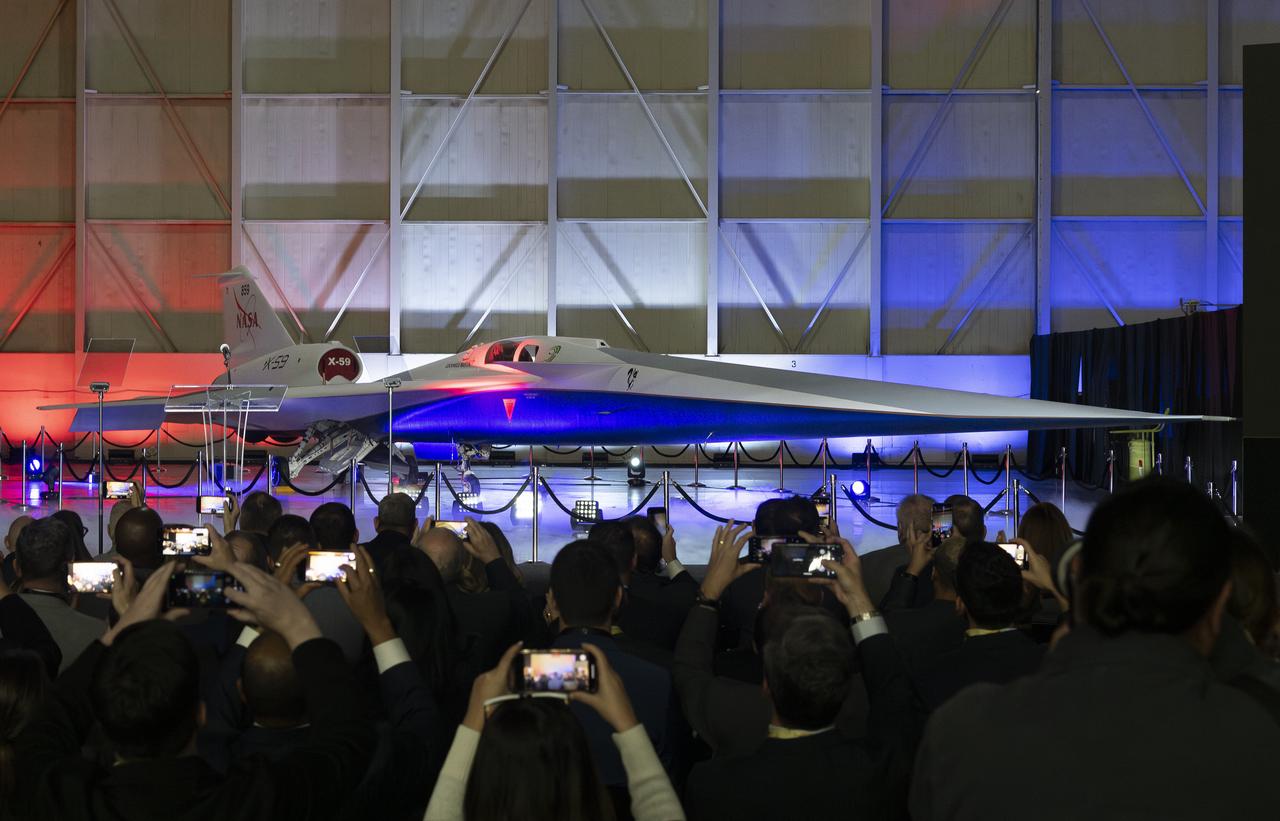

NASA and Lockheed Martin publicly unveil the X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a ceremony in Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.

On March 22, 1946, 250 members of the Institute of Aeronautical Science toured the NACA’s Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory. NACA Chairman Jerome Hunsaker and Secretary John Victory were on hand to brief the attendees in the Administration Building before the visited the lab’s test facilities. At each of the twelve stops, researchers provided brief presentations on their work. Topics included axial flow combustors, materials for turbine blades, engine cooling, icing prevention, and supersonic flight. The laboratory reorganized itself in October 1945 as World War II came to an end to address newly emerging technologies such as the jet engine, rockets, and high-speed flight. While design work began on what would eventually become the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel, NACA Lewis quickly built several small supersonic tunnels. These small facilities utilized the Altitude Wind Tunnel’s massive air handling equipment to generate high-speed airflow. The display seen in this photograph was set up in the building that housed the first of these wind tunnels. Eventually the building would contain three small supersonic tunnels, referred to as the “stack tunnels” because of the vertical alignment. The two other tunnels were added to this structure in 1949 and 1951. The small tunnels were used until the early 1960s to study the aerodynamic characteristics of supersonic inlets and exits.
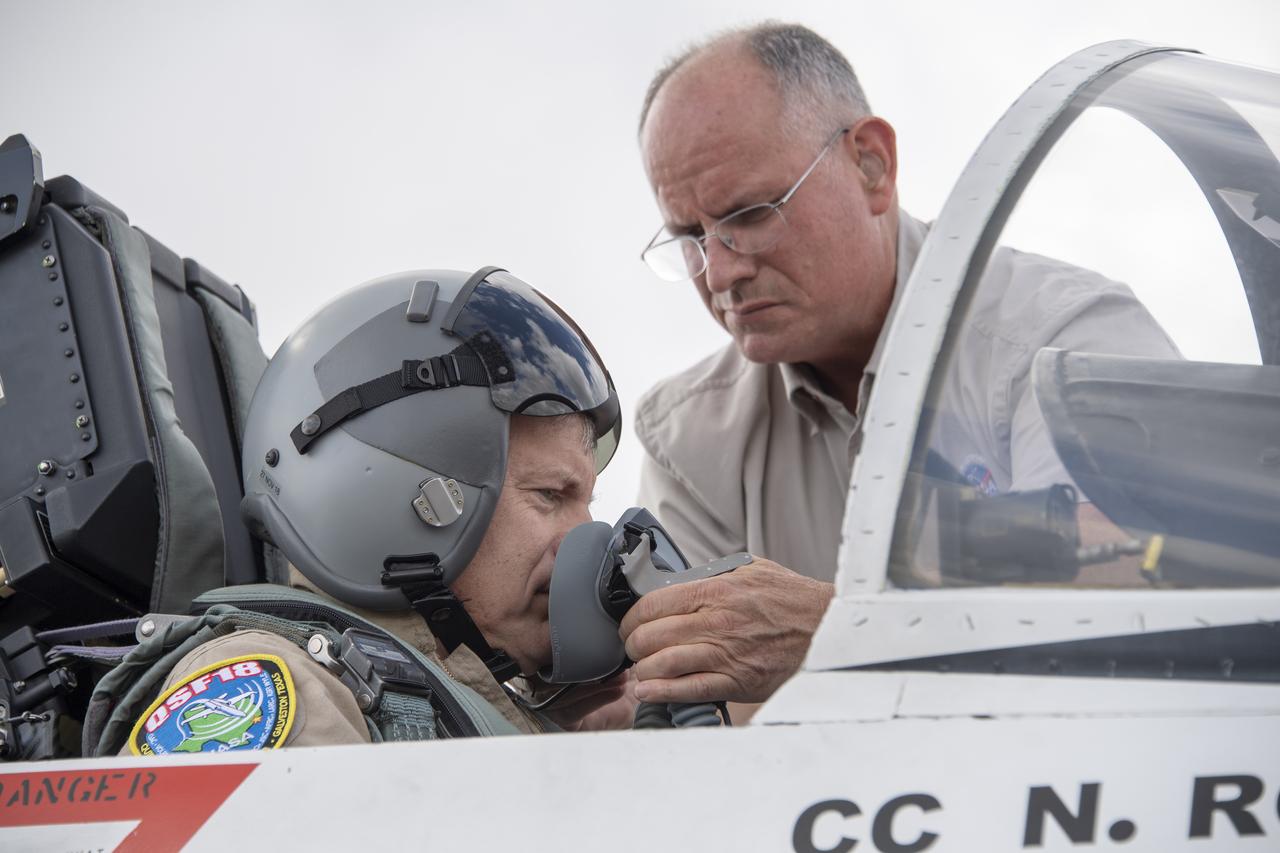

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
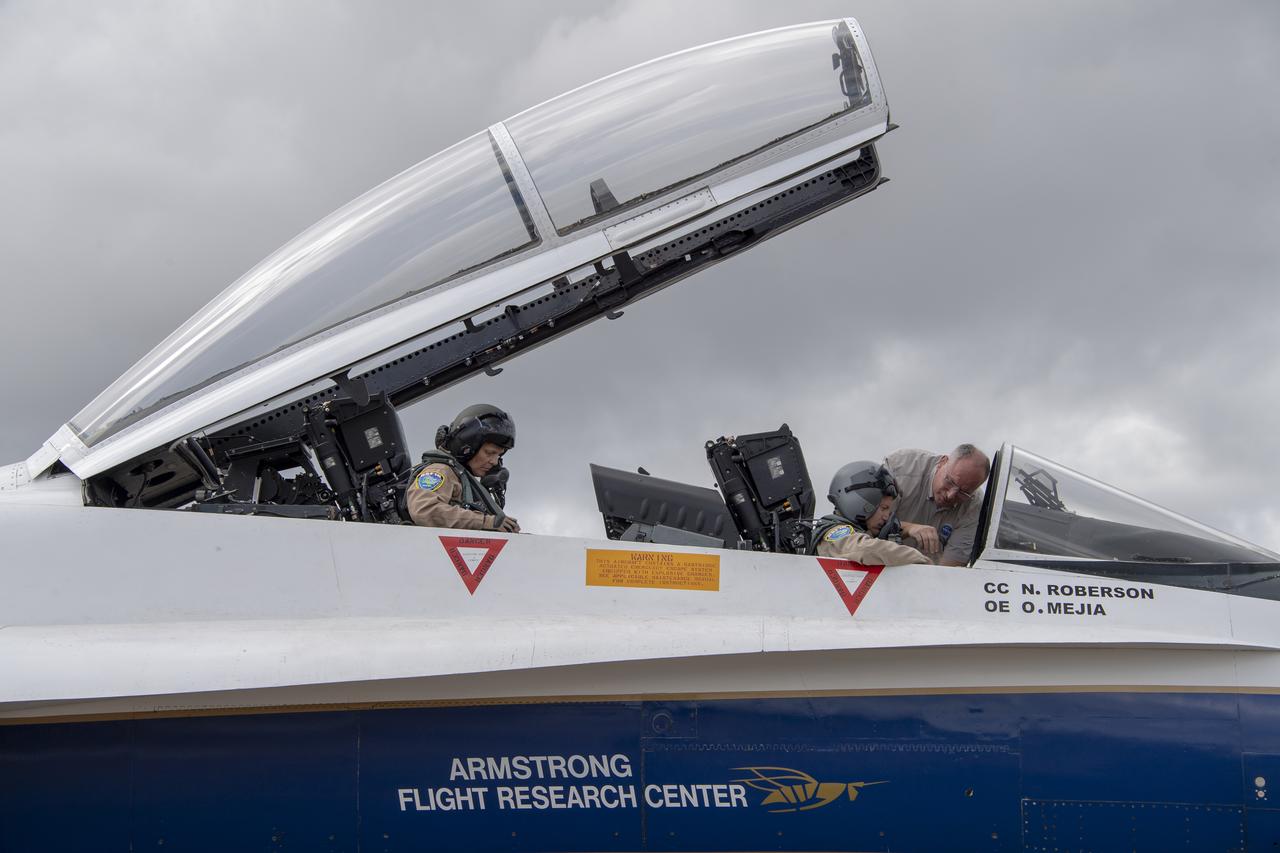

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
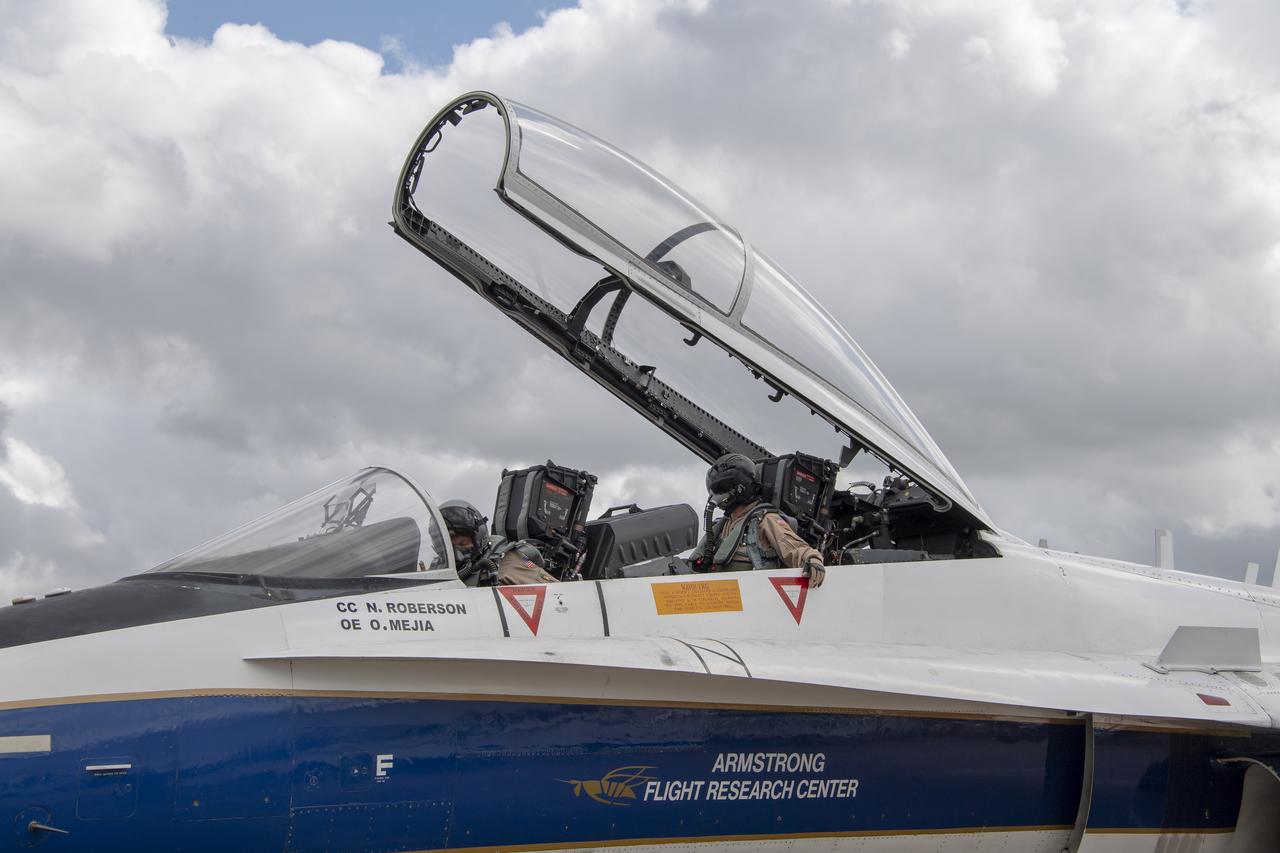

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
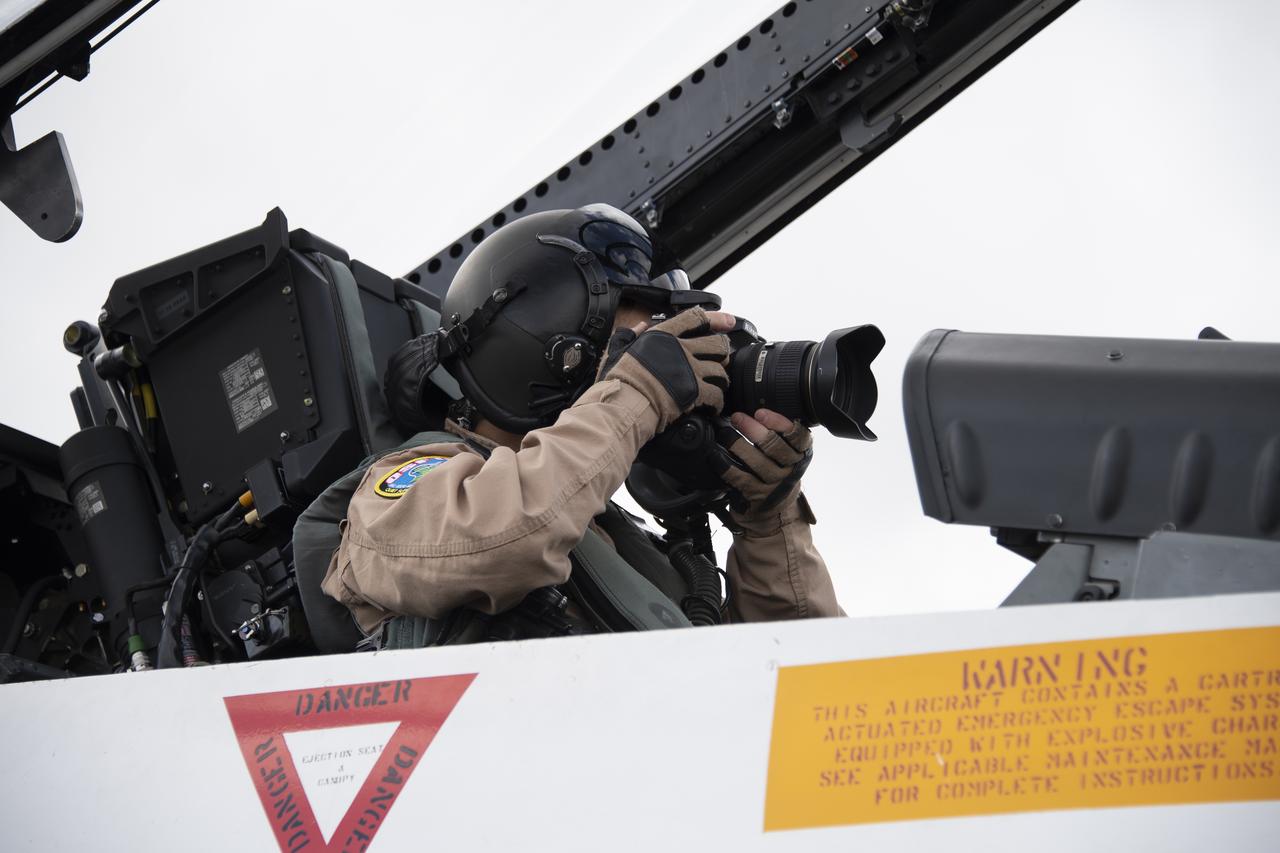

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
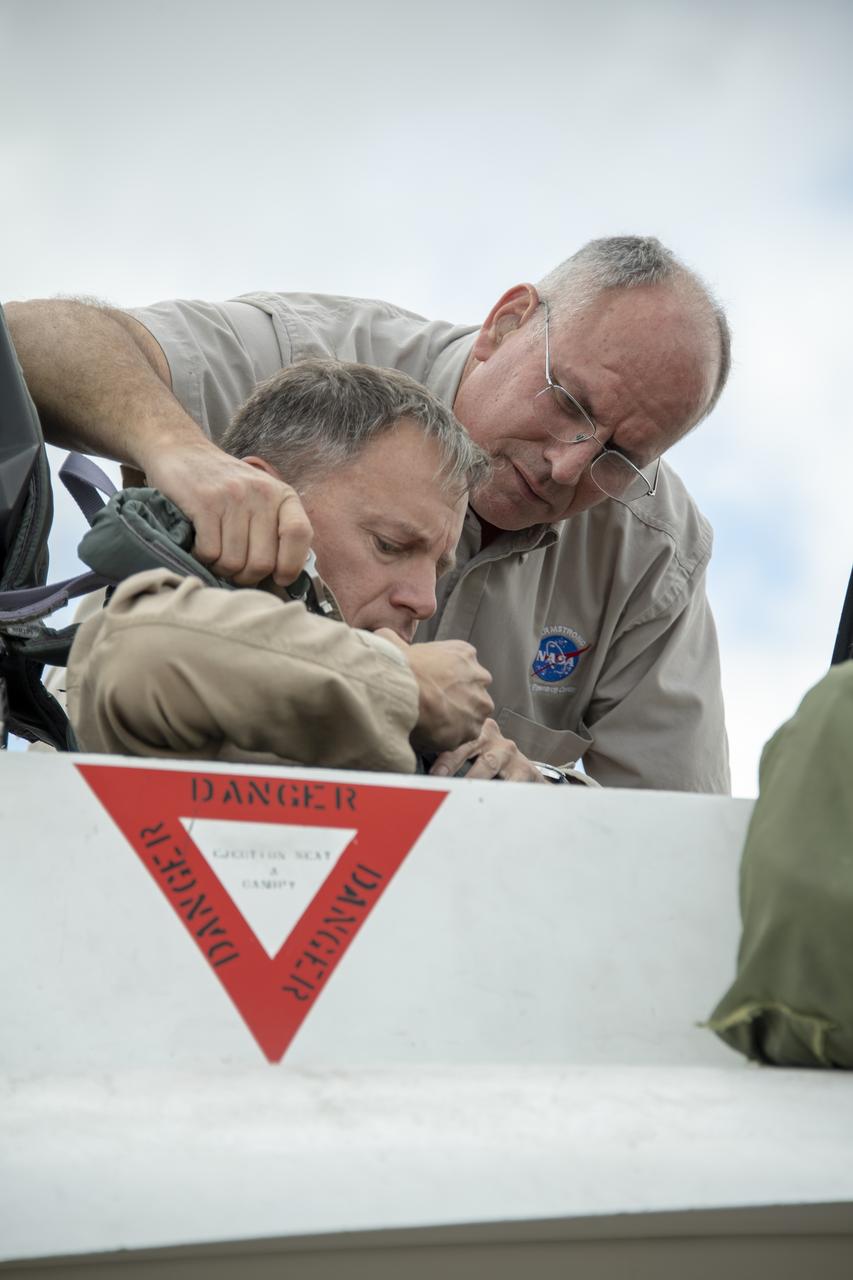

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
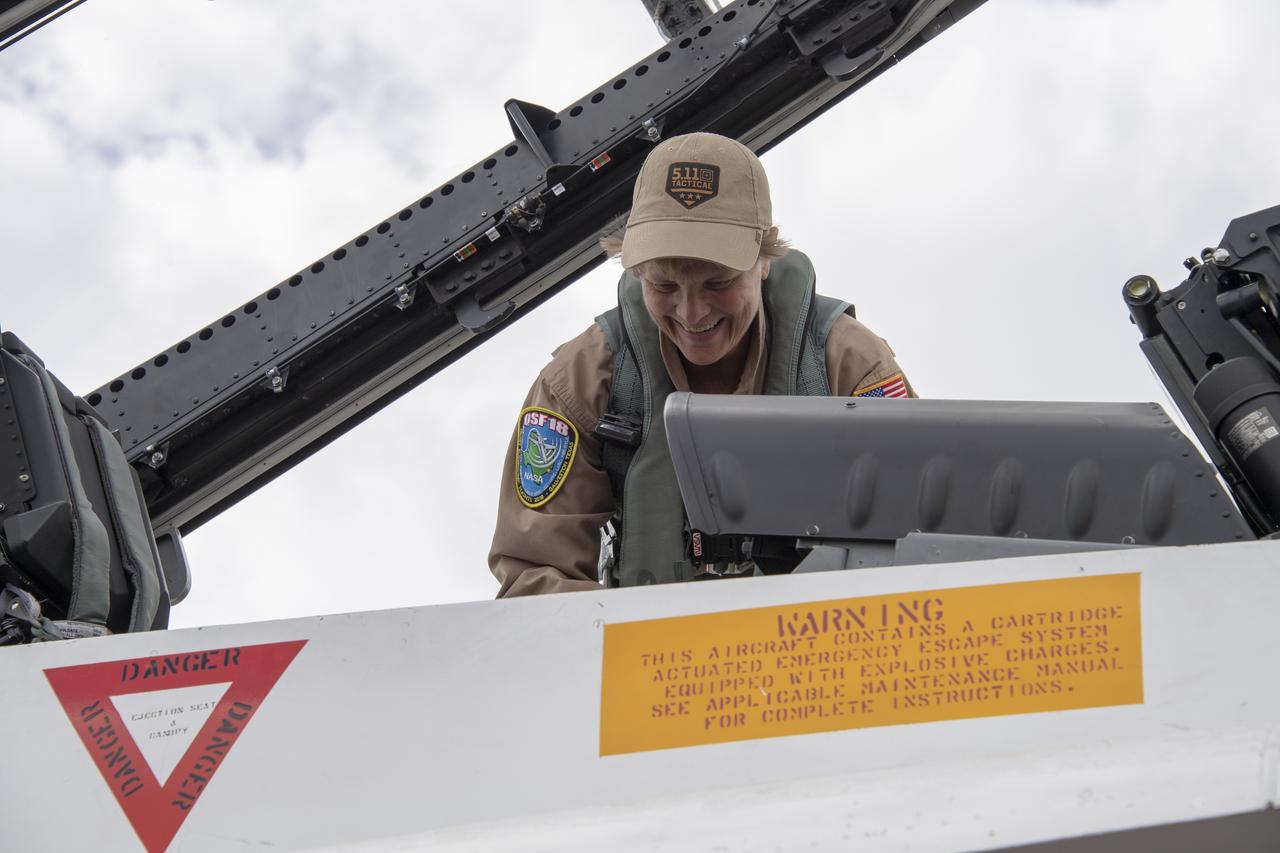

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
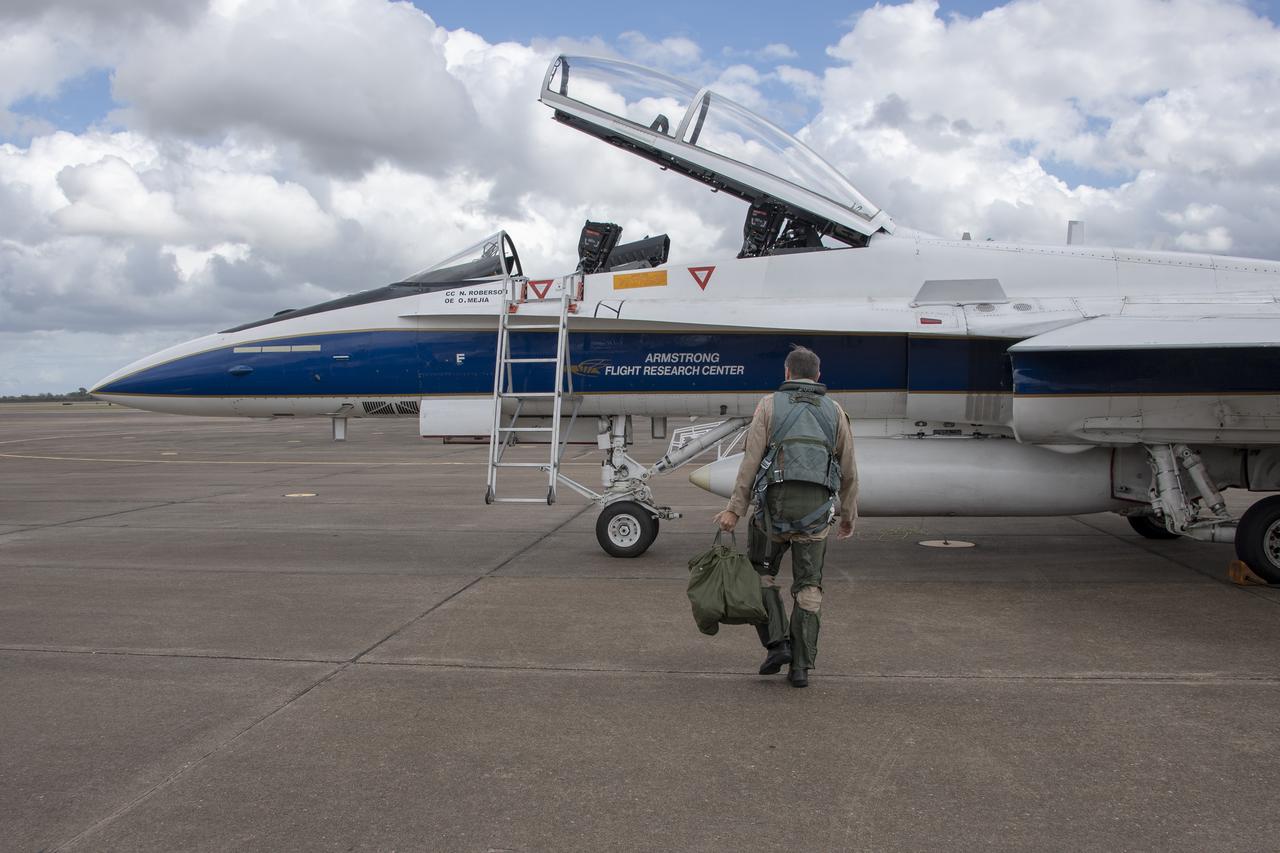

NASA test pilot Wayne "Ringo" Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
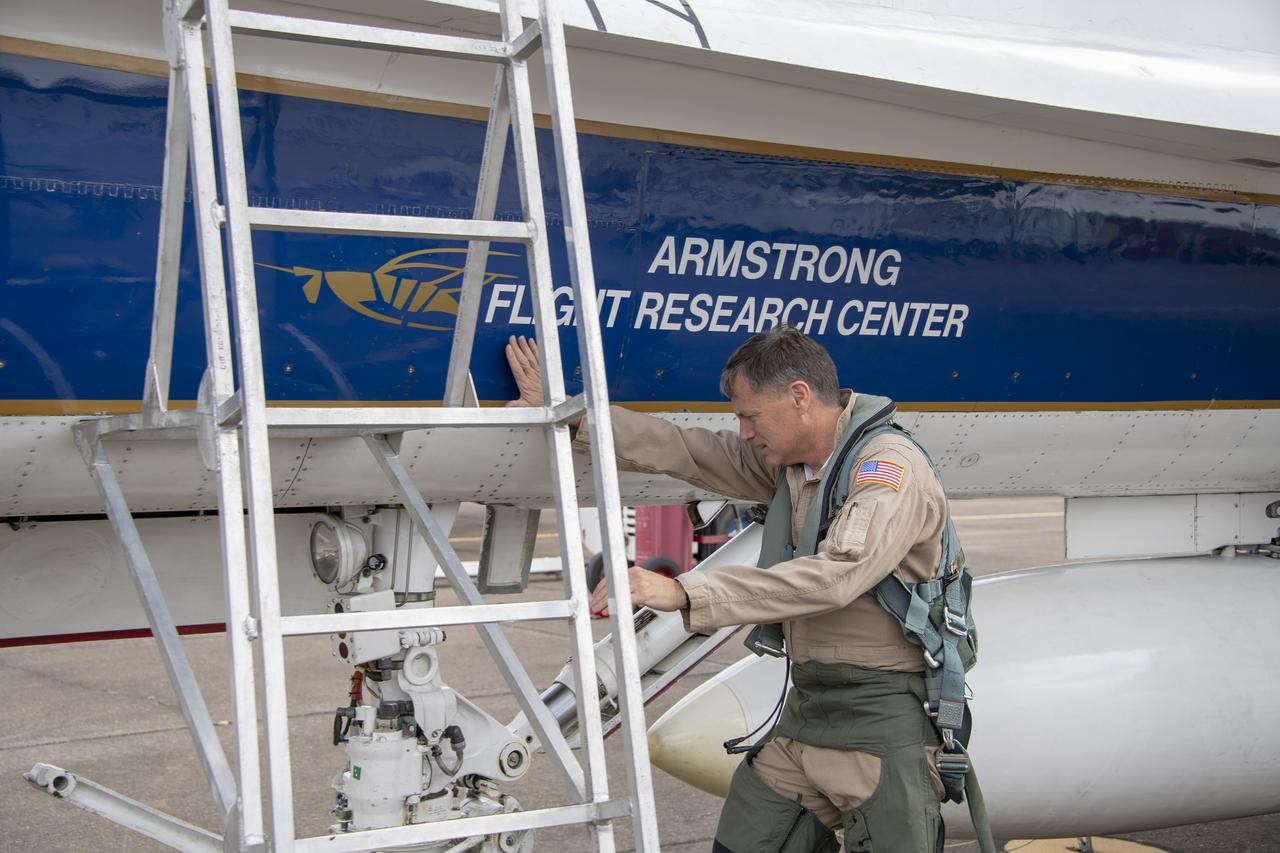

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
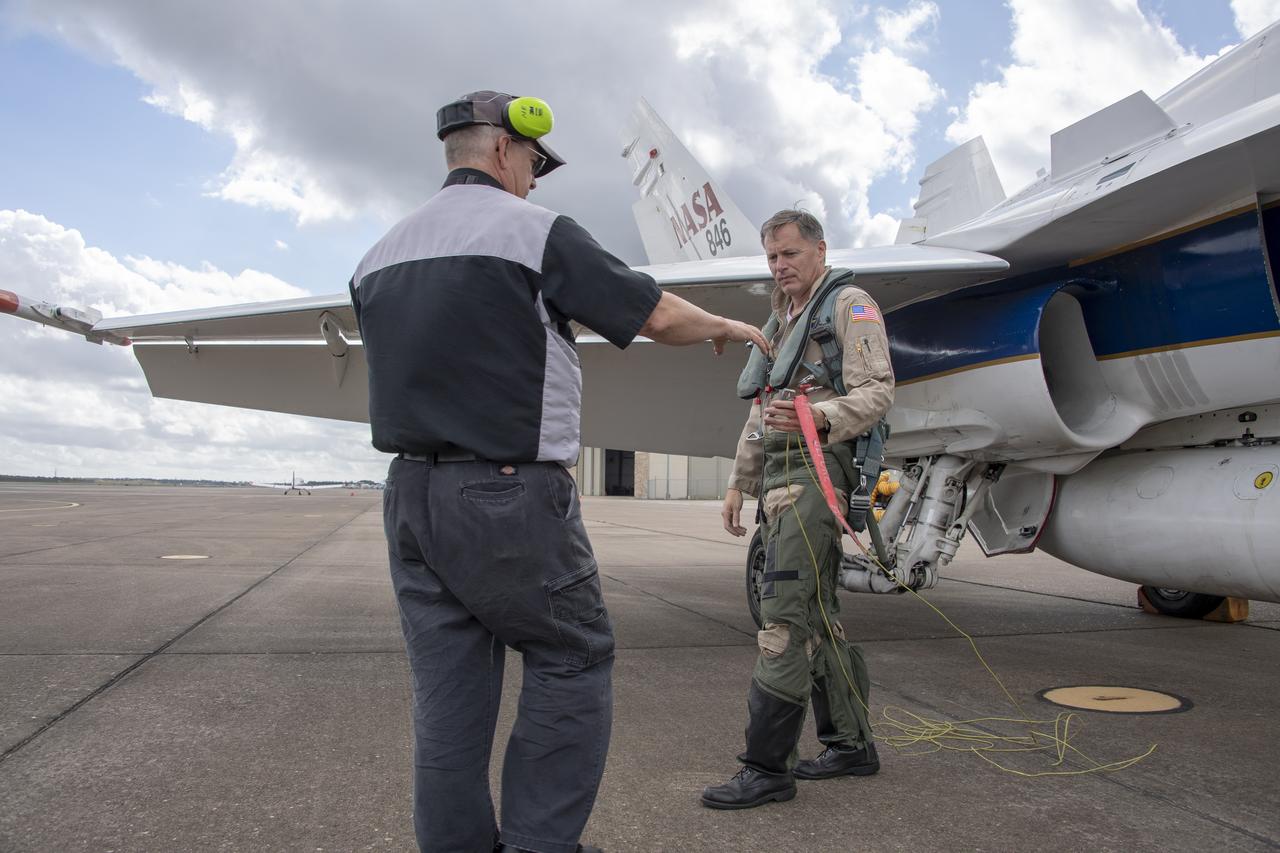

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
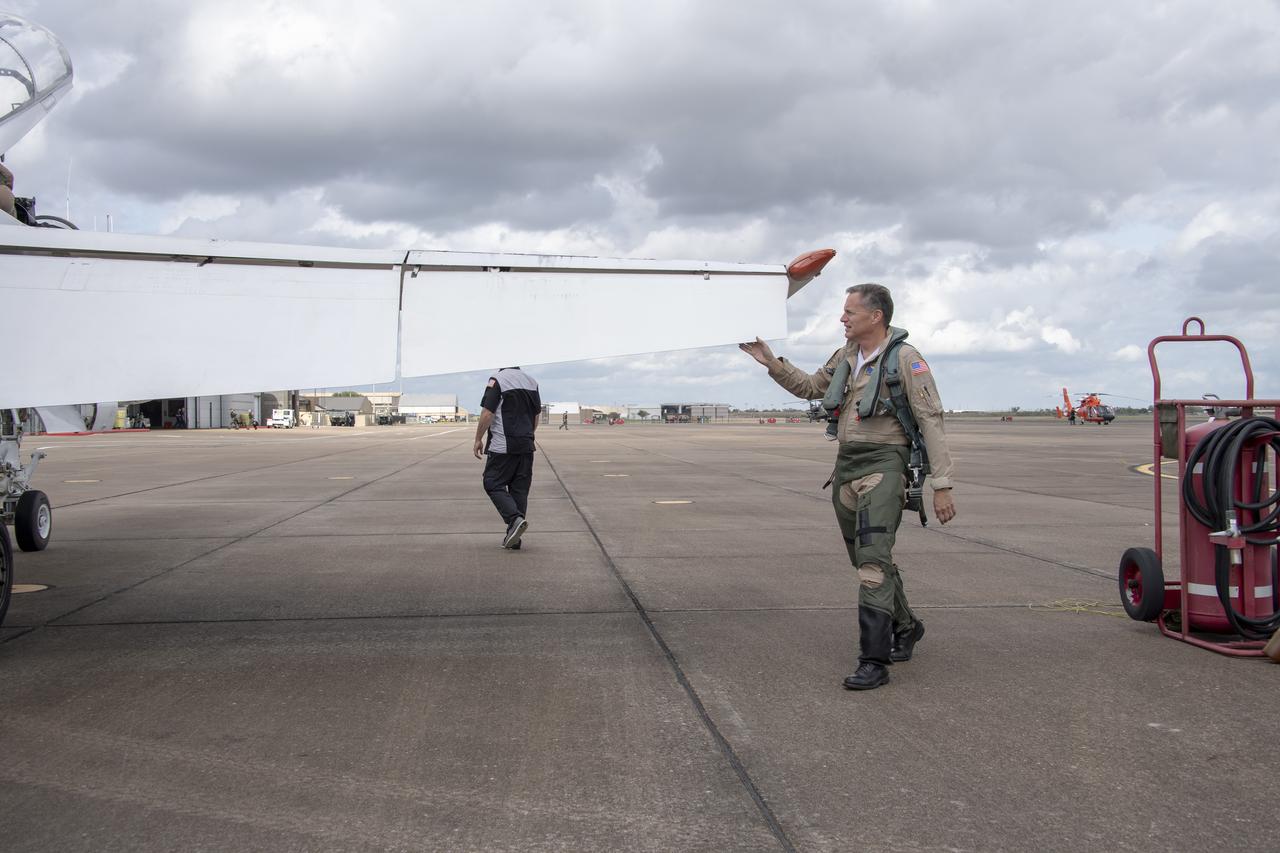

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.

NASA test pilot Wayne "Ringo" Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
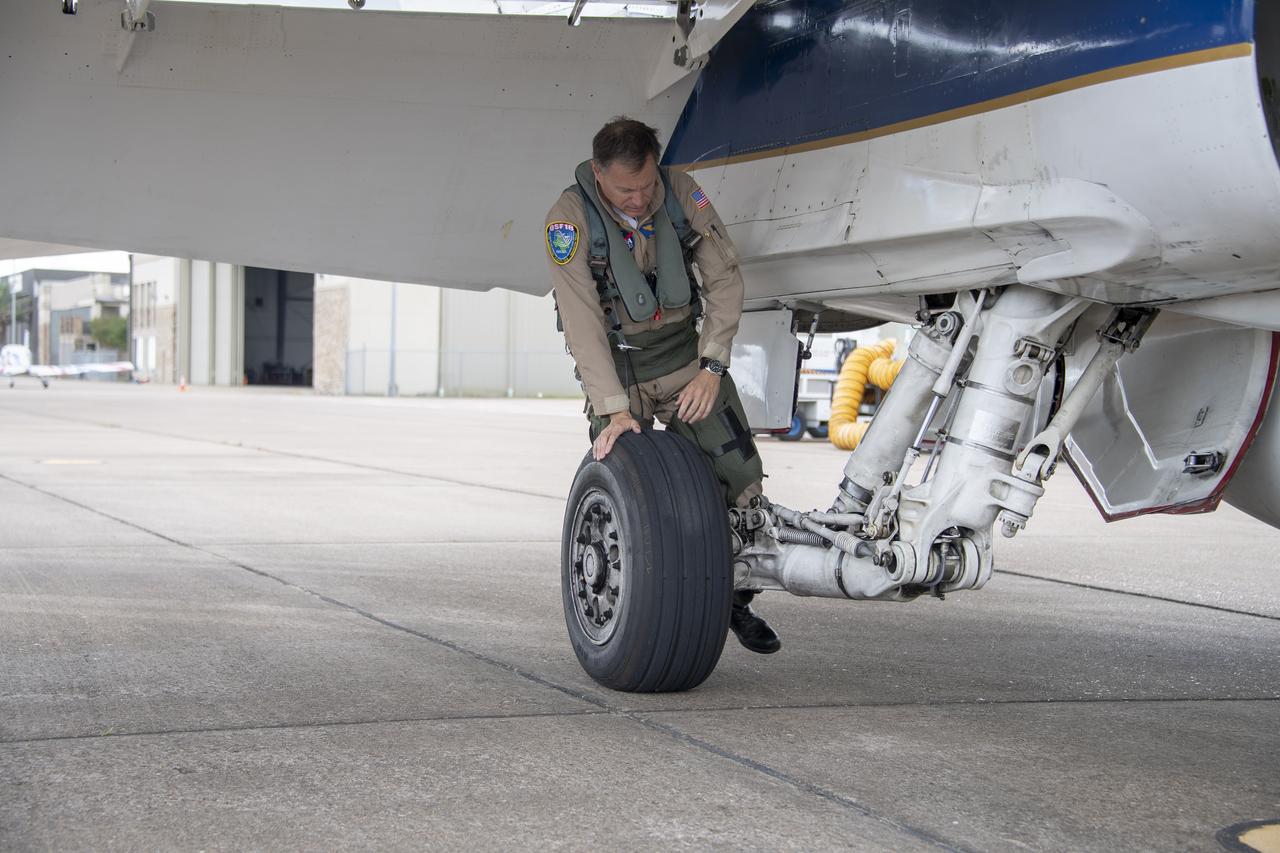

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
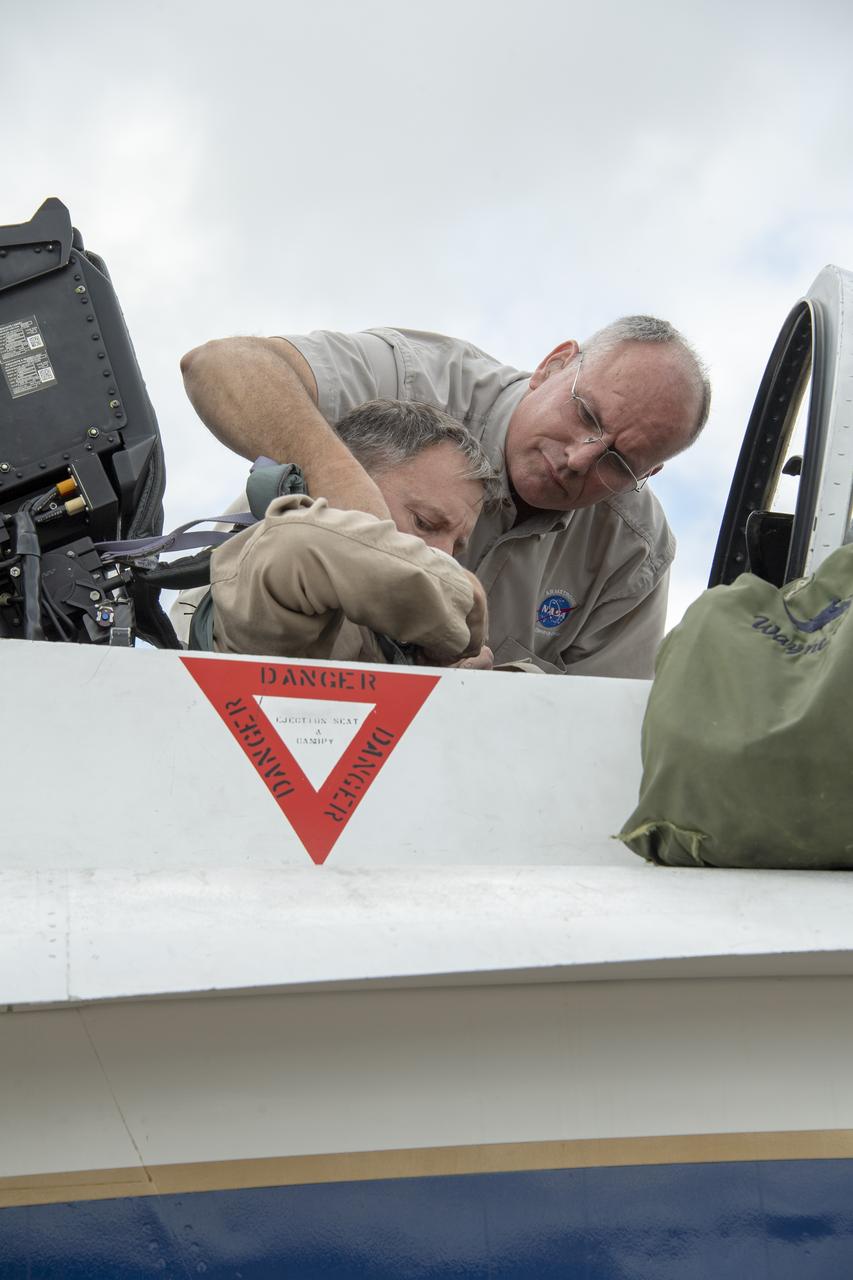

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
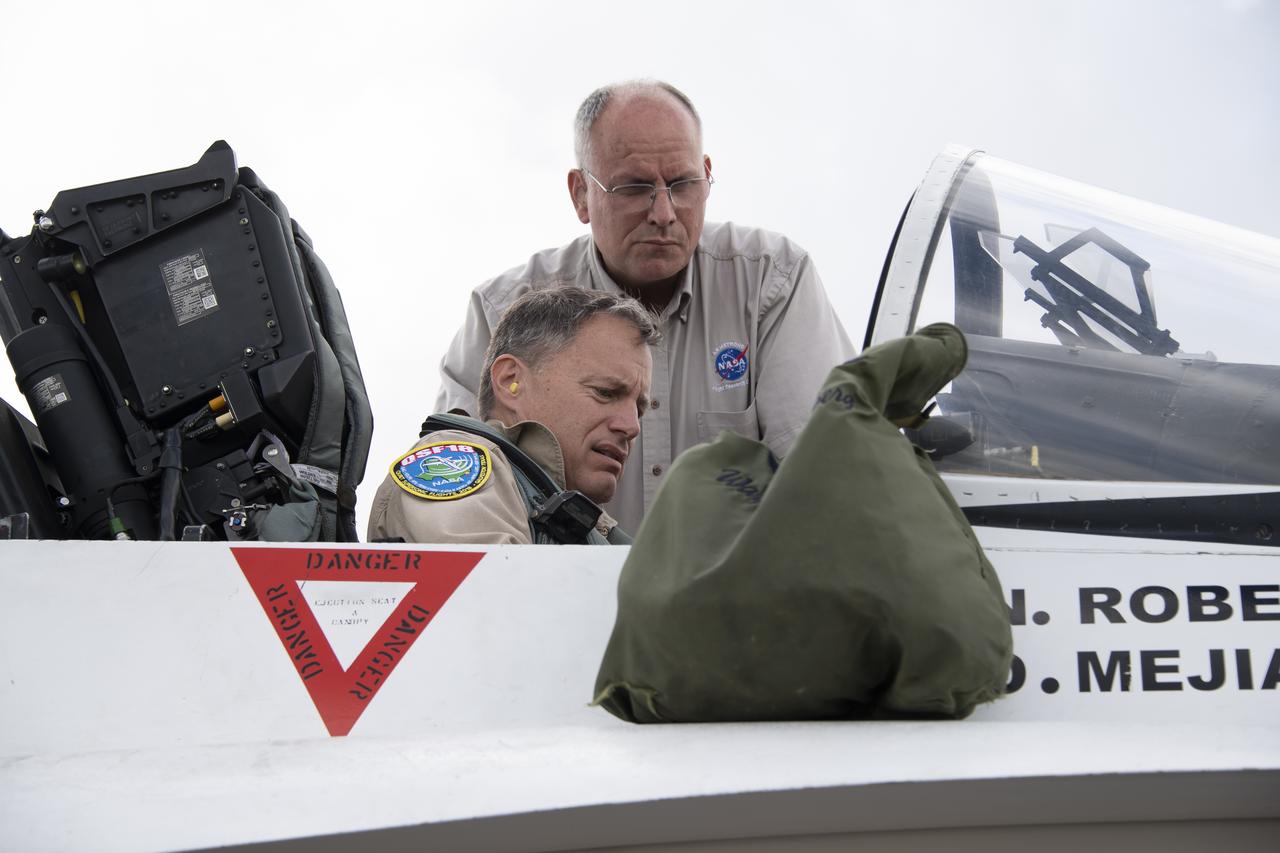

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
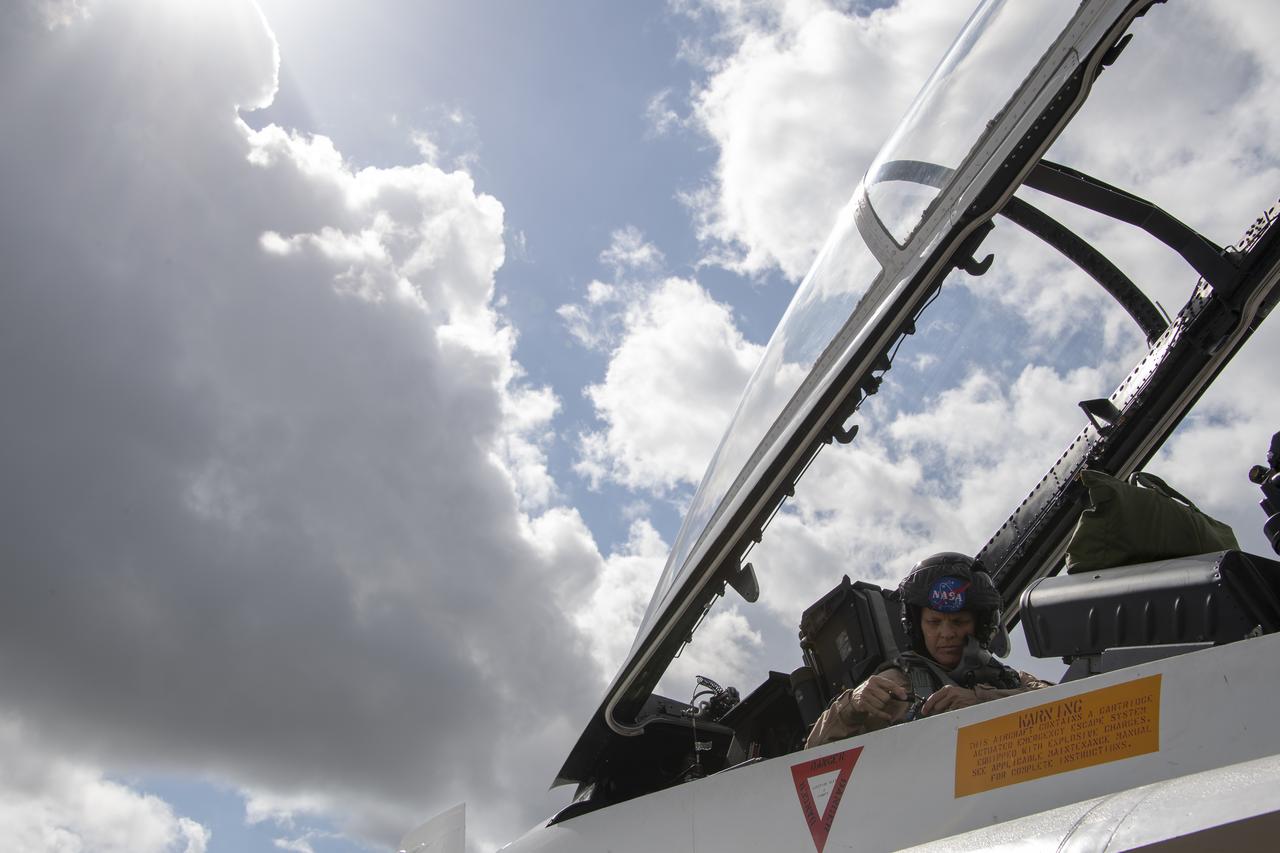

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
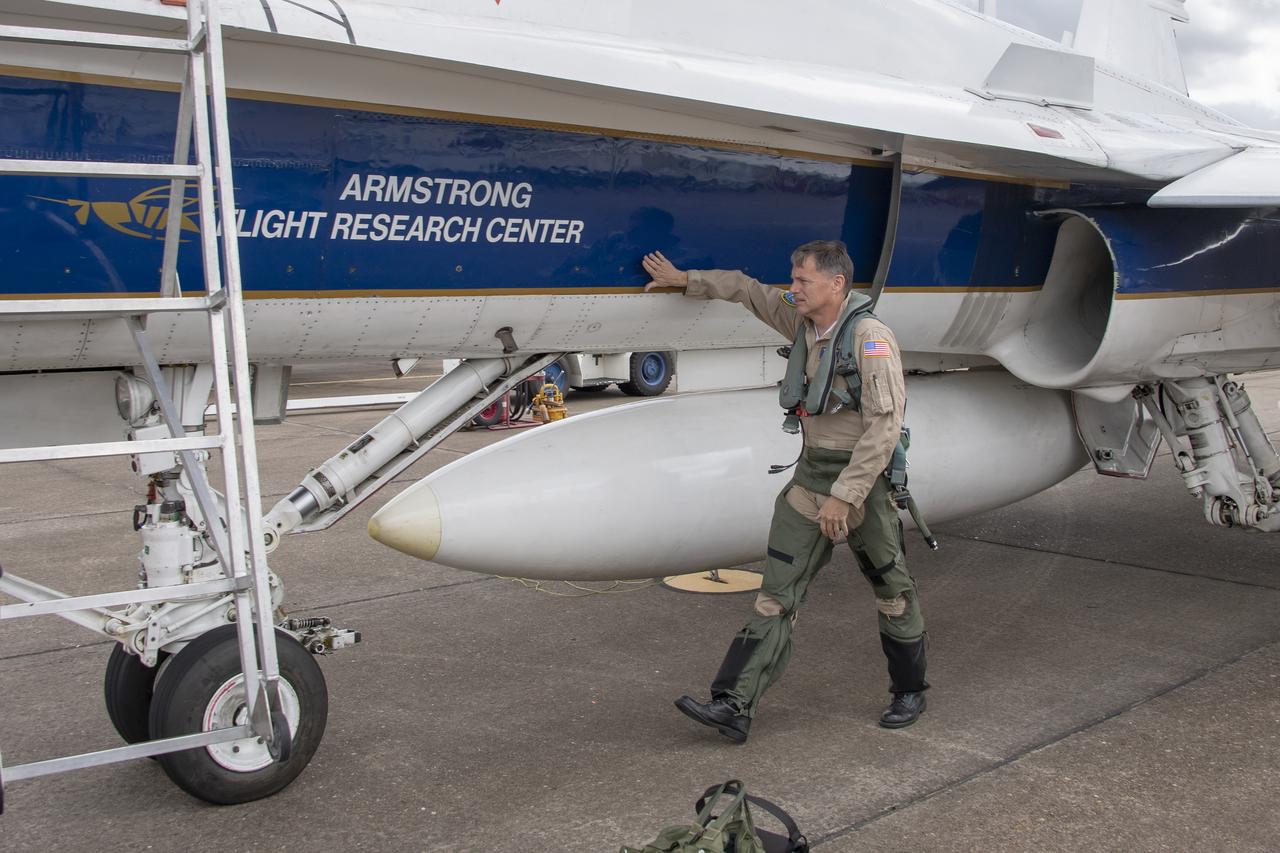

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
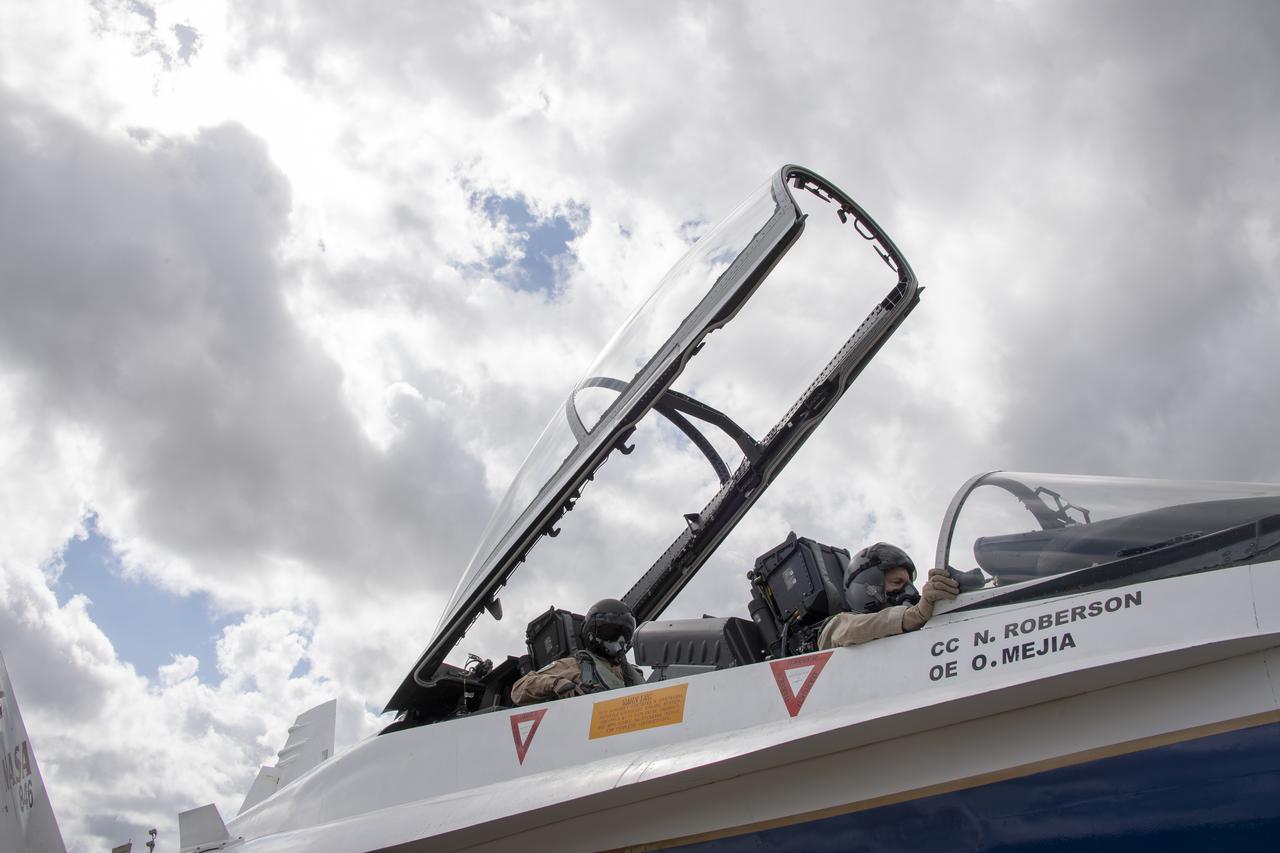

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
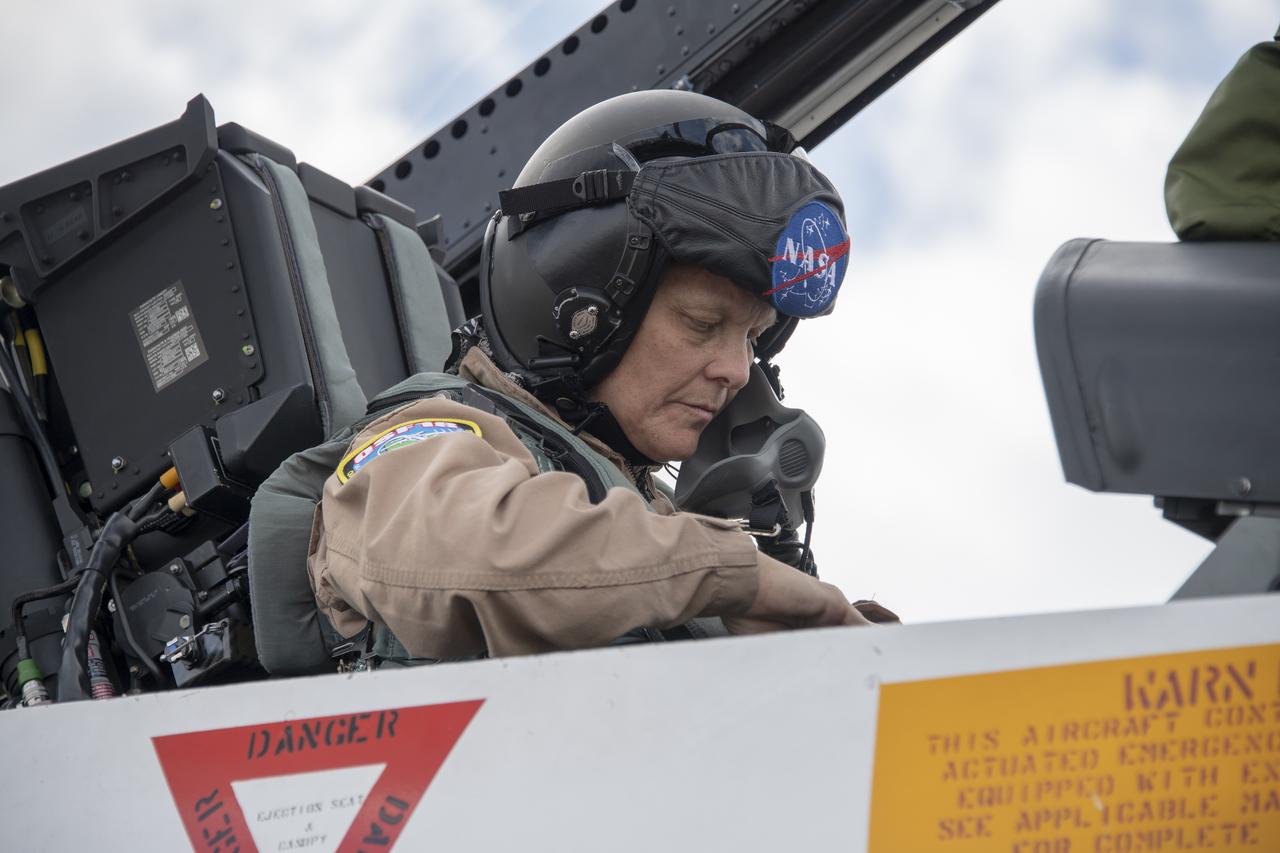

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
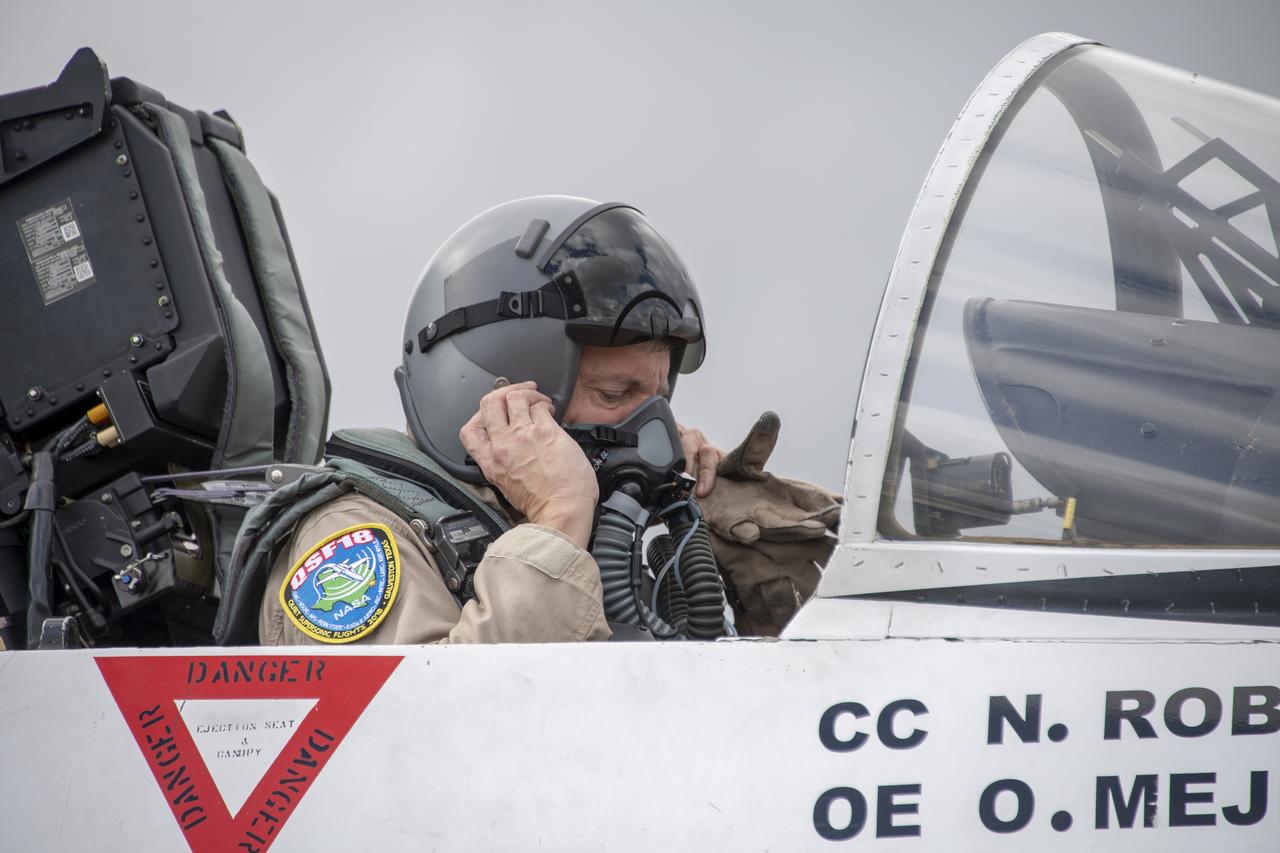

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
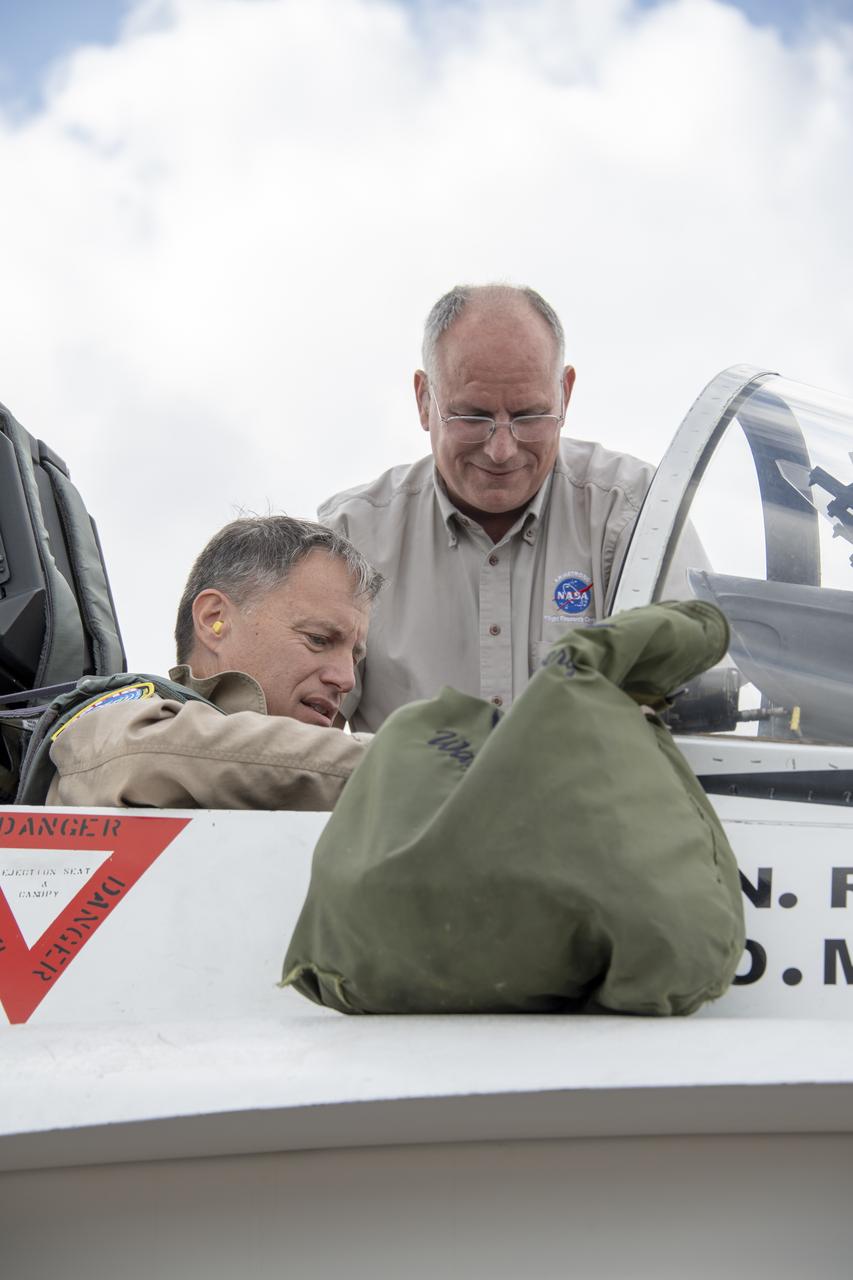

NASA test pilot Wayne “Ringo” Ringelberg and photographer Carla Thomas prepare to take off for a supersonic research flight in support of the QSF18 campaign off the coast of Texas. NASA photographers and videographers take part in operations to support mission documentation.
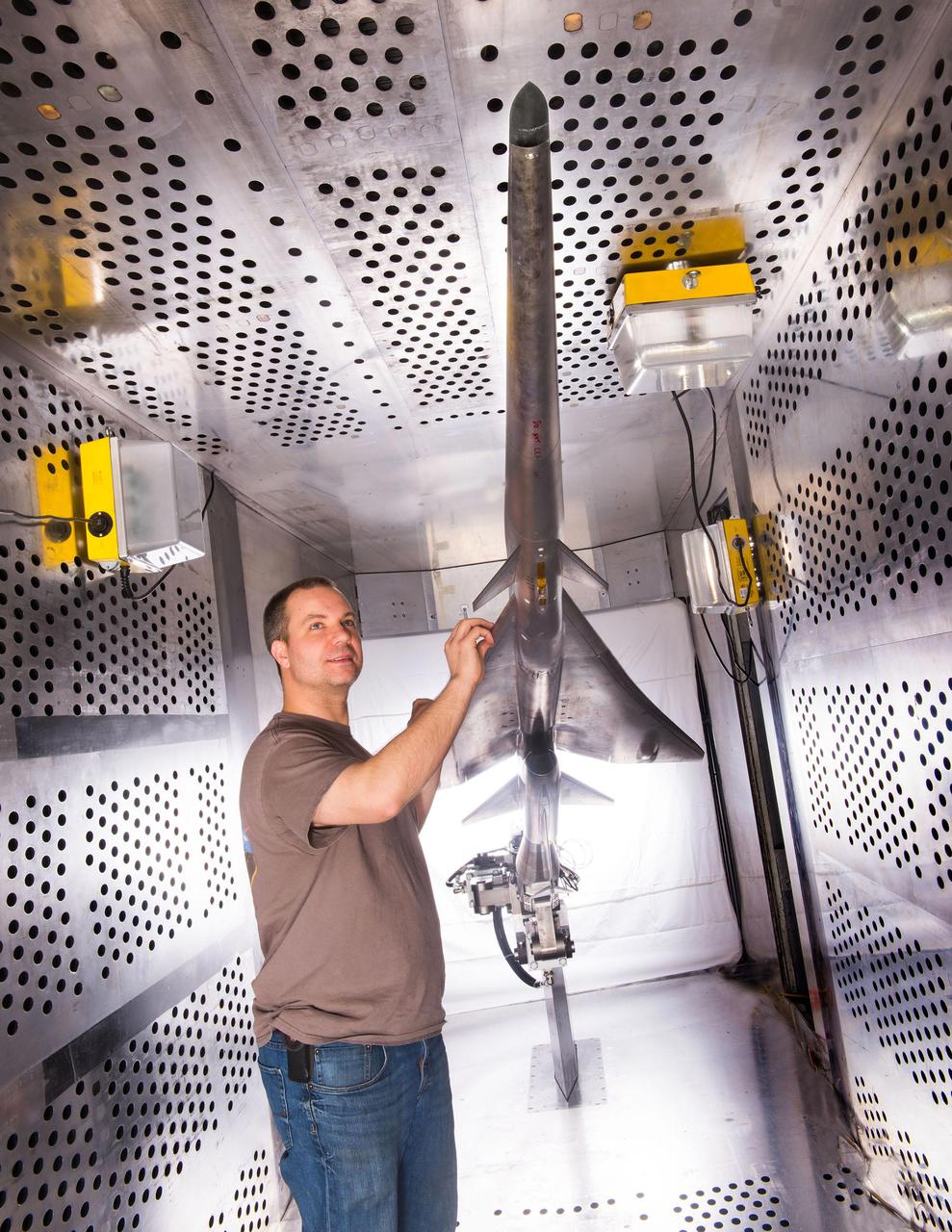

Mechanical technician Dan Pitts prepares a scale model of Lockheed Martin's Quiet Supersonic Technology (QueSST) X-plane preliminary design for its first high-speed wind tunnel tests at NASA's Glenn Research Center.
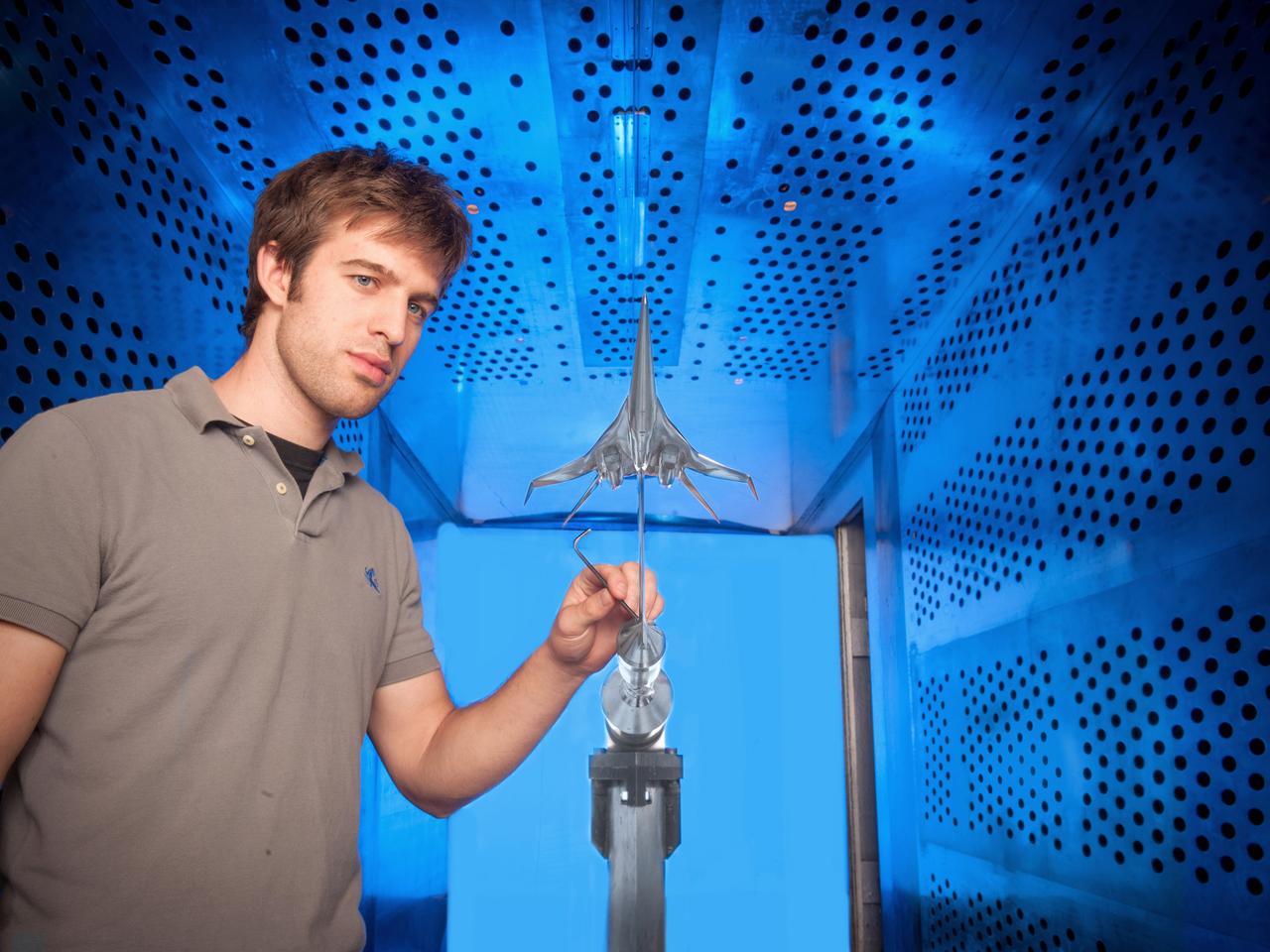
NASA Glenn engineer Gary Williamson with a small model of a future low-boom supersonic aircraft used for testing in the 8' x 6' Supersonic Wind Tunnel at NASA Glenn Research Center.
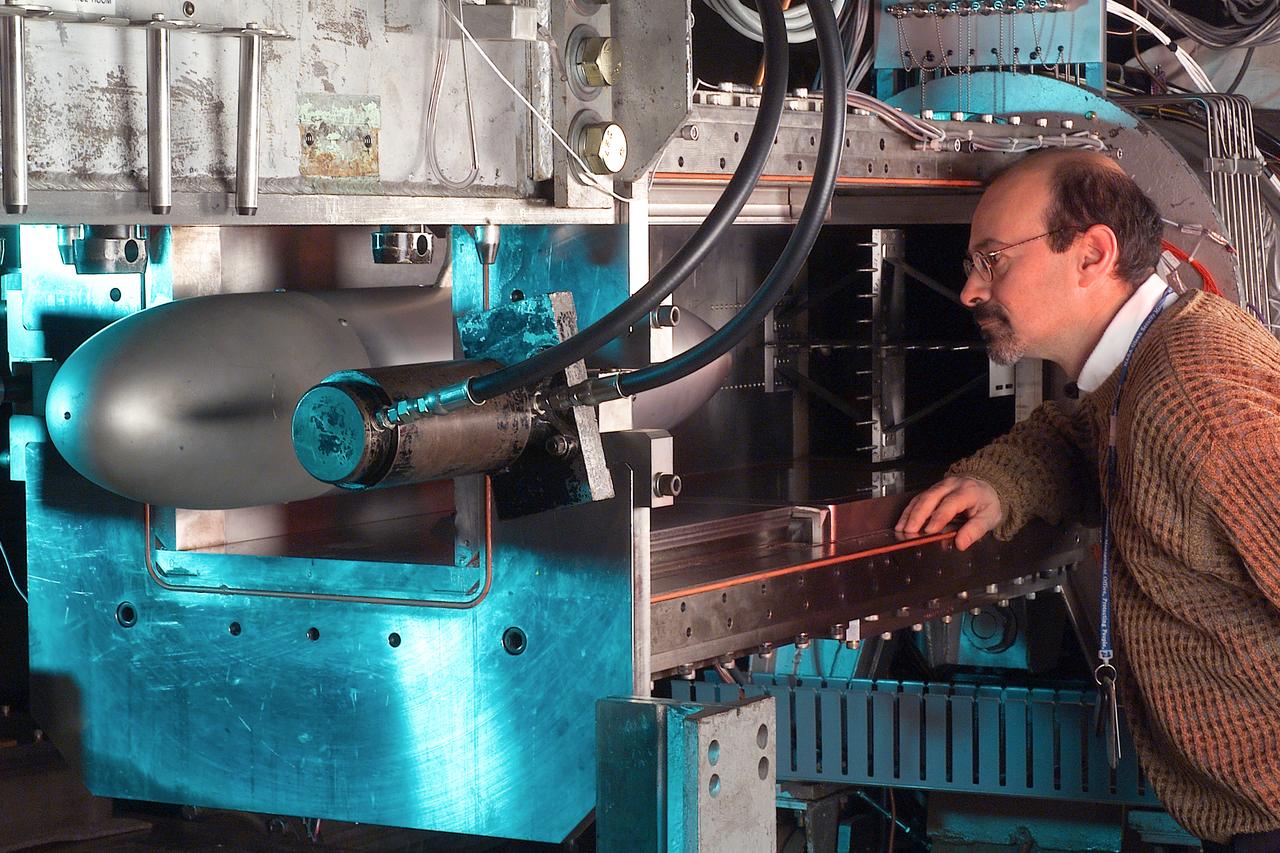
A researcher stands next to the Pulsed Ejector Wave Propagation Test Rig in an opened section of the 1'x1' Supersonic Wind Tunnel at NASA Glenn Research Center.
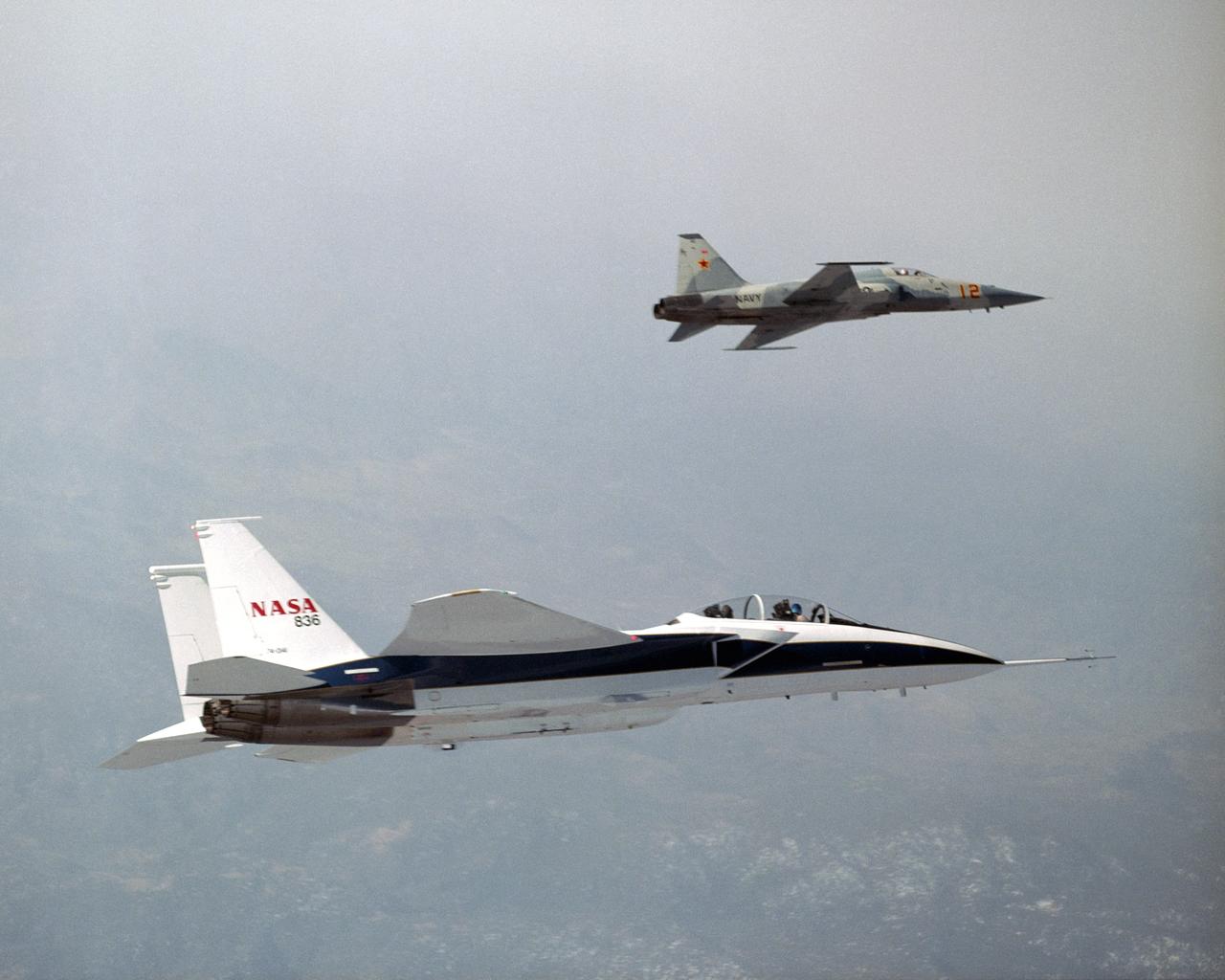

NASA's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft recently flew in the supersonic shock wave of a U.S. Navy F-5E in support of the F-5 Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency's (DARPA) Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. The flights originated from the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. Four flights were flown in order to measure the F-5E's near-field (close-up) sonic boom signature at Mach 1.4, during which more than 50 shockwave patterns were measured at distances as close as 100 feet below the F-5E.
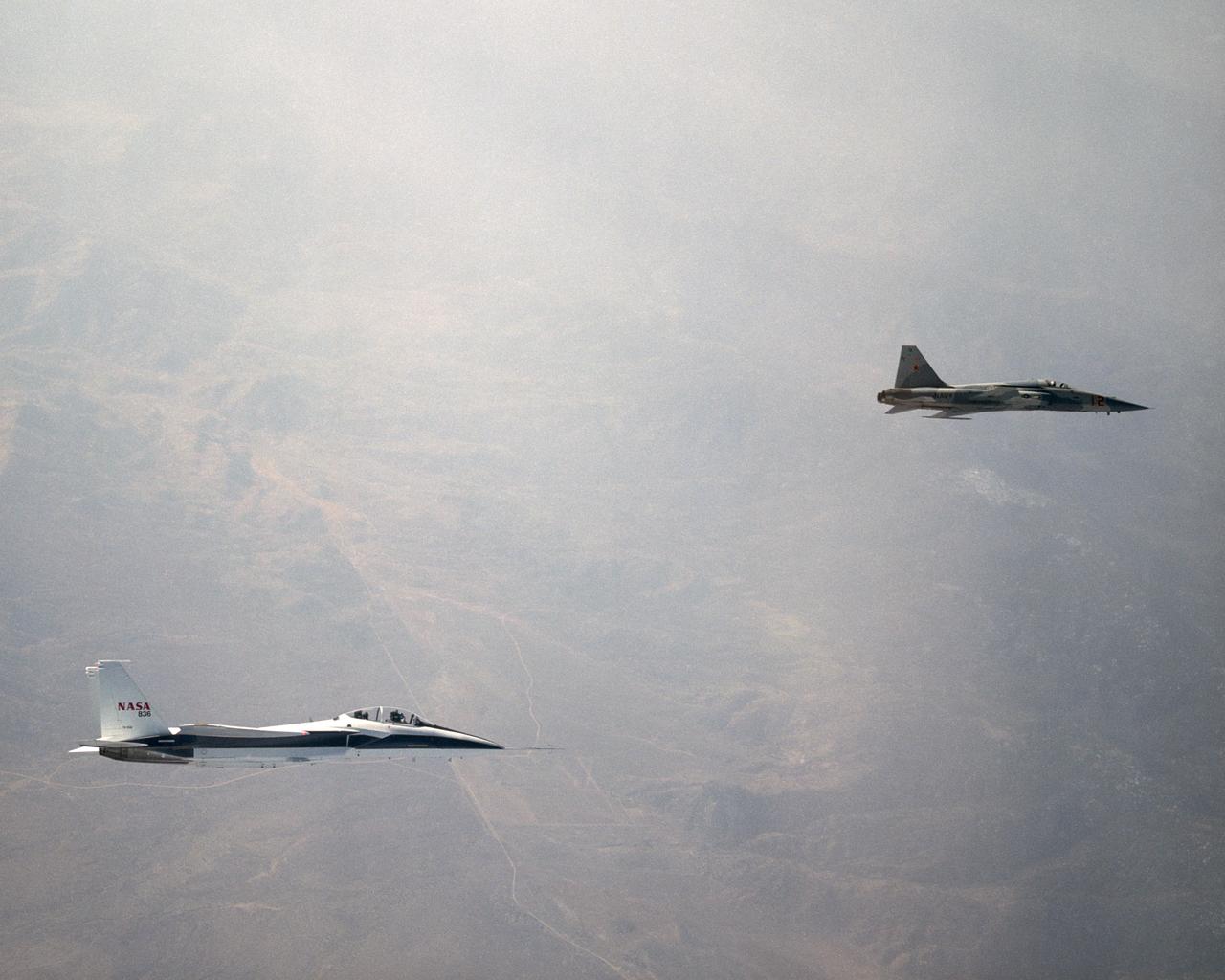

NASA's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft recently flew in the supersonic shock wave of a U.S. Navy F-5E in support of the F-5 Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency's (DARPA) Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. The flights originated from the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. Four flights were flown in order to measure the F-5E's near-field (close-up) sonic boom signature at Mach 1.4, during which more than 50 shockwave patterns were measured at distances as close as 100 feet below the F-5E.

Raised Floor Calibration Hardware for the Boundary Layer Ingesting Inlet Distortion Tolerant Fan tests to be performed in the 8' x 6' Supersonic Wind Tunnel at NASA Glenn Research Center.
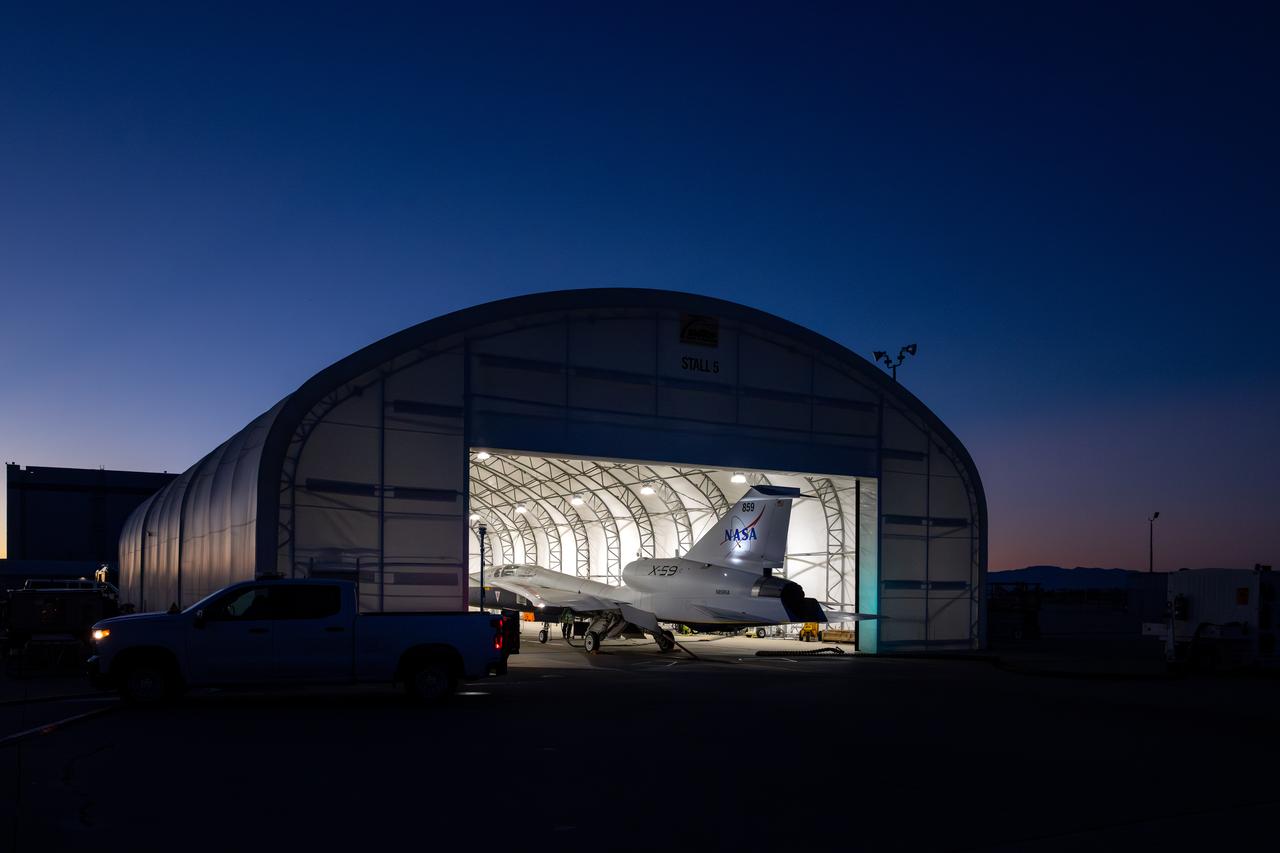

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits inside its run stall following maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. The test demonstrates the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight, advancing NASA’s Quesst mission. The X-59 is the centerpiece of the mission, designed to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight over land, addressing a key barrier to commercial supersonic travel.
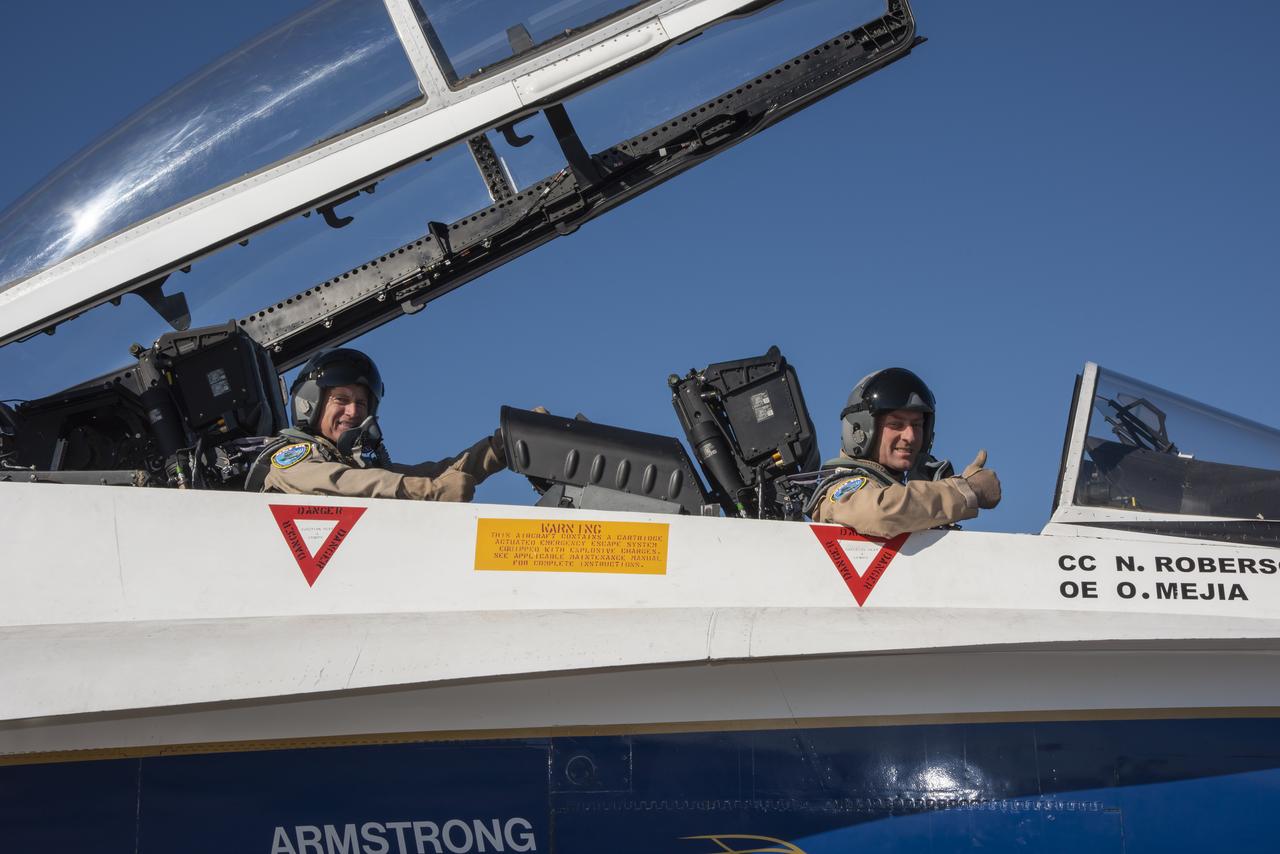

NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center test pilots Jim "Clue" Less (front) and Wayne "Ringo" Ringelberg (back) taxi out in a NASA F/A-18 at Ellington Field in Houston, Texas, in preparation of a training flight for the Quiet Supersonic Flights 2018 series, or QSF18. The QSF18 flights will provide NASA with feedback necessary to validate community response techniques for future quiet supersonic research flights for the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology, or QueSST.
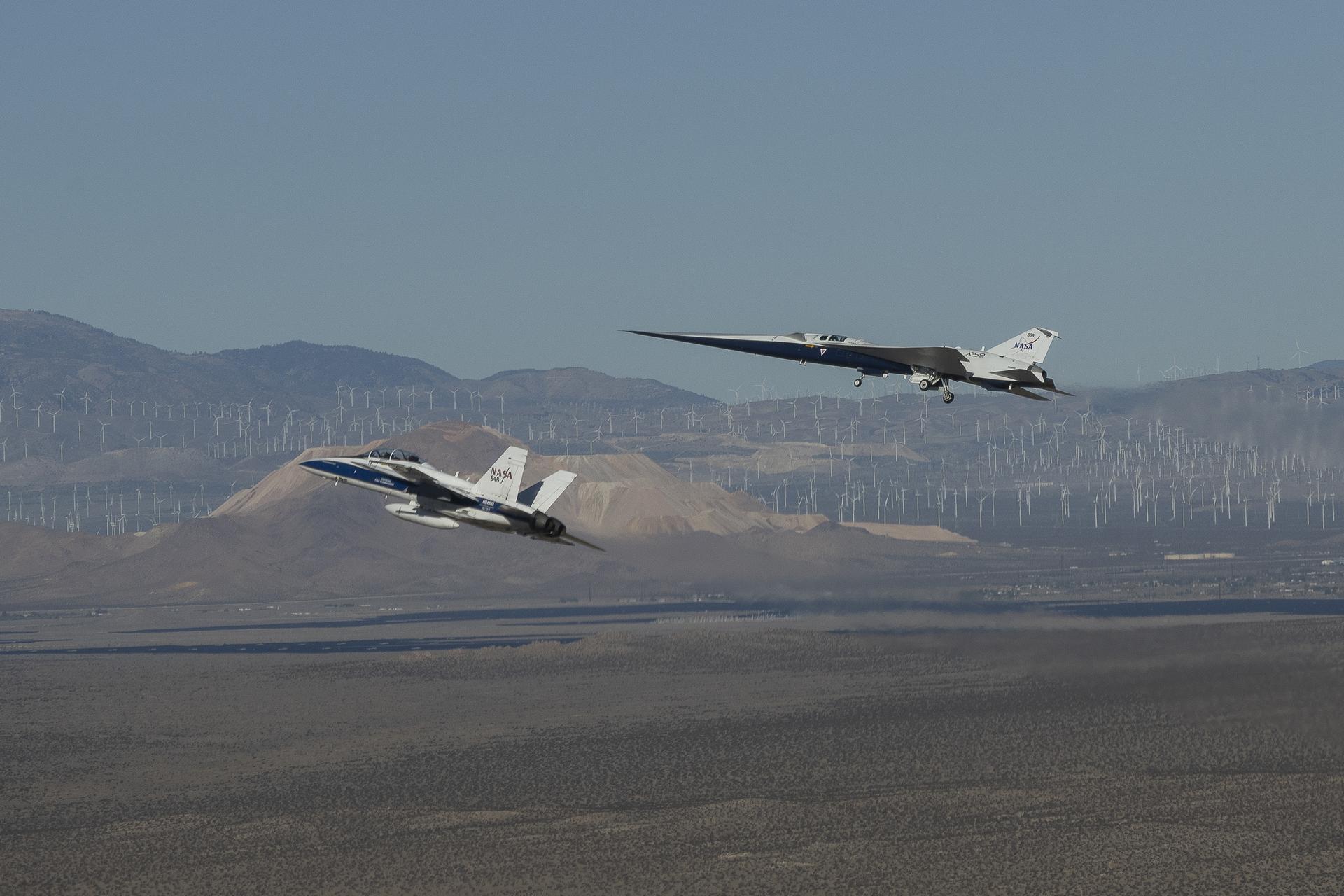

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft flies above Palmdale and Edwards, California, on its first flight Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025, accompanied by a NASA F-15 research aircraft. The F-15 monitored the X-59 during the flight as it traveled to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, where it will begin flight testing for NASA’s Quesst mission, which aims to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight over land.
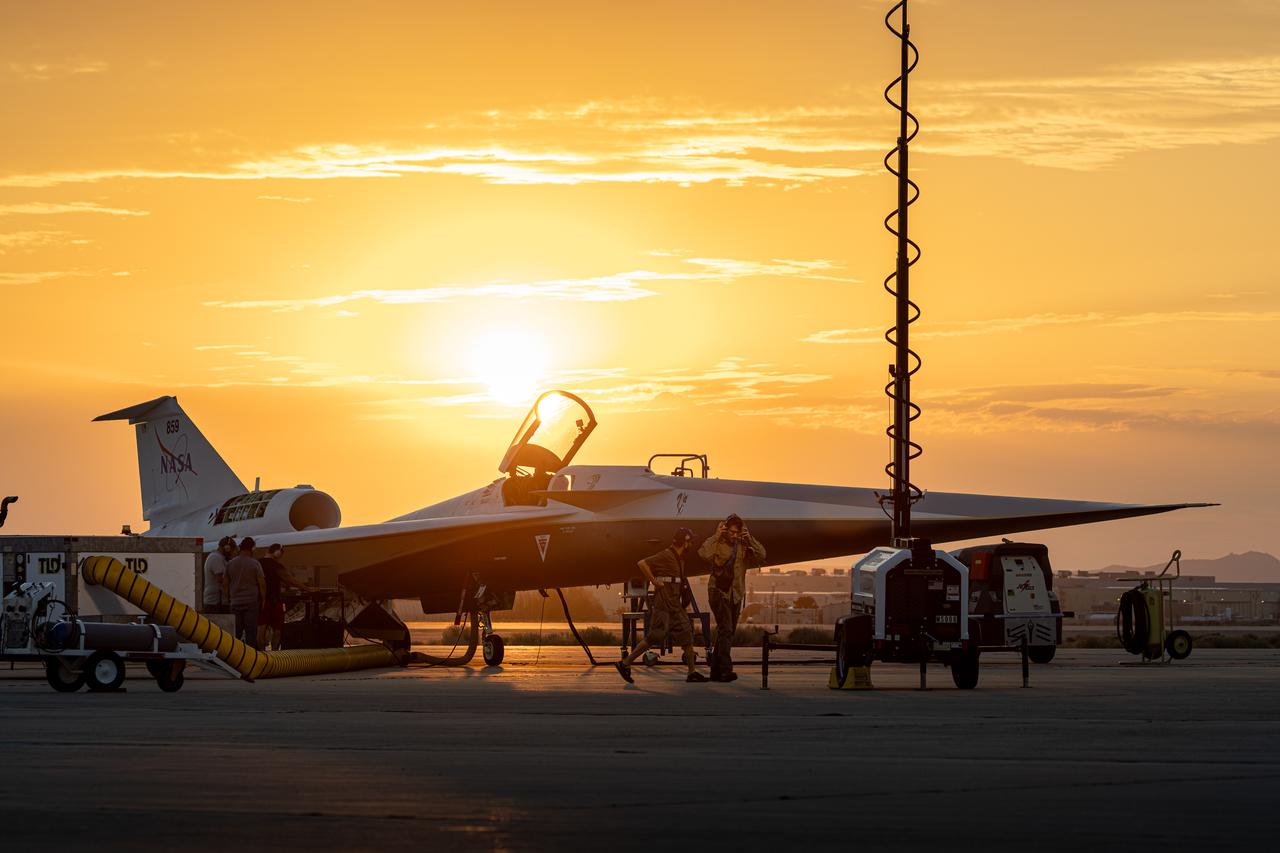

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on the ramp at sunrise before ground tests at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California, on July 18, 2025. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight and the aircraft is scheduled to make its first flight later this year.

NASA Associate Administrator for the Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate Bob Pearce speaks on stage prior to the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.

NASA Associate Administrator for the Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate Bob Pearce speaks on stage prior to the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.

NASA Associate Administrator for the Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate Bob Pearce speaks on stage prior to the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.

A NASA F/A-18 sits on the apron at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, prior to a supersonic research flight.
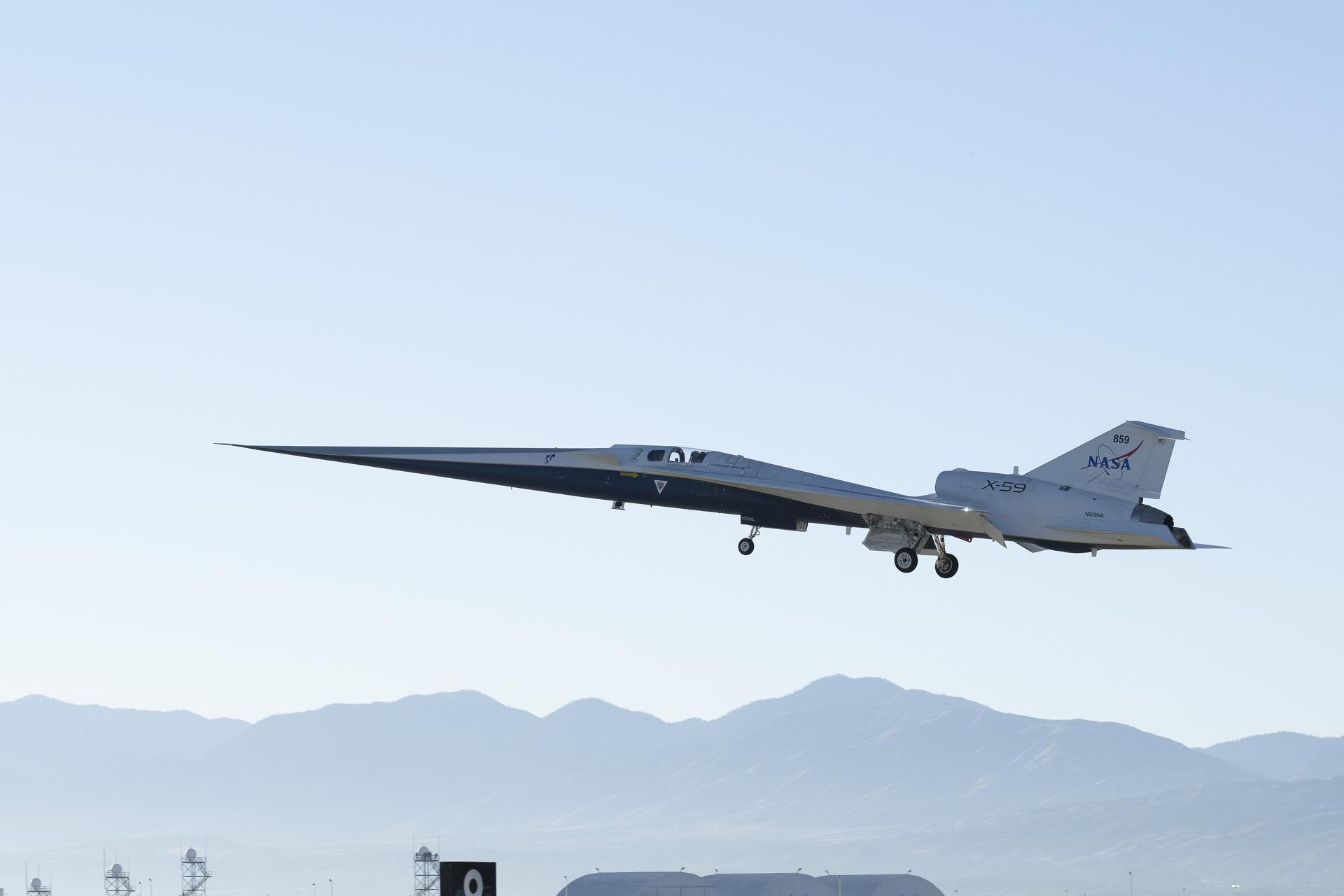

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft lifts off for its first flight Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025, from U.S. Air Force Plant 42 in Palmdale, California. The aircraft’s first flight marks the start of flight testing for NASA’s Quesst mission, the result of years of design, integration, and ground testing and begins a new chapter in NASA’s aeronautics research legacy.

NASA test pilot Nils Larson inspects the agency’s F-15D research aircraft at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, ahead of a calibration flight for a newly installed near-field shock-sensing probe. Mounted on the F-15D, the probe is designed to measure shock waves generated by the X-59 quiet supersonic aircraft during flight. The data will help researchers better understand how shock waves behave in close proximity to the aircraft, supporting NASA’s Quesst mission to enable quiet supersonic flight over land.
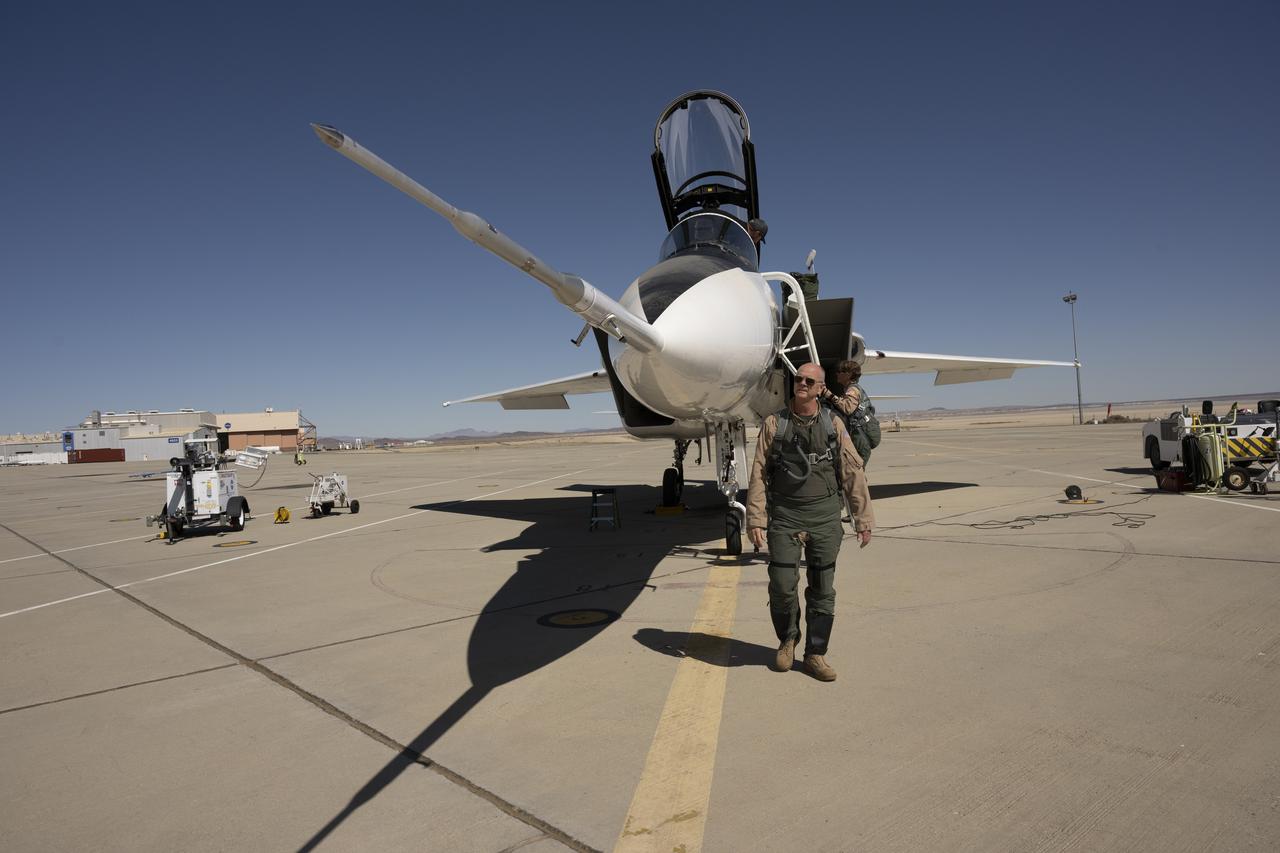

NASA test pilot Nils Larson inspects the agency’s F-15D research aircraft at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, ahead of a calibration flight for a newly installed near-field shock-sensing probe. Mounted on the F-15D, the probe is designed to measure shock waves generated by the X-59 quiet supersonic aircraft during flight. The data will help researchers better understand how shock waves behave in close proximity to the aircraft, supporting NASA’s Quesst mission to enable quiet supersonic flight over land.
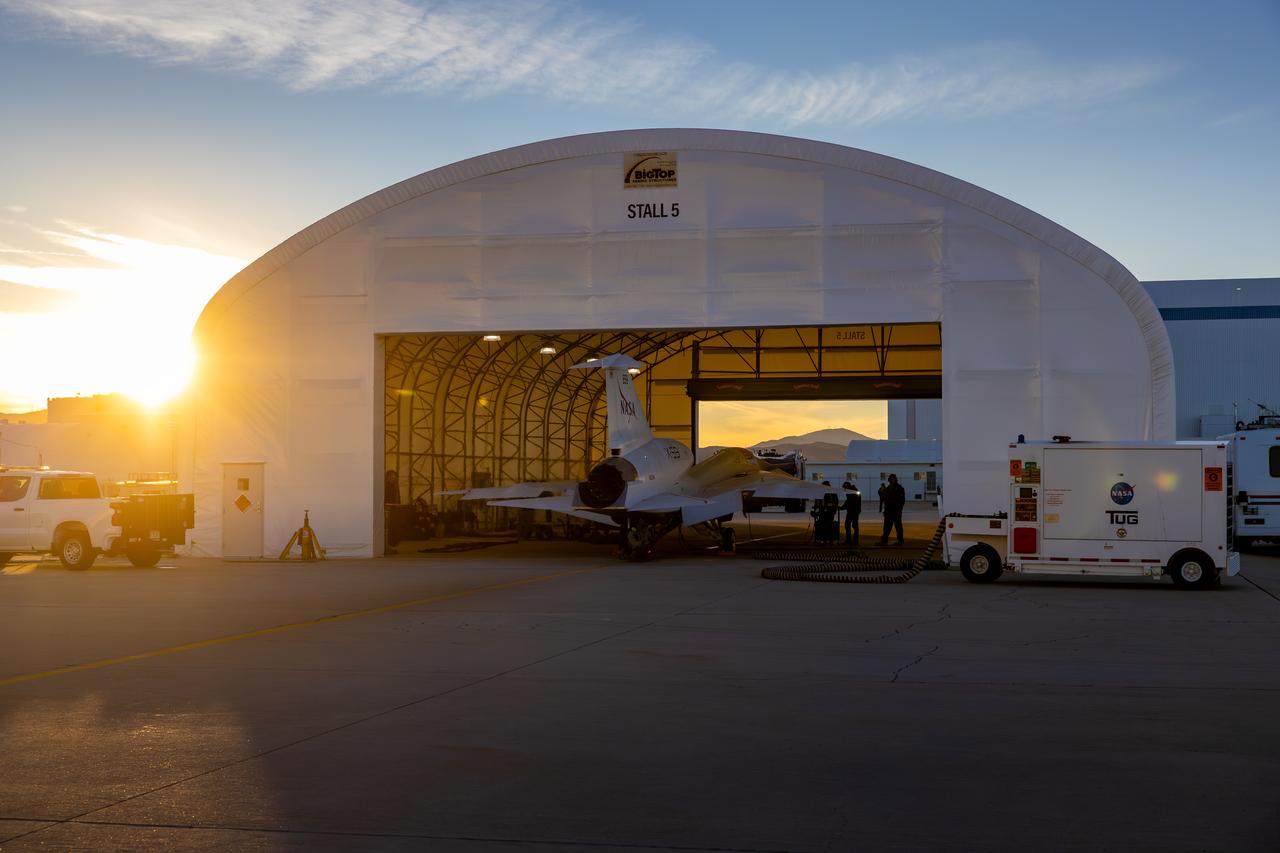

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits inside its run stall in preparation for maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. Teams conduct final checks on the aircraft before its high-thrust engine runs. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission designed to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight over land, addressing a key barrier to commercial supersonic travel.
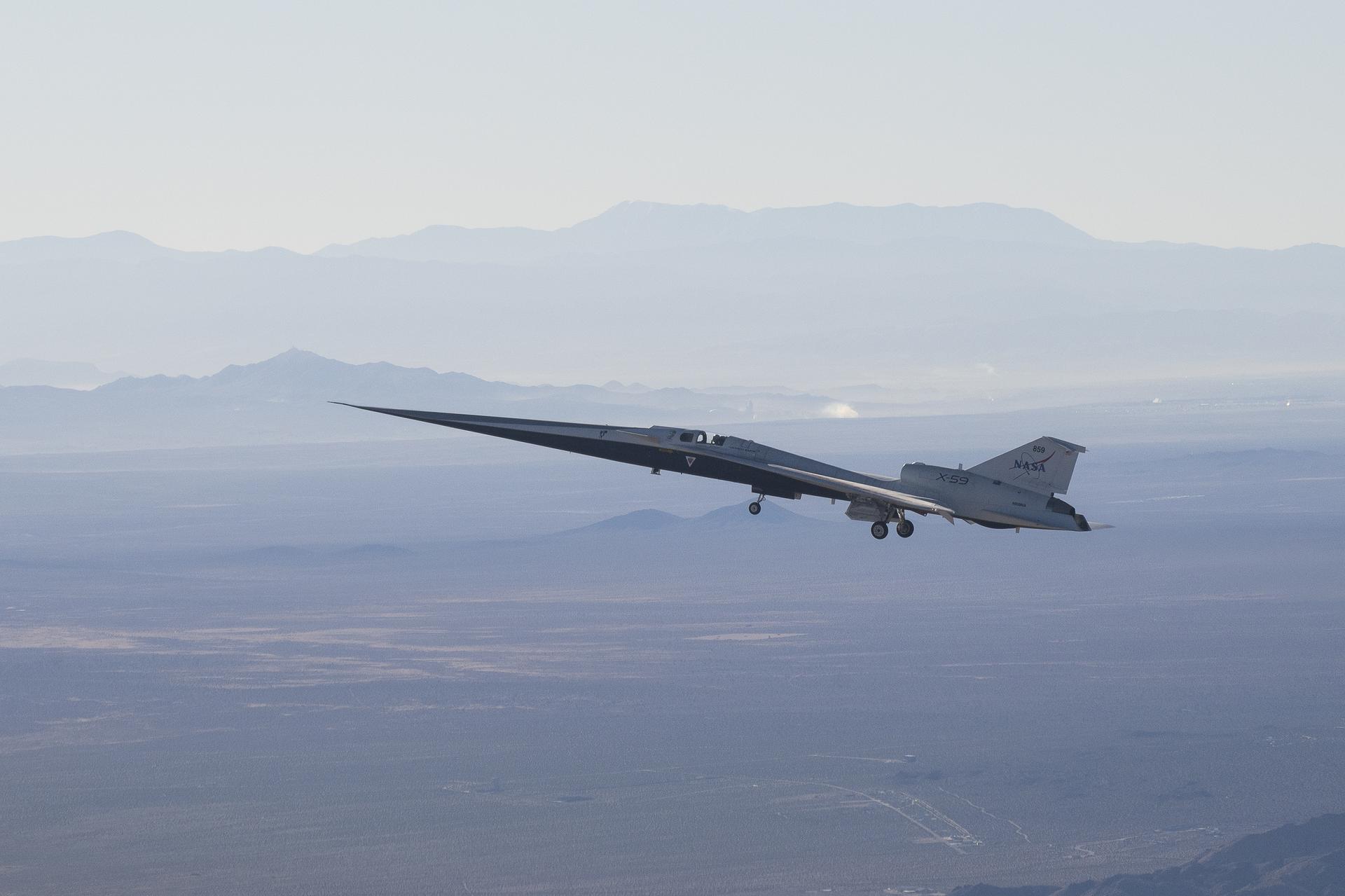

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft flies above Palmdale and Edwards, California, on its first flight Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025. The aircraft traveled to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, where it will begin flight testing for NASA’s Quesst mission, which aims to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight over land.
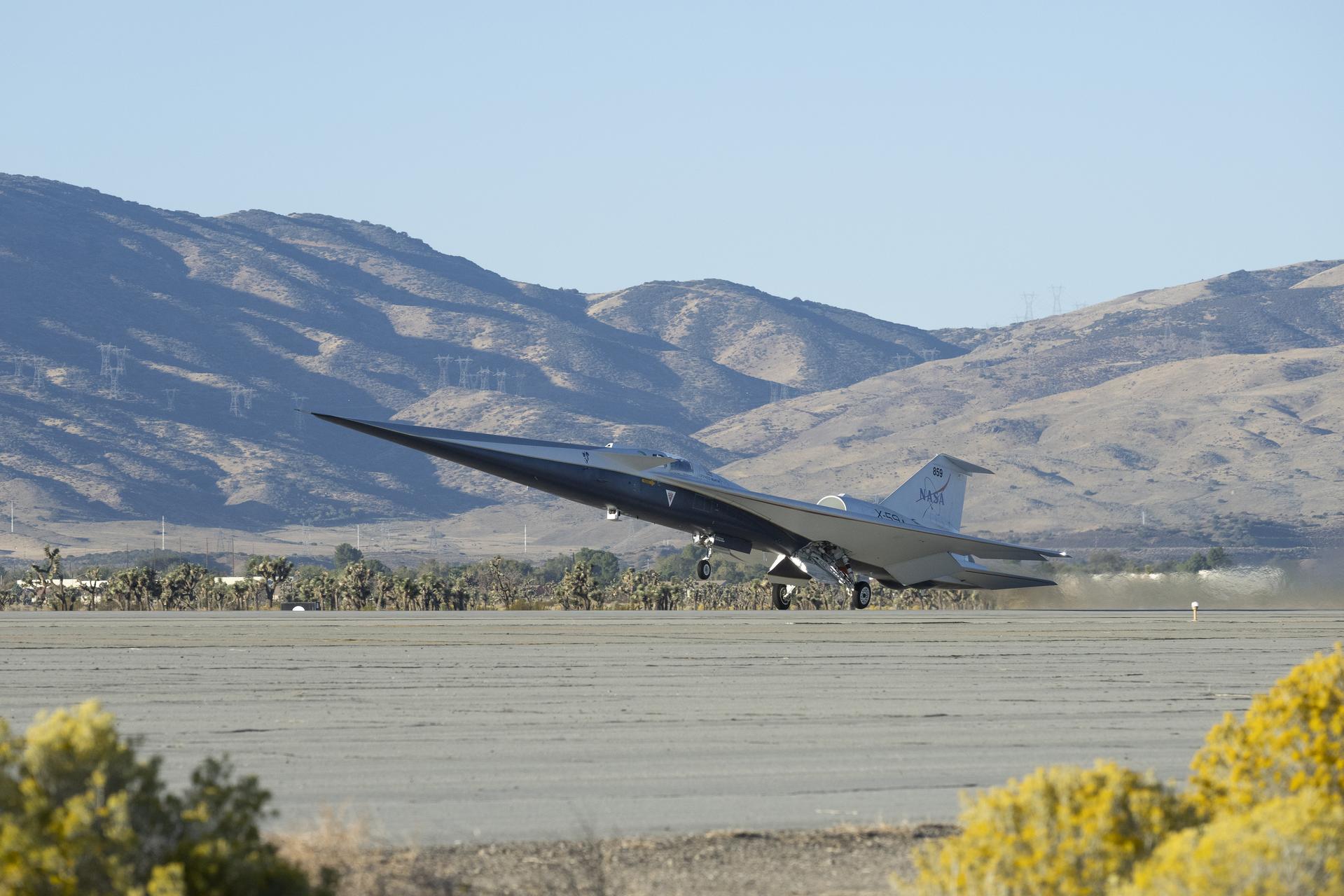

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft lifts off for its first flight Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025, from U.S. Air Force Plant 42 in Palmdale, California. The aircraft’s first flight marks the start of flight testing for NASA’s Quesst mission, the result of years of design, integration, and ground testing and begins a new chapter in NASA’s aeronautics research legacy.
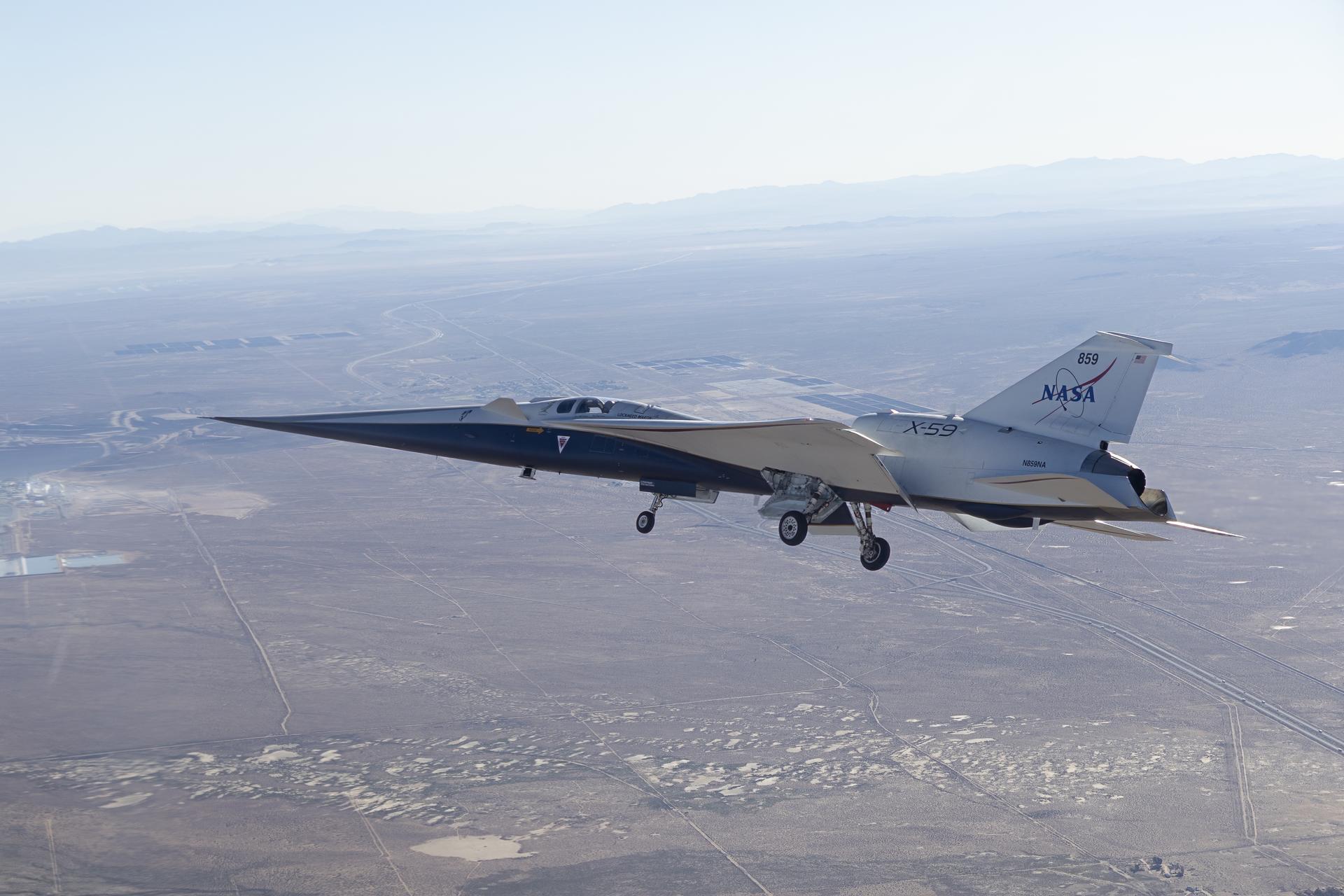

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft cruises above Palmdale and Edwards, California, during its first flight, Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025. The aircraft traveled to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
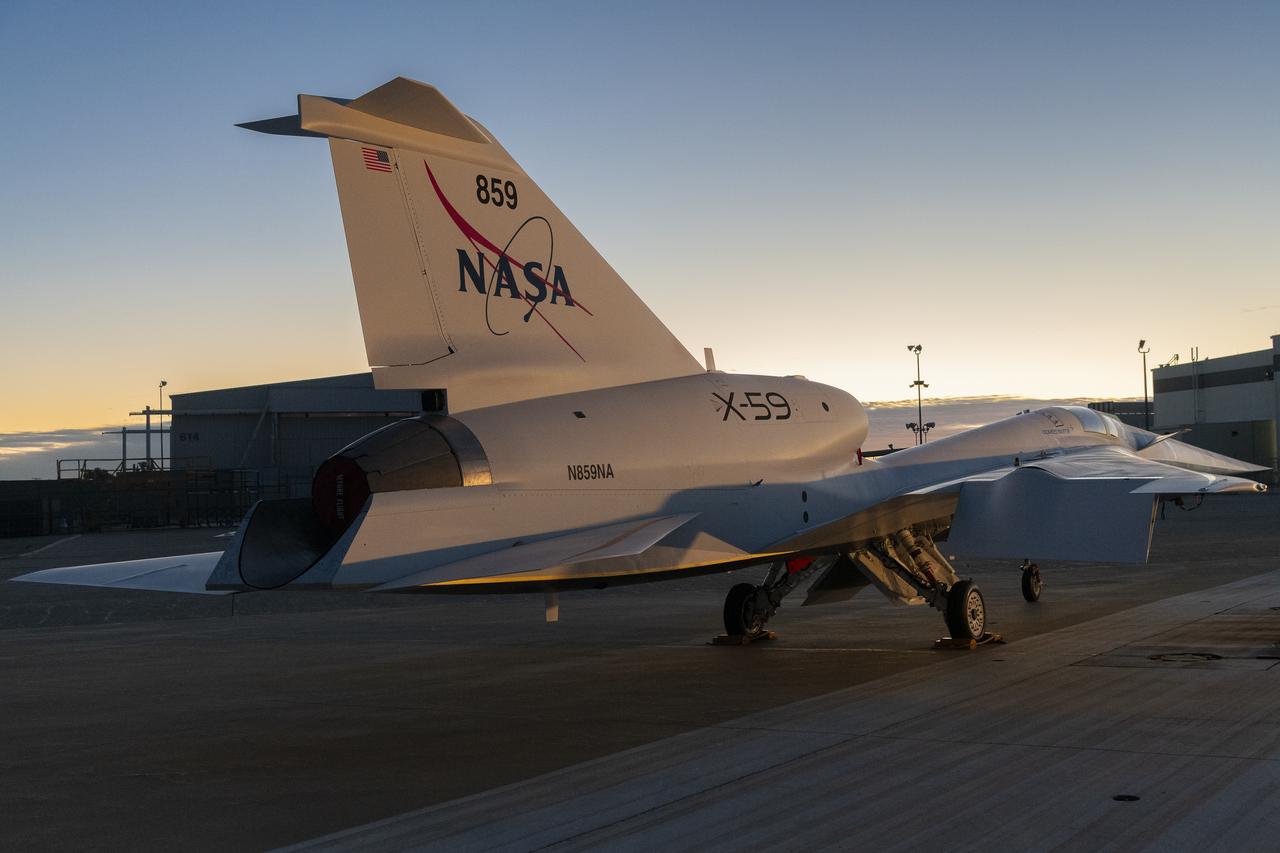

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California during sunrise, shortly after completion of painting. With its unique design, including a 38-foot-long nose, the X-59 was built to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic, or faster than the speed of sound, while reducing the typically loud sonic boom produced by aircraft at such speeds to a quieter sonic “thump”. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
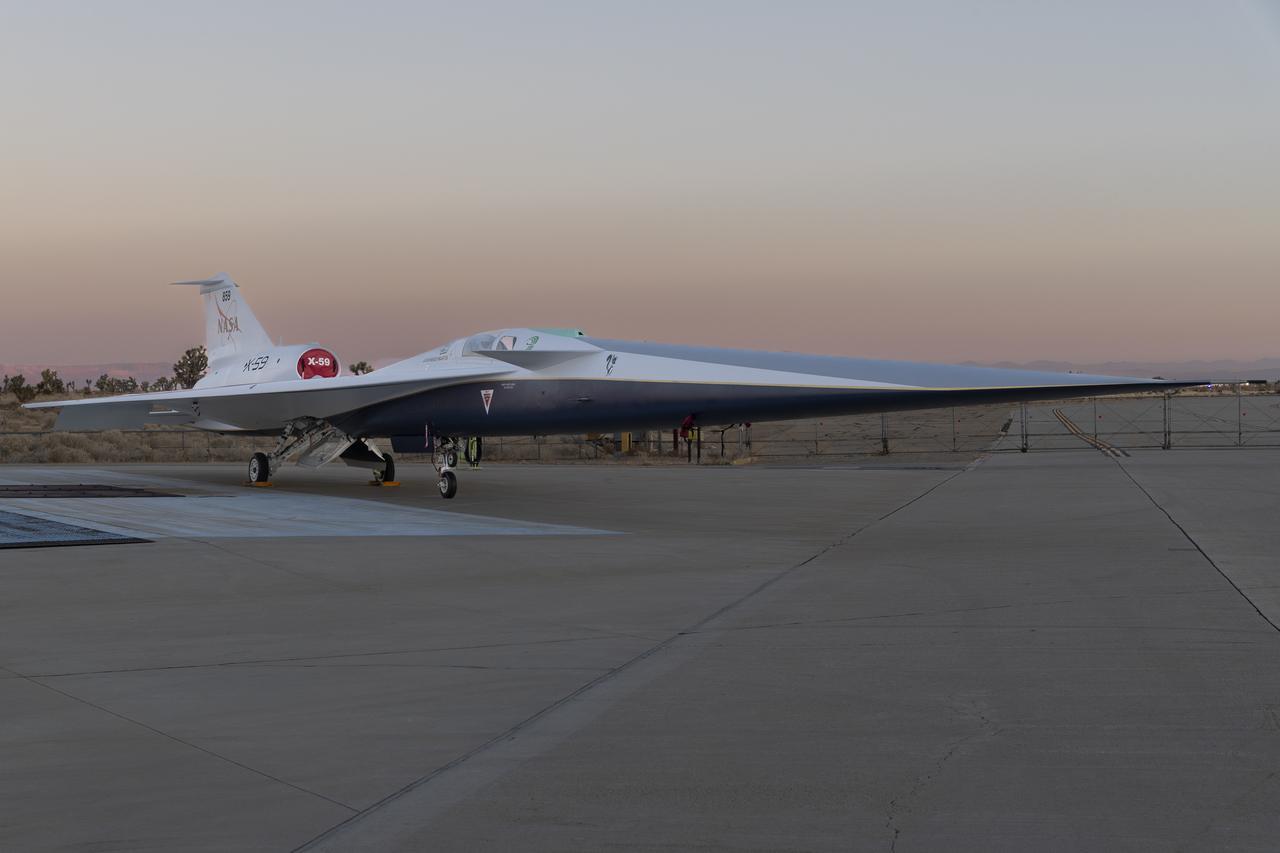

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California during sunrise, shortly after completion of painting. With its unique design, including a 38-foot-long nose, the X-59 was built to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic, or faster than the speed of sound, while reducing the typically loud sonic boom produced by aircraft at such speeds to a quieter sonic “thump”. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
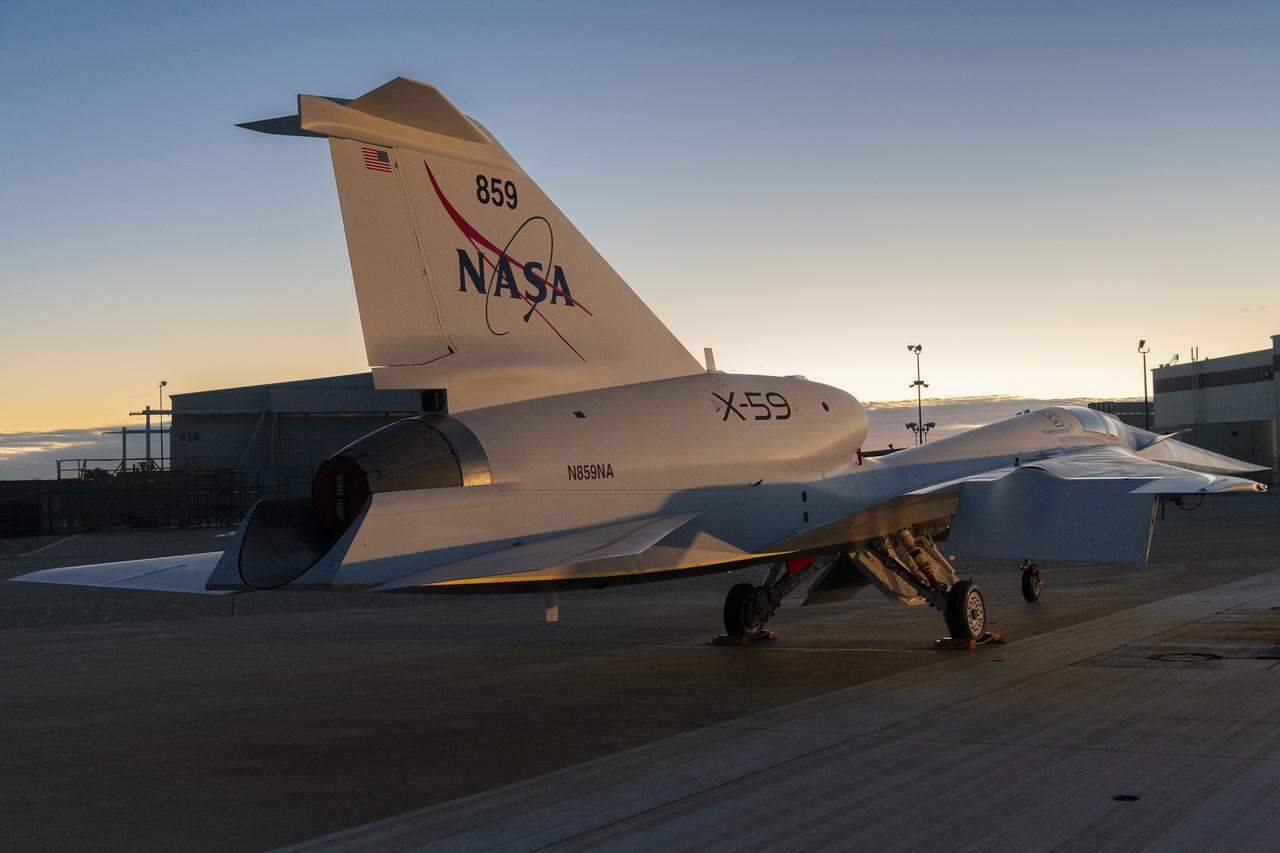

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California during sunrise, shortly after completion of painting. With its unique design, including a 38-foot-long nose, the X-59 was built to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic, or faster than the speed of sound, while reducing the typically loud sonic boom produced by aircraft at such speeds to a quieter sonic “thump”. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
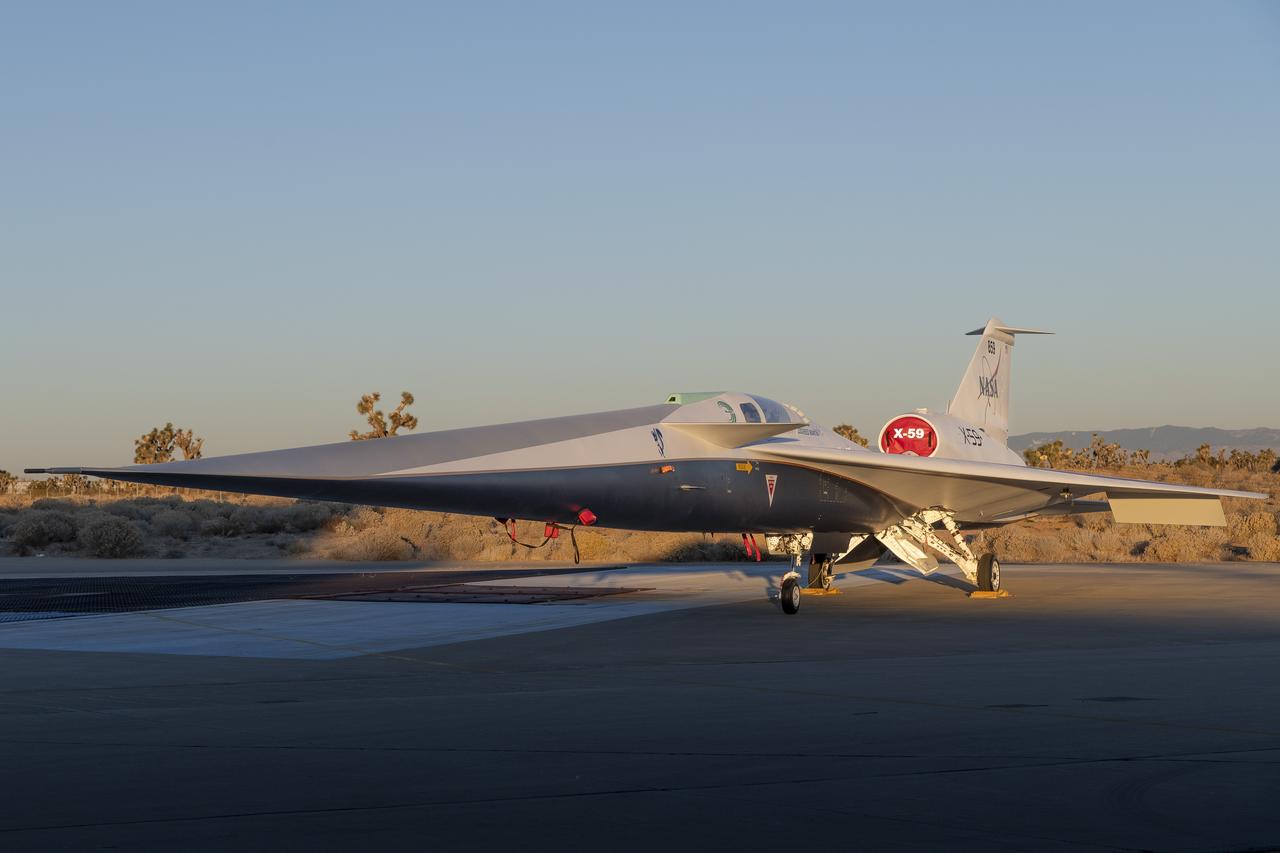

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California during sunrise, shortly after completion of painting. With its unique design, including a 38-foot-long nose, the X-59 was built to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic, or faster than the speed of sound, while reducing the typically loud sonic boom produced by aircraft at such speeds to a quieter sonic “thump”. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
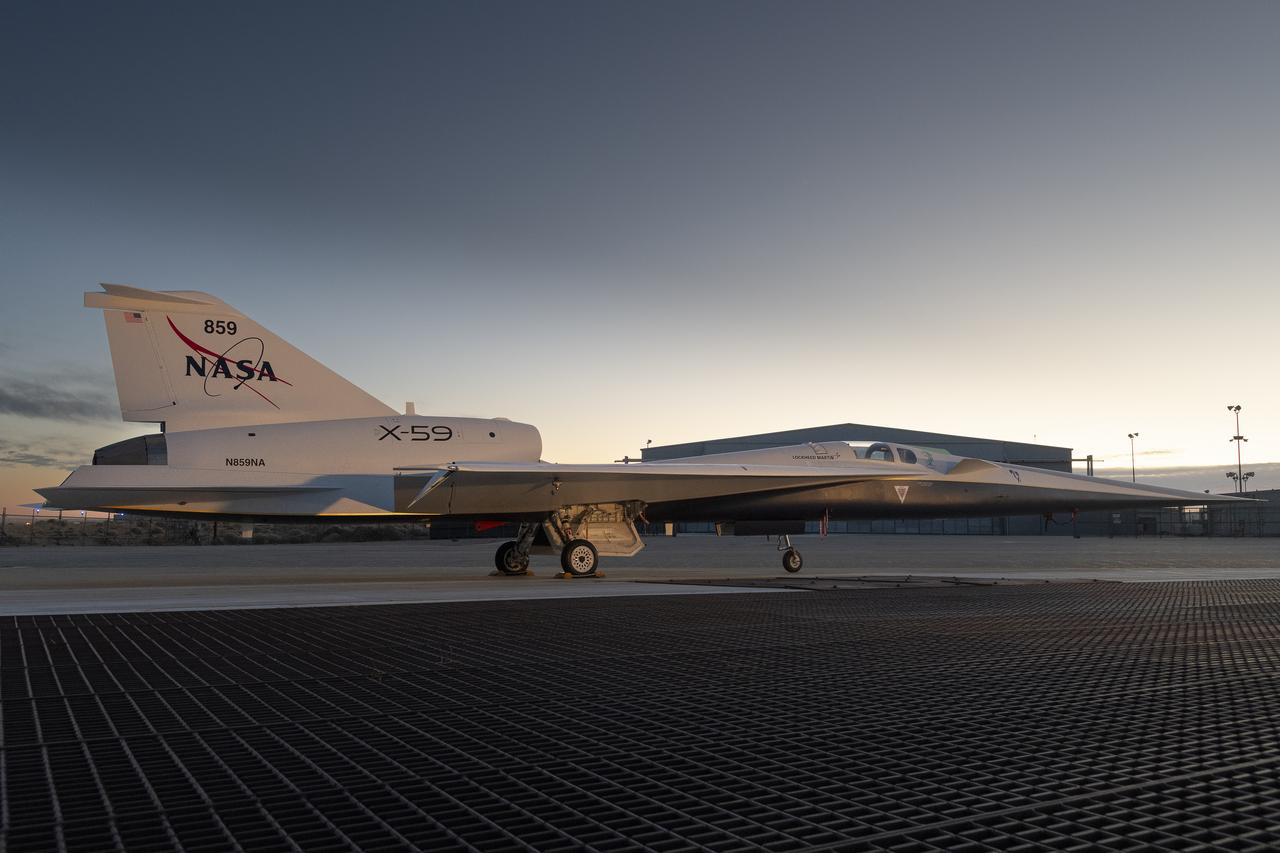

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California during sunrise, shortly after completion of painting. With its unique design, including a 38-foot-long nose, the X-59 was built to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic, or faster than the speed of sound, while reducing the typically loud sonic boom produced by aircraft at such speeds to a quieter sonic “thump”. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
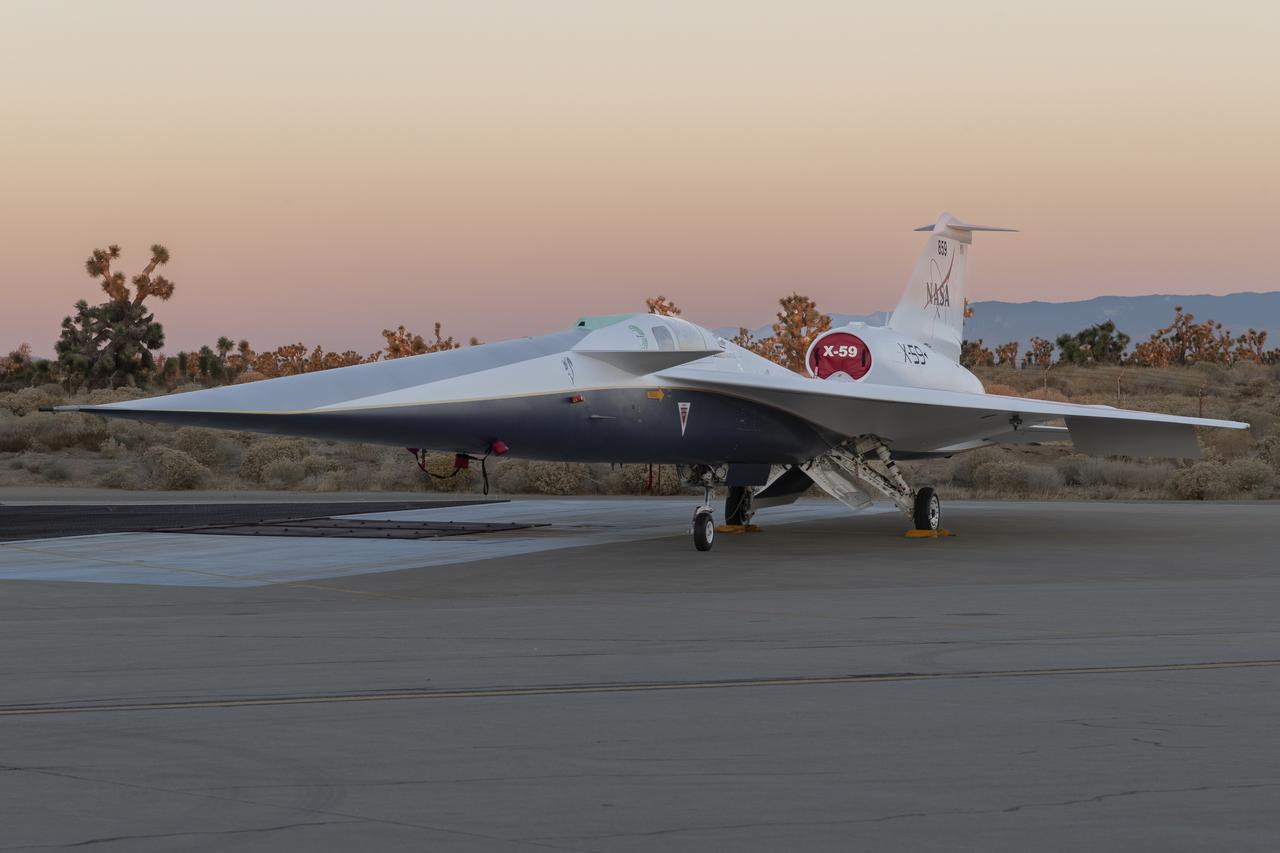

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California during sunrise, shortly after completion of painting. With its unique design, including a 38-foot-long nose, the X-59 was built to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic, or faster than the speed of sound, while reducing the typically loud sonic boom produced by aircraft at such speeds to a quieter sonic “thump”. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
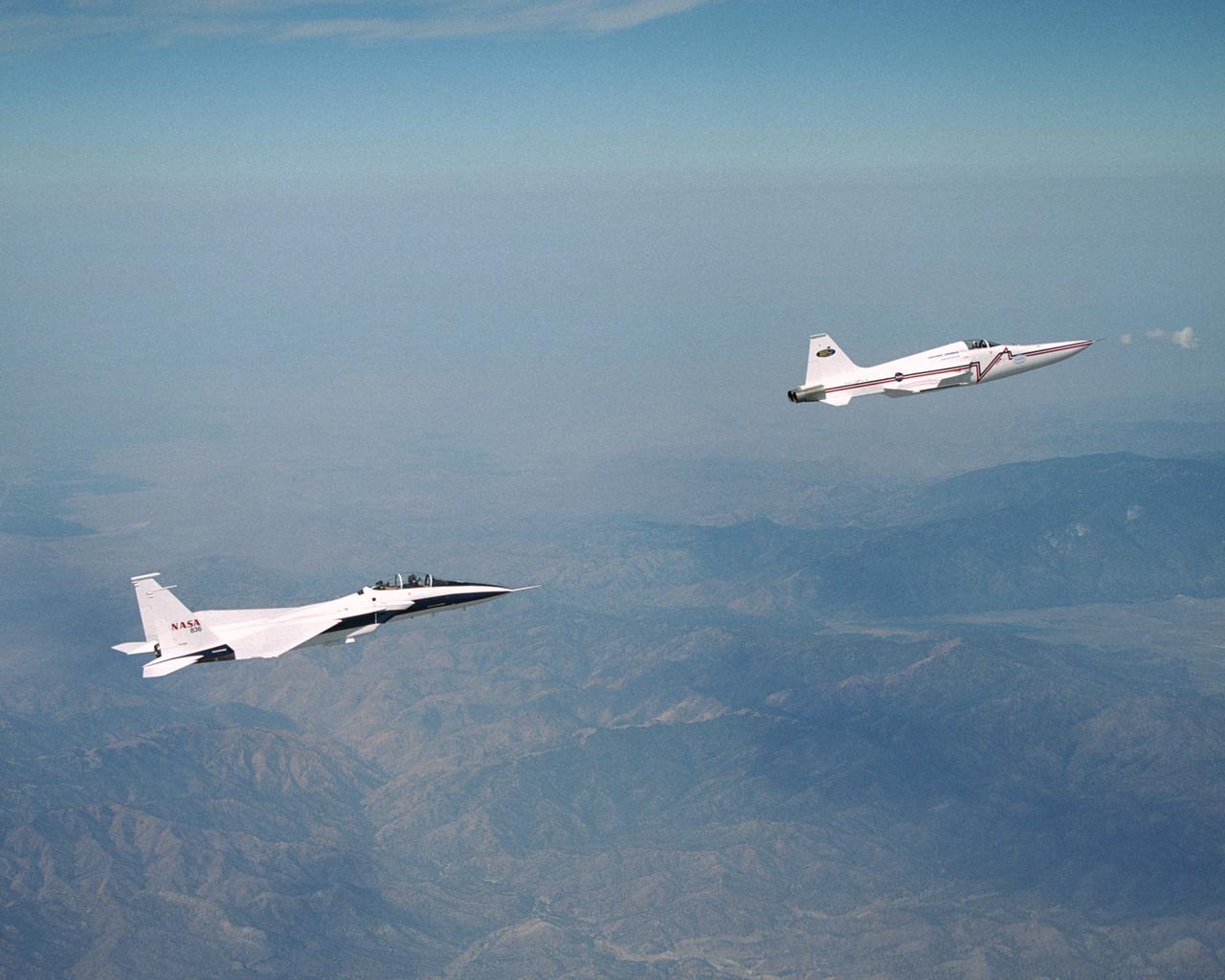

NASA's F-15B research testbed jet from the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center flew in the supersonic shockwave of a Northrop Grumman Corp. modified F-5E in support of the Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, which is part of the DARPA's Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program.
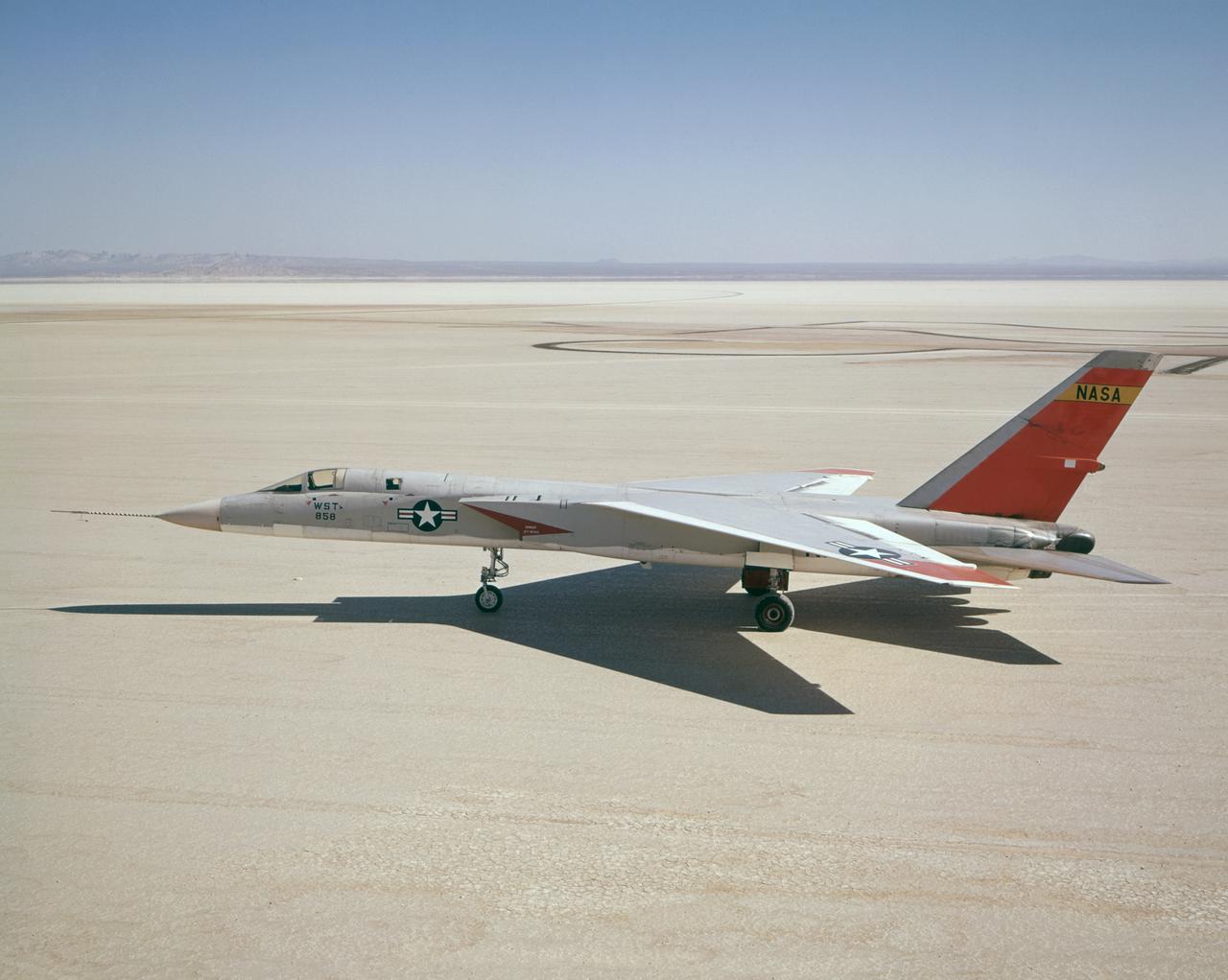

A North American Aviation A-5A Vigilante (Navy serial number 147858/NASA tail number 858) arrived from the Naval Air Test Center, Patuxent River, MD, on December 19, 1962, at the NASA Flight Research Center (now, Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, CA). The Center flew the A-5A in a year-long series of flights in support of the U.S. supersonic transport program. The Center flew the aircraft to determine the let-down and approach conditions of a supersonic transport flying into a dense air traffic network. With the completion of the research flights, the Center sent the A-5A back to the Navy on December 20, 1963.
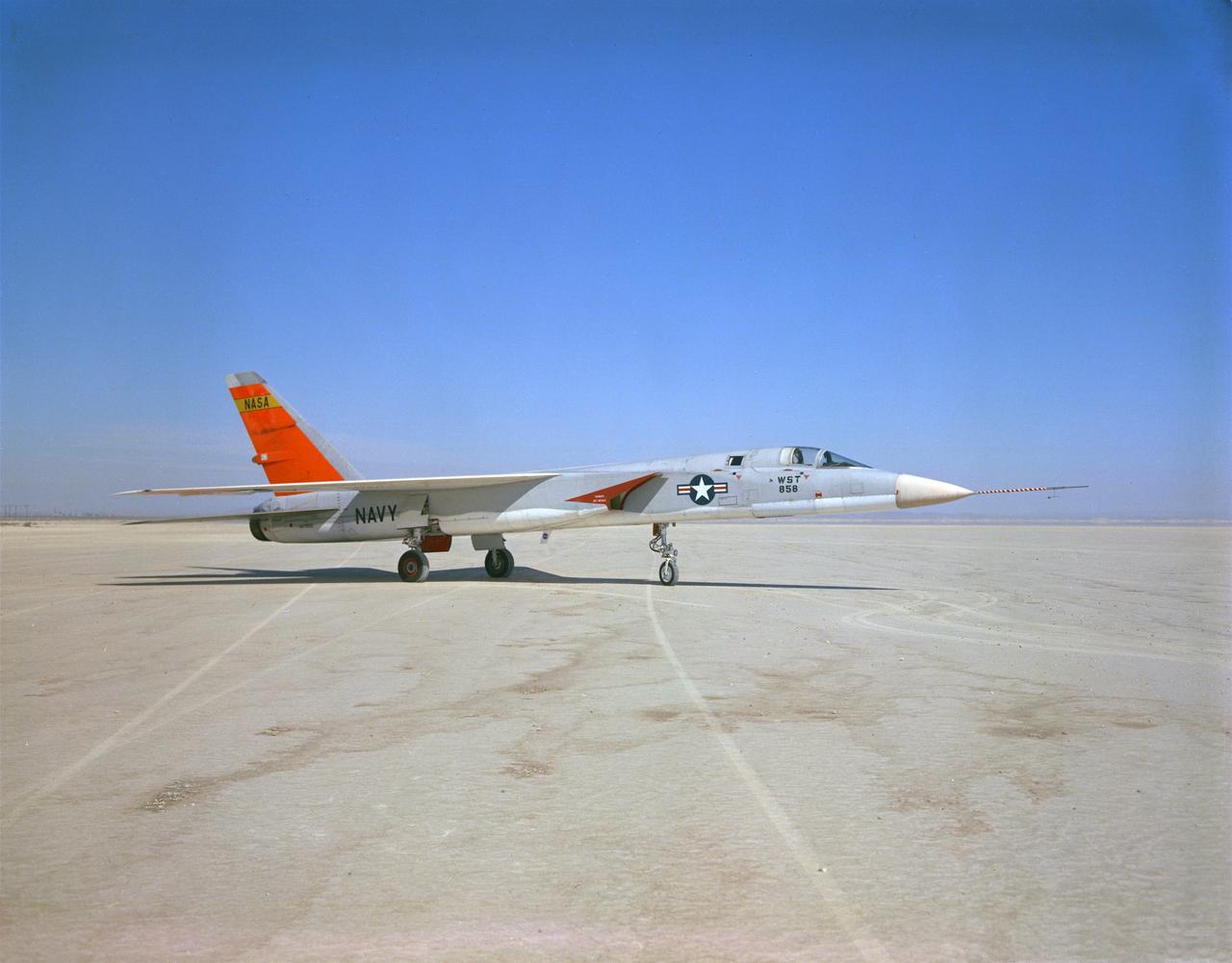

A North American Aviation A-5A Vigilante (Navy serial number 147858/NASA tail number 858) arrived from the Naval Air Test Center, Patuxent River, MD, on December 19, 1962, at the NASA Flight Research Center (now, Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, CA). The Center flew the A-5A in a year-long series of flights in support of the U.S. supersonic transport program. The Center flew the aircraft to determine the let-down and approach conditions of a supersonic transport flying into a dense air traffic network. With the completion of the research flights, the Center sent the A-5A back to the Navy on December 20, 1963.

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits in its run stall at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California, prior to its first engine run. Engine runs are part of a series of integrated ground tests needed to ensure safe flight and successful achievement of mission goals. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land by making sonic booms quieter.

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits in its run stall at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California, firing up its engine for the first time. These engine-run tests start at low power and allow the X-59 team to verify the aircraft’s systems are working together while powered by its own engine. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land by making sonic booms quieter.
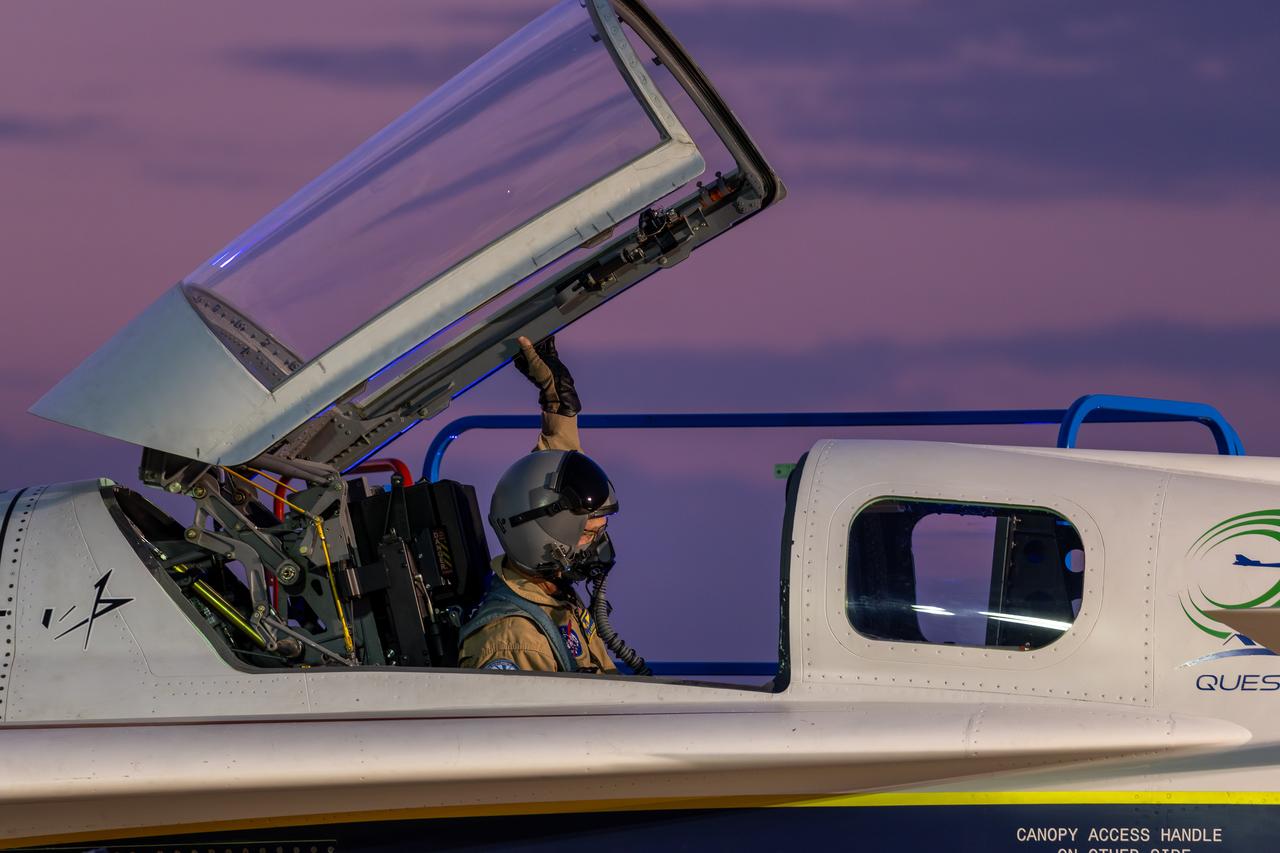

NASA test pilot Nils Larson lowers the canopy of the X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft during ground tests at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California, on July 18, 2025. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight and the aircraft is scheduled to make its first flight later this year.
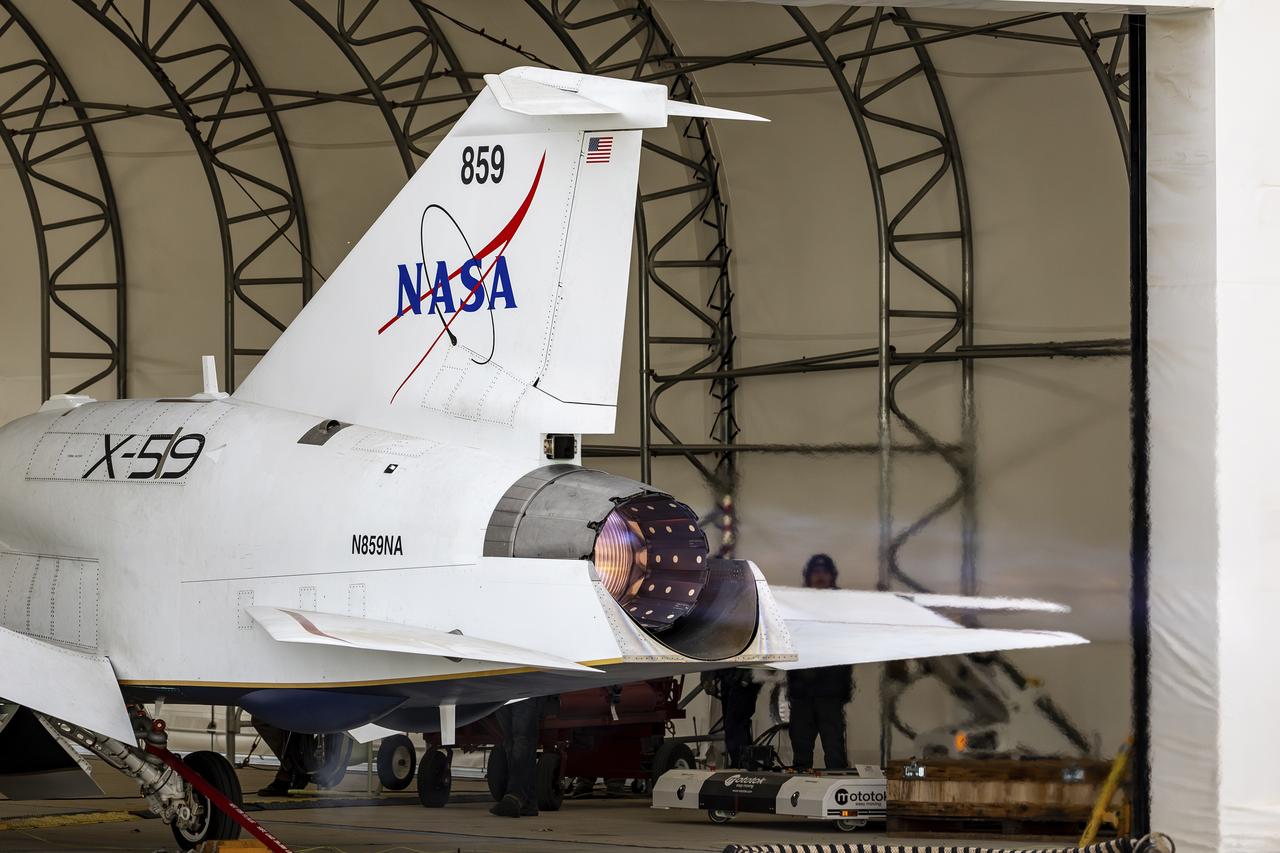

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft completed its first maximum afterburner test at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. This full-power test, during which the engine generates additional thrust, validates the additional power needed for meeting the testing conditions of the aircraft. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which aims to overcome a major barrier to supersonic flight over land by reducing the noise of sonic booms.
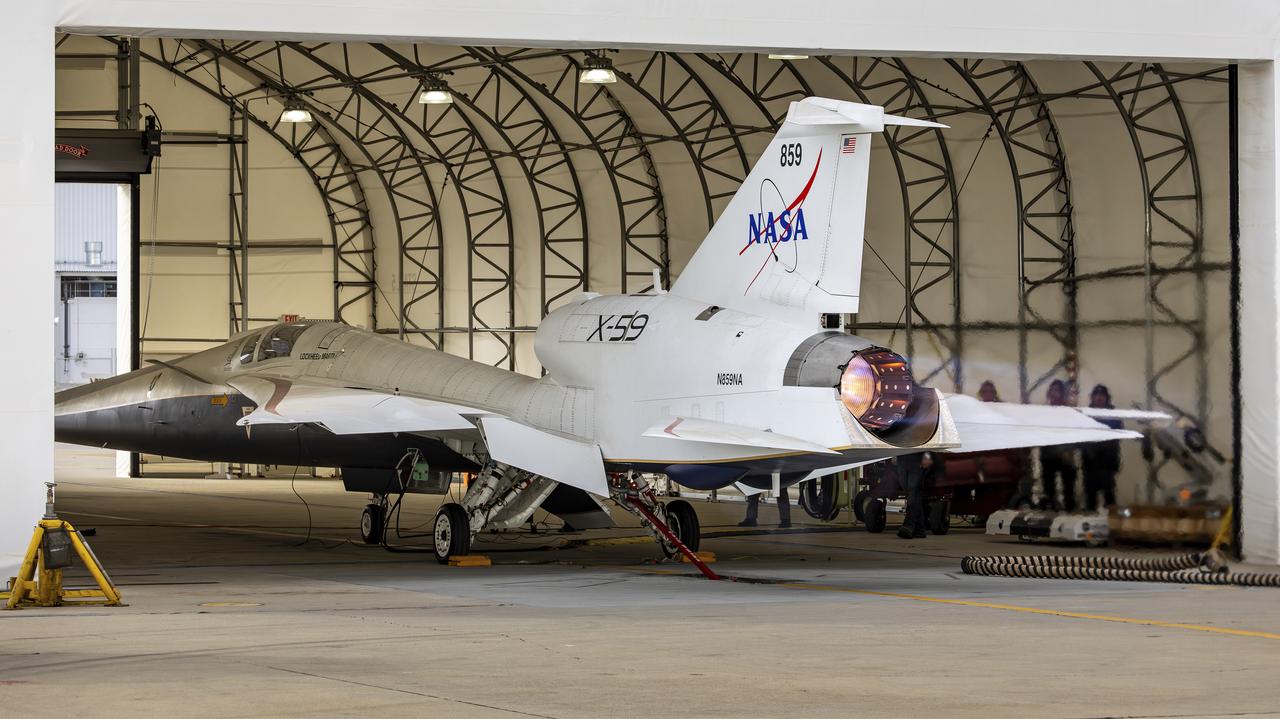

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft completed its first maximum afterburner test at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. This full-power test, during which the engine generates additional thrust, validates the additional power needed for meeting the testing conditions of the aircraft. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which aims to overcome a major barrier to supersonic flight over land by reducing the noise of sonic booms.
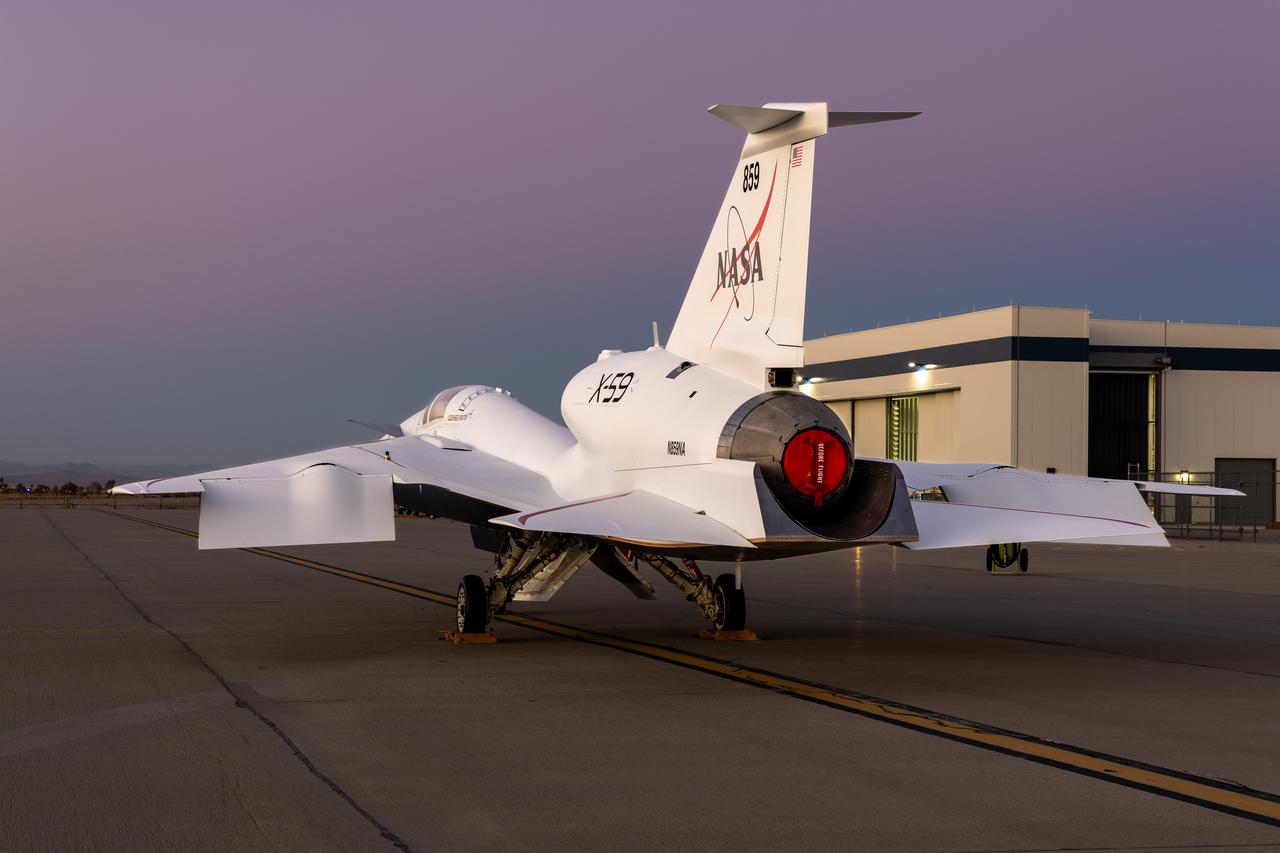

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on a ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, during sunset. The one-of-a-kind aircraft is powered by a General Electric F414 engine, a variant of the engines used on F/A-18 fighter jets. The engine is mounted above the fuselage to reduce the number of shockwaves that reach the ground. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA's Quesst mission, which aims to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight and enable future commercial travel over land – faster than the speed of sound.
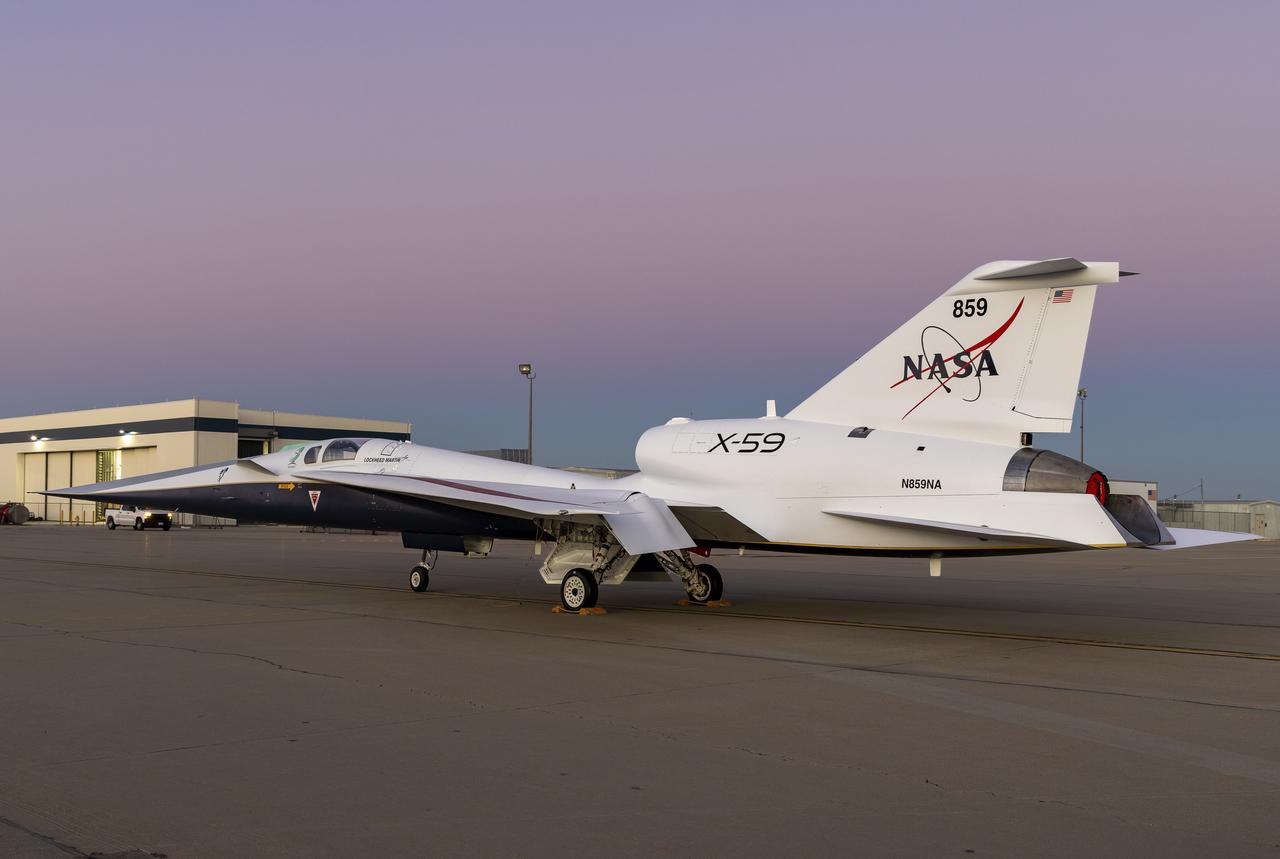

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on a ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, during sunset. The one-of-a-kind aircraft is powered by a General Electric F414 engine, a variant of the engines used on F/A-18 fighter jets. The engine is mounted above the fuselage to reduce the number of shockwaves that reach the ground. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA's Quesst mission, which aims to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight and enable future commercial travel over land – faster than the speed of sound.

Lockheed Martin Skunk Works Vice President and General Manager John Clark speaks on stage prior to the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
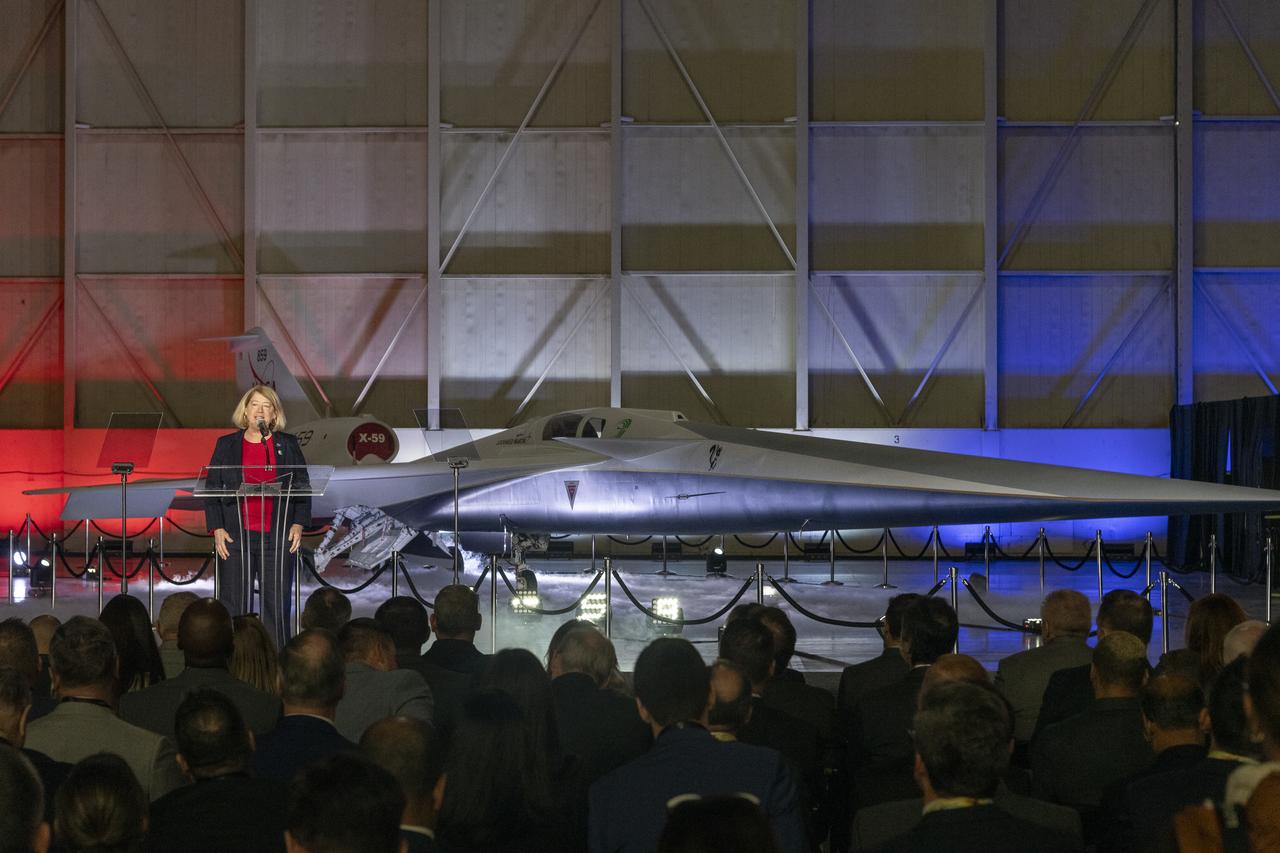

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks on stage immediately following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
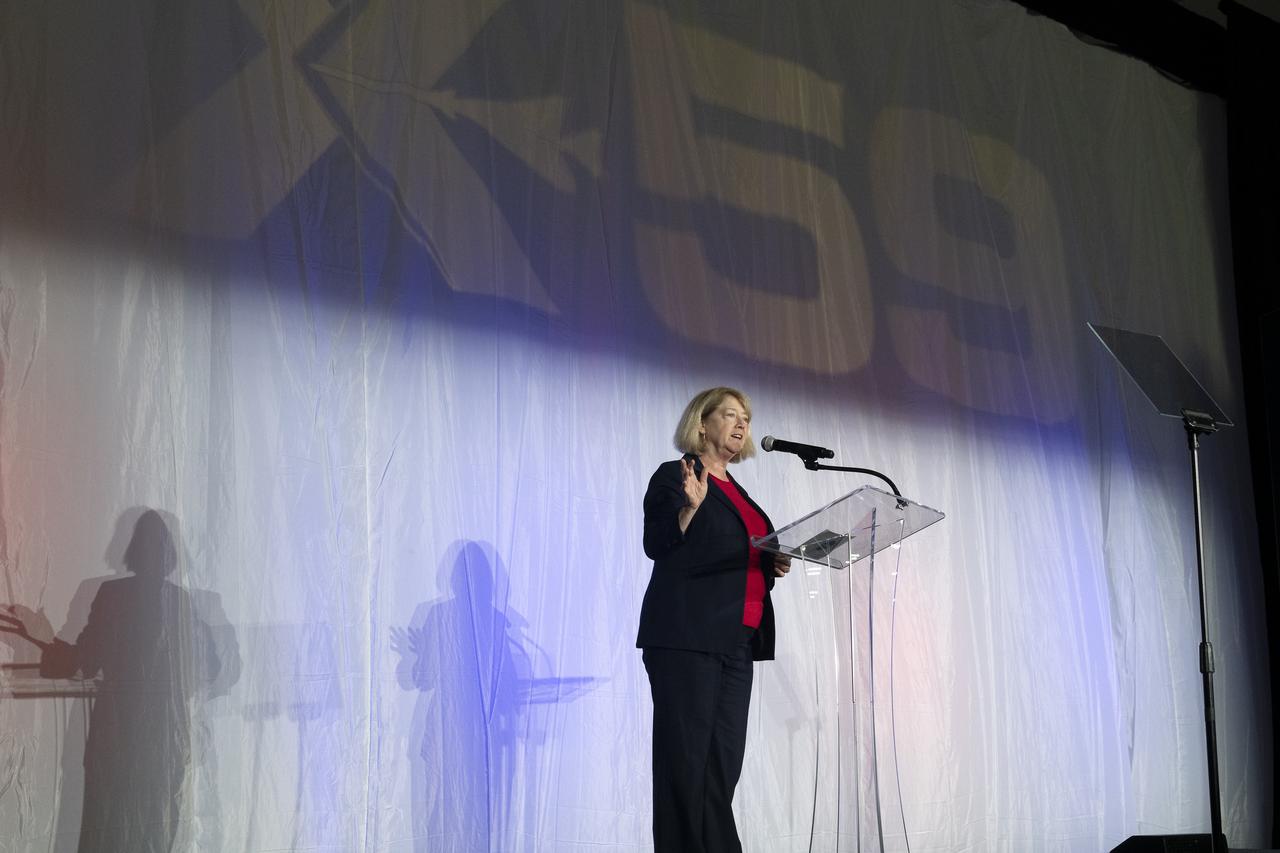

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks on stage prior to the official unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
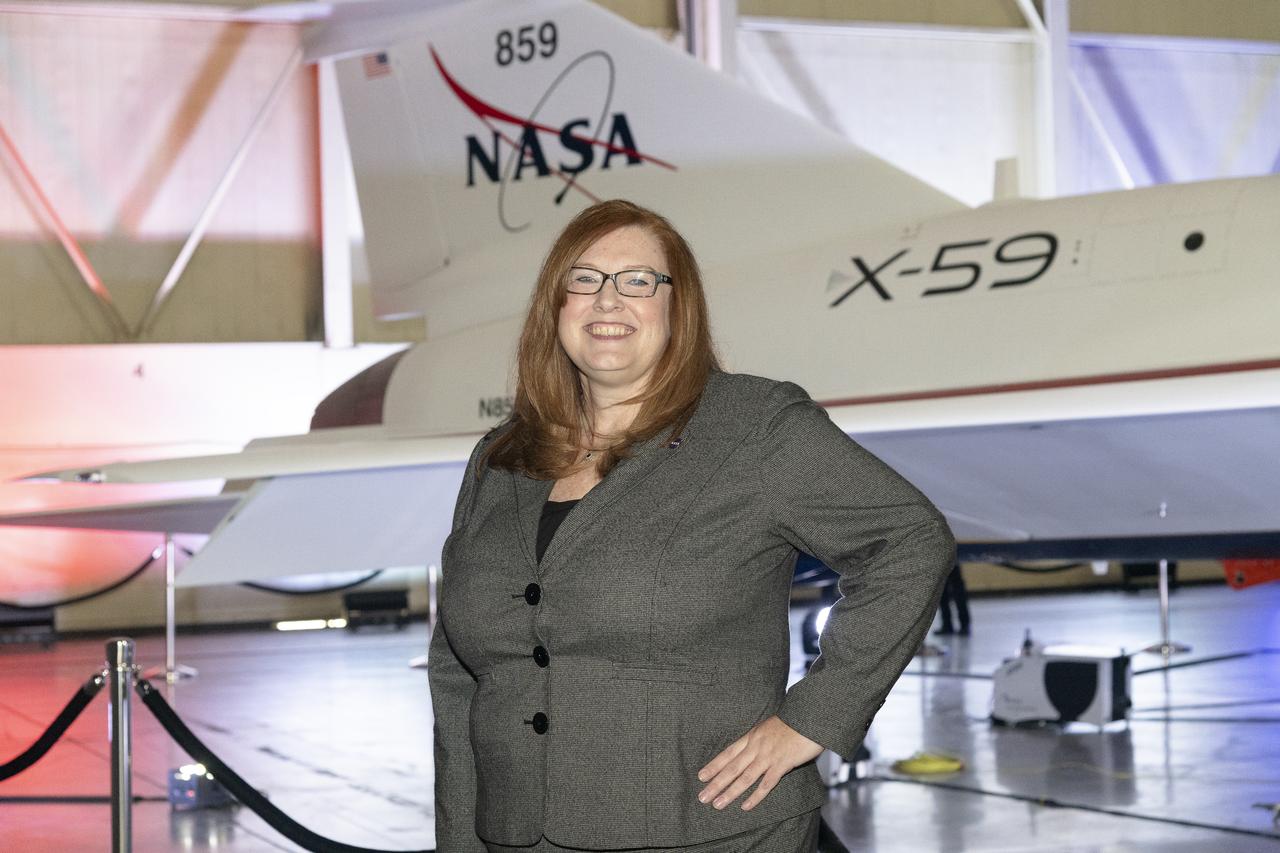

NASA’s project manager for the Low Boom Flight Demonstrator project, Cathy Bahm, poses in front of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
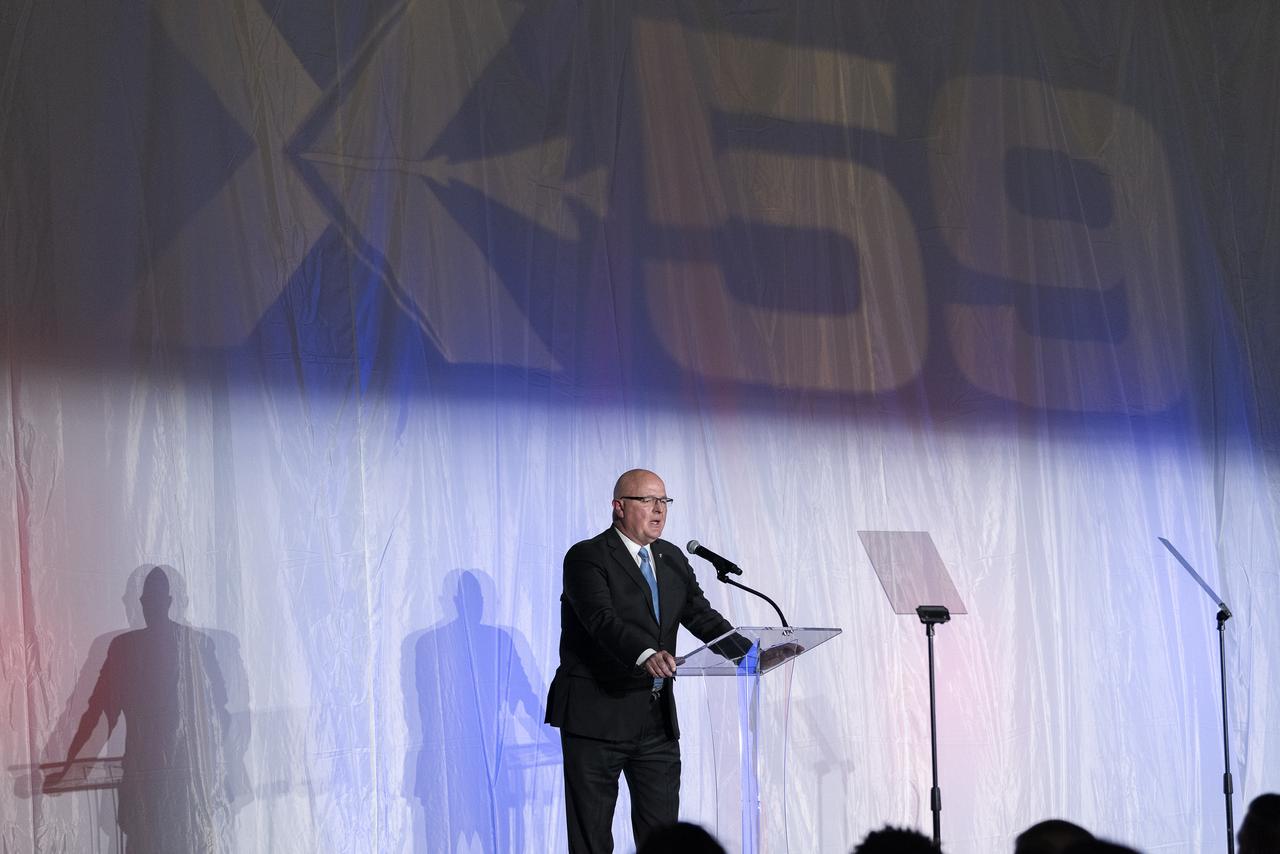

Lockheed Martin Skunk Works Director of Government Affairs Eric Fox speaks on stage prior to the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
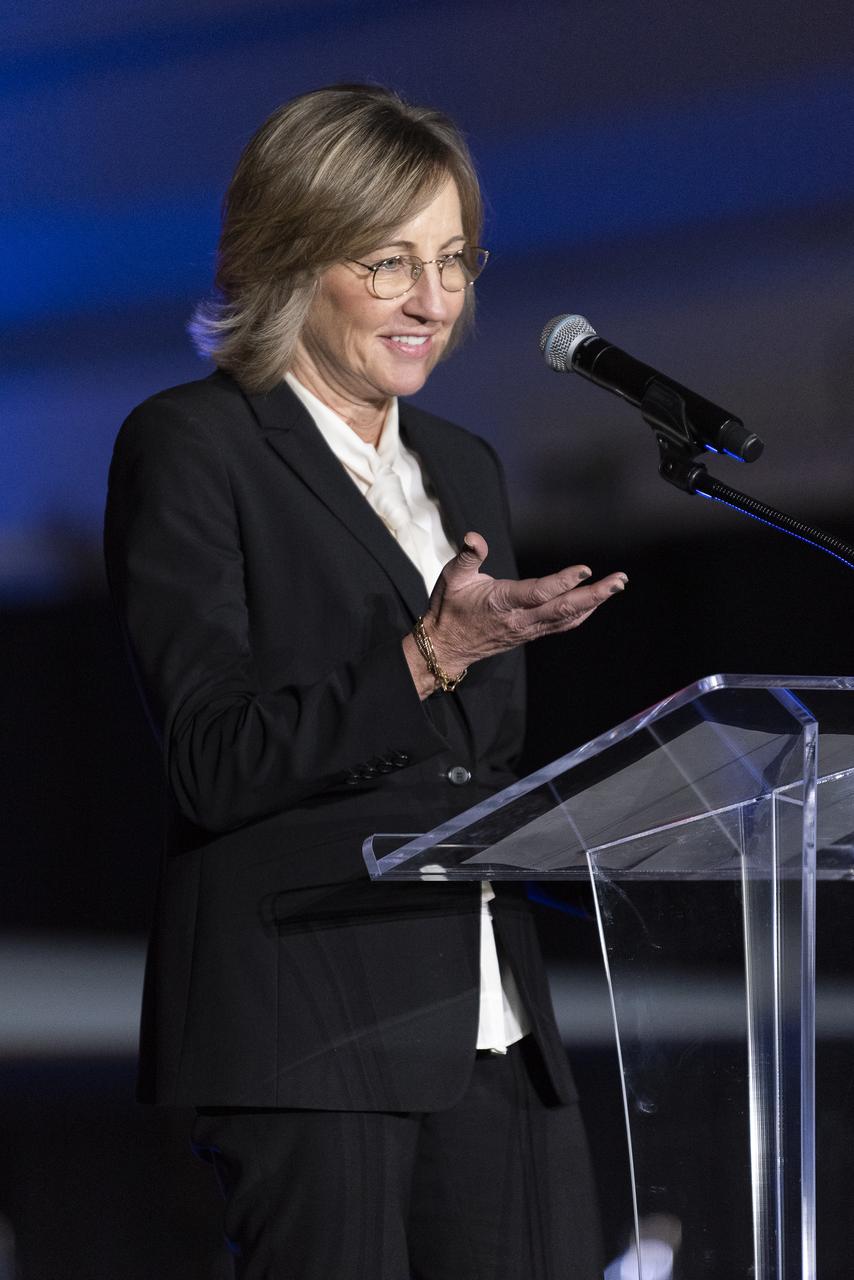

California Senior Economic Advisor to the Governor Dee Dee Myers speaks on stage following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.

NASA’s structures lead for the X-59, Dr. Walt Silva, poses in front of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks on stage immediately following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
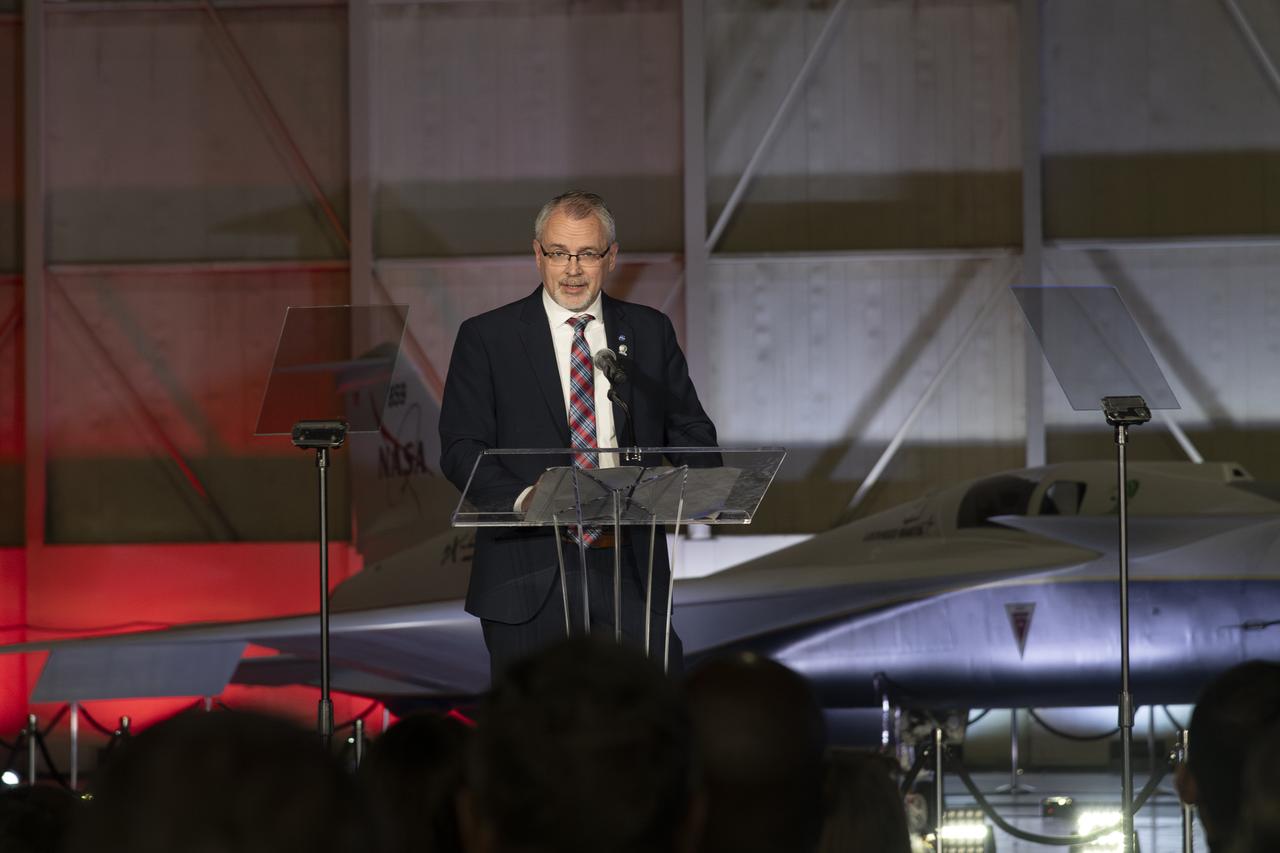

NASA Associate Administrator Jim Free speaks on stage following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
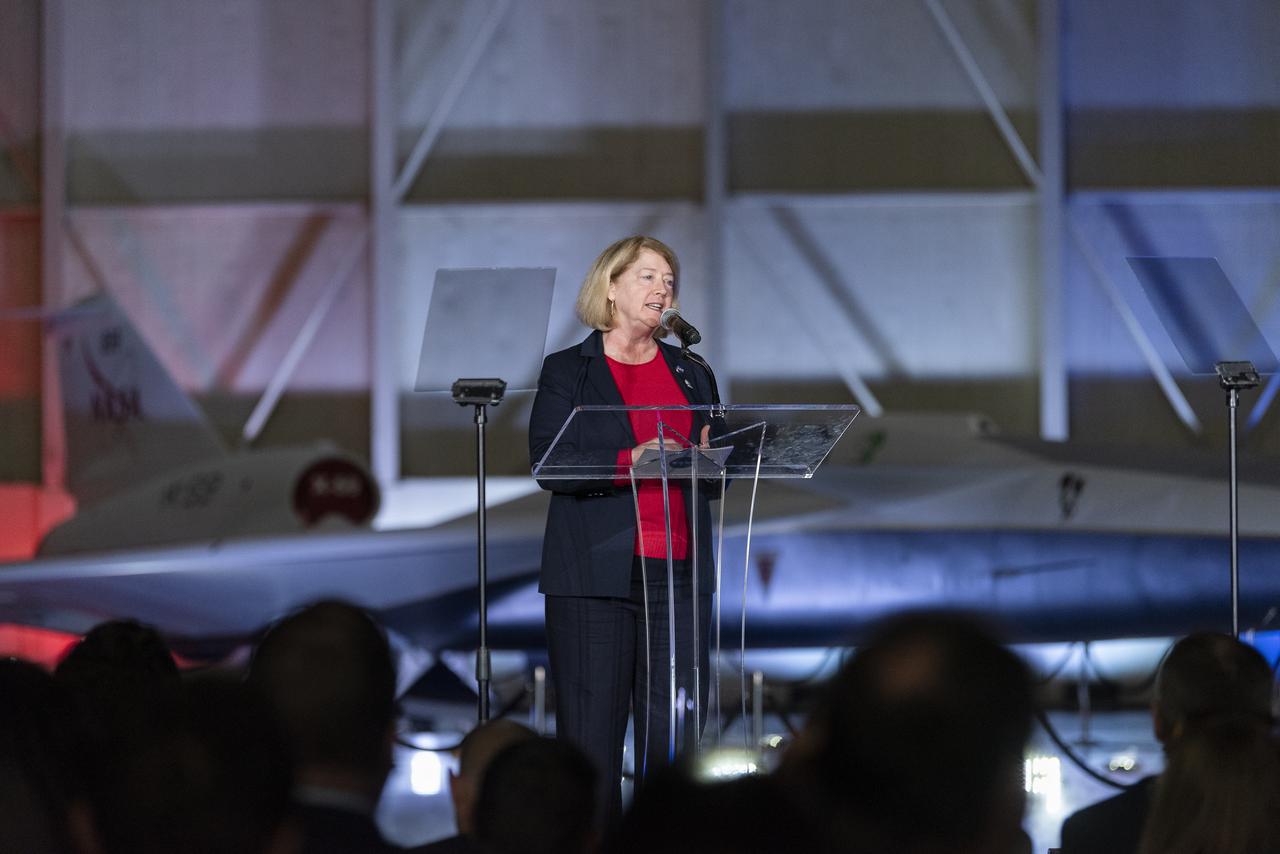

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks on stage immediately following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
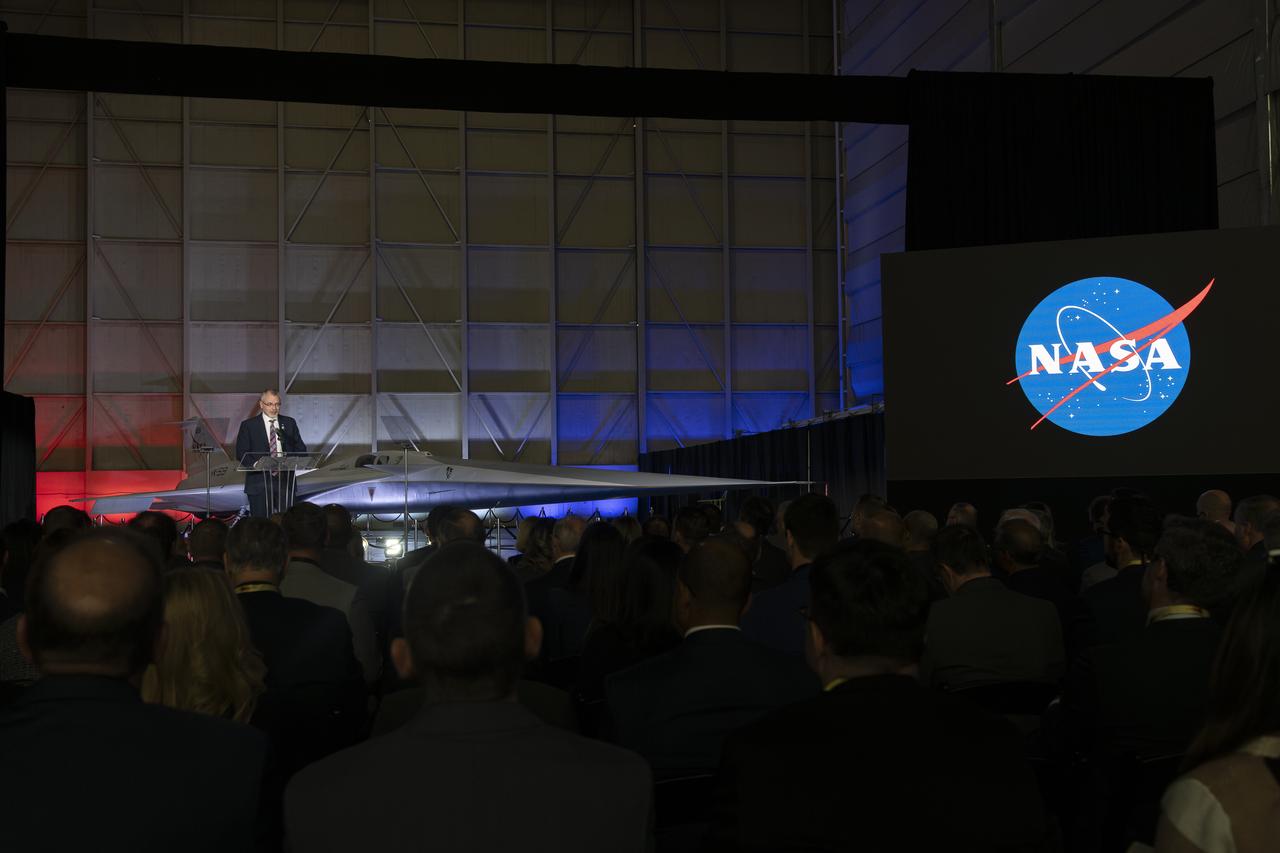

NASA Associate Administrator Jim Free speaks on stage following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
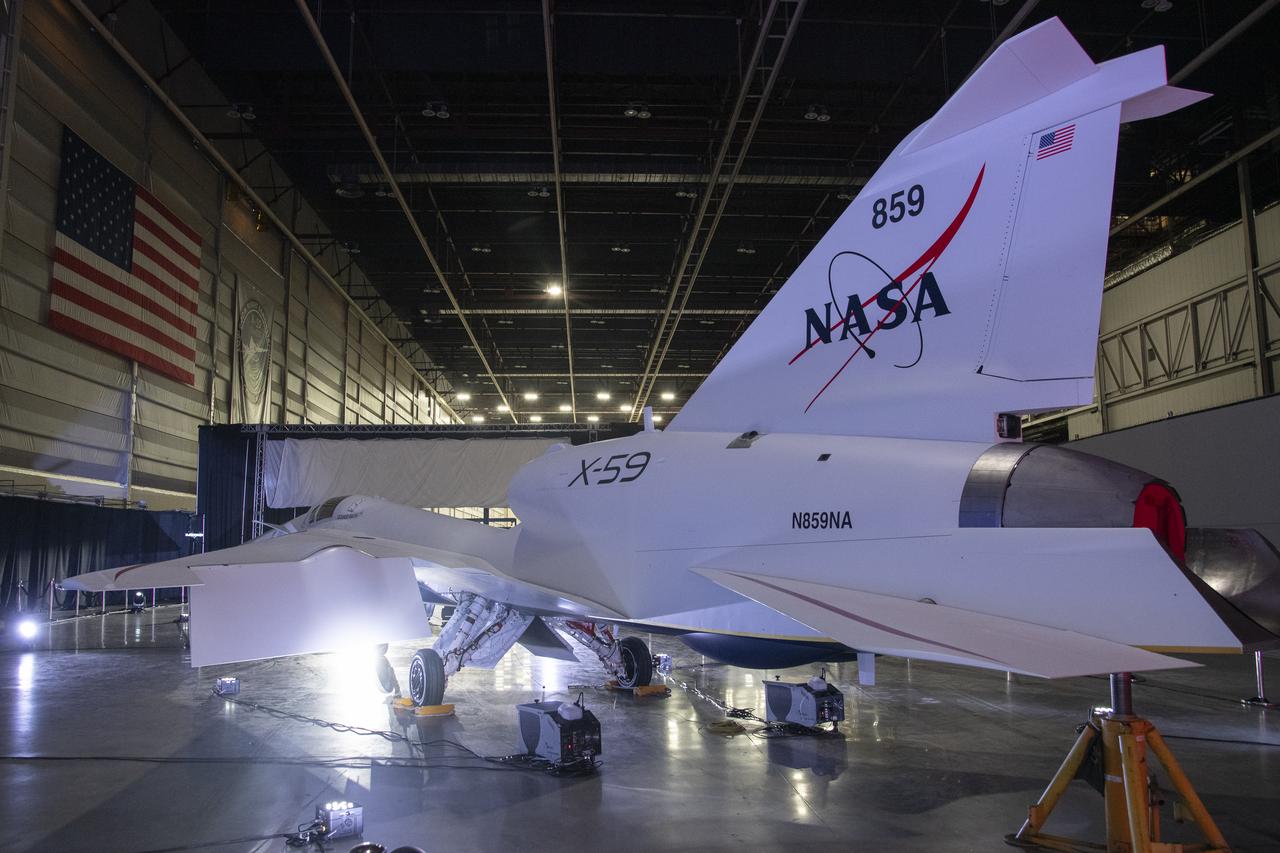

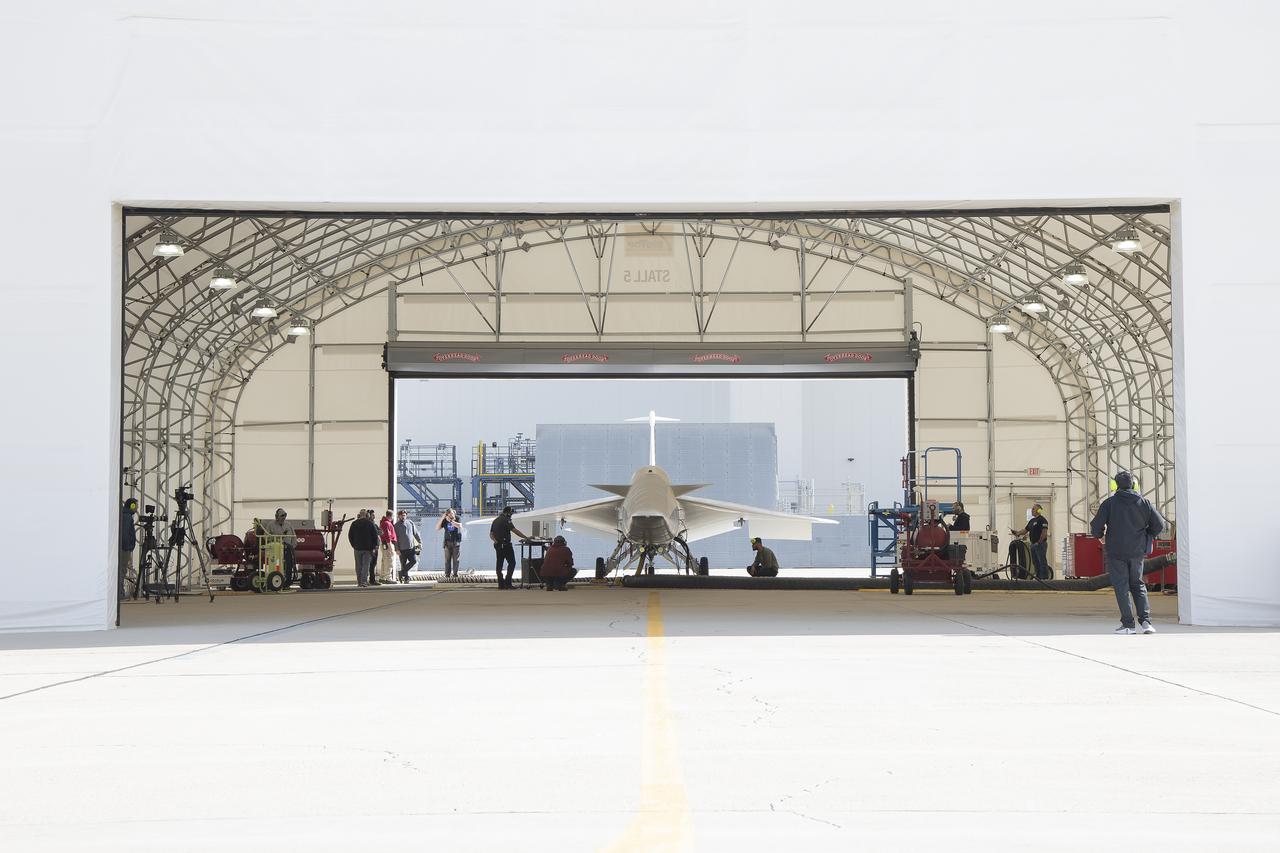
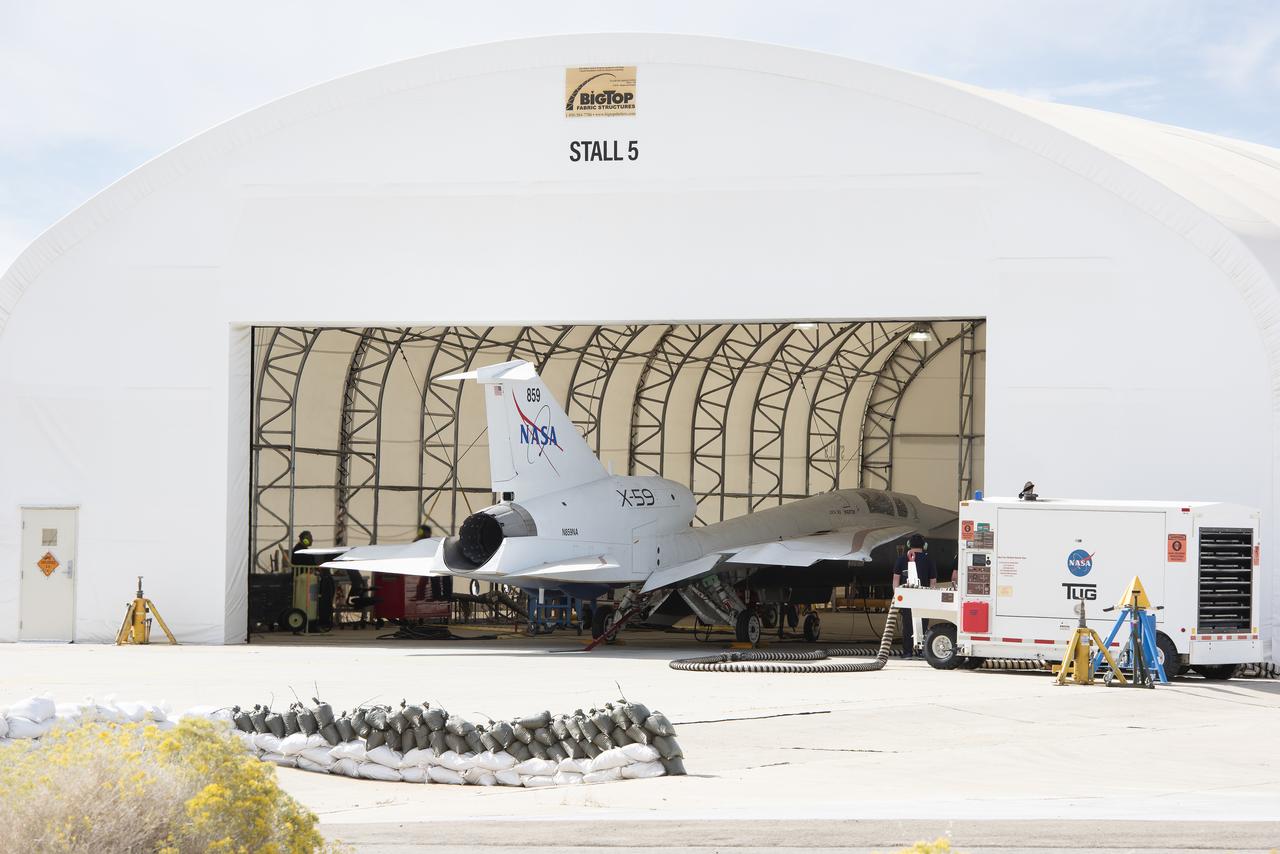
NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits in position inside a hangar at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California prior to its January 12, 2024 unveiling. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
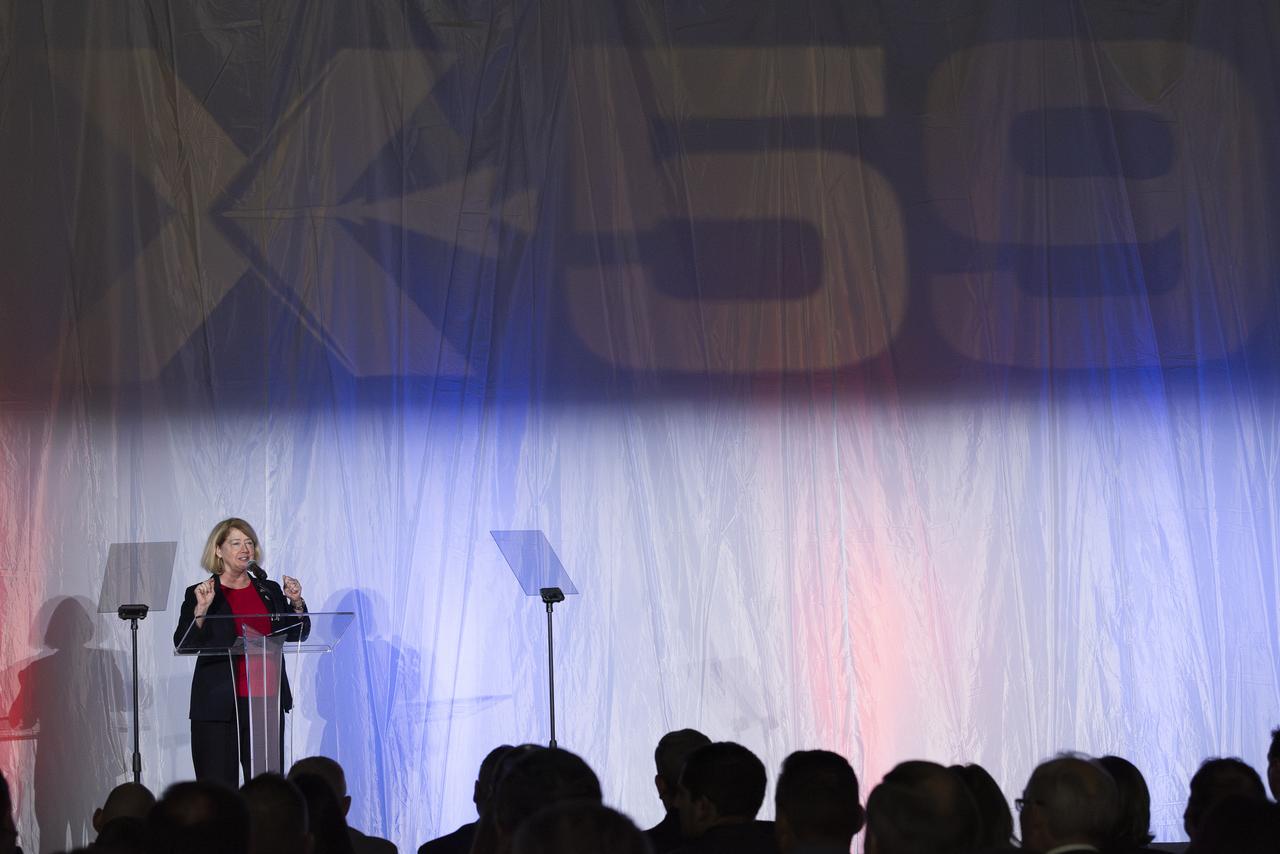

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks on stage prior to the official unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
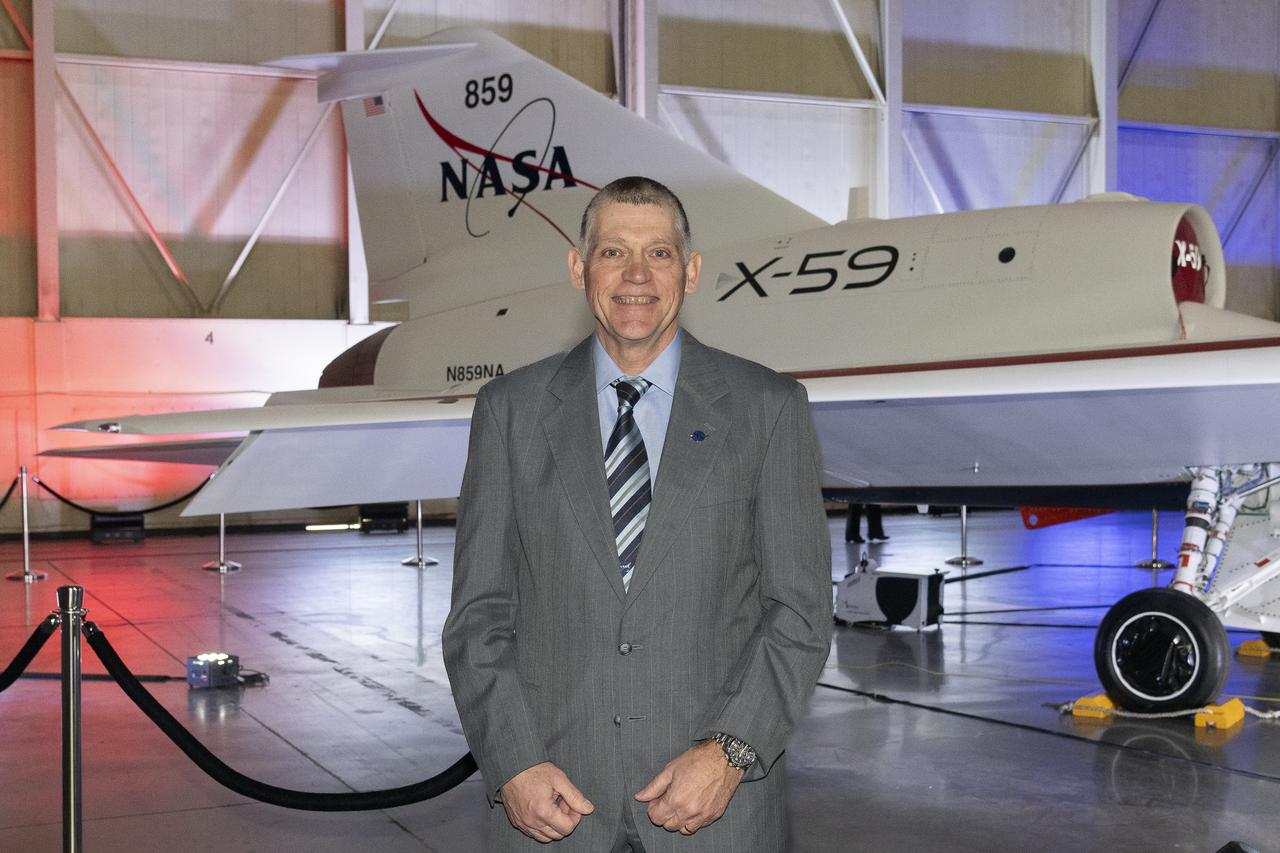

NASA’s chief engineer for the Low Boom Flight Demonstrator project, Jay Brandon, poses in front of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks on stage prior to the official unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft is unveiled at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
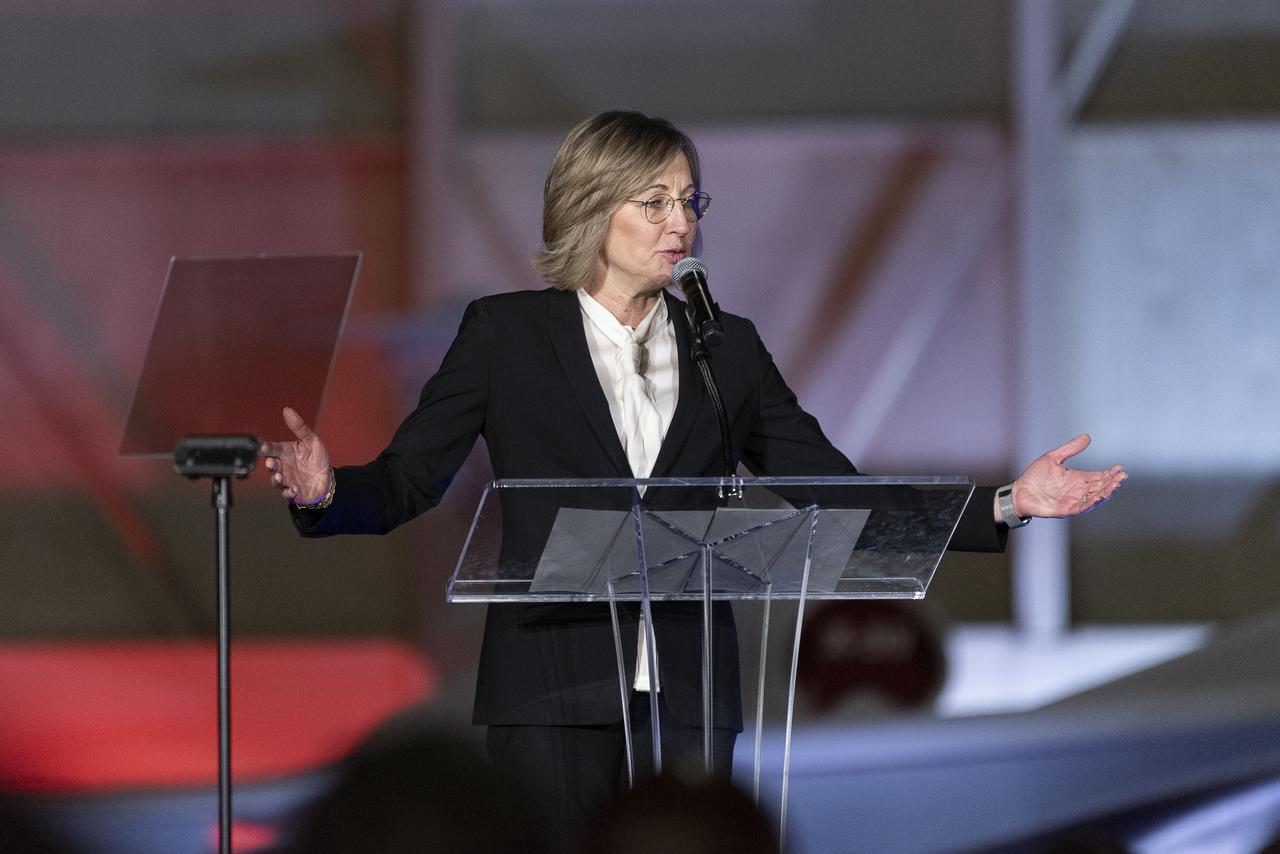

California Senior Economic Advisor to the Governor Dee Dee Myers speaks on stage following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
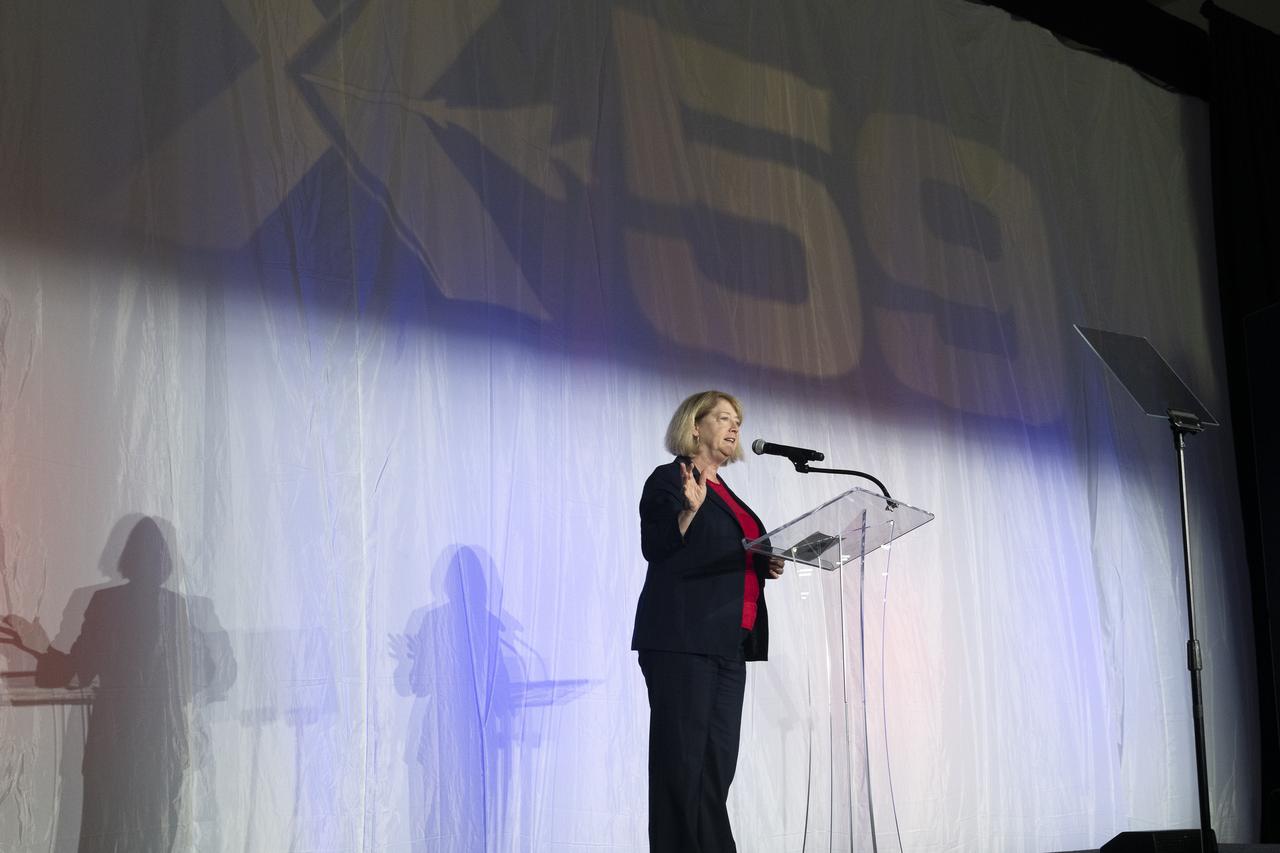

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks on stage prior to the official unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks on stage immediately following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
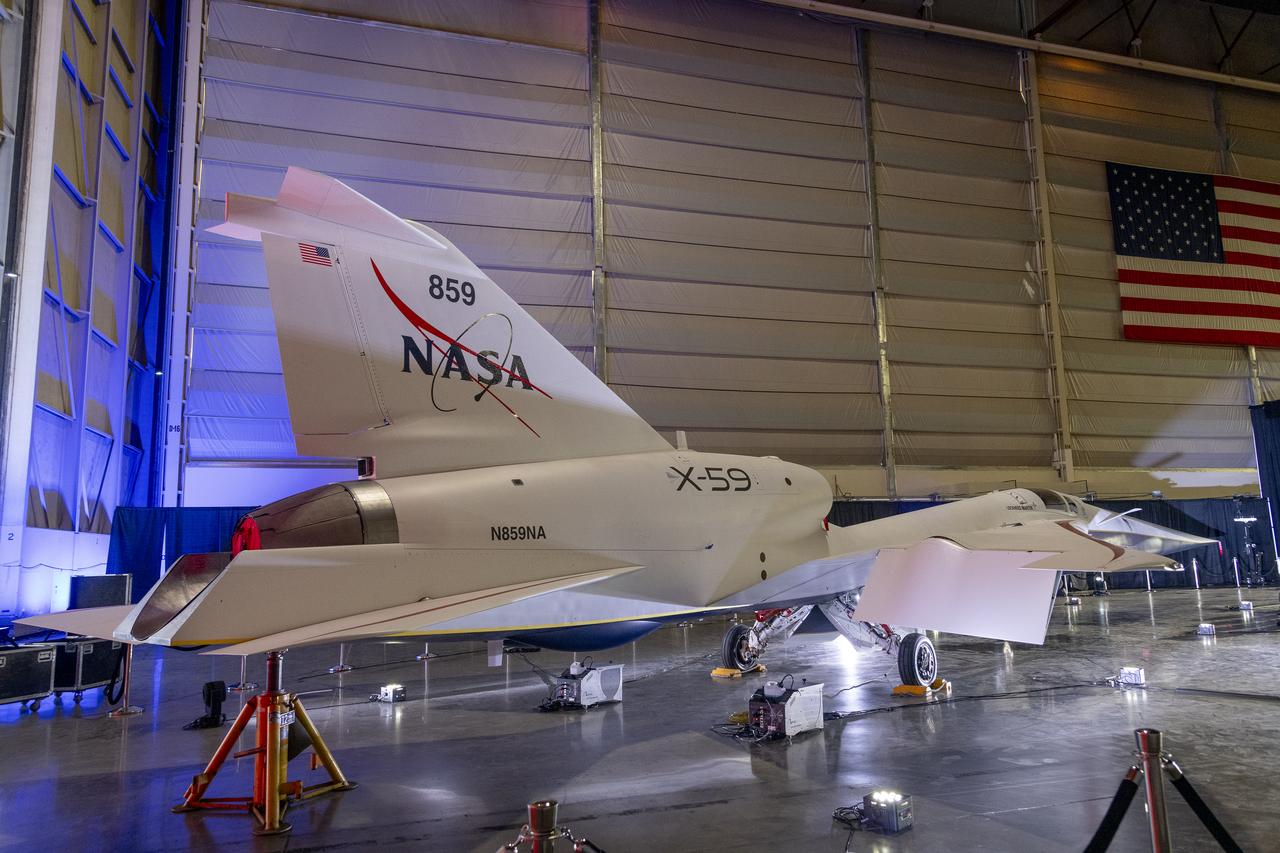

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits in position inside a hangar at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California prior to its January 12, 2024 unveiling. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
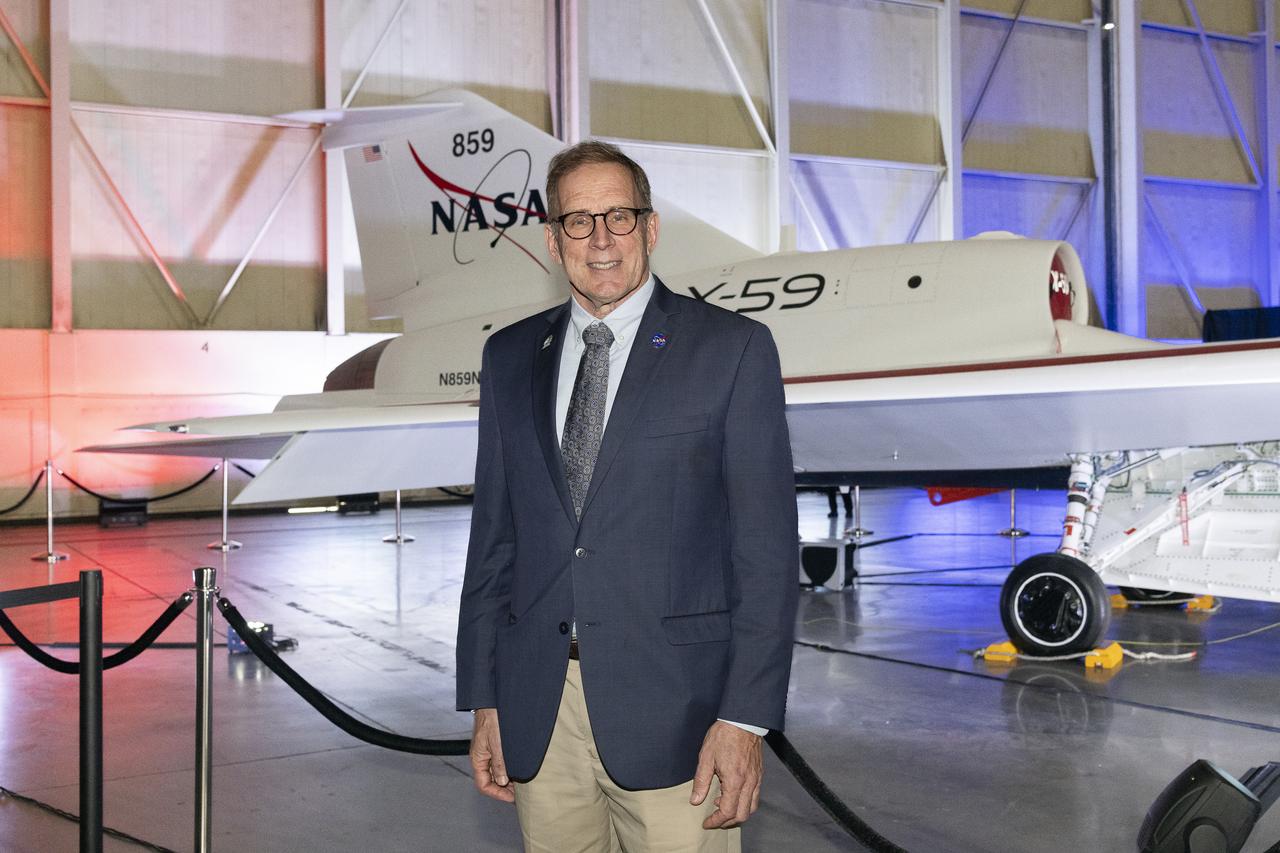

NASA’s mission integration manager for the Quesst mission, Peter Coen, poses in front of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
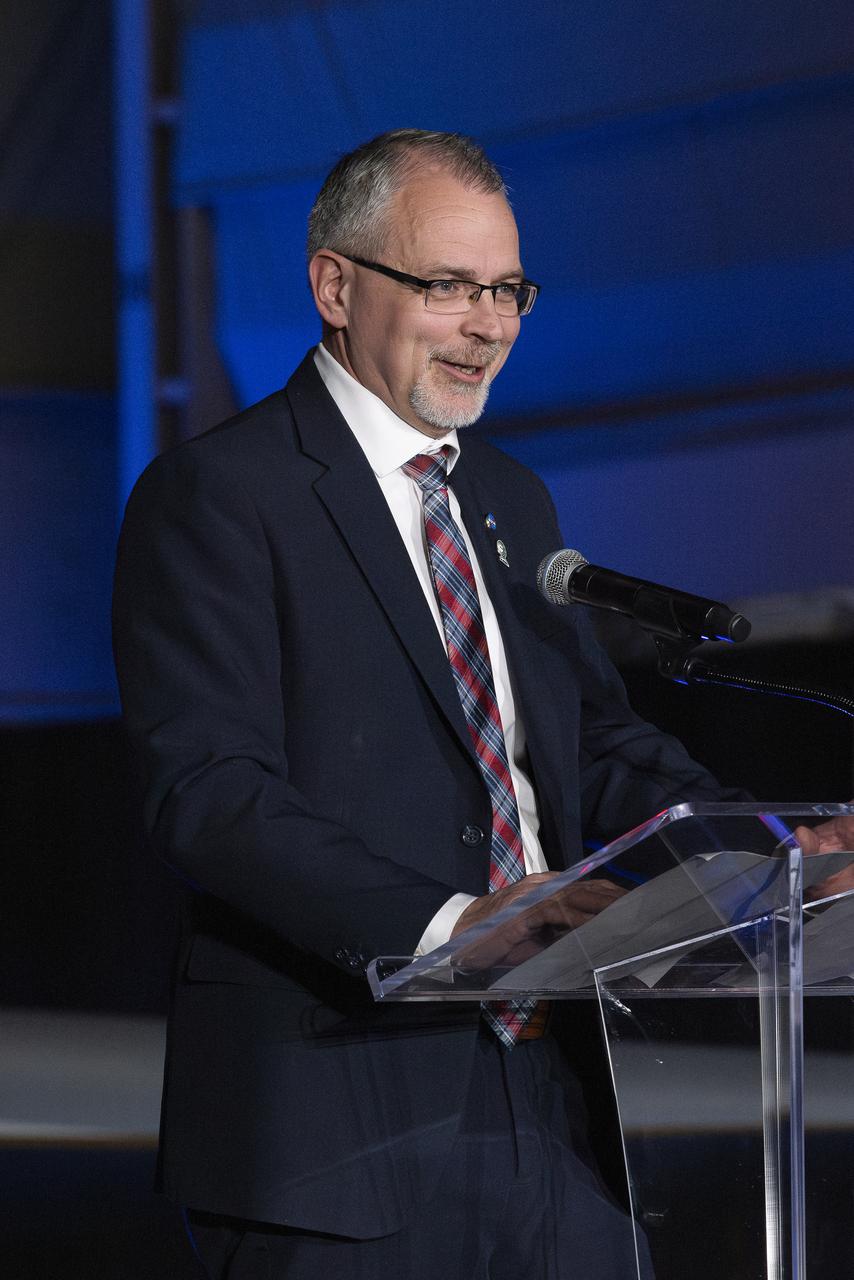

NASA Associate Administrator Jim Free speaks on stage following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
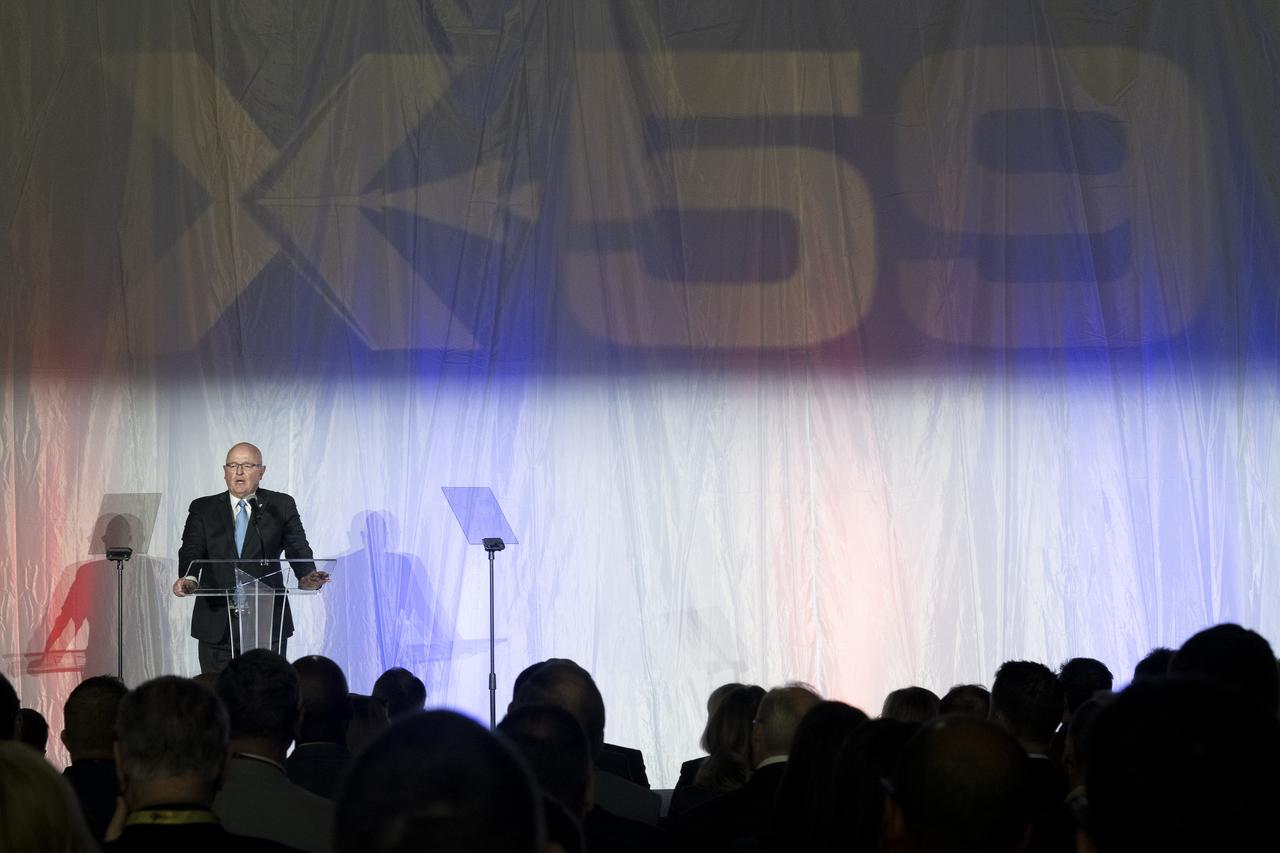

Lockheed Martin Skunk Works Director of Government Affairs Eric Fox speaks on stage prior to the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
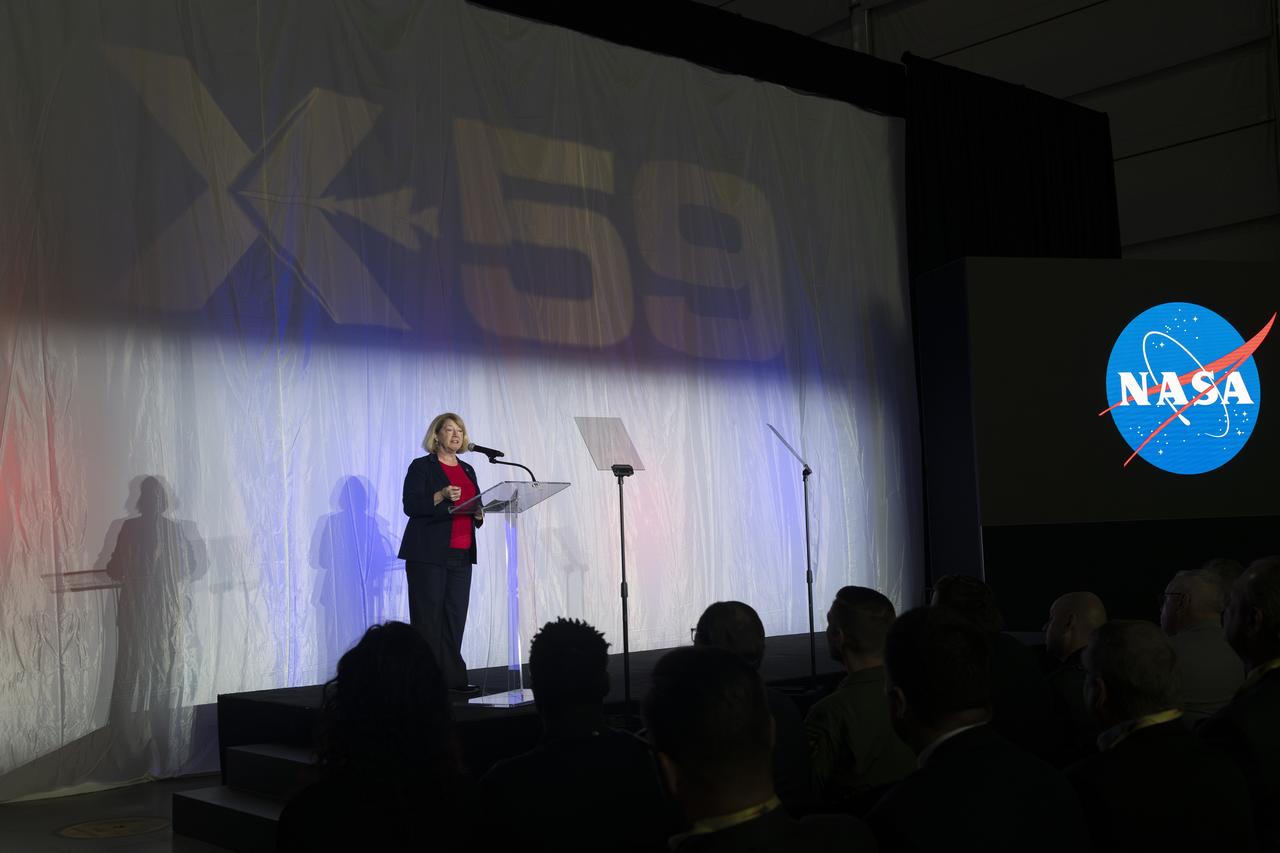

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks on stage prior to the official unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
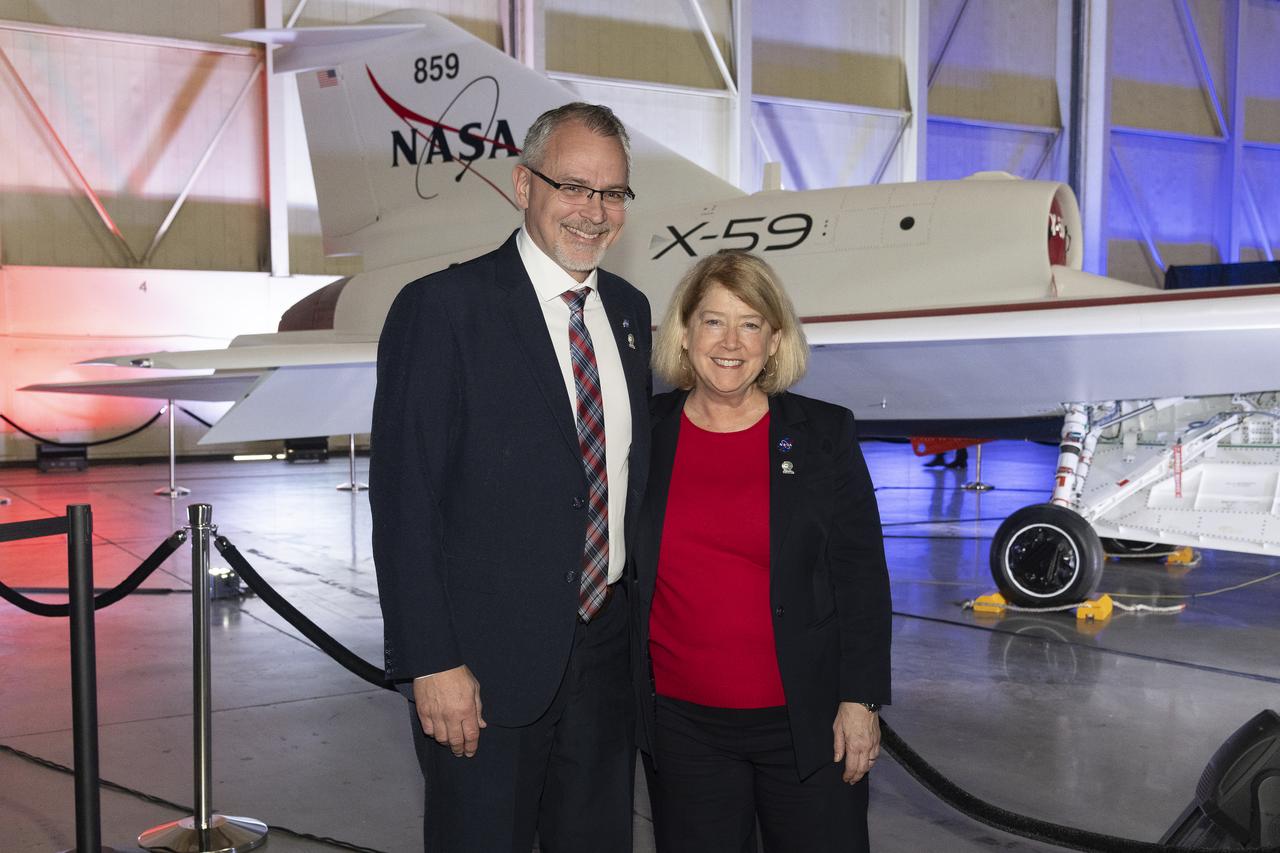

NASA Associate Administrator Jim Free (left) and Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy (right) stand in front of the newly unveiled X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
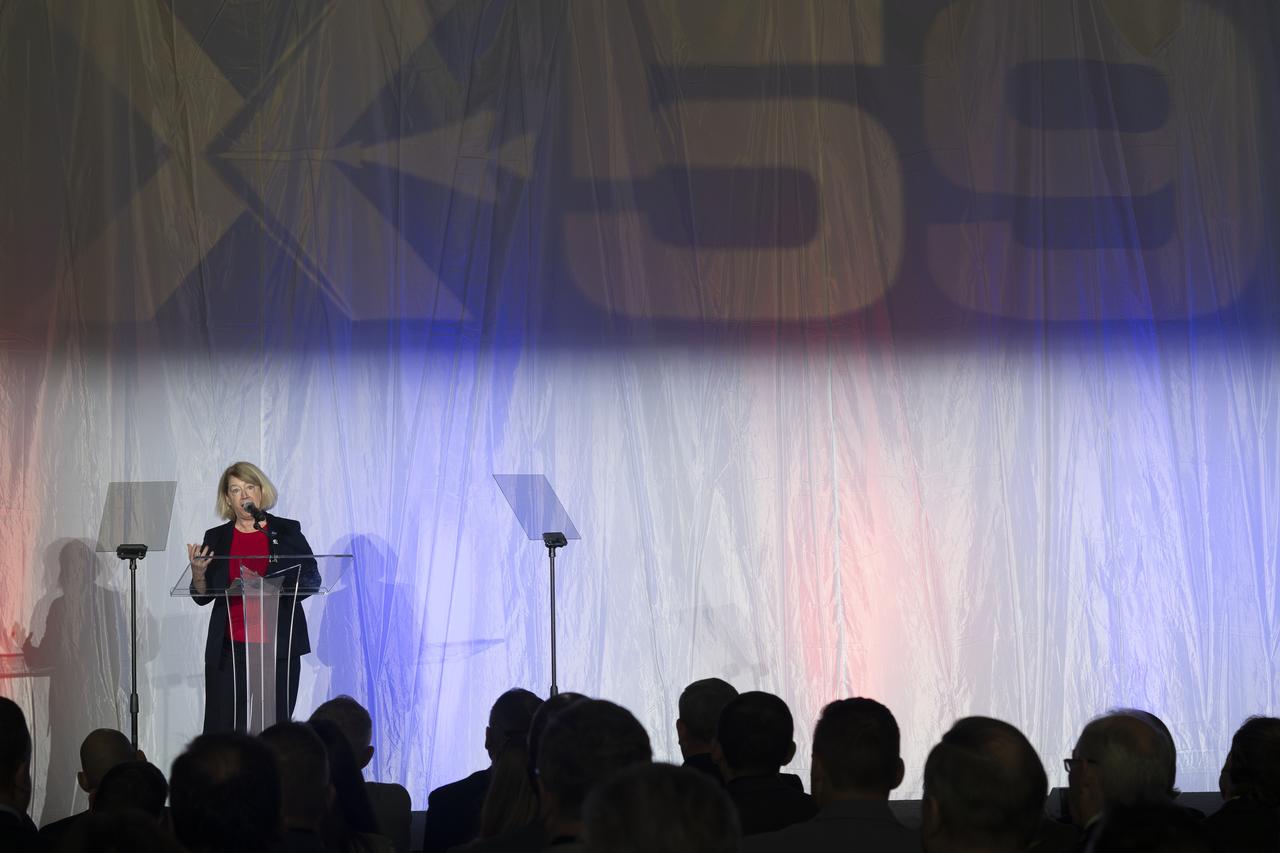

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks on stage prior to the official unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
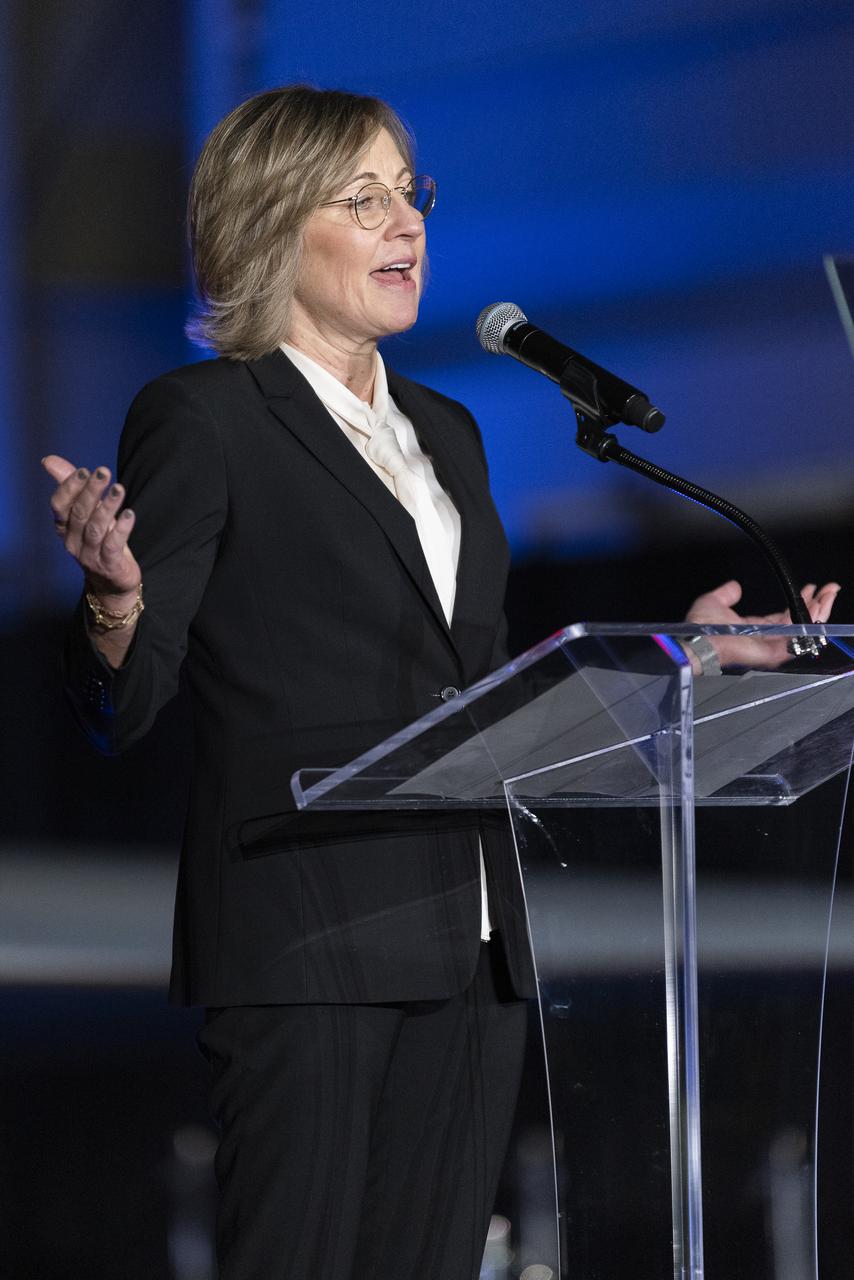

California Senior Economic Advisor to the Governor Dee Dee Myers speaks on stage following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
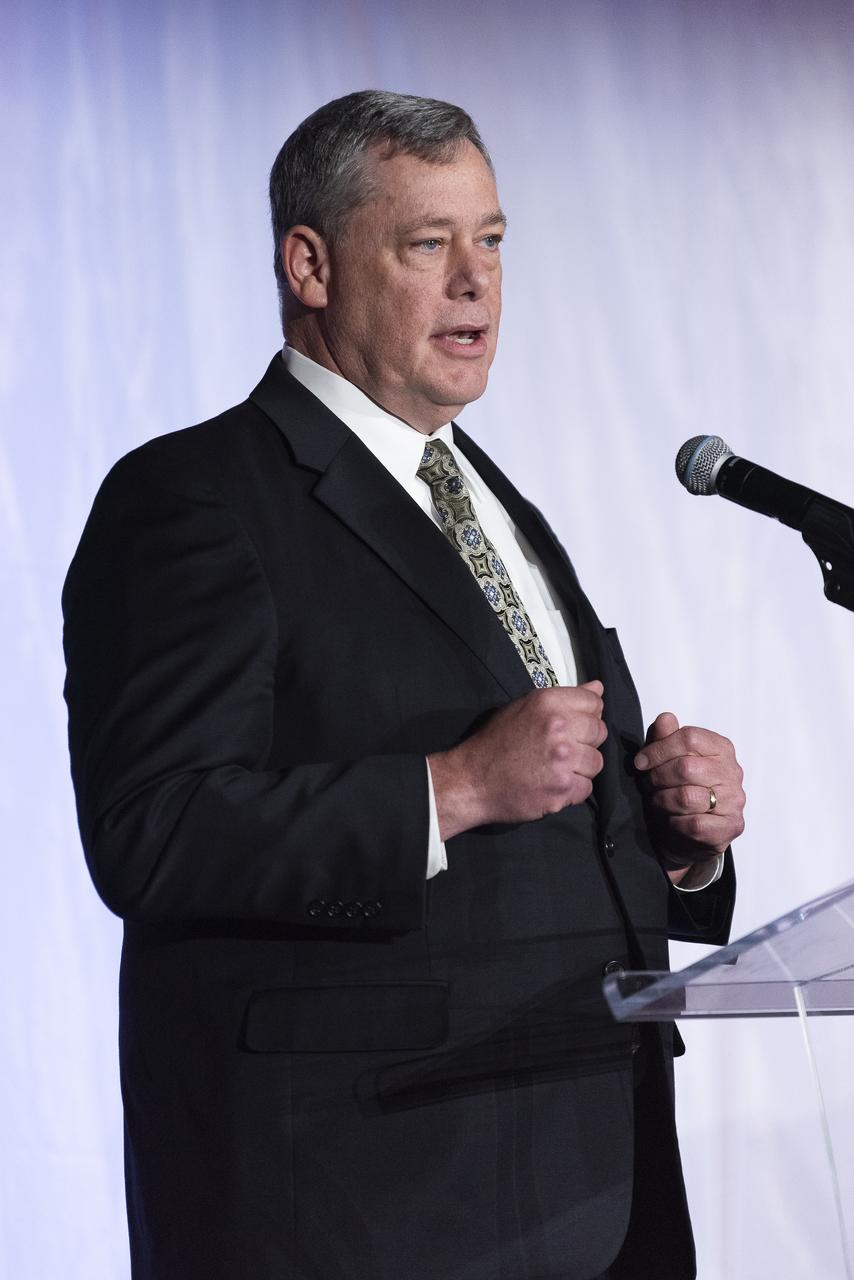

Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Executive Vice President Greg Ulmer speaks on stage prior to the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
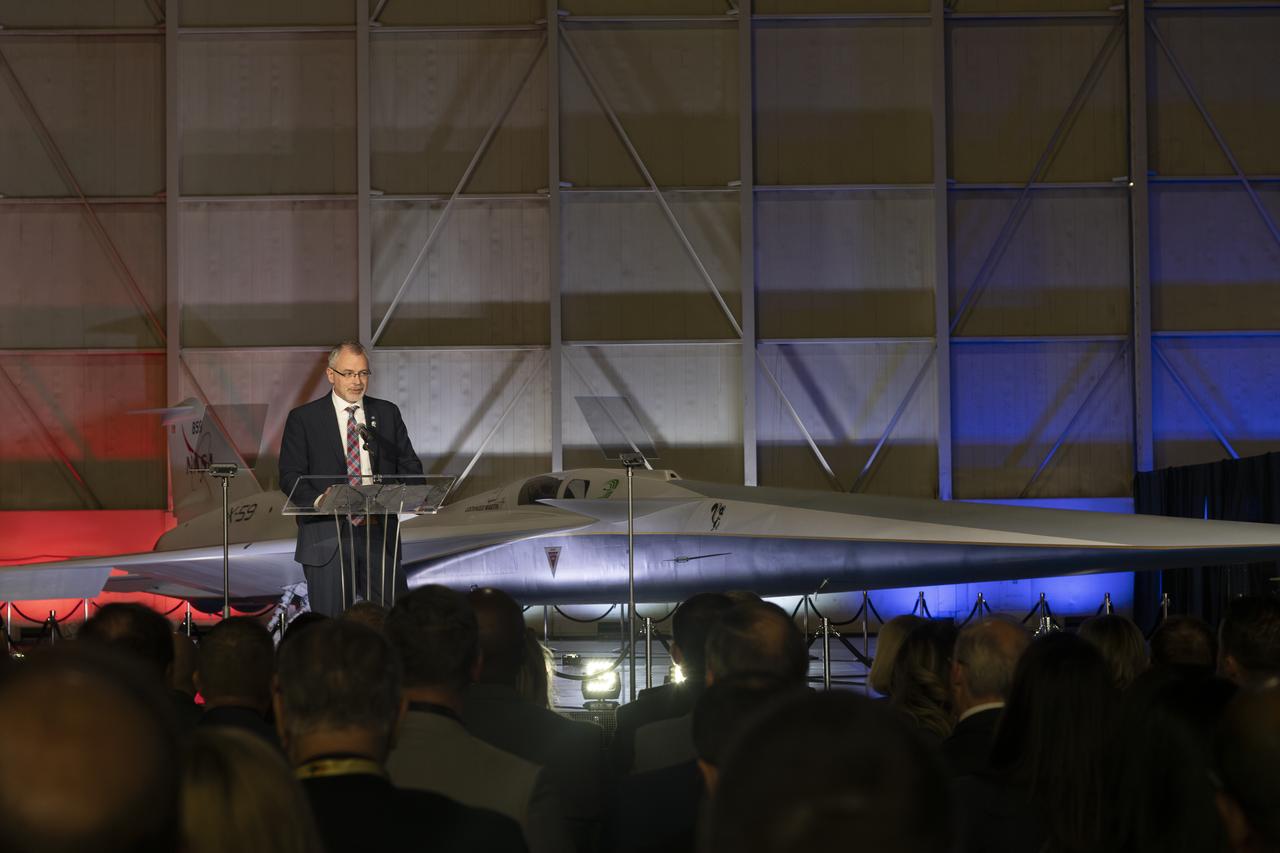

NASA Associate Administrator Jim Free speaks on stage following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
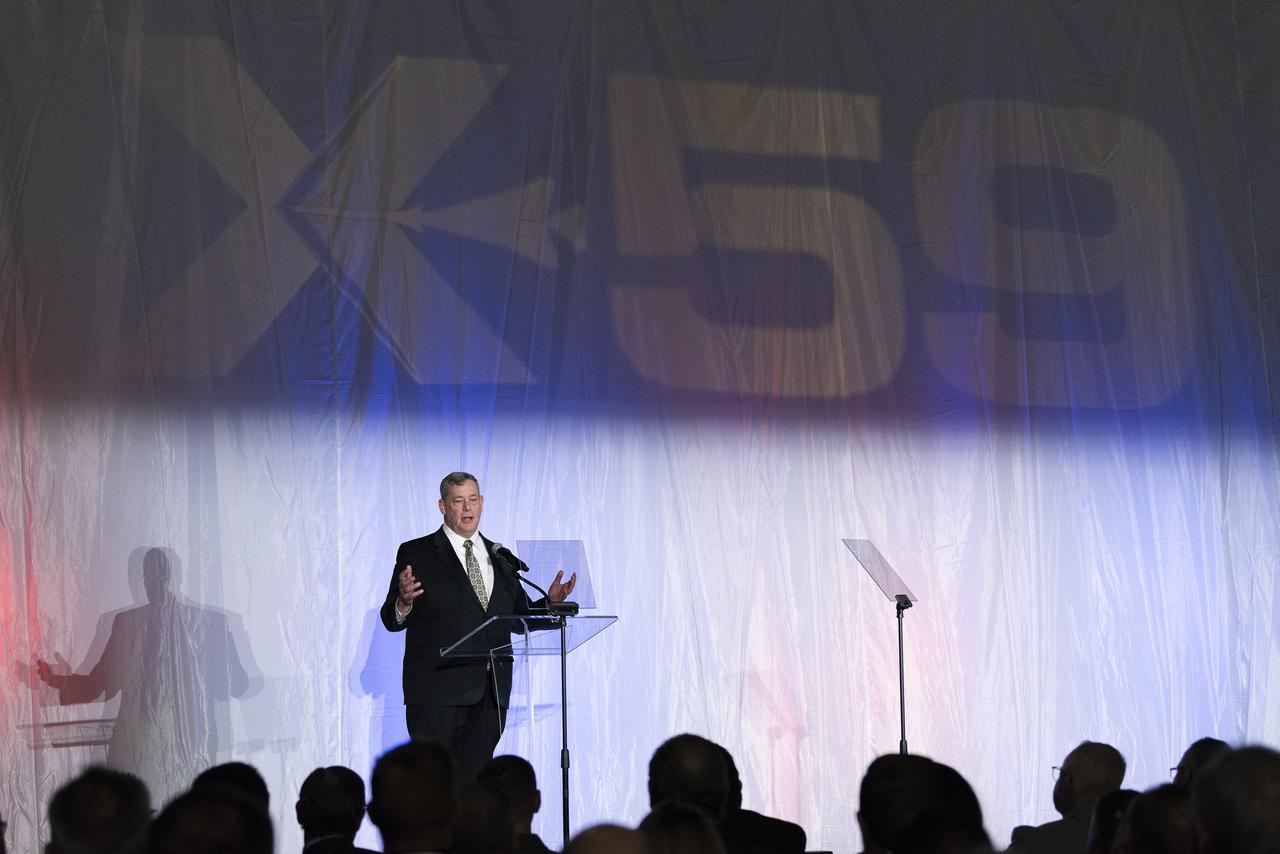

Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Executive Vice President Greg Ulmer speaks on stage prior to the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
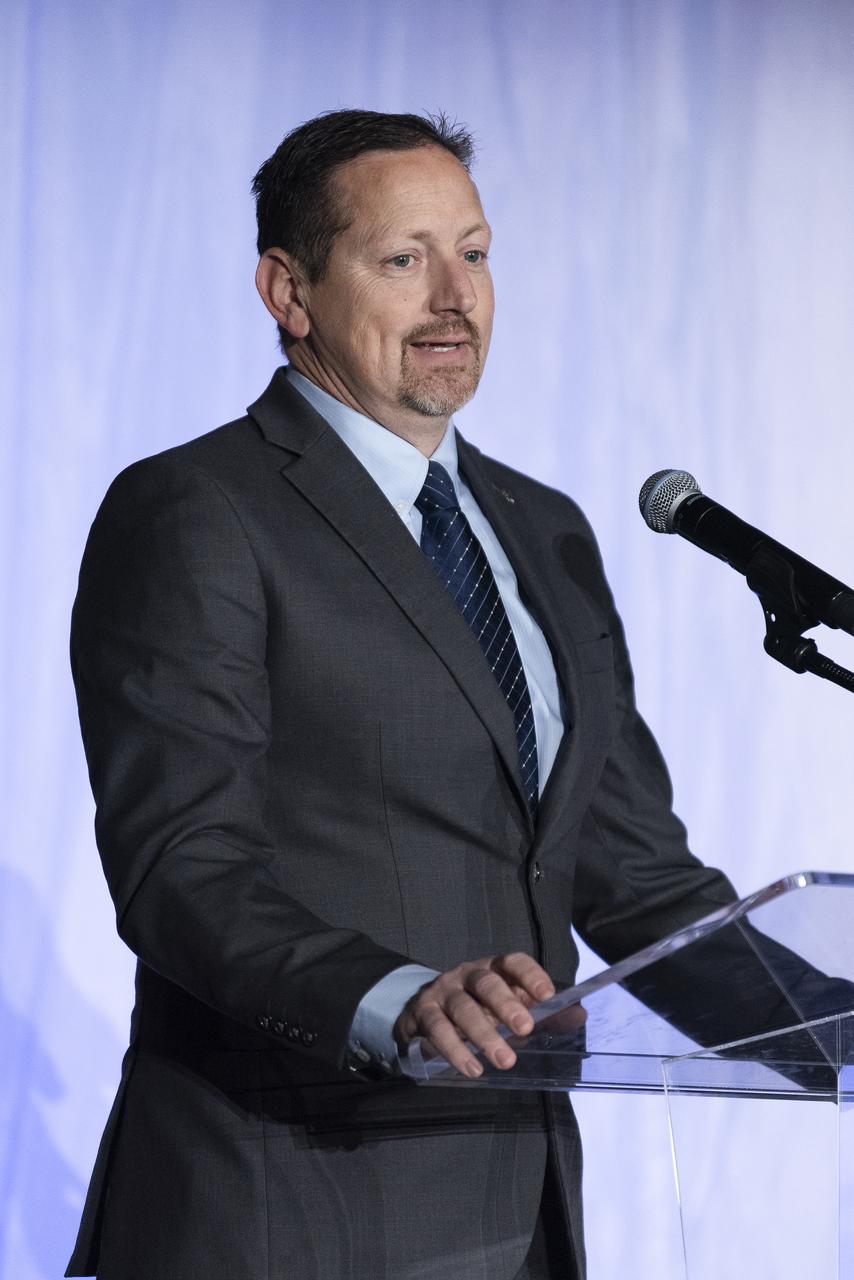

Lockheed Martin Skunk Works Vice President and General Manager John Clark speaks on stage prior to the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
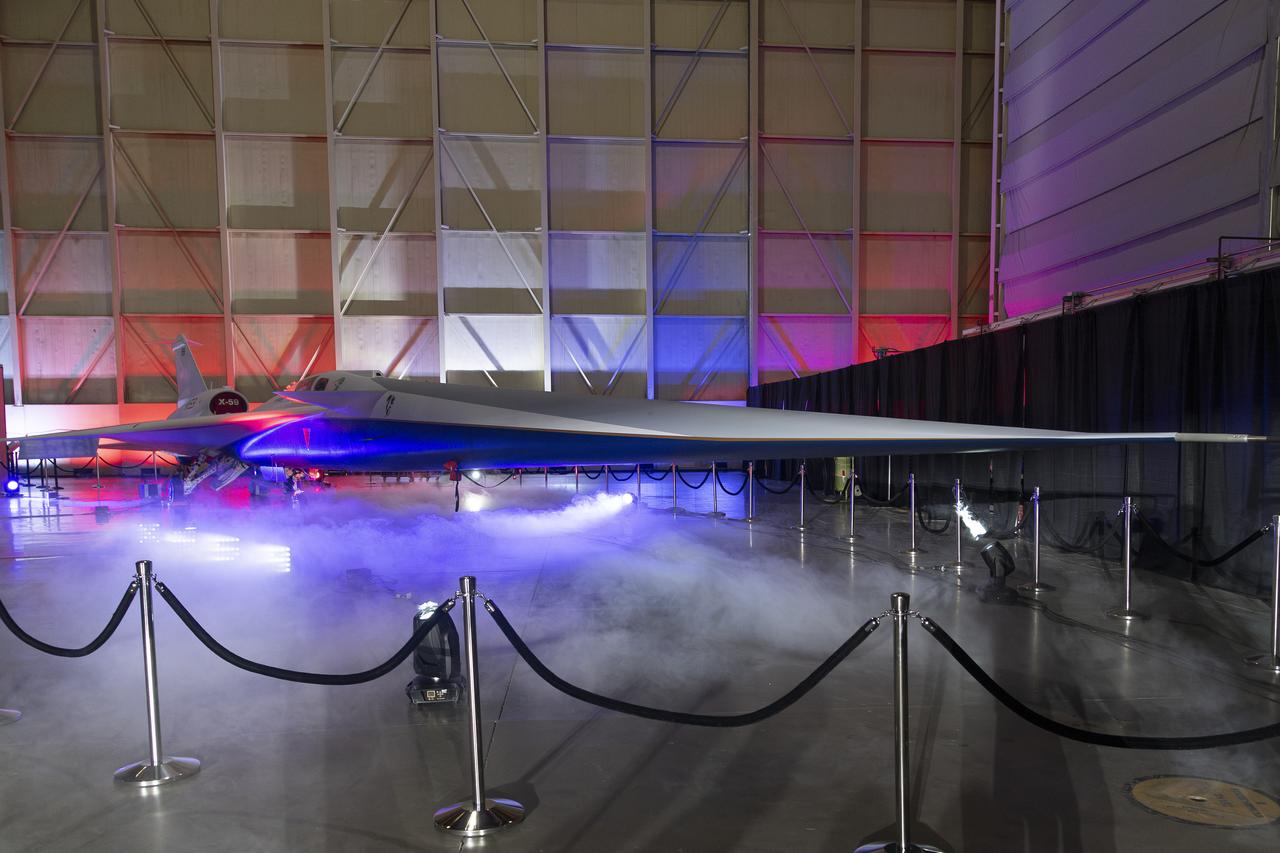

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits in position inside a hangar at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California prior to its January 12, 2024 unveiling. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks on stage immediately following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
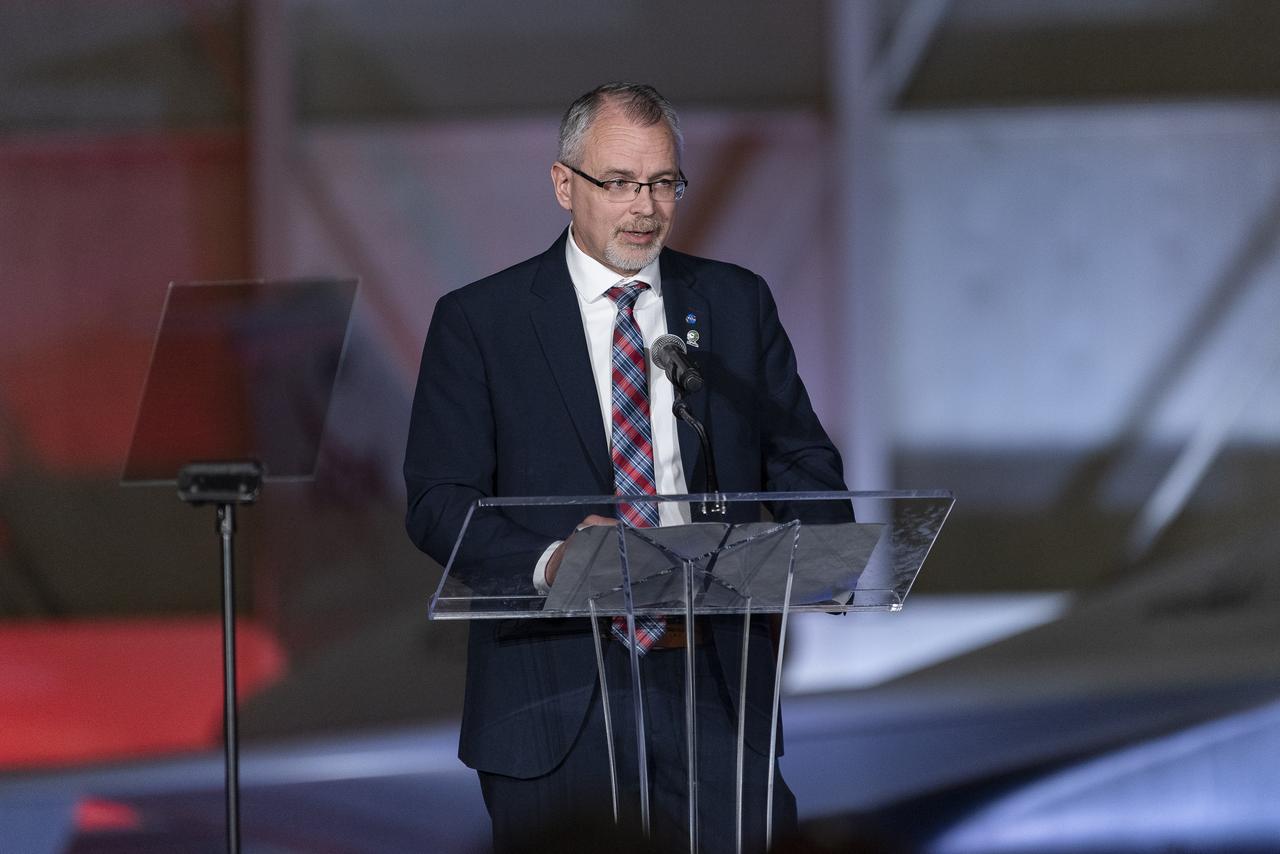

NASA Associate Administrator Jim Free speaks on stage following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
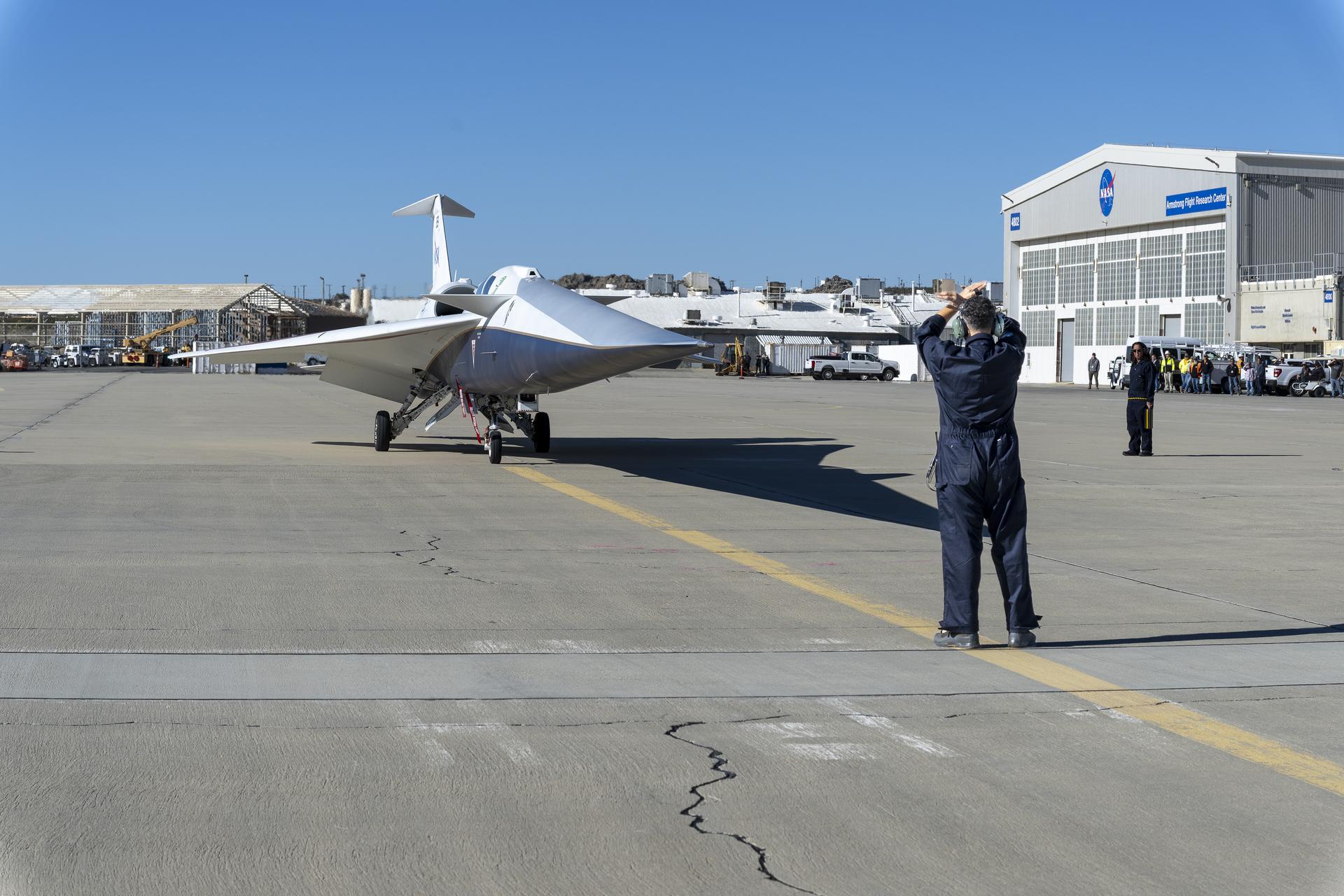

The X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft arrives at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, following its first flight Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025. The arrival marks the aircraft’s transition from ground testing to flight operations. Next, the aircraft will undergo scheduled maintenance followed by a series of additional test flights, gradually building toward its first supersonic flight.

NASA's F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.

NASA's F/A-18 research aircraft stands ready prior to a QSF18 supersonic research flight off the coast of Galveston, Texas.