
The 10- by 10-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel (10×10) is the largest and fastest wind tunnel facility at NASA’s Glenn Research Center and is specifically designed to test supersonic propulsion components from inlets and nozzles to full-scale jet and rocket engines.

NASA Dryden's new in-house designed Propulsion Flight Test Fixture (PFTF) flew mated to a specially-equipped supersonic F-15B research aircraft during December 2001 and January 2002.

The main structural body of the second flight test vehicle in NASA Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator LDSD project is seen during its assembly in a cleanroom at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
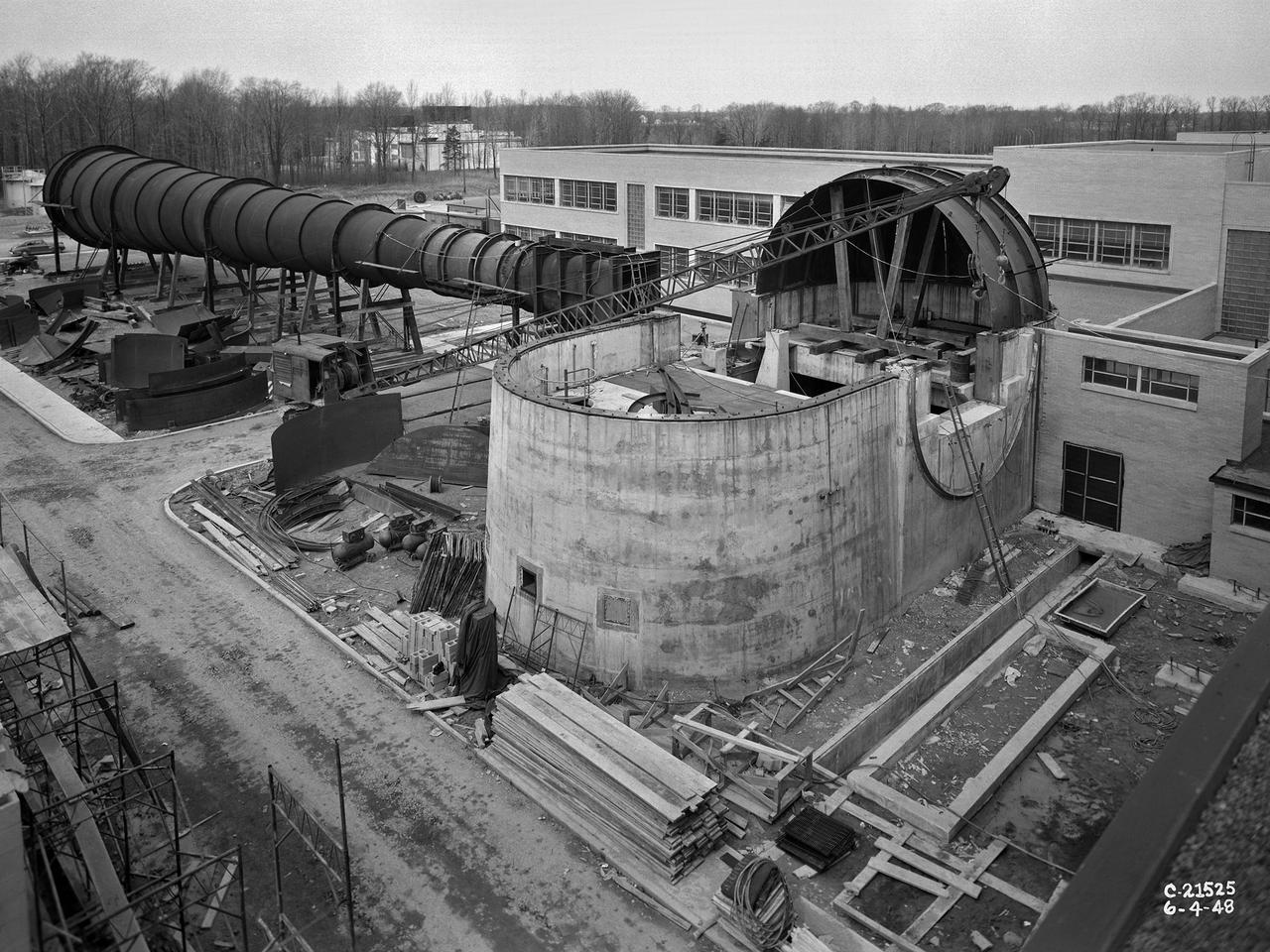

The 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory was the nation’s largest supersonic facility when it began operation in April 1949. The emergence of new propulsion technologies such as turbojets, ramjets, and rockets during World War II forced the NACA and the aircraft industry to develop new research tools. In late 1945 the NACA began design work for new large supersonic wind tunnels at its three laboratories. The result was the 4- by 4-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory, 6- by 6-foot supersonic wind tunnel at Ames Aeronautical Laboratory, and the largest facility, the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel in Cleveland. The two former tunnels were to study aerodynamics, while the 8- by 6 facility was designed for supersonic propulsion. The 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel was used to study propulsion systems, including inlets and exit nozzles, combustion fuel injectors, flame holders, exit nozzles, and controls on ramjet and turbojet engines. Flexible sidewalls alter the tunnel’s nozzle shape to vary the Mach number during operation. A seven-stage axial compressor, driven by three electric motors that yield a total of 87,000 horsepower, generates air speeds from Mach 0.36 to 2.0. A section of the tunnel is seen being erected in this photograph.
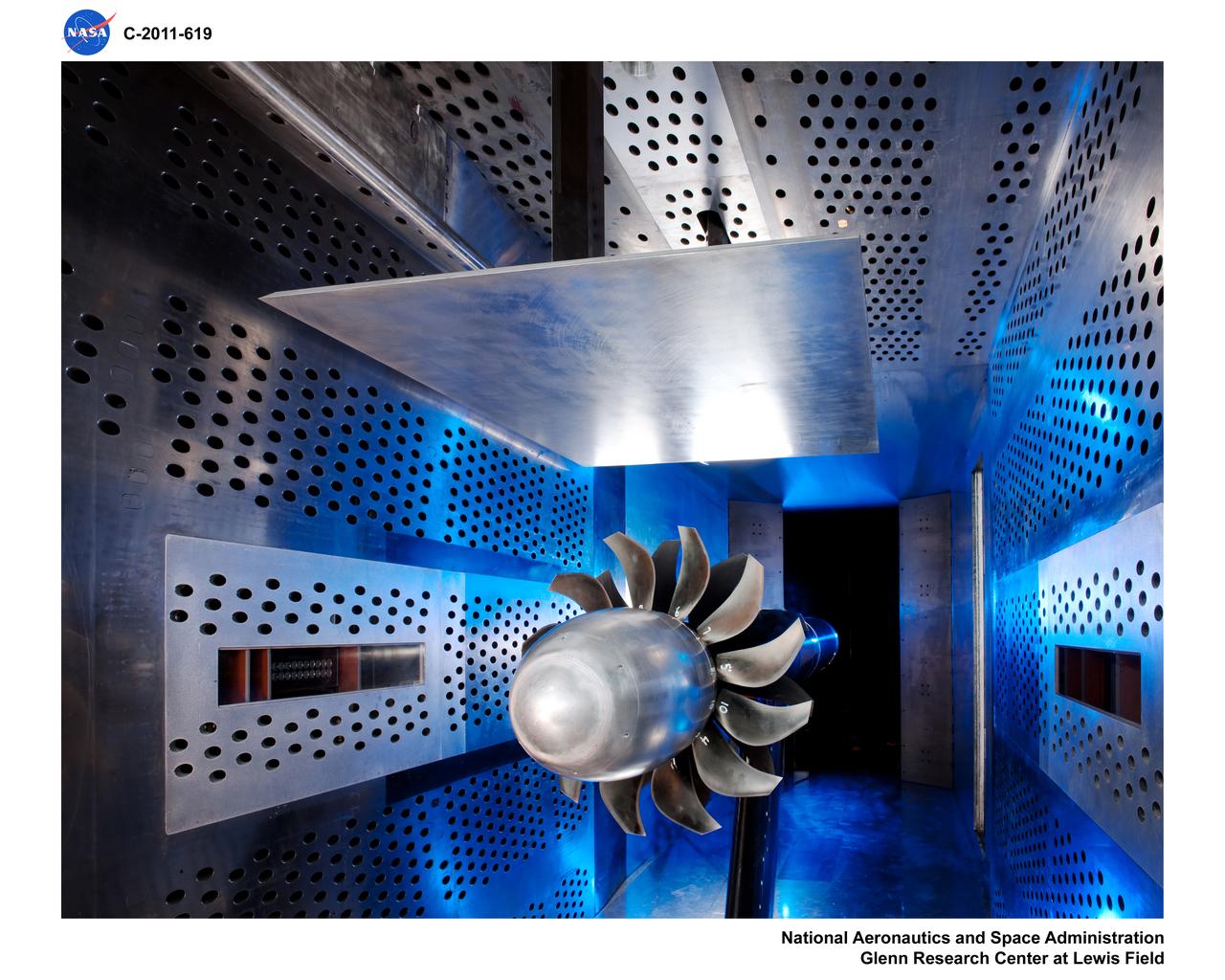
Air-Breathing Propulsion - General Electric Open Rotor Model in the 8x6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

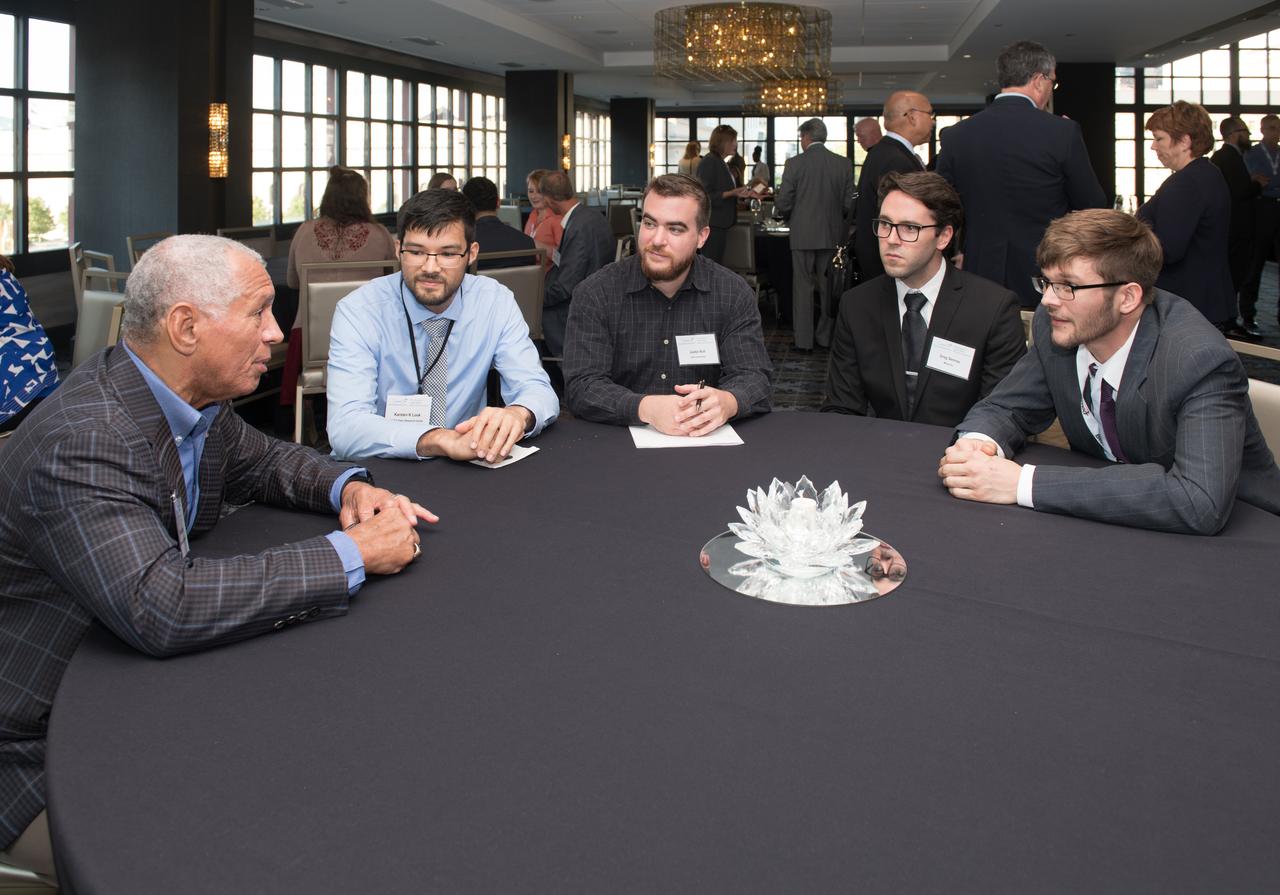
The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

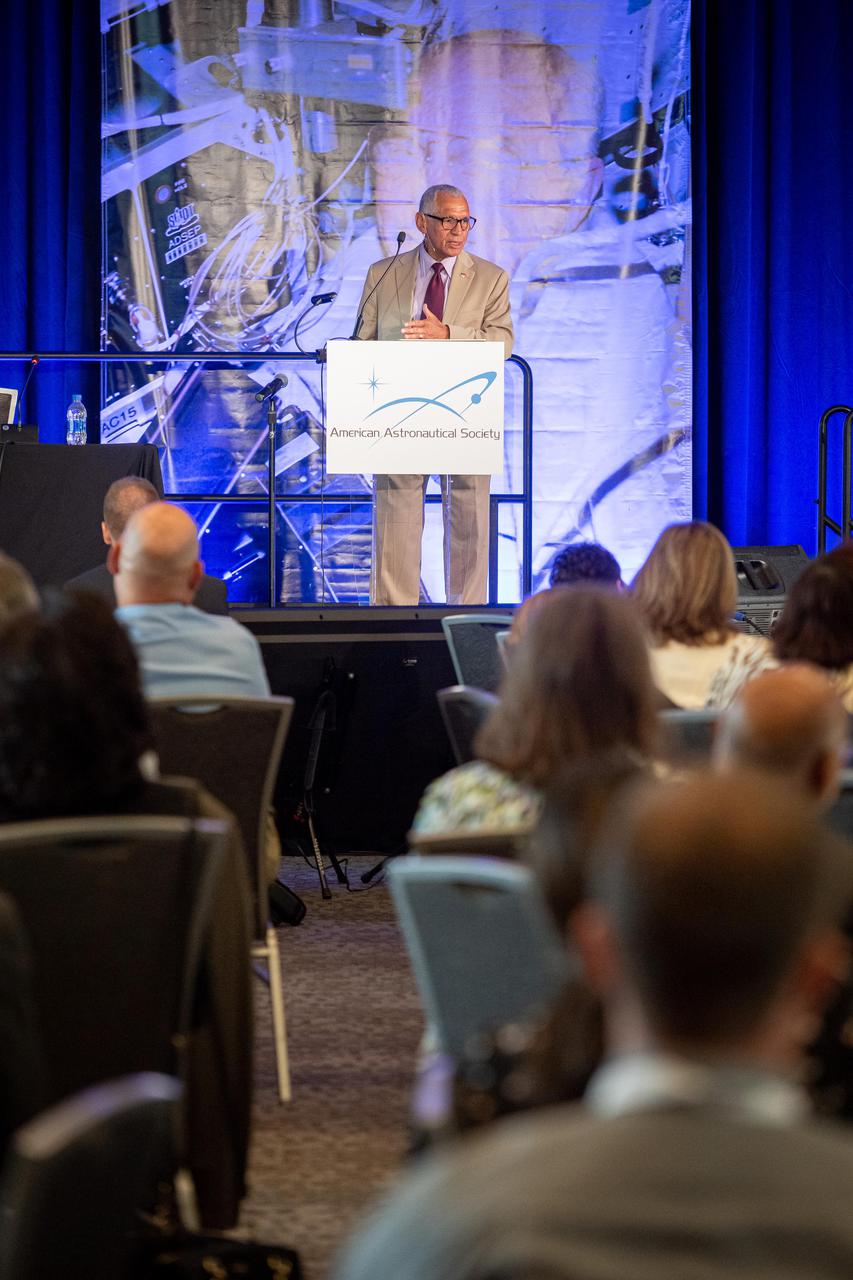
The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

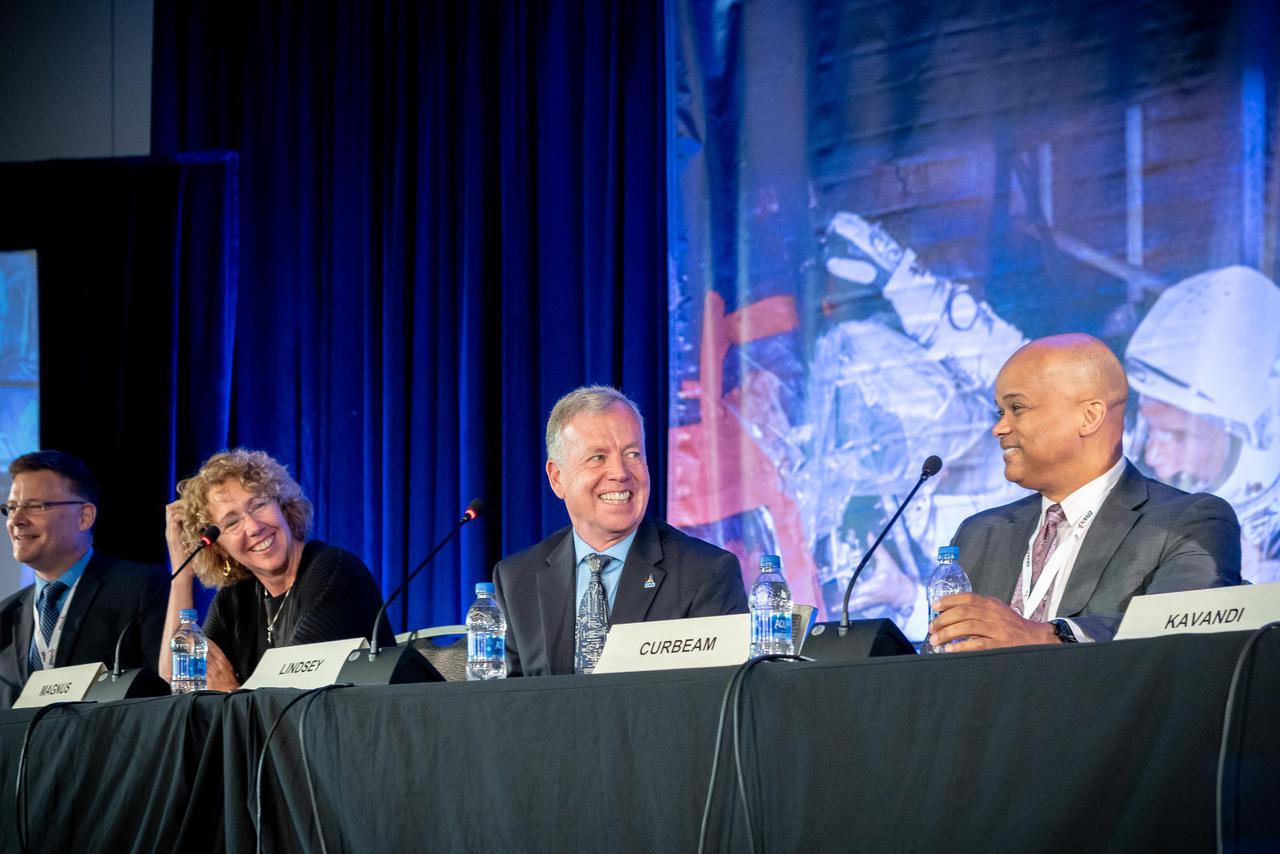
The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

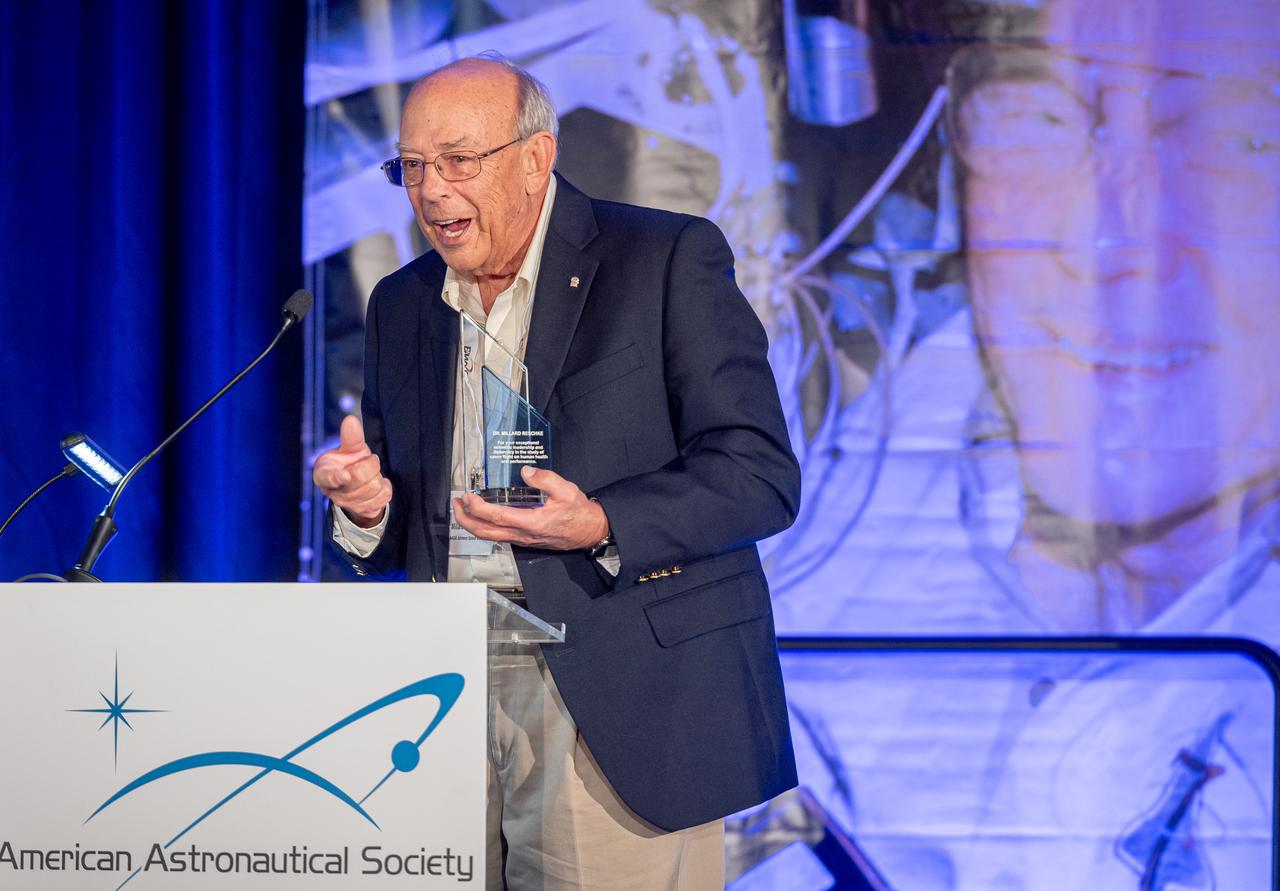
The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.
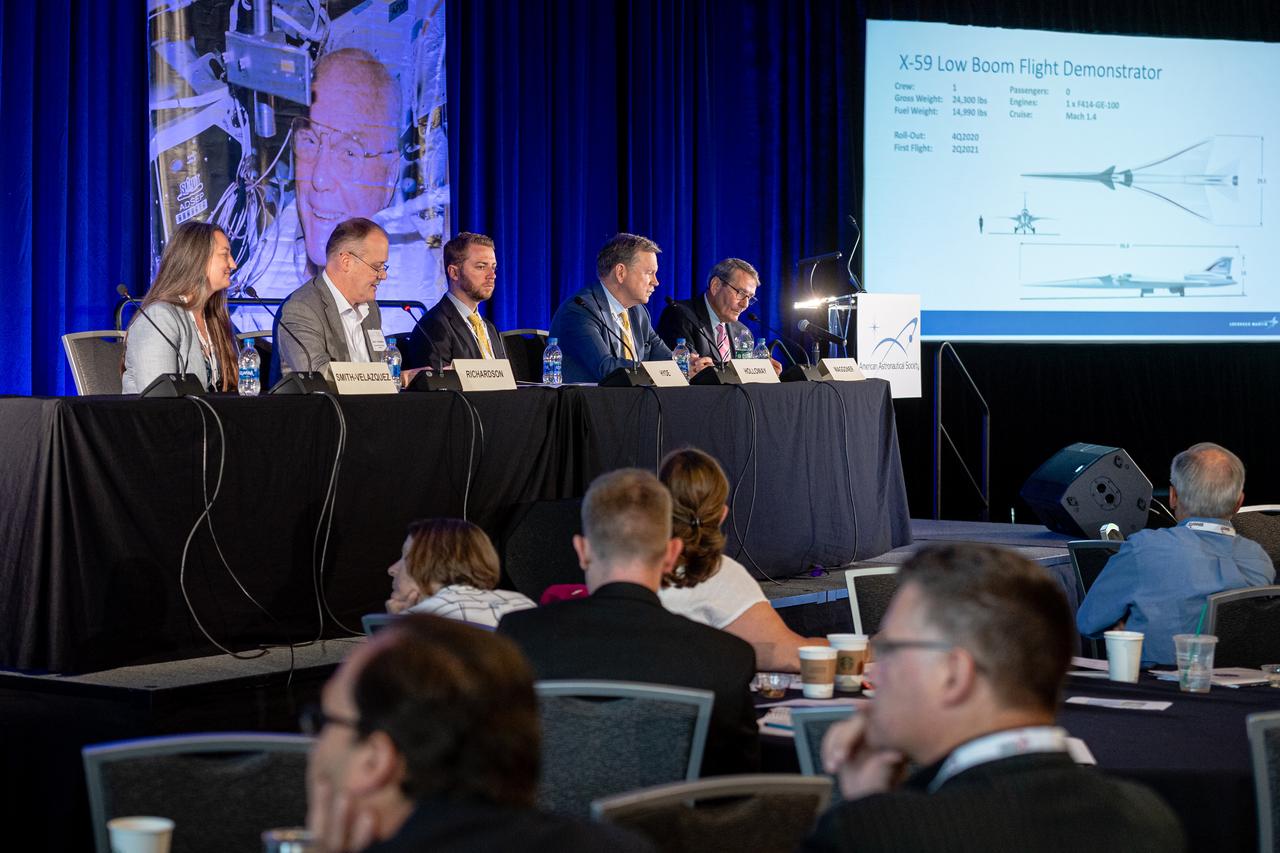

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.
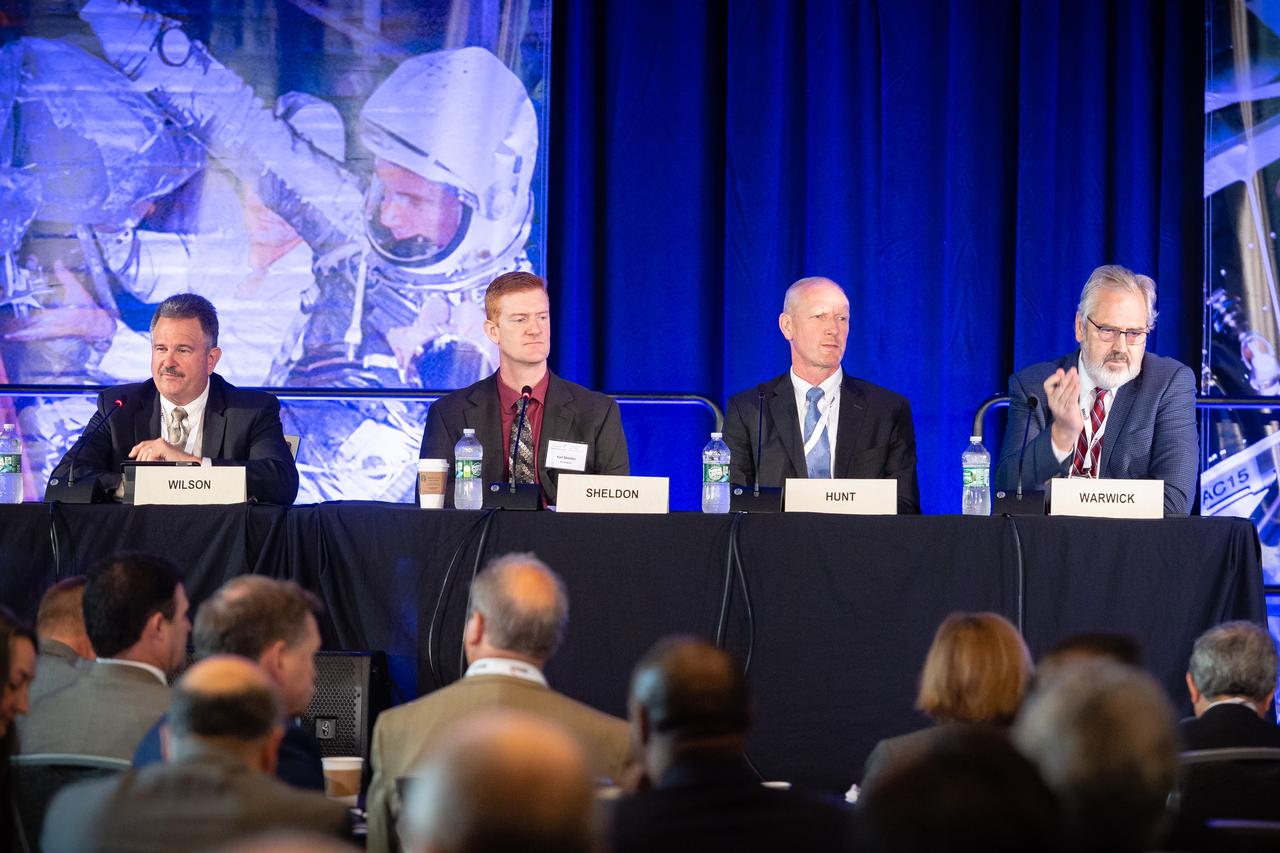

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.
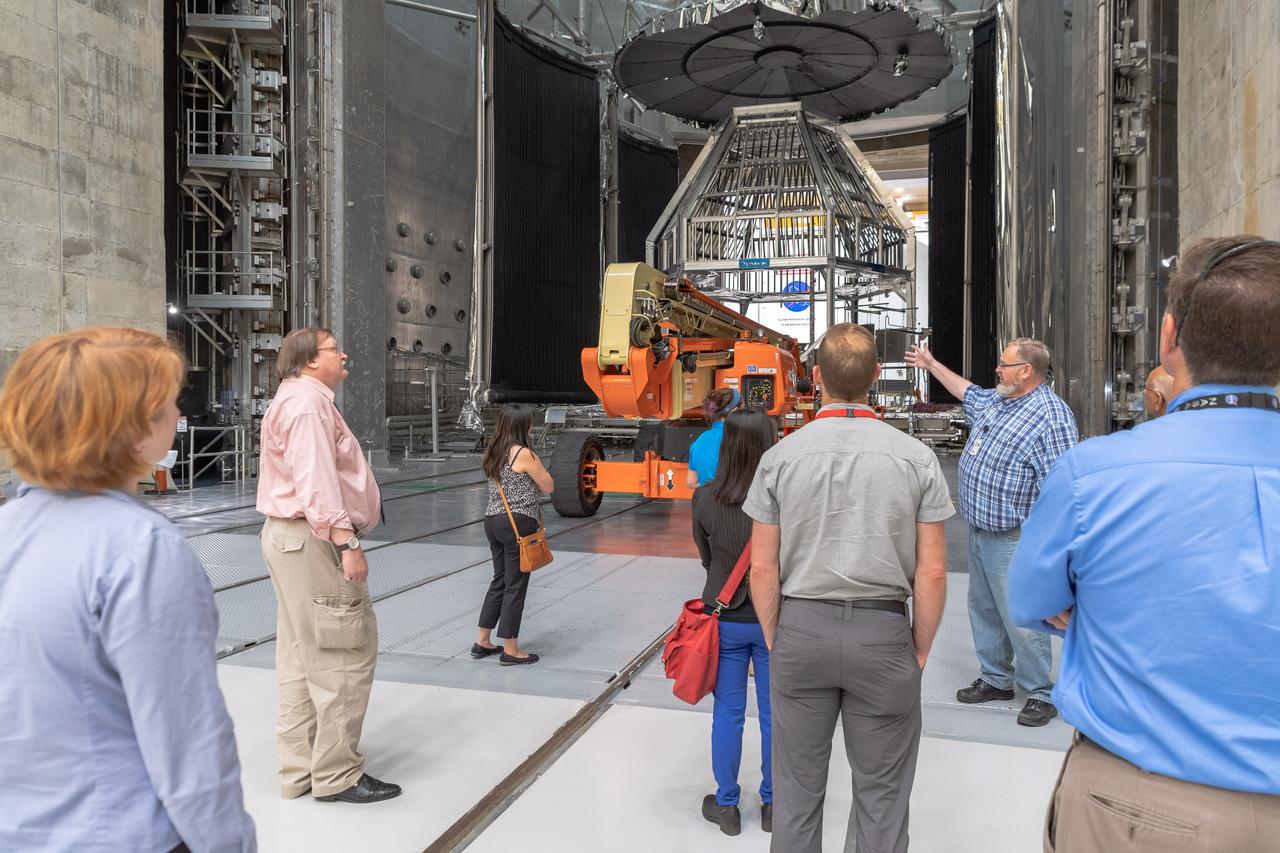

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.
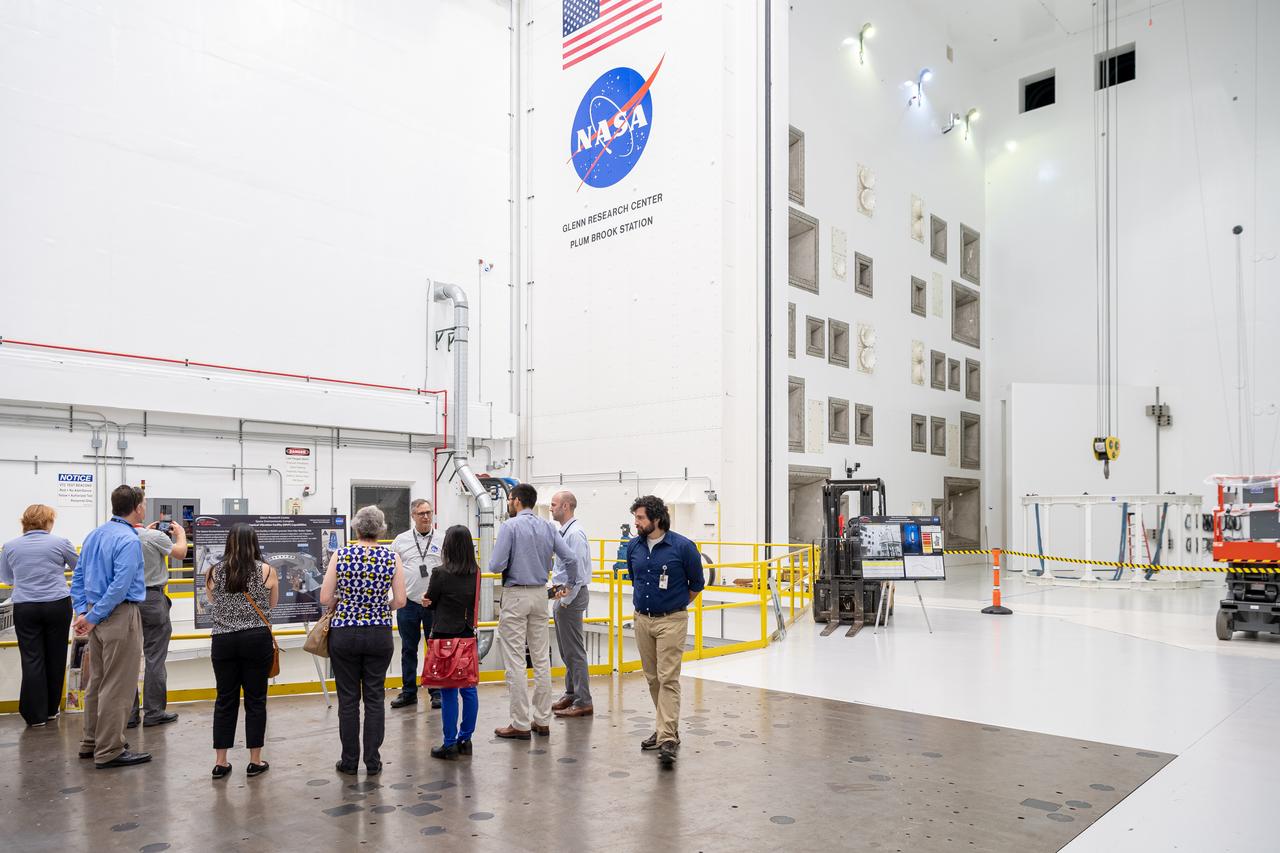

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.
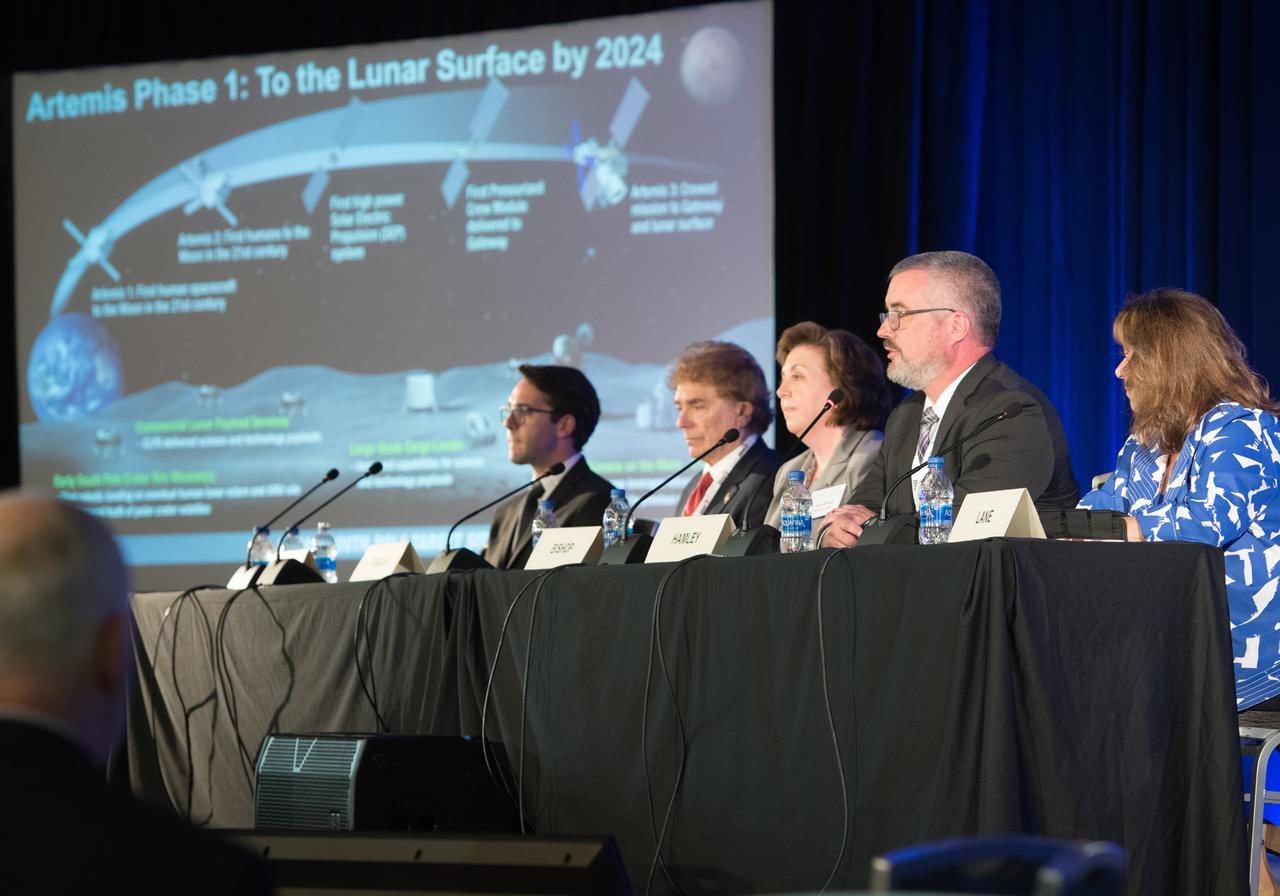

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.
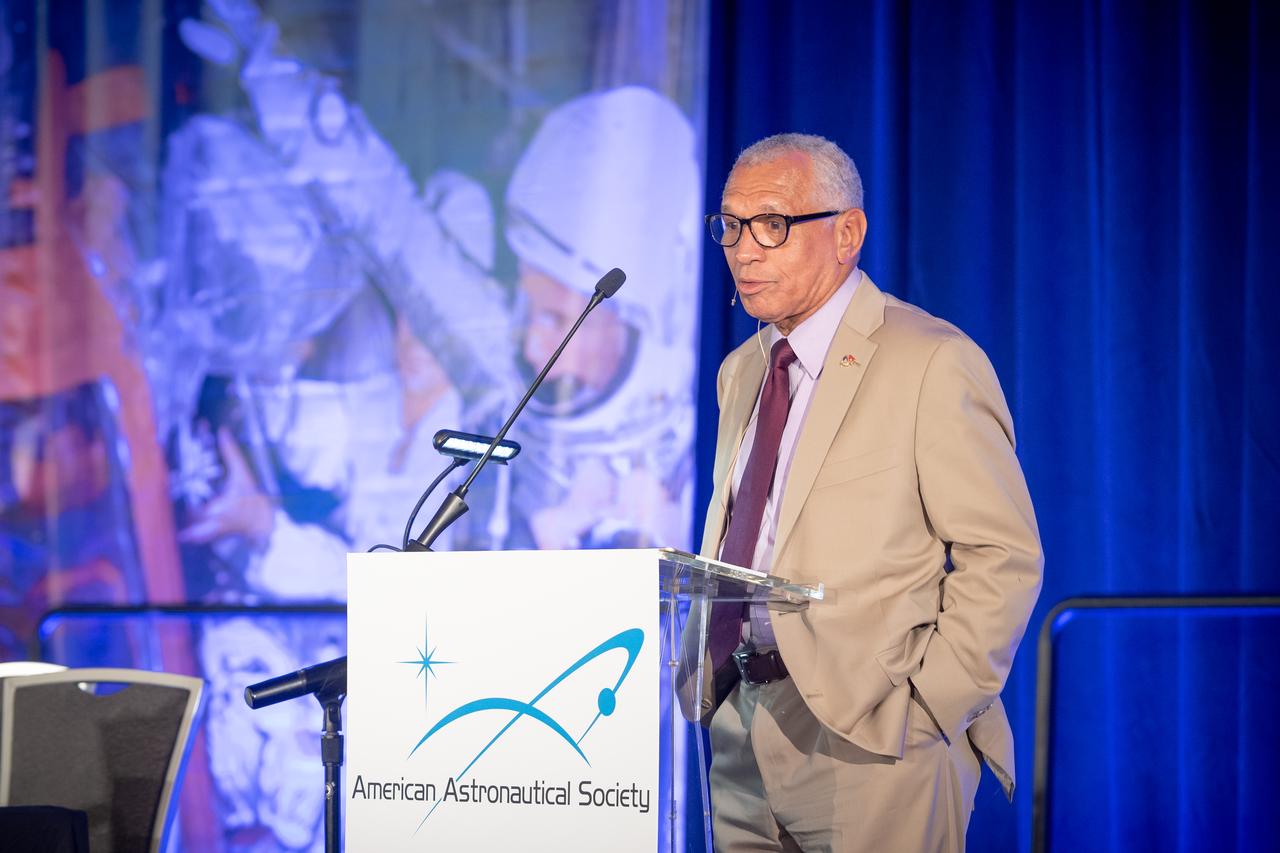

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.
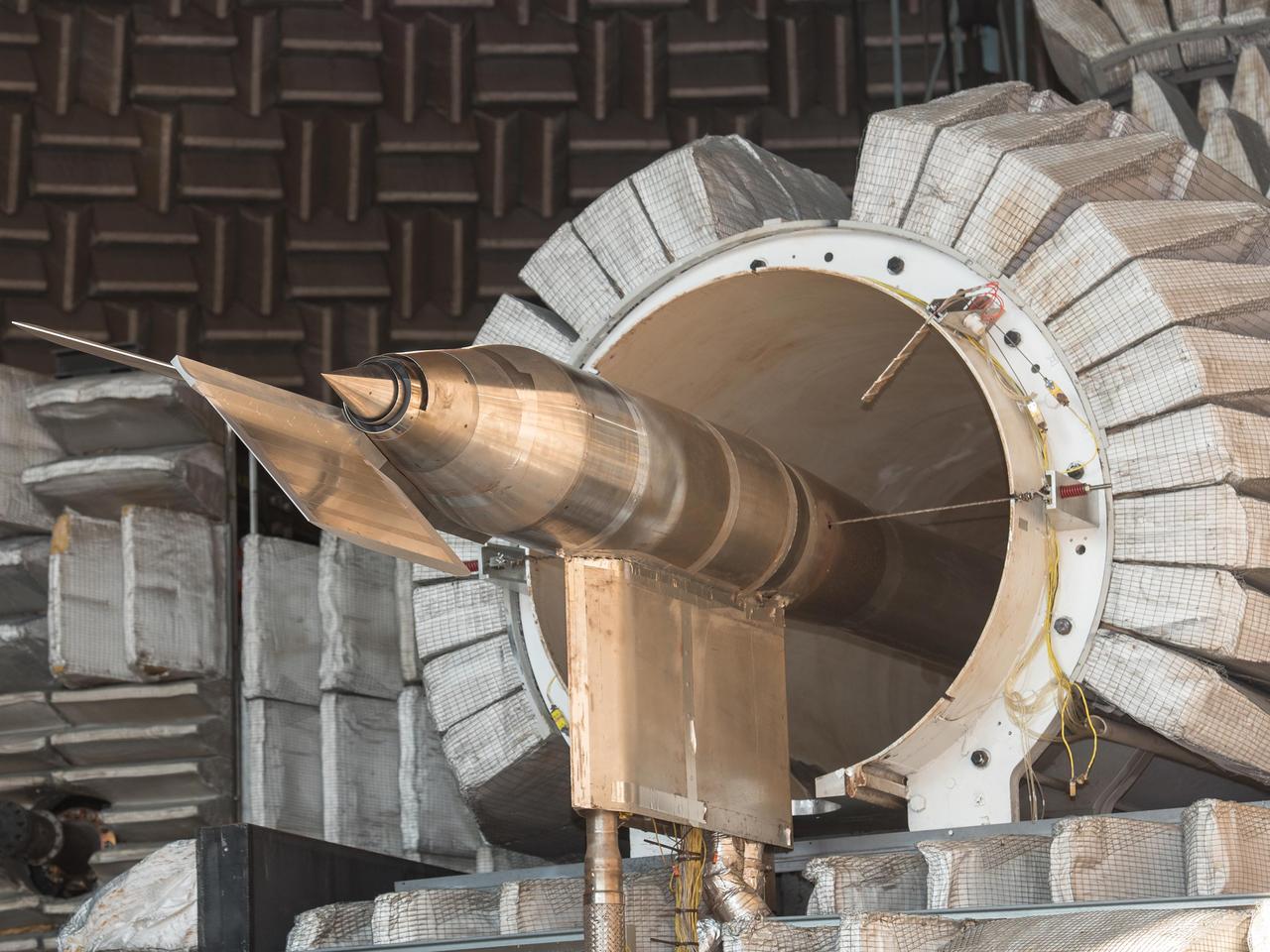

N+2 Nozzle in the Aero-Acoustic Propulsion Lab. As NASA works toward demonstrating low-sonic boom design, engineers at NASA Glenn have tested an engine nozzle that could make supersonic aircraft much quieter.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.
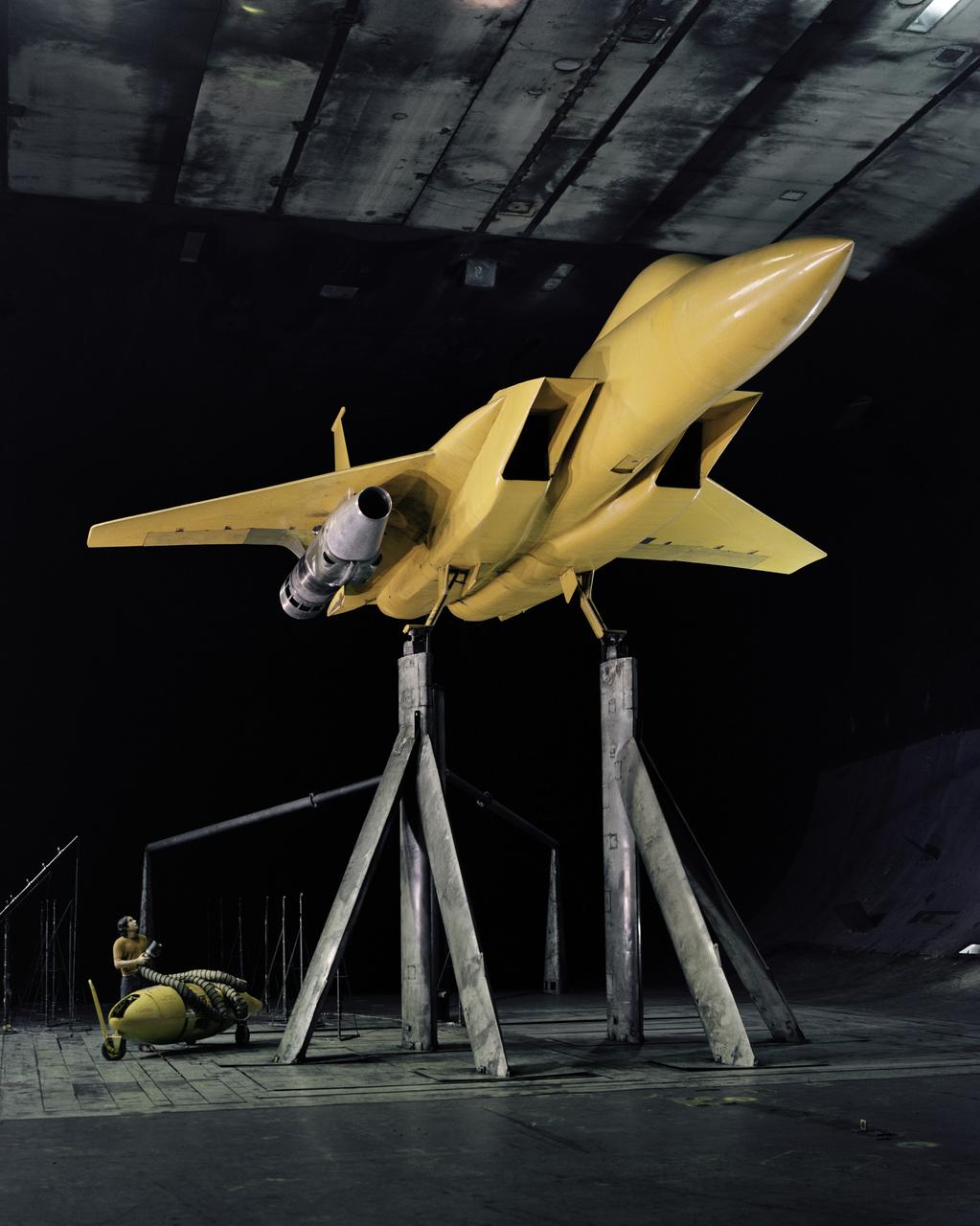

AST (Advanced Supersonic Technology) Propulsion Noise Research test on the F-15 model with nacelle in the 40x80ft Subsonic Wind Tunnel at Ames Research Center, Mt View, CA

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.
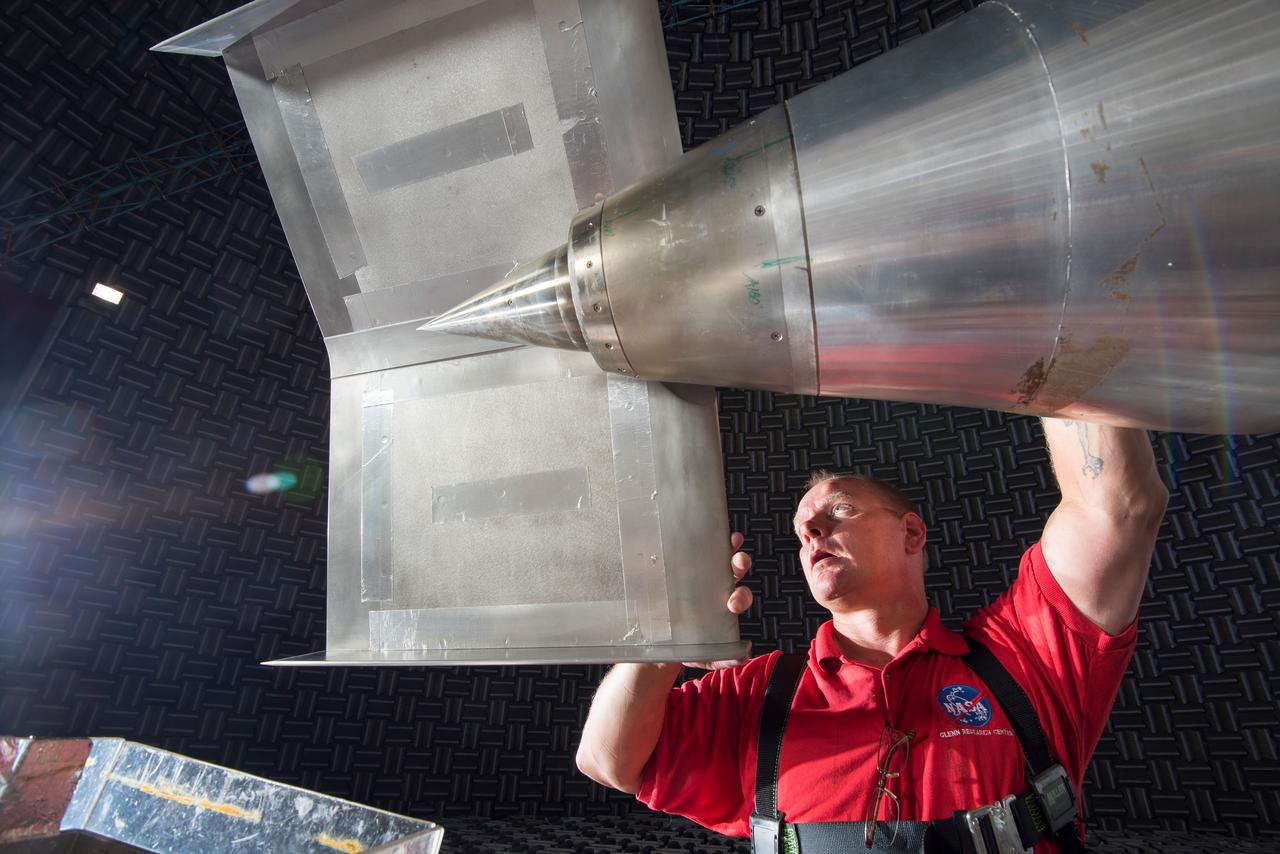

N+2 Nozzle in the Aero-Acoustic Propulsion Lab. As NASA works toward demonstrating low-sonic boom design, engineers at NASA Glenn have tested an engine nozzle that could make supersonic aircraft much quieter.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.
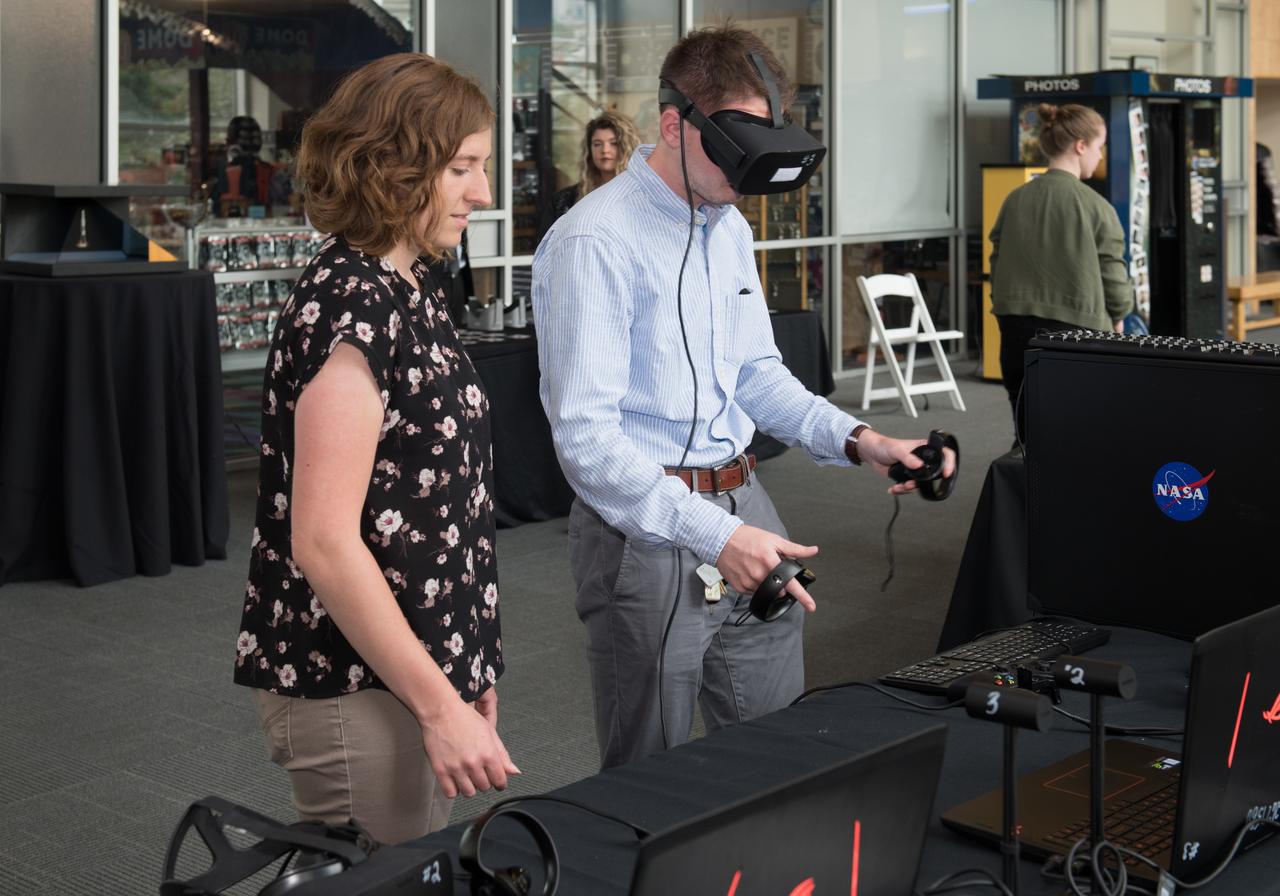

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.
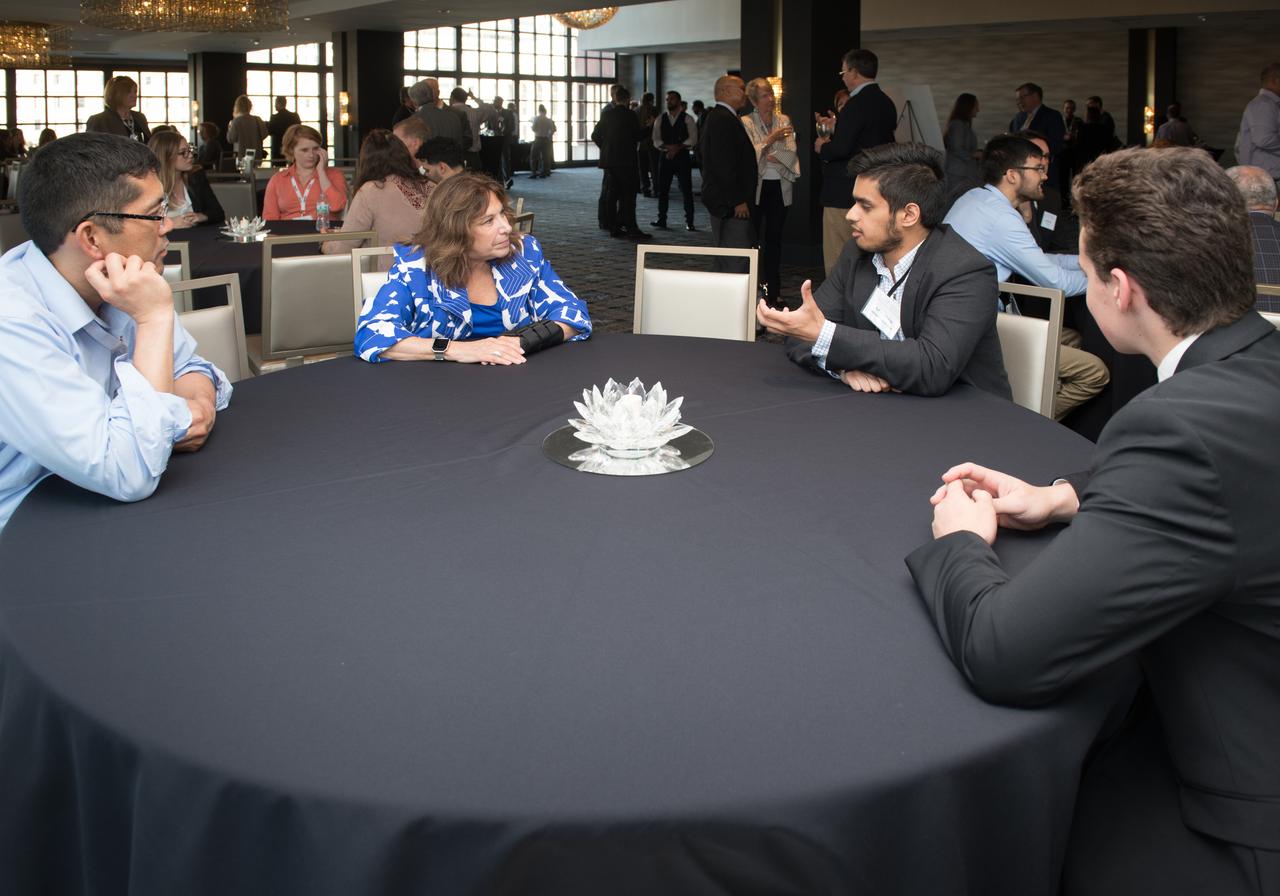

The inaugural Glenn Symposium focused on advancements in aerospace technology including power and propulsion, autonomy and communications, low boom supersonics, hypersonics, and more. Discussion also encompassed humans returning to the moon, including challenges associated with the 2024 mission.
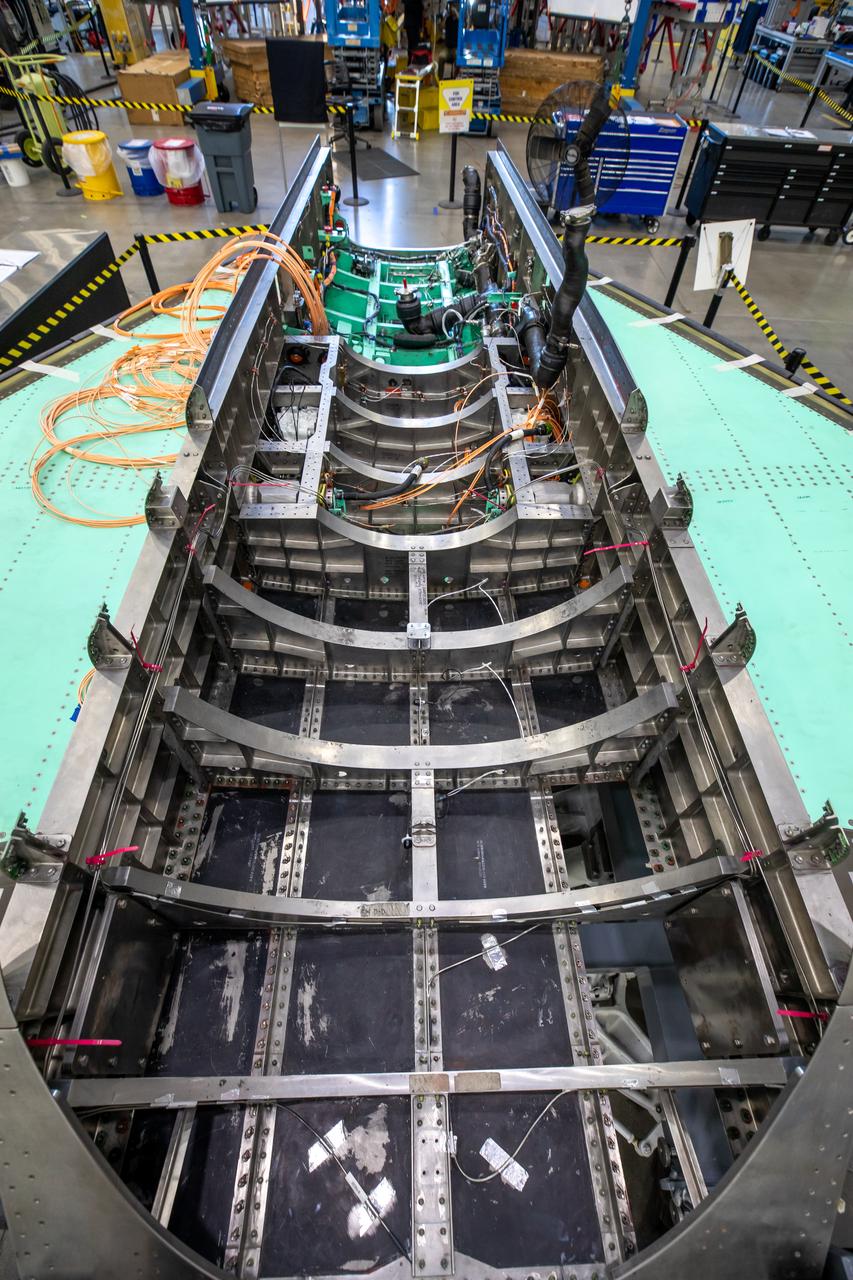
This image shows the X-59 aircraft’s lower empennage structure, or tail section of the plane, that was installed. The stabilators, the outer surfaces also seen in the photo, attach to the lower empennage and are used to help regulate the aircraft pitch which controls the up and down movement of the motion of the plane. The 13-foot engine will pack 22,000 pounds of propulsion and energy and power the X-plane to its planned cruising speed of Mach 1.4. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.
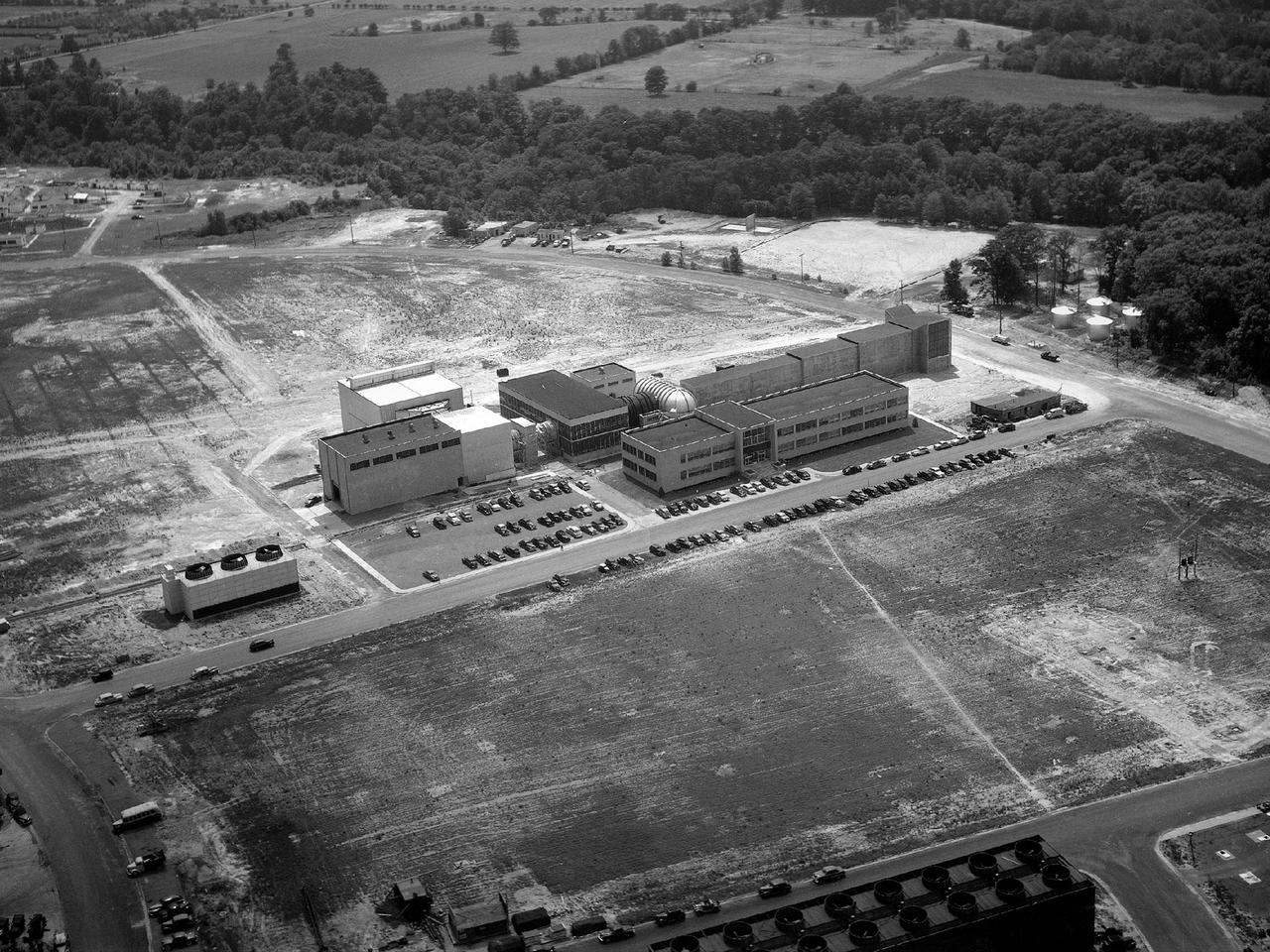

Aerial view of the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel in its original configuration at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The 8- by 6 was the laboratory’s first large supersonic wind tunnel. It was also the NACA’s most powerful supersonic tunnel, and its first facility capable of running an engine at supersonic speeds. The 8- by 6-foot tunnel has been used to study inlets and exit nozzles, fuel injectors, flameholders, exit nozzles, and controls on ramjet and turbojet propulsion systems. The 8- by 6 was originally an open-throat and non-return tunnel. This meant that the supersonic air flow was blown through the test section and out the other end into the atmosphere. In this photograph, the three drive motors in the structure at the left supplied power to the seven-stage axial-flow compressor in the light-colored structure. The air flow passed through flexible walls which were bent to create the desired speed. The test article was located in the 8- by 6-foot stainless steel test section located inside the steel pressure chamber at the center of this photograph. The tunnel dimensions were then gradually increased to slow the air flow before it exited into the atmosphere. The large two-story building in front of the tunnel was used as office space for the researchers.

New testing is underway in the Aero-Acoustic Propulsion Laboratory (AAPL) at NASA's Glenn Research Center. The research focuses on a model called the Highly Variable Cycle Exhaust System -- a 0.17 scale model of an exhaust system that will operate at subsonic, transonic and supersonic exhaust speeds in a future supersonic business jet. The model features ejector doors used at different angles. Researchers are investigating the impact of these ejectors on the resulting acoustic radiation. Here, Steven Sedensky, a mechanical engineer with Jacobs Sverdrup, takes measurements of the ejector door positions.
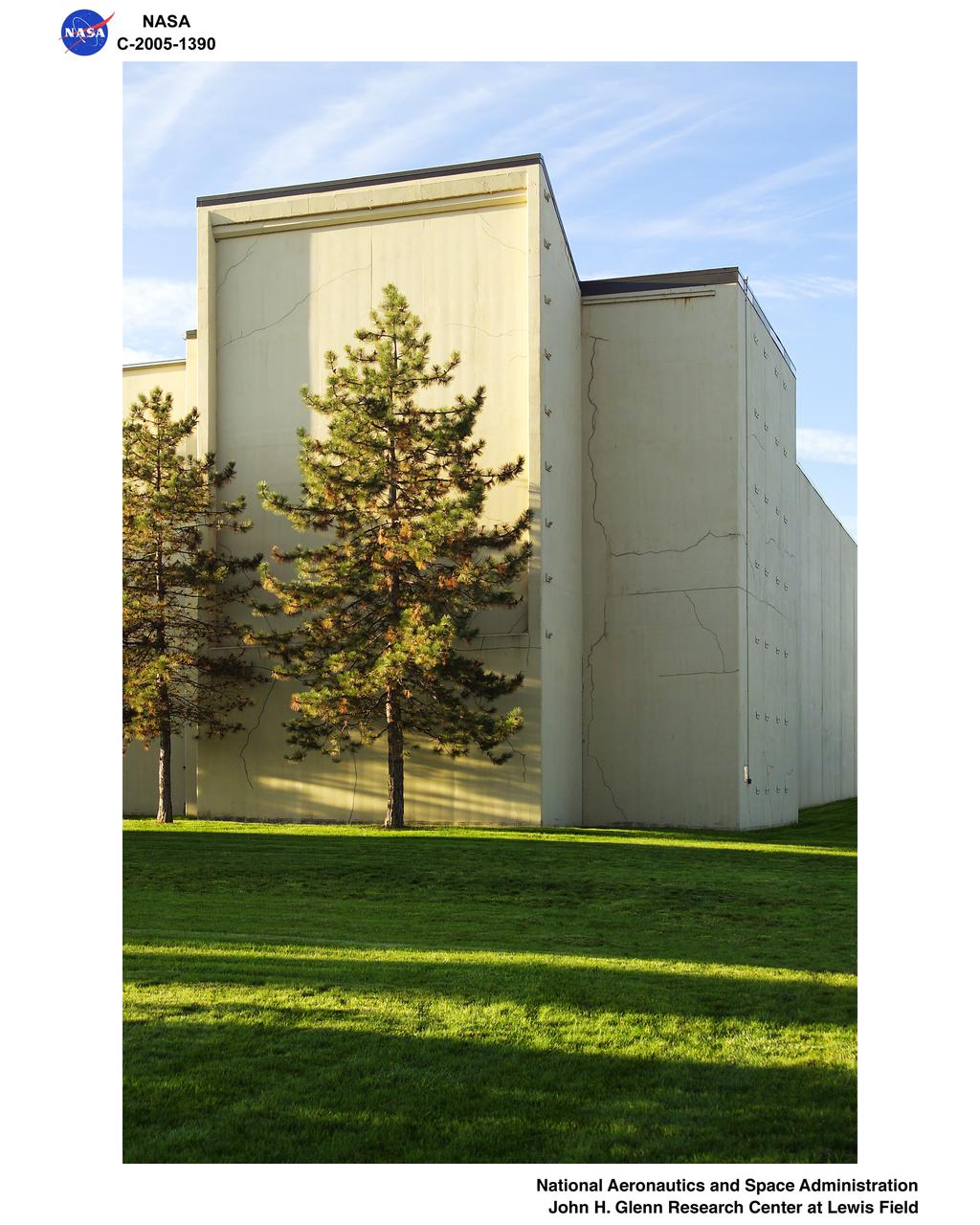

North and West-facing facades of the 8x6 Supersonic Wind Tunnel in the early morning light. Caption: In the early morning light, the strong geometric lines behind the soft pine trees caught the eye of a photographer at Glenn Research Center. Behind the commanding facade lies the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel (8x6 SWT), an atmospheric tunnel with perforated stainless steel walls that provide boundary control during transonic operations. It is NASA's only transonic propulsion wind tunnel. http://facilities.grc.nasa.gov/8x6/8x6_quick.html

A technician at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory examines one of the massive axial-flow compressor stages that created the high-speed air flow through the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel. The tunnel’s first run was on April 3, 1949, just over a week before this photograph was taken. The 8- by 6 was the laboratory’s first large supersonic wind tunnel and the NACA’s largest supersonic tunnel at the time. The 8- by 6-foot tunnel was originally an open-throat non-return tunnel. The supersonic air flow was blown through the tubular facility and expelled out the other end into the atmosphere with a roar. Complaints from the local community led to the addition of a muffler at the tunnel exit in 1956 and the eventual addition of a return leg. The return leg allowed the tunnel to be operated as either an open system with large doors venting directly to the atmosphere for propulsion system tests or as a closed loop for aerodynamic tests. The air flow was generated by a large seven-stage axial-flow compressor, seen in this photograph, that was powered by three electric motors with a combined 87,000 horsepower. The system required 36,000 kilowatts of power per hour to generate wind velocities of Mach 1.5, and 72,000 kilowatts per hour for Mach 2.0.
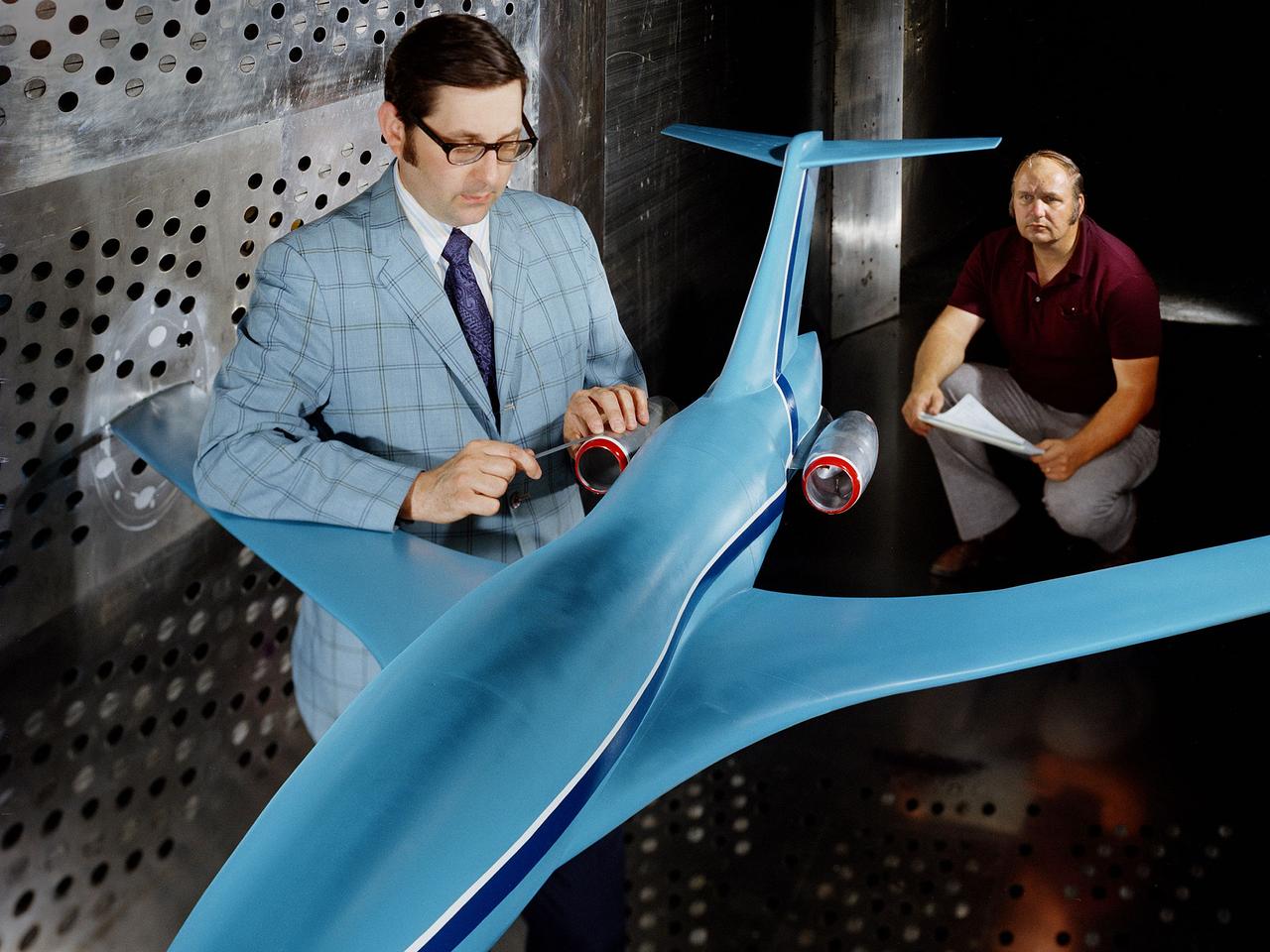

A researcher examines an Advanced Technology Transport model installed in the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The Advanced Technology Transport concept was a 200-person supersonic transport aircraft that could cruise at Mach 0.9 to 0.98 with low noise and pollution outputs. General Electric and Pratt and Whitney responded to NASA Lewis’ call to design a propulsion system for the aircraft. The integration of the propulsion system with the airframe was one of the greatest challenges facing the designers of supersonic aircraft. The aircraft’s flow patterns and engine nacelles could significantly affect the performance of the engines. NASA Lewis researchers undertook a study of this 0.30-scale model of the Advanced Technology Transport in the 8- by 6-foot tunnel. The flow-through nacelles were located near the rear of the fuselage during the initial tests, seen here, and then moved under the wings for ensuing runs. Different engine cowl shapes were also analyzed. The researchers determined that nacelles mounted at the rear of the aircraft produced more efficient airflow patterns during cruising conditions at the desired velocities. The concept of the Advanced Technology Transport, nor any other US supersonic transport, has ever come to fruition. The energy crisis, environmental concerns, and inadequate turbofan technology of the 1970s were among the most significant reasons.
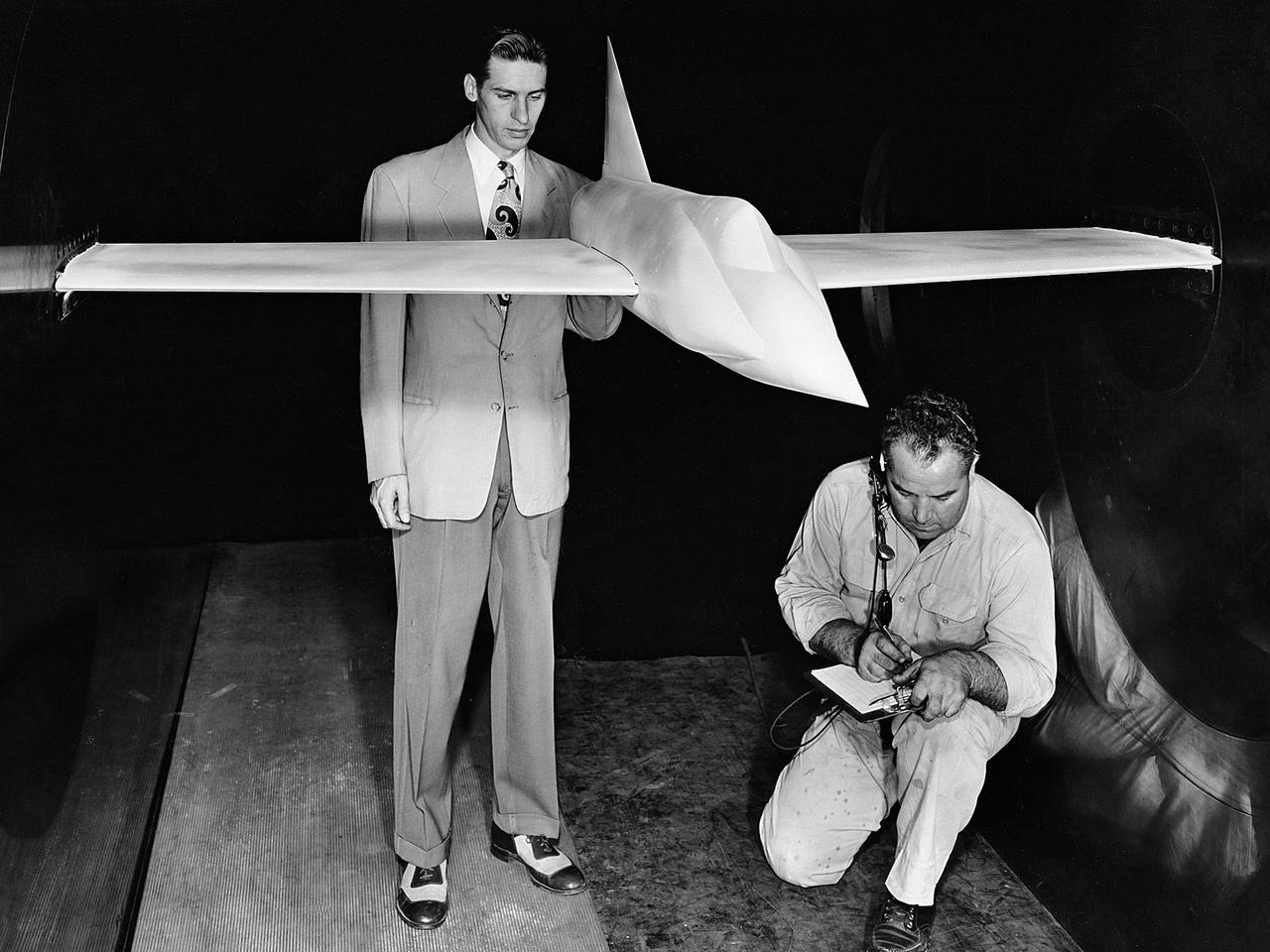

A .10-scale model of Convair’s XF-102 in the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory for jet exit studies. The XF-102 was a prototype of the F-102 Delta Dagger. The F-102 served as an interceptor against long range bombers from the Soviet Union. The aircraft was powered by a Pratt and Whitney J57 turbojet. The first prototype crashed two weeks after is first flight on October 24, 1953, just months after this photograph. Engineers then incorporated the fixed-wing design to reduce drag at supersonic speeds. The production model F-102 became the first delta-wing supersonic aircraft in operation. The 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel is used to study propulsion systems, including inlets and exit nozzles, combustion fuel injectors, flame holders, exit nozzles, and controls on ramjet and turbojet engines. Flexible sidewalls alter the tunnel’s nozzle shape to vary the Mach number during operation. A seven-stage axial compressor, driven by three electric motors that yield a total of 87,000 horsepower, generates air speeds from Mach 0.36 to 2.0.
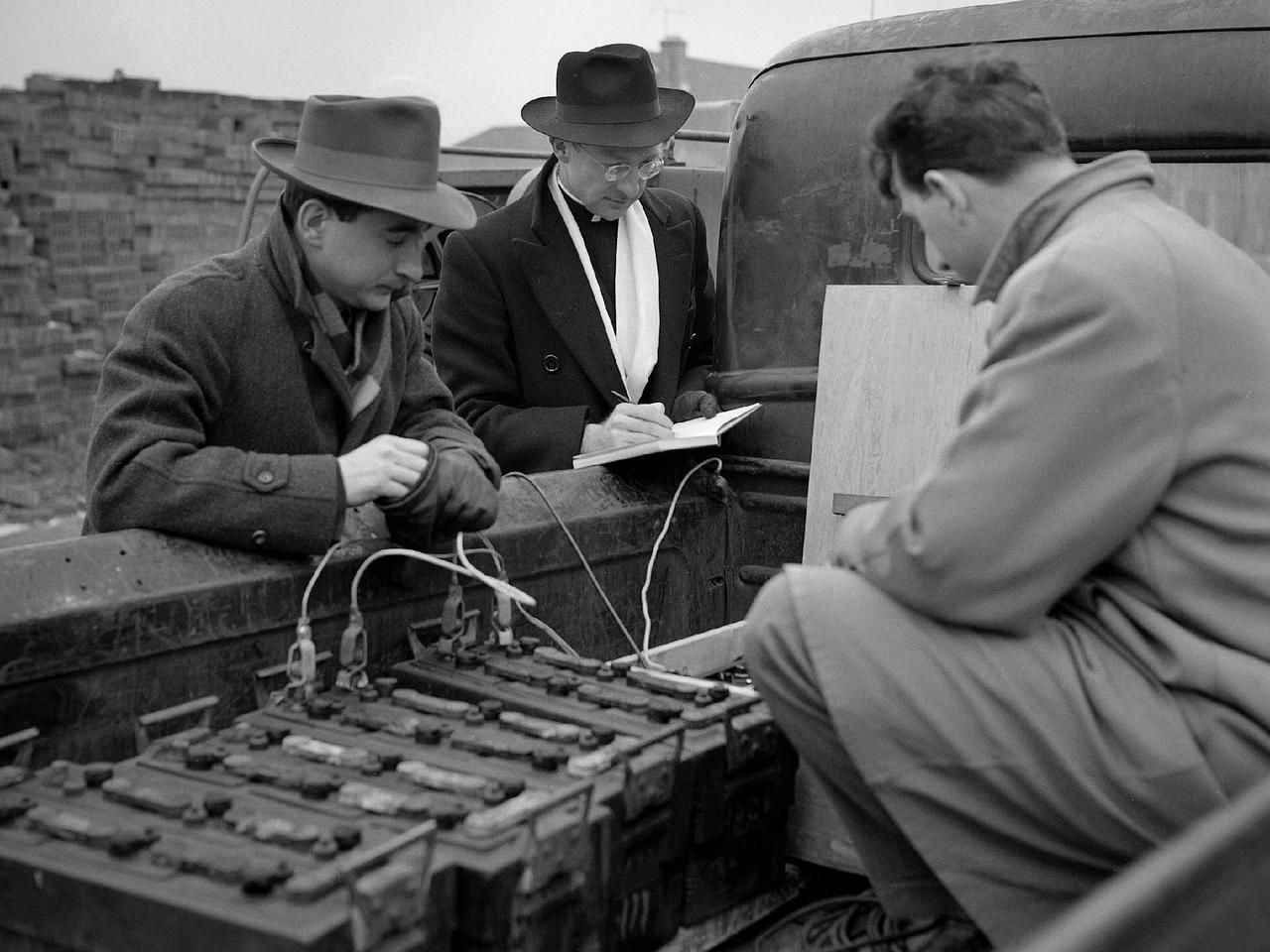

Reverend Henry Birkenhauer and E.F. Carome measure ground vibrations on West 220th Street caused by the operation of the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The 8- by 6 was the laboratory’s first large supersonic wind tunnel. It was also the NACA’s most powerful supersonic tunnel, and the NACA’s first facility capable of running an engine at supersonic speeds. The 8- by 6 was originally an open-throat and non-return tunnel. This meant that the supersonic air flow was blown through the test section and out the other end into the atmosphere. Complaints from the local community led to the installation of a muffler at the tunnel exit and the eventual addition of a return leg. Reverend Brikenhauer, a seismologist, and Carome, an electrical technician were brought in from John Carroll University to take vibration measurements during the 8- by 6 tunnel’s first run with a supersonic engine. They found that the majority of the vibrations came from the air and not the ground. The tunnel’s original muffler offered some relief during the facility checkout runs, but it proved inadequate during the operation of an engine in the test section. Tunnel operation was suspended until a new muffler was designed and installed. The NACA researchers, however, were pleased with the tunnel’s operation. They claimed it was the first time a jet engine was operated in an airflow faster than Mach 2.
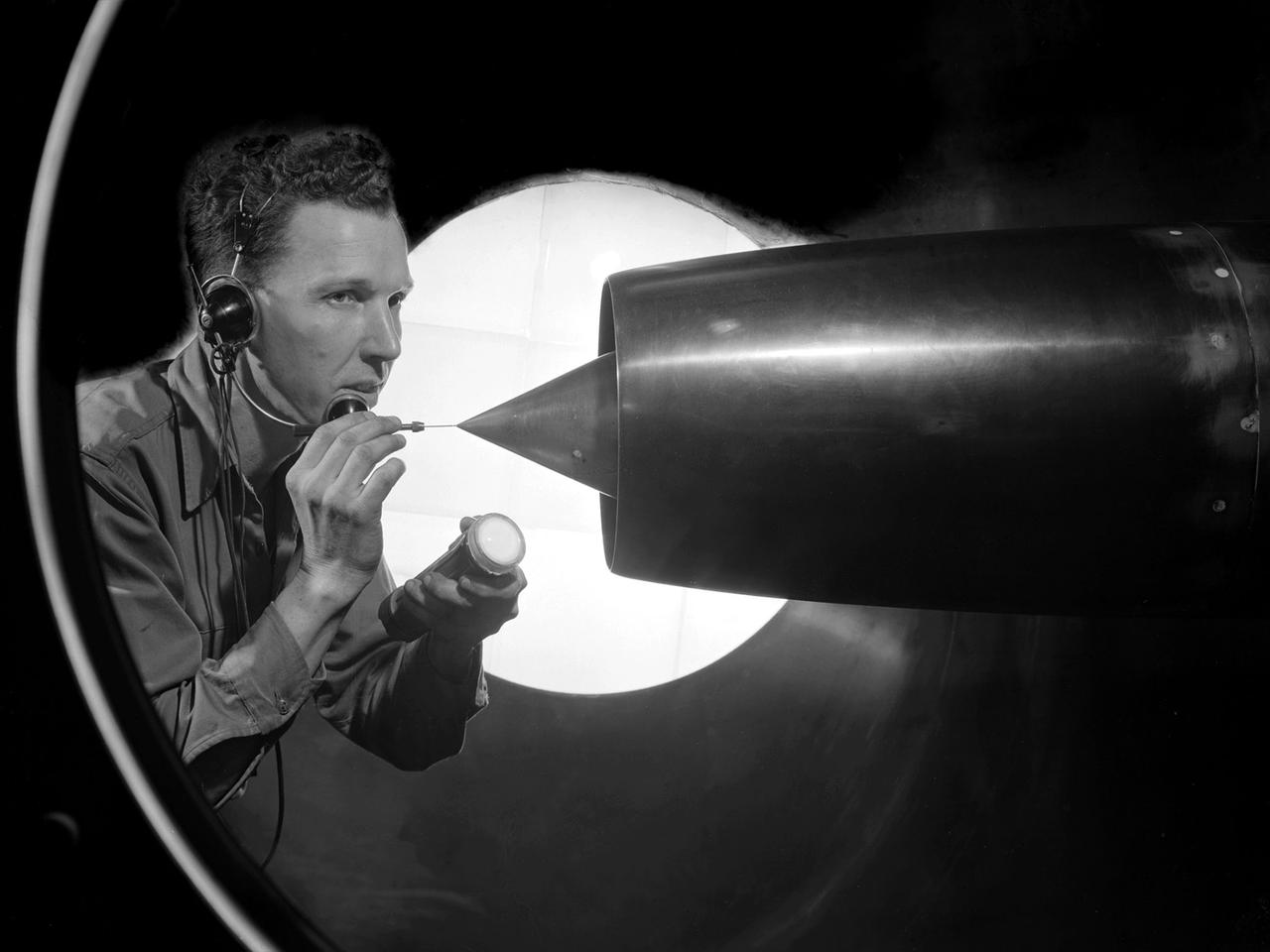

A technician at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory cleans the pitot tube on a 16-inch diameter ramjet in the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel. Pitot tubes are a measurement device used to determine the flow velocity at a specific location in the air stream, not the average velocity of the entire wind stream. NACA Lewis was in the midst of a multi-year program to determine the feasibility of ramjets and design improvements that could be employed for all models. The advantage of the ramjet was its ability to process large volumes of combustion air, resulting in the burning of fuel at the optimal stoichiometric temperatures. This was not possible with turbojets. The higher the Mach number, the more efficient the ramjet operated. The 8- by 6 Supersonic Wind Tunnel had been in operation for just over one year when this photograph was taken. The facility was the NACA’s largest supersonic tunnel and the only facility capable of running an engine at supersonic speeds. The 8- by 6 tunnel was also equipped with a Schlieren camera system that captured the air flow gradient as it passes over the test setup. The ramjet tests in the 8- by 6 tunnel complemented the NACA Lewis investigations using aircraft, the Altitude Wind Tunnel and smaller supersonic tunnels. Researchers studied the ramjet’s performance at different speeds and varying angles -of -attack.
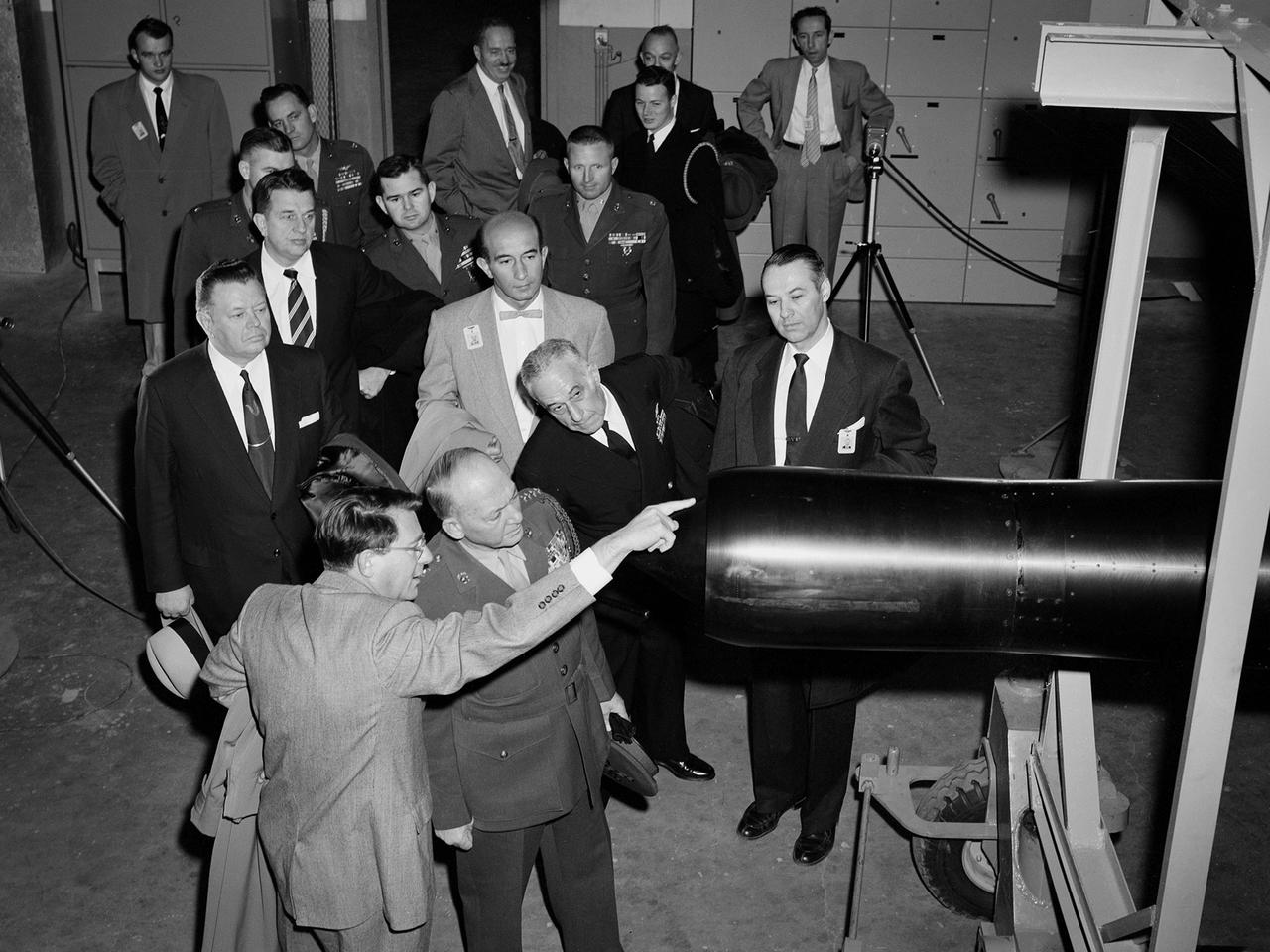

Abe Silverstein, Associate Director of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory, provides a personal tour of the new 10- by 10-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel for US Senator George Bender (hat in hand) and General Lemuel Shepherd. Shepherd was Commandant of the Marine Corps and had served in World War I, World War II, and the Korean War. The general was accompanied by Admiral Herbert Leary, in dark uniform. Bender was a Republican Senator from Ohio. Behind Bender is President of the Cleveland Chamber of Commerce Curtis Smith. NACA Lewis managers Eugene Manganiello and Wilson Hunter assist with the tour. Abe Silverstein oversaw all research at the laboratory. Upon taking his post in 1952 he reorganized the research staff and began shifting the focus away from airbreathing aircraft engines to new fields such as high energy fuels, electric propulsion, and nuclear power and propulsion. He was an early advocate of the NACA’s involvement in the space program and crucial to the founding of National Aeronautics and Space Administration in 1958. Silverstein began his career helping design and conduct research in the Full Scale Tunnel in 1929 at the Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory. Silverstein advocated a series of increasingly large supersonic wind tunnels after the war, culminating in the 10- by 10.
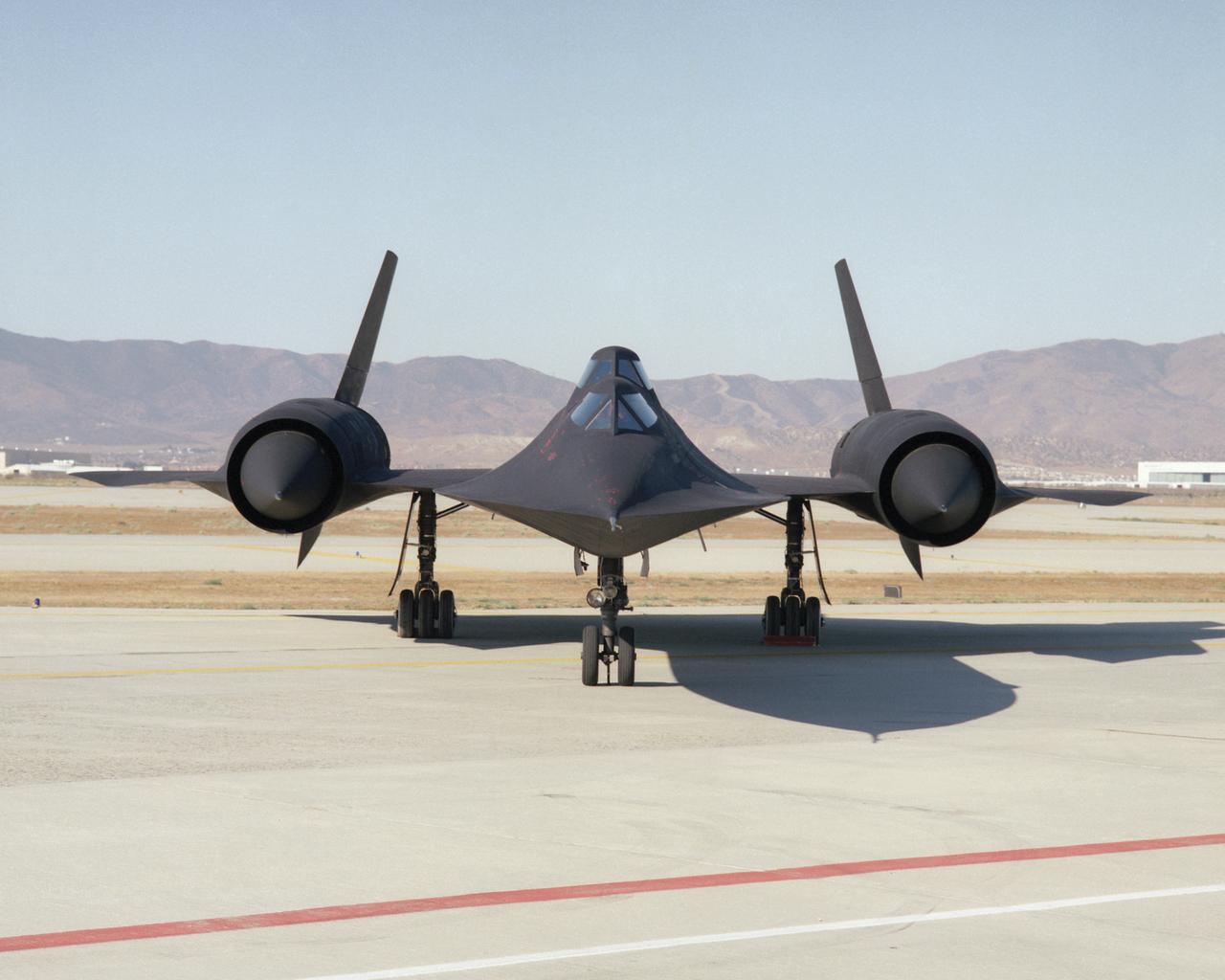

This photo shows a head-on view of NASA's SR-71B, used for pilot proficiency and training, on the ramp at the Air Force's Plant 42 in Palmdale, California, shortly before delivery to the Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility (later, Dryden Flight Research Center) at Edwards, California. NASA operated two of these unique aircraft, an SR-71A, for high-speed, high altitude research, and this SR- 71B pilot trainer for most of the decade of the 1990s. The "B" model is special because of its raised rear cockpit, which provided a second pilot position so a trainer and an experienced pilot could both see what was going on during flights. The SR-71 was designed and built by the Lockheed Skunk Works, now the Lockheed Martin Skunk Works. Studies have shown that less than 20 percent of the total thrust used to fly at Mach 3 is produced by the basic engine itself. The balance of the total thrust is produced by the unique design of the engine inlet and "moveable spike" system at the front of the engine nacelles, and by the ejector nozzles at the exhaust which burn air compressed in the engine bypass system. Data from the SR-71 high speed research program will be used to aid designers of future supersonic/hypersonic aircraft and propulsion systems, including a high speed civil transport.
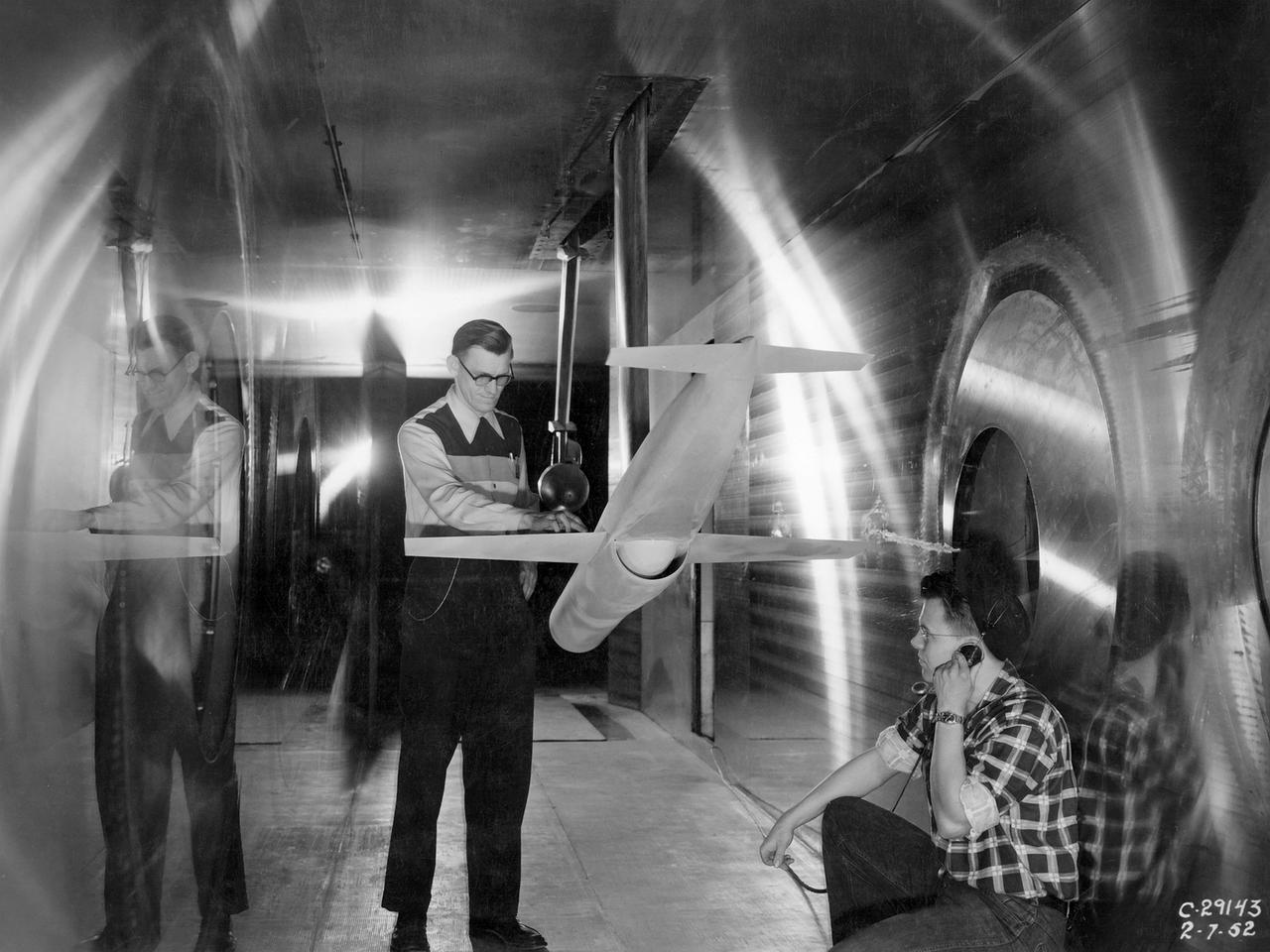

A researcher at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory checks the setup of a RJM-2 ramjet model in the test section of the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel. The 8- by 6 was not only the laboratory’s first large supersonic wind tunnel, but it was also the NACA’s first facility capable of testing an operating engine at supersonic speeds. The 8- by 6-foot tunnel has been used to study engine inlets, fuel injectors, flameholders, exit nozzles, and controls on ramjet and turbojet propulsion systems. The 8-foot wide and 6-foot tall test section consisted of 1-inch thick steel plates with hatches on the floor and ceiling to facilitate the installation of the test article. The two windows seen on the right wall allowed photographic equipment to be set up. The test section was modified in 1956 to accommodate transonic research. NACA engineers drilled 4,700 holes into the test section walls to reduce transonic pressure disturbances and shock waves. NACA Lewis undertook an extensive research program on ramjets in the 1940s using several of its facilities. Ramjets provide a very simple source of propulsion. They are basically a tube which ingests high speed air, ignites it, and then expels the heated air at a significantly higher velocity. Ramjets are extremely efficient and powerful but can only operate at high speeds. Therefore, they require a booster rocket or aircraft drop to accelerate them to high speeds before they can operate.
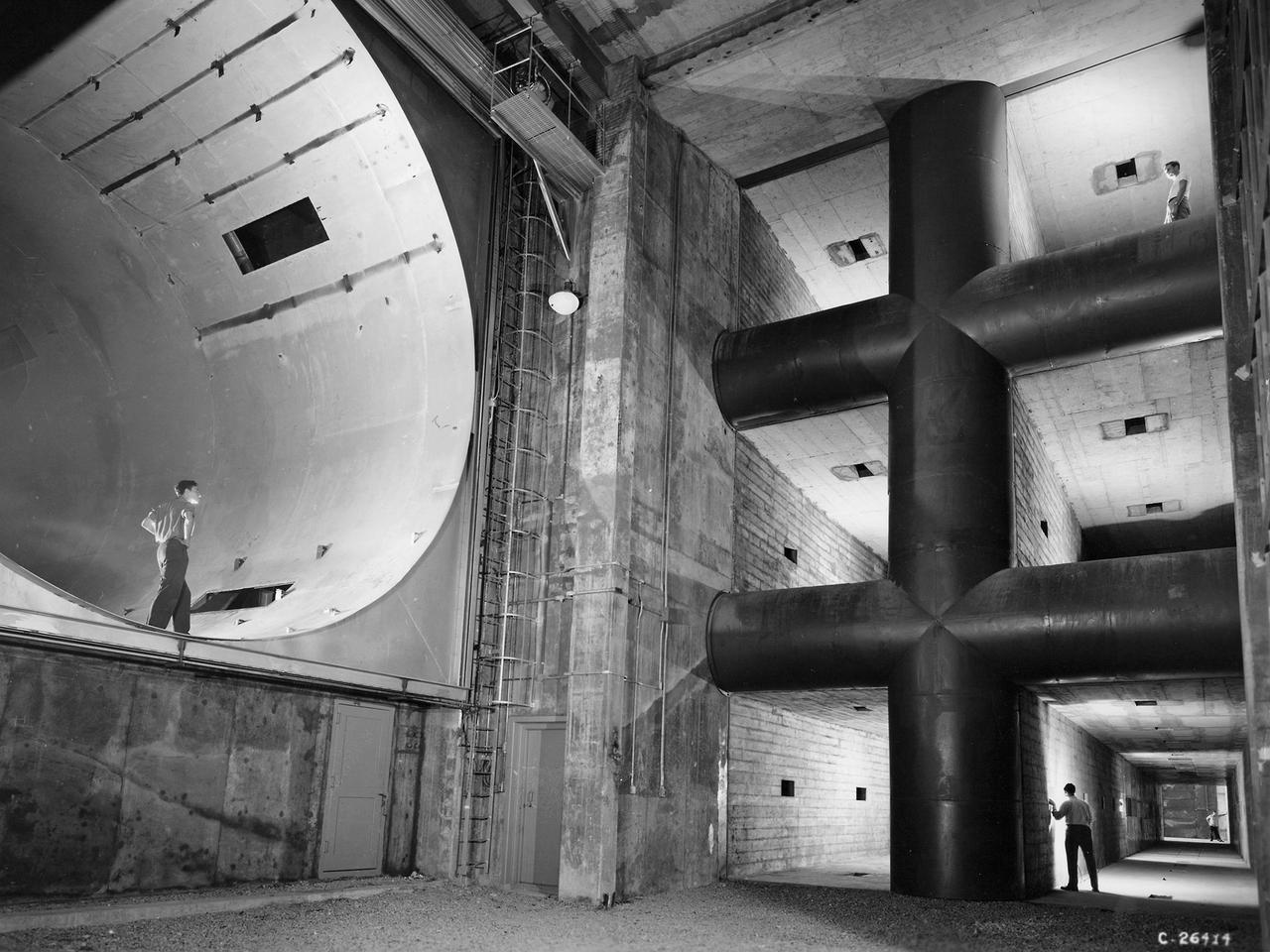

The 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory was the largest supersonic wind tunnel in the nation at the time and the only one able to test full-scale engines at supersonic speeds. The 8- by 6 was designed as a non-return and open-throat tunnel. A large compressor created the air flow at one end of the tunnel, squeezed the flow to increase its velocity just before the test section, then reduced the velocity, and expelled it into the atmosphere at the other end of the tunnel. This design worked well for initial aerodynamic testing, but the local community was literally rattled by the noise and vibrations when researchers began running engines in the test section in January 1950. The NACA’s most modern wind tunnel was referred to as “an 87,000-horsepower bugle aimed at the heart of Cleveland.” NACA Lewis responded to the complaints by adding an acoustic housing at the end of the tunnel to dampen the noise. The structure included resonator chambers and a reinforced concrete muffler structure. Modifications continued over the years. A return leg was added, and a second test section, 9 -by 15-foot, was incorporated in the return leg in the 1960s. Since its initial operation in 1948, the 8- by 6-foot tunnel has been aggressively used to support the nation's aeronautics and space programs for the military, industry, and academia.
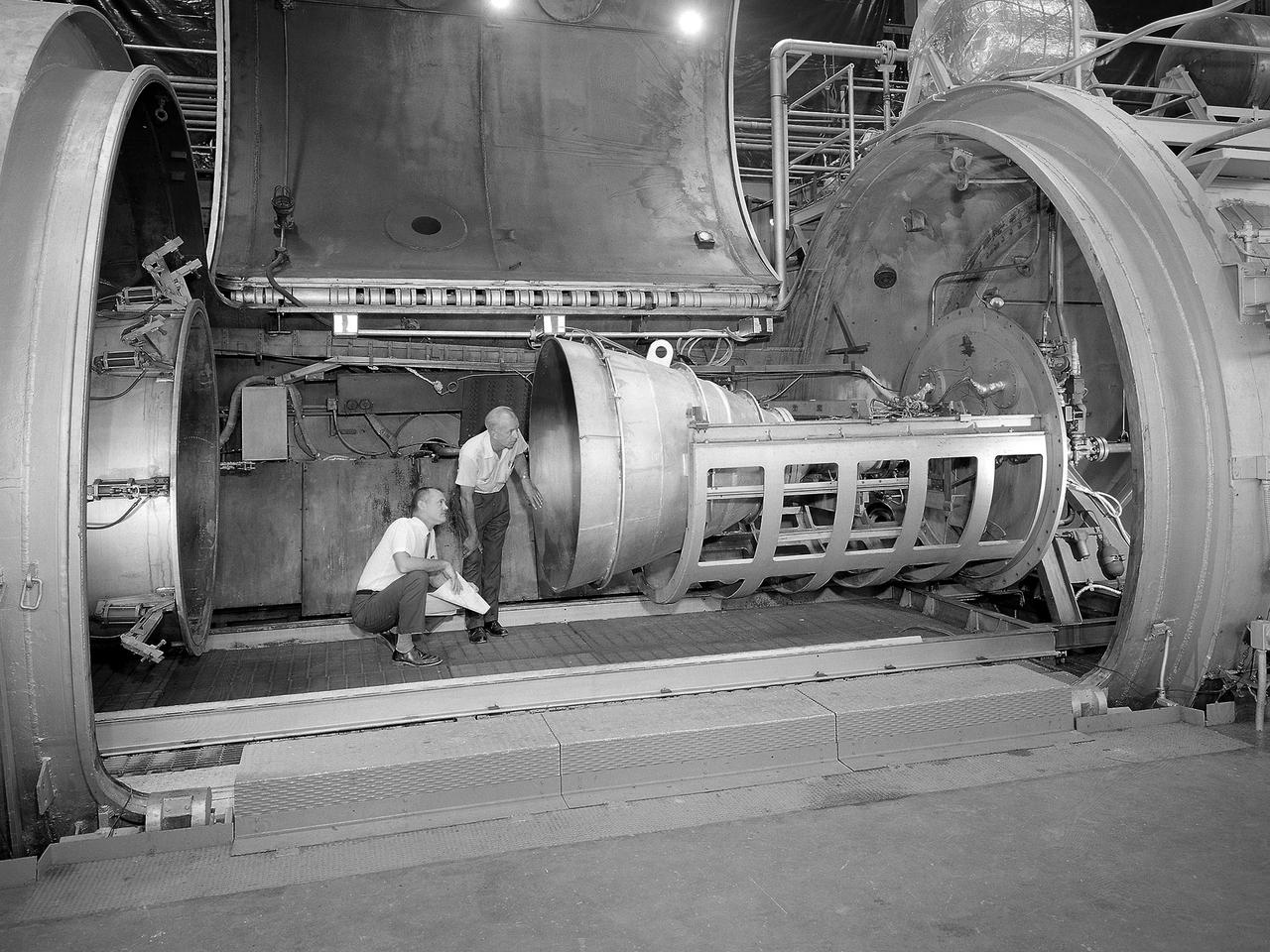

Bill Harrison and Bud Meilander check the setup of an Apollo Contour rocket nozzle in the Propulsion Systems Laboratory at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The Propulsion Systems Laboratory contained two 14-foot diameter test chambers that could simulate conditions found at very high altitudes. The facility was used in the 1960s to study complex rocket engines such as the Pratt and Whitney RL-10 and rocket components such as the Apollo Contour nozzle, seen here. Meilander oversaw the facility’s mechanics and the installation of test articles into the chambers. Harrison was head of the Supersonic Tunnels Branch in the Test Installations Division. Researchers sought to determine the impulse value of the storable propellant mix, classify and improve the internal engine performance, and compare the results with analytical tools. A special setup was installed in the chamber that included a device to measure the thrust load and a calibration stand. Both cylindrical and conical combustion chambers were examined with the conical large area ratio nozzles. In addition, two contour nozzles were tested, one based on the Apollo Service Propulsion System and the other on the Air Force’s Titan transtage engine. Three types of injectors were investigated, including a Lewis-designed model that produced 98-percent efficiency. It was determined that combustion instability did not affect the nozzle performance. Although much valuable information was obtained during the tests, attempts to improve the engine performance were not successful.
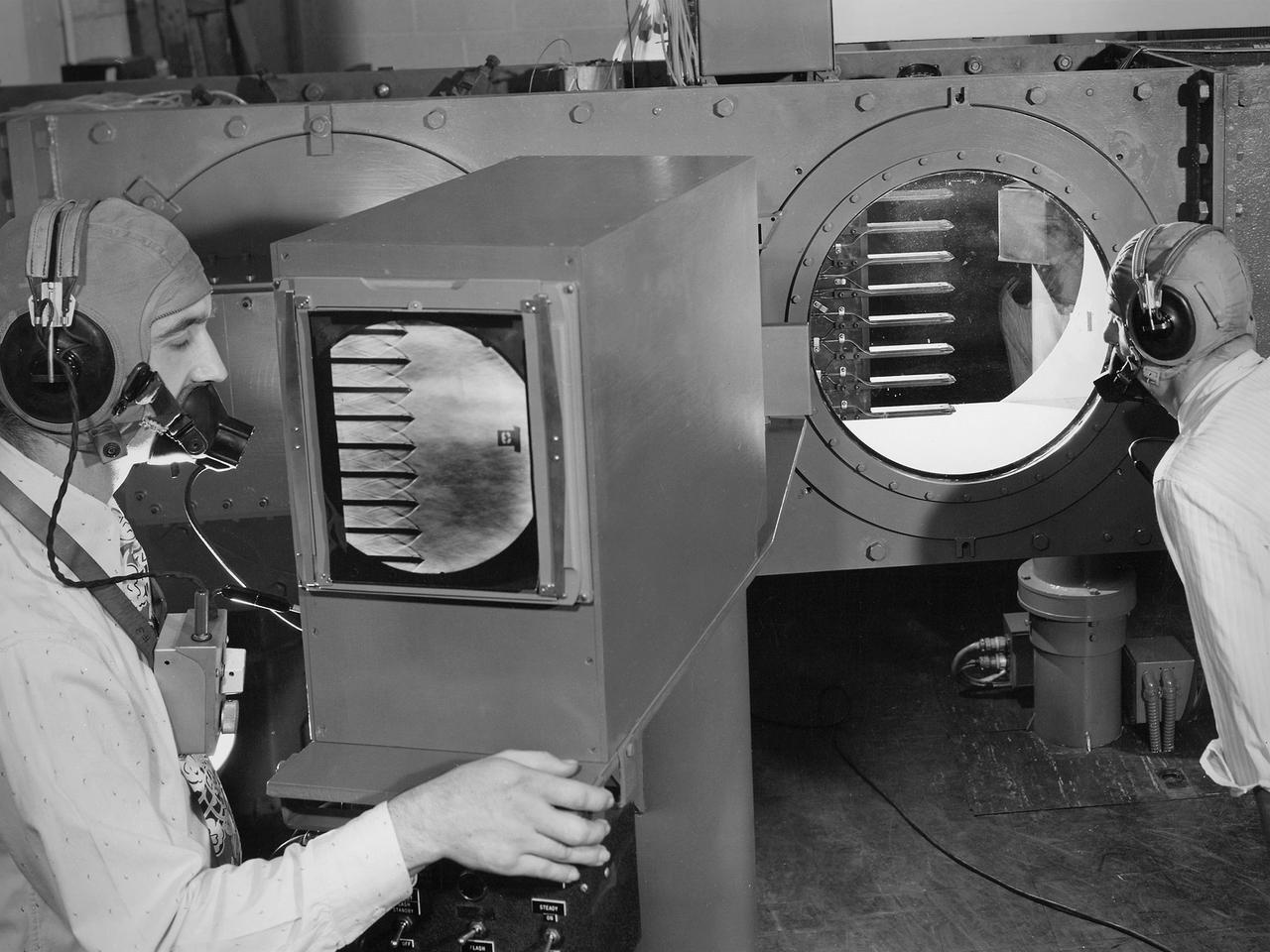

Engineers calibrate one of three small supersonic wind tunnels that were collectively referred to as the “Stack Tunnels” at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. In late 1945 NACA Lewis reorganized its staff and began constructing a new wave of facilities to address high-speed flight and the turbojet and rocket technologies that emerged during World War II. While design work began on what would eventually become the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel, NACA Lewis quickly built several small supersonic tunnels. These small facilities utilized the Altitude Wind Tunnel’s massive air handling equipment. Three of the small tunnels were built vertically on top of each other and thus were known as the Stack Tunnels. The first of the Stack Tunnels was an 18- by 18-inch tunnel that began operating in August 1945 at speeds up to Mach 1.91. The second tunnel, whose 24- by 24-inch test section is shown here, was added in 1949. It could generate air flows up to Mach 3.96. A third tunnel with an 18- by 18-inch test section began operating in 1951 with speeds up to Mach 3.05. The small tunnels were used until the early 1960s to study the aerodynamic characteristics of supersonic inlets and exits. The technician to the left in this photograph is operating a Schlieren camera to view the air flow dynamics inside the 24- by 24-inch test section. The technician on the right is viewing the pronged test article through the circular window. They are calibrating the tunnel and its equipment to prepare for the initial test runs.