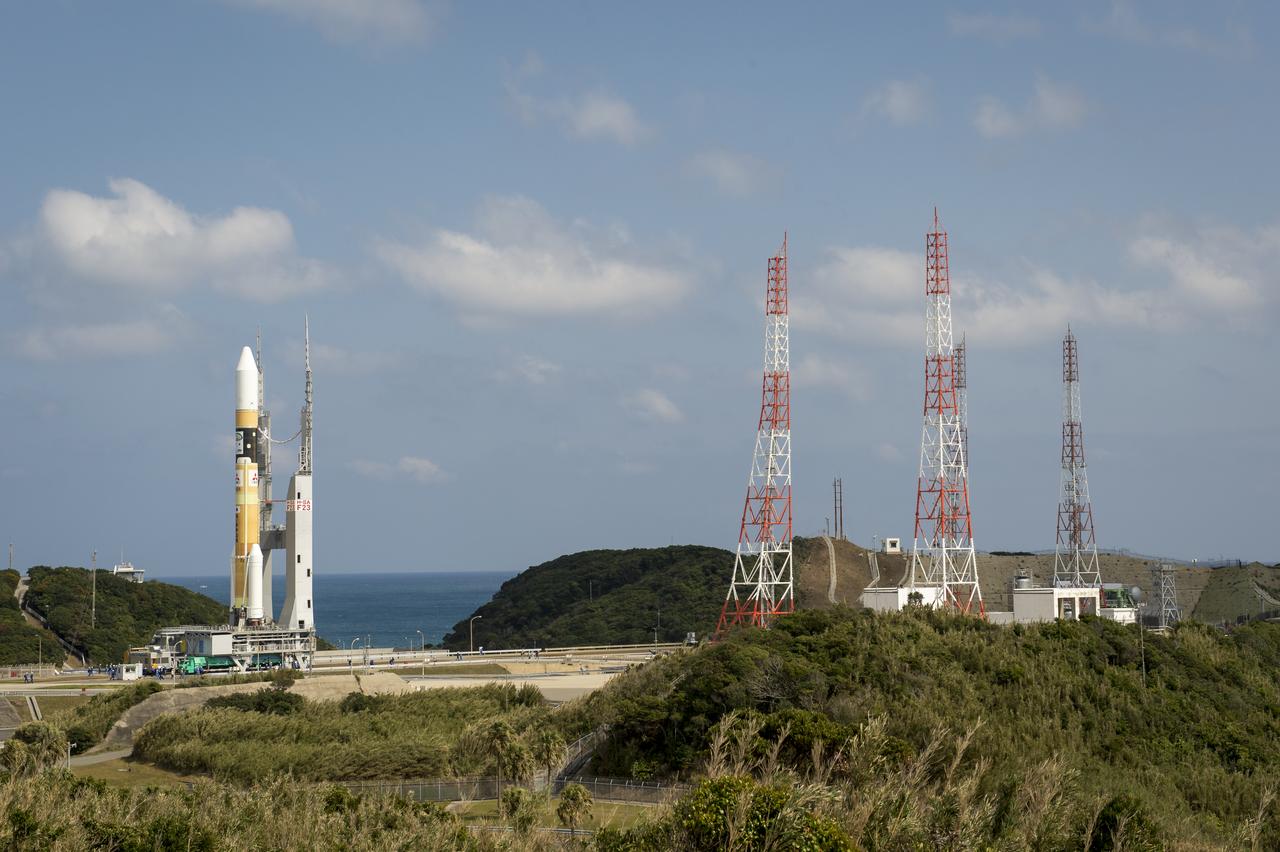

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

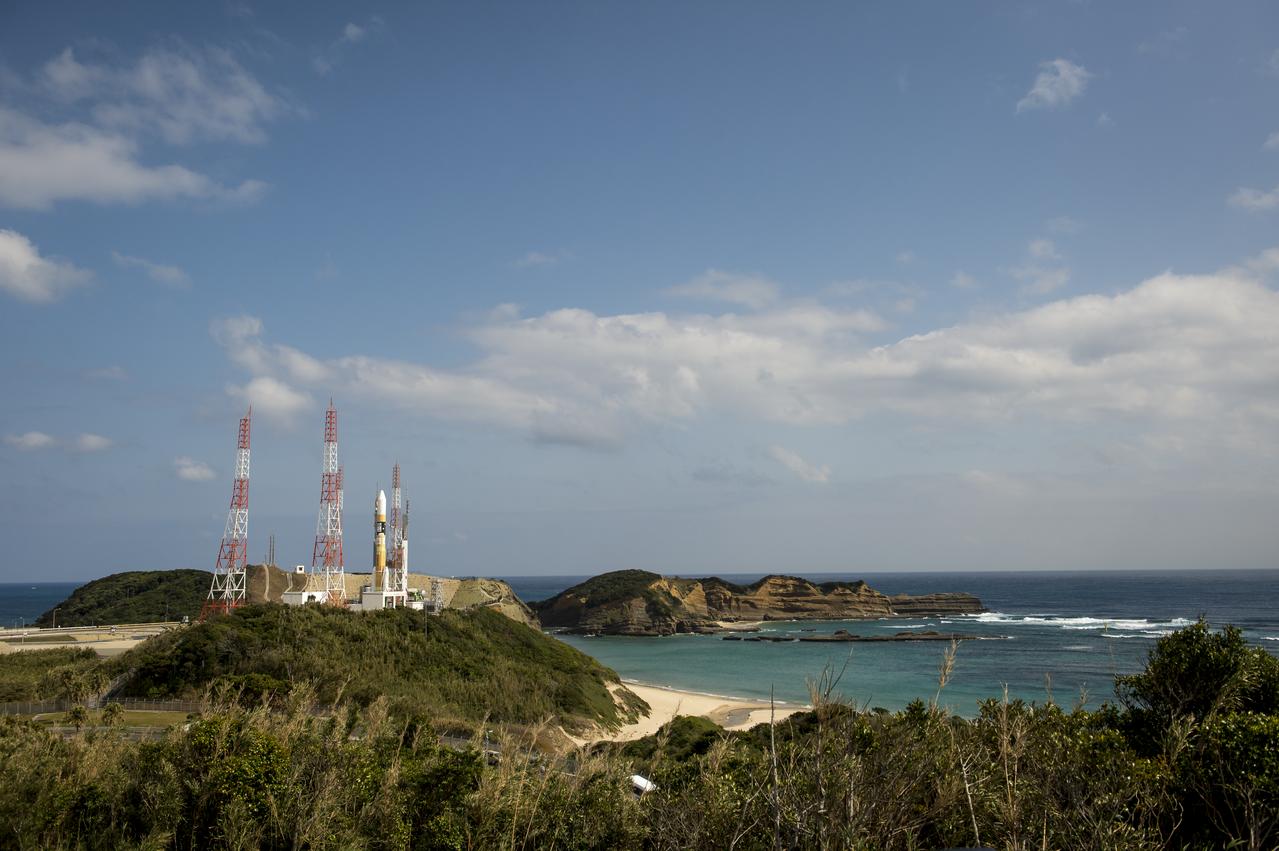
A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard is seen on launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

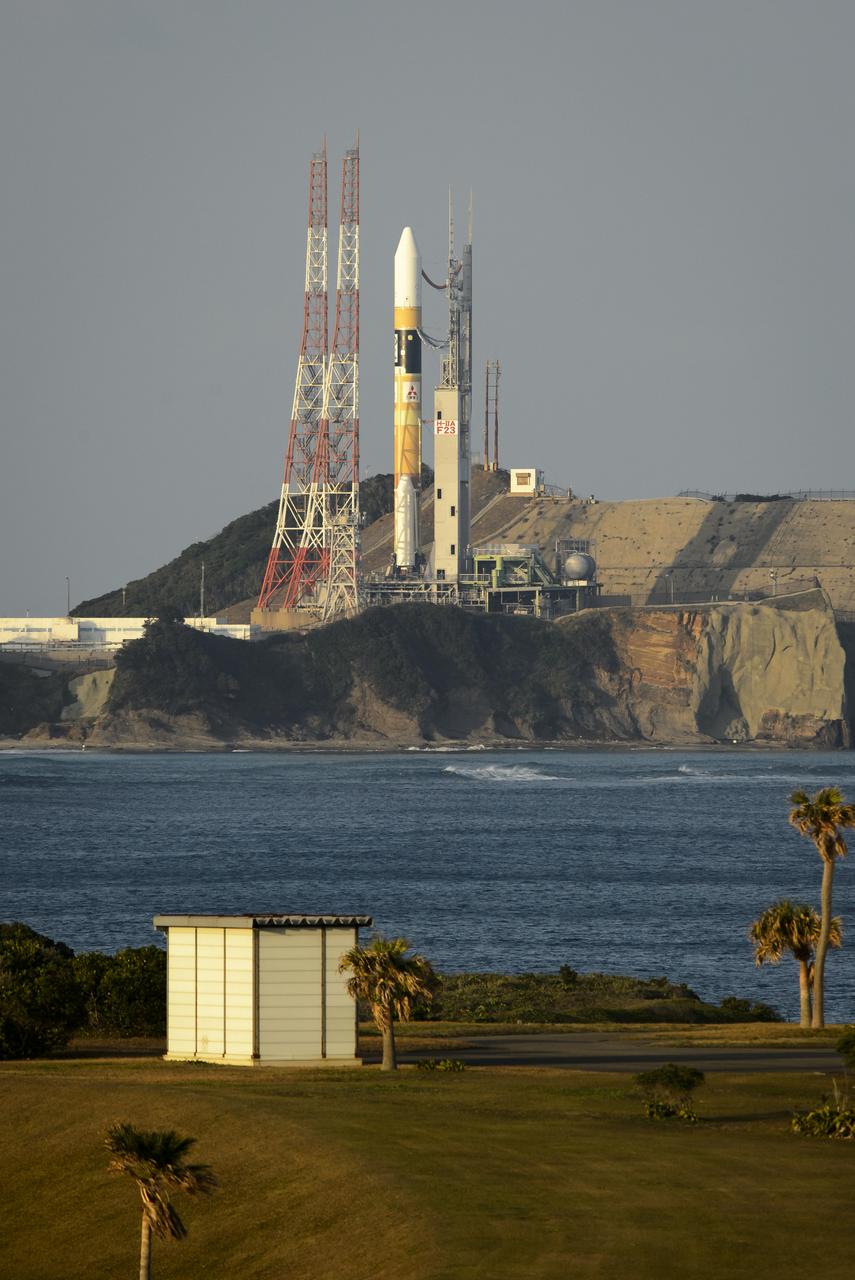
A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, is seen on launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Friday, Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
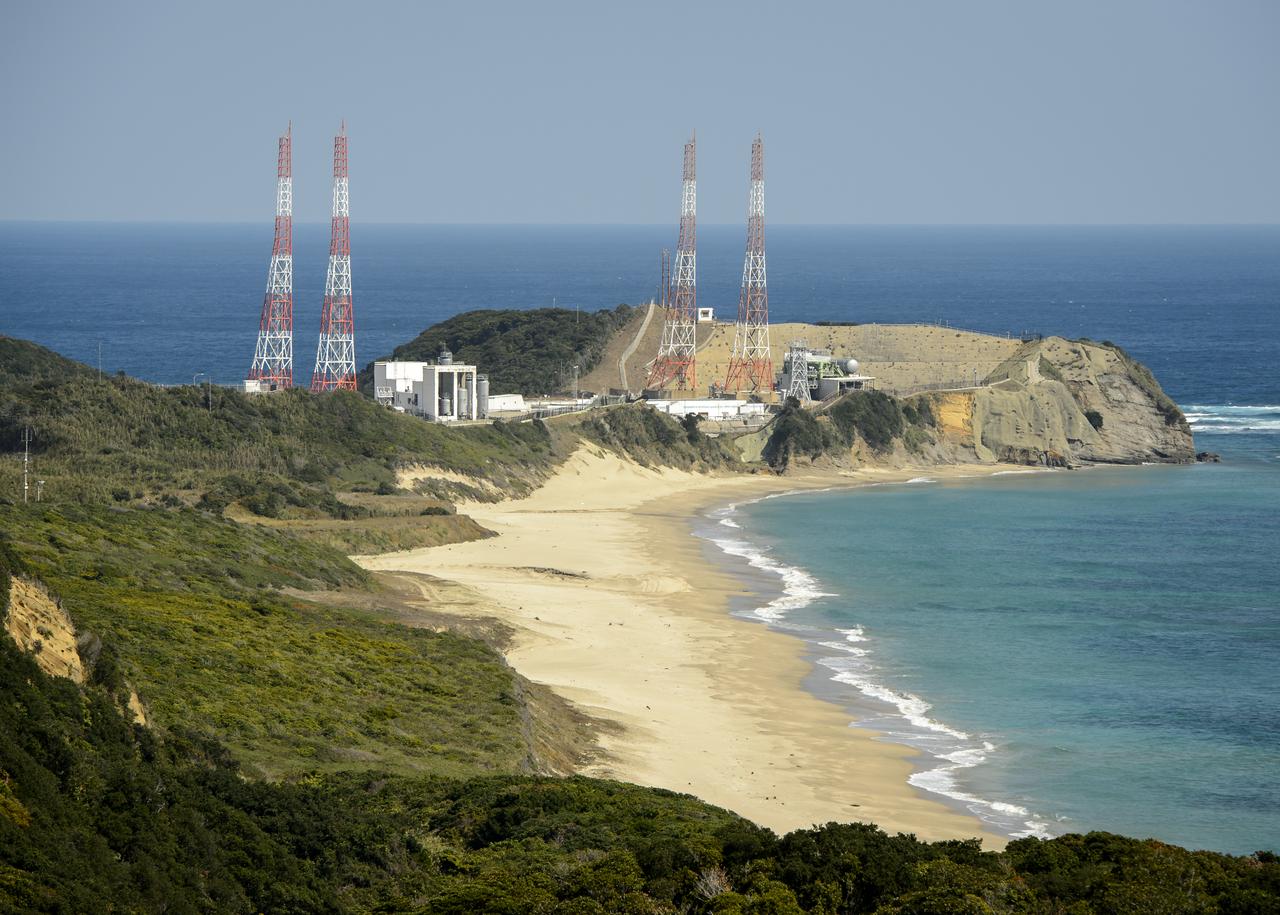

The launch pads at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center are seen a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
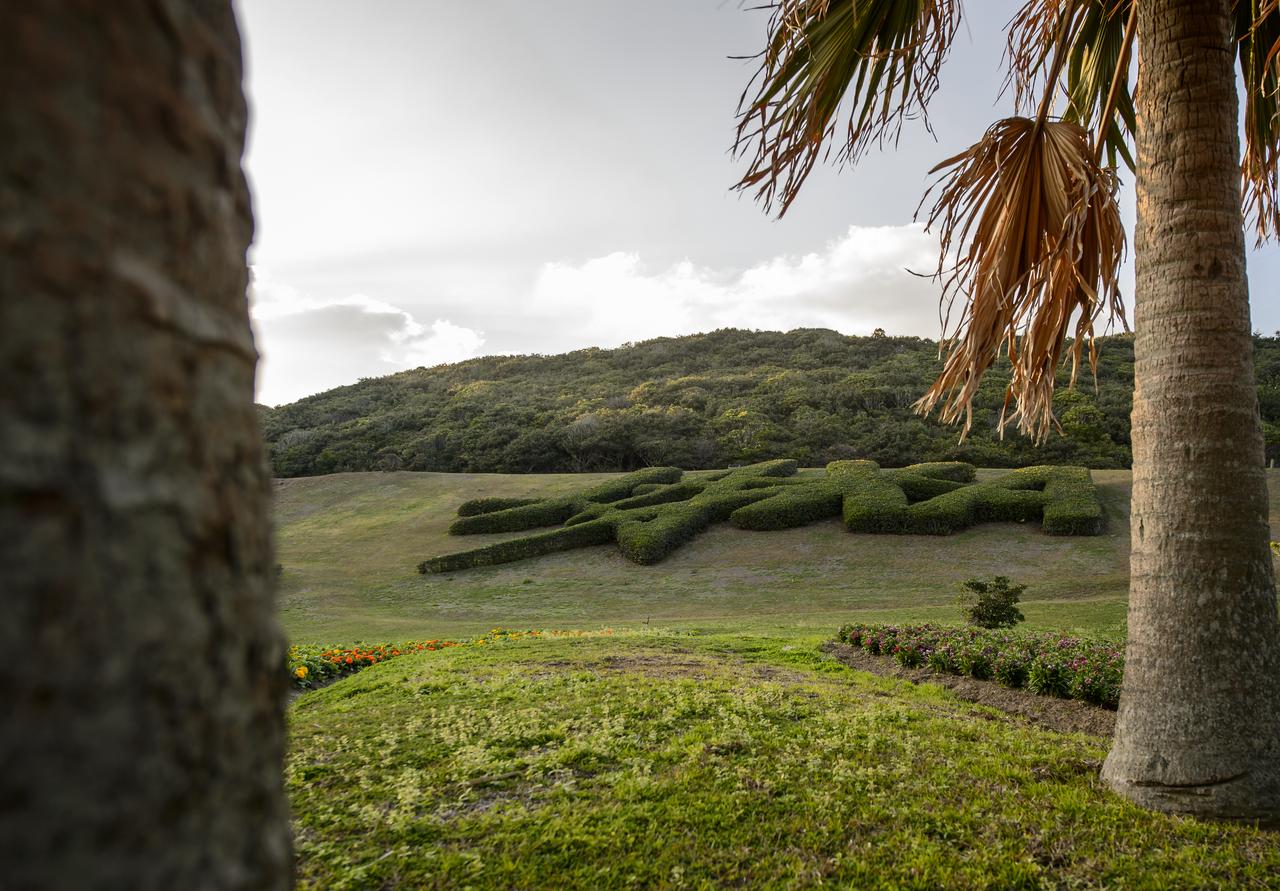

Topiary shaped into the logo of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) is seen at the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
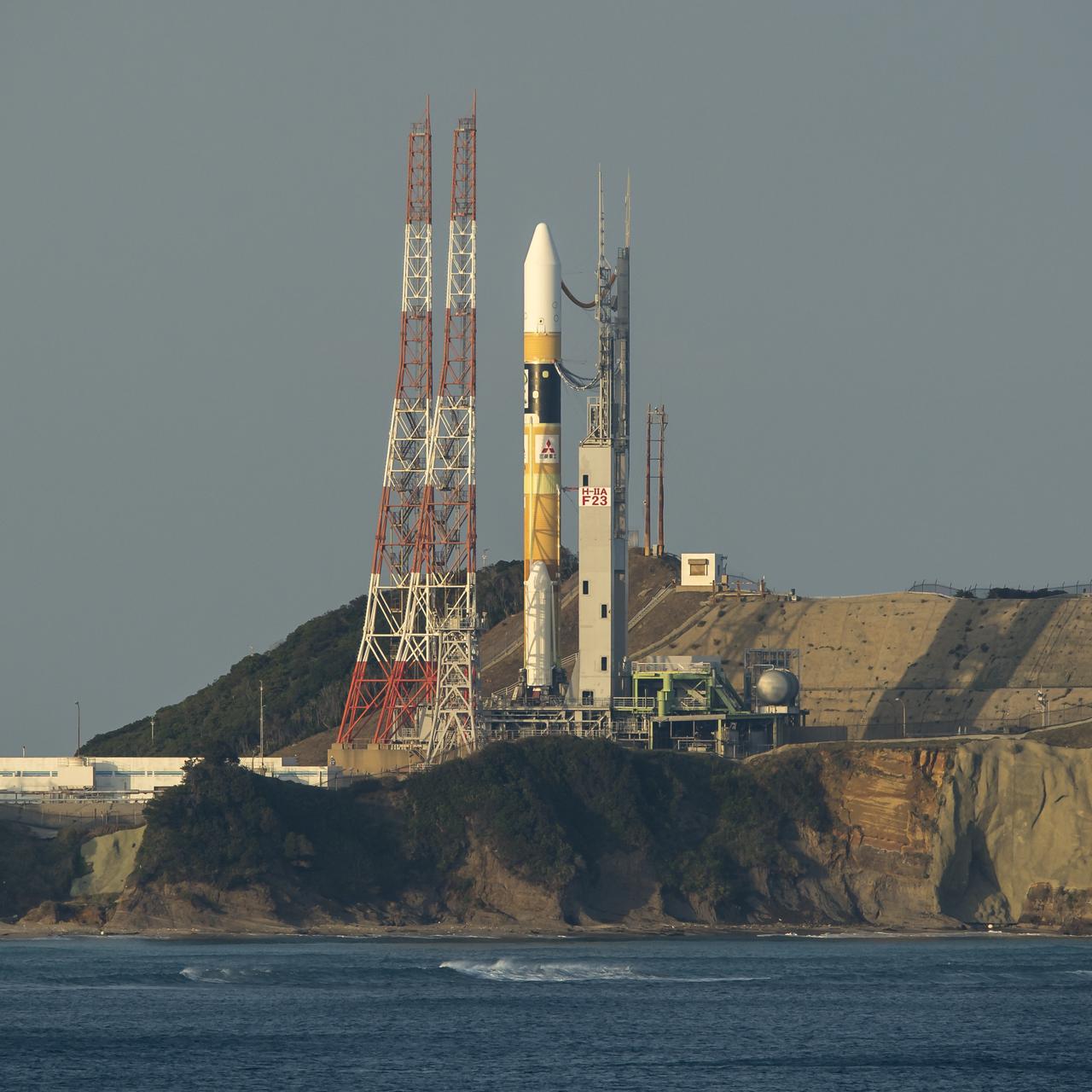

A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard is seen on launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
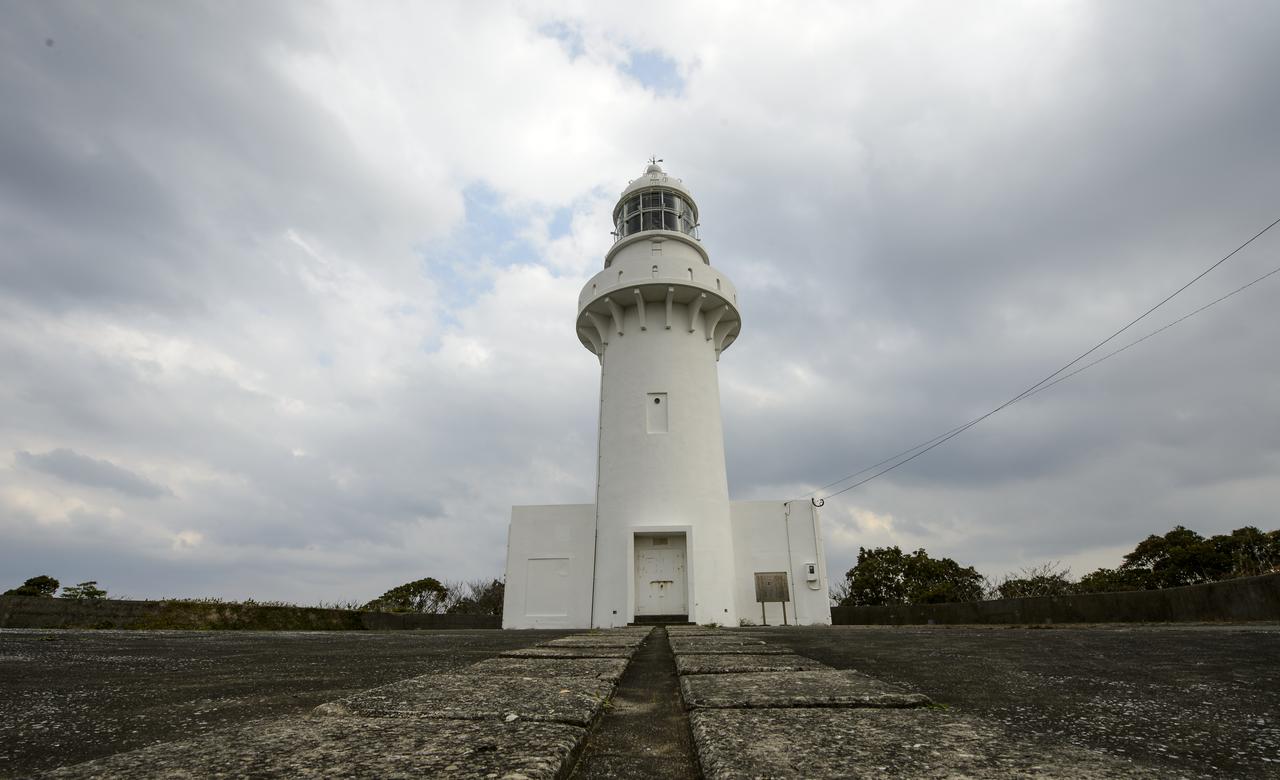

The Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) lighthouse is seen on Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
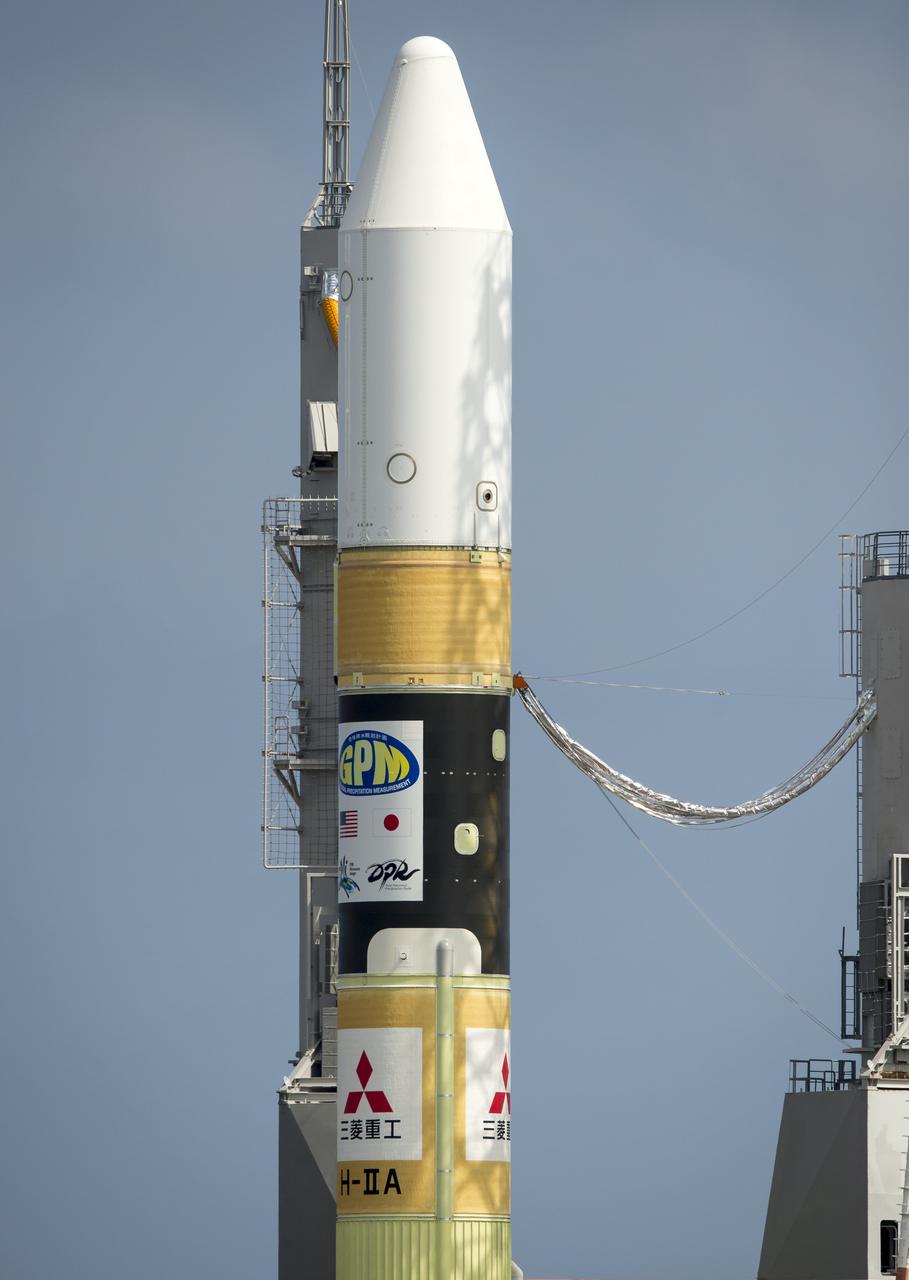

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
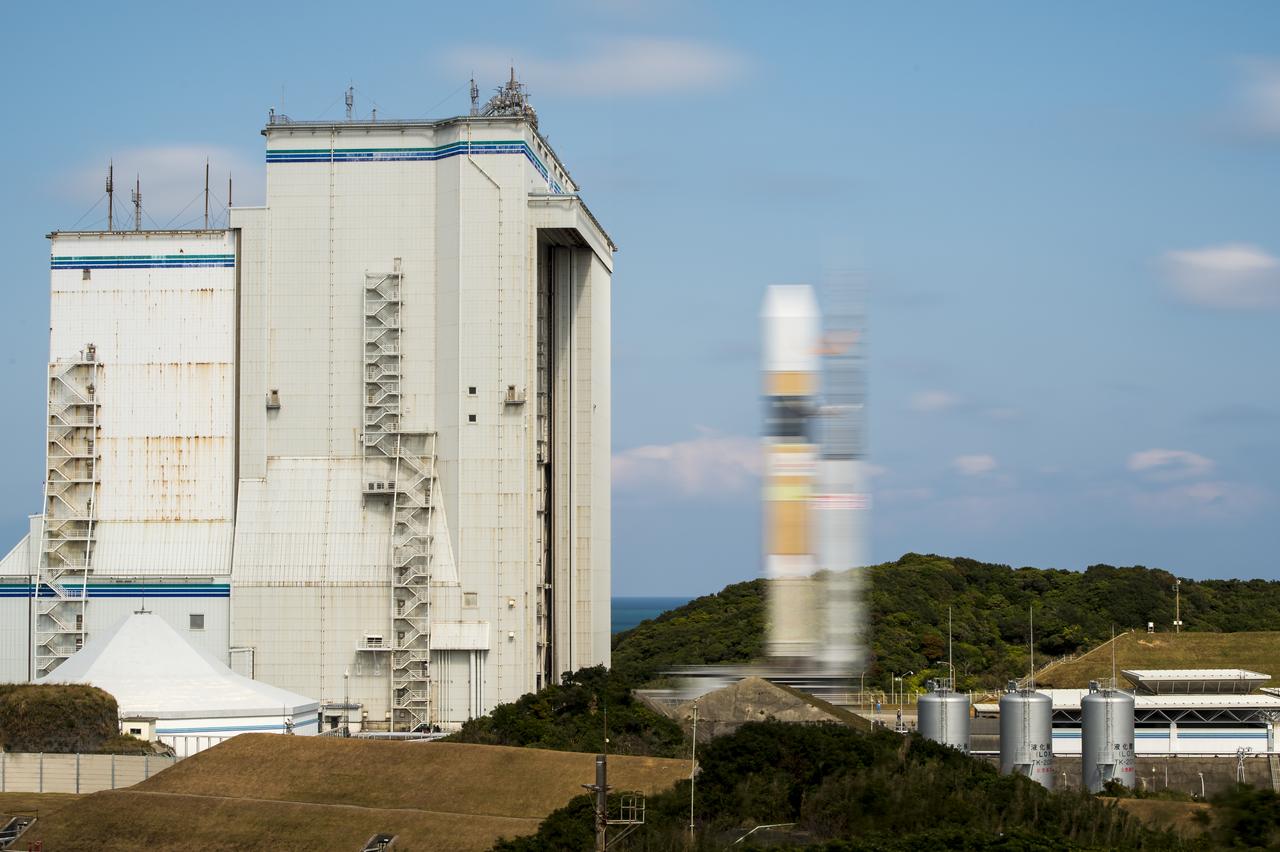

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen in this 10 second exposure as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

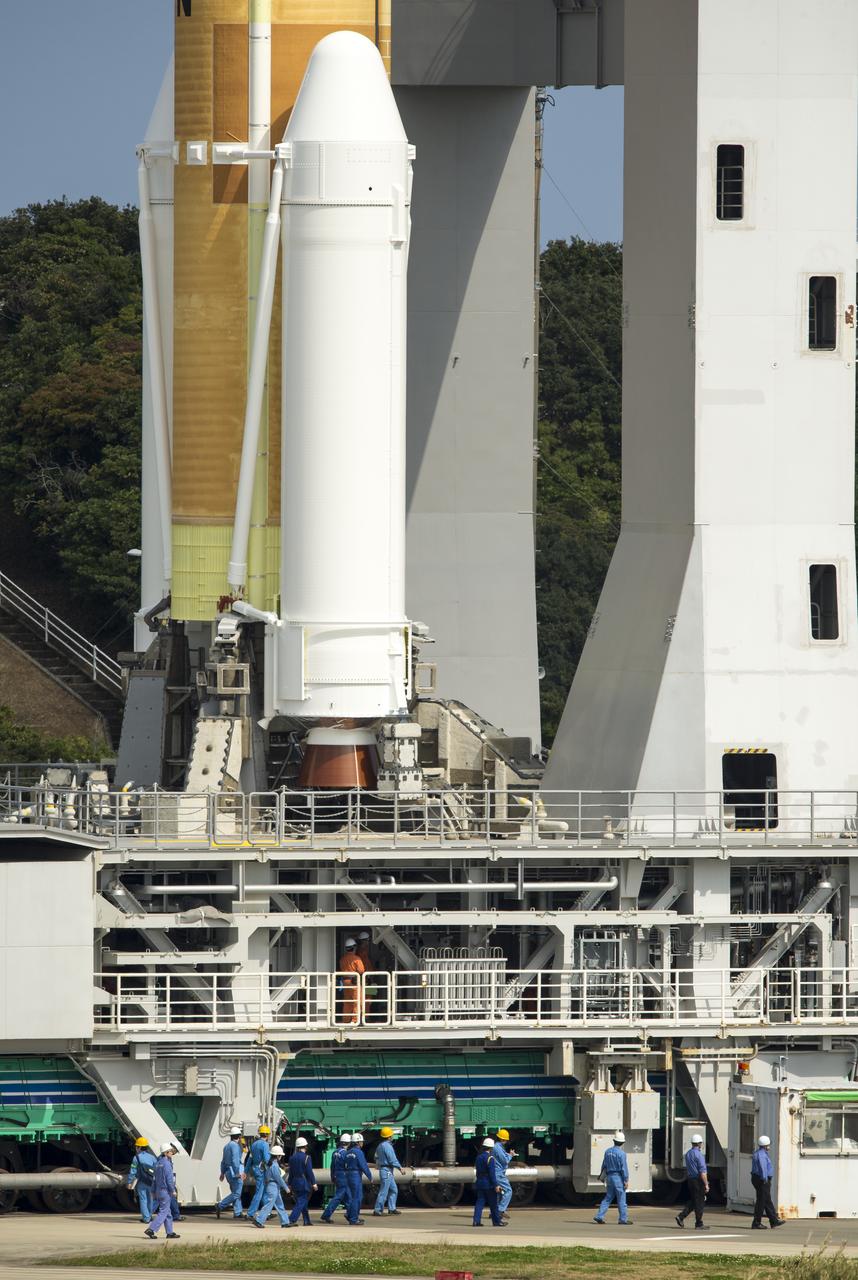
A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard is seen on launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
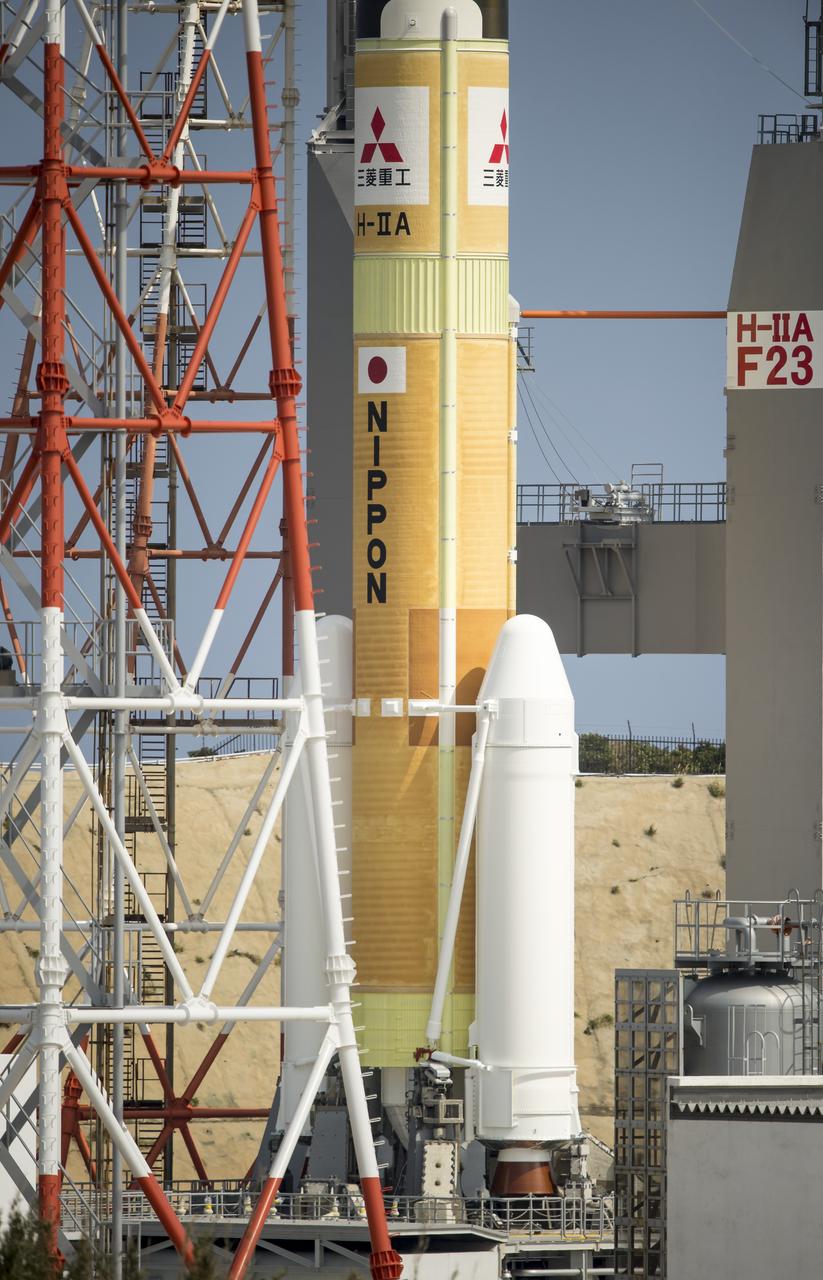

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
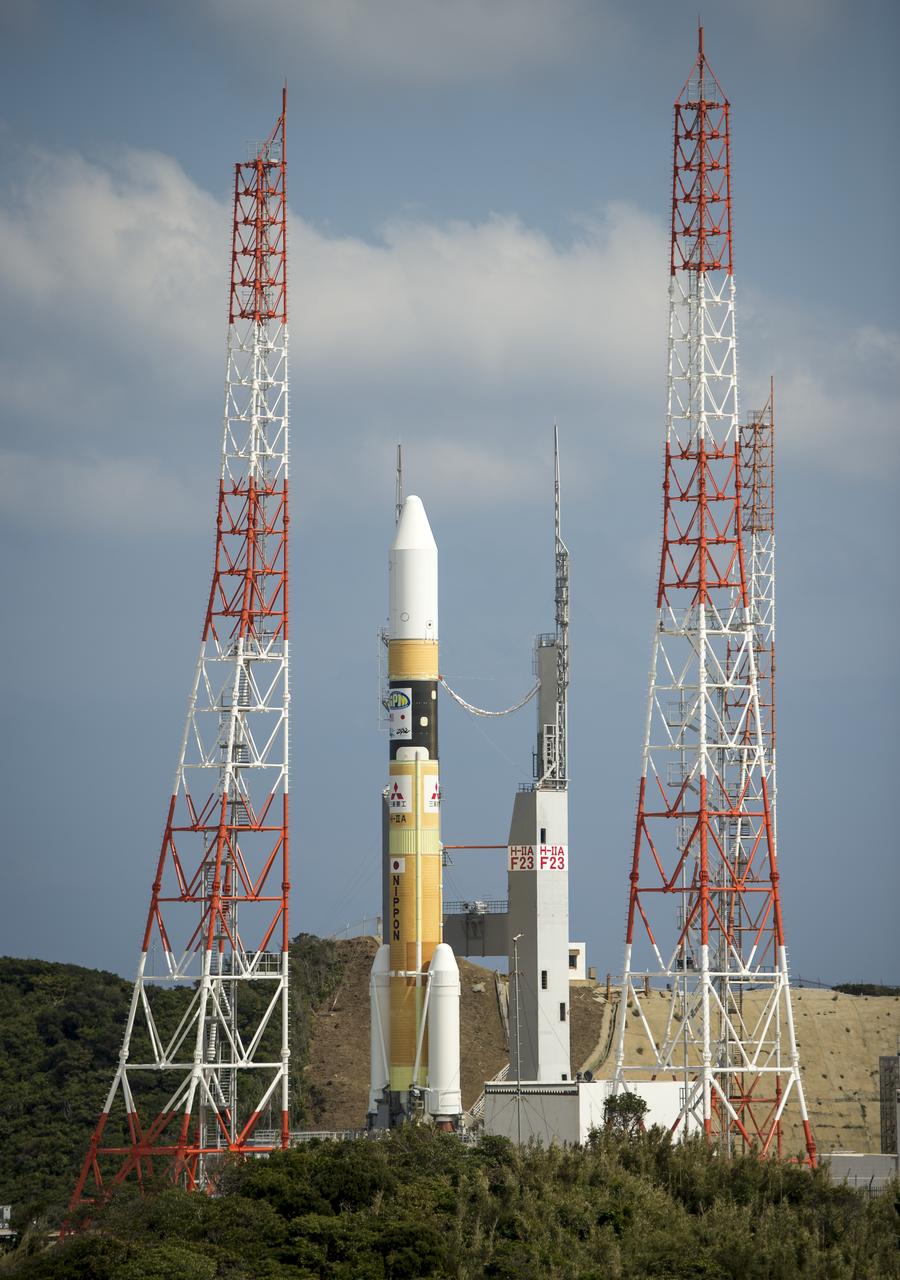

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The entrance sign to the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) is seen a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
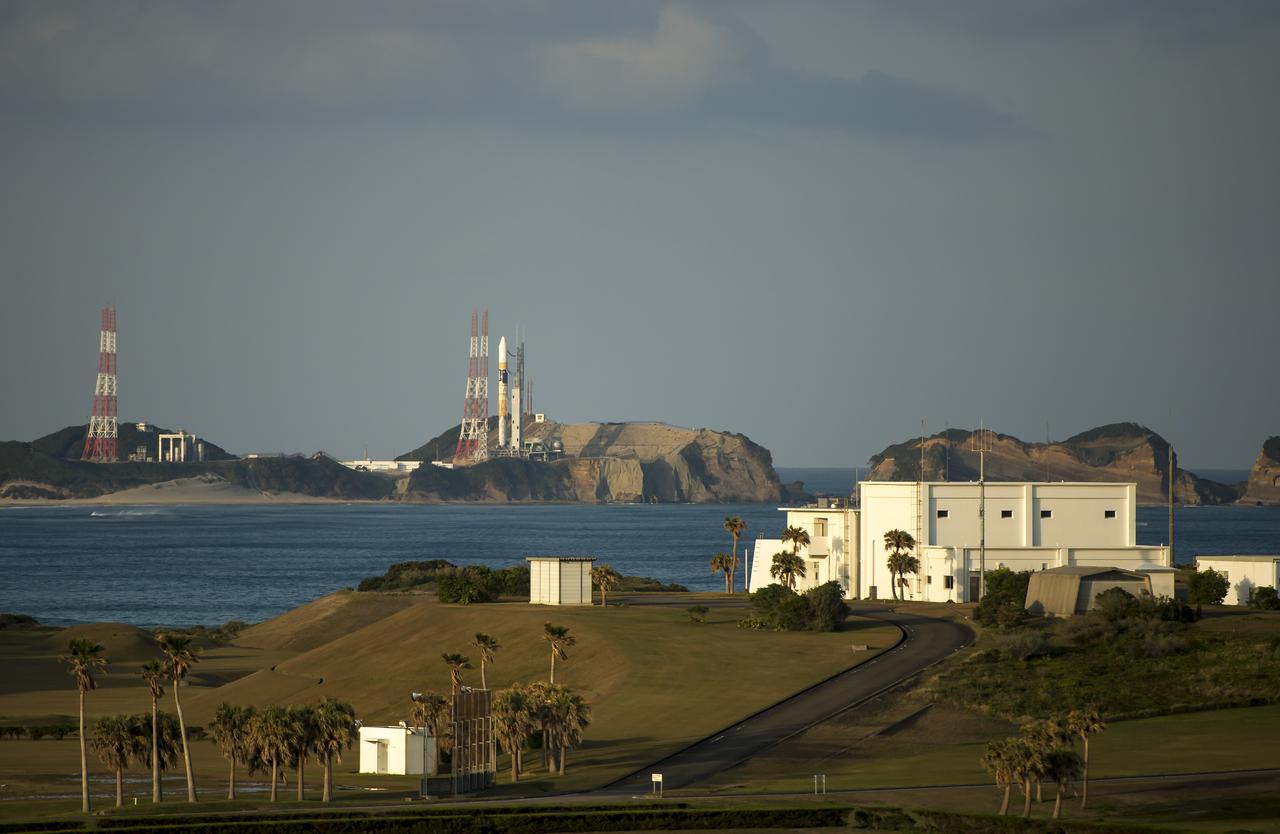

A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard is seen on launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
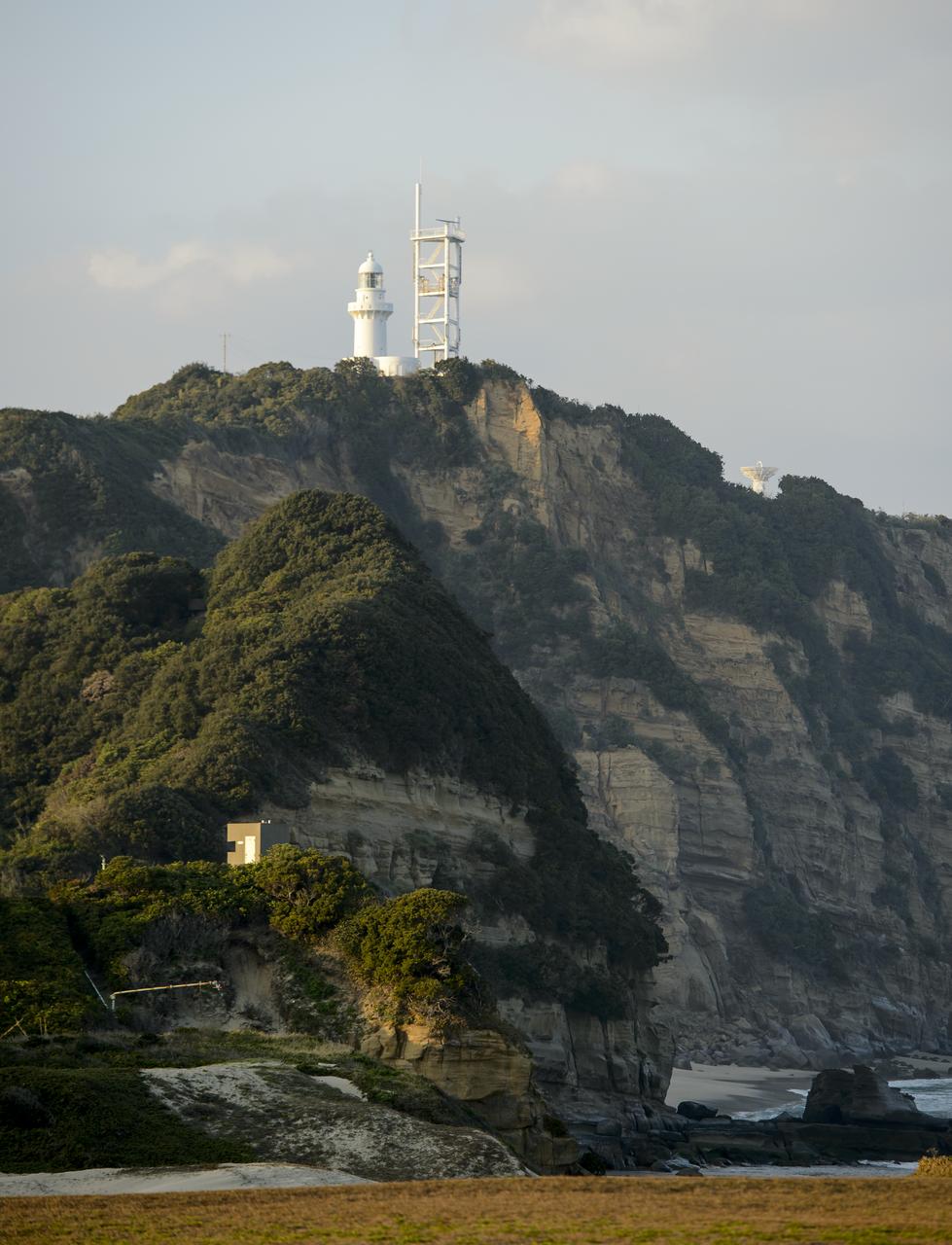

A light house and weather station is seen at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
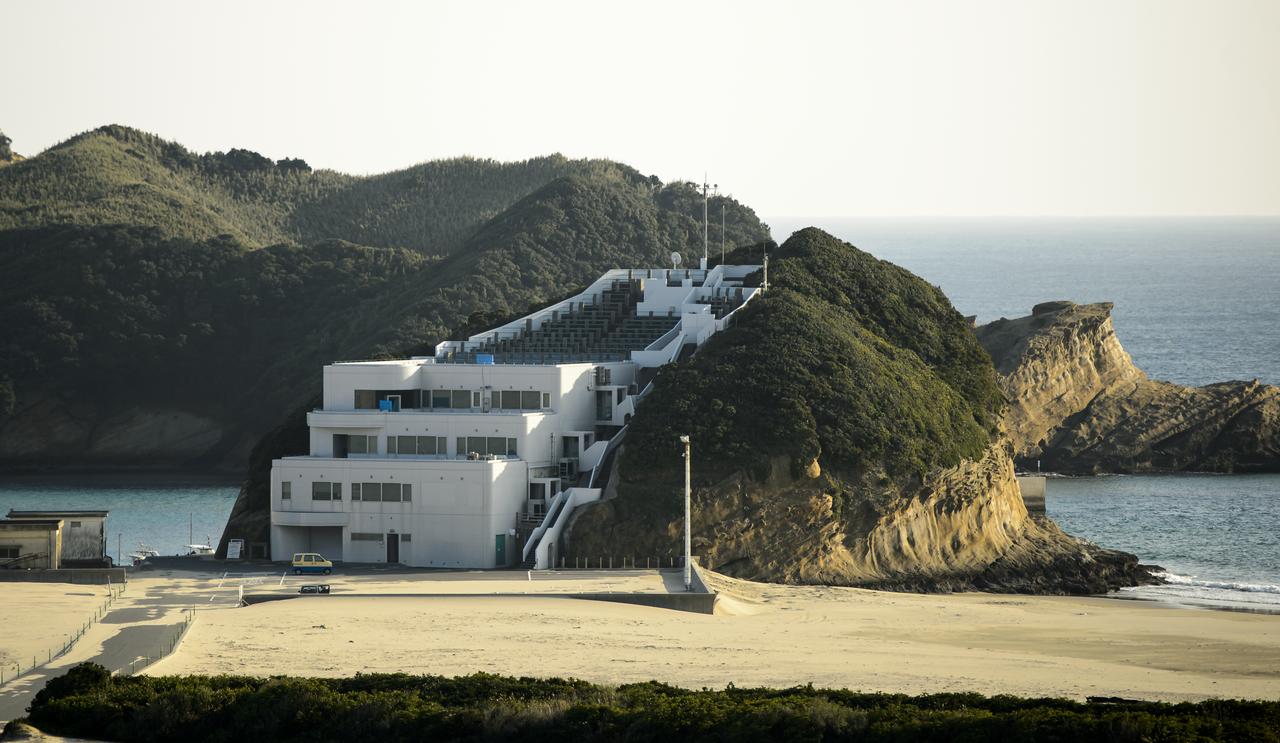

The Takesaki Observation Center is seen at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
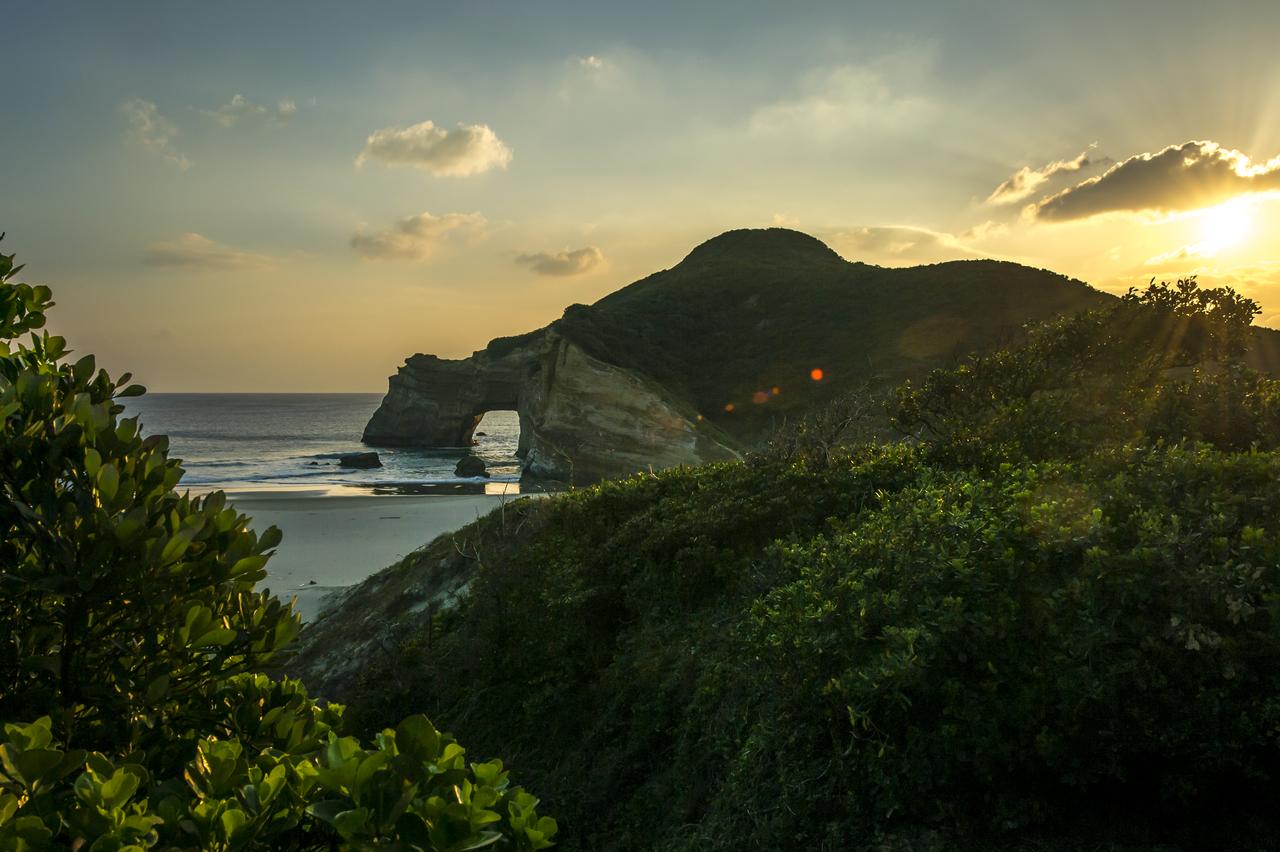

The sun sets just outside the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
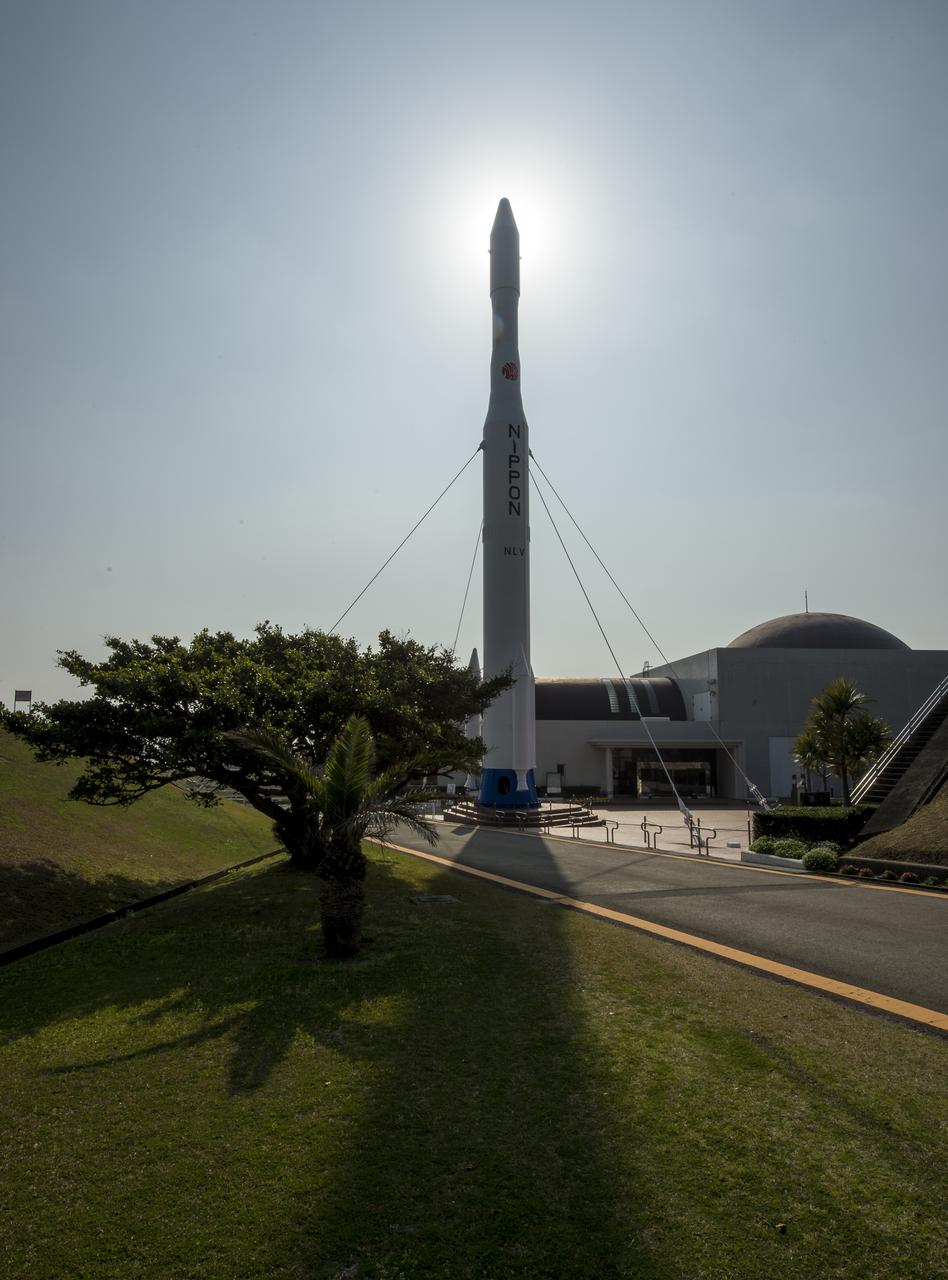

A rocket is seen at the entrance to the visitor's center of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
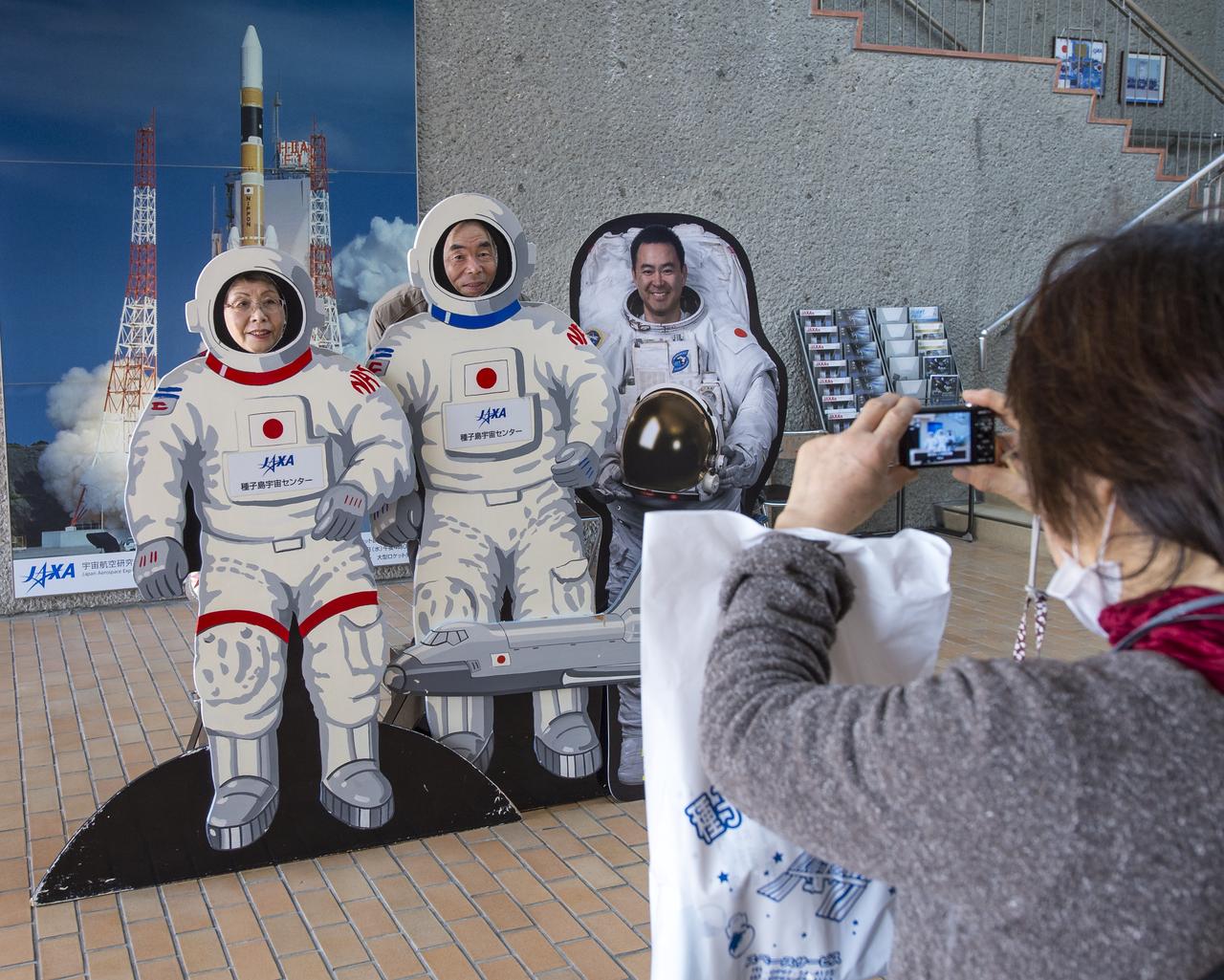

Tourist photograph themselves in astronaut space suites next to a cardboard cutout of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Astronaut Akihiko Hoshide at the visitor's center of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
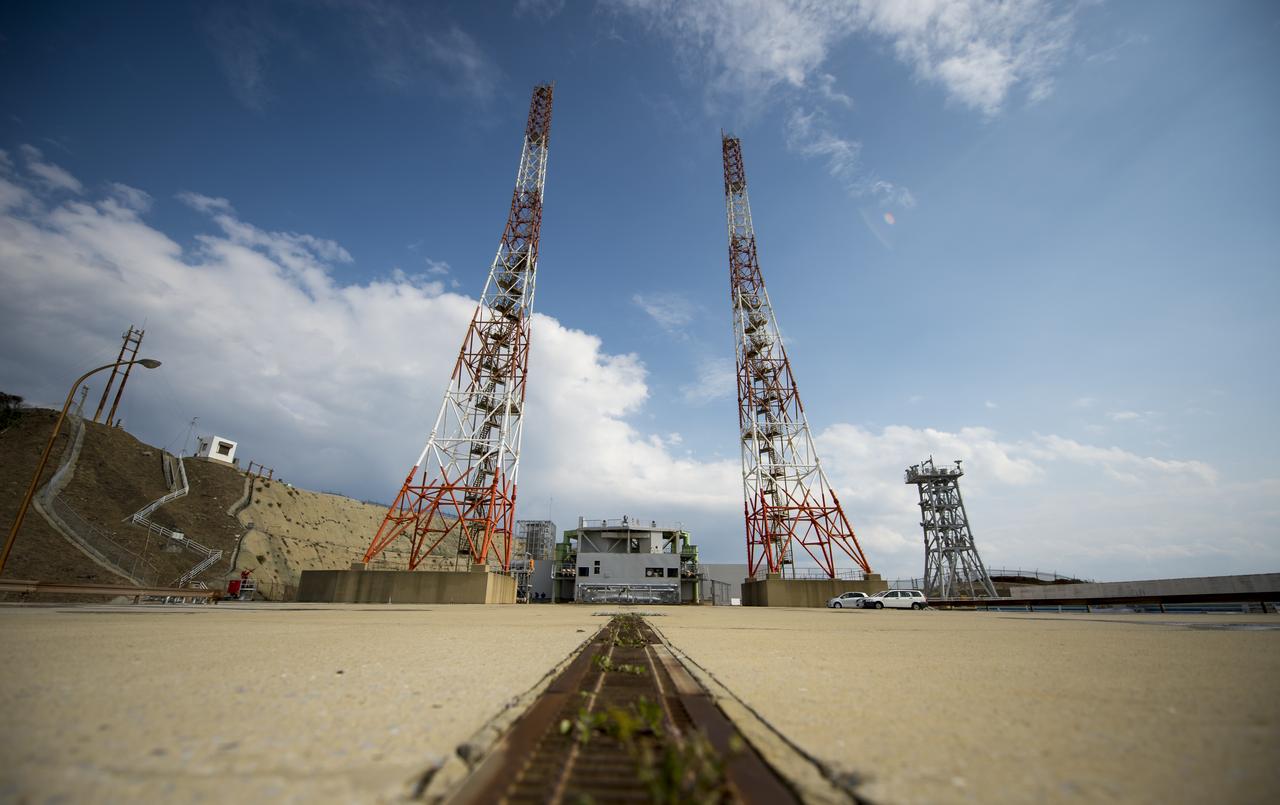

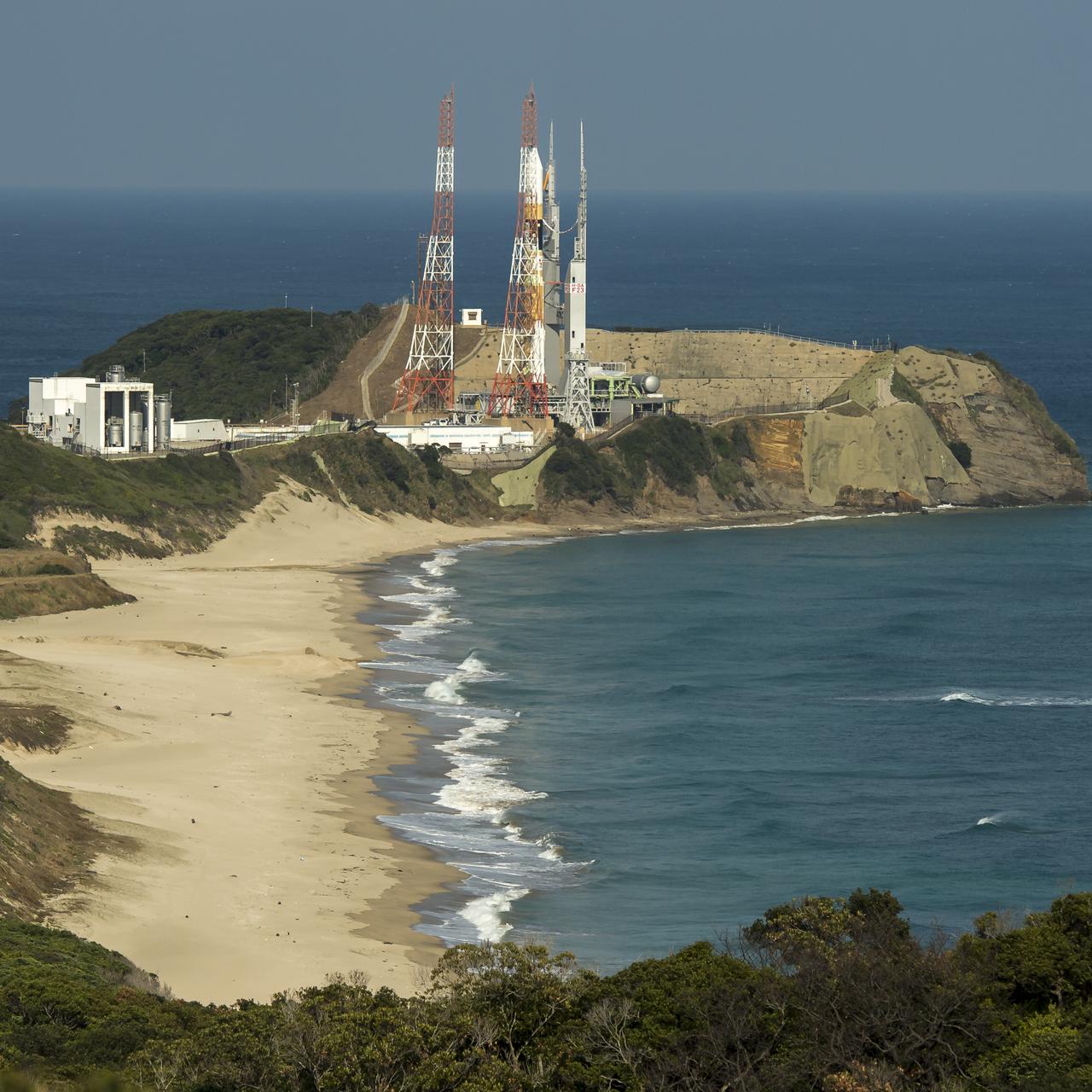
Launch pad 1 is seen at the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Monday, Feb. 24, 2014 in Tanegashima, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from pad 1 on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
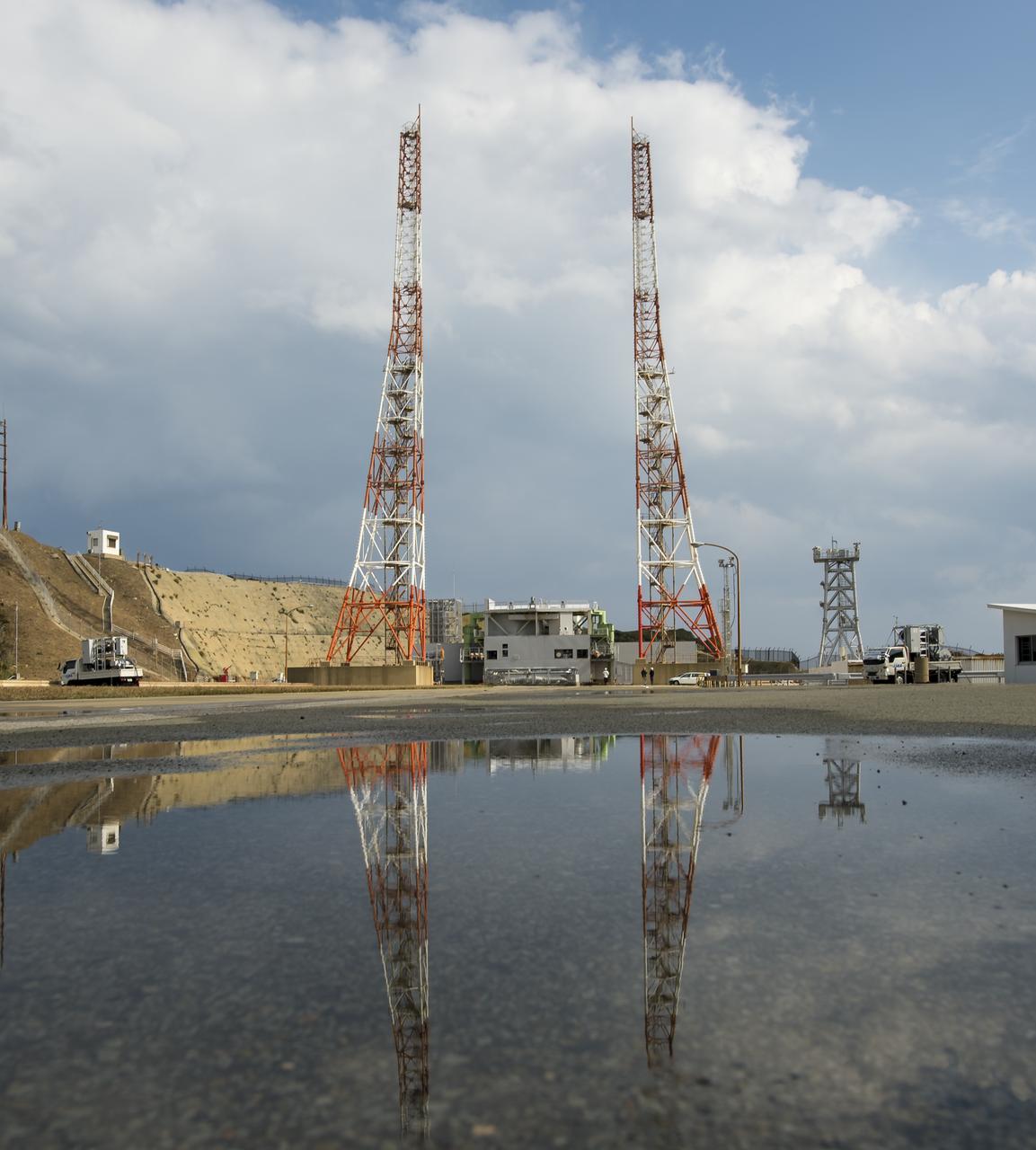

Launch pad 1 is seen at the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Monday, Feb. 24, 2014 in Tanegashima, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from pad 1 on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
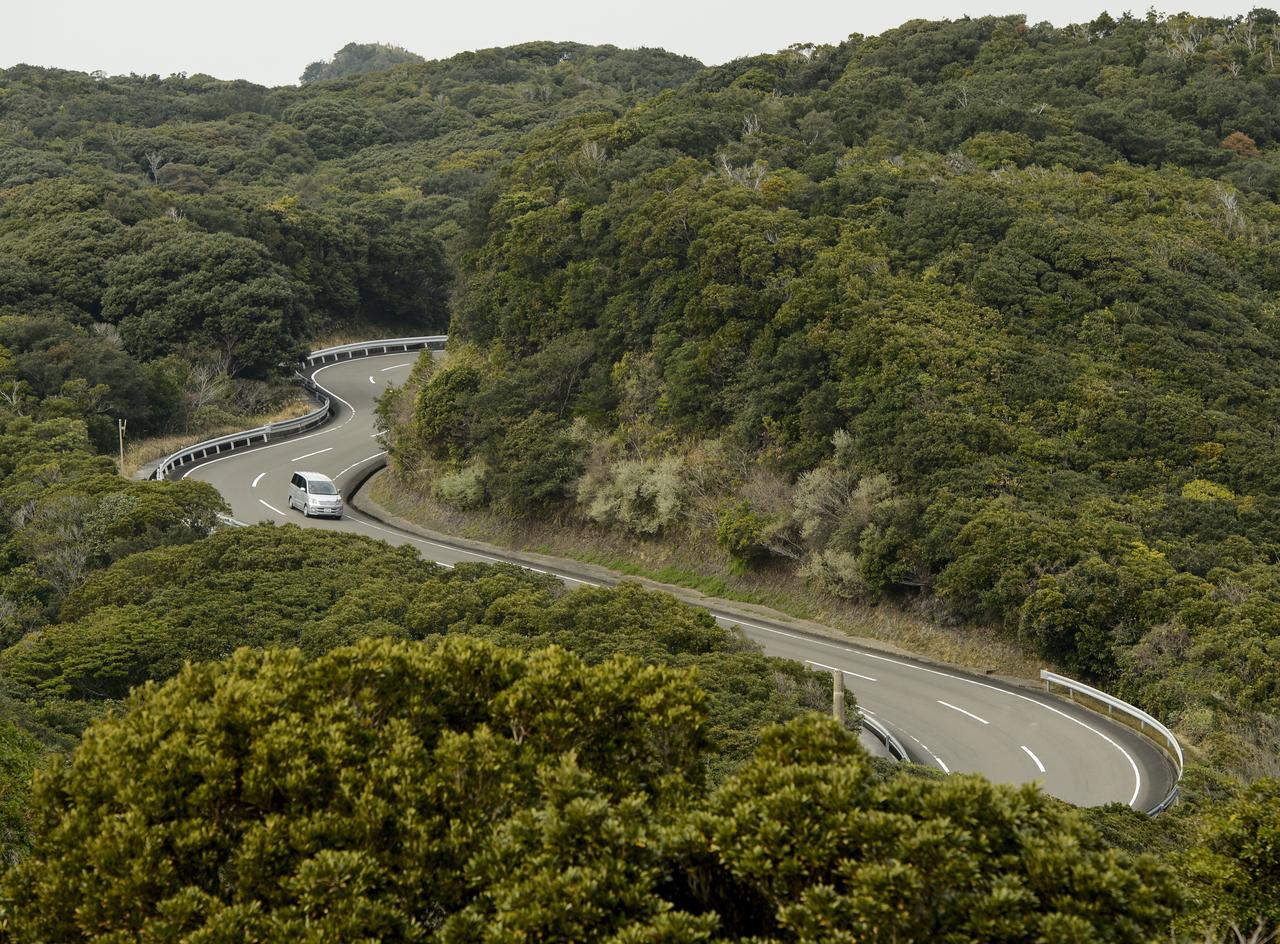

A car drives on the twisty roads that hug the coast line of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
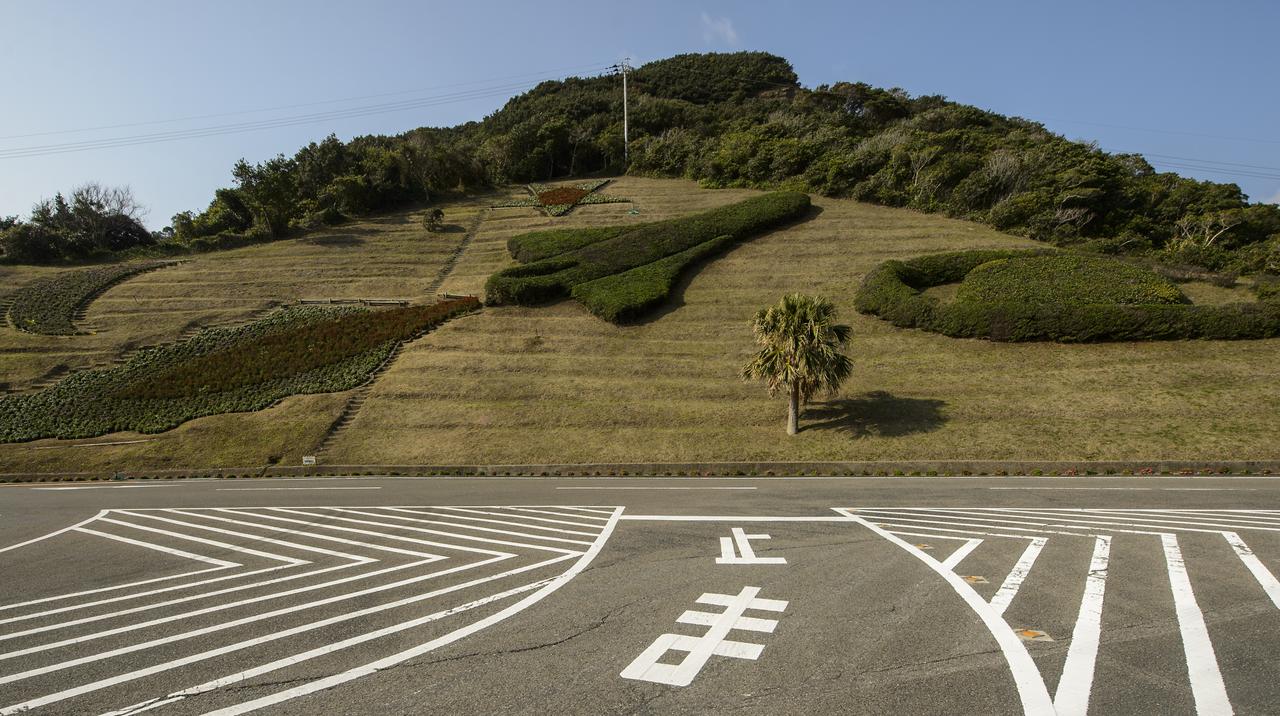

Shrubs and flowers in the shape of a space shuttle, star and planet are seen just outside the visitor's center of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
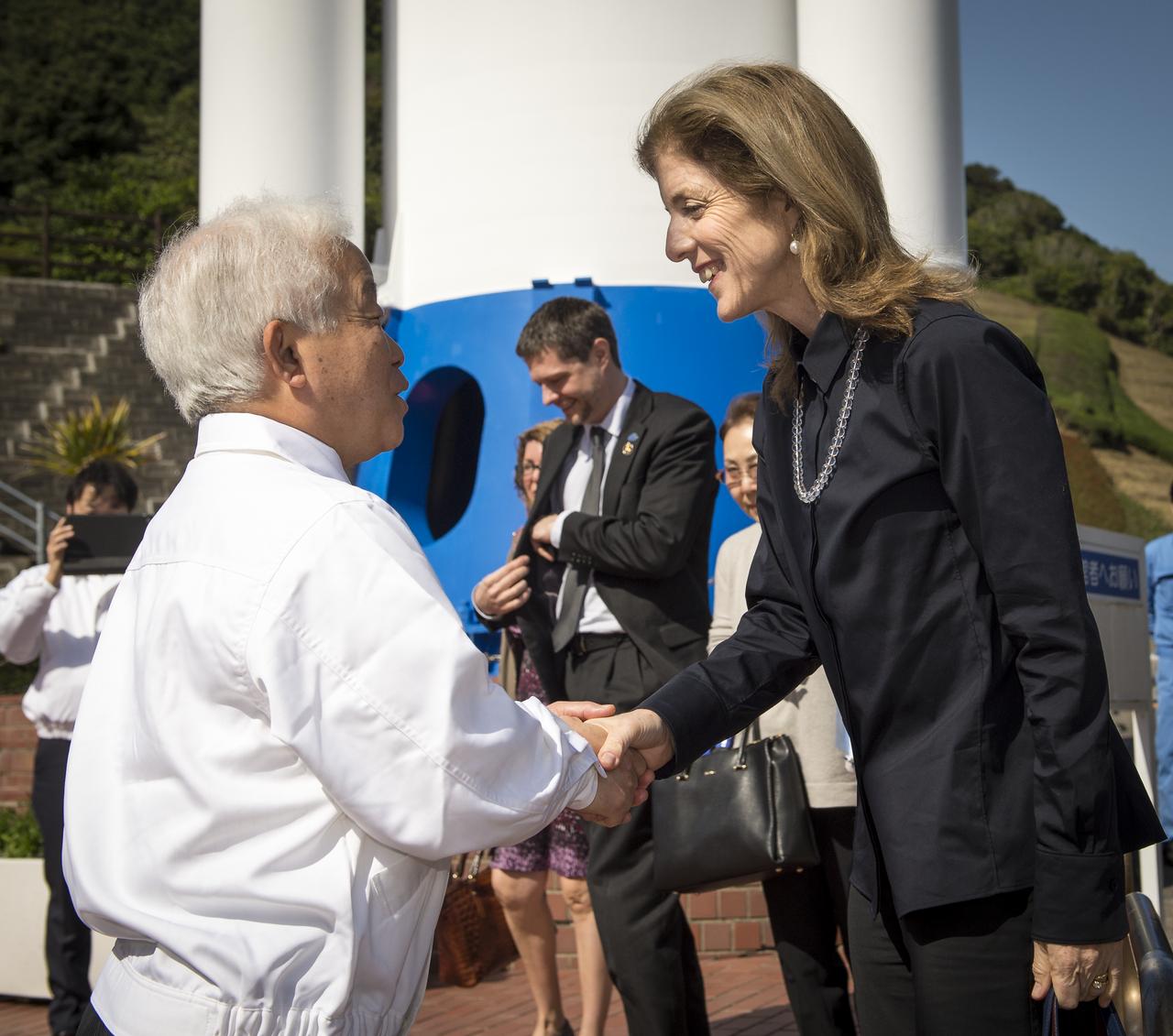

Caroline Kennedy, U.S. Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary to Japan, right, is welcomed by Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), President, Naoki Okumura, at the Tanegashima Space Center Visitors Center on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. The Ambassador is visiting the space center and hopes to witness the planned launch of a Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
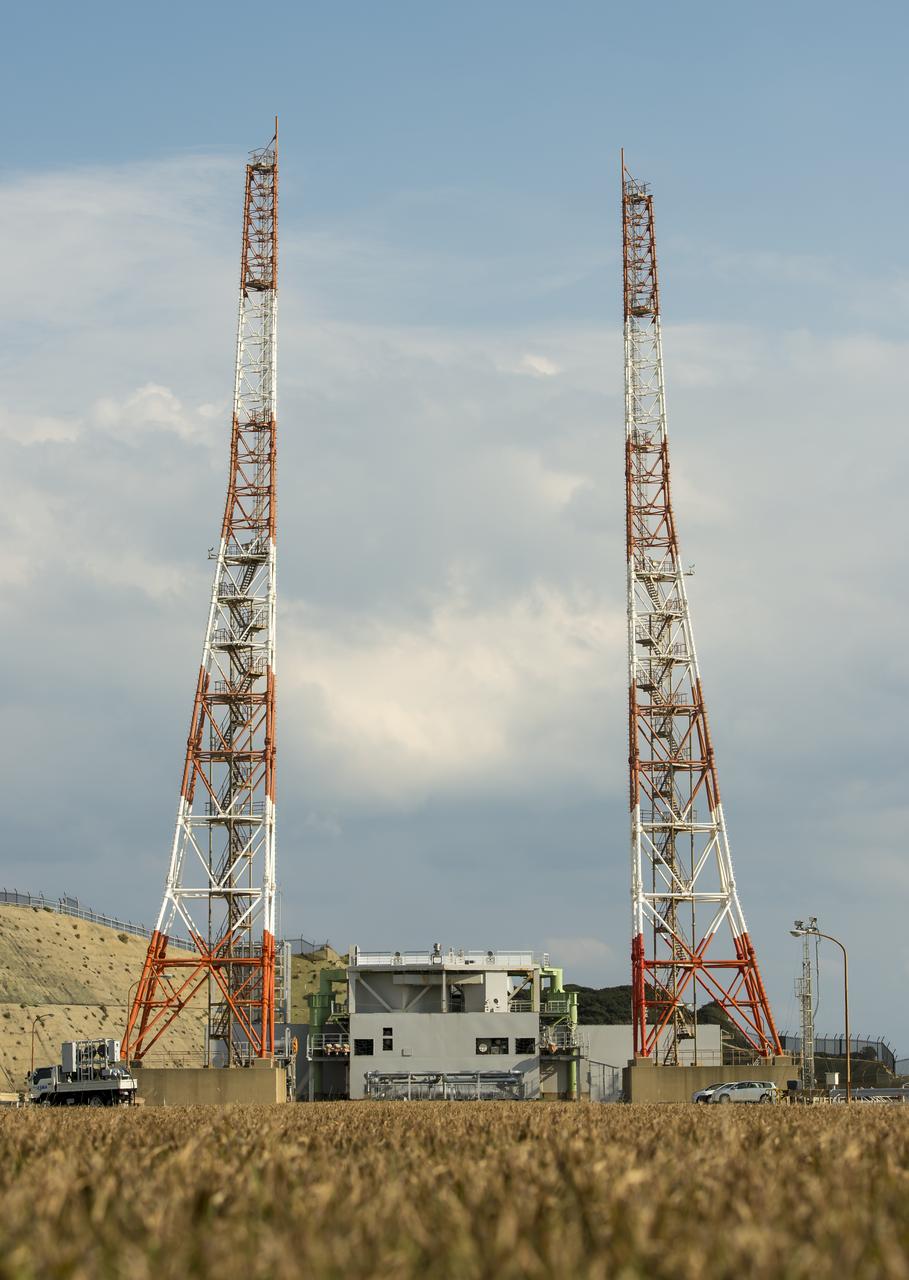

Launch pad 1 is seen at the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Monday, Feb. 24, 2014 in Tanegashima, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from pad 1 on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
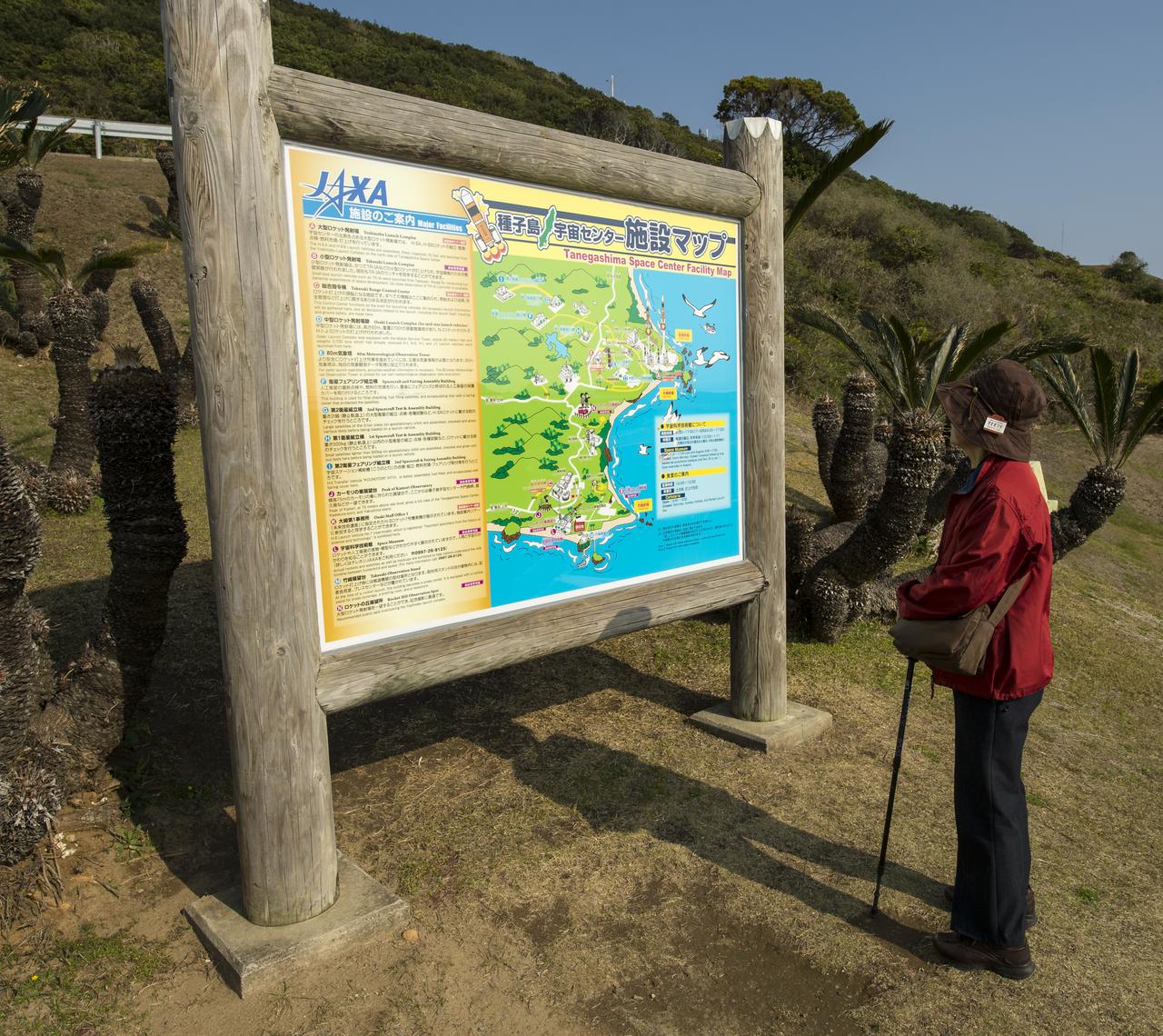
A visitor looks over a Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) Facility Map, Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Caroline Bouvier Kennedy, U.S. Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary to Japan, center, tours the Tanegashima Space Center, Visitors Center with Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), President, Naoki Okumura, right, on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. The Ambassador visiting the space center and hopes to witness the planned launch of a Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
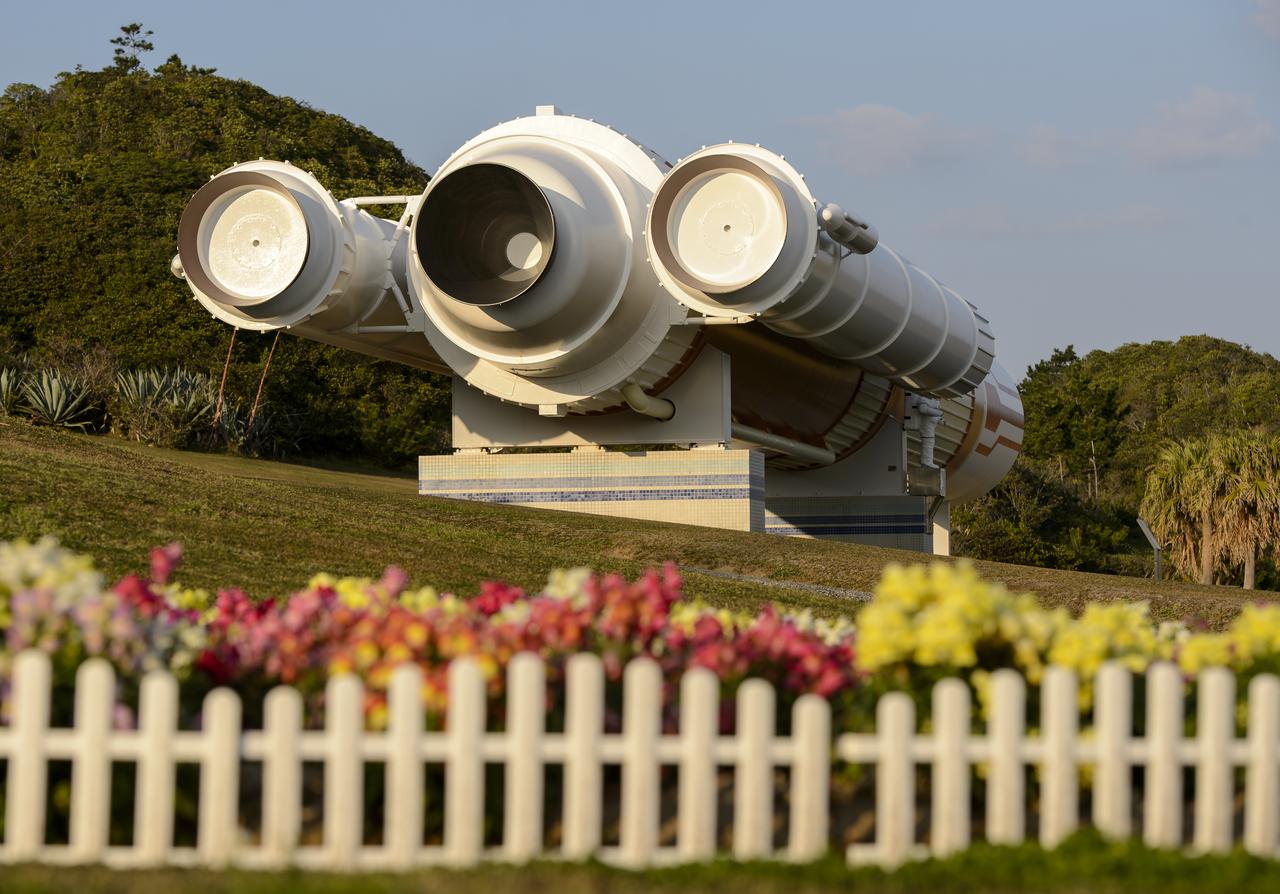
A full size model of an H-II rocket is seen at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) visitors center a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
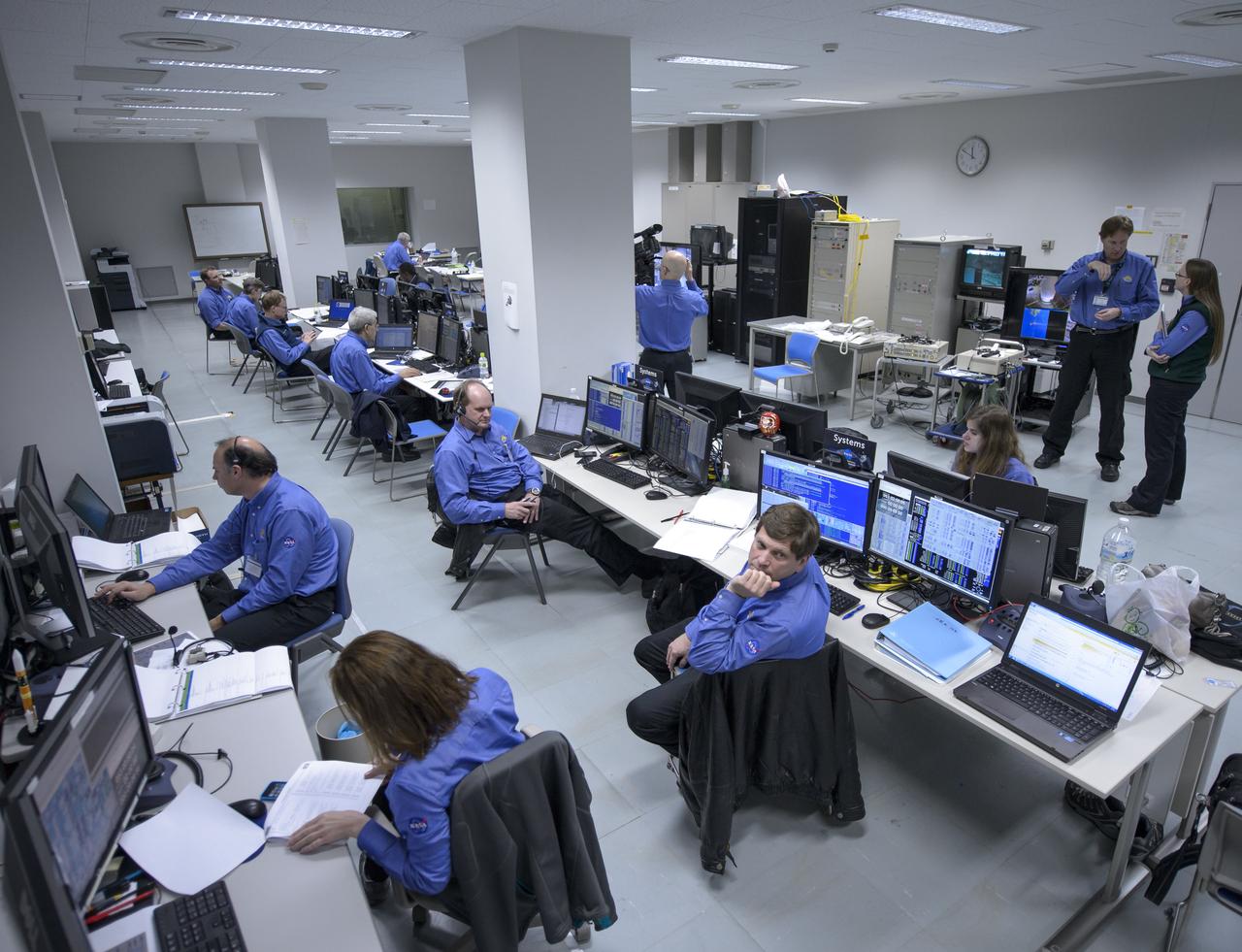

The NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory team is seen during an all-day launch simulation for GPM at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
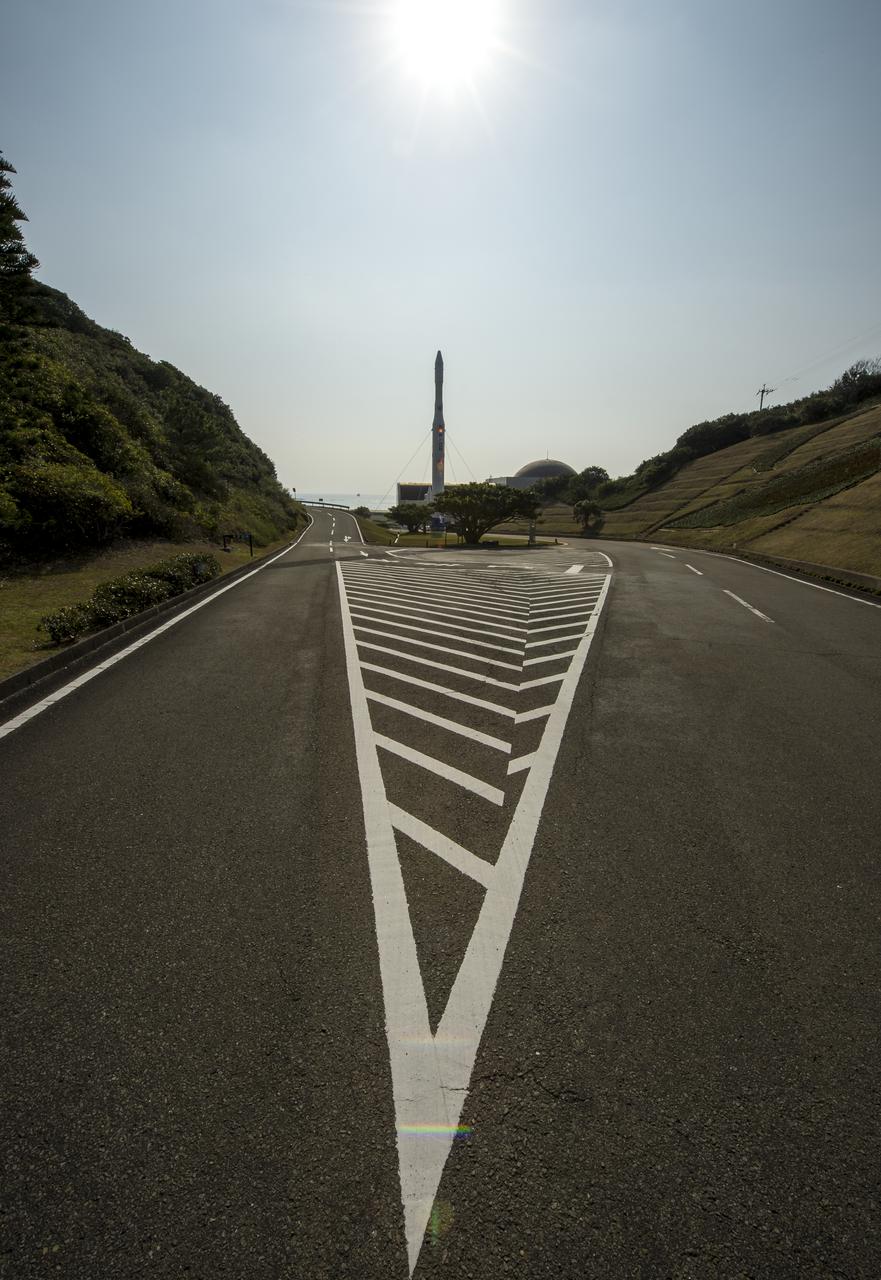

A rocket is seen at the entrance to the visitor's center of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
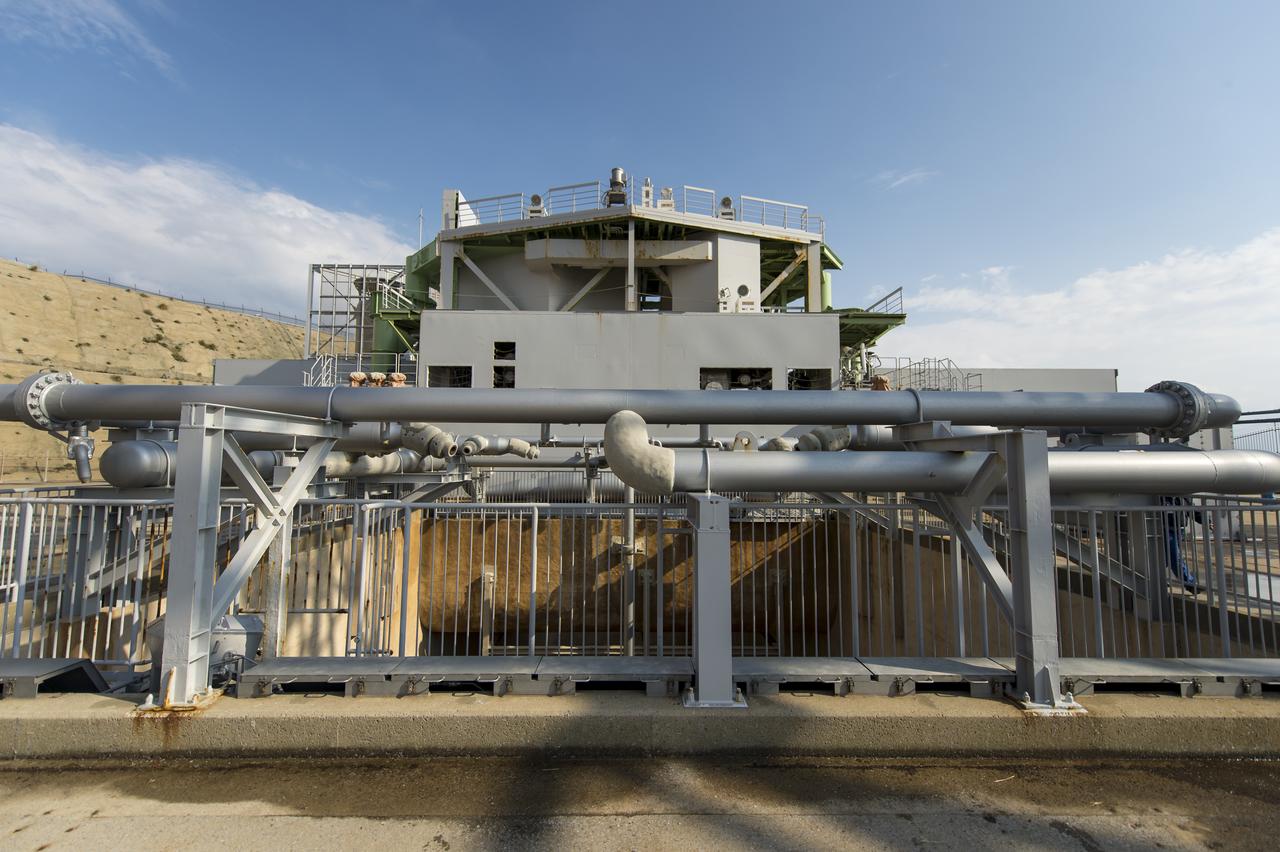

Launch pad 1 is seen at the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Monday, Feb. 24, 2014 in Tanegashima, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from pad 1 on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
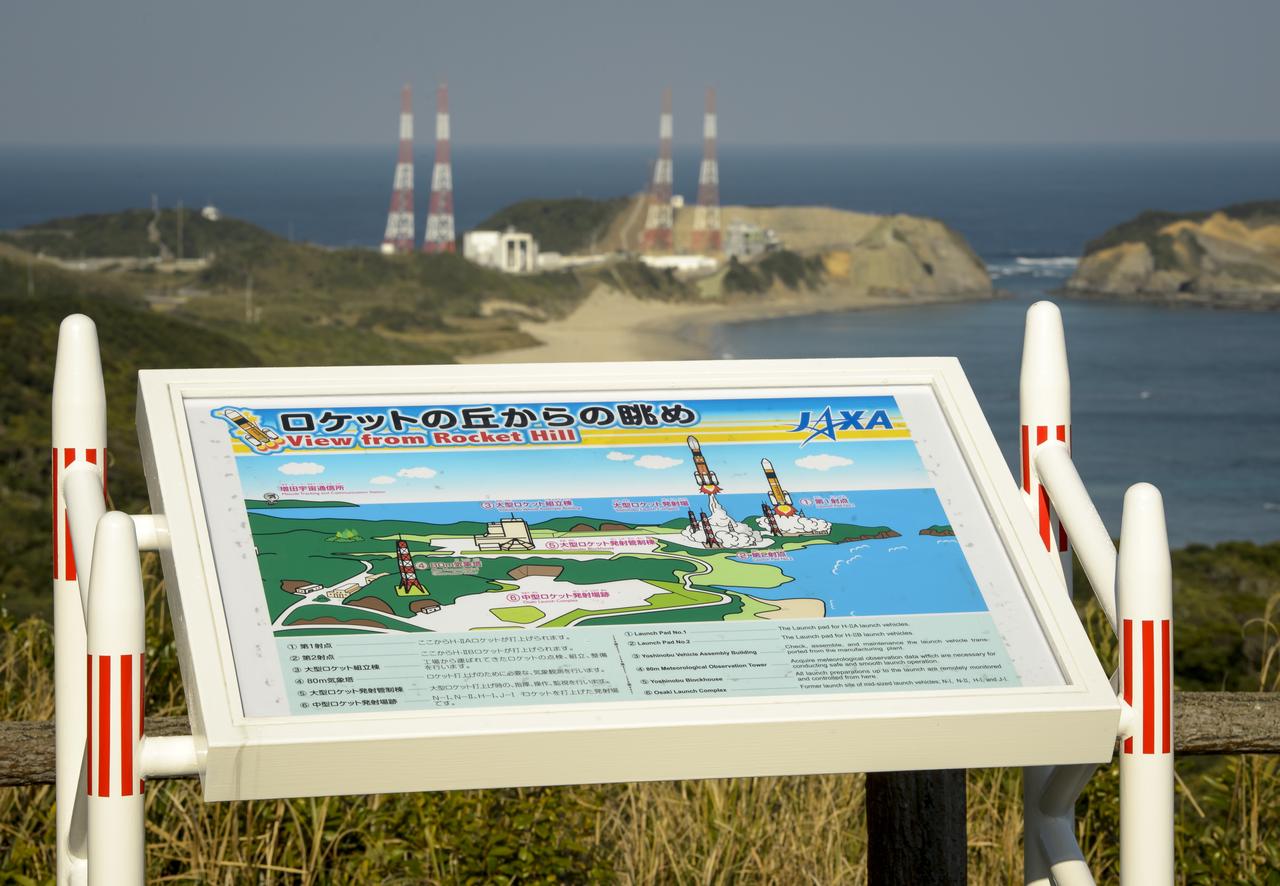

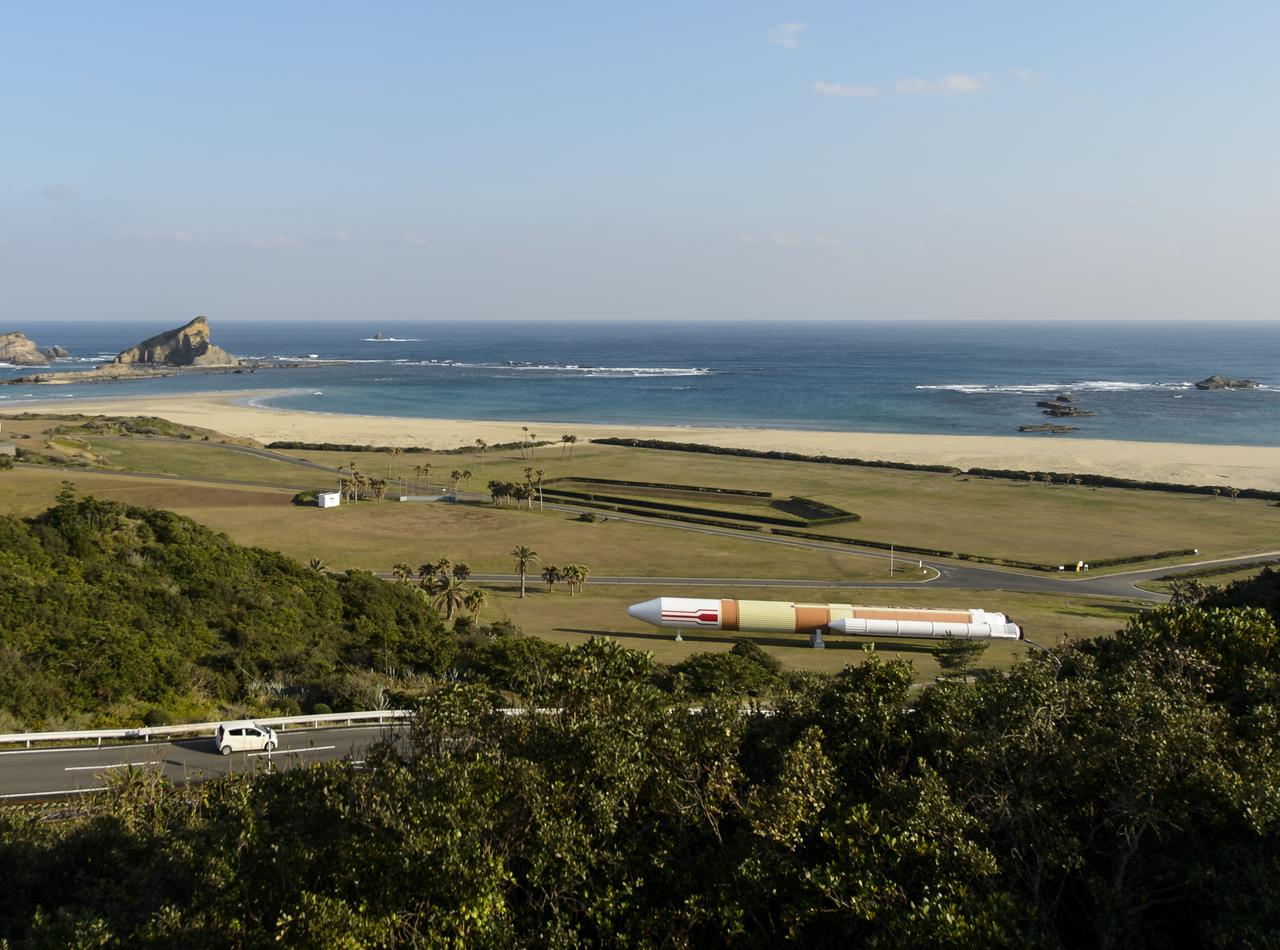
A sign at an overlook, named Rocket Hill, helps viewers identify the various facilities of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), including launch pad 1 that will be used Feb. 28, 2014 for the launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A full size model of an H-II rocket is seen at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) visitors center a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
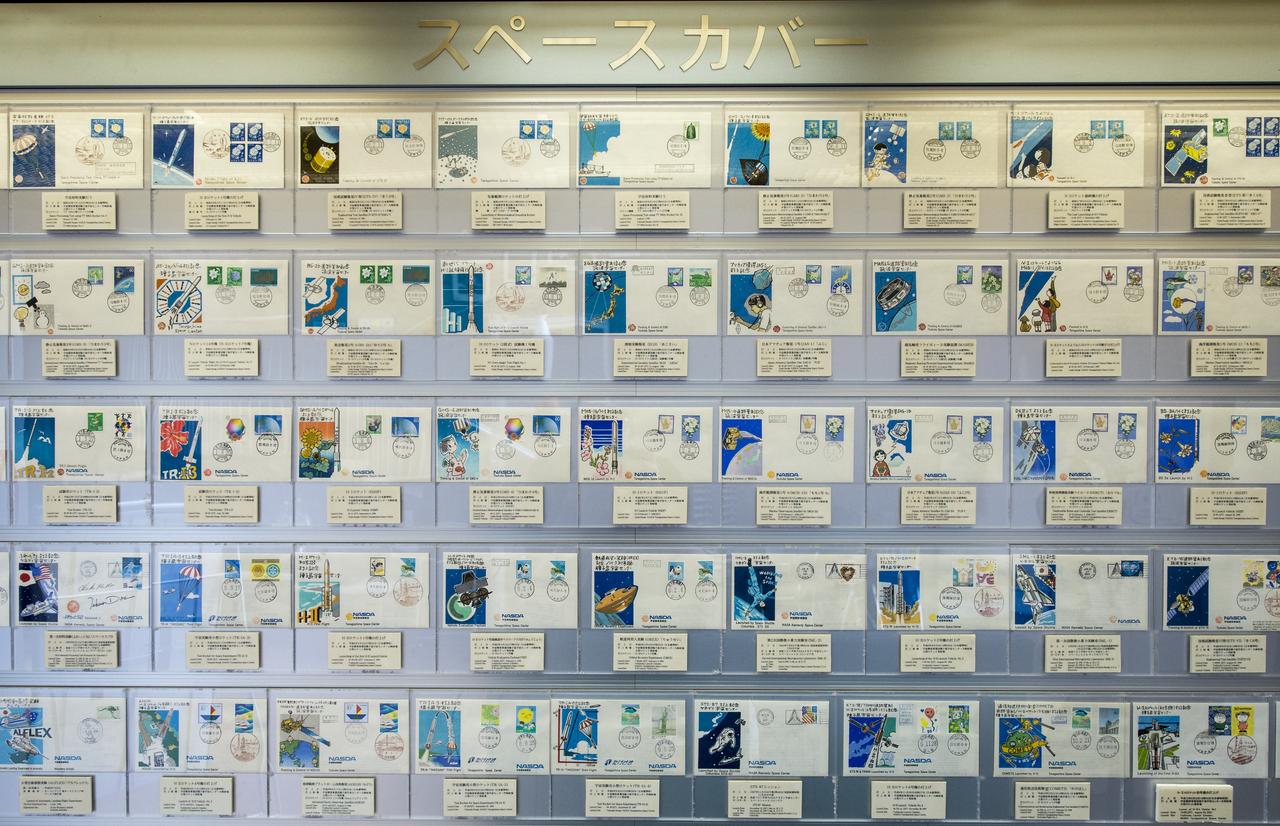

Envelopes with stamps depicting various space missions are shown at the visitor's center of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The launch vehicle for the Global Precipitation Measurement, or GPM, mission's Core Observatory arrived at Tanegashima Space Center, Japan, in the pre-dawn hours of Tuesday, Jan. 21, local time. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Warren Schultzaburger GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Mitsubishi Heavy Industries <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
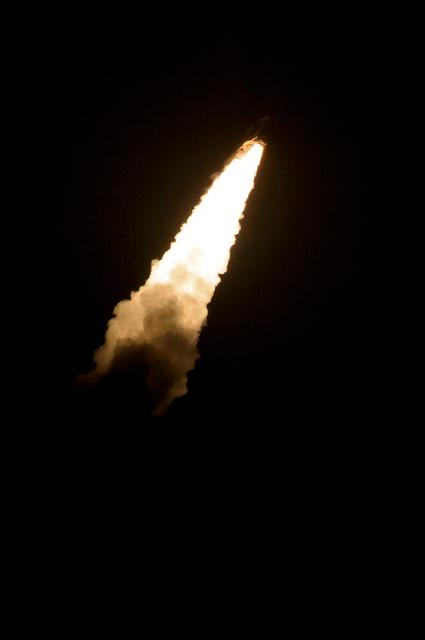

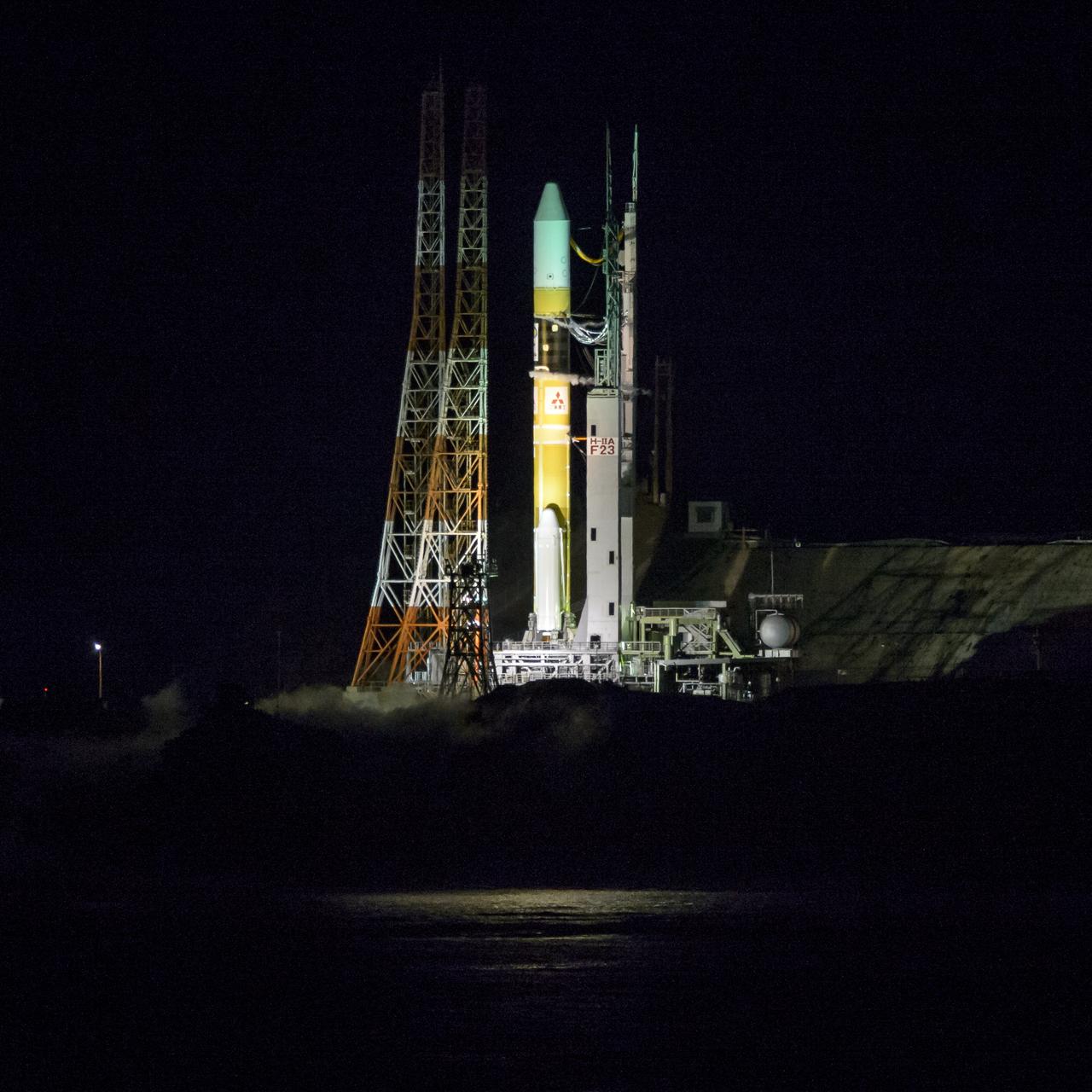
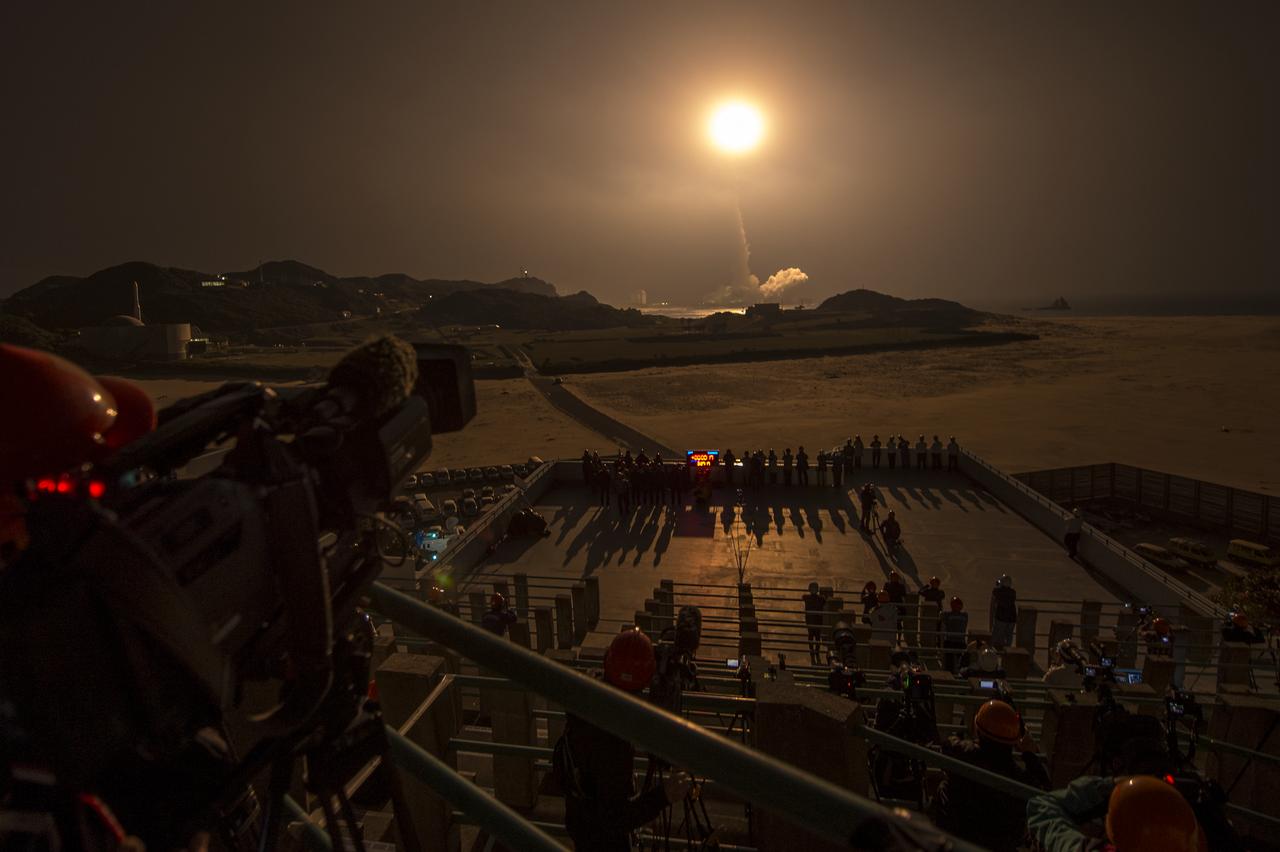
A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, fades into the dark as it launches from the Tanegashima Space Center, Friday, Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. The GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
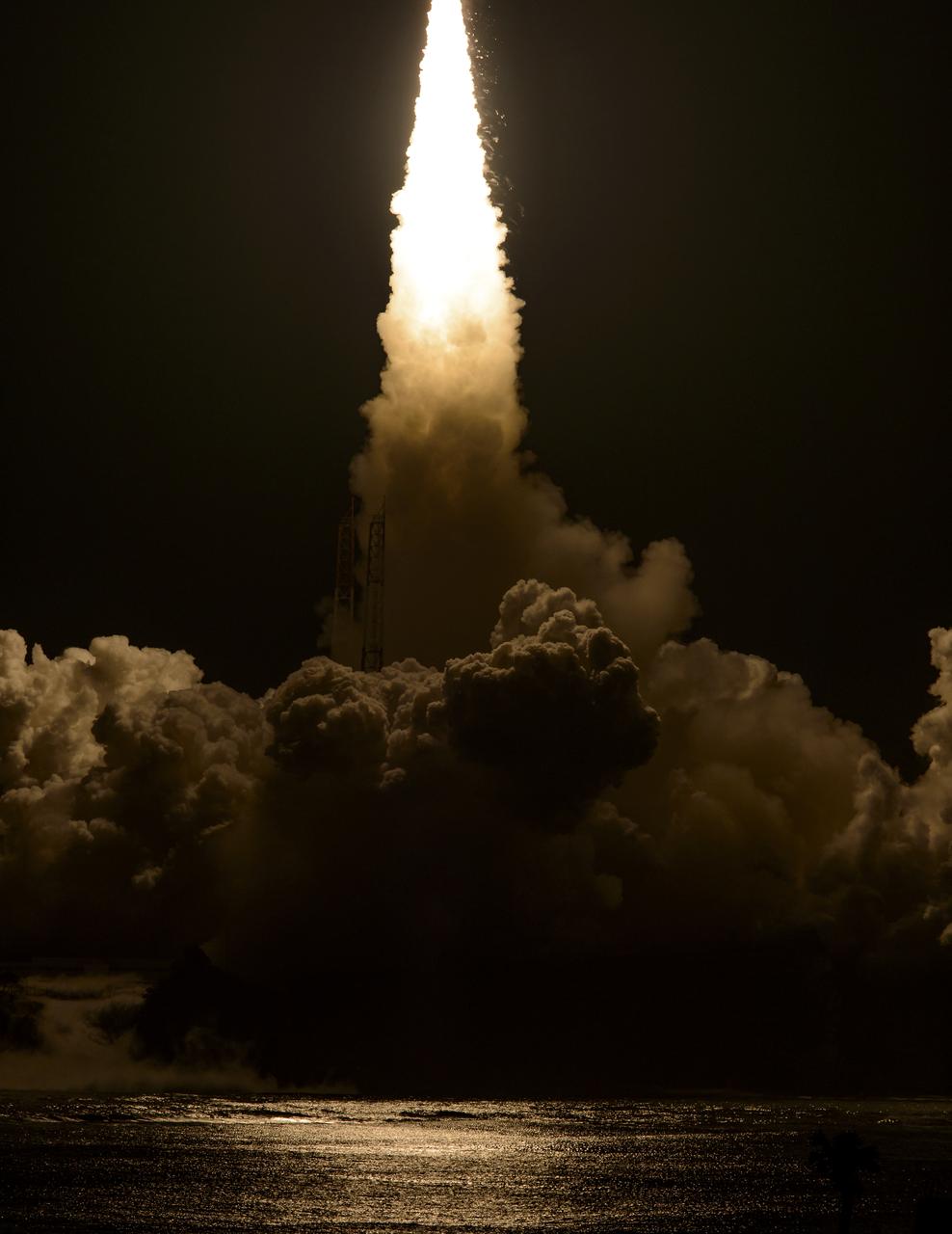

Flames and smoke from a Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, are seen during the launch from the Tanegashima Space Center, Friday, Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. The GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
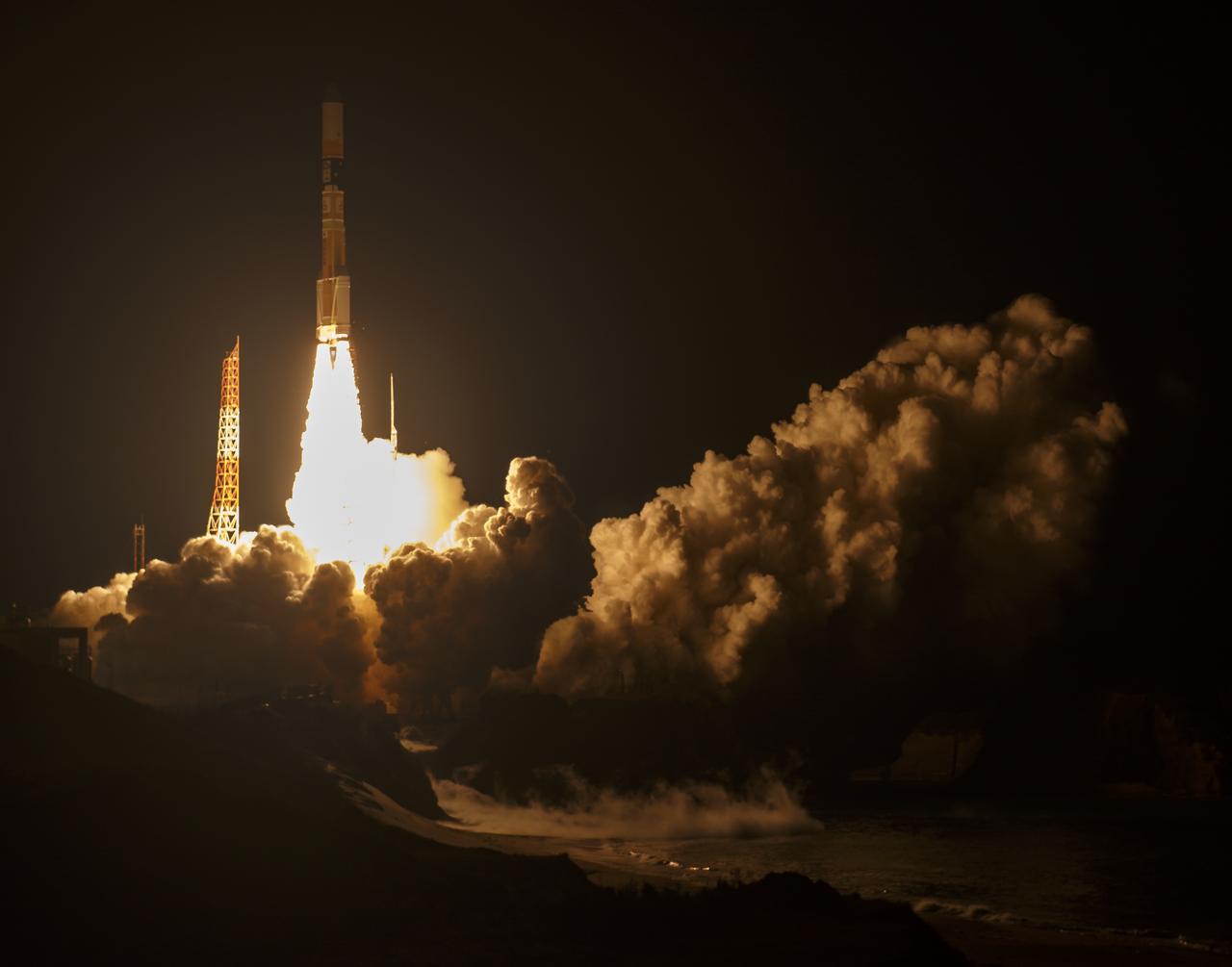

A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, is seen launching from the Tanegashima Space Center, Friday, Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. The GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, is seen launching from the Tanegashima Space Center, Friday, Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. The GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
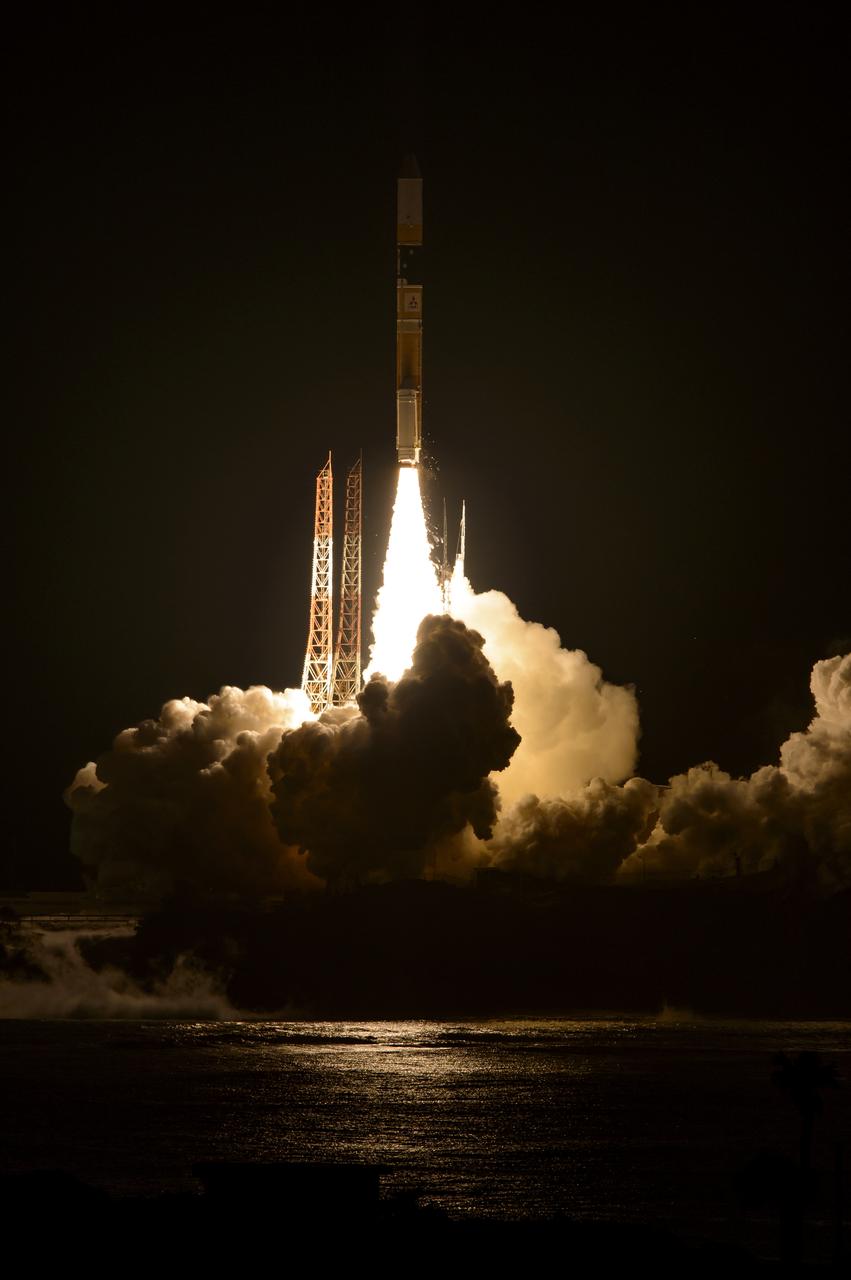

A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, is seen launching from the Tanegashima Space Center, Friday, Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. The GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
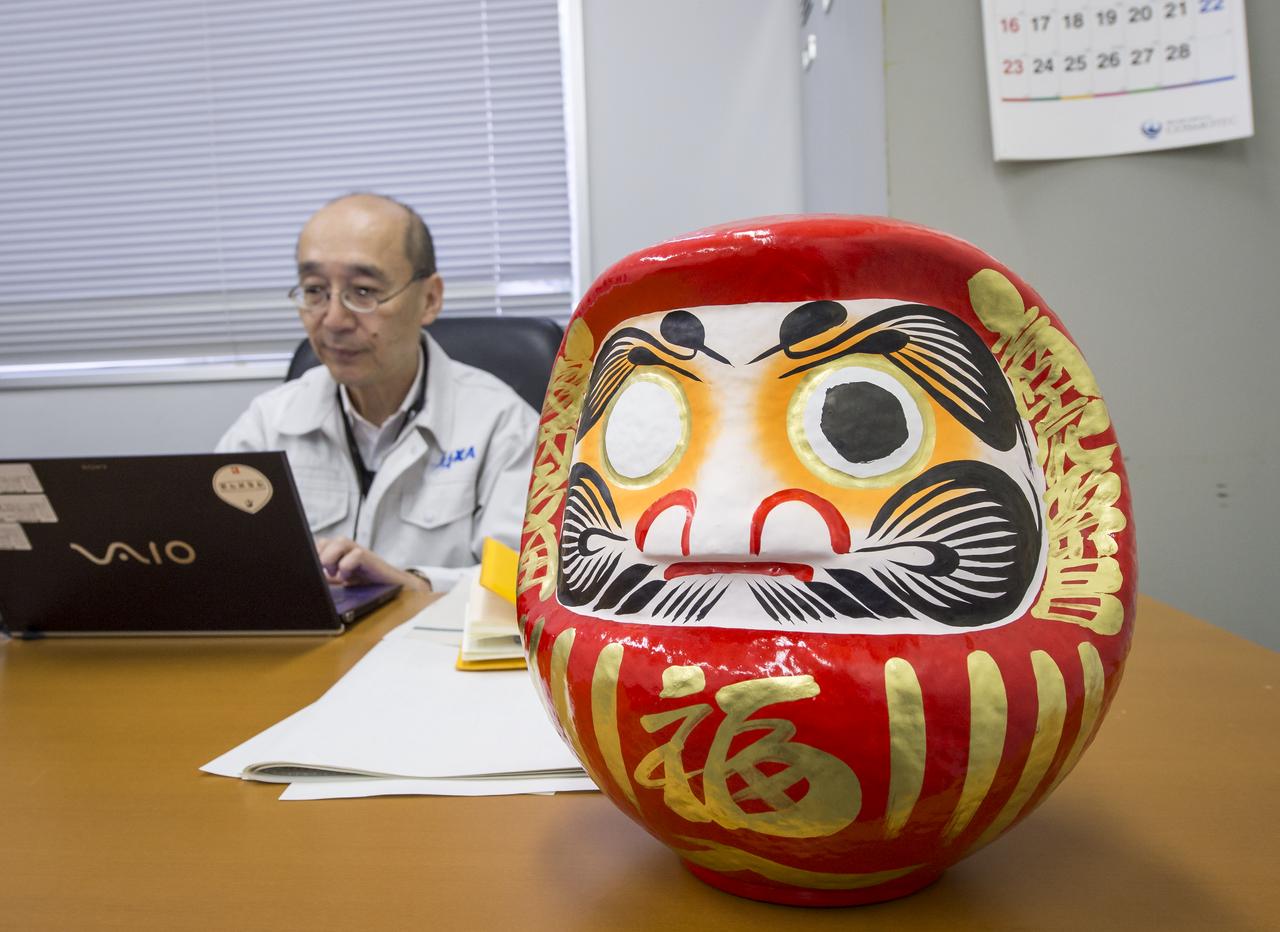

A daruma doll is seen on the desk of Masahiro Kojima, GPM Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar project manager, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), at the Tanegashima Space Cener's Range Control Center (RCC), Wednesday, Feb. 26, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. One eye of the daruma doll is colored in when a goal is set and the second eye is colored in at the completion of the goal. JAXA plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
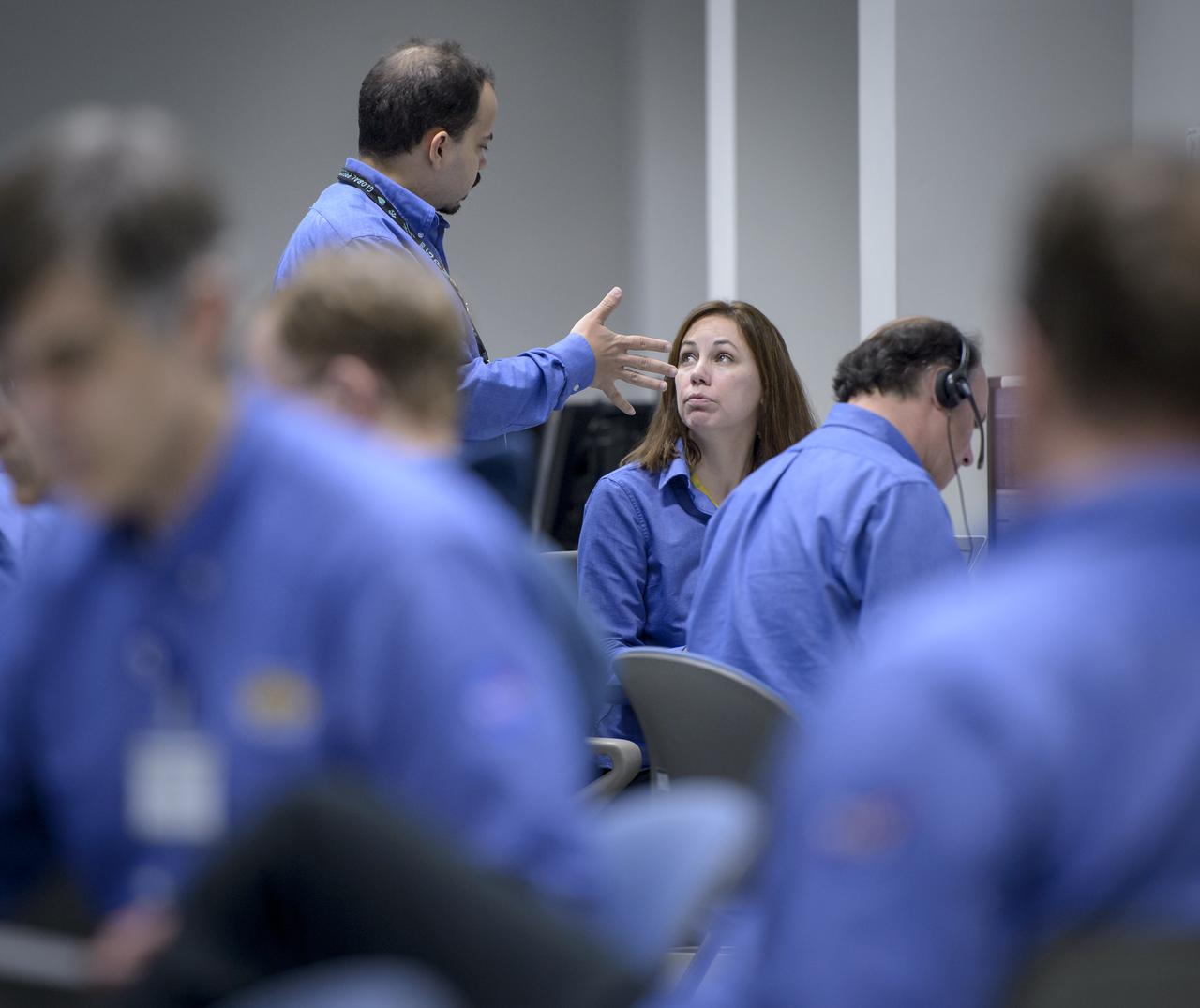

NASA GPM Test Conductors John Pope, and, Michelle Lacombe talk during the all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
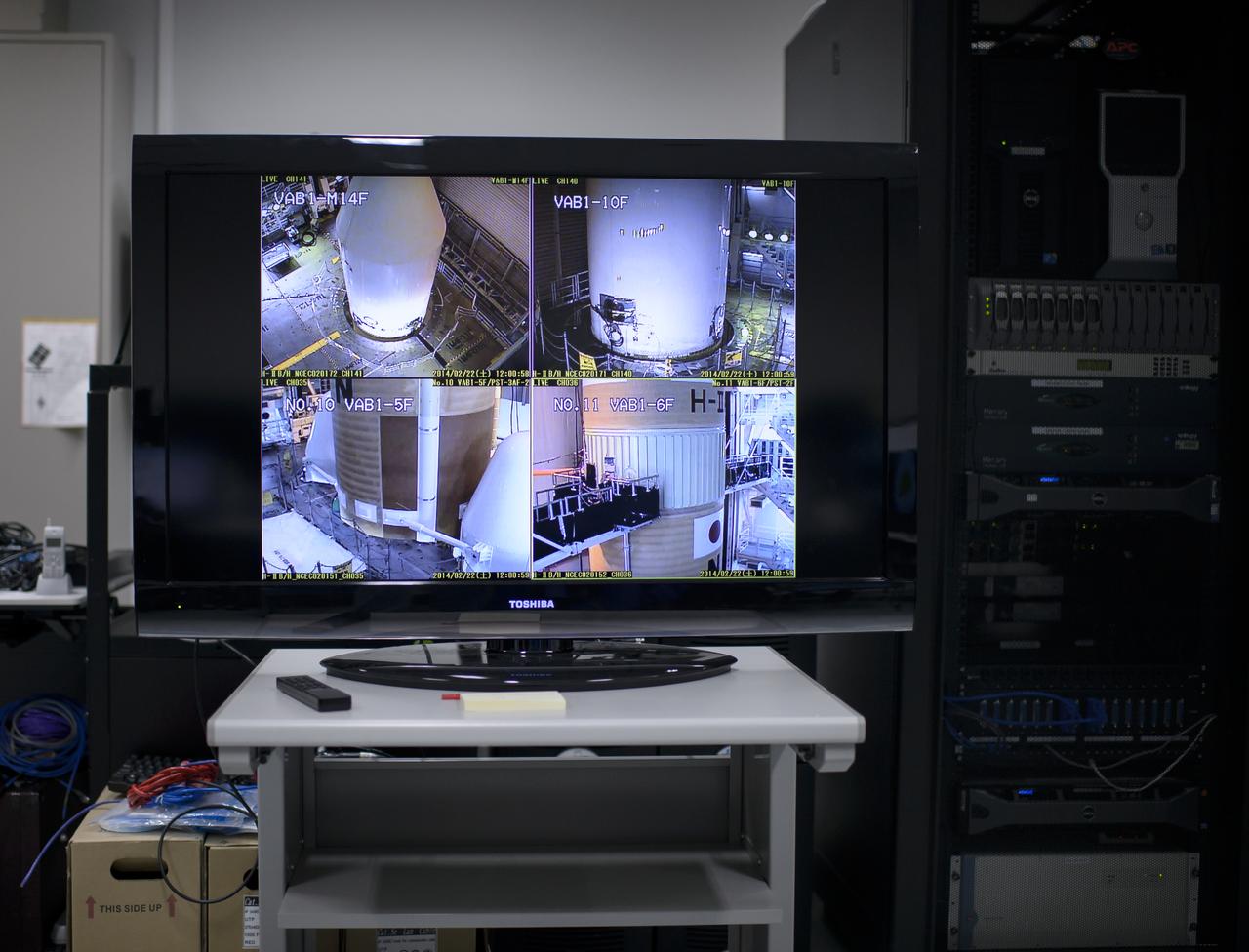

A live television view of the H-IIA rocket, with the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, is seen inside the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2) during an all-day launch simulation, Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
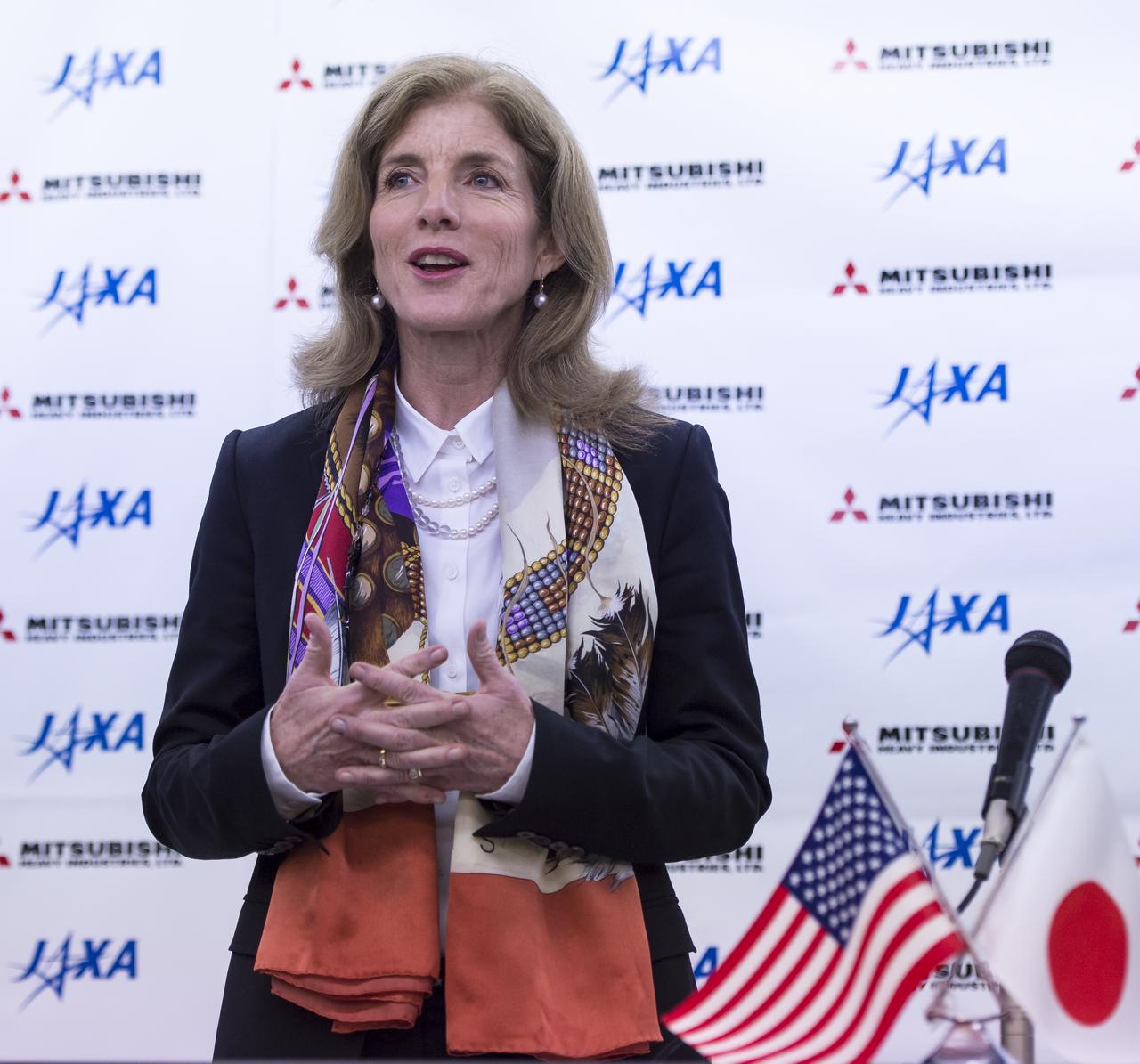

Caroline Kennedy, U.S. Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary to Japan, congratulated both NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory teams and noted it was an example of over 40 years of strong U.S. and Japan relations, Friday Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) Tanegashima, Japan. The Ambassador witnessed the launch of a Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, GPM Core Observatory. The GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
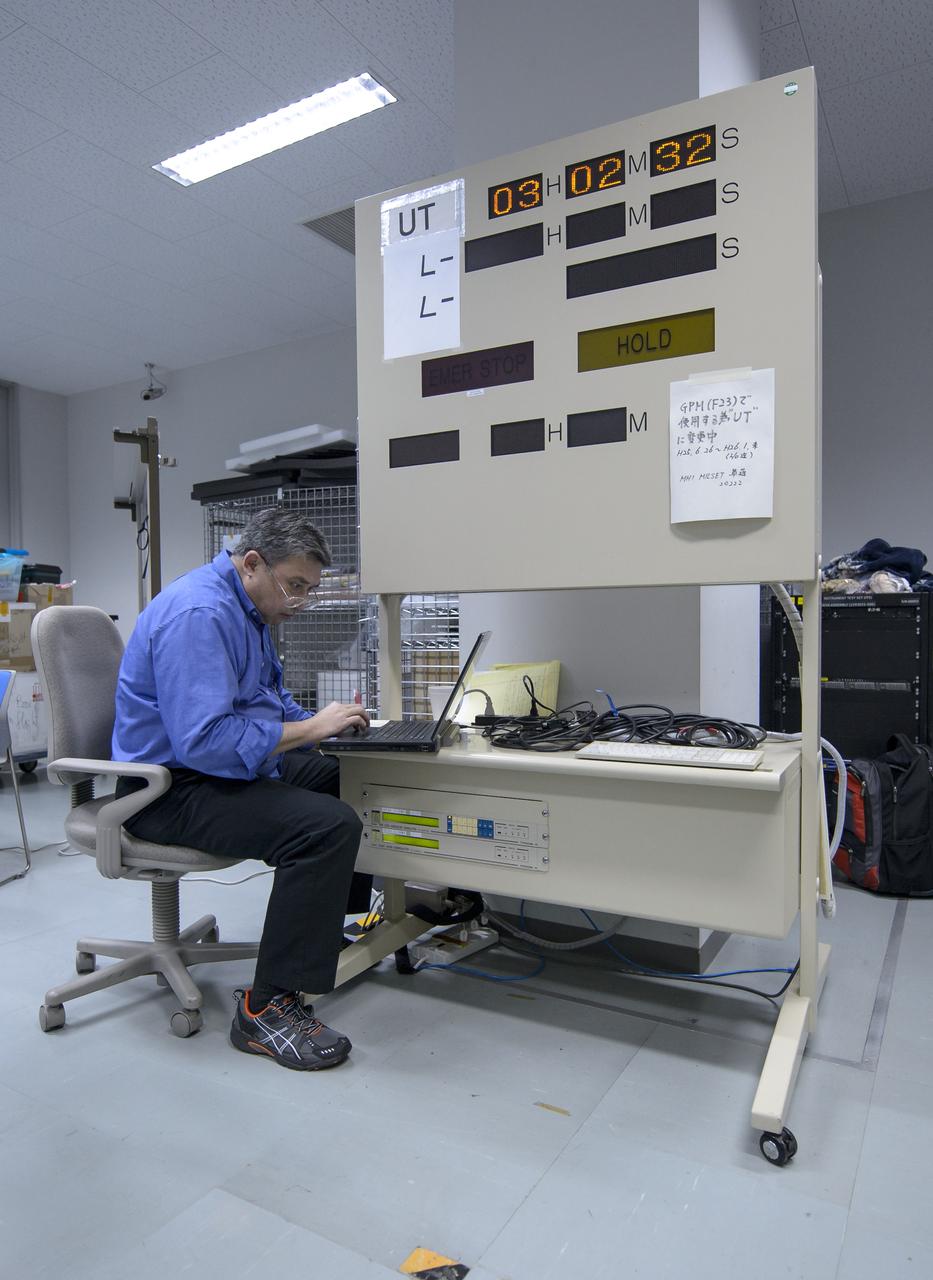

Clyde Woodall, NASA GPM launch services, is seen during the all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

George Dakermanji, NASA GPM Power, monitors the progress of an all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA GPM Radio Frequency Engineer David Lassiter monitors the progress of an all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Andy Aylward, GPM EGSE, monitors the progress of an all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
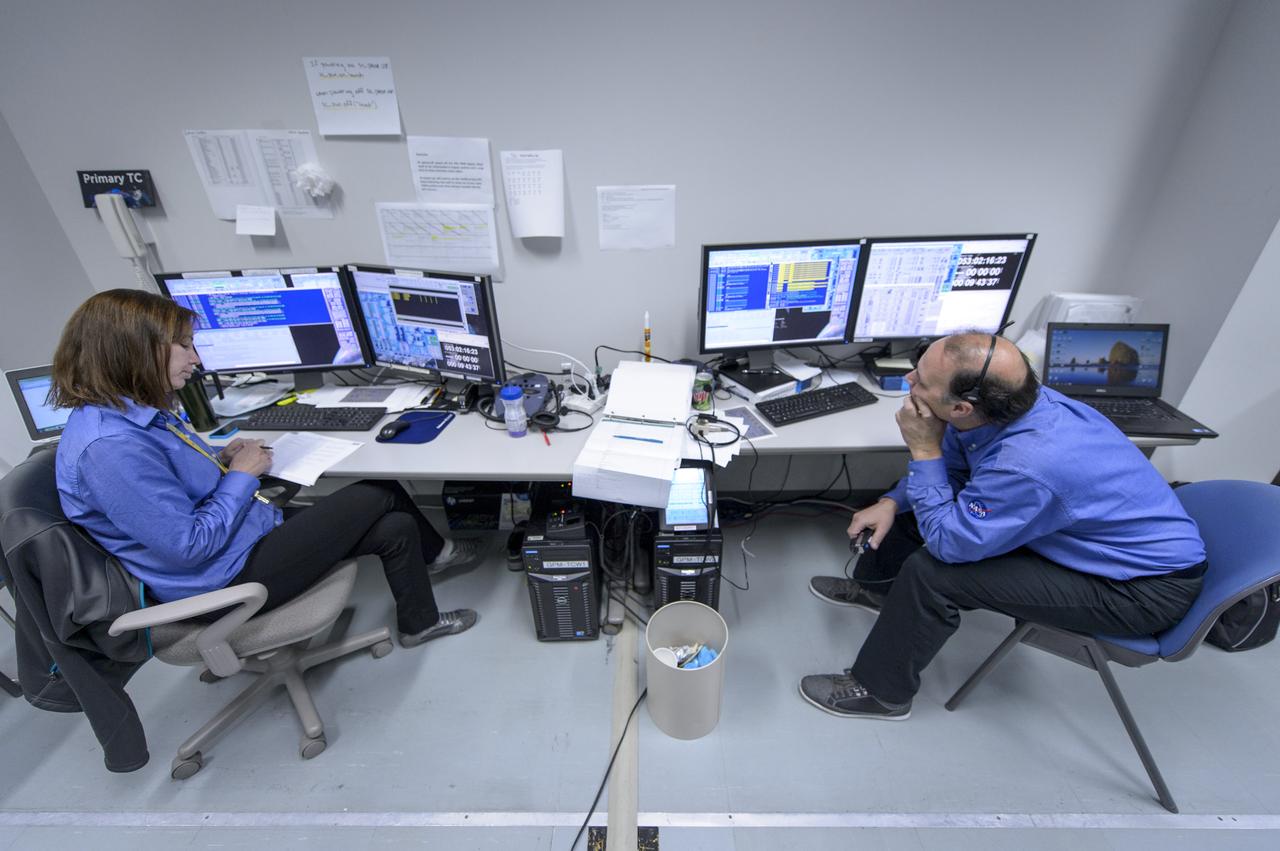

NASA GPM Test Conductors, Michelle Lacombe, left, and Bill Dehaven participate in an all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
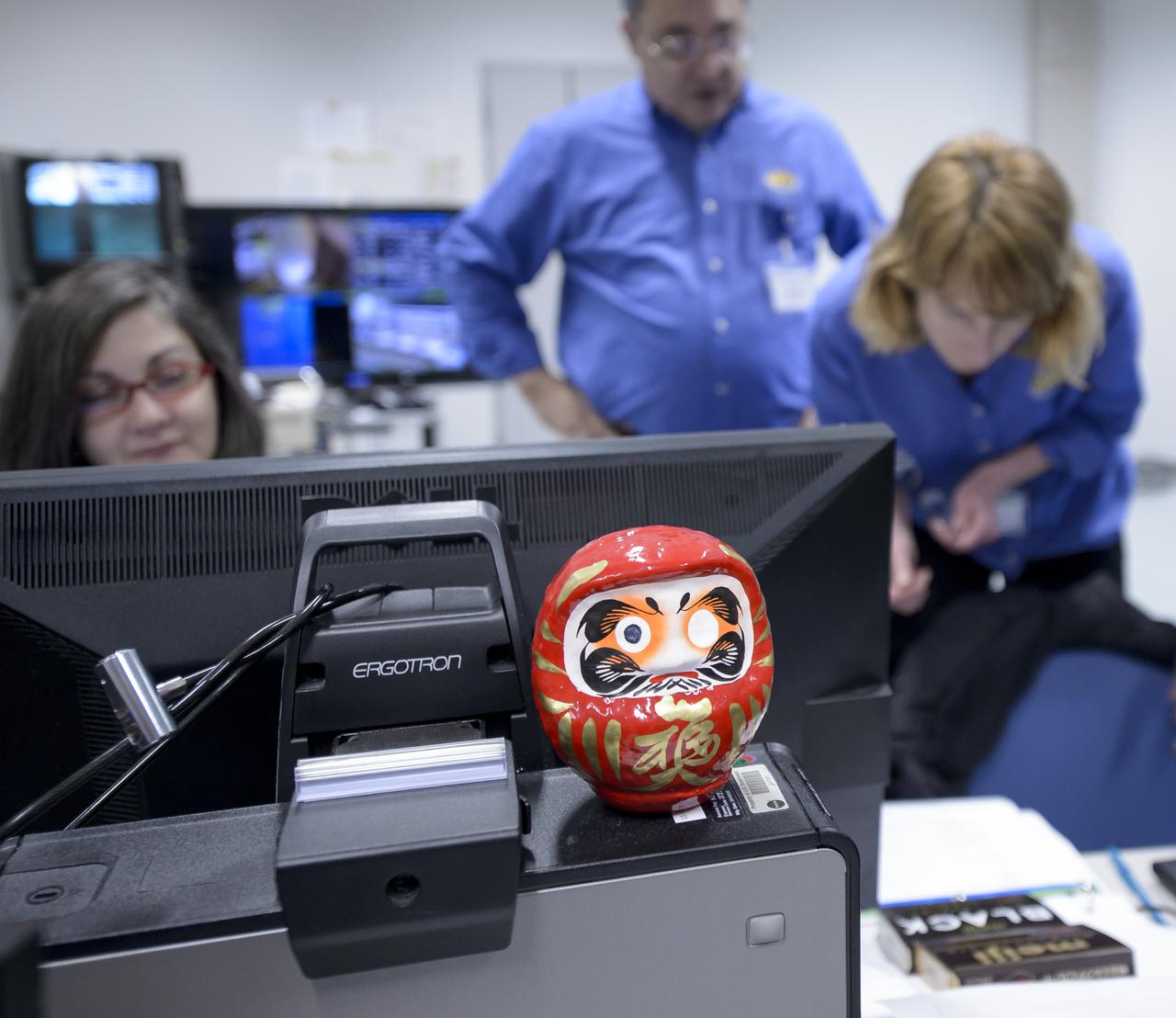

A daruma doll is seen amongst the NASA GPM Mission launch team in the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2) during the all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. One eye of the daruma doll is colored in when a goal is set, in this case a successful launch of GPM, and the second eye is colored in at the completion of the goal. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
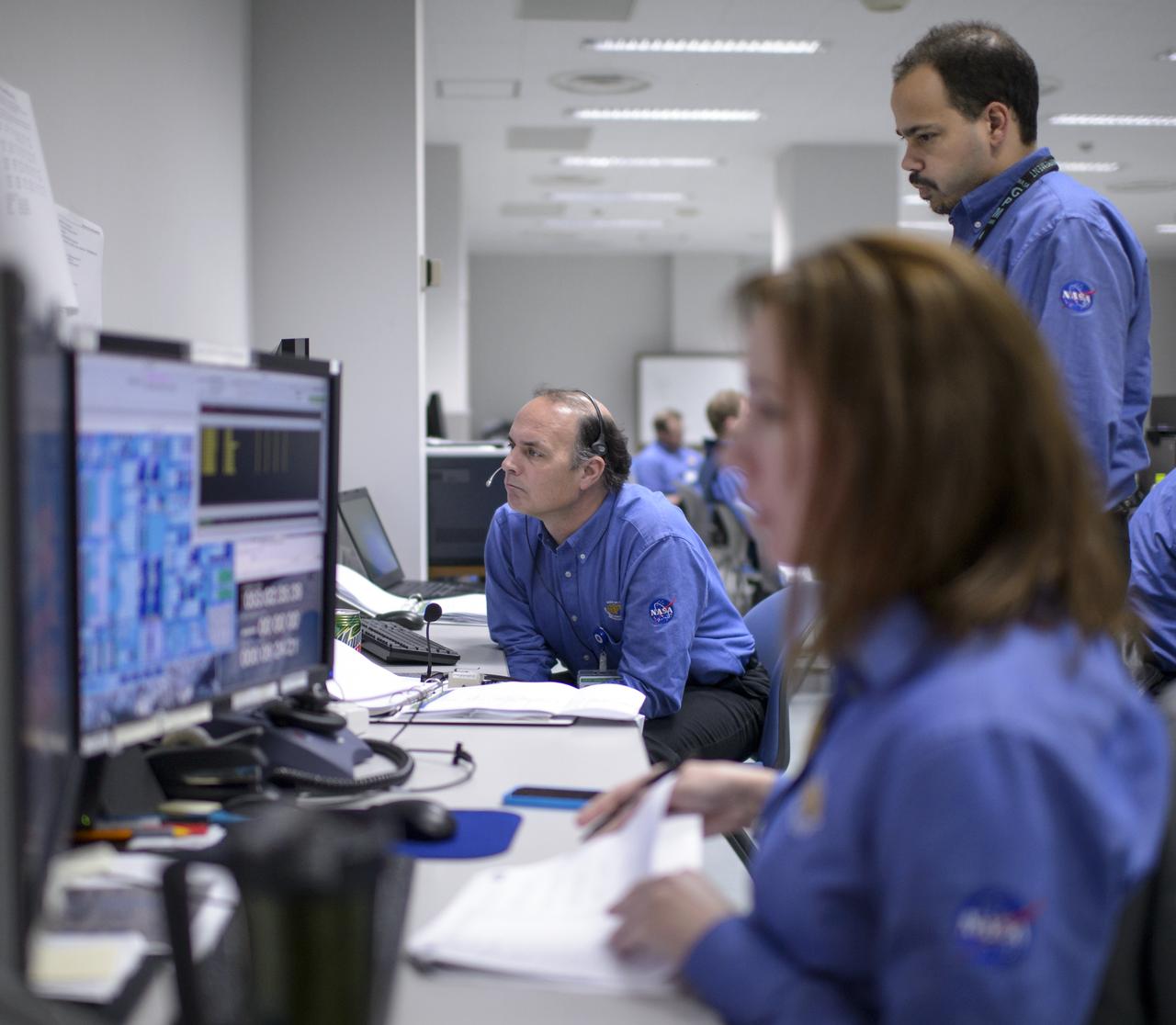

NASA GPM Test Conductors, Bill Dehaven, left, and John Pope, standing, and other GPM team members, participate in an all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
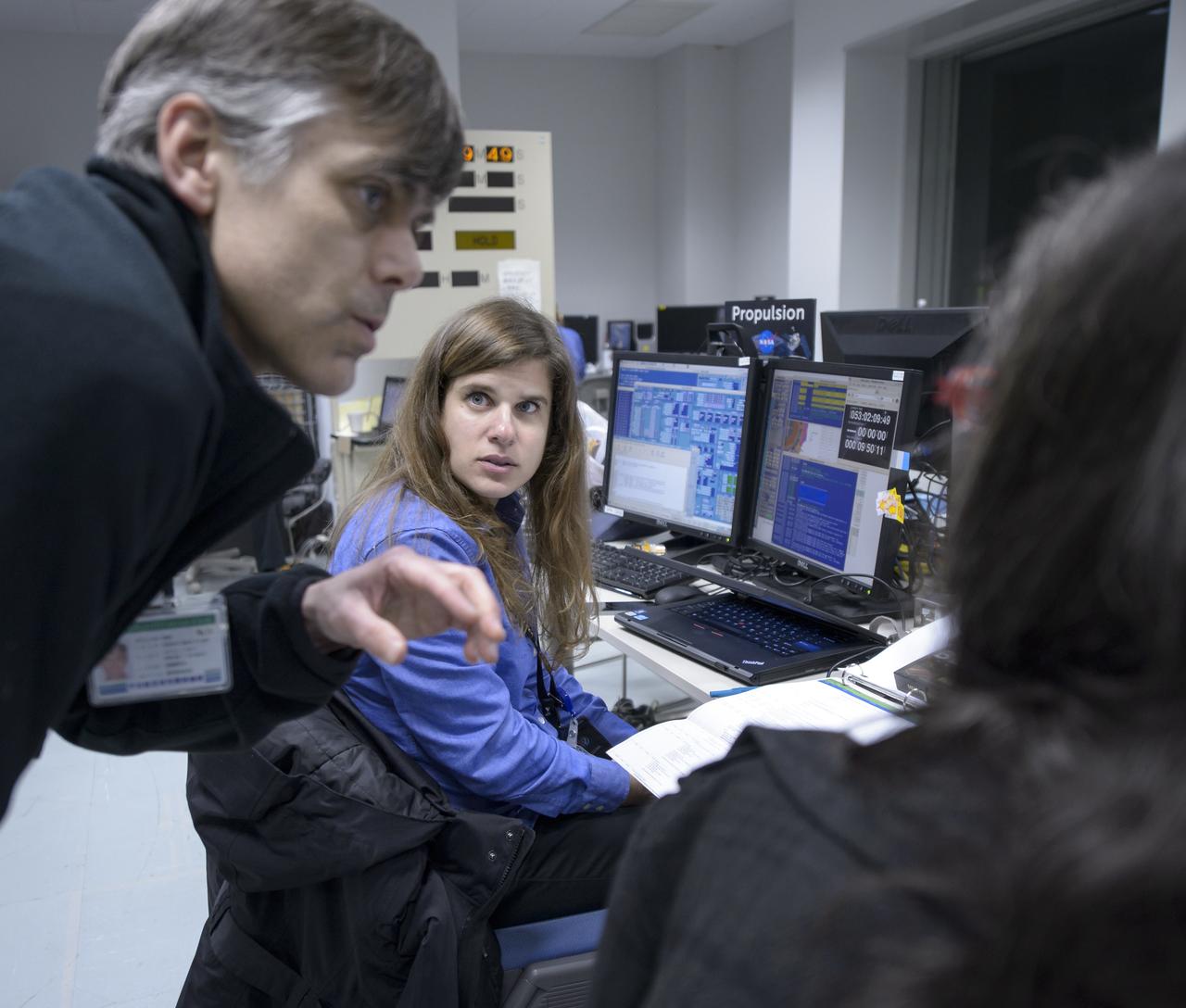

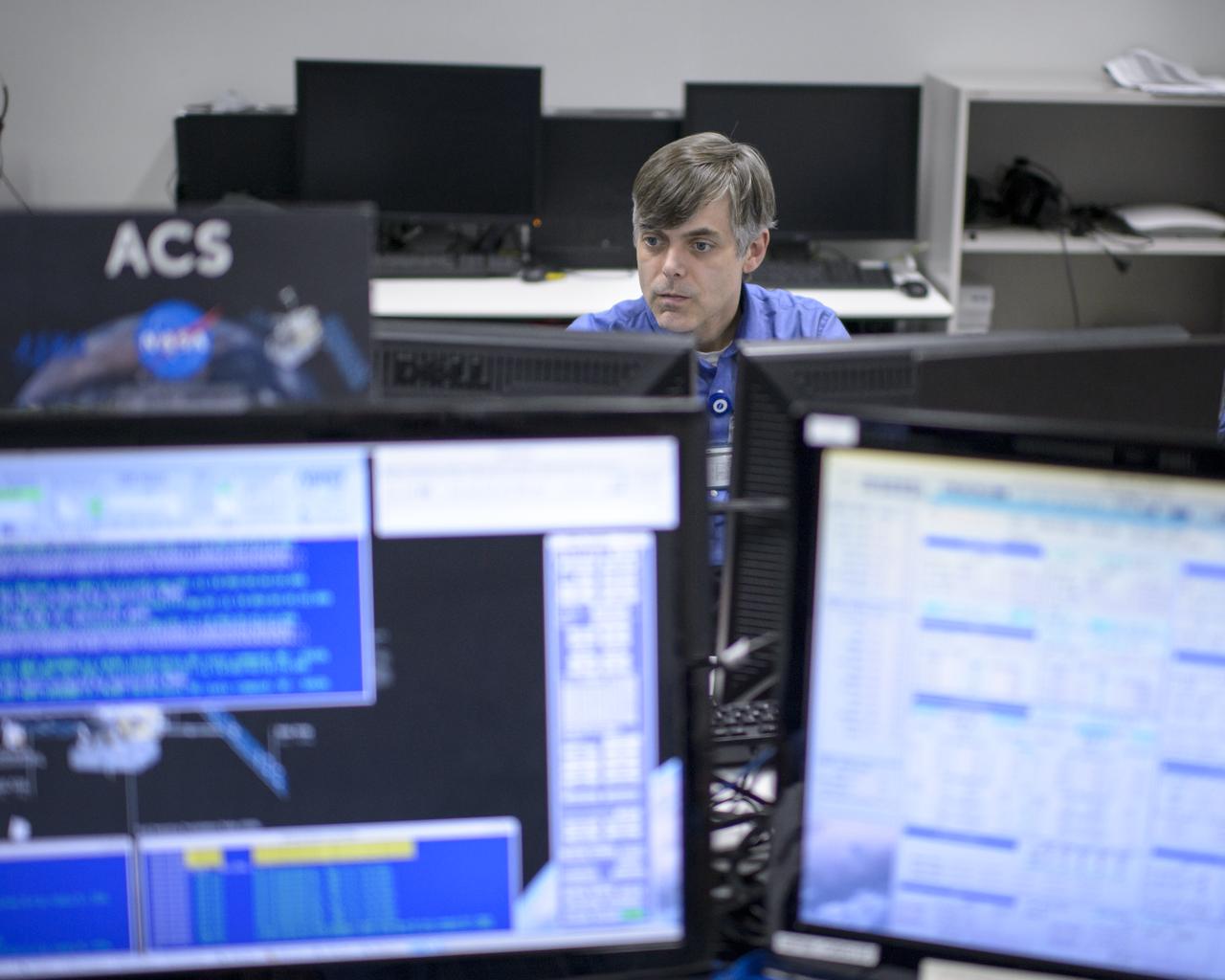
Andy Aylward, NASA GPM EGSE, left, Beth Weinsteen, NASA GPM Integration and Testing Team, center, and another GPM team member, talk during the all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
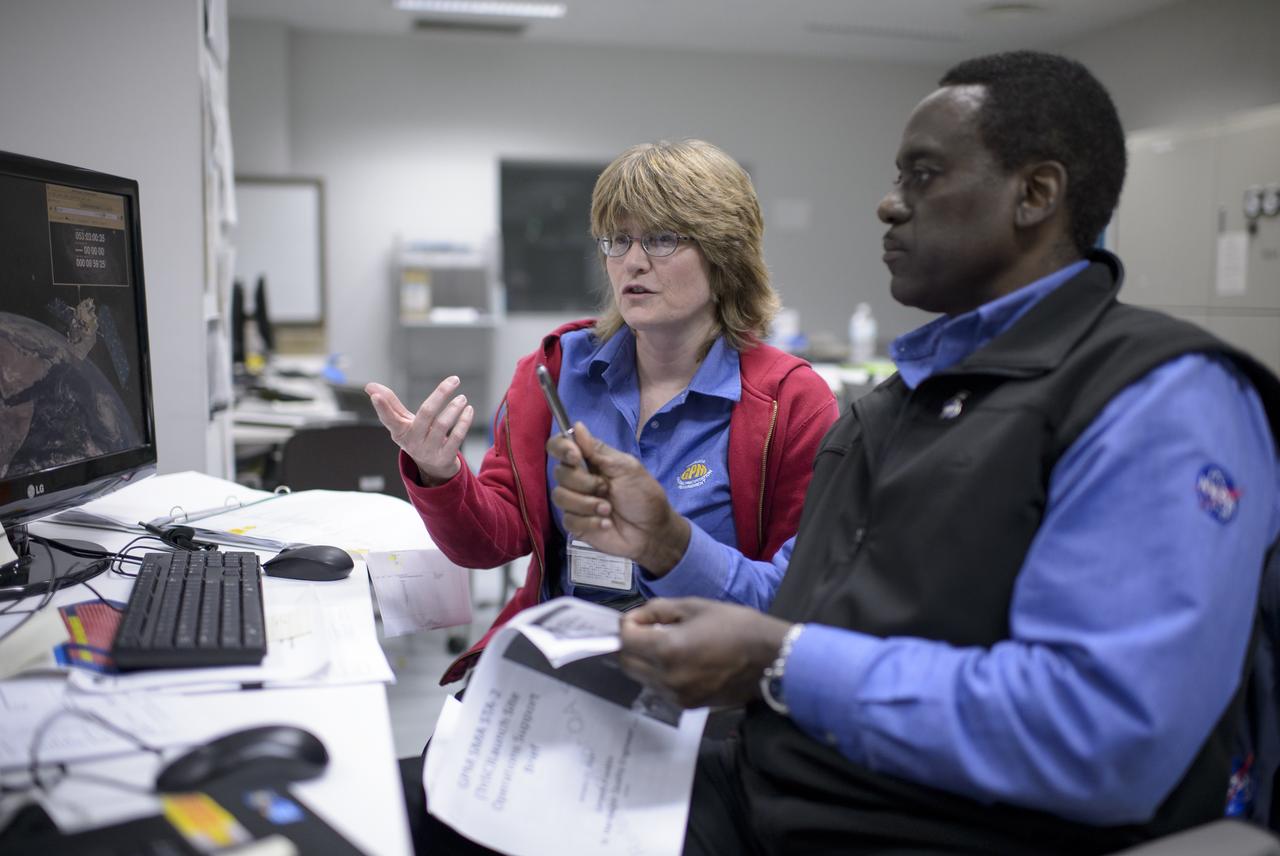

NASA GPM Safety Quality and Assurance, Shirley Dion, and, NASA GPM Quality and Assurance, Larry Morgan, monitor the all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
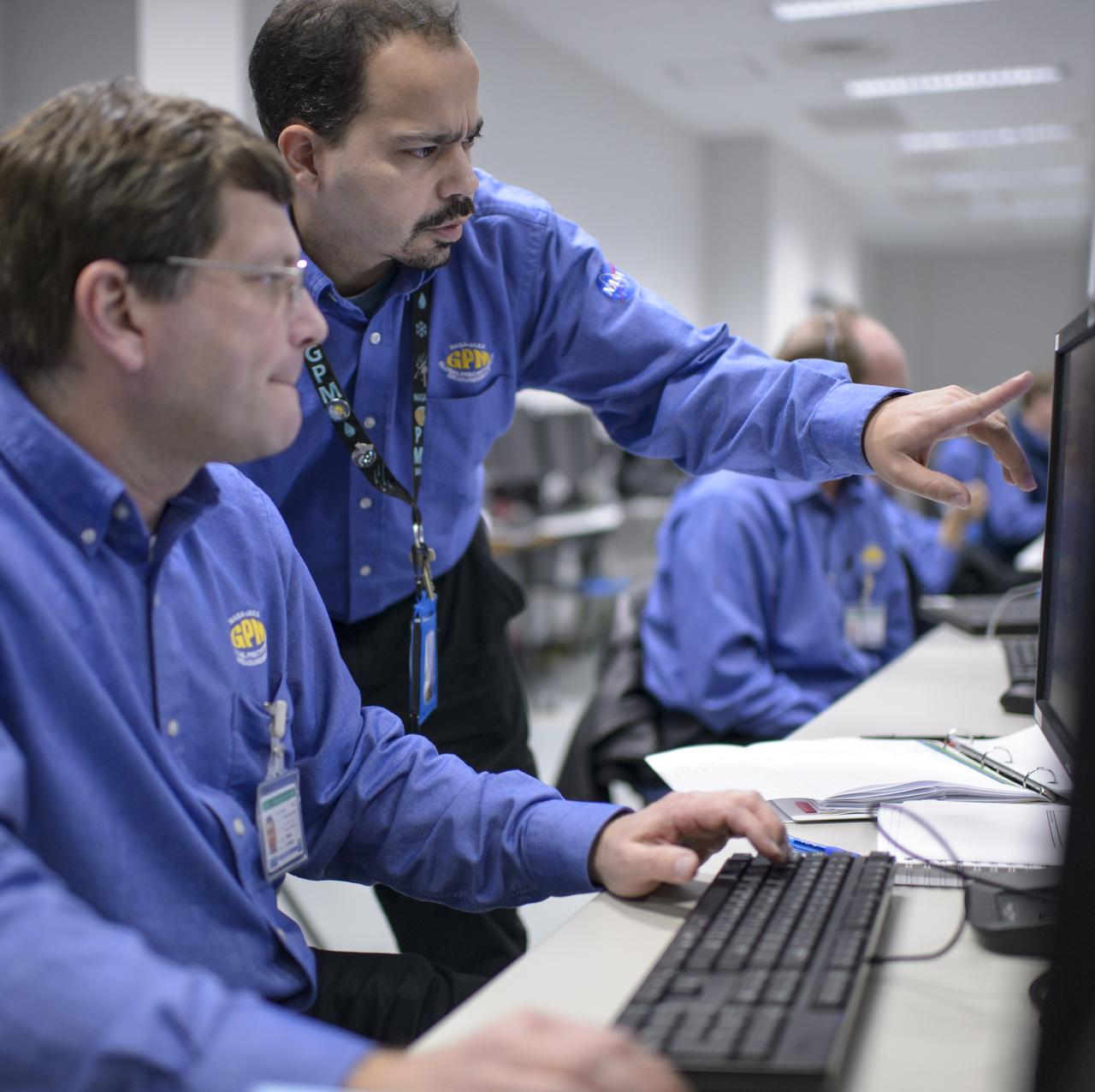

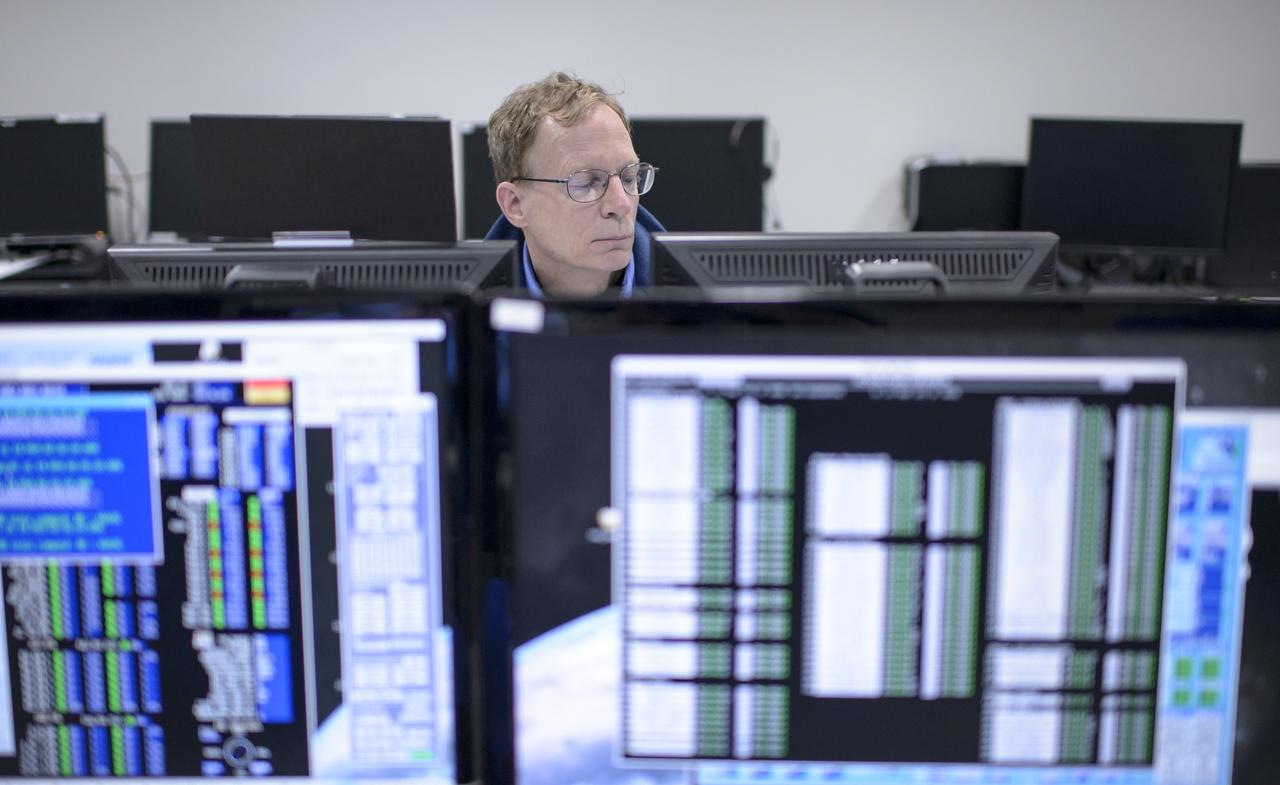
NASA GPM Systems team member Tim Grunner, left, and NASA GPM Test Conductor John Pope talk during an all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
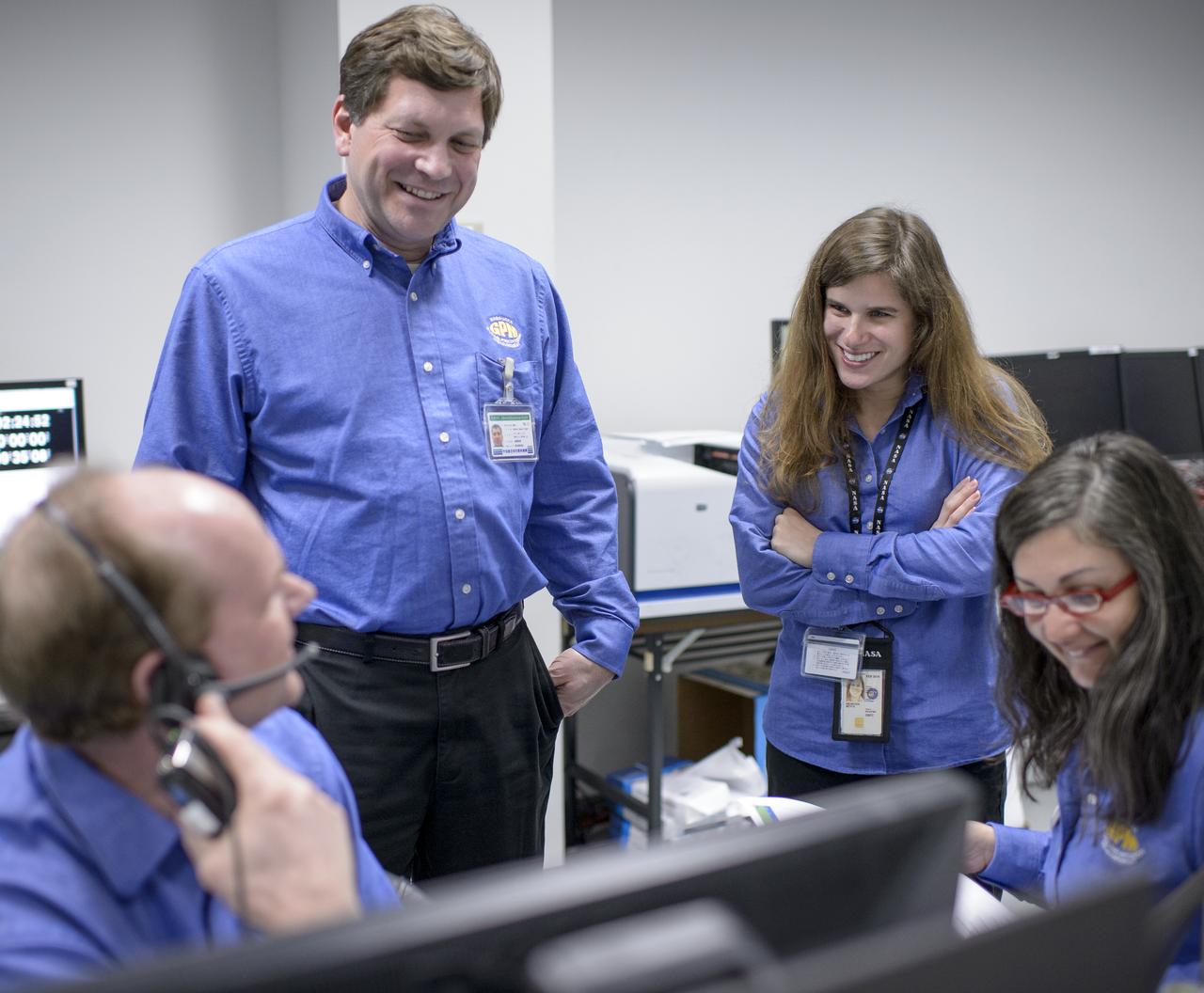

NASA GPM Systems team members, Tim Grunner, left, Harry Culver, 2nd from left, and, Liza Bartusek, right, talk, along with with GPM Testing team member Beth Weinsteen, during an all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
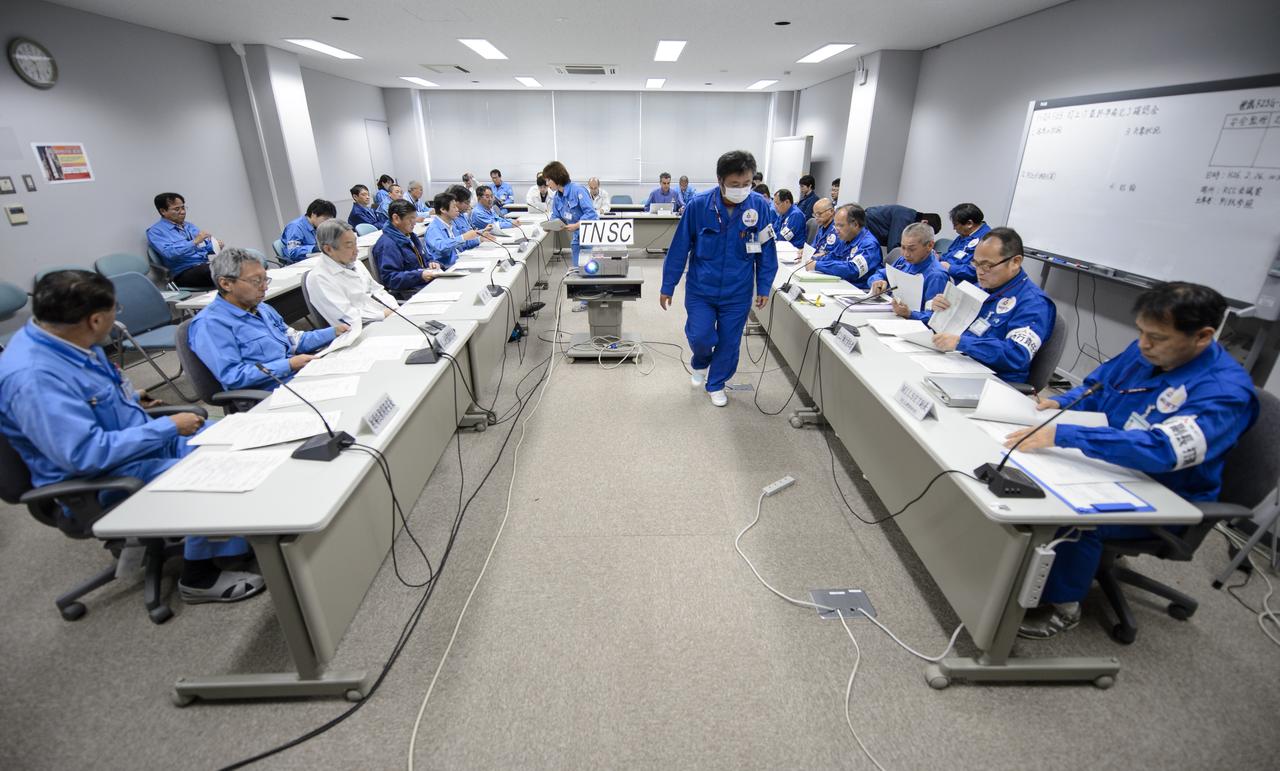

Chief officers from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd., the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and NASA met on Wednesday, Feb. 26, 2014 in the Range Control Center (RCC) of the Tanegashima Space Center, Japan, to review the readiness of the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory for launch. The spacecraft is scheduled to launch aboard an H-IIA rocket early on the morning of Feb. 28 Japan time. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
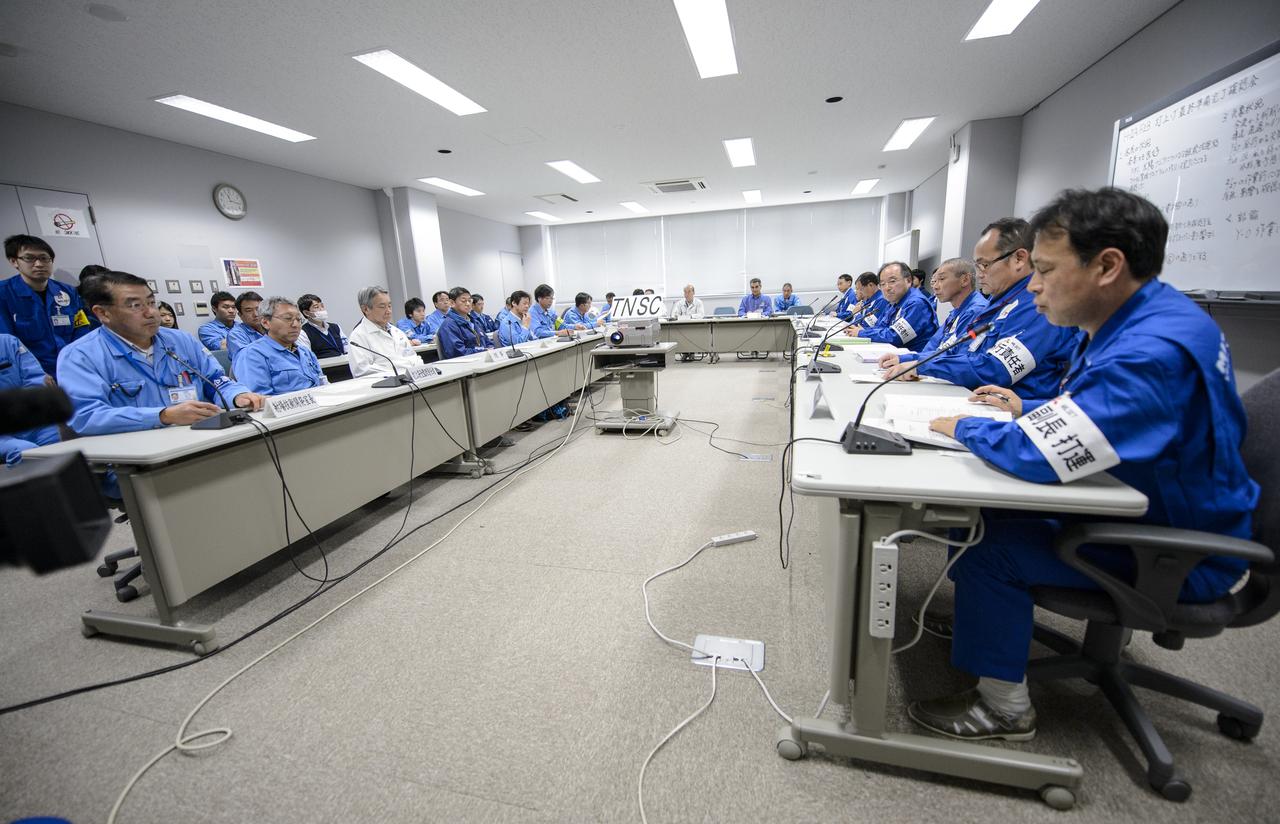

Chief officers from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd., the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and NASA met on Wednesday, Feb. 26, 2014 in the Range Control Center (RCC) of the Tanegashima Space Center, Japan, to review the readiness of the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory for launch. The spacecraft is scheduled to launch aboard an H-IIA rocket early on the morning of Feb. 28 Japan time. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
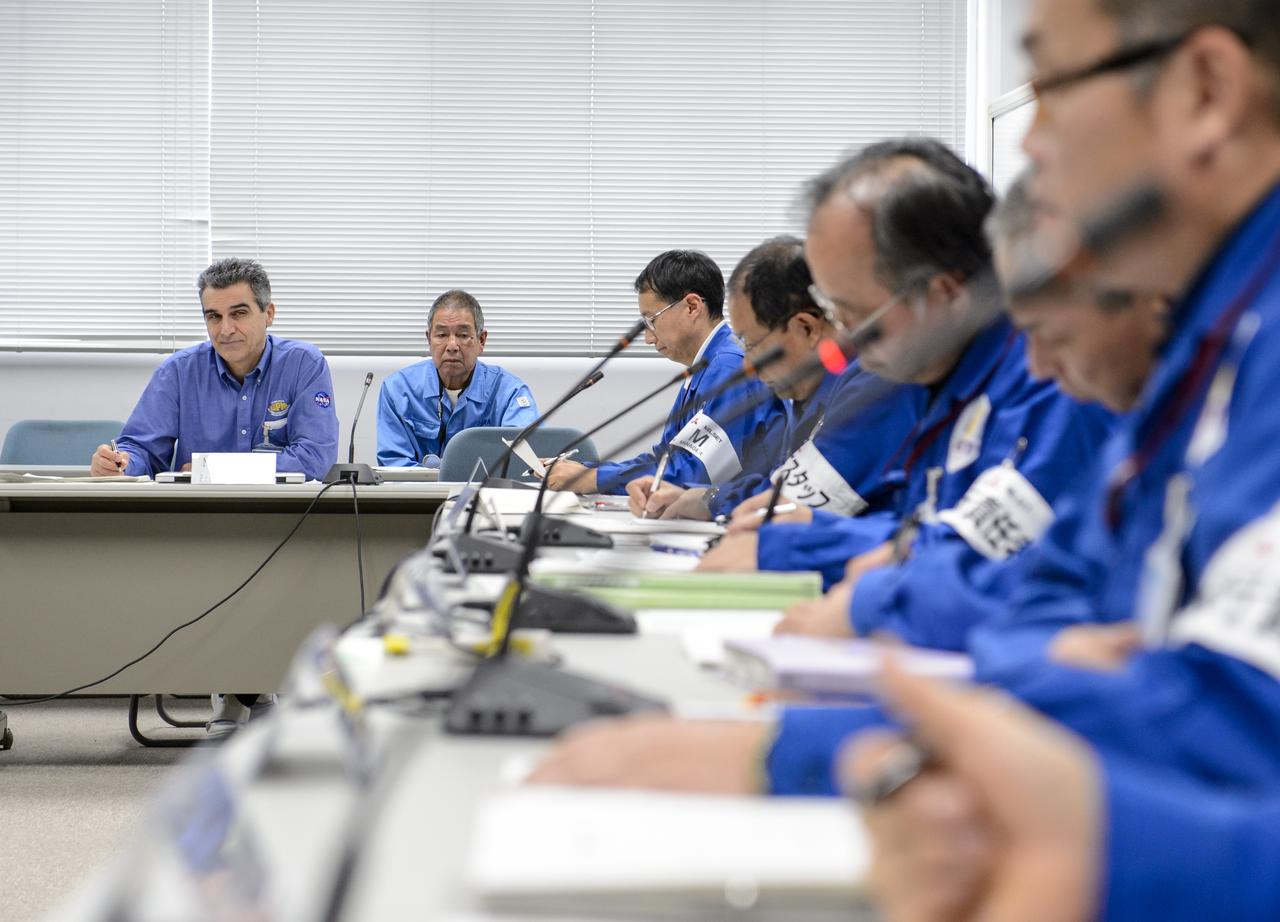

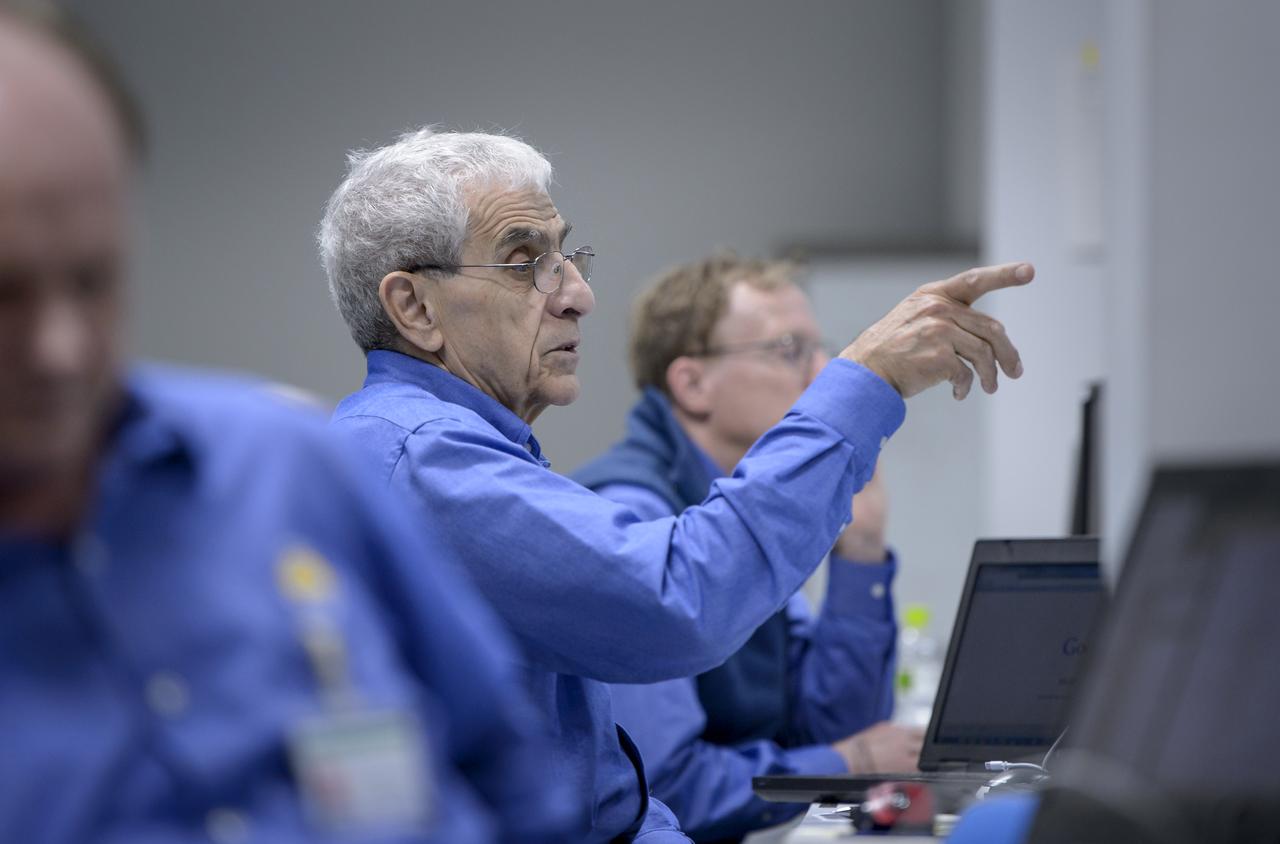
Art Azarbarzin, NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) project manager, left, participates in the GPM Launch Readiness Review (LRR) along with Chief officers from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd., and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) on Wednesday, Feb. 26, 2014 at Tanegashima Space Center, Japan. The spacecraft is scheduled to launch aboard an H-IIA rocket early on the morning of Feb. 28 Japan time. At the meeting in the space center's Range Control Center, all preparations to date were reviewed and approval was given to proceed with launch on schedule. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
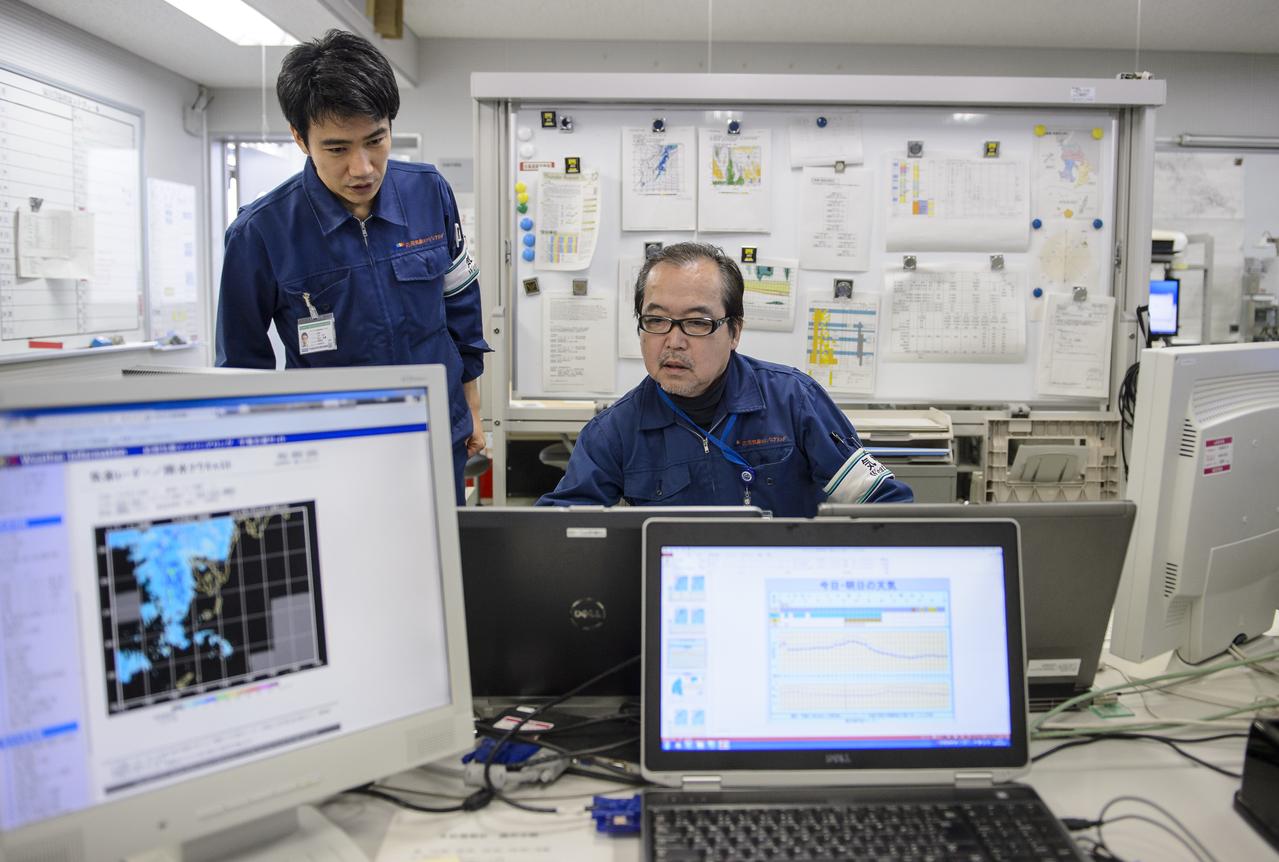

Members of the weather team prepare reports for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory Launch Readiness Review (LRR) with Chief officers from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd., the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), and NASA, on Wednesday, Feb. 26, 2014 at Tanegashima Space Center, Japan. The GPM spacecraft is scheduled to launch aboard an H-IIA rocket early on the morning of Feb. 28 Japan time. At the meeting in the space center's Range Control Center, all preparations to date were reviewed and approval was given to proceed with launch on schedule. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
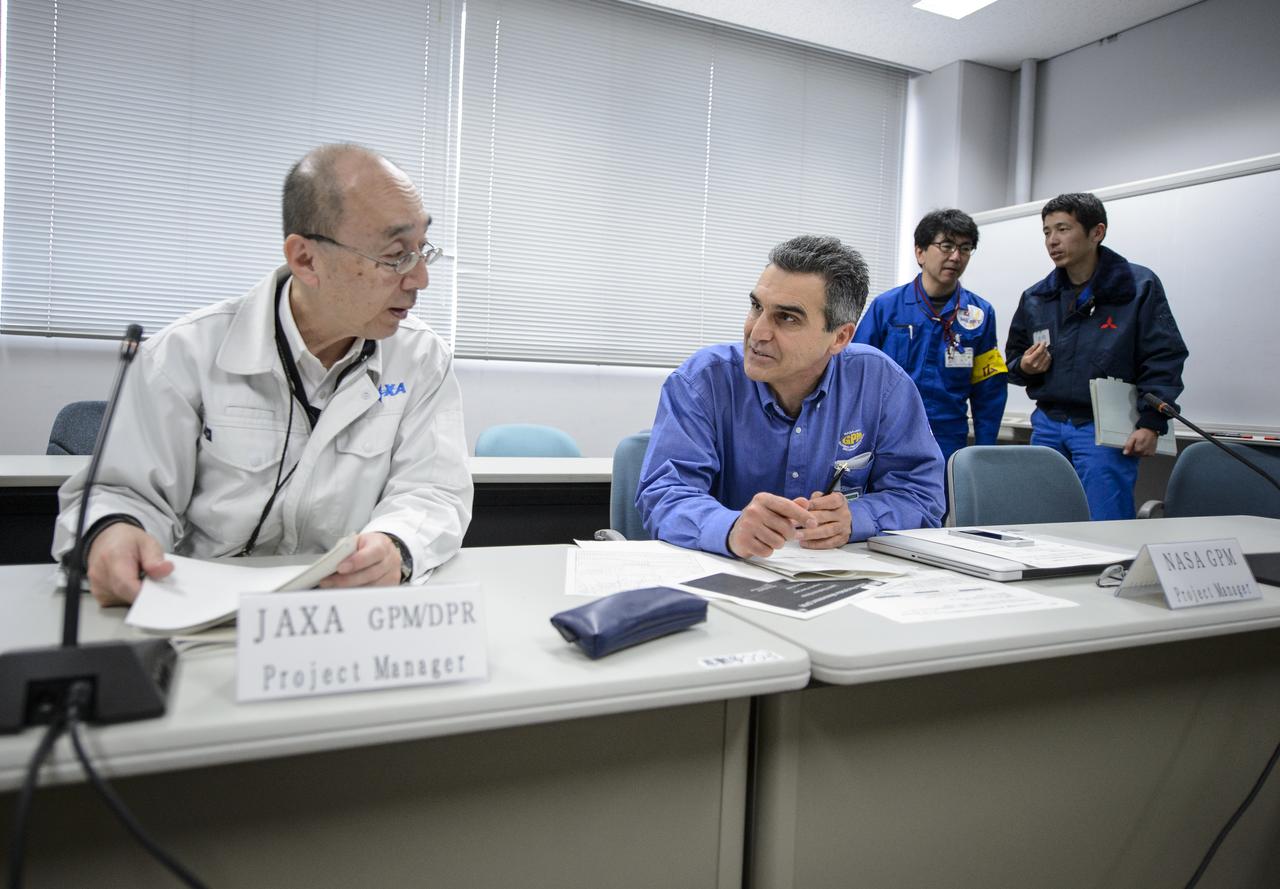

Masahiro Kojima, GPM Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar project manager, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), left, and, Art Azarbarzin, NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) project manager, talk after the GPM Launch Readiness Review (LRR), Wednesday, Feb. 26, 2014 at Tanegashima Space Center, Japan. The GPM spacecraft is scheduled to launch aboard an H-IIA rocket early on the morning of Feb. 28 Japan time. At the meeting in the space center's Range Control Center, all preparations to date were reviewed and approval was given to proceed with launch on schedule. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, is seen on launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Friday, Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Caroline Bouvier Kennedy, U.S. Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary to Japan, right, is welcomed by Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), President, Naoki Okumura, at the Tanegashima Space Center Visitors Center on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. The Ambassador is visiting the space center and hopes to witness the planned launch of a Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Caroline Bouvier Kennedy, U.S. Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary to Japan, center, tours the Tanegashima Space Center, Visitors Center with Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), President, Naoki Okumura, right, on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. The Ambassador visiting the space center and hopes to witness the planned launch of a Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A sign guides travelers to the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for Feb. 28, 2014 from the space center. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
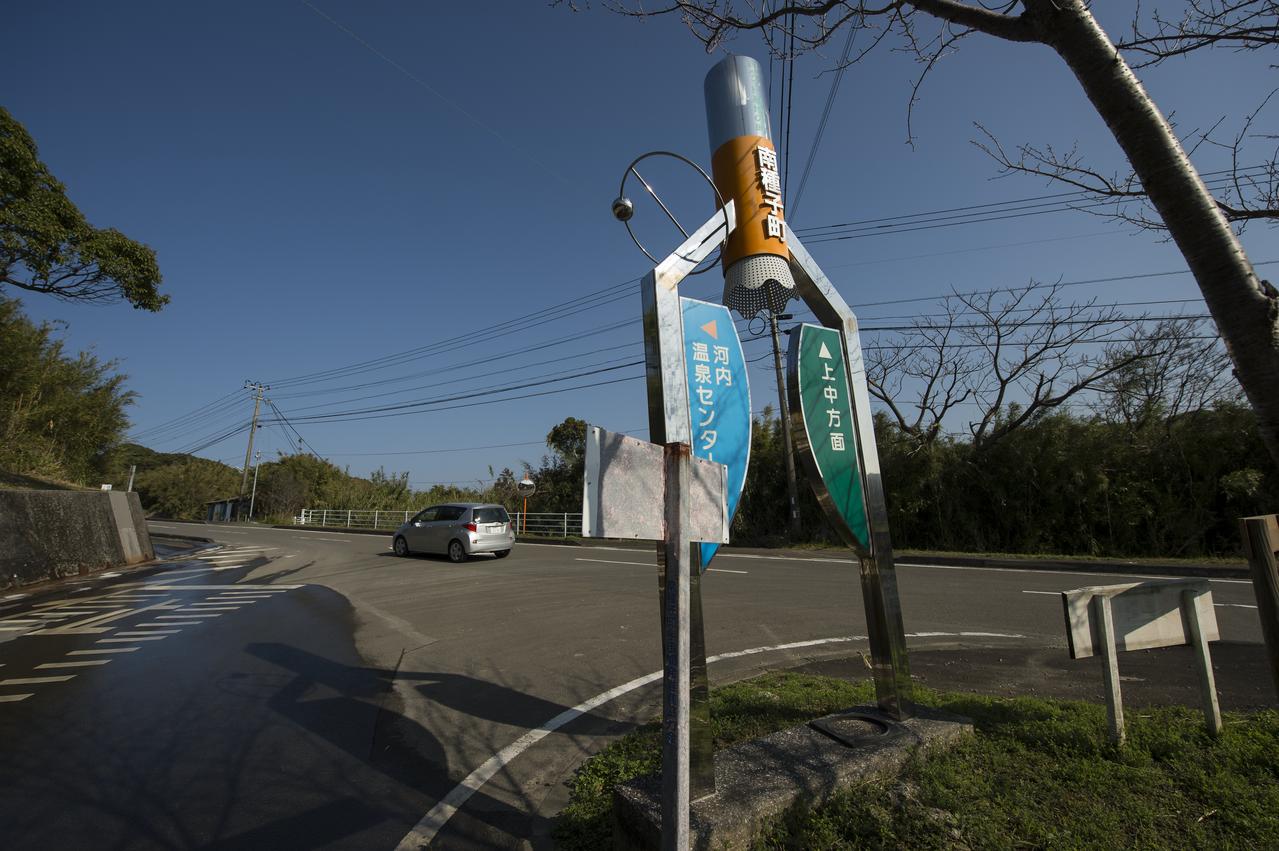

Space themed signs are seen along the roads to and from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for Feb. 28, 2014 from the space center. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
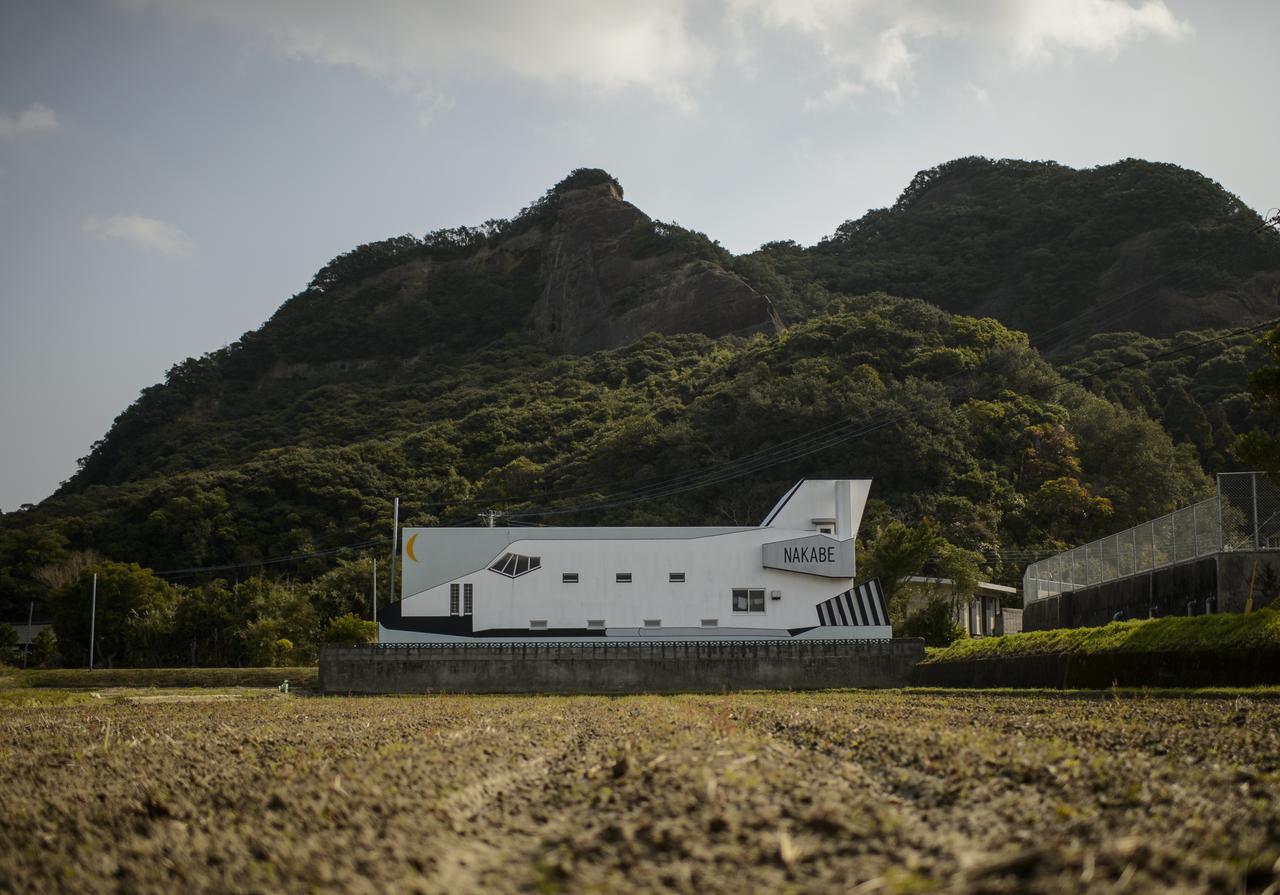

A building designed to look like a space shuttle is seen a few kilometers outside of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
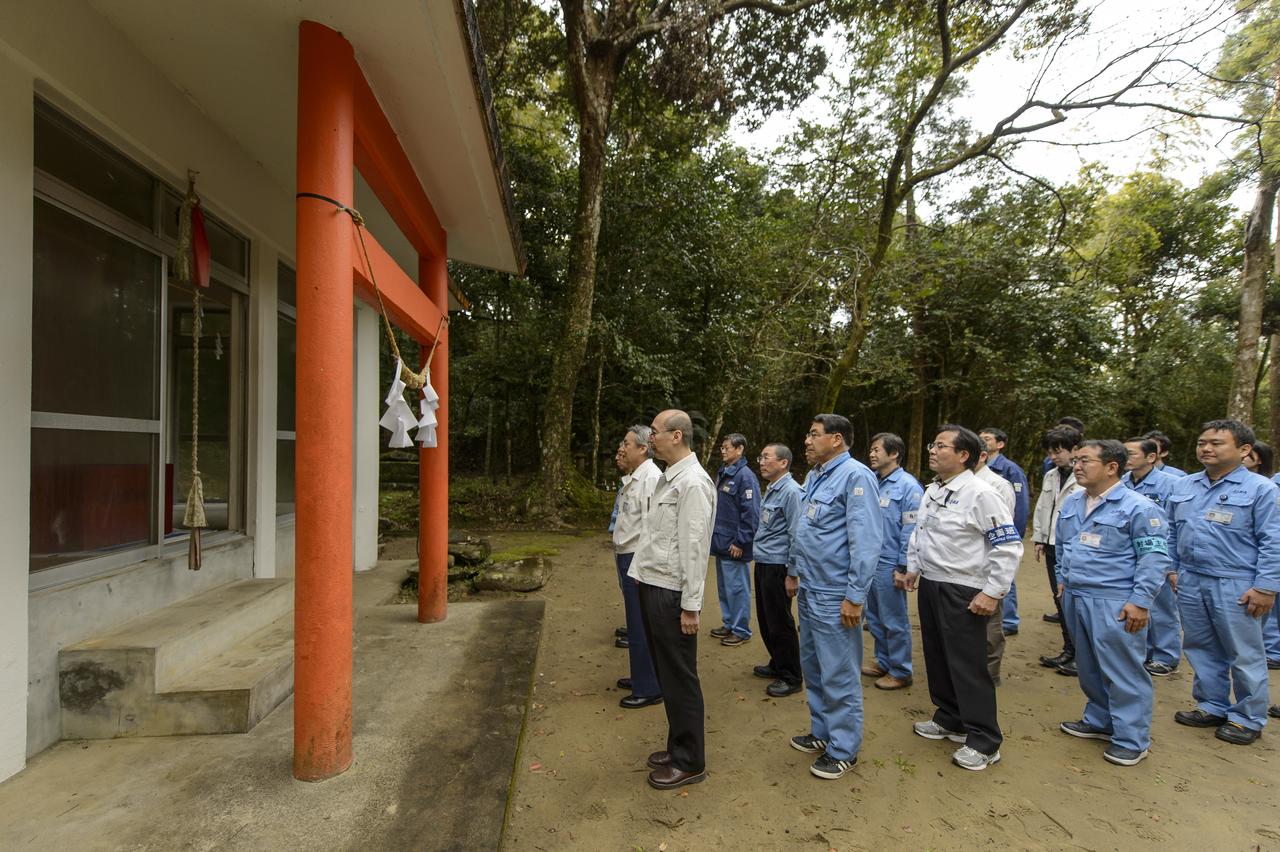

Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) team members stand before at the Kawachi Shrine, the second shrine in a traditional San-ja Mairi, or Three Shrine Pilgrimage, where the team prays for a successful launch, Tuesday, Feb. 25, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
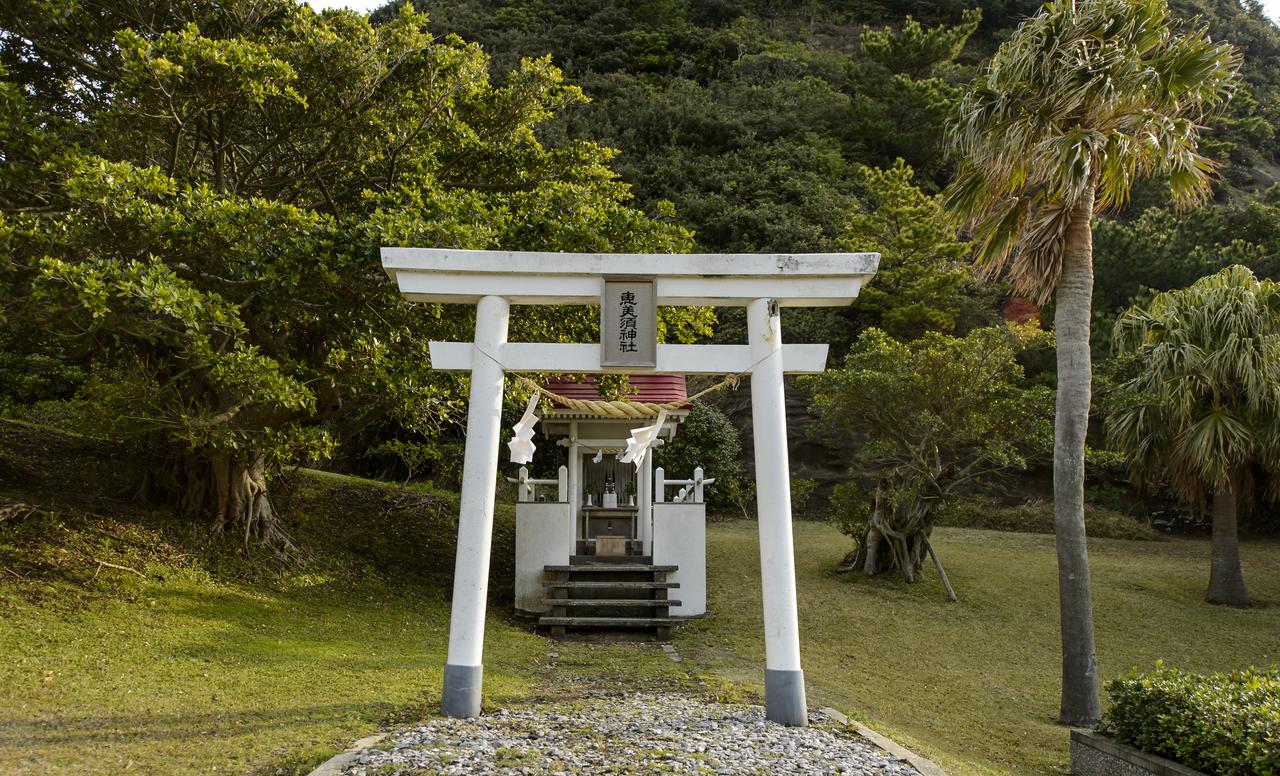

The Ebisu Shrine, the first shrine in a traditional San-ja Mairi, or Three Shrine Pilgrimage, is seen just after members of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) team prayed for a successful launch, Tuesday, Feb. 25, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
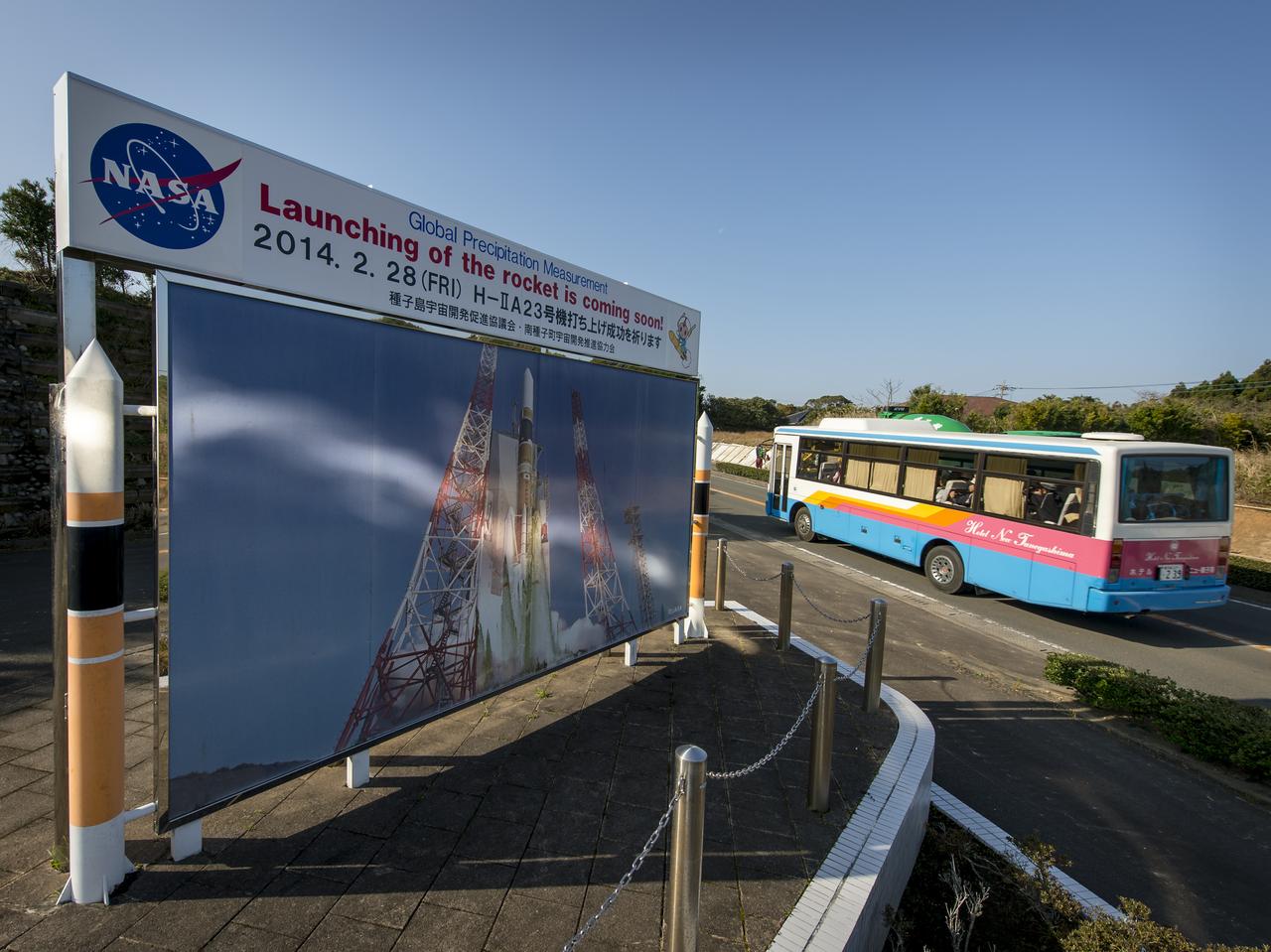

A roadside sign announces the upcoming launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Minamitane Town, Tanegashima Island, Japan. Once launched from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) the NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. The launch is planned for Feb. 28, 2014. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
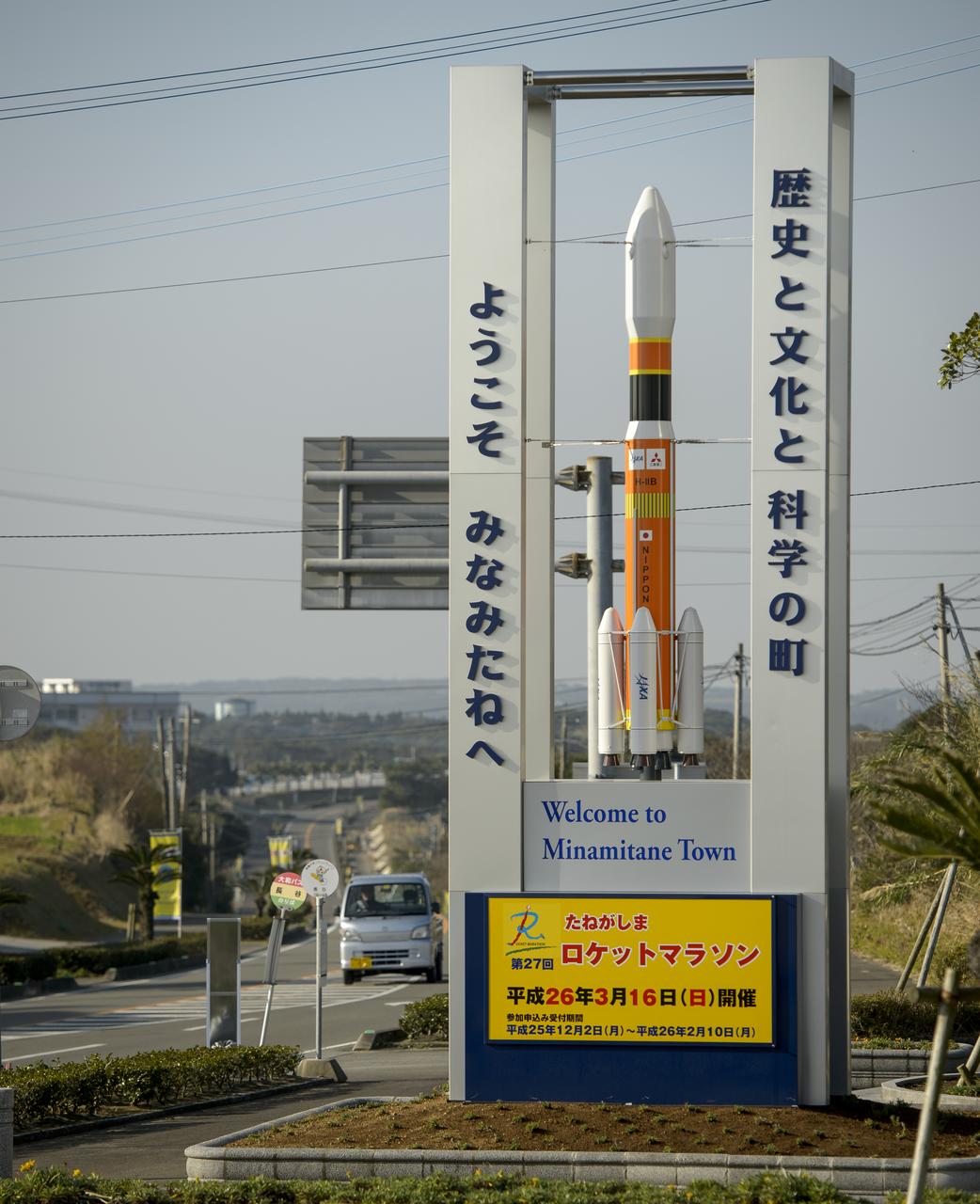

A sign with a model of the Japanese H-IIB rocket welcomes visitors to Minamitane Town, one of only a few small towns located outside of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), where the launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory will take place in the next week, Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
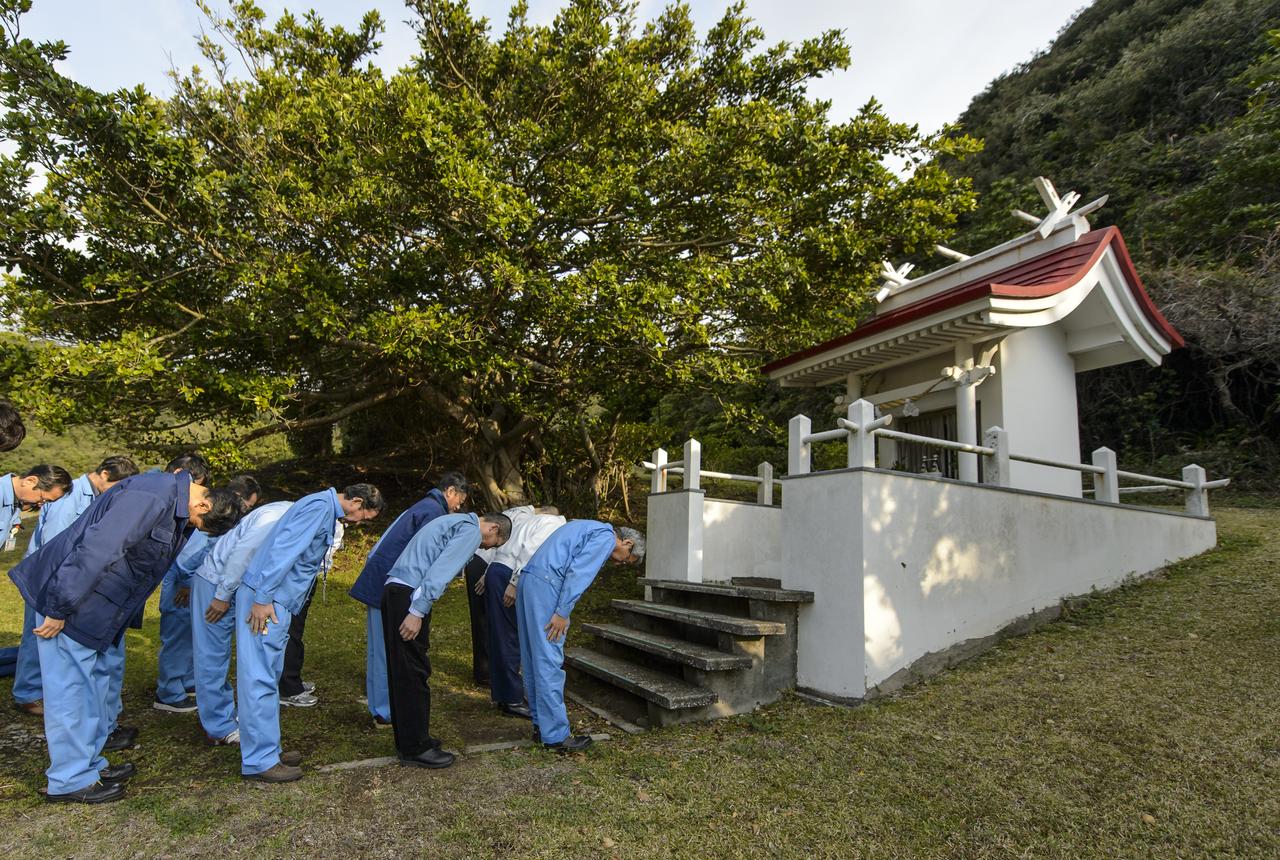

Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) team members bow at the Ebisu Shrine, the first shrine in a traditional San-ja Mairi, or Three Shrine Pilgrimage, where the team prays for a successful launch, Tuesday, Feb. 25, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
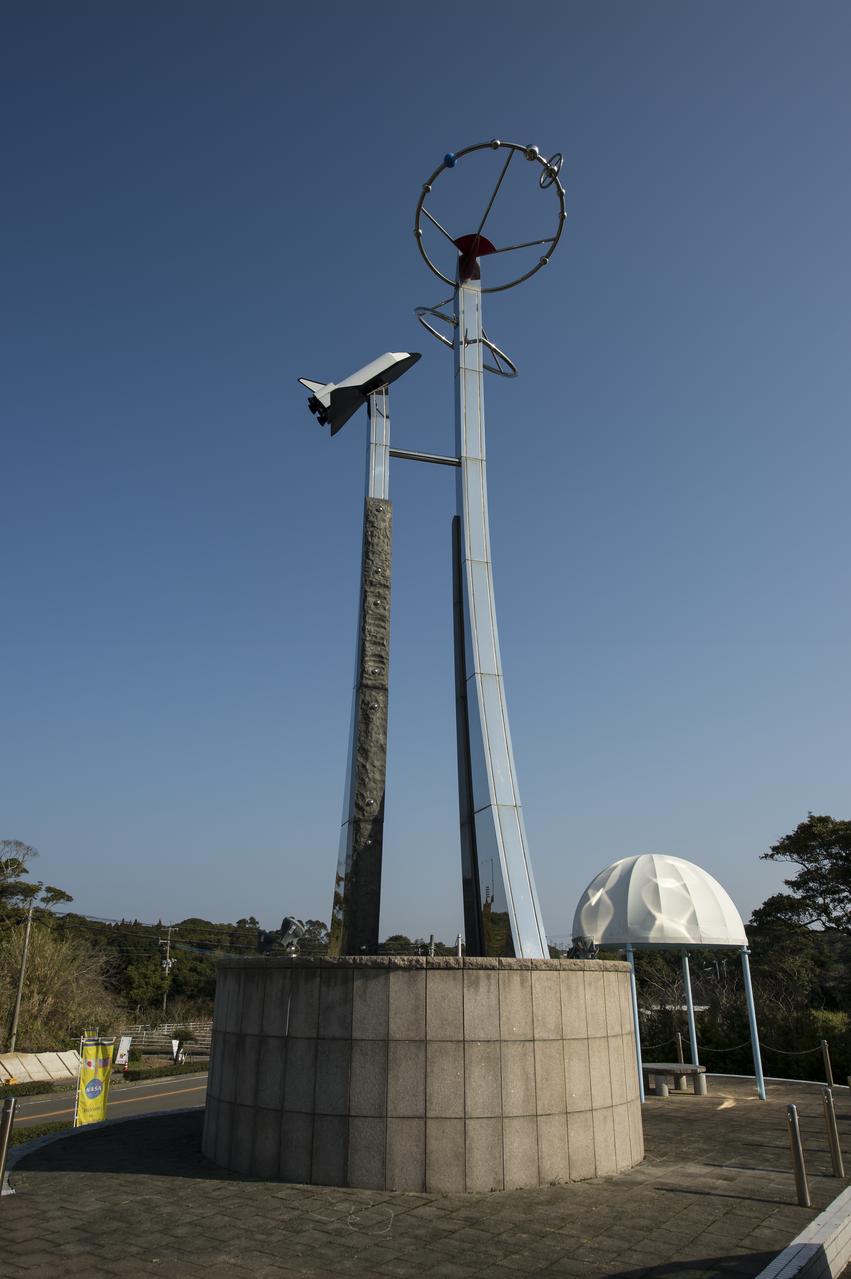

A small roadside park honoring spaceflight is seen in Minamitane Town, Saturday Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. Minamitane Town is located not far from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), where the launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
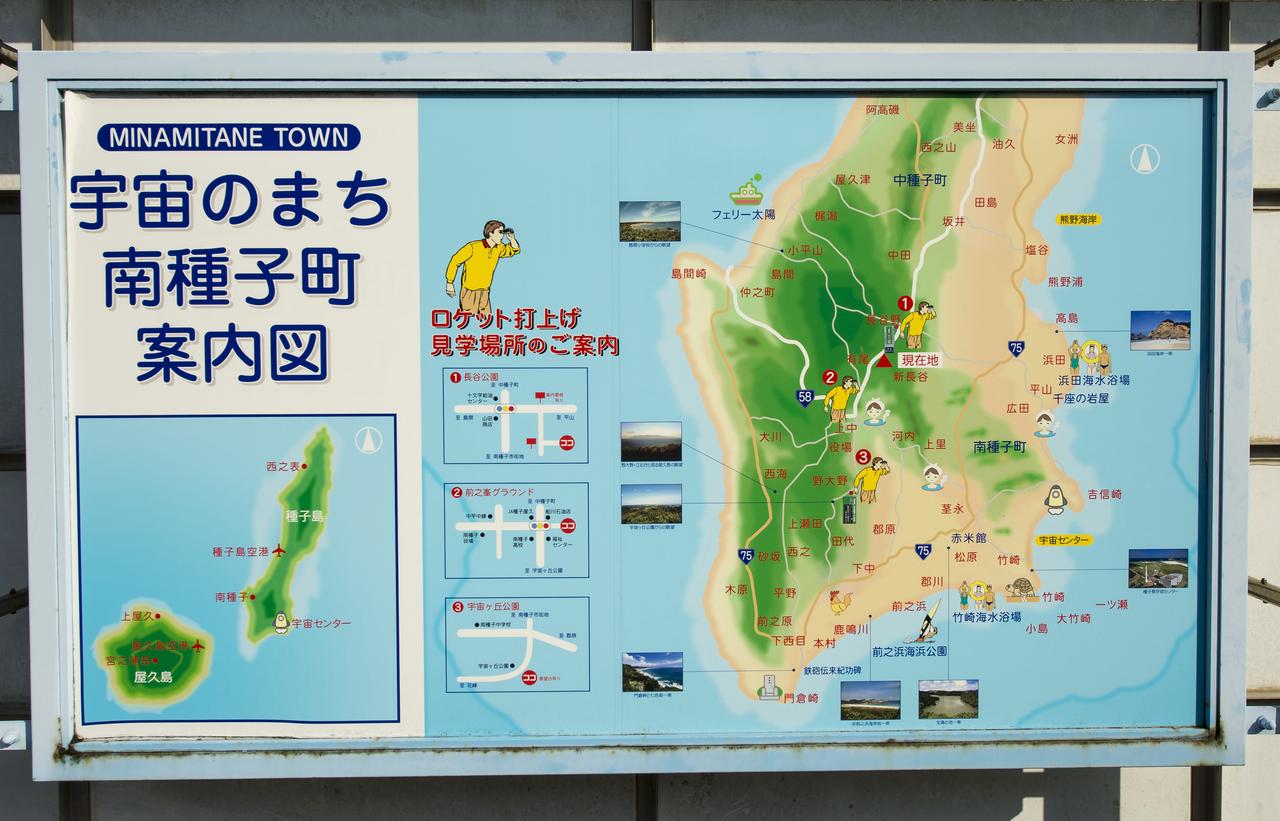
A roadside sign shows visitors of Minamitane Town various locations for activities, including the viewing of rocket launches from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), where the launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is scheduled to take place in the next week, Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Minamitane Town, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Launch is planned for Feb. 28, 2014. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
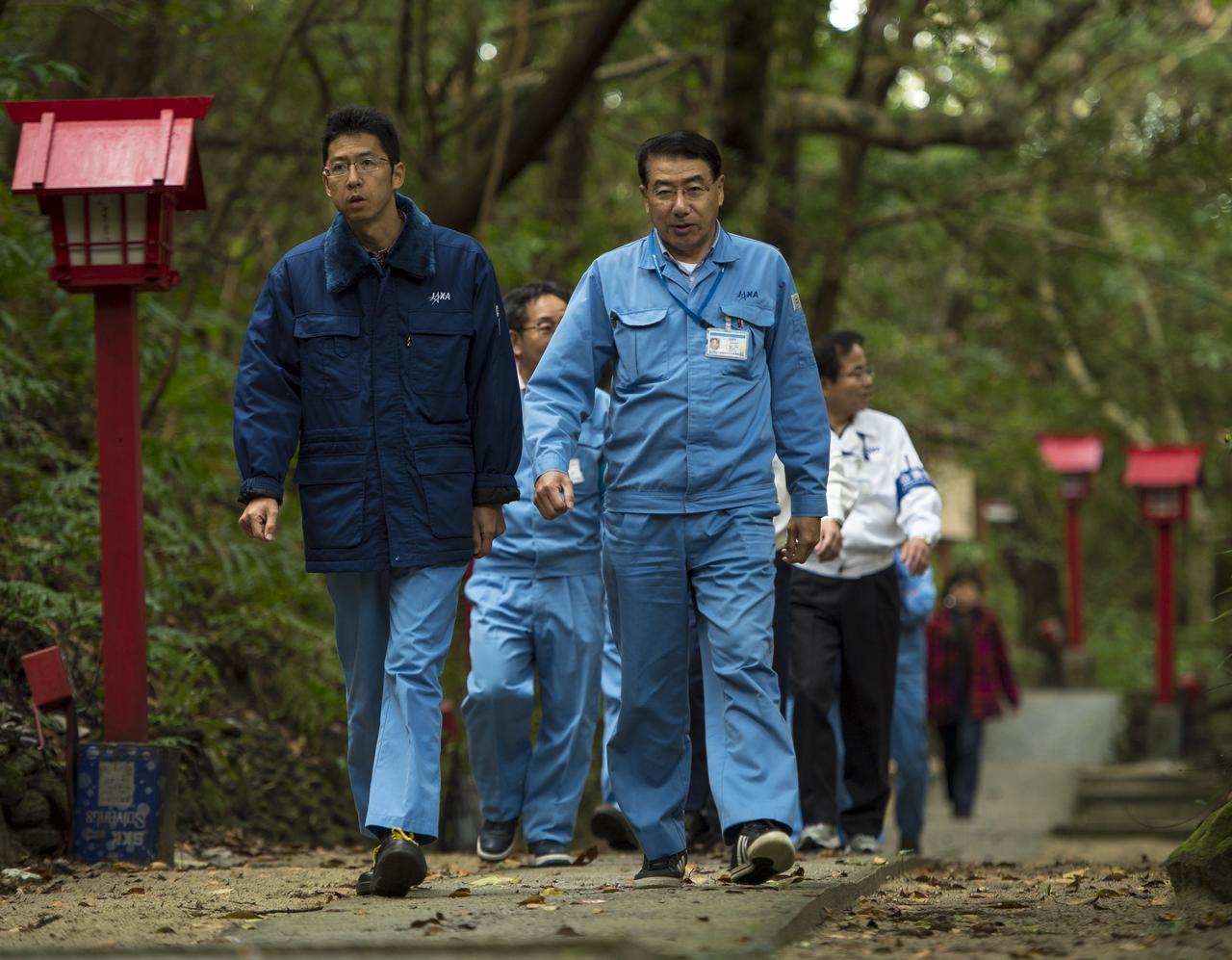

Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are seen as they depart the Houman Shrine, the third, and final, shrine in a traditional San-ja Mairi, or Three Shrine Pilgrimage, where the team prays for a successful launch, Tuesday, Feb. 25, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
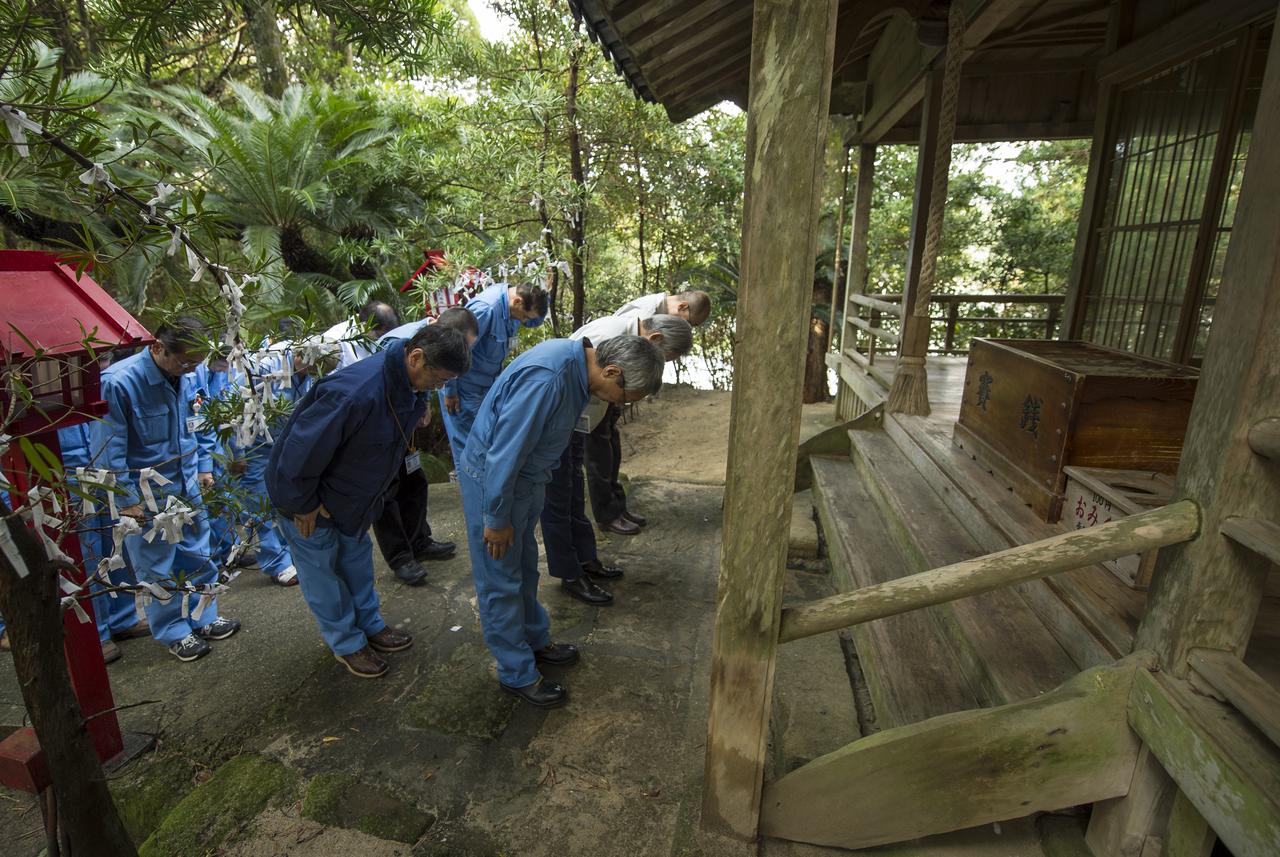

Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) team members pray at the Houman Shrine, the third, and final, shrine in a traditional San-ja Mairi, or Three Shrine Pilgrimage, where the team prays for a successful launch, Tuesday, Feb. 25, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
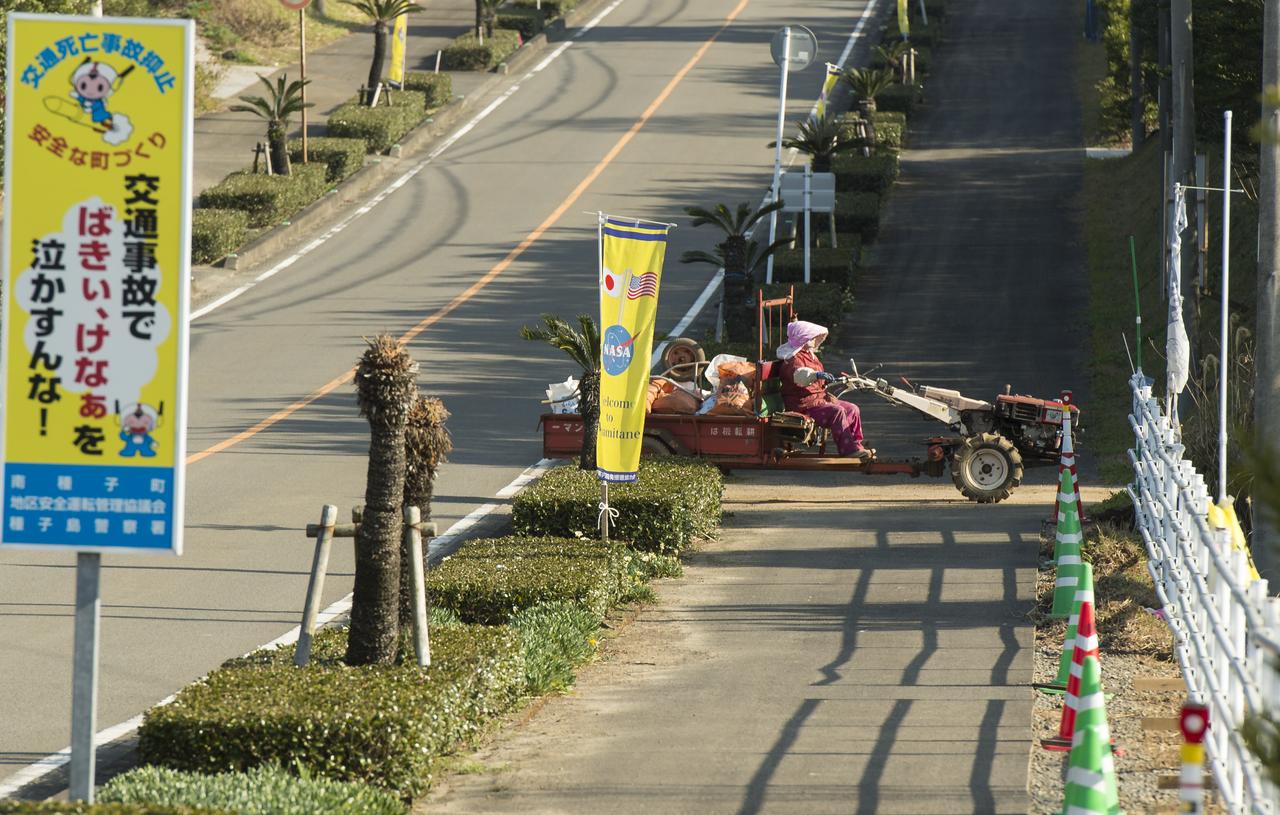

Roadside flags welcome the NASA team and visitors to Minamitame Town, one of only a few small towns located outside of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), where the launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory will take place in the next week, Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. The launch is planned for Feb. 28, 2014. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
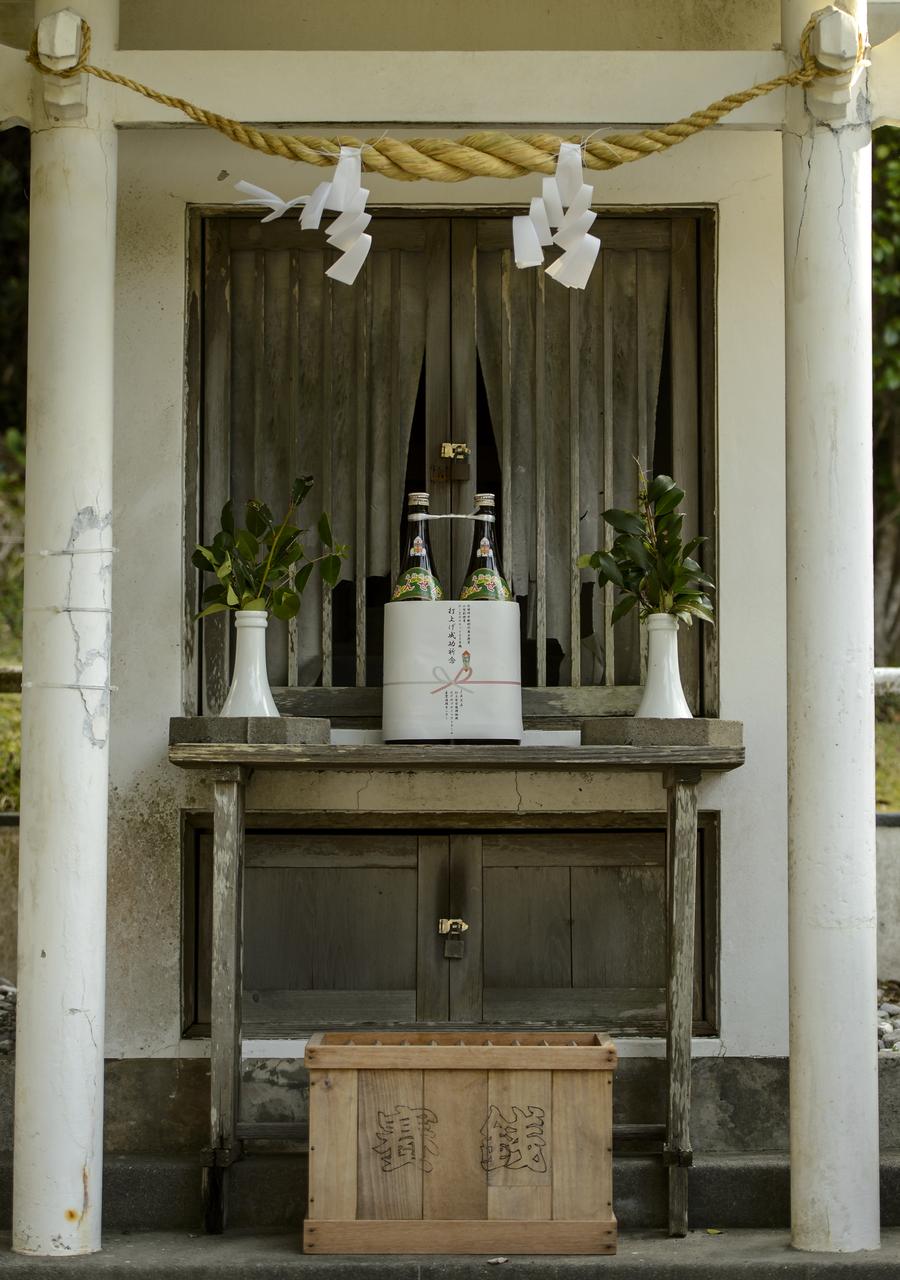

An offering of sake can be seen at the Ebisu Shrine, the first shrine in a traditional San-ja Mairi, or Three Shrine Pilgrimage, in which members of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) team pray for a successful launch, Tuesday, Feb. 25, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
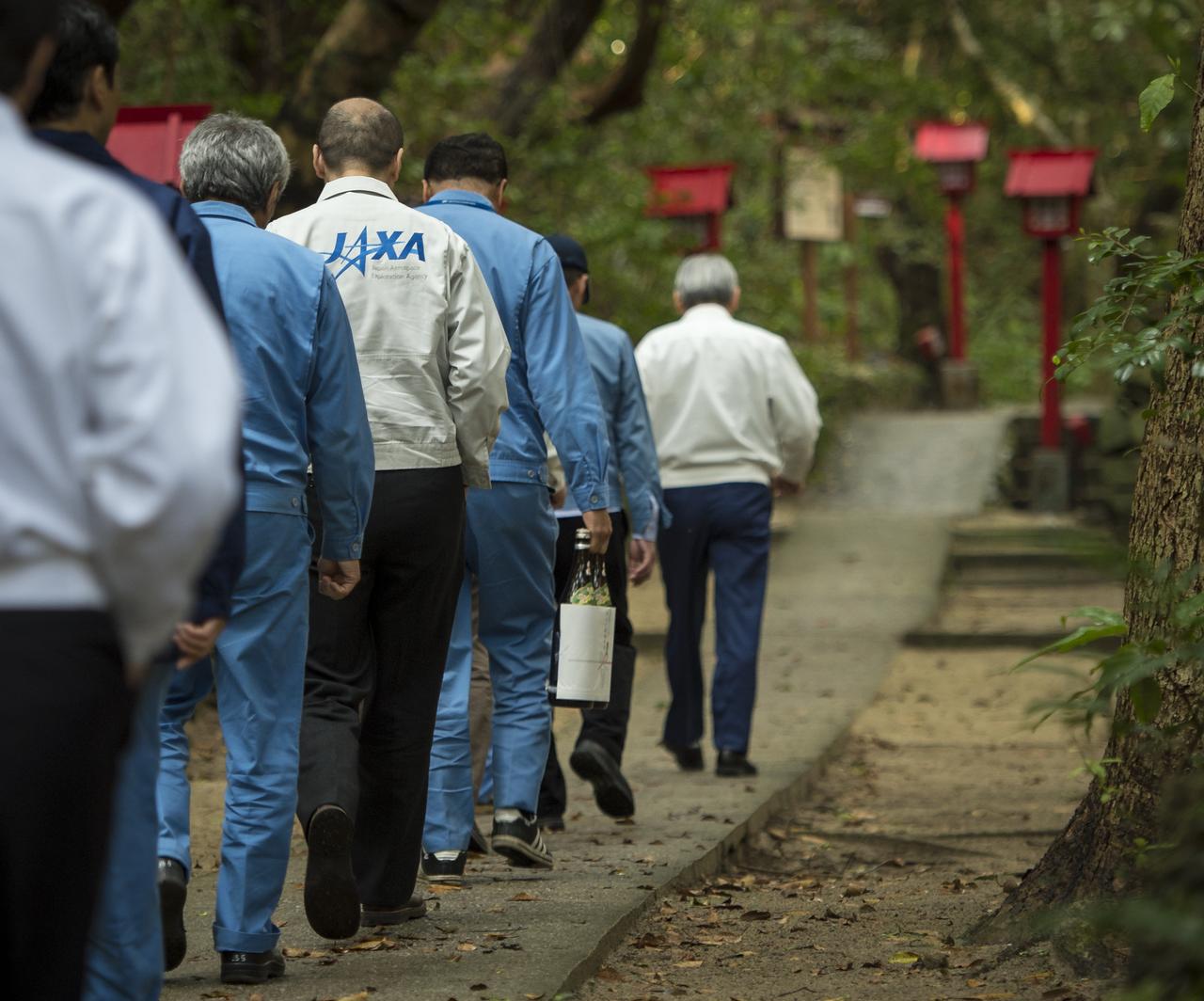

Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) team members walk with their offering of sake to the Houman Shrine, the third, and final, shrine in a traditional San-ja Mairi, or Three Shrine Pilgrimage, where the team prays for a successful launch, Tuesday, Feb. 25, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
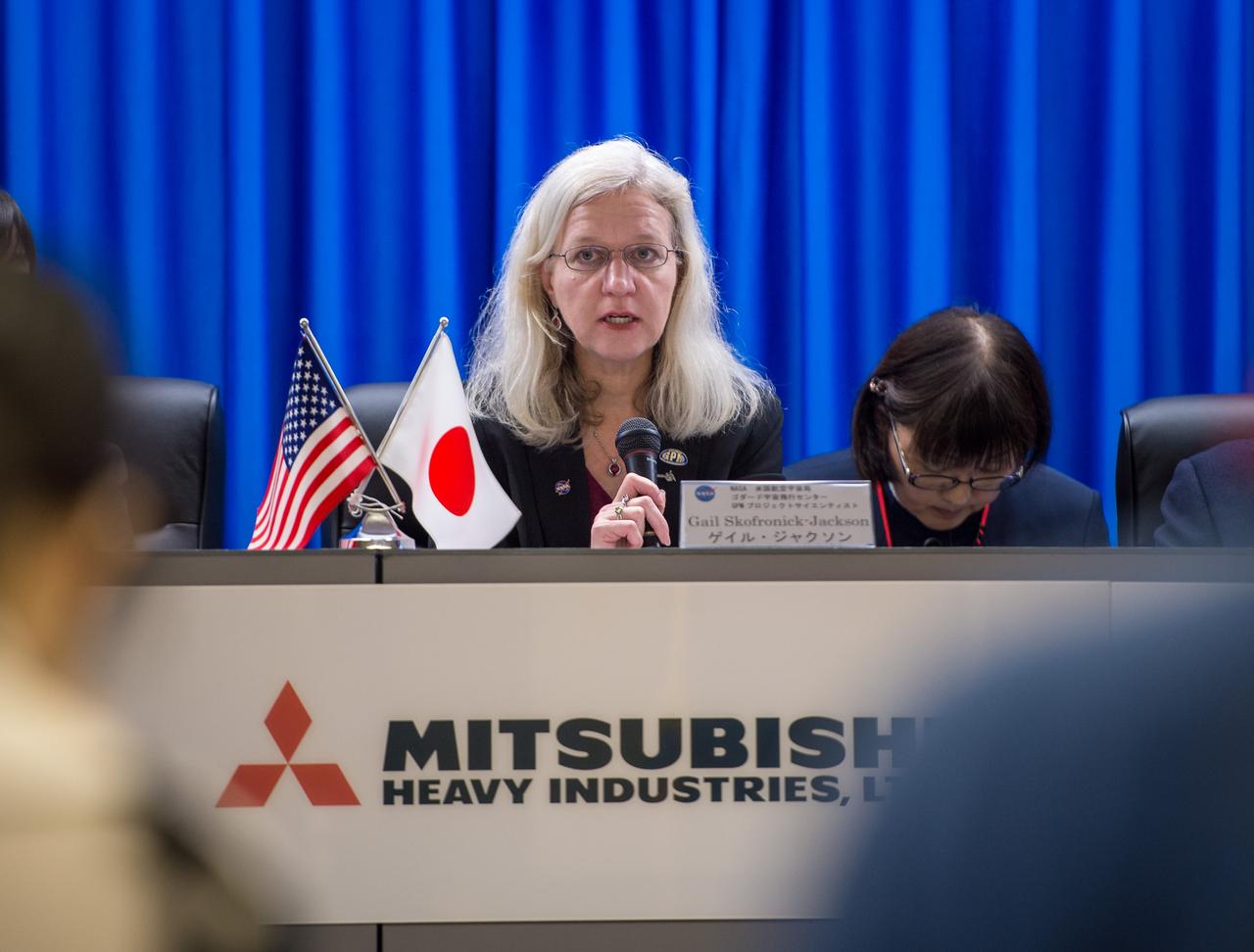

Gail Skofronick-Jackson, NASA GPM Project Scientist, talks during a science briefing for the launch of the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory aboard an H-IIA rocket, Wednesday, Feb. 26, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center, Japan. Launch is scheduled for early in the morning of Feb. 28 Japan time. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
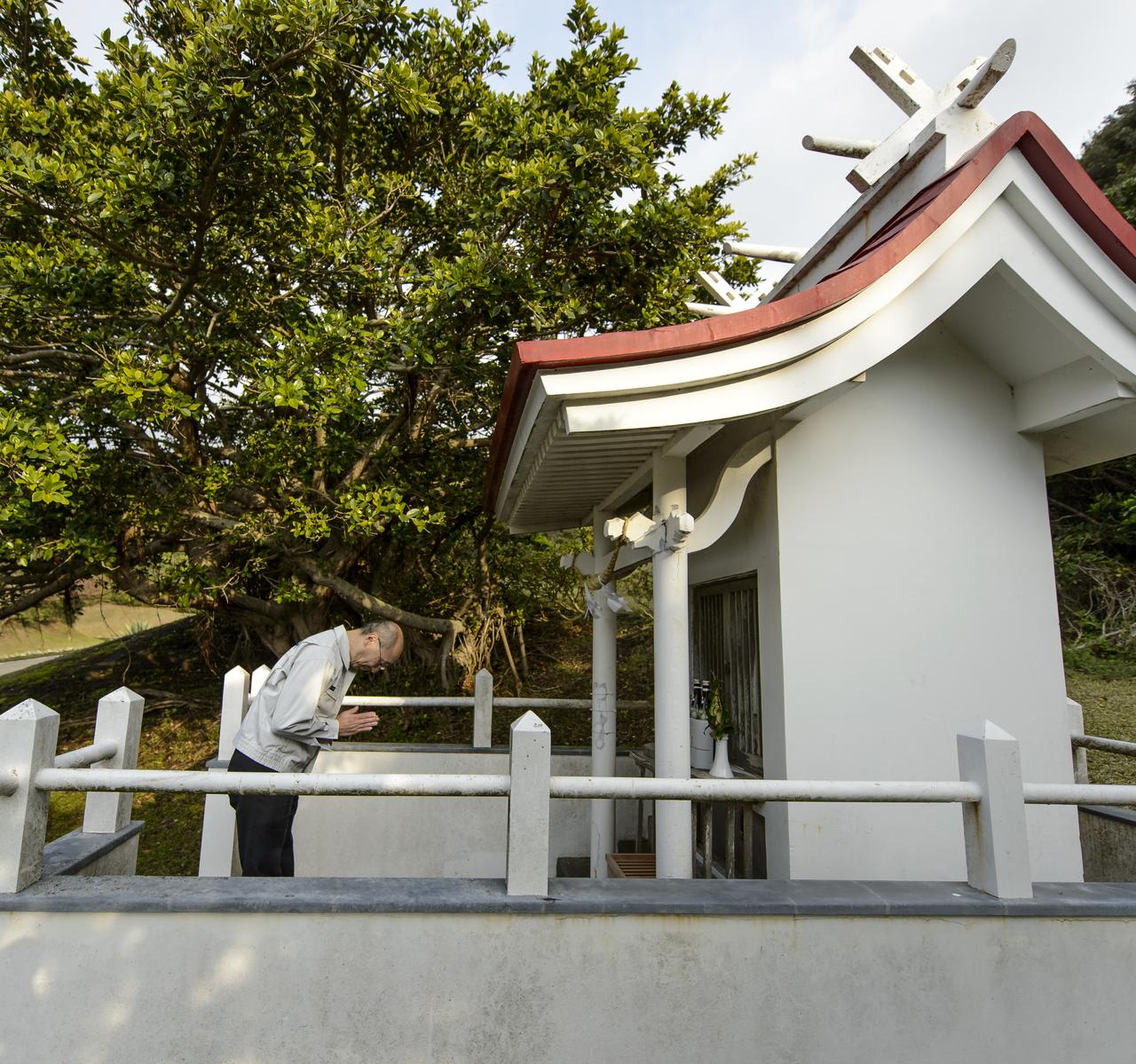

Masahiro Kojima, GPM Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar project manager, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Tsukuba, bows at the Ebisu Shrine, the first shrine in a traditional San-ja Mairi, or Three Shrine Pilgrimage, in which members of the JAXA team pray for a successful launch, Tuesday, Feb. 25, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) team members wash their hands before praying at the Houman Shrine, the third, and final, shrine in a traditional San-ja Mairi, or Three Shrine Pilgrimage, where the team prays for a successful launch, Tuesday, Feb. 25, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission shirt is seen drying in the mid-day sun outside the Sun Pearl Hotel where many of the NASA GPM team are staying, Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
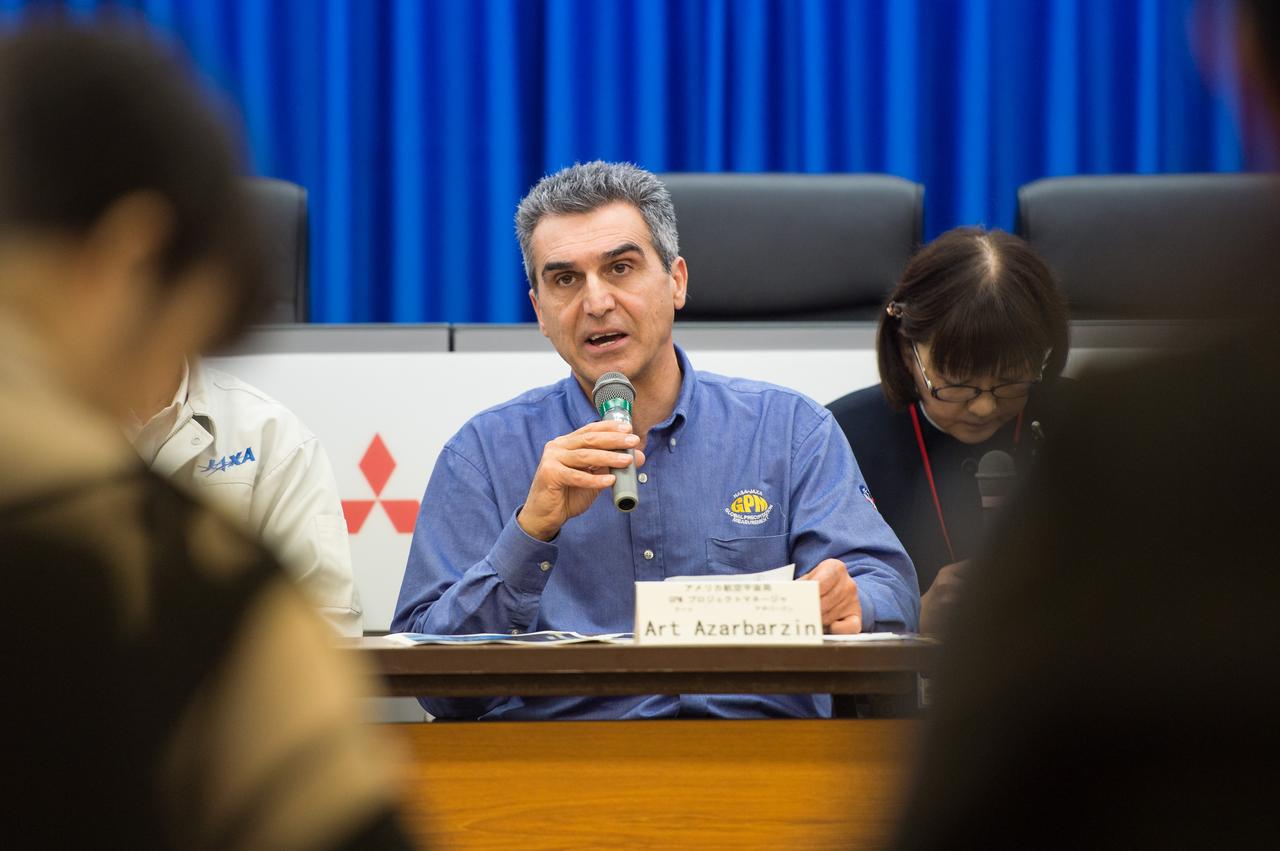

Art Azarbarzin, NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) project manager talks during a technical briefing for the launch of the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory aboard an H-IIA rocket, Wednesday, Feb. 26, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center, Japan. Launch is scheduled for early in the morning of Feb. 28 Japan time. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
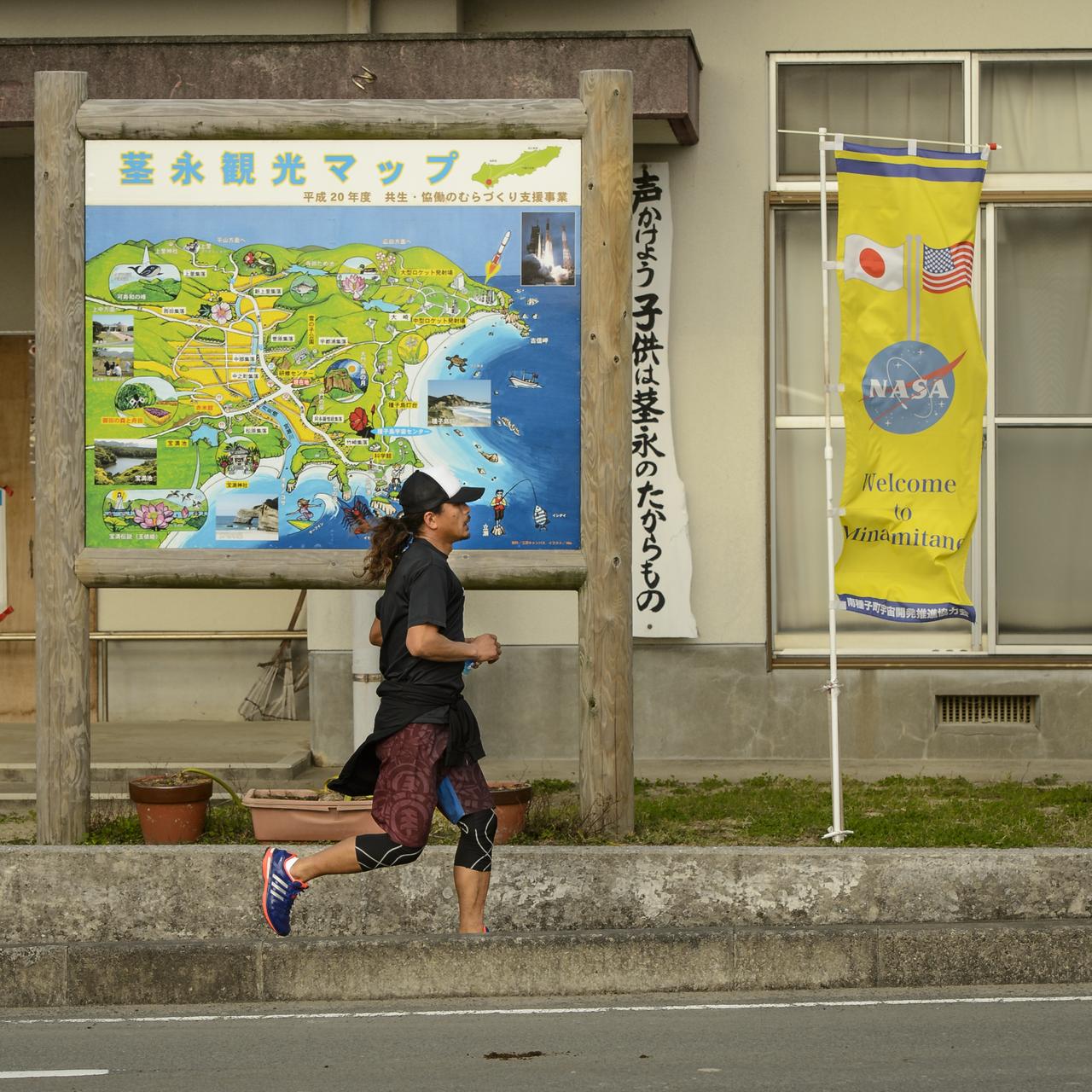

A jogger runs past a sign welcoming NASA and other visitors to Minamitane Town on Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
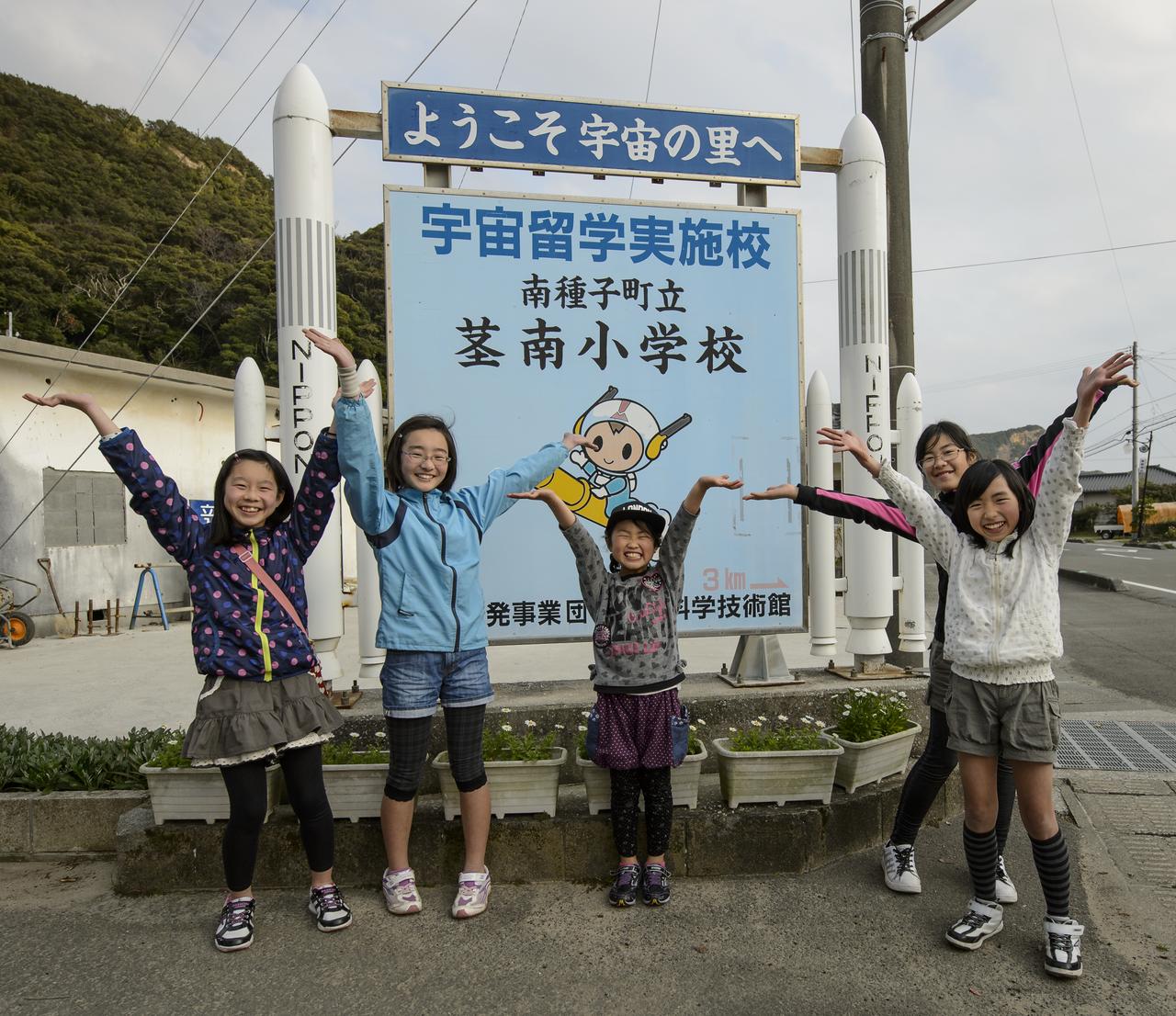

Minamitane elementary school girls pose for a photo in front of a sign featuring the town's mascot "Chuta-kun", Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The Chuta-kun mascot rides a rocket and has guns on the side of his helmet to show the areas history as the site of the first known contact of Europe and the Japanese, in 1543 and the introduction of the gun. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The H-IIA No. 23 rocket that will carry the GPM Core Observatory into space arrived at Tanegashima Space Center on Jan. 20, 2014. The rocket has two stages, an lower first stage that, with the help of two solid rocket boosters gets them off the ground, and an upper second stage that lights up a few minutes after launch to boost the satellite the rest of the way to orbit. The launch services provider, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI), immediately began assembling the rocket. On Jan. 22, the GPM team in Tanegashima was invited to participate in a blessing ceremony for the rocket. Lynette Marbley, the Instruments Chief Safety and Mission Assurance Officer for GPM, represented the NASA team.
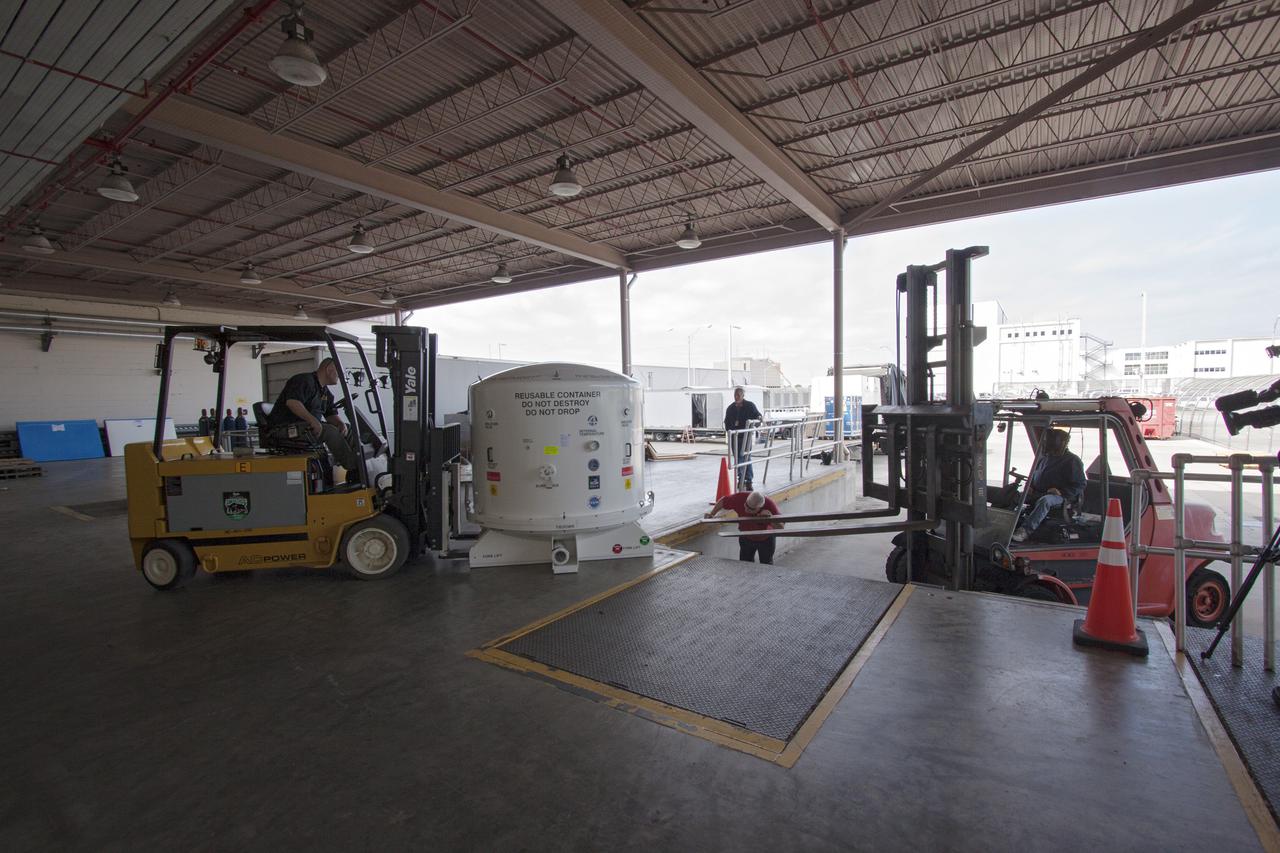

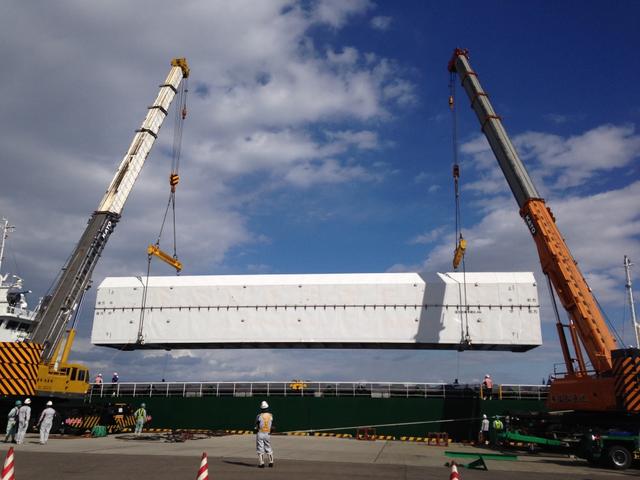
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers prepare to load the payload shipping container that holds the Space Test Program-Houston 4 STP H-4 experiments on a transport that will also carry containers with the unpressurized Orbital Replacement Units ORU for the International Space Station's Main Bus Switching Unit MBSU and Utility Transfer Assembly UTA. The payloads were processed at Kennedy and will be trucked to Chicago. From Chicago, they will be moved by air freight to Narita, Japan, where a complicated combination of ground and ocean ferry transfers will be used to deliver them to the Tanegashima Space Center. At Tanegashima the payloads will be turned over to the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency JAXA in preparation for launch on the H-II Transfer Vehicle 4 HTV-4 mission this summer. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
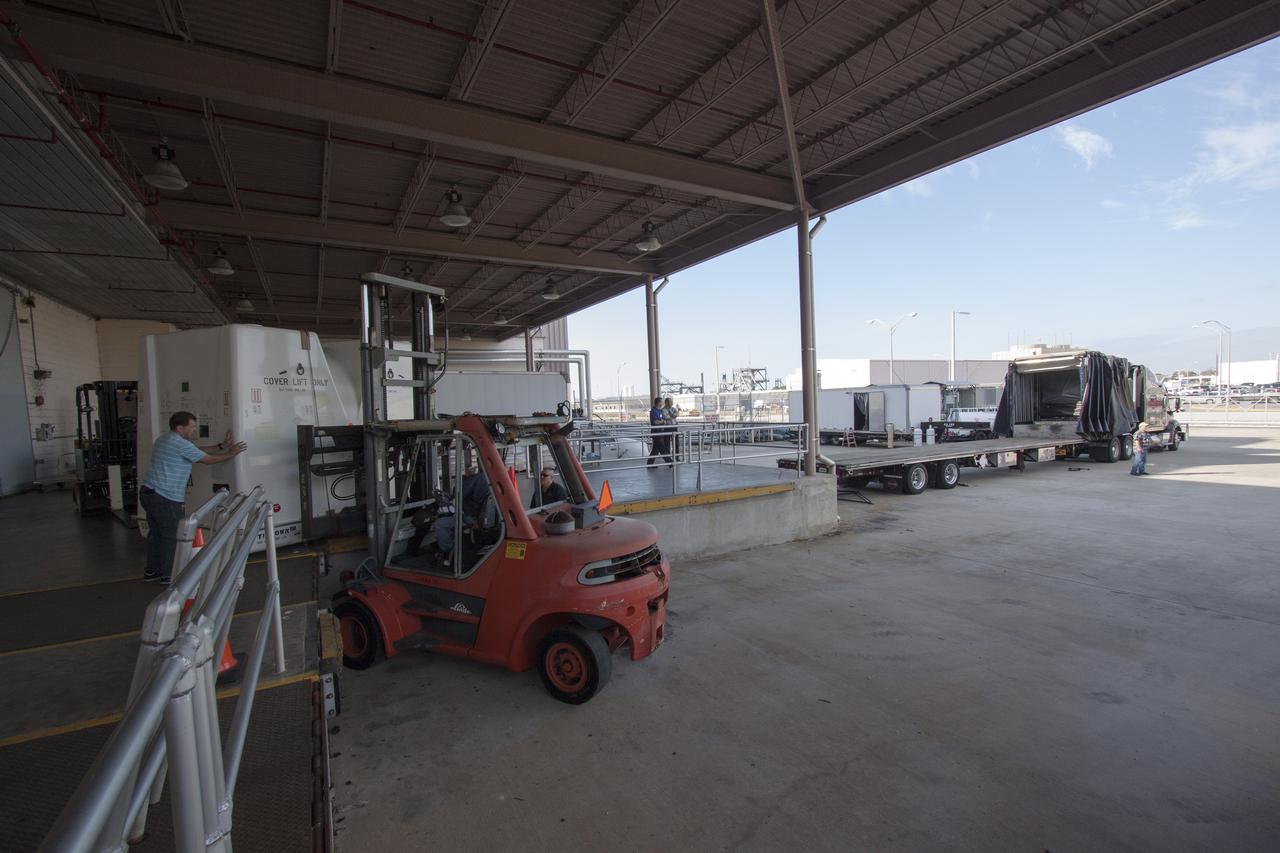

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers prepare to load the payload shipping containers that hold the unpressurized Orbital Replacement Units ORU for the International Space Station's Main Bus Switching Unit MBSU and Utility Transfer Assembly UTA, as well as the Space Test Program-Houston 4 STP H-4 experiments, on a transport. The payloads were processed at Kennedy and will be trucked to Chicago. From Chicago, they will be moved by air freight to Narita, Japan, where a complicated combination of ground and ocean ferry transfers will be used to deliver them to the Tanegashima Space Center. At Tanegashima the payloads will be turned over to the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency JAXA in preparation for launch on the H-II Transfer Vehicle 4 HTV-4 mission this summer. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
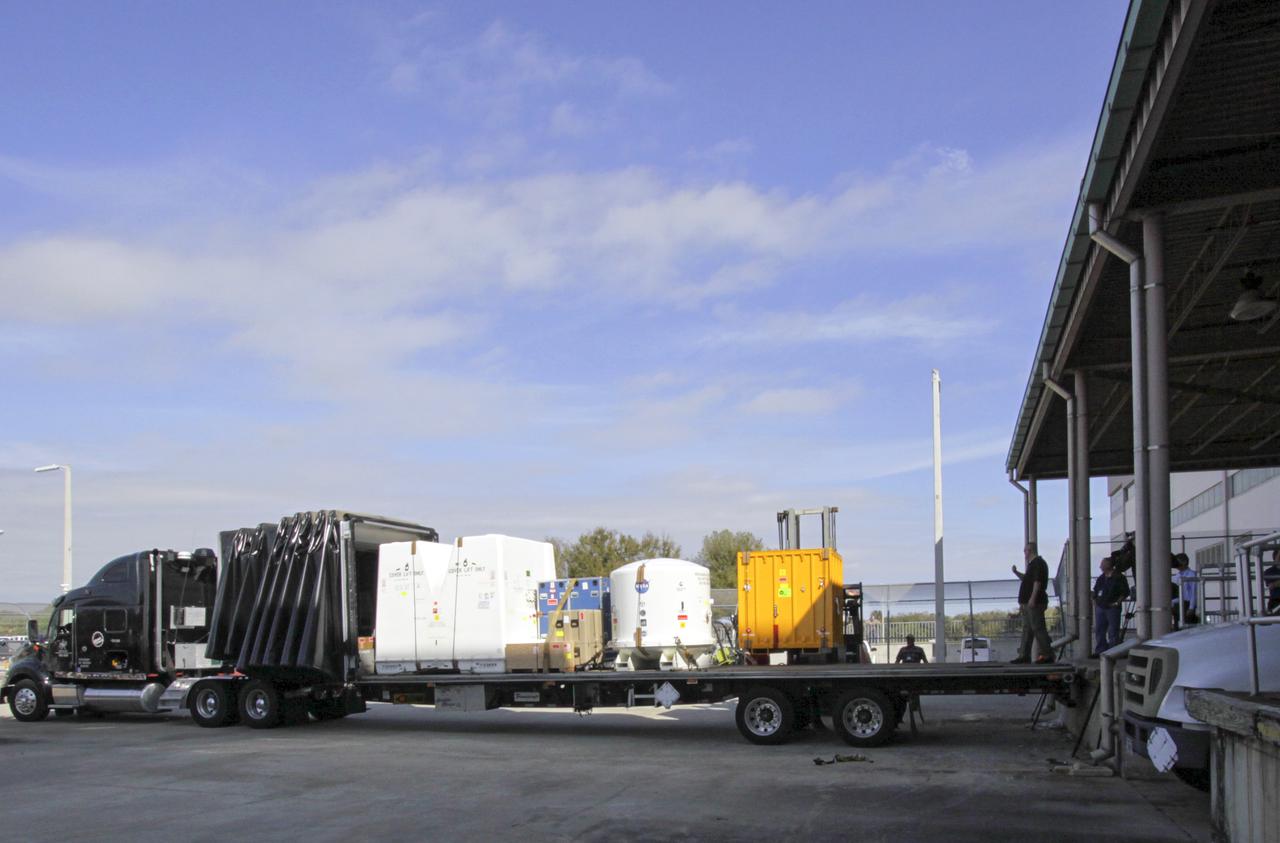

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Payload shipping containers that hold the unpressurized Orbital Replacement Units ORU for the International Space Station's Main Bus Switching Unit MBSU and Utility Transfer Assembly UTA, as well as the Space Test Program-Houston 4 STP H-4 experiments, are loaded on a transport. The payloads were processed at Kennedy and will be trucked to Chicago. From Chicago, they will be moved by air freight to Narita, Japan, where a complicated combination of ground and ocean ferry transfers will be used to deliver them to the Tanegashima Space Center. At Tanegashima the payloads will be turned over to the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency JAXA in preparation for launch on the H-II Transfer Vehicle 4 HTV-4 mission this summer. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
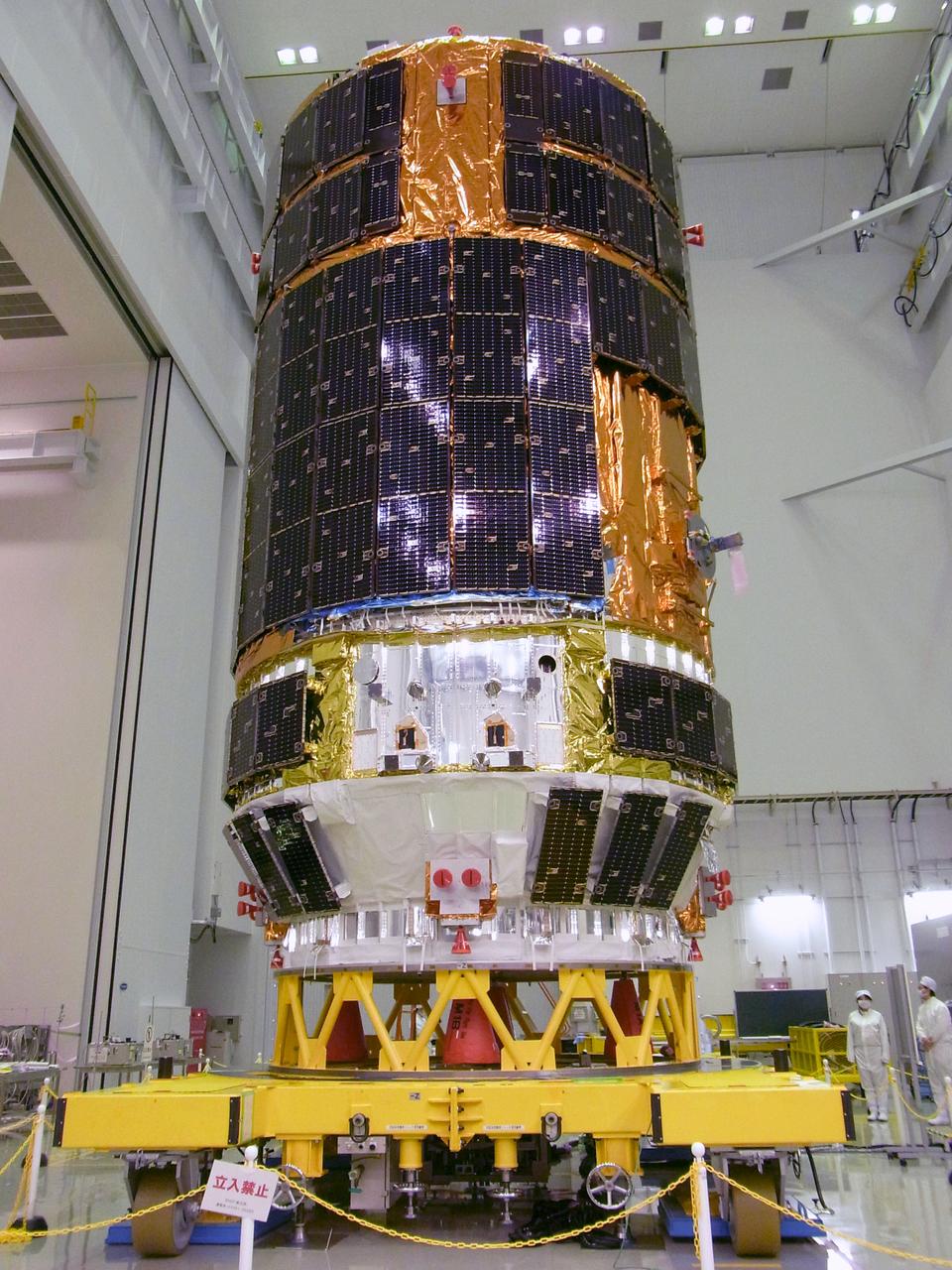

JSC2010-E-188665 (25 Nov. 2010) --- The H-II Transfer Vehicle 2 (Kounotori 2) is pictured during media day at the JAXA Tanegashima Space Center, Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan on Nov. 25, 2010. Reporters were invited to the Space Center to see the fully assembled HTV2. Photo credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
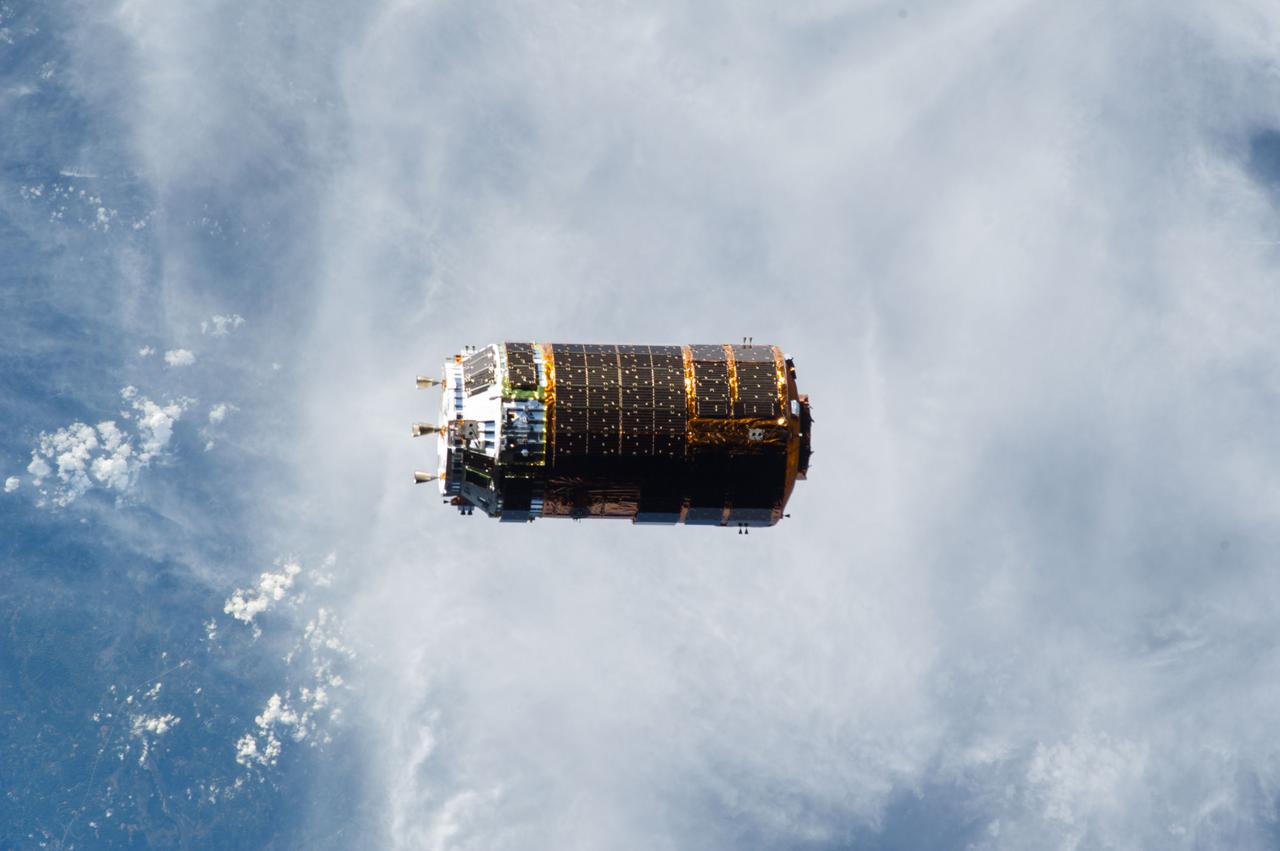

ISS036-E-030064 (9 Aug. 2013) --- The unpiloted Japanese "Kounotori" H2 Transfer Vehicle-4 (HTV-4) approaches the International Space Station. The HTV, a 33-foot-long, 13-foot-diameter unmanned cargo transfer spacecraft, is delivering 3.6 tons of science experiments, equipment and supplies to the orbiting complex. HTV-4 launched from the Tanegashima Space Center in southern Japan on Aug.3 at 3:48 p.m. (Aug. 4 at 4:48 a.m., Japan time).