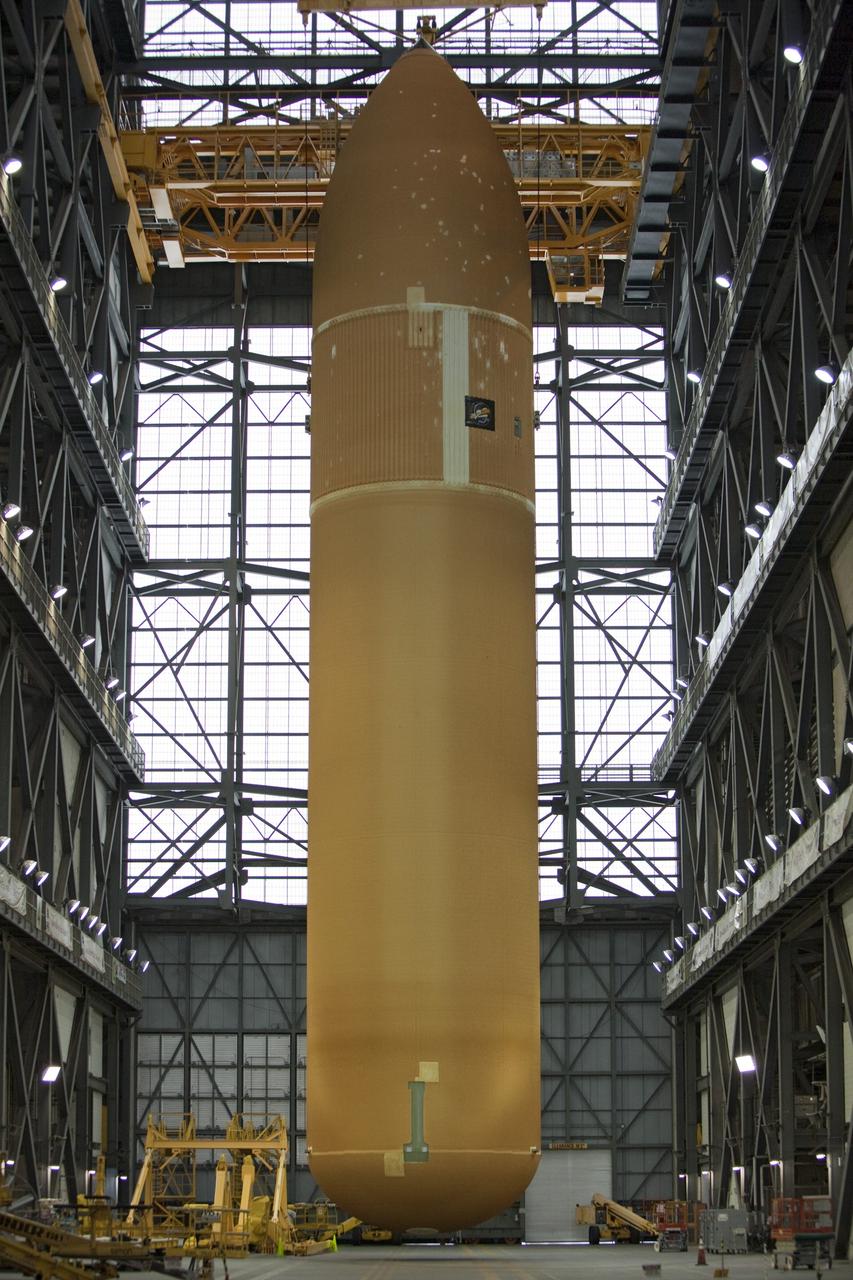

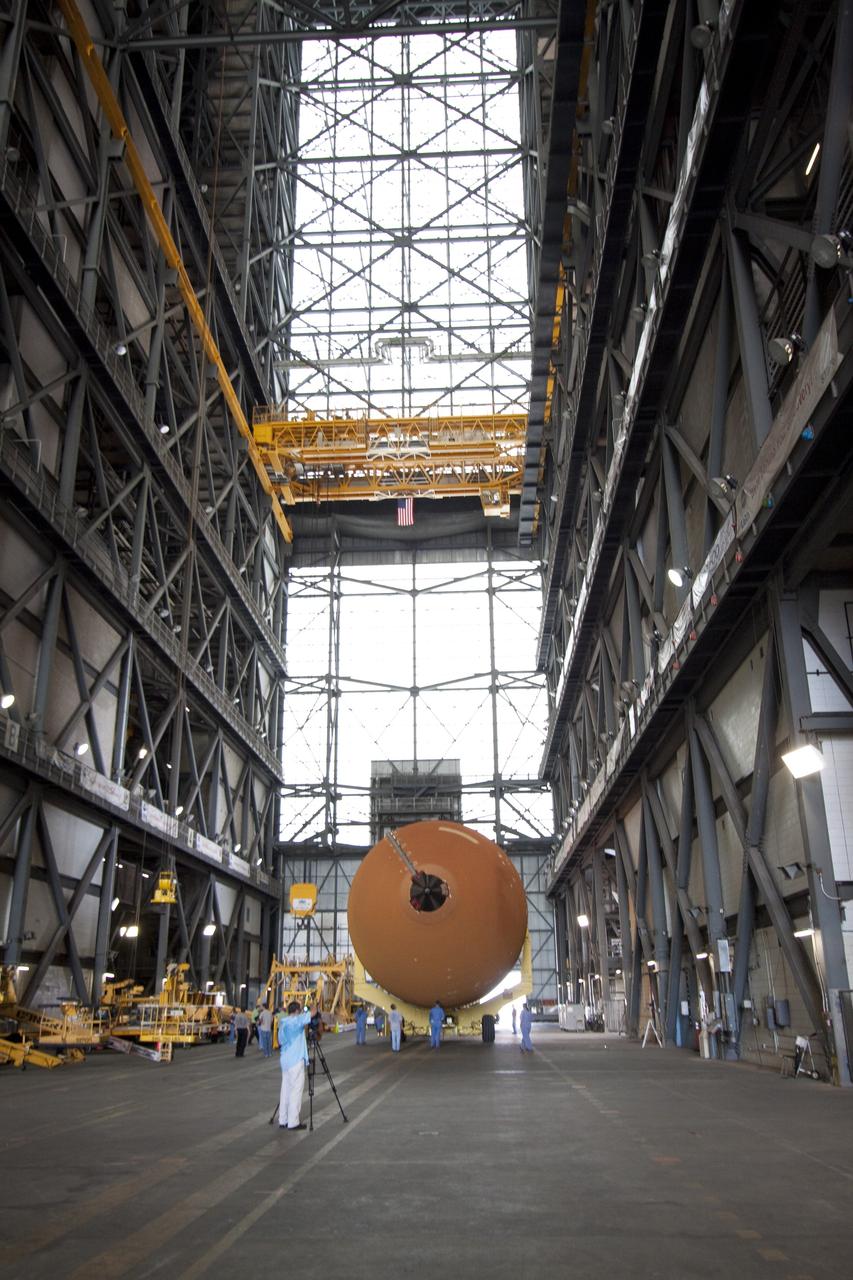
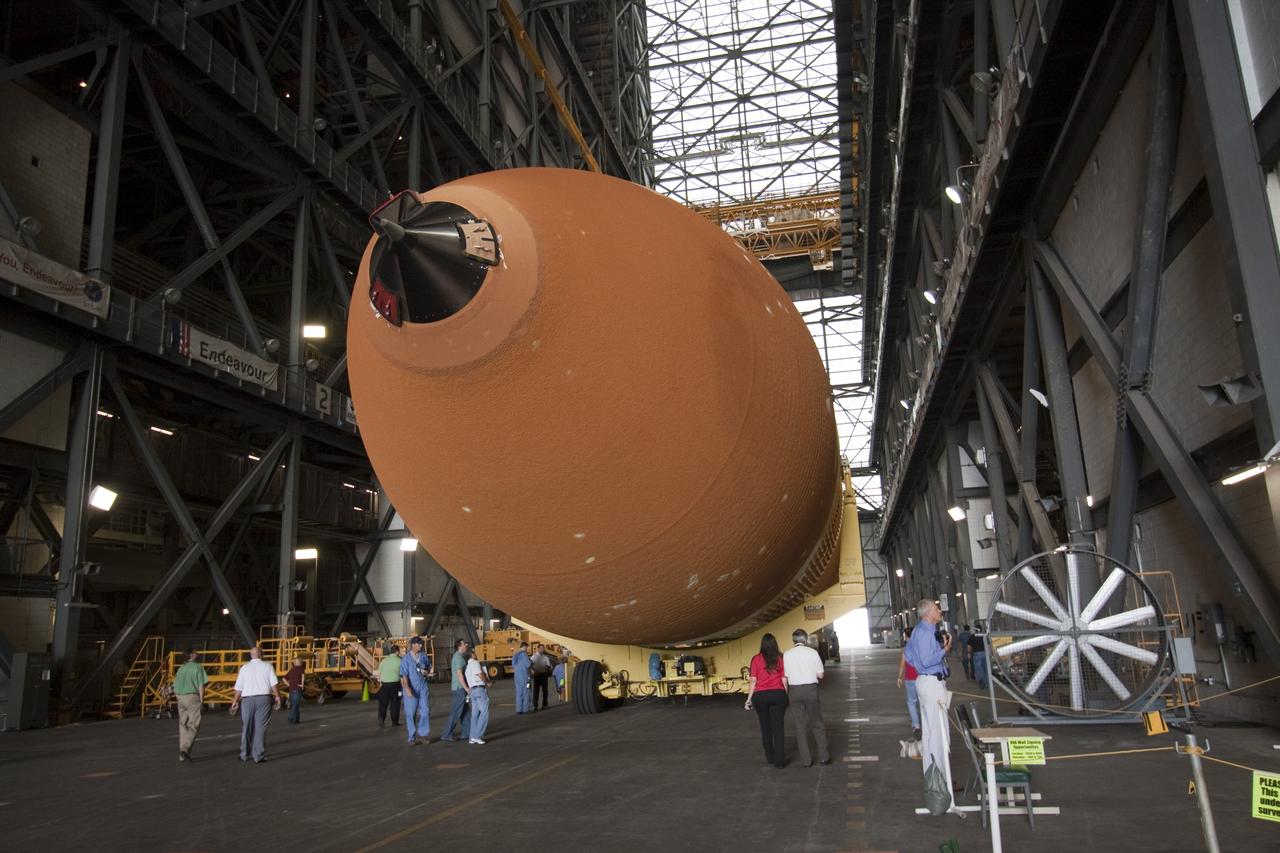
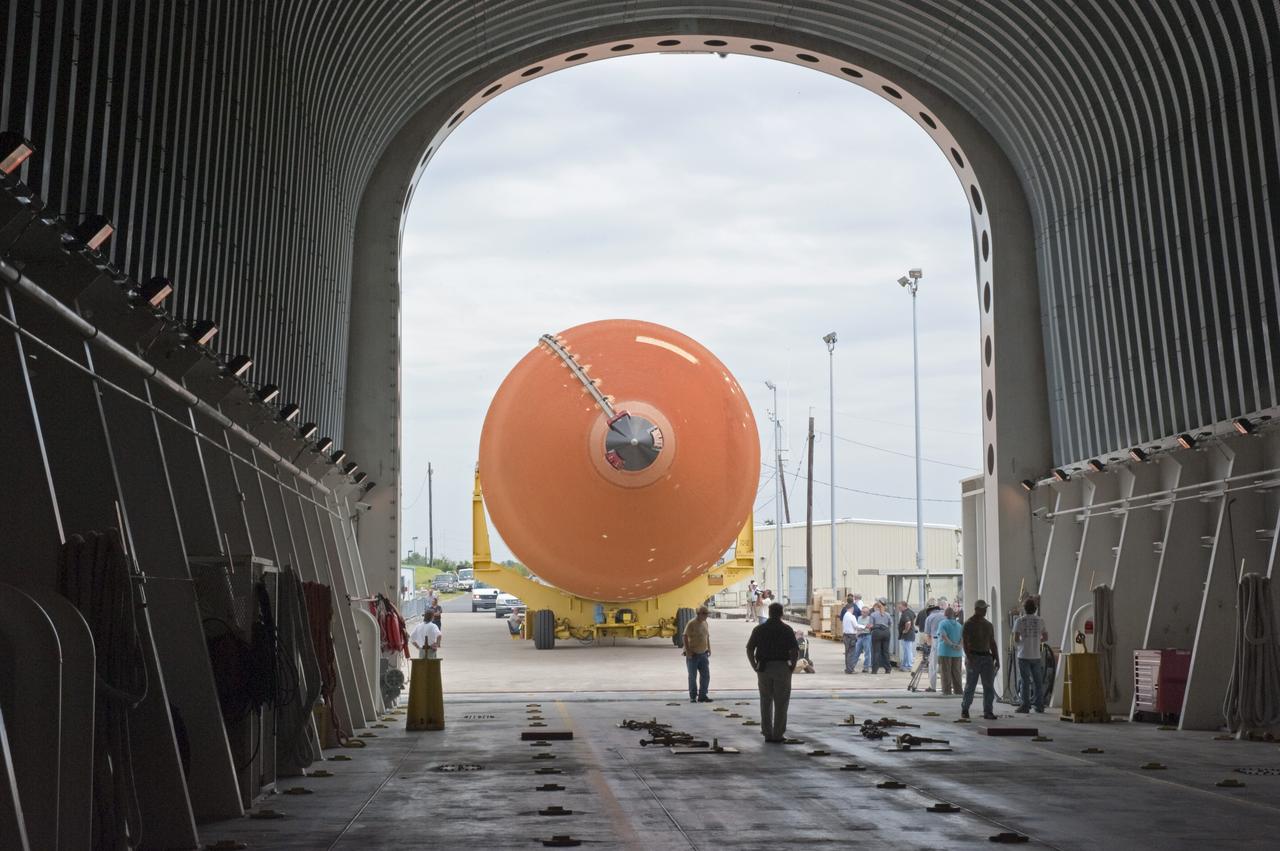
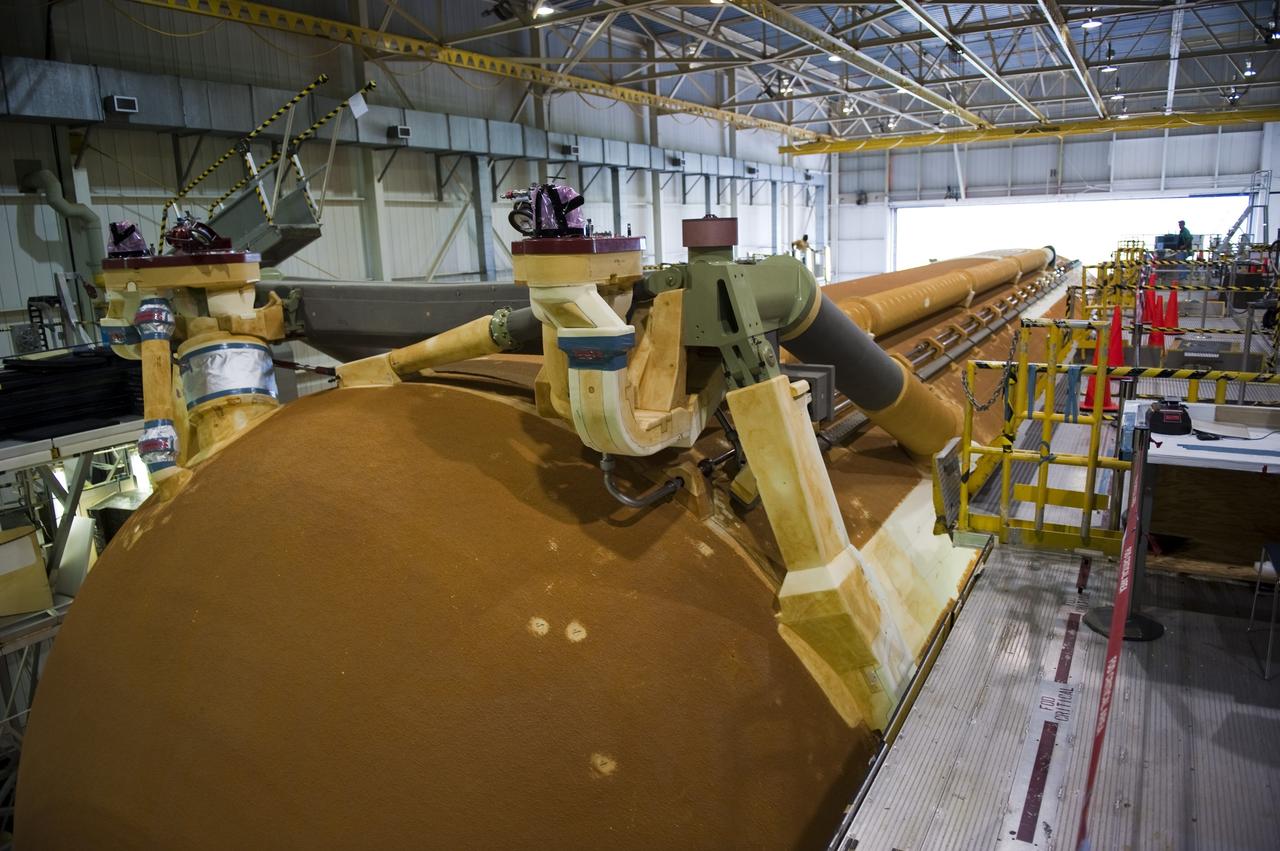
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, External Fuel Tank-122 is suspended vertically over the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building as it is lifted toward a test cell. ET-122, the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank was delivered to Kennedy's Turn Basin from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After testing, ET-122 eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch February, 2011. For more information visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, External Fuel Tank-122 sits on its transporter in the transfer aisle waiting to be lifted into a test cell. ET-122, the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank was delivered to Kennedy's Turn Basin from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After testing, ET-122 eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch February, 2011. For more information visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
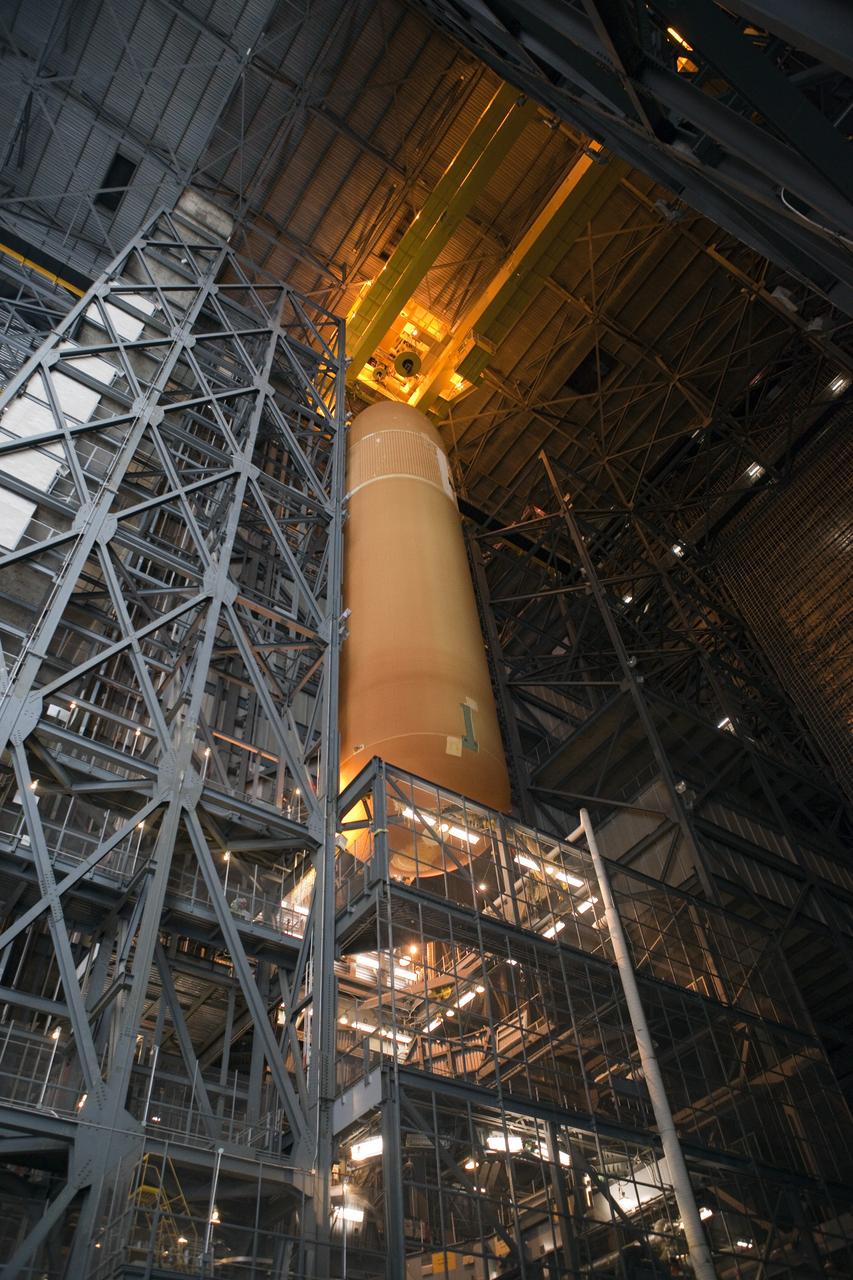

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, External Fuel Tank-122 is being lowered toward a test stand where it will be checked out before launch. ET-122, the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank was delivered to Kennedy's Turn Basin from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After testing, ET-122 eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch February, 2011. For more information visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
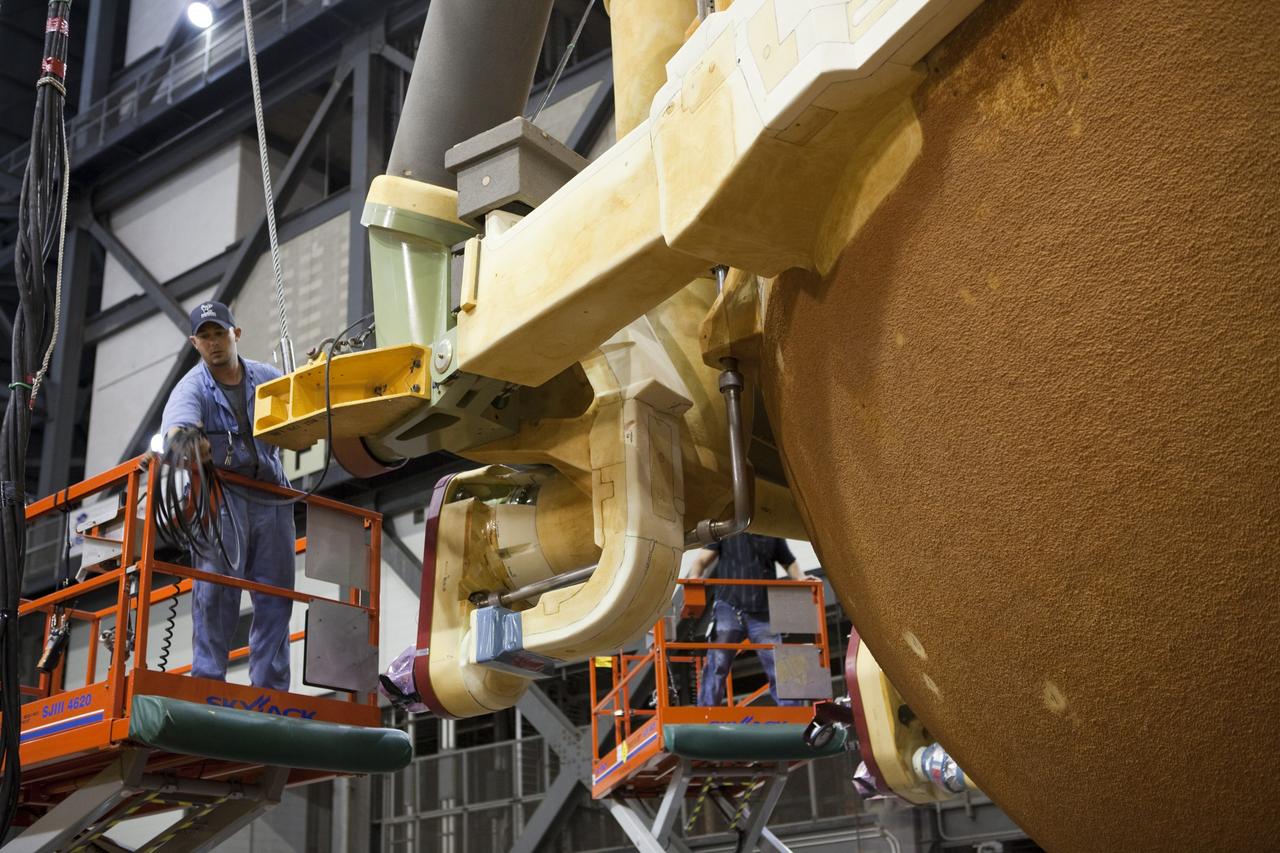

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers check the hoist connections on External Fuel Tank-122 as it is lifted toward a test cell. ET-122, the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank was delivered to Kennedy's Turn Basin from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After testing, ET-122 eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch February, 2011. For more information visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
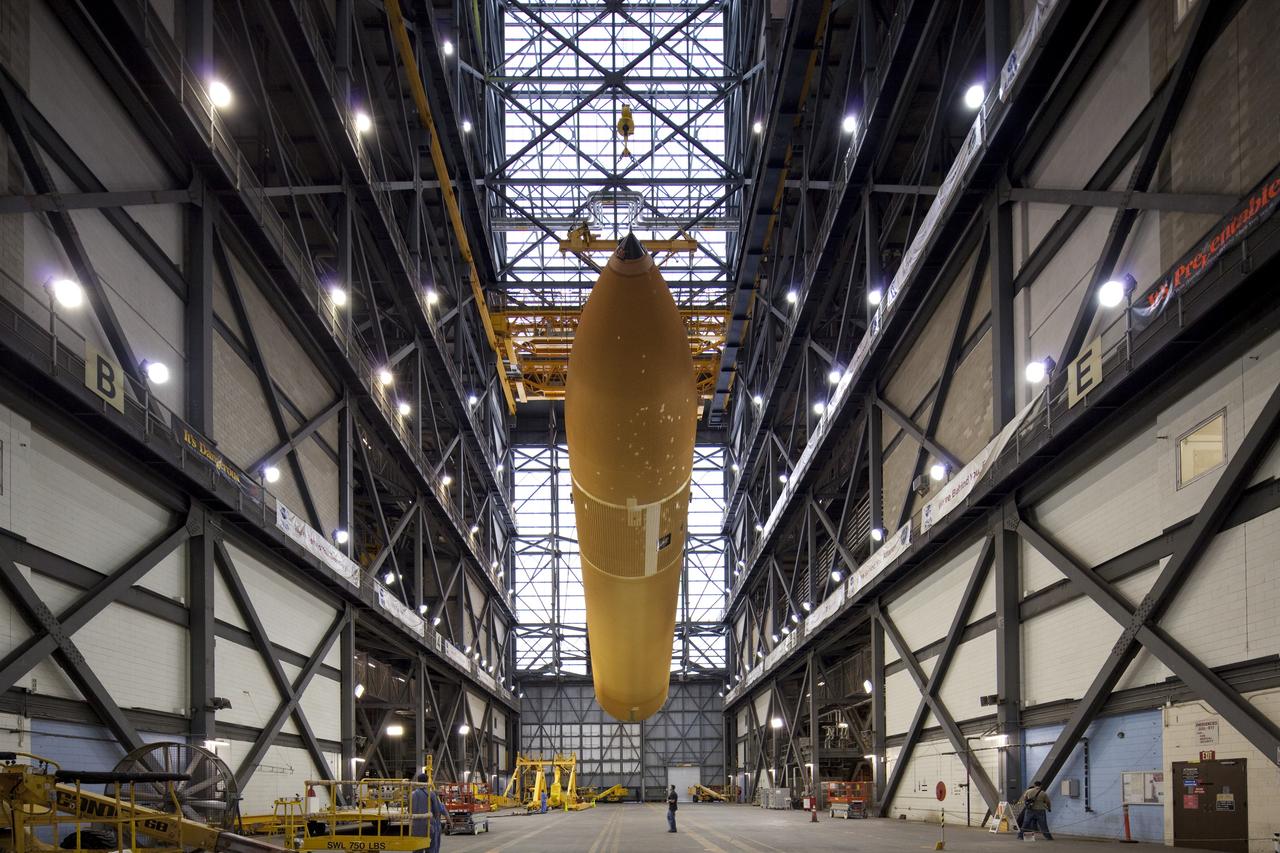

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers monitor the progress of External Fuel Tank-122 as it is lifted toward a test cell. ET-122, the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank was delivered to Kennedy's Turn Basin from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After testing, ET-122 eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch February, 2011. For more information visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, External Fuel Tank-122 is being lowered onto a test stand where it will be checked out before launch. ET-122, the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank was delivered to Kennedy's Turn Basin from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After testing ET-122 eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch February, 2011. For more information visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

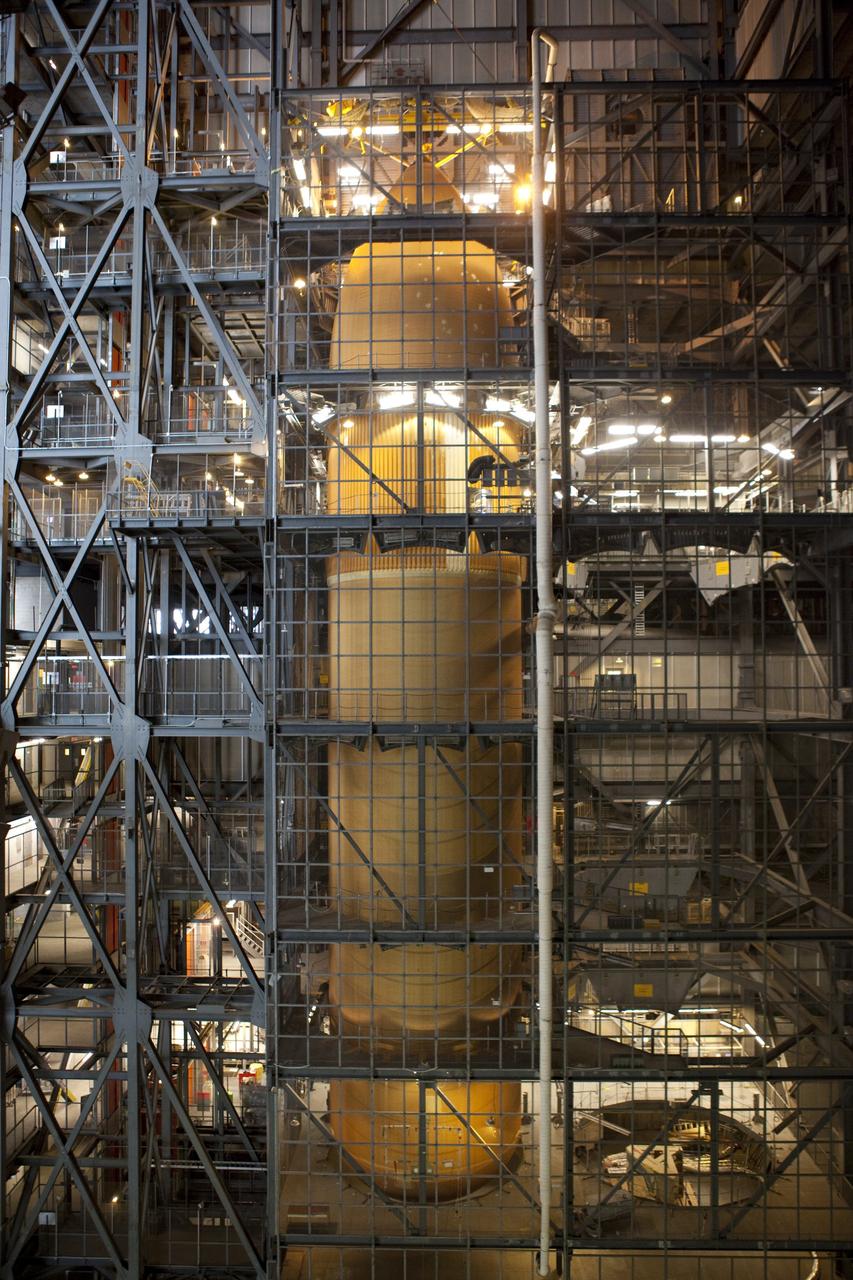
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, External Fuel Tank-122 is being lowered toward a test stand where it will be checked out before launch. ET-122, the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank was delivered to Kennedy's Turn Basin from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After testing, ET-122 eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch February, 2011. For more information visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
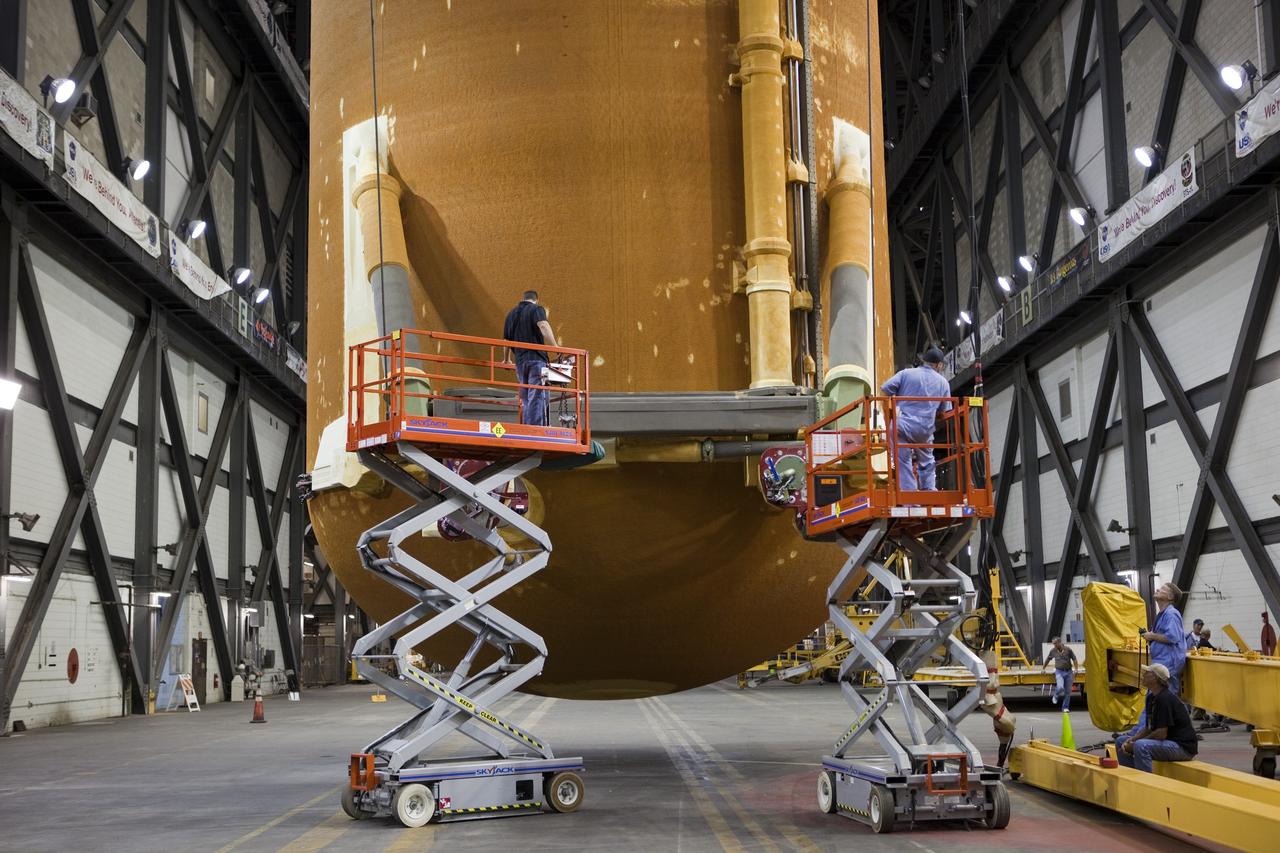

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers check the hoist connections on External Fuel Tank-122 as it is lifted toward a test cell. ET-122, the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank was delivered to Kennedy's Turn Basin from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After testing, ET-122 eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch February, 2011. For more information visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
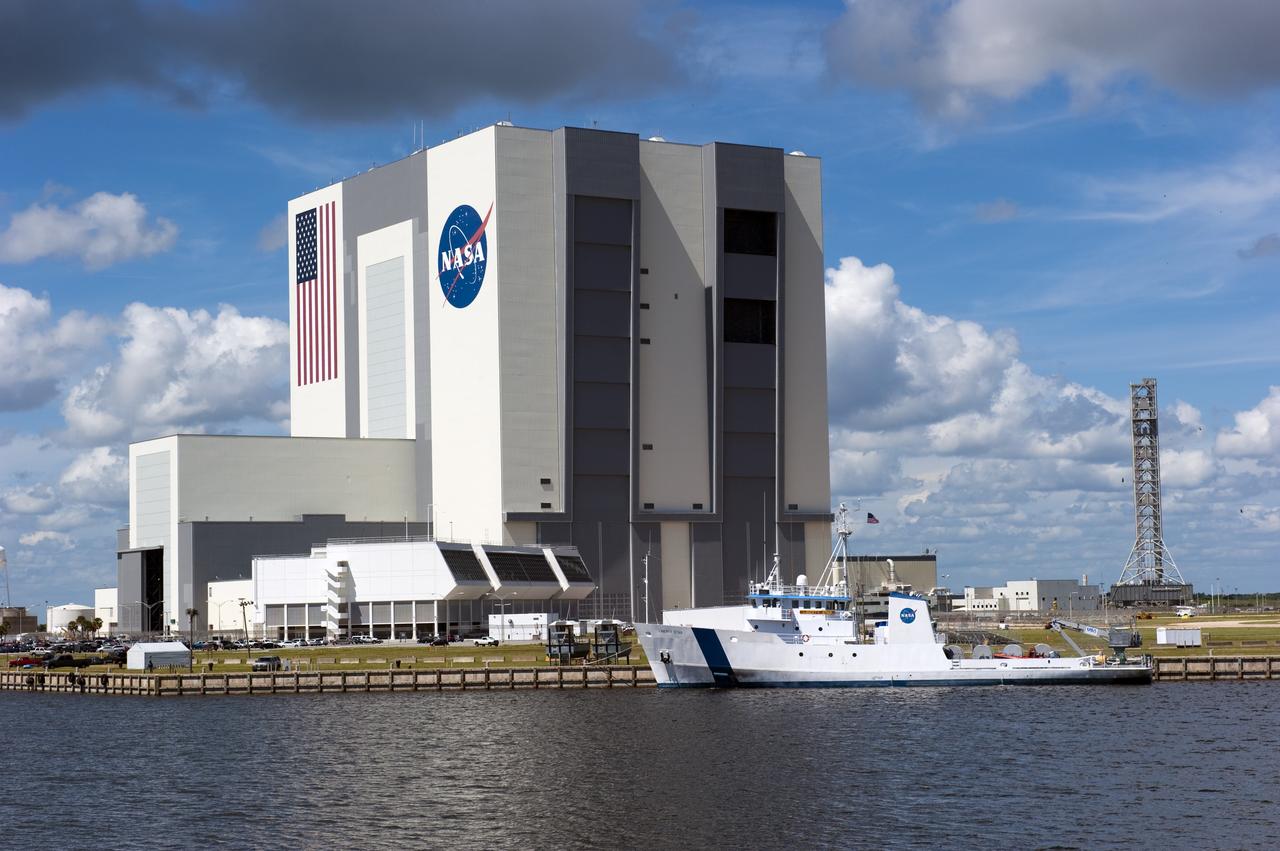

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, is pictured in the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the background is the Vehicle Assembly Building where External Tank ET-122 was just delivered from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans for Endeavour's STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
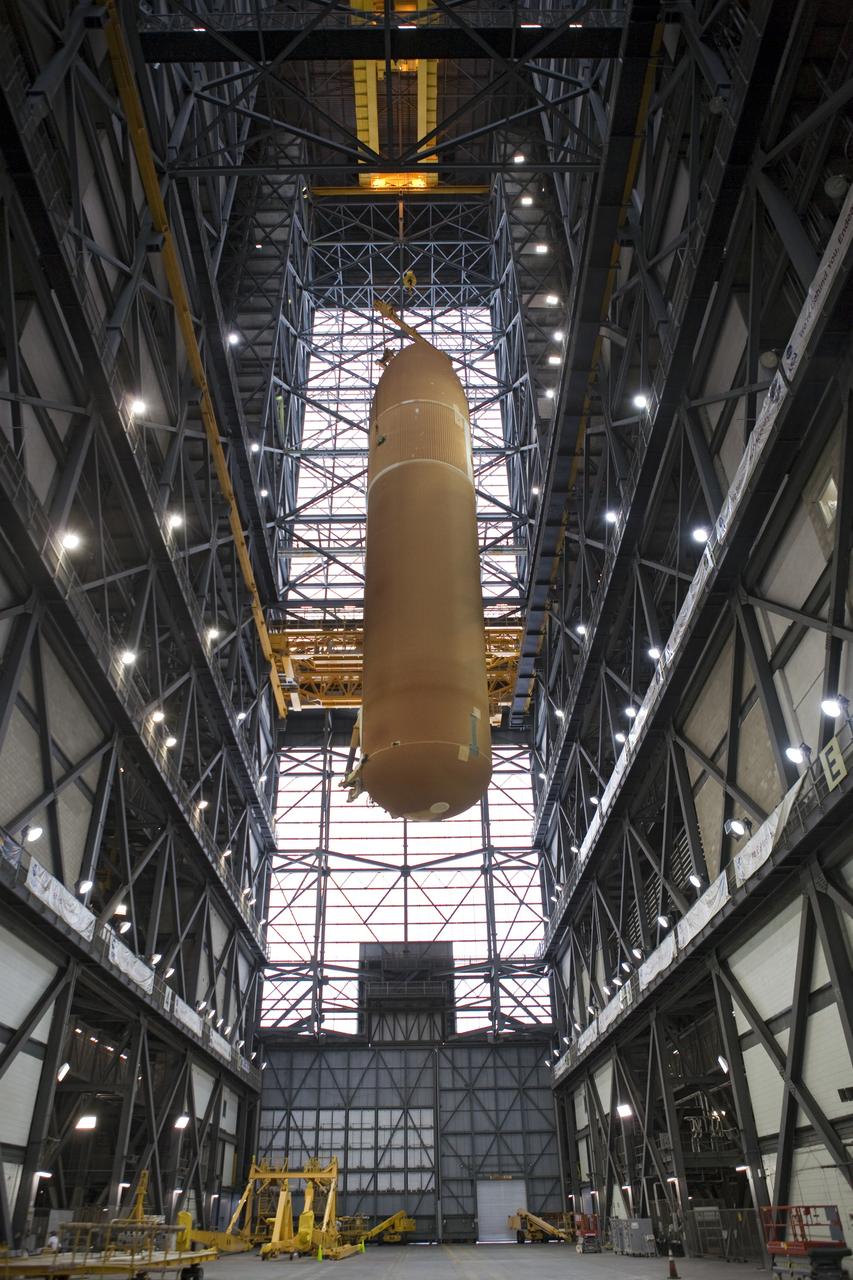

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, External Fuel Tank-122 is lifted into a vertical position above the transfer aisle. The external tank is being moved to a test cell where it will be checked out before launch. ET-122, the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank was delivered to Kennedy's Turn Basin from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After testing ET-122 eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch February, 2011. For more information visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
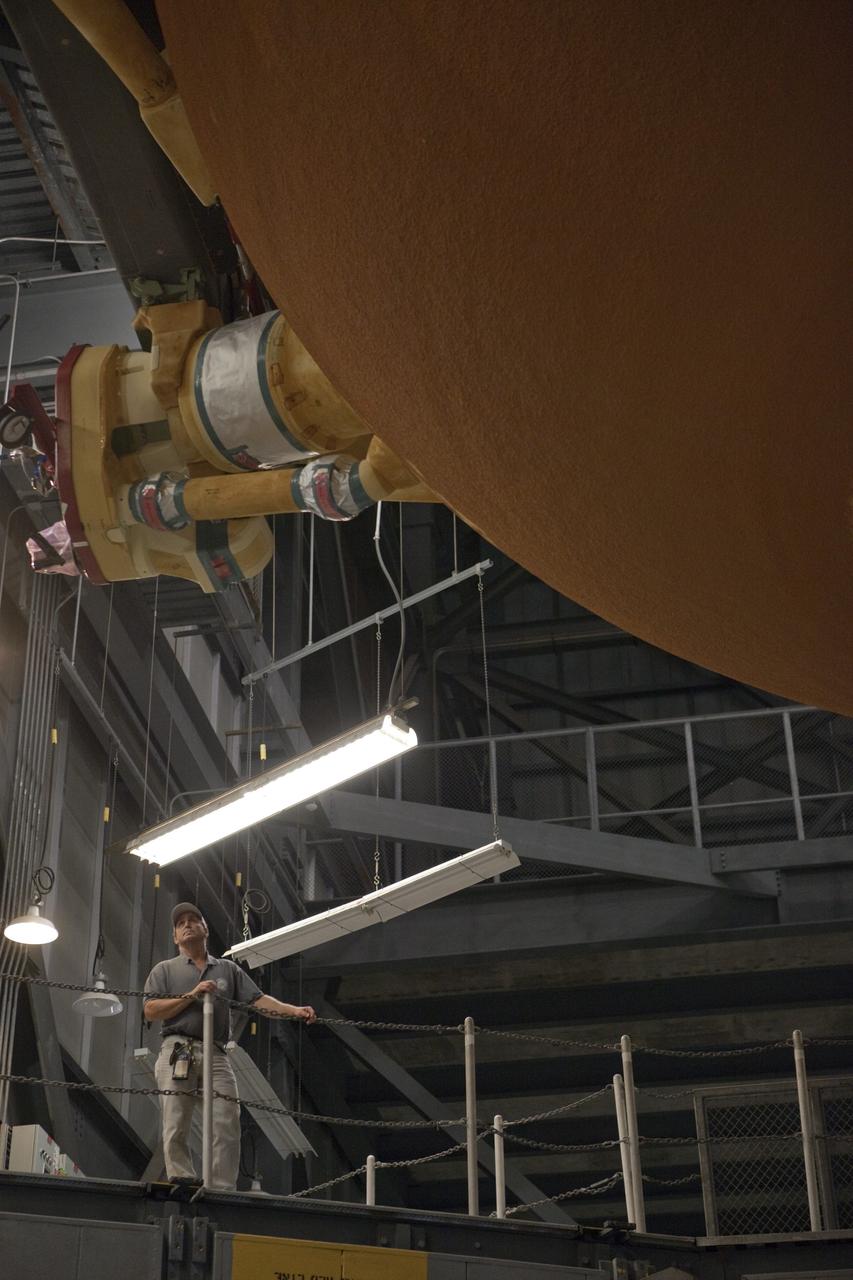

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a worker checks the progress of External Fuel Tank-122 as it is being lowered into a test stand where it will be checked out before launch. ET-122, the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank was delivered to Kennedy's Turn Basin from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After testing, ET-122 eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch February, 2011. For more information visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
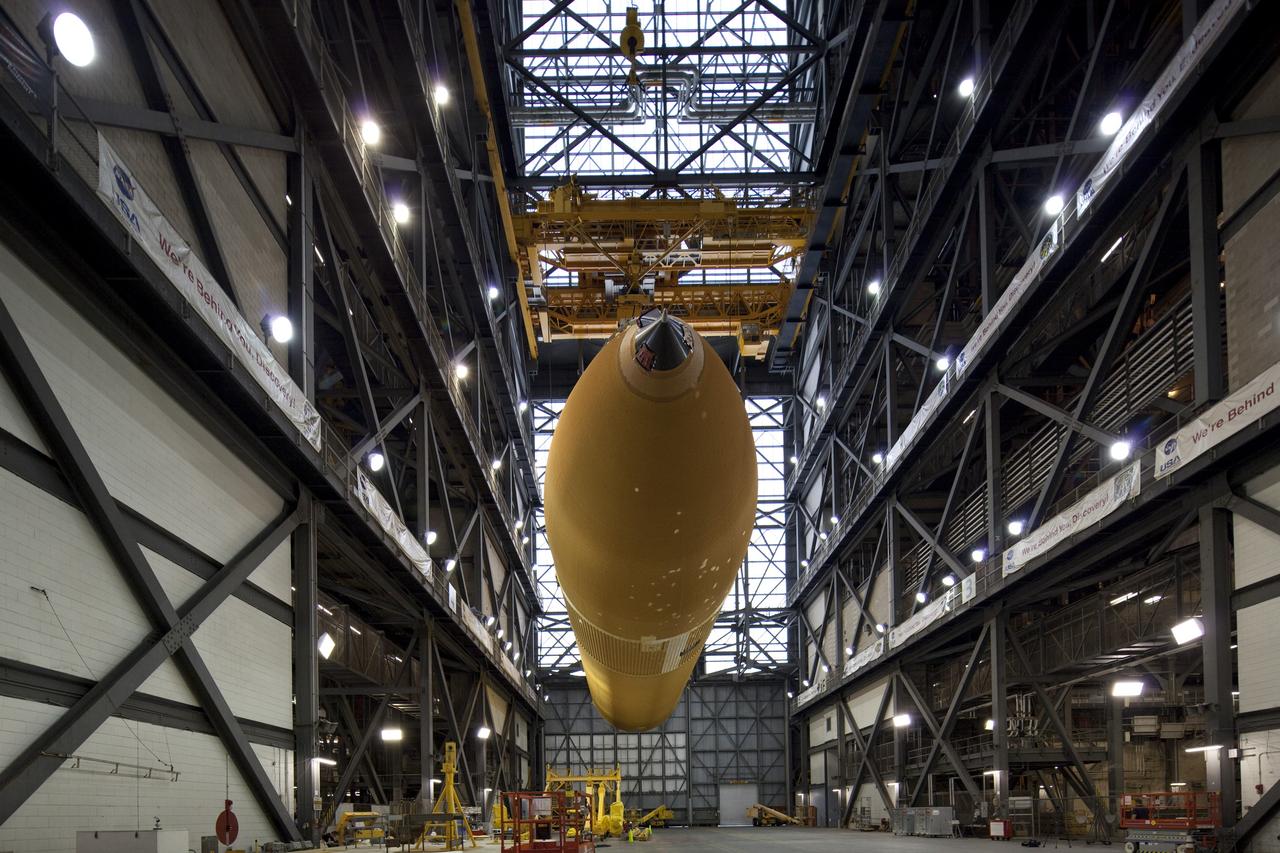

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, External Fuel Tank-122 is lifted above the transfer aisle. The external tank is being moved into a test cell where it will be checked out before launch. ET-122, the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank was delivered to Kennedy's Turn Basin from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After testing ET-122 eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch February, 2011. For more information visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
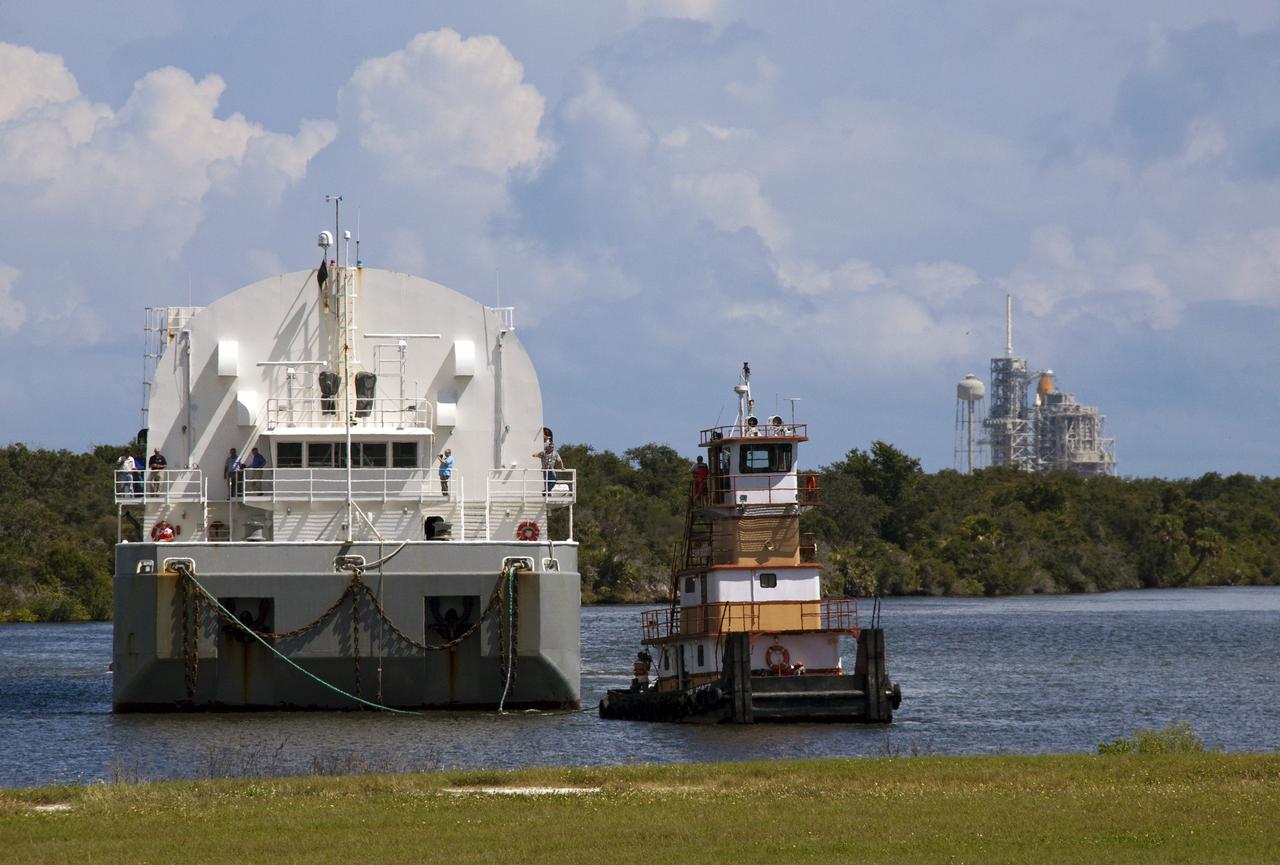

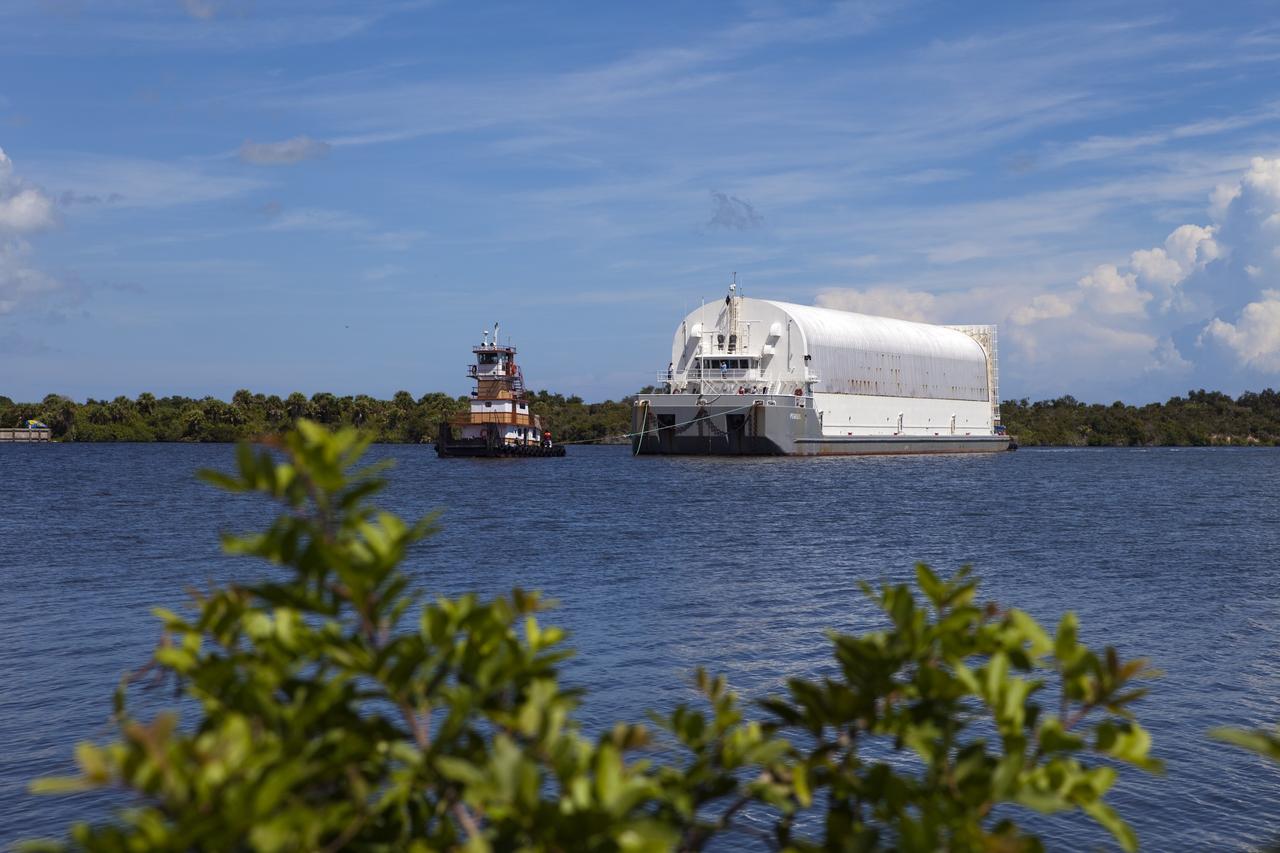
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tugboat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In the background, space shuttle Discovery is on Launch Pad 39A awaiting liftoff on the STS-133 mission to the International Space Station. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
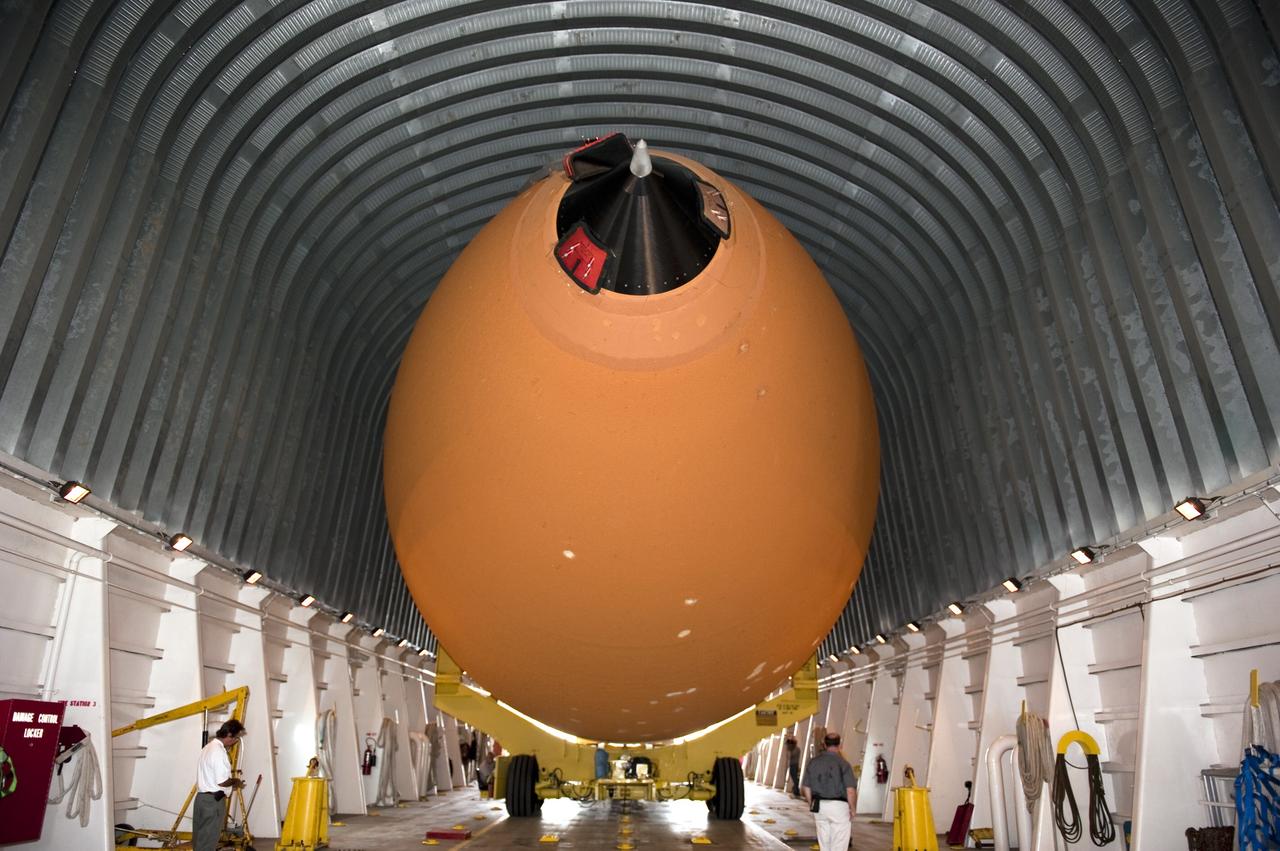

NEW ORLEANS -- Workers monitor the progress of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it is being loaded onto the Pegasus BargeThe tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida secured aboard the barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

NEW ORLEANS -- A tug boat is pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

LOUISIANA -- A tug boat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans toward a dock in Gulfport, La. The barge will meet up with Freedom Star, NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ship, which will escort it to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This overhead view shows the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, as it is being transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea, carried in the Pegasus Barge, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Once inside the VAB, it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch Feb. 2011. STS-134 currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell

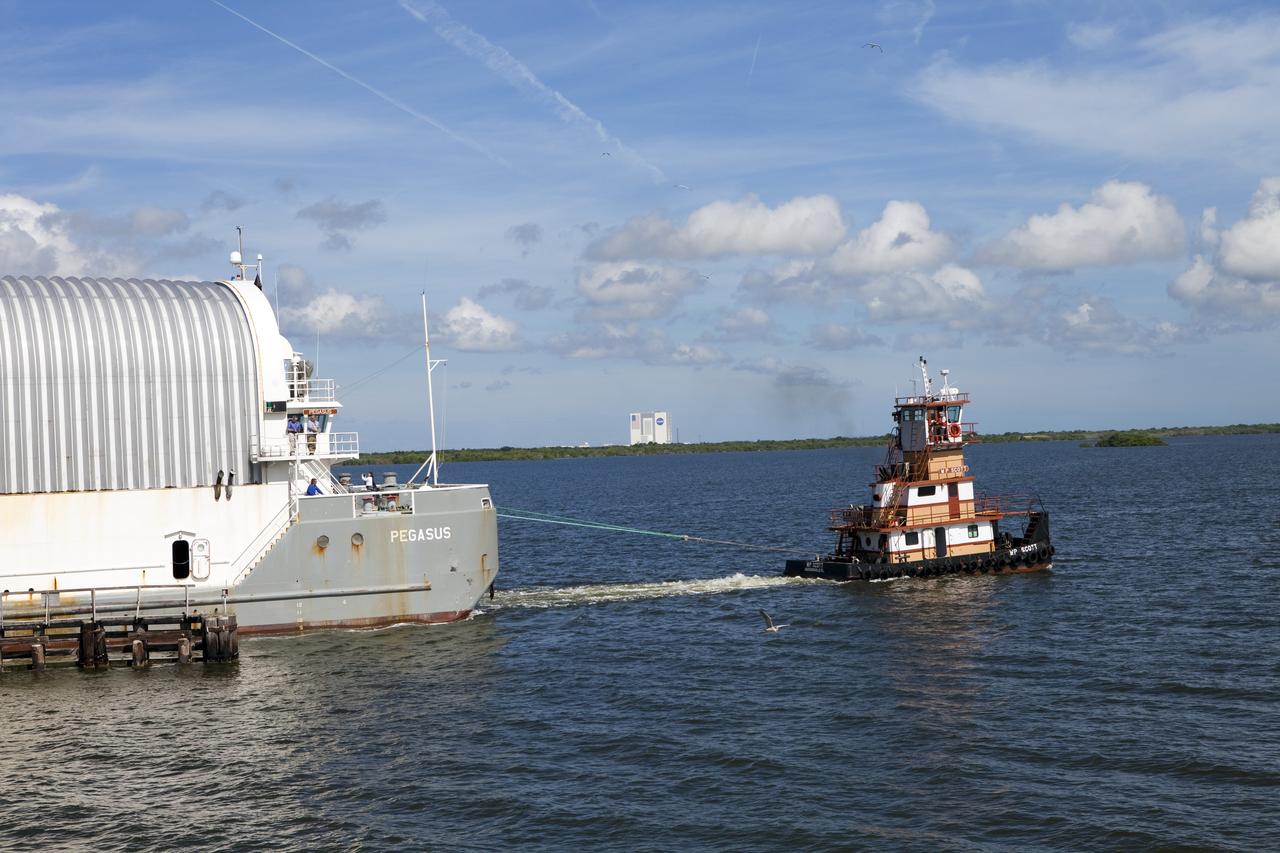
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

NEW ORLEANS -- Associate Administrator for Space Operations Bill Gerstenmaier and Manny Zulueta, Lockheed Martin vice president and site executive at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, watch the progress of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, as it is being transported from the facility to the Pegasus Barge. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida secured aboard the barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
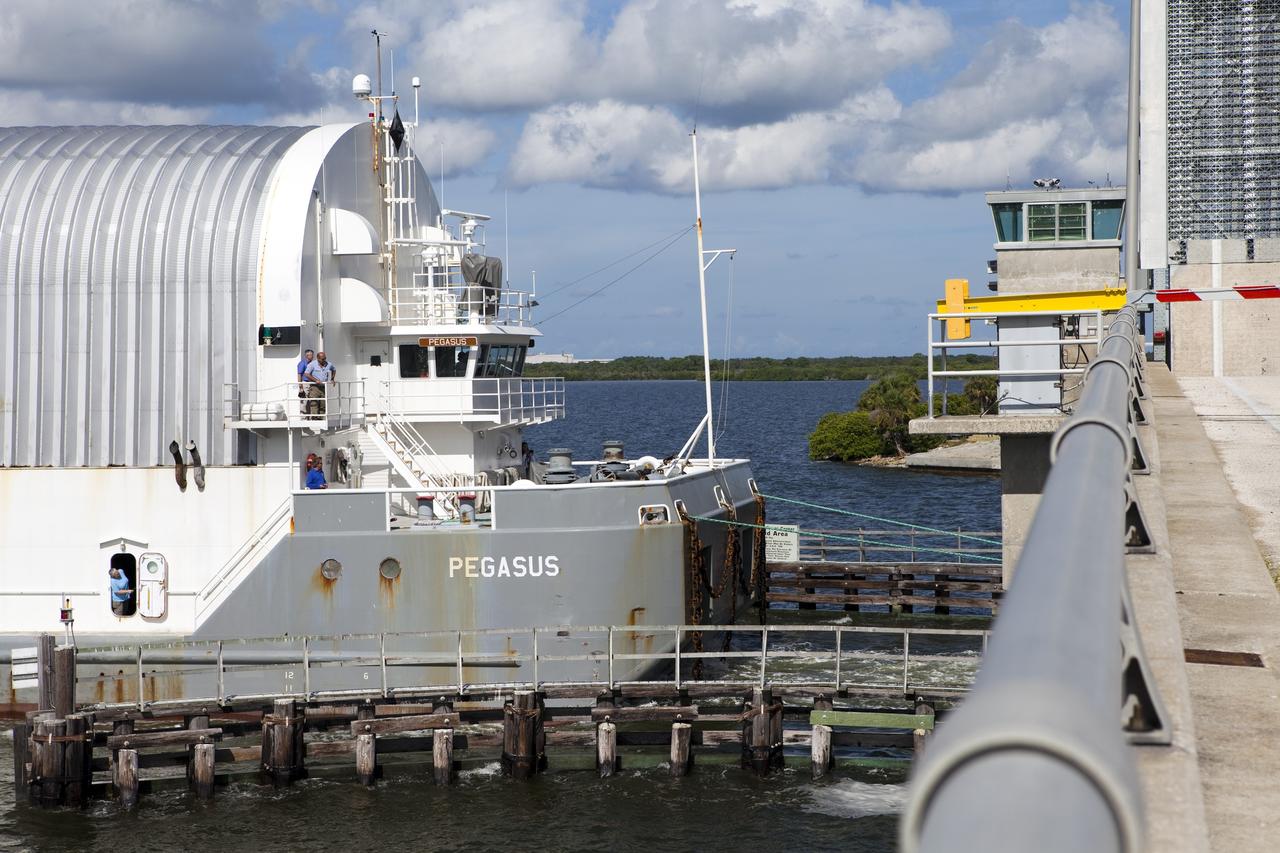

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Pegasus Barge, carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, arrives at the Turn Basin. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
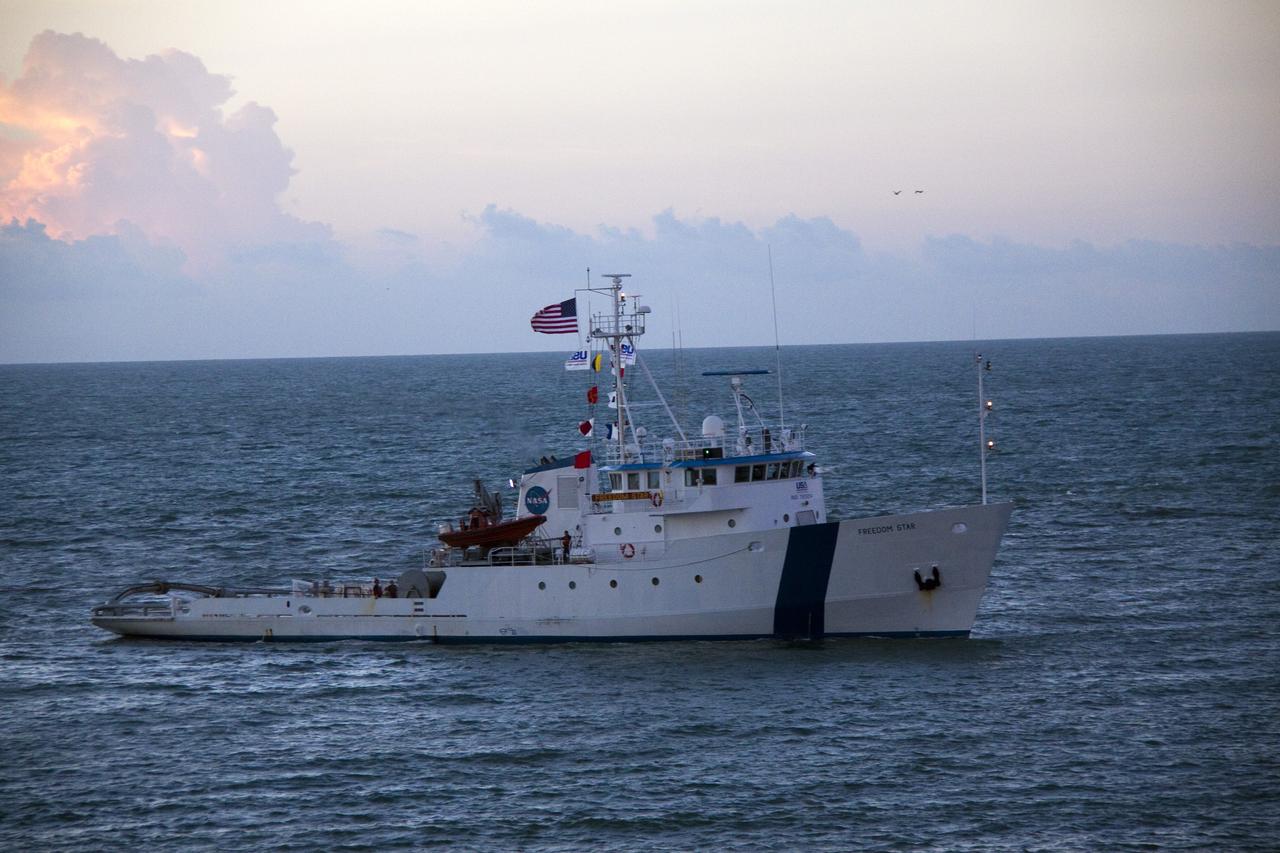

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

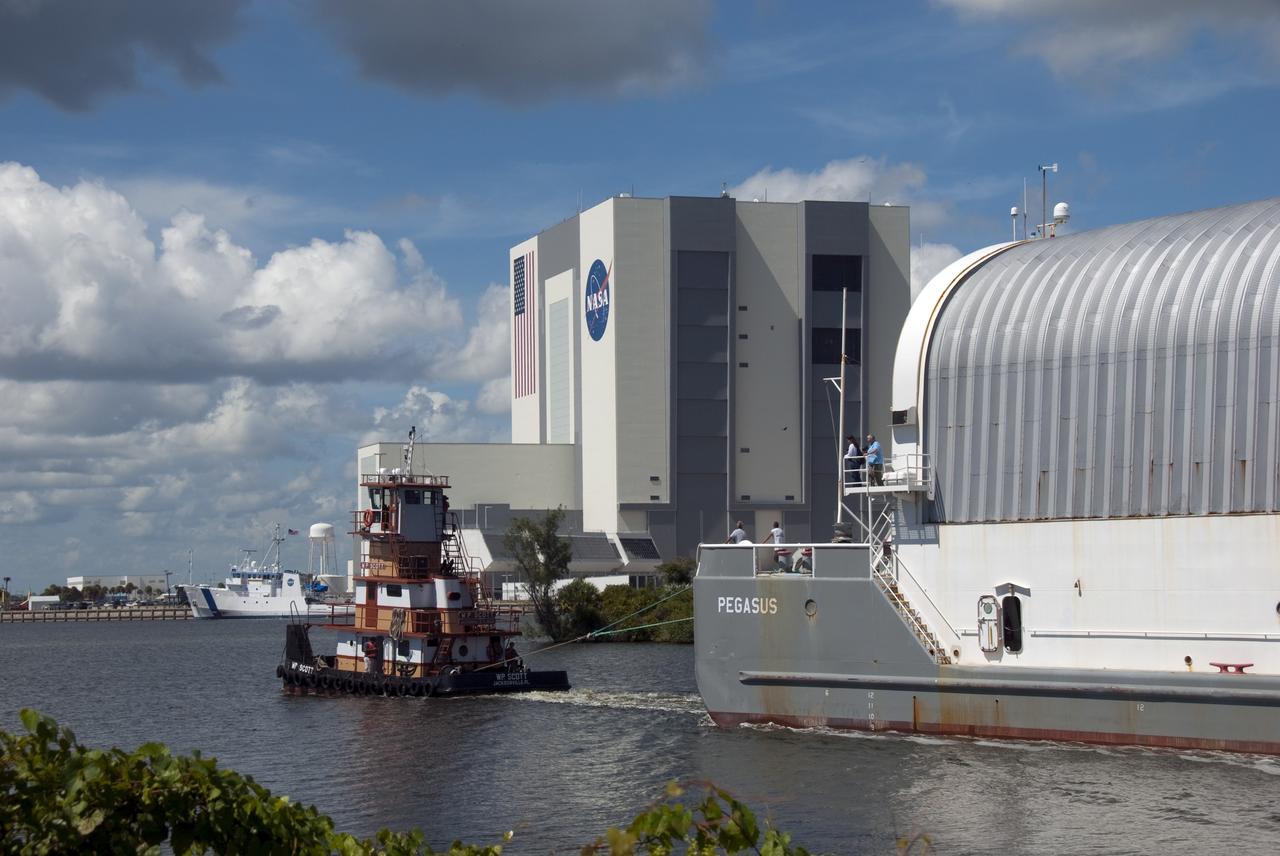
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, has been moved inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to Kennedy's Turn Basin aboard the Pegasus Barge. The tank eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
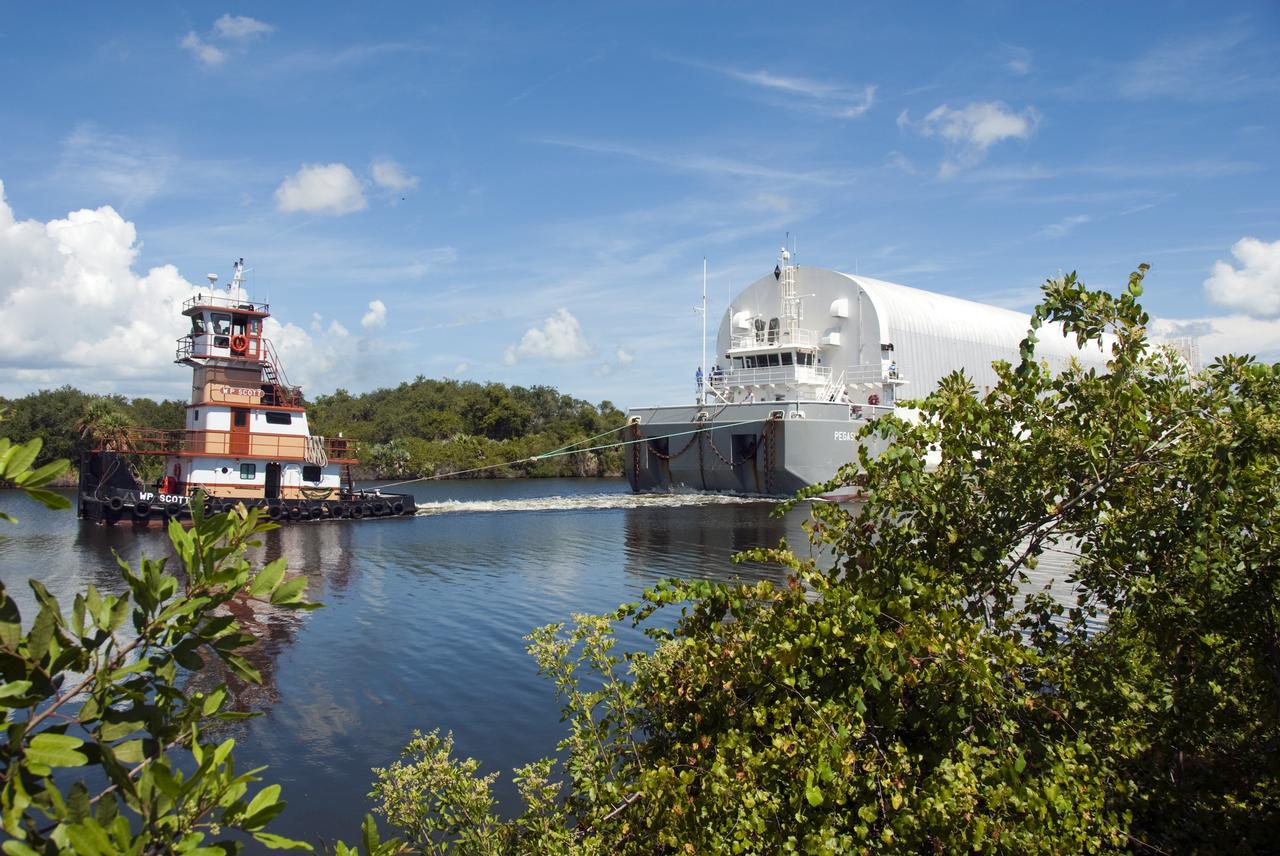

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tugboat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
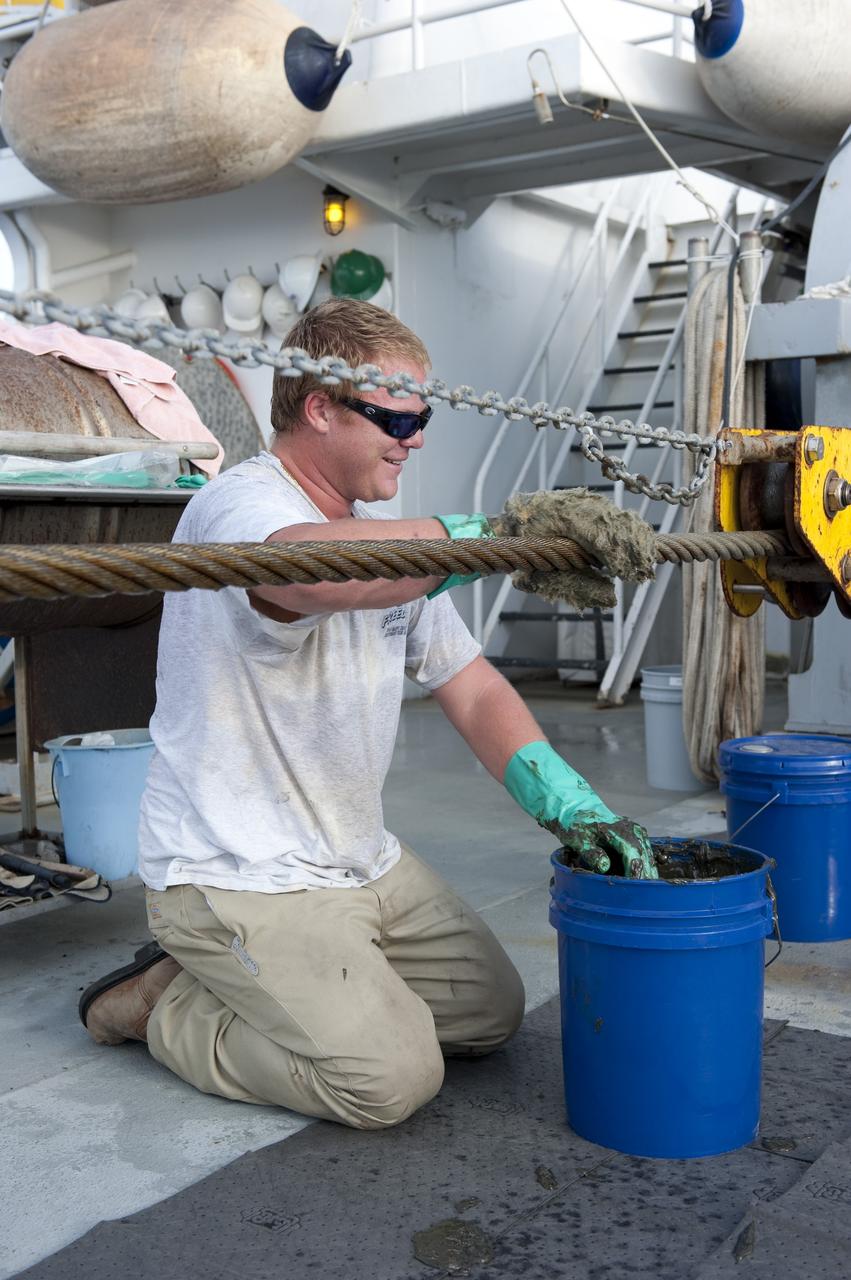

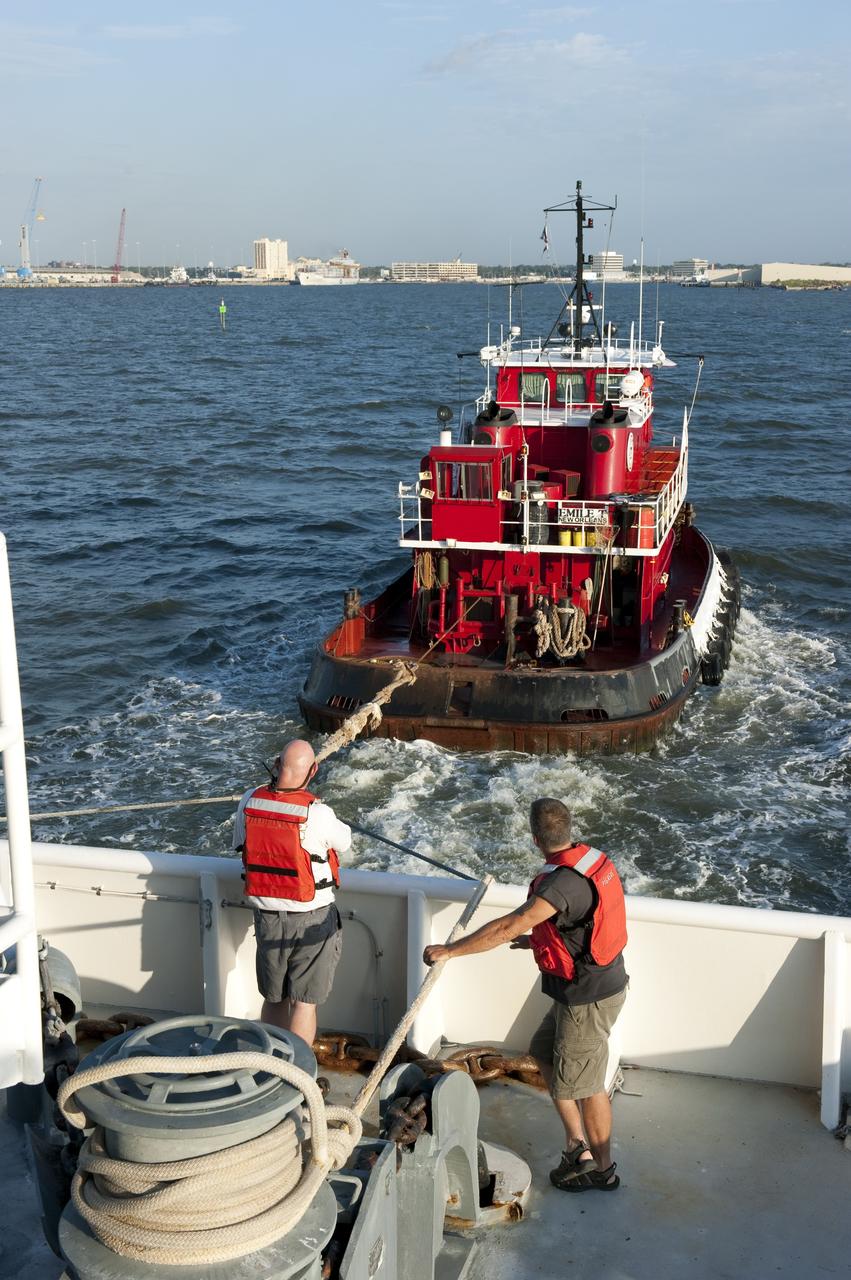
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A deckhand on Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, keeps the ship in good repair as it pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
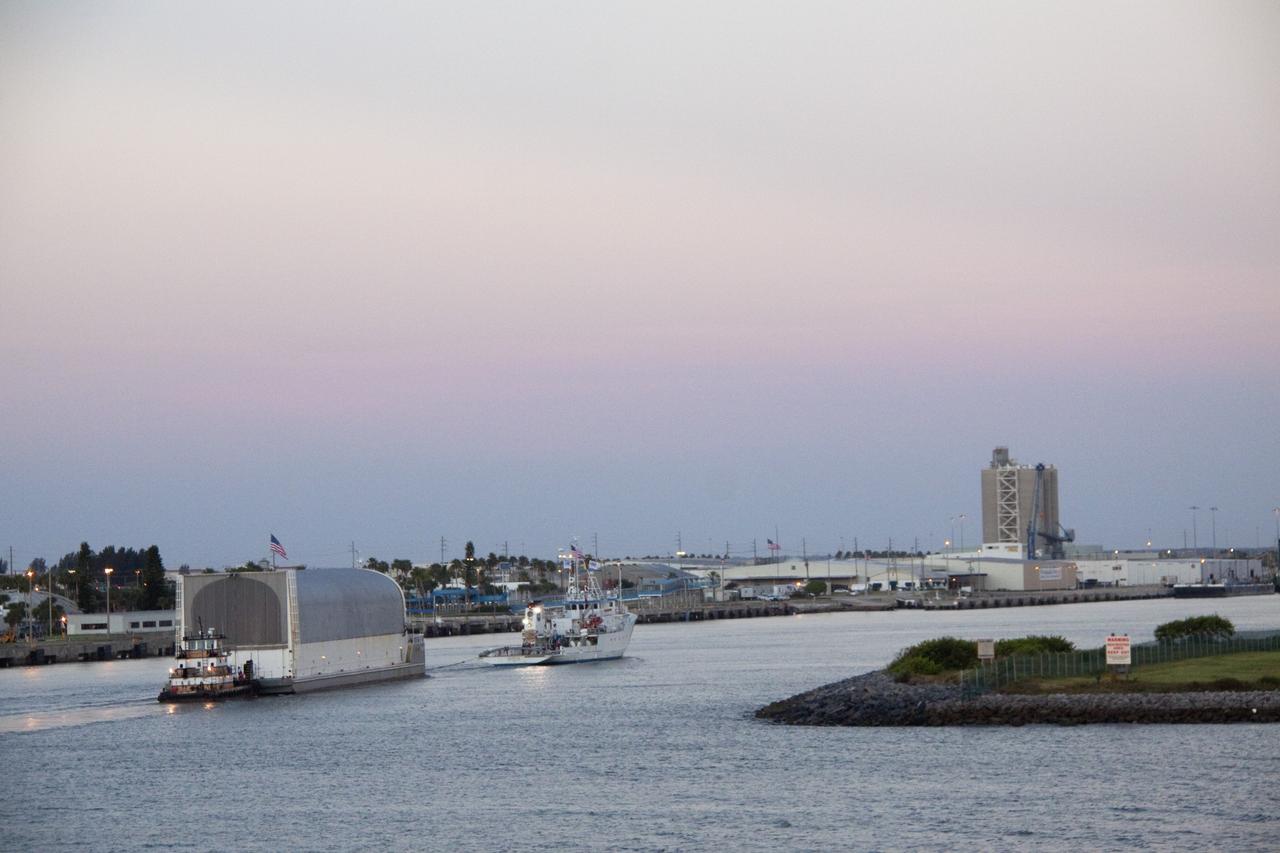

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
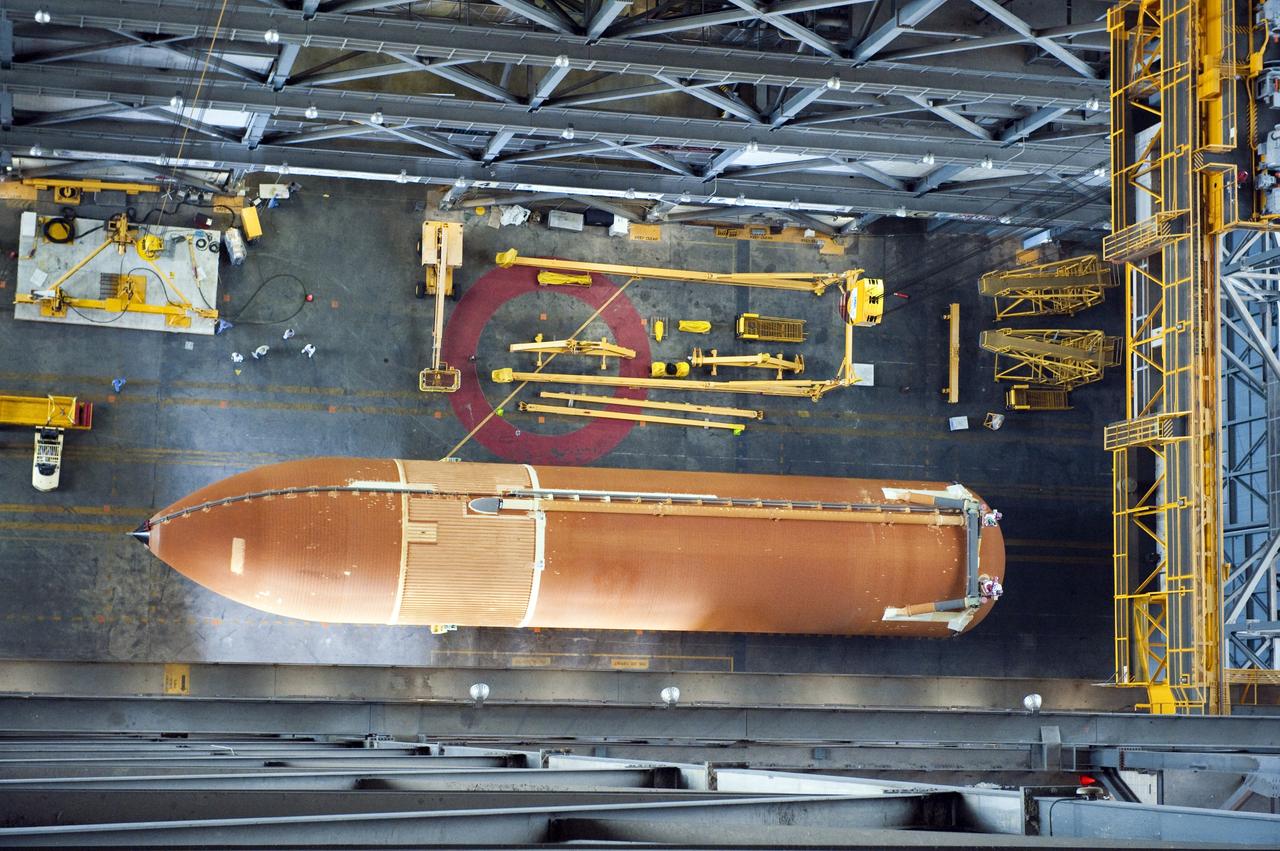
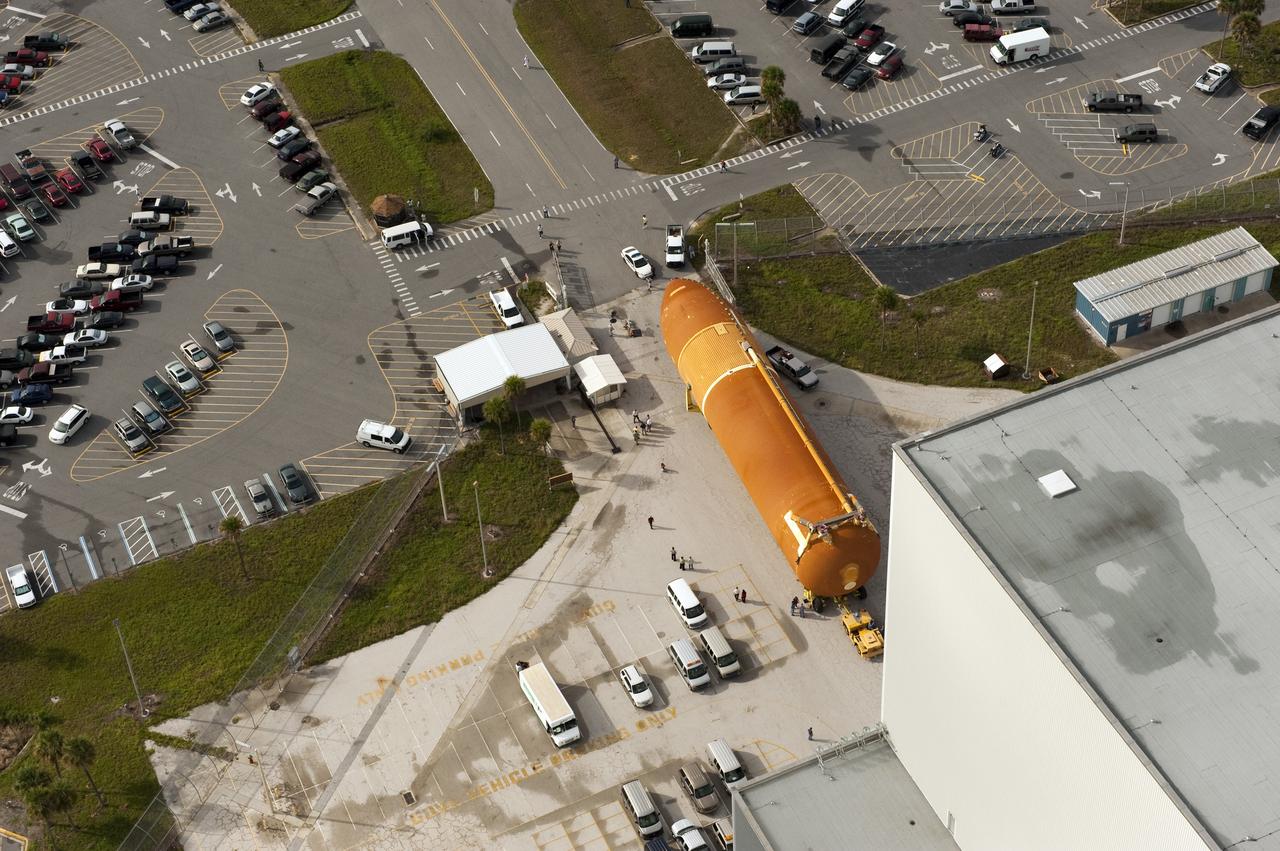
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, this overhead image shows the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, after it was delivered to the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The tank traveled 900 miles by sea, carried in the Pegasus Barge, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Once inside the VAB, it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch Feb. 2011. STS-134 currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell
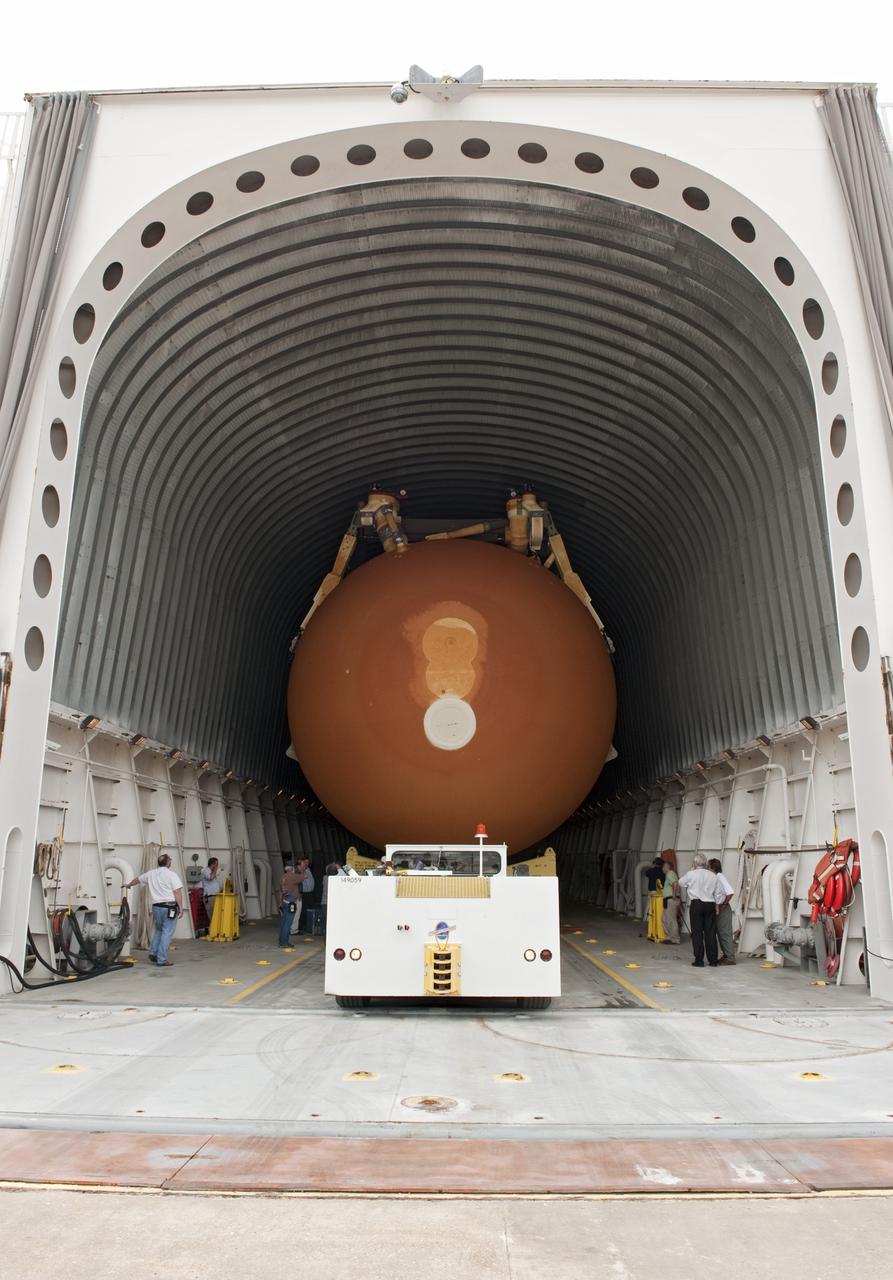

NEW ORLEANS -- Workers check the progress of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it is being loaded onto the Pegasus Barge. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida secured aboard the barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
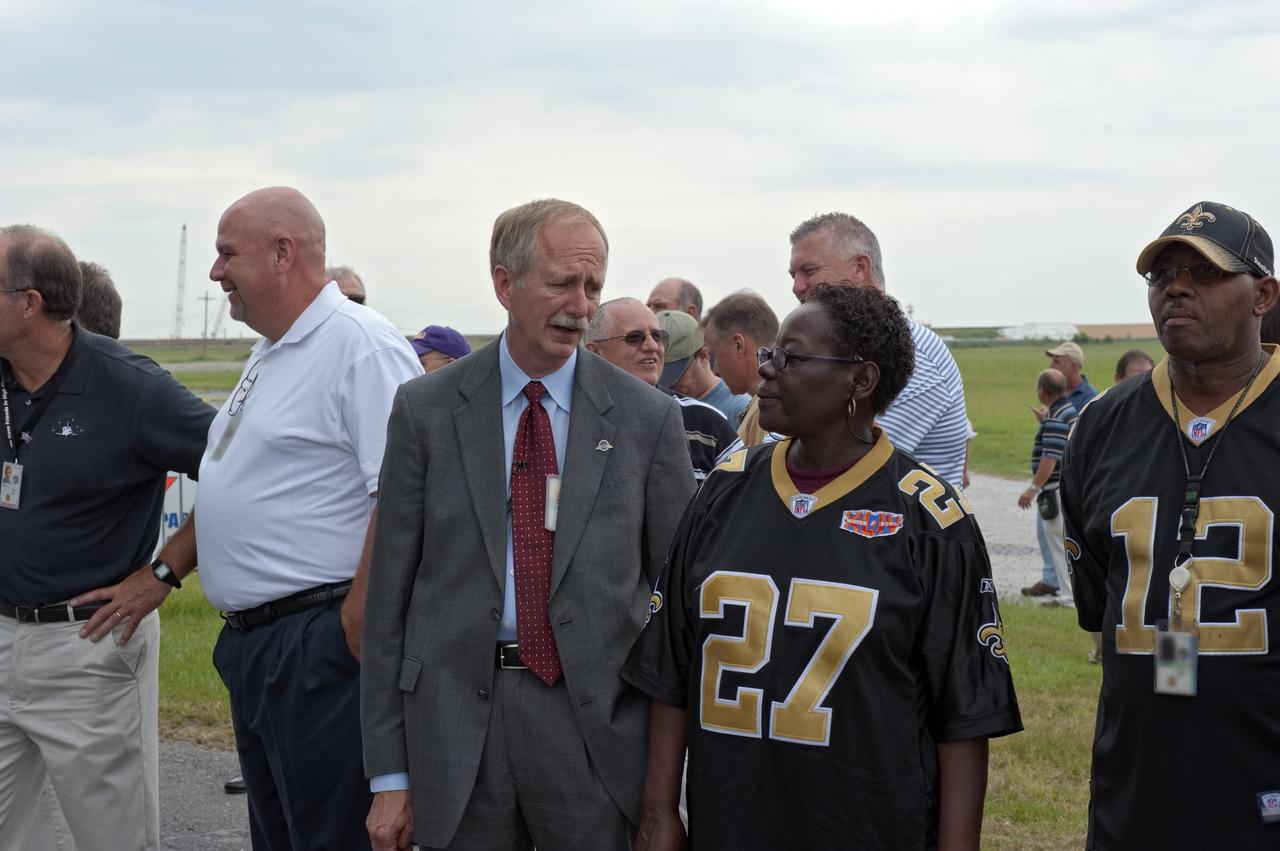

NEW ORLEANS -- At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Associate Administrator for Space Operations Bill Gerstenmaier and a Michoud employee discuss the progress of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, as it is being transported from the facility to the Pegasus Barge. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida secured aboard the barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
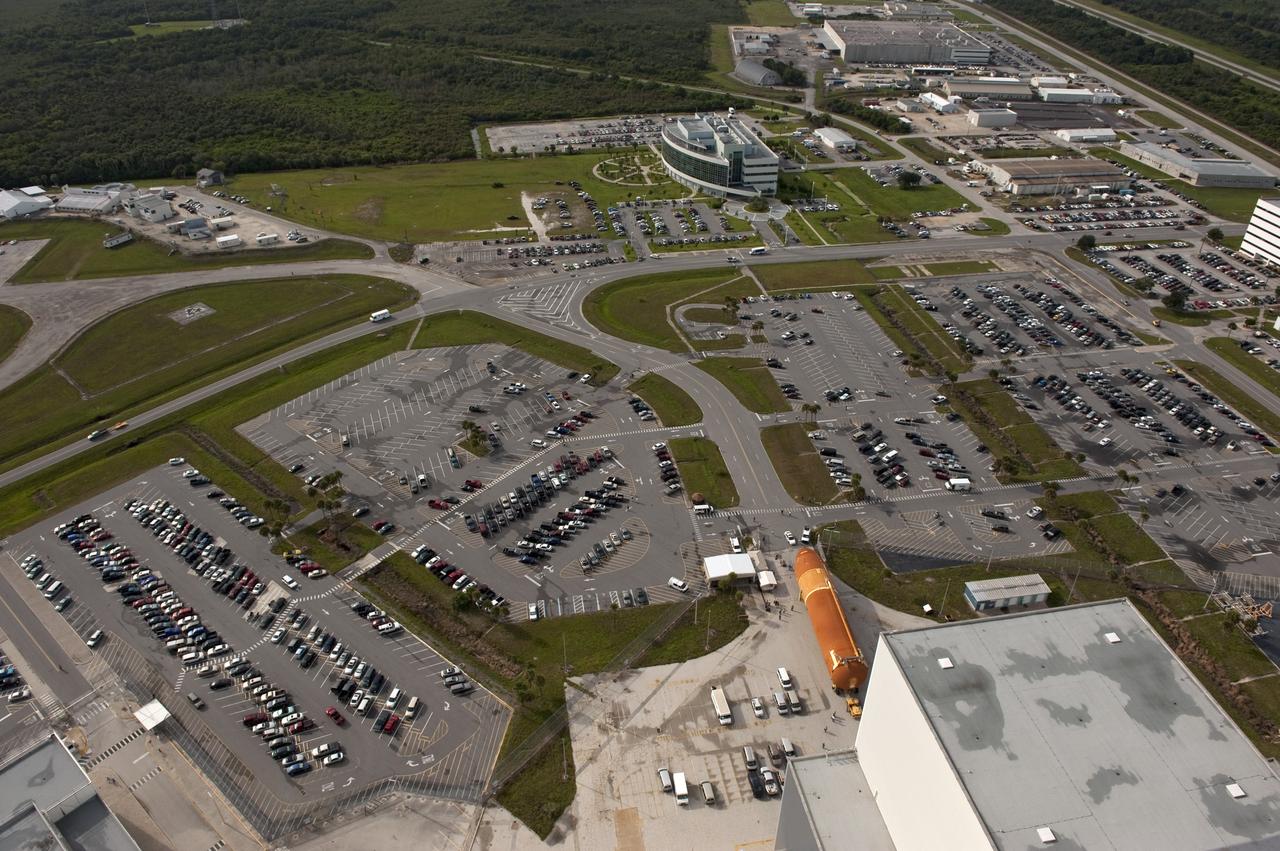

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This overhead view shows the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122 (right), as it is being transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea, carried in the Pegasus Barge, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Once inside the VAB, it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch Feb. 2011. STS-134 currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

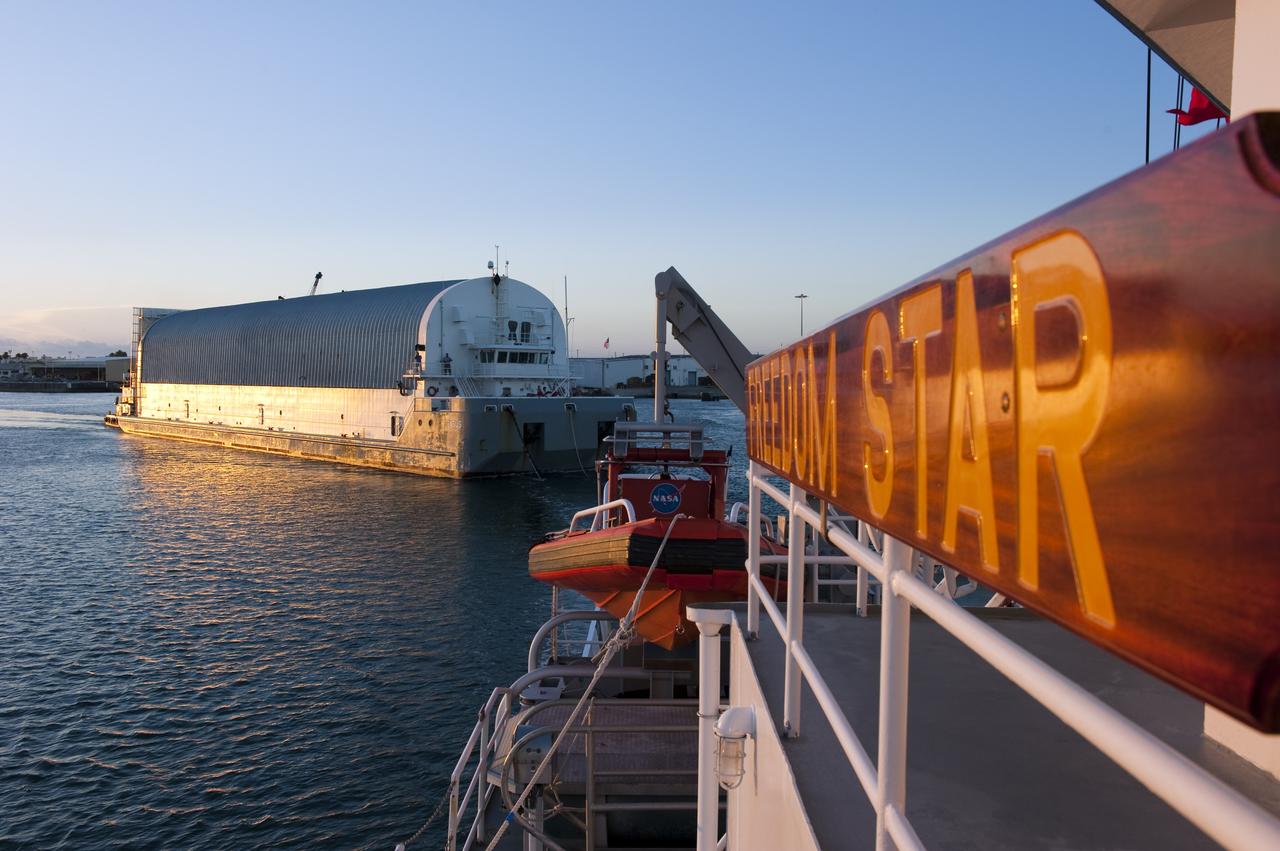
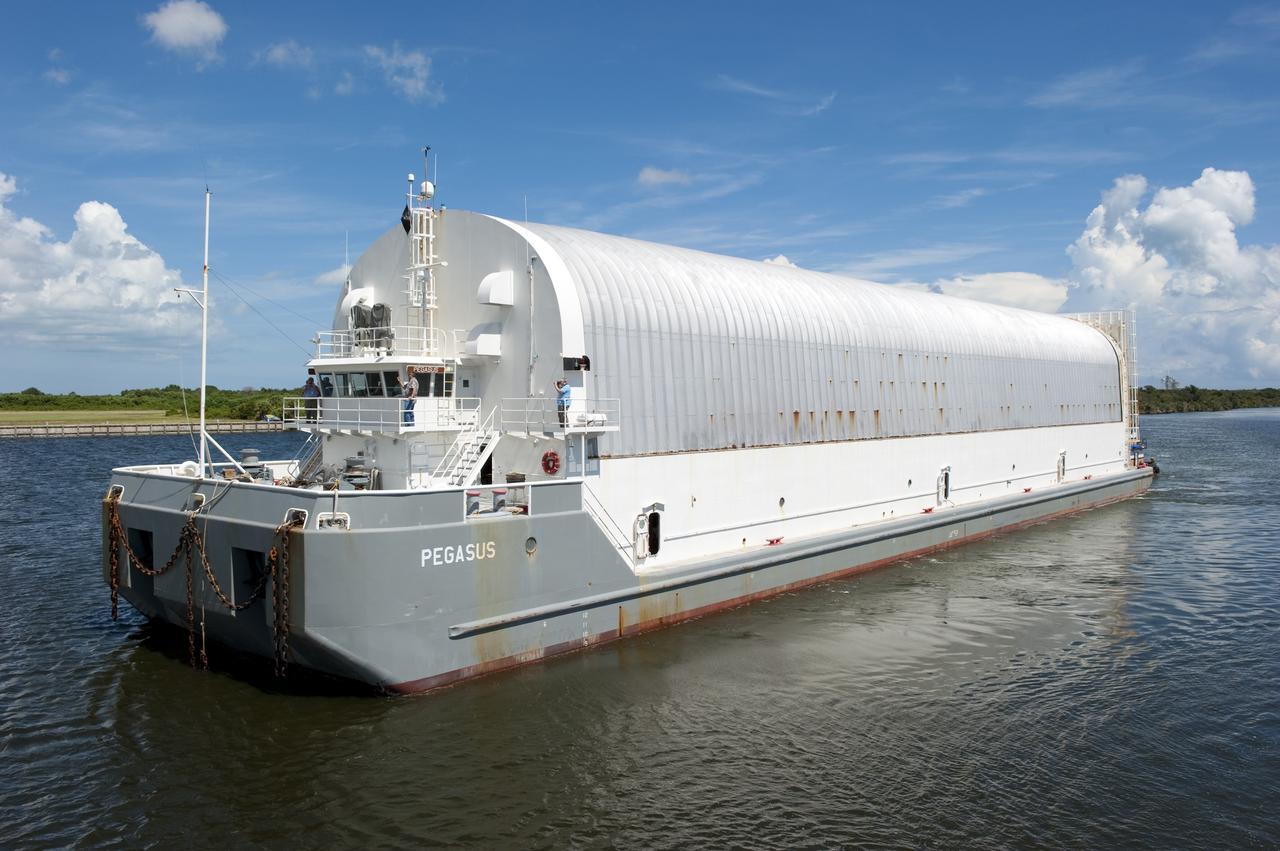
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This view from the stern of Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, shows the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
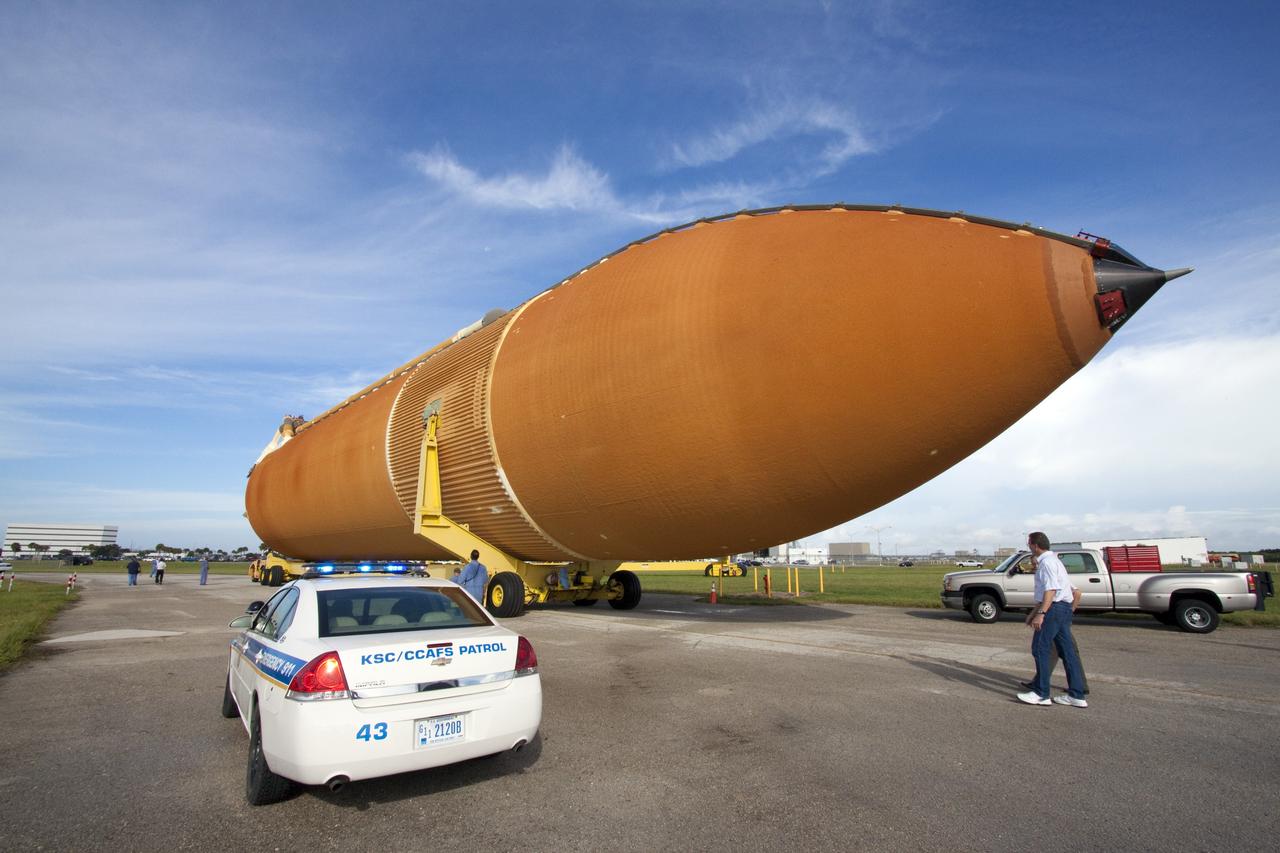

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, moves from the Turn Basin to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Once inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This view from the stern of Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, shows the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, as it is transported to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
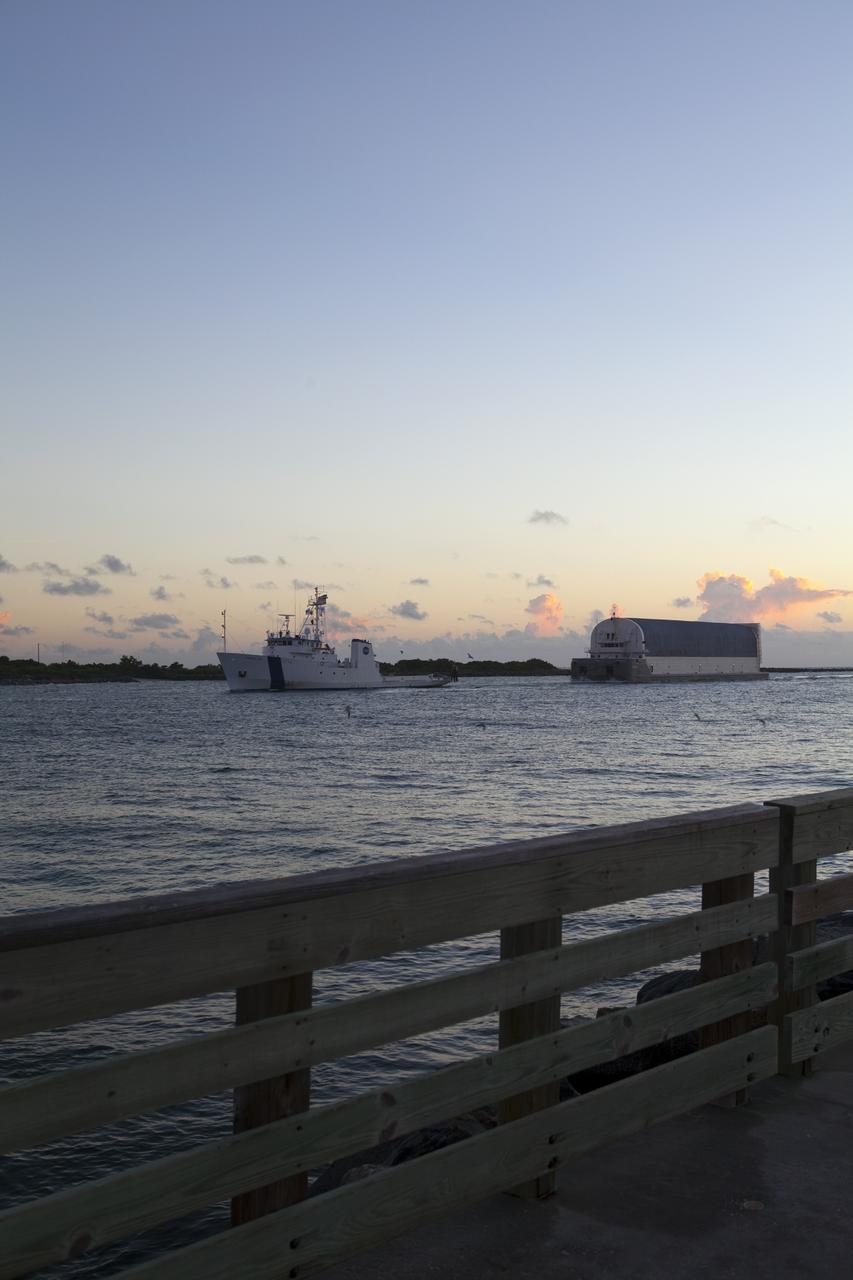

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, ushers the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
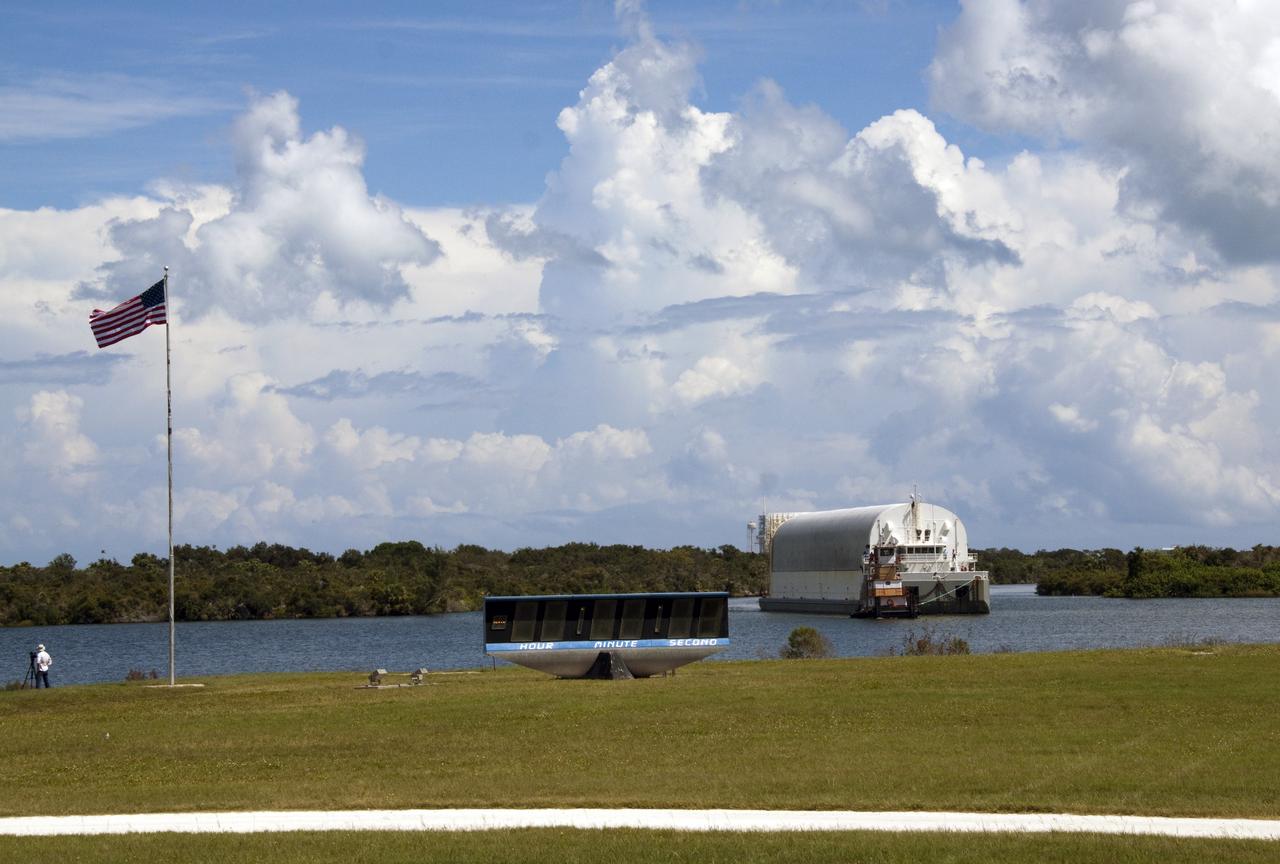

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tugboat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
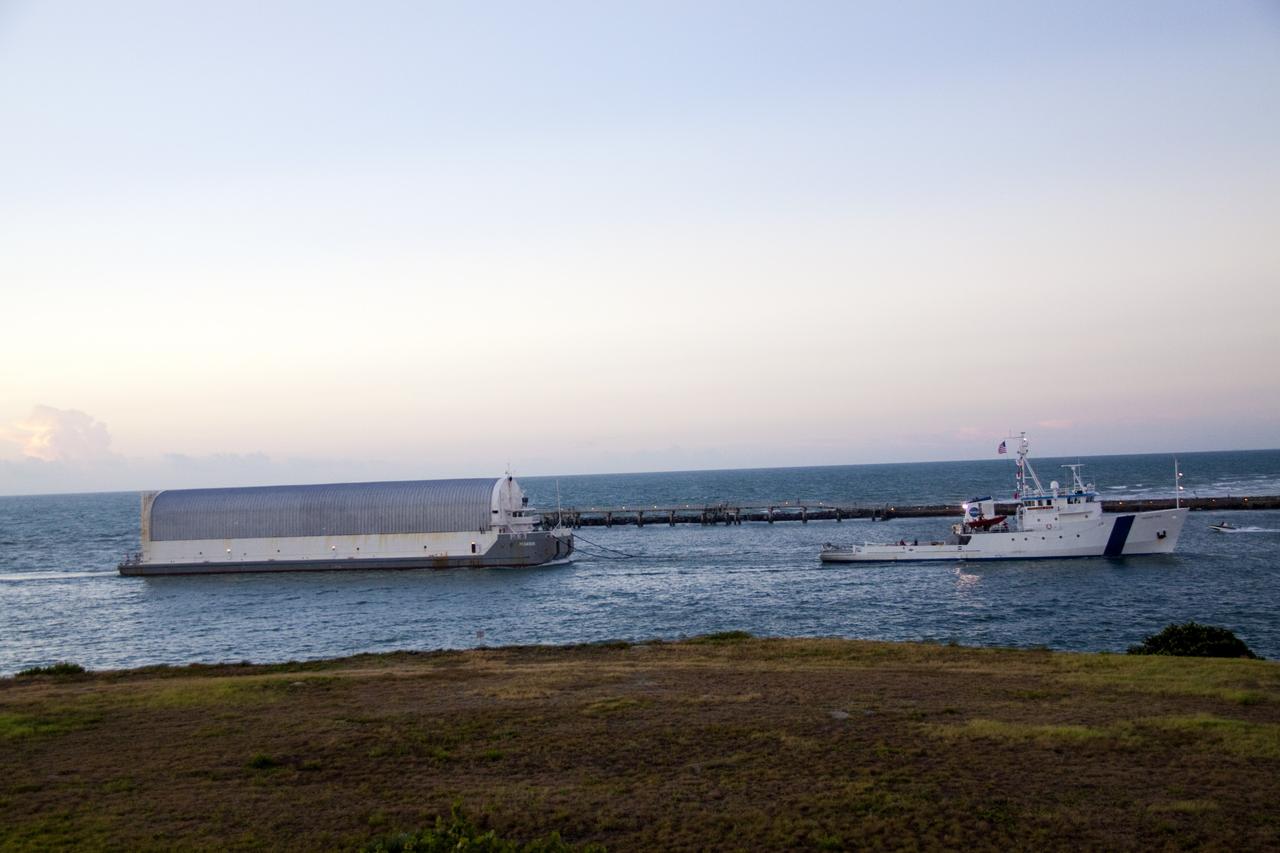

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
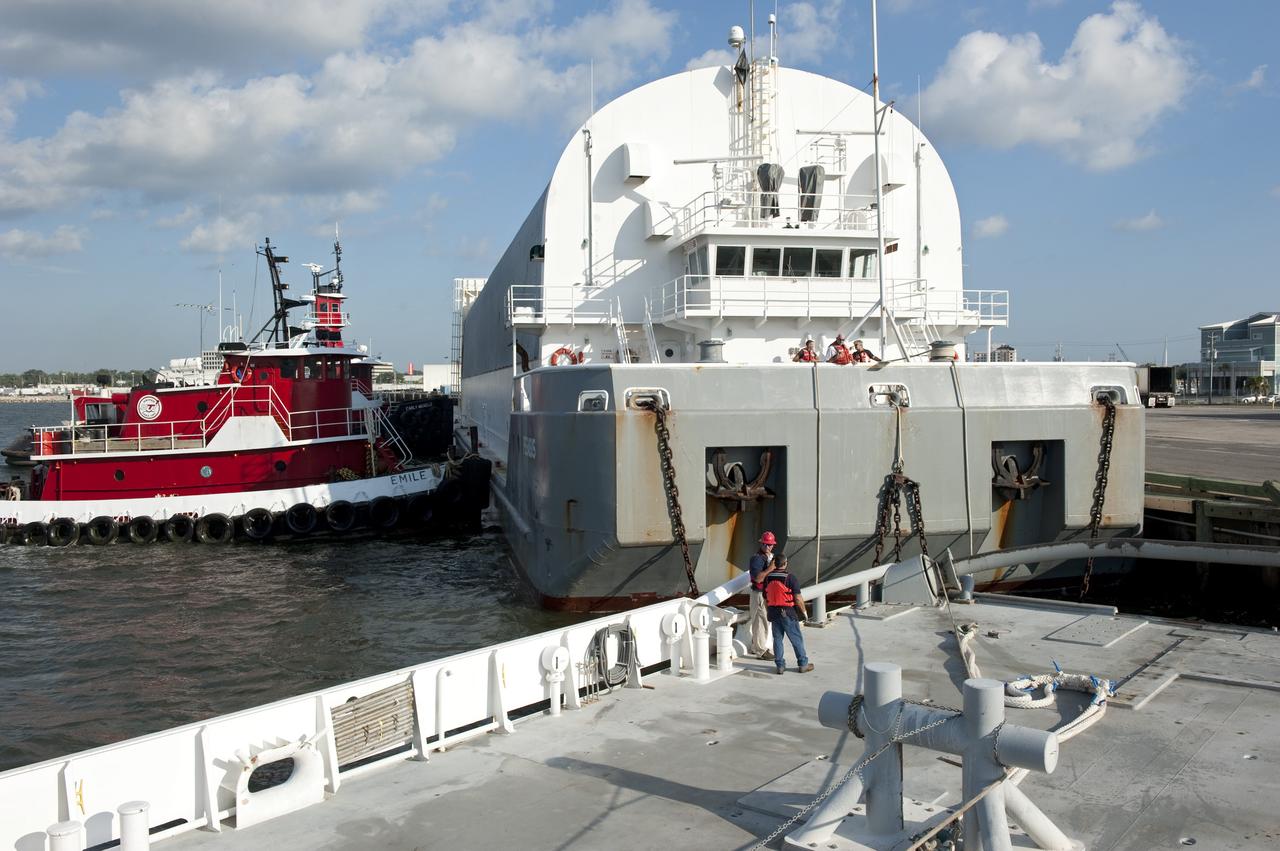

LOUISIANA -- In Gulfport, La., workers connect the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, to Freedom Star, NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ship. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
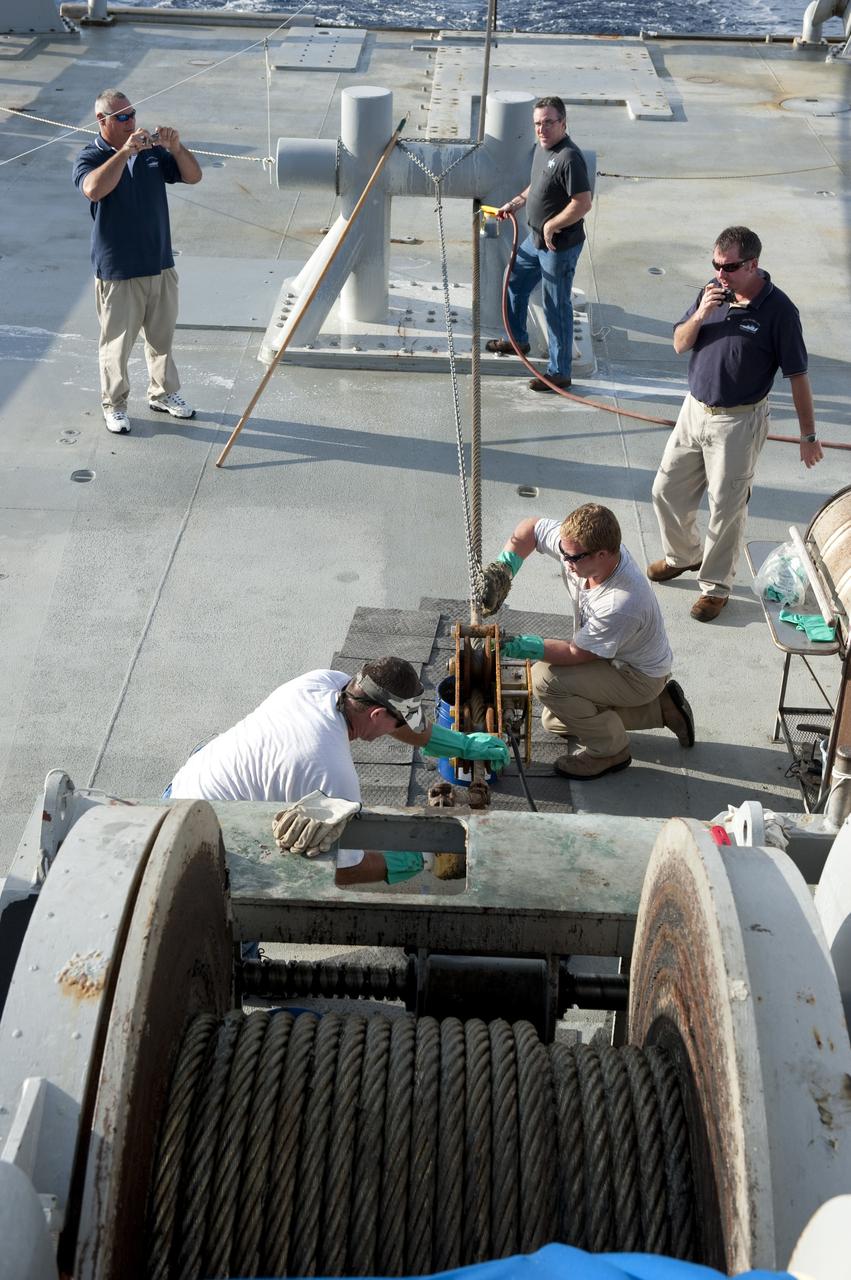

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Deckhands on Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, keep the ship in good repair as it pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
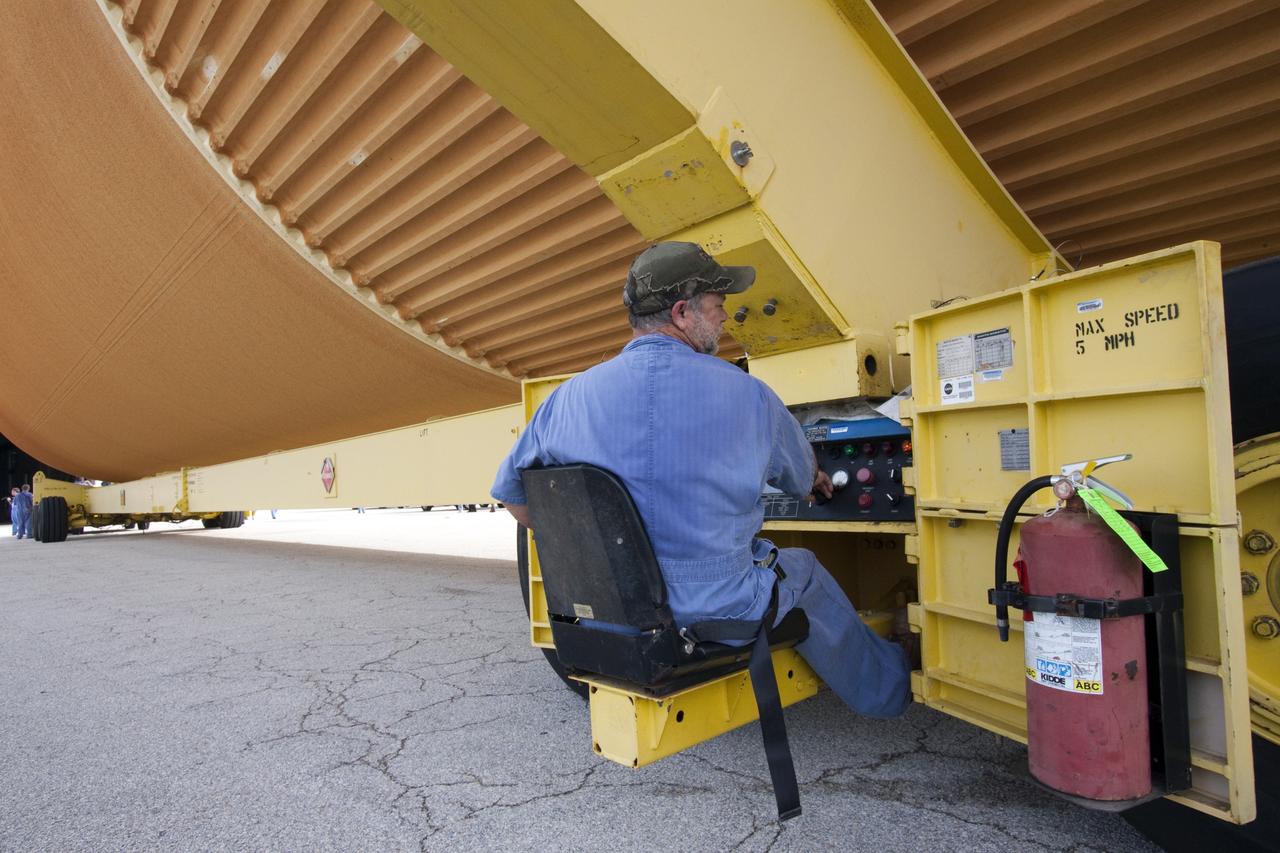

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A United Space Alliance technician monitors the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, as it moves from the Turn Basin to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Once inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
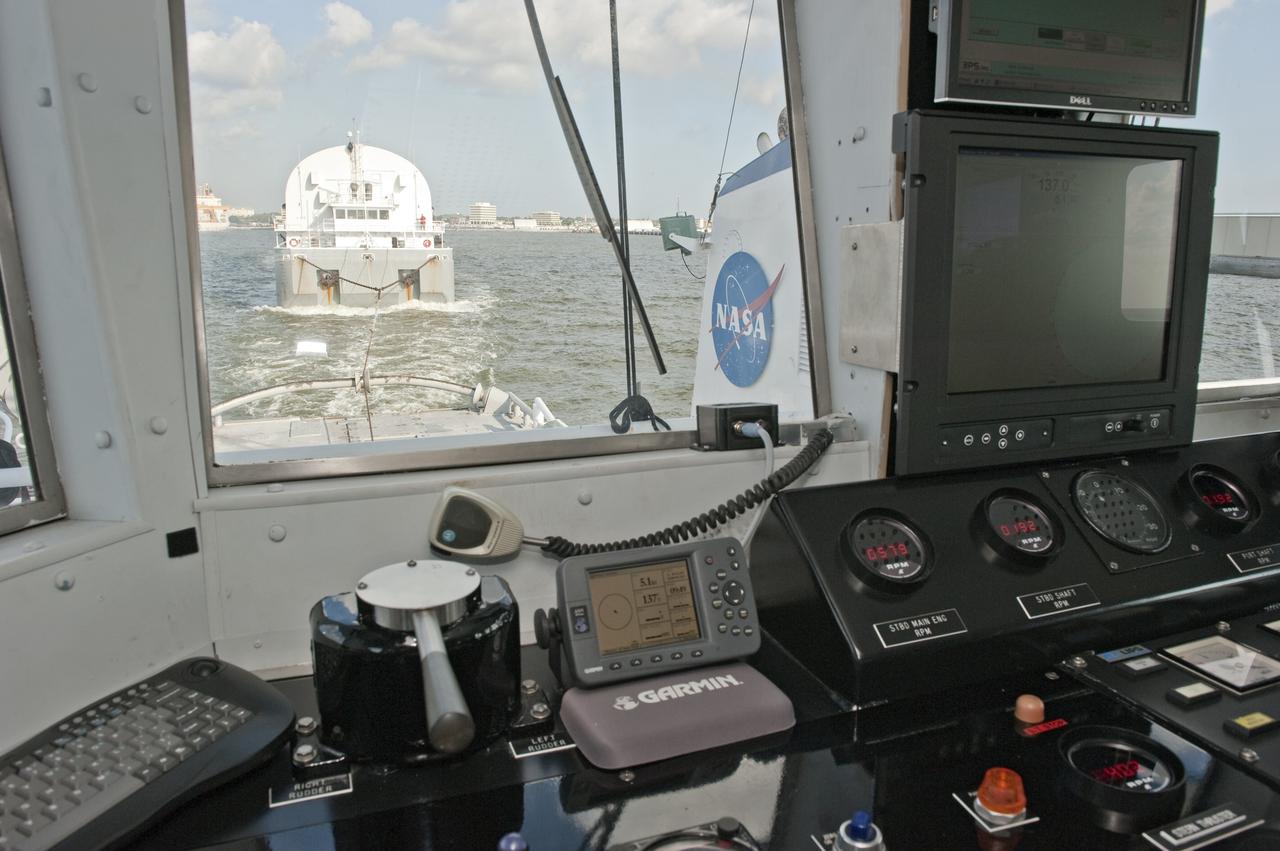

GULFPORT, La. -- This view from the captain's deck of Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, shows the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, as it is escorted from Gulfport, La., to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
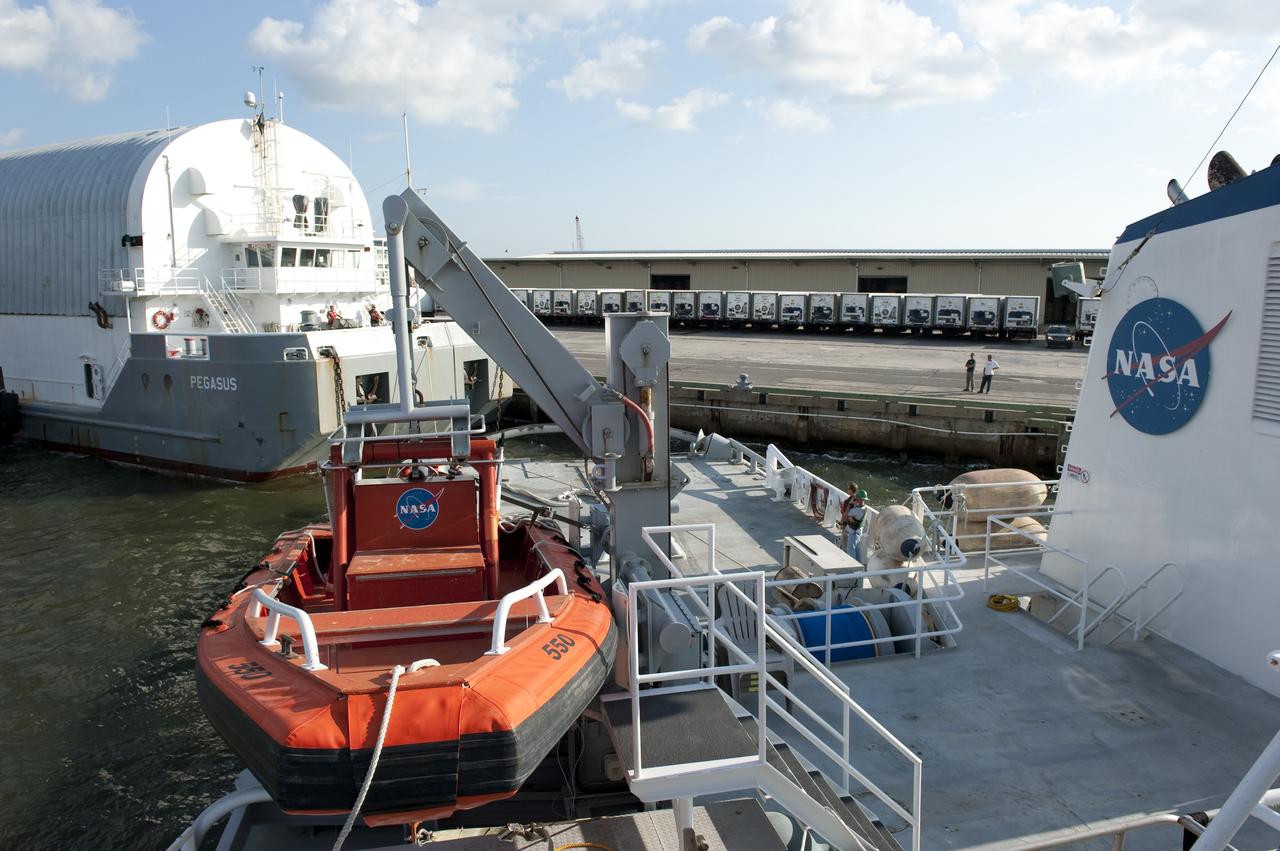

LOUISIANA -- In Gulfport, La., workers connect the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, to Freedom Star, NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ship. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
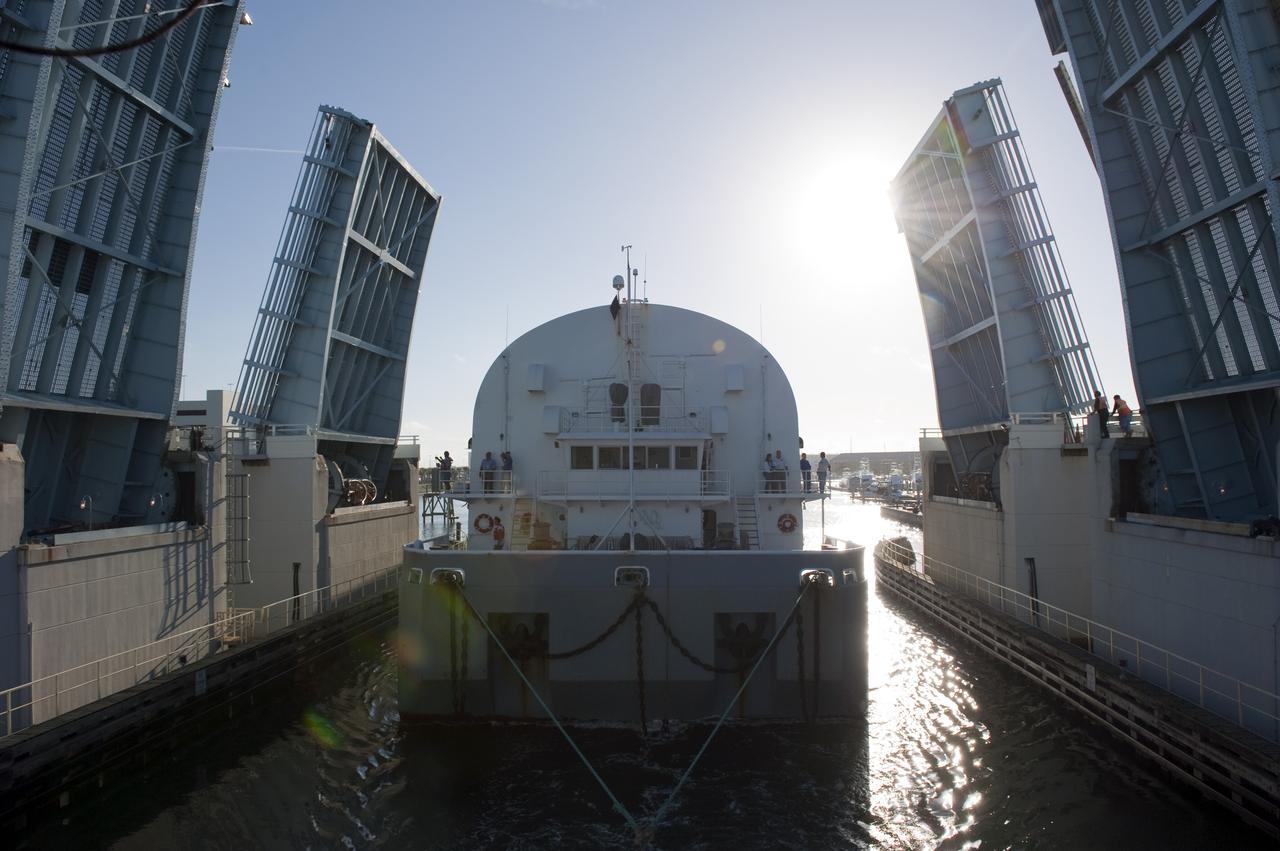

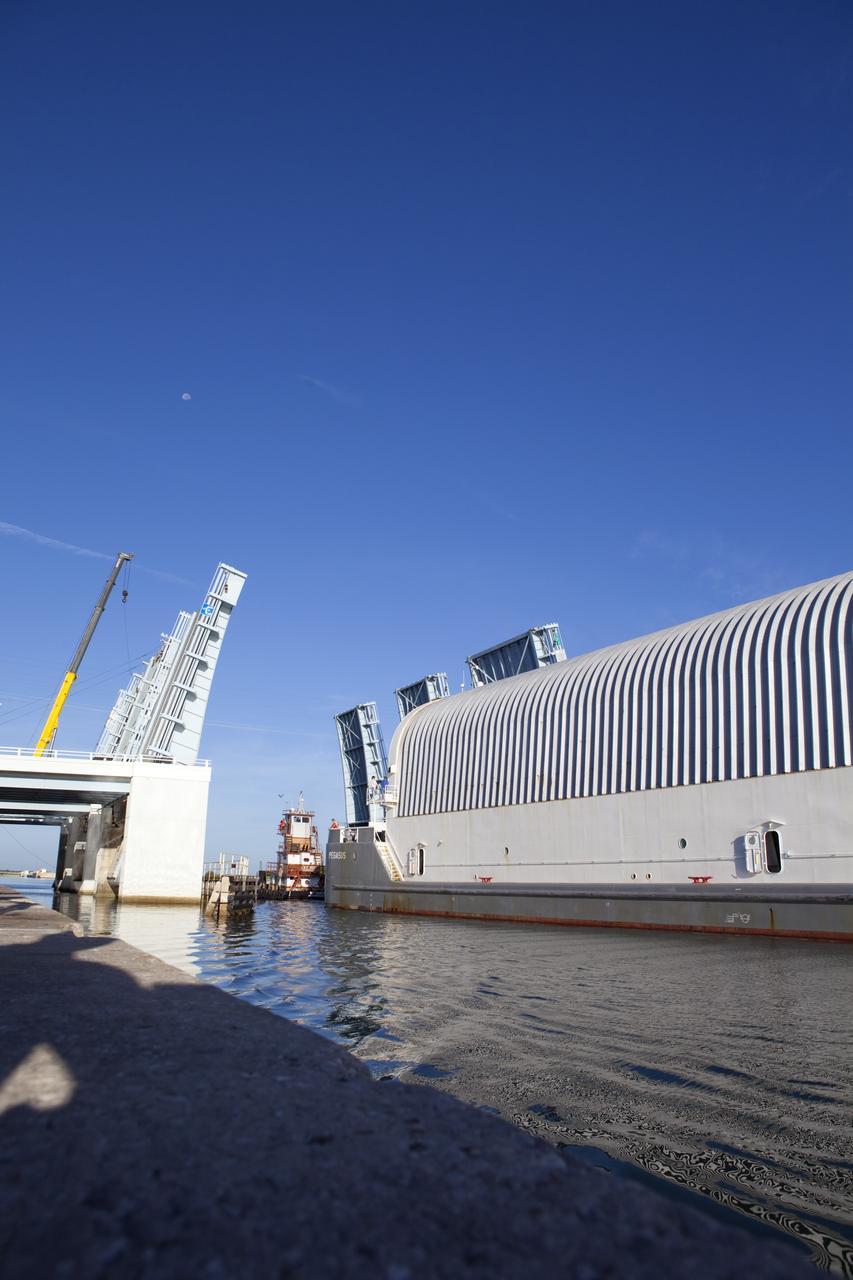
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Pegasus barge moves through the bridge at Port Canaveral, Fla. The barge is carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
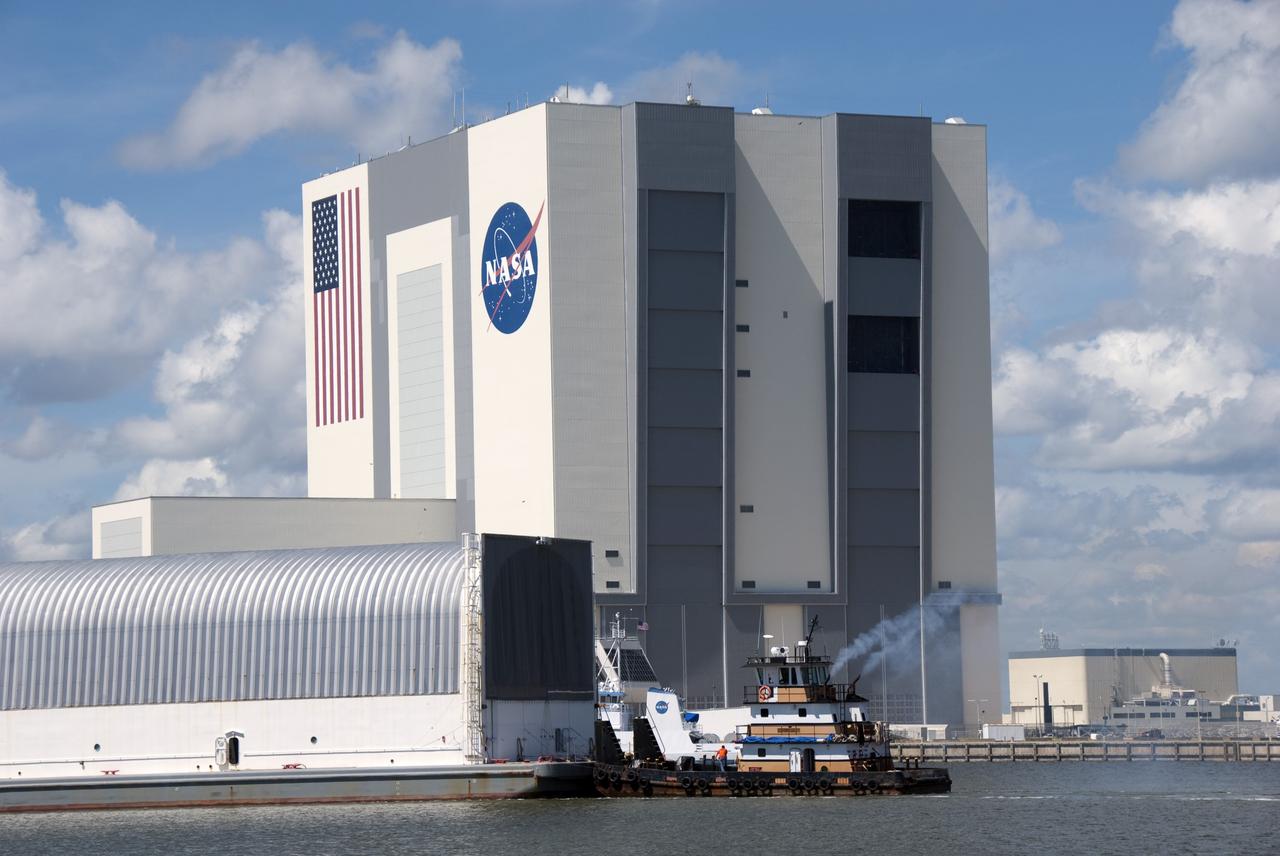

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tugboat pushes the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
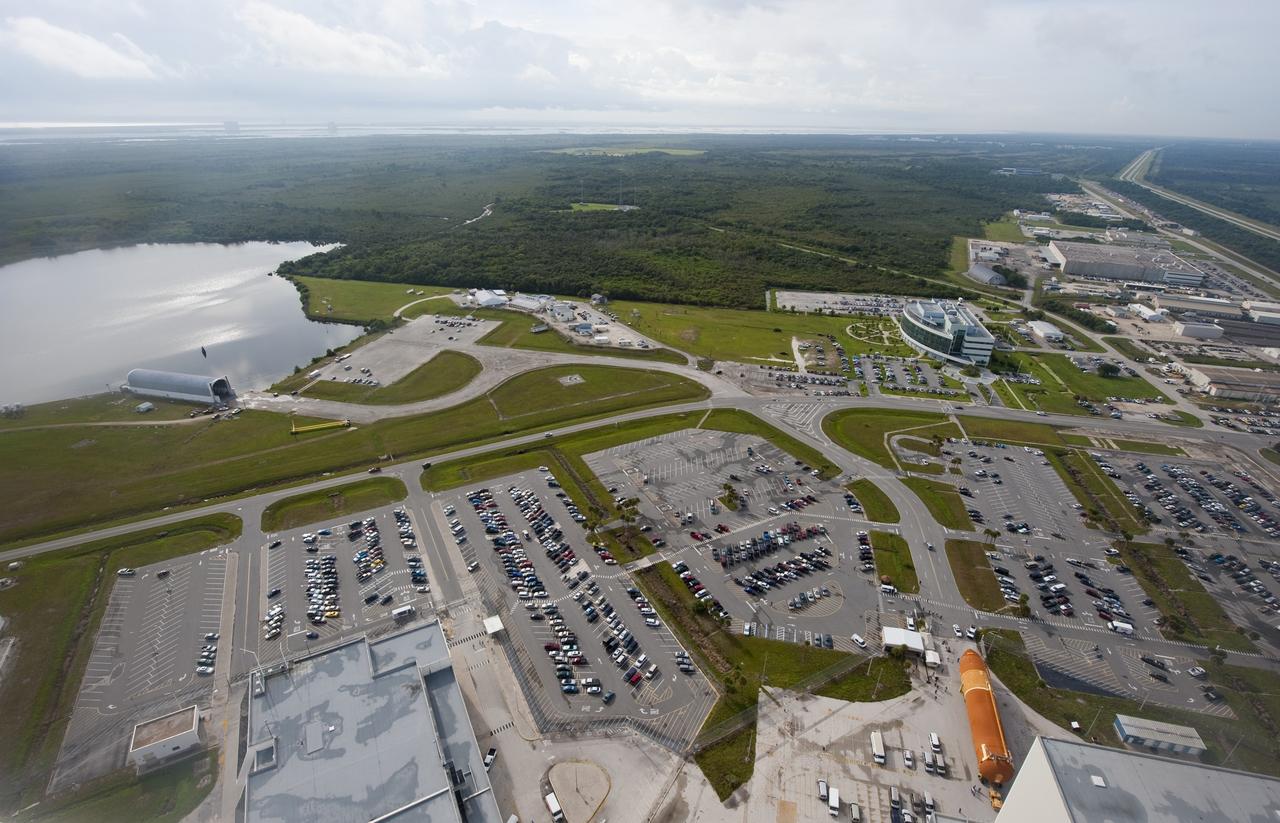

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This overhead view shows the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122 (right), as it is being transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea, carried in the Pegasus Barge, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Once inside the VAB, it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch Feb. 2011. STS-134 currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell
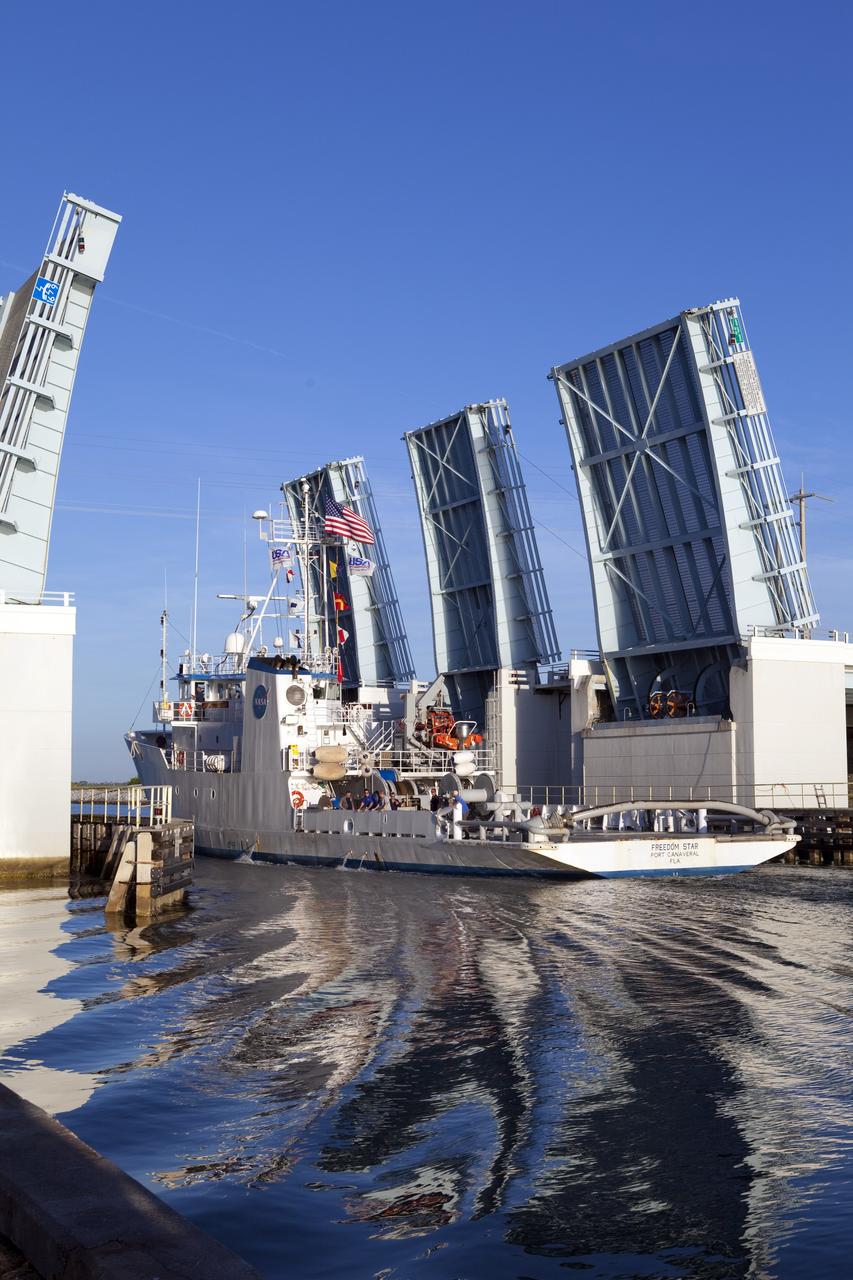

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, ushers the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
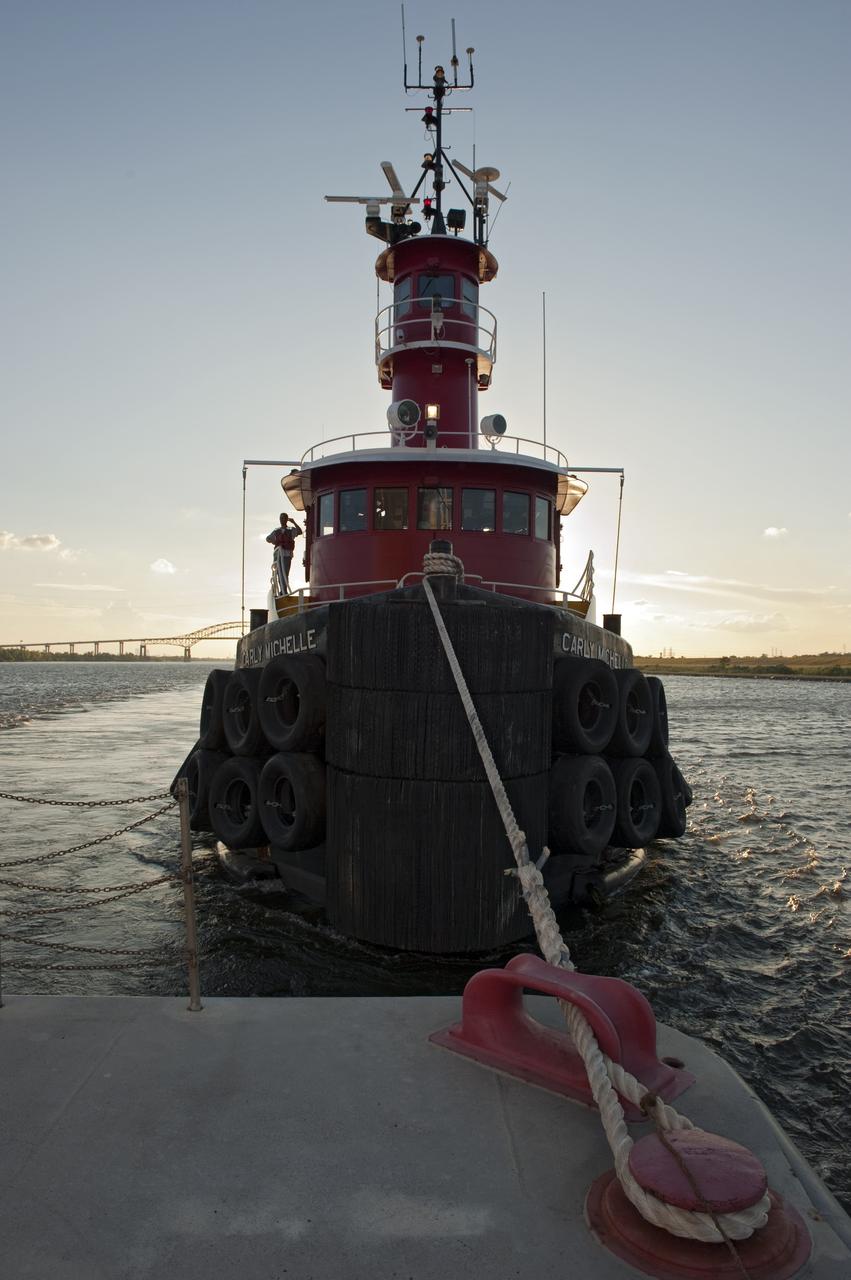

NEW ORLEANS -- A tug boat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
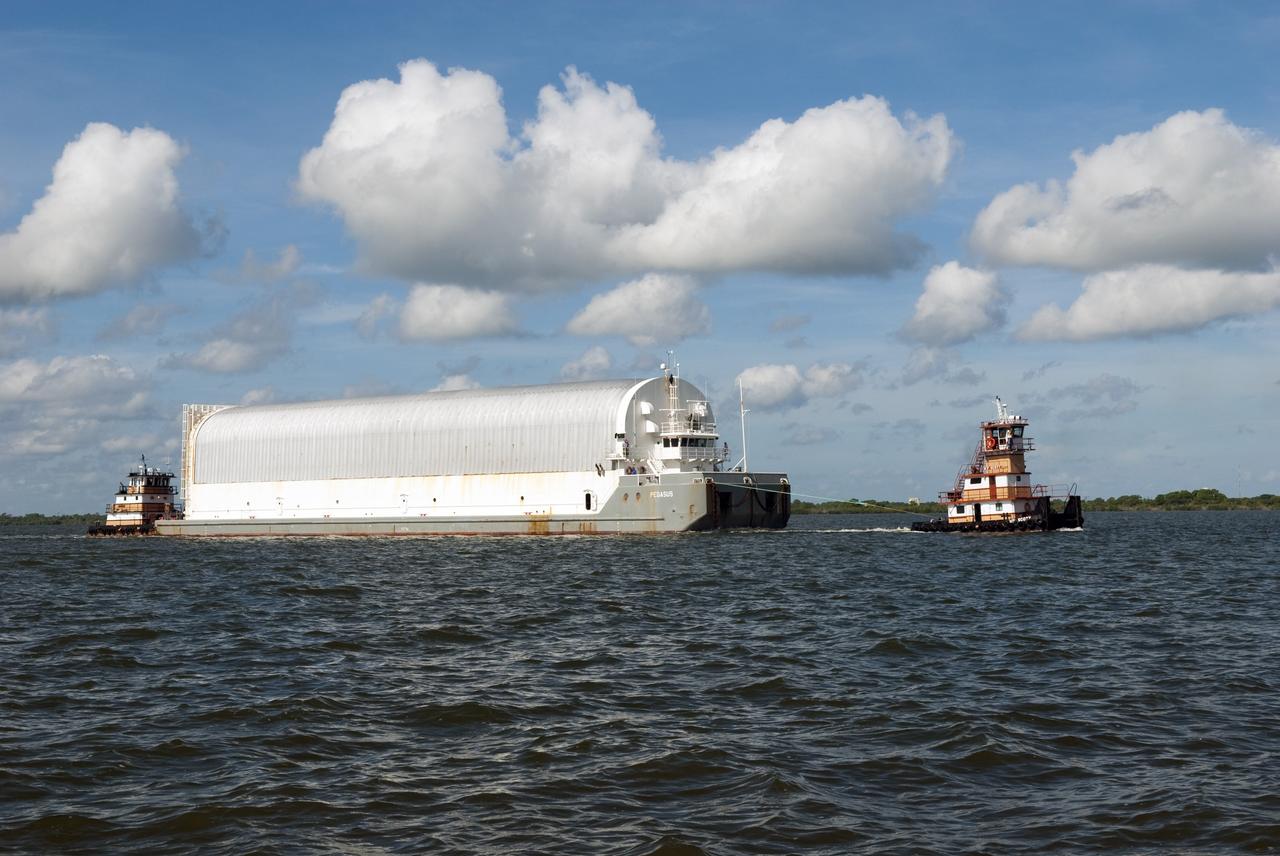

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- One tugboat pulls while another pushes the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
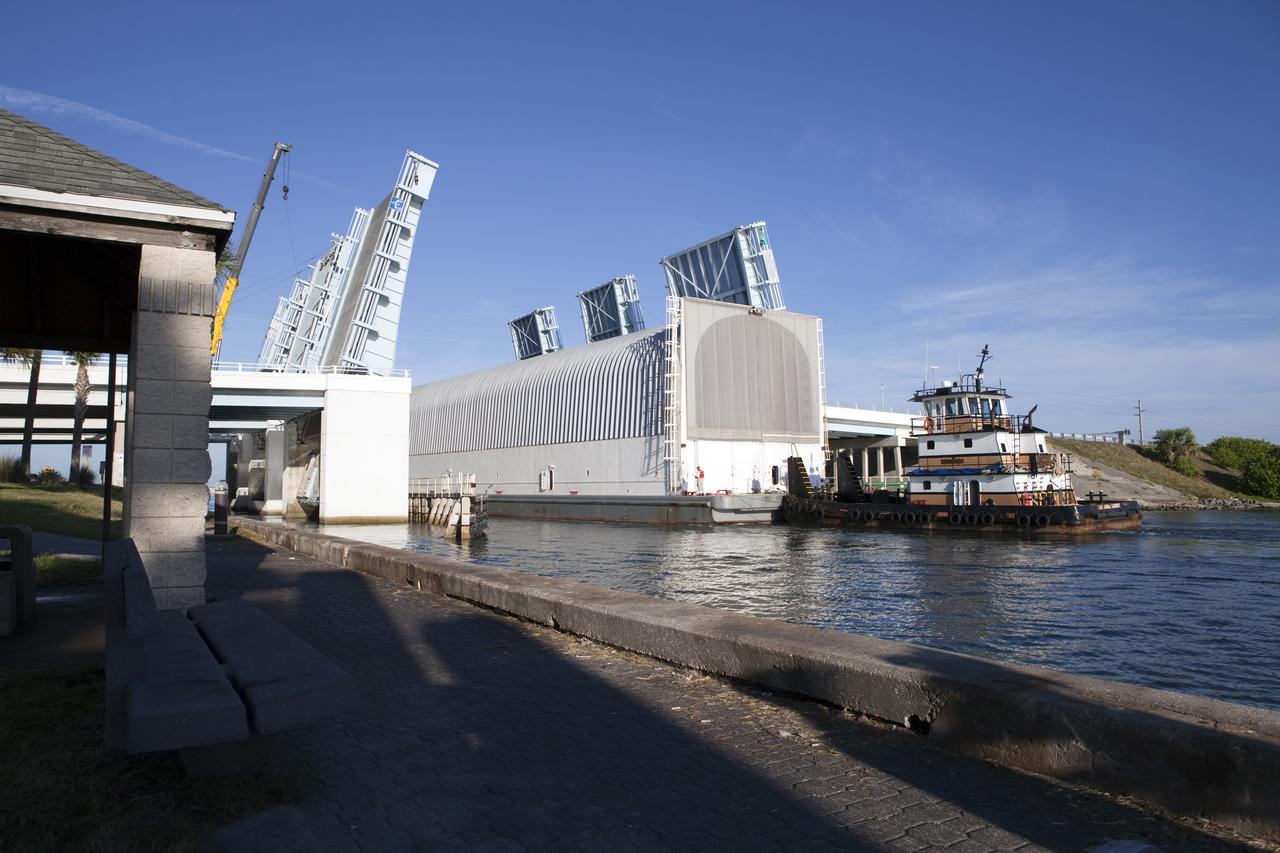

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tug boat pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb., 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
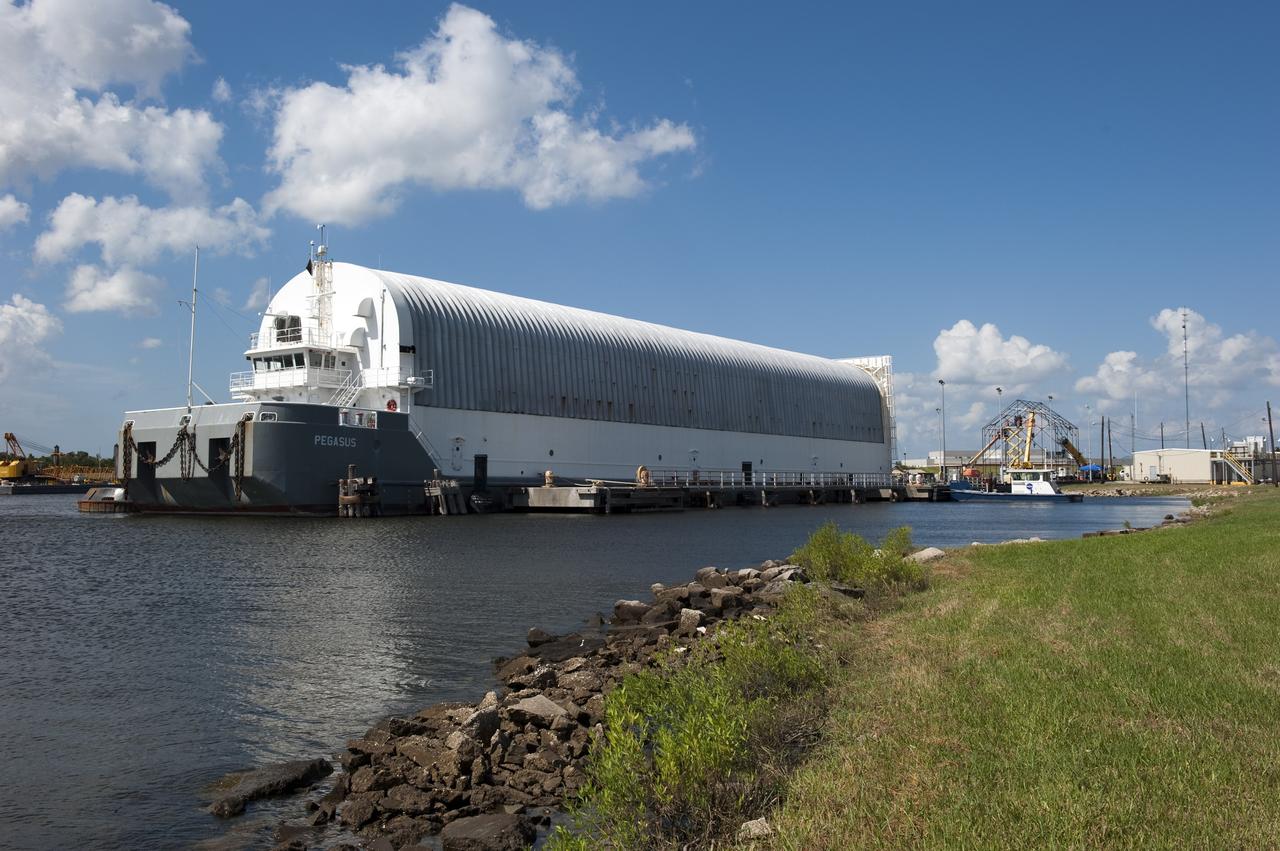

NEW ORLEANS -- At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, is ready for transportation to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Secured aboard the Pegasus Barge the tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
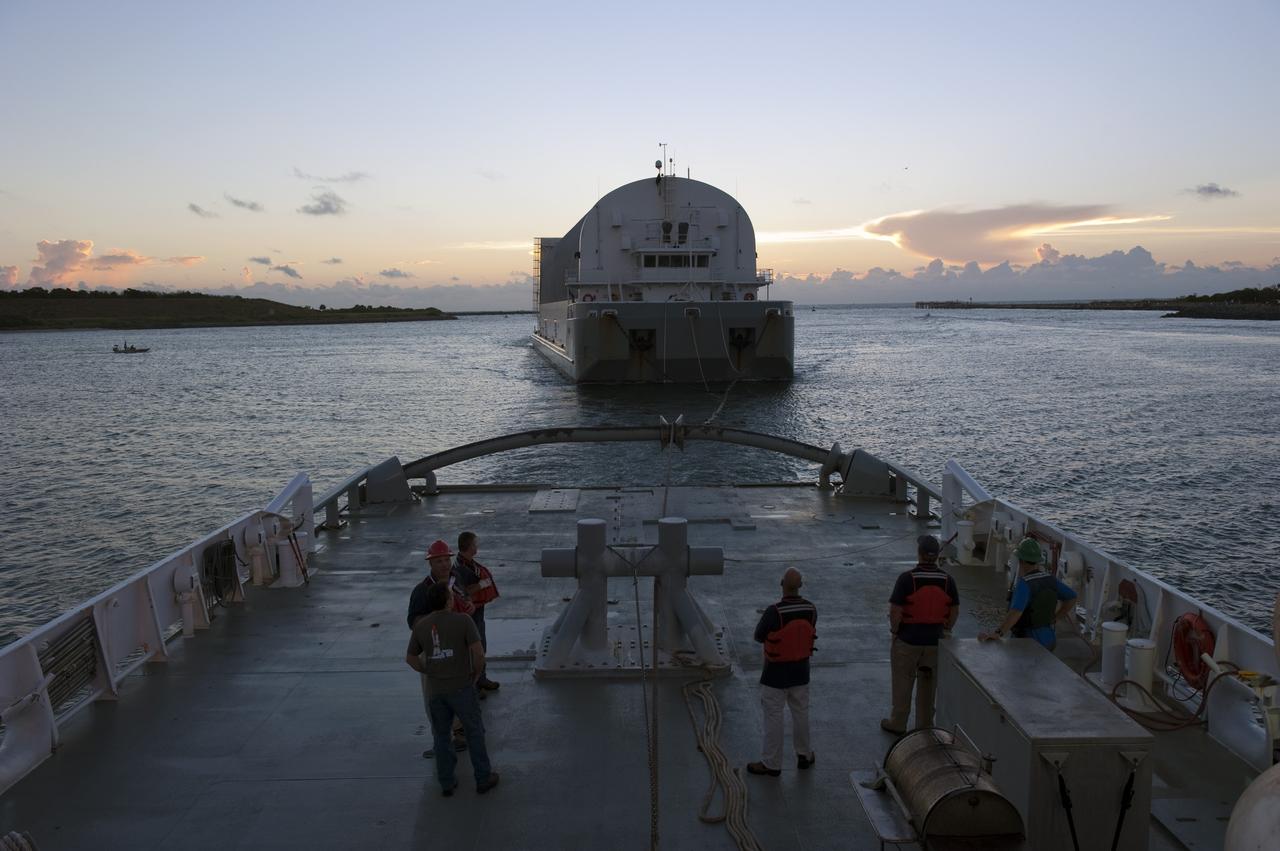

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

NEW ORLEANS -- To commemorate the history of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, its intertank door is emblazoned with an ET-122 insignia. The external tank will travel 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida secured aboard the Pegasus Barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
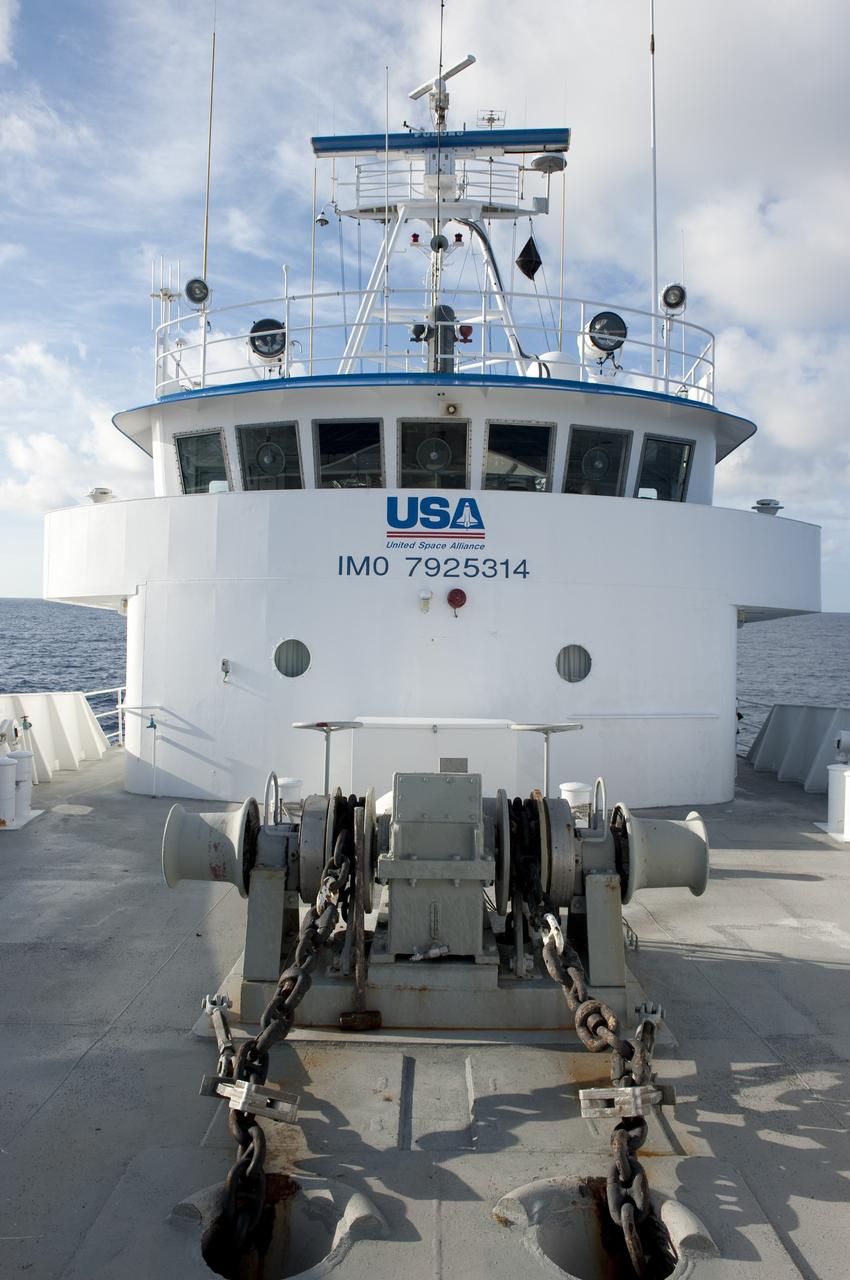

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This view is from the deck of Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, as it pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
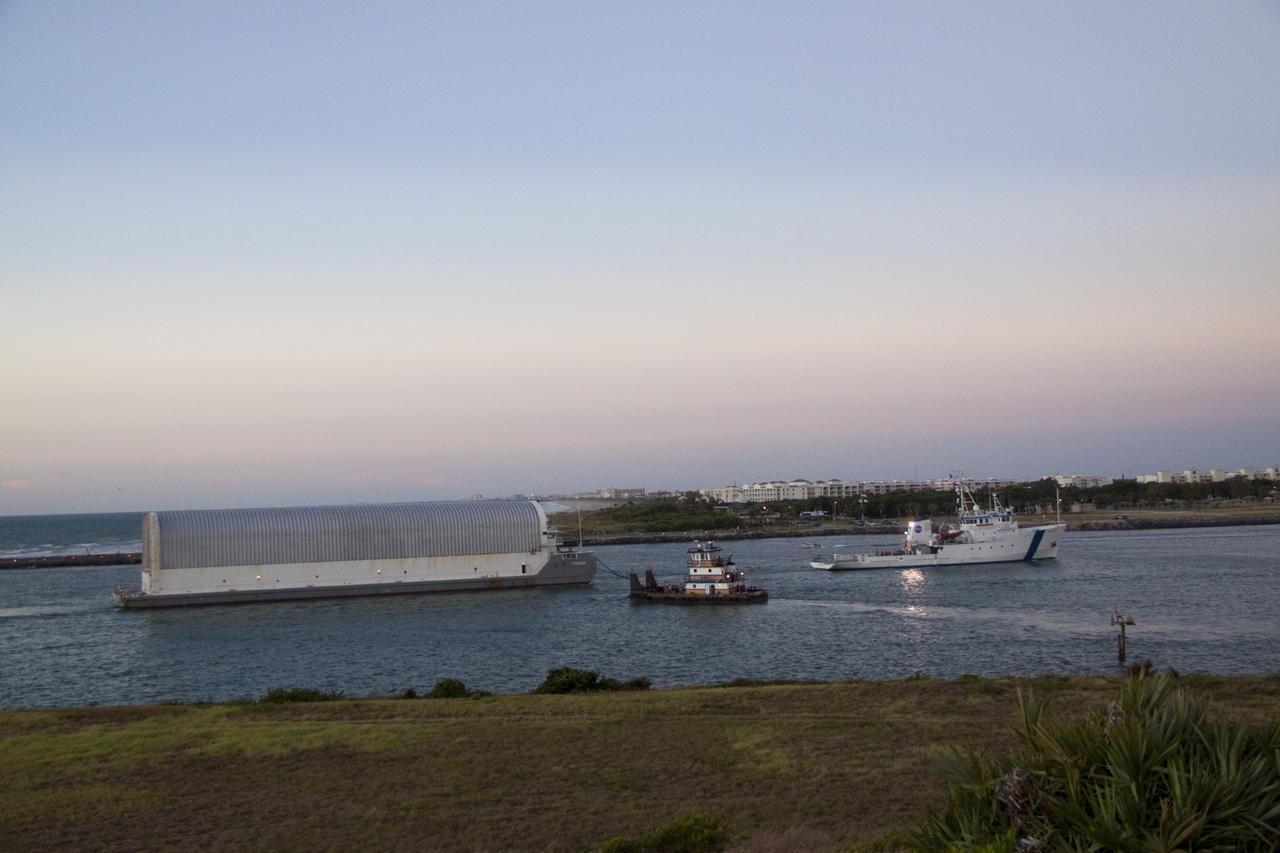

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
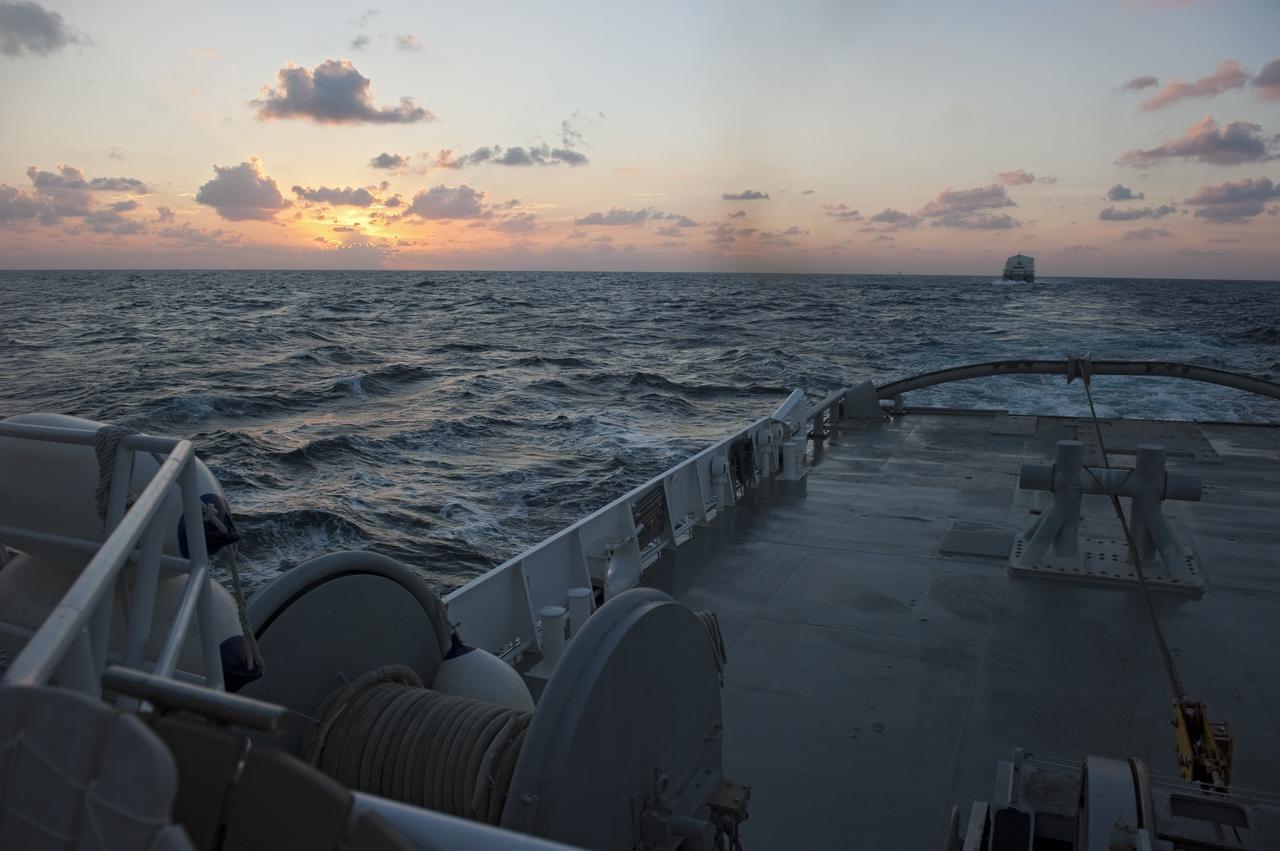

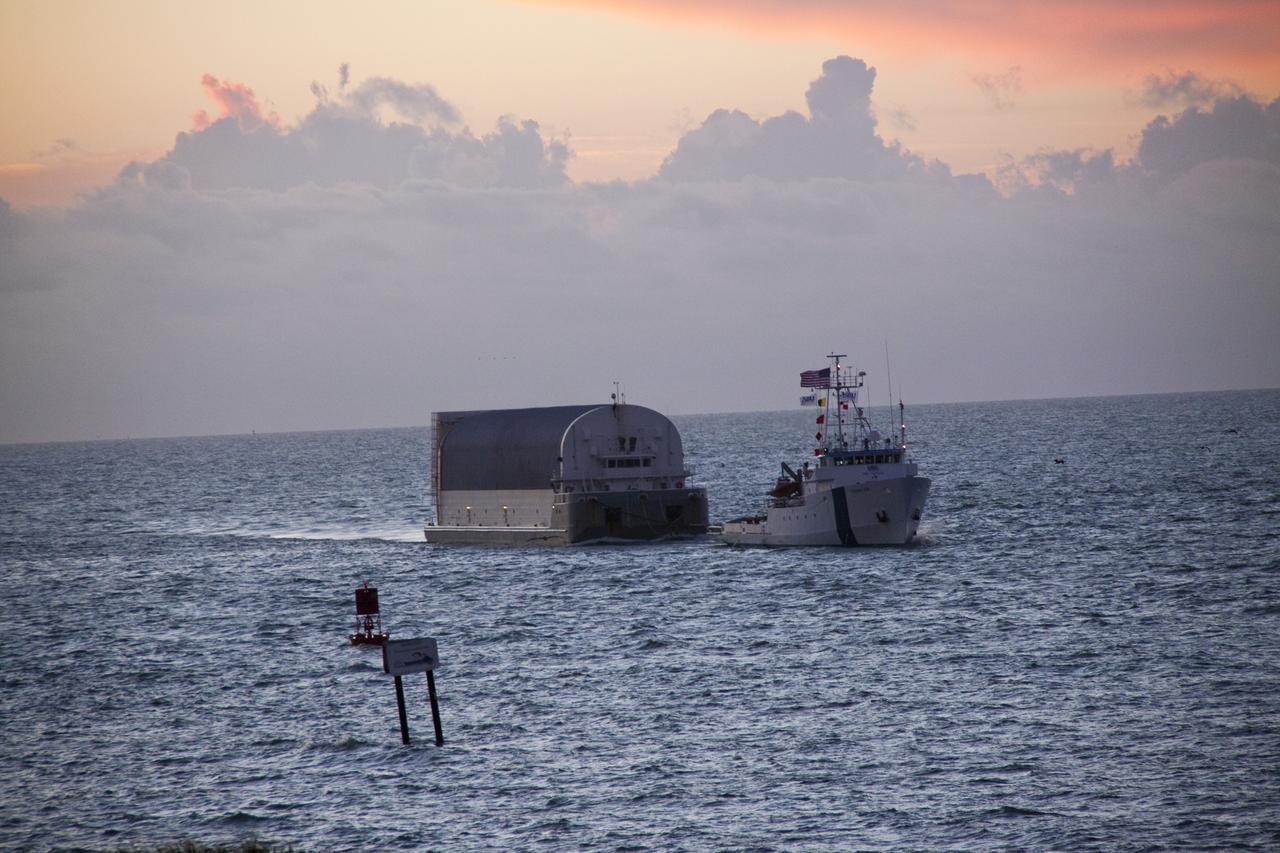
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This view at dusk from the stern of Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, shows the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, as it is transported to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
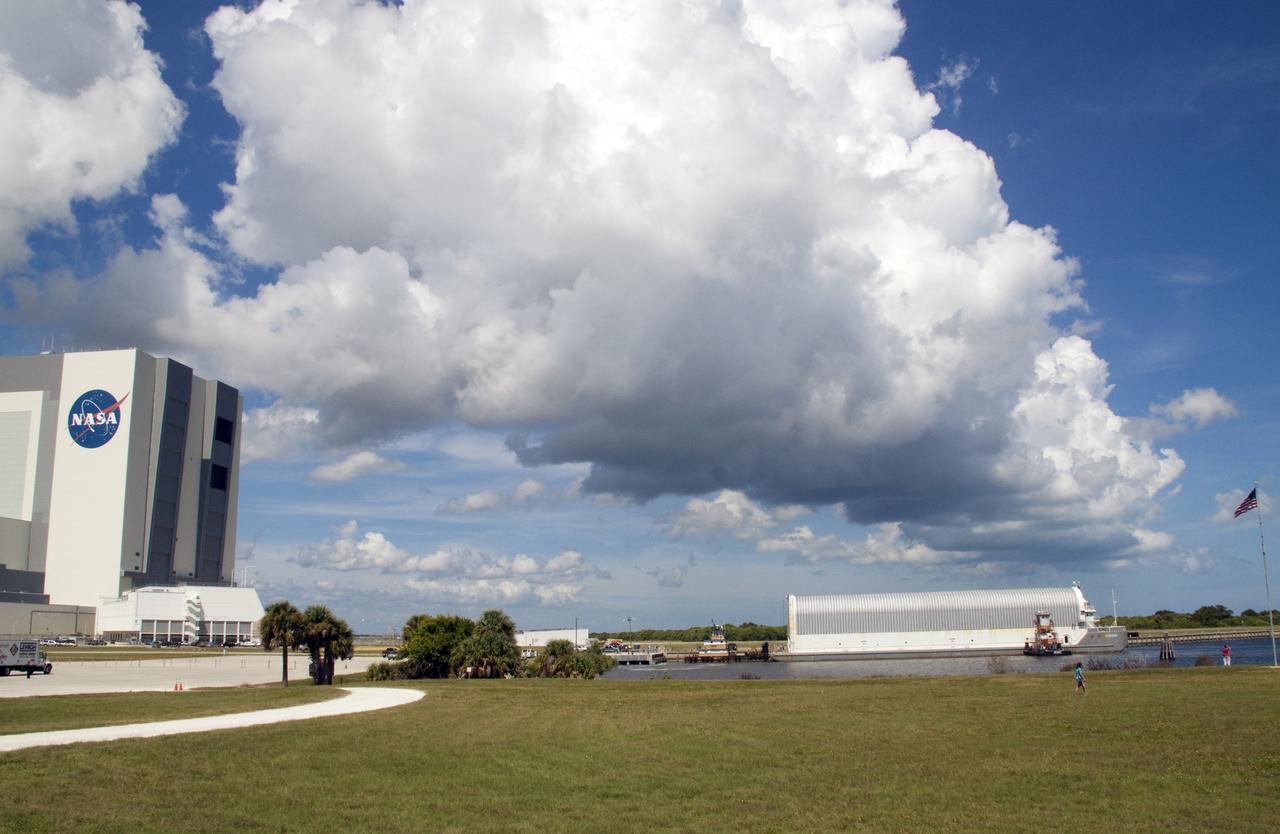

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, arrives at the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
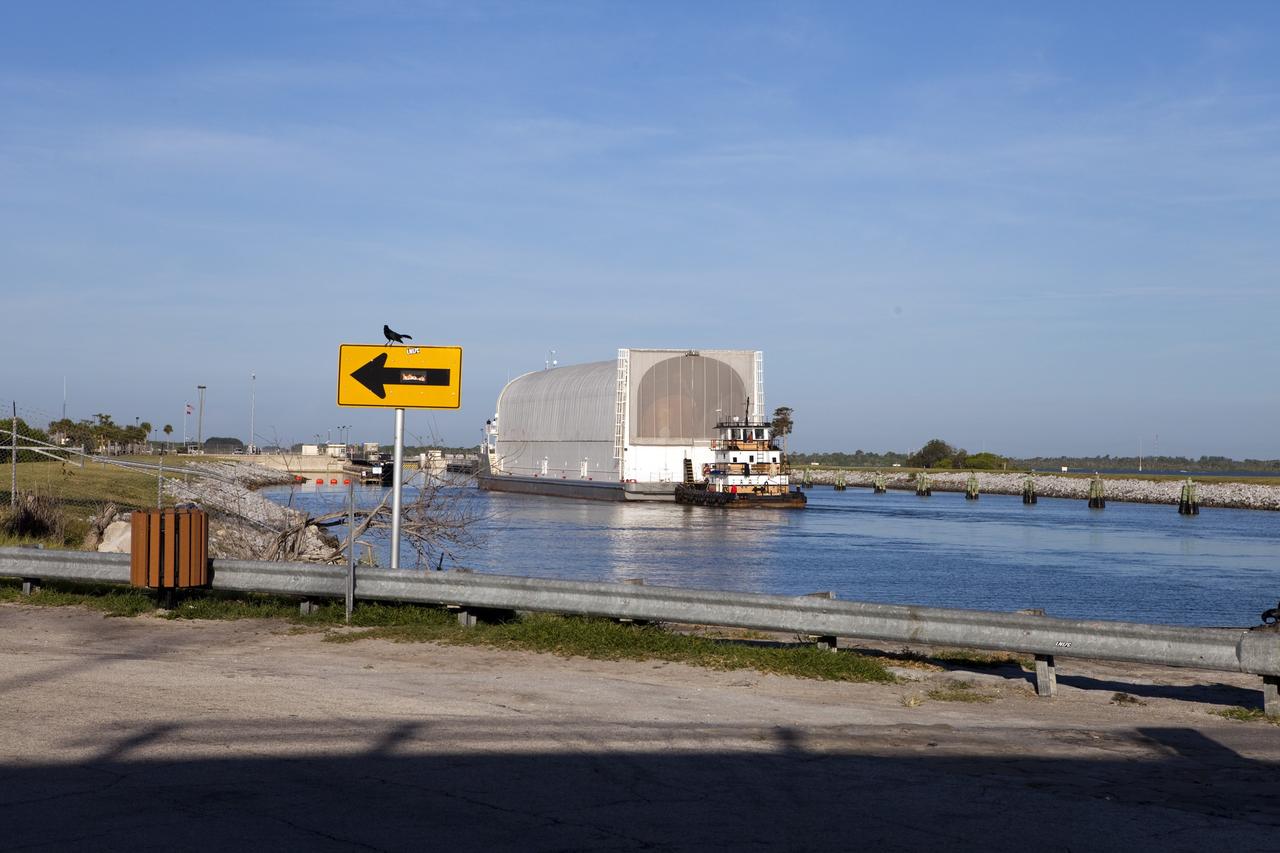

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tug boat pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb., 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, has been moved inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to Kennedy's Turn Basin aboard the Pegasus Barge. The tank eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
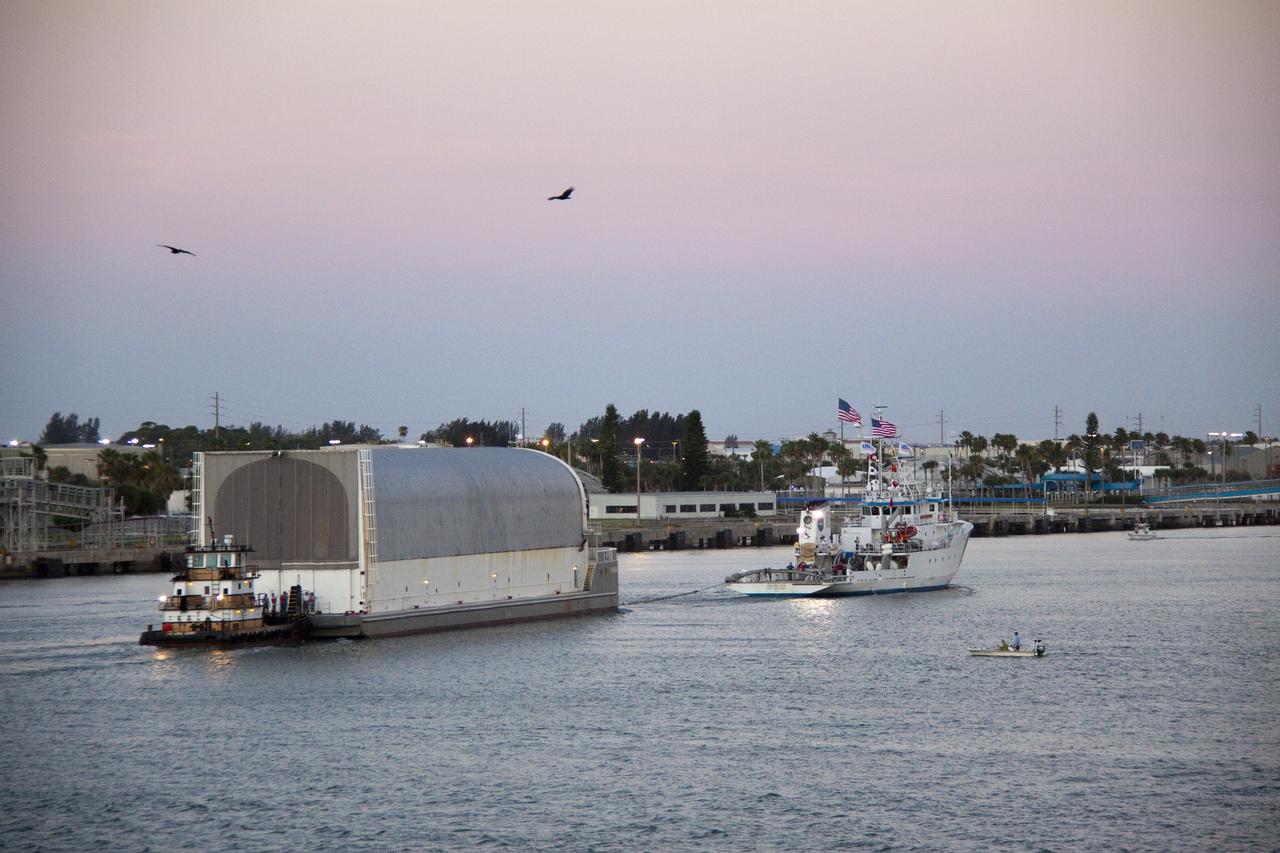

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Boaters watch as Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tug boat pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

LOUISIANA -- In Gulfport, La., tugboats are preparing the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, for connection to Freedom Star, NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ship. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
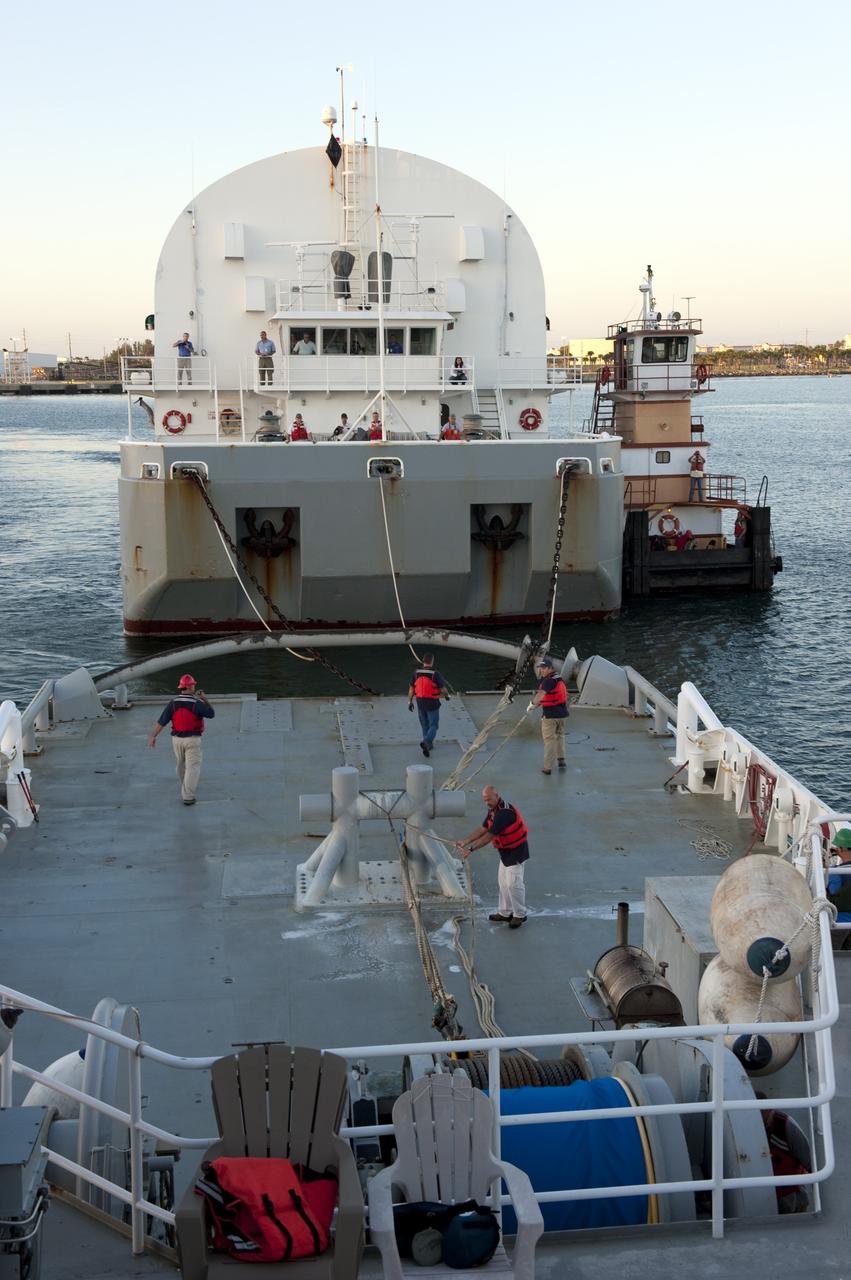

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers aboard Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, disconnect their ship from the Pegasus Barge, which is carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space Coast residents watch as the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, approaches NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
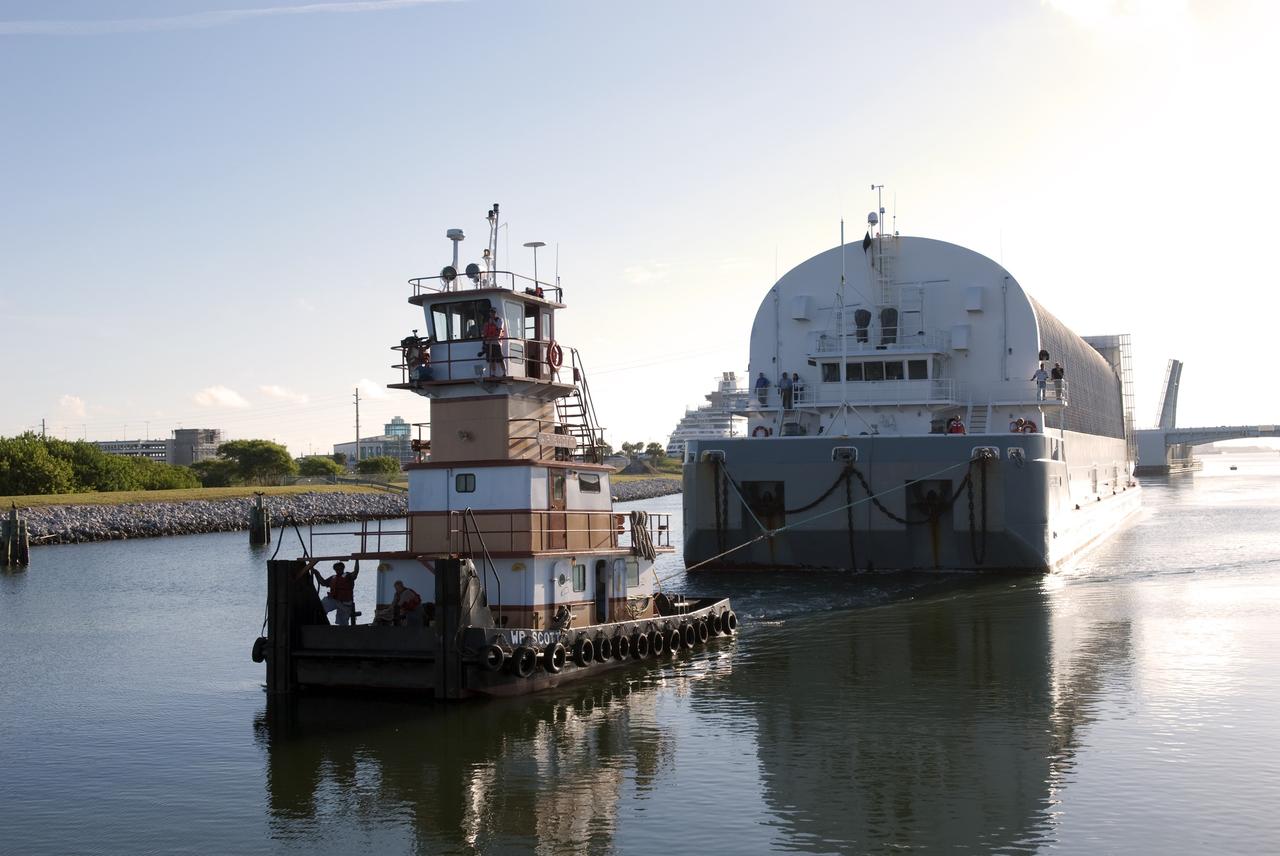

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tugboat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
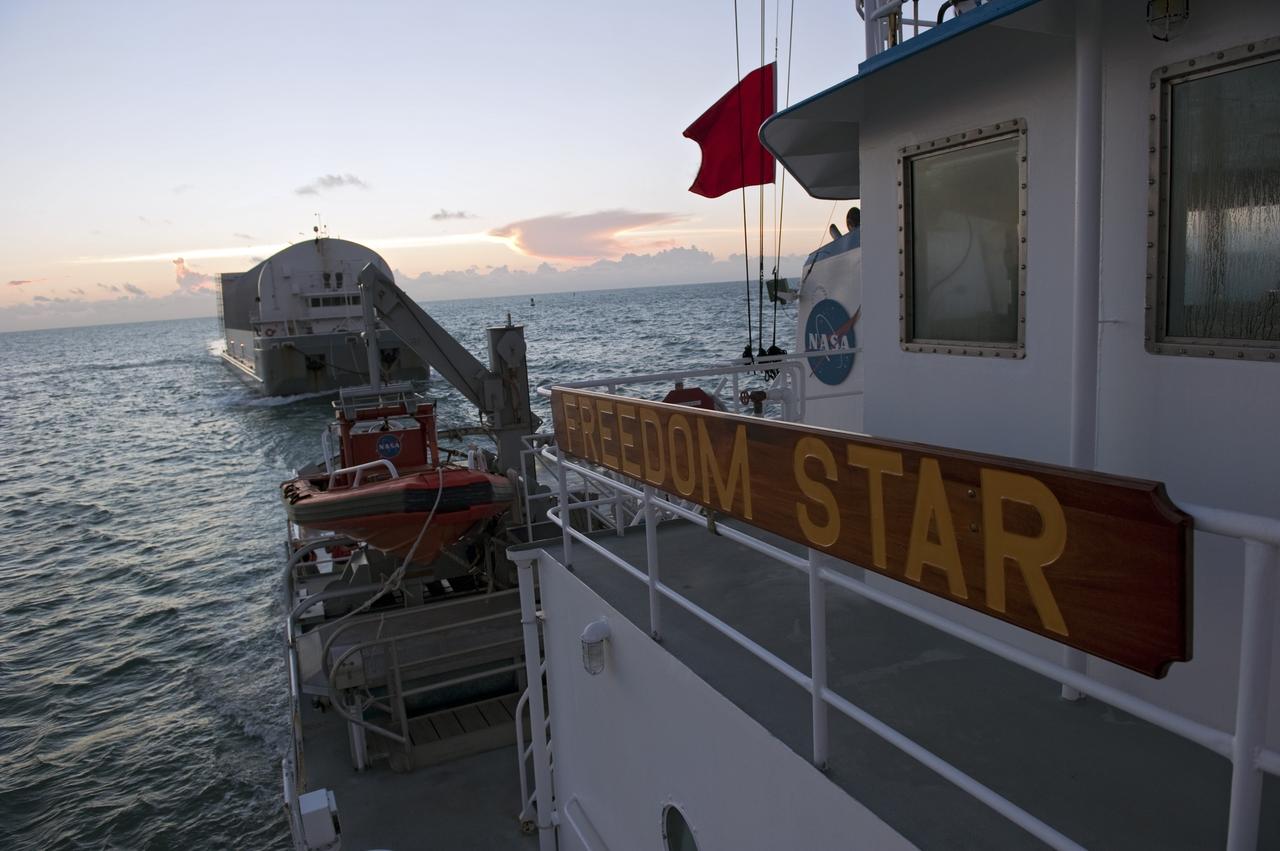

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
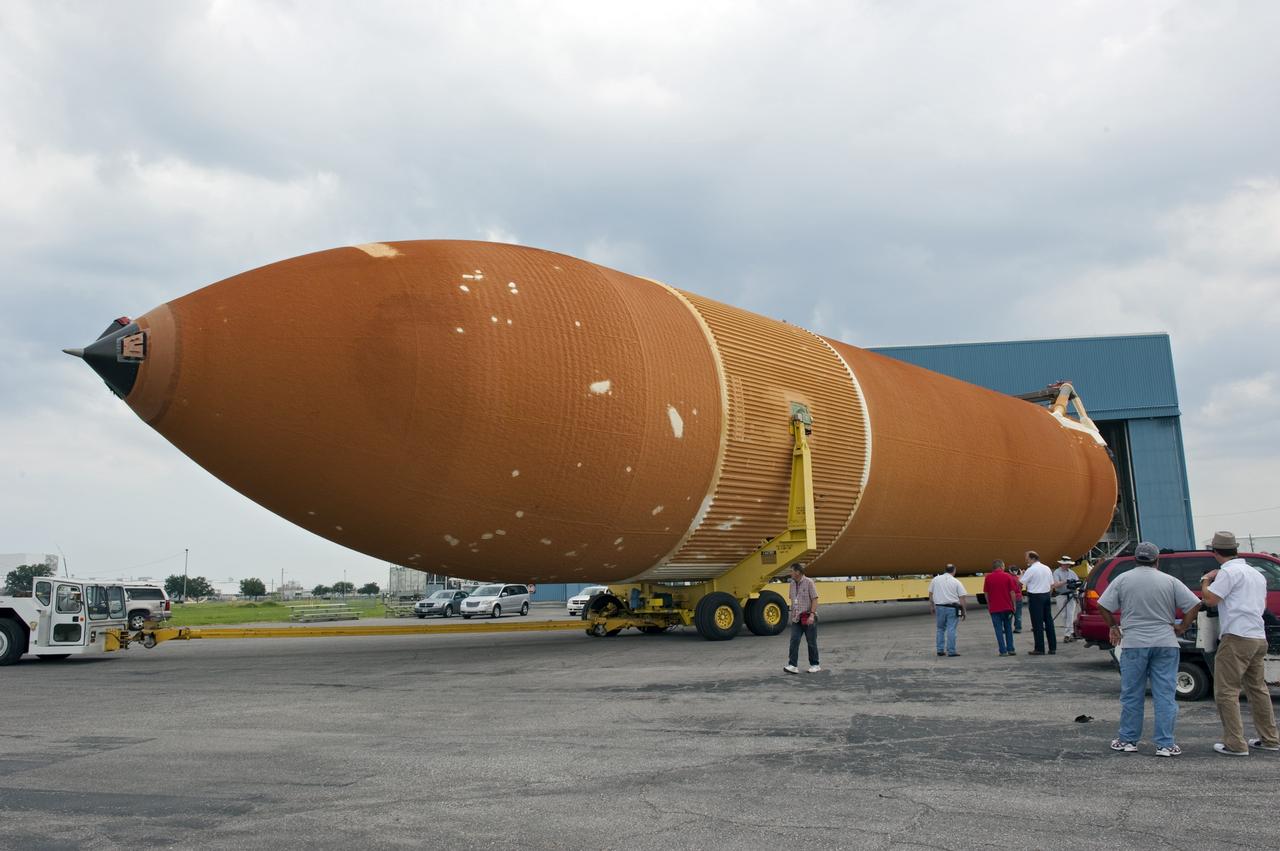

NEW ORLEANS -- Workers escort the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans onto the Pegasus Barge. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida secured aboard the barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
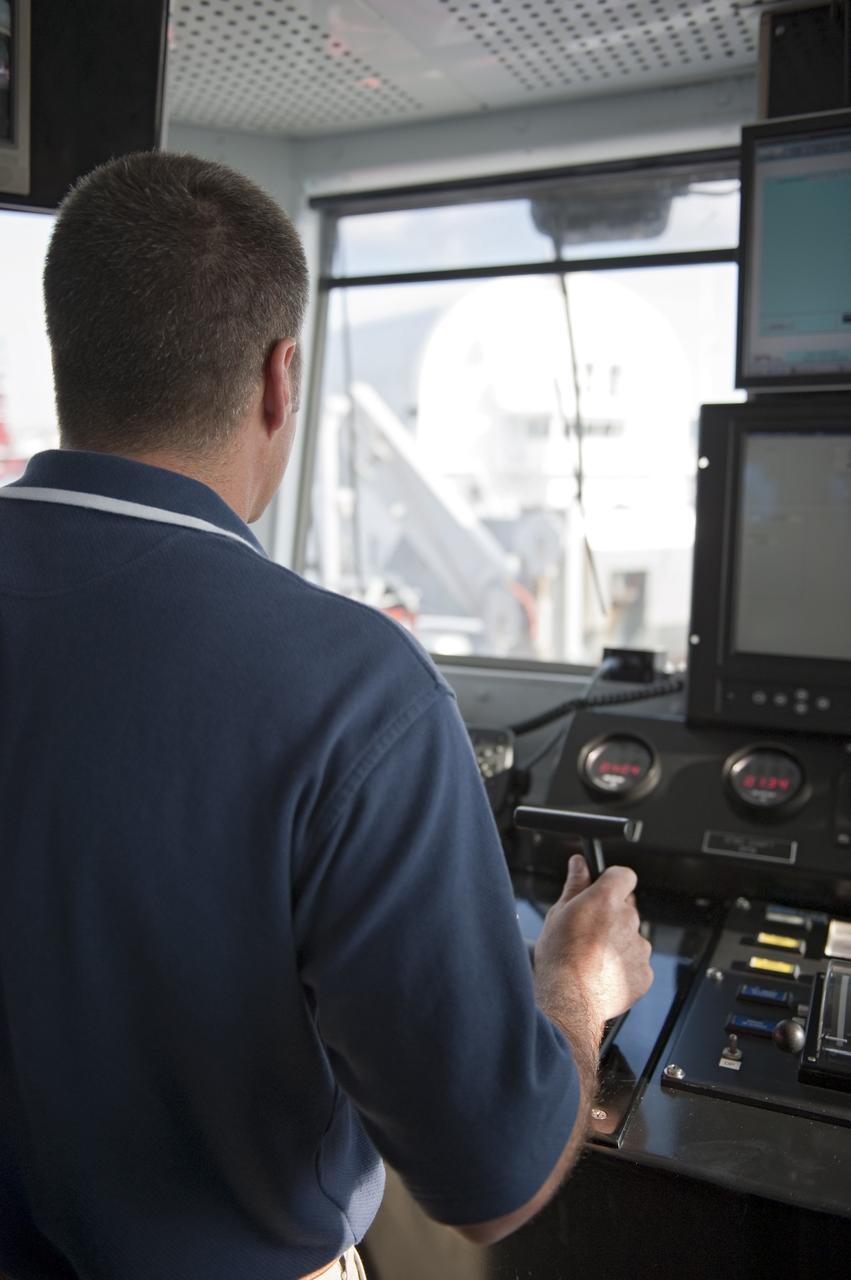

GULFPORT, La. -- At Gulfport, La., Michael Nicholas, captain M/V Freedom Star, guides NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ship out of port pulling the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

NEW ORLEANS -- Workers monitor the progress of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it is being loaded onto the Pegasus Barge. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida secured aboard the barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

NEW ORLEANS -- A tug boat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
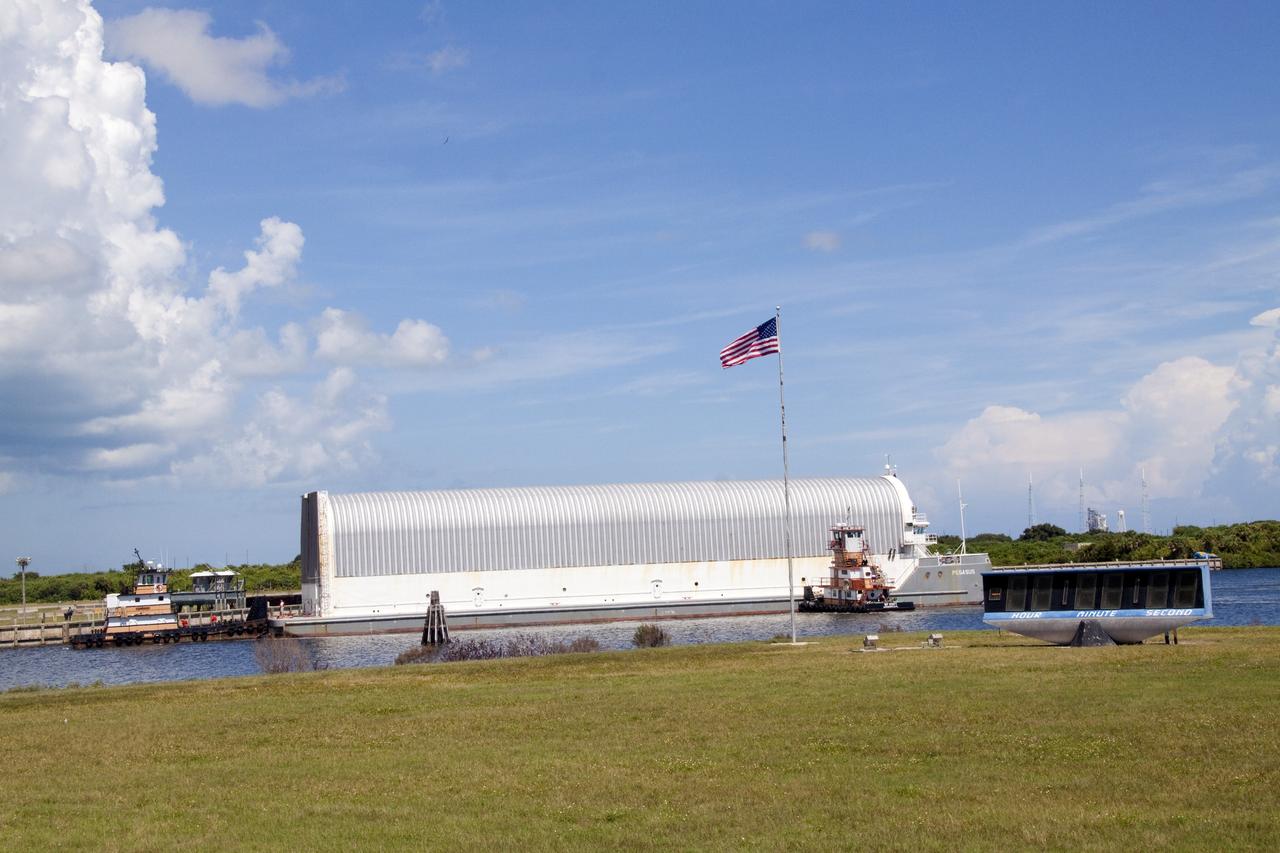

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, arrives at the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tugboat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Pegasus barge, carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, arrives at the Turn Basin of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
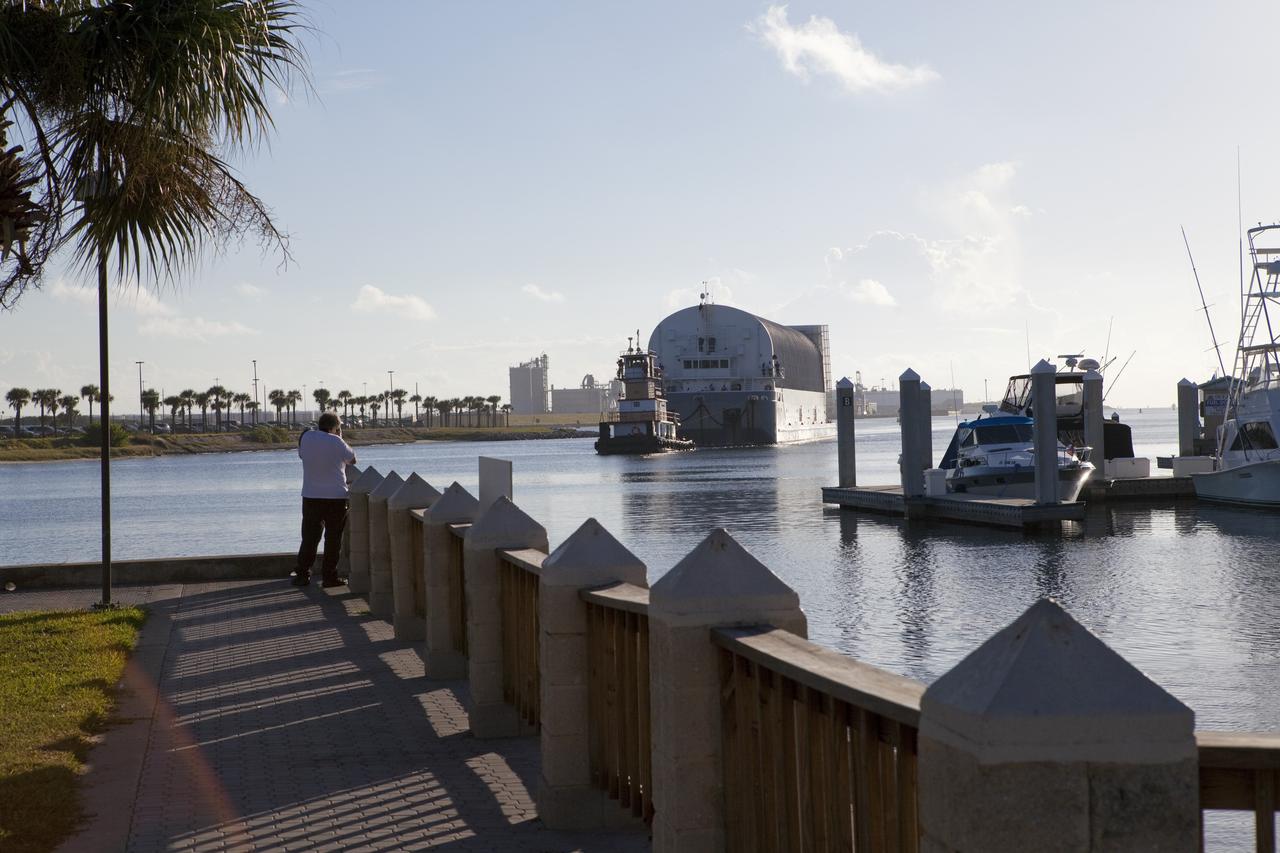

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tug boat pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
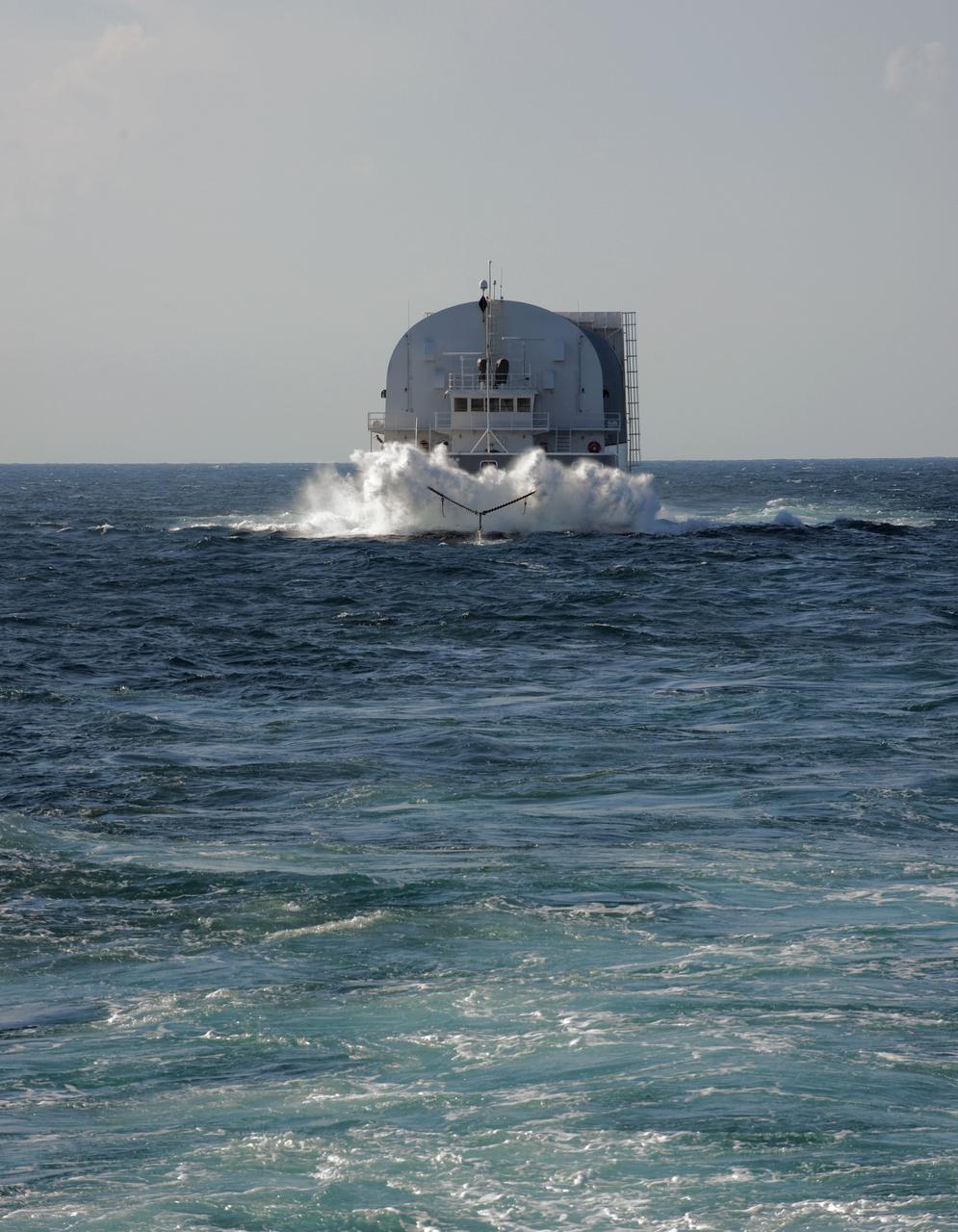

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This view from Freedom Star, one NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, shows the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, as it is transported to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
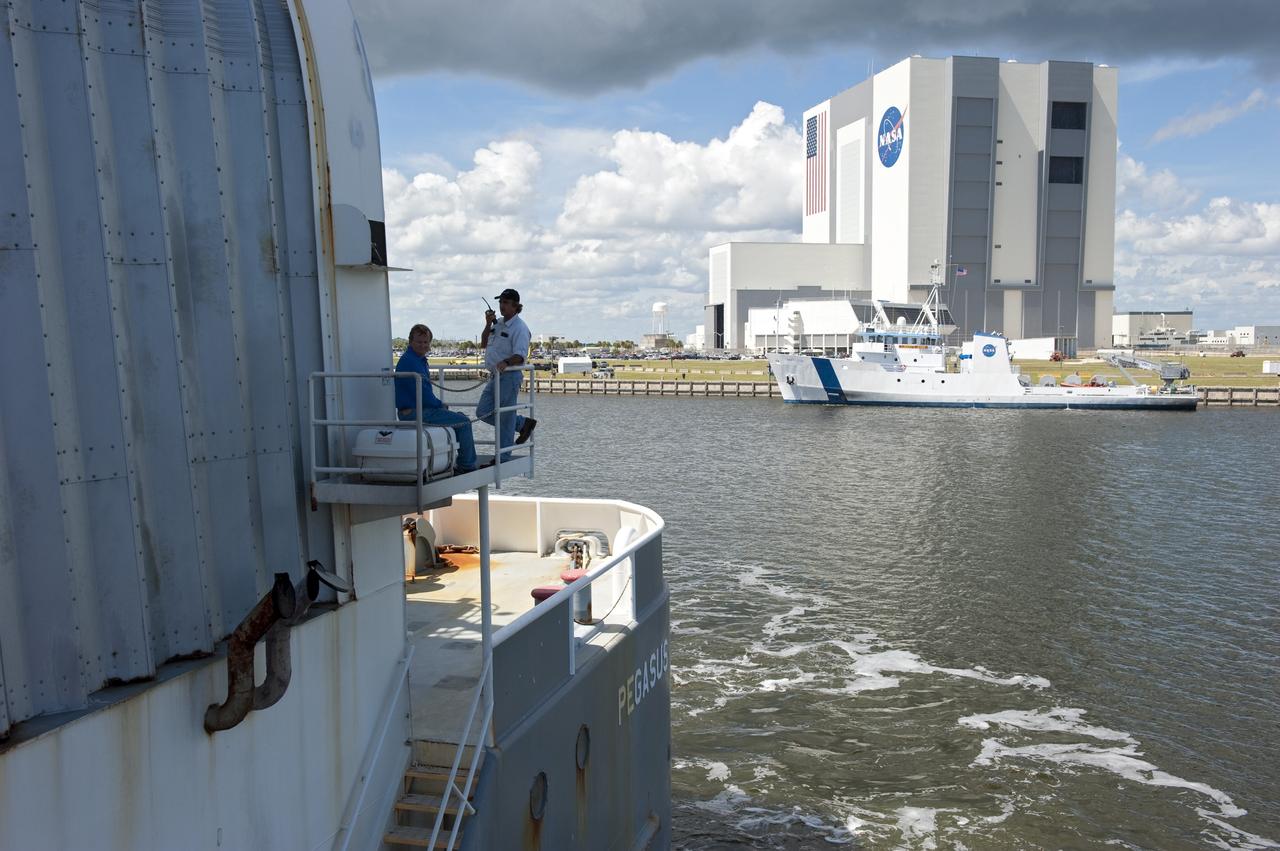

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Pegasus barge, carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, arrives at the Turn Basin of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
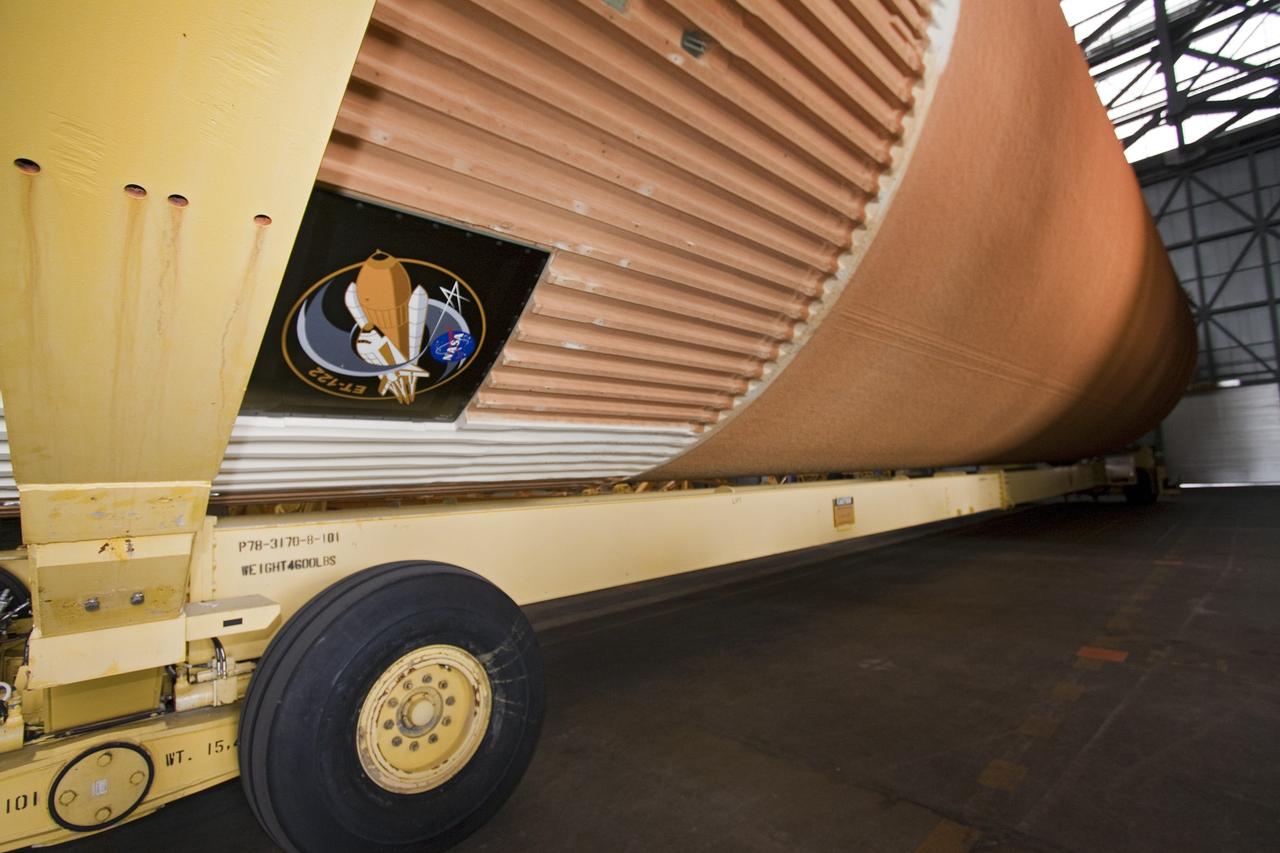

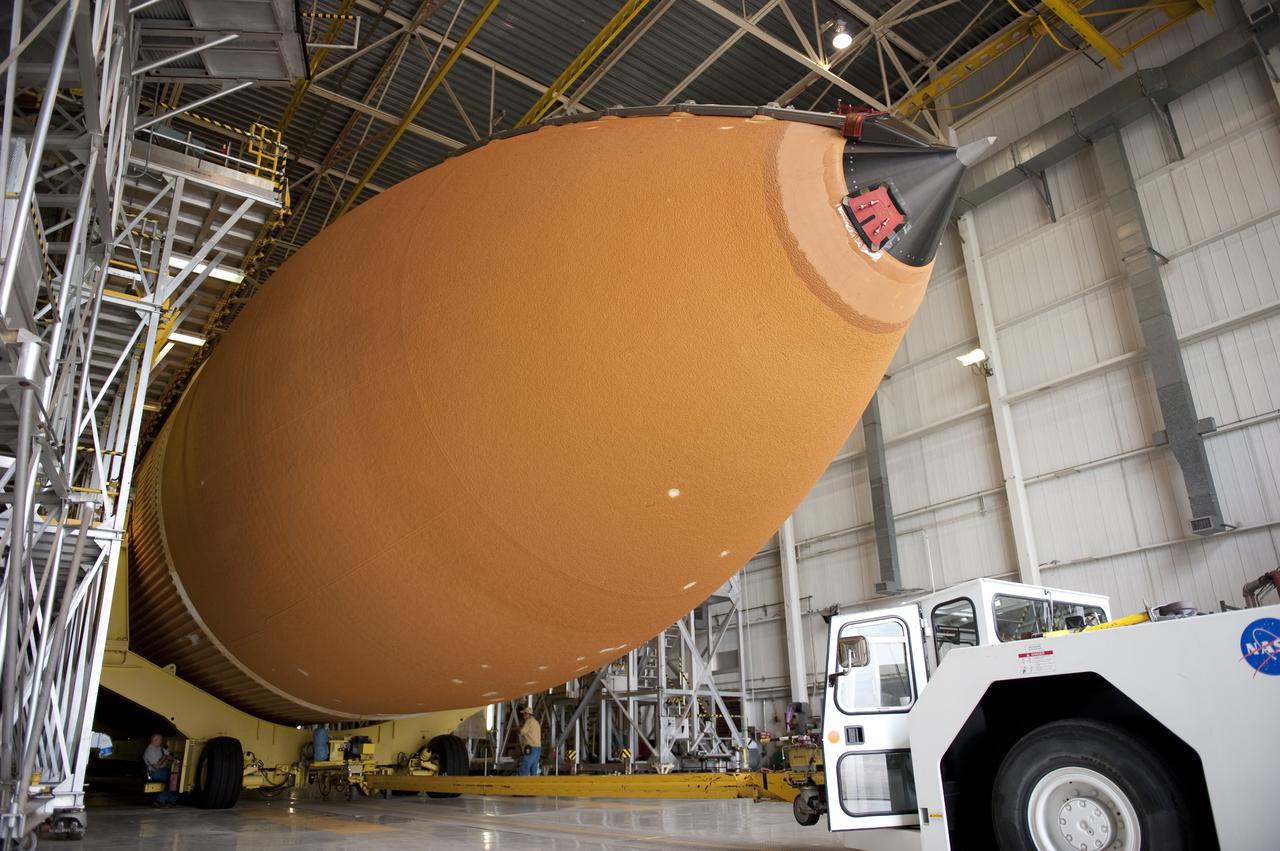
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- To commemorate the history of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, its intertank door is emblazoned with an ET-122 insignia. The tank is in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after traveling 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. It eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was completed in 2002, modified during Return to Flight operations in 2003 and 2004, damaged during Hurricane Katrina in 2005, and then restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees in 2008 at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
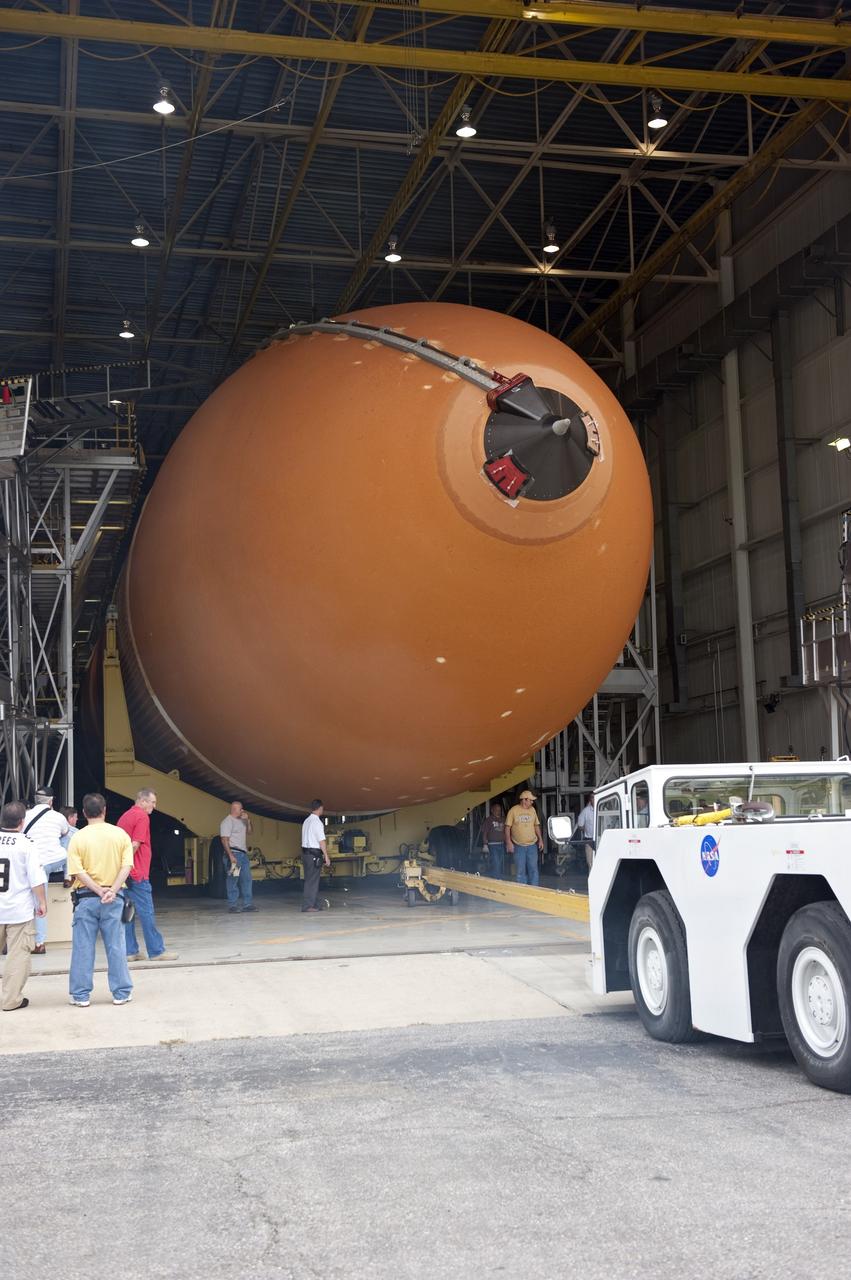

NEW ORLEANS -- Workers escort the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans for transportation to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea secured aboard the Pegasus Barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
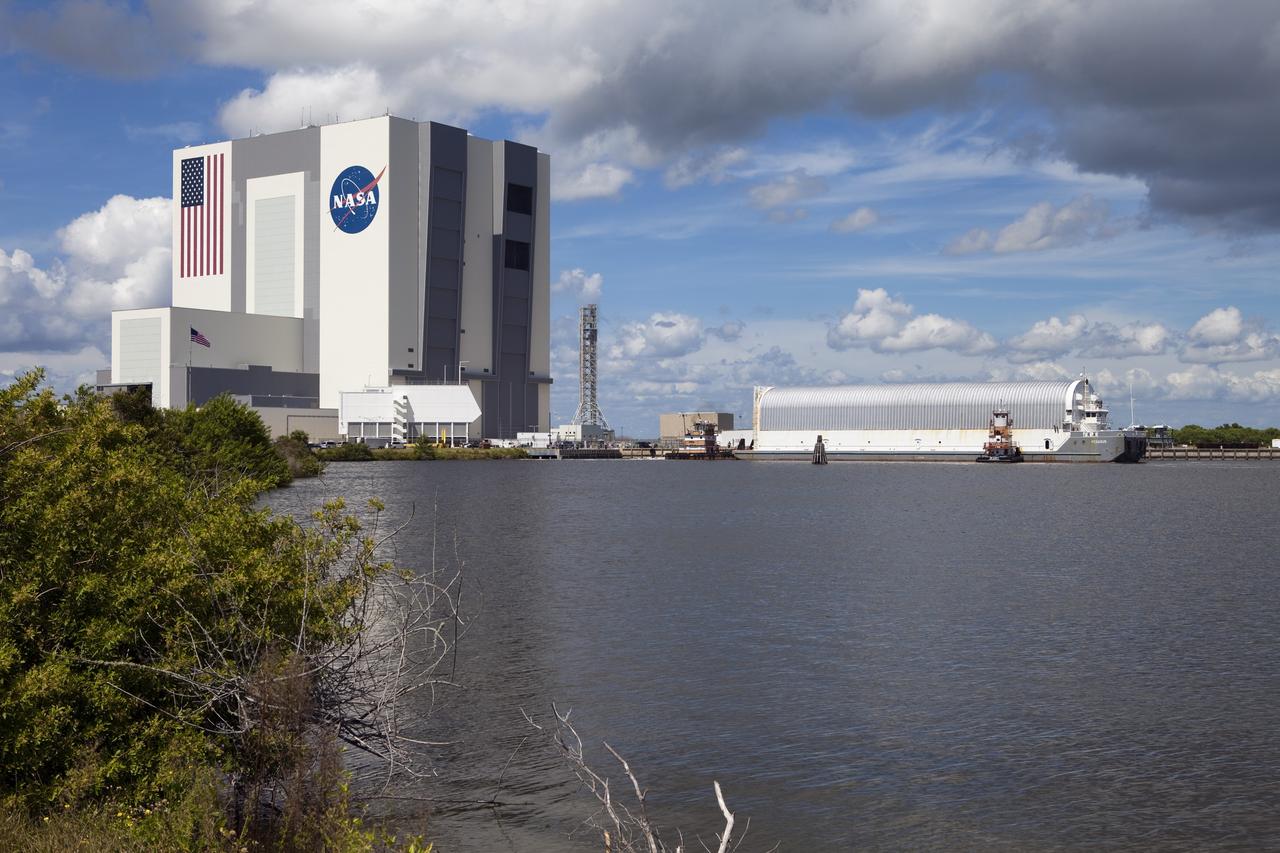

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Pegasus Barge, carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, arrives at the Turn Basin. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
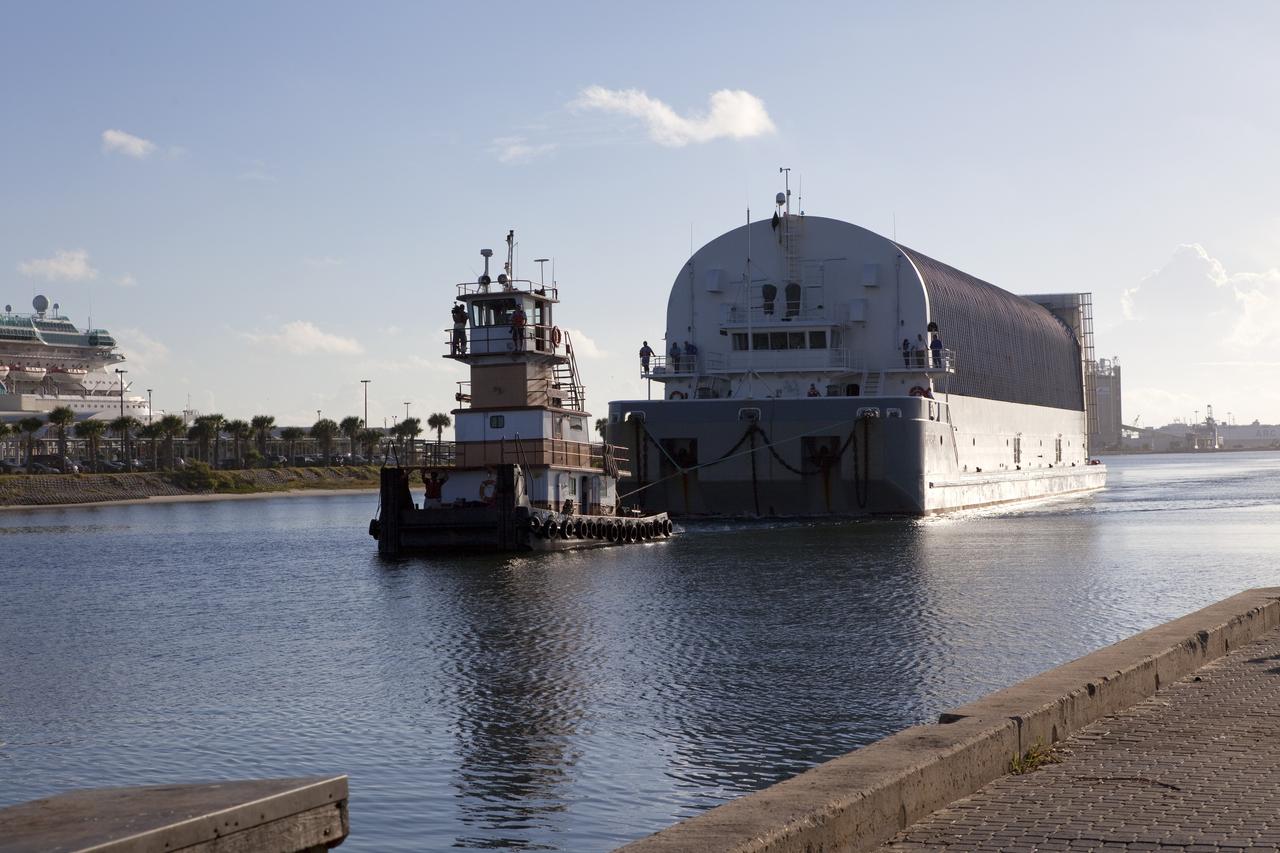

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tug boat pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb., 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
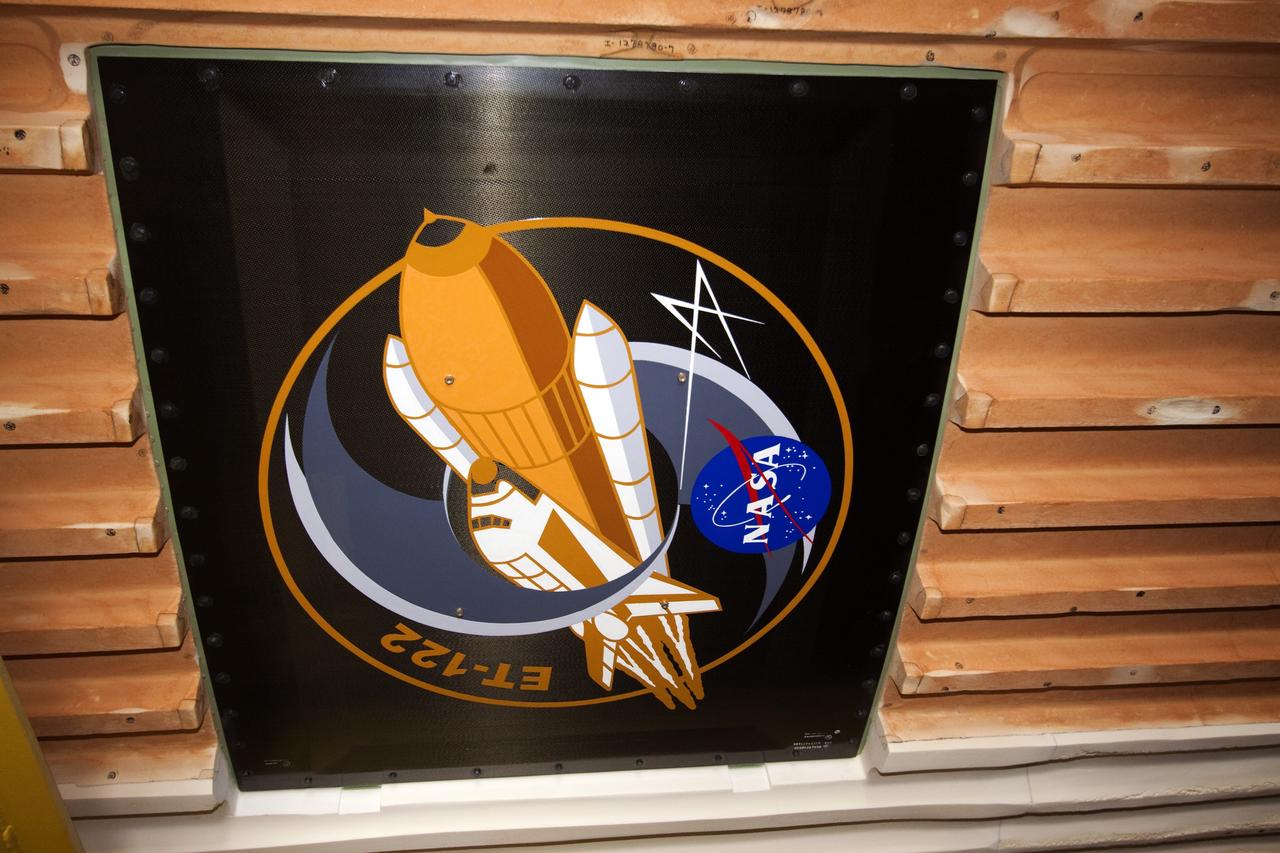

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- To commemorate the history of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, its intertank door is emblazoned with an ET-122 insignia. The tank is in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after traveling 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. It eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was completed in 2002, modified during Return to Flight operations in 2003 and 2004, damaged during Hurricane Katrina in 2005, and then restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees in 2008 at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
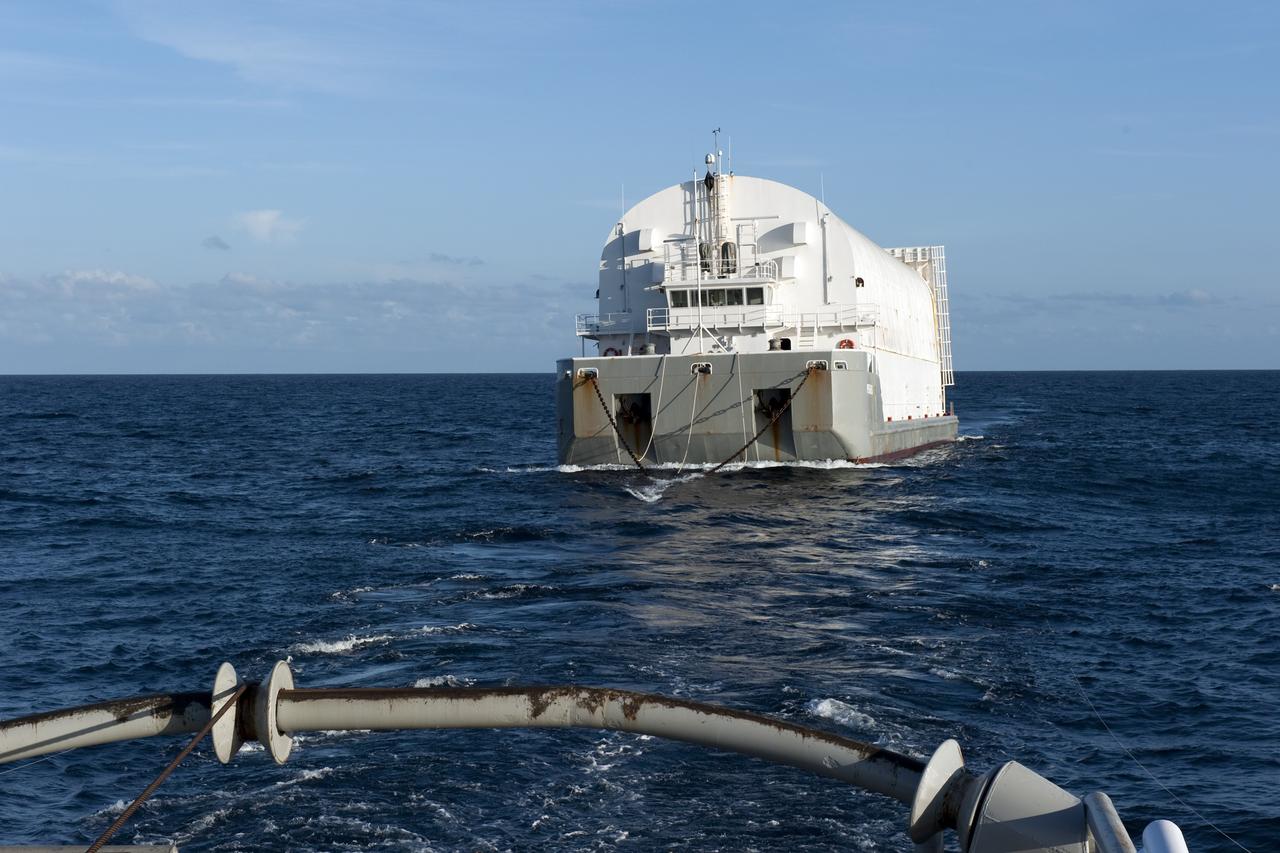

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This view from the stern of Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, shows the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
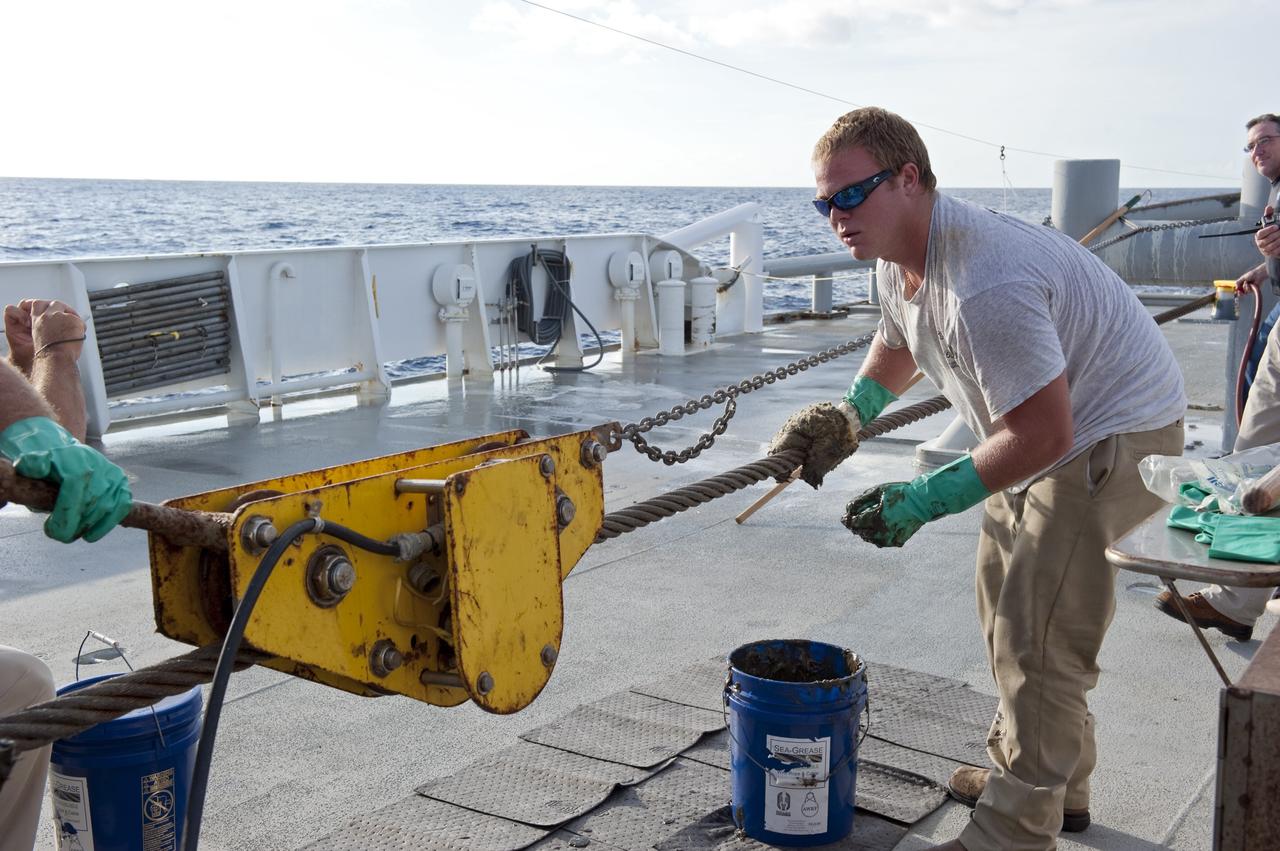

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Deckhands on Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, keep the ship in good repair as it pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
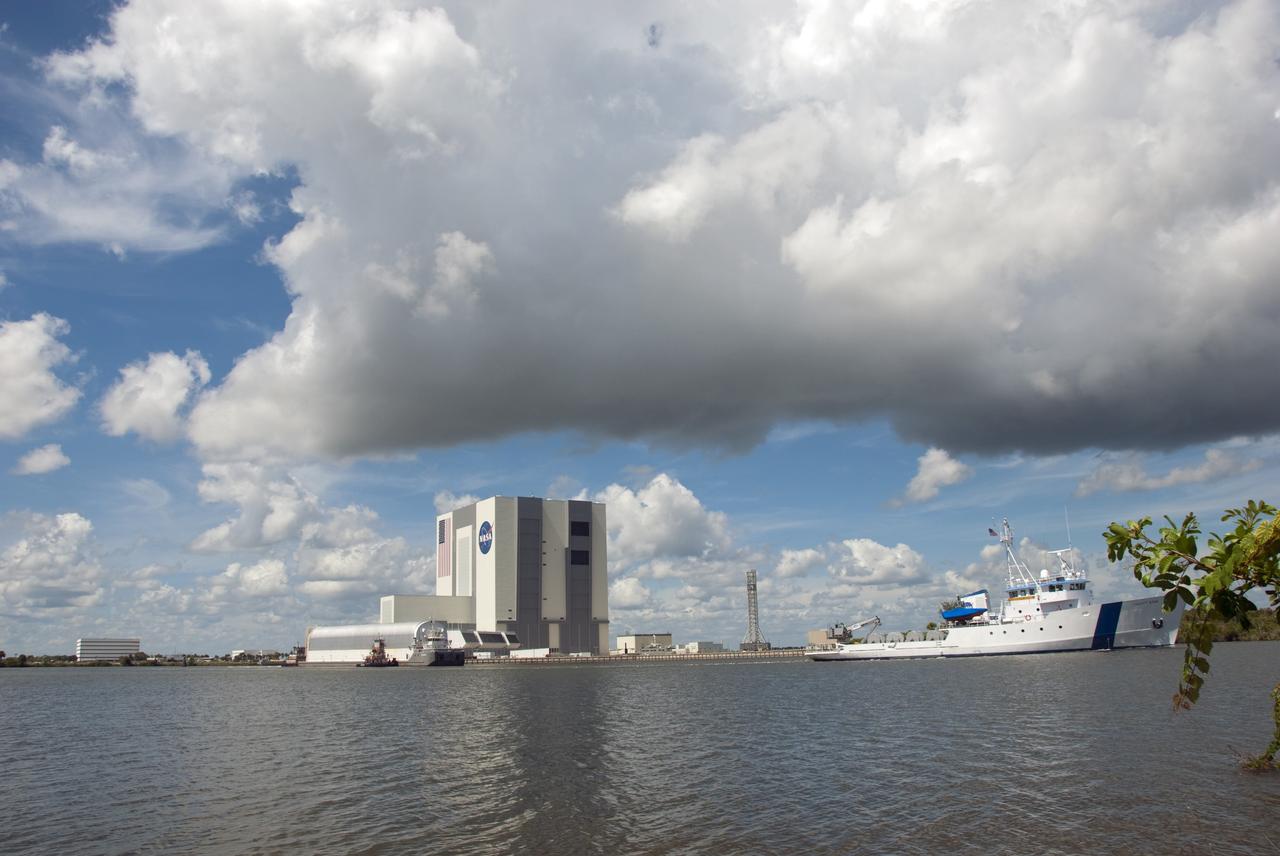

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Pegasus barge, which was ushered by two tug boats and Liberty Star, arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The barge is carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122 and traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
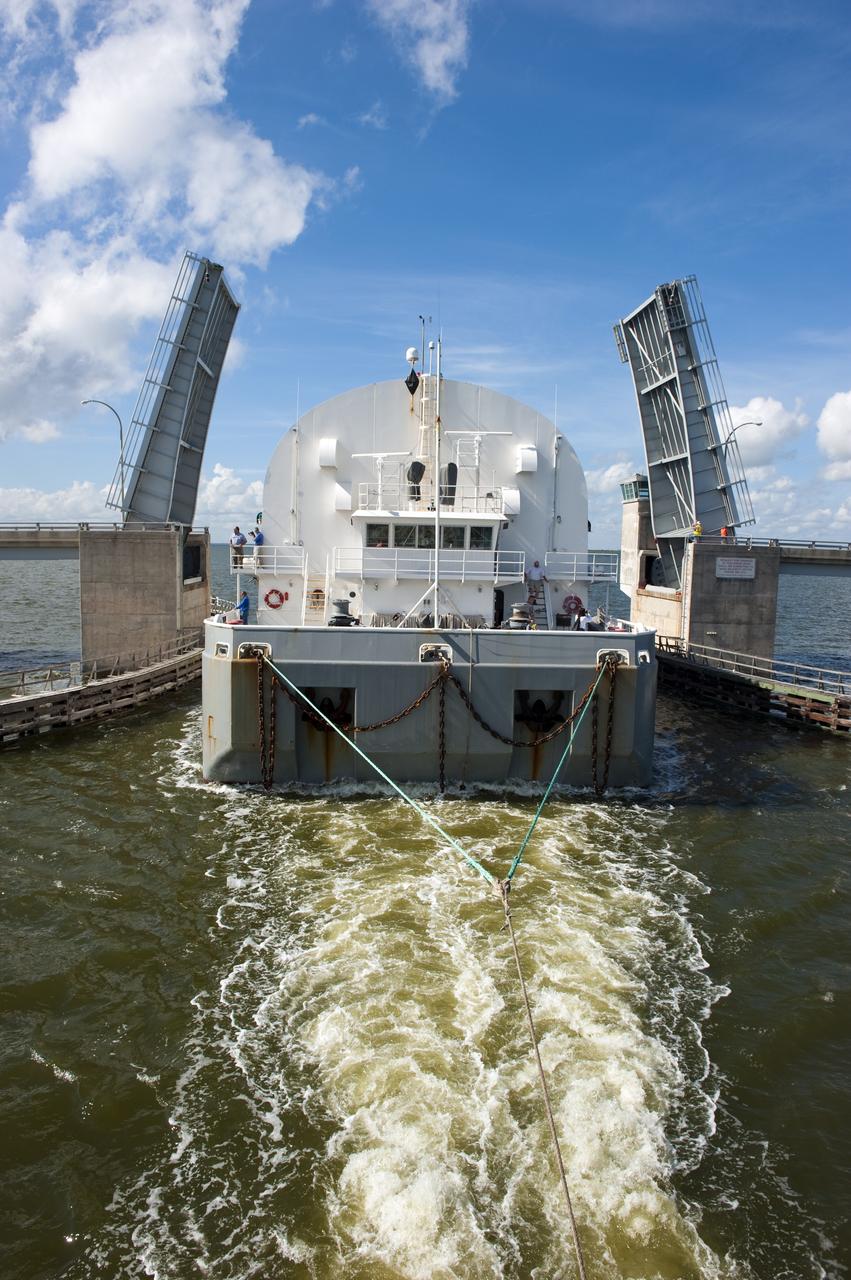

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Pegasus barge is pulled through the bridge at the NASA Causeway. The barge is carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

NEW ORLEANS -- Workers at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans prepare the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, for transportation to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea secured aboard the Pegasus Barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tug boat pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, to the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tug boat pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, to the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

NEW ORLEANS -- Workers at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans prepare the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, for transportation to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea secured aboard the Pegasus Barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
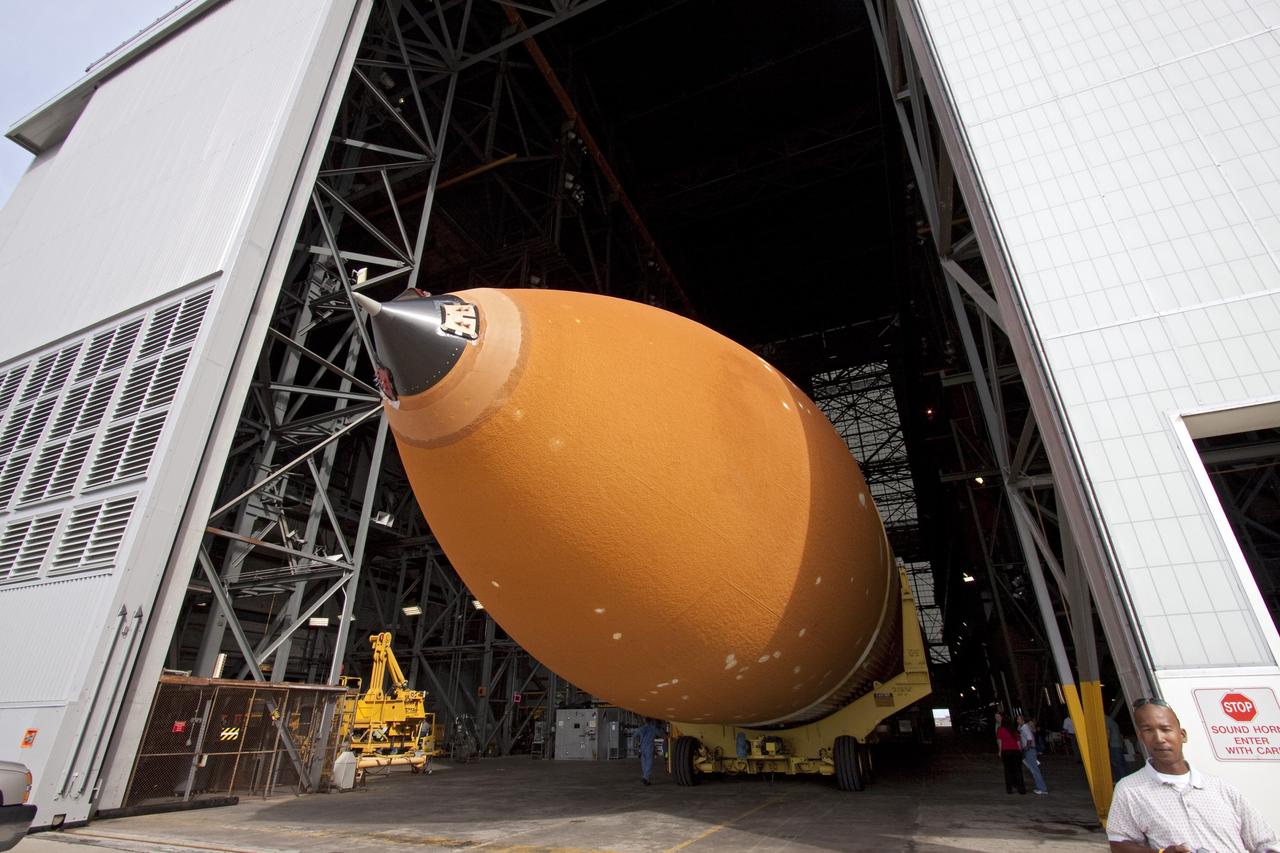

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, enters the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to Kennedy's Turn Basin aboard the Pegasus Barge. The tank eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
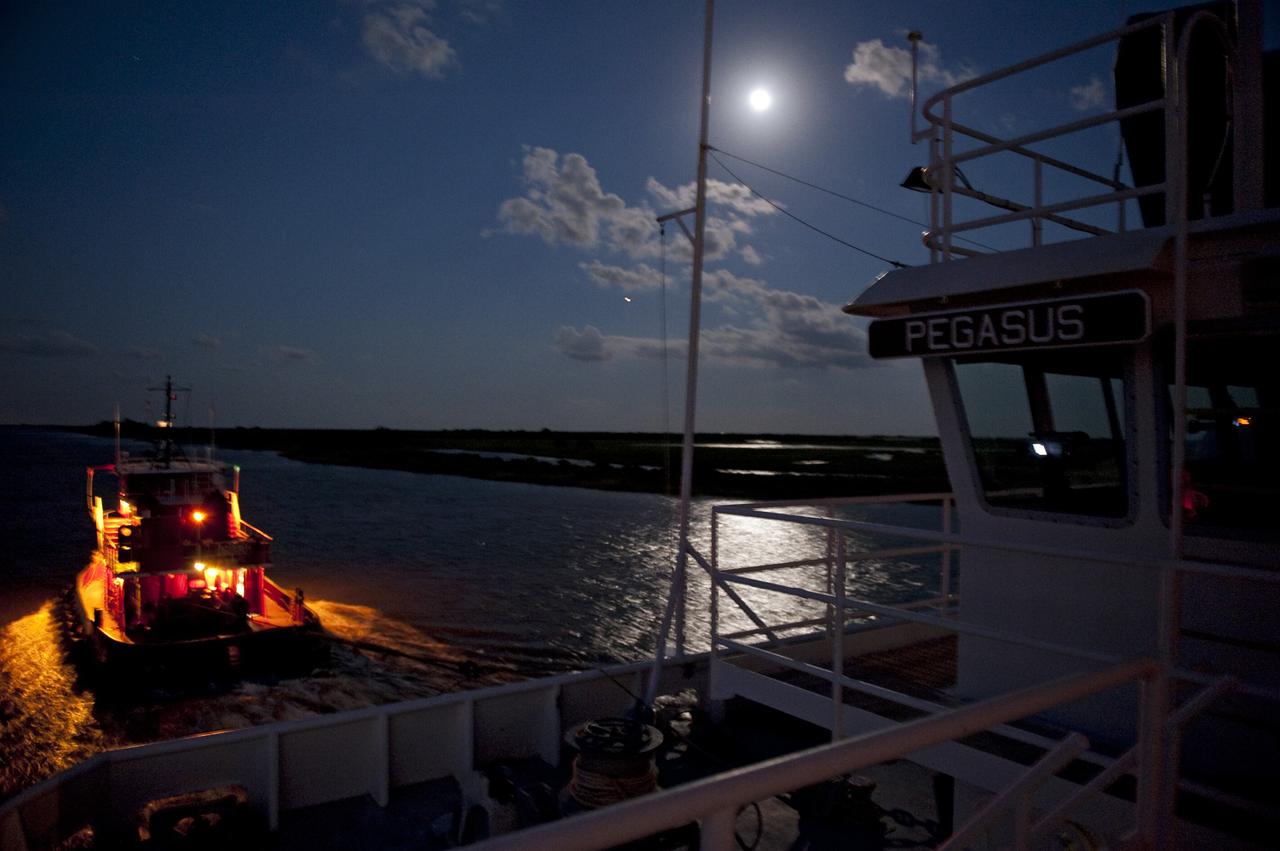

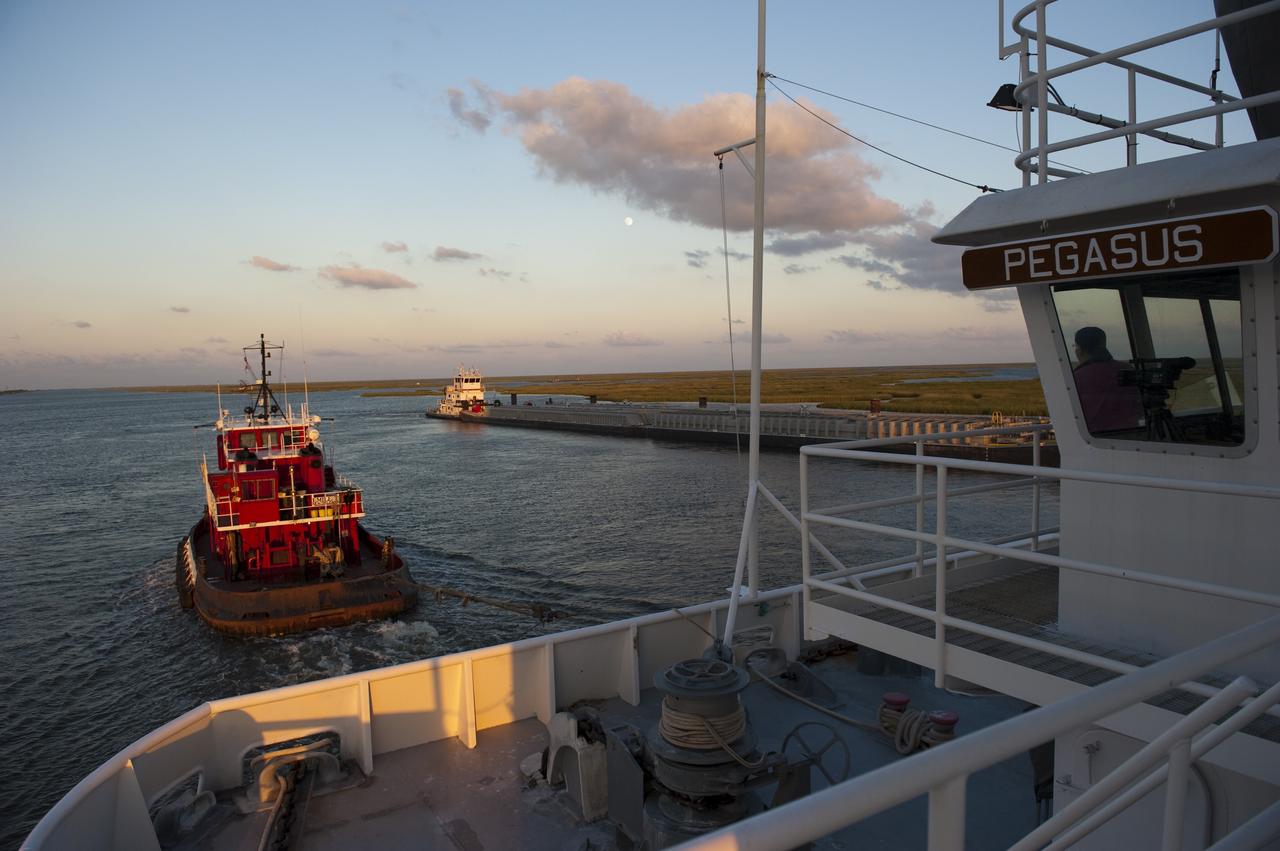
NEW ORLEANS -- As the moon lights up the water, as tug boat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved for Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
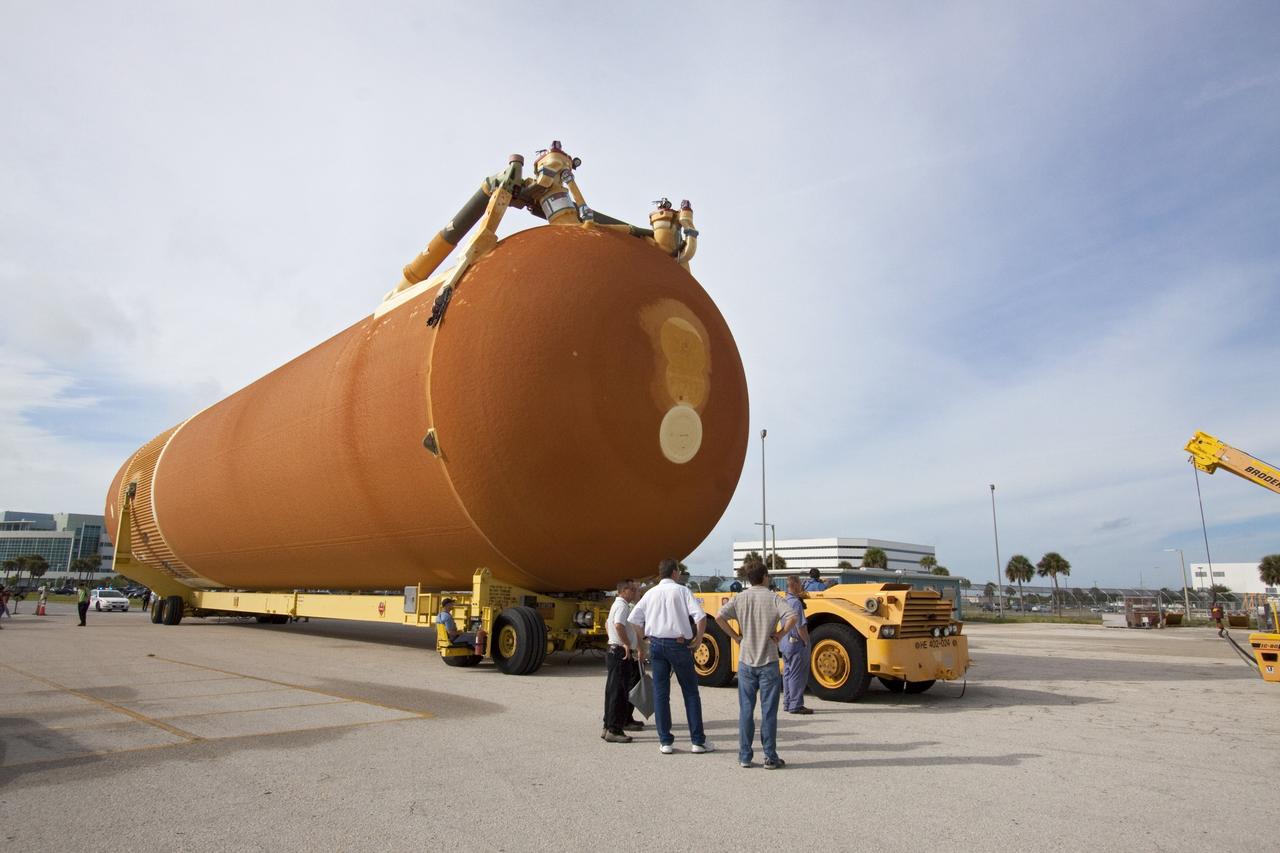

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, moves from the Turn Basin to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Once inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
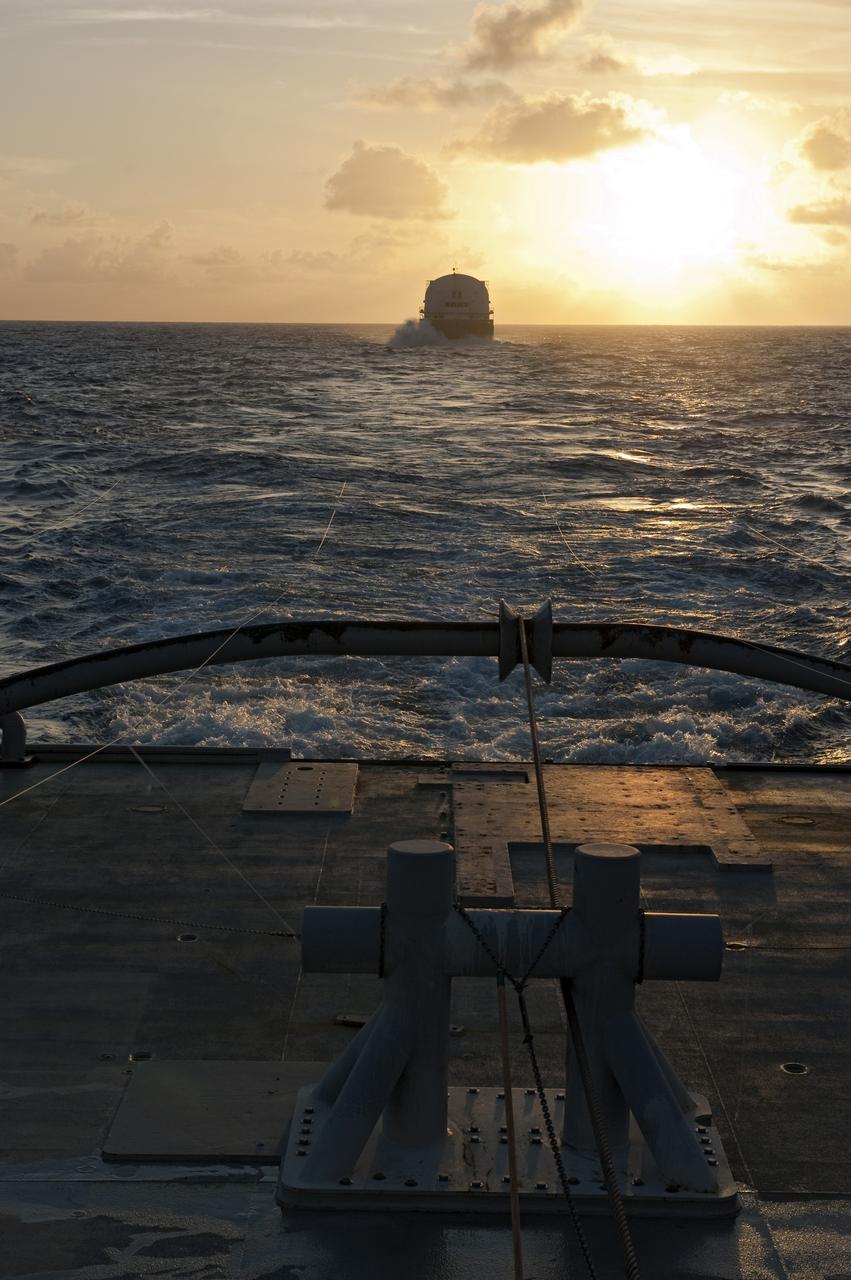

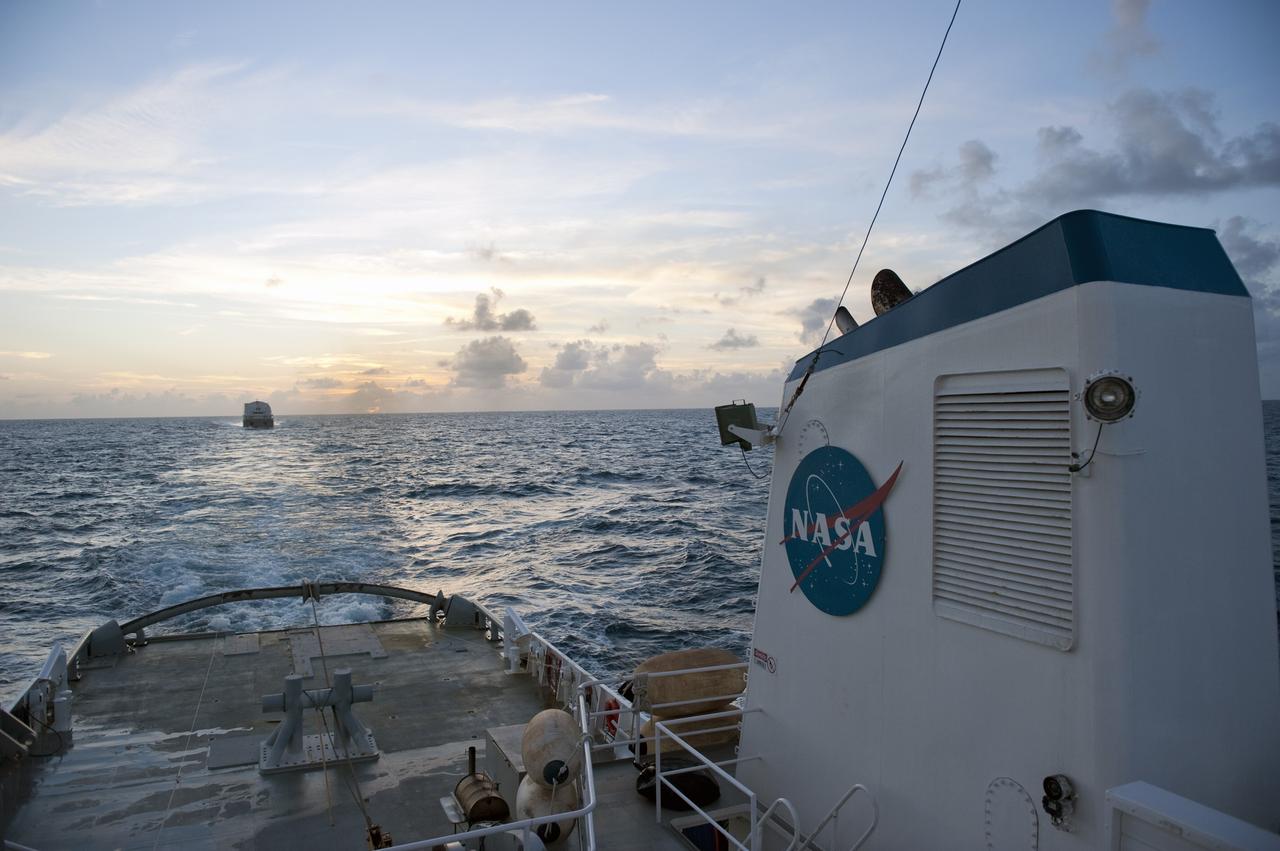
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This sunrise view from the stern of Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, shows the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Pegasus Barge, carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, nears NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
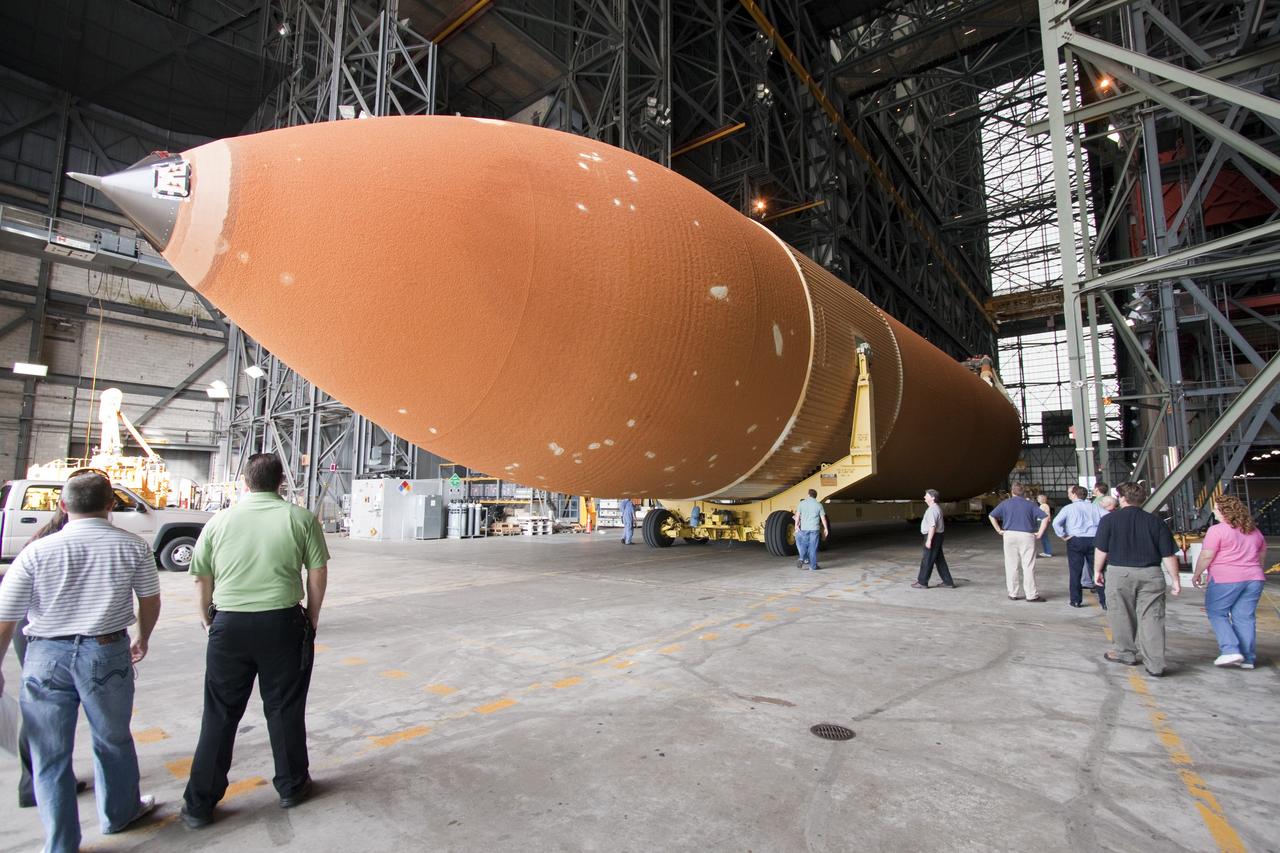

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, moves into the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to Kennedy's Turn Basin aboard the Pegasus Barge. The tank eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
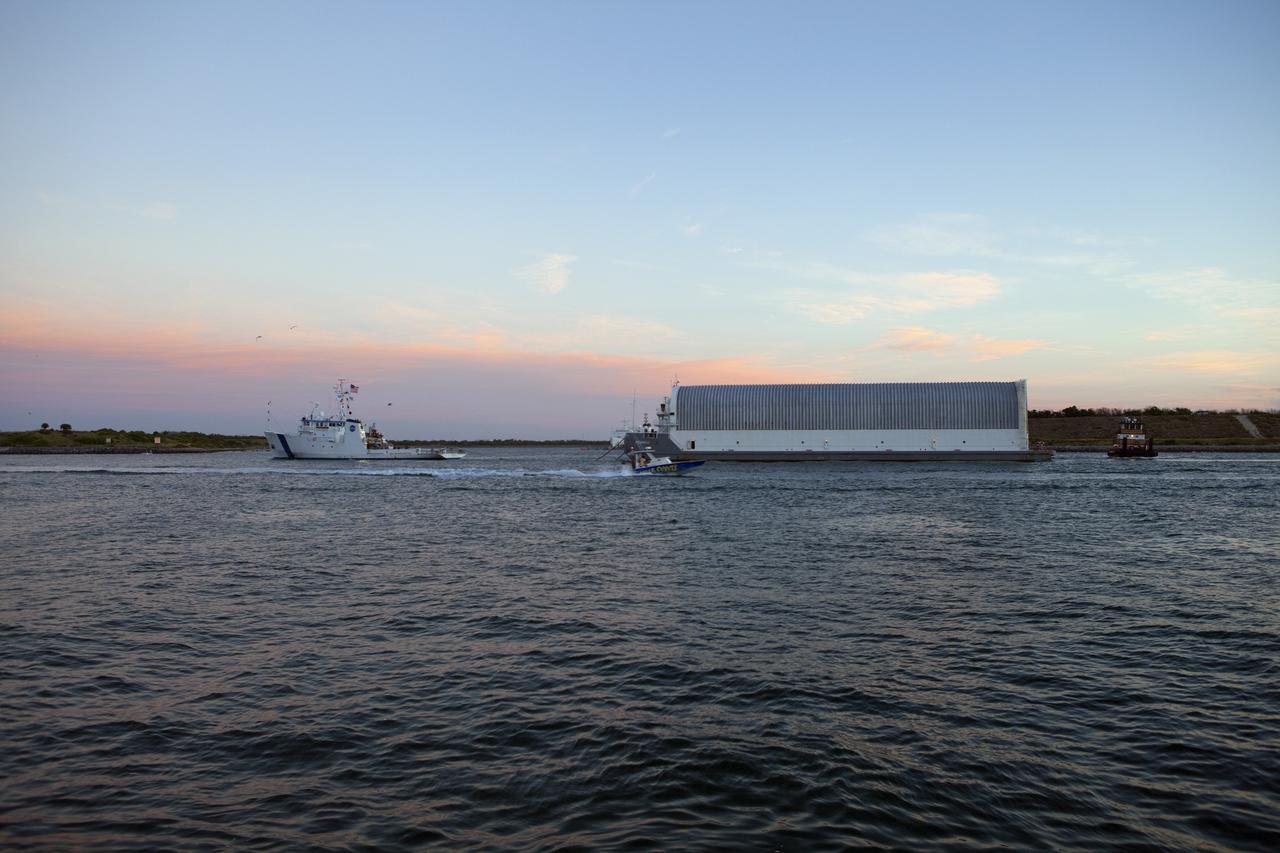

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, ushers the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
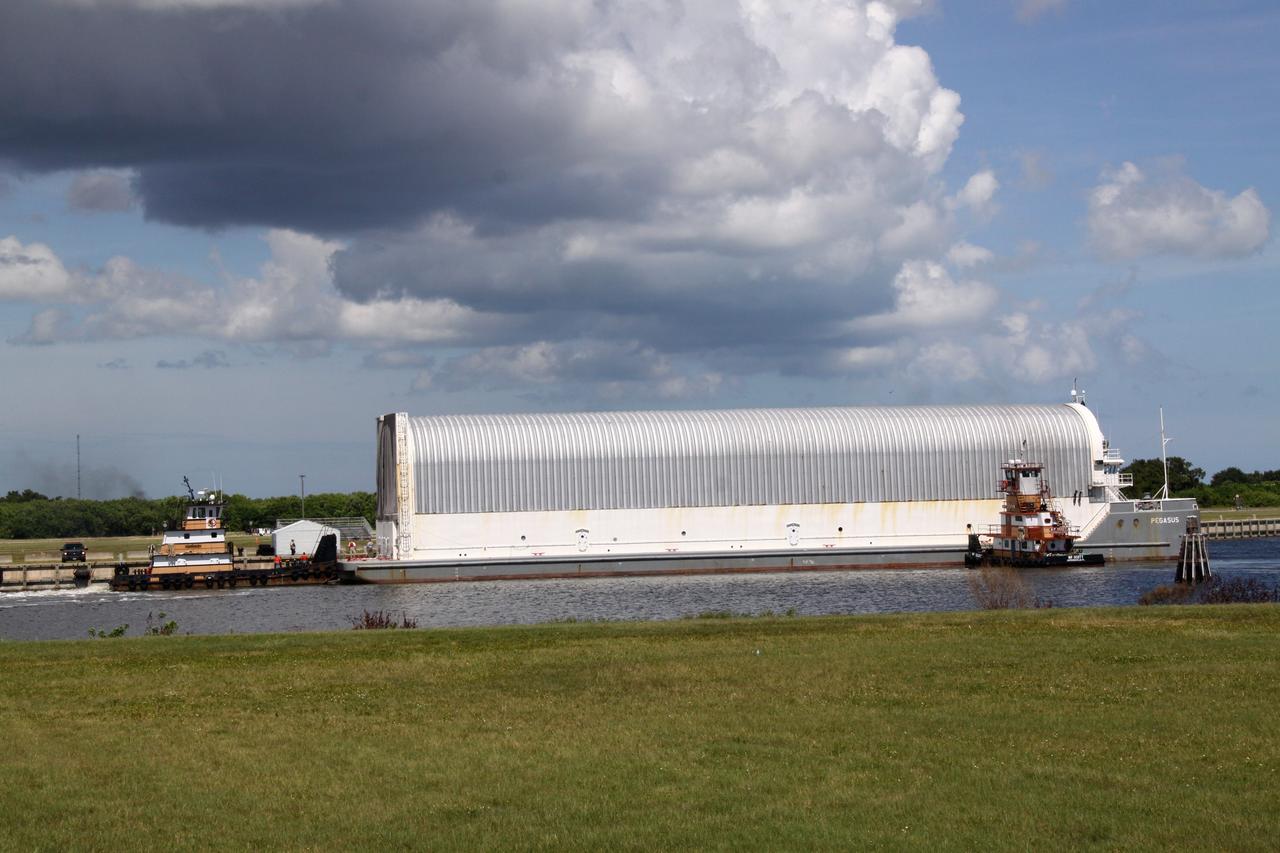

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, arrives at the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
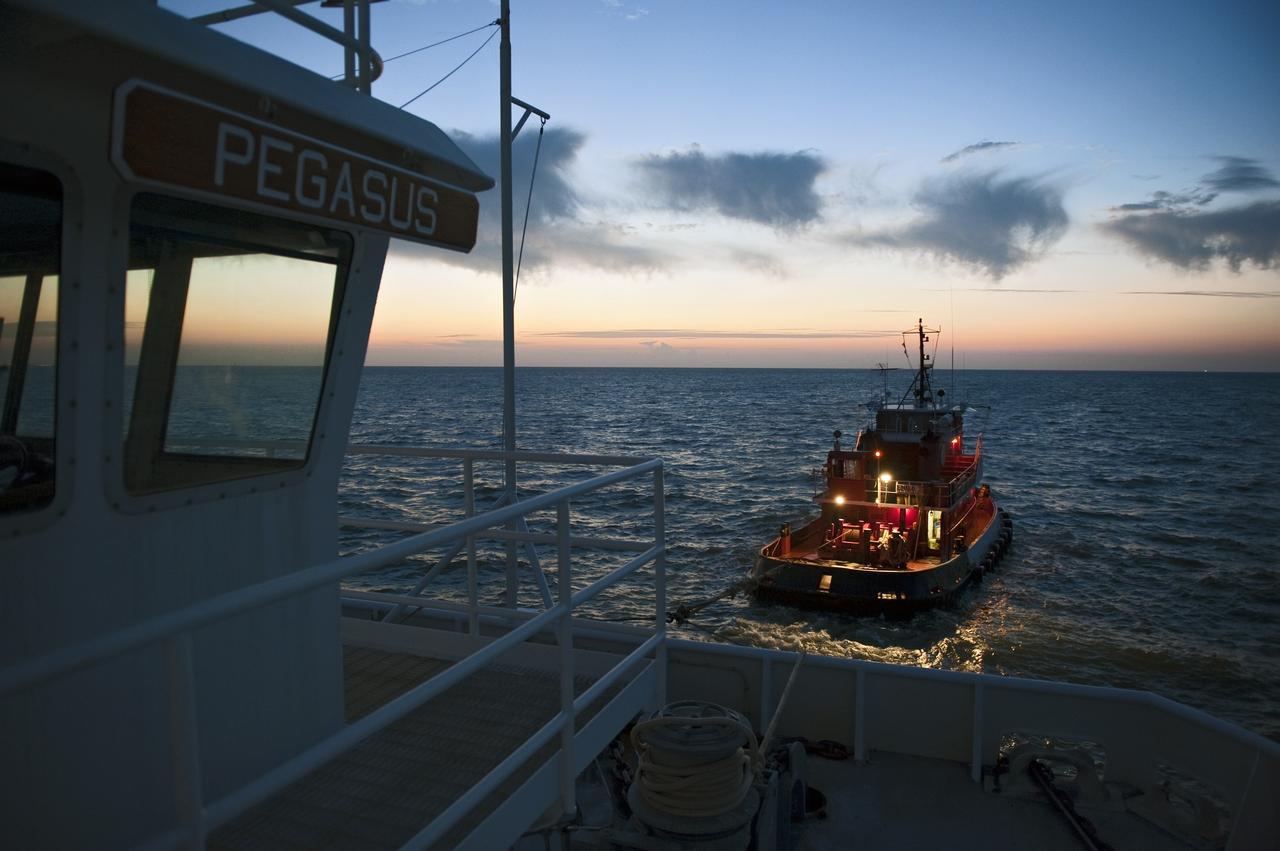

LOUISIANA -- A tug boat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans toward Gulfport, La. The barge will meet up with Freedom Star, NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ship, which will escort it to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
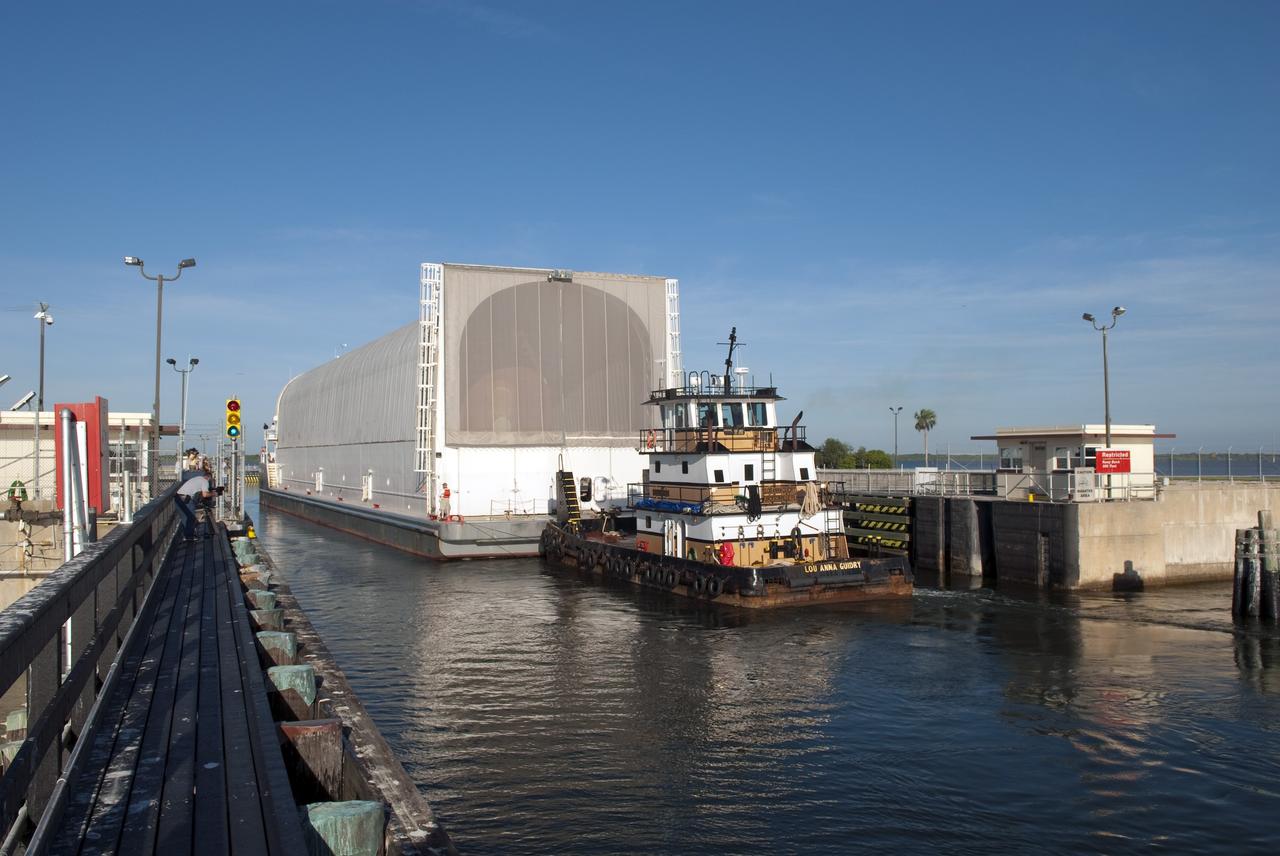

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tugboat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tug boat pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, to the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
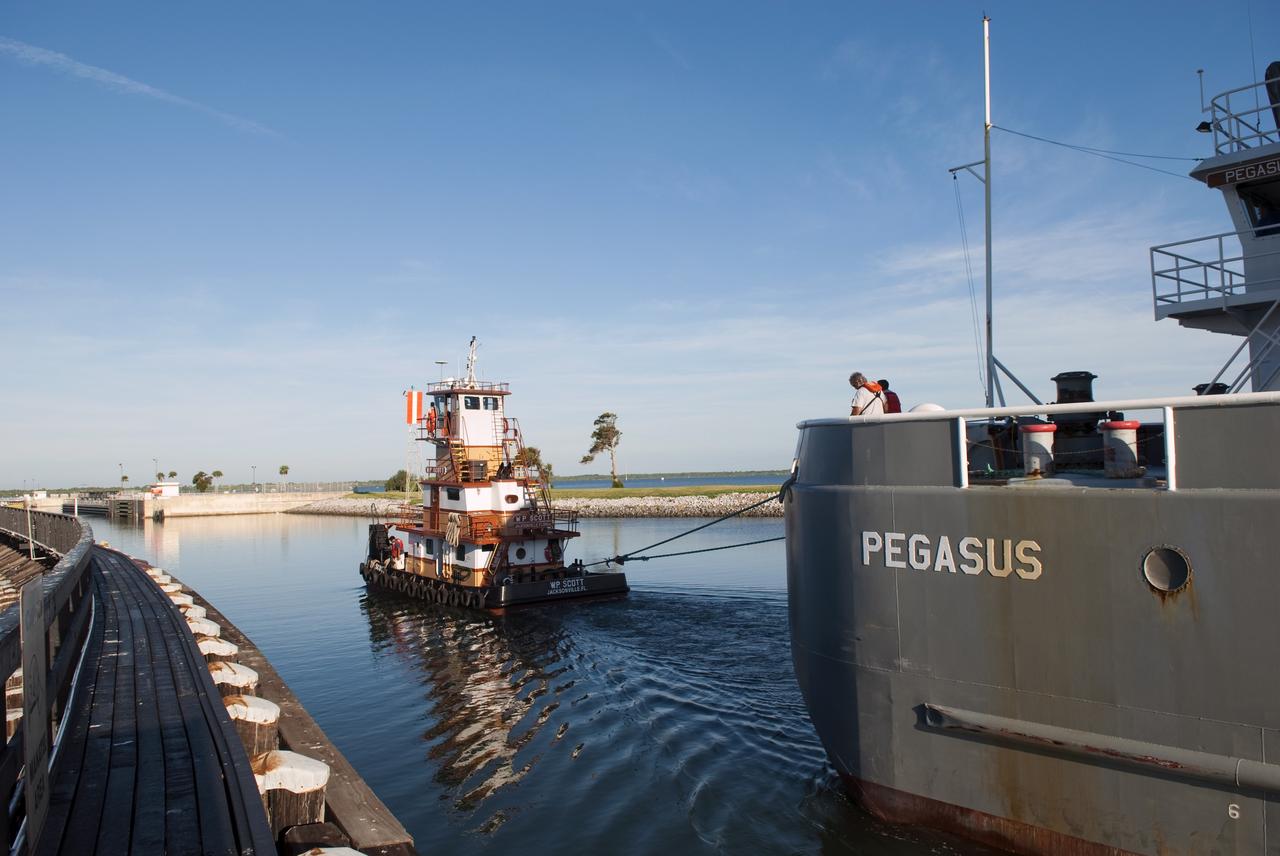

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tugboat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
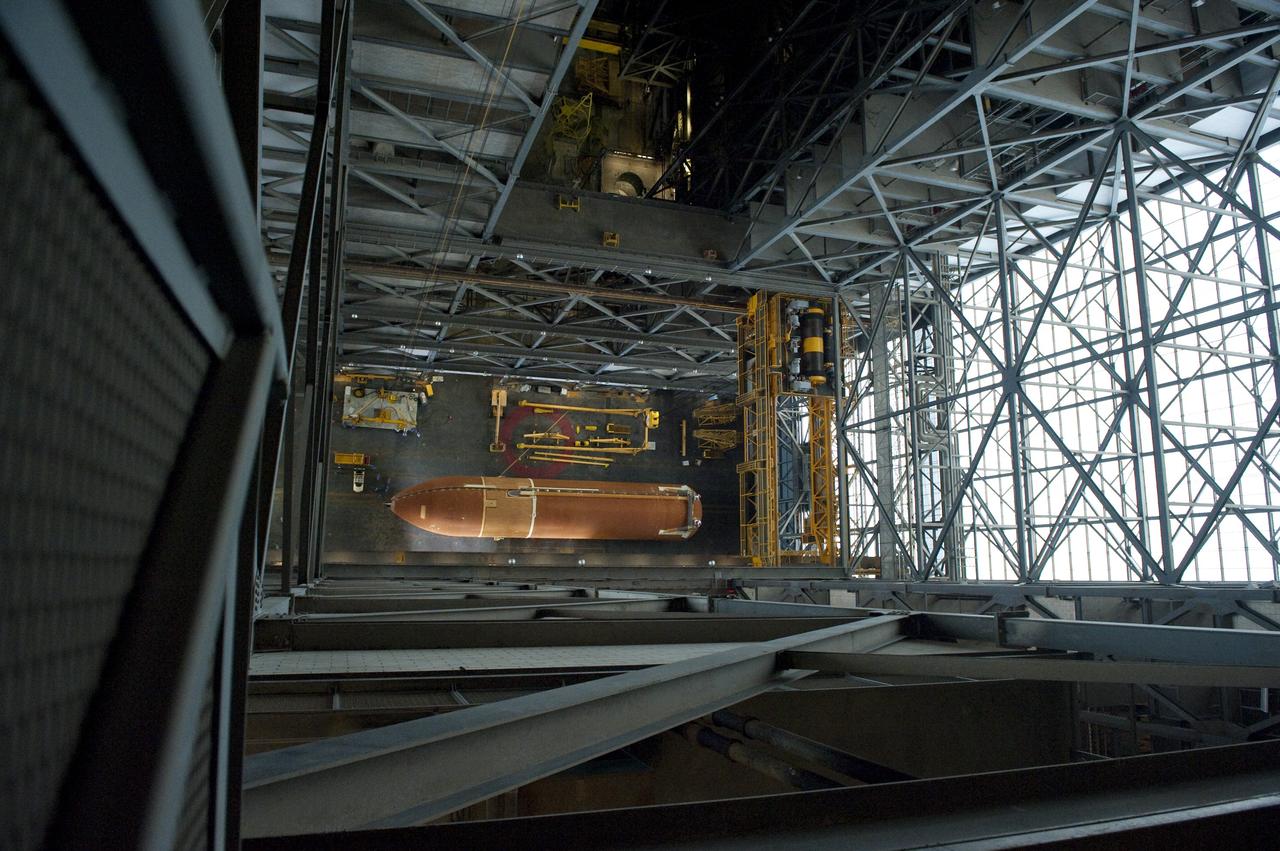

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, this overhead image shows the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, after it was delivered to the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The tank traveled 900 miles by sea, carried in the Pegasus Barge, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Once inside the VAB, it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch Feb. 2011. STS-134 currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell