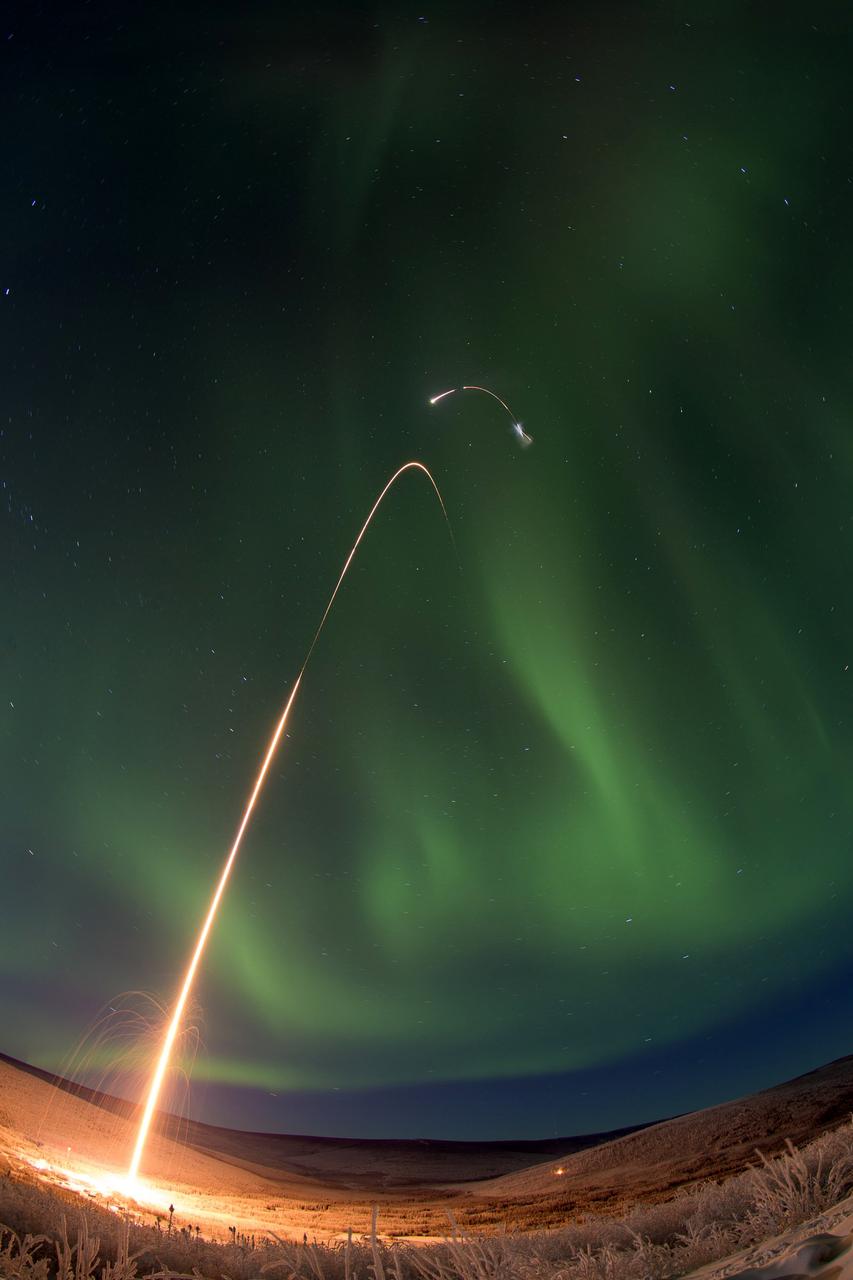

Caption: Time lapse photo of the NASA Oriole IV sounding rocket with Aural Spatial Structures Probe as an aurora dances over Alaska. All four stages of the rocket are visible in this image. Credit: NASA/Jamie Adkins More info: On count day number 15, the Aural Spatial Structures Probe, or ASSP, was successfully launched on a NASA Oriole IV sounding rocket at 5:41 a.m. EST on Jan. 28, 2015, from the Poker Flat Research Range in Alaska. Preliminary data show that all aspects of the payload worked as designed and the principal investigator Charles Swenson at Utah State University described the mission as a “raging success.” “This is likely the most complicated mission the sounding rocket program has ever undertaken and it was not easy by any stretch," said John Hickman, operations manager of the NASA sounding rocket program office at the Wallops Flight Facility, Virginia. "It was technically challenging every step of the way.” “The payload deployed all six sub-payloads in formation as planned and all appeared to function as planned. Quite an amazing feat to maneuver and align the main payload, maintain the proper attitude while deploying all six 7.3-pound sub payloads at about 40 meters per second," said Hickman. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/assp-sounding-rocket-launches-successfully-from-alaska/#.VMkOnEhpEhJ" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/assp-sounding-rocket-launches-succes...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
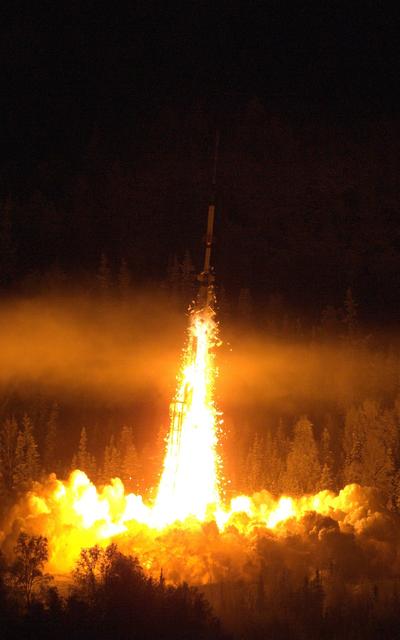

A NASA Oriole IV sounding rocket with the Aural Spatial Structures Probe leaves the launch pad on Jan. 28, 2015, from the Poker Flat Research Range in Alaska. Credit: NASA/Lee Wingfield More info: On count day number 15, the Aural Spatial Structures Probe, or ASSP, was successfully launched on a NASA Oriole IV sounding rocket at 5:41 a.m. EST on Jan. 28, 2015, from the Poker Flat Research Range in Alaska. Preliminary data show that all aspects of the payload worked as designed and the principal investigator Charles Swenson at Utah State University described the mission as a “raging success.” “This is likely the most complicated mission the sounding rocket program has ever undertaken and it was not easy by any stretch," said John Hickman, operations manager of the NASA sounding rocket program office at the Wallops Flight Facility, Virginia. "It was technically challenging every step of the way.” “The payload deployed all six sub-payloads in formation as planned and all appeared to function as planned. Quite an amazing feat to maneuver and align the main payload, maintain the proper attitude while deploying all six 7.3-pound sub payloads at about 40 meters per second," said Hickman. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/assp-sounding-rocket-launches-successfully-from-alaska/#.VMkOnEhpEhJ" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/assp-sounding-rocket-launches-succes...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
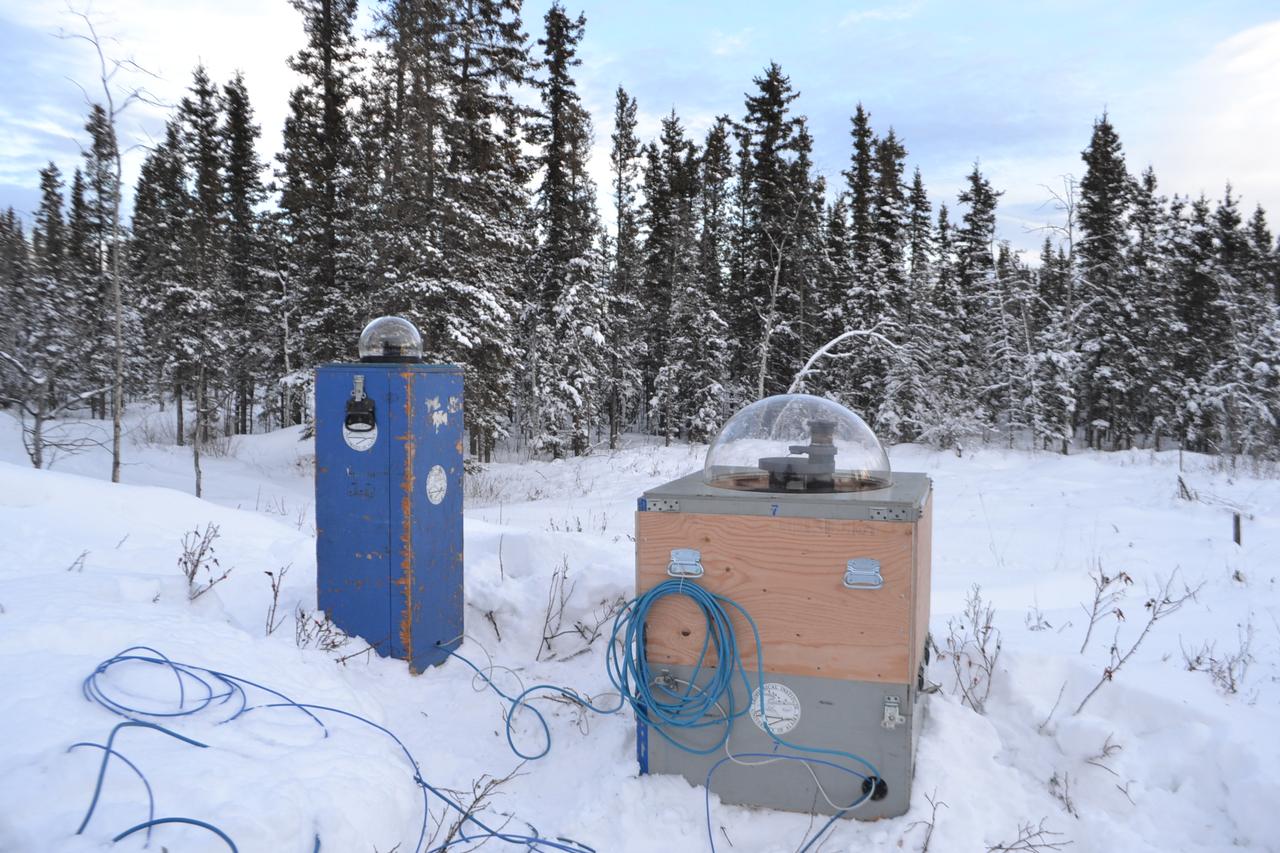

The NASA-funded Ground-to-Rocket Electron-Electrodynamics Correlative Experiment, or GREECE, wants to understand aurora. Specifically, it will study classic auroral curls that swirl through the sky like cream in a cup of coffee. The GREECE instruments travel on a sounding rocket that launches for a ten-minute ride right through the heart of the aurora reaching its zenith over the native village of Venetie, Alaska. To study the curl structures, GREECE consists of two parts: ground-based imagers located in Venetie to track the aurora from the ground and the rocket to take measurements from the middle of the aurora itself. At their simplest, auroras are caused when particles from the sun funnel over to Earth's night side, generate electric currents, and trigger a shower of particles that strike oxygen and nitrogen some 60 to 200 miles up in Earth's atmosphere, releasing a flash of light. But the details are always more complicated, of course. Researchers wish to understand the aurora, and movement of plasma in general, at much smaller scales including such things as how different structures are formed there. This is a piece of information, which in turn, helps paint a picture of the sun-Earth connection and how energy and particles from the sun interact with Earth's own magnetic system, the magnetosphere. GREECE is a collaborative effort between SWRI, which developed particle instruments and the ground-based imaging, and the University of California, Berkeley, measuring the electric and magnetic fields. The launch is supported by a sounding rocket team from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Va. The Poker Flat Research Range is operated by the University of Alaska, Fairbanks. Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

The NASA-funded Ground-to-Rocket Electron-Electrodynamics Correlative Experiment, or GREECE, wants to understand aurora. Specifically, it will study classic auroral curls that swirl through the sky like cream in a cup of coffee. The GREECE instruments travel on a sounding rocket that launches for a ten-minute ride right through the heart of the aurora reaching its zenith over the native village of Venetie, Alaska. To study the curl structures, GREECE consists of two parts: ground-based imagers located in Venetie to track the aurora from the ground and the rocket to take measurements from the middle of the aurora itself. At their simplest, auroras are caused when particles from the sun funnel over to Earth's night side, generate electric currents, and trigger a shower of particles that strike oxygen and nitrogen some 60 to 200 miles up in Earth's atmosphere, releasing a flash of light. But the details are always more complicated, of course. Researchers wish to understand the aurora, and movement of plasma in general, at much smaller scales including such things as how different structures are formed there. This is a piece of information, which in turn, helps paint a picture of the sun-Earth connection and how energy and particles from the sun interact with Earth's own magnetic system, the magnetosphere. GREECE is a collaborative effort between SWRI, which developed particle instruments and the ground-based imaging, and the University of California, Berkeley, measuring the electric and magnetic fields. The launch is supported by a sounding rocket team from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Va. The Poker Flat Research Range is operated by the University of Alaska, Fairbanks. Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

The NASA-funded Ground-to-Rocket Electron-Electrodynamics Correlative Experiment, or GREECE, wants to understand aurora. Specifically, it will study classic auroral curls that swirl through the sky like cream in a cup of coffee. The GREECE instruments travel on a sounding rocket that launches for a ten-minute ride right through the heart of the aurora reaching its zenith over the native village of Venetie, Alaska. To study the curl structures, GREECE consists of two parts: ground-based imagers located in Venetie to track the aurora from the ground and the rocket to take measurements from the middle of the aurora itself. At their simplest, auroras are caused when particles from the sun funnel over to Earth's night side, generate electric currents, and trigger a shower of particles that strike oxygen and nitrogen some 60 to 200 miles up in Earth's atmosphere, releasing a flash of light. But the details are always more complicated, of course. Researchers wish to understand the aurora, and movement of plasma in general, at much smaller scales including such things as how different structures are formed there. This is a piece of information, which in turn, helps paint a picture of the sun-Earth connection and how energy and particles from the sun interact with Earth's own magnetic system, the magnetosphere. GREECE is a collaborative effort between SWRI, which developed particle instruments and the ground-based imaging, and the University of California, Berkeley, measuring the electric and magnetic fields. The launch is supported by a sounding rocket team from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Va. The Poker Flat Research Range is operated by the University of Alaska, Fairbanks. Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Air Force Javelin Rocket on Launcher (USAF JV-1) Wallops Model D4-78 L59-5144 First AFSWC Javelin sounding rocket ready for flight test, July 7, 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 704.

Air Force Javelin Rocket on Launcher (USAF JV-1) Wallops Model D4-78 L59-5144 First AFSWC Javelin sounding rocket ready for flight test, July 7, 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 704.

Air Force Javelin Rocket on Launcher (USAF JV-1) Wallops Model D4-78 L59-5144 First AFSWC Javelin sounding rocket ready for flight test, July 7, 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 704.

Air Force Javelin Rocket on Launcher (USAF JV-1) Wallops Model D4-78 L59-5144 First AFSWC Javelin sounding rocket ready for flight test, July 7, 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 704.

Air Force Javelin Rocket on Launcher (USAF JV-1) Wallops Model D4-78 L59-5144 First AFSWC Javelin sounding rocket ready for flight test, July 7, 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 704.

L59-7932 First University of Michigan Strongarm sounding rocket on launcher at Wallops for test, November 10, 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 701.E5-188 Shop and Launcher Pictures

L59-7932 First University of Michigan Strongarm sounding rocket on launcher at Wallops for test, November 10, 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 701.E5-188 Shop and Launcher Pictures

L59-7932 First University of Michigan Strongarm sounding rocket on launcher at Wallops for test, November 10, 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 701.E5-188 Shop and Launcher Pictures

L59-7932 First University of Michigan Strongarm sounding rocket on launcher at Wallops for test, November 10, 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 701.E5-188 Shop and Launcher Pictures

L59-7932 First University of Michigan Strongarm sounding rocket on launcher at Wallops for test, November 10, 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 701.E5-188 Shop and Launcher Pictures

L59-7932 First University of Michigan Strongarm sounding rocket on launcher at Wallops for test, November 10, 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 701.E5-188 Shop and Launcher Pictures

L59-3802 Nike-Cajun sounding rocket with University of Iowa payload on launcher at Wallops for flight test, May 20, 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 698.

L59-3802 Nike-Cajun sounding rocket with University of Iowa payload on launcher at Wallops for flight test, May 20, 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 698.
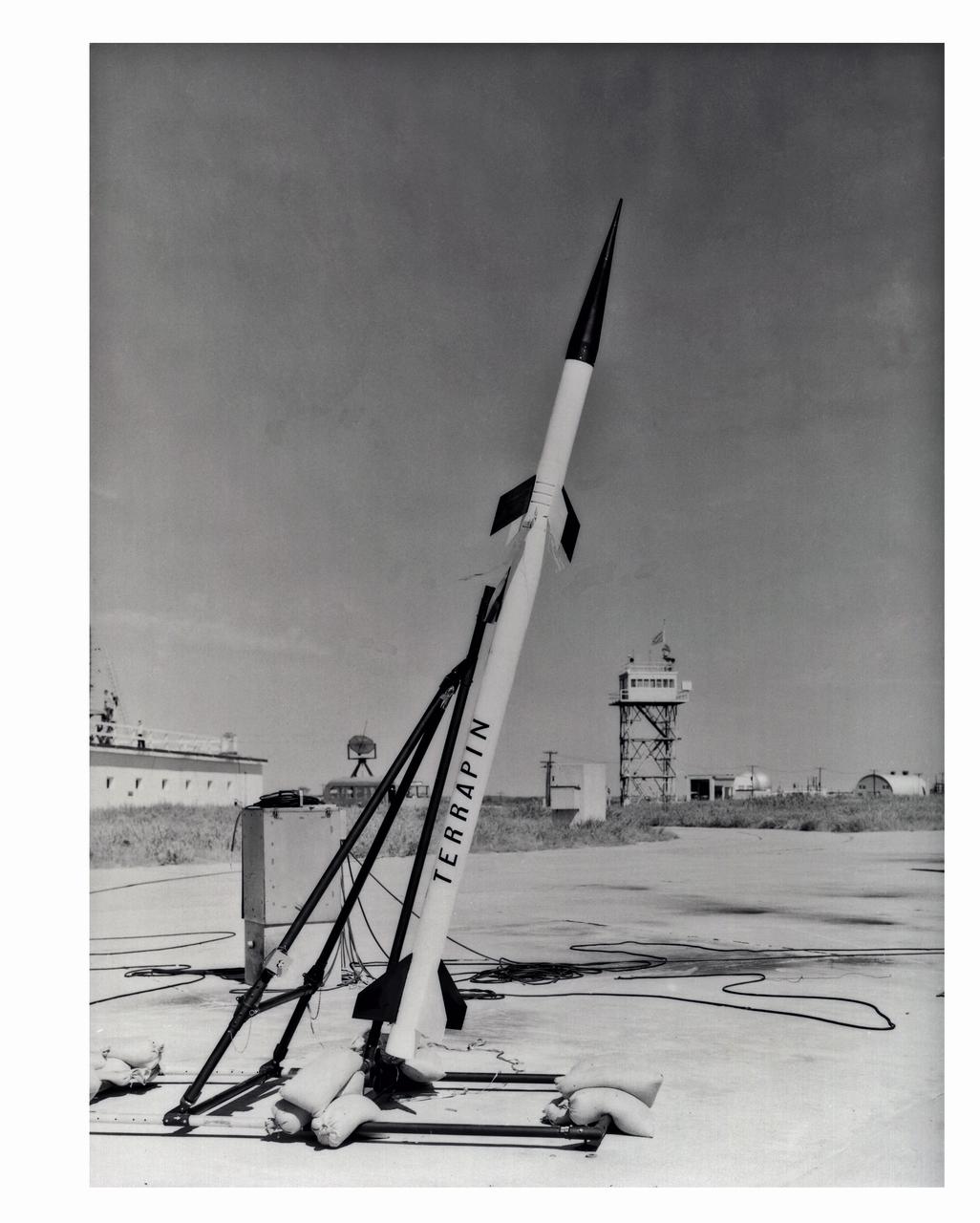

LAL 95,647 University of Maryland-Republic Terrapin sounding rocket mounted on special launcher, September 21, 1956. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 506.
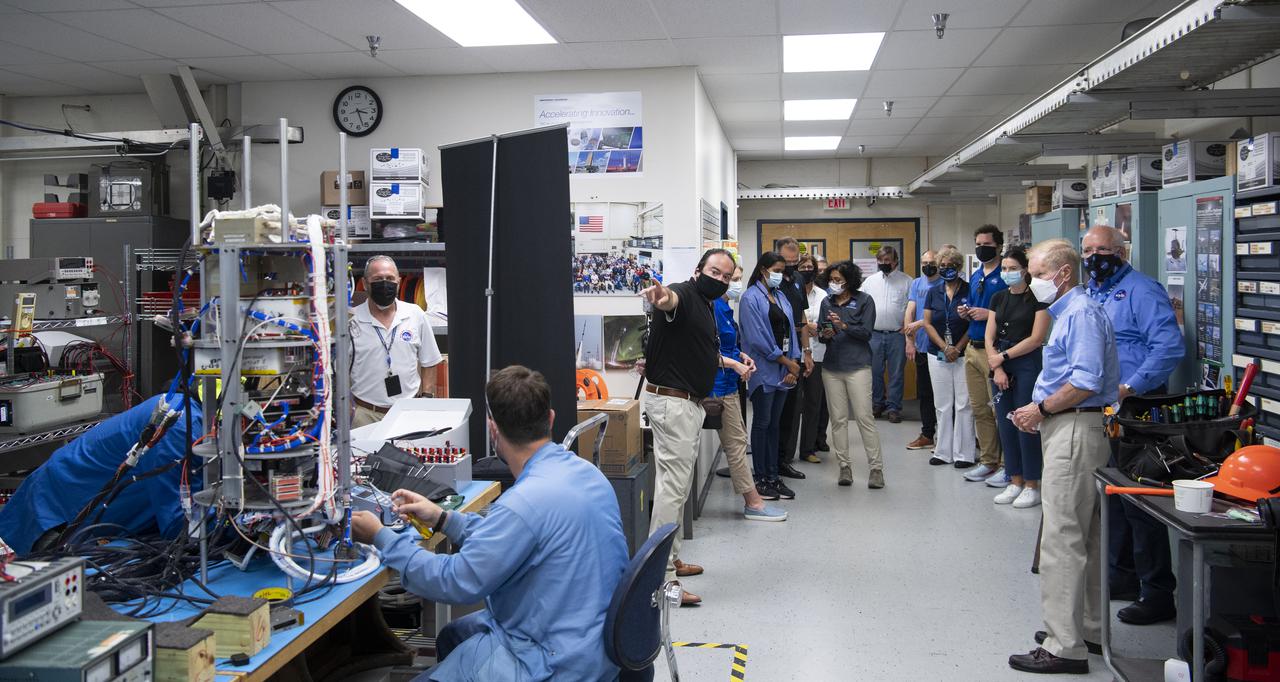

Giovanni Rosanova, chief of the Sounding Rocket Program Office at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility, center, describes work done in the Payload Integration Laboratory of the Sounding Rockets Machine Shop, Test and Evaluation Facility during a tour with NASA Administrator Bill Nelson and Dennis Andrucyk, director of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Tuesday, Aug. 10, 2021, at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
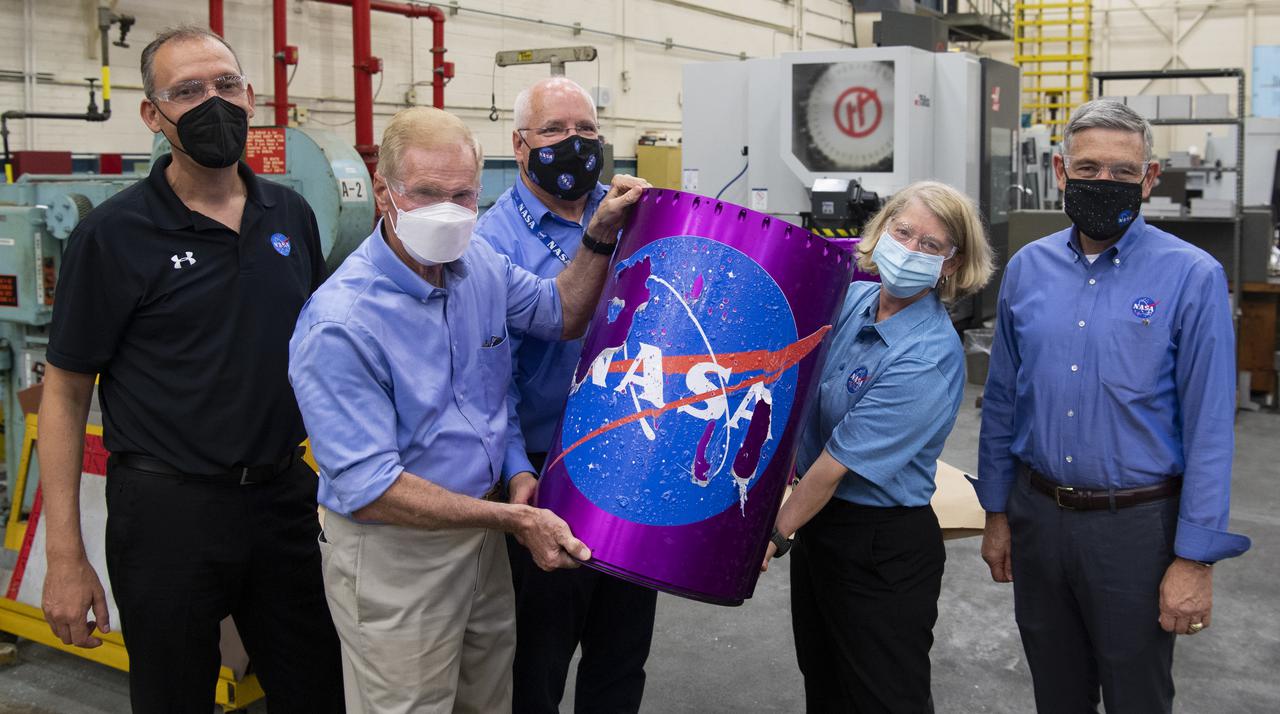

Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, left, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson second from left, Dennis Andrucyk, director of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, center, NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, second from right, and Bob Cabana, NASA associate administrator, right, hold a recovered portion of the Black Brant IX sounding rocket used for the Advanced Supersonic Parachute Inflation Research Experiment (ASPIRE), during a tour of the Sounding Rockets Machine Shop, Test and Evaluation Facility, Tuesday, Aug. 10, 2021, at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
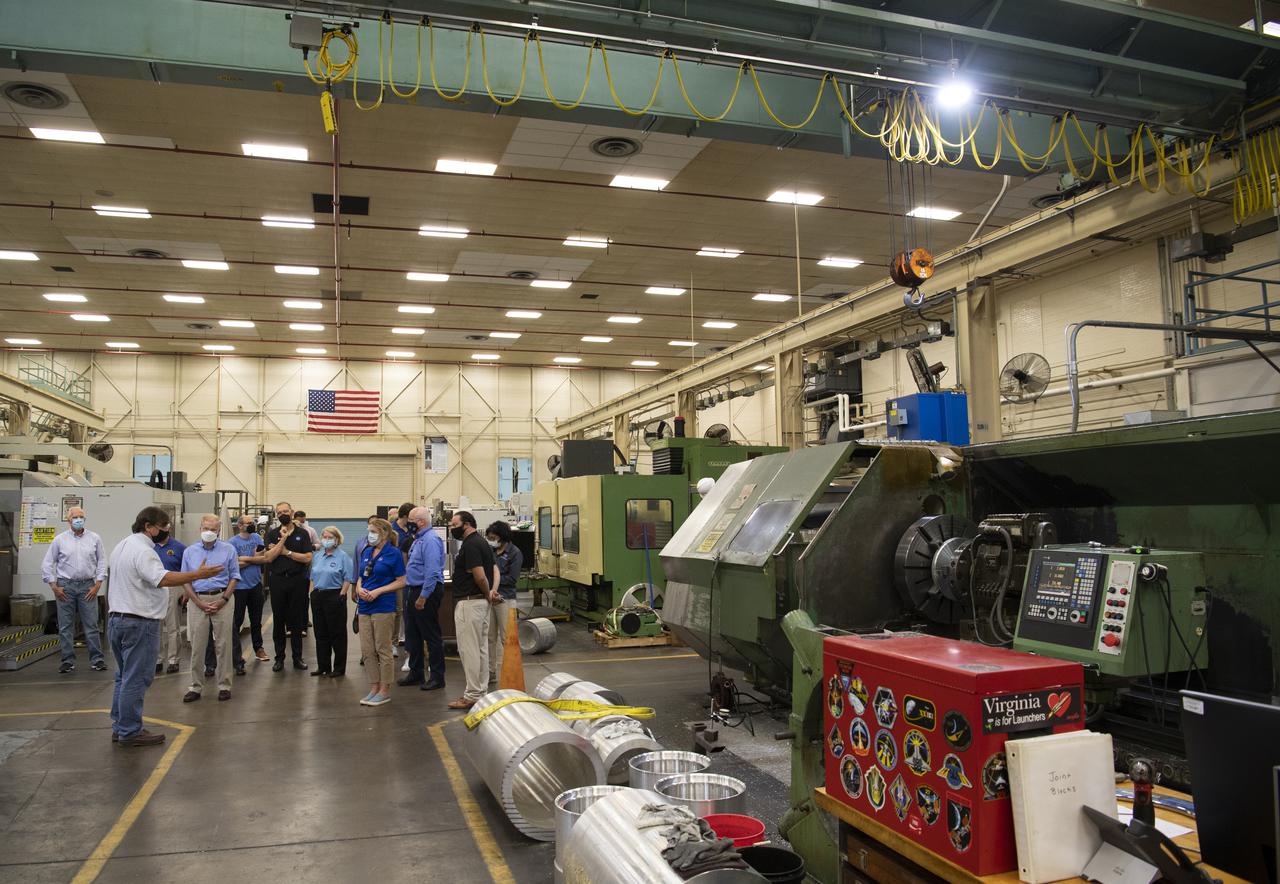

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Dave Pierce, director of NASA's Wallops Flight Facility, and Dennis Andrucyk, director of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, are seen during a tour of the Sounding Rockets Machine Shop, Test and Evaluation Facility, Tuesday, Aug. 10, 2021, at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

They sounded more like fireworks than rockets but the Chinese used rockets in battle.
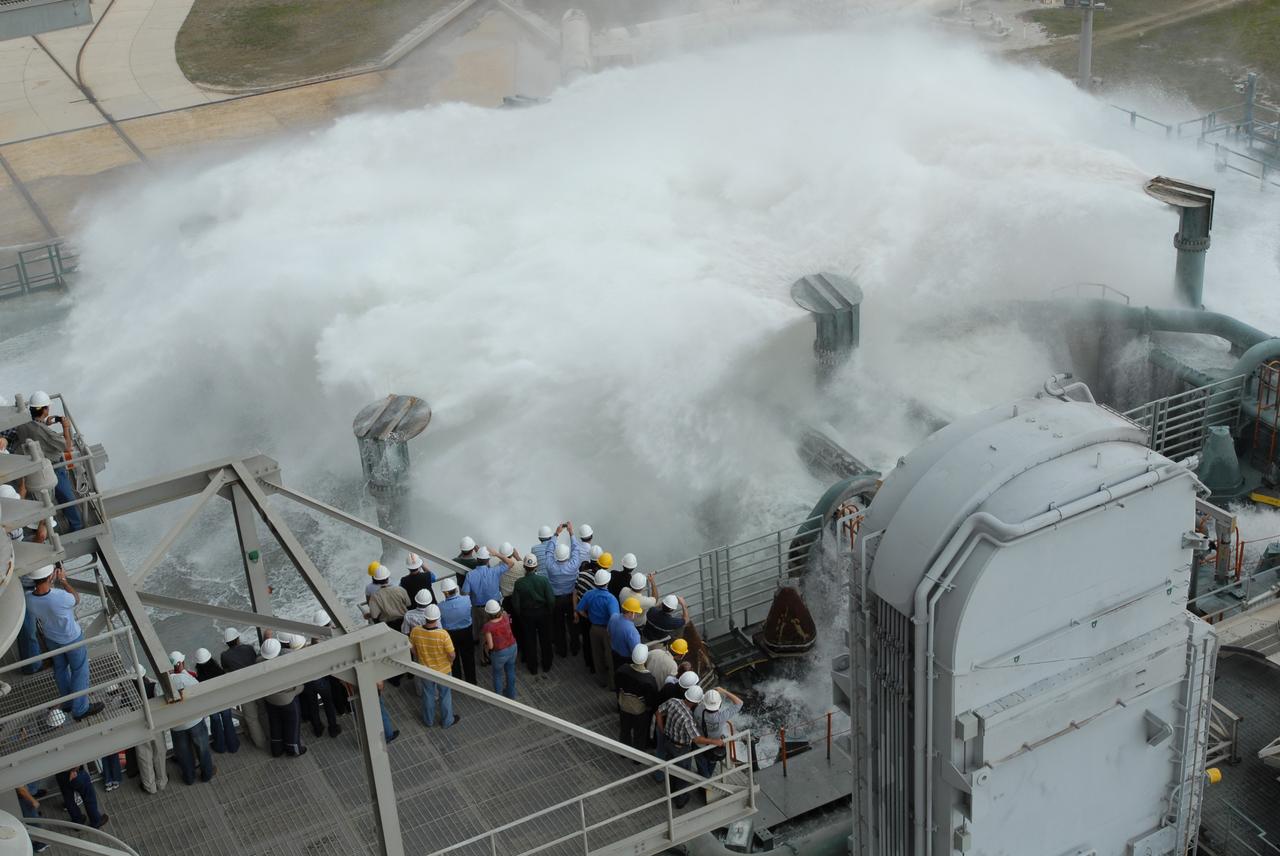

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The sound suppression system is tested on the mobile launcher platform on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X flight test that is targeted for summer 2009. The mobile launcher platform was handed over to the Constellation Program and modified for the Ares I-X flight test. It is being tested before being moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building for assembly of the Ares I-X rocket. A sound suppression water system is in¬stalled on the pads to protect against damage by acoustical energy and rocket exhaust reflected from the flame trench and mobile launcher plat¬form during a launch. The sound suppression system includes an elevated 290-foot-high water tank with a capacity of 300,000 gallons. The water releases just prior to the ignition of the rocket and flows through 7-foot-diameter pipes for about 20 seconds. A torrent of water will flow onto the mobile launcher platform from six large quench nozzles, or “rainbirds,” mounted on its surface. The rainbirds are 12 feet high. The two in the center are 42 inches in diameter; the other four have a 30-inch diameter. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
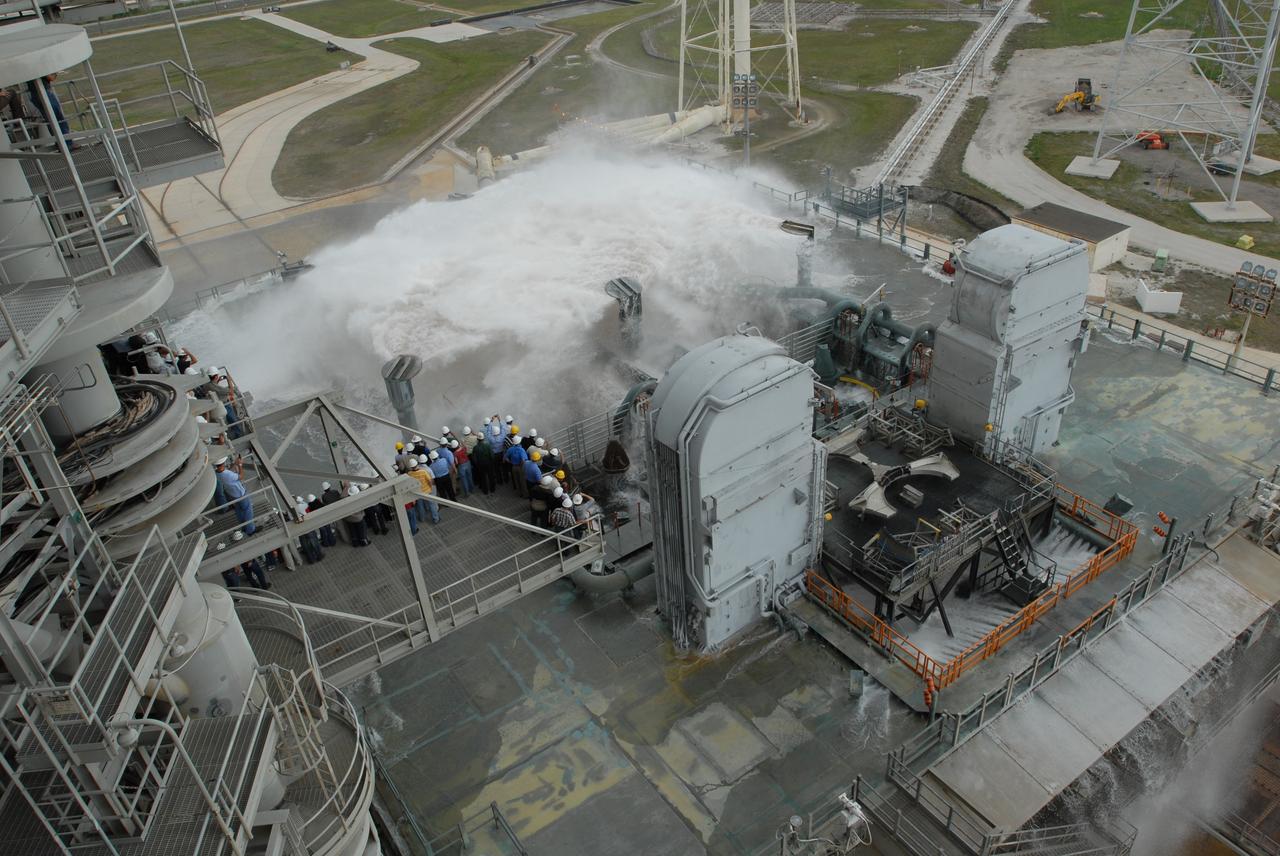

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The sound suppression system is tested on the mobile launcher platform on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X flight test that is targeted for summer 2009. The mobile launcher platform was handed over to the Constellation Program and modified for the Ares I-X flight test. It is being tested before being moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building for assembly of the Ares I-X rocket. A sound suppression water system is in¬stalled on the pads to protect against damage by acoustical energy and rocket exhaust reflected from the flame trench and mobile launcher plat¬form during a launch. The sound suppression system includes an elevated 290-foot-high water tank with a capacity of 300,000 gallons. The water releases just prior to the ignition of the rocket and flows through 7-foot-diameter pipes for about 20 seconds. A torrent of water will flow onto the mobile launcher platform from six large quench nozzles, or “rainbirds,” mounted on its surface. The rainbirds are 12 feet high. The two in the center are 42 inches in diameter; the other four have a 30-inch diameter. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
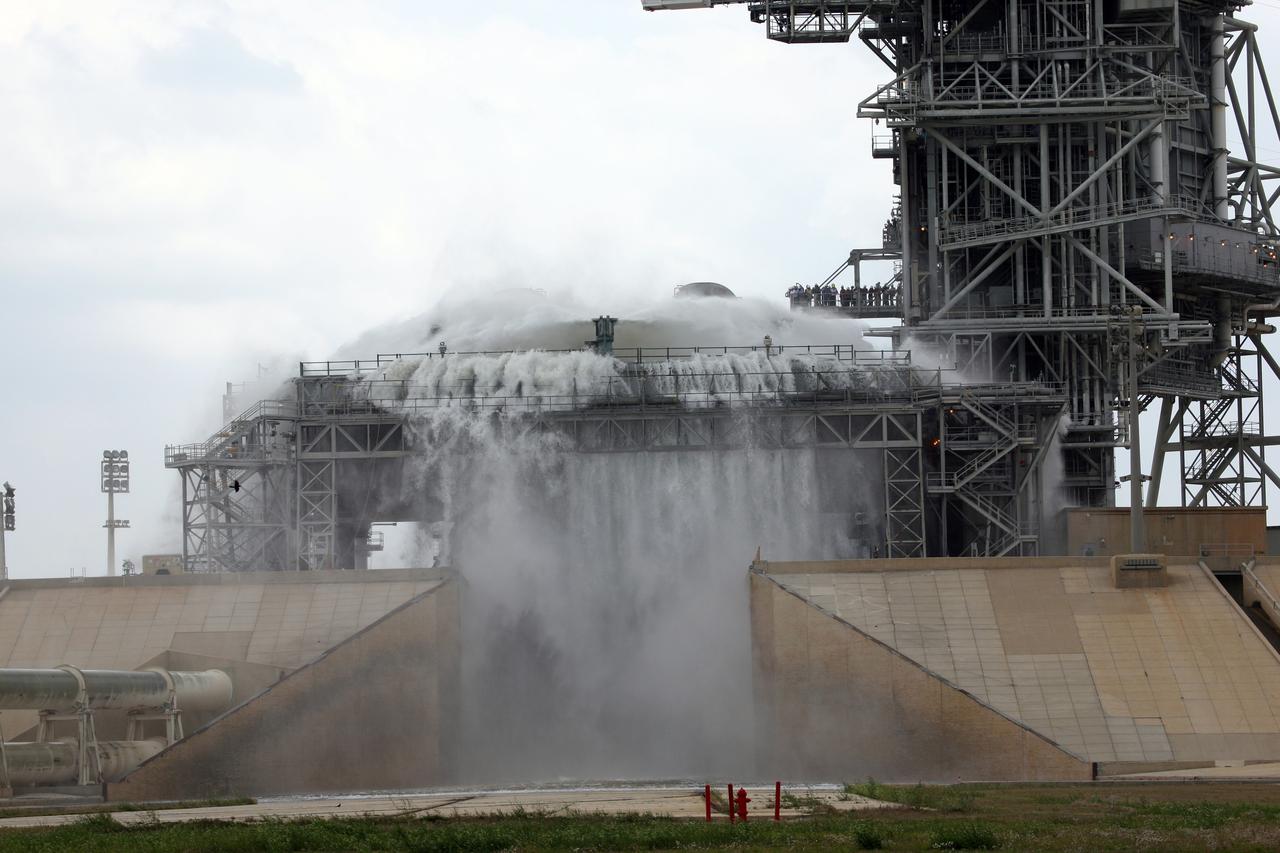

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Water cascades over the side of the mobile launcher platform on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The sound suppression system is being tested on the platform. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X flight test that is targeted for summer 2009. The mobile launcher platform was handed over to the Constellation Program and modified for the Ares I-X flight test. It is being tested before being moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building for assembly of the Ares I-X rocket. A sound suppression water system is in¬stalled on the pads to protect against damage by acoustical energy and rocket exhaust reflected from the flame trench and mobile launcher plat¬form during a launch. The sound suppression system includes an elevated 290-foot-high water tank with a capacity of 300,000 gallons. The water releases just prior to the ignition of the rocket and flows through 7-foot-diameter pipes for about 20 seconds. A torrent of water will flow onto the mobile launcher platform from six large quench nozzles, or “rainbirds,” mounted on its surface. The rainbirds are 12 feet high. The two in the center are 42 inches in diameter; the other four have a 30-inch diameter. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
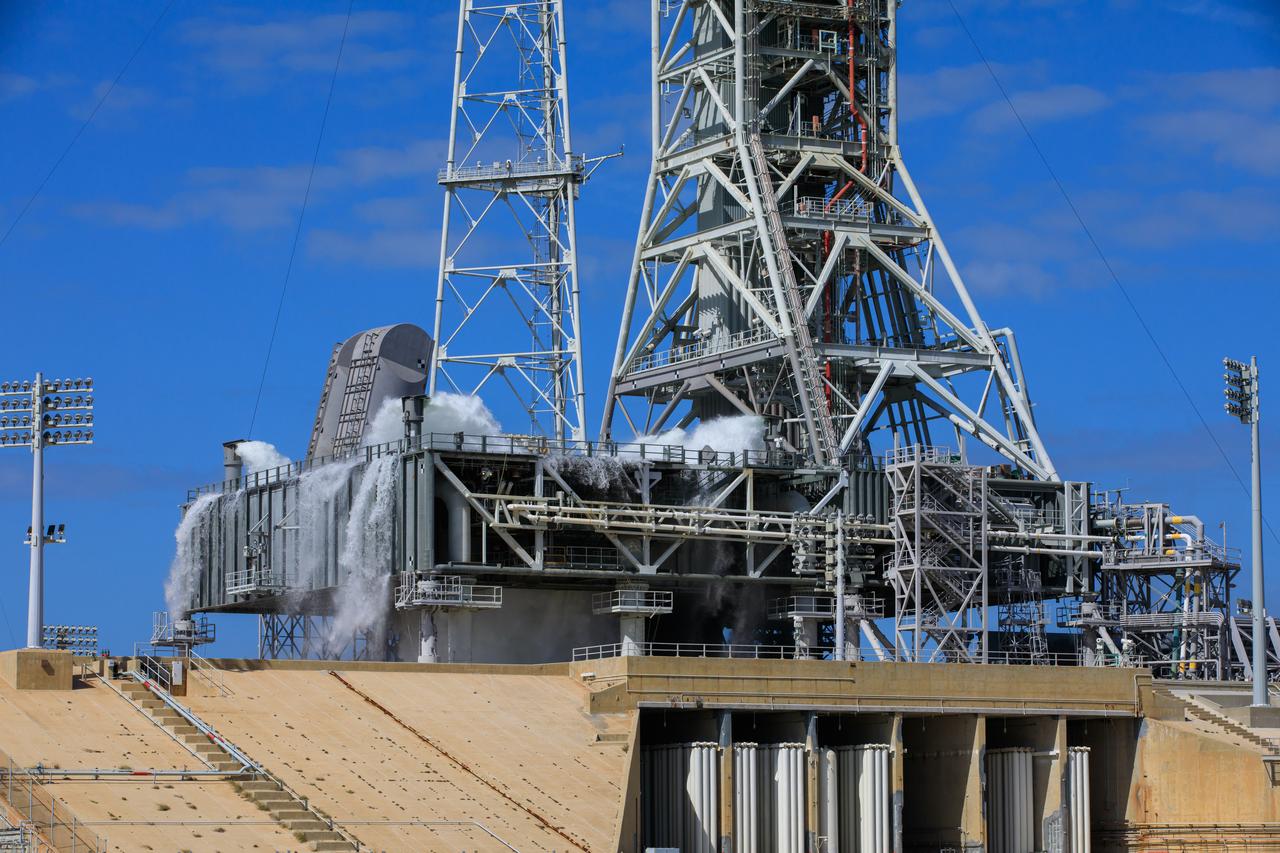

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems conducts a water flow test with the mobile launcher at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida on Oct. 24, 2023. It is the third in a series of tests to verify the overpressure protection and sound suppression system is ready for launch of the Artemis II mission. During liftoff, 400,000 gallons of water will rush onto the pad to help protect NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, Orion spacecraft, mobile launcher, and launch pad from any over pressurization and extreme sound produced during ignition and liftoff.
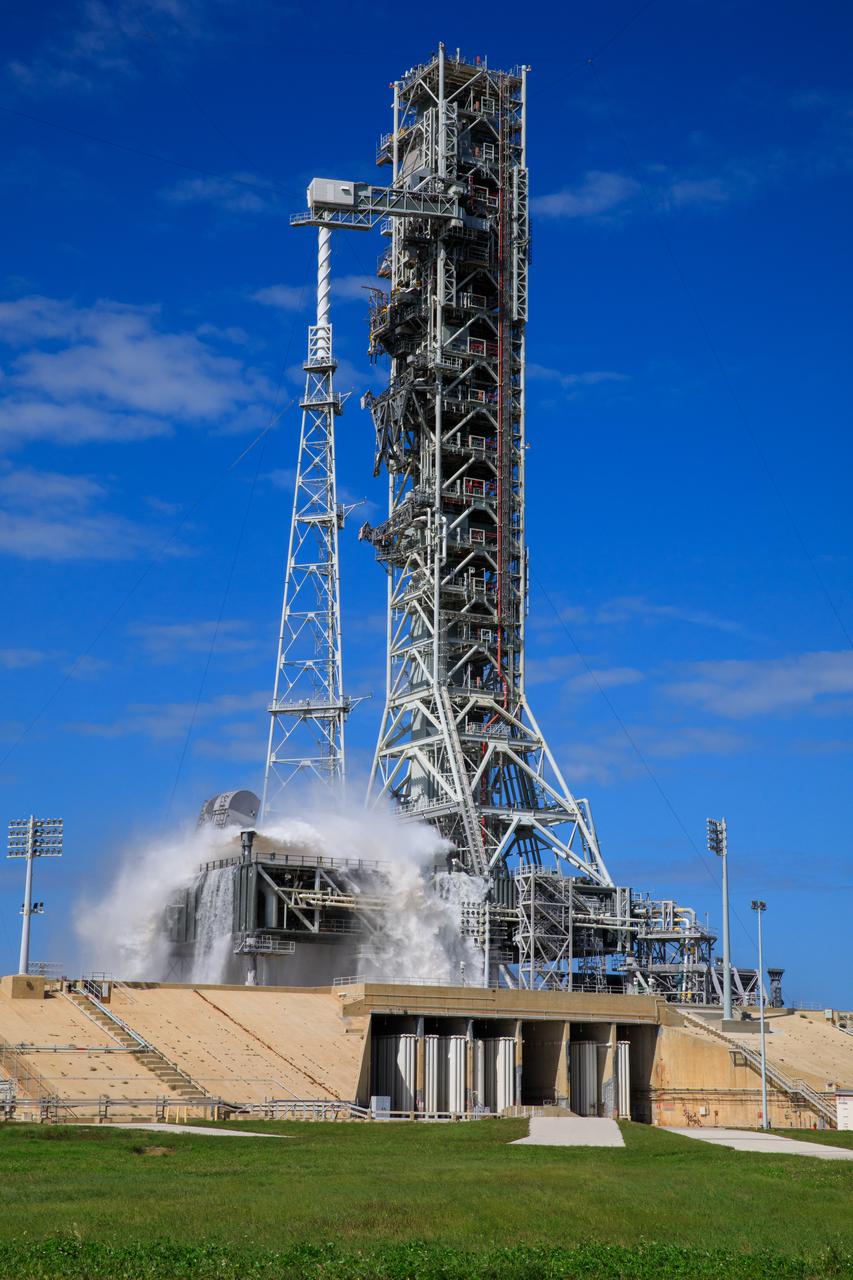

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems conducts a water flow test with the mobile launcher at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida on Oct. 24, 2023. It is the third in a series of tests to verify the overpressure protection and sound suppression system is ready for launch of the Artemis II mission. During liftoff, 400,000 gallons of water will rush onto the pad to help protect NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, Orion spacecraft, mobile launcher, and launch pad from any over pressurization and extreme sound produced during ignition and liftoff.
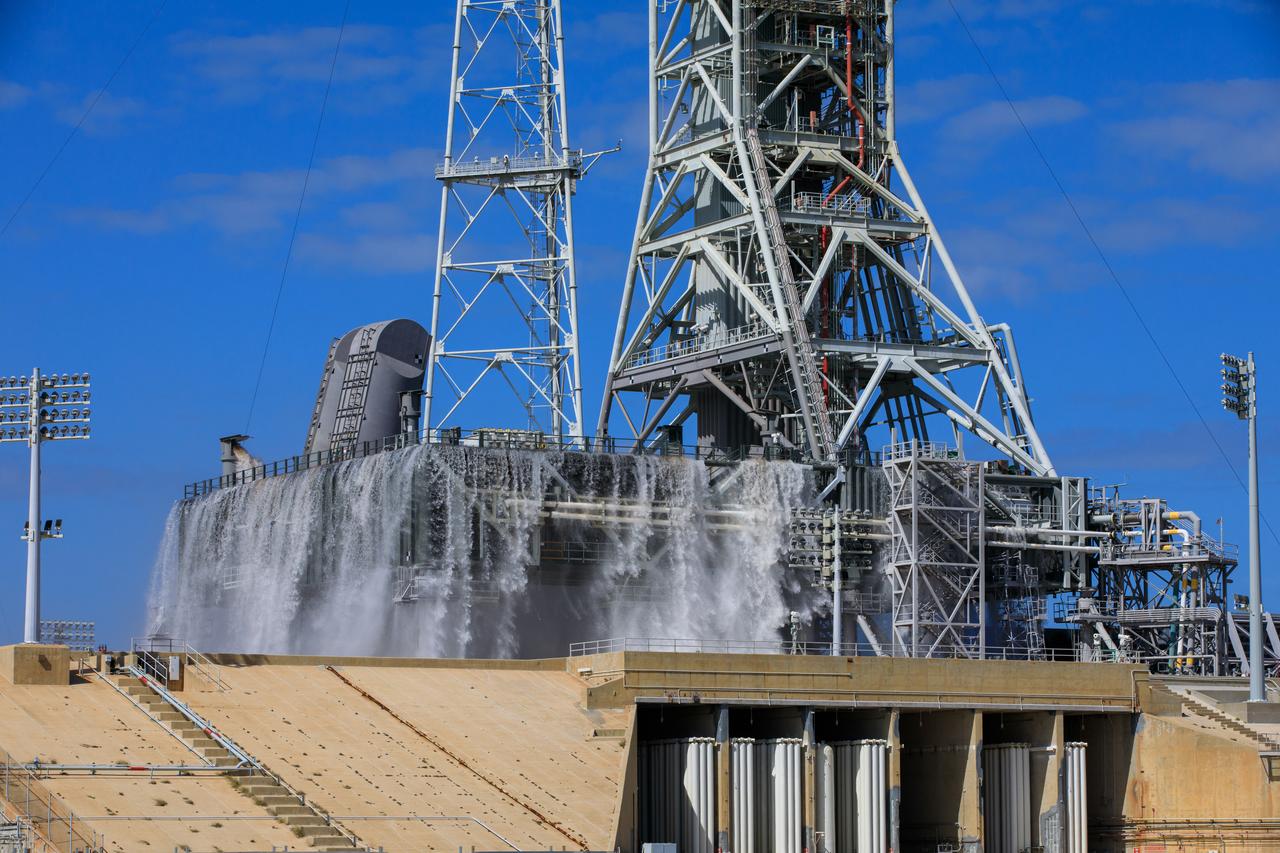

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems conducts a water flow test with the mobile launcher at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida on Oct. 24, 2023. It is the third in a series of tests to verify the overpressure protection and sound suppression system is ready for launch of the Artemis II mission. During liftoff, 400,000 gallons of water will rush onto the pad to help protect NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, Orion spacecraft, mobile launcher, and launch pad from any over pressurization and extreme sound produced during ignition and liftoff.
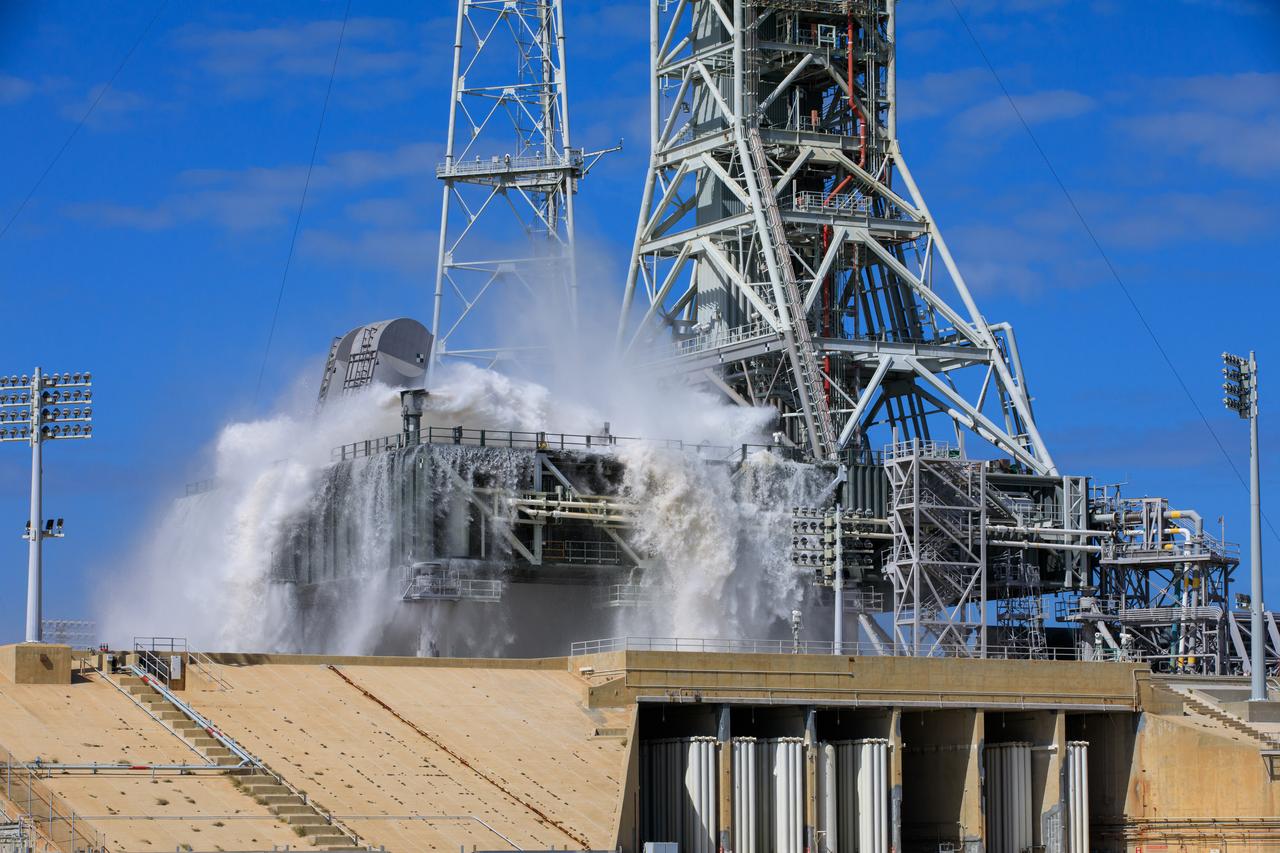

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems conducts a water flow test with the mobile launcher at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida on Oct. 24, 2023. It is the third in a series of tests to verify the overpressure protection and sound suppression system is ready for launch of the Artemis II mission. During liftoff, 400,000 gallons of water will rush onto the pad to help protect NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, Orion spacecraft, mobile launcher, and launch pad from any over pressurization and extreme sound produced during ignition and liftoff.

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems conducts a water flow test with the mobile launcher at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida on Oct. 24, 2023. It is the third in a series of tests to verify the overpressure protection and sound suppression system is ready for launch of the Artemis II mission. During liftoff, 400,000 gallons of water will rush onto the pad to help protect NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, Orion spacecraft, mobile launcher, and launch pad from any over pressurization and extreme sound produced during ignition and liftoff.
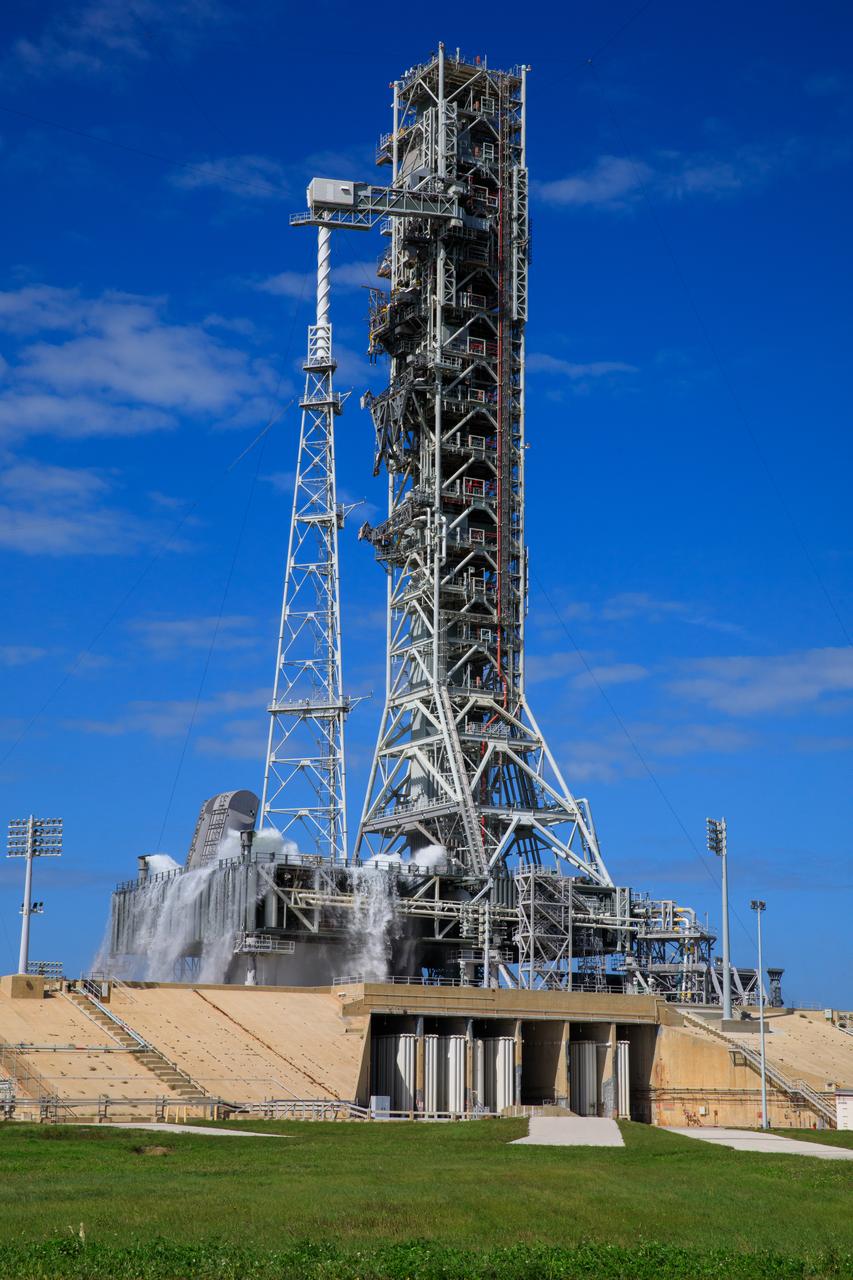

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems conducts a water flow test with the mobile launcher at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida on Oct. 24, 2023. It is the third in a series of tests to verify the overpressure protection and sound suppression system is ready for launch of the Artemis II mission. During liftoff, 400,000 gallons of water will rush onto the pad to help protect NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, Orion spacecraft, mobile launcher, and launch pad from any over pressurization and extreme sound produced during ignition and liftoff.
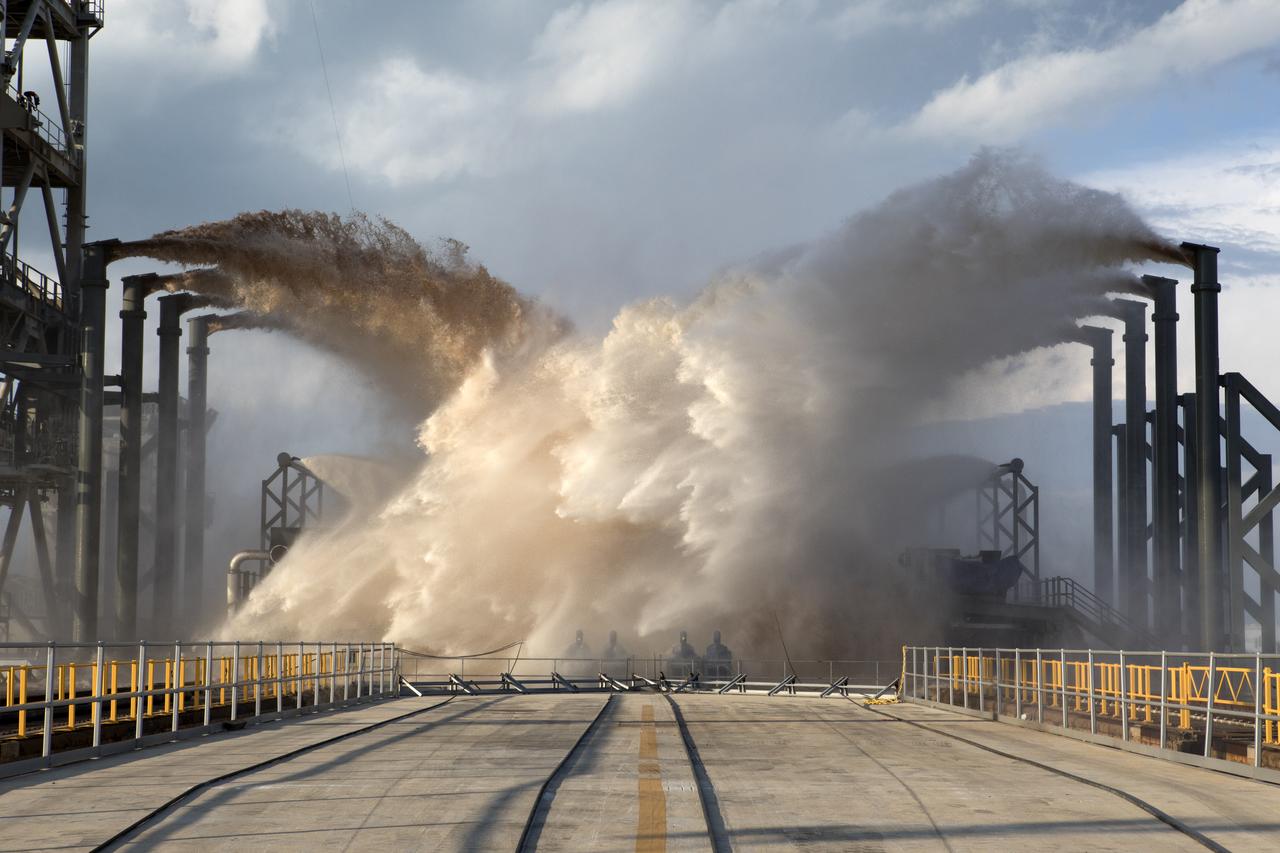

Water sprays onto Launch Complex 39A during a test by SpaceX of the sound suppression system at the launch pad. The water deluge diminishes vibration at the pad during a liftoff to protect the pad structures and rocket itself from excessive shaking. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Caption: A NASA-funded sounding rocket launches into an aurora in the early morning of March 3, 2014, over Venetie, Alaska. The GREECE mission studies how certain structures – classic curls like swirls of cream in coffee -- form in the aurora. Credit: NASA/Christopher Perry More info: On March 3, 2014, at 6:09 a.m. EST, a NASA-funded sounding rocket launched straight into an aurora over Venetie, Alaska. The Ground-to-Rocket Electrodynamics – Electron Correlative Experiment, or GREECE, sounding rocket mission, which launched from Poker Flat Research Range in Poker Flat, Alaska, will study classic curls in the aurora in the night sky. The GREECE instruments travel on a sounding rocket that launches for a ten-minute ride right through the heart of the aurora reaching its zenith over the native village of Venetie, Alaska. To study the curl structures, GREECE consists of two parts: ground-based imagers located in Venetie to track the aurora from the ground and the rocket to take measurements from the middle of the aurora itself. At their simplest, auroras are caused when particles from the sun funnel over to Earth's night side, generate electric currents, and trigger a shower of particles that strike oxygen and nitrogen some 60 to 200 miles up in Earth's atmosphere, releasing a flash of light. But the details are always more complicated, of course. Researchers wish to understand the aurora, and movement of plasma in general, at much smaller scales including such things as how different structures are formed there. This is a piece of information, which in turn, helps paint a picture of the sun-Earth connection and how energy and particles from the sun interact with Earth's own magnetic system, the magnetosphere. GREECE is a collaborative effort between SWRI, which developed particle instruments and the ground-based imaging, and the University of California, Berkeley, measuring the electric and magnetic fields. The launch is supported by a sounding rocket team from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Va. The Poker Flat Research Range is operated by the University of Alaska, Fairbanks. “The conditions were optimal,” said Marilia Samara, principal investigator for the mission at Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio, Texas. “We can’t wait to dig into the data.” For more information on the GREECE mission visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasa-funded-sounding-rocket-to-catch-aurora-in-the-act/." rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasa-funded-sounding-rocket- </a>.<b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Caption: A NASA-funded sounding rocket launches into an aurora in the early morning of March 3, 2014, over Venetie, Alaska. The GREECE mission studies how certain structures – classic curls like swirls of cream in coffee -- form in the aurora. Credit: NASA/Christopher Perry More info: On March 3, 2014, at 6:09 a.m. EST, a NASA-funded sounding rocket launched straight into an aurora over Venetie, Alaska. The Ground-to-Rocket Electrodynamics – Electron Correlative Experiment, or GREECE, sounding rocket mission, which launched from Poker Flat Research Range in Poker Flat, Alaska, will study classic curls in the aurora in the night sky. The GREECE instruments travel on a sounding rocket that launches for a ten-minute ride right through the heart of the aurora reaching its zenith over the native village of Venetie, Alaska. To study the curl structures, GREECE consists of two parts: ground-based imagers located in Venetie to track the aurora from the ground and the rocket to take measurements from the middle of the aurora itself. At their simplest, auroras are caused when particles from the sun funnel over to Earth's night side, generate electric currents, and trigger a shower of particles that strike oxygen and nitrogen some 60 to 200 miles up in Earth's atmosphere, releasing a flash of light. But the details are always more complicated, of course. Researchers wish to understand the aurora, and movement of plasma in general, at much smaller scales including such things as how different structures are formed there. This is a piece of information, which in turn, helps paint a picture of the sun-Earth connection and how energy and particles from the sun interact with Earth's own magnetic system, the magnetosphere. GREECE is a collaborative effort between SWRI, which developed particle instruments and the ground-based imaging, and the University of California, Berkeley, measuring the electric and magnetic fields. The launch is supported by a sounding rocket team from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Va. The Poker Flat Research Range is operated by the University of Alaska, Fairbanks. “The conditions were optimal,” said Marilia Samara, principal investigator for the mission at Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio, Texas. “We can’t wait to dig into the data.” For more information on the GREECE mission visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasa-funded-sounding-rocket-to-catch-aurora-in-the-act/." rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasa-funded-sounding-rocket- </a>.<b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Caption: A NASA-funded sounding rocket launches into an aurora in the early morning of March 3, 2014, over Venetie, Alaska. The GREECE mission studies how certain structures – classic curls like swirls of cream in coffee -- form in the aurora. Credit: NASA/Christopher Perry More info: On March 3, 2014, at 6:09 a.m. EST, a NASA-funded sounding rocket launched straight into an aurora over Venetie, Alaska. The Ground-to-Rocket Electrodynamics – Electron Correlative Experiment, or GREECE, sounding rocket mission, which launched from Poker Flat Research Range in Poker Flat, Alaska, will study classic curls in the aurora in the night sky. The GREECE instruments travel on a sounding rocket that launches for a ten-minute ride right through the heart of the aurora reaching its zenith over the native village of Venetie, Alaska. To study the curl structures, GREECE consists of two parts: ground-based imagers located in Venetie to track the aurora from the ground and the rocket to take measurements from the middle of the aurora itself. At their simplest, auroras are caused when particles from the sun funnel over to Earth's night side, generate electric currents, and trigger a shower of particles that strike oxygen and nitrogen some 60 to 200 miles up in Earth's atmosphere, releasing a flash of light. But the details are always more complicated, of course. Researchers wish to understand the aurora, and movement of plasma in general, at much smaller scales including such things as how different structures are formed there. This is a piece of information, which in turn, helps paint a picture of the sun-Earth connection and how energy and particles from the sun interact with Earth's own magnetic system, the magnetosphere. GREECE is a collaborative effort between SWRI, which developed particle instruments and the ground-based imaging, and the University of California, Berkeley, measuring the electric and magnetic fields. The launch is supported by a sounding rocket team from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Va. The Poker Flat Research Range is operated by the University of Alaska, Fairbanks. “The conditions were optimal,” said Marilia Samara, principal investigator for the mission at Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio, Texas. “We can’t wait to dig into the data.” For more information on the GREECE mission visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasa-funded-sounding-rocket-to-catch-aurora-in-the-act/." rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasa-funded-sounding-rocket- </a>.<b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Caption: A NASA-funded sounding rocket launches into an aurora in the early morning of March 3, 2014, over Venetie, Alaska. The GREECE mission studies how certain structures – classic curls like swirls of cream in coffee -- form in the aurora. Credit: NASA/Christopher Perry More info: On March 3, 2014, at 6:09 a.m. EST, a NASA-funded sounding rocket launched straight into an aurora over Venetie, Alaska. The Ground-to-Rocket Electrodynamics – Electron Correlative Experiment, or GREECE, sounding rocket mission, which launched from Poker Flat Research Range in Poker Flat, Alaska, will study classic curls in the aurora in the night sky. The GREECE instruments travel on a sounding rocket that launches for a ten-minute ride right through the heart of the aurora reaching its zenith over the native village of Venetie, Alaska. To study the curl structures, GREECE consists of two parts: ground-based imagers located in Venetie to track the aurora from the ground and the rocket to take measurements from the middle of the aurora itself. At their simplest, auroras are caused when particles from the sun funnel over to Earth's night side, generate electric currents, and trigger a shower of particles that strike oxygen and nitrogen some 60 to 200 miles up in Earth's atmosphere, releasing a flash of light. But the details are always more complicated, of course. Researchers wish to understand the aurora, and movement of plasma in general, at much smaller scales including such things as how different structures are formed there. This is a piece of information, which in turn, helps paint a picture of the sun-Earth connection and how energy and particles from the sun interact with Earth's own magnetic system, the magnetosphere. GREECE is a collaborative effort between SWRI, which developed particle instruments and the ground-based imaging, and the University of California, Berkeley, measuring the electric and magnetic fields. The launch is supported by a sounding rocket team from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Va. The Poker Flat Research Range is operated by the University of Alaska, Fairbanks. “The conditions were optimal,” said Marilia Samara, principal investigator for the mission at Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio, Texas. “We can’t wait to dig into the data.” For more information on the GREECE mission visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasa-funded-sounding-rocket-to-catch-aurora-in-the-act/." rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasa-funded-sounding-rocket- </a>.<b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Caption: A NASA-funded sounding rocket launches into an aurora in the early morning of March 3, 2014, over Venetie, Alaska. The GREECE mission studies how certain structures – classic curls like swirls of cream in coffee -- form in the aurora. Credit: NASA/Christopher Perry More info: On March 3, 2014, at 6:09 a.m. EST, a NASA-funded sounding rocket launched straight into an aurora over Venetie, Alaska. The Ground-to-Rocket Electrodynamics – Electron Correlative Experiment, or GREECE, sounding rocket mission, which launched from Poker Flat Research Range in Poker Flat, Alaska, will study classic curls in the aurora in the night sky. The GREECE instruments travel on a sounding rocket that launches for a ten-minute ride right through the heart of the aurora reaching its zenith over the native village of Venetie, Alaska. To study the curl structures, GREECE consists of two parts: ground-based imagers located in Venetie to track the aurora from the ground and the rocket to take measurements from the middle of the aurora itself. At their simplest, auroras are caused when particles from the sun funnel over to Earth's night side, generate electric currents, and trigger a shower of particles that strike oxygen and nitrogen some 60 to 200 miles up in Earth's atmosphere, releasing a flash of light. But the details are always more complicated, of course. Researchers wish to understand the aurora, and movement of plasma in general, at much smaller scales including such things as how different structures are formed there. This is a piece of information, which in turn, helps paint a picture of the sun-Earth connection and how energy and particles from the sun interact with Earth's own magnetic system, the magnetosphere. GREECE is a collaborative effort between SWRI, which developed particle instruments and the ground-based imaging, and the University of California, Berkeley, measuring the electric and magnetic fields. The launch is supported by a sounding rocket team from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Va. The Poker Flat Research Range is operated by the University of Alaska, Fairbanks. “The conditions were optimal,” said Marilia Samara, principal investigator for the mission at Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio, Texas. “We can’t wait to dig into the data.” For more information on the GREECE mission visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasa-funded-sounding-rocket-to-catch-aurora-in-the-act/." rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasa-funded-sounding-rocket- </a>.<b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This photograph depicts an air-breathing rocket engine prototype in the test bay at the General Applied Science Lab facility in Ronkonkoma, New York. Air-breathing engines, known as rocket based, combined-cycle engines, get their initial take-off power from specially designed rockets, called air-augmented rockets, that boost performance about 15 percent over conventional rockets. When the vehicle's velocity reaches twice the speed of sound, the rockets are turned off and the engine relies totally on oxygen in the atmosphere to burn hydrogen fuel, as opposed to a rocket that must carry its own oxygen, thus reducing weight and flight costs. Once the vehicle has accelerated to about 10 times the speed of sound, the engine converts to a conventional rocket-powered system to propel the craft into orbit or sustain it to suborbital flight speed. NASA's Advanced Space Transportation Program at Marshall Space Flight Center, along with several industry partners and collegiate forces, is developing this technology to make space transportation affordable for everyone from business travelers to tourists. The goal is to reduce launch costs from today's price tag of $10,000 per pound to only hundreds of dollars per pound. NASA's series of hypersonic flight demonstrators currently include three air-breathing vehicles: the X-43A, X-43B and X-43C.
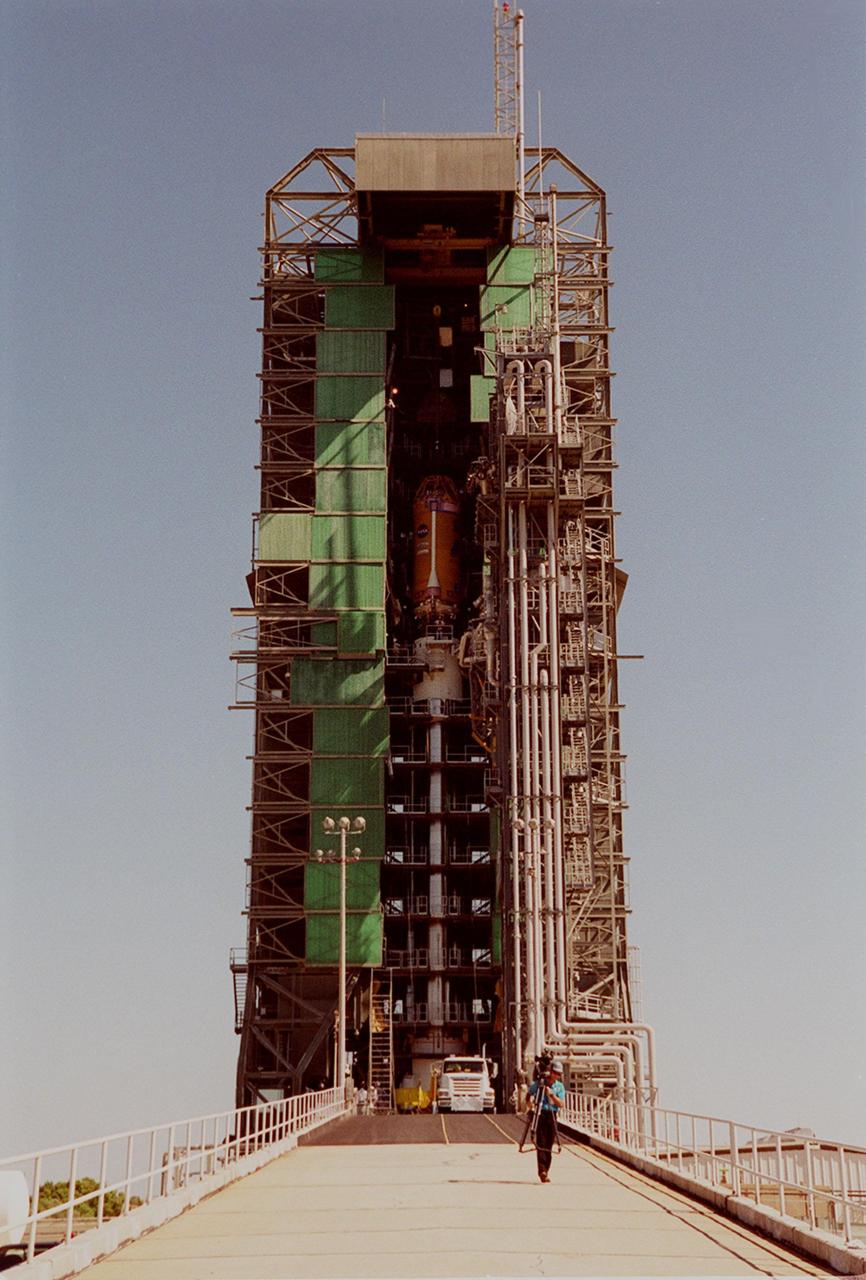

At launch pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, lifting of the second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket in the launch gantry is completed. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
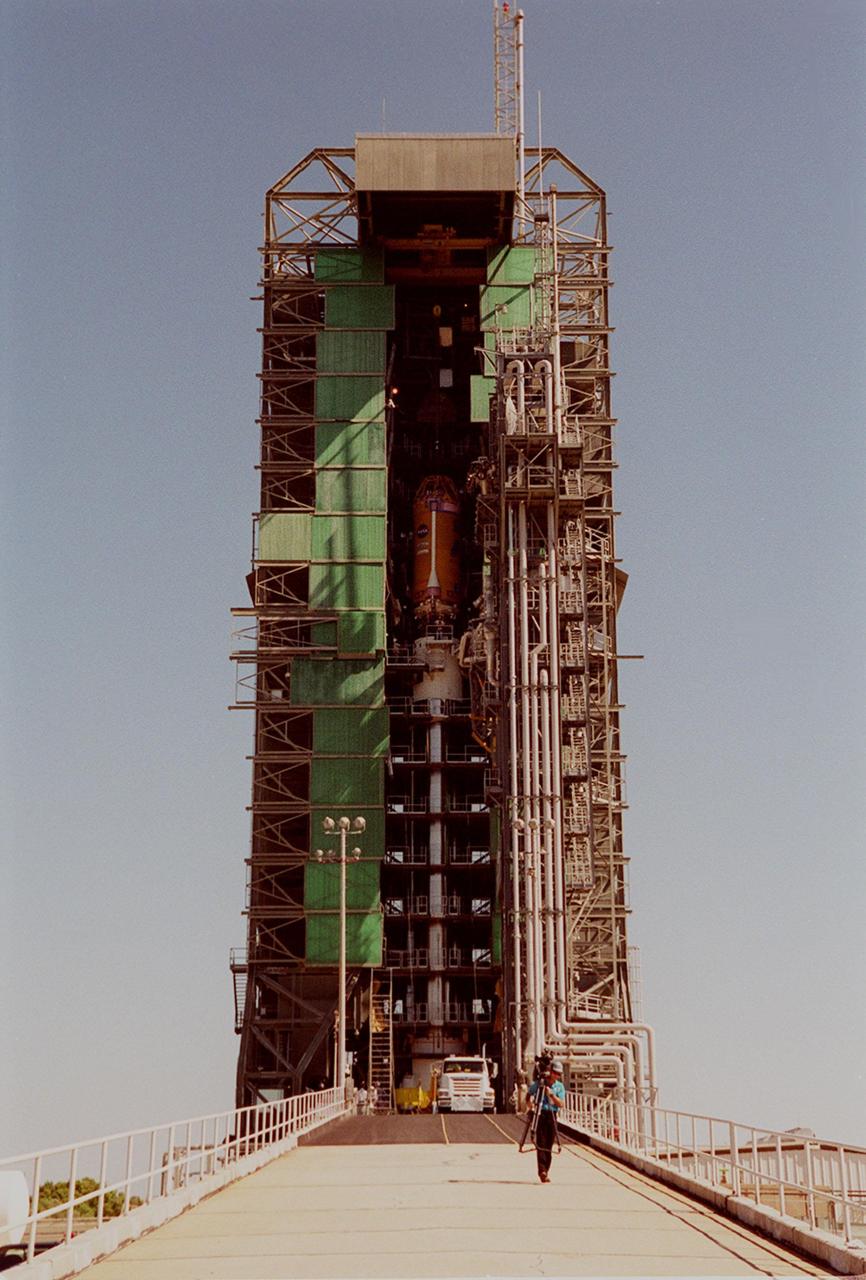

At launch pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, lifting of the second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket in the launch gantry is completed. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing

Red and white vapor clouds filled the skies over the Marshall Islands as part of NASA’s Equatorial Vortex Experiment (EVEX). The red cloud was formed by the release of lithium vapor and the white tracer clouds were formed by the release of trimethyl aluminum (TMA). These clouds allowed scientists on the ground from various locations in the Marshall Islands to observe the neutral winds in the ionosphere. Credit: NASA/Jon Grant --- The Equatorial Vortex Experiment (EVEX) was successfully conducted during the early morning hours (eastern time) May 7 from Roi Namur, Republic of the Marshall Islands. A NASA Terrier-Oriole sounding rocket was launched at 3:39 a.m. EDT and was followed by a launch of Terrier-Improved Malemute sounding rocket 90 seconds later. Preliminary indications are that both rockets released their vapor clouds of lithium or trimethyl aluminum, which were observed from various locations in the area, and all science instruments on the rockets worked as planned. More information on EVEX can be found at <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sounding-rockets/news/evex.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sounding-rockets/news/evex.html</a> These were the second and third rockets of four planned for launch during this year’s campaign in the Marshall Islands. The first and fourth rockets are supporting the Metal Oxide Space Cloud experiment (MOSC), which is studying radio frequency propagation. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
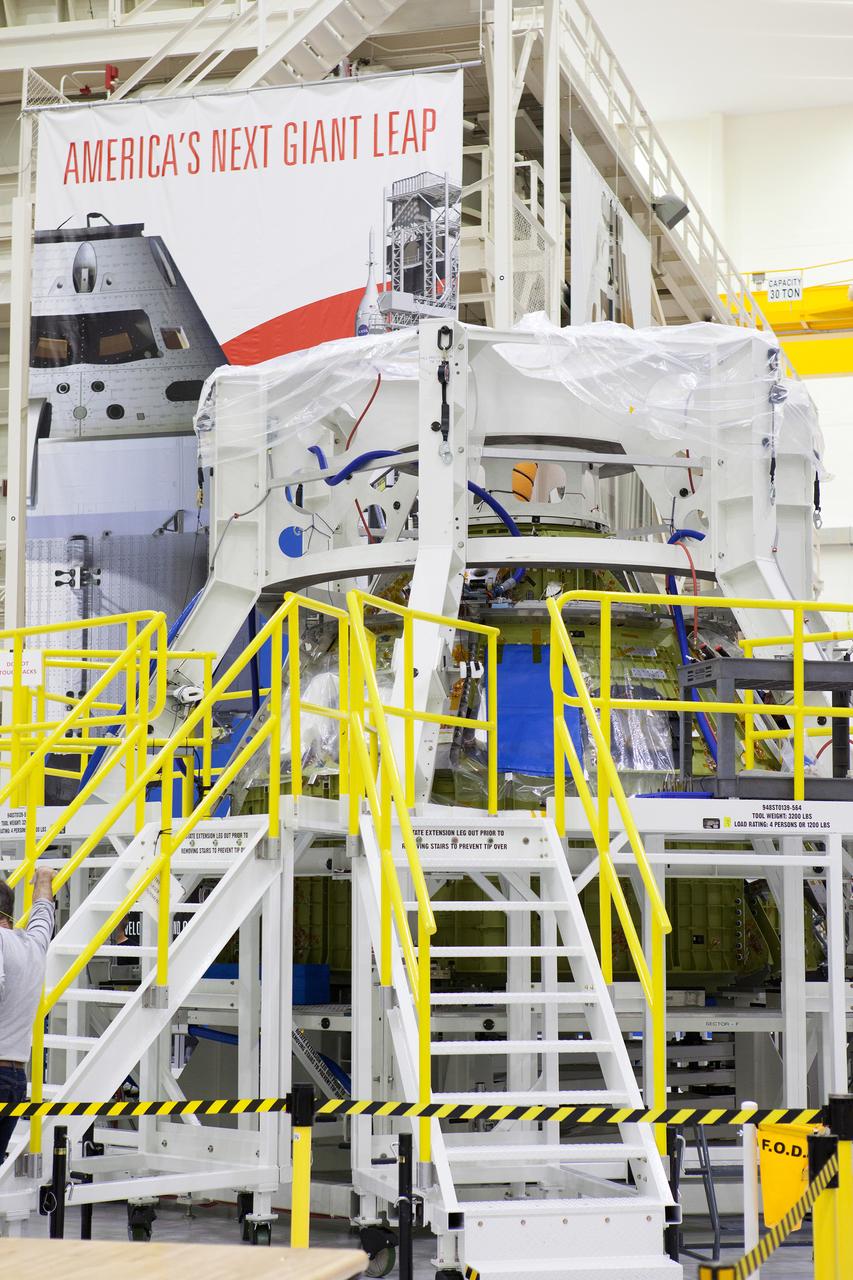

Engineers and technicians moved the Orion service module test article into the Reverberant Acoustic Test Facility at NASA Glenn Research Center’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio on April 8, 2016. Acoustic testing is scheduled to begin April 18. The blue structure sitting on top of the test article is a mass simulator that represents the Orion crew module...The test article will be blasted with at least 152 decibels and 20-10,000 hertz of sound pressure and vibration to simulate the intense sounds the Orion service module will be subjected to during launch and ascent into space atop the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. This is part of a series of tests to verify the structural integrity of Orion’s service module for Exploration Mission-1, the spacecraft’s first flight atop SLS...Provided by ESA (European Space Agency) and built by Airbus Defence and Space, the service module will power, propel and cool the vehicle and also supply it with air and water.
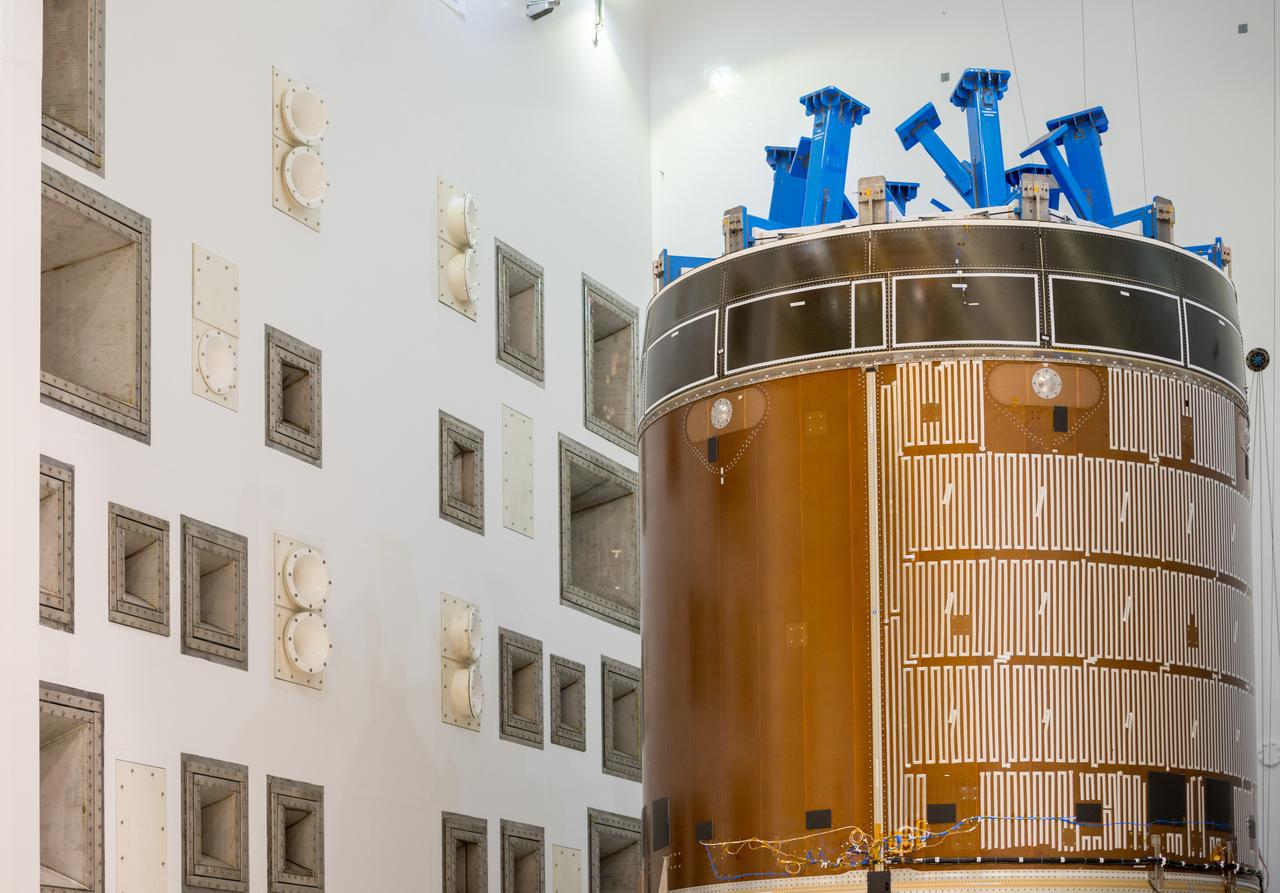

Engineers and technicians moved the Orion service module test article into the Reverberant Acoustic Test Facility at NASA Glenn Research Center’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio on April 8, 2016. Acoustic testing is scheduled to begin April 18. The blue structure sitting on top of the test article is a mass simulator that represents the Orion crew module...The test article will be blasted with at least 152 decibels and 20-10,000 hertz of sound pressure and vibration to simulate the intense sounds the Orion service module will be subjected to during launch and ascent into space atop the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. This is part of a series of tests to verify the structural integrity of Orion’s service module for Exploration Mission-1, the spacecraft’s first flight atop SLS...Provided by ESA (European Space Agency) and built by Airbus Defence and Space, the service module will power, propel and cool the vehicle and also supply it with air and water.
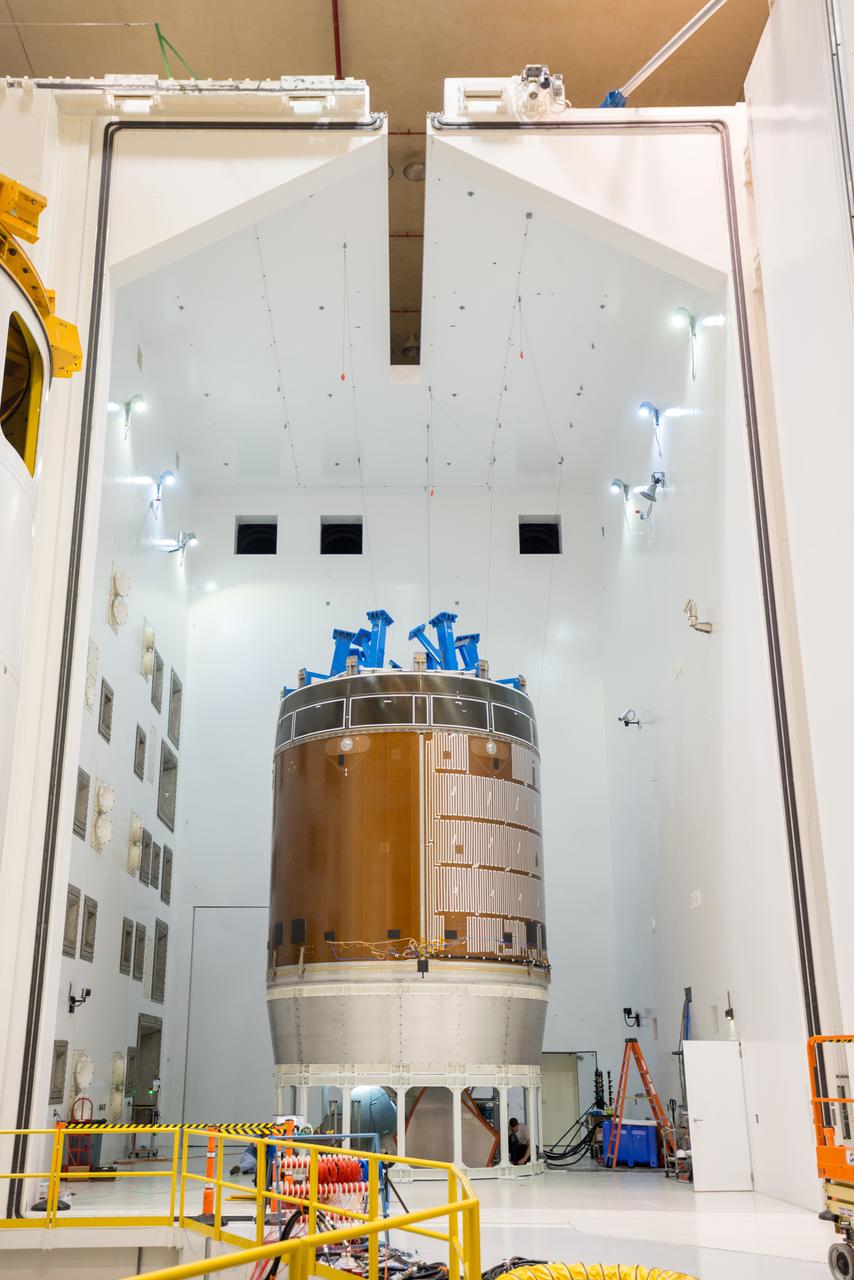

Engineers and technicians moved the Orion service module test article into the Reverberant Acoustic Test Facility at NASA Glenn Research Center’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio on April 8, 2016. Acoustic testing is scheduled to begin April 18. The blue structure sitting on top of the test article is a mass simulator that represents the Orion crew module...The test article will be blasted with at least 152 decibels and 20-10,000 hertz of sound pressure and vibration to simulate the intense sounds the Orion service module will be subjected to during launch and ascent into space atop the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. This is part of a series of tests to verify the structural integrity of Orion’s service module for Exploration Mission-1, the spacecraft’s first flight atop SLS...Provided by ESA (European Space Agency) and built by Airbus Defence and Space, the service module will power, propel and cool the vehicle and also supply it with air and water.
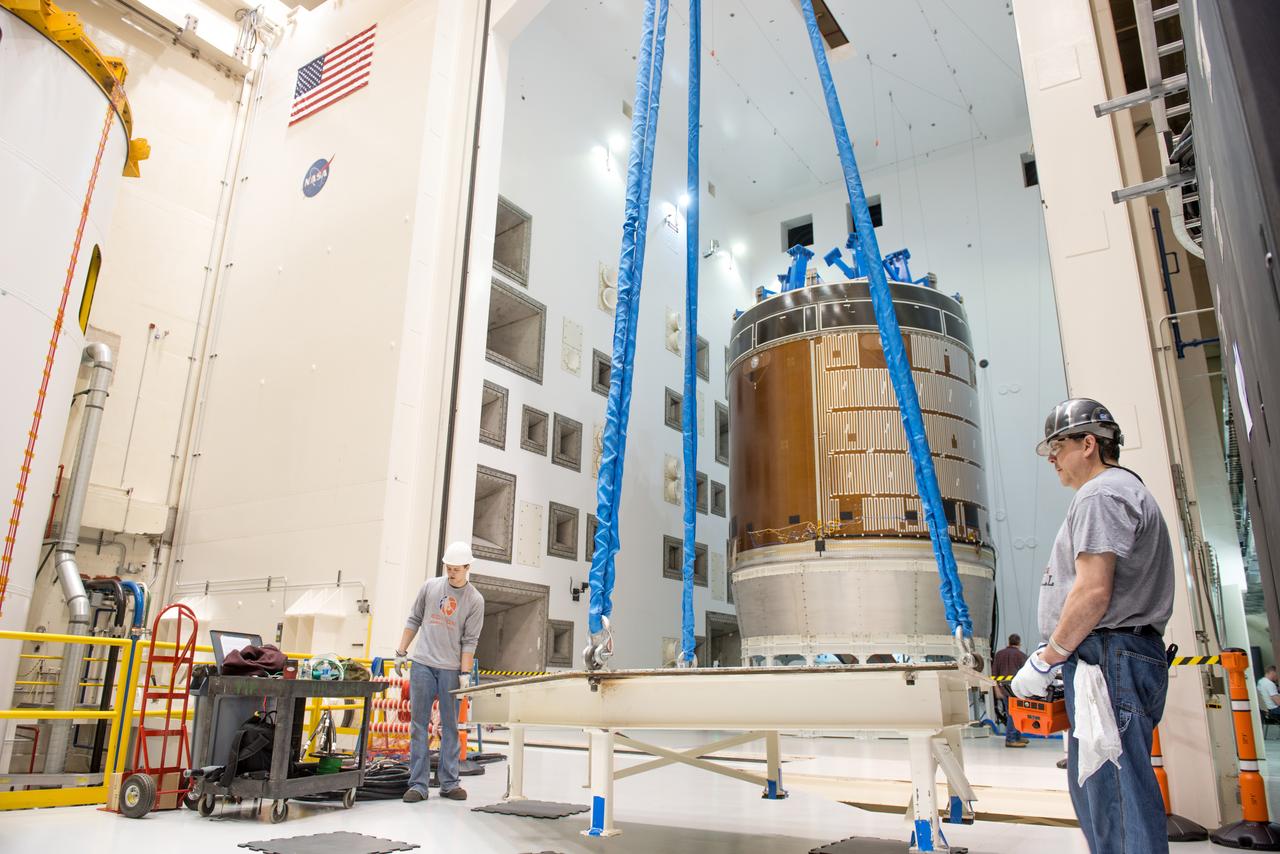

Engineers and technicians moved the Orion service module test article into the Reverberant Acoustic Test Facility at NASA Glenn Research Center’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio on April 8, 2016. Acoustic testing is scheduled to begin April 18. The blue structure sitting on top of the test article is a mass simulator that represents the Orion crew module...The test article will be blasted with at least 152 decibels and 20-10,000 hertz of sound pressure and vibration to simulate the intense sounds the Orion service module will be subjected to during launch and ascent into space atop the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. This is part of a series of tests to verify the structural integrity of Orion’s service module for Exploration Mission-1, the spacecraft’s first flight atop SLS...Provided by ESA (European Space Agency) and built by Airbus Defence and Space, the service module will power, propel and cool the vehicle and also supply it with air and water.

Engineers and technicians moved the Orion service module test article into the Reverberant Acoustic Test Facility at NASA Glenn Research Center’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio on April 8, 2016. Acoustic testing is scheduled to begin April 18. The blue structure sitting on top of the test article is a mass simulator that represents the Orion crew module...The test article will be blasted with at least 152 decibels and 20-10,000 hertz of sound pressure and vibration to simulate the intense sounds the Orion service module will be subjected to during launch and ascent into space atop the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. This is part of a series of tests to verify the structural integrity of Orion’s service module for Exploration Mission-1, the spacecraft’s first flight atop SLS...Provided by ESA (European Space Agency) and built by Airbus Defence and Space, the service module will power, propel and cool the vehicle and also supply it with air and water.
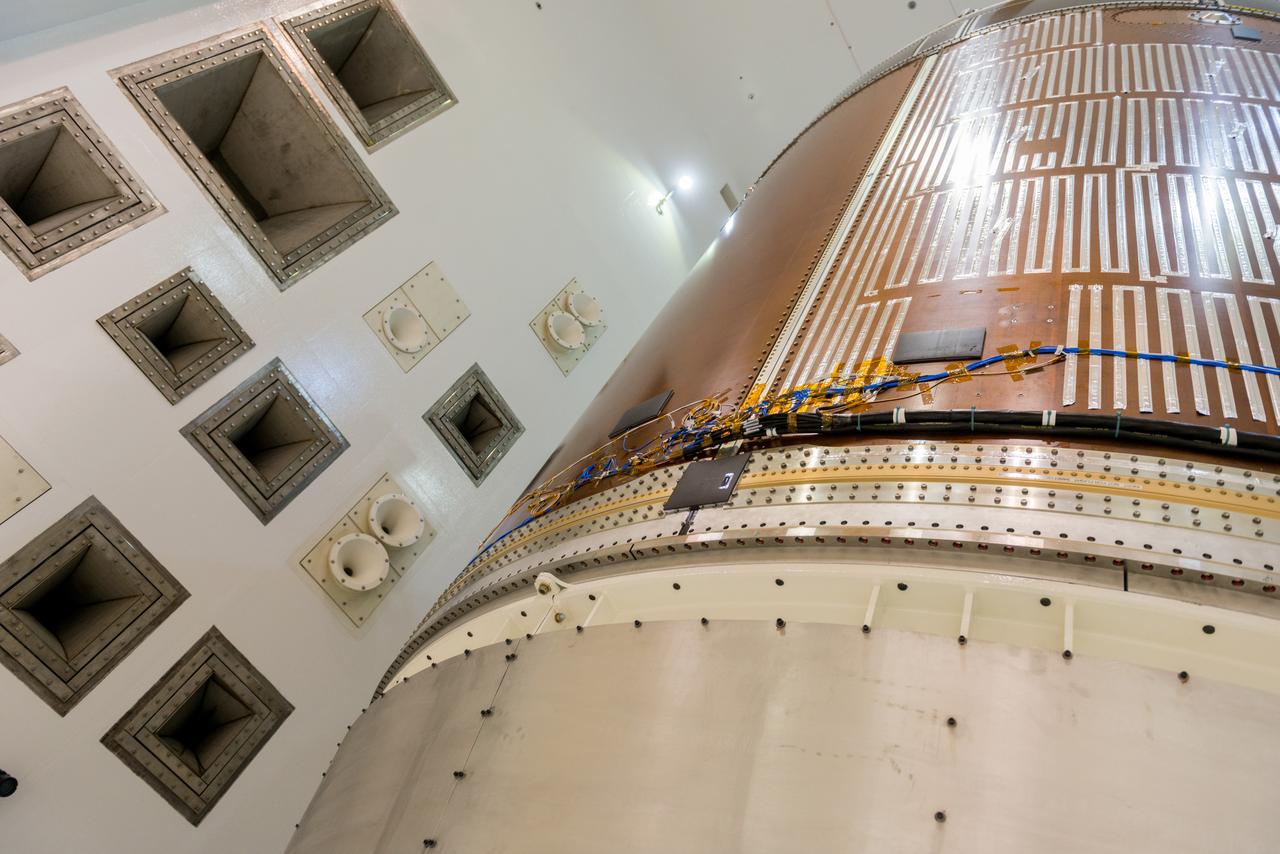

Engineers and technicians moved the Orion service module test article into the Reverberant Acoustic Test Facility at NASA Glenn Research Center’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio on April 8, 2016. Acoustic testing is scheduled to begin April 18. The blue structure sitting on top of the test article is a mass simulator that represents the Orion crew module...The test article will be blasted with at least 152 decibels and 20-10,000 hertz of sound pressure and vibration to simulate the intense sounds the Orion service module will be subjected to during launch and ascent into space atop the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. This is part of a series of tests to verify the structural integrity of Orion’s service module for Exploration Mission-1, the spacecraft’s first flight atop SLS...Provided by ESA (European Space Agency) and built by Airbus Defence and Space, the service module will power, propel and cool the vehicle and also supply it with air and water.
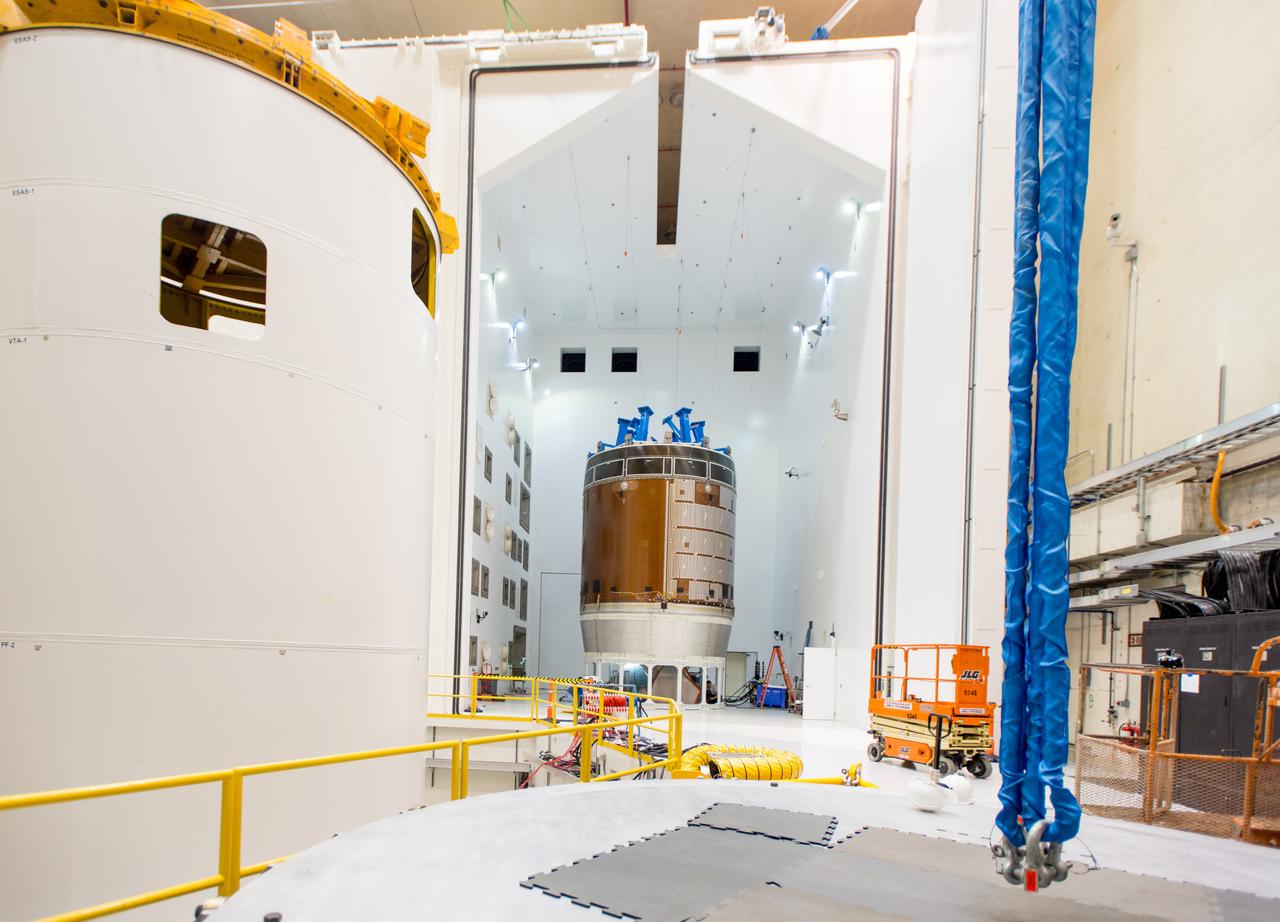

Engineers and technicians moved the Orion service module test article into the Reverberant Acoustic Test Facility at NASA Glenn Research Center’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio on April 8, 2016. Acoustic testing is scheduled to begin April 18. The blue structure sitting on top of the test article is a mass simulator that represents the Orion crew module...The test article will be blasted with at least 152 decibels and 20-10,000 hertz of sound pressure and vibration to simulate the intense sounds the Orion service module will be subjected to during launch and ascent into space atop the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. This is part of a series of tests to verify the structural integrity of Orion’s service module for Exploration Mission-1, the spacecraft’s first flight atop SLS...Provided by ESA (European Space Agency) and built by Airbus Defence and Space, the service module will power, propel and cool the vehicle and also supply it with air and water.
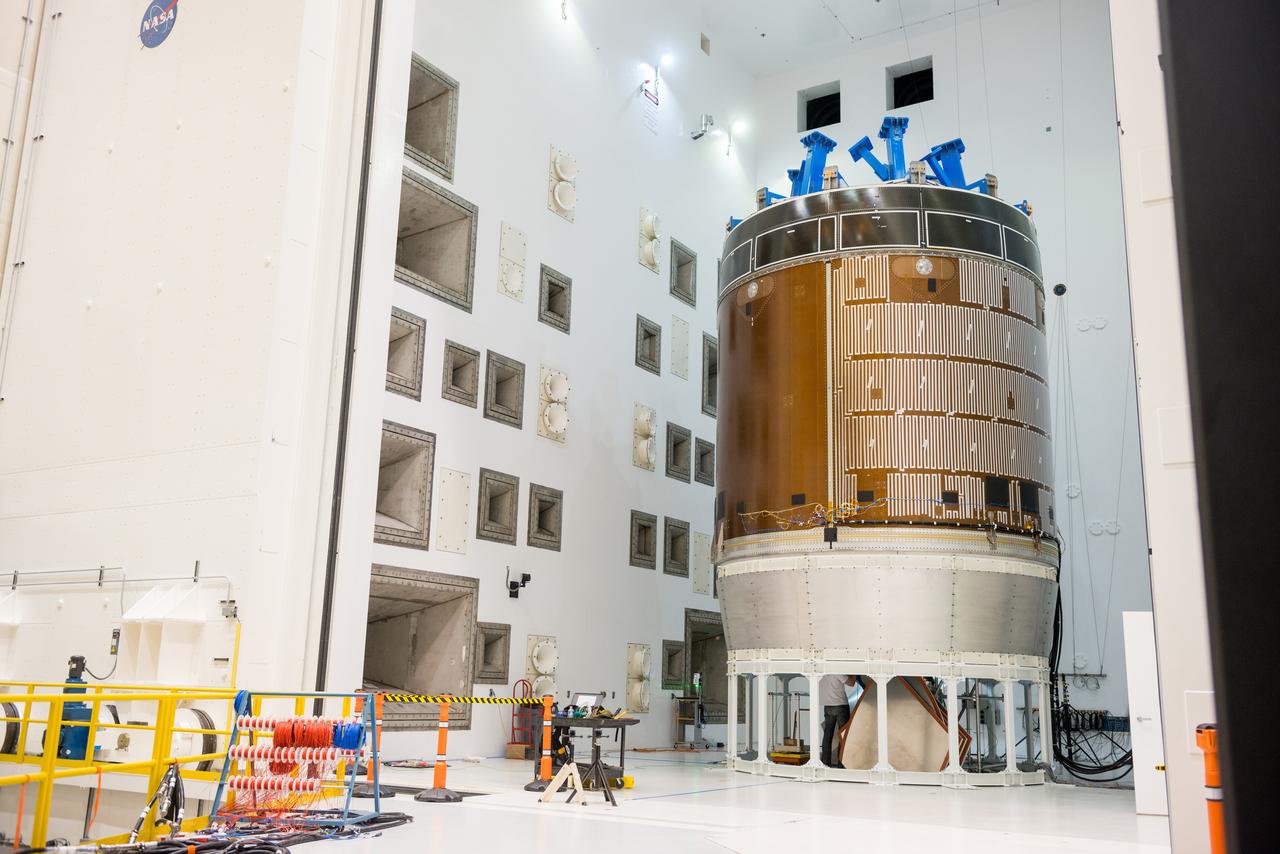

Engineers and technicians moved the Orion service module test article into the Reverberant Acoustic Test Facility at NASA Glenn Research Center’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio on April 8, 2016. Acoustic testing is scheduled to begin April 18. The blue structure sitting on top of the test article is a mass simulator that represents the Orion crew module...The test article will be blasted with at least 152 decibels and 20-10,000 hertz of sound pressure and vibration to simulate the intense sounds the Orion service module will be subjected to during launch and ascent into space atop the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. This is part of a series of tests to verify the structural integrity of Orion’s service module for Exploration Mission-1, the spacecraft’s first flight atop SLS...Provided by ESA (European Space Agency) and built by Airbus Defence and Space, the service module will power, propel and cool the vehicle and also supply it with air and water.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- David Dickinson, the acting director of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Public Affairs Office at Kennedy Space Center, accepts a copy of Bulgarian singer Dyana Dafova's latest compact disc (CD) from her on behalf of NASA. The 525-foot tall Vehicle Assembly Building, where Space Shuttle orbiters are mated to their external tank/solid rocket booster stacks, looms in the background. Dyana is touring the United States to promote her CD, entitled "Sounds of the Earth," and was an invited guest of NASA for the launch of Columbia on STS-90, the Neurolab mission, earlier in the day. Columbia lifted off from Launch Pad 39B at 2:19 p.m. EDT. Dyana characterized the music on her CD as a new sound, incorporating jazz and new age classics, sung in a newly created language comprised of Bulgarian, English, Sanskrit, Aramski and Hebrew
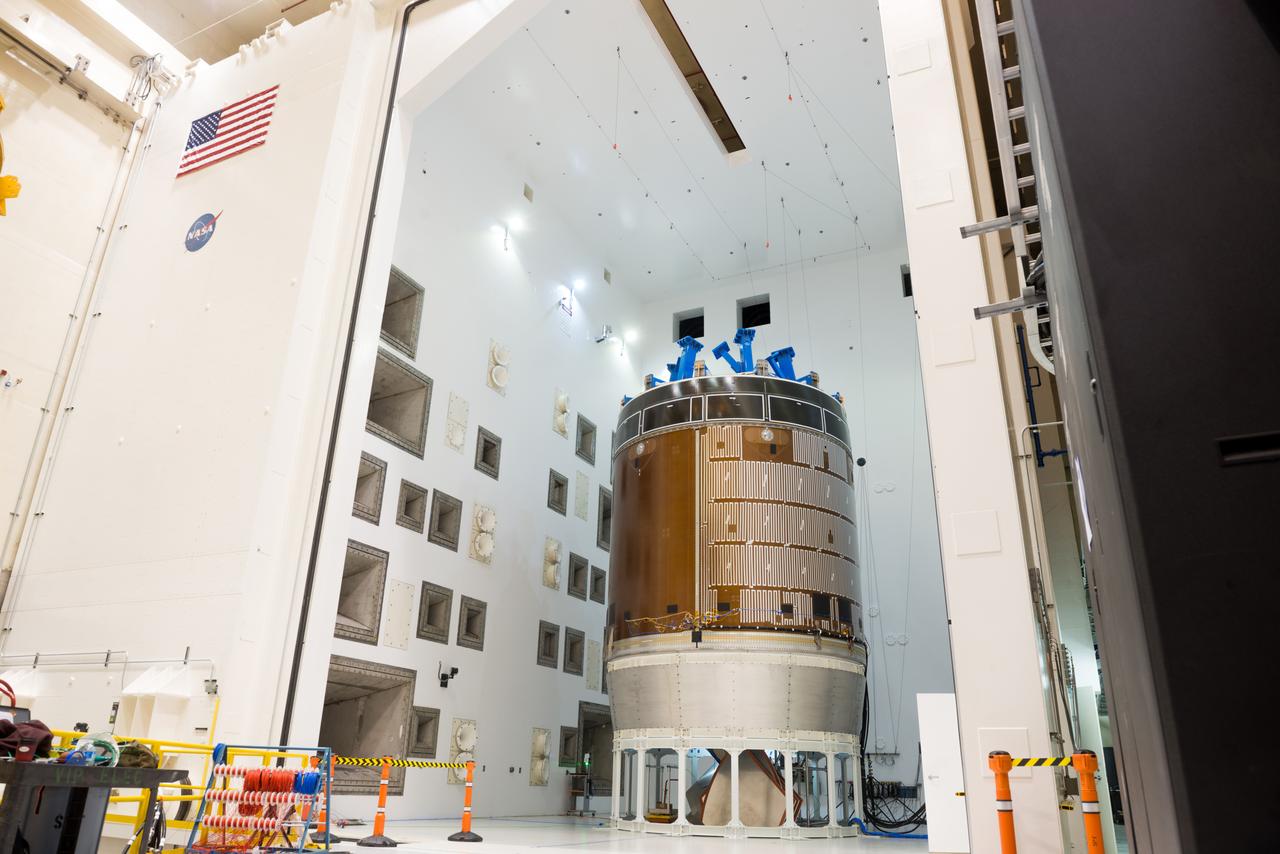

Engineers and technicians moved the Orion service module test article into the Reverberant Acoustic Test Facility at NASA Glenn Research Center’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio on April 8, 2016. Acoustic testing is scheduled to begin April 18. The blue structure sitting on top of the test article is a mass simulator that represents the Orion crew module...The test article will be blasted with at least 152 decibels and 20-10,000 hertz of sound pressure and vibration to simulate the intense sounds the Orion service module will be subjected to during launch and ascent into space atop the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. This is part of a series of tests to verify the structural integrity of Orion’s service module for Exploration Mission-1, the spacecraft’s first flight atop SLS...Provided by ESA (European Space Agency) and built by Airbus Defence and Space, the service module will power, propel and cool the vehicle and also supply it with air and water.
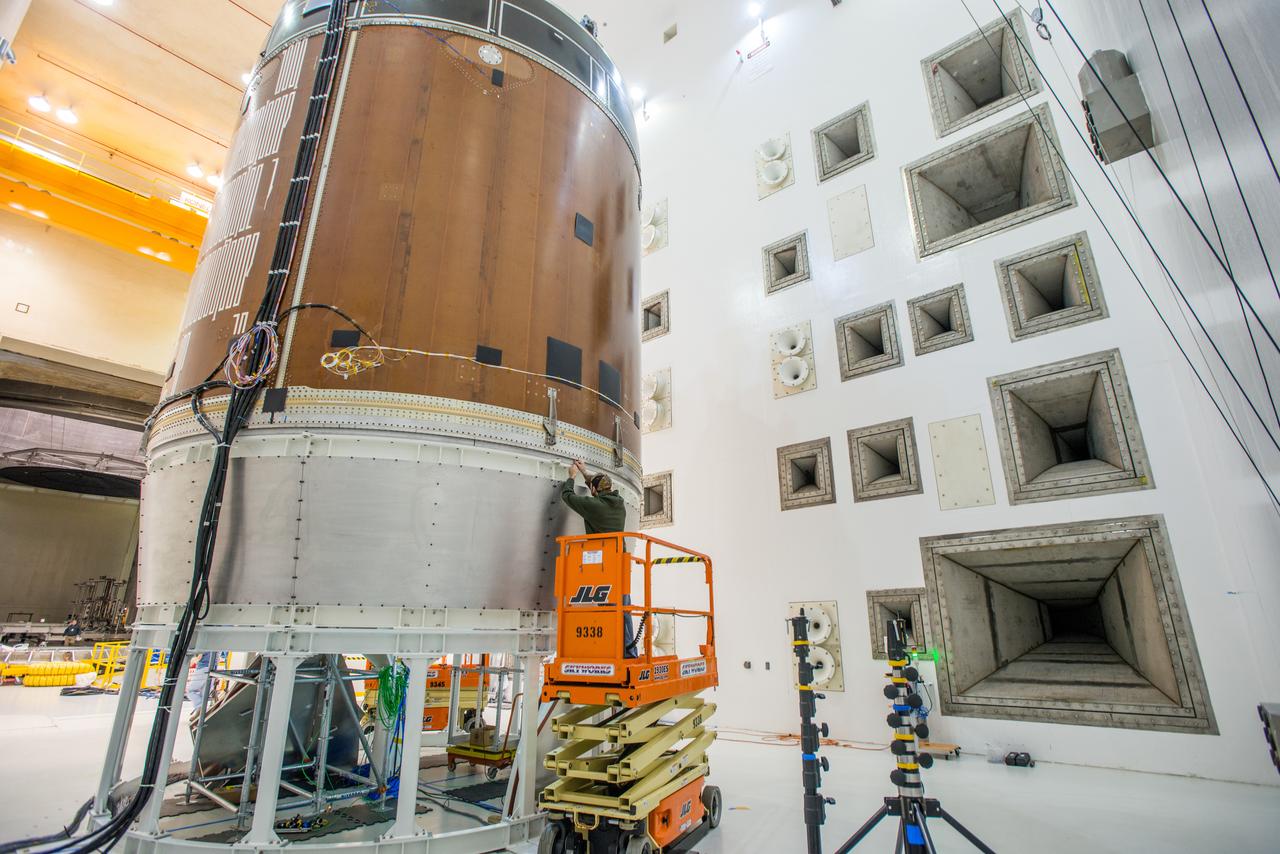

Engineers and technicians moved the Orion service module test article into the Reverberant Acoustic Test Facility at NASA Glenn Research Center’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio on April 8, 2016. Acoustic testing is scheduled to begin April 18. The blue structure sitting on top of the test article is a mass simulator that represents the Orion crew module...The test article will be blasted with at least 152 decibels and 20-10,000 hertz of sound pressure and vibration to simulate the intense sounds the Orion service module will be subjected to during launch and ascent into space atop the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. This is part of a series of tests to verify the structural integrity of Orion’s service module for Exploration Mission-1, the spacecraft’s first flight atop SLS...Provided by ESA (European Space Agency) and built by Airbus Defence and Space, the service module will power, propel and cool the vehicle and also supply it with air and water.
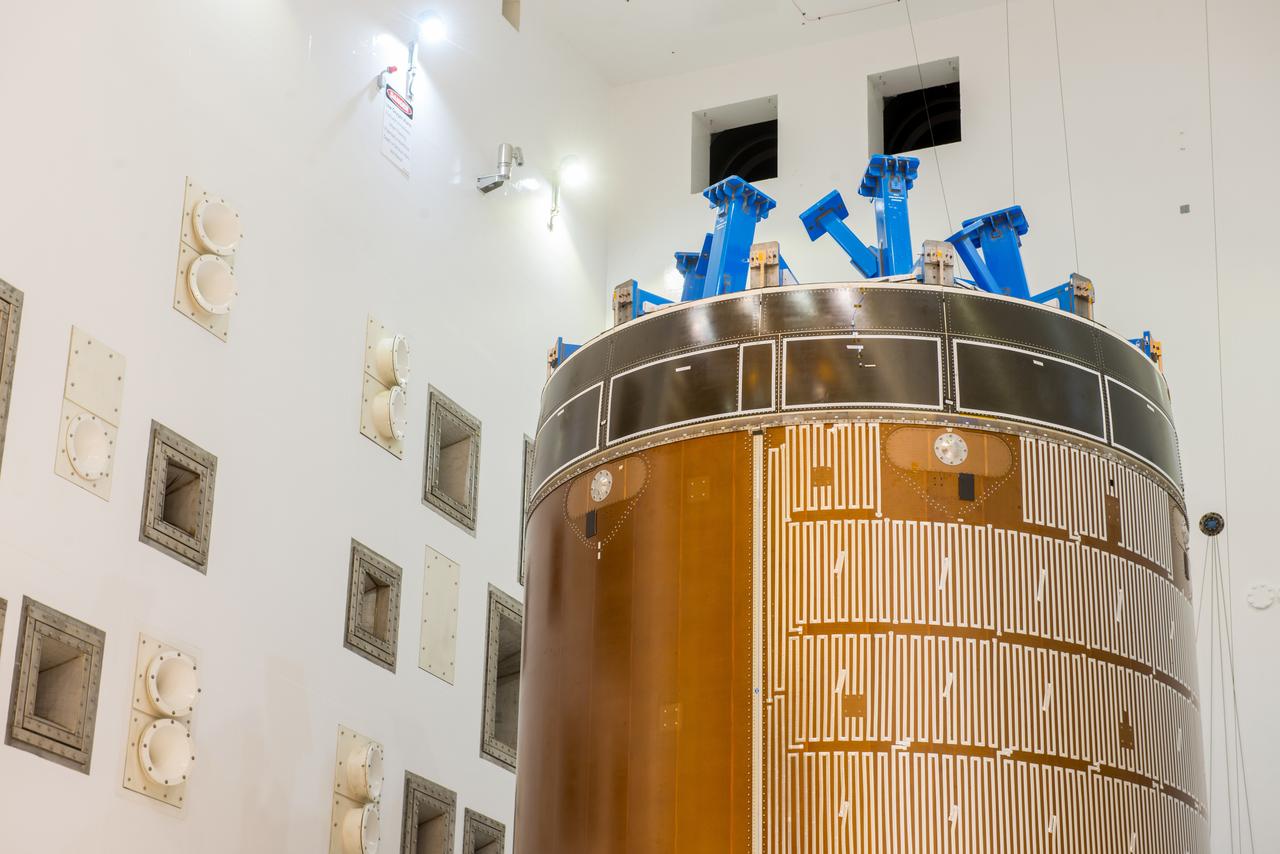

Engineers and technicians moved the Orion service module test article into the Reverberant Acoustic Test Facility at NASA Glenn Research Center’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio on April 8, 2016. Acoustic testing is scheduled to begin April 18. The blue structure sitting on top of the test article is a mass simulator that represents the Orion crew module...The test article will be blasted with at least 152 decibels and 20-10,000 hertz of sound pressure and vibration to simulate the intense sounds the Orion service module will be subjected to during launch and ascent into space atop the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. This is part of a series of tests to verify the structural integrity of Orion’s service module for Exploration Mission-1, the spacecraft’s first flight atop SLS...Provided by ESA (European Space Agency) and built by Airbus Defence and Space, the service module will power, propel and cool the vehicle and also supply it with air and water.

Engineers and technicians moved the Orion service module test article into the Reverberant Acoustic Test Facility at NASA Glenn Research Center’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio on April 8, 2016. Acoustic testing is scheduled to begin April 18. The blue structure sitting on top of the test article is a mass simulator that represents the Orion crew module...The test article will be blasted with at least 152 decibels and 20-10,000 hertz of sound pressure and vibration to simulate the intense sounds the Orion service module will be subjected to during launch and ascent into space atop the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. This is part of a series of tests to verify the structural integrity of Orion’s service module for Exploration Mission-1, the spacecraft’s first flight atop SLS...Provided by ESA (European Space Agency) and built by Airbus Defence and Space, the service module will power, propel and cool the vehicle and also supply it with air and water.
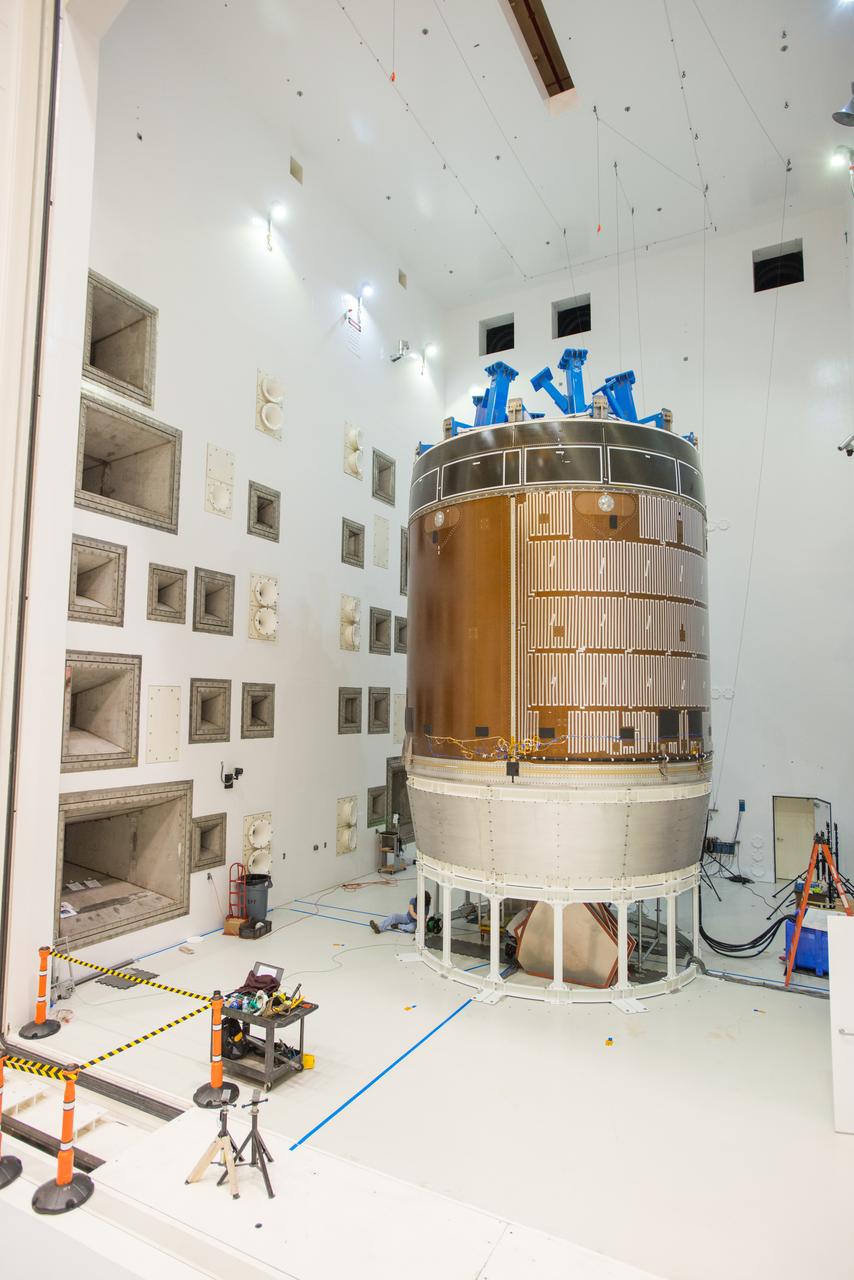

Engineers and technicians moved the Orion service module test article into the Reverberant Acoustic Test Facility at NASA Glenn Research Center’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio on April 8, 2016. Acoustic testing is scheduled to begin April 18. The blue structure sitting on top of the test article is a mass simulator that represents the Orion crew module...The test article will be blasted with at least 152 decibels and 20-10,000 hertz of sound pressure and vibration to simulate the intense sounds the Orion service module will be subjected to during launch and ascent into space atop the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. This is part of a series of tests to verify the structural integrity of Orion’s service module for Exploration Mission-1, the spacecraft’s first flight atop SLS...Provided by ESA (European Space Agency) and built by Airbus Defence and Space, the service module will power, propel and cool the vehicle and also supply it with air and water.
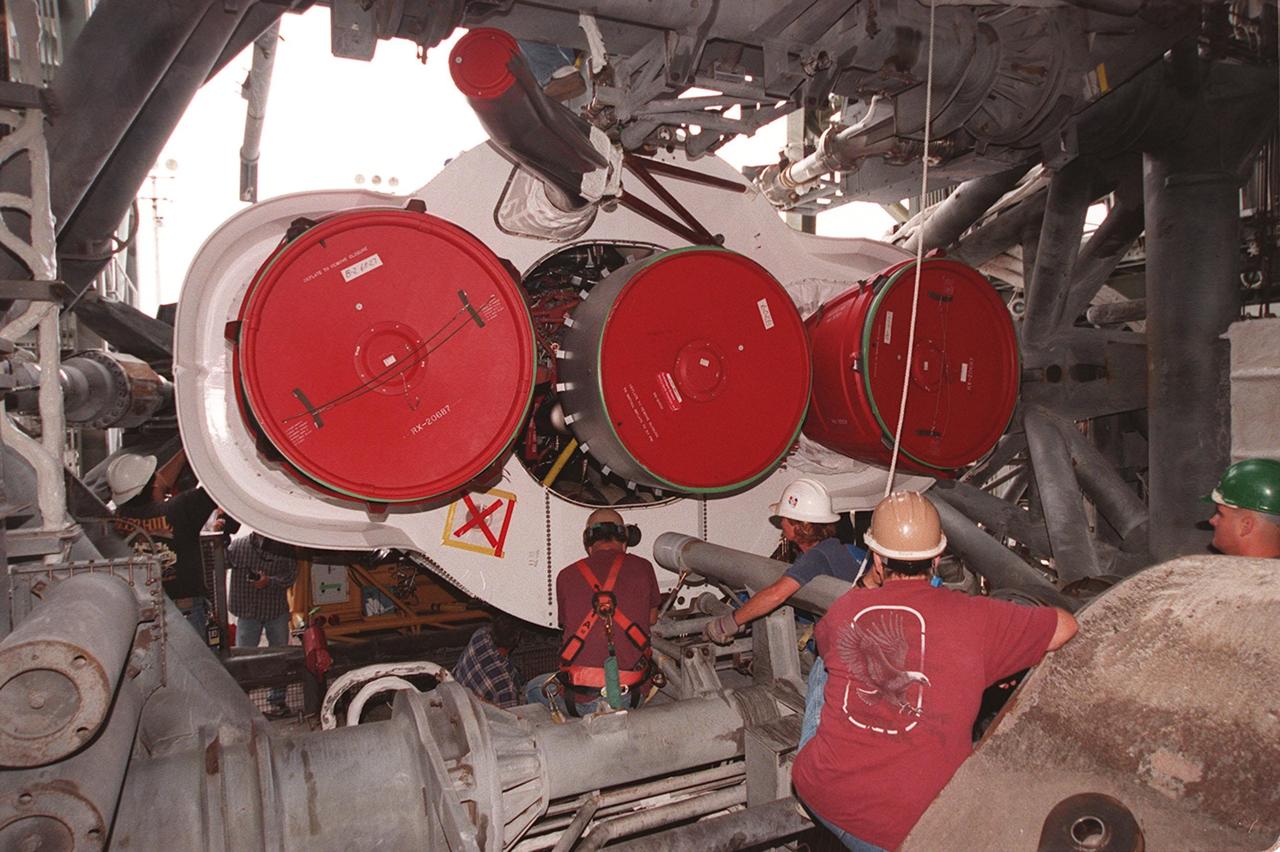

Workers at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station prepare to erect the first stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket in the launch gantry on pad 36A. Shown are the rocket thrusters. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the NASA/Lockheed Martin GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
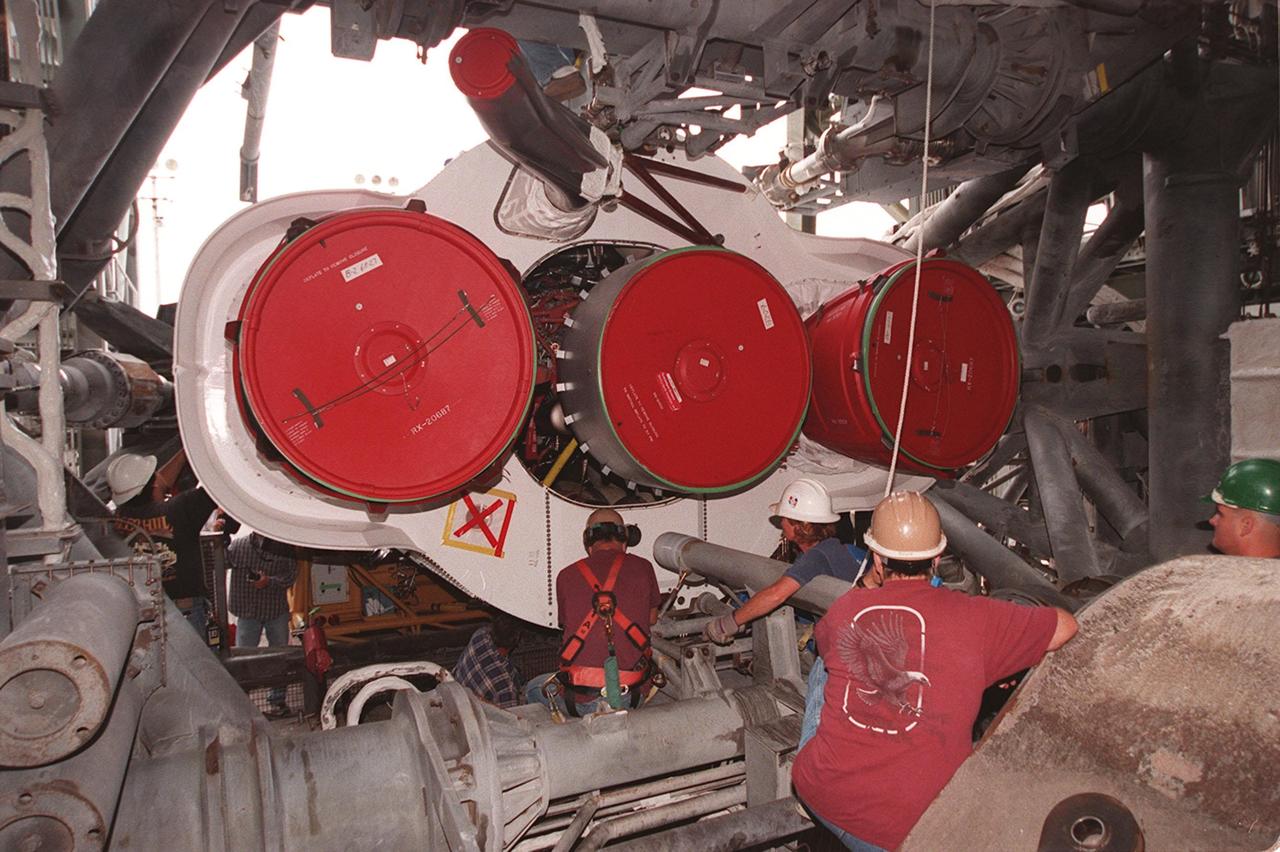

Workers at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station prepare to erect the first stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket in the launch gantry on pad 36A. Shown are the rocket thrusters. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the NASA/Lockheed Martin GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
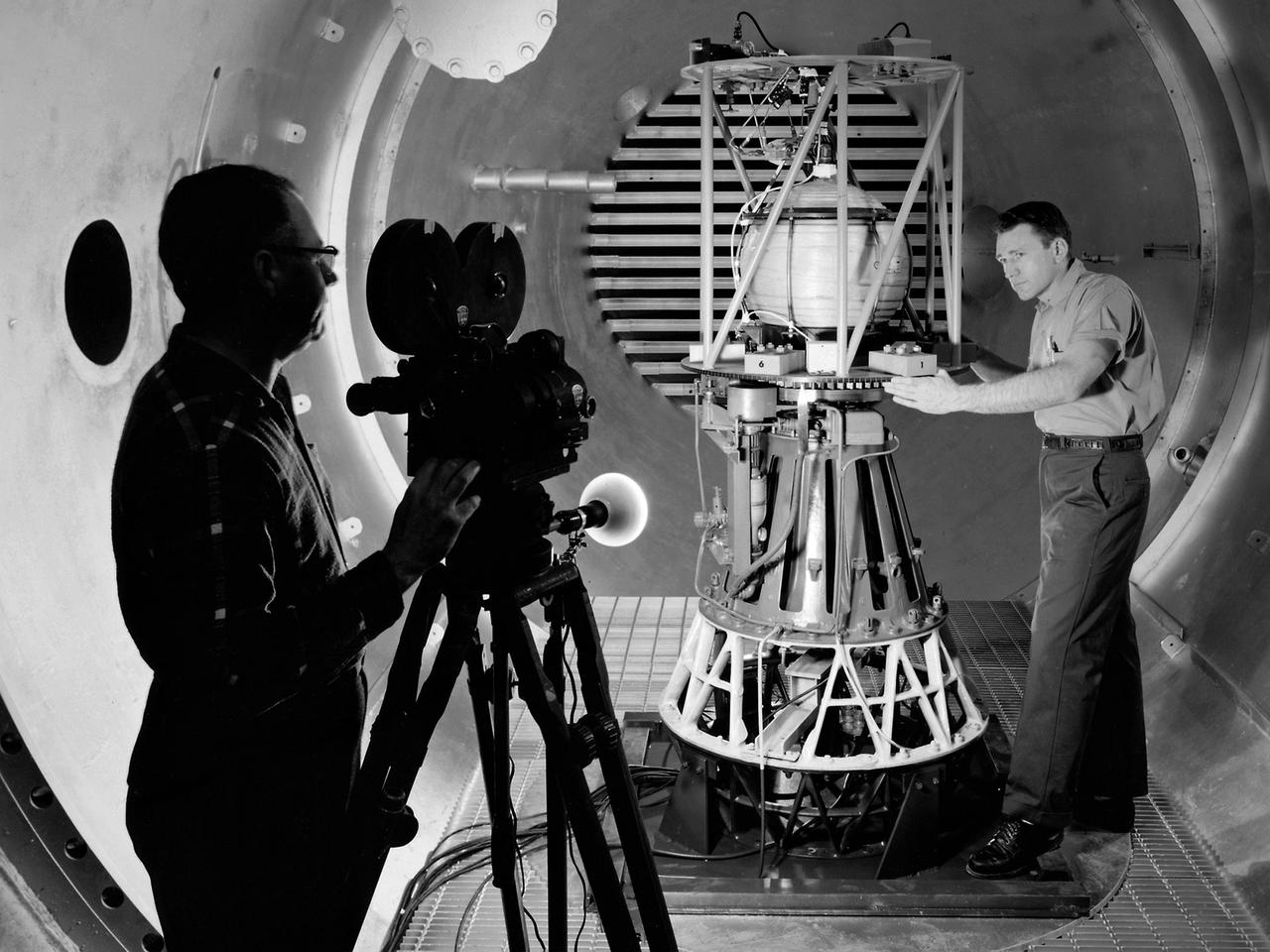

Mechanic Howard Wine inspects the setup of a spin isolator in Cell 2 of the Propulsion Systems Laboratory at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Photographer Al Jecko filmed the proceedings. This test was unique in that the chamber’s altitude system was used, but not its inlet air flow. The test was in preparation for an upcoming launch of modified liquid hydrogen propellant tank on a sounding rocket. This Weightlessness Analysis Sounding Probe (WASP) was part of Lewis investigation into methods for controlling partially filled liquid hydrogen fuel tanks during flight. Second-stage rockets, the Centaur in particular, were designed to stop their engines and coast, then restart them when needed. During this coast period, the propellant often shifted inside the tank. This movement could throw the rocket off course or result in the sloshing of fuel away from the fuel pump. Wine was one of only three journeymen mechanics at Lewis when he was hired in January 1954. He spent his first decade in the Propulsion Systems Laboratory and was soon named a section head. Wine went on to serve as Assistant Division Chief and later served as an assistant to the director. Jecko joined the center in 1947 as a photographer and artist. He studied at the Cleveland School or Art and was known for his cartoon drawing. He worked at the center for 26 years.
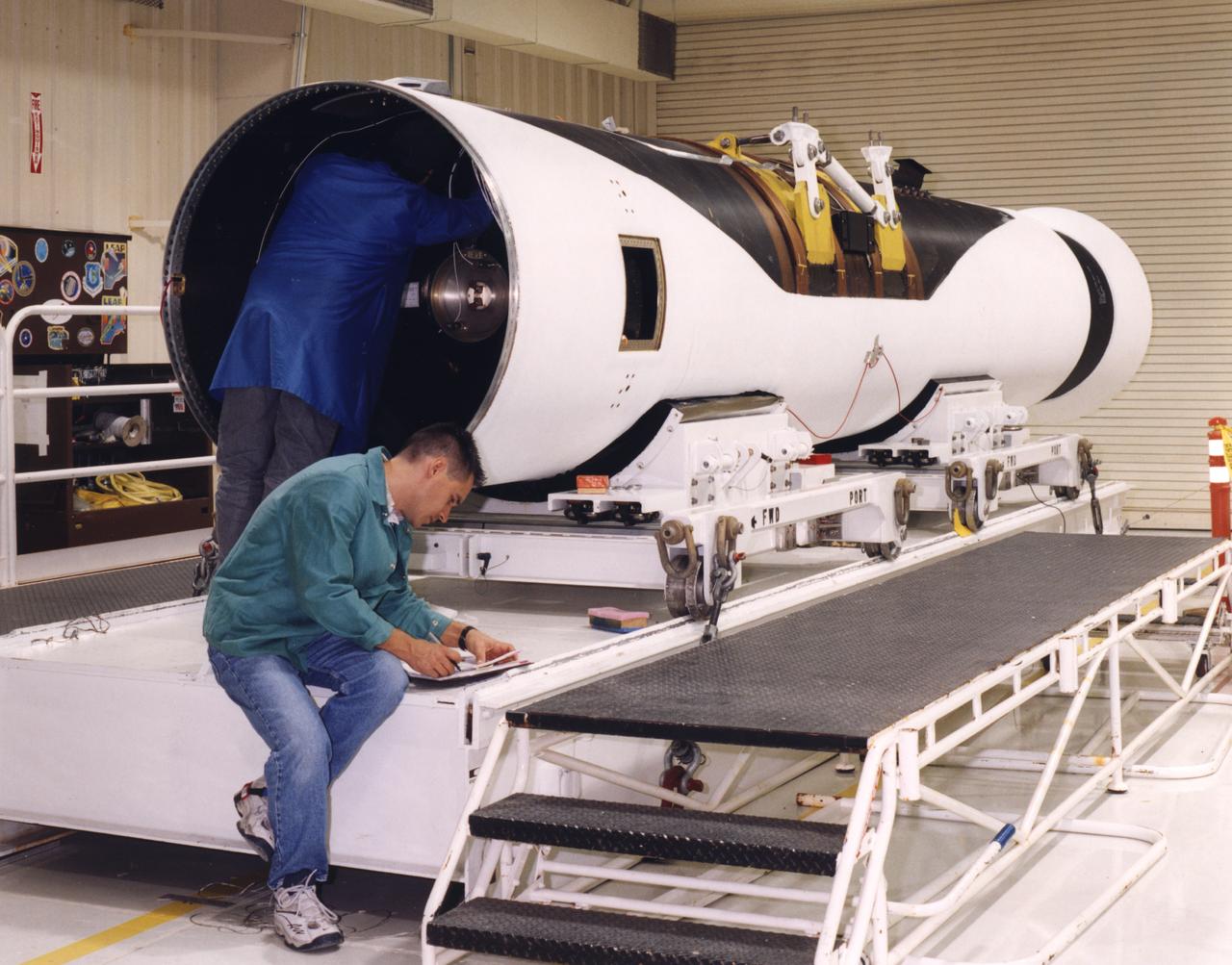

Technicians prepare a Pegasus rocket booster for flight tests with the X-43A "Hypersonic Experimental Vehicle," or "Hyper-X." The X-43A, which will be attached to the Pegasus booster and drop launched from NASA's B-52 mothership, was developed to research dual-mode ramjet/scramjet propulsion system at speeds from Mach 7 up to Mach 10 (7 to 10 times the speed of sound, which varies with temperature and altitude).
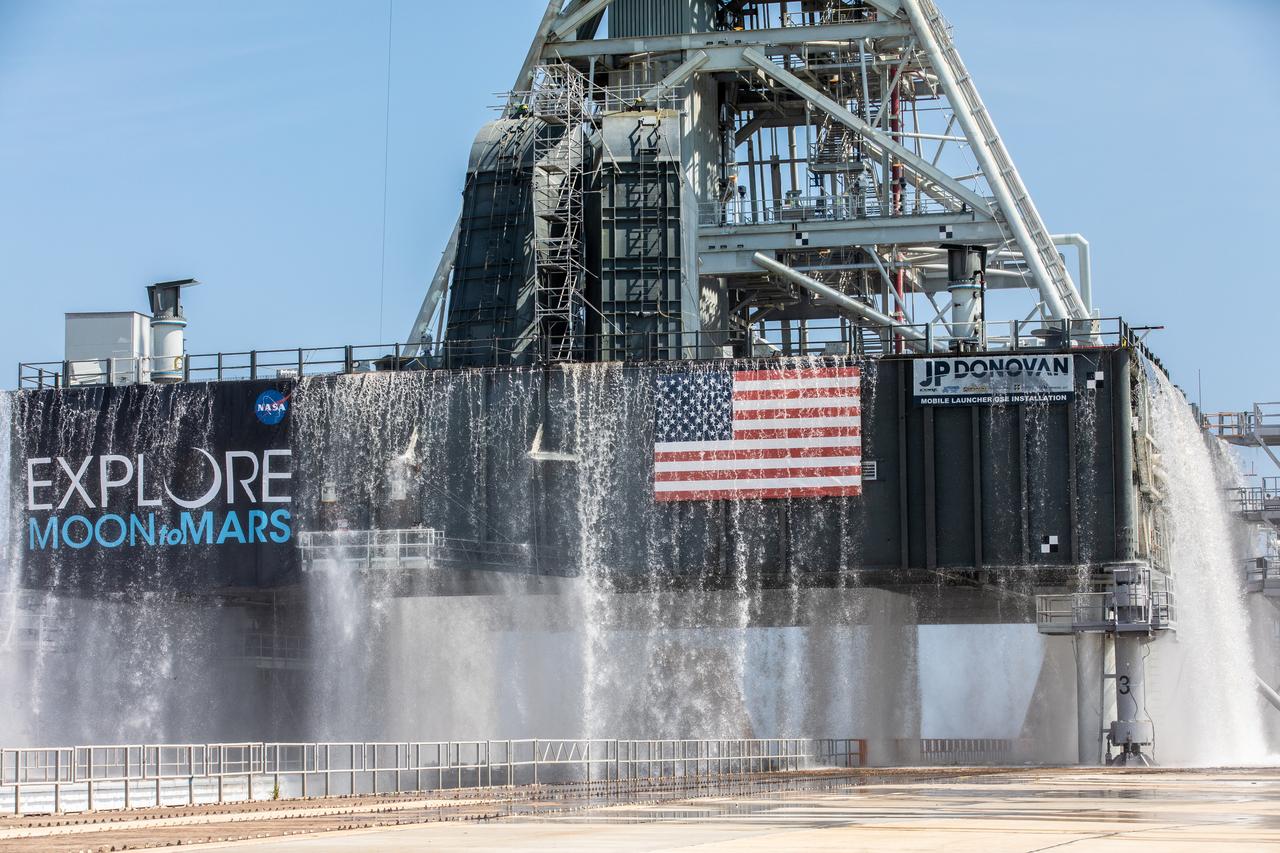

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems conducts a water flow test with the mobile launcher at Kennedy Space Center’s Pad 39B in Florida on July 2, 2019. It is the first of nine tests to verify the sound suppression system is ready for launch of NASA’s Space Launch System for the first Artemis mission. During launch, 400,000 gallons of water will rush onto the pad to help protect the rocket, NASA’s Orion Spacecraft, mobile launcher, and launch pad from the extreme acoustic and temperature environment.
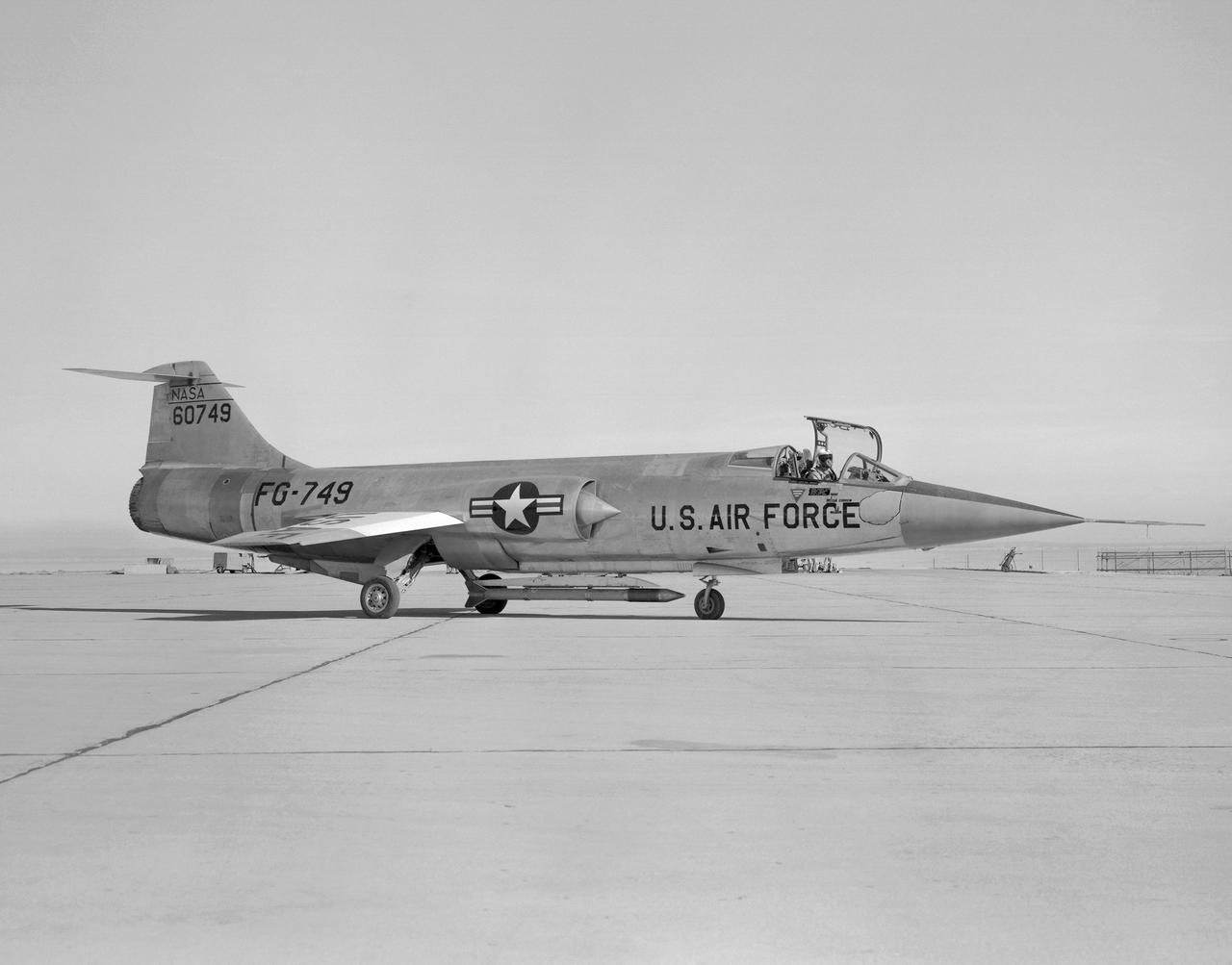

JF-104A (Serial #56-0749) on the ramp at the NASA Flight Research Center (now the Dryden Flight Research Center) at Edwards AFB. The aircraft is shown with the Air Launched Sounding Rocket (ALSOR) attached to the underside. NASA test pilot Milton O. Thompson ejected from this aircraft on 20 December 1962, after an asymmetrical flap condition made the jet uncontrollable.
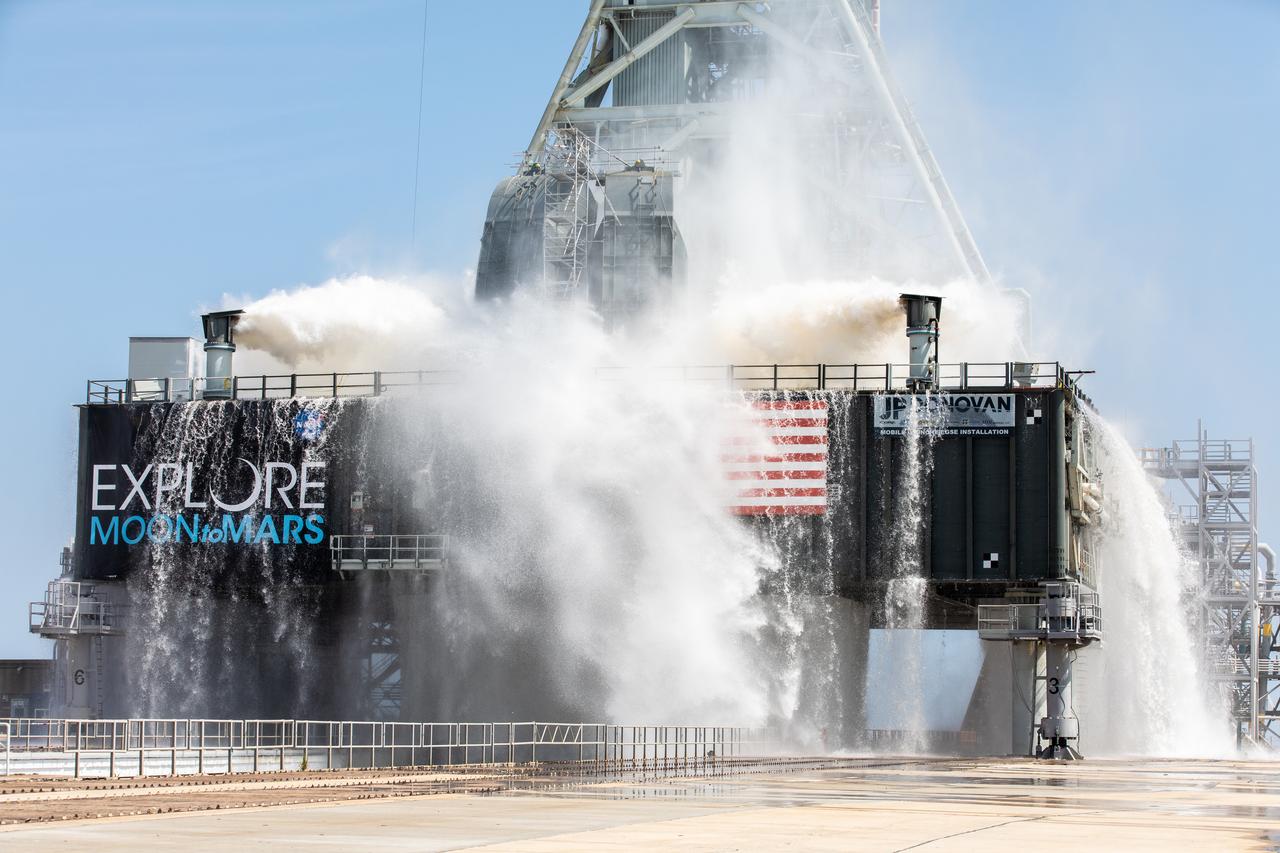

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems conducts a water flow test with the mobile launcher at Kennedy Space Center’s Pad 39B in Florida on July 2, 2019. It is the first of nine tests to verify the sound suppression system is ready for launch of NASA’s Space Launch System for the first Artemis mission. During launch, 400,000 gallons of water will rush onto the pad to help protect the rocket, NASA’s Orion Spacecraft, mobile launcher, and launch pad from the extreme acoustic and temperature environment.
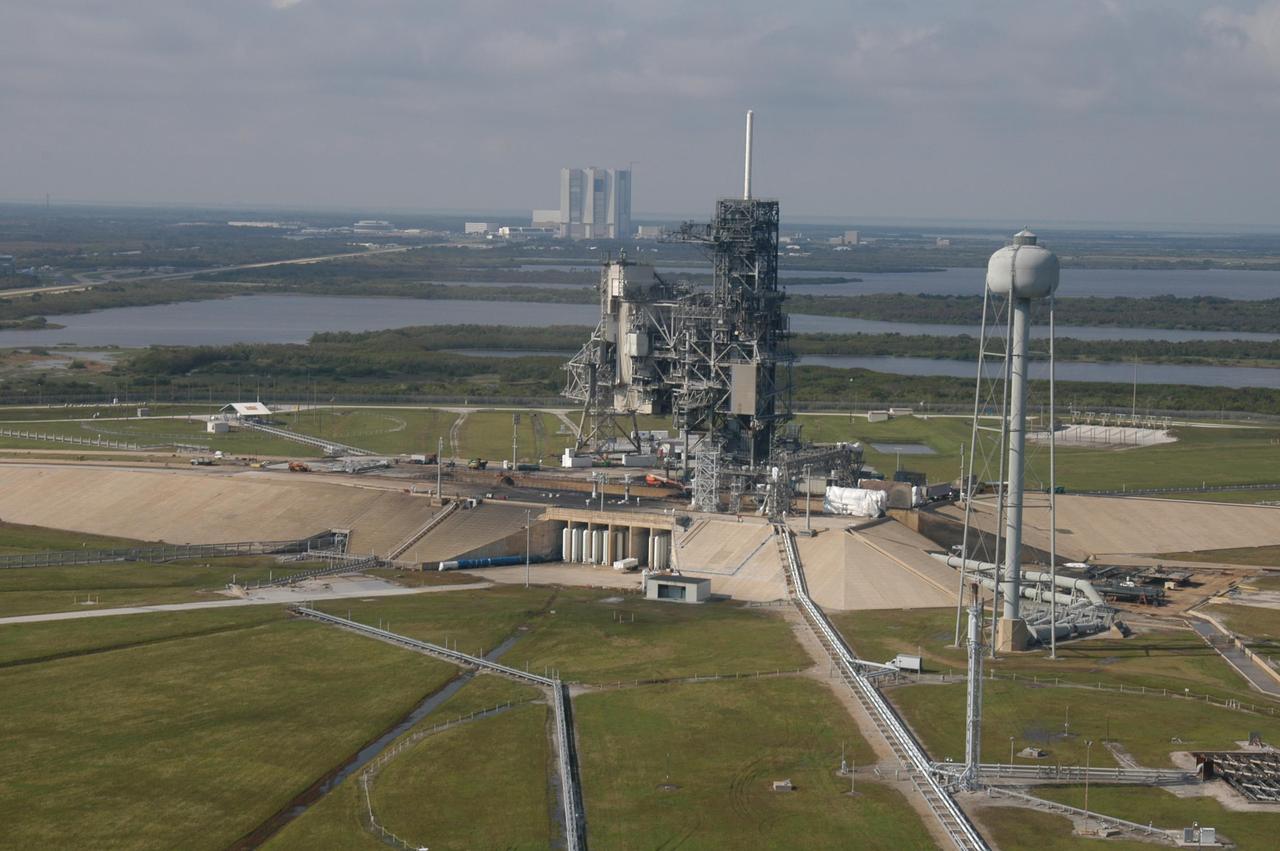

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - An aerial view of Launch Pad 39A at NASA Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the background is the Vehicle Assembly Building. Atop the fixed service structure is the 80-foot-tall lightning mast. At right is the 290-foot-tall water tower that holds 300,000 gallons of water used at launch for sound suppression to protect the orbiter and its payloads from damage by acoustical energy and rocket exhaust reflected from the flame trench and Mobile Launcher Platform during launch.
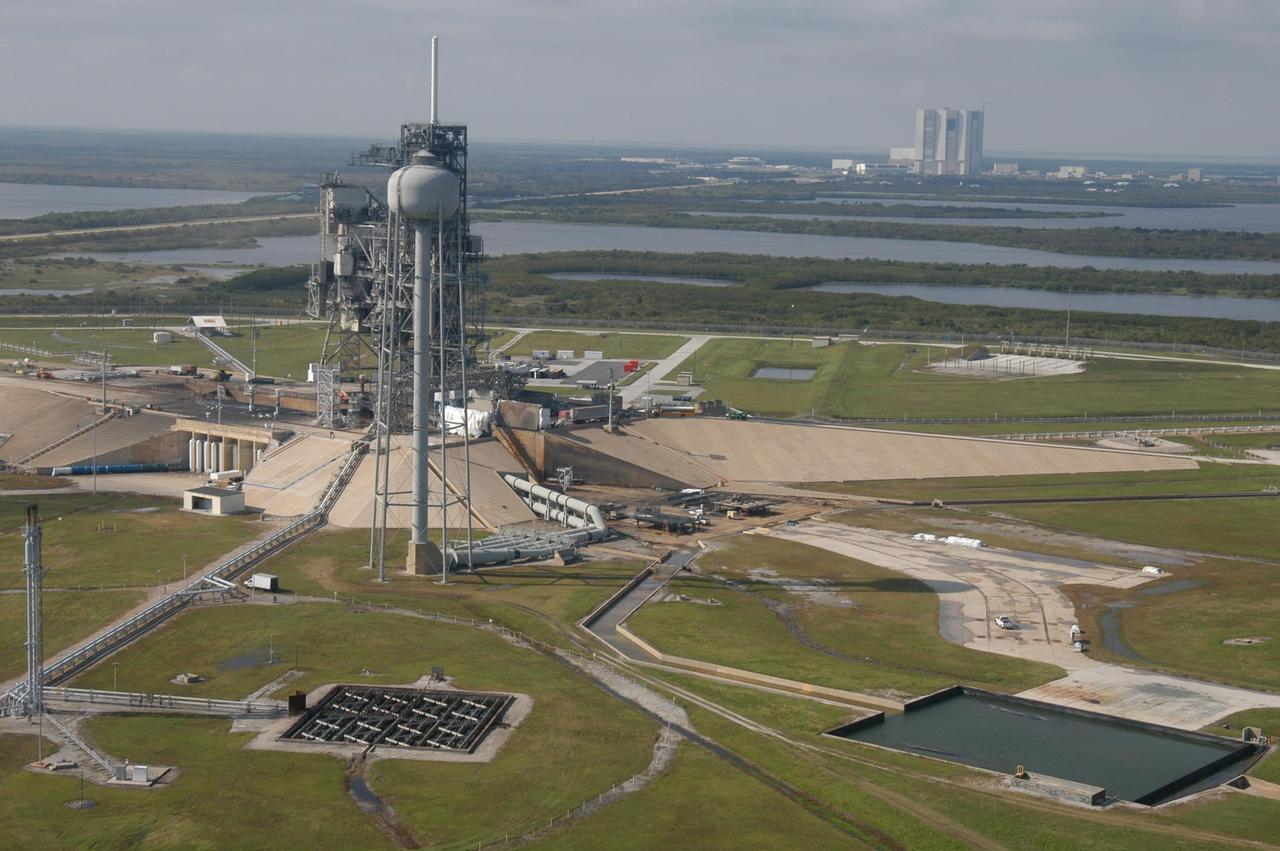

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Another aerial view of Launch Pad 39A at NASA Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the background at right is the Vehicle Assembly Building. Atop the fixed service structure is the 80-foot-tall lightning mast. In front is the 290-foot-tall water tower that holds 300,000 gallons of water used at launch for sound suppression to protect the orbiter and its payloads from damage by acoustical energy and rocket exhaust reflected from the flame trench and Mobile Launcher Platform during launch.

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems conducts a water flow test with the mobile launcher at Kennedy Space Center’s Pad 39B in Florida on July 2, 2019. It is the first of nine tests to verify the sound suppression system is ready for launch of NASA’s Space Launch System for the first Artemis mission. During launch, 400,000 gallons of water will rush onto the pad to help protect the rocket, NASA’s Orion Spacecraft, mobile launcher, and launch pad from the extreme acoustic and temperature environment.
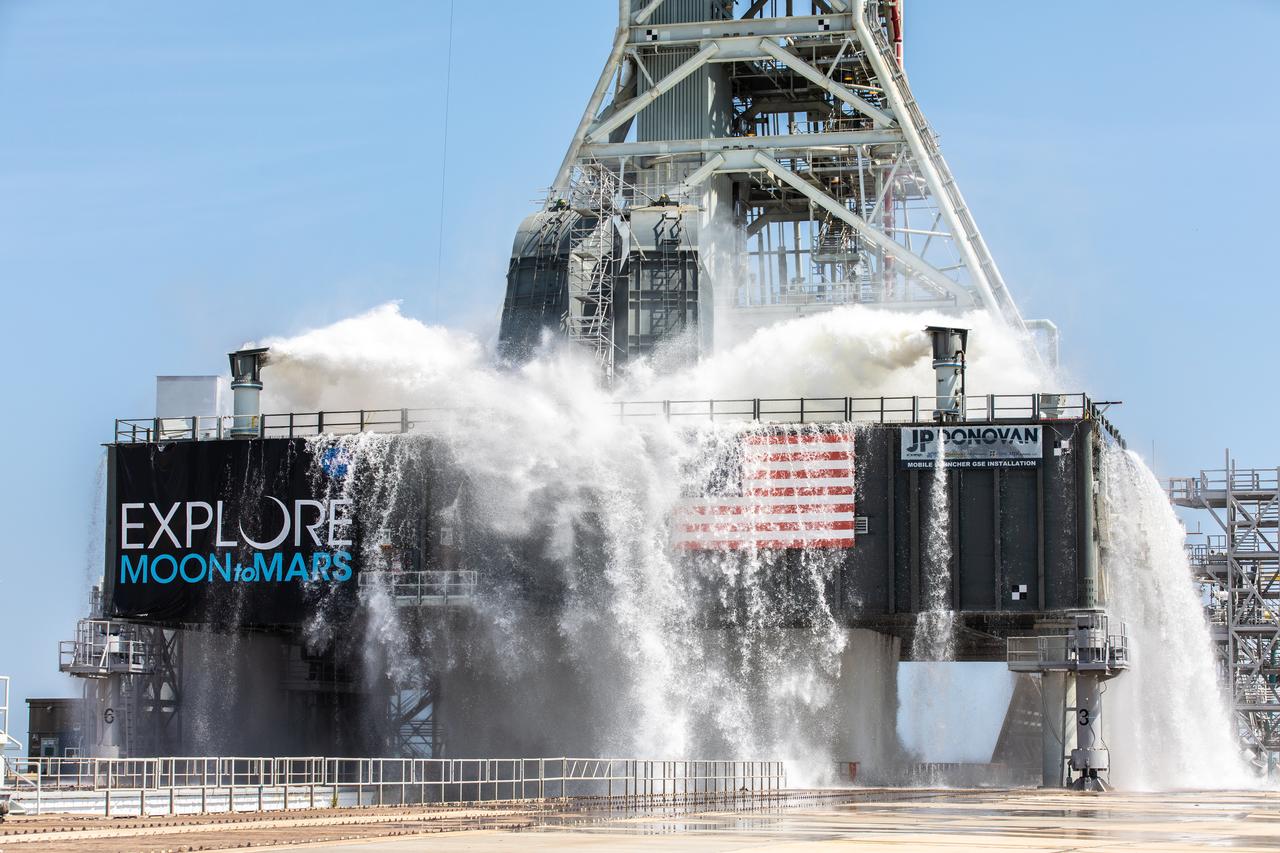

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems conducts a water flow test with the mobile launcher at Kennedy Space Center’s Pad 39B in Florida on July 2, 2019. It is the first of nine tests to verify the sound suppression system is ready for launch of NASA’s Space Launch System for the first Artemis mission. During launch, 400,000 gallons of water will rush onto the pad to help protect the rocket, NASA’s Orion Spacecraft, mobile launcher, and launch pad from the extreme acoustic and temperature environment.
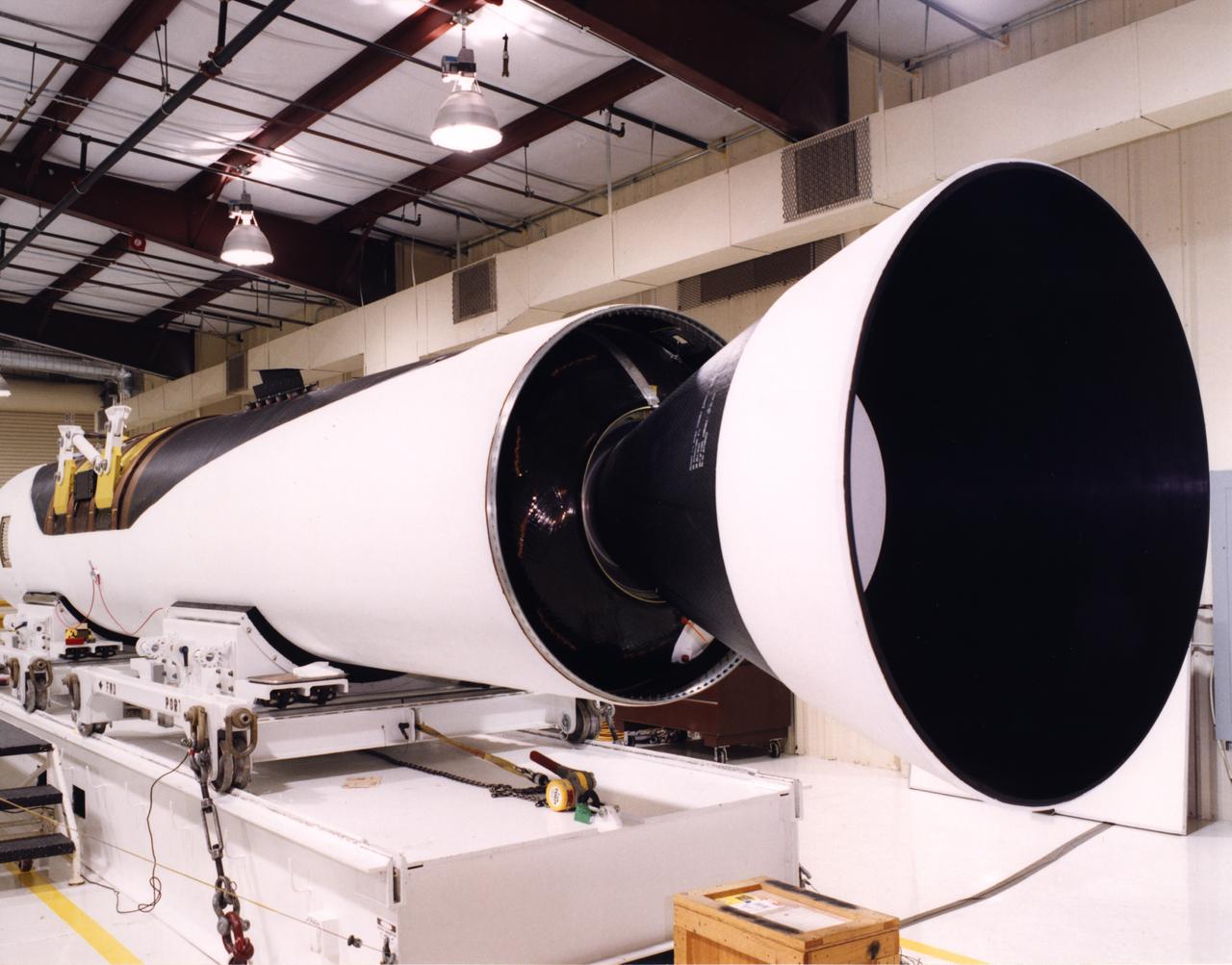

A close-up view of the front end of a Pegasus rocket booster being prepared by technicians at the Dryden Flight Research Center for flight tests with the X-43A "Hypersonic Experimental Vehicle," or "Hyper-X." The X-43A, which will be attached to the Pegasus booster and drop launched from NASA's B-52 mothership, was developed to research dual-mode ramjet/scramjet propulsion system at speeds from Mach 7 up to Mach 10 (7 to 10 times the speed of sound, which varies with temperature and altitude).
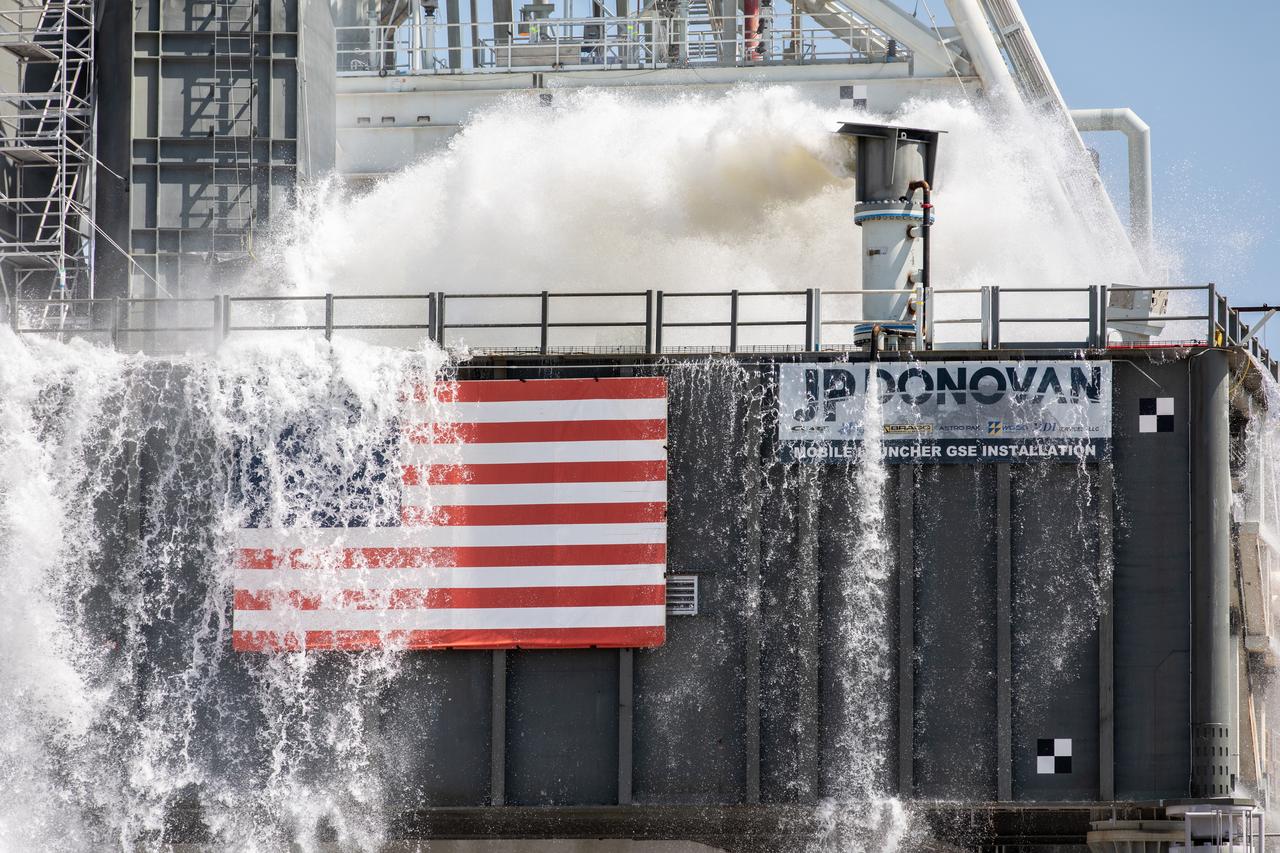

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems conducts a water flow test with the mobile launcher at Kennedy Space Center’s Pad 39B in Florida on July 2, 2019. It is the first of nine tests to verify the sound suppression system is ready for launch of NASA’s Space Launch System for the first Artemis mission. During launch, 400,000 gallons of water will rush onto the pad to help protect the rocket, NASA’s Orion Spacecraft, mobile launcher, and launch pad from the extreme acoustic and temperature environment.
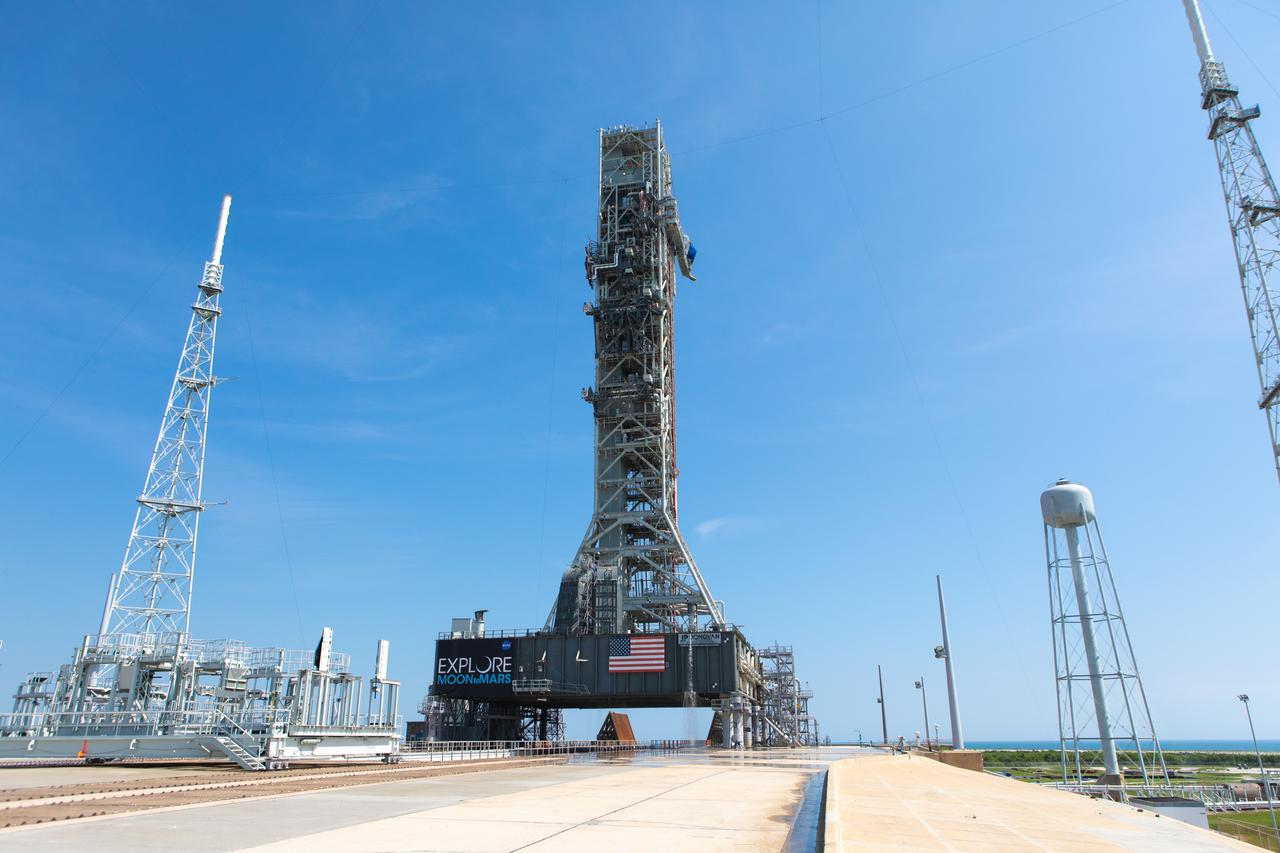

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems conducts a water flow test with the mobile launcher at Kennedy Space Center’s Pad 39B in Florida on July 2, 2019. It is the first of nine tests to verify the sound suppression system is ready for launch of NASA’s Space Launch System for the first Artemis mission. During launch, 400,000 gallons of water will rush onto the pad to help protect the rocket, NASA’s Orion Spacecraft, mobile launcher, and launch pad from the extreme acoustic and temperature environment.
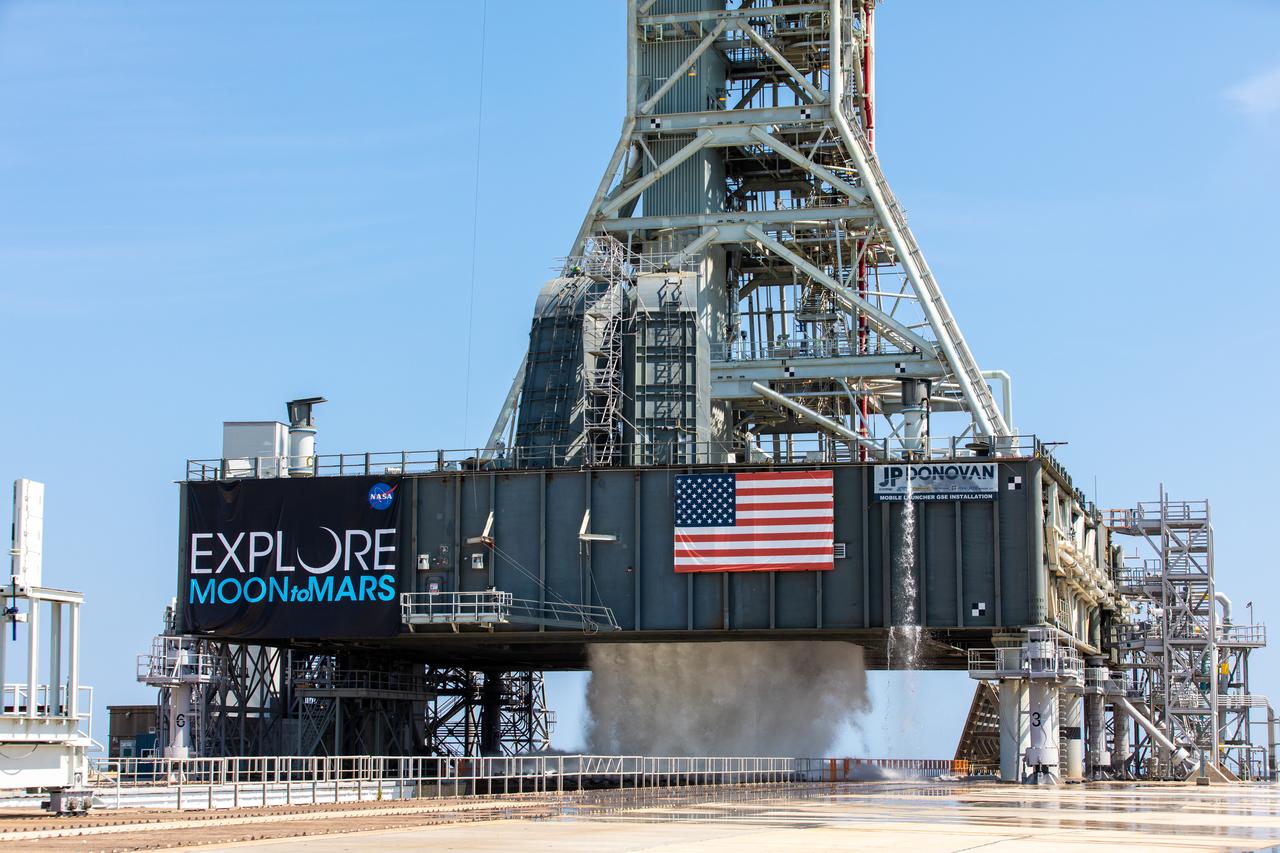

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems conducts a water flow test with the mobile launcher at Kennedy Space Center’s Pad 39B in Florida on July 2, 2019. It is the first of nine tests to verify the sound suppression system is ready for launch of NASA’s Space Launch System for the first Artemis mission. During launch, 400,000 gallons of water will rush onto the pad to help protect the rocket, NASA’s Orion Spacecraft, mobile launcher, and launch pad from the extreme acoustic and temperature environment.
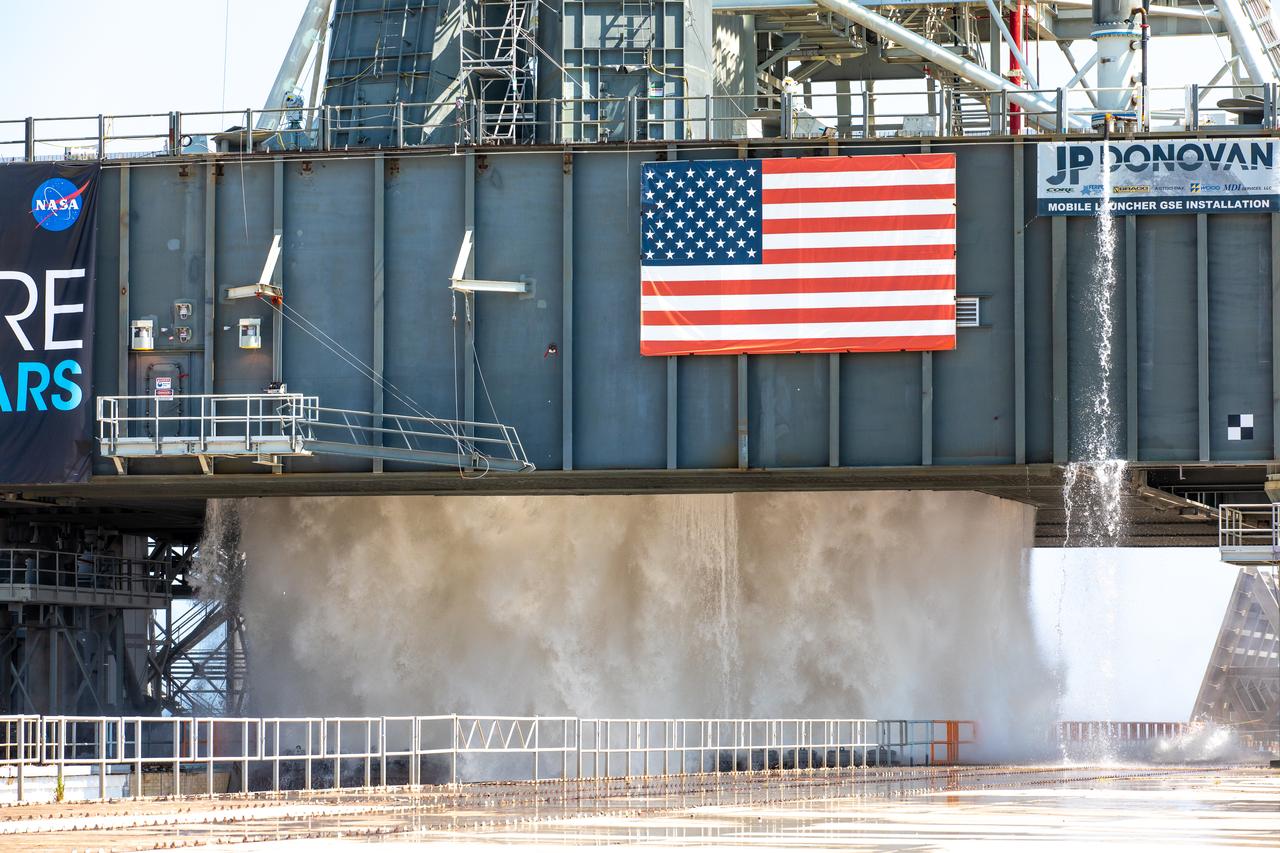

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems conducts a water flow test with the mobile launcher at Kennedy Space Center’s Pad 39B in Florida on July 2, 2019. It is the first of nine tests to verify the sound suppression system is ready for launch of NASA’s Space Launch System for the first Artemis mission. During launch, 400,000 gallons of water will rush onto the pad to help protect the rocket, NASA’s Orion Spacecraft, mobile launcher, and launch pad from the extreme acoustic and temperature environment.
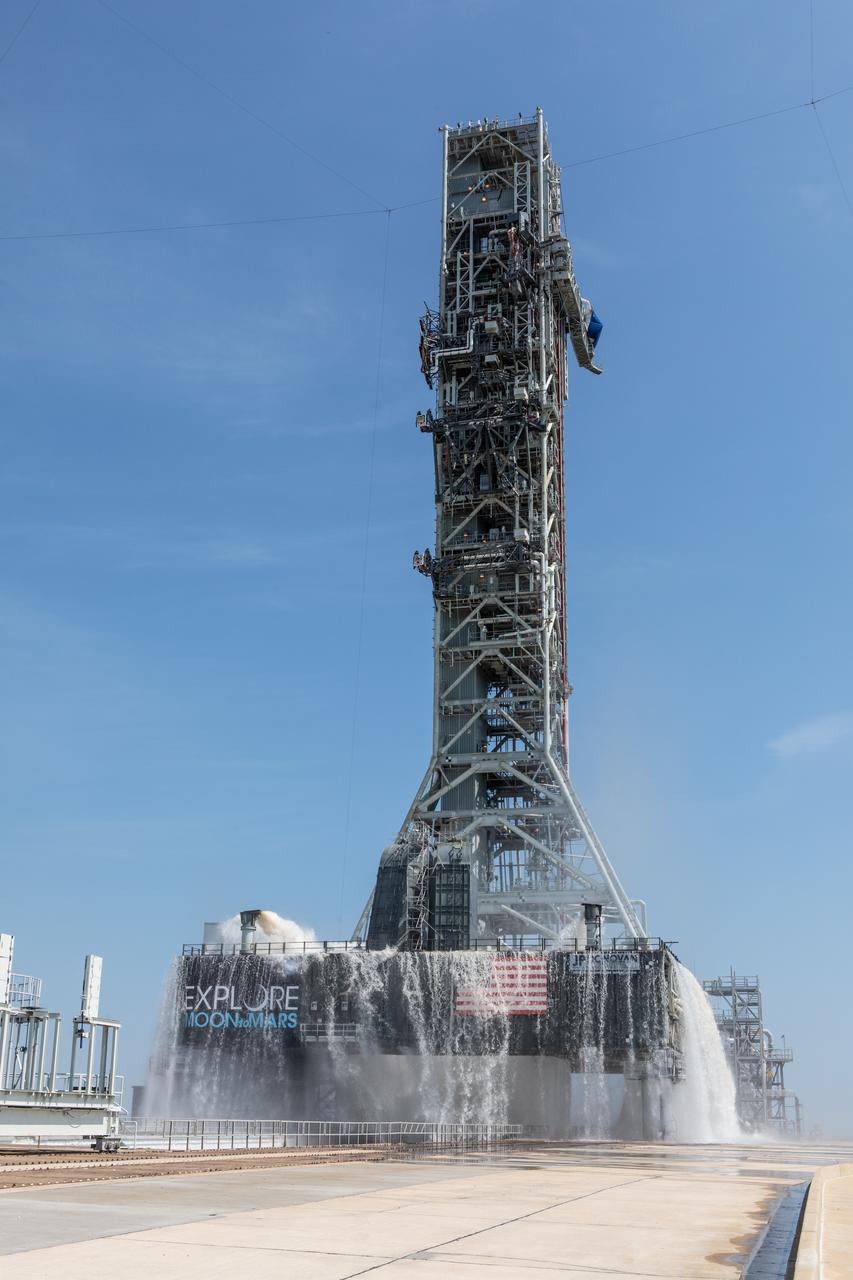

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems conducts a water flow test with the mobile launcher at Kennedy Space Center’s Pad 39B in Florida on July 2, 2019. It is the first of nine tests to verify the sound suppression system is ready for launch of NASA’s Space Launch System for the first Artemis mission. During launch, 400,000 gallons of water will rush onto the pad to help protect the rocket, NASA’s Orion Spacecraft, mobile launcher, and launch pad from the extreme acoustic and temperature environment.
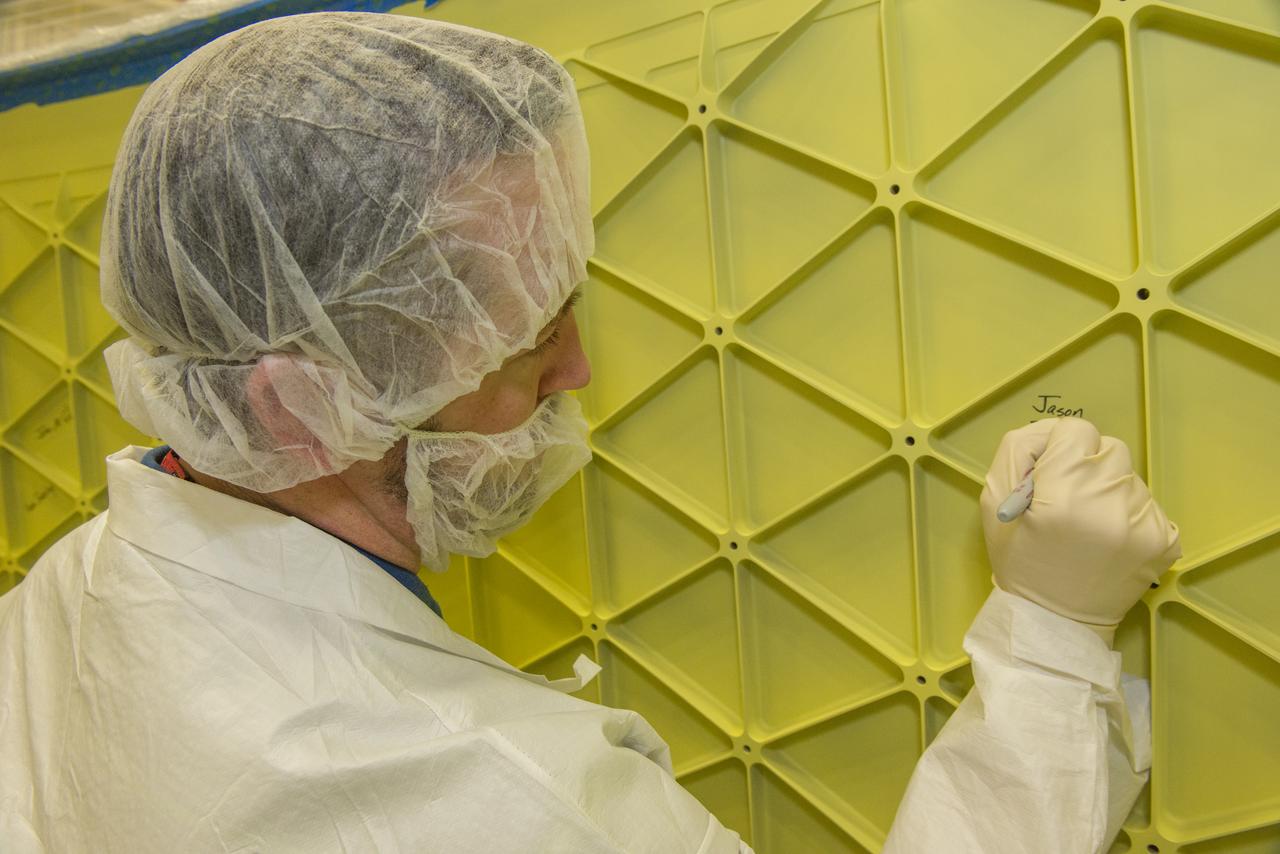

JASON ELDRIDGE, AN ERC INCORPORATED EMPLOYEE SUPPORTING THE MATERIALS & PROCESSES LABORATORY AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER, SIGNS HIS NAME ON THE INTERIOR OF THE ADAPTER THAT WILL CONNECT THE ORION SPACECRAFT TO A UNITED LAUNCH ALLIANCE DELTA IV ROCKET FOR EXPLORATION FLIGHT TEST (EFT)-1. MARSHALL CENTER TEAM MEMBERS WHO WERE INVOLVED IN THE DESIGN, CONSTRUCTION AND TESTING OF THE ADAPTER HAD THE OPPORTUNITY TO AUTOGRAPH IT BEFORE THE HARDWARE IS SHIPPED TO NASA'S KENNEDY SPACE CENTER IN FEBRUARY. ELDRIDGE WAS ON A TEAM THAT PERFORMED ULTRASONIC INSPECTIONS ON THE ADAPTER'S WELDS -- ENSURING THEY ARE STRUCTURALLY SOUND. EFT-1, SCHEDULED FOR 2014, WILL PROVIDE EARLY EXPERIENCE FOR NASA SPACE LAUNCH SYSTEM (SLS) HARDWARE AHEAD OF THE ROCKET'S FIRST FLIGHT IN 2017.
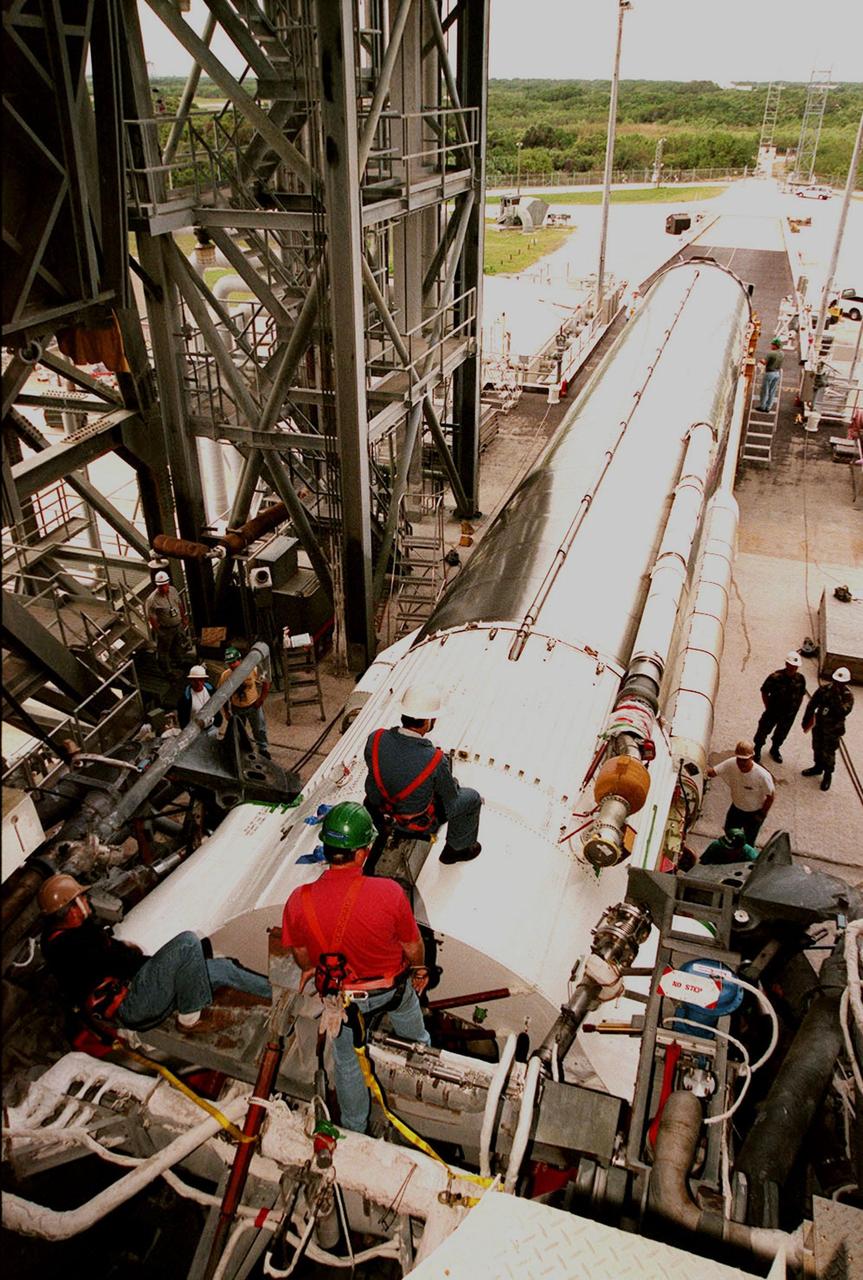

Workers at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station prepare to erect the first stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket in the launch gantry on pad 36A. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the NASA/Lockheed Martin GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
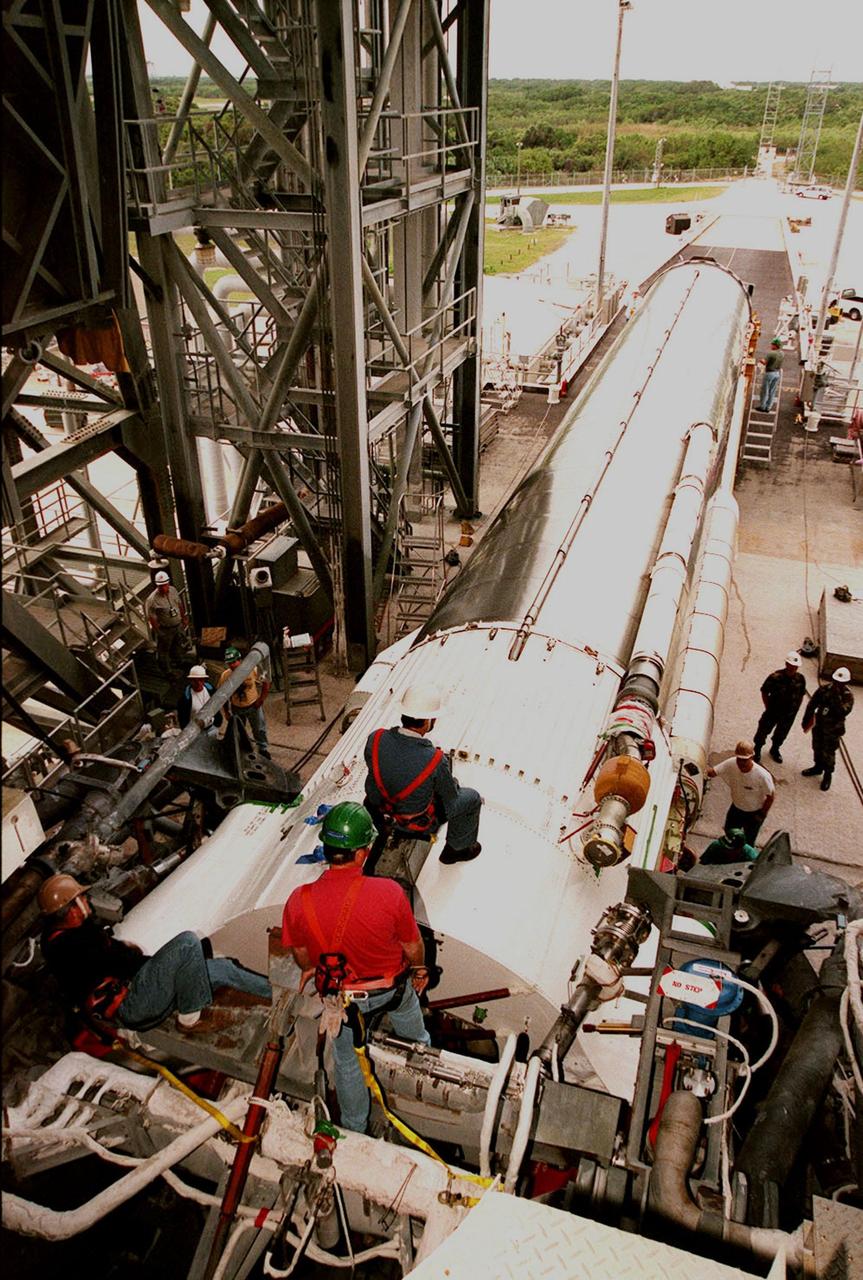

Workers at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station prepare to erect the first stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket in the launch gantry on pad 36A. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the NASA/Lockheed Martin GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
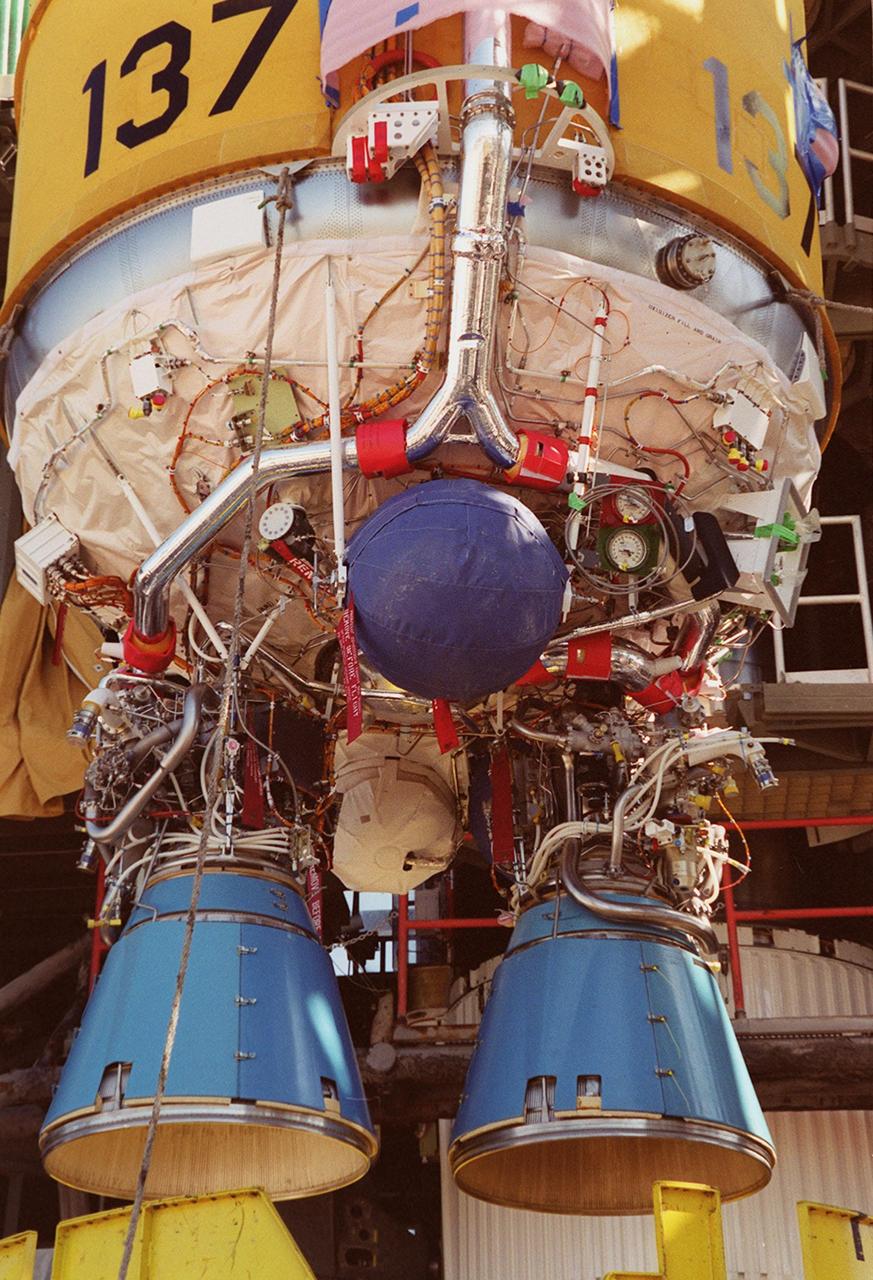
At launch pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket is lifted up the gantry (behind it) for mating with the first stage. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing

The GOES-L satellite is ready for mating with the lower stages of the Atlas IIA rocket on pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing. Launch is scheduled for May 3
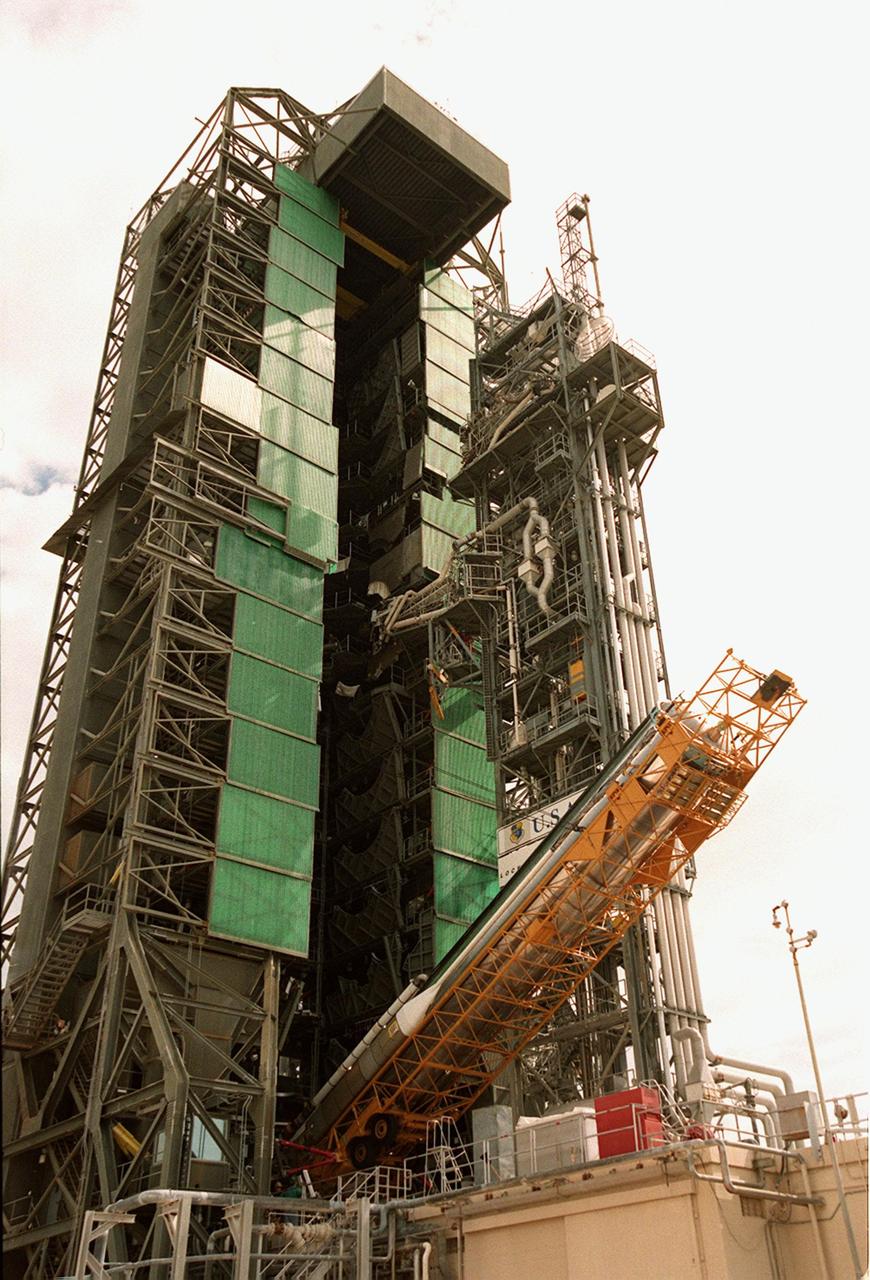

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the first stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket is slowly raised in the launch gantry on pad 36A. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the NASA/Lockheed Martin GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
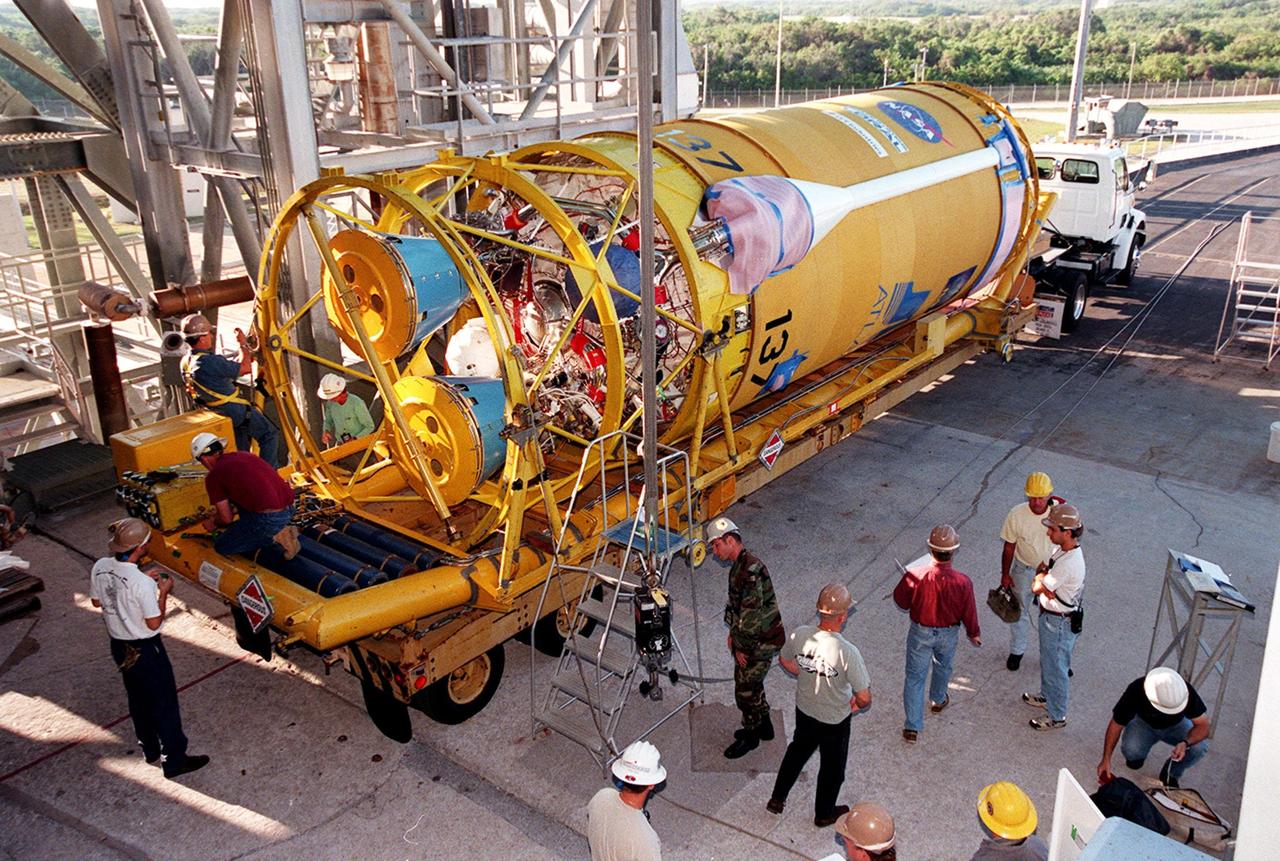

The second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket arrives on pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, for mating with the first stage. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
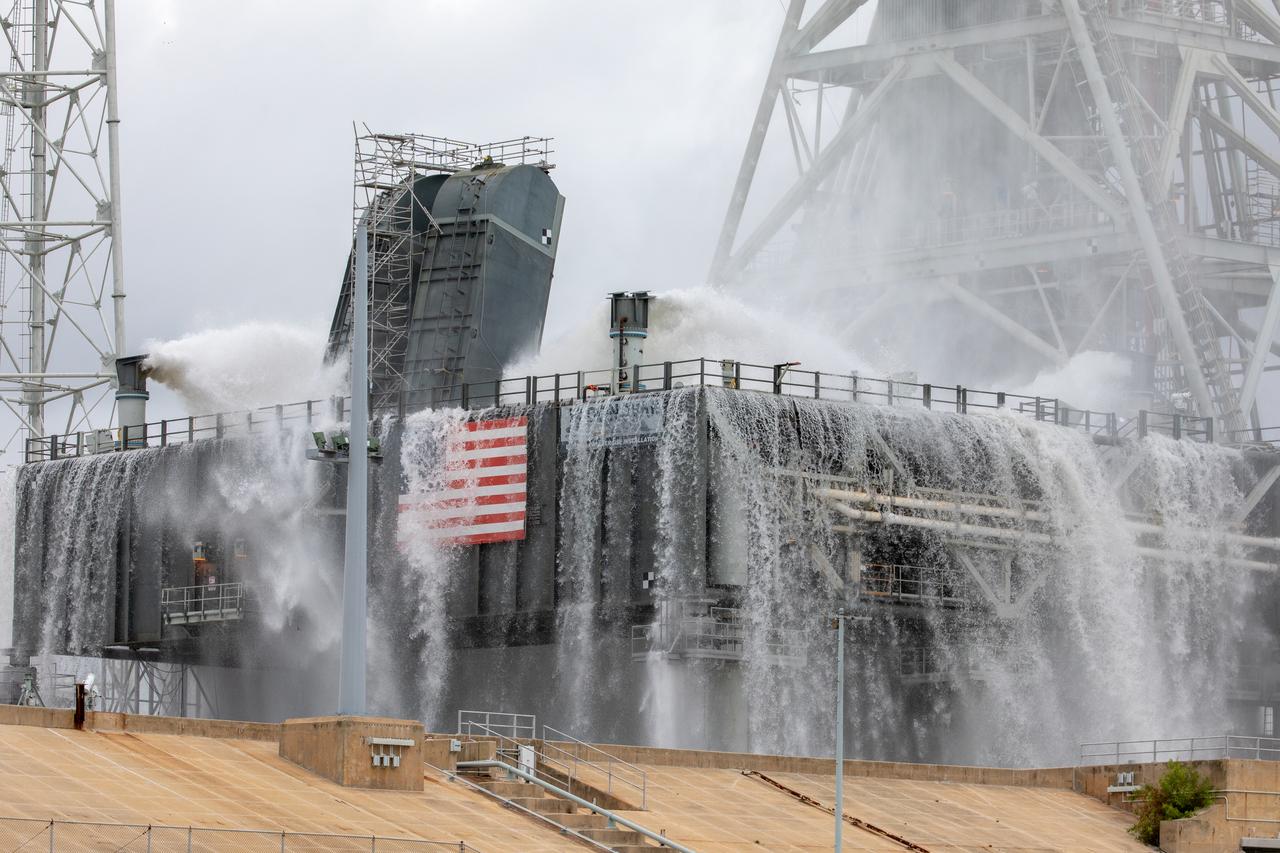

A flow test of the Ignition Overpressure Protection and Sound Suppression water deluge system is underway on the mobile launcher at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on July 25, 2019. The testing is part of a series of tests that Exploration Ground System is doing to verify the system is ready for the new Space Launch System rocket. Modifications were made to the pad after a previous wet flow test, increasing the performance of the system. During the launch of Artemis 1 and subsequent missions, this water deluge system will release about 450,000 gallons of water across the mobile launcher and Flame Deflector to reduce the extreme heat and energy generated by the rocket during ignition and liftoff.
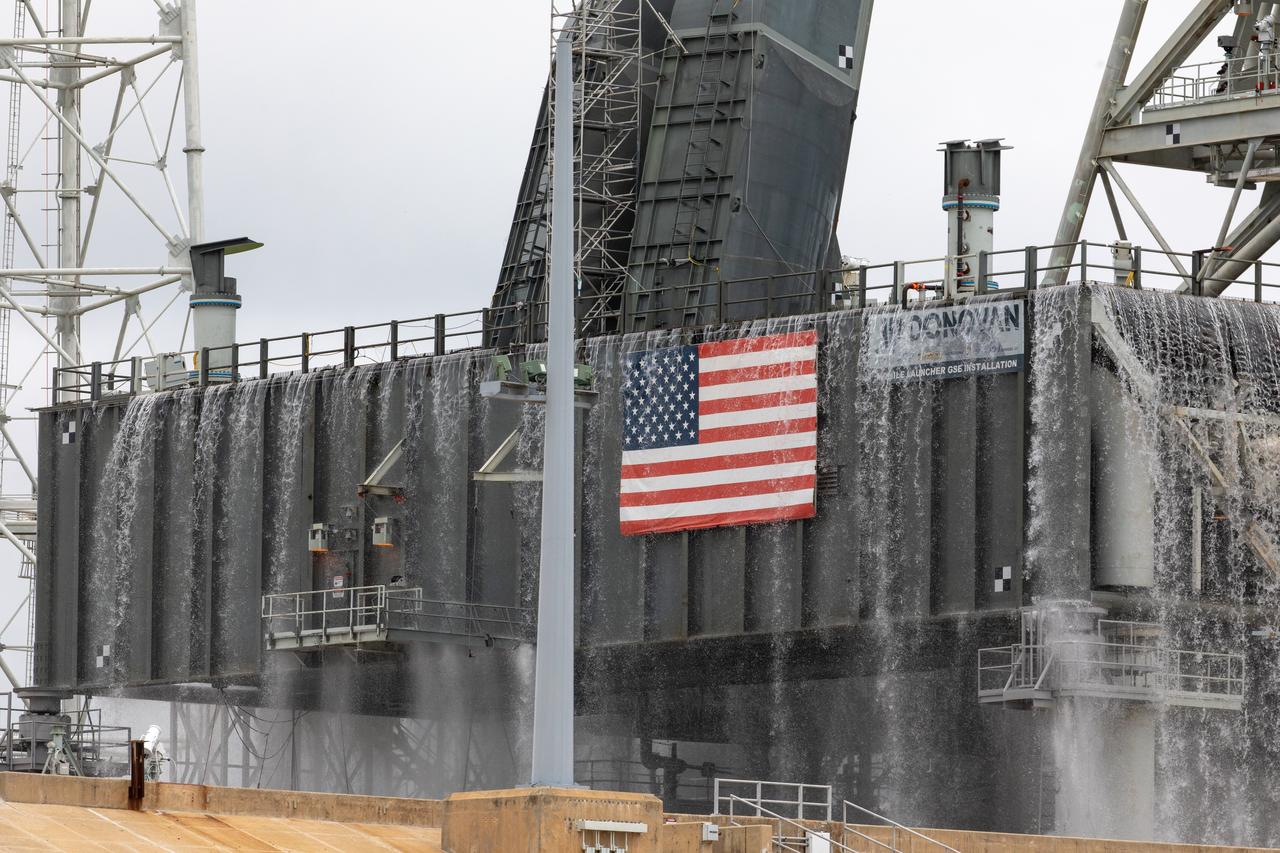

A flow test of the Ignition Overpressure Protection and Sound Suppression water deluge system is underway on the mobile launcher at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on July 25, 2019. The testing is part of a series of tests that Exploration Ground System is doing to verify the system is ready for the new Space Launch System rocket. Modifications were made to the pad after a previous wet flow test, increasing the performance of the system. During the launch of Artemis 1 and subsequent missions, this water deluge system will release about 450,000 gallons of water across the mobile launcher and Flame Deflector to reduce the extreme heat and energy generated by the rocket during ignition and liftoff.
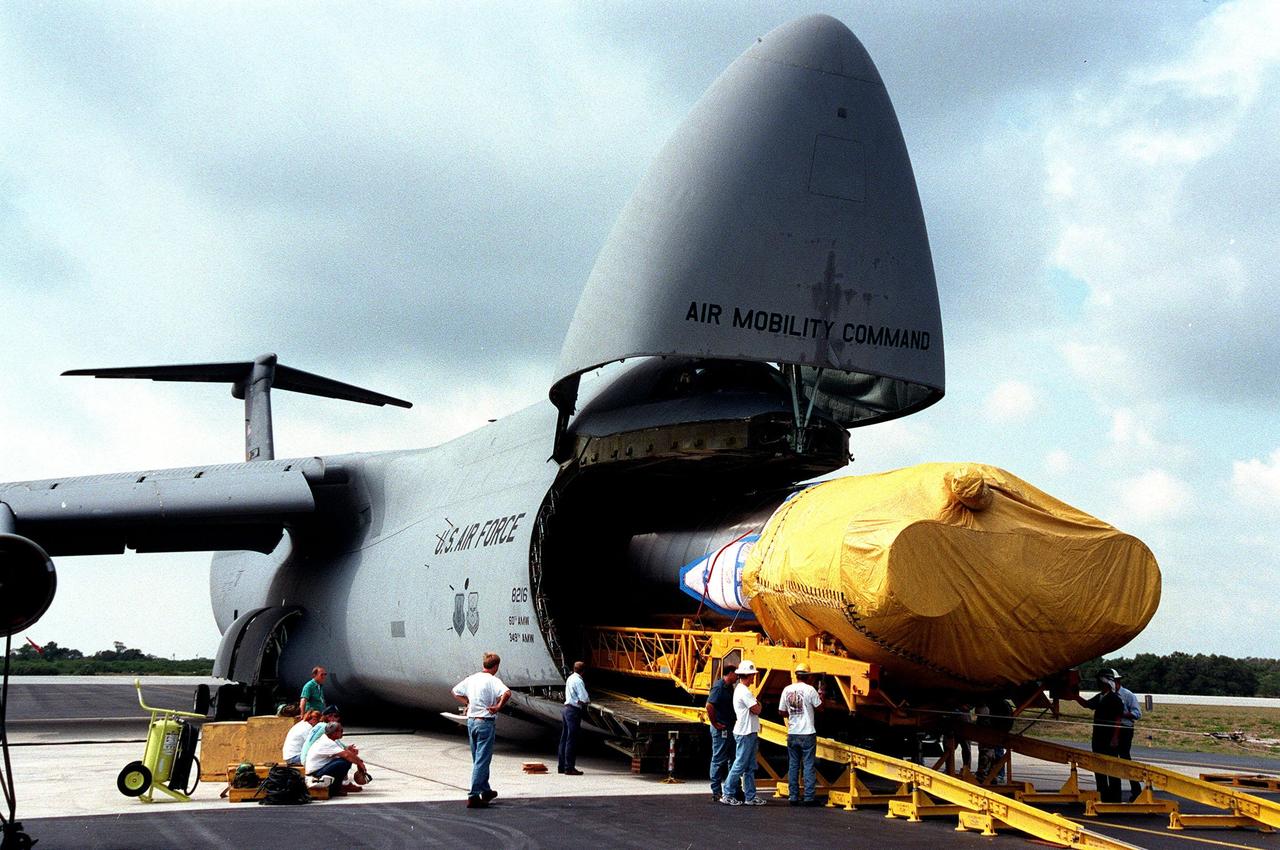

At Cape Canaveral Air Station, workers begin offloading an Atlas IIA rocket from a U.S. Air Force C-5c. The rocket is scheduled to launch the NASA GOES-L satellite from Launch Pad 36B on May 15. Once in orbit, the satellite will become GOES-11, joining GOES-8, GOES-9 and GOES-10 in space. The fourth of a new advanced series of geostationary weather satellites for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), GOES-L is a three-axis inertially stabilized spacecraft that will provide pictures and perform atmospheric sounding at the same time. Once launched, the satellite will undergo checkout and then provide backup capabilities for the existing, aging operational satellites
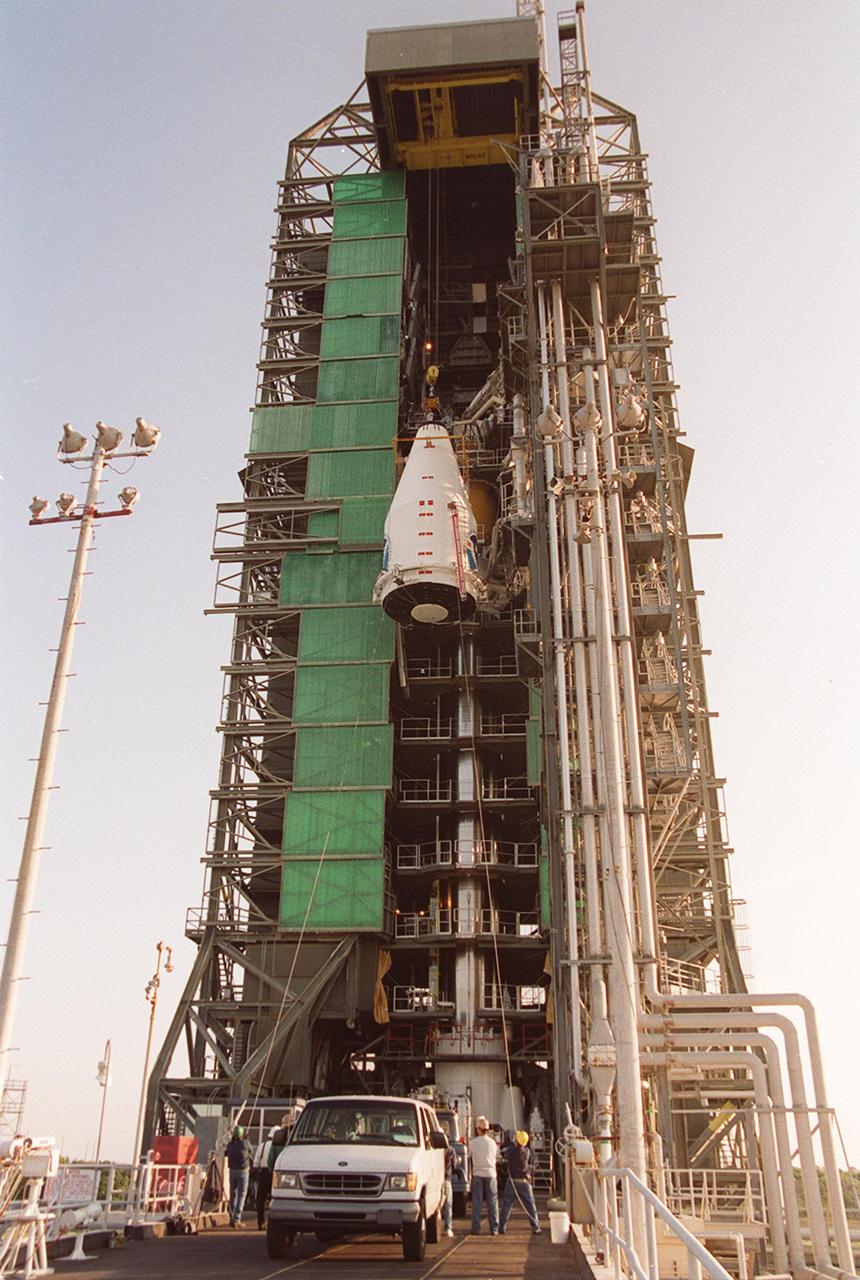
The GOES-L satellite is about midway in its journey up the gantry on pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The Atlas IIA rocket is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing. Launch is scheduled for May 3
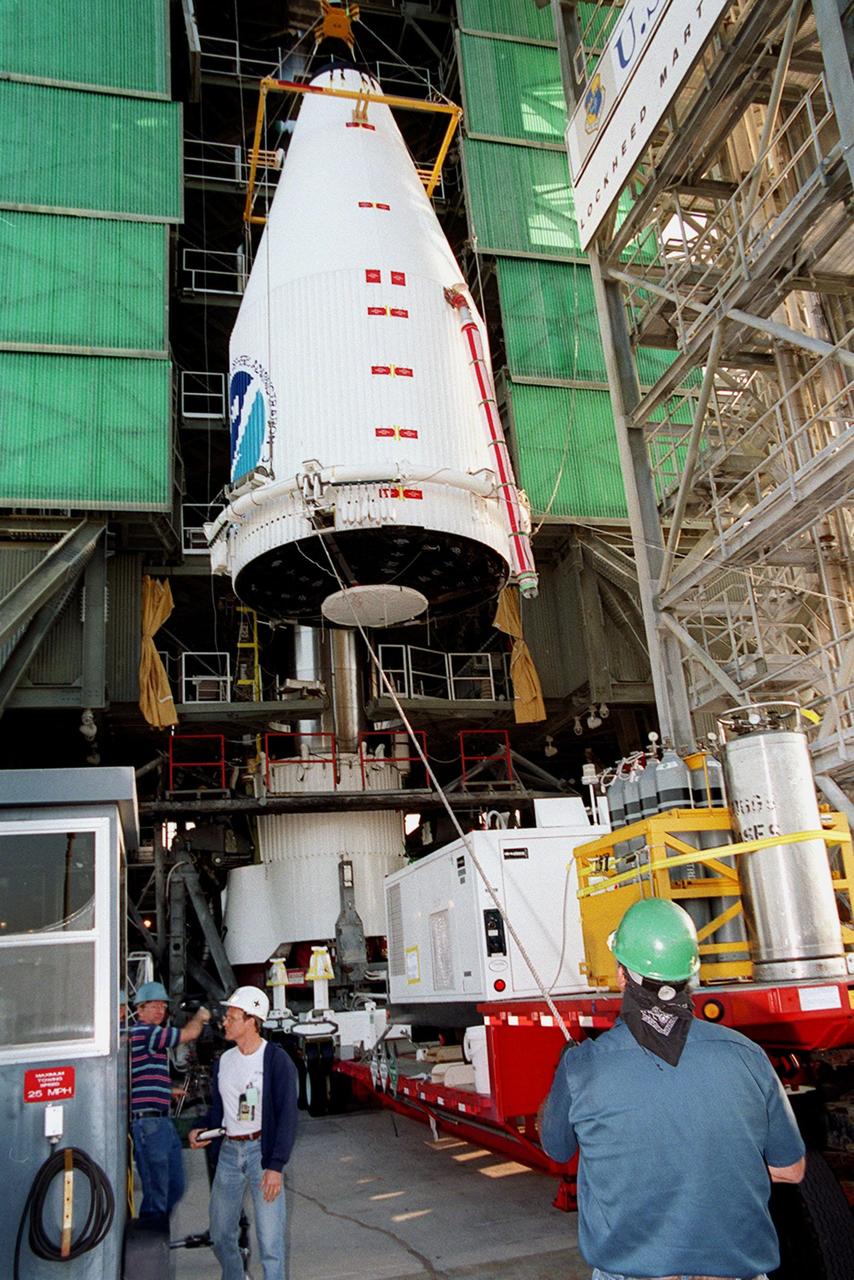

The GOES-L satellite is ready for mating with the lower stages of the Atlas IIA rocket on pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing. Launch is scheduled for May 3
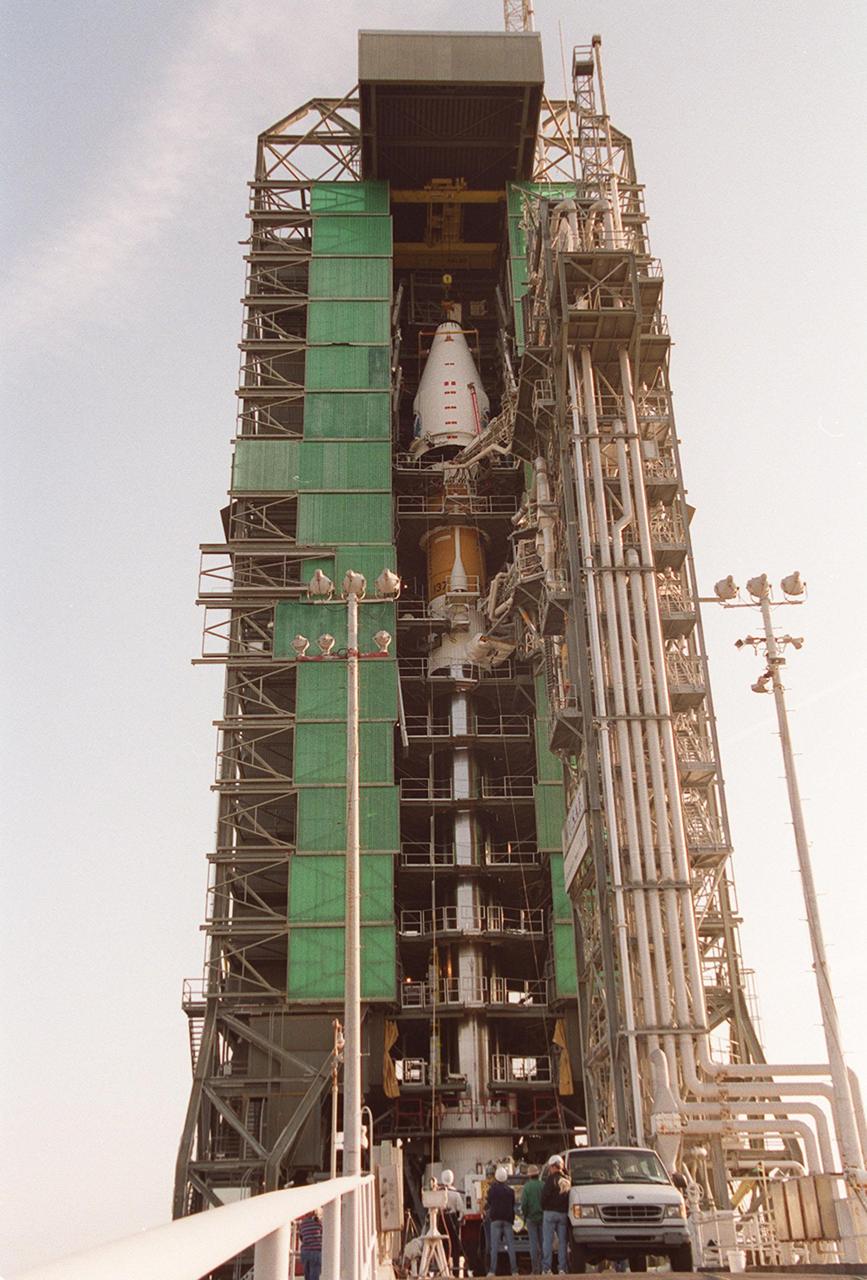
The GOES-L satellite, after being lifted up to the top of the gantry on pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, is ready for mating with the Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. Atlas IIA is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing. Launch is scheduled for May 3
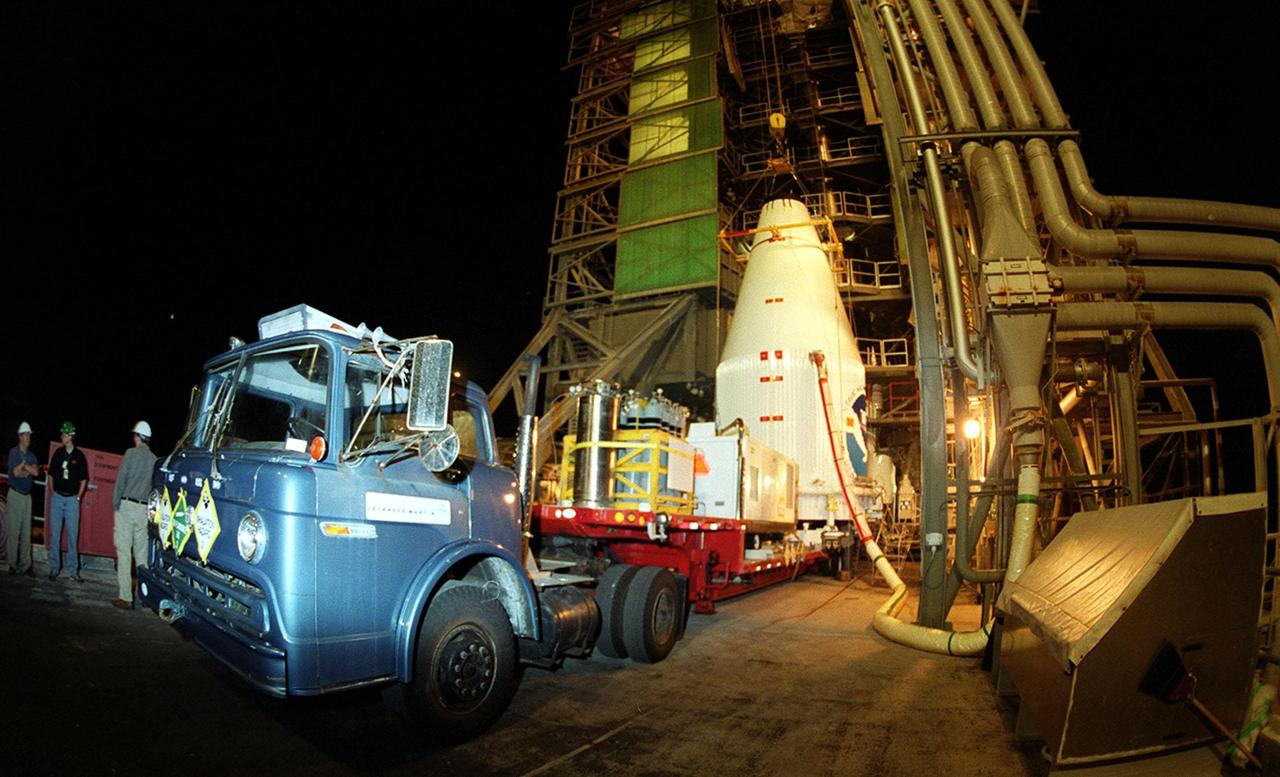

The GOES-L satellite arrives on pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The Atlas IIA rocket is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing. Launch is scheduled for May 3
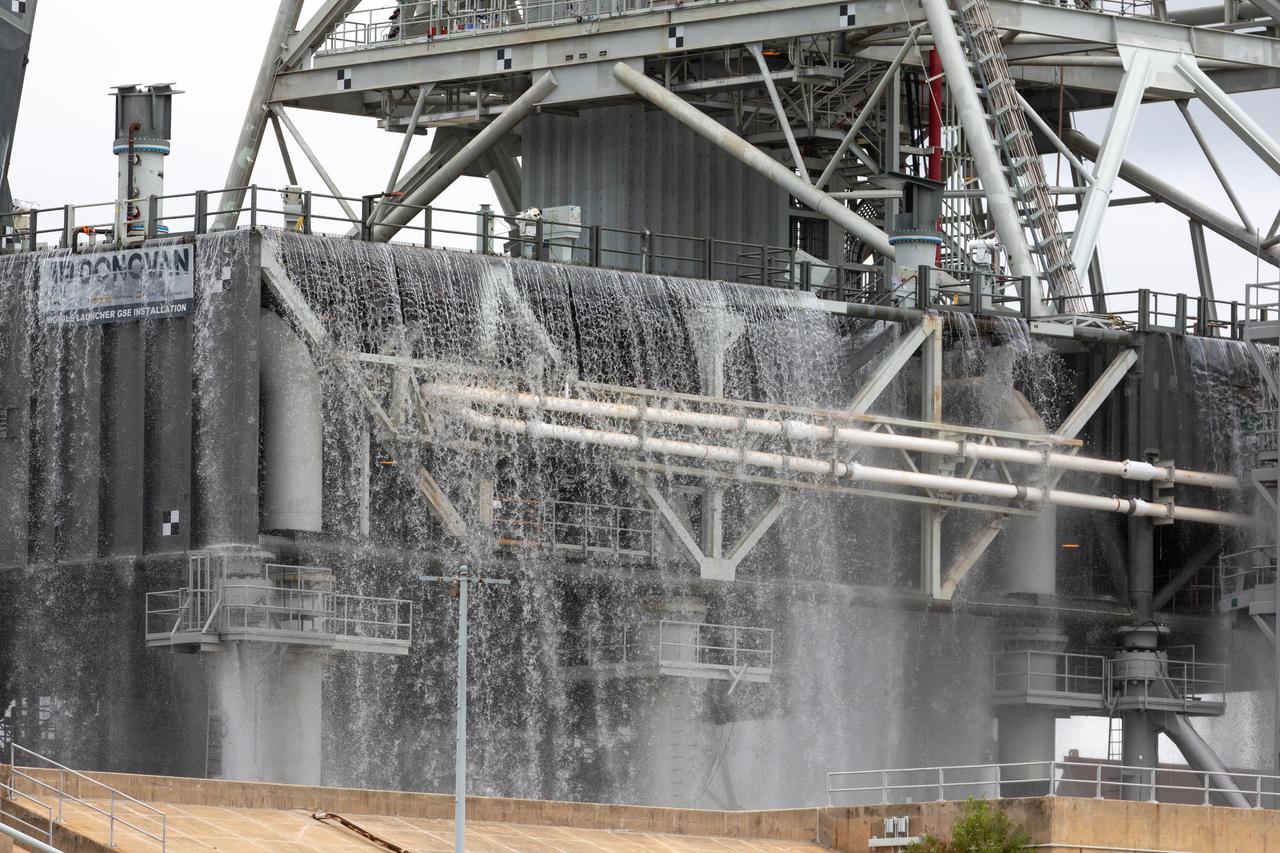

A flow test of the Ignition Overpressure Protection and Sound Suppression water deluge system is underway on the mobile launcher at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on July 25, 2019. The testing is part of a series of tests that Exploration Ground System is doing to verify the system is ready for the new Space Launch System rocket. Modifications were made to the pad after a previous wet flow test, increasing the performance of the system. During the launch of Artemis 1 and subsequent missions, this water deluge system will release about 450,000 gallons of water across the mobile launcher and Flame Deflector to reduce the extreme heat and energy generated by the rocket during ignition and liftoff.

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the first stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket is slowly raised in the launch gantry on pad 36A. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the NASA/Lockheed Martin GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
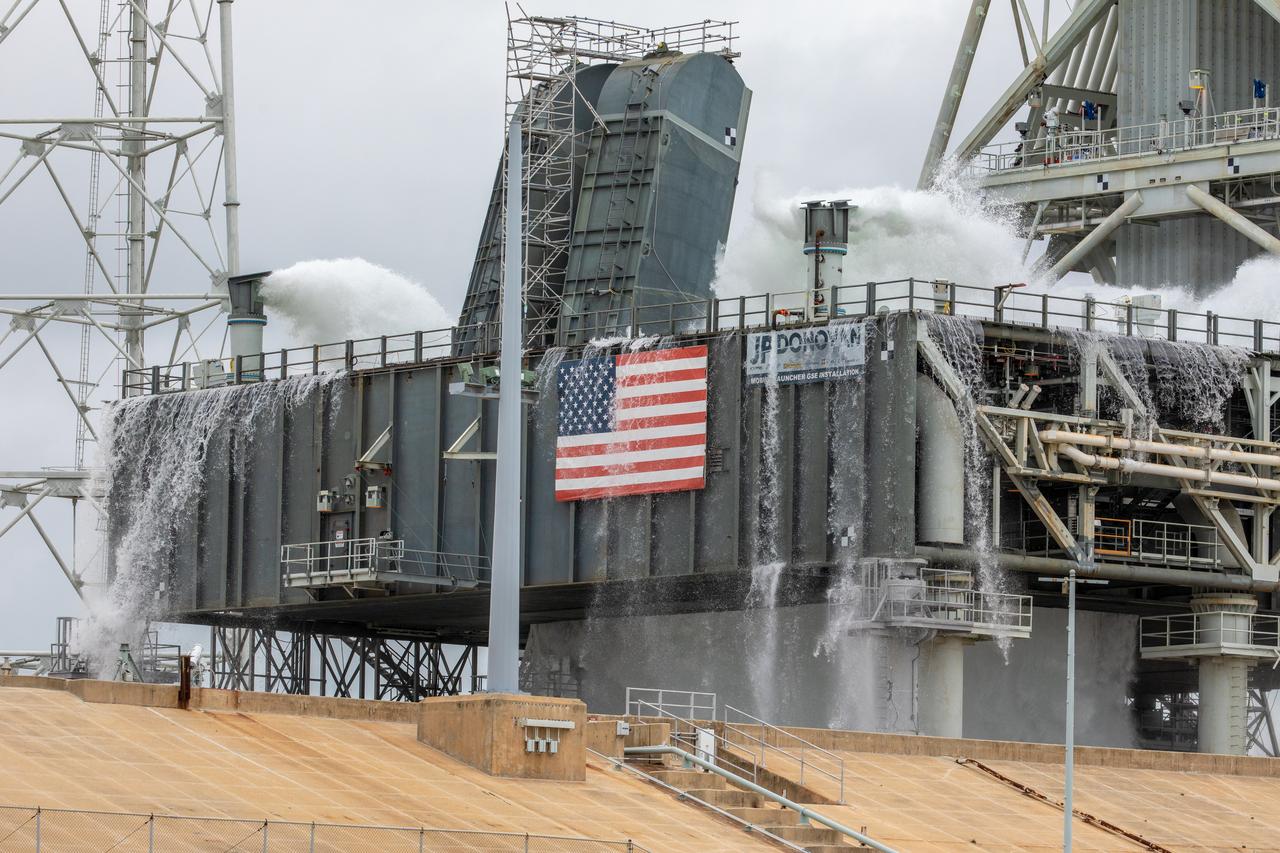

A flow test of the Ignition Overpressure Protection and Sound Suppression water deluge system begins on the mobile launcher at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on July 25, 2019. The testing is part of a series of tests that Exploration Ground System is doing to verify the system is ready for the new Space Launch System rocket. Modifications were made to the pad after a previous wet flow test, increasing the performance of the system. During the launch of Artemis 1 and subsequent missions, this water deluge system will release about 450,000 gallons of water across the mobile launcher and Flame Deflector to reduce the extreme heat and energy generated by the rocket during ignition and liftoff.
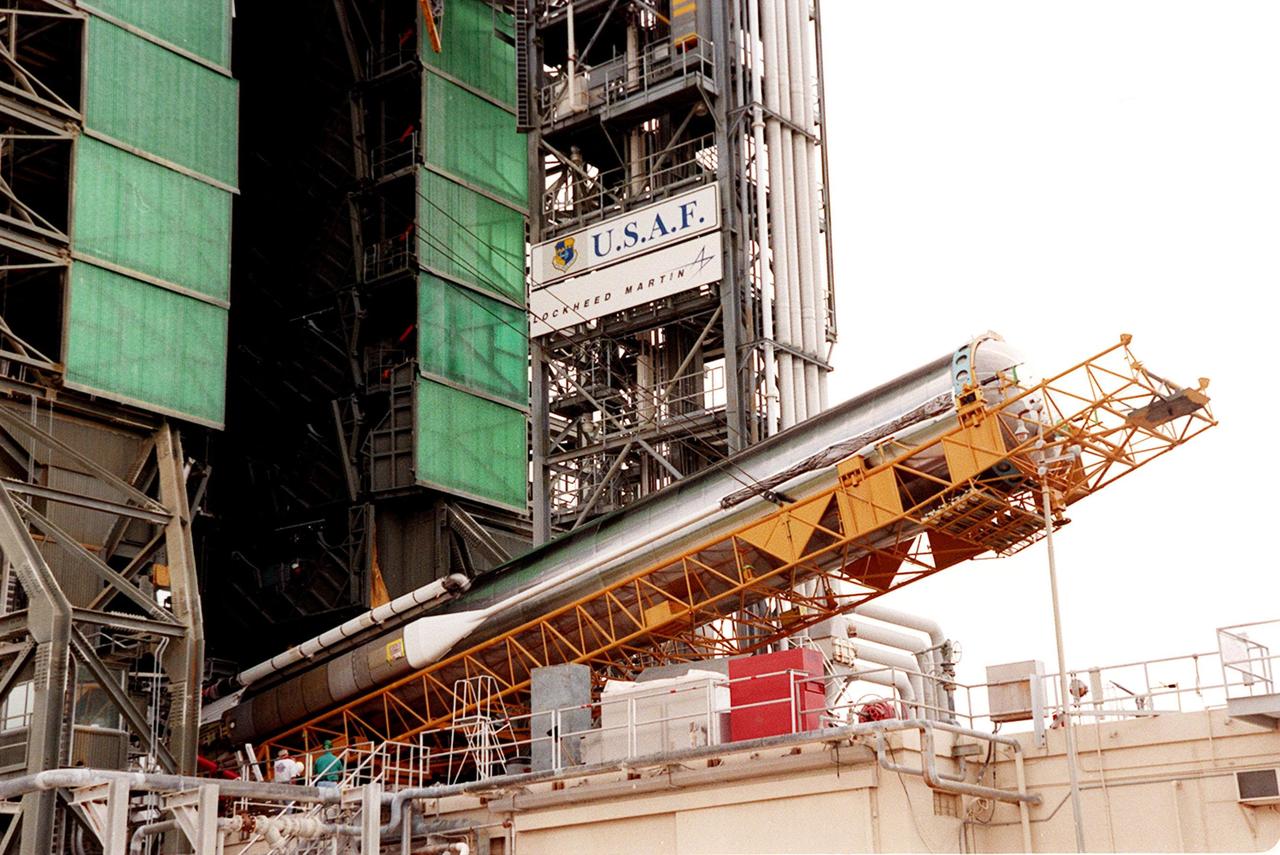

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the first stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket begins erection in the launch gantry on pad 36A. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the NASA/Lockheed Martin GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
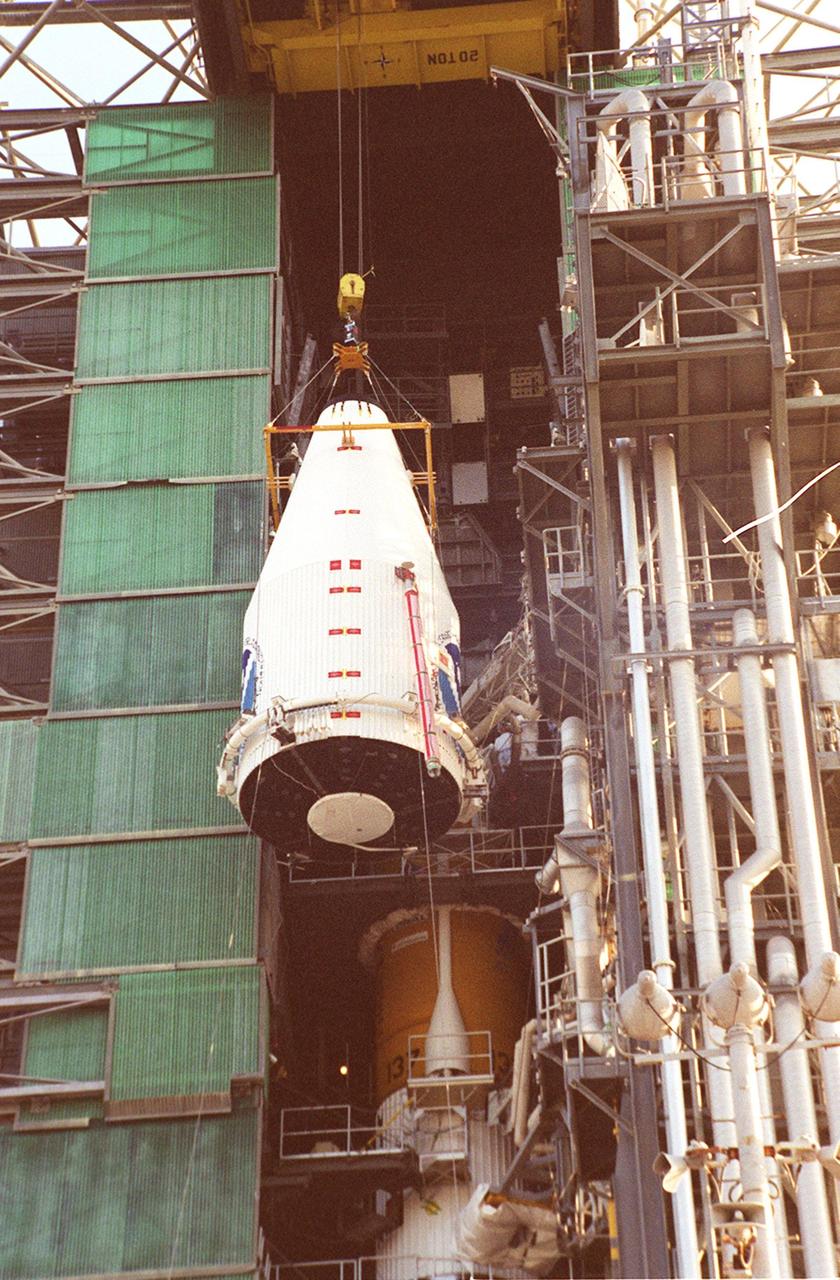
The GOES-L satellite approaches the end of its journey up the gantry on pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, for mating with the Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. The Atlas IIA is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing. Launch is scheduled for May 3
At launch pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket is lifted up the gantry (behind it) for mating with the first stage. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
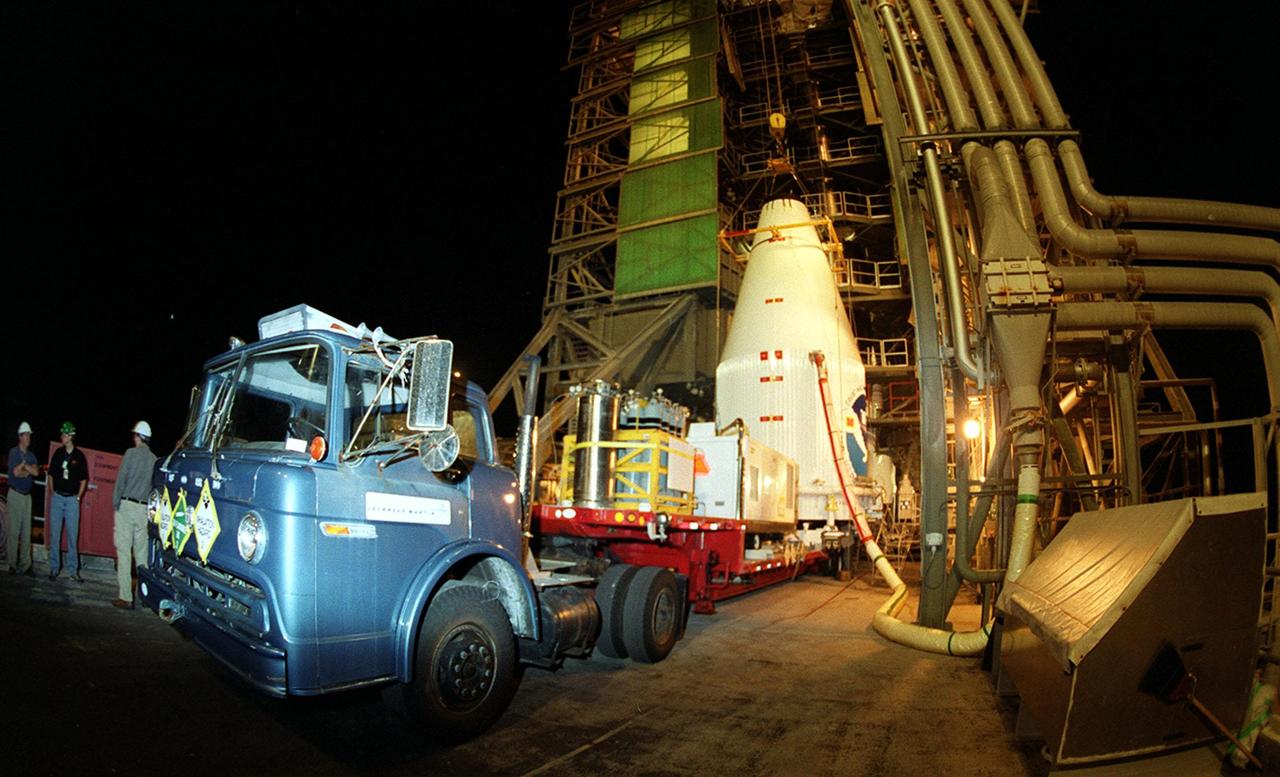

The GOES-L satellite arrives on pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The Atlas IIA rocket is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing. Launch is scheduled for May 3
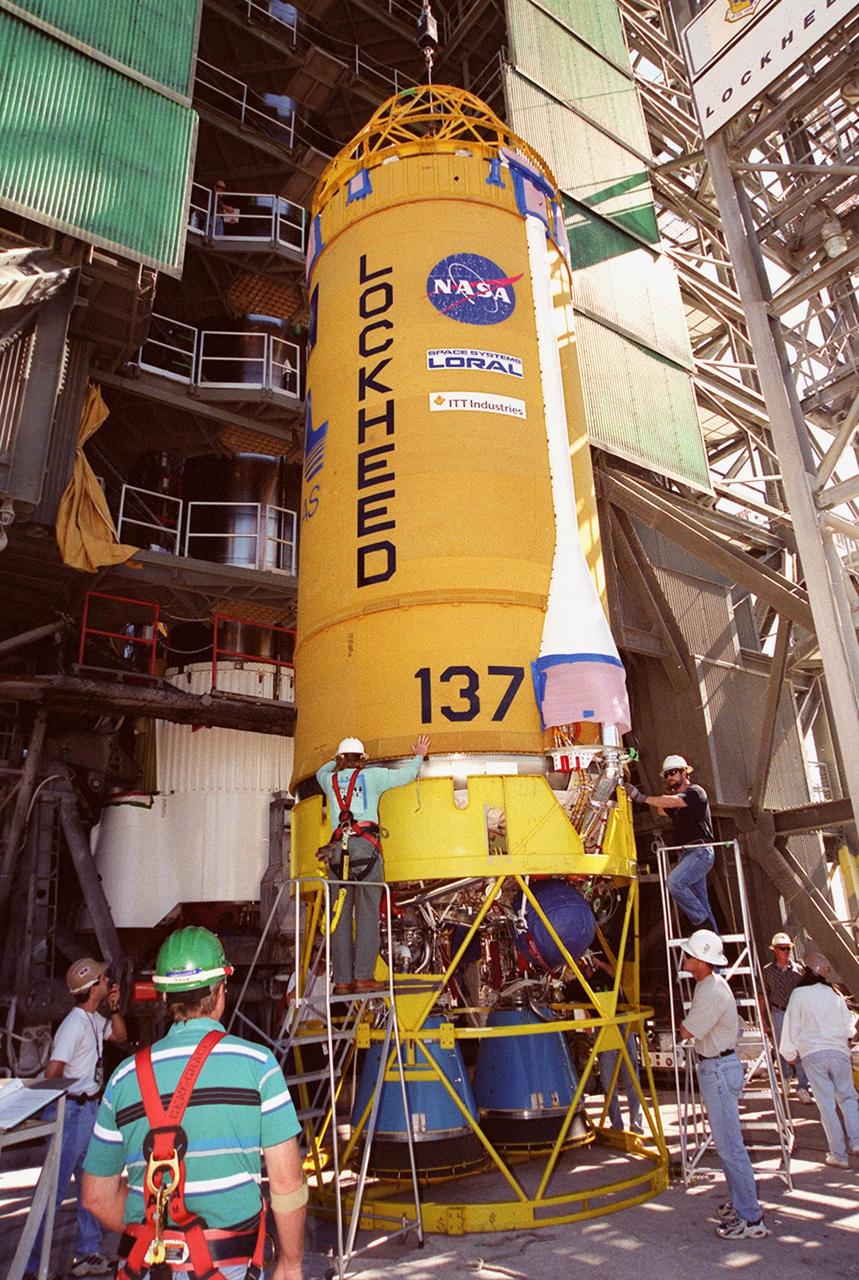

At launch pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers check over the second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket before it is lifted up the gantry (behind it) for mating with the first stage. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing

The second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket is raised to a vertical position in front of the gantry on pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, for mating with the first stage. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
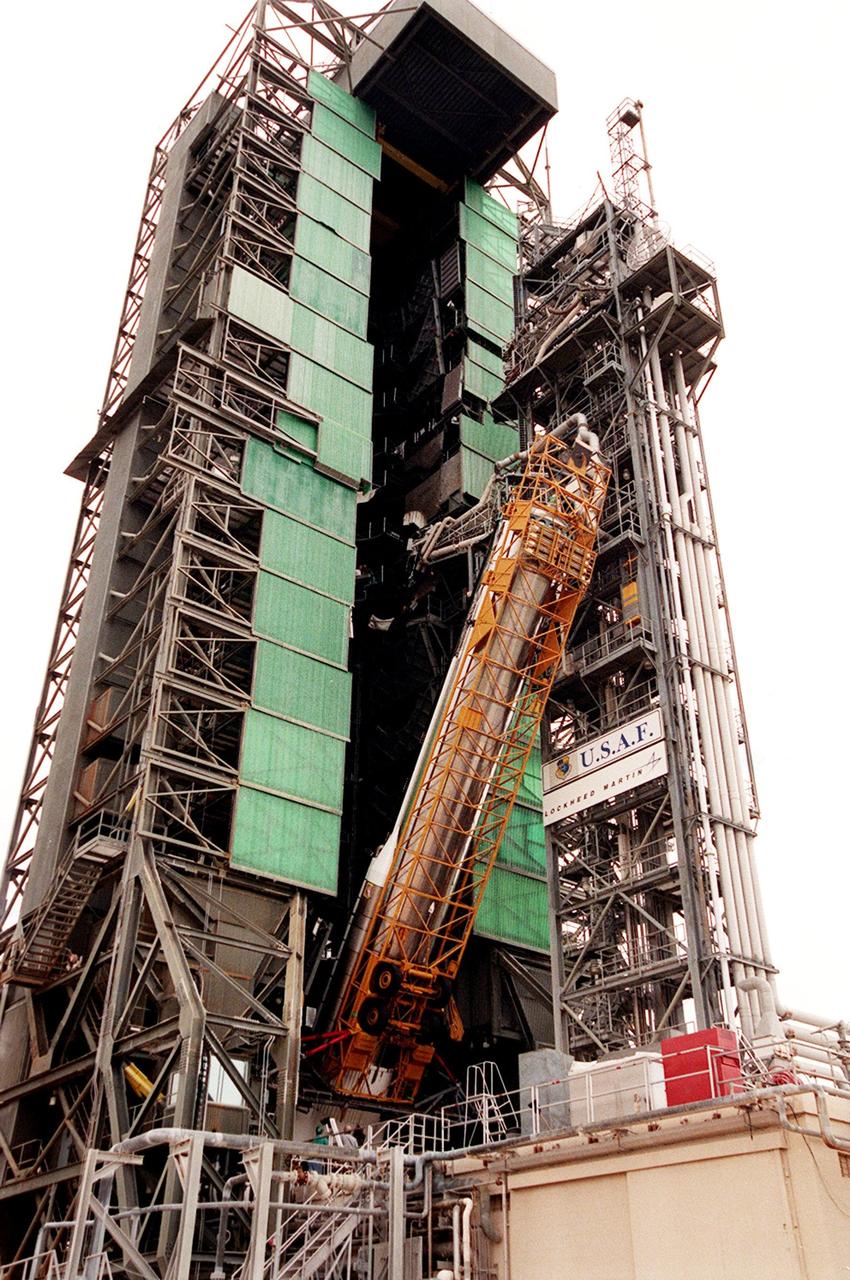

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the first stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket is nearing erection in the launch gantry on pad 36A. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the NASA/Lockheed Martin GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
The GOES-L satellite is about midway in its journey up the gantry on pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The Atlas IIA rocket is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing. Launch is scheduled for May 3
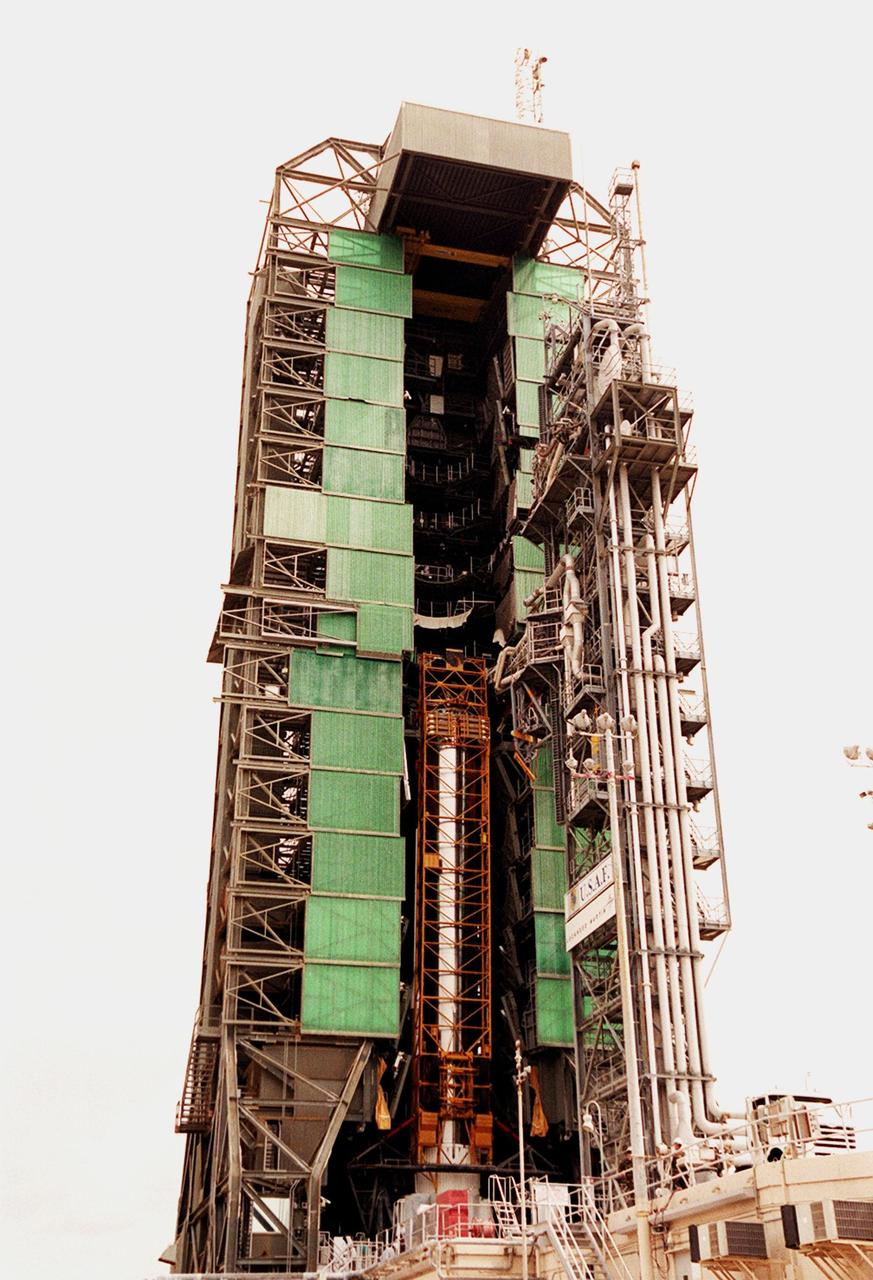

The first stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket stands erect in the launch gantry on pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the NASA/Lockheed Martin GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing

A flow test of the Ignition Overpressure Protection and Sound Suppression water deluge system is underway on the mobile launcher at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on July 25, 2019. The testing is part of a series of tests that Exploration Ground System is doing to verify the system is ready for the new Space Launch System rocket. Modifications were made to the pad after a previous wet flow test, increasing the performance of the system. During the launch of Artemis 1 and subsequent missions, this water deluge system will release about 450,000 gallons of water across the mobile launcher and Flame Deflector to reduce the extreme heat and energy generated by the rocket during ignition and liftoff.