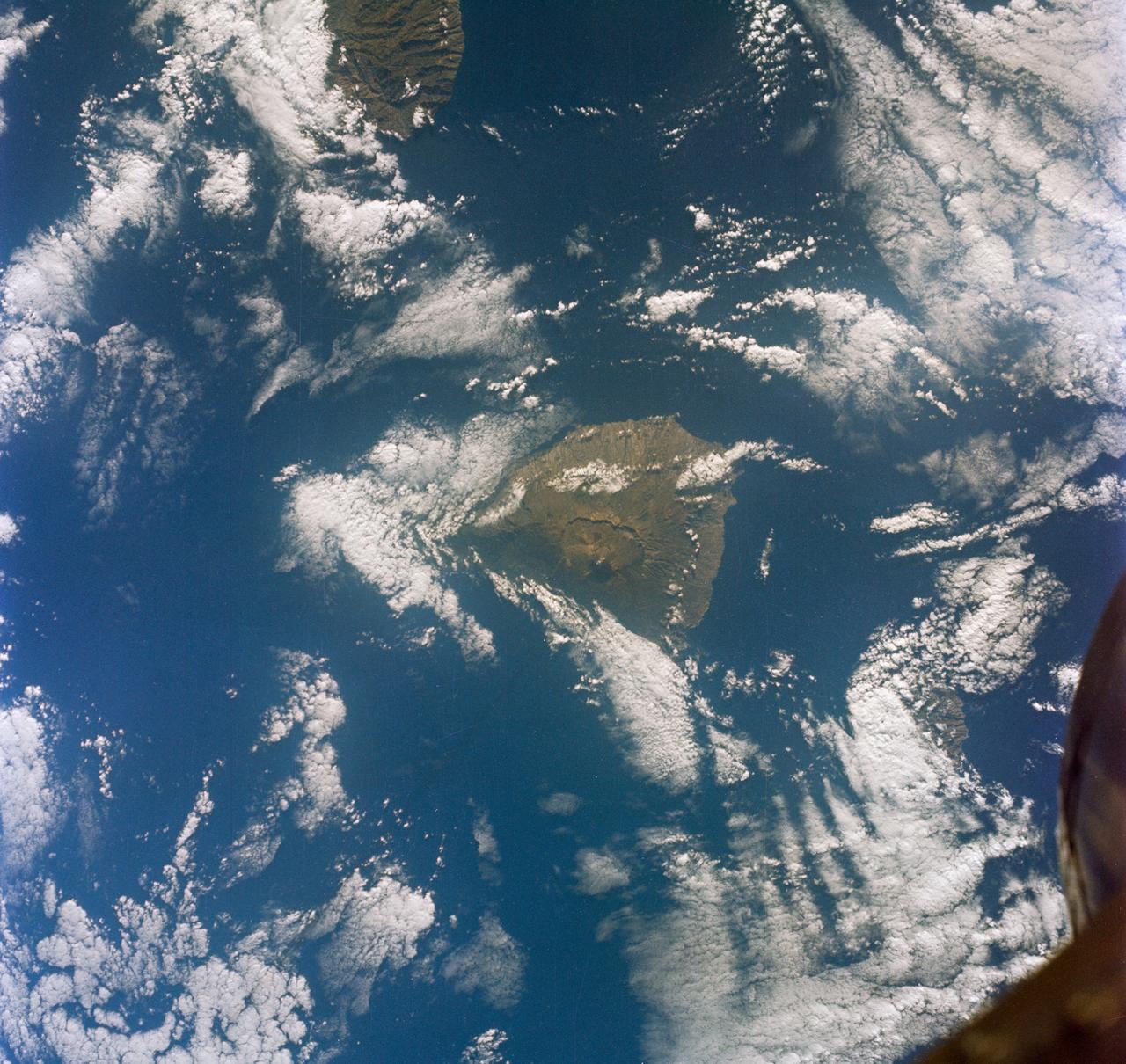

S65-63150 (16 Dec. 1965) --- Eddies in stratocumulus clouds over the Canary Islands as seen from the Gemini-6 spacecraft during its 14th revolution of Earth. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
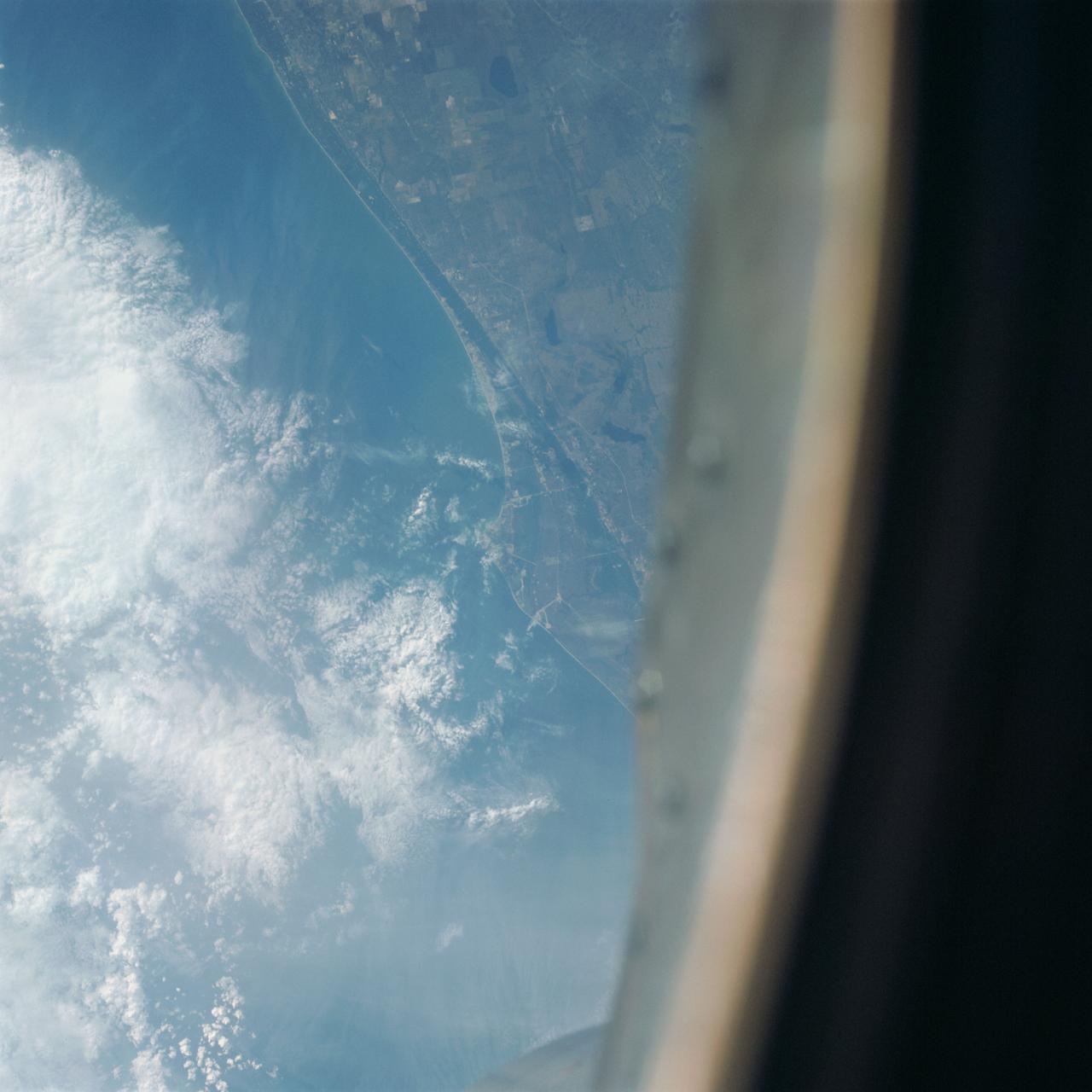

S65-63771 (12 Dec. 1965) --- Kennedy Space Center area on the east coast of Florida as seen from the Gemini-7 spacecraft, during Gemini-6 abort, on its 118th revolution of Earth. Photo credit: NASA
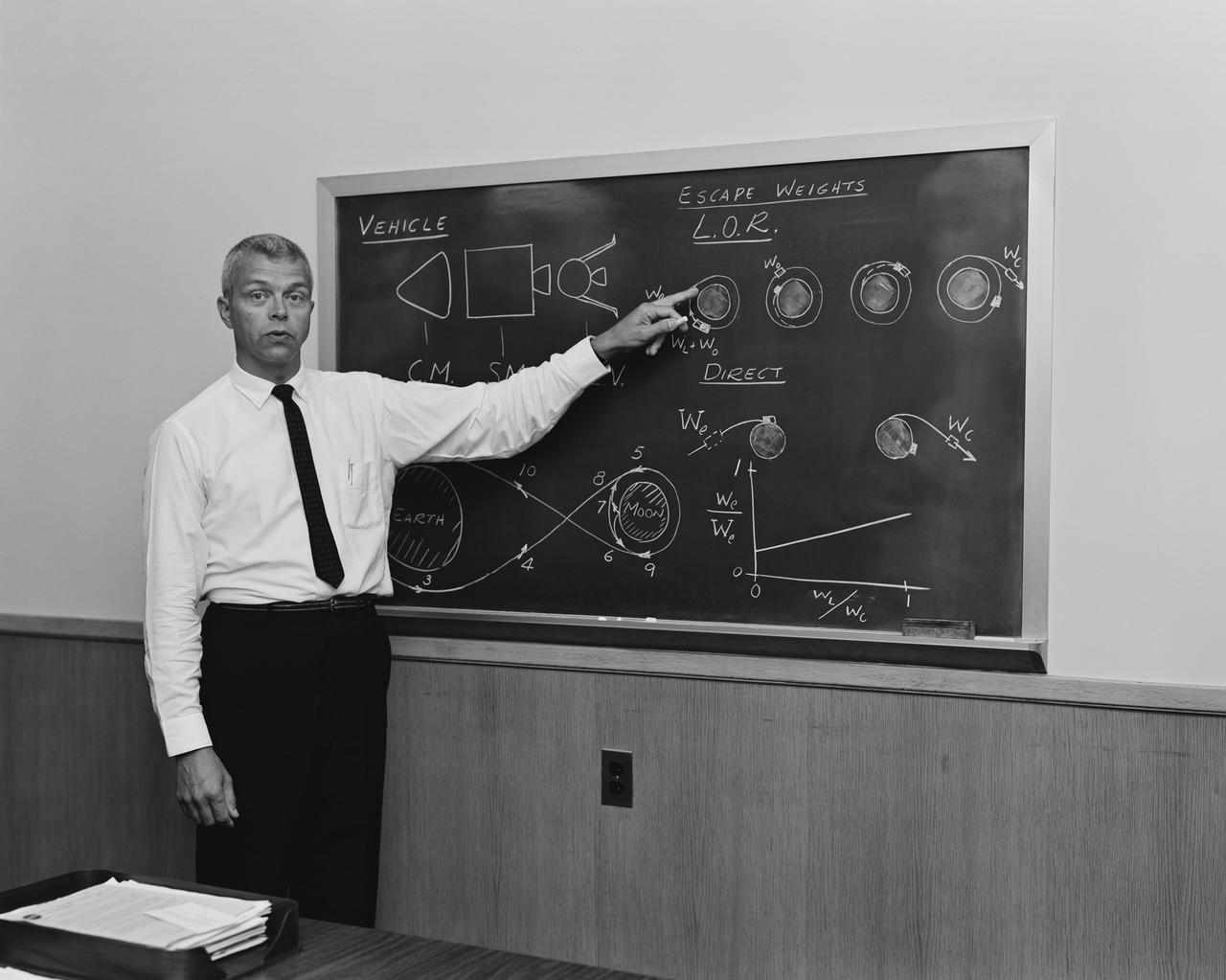

At blackboard, showing his space rendezvous concept for lunar landings. Lunar Orbital Rendezvous (LOR) would be used in the Apollo program. Photograph published in Space Flight Revolution - NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo (page 247), by James R. Hansen.

S65-63256 (16 Dec. 1965) --- Cap Blanc and Levrier Bay on the coast of Spanish Sahara and Mauritania, as seen from the Gemini-6 spacecraft during its 15th revolution of Earth. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

S65-63282 (16 Dec. 1965) --- Area of Indian Ocean, just east of the island of Madagascar, as seen from the Gemini-6 spacecraft during its 15th revolution of Earth. Land mass at top of picture is the Malagasy Republic (Madagascar). Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
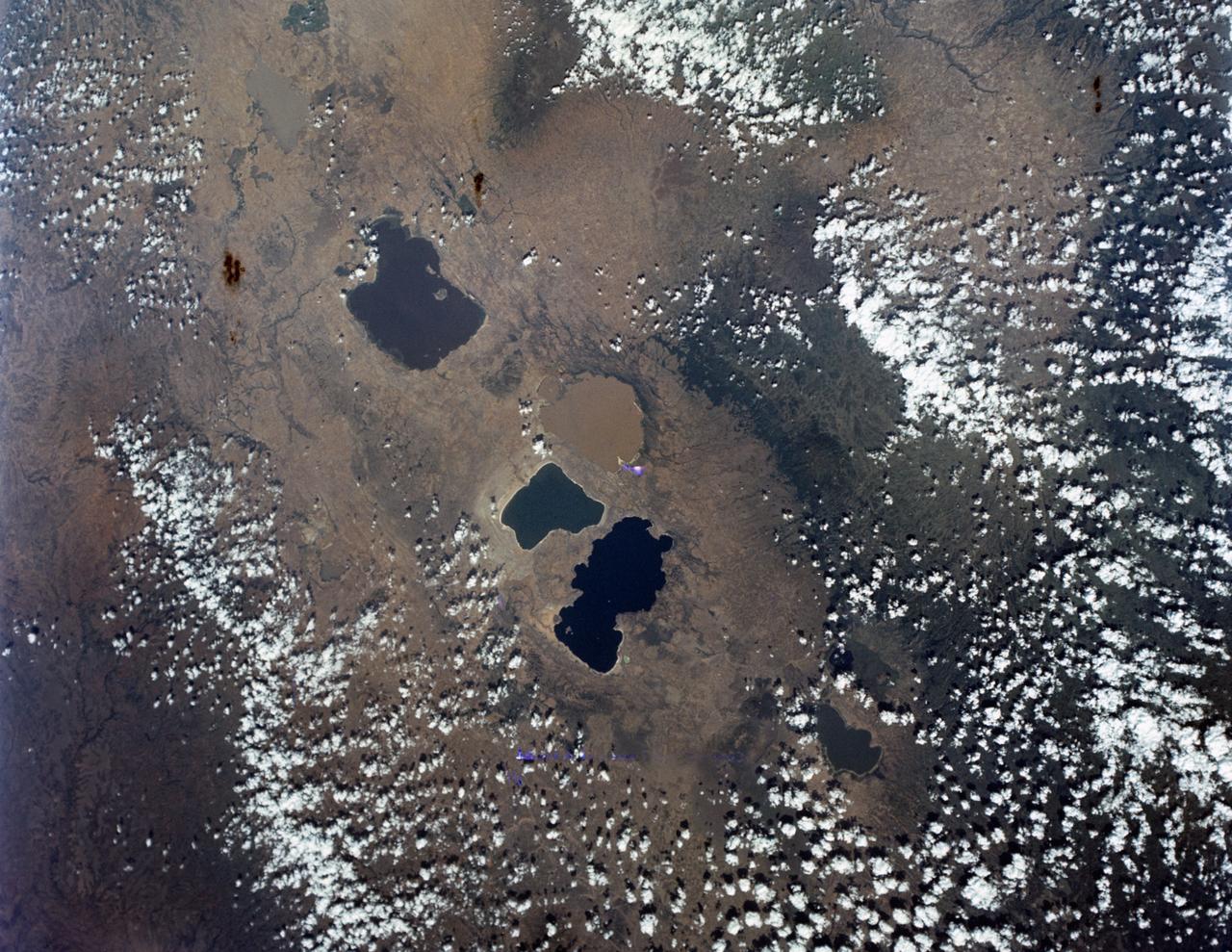

S65-63162 (16 Dec. 1965) --- Central area of Ethiopia, south of Addis Ababa, showing Lakes Zwai, Langana, and Shala, as seen from the Gemini-6 spacecraft during its 14th revolution of Earth. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
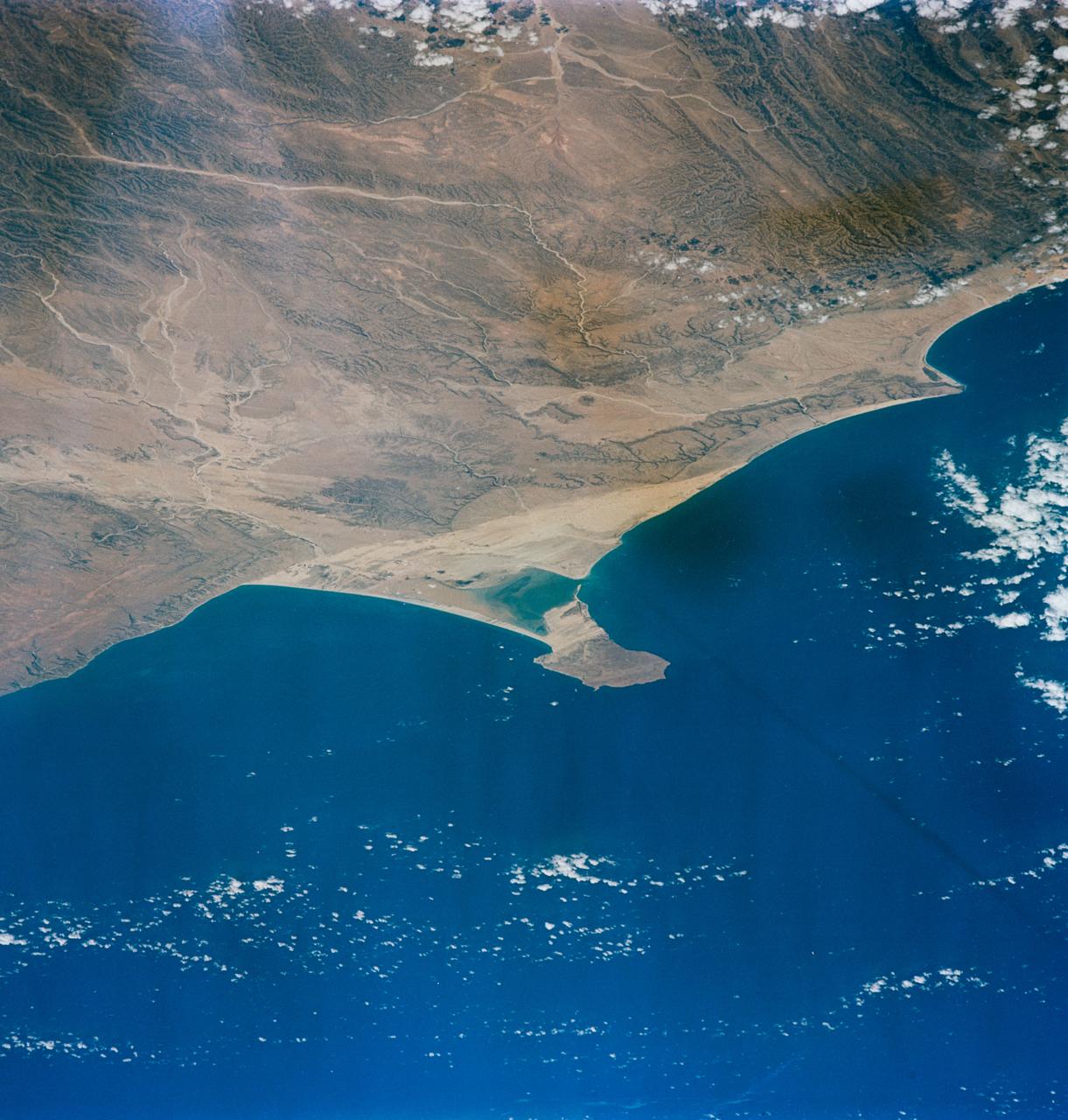

S65-63130 (16 Dec. 1965) --- Ras Hafum, coast of Somali Republic, northeast Africa, as seen from the Gemini-6 spacecraft during its 13th revolution of Earth. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
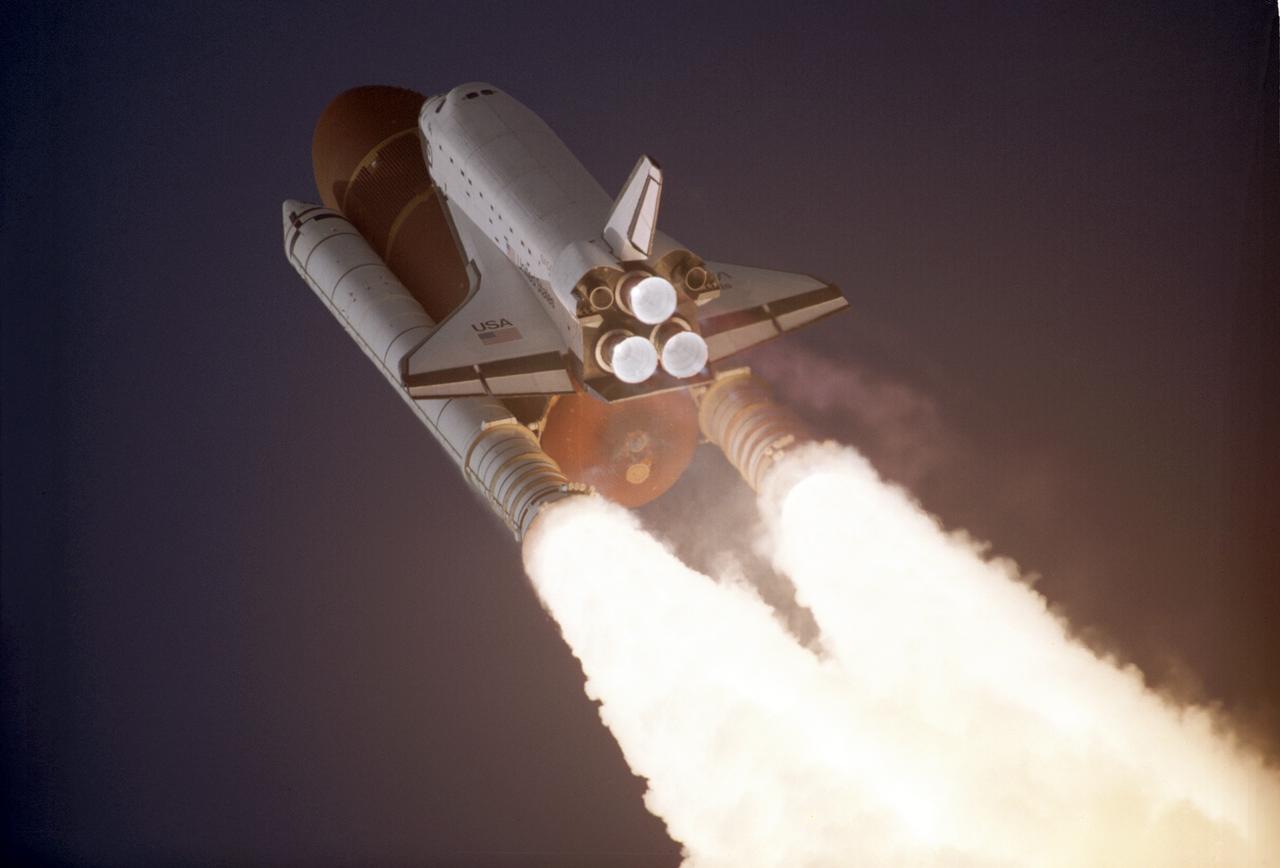

Space Shuttle Atlantis takes flight on its STS-27 mission, December 2, 1988, utilizing 375,000 pounds of thrust produced by its three main engines. The engines start in 3.9 seconds of ignition and go to static pump speeds of approximately 35,000 revolutions per minute during that time. The Marshall Space Flight Center had management responsibility of Space Shuttle propulsion elements, including the Main Engines.
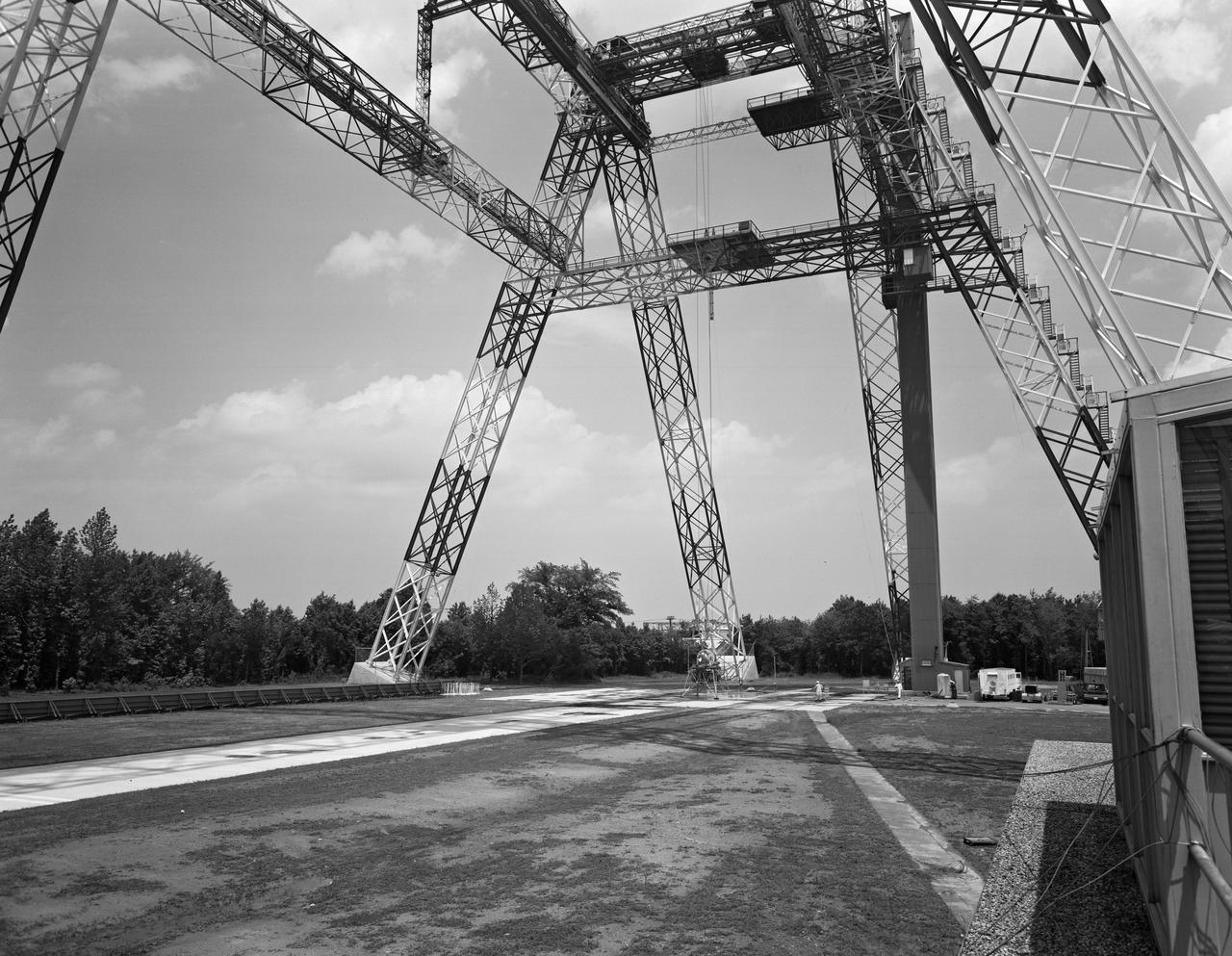

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
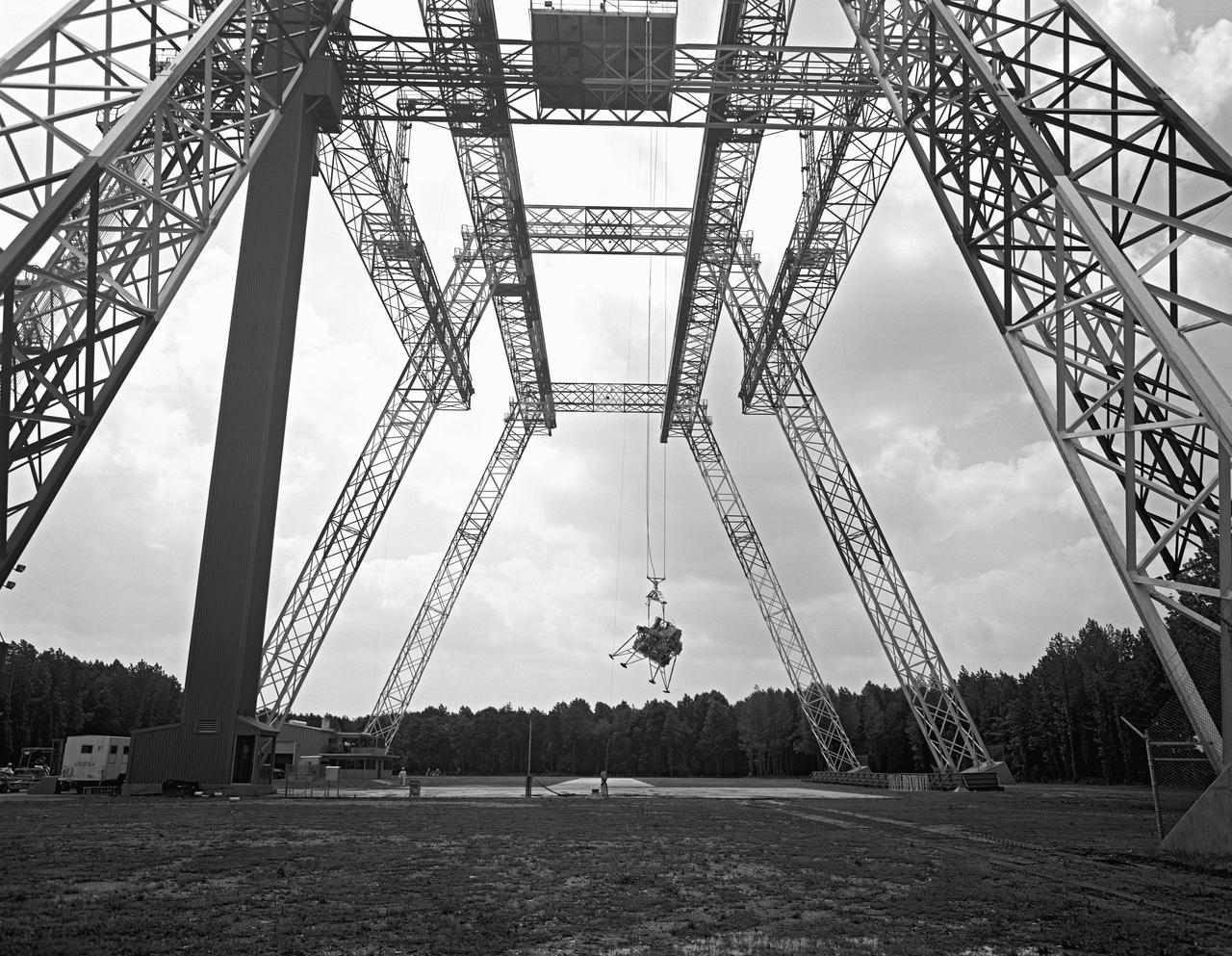

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
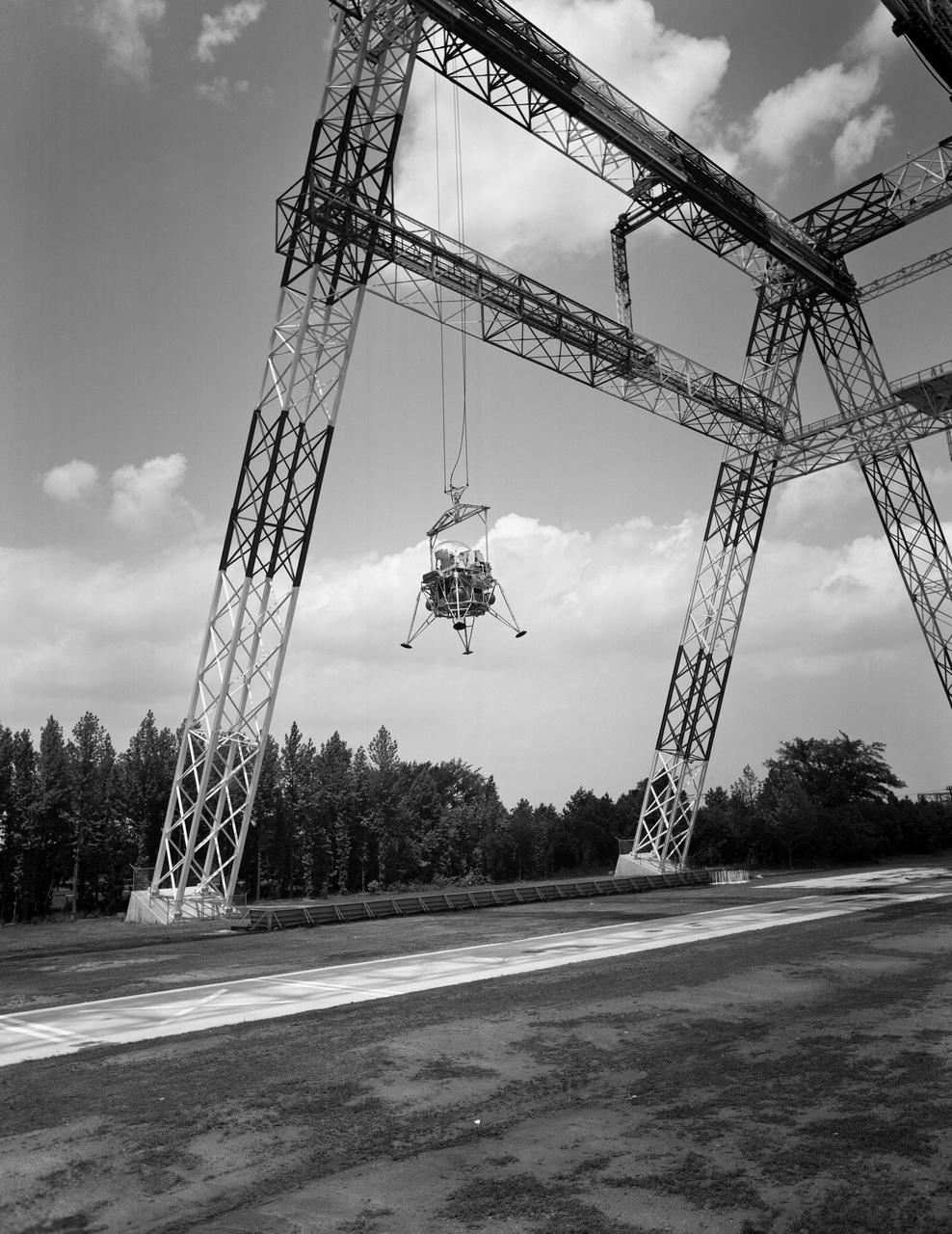

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
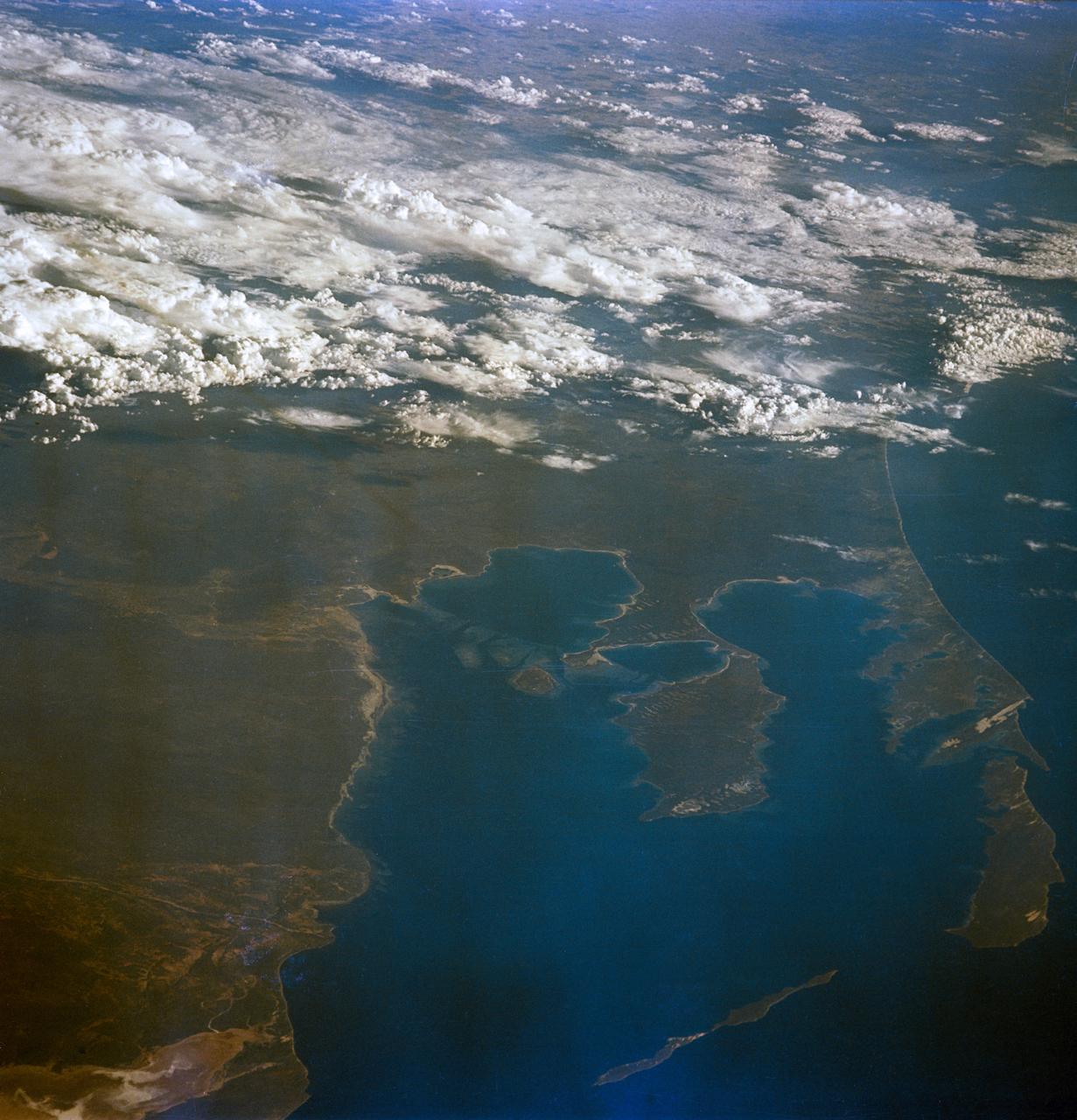

S65-63136 (16 Dec. 1965) --- Shark Bay area on the western coast of Western Australia as seen from the Gemini-6 spacecraft during its 16th revolution of Earth. City of Carnarven, where NASA has a tracking station, is located near the bottom of picture in lower left corner, near mouth of stream. Indian Ocean is body of water at upper right. South is toward top of picture. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
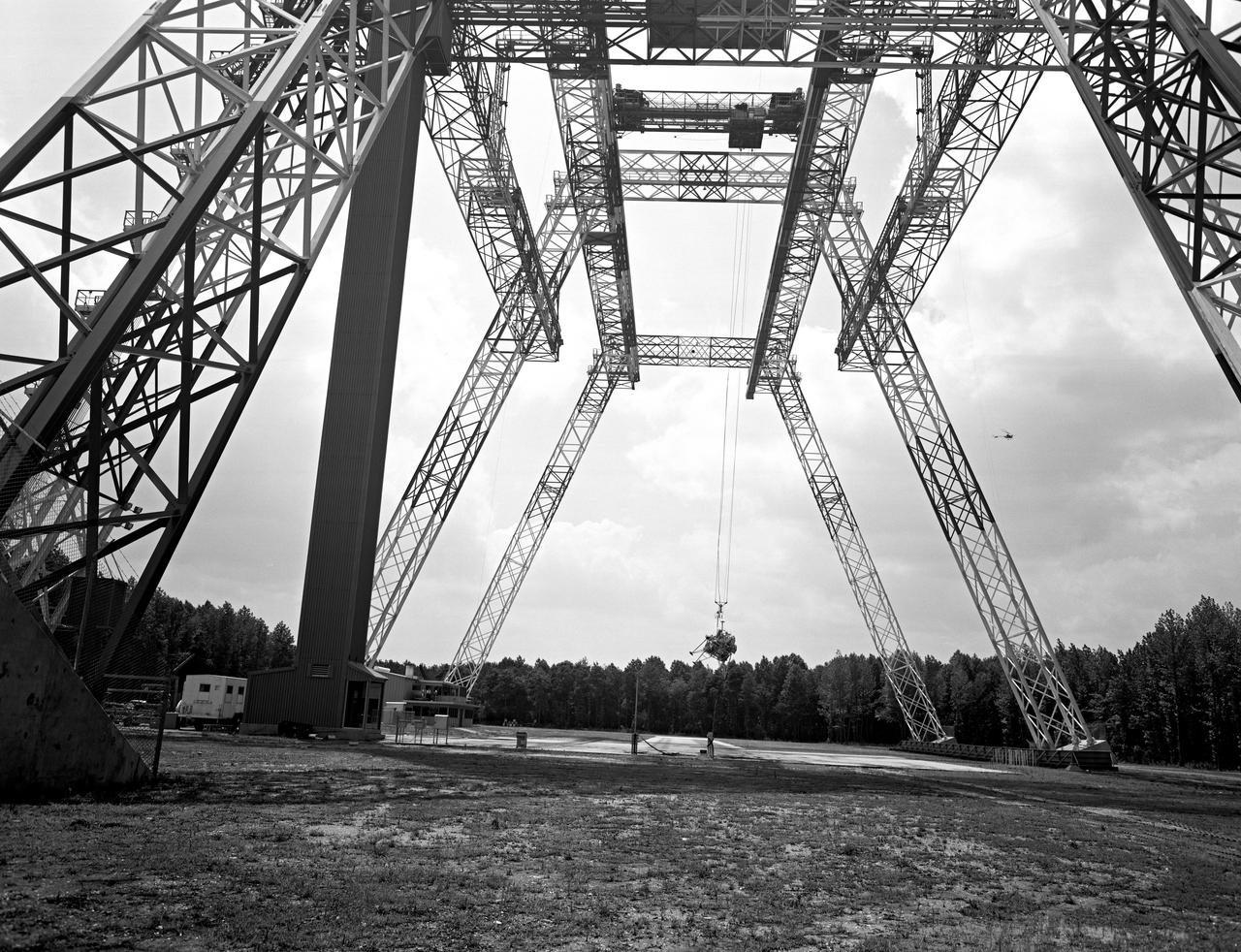

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376

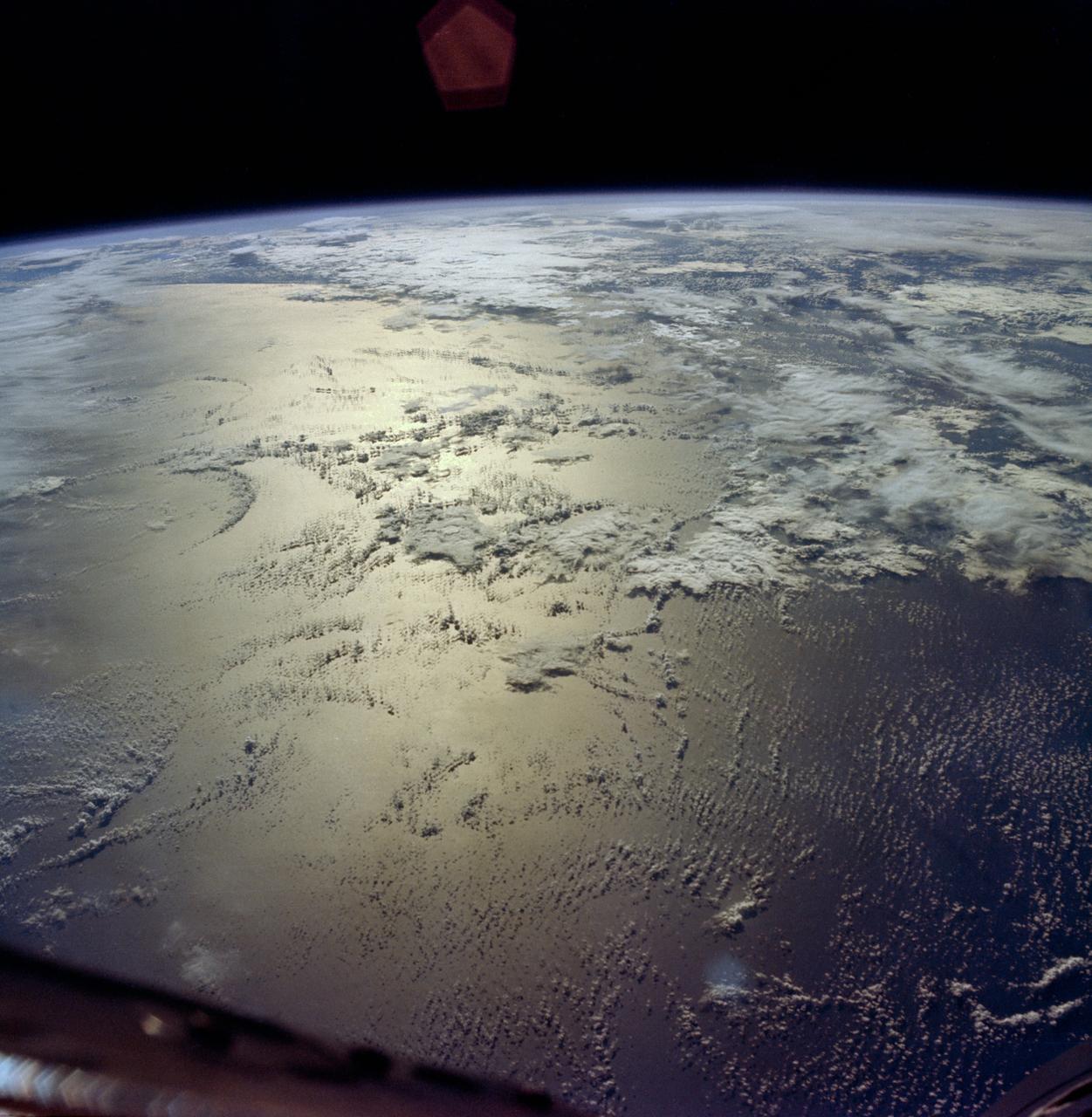
AS09-23-3592 (3-13 March 1969) --- Cyclonic storm system, located 1,200 miles north of Hawaii, as photographed from the Apollo 9 spacecraft during its 10-day, Earth-orbital space mission. This picture was made on the 124th revolution of Apollo 9. This cyclonic storm system can also be seen in the ESSA-7 photograph taken on March 11, 1969.
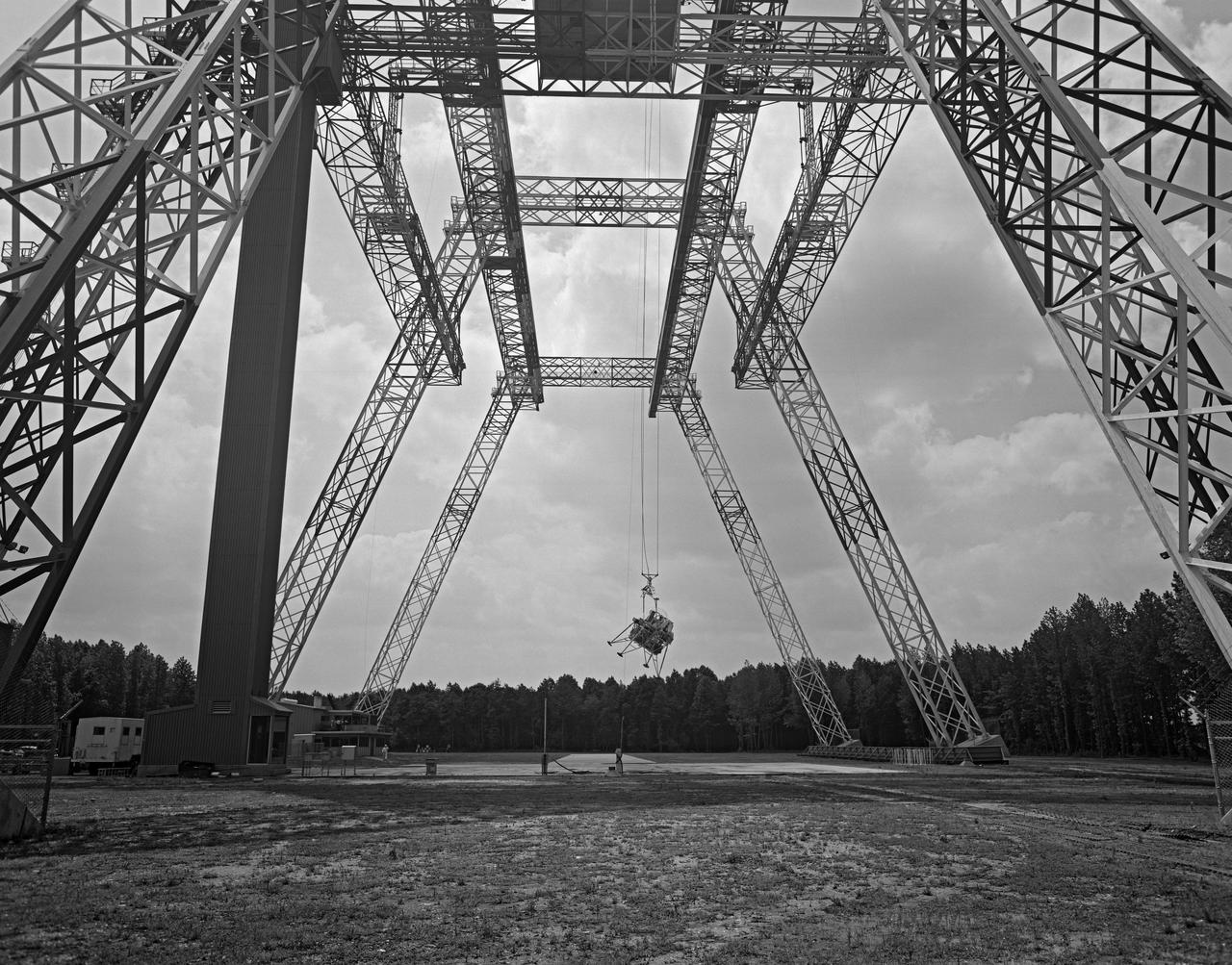

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
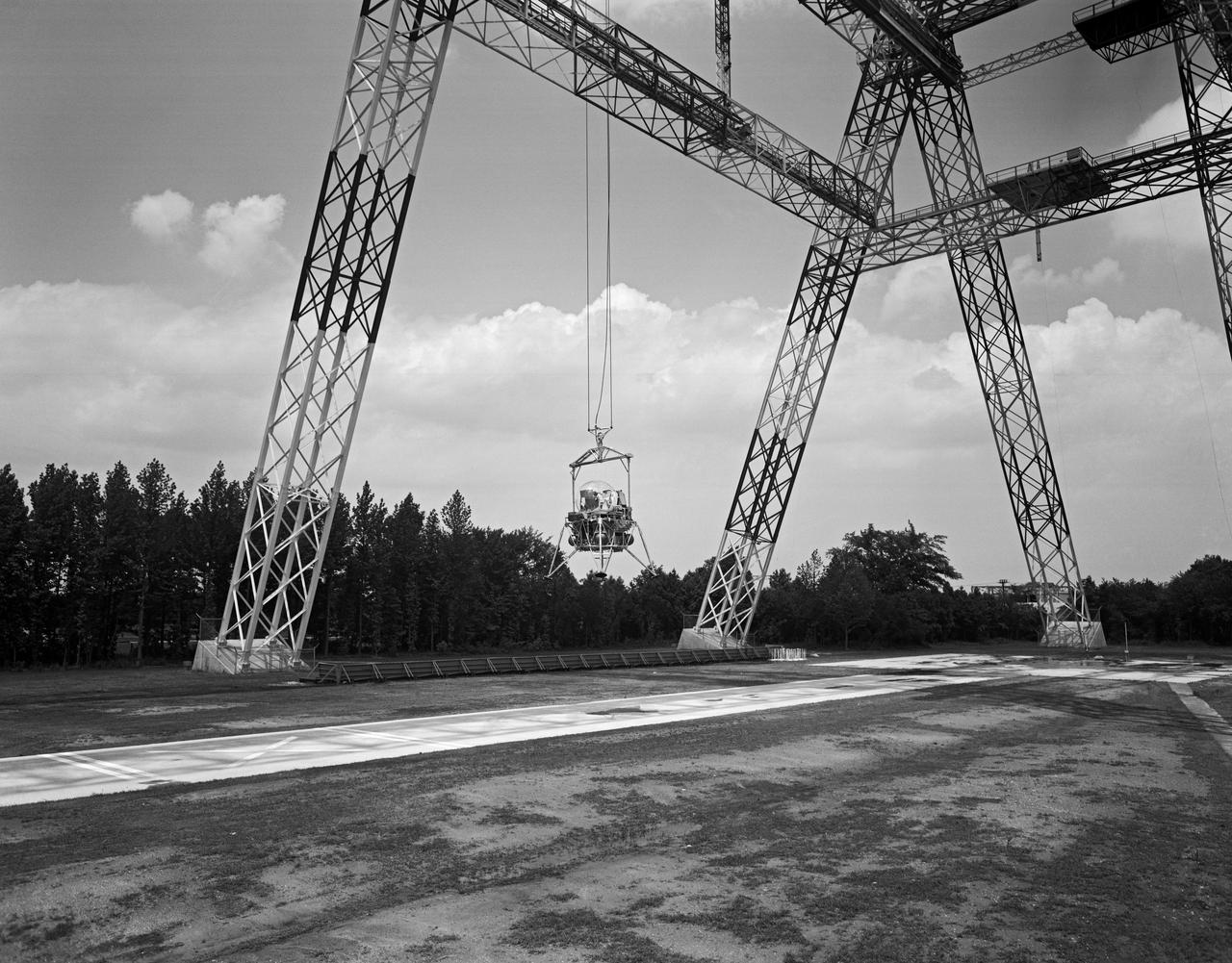

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
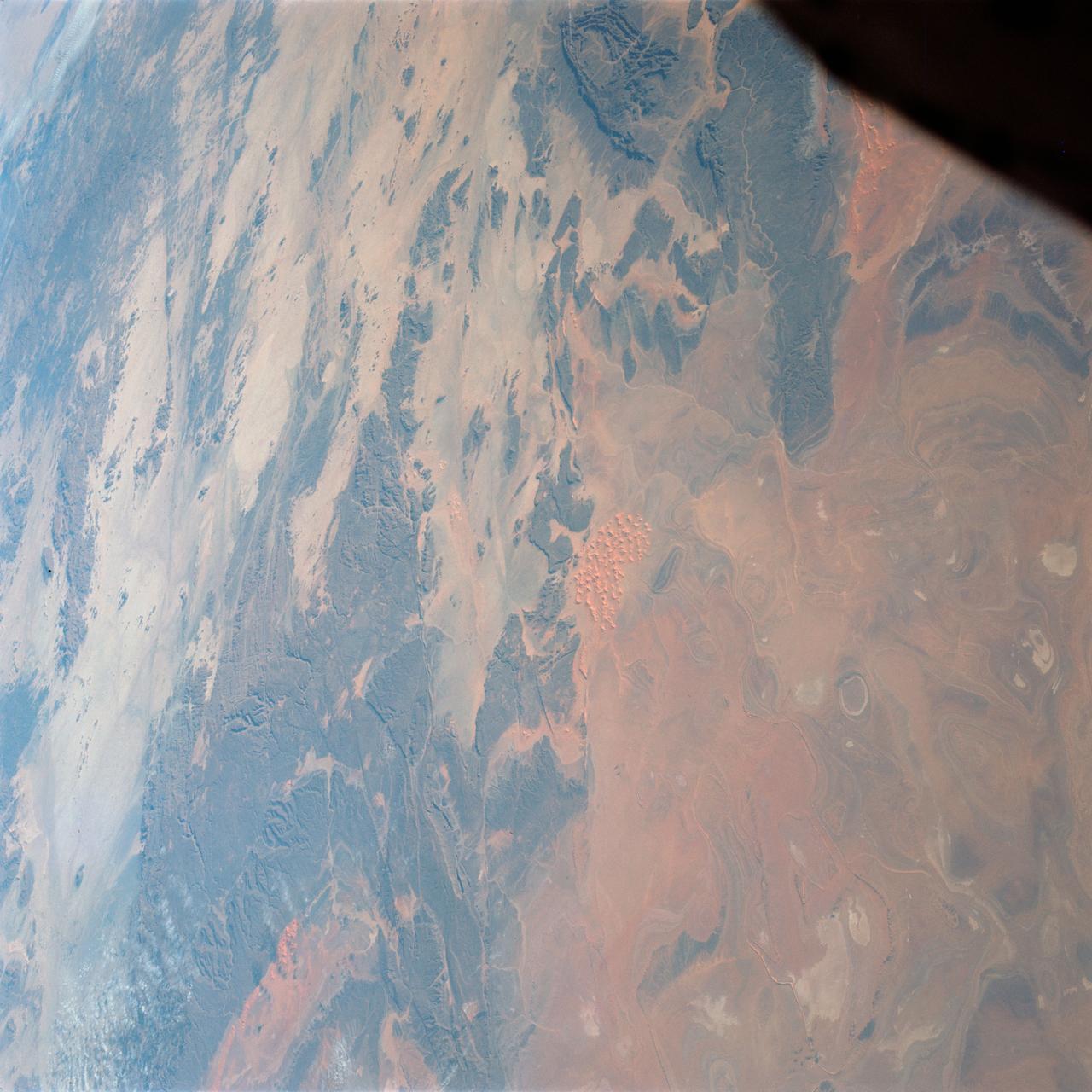

S65-63784 (7 Dec. 1965) --- Algeria, south of Celemb Bechar, as seen from the orbiting Gemini-7 spacecraft during its 42nd revolution of Earth. Note rain runoff on the desert floor. Astronaut Frank Borman and James A. Lovell Jr. were aboard the National Aeronautics and Space Administration?s Gemini-7 spacecraft. The photograph was taken with a modified 70mm Hasselblad camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome MS (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA
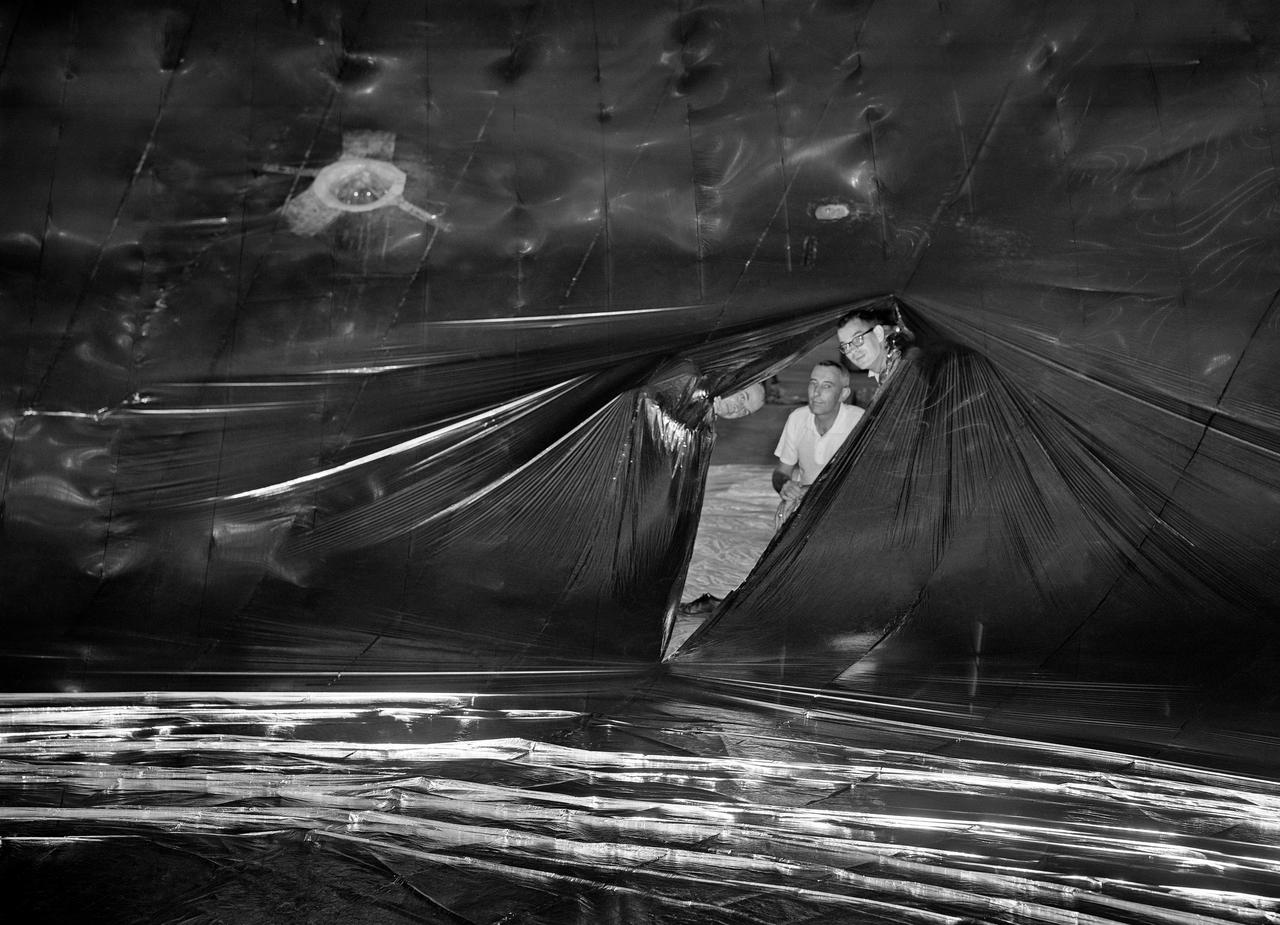

Inflation Tests of the Echo 1 Satellite in Weeksville, N.C. 1958-L-03603 Image Langley engineers Edwin Kilgore (center), Norman Crabill (right) and an unidentified man take a peek inside the vast balloon during inflation tests. Page. 183 Space Flight Revolution NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo. NASA SP-4308.
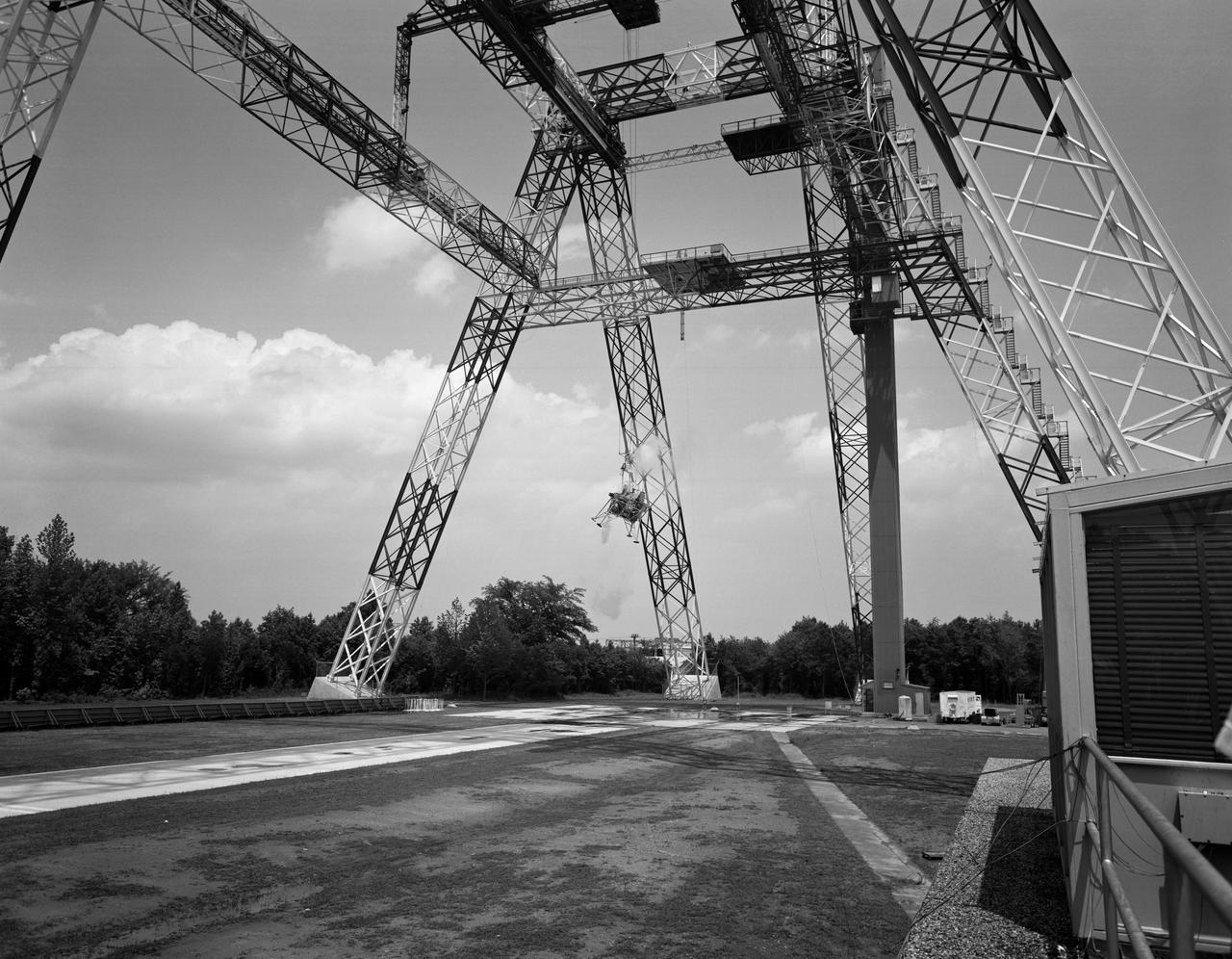

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
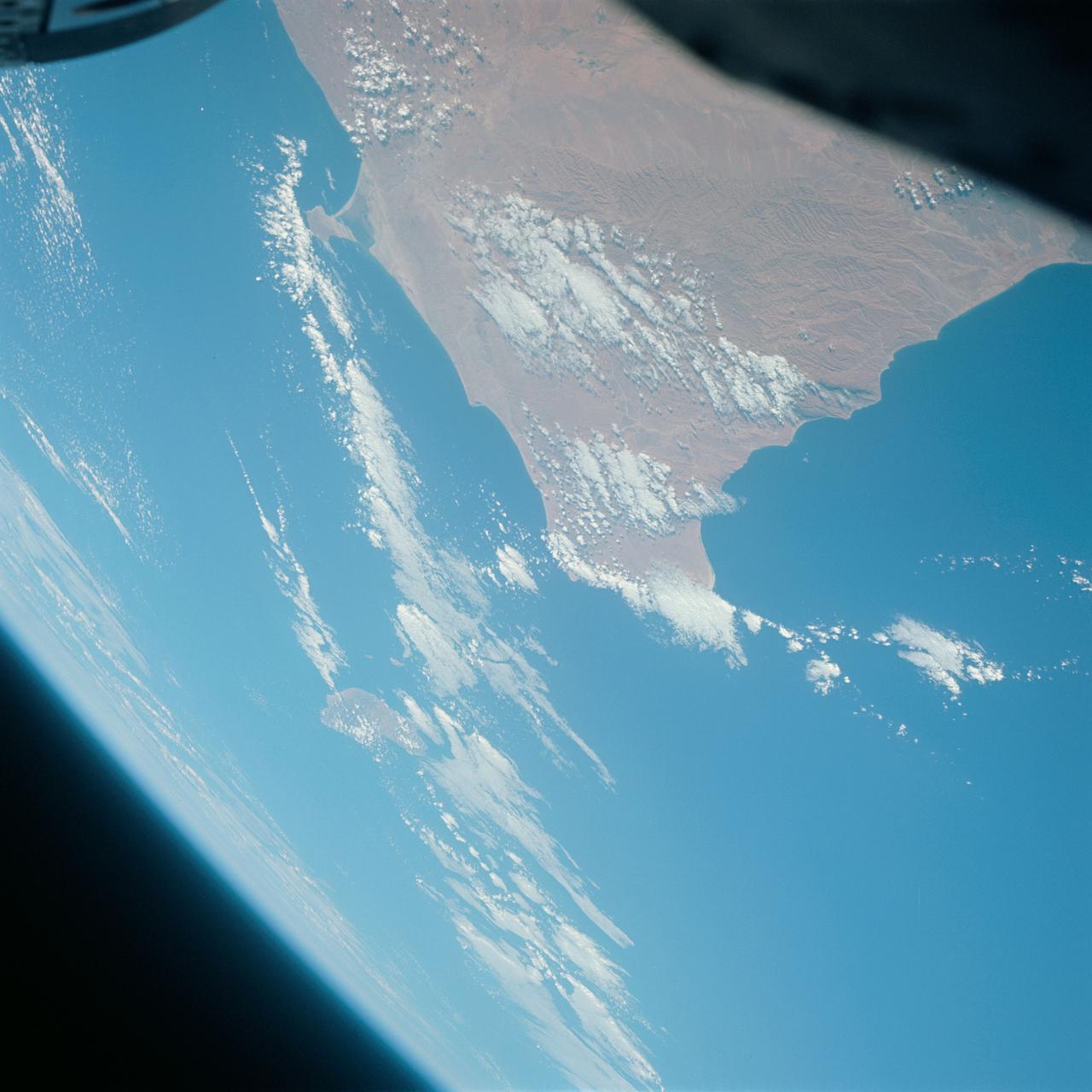

S65-63766 (12 Dec. 1965) --- Ras Azir on the coast of the Republic of Somali, looking east, as seen from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's Gemini-7 spacecraft during its 117th revolution of Earth. Taken with a modified 70mm Hasselblad camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome MS (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA
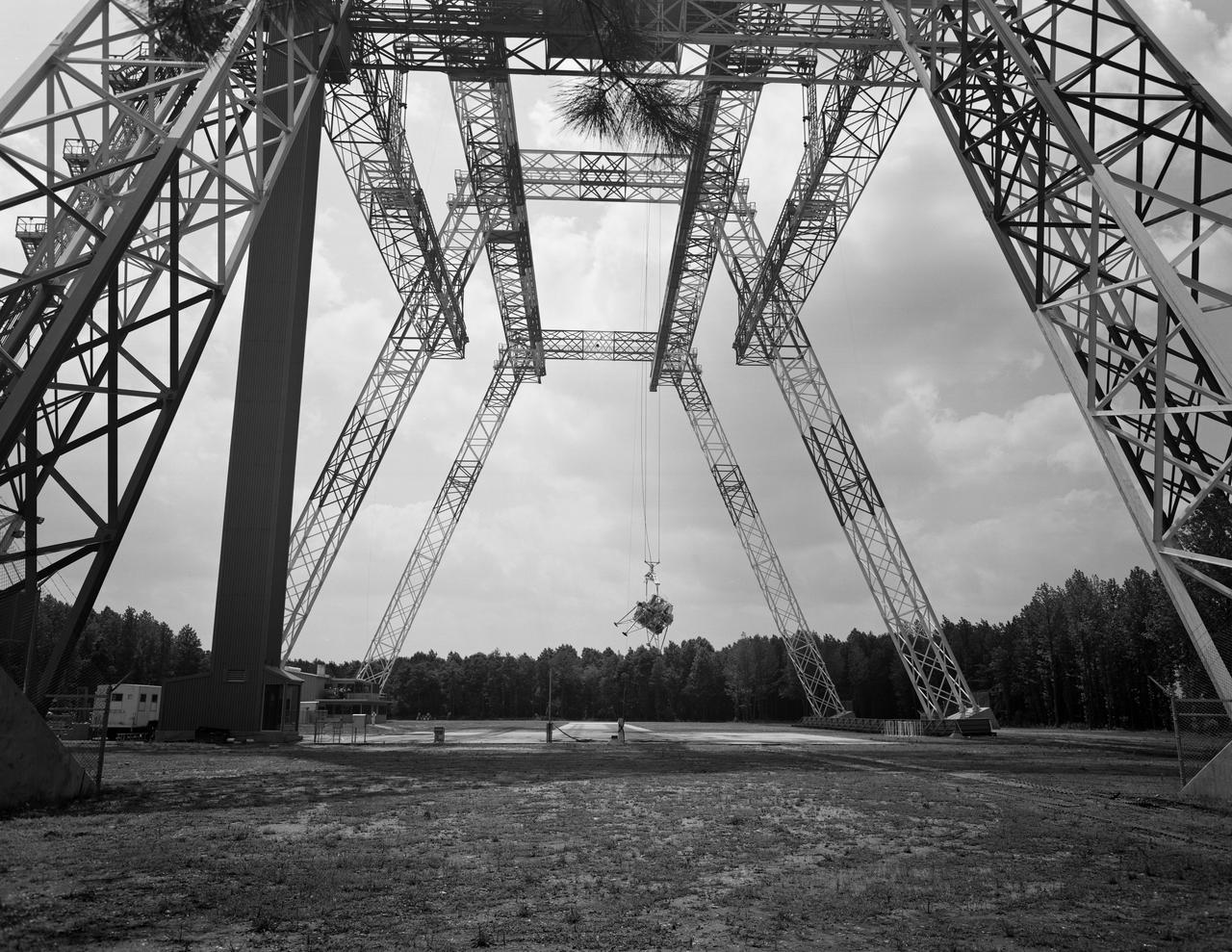

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
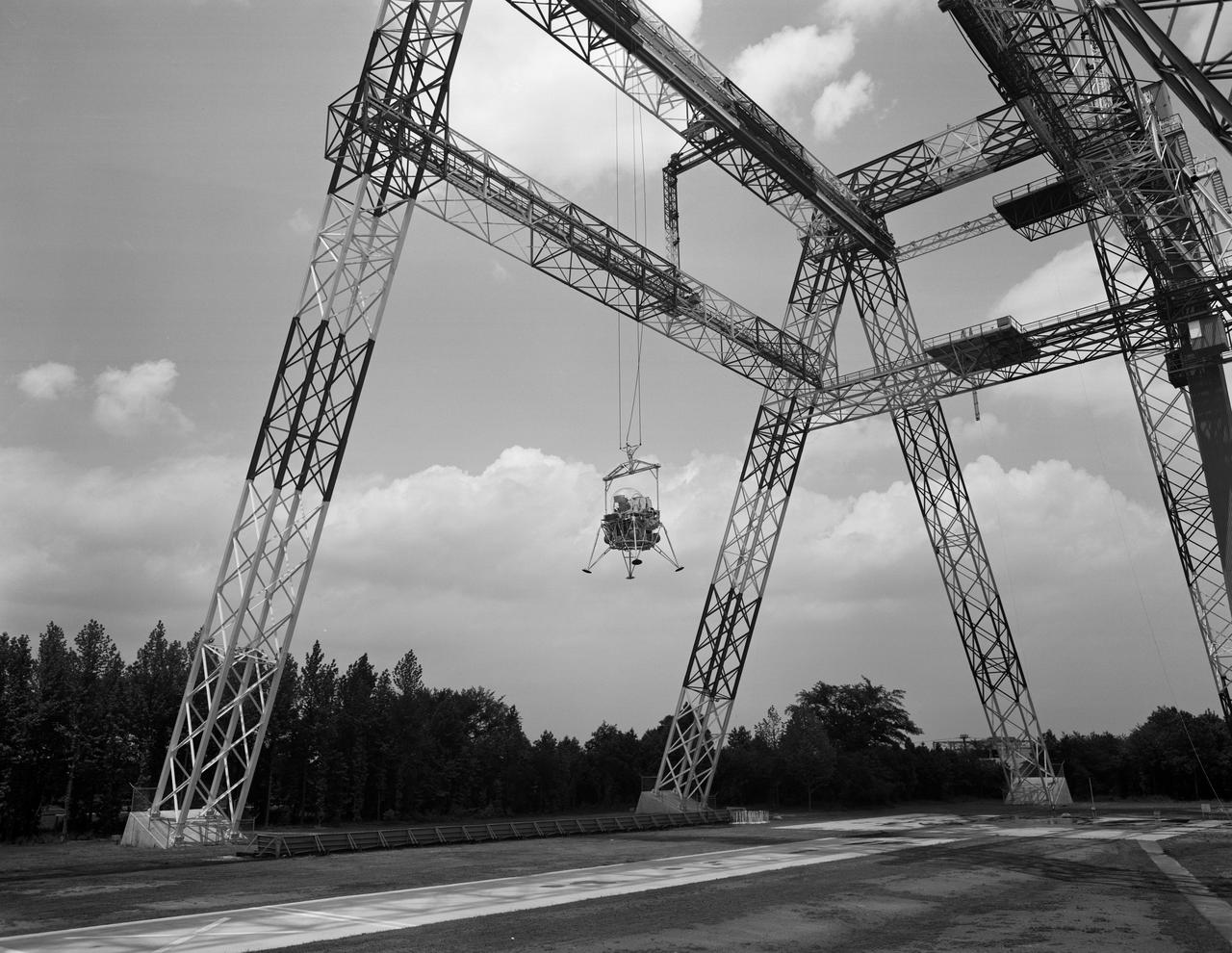

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
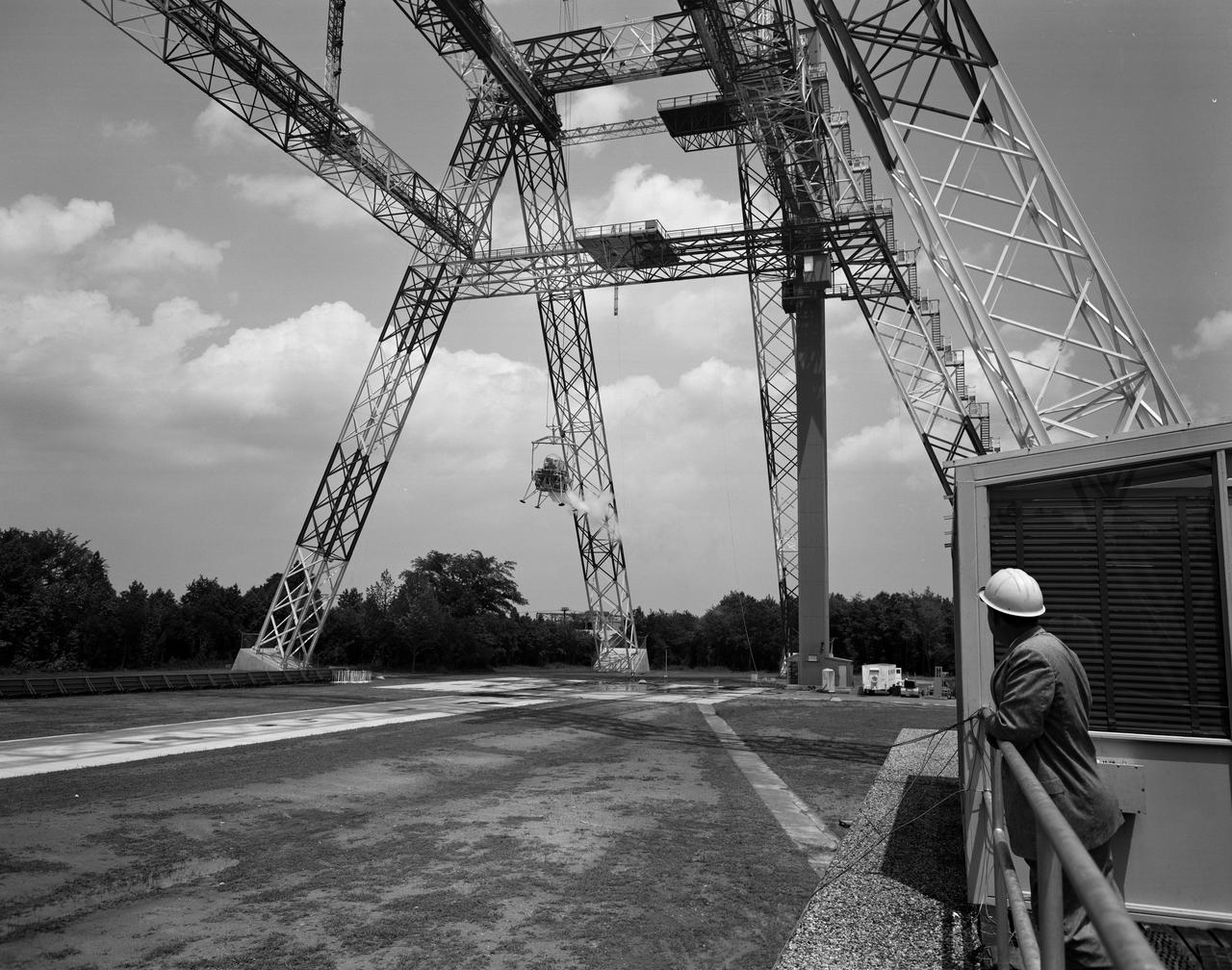

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
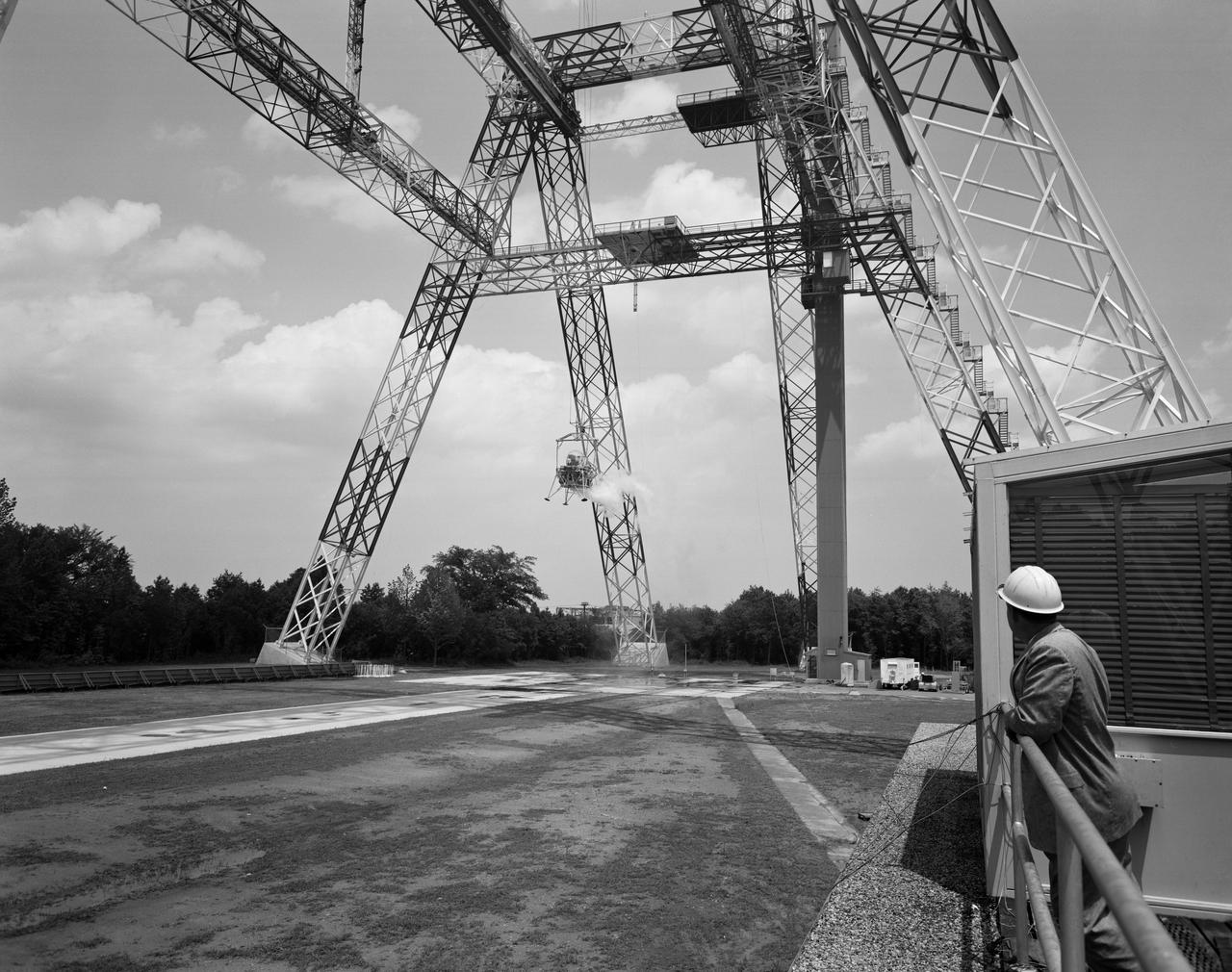

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
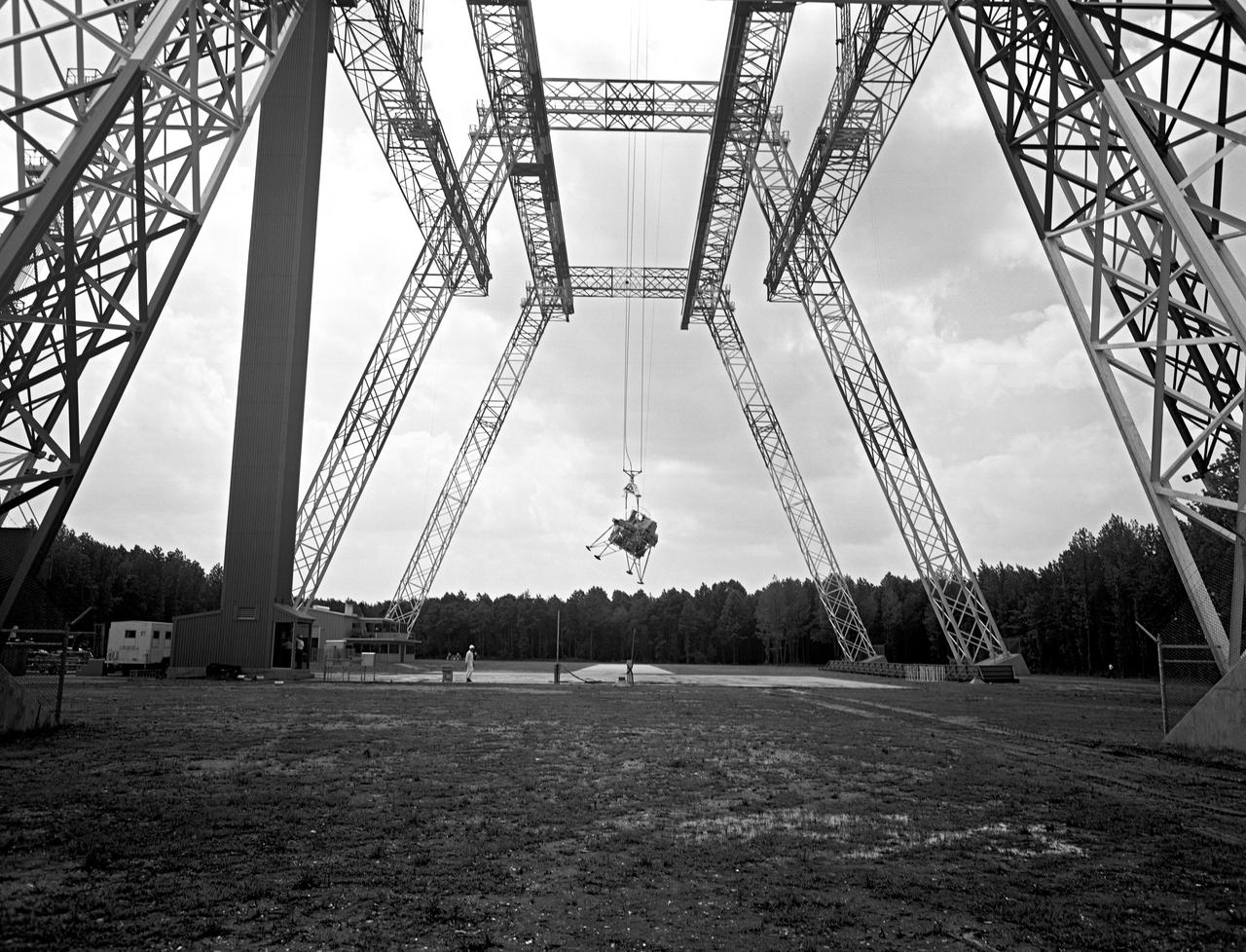

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
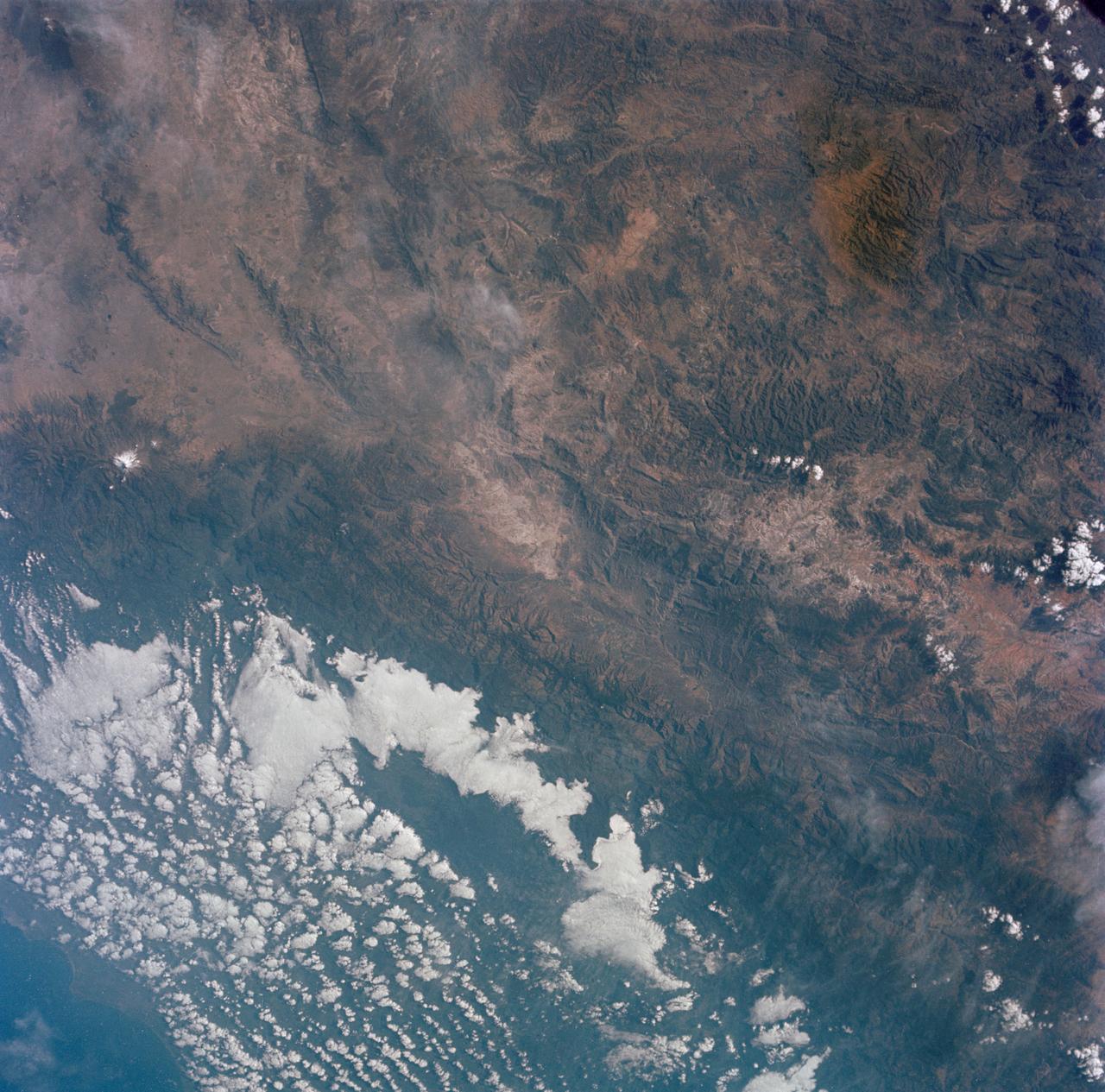

S65-63758 (11 Dec. 1965) --- The states of Puebla, Vera Cruz, Tlaxcala and Oaxaca in Mexico, as seen from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration?s Gemini-7 spacecraft during its 107th revolution of Earth. Taken with a modified 70mm Hasselblad camera, with Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome MS (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA
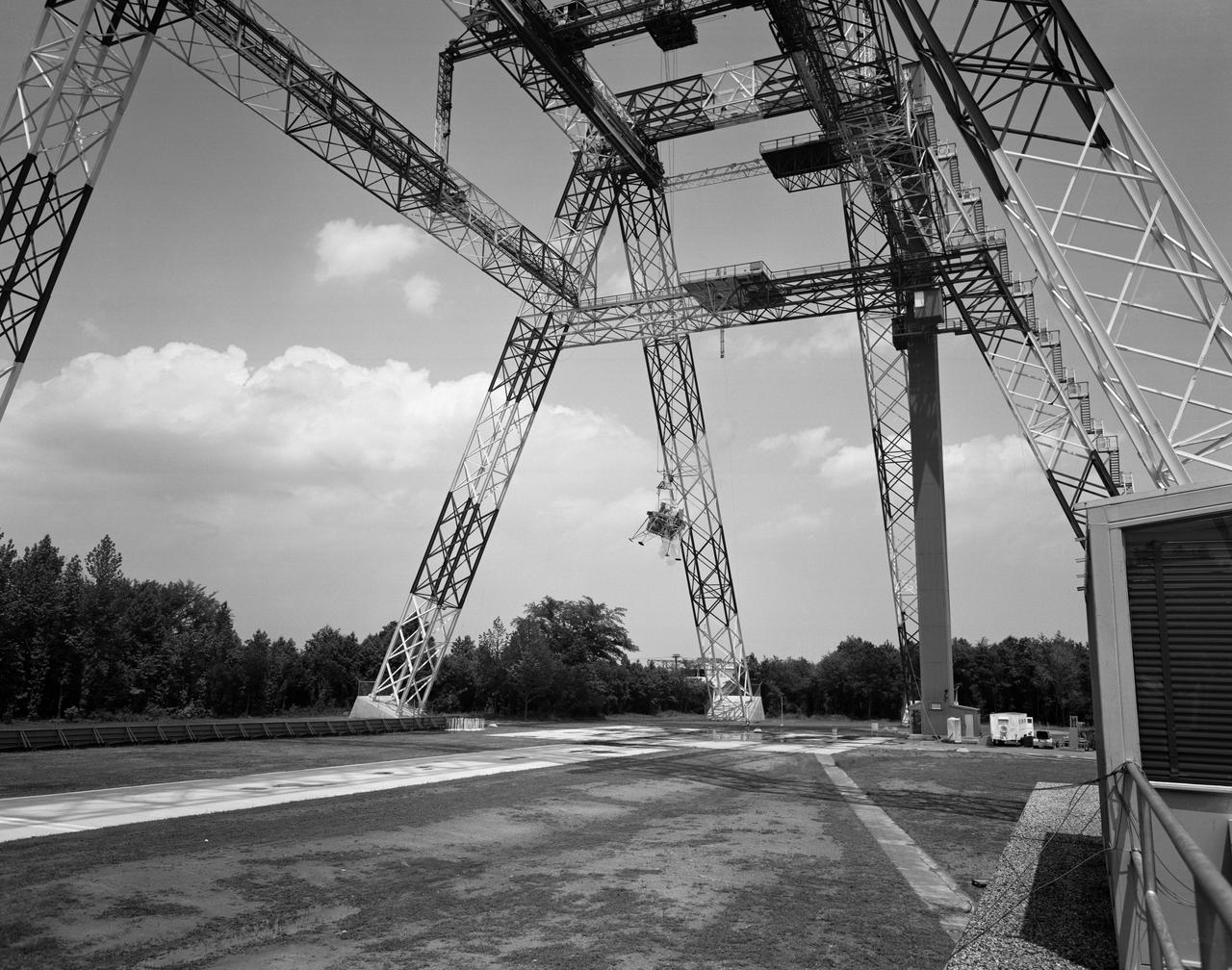

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
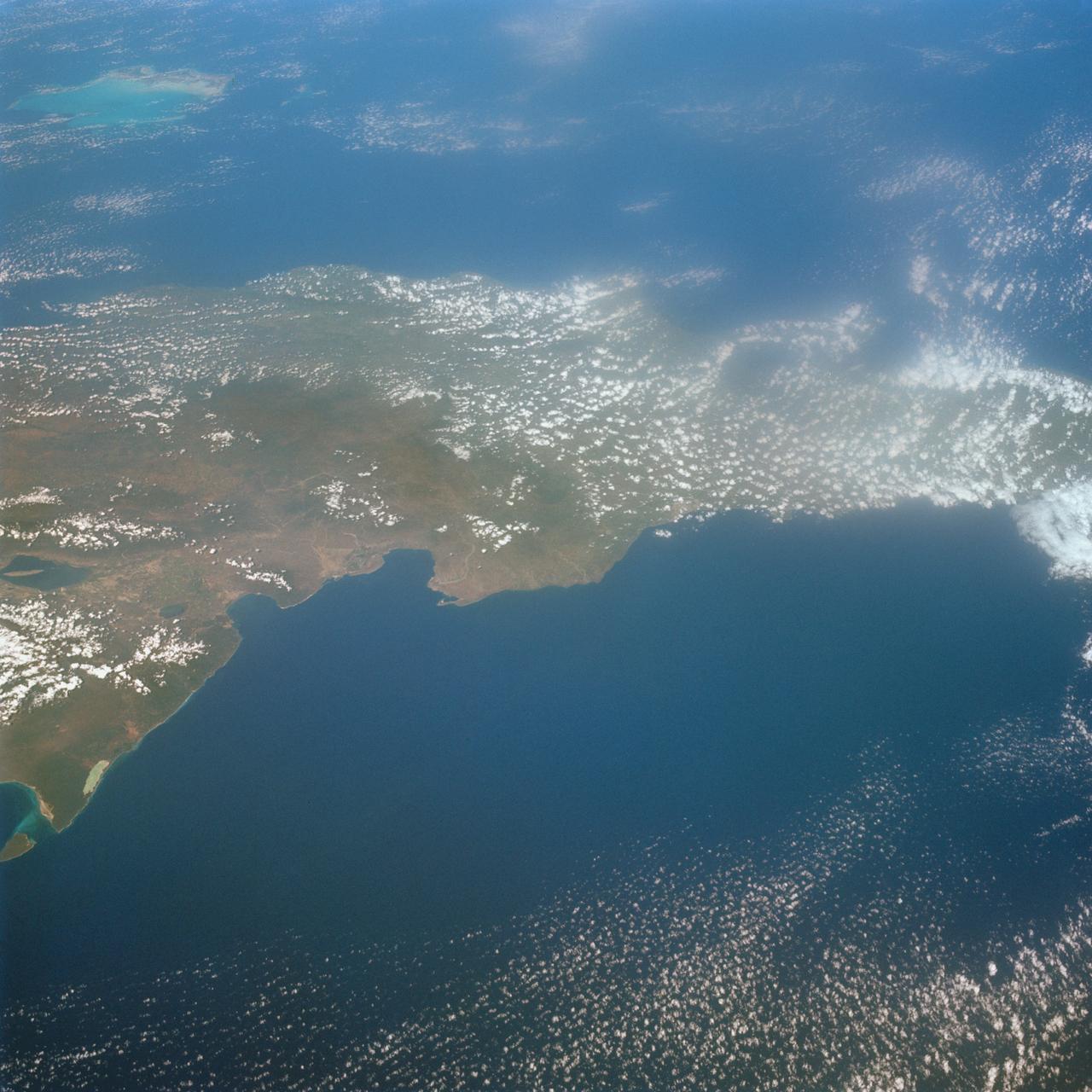

S65-63926 (16 Dec. 1965) --- Island of Hispaniola, Dominican Republic end, as seen from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's Gemini-7 spacecraft during its 179th revolution of Earth. North is toward the left of the picture. This photograph was taken with a modified 70mm Hasselblad camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome MS (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA
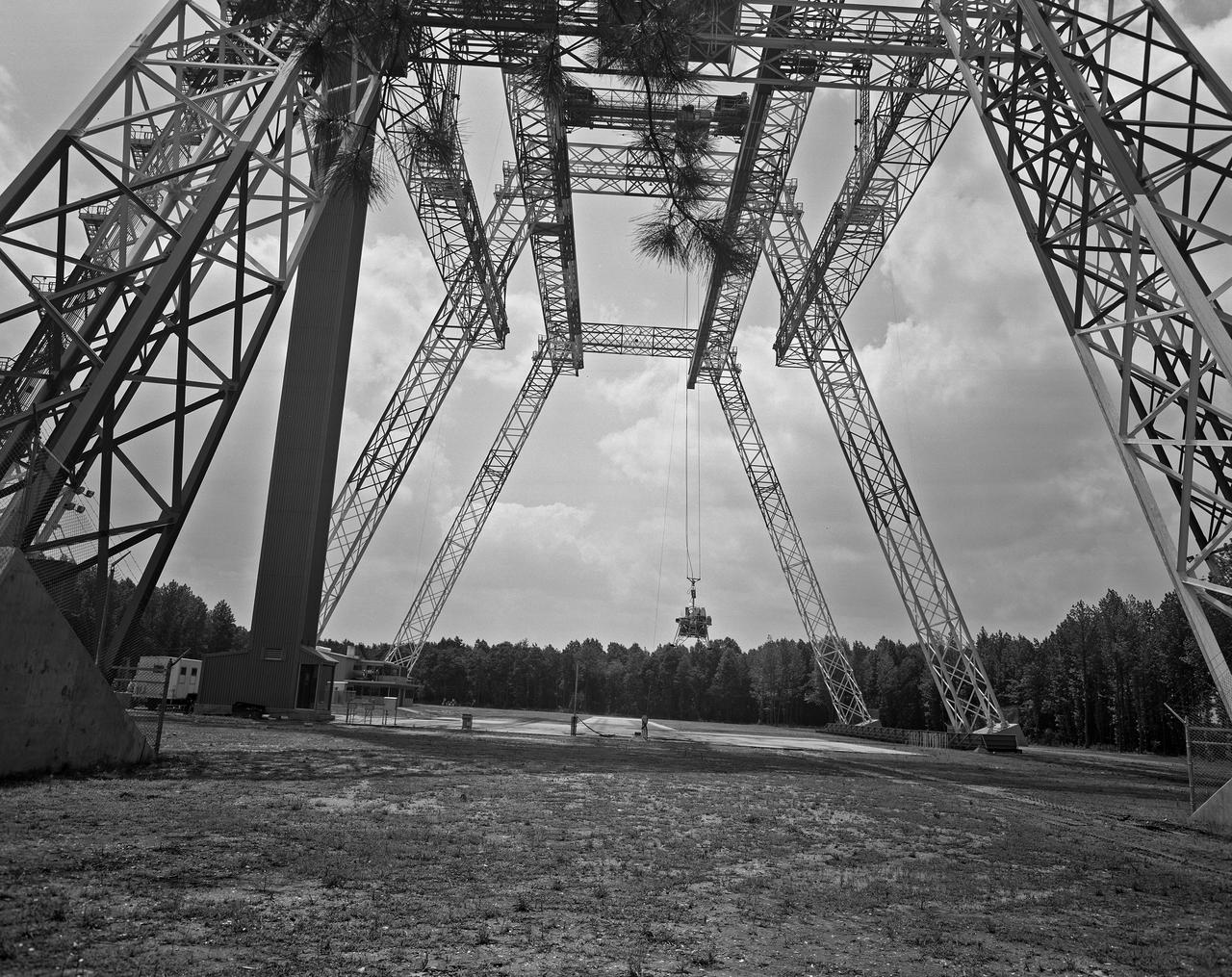

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
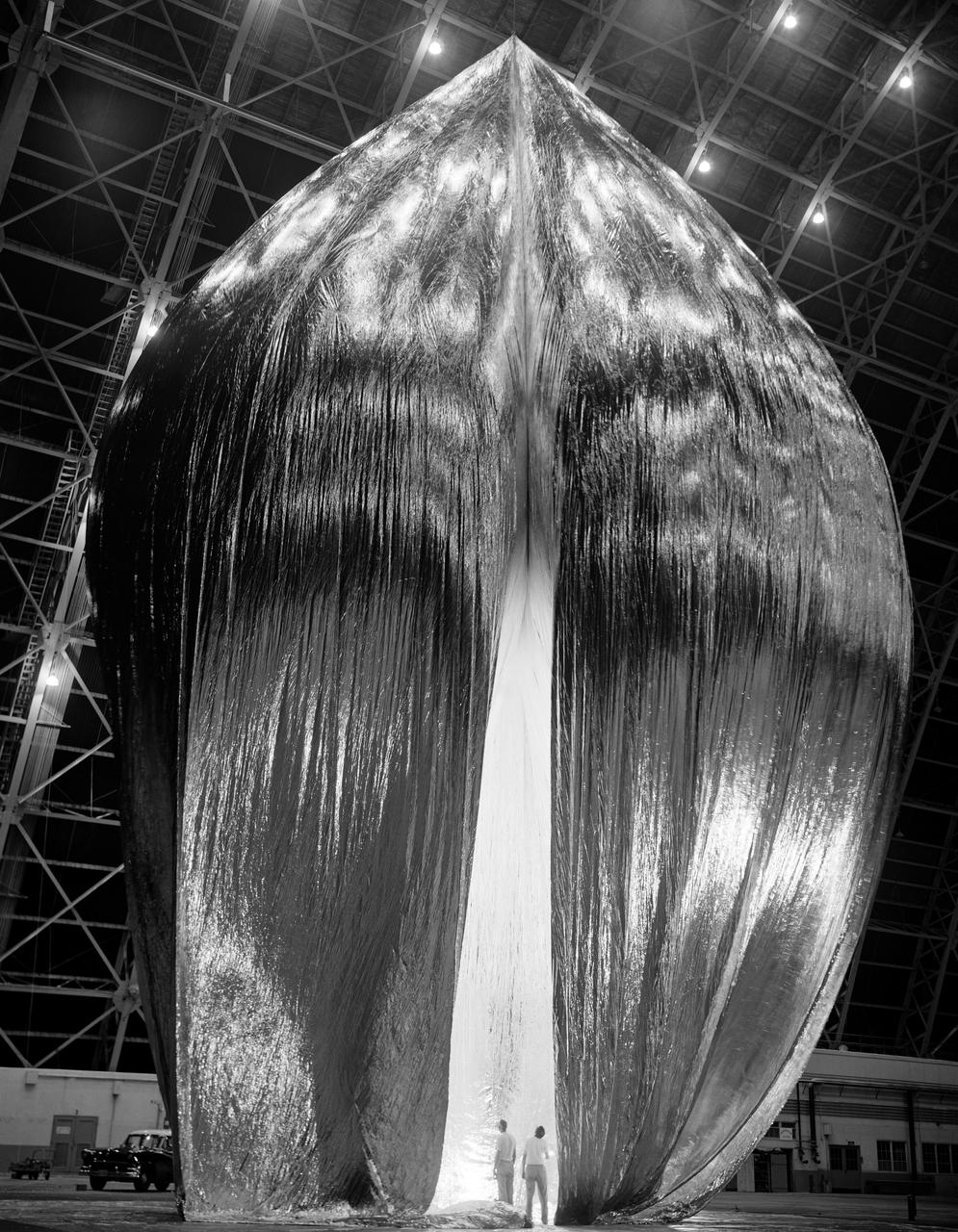

Inflation Tests of the Echo 1 Satellite in Weeksville, N.C. 1958-L-03603 Image Langley engineers Edwin Kilgore (center), Norman Crabill (right) and an unidentified man take a peek inside the vast balloon during inflation tests. Page. 183 Space Flight Revolution NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo. NASA SP-4308.
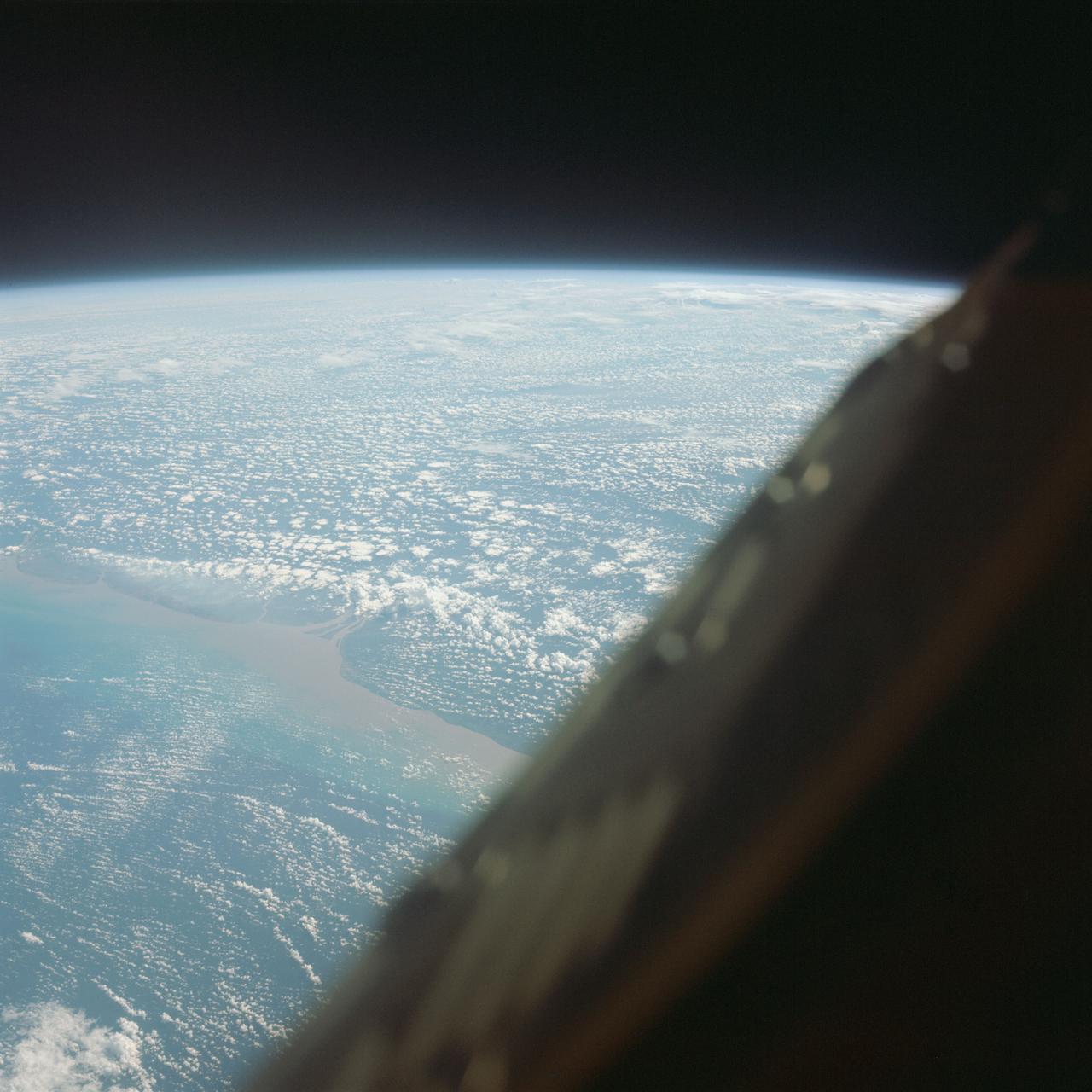

S65-64029 (13 Dec. 1965) --- Coast of British Guiana, South America, looking south, as seen from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration?s Gemini-7 spacecraft during its 135th revolution of Earth. This photograph was taken with a modified 70mm Hasselblad camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome MS (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA
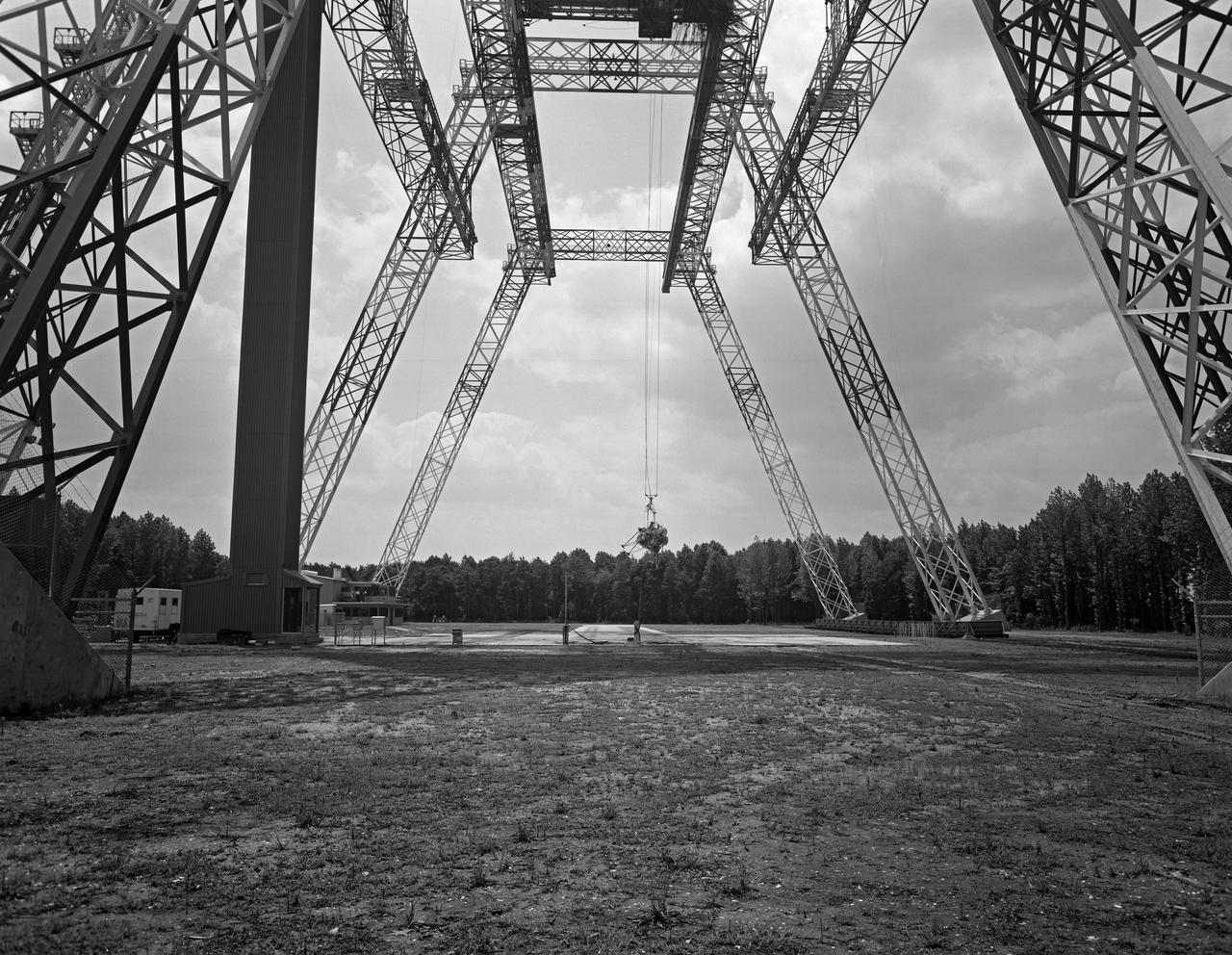

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
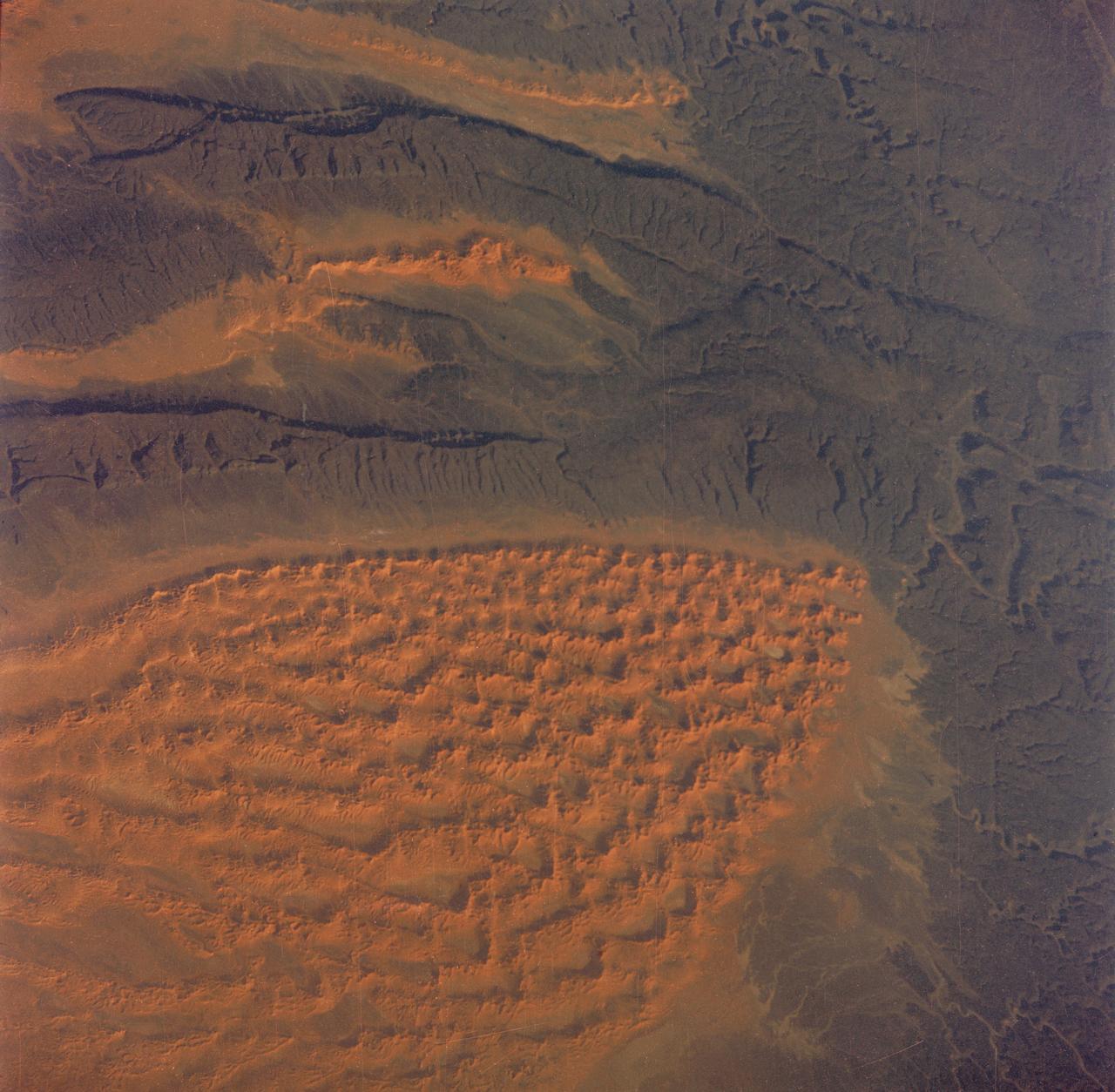
S65-63829 (5 Dec. 1965) --- Algeria, south of the Fort Flatters area, as seen from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration?s Gemini-7 spacecraft during its 13th revolution of Earth. The orange color area is the Tifermine Sand Dunes that reach a height of 1,000 feet. The photograph was taken with a modified 70mm Hasselblad camera, with Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome MS (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA
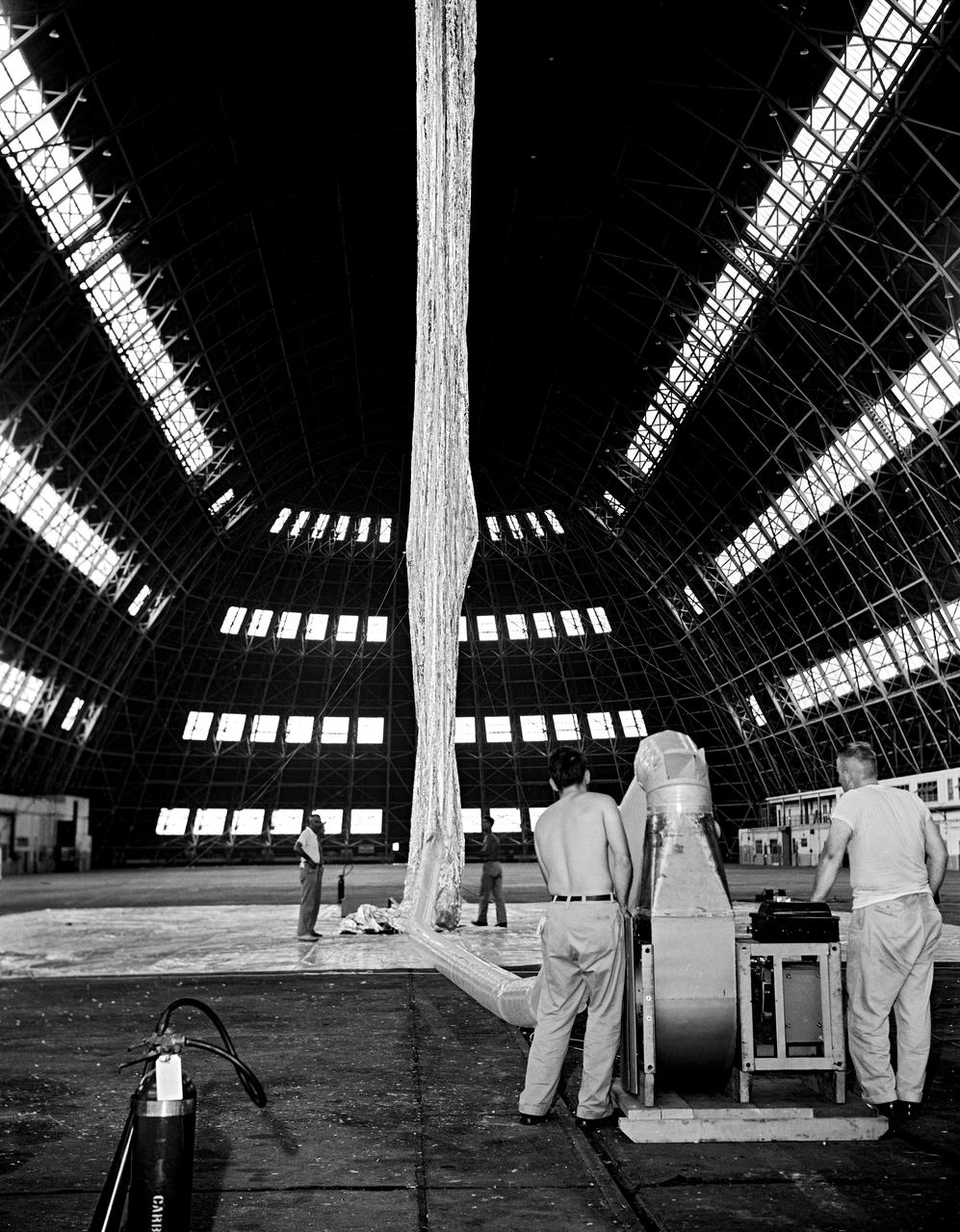

Inflation Tests of the Echo 1 Satellite in Weeksville, N.C. 1958-L-03603 Image Langley engineers Edwin Kilgore (center), Norman Crabill (right) and an unidentified man take a peek inside the vast balloon during inflation tests. Page. 183 Space Flight Revolution NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo. NASA SP-4308.
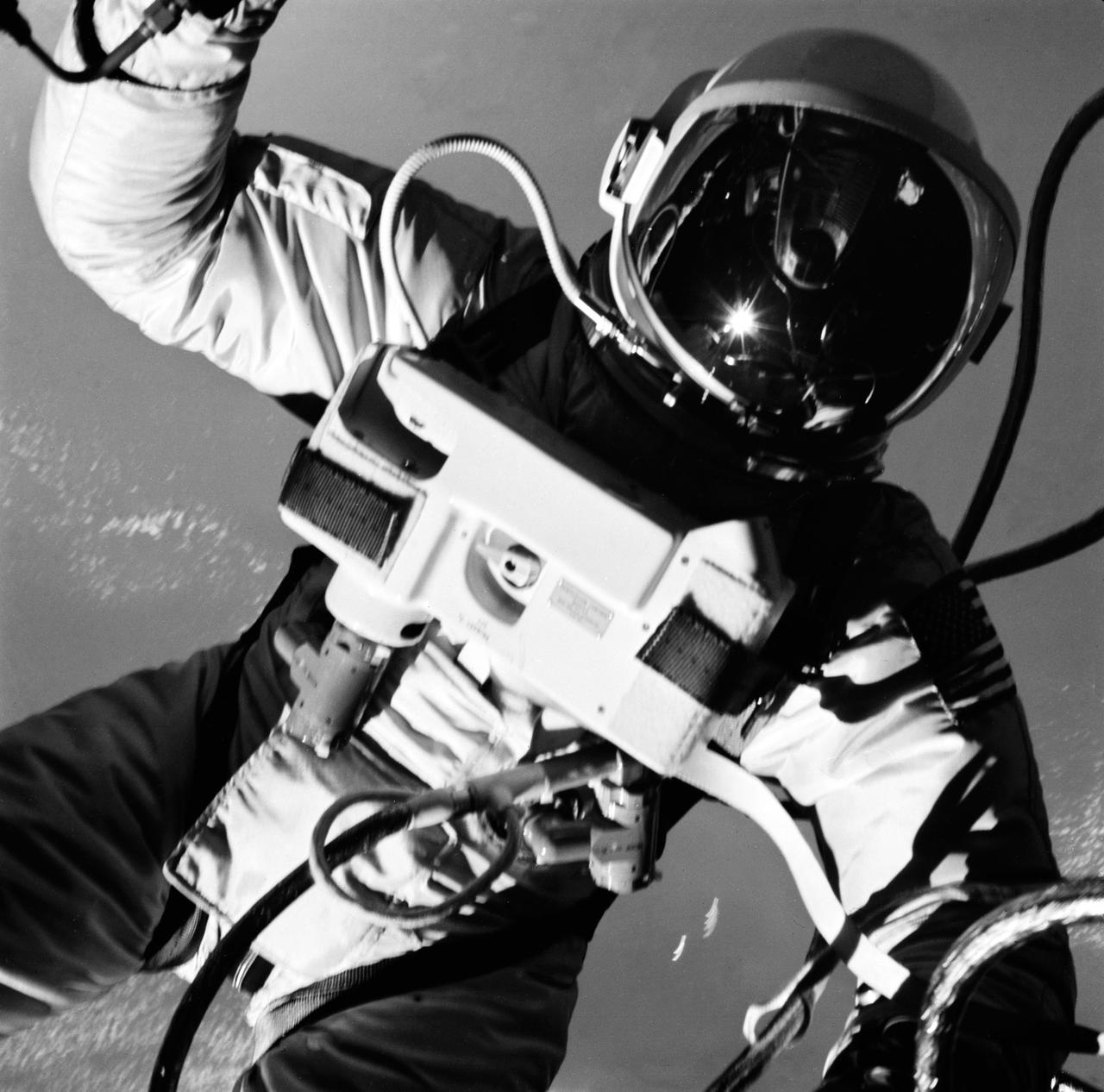

S65-30271 (3 June 1965) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot on the Gemini-Titan IV (GT-4) spaceflight, floats in the zero gravity of space outside the Gemini IV spacecraft. His face is covered by a shaded visor to protect him from the unfiltered rays of the sun. White became the first American astronaut to walk in space. He remained outside the spacecraft for 21 minutes during the third revolution of the Gemini IV mission. He wears a specially designed spacesuit for the EVA. His right hand (out of frame) is holding the Hand-Held Self-Maneuvering Unit (HHSMU), with which he controlled his movements while in space, and a camera is attached to the HHSMU. He was attached to the spacecraft by a 25-feet umbilical line and a 23-feet tether line, both wrapped together with gold tape to form one cord. He wears an emergency oxygen supply check pack. Astronaut James A. McDivitt is command pilot for the GT-4 mission. The mission was a four-day, 62-revolution flight, during which McDivitt and White performed a series of scientific and engineering experiments. (This image is black and white) Photo credit: NASA EDITOR?S NOTE: Astronaut Edward H. White II died in the Apollo/Saturn 204 fire at Cape Kennedy, Florida, on Jan. 27, 1967.
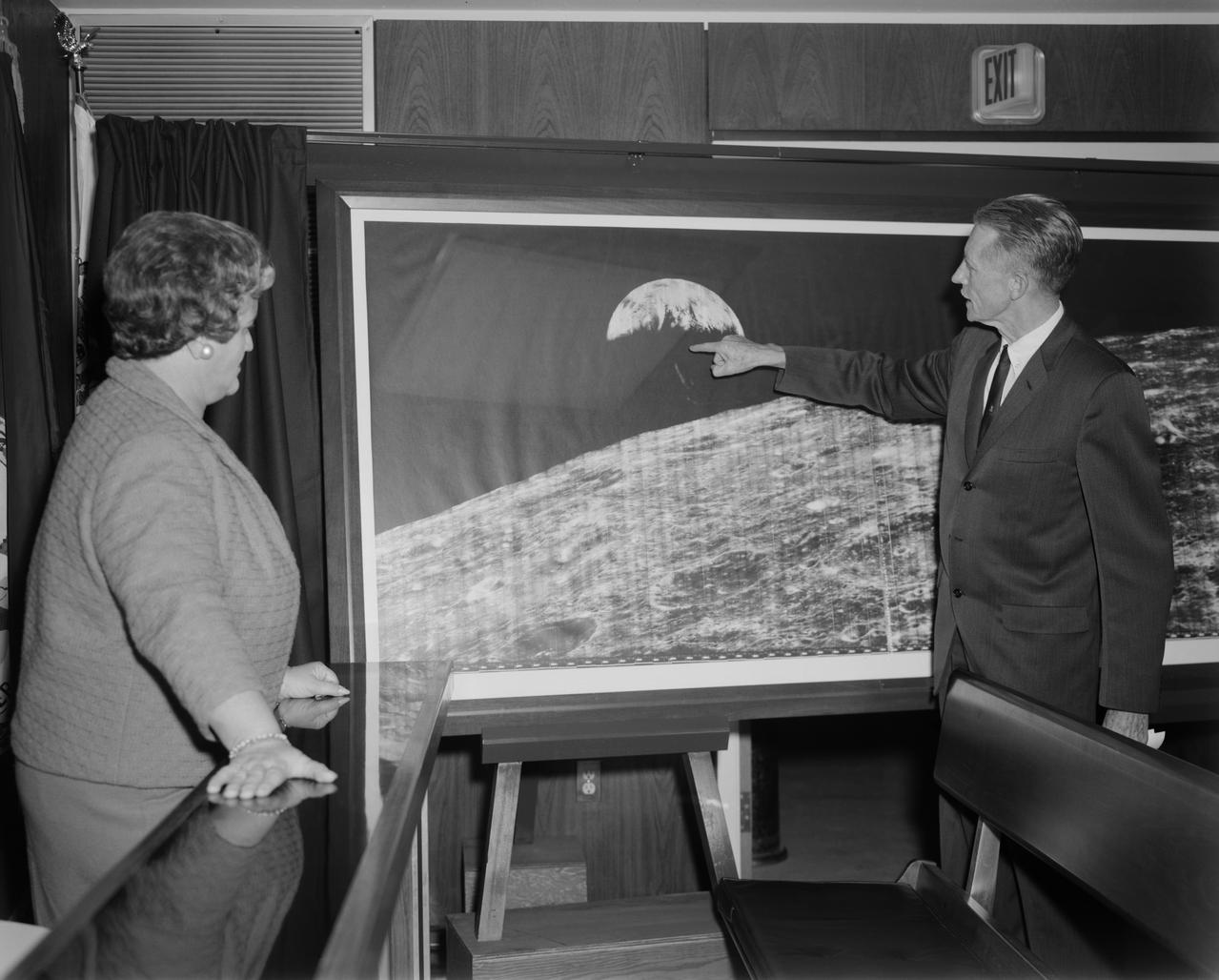

Langley Center Director Floyd Thompson shows Ann Kilgore the "picture of the century." This was the first picture of the earth taken from space. From Spaceflight Revolution: "On 23 August 1966 just as Lunar Orbiter I was about to pass behind the moon, mission controllers executed the necessary maneuvers to point the camera away from the lunar surface and toward the earth. The result was the world's first view of the earth from space. It was called "the picture of the century' and "the greatest shot taken since the invention of photography." Not even the color photos of the earth taken during the Apollo missions superseded the impact of this first image of our planet as a little island of life floating in the black and infinite sea of space." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), pp. 345-346. Mayor Ann Kilgore was married to NASA researcher Edwin Carroll Kilgore. Mrs. Kilgore was Mayor from 1963-1971 and again from 1974-1978.
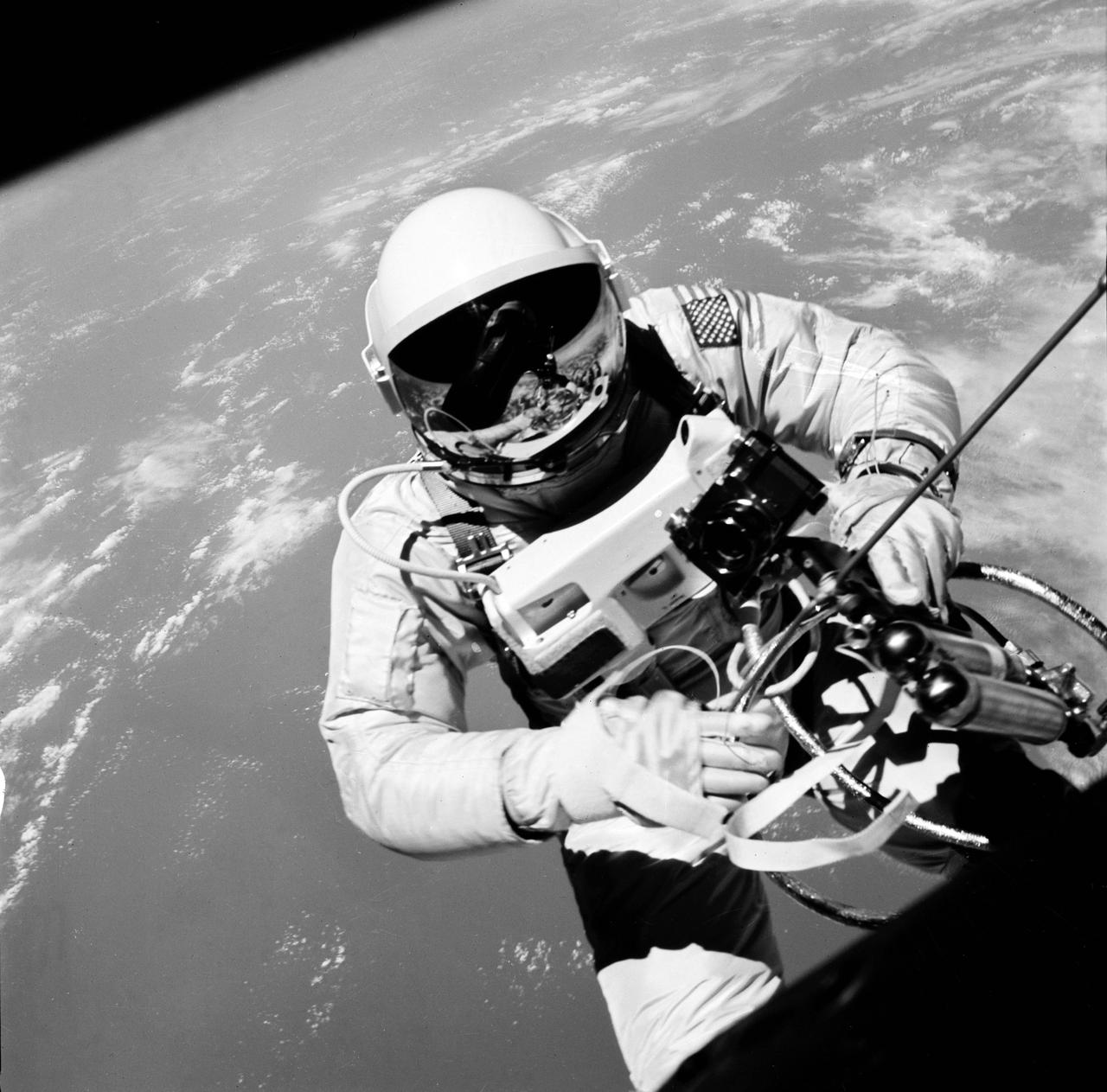

S65-30202 (3 June 1965) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot on the Gemini-Titan IV (GT-4) spaceflight, floats in the zero gravity of space outside the Gemini IV spacecraft. His face is covered by a shaded visor to protect him from the unfiltered rays of the sun. White became the first American astronaut to walk in space. He remained outside the spacecraft for 21 minutes during the third revolution of the Gemini IV mission. He wears a specially designed spacesuit for the EVA. He?s holding the Hand-Held Self-Maneuvering Unit (HHSMU), with which he controlled his movements while in space, and a camera is attached to the HHSMU. He was attached to the spacecraft by a 25-feet umbilical line and a 23-feet tether line, both wrapped together with gold tape to form one cord. He wears an emergency oxygen supply check pack. Astronaut James A. McDivitt is command pilot for the GT-4 mission. The mission was a four-day, 62-revolution flight, during which McDivitt and White performed a series of scientific and engineering experiments. (This image is black and white) Photo credit: NASA EDITOR?S NOTE: Astronaut Edward H. White II died in the Apollo/Saturn 204 fire at Cape Kennedy, Florida, on Jan. 27, 1967.
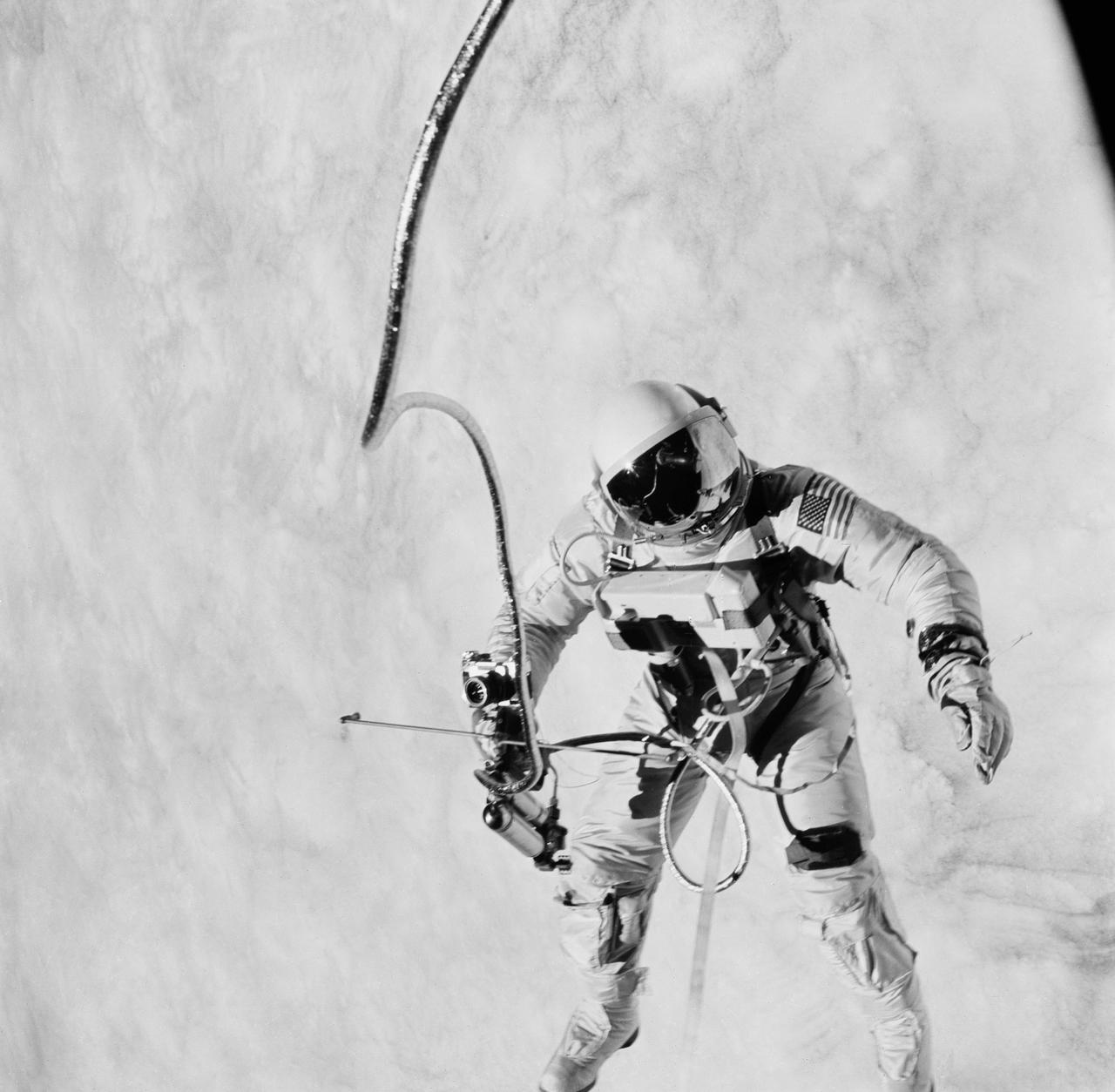

S65-30272 (3 June 1965) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot on the Gemini-Titan IV (GT-4) spaceflight, floats in the zero gravity of space outside the Gemini IV spacecraft. His face is covered by a shaded visor to protect him from the unfiltered rays of the sun. White became the first American astronaut to walk in space. He remained outside the spacecraft for 21 minutes during the third revolution of the Gemini IV mission. He wears a specially designed spacesuit for the EVA. His right hand is holding the Hand-Held Self-Maneuvering Unit (HHSMU), with which he controlled his movements while in space, and a camera is attached to the HHSMU. He was attached to the spacecraft by a 25-feet umbilical line and a 23-feet tether line, both wrapped together with gold tape to form one cord. He wears an emergency oxygen supply check pack. Astronaut James A. McDivitt is command pilot for the GT-4 mission. The mission was a four-day, 62-revolution flight, during which McDivitt and White performed a series of scientific and engineering experiments. (This image is black and white) Photo credit: NASA EDITOR?S NOTE: Astronaut Edward H. White II died in the Apollo/Saturn 204 fire at Cape Kennedy, Florida, on Jan. 27, 1967.
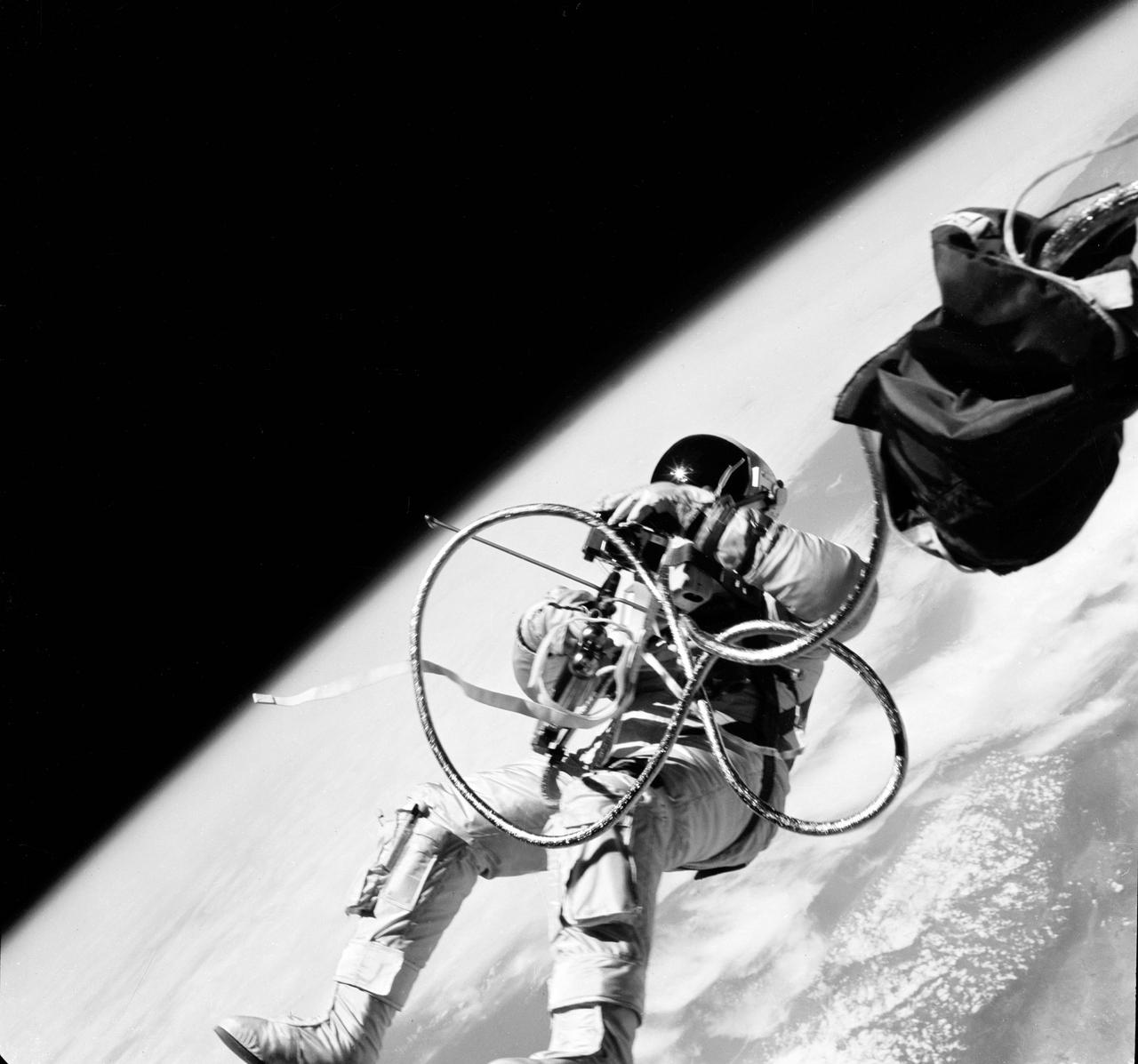

S65-30273 (3 June 1965) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot on the Gemini-Titan IV (GT-4) spaceflight, floats in the zero gravity of space outside the Gemini IV spacecraft. His face is covered by a shaded visor to protect him from the unfiltered rays of the sun. White became the first American astronaut to walk in space. He remained outside the spacecraft for 21 minutes during the third revolution of the Gemini IV mission. He wears a specially designed spacesuit for the EVA. His right hand is holding the Hand-Held Self-Maneuvering Unit (HHSMU), with which he controlled his movements while in space, and a camera is attached to the HHSMU. He was attached to the spacecraft by a 25-feet umbilical line and a 23-feet tether line, both wrapped together with gold tape to form one cord. He wears an emergency oxygen supply check pack. Astronaut James A. McDivitt is command pilot for the GT-4 mission. The mission was a four-day, 62-revolution flight, during which McDivitt and White performed a series of scientific and engineering experiments. (This image is black and white) Photo credit: NASA EDITOR?S NOTE: Astronaut Edward H. White II died in the Apollo/Saturn 204 fire at Cape Kennedy, Florida, on Jan. 27, 1967.

Portrait of John M. Eggleston. Served with John Houbolt on the Manned Space Lab group.
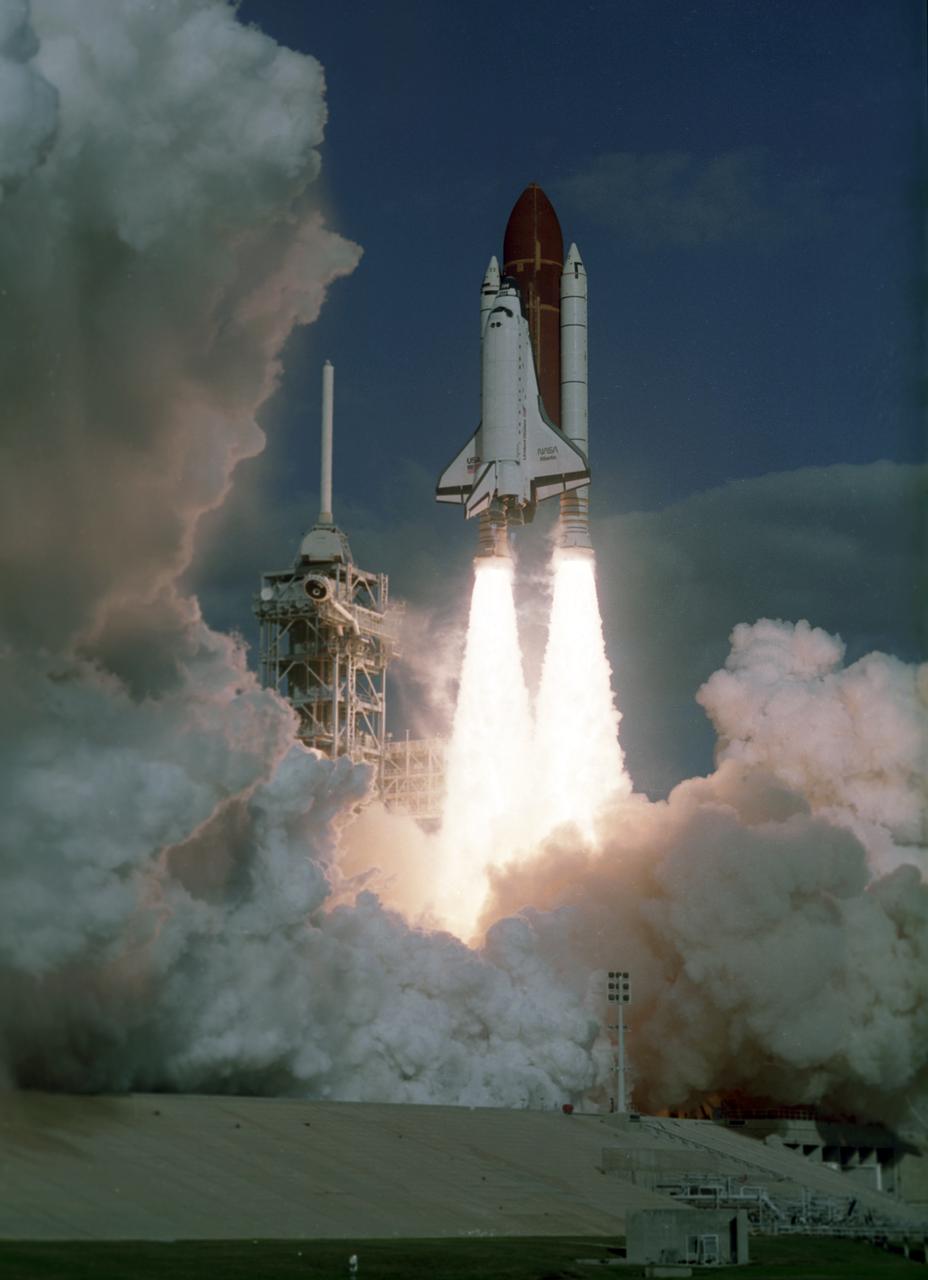

Space Shuttle orbiter Atlantis takes flight on its STS-27 mission, December 2, 1988, utilizing 375,000 pounds of thrust produced by its three main engines. The engines start in 3.9 seconds of ignition and go to static pump speeds of approximately 35,000 revolutions per minute during that time. The Marshall Space Flight Center had management responsibility of Space Shuttle propulsion elements, including the Main Engines. The STS-27 mission, the third mission dedicated to the Department of Defense (DOD), was crewed by five astronauts: Robert L. Gibson, commander; Guy S. Gardner, pilot; and mission specialists Richard M. Mullane, Jerry L. Ross, and William M. Shepherd.
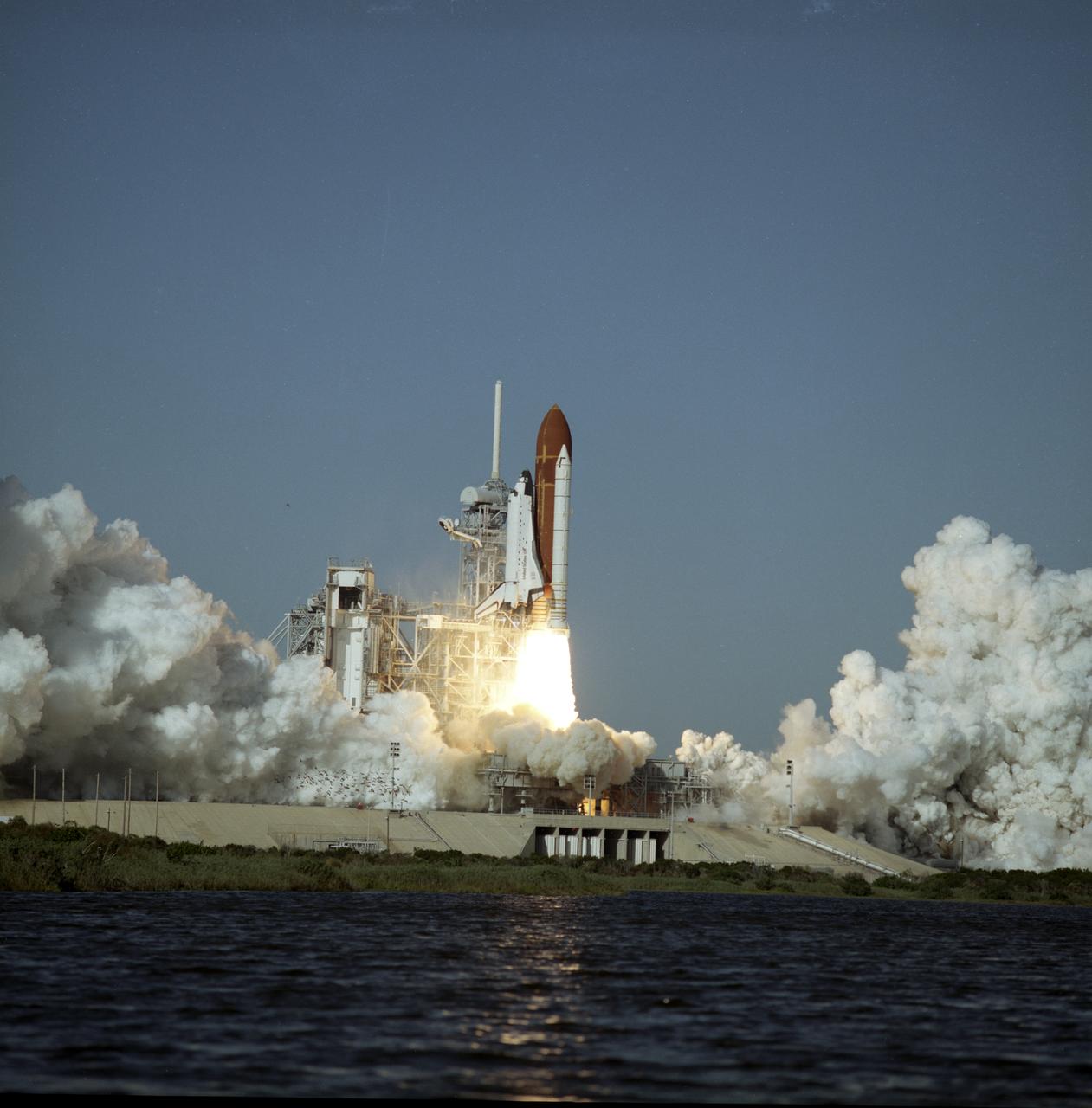

Space Shuttle orbiter Atlantis takes flight on its STS-27 mission, December 2, 1988, utilizing 375,000 pounds of thrust produced by its three main engines. The engines start in 3.9 seconds of ignition and go to static pump speeds of approximately 35,000 revolutions per minute during that time. The Marshall Space Flight Center had management responsibility of Space Shuttle propulsion elements, including the Main Engines. The STS-27 mission, the third mission dedicated to the Department of Defense (DOD), was crewed by five astronauts: Robert L. Gibson, commander; Guy S. Gardner, pilot; and mission specialists Richard M. Mullane, Jerry L. Ross, and William M. Shepherd.
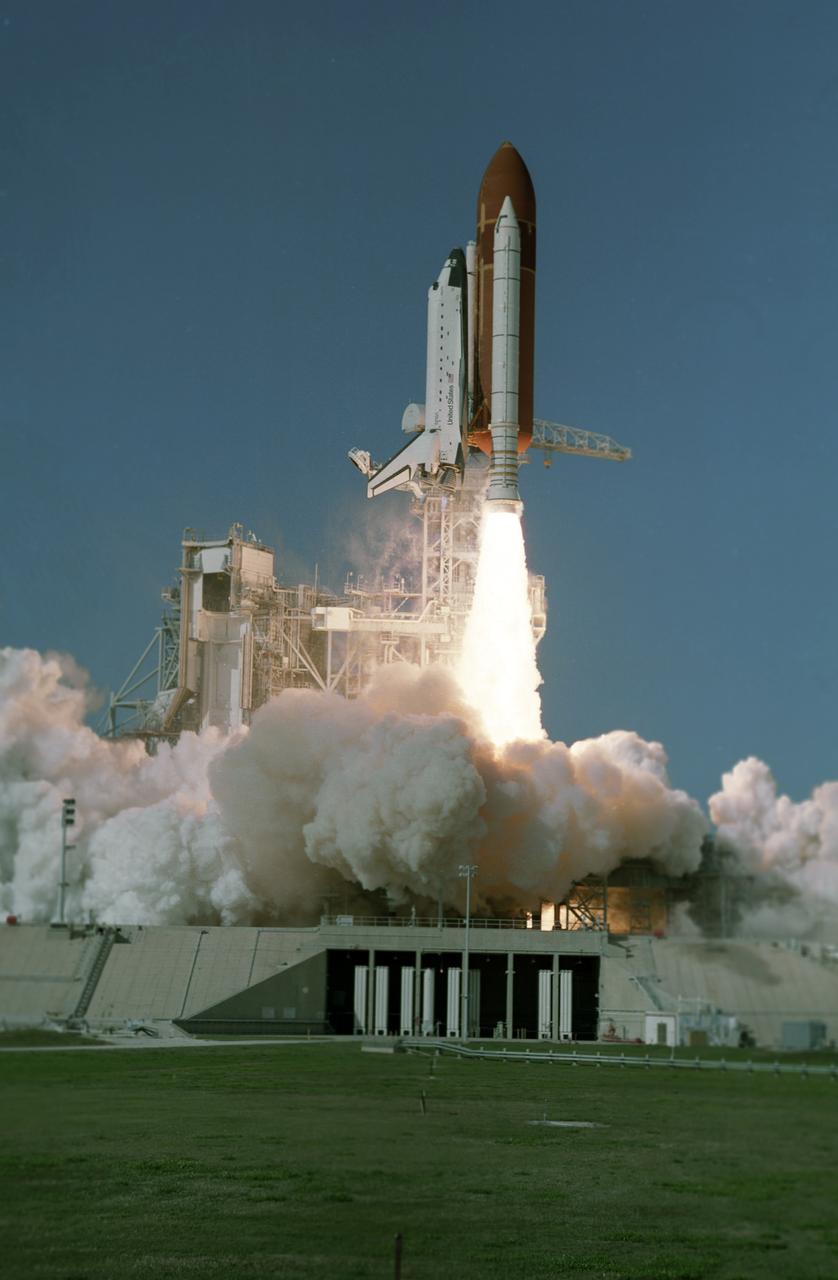

Space Shuttle orbiter Atlantis takes flight on its STS-27 mission, December 2, 1988, utilizing 375,000 pounds of thrust produced by its three main engines. The engines start in 3.9 seconds of ignition and go to static pump speeds of approximately 35,000 revolutions per minute during that time. The Marshall Space Flight Center had management responsibility of Space Shuttle propulsion elements, including the Main Engines. The STS-27 mission, the third mission dedicated to the Department of Defense (DOD), was crewed by five astronauts: Robert L. Gibson, commander; Guy S. Gardner, pilot; and mission specialists Richard M. Mullane, Jerry L. Ross, and William M. Shepherd.
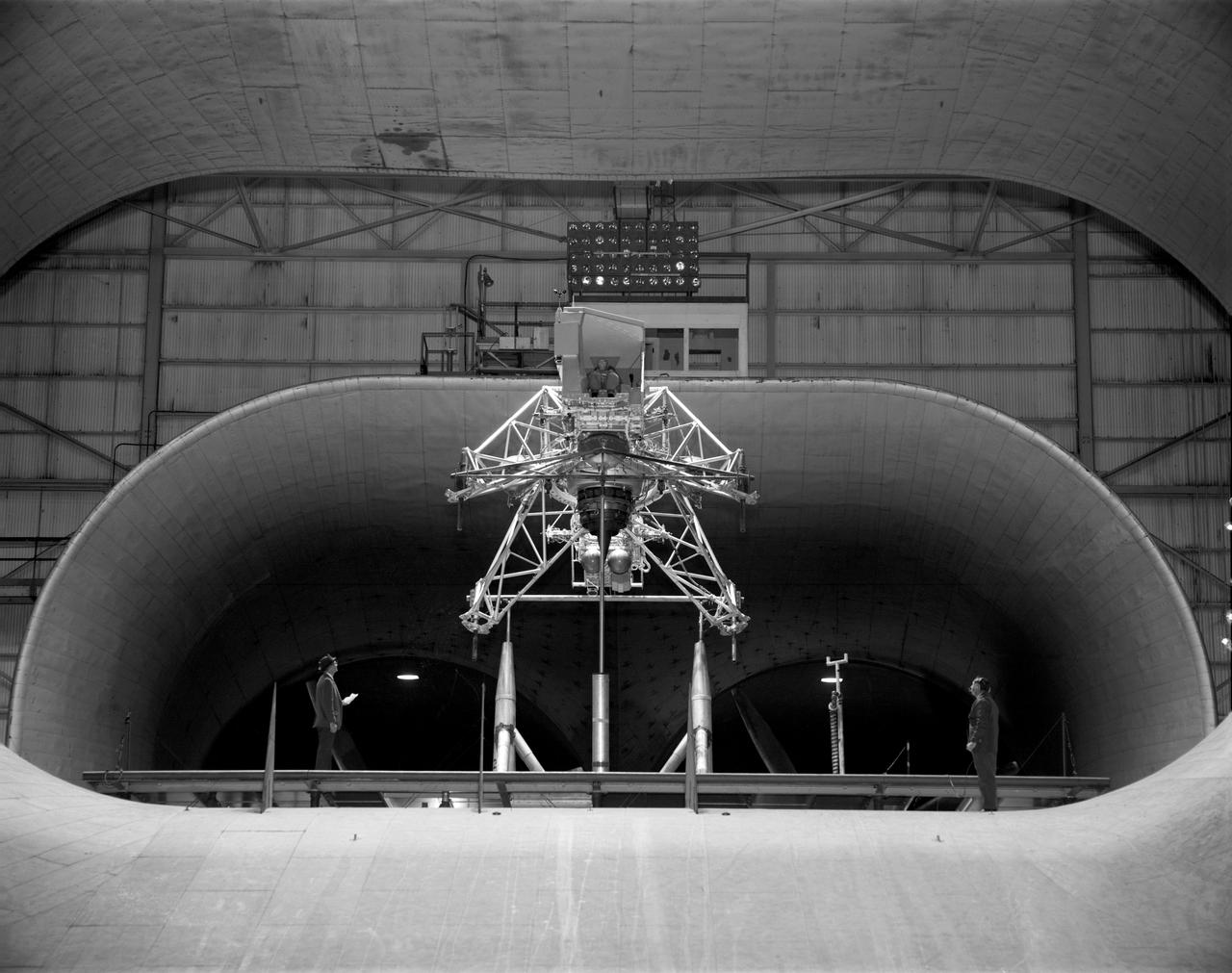
Concept model of the Lunar Excursion Module tested in the Full-Scale wind tunnel. -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 356.-L69-670 Bell Lunar Landing Training Vehicle (LLTV): Following the crash of a sister Lunar Landing Training Vehicle at Ellington Field in Houston, Texas, the LLTV NASA 952 was sent from Houston to Langley for tests in the 30 x 60 Full Scale Tunnel. The LLTV was returned to Houston for further training use a short time later. NASA 952 is now on exhibit at the Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas.
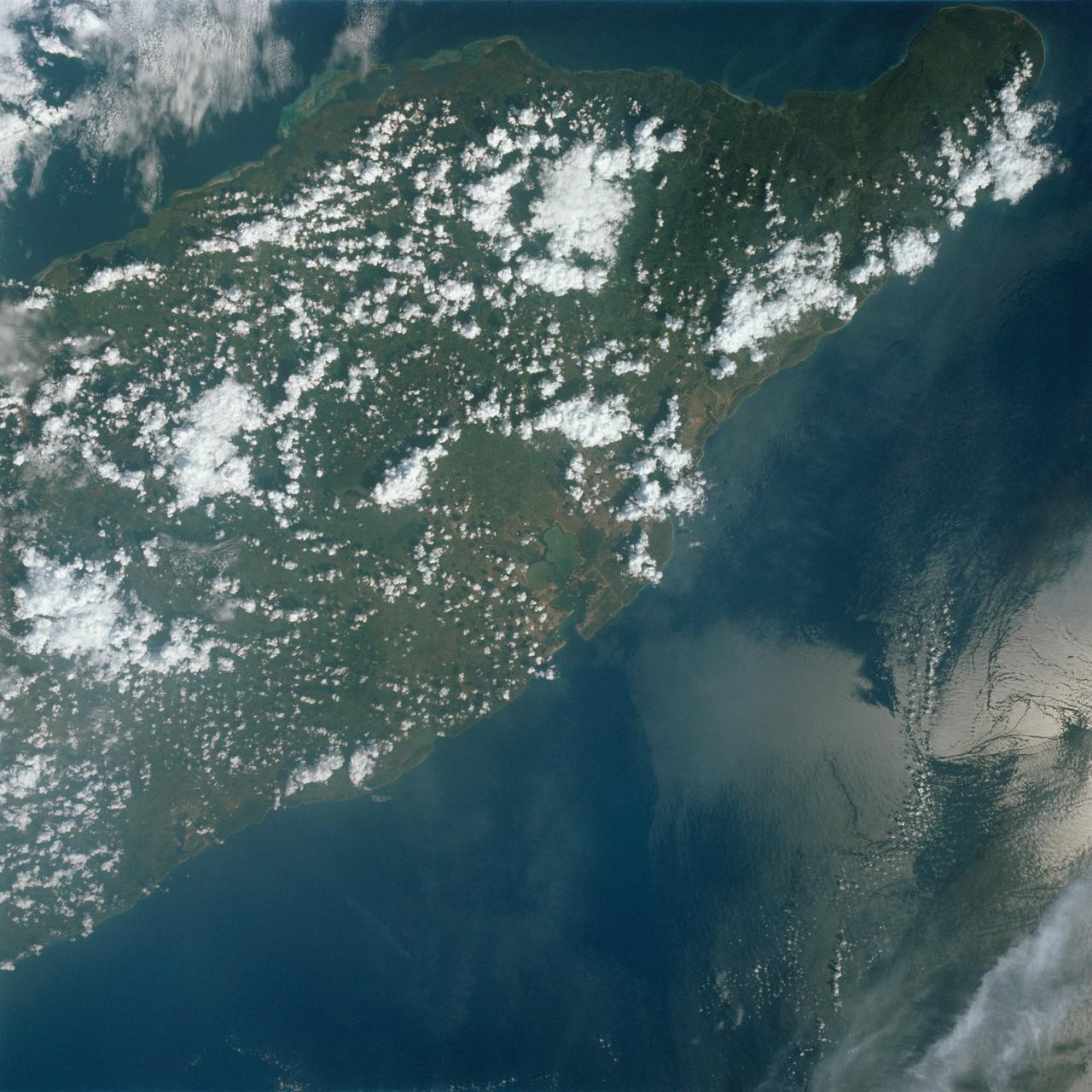

S65-63826 (5 Dec. 1965) --- Oriente Province, eastern end of Cuba, as seen from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's Gemini-7 spacecraft during its 14th revolution of Earth. Guantanamo Bay is in the center of the picture on the southern coast of Cuba. Santiago de Cuba is located about one inch from the bottom edge of the picture, or about three inches westward down the coast from Guantanamo. This photograph was taken with a modified 70mm Hasselblad camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome MS (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA
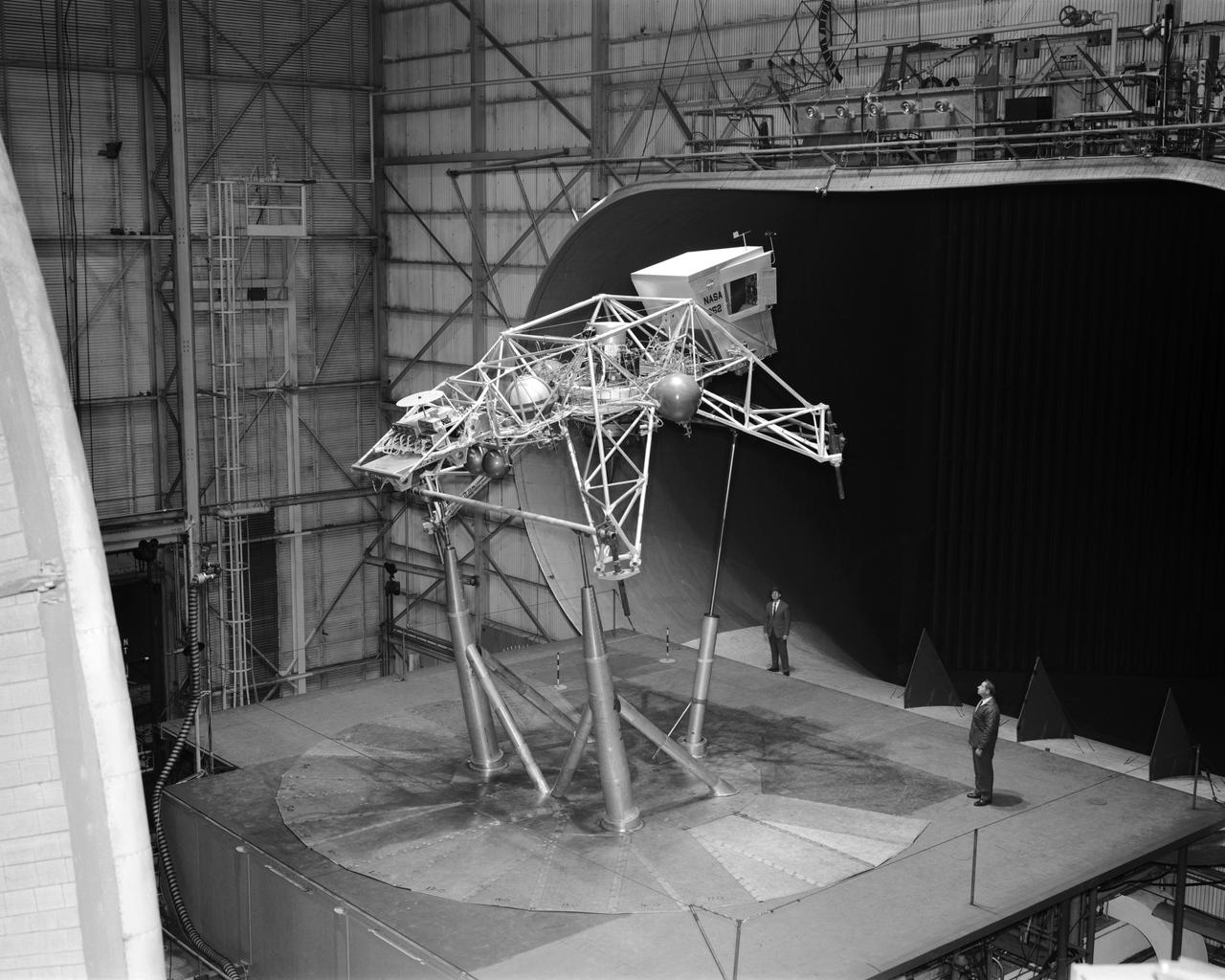

Concept model of the Lunar Excursion Module tested in the Full-Scale wind tunnel. -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 356.-L69-670 Bell Lunar Landing Training Vehicle (LLTV): Following the crash of a sister Lunar Landing Training Vehicle at Ellington Field in Houston, Texas, the LLTV NASA 952 was sent from Houston to Langley for tests in the 30 x 60 Full Scale Tunnel. The LLTV was returned to Houston for further training use a short time later. NASA 952 is now on exhibit at the Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas.
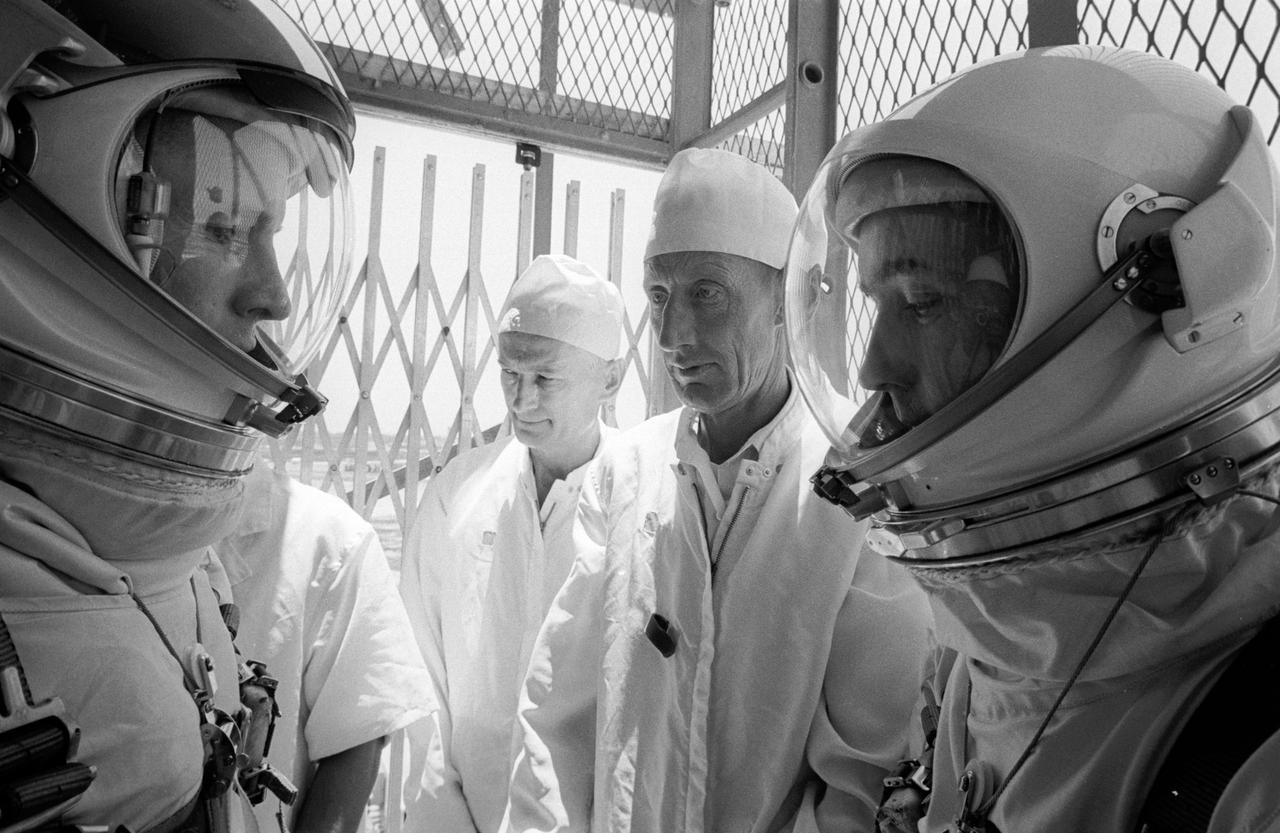

S65-30266 (29 May 1965) --- In the elevator on the way to the White Room at Pad 19 for simulations on May 29, 1965, astronauts James A. McDivitt (right), command pilot, and Edward H. White II, pilot, are shown with suit technicians Clyde Teague (right center) and Joe Schmitt. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration's two-man Gemini-4 mission is scheduled for 62 revolutions in four days. The backup crew, astronauts Frank Borman and James A. Lovell Jr. (both out of frame), will replace the prime crew if either crewman should become ineligible for the flight.
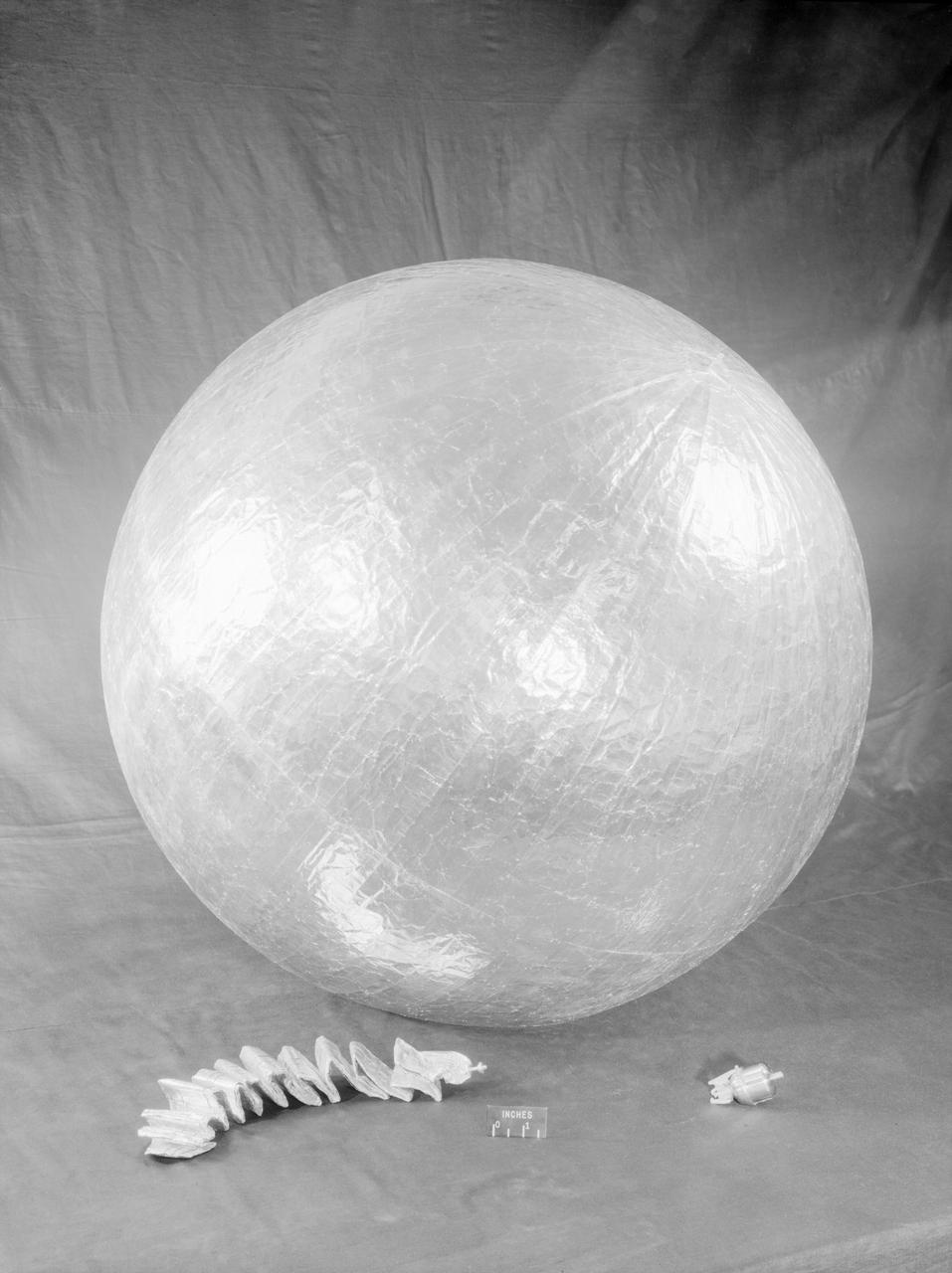

James Hansen describes the work on Project Echo s air density experiment known as the Sub-Satellite. Before launch engineers subjected the sub-satellite to many tests. Here, the sub-satellite is shown prior to tests to determine the capacity of the 30-inch Sub-Satellite to withstand the high temperature of direct sunlight in space, Langley researchers subjected it to 450 F heat test. Results indicated that the aluminum-covered Mylar plastic would effectively reflect the dangerous heat. -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, NASA SP-4308, p. 168.
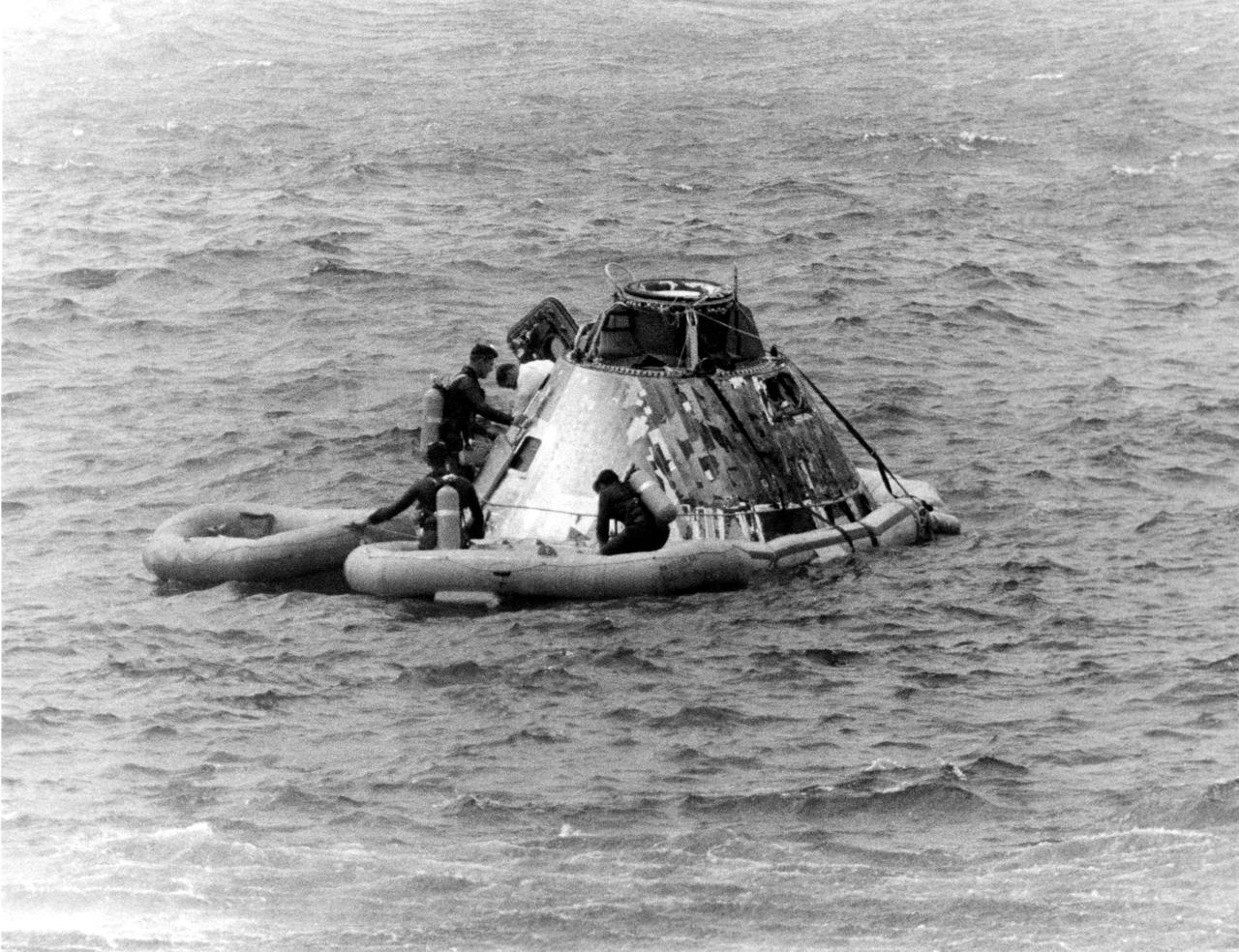

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Pararescueman helps Apollo 9 Command Module Pilot David R. Scott from the spacecraft today during recovery at completion of the 10-day Earth orbital flight with James A. McDivitt and Russell L. Schweickart, still in the spacecraft. The astronauts splashed down less than five miles from the USS Guadalcanal, prime recovery ship, at the beginning of their 152nd revolution. During the highly successful flight, they extensively tested the lunar module spacecraft, paving the way for a similar one to carry Americans to the Moon later this year. They were lalunched March 3 by an Apollo_Saturn V space vehicle from the Kennedy Space Center at the start of NASA's third manned mission using an Apollo spacecraft.
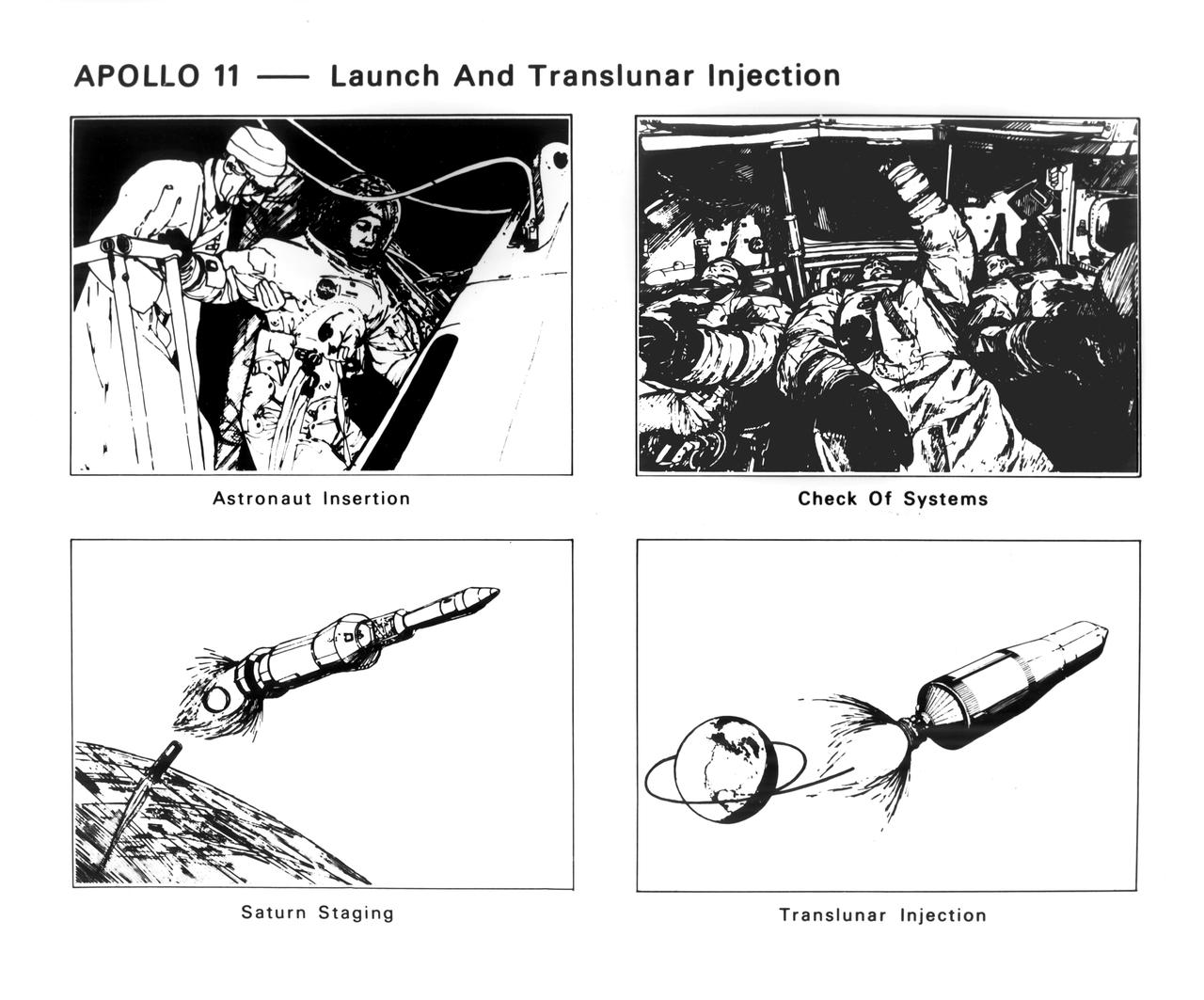
The Apollo 11 mission launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished. These sketches illustrate four of the early steps in the first manned lunar landing mission. The series begins with insertion of astronauts Neil Armstrong, Edwin Aldrin, and Michael Collins in the Apollo Command Module (CM). They checked out spacecraft systems and prepared for the launch. After two revolutions in Earth orbit, the Saturn V third stage reignited to place them into the translunar trajectory.
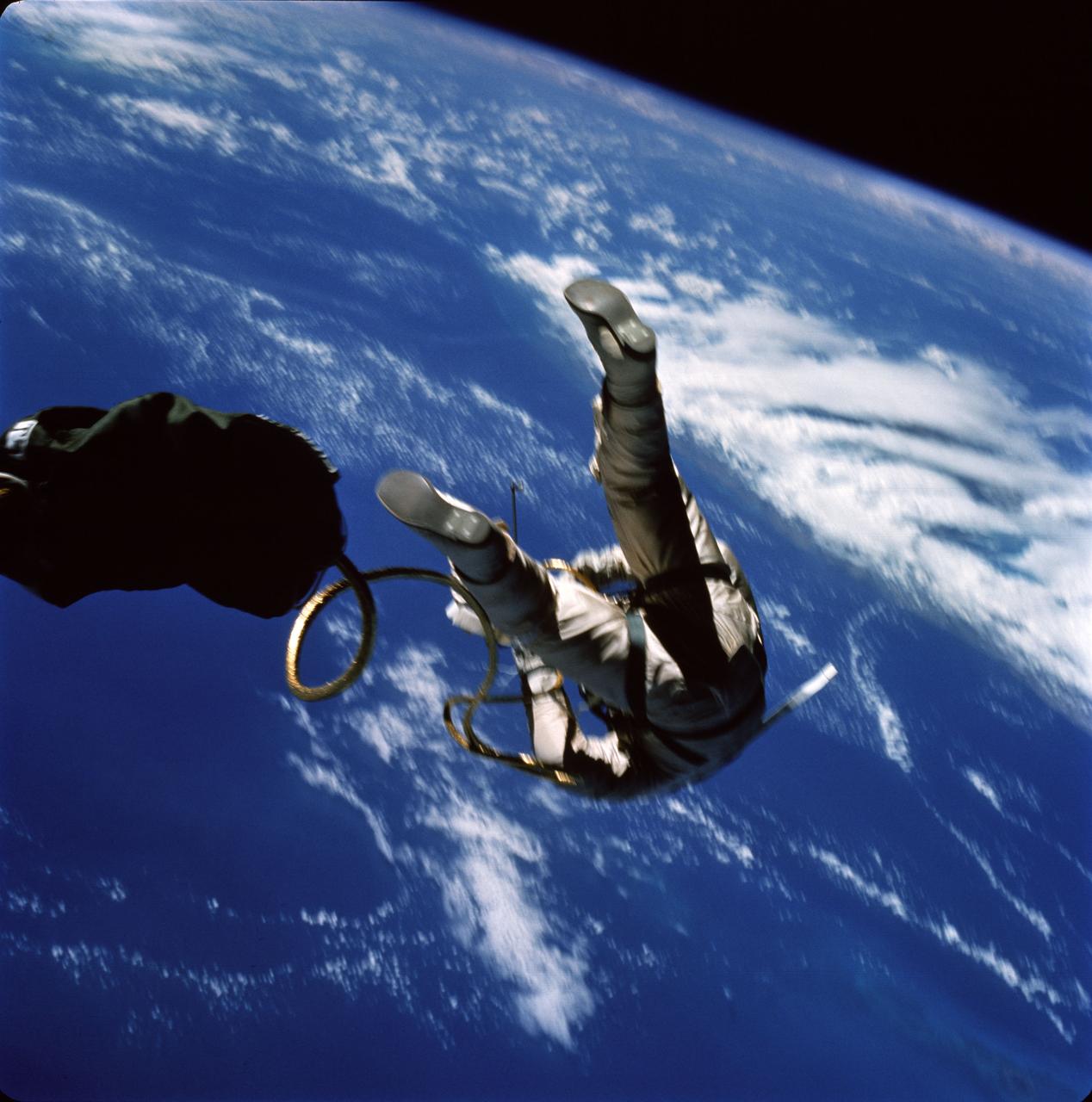

View of Astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot for the Gemini-Titan 4 space flight, as he floats in zero gravity of space. The extravehicular activity was performed during the third revolution of the Gemini 4 spacecraft. White is attached to the spacecraft by a 25-ft. umbilical line and a 23-ft. tether line,both wrapped in gold tape to form one cord. In his right hand White carries a Hand-Held Self-Maneuvering Unit (HHSMU). The visor of his helmet is gold plated to protect him from the unfiltered rays of the sun. Photo was taken on June 3,1965. G.E.T. time was 4:45 / GMT time was 20:00. Original magazine number was GEM04-16-34642, taken with a Hasselblad camera and a 70mm lens. Film type was Kodak Ektachrome MS (S.O. -217). The original photo was a color negative. It's image number is S65-34642.
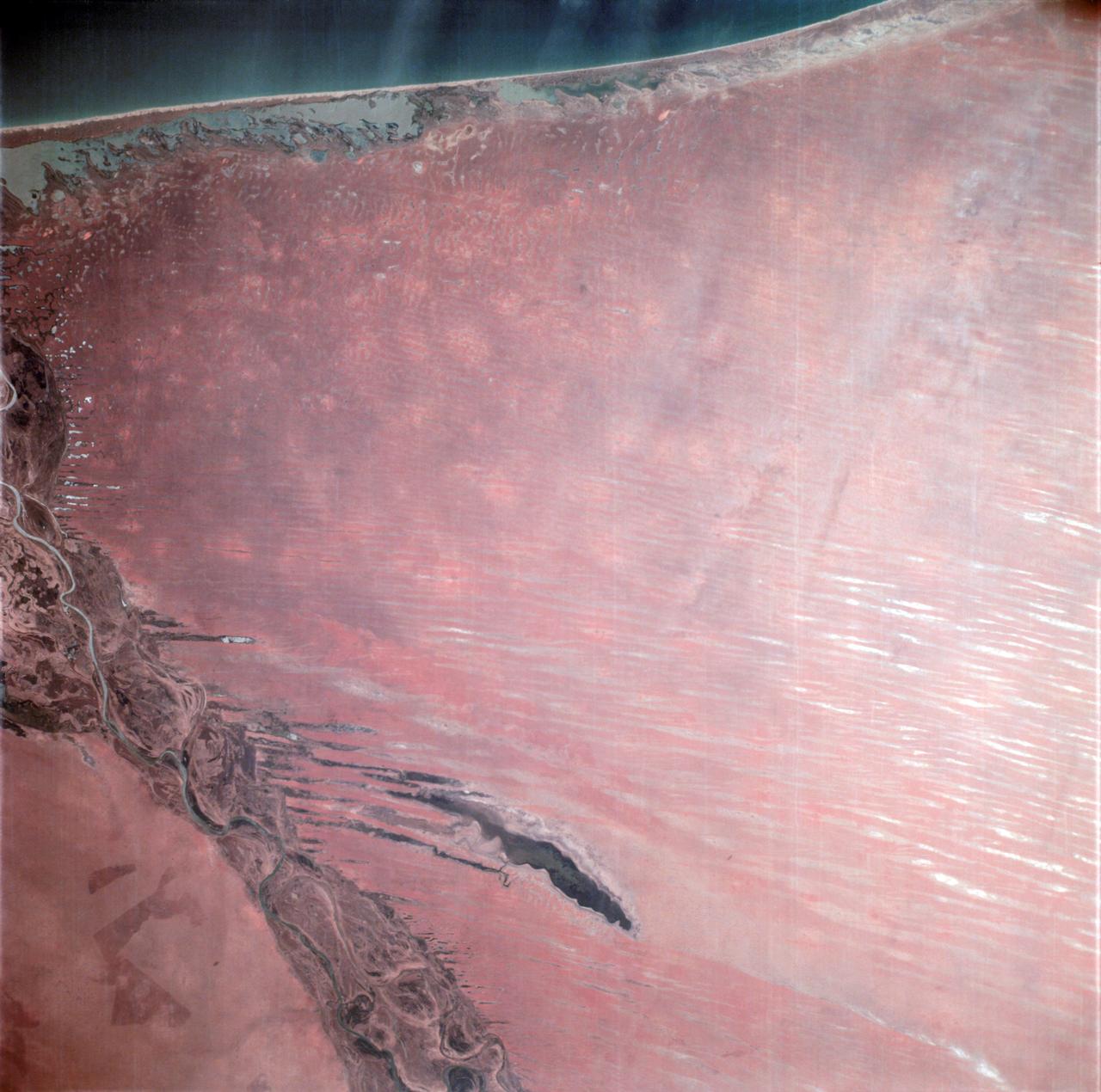
AS06-02-938 (6 April 1968) --- During the second revolution of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's Apollo 6 spacecraft, this photograph of Senegal and Mauritania was taken at an altitude of 125 nautical miles. The predominant feature is the valley of the Senegal River (flowing to lower right). Lake Rkiz is to the left of the river in Mauritania. The Trarza Scrub Hills, a large area of elongated, fixed dunes, is in the lower left of the print. The land area seen in this photo is approximately 10,000 square miles or about the size of the state of Maryland. The photo was made one hour and fifty minutes after liftoff using a J.A. Maurer model 220G camera with Eastman Kodak SO-121 high resolution aerial Ektachrome film (exposure setting of f: 5.6 at 1/500 sec.).
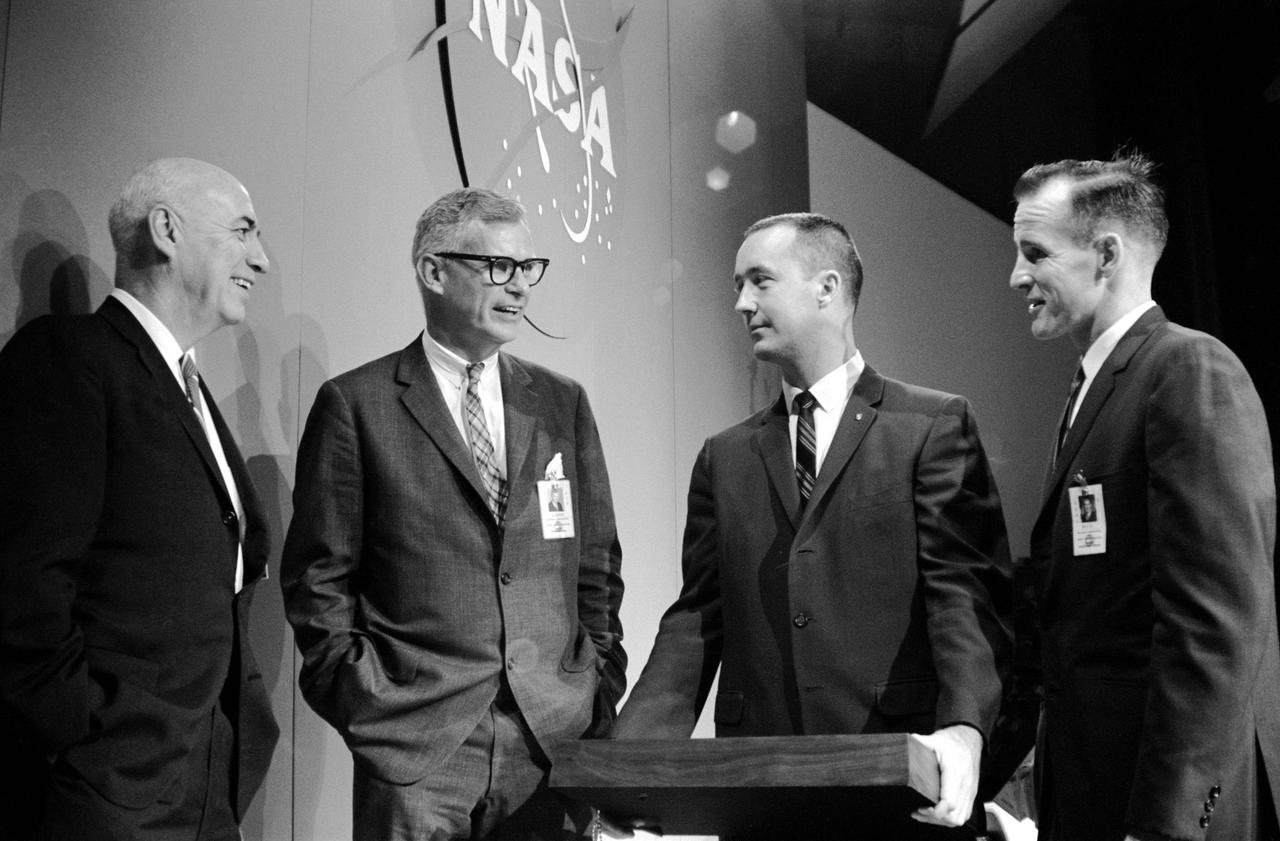

S65-33352 (11 June 1965) --- The Gemini-4 prime crew pose with two NASA officials after a press conference in the MSC auditorium. Left to right, are Dr. Robert R. Gilruth, MSC director; Dr. Robert C. Seamans Jr., associate administrator, National Aeronautics and Space Administration; astronaut James A. McDivitt, command pilot of the Gemini-4 flight; and astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot of the mission. The two astronauts had just returned to Houston following their debriefings at Cape Kennedy. The Gt-4 liftoff was at 10:16 a.m. (EST) on June 3, 1965. Time of splashdown ending the four-day, 62-revolution mission was at 12:12 p.m. on June 7, 1965.
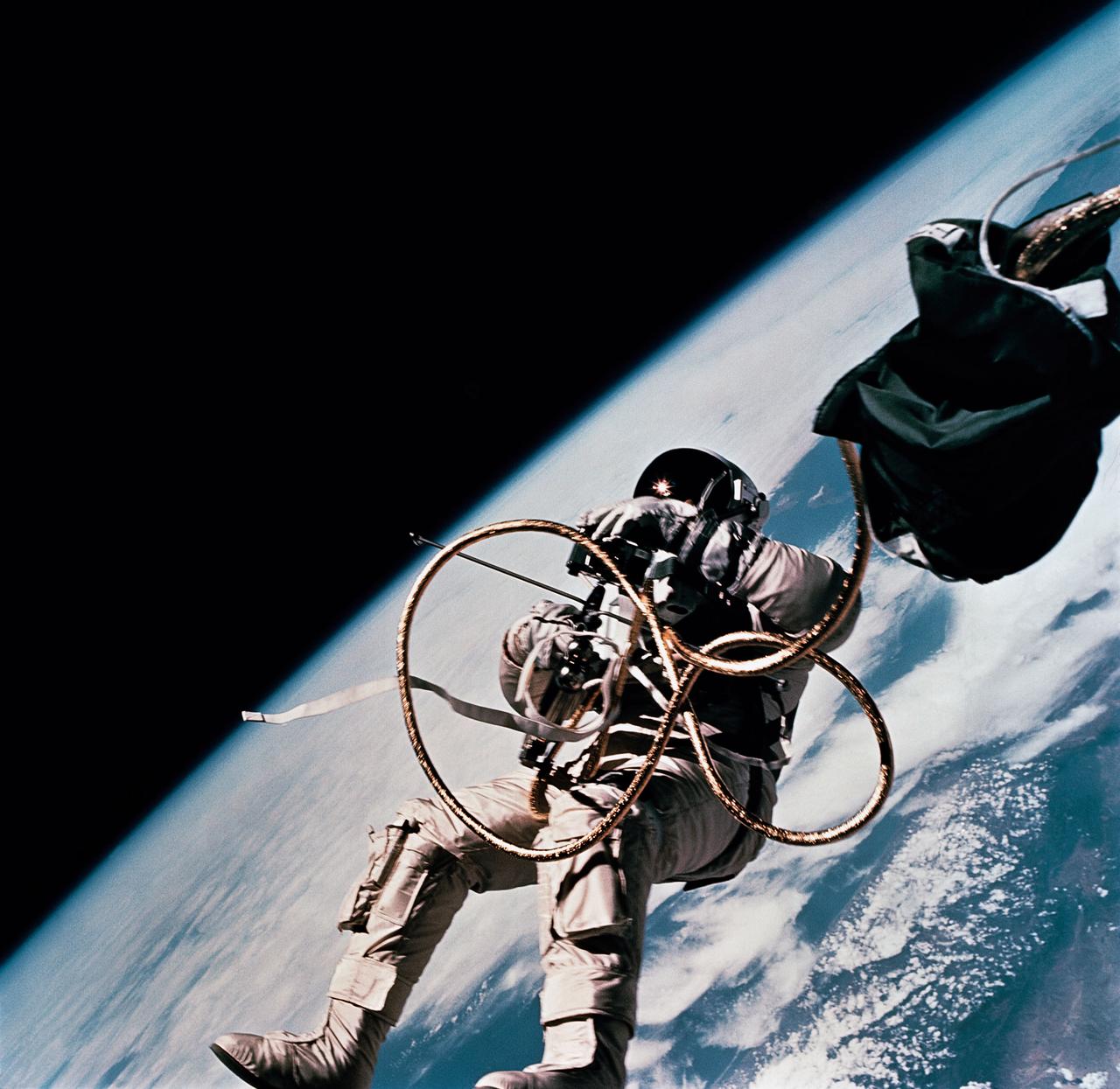

S65-30430 (3 June 1965) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot on the Gemini-Titan 4 spaceflight, is shown during his egress from the spacecraft. His face is covered by a shaded visor to protect him from the unfiltered rays of the sun. White became the first American astronaut to walk in space. He remained outside the spacecraft for 21 minutes during the third revolution of the Gemini-4 mission. He wears a specially designed spacesuit for the extravehicular activity (EVA). In his right hand, he carries a Hand-Held Self-Maneuvering Unit (HHSMU) with which he controlled his movements while in space. He was attached to the spacecraft by a 25-feet umbilical line and a 23-feet tether line, both wrapped together with gold tape to form one cord. He wears an emergency oxygen supply chest pack. Astronaut James A. McDivitt is command pilot for the Gemini-4 mission. Photo credit: NASA EDITOR'S NOTE: Astronaut Edward H. White II died in the Apollo/Saturn 204 fire at Cape Kennedy on Jan. 27, 1967.
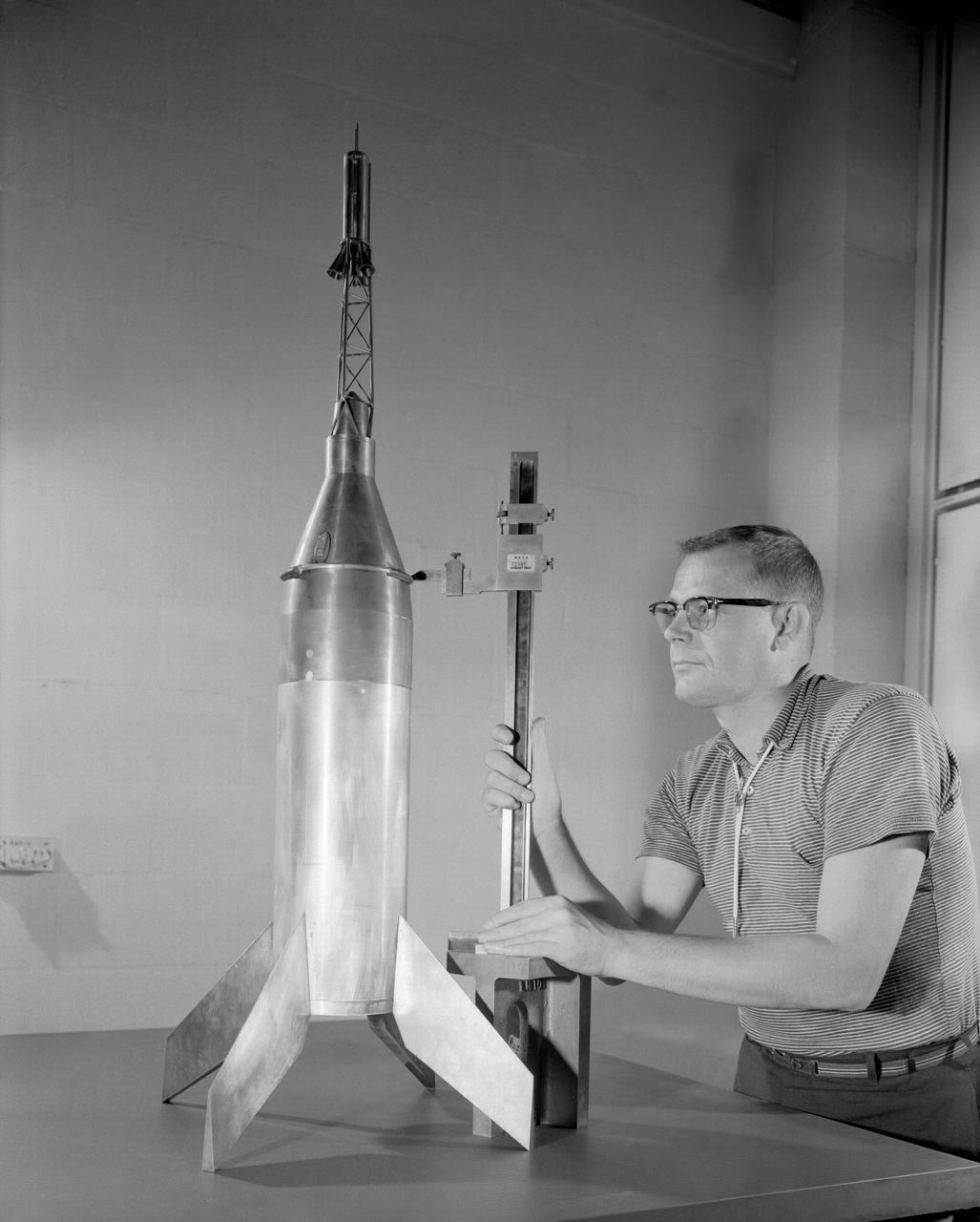

Publicity photograph of a technician measuring a wind tunnel model of the Little Joe test vehicle. Joseph Shortal noted that (vol. 3, p. 29): The largest project at Wallops in support of Mercury was the Little Joe project, designed to qualify the abort-escape system under flight conditions. James Hansen (p. 47) writes: STG engineers Max Faget and Paul Purser, then of Langley's PARD, had conceived Little Joe as a space capsule test vehicle even before the establishment of NASA and the formation of the STG. Girlruth understood the importance of the Little Joe tests: We had to be sure there were no serious performance and operational problems that we had simply not thought of in such a new and radical type of flight vehicle. -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 47 Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.
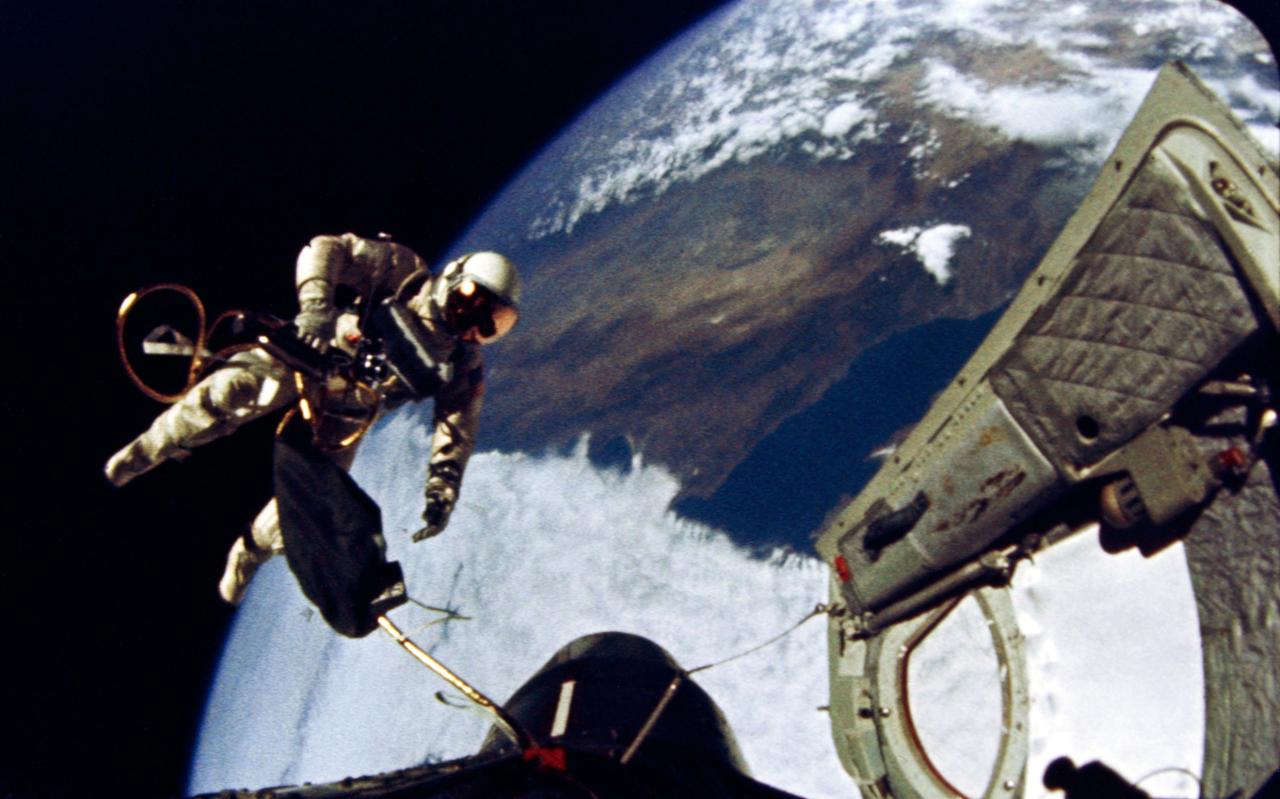

S65-29730 (3 June 1965) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot for the Gemini-Titan 4 (GT-4) spaceflight, floats in the zero-gravity of space during the third revolution of the GT-4 spacecraft. White wears a specially designed spacesuit. His face is shaded by a gold-plated visor to protect him from unfiltered rays of the sun. In his right hand he carries a Hand-Held Self-Maneuvering Unit (HHSMU) that gives him control over his movements in space. White also wears an emergency oxygen chest pack; and he carries a camera mounted on the HHSMU for taking pictures of the sky, Earth and the GT-4 spacecraft. He is secured to the spacecraft by a 25-feet umbilical line and a 23-feet tether line. Both lines are wrapped together in gold tape to form one cord. Astronaut James A. McDivitt, command pilot, remained inside the spacecraft during the extravehicular activity (EVA). Photo credit: NASA EDITOR'S NOTE: Astronaut Edward H. White II died in the Apollo/Saturn 204 fire at Cape Kennedy on Jan. 27, 1967.

S65-34635 (3 June 1965) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot on the Gemini-Titan 4 spaceflight, is shown during his egress from the spacecraft. His face is covered by a shaded visor to protect him from the unfiltered rays of the sun. White became the first American astronaut to walk in space. He remained outside the spacecraft for 21 minutes during the third revolution of the Gemini-4 mission. He wears a specially designed spacesuit for the extravehicular activity (EVA). In his right hand, he carries a Hand-Held Self-Maneuvering Unit (HHSMU) with which he controlled his movements while in space. He was attached to the spacecraft by a 25-feet umbilical line and a 23-feet tether line, both wrapped together with gold tape to form one cord. He wears an emergency oxygen supply chest pack. Astronaut James A. McDivitt is command pilot for the Gemini-4 mission. EDITOR'S NOTE: Astronaut Edward H. White II died in the Apollo/Saturn 204 fire at Cape Kennedy on Jan. 27, 1967.
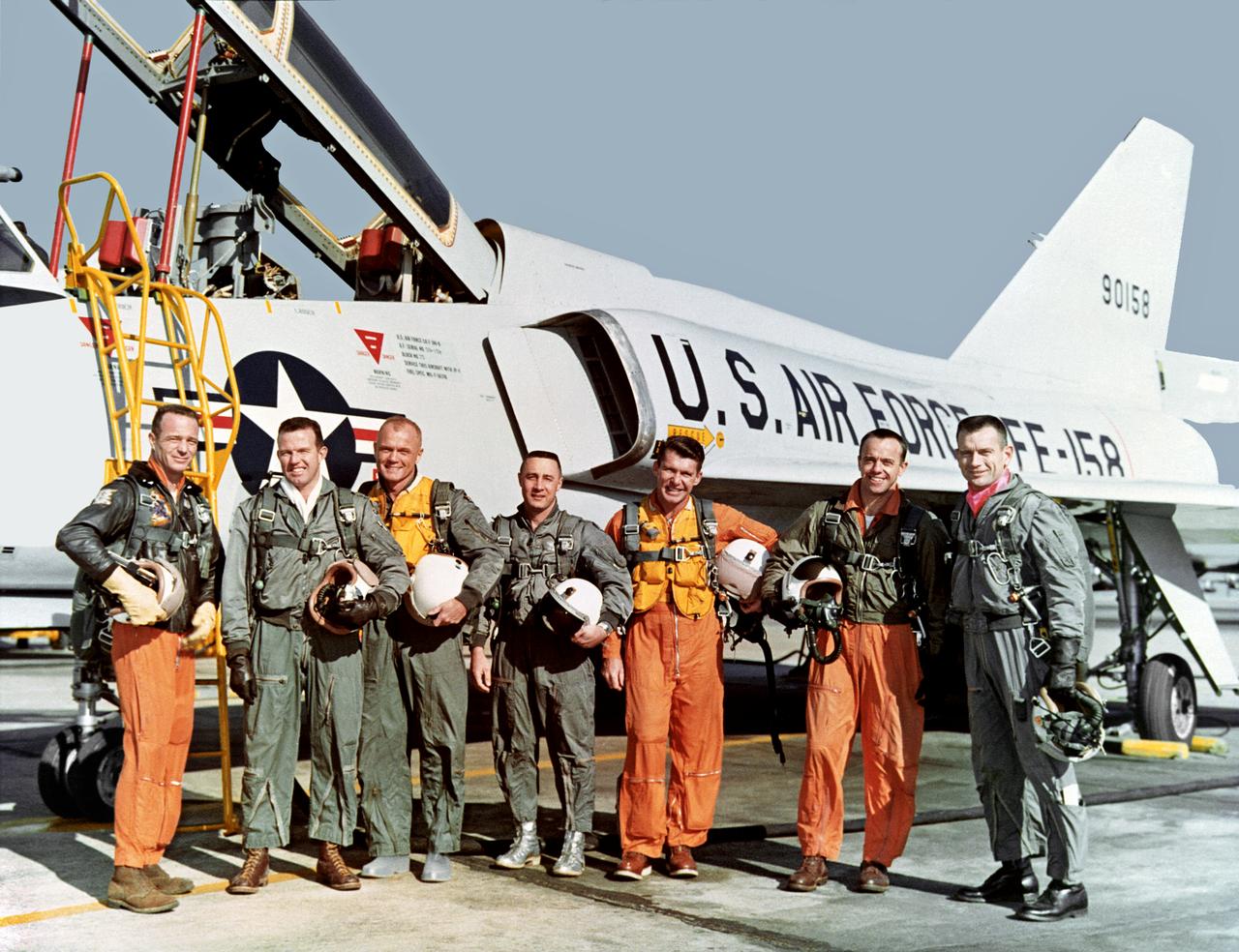

The original seven Mercury astronauts during training at NASA Langley Research Center Project Mercury. The original seven astronauts trained at NASA Langley Research Center. Chosen from among hundreds of applicants, the seven men were all test pilots. Standing in front of the U.S. Air Force Convair F-106B aircraft, the astronauts are, from left, Lt. M. Scott Carpenter, Capt. Gordon Cooper, Col. John H. Glenn Jr., Capt. Virgil "Gus" Grissom, Lt. Comdr. Walter Schirra, Lt. Comdr. Alan B. Shepard Jr. and Capt. Donald K. "Deke" Slayton. While familiarizing the astronauts with the Mercury set-up, Langley employees helped them to specialize in the technical areas crucial to the overall success of Project Mercury. Langley people also guided and monitored the astronauts activities through the many spaceflight simulators and other training devices built at the Center expressly for the manned space program. In less than three years, Project Mercury proved that men could be sent into space and returned safely to Earth, setting the stage for the longer duration Gemini flights and the Apollo lunar landings. This photograph was originally taken on 01/20/1961 and is published in Spaceflight Revolution NASA Langley Research Center from Sputnik to Apollo, NASA SP-4308, by James R. Hansen, 1995, page 40.
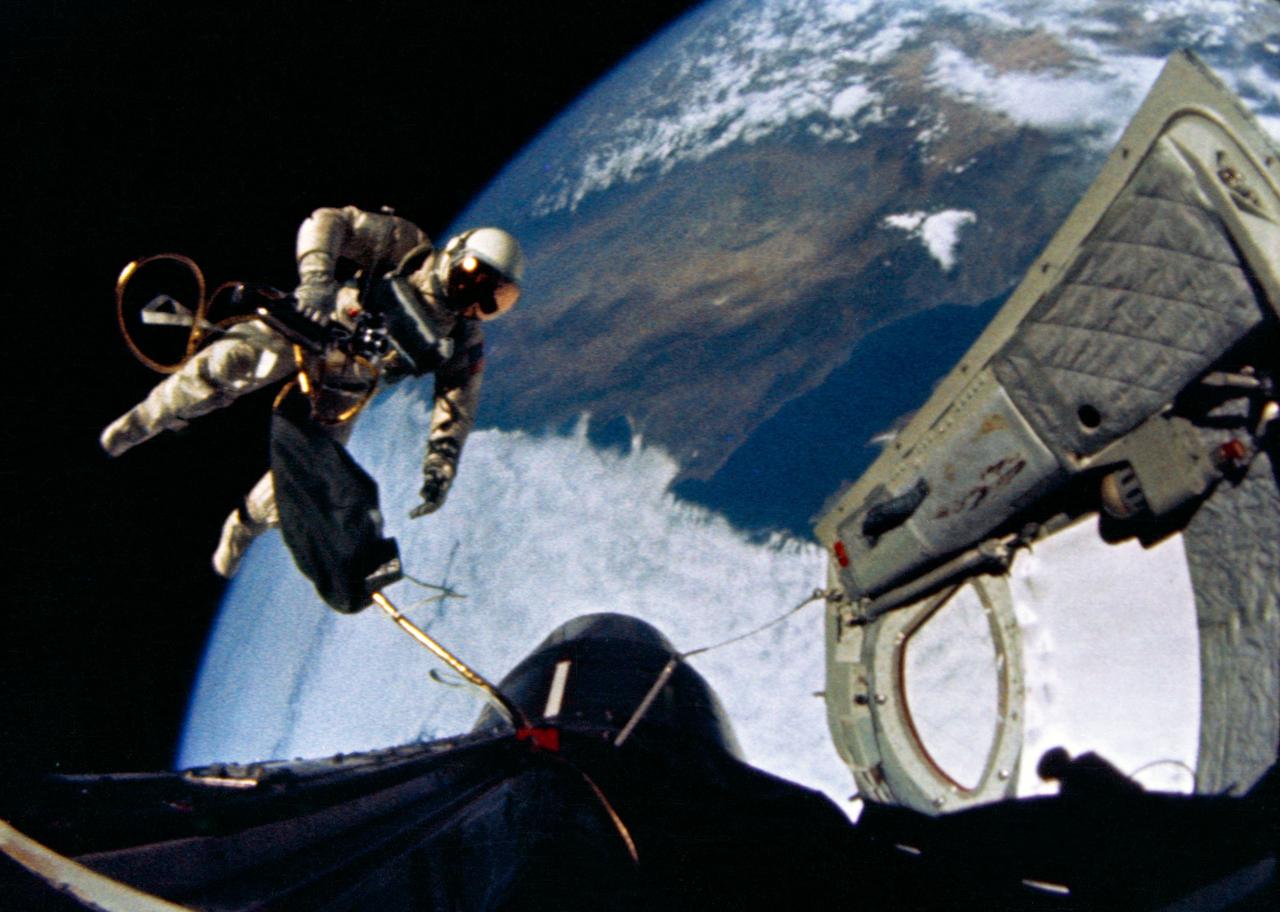

S65-29766 (3 June 1965) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot for the Gemini-Titan 4 (GT-4) spaceflight, floats in the zero-gravity of space during the third revolution of the GT-4 spacecraft. White wears a specially designed spacesuit. His face is shaded by a gold-plated visor to protect him from unfiltered rays of the sun. In his right hand he carries a Hand-Held Self-Maneuvering Unit (HHSMU) that gives him control over his movements in space. White also wears an emergency oxygen chest pack; and he carries a camera mounted on the HHSMU for taking pictures of the sky, Earth and the GT-4 spacecraft. He is secured to the spacecraft by a 25-feet umbilical line and a 23-feet tether line. Both lines are wrapped together in gold tape to form one cord. Astronaut James A. McDivitt, command pilot, remained inside the spacecraft during the extravehicular activity (EVA). Photo credit: NASA EDITOR'S NOTE: Astronaut Edward H. White II died in the Apollo/Saturn 204 fire at Cape Kennedy on Jan. 27, 1967.
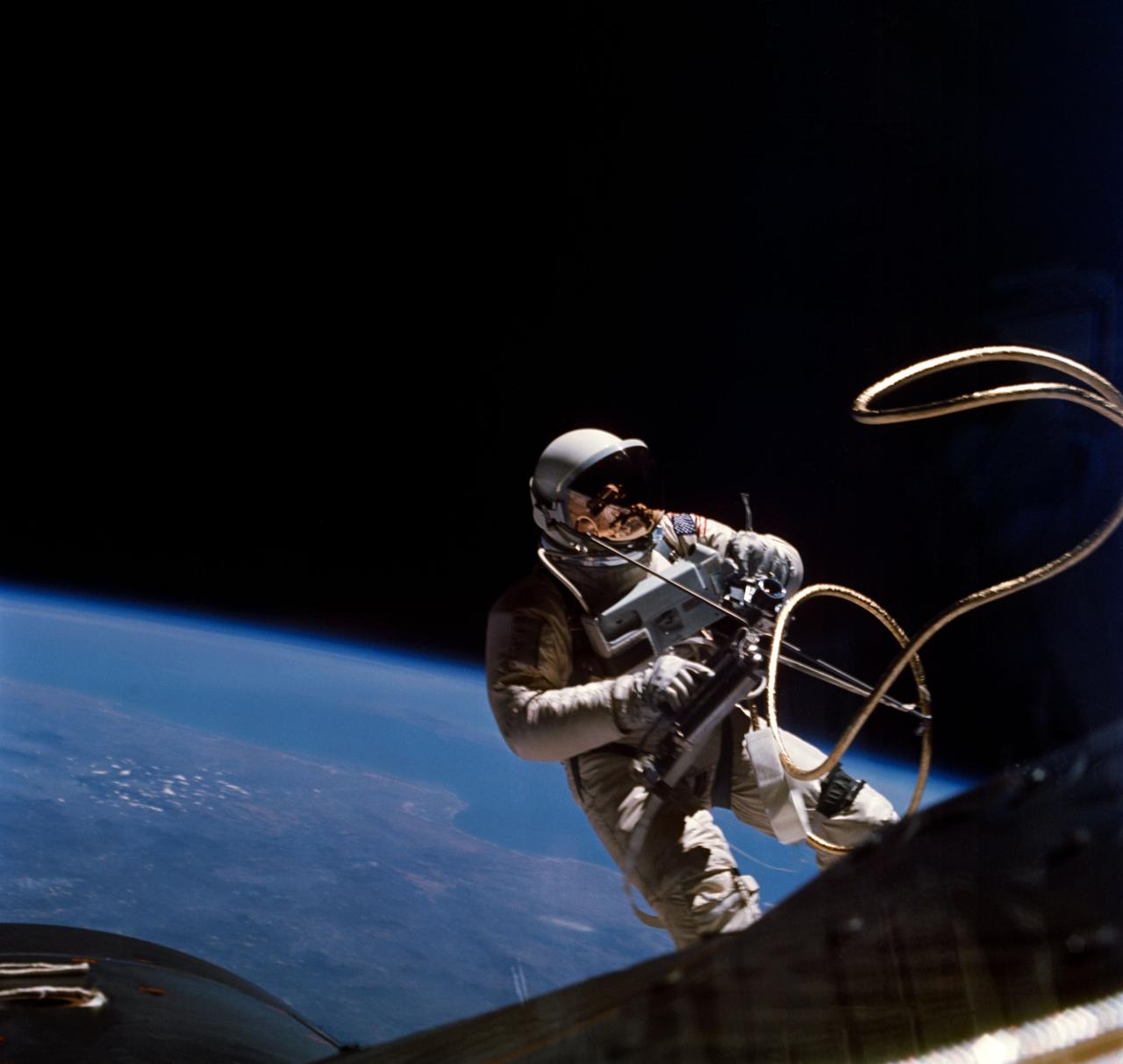

S65-30428 (3 June 1965) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot on the Gemini-Titan 4 spaceflight, is shown during his egress from the spacecraft. His face is covered by a shaded visor to protect him from the unfiltered rays of the sun. White became the first American astronaut to walk in space. He remained outside the spacecraft for 21 minutes during the third revolution of the Gemini-4 mission. He wears a specially designed spacesuit for the extravehicular activity (EVA). In his right hand, he carries a Hand-Held Self-Maneuvering Unit (HHSMU) with which he controlled his movements while in space. He was attached to the spacecraft by a 25-feet umbilical line and a 23-feet tether line, both wrapped together with gold tape to form one cord. He wears an emergency oxygen supply chest pack. Astronaut James A. McDivitt is command pilot for the Gemini-4 mission. EDITOR'S NOTE: Astronaut Edward H. White II died in the Apollo/Saturn 204 fire at Cape Kennedy on Jan. 27, 1967.
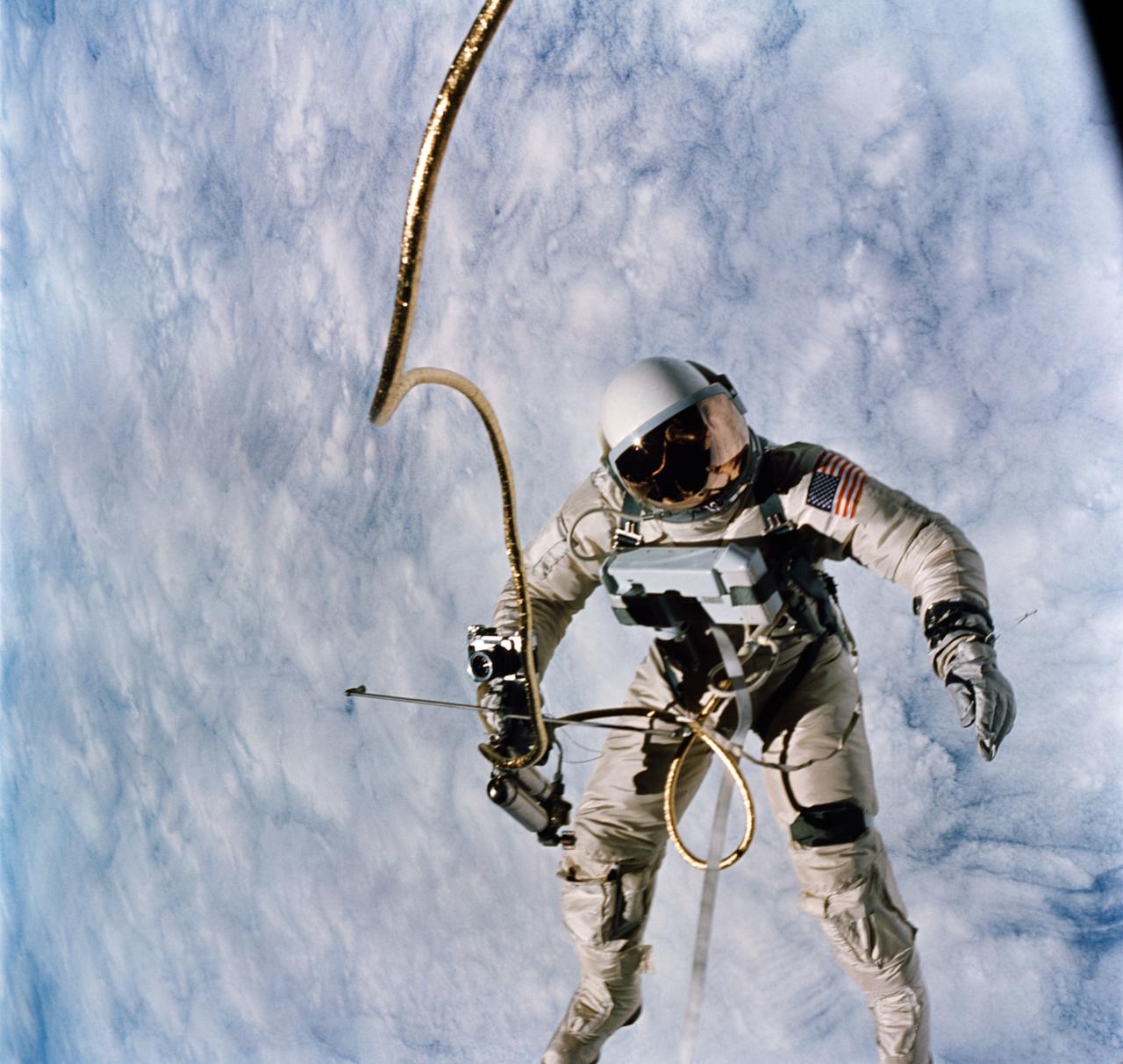

S65-30427 (3 June 1965) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot for the Gemini-Titan 4 (GT-4) spaceflight, floats in the zero-gravity of space during the third revolution of the GT-4 spacecraft. White wears a specially designed spacesuit. His face is shaded by a gold-plated visor to protect him from unfiltered rays of the sun. In his right hand he carries a Hand-Held Self-Maneuvering Unit (HHSMU) that gives him control over his movements in space. White also wears an emergency oxygen chest pack; and he carries a camera mounted on the HHSMU for taking pictures of the sky, Earth and the GT-4 spacecraft. He is secured to the spacecraft by a 25-feet umbilical line and a 23-feet tether line. Both lines are wrapped together in gold tape to form one cord. Astronaut James A. McDivitt, command pilot, remained inside the spacecraft during the extravehicular activity (EVA). Photo credit: NASA EDITOR'S NOTE: Astronaut Edward H. White II died in the Apollo/Saturn 204 fire at Cape Kennedy on Jan. 27, 1967.

Using data collected by NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, this animation shows the trajectories of rocky particles after being ejected from asteroid (101955) Bennu's surface. The animation emphasizes the four largest particle-ejection events detected at Bennu between December 2018 and September 2019. Additional particles not related to the ejections are also visible. Most of these pebble-size pieces of rock, typically measuring around a quarter inch (7 millimeters), were pulled back to Bennu under the asteroid's weak gravity after a short hop, sometimes even ricocheting back into space after colliding with the surface. Others remained in orbit for a few days and up to 16 revolutions. And some were ejected with enough force to completely escape from the Bennu environs. OSIRIS-REx — which stands for Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, and Security-Regolith Explorer — arrived at Bennu in December 2018. On Oct. 20, 2020, the mission will attempt to briefly touch down on the asteroid to scoop up material likely to include particles that were ejected before dropping back to the surface. If all goes as planned, the spacecraft will return to Earth in September 2023 with a cache of Bennu's particles for further study, including of which may even hold the physical clues as to what ejection mechanisms are at play. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24101

Special "space" suit for the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil described the purpose of the simulator in his paper "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," "When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject's weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 377; A.W. Vigil, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology," Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.
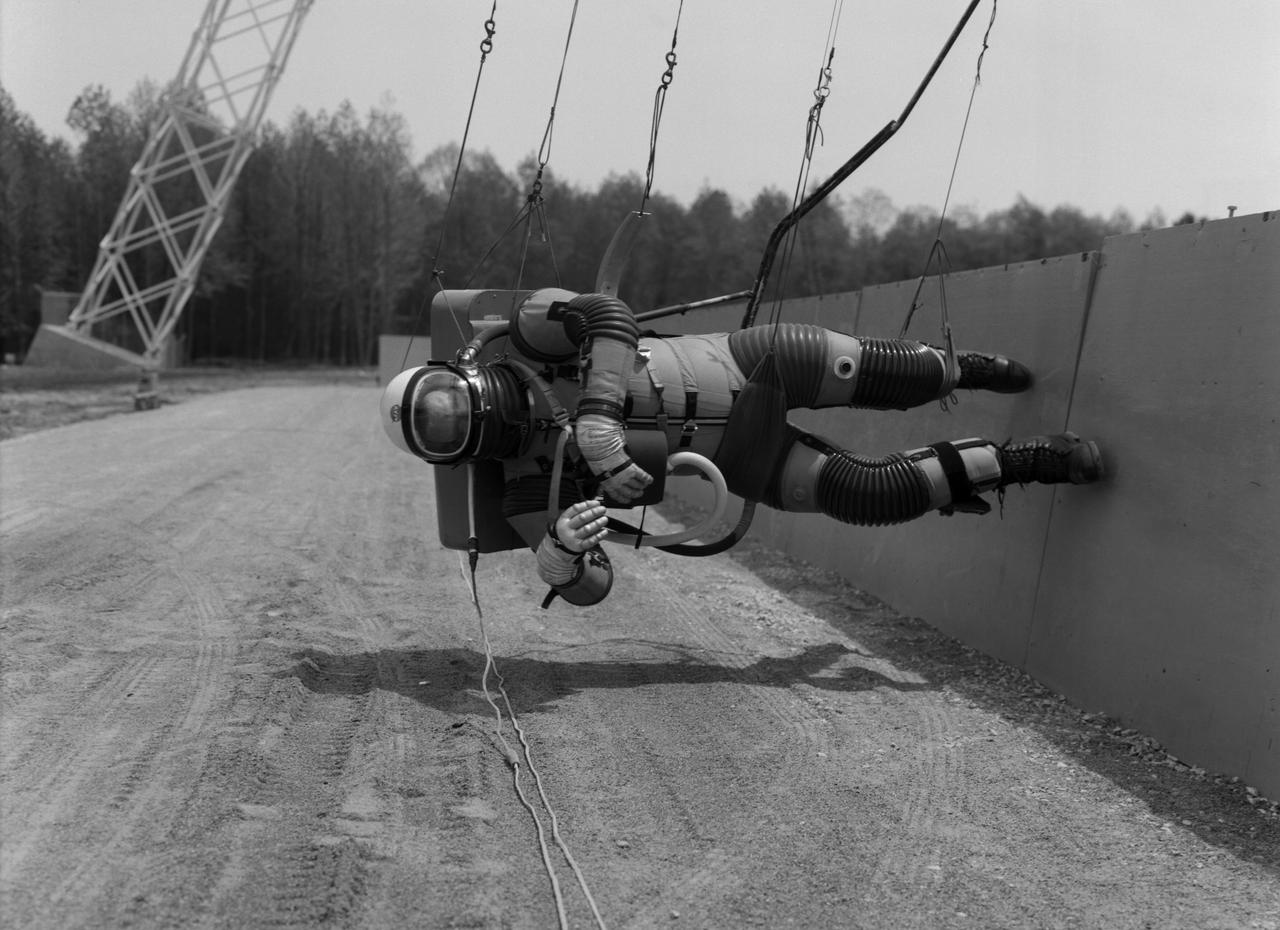

Test subject wearing the pressurized "space" suit for the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil described the purpose of the simulator in his paper "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," "When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject's weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 377; A.W. Vigil, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology," Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.
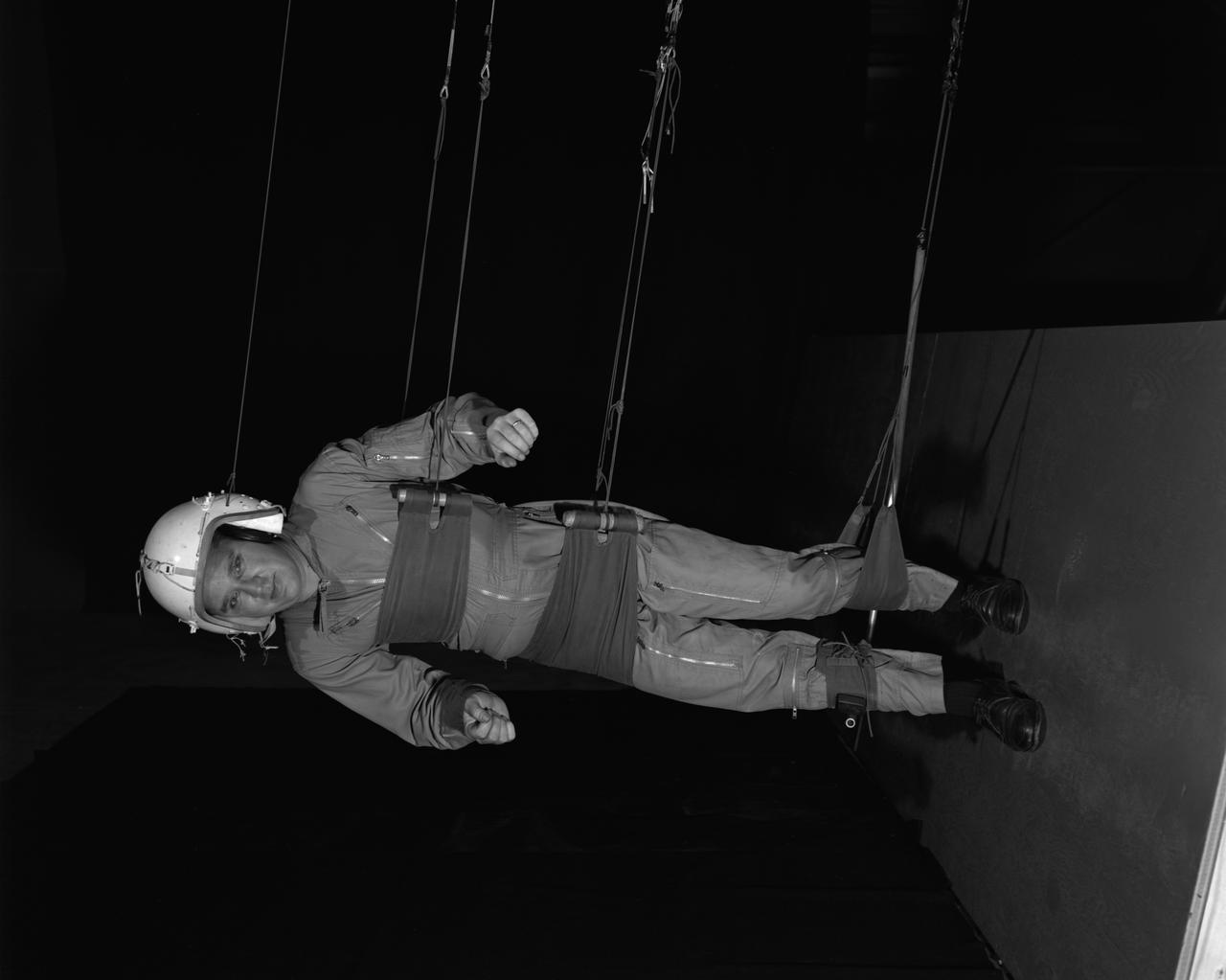

Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located in the hangar at Langley Research Center. The initial version of this simulator was located inside the hangar. Later a larger version would be located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil wrote in his paper Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research, When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject' s weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed. -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, NASA SP-4308, p. 377 A.W. Vigil, Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research, Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.

NASA image release July 12, 2011 Neptune: 23:09 UT (June 25, 2011) Today, Neptune has arrived at the same location in space where it was discovered nearly 165 years ago. To commemorate the event, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has taken these "anniversary pictures" of the blue-green giant planet. Neptune is the most distant major planet in our solar system. German astronomer Johann Galle discovered the planet on September 23, 1846. At the time, the discovery doubled the size of the known solar system. The planet is 2.8 billion miles (4.5 billion kilometers) from the Sun, 30 times farther than Earth. Under the Sun's weak pull at that distance, Neptune plods along in its huge orbit, slowly completing one revolution approximately every 165 years. <b>To read more go <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/neptune-circuit.html" rel="nofollow"> here</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
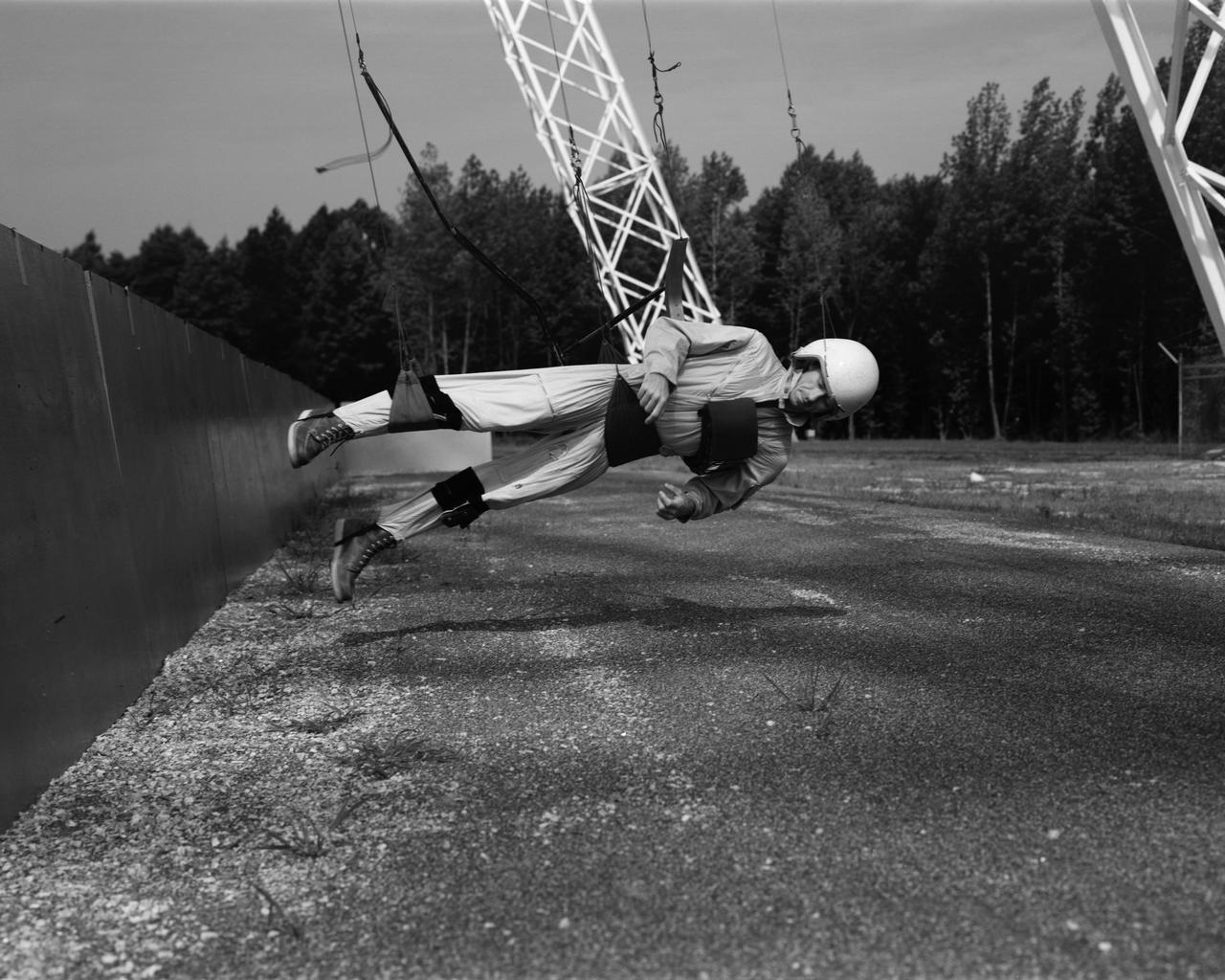

Astronaut Walt Cunningham on the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil described the purpose of the simulator in his paper "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," "When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject's weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 377; A.W. Vigil, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology," Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.
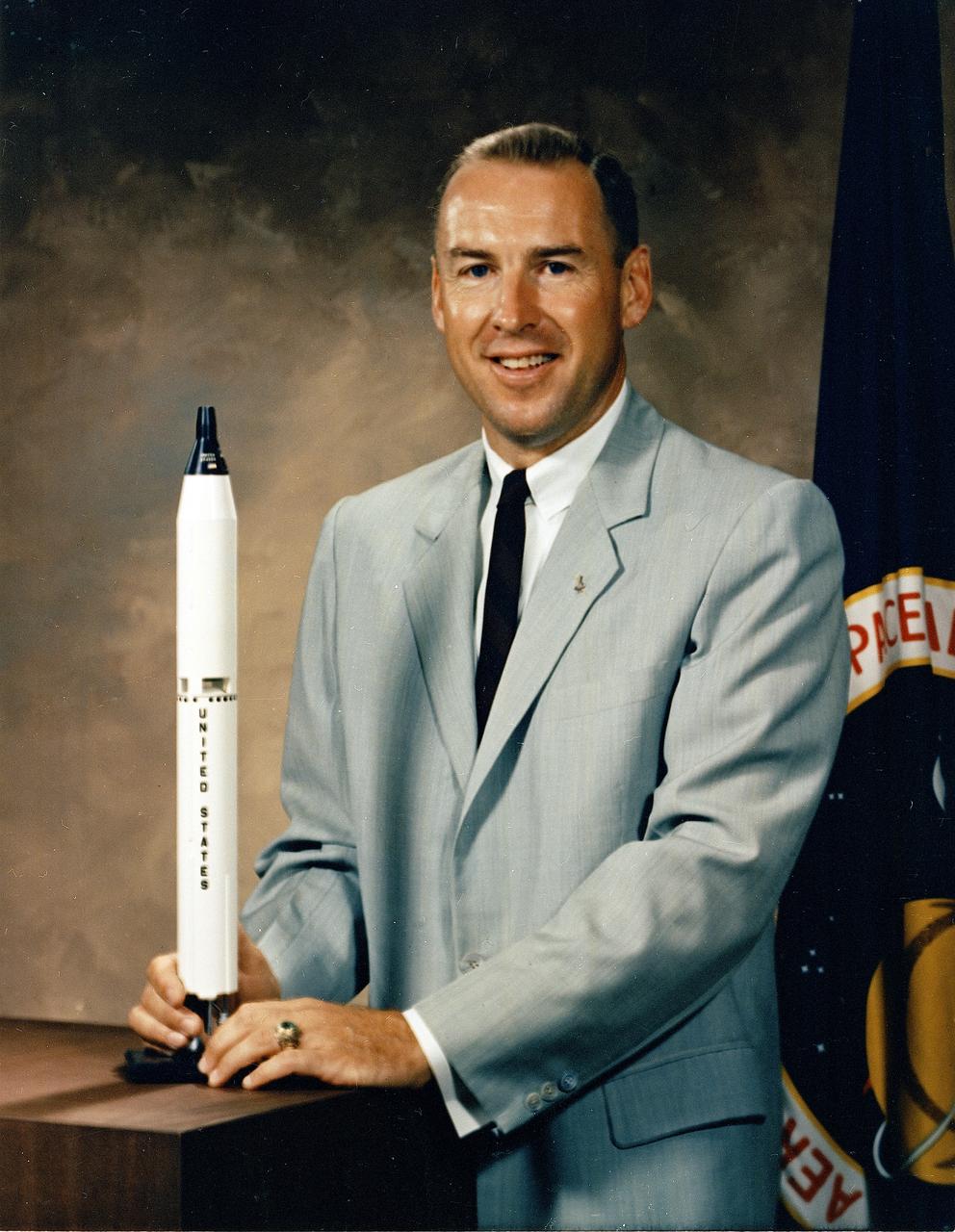

This is the official NASA portrait of astronaut James Lovell. Captain Lovell was selected as an Astronaut by NASA in September 1962. He has since served as backup pilot for the Gemini 4 flight and backup Commander for the Gemini 9 flight, as well as backup Commander to Neil Armstrong for the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. On December 4, 1965, he and Frank Borman were launched into space on the history making Gemini 7 mission. The flight lasted 330 hours and 35 minutes and included the first rendezvous of two manned maneuverable spacecraft. The Gemini 12 mission, commanded by Lovell with Pilot Edwin Aldrin, began on November 11, 1966 for a 4-day, 59-revolution flight that brought the Gemini program to a successful close. Lovell served as Command Module Pilot and Navigator on the epic six-day journey of Apollo 8, the first manned Saturn V liftoff responsible for allowing the first humans to leave the gravitational influence of Earth. He completed his fourth mission as Spacecraft Commander of the Apollo 13 flight, April 11-17, 1970, and became the first man to journey twice to the moon. The Apollo 13 mission was cut short due to a failure of the Service Module cryogenic oxygen system. Aborting the lunar course, Lovell and fellow crewmen, John L. Swigert and Fred W. Haise, working closely with Houston ground controllers, converted their lunar module, Aquarius, into an effective lifeboat that got them safely back to Earth. Captain Lovell held the record for time in space with a total of 715 hours and 5 minutes until surpassed by the Skylab flights. On March 1, 1973, Captain Lovell retired from the Navy and the Space Program.
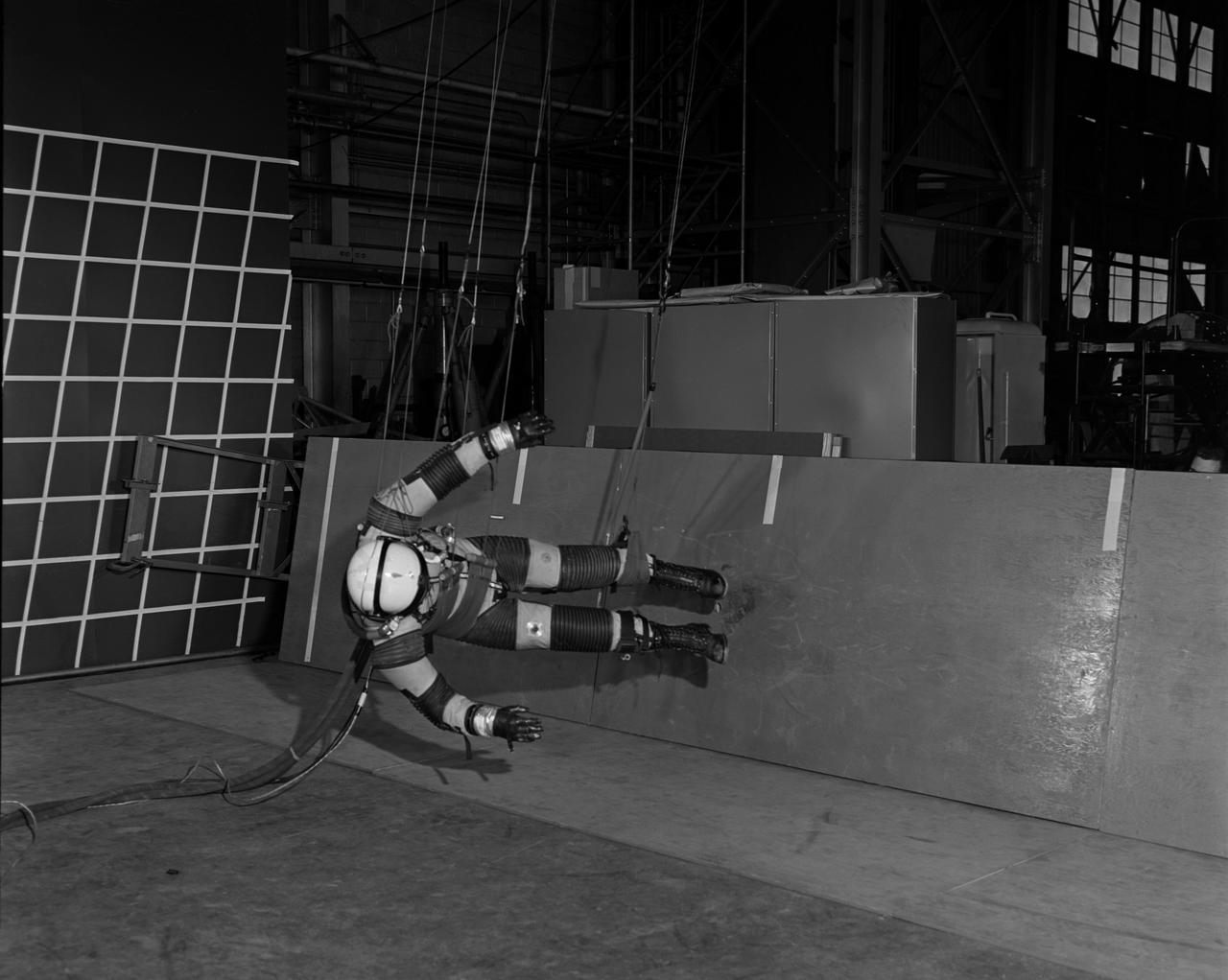

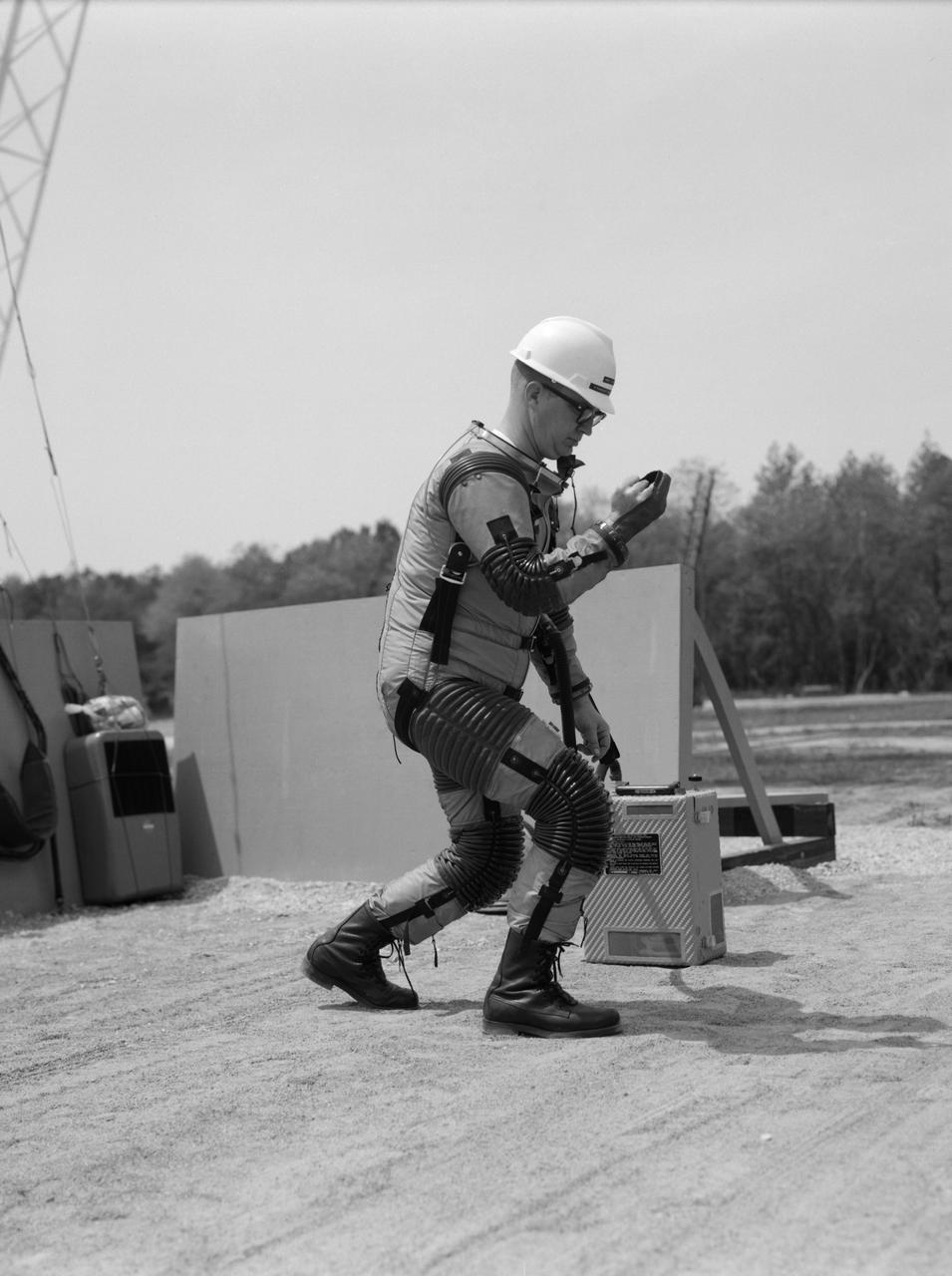
A "suited" test subject on the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located in the hangar at Langley Research Center. The initial version of this simulator was located inside the hangar. Later a larger version would be located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. Francis B. Smith wrote in "Simulators For Manned Space Research:" "The cables which support the astronaut are supported by an overhead trolley about 150 feet above the center line of the walkway and the support is arranged so that the subject is free to walk, run, jump, and perform other self-locomotive tasks in a more-or-less normal manner, even though he is constrained to move in one place." "The studies thus far show that an astronaut should have no particular difficulty in walking in a pressurized space suit on a hard lunar surface. Rather, the pace was faster and the suit was found to be more comfortable and less fatiguing under lunar "g" than under earth "g." When the test subject wished to travel hurriedly any appreciable distance, a long loping gait at about 10 feet per second was found to be most comfortable." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 377; Francis B. Smith, "Simulators For Manned Space Research," Paper for 1966 IEEE International Convention, New York, NY, March 21-25, 1966.
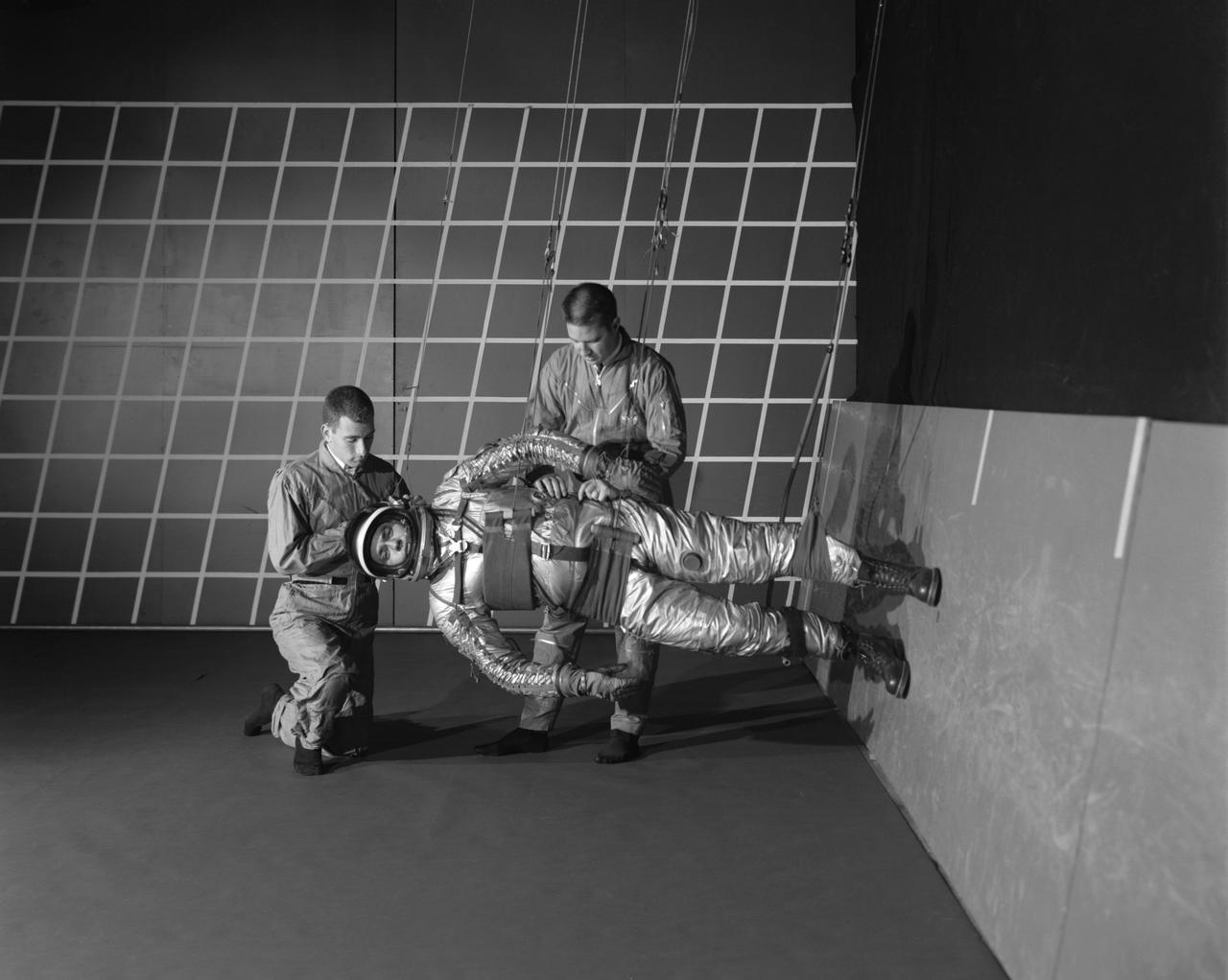

A test subject being suited up for studies on the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located in the hangar at Langley Research Center. The initial version of this simulator was located inside the hangar. Later a larger version would be located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. Francis B. Smith wrote in his paper "Simulators For Manned Space Research," "I would like to conclude this talk with a discussion of a device for simulating lunar gravity which is very effective and yet which is so simple that its cost is in the order of a few thousand dollars at most, rather than hundreds of thousands. With a little ingenuity, one could almost build this type simulator in his backyard for children to play on. The principle is ...if a test subject is suspended in a sling so that his body axis makes an angle of 9 1/2 degrees with the horizontal and if he then "stands" on a platform perpendicular to his body axis, the component of the earth's gravity forcing him toward the platform is one times the sine of 9 1/2 degrees or approximately 1/6 of the earth's normal gravity field. That is, a 180 pound astronaut "standing" on the platform would exert a force of only 30 pounds - the same as if he were standing upright on the lunar surface." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, NASA SP-4308; Francis B. Smith, "Simulators For Manned Space Research," Paper for 1966 IEEE International Convention, New York, NY, March 21-25, 1966

Astronaut Roger Chaffee on the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil, described the simulator as follows: "When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject's weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, NASA SP-4308, p. 377; A.W. Vigil, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology," Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.

This artist's illustration depicts the exoplanet LHS 3844b, which is 1.3 times the mass of Earth and orbits an M dwarf star. The planet has no apparent atmosphere, and its surface may be covered mostly in dark lava rock, according to observations by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. Discovered in 2018 by NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Satellite Survey (TESS), planet LHS 3844b is located 48.6 light-years from Earth and makes one full revolution around its parent star in just 11 hours. Because it has such a tight orbit, LHS 3844b is most likely tidally locked, meaning one side of the planet always faces the star while another side always faces away. Spitzer was able to detect light directly emitted by LHS 3844b in part because the planet is extremely hot, so it radiates a relatively high amount of infrared light. The star-facing side is heated to about 1,410 degrees Fahrenheit (770 degrees Celsius). In addition, the planet's parent star is relatively dim as far as stars go. By measuring the temperature difference between the planet's star-facing dayside and its space-facing nightside, the new study found that a negligible amount of heat is being transferred from one side to the other. If an atmosphere were present, hot air on the dayside would naturally expand and generate winds that would transfer heat around the planet. On a rock with little to no atmosphere, like the Moon, there is no air present to transfer heat. The planet has a low infrared albedo, or reflectivity, leading scientists to conclude that its surface may be covered with basalt, which also composes the dark mare on the Moon. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23130
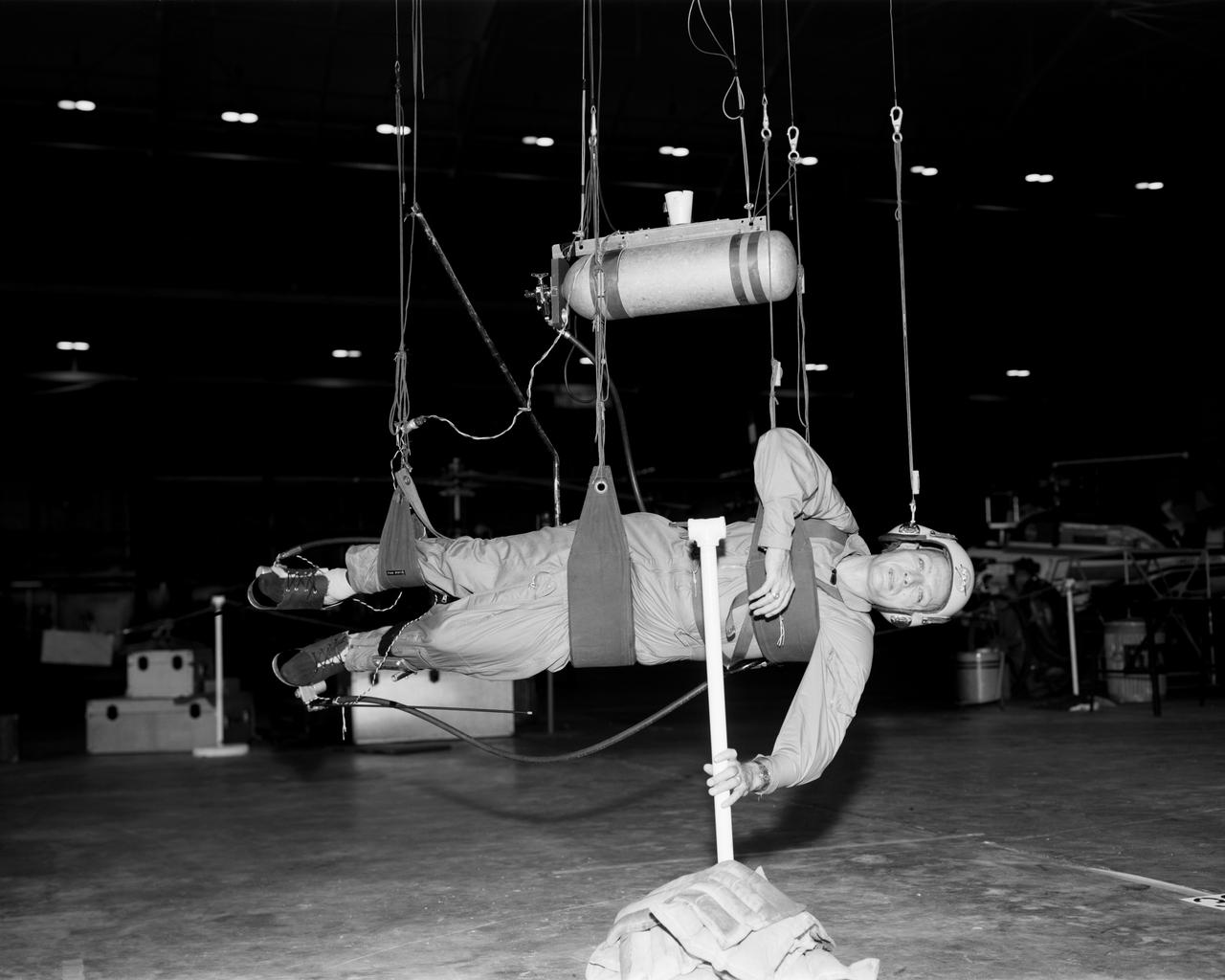

Cable system which supports the test subject on the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil described the purpose of the simulator as follows: "When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject's weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995); A.W. Vigil, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology," Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.
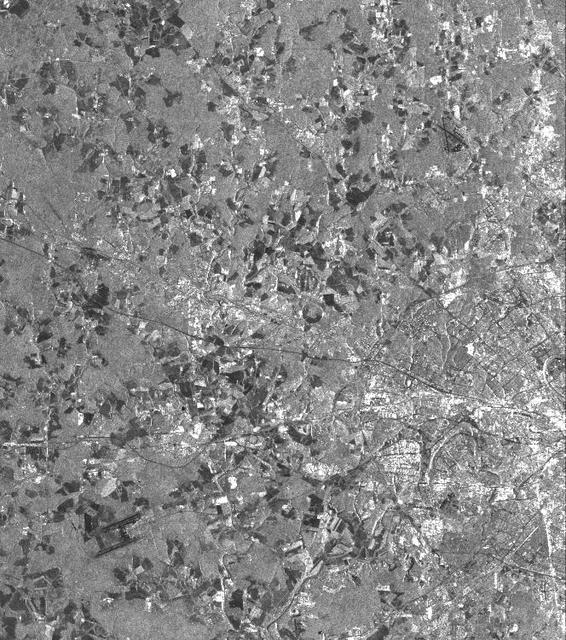
This is a vertically polarized L-band image of the southern half of Moscow, an area which has been inhabited for 2,000 years. The image covers a diameter of approximately 50 kilometers (31 miles) and was taken on September 30, 1994 by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar aboard the space shuttle Endeavour. The city of Moscow was founded about 750 years ago and today is home to about 8 million residents. The southern half of the circular highway (a road that looks like a ring) can easily be identified as well as the roads and railways radiating out from the center of the city. The city was named after the Moskwa River and replaced Russia's former capital, St. Petersburg, after the Russian Revolution in 1917. The river winding through Moscow shows up in various gray shades. The circular structure of many city roads can easily be identified, although subway connections covering several hundred kilometers are not visible in this image. The white areas within the ring road and outside of it are buildings of the city itself and it suburban towns. Two of many airports are located in the west and southeast of Moscow, near the corners of the image. The Kremlin is located north just outside of the imaged city center. It was actually built in the 16th century, when Ivan III was czar, and is famous for its various churches. In the surrounding area, light gray indicates forests, while the dark patches are agricultural areas. The various shades from middle gray to dark gray indicate different stages of harvesting, ploughing and grassland. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01752
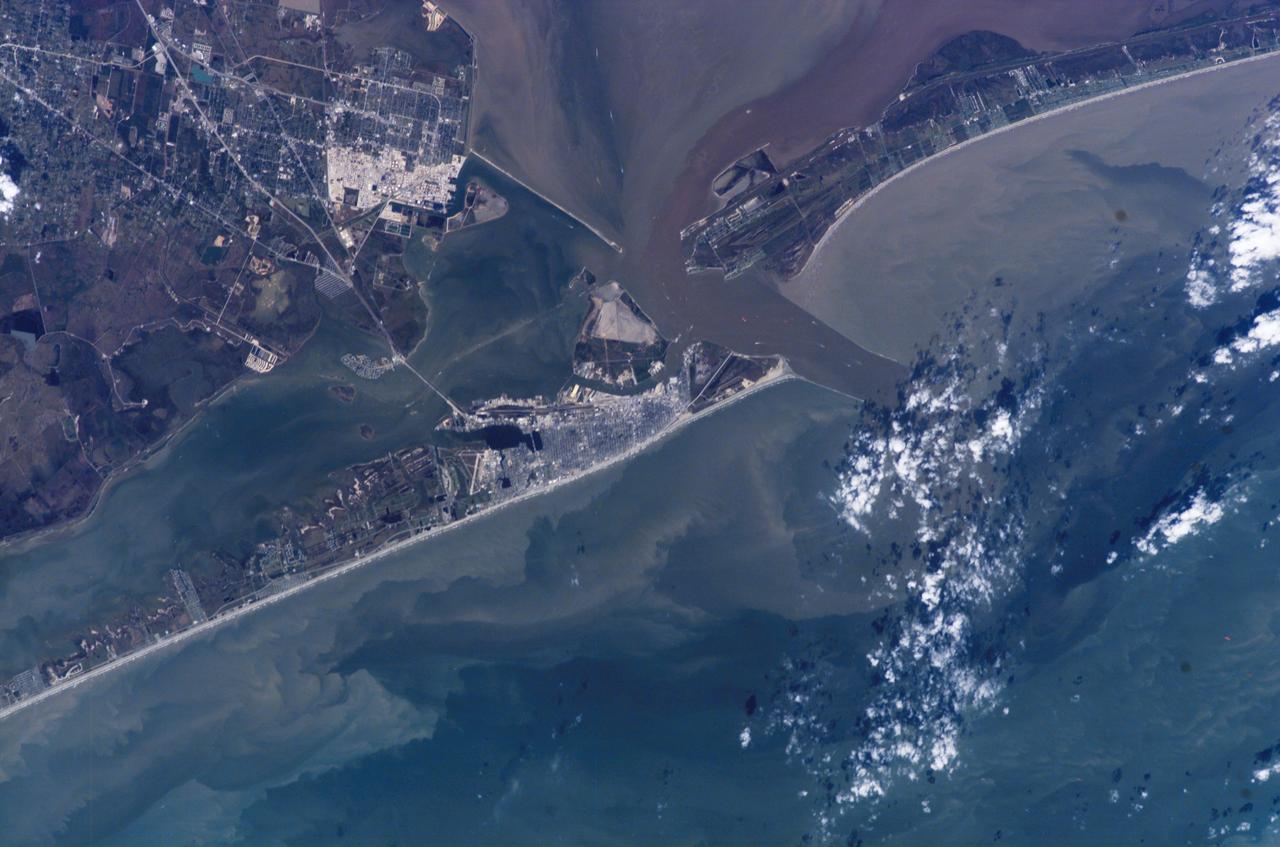

ISS014-E-07258 (4 Nov. 2006) --- Galveston, Texas is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 14 crewmember on the International Space Station (ISS). Mexico established a port of entry (known as Galveston) in 1825, and following the Texas Revolution it was the capital of the Republic of Texas during 1836. The modern-day city of Galveston was incorporated in 1839, and became the major trading seaport of Texas during the latter half of the 19th century. The city was largely destroyed in early September of 1900 by a powerful hurricane; this, coupled with construction of the Houston Ship Channel and discovery of oil in eastern Texas shifted the center of trade northwest to Houston. Many human footprints are easily observed from the vantage point of low Earth orbit. The eastern half of Galveston Island is dominated by the city of Galveston (gray-white region at center). A large seawall along the Gulf of Mexico (southern coastline of Galveston Island) protects most of the city. To the west of Galveston, coastal wetlands are largely submerged by regional subsidence--a result of ground water withdrawal by the petrochemical industry of Houston and Texas City. The entrance to Galveston Bay and the Houston Ship Channel is located between Galveston Island and the Bolivar Peninsula (upper right). Numerous ship wakes are visible along the Houston Ship Channel. Other visible features of the entrance to Galveston Bay include the five-mile long Texas City Dike, a structure that protects the Texas City channel and includes a fishing pier that extends 600 feet beyond the end of the Dike. Extensive petroleum processing facilities are located to the west of the Dike in Texas City. The Intracoastal Waterway runs through western Galveston Bay; new subdivisions built on dredge spoils are visible along the northern boundary of the Waterway. Geologists studying the ISS collection of down linked still imagery observe that complex estuarine sediment patterns are visible in this image. Dark brown to tan waters adjacent to the Bolivar Peninsula and Texas City Dike reflect increased sediment loads following heavy rains in mid-to-late October, coupled with northerly winds moving Bay water southwards. Turbidity currents to both the northwest and southeast of Galveston Island produce a more chaotic pattern of sediment-laden (light green to tan) and relatively sediment-free (dark green) water leading into the dark green Gulf of Mexico (lower right).

For the 26th birthday of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers are highlighting a Hubble image of an enormous bubble being blown into space by a super-hot, massive star. The Hubble image of the Bubble Nebula, or NGC 7635, was chosen to mark the 26th anniversary of the launch of Hubble into Earth orbit by the STS-31 space shuttle crew on April 24, 1990 “As Hubble makes its 26th revolution around our home star, the sun, we celebrate the event with a spectacular image of a dynamic and exciting interaction of a young star with its environment. The view of the Bubble Nebula, crafted from WFC-3 images, reminds us that Hubble gives us a front row seat to the awe inspiring universe we live in,” said John Grunsfeld, Hubble astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, in Washington, D.C. The Bubble Nebula is seven light-years across—about one-and-a-half times the distance from our sun to its nearest stellar neighbor, Alpha Centauri, and resides 7,100 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cassiopeia. The seething star forming this nebula is 45 times more massive than our sun. Gas on the star gets so hot that it escapes away into space as a “stellar wind” moving at over four million miles per hour. This outflow sweeps up the cold, interstellar gas in front of it, forming the outer edge of the bubble much like a snowplow piles up snow in front of it as it moves forward. As the surface of the bubble's shell expands outward, it slams into dense regions of cold gas on one side of the bubble. This asymmetry makes the star appear dramatically off-center from the bubble, with its location in the 10 o’clock position in the Hubble view. Dense pillars of cool hydrogen gas laced with dust appear at the upper left of the picture, and more “fingers” can be seen nearly face-on, behind the translucent bubble. The gases heated to varying temperatures emit different colors: oxygen is hot enough to emit blue light in the bubble near the star, while the cooler pillars are yellow from the combined light of hydrogen and nitrogen. The pillars are similar to the iconic columns in the “Pillars of Creation” Eagle Nebula. As seen with the structures in the Eagle Nebula, the Bubble Nebula pillars are being illuminated by the strong ultraviolet radiation from the brilliant star inside the bubble. The Bubble Nebula was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, a prominent British astronomer. It is being formed by a proto-typical Wolf-Rayet star, BD +60º2522, an extremely bright, massive, and short-lived star that has lost most of its outer hydrogen and is now fusing helium into heavier elements. The star is about four million years old, and in 10 million to 20 million years, it will likely detonate as a supernova. Hubble’s Wide Field Camera-3 imaged the nebula in visible light with unprecedented clarity in February 2016. The colors correspond to blue for oxygen, green for hydrogen, and red for nitrogen. This information will help astronomers understand the geometry and dynamics of this complex system. The Bubble Nebula is one of only a handful of astronomical objects that have been observed with several different instruments onboard Hubble. Hubble also imaged it with the Wide Field Planetary Camera (WFPC) in September 1992, and with Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (WFPC2) in April 1999. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)

For the 26th birthday of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers are highlighting a Hubble image of an enormous bubble being blown into space by a super-hot, massive star. The Hubble image of the Bubble Nebula, or NGC 7635, was chosen to mark the 26th anniversary of the launch of Hubble into Earth orbit by the STS-31 space shuttle crew on April 24, 1990 “As Hubble makes its 26th revolution around our home star, the sun, we celebrate the event with a spectacular image of a dynamic and exciting interaction of a young star with its environment. The view of the Bubble Nebula, crafted from WFC-3 images, reminds us that Hubble gives us a front row seat to the awe inspiring universe we live in,” said John Grunsfeld, Hubble astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, in Washington, D.C. The Bubble Nebula is seven light-years across—about one-and-a-half times the distance from our sun to its nearest stellar neighbor, Alpha Centauri, and resides 7,100 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cassiopeia. The seething star forming this nebula is 45 times more massive than our sun. Gas on the star gets so hot that it escapes away into space as a “stellar wind” moving at over four million miles per hour. This outflow sweeps up the cold, interstellar gas in front of it, forming the outer edge of the bubble much like a snowplow piles up snow in front of it as it moves forward. As the surface of the bubble's shell expands outward, it slams into dense regions of cold gas on one side of the bubble. This asymmetry makes the star appear dramatically off-center from the bubble, with its location in the 10 o’clock position in the Hubble view. Dense pillars of cool hydrogen gas laced with dust appear at the upper left of the picture, and more “fingers” can be seen nearly face-on, behind the translucent bubble. The gases heated to varying temperatures emit different colors: oxygen is hot enough to emit blue light in the bubble near the star, while the cooler pillars are yellow from the combined light of hydrogen and nitrogen. The pillars are similar to the iconic columns in the “Pillars of Creation” Eagle Nebula. As seen with the structures in the Eagle Nebula, the Bubble Nebula pillars are being illuminated by the strong ultraviolet radiation from the brilliant star inside the bubble. The Bubble Nebula was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, a prominent British astronomer. It is being formed by a proto-typical Wolf-Rayet star, BD +60º2522, an extremely bright, massive, and short-lived star that has lost most of its outer hydrogen and is now fusing helium into heavier elements. The star is about four million years old, and in 10 million to 20 million years, it will likely detonate as a supernova. Hubble’s Wide Field Camera-3 imaged the nebula in visible light with unprecedented clarity in February 2016. The colors correspond to blue for oxygen, green for hydrogen, and red for nitrogen. This information will help astronomers understand the geometry and dynamics of this complex system. The Bubble Nebula is one of only a handful of astronomical objects that have been observed with several different instruments onboard Hubble. Hubble also imaged it with the Wide Field Planetary Camera (WFPC) in September 1992, and with Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (WFPC2) in April 1999. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
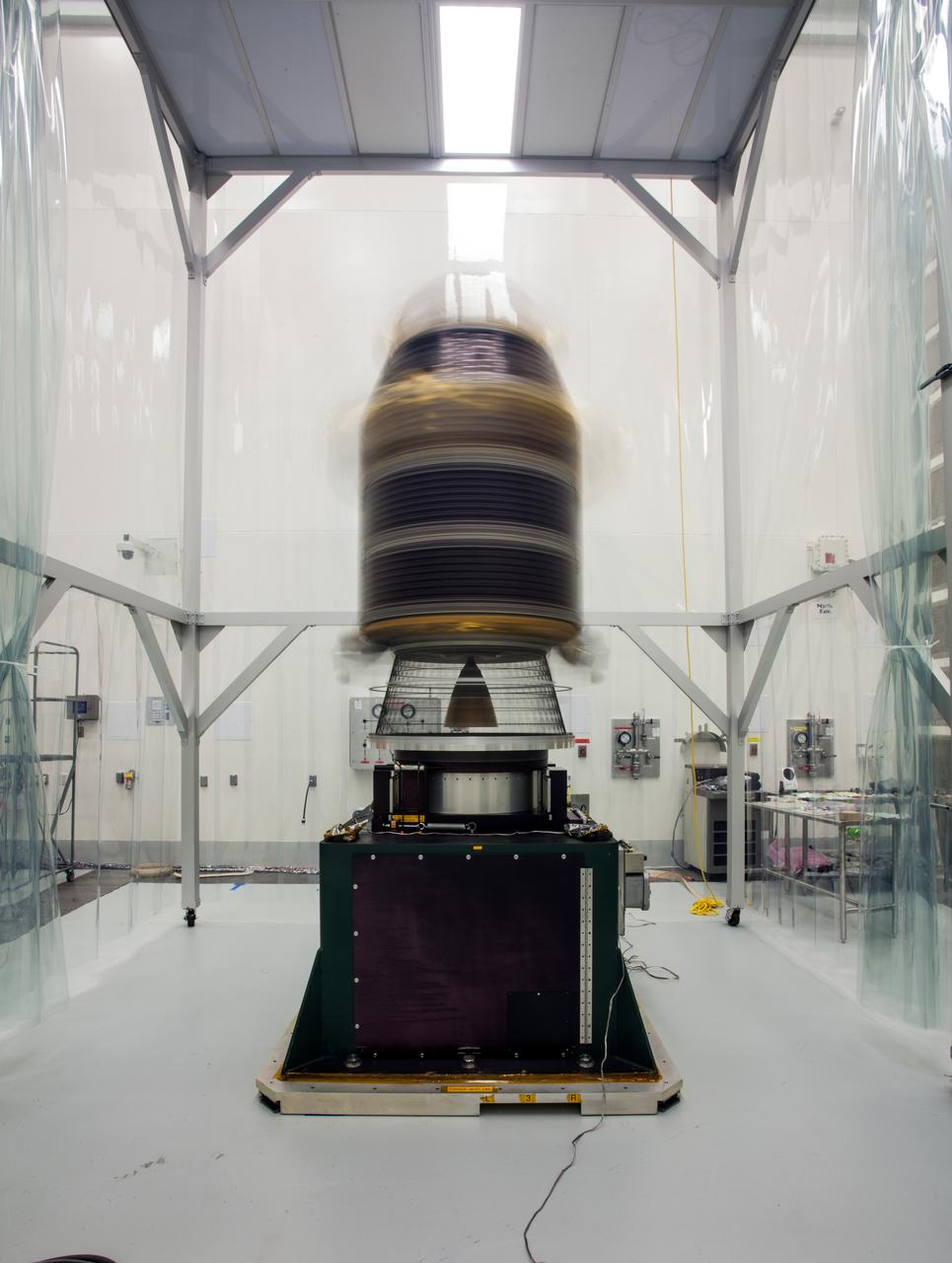

During preparations for NASA's Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) observatory launch on Sept. 6, 2013, the spacecraft went through final preparations and close-outs, which included checking alignment after its cross-country shipment, checking the propulsion system for leaks, inspecting and repairing solar panels, and final electrical tests. After these activities were completed, more challenging portions of the launch preparations began: spin testing and fueling. To make sure that the spacecraft is perfectly balanced for flight, engineers mounted it onto a spin table and rotate it at high speeds, approximately one revolution per second. The team measured any offsets during the spinning, and then added small weights to the spacecraft to balance it. Once the spacecraft was balanced dry, the team loaded the propulsion tanks with fuel, oxidizer, and pressurant. The spin testing was performed again "wet," or with fuel, in order to see if the balance changed with the full fuel tanks. Engineers from NASA's Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, Calif., have now successfully completed launch preparation activities for LADEE, which has been encapsulated into the nose-cone of the Minotaur V rocket at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. LADEE is ready to launch when the window opens on Friday. Image Credit: NASA ----- What is LADEE? The Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) is designed to study the Moon's thin exosphere and the lunar dust environment. An "exosphere" is an atmosphere that is so thin and tenuous that molecules don't collide with each other. Studying the Moon's exosphere will help scientists understand other planetary bodies with exospheres too, like Mercury and some of Jupiter's bigger moons. The orbiter will determine the density, composition and temporal and spatial variability of the Moon's exosphere to help us understand where the species in the exosphere come from and the role of the solar wind, lunar surface and interior, and meteoric infall as sources. The mission will also examine the density and temporal and spatial variability of dust particles that may get lofted into the atmosphere. The mission also will test several new technologies, including a modular spacecraft bus that may reduce the cost of future deep space missions and demonstrate two-way high rate laser communication for the first time from the Moon. LADEE now is ready to launch when the window opens on Sept. 6, 2013. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/ladee" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/ladee</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>