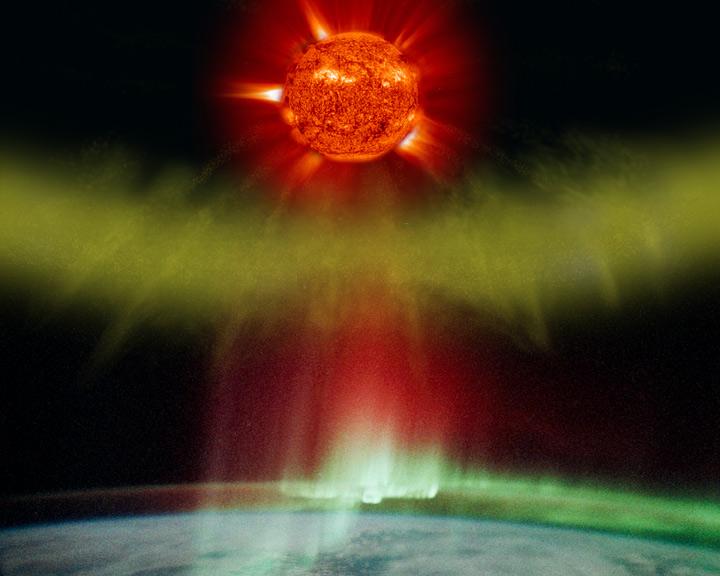

Illustration of a CME particle cloud blasted from the sun impacting Earth and creating aurora (in actual photo of aurora as taken by an astronaut on the space station). Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO/ESA To learn more go to the SOHO website: <a href="http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>
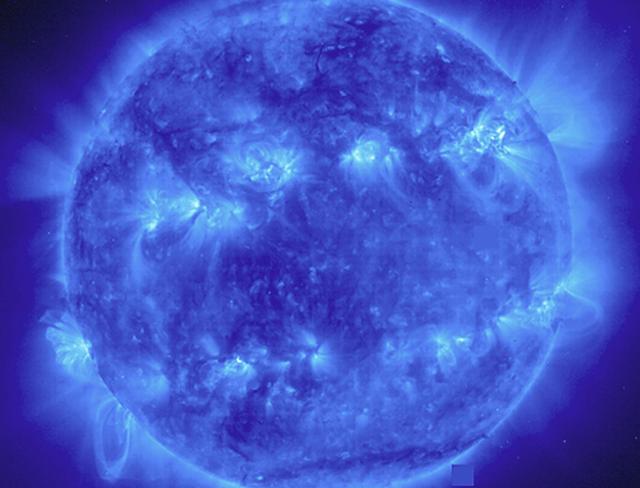
This EIT 171 image shows a wide variety of loops and active regions (lighter areas on the surface). Taken on November 9, 1998. The 171 filter shows emission from 8 and 9 times ionized iron at about 1 million degrees C. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO/ESA To learn more go to the SOHO website: <a href="http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>

This LASCO C2 image, taken 8 January 2002, shows a widely spreading coronal mass ejection (CME) as it blasts more than a billion tons of matter out into space at millions of kilometers per hour. The C2 image was turned 90 degrees so that the blast seems to be pointing down. An EIT 304 Angstrom image from a different day was enlarged and superimposed on the C2 image so that it filled the occulting disk for effect. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO/ESA To learn more go to the SOHO website: <a href="http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>
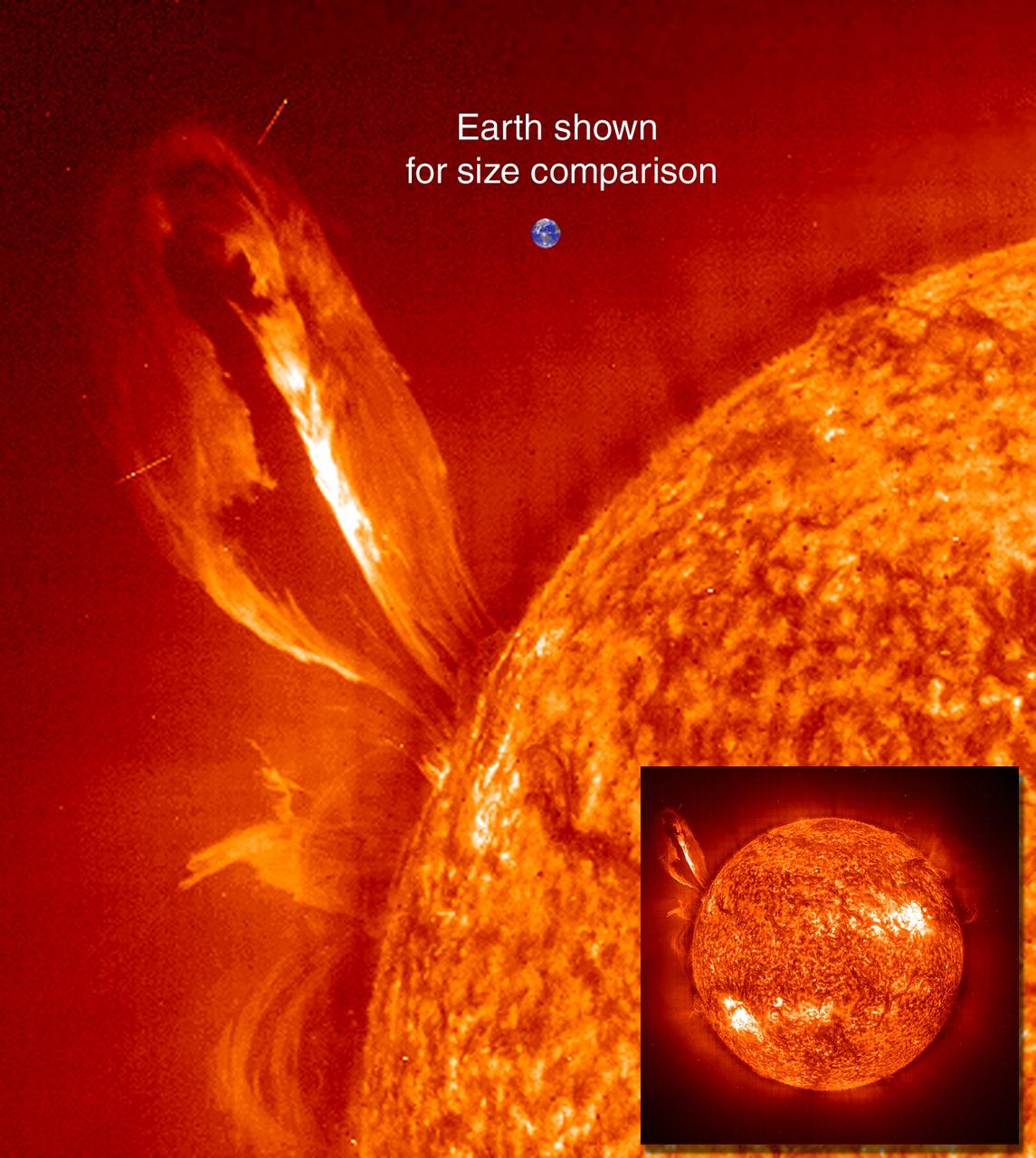

Large, eruptive prominence in He II at 304Å, with an image of the Earth added for size comparison. This prominence from 24 July 1999 is particularly large and looping, extending over 35 Earths out from the Sun. Erupting prominences (when Earthward directed) can affect communications, navigation systems, even power grids, while also producing auroras visible in the night skies. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO/ESA To learn more go to the SOHO website: <a href="http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>

Animation of solar wind impacting the magnetosphere and creating aurora. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO/ESA Sound: Juan Carlos Garcia To learn more go to the SOHO website: <a href="http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>
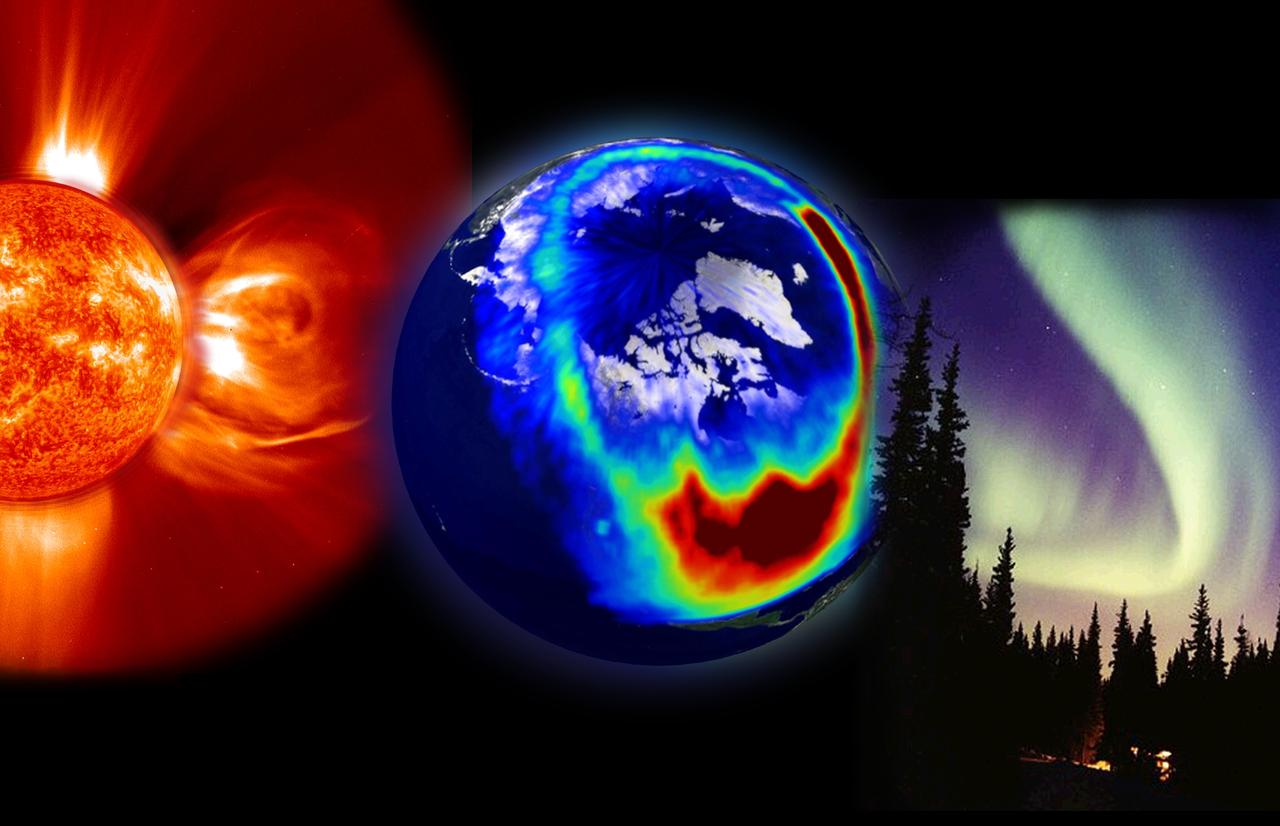
This composite image presents the three most visible elements of space weather: a storm from the Sun, aurora as seen from space, and aurora as seen from the Earth. The solar storm is a corona mass ejection (CME) composite from EIT 304Å superimposed on a LASCO C2 image, both from SOHO. The middle image from Polar’s VIS imager shows charged particles as they spread down across the U.S. during a large solar storm event on July 14, 2000. Lastly, Jan Curtis took this image of an aurora display in Alaska, the visible evidence of space weather that we see here on Earth. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO/ESA To learn more go to the SOHO website: <a href="http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>
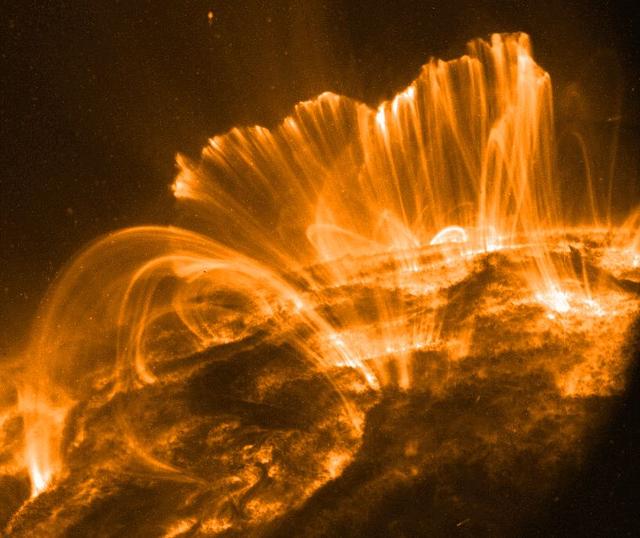

Explanation: In this picture, the Sun's surface is quite dark. A frame from a movie recorded on November 9th by the orbiting TRACE telescope, it shows coronal loops lofted over a solar active region. Glowing brightly in extreme ultraviolet light, the hot plasma entrained above the Sun along arching magnetic fields is cooling and raining back down on the solar surface. Hours earlier, on November 8th, astronomers had watched this particular active region produce a not so spectacular solar flare. Still, the M-class flare spewed forth an intense storm of particles, suddenly showering satellites near the Earth with high energy protons. The flare event was also associated with a large coronal mass ejection, a massive cloud of material which impacted our fair planet's magnetic field about 31 hours later. The result ... a strong geomagnetic storm. Credit: NASA/GSFC/TRACE To learn more go to: <a href="http://nasascience.nasa.gov/missions/trace" rel="nofollow">nasascience.nasa.gov/missions/trace</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>
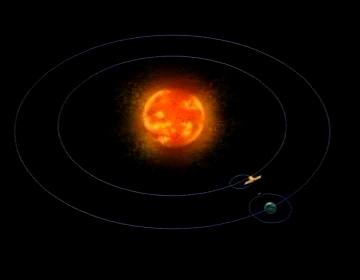
SOHO's orbit around the Lagrangian L1 point and the Sun Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO/ESA Sound: Juan Carlos Garcia To learn more go to the SOHO website: <a href="http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>
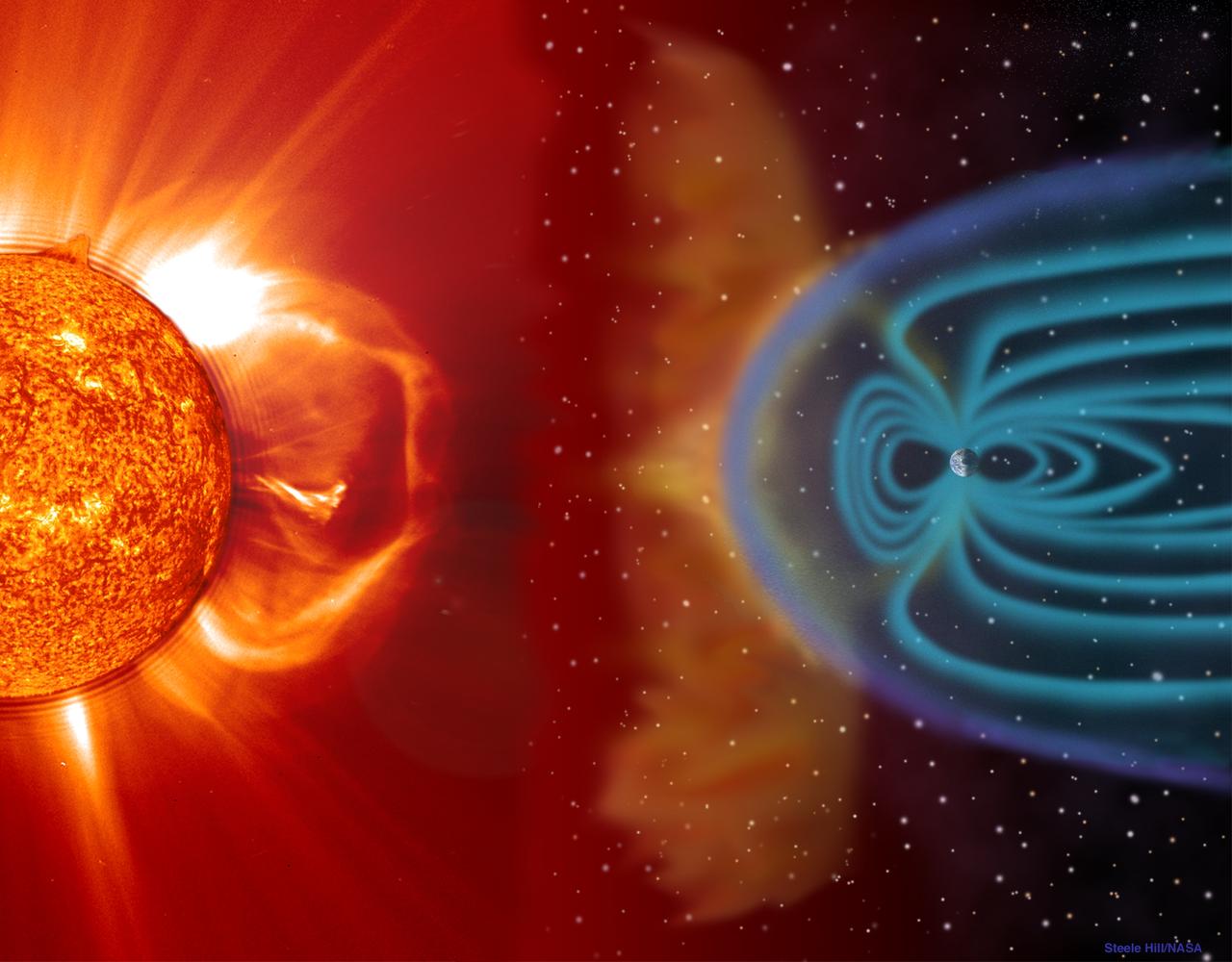
CME blast and subsequent impact at Earth -- This illustration shows a CME blasting off the Sun’s surface in the direction of Ea CME blast and subsequent impact at Earth -- This illustration shows a CME blasting off the Sun’s surface in the direction of Earth. This left portion is composed of an EIT 304 image superimposed on a LASCO C2 coronagraph. Two to four days later, the CME cloud is shown striking and beginning to be mostly deflected around the Earth’s magnetosphere. The blue paths emanating from the Earth’s poles represent some of its magnetic field lines. The magnetic cloud of plasma can extend to 30 million miles wide by the time it reaches earth. These storms, which occur frequently, can disrupt communications and navigational equipment, damage satellites, and even cause blackouts. (Objects in the illustration are not drawn to scale.) Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO/ESA To learn more go to the SOHO website: <a href="http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>
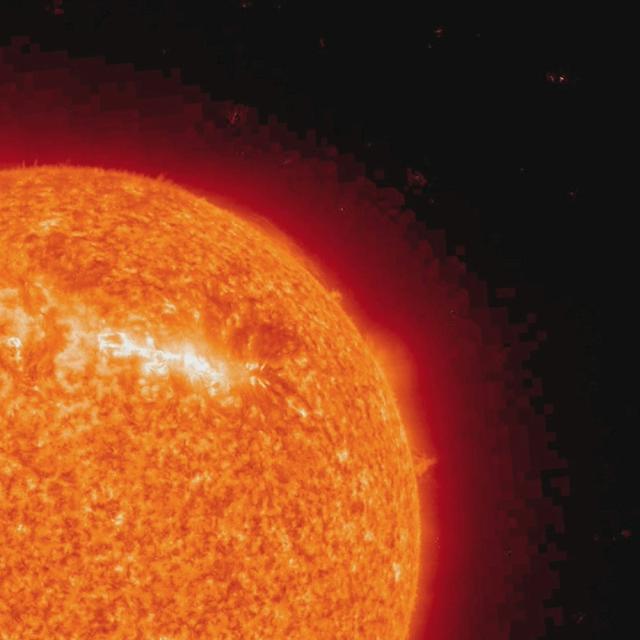

STEREO (Ahead) caught the action as one edge of a single active region spurted out more than a dozen surges of plasma in less than two days (Feb. 15-16, 2010). As seen in extreme UV light, the surges were narrow and directional outbursts driven by intense magnetic activity in the active region. While these kinds of outbursts have been observed numerous times, it was the frequency of so many surges in a short span of time that caught our attention. In this wavelength of UV light we are seeing singly ionized Helium at about 60,000 degrees C. For more information: <a href="http://stereo.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">stereo.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/STEREO To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>

Animation of a CME leaving the Sun, slamming into our magnetosphere. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO/ESA Sound: Juan Carlos Garcia To learn more go to the SOHO website: <a href="http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>
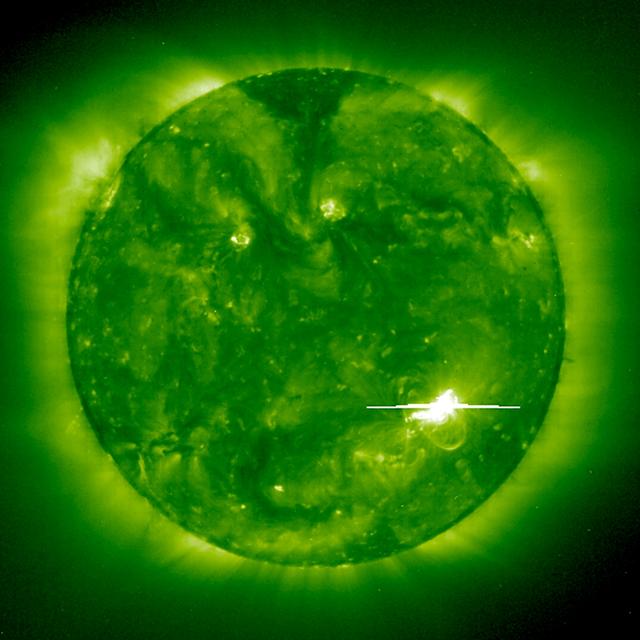
A bright solar flare is captured by the EIT 195Å instrument on 1998 May 2. A solar flare (a sudden, rapid, and intense variation in brightness) occurs when magnetic energy that has built up in the solar atmosphere is suddenly released, launching material outward at millions of km per hour. The Sun’s magnetic fields tend to restrain each other and force the buildup of tremendous energy, like twisting rubber bands, so much that they eventually break. At some point, the magnetic lines of force merge and cancel in a process known as magnetic reconnection, causing plasma to forcefully escape from the Sun. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO/ESA To learn more go to the SOHO website: <a href="http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>
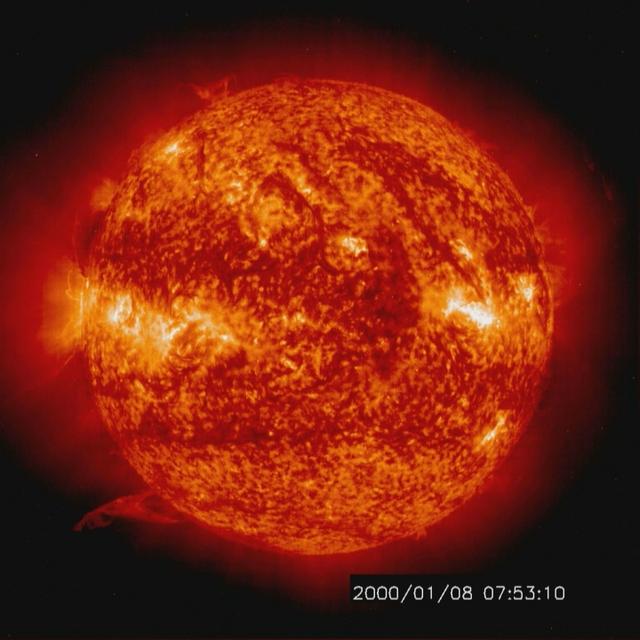

Solar activity and erupting prominences. EIT 304A (Jan. 8-10, 2000) Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO/ESA To learn more go to the SOHO website: <a href="http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>