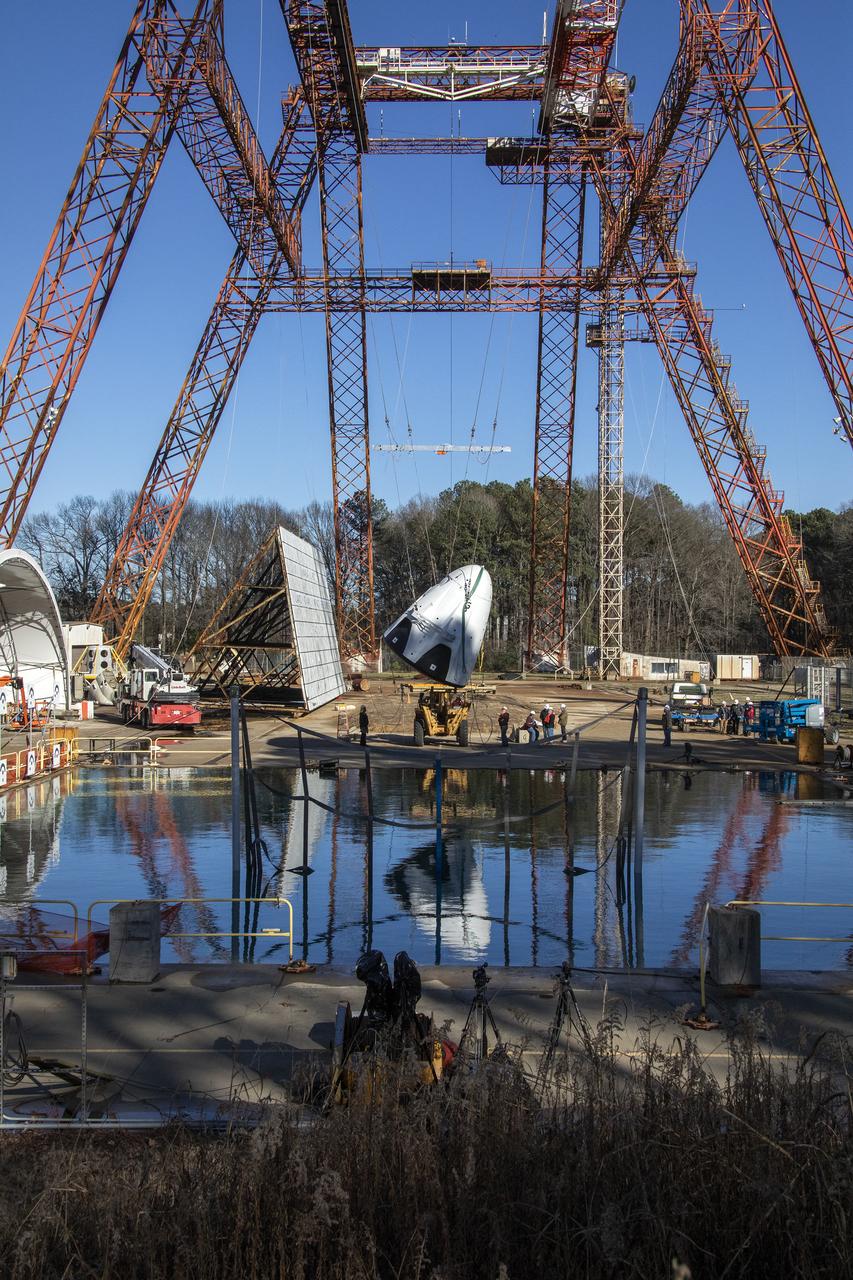

The Space X capsule being tested at NASA Langley’s Splash Test Basin. A series of drop tests into the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia helped SpaceX’s Crew Dragon capsule prepare to safely land astronauts. A mock-up of the capsule with two instrumented crash test devices seated inside was tested in March 2019, representing how the capsule may impact the water during splashdown with different wind and parachute dynamics. Data collected helps understand pressures on the capsule and how those forces affect the spacecraft and occupants. Crew Dragon will carry NASA astronauts Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley to the International Space Station in the Demo-2 mission, the final SpaceX flight test for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and the first flight of astronauts to orbit from U.S. soil since the space shuttle’s retirement in 2011. (NASA/ David C. Bowman)
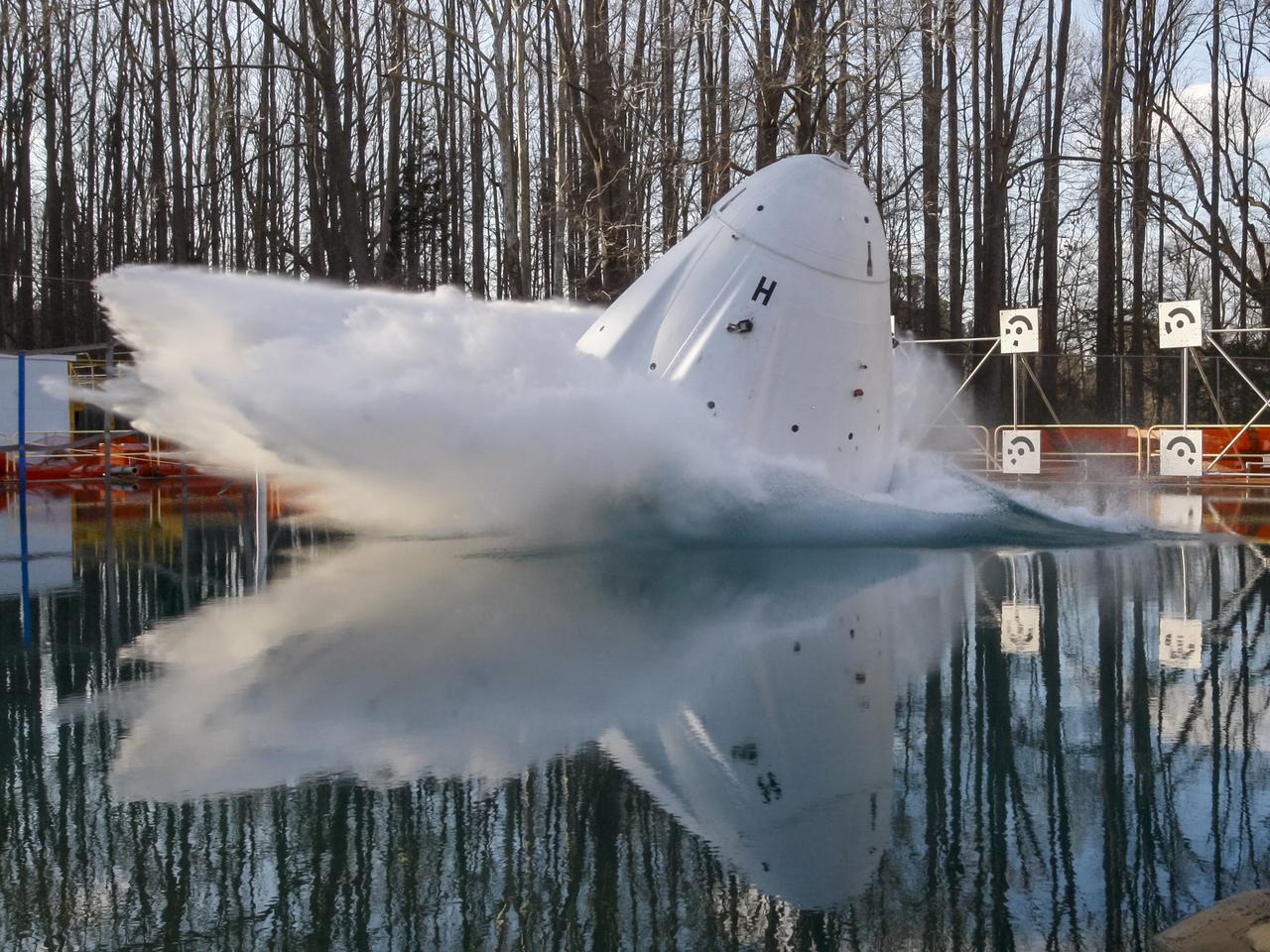

The Space X capsule being tested at NASA Langley’s Splash Test Basin. A series of drop tests into the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia helped SpaceX’s Crew Dragon capsule prepare to safely land astronauts. A mock-up of the capsule with two instrumented crash test devices seated inside was tested in March 2019, representing how the capsule may impact the water during splashdown with different wind and parachute dynamics. Data collected helps understand pressures on the capsule and how those forces affect the spacecraft and occupants. Crew Dragon will carry NASA astronauts Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley to the International Space Station in the Demo-2 mission, the final SpaceX flight test for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and the first flight of astronauts to orbit from U.S. soil since the space shuttle’s retirement in 2011. (NASA/ David C. Bowman)

Space Station Freedom option A showing two Soyuz Assured Crew Return Vehicle (ACRV) capsules docked at berthing ports.
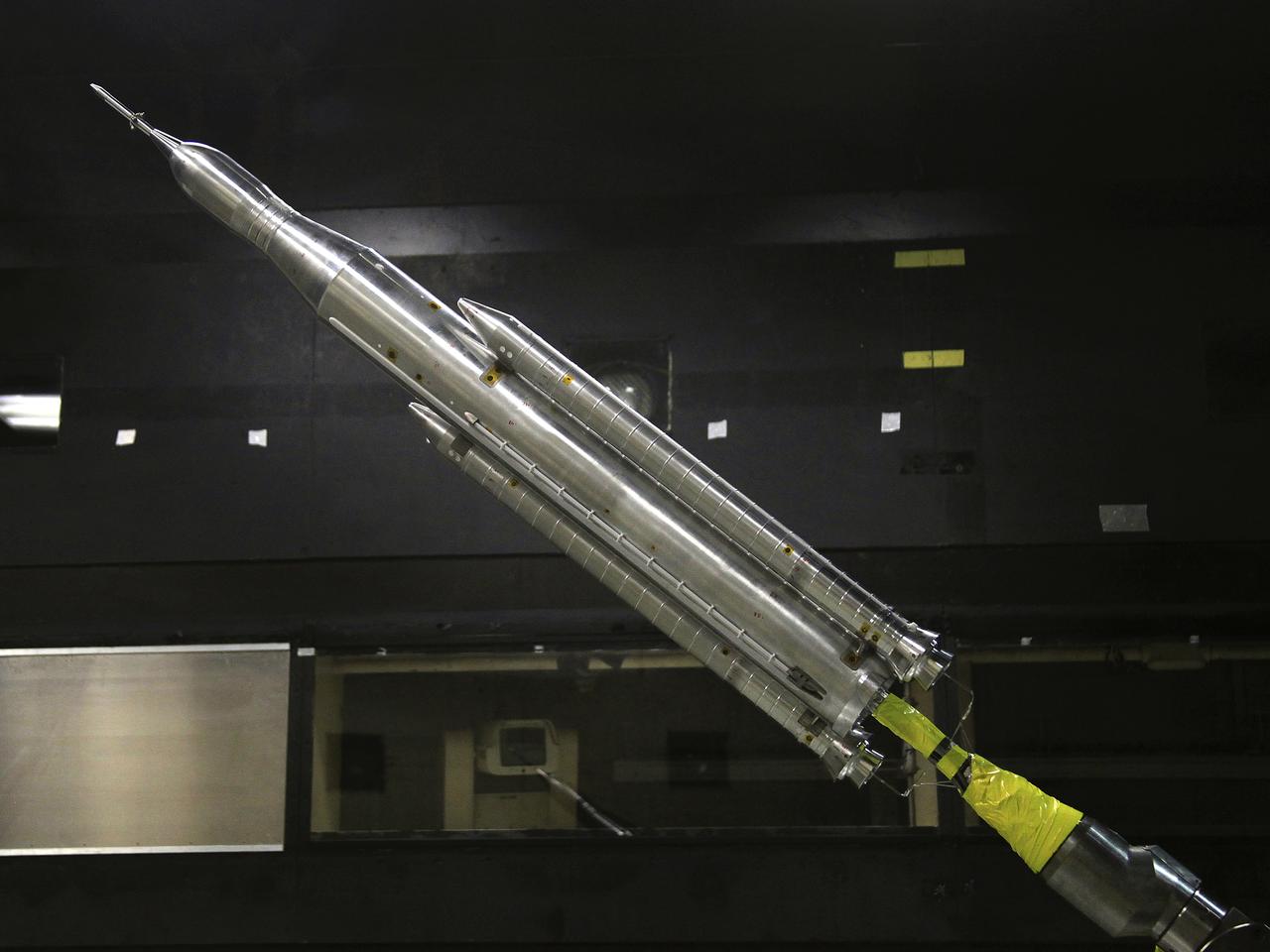

The model of the Space Launch System for the Orion Space Capsule is being prepared for windtunnel test in the 14x22 Subsonic windtunnel at NASA Langley.
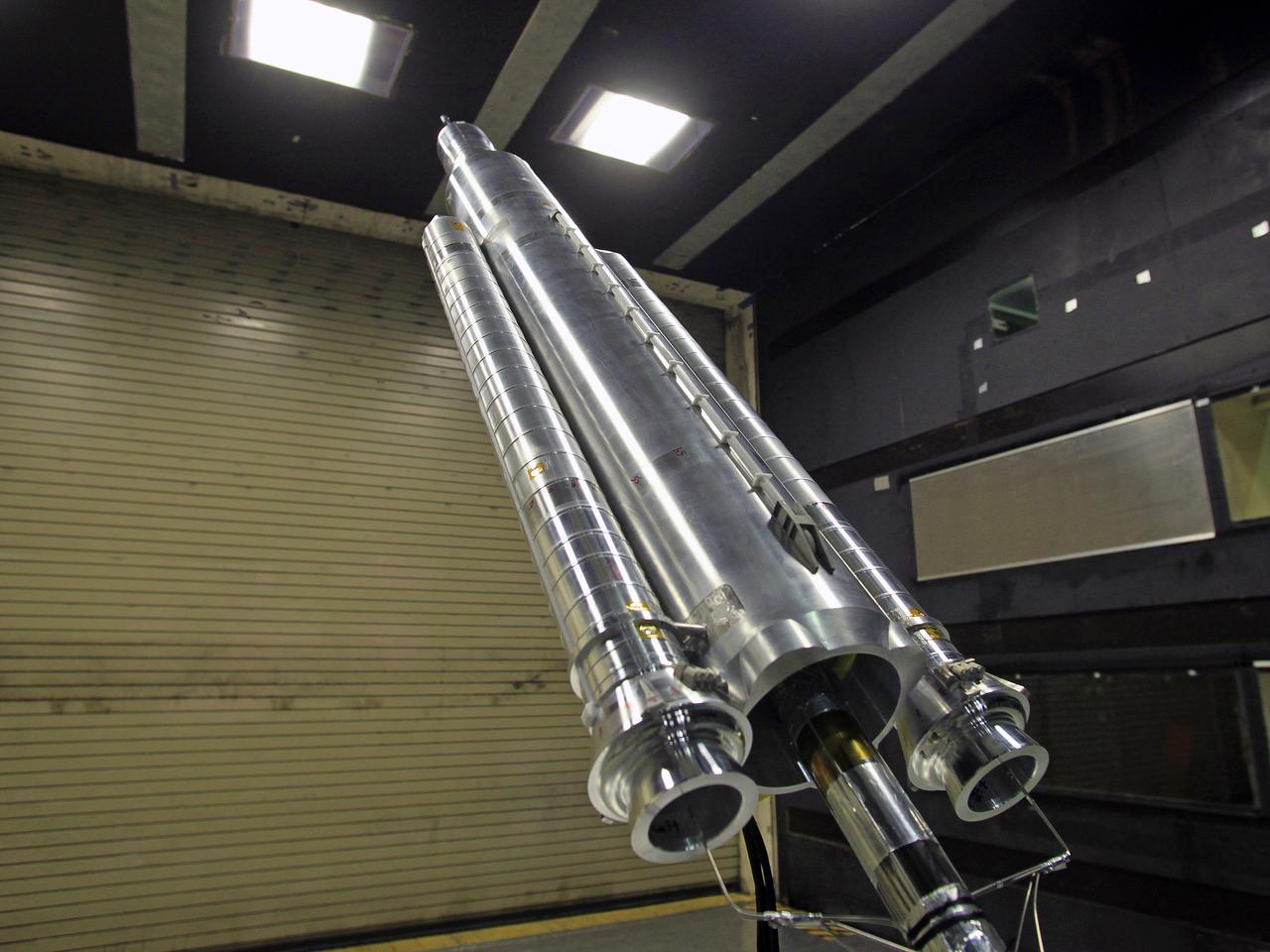

The model of the Space Launch System for the Orion Space Capsule is being prepared for windtunnel test in the 14x22 Subsonic windtunnel at NASA Langley.
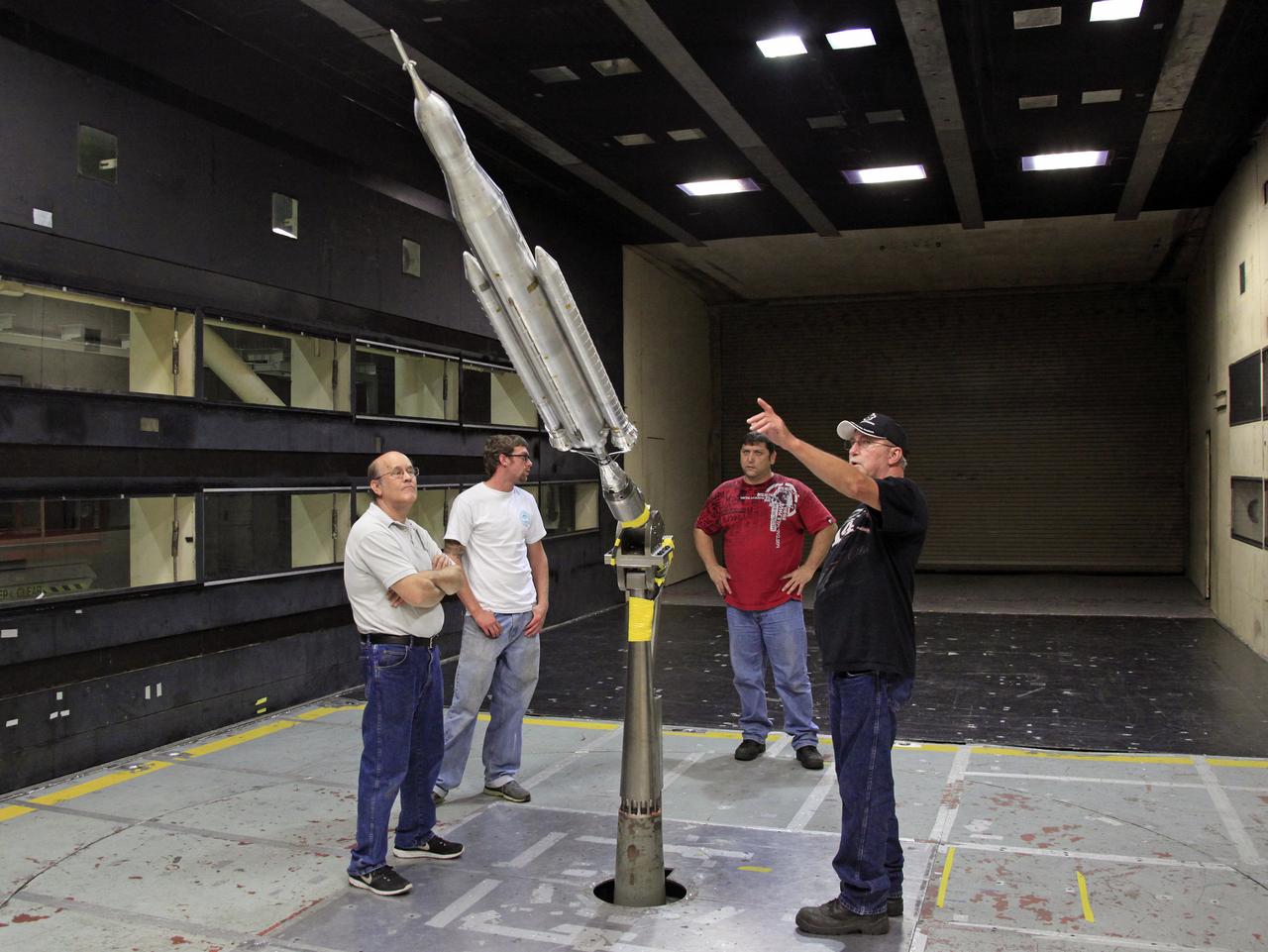

The model of the Space Launch System for the Orion Space Capsule is being prepared for windtunnel test in the 14x22 Subsonic windtunnel at NASA Langley.
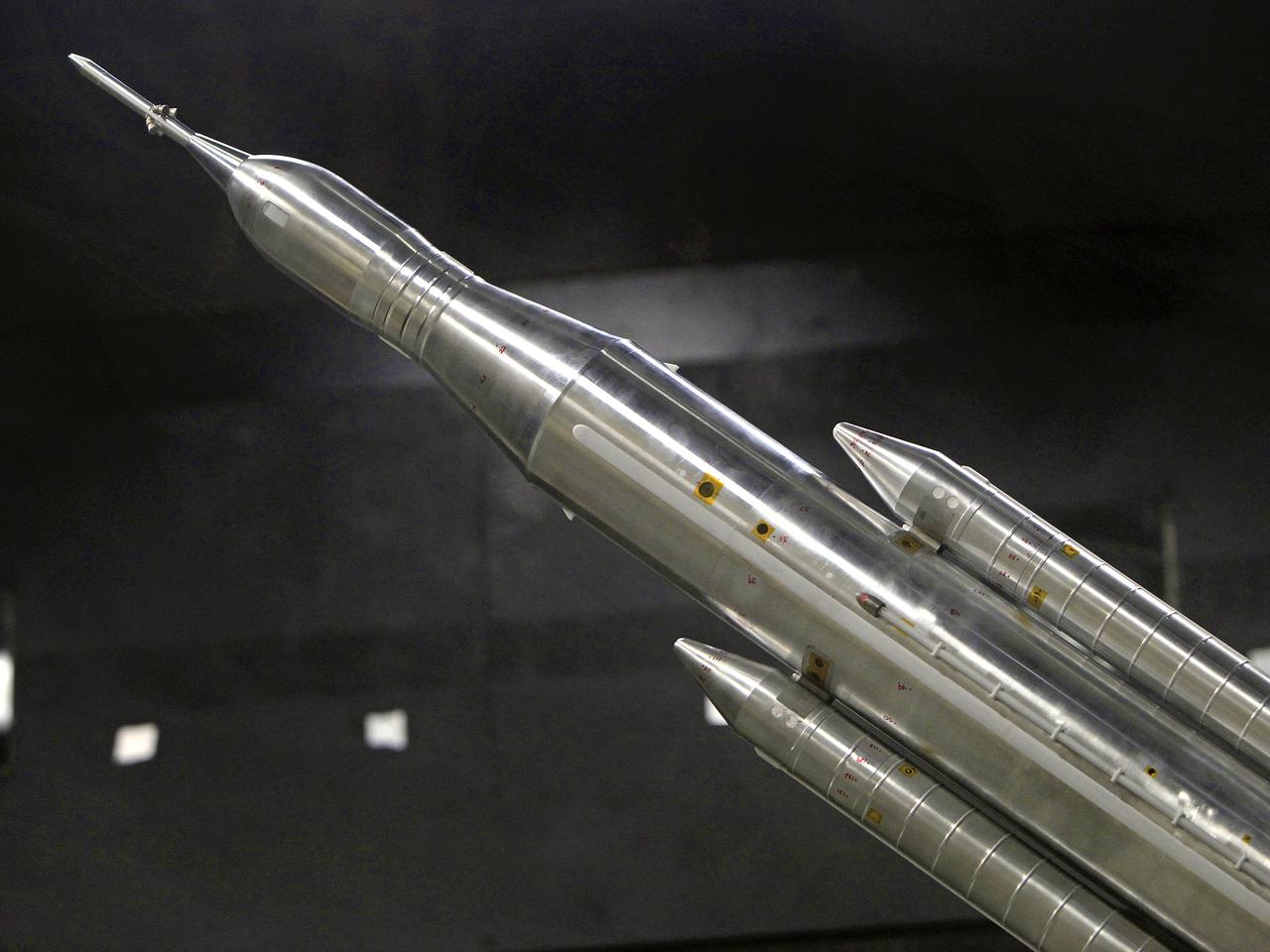

The model of the Space Launch System for the Orion Space Capsule is being prepared for windtunnel test in the 14x22 Subsonic windtunnel at NASA Langley.
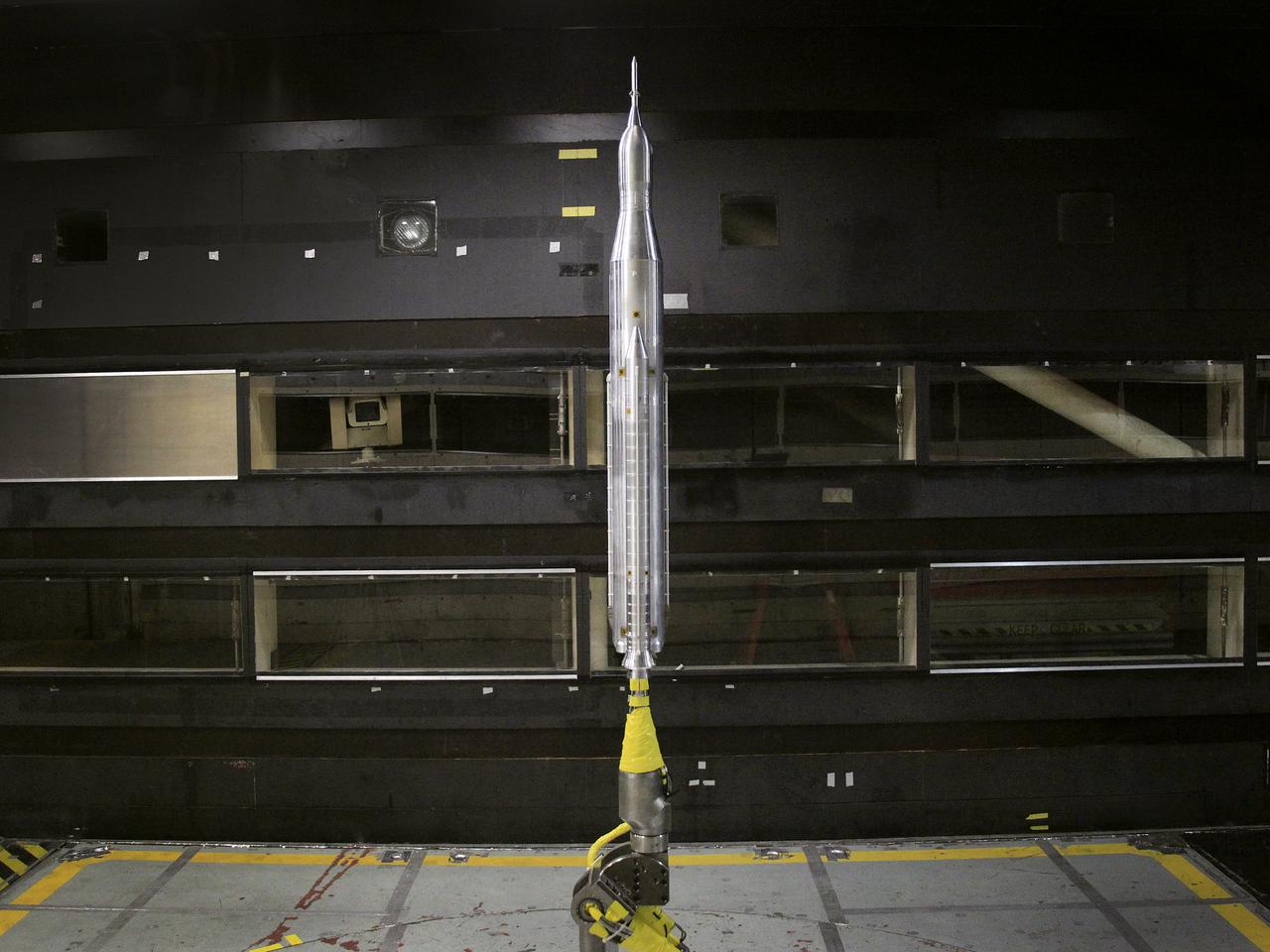

The model of the Space Launch System for the Orion Space Capsule is being prepared for windtunnel test in the 14x22 Subsonic windtunnel at NASA Langley.
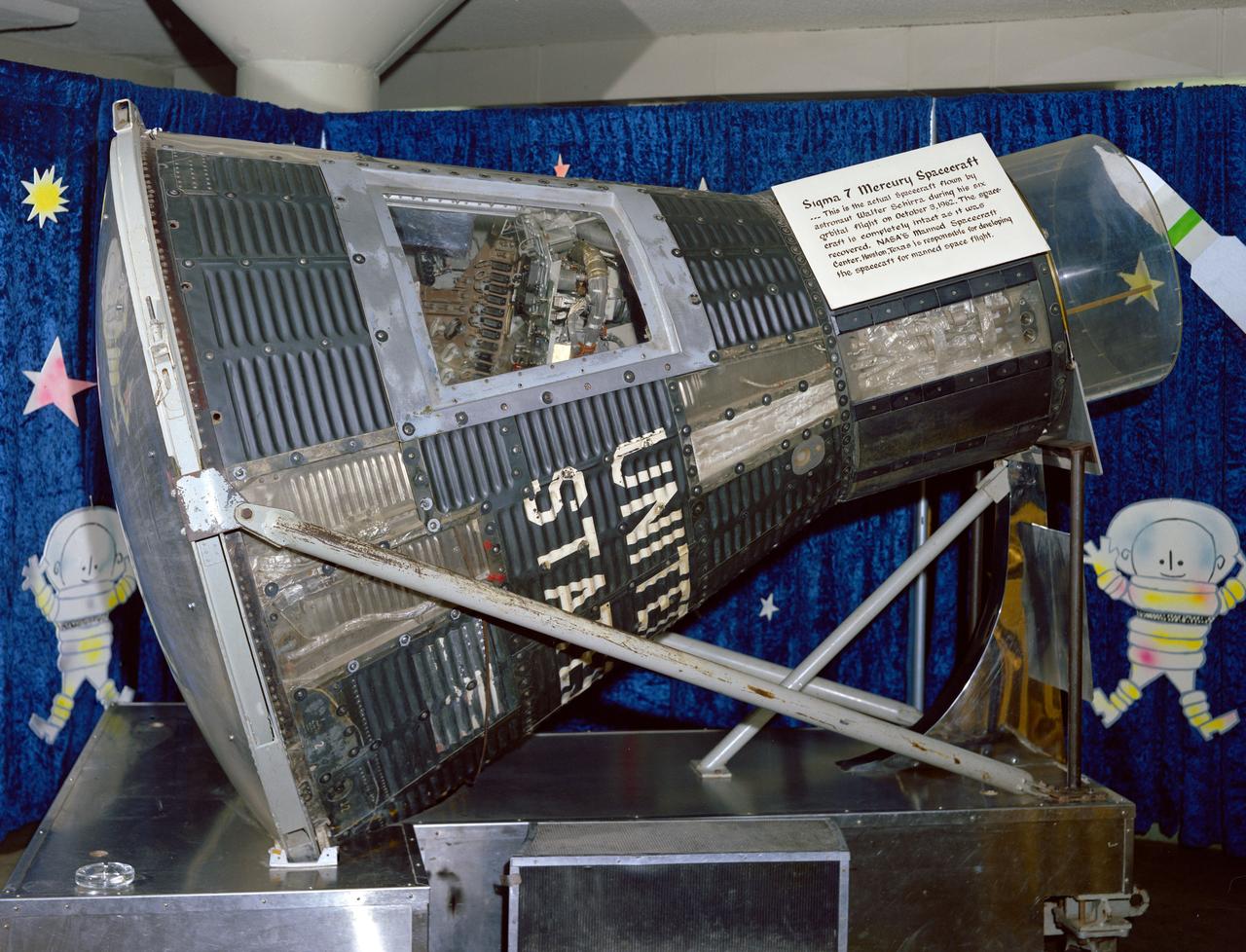
S66-53205 (1966) --- Mercury Atlas (MA-8) Sigma 7 capsule on display at the Johnson Space Center. Photo credit: NASA
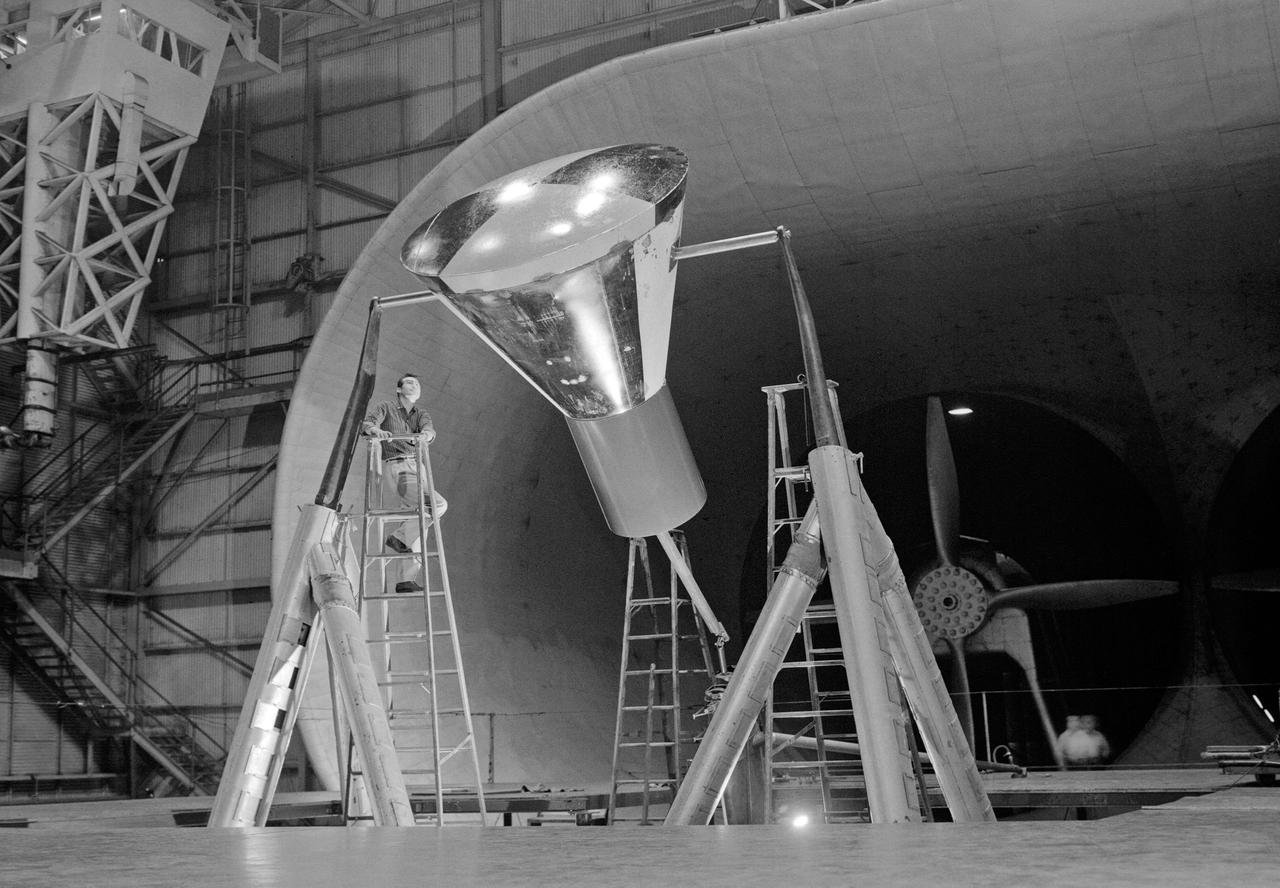

The Mercury space capsule undergoing tests in Full Scale Wind Tunnel, January 1959. Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, page 75, by James Schultz. Also Photograph published in Engineer in Charge: A History of the Langley Aeronautical Laboratory, 1917-1958, page 389, by James R. Hansen.

Miscellaneous Charts, Space Capsule

Miscellaneous Charts, Space Capsule

Vehicles and Missions Studies Charts, Space Capsule

Vehicles and Missions Studies Charts, Space Capsule

Vehicles and Missions Studies Charts, Space Capsule

Vehicles and Missions Studies Charts, Space Capsule

Vehicles and Missions Studies Charts, Space Capsule

Vehicles and Missions Studies Charts, Space Capsule

Vehicles and Missions Studies Charts, Space Capsule

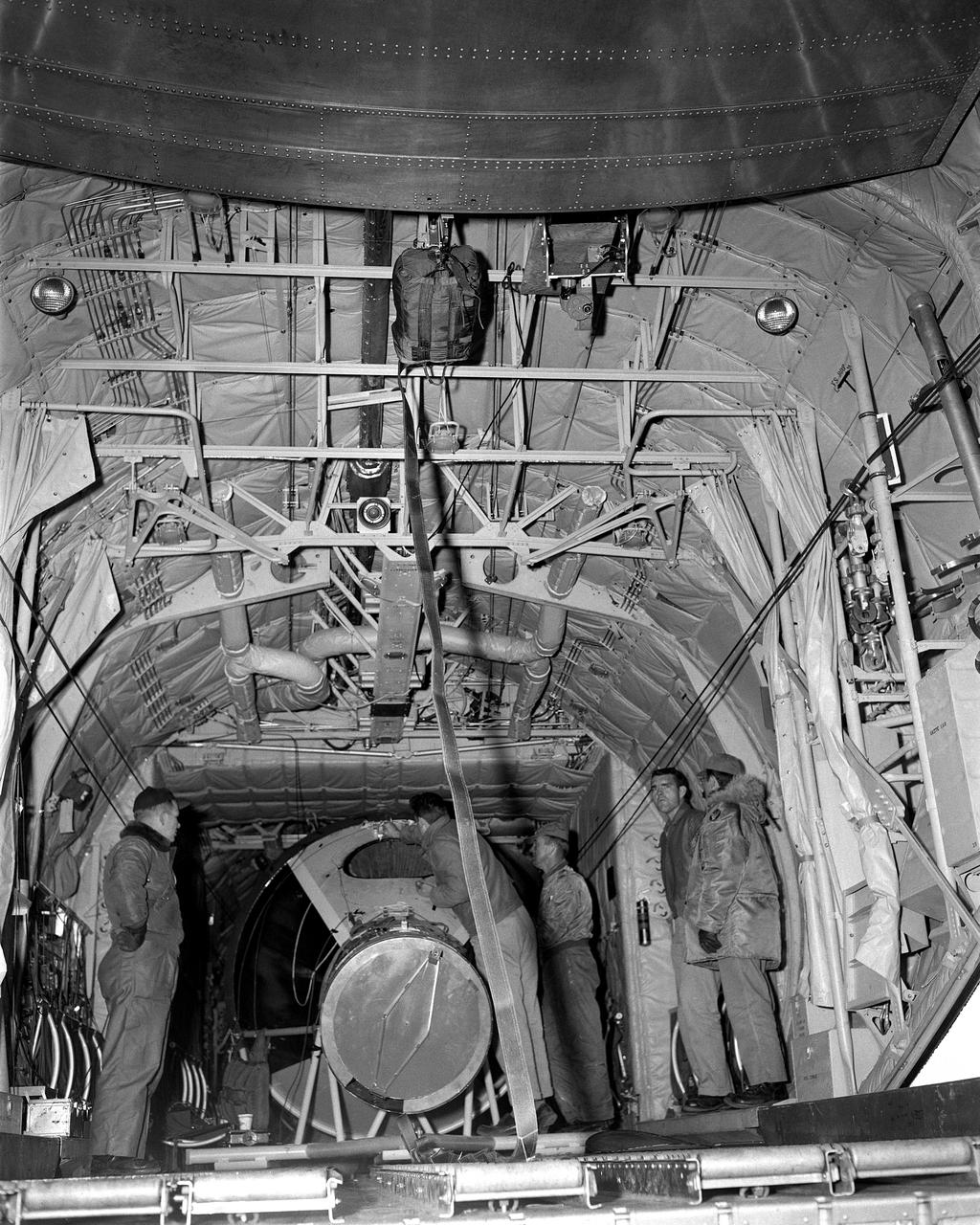
Assembling the Little Joe capsules. The capsules were manufactured in-house by Langley technicians. Three capsules are shown here in various stages of assembly. The escape tower and rocket motors shown on the completed capsule would be removed before shipping and finally assembly for launching at Wallops Island. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3, p. 32): Design of the Little Joe capsules began at Langley before McDonnell started on the design of the Mercury capsule and was, therefore, a separate design. Although it was not designed to carry a man, it did have to carry a monkey. It had to meet the weight and center of gravity requirements of Mercury and withstand the same aerodynamic loads during the exit trajectory. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. Project Mercury: Little Joe: Boilerplate Mercury spacecraft undergo fabrication at the shops of the Langley Research Center. They will launched atop Little Joe rockets to test the spacecraft recovery systems. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition. L59-4947 Technicians prepare a Little Joe launch vehicle prototype for the Mercury space program, 1959. Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, page 76, by James Schultz
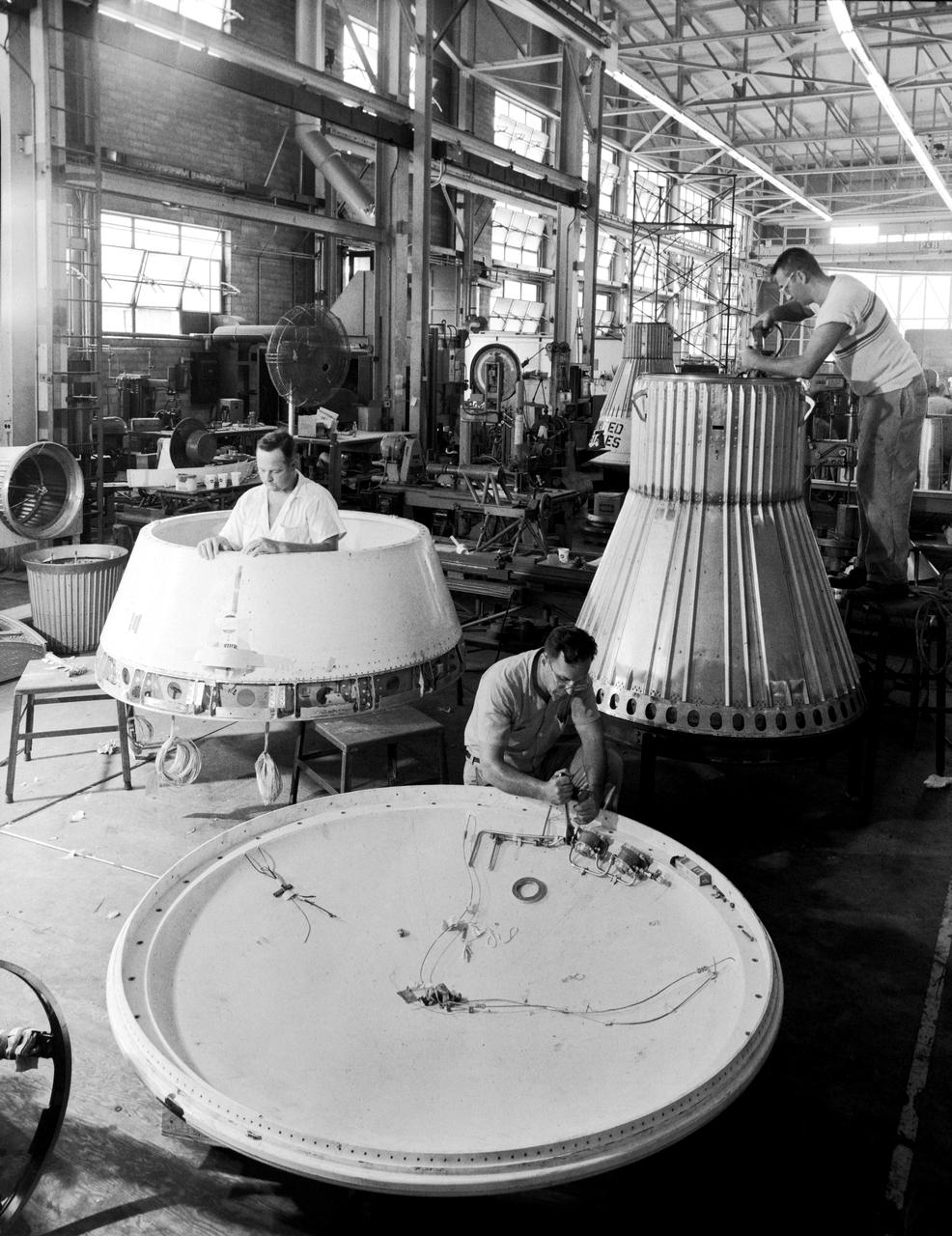

Assembling the Little Joe capsules. The capsules were manufactured in-house by Langley technicians. Three capsules are shown here in various stages of assembly. The escape tower and rocket motors shown on the completed capsule would be removed before shipping and finally assembly for launching at Wallops Island. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3, p. 32): Design of the Little Joe capsules began at Langley before McDonnell started on the design of the Mercury capsule and was, therefore, a separate design. Although it was not designed to carry a man, it did have to carry a monkey. It had to meet the weight and center of gravity requirements of Mercury and withstand the same aerodynamic loads during the exit trajectory. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. Project Mercury: Little Joe: Boilerplate Mercury spacecraft undergo fabrication at the shops of the Langley Research Center. They will launched atop Little Joe rockets to test the spacecraft recovery systems. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition. L59-4947 Technicians prepare a Little Joe launch vehicle prototype for the Mercury space program, 1959. Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, page 76, by James Schultz

Assembling the Little Joe capsules. The capsules were manufactured in-house by Langley technicians. Three capsules are shown here in various stages of assembly. The escape tower and rocket motors shown on the completed capsule would be removed before shipping and finally assembly for launching at Wallops Island. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3, p. 32): Design of the Little Joe capsules began at Langley before McDonnell started on the design of the Mercury capsule and was, therefore, a separate design. Although it was not designed to carry a man, it did have to carry a monkey. It had to meet the weight and center of gravity requirements of Mercury and withstand the same aerodynamic loads during the exit trajectory. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. Project Mercury: Little Joe: Boilerplate Mercury spacecraft undergo fabrication at the shops of the Langley Research Center. They will launched atop Little Joe rockets to test the spacecraft recovery systems. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition. L59-4947 Technicians prepare a Little Joe launch vehicle prototype for the Mercury space program, 1959. Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, page 76, by James Schultz

Assembling the Little Joe capsules. The capsules were manufactured in-house by Langley technicians. Three capsules are shown here in various stages of assembly. The escape tower and rocket motors shown on the completed capsule would be removed before shipping and finally assembly for launching at Wallops Island. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3, p. 32): Design of the Little Joe capsules began at Langley before McDonnell started on the design of the Mercury capsule and was, therefore, a separate design. Although it was not designed to carry a man, it did have to carry a monkey. It had to meet the weight and center of gravity requirements of Mercury and withstand the same aerodynamic loads during the exit trajectory. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. Project Mercury: Little Joe: Boilerplate Mercury spacecraft undergo fabrication at the shops of the Langley Research Center. They will launched atop Little Joe rockets to test the spacecraft recovery systems. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition. L59-4947 Technicians prepare a Little Joe launch vehicle prototype for the Mercury space program, 1959. Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, page 76, by James Schultz
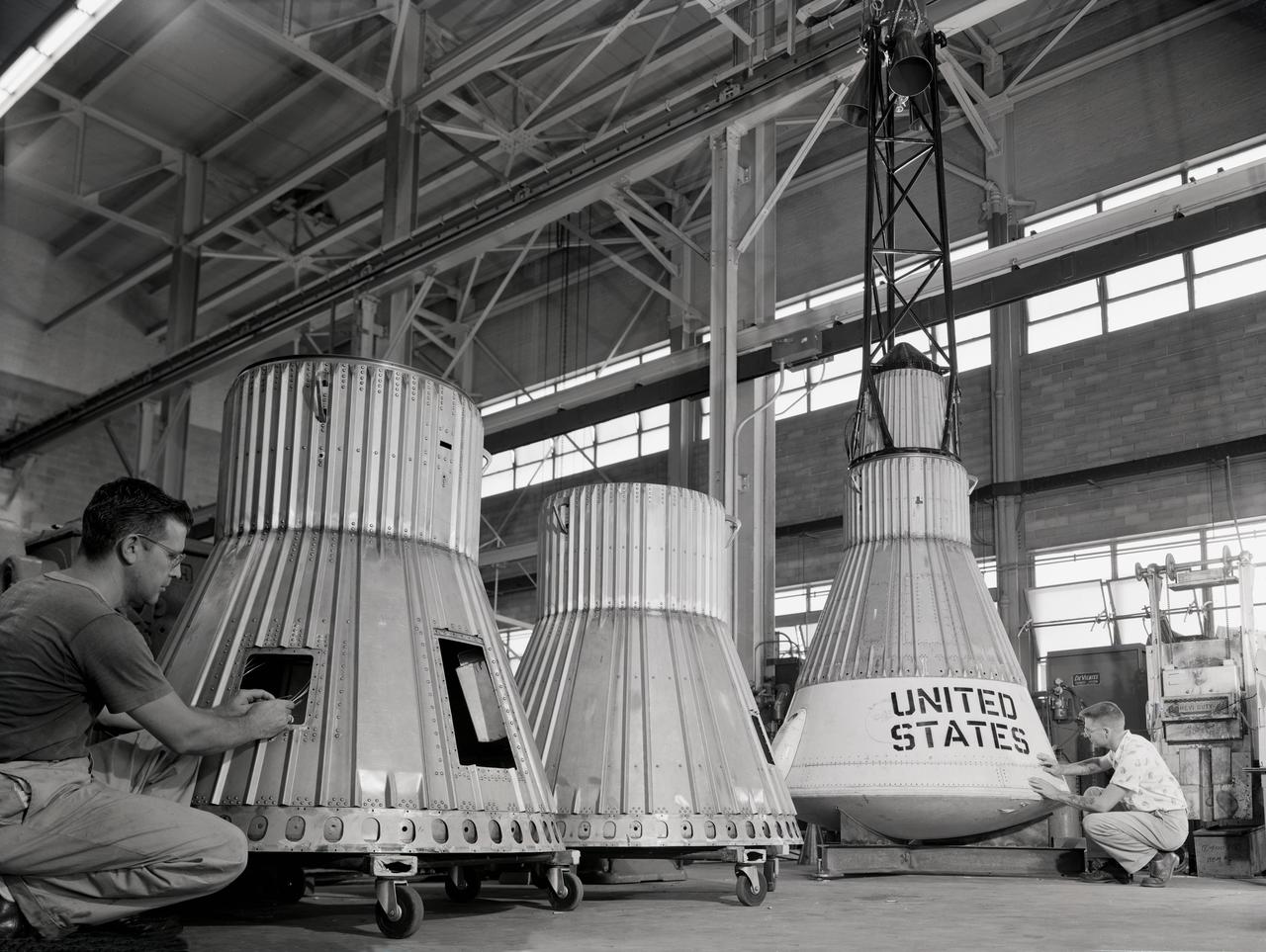

Assembling the Little Joe capsules. The capsules were manufactured in-house by Langley technicians. Three capsules are shown here in various stages of assembly. The escape tower and rocket motors shown on the completed capsule would be removed before shipping and finally assembly for launching at Wallops Island. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3, p. 32): Design of the Little Joe capsules began at Langley before McDonnell started on the design of the Mercury capsule and was, therefore, a separate design. Although it was not designed to carry a man, it did have to carry a monkey. It had to meet the weight and center of gravity requirements of Mercury and withstand the same aerodynamic loads during the exit trajectory. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. Project Mercury: Little Joe: Boilerplate Mercury spacecraft undergo fabrication at the shops of the Langley Research Center. They will launched atop Little Joe rockets to test the spacecraft recovery systems. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition. L59-4947 Technicians prepare a Little Joe launch vehicle prototype for the Mercury space program, 1959. Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, page 76, by James Schultz

Assembling the Little Joe capsules. The capsules were manufactured in-house by Langley technicians. Three capsules are shown here in various stages of assembly. The escape tower and rocket motors shown on the completed capsule would be removed before shipping and finally assembly for launching at Wallops Island. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3, p. 32): Design of the Little Joe capsules began at Langley before McDonnell started on the design of the Mercury capsule and was, therefore, a separate design. Although it was not designed to carry a man, it did have to carry a monkey. It had to meet the weight and center of gravity requirements of Mercury and withstand the same aerodynamic loads during the exit trajectory. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. Project Mercury: Little Joe: Boilerplate Mercury spacecraft undergo fabrication at the shops of the Langley Research Center. They will launched atop Little Joe rockets to test the spacecraft recovery systems. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition. L59-4947 Technicians prepare a Little Joe launch vehicle prototype for the Mercury space program, 1959. Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, page 76, by James Schultz
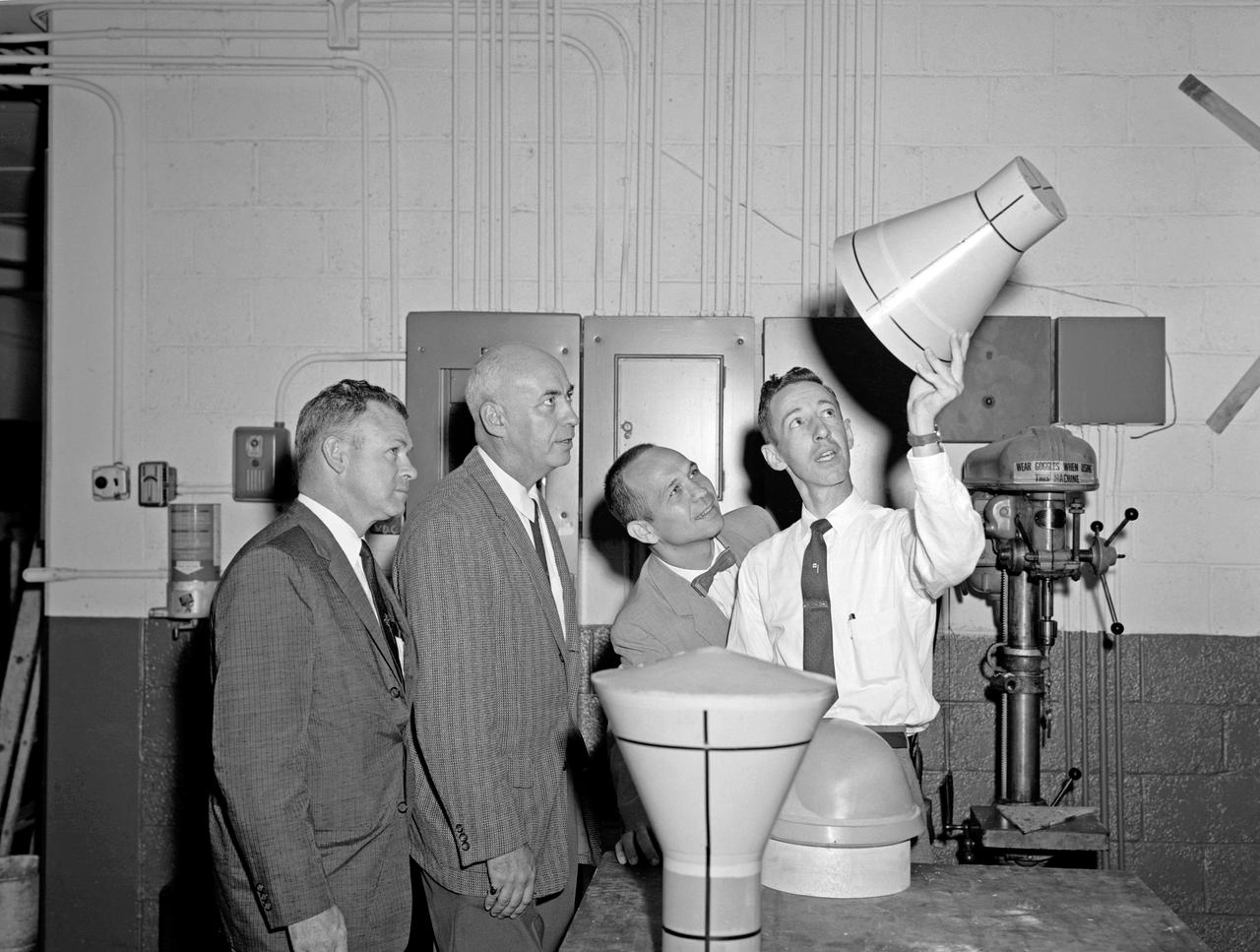

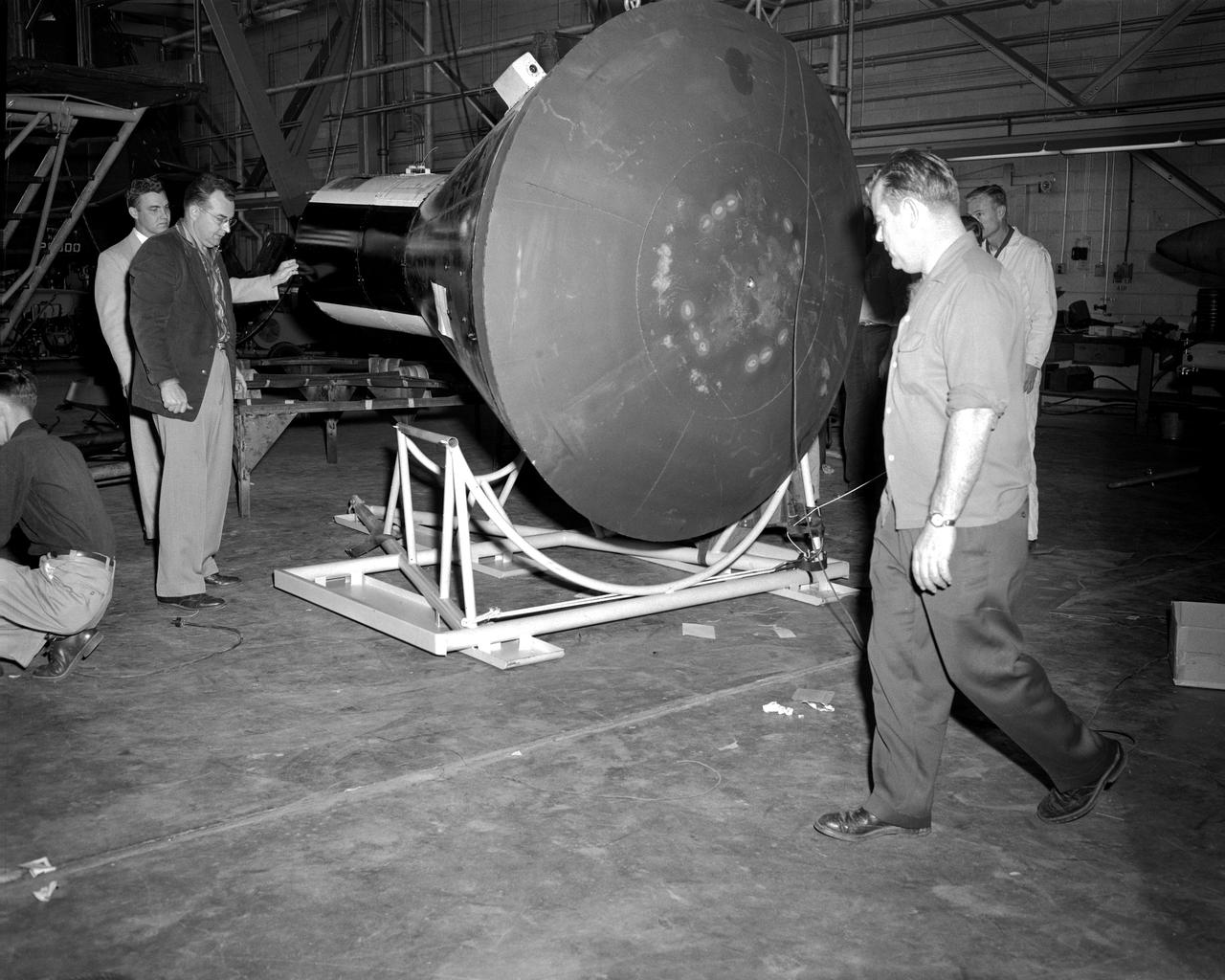
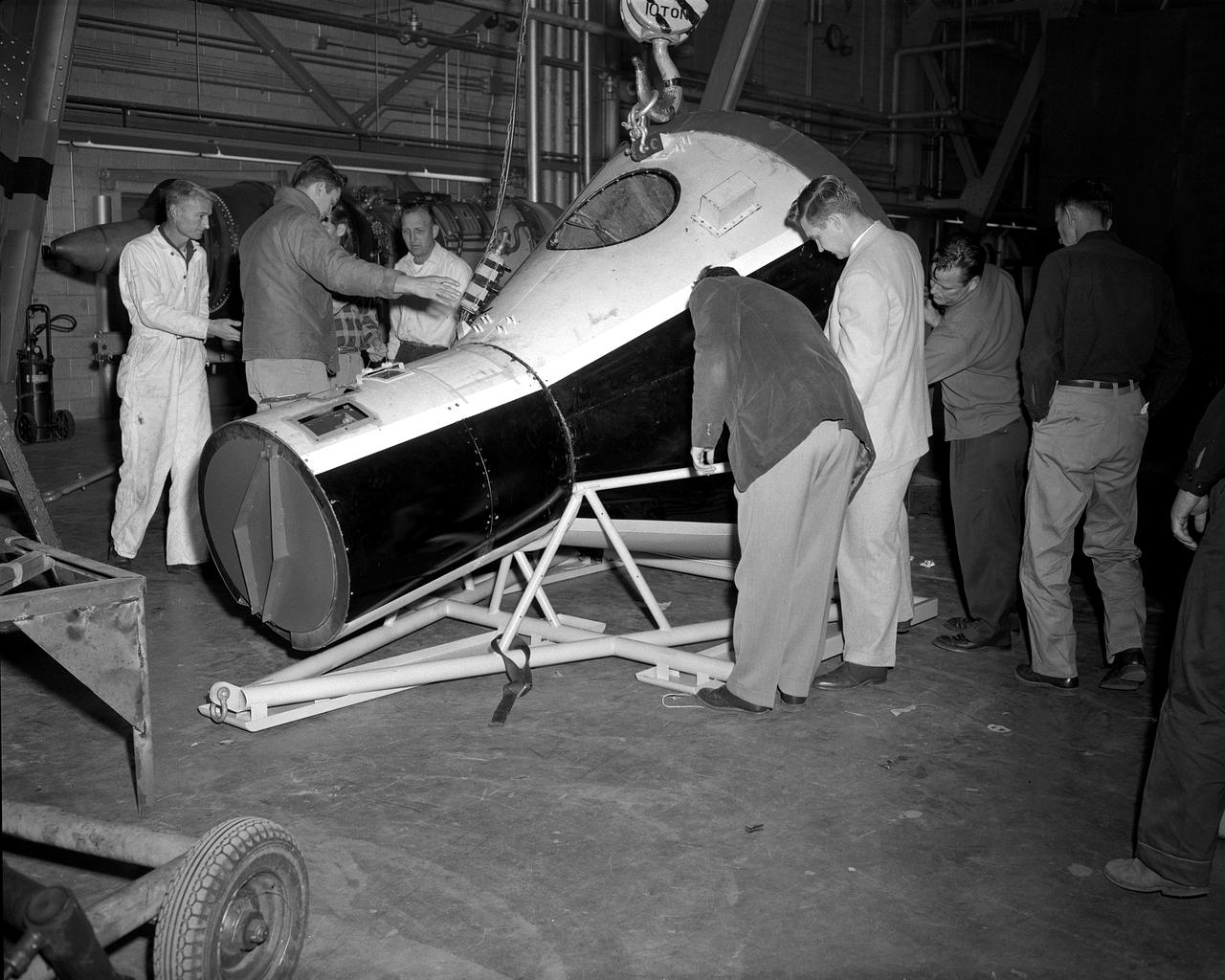
From left to right: Charles Donlan, deputy head, and Robert Gilruth, head of STG, look at a scale model of a Mercury space capsule.
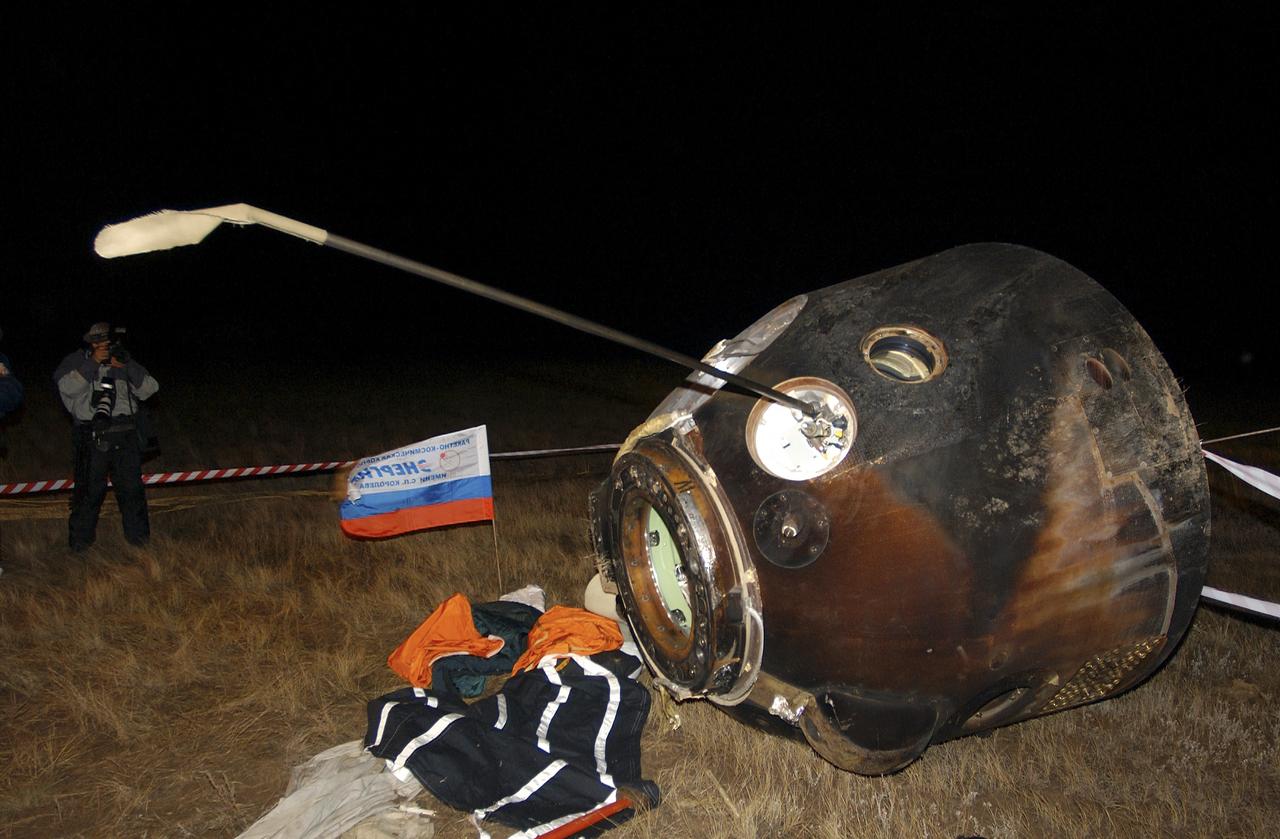

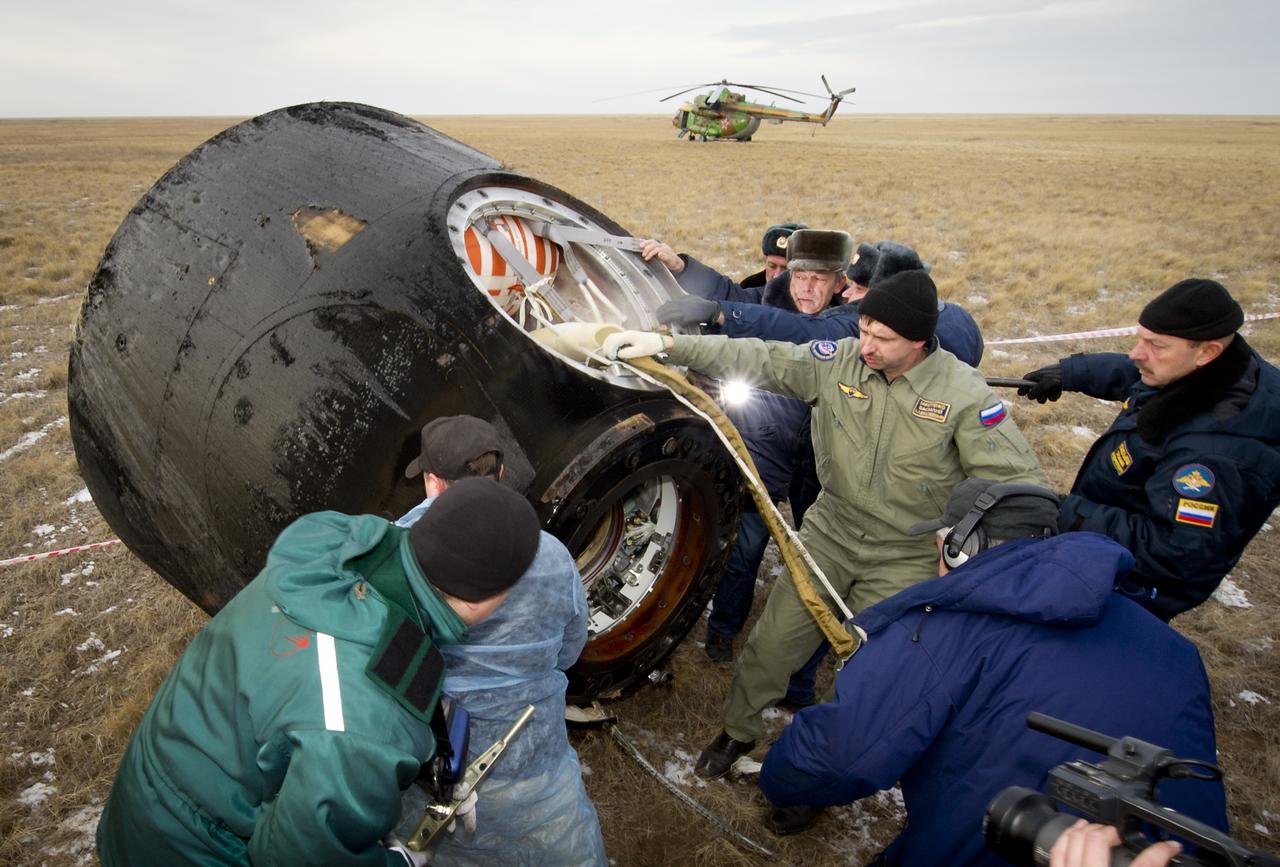
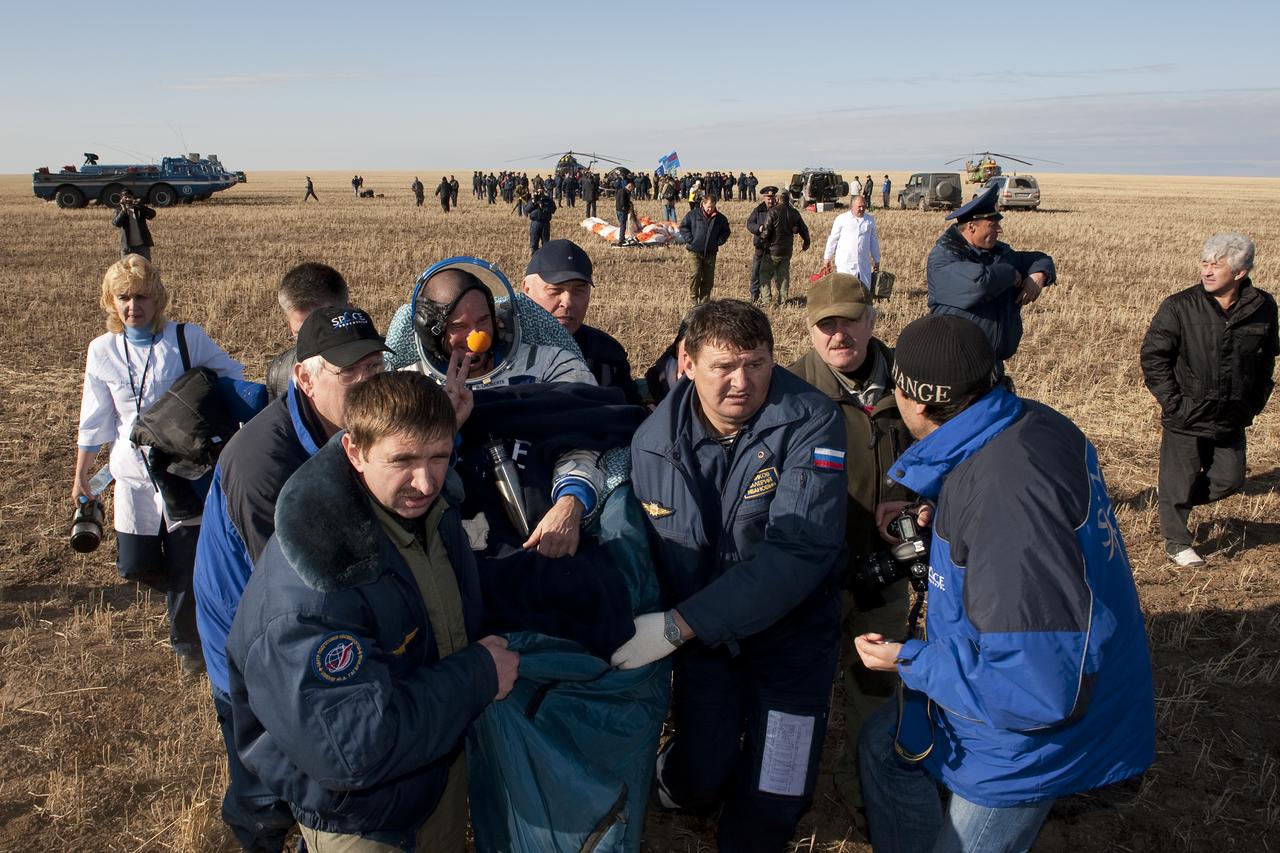
The Soyuz capsule lays on its side after landing approximately 85 kilometers northeast of Arkalyk in northern Kazakhstan with the crew of Expedition 9 and Russian Space Forces cosmonaut Yuri Shargin, Sunday, October 24, 2004. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
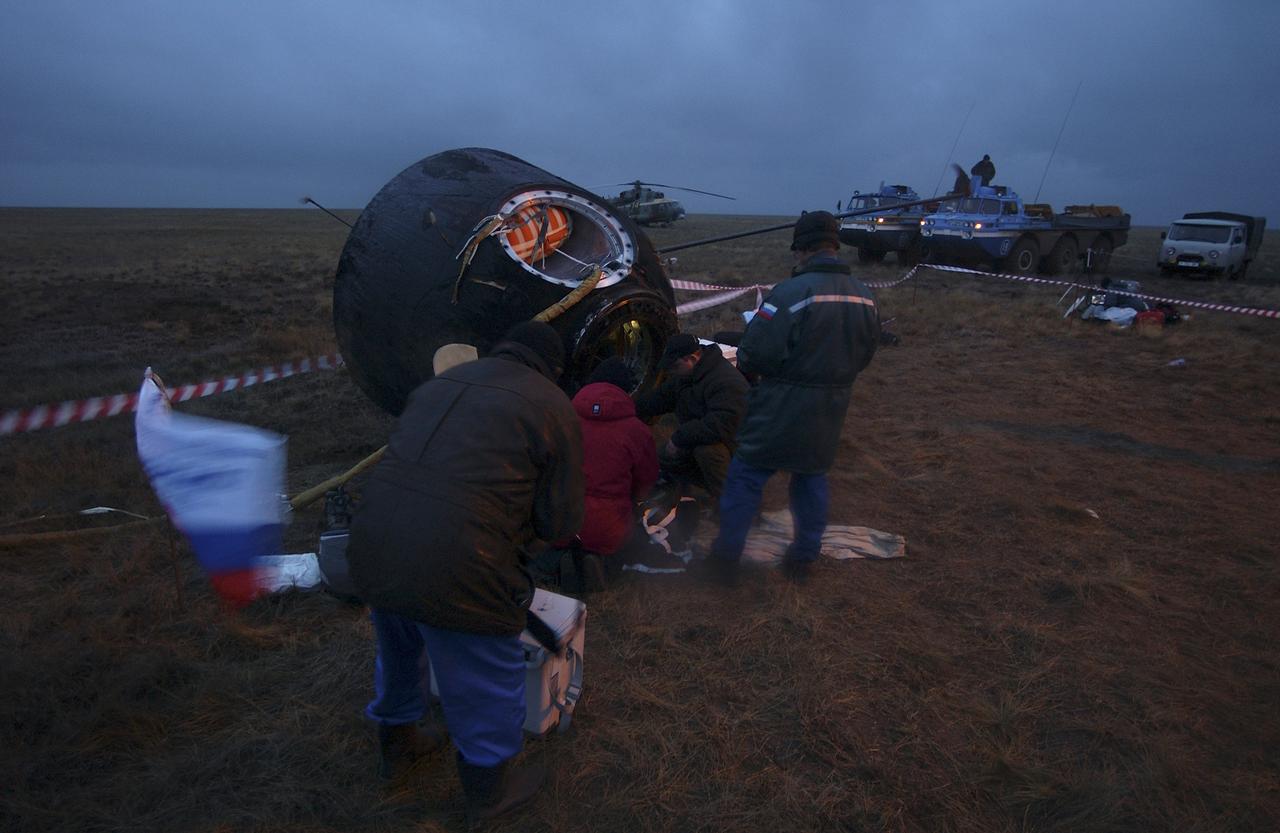

The Soyuz capsule lays on its side after landing approximately 85 kilometers northeast of Arkalyk in northern Kazakhstan with the crew of Expedition 9 and Russian Space Forces cosmonaut Yuri Shargin, Sunday, October 24, 2004. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
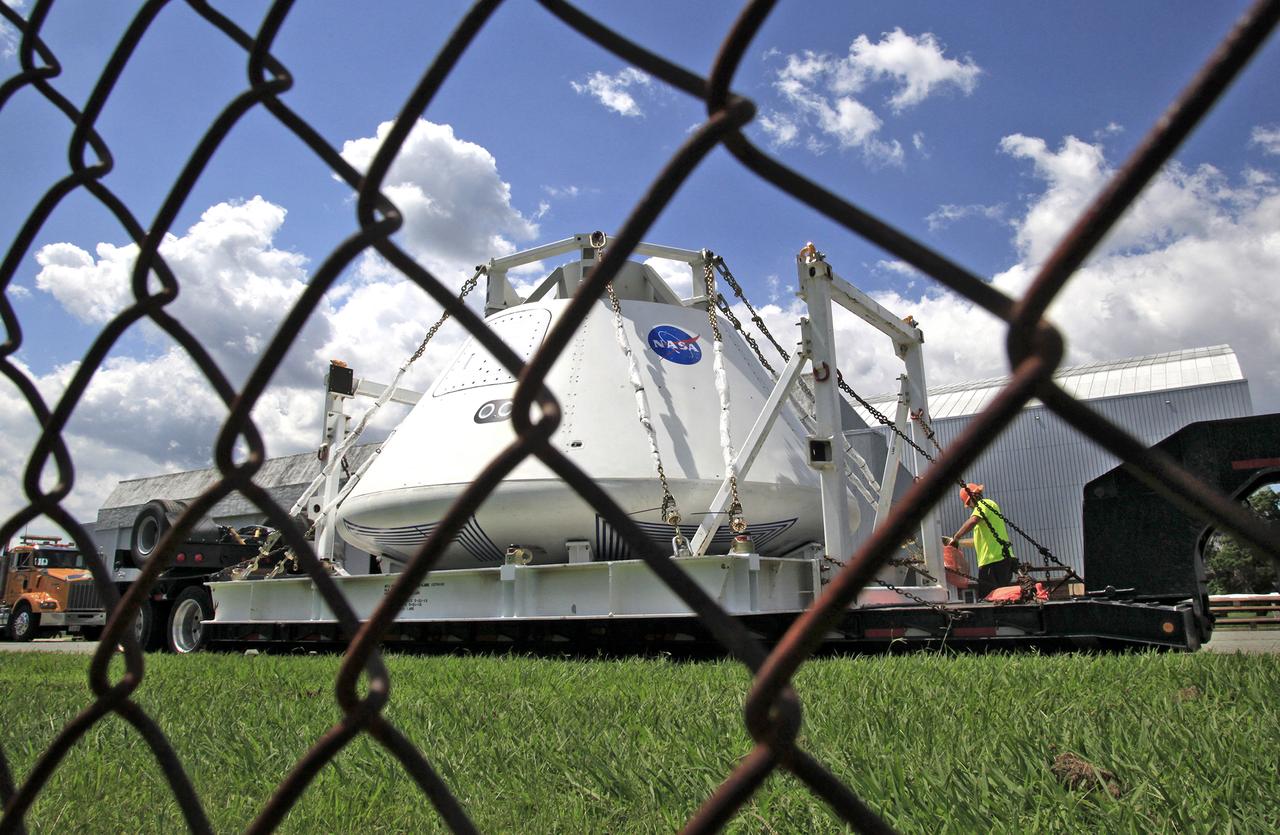

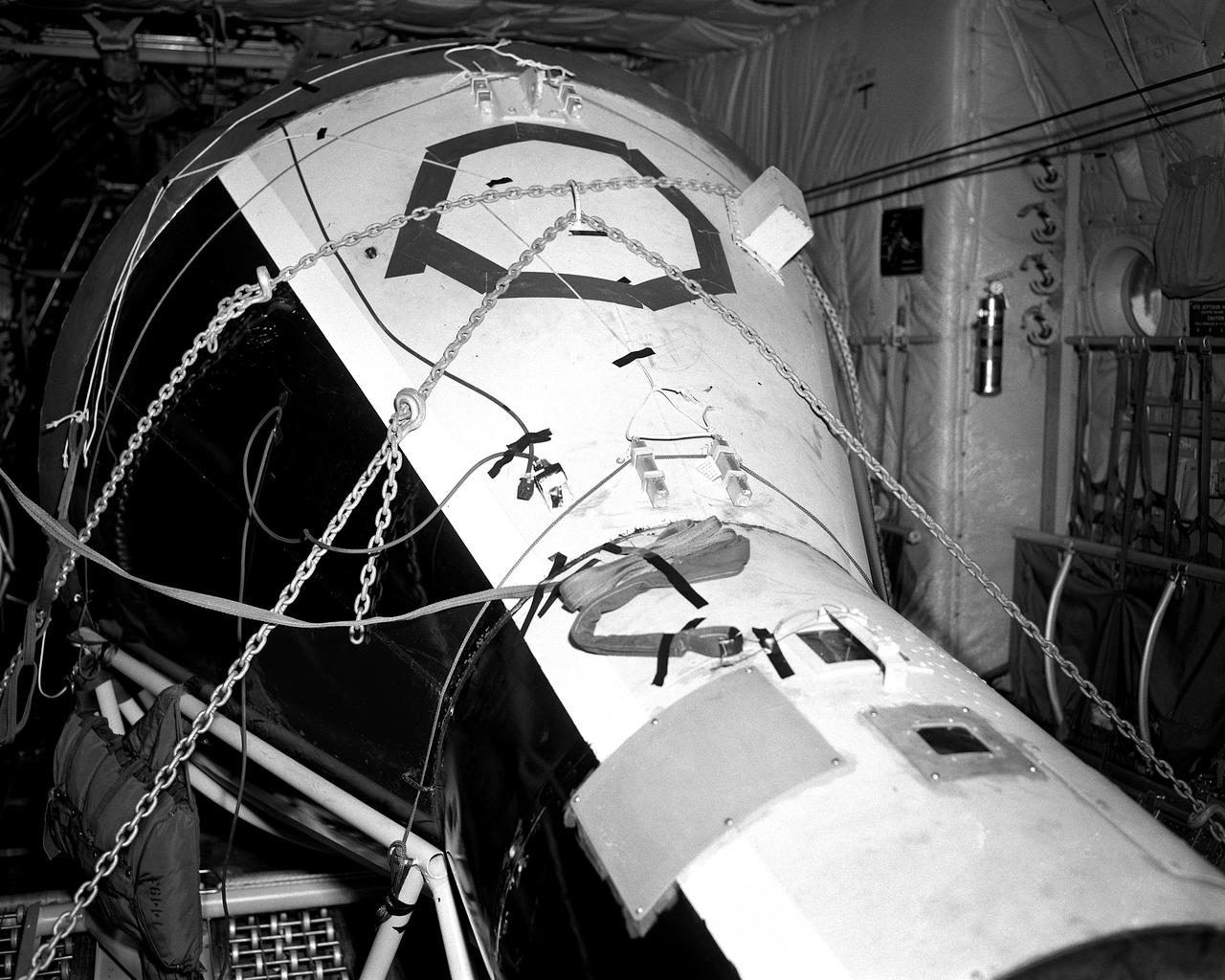
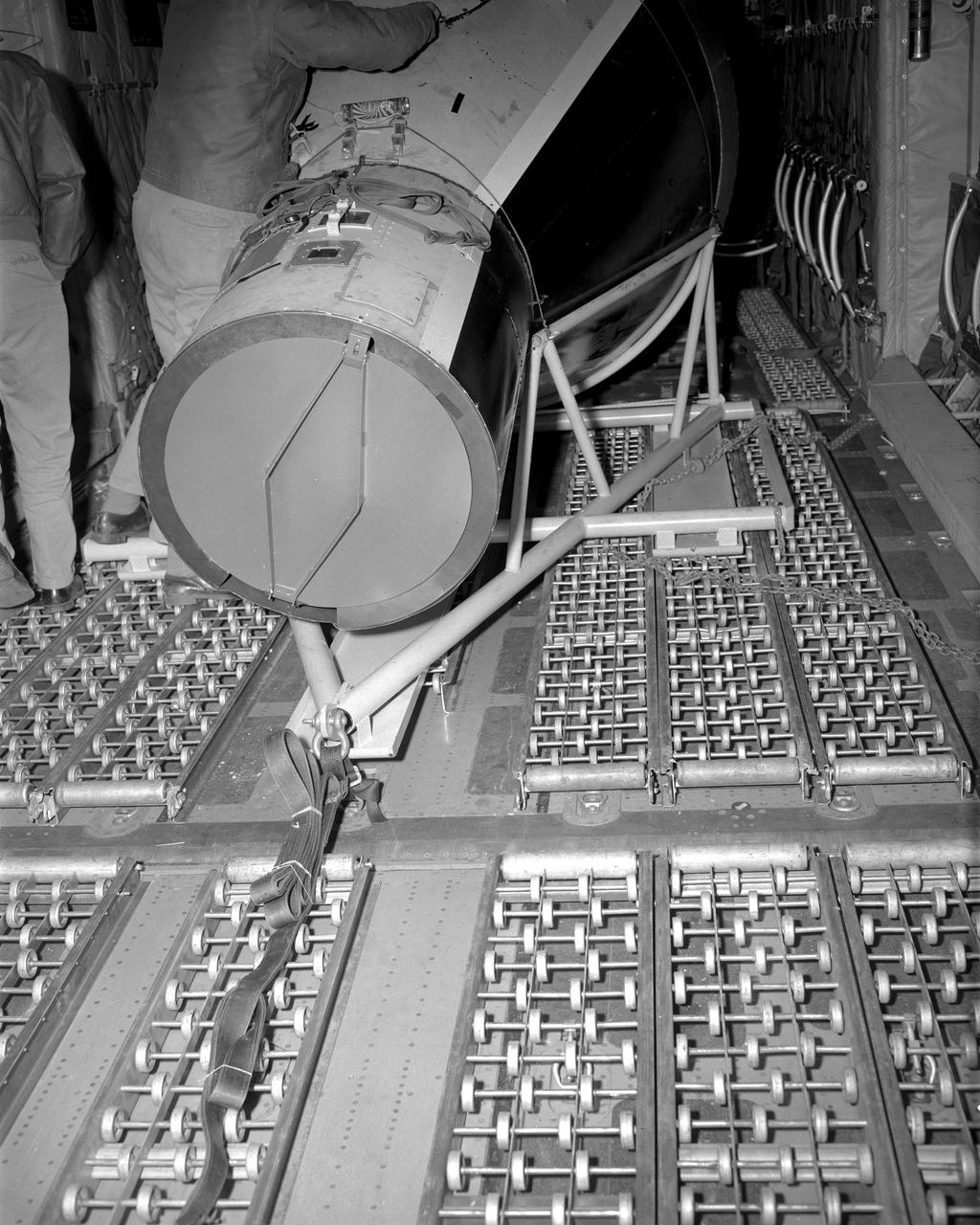
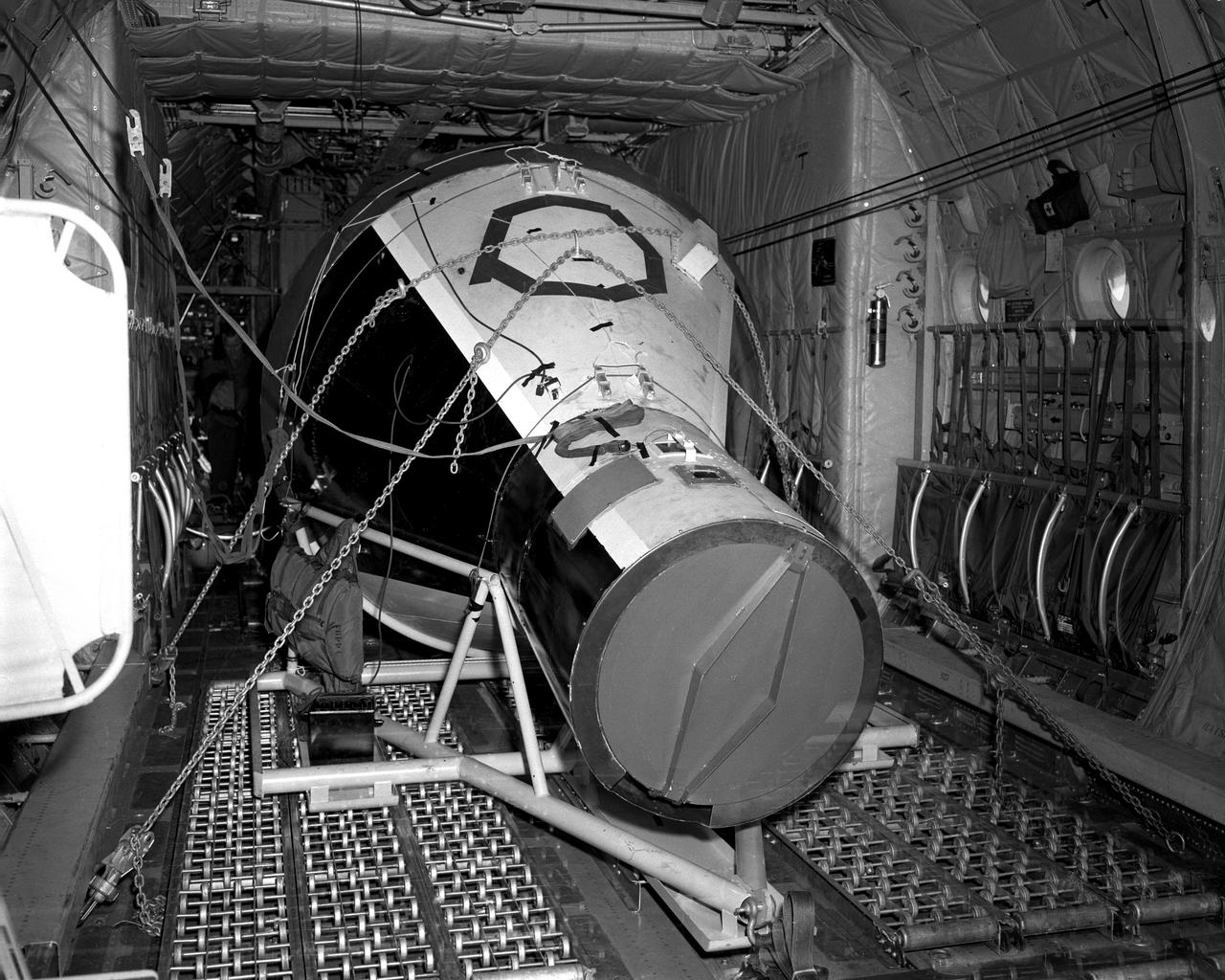
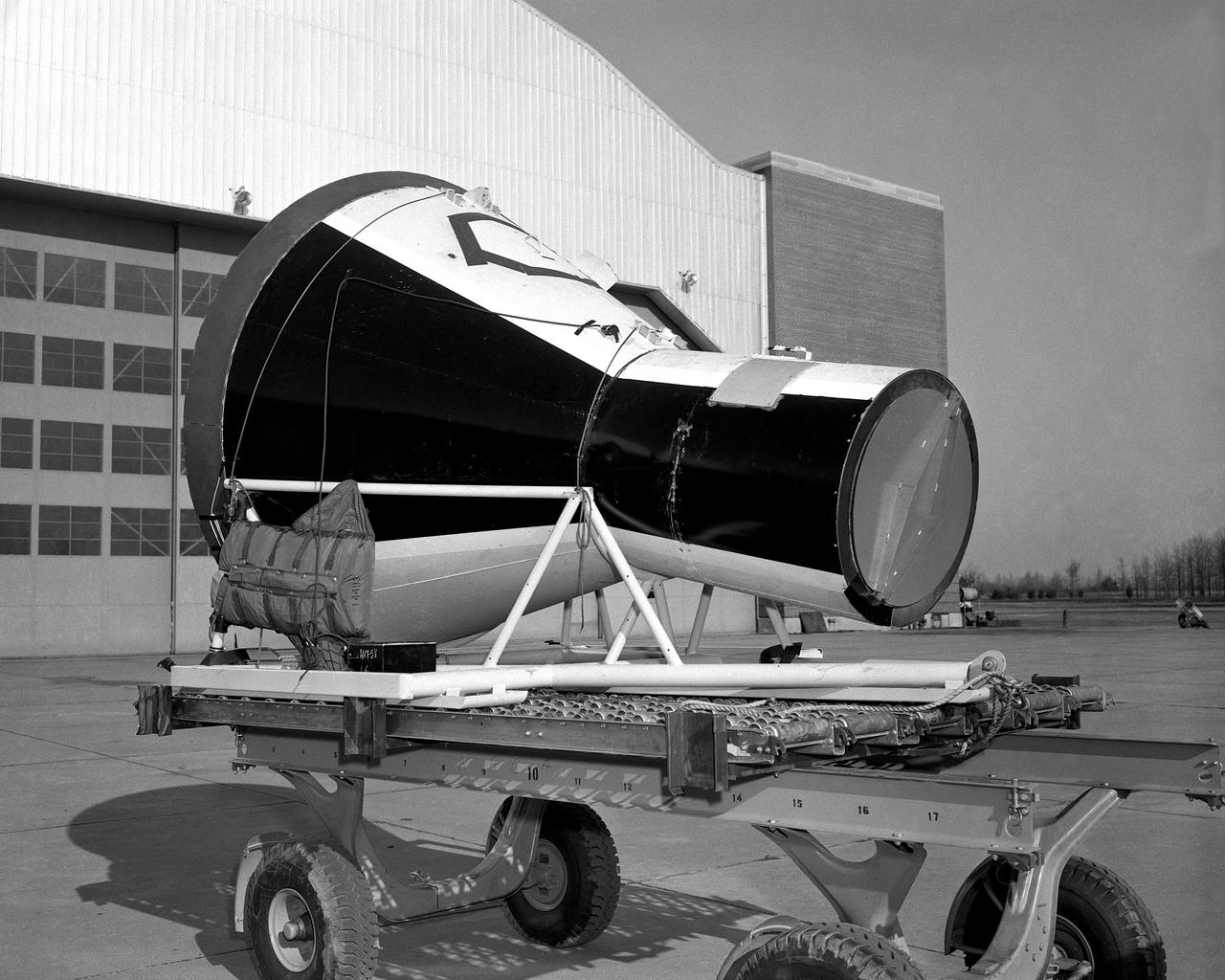
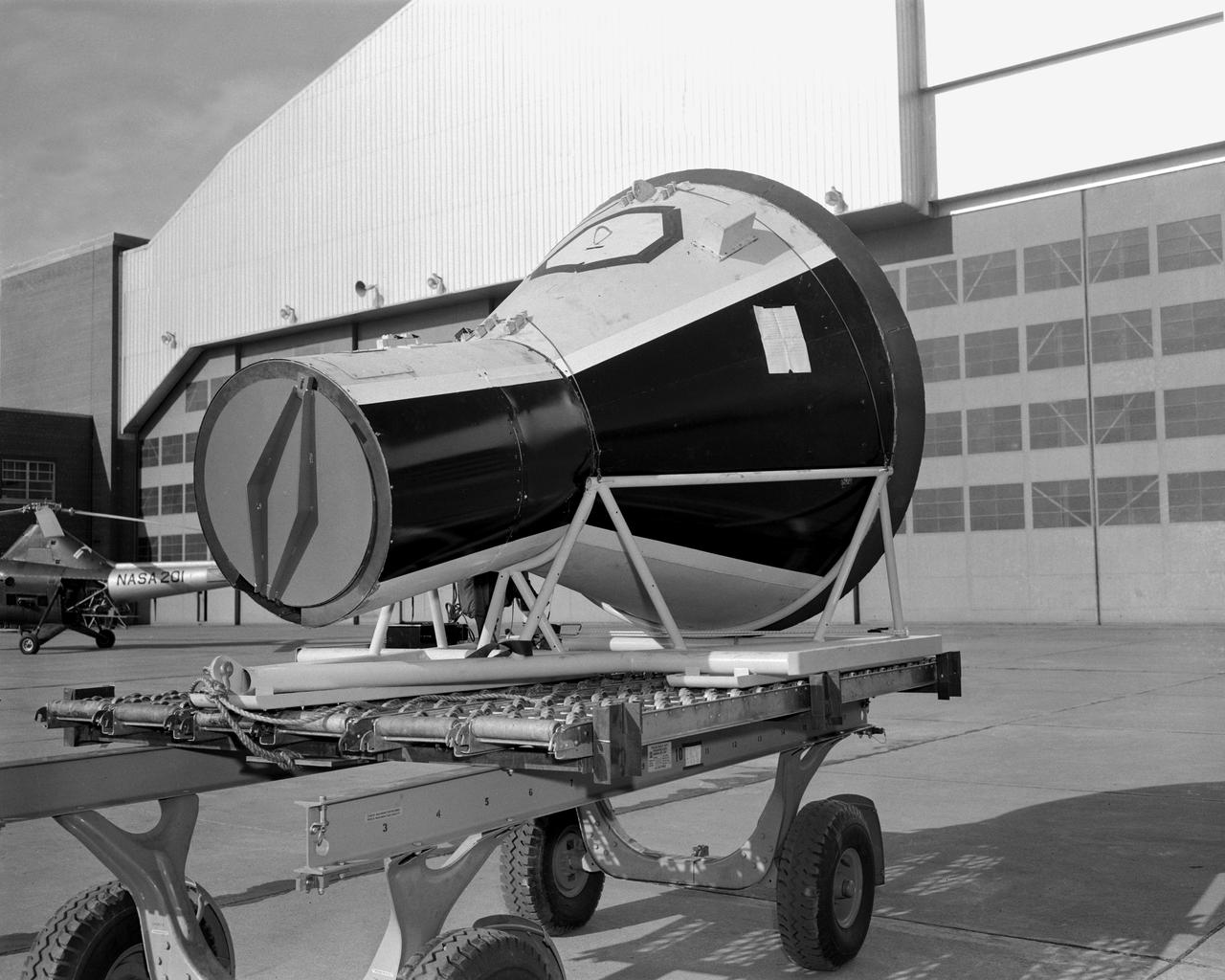
Orion Test Capsule loaded on a flatbed trailer at NASA Langley to be transport to Fort Eustis, VA. where it will be transported by barge to Norfolk Va. for open water recovery test.
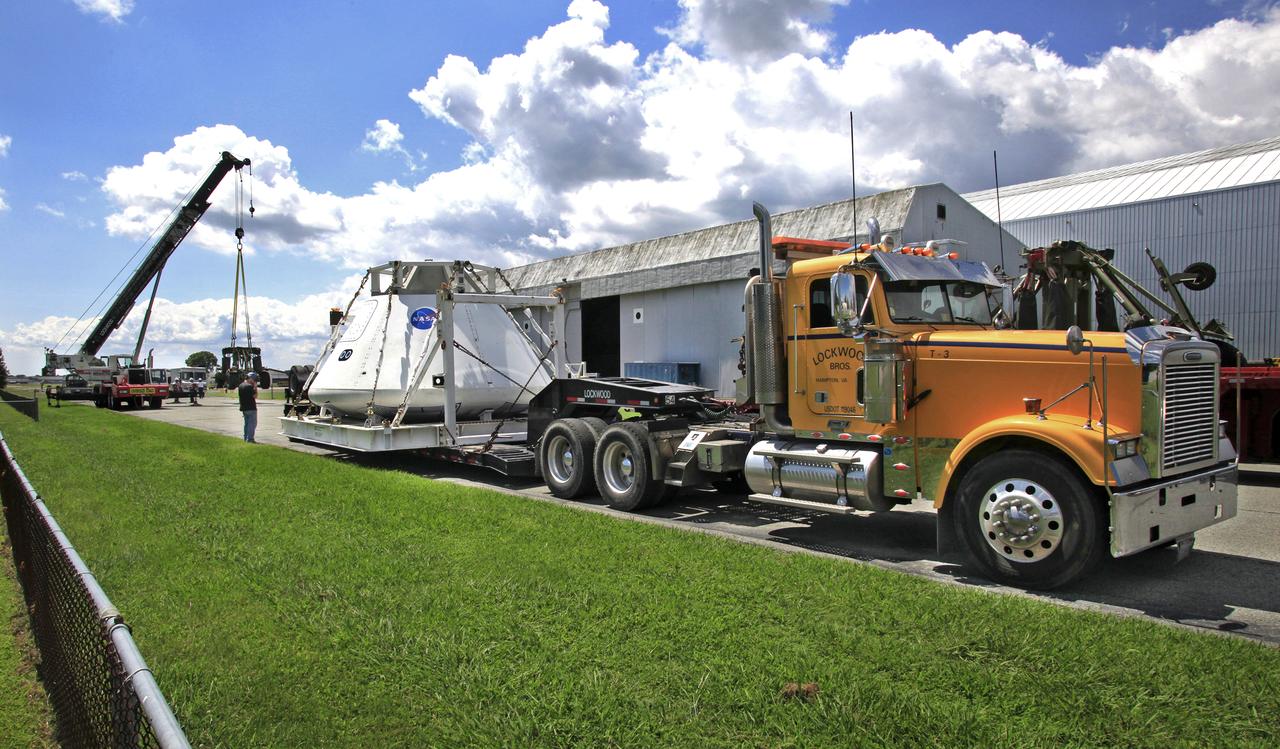

Orion Test Capsule loaded on a flatbed trailer at NASA Langley to be transport to Fort Eustis, VA. where it will be transported by barge to Norfolk Va. for open water recovery test.
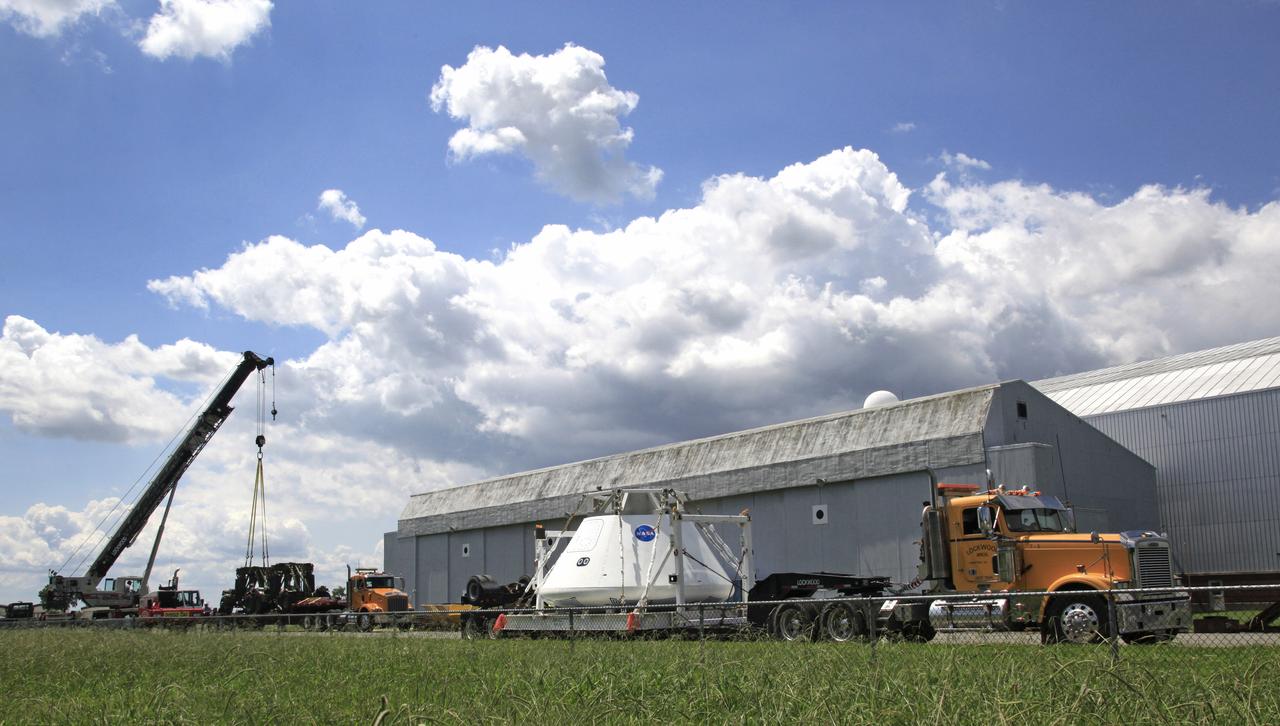

Orion Test Capsule loaded on a flatbed trailer at NASA Langley to be transport to Fort Eustis, VA. where it will be transported by barge to Norfolk Va. for open water recovery test.
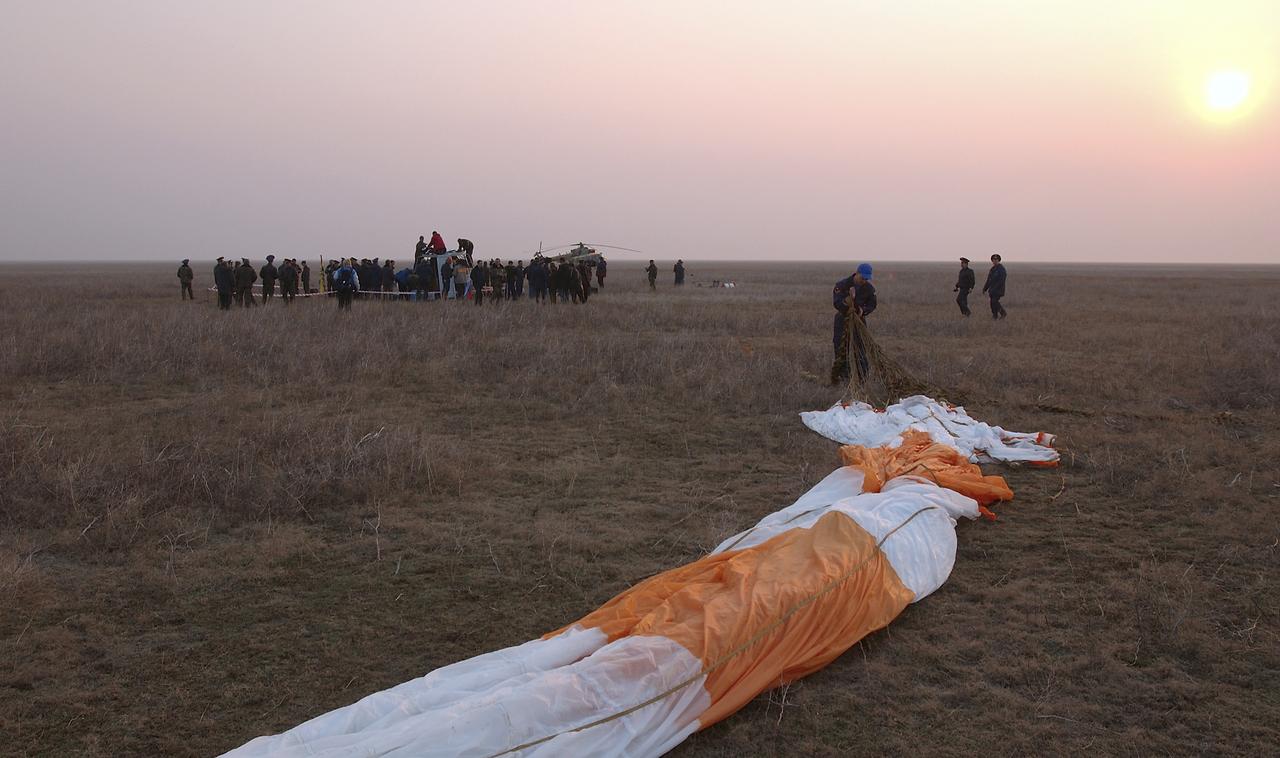

The main chute for the Soyuz capsule is prepared for folding, Friday, April 30, 2004, following the landing of the Expedition 8. Commander Michael Foale, Soyuz Flight Engineer Alexander Kaleri and European Space Agency astronaut Andre Kuipers of the Netherlands landed in north central Kazakhstan in a Soyuz TMA-3 capsule. Foale and Kaleri completed 195 days in space aboard the International Space Station, while Kuipers returned after an 11-day research mission as part of a commercial agreement between ESA and the Russian Federal Space Agency. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
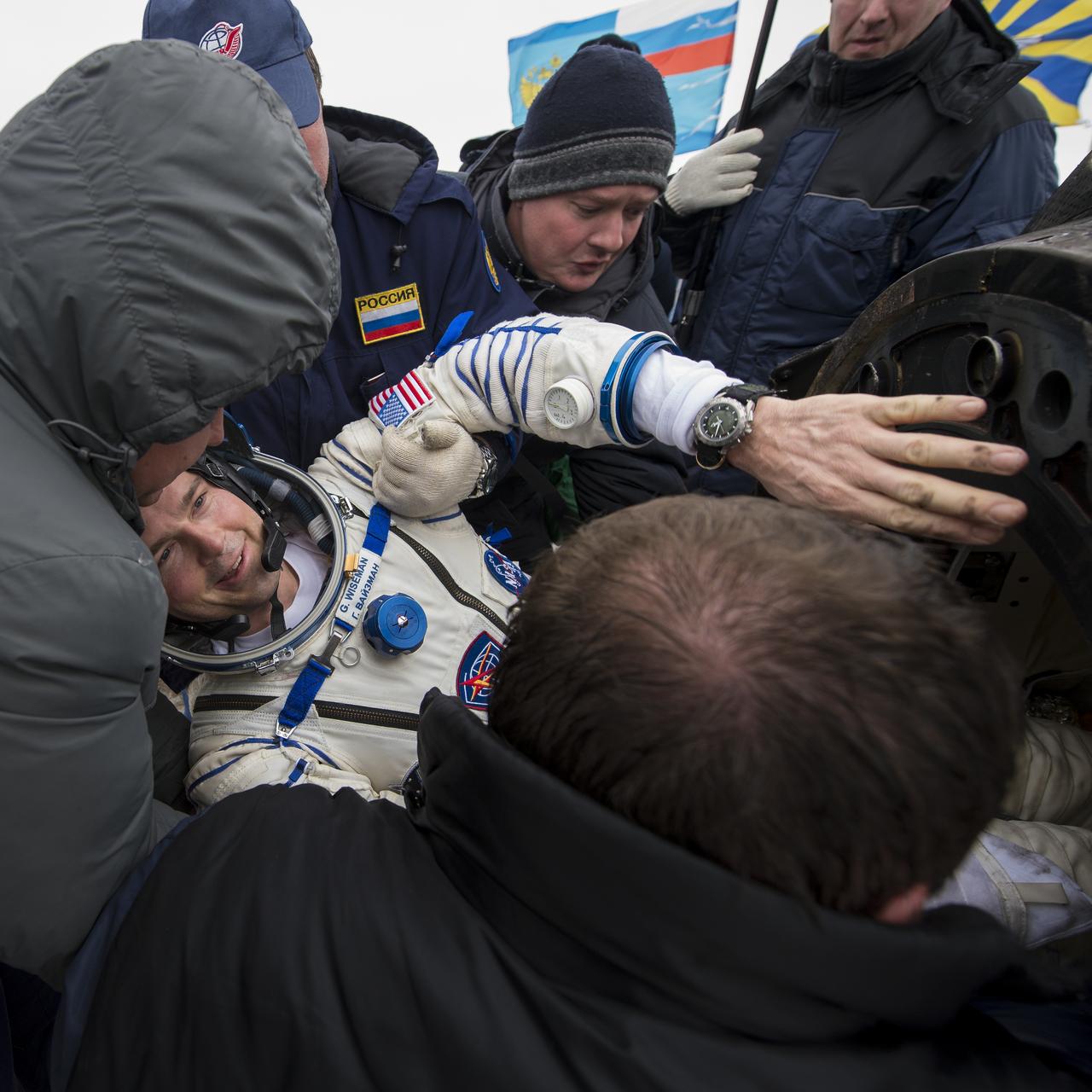

Expedition 41 Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman of NASA is helped out of the Soyuz Capsule just minutes after he and Expedition 41 Commander Max Suraev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) and Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency (ESA) landed in their Soyuz TMA-13M capsule in a remote area near the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Monday, Nov. 10, 2014. Suraev, Wiseman and Gerst returned to Earth after more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 40 and 41 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
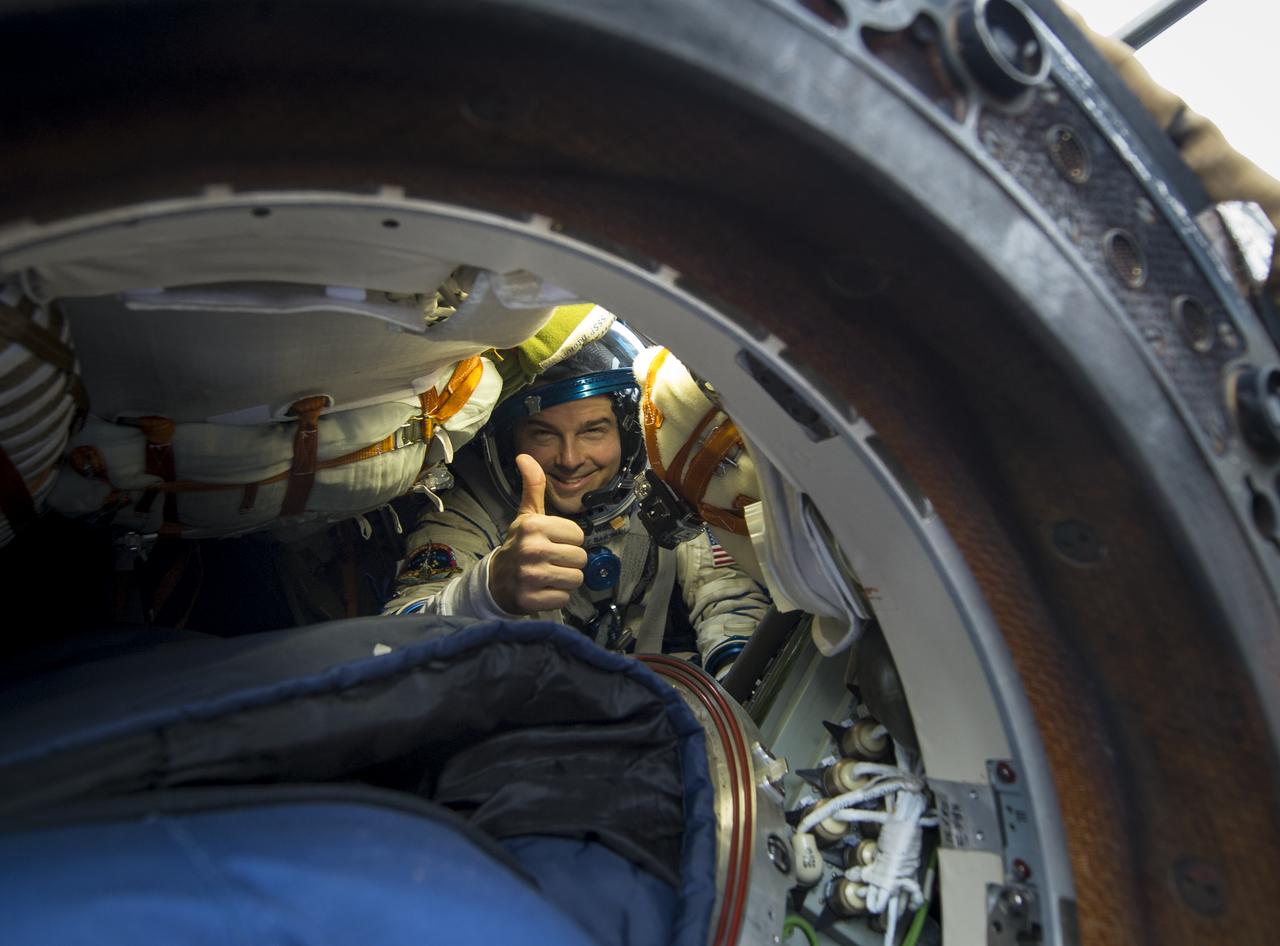

Expedition 41 Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman of NASA gives a thumbs up from inside the Soyuz Capsule just minutes after he and Expedition 41 Commander Max Suraev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) and Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency (ESA) landed in their Soyuz TMA-13M capsule in a remote area near the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Monday, Nov. 10, 2014. Suraev, Wiseman and Gerst returned to Earth after more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 40 and 41 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
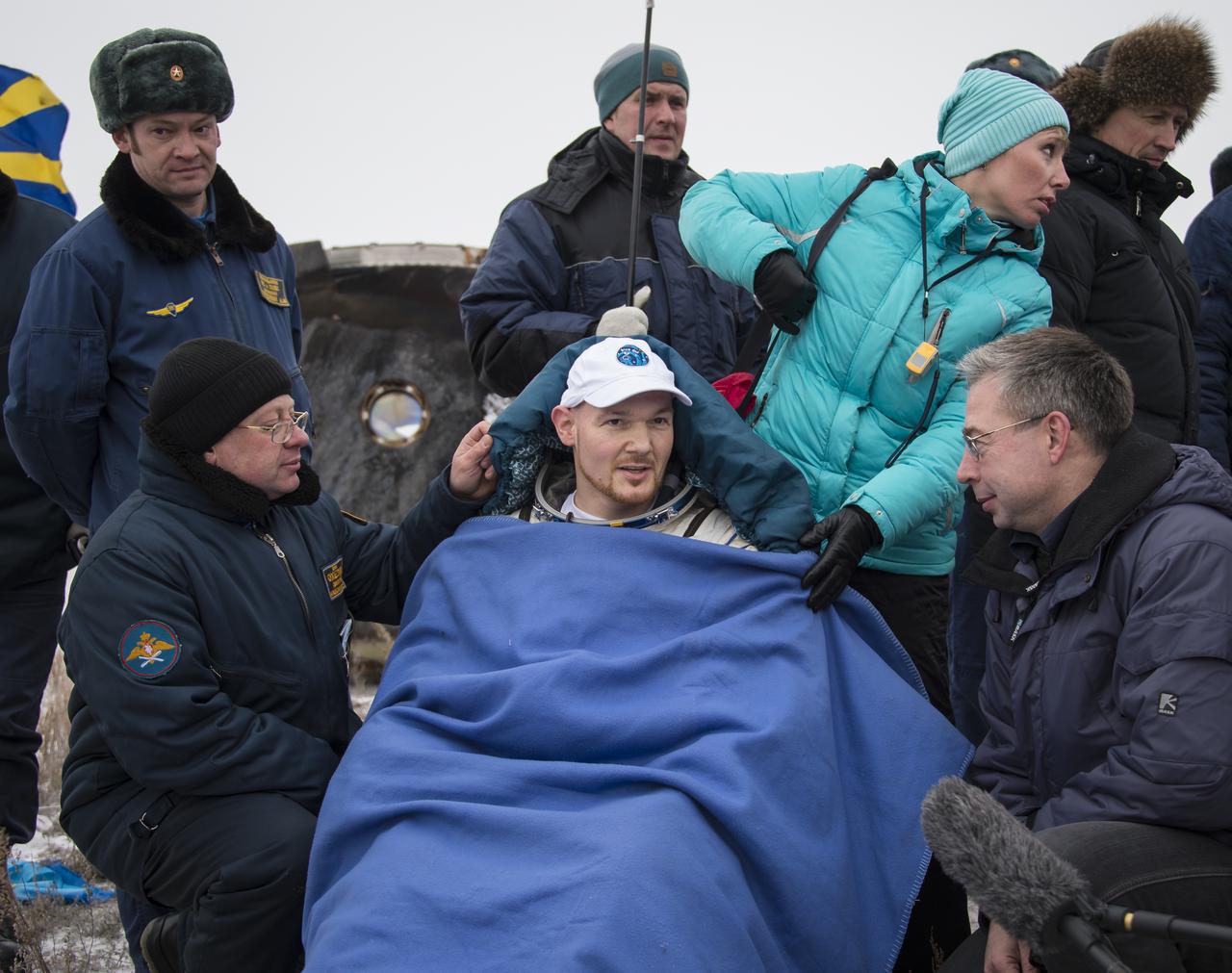

Expedition 41 Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency (ESA) rests in a chair outside the Soyuz Capsule just minutes after he and Expedition 41 Commander Max Suraev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), and NASA Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman landed in their Soyuz TMA-13M capsule in a remote area near the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Monday, Nov. 10, 2014. Suraev, Wiseman and Gerst returned to Earth after more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 40 and 41 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
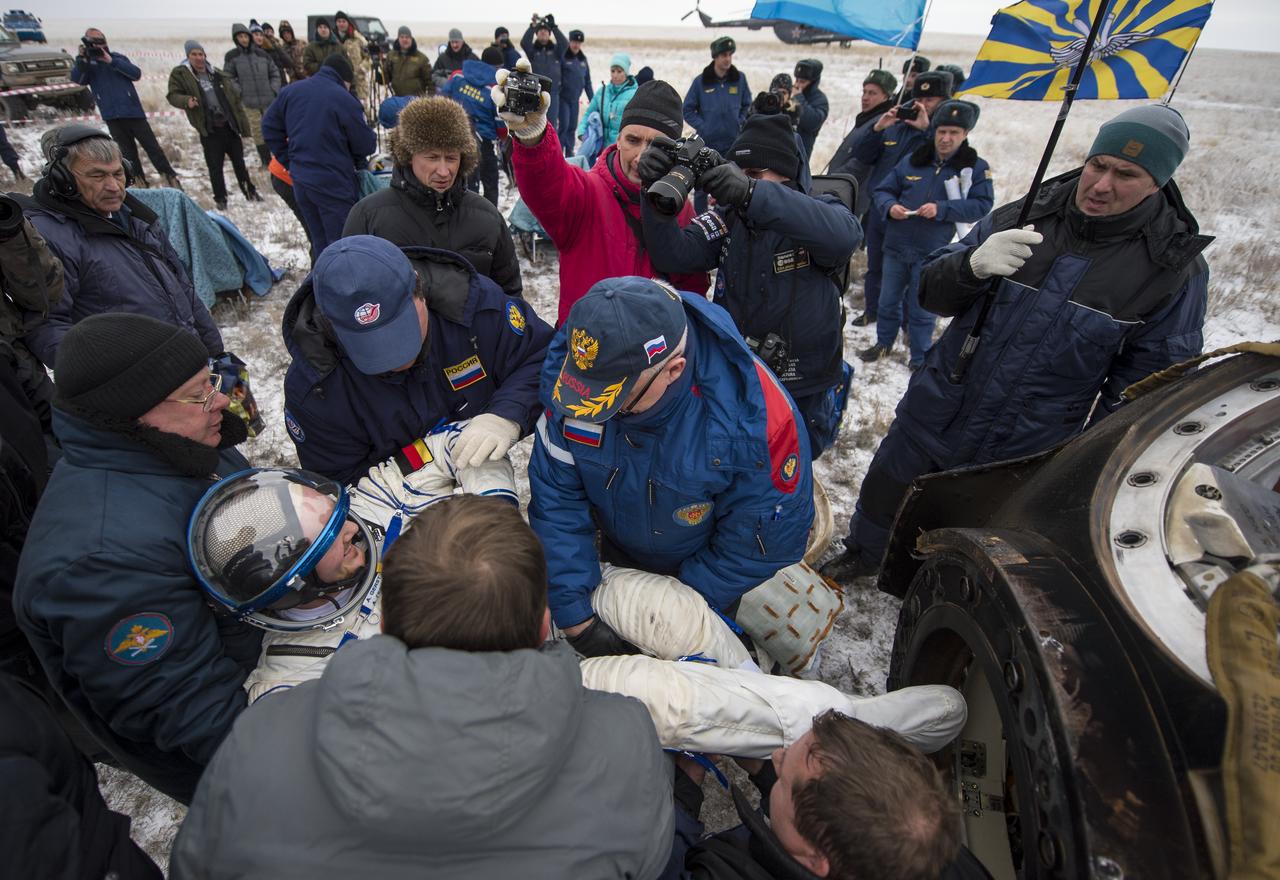

Expedition 41 Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency (ESA) is helped out of the Soyuz Capsule just minutes after he and Expedition 41 Commander Max Suraev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), and NASA Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman landed in their Soyuz TMA-13M capsule in a remote area near the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Monday, Nov. 10, 2014. Suraev, Wiseman and Gerst returned to Earth after more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 40 and 41 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Technicians prepare a full-scale capsule which would be used for the first rocket-launching on March 11, 1959. The purpose of the test would be to simulate a ground-level or beach abort. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3, p. 27): It was a test of the ability of the escape system to rescue the astronaut in case of a malfunction of the launch vehicle prior to flight. This test was carried out by PARD under the direction of W.S. Blanchard, Jr., and was part of the program designated F57 at PARD. For these tests capsule shape C was used. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.
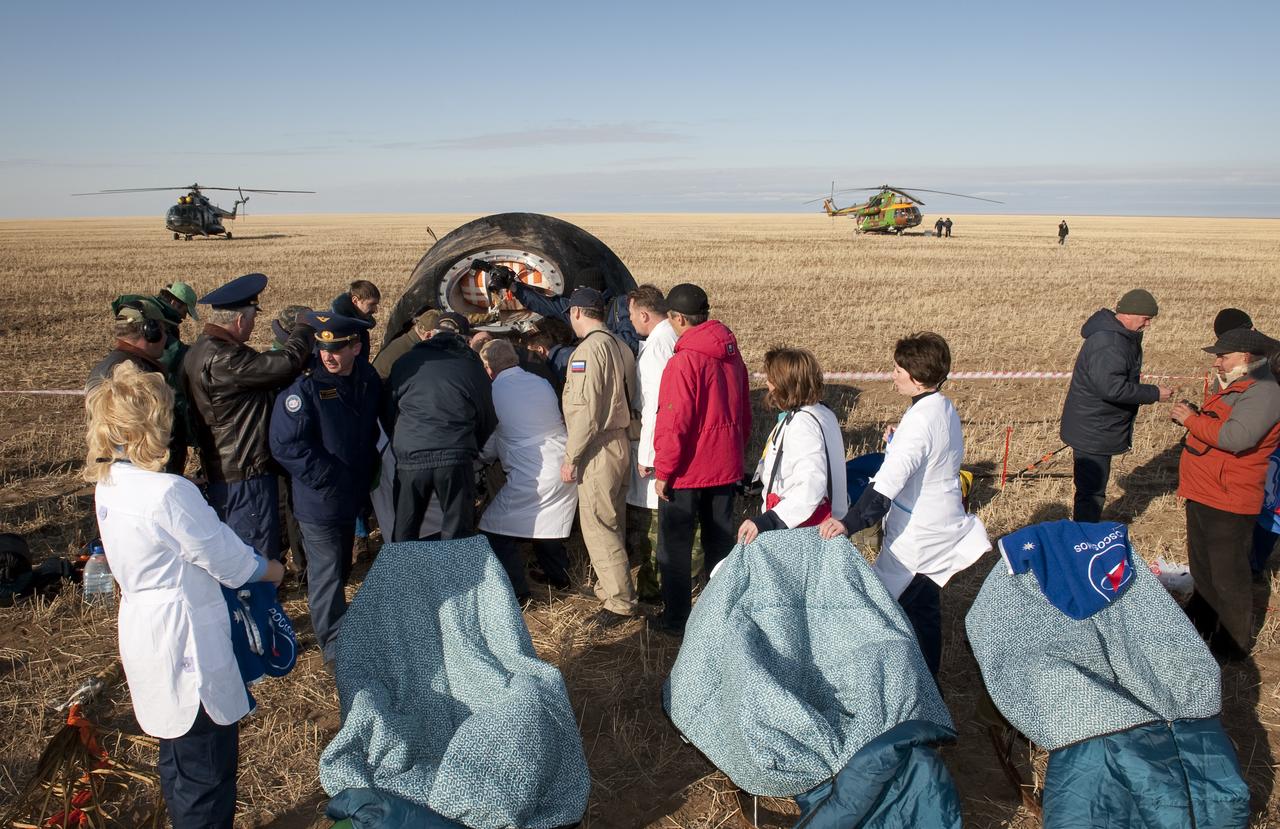

Empty chairs outside the Soyuz Capsule await Spaceflight participant Guy Laliberté, Expedition 20 Commander Gennady Padalka, and Expedition 20 Flight Engineer Michael Barratt just minutes after they landed in their Soyuz TMA-14 capsule near the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Sunday, Oct. 11, 2009. Padalka and Barratt are returning from six months onboard the International Space Station, along with Laliberté who arrived at the station on Oct. 2 with Expedition 21 Flight Engineers Jeff Williams and Maxim Suraev aboard the Soyuz TMA-16 spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
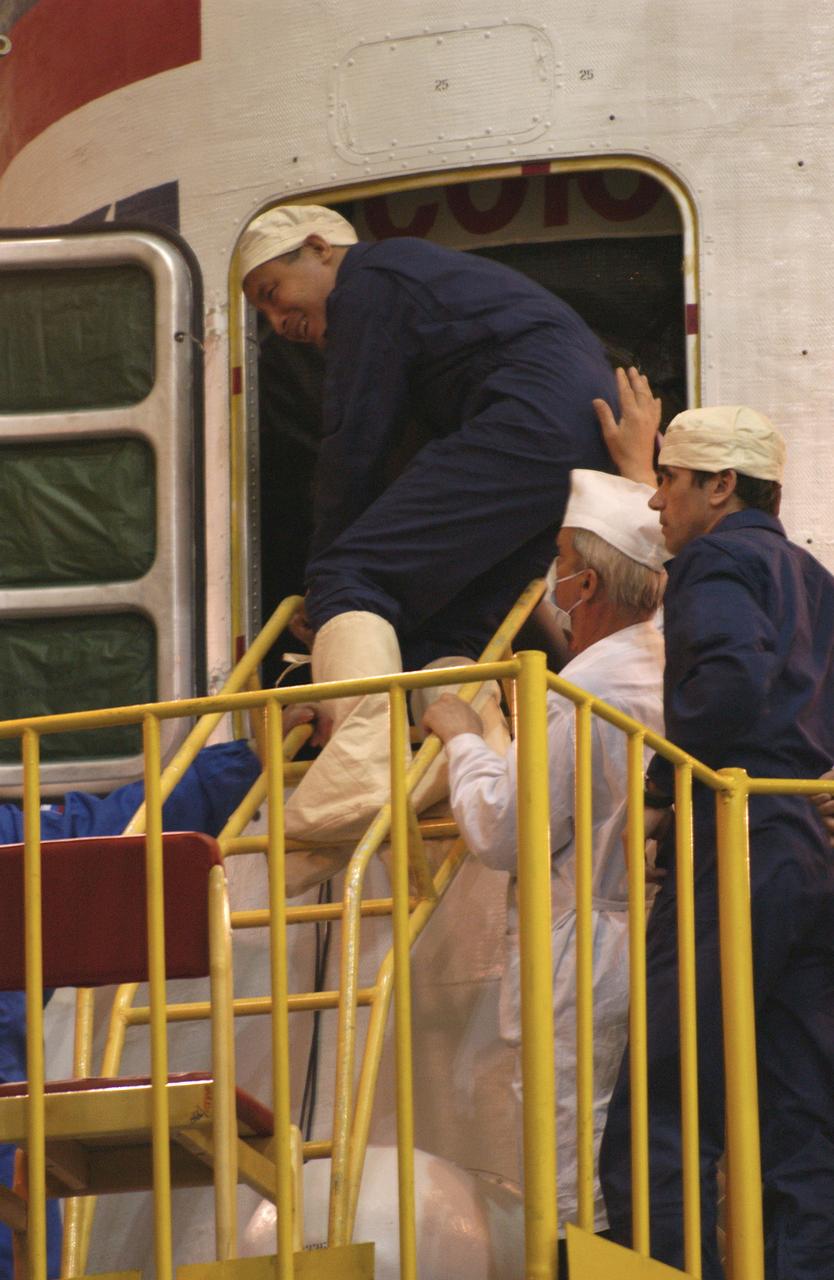

Expedition 7 NASA International Space Station Science Officer and Flight Engineer Edward T. Lu steps out of the Soyuz capsule while Mission Commander Yuri I. Malenchenko looks on. The crew entered the Soyuz capsule for final checks, Tuesday, April 22, 2003, prior to their scheduled launch on Saturday April 26, 2003 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baiknour, Kazakhstan. Photo credit: (NASA/Scott Andrews)
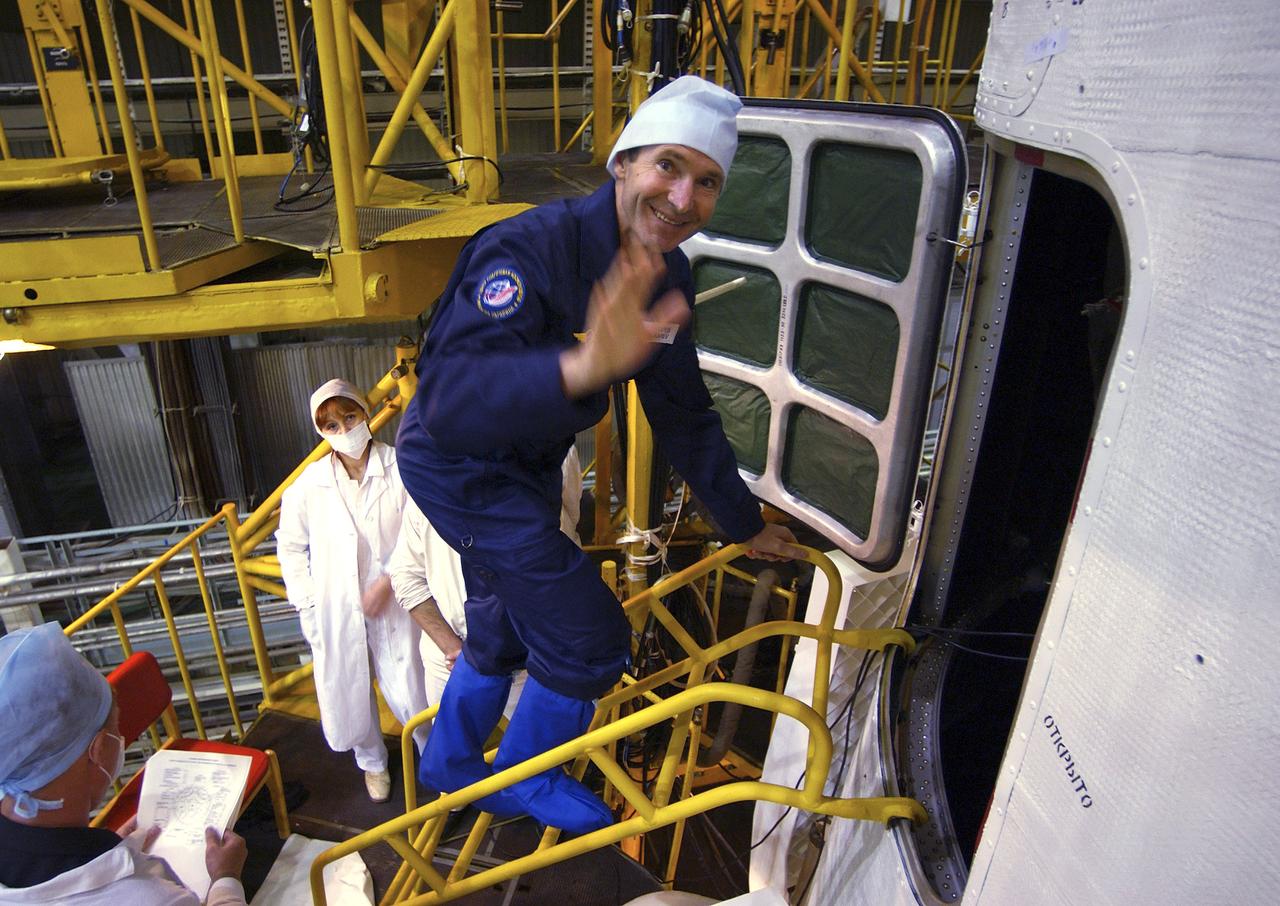

Expedition 10 backup Soyuz Commander Valery Tokarev enters the Soyuz capsule for a final check Saturday, Oct. 9, 2004, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 10 is scheduled to launch October 14 on the Soyuz TMA-5 spacecraft to the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
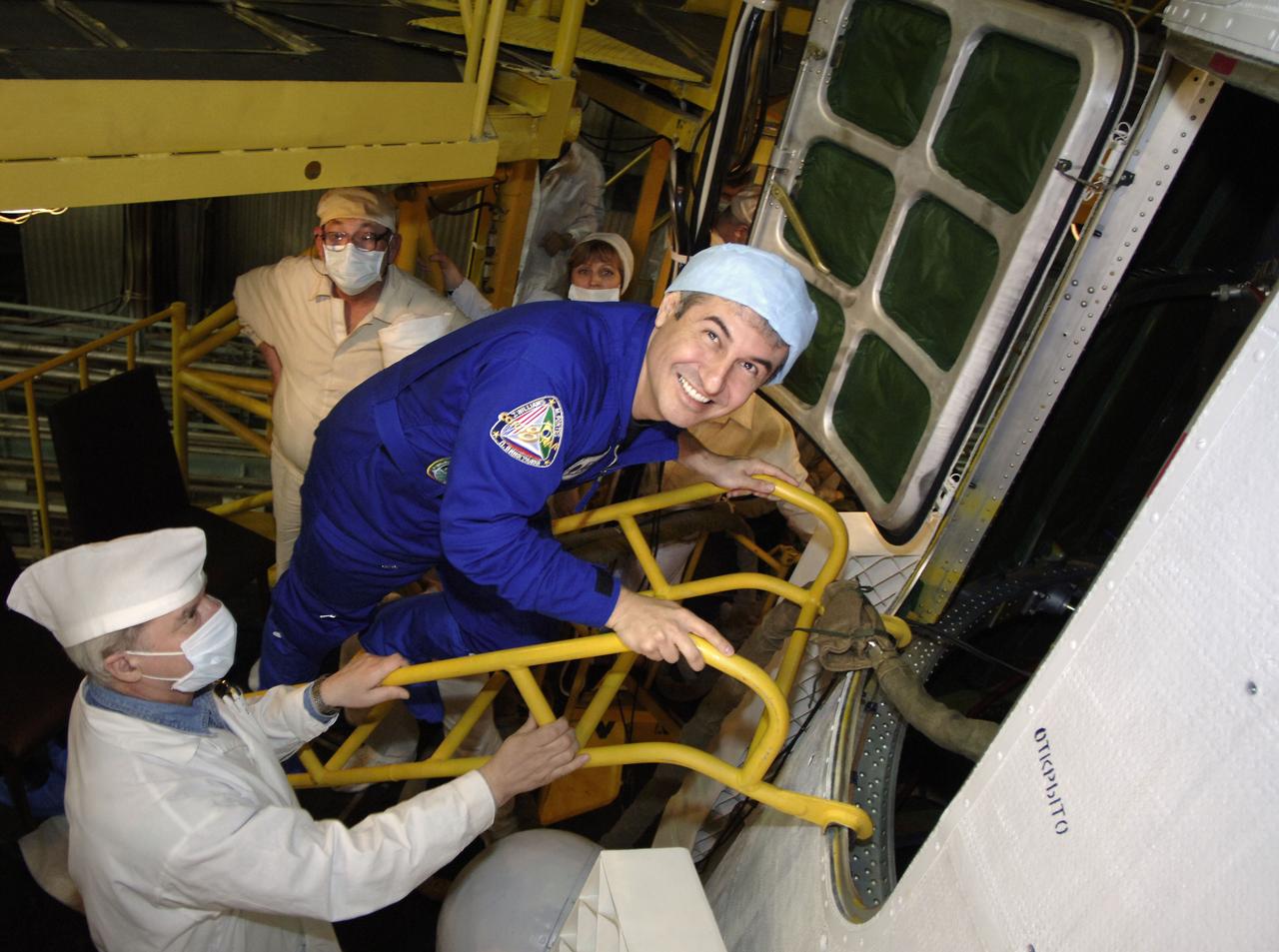

Marcos Pontes, Brazilian Space Agency Soyuz crew member, climbs into the Soyuz capsule for his final check at building 254 of the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan days before launch to the International Space Station. Sunday, March 26, 2006. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
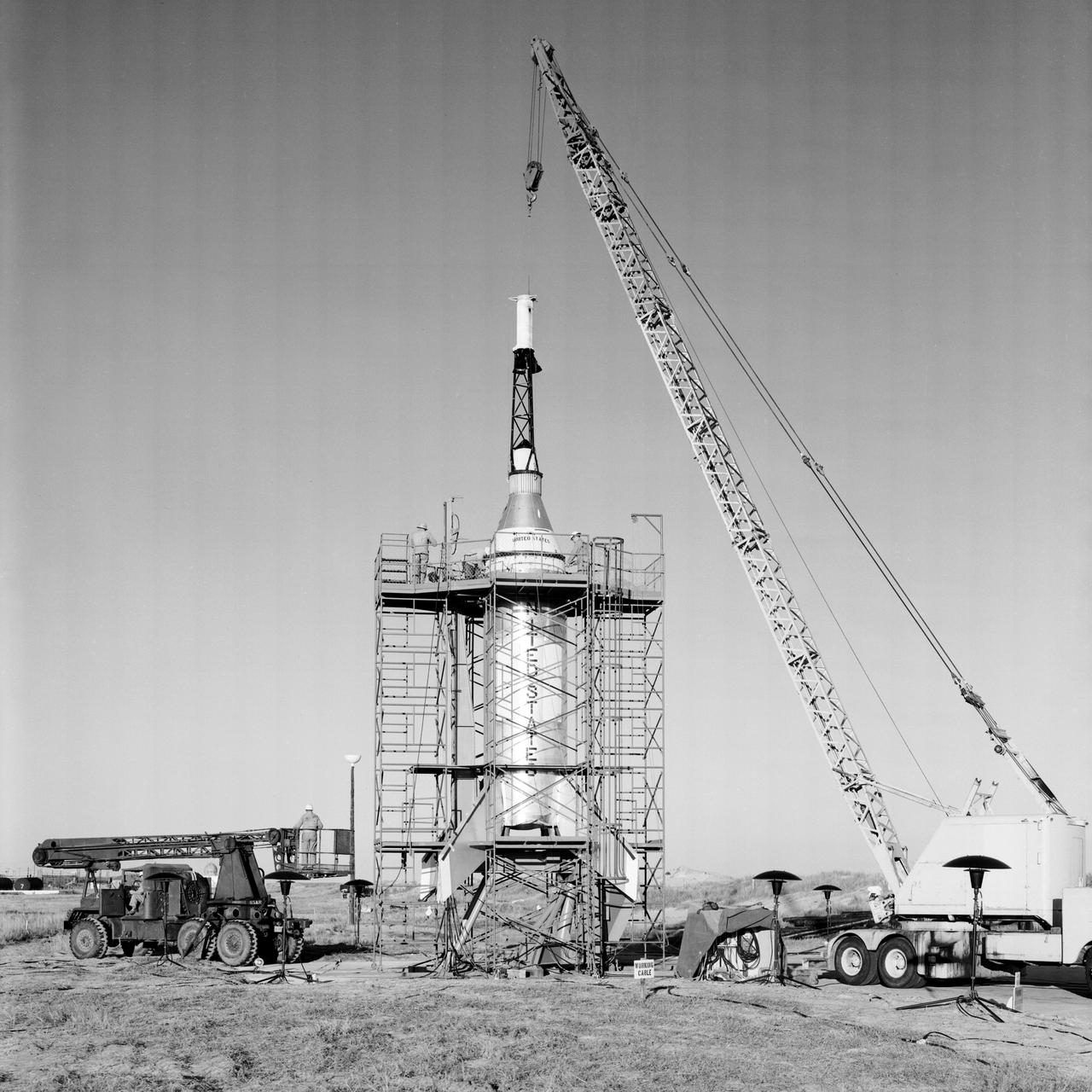

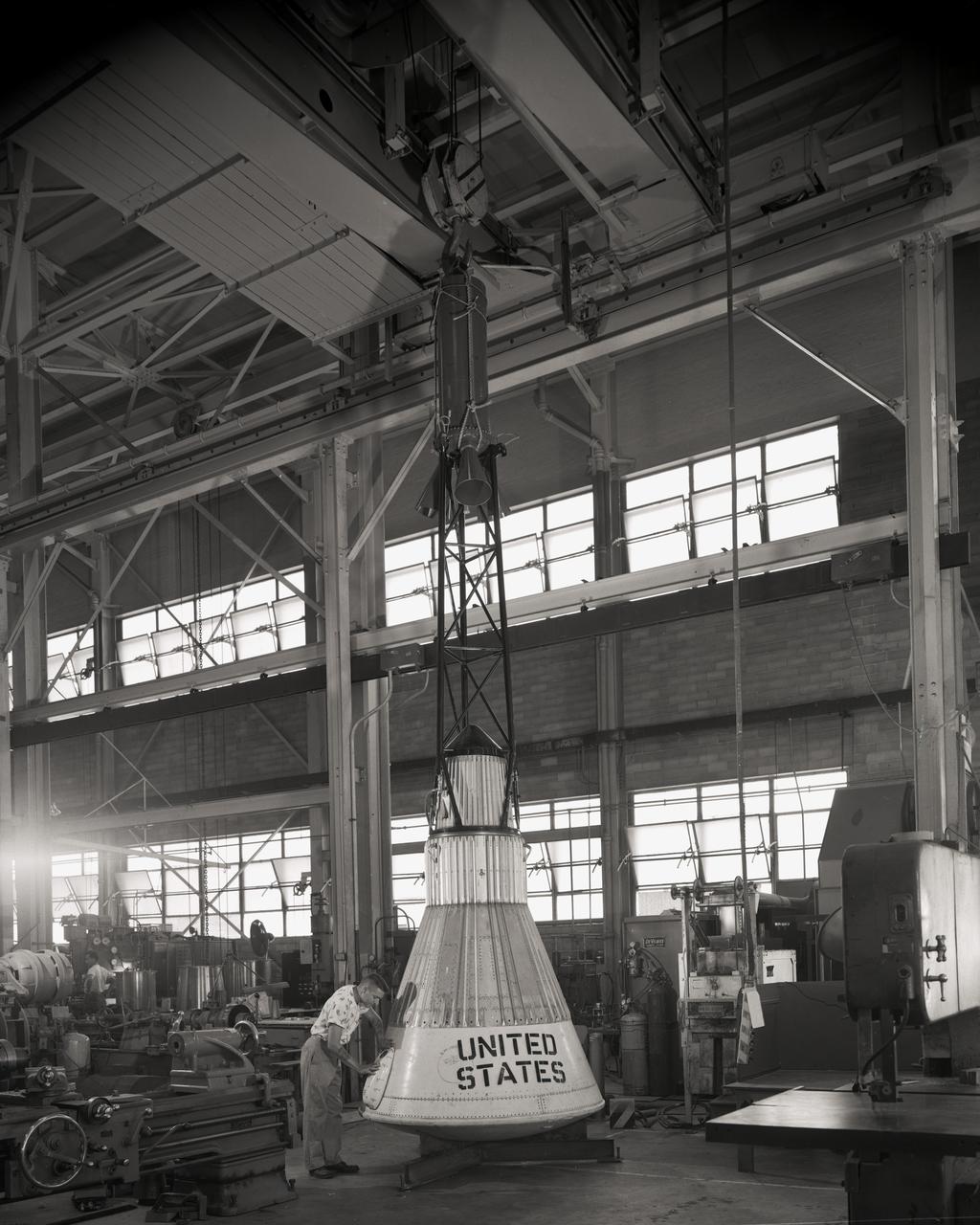
The Mercury capsule and escape tower are being lowered onto the Little Joe booster for launch on August 21, 1959. Joseph Shortal described this as follows (vol. 3, p. 33): The Little Joe booster was assembled at Wallops on its special launcher in a vertical attitude. It is shown in the on the left with the work platform in place. The launcher was located on a special concrete slab in Launching Area 1. The capsule was lowered onto the booster by crane.... After the assembly was completed, the scaffolding was disassembled and the launcher pitched over to its normal launch angle of 80 degrees.... Little Joe had a diameter of 80 inches and an overall length, including the capsule and escape tower of 48 feet. The total weight at launch was about 43,000 pounds. The overall span of the stabilizing fins was 21.3 feet. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.
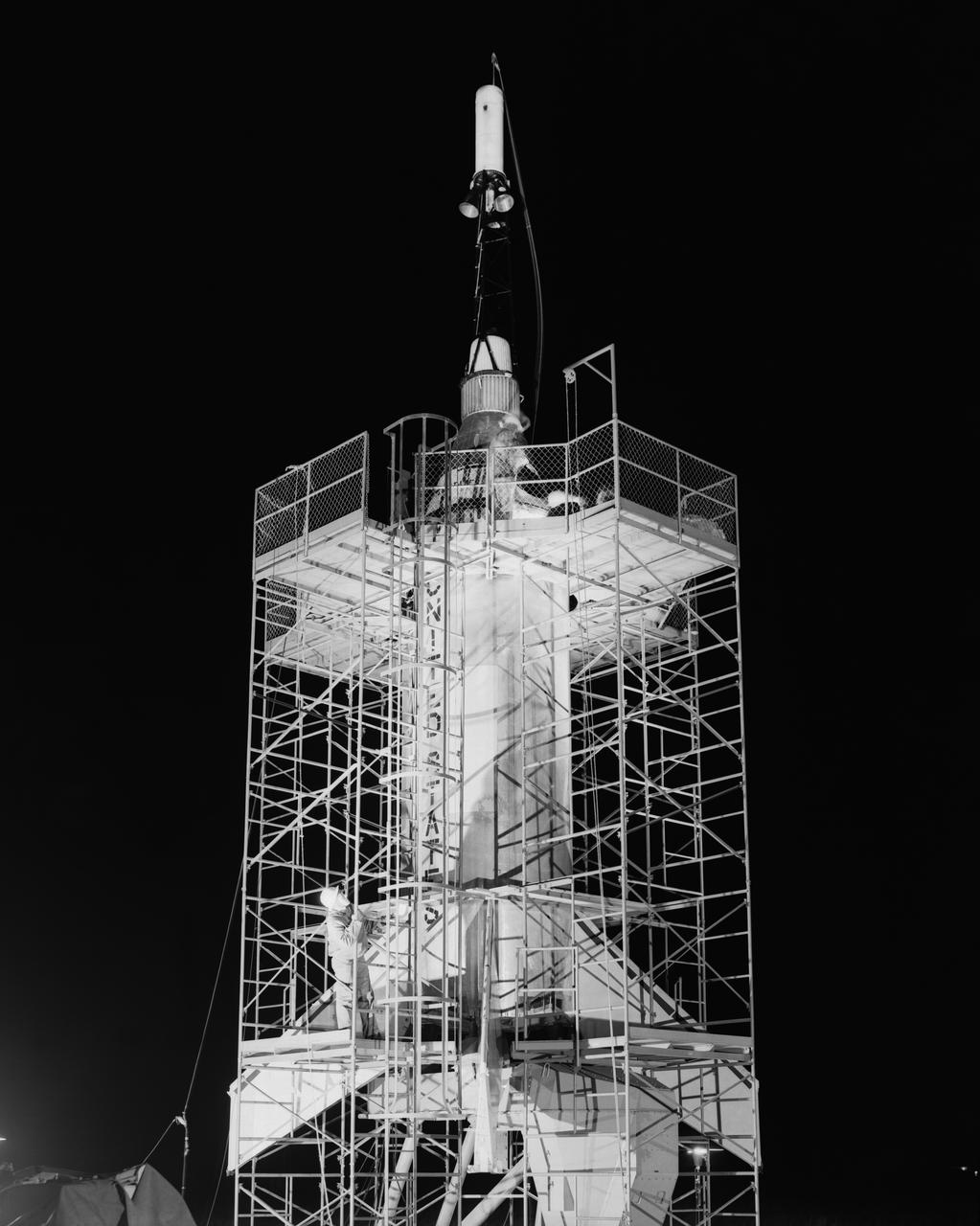

The Mercury capsule and escape tower are being lowered onto the Little Joe booster for launch on August 21, 1959. Joseph Shortal described this as follows (vol. 3, p. 33): The Little Joe booster was assembled at Wallops on its special launcher in a vertical attitude. It is shown in the on the left with the work platform in place. The launcher was located on a special concrete slab in Launching Area 1. The capsule was lowered onto the booster by crane.... After the assembly was completed, the scaffolding was disassembled and the launcher pitched over to its normal launch angle of 80 degrees.... Little Joe had a diameter of 80 inches and an overall length, including the capsule and escape tower of 48 feet. The total weight at launch was about 43,000 pounds. The overall span of the stabilizing fins was 21.3 feet. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.
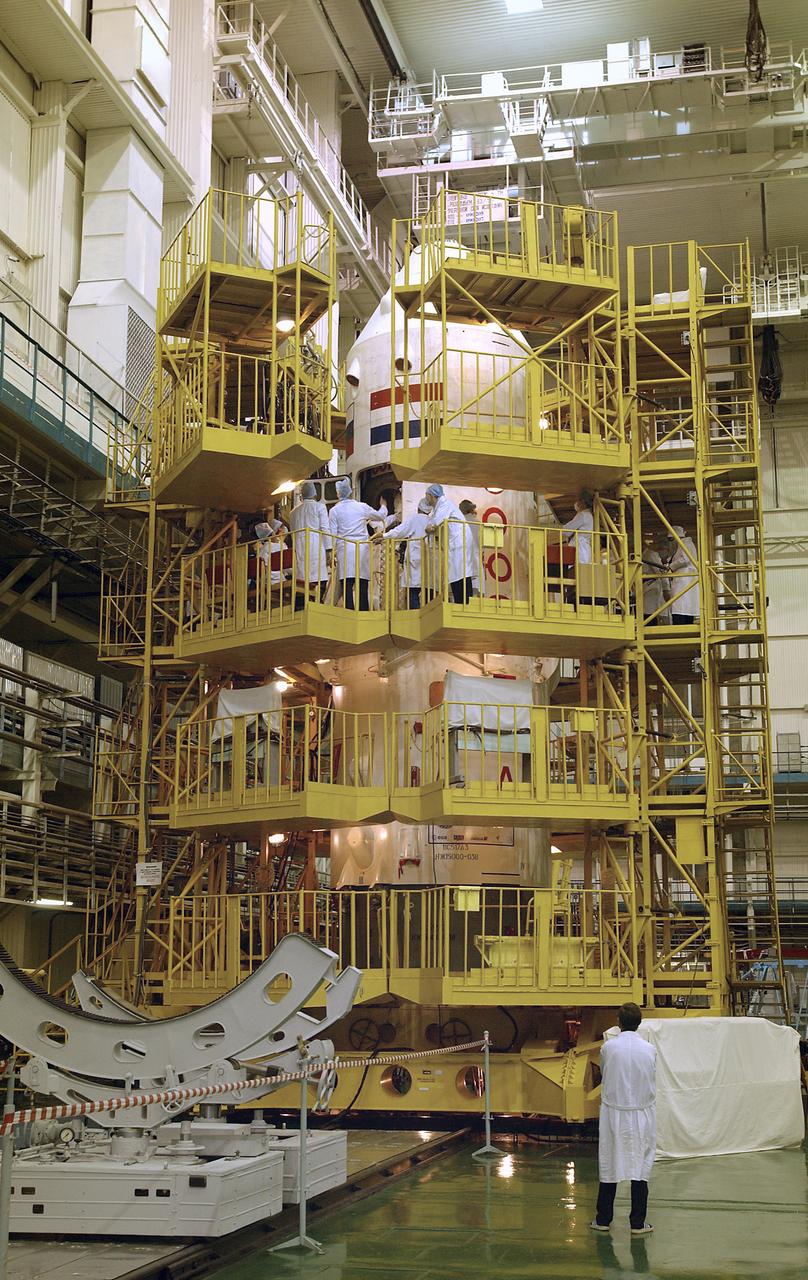

Expedition 9 Commander Gennady Padalka, Flight Engineer, NASA Science Officer Mike Fincke and European Space Agency astronaut Andre Kuipers of the Netherlands do their final fit check in the Soyuz capsule at building 254 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, Wednesday, April 14, 2004. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
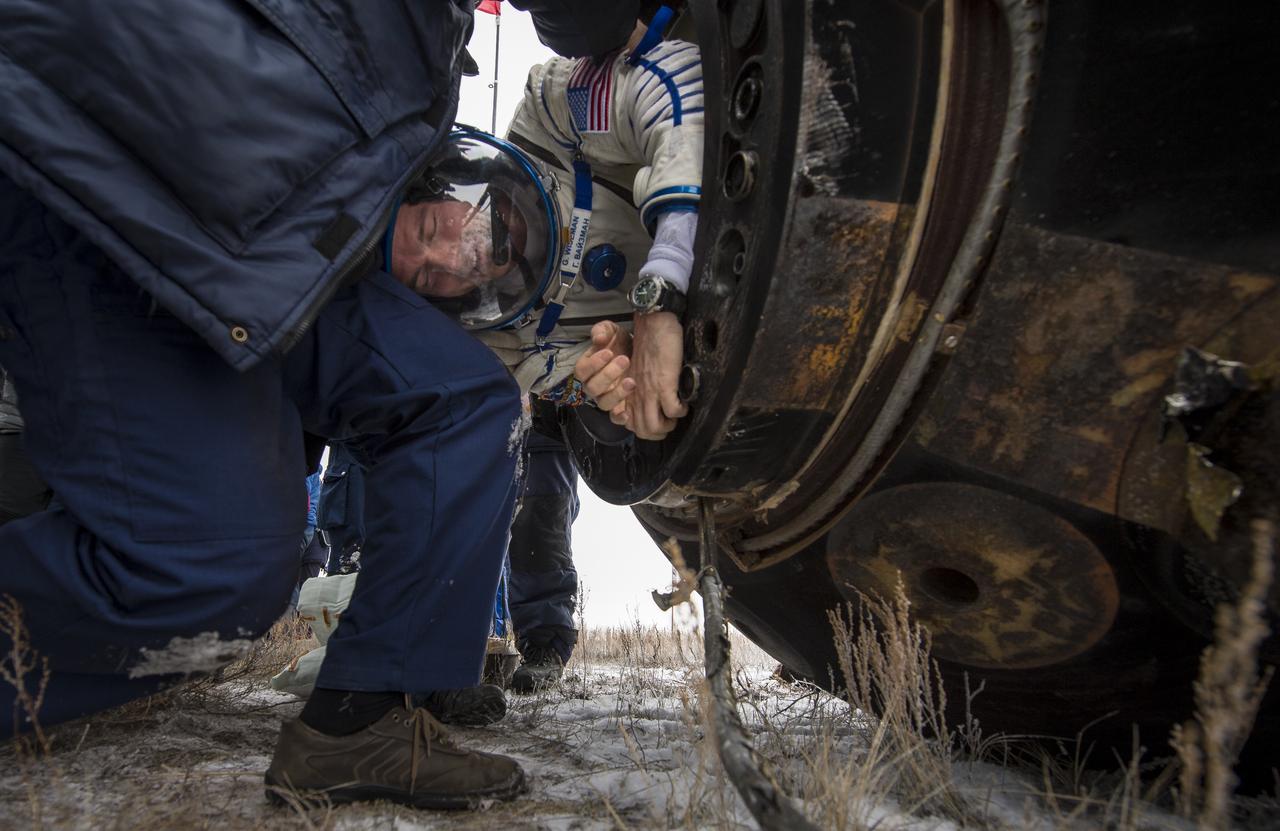

Expedition 41 Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman of NASA is helped out of the Soyuz Capsule just minutes after he and Expedition 41 Commander Max Suraev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) and Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency (ESA) landed in their Soyuz TMA-13M capsule in a remote area near the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Monday, Nov. 10, 2014. Suraev, Wiseman and Gerst returned to Earth after more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 40 and 41 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
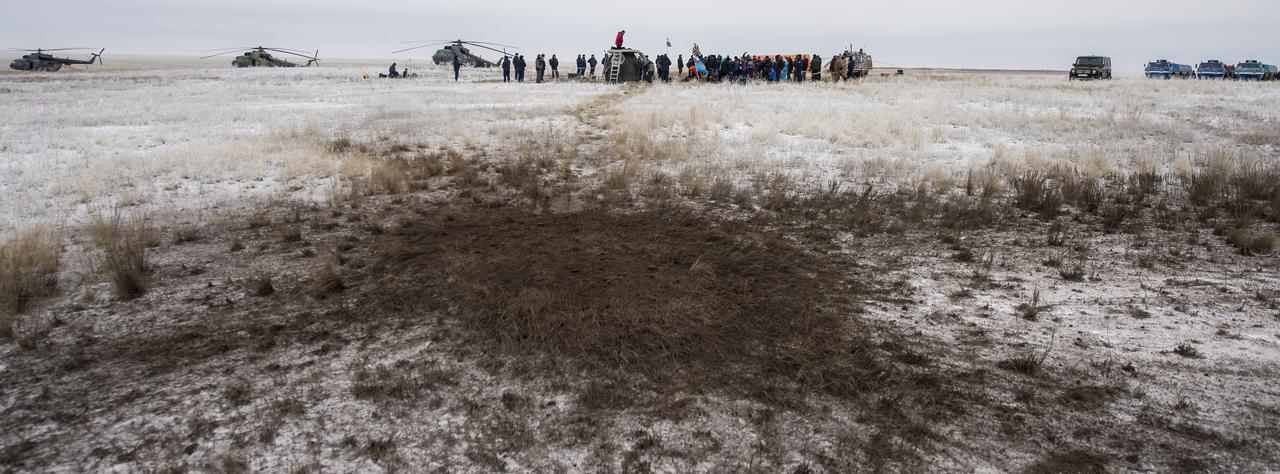

The ground where the Soyuz TMA-13M spacecraft landed, and then was dragged by it’s parachute, is seen after the capsule landed with Expedition 41 Commander Max Suraev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), NASA Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman and Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency (ESA) near the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Monday, Nov. 10, 2014. Suraev, Wiseman and Gerst returned to Earth after more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 40 and 41 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
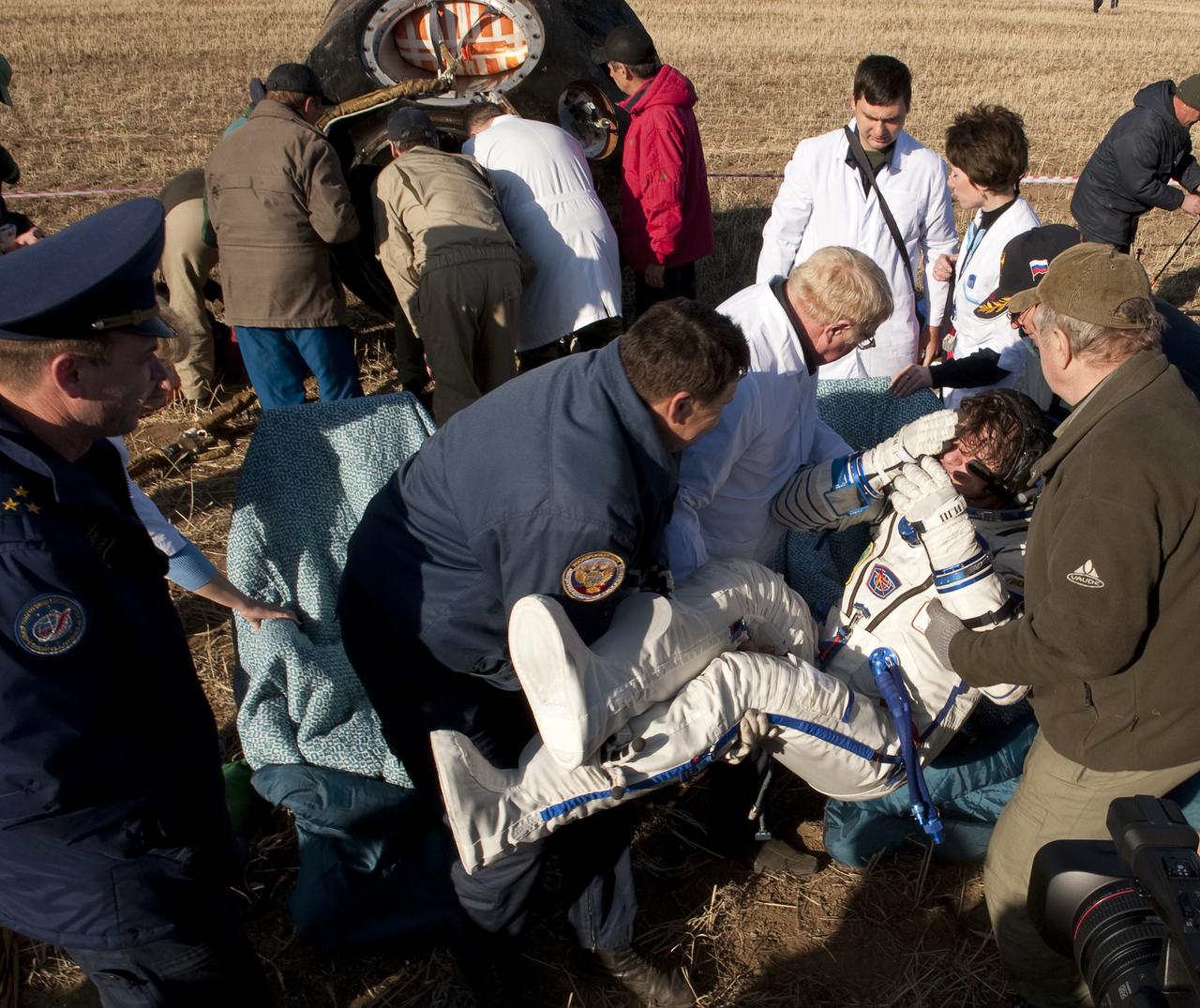

Expedition 20 Commander Gennady Padalka is helped of the Soyuz capsule shortly after he and Spaceflight participant Guy Laliberté, and Expedition 20 Flight Engineer Michael Barratt landed in their Soyuz TMA-14 capsule near the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Sunday, Oct. 11, 2009. Padalka and Barratt are returning from six months onboard the International Space Station, along with Laliberté who arrived at the station on Oct. 2 with Expedition 21 Flight Engineers Jeff Williams and Maxim Suraev aboard the Soyuz TMA-16 spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Expedition 53 Commander Randy Bresnik of NASA is seen holding documents inside the Soyuz Capsule after having landed with Flight Engineers Paolo Nespoli of ESA (European Space Agency) and Sergey Ryazanskiy of the Russian space agency Roscosmos near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Thursday, Dec. 14, 2017. Bresnik, Nespoli and Ryazanskiy are returning after 139 days in space where they served as members of the Expedition 52 and 53 crews onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
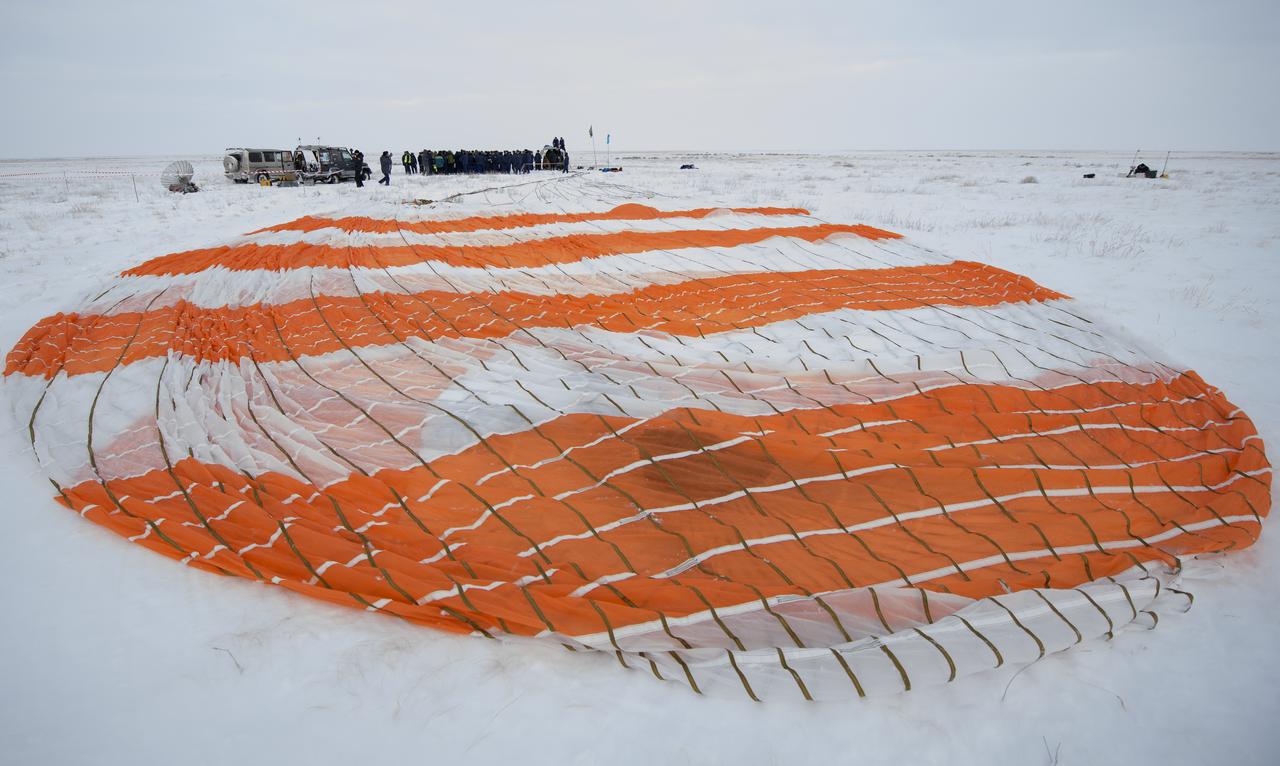

The parachute of the Soyuz MS-09 spacecraft is seen shortly the capsule landed with Expedition 57 crew members Serena Auñón-Chancellor of NASA, Alexander Gerst of ESA (European Space Agency), and Sergey Prokopyev of Roscosmos near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Thursday, Dec. 20, 2018. Auñón-Chancellor, Gerst, and Prokopyev are returning after 197 days in space where they served as members of the Expedition 56 and 57 crews onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
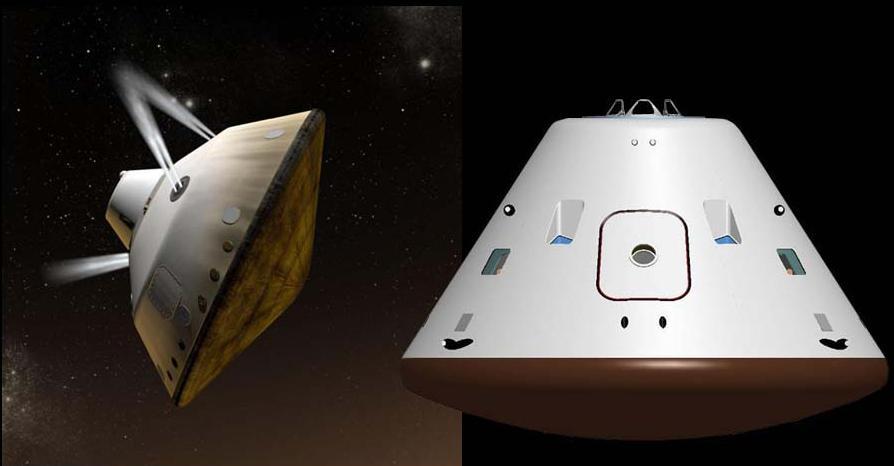
This set of artist concepts shows NASA Mars Science Laboratory cruise capsule and NASA Orion spacecraft, which is being built now at NASA Johnson Space Center and will one day send astronauts to Mars.
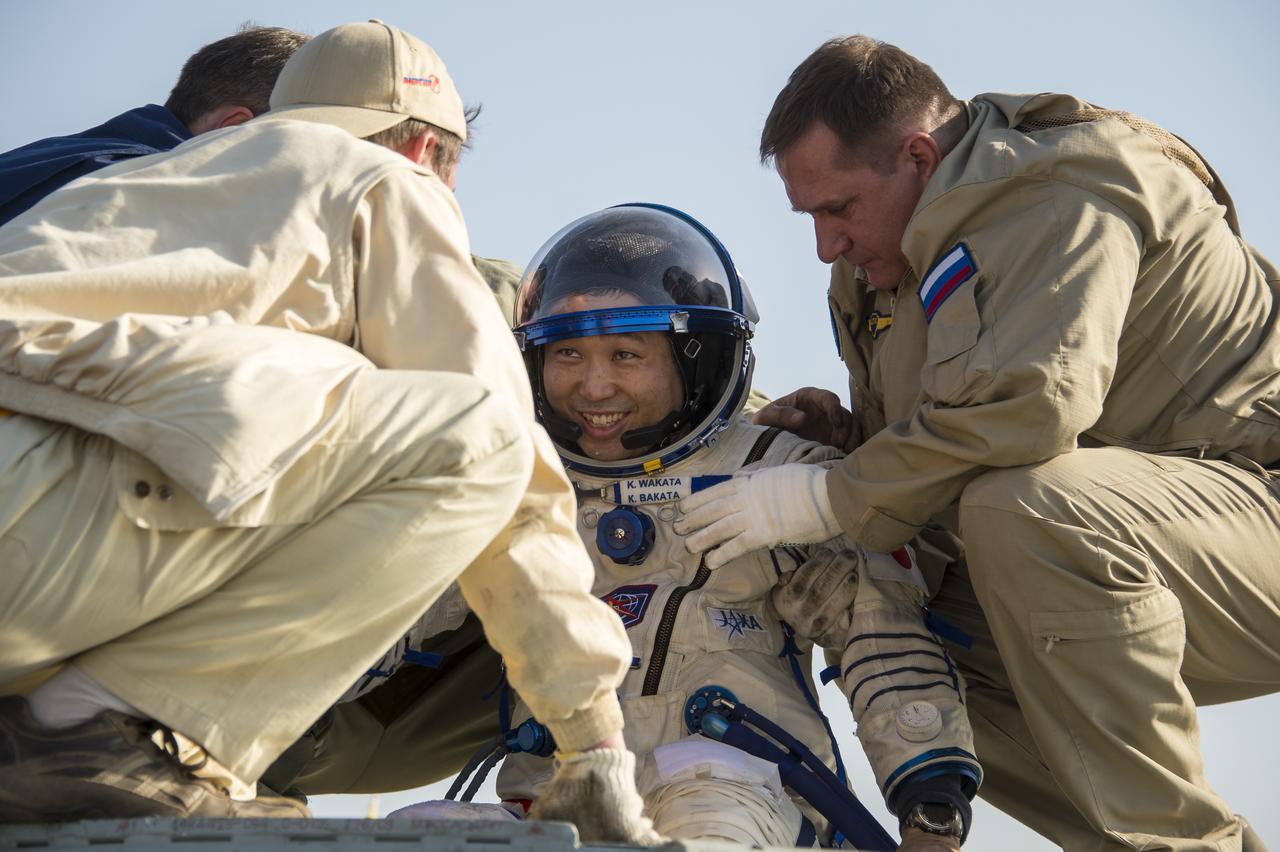

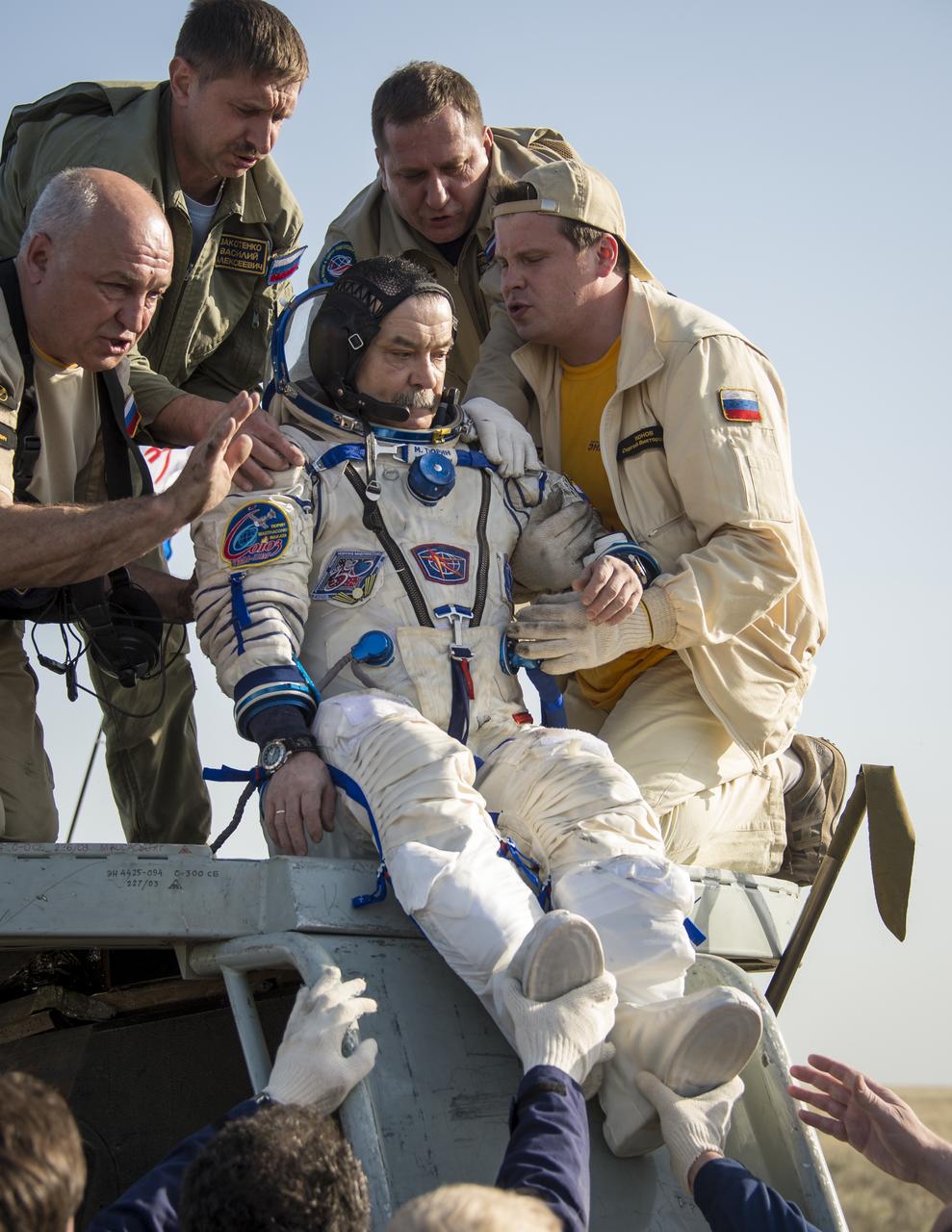
Expedition 39 Commander Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) is helped of the Soyuz Capsule just minutes after he and Soyuz Commander Mikhail Tyurin of Roscosmos, and Flight Engineer Rick Mastracchio of NASA, landed in their Soyuz TMA-11M spacecraft near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Wednesday, May 14, 2014. Wakata, Tyurin and Mastracchio returned to Earth after more than six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 38 and 39 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
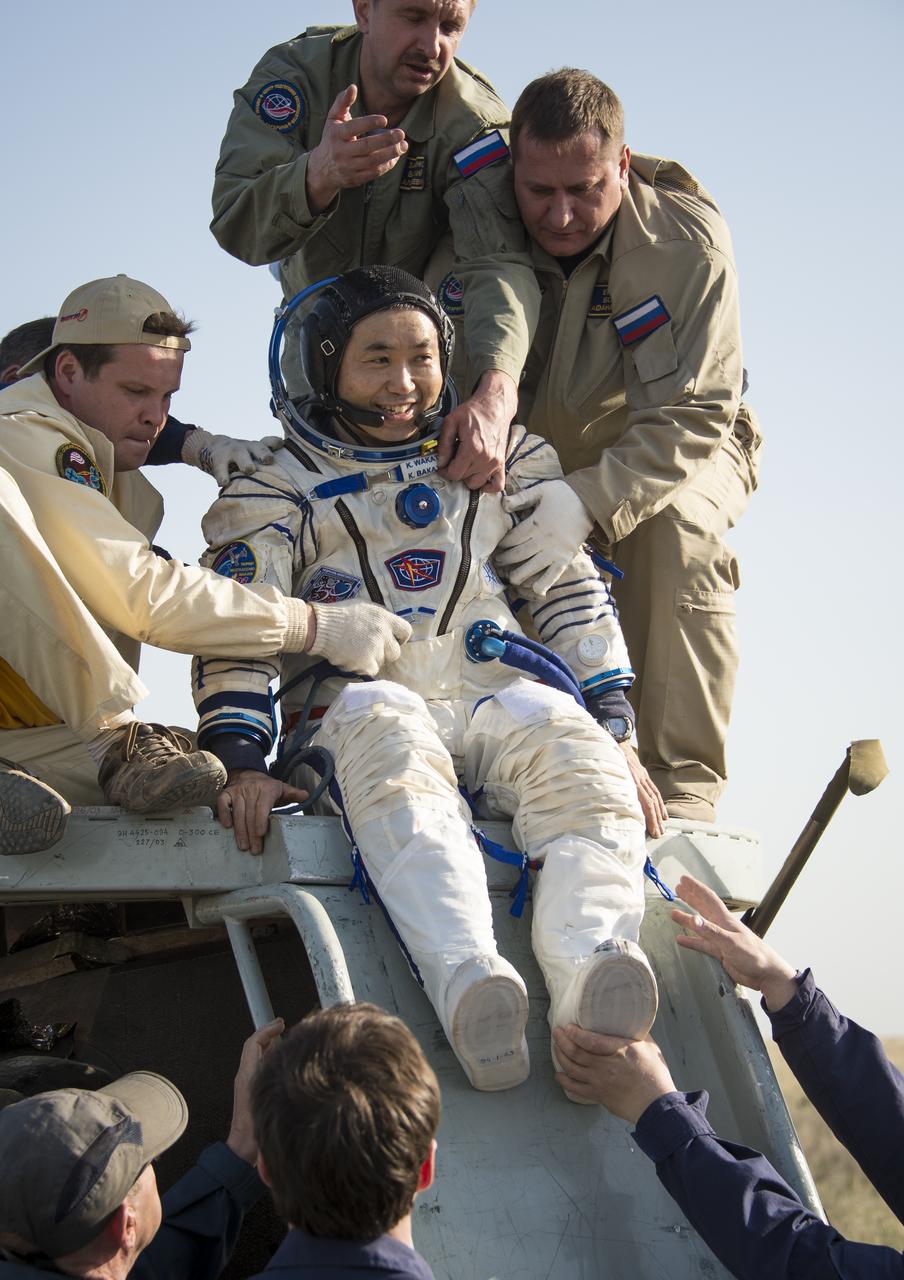

Expedition 39 Commander Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) is helped of the Soyuz Capsule just minutes after he and Soyuz Commander Mikhail Tyurin of Roscosmos, and Flight Engineer Rick Mastracchio of NASA, landed in their Soyuz TMA-11M spacecraft near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Wednesday, May 14, 2014. Wakata, Tyurin and Mastracchio returned to Earth after more than six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 38 and 39 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
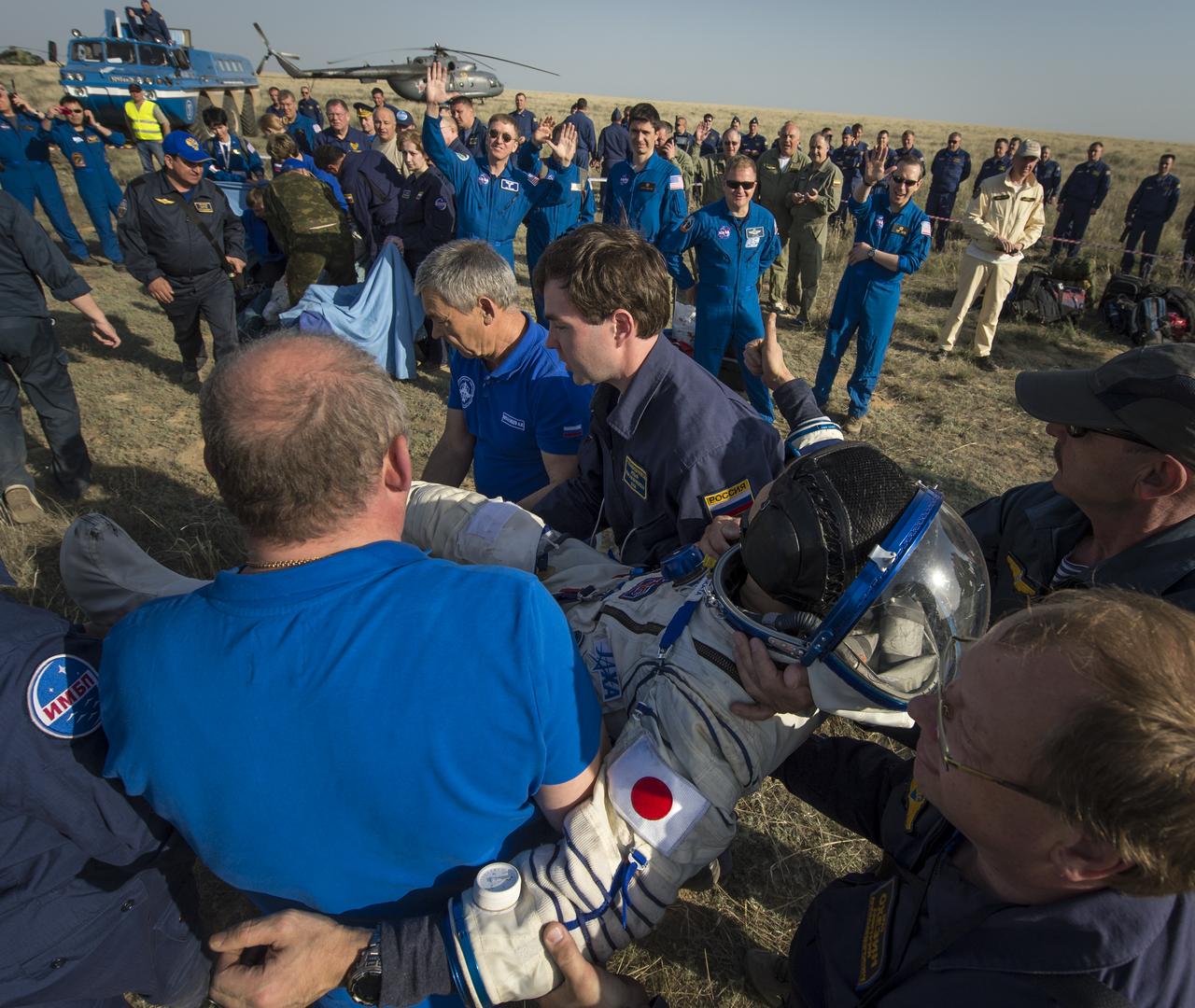

Expedition 39 Commander Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) gives a thumbs up to his NASA and Russian partners as he is carried from the Soyuz Capsule just minutes after he and Soyuz Commander Mikhail Tyurin of Roscosmos, and Flight Engineer Rick Mastracchio of NASA, landed in their Soyuz TMA-11M spacecraft near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Wednesday, May 14, 2014. Wakata, Tyurin and Mastracchio returned to Earth after more than six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 38 and 39 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Soyuz Commander Mikhail Tyurin of Roscosmos is helped out of the Soyuz Capsule just minutes after he and Expedition 39 Commander Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), and Flight Engineer Rick Mastracchio of NASA, landed in their Soyuz TMA-11M spacecraft near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Wednesday, May 14, 2014. Wakata, Tyurin and Mastracchio returned to Earth after more than six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 38 and 39 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
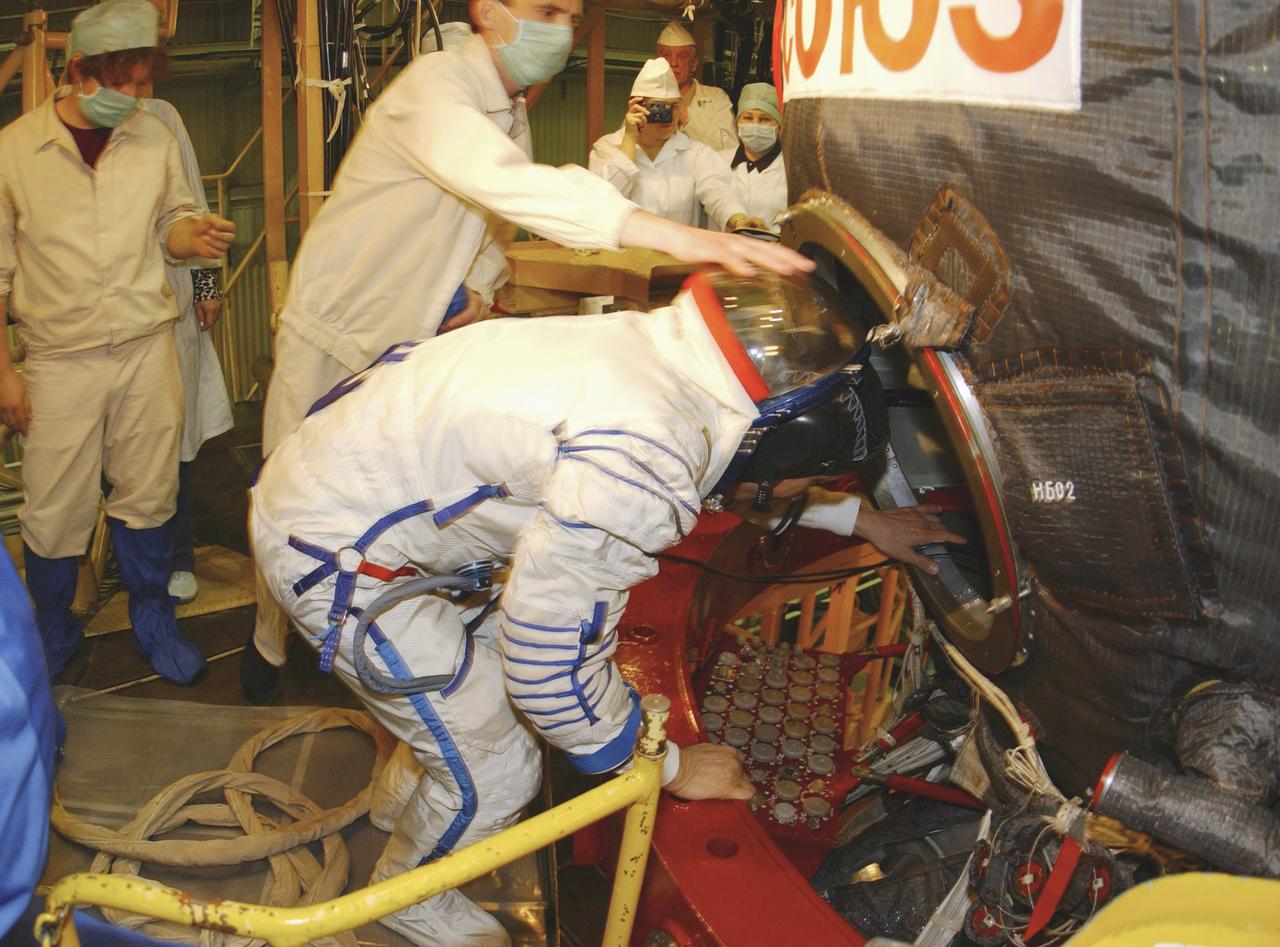

Edward T. Lu, NASA International Space Station Science Officer and Flight Engineer for Expedition 7, enters the Soyuz TMA-2 capsule for inspection and seat liner check in the Soyuz Integration Facility at the Baikonur Cosmodrome, in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Thursday, April 10, 2003. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The Soyuz TMA-19 spacecraft with Expedition 25 Commander Doug Wheelock and Flight Engineers Shannon Walker and Fyodor Yurchikhin is rolled by technicians in order to assist with getting the crew out of the capsule, near Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Friday, Nov. 26, 2010. Russian Cosmonaut Yurchikhin and NASA Astronauts Wheelock and Walker, are returning from nearly six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 24 and 25 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
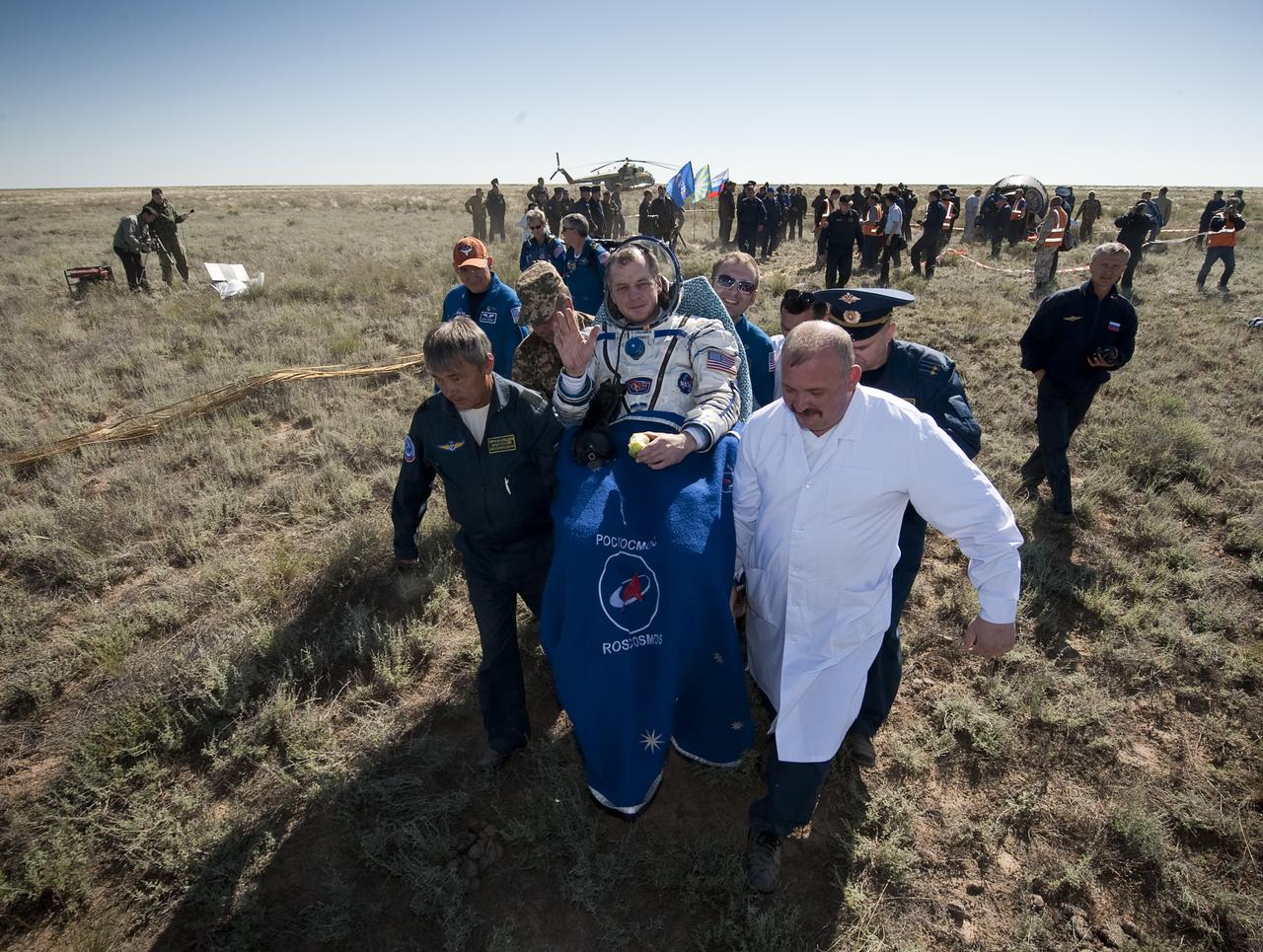

Expedition 23 Flight Engineer T.J. Creamer is carried in a chair to the medical tent just minutes after he and fellow crew members Soichi Noguchi and Commander Oleg Kotov landed in their Soyuz TMA-17 capsule near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Wednesday, June 2, 2010. NASA Astronaut Creamer, Russian Cosmonaut Kotov and Japanese Astronaut Noguchi are returning from six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 22 and 23 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
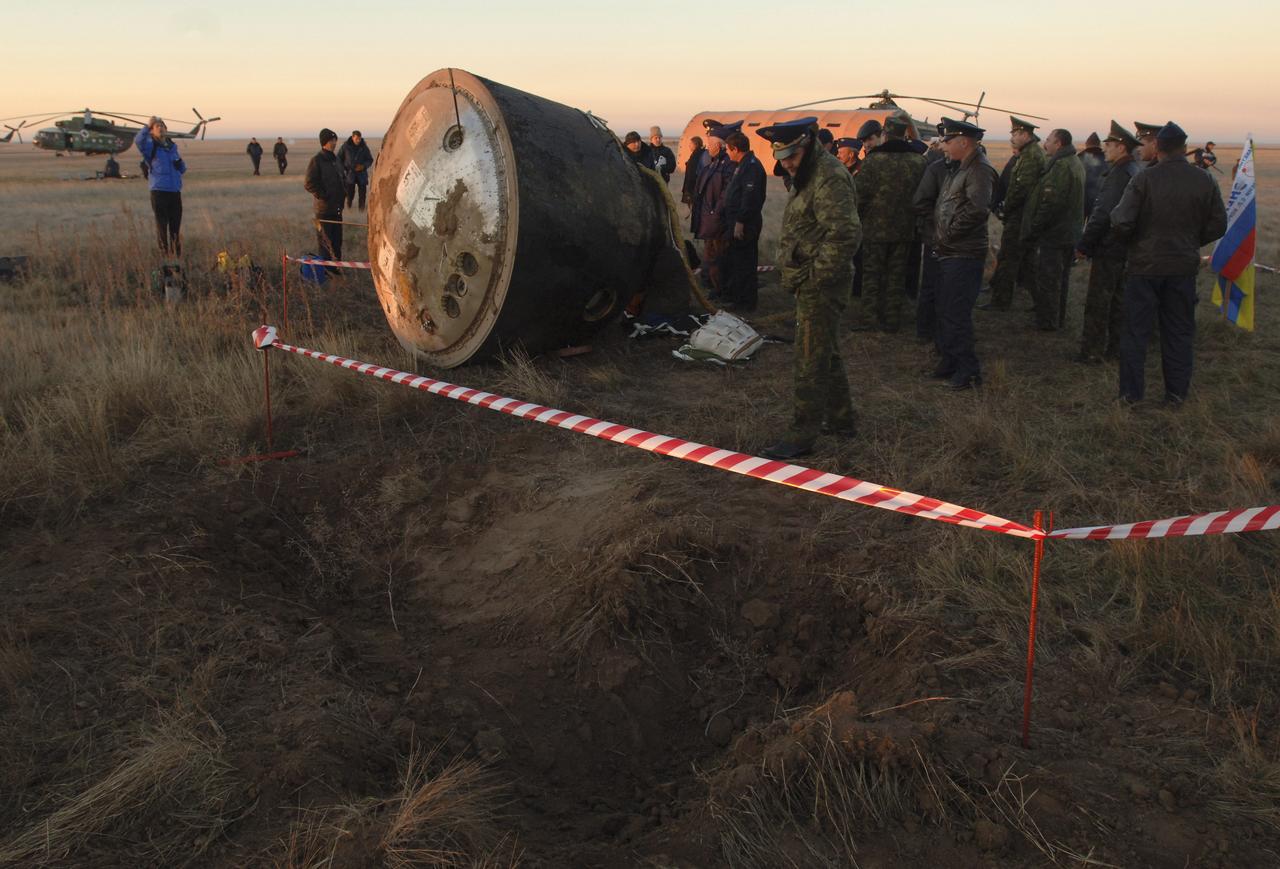

Divits made by the landing jets of the Soyuz capsule, background, are seen after touchdown, Tuesday, Oct. 11, 2005, near Arlalyk, Kazakhstan. Members of the 11th expedition to the international space station, astronaut John Phillips and cosmonaut Sergei Krikalev landed after a six-month mission in orbit. Along with American businessman Greg Olsen, who visited the station for more than a week, Phillips and Krikalev returned to Earth aboard a Russian Soyuz spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
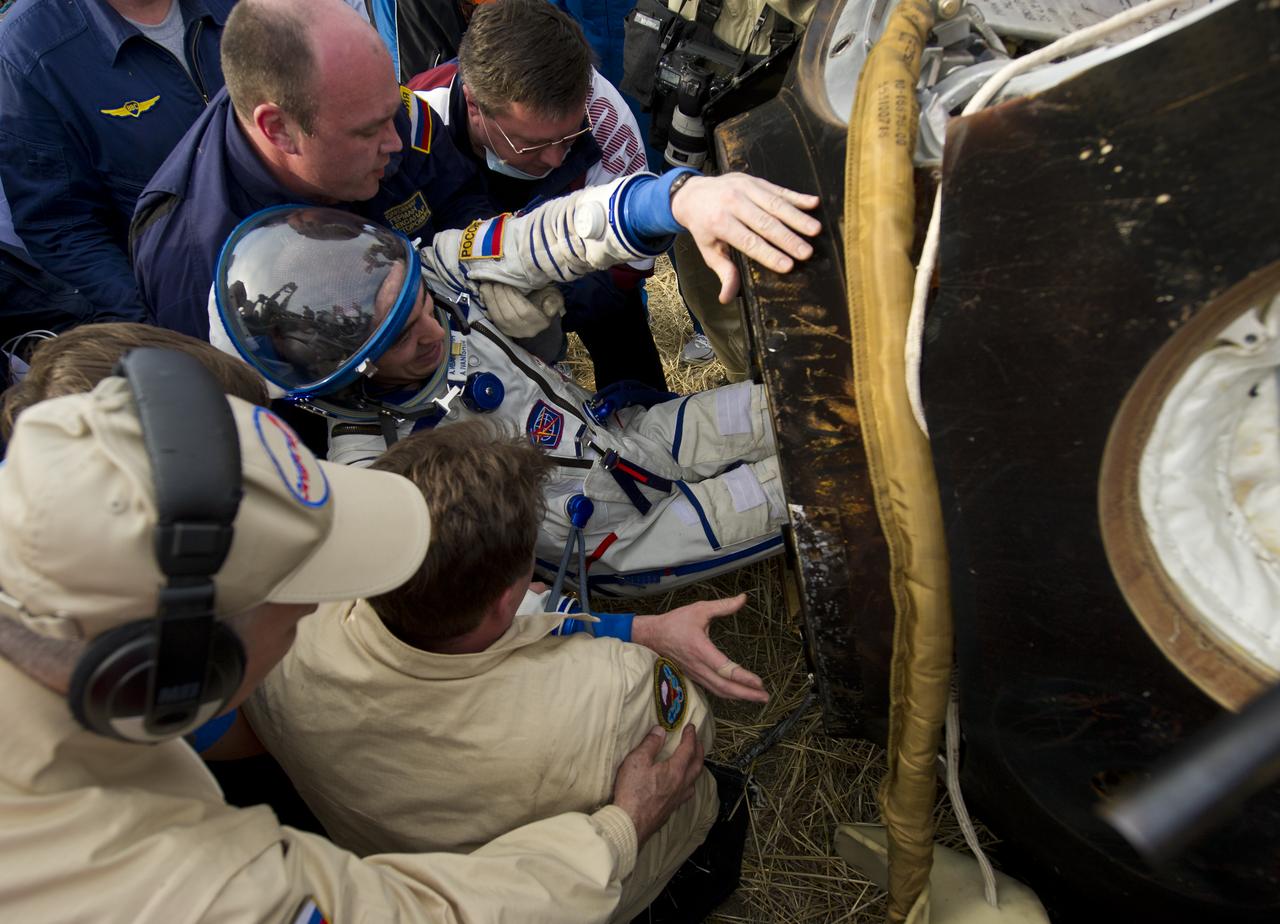

Expedition 30 flight engineer and Russian cosmonaut Anatoly Ivanishin is seen as he is extracted from the Soyuz TMA-22 spacecraft shortly after the capsule landed with Expedition 30 Commander Dan Burbank and flight engineer Anton Shkaplerov in a remote area outside of the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Friday, April 27, 2012. Ivanishin, Burbank and Shkaplerov are returning from more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 29 and 30 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
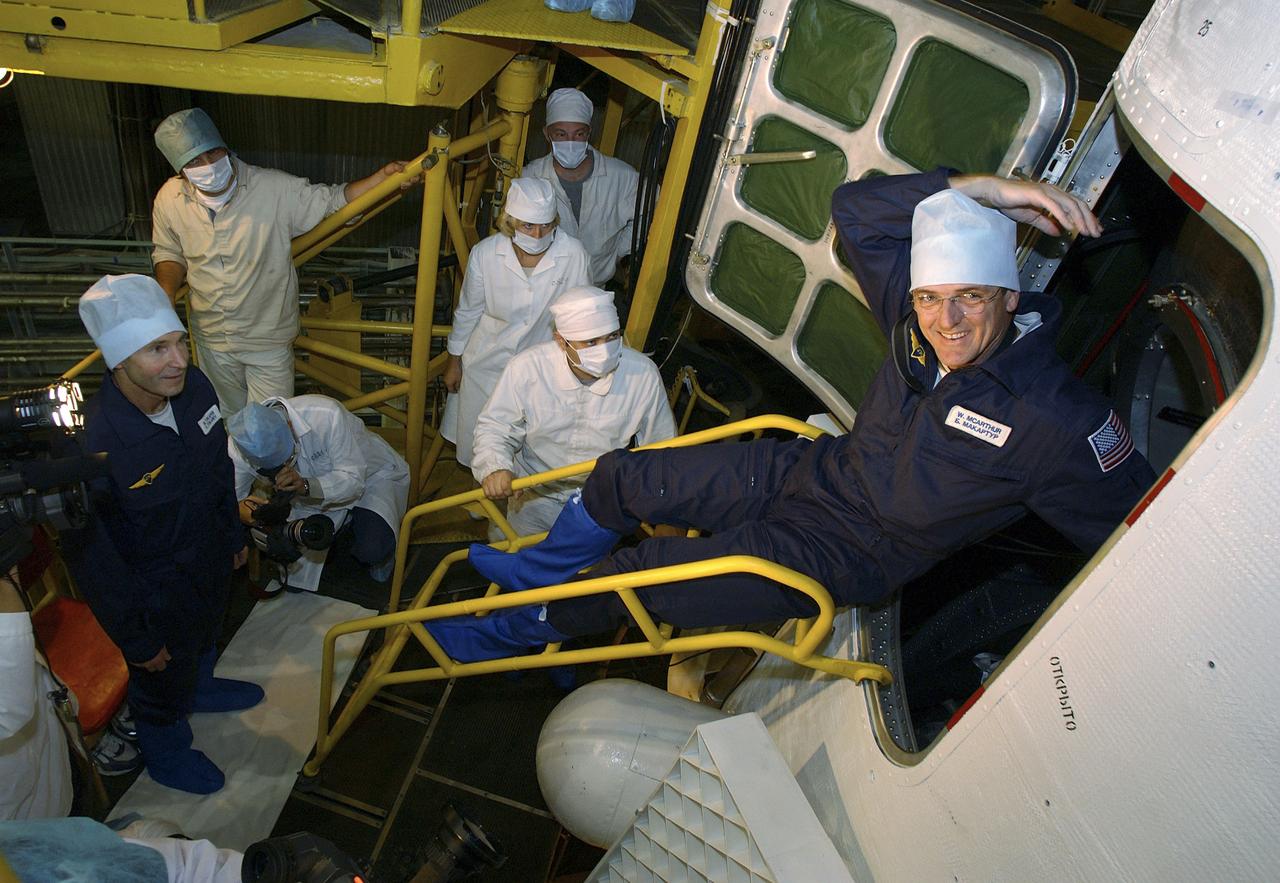

Expedition 10 backup Soyuz Commander Valery Tokarev, left, watches backup Expedition 10 Commander Bill McArthur exit the Soyuz capsule after their final check of the spacecraft Saturday, October 9, 2004 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 10 is scheduled to launch October 14 on the Soyuz TMA-5 spacecraft to the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
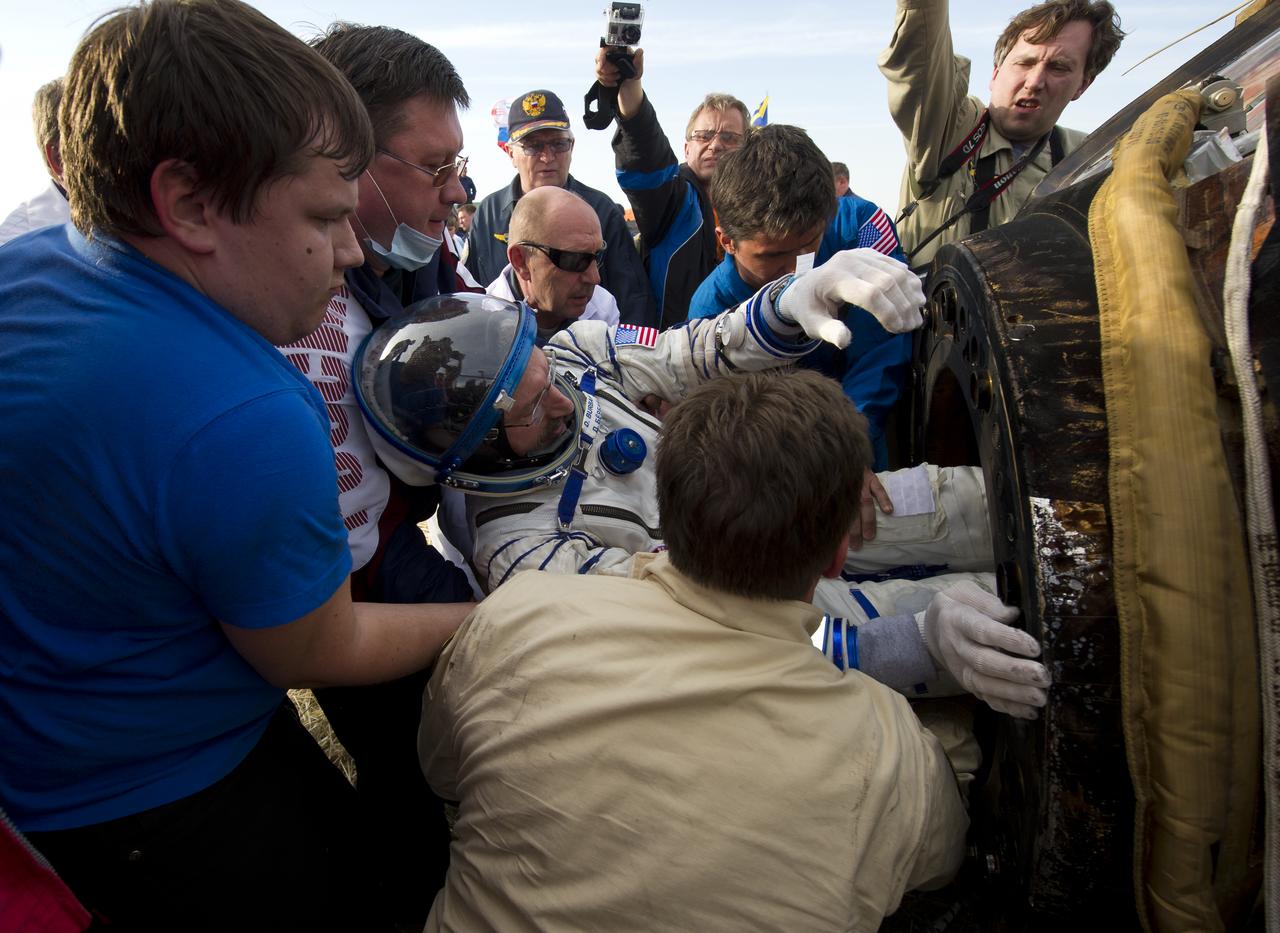

Expedition 30 Commander Dan Burbank is seen as he is extracted from the Soyuz TMA-22 spacecraft shortly after the capsule landed with Russian flight engineers Anton Shkaplerov and Anatoly Ivanishin in a remote area outside of the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Friday, April 27, 2012. Burbank, Ivanishin, and Shkaplerov are returning from more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 29 and 30 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
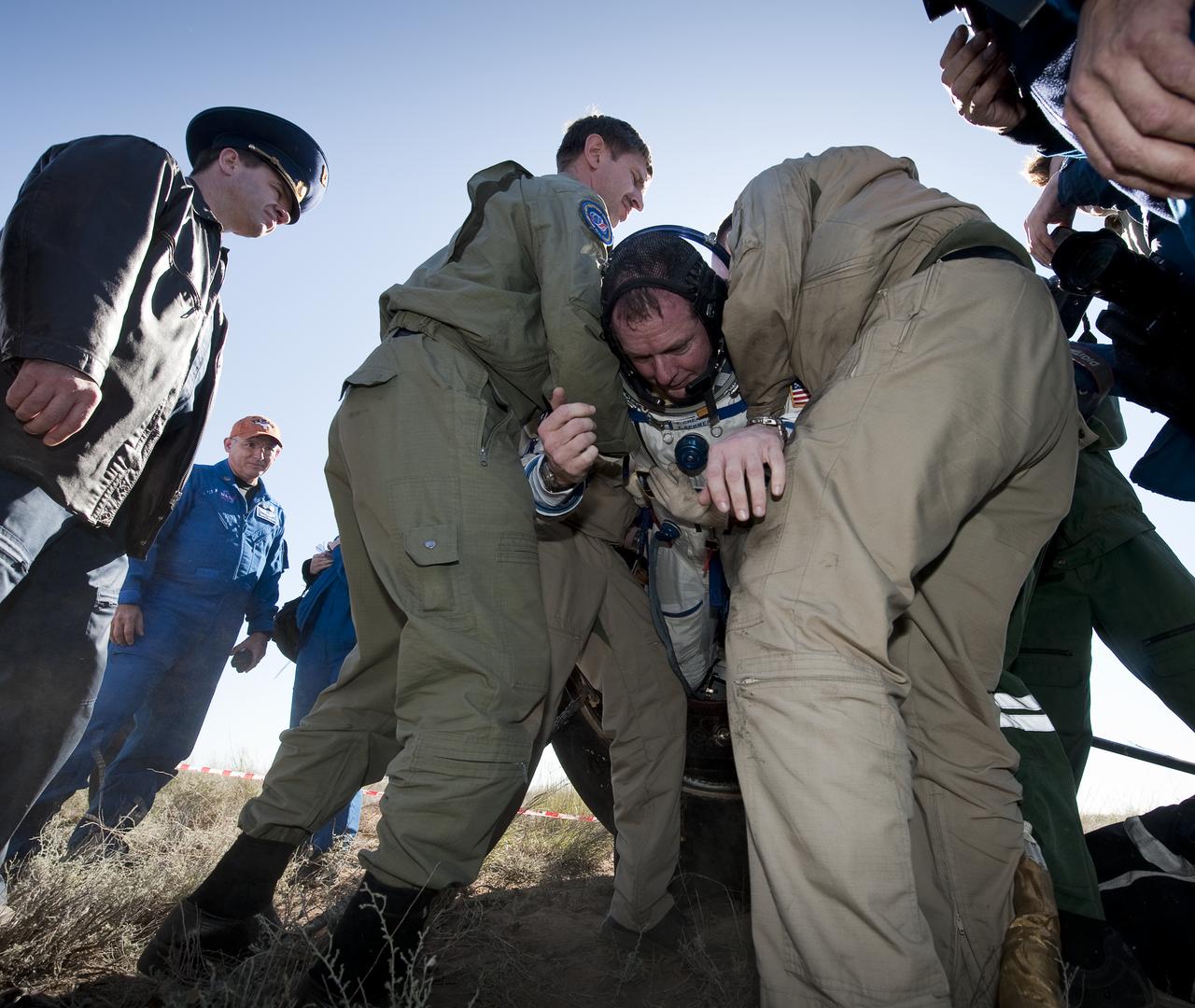

Expedition 23 Flight Engineer T.J. Creamer is helped out of the Soyuz TMA-17 capsule just minutes after he and fellow crew members Soichi Noguchi and Commander Oleg Kotov landed near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Wednesday, June 2, 2010. NASA Astronaut Creamer, Russian Cosmonaut Kotov and Japanese Astronaut Noguchi are returning from six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 22 and 23 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, and SpaceX CEO and Chief Designer Elon Musk, view the historic Dragon capsule that returned to Earth on May 31 following the first successful mission by a private company to carry supplies to the International Space Station on Wednesday, June 13, 2012 at the SpaceX facility in McGregor, Texas. Bolden and Musk also thanked the more than 150 SpaceX employees working at the McGregor facility for their role in the historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, and SpaceX CEO and Chief Designer Elon Musk, view the historic Dragon capsule that returned to Earth on May 31 following the first successful mission by a private company to carry supplies to the International Space Station on Wednesday, June 13, 2012 at the SpaceX facility in McGregor, Texas. Bolden and Musk also thanked the more than 150 SpaceX employees working at the McGregor facility for their role in the historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
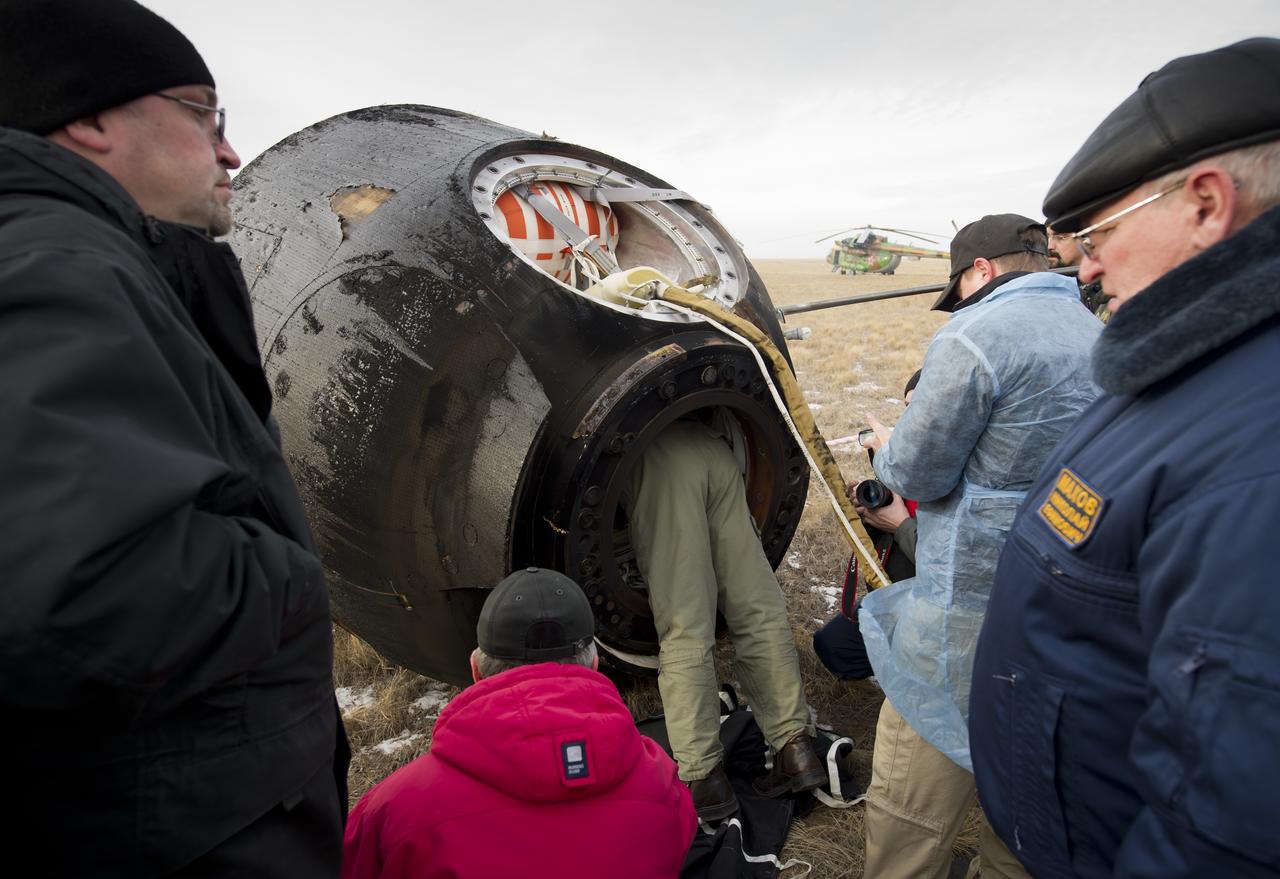

A technician enters the Soyuz TMA-19 spacecraft with Expedition 25 Commander Doug Wheelock and Flight Engineers Shannon Walker and Fyodor Yurchikhin in order to assist with getting the crew out of the capsule, near Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Friday, Nov. 26, 2010. Russian Cosmonaut Yurchikhin and NASA Astronauts Wheelock and Walker, are returning from nearly six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 24 and 25 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, and SpaceX CEO and Chief Designer Elon Musk, view the historic Dragon capsule that returned to Earth on May 31 following the first successful mission by a private company to carry supplies to the International Space Station on Wednesday, June 13, 2012 at the SpaceX facility in McGregor, Texas. Bolden and Musk also thanked the more than 150 SpaceX employees working at the McGregor facility for their role in the historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
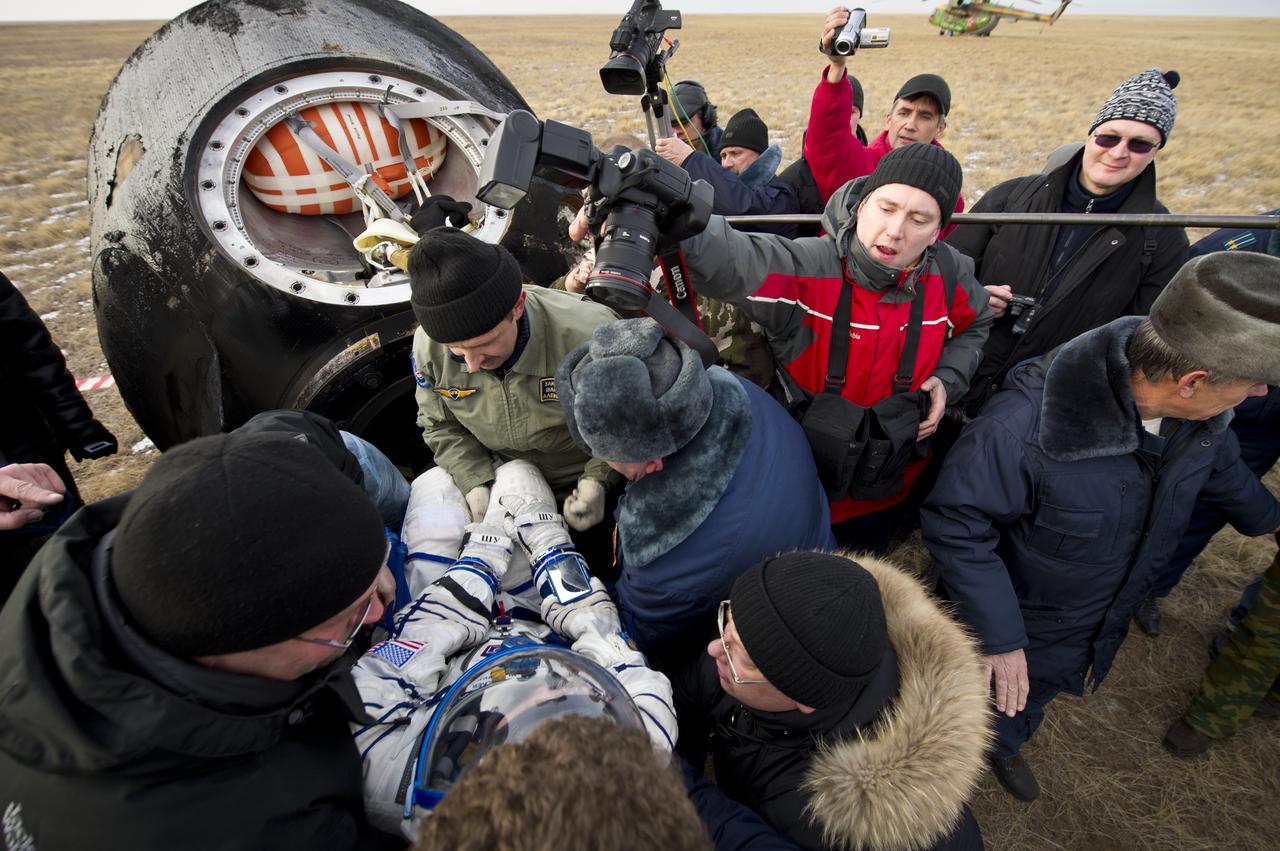

Engineer Shannon Walker out of the Soyuz TMA-19 spacecraft shortly after the capsule landed with her, Expedition 25 Commander Doug Wheelock and Flight Engineer Fyodor Yurchikhin near Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Friday, Nov. 26, 2010. Russian Cosmonaut Yurchikhin and NASA Astronauts Wheelock and Walker, are returning from nearly six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 24 and 25 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
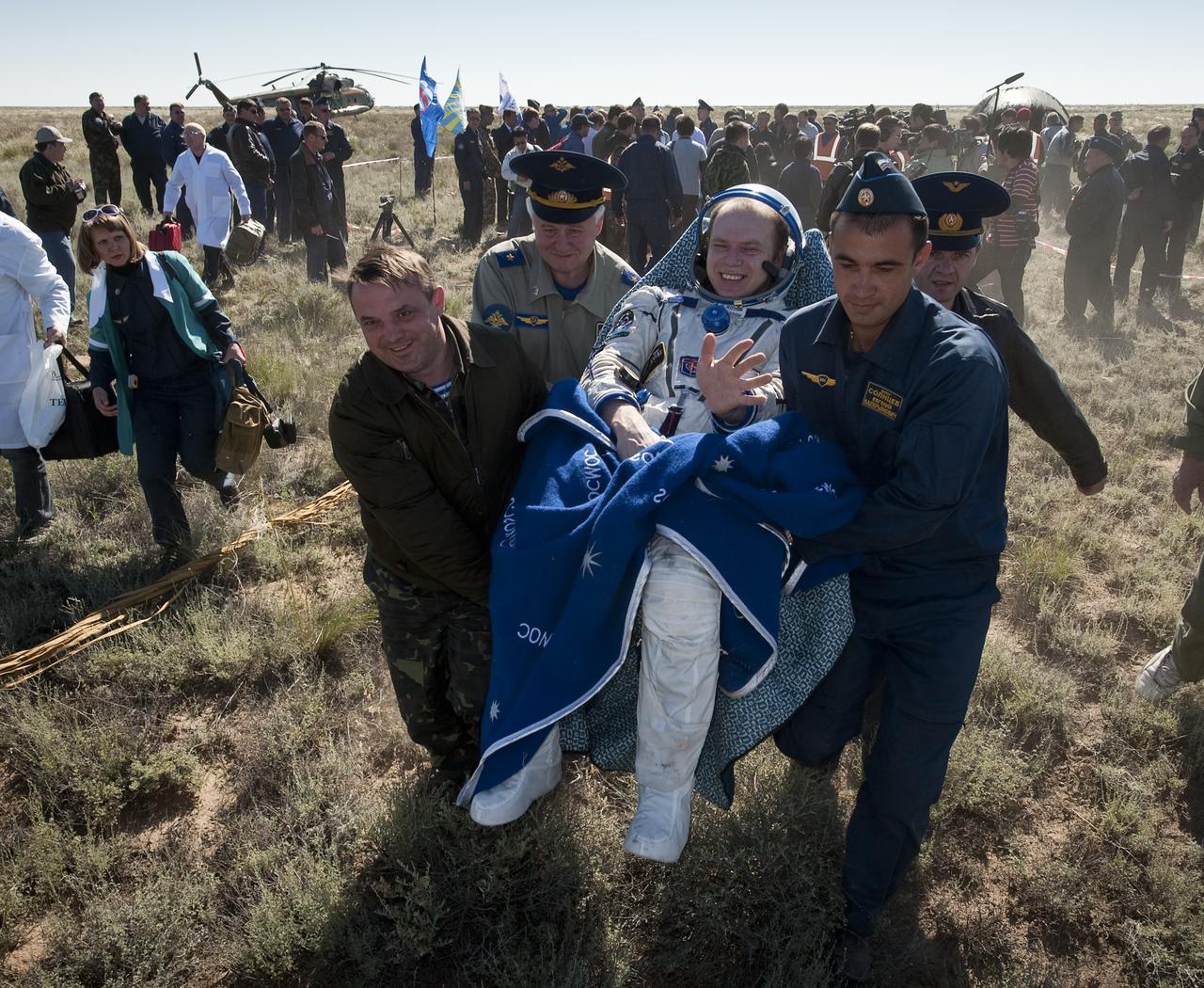

Expedition 23 Commander Oleg Kotov is carried in a chair to the medical tent just minutes after he and fellow crew members T.J. Creamer and Soichi Noguchi landed in their Soyuz TMA-17 capsule near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Wednesday, June 2, 2010. NASA Astronaut Creamer, Russian Cosmonaut Kotov and Japanese Astronaut Noguchi are returning from six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 22 and 23 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, and SpaceX CEO and Chief Designer Elon Musk, view the historic Dragon capsule that returned to Earth on May 31 following the first successful mission by a private company to carry supplies to the International Space Station on Wednesday, June 13, 2012 at the SpaceX facility in McGregor, Texas. Bolden and Musk also thanked the more than 150 SpaceX employees working at the McGregor facility for their role in the historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
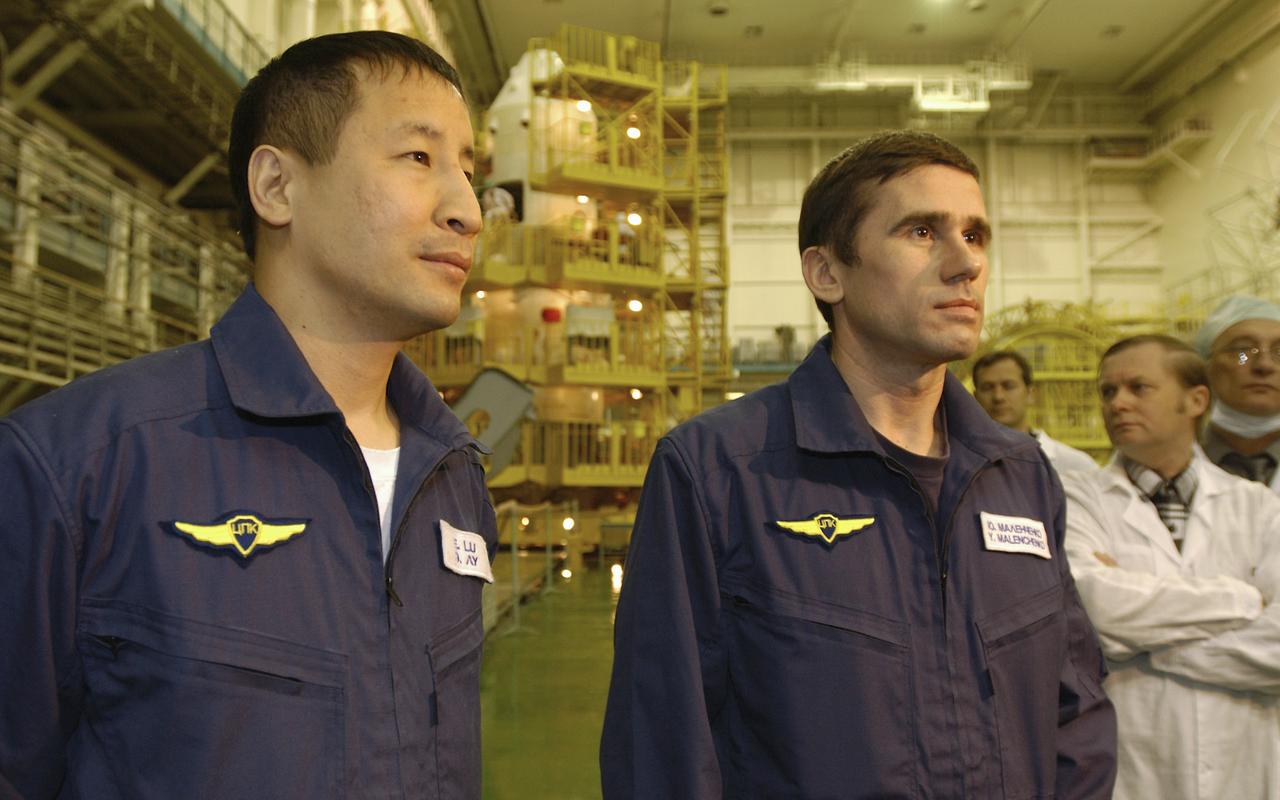

Expedition 7 NASA International Space Station Science Officer and Flight Engineer Edward T. Lu, left and Commander Yuri I. Malenchenko stop to take questions after their final check of the Soyuz capsule prior to their scheduled launch on Saturday April 26, 2003 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Tuesday, April 22. 2003. Photo credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, congratulates SpaceX CEO and Chief Designer Elon Musk in front of the historic Dragon capsule that returned to Earth on May 31 following the first successful mission by a private company to carry supplies to the International Space Station on Wednesday, June 13, 2012 at the SpaceX facility in McGregor, Texas. Bolden and Musk also thanked the more than 150 SpaceX employees working at the McGregor facility for their role in the historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

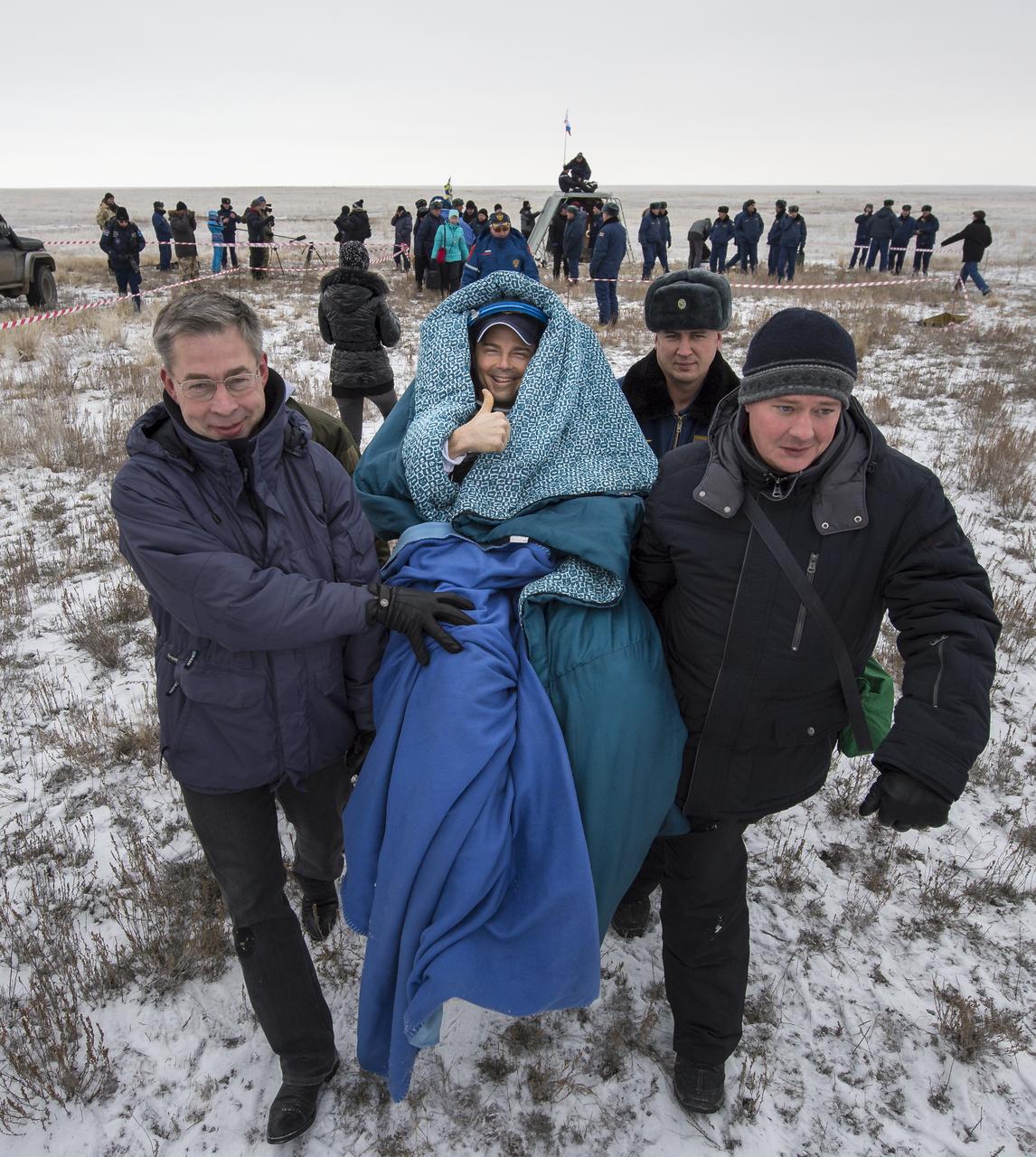
Expedition 41 Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency (ESA) is carried in a chair to a medical tent after he and Expedition 41 Commander Max Suraev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), and NASA Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman landed in their Soyuz TMA-13M capsule in a remote area near the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Monday, Nov. 10, 2014. Suraev, Wiseman and Gerst returned to Earth after more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 40 and 41 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

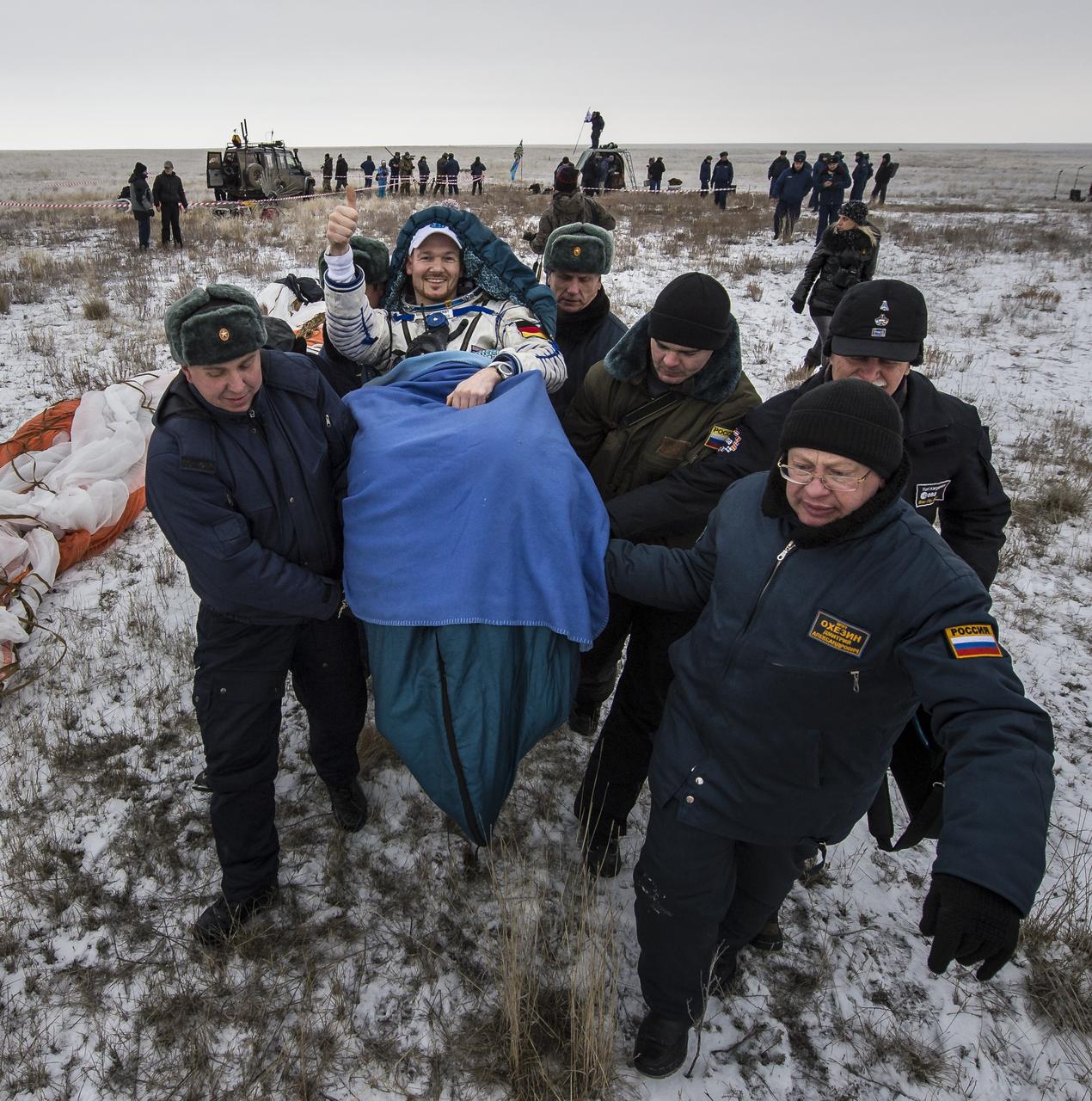
Expedition 41 Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman of NASA is carried in a chair to a medical tent after he and Expedition 41 Commander Max Suraev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) and Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency (ESA) landed in their Soyuz TMA-13M capsule in a remote area near the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Monday, Nov. 10, 2014. Suraev, Wiseman and Gerst returned to Earth after more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 40 and 41 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
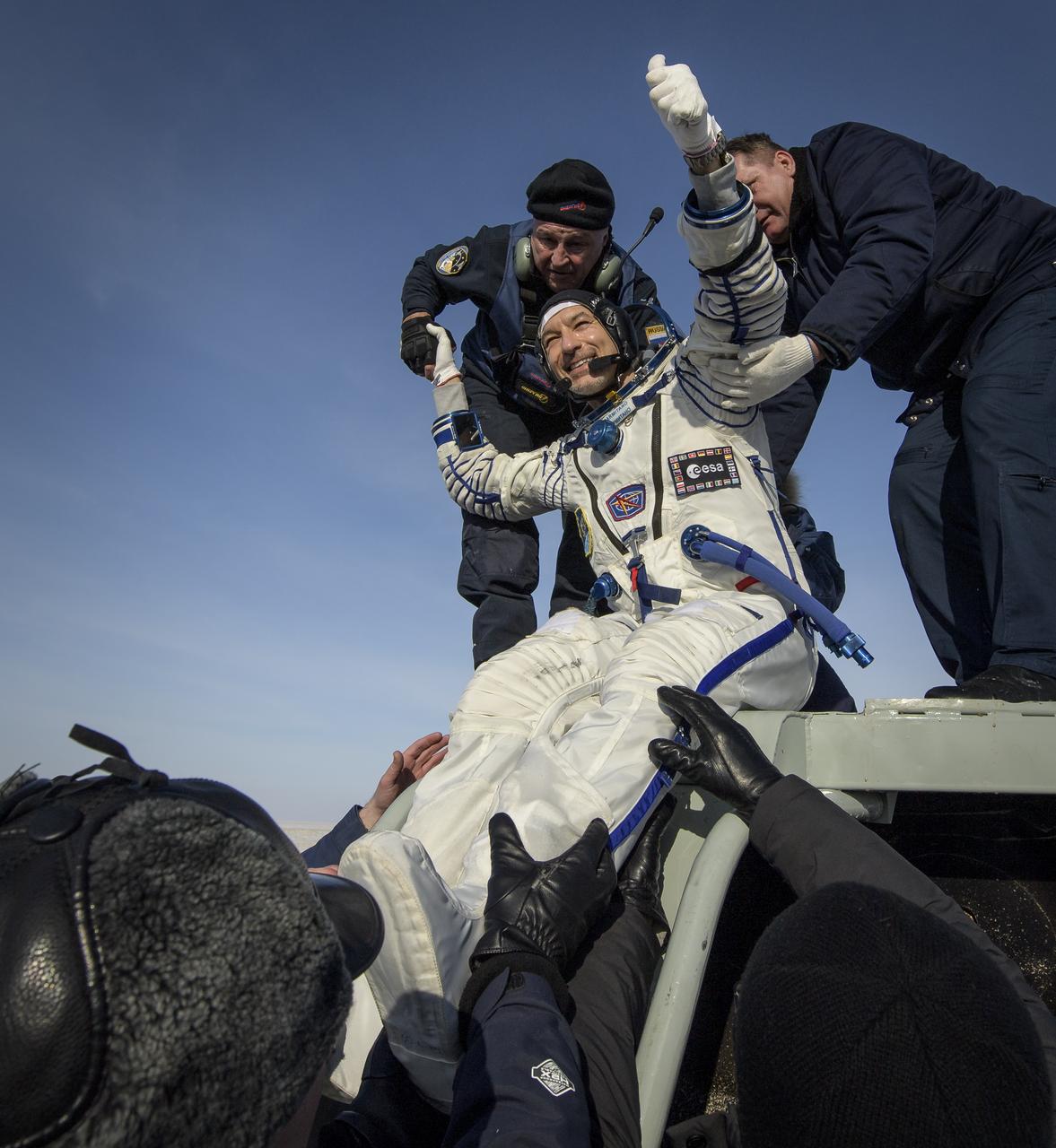

ESA astronaut Luca Parmitano is helped out of the Soyuz MS-13 spacecraft just minutes after he, NASA astronaut Christina Koch, and Roscosmos cosmonaut Alexander Skvortsov, landed their Soyuz MS-13 capsule in a remote area near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Thursday, Feb. 6, 2020. Koch returned to Earth after logging 328 days in space --- the longest spaceflight in history by a woman --- as a member of Expeditions 59-60-61 on the International Space Station. Skvortsov and Parmitano returned after 201 days in space where they served as Expedition 60-61 crew members onboard the station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, and SpaceX CEO and Chief Designer Elon Musk, view the historic Dragon capsule, right, that returned to Earth on May 31 following the first successful mission by a private company to carry supplies to the International Space Station on Wednesday, June 13, 2012 at the SpaceX facility in McGregor, Texas. Bolden and Musk also thanked the more than 150 SpaceX employees working at the McGregor facility for their role in the historic mission. Some of the 1,367 pounds of cargo the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft returned to Earth from the space station are seen in a clean room to the left. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
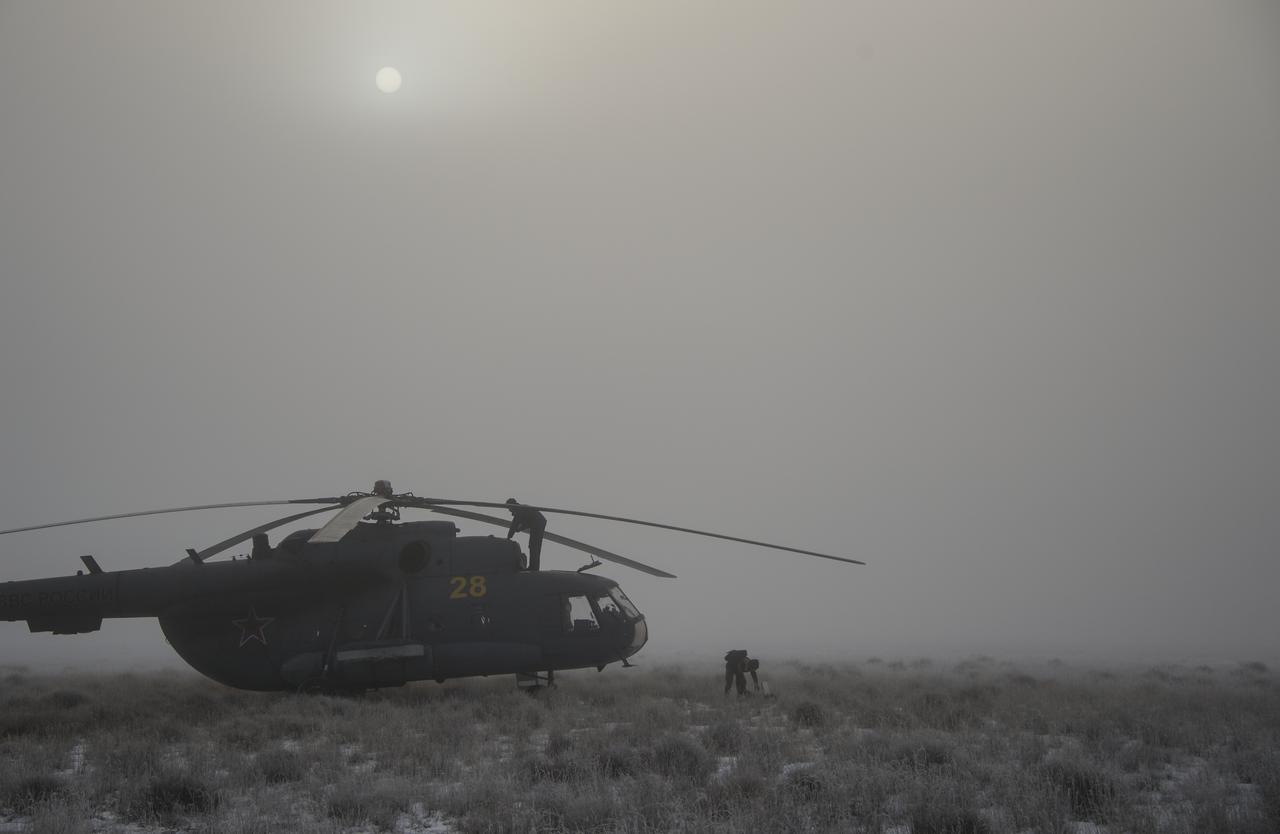

Russian MI-8 helicopter personnel work on their helicopters at the Soyuz TMA-14M spacecraft landing site shortly after the capsule landed with Expedition 42 commander Barry Wilmore of NASA, Alexander Samokutyaev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) and Elena Serova of Roscosmos near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Thursday, March 12, 2015. NASA Astronaut Wilmore, Russian Cosmonauts Samokutyaev and Serova are returning after almost six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 41 and 42 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
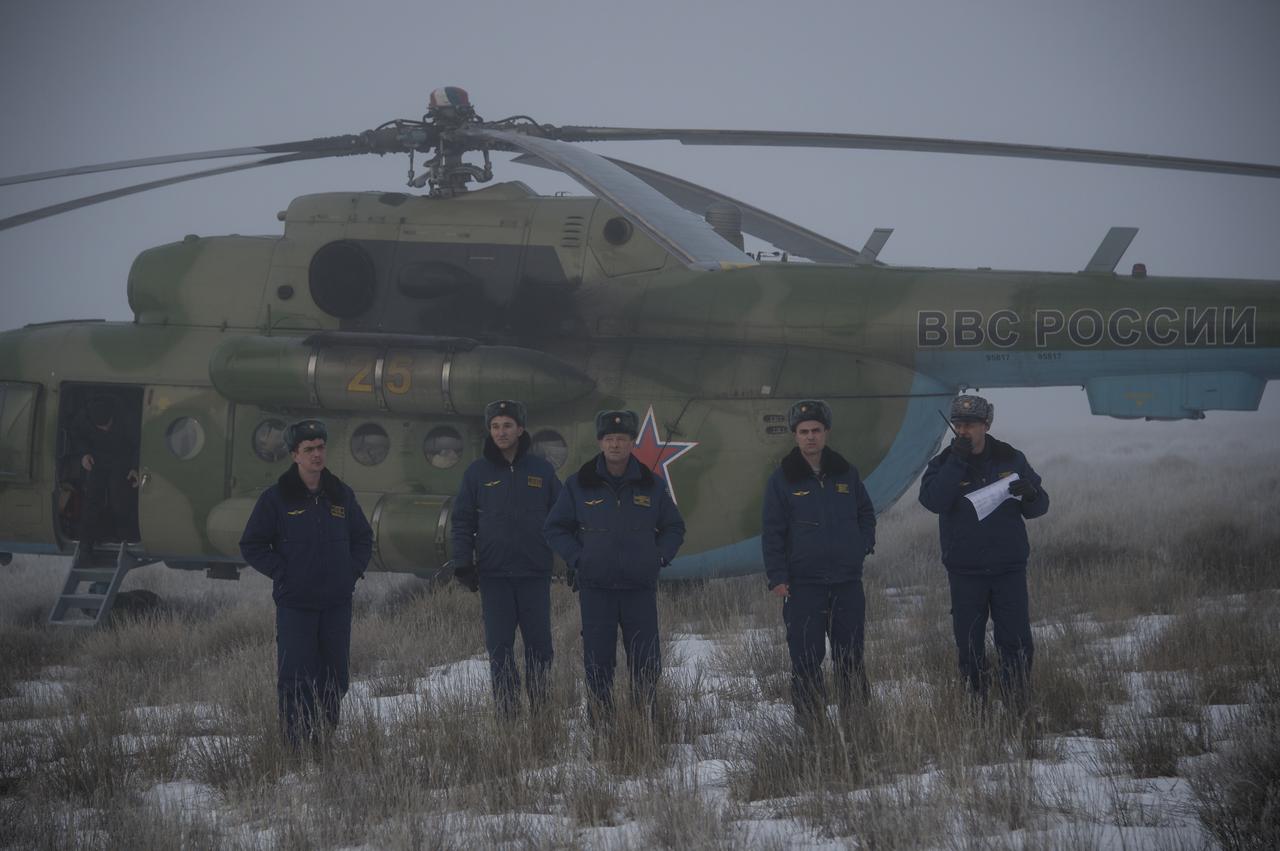

Russian MI-8 helicopter personnel look on at the Soyuz TMA-14M spacecraft landing site shortly after the capsule landed with Expedition 42 commander Barry Wilmore of NASA, Alexander Samokutyaev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) and Elena Serova of Roscosmos near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Thursday, March 12, 2015. NASA Astronaut Wilmore, Russian Cosmonauts Samokutyaev and Serova are returning after almost six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 41 and 42 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
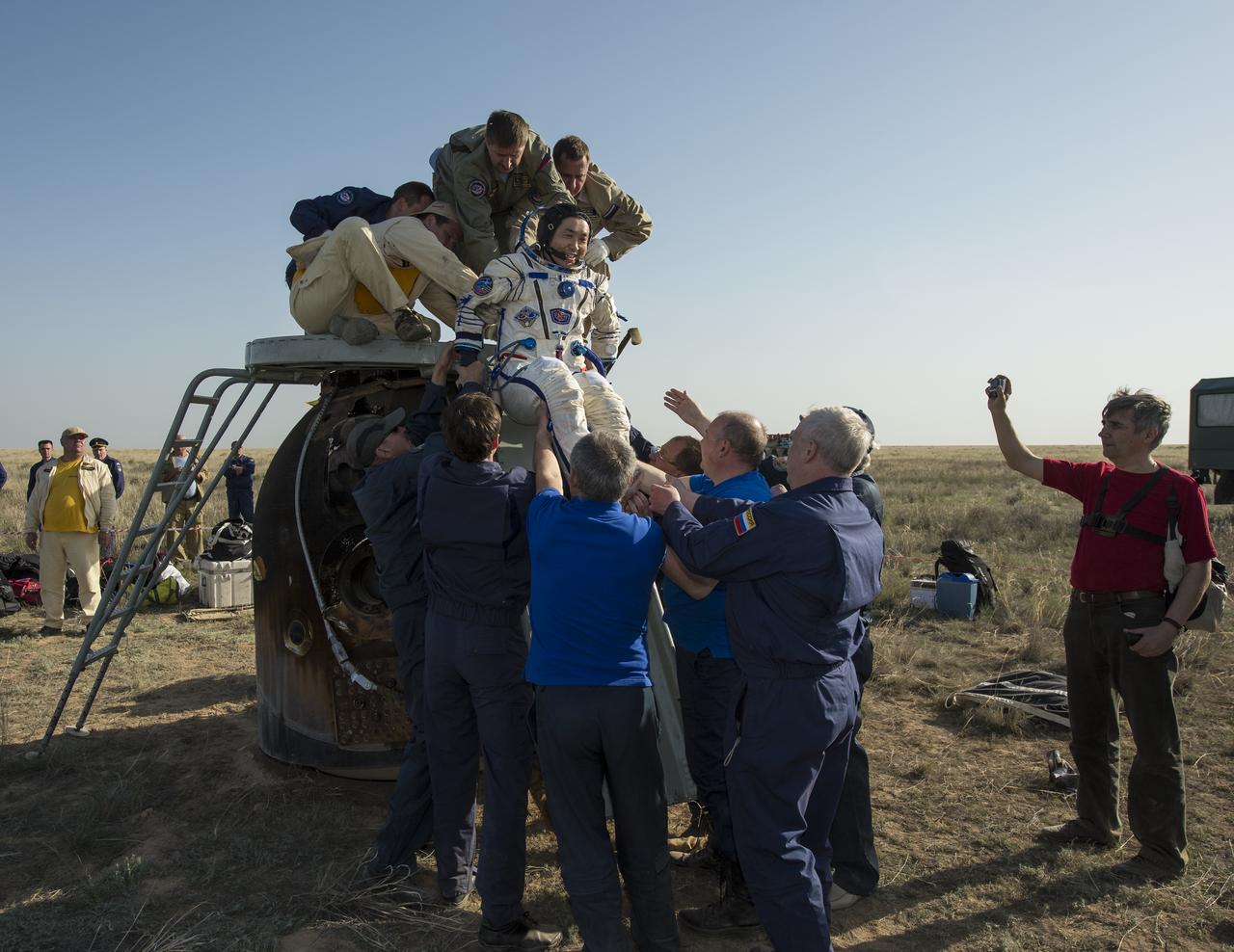

Expedition 39 Commander Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) is helped of the Soyuz Capsule just minutes after he and Soyuz Commander Mikhail Tyurin of Roscosmos, and Flight Engineer Rick Mastracchio of NASA, landed in their Soyuz TMA-11M spacecraft near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Wednesday, May 14, 2014. Wakata, Tyurin and Mastracchio returned to Earth after more than six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 38 and 39 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Russian Search and Rescue teams and medical personnel help Expedition 25 Commander Doug Wheelock out of the Soyuz TMA-19 spacecraft shortly after the capsule landed with him, Expedition 25 Flight Engineer Shannon Walker and Flight Engineer Fyodor Yurchikhin near Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Friday, Nov. 26, 2010. Russian Cosmonaut Yurchikhin and NASA Astronauts Wheelock and Walker, are returning from nearly six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 24 and 25 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
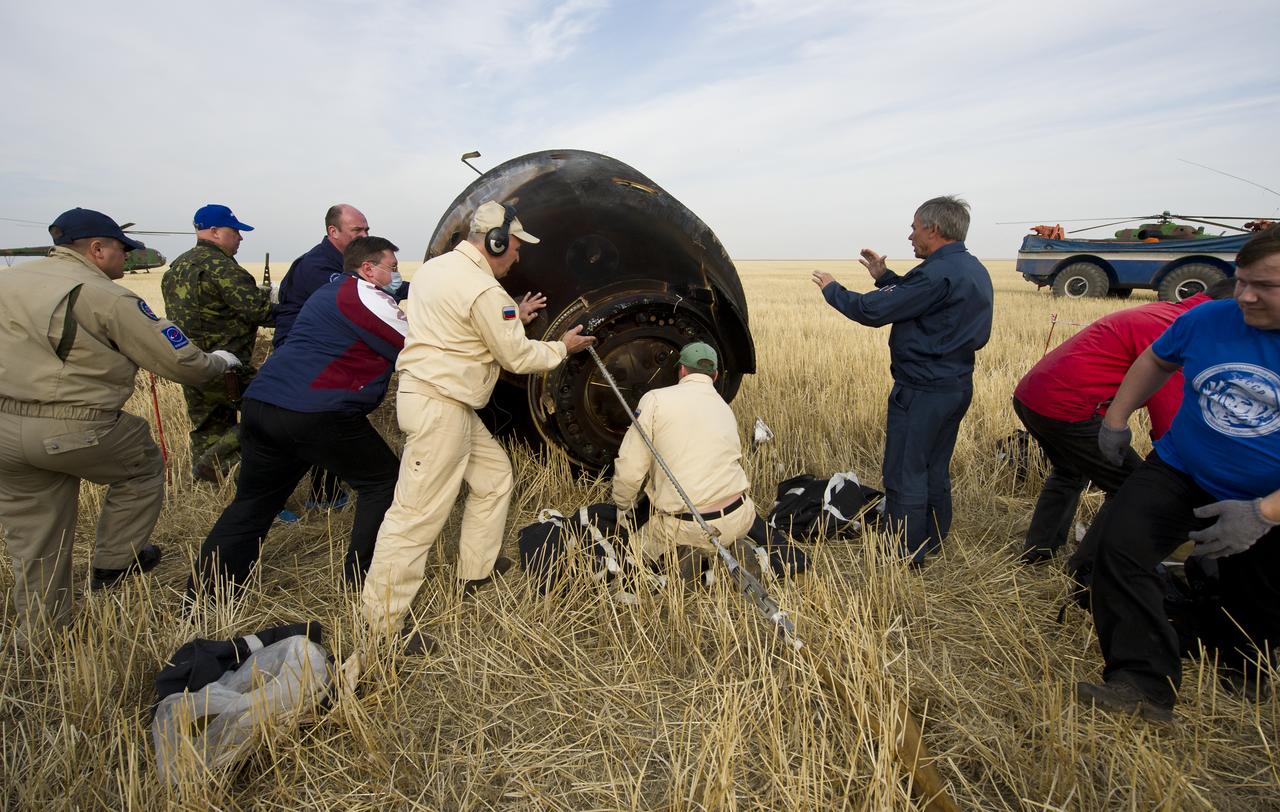

Russian support personnel work to help get crew members out of the Soyuz TMA-22 spacecraft shortly after the capsule landed with Expedition 30 Commander Dan Burbank, and Flight Engineers Anton Skhaplerov and Anatoly Ivanishin in a remote area outside of the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan, on Friday, April 27, 2012. NASA Astronaut Burbank, Russian Cosmonauts Shkaplerov and Ivanishin are returning from more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 29 and 30 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
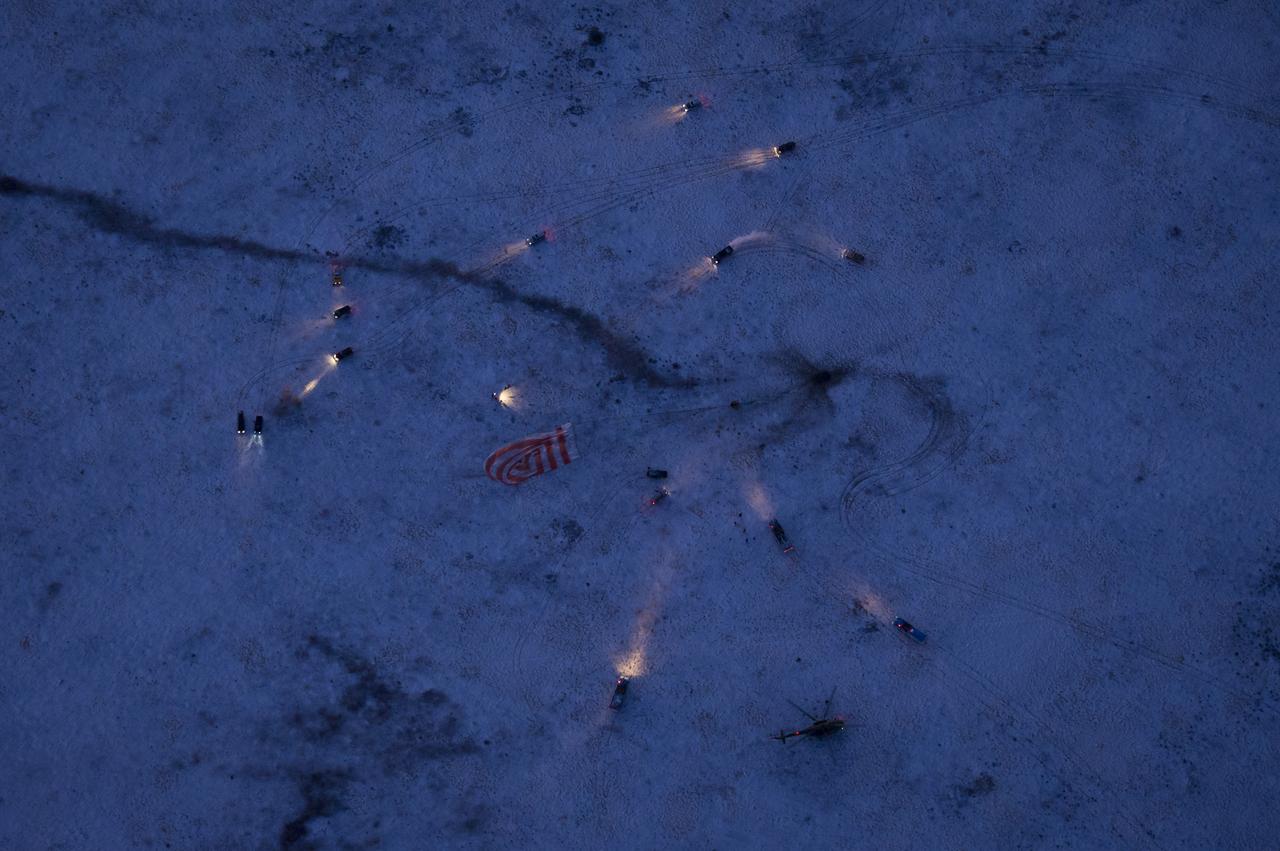

Russian support personnel arrive to help meet the Soyuz TMA-02M spacecraft shortly after the capsule landed with Expedition 29 Commander Mike Fossum, and Flight Engineers Sergei Volkov and Satoshi Furukawa in a remote area outside of the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan, on Tuesday, Nov. 22, 2011. NASA Astronaut Fossum, Russian Cosmonaut Volkov and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Astronaut Furukawa are returning from more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 28 and 29 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Russian support personnel work to help get crew members out of the Soyuz TMA-22 spacecraft shortly after the capsule landed with Expedition 30 Commander Dan Burbank, and Flight Engineers Anton Skhaplerov and Anatoly Ivanishin in a remote area outside of the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan, on Friday, April 27, 2012. NASA Astronaut Burbank, Russian Cosmonauts Shkaplerov and Ivanishin are returning from more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 29 and 30 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Expedition 39 Commander Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) is helped of the Soyuz Capsule just minutes after he and Soyuz Commander Mikhail Tyurin of Roscosmos, and Flight Engineer Rick Mastracchio of NASA, landed in their Soyuz TMA-11M spacecraft near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Wednesday, May 14, 2014. Wakata, Tyurin and Mastracchio returned to Earth after more than six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 38 and 39 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

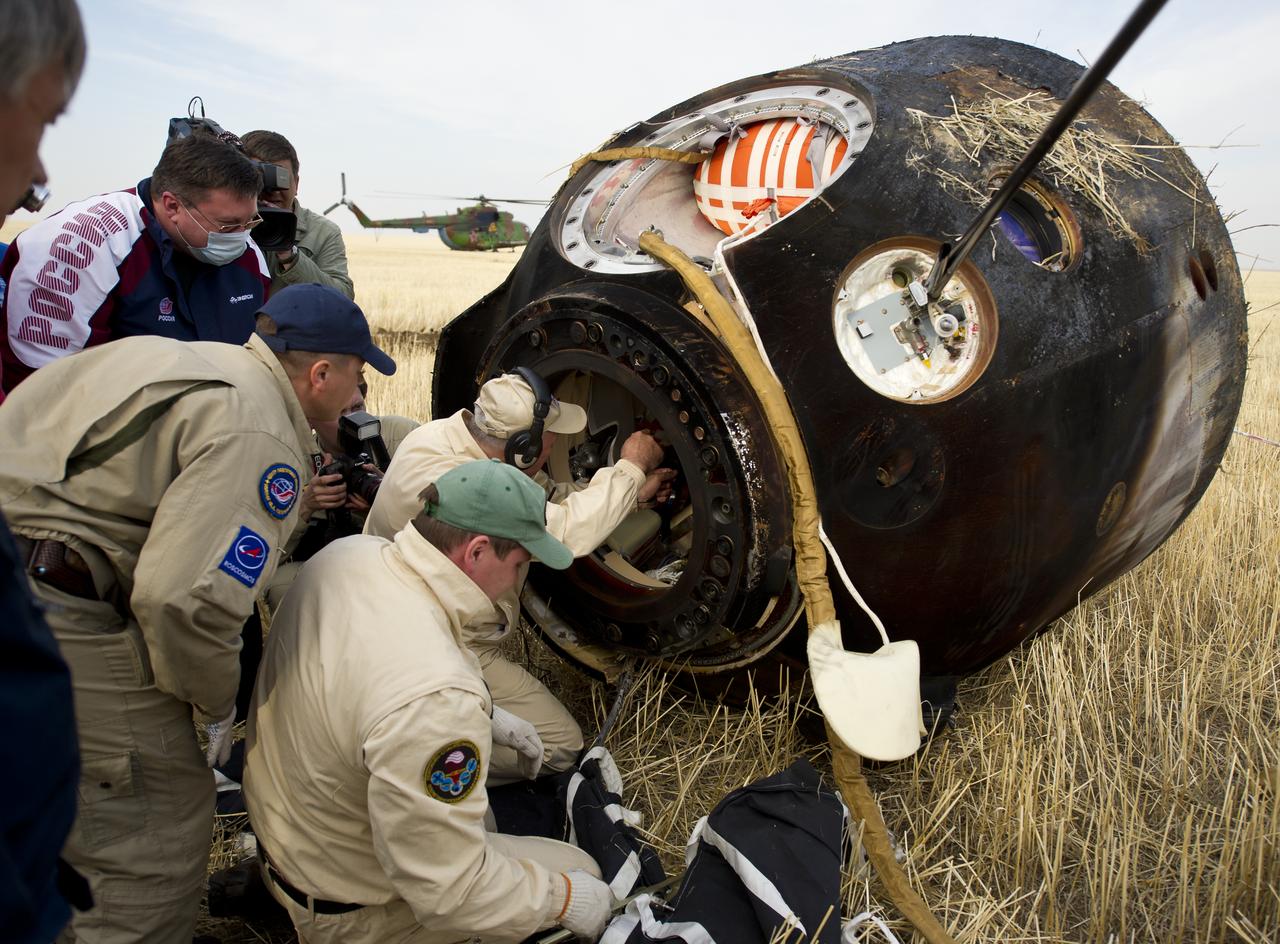
Spaceflight participant Guy Laliberté is carried in a chair to the medical tent shortly after he and Expedition 20 Flight Engineer Michael Barratt, and Expedition 20 Commander Gennady Padalka landed in their Soyuz TMA-14 capsule near the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Sunday, Oct. 11, 2009. Padalka and Barratt are returning from six months onboard the International Space Station, along with Laliberté who arrived at the station on Oct. 2 with Expedition 21 Flight Engineers Jeff Williams and Maxim Suraev aboard the Soyuz TMA-16 spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
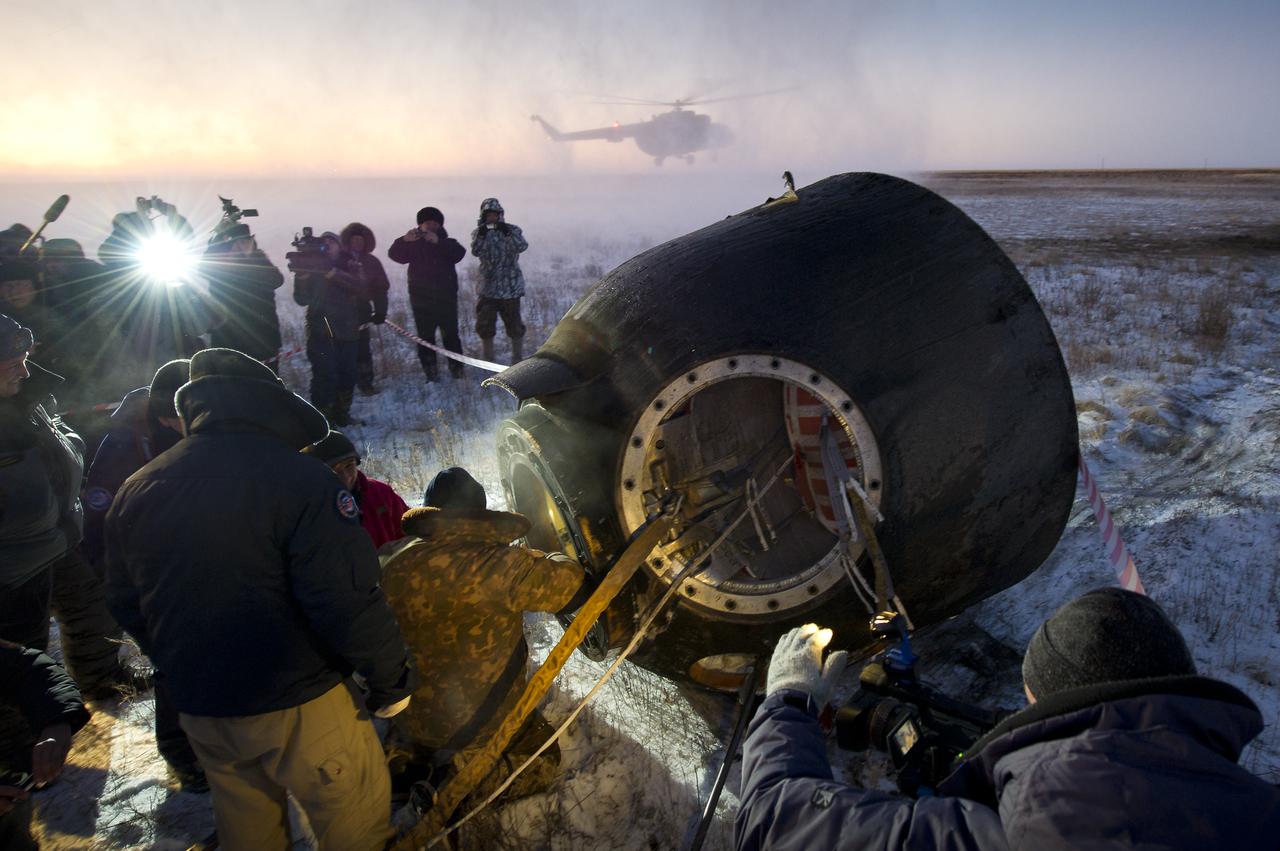

Russian support personnel work to help get Expedition 29 crew members out of the Soyuz TMA-02M spacecraft shortly after the capsule landed with Expedition 29 Commander Mike Fossum, and Flight Engineers Sergei Volkov and Satoshi Furukawa in a remote area outside of the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan, on Tuesday, Nov. 22, 2011. NASA Astronaut Fossum, Russian Cosmonaut Volkov and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Astronaut Furukawa are returning from more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 28 and 29 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
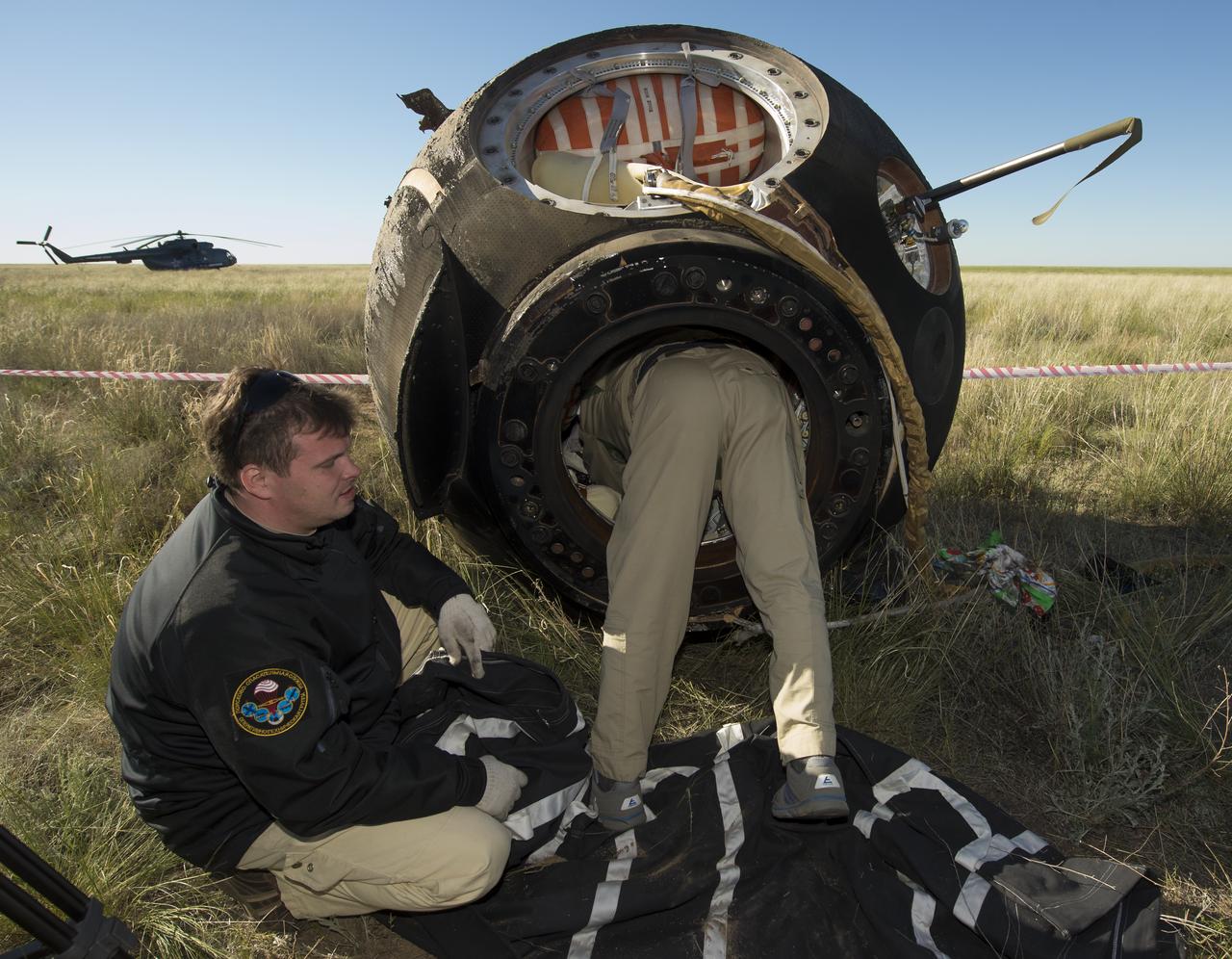

Russian support personnel start to access the crew of Soyuz TMA-07M capsule shortly after it landed with Expedition 35 Commander Chris Hadfield of the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), NASA Flight Engineers Tom Marshburn and Russian Flight Engineer Roman Romanenko of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) in a remote area near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan, Tuesday, May 14, 2013. Hadfield, Marshburn and Romanenko are returning from five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 34 and 35 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
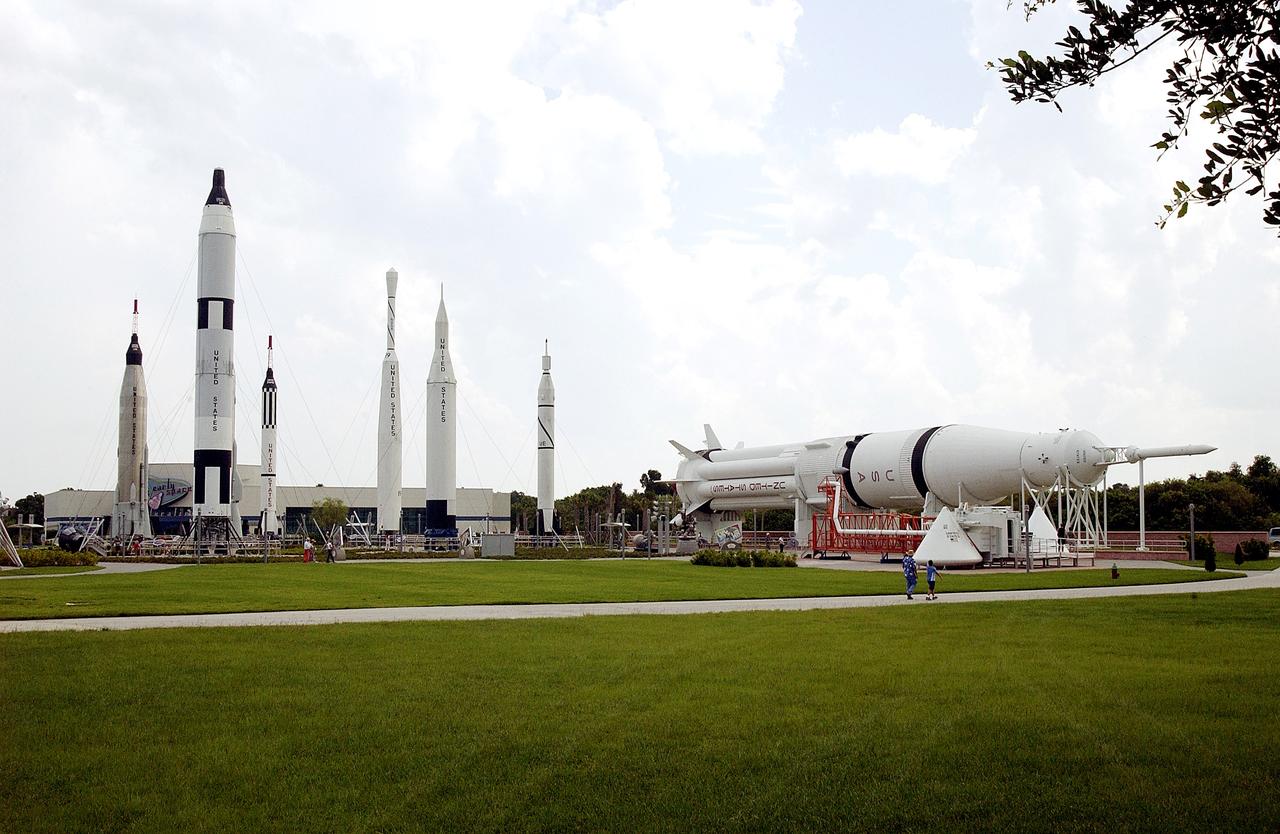

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Rocket Garden at the KSC Visitor Complex features eight authentic rockets from the past, including a Mercury-Atlas rocket. The garden also features a climb-in Mercury, Gemino and Apollo capsule replicas, seating pods and informative graphic elements.
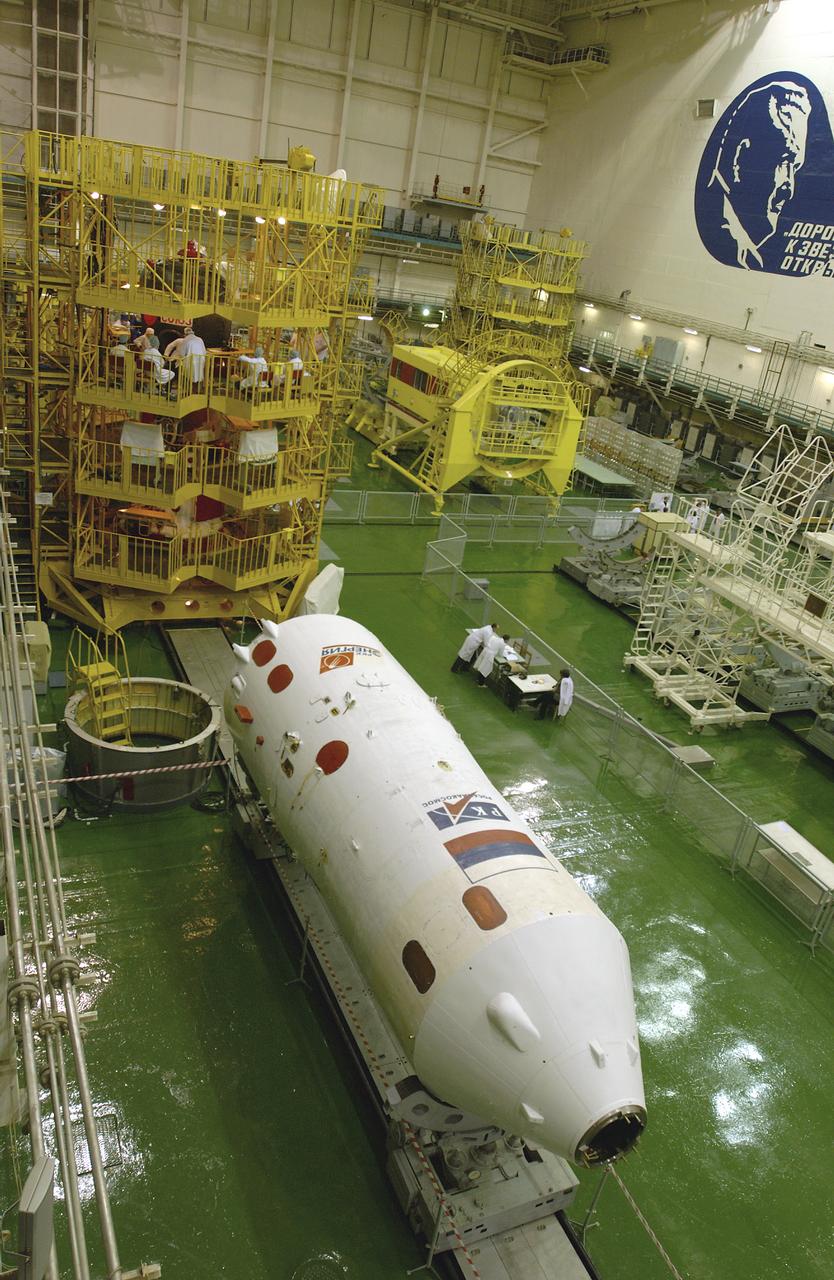

The interior of the Soyuz Integration Facility at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan is seen, Thursday, April 10, 2003. The Soyuz module is in the yellow work stand with its payload fairing ready in the foreground. Expedition 7 NASA International Space Station Science Officer and Flight Engineer Edward T. Lu and Expedition 7 Commander Yuri I. Malenchenko (both out of view) are in the Soyuz TMA-2 capsule for an inspection and seat liner check.
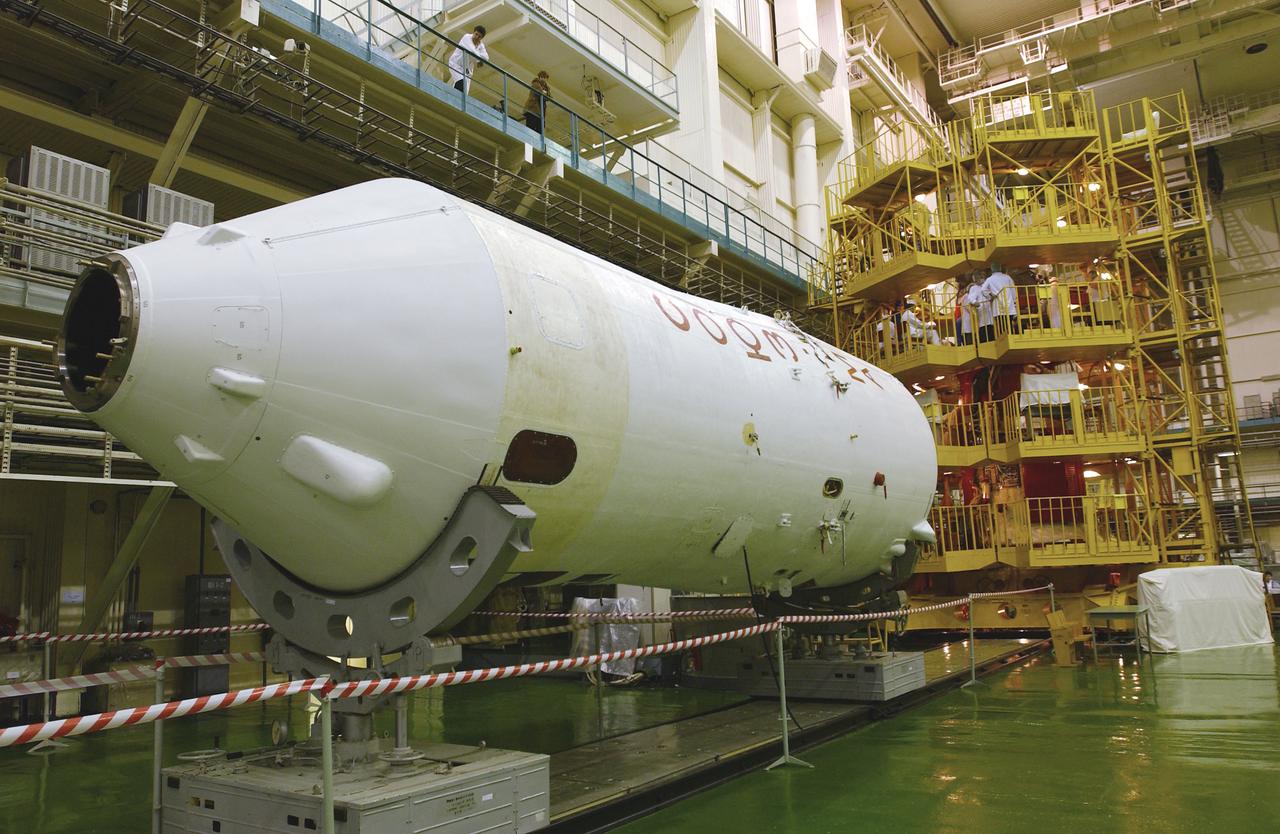

The interior of the Soyuz Integration Facility at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan is seen, Thursday, April 10, 2003. The Soyuz module is in the yellow work stand with its payload fairing ready in the foreground. Expedition 7 NASA International Space Station Science Officer and Flight Engineer Edward T. Lu and Expedition 7 Commander Yuri I. Malenchenko (both out of view) are in the Soyuz TMA-2 capsule for an inspection and seat liner check.
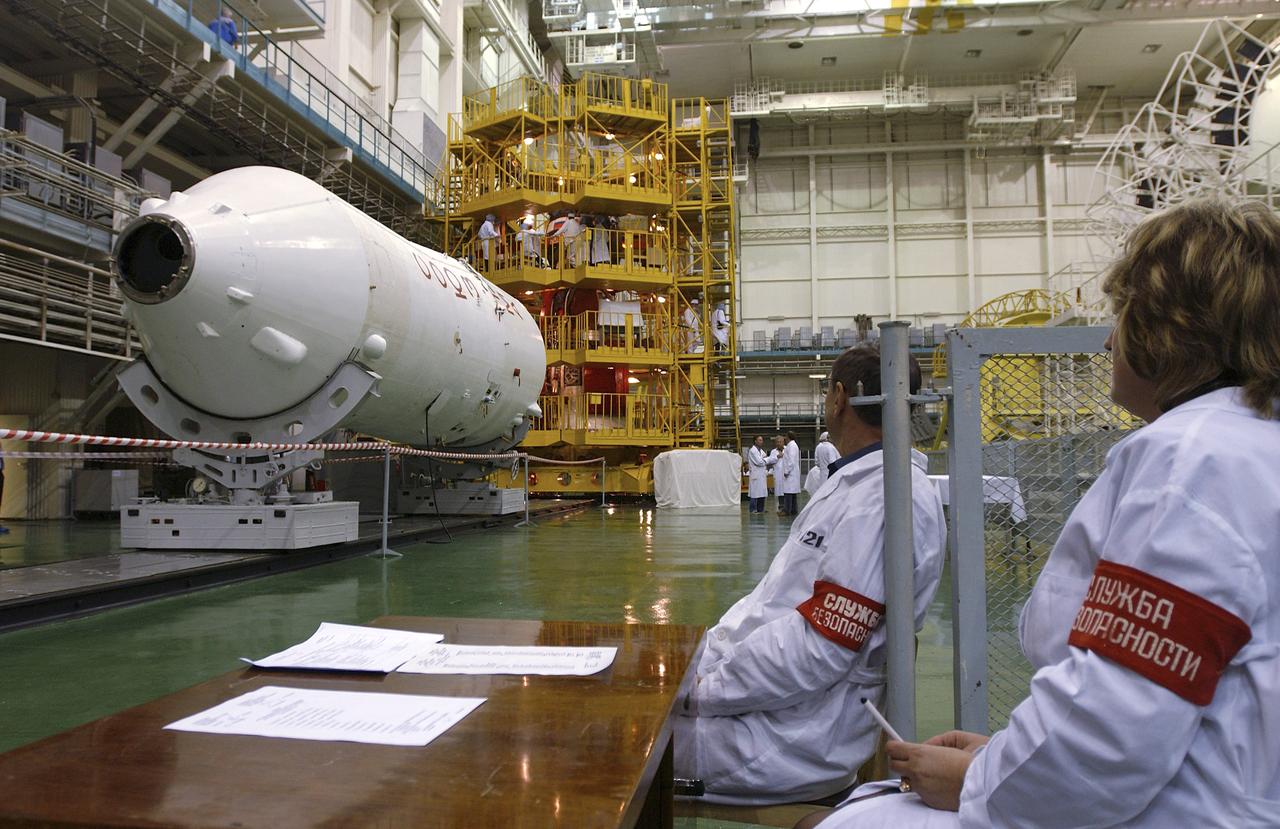

Security controls access to the Soyuz capsule and test stand area, Friday, Oct. 5, 2004, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome. Expedition 10 Commander and NASA Science Officer Leroy Chiao, Flight Engineer and Soyuz Commander Salizhan Sharipov and Russian Space Forces Cosmonaut Yuri Shargin donned their launch and entry suits and climbed aboard their Soyuz TMA-5 for a dress rehearsal of launch day activities leading to their liftoff October 14 to the International Space Station. Chiao and Sharipov, the first crew of all-Asian extraction, will spend six months on the Station. Shargin will return to Earth October 24 with the Stations' current residents, Expedition 9 Commander Gennady Padalka and NASA Flight Engineer and Science Officer Mike Fincke. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
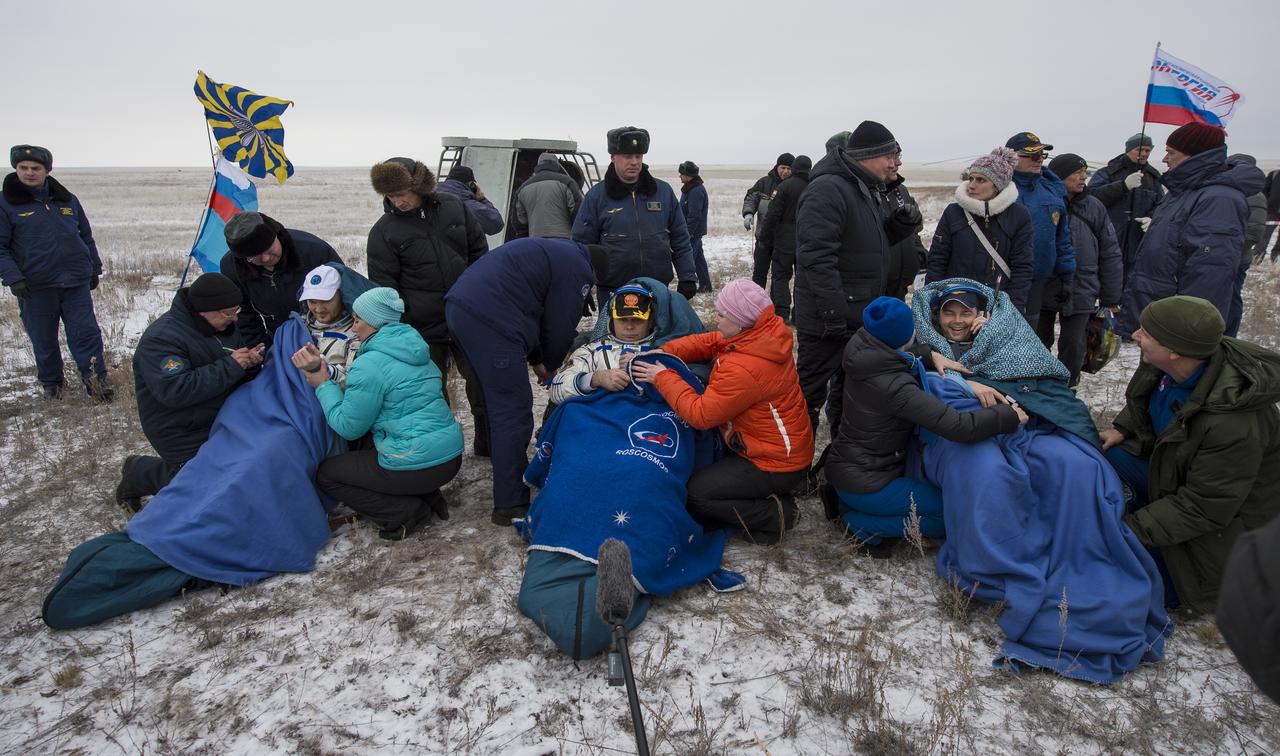

Expedition 41 light Engineer Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency (ESA), left, Commander Max Suraev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), center, and NASA Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman, sit in chairs outside the Soyuz TMA-13M capsule just minutes after they landed in a remote area near the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Monday, Nov. 10, 2014. Suraev, Wiseman and Gerst returned to Earth after more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 40 and 41 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
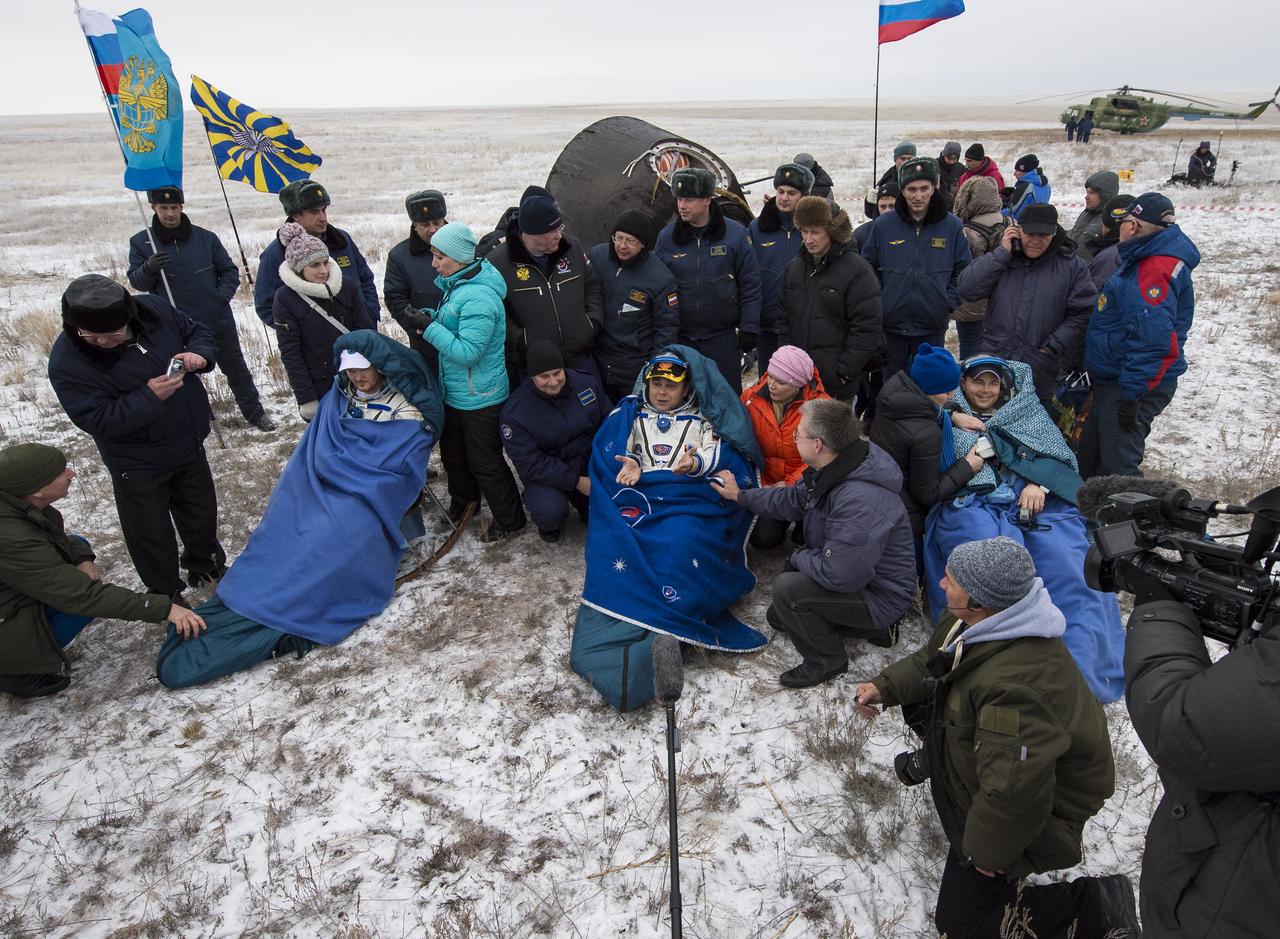

Expedition 41 light Engineer Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency (ESA), left, Commander Max Suraev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), center, and NASA Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman, sit in chairs outside the Soyuz TMA-13M capsule just minutes after they landed in a remote area near the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan on Monday, Nov. 10, 2014. Suraev, Wiseman and Gerst returned to Earth after more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 40 and 41 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
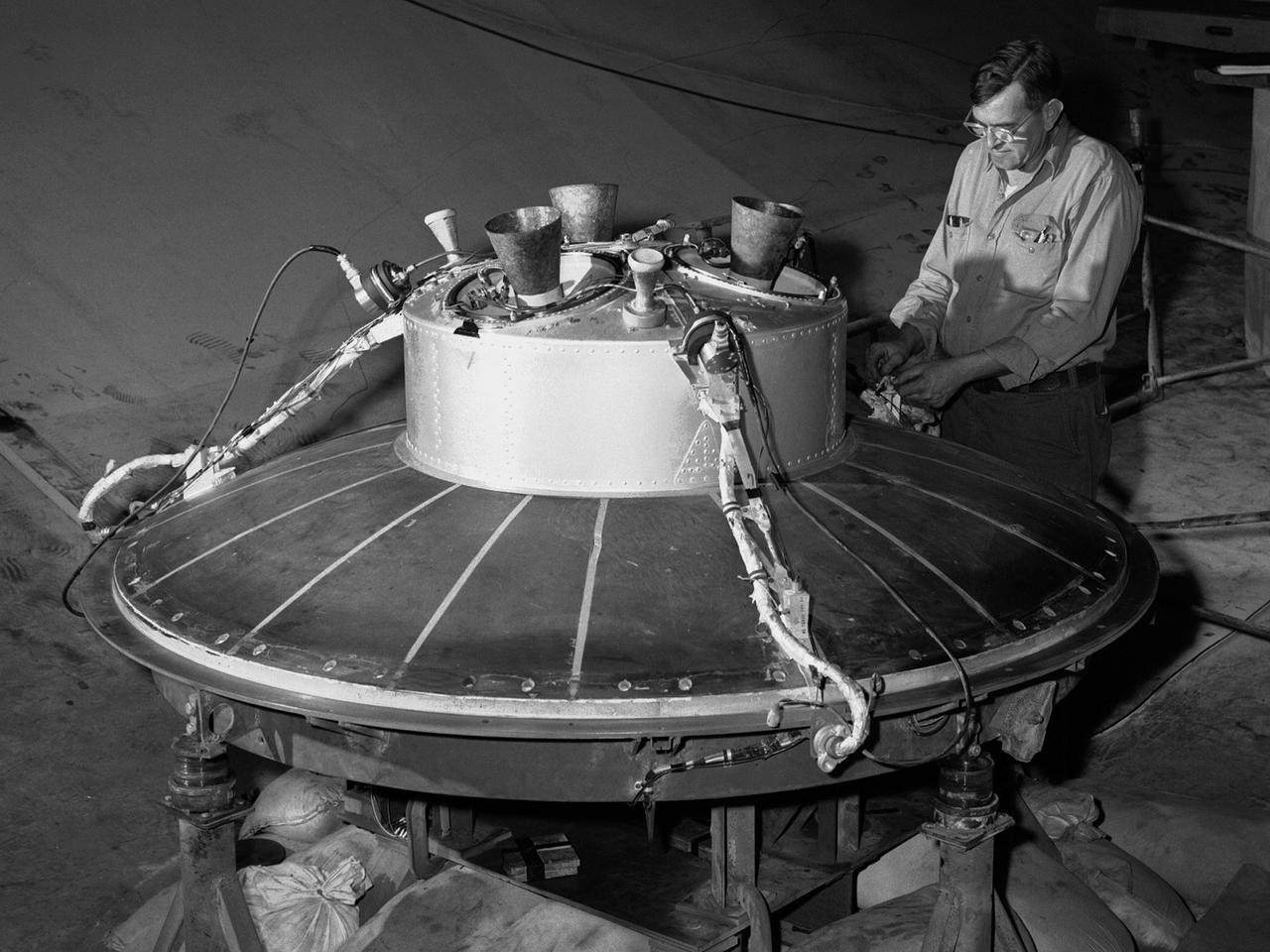

A mechanic at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center prepares the inverted base of a Mercury capsule for a test of its posigrade retrorockets inside the Altitude Wind Tunnel. In October 1959 NASA’s Space Task Group allocated several Project Mercury assignments to Lewis. The Altitude Wind Tunnel was modified to test the Atlas separation system, study the escape tower rocket plume, train astronauts to bring a spinning capsule under control, and calibrate the capsule’s retrorockets. The turning vanes, makeup air pipes, and cooling coils were removed from the wide western end of the tunnel to create a 51-foot diameter test chamber. The Mercury capsule had a six-rocket retro-package affixed to the bottom of the capsule. Three of these were posigrade rockets used to separate the capsule from the booster and three were retrograde rockets used to slow the capsule for reentry into the earth’s atmosphere. Performance of the retrorockets was vital since there was no backup system. Qualification tests of the retrorockets began in April 1960 on a retrograde thrust stand inside the southwest corner of the Altitude Wind Tunnel. These studies showed that a previous issue concerning the delayed ignition of the propellant had been resolved. Follow-up test runs verified reliability of the igniter’s attachment to the propellant. In addition, the capsule’s retrorockets were calibrated so they would not alter the capsule’s attitude when fired.
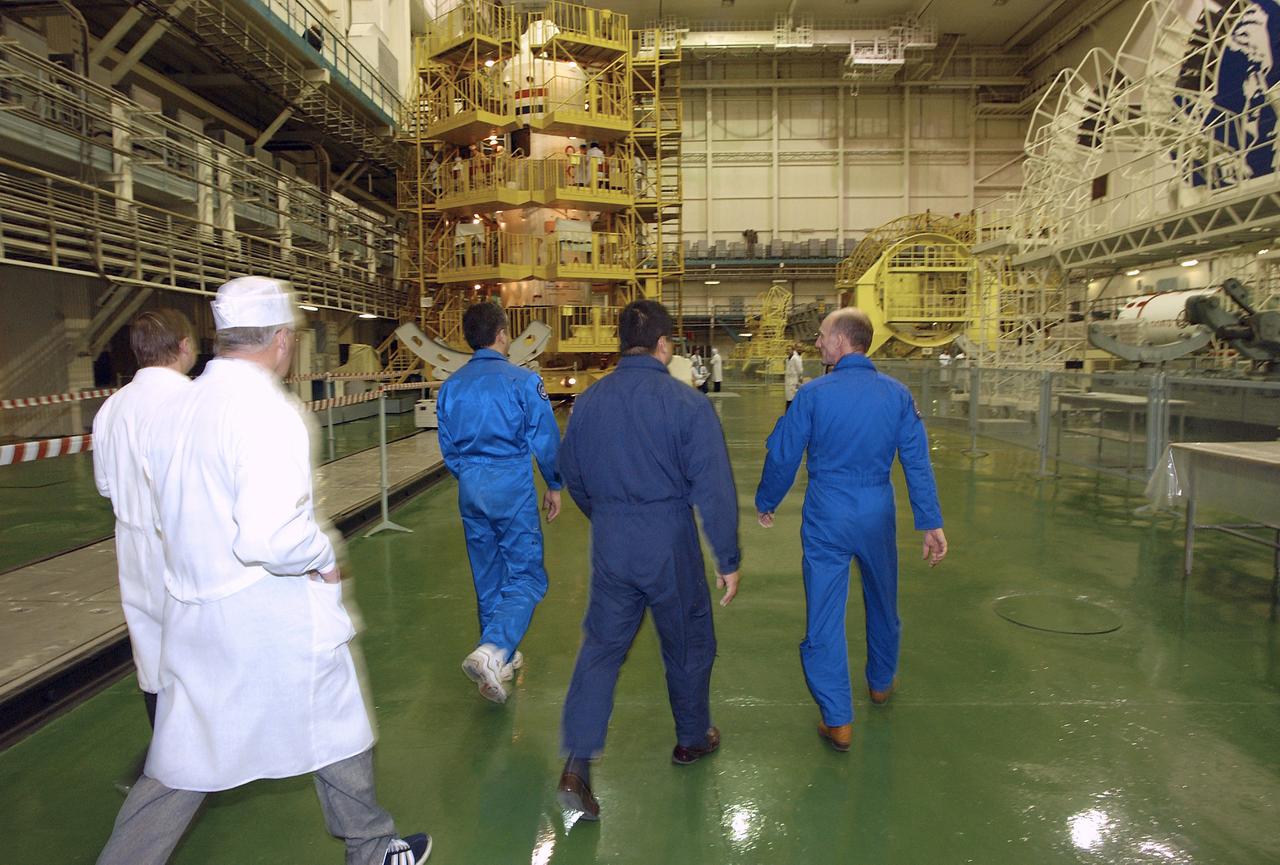

Backup Flight Engineer Salizhan Sharipov, left, Expedition 9 backup Commander Leroy Chiao, center and backup European Space Agency astronaut Gerhard Thiele of Germany walk out to the Soyuz capsule at building 254 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome for their final fit check, Wednesday, April 14, 2004, in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
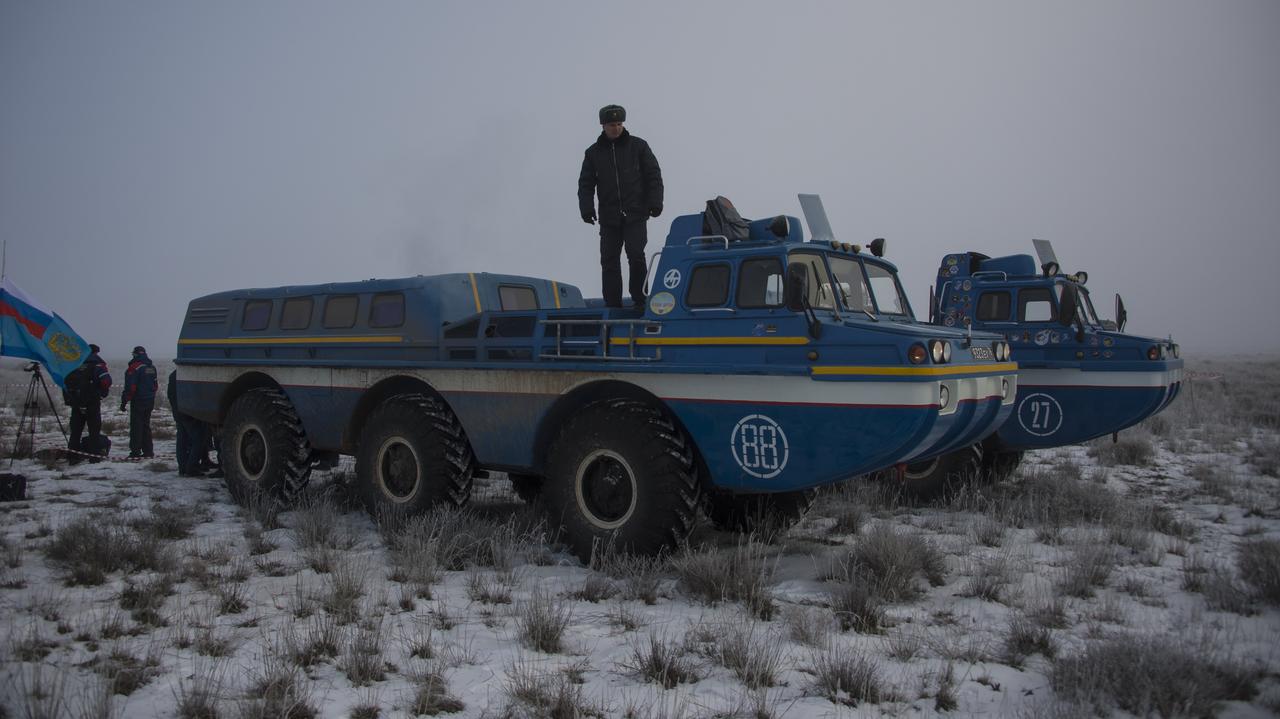

Russian all terrain vehicles (ATVs) are seen at the Soyuz TMA-14M spacecraft landing site shortly after the capsule landed with Expedition 42 commander Barry Wilmore of NASA, Alexander Samokutyaev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) and Elena Serova of Roscosmos near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Thursday, March 12, 2015. NASA Astronaut Wilmore, Russian Cosmonauts Samokutyaev and Serova are returning after almost six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 41 and 42 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
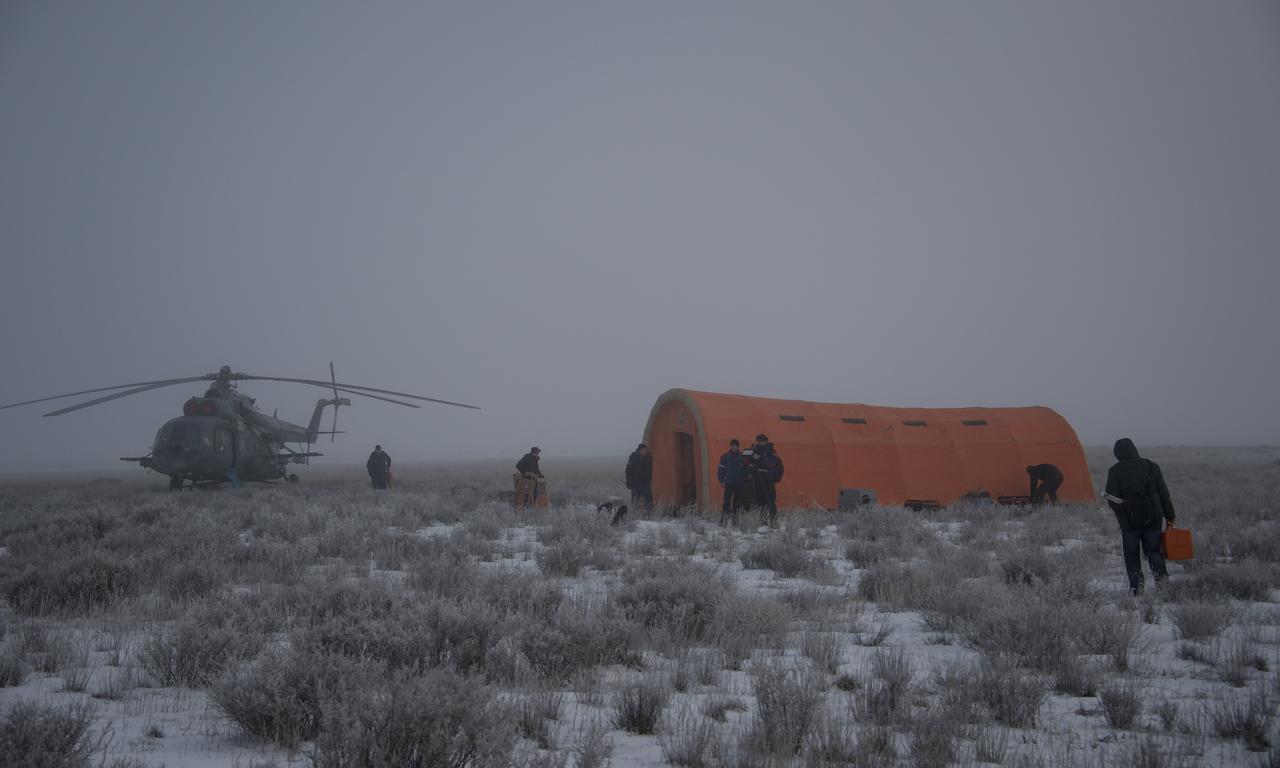

Russian ground support personnel assemble a portable medical tent at the Soyuz TMA-14M spacecraft landing site shortly after the capsule landed with Expedition 42 commander Barry Wilmore of NASA, Alexander Samokutyaev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) and Elena Serova of Roscosmos near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Thursday, March 12, 2015. NASA Astronaut Wilmore, Russian Cosmonauts Samokutyaev and Serova are returning after almost six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 41 and 42 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
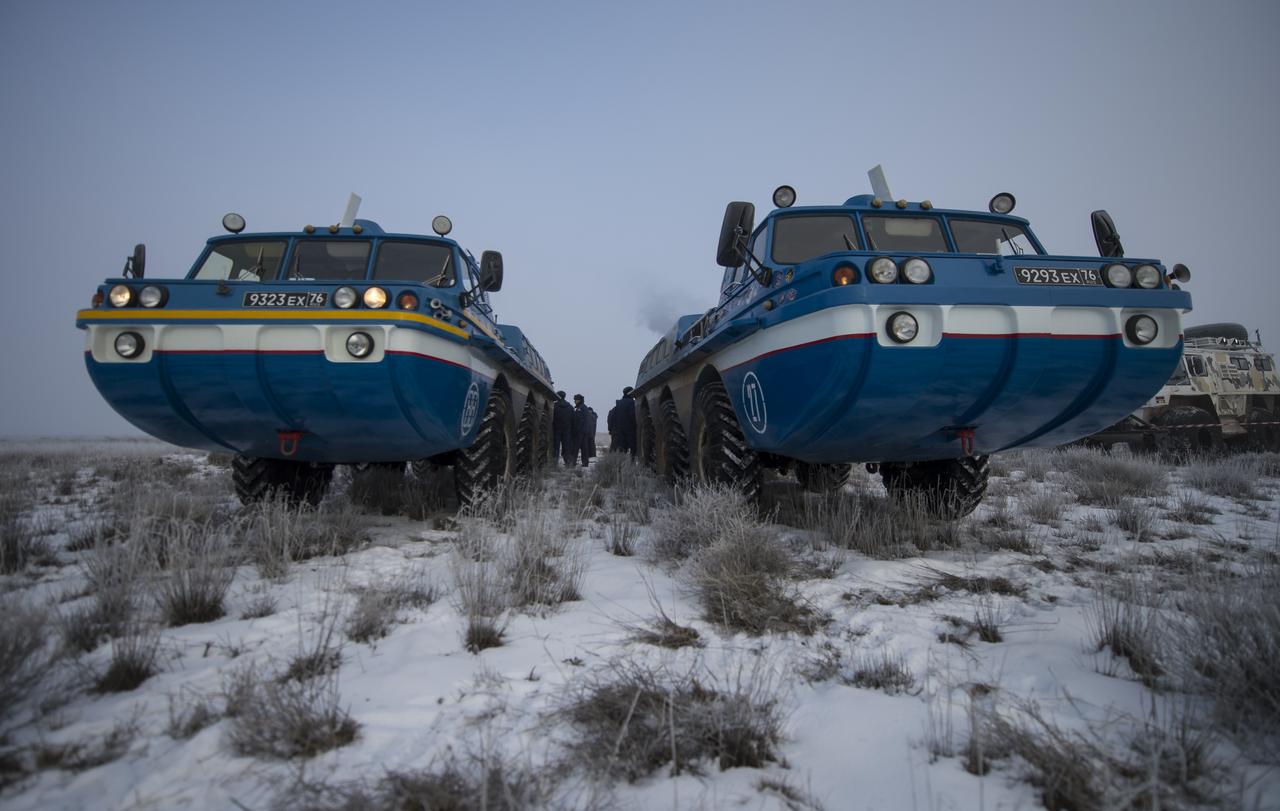

Russian all terrain vehicles (ATVs) are seen at the Soyuz TMA-14M spacecraft landing site shortly after the capsule landed with Expedition 42 commander Barry Wilmore of NASA, Alexander Samokutyaev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) and Elena Serova of Roscosmos near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Thursday, March 12, 2015. NASA Astronaut Wilmore, Russian Cosmonauts Samokutyaev and Serova are returning after almost six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 41 and 42 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Space Flight Charts, Space Capsule

Space Flight Charts, Space Capsule

Space Flight Charts, Space Capsule