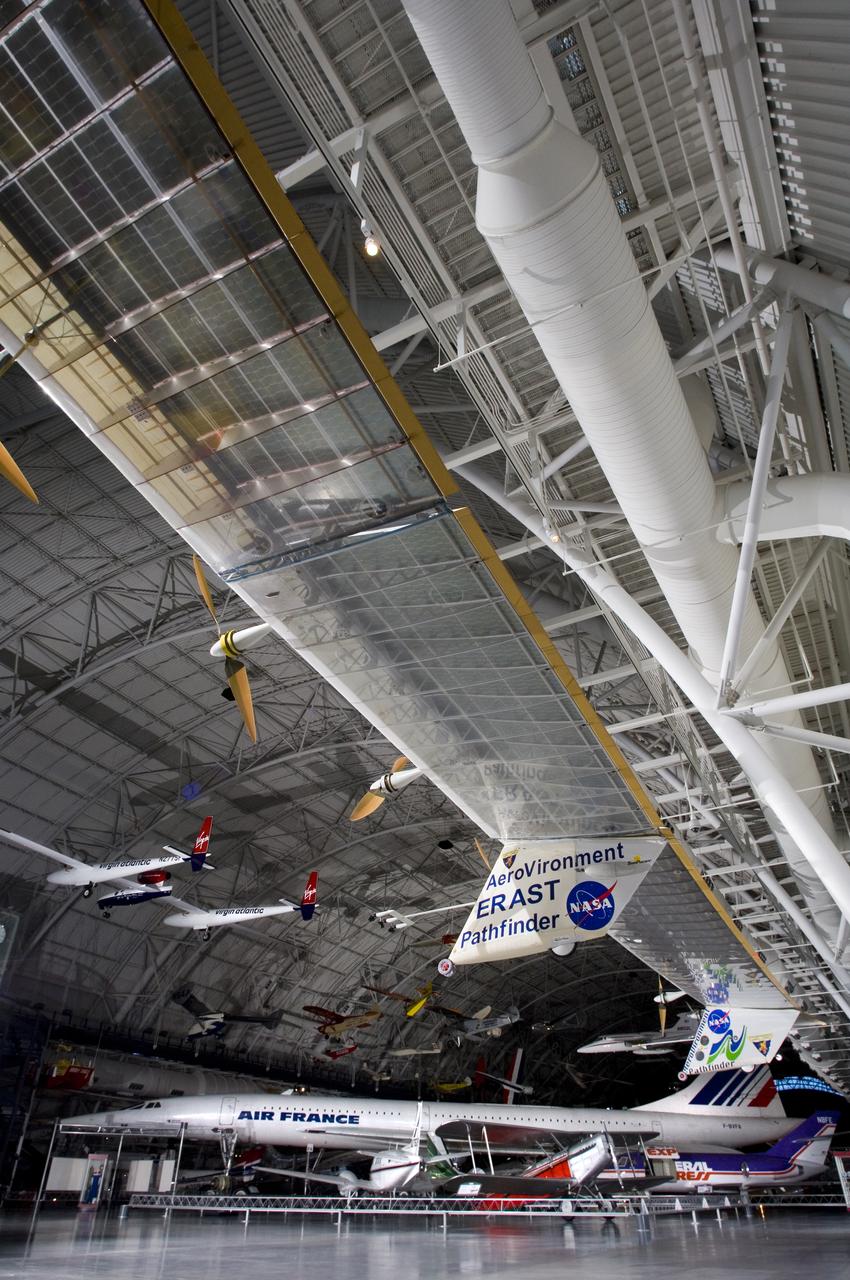

The record-setting AeroVironment/NASA Pathfinder-Plus solar-electric flying wing is enshrined in the National Air & Space Museum's Udvar-Hazy Center in Virginia.
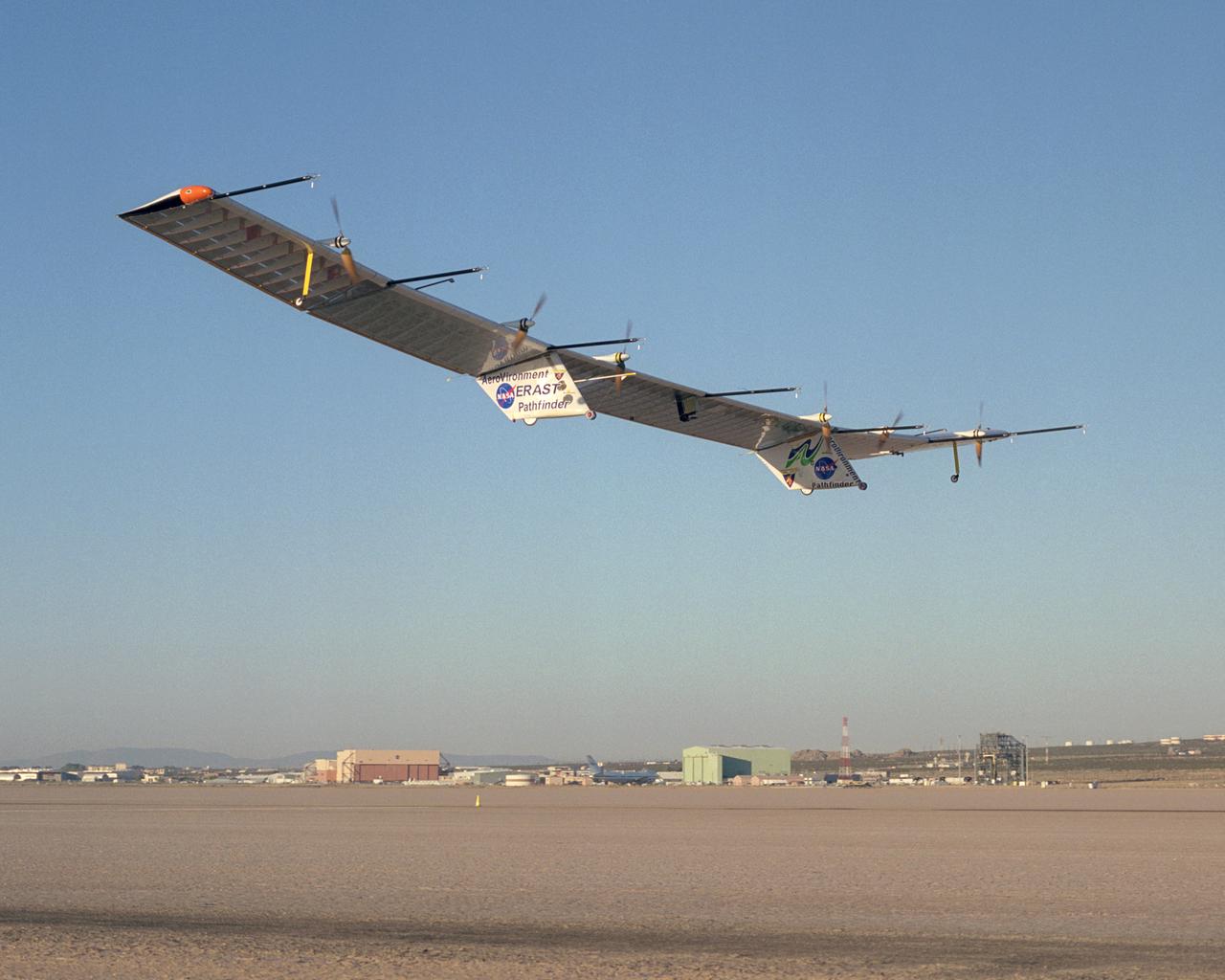

The Pathfinder-Plus solar-electric flying wing lifts off Rogers Dry Lake adjoining NASA Dryden Flight Research Center on a turbulence-measurement flight.
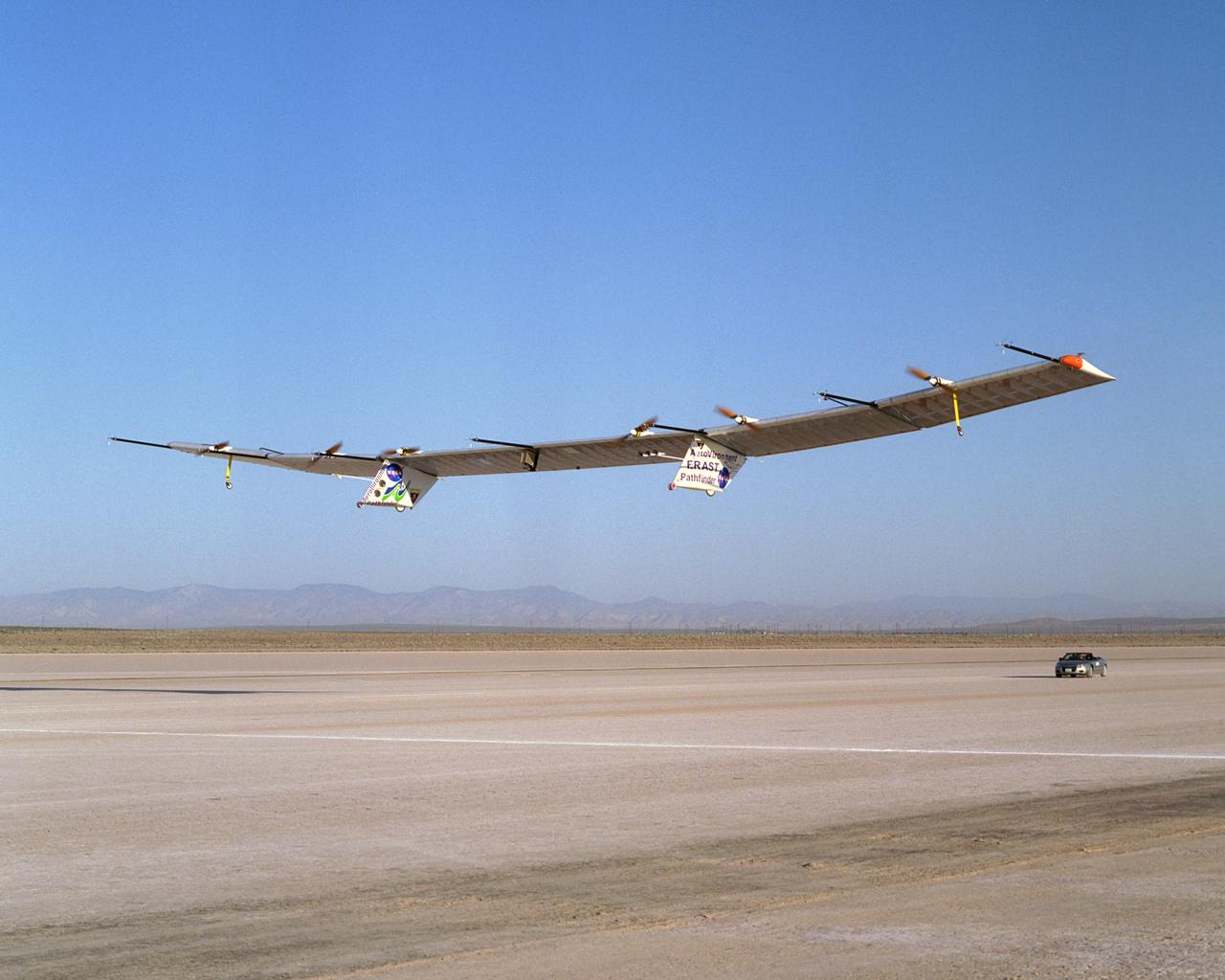

The Pathfinder-Plus solar-electric flying wing lifts off Rogers Dry Lake adjoining NASA Dryden Flight Research Center on a turbulence-measurement flight.
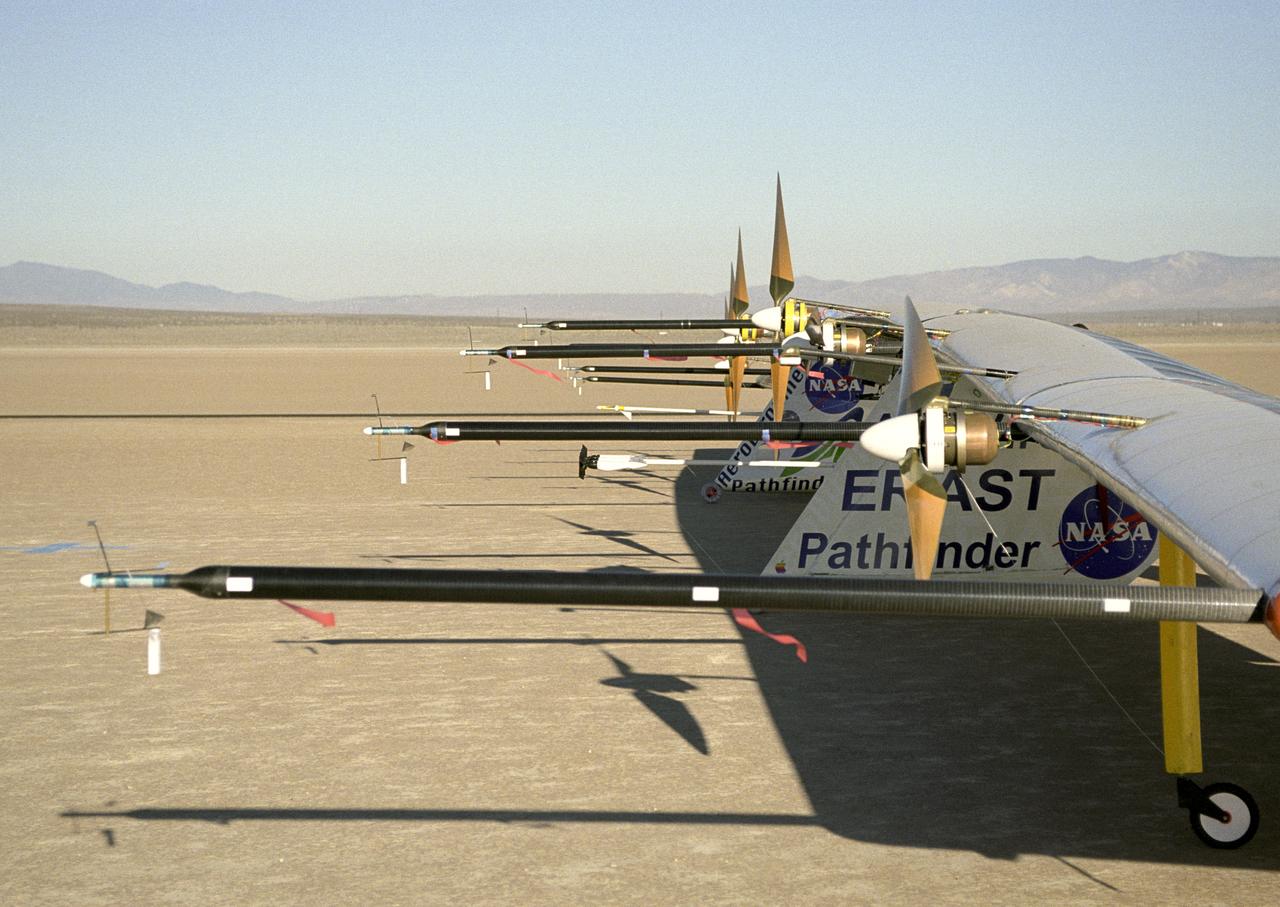

Sensitive instruments mounted on booms extending forward of the wing measure air turbulence and its effect on the stability of the Pathfinder-Plus solar-electric flying wing.
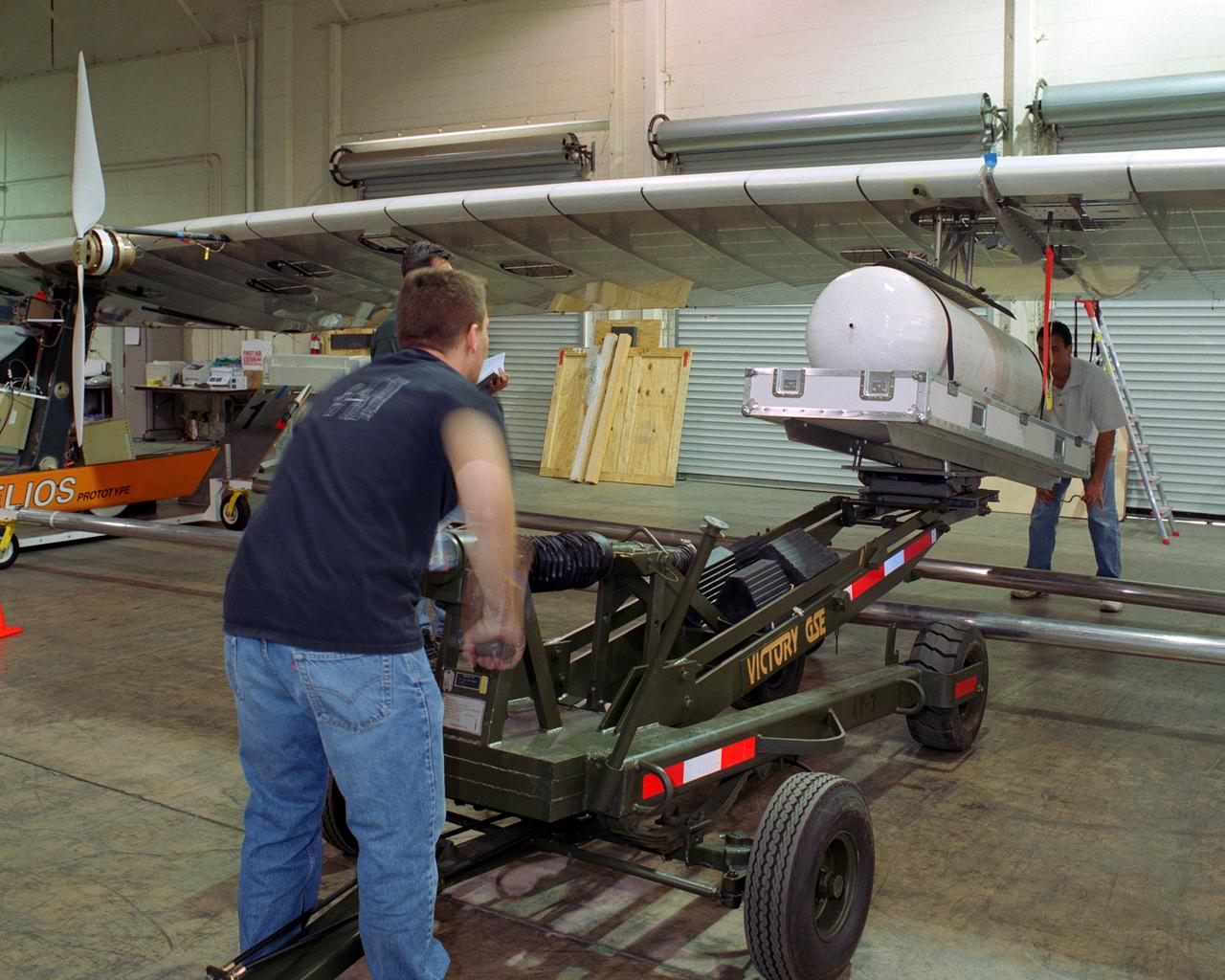

Technicians for AeroVironment, Inc., jack up a pressure tank to the wing of the Helios Prototype solar-electric flying wing. The tank carries pressurized hydrogen to fuel an experimental fuel cell system that powered the aircraft at night during an almost two-day long-endurance flight demonstration in the summer of 2003.
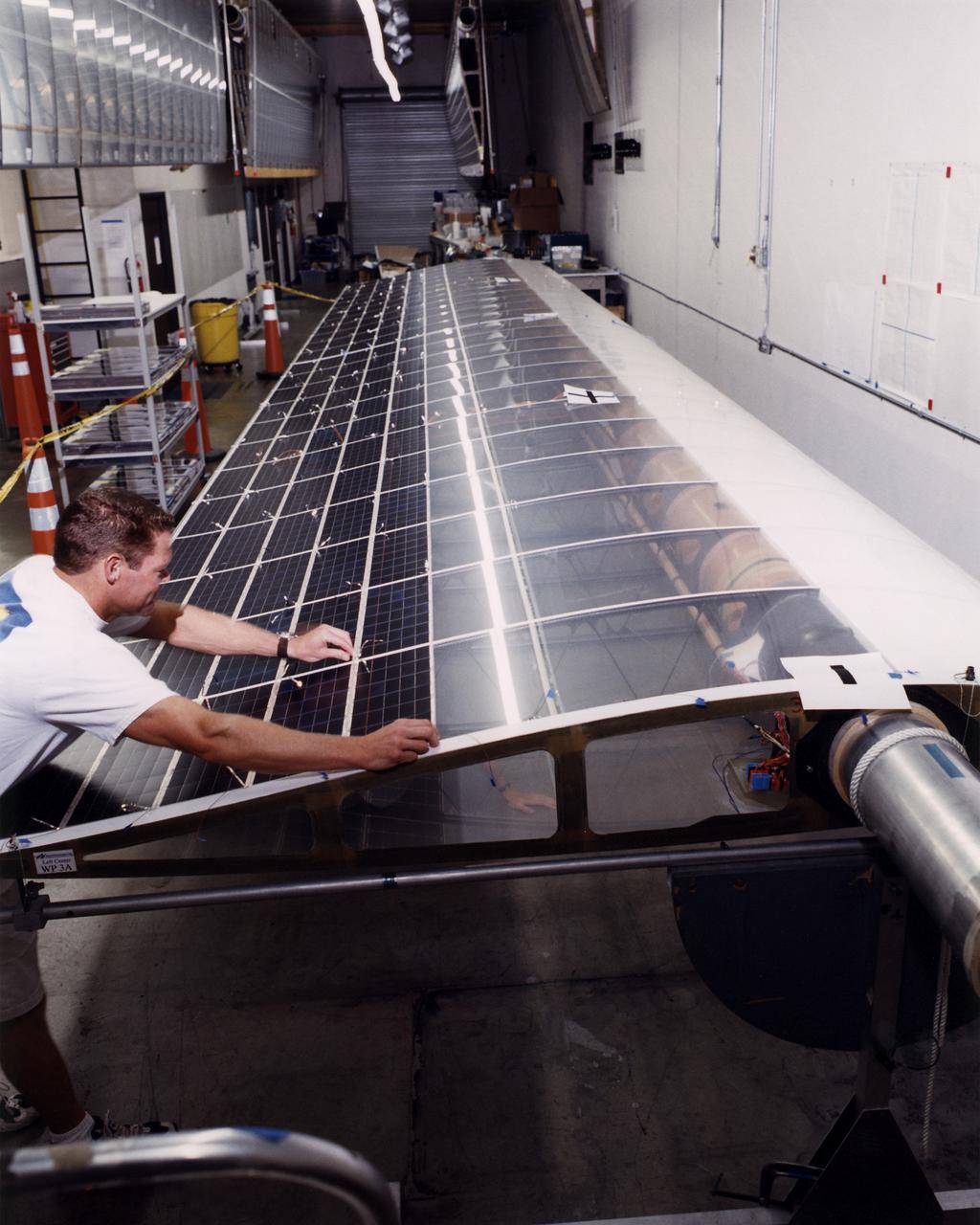

Technician Marshall MacCready carefully lays a panel of solar cells into place on a wing section of the Helios Prototype flying wing at AeroVironment's Design Development Center in Simi Valley, California. The bi-facial cells, manufactured by SunPower, Inc., of Sunnyvale, California, are among 64,000 solar cells which have been installed on the solar-powered aircraft to provide electricity to its 14 motors and operating systems.
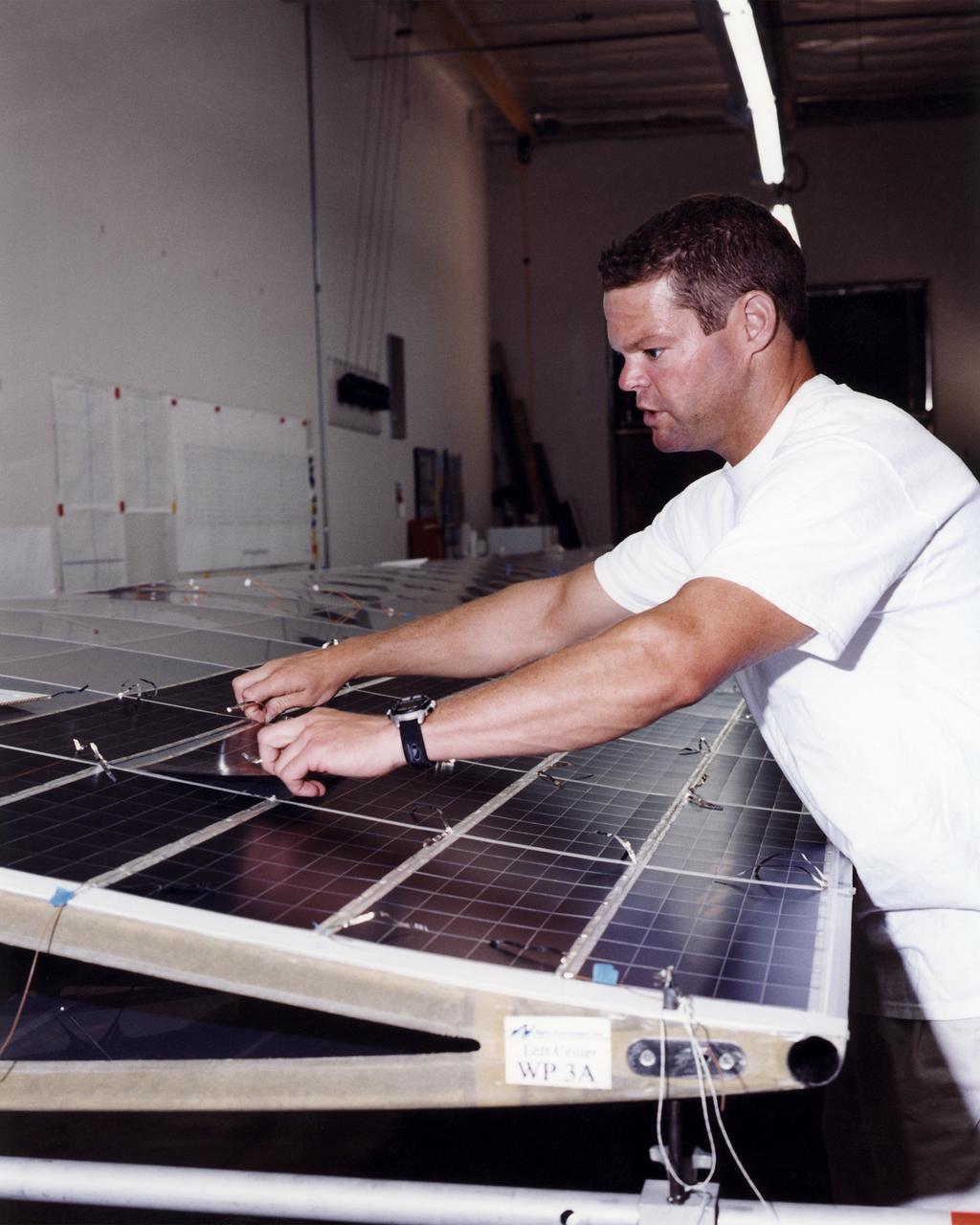

Technician Marshall MacCready carefully lays a panel of solar cells into place on a wing section of the Helios Prototype flying wing at AeroVironment's Design Development Center in Simi Valley, California. More than 1,800 panels containing some 64,000 bi-facial cells, fabricated by SunPower, Inc., of Sunnyvale, California, have been installed on the solar-powered aircraft to provide electricity to its 14 motors and operating systems.
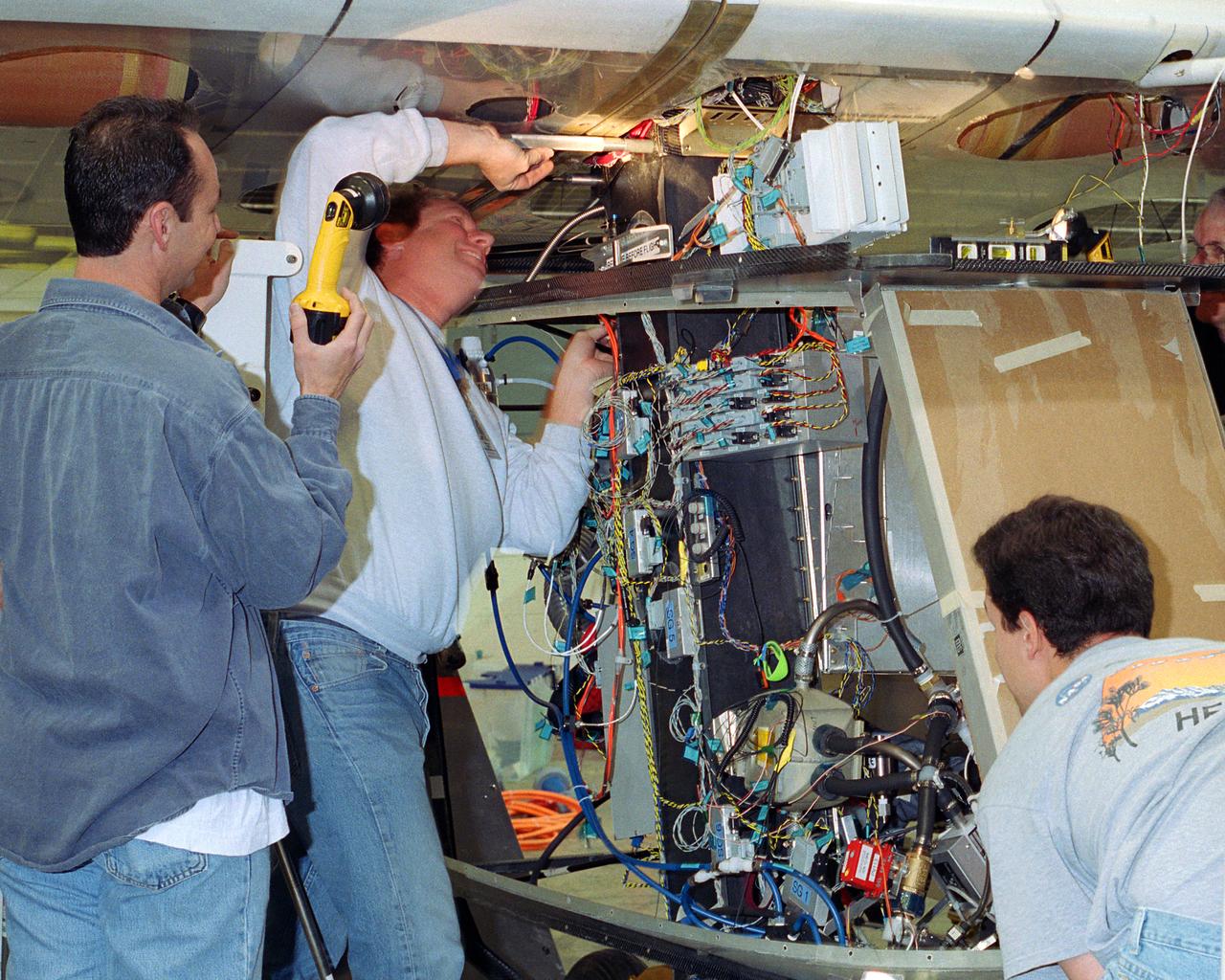

Aerovironment technicians carefully line up attachments as a fuel cell electrical system is installed on the Helios Prototype solar powered flying wing. The fuel cell system will power the aircraft at night during NASA-sponsored long-endurance demonstration flight in the summer of 2003.
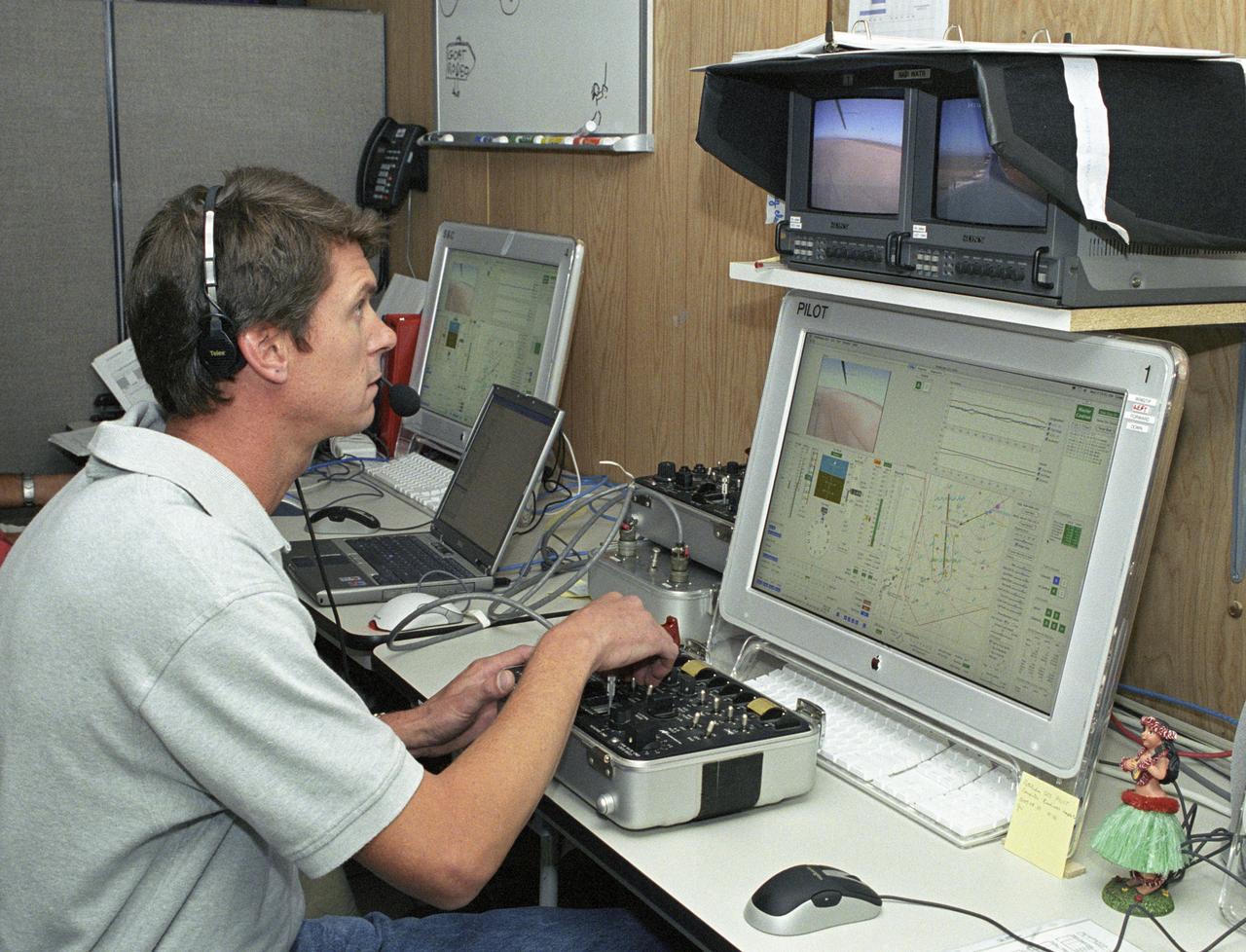

AeroVironment pilot Wyatt Sadler controls the Pathfinder-Plus flying wing from a small console, video and computer monitors in the ground station.
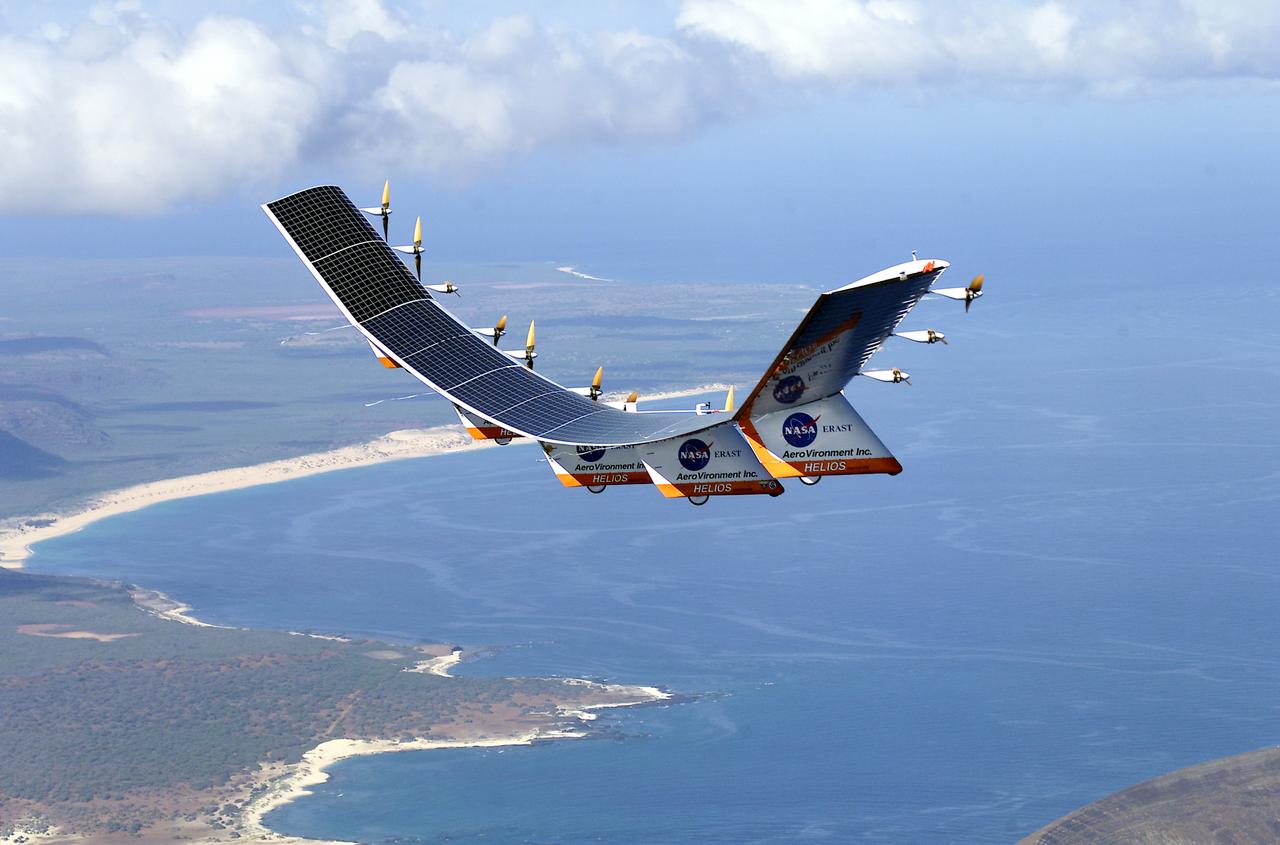

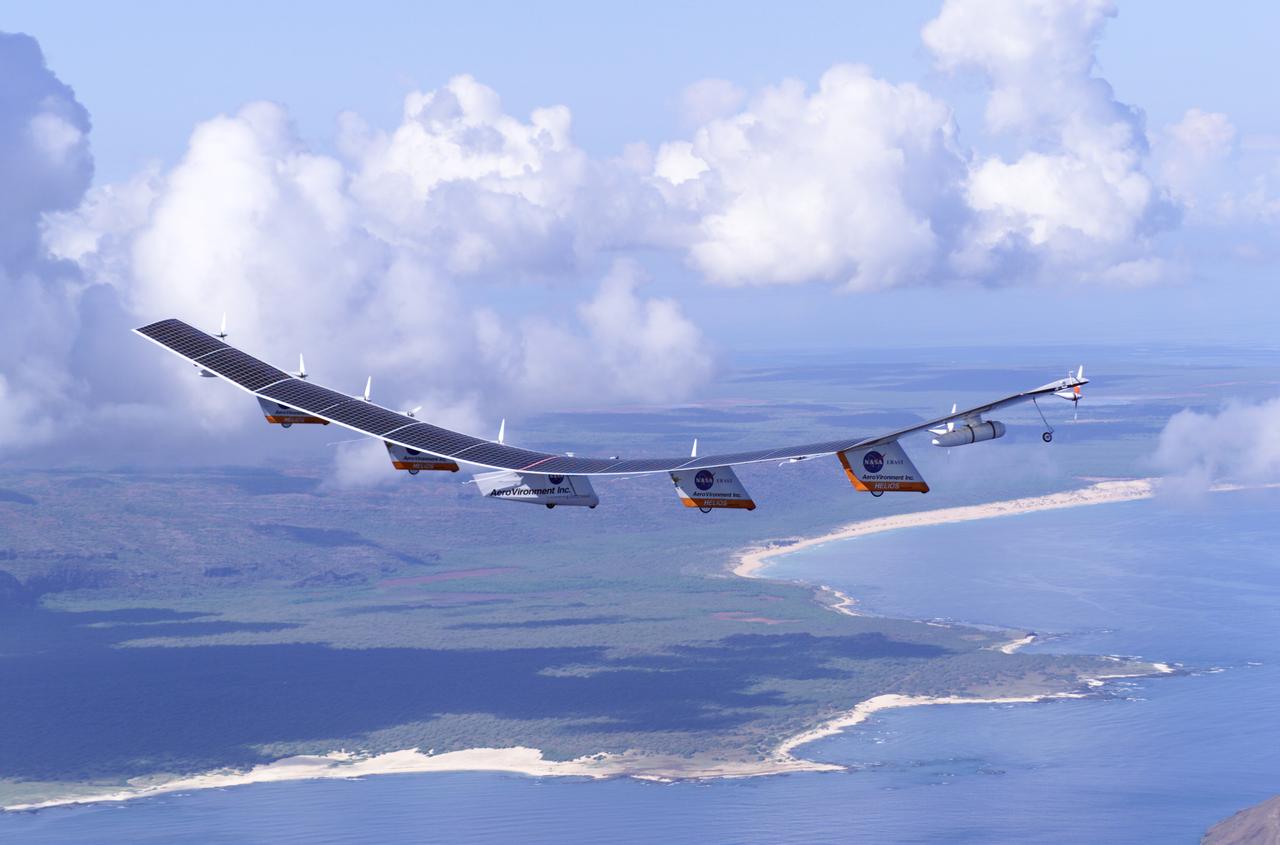
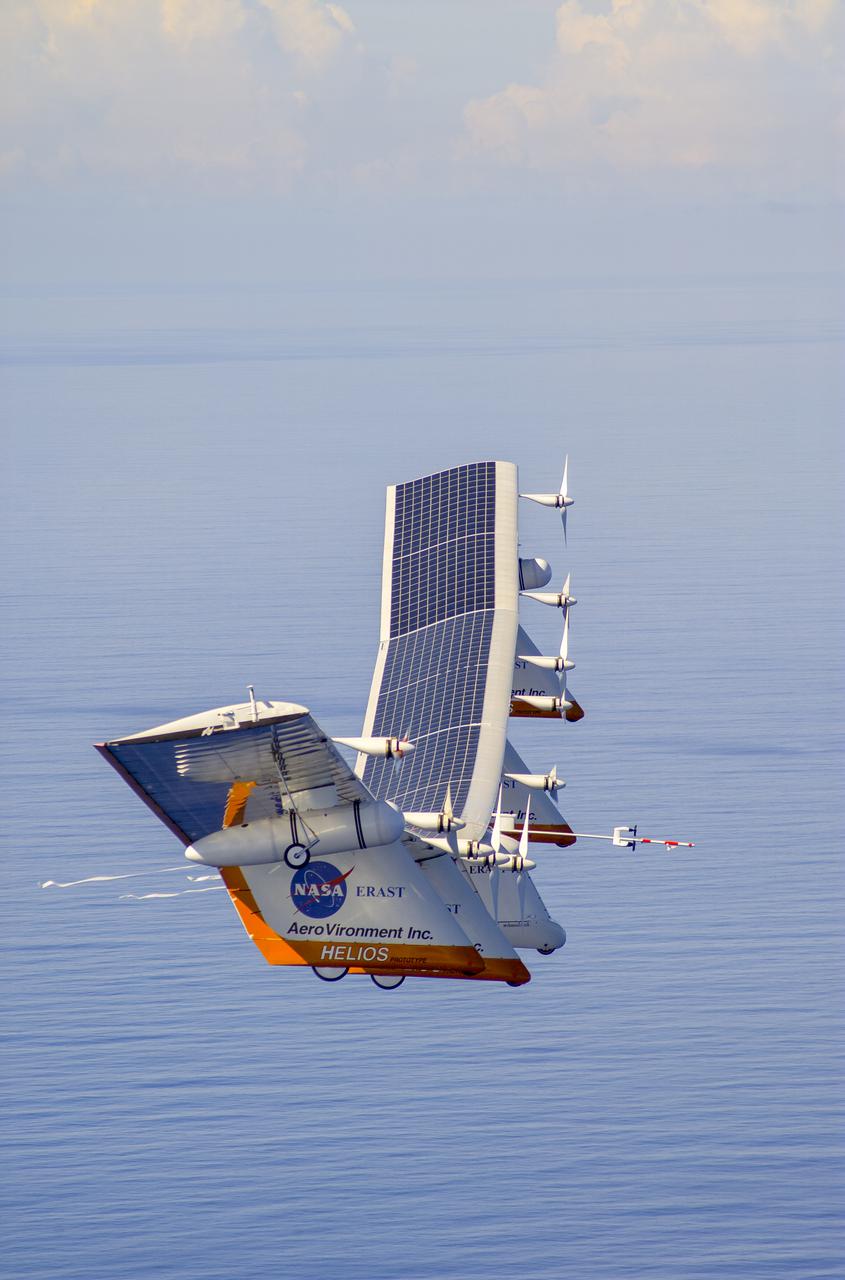
The solar-electric Helios Prototype flying wing is shown near the Hawaiian islands of Niihau and Lehua during its first test flight on solar power from the U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility on Kauai, Hawaii, July 14, 2001. The 18-hour flight was a functional checkout of the aircraft's systems and performance in preparation for an attempt to reach sustained flight at 100,000 feet altitude later this summer.
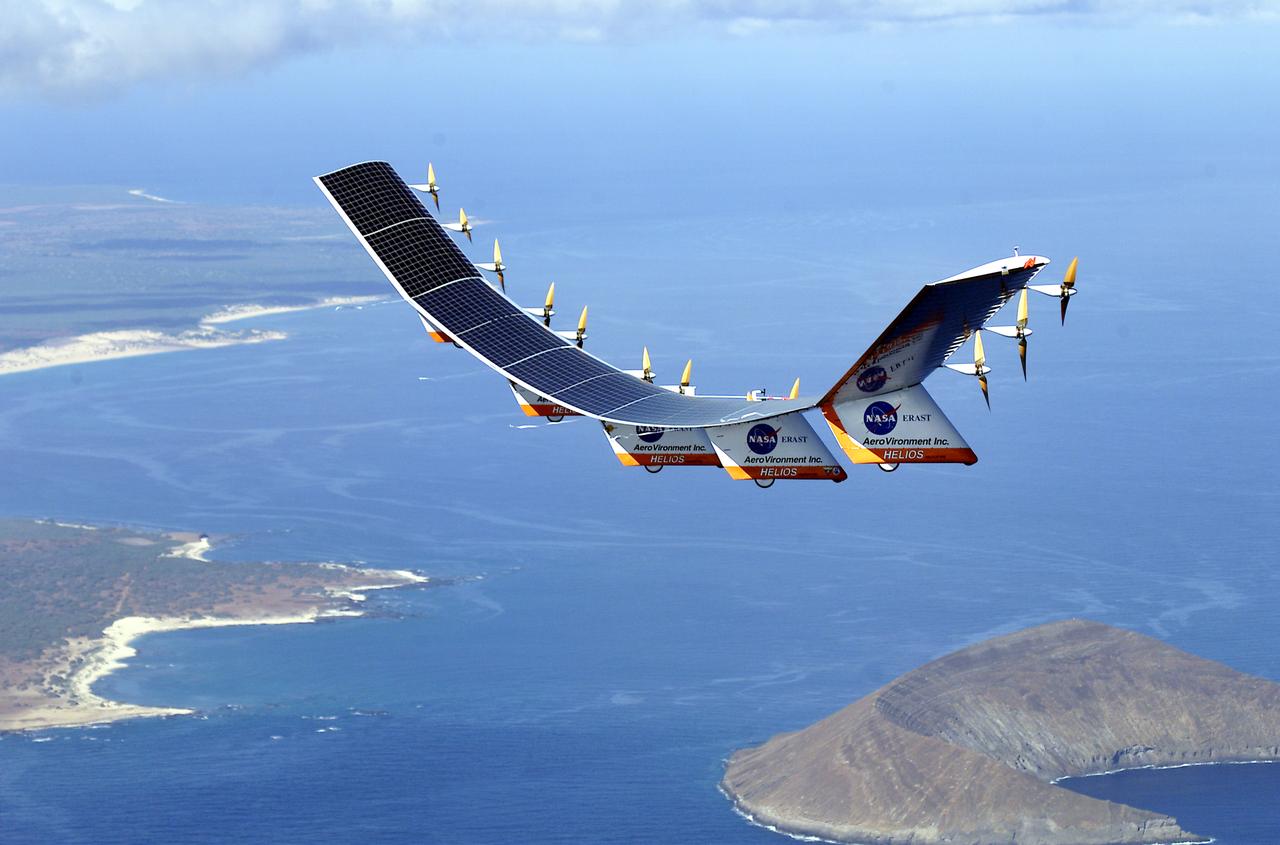

The solar-electric Helios Prototype flying wing is shown near the Hawaiian islands of Niihau and Lehua during its first test flight on solar power from the U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility on Kauai, Hawaii, July 14, 2001. The 18-hour flight was a functional checkout of the aircraft's systems and performance in preparation for an attempt to reach sustained flight at 100,000 feet altitude later this summer.
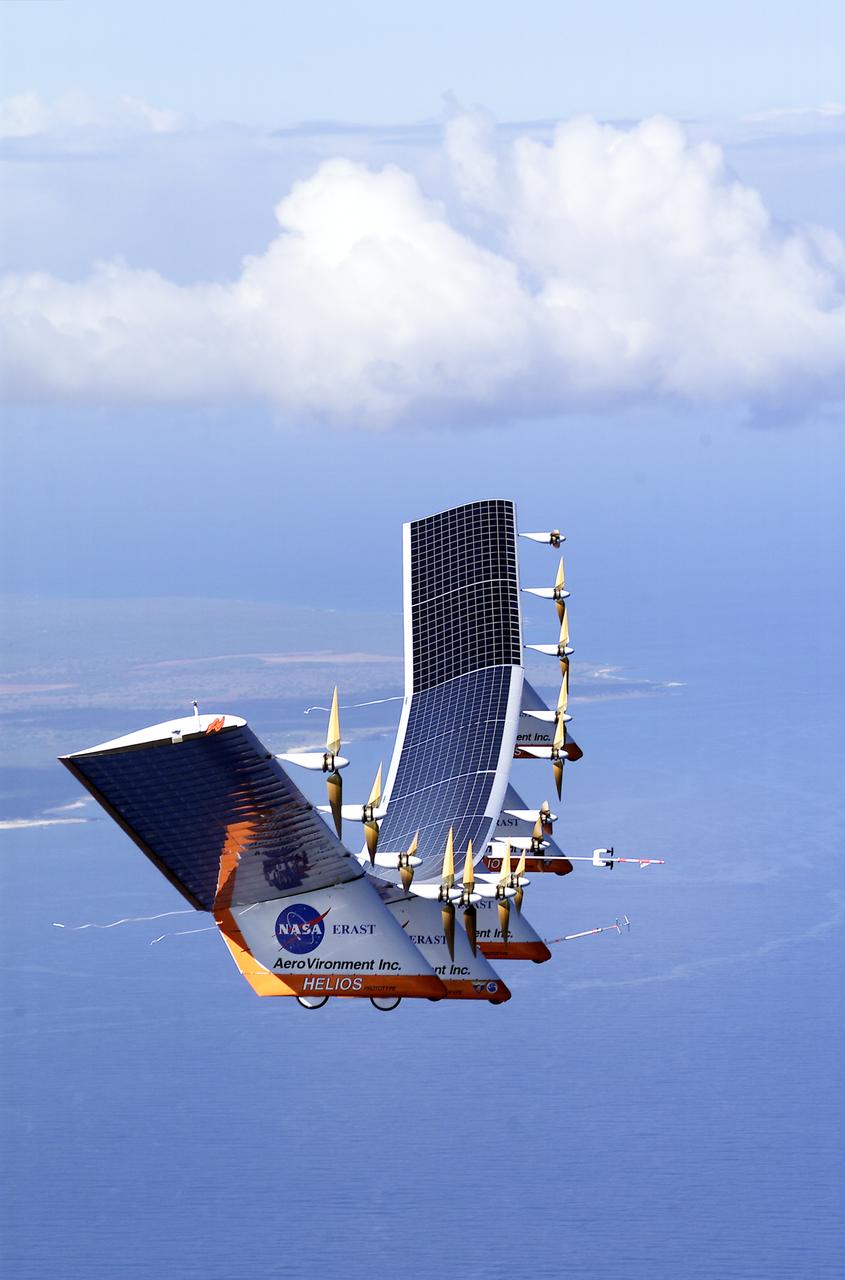

The solar-electric Helios Prototype flying wing is shown near the Hawaiian island of Niihau during its first test flight on solar power from the U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility on Kauai, Hawaii, July 14, 2001. The 18-hour flight was a functional checkout of the aircraft's systems and performance in preparation for an attempt to reach sustained flight at 100,000 feet altitude later this summer.
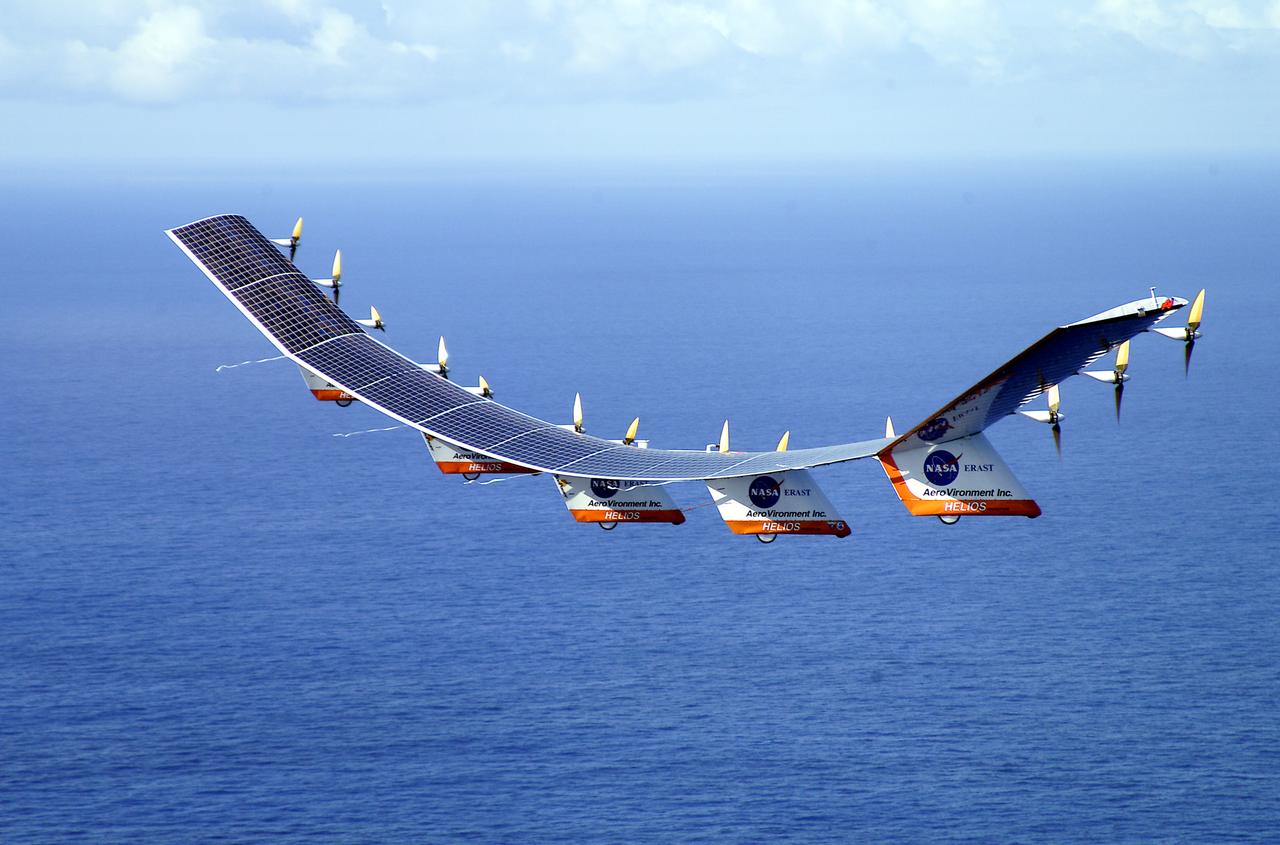

The solar-electric Helios Prototype flying wing is shown over the Pacific Ocean during its first test flight on solar power from the U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility on Kauai, Hawaii, July 14, 2001. The 18-hour flight was a functional checkout of the aircraft's systems and performance in preparation for an attempt to reach sustained flight at 100,000 feet altitude later this summer.
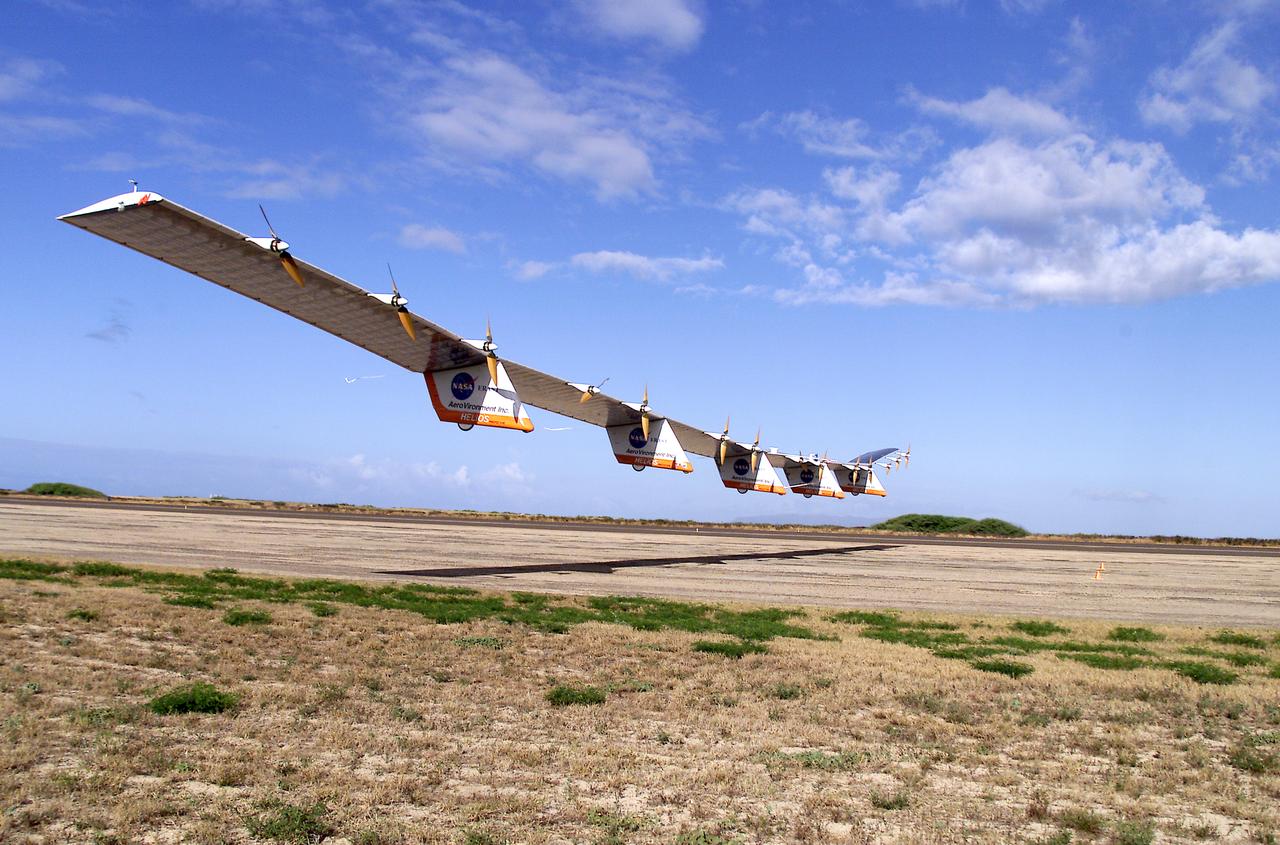

The solar-electric Helios Prototype flying wing is shown moments after takeoff, beginning its first test flight on solar power from the U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility on Kauai, Hawaii, July 14, 2001. The 18-hour flight was a functional checkout of the aircraft's systems and performance in preparation for an attempt to reach sustained flight at 100,000 feet altitude later this summer.
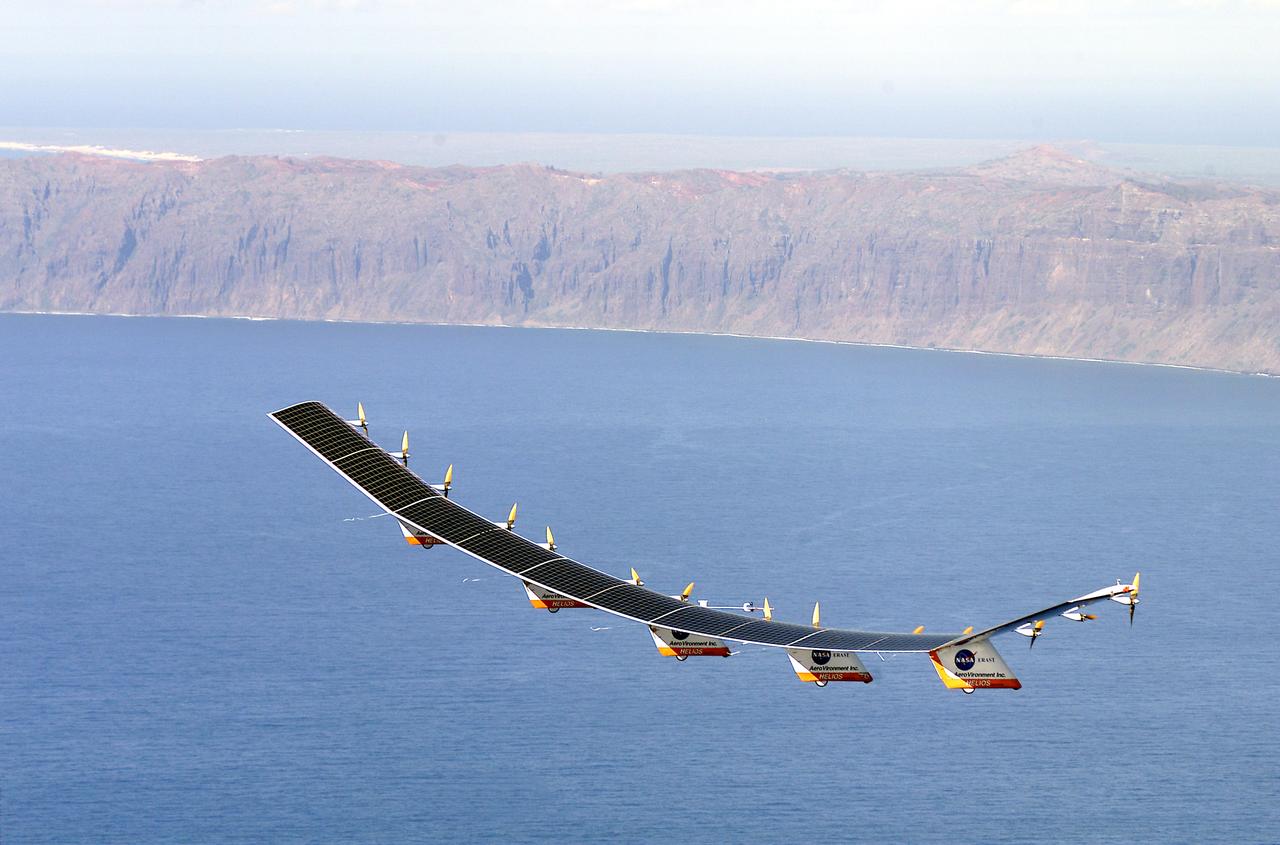

The solar-electric Helios Prototype flying wing is shown near the Hawaiian island of Niihau during its first test flight on solar power from the U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility on Kauai, Hawaii, July 14, 2001. The 18-hour flight was a functional checkout of the aircraft's systems and performance in preparation for an attempt to reach sustained flight at 100,000 feet altitude later this summer.
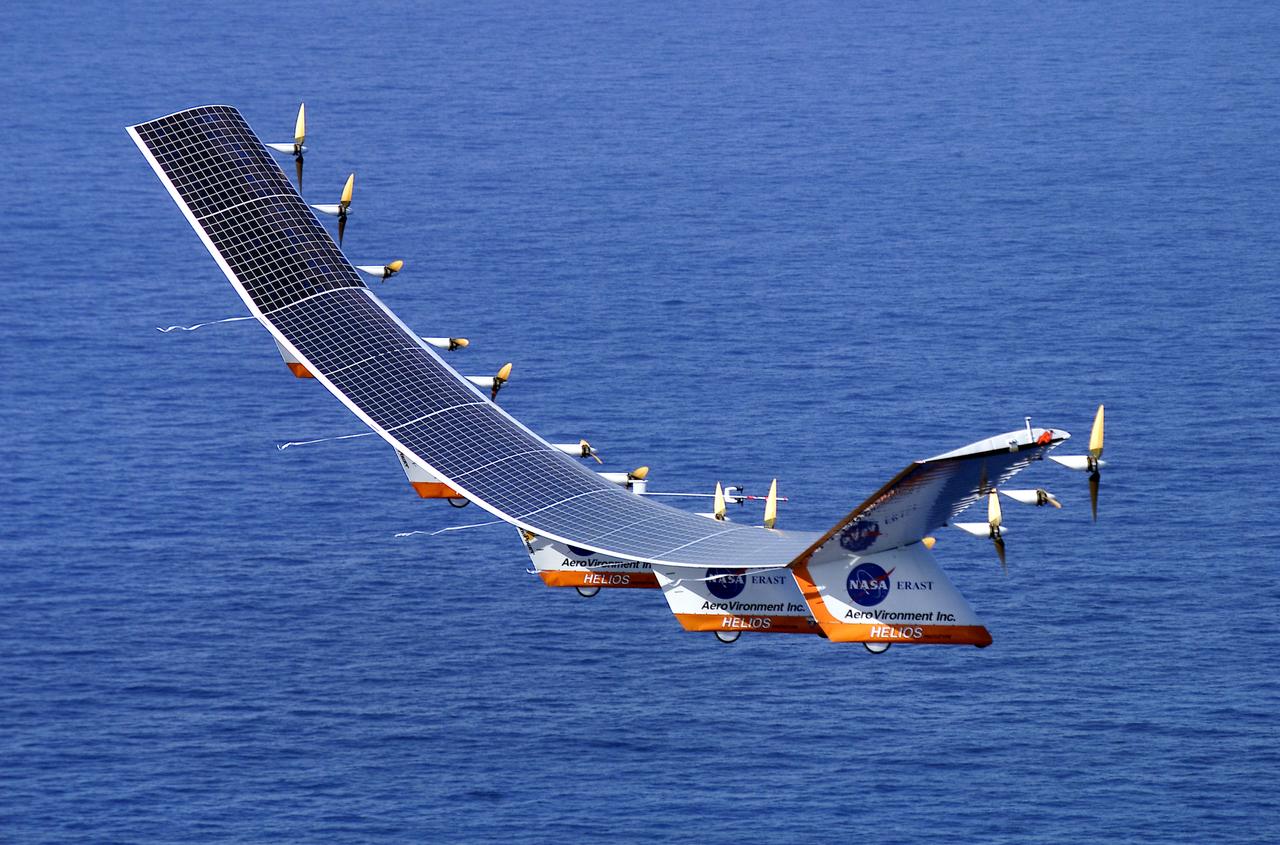

The solar-electric Helios Prototype flying wing is shown over the Pacific Ocean during its first test flight on solar power from the U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility on Kauai, Hawaii, July 14, 2001. The 18-hour flight was a functional checkout of the aircraft's systems and performance in preparation for an attempt to reach sustained flight at 100,000 feet altitude later this summer.
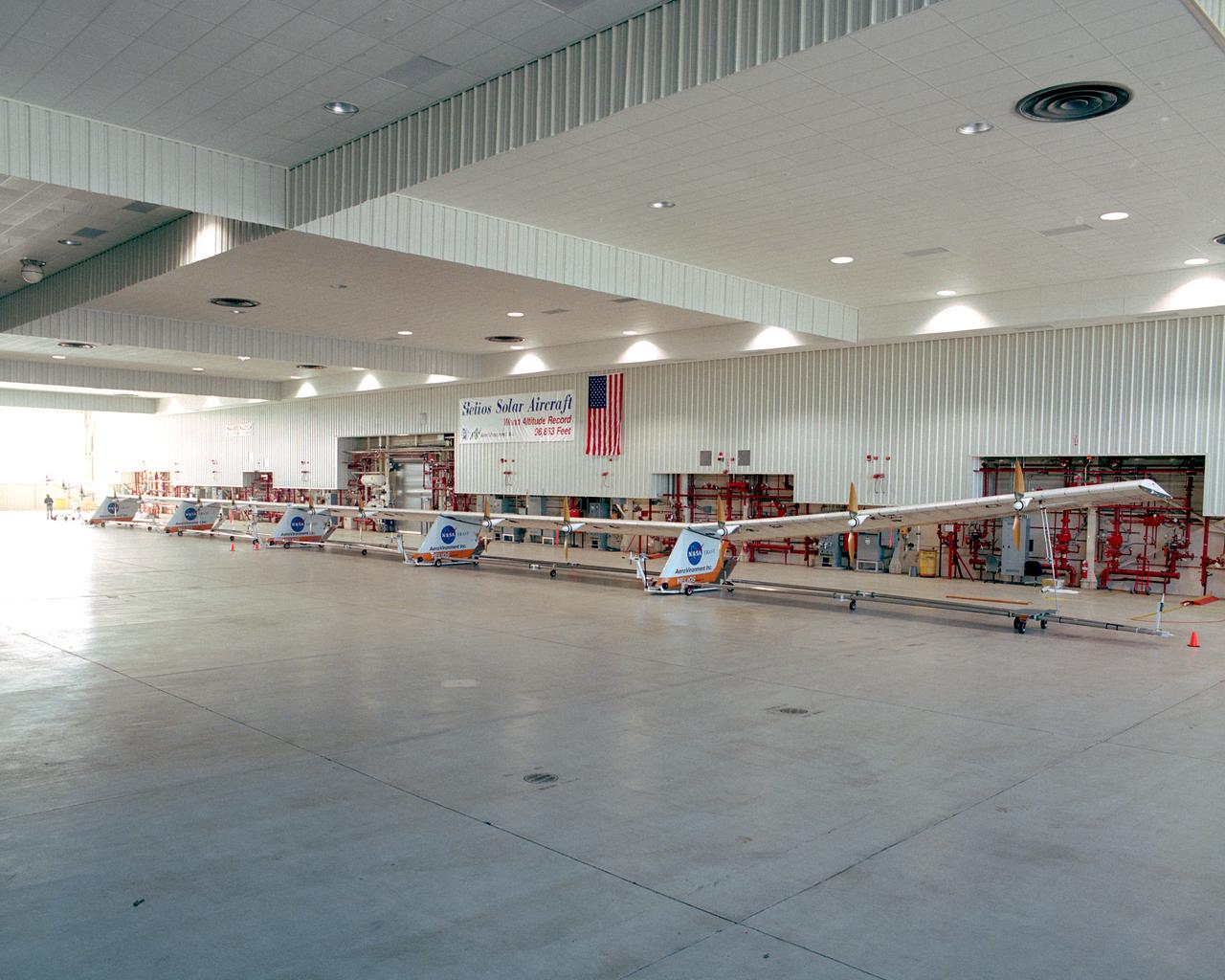

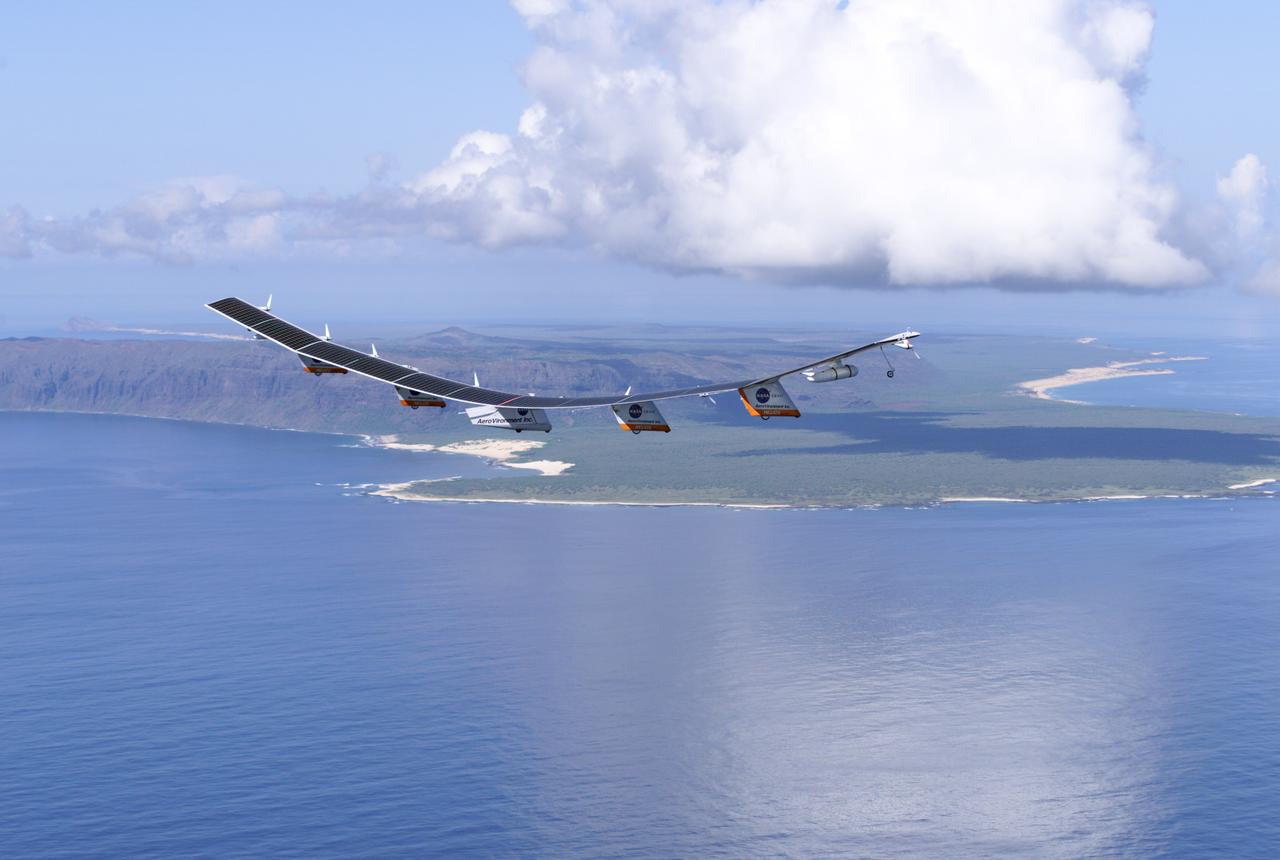
The Helios Prototype flying wing stretches almost the full length of the 300-foot-long hangar at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The 247-foot span solar-powered aircraft, resting on its ground maneuvering dolly, was on display for a visit of NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe and other NASA officials on January 31, 2002. The unique solar-electric flying wing reached an altitude of 96,863 feet during an almost 17-hour flight near Hawaii on August 13, 2001, a world record for sustained horizontal flight by a non-rocket powered aircraft. Developed by AeroVironment, Inc., under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) project, the Helios Prototype is the forerunner of a planned fleet of slow-flying, long duration, high-altitude uninhabited aerial vehicles (UAV) which can serve as "atmospheric satellites," performing Earth science missions or functioning as telecommunications relay platforms in the stratosphere.
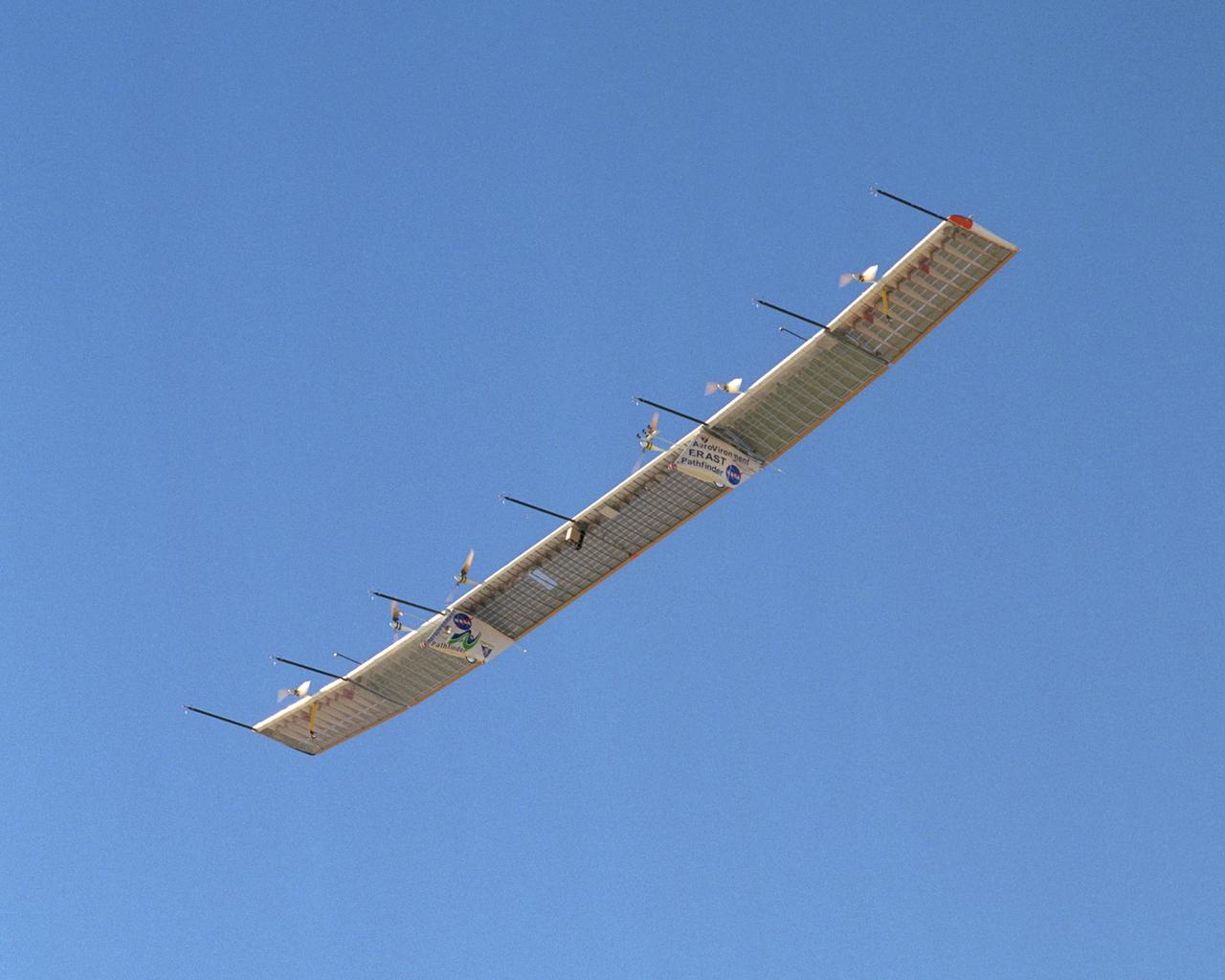

With its sensor booms projecting ahead of the wing, the Pathfinder-Plus solar-electric aircraft soars under a blue sky on a turbulence measurement research flight.
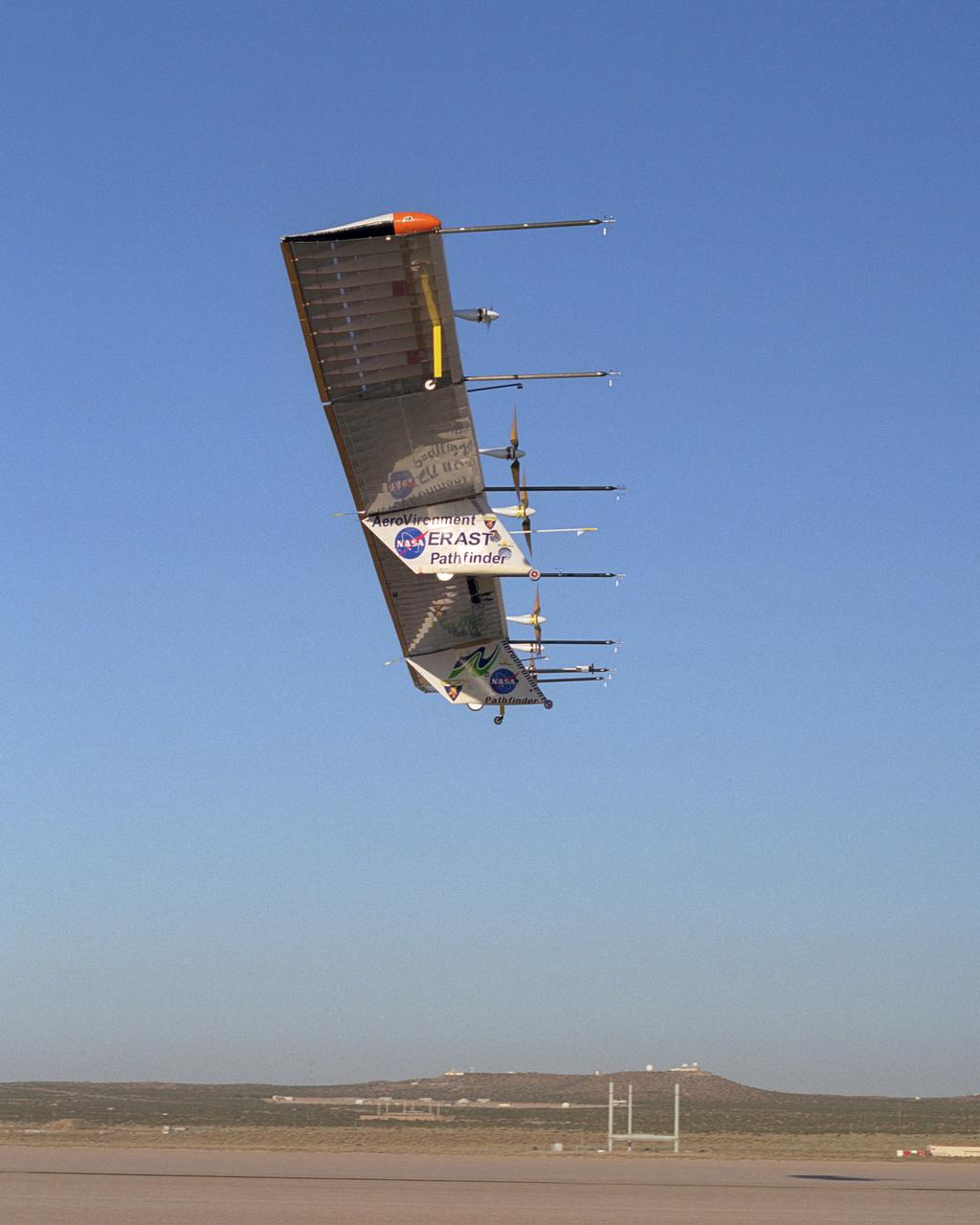

The Atmospheric Turbulence Measurement System booms are clearly evident in this view of the Pathfinder-Plus solar aircraft as it flies over Rogers Dry Lake.
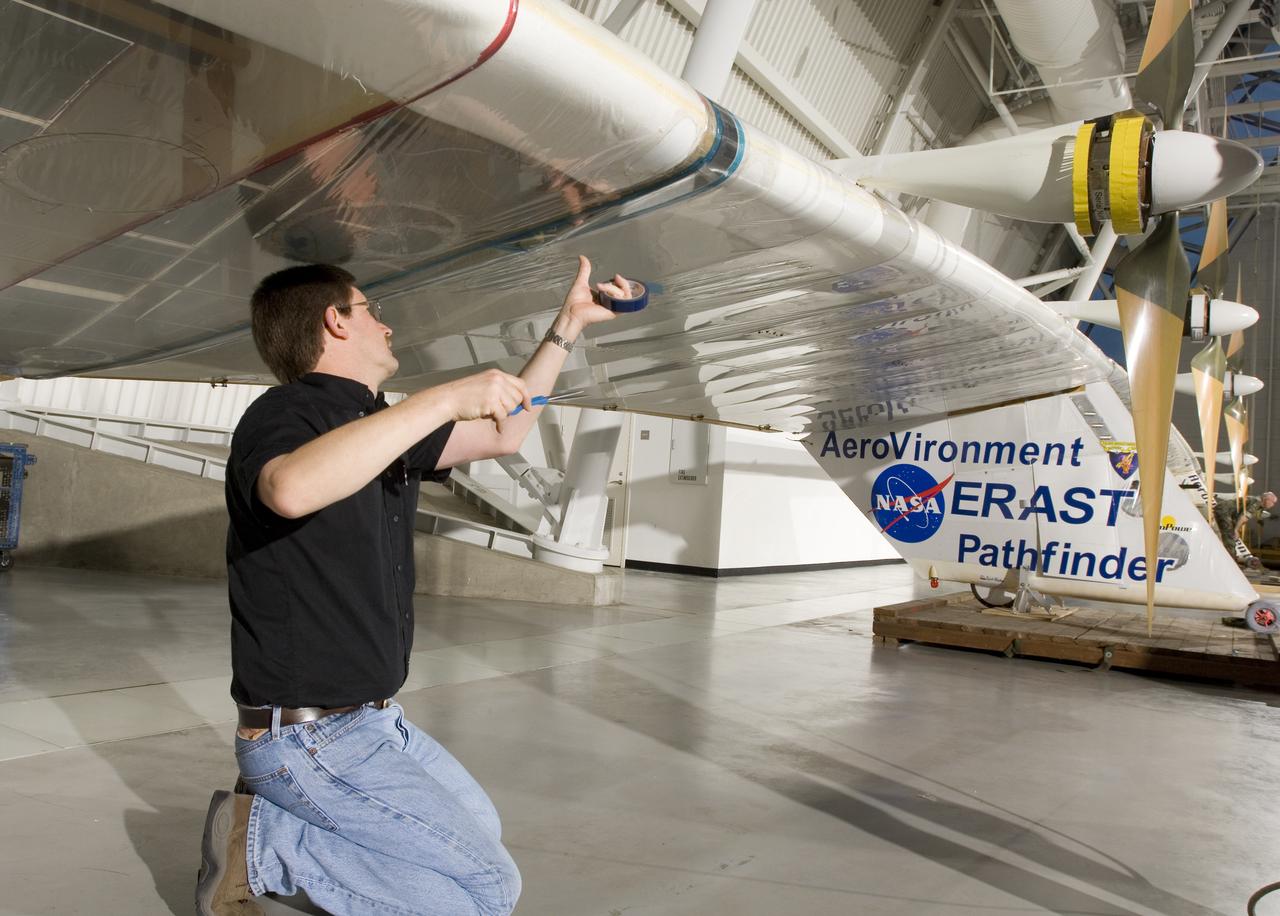

AeroVironment crew chief Mark Shipley applies sealing tape to a wing joint on Pathfinder-Plus before it is hoisted into place at the NASM's Udvar-Hazy Center.
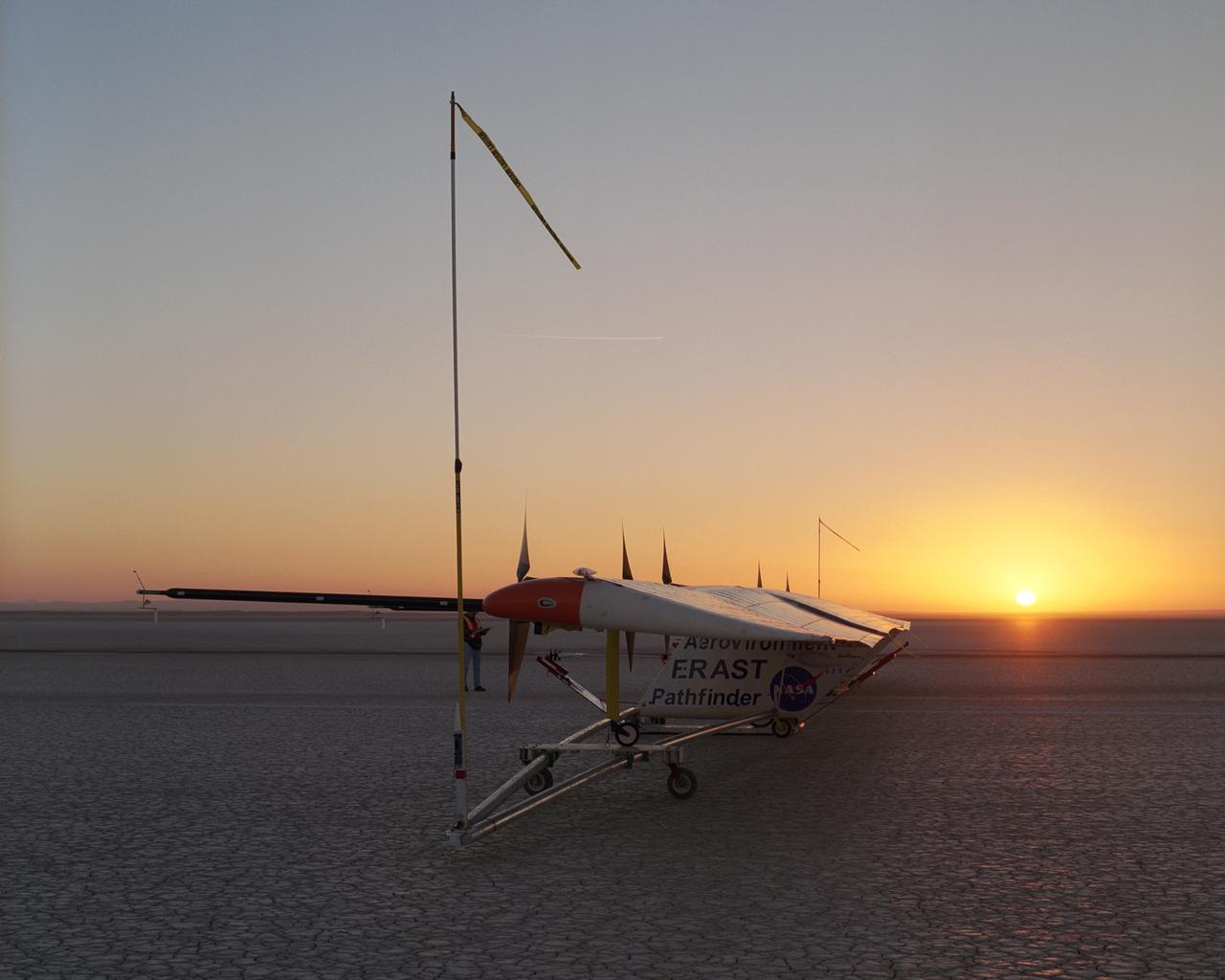

As the rising sun dawns over the parched bed of Rogers Dry Lake, AeroVironment's solar-electric Pathfinder-Plus awaits takeoff on its final research flight.
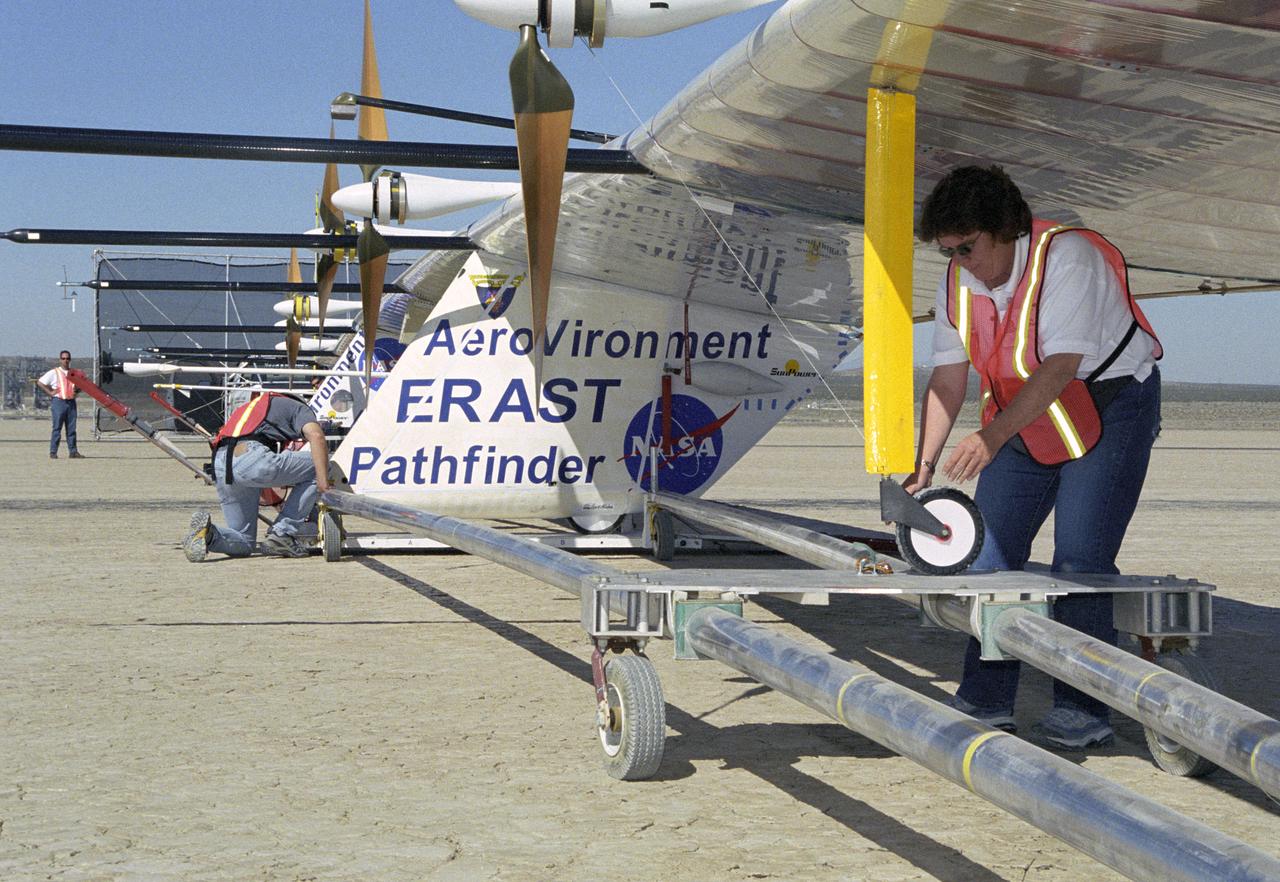

AeroVironment technicians prepare to remove the Pathfinder-Plus solar aircraft from its ground dolly before a turbulence measurement flight from Rogers Dry Lake.
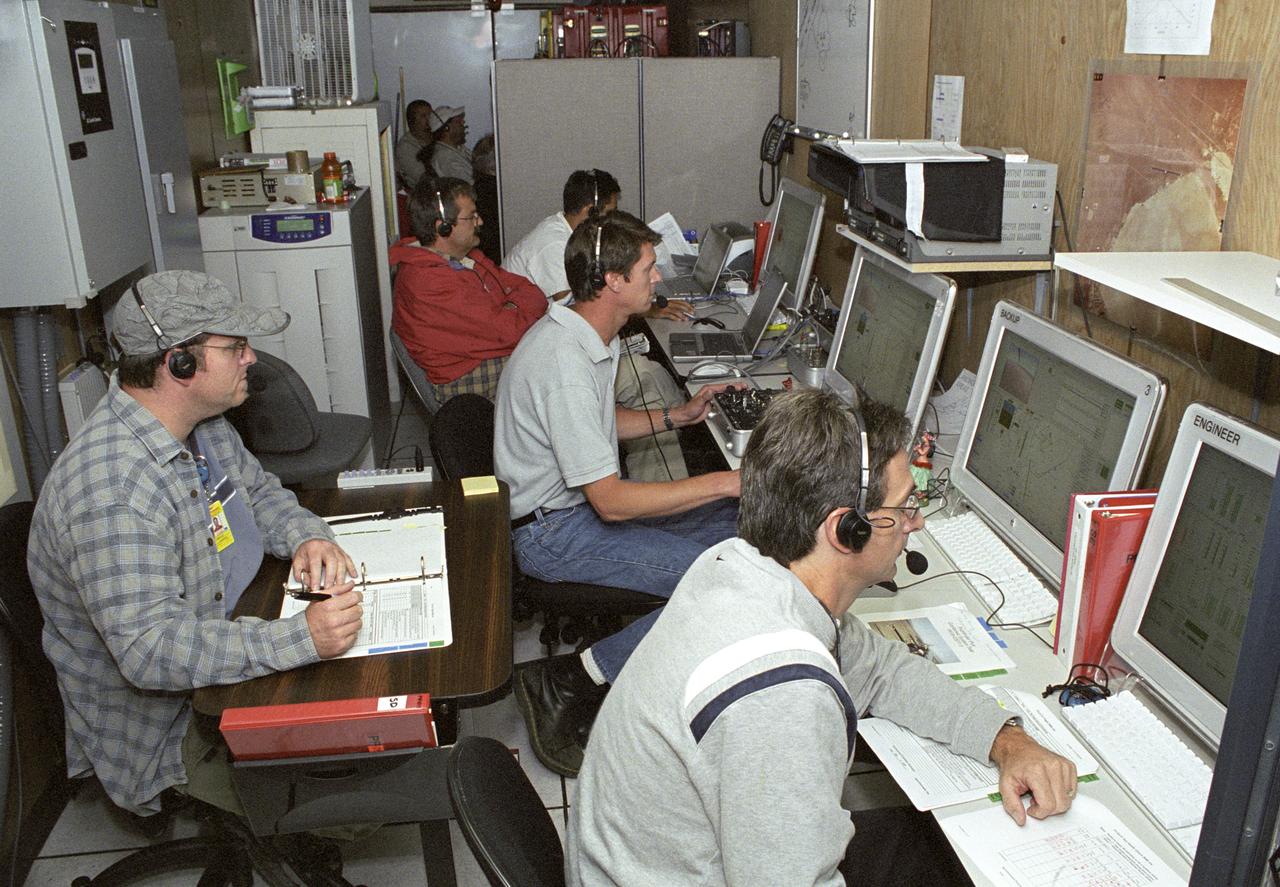

AeroVironment engineers and technicians closely monitor flight data in the ground control station during the Pathfinder-Plus' turbulence measurement flights.
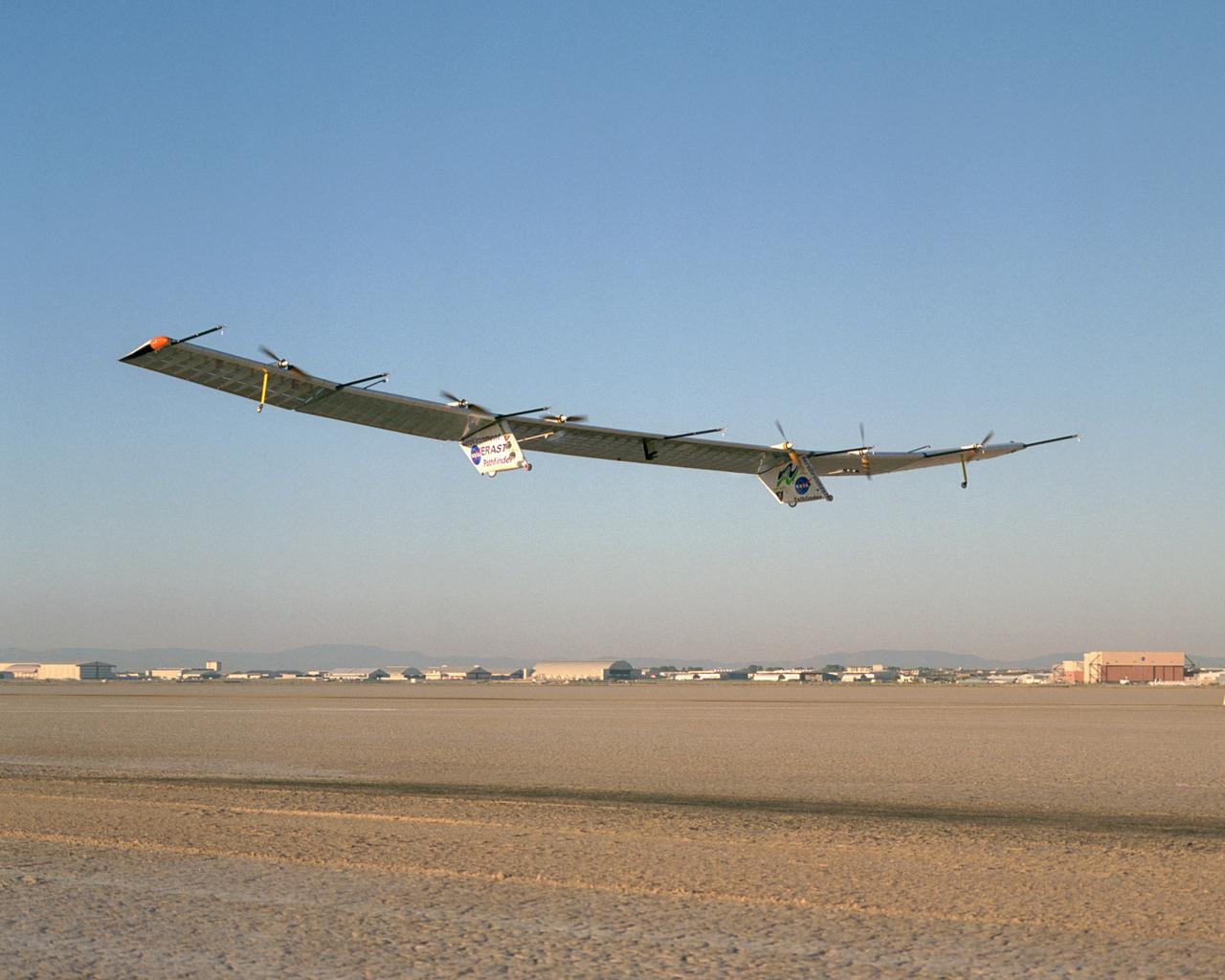

With turbulence-measurement booms projecting ahead of the wing, Pathfinder-Plus soars aloft over Rogers Dry Lake on its final research flight from NASA Dryden.
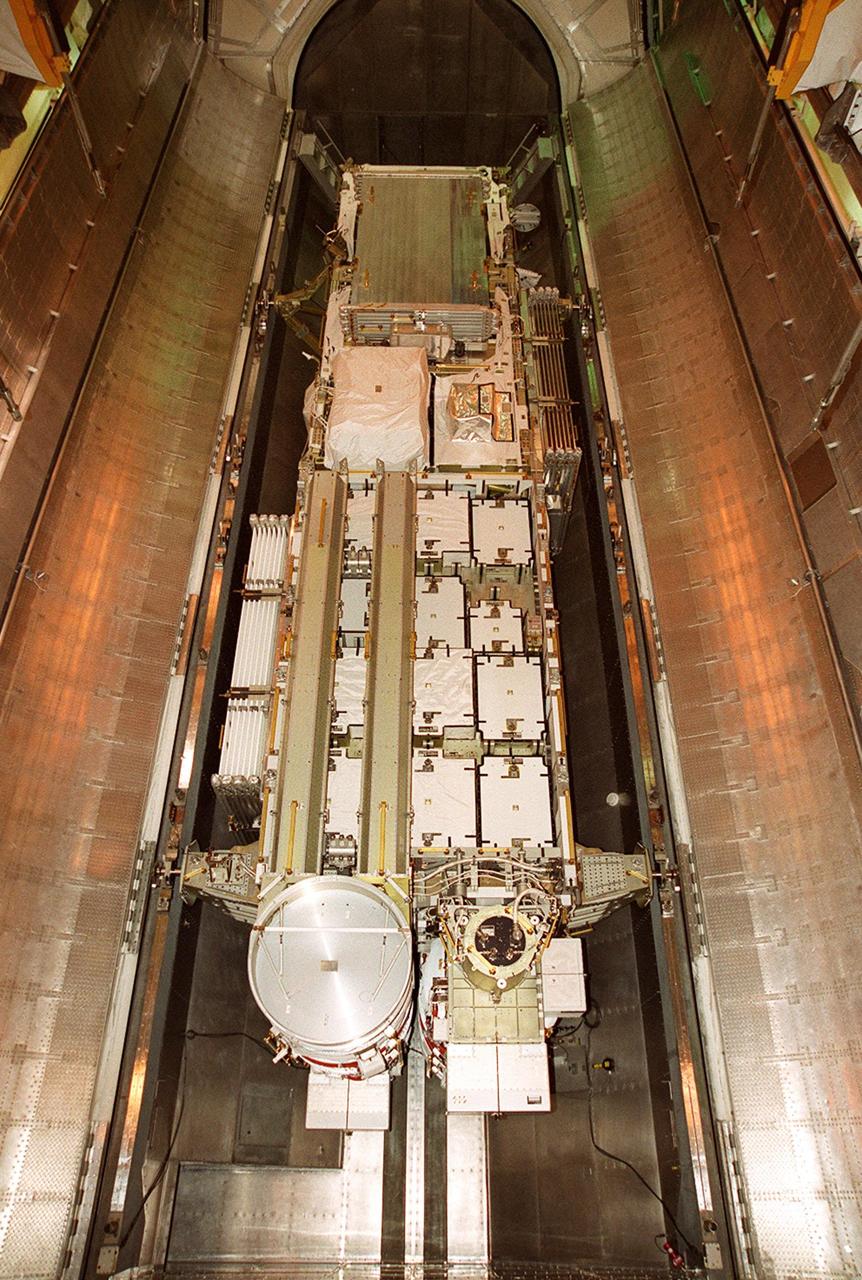
The doors of the payload transport canister are open wide in the payload changeout room on Launch Pad 39B. Revealed is the P6 integrated truss segment, which will fly on mission STS-97. The P6 comprises Solar Array Wing-3 and the Integrated Electronic Assembly, to be installed on the International Space Station. The Station’s electrical power system will use eight photovoltaic solar arrays, each 112 feet long by 39 feet wide, to convert sunlight to electricity. The solar arrays are mounted on a “blanket” that can be folded like an accordion for delivery. Once in orbit, astronauts will deploy the blankets to their full size. Gimbals will be used to rotate the arrays so that they will face the Sun to provide maximum power to the Space Station. Launch of STS-97 is scheduled for Nov. 30 at 10:06 p.m. EST
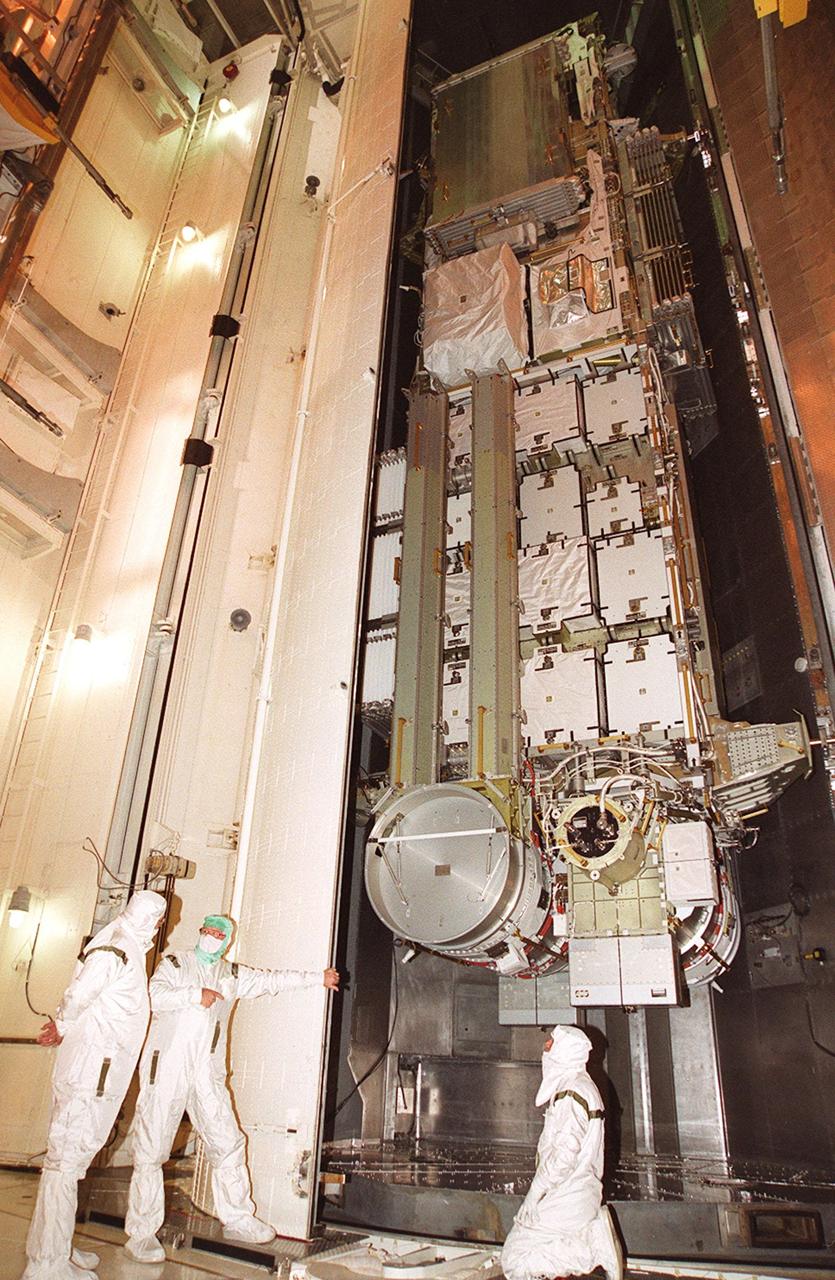
Workers in the payload changeout room stand by as the doors open on the payload transport canister. Inside is the P6 integrated truss segment, which will fly on mission STS-97. The P6 comprises Solar Array Wing-3 and the Integrated Electronic Assembly, to be installed on the International Space Station. The Station’s electrical power system will use eight photovoltaic solar arrays, each 112 feet long by 39 feet wide, to convert sunlight to electricity. The solar arrays are mounted on a “blanket” that can be folded like an accordion for delivery. Once in orbit, astronauts will deploy the blankets to their full size. Gimbals will be used to rotate the arrays so that they will face the Sun to provide maximum power to the Space Station. Launch of STS-97 is scheduled for Nov. 30 at 10:06 p.m. EST
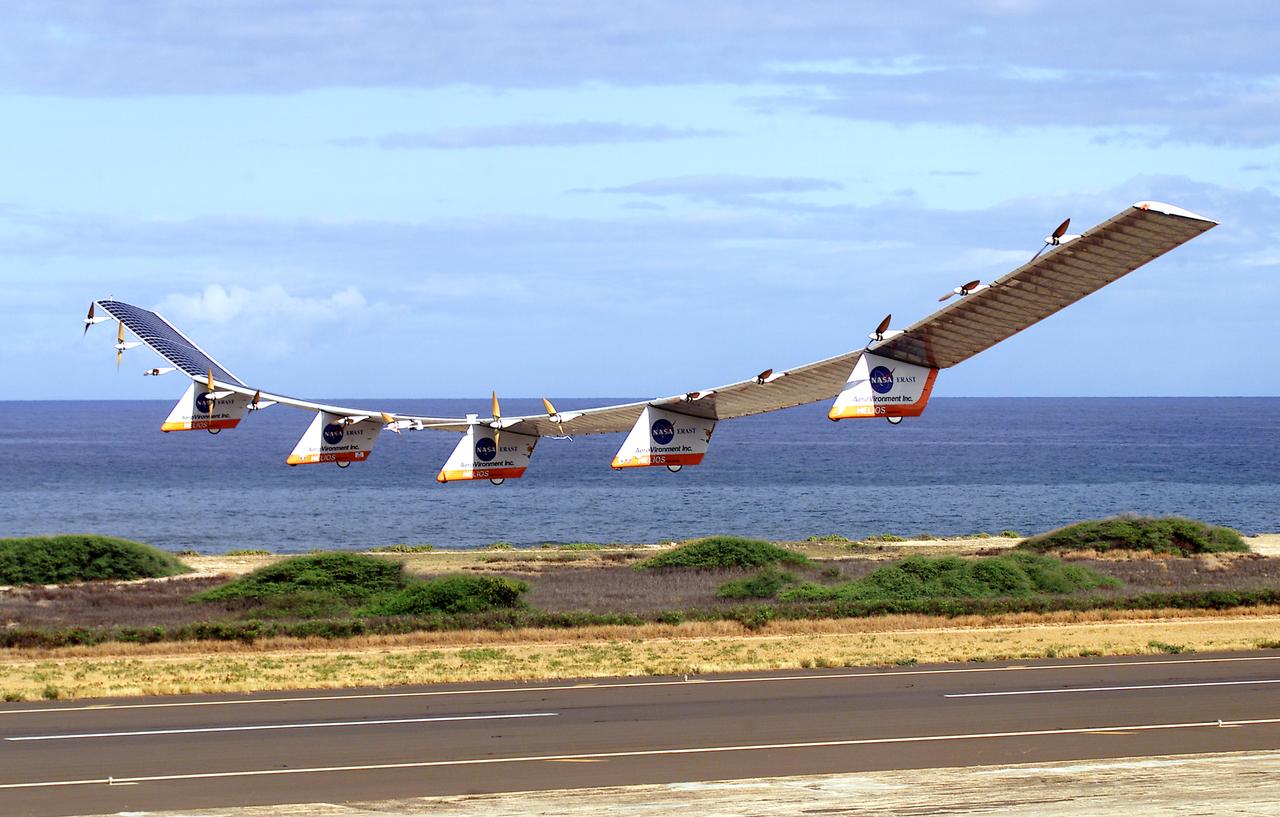

NASA's Helios Prototype aircraft taking off from the Pacific Missile Range Facility, Kauai, Hawaii, for the record flight. As a follow-on to the Centurion (and earlier Pathfinder and Pathfinder-Plus) aircraft, the solar-powered Helios Prototype is the latest and largest example of a slow-flying ultralight flying wing designed for long-duration, high-altitude Earth science or telecommunications relay missions in the stratosphere. Developed by AeroVironment, Inc., of Monrovia, California, under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) project, the unique craft is intended to demonstrate two key missions: the ability to reach and sustain horizontal flight at 100,000 feet altitude on a single-day flight in 2001, and to maintain flight above 50,000 feet altitude for at least four days in 2003, with the aid of a regenerative fuel cell-based energy storage system now in development. Both of these missions will be powered by electricity derived from non-polluting solar energy. The Helios Prototype is an enlarged version of the Centurion flying wing, which flew a series of test flights at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in late 1998. The craft has a wingspan of 247 feet, 41 feet greater than the Centurion, 2 1/2 times that of its solar-powered Pathfinder flying wing, and longer than the wingspans of either the Boeing 747 jetliner or Lockheed C-5 transport aircraft. The remotely piloted, electrically powered Helios Prototype went aloft on its maiden low-altitude checkout flight Sept. 8, 1999, over Rogers Dry Lake adjacent to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in the Southern California desert. The initial flight series was flown on battery power as a risk-reduction measure. In all, six flights were flown in the Helios Protoype's initial development series. In upgrading the Centurion to the Helios Prototype configuration, AeroVironment added a sixth wing section and a fifth landing gear pod, among other improvements. The additional wingsp
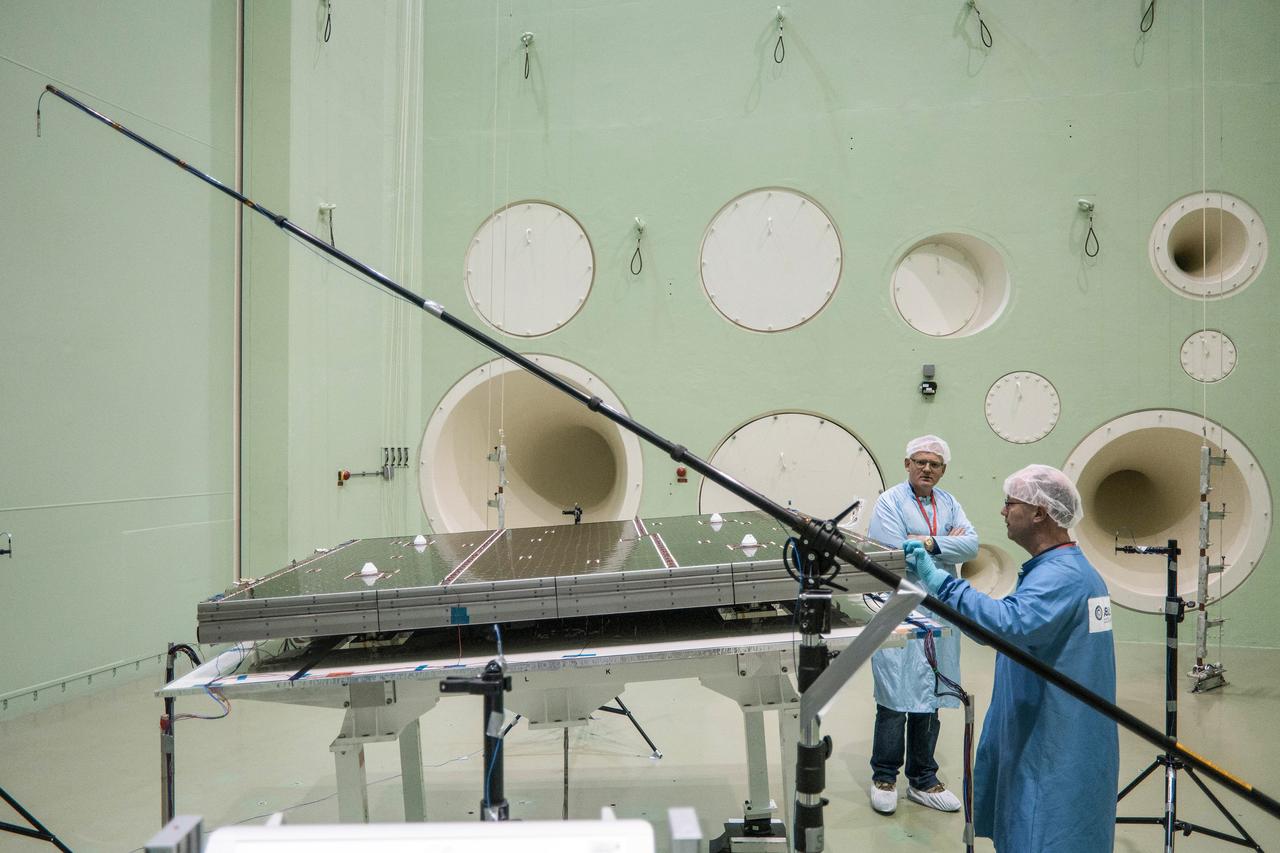

The solar arrays that will provide electricity to the Orion spacecraft were put through launch-day paces at ESA’s Test Centre in the Netherlands to verify that they can handle the rigours of the trip around the Moon... .The wings are seen here on April 11, 2018, on the shaking table that vibrates with the full force of a rumbling rocket. They were also placed in front of enormous speakers that recreate the harsh conditions they can expect on launch day. The solar arrays passed with flying colours... .The wings will be tested on how they deploy before shipping to Bremen, Germany, for integration with the European service module. ESA’s contribution to the Orion mission will provide power, propulsion, water, and air... .The first mission will take Orion around the Moon without astronauts. The solar panels will be folded inside the rocket fairing, once released from NASA’s Space Launch System rocket they will unfold and rotate towards the Sun to start delivering power... .With solar wings tested and fuel tanks installed, Orion is one step closer to its maiden voyage.
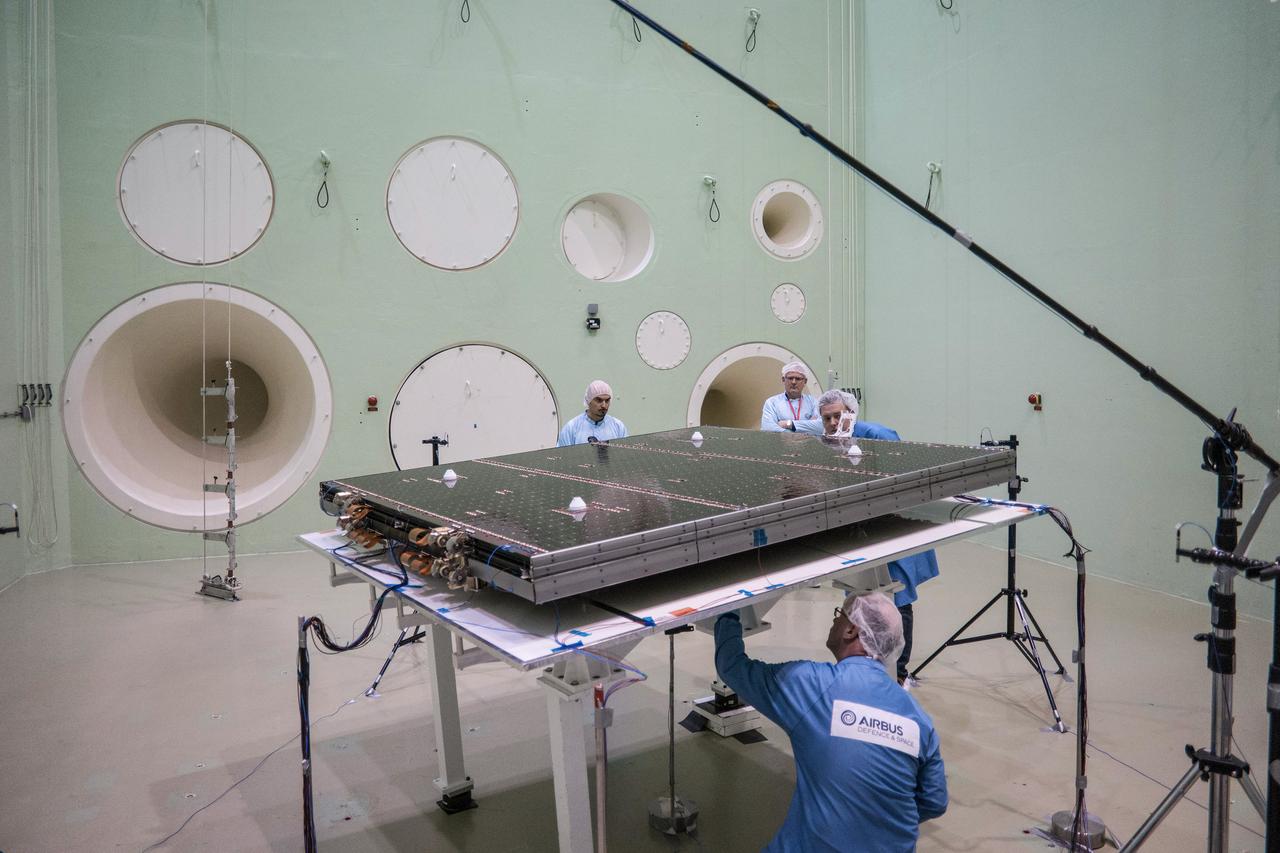

The solar arrays that will provide electricity to the Orion spacecraft were put through launch-day paces at ESA’s Test Centre in the Netherlands to verify that they can handle the rigours of the trip around the Moon... .The wings are seen here on April 11, 2018, on the shaking table that vibrates with the full force of a rumbling rocket. They were also placed in front of enormous speakers that recreate the harsh conditions they can expect on launch day. The solar arrays passed with flying colours... .The wings will be tested on how they deploy before shipping to Bremen, Germany, for integration with the European service module. ESA’s contribution to the Orion mission will provide power, propulsion, water, and air... .The first mission will take Orion around the Moon without astronauts. The solar panels will be folded inside the rocket fairing, once released from NASA’s Space Launch System rocket they will unfold and rotate towards the Sun to start delivering power... .With solar wings tested and fuel tanks installed, Orion is one step closer to its maiden voyage.
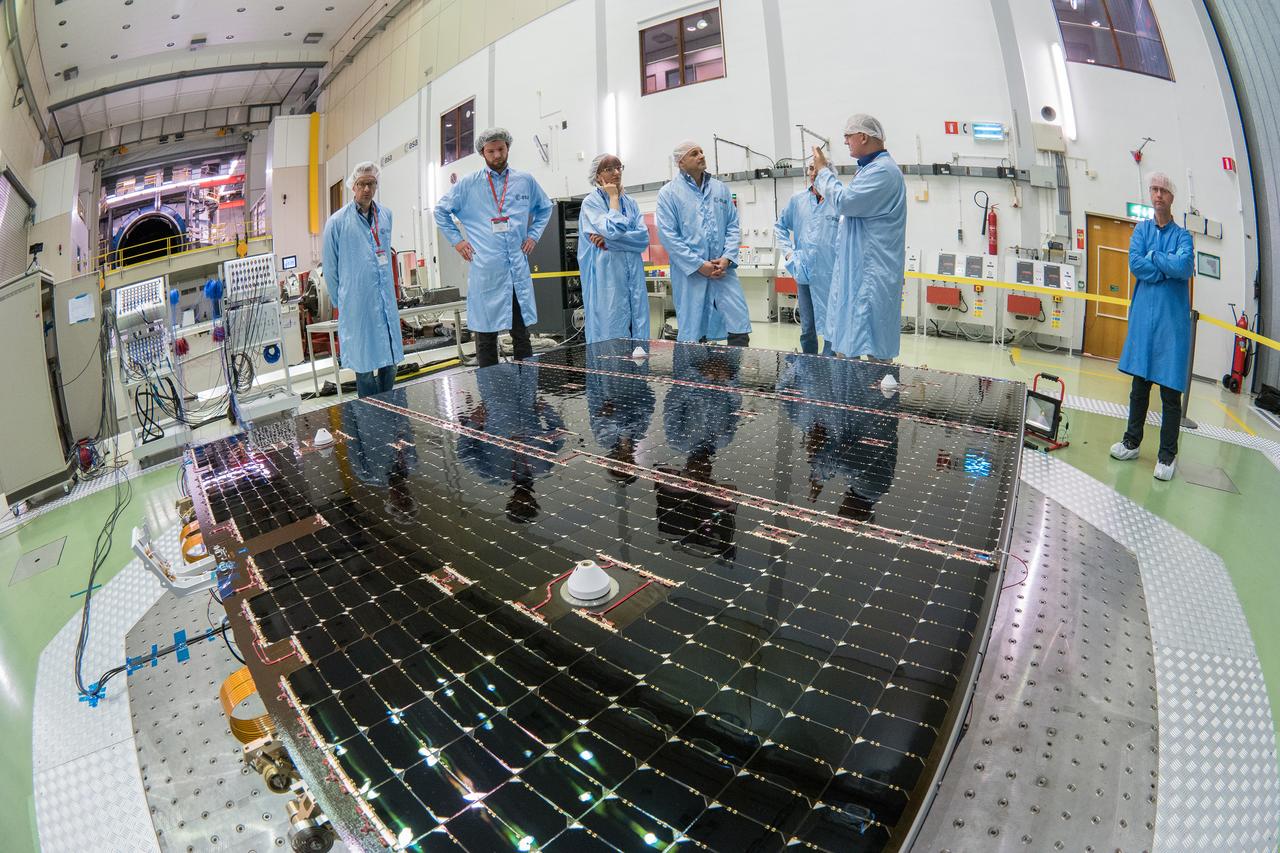

The solar arrays that will provide electricity to the Orion spacecraft were put through launch-day paces at ESA’s Test Centre in the Netherlands to verify that they can handle the rigours of the trip around the Moon... .The wings are seen here on April 11, 2018, on the shaking table that vibrates with the full force of a rumbling rocket. They were also placed in front of enormous speakers that recreate the harsh conditions they can expect on launch day. The solar arrays passed with flying colours... .The wings will be tested on how they deploy before shipping to Bremen, Germany, for integration with the European service module. ESA’s contribution to the Orion mission will provide power, propulsion, water, and air... .The first mission will take Orion around the Moon without astronauts. The solar panels will be folded inside the rocket fairing, once released from NASA’s Space Launch System rocket they will unfold and rotate towards the Sun to start delivering power... .With solar wings tested and fuel tanks installed, Orion is one step closer to its maiden voyage.
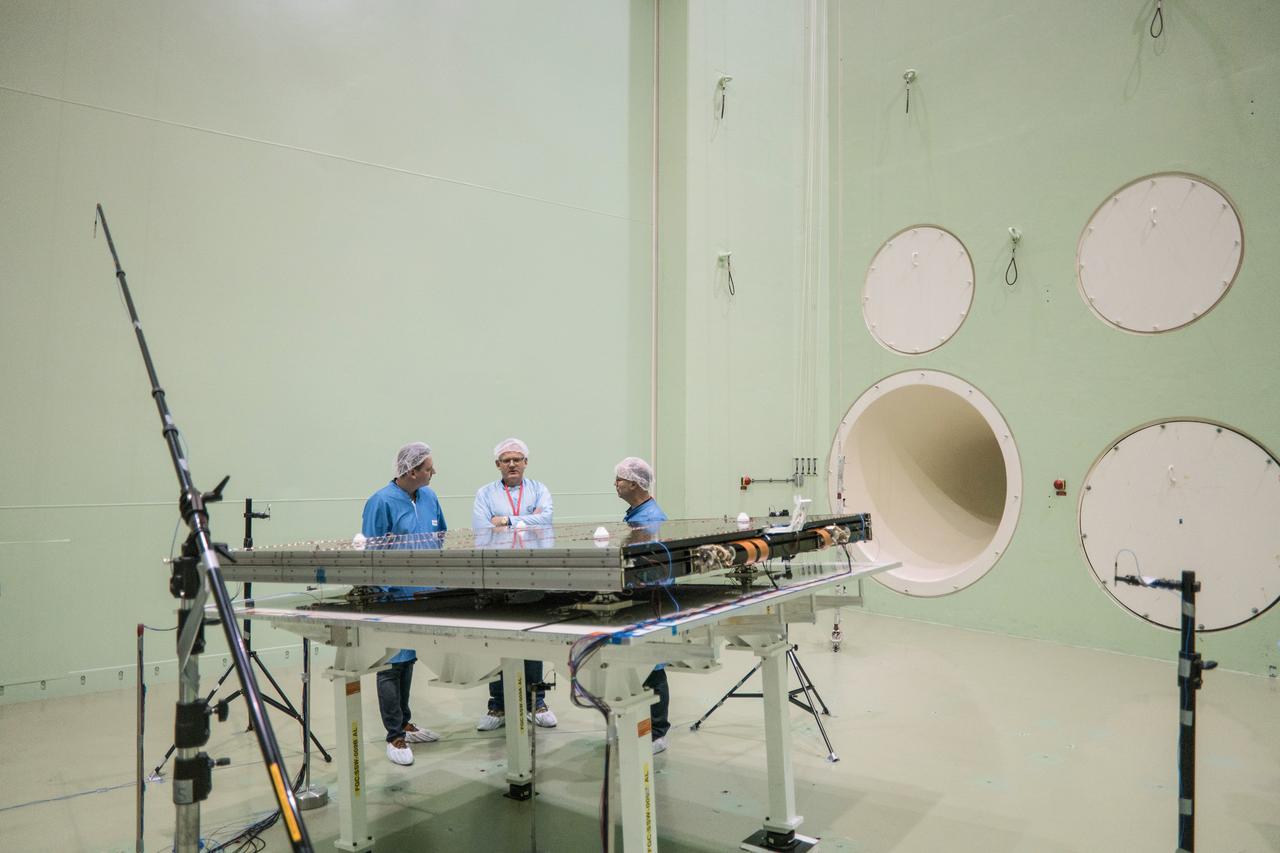

The solar arrays that will provide electricity to the Orion spacecraft were put through launch-day paces at ESA’s Test Centre in the Netherlands to verify that they can handle the rigours of the trip around the Moon... .The wings are seen here on April 11, 2018, on the shaking table that vibrates with the full force of a rumbling rocket. They were also placed in front of enormous speakers that recreate the harsh conditions they can expect on launch day. The solar arrays passed with flying colours... .The wings will be tested on how they deploy before shipping to Bremen, Germany, for integration with the European service module. ESA’s contribution to the Orion mission will provide power, propulsion, water, and air... .The first mission will take Orion around the Moon without astronauts. The solar panels will be folded inside the rocket fairing, once released from NASA’s Space Launch System rocket they will unfold and rotate towards the Sun to start delivering power... .With solar wings tested and fuel tanks installed, Orion is one step closer to its maiden voyage.
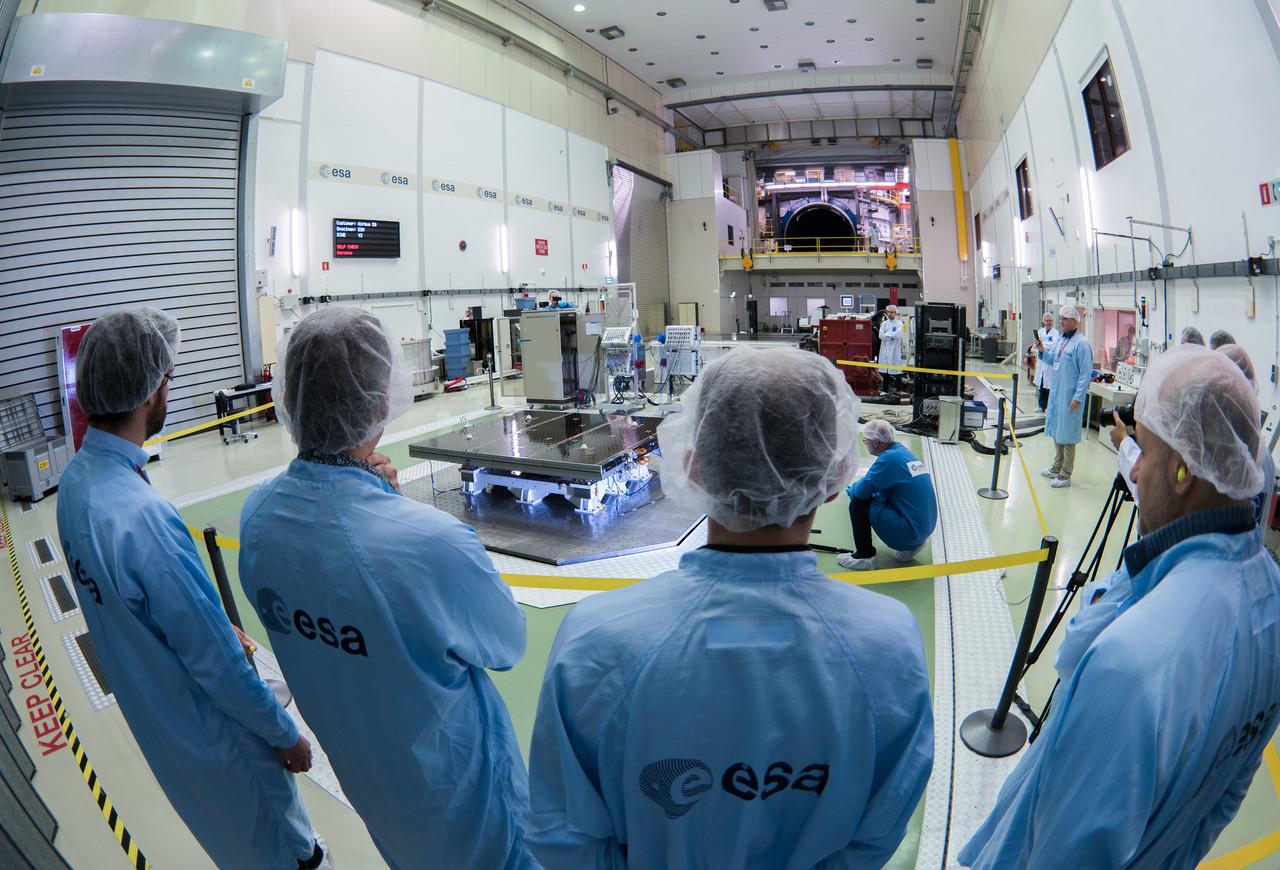

The solar arrays that will provide electricity to the Orion spacecraft were put through launch-day paces at ESA’s Test Centre in the Netherlands to verify that they can handle the rigours of the trip around the Moon... .The wings are seen here on April 11, 2018, on the shaking table that vibrates with the full force of a rumbling rocket. They were also placed in front of enormous speakers that recreate the harsh conditions they can expect on launch day. The solar arrays passed with flying colours... .The wings will be tested on how they deploy before shipping to Bremen, Germany, for integration with the European service module. ESA’s contribution to the Orion mission will provide power, propulsion, water, and air... .The first mission will take Orion around the Moon without astronauts. The solar panels will be folded inside the rocket fairing, once released from NASA’s Space Launch System rocket they will unfold and rotate towards the Sun to start delivering power... .With solar wings tested and fuel tanks installed, Orion is one step closer to its maiden voyage.
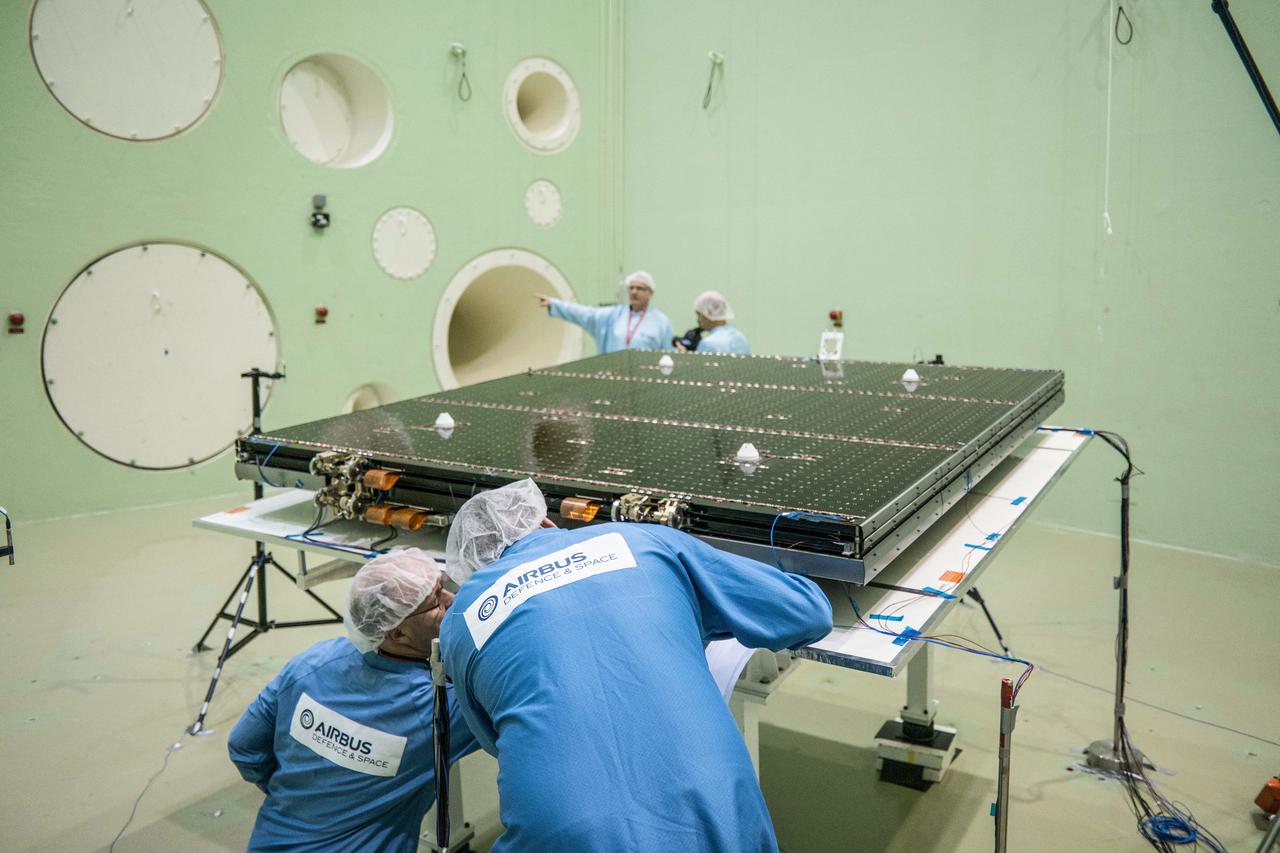

The solar arrays that will provide electricity to the Orion spacecraft were put through launch-day paces at ESA’s Test Centre in the Netherlands to verify that they can handle the rigours of the trip around the Moon... .The wings are seen here on April 11, 2018, on the shaking table that vibrates with the full force of a rumbling rocket. They were also placed in front of enormous speakers that recreate the harsh conditions they can expect on launch day. The solar arrays passed with flying colours... .The wings will be tested on how they deploy before shipping to Bremen, Germany, for integration with the European service module. ESA’s contribution to the Orion mission will provide power, propulsion, water, and air... .The first mission will take Orion around the Moon without astronauts. The solar panels will be folded inside the rocket fairing, once released from NASA’s Space Launch System rocket they will unfold and rotate towards the Sun to start delivering power... .With solar wings tested and fuel tanks installed, Orion is one step closer to its maiden voyage.
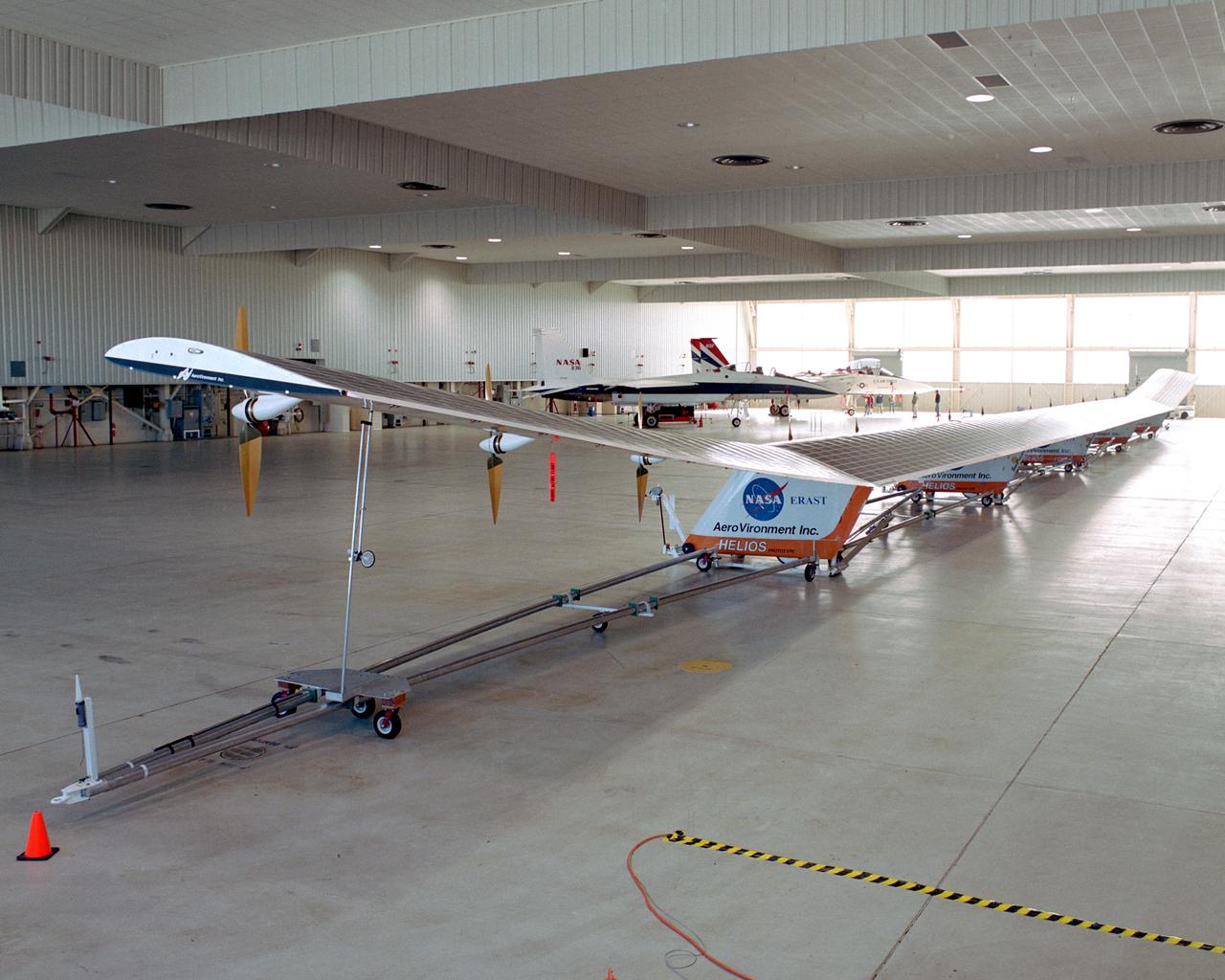

The solar-powered Helios Prototype flying wing frames two modified F-15 research aircraft in a hangar at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The elongated 247-foot span lightweight aircraft, resting on its ground maneuvering dolly, stretched almost the full length of the 300-foot long hangar while on display during a visit of NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe and other NASA officials on Jan. 31, 2002. The unique solar-electric flying wing reached an altitude of 96,863 feet during an almost 17-hour flight near Hawaii on Aug. 13, 2001, a world record for sustained horizontal flight by a non-rocket powered aircraft. Developed by AeroVironment, Inc., under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) project, the Helios Prototype is the forerunner of a planned fleet of slow-flying, long duration, high-altitude uninhabited aerial vehicles (UAV) which can serve as "atmospheric satellites," performing Earth science missions or functioning as telecommunications relay platforms in the stratosphere.

The first flight of a large aircraft to be powered by electric fuel cells began with a takeoff at 8:43 a.m. HST today from the Hawaiian island of Kauai. The Helios Prototype flying wing, built by AeroVironment, Inc., of Monrovia, Calif., as part of NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program, used solar panels to power its 10 electric motors for takeoff and during daylight portions of its planned 20-hour shakedown flight. As sunlight diminishes, Helios will switch to a fuel cell system to continue flight into the night. The takeoff set the stage for a two-day Helios endurance flight in the stratosphere planned for mid-July. The Helios wing, spanning 247 feet and weighing about 2,400 pounds, is giving NASA and industry engineers confidence that remotely piloted aircraft will be able to stay aloft for weeks at a time, providing environmental monitoring capabilities and telecommunications relay services. Helios is an all-electric airplane. In addition to being non-polluting, Helios can fly above storms, and use the power of the sun to stay aloft during daylight. Key to the success of this type of aircraft is the ability to fly in darkness, using fuel cells when sunlight cannot furnish energy. Helios flew over the Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility where favorable sun exposure and test ranges closed to other air traffic benefited the NASA research effort. In 2003 the aircraft was lost to a crash.
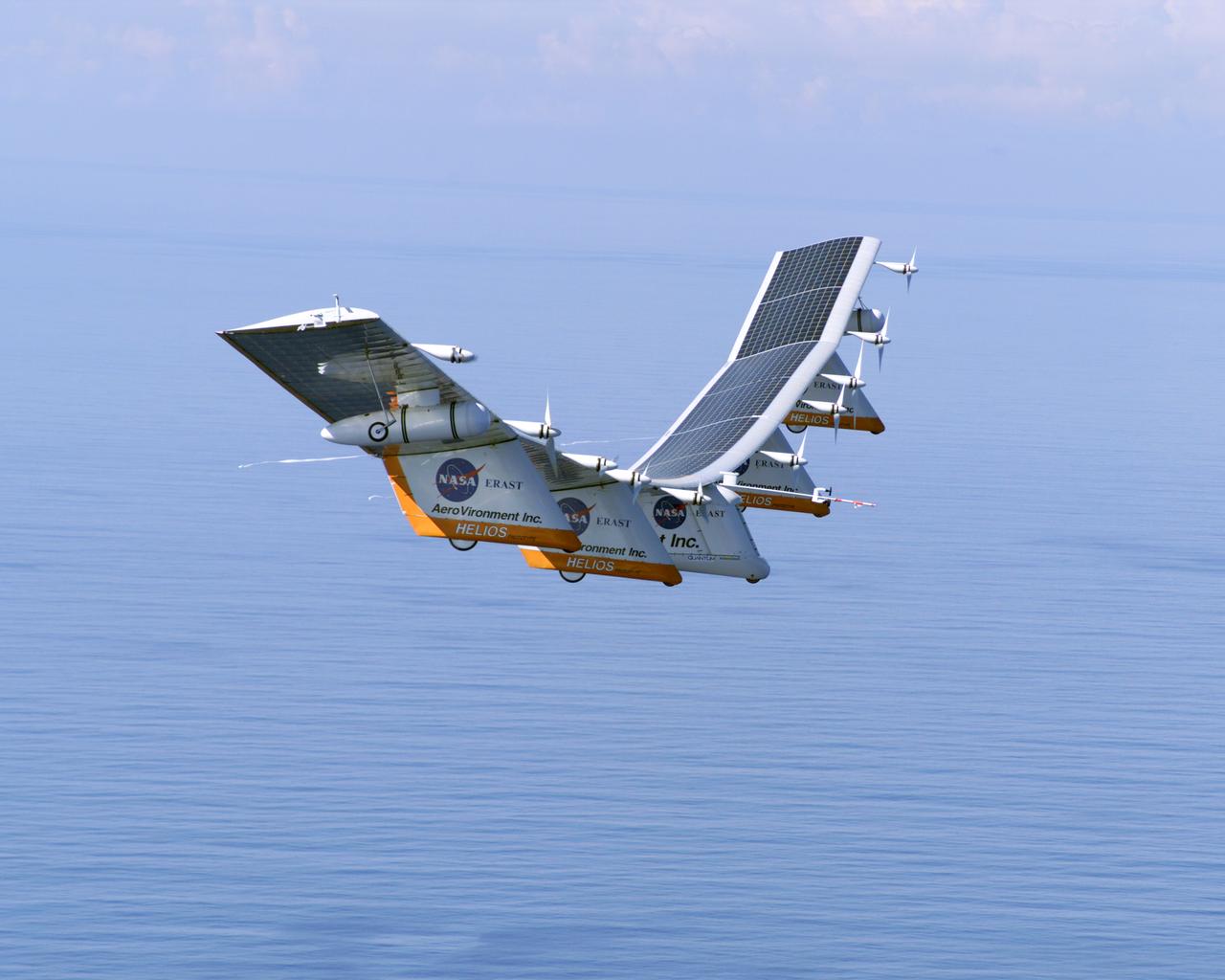

The first flight of a large aircraft to be powered by electric fuel cells began with a takeoff at 8:43 a.m. HST today from the Hawaiian island of Kauai. The Helios Prototype flying wing, built by AeroVironment, Inc., of Monrovia, Calif., as part of NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program, used solar panels to power its 10 electric motors for takeoff and during daylight portions of its planned 20-hour shakedown flight. As sunlight diminishes, Helios will switch to a fuel cell system to continue flight into the night. The takeoff set the stage for a two-day Helios endurance flight in the stratosphere planned for mid-July. The Helios wing, spanning 247 feet and weighing about 2,400 pounds, is giving NASA and industry engineers confidence that remotely piloted aircraft will be able to stay aloft for weeks at a time, providing environmental monitoring capabilities and telecommunications relay services. Helios is an all-electric airplane. In addition to being non-polluting, Helios can fly above storms, and use the power of the sun to stay aloft during daylight. Key to the success of this type of aircraft is the ability to fly in darkness, using fuel cells when sunlight cannot furnish energy. Helios flew over the Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility where favorable sun exposure and test ranges closed to other air traffic benefited the NASA research effort. In 2003 the aircraft was lost to a crash.

The first flight of a large aircraft to be powered by electric fuel cells began with a takeoff at 8:43 a.m. HST today from the Hawaiian island of Kauai. The Helios Prototype flying wing, built by AeroVironment, Inc., of Monrovia, Calif., as part of NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program, used solar panels to power its 10 electric motors for takeoff and during daylight portions of its planned 20-hour shakedown flight. As sunlight diminishes, Helios will switch to a fuel cell system to continue flight into the night. The takeoff set the stage for a two-day Helios endurance flight in the stratosphere planned for mid-July. The Helios wing, spanning 247 feet and weighing about 2,400 pounds, is giving NASA and industry engineers confidence that remotely piloted aircraft will be able to stay aloft for weeks at a time, providing environmental monitoring capabilities and telecommunications relay services. Helios is an all-electric airplane. In addition to being non-polluting, Helios can fly above storms, and use the power of the sun to stay aloft during daylight. Key to the success of this type of aircraft is the ability to fly in darkness, using fuel cells when sunlight cannot furnish energy. Helios flew over the Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility where favorable sun exposure and test ranges closed to other air traffic benefited the NASA research effort. In 2003 the aircraft was lost to a crash.

The first flight of a large aircraft to be powered by electric fuel cells began with a takeoff at 8:43 a.m. HST today from the Hawaiian island of Kauai. The Helios Prototype flying wing, built by AeroVironment, Inc., of Monrovia, Calif., as part of NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program, used solar panels to power its 10 electric motors for takeoff and during daylight portions of its planned 20-hour shakedown flight. As sunlight diminishes, Helios will switch to a fuel cell system to continue flight into the night. The takeoff set the stage for a two-day Helios endurance flight in the stratosphere planned for mid-July. The Helios wing, spanning 247 feet and weighing about 2,400 pounds, is giving NASA and industry engineers confidence that remotely piloted aircraft will be able to stay aloft for weeks at a time, providing environmental monitoring capabilities and telecommunications relay services. Helios is an all-electric airplane. In addition to being non-polluting, Helios can fly above storms, and use the power of the sun to stay aloft during daylight. Key to the success of this type of aircraft is the ability to fly in darkness, using fuel cells when sunlight cannot furnish energy. Helios flew over the Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility where favorable sun exposure and test ranges closed to other air traffic benefited the NASA research effort. In 2003 the aircraft was lost to a crash.
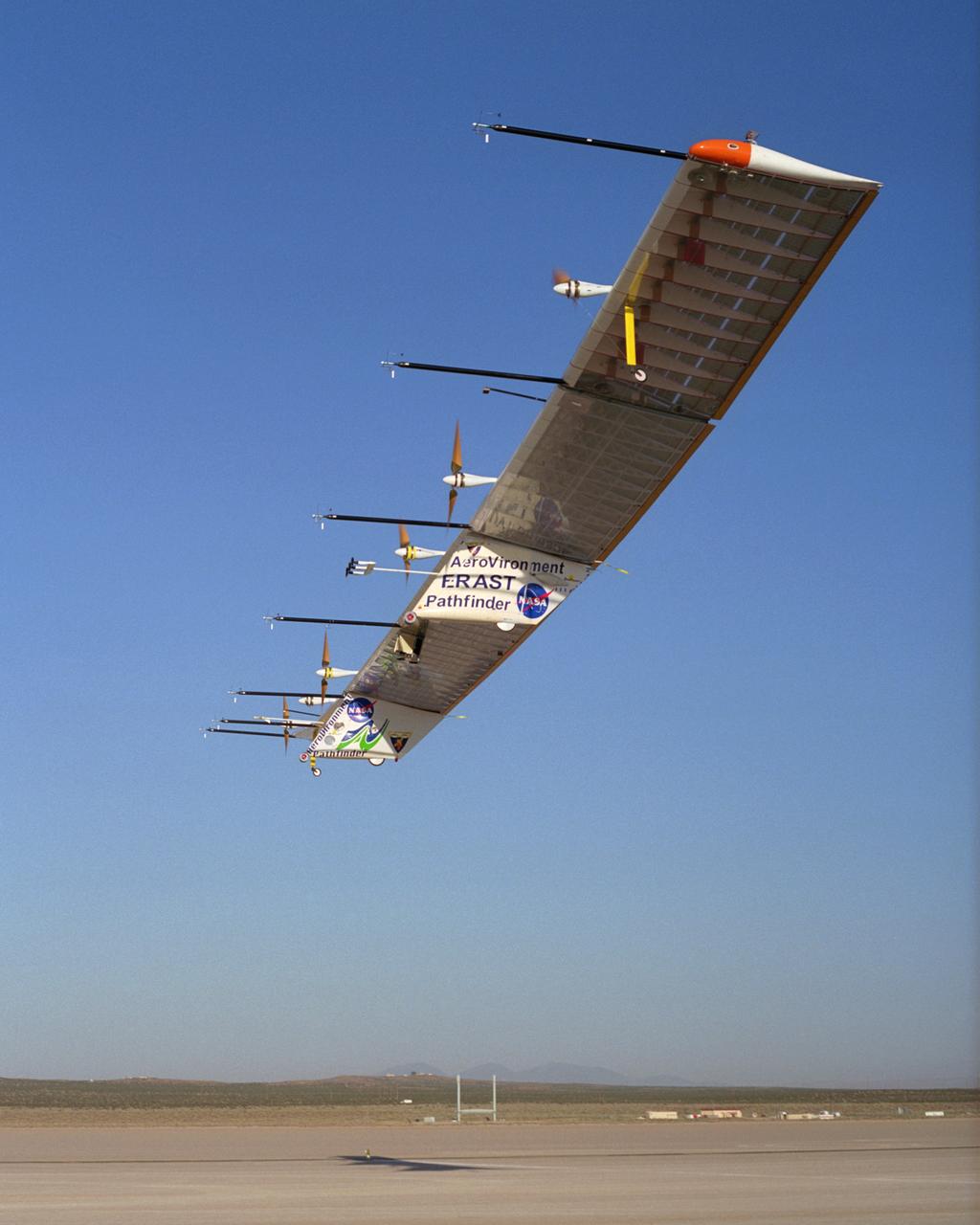

The Atmospheric Turbulence Measurement System booms extend forward from the Pathfinder-Plus solar wing as it soars over Rogers Dry Lake on its final flight.
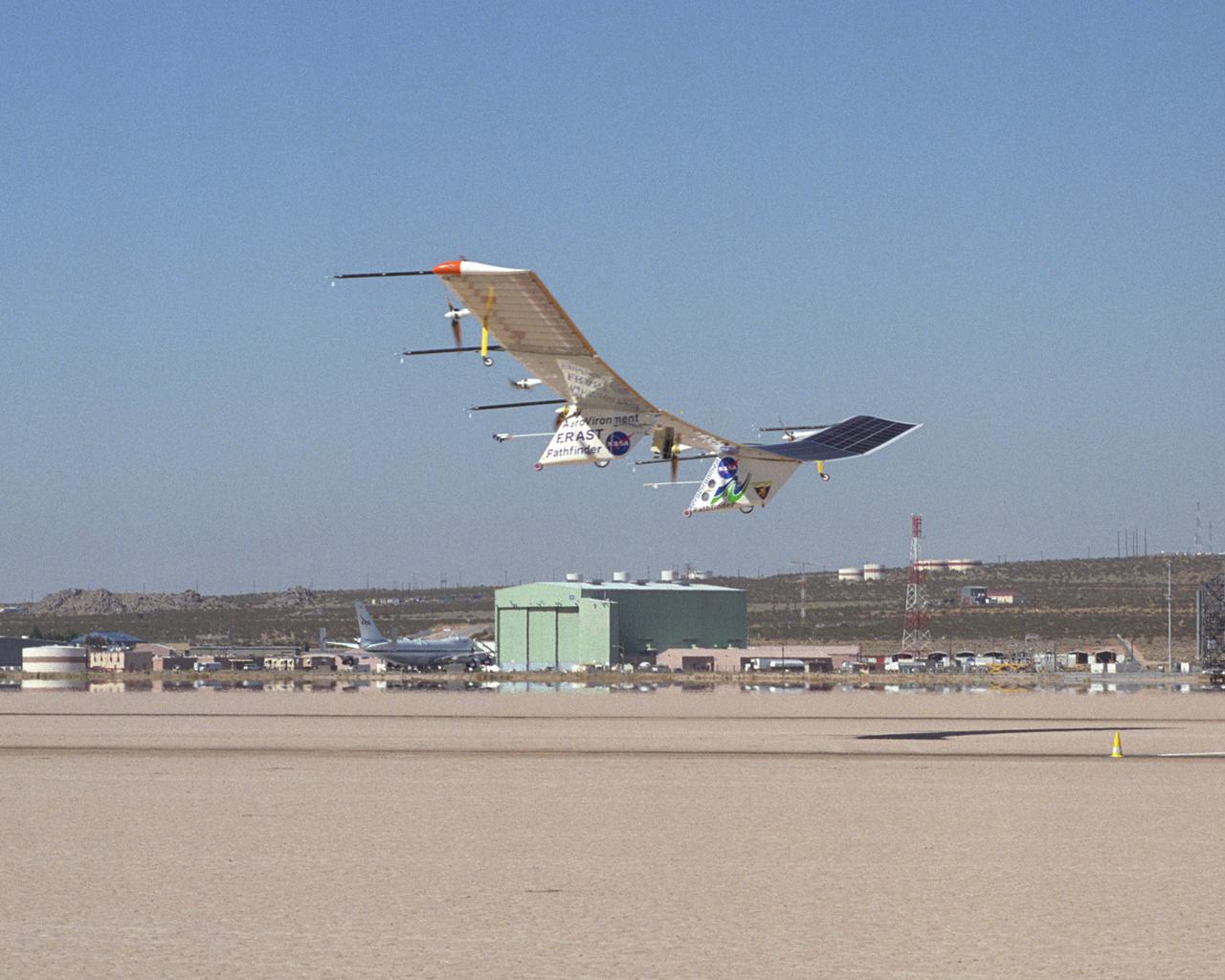

The Pathfinder-Plus solar aircraft flies past NASA Dryden's space shuttle hangar and shuttle carrier aircraft as it descends for landing on Rogers Dry Lake.
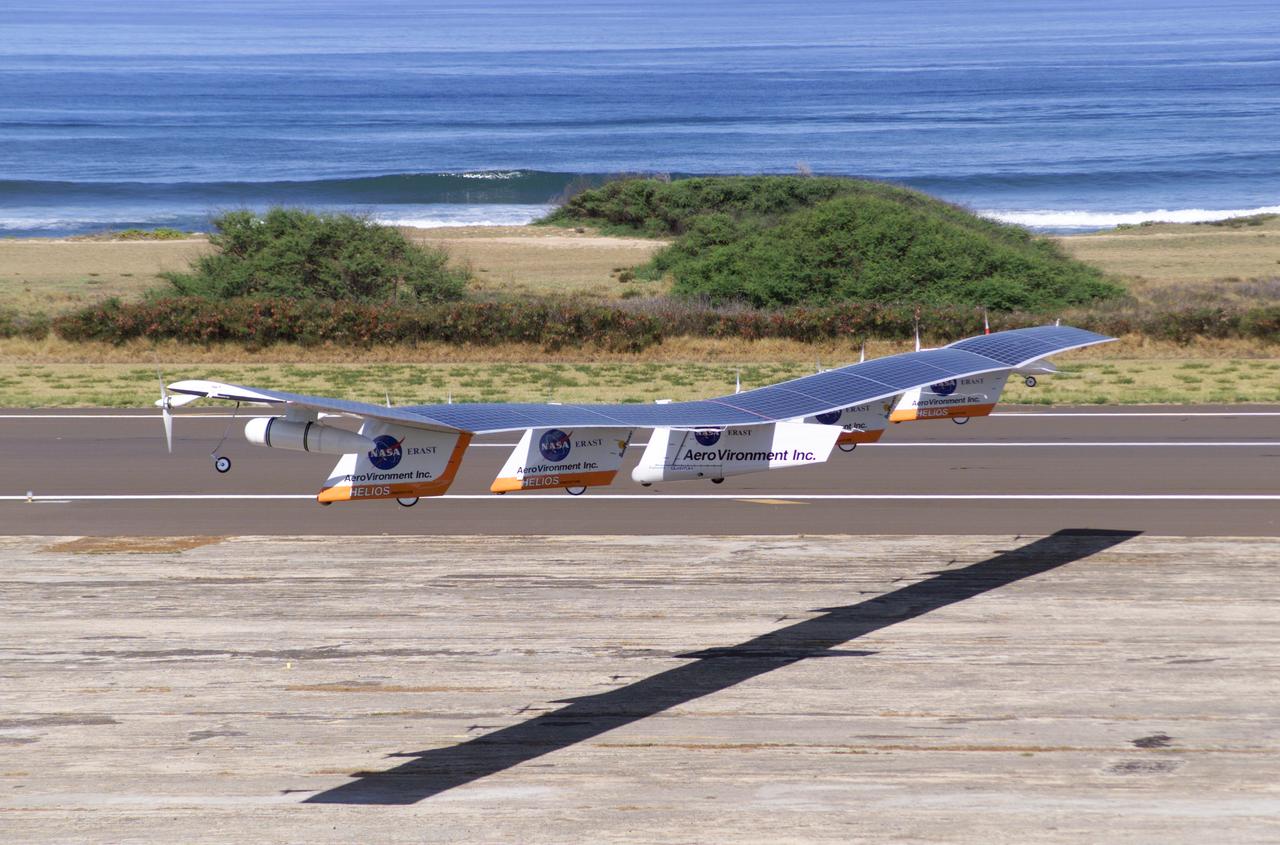

The first flight of a large aircraft to be powered by electric fuel cells began with a takeoff at 8:43 a.m. HST today from the Hawaiian island of Kauai. The Helios Prototype flying wing, built by AeroVironment, Inc., of Monrovia, Calif., as part of NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program, used solar panels to power its 10 electric motors for takeoff and during daylight portions of its planned 20-hour shakedown flight. As sunlight diminishes, Helios will switch to a fuel cell system to continue flight into the night. The takeoff set the stage for a two-day Helios endurance flight in the stratosphere planned for mid-July. The Helios wing, spanning 247 feet and weighing about 2,400 pounds, gave NASA and industry engineers confidence that remotely piloted aircraft would be able to stay aloft for weeks at a time, providing environmental monitoring capabilities and telecommunications relay services. Helios was an all-electric airplane. In addition to being non-polluting, Helios flew above storms, and used the power of the sun to stay aloft during daylight. Key to the success of this type of aircraft was the ability to fly in darkness, using fuel cells when sunlight cannot furnish energy. Helios flew over the Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility where favorable sun exposure and test ranges closed to other air traffic benefited the NASA research effort. In 2003 the aircraft was lost to a crash.
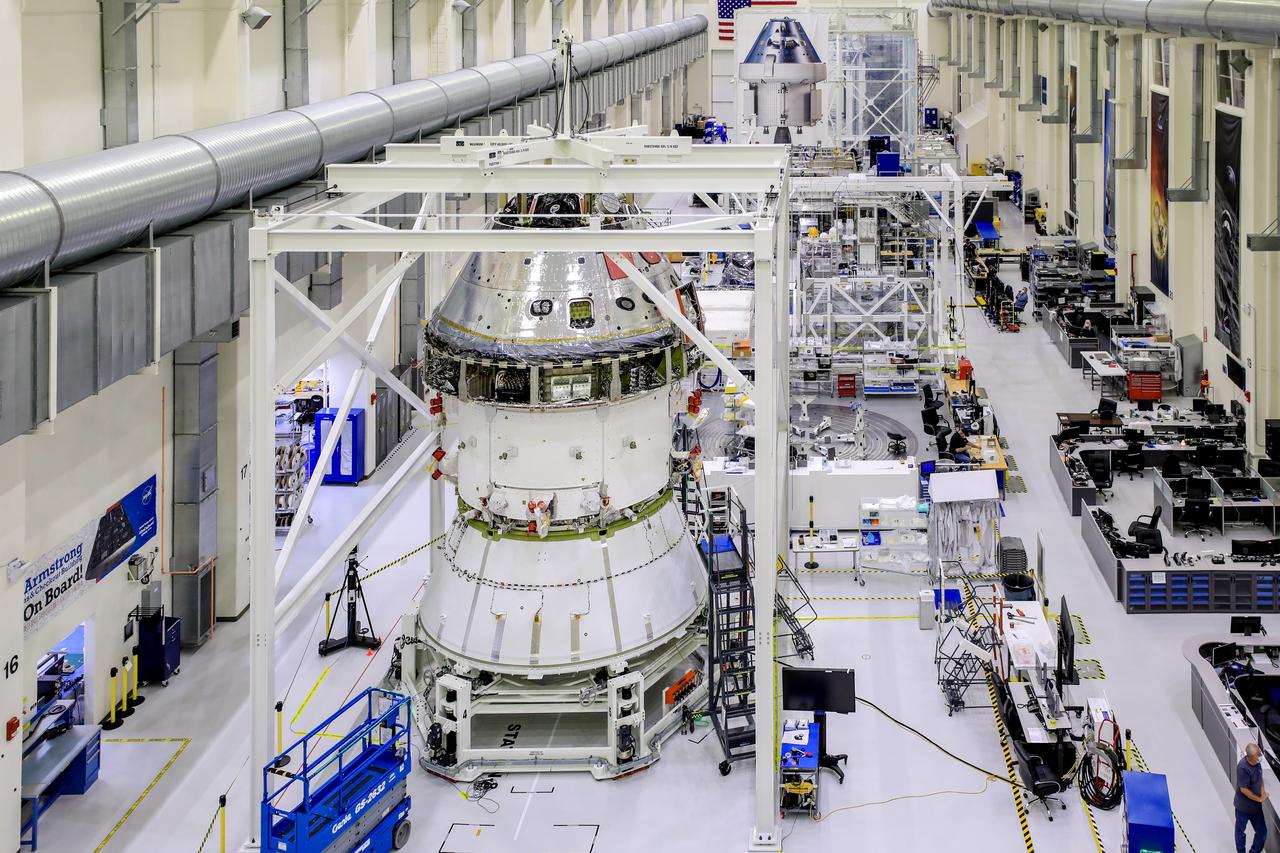

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida are working to install an adapter that will connect the Orion spacecraft to its rocket for the Artemis I mission around the Moon. This is one of the final major hardware operations for Orion inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building prior to integration with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket...The spacecraft adapter cone (seen at the bottom of the stack pictured above) connects to the bottom of Orion’s service module and will later join another adapter connected to the top of the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). During the process to install the cone on Orion, the spacecraft is lifted out of the Final Assembly and Systems Testing, or FAST, cell and placed into the Super Station support fixture...During flight, the SLS rocket separates in multiple stages as it pushes Orion into deep space. After accelerating Orion towards the Moon, the spacecraft will separate from the ICPS and adapter cone using pyrotechnics and springs...Next up before stacking Orion on the rocket, technicians will install coverings to protect fluid lines and electrical components on the crew module adapter that connects Orion to the service module. Workers also will install the solar array wings that will provide Orion with power, spacecraft adapter jettison fairings that enclose the service module for launch, and the forward bay cover that protects the parachute system. ..Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will lead to human exploration of Mars. Through the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024
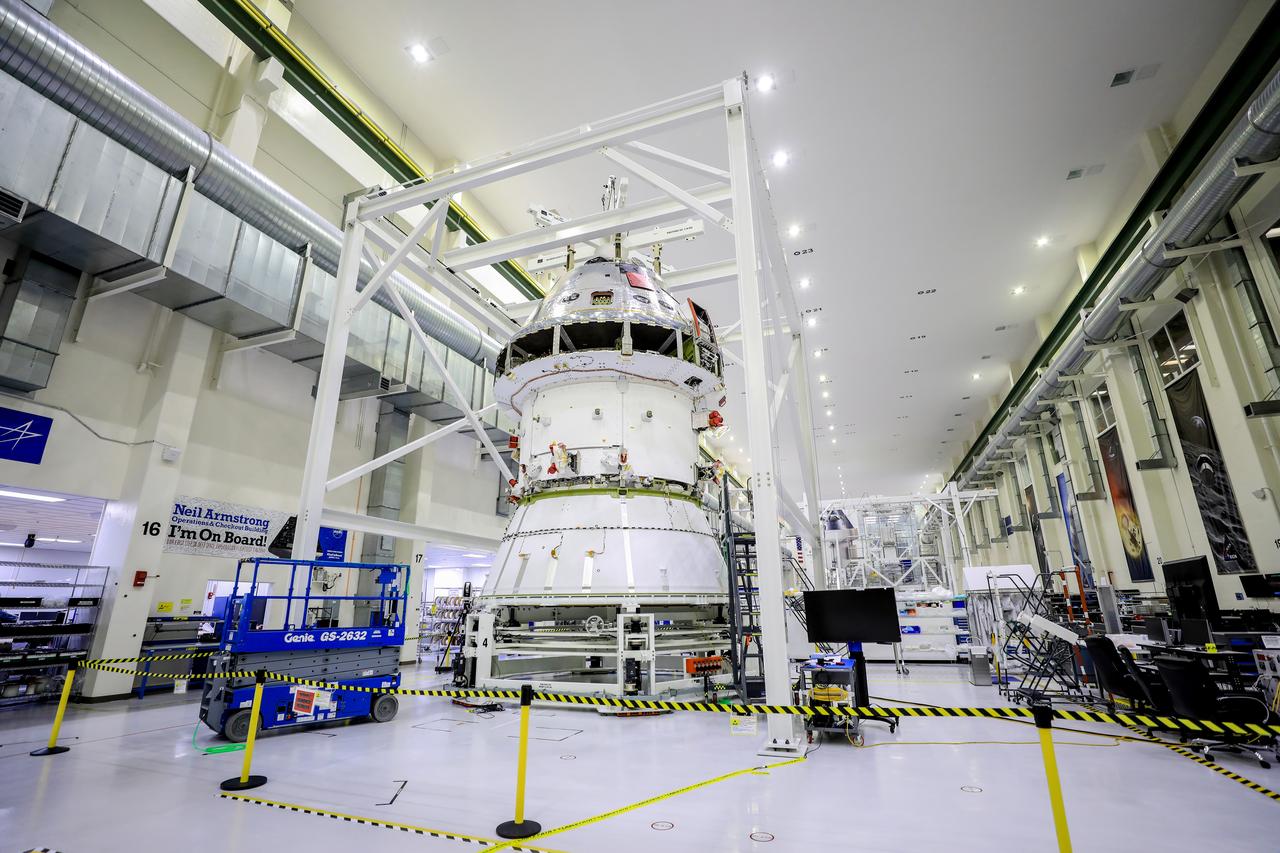

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida working to install an adapter that will connect the Orion spacecraft to its rocket for the Artemis I mission around the Moon on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations for Orion inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building prior to integration with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket...The spacecraft adapter cone (seen at the bottom of the stack pictured above) connects to the bottom of Orion’s service module and will later join another adapter connected to the top of the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). During the process to install the cone on Orion, the spacecraft is lifted out of the Final Assembly and Systems Testing, or FAST, cell and placed into the Super Station support fixture...During flight, the SLS rocket separates in multiple stages as it pushes Orion into deep space. After accelerating Orion towards the Moon, the spacecraft will separate from the ICPS and adapter cone using pyrotechnics and springs...Next up before stacking Orion on the rocket, technicians will install coverings to protect fluid lines and electrical components on the crew module adapter that connects Orion to the service module. Workers also will install the solar array wings that will provide Orion with power, spacecraft adapter jettison fairings that enclose the service module for launch, and the forward bay cover that protects the parachute system. ..Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will lead to human exploration of Mars.