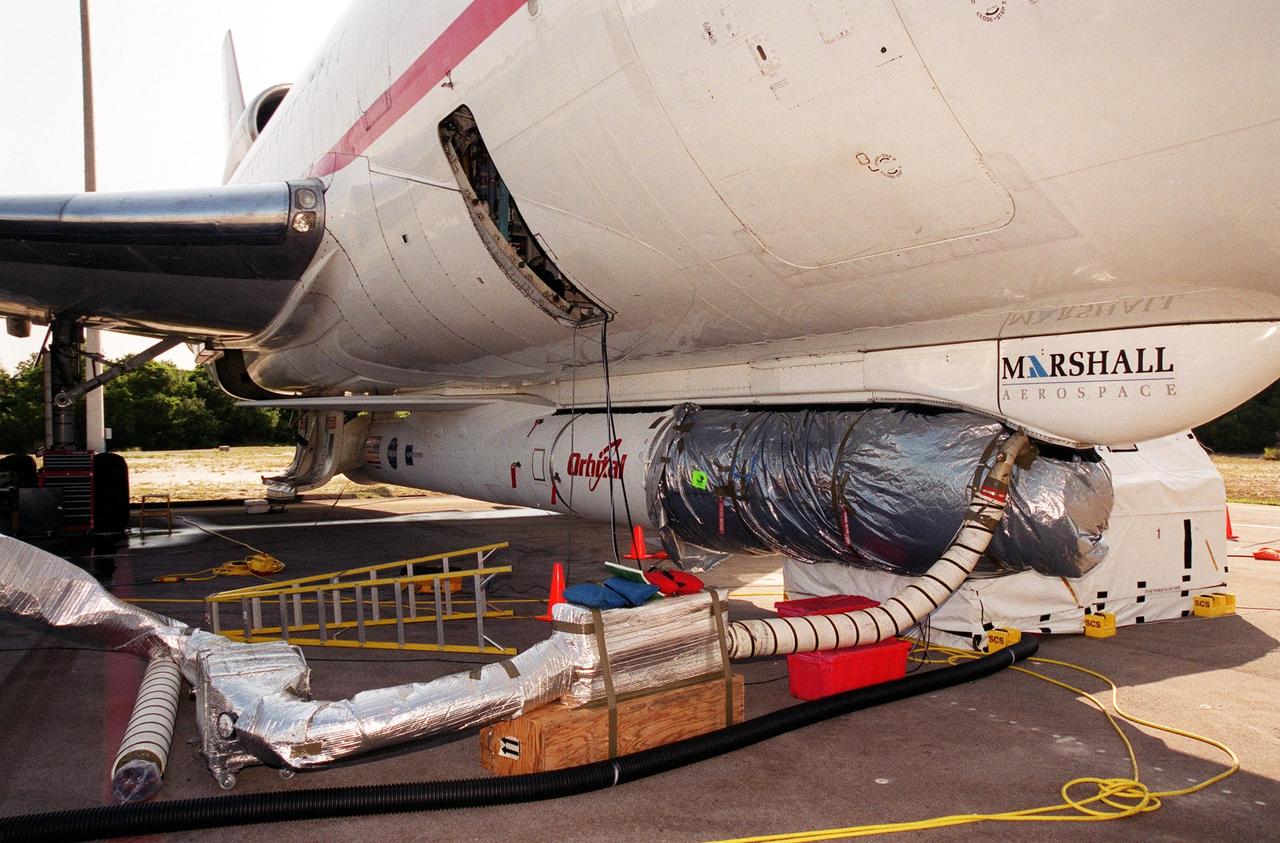

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (HESSI) spacecraft, which will be launched by a Pegasus XL rocket, arrives at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Part of NASA's Small Explorer Program, HESSI's primary mission is to explore the basic physics of particle acceleration and explosive energy release in solar flares. Launch is scheduled for no earlier than June 14
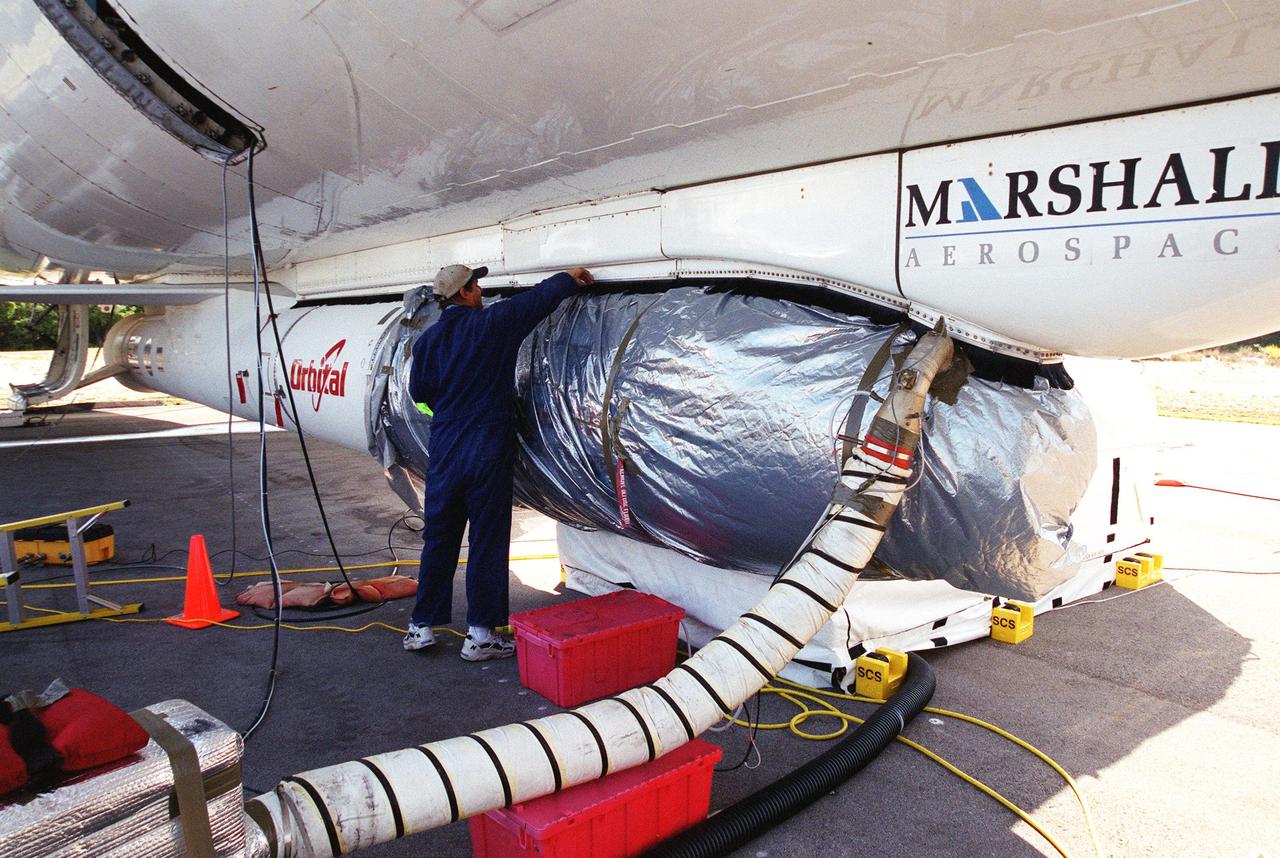

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (HESSI) spacecraft, which will be launched by a Pegasus XL rocket, arrives at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Part of NASA's Small Explorer Program, HESSI's primary mission is to explore the basic physics of particle acceleration and explosive energy release in solar flares. Launch is scheduled for no earlier than June 14
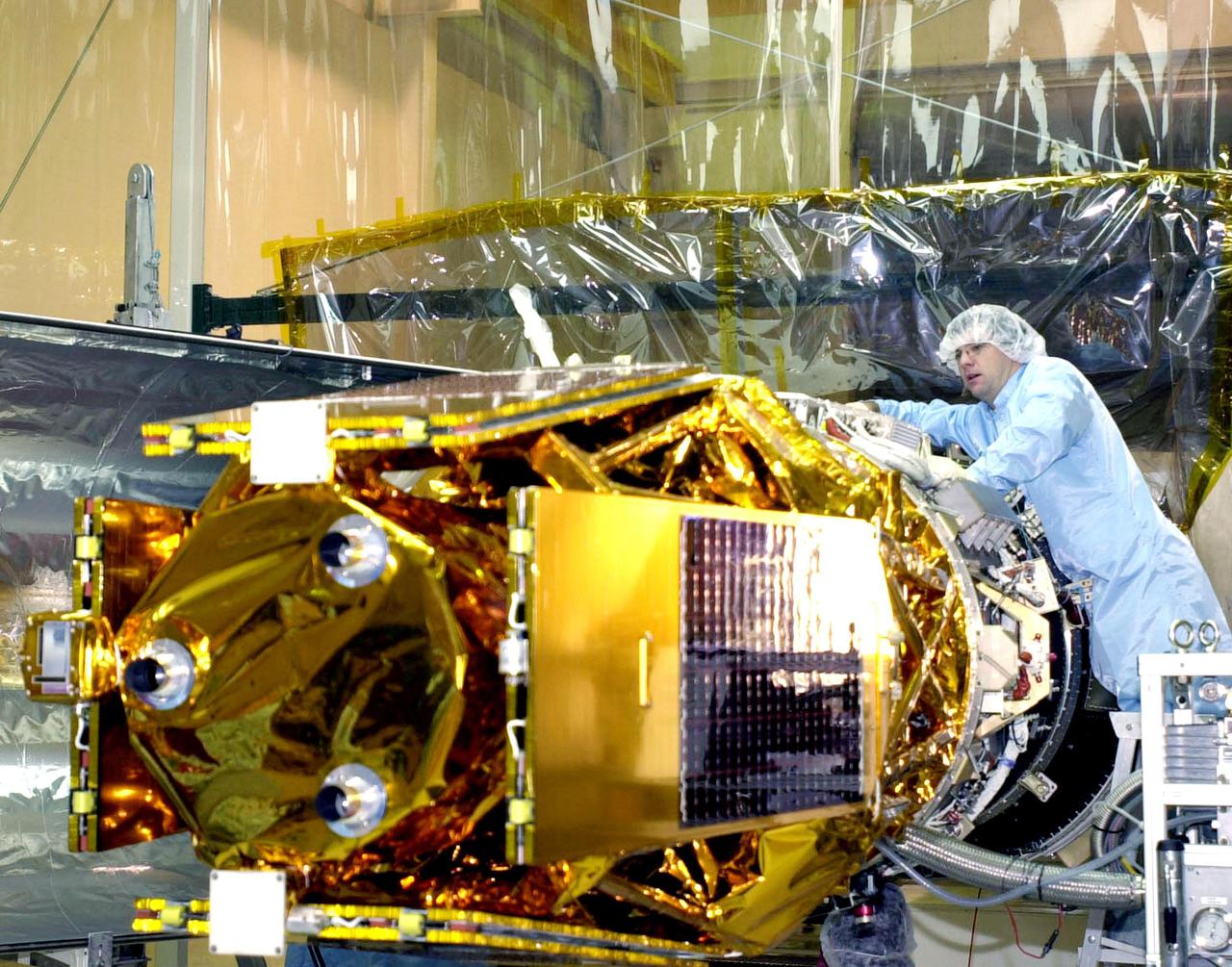

VANDENBERG AFB, CALIF. - A worker prepares the High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (HESSI) for encapsulation atop the Pegasus XL rocket before its transport to Florida. The Pegasus is the vehicle that will launch HESSI on its primary mission to explore the basic physics of particle acceleration and energy release in solar flares. The launch of PegasusXL_HESSI is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2002, from beneath an Orbital Sciences Corp. L-1011 aircraft over the Atlantic Ocean
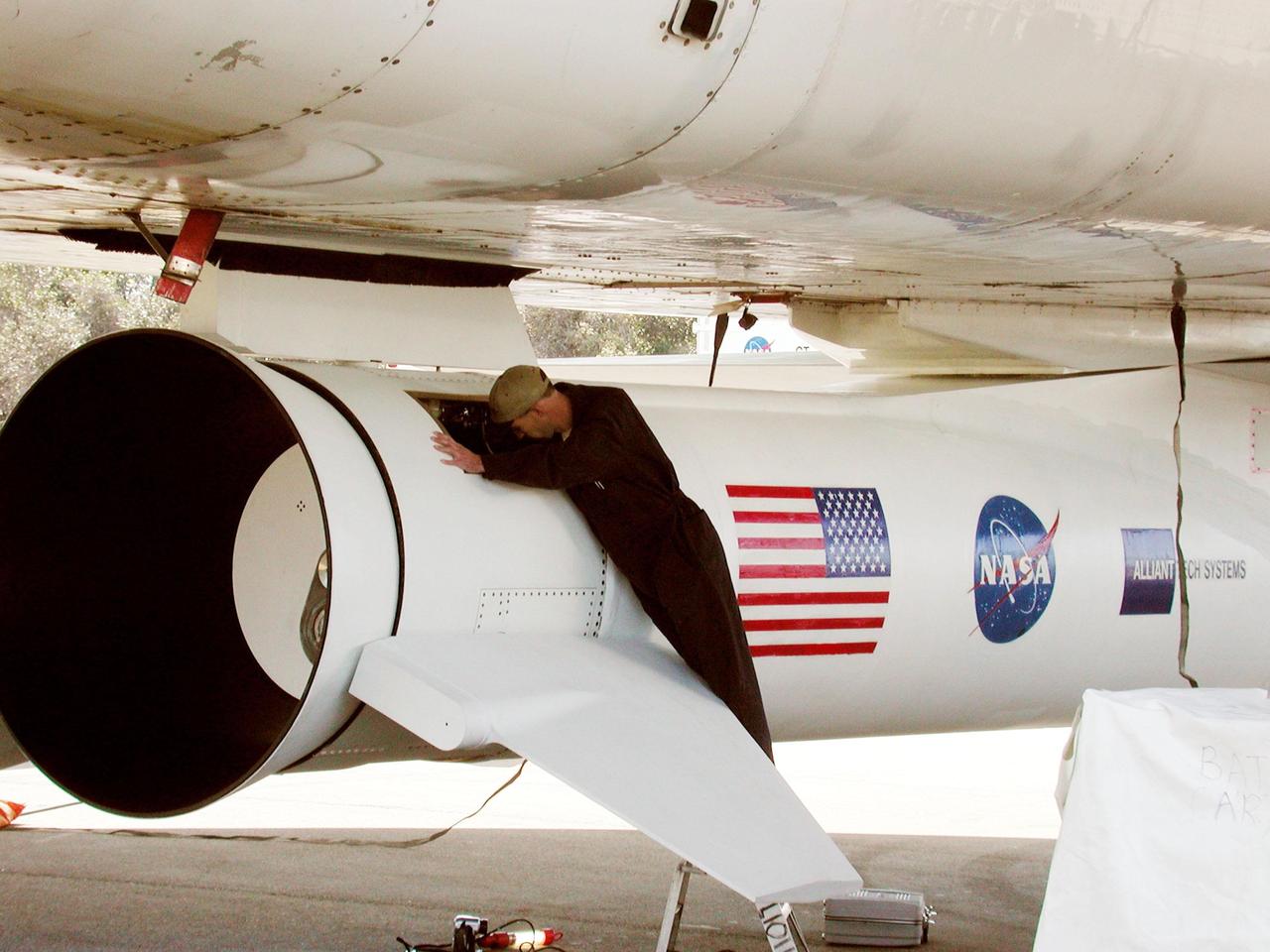

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., Mark McManus makes a final inspection of the first stage aft skirt on the Pegasus XL rocket, the vehicle that will launch the High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (HESSI). The primary mission of HESSI is to explore the basic physics of particle acceleration and energy release in solar flares. The launch of PegasusXL/HESSI is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2002, from beneath the Orbital Sciences Corp. L-1011 aircraft seen here

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Orbital Sciences Corp. L-1011 aircraft waits at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., for its mission, to carry the Pegasus XL rocket attached beneath it to the rocket's mid-air launch site. The Pegasus will launch the High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (HESSI) encased in its top to explore the basic physics of particle acceleration and energy release in solar flares. The launch is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2002
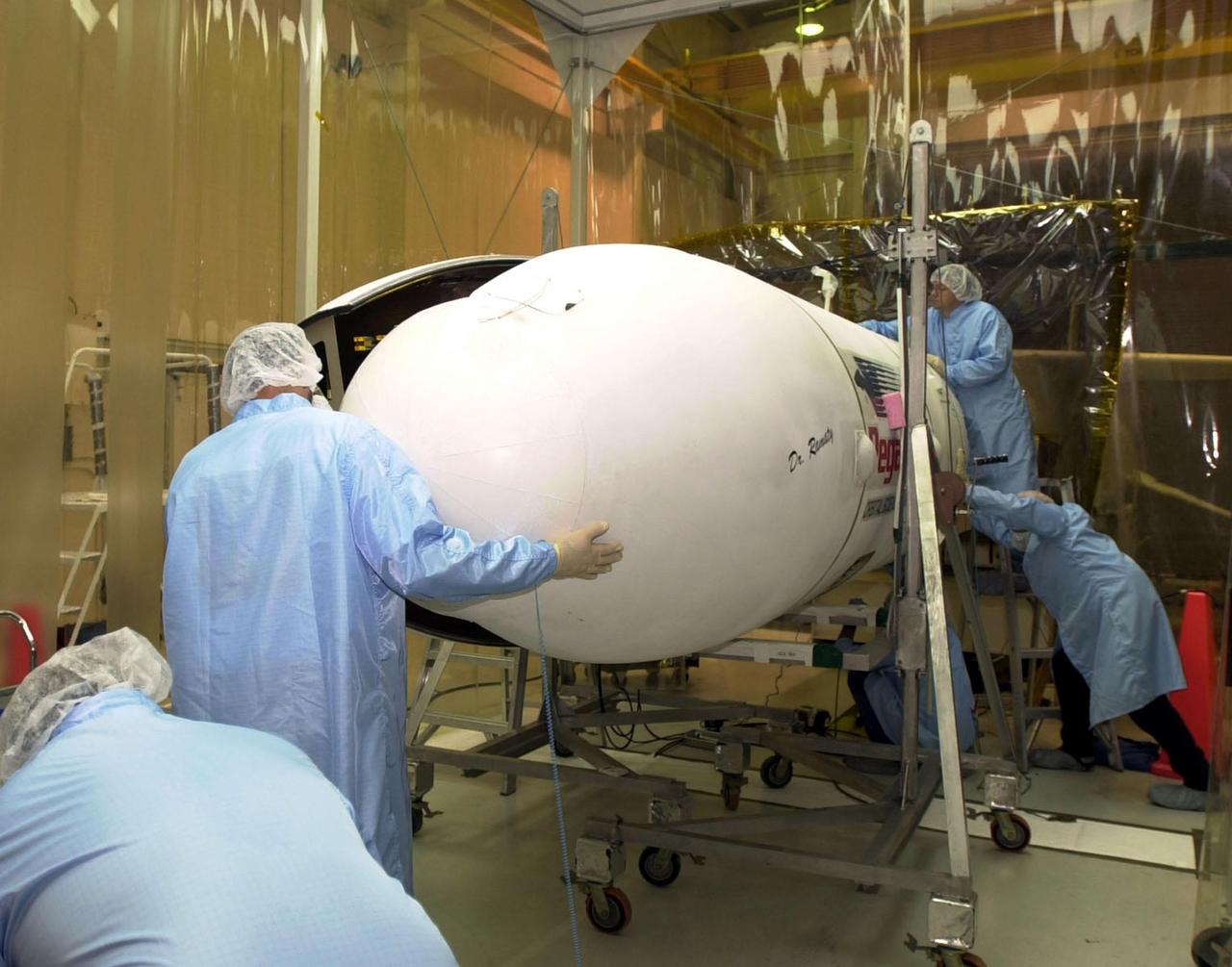
VANDENBERG AFB, CALIF. -- Technicians ready the Pegasus XL rocket, the vehicle that will launch the High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (HESSI), for flight to Florida. The primary mission of HESSI is to explore the basic physics of particle acceleration and energy release in solar flares. The launch of PegasusXL/HESSI is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2002, from beneath an Orbital Sciences Corp. L-1011 aircraft over the Atlantic Ocean
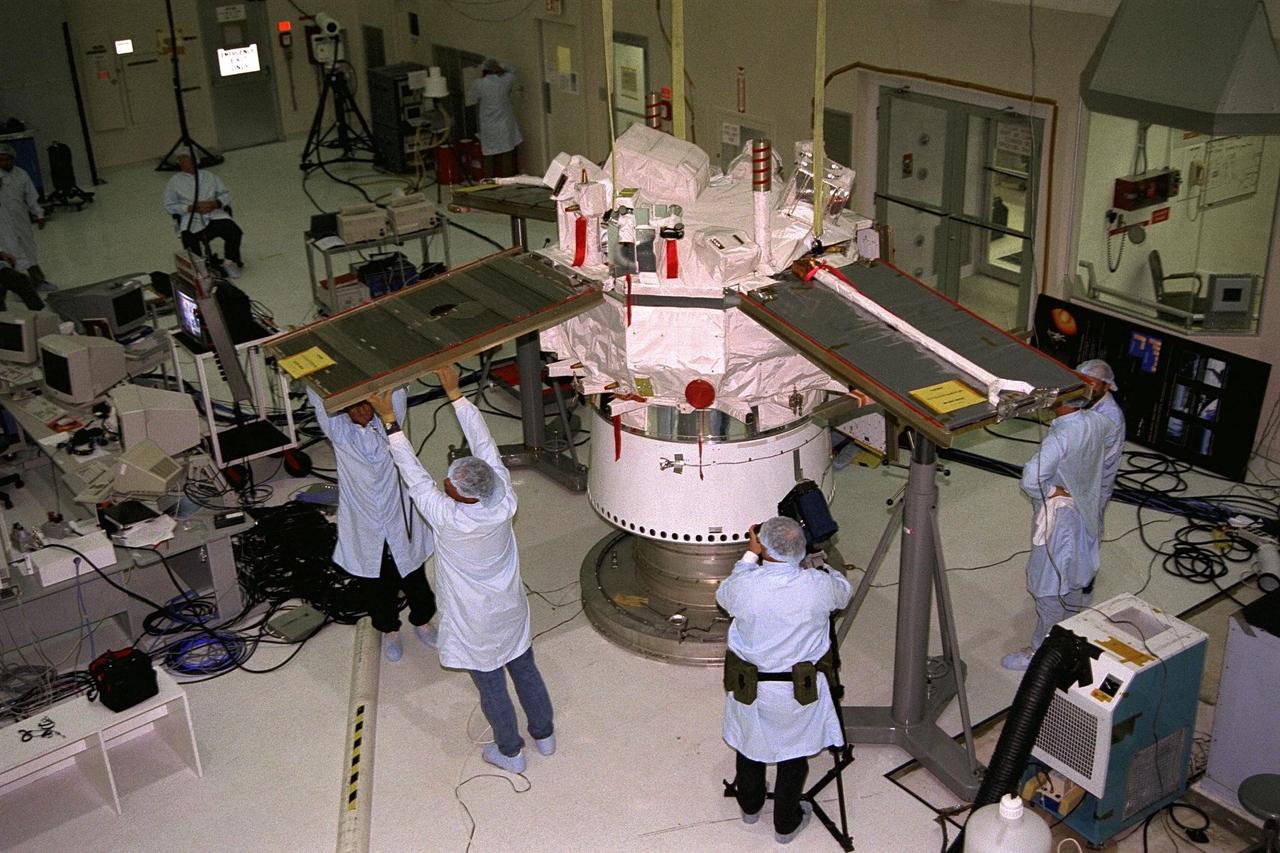

Extension of the solar panels is tested on the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) spacecraft in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-II (SAEF-II). Scheduled for launch on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Station on Aug. 25, ACE will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles. The collecting power of instruments aboard ACE is 10 to 1,000 times greater than anything previously flown to collect similar data by NASA
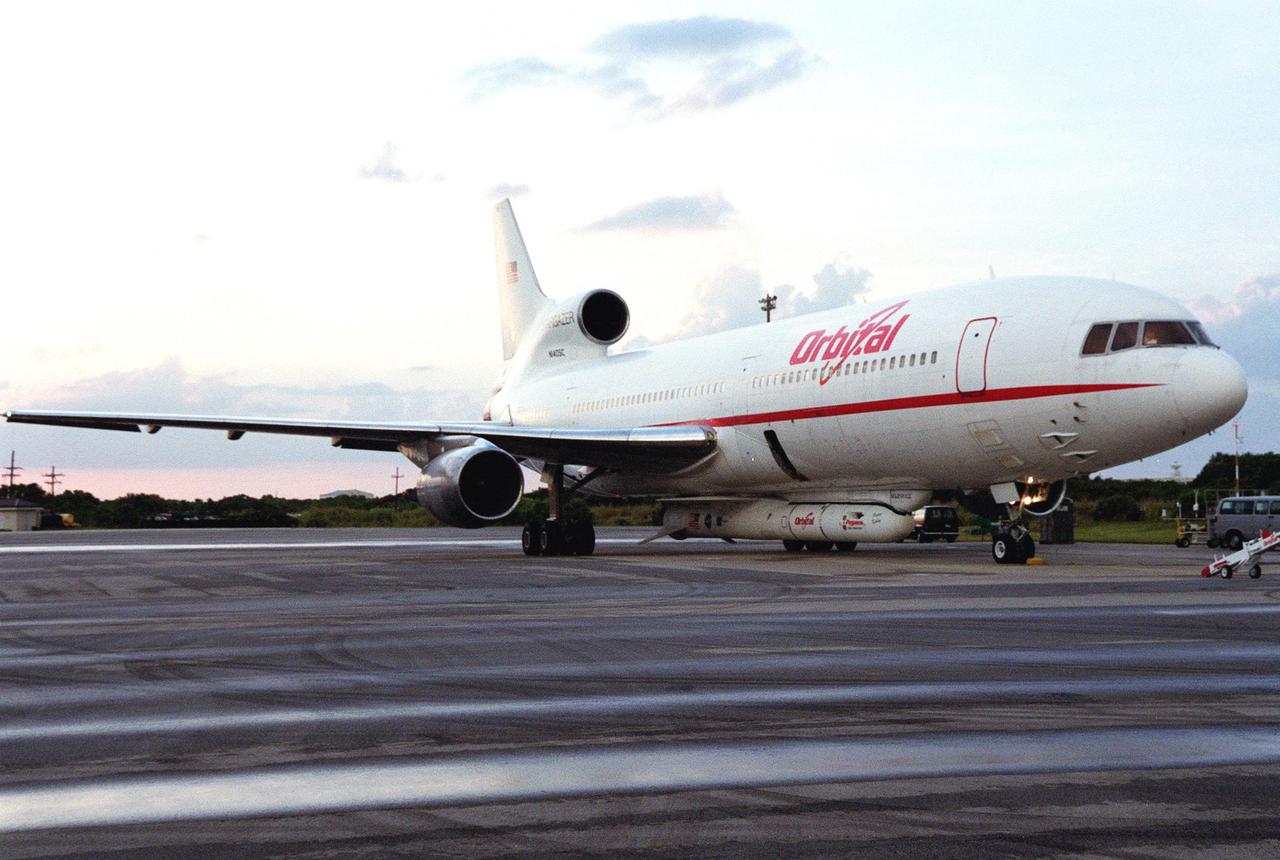

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- An L-1011 aircraft called the Stargazer is parked after landing at the Skid Strip, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Underneath its belly it carries the Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus XL launch vehicle with the High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (HESSI) attached. The Pegasus XL will launch the HESSI no earlier than June 12 from CCAFS. The primary mission of HESSI is to explore the basic physics of particle acceleration and energy release in solar flares
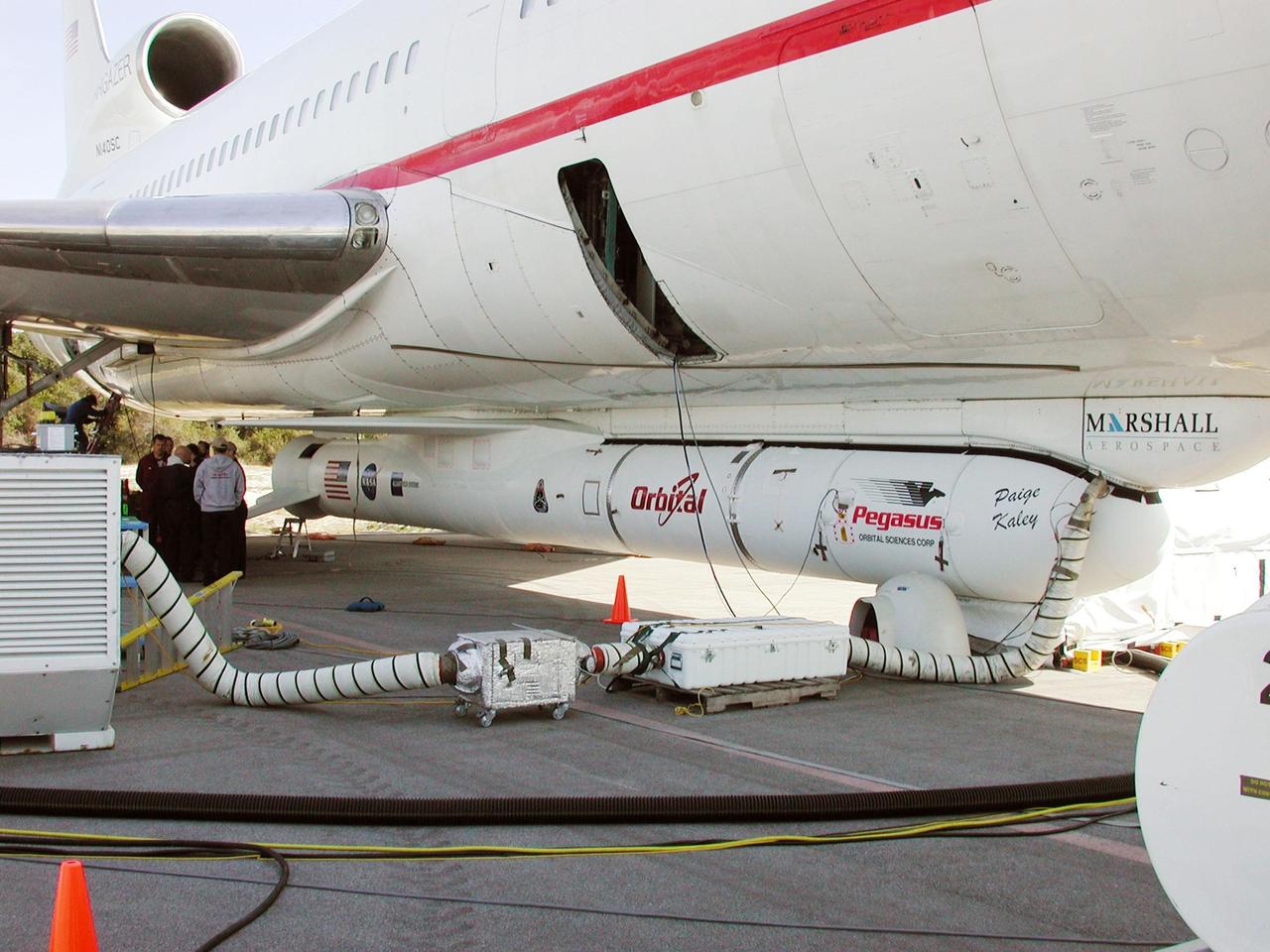

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Underneath the belly of Orbital Sciences Corp.'s L-1011 aircraft is the Pegasus XL rocket, the vehicle that will launch the High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (HESSI), on display at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The primary mission of HESSI is to explore the basic physics of particle acceleration and energy release in solar flares. The launch of PegasusXL/HESSI is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2002
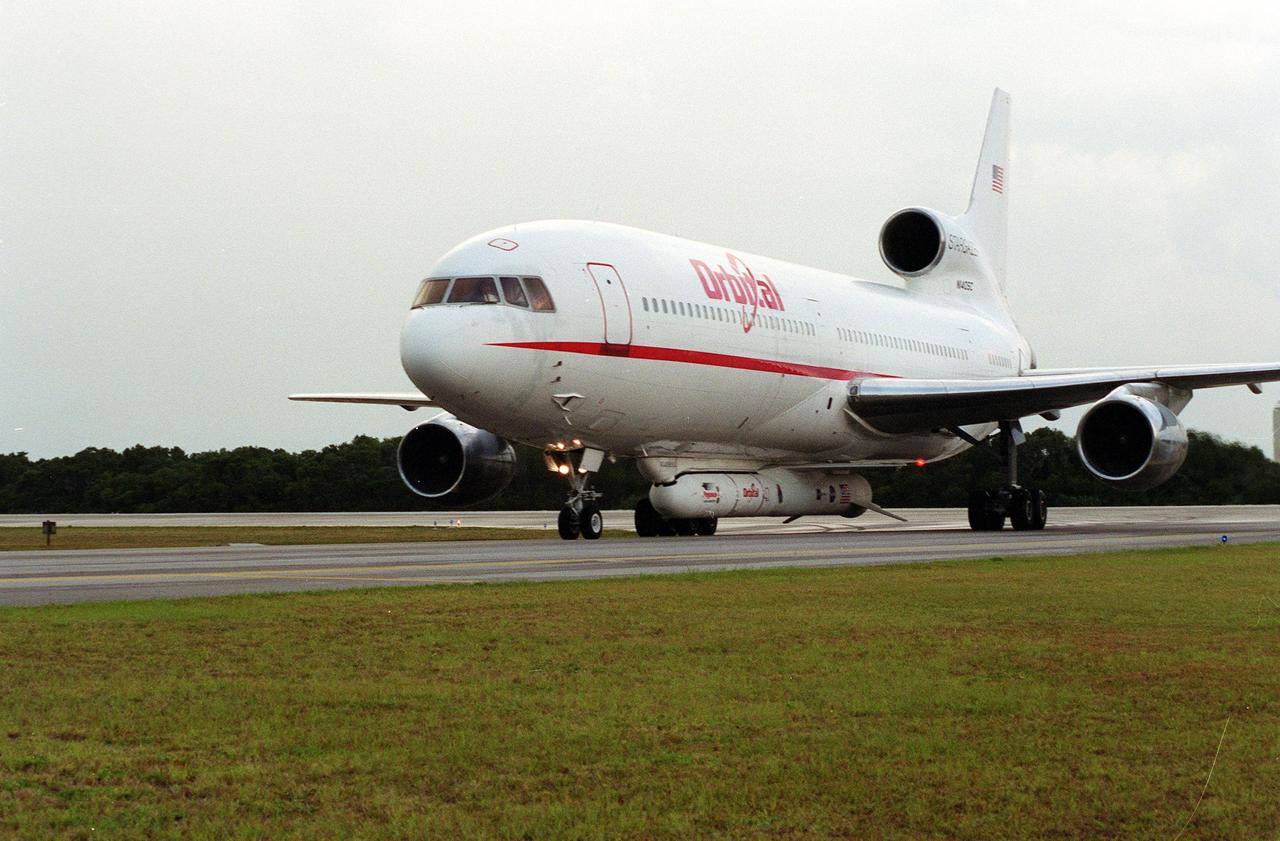

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- An L-1011 aircraft called the Stargazer lands at the Skid Strip, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Underneath its belly it carries the Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus XL launch vehicle with the High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (HESSI) attached. The Pegasus XL will launch the HESSI no earlier than June 12 from CCAFS. The primary mission of HESSI is to explore the basic physics of particle acceleration and energy release in solar flares
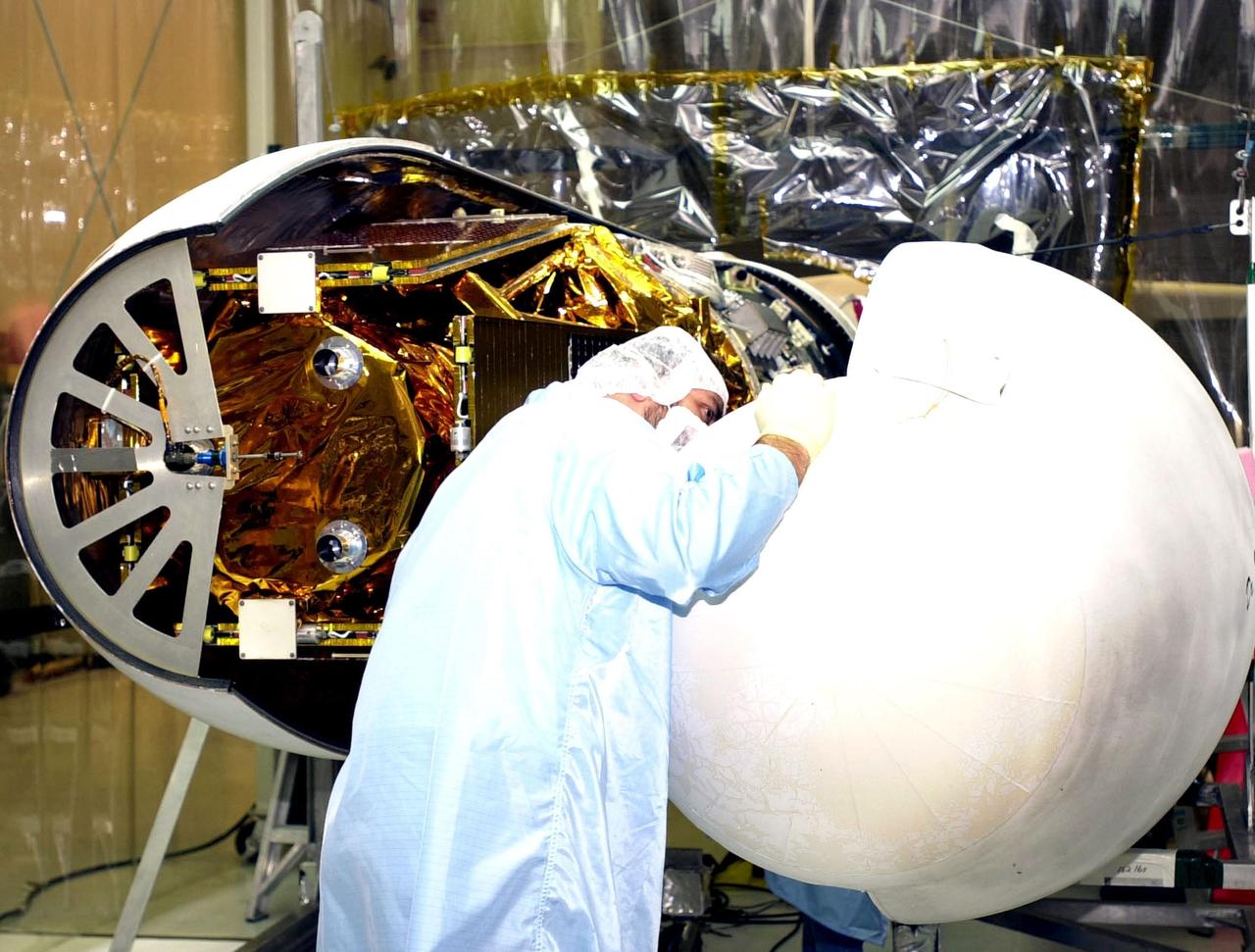

VANDENBERG AFB, CALIF. -- A worker helps guide the second half of the encapsulation around the High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (HESSI) atop the Pegasus XL rocket before its transport to Florida. The Pegasus is the vehicle that will launch HESSI on its primary mission to explore the basic physics of particle acceleration and energy release in solar flares. The launch of PegasusXL/HESSI is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2002, from beneath an Orbital Sciences Corp. L-1011 aircraft over the Atlantic Ocean
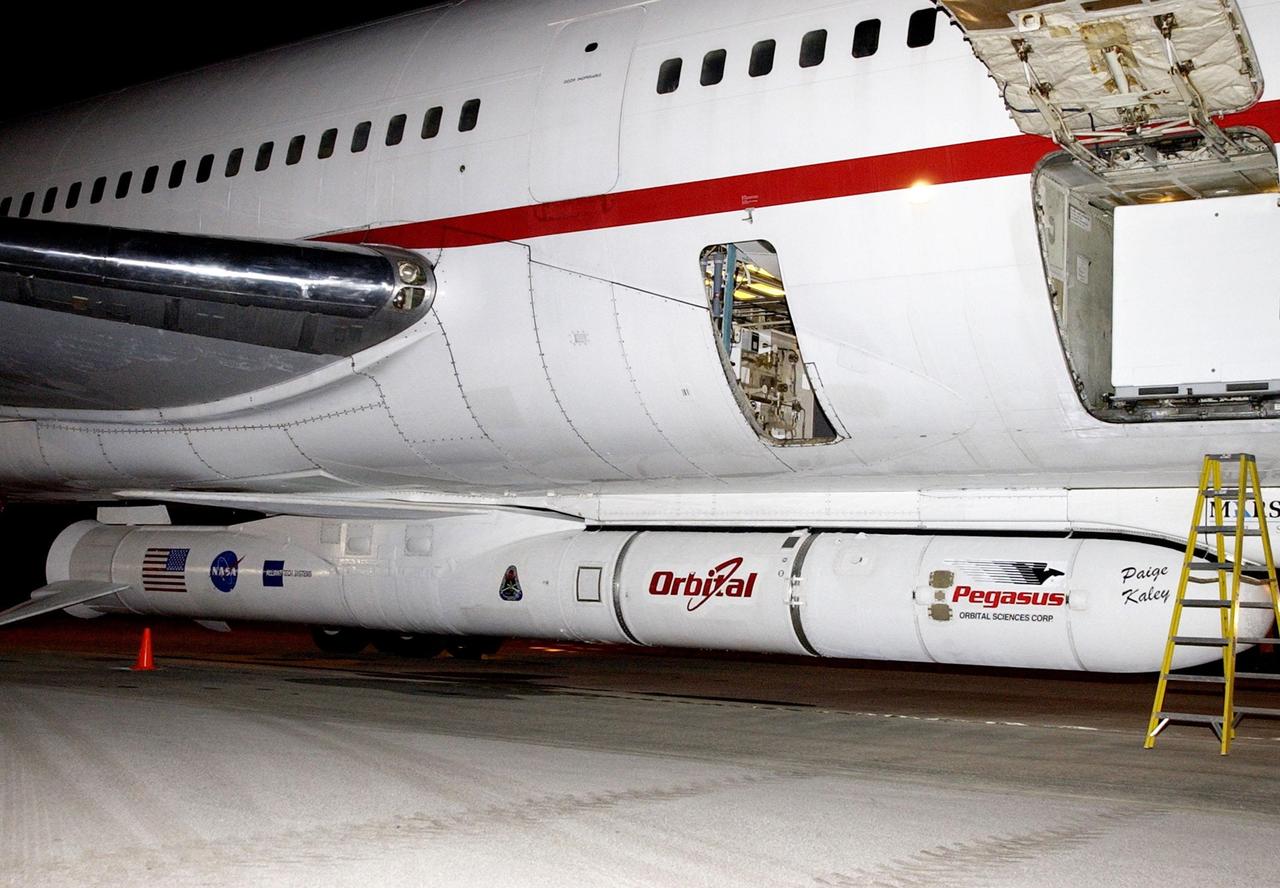

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This closeup shows the Pegasus XL rocket with the High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (HESSI) attached at its top, on the right. The Pegasus will launch HESSI to explore the basic physics of particle acceleration and energy release in solar flares. The launch is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2002, from beneath the Orbital Sciences Corp. L-1011 aircraft seen here
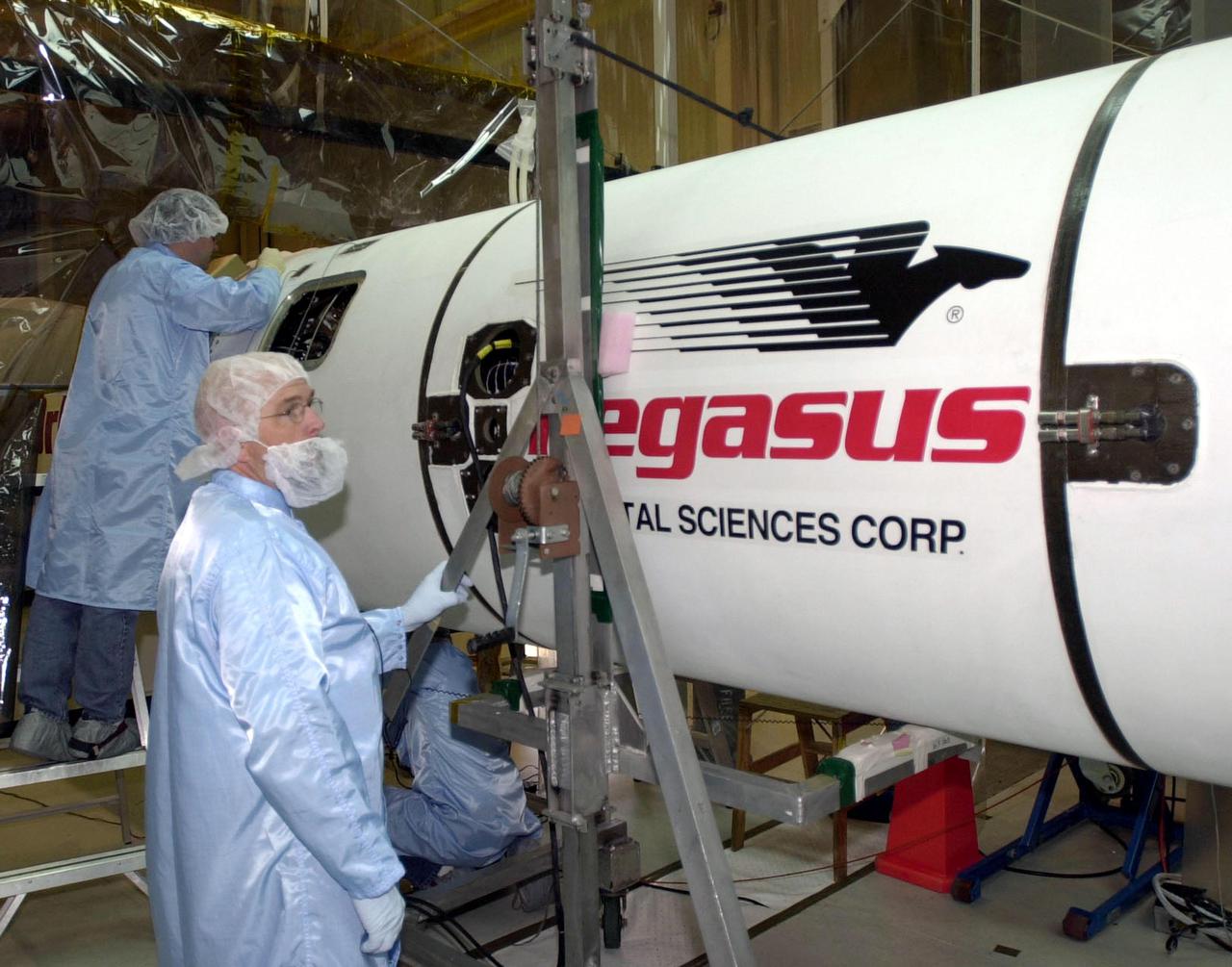

VANDENBERG AFB, CALIF. -- Technicians work on the Pegasus XL rocket, the vehicle that will launch the High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (HESSI). The primary mission of HESSI is to explore the basic physics of particle acceleration and energy release in solar flares. The launch of PegasusXL_HESSI is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2002, from beneath an Orbital Sciences Corp. L-1011 aircraft over the Atlantic Ocean

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Orbital Sciences Corp.'s L-1011 aircraft is on display for a press showing at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. Underneath is the Pegasus XL rocket, the vehicle that will launch the High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (HESSI). The primary mission of HESSI is to explore the basic physics of particle acceleration and energy release in solar flares. The launch of PegasusXL/HESSI is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2002
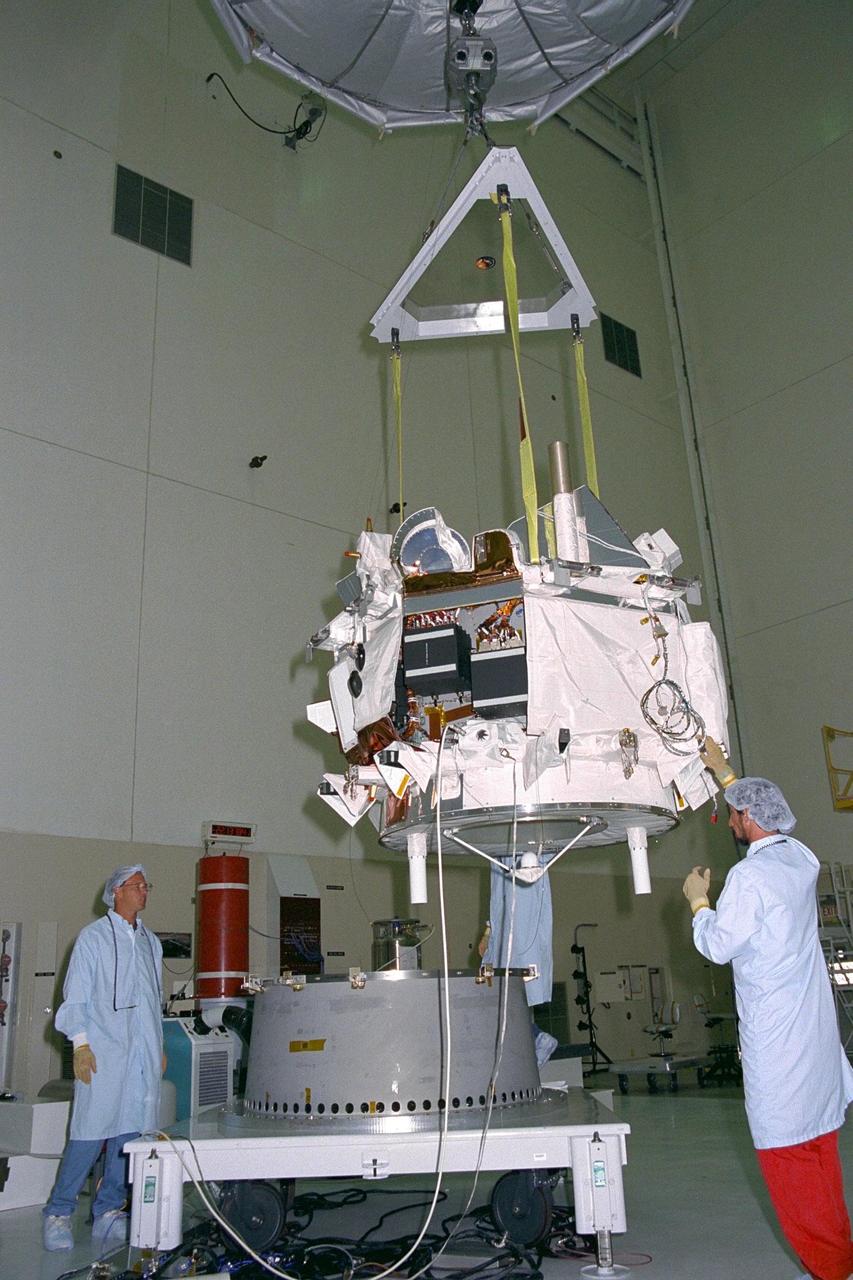

Applied Physics Laboratory engineers and technicians from Johns Hopkins University assist in guiding the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) as it is hoisted over a platform for solar array installation in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-II. Scheduled for launch on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Station on Aug. 25, ACE will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles. The ACE observatory will contribute to the understanding of the formation and evolution of the solar system as well as the astrophysical processes involved. The collecting power of instruments aboard ACE is 10 to 1,000 times greater than anything previously flown to collect similar data by NASA
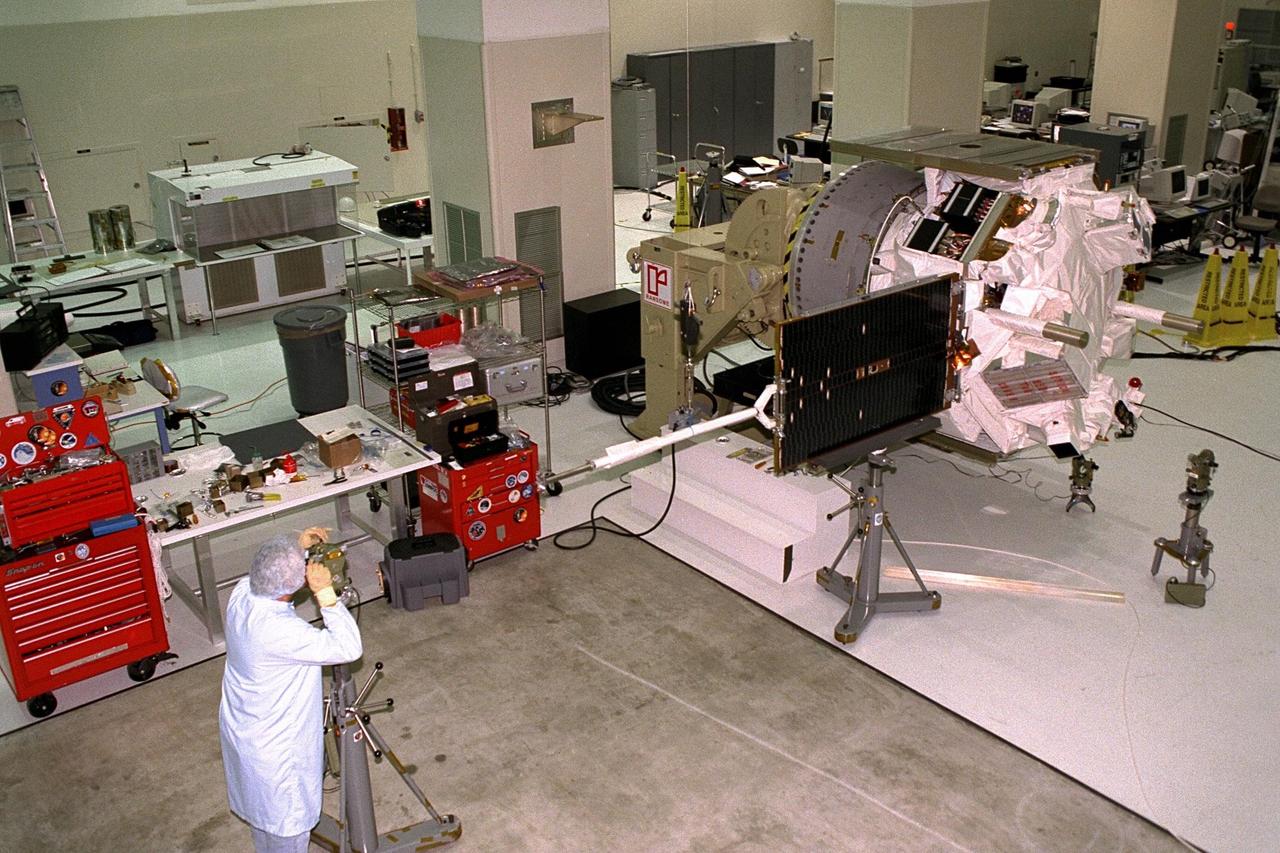

An Applied Physics Laboratory engineer from Johns Hopkins University tests for true perpendicular solar array deployment of the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-II (SAEF-II). The white magnetometer boom seen across the solar array panel will deploy the panel once in space. Scheduled for launch on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Station on Aug. 25, ACE will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles. The ACE observatory will be placed into an orbit almost a million miles (1.5 million kilometers) away from the Earth, about 1/100 the distance from the Earth to the Sun
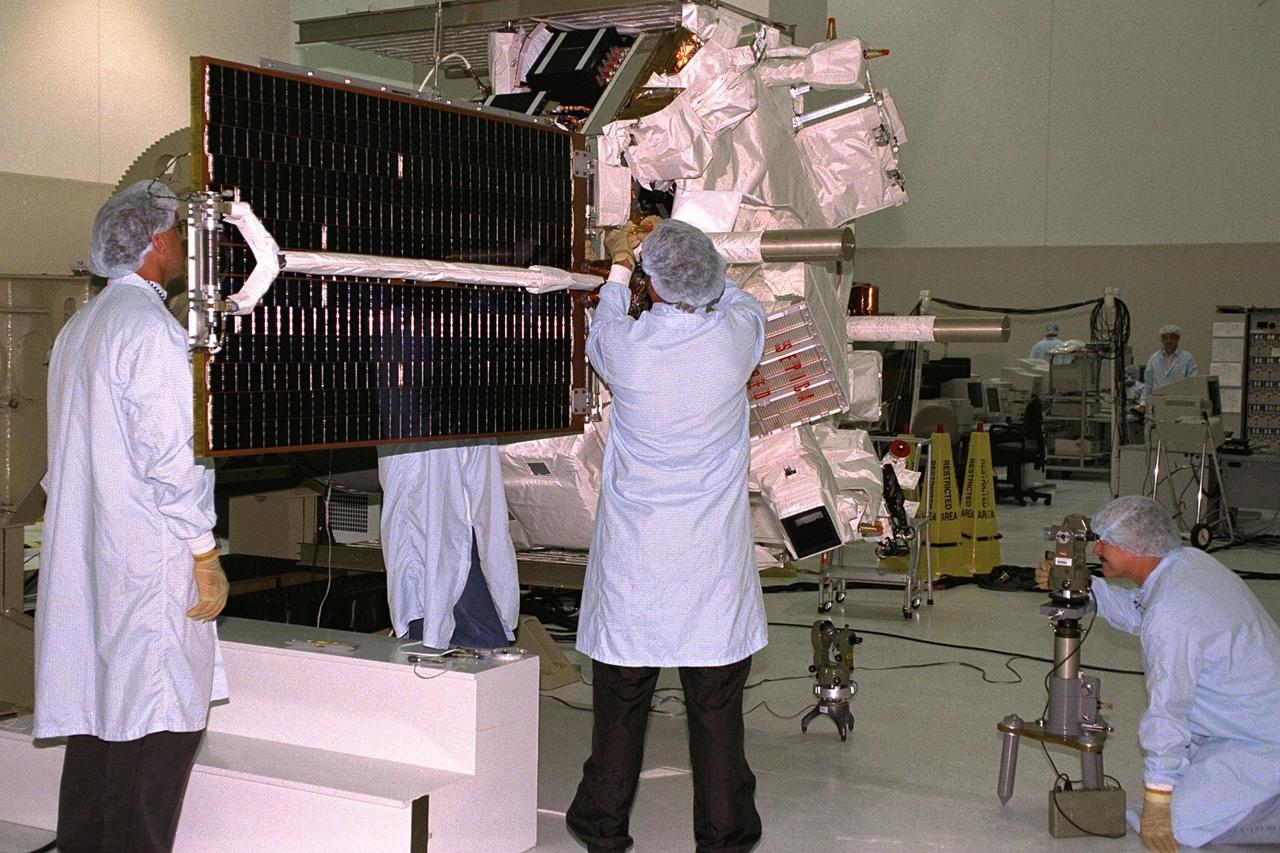

Applied Physics Laboratory engineers and technicians from Johns Hopkins University test for true perpendicular solar array deployment of the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-II (SAEF-II). The white magnetometer boom seen across the solar array panel will deploy the panel once in space. Scheduled for launch on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Station on Aug. 25, ACE will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles. The ACE observatory will be placed into an orbit almost a million miles (1.5 million kilometers) away from the Earth, about 1/100 the distance from the Earth to the Sun
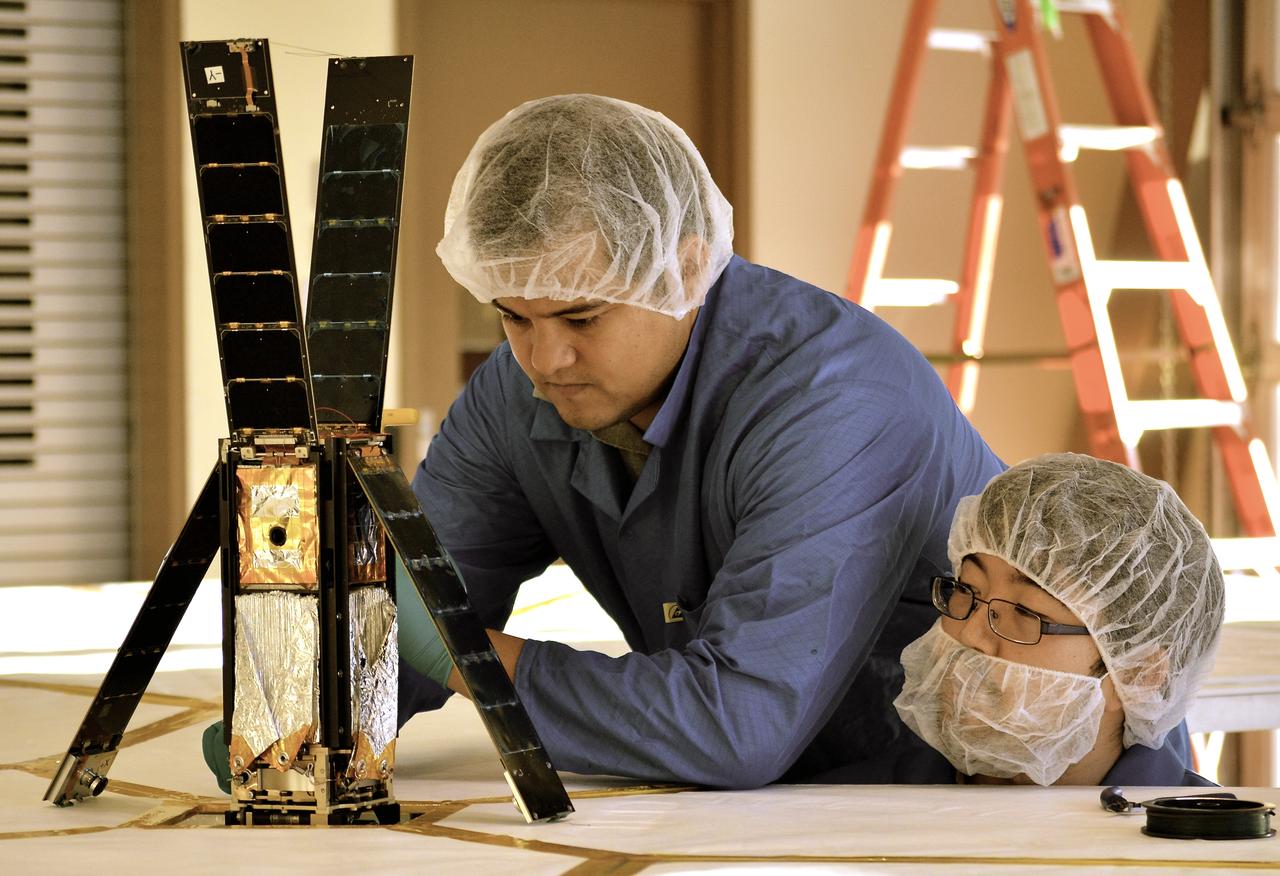

Students Alex Diaz and Riki Munakata of California Polytechnic State University testing the LightSail CubeSat. LightSail is a citizen-funded technology demonstration mission sponsored by the Planetary Society using solar propulsion for CubeSats. The spacecraft is designed to “sail” on the energy of solar photons striking the thin, reflective sail material. The first LightSail mission is designed to test the spacecraft’s critical systems, including the sequence to autonomously deploy a Mylar solar sail with an area of 32 square meters (344 square feet). The Planetary Society is planning a second, full solar sailing demonstration flight for 2016. Light is made of packets of energy called photons. While photons have no mass, they have energy and momentum. Solar sails use this momentum as a method of propulsion, creating flight by light. LightSail’s solar sail is packaged into a three-unit CubeSat about the size of a loaf of bread. Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative on the ELaNa XI mission as an auxiliary payload aboard the U.S. Air Force X-37B space plane mission on May 20, 2015.
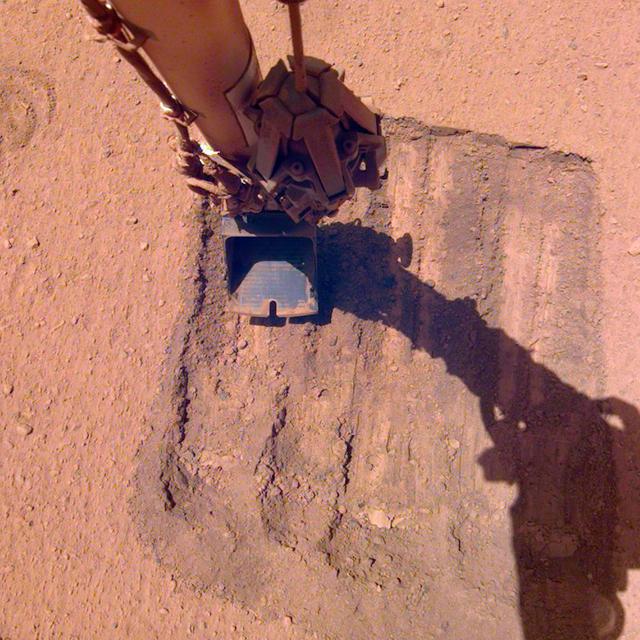

NASA's InSight lander tried a novel approach to remove dust clinging to one of its solar panels. On May 22, 2021, the 884th Martian day, or sol, of the mission, the lander's robotic arm trickled sand above the panel. As wind carried the sand grains across the panel, they picked up some dust along the way, enabling the lander to gain about 30 watt-hours of energy per sol. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24664
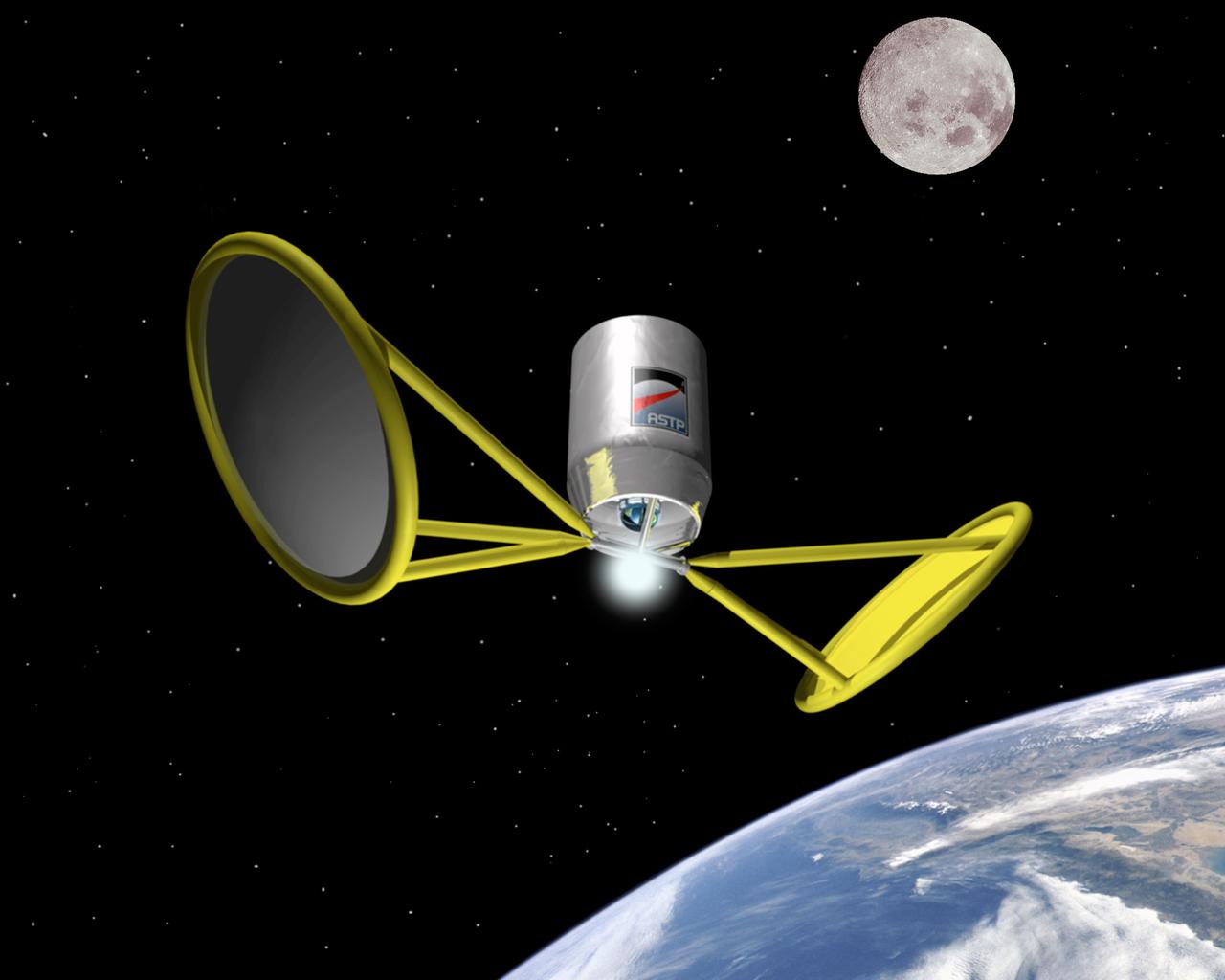
Harnessing the Sun's energy through Solar Thermal Propulsion will propel vehicles through space by significantly reducing weight, complexity, and cost while boosting performance over current conventional upper stages. Another solar powered system, solar electric propulsion, demonstrates ion propulsion is suitable for long duration missions. Pictured is an artist's concept of space flight using solar thermal propulsion.

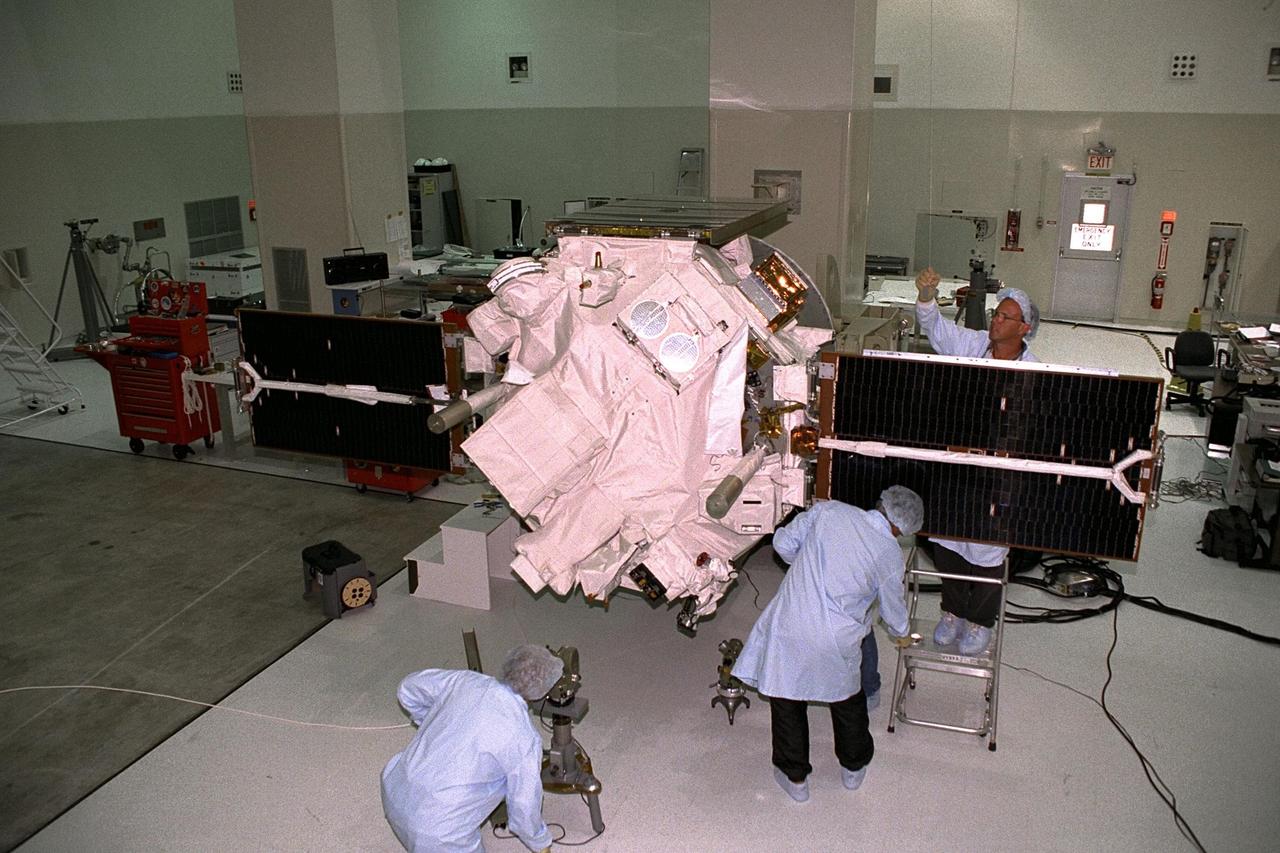
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's first large-scale solar power generation facility opens at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Representatives from NASA, Florida Power & Light Company, or FPL, and SunPower Corporation formally commissioned the one-megawatt facility and announced plans to pursue a new research, development and demonstration project at Kennedy to advance America's use of renewable energy. The facility is the first element of a major renewable energy project currently under construction at Kennedy. The completed system features a fixed-tilt, ground-mounted solar power system designed and built by SunPower, along with SunPower solar panels. A 10-megawatt solar farm, which SunPower is building on nearby Kennedy property, will supply power to FPL's customers when it is completed in April 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

Applied Physics Laboratory engineers and technicians from Johns Hopkins University test solar array deployment of the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-II (SAEF-II). The wire hanging from the ceiling above the black solar array panel is used for "g-negation," which takes the weight off of the panel’s hinges to simulate zero gravity, mimicking deployment in space. Scheduled for launch on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Station on Aug. 25, ACE will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles for a better understanding of the formation and evolution of the solar system as well as the astrophysical processes involved. The collecting power of instrumentation aboard ACE is at least 100 times more sensitive than anything previously flown to collect similar data by NASA
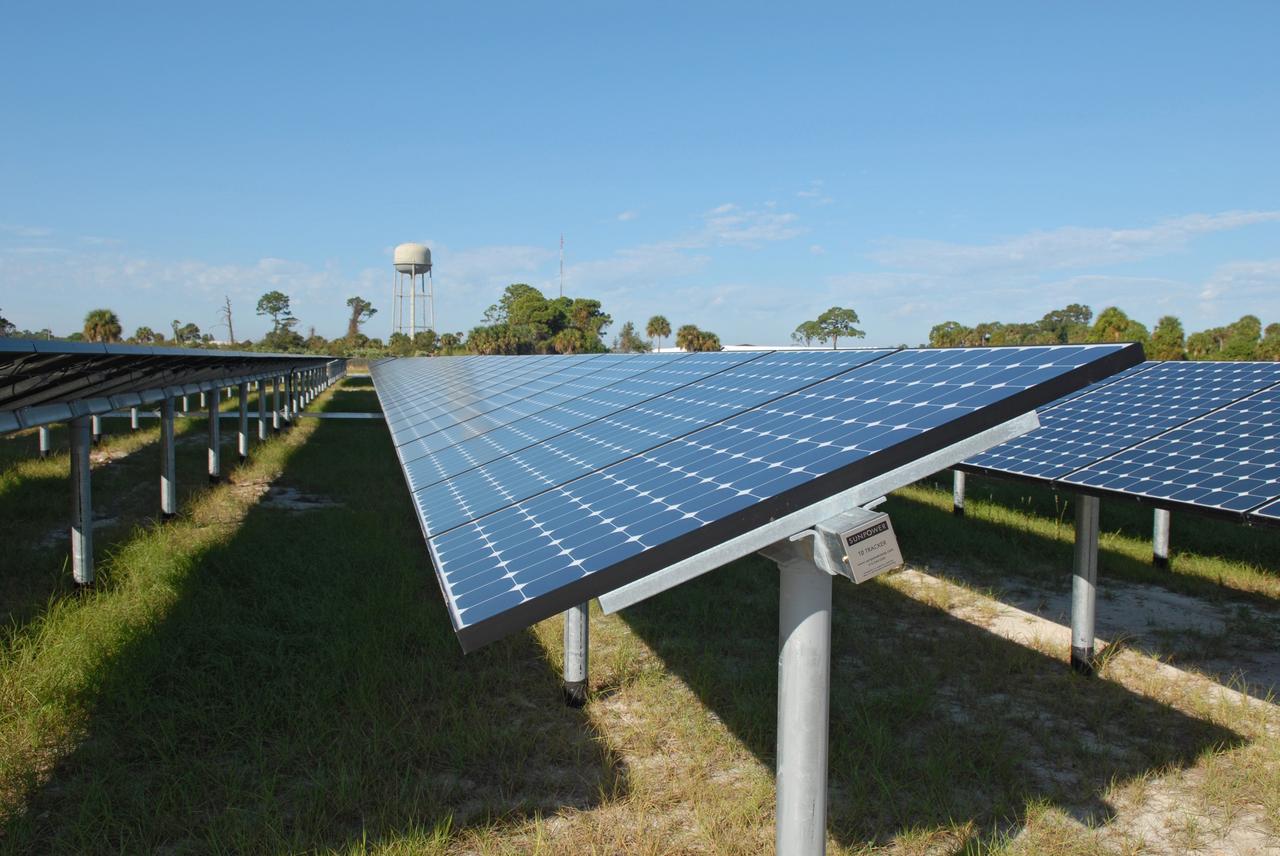

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's first large-scale solar power generation facility is unveiled at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Representatives from NASA, Florida Power & Light Company, or FPL, and SunPower Corporation formally commissioned the one-megawatt facility and announced plans to pursue a new research, development and demonstration project at Kennedy to advance America's use of renewable energy. The facility is the first element of a major renewable energy project currently under construction at Kennedy. The completed system features a fixed-tilt, ground-mounted solar power system designed and built by SunPower, along with SunPower solar panels. A 10-megawatt solar farm, which SunPower is building on nearby Kennedy property, will supply power to FPL's customers when it is completed in April 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
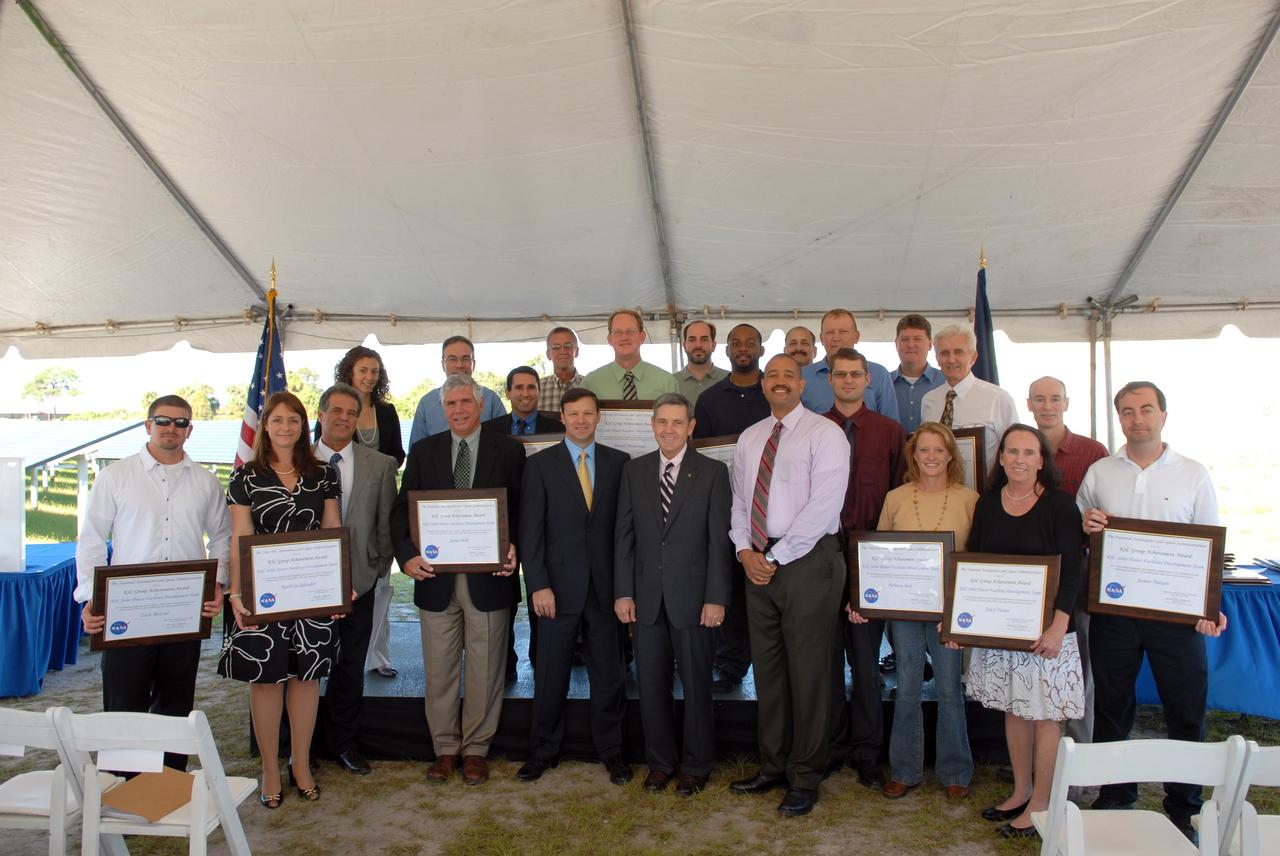

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, recipients of a NASA Team Award for their parts in the successful construction of NASA's first large-scale solar power generation facility pose for a group portrait. Representatives from NASA, Florida Power & Light Company, or FPL, and SunPower Corporation formally commissioned the one-megawatt facility and announced plans to pursue a new research, development and demonstration project at Kennedy to advance America's use of renewable energy. The facility is the first element of a major renewable energy project currently under construction at Kennedy. The completed system features a fixed-tilt, ground-mounted solar power system designed and built by SunPower, along with SunPower solar panels. A 10-megawatt solar farm, which SunPower is building on nearby Kennedy property, will supply power to FPL's customers when it is completed in April 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
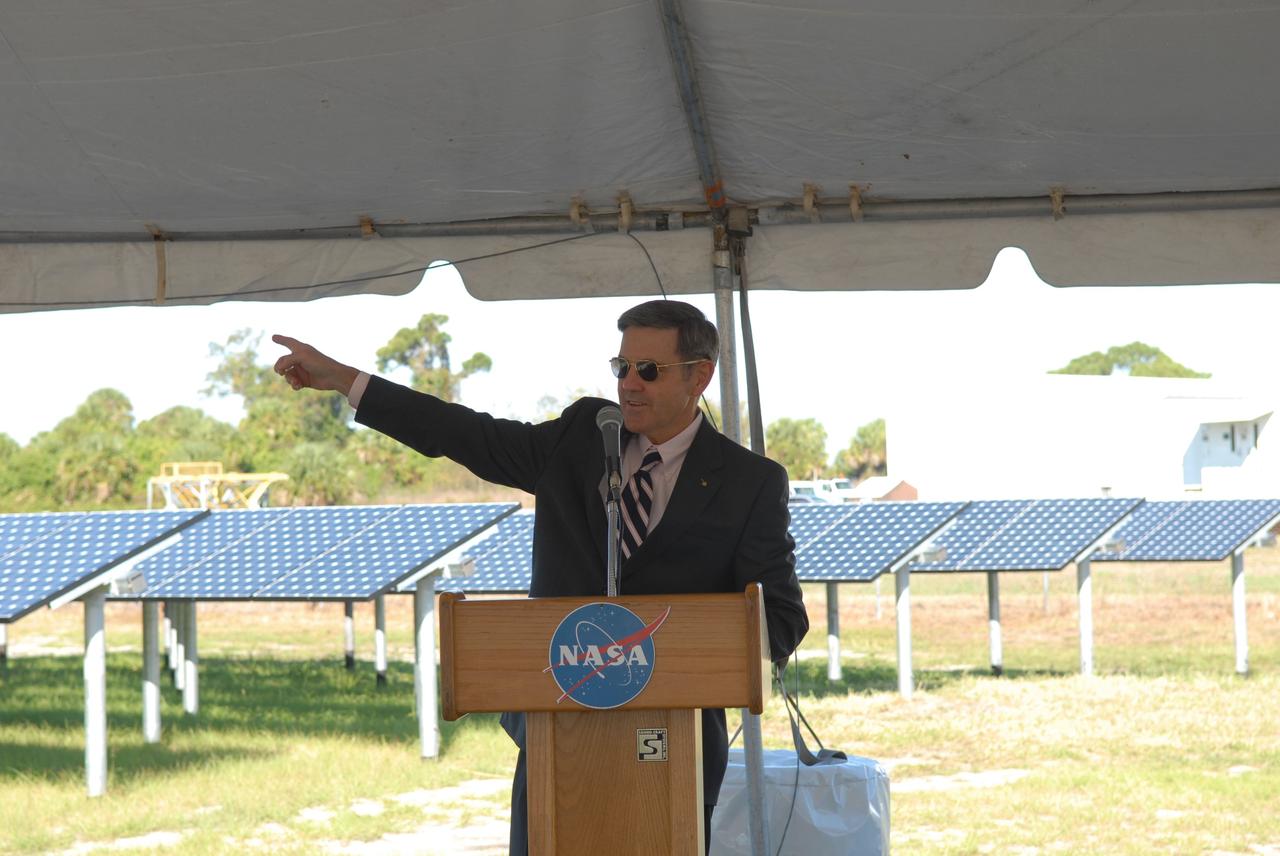

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana addresses the audience on hand for the unveiling of NASA's first large-scale solar power generation facility at Kennedy in Florida. Representatives from NASA, Florida Power & Light Company, or FPL, and SunPower Corporation formally commissioned the one-megawatt facility and announced plans to pursue a new research, development and demonstration project at Kennedy to advance America's use of renewable energy. The facility is the first element of a major renewable energy project currently under construction at Kennedy. The completed system features a fixed-tilt, ground-mounted solar power system designed and built by SunPower, along with SunPower solar panels. A 10-megawatt solar farm, which SunPower is building on nearby Kennedy property, will supply power to FPL's customers when it is completed in April 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
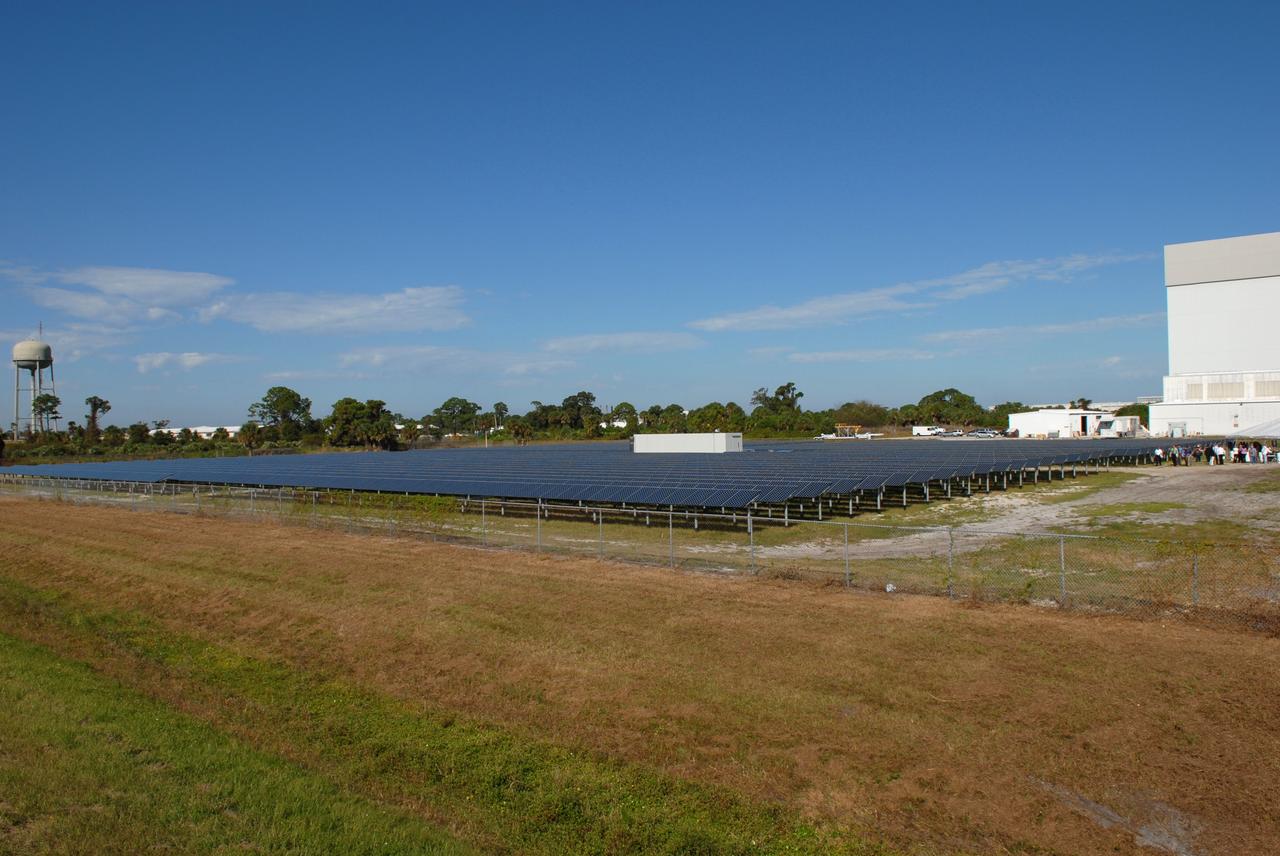

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's first large-scale solar power generation facility is ready for operation at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Representatives from NASA, Florida Power & Light Company, or FPL, and SunPower Corporation formally commissioned the one-megawatt facility and announced plans to pursue a new research, development and demonstration project at Kennedy to advance America's use of renewable energy. The facility is the first element of a major renewable energy project currently under construction at Kennedy. The completed system features a fixed-tilt, ground-mounted solar power system designed and built by SunPower, along with SunPower solar panels. A 10-megawatt solar farm, which SunPower is building on nearby Kennedy property, will supply power to FPL's customers when it is completed in April 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
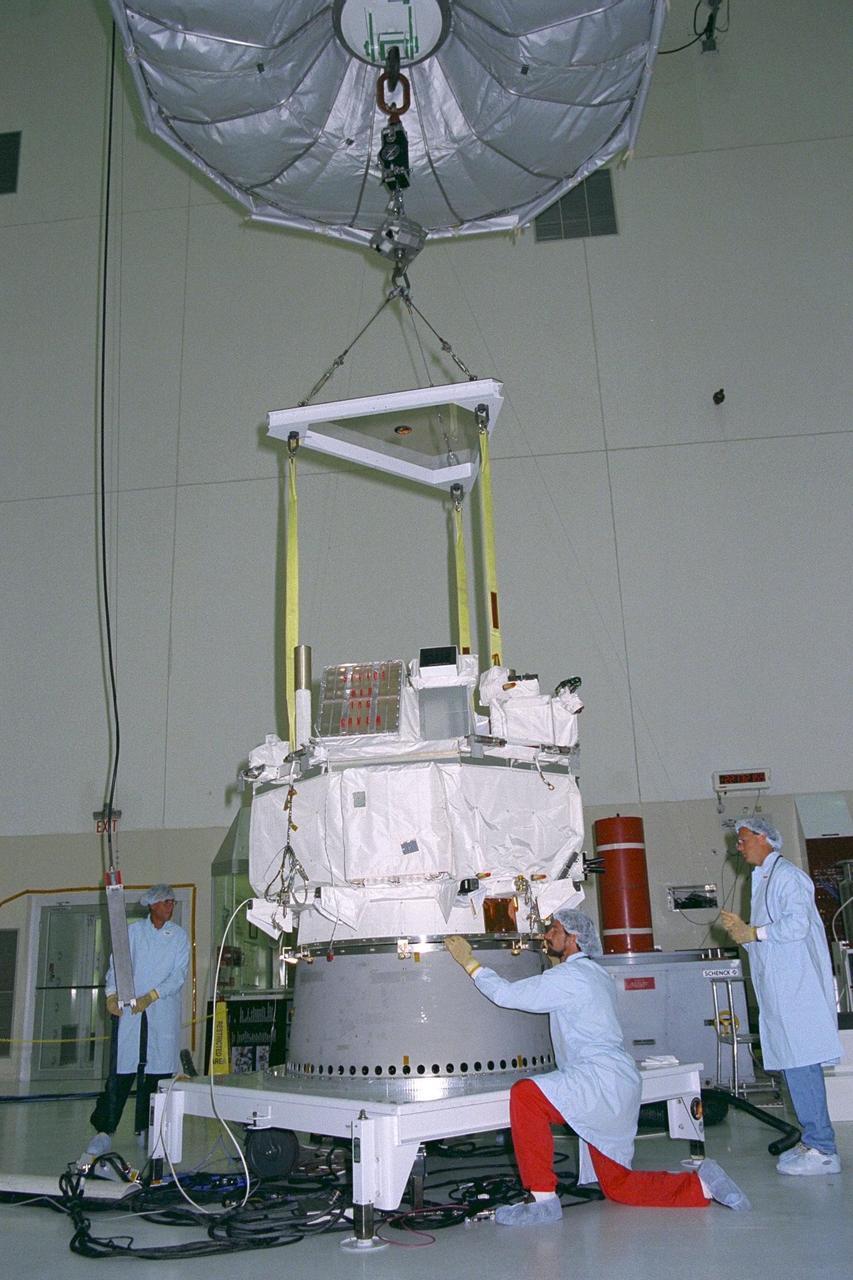

Applied Physics Laboratory engineers and technicians from Johns Hopkins University assist in leveling and orienting the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) as it is seated on a platform for solar array installation in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-II. Scheduled for launch on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Station on Aug. 25, ACE will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles. The ACE observatory has six high-resolution particle detection sensors and three monitoring instruments. The collecting power of instrumentation aboard ACE is at least 100 times more sensitive than anything previously flown to collect similar data by NASA
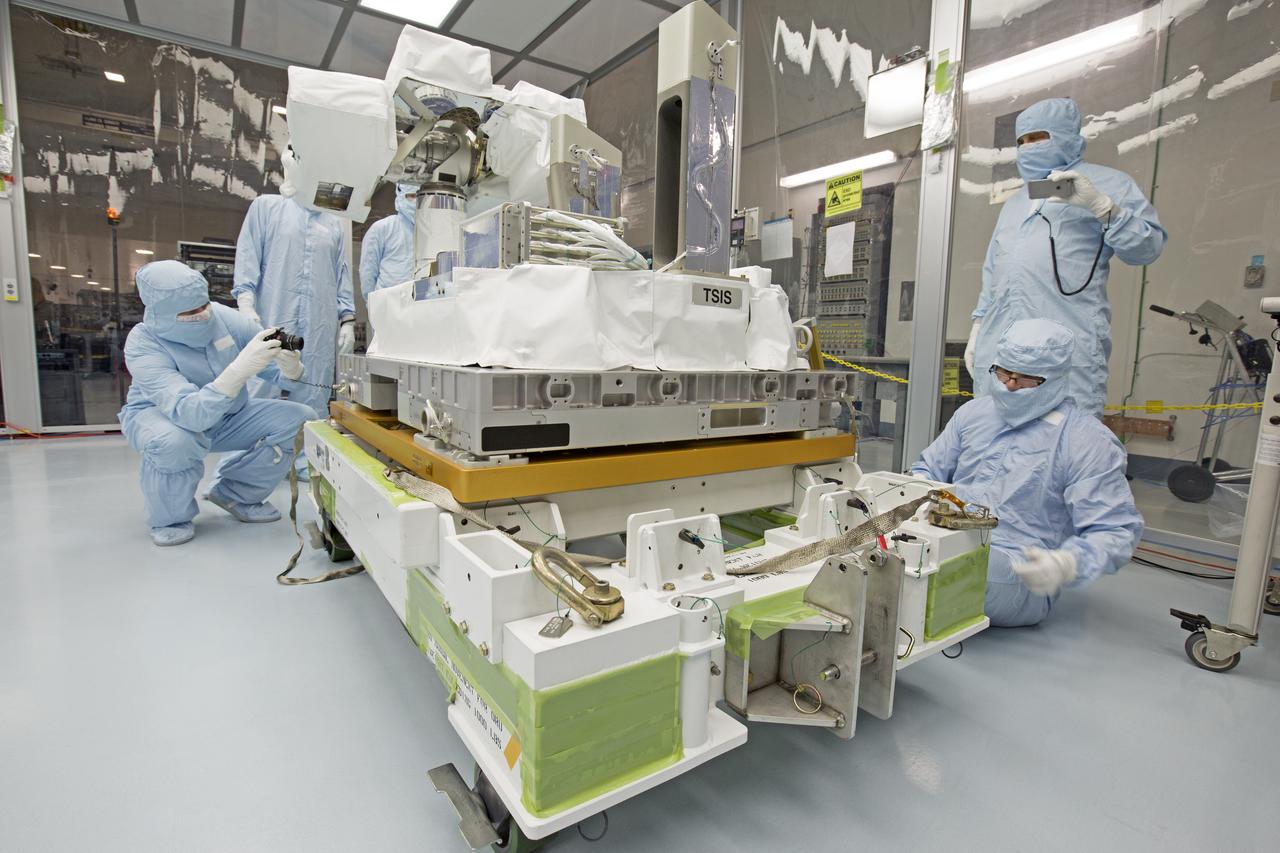

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle, left, of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies, and other payload team members performs spacewalk tool fit-checks of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.
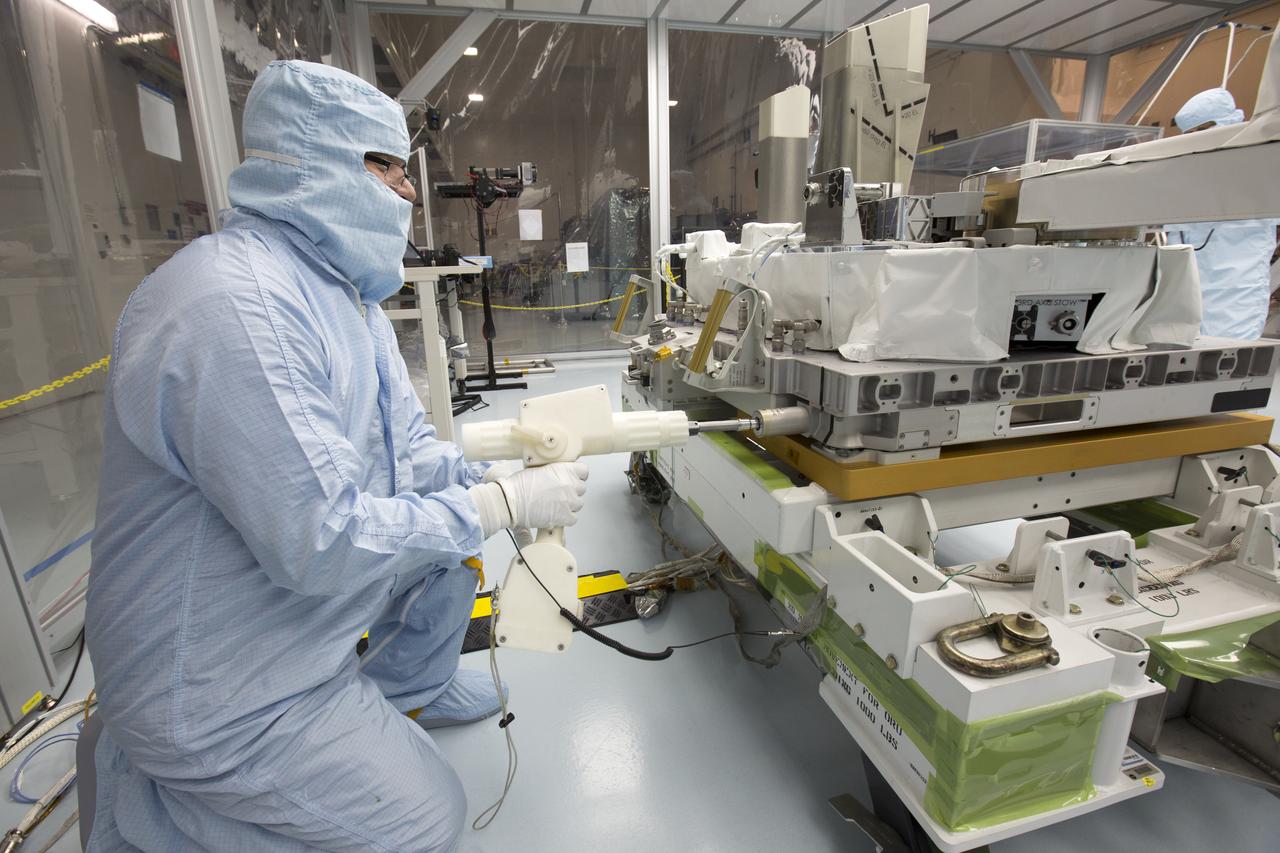

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies performs spacewalk tool fit-checks of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.
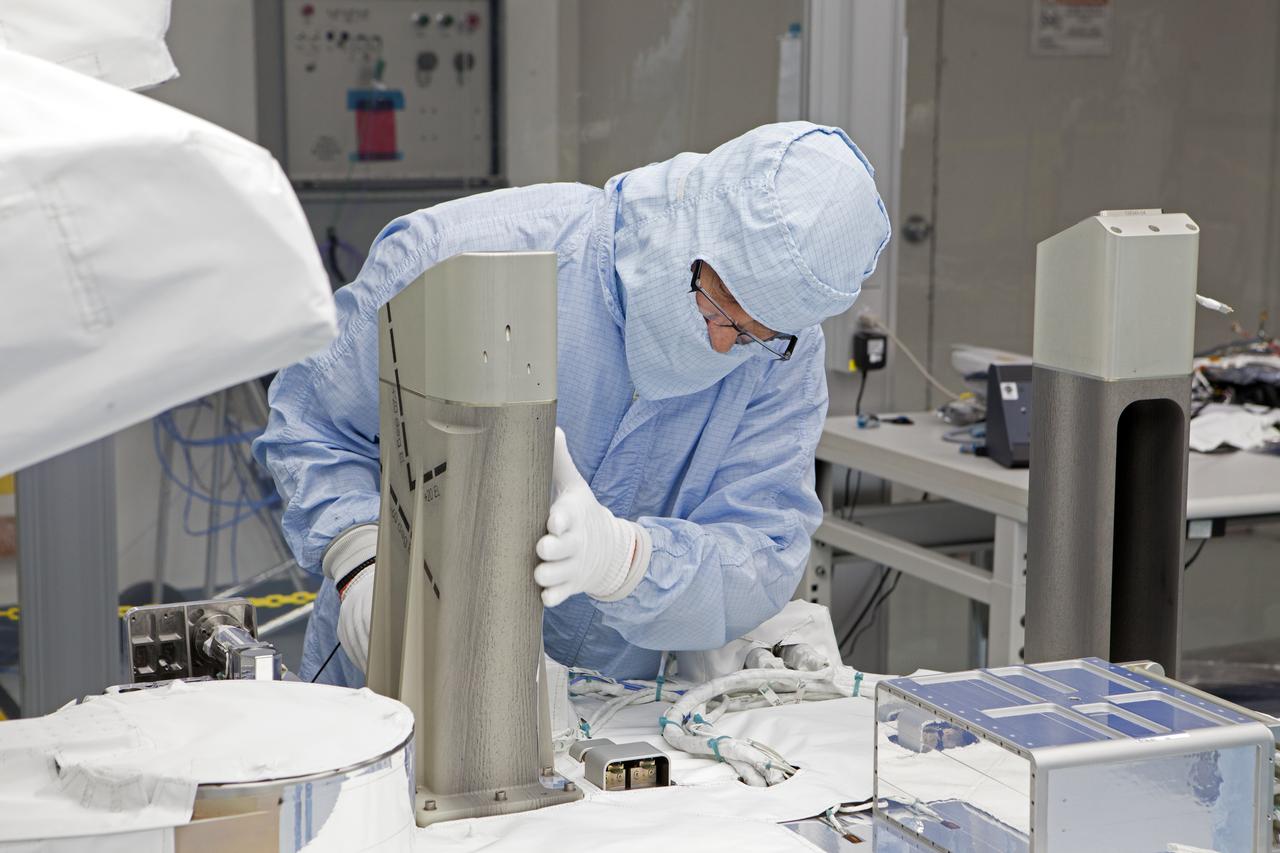

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies performs a sharp edge inspection of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.
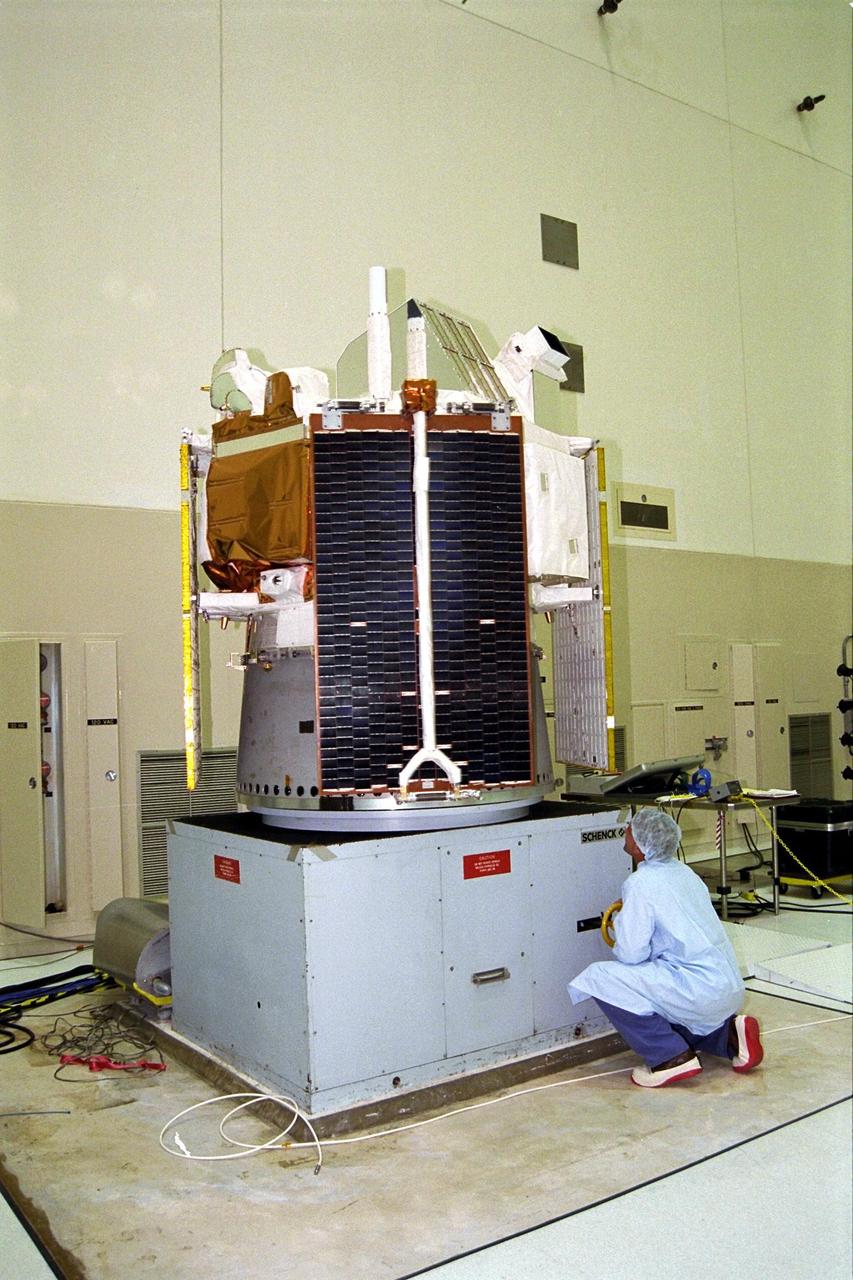

The Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) spacecraft undergoes a spin test in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-II (SAEF-II). Scheduled for launch on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Station on Aug. 25, ACE will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles. The collecting power of instruments aboard ACE is 10 to 1,000 times greater than anything previously flown to collect similar data by NASA
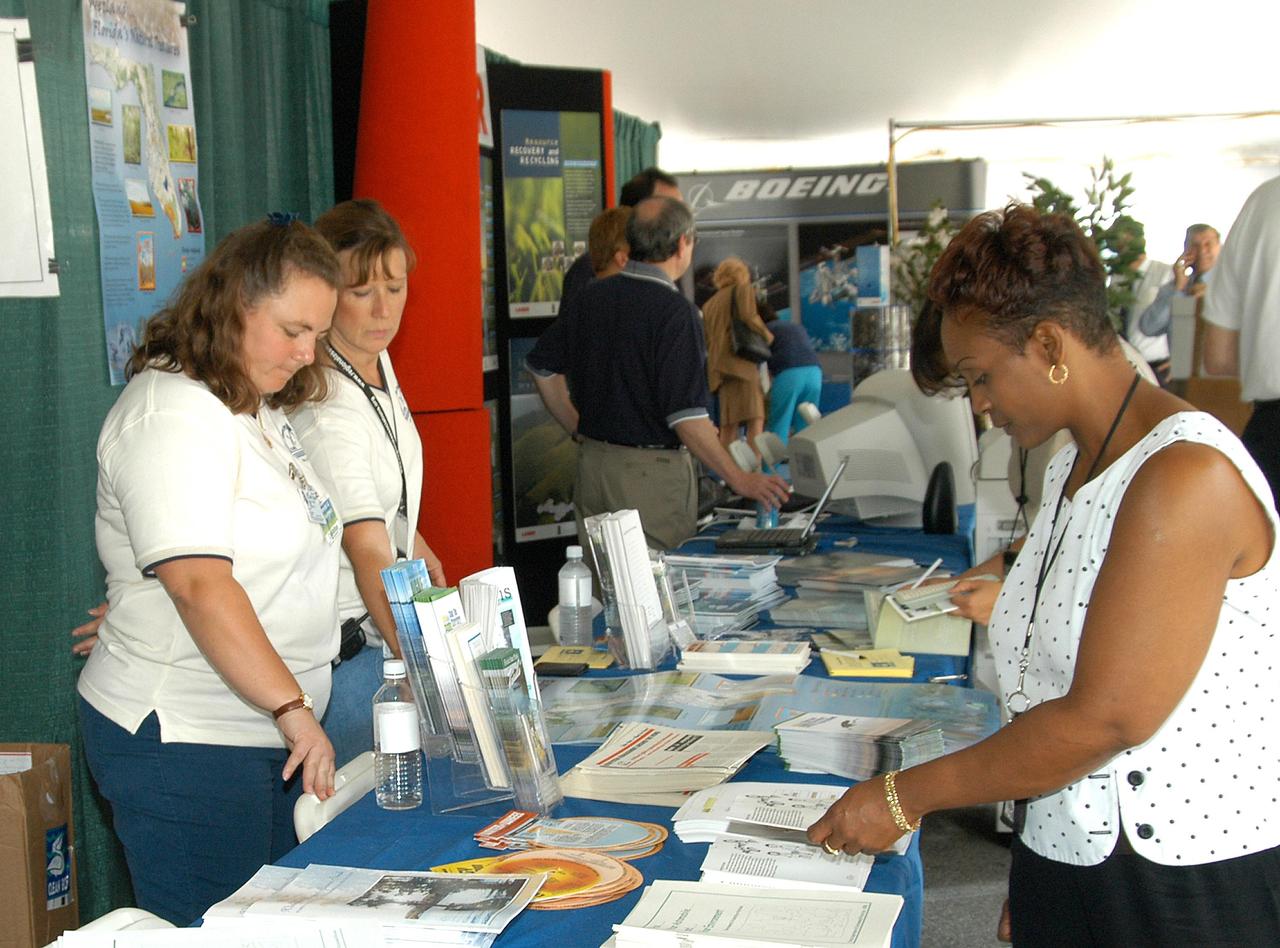

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - KSC employees stop at display tables set up in a tent near the Operations and Checkout Building for KSC’s annual Environmental and Energy Awareness Week, held April 20-22. The slogan for this year’s event was “Today's Conservation Defines Tomorrow's Future.” Presentations included Chemistry Safety, Cost-Effective Solar Applications, Non-Native Invasive Plant Identification and Control, Energy Efficient Lighting Systems, and Historical Changes in KSC’s Ecosystems.
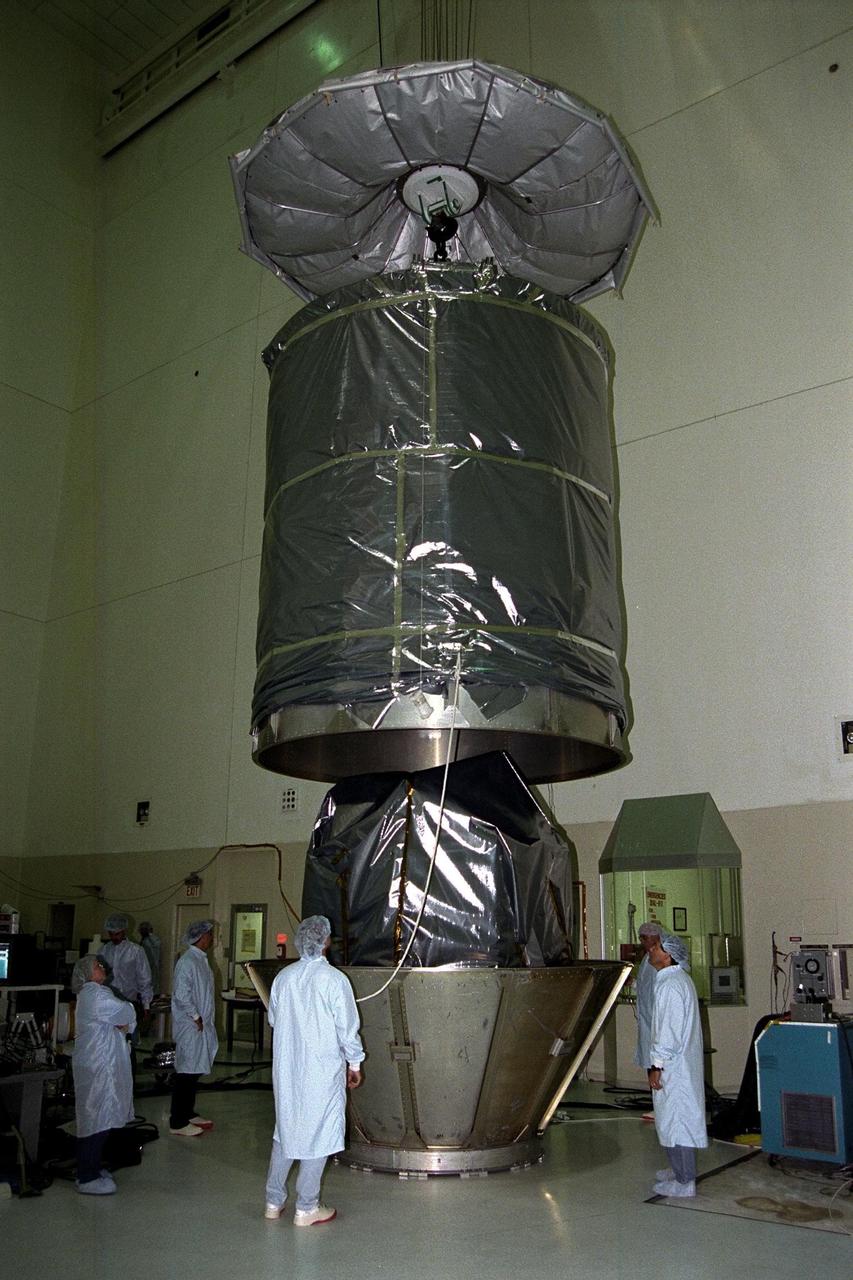

In KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-II (SAEF-II), the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) spacecraft is encapsulated and placed into the transporter which will move it to Launch Complex 17A. Scheduled for launch on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Station on Aug. 24, ACE will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles. The collecting power of instruments aboard ACE is 10 to 1,000 times greater than anything previously flown to collect similar data by NASA
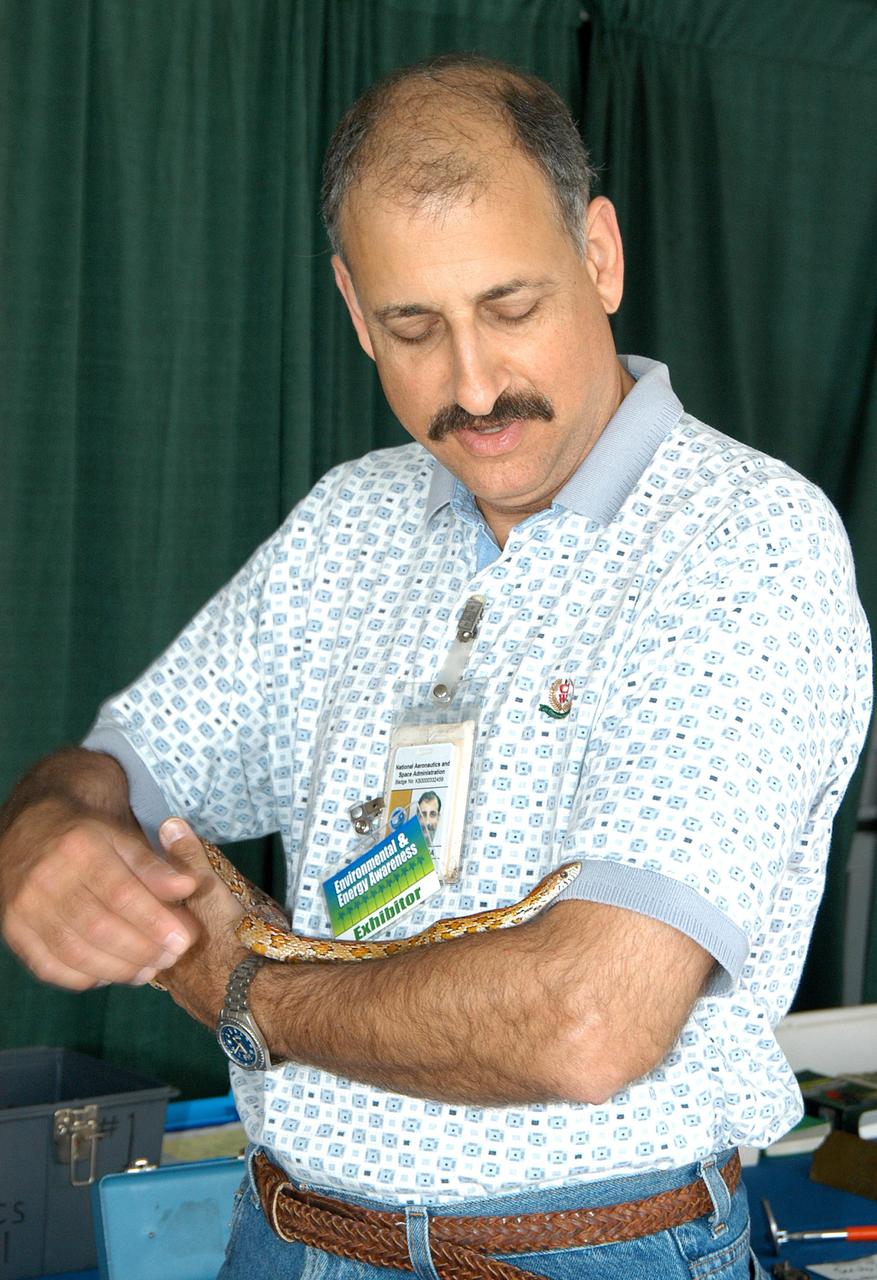
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Mario Busacca, with the Safety, Occupational Health and Environmental Division, handles a snake at one of the exhibits for KSC’s annual Environmental and Energy Awareness Week, held April 20-22. Presentations included Chemistry Safety, Cost-Effective Solar Applications, Non-Native Invasive Plant Identification and Control, Energy Efficient Lighting Systems, and Historical Changes in KSC’s Ecosystems. The slogan for this year’s event was “Today's Conservation Defines Tomorrow's Future.”
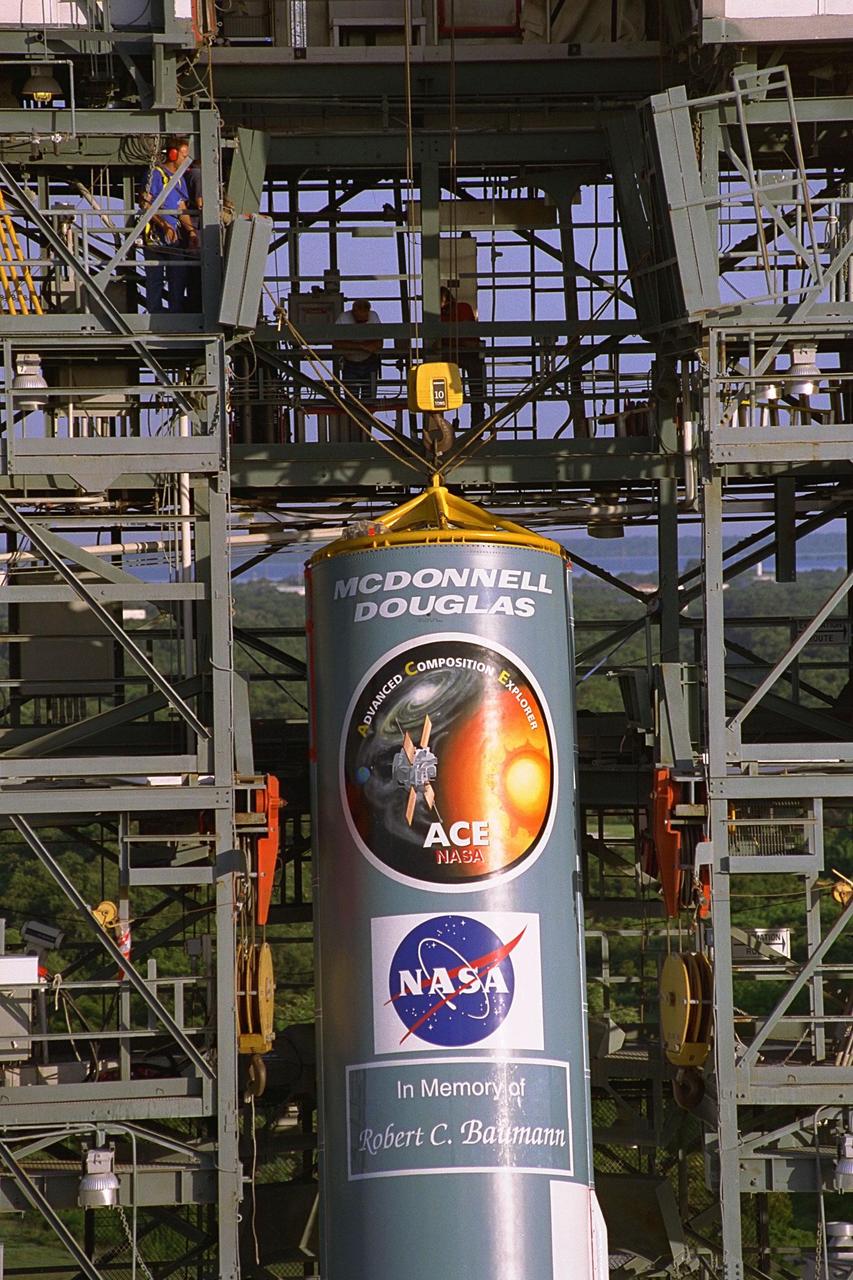

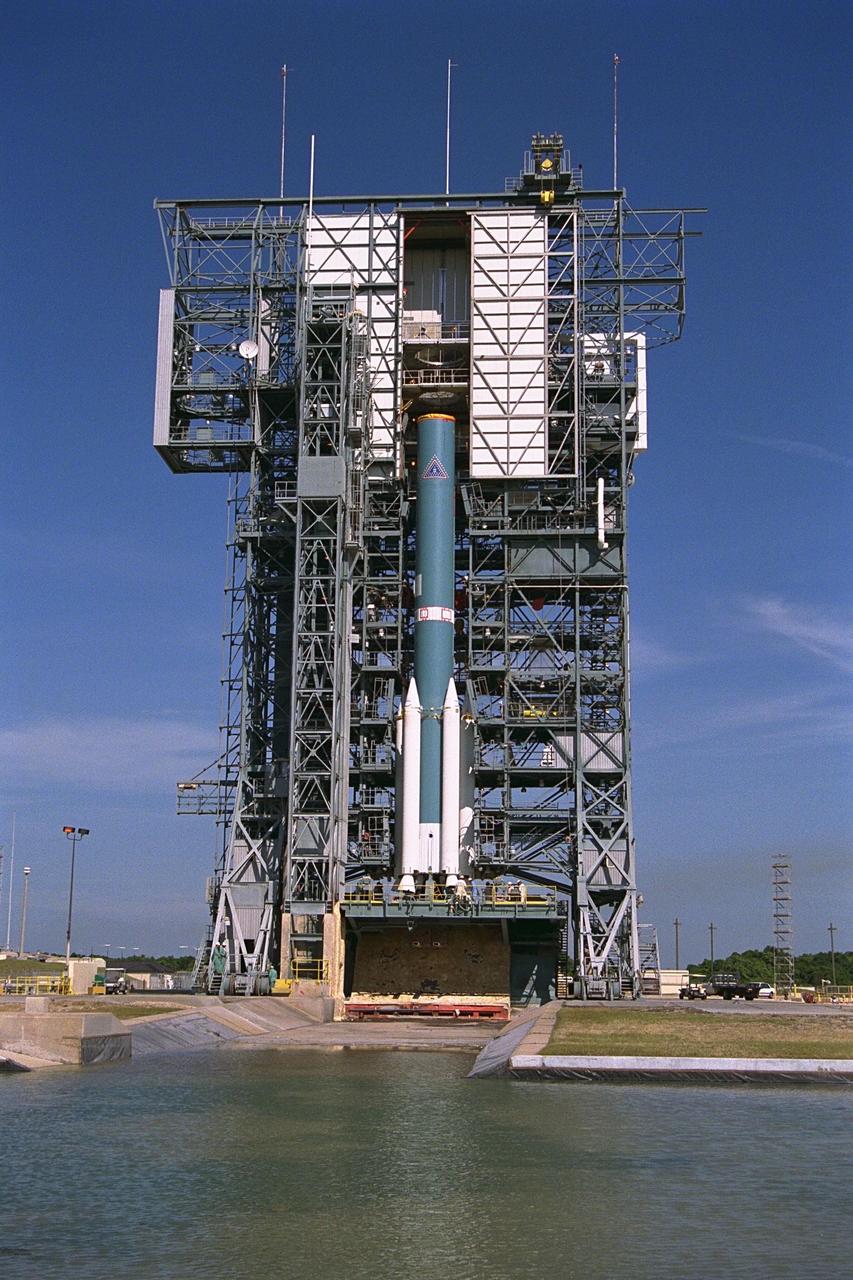
The first stage of the Delta II rocket which will to be used to launch the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) spacecraft is erected at Launch Complex 17A at Cape Canaveral Air Station. Scheduled for launch on Aug. 25, ACE will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles. The ACE observatory will be placed into an orbit almost a million miles (1.5 million kilometers) away from the Earth, about 1/100 the distance from the Earth to the Sun

The solid rocket motors of the Delta II rocket which will to be used to launch the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) spacecraft are erected at Launch Complex 17A at Cape Canaveral Air Station. Scheduled for launch on Aug. 25, ACE will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles. The ACE observatory will be placed into an orbit almost a million miles (1.5 million kilometers) away from the Earth, about 1/100 the distance from the Earth to the Sun
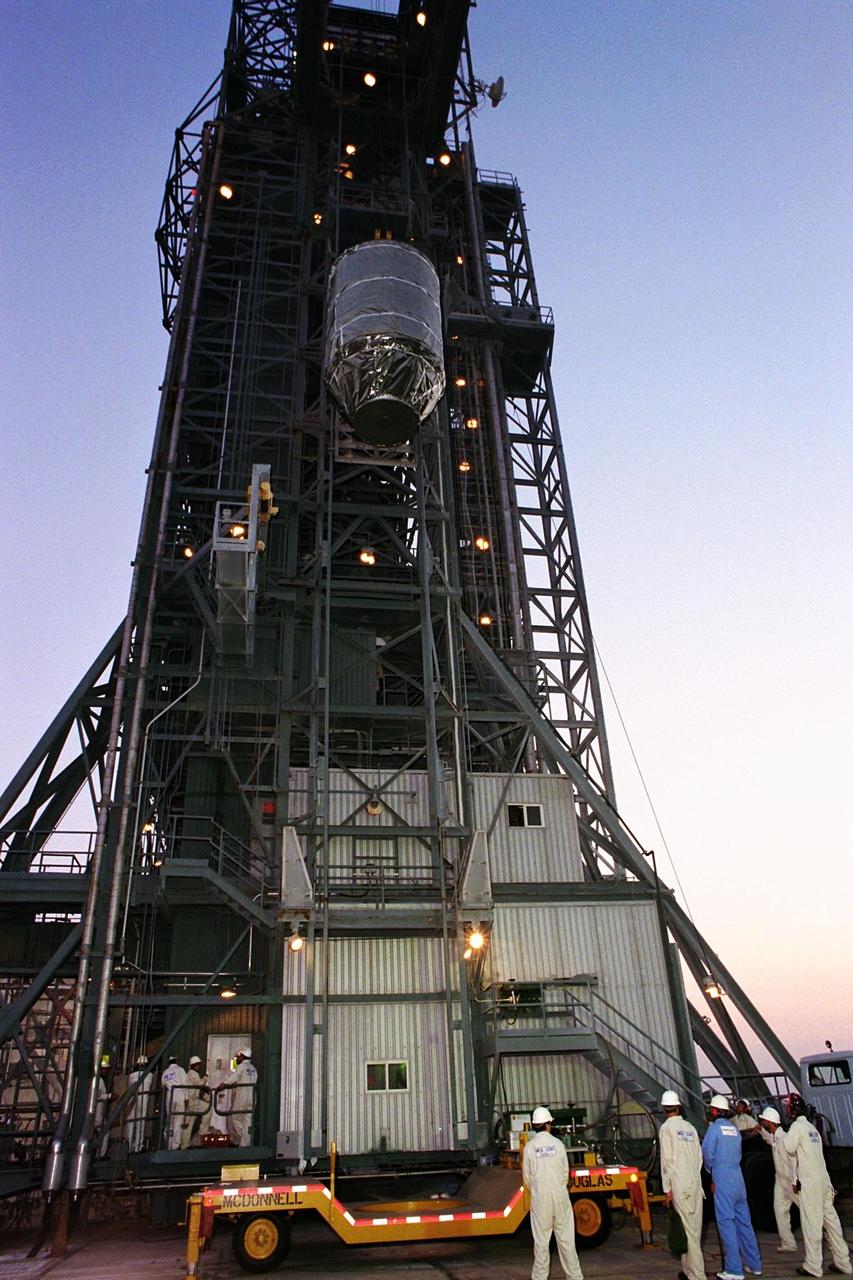

The Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) spacecraft is placed atop its launch vehicle at Launch Complex 17A. Scheduled for launch on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Station on Aug. 24, ACE will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles. The collecting power of instruments aboard ACE is 10 to 1,000 times greater than anything previously flown to collect similar data by NASA
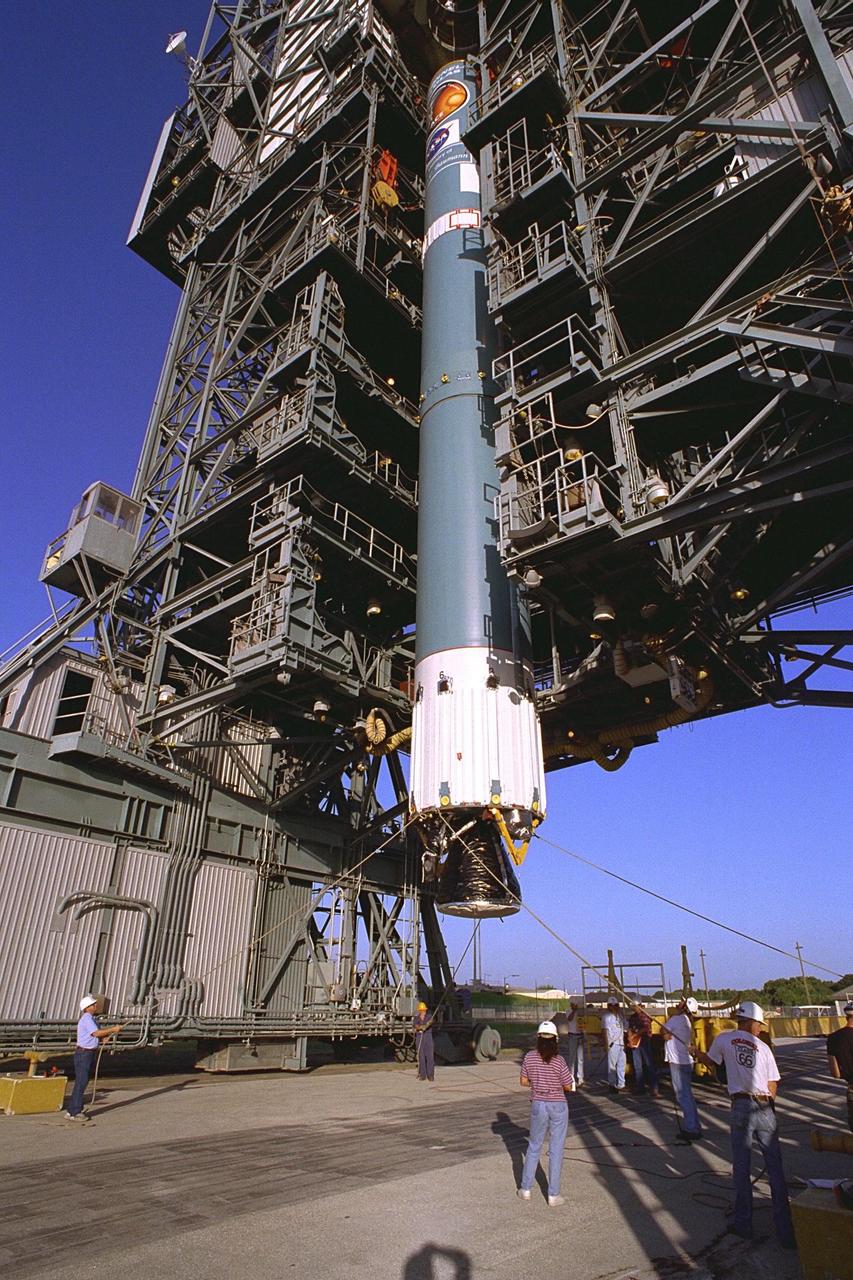

The first stage of the Delta II rocket which will to be used to launch the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) spacecraft is erected at Launch Complex 17A at Cape Canaveral Air Station. Scheduled for launch on Aug. 25, ACE will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles. The ACE observatory will be placed into an orbit almost a million miles (1.5 million kilometers) away from the Earth, about 1/100 the distance from the Earth to the Sun
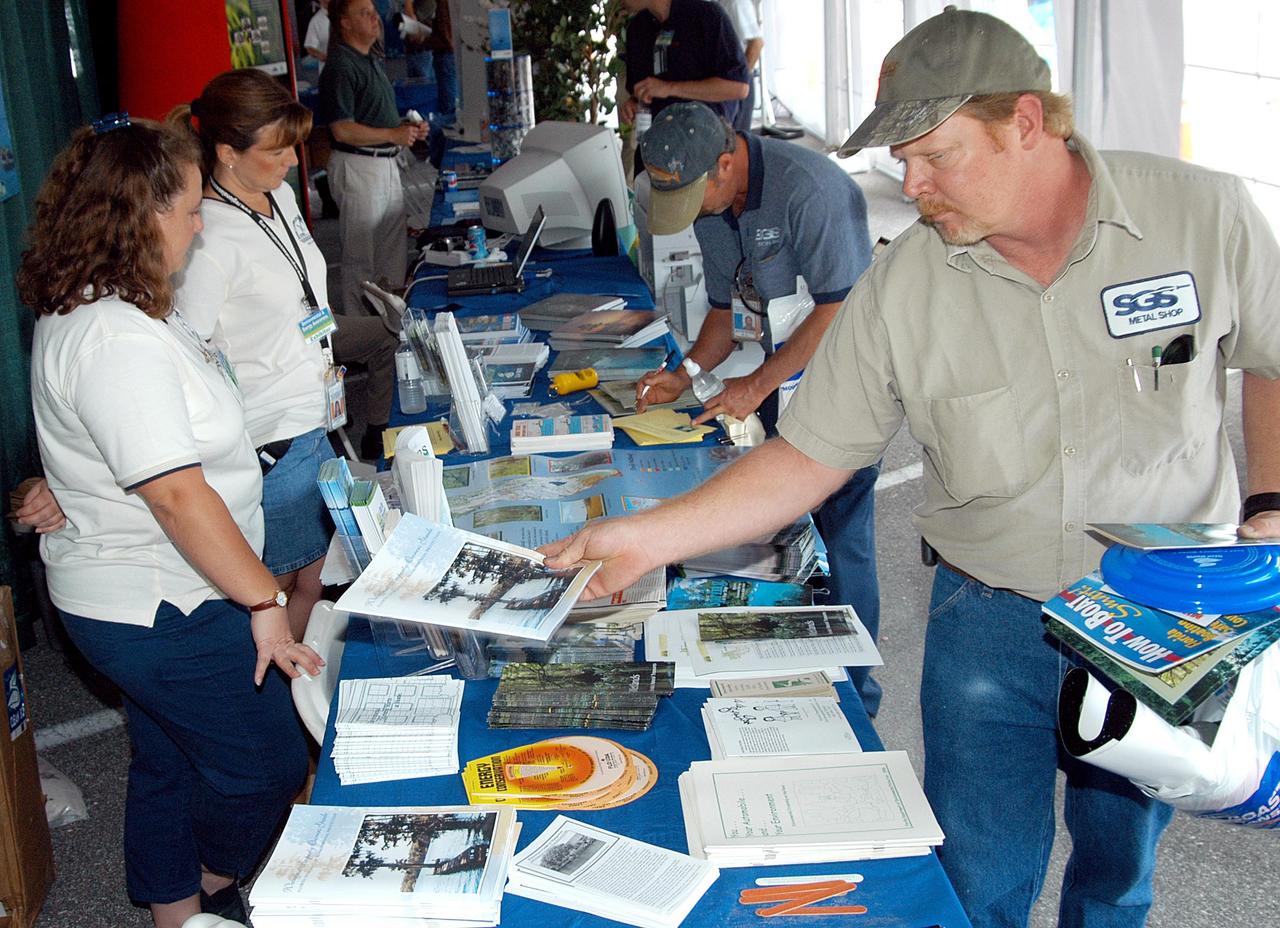

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - KSC employees stop at display tables set up in a tent near the Operations and Checkout Building for KSC’s annual Environmental and Energy Awareness Week, held April 20-22. The slogan for this year’s event was “Today's Conservation Defines Tomorrow's Future.” Presentations included Chemistry Safety, Cost-Effective Solar Applications, Non-Native Invasive Plant Identification and Control, Energy Efficient Lighting Systems, and Historical Changes in KSC’s Ecosystems.