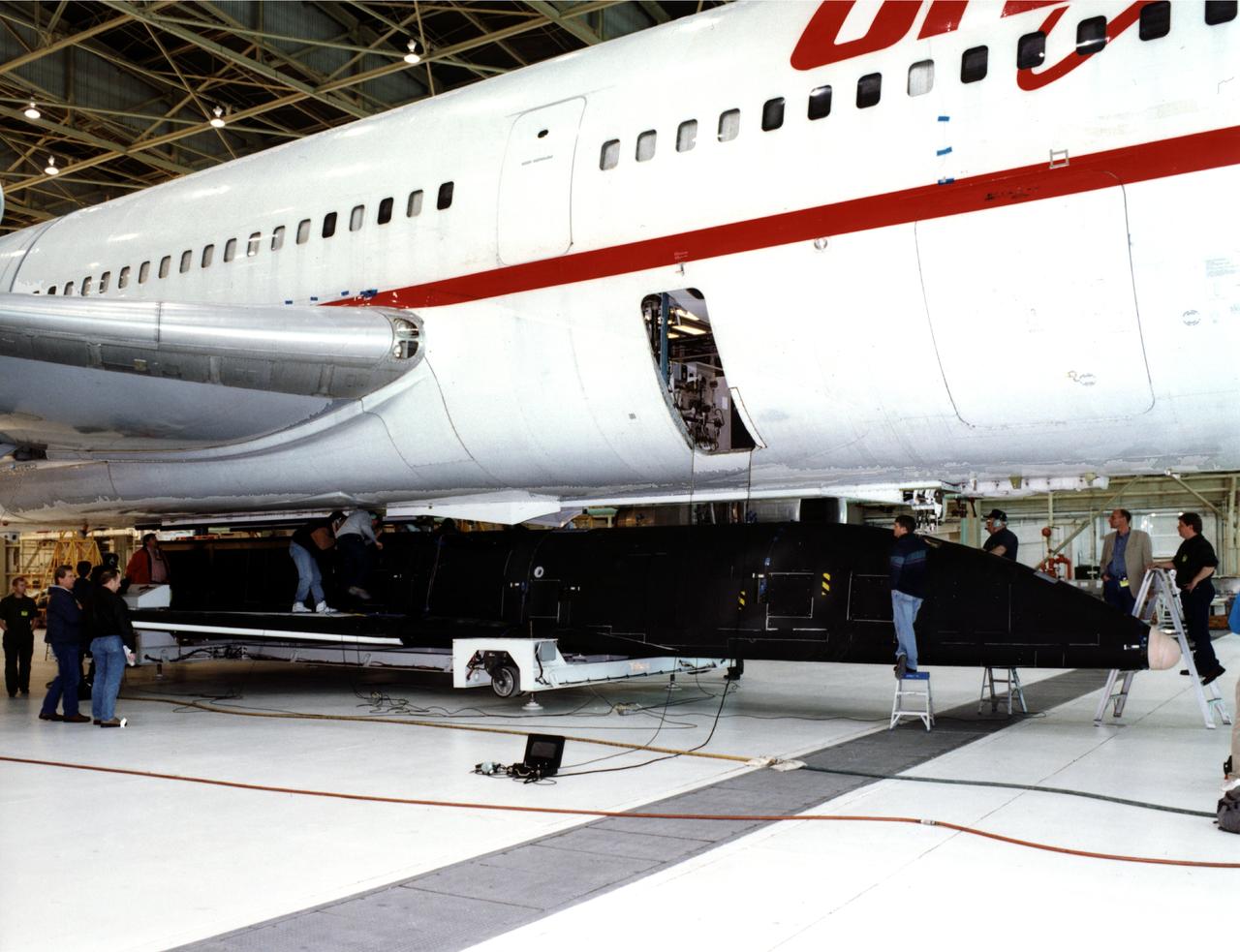

This is the X-34 Technology Testbed Demonstrator being mated with the L-1011 mothership. The X-34 will demonstrate key vehicle and operational technologies applicable to future low-cost resuable launch vehicles.
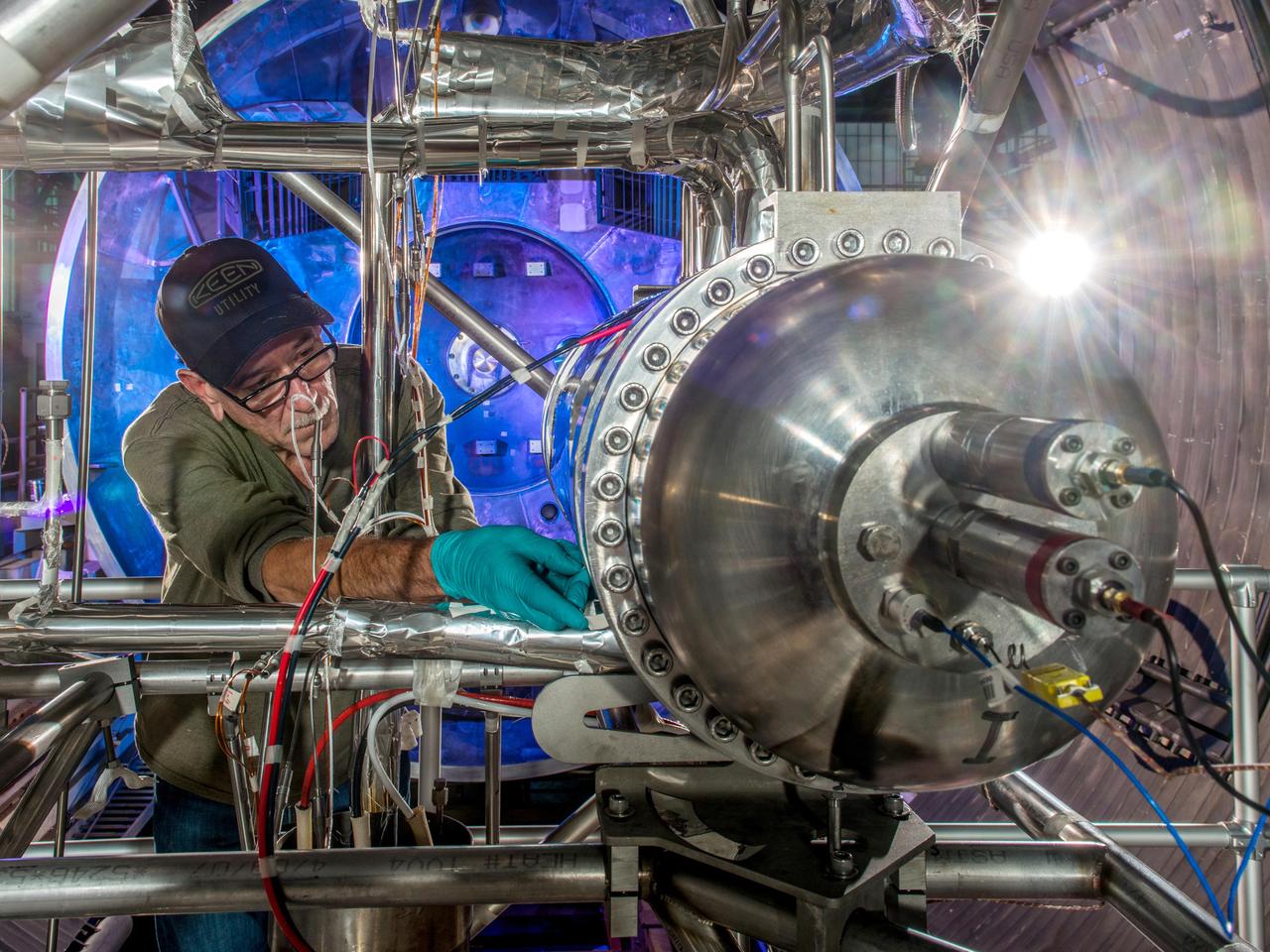
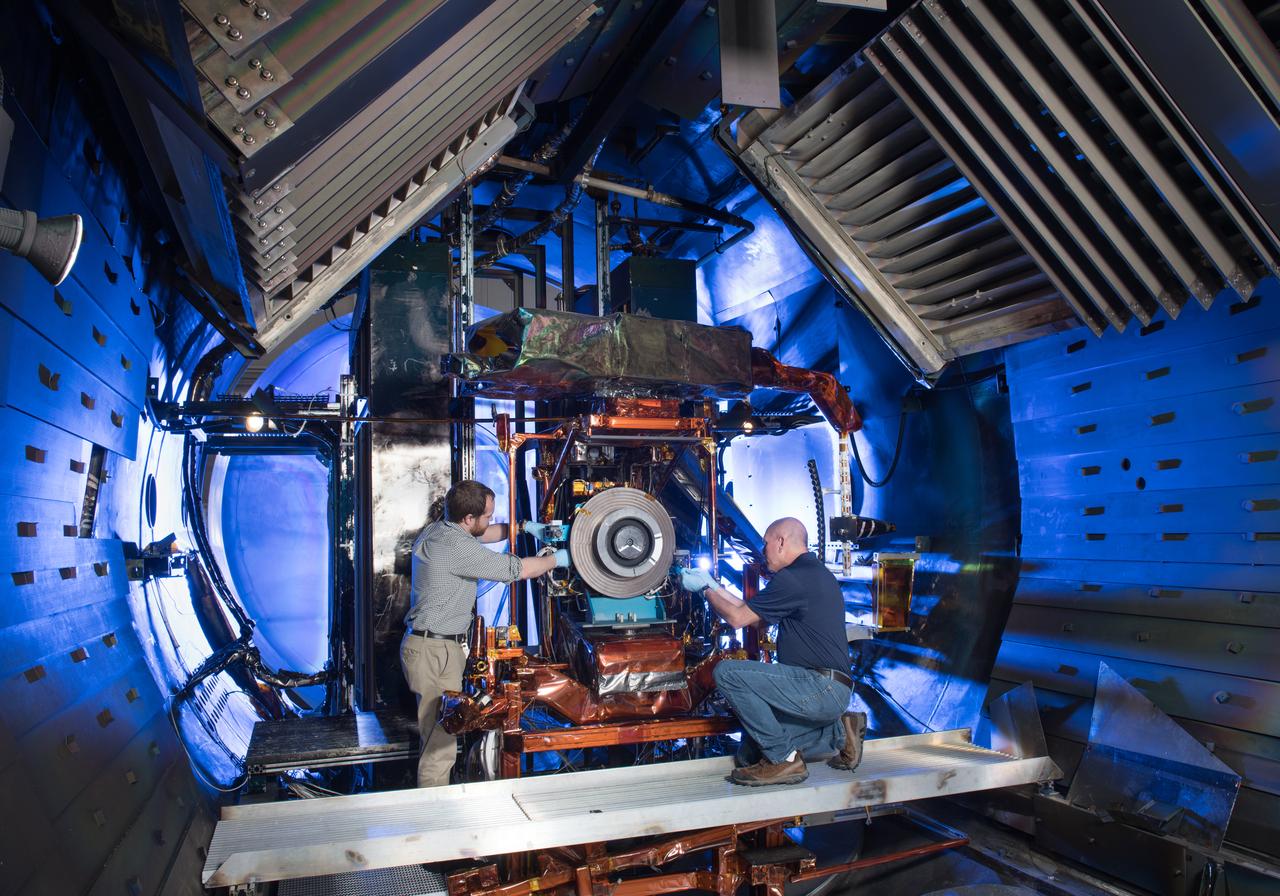
NASA Glenn Technician Mark Springowski works on a 10-kilowatt Stirling Power Conversion Unit, which is part of the Fission Surface Power Technology Demonstration Unit. This is a system level demonstration of a surface power system, which could potentially be used to support manned missions to the moon or Mars. A flight system would use 180 kilowatt nuclear fission reactor and four Stirling PCU’s to produce 40 kW of electricity for manned surface missions.
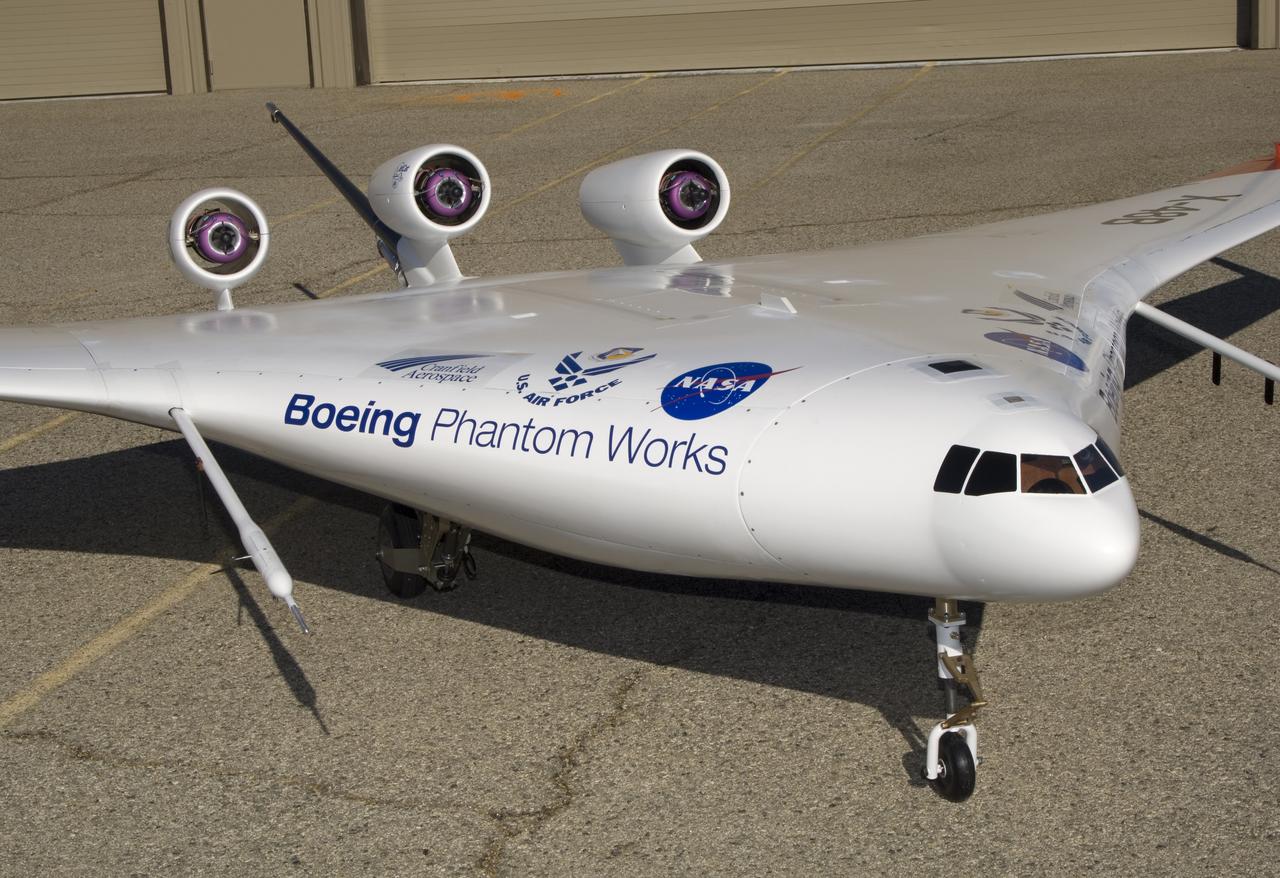

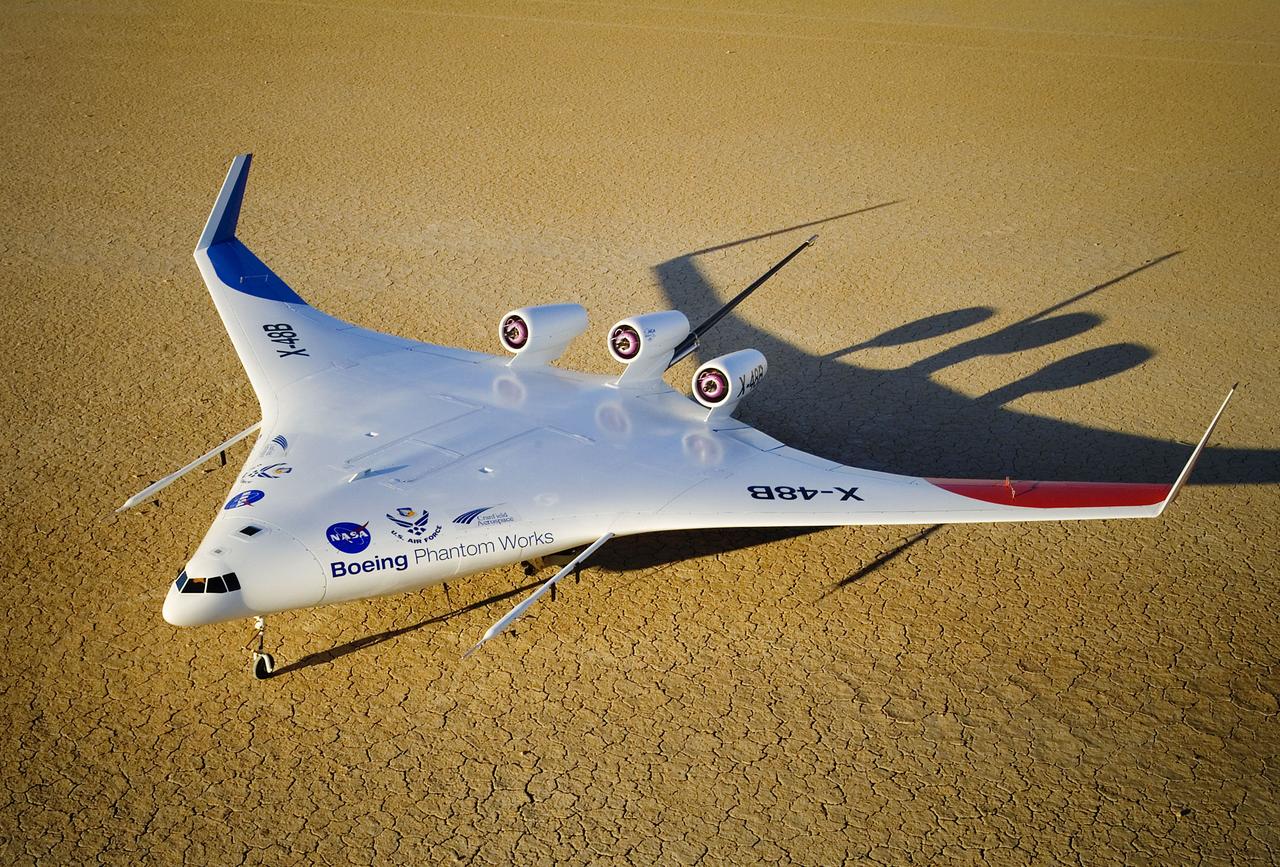
This closeup of Boeing Phantom Works' unique X-48B Blended Wing Body technology demonstrator shows off its unusual engine placement and supercritical airfoil.
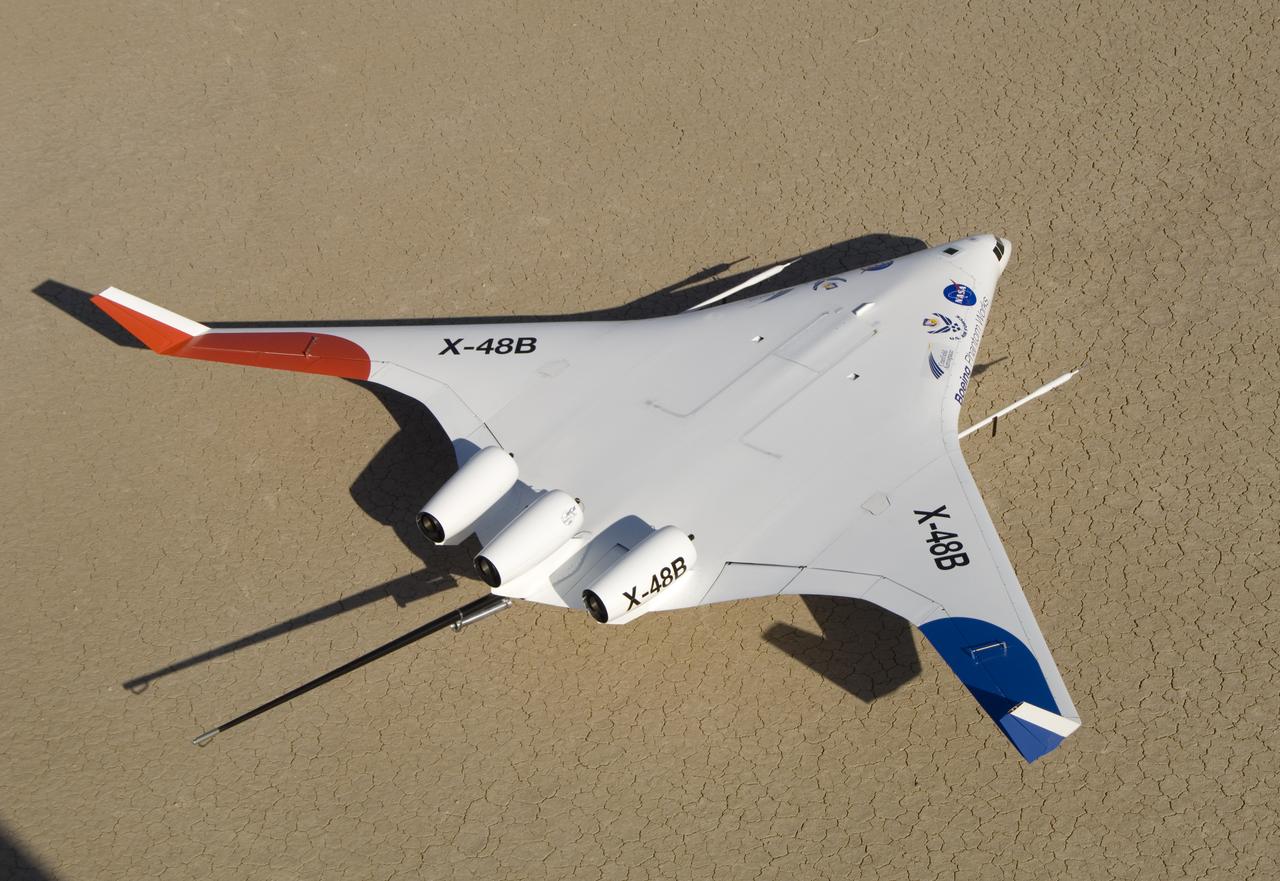

This rear-quarter view shows off the unique lines of Boeing's X-48B Blended Wing Body technology demonstrator on Rogers Dry Lake adjacent to NASA Dryden.
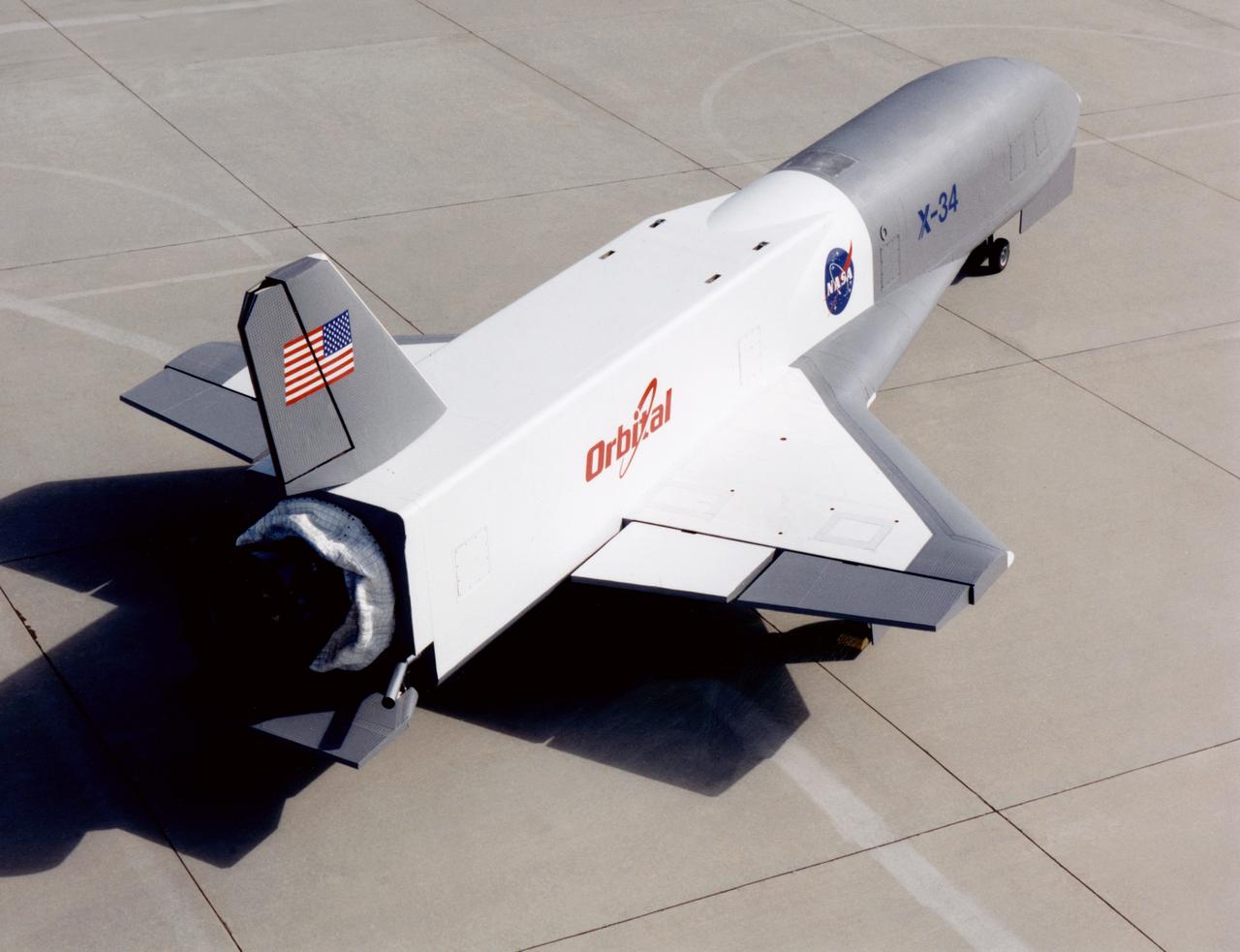

X-34 Technology Testbed Demonstrator on NASA Dryden ramp

The test subject of Airspace Technology Demonstration 2 is “Integrated Arrivals Departures Scheduling,” a software tool that coordinates schedules between the ramp, tower, terminal and center control facilities, allowing air traffic controllers to better predict where and when to send aircraft in order to reduce congestion.
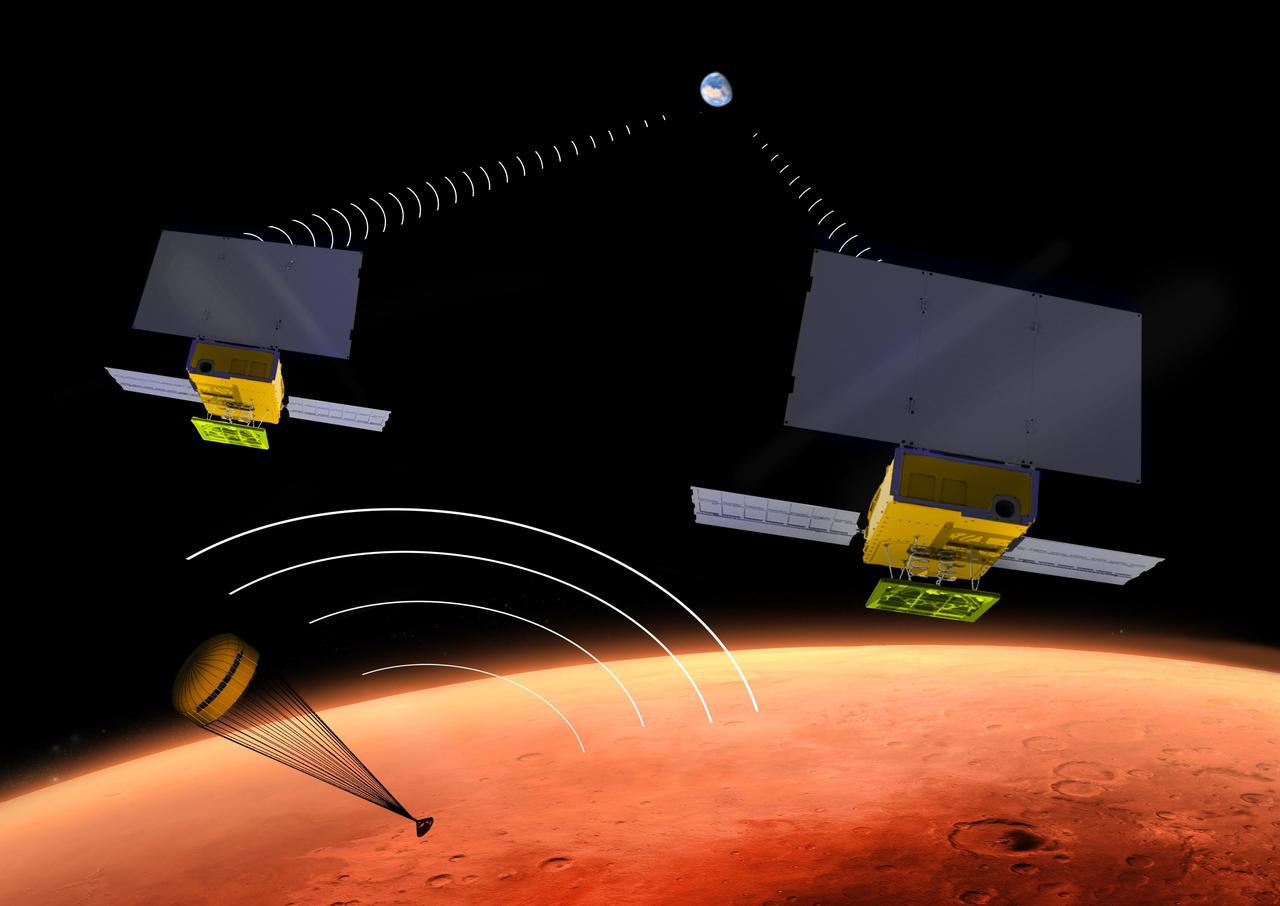

NASA's two MarCO CubeSats will be flying past Mars in September 2016 just as NASA's next Mars lander, InSight, is descending through the Martian atmosphere and landing on the surface. MarCO, for Mars Cube One, will provide an experimental communications relay to inform Earth quickly about the landing. This illustration depicts a moment during the lander's descent when it is transmitting data in the UHF radio band, and the twin MarCO craft are receiving those transmissions while simultaneously relaying the data to Earth in a different radio band. Each of the MarCO twins carries two solar panels for power, and both UHF-band and X-band radio antennas. As a technology demonstration, MarCO could lead to other "bring-your-own-relay" mission designs and also to use of miniature spacecraft for a wide diversity of interplanetary missions. MarCO is the first interplanetary use of CubeSat technologies for small spacecraft. CubeSats are a class of spacecraft based on a standardized small size and modular use of off-the-shelf technologies to streamline development. Many have been made by university students, and dozens have been launched into Earth orbit using extra payload mass available on launches of larger spacecraft. The two briefcase-size MarCO CubeSats will ride along with InSight on an Atlas V launch vehicle lifting off in March 2016 from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. MarCO is a technology demonstration aspect of the InSight mission and not needed for that mission's success. InSight, an acronym for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, will investigate the deep interior of Mars to advance understanding of how rocky planets, including Earth, formed and evolved. After launch, the MarCO twins and InSight will be navigated separately to Mars. Note: After thorough examination, NASA managers have decided to suspend the planned March 2016 launch of the Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) mission. The decision follows unsuccessful attempts to repair a leak in a section of the prime instrument in the science payload. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19388
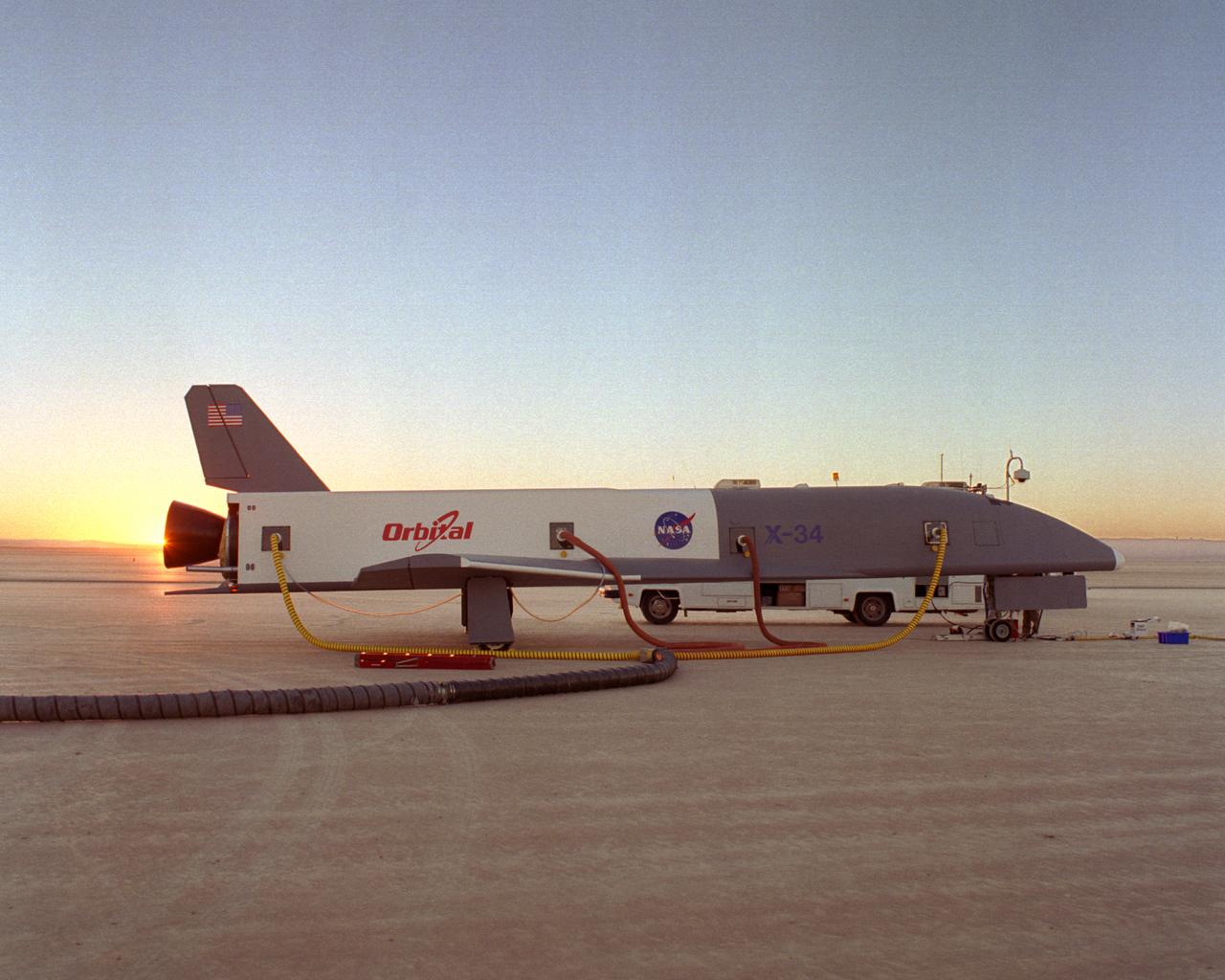

Following initial captive flight tests last year at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards Air Force Base, California, the X-34 technology demonstrator began a new series of tests last week in which it is being towed behind a semi-truck and released to coast on the Edwards dry lakebed. On July 20, 2000, it was towed and released twice at speeds of five and 10 miles per hour. On July 24, 2000, it was towed and released twice at 10 and 30 miles per hour. Twelve tests are planned during which the X-34 will be towed for distances up to 10,000 feet and released at speeds up to 80 miles per hour. The test series is expected to last at least six weeks.

Following initial captive flight tests last year at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards Air Force Base, California, the X-34 technology demonstrator began a new series of tests last week in which it is being towed behind a semi-truck and released to coast on the Edwards dry lakebed. On July 20, 2000, it was towed and released twice at speeds of five and 10 miles per hour. On July 24, 2000, it was towed and released twice at 10 and 30 miles per hour. Twelve tests are planned during which the X-34 will be towed for distances up to 10,000 feet and released at speeds up to 80 miles per hour. The test series is expected to last at least six weeks.
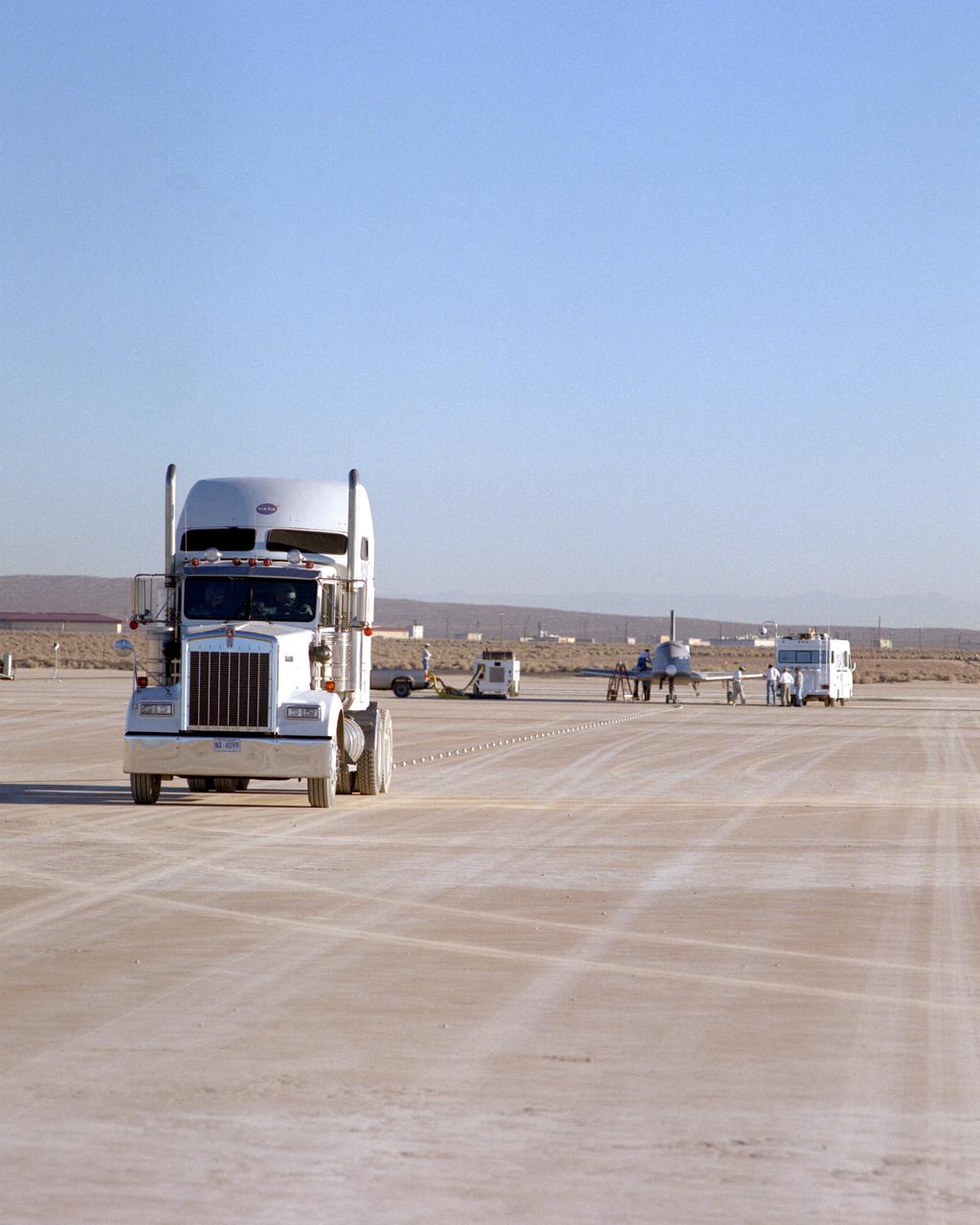

Following initial captive flight tests last year at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards Air Force Base, California, the X-34 technology demonstrator began a new series of tests last week in which it is being towed behind a semi-truck and released to coast on the Edwards dry lakebed. On July 20, 2000, it was towed and released twice at speeds of five and 10 miles per hour. On July 24, 2000, it was towed and released twice at 10 and 30 miles per hour. Twelve tests are planned during which the X-34 will be towed for distances up to 10,000 feet and released at speeds up to 80 miles per hour. The test series is expected to last at least six weeks.
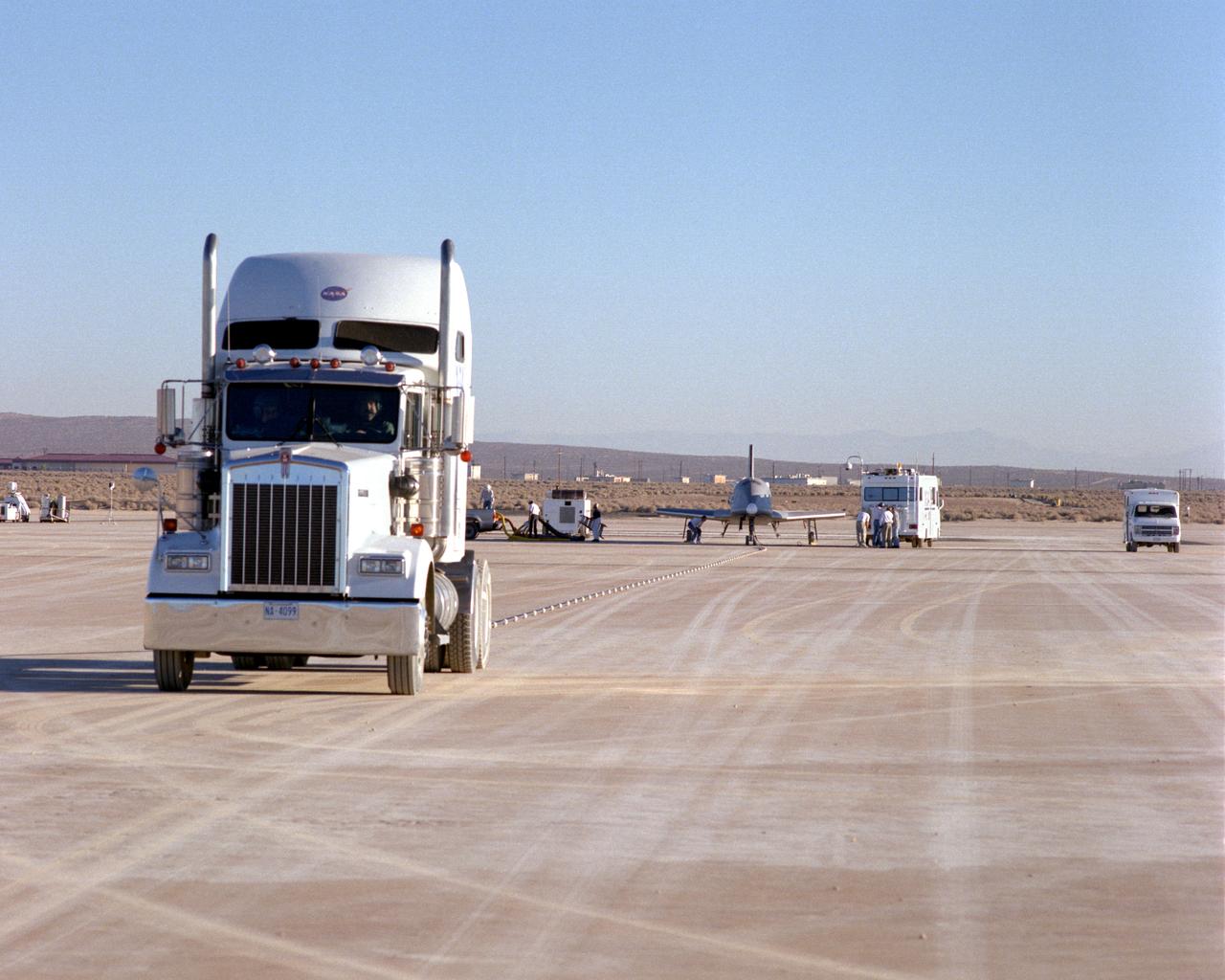

Following initial captive flight tests last year at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards Air Force Base, California, the X-34 technology demonstrator began a new series of tests last week in which it is being towed behind a semi-truck and released to coast on the Edwards dry lakebed. On July 20, 2000, it was towed and released twice at speeds of five and 10 miles per hour. On July 24, 2000, it was towed and released twice at 10 and 30 miles per hour. Twelve tests are planned during which the X-34 will be towed for distances up to 10,000 feet and released at speeds up to 80 miles per hour. The test series is expected to last at least six weeks.
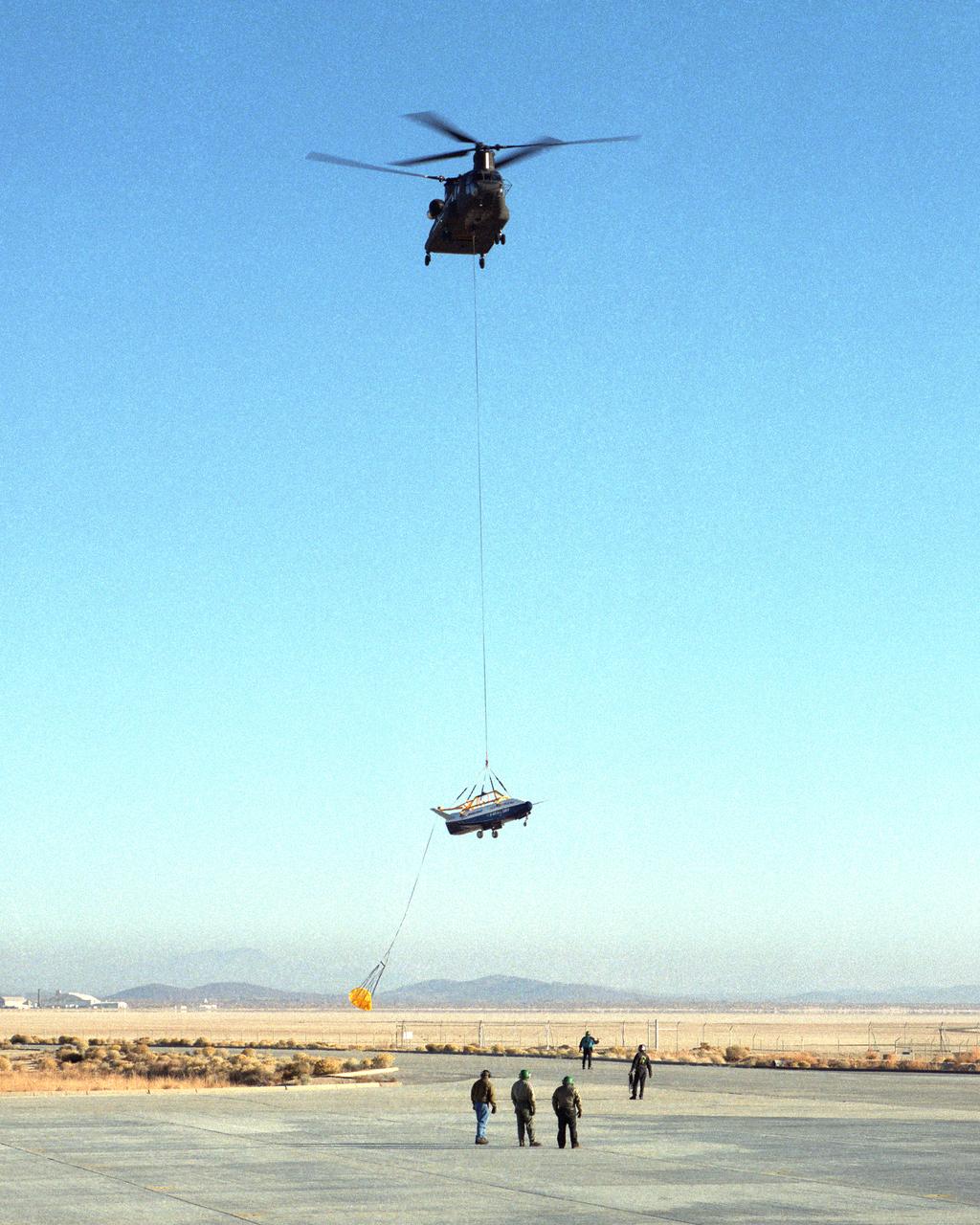

A U.S. Army CH-47 Chinook helicopter slowly lowers the X-40 sub-scale technology demonstrator to the ground under the watchful eyes of ground crew at the conclusion of a captive-carry test flight at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. Several captive-carry flights were conducted to check out all operating systems and procedures before the X-40 made its first free flight at Edwards, gliding to a fully-autonomous approach and landing on the Edwards runway. The X-40 is an unpowered 82 percent scale version of the X-37, a Boeing-developed spaceplane designed to demonstrate various advanced technologies for development of future lower-cost access to space vehicles. Flight tests of the X-40 are designed to reduce the risks associated with research flights of the larger, more complex X-37.
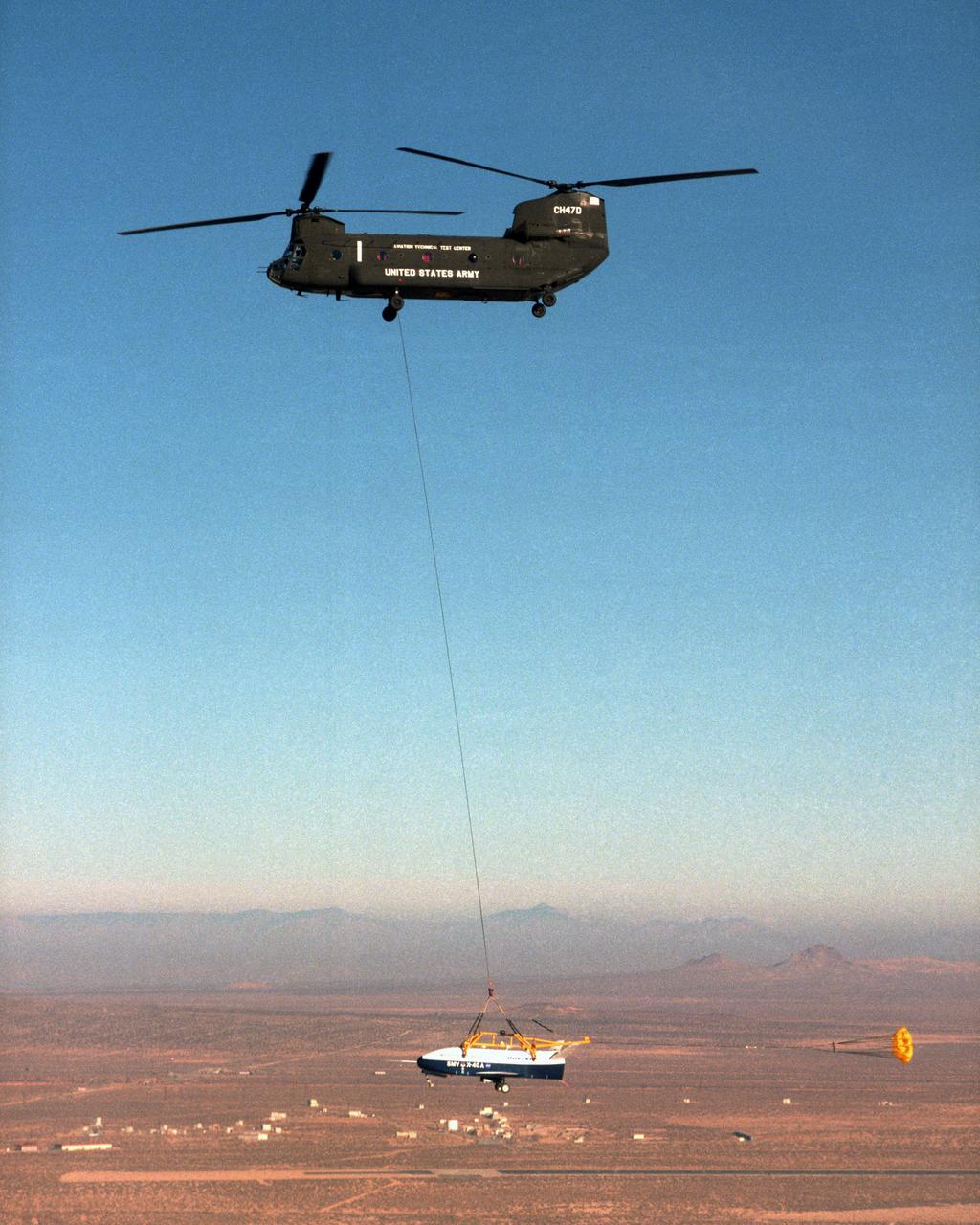

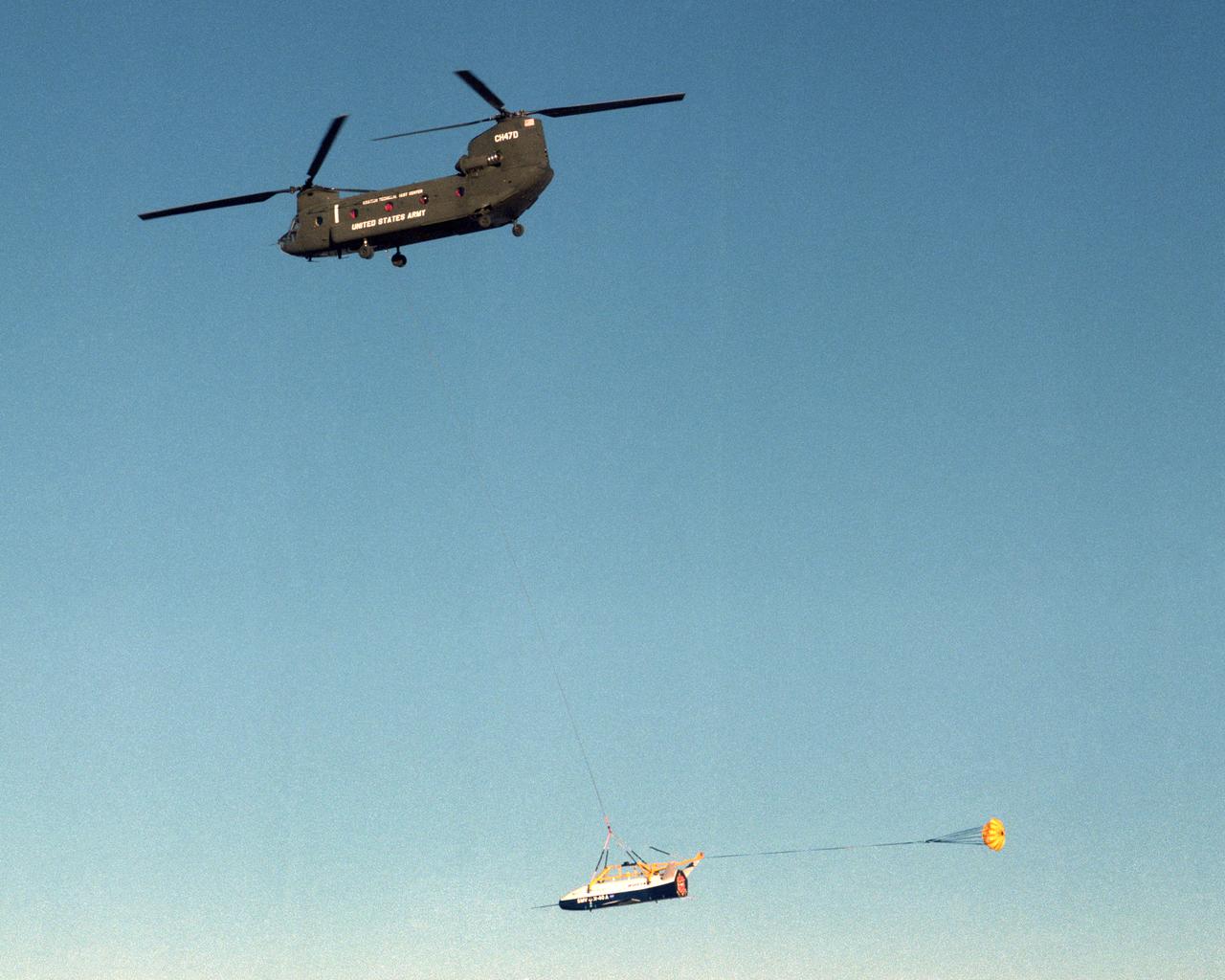
With a small stabilization parachute trailing behind, the X-40 sub-scale technology demonstrator is suspended under a U.S. Army CH-47 Chinook cargo helicopter during a captive-carry test flight at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The captive carry flights are designed to verify the X-40's navigation and control systems, rigging angles for its sling, and stability and control of the helicopter while carrying the X-40 on a tether. Following a series of captive-carry flights, the X-40 made free flights from a launch altitude of about 15,000 feet above ground, gliding to a fully autonomous landing. The X-40 is an unpowered 82 percent scale version of the X-37, a Boeing-developed spaceplane designed to demonstrate various advanced technologies for development of future lower-cost access to space vehicles.

The X-40 sub-scale technology demonstrator is suspended under a U.S. Army CH-47 Chinook cargo helicopter during a captive-carry test flight at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The captive carry flights are designed to verify the X-40's navigation and control systems, rigging angles for its sling, and stability and control of the helicopter while carrying the X-40 on a tether. Following a series of captive-carry flights, the X-40 made free flights from a launch altitude of about 15,000 feet above ground, gliding to a fully autonomous landing. The X-40 is an unpowered 82 percent scale version of the X-37, a Boeing-developed spaceplane designed to demonstrate various advanced technologies for development of future lower-cost access to space vehicles.
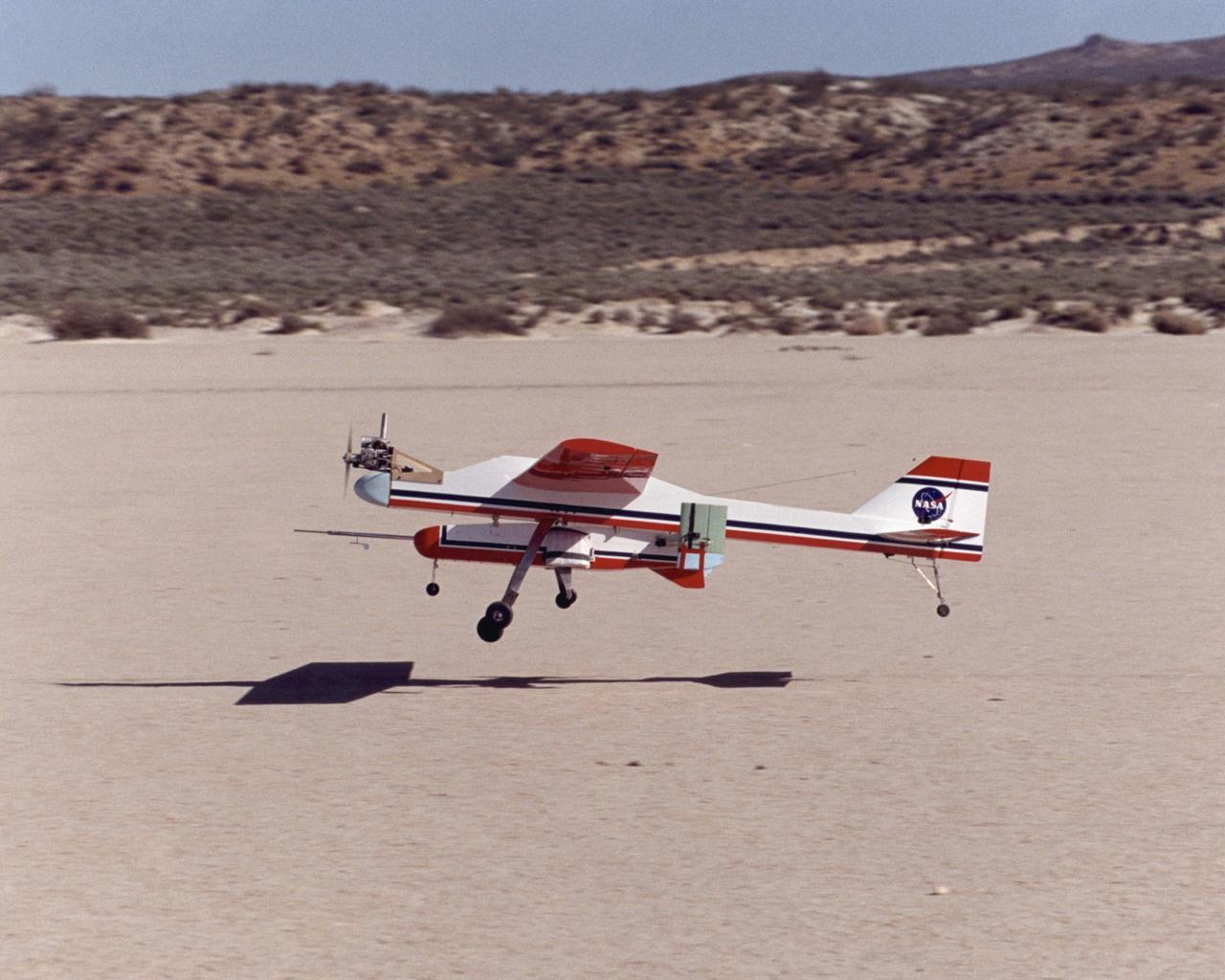

The I2000, a deployable, inflatable wing technology demonstrator experiment aircraft, leaves the ground during a flight conducted by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California.
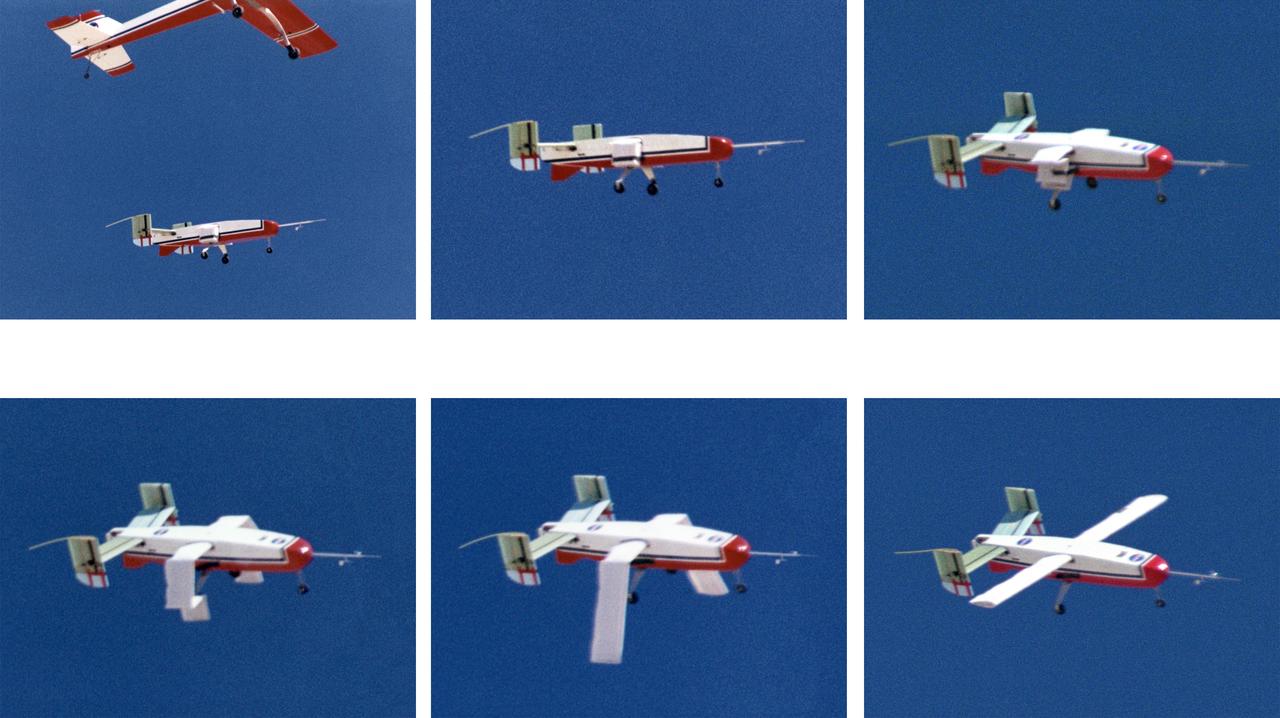
The deployable, inflatable wing technology demonstrator aircraft's wings begin deploying following separation from its carrier aircraft during a flight experiment conducted by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. Wing deployment time is typically on the order of a third of a second, almost faster than the human eye can see. Three successful flights of the I2000 inflatable wing aircraft occurred. During the flights, the team air-launched the radio-controlled (R/C) I2000 from an R/C utility airplane at an altitude of 800-1000 feet. As the I2000 separated from the carrier aircraft, its inflatable wings "popped-out," deploying rapidly via an on-board nitrogen bottle. The aircraft remained stable as it transitioned from wingless to winged flight. The unpowered I2000 glided down to a smooth landing under complete control.
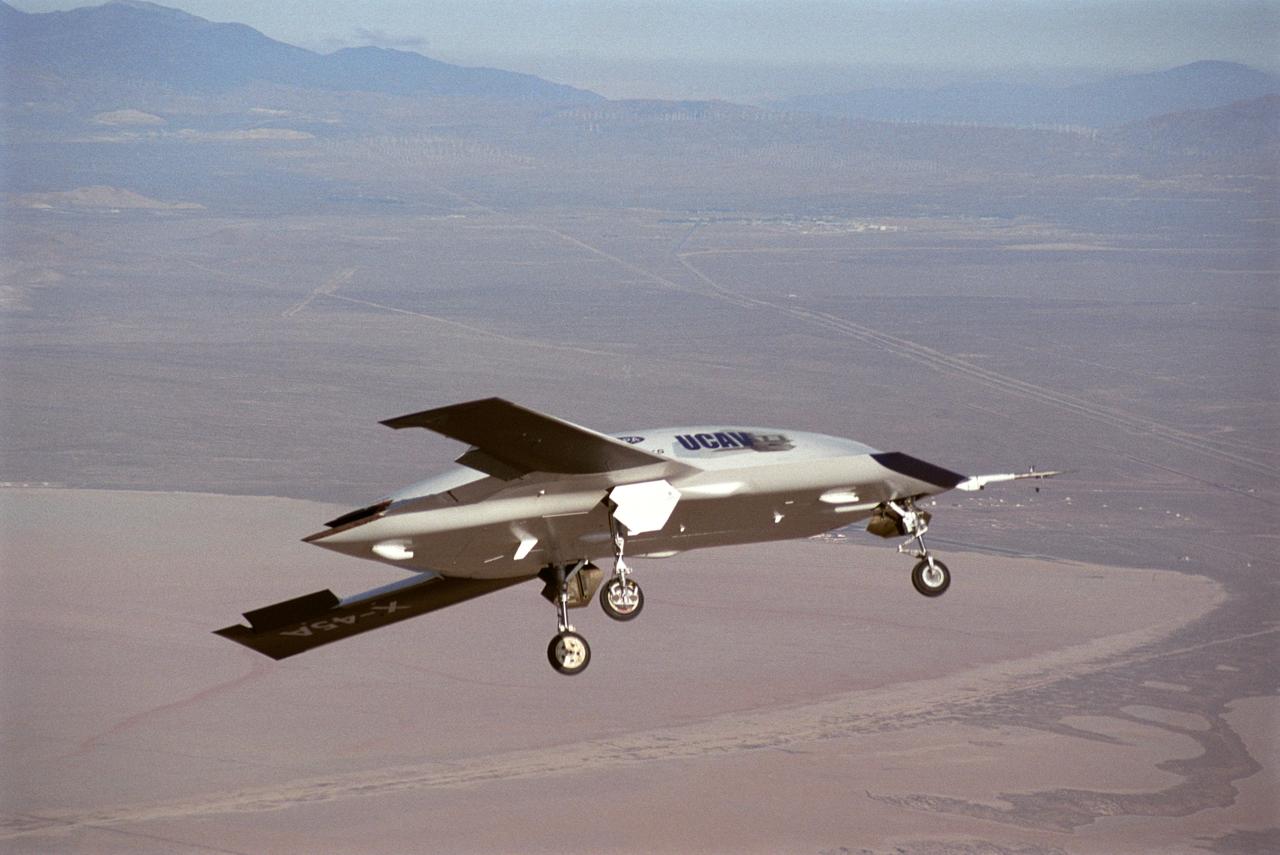

X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle, or UCAV, technology demonstration aircraft in flight during its first flight at Edwards Air Force Base, California.
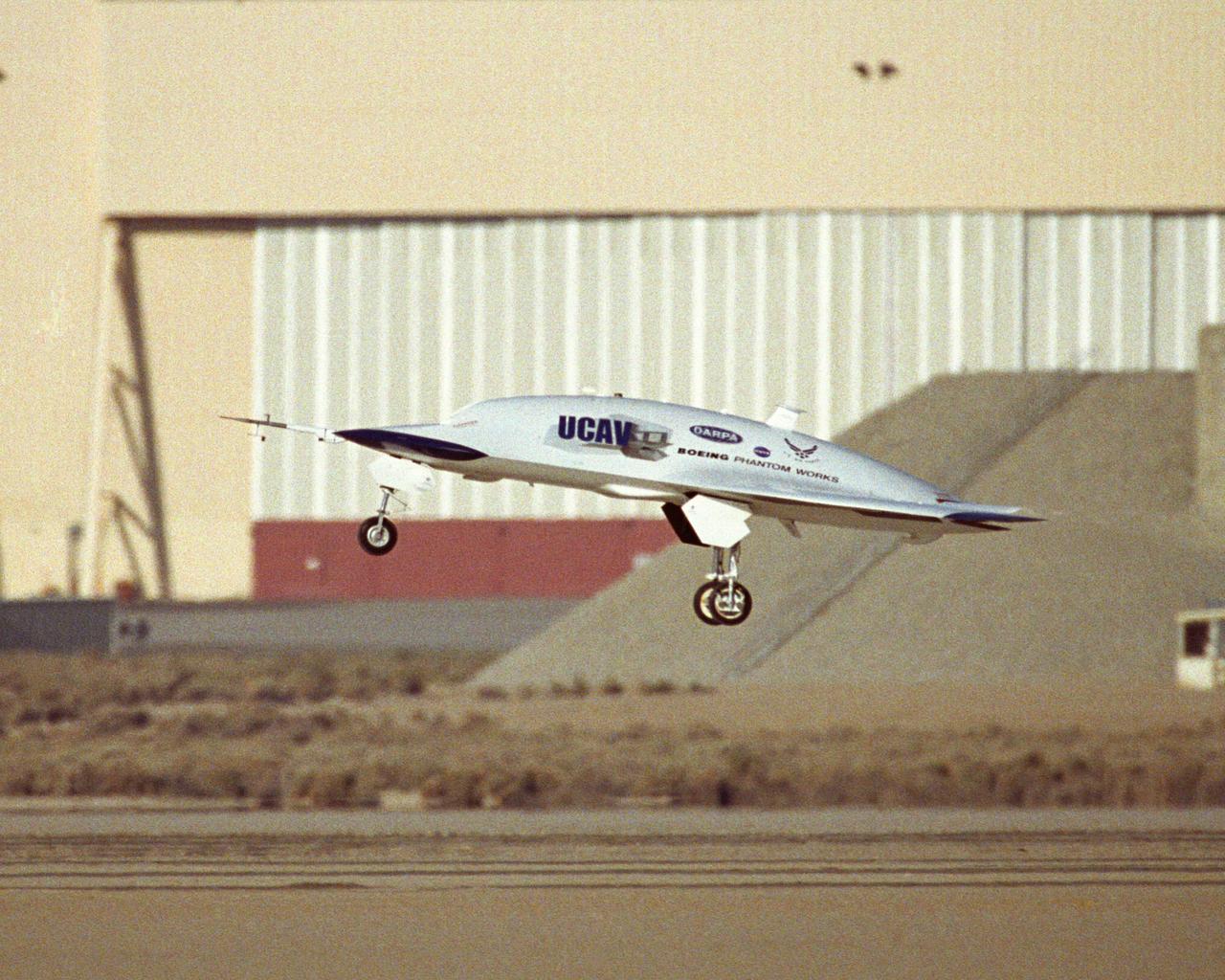

X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle, or UCAV, technology demonstration aircraft in flight during its first flight at Edwards Air Force Base, California.
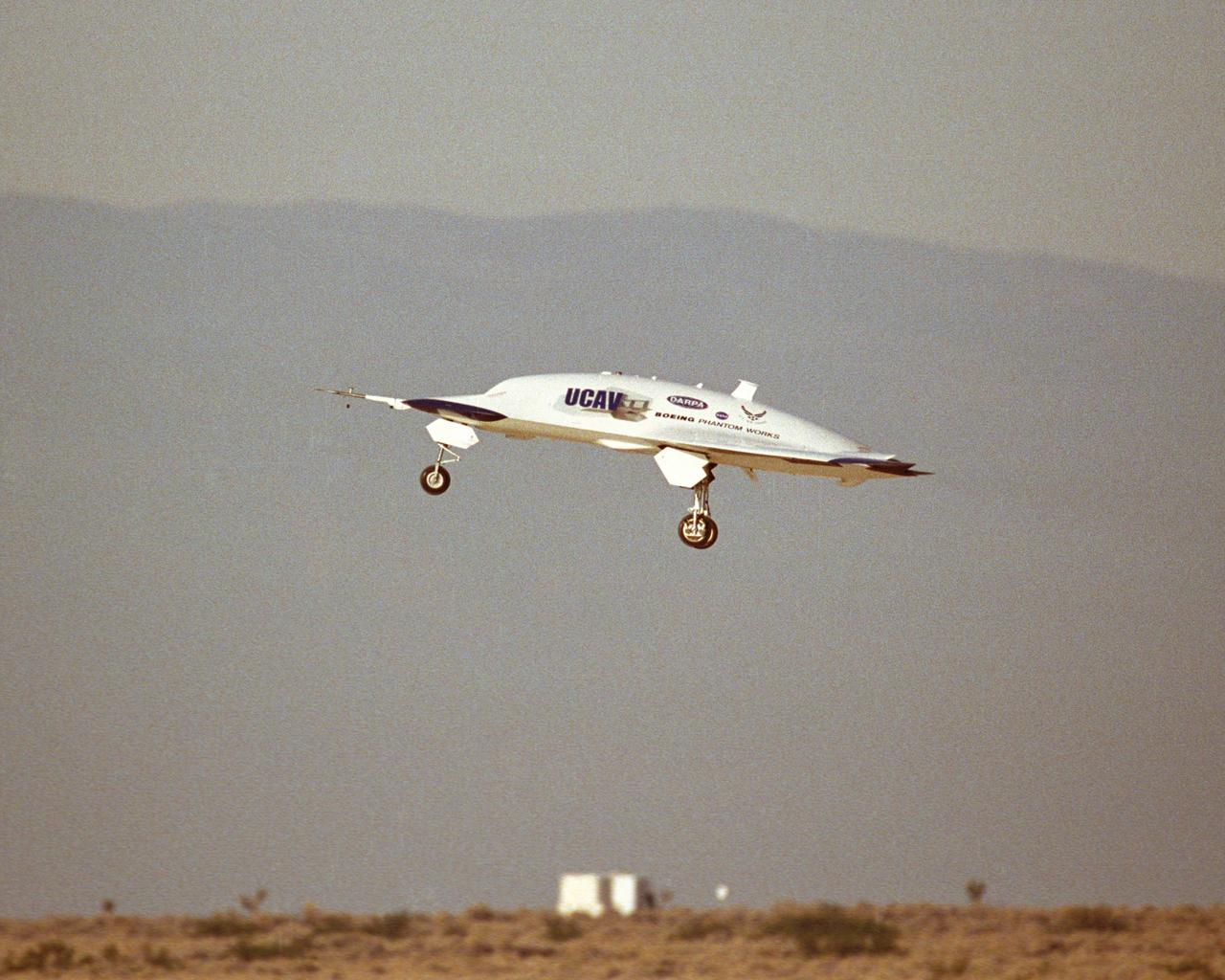

X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle, or UCAV, technology demonstration aircraft in flight during its first flight at Edwards Air Force Base, California.
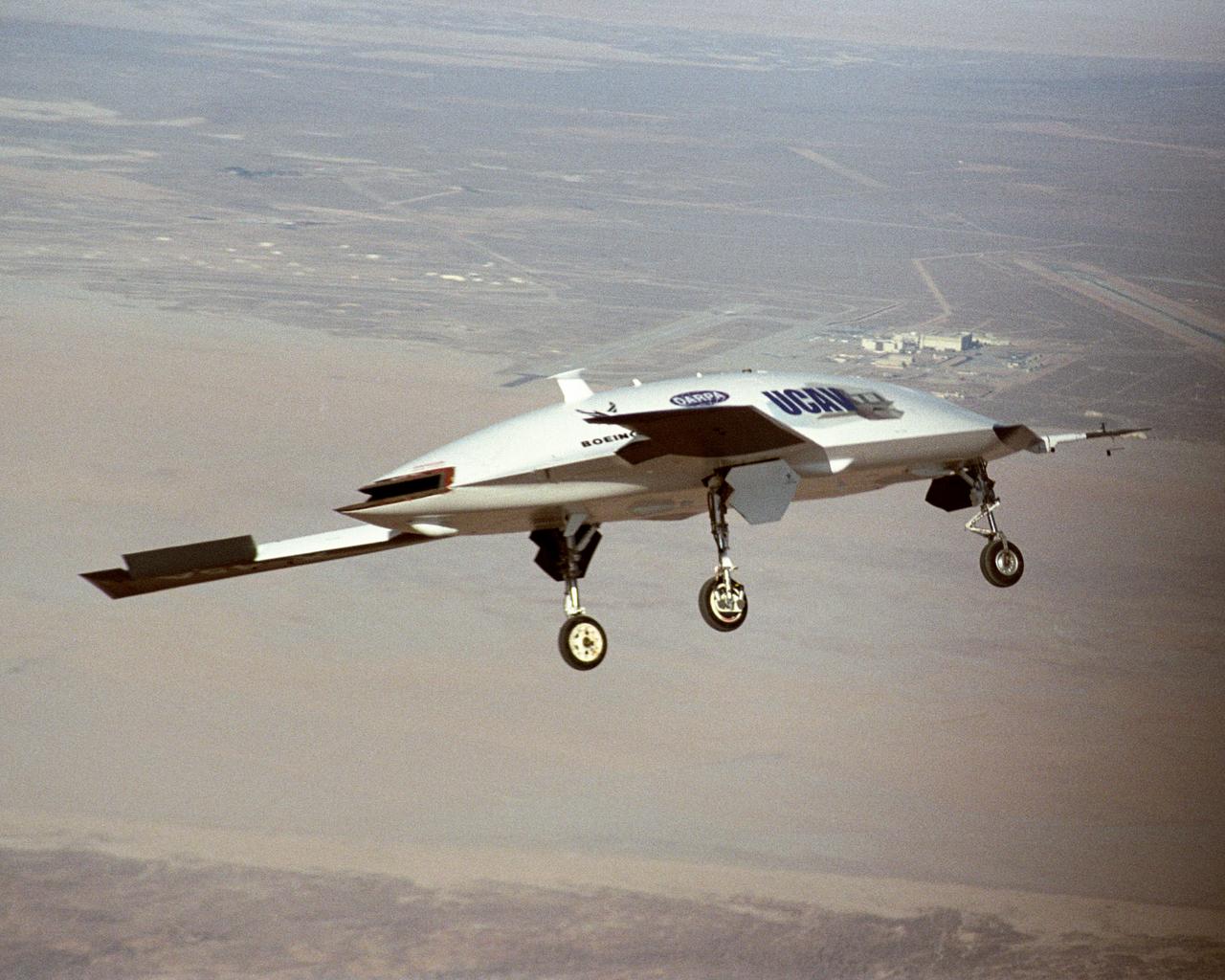

X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle, or UCAV, technology demonstration aircraft in flight during its first flight at Edwards Air Force Base, California.
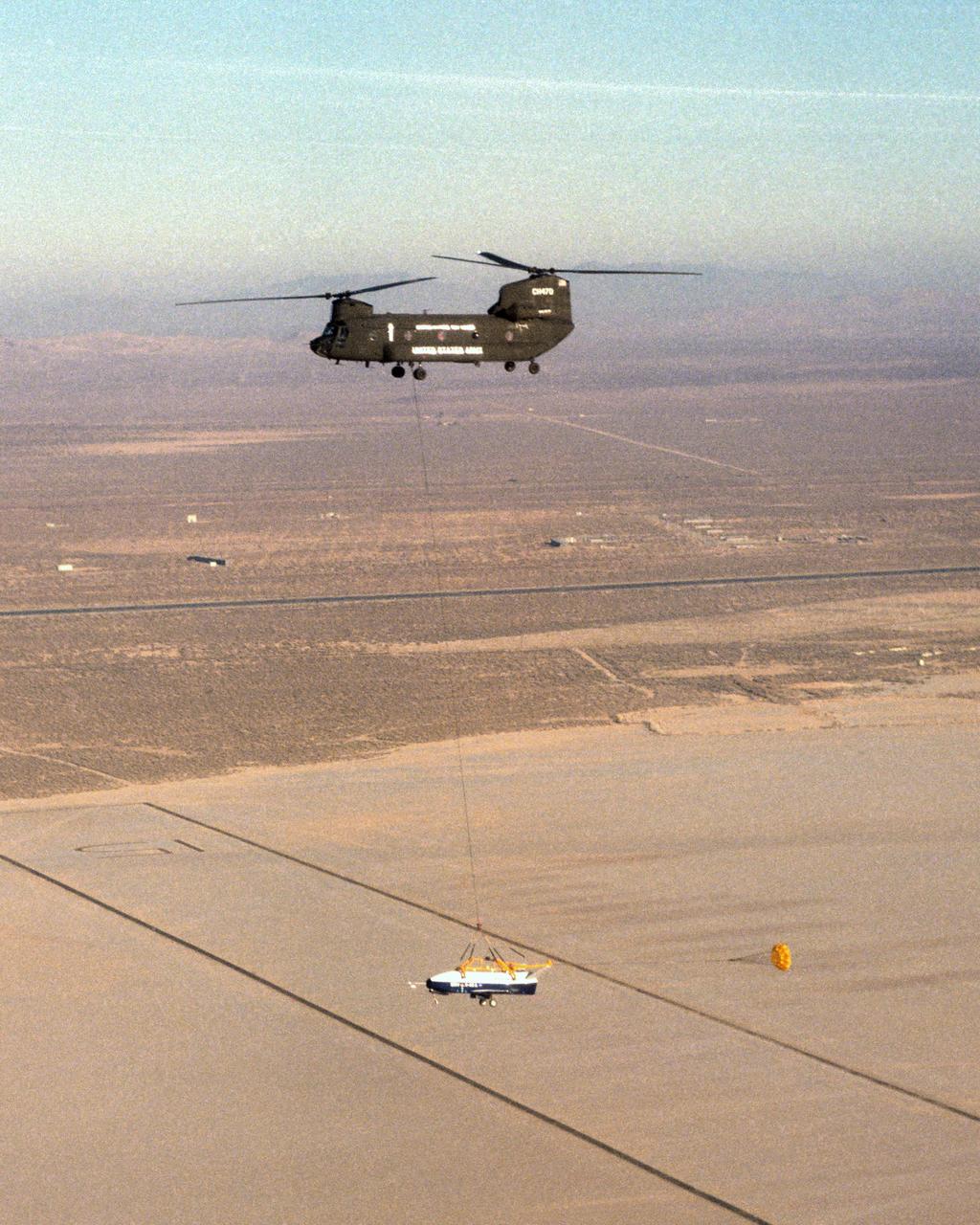

The X-40 sub-scale technology demonstrator and its U.S. Army CH-47 Chinook helicopter mothership fly over a dry lakebed runway during a captive-carry test flight from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The X-40 is attached to a sling which is suspended from the CH-47 by a 110-foot-long cable during the tests, while a small parachute trails behind to provide stability. The captive carry flights are designed to verify the X-40's navigation and control systems, rigging angles for its sling, and stability and control of the helicopter while carrying the X-40 on a tether. Following a series of captive-carry flights, the X-40 made free flights from a launch altitude of about 15,000 feet above ground, gliding to a fully autonomous landing. The X-40 is an unpowered 82 percent scale version of the X-37, a Boeing-developed spaceplane designed to demonstrate various advanced technologies for development of future lower-cost access to space vehicles.

Boeing's X-48B Blended Wing Body technology demonstrator shows off its unique lines at sunset on Rogers Dry Lake adjacent to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. (Boeing photo # SMF06_F_KOEH_X48B-0900a)
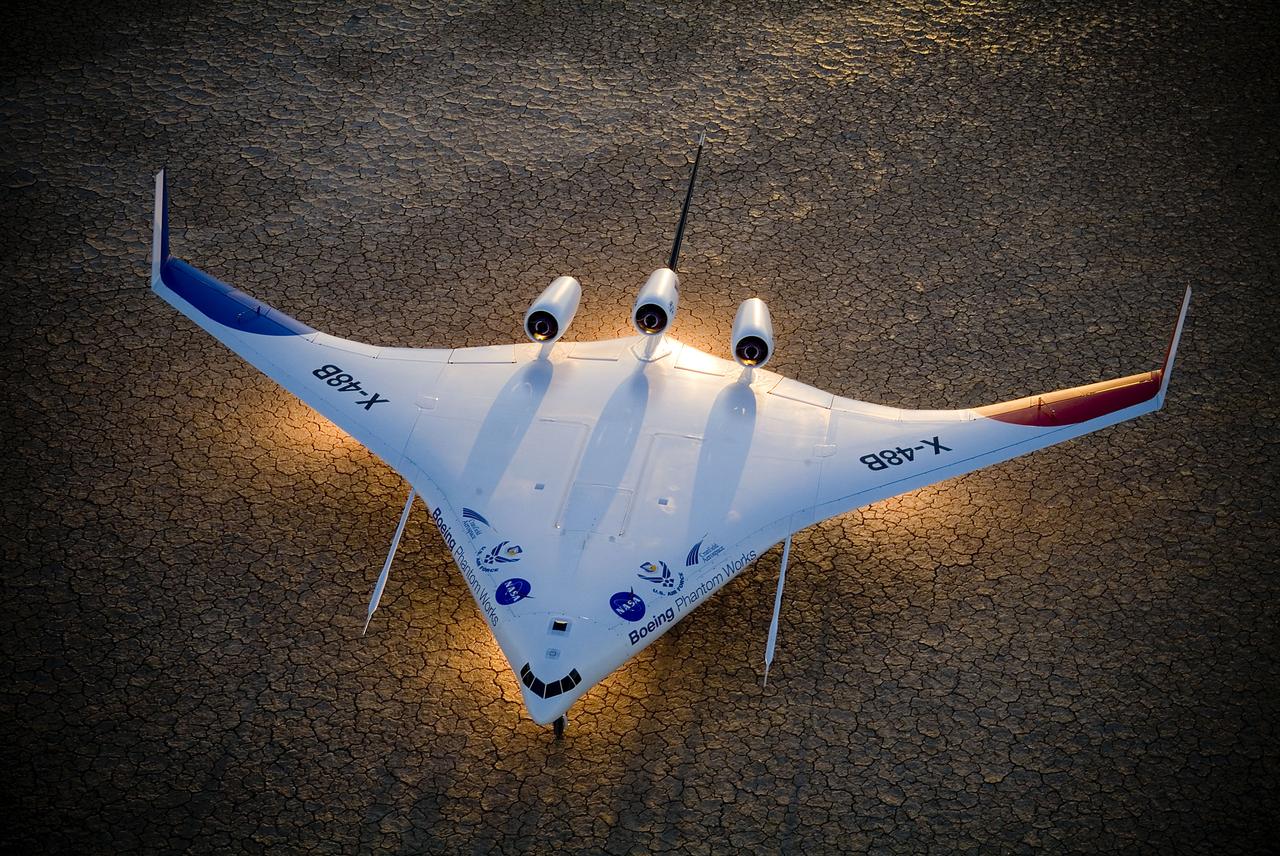

Boeing's X-48B Blended Wing Body technology demonstrator shows off its unique lines at sunset on Rogers Dry Lake adjacent to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. (Boeing photo # SMF06_F_KOEH_X48B-0955)
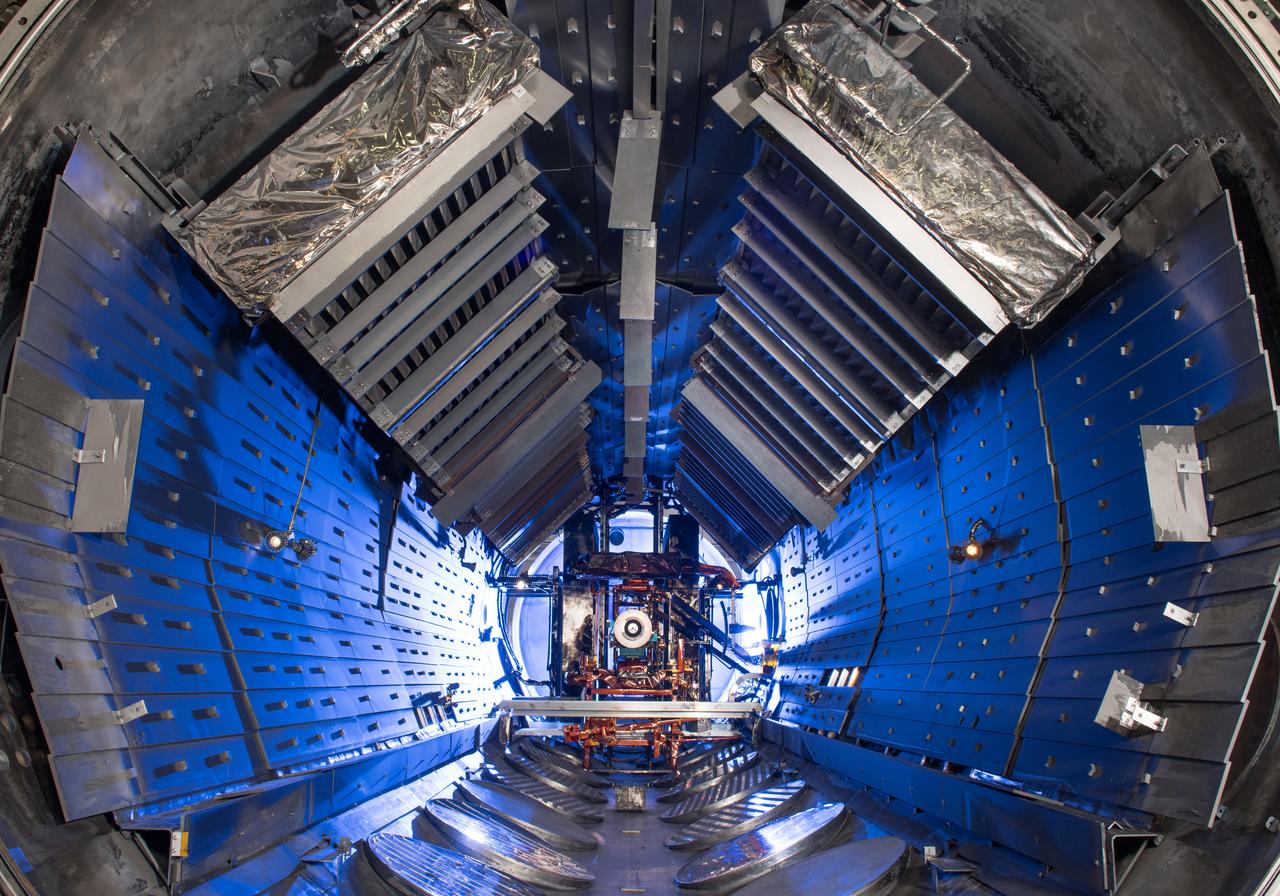

Advanced Electric Propulsion Systems Contract, Technology Demonstration Unit, TDU-3 Checkout Test Hardware Installed in Vacuum Facility 5, VF-5
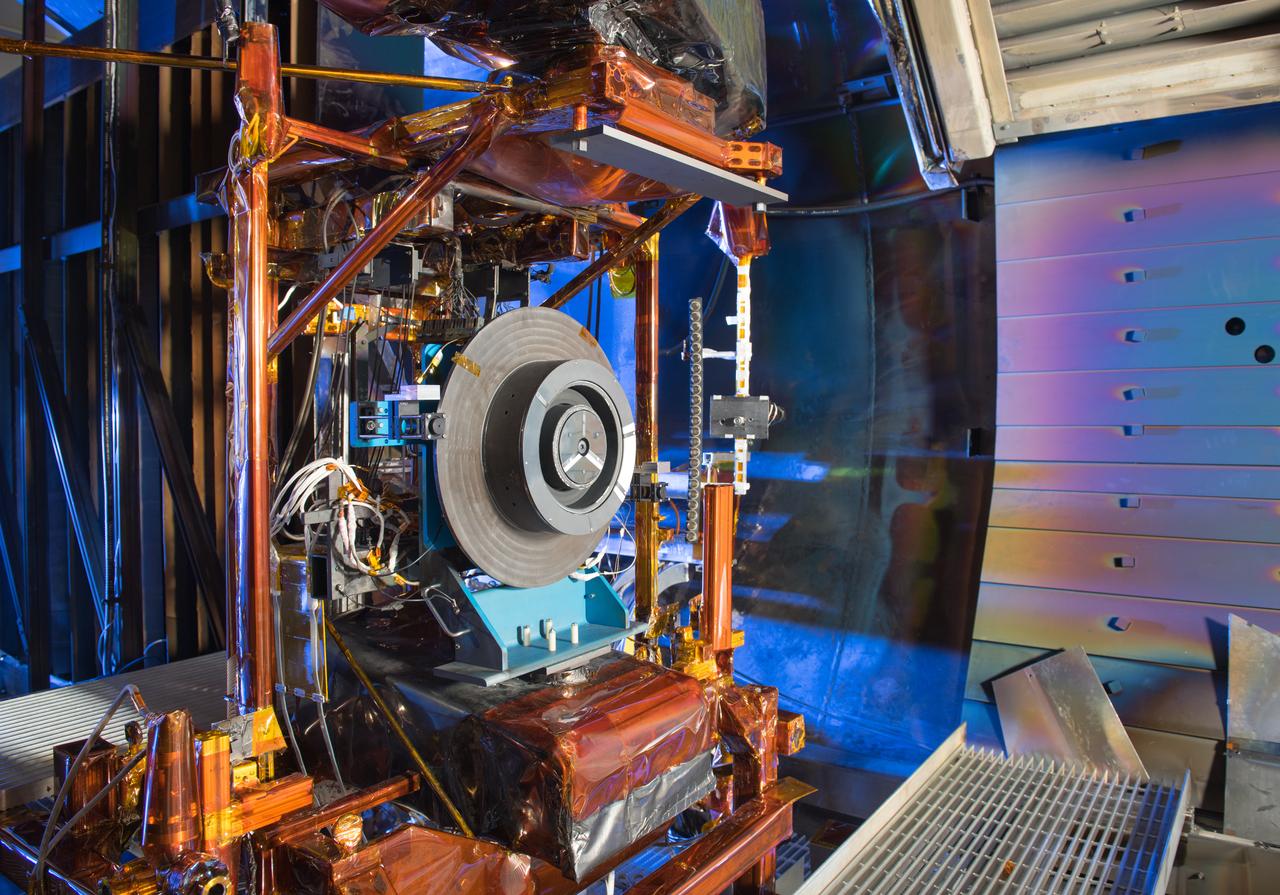
Advanced Electric Propulsion Systems Contract, Technology Demonstration Unit, TDU-3 Checkout Test Hardware Installed in Vacuum Facility 5, VF-5
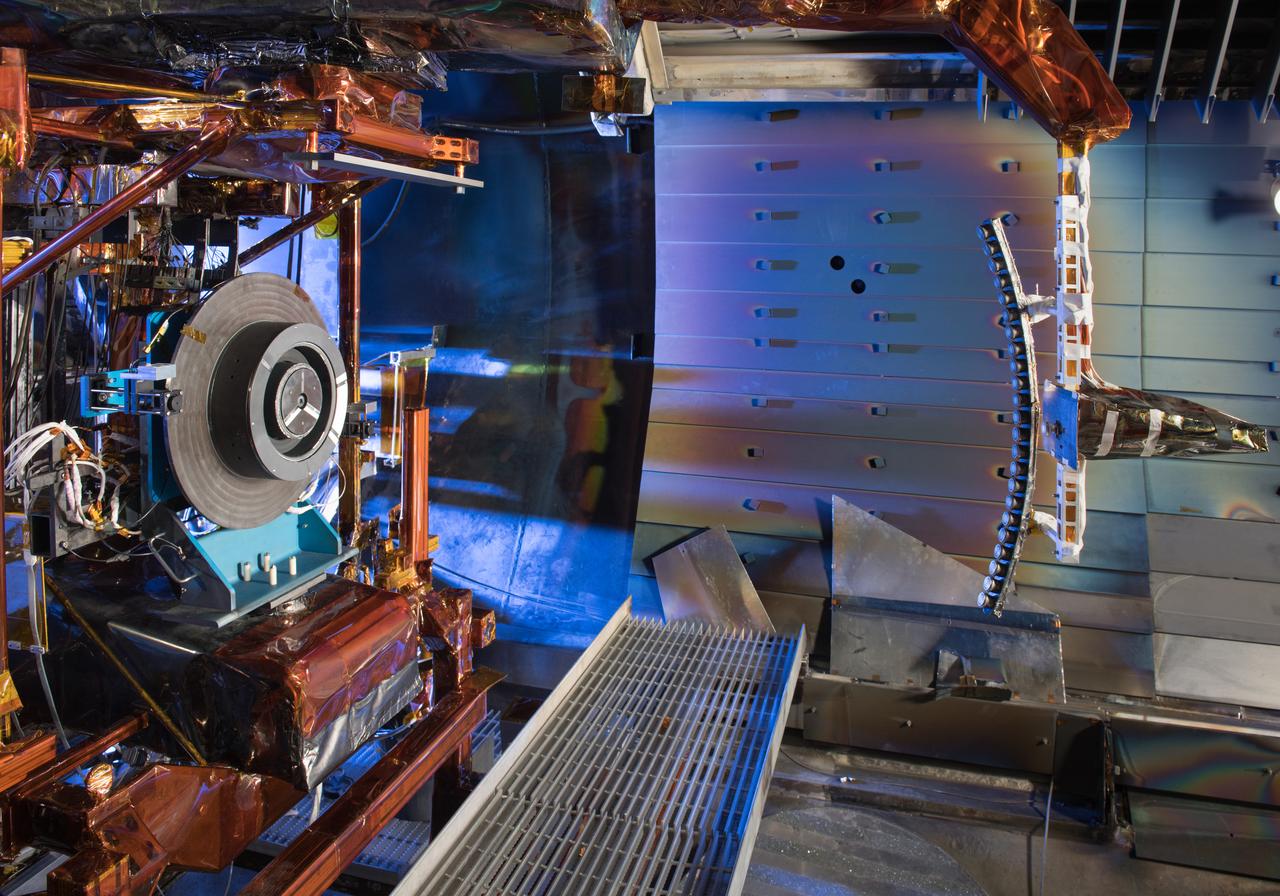
Advanced Electric Propulsion Systems Contract, Technology Demonstration Unit, TDU-3 Checkout Test Hardware Installed in Vacuum Facility 5, VF-5
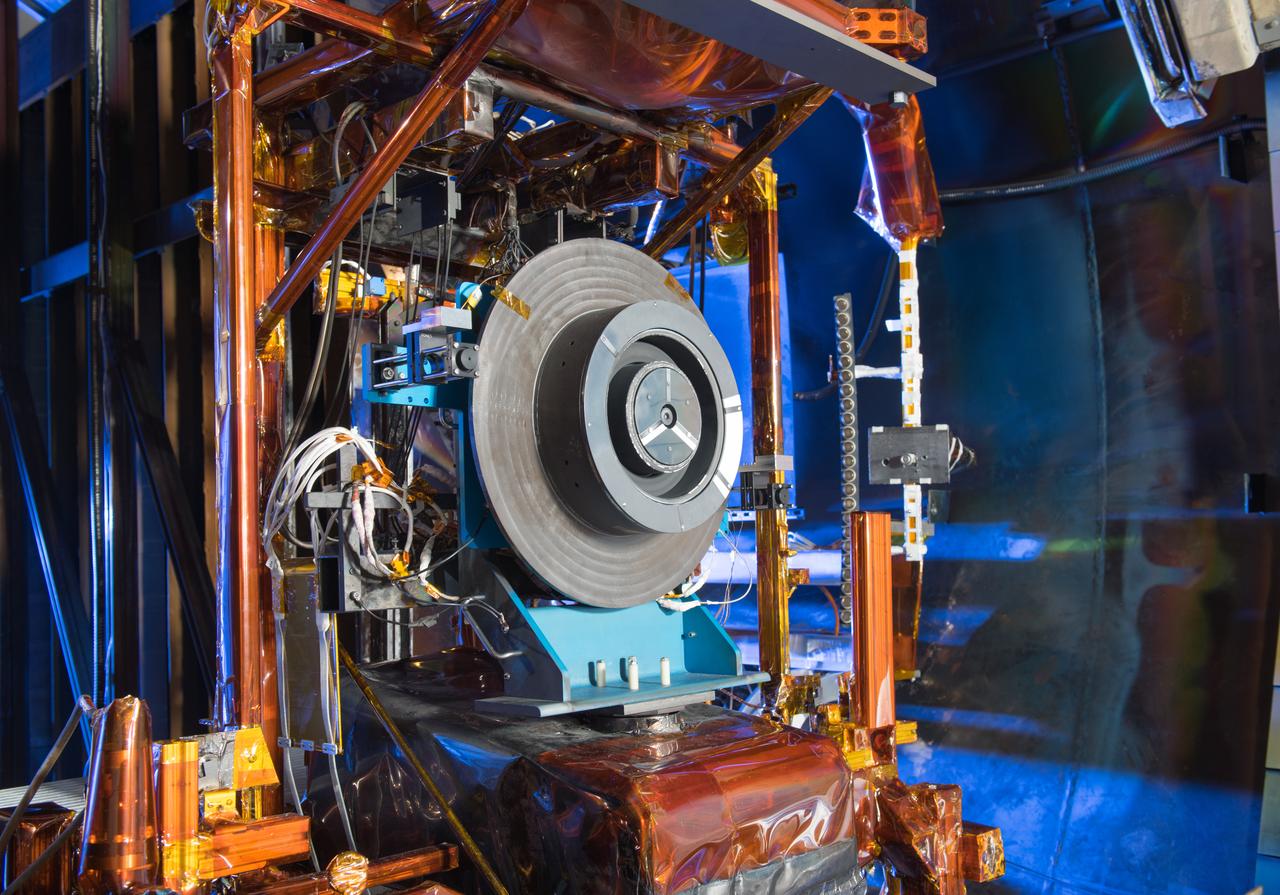
Advanced Electric Propulsion Systems Contract, Technology Demonstration Unit, TDU-3 Checkout Test Hardware Installed in Vacuum Facility 5, VF-5
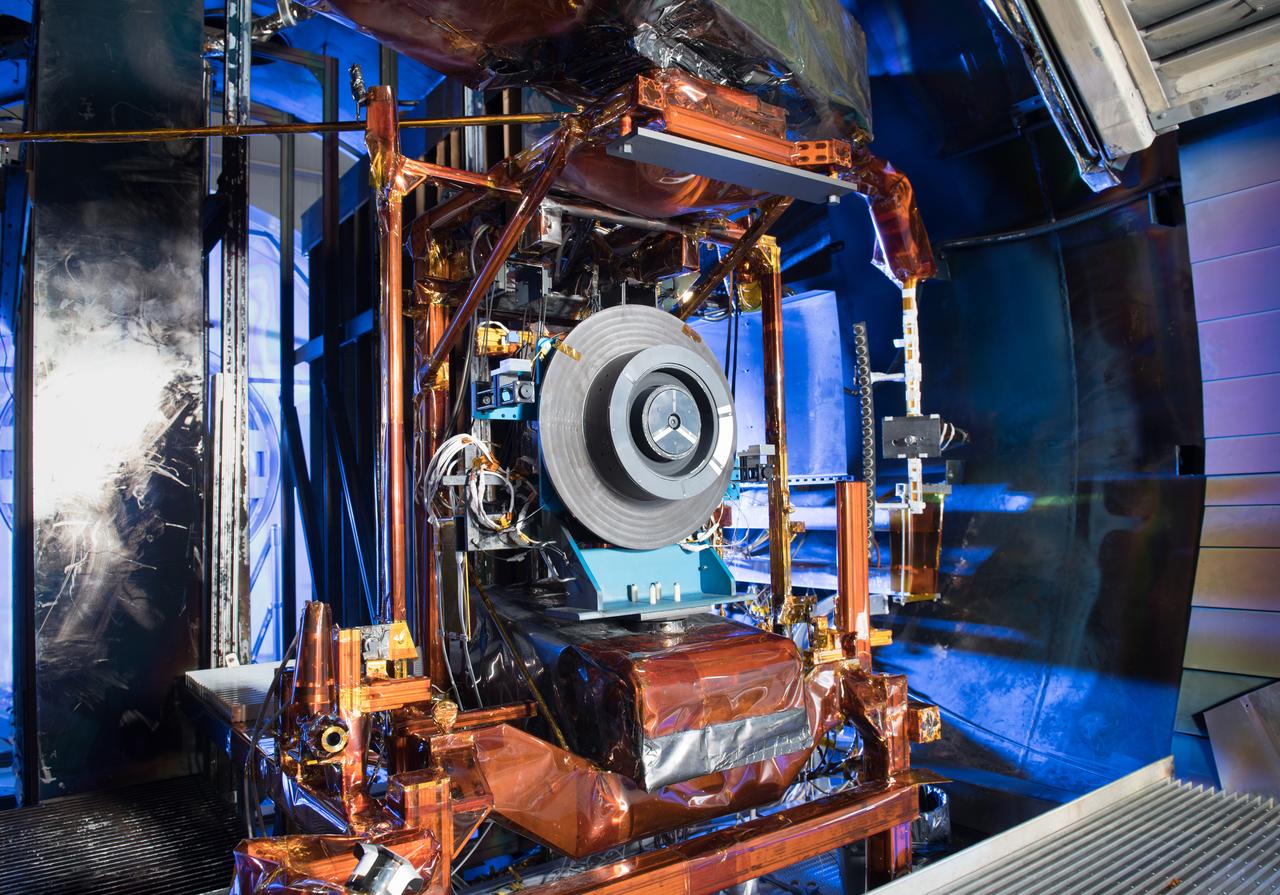
Advanced Electric Propulsion Systems Contract, Technology Demonstration Unit, TDU-3 Checkout Test Hardware Installed in Vacuum Facility 5, VF-5
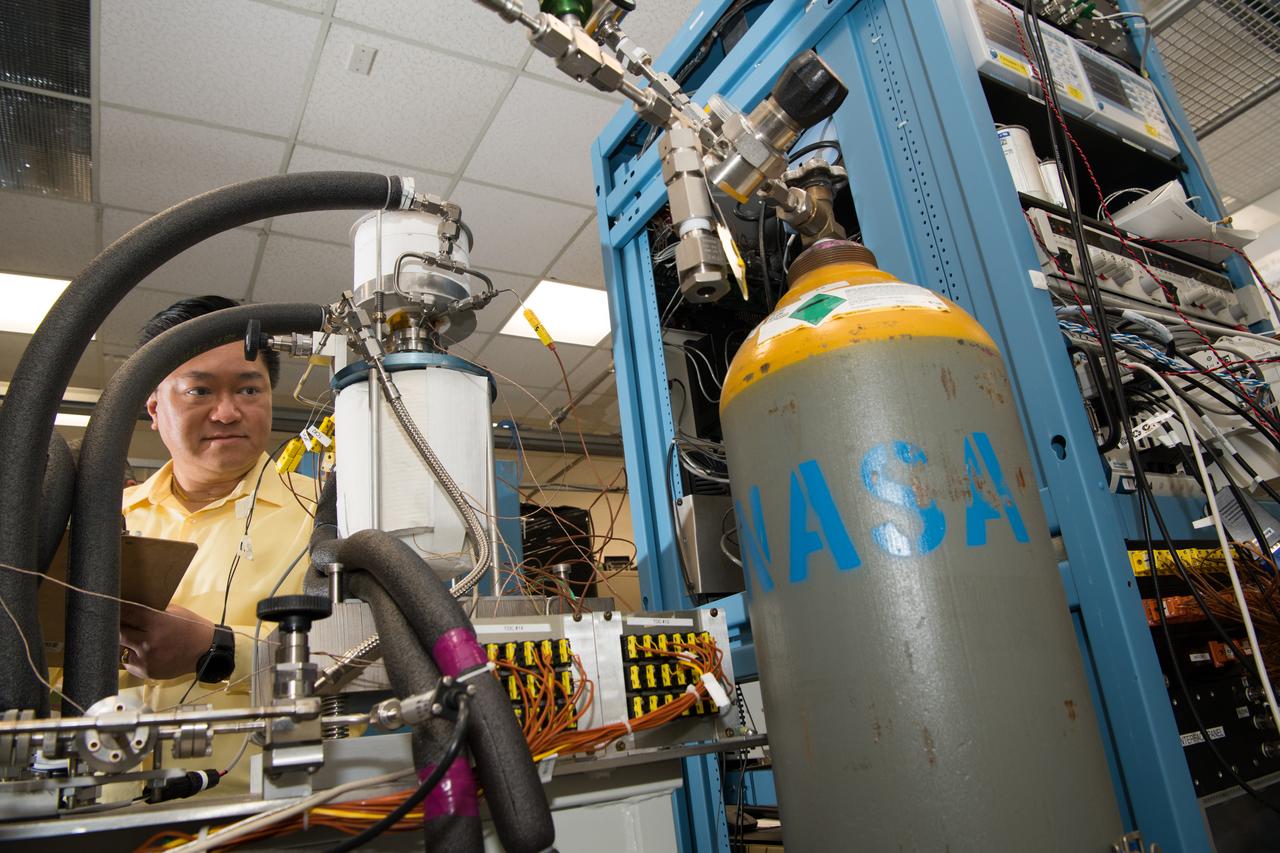

Glenn’s Technology Demonstration Convertor (TDC) #13, a free-piston Stirling power convertor, achieved a milestone of 14 years of maintenance-free operation in the Stirling Research Laboratory in building 301. This technology is proving our capability to power spacecraft on longer-duration future scientific missions.
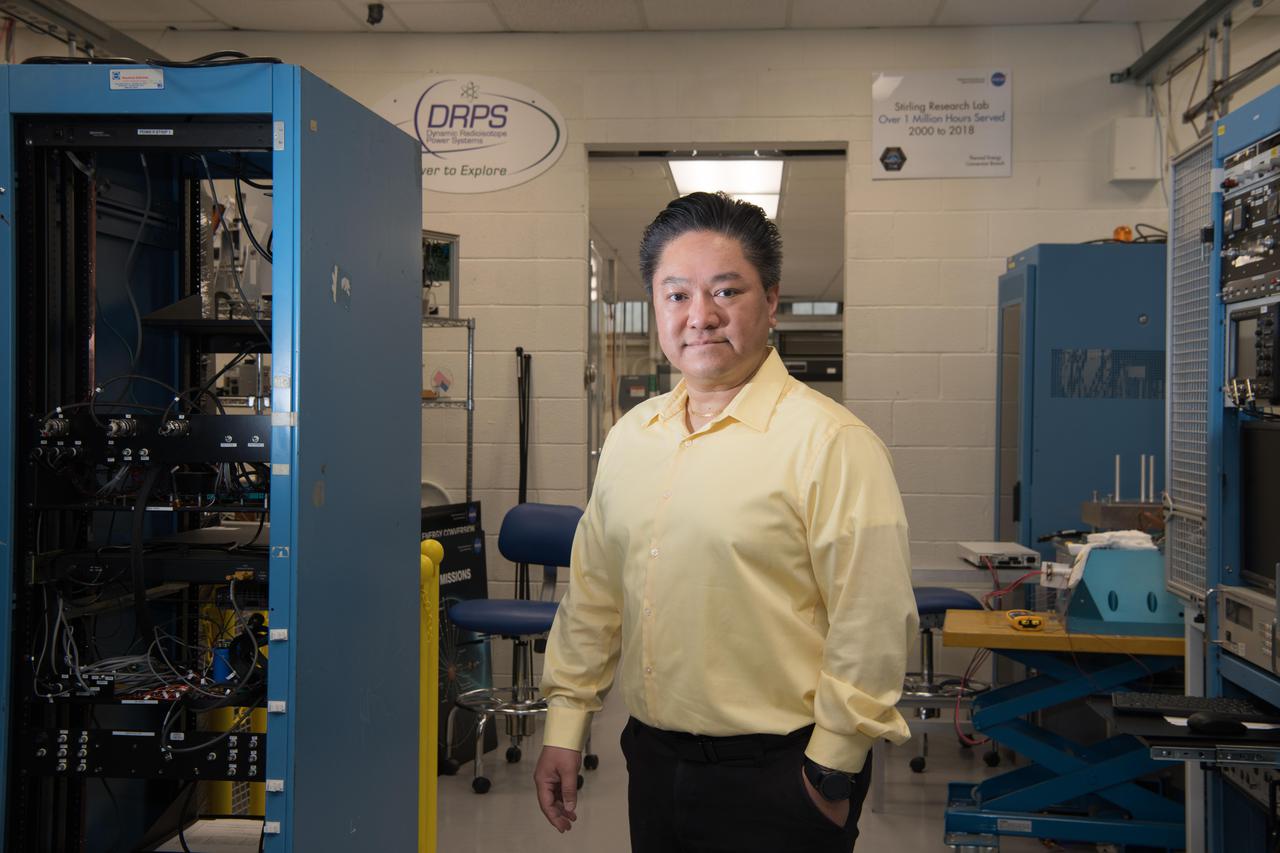
Glenn’s Technology Demonstration Convertor (TDC) #13, a free-piston Stirling power convertor, achieved a milestone of 14 years of maintenance-free operation in the Stirling Research Laboratory in building 301. This technology is proving our capability to power spacecraft on longer-duration future scientific missions.
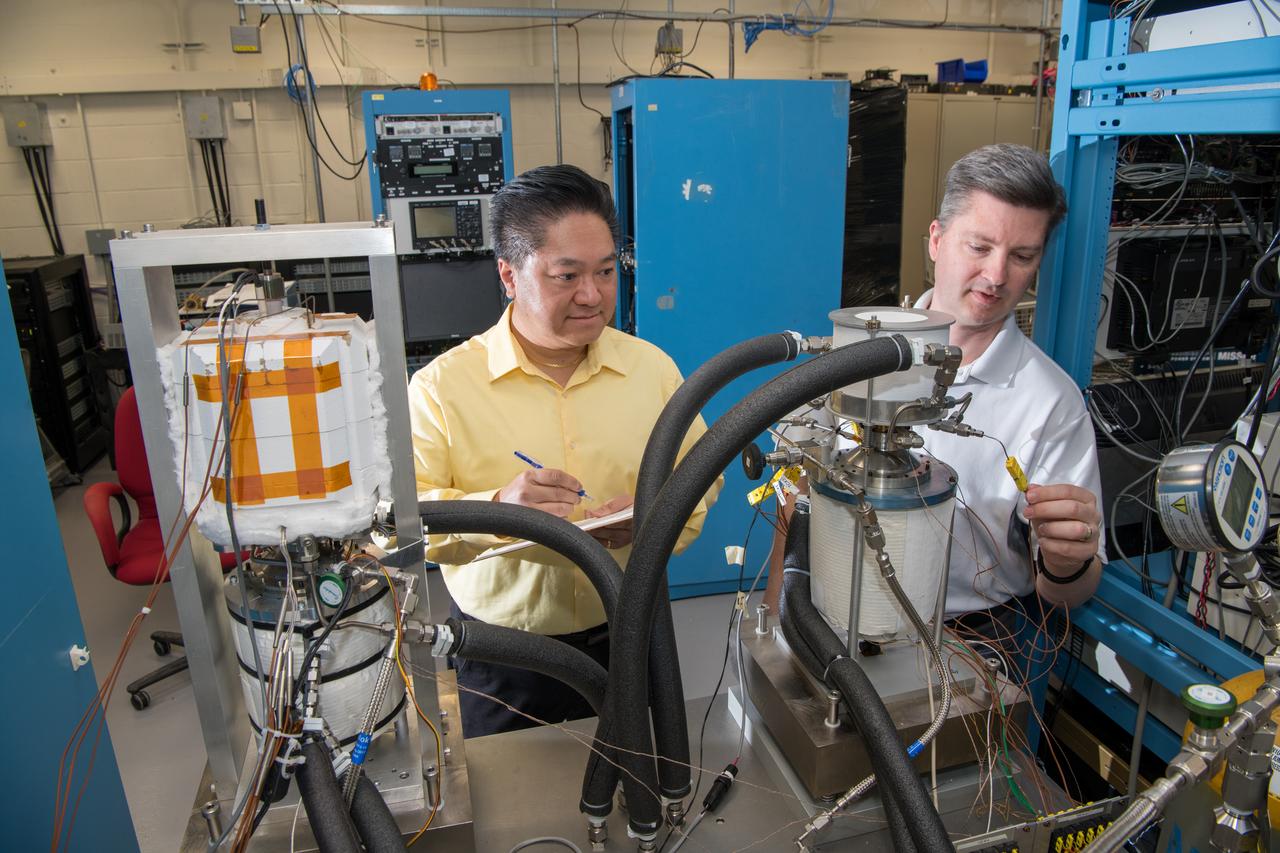
Glenn’s Technology Demonstration Convertor (TDC) #13, a free-piston Stirling power convertor, achieved a milestone of 14 years of maintenance-free operation in the Stirling Research Laboratory in building 301. This technology is proving our capability to power spacecraft on longer-duration future scientific missions.
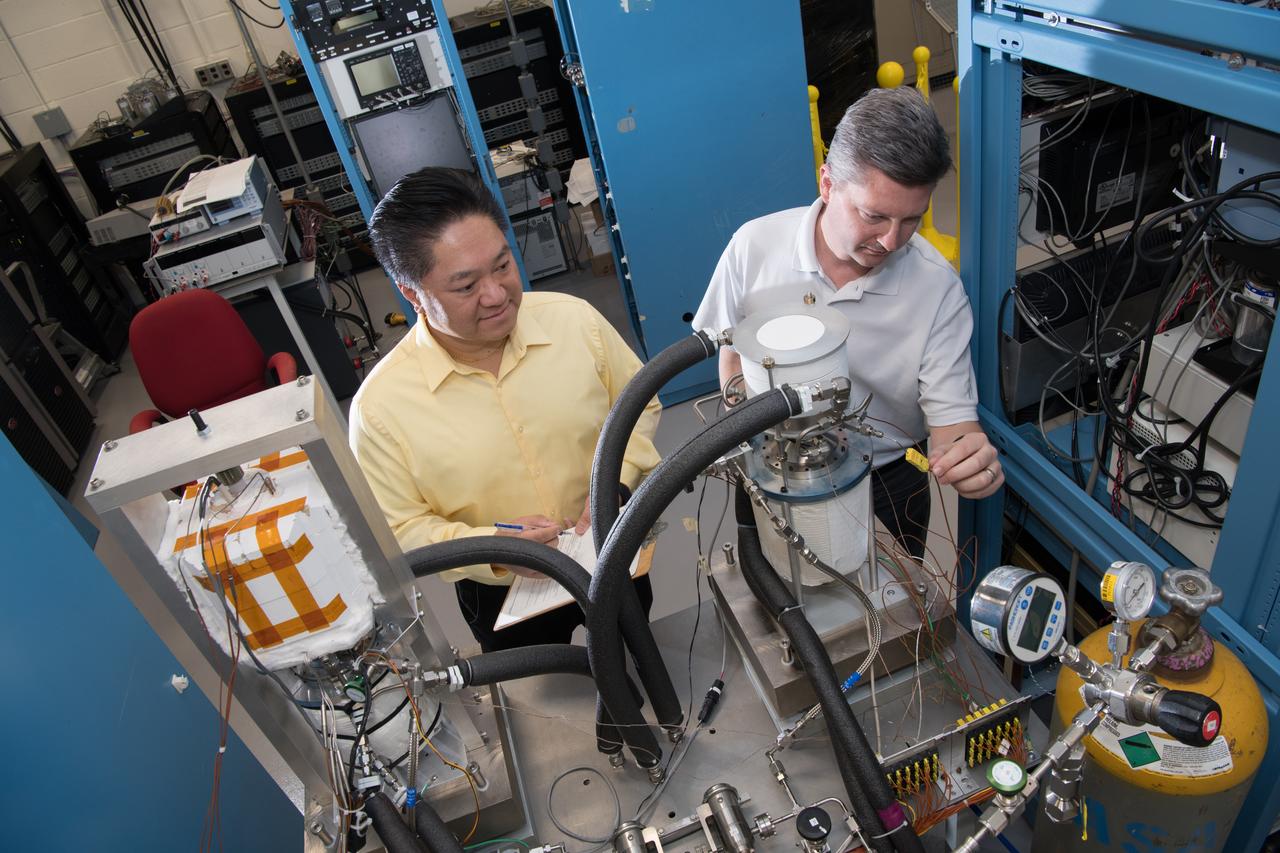

Glenn’s Technology Demonstration Convertor (TDC) #13, a free-piston Stirling power convertor, achieved a milestone of 14 years of maintenance-free operation in the Stirling Research Laboratory in building 301. This technology is proving our capability to power spacecraft on longer-duration future scientific missions.
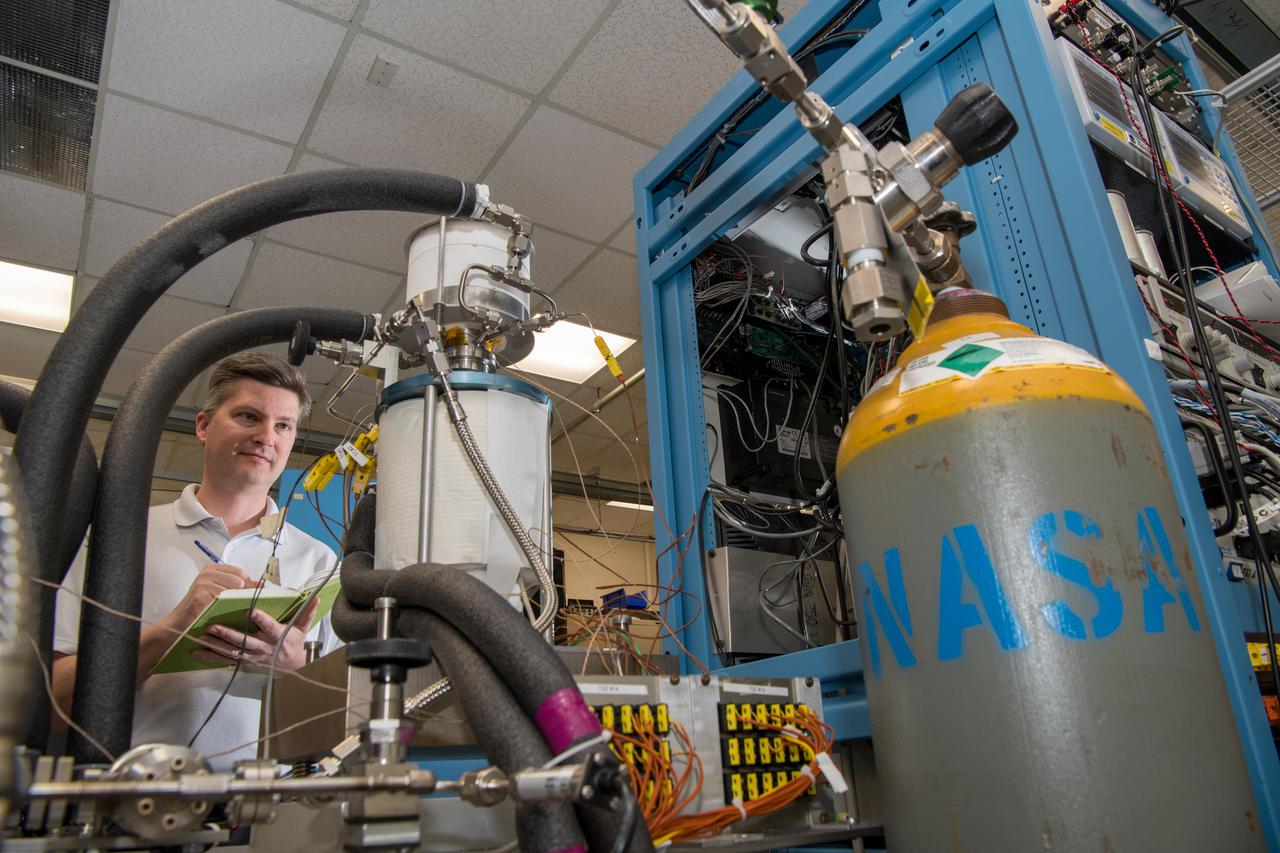

Glenn’s Technology Demonstration Convertor (TDC) #13, a free-piston Stirling power convertor, achieved a milestone of 14 years of maintenance-free operation in the Stirling Research Laboratory in building 301. This technology is proving our capability to power spacecraft on longer-duration future scientific missions.
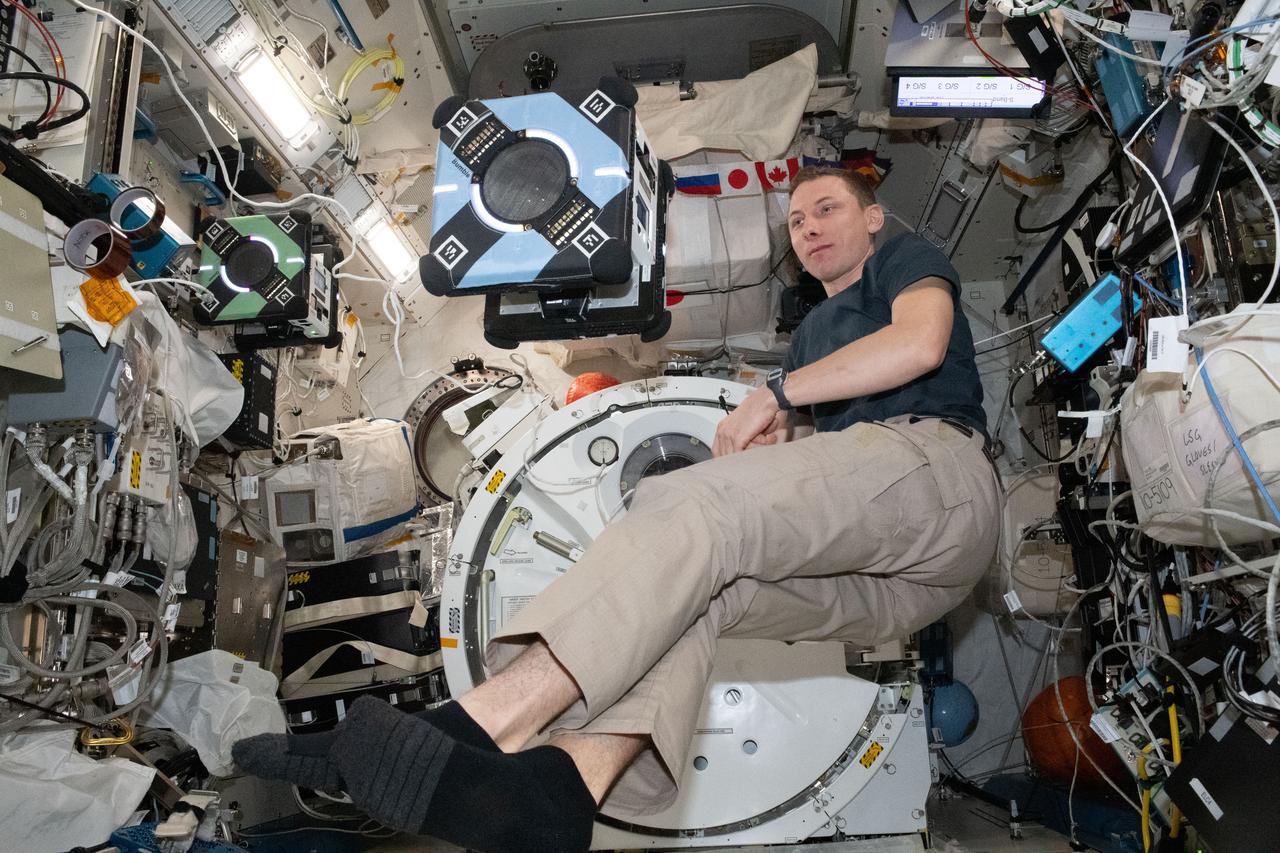

iss069e008378 (May 2, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Woody Hoburg tests one of the space station’s Astrobee robots for Zero Robotics, a student competition to write software to control the free-flying robots. The program promotes teamwork and awareness of space career opportunities and students learn about artificial intelligence, systems engineering, and human-robot collaboration.
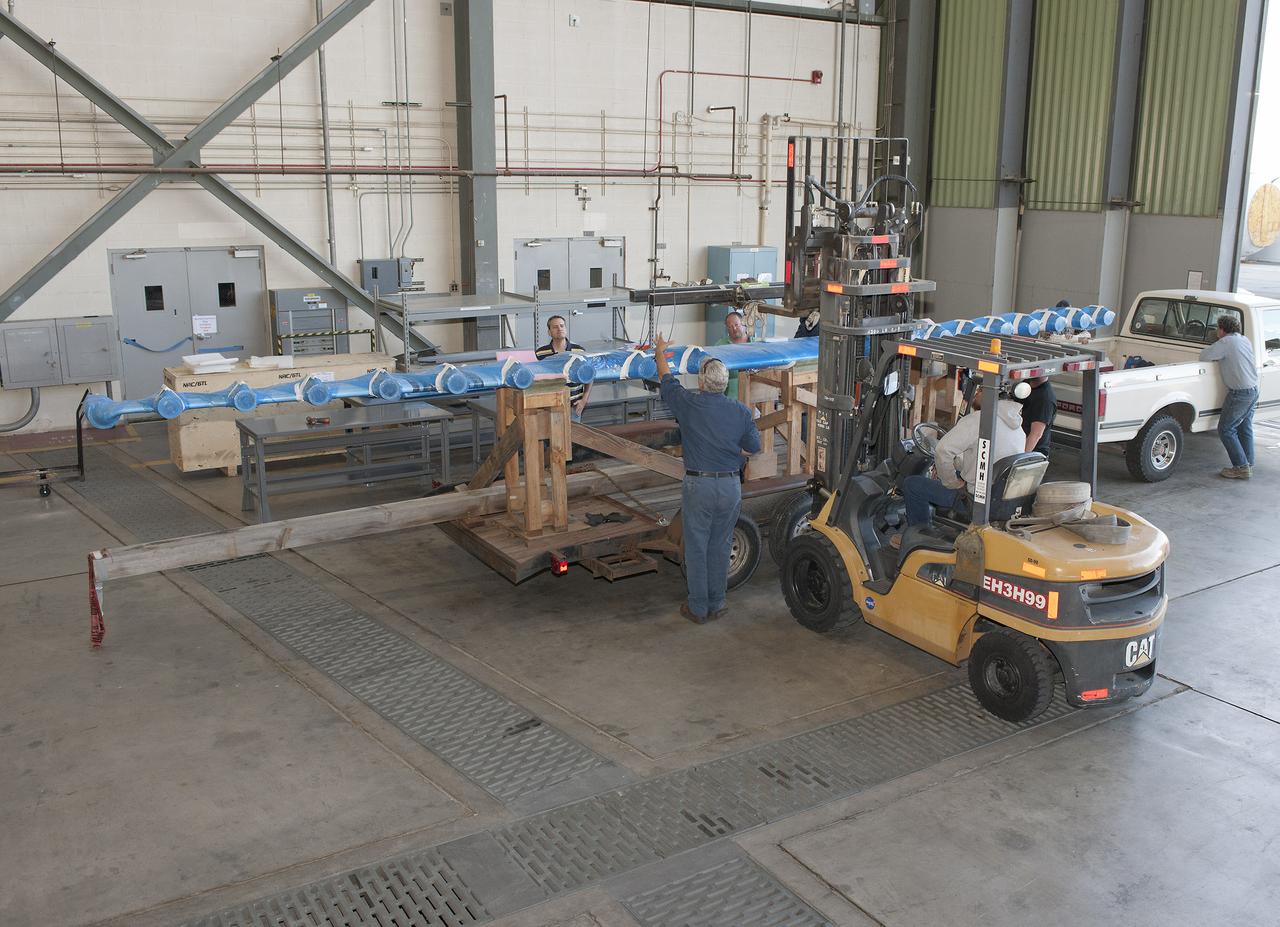

Technicians unload the LEAPTech experimental wing upon its arrival at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center. Ground testing will begin after the wing is mounted on a specially modified truck.
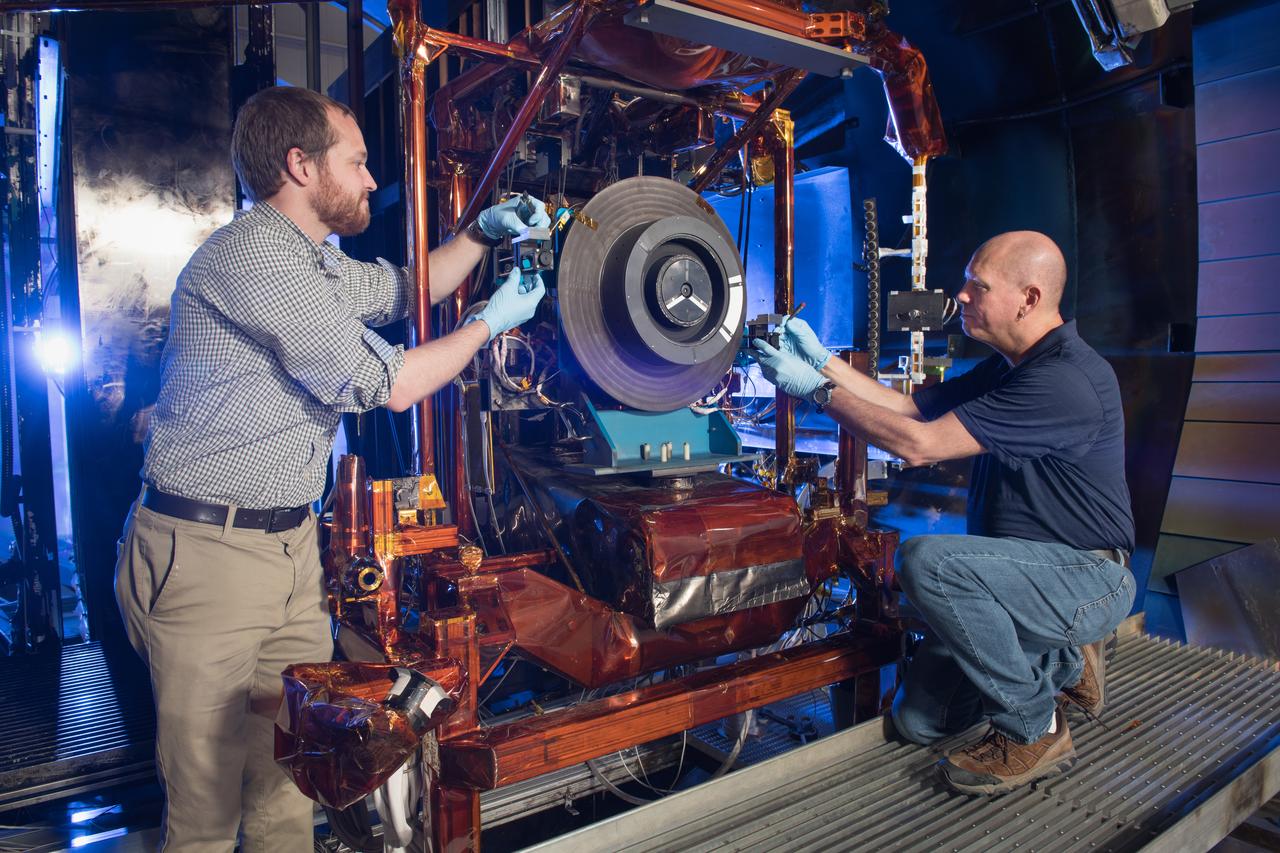

Advanced Electric Propulsion Systems Contract, Technology Demonstration Unit, TDU-3 Checkout Test Hardware Installed in Vacuum Facility 5, VF-5
Advanced Electric Propulsion Systems Contract, Technology Demonstration Unit, TDU-3 Checkout Test Hardware Installed in Vacuum Facility 5, VF-5
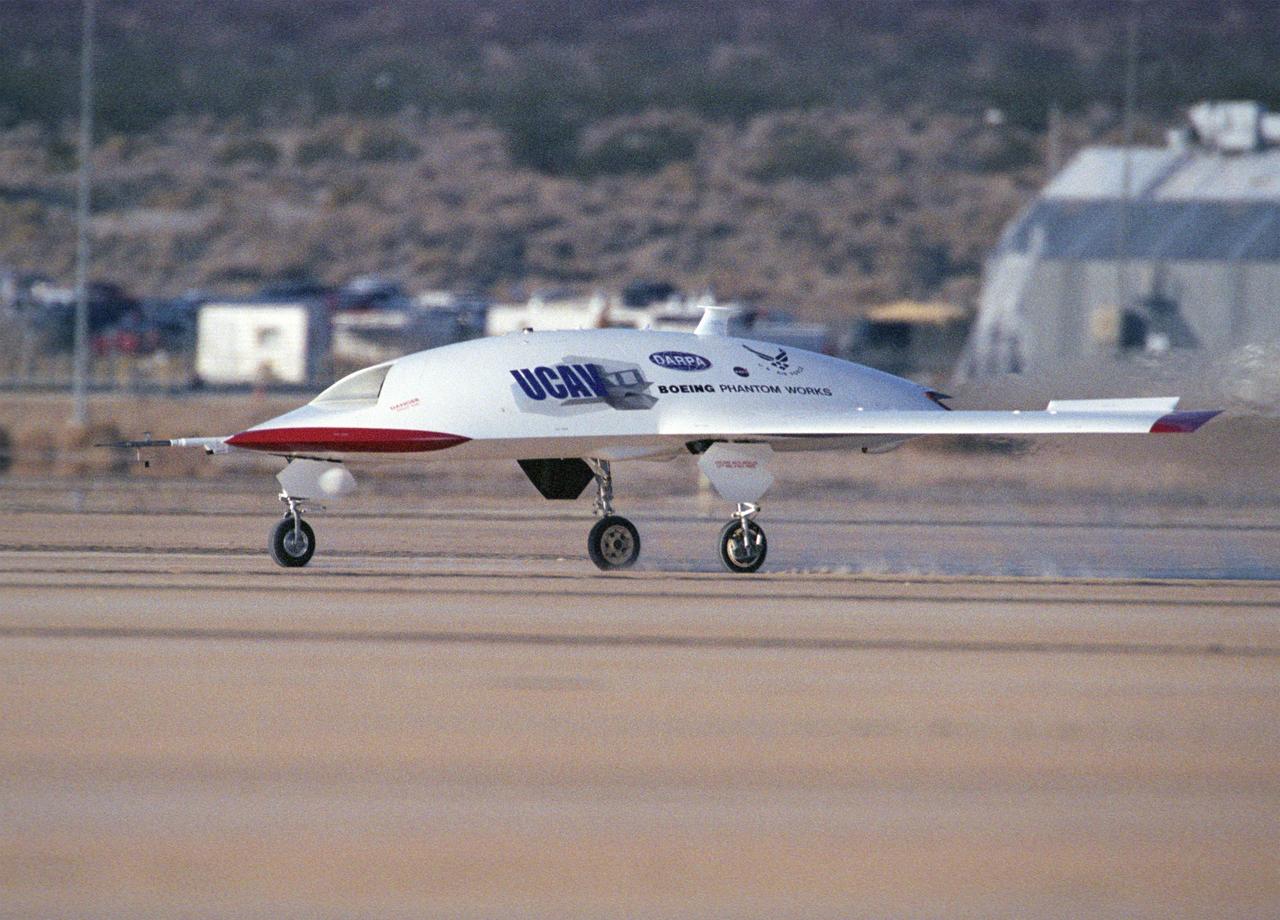

The second X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its first flight on November 21, 2002, after taking off from a dry lakebed at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards Air Force Base, California. X-45A vehicle two flew for approximately 30 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7500 feet. This flight validated the functionality of the UCAV flight software on the second air vehicle. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.
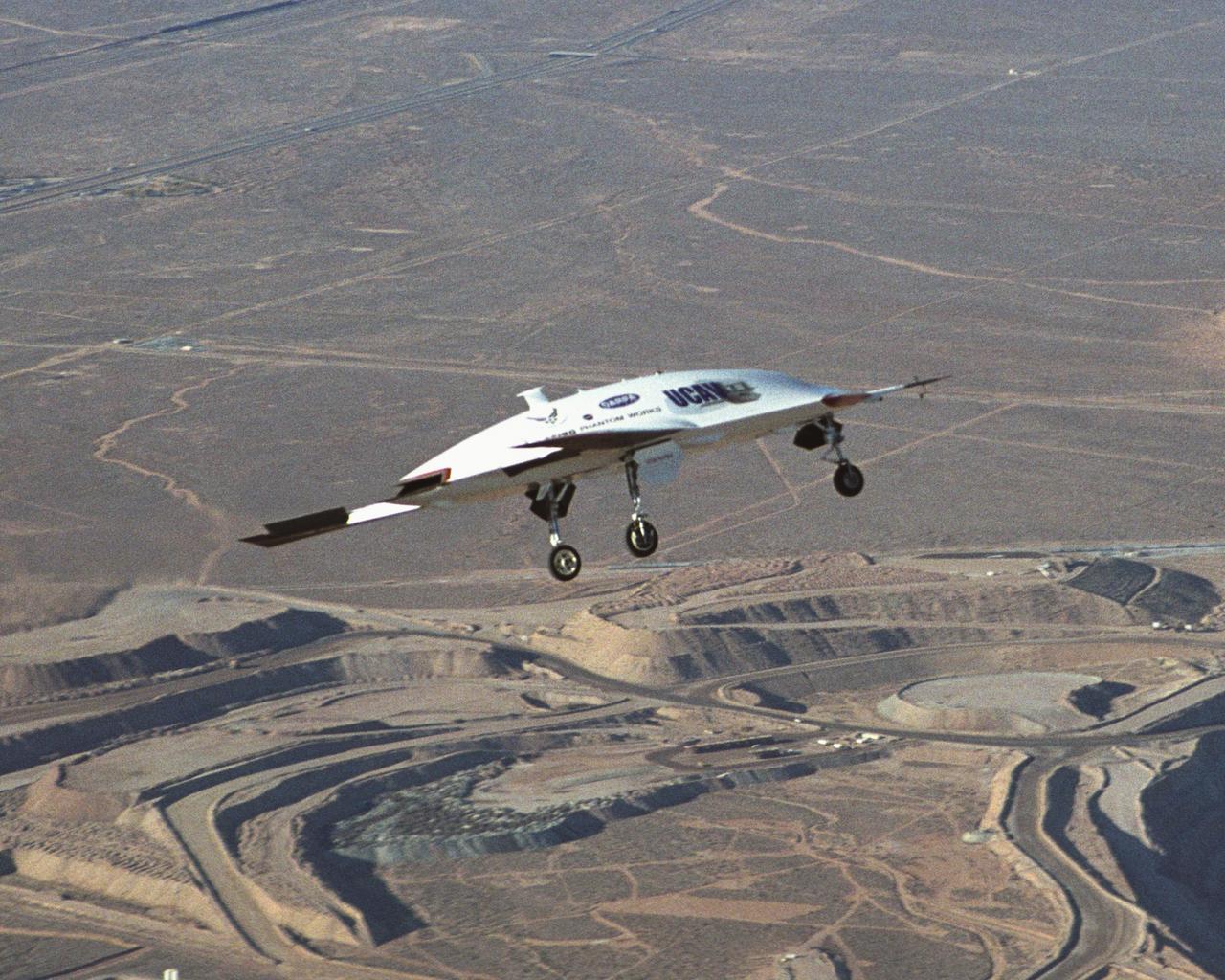

The second X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its first flight on November 21, 2002, after taking off from a dry lakebed at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards Air Force Base, California. X-45A vehicle two flew for approximately 30 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7500 feet. This flight validated the functionality of the UCAV flight software on the second air vehicle. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.

The second X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its first flight on November 21, 2002, after taking off from a dry lakebed at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards Air Force Base, California. X-45A vehicle two flew for approximately 30 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7500 feet. This flight validated the functionality of the UCAV flight software on the second air vehicle. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.
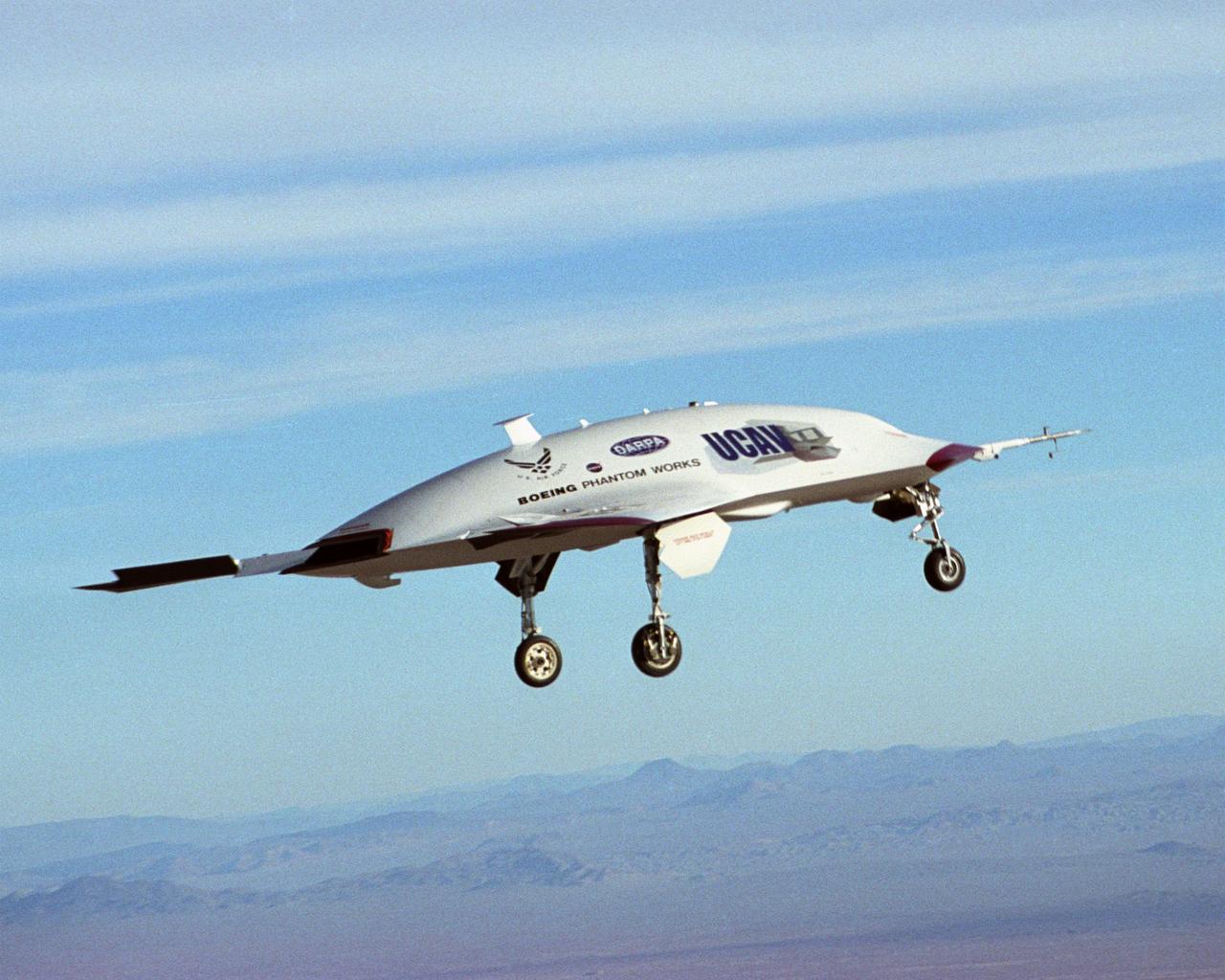

The second X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its first flight on November 21, 2002, after taking off from a dry lakebed at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards Air Force Base, California. X-45A vehicle two flew for approximately 30 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7500 feet. This flight validated the functionality of the UCAV flight software on the second air vehicle. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.
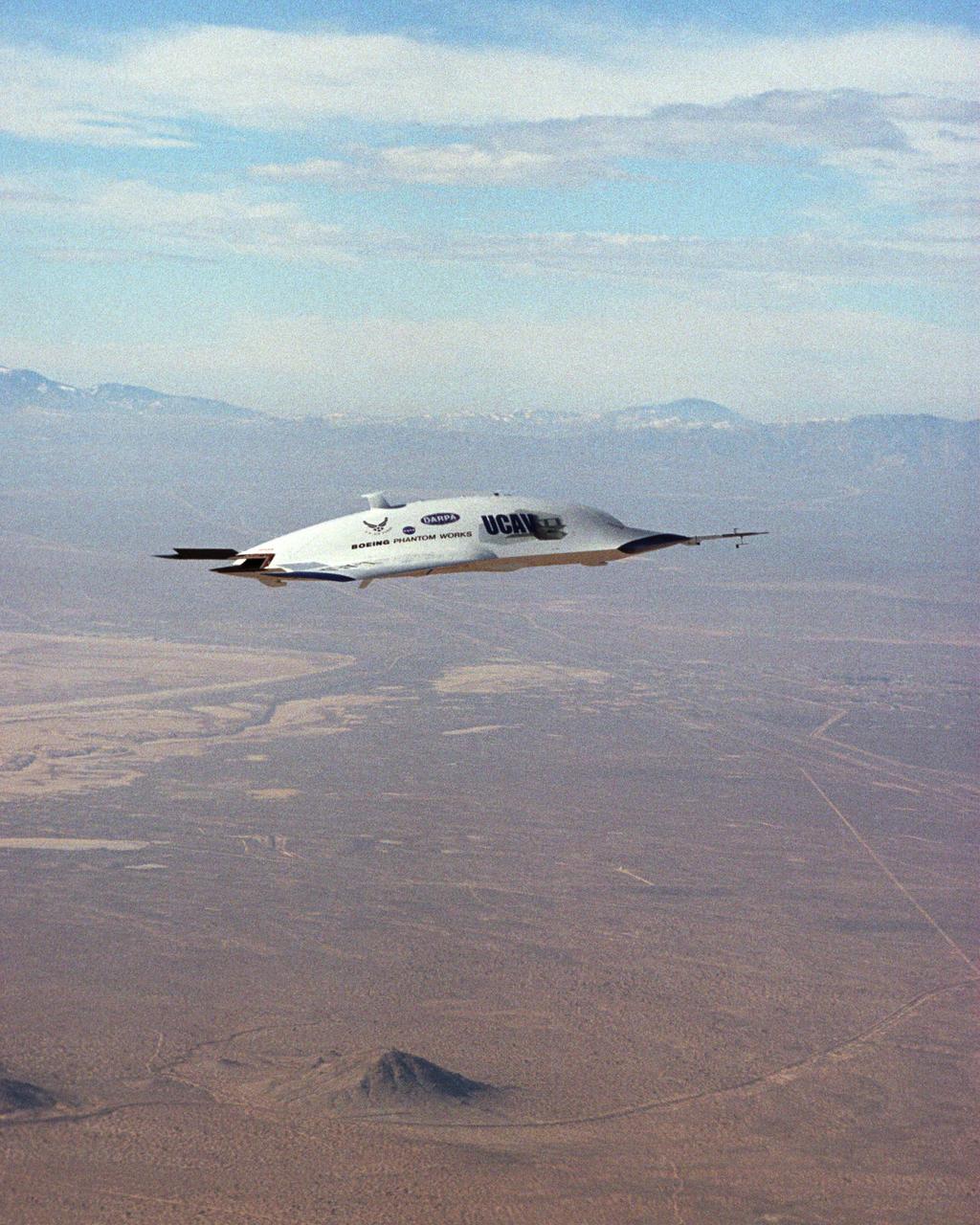

The first X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its sixth flight on Dec. 19, 2002, raising its landing gear in flight for the first time. The X-45A flew for 40 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7,500 feet. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.

The first X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its sixth flight on Dec. 19, 2002, raising its landing gear in flight for the first time. The X-45A flew for 40 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7,500 feet. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.
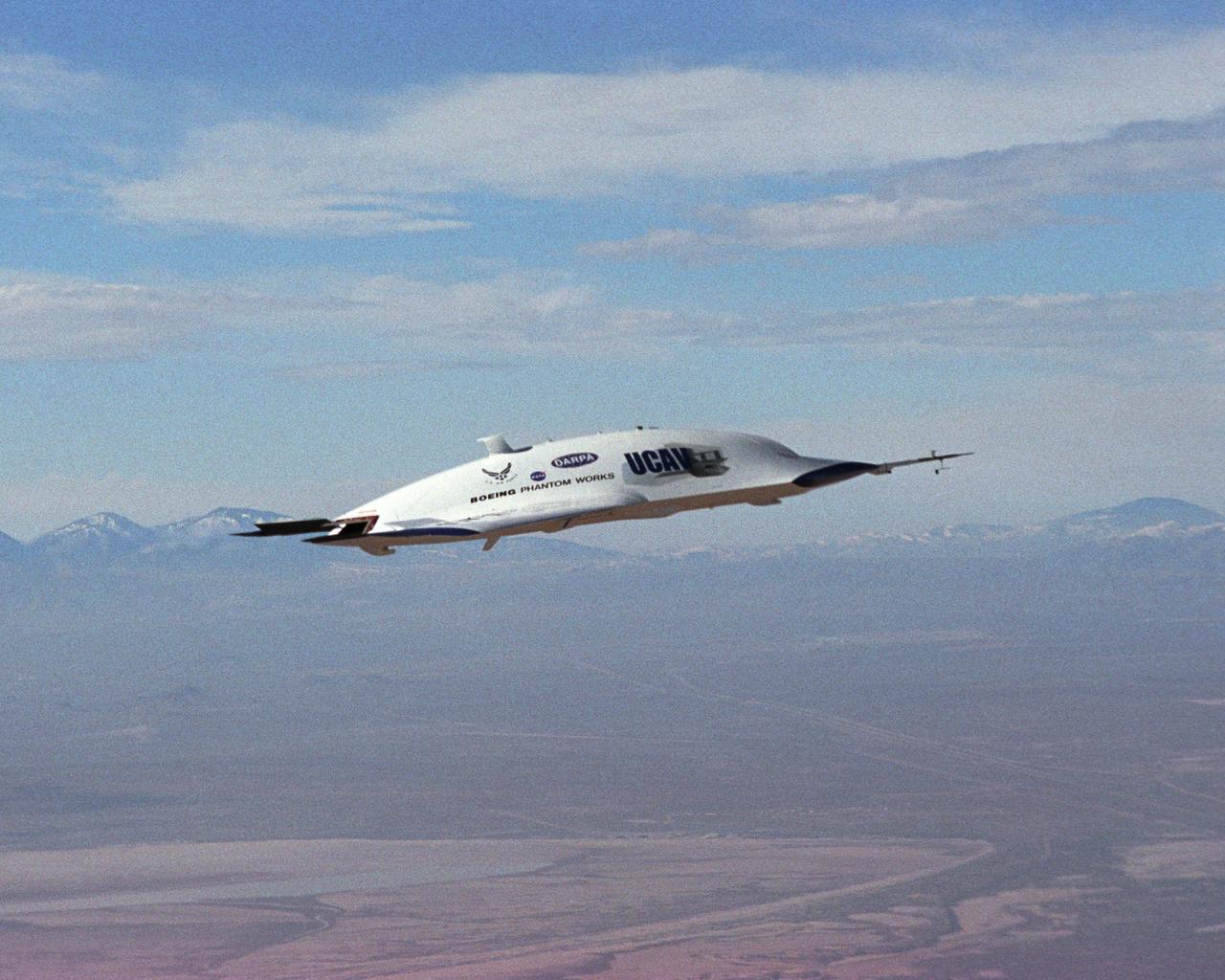

The first X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its sixth flight on Dec. 19, 2002, raising its landing gear in flight for the first time. The X-45A flew for 40 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7,500 feet. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.
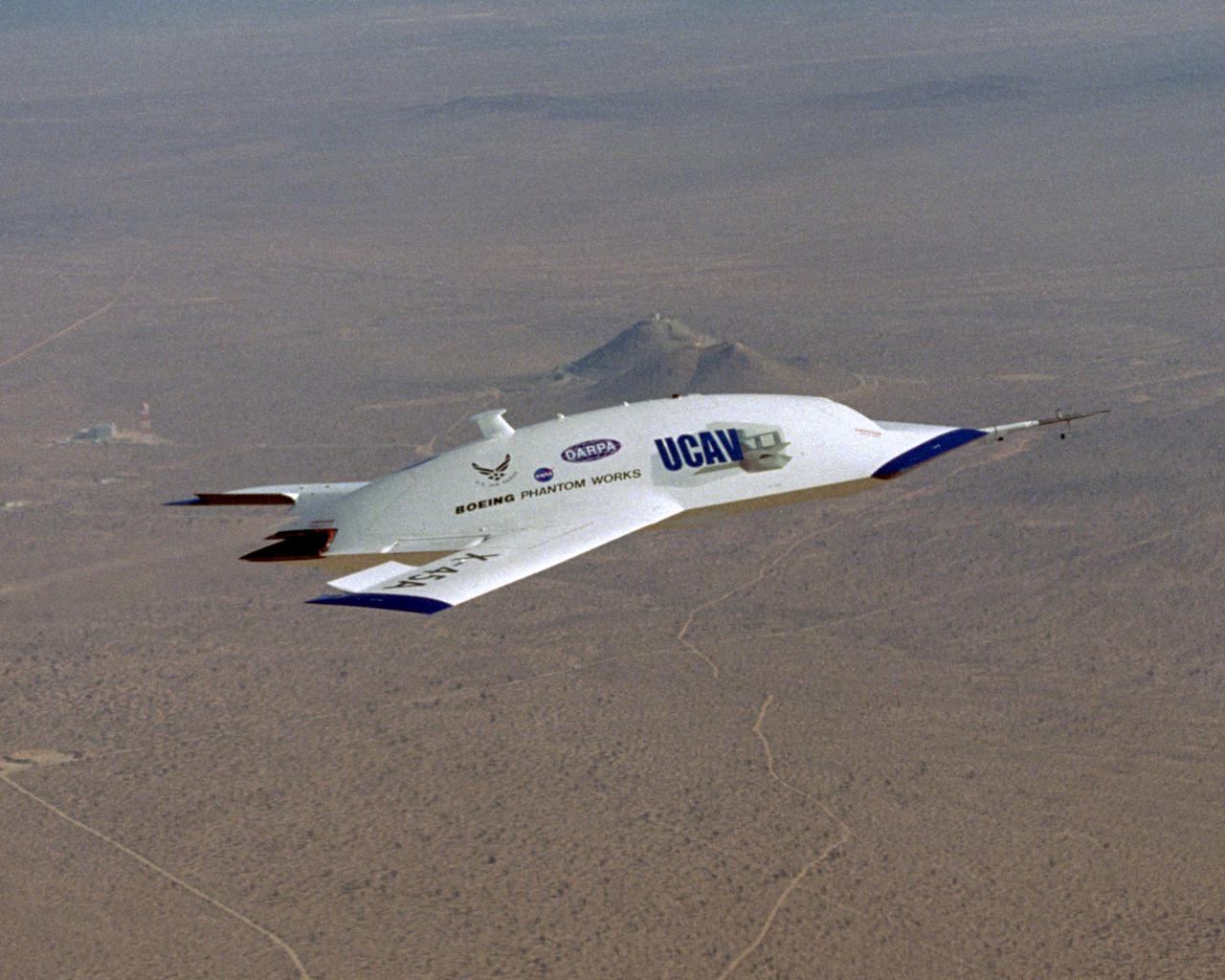

The first X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its sixth flight on Dec. 19, 2002, raising its landing gear in flight for the first time. The X-45A flew for 40 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7,500 feet. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.
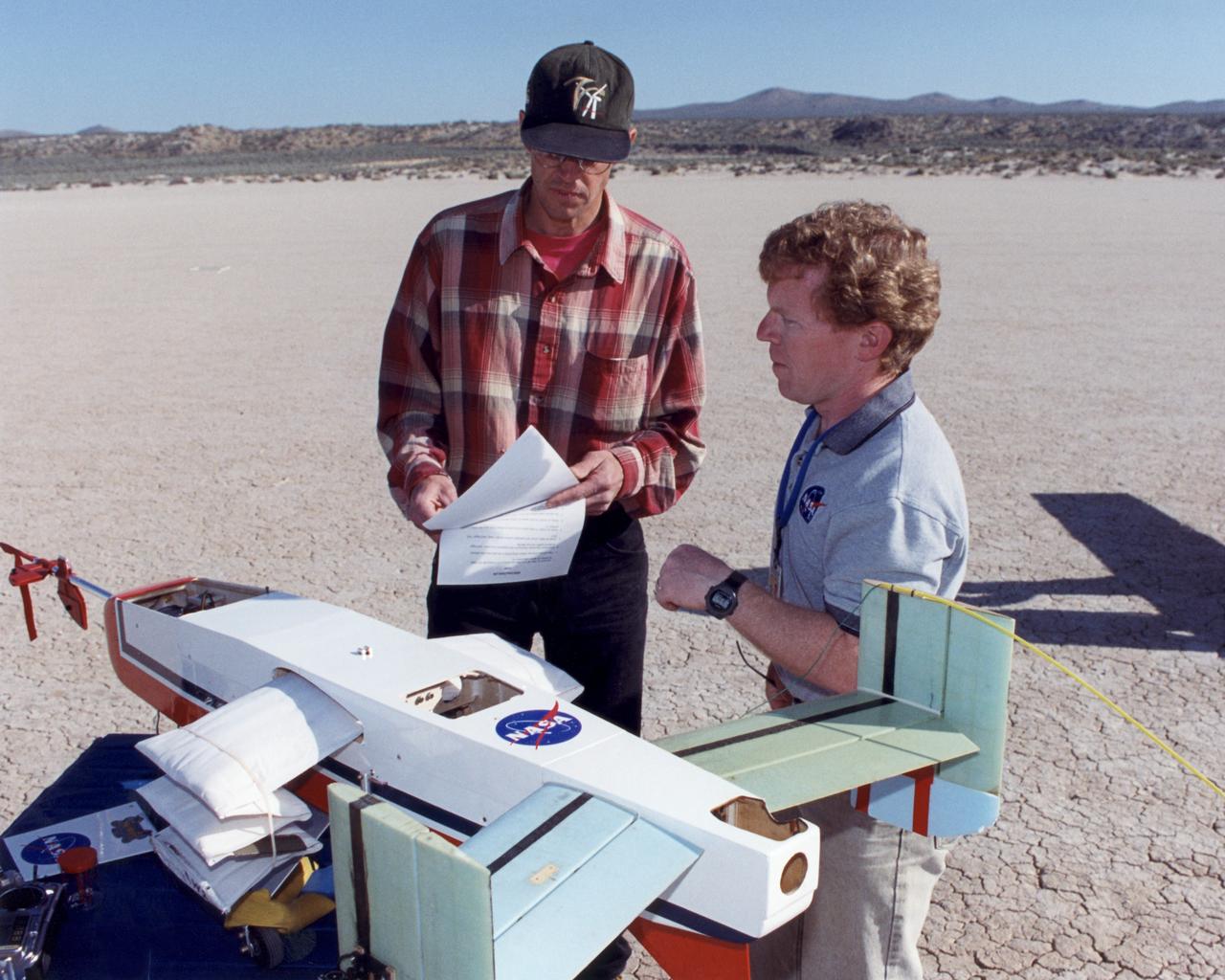

Engineers Jim Murray and Joe Pahle prepare a deployable, inflatable wing technology demonstrator experiment flown by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The inflatable wing project represented a basic flight research effort by Dryden personnel. Three successful flights of the I2000 inflatable wing aircraft occurred. During the flights, the team air-launched the radio-controlled (R/C) I2000 from an R/C utility airplane at an altitude of 800-1000 feet. As the I2000 separated from the carrier aircraft, its inflatable wings "popped-out," deploying rapidly via an on-board nitrogen bottle. The aircraft remained stable as it transitioned from wingless to winged flight. The unpowered I2000 glided down to a smooth landing under complete control.

The deployable, inflatable wing technology demonstrator experiment aircraft maintains a steady attitude following separation from its carrier aircraft during a flight conducted by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The inflatable wing project represented a basic flight research effort by Dryden personnel. Three successful flights of the I2000 inflatable wing aircraft occurred. During the flights, the team air-launched the radio-controlled (R/C) I2000 from an R/C utility airplane at an altitude of 800-1000 feet. As the I2000 separated from the carrier aircraft, its inflatable wings "popped-out," deploying rapidly via an on-board nitrogen bottle. The aircraft remained stable as it transitioned from wingless to winged flight. The unpowered I2000 glided down to a smooth landing under complete control.
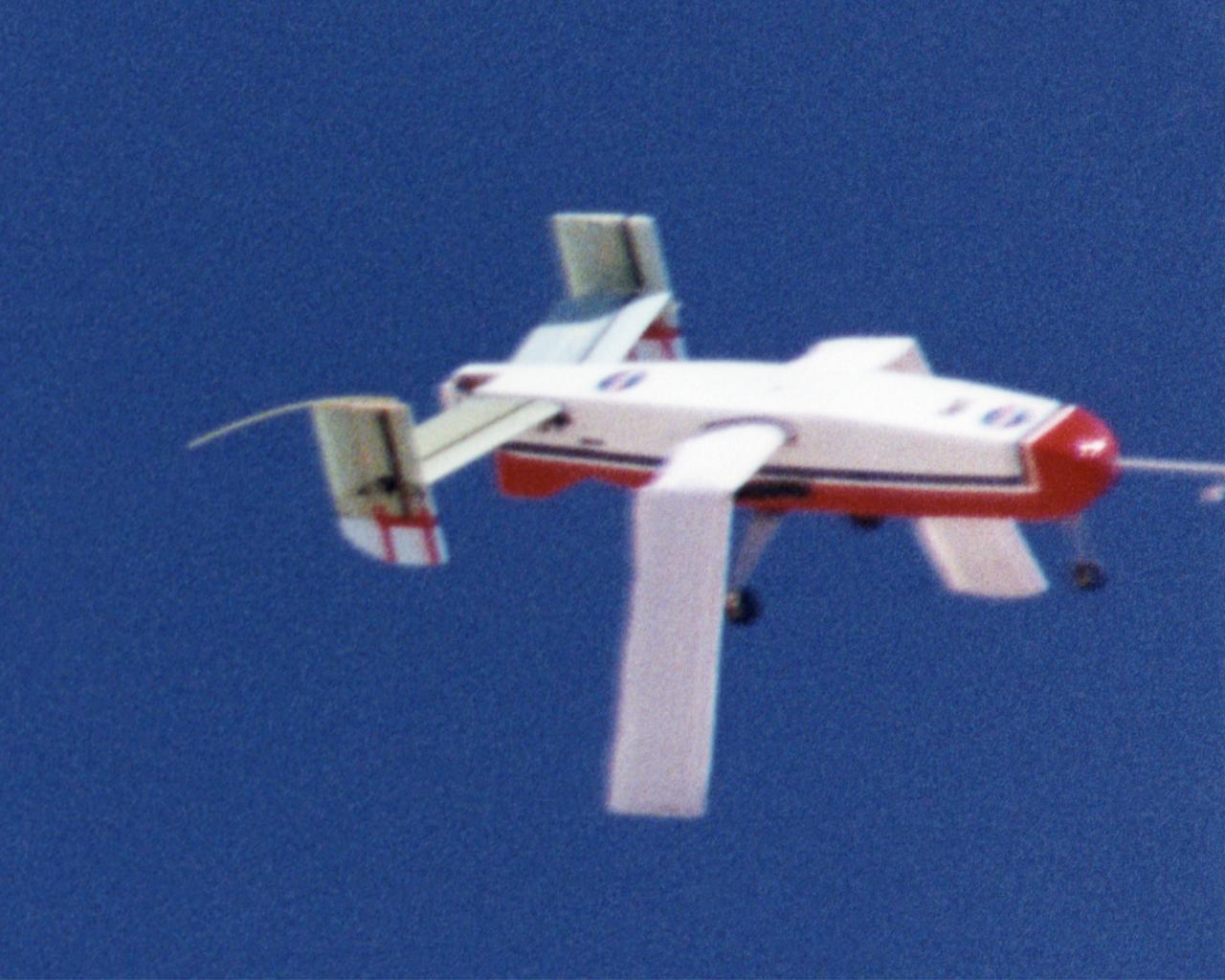

Wing Deployment Sequence #2: The deployable, inflatable wing technology demonstrator experiment aircraft's wings continue deploying following separation from its carrier aircraft during a flight conducted by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The inflatable wing project represented a basic flight research effort by Dryden personnel. Three successful flights of the I2000 inflatable wing aircraft occurred. During the flights, the team air-launched the radio-controlled (R/C) I2000 from an R/C utility airplane at an altitude of 800-1000 feet. As the I2000 separated from the carrier aircraft, its inflatable wings "popped-out," deploying rapidly via an on-board nitrogen bottle. The aircraft remained stable as it transitioned from wingless to winged flight. The unpowered I2000 glided down to a smooth landing under complete control.
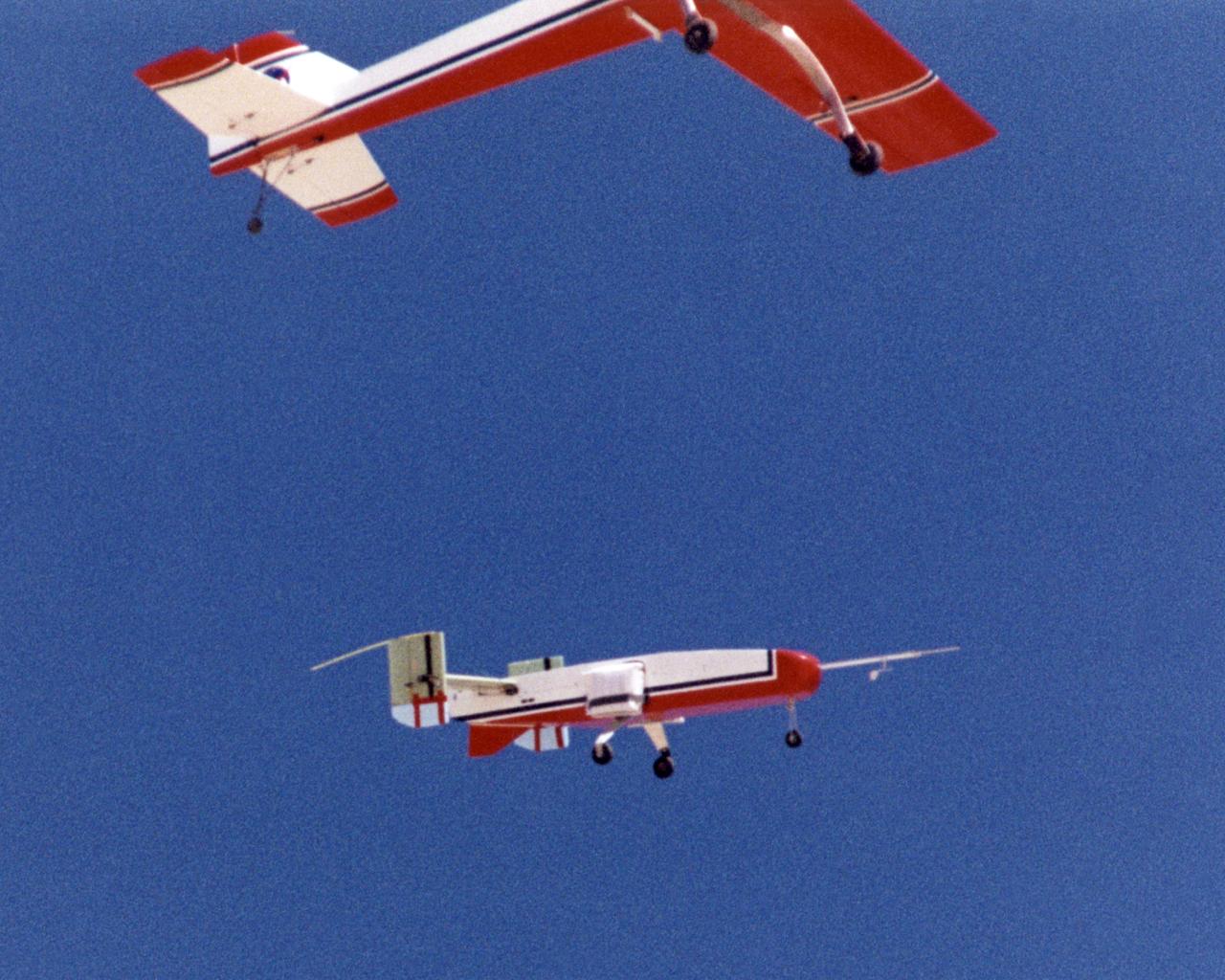
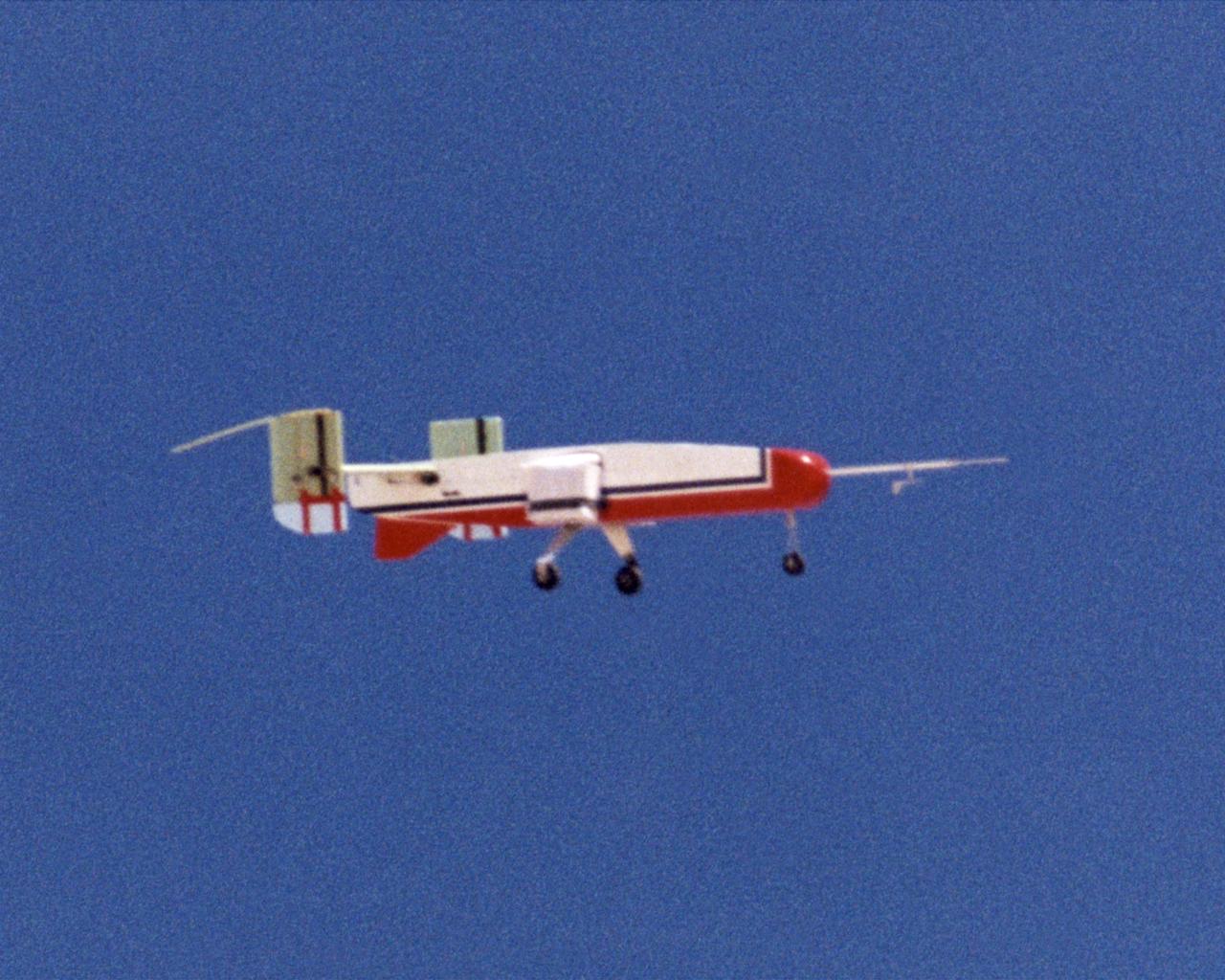
The deployable, inflatable wing technology demonstrator experiment separates from its carrier aircraft during a flight conducted by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The inflatable wing project represented a basic flight research effort by Dryden personnel. Three successful flights of the I2000 inflatable wing aircraft occurred. During the flights, the team air-launched the radio-controlled (R/C) I2000 from an R/C utility airplane at an altitude of 800-1000 feet. As the I2000 separated from the carrier aircraft, its inflatable wings "popped-out," deploying rapidly via an on-board nitrogen bottle. The aircraft remained stable as it transitioned from wingless to winged flight. The unpowered I2000 glided down to a smooth landing under complete control.
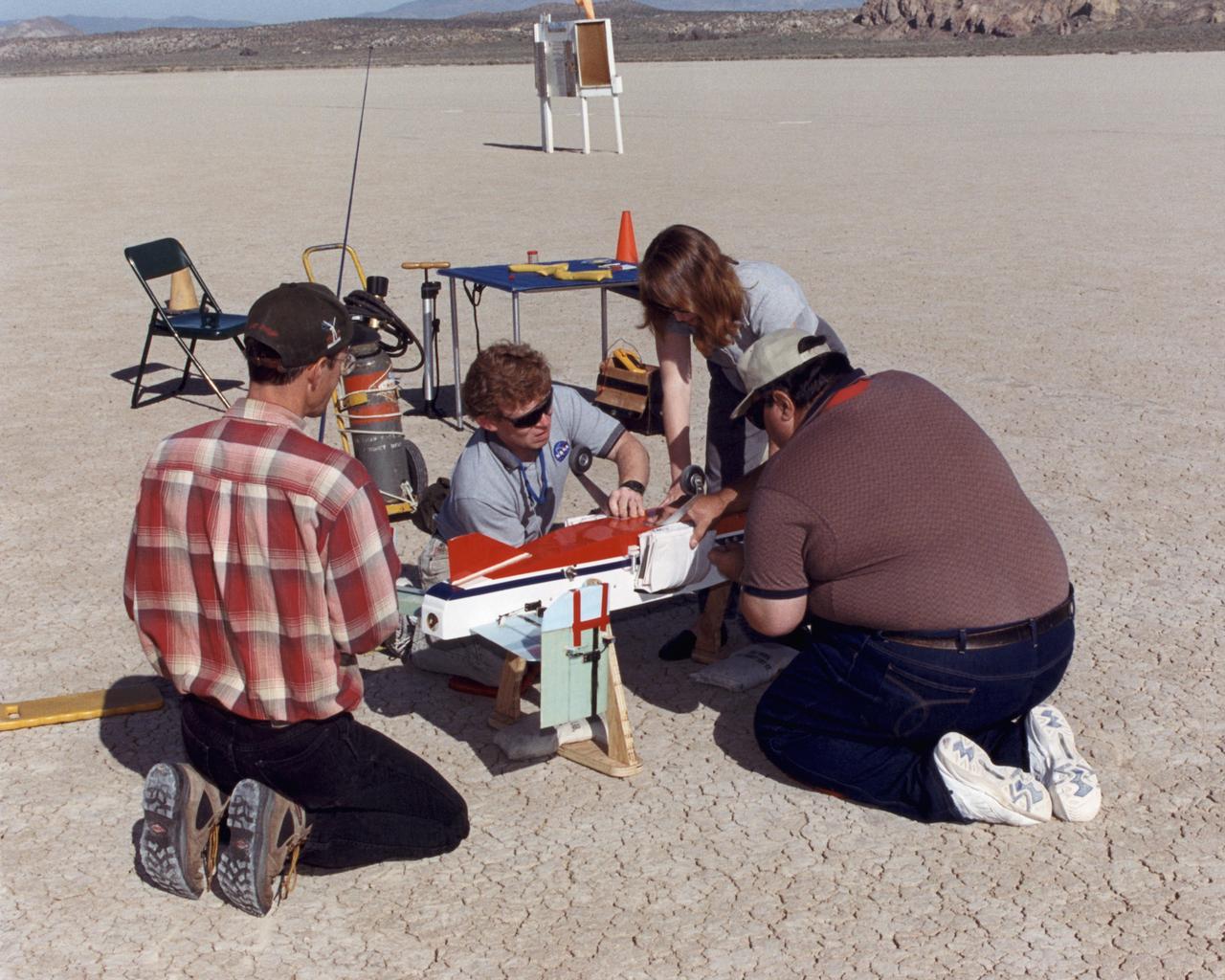

Inflatable Wing project personnel prepare a deployable, inflatable wing technology demonstrator experiment flown by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The inflatable wing project represented a basic flight research effort by Dryden personnel. Three successful flights of the I2000 inflatable wing aircraft occurred. During the flights, the team air-launched the radio-controlled (R/C) I2000 from an R/C utility airplane at an altitude of 800-1000 feet. As the I2000 separated from the carrier aircraft, its inflatable wings "popped-out," deploying rapidly via an on-board nitrogen bottle. The aircraft remained stable as it transitioned from wingless to winged flight. The unpowered I2000 glided down to a smooth landing under complete control.
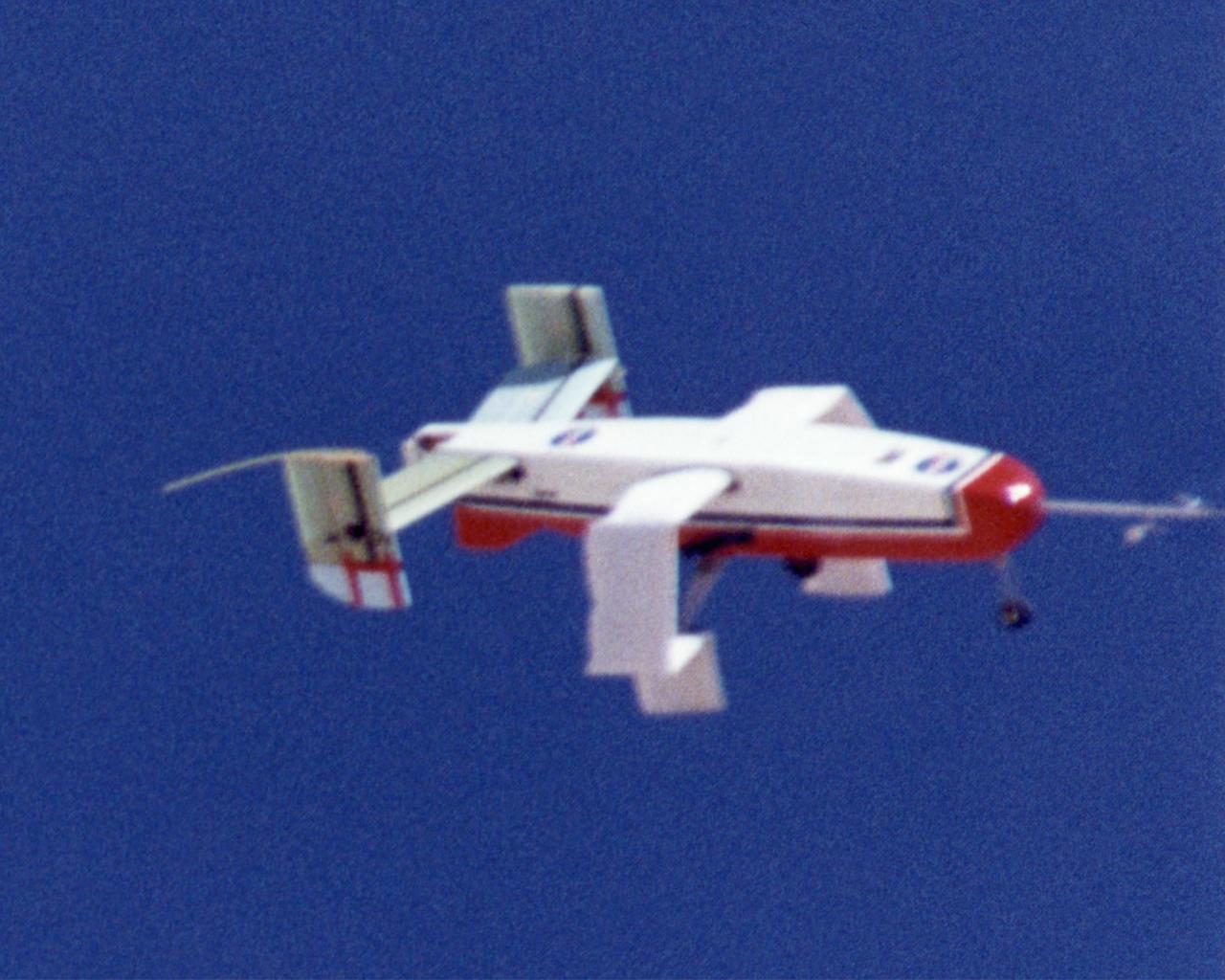

Wing Deployment Sequence #1: The deployable, inflatable wing technology demonstrator experiment aircraft's wings begin deploying following separation from its carrier aircraft during a flight conducted by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The inflatable wing project represented a basic flight research effort by Dryden personnel. Three successful flights of the I2000 inflatable wing aircraft occurred. During the flights, the team air-launched the radio-controlled (R/C) I2000 from an R/C utility airplane at an altitude of 800-1000 feet. As the I2000 separated from the carrier aircraft, its inflatable wings "popped-out," deploying rapidly via an on-board nitrogen bottle. The aircraft remained stable as it transitioned from wingless to winged flight. The unpowered I2000 glided down to a smooth landing under complete control.
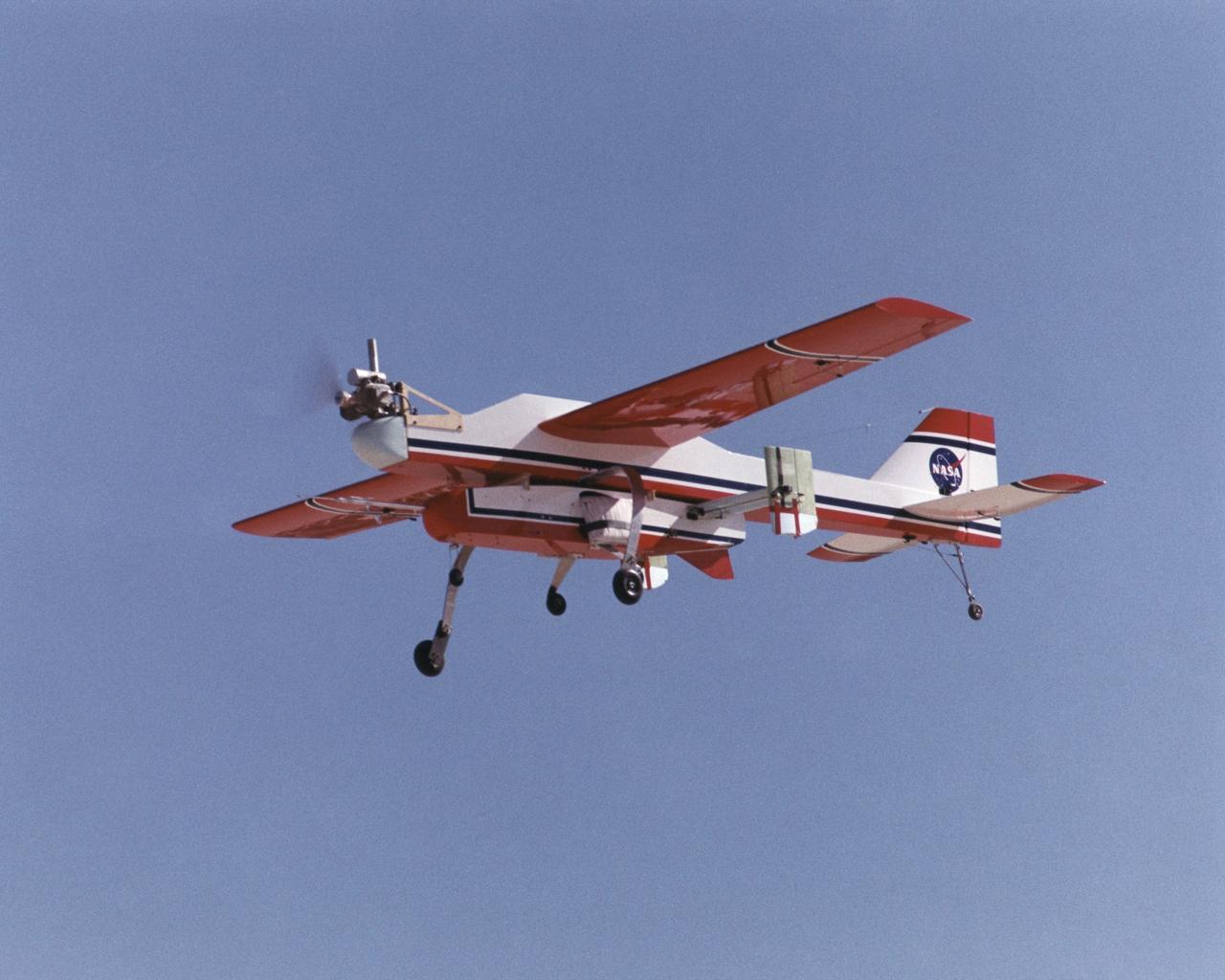

The deployable, inflatable wing technology demonstrator experiment aircraft looks good during a flight conducted by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The inflatable wing project represented a basic flight research effort by Dryden personnel. Three successful flights of the I2000 inflatable wing aircraft occurred. During the flights, the team air-launched the radio-controlled (R/C) I2000 from an R/C utility airplane at an altitude of 800-1000 feet. As the I2000 separated from the carrier aircraft, its inflatable wings "popped-out," deploying rapidly via an on-board nitrogen bottle. The aircraft remained stable as it transitioned from wingless to winged flight. The unpowered I2000 glided down to a smooth landing under complete control.
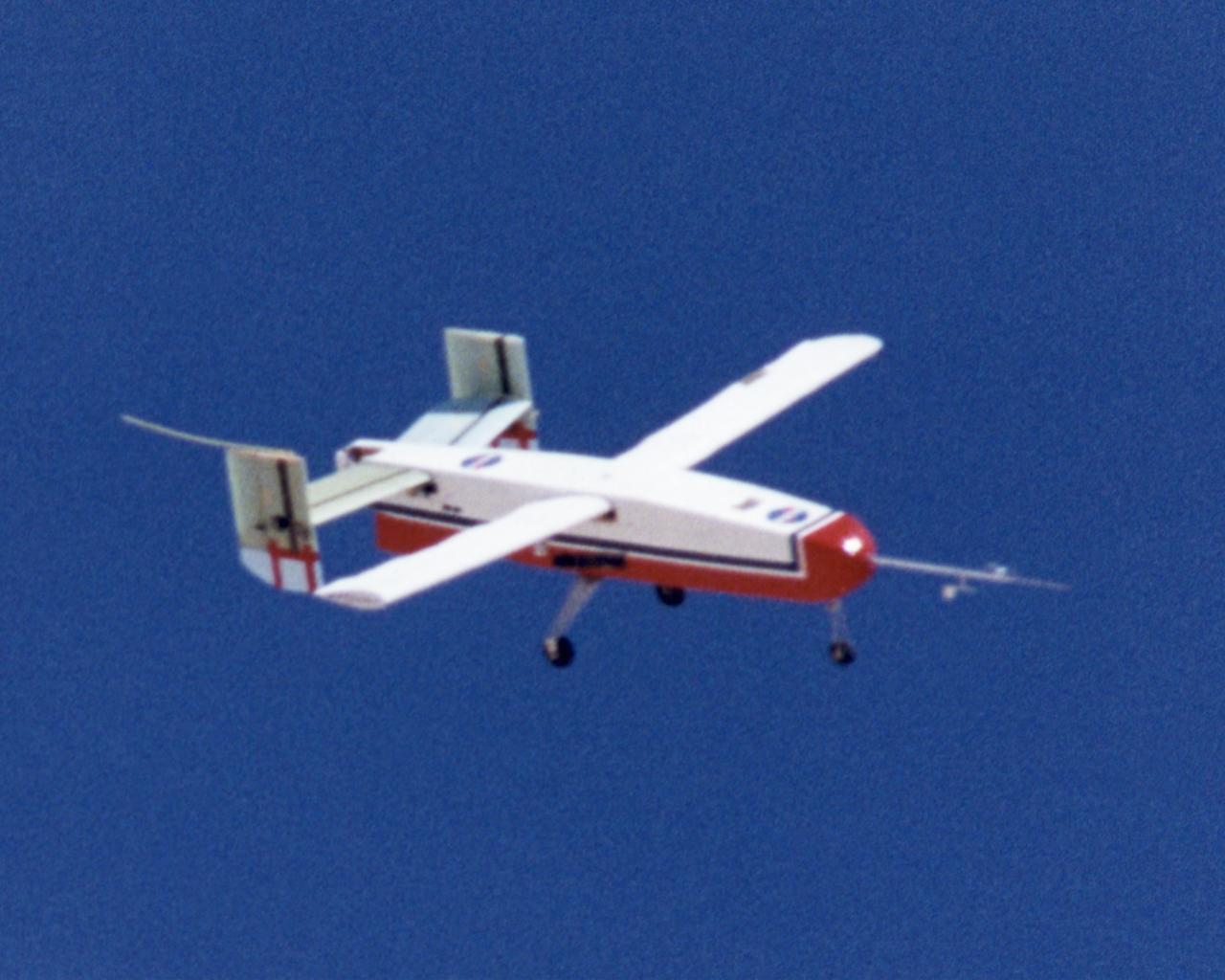

Wing Deployment Sequence #3: The deployable, inflatable wing technology demonstrator experiment aircraft's wings fully deployed during flight following separation from its carrier aircraft during a flight conducted by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Californiaornia. The inflatable wing project represented a basic flight research effort by Dryden personnel. Three successful flights of the I2000 inflatable wing aircraft occurred. During the flights, the team air-launched the radio-controlled (R/C) I2000 from an R/C utility airplane at an altitude of 800-1000 feet. As the I2000 separated from the carrier aircraft, its inflatable wings "popped-out," deploying rapidly via an on-board nitrogen bottle. The aircraft remained stable as it transitioned from wingless to winged flight. The unpowered I2000 glided down to a smooth landing under complete control.
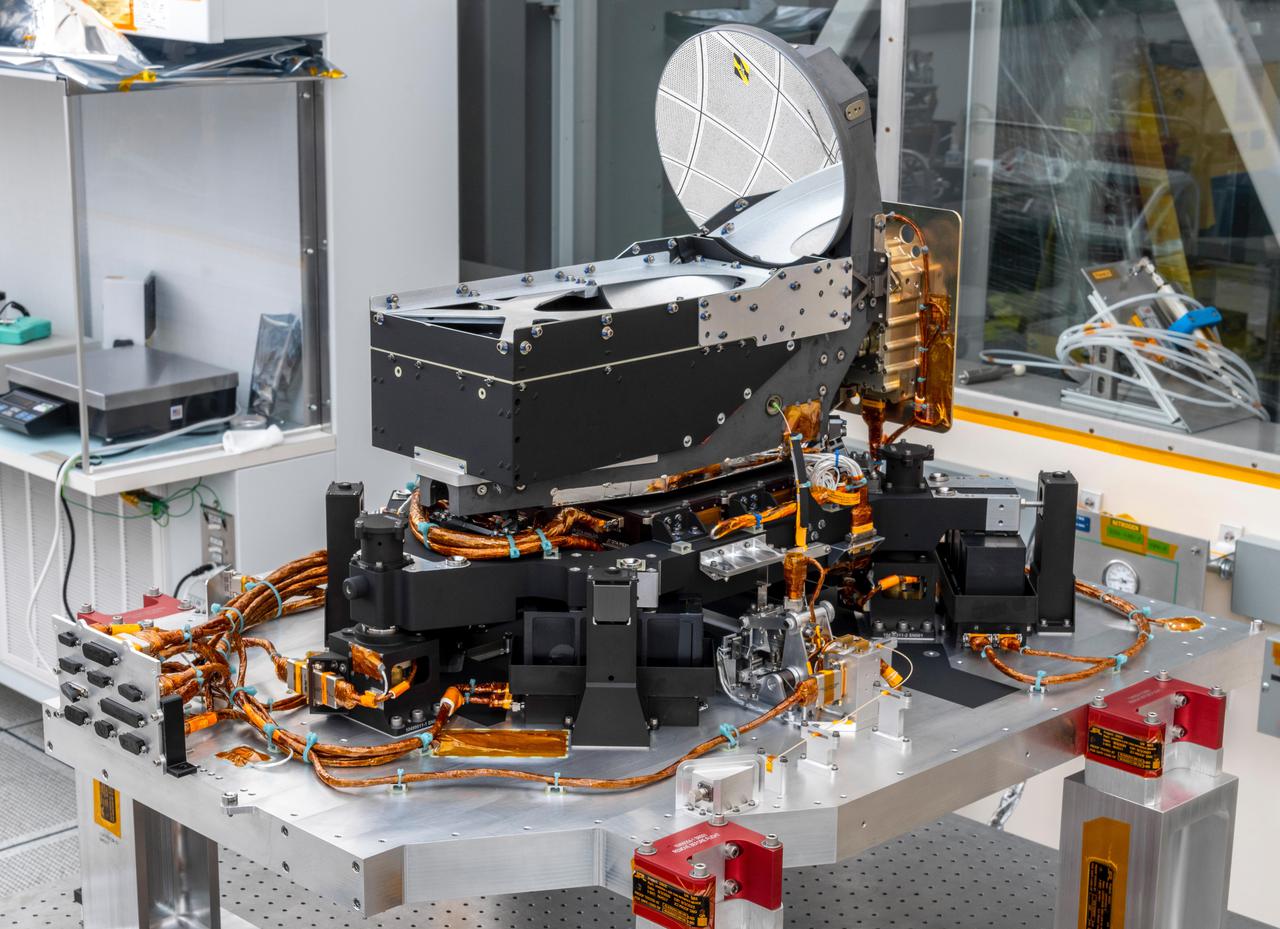
The Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) technology demonstration's flight laser transceiver is shown at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in April 2021, before being installed inside its box-like enclosure that was later integrated with NASA's Psyche spacecraft. The transceiver consists of a near-infrared laser transmitter to send high-rate data to Earth, and a sensitive photon-counting camera to receive ground-transmitted low-rate data. The transceiver is mounted on an assembly of struts and actuators – shown in this photograph – that stabilizes the optics from spacecraft vibrations. The DSOC experiment is the agency's first demonstration of optical communications beyond the Earth-Moon system. DSOC is a system that consists of this flight laser transceiver, a ground laser transmitter, and a ground laser receiver. New advanced technologies have been implemented in each of these elements. The transceiver will "piggyback" on NASA's Psyche spacecraft when it launches in August 2022 to the metal-rich asteroid of the same name. The DSOC technology demonstration will begin shortly after launch and continue as the spacecraft travels from Earth to its gravity-assist flyby of Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24569
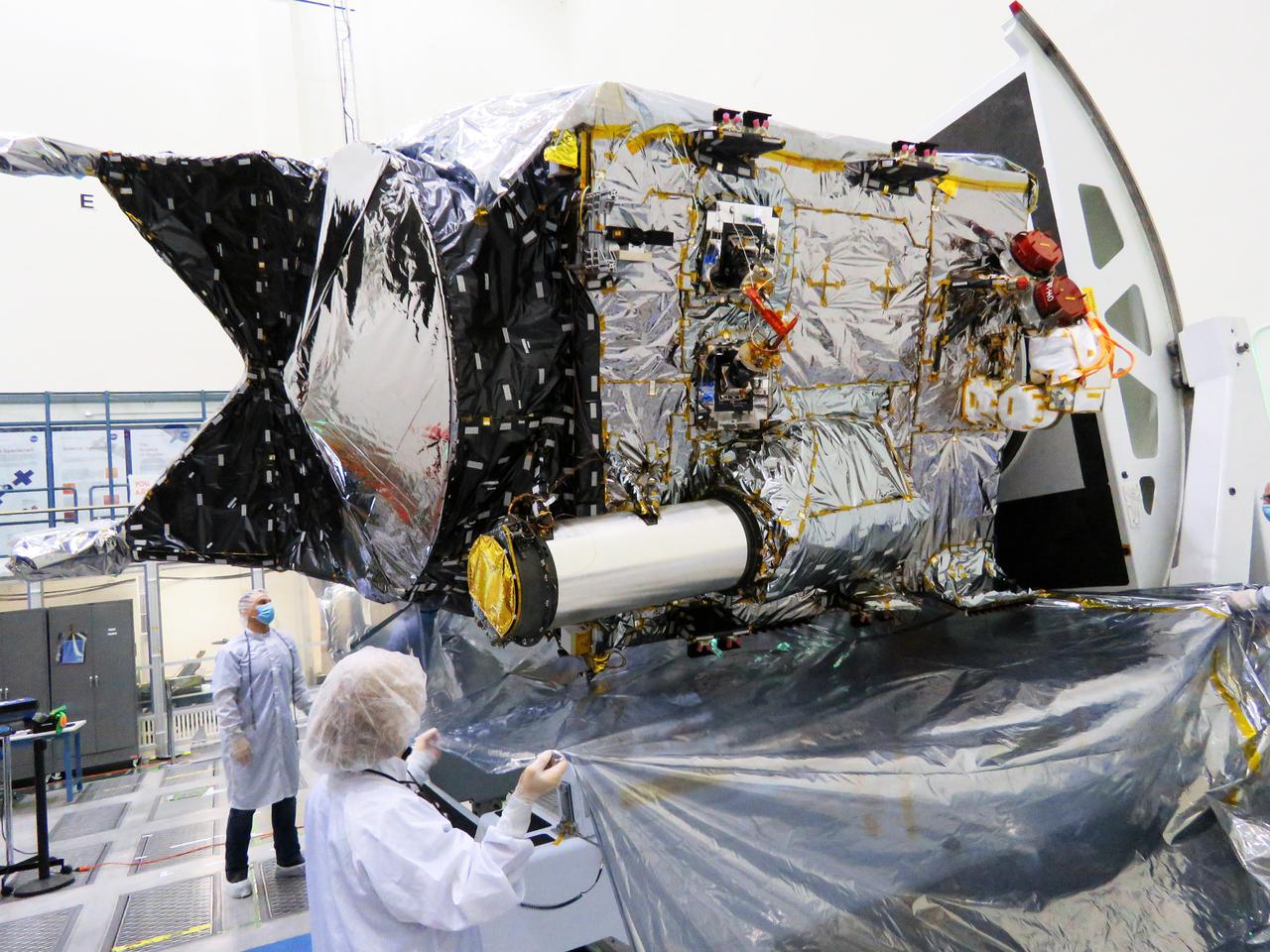

The Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) technology demonstration's flight laser transceiver can be easily identified on NASA's Psyche spacecraft, seen in this December 2021 photograph inside a clean room at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. DSOC's tube-like gray/silver sunshade can be seen protruding from the side of the spacecraft. The bulge to which the sunshade is attached is DSOC's transceiver, which consists of a near-infrared laser transmitter to send high-rate data to Earth and a sensitive photon-counting camera to receive ground-transmitted low-rate data. The DSOC experiment is the agency's first demonstration of optical communications beyond the Earth-Moon system. DSOC is a system that consists of this flight laser transceiver, a ground laser transmitter, and a ground laser receiver. New advanced technologies have been implemented in each of these elements. The transceiver will "piggyback" on NASA's Psyche spacecraft when it launches in August 2022 to the metal-rich asteroid of the same name. The DSOC technology demonstration will begin shortly after launch and continue as the spacecraft travels from Earth to its gravity-assist flyby of Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24570
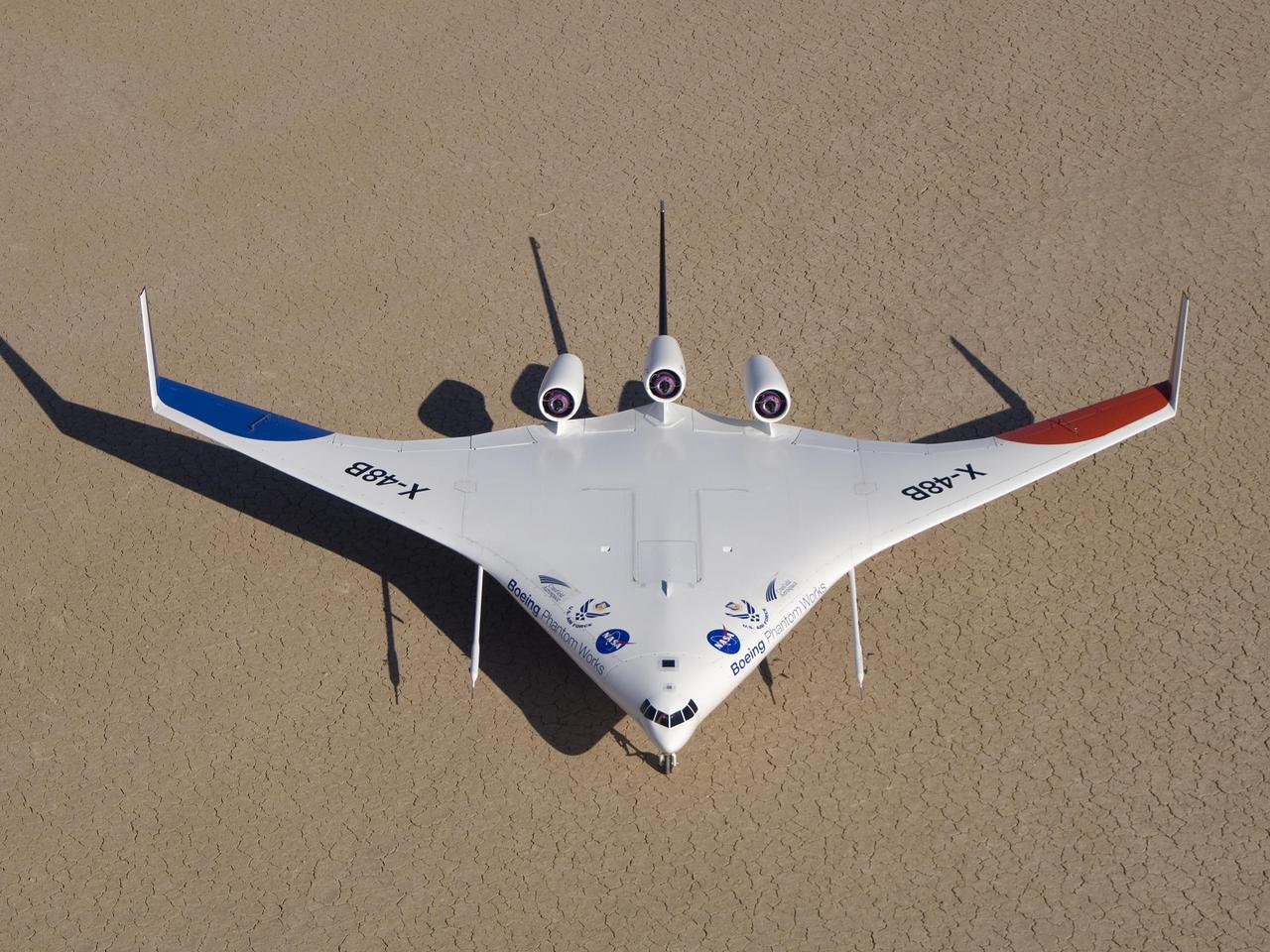

Boeing's colorful X-48B Blended Wing Body technology demonstrator showed off its unique triangular lines while parked on Rogers Dry Lake adjacent to NASA Dryden.
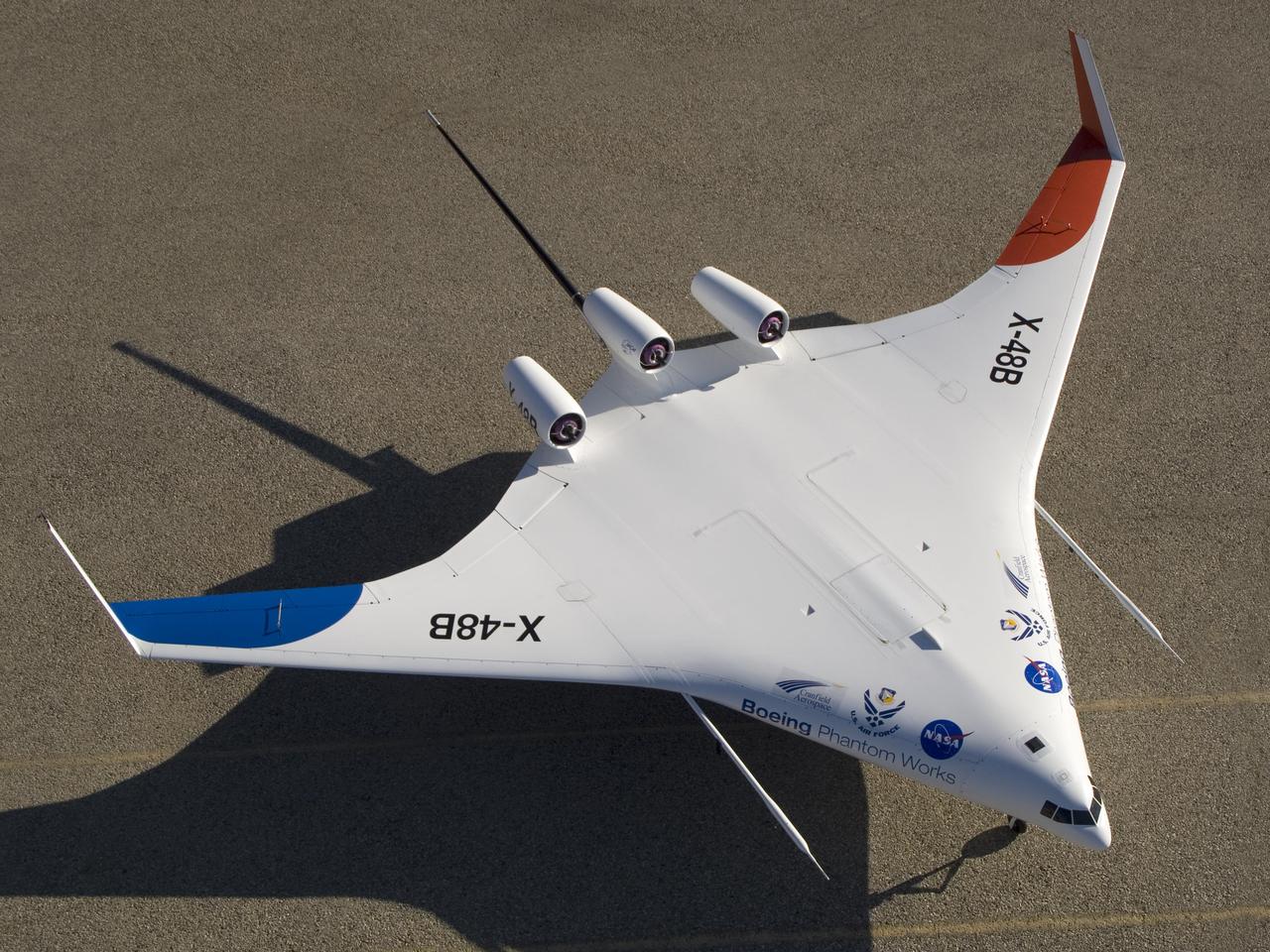

With its spin parachute tail stinger extending aft, Boeing's sub-scale X-48B BWB technology demonstrator showed off its clean semi-triangular shape.
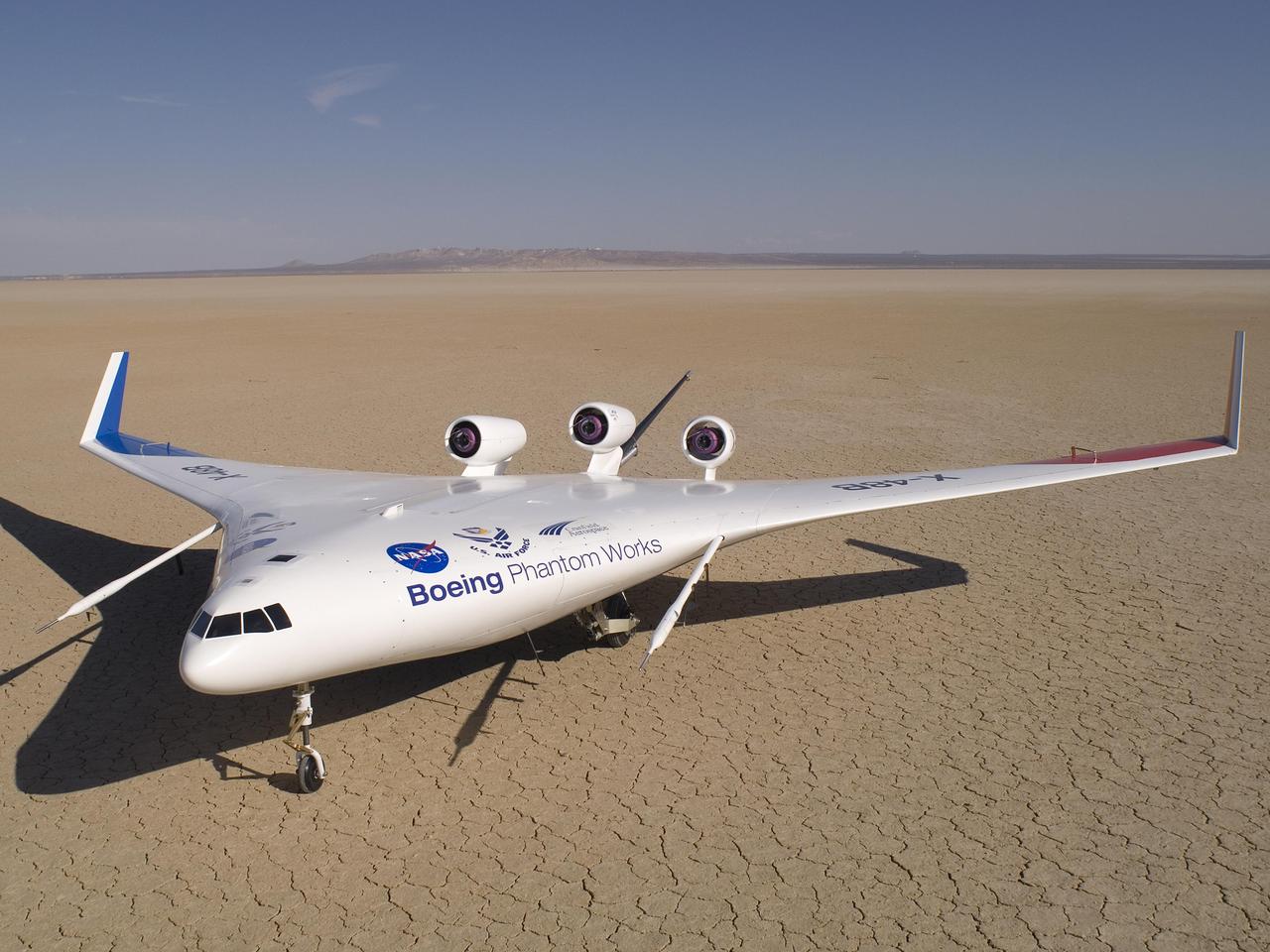

Boeing's sub-scale X-48B Blended Wing Body technology demonstrator showed off its unique lines on the vast expanse of Rogers Dry Lake adjacent to NASA Dryden.

This image showing the position of the Martian moon Deimos against a background of stars is part of a successful technology demonstration completed by NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter before arrival at Mars
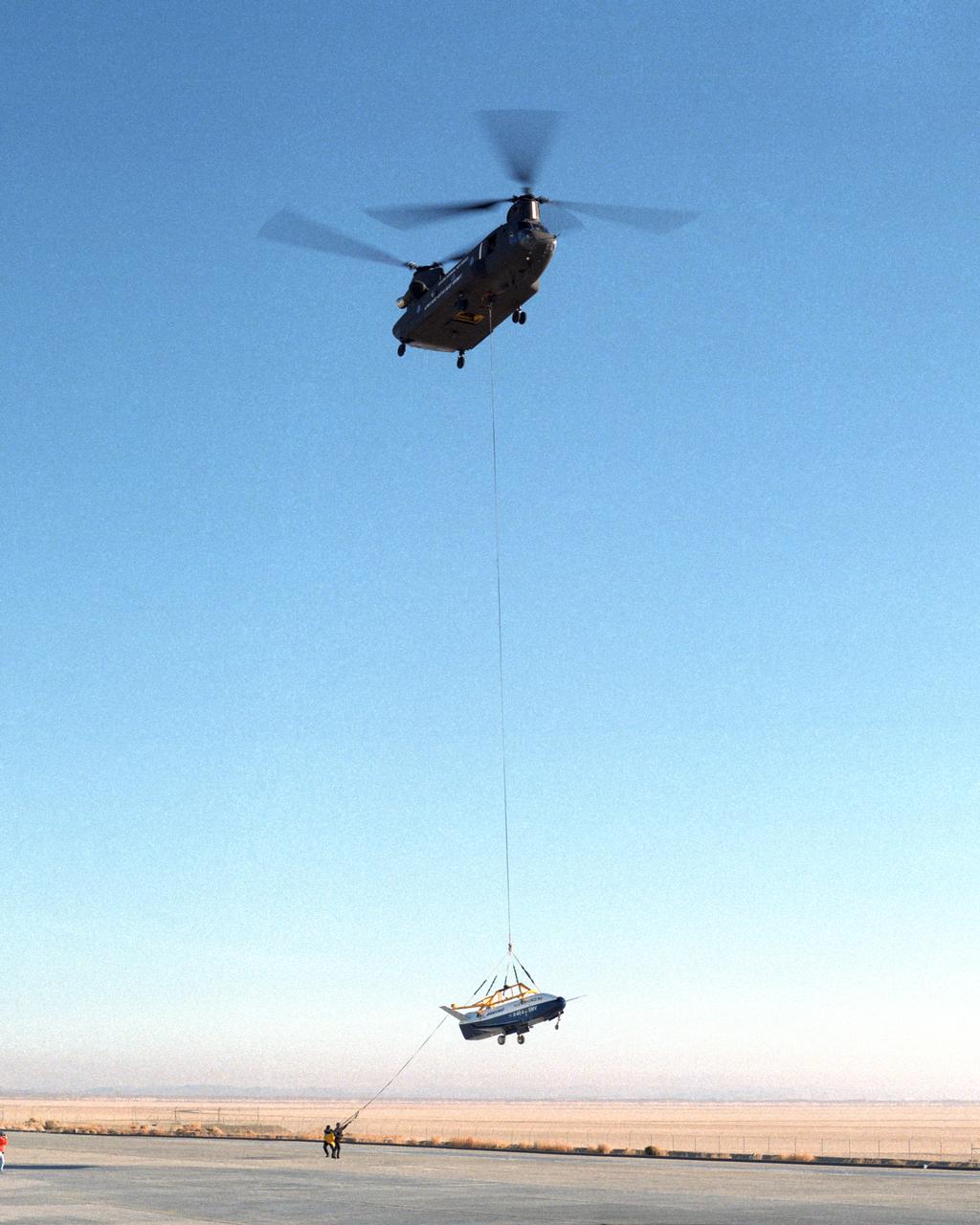

Ground crewmen help guide the alignment of the X-40 technology demonstrator as the experimental craft is gently lowered to the ground by a U.S. Army CH-47 Chinook cargo helicopter following a captive-carry test flight at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The X-40 is an unpowered 82 percent scale version of the X-37, a Boeing-developed spaceplane designed to demonstrate various advanced technologies for development of future lower-cost access to space vehicles. The X-37 will be carried into space aboard a space shuttle and then released to perform various maneuvers and a controlled re-entry through the Earth's atmosphere to an airplane-style landing on a runway, controlled entirely by pre-programmed computer software. Following a series of captive-carry flights, the X-40 made several free flights from a launch altitude of about 15,000 feet above ground, gliding to a fully autonomous landing. The captive carry flights helped verify the X-40's navigation and control systems, rigging angles for its sling, and stability and control of the helicopter while carrying the X-40 on a tether.

Justin Link, pilot for small uncrewed aircraft systems, installs weather instruments on NASA’s Alta X drone at the agency’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. Members of the center’s Dale Reed Subscale Flight Research Laboratory used the Alta X to support the agency’s FireSense project in March 2025 for a prescribed burn in Geneva State Forest, which is about 100 miles south of Montgomery, Alabama.
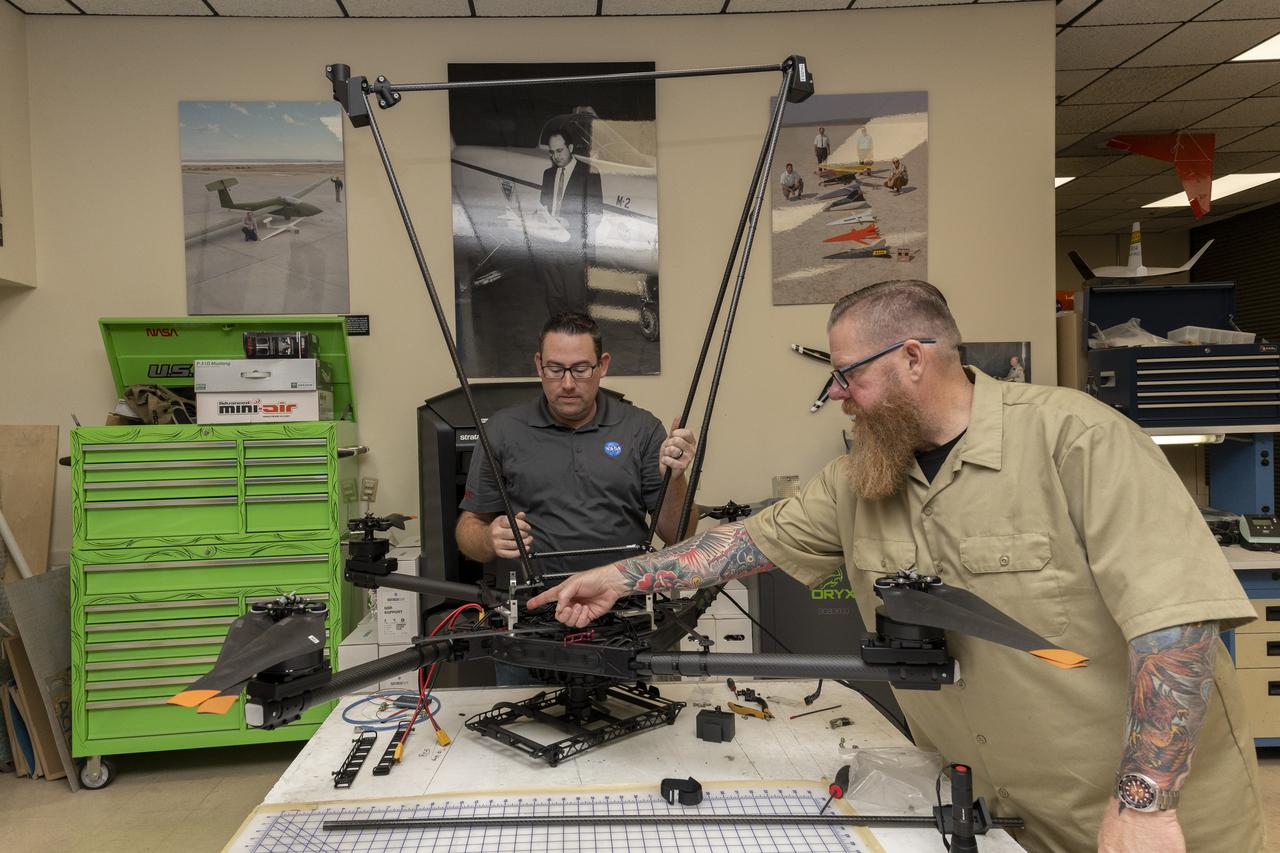

Justin Link, left, pilot for small uncrewed aircraft systems, and Justin Hall, chief pilot for small uncrewed aircraft systems, install weather instruments on NASA’s Alta X drone at the agency’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. Members of the center’s NASA Armstrong Dale Reed Subscale Flight Research Laboratory used the Alta X to support the NASA’s FireSense project in March 2025 for a prescribed burn in Geneva State Forest, which is about 100 miles south of Montgomery, Alabama.
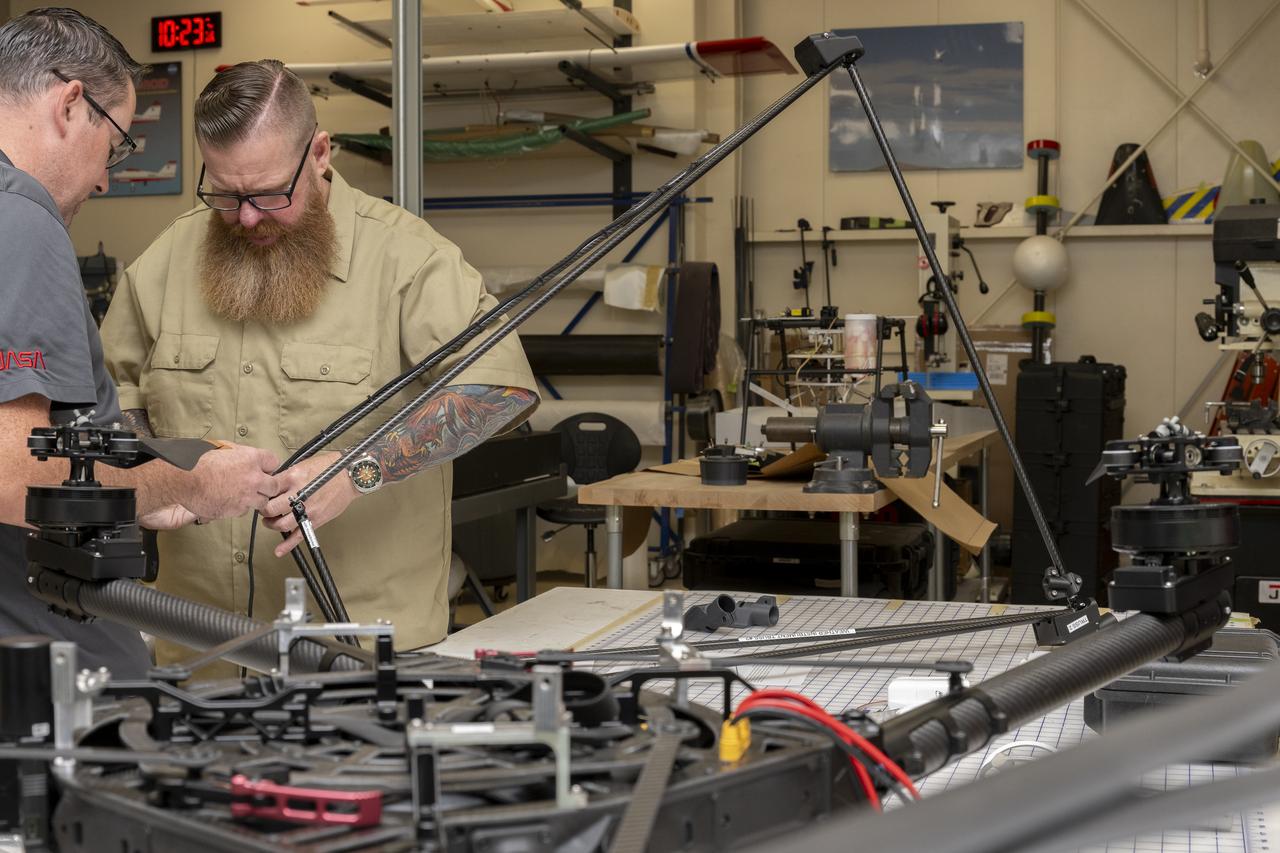

Justin Link, left, pilot for small uncrewed aircraft systems, and Justin Hall, chief pilot for small uncrewed aircraft systems, install weather instruments on NASA’s Alta X drone at the agency’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. Members of the center’s NASA Armstrong Dale Reed Subscale Flight Research Laboratory used the Alta X to support the NASA’s FireSense project in March 2025 for a prescribed burn in Geneva State Forest, which is about 100 miles south of Montgomery, Alabama.
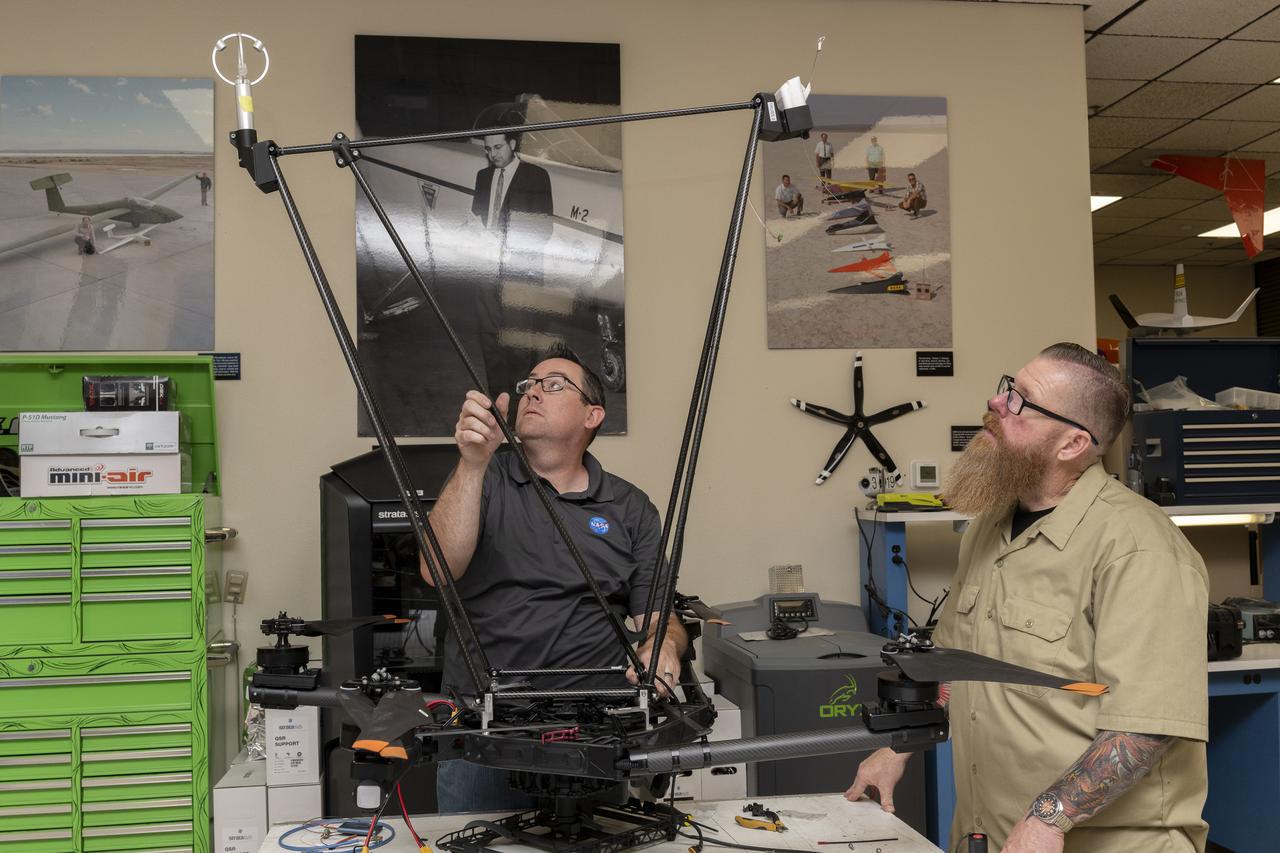

Justin Link, left, pilot for small uncrewed aircraft systems, and Justin Hall, chief pilot for small uncrewed aircraft systems, install weather instruments on NASA’s Alta X drone at the agency’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. Members of the center’s Dale Reed Subscale Flight Research Laboratory used the Alta X to support the agency’s FireSense project in March 2025 for a prescribed burn in Geneva State Forest, which is about 100 miles south of Montgomery, Alabama.

An example of collaboration between NASA and the FAA, at NASA’s air traffic management laboratory near the Dallas/Ft. Worth International Airport in Texas, researchers Al Capps (seated) and Paul Borchers demonstrate tools that air traffic managers have been successfully testing since 2017 at the Charlotte Douglas International Airport in North Carolina to more efficiently direct departing traffic.

Data from the American Airlines ramp tower at Charlotte airport is among the information to be coordinated as part of ATD-2.

American Airlines aircraft in the gate area at Charlotte Douglas International Airport where ATD-2 began in 2017.
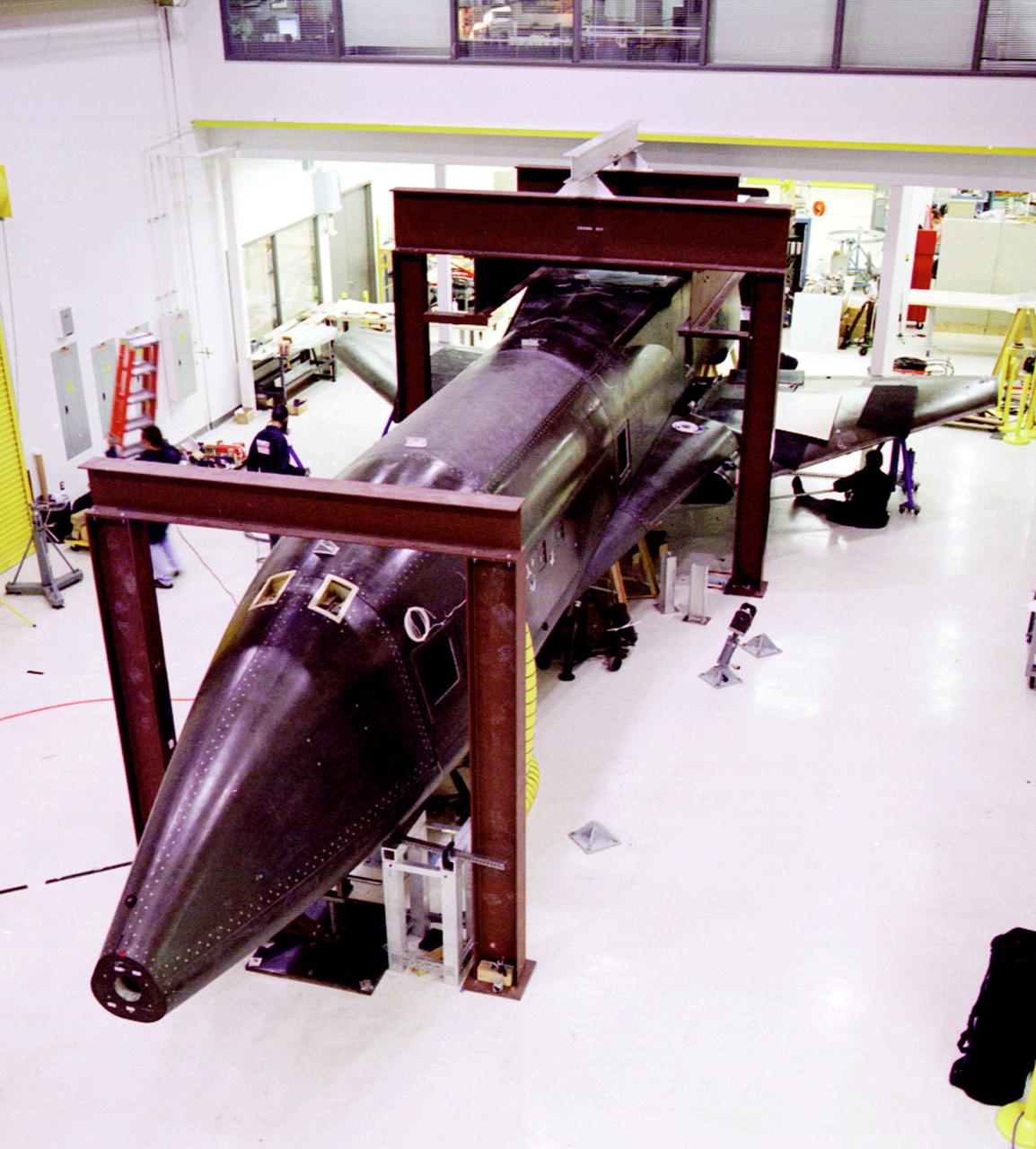

Pictured in the high bay, is the X-34 Technology Demonstrator in the process of completion. The X-34 wass part of NASA's Pathfinder Program which demonstrated advanced space transportation technologies through the use of flight experiments and experimental vehicles. These technology demonstrators and flight experiments supported the Agency's goal of dramatically reducing the cost of access to space and defined the future of space transportation pushing technology into a new era of space development and exploration at the dawn of the new century. The X-34 program was cancelled in 2001.
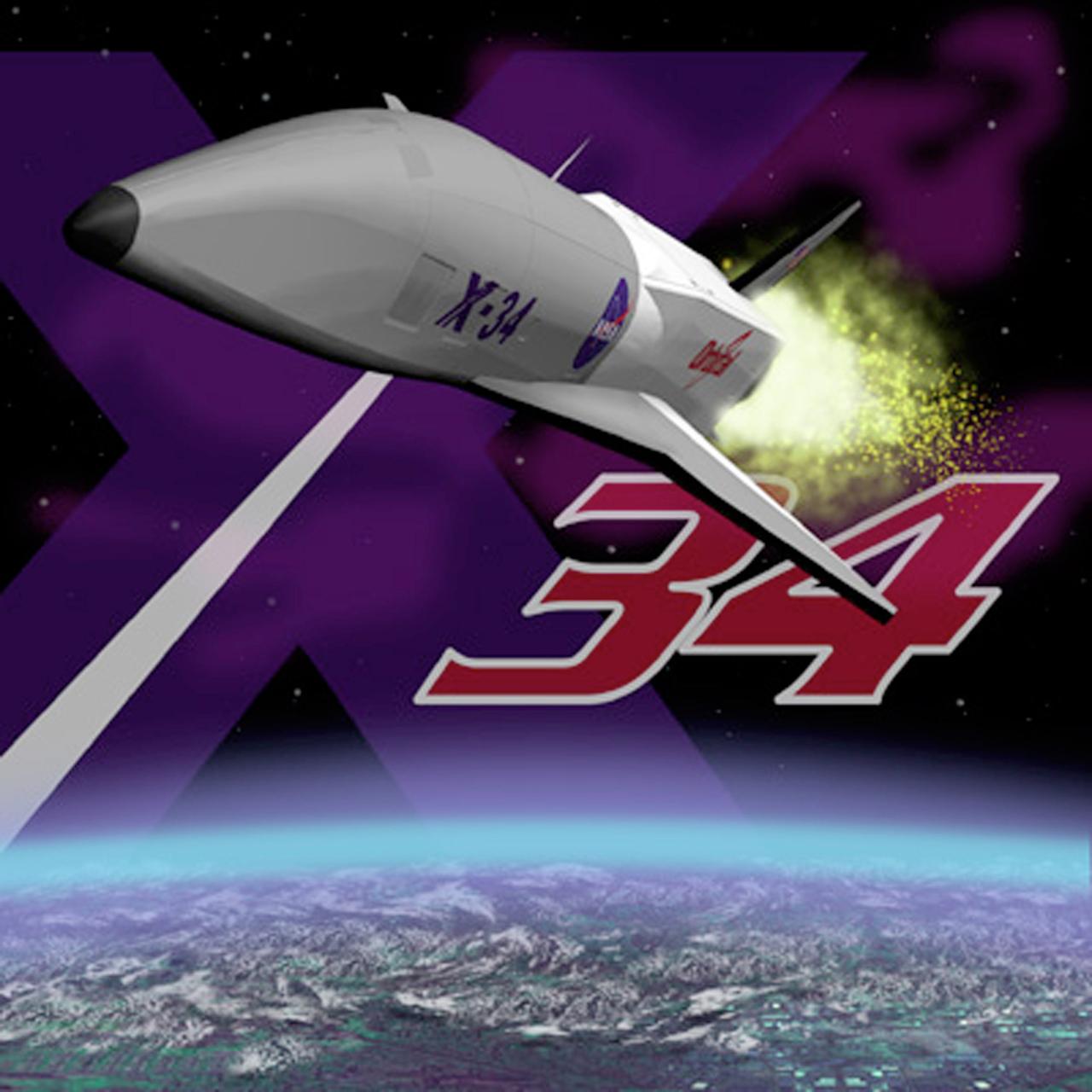

Pictured is NASA's poster art for the X-34 technology Demonstrator. The X-34 was part of NASA's Pathfinder Program which demonstrated advanced space transportation technologies through the use of flight experiments and experimental vehicles. These technology demonstrators and flight experiments would support the Agency's goal of dramatically reducing the cost of access to space and would define the future of space transportation pushing technology into a new era of space development and exploration at the dawn of the new century. The X-34 program was cancelled in 2001.
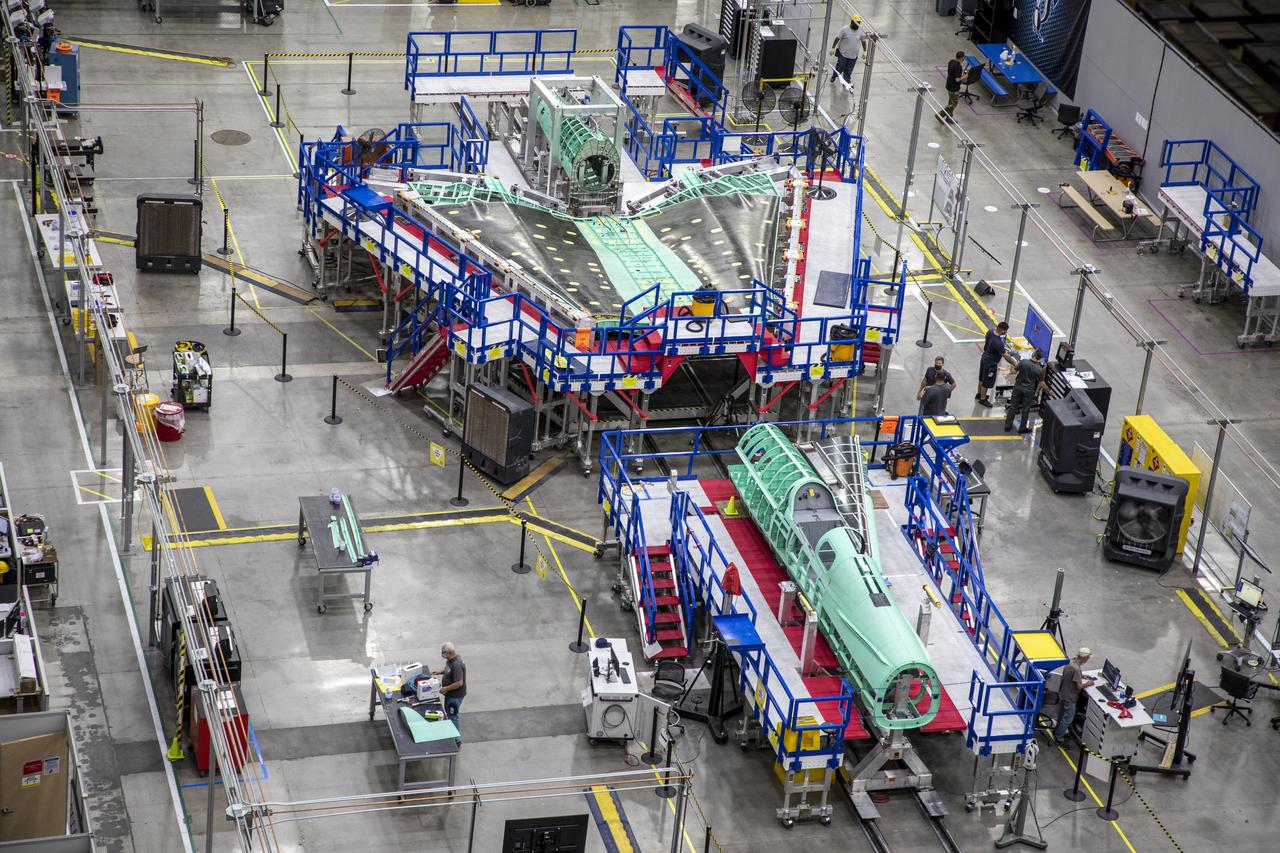

This overhead shot of the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology or QueSST aircraft shows the assembly progress of the vehicle during Spring 2021. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599
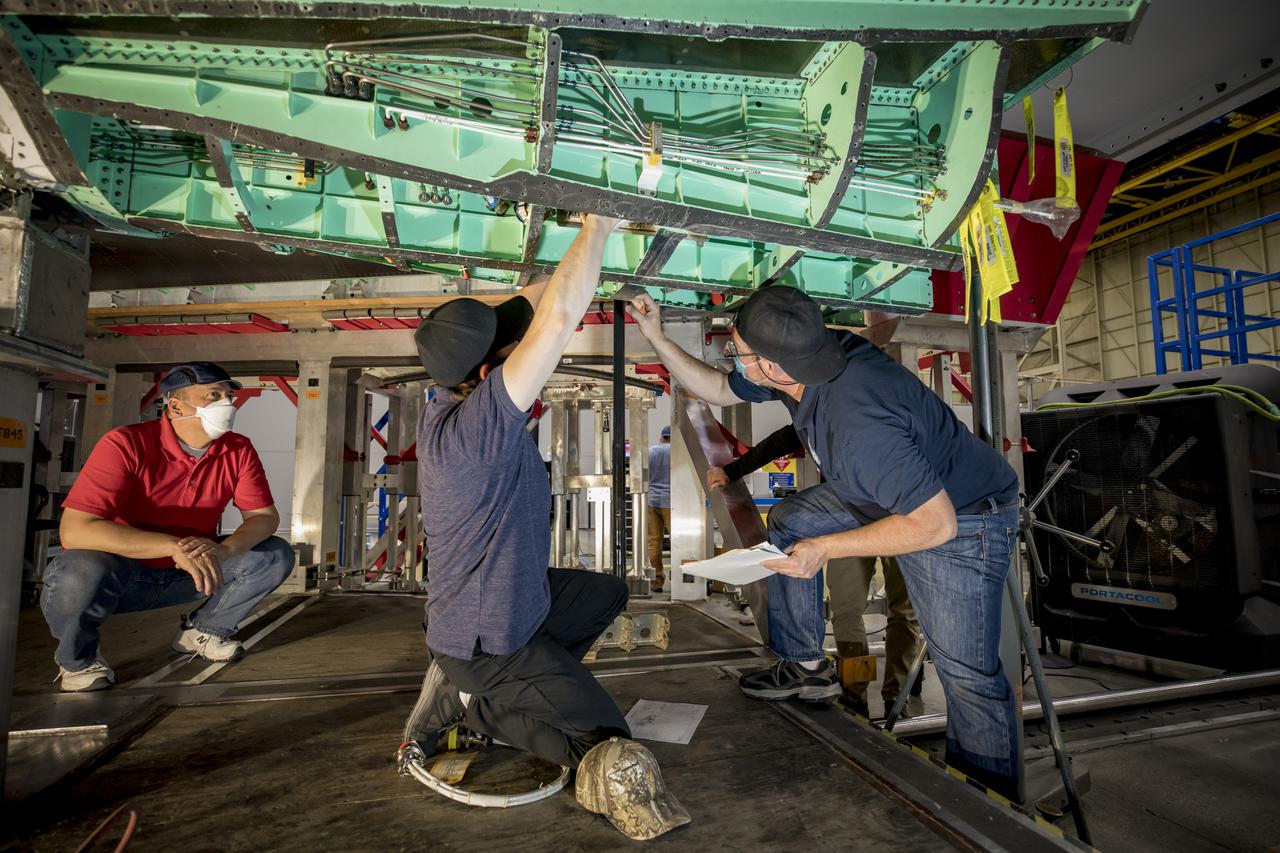

Technicians preform some installation work in the mid-bay on the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology or QueSST aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 450 Mid Bay - Encoders Date: 4/28/2021
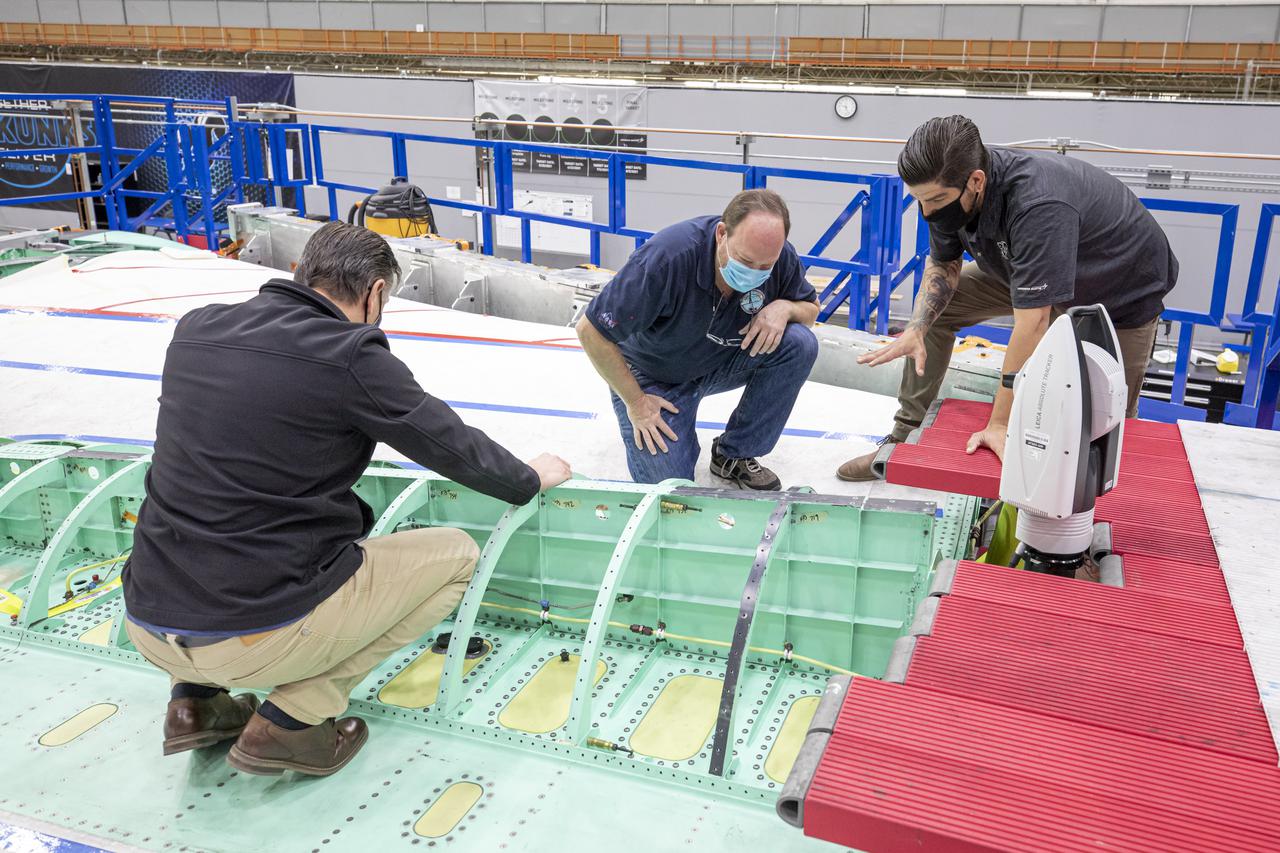

Technicians work with a laser measuring system on the X-59 spine. The X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology, or QueSST, aircraft is under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, and will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 400 Main Wing Assembly, SEG 430 Spine, SEG 500 Empennage Date: 4/28/2021

NASA’s F-15D research aircraft is positioned behind the X-59 during electromagnetic compatibility testing at U.S. Air Force Plant 42 in Palmdale, California. During this test, the F-15D’s radar and avionics were turned on one at a time while engineers evaluated each signal’s interaction with the X-59 for possible interference. NASA’s Quesst mission will demonstrate quiet supersonic technology that will provide data to help determine an acceptable sound limit in the sky.
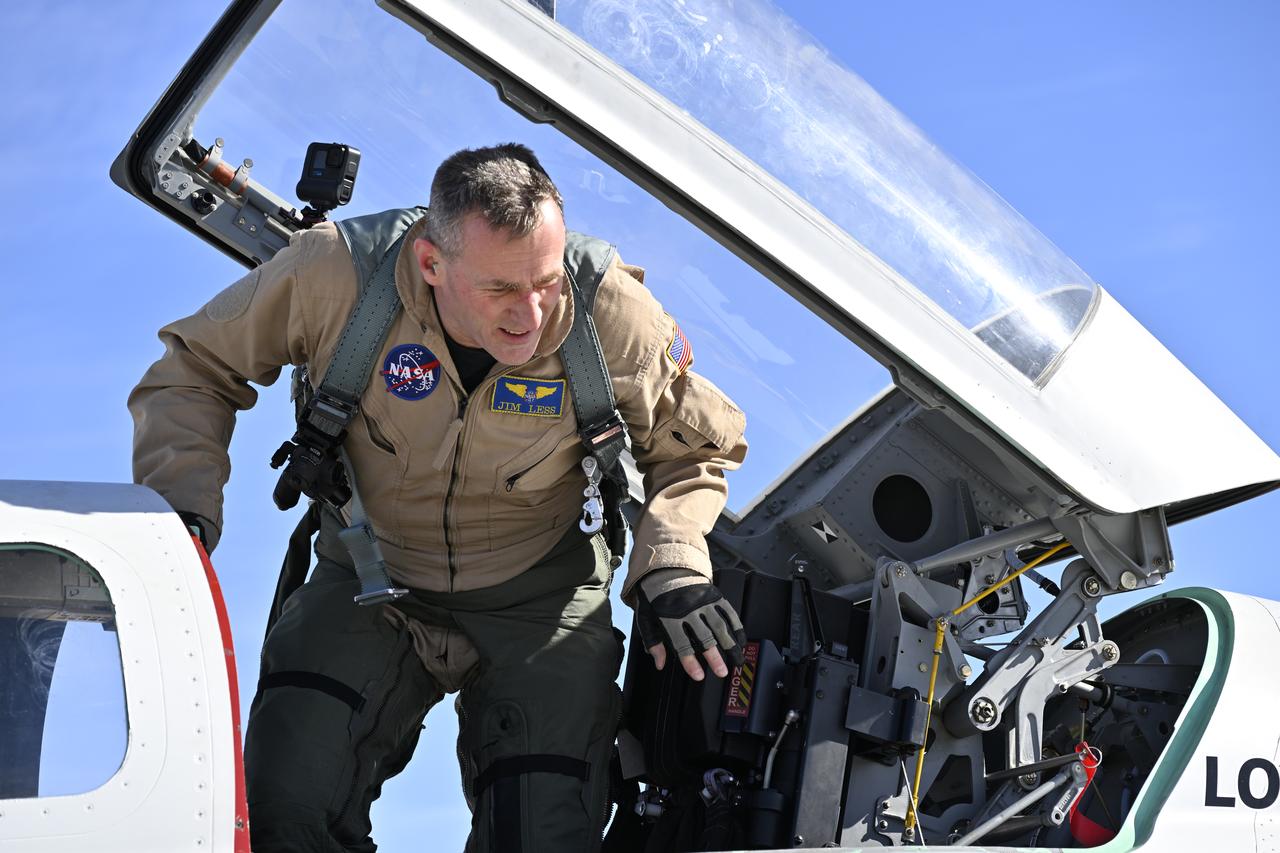

NASA test pilot Jim Less prepares to exit the cockpit of the quiet supersonic X-59 aircraft in between electromagnetic interference (EMI) testing. The EMI testing ensures an aircraft’s systems function properly under various conditions of electromagnetic radiation. The X-59 is the centerpiece of the NASA’s Quesst mission, designed to demonstrate quiet supersonic technology and provide data to address a key barrier to commercial supersonic travel.
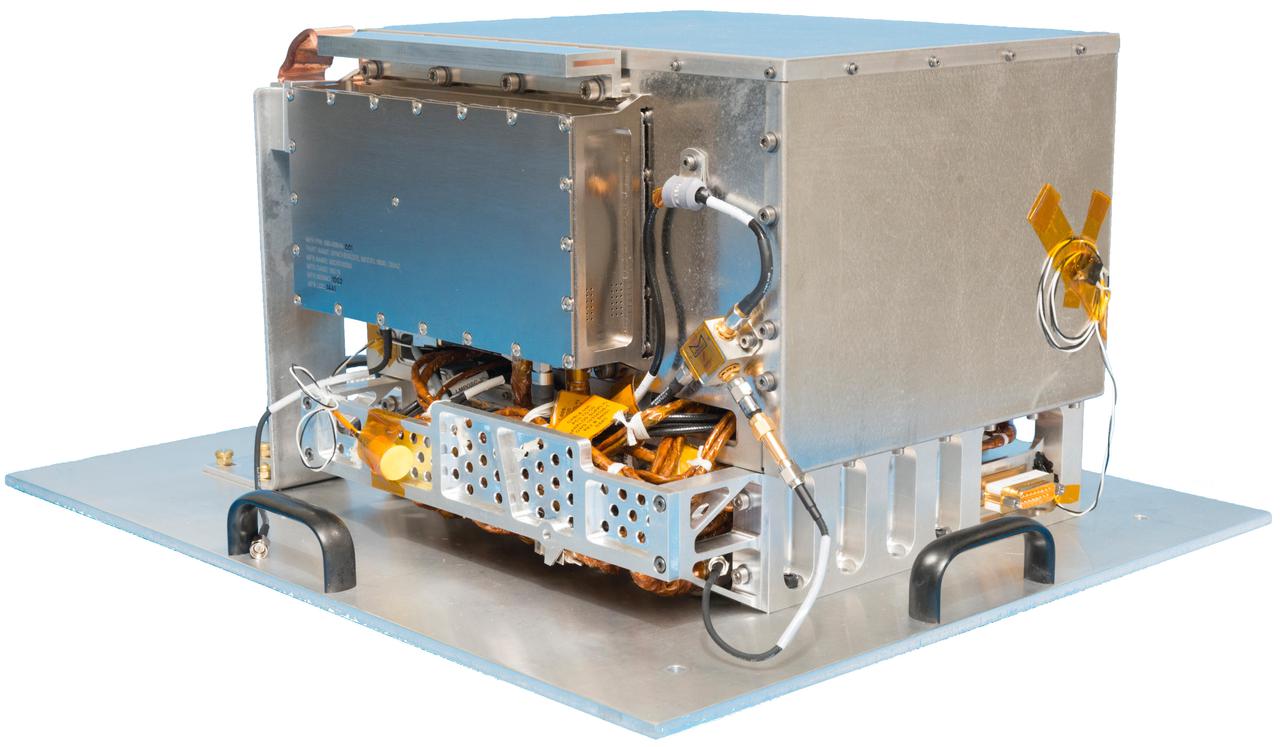
NASA's Deep Space Atomic Clock could revolutionize deep space navigation. One key requirement for the technology demonstration was a compact design. The complete hardware package is shown here and is only about 10 inches (25 centimeters) on each side. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24573
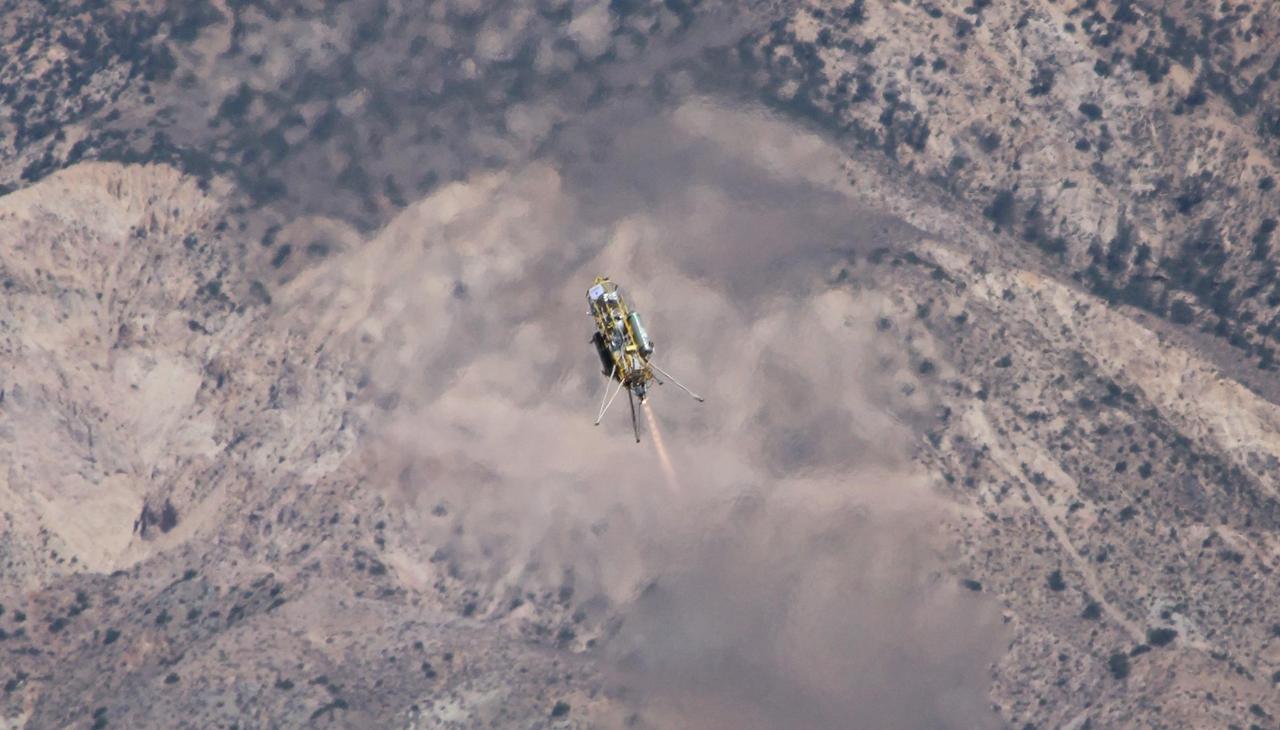

A Xombie technology demonstrator from Masten Space Systems, Mojave, Calif., ascends from its pad at Mojave Air and Space Port on a test for NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The vehicle is a vertical-takeoff, vertical-landing experimental rocket.
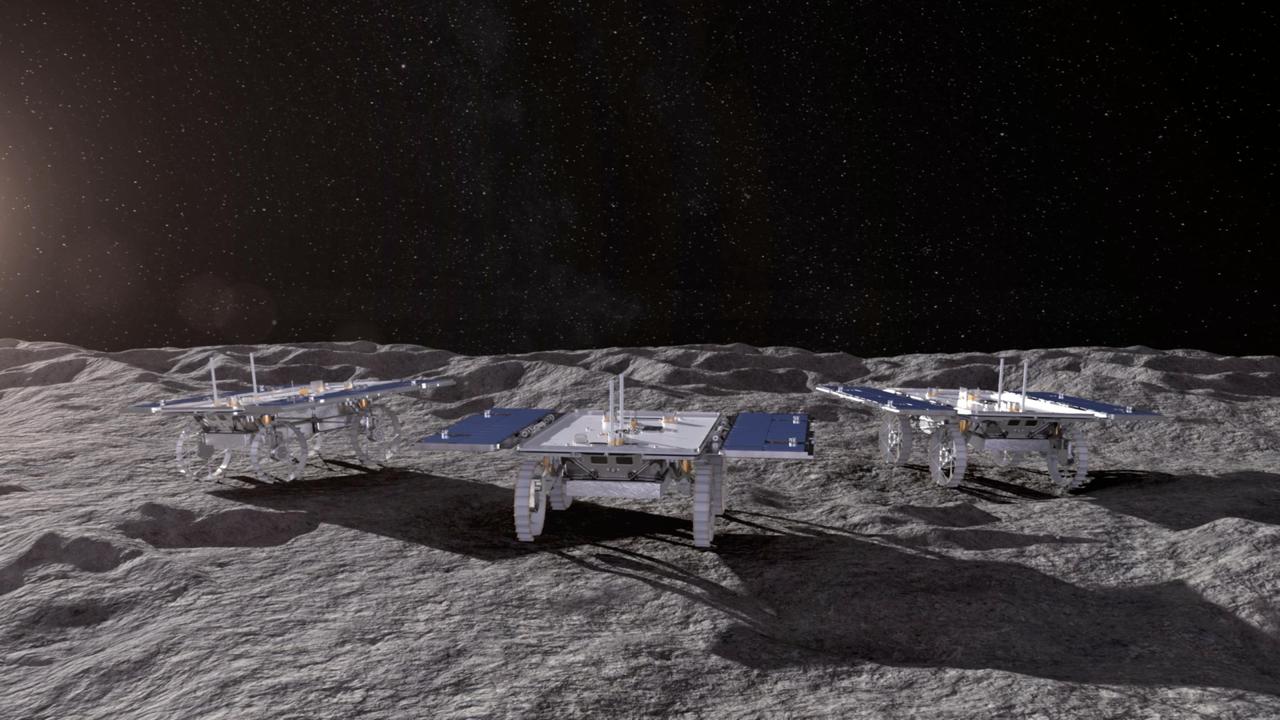
This animated artist's concept depicts three small rovers – part of NASA's CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration) technology demonstration headed for the Moon – driving together on the lunar surface. Motiv Space Systems in Pasadena, California, created the rendering and collaborated with NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on critical rover and mobility functions. Slated to arrive aboard a lunar lander at the Reiner Gamma region of the Moon under NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, CADRE is designed to demonstrate that multiple robots can cooperate and explore together autonomously – without direct input from human mission controllers. A trio of the miniature solar-powered rovers, each about the size of a carry-on suitcase, will explore the Moon as a team, communicating via radio with each other and a base station aboard the lander. By taking simultaneous measurements from multiple locations, CADRE will also demonstrate how multirobot missions can record data impossible for a single robot to achieve – a tantalizing prospect for future missions. Motiv contributed subsystems and hardware elements for three of four CADRE systems, including designing and building the mobility system and rover chassis, the base station, the rover deployers, and the motor controller boards. The company also procured and tested the actuators with the flight motor controller boards. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26296

A development model rover that is part of NASA's CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration) technology demonstration took its first autonomous drive around the Mars Yard at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in June 2023. The CADRE team tested a new wheel design, surface navigation software, and mobility capabilities, among other aspects of the project. Engineer Kristopher Sherrill is shown recording video of the test. The rover being tested is similar in size and appearance to the flight models of the CADRE rovers, which are still being built. Slated to arrive at the Moon in spring 2024 as part of NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, CADRE is designed to demonstrate that multiple robots can cooperate and explore together autonomously – without direct input from human mission controllers. A trio of the miniature solar-powered rovers, each about the size of a carry-on suitcase, will explore the Moon as a team, communicating via radio with each other and a base station aboard a lunar lander. By taking simultaneous measurements from multiple locations, CADRE will also demonstrate how multirobot missions can record data impossible for a single robot to achieve – a tantalizing prospect for future missions. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25665
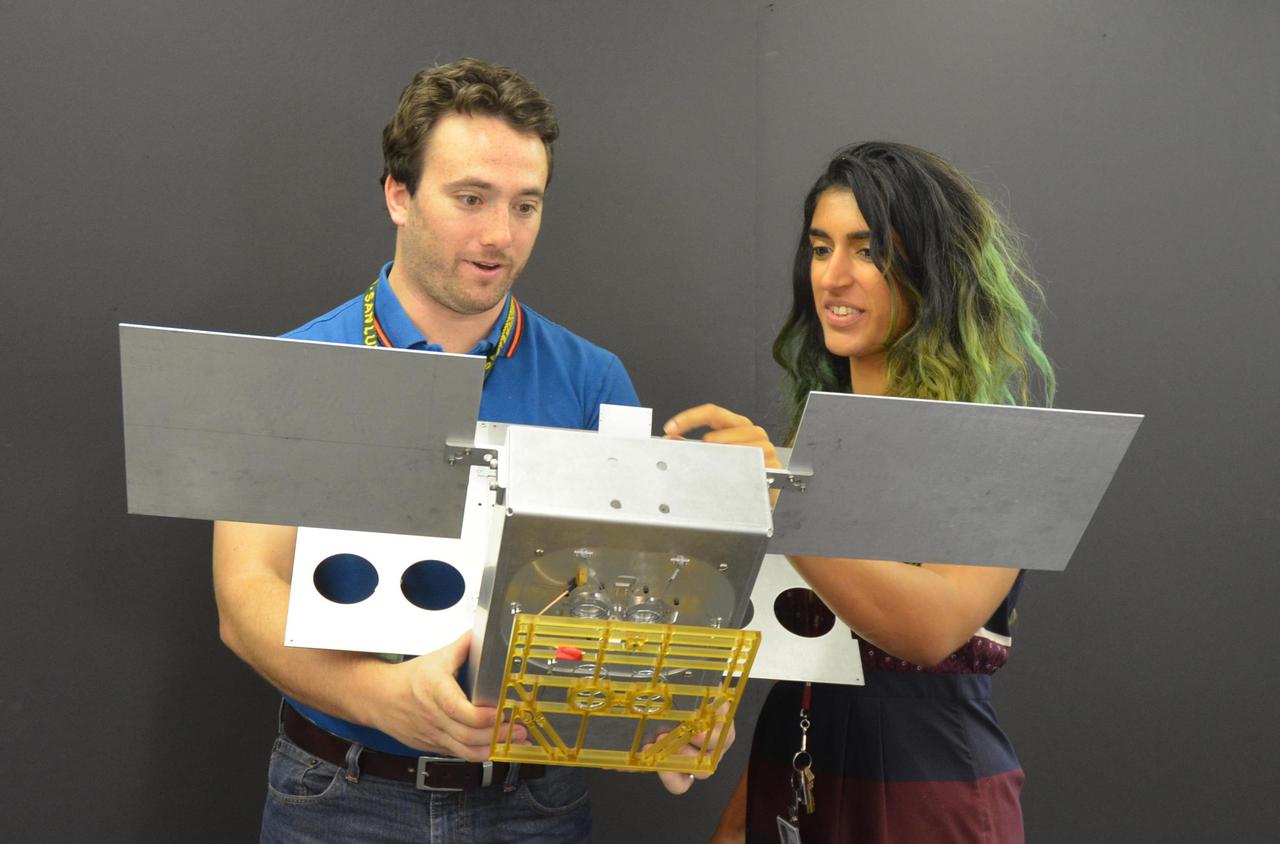

Engineers for NASA's MarCO technology demonstration display a full-scale mechanical mock-up of the small craft in development as part of NASA's next mission to Mars. Mechanical engineer Joel Steinkraus and systems engineer Farah Alibay are on the team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, preparing twin MarCO (Mars Cube One) CubeSats for a March 2016 launch. MarCO is the first interplanetary mission using CubeSat technologies for small spacecraft. The briefcase-size MarCO twins will ride along on an Atlas V launch vehicle lifting off from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, with NASA's next Mars lander, InSight. The mock-up in the photo is in a configuration to show the deployed position of components that correspond to MarCO's two solar panels and two antennas. During launch, those components will be stowed for a total vehicle size of about 14.4 inches (36.6 centimeters) by 9.5 inches (24.3 centimeters) by 4.6 inches (11.8 centimeters). After launch, the two MarCO CubeSats and InSight will be navigated separately to Mars. The MarCO twins will fly past the planet in September 2016 just as InSight is descending through the atmosphere and landing on the surface. MarCO is a technology demonstration mission to relay communications from InSight to Earth during InSight's descent and landing. InSight communications during that critical period will also be recorded by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter for delayed transmission to Earth. InSight -- an acronym for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport -- will study the interior of Mars to improve understanding of the processes that formed and shaped rocky planets, including Earth. After launch, the MarCO twins and InSight will be navigated separately to Mars. Note: After thorough examination, NASA managers have decided to suspend the planned March 2016 launch of the Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) mission. The decision follows unsuccessful attempts to repair a leak in a section of the prime instrument in the science payload. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19389
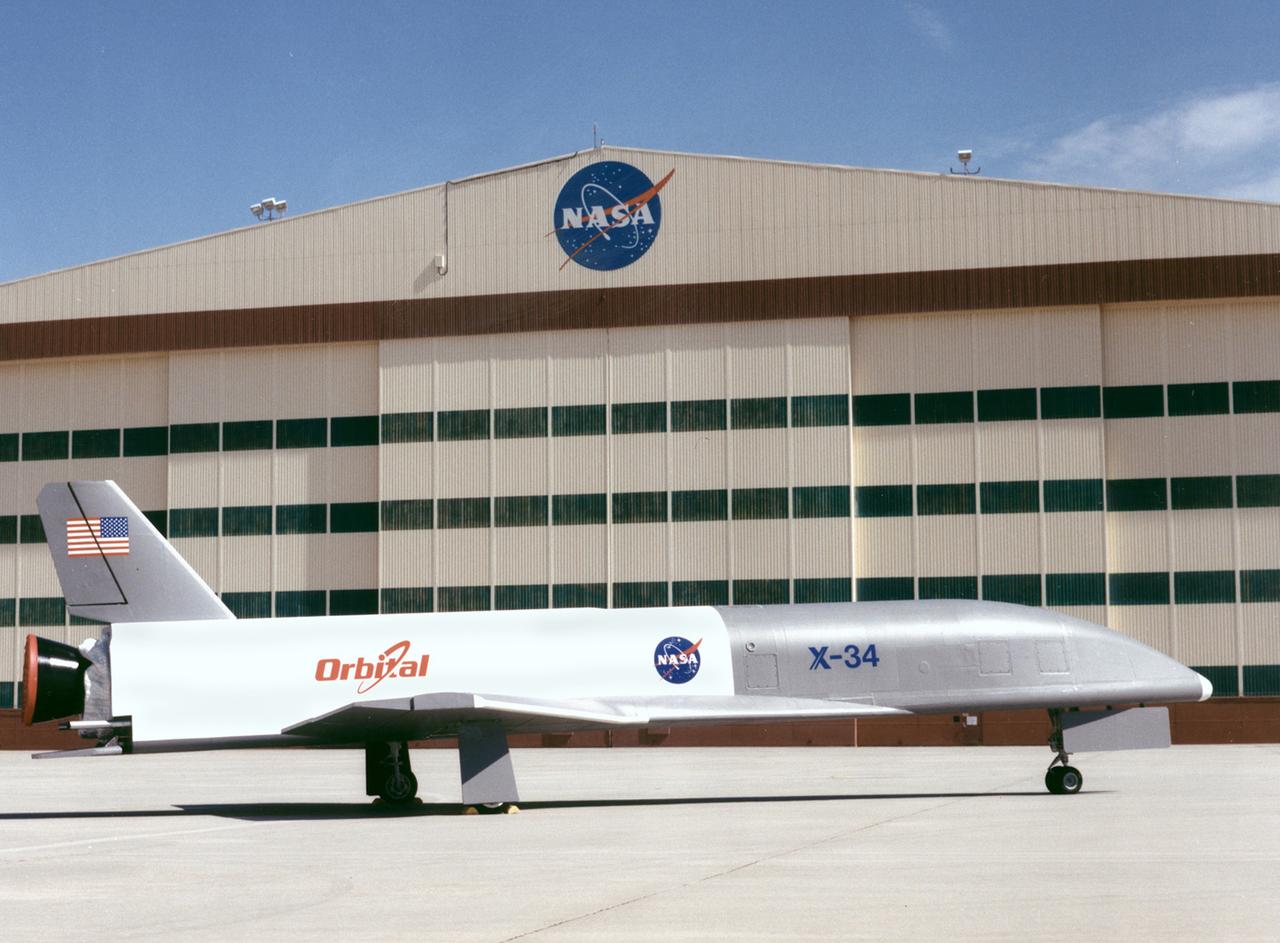

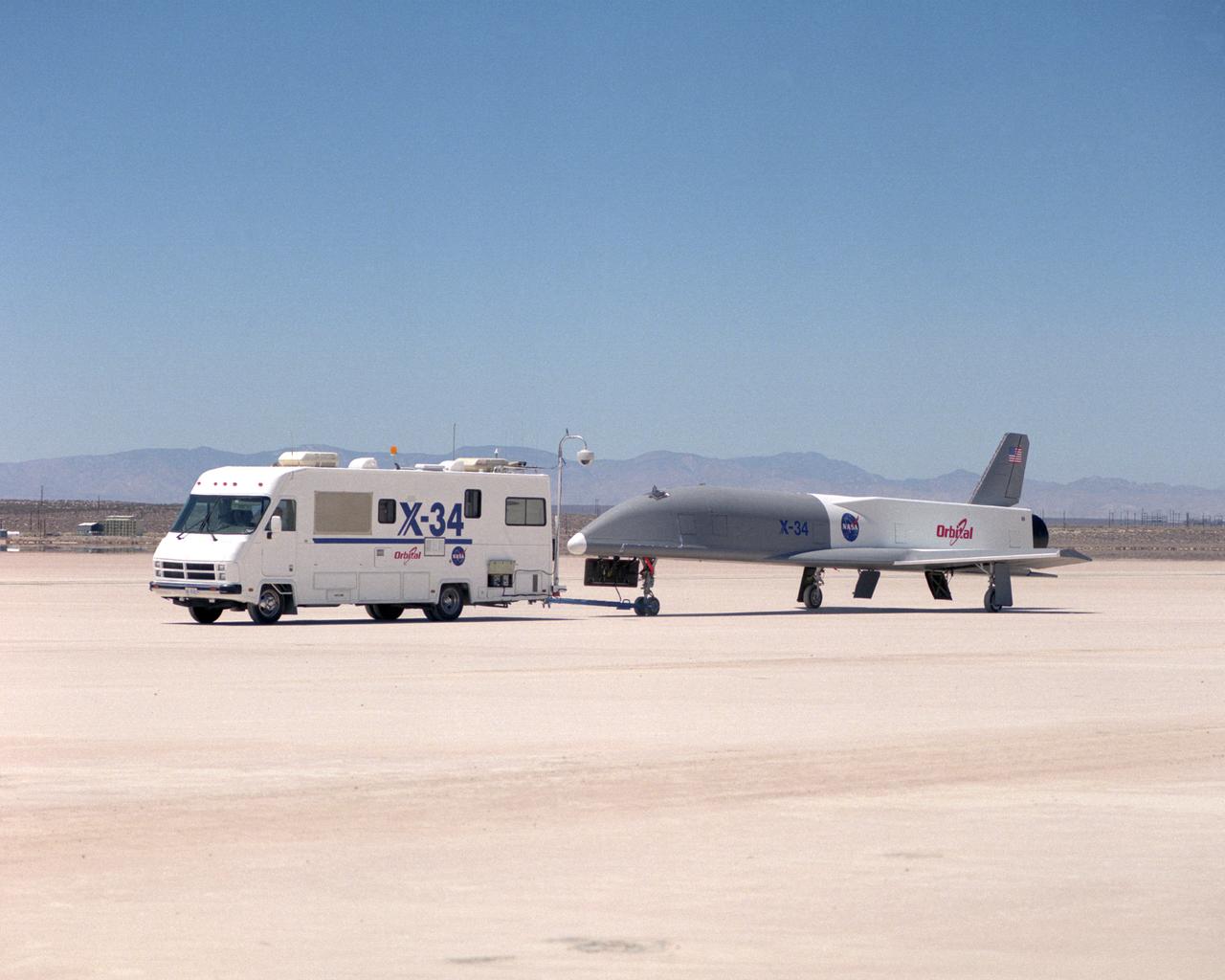
The X-34 demonstrator is shown being taken out of its hangar and placed on the tarmac. The X-34 was classified as part of the Pathfinder class demonstrators which include small experimental vehicles or less expensive flight experiments. These demonstrators were driven by technology and were executed every one to two years. They were done quickly, for low cost, and for a wide range of technologies and applications. The X-34 program was cancelled in 2001.
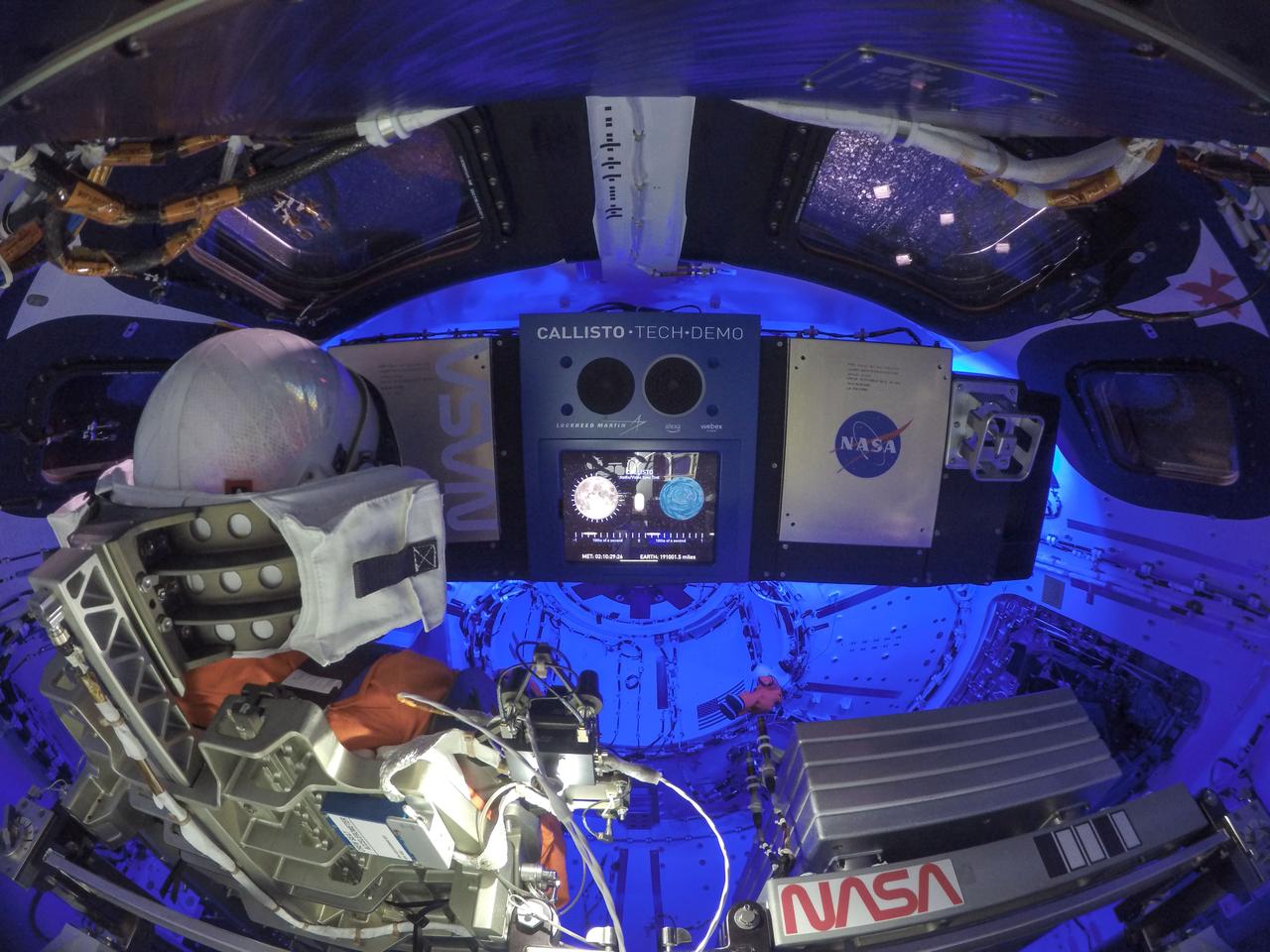
Engineers activated the Callisto payload, Lockheed Martin’s technology demonstration in collaboration with Amazon and Cisco. Callisto will test voice-activated and video technology that may assist future astronauts on deep space missions.
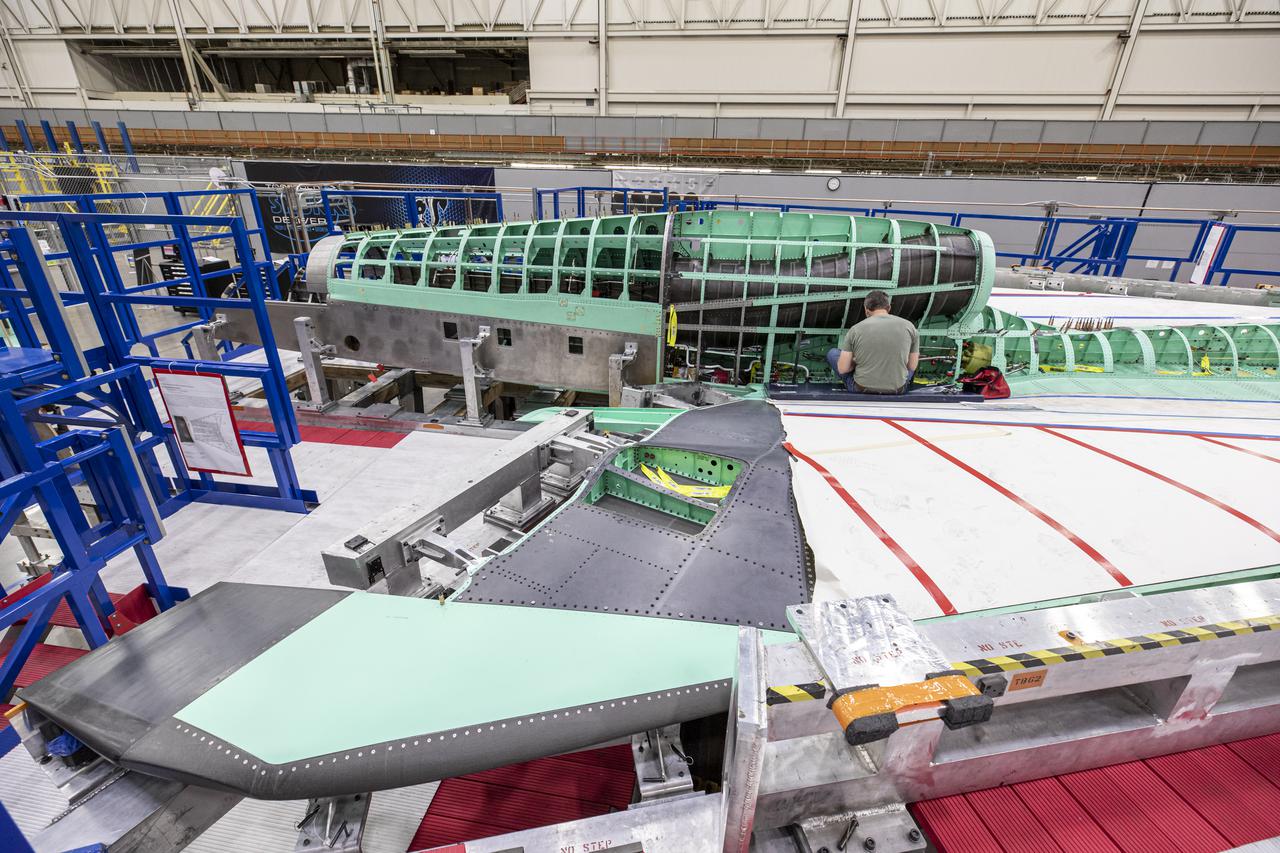

Here is a wide shot of the wing, engine and engine inlet area of NASA’s X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology or QueSST aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 400 Main Wing Assembly, SEG 430 Spine, SEG 500 Empennage Date: 4/28/2021
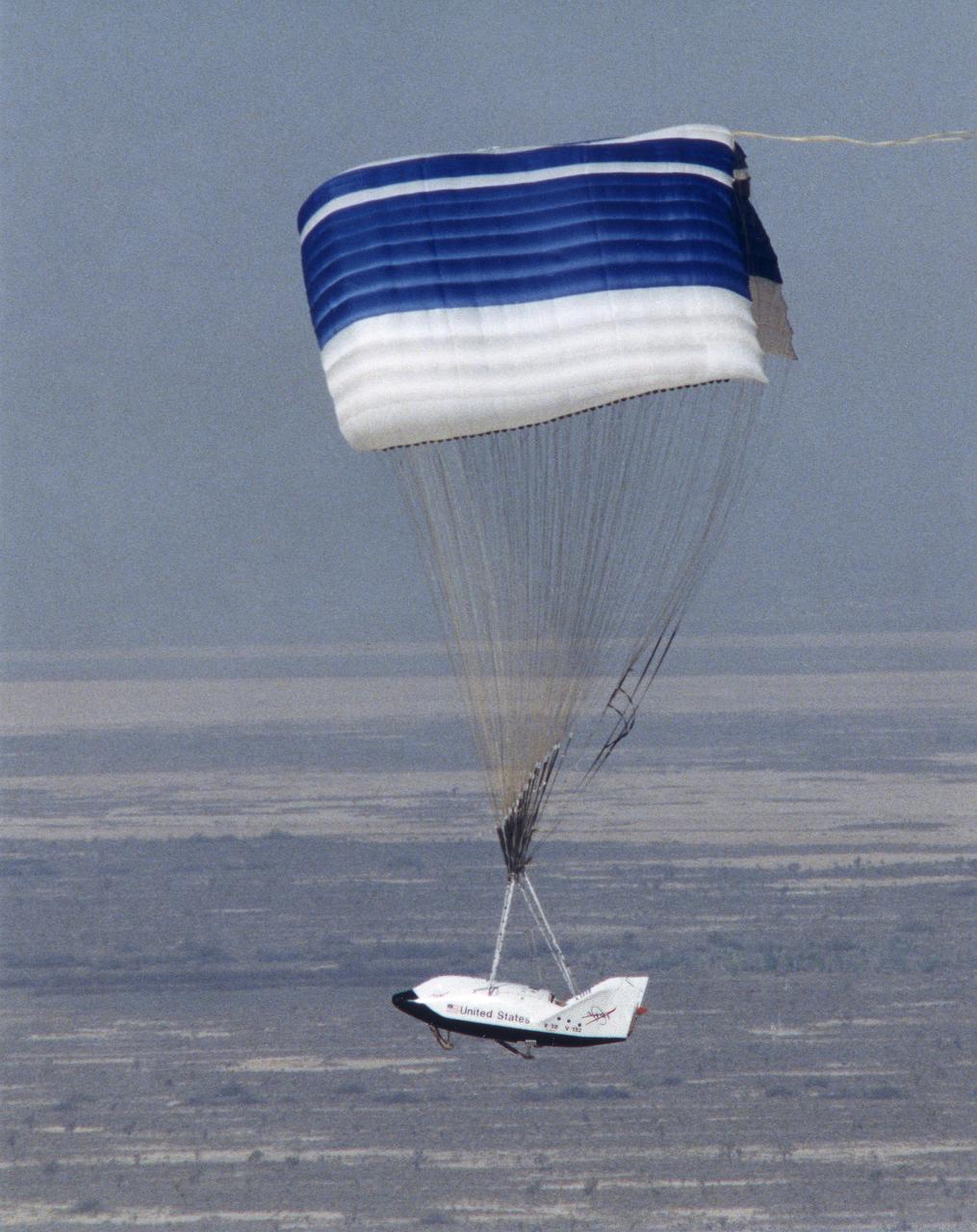

The X-38 technology demonstrator descends under its steerable parafoil toward a lakebed landing in a March 2000 test flight.
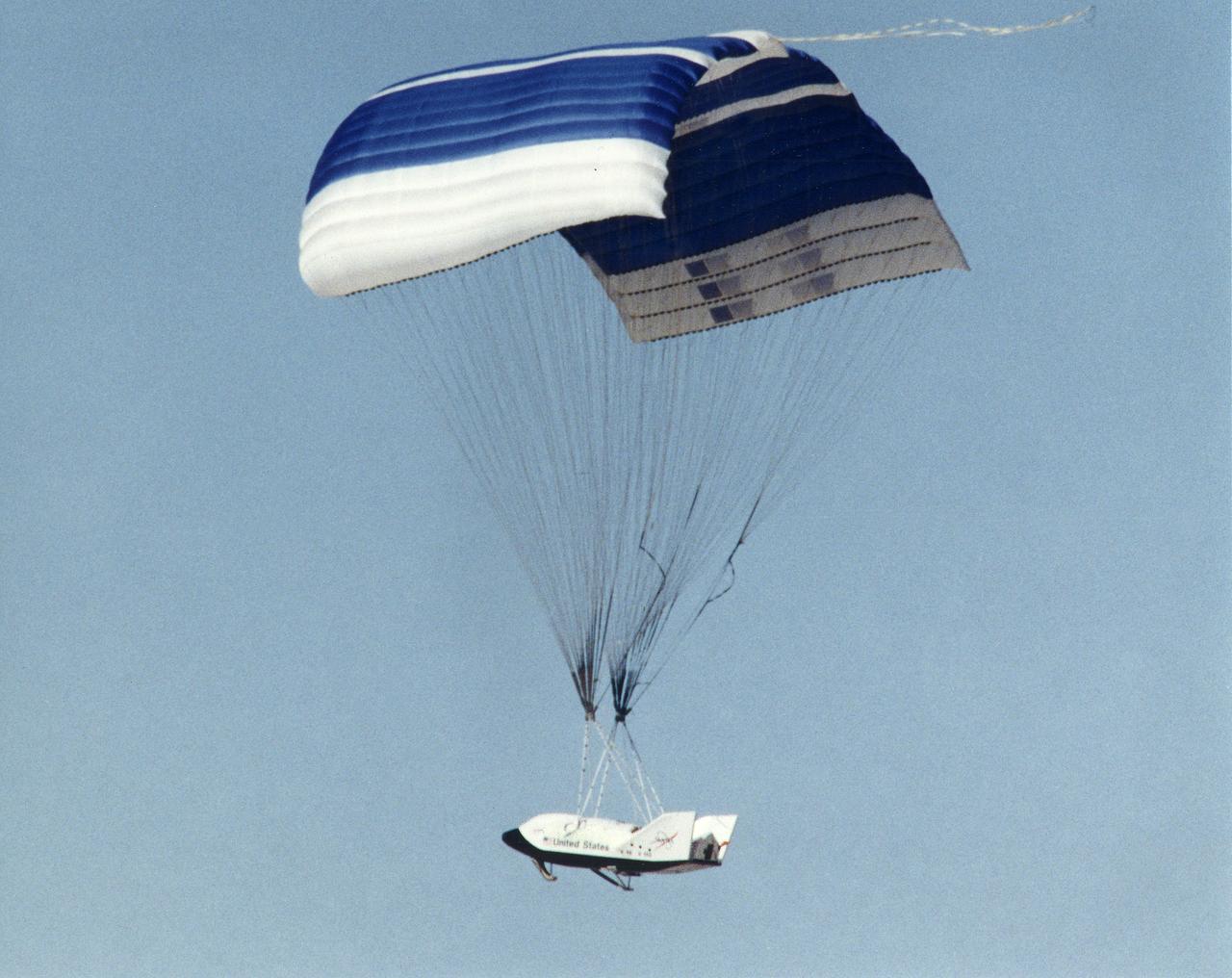

The X-38 technology demonstrator descends under its steerable parafoil toward a lakebed landing in a March 2000 test flight.
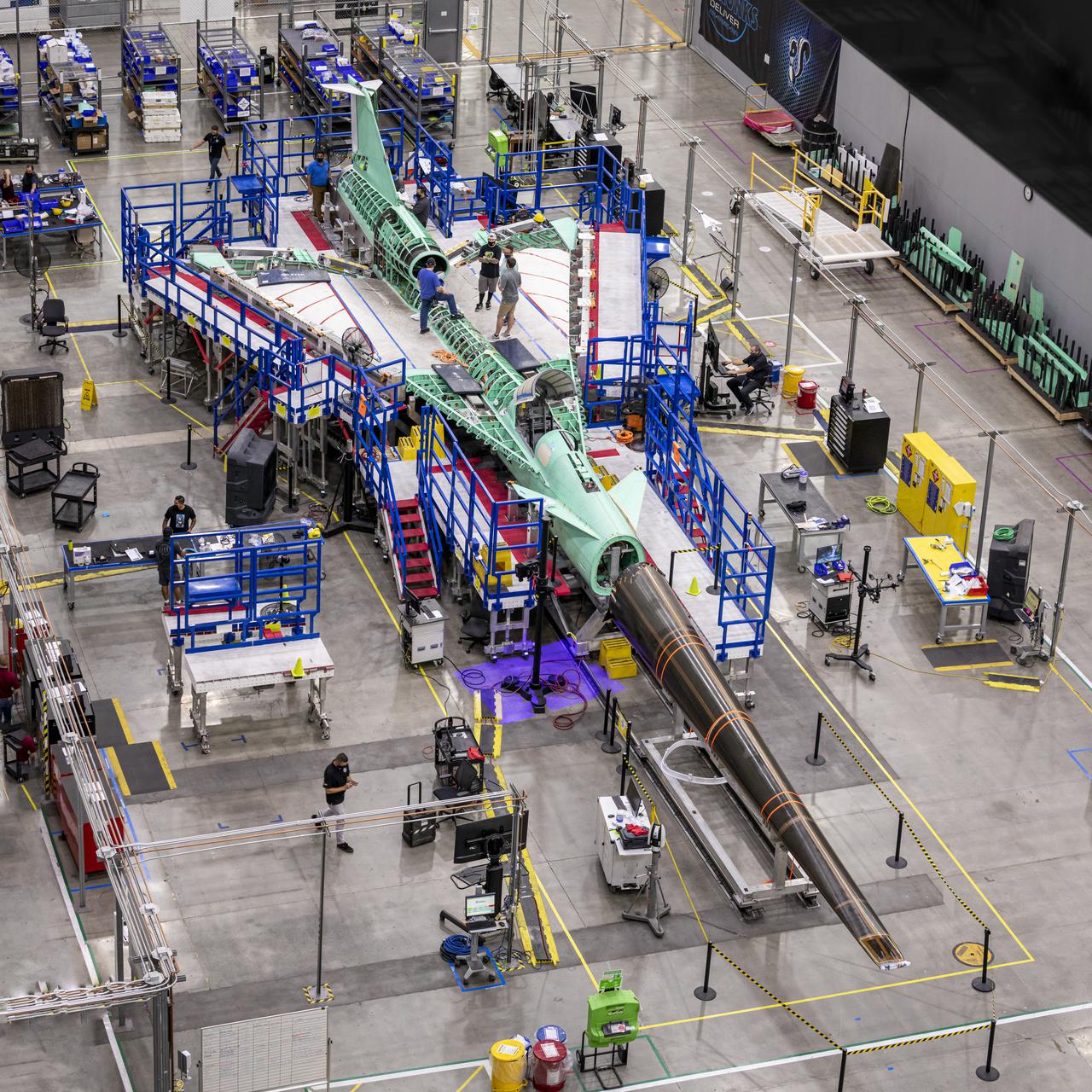

The X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology (QueSST) aircraft is taking shape at the Lockheed Martin Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. The team positioned the X-59 QueSST's nose at the front of the aircraft. As one of the more recognizable features of the X-59, the nose makes up almost a third of the aircraft length and will be essential in shaping shock waves during supersonic flight, resulting in quiet sonic thumps instead of loud sonic booms. The nose was attached and then removed from the front of the aircraft in preparation for its shipment to Fort Worth, Texas where it will undergo additional testing. The X-59 will fly at supersonic speeds above communities as part of the Low-Boom Flight Demonstration mission, during which NASA will gather community feedback to the sound of quiet supersonic flight. These findings will be shared with regulators to inform decisions on current restrictions of supersonic flight over land. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: Manufacturing Area From Above Date: 8/18/2021 Additional Info:
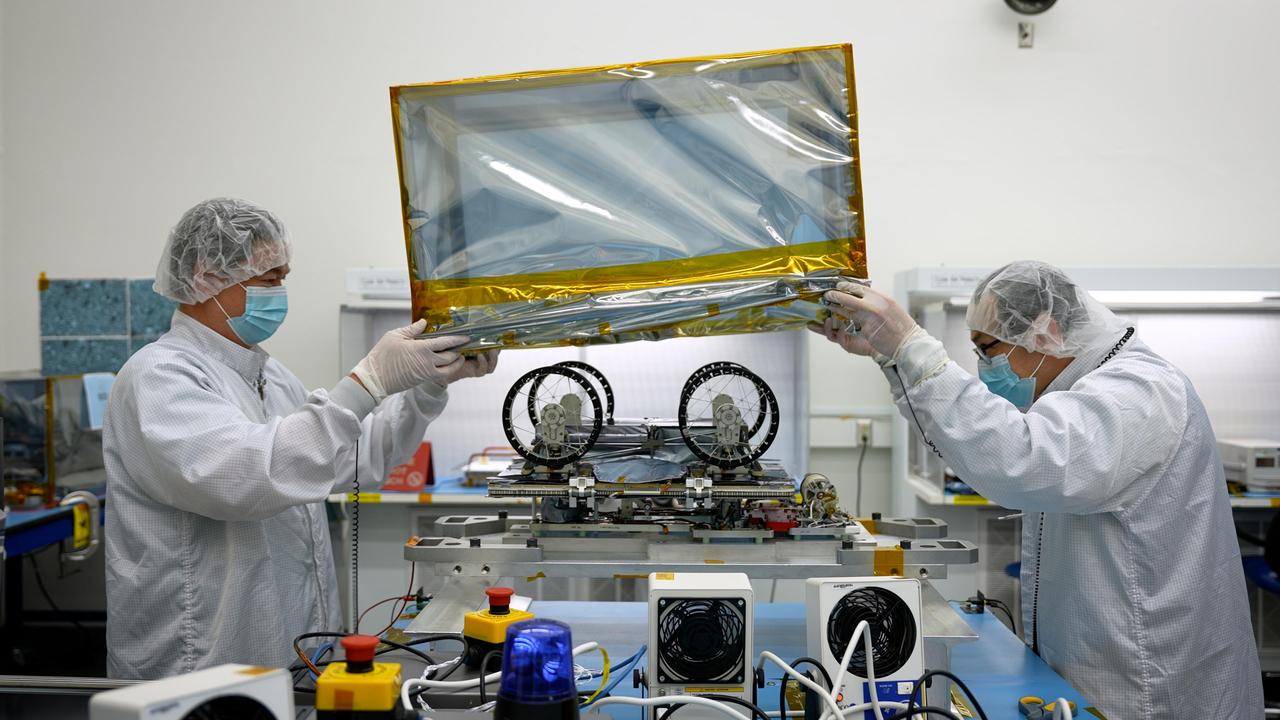

Engineers and technicians prepare one of three small lunar rovers that are part of a NASA technology demonstration called CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration). Mechanical engineer Kristopher Sherrill, left, and technician Leroy Montalvo lower an enclosure over the upside-down rover in a clean room at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Jan. 29, 2025. CADRE aims to prove that a group of robots can collaborate to gather data without receiving direct commands from mission controllers on Earth. Its trio of rovers will use their cameras and ground-penetrating radars to send back imagery of the lunar surface and subsurface while testing out the novel software systems that enable them to work together as a team autonomously. Before embarking on the first leg of a multistage journey to the Moon, each rover was mated to its deployer system, which will lower it via tether from an Intuitive Machines lander onto the dusty lunar surface. Engineers flipped each rover-deployer pair over and attached it to an aluminum plate for safe transit. The rovers were then sealed into protective metal-frame enclosures that were fitted snuggly into metal shipping containers and loaded onto a truck for the drive to Intuitive Machines' Houston facility. A division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, JPL manages CADRE for the Game Changing Development program within NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate in Washington. The technology demonstration was selected under the agency's Lunar Surface Innovation Initiative, which was established to expedite the development of technologies for sustained presence on the lunar surface. CADRE will launch as a payload on the third lunar lander mission by Intuitive Machines, called IM-3, under NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, which is managed by the agency's Science Mission Directorate, also in Washington. The agency's Glenn Research Center in Cleveland and its Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley, California, both supported the project. Motiv Space Systems designed and built key hardware elements at the company's Pasadena facility. Clemson University in South Carolina contributed research in support of the project. For more about CADRE, go to: https://go.nasa.gov/cadre https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26426
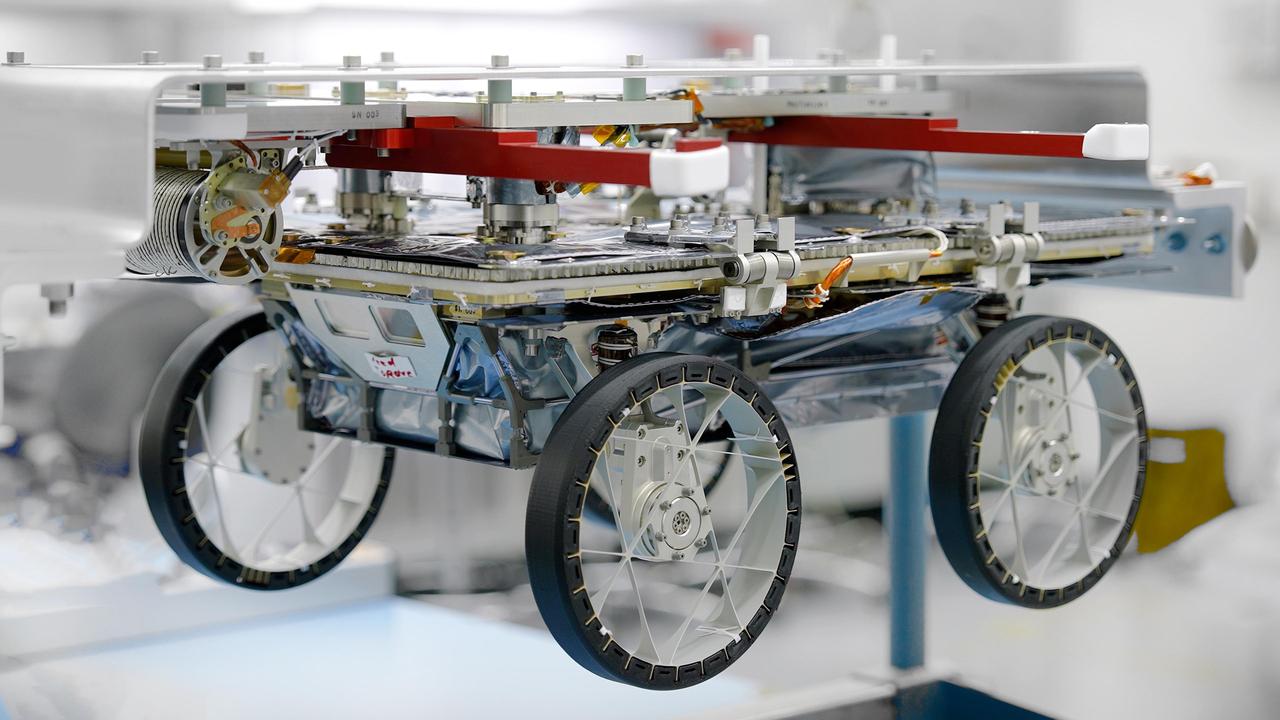
One of three small lunar rovers that are part of a NASA technology demonstration called CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration) is attached to a fixture in a clean room at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Jan. 29, 2025. Less than two weeks later, the rover had been packed up and shipped off in preparation for launch. CADRE aims to prove that a group of robots can collaborate to gather data without receiving direct commands from mission controllers on Earth. Its trio of rovers will use their cameras and ground-penetrating radars to send back imagery of the lunar surface and subsurface while testing out the novel software systems that enable them to work together as a team autonomously. Before embarking on the first leg of a multistage journey to the Moon, each rover was mated to its deployer system, which will lower it via tether from an Intuitive Machines lander onto the dusty lunar surface. Engineers flipped each rover-deployer pair over and attached it to an aluminum plate for safe transit. The rovers were then sealed into protective metal-frame enclosures that were fitted snuggly into metal shipping containers and loaded onto a truck for the drive to Intuitive Machines' Houston facility. A division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, JPL manages CADRE for the Game Changing Development program within NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate in Washington. The technology demonstration was selected under the agency's Lunar Surface Innovation Initiative, which was established to expedite the development of technologies for sustained presence on the lunar surface. CADRE will launch as a payload on the third lunar lander mission by Intuitive Machines, called IM-3, under NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, which is managed by the agency's Science Mission Directorate, also in Washington. The agency's Glenn Research Center in Cleveland and its Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley, California, both supported the project. Motiv Space Systems designed and built key hardware elements at the company's Pasadena facility. Clemson University in South Carolina contributed research in support of the project. For more about CADRE, go to: https://go.nasa.gov/cadre https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26428

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden at the Air Traffic Operations Lab , observed a simulation of cockpit technologies for the Air Traffic Management Demonstration-1 (ATD-1)
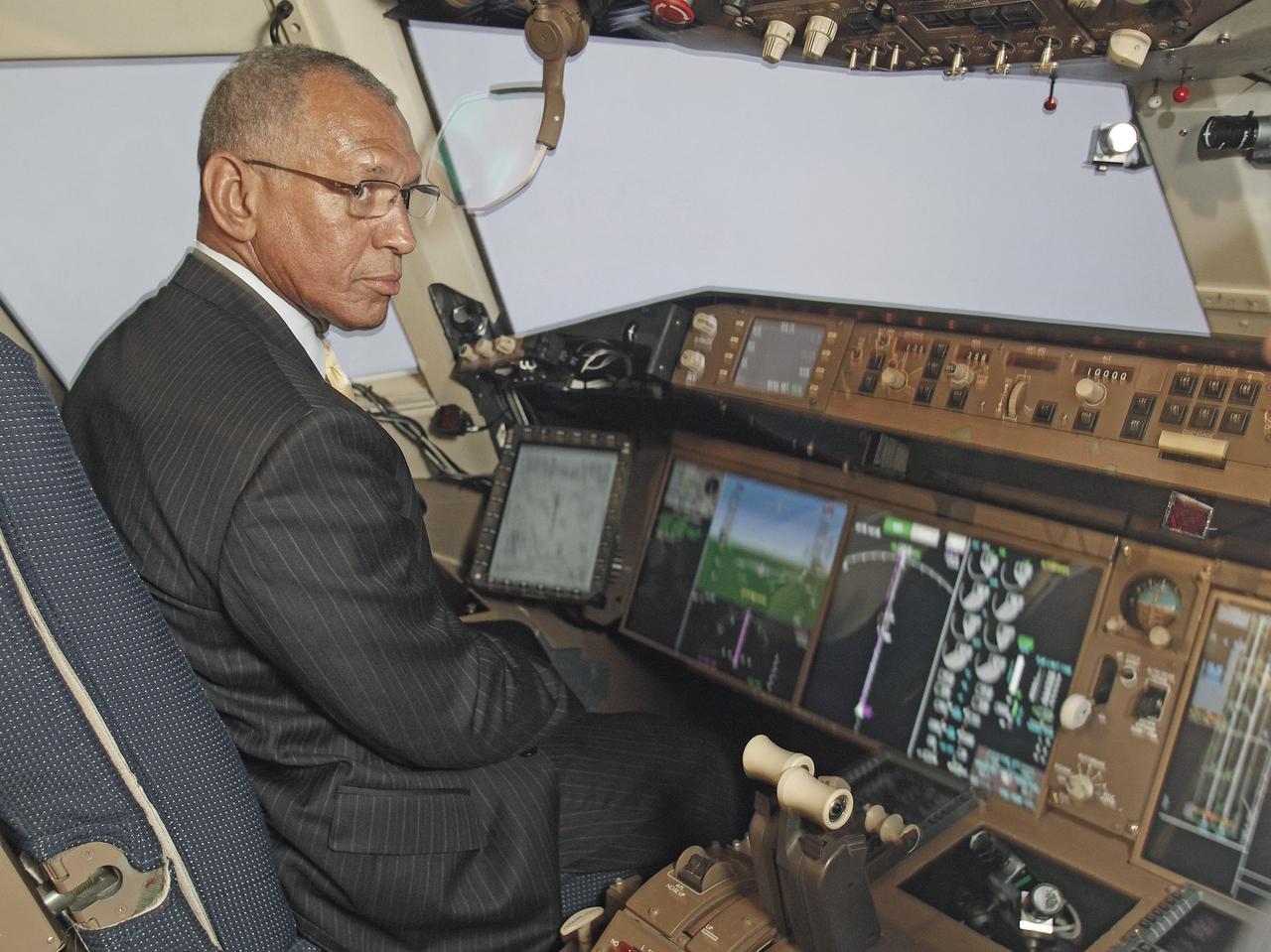

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden at the Air Traffic Operations Lab , observed a simulation of cockpit technologies for the Air Traffic Management Demonstration-1 (ATD-1)
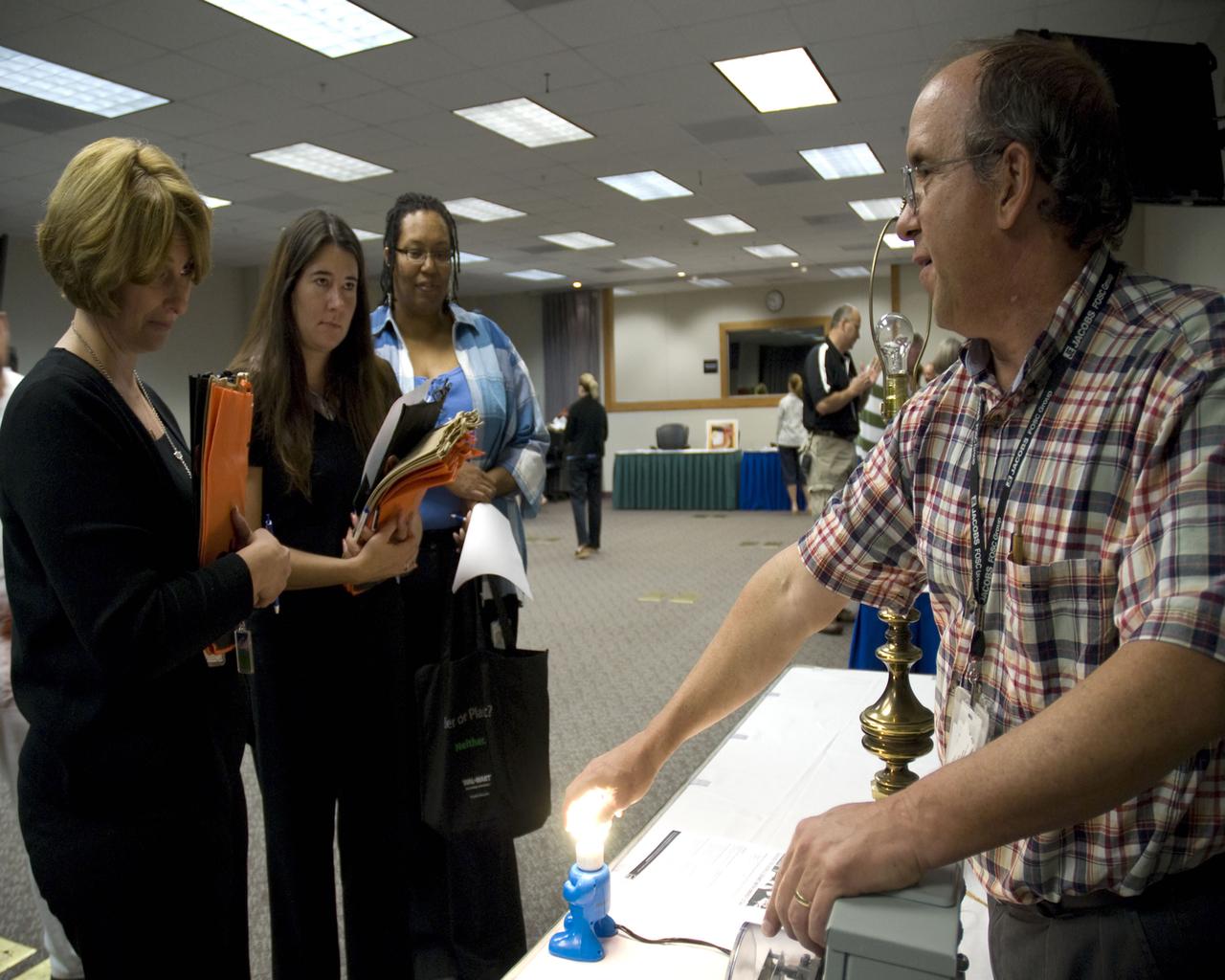

Donnie Thompson, site energy manager for the Jacobs Technology FOSC Group, demonstrates the efficiency of fluorescent bulbs during Energy Awareness Day at Stennis on Sept. 30.
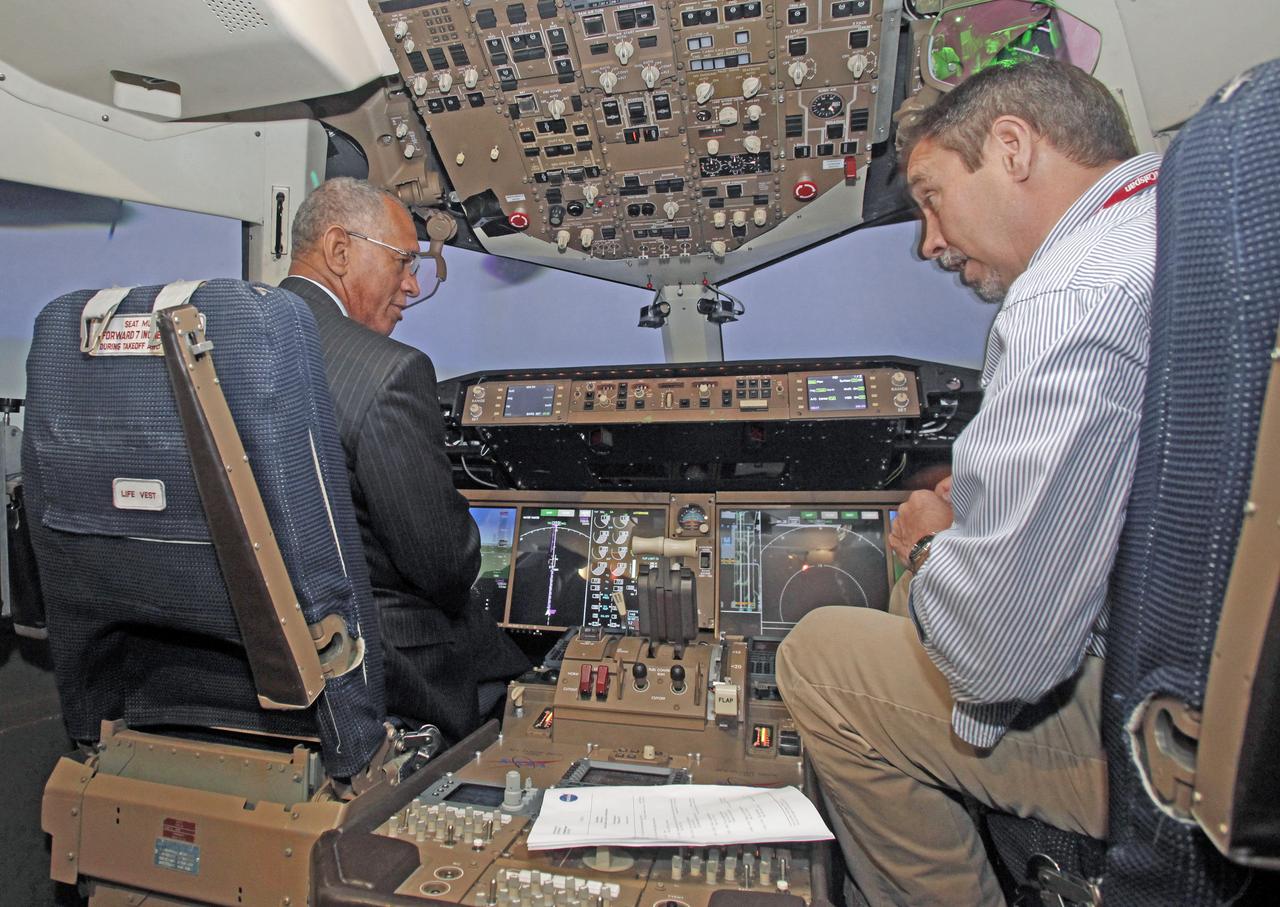

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden at the Air Traffic Operations Lab , observed a simulation of cockpit technologies for the Air Traffic Management Demonstration-1 (ATD-1)
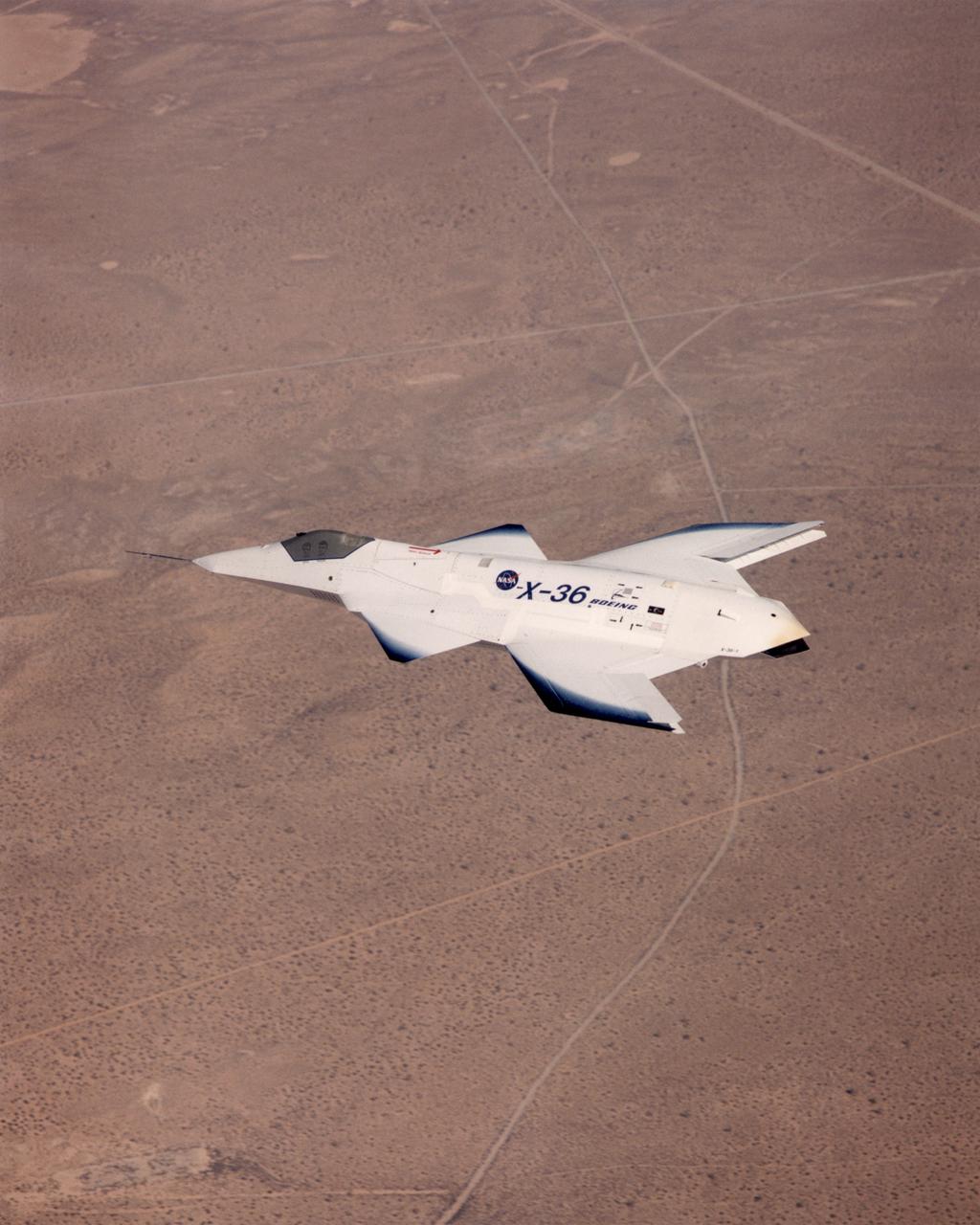

The tailless X-36 technology demonstrator research aircraft cruises over the California desert at low altitude during a 1997 research flight.
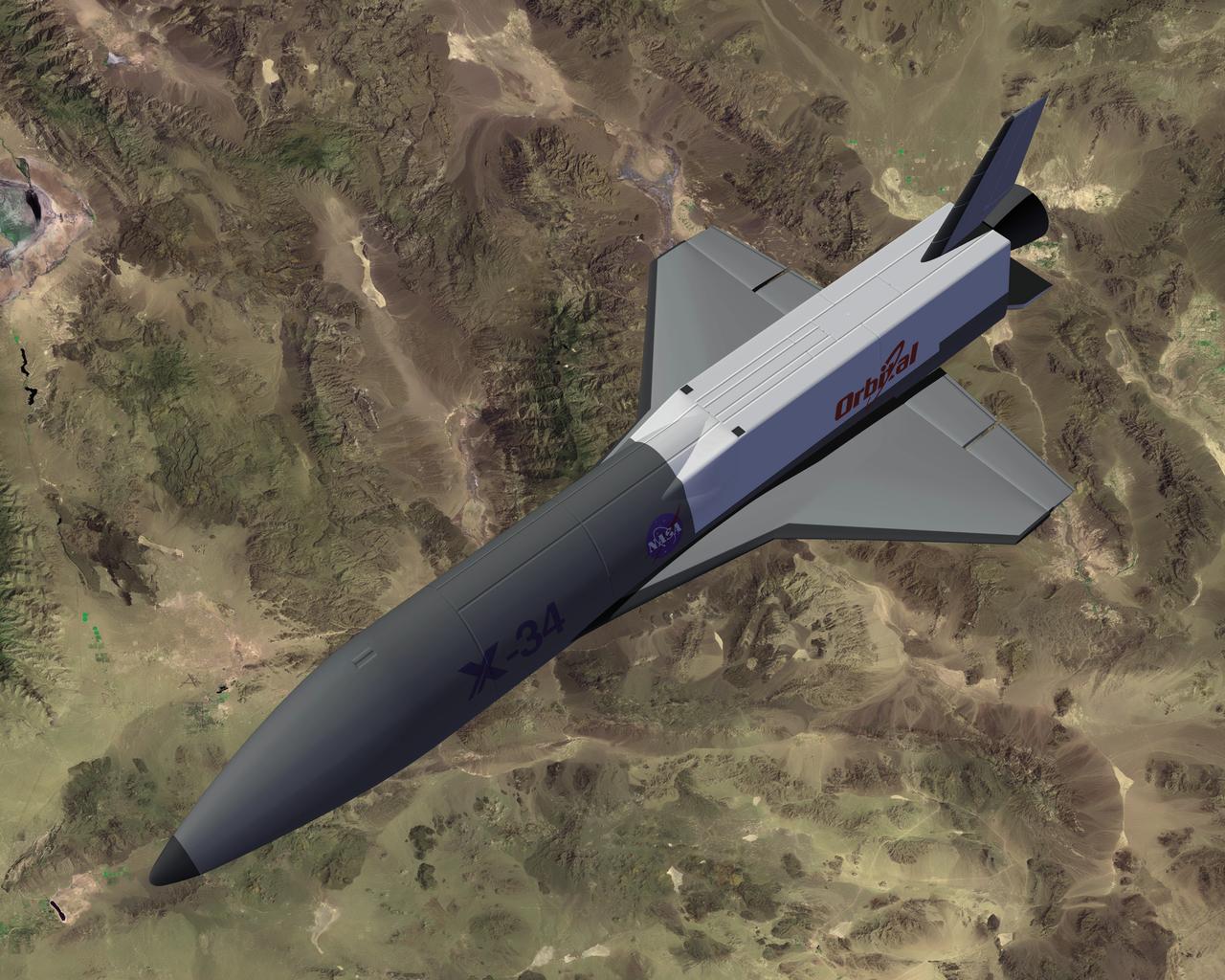

This artist's concept depicts the X-34 Demonstrator in flight. Part of the Pathfinder Program, the X-34 was a reusable technology testbed vehicle that was designed and built by the Marshall Space Flight Center to demonstrate technologies that were essential to lowering the cost of access to space. Powered by a LOX and RP-1 liquid Fastrac engine, the X-34 would be capable of speeds up to Mach 8 and altitudes of 250,000-feet. The X-34 program was cancelled in 2001.
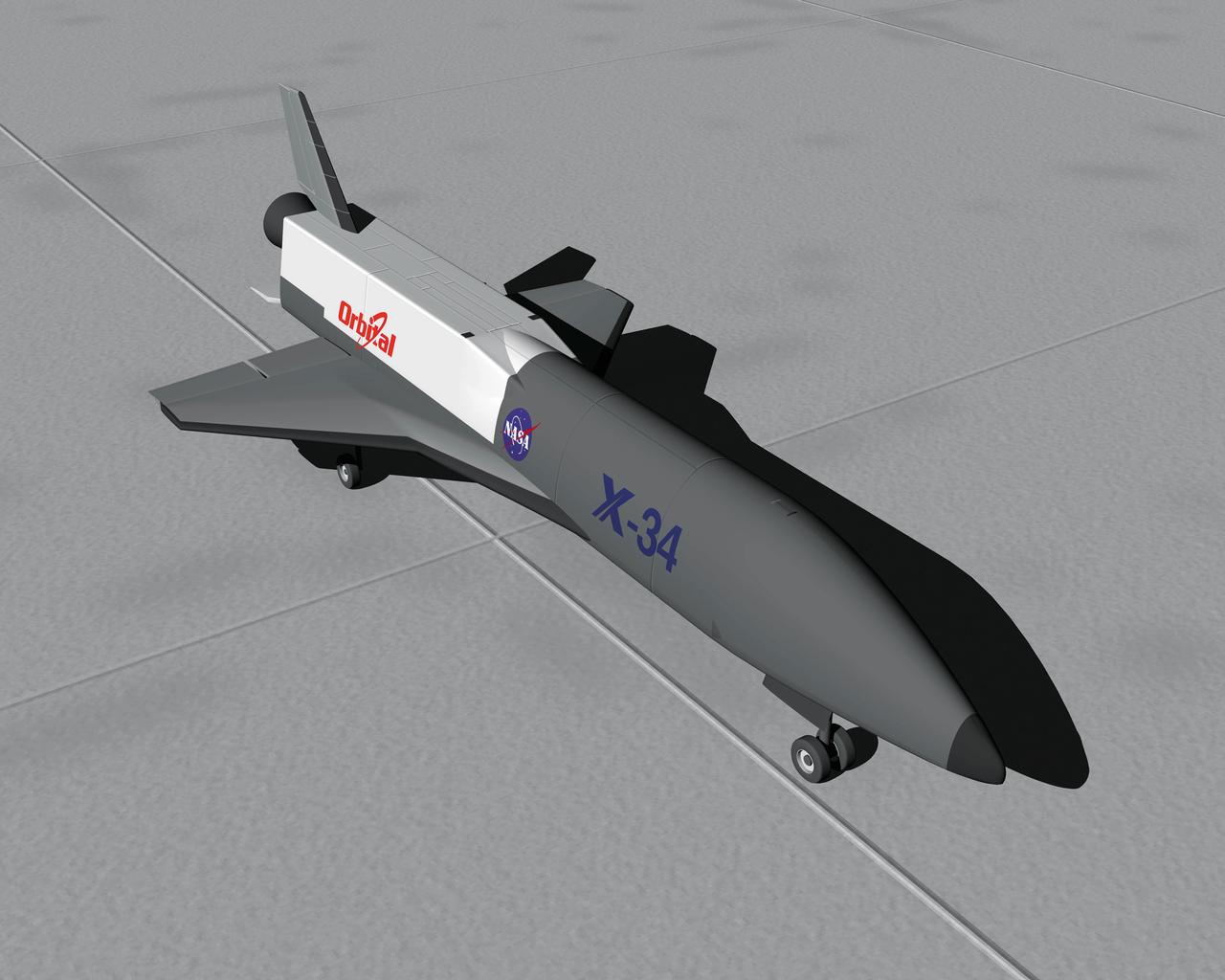

This artist's concept depicts the X-34 Demonstrator sitting on a runway. Part of the Pathfinder Program, the X-34 was a reusable technology testbed vehicle that was designed and built by the Marshall Space Flight Center to demonstrate technologies that were essential to lowering the cost of access to space. Powered by a LOX and RP-1 liquid Fastrac engine, the X-34 would be capable of speeds up to Mach 8 and altitudes of 250,000-feet. The X-34 program was cancelled in 2001.
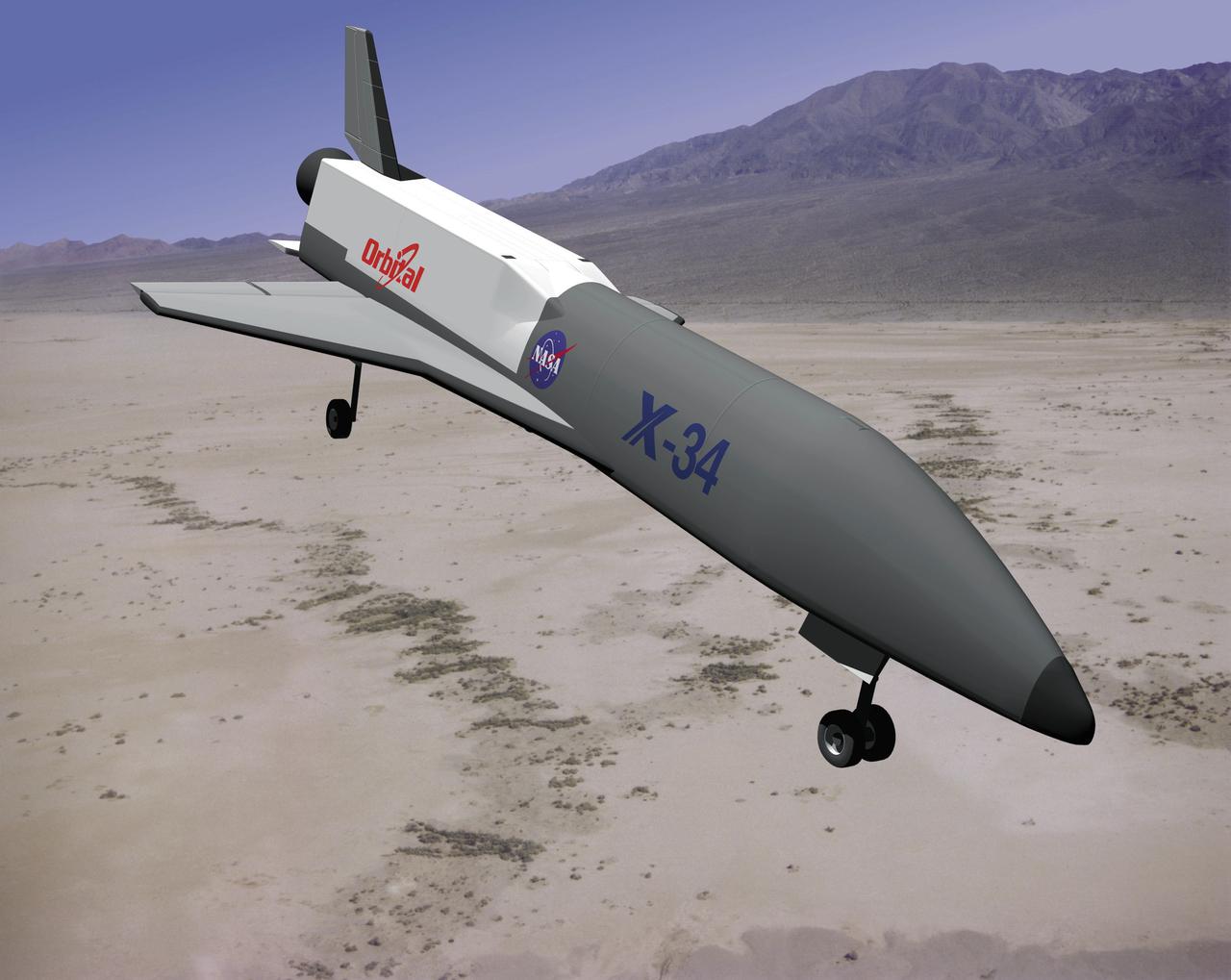

This artist's concept depicts the X-34 Demonstrator landing in a dessert. Part of the Pathfinder Program, the X-34 was a reusable technology testbed vehicle that was designed and built by the Marshall Space Flight Center to demonstrate technologies that were essential to lowering the cost of access to space. Powered by a LOX and RP-1 liquid Fastrac engine, the X-34 would be capable of speeds up to Mach 8 and altitudes of 250,000-feet. The X-34 program was cancelled in 2001.
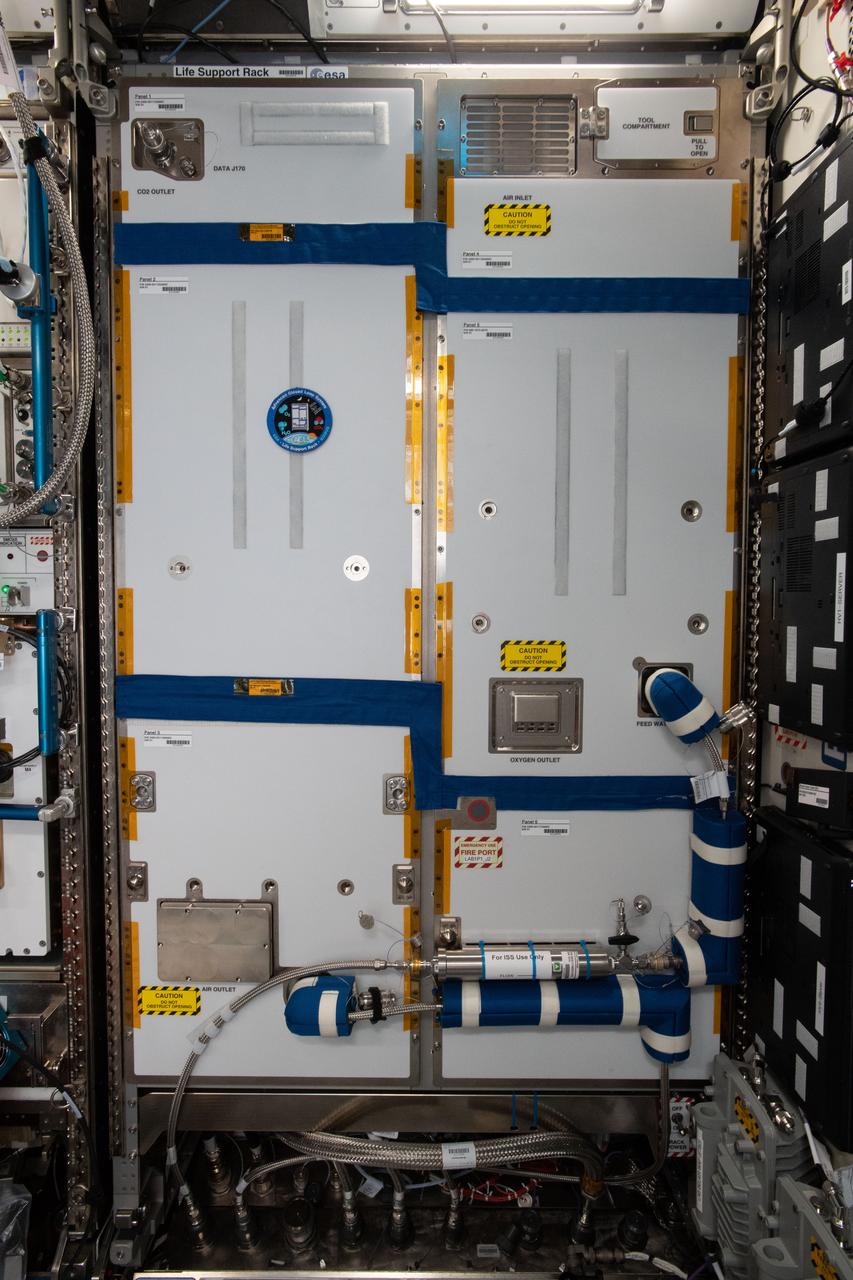

iss057e055217 (10/19/2018) --- A view of the LSR rack inside the Destiny laboratory onboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Life Support Rack (LSR) is a Technology Demonstrator for Closed Loop Air Revitalisation. LSR captures carbon dioxide from cabin air and recovers 50% of its oxygen for use by the astronauts. LSR operates for a minimum of one year on the International Space Station to demonstrate the robustness of the technology for future Exploration Missions.
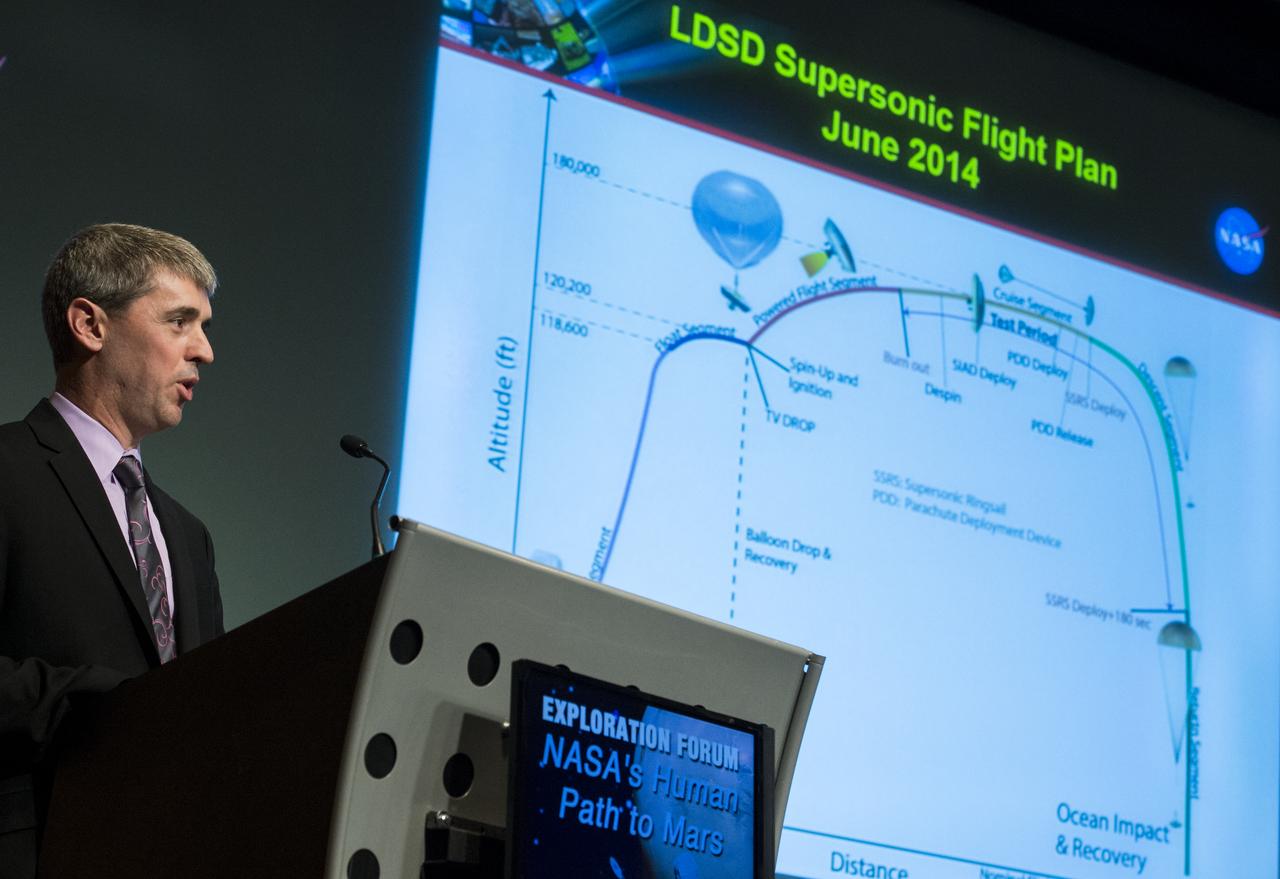
Randy Lillard, Program Executive for Technology Demonstration Missions of NASA's Space Technology Mission DIrectorate, speaks about the upcoming Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator demonstration during an Exploration Forum showcasing NASA's human exploration path to Mars in the James E. Webb Auditorium at NASA Headquarters on Tuesday, April 29, 2014. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
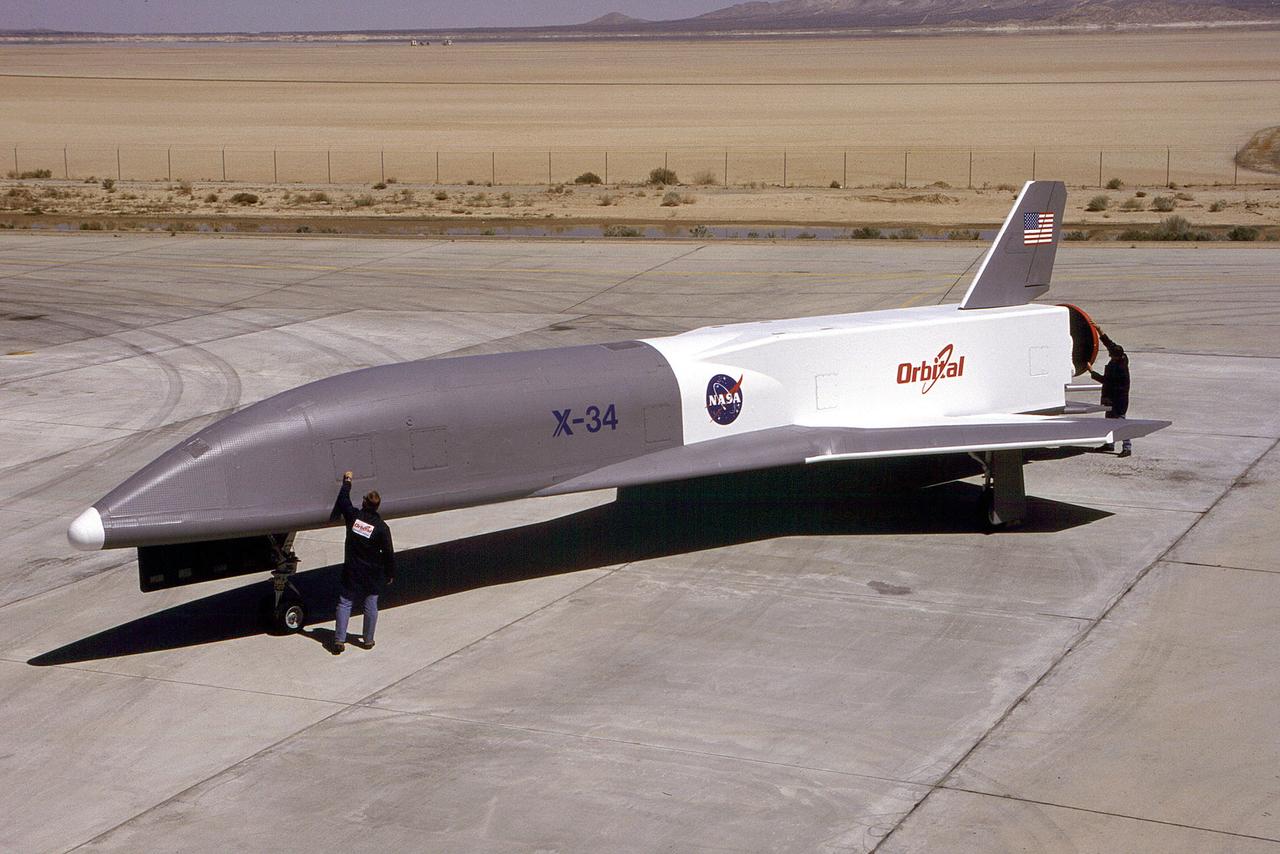

Pictured is the X-34 Demonstrator parked on the runway. Part of the Pathfinder Program, the X-34 was a reusable technology testbed vehicle that was designed and built by the Marshall Space Flight Center to demonstrate technologies that are essential to lowering the cost of access to space. Powered by a LOX and RP-1 liquid Fastrac engine, the X-34 would be capable of speeds up to Mach 8 and altitudes of 250,000-feet. The X-34 program was cancelled in 2001.
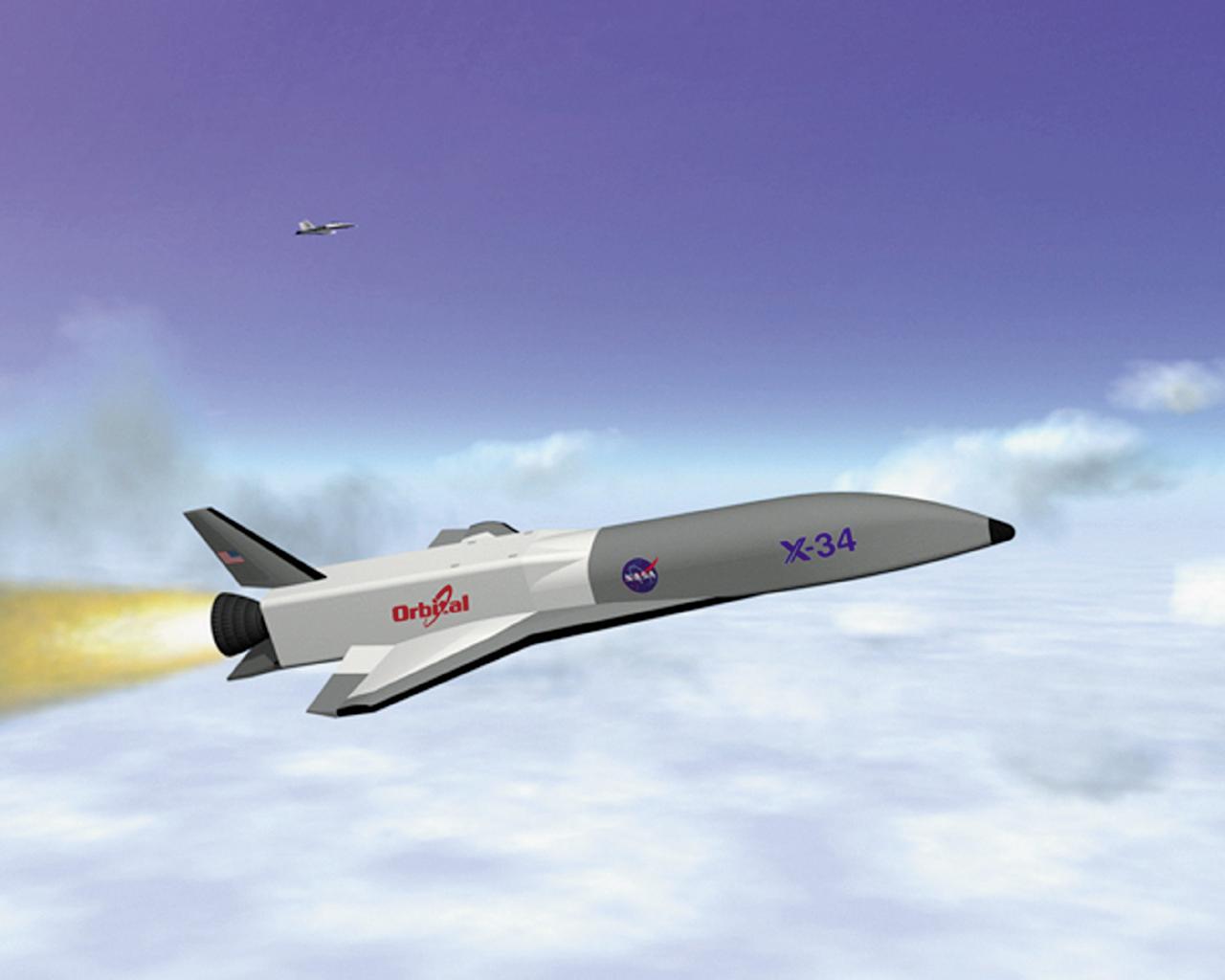

This artist's concept depicts the X-34 Demonstrator in flight. Part of the Pathfinder Program, the X-34 was a reusable technology testbed vehicle that was designed and built by the Marshall Space Flight Center to demonstrate technologies that were essential to lowering the cost of access to space. Powered by a LOX and RP-1 liquid Fastrac engine, the X-34 would be capable of speeds up to Mach 8 and altitudes of 250,000-feet. The X-34 program was cancelled in 2001.
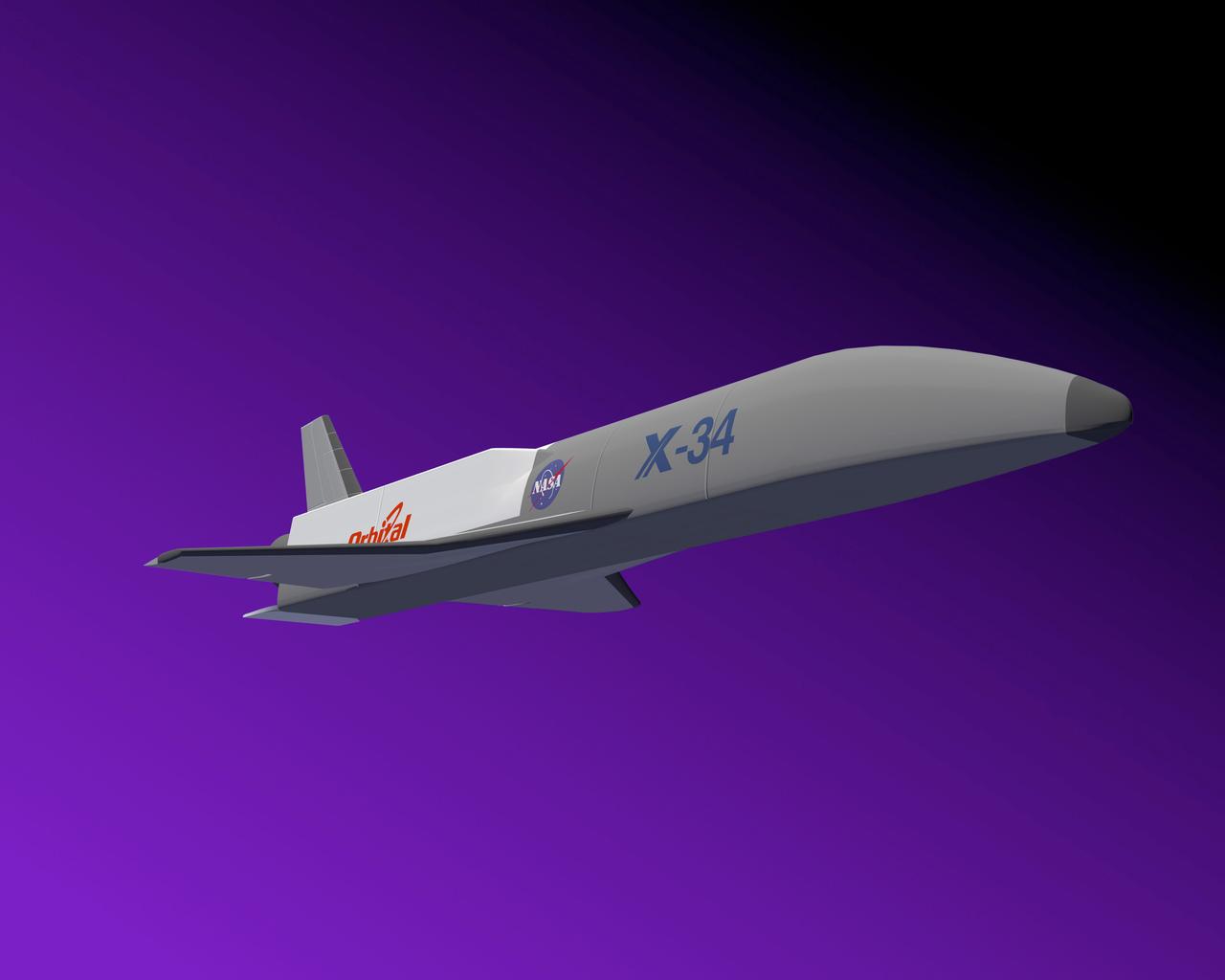

This is an artist's concept of the X-34 Demonstrator, a reusable technology testbed vehicle that was designed to demonstrate technologies that were essential to lowering the cost of access to space. Powered by a LOX and RP-1 liquid Fastrac engine that was designed and built by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the X-34 would be capable of speeds up to Mach 8 and altitudes of 250,000-feet. The X-34 program was cancelled in 2001.