
William J. O Sullivan at desk with folded subsatellite, 30 inch subsatellite, 12 foot subsatellite, and corner reflector.

William J. O Sullivan at desk with folded subsatellite, 30 inch subsatellite, 12 foot subsatellite, and corner reflector.
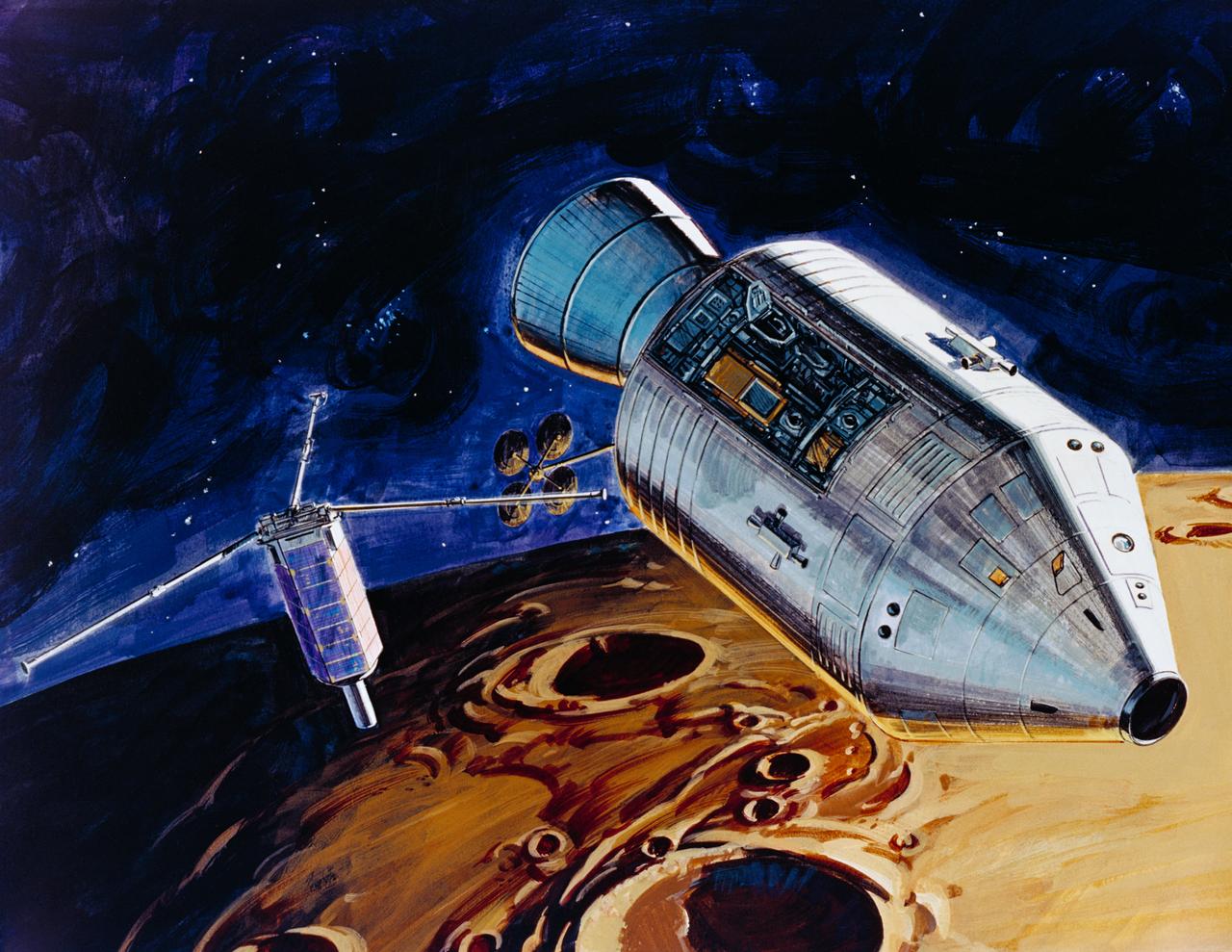

S71-39481 (July 1971) --- An artist's concept showing TRW's small lunar subsatellite being ejected into lunar orbit from the SIM bay of the Apollo 15 Service Module. The 80-pound satellite will remain in orbit a year or more, carrying scientific experiments to study space in the vicinity of the moon. The satellite carries three experiments: S-Band Transponder; Particle Shadows/Boundary Layer Experiment; and Subsatellite Magnetometer Experiment. The subsatellite is housed in a container resembling a rural mailbox, and when deployed is spring-ejected out-of-plane at 4 fps with a spin rate of 140 rpm. After the satellite booms are deployed, the spin rate is stabilized at about 12 rpm. The subsatellite is 31 inches long and has a 14 inch hexagonal diameter. The exact weight is 78.5 pounds. The folded booms deploy to a length of five feet. Subsatellite electrical power is supplied by a solar cell array outputting 25 watts for dayside operation and a rechargeable silver-cadmium battery for nightside passes.

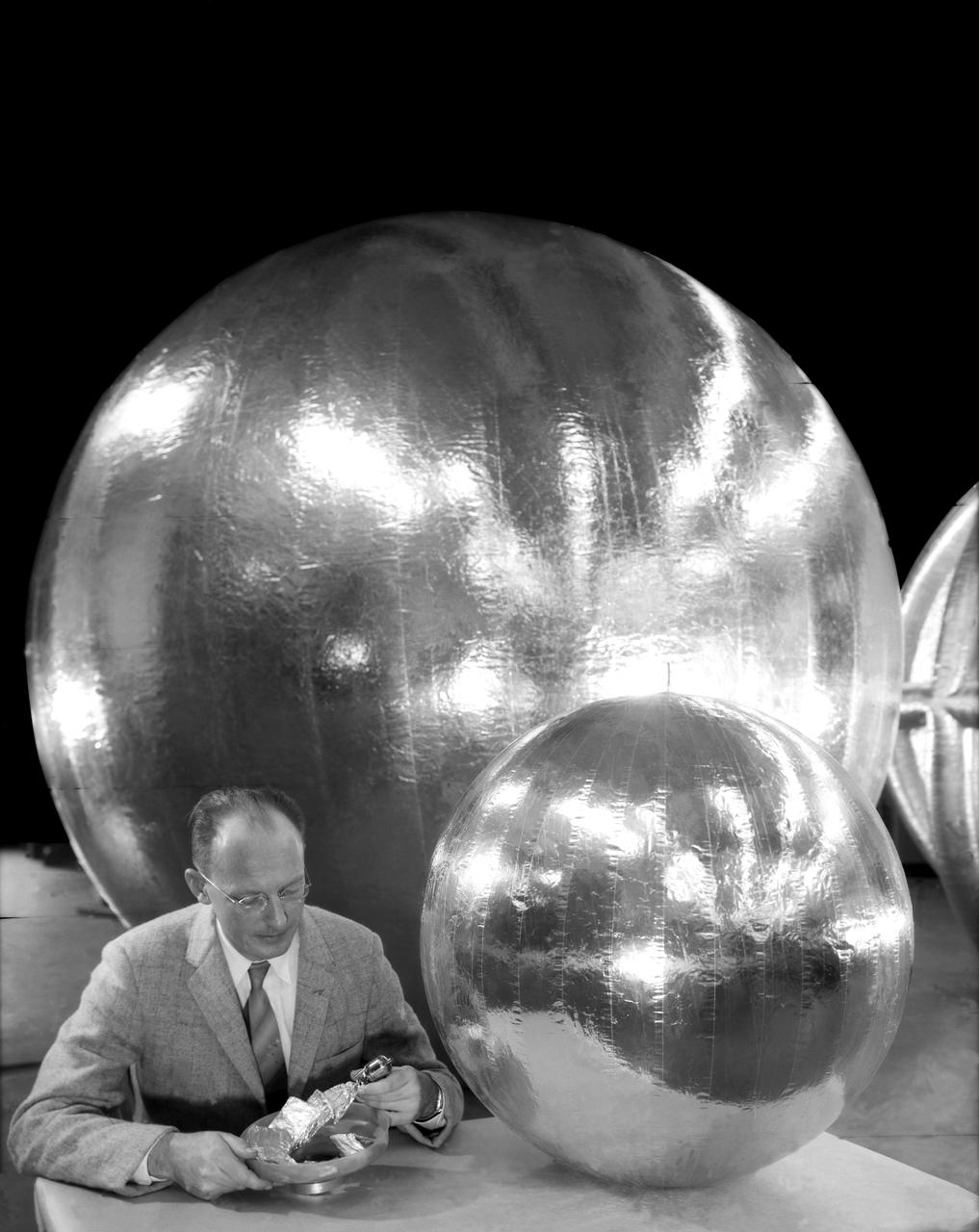
Engineer W.J. O Sullivan, Jr., seated beside 30 inch subsatellite. He holds inflation bottle and folded duplicate copy, July 1957.

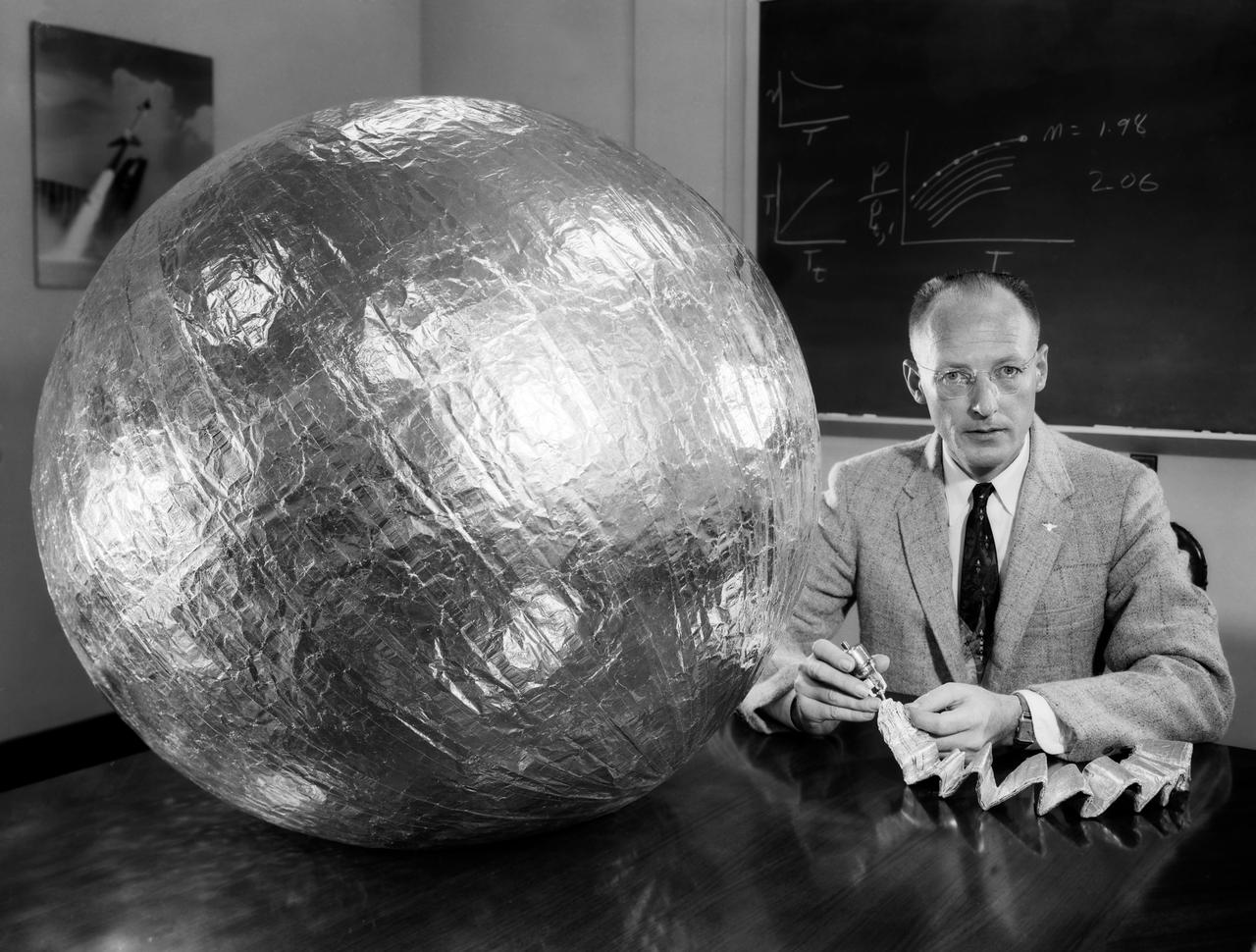
L57-525 Engineer W.J. O Sullivan, Jr., looks at inflated 20 inch subsatellite while holding inflation bottle and folded duplicate copy, February 1957. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 601.
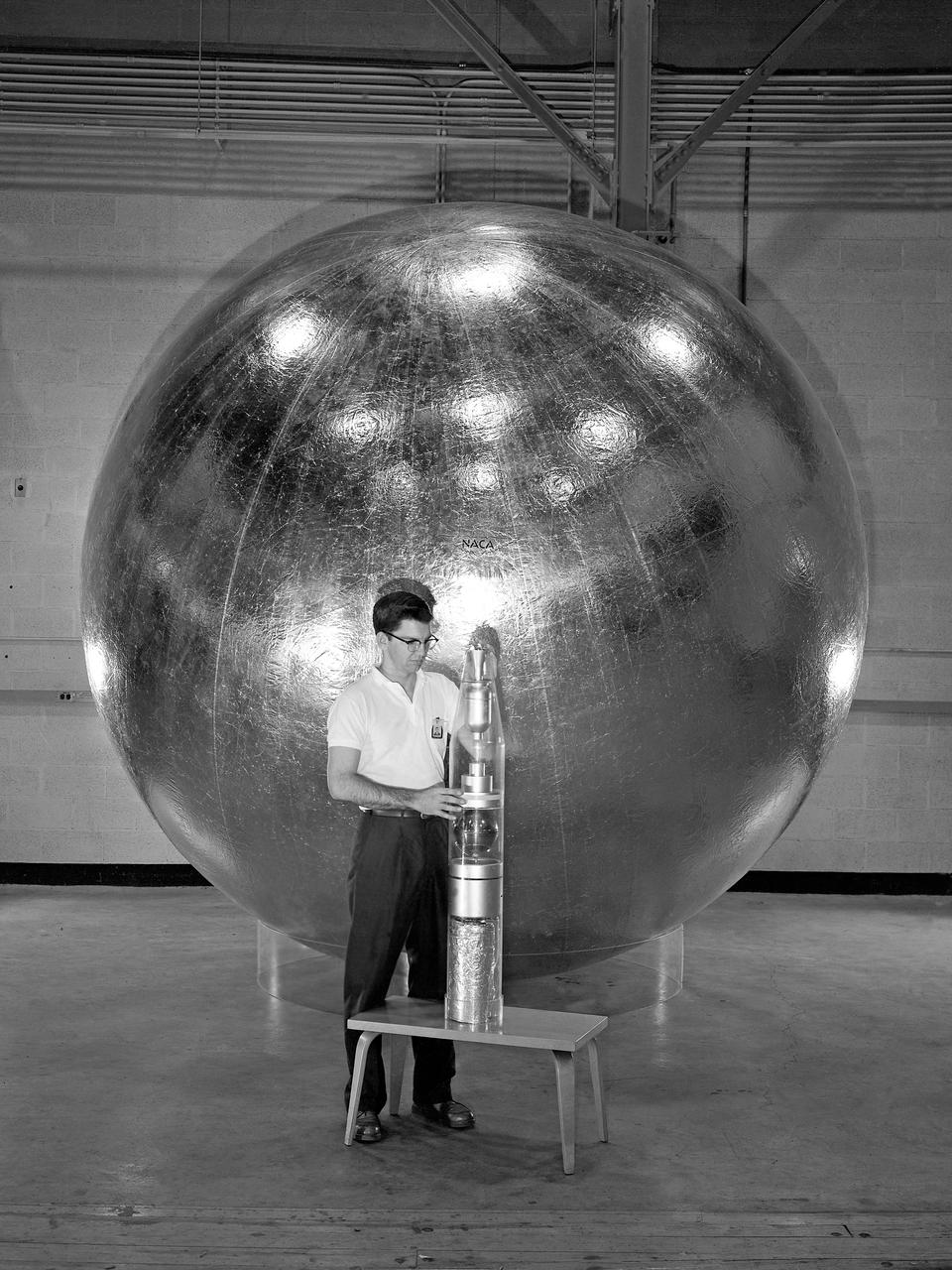

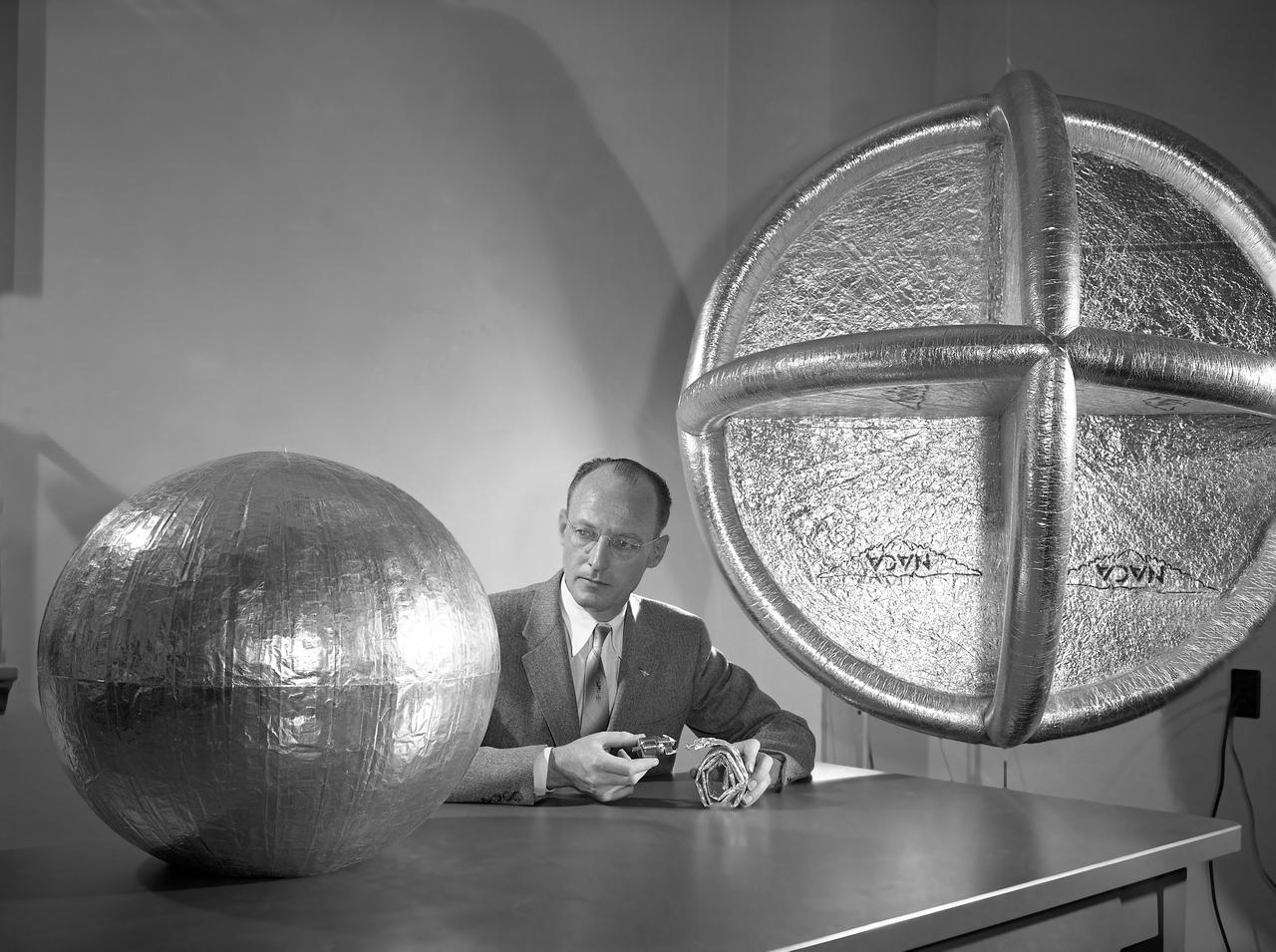
Engineer and 12 foot Beacon showing NACA emblem on inflated satelloon . For related information see, Spaceflight Revolution, NASA from Sputnik to Apollo, by James R. Hansen. NASA SP-4308, 1995. p. 173.
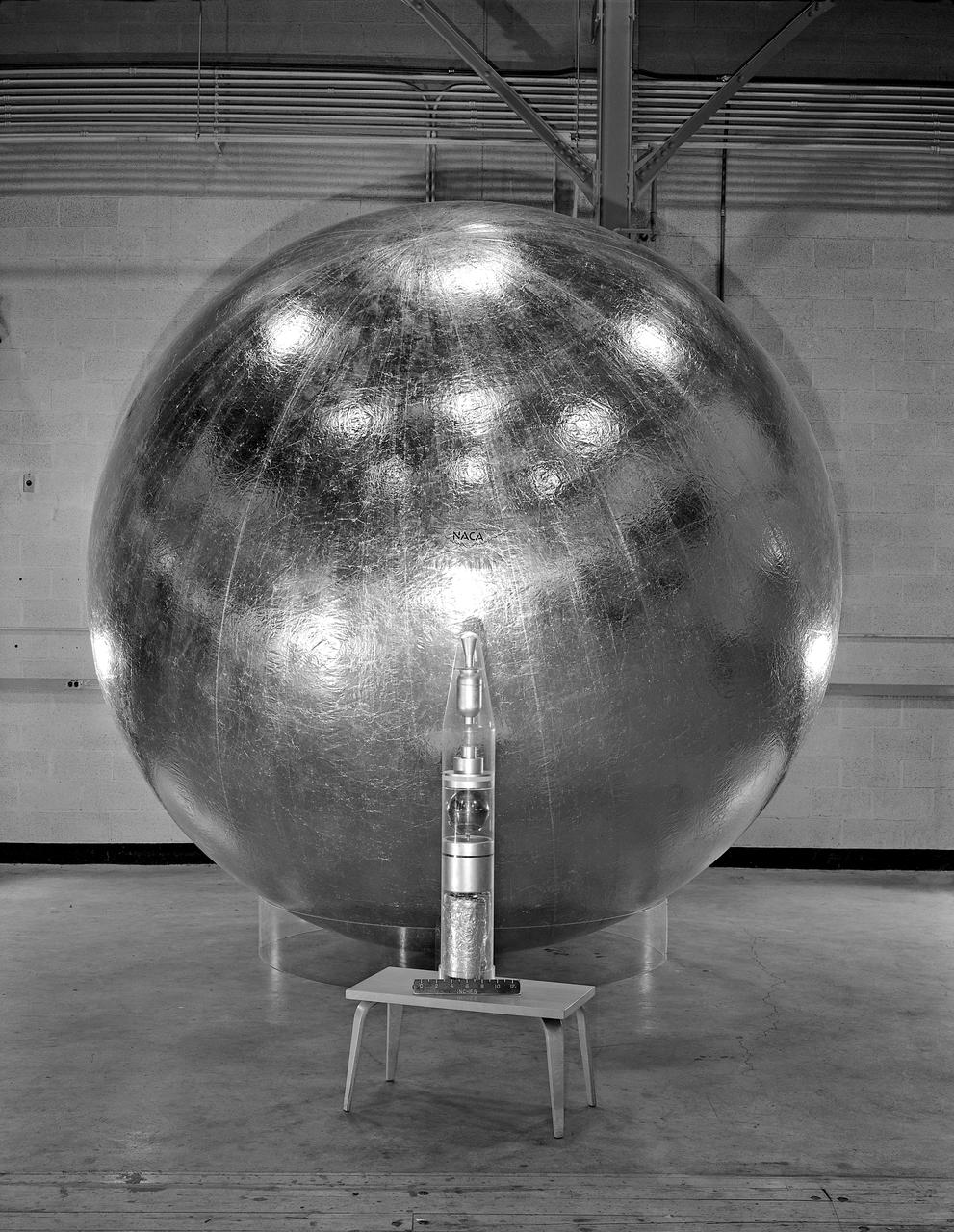

Engineer and 12 foot Beacon showing NACA emblem on inflated satelloon . For related information see, Spaceflight Revolution, NASA from Sputnik to Apollo, by James R. Hansen. NASA SP-4308, 1995. p. 173.
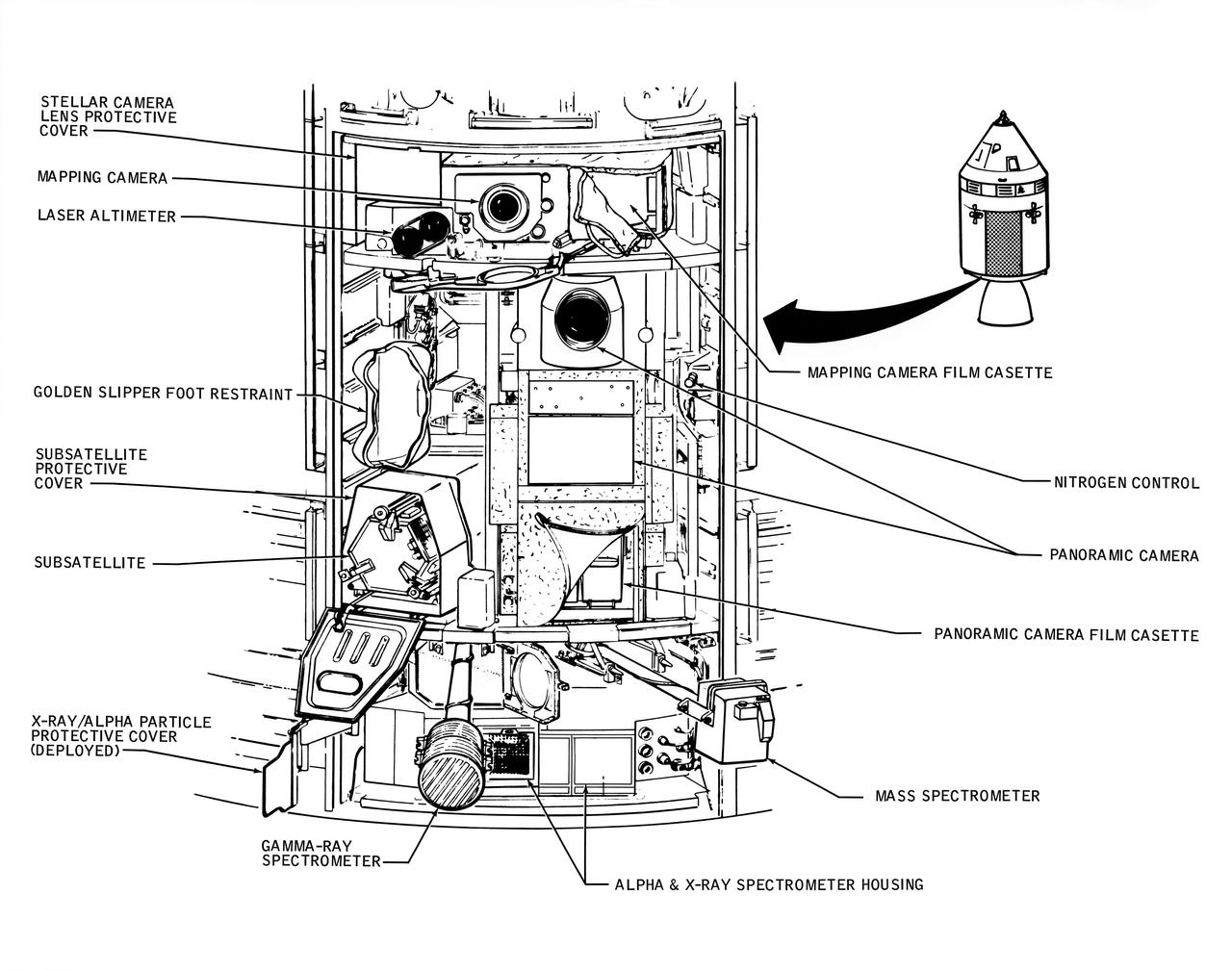
A line drawing illustrating the layout of the Scietific Instrument Module (SIM) of the Apollo 16 Service Module. Shown here is the location in the SIM bay of the equipment for each orbital experiment. Arrows point to various components of the SIM bay. The sensors for the gamma ray spectrometer and the mas spectrometer both extend outward on a boom about 25 feet when the instruments are in use. The subsatellite is launched while the Service Module is in orbit around the moon. The film cassettes must be retrieved prior to Command Module/Service Module separation.

S71-22401 (March 1971) --- These three astronauts have been named by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as the prime crew members of the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission. They are, left to right, David R. Scott, commander; Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. The crew is posed behind the subsatellite that they will deploy from the lunar surface during the Apollo 15 mission. Astronauts Scott and Irwin will descend in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, while astronaut Worden will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
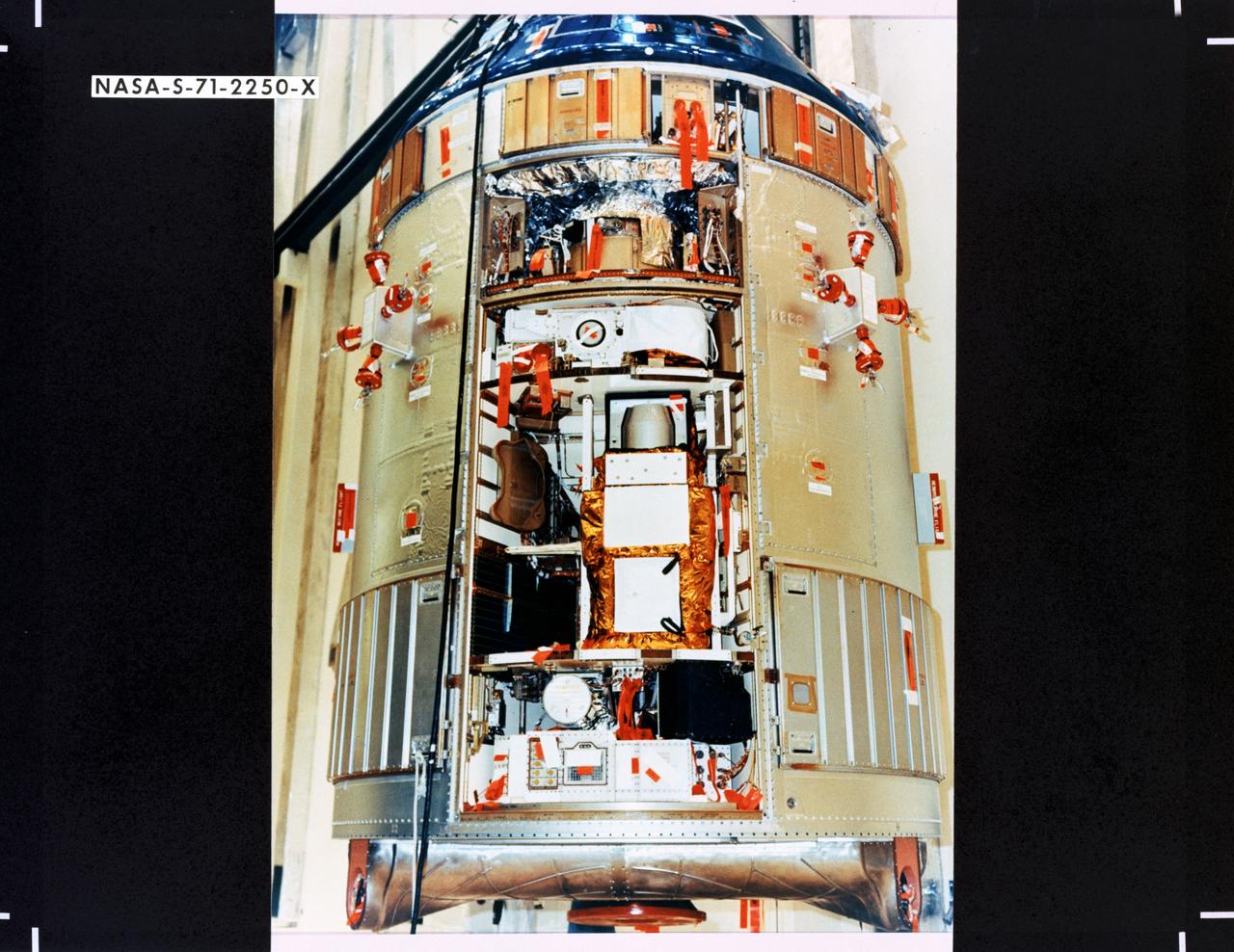
S71-2250X (June 1971) --- A close-up view of the Scientific Instrument Module (SIM) to be flown for the first time on the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission. Mounted in a previously vacant sector of the Apollo Service Module (SM), the SIM carries specialized cameras and instrumentation for gathering lunar orbit scientific data. SIM equipment includes a laser altimeter for accurate measurement of height above the lunar surface; a large-format panoramic camera for mapping, correlated with a metric camera and the laser altimeter for surface mapping; a gamma ray spectrometer on a 25-feet extendible boom; a mass spectrometer on a 21-feet extendible boom; X-ray and alpha particle spectrometers; and a subsatellite which will be injected into lunar orbit carrying a particle and magnetometer, and the S-Band transponder.
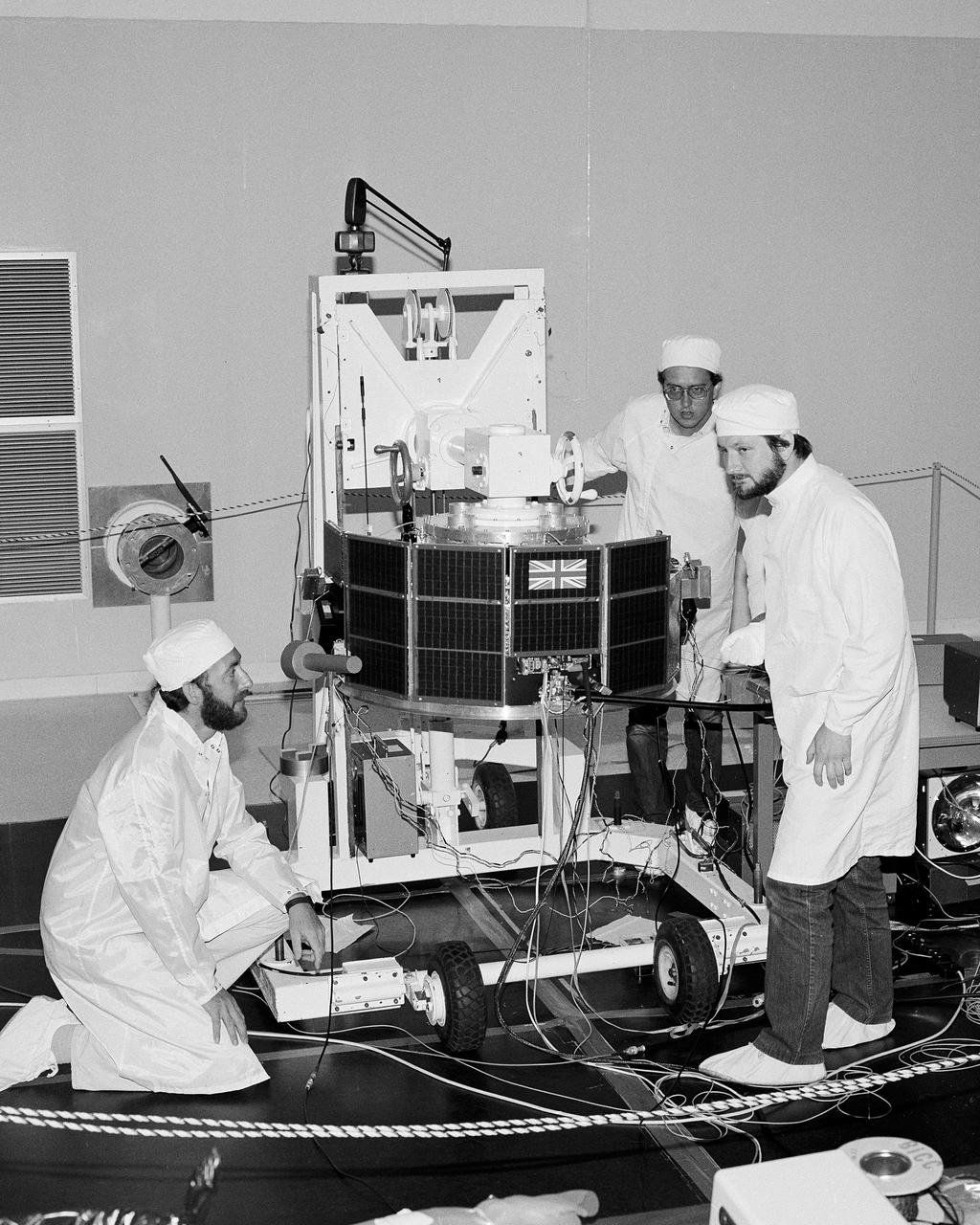

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, British engineers conduct tests on the United Kingdom Subsatellite, part of the three-spacecraft international Active Magnetospheric Particle Tracer Explorer AMPTE mission scheduled for launch on Aug. 9, 1984 aboard a Delta rocket. The 172-pound UKS contains a comprehensive set of plasma measuring instruments to record the effects of chemical clouds released by the West German built Ion Release Module. The other AMPTE spacecraft – the Charged Composition Explorer CCEUnited States) – will operate far below, from inside the Earth’s magnetosphere, where it will track the ionized clouds as it is swept along by the solar wind. With the CCE studying this activity from below, and the IRM and UKS studying it from above, scientists expect to acquire valuable new data on exactly how the solar wind interacts with the Earth’s magnetic fields. Photo Credit: NASA
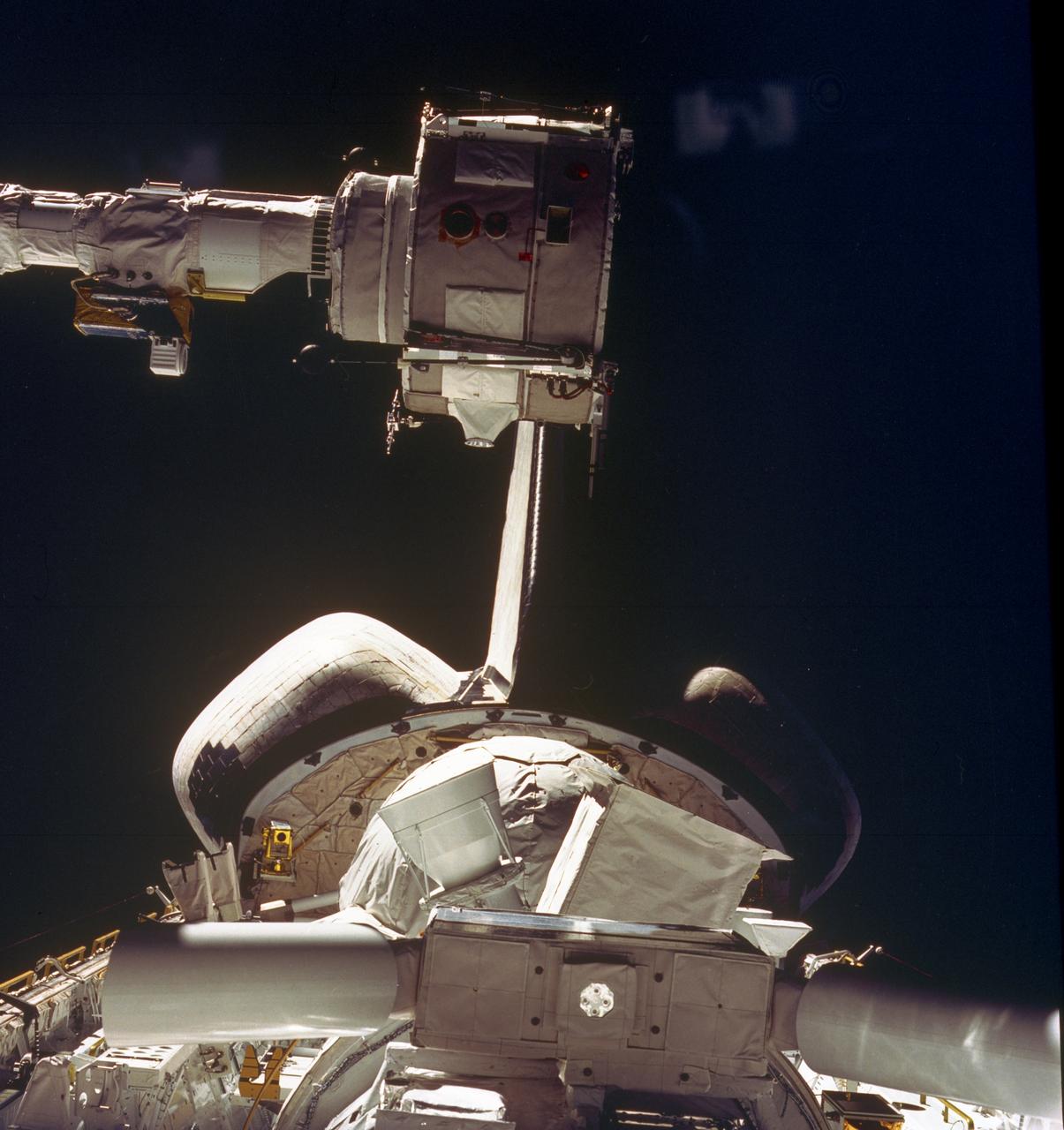

This STS-51F mission onboard Photograph shows some of the Spacelab-2 instruments in the cargo bay of the Orbiter Challenger. The Plasma Diagnostics Package (PDP). shown at the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), used instruments on a subsatellite to study natural plasma processes, orbiter-induced plasma processes, and beam plasma physics. Fourteen instruments were mounted on the PDP for measurements of various plasma characteristics. The X-ray Telescope (XRT), is at the front. The goal of this investigation was to image and examine the X-ray emissions from clusters of galaxies in order to study the mechanisms that cause high-temperature emissions and to determine the weight of galactic clusters. The Small Helium-Cooled Infrared Telescope (IRT) is at the right behind the XRT. The objective of this investigation was to measure and map diffused and discrete infrared astronomical sources while evaluating the Space Shuttle as a platform for infrared astronomy. At the same time, a new large superfluid helium dewar system for cooling the telescope was evaluated. The egg-shaped Cosmic Ray Nuclei experiment (CRNE) is shown at the rear. This investigation was to study the composition of high-energy cosmic rays by using a large instrument exposed to space for a considerable period of time. Spacelab-2 (STS-51F, 19th Shuttle mission) was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger on July 29, 1985.