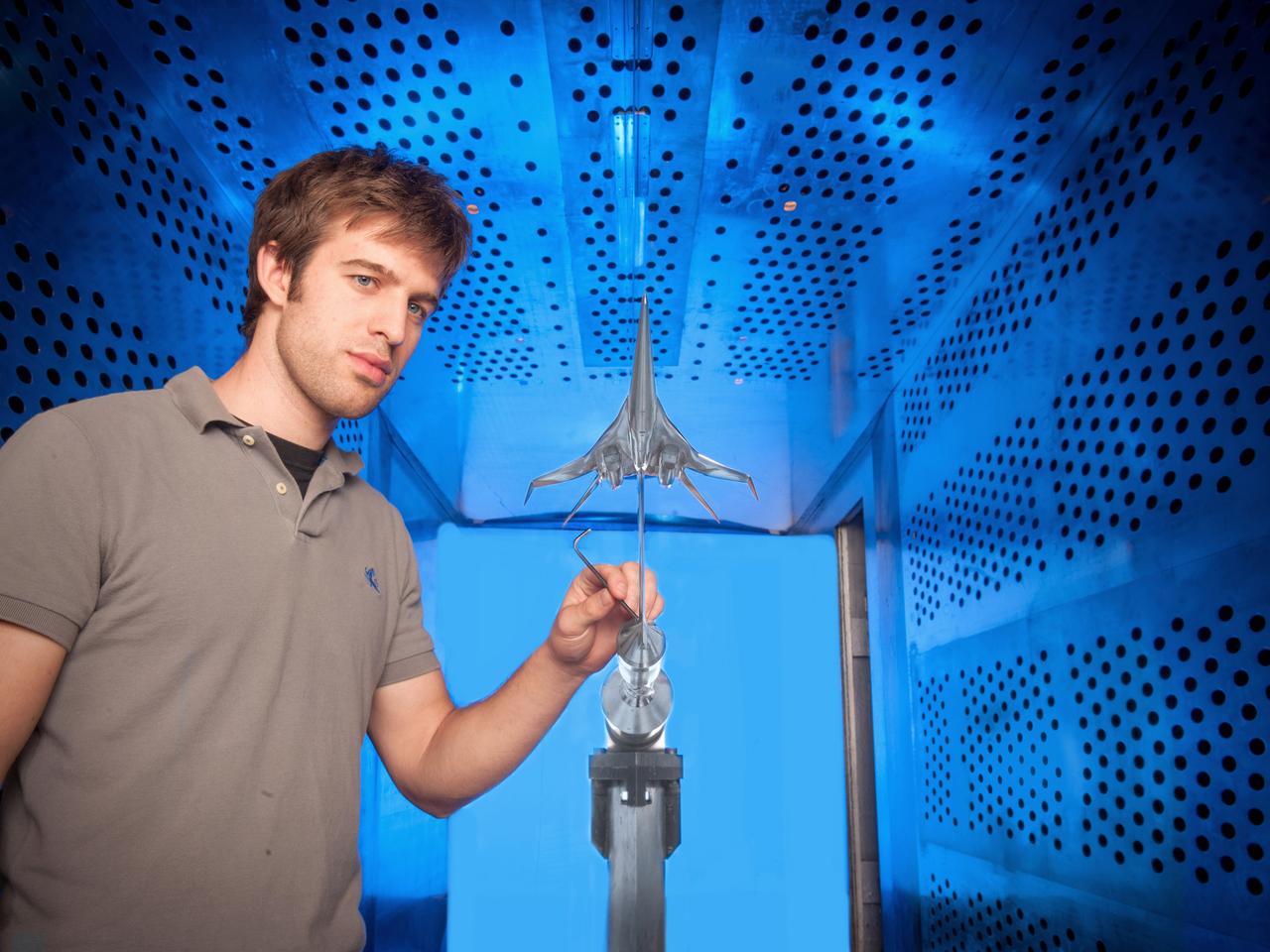
NASA Glenn engineer Gary Williamson with a small model of a future low-boom supersonic aircraft used for testing in the 8' x 6' Supersonic Wind Tunnel at NASA Glenn Research Center.

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft is unveiled at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
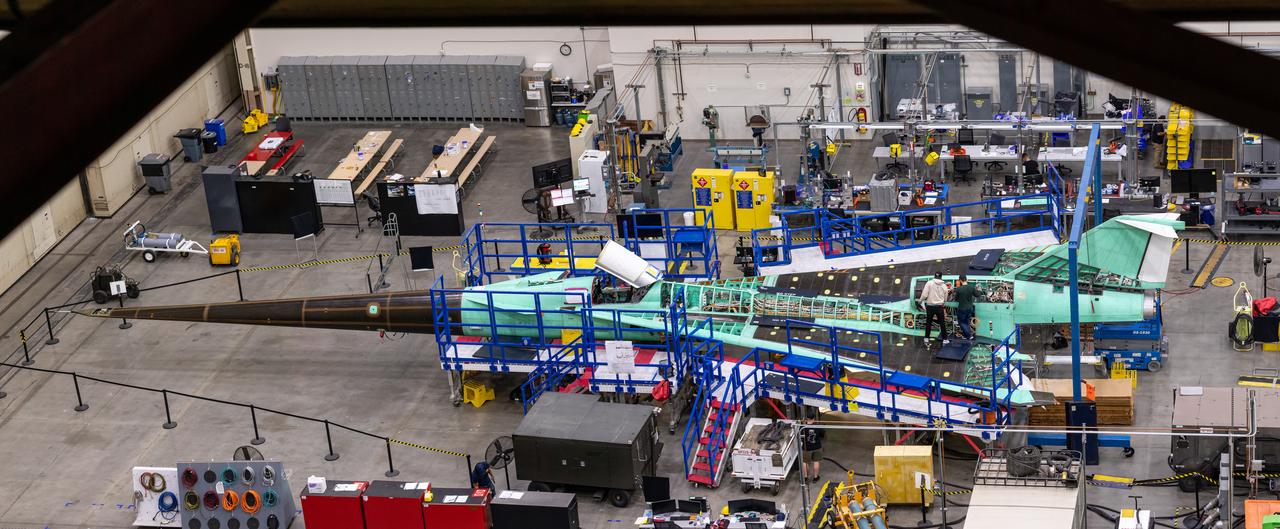

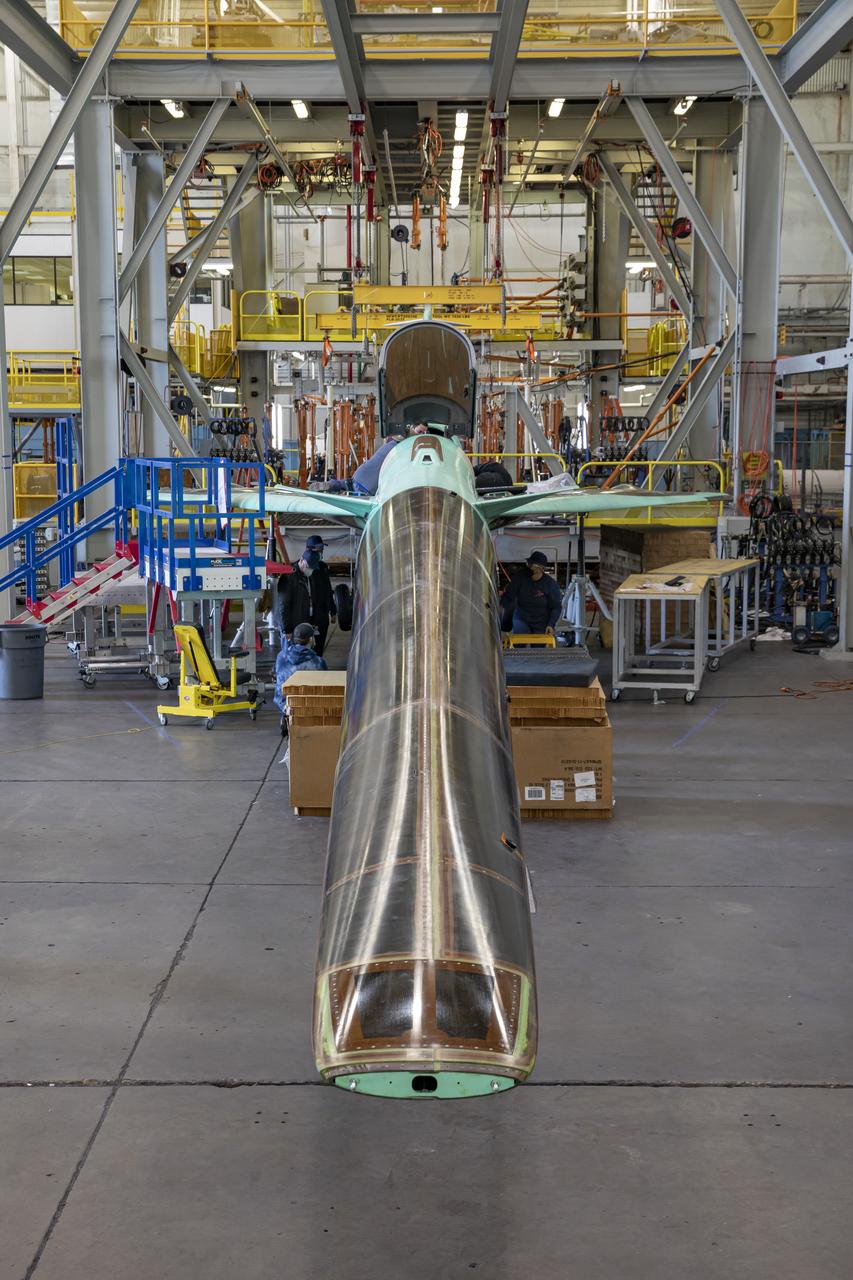
This is an overhead view of the X-59 aircraft at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The nose was installed, and the plane awaits engine installation. Technicians continue to wire the aircraft as the team preforms several system checkouts to ensure the safety of the aircraft. The X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
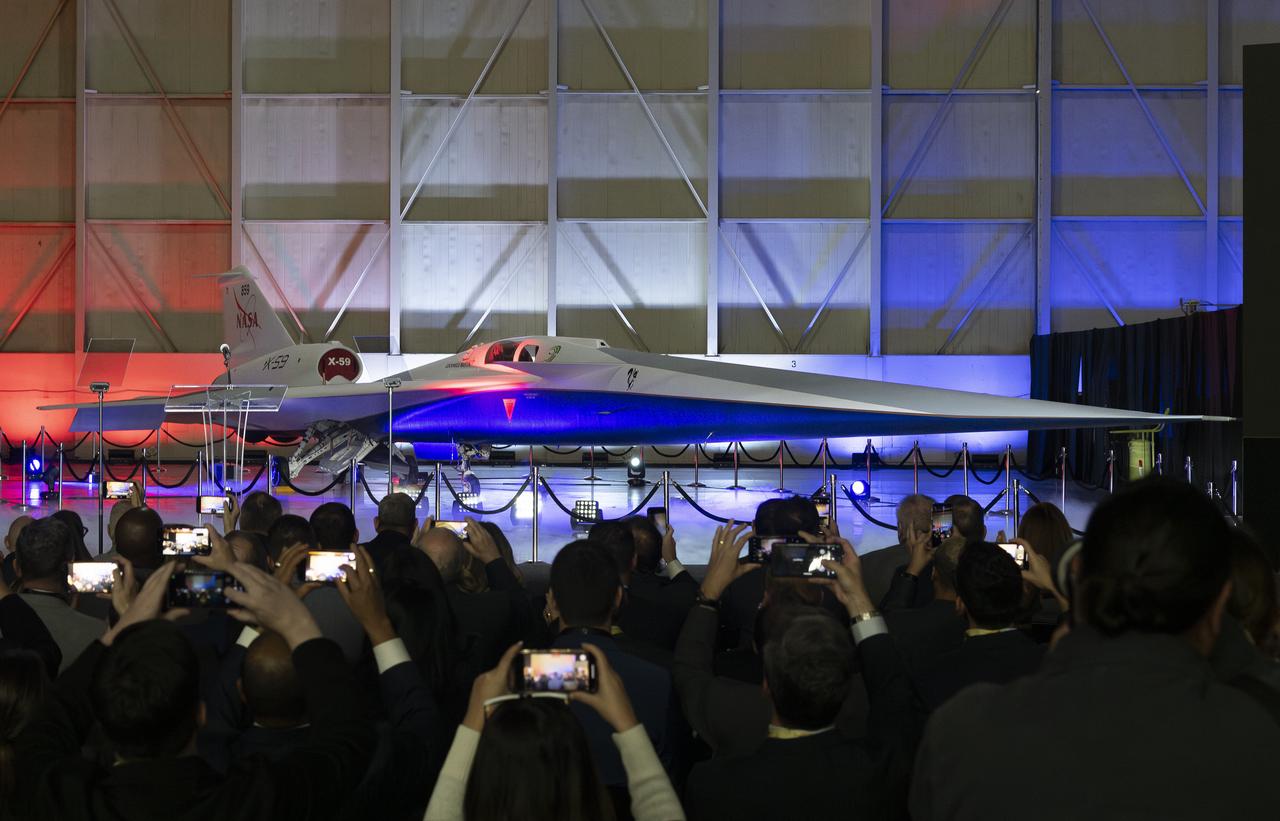

NASA and Lockheed Martin publicly unveil the X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a ceremony in Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
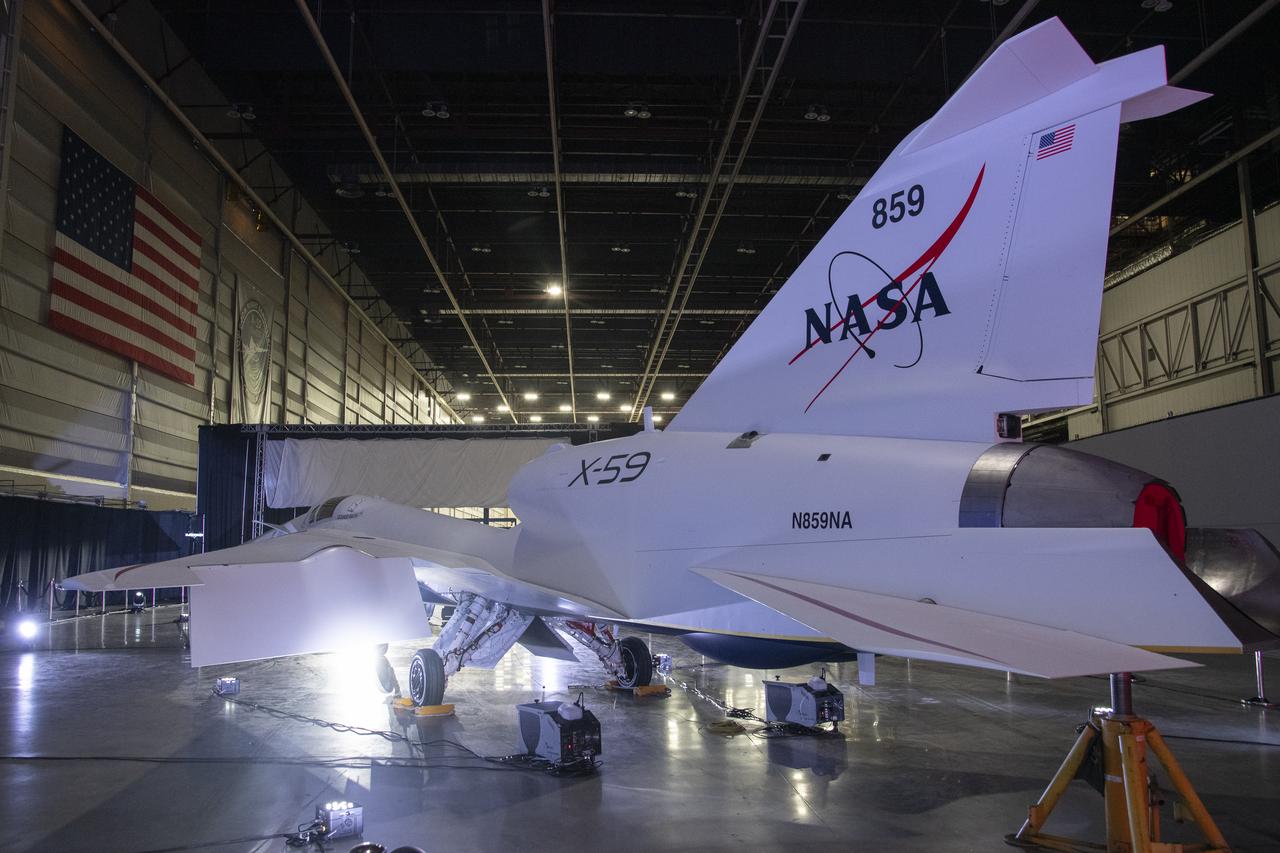

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits in position inside a hangar at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California prior to its January 12, 2024 unveiling. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
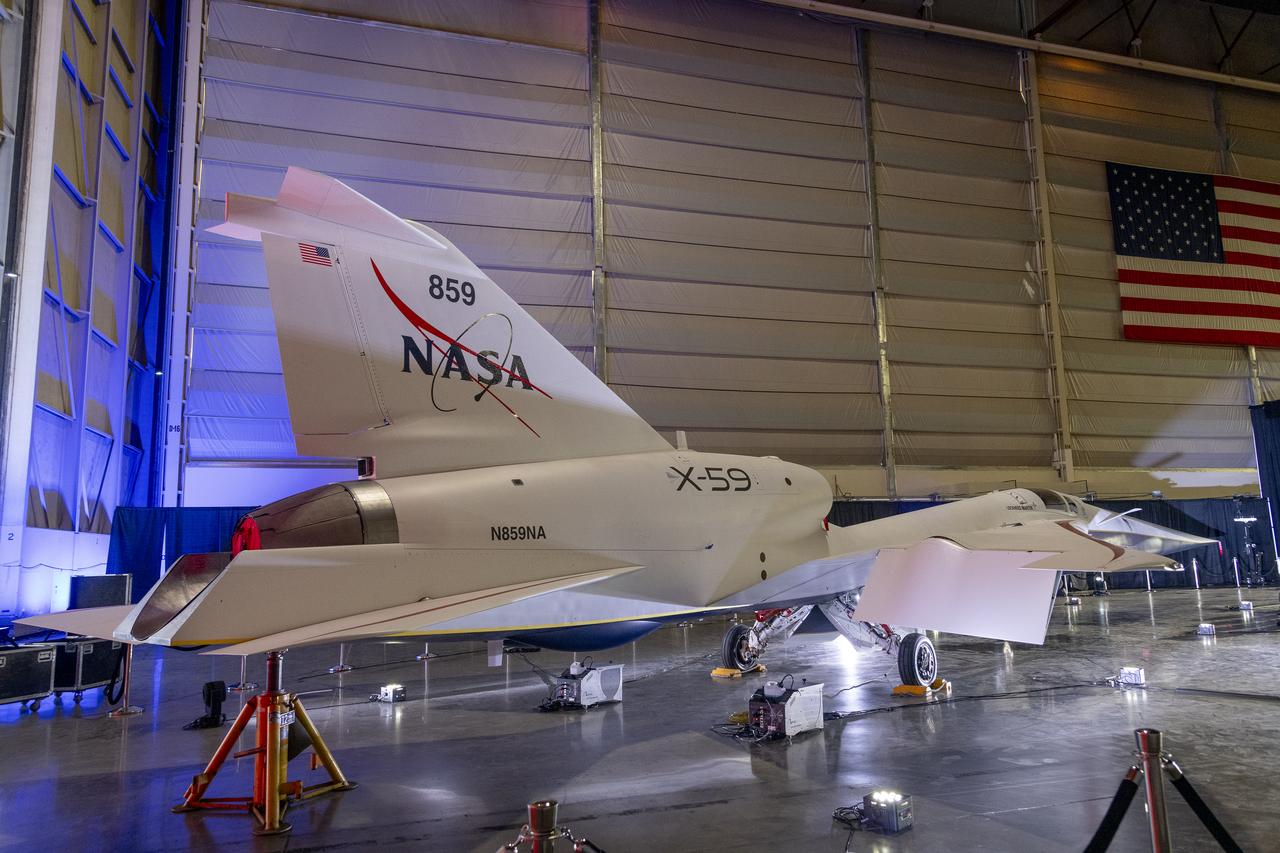

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits in position inside a hangar at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California prior to its January 12, 2024 unveiling. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
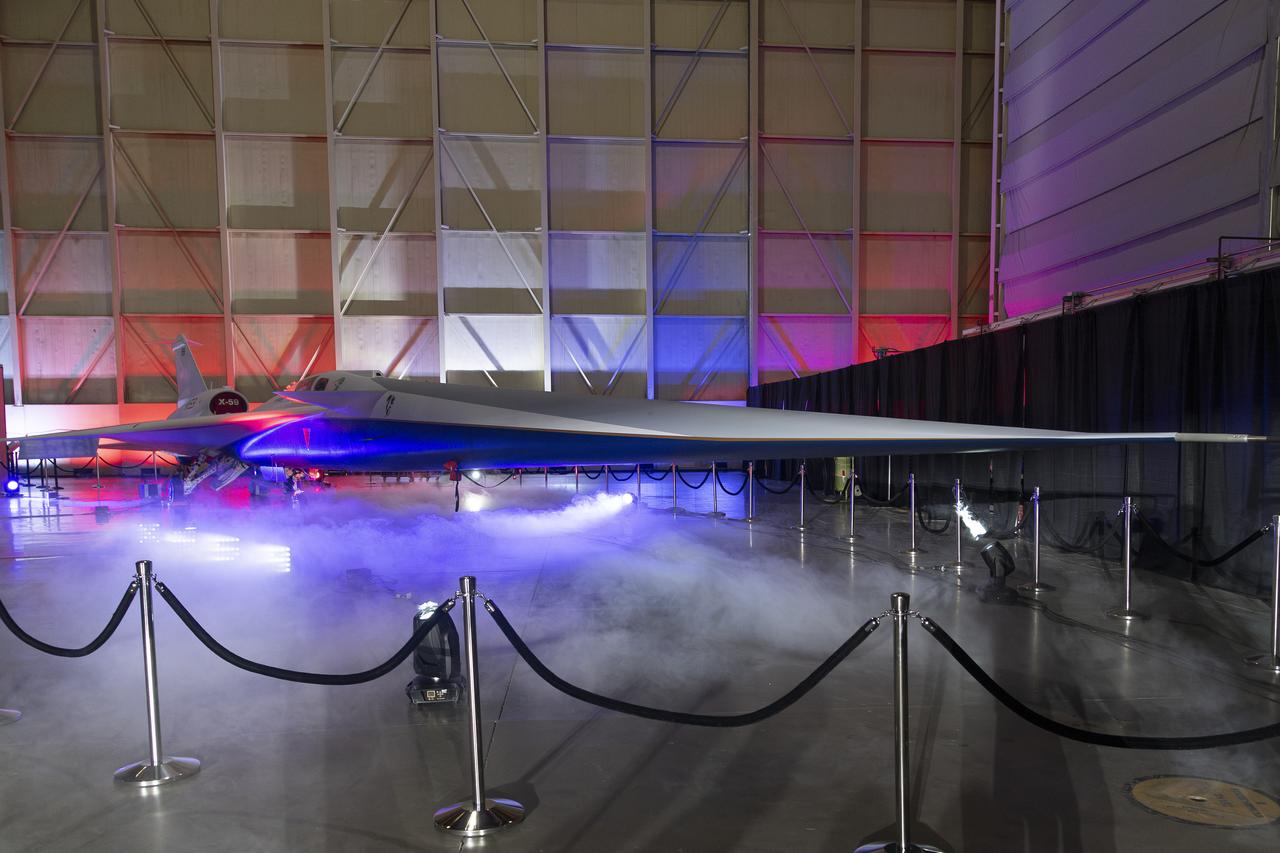

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits in position inside a hangar at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California prior to its January 12, 2024 unveiling. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
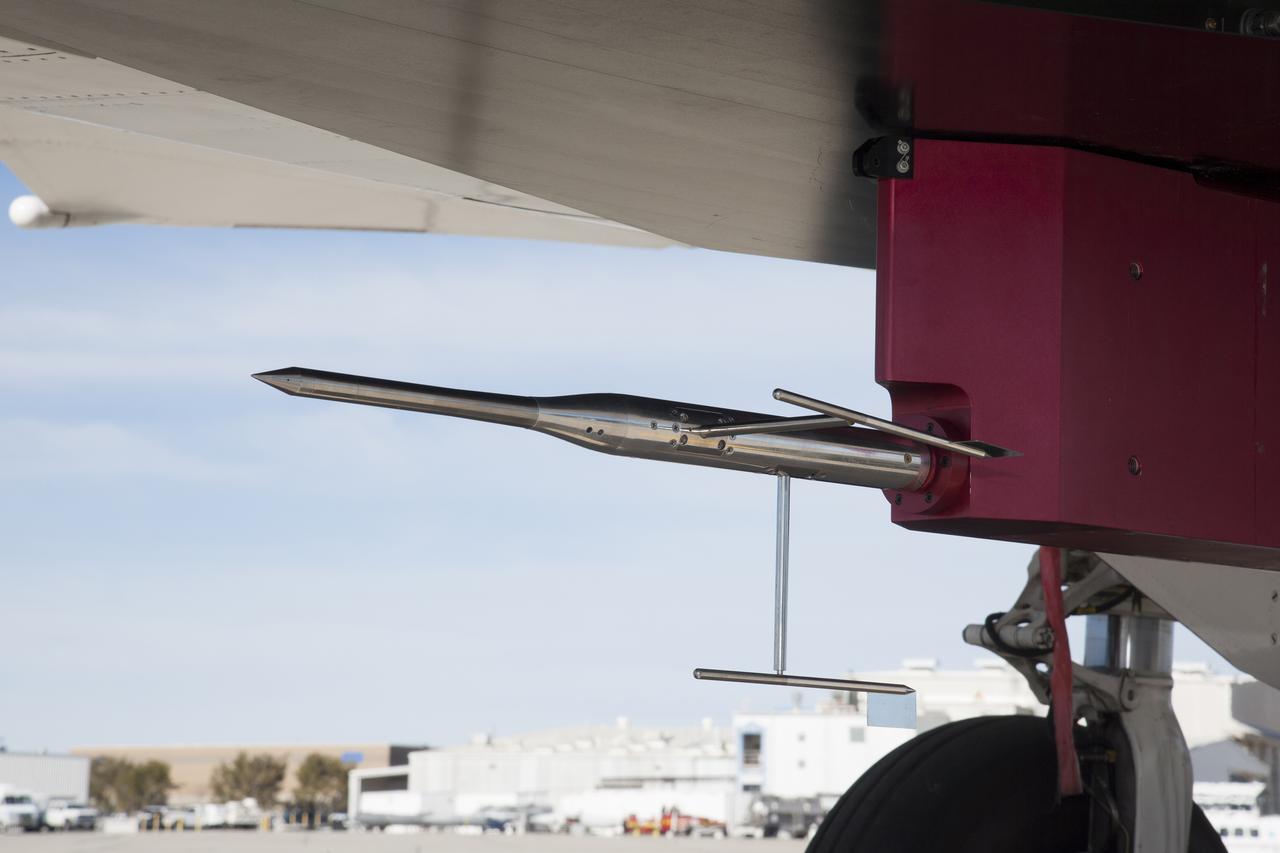

A new supersonic probe seen affixed to a F-15B flight test fixture might one day measure the sonic booms of a new generation of supersonic aircraft.
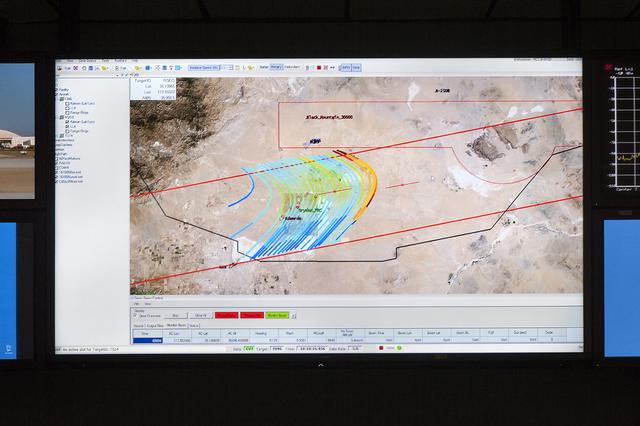
The CISBoomDA display allows the pilot of a supersonic aircraft to monitor the locations of any sonic booms produced, to prevent the aircraft from positioning booms in restricted area.
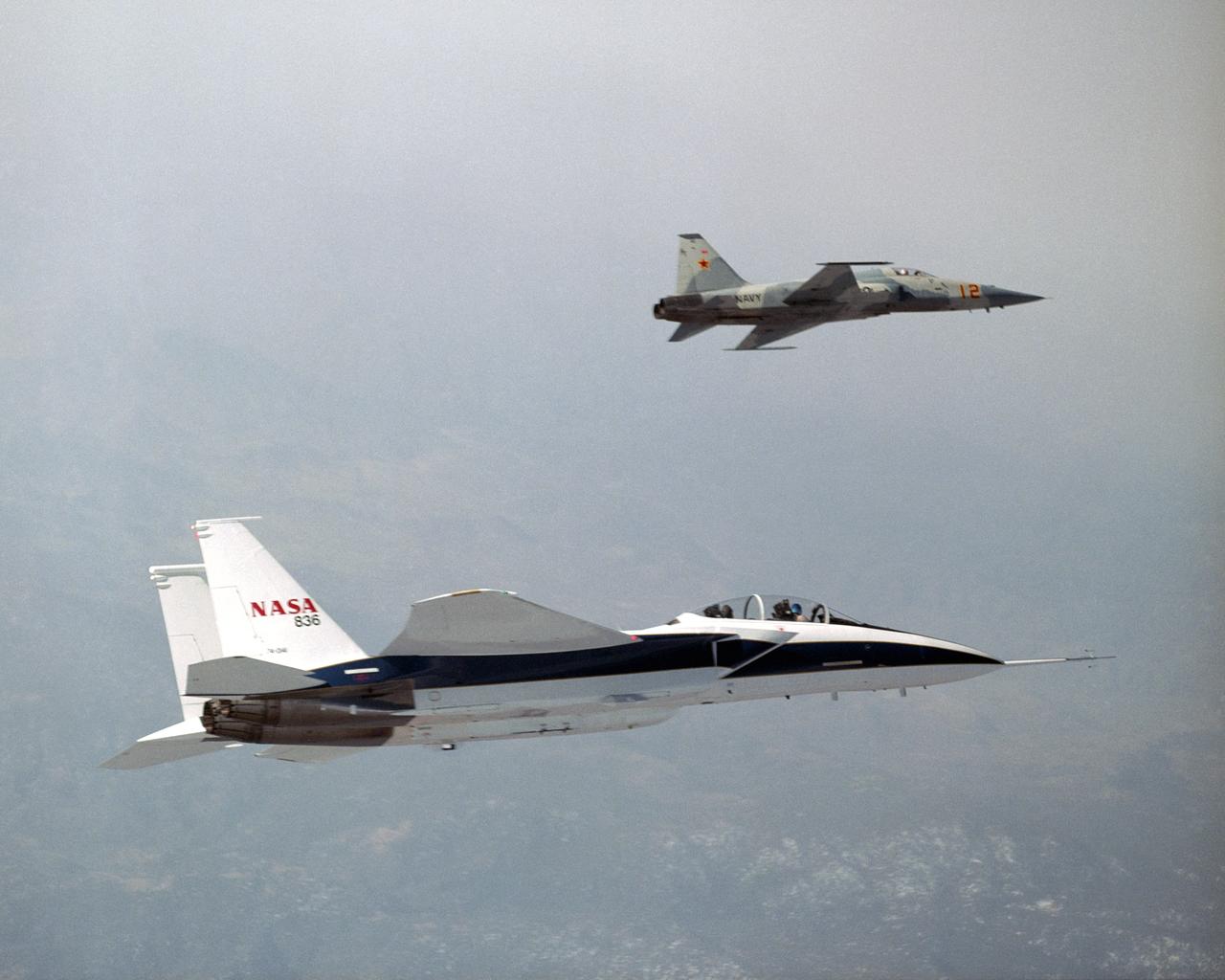

NASA's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft recently flew in the supersonic shock wave of a U.S. Navy F-5E in support of the F-5 Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency's (DARPA) Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. The flights originated from the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. Four flights were flown in order to measure the F-5E's near-field (close-up) sonic boom signature at Mach 1.4, during which more than 50 shockwave patterns were measured at distances as close as 100 feet below the F-5E.
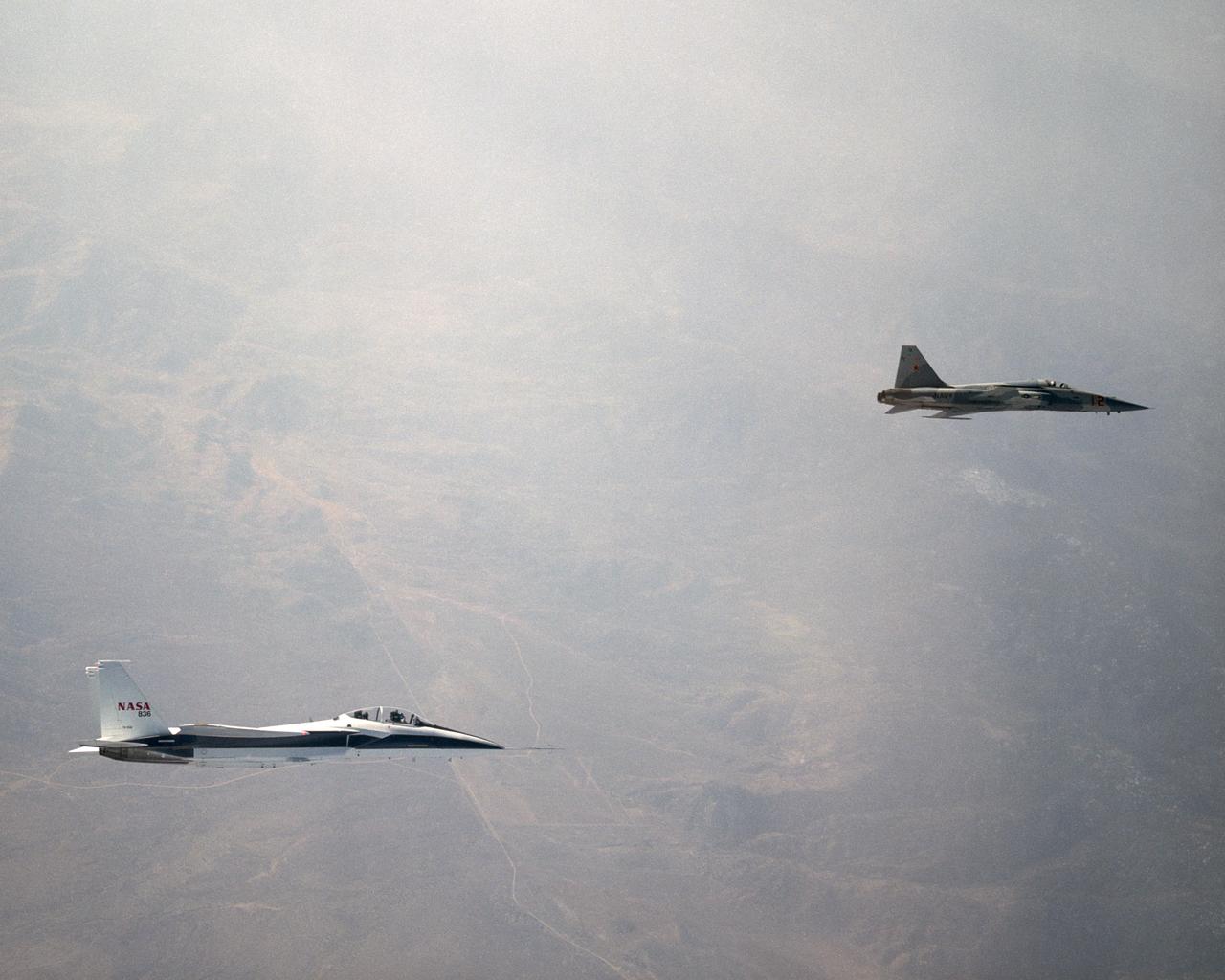

NASA's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft recently flew in the supersonic shock wave of a U.S. Navy F-5E in support of the F-5 Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency's (DARPA) Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. The flights originated from the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. Four flights were flown in order to measure the F-5E's near-field (close-up) sonic boom signature at Mach 1.4, during which more than 50 shockwave patterns were measured at distances as close as 100 feet below the F-5E.
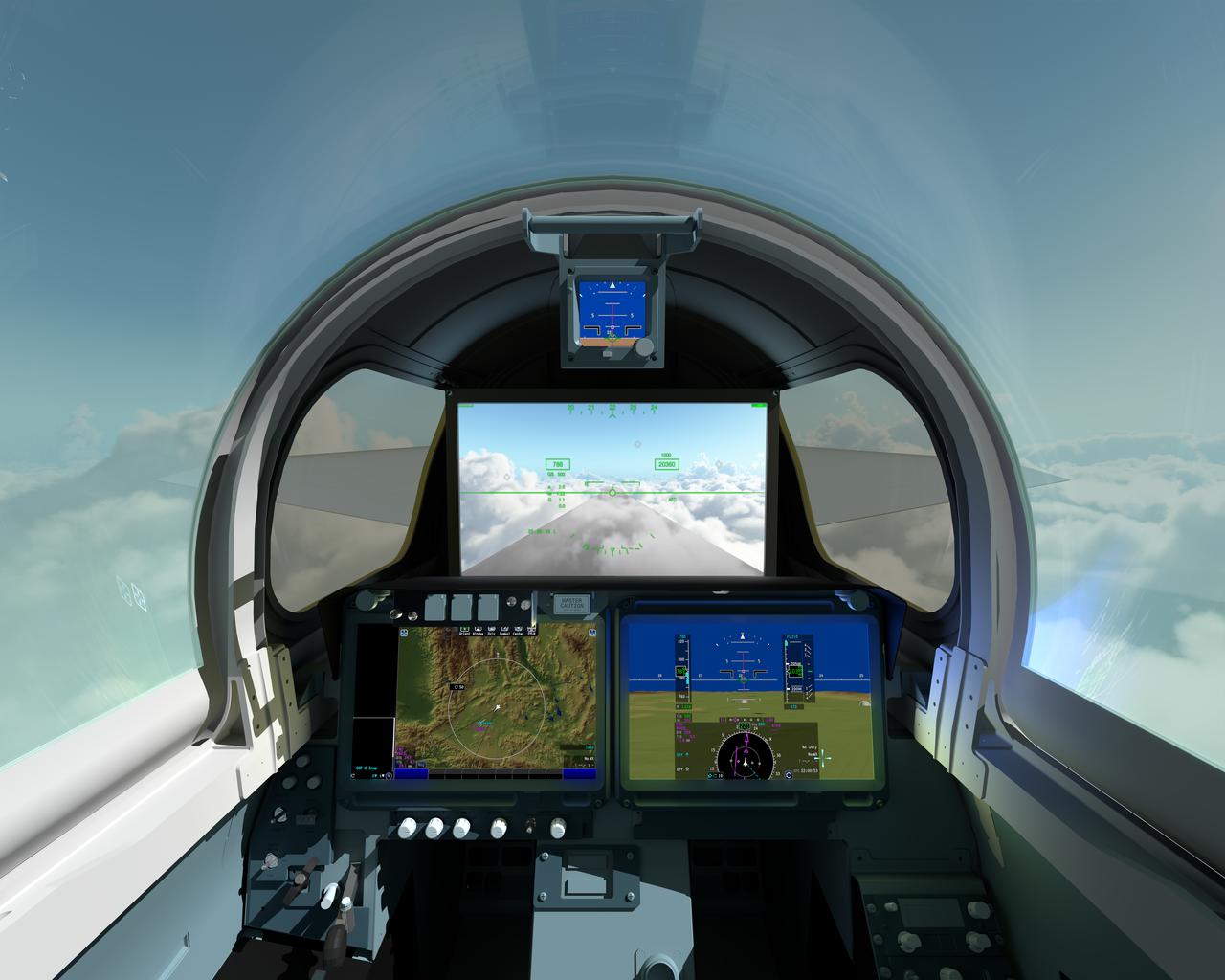

The pilot of NASAÕs X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology, or QueSST, aircraft will navigate the skies in a cockpit unlike any other. There wonÕt be a forward-facing window. ThatÕs right; itÕs actually a 4K monitor that serves as the central window and allows the pilot to safely see traffic in his or her flight path, and provides additional visual aids for airport approaches, landings and takeoffs. The 4K monitor, which is part of the aircraftÕs eXternal Visibility System, or XVS, displays stitched images from two cameras outside the aircraft combined with terrain data from an advanced computing system. The two portals and traditional canopy are real windows however, and help the pilot see the horizon. The displays below the XVS will provide a variety of aircraft systems and trajectory data for the pilot to safely fly. The XVS is one of several innovative solutions to help ensure the X-59Õs design shape reduces a sonic boom to a gentle thump heard by people on the ground. Though not intended to ever carry passengers, the X-59 boom-suppressing technology and community response data could help lift current bans on supersonic flight over land and enable a new generation of quiet supersonic commercial aircraft.
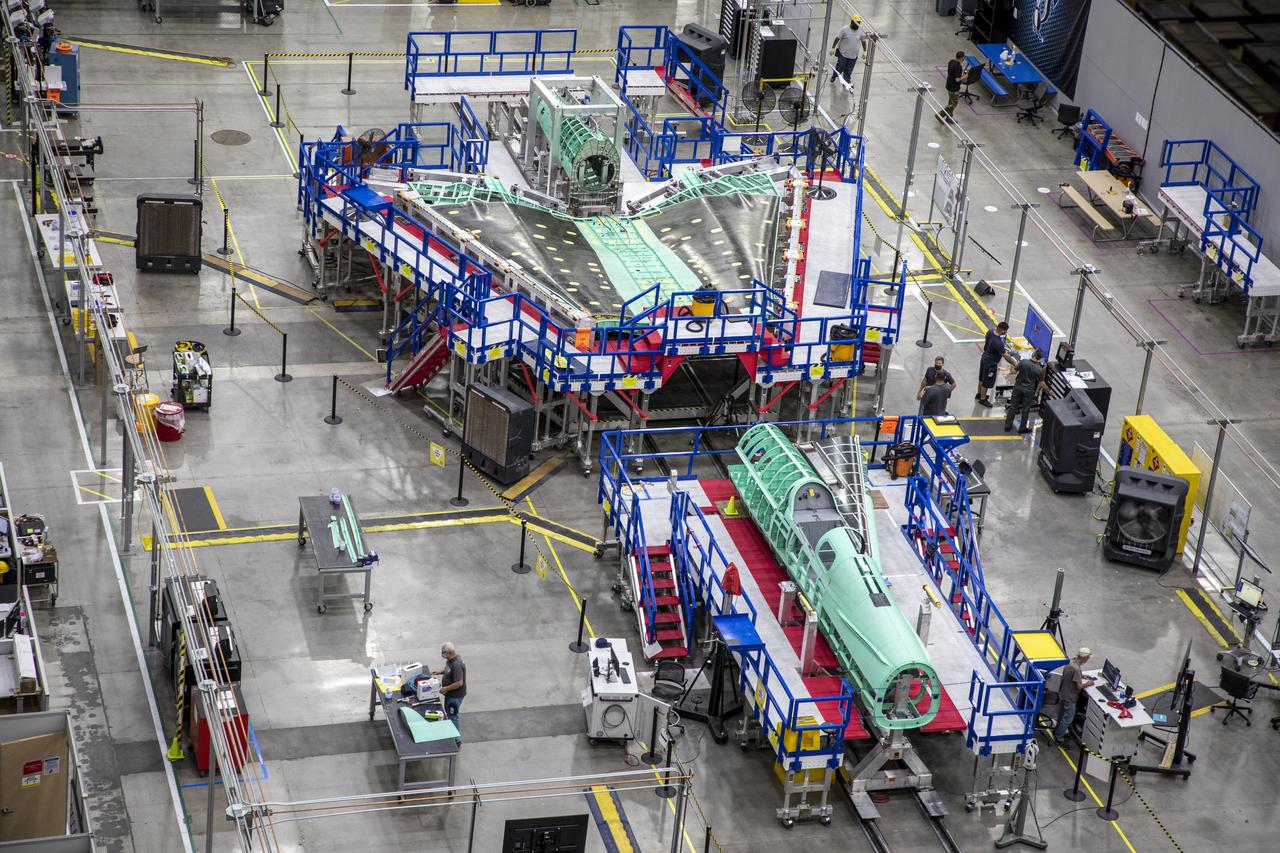

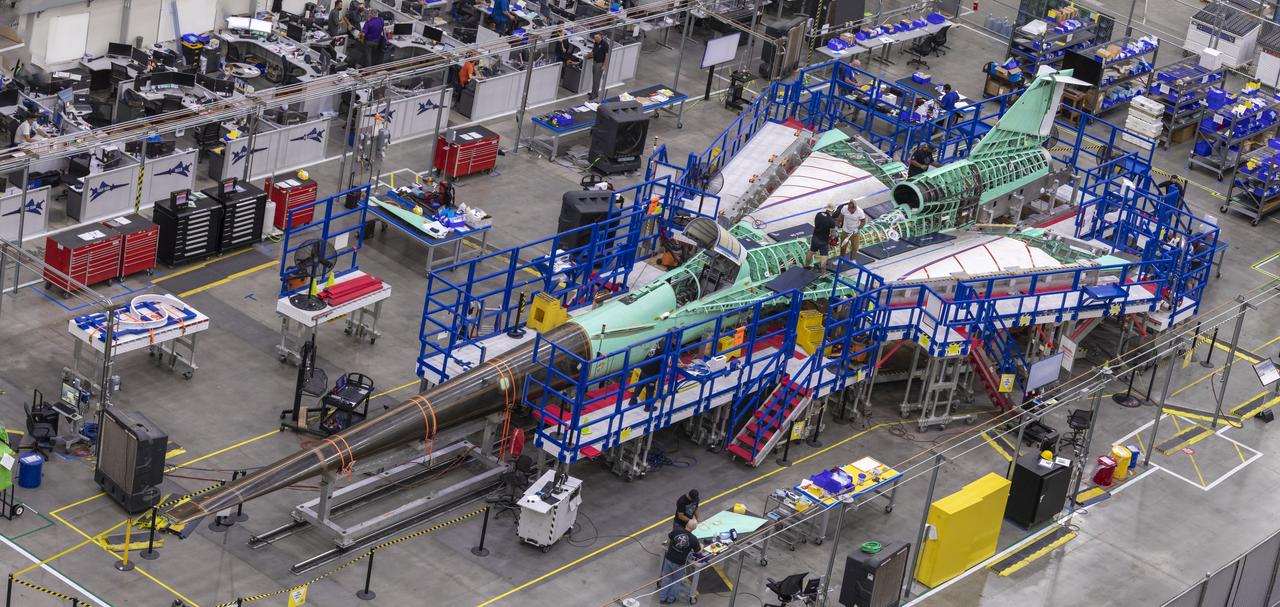
This overhead shot of the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology or QueSST aircraft shows the assembly progress of the vehicle during Spring 2021. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599
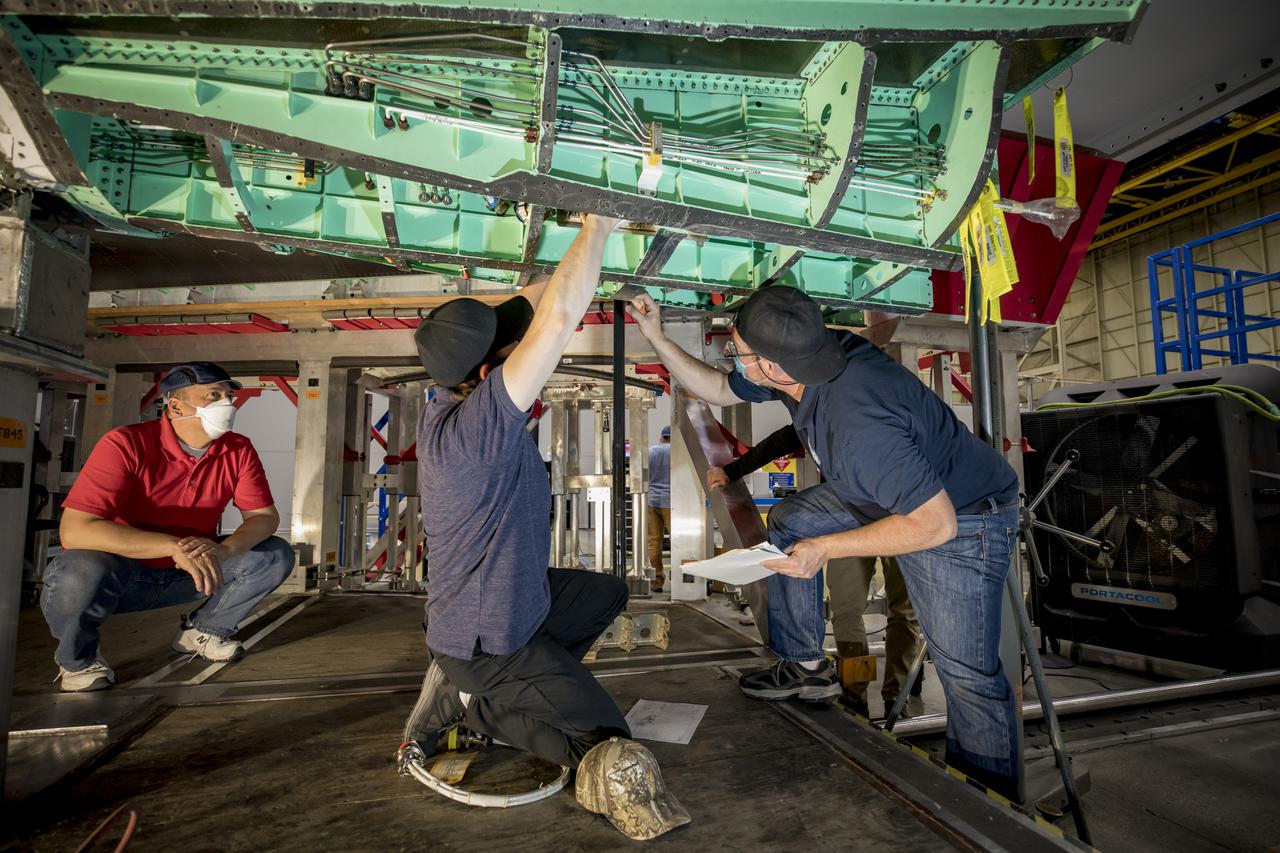

Technicians preform some installation work in the mid-bay on the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology or QueSST aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 450 Mid Bay - Encoders Date: 4/28/2021
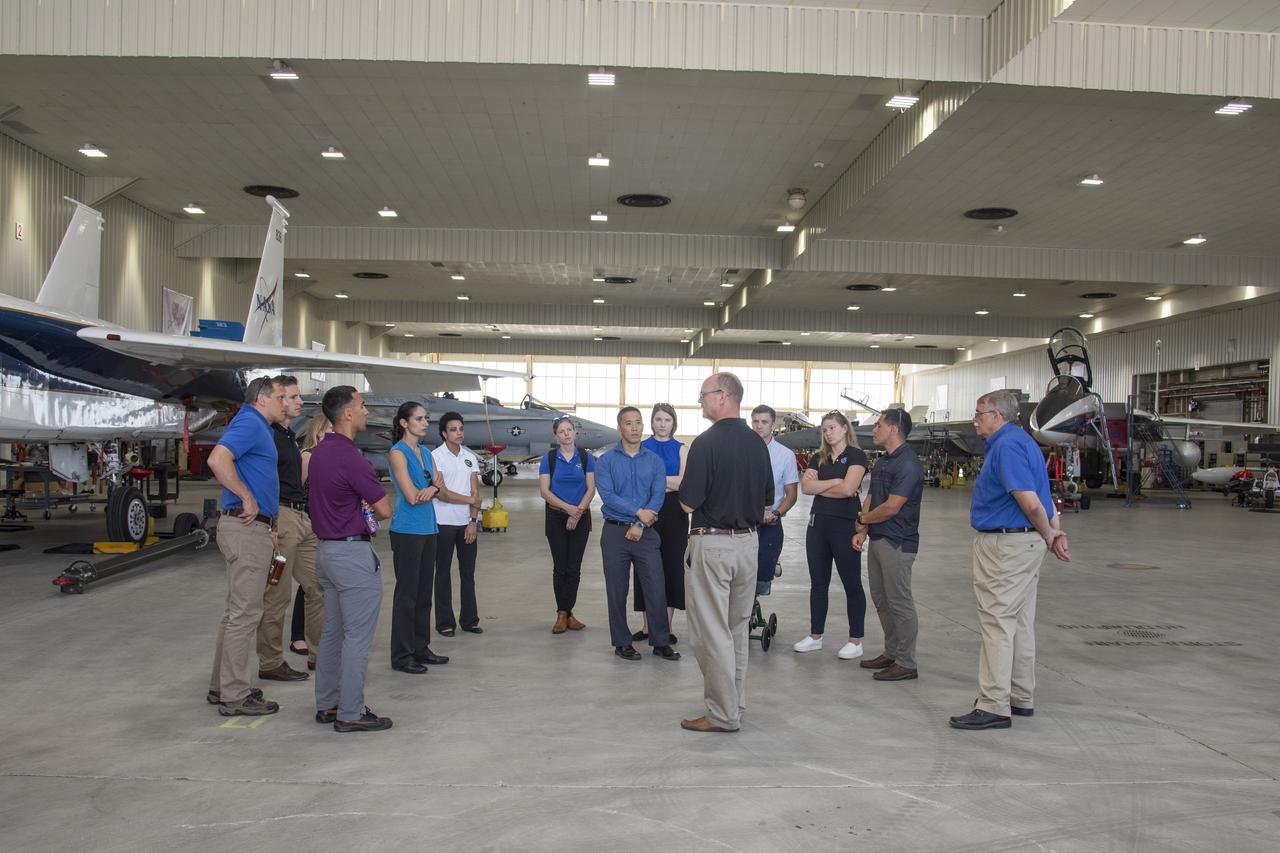

NASA's 2017 astronaut candidates toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California. On the right, NASA's, X-59 pilot Nils Larsen, briefs the astronauts as they look at Armstrong's fleet of supersonic research support aircraft, including the F-15, which will fly in tandem with the X-59 QueSST during early flight test stages, and the F-18, which is conducting supersonic research in support of the overall mission.
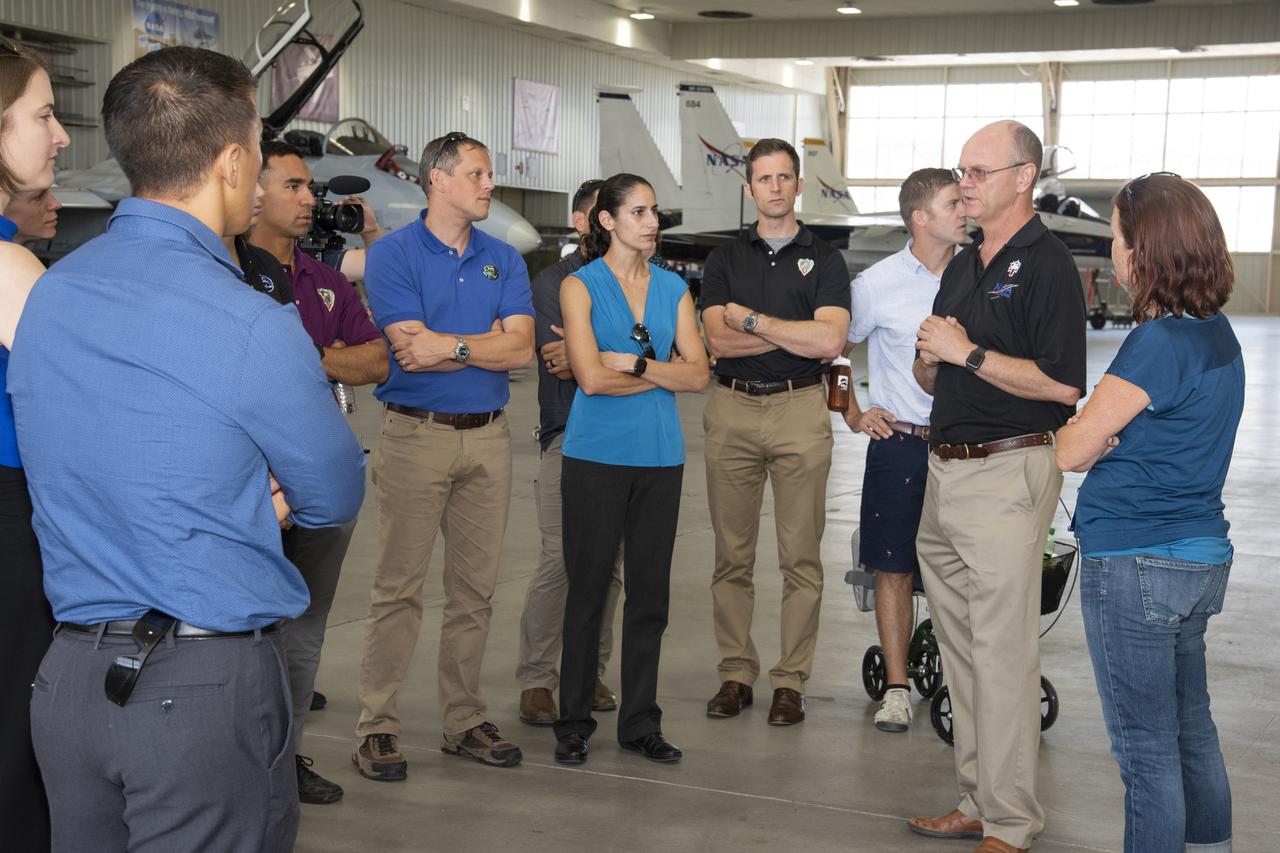

NASA’s 2017 astronaut candidates toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California. On the right, NASA’s, X-59 pilot Nils Larsen, briefs the astronauts as they look at Armstrong’s fleet of supersonic research support aircraft, including the F-15, which will fly in tandem with the X-59 QueSST during early flight test stages, and the F-18, which is conducting supersonic research in support of the overall mission.
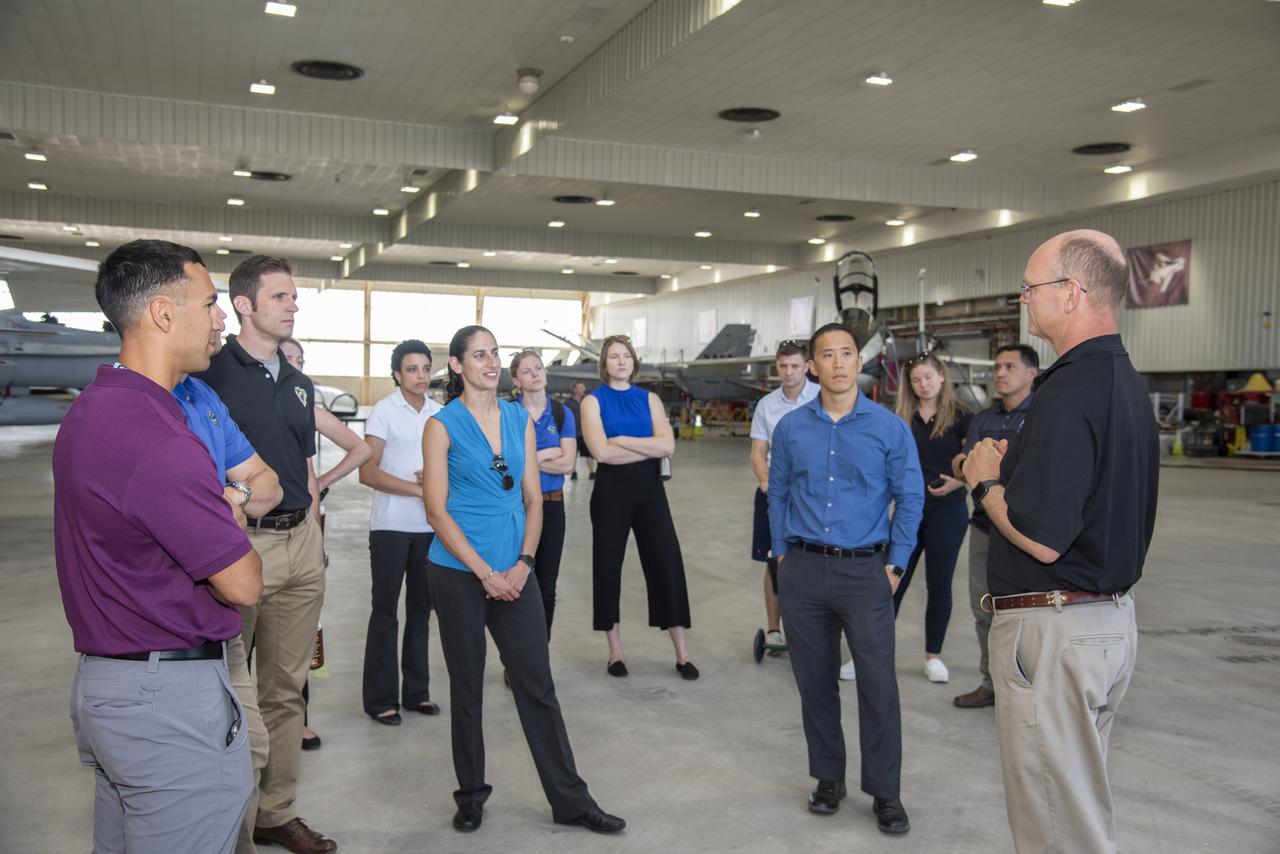

NASA's 2017 astronaut candidates toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California. On the right, NASA's, X-59 pilot Nils Larsen, briefs the astronauts as they look at Armstrong's fleet of supersonic research support aircraft, including the F-15, which will fly in tandem with the X-59 QueSST during early flight test stages, and the F-18, which is conducting supersonic research in support of the overall mission.
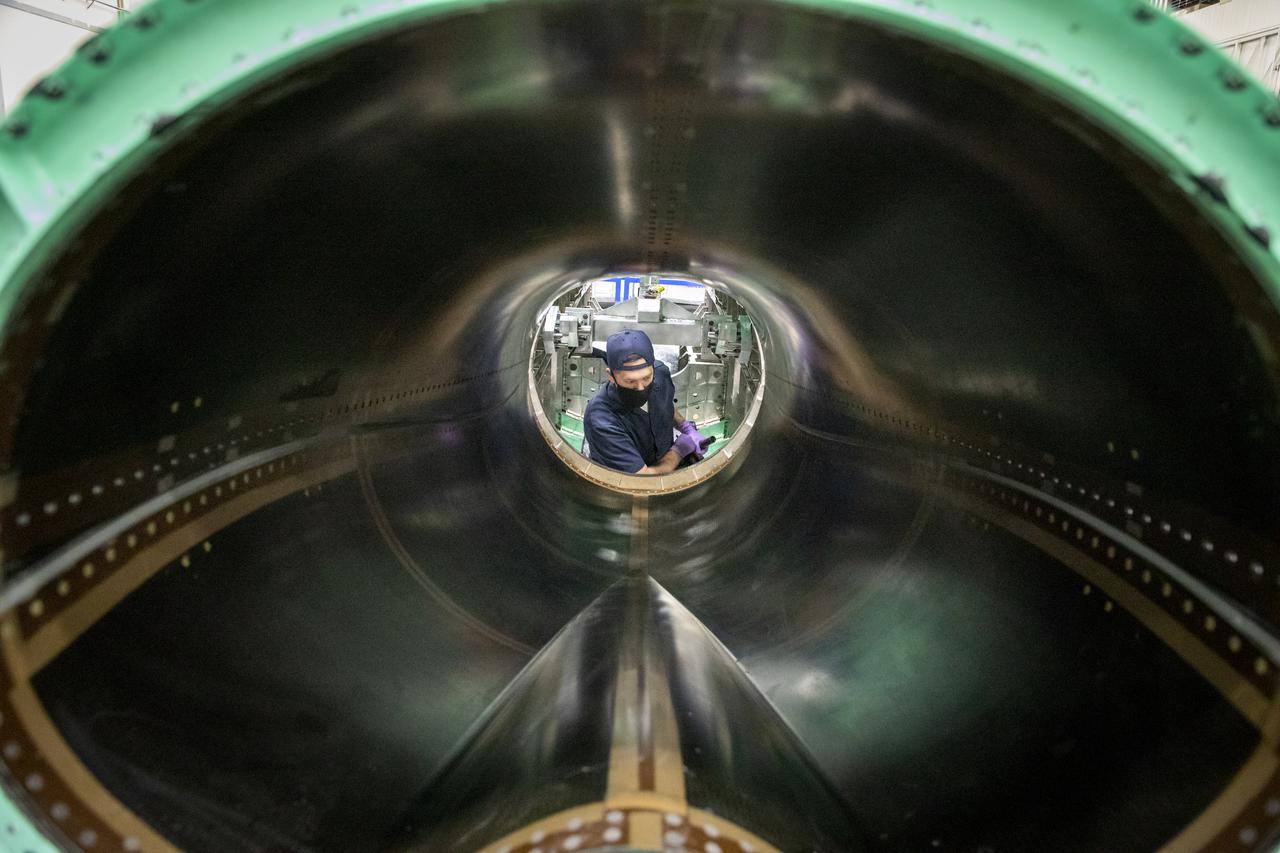

A technician is working on the engine inlet of NASA’s X-59 Quiet Supersonic Technology (QueSST) aircraft at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California.
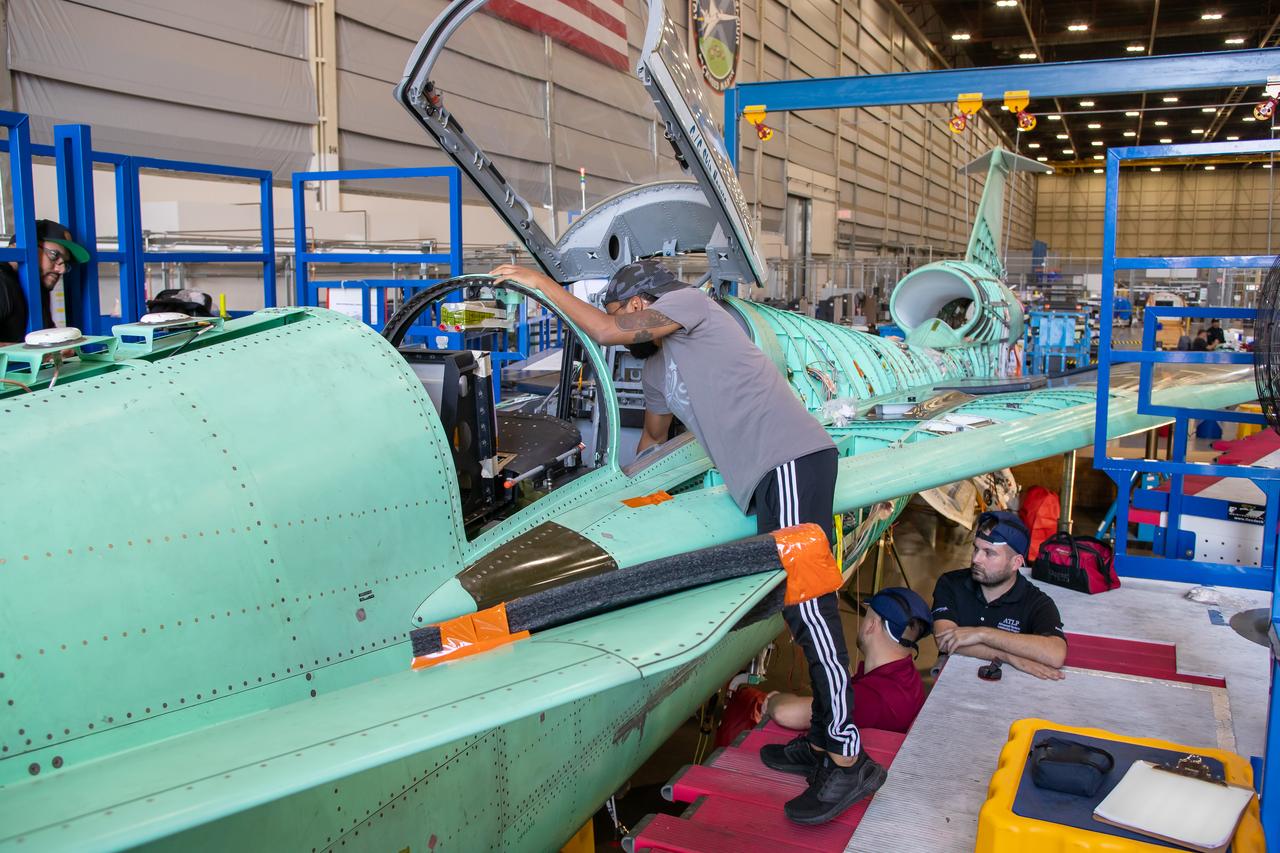

A Lockheed Martin Skunk Works technician inspects some of the wiring and sensors on the X-59 aircraft in preparation for the first power-on system checkouts. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.
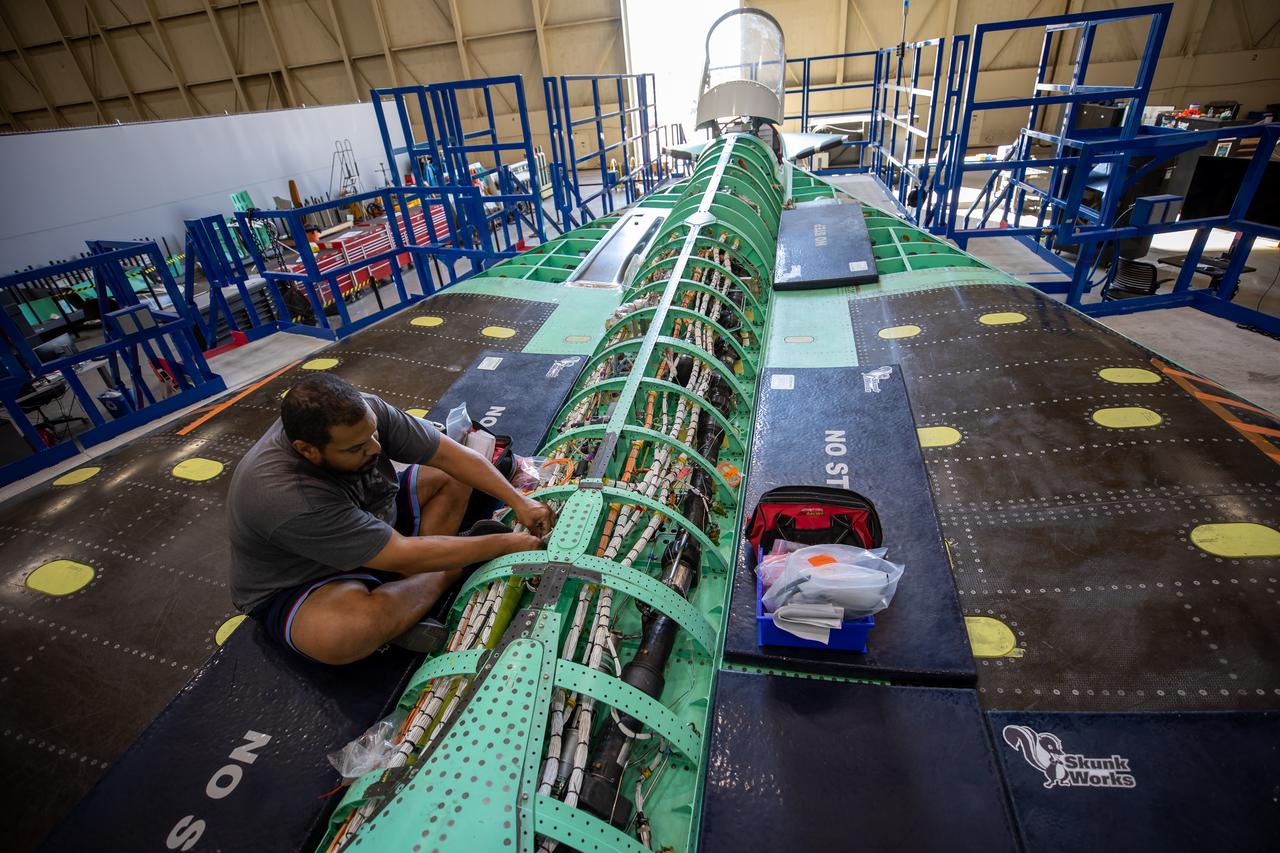

A Lockheed Martin technician works to complete wiring on the X-59 aircraft in preparation for the power-on system checkouts. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.
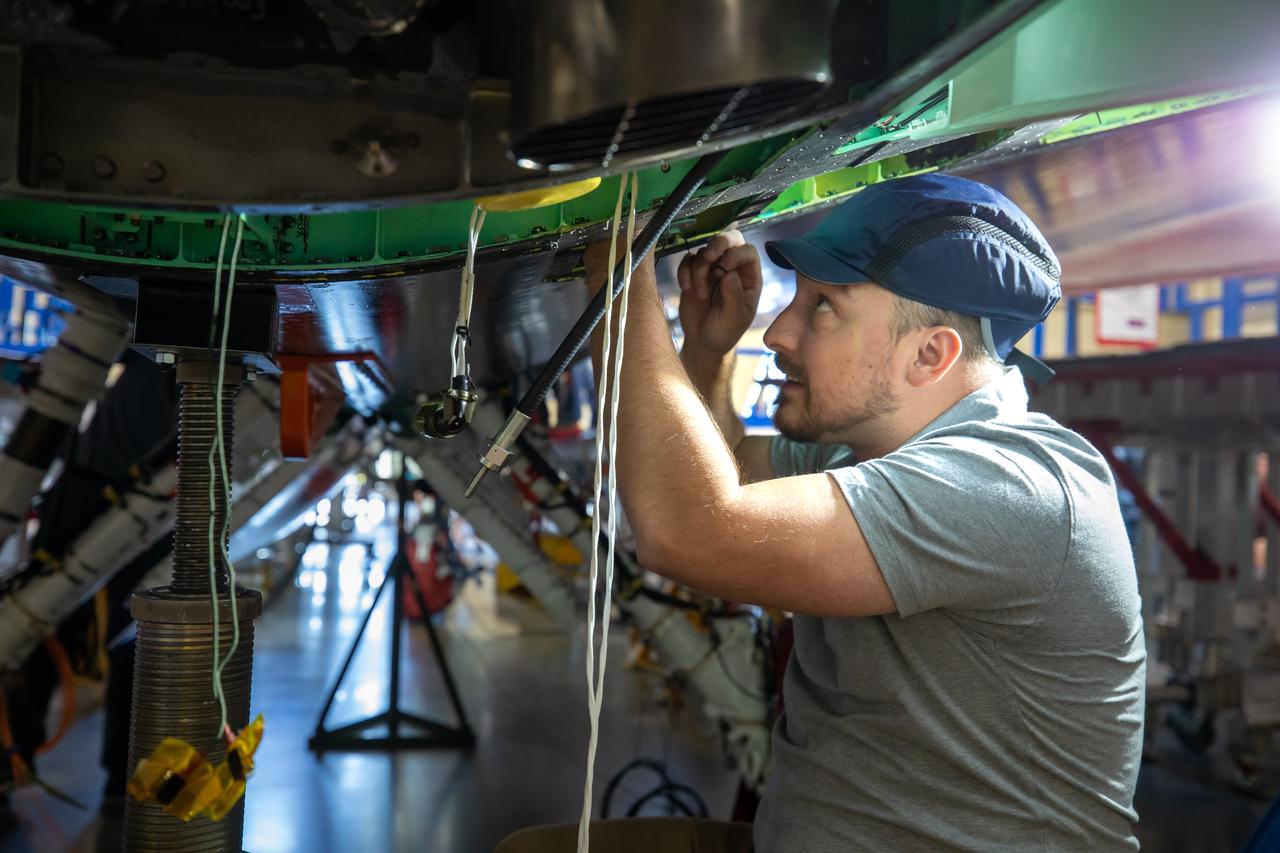

A Lockheed Martin Skunk Works technician works to complete wiring on the X-59 aircraft in preparation for the power-on system checkouts. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.
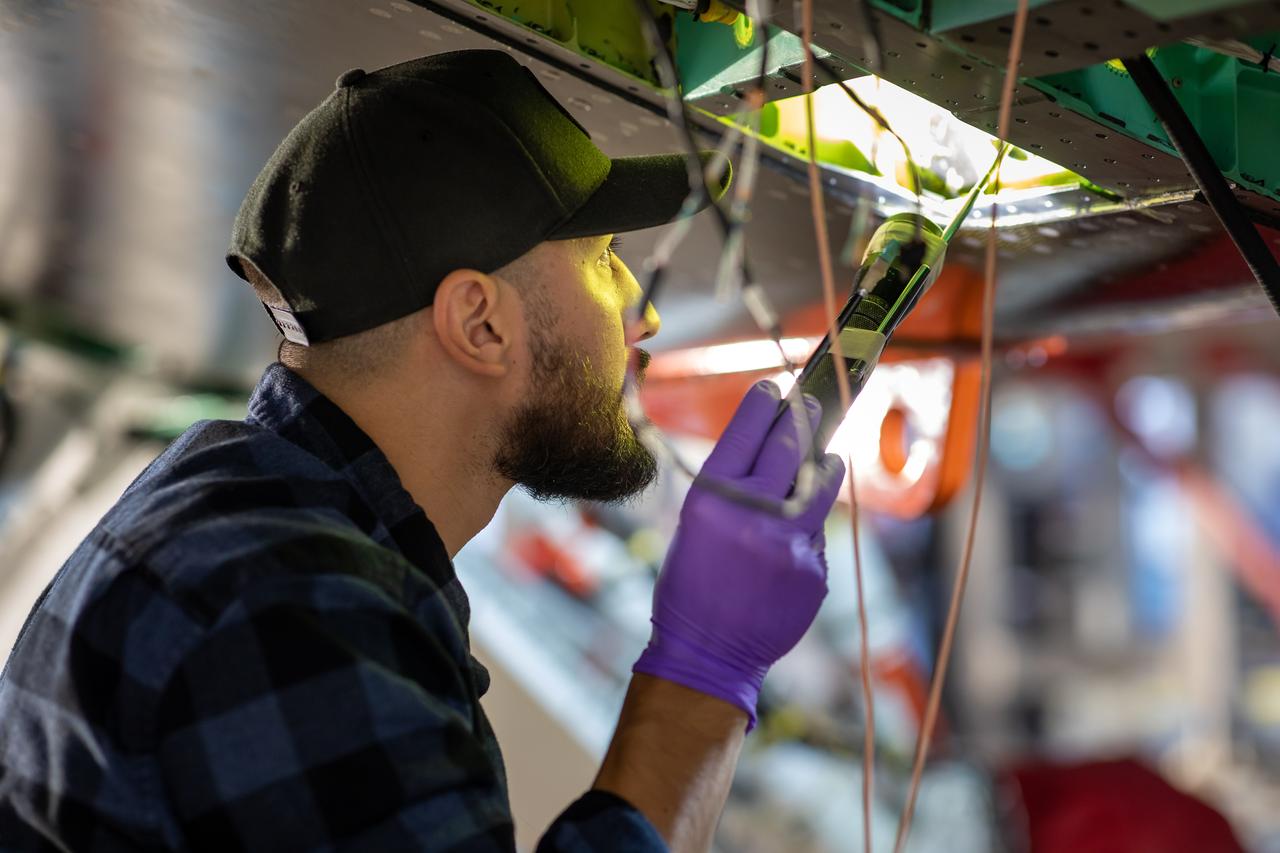

A Lockheed Martin Skunk Works technician inspects some of the wiring and sensors on the X-59 aircraft in preparation for the first power-on system checkouts. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.

Here is an image of the X-59’s 13-foot General Electric F414 engine as the team prepares for a fit check. Making sure components, like the aircraft’s hydraulic lines, which help control functions like brakes or landing gear, and wiring of the engine, fit properly is essential to the aircraft’s safety. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
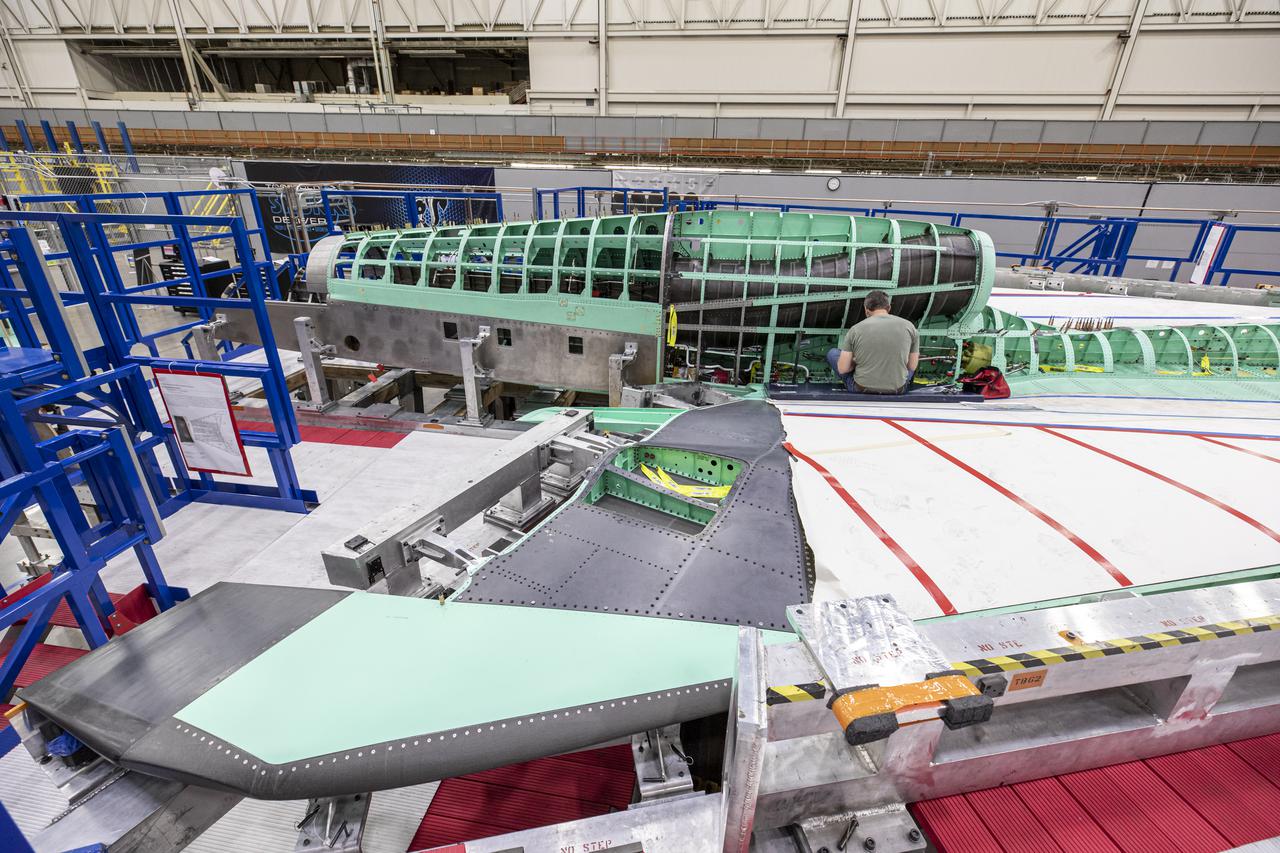

Here is a wide shot of the wing, engine and engine inlet area of NASA’s X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology or QueSST aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 400 Main Wing Assembly, SEG 430 Spine, SEG 500 Empennage Date: 4/28/2021
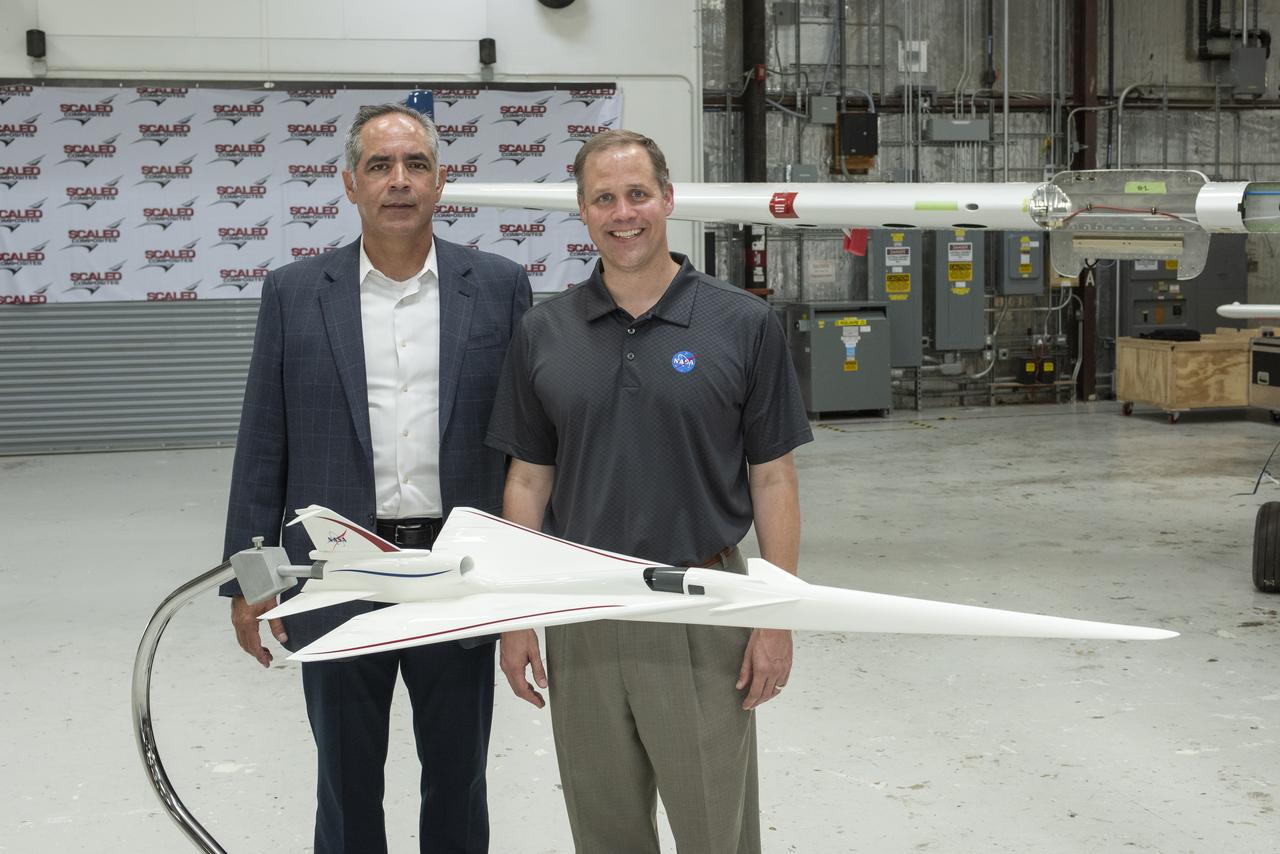

NASA Administrator Bridenstine stands with AFRC center director McBride by model NASA's Supersonic X-Plane, X-59 Quiet Supersonic Technology or QueSST. Bridenstine spoke at press event at Mojave Air and Space Port in California. The goal of X-59 is to quiet the sound when aircraft pierce the speed of sound and make a loud sonic boom on the ground.

Here is an overhead view of the X-59 aircraft (left) prior to the installation of the General Electric F414 engine (center, located under the blue cover). After the engine is installed, the lower empennage (right), the last remaining major aircraft component, will be installed in preparation for integrated system checkouts. The X-59 is the centerpiece of the Quesst mission which plans to help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
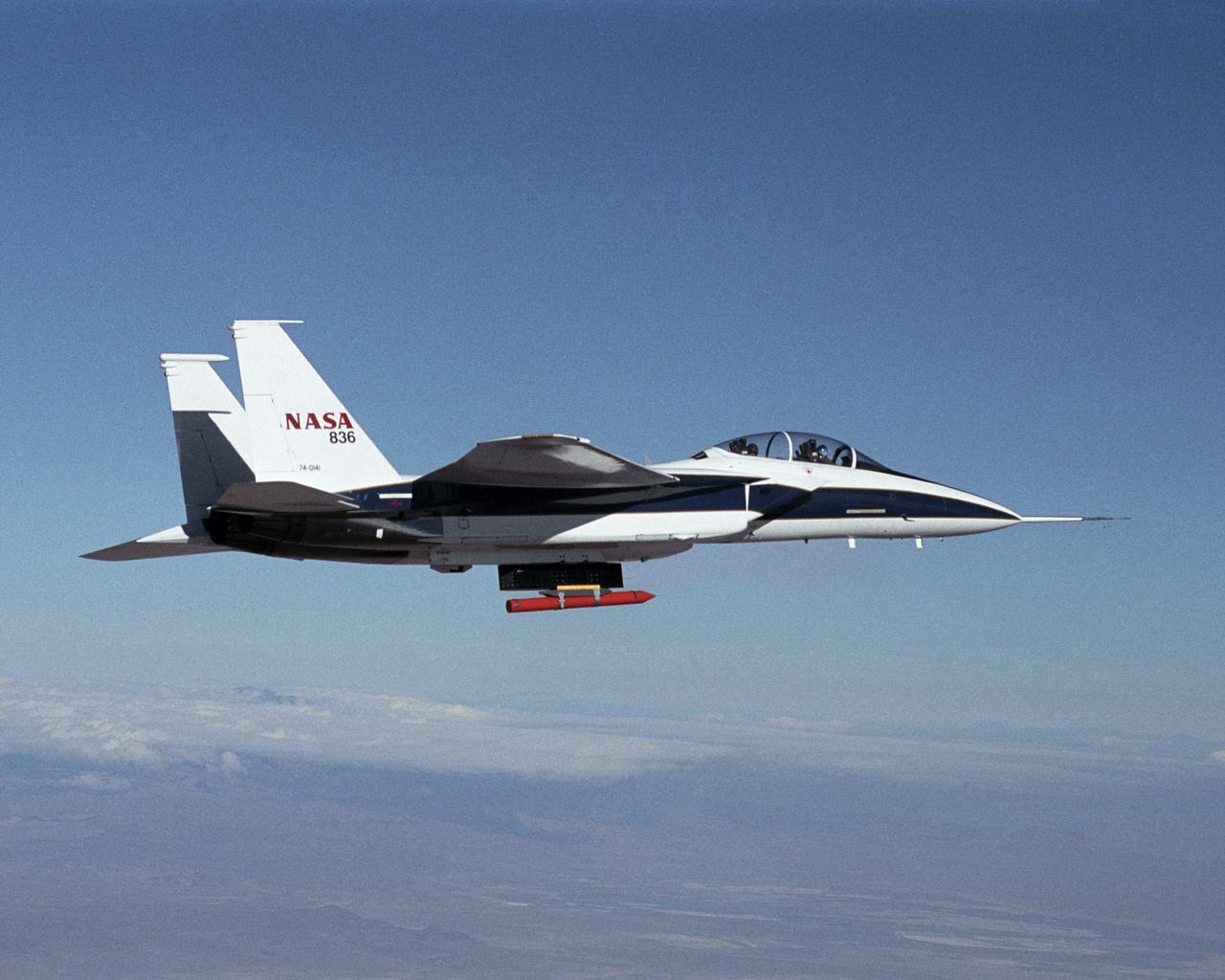

NASA Dryden's new in-house designed Propulsion Flight Test Fixture (PFTF) flew mated to a specially-equipped supersonic F-15B research aircraft during December 2001 and January 2002.
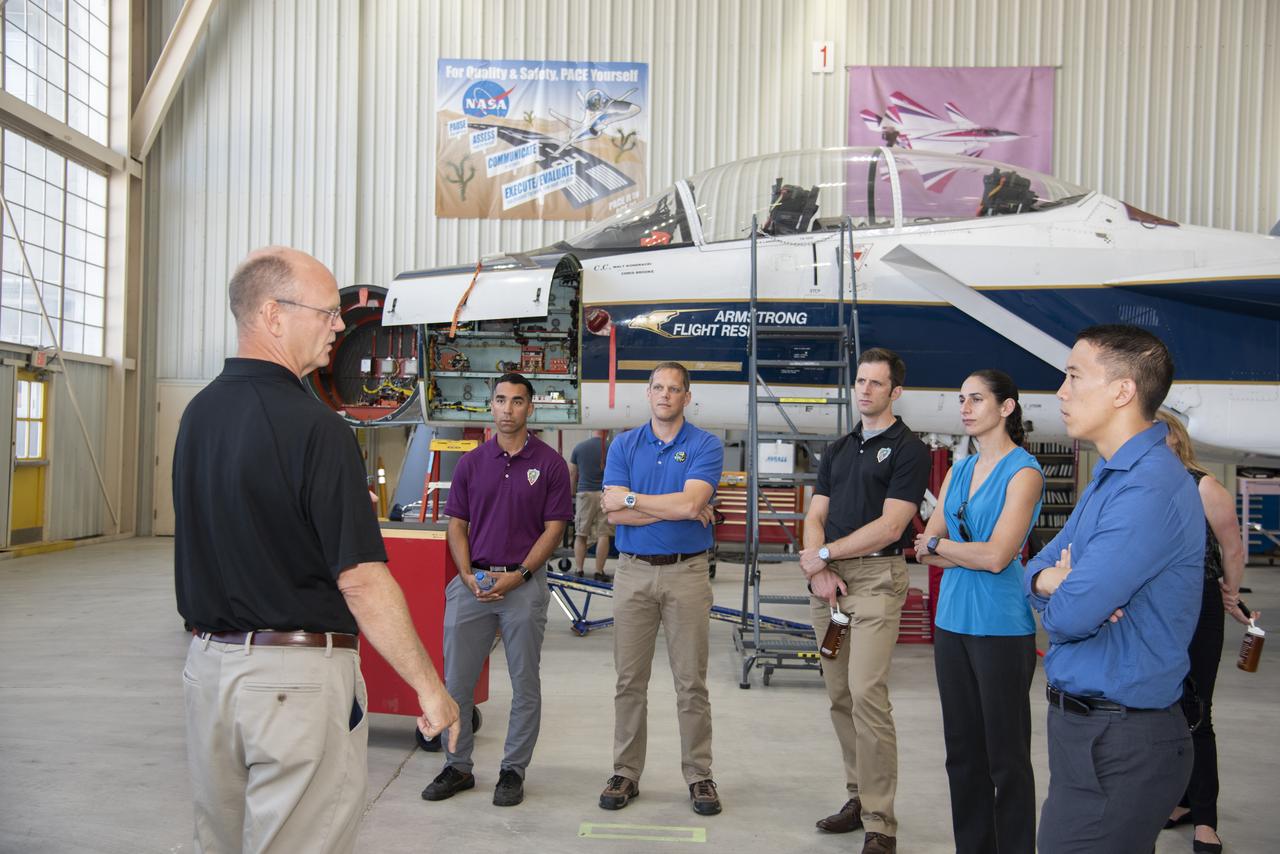

NASA’s 2017 astronaut candidates (L to R) Raja Chari, Bob Hines, Joshua Kutryk, Jasmin Moghbeli, Jonny Kim, and Jessica Watkins toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California. On the left, NASA’s, X-59 pilot, briefs them on use of F-15 for studying sonic booms during the development of the low-boom X-59 aircraft that is planned to fly supersonically over land. Low-level supersonic flight is not allowed at this time because of the loud noise levels generated when flying beyond the speed of sound.
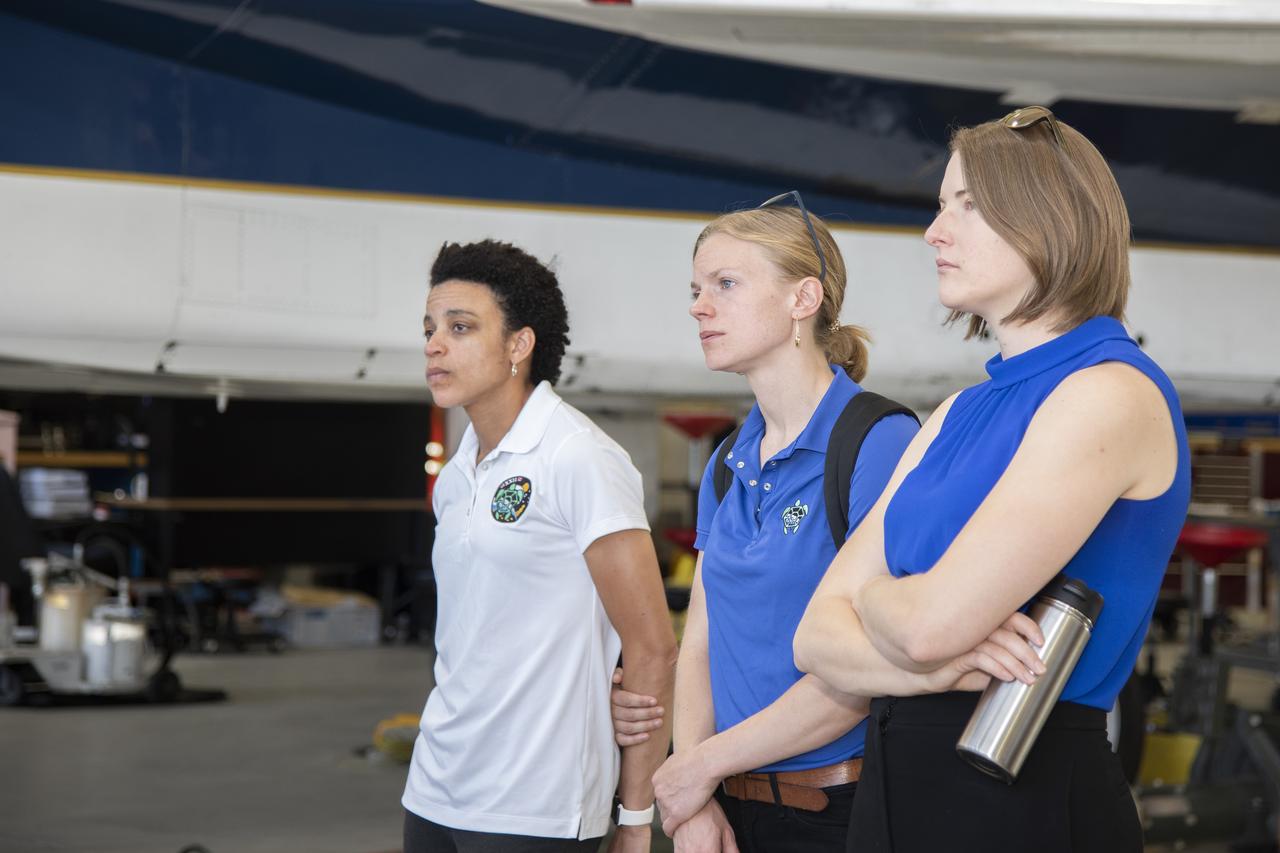

NASA’s 2017 astronaut candidates (L to R) Jessica Watkins, Zena Cardman, Kayla Barron toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California where they were briefed on the use of Armstrong's F-15 and F-18 aircraft for studying sonic booms. The aircraft will be used during the development of the low-boom X-59 aircraft that is planned to fly supersonically over land, which is not allowed at this time because of the loud noise created when flying beyond the speed of sound.
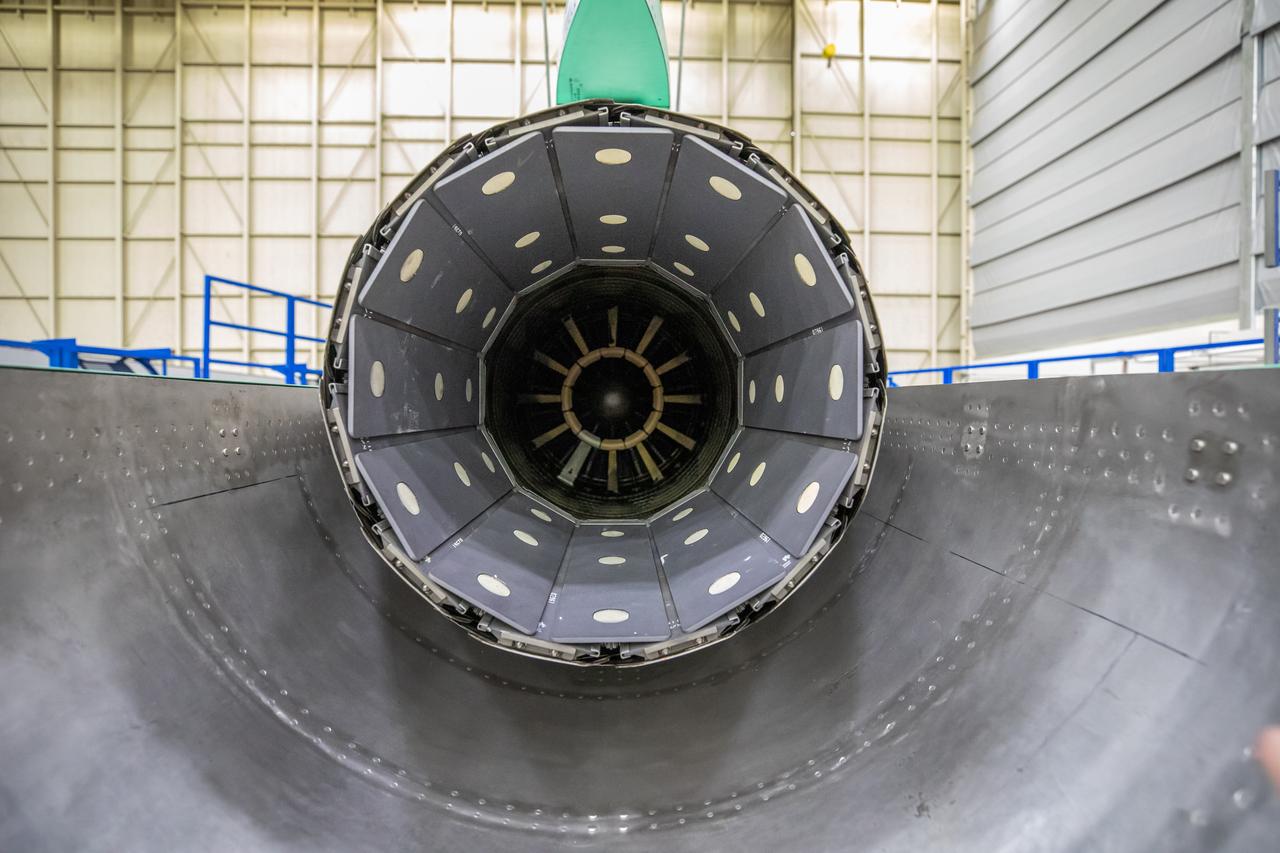

A look at the X-59’s engine nozzle, where the thrust -the force that moves the aircraft- will exit. Once complete, the X-59 is designed to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom. The Quesst mission could help change the rules for commercial supersonic air travel over land.
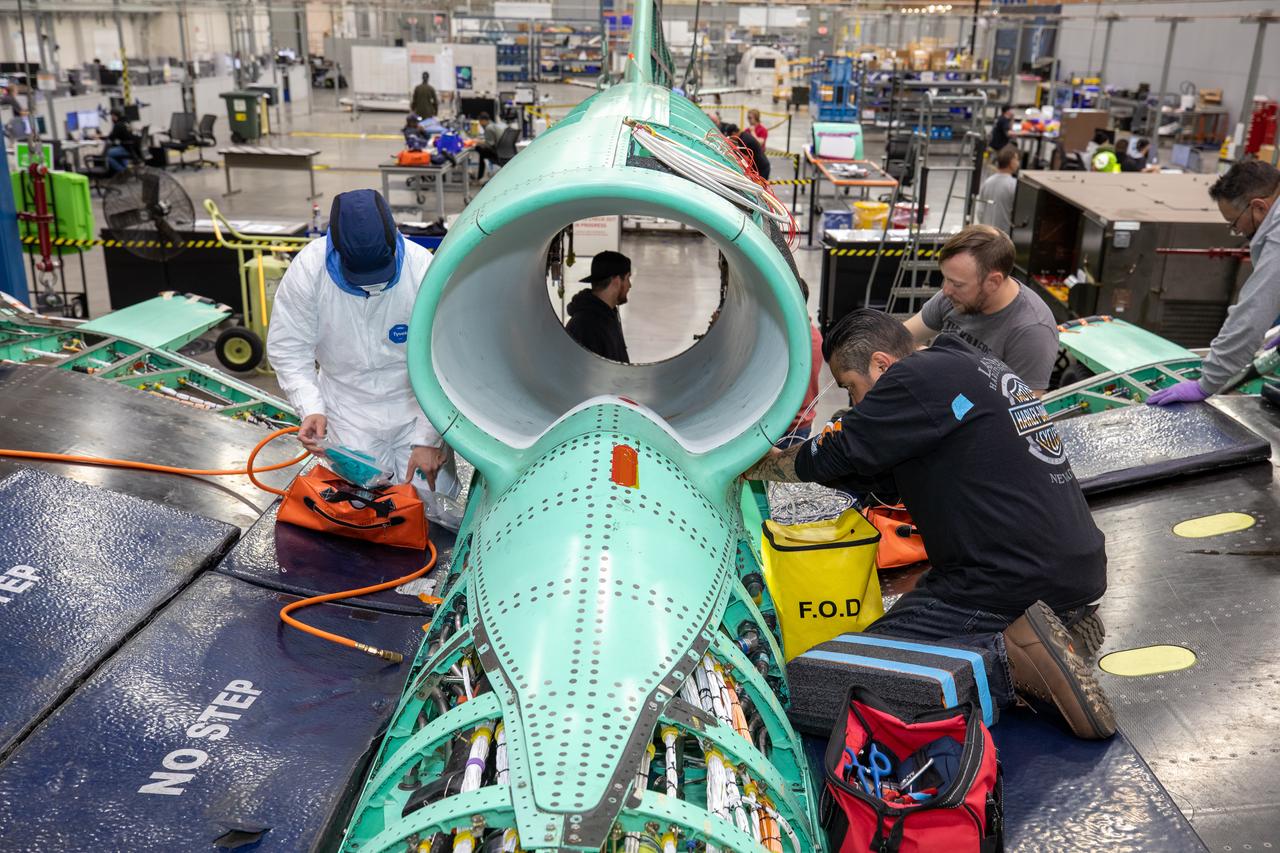

The X-59 team working on the aircraft’s wiring around the engine inlet prior to the engine being installed. Once complete, the X-59 is designed to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom. The Quesst mission could help change the rules for commercial supersonic air travel over land.
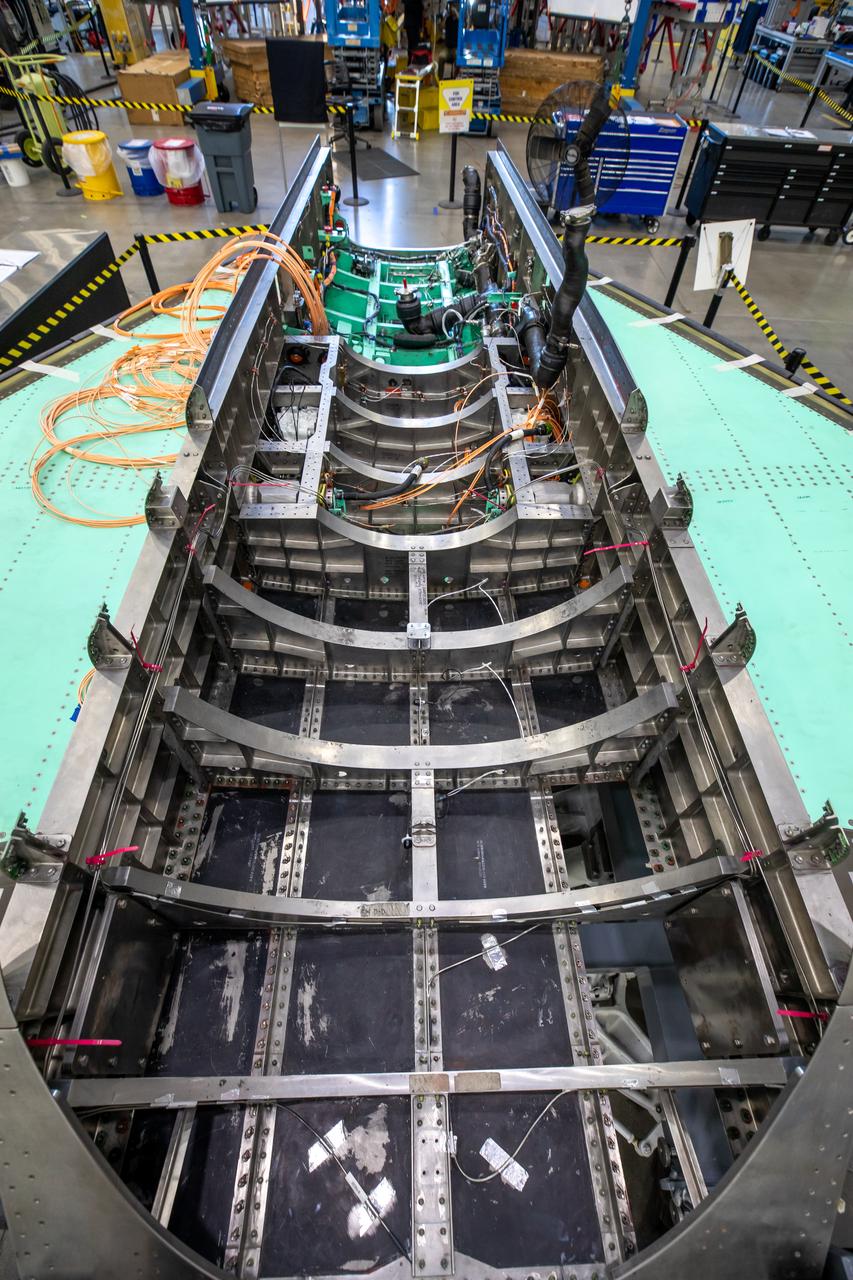
This image shows the X-59 aircraft’s lower empennage structure, or tail section of the plane, that was installed. The stabilators, the outer surfaces also seen in the photo, attach to the lower empennage and are used to help regulate the aircraft pitch which controls the up and down movement of the motion of the plane. The 13-foot engine will pack 22,000 pounds of propulsion and energy and power the X-plane to its planned cruising speed of Mach 1.4. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.
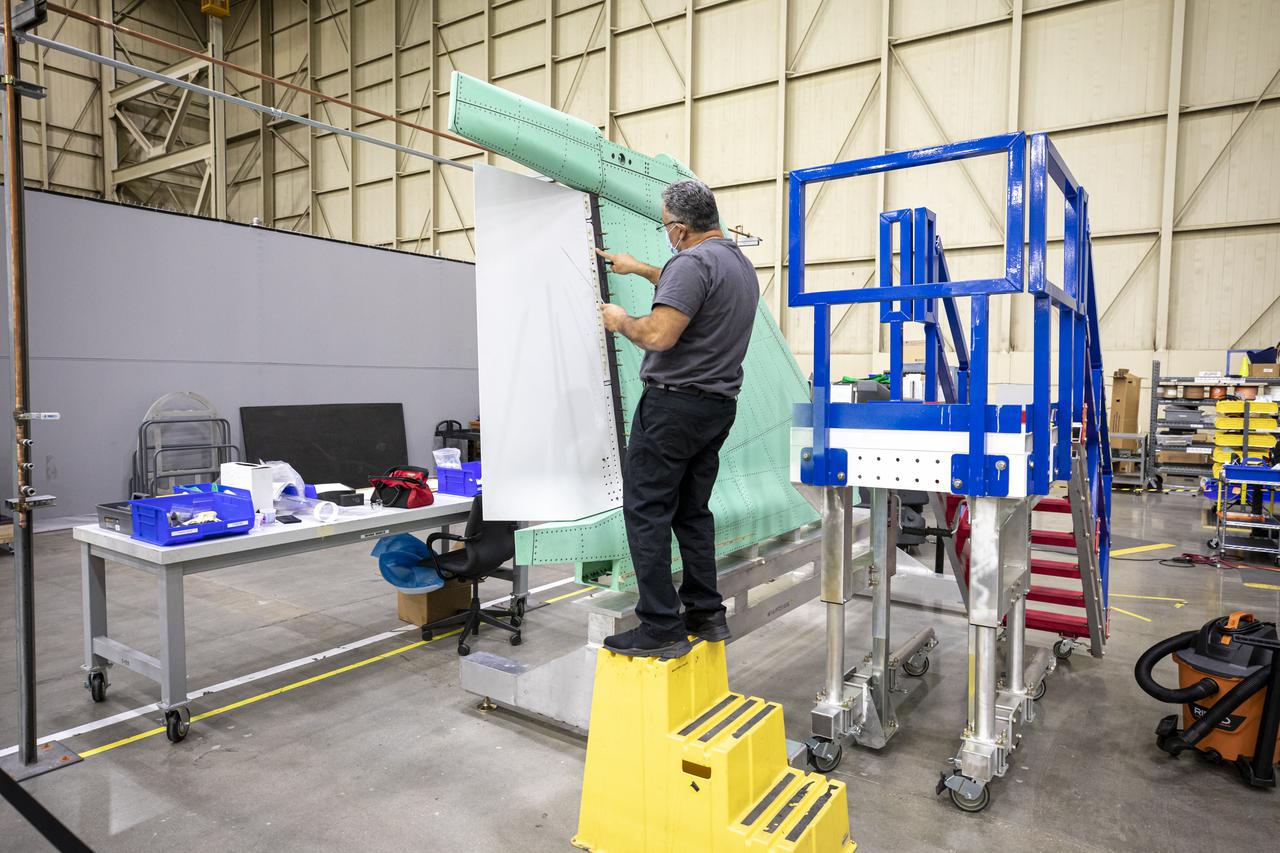

A technician is shown working on the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology or QueSST aircraft’s vertical tail prior to installation. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 530 Vertical Tail - Rudder Installed Date: 5/12/2021
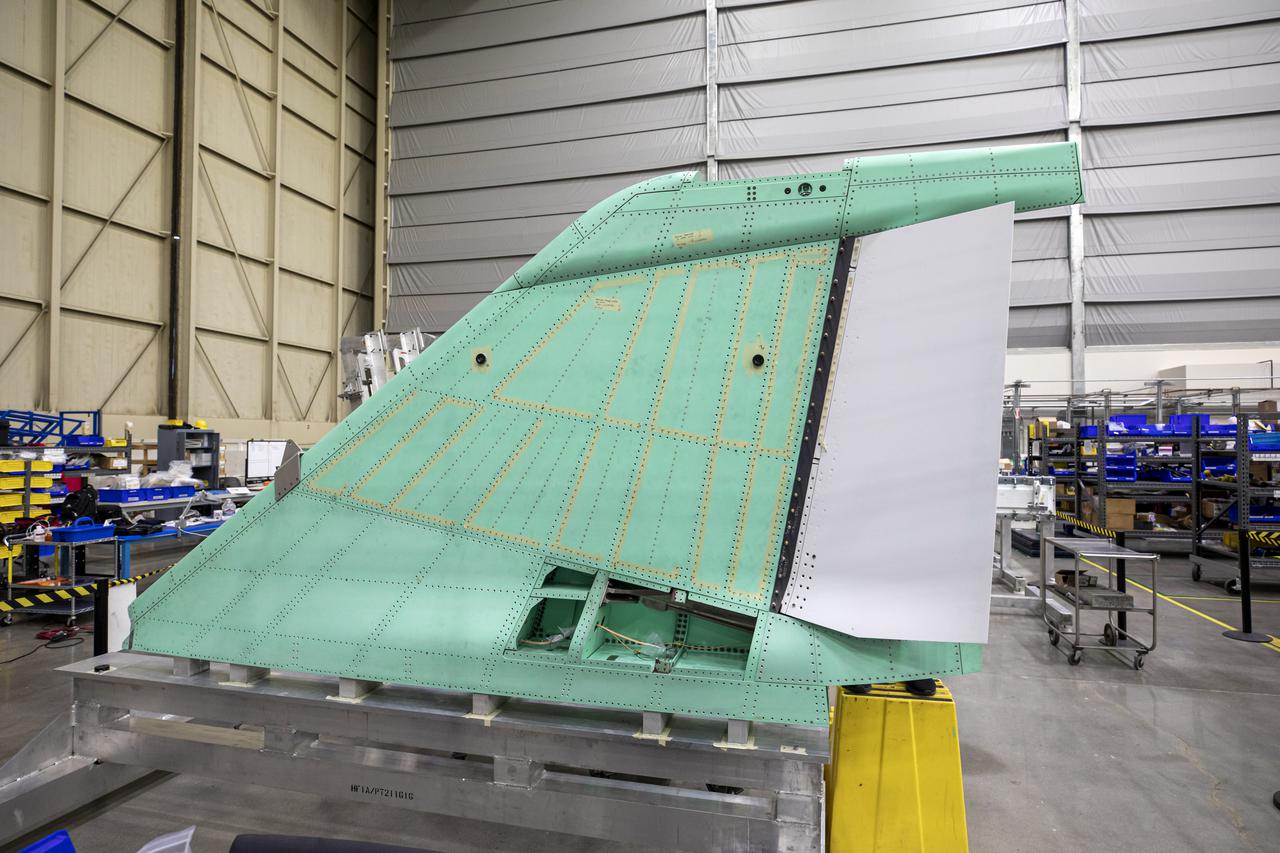

Pictured here is a close up view of the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology or QueSST aircraft’s vertical tail prior to installation. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 530 Vertical Tail - Rudder Installed Date: 5/12/2021
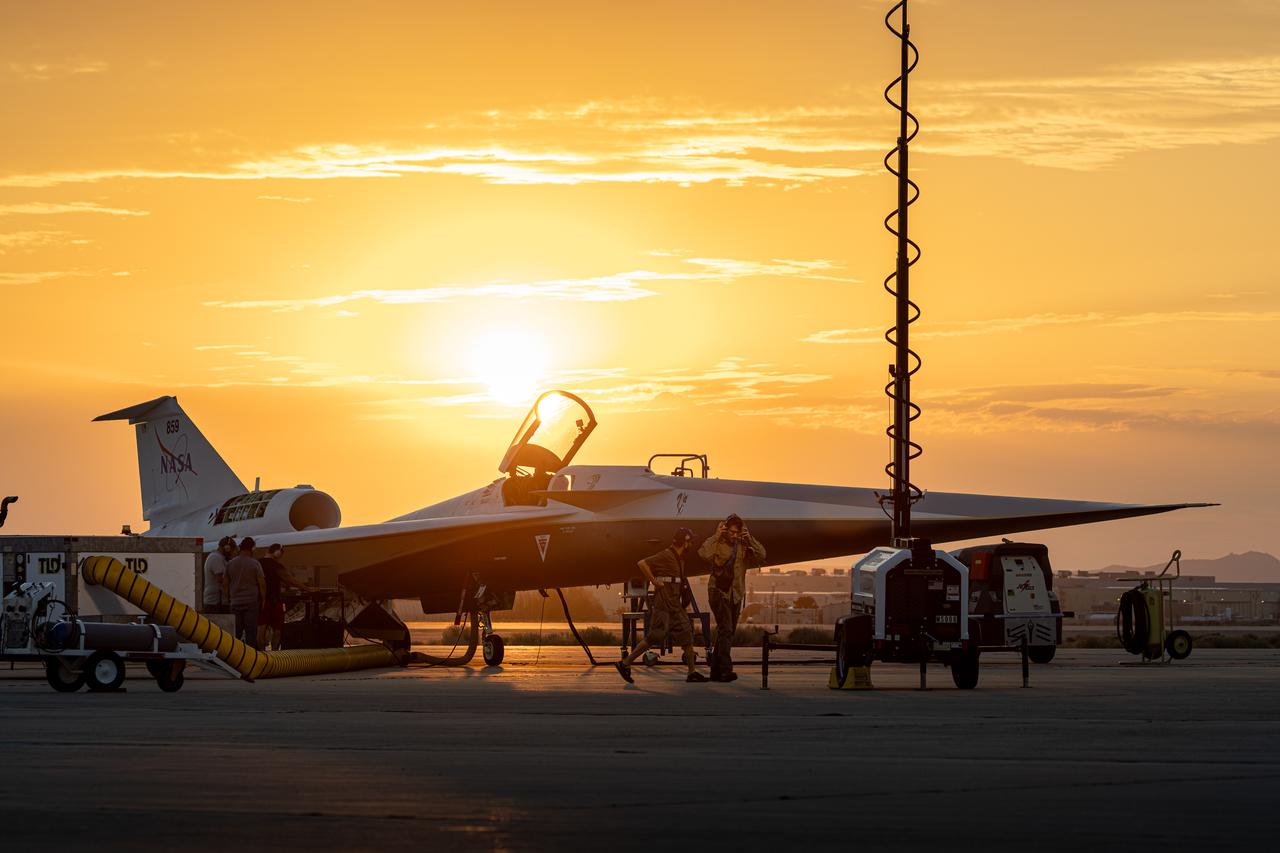

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on the ramp at sunrise before ground tests at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California, on July 18, 2025. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight and the aircraft is scheduled to make its first flight later this year.

This overview shot of the X-59 Quiet Supersonic Technology or QueSST aircraft shows the vehicle before a major merger of three major aircraft sections – the fuselage, the wing, and the tail assembly – together, making it looks more like an airplane. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: Manufacture Area From Above Date: 3/30/2021
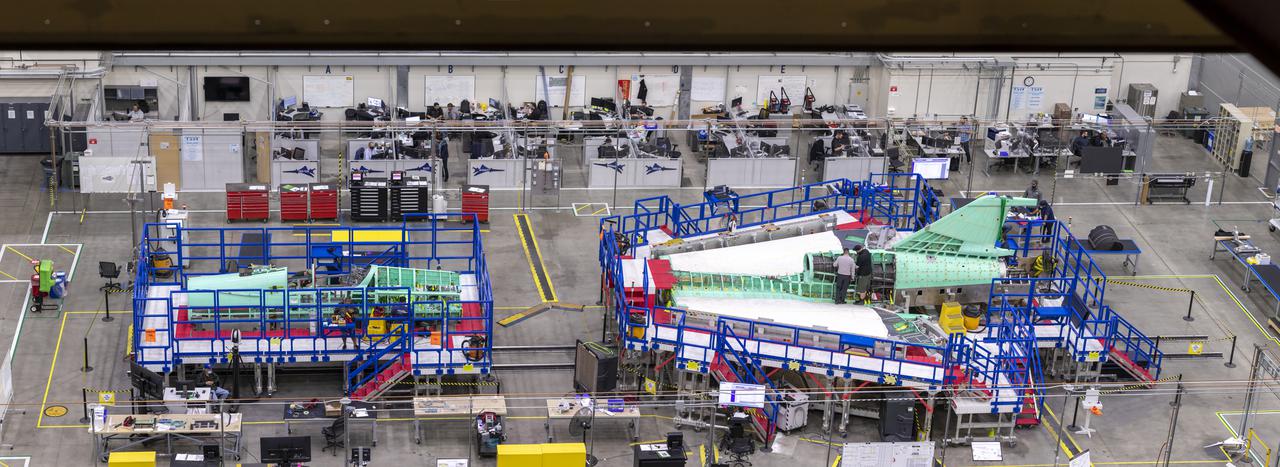

This overhead shot of the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology or QueSST aircraft shows the assembly progress of the vehicle during Spring 2021. In the left side of the picture, the fuselage which contains the cockpit is shown and the right side of the photo shows the wing and the tail section of the aircraft. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: Manufacture Area From Above Date: 3/30/2021
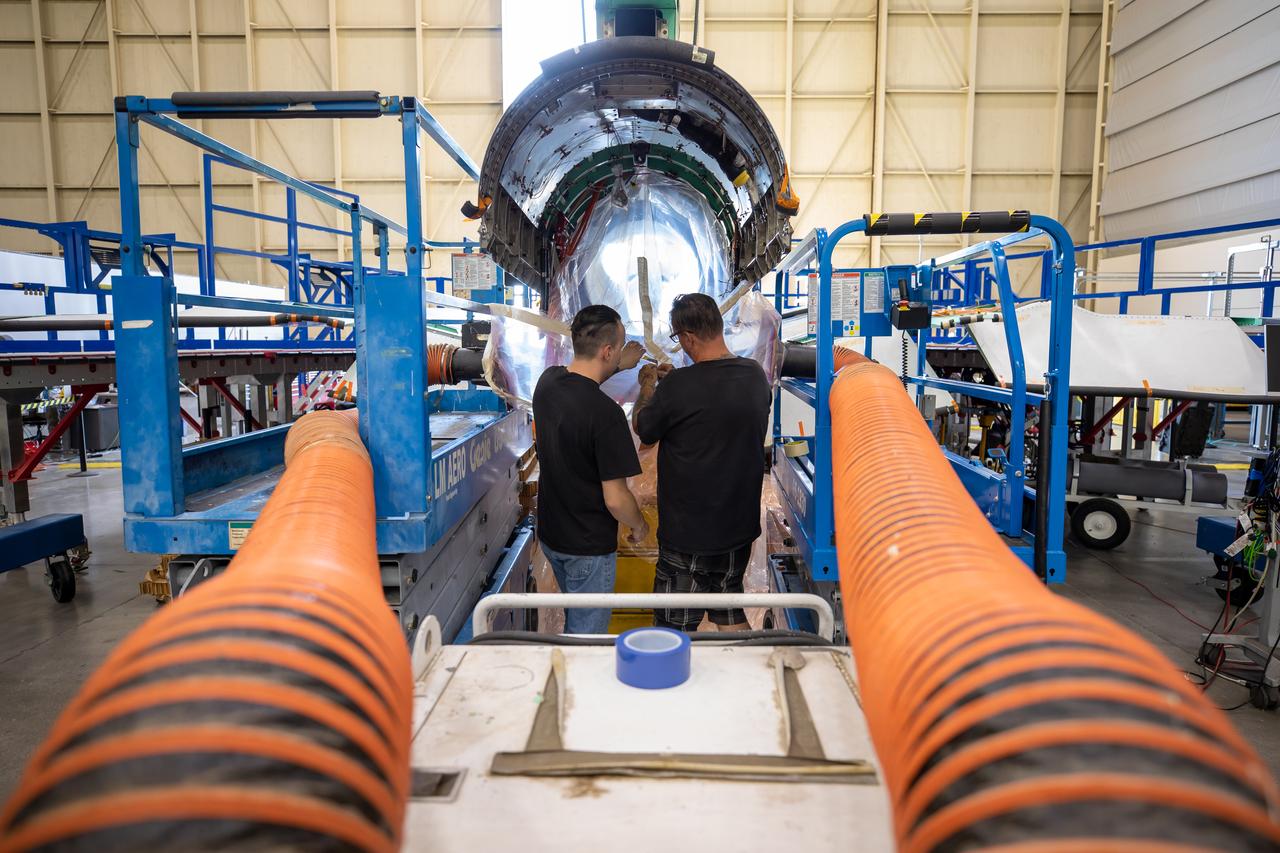

This image shows the extensive ventilation system that has been placed adjacent to the X-59 during the recent painting of the aircraft’s engine inlet. Once the aircraft build and ground testing are complete, the X-59 airplane will begin flight testing, working towards demonstrating the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
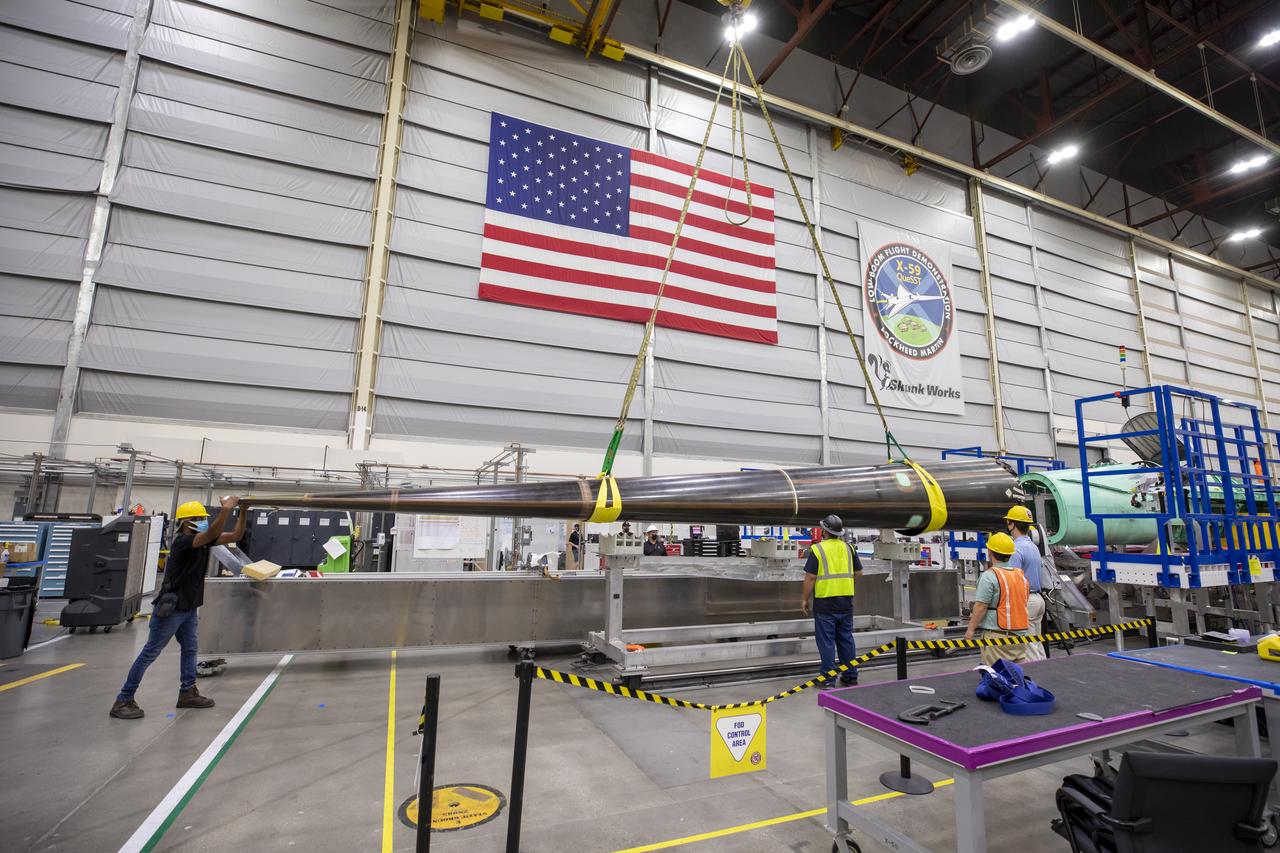

Event: SEG 230 Nose - Craned Onto Tooling A close up of the X-59’s duckbill nose, which is a crucial part of its supersonic design shaping. The team prepares the nose for a fit check. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
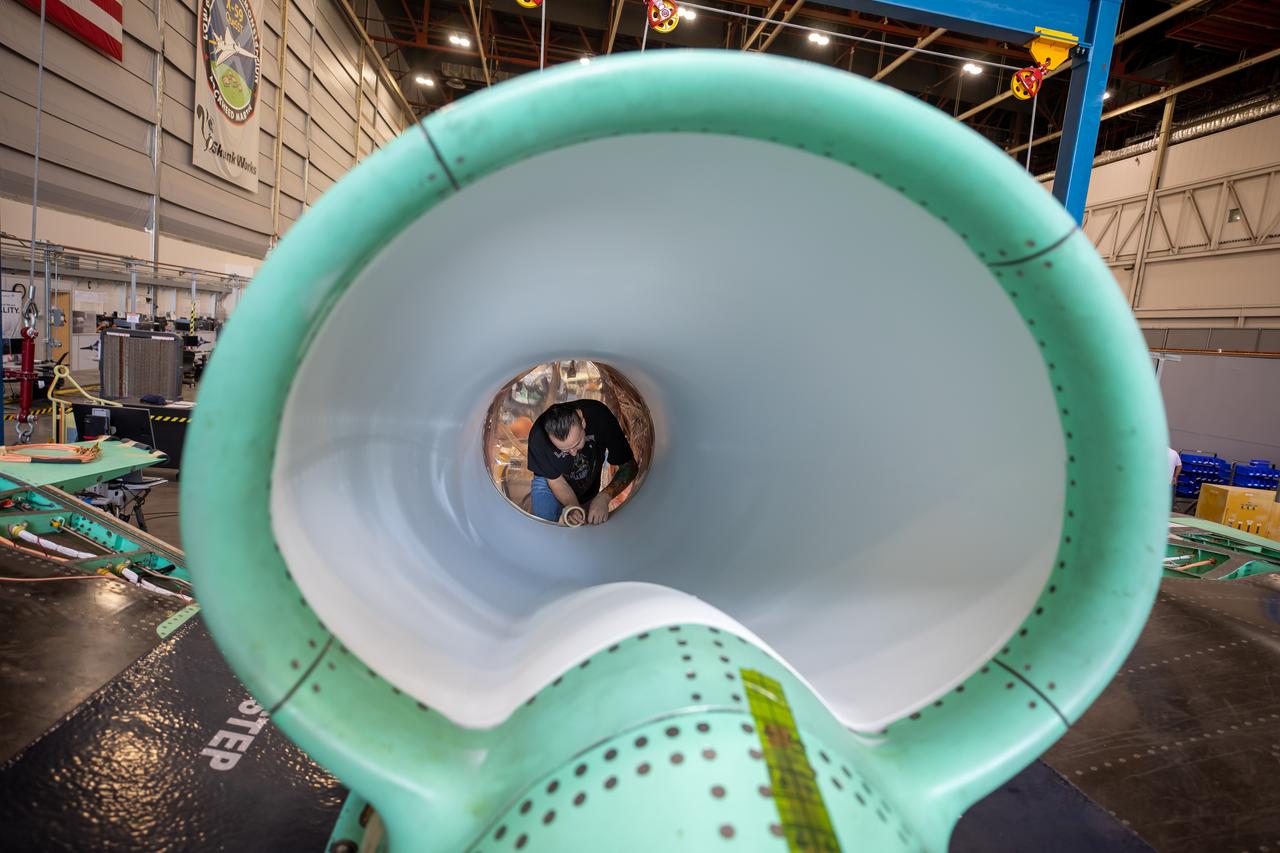

This is an up-close view of the X-59’s engine inlet – fresh after being painted. The 13-foot F414-GE-100 engine will be placed inside the inlet bringing the X-59 aircraft one step closer to completion. Once fully assembled, the X-59 aircraft will begin flight operations, working toward demonstration of the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump, helping to enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
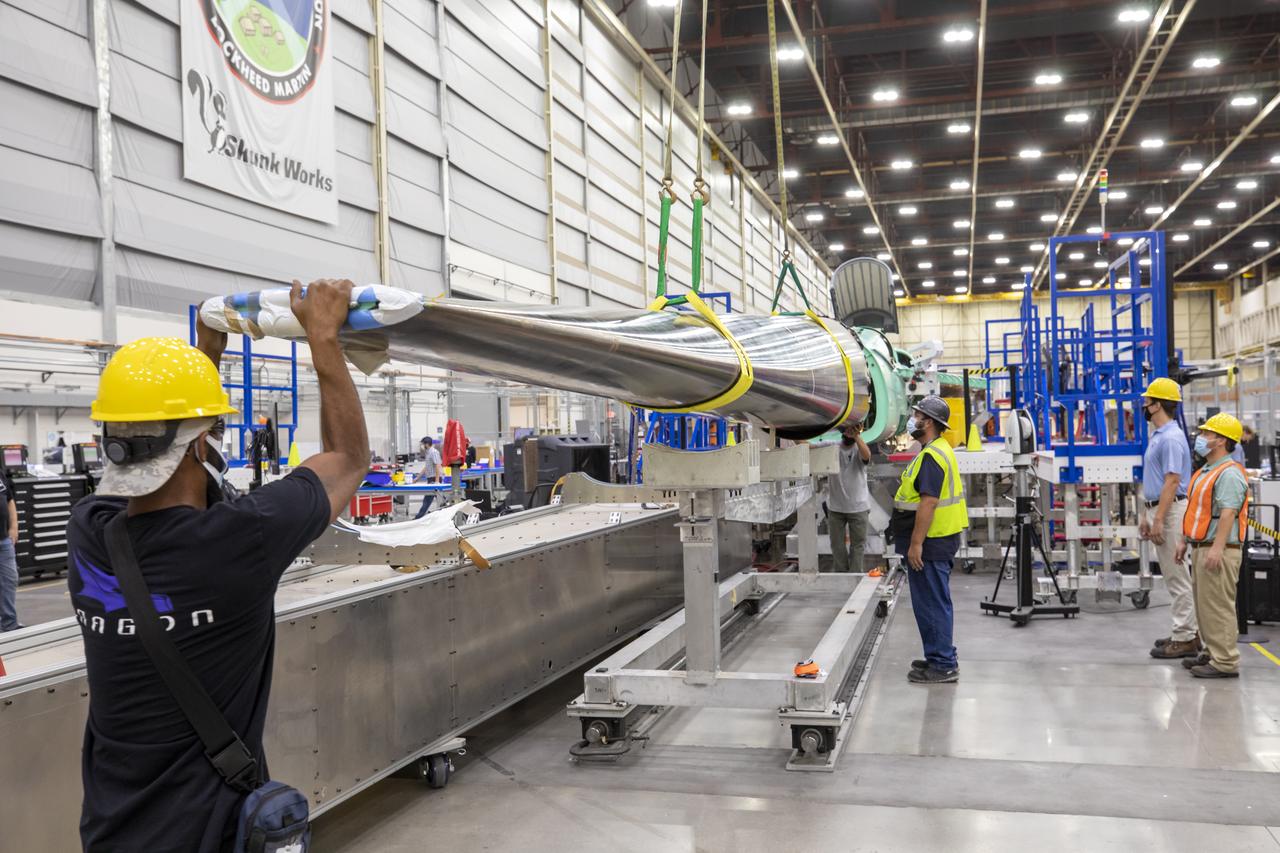

Event: SEG 230 Nose - Craned Onto Tooling A close-up of the X-59’s duckbill nose, which is a crucial part of its supersonic design shaping. The team prepares the nose for a fit check. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
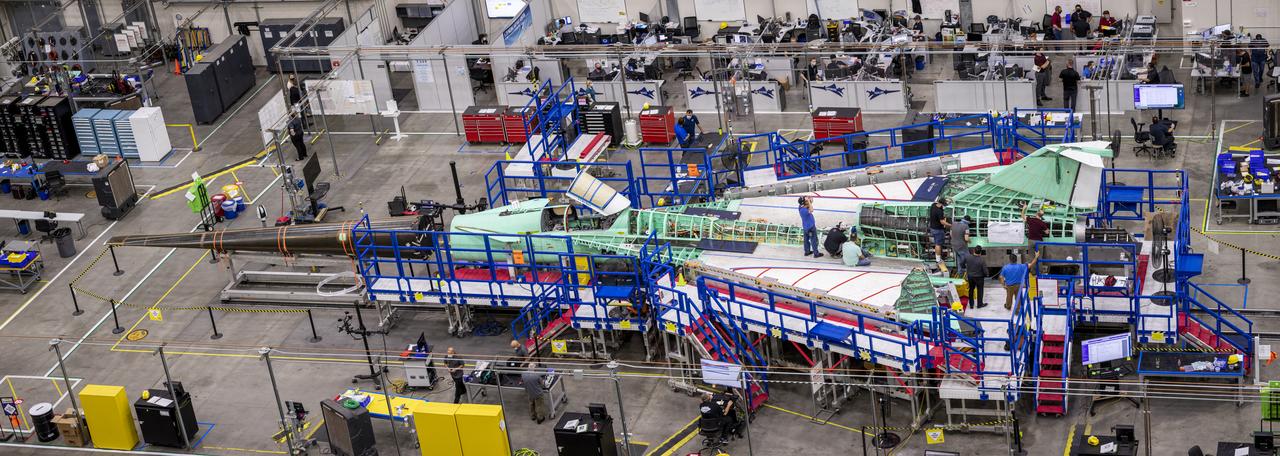

A panoramic side view of the left top of the X-59 supersonic plane with the tail on and the nose in the process of installation. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
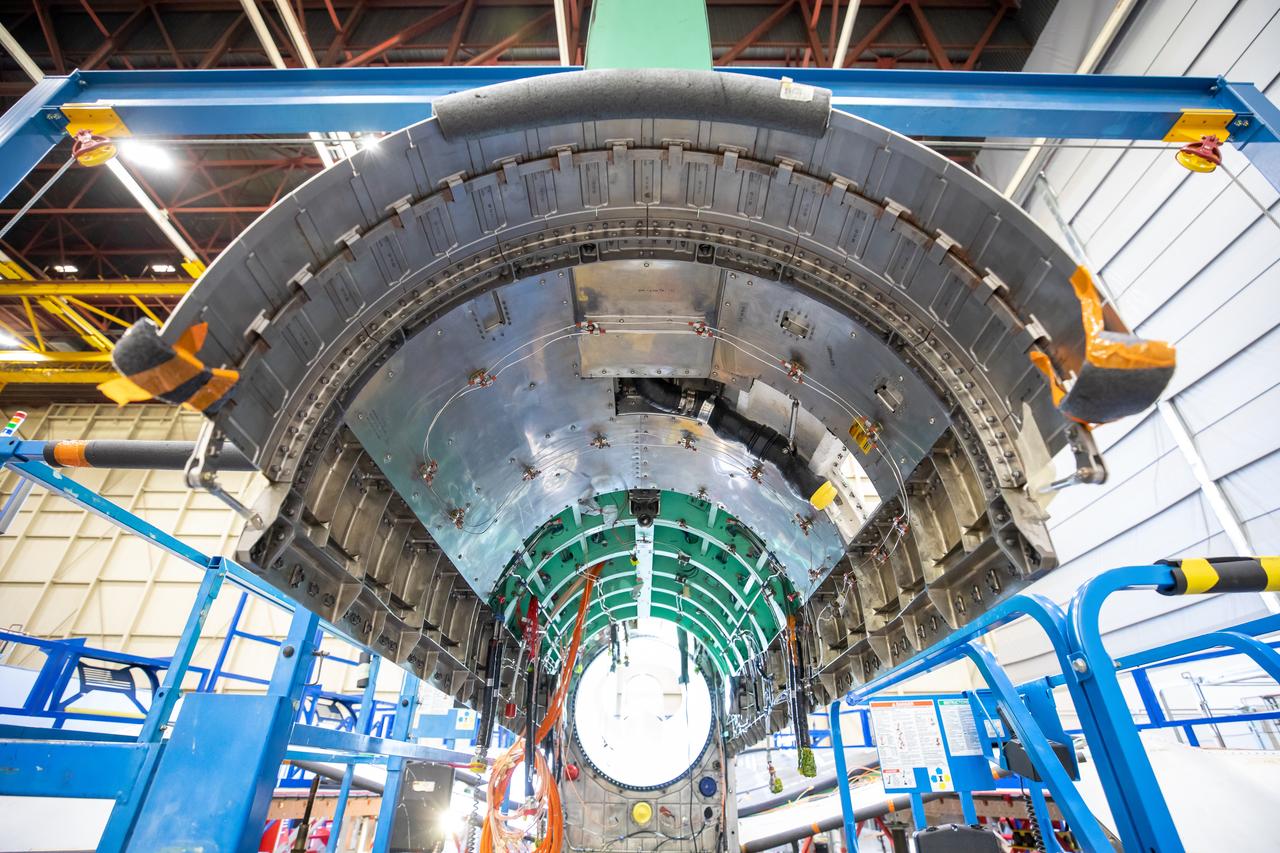

The upper empennage, or tail section of the plane, and engine bay is surrounded by a blue gantry that is used to assist with ground installation and removal of the X-59’s lower empennage and engine. Once fully assembled, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.
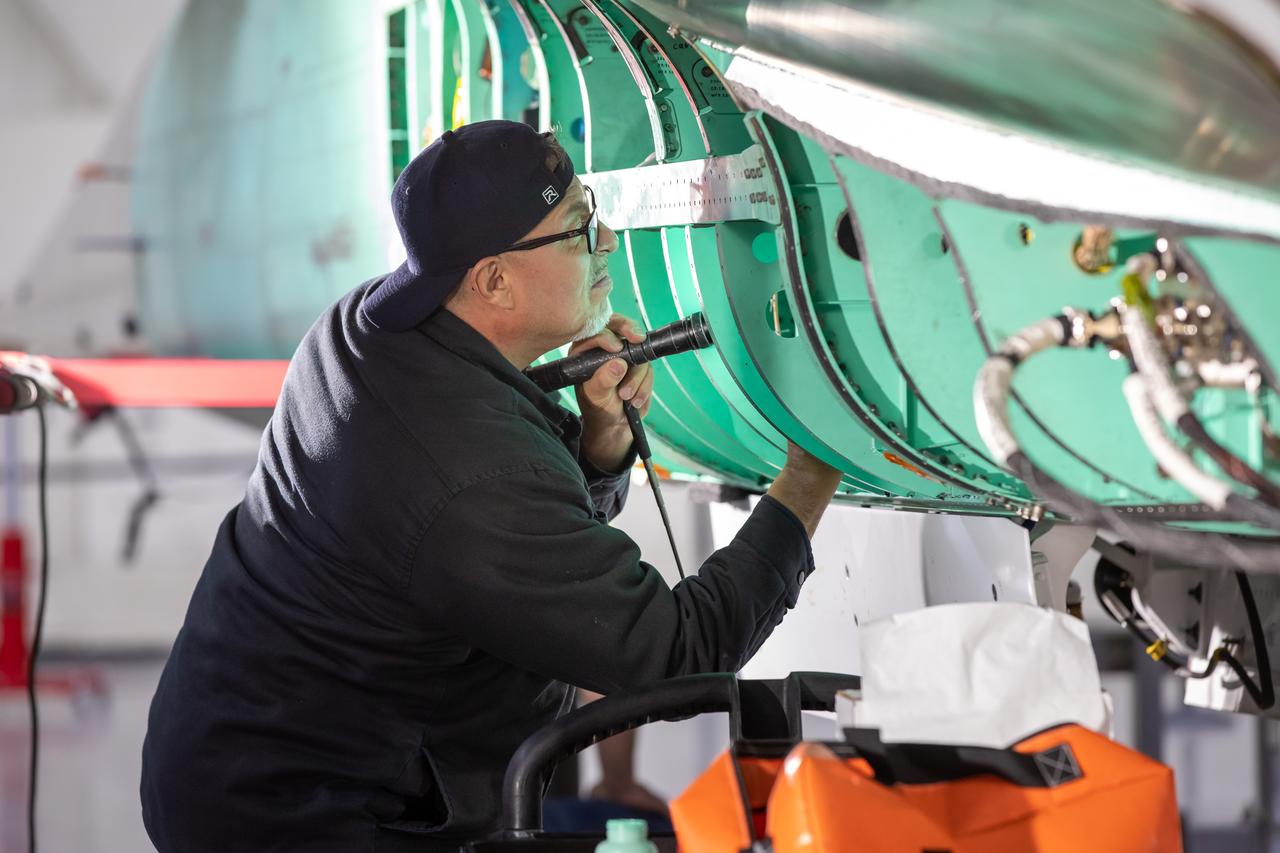

A quality inspector checks NASA’s X-59 aircraft during the construction phase. The X-59 was built in Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. Once the aircraft and ground testing are complete, the X-59 will undergo flight testing, which will demonstrate the plane’s ability to fly supersonic - faster than the speed of sound - while reducing the loud sonic boom. This could enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
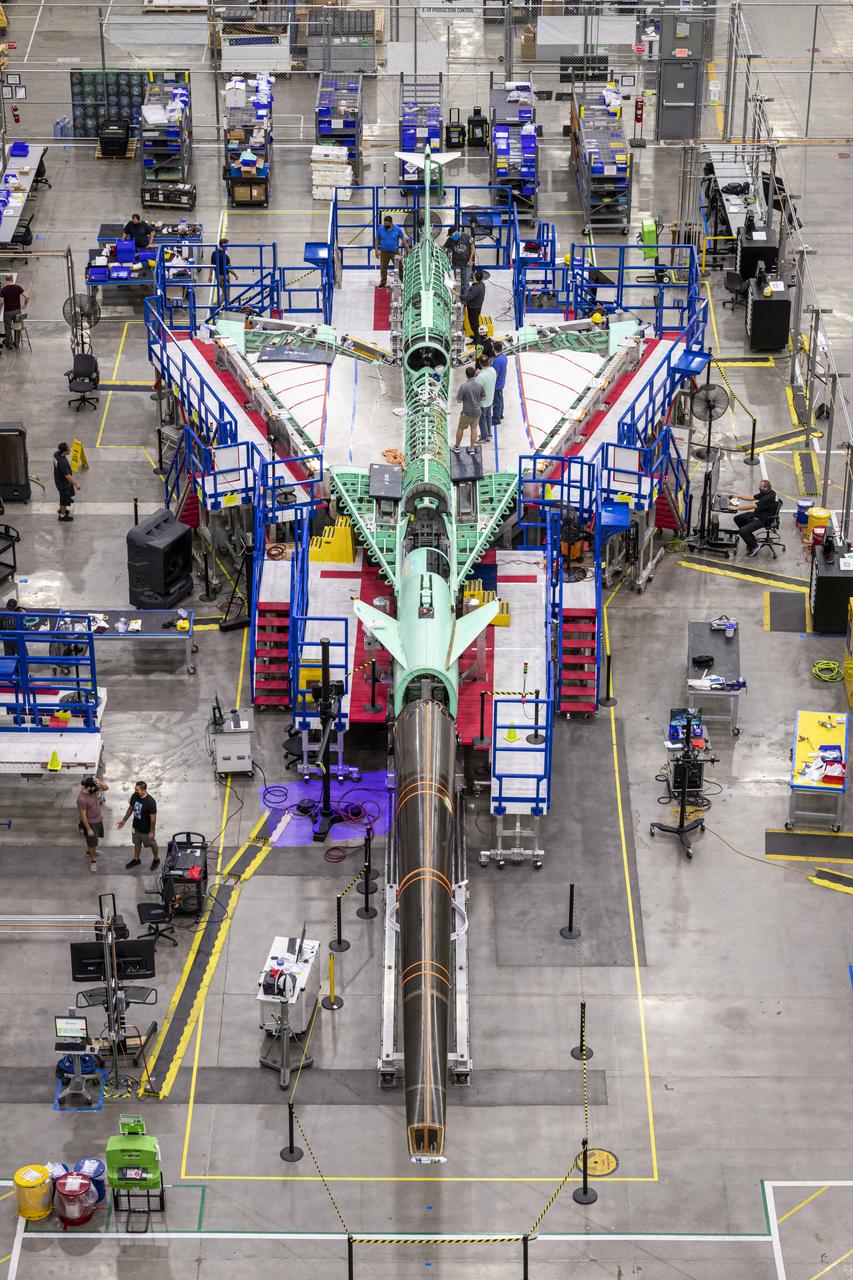

An overhead view of the X-59 supersonic plane with the tail on and the nose in the process of installation. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
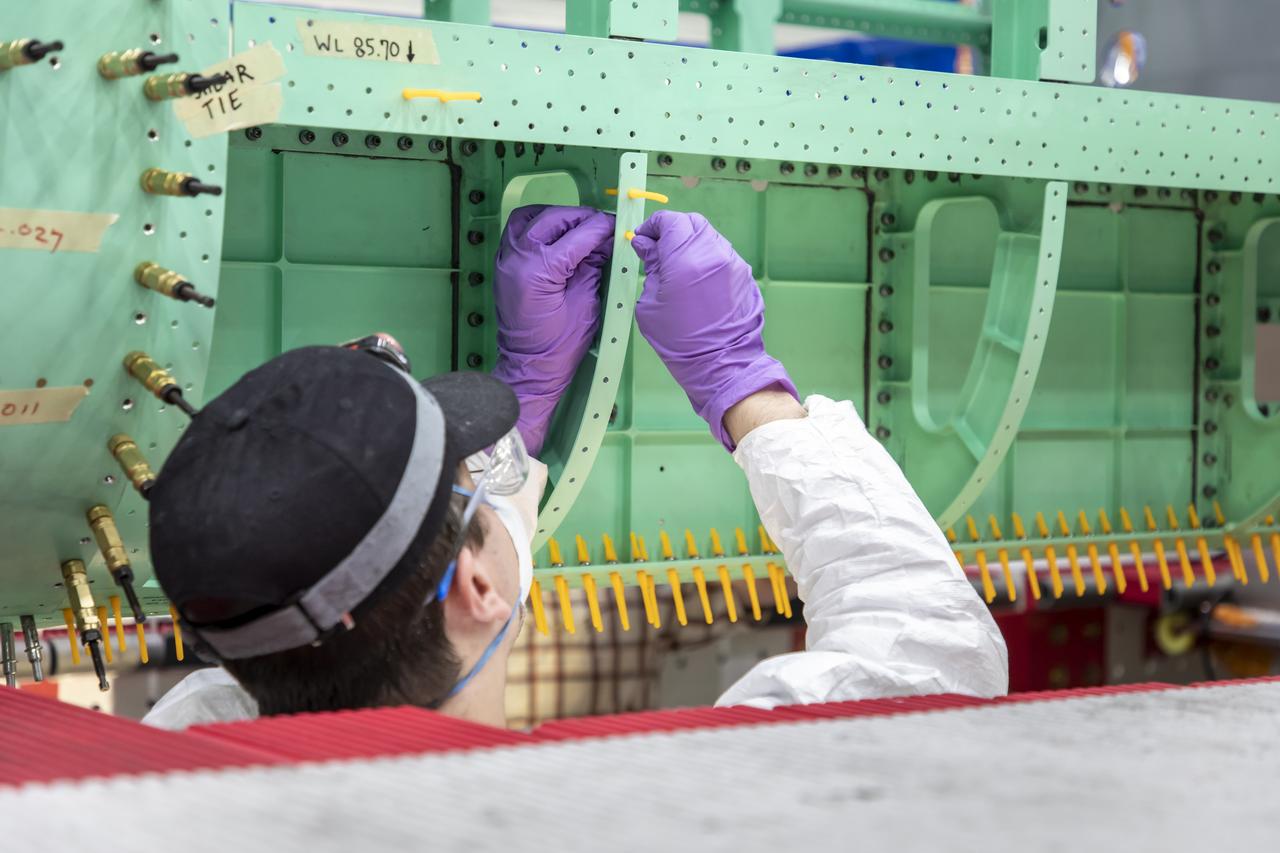

A Lockheed Martin technician prepares holes for installation of the fuselage panel on the X-59. The fuselage is the section of the aircraft that contains the cockpit. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
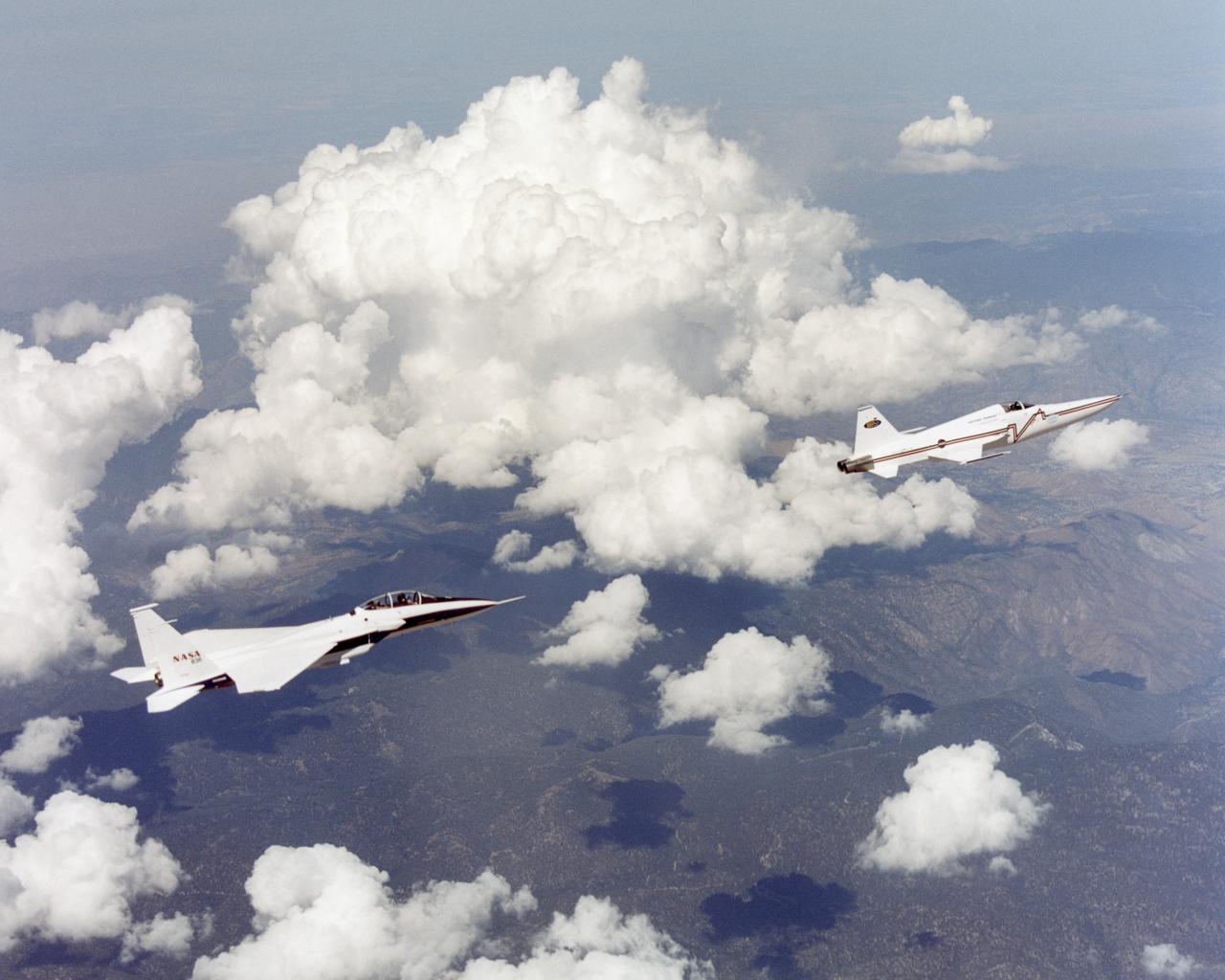

NASA's F-15B research testbed jet from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center flew in the supersonic shockwave of a Northrop Grumman Corp. modified U.S. Navy F-5E jet in support of the Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, which is part of the DARPA's Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. On Aug. 27, 2003, the F-5 SSBD aircraft demonstrated a method to reduce the intensity of sonic booms.

This overhead shot of the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology or QueSST aircraft shows the assembly progress of the vehicle during Spring 2021. Pictured here you can see the nose (far left) which will later be mounted to the middle section in the photo known as the fuselage and the last section is the wing and tail in the far right of the photo. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: Manufacture Area From Above Date: 3/30/2021
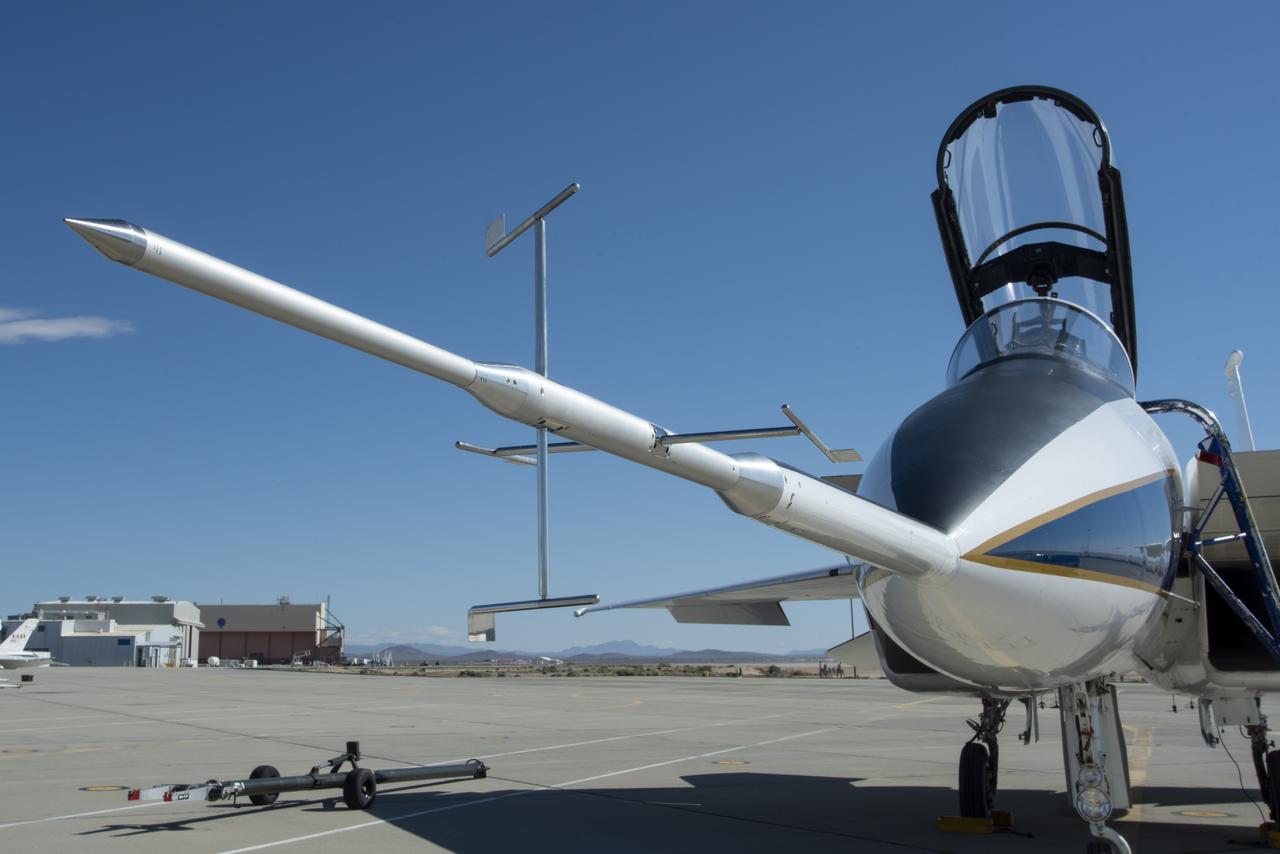

NASA recently completed flight testing a state-of-the-art instrument designed to capture high-quality measurements of shock waves created by supersonic aircraft in flight. It's called the Shock Sensing Probe. The probe's performance was tested in flight at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, using an innovative technique originated by NASA's predecessor, the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics.

NASA recently completed flight testing a state-of-the-art instrument designed to capture high-quality measurements of shock waves created by supersonic aircraft in flight. It’s called the Shock Sensing Probe. The probe’s performance was tested in flight at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, using an innovative technique originated by NASA’s predecessor, the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics.

This overhead view of the X-59 shows the aircraft at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. During the assembly of this experimental aircraft, the team often has to remove components to effectively and safely assemble other sections of the aircraft. In this image, the nose is not attached and the horizontal stabilators are shown behind the tail. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission which plans to produce data that will help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
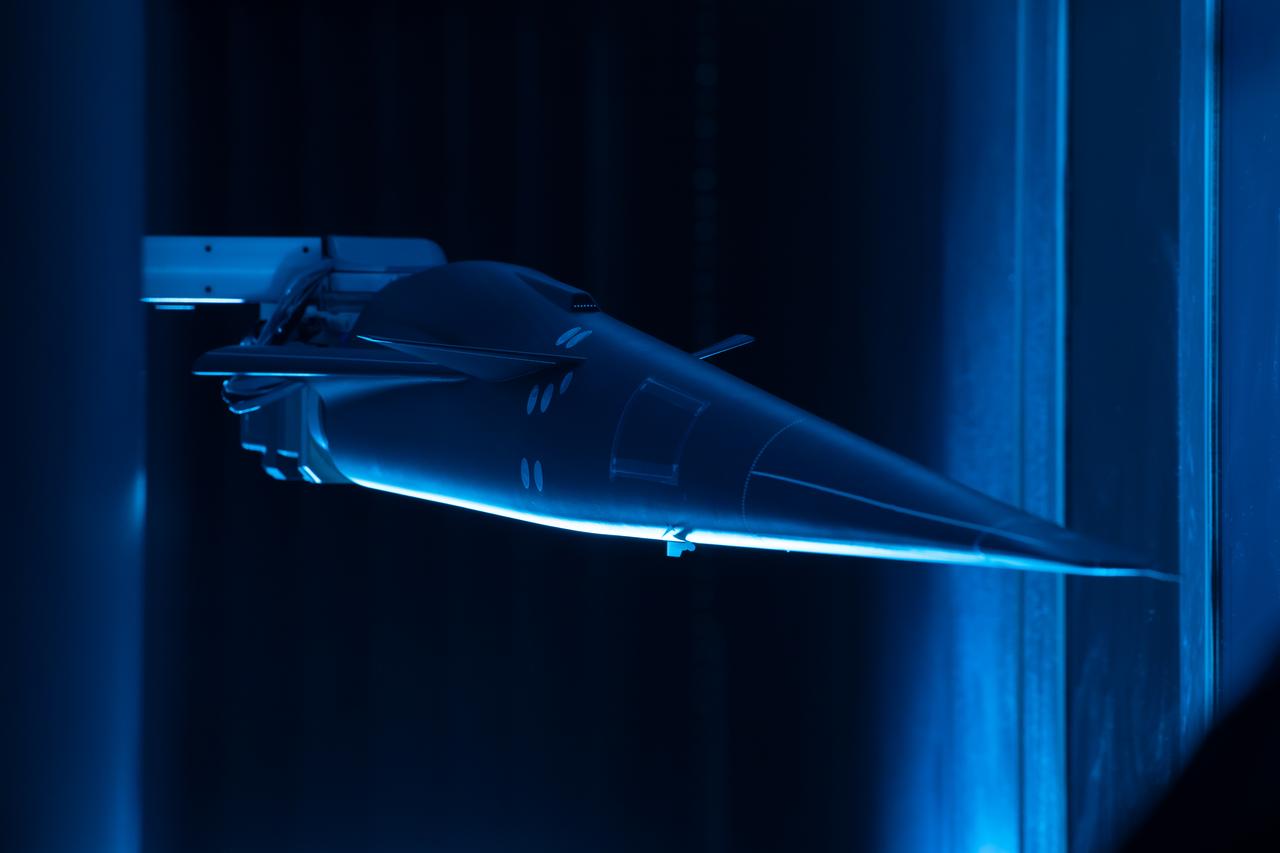

Event: Forebody and Nose - Windtunnel Testing A model of the X-59 forebody is shown in the Lockheed Martin Skunk Works’ wind tunnel in Palmdale, California. These tests gave the team measurements of wind flow angle around the aircraft’s nose and confirmed computer predictions made using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software tools. The data will be fed into the aircraft flight control system to tell the pilot the aircraft’s altitude, speed and angle. This is part of NASA’s Quesst mission which plans to help enable supersonic air travel over land.

This overhead view of the X-59 shows the aircraft at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. During the assembly of this experimental aircraft, the team often has to remove components to effectively and safely assemble other sections of the aircraft. In this image, the nose is not attached and the horizontal stabilators are shown behind the tail. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission which plans to produce data that will help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
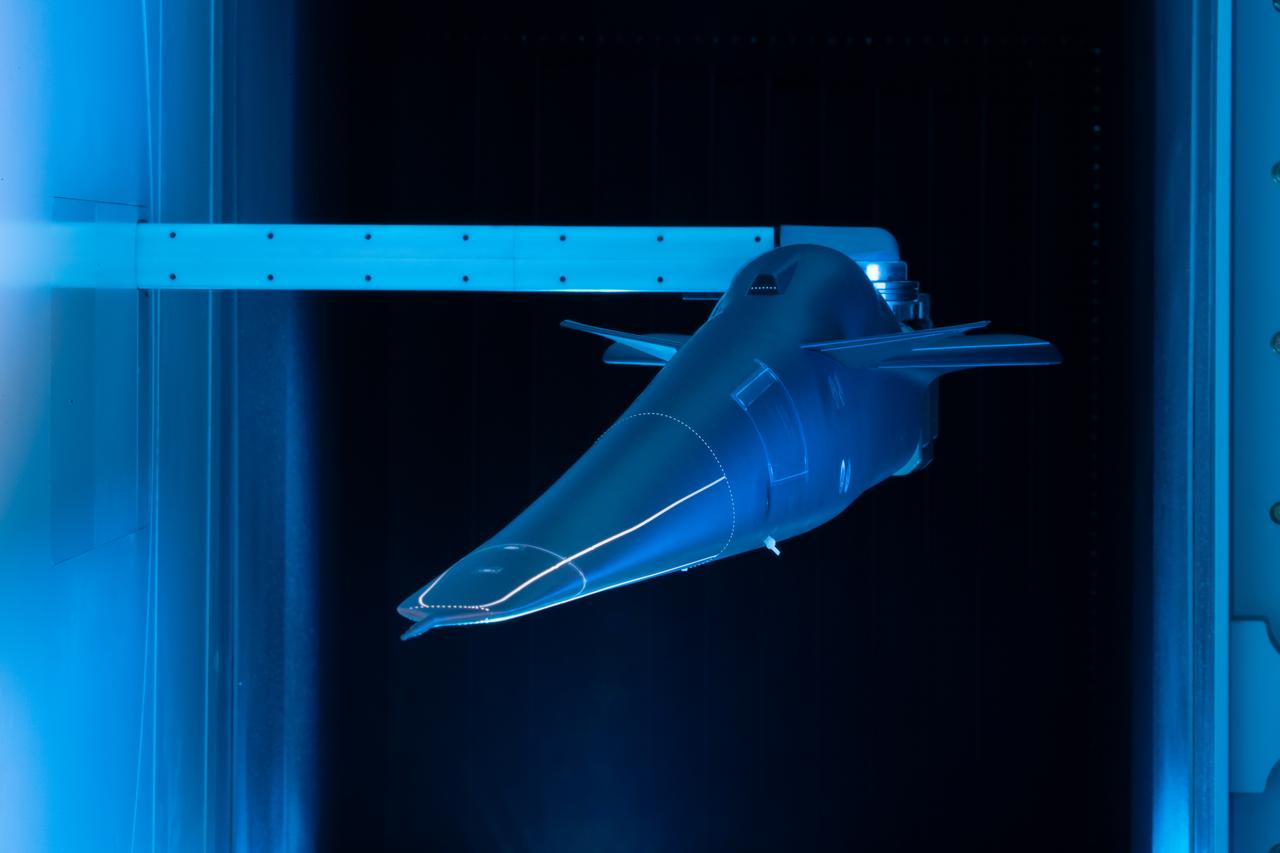

Event: Forebody and Nose - Windtunnel Testing A model of the X-59 forebody is shown in the Lockheed Martin Skunk Works’ wind tunnel in Palmdale, California. These tests gave the team measurements of wind flow angle around the aircraft’s nose and confirmed computer predictions made using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software tools. The data will be fed into the aircraft flight control system to tell the pilot the aircraft’s altitude, speed and angle. This is part of NASA’s Quesst mission which plans to help enable supersonic air travel over land.

Event: Manufacturing Area From Above A overhead view of the X-59 with its nose on. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
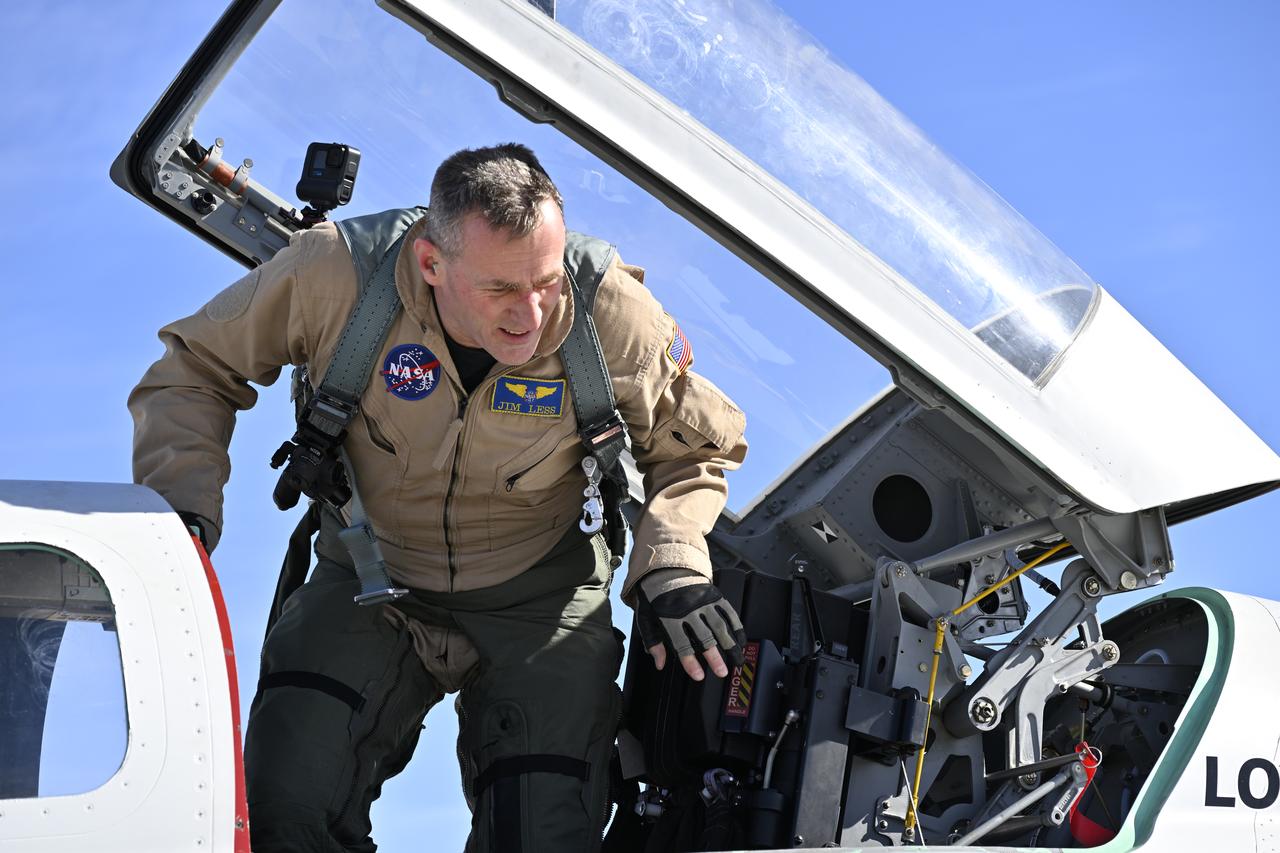

NASA test pilot Jim Less prepares to exit the cockpit of the quiet supersonic X-59 aircraft in between electromagnetic interference (EMI) testing. The EMI testing ensures an aircraft’s systems function properly under various conditions of electromagnetic radiation. The X-59 is the centerpiece of the NASA’s Quesst mission, designed to demonstrate quiet supersonic technology and provide data to address a key barrier to commercial supersonic travel.
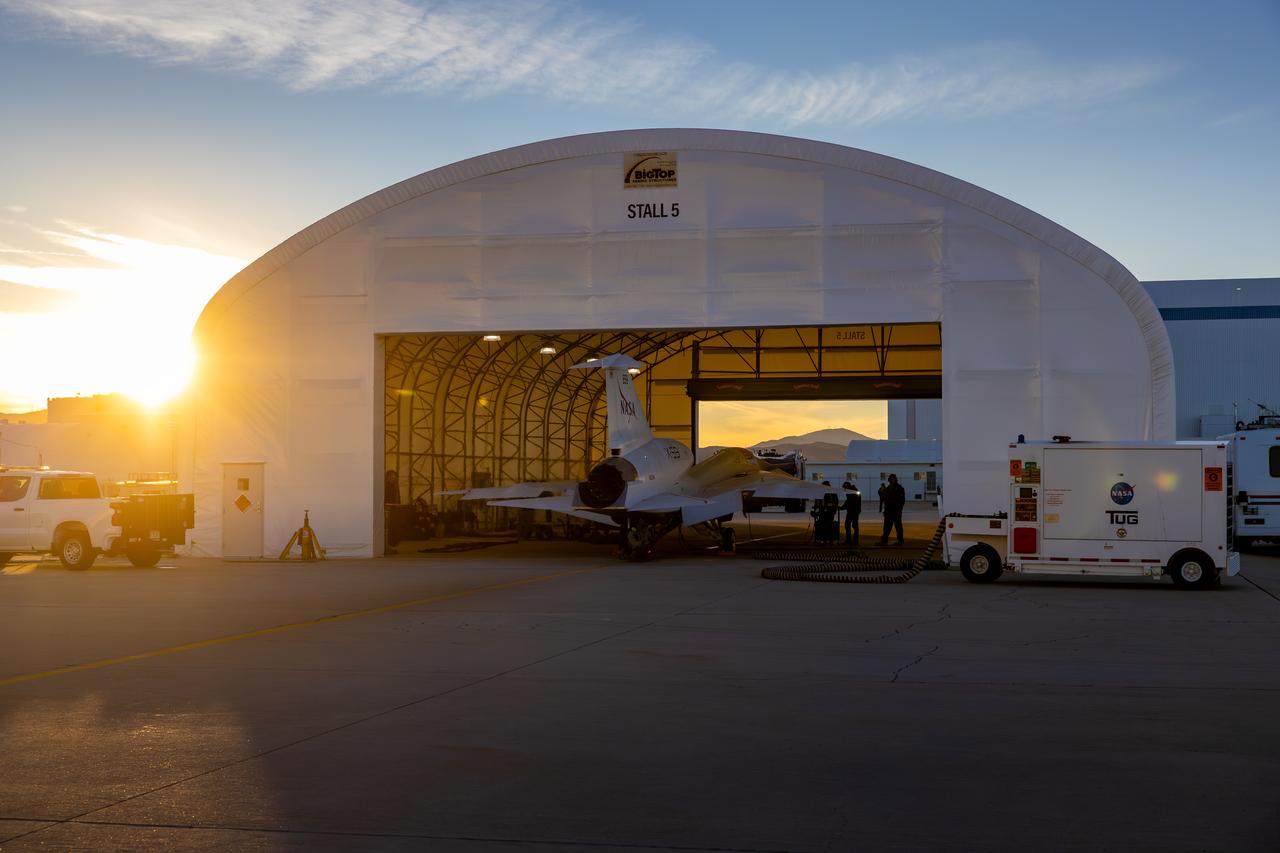

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits inside its run stall in preparation for maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. Teams conduct final checks on the aircraft before its high-thrust engine runs. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission designed to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight over land, addressing a key barrier to commercial supersonic travel.

A panoramic view of NASA’s X-59 in Fort Worth, Texas to undergo structural and fuel testing. The X-59’s nose makes up one third of the aircraft, at 38-feet in length. The X-59 is a one-of-a-kind airplane designed to fly at supersonic speeds without making a startling sonic boom sound for the communities below. This is part of NASA’s Quesst mission which plans to help enable supersonic air travel over land.
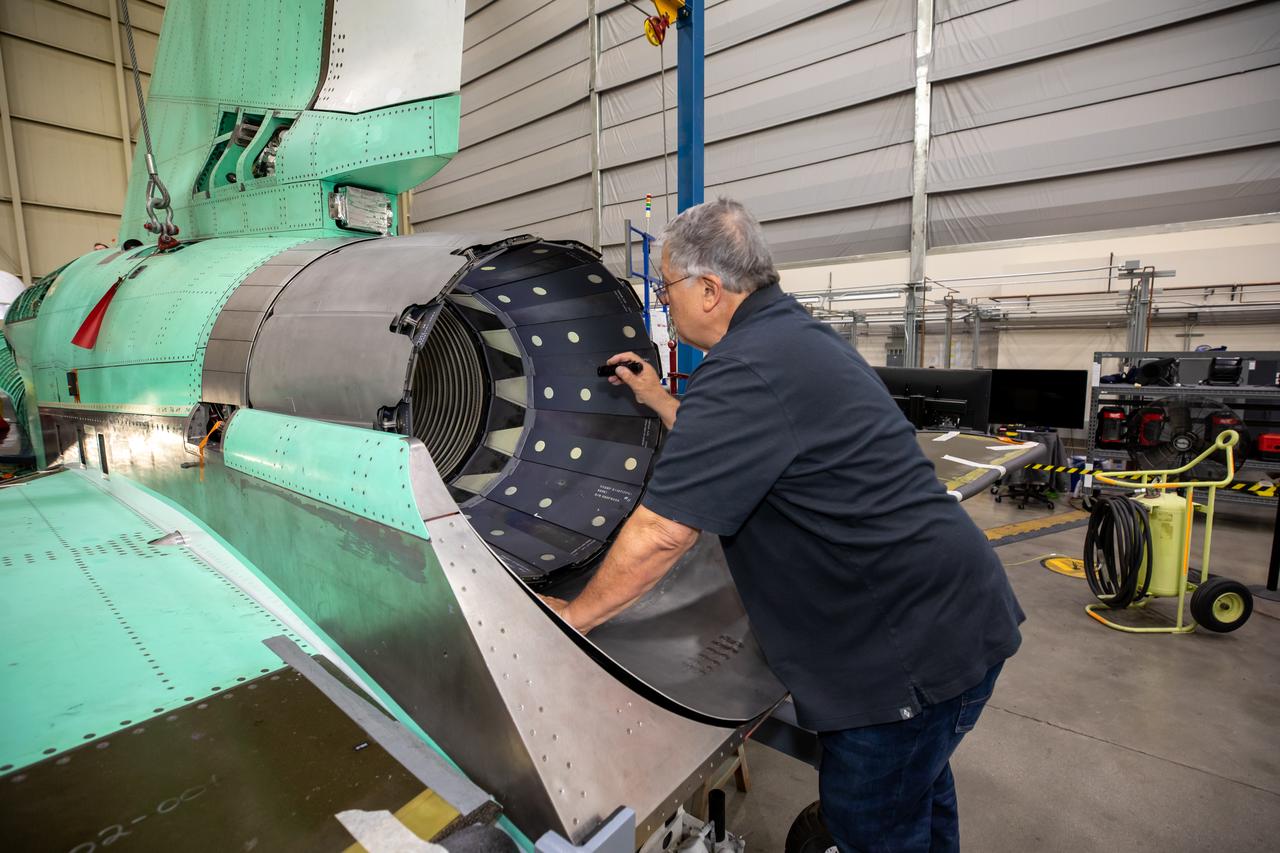

A quality inspector inspects the GE F-414 engine nozzle after installation at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. Once the aircraft and ground testing are complete, the X-59 will undergo flight testing, which will demonstrate the plane’s ability to fly supersonic - faster than the speed of sound - while reducing the loud sonic boom. This could enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
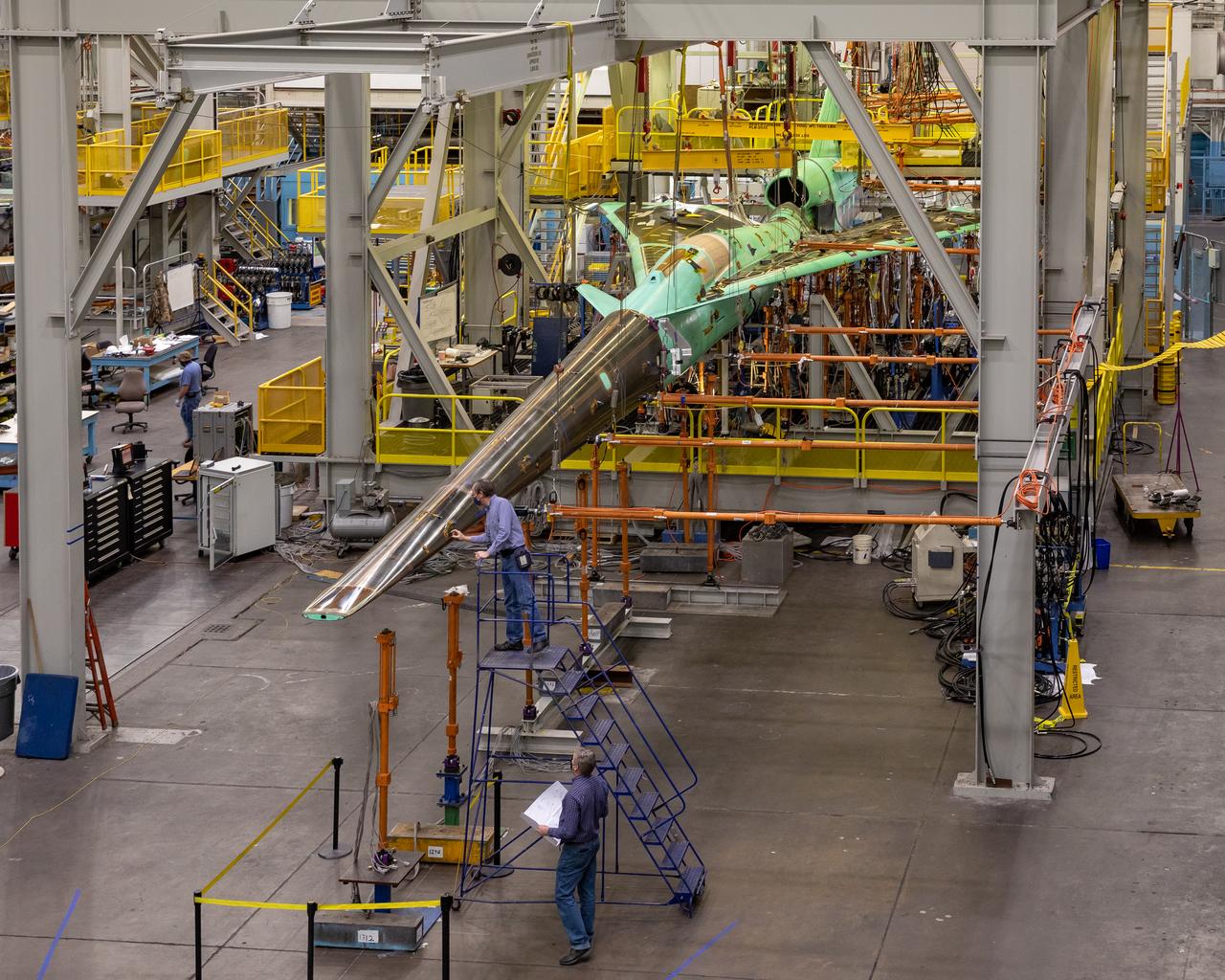

NASA’s X-59 undergoes a structural stress test at Lockheed Martin’s facility in Fort Worth, Texas. The X-59’s nose makes up one third of the aircraft, at 38-feet in length. The X-59 is a one-of-a-kind airplane designed to fly at supersonic speeds without making a startling sonic boom sound for the communities below. This is part of NASA’s Quesst mission, which plans to help enable supersonic air travel over land

NASA’s X-59 undergoes a structural stress test at a Lockheed Martin facility in Fort Worth, Texas. The X-59’s nose makes up one third of the aircraft, at 38-feet in length. The X-59 is a one-of-a-kind airplane designed to fly at supersonic speeds without making aa startling sonic boom sound for the communities below. This is part of NASA’s Quesst mission which plans to help enable supersonic air travel over land
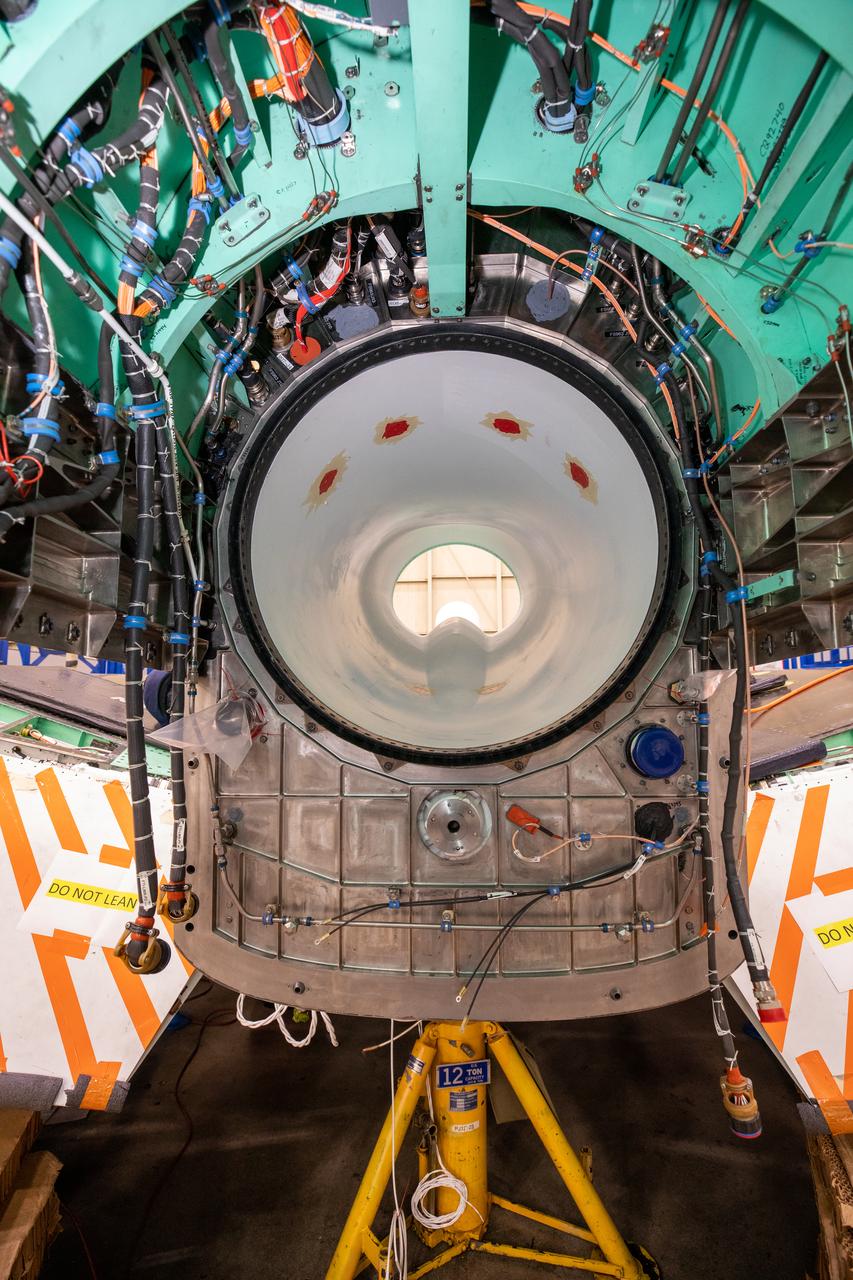

This image shows the X-59’s engine inlet from the aft view, which is the rear of the airplane, looking forward. Once the aircraft and ground testing are complete, the X-59 will undergo flight testing, which will demonstrate the plane’s ability to fly supersonic - faster than the speed of sound - while reducing the loud sonic boom. This could enable commercial supersonic air travel over land again.
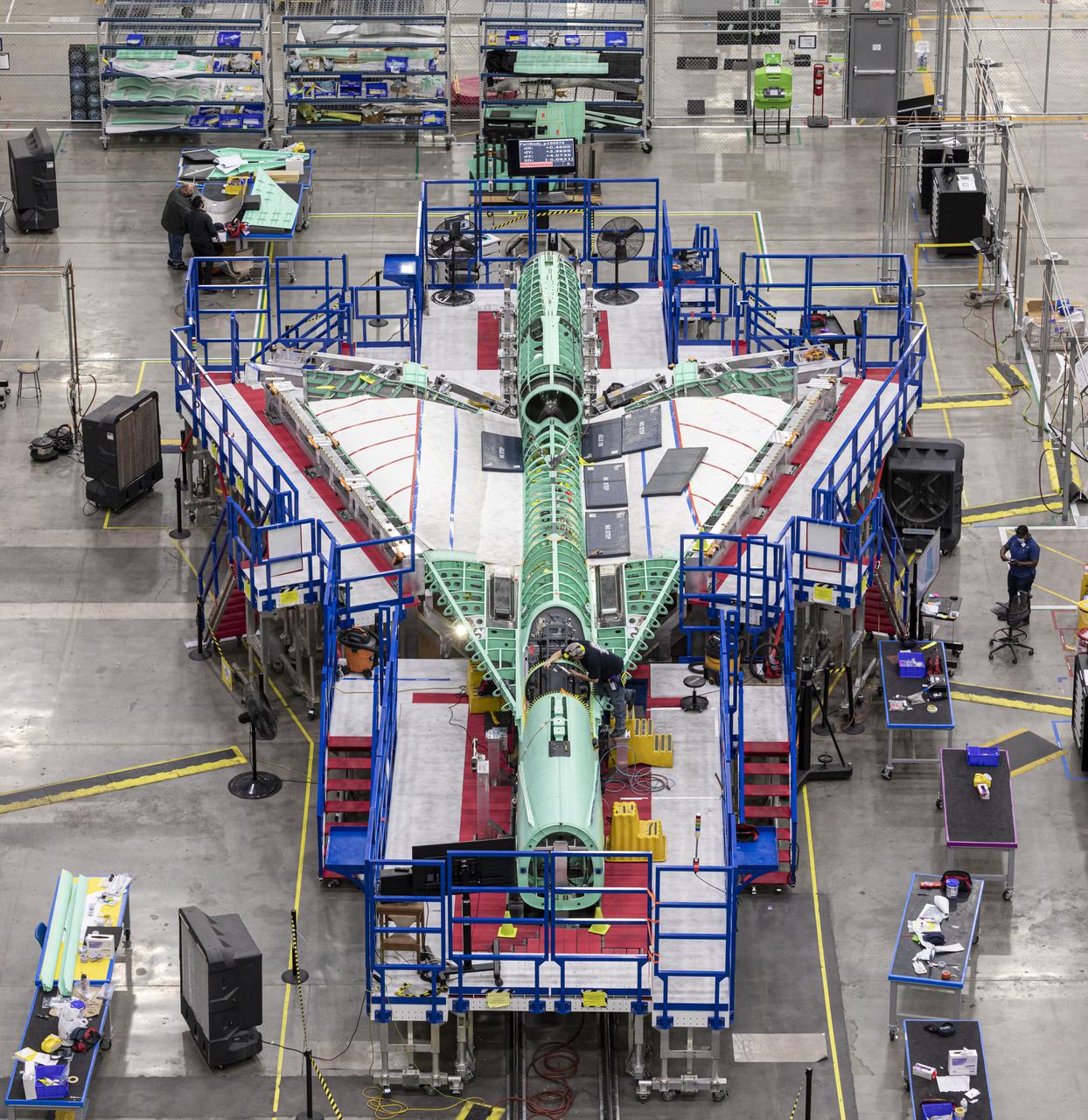

This overhead view shows NASA’s X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology or QueSST aircraft as it comes together for the merger of its main parts – the wing, forward section and tail assembly. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: Manufacturing Area From Above Date: 5/26/2021
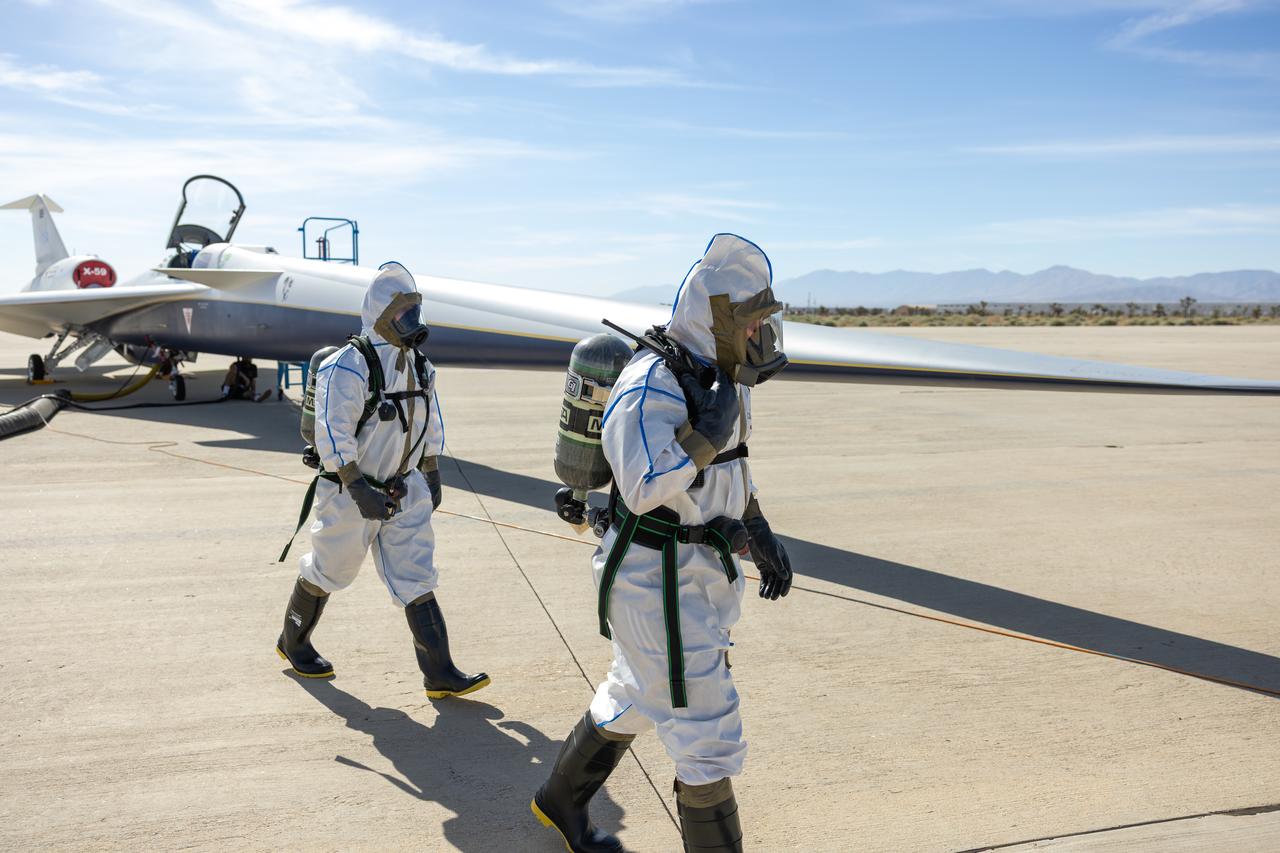

Maintainers perform a hydrazine safety check on NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 aircraft at U.S. Air Force Plant 42 in Palmdale, California, on Aug. 18, 2025. Hydrazine is a highly toxic chemical, but it serves as a critical backup to restart the engine in flight, if necessary, which is one of several safety features being validated ahead of the aircraft’s first flight.
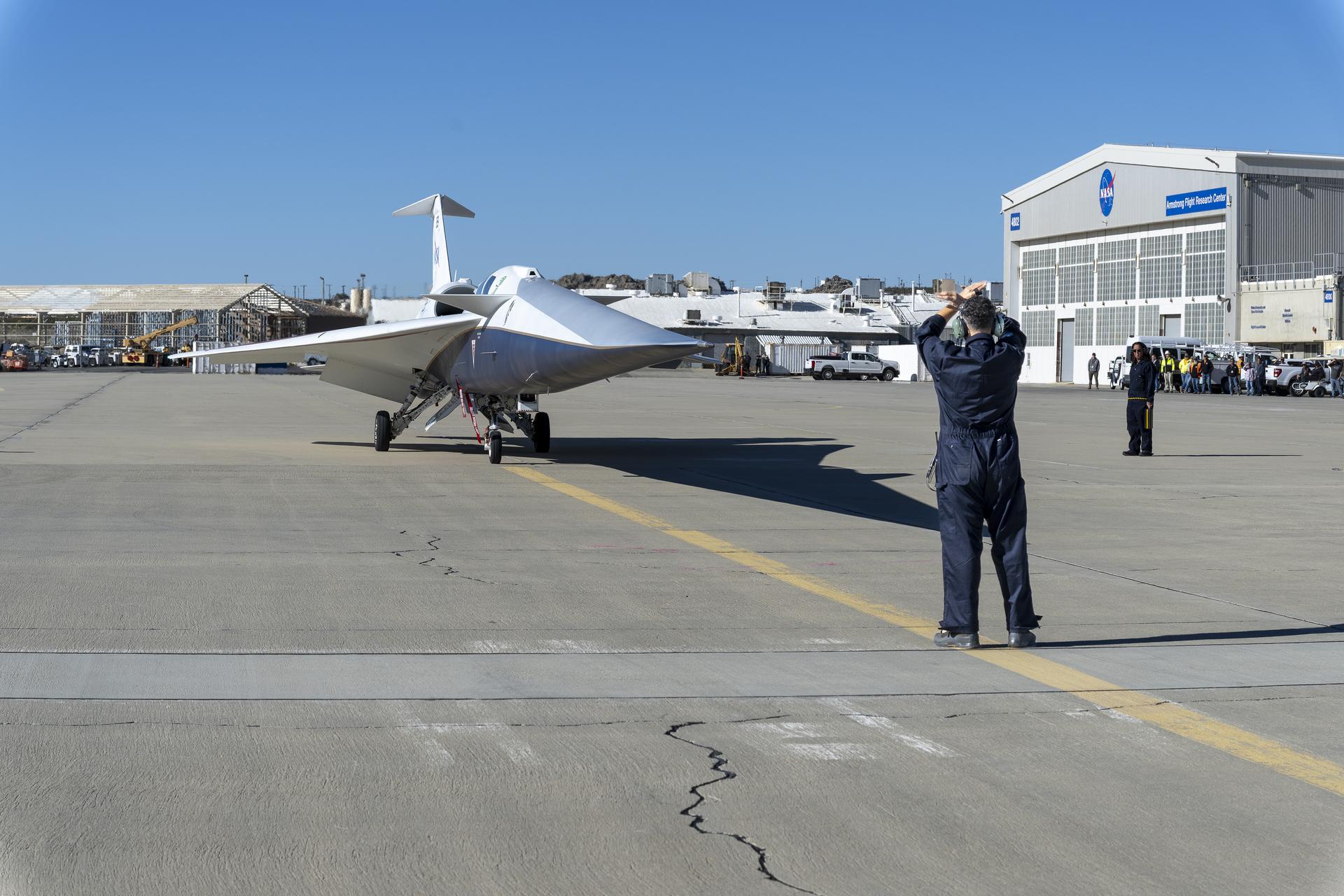

The X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft arrives at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, following its first flight Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025. The arrival marks the aircraft’s transition from ground testing to flight operations. Next, the aircraft will undergo scheduled maintenance followed by a series of additional test flights, gradually building toward its first supersonic flight.

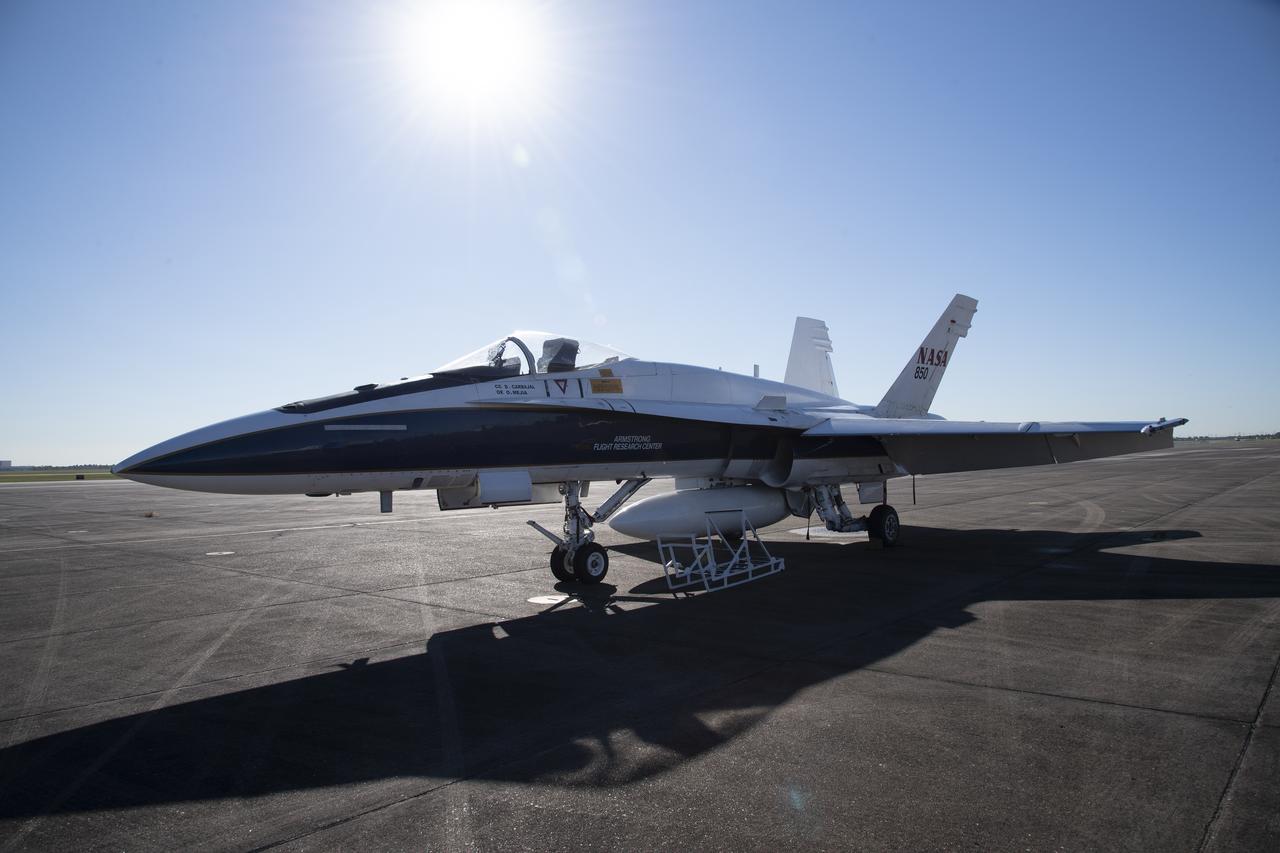
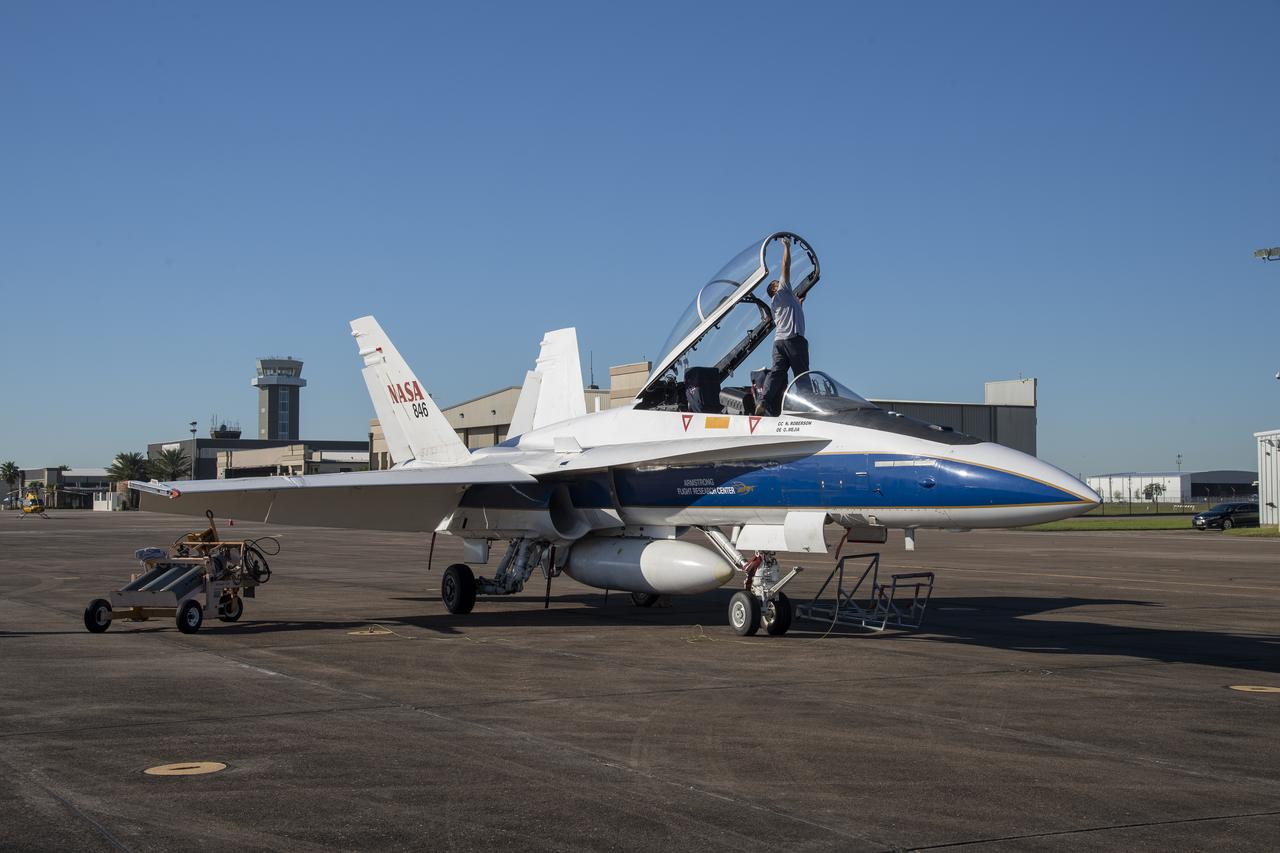
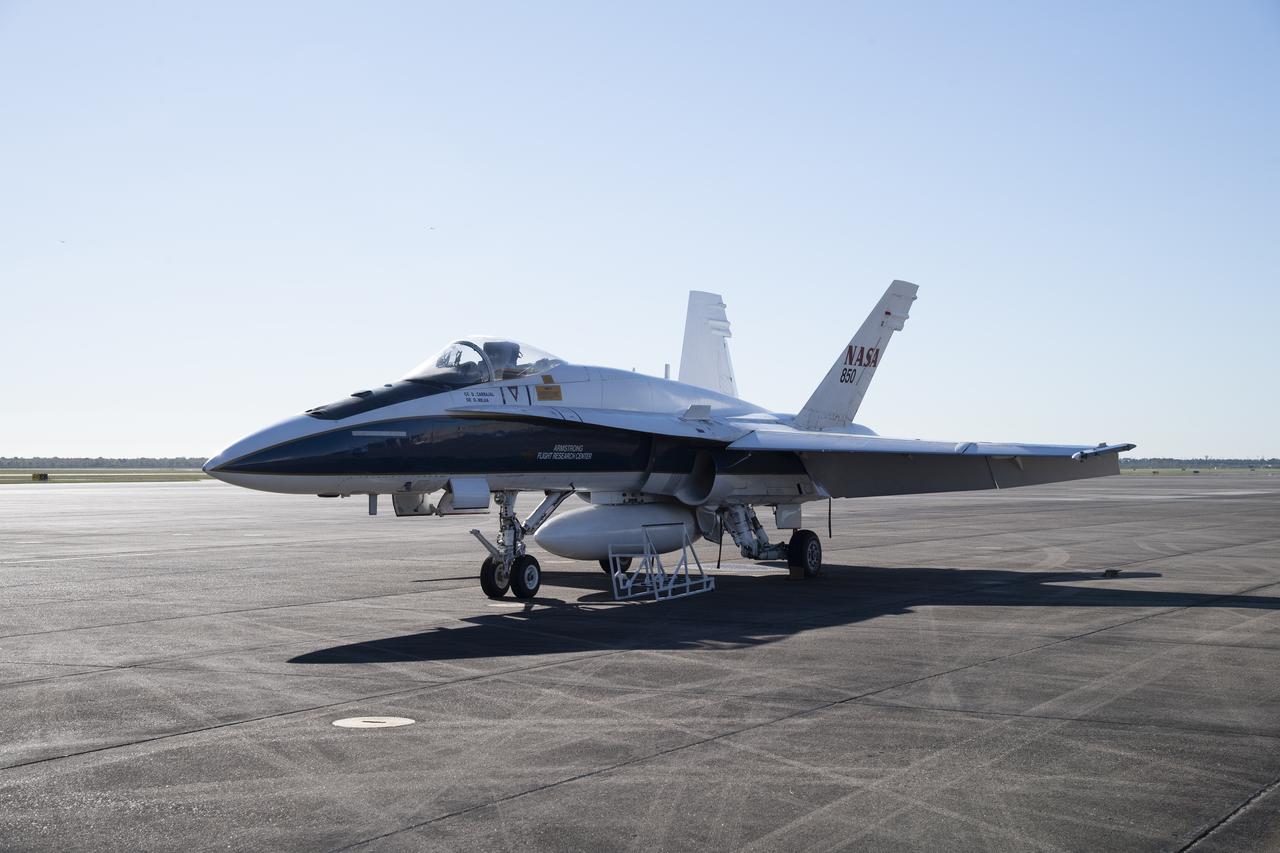
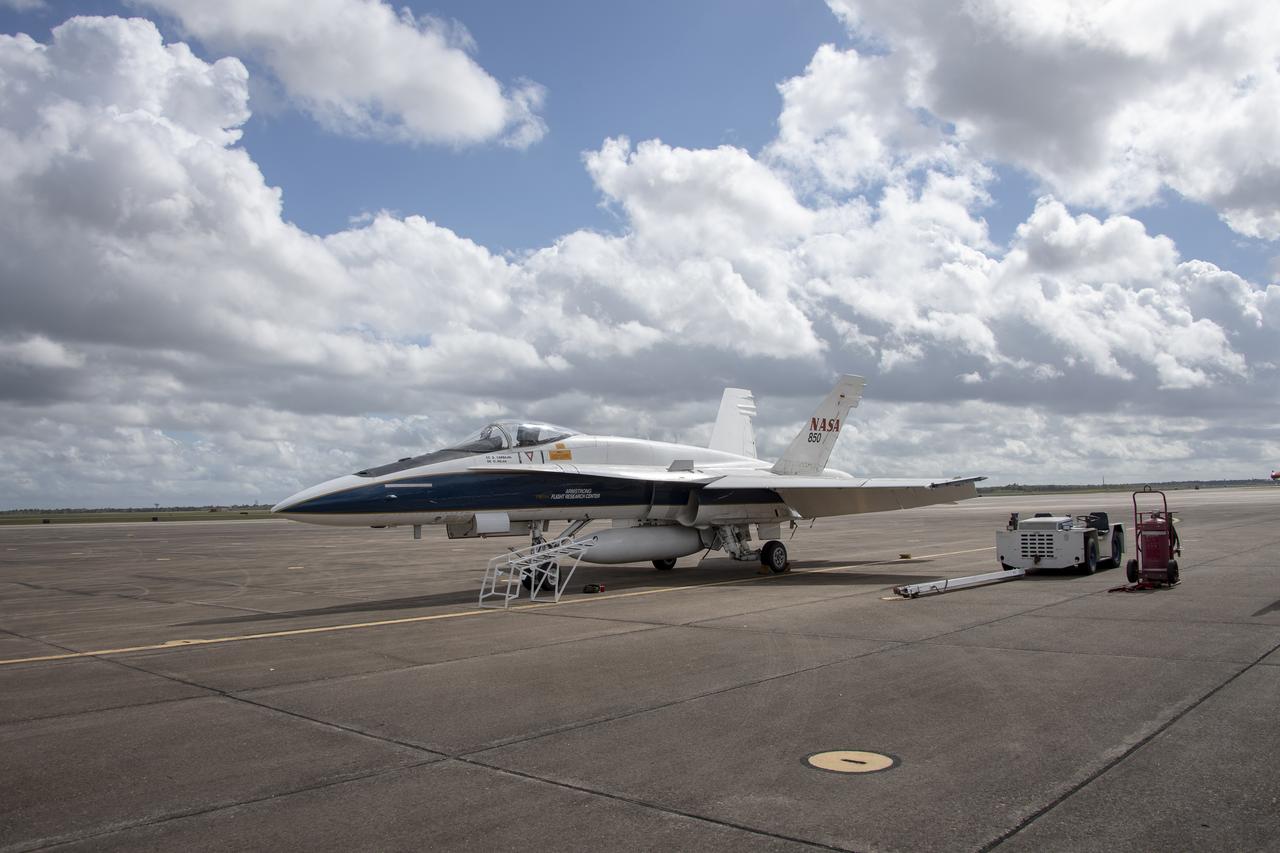
NASA's F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.
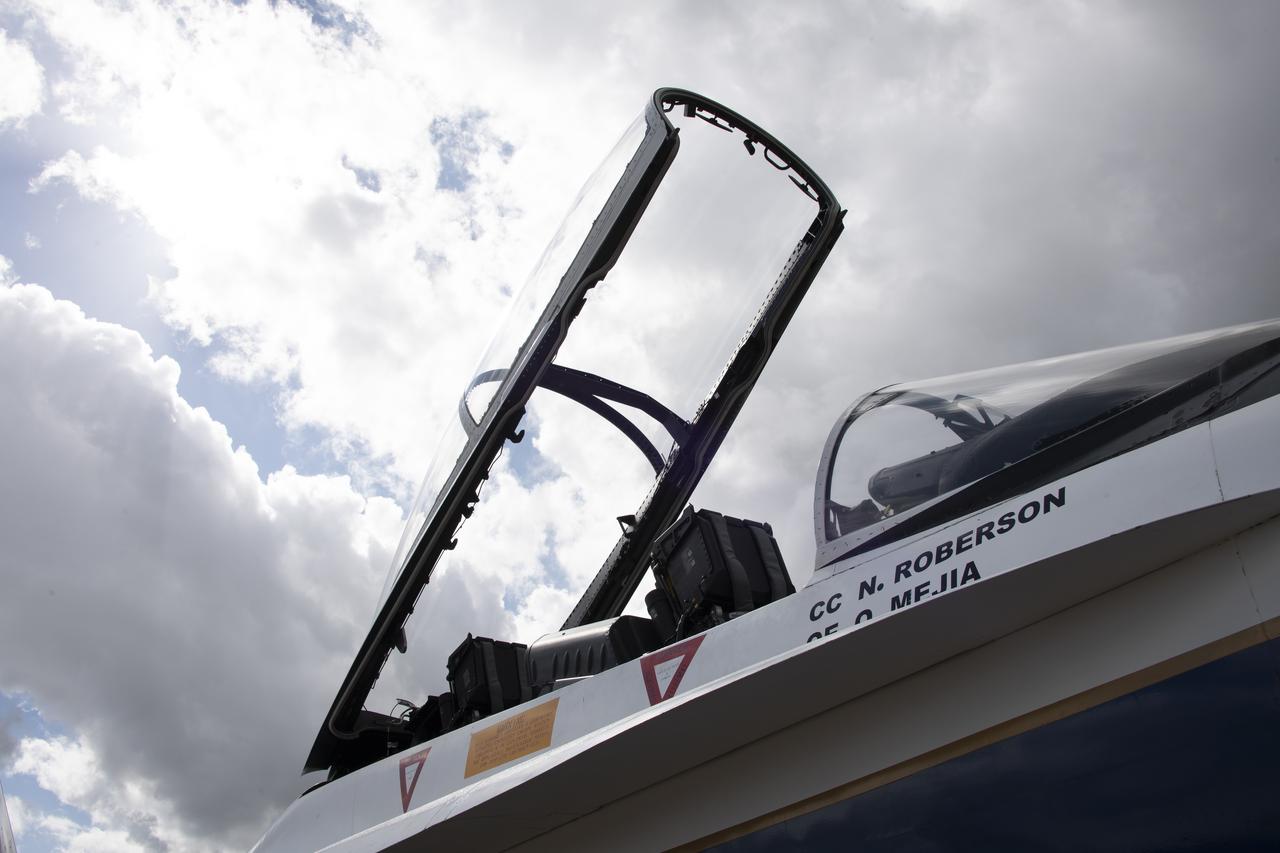

NASA's F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.
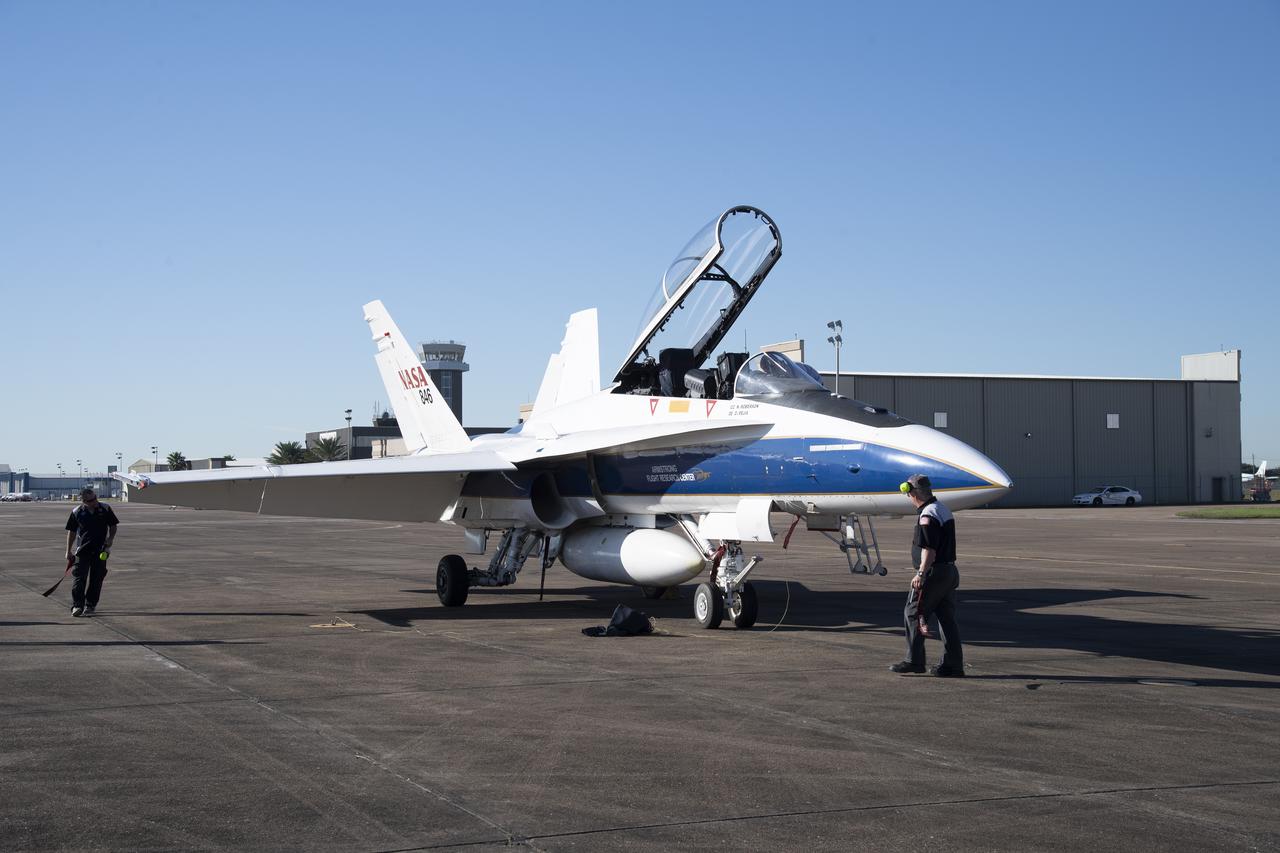

NASA's F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.
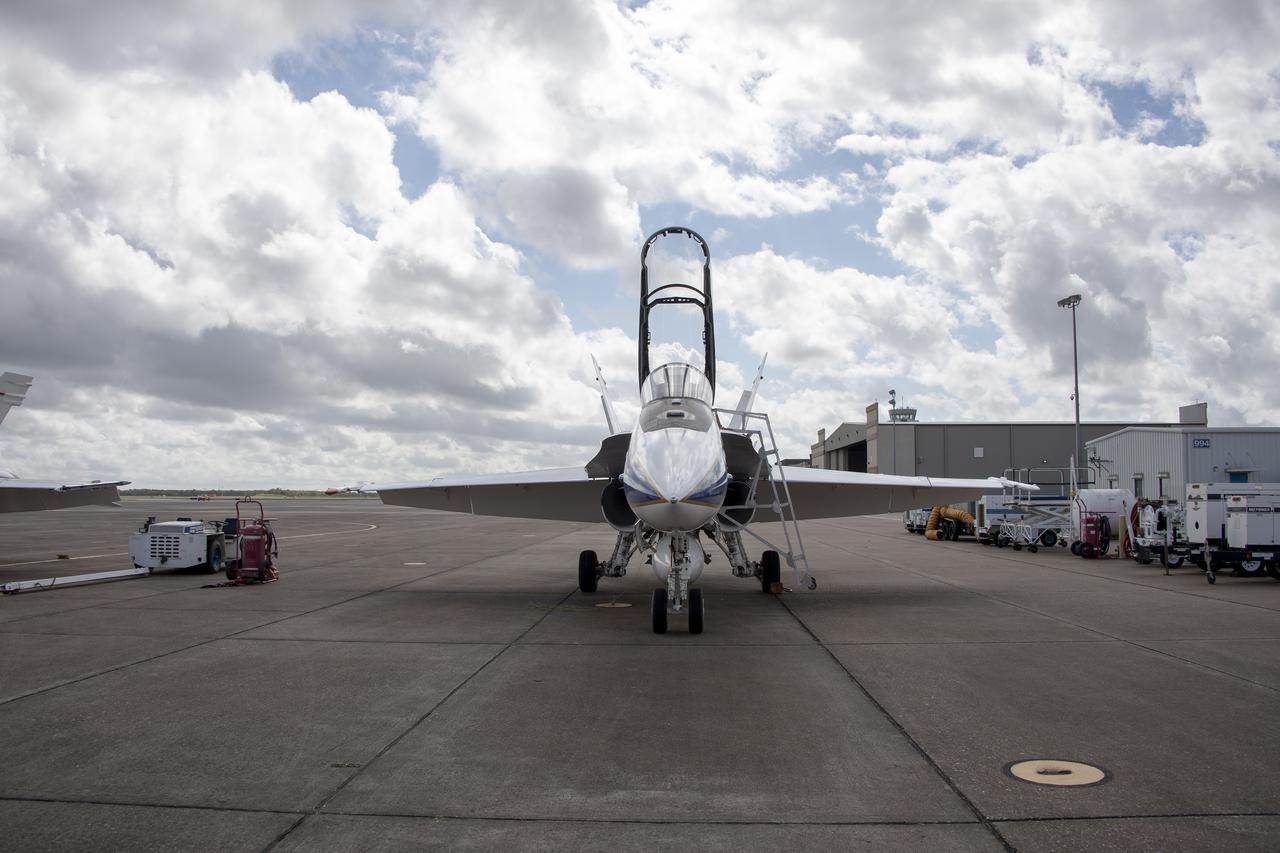

NASA's F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.
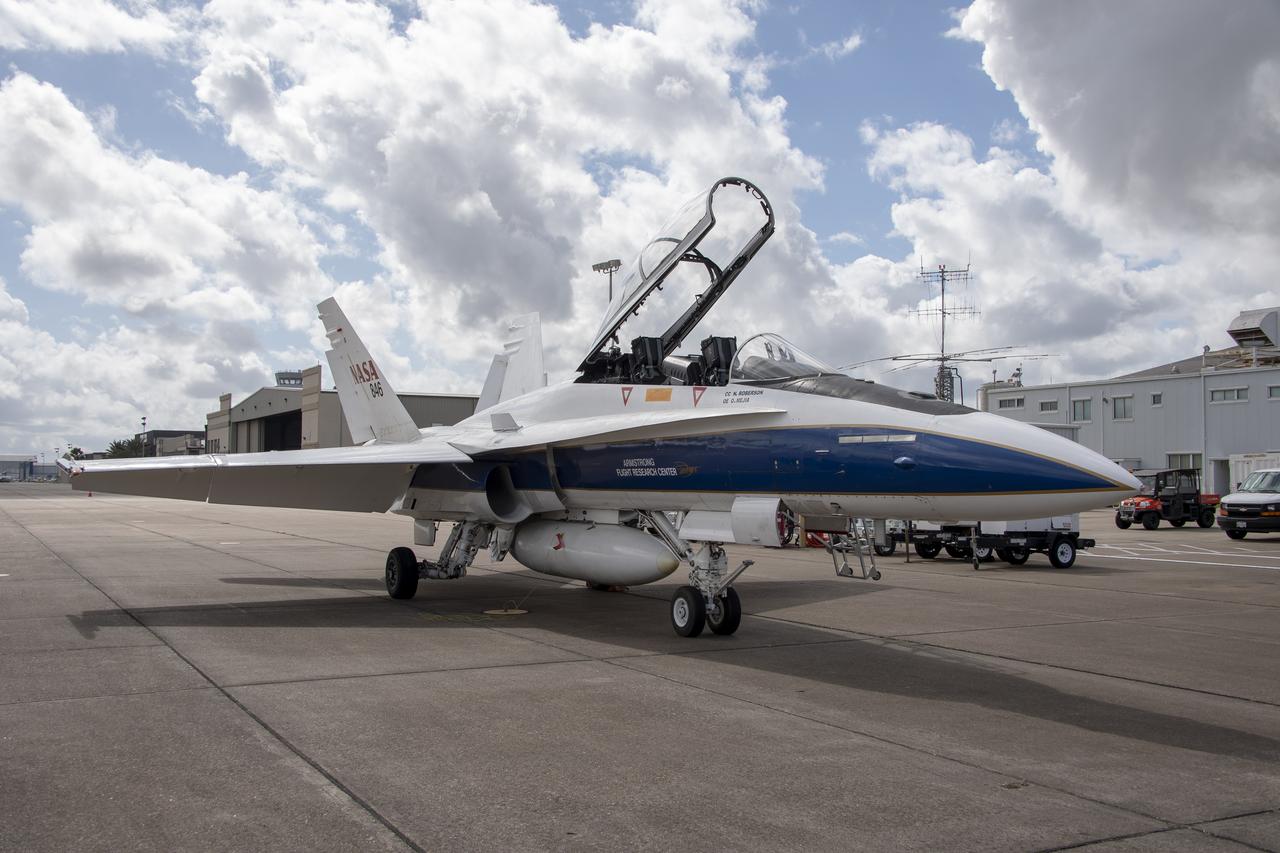

NASA’s F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.
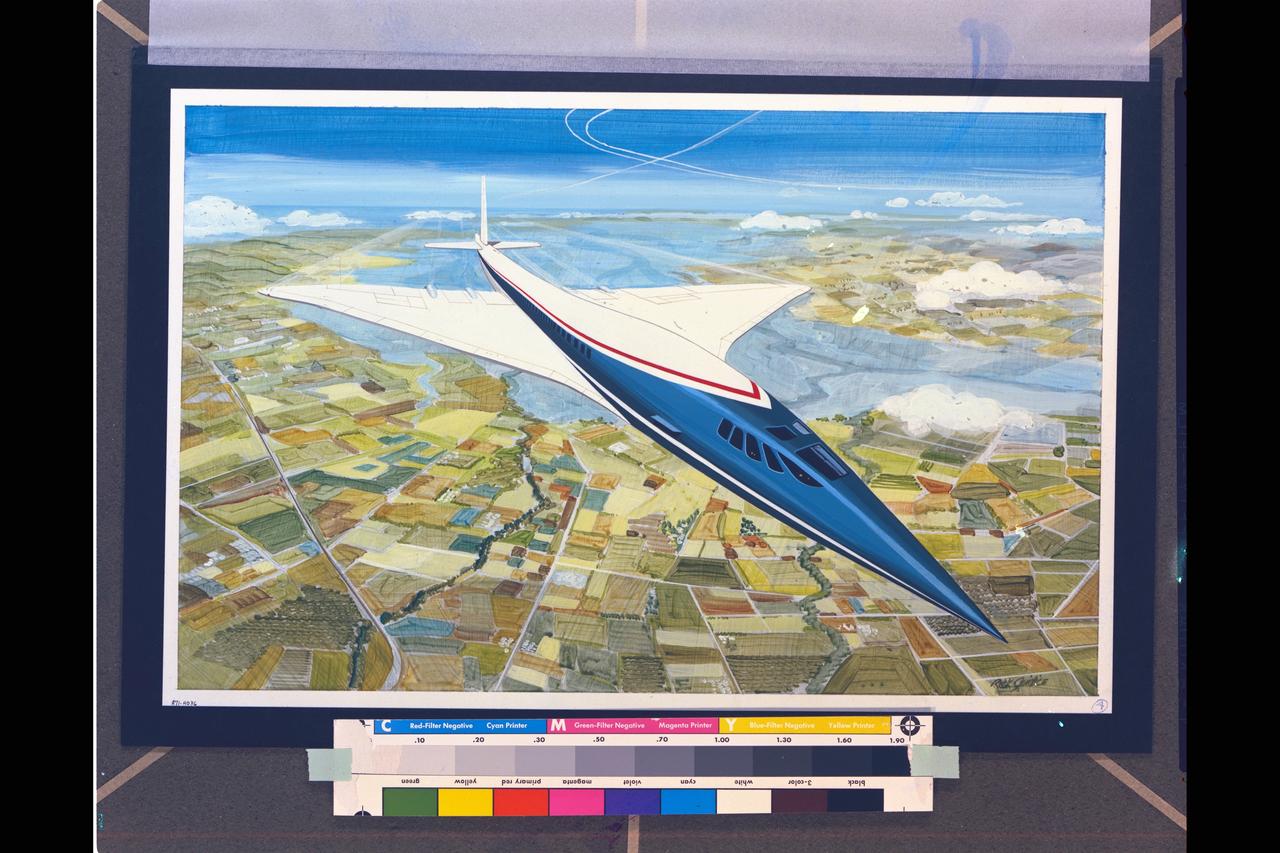

NASA ART by Rick Guidice Supersonic (SST) aircraft technology concept in flight artwork (OART)
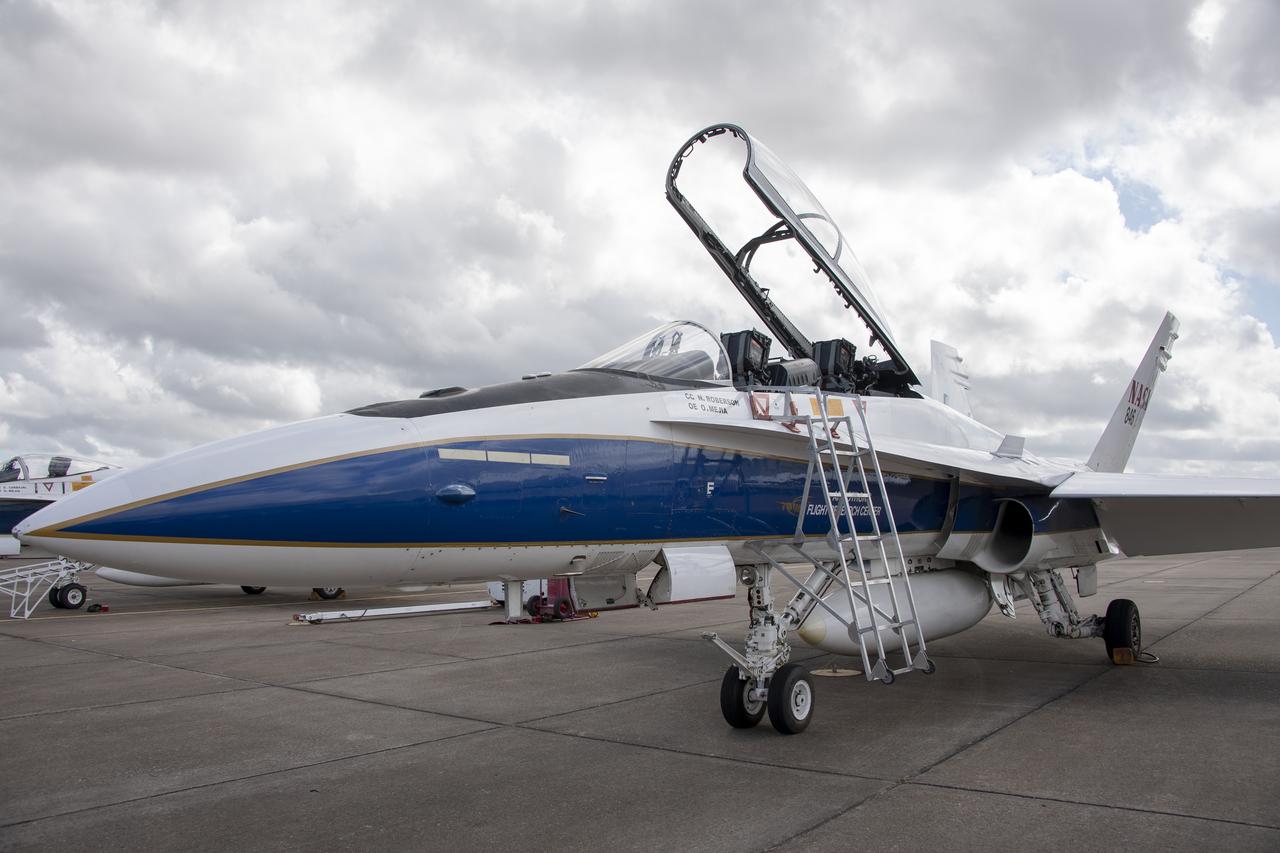

NASA’s F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.
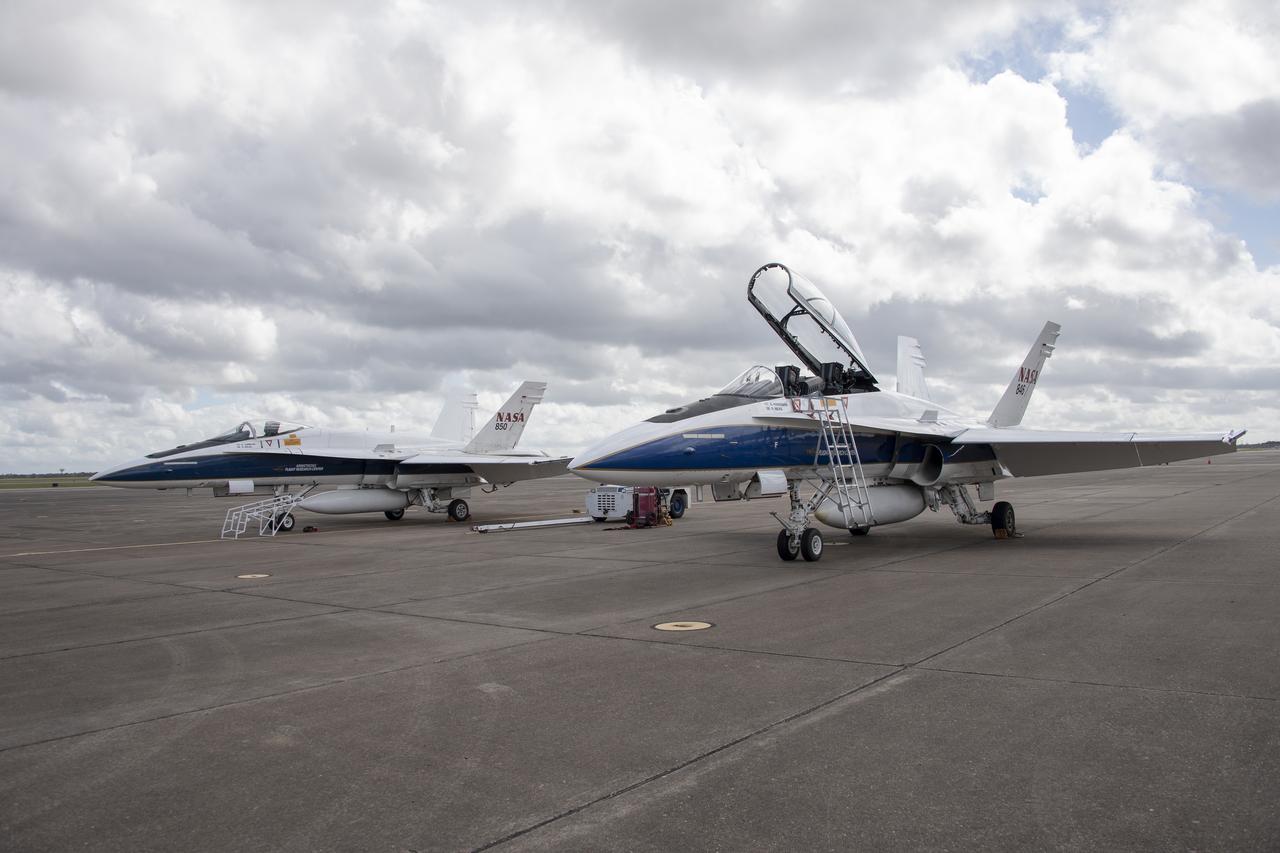

NASA's F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.

NASA’s F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.

NASA's F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.

NASA's F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.

NASA's F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.
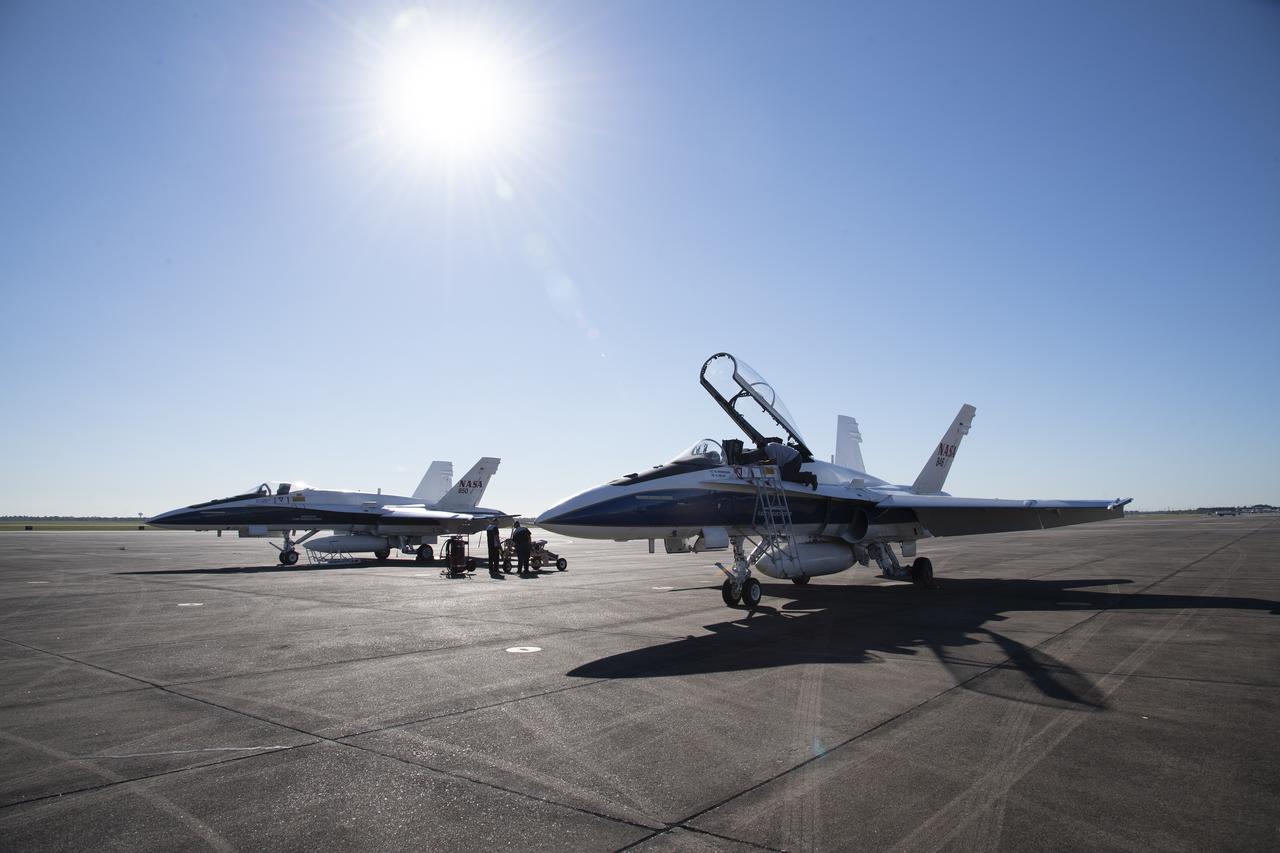

NASA’s F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.
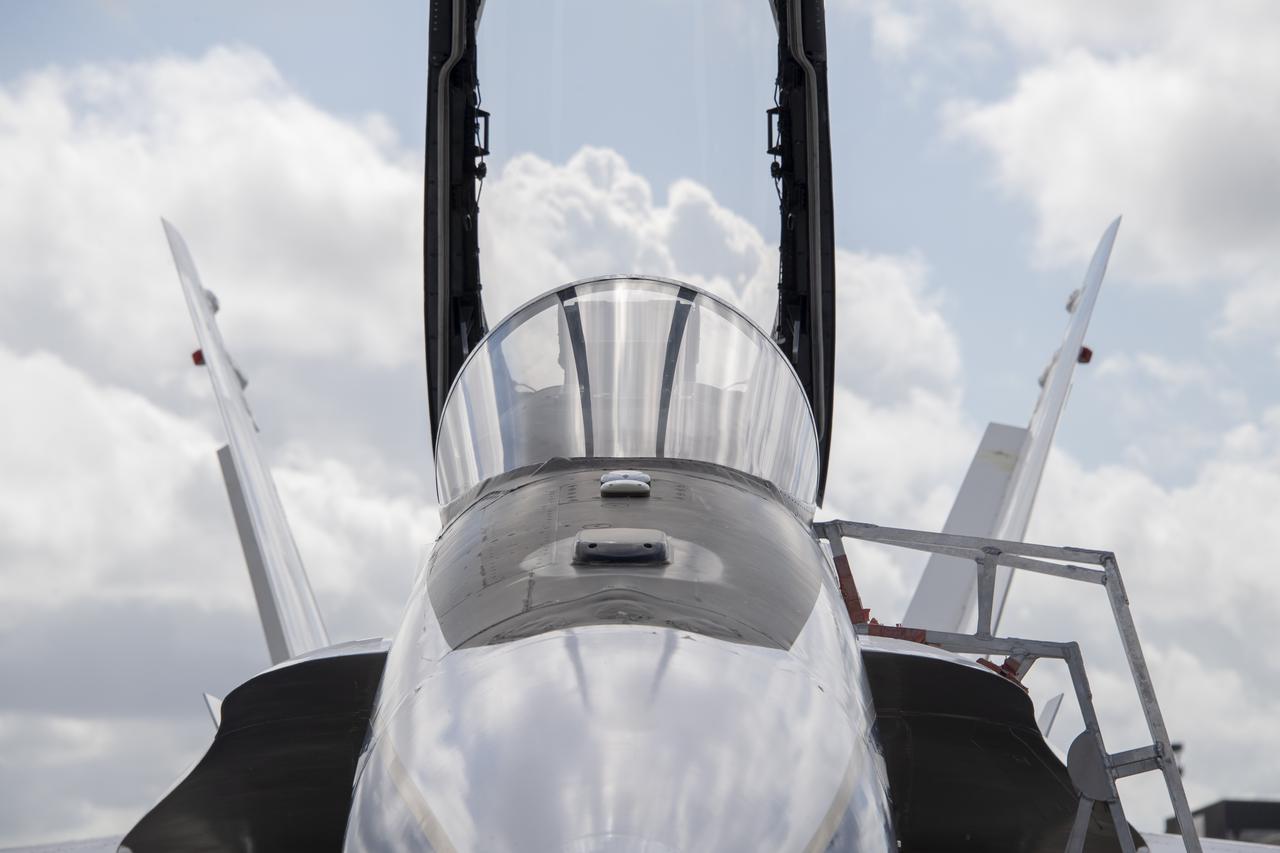

NASA’s F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.
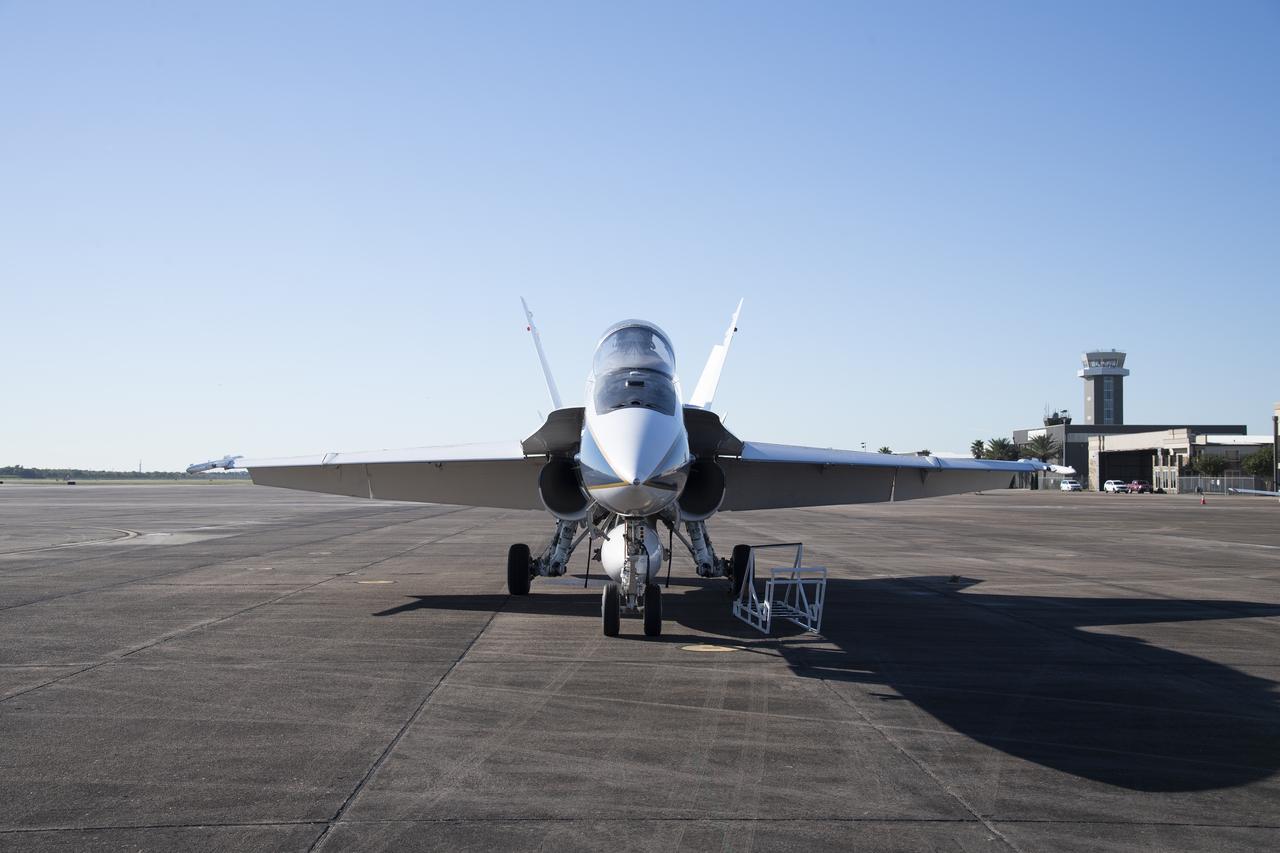

NASA's F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.
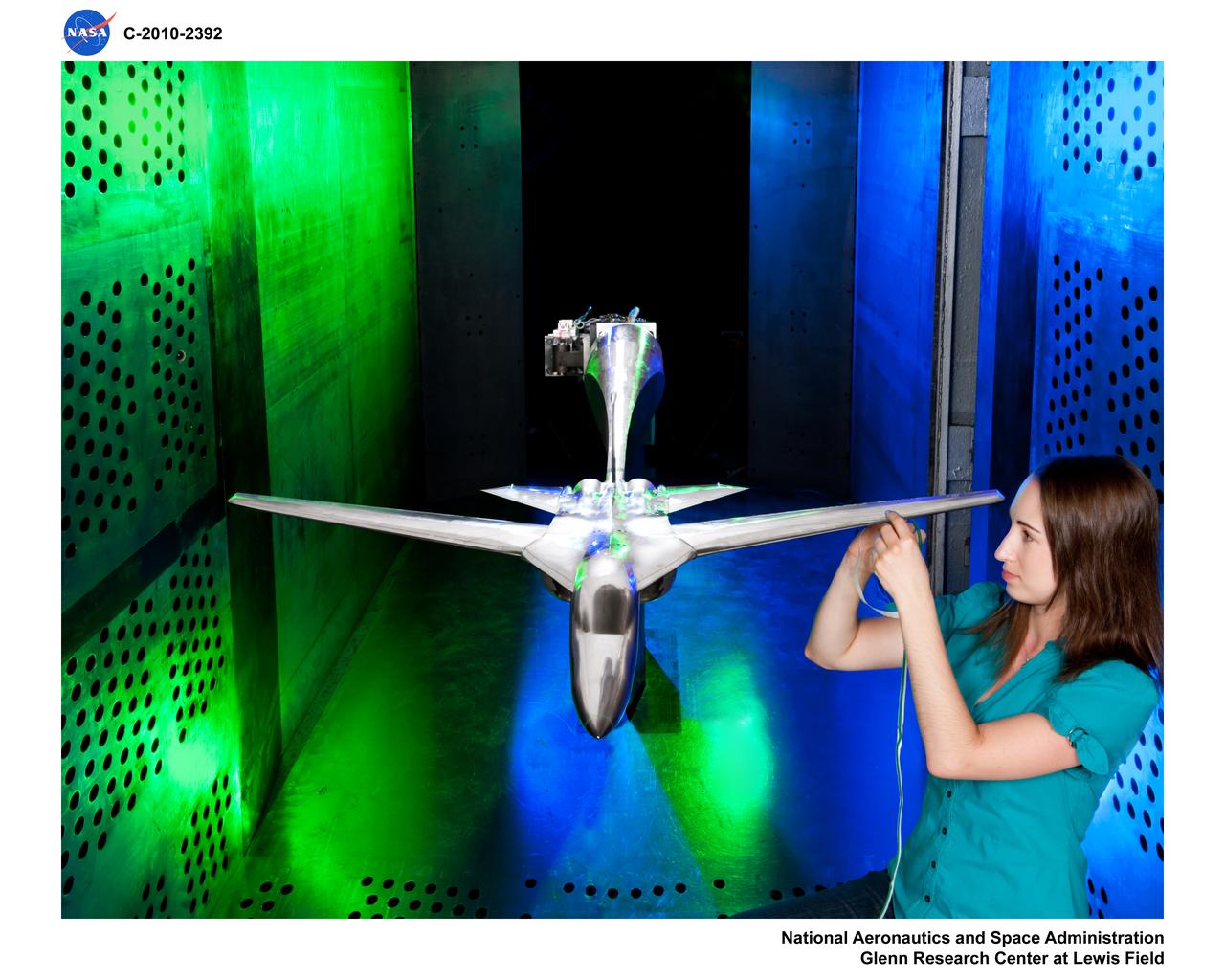

Facility Aerodynamic Validation and Operational Research (FAVOR) aircraft model hardware in 8x6 Supersonic Wind Tunnel (SWT)
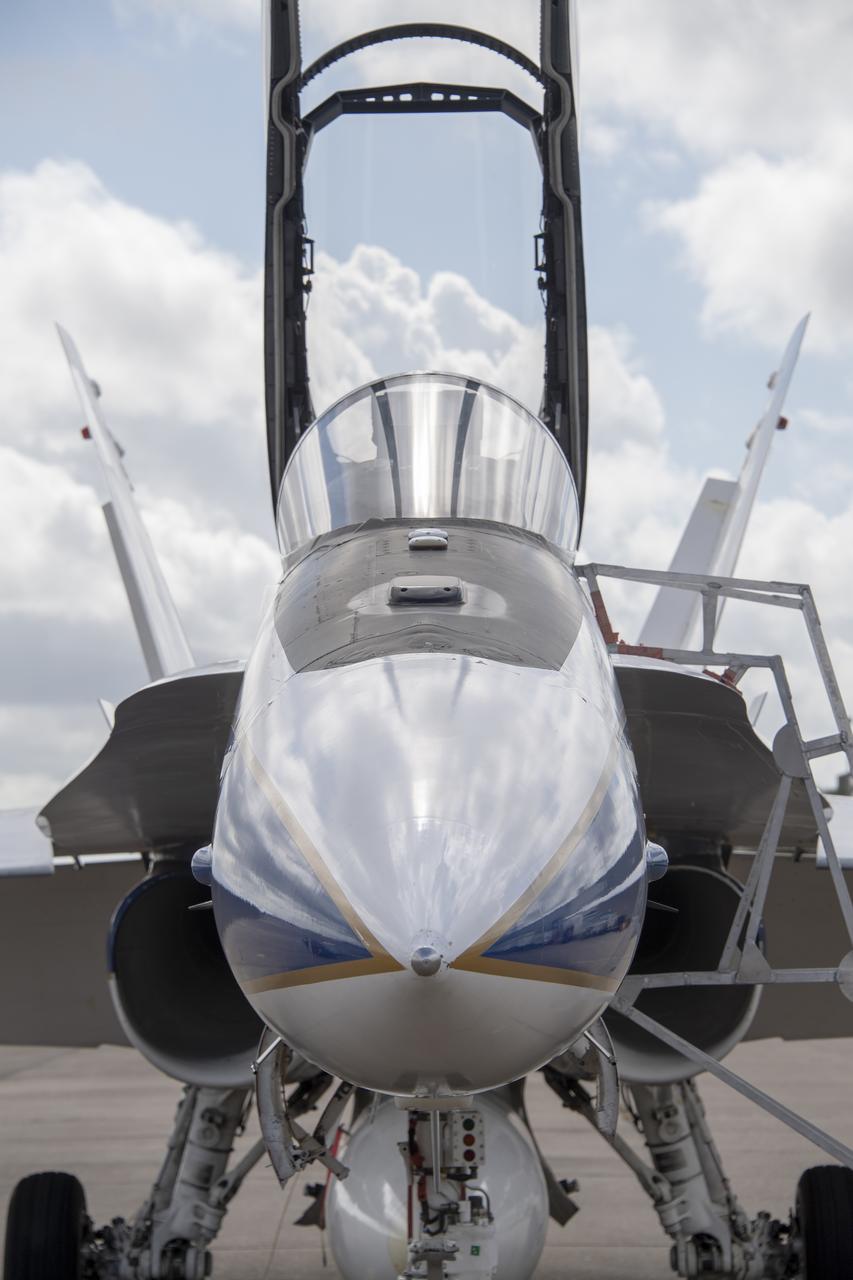

NASA’s F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.

Facility Aerodynamic Validation and Operational Research (FAVOR) aircraft model hardware in 8x6 Supersonic Wind Tunnel (SWT)
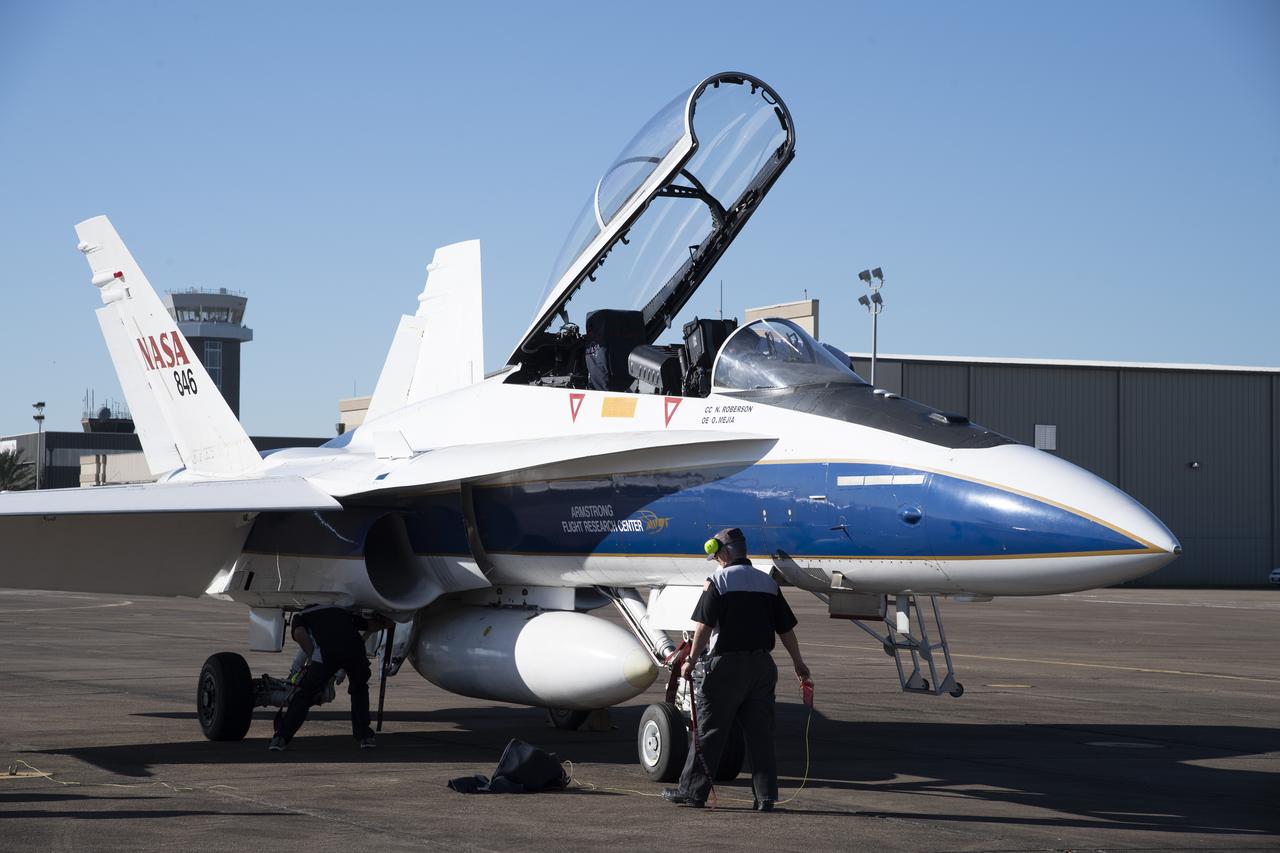

NASA’s F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.
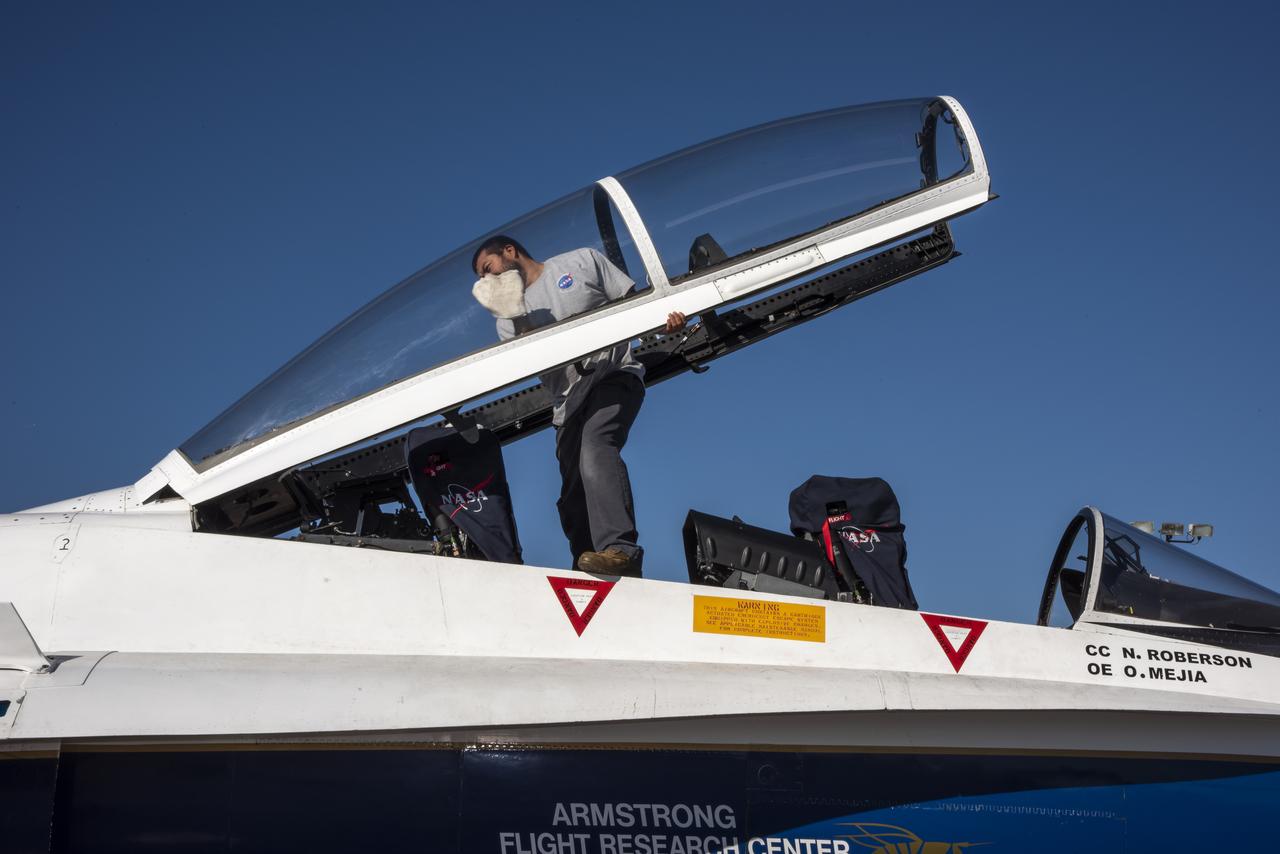

NASA’s F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.
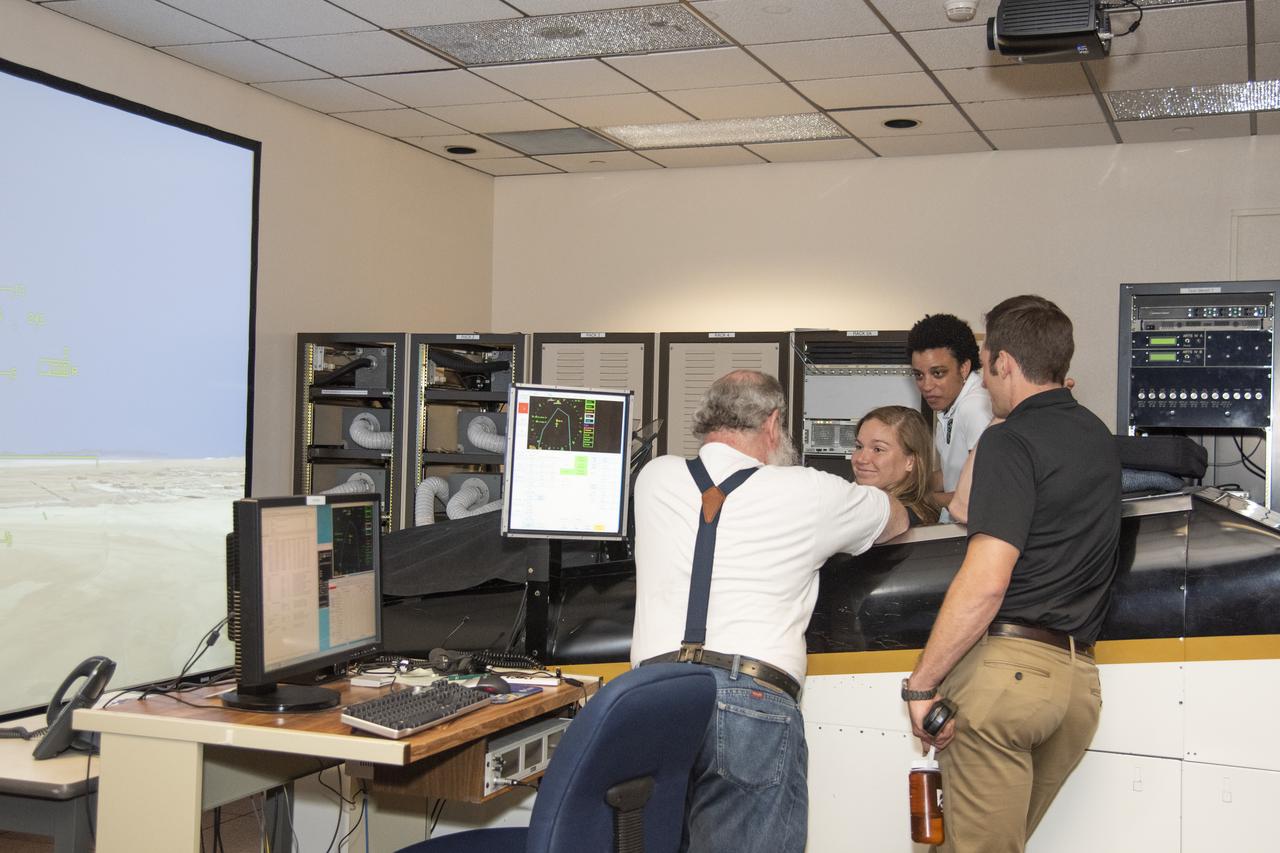

NASA's 2017 astronaut candidates (L to R) Jenni Sidey-Gibbons, Jessica Watkins and Joshua Kutryk practice flying in an F-18 aircraft cockpit simulator at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California. The F-18's are flown for research support and pilot proficiency. Currently, the F-18 is conducting supersonic research in support of the X-59 QueSST overall mission.
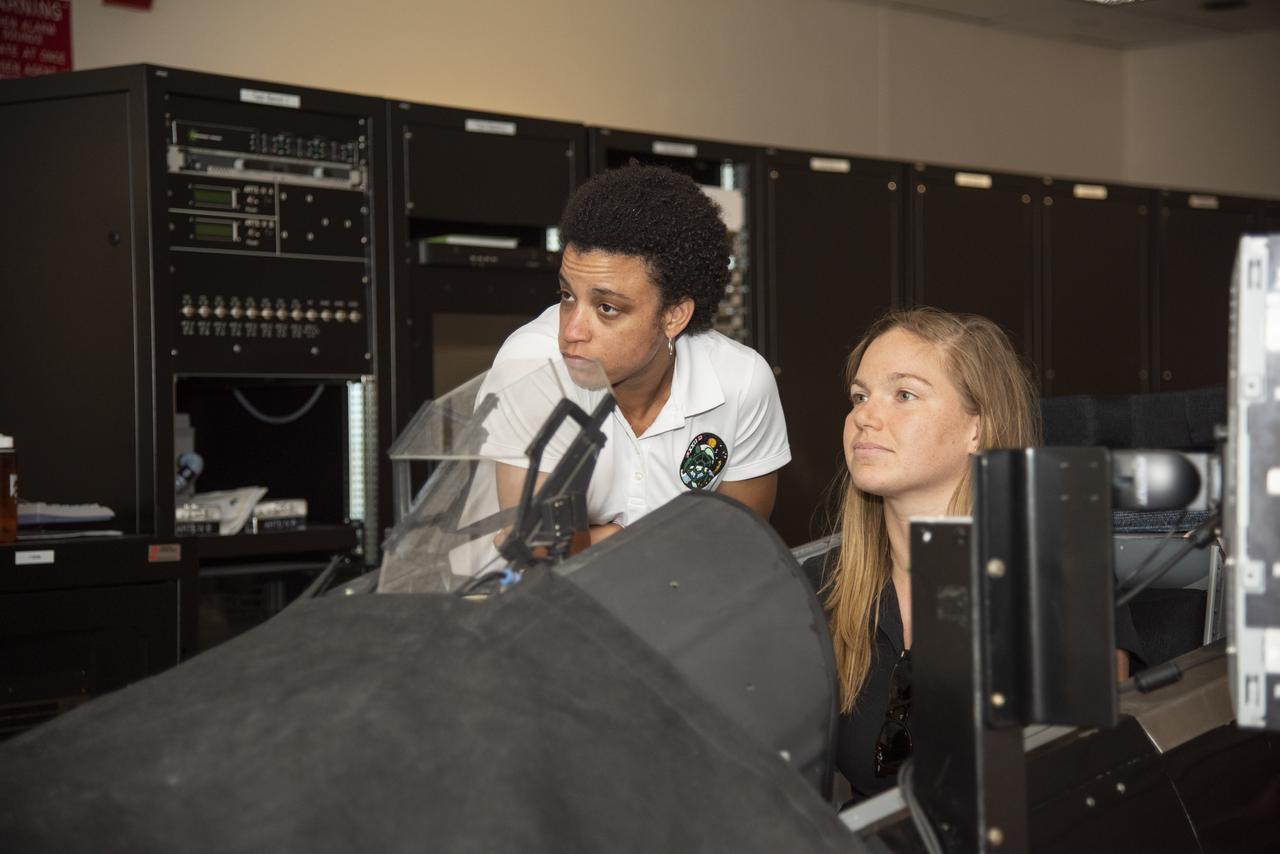

NASA's 2017 astronaut candidates (L to R) Jessica Watkins and Jenni Sidey-Gibbons practice flying in an F-18 aircraft cockpit simulator at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California. The F-18's are flown for research support and pilot proficiency. Currently, the F-18's are being used to conduct supersonic research in support of the X-59 QueSST overall mission.
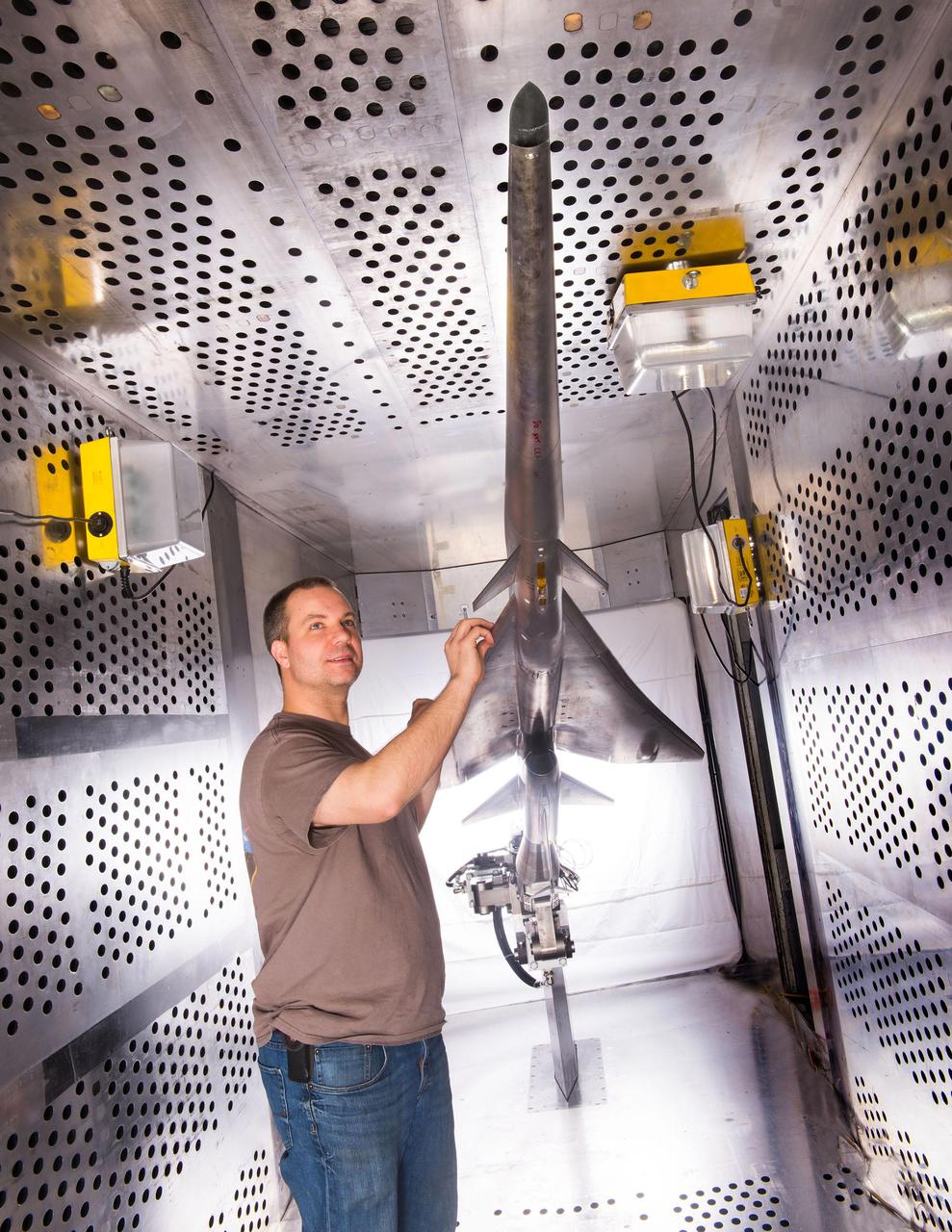

Mechanical technician Dan Pitts prepares a scale model of Lockheed Martin's Quiet Supersonic Technology (QueSST) X-plane preliminary design for its first high-speed wind tunnel tests at NASA's Glenn Research Center.

An aerospace research engineer and technicians inspect the X-59 Commercial Supersonic Transport model’s installation and alignment before testing. The blade hanging from the top of the tunnel will be measuring the shock waves coming from the model during testing. The intent is to develop a supersonic aircraft with less sonic boom. Commercial Supersonic Transport, CST Project, X-59 Sonic Boom Test Model, in the 8x6-foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel, SWT
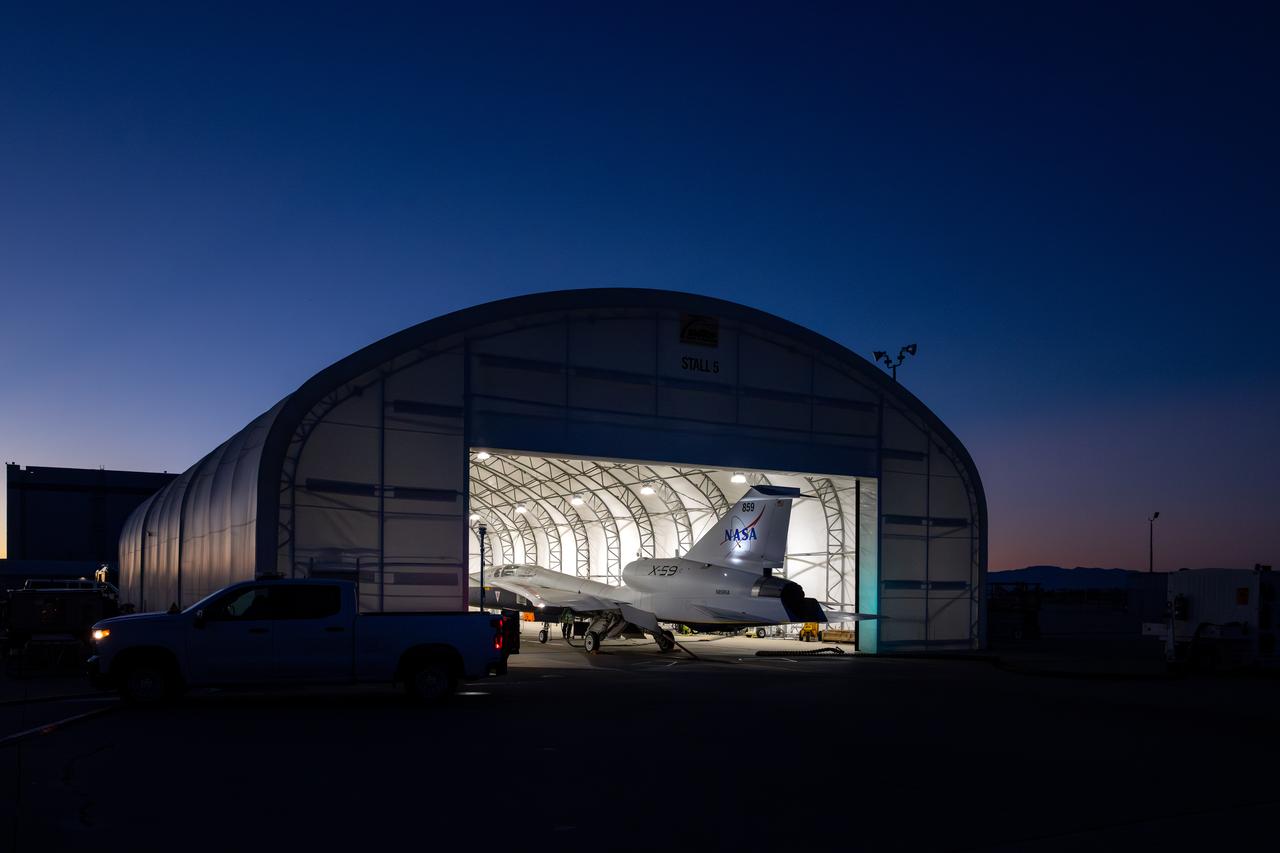

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits inside its run stall following maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. The test demonstrates the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight, advancing NASA’s Quesst mission. The X-59 is the centerpiece of the mission, designed to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight over land, addressing a key barrier to commercial supersonic travel.
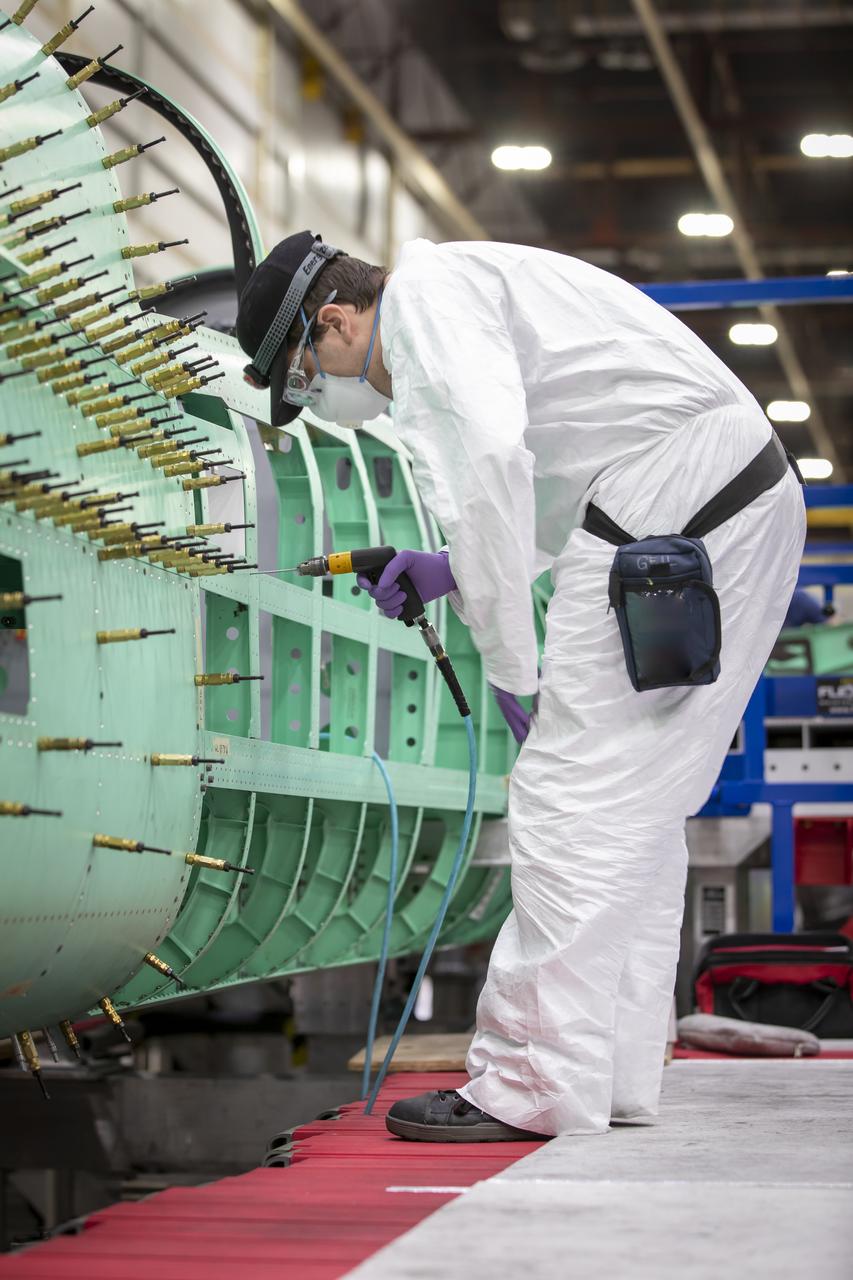

Event: SEG 210 Forebody A Lockheed Martin technician prepares to install the left fuselage skins onto the X-59. Once in the air, the aircraft, currently under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
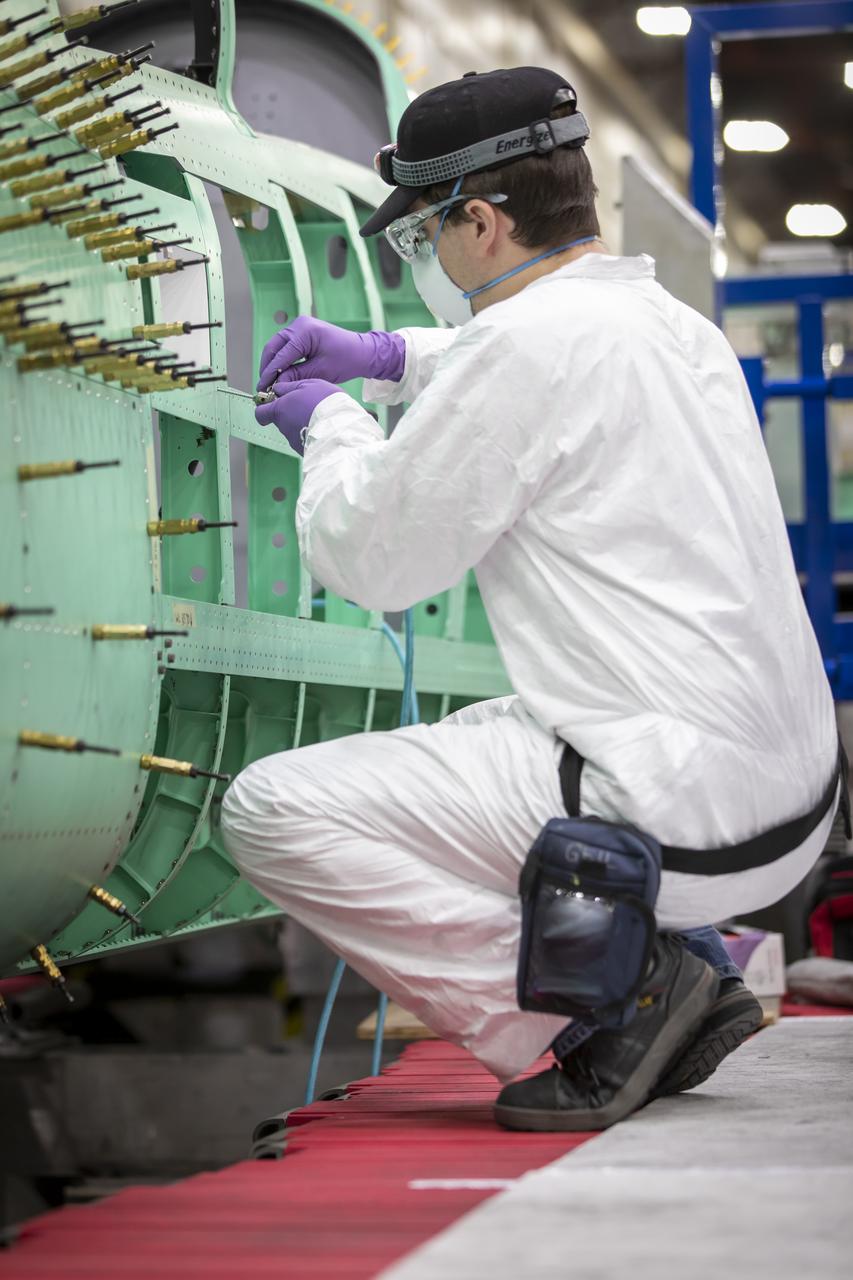

Event: SEG 210 Forebody A Lockheed Martin technician prepares to install the left fuselage skins onto the X-59. Once in the air, the aircraft, currently under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.

Lockheed Martin technicians work to align and check the fastener holes on the X-59’s fuselage skin. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
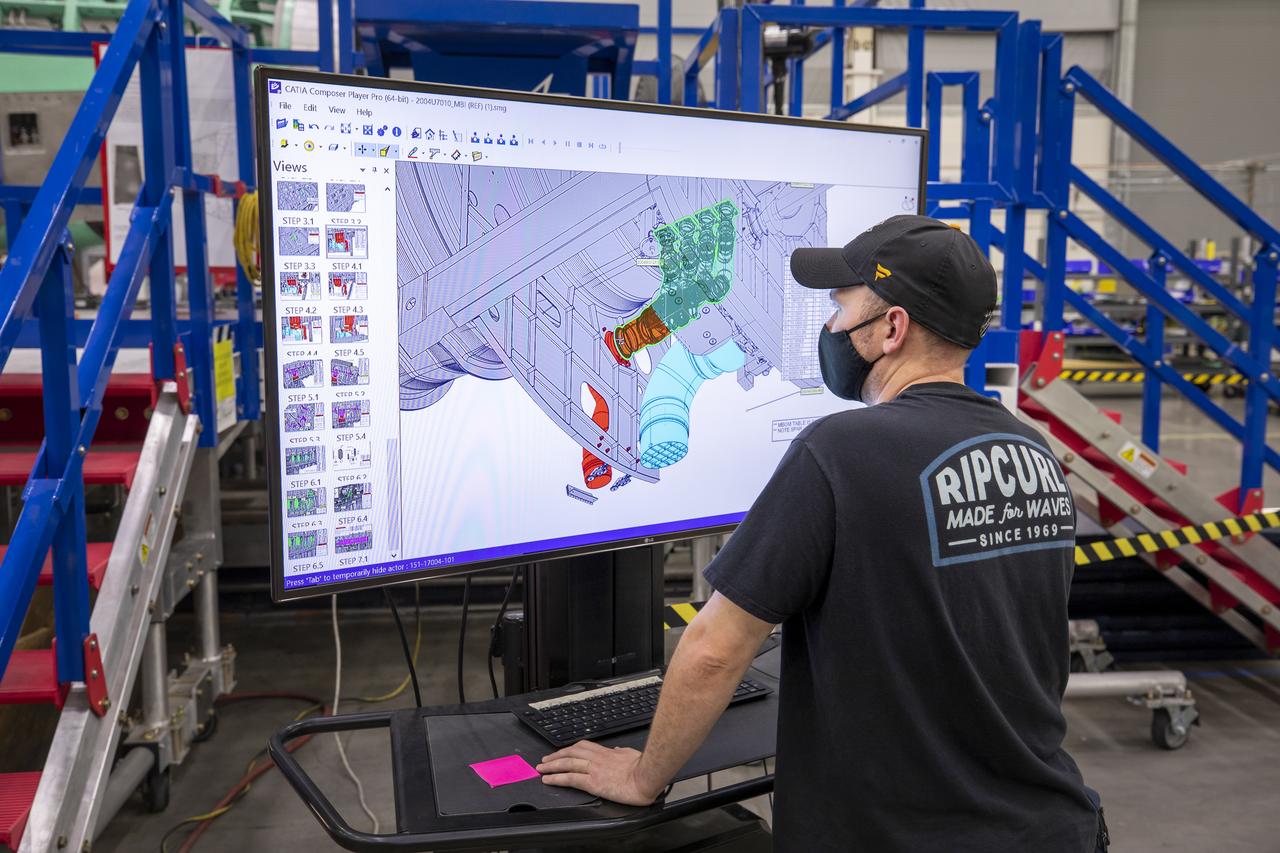

A Lockheed Martin technician looks at the connector installation on the cad model of the X-59 airplane. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
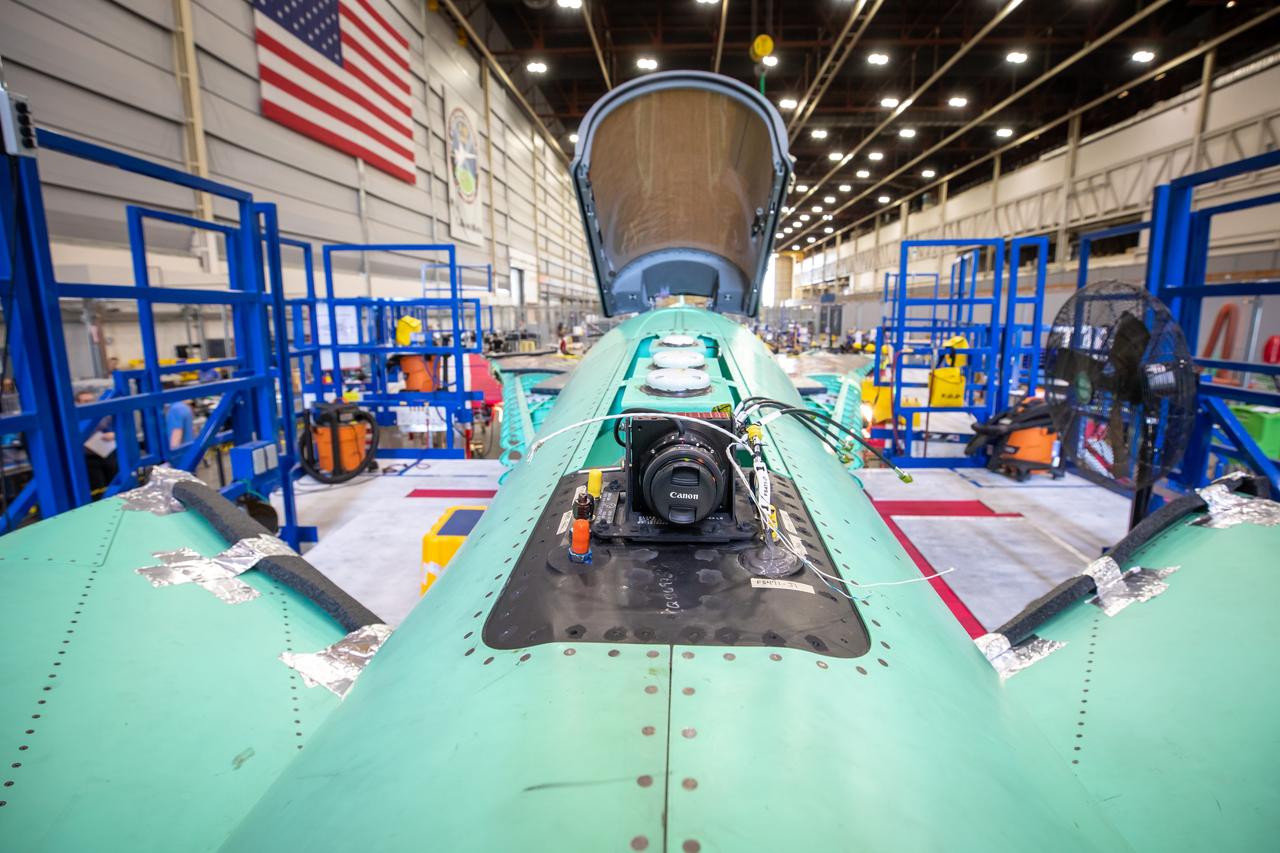

Event: Horizontal Stabilator Install A close up of the camera from the X-59’s eXternal Vision System. This camera is on the top of the X-59, but there will also be one on the belly of the aircraft. This visuals from this camera will be displayed on a 4K monitor for the pilot. As part of the supersonic shaping technology, the X-plane will not have a forward-facing window in the cockpit.
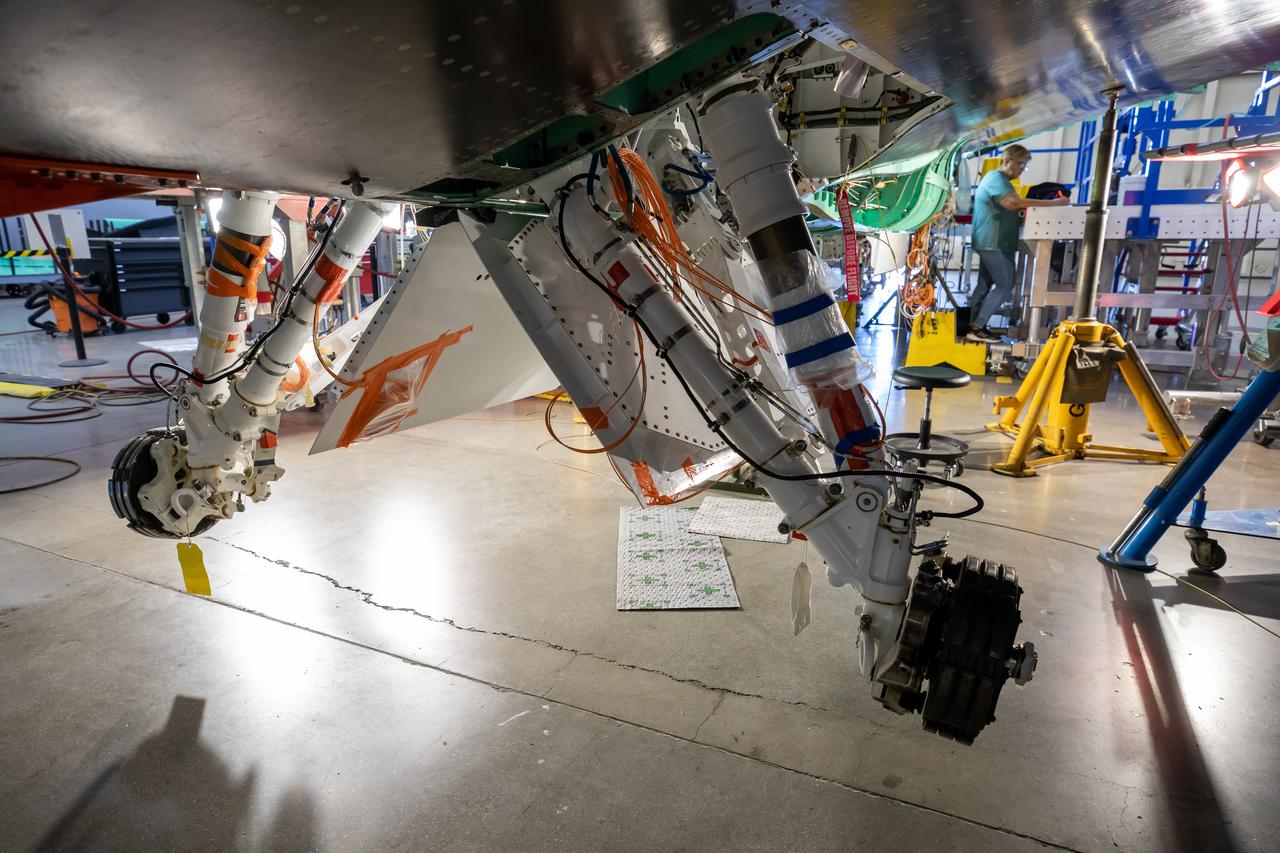

The Quesst team has repurposed the landing gear from an F-16 Fighting Falcon aircraft and is working on adjusting the fit onto the X-59 airplane. This is part of NASA’s Quesst mission which plans to help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
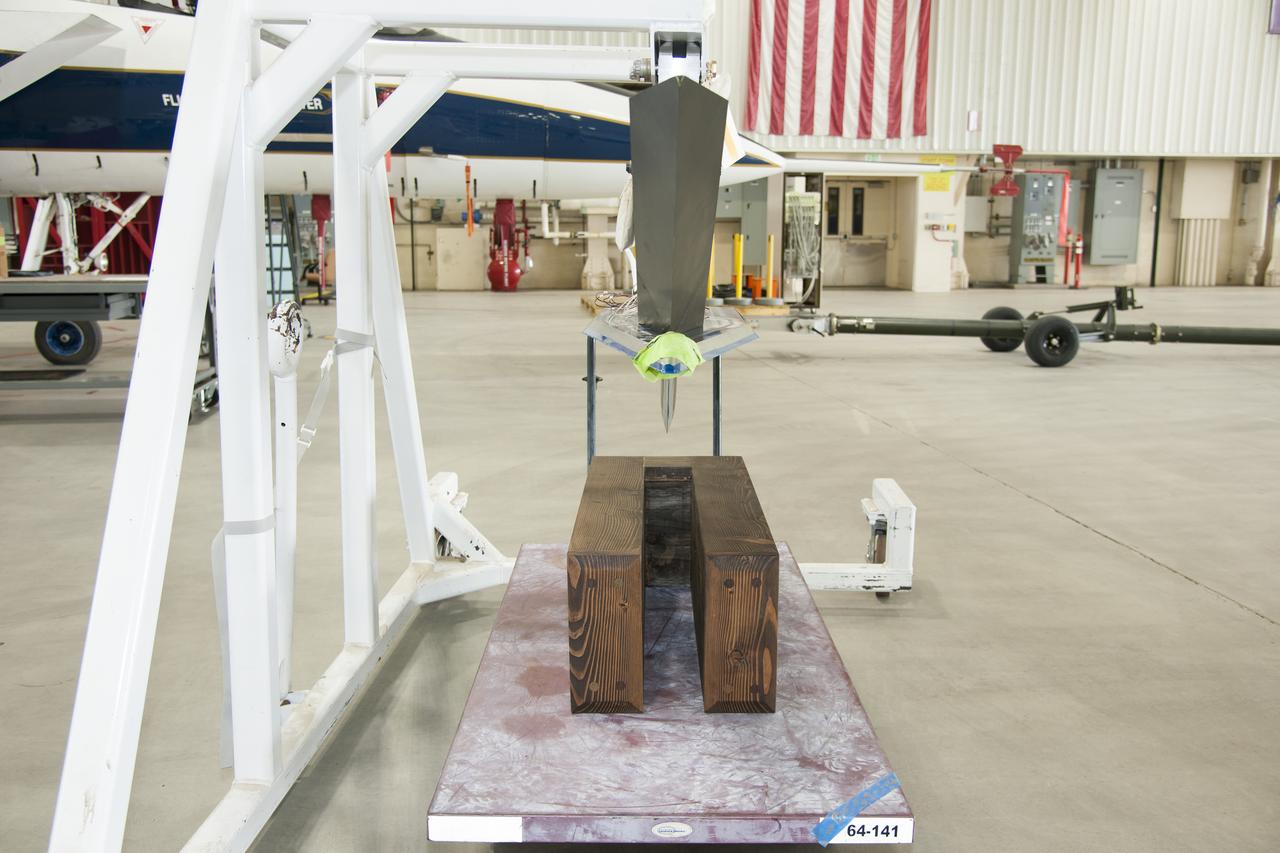

Testing different configurations of distributed roughness elements on the Swept Wing Laminar Flow test article, seen suspended above, will allow NASA researchers to observe which distributions are most efficient in extending laminar flow over a supersonic aircraft’s wing.
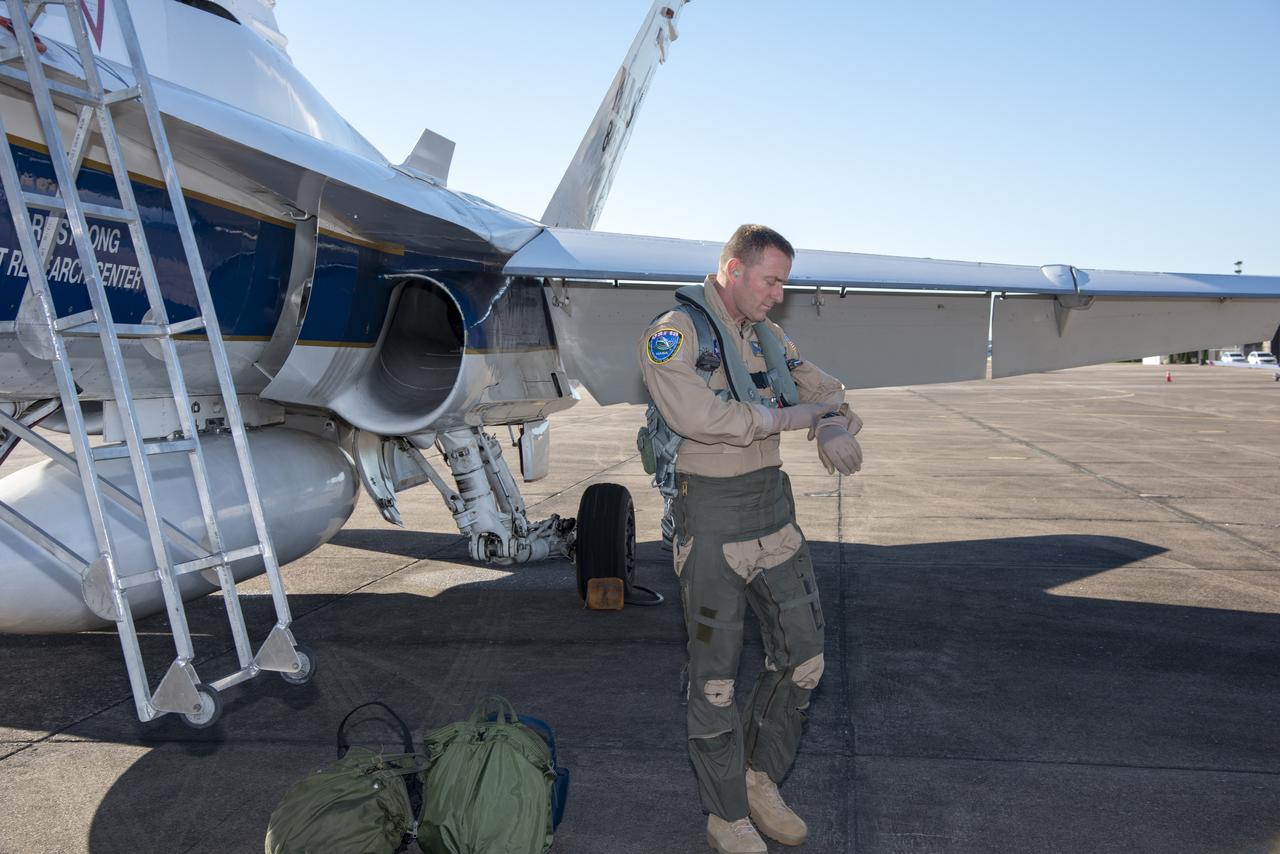

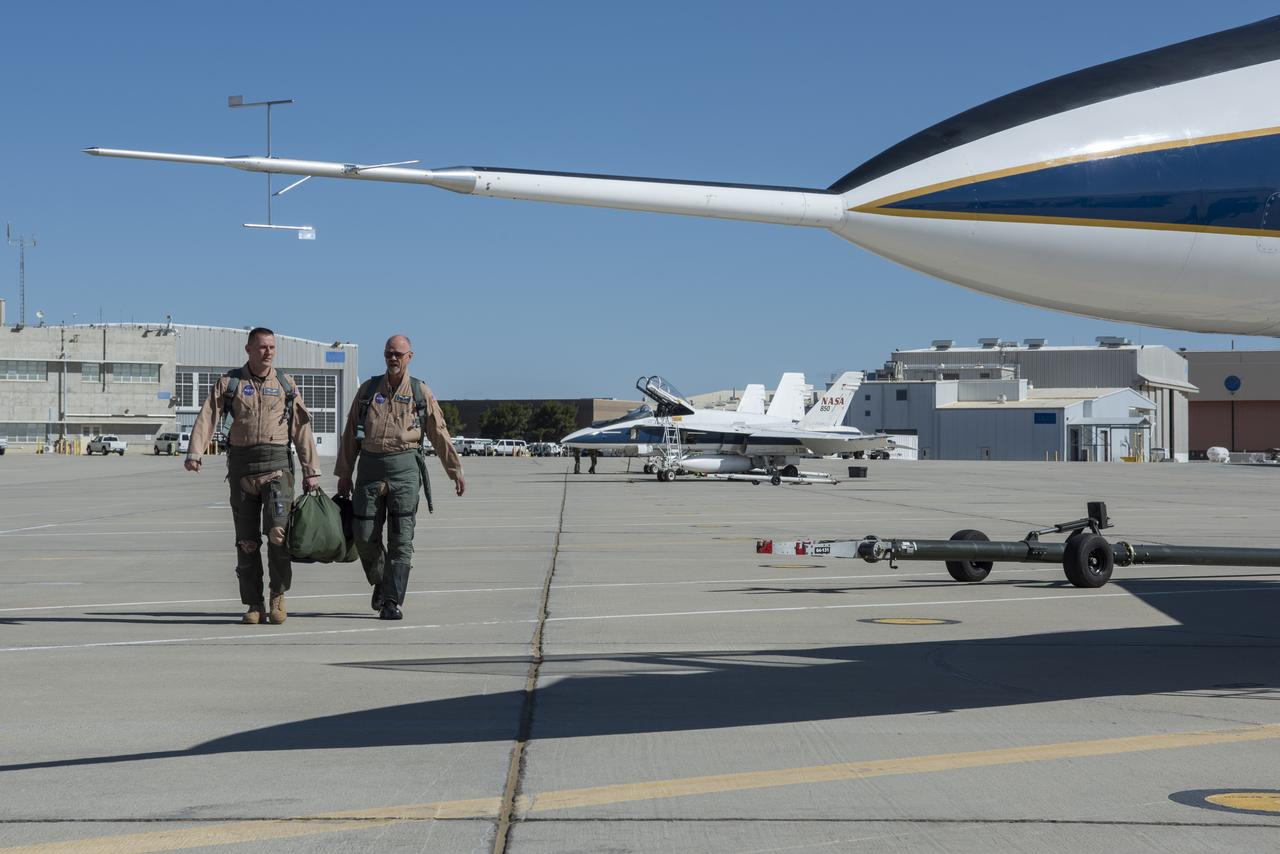
NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
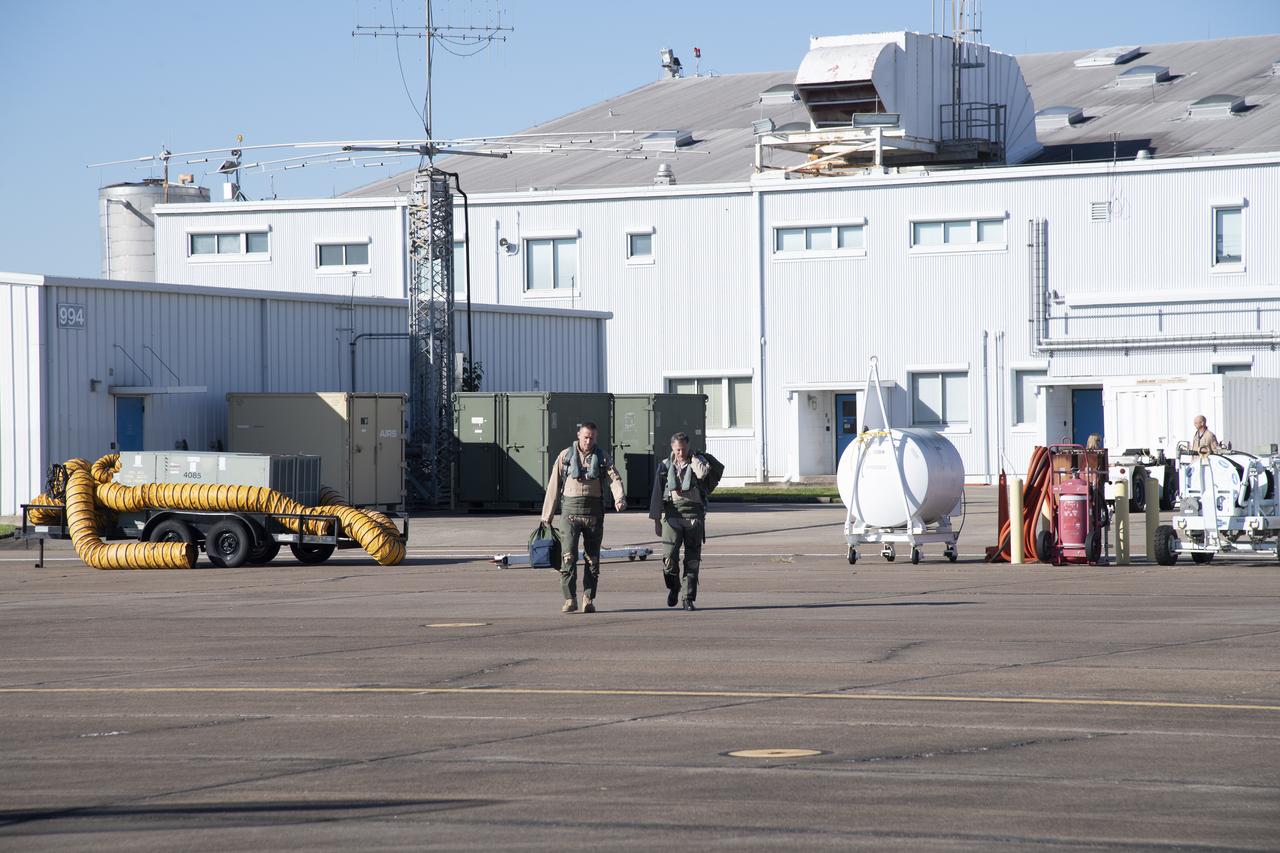

NASA test pilots Jim “Clue” Less and Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.
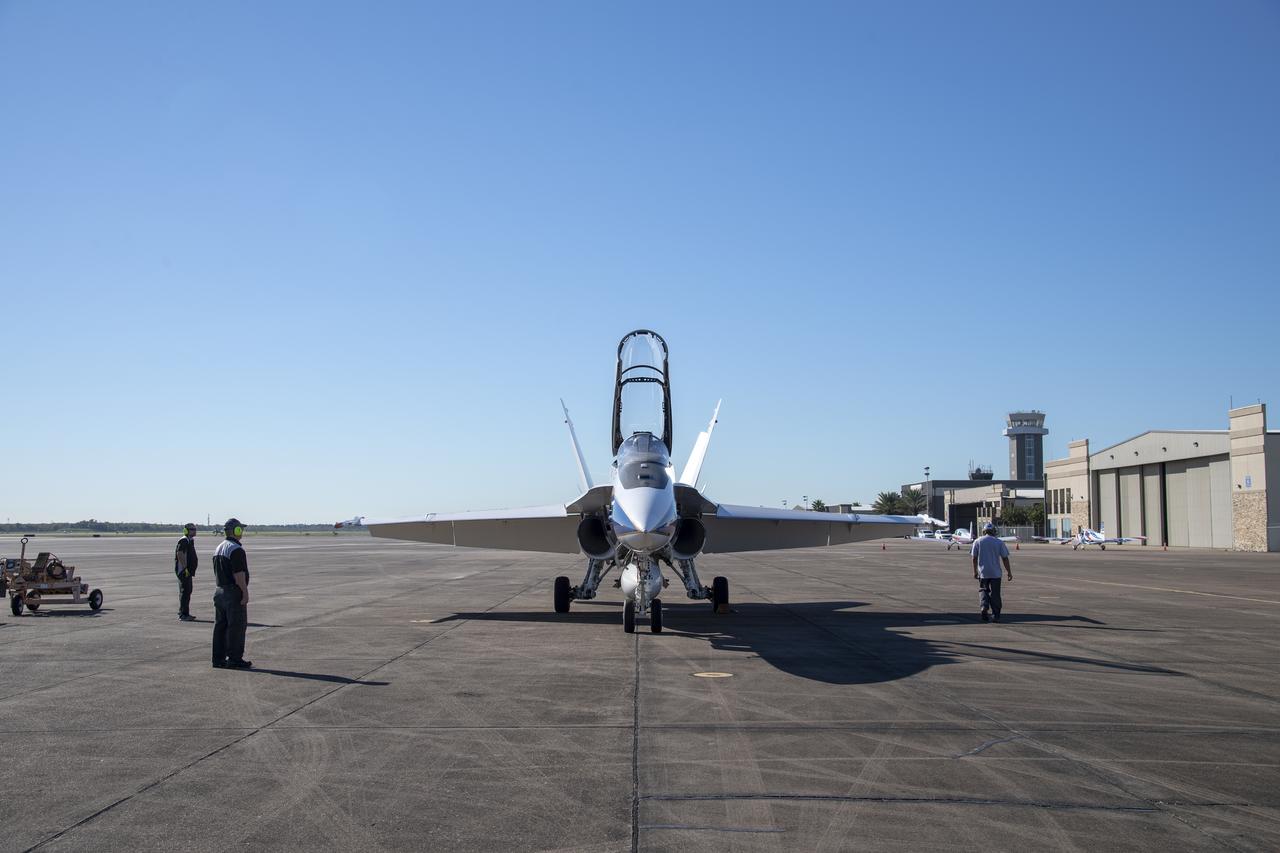

NASA test pilots Jim "Clue" Less and Wayne "Ringo" Ringelberg step to the F/A-18 research aircraft at Ellington Field and conduct pre-flight safety checks on the aircraft prior to a supersonic research flight for the QSF18 series.