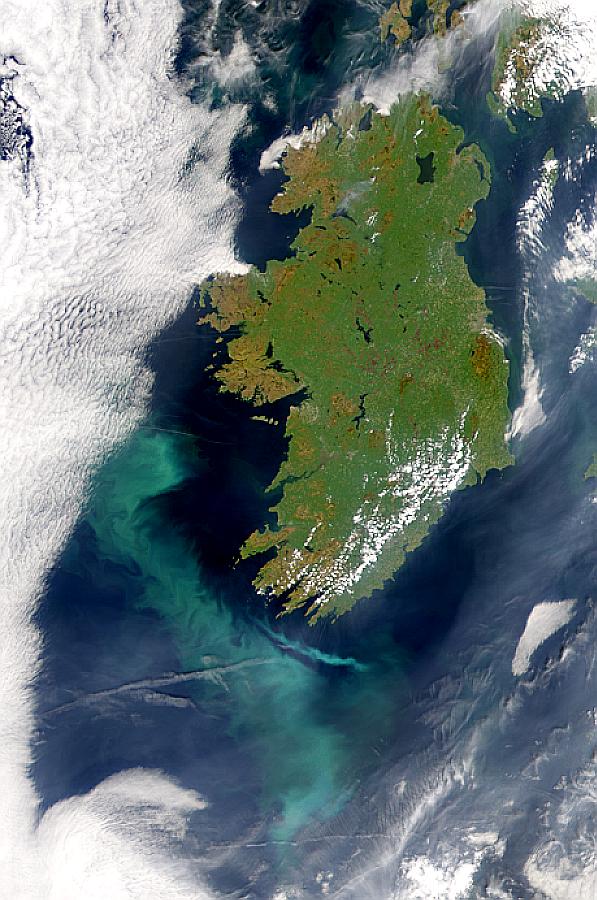

Visualization Date 2000-05-10 A possible coccolithophore bloom is seen to the southwest of Ireland in this SeaWiFS image. Sensor OrbView-2/SeaWiFS Credit Provided by the SeaWiFS Project, NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, and ORBIMAGE For more information go to: <a href="http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view_rec.php?id=785" rel="nofollow">visibleearth.nasa.gov/view_rec.php?id=785</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
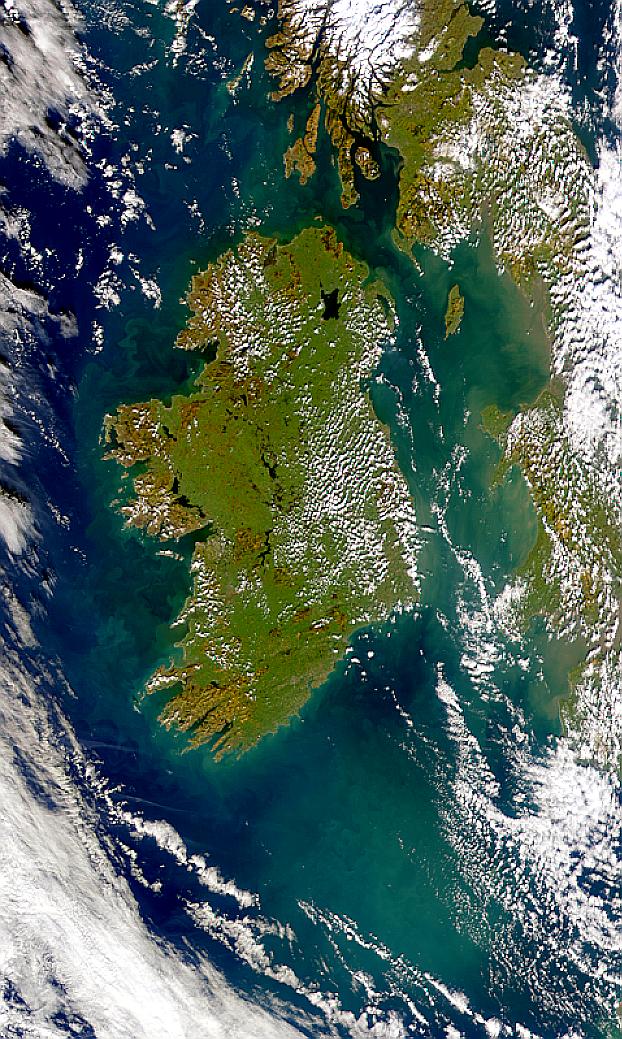
Visualization Date 2000-02-19 Possible coccolithophore blooms are visible in this SeaWiFS image of Ireland. Sensor OrbView-2/SeaWiFS Credit Provided by the SeaWiFS Project, NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, and ORBIMAGE For more information go to: <a href="http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view_rec.php?id=920" rel="nofollow">visibleearth.nasa.gov/view_rec.php?id=920</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
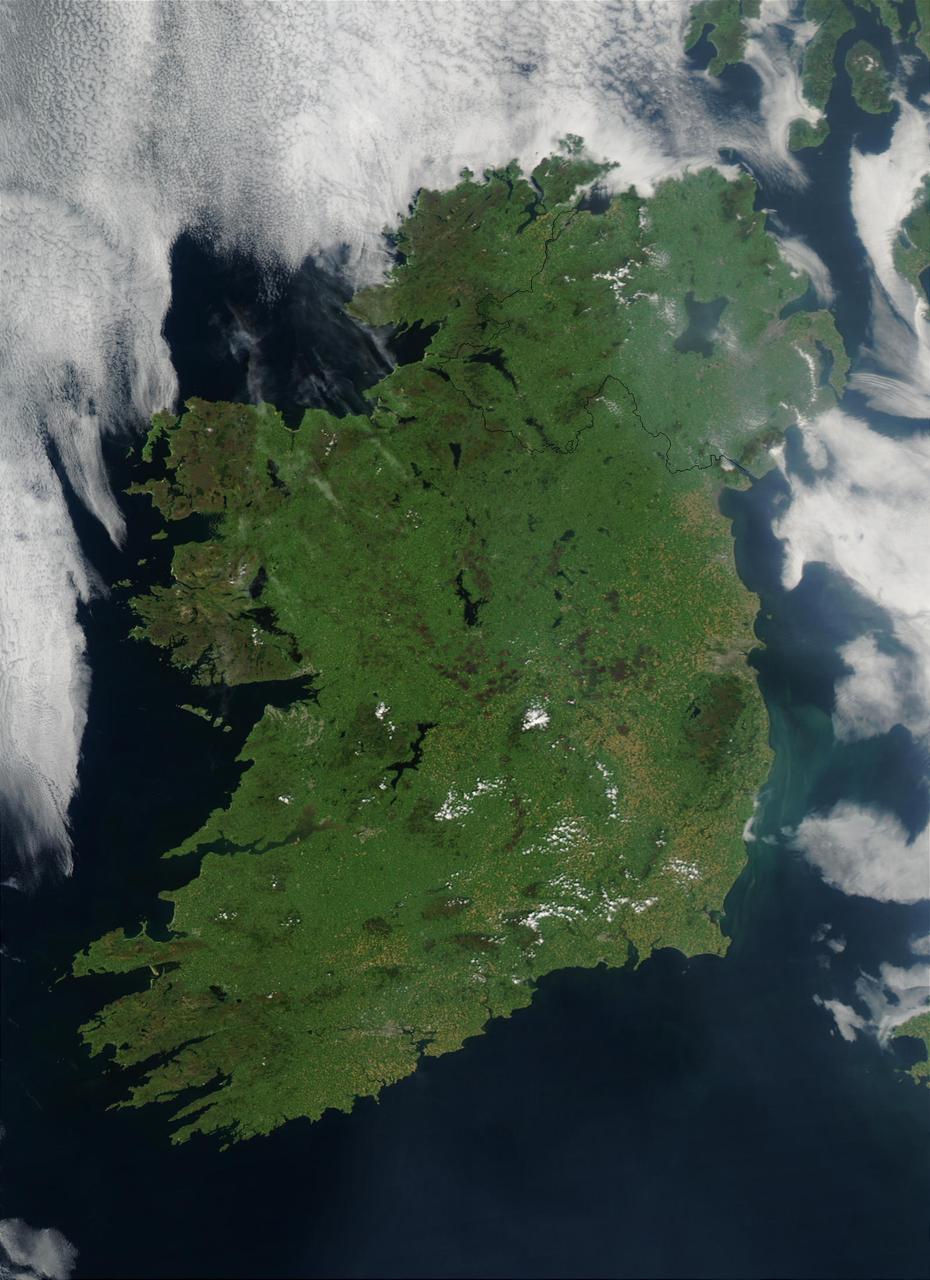

On August 7, 2003, the NASA Aqua MODIS instrument acquired this image of Ireland on the first day this summer that most of the island hasn´t been completely obscured by cloud cover. Called the Emerald Isle for a good reason, Ireland is draped in vibrant shades of green amidst the blue Atlantic Ocean and Celtic (south) and Irish (east) Seas. Faint ribbons of blue-green phytoplankton drift in the waters of the Celtic Sea, just south of Dublin. Dublin itself appears as a large grayish-brown spot on the Republic of Ireland´s northeastern coast. This large capital city (population 1.12 million) sits on the River Liffey, effectively splitting the city in half. Northern Ireland´s capital city, Belfast, also sits on a river: the River Lagan. This city, though its population is only a fifth of the size of Dublin´s, is also clearly visible in the image as a grayish-brown spot on the coast of the Irish Sea. Sensor Aqua/MODIS Credit Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team, NASA/GSFC For more information go to: <a href="http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view_rec.php?id=5744" rel="nofollow">visibleearth.nasa.gov/view_rec.php?id=5744</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a><b> </b></b>
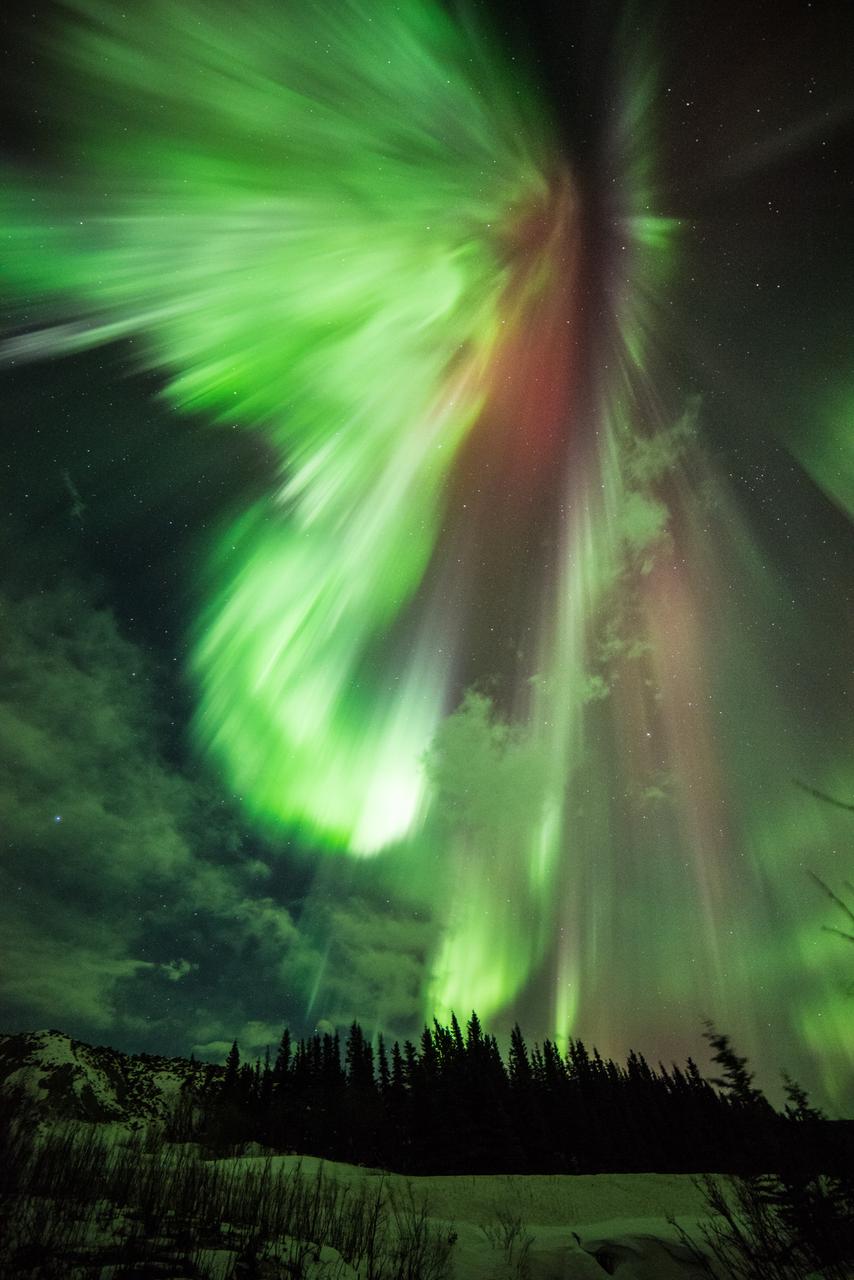

Geomagnetic Storms Sometimes during the solar magnetic events, solar explosions hurl clouds of magnetized particles into space. Traveling more than a million miles per hour, these coronal mass ejections, or CMEs, made up of hot material called plasma take up to three days to reach Earth. Spacecraft and satellites in the path of CMEs can experience glitches as these plasma clouds pass by. In near-Earth space, magnetic reconnection incites explosions of energy driving charged solar particles to collide with atoms in Earth’s upper atmosphere. We see these collisions near Earth’s polar regions as the aurora. The prevalence of specific gases in the atmosphere determines the color of the aurora. For example, if charged particles strike oxygen atoms, the aurora will appear green. Excited nitrogen closer to 60 miles above Earth’s surface will produce a blood red color. Three spacecraft from NASA’s Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms (THEMIS) mission, observe these outbursts known as substorms. Substorms can intensify aurora’s near Earth’s poles. To learn more about the aurora, go to NASA’s THEMIS mission: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/themis/main/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/themis/main/index.html</a> ---------- Original caption: How about a little something green for St. Patrick's Day? "St. Patrick's Aurora" was taken at Donnelly Creek, Alaska at 1:30 am, March 17, 2015 by our good friend Sebastian Saarloos! You can see more images from Sebastian here: <a href="http://www.facebook.com/SebastianSaarloos" rel="nofollow">www.facebook.com/SebastianSaarloos</a> Credit: Sebastian Saarloos <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
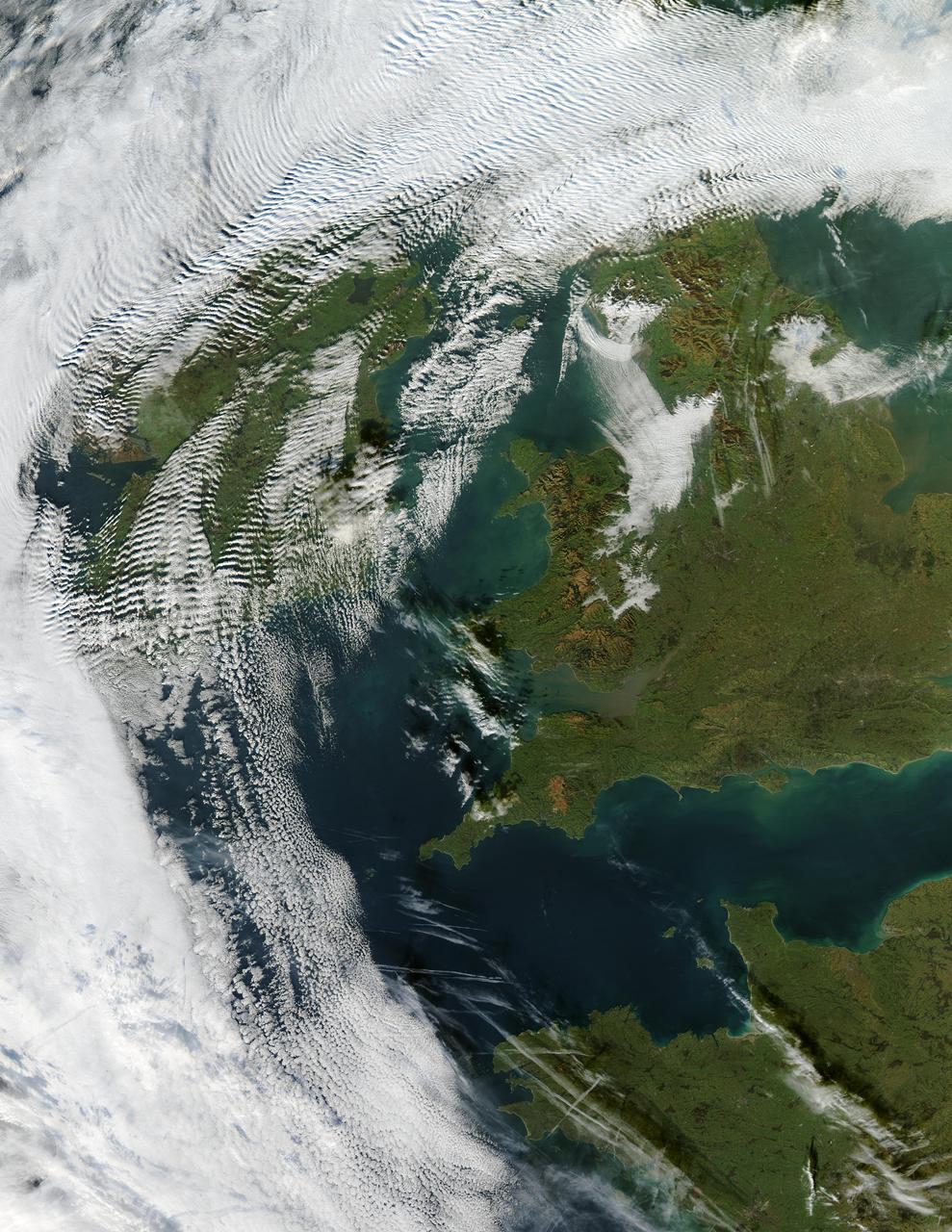
Visualization Date 2003-12-18 Clouds ripple over Ireland and Scotland in a wave pattern, similar to the pattern of waves along a seashore. The similarity is not coincidental — the atmosphere behaves like a fluid, so when it encounters an obstacle, it must move around it. This movement forms a wave, and the wave movement can continue for long distances. In this case, the waves were caused by the air moving over and around the mountains of Scotland and Ireland. As the air crested a wave, it cooled, and clouds formed. Then, as the air sank into the trough, the air warmed, and clouds did not form. This pattern repeated itself, with clouds appearing at the peak of every wave. Other types of clouds are also visible in the scene. Along the northwestern and southwestern edges of this true-color image from December 17, 2003, are normal mid-altitude clouds with fairly uniform appearances. High altitude cirrus-clouds float over these, casting their shadows on the lower clouds. Open- and closed-cell clouds formed off the coast of northwestern France, and thin contrail clouds are visible just east of these. Contrail clouds form around the particles carried in airplane exhaust. Fog is also visible in the valleys east of the Cambrian Mountains, along the border between northern/central Wales and England. This is an Aqua MODIS image. Sensor Aqua/MODIS Credit Jacques Descloitres, MODIS Rapid Response Team, NASA/GSFC For more information go to: <a href="http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view_rec.php?id=6146" rel="nofollow">visibleearth.nasa.gov/view_rec.php?id=6146</a>
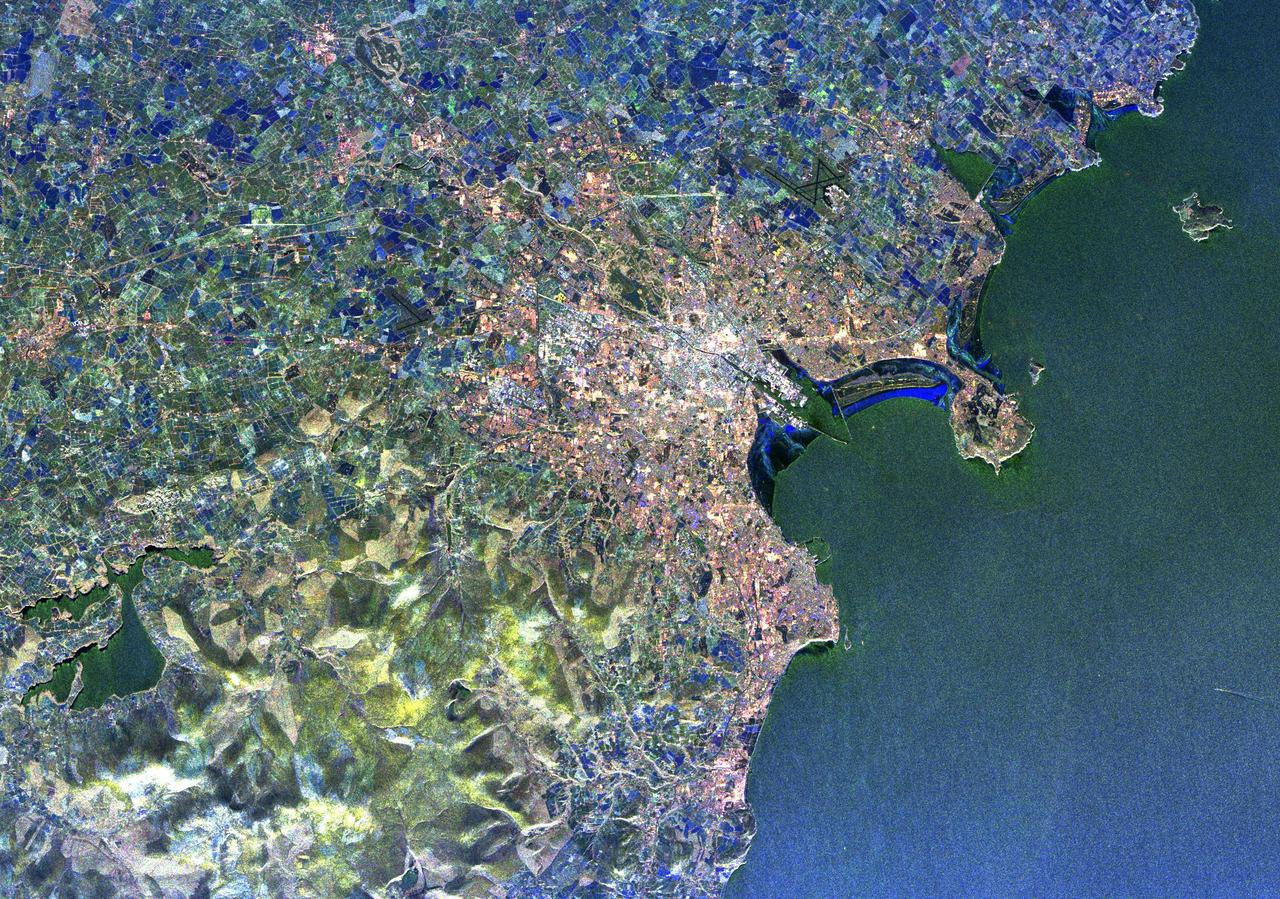

Visualization Date 1994-04-11 This radar image of Dublin, Ireland, shows how the radar distingishes between densely populated urban areas and nearby areas that are relatively unsettled. In the center of the image is the city's natural harbor along the Irish Sea. The pinkish areas in the center are the densely populated parts of the city and the blue/green areas are the suburbs. The two ends of the Dublin Bay are Howth Point, the circular peninsula near the upper right side of the image, and Dun Laoghaire, the point to the south. The small island just north of Howth is called "Ireland's Eye," and the larger island, near the upper right corner of the image is Lambay Island. The yellow/green mountains in the lower left of the image (south) are the Wicklow Mountains. The large lake in the lower left, nestled within these mountains, is the Poulaphouca Reservoir along River Liffey. The River Liffey, the River Dodder and the Tolka River are the three rivers that flow into Dublin. The straight features west of the city are the Grand Canal and the three rivers are the faint lines above and below these structures. The dark X-shaped feature just to the north of the city is the Dublin International Airport. The image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture (SIR-C/X-SAR) when it flew aboard the space shuttle Endeavour on April 11, 1994. This area is centered at 53.3 degrees north latitude, 6.2 degrees west longitude. The area shown is approximately 55 kilometers by 42 kilometers (34 miles by 26 miles). The colors are assigned to different frequencies and polarizations of the radar as follows: Red is L-band horizontally transmitted, horizontally received; green is L-band vertically transmitted, vertically received; and blue is C-band vertically transmitted, vertically received. SIR-C/X-SAR, a joint mission of the German, Italian, and the United States space agencies, is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth. Credit: NASA/GSFC For more information go to: <a href="http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view_rec.php?id=467" rel="nofollow">visibleearth.nasa.gov/view_rec.php?id=467</a>