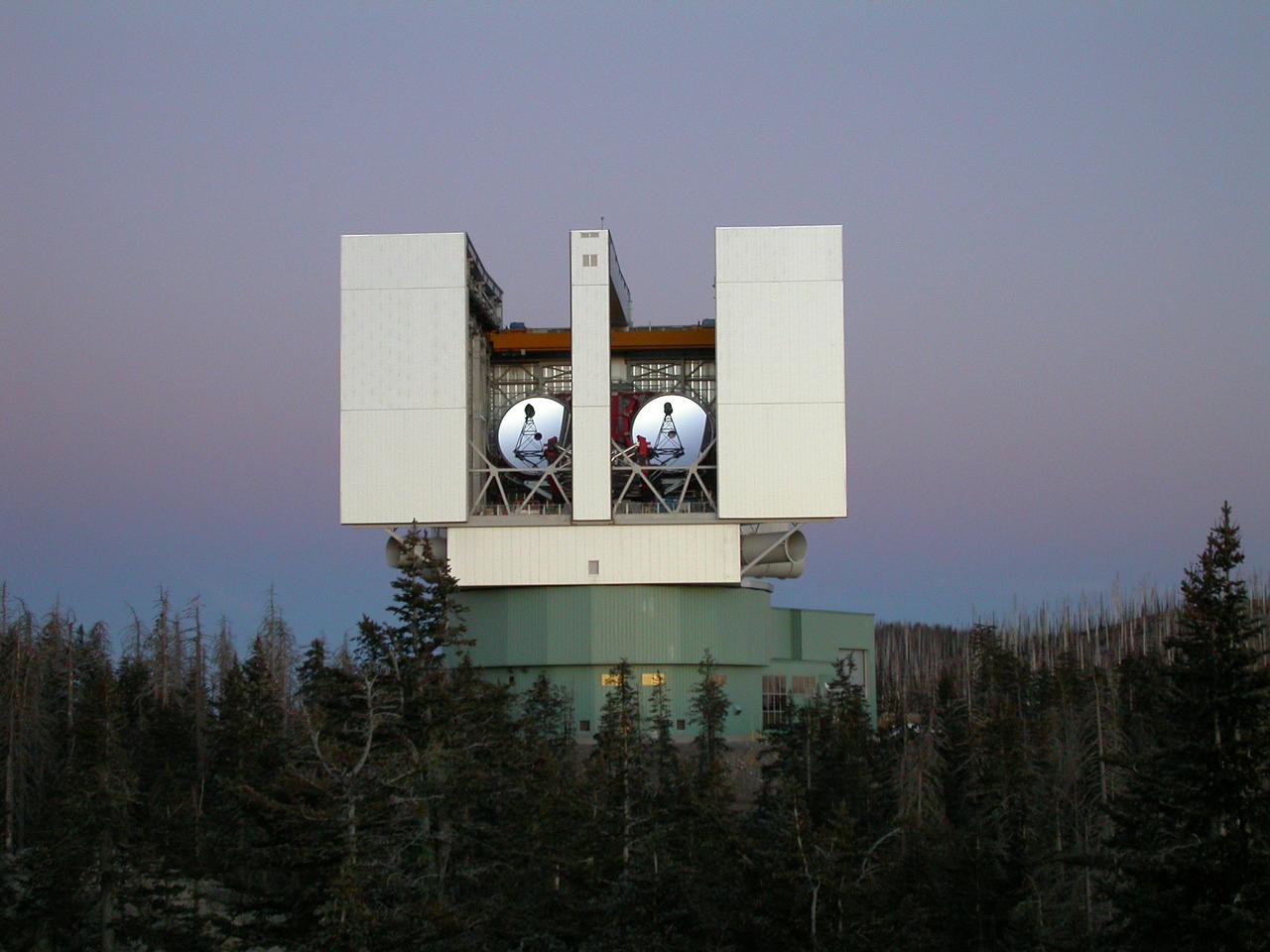

The Large Binocular Telescope Interferometer, or LBTI, is a ground-based instrument connecting two 8-meter class telescopes on Mount Graham in Arizona to form the largest single-mount telescope in the world. The interferometer is designed to detect and study stars and planets outside our solar system. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22354
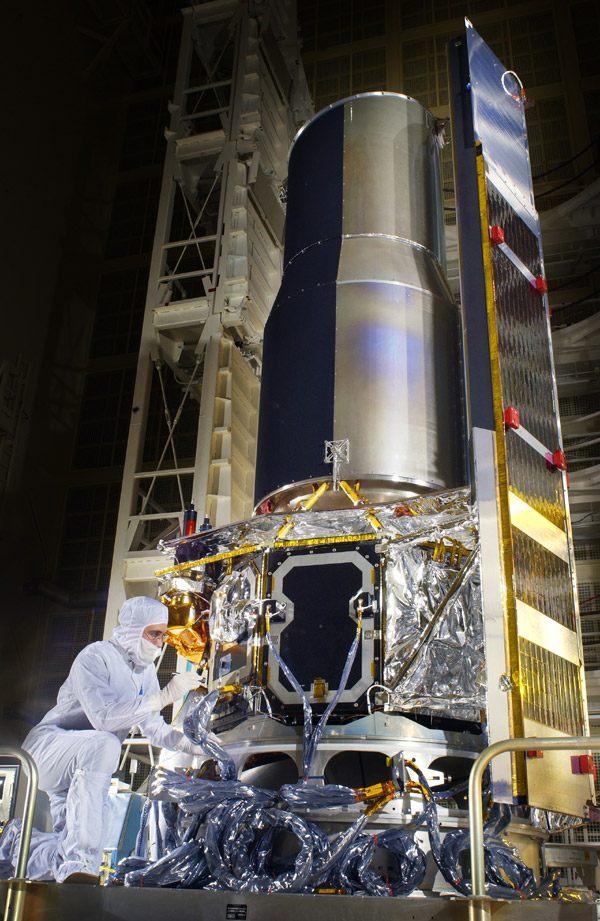

Technicians put final touches on NASA Space Infrared Telescope Facility at Lockheed Martin Aeronautics in Sunnyvale, Calif., which launched on August 25, 2003. The telescope is now known as the Spitzer Space Telescope.
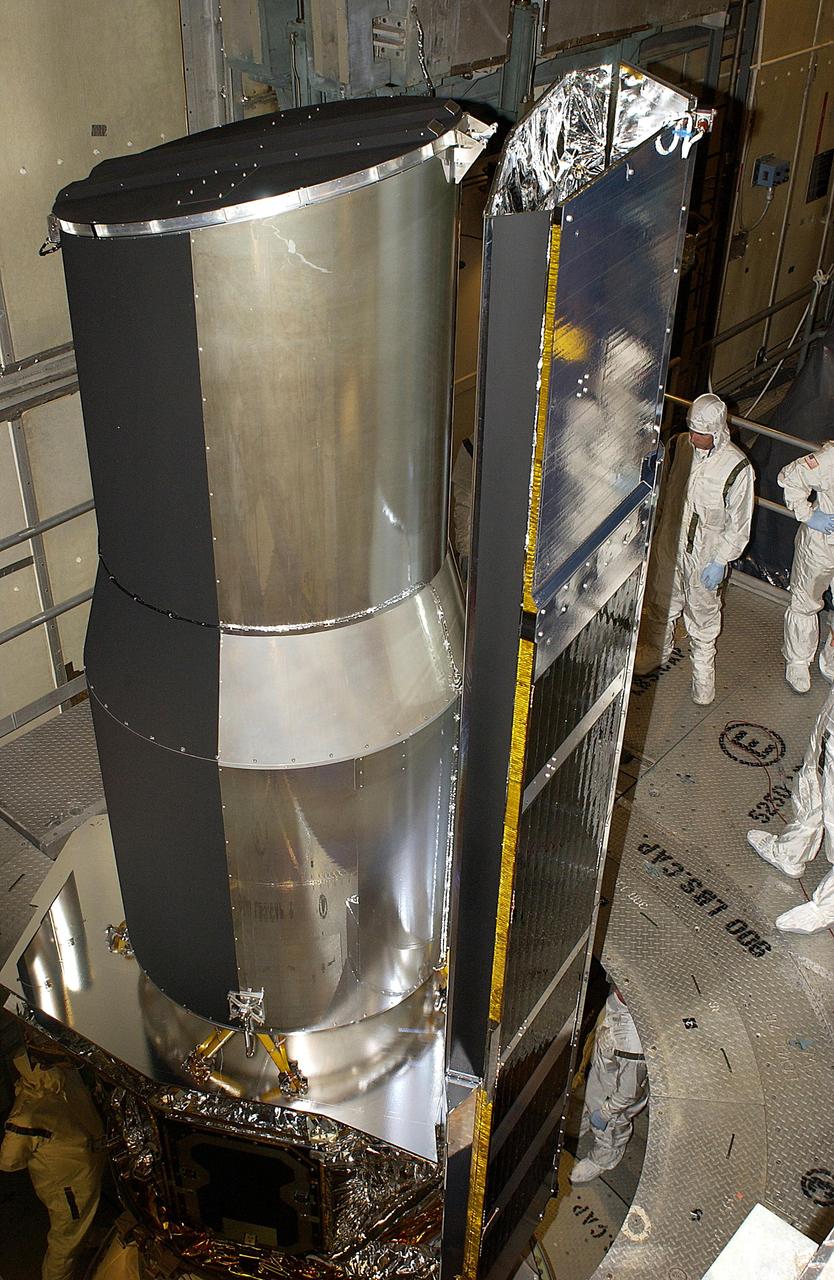

The Spitzer Space Telescope (formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility or SIRTF) is readied for launch at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, in 2003. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23644

Saturn from Far and Near Hubble Space Telescope

Hubble Space Telescope Resolves Volcanoes on Io
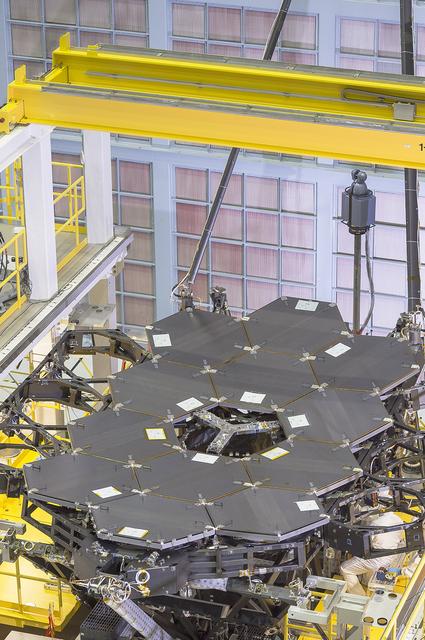

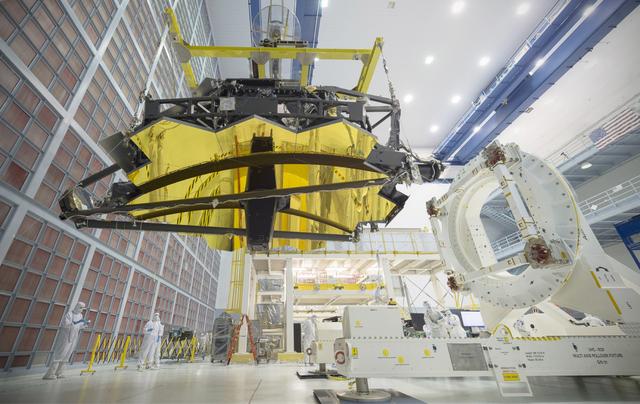
A view of the one dozen (out of 18) flight mirror segments that make up the primary mirror on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have been installed at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn More: Since December 2015, the team of scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to install all the primary mirror segments onto the telescope structure in the large clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The twelfth mirror was installed on January 2, 2016. "This milestone signifies that all of the hexagonal shaped mirrors on the fixed central section of the telescope structure are installed and only the 3 mirrors on each wing are left for installation," said Lee Feinberg, NASA's Optical Telescope Element Manager at NASA Goddard. "The incredibly skilled and dedicated team assembling the telescope continues to find ways to do things faster and more efficiently." Each hexagonal-shaped segment measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). After being pieced together, the 18 primary mirror segments will work together as one large 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) mirror. The primary mirror will unfold and adjust to shape after launch. The mirrors are made of ultra-lightweight beryllium. The mirrors are placed on the telescope's backplane using a robotic arm, guided by engineers. The full installation is expected to be completed in a few months. The mirrors were built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. Ball is the principal subcontractor to Northrop Grumman for the optical technology and lightweight mirror system. The installation of the mirrors onto the telescope structure is performed by Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York. Harris Corporation leads integration and testing for the telescope. While the mirror assembly is a very significant milestone, there are many more steps involved in assembling the Webb telescope. The primary mirror and the tennis-court-sized sunshield are the largest and most visible components of the Webb telescope. However, there are four smaller components that are less visible, yet critical. The instruments that will fly aboard Webb - cameras and spectrographs with detectors able to record extremely faint signals — are part of the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), which is currently undergoing its final cryogenic vacuum test and will be integrated with the mirror later this year.
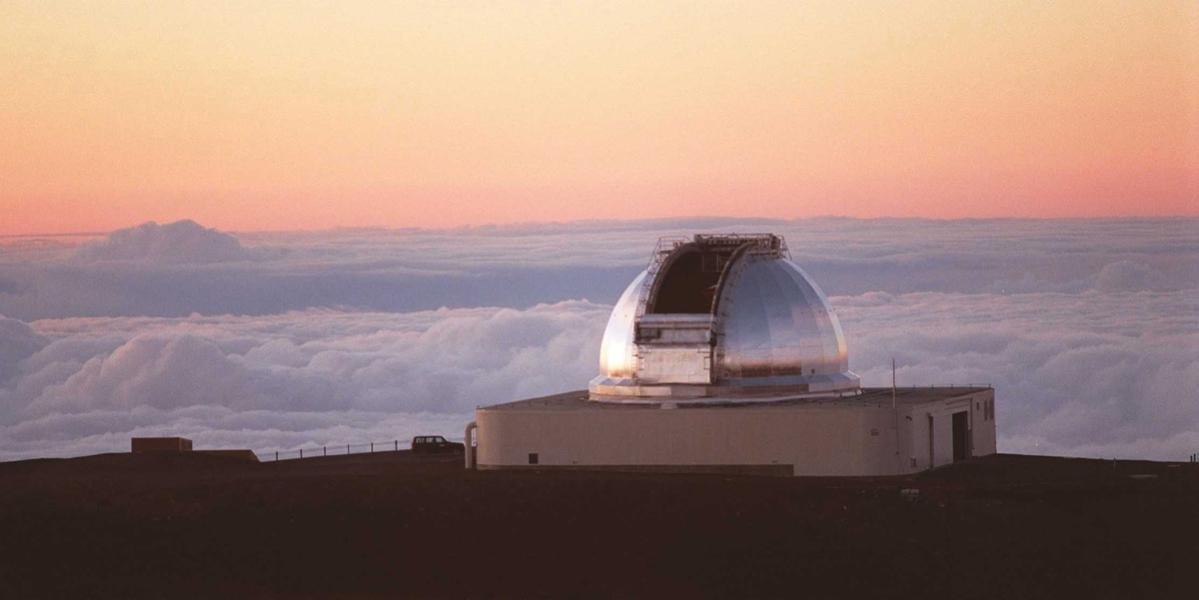

NASA Infrared Telescope Facility atop Mauna Kea, Hawaii. The IRTF is a venerable 30-year-old, 3-meter-diameter 10-foot telescope that ranks 40th among ground-based telescopes.

In this artist's rendering of NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope in space, the background is shown in infrared light. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23643
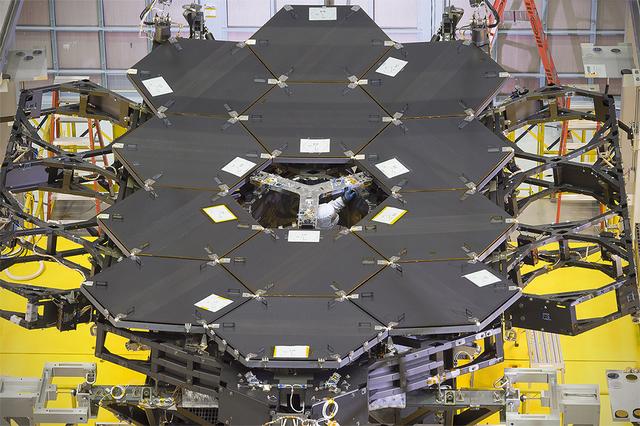

Caption: One dozen (out of 18) flight mirror segments that make up the primary mirror on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have been installed at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn More: Since December 2015, the team of scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to install all the primary mirror segments onto the telescope structure in the large clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The twelfth mirror was installed on January 2, 2016. "This milestone signifies that all of the hexagonal shaped mirrors on the fixed central section of the telescope structure are installed and only the 3 mirrors on each wing are left for installation," said Lee Feinberg, NASA's Optical Telescope Element Manager at NASA Goddard. "The incredibly skilled and dedicated team assembling the telescope continues to find ways to do things faster and more efficiently." Each hexagonal-shaped segment measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). After being pieced together, the 18 primary mirror segments will work together as one large 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) mirror. The primary mirror will unfold and adjust to shape after launch. The mirrors are made of ultra-lightweight beryllium. The mirrors are placed on the telescope's backplane using a robotic arm, guided by engineers. The full installation is expected to be completed in a few months. The mirrors were built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. Ball is the principal subcontractor to Northrop Grumman for the optical technology and lightweight mirror system. The installation of the mirrors onto the telescope structure is performed by Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York. Harris Corporation leads integration and testing for the telescope. While the mirror assembly is a very significant milestone, there are many more steps involved in assembling the Webb telescope. The primary mirror and the tennis-court-sized sunshield are the largest and most visible components of the Webb telescope. However, there are four smaller components that are less visible, yet critical. The instruments that will fly aboard Webb - cameras and spectrographs with detectors able to record extremely faint signals — are part of the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), which is currently undergoing its final cryogenic vacuum test and will be integrated with the mirror later this year.

Jupiter Upper Atmospheric Winds Revealed in Ultraviolet Images by Hubble Telescope
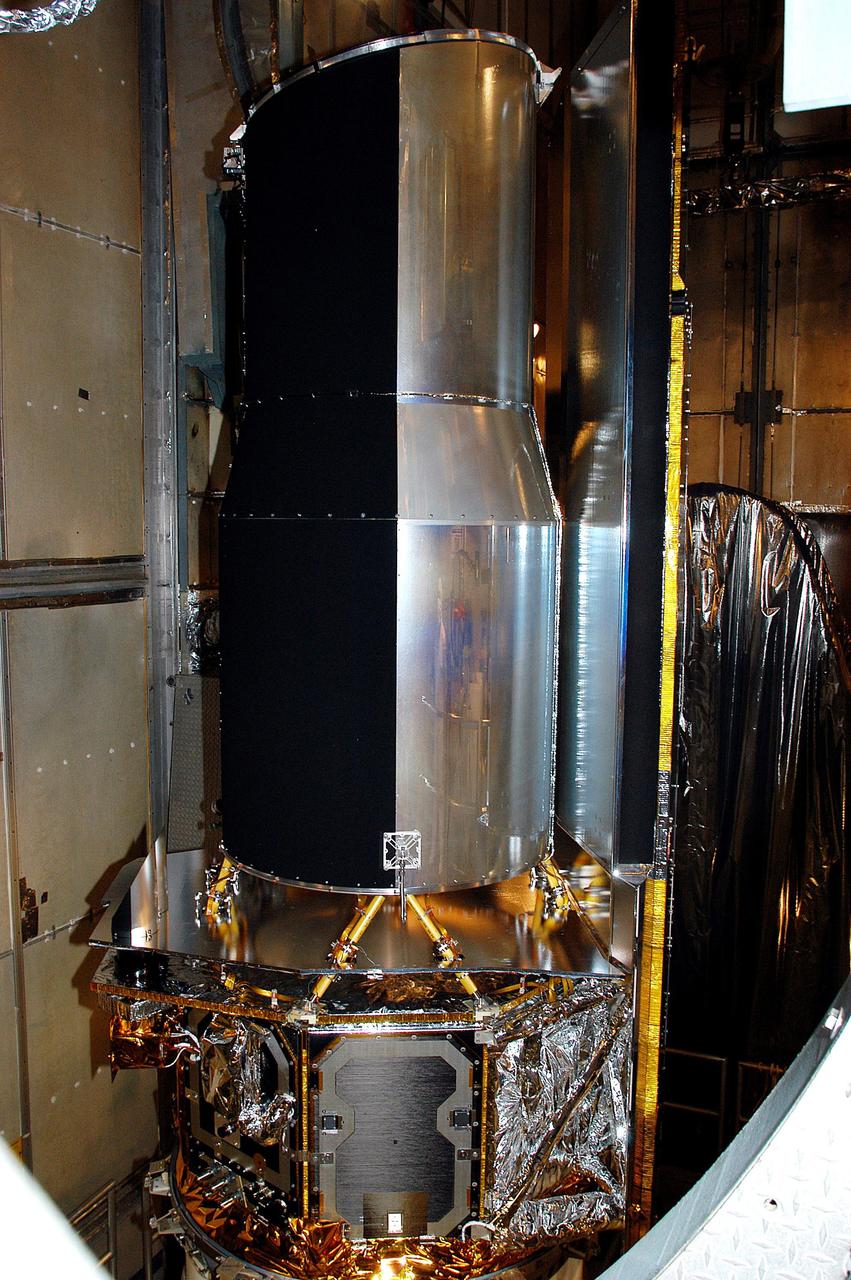

At the time of launch, the Spitzer Space Telescope bore its original name: the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF). It's shown here in the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, waiting for encapsulation. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23649
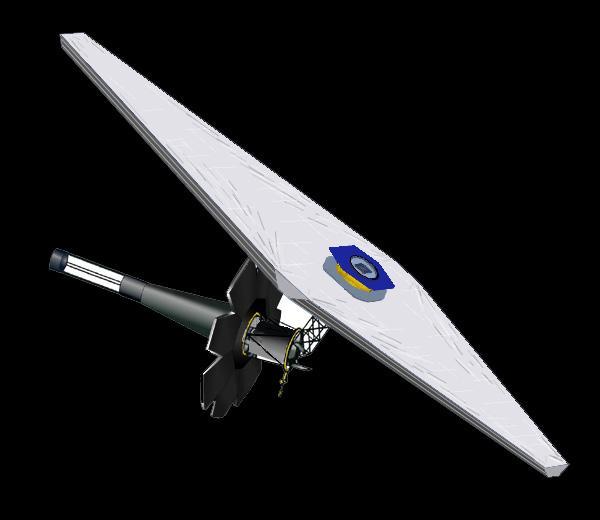

Artist concept of Next Generation Space Telescope from December, 2002. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04243
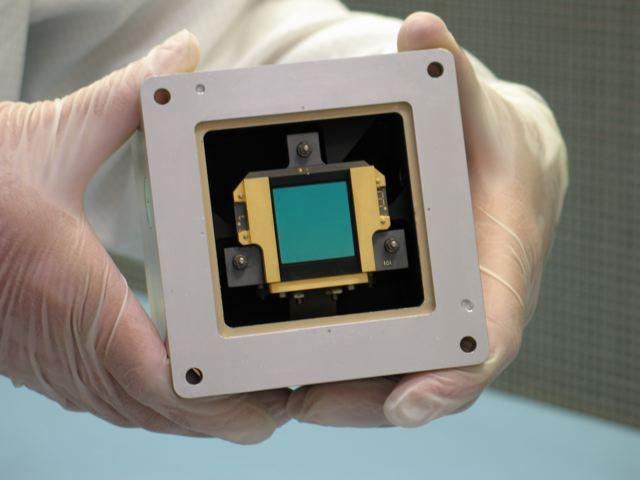
This image shows a model of one of three detectors for the Mid-Infrared Instrument on NASA James Webb Space Telescope.
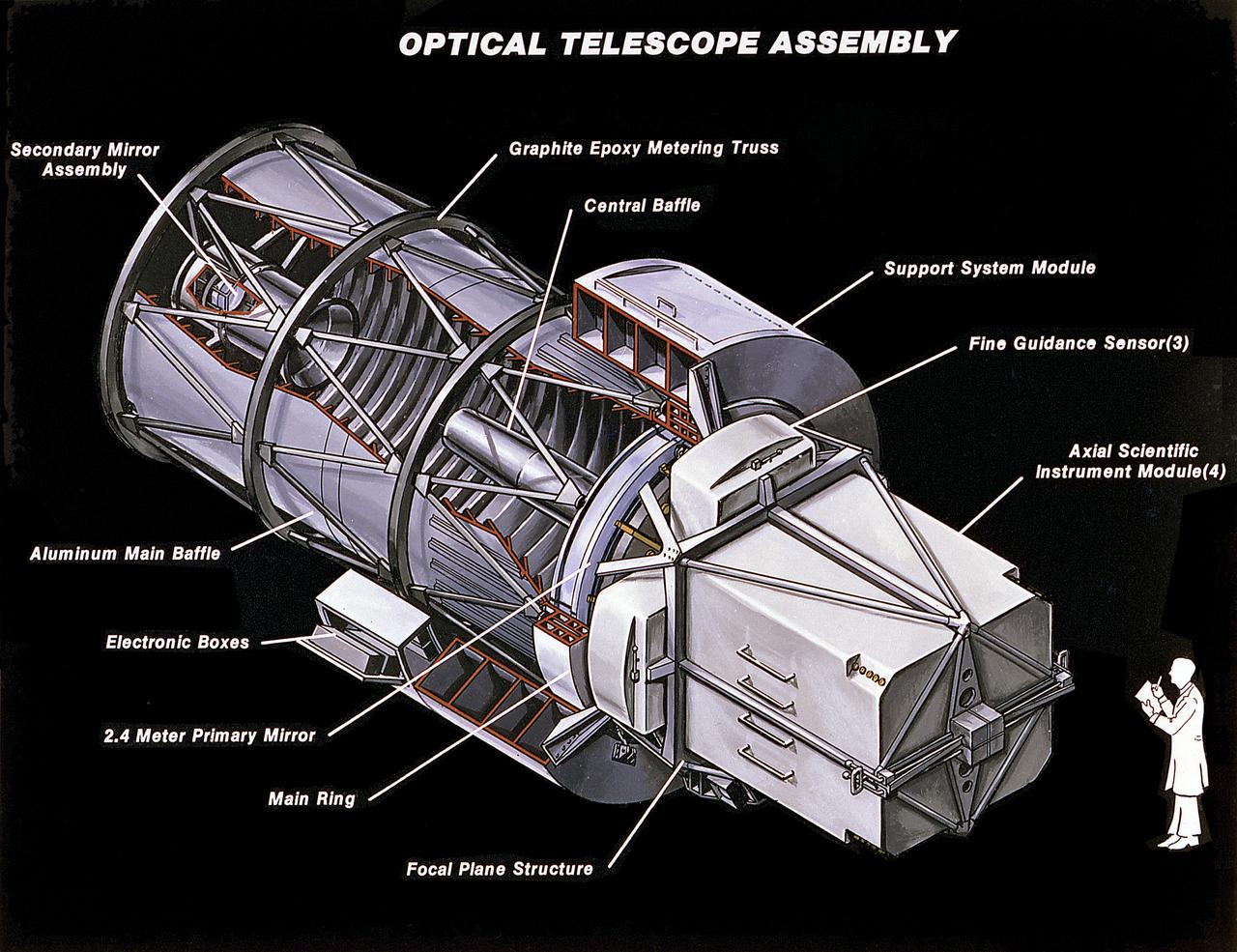
This image illustrates the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA). One of the three major elements of the HST, the OTA consists of two mirrors (a primary mirror and a secondary mirror), support trusses, and the focal plane structure. The mirrors collect and focus light from selected celestial objects and are housed near the center of the telescope. The primary mirror captures light from objects in space and focuses it toward the secondary mirror. The secondary mirror redirects the light to a focal plane where the Scientific Instruments are located. The primary mirror is 94.5 inches (2.4 meters) in diameter and the secondary mirror is 12.2 inches (0.3 meters) in diameter. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth Orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from the Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The spacecraft is 42.5 feet (13 meters) long and weighs 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
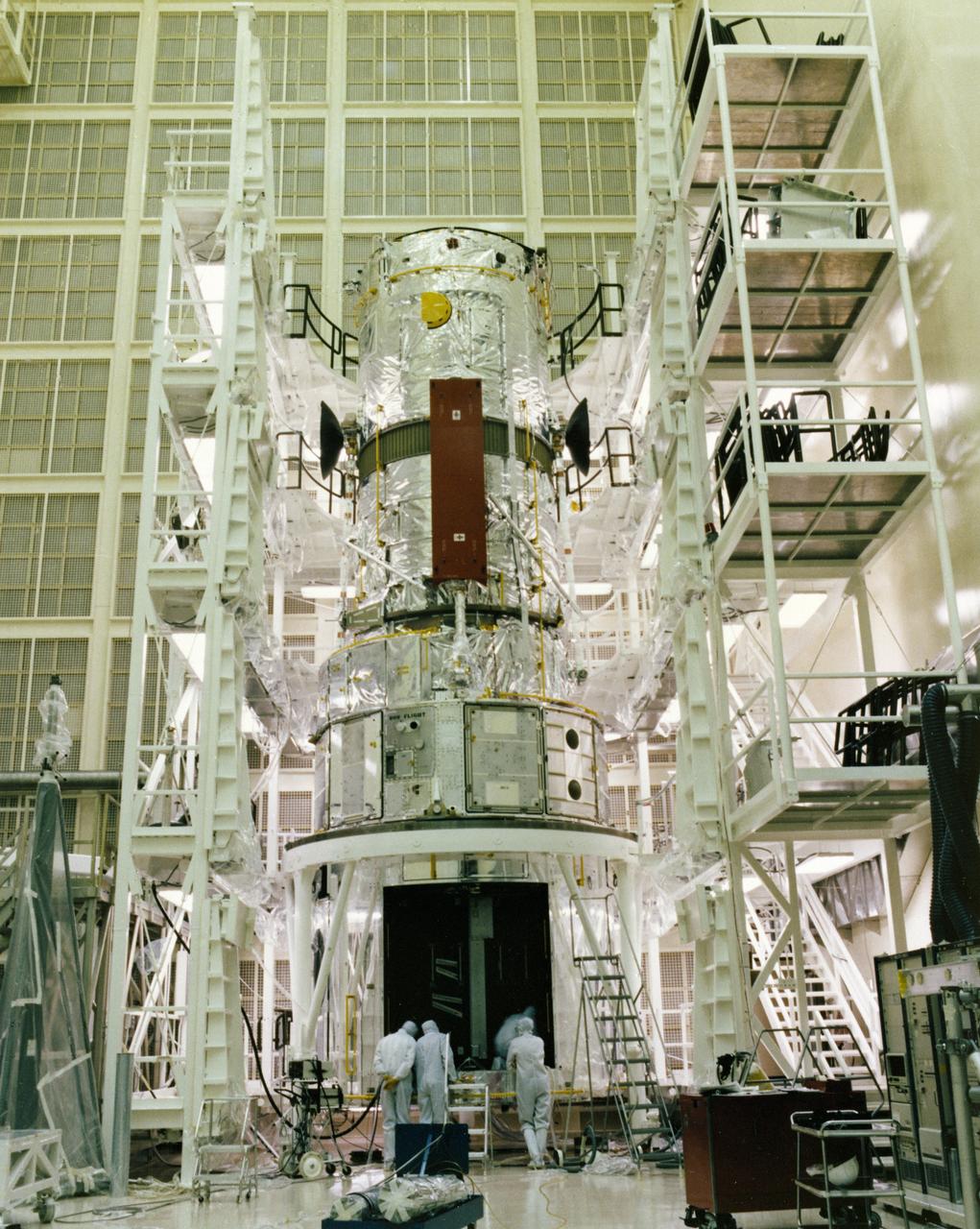
This photograph shows the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) flight article assembly with multilayer insulation, high gain anterna, and solar arrays in a clean room of the Lockheed Missile and Space Company. The HST is the first of NASA's great observatories and the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made. The purpose of the HST is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit by placing the telescope in space, enabling astronomers to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had overall responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company, Sunnyvale, California, produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
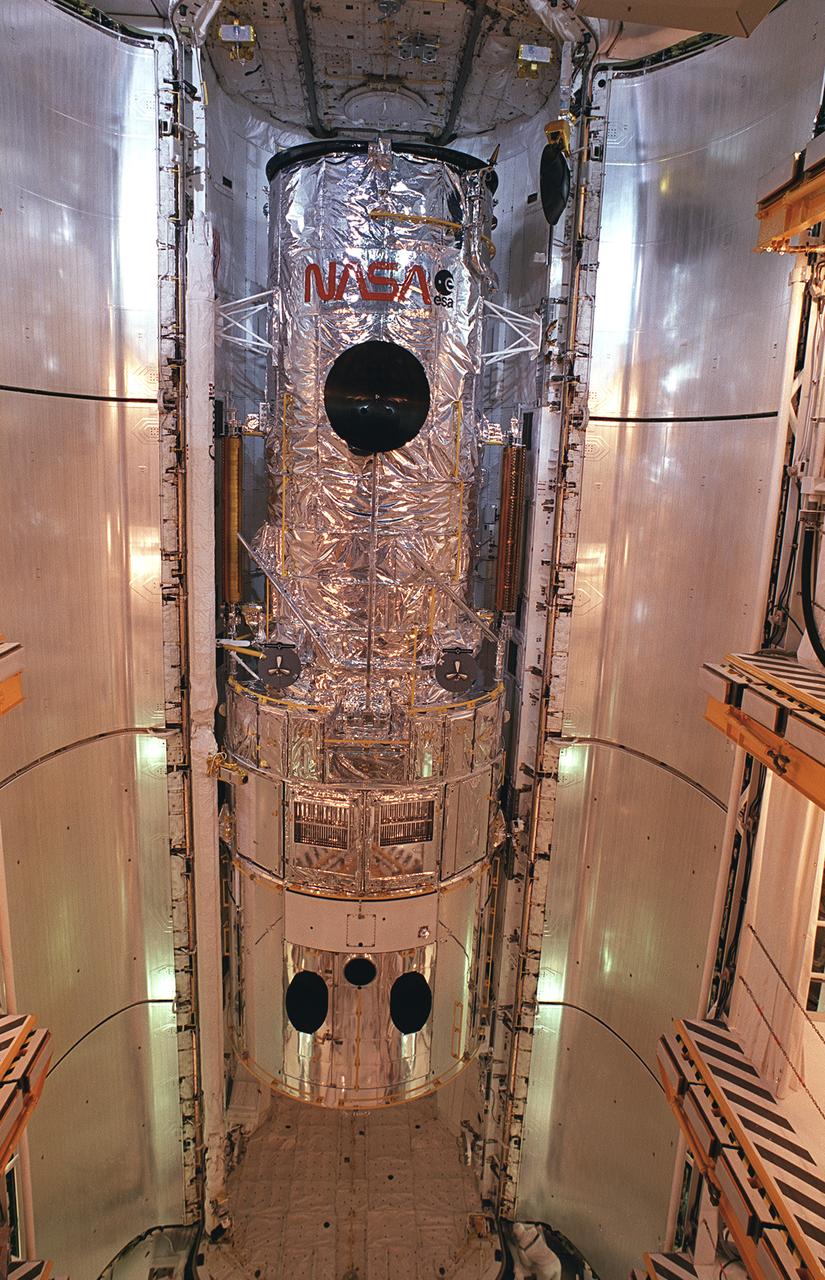

This photograph shows the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) installed in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery for the STS-31 Mission at The Kennedy Space Center prior to launch on April 24, 1990. The HST is the first of NASA's great observatories and the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made. The purpose of the HST is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit by placing the telescope in space, enabling astronomers to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The Marshall Space Flight Center had overall responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company, Sunnyvale, California, produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.

This is an artist's concept of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than is visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is approximately the size of a railroad car, with two cylinders joined together and wrapped in a silvery reflective heat shield blanket. Wing-like solar arrays extend horizontally from each side of these cylinders, and dish-shaped anternas extend above and below the body of the telescope. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
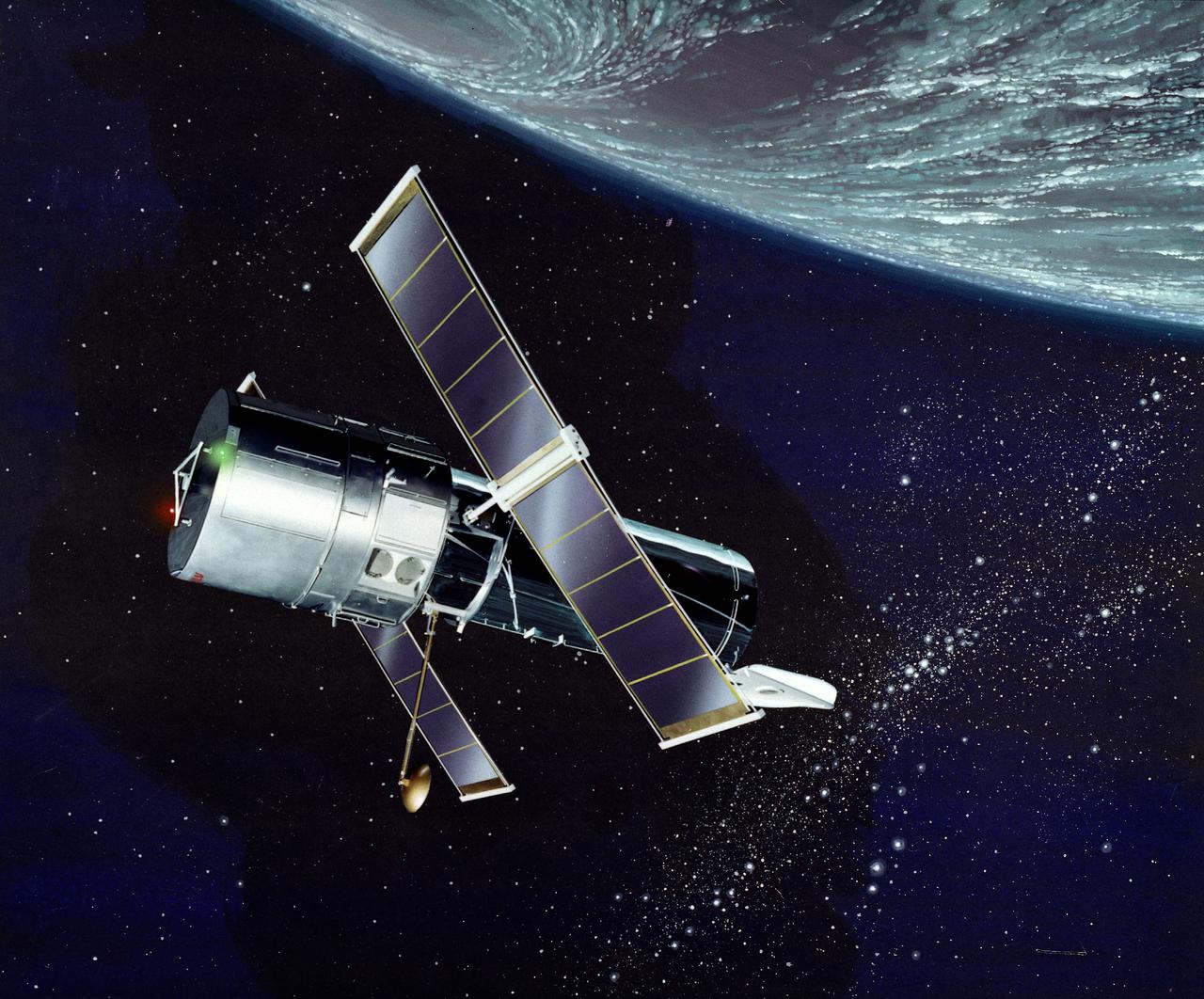

This illustration depicts a side view of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is approximately the size of a railroad car, with two cylinders joined together and wrapped in a silvery reflective heat shield blanket. Wing-like solar arrays extend horizontally from each side of these cylinders, and dish-shaped anternas extend above and below the body of the telescope. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
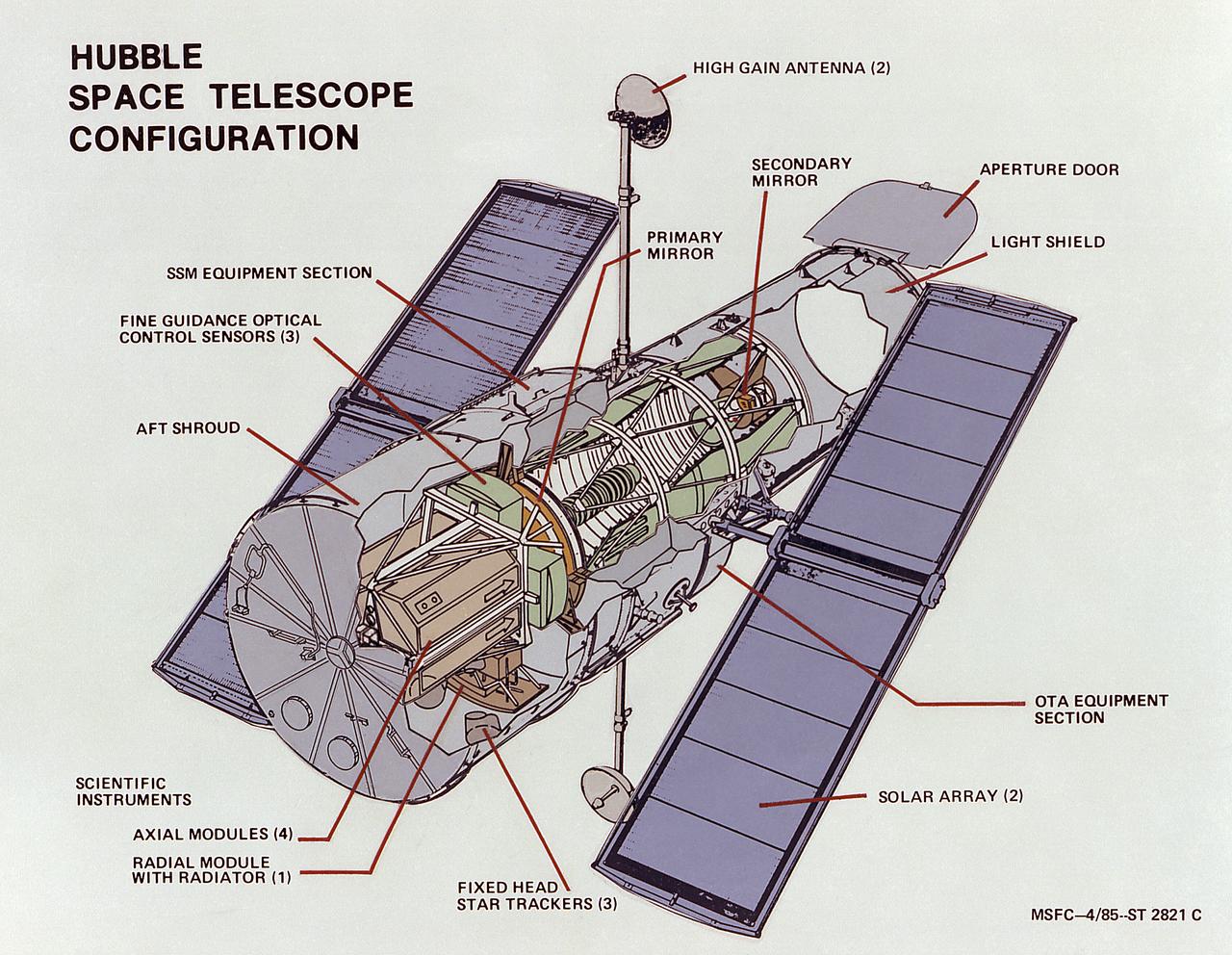
This image illustrates the overall Hubble Space Telescope (HST) configuration. The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is approximately the size of a railroad car, with two cylinders joined together and wrapped in a silvery reflective heat shield blanket. Wing-like solar arrays extend horizontally from each side of these cylinders, and dish-shaped anternas extend above and below the body of the telescope. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
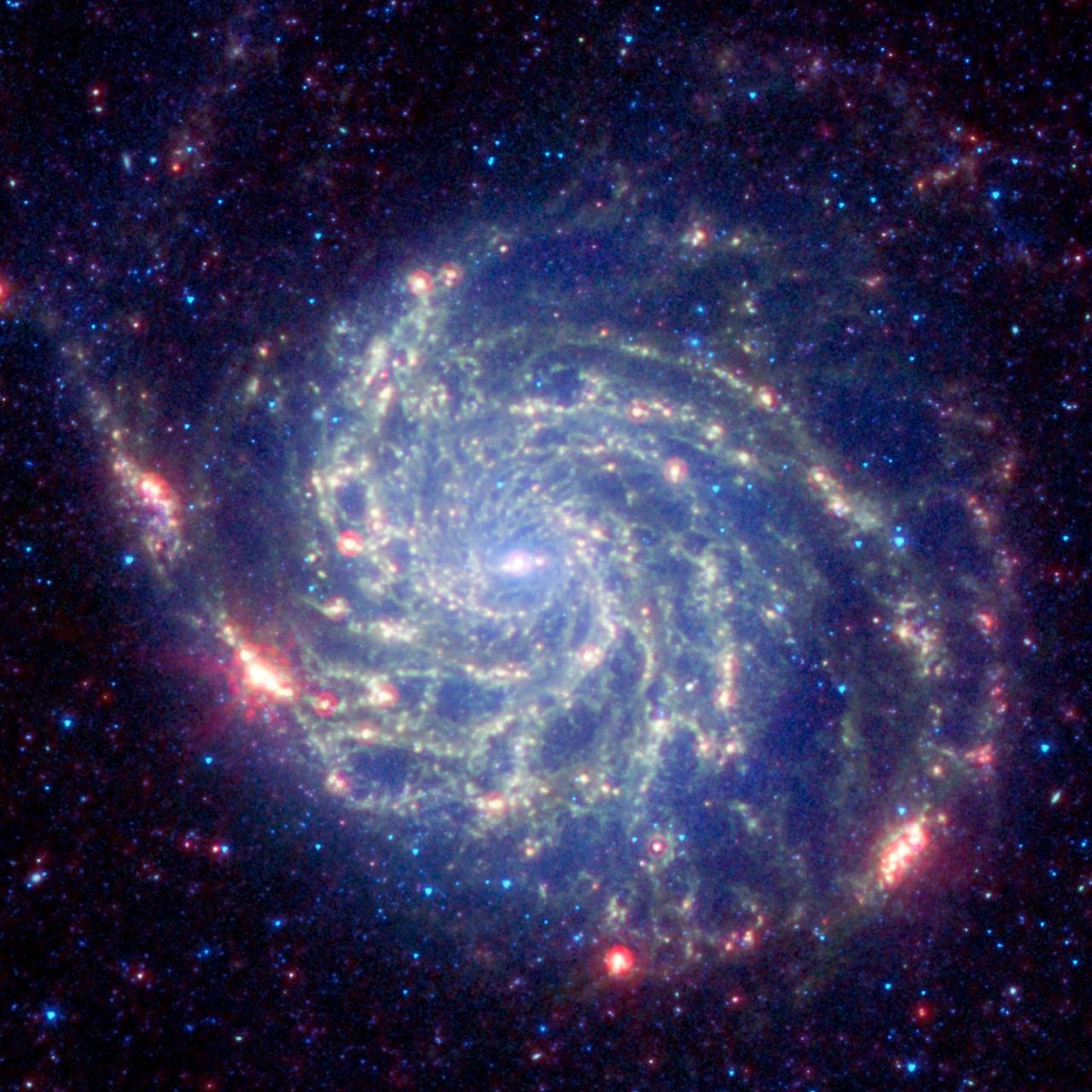

The galaxy Messier 101 is a swirling spiral of stars, gas, and dust. Messier 101 is nearly twice as wide as our Milky Way galaxy in this image as seen by NASA Spitzer Space Telescope.
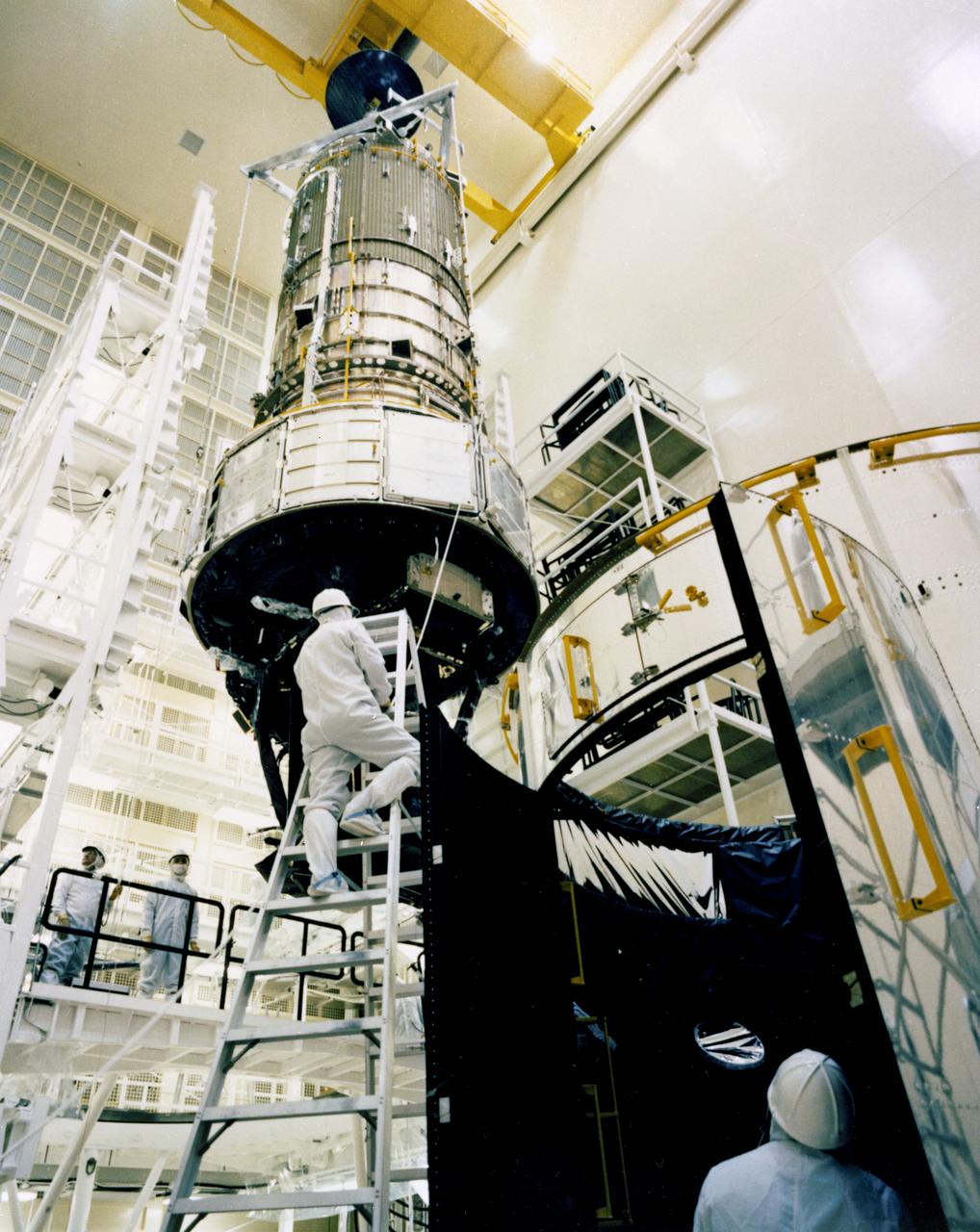

This photograph shows the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) being assembled in the clean room of the Lockheed Missile Space Company. The Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA) is being readied for the installation of the AFT shroud. The OTA contains two mirrors, primary and secondary, to collect and focus light from selected celestial objects. The HST is the first of NASA's great observatories and the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made. The purpose of the HST is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit by placing the telescope in space, enabling astronomers to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had overall responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company, Sunnyvale, California, produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
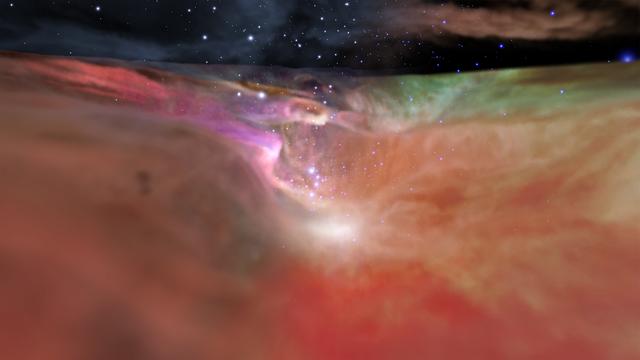
This image showcases both the visible and infrared visualizations of the Orion Nebula. This view from a movie sequence looks down the 'valley' leading to the star cluster at the far end. The left side of the image shows the visible-light visualization, which fades to the infrared-light visualization on the right. These two contrasting models derive from observations by the Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes. An animation is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22089
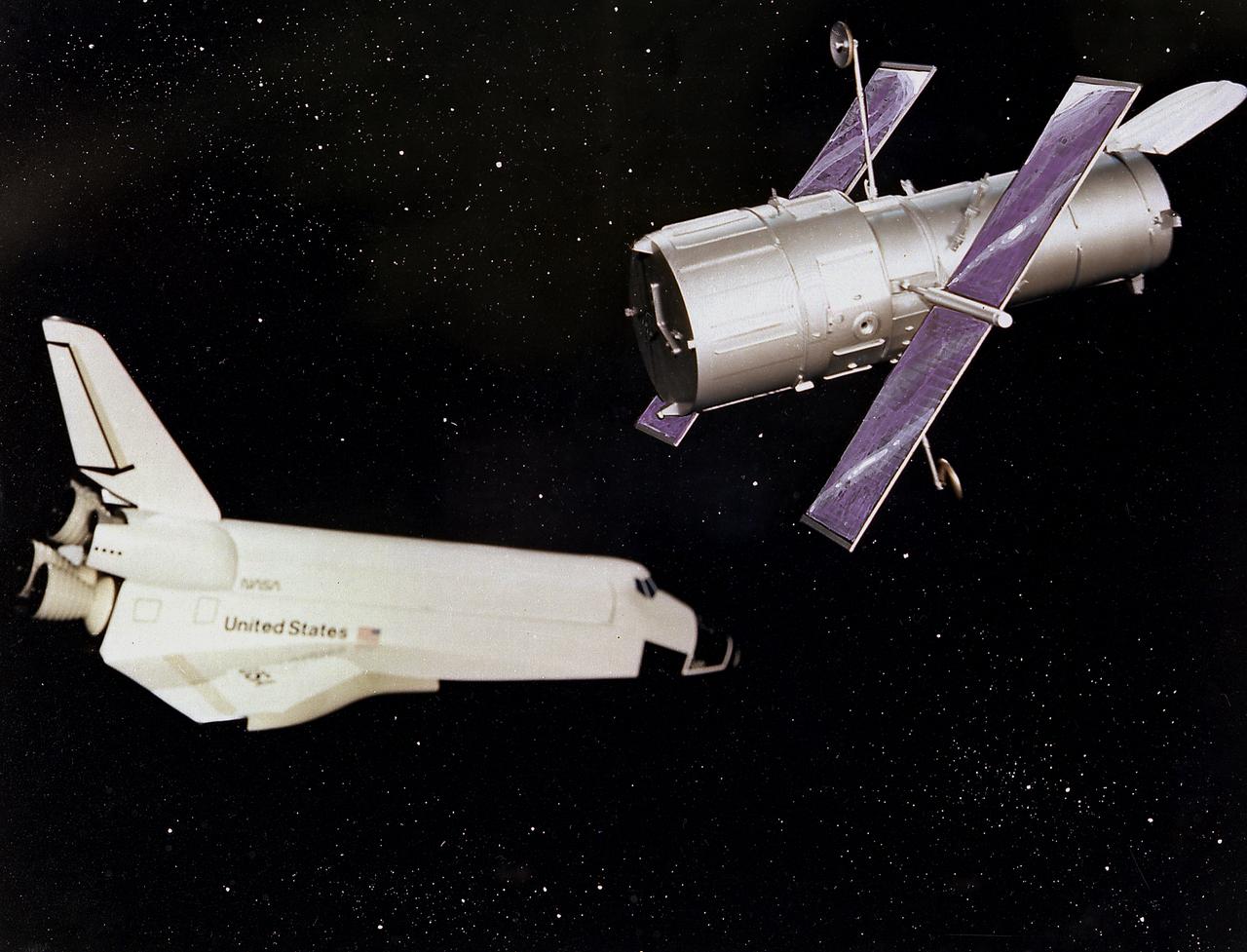
This artist's concept depicts the Hubble Space Telescope after being released into orbit, with the high gain anternas and solar arrays deployed and the aperture doors opened. The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is 42.5-feet (13-meters) long and weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
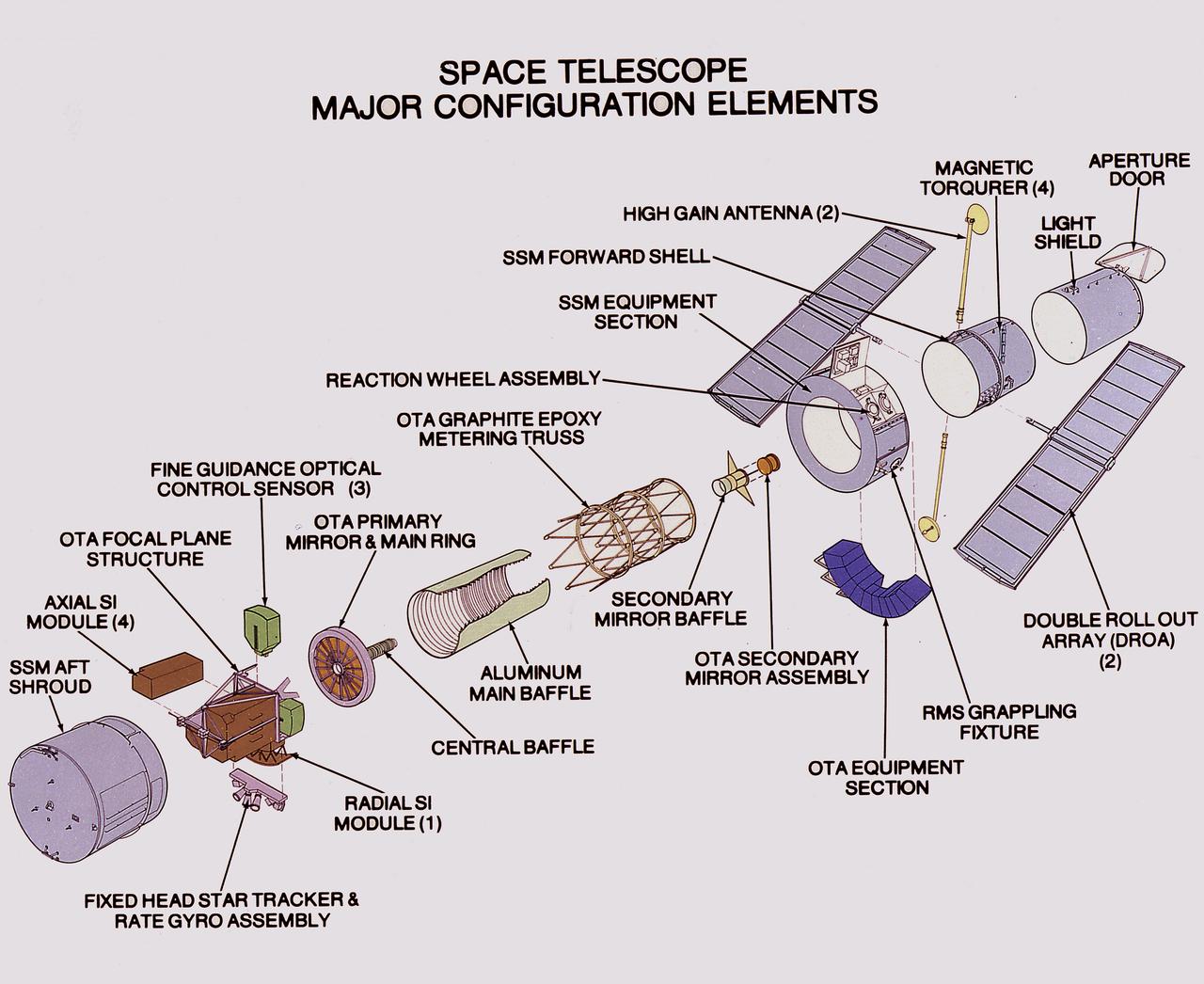
This illustration shows the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) major configuration elements. The spacecraft has three interacting systems: The Support System Module (SSM), an outer structure that houses the other systems and provides services such as power, communication, and control; The Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), which collects and concentrates the incoming light in the focal plane for use by the Scientific Instruments (SI); and five SIs. The SI Control and Data Handling (CDH) unit controls the five SI's, four that are housed in an aft section focal plane structure and one that is placed along the circumference of the spacecraft. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
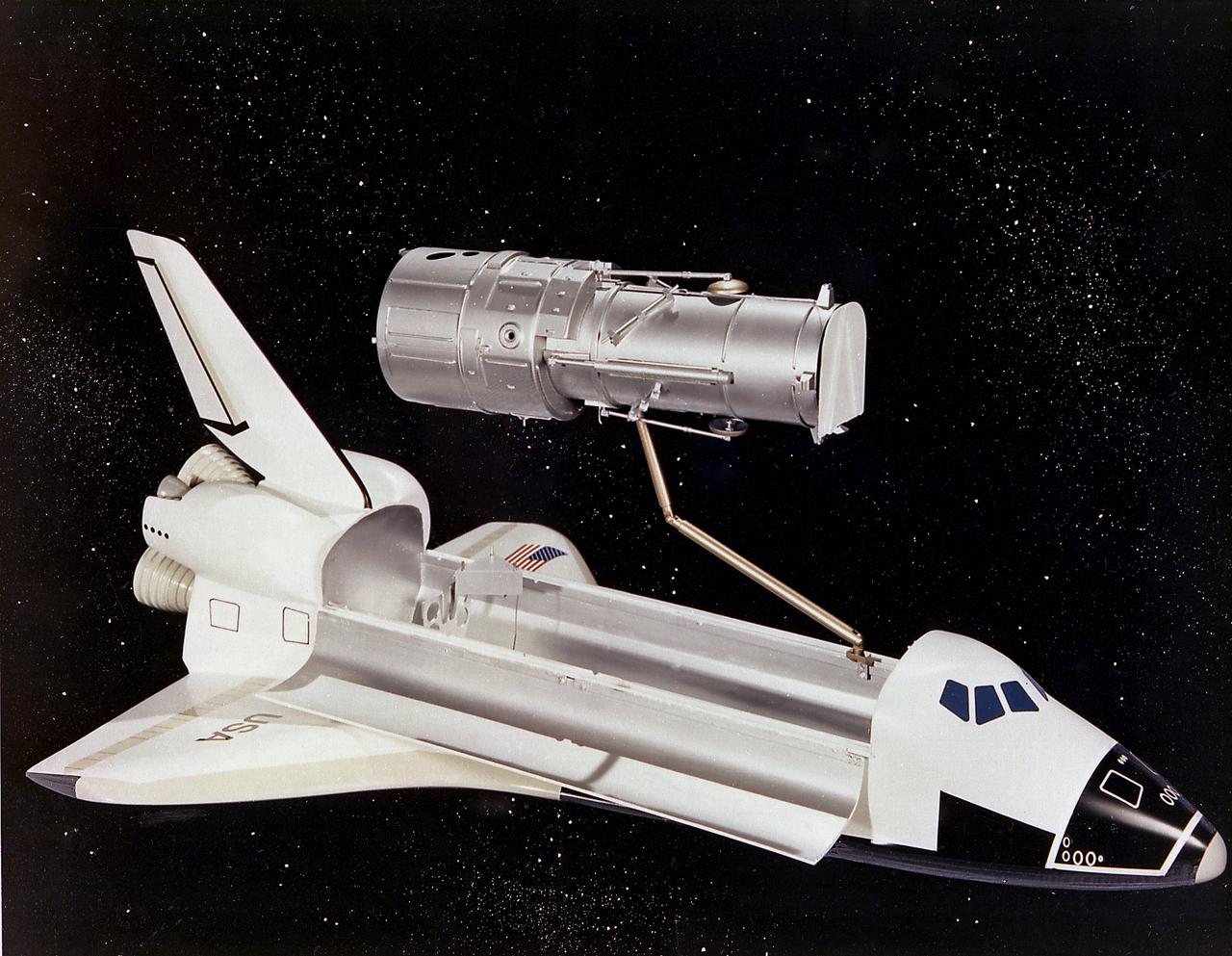
This artist's concept depicts the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) being positioned for release from the Space Shuttle orbiter by the Remote Manipulator System (RMS). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is 42.5-feet (13- meters) long and weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
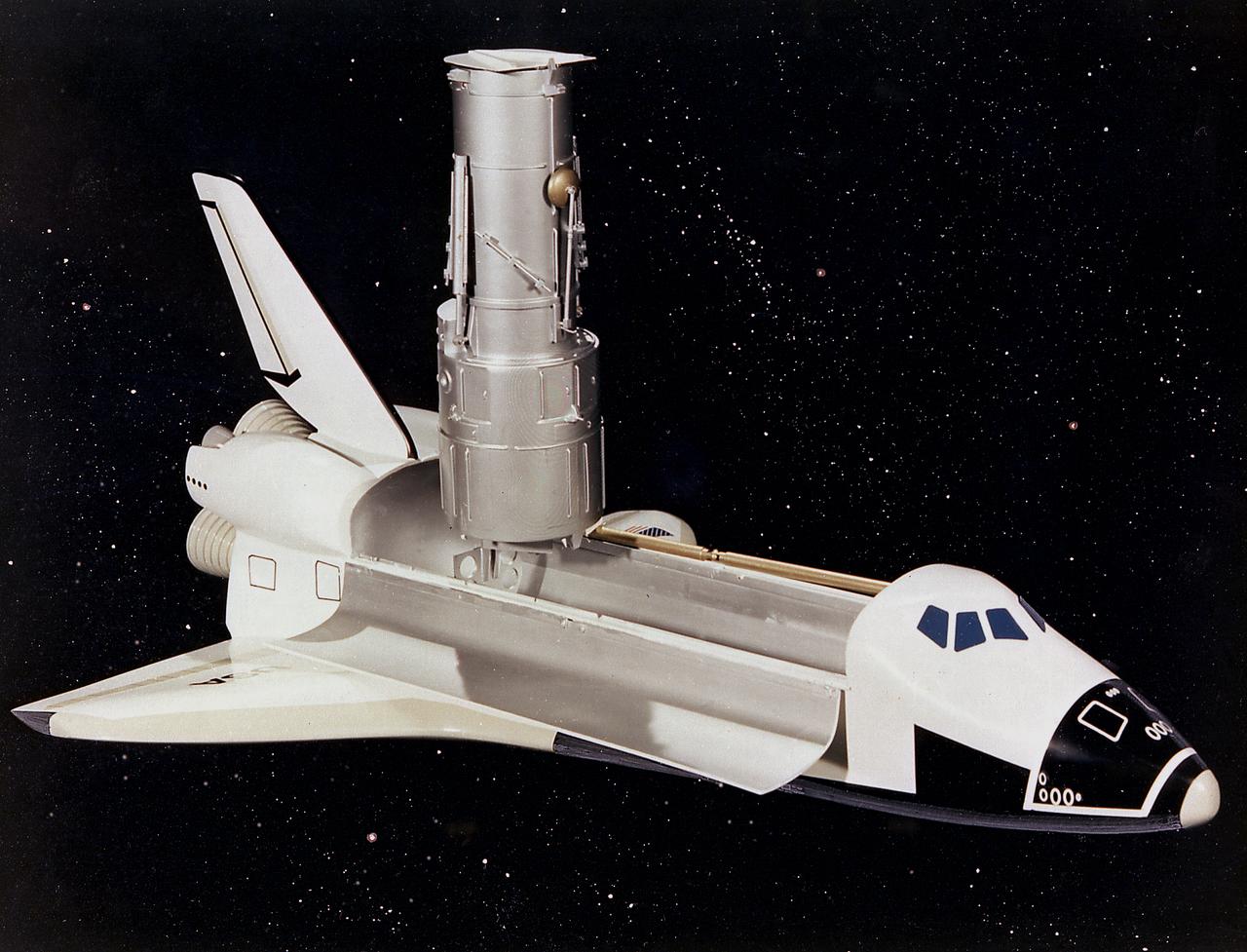
This artist's concept depicts the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) being raised to a vertical position in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle orbiter. The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is 42.5-feet (13-meters) long and weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.

The Hubble Space Telescope in a picture snapped by a Servicing Mission 4 crewmember just after the Space Shuttle Atlantis captured Hubble with its robotic arm on May 13, 2009, beginning the mission to upgrade and repair the telescope. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute conducts Hubble science operations. Goddard is responsible for HST project management, including mission and science operations, servicing missions, and all associated development activities. To learn more about the Hubble Space Telescope go here: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html</a>
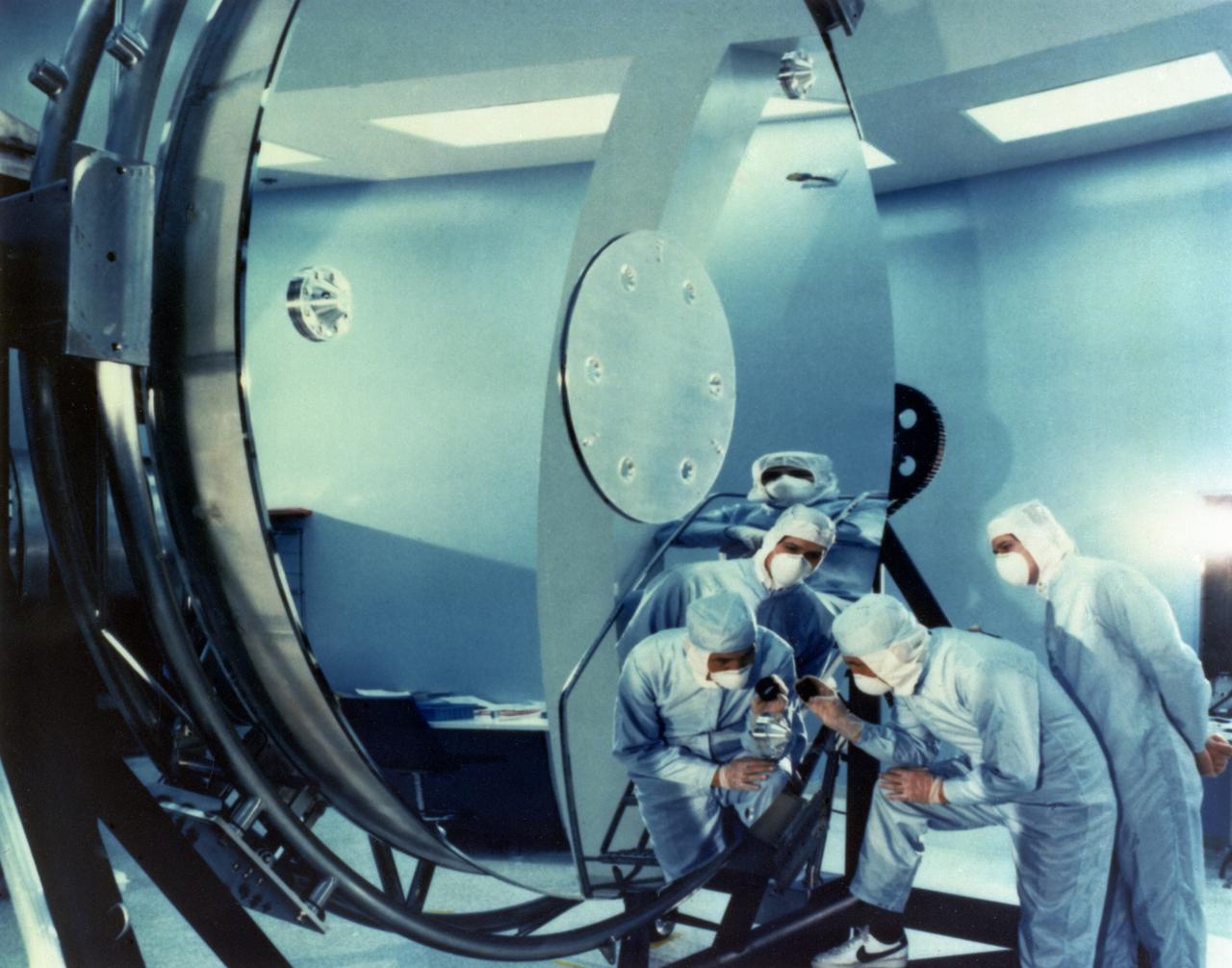
Prior to installation, technicians inspect the primary mirror of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The first in a series of great observatories launched by NASA, the HST was designed to last approximately 15 years. The Marshall Space Flight Center had management responsibility for the development of the HST and played a major role in ground tests and orbital checkout of the telescope. The HST was launched April 24, 1990 aboard Space Shuttle Discovery's STS-31 mission.
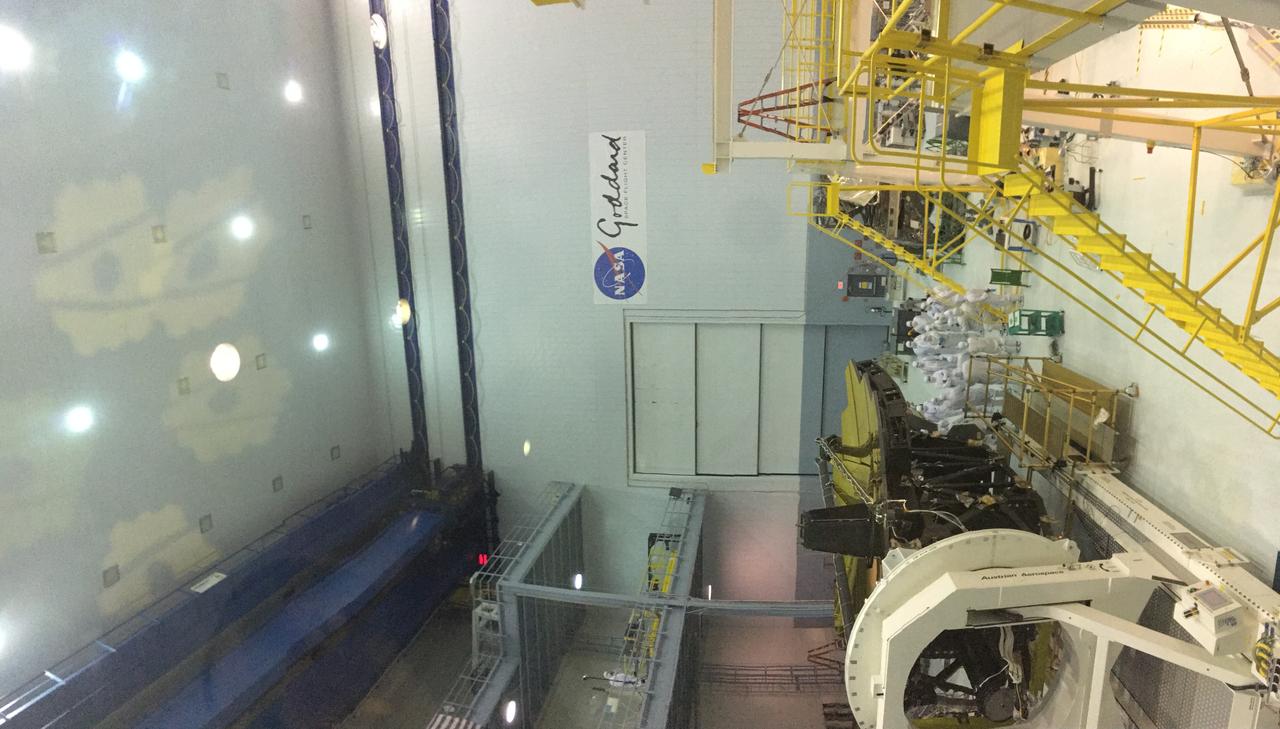

A rare view of the James Webb Space Telescope face-on, from the NASA Goddard cleanroom observation window.

A rare view of the James Webb Space Telescope face-on, from the NASA Goddard cleanroom observation window.
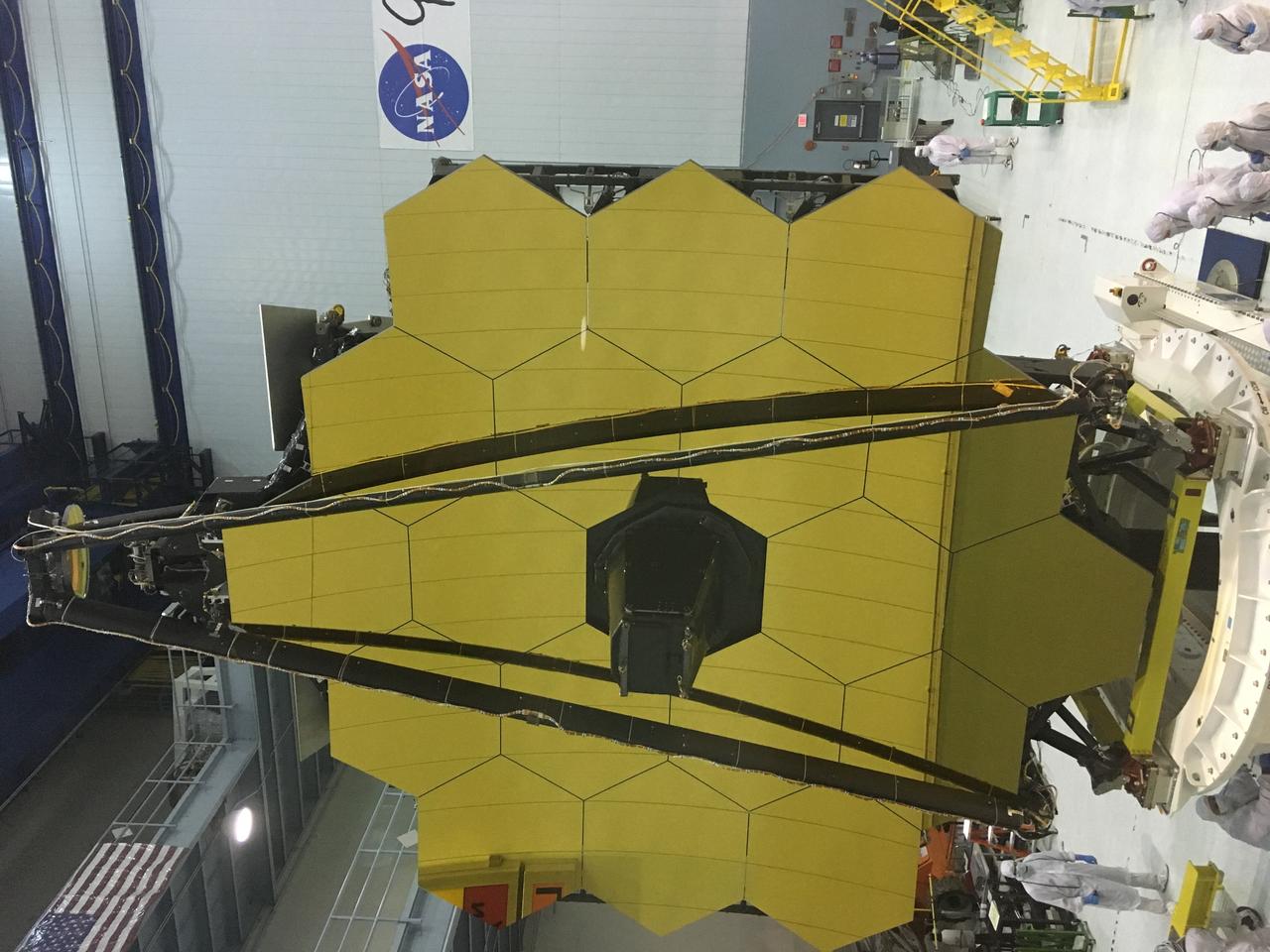
A rare view of the James Webb Space Telescope face-on, from the NASA Goddard cleanroom observation window.

A rare view of the James Webb Space Telescope face-on, from the NASA Goddard cleanroom observation window.
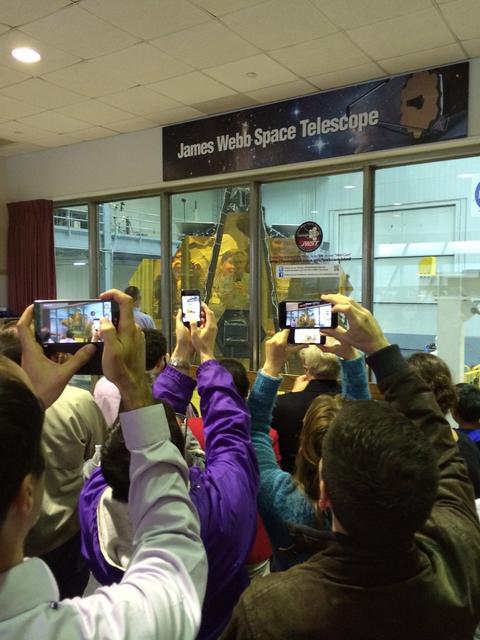

A rare view of the James Webb Space Telescope face-on, from the NASA Goddard cleanroom observation window.
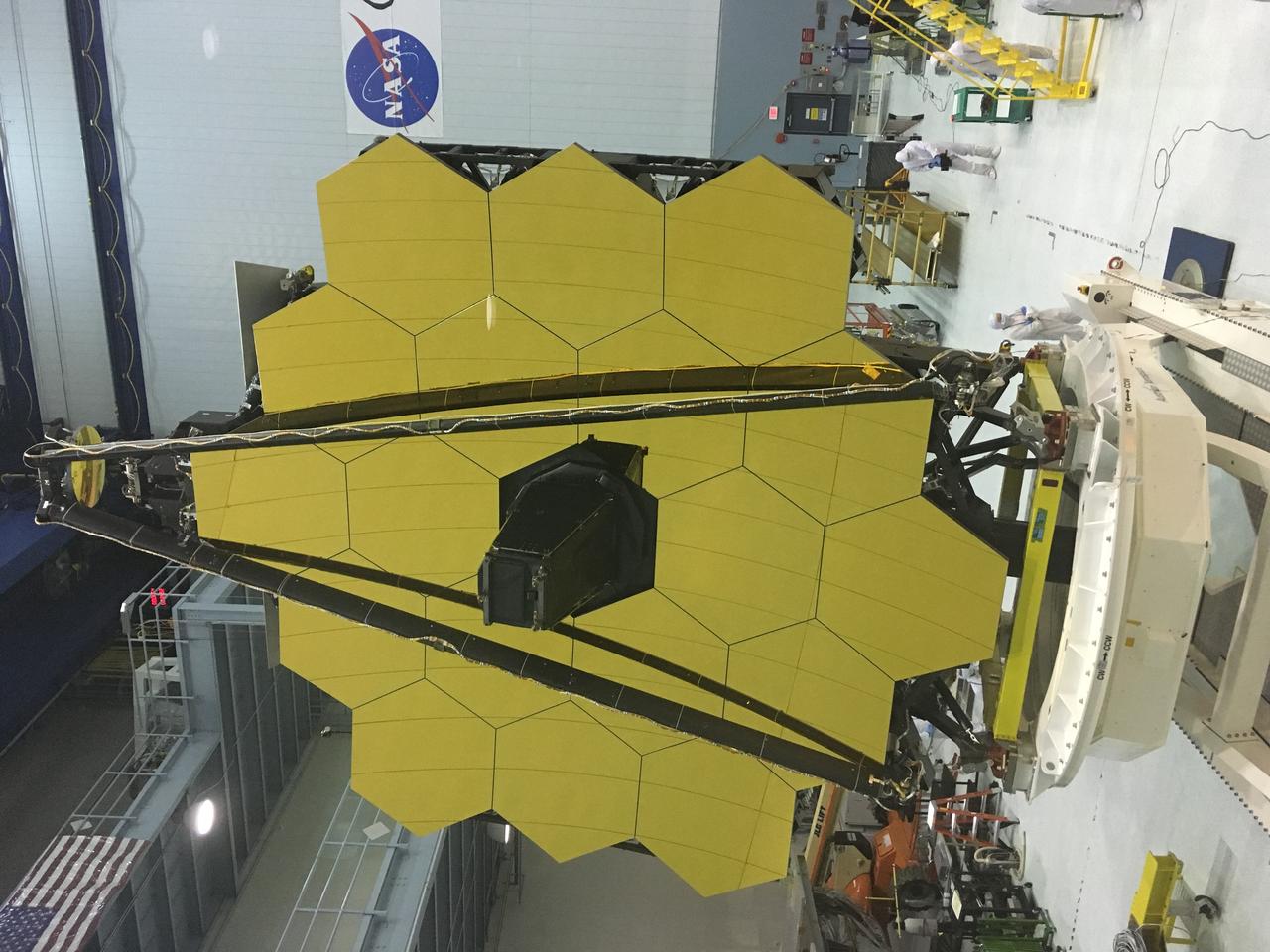

A rare view of the James Webb Space Telescope face-on, from the NASA Goddard cleanroom observation window.
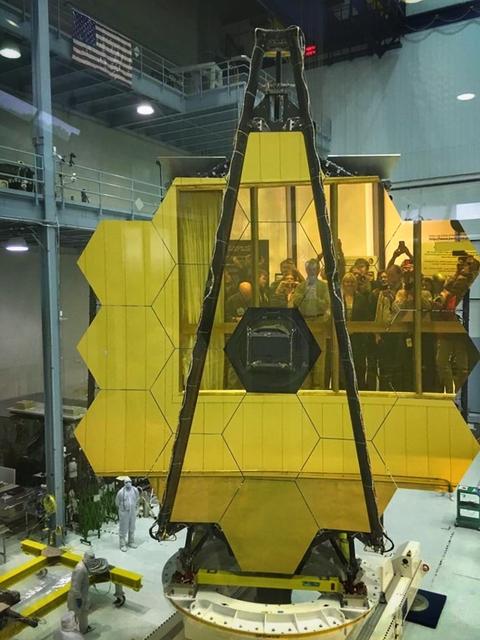

A rare view of the James Webb Space Telescope face-on, from the NASA Goddard cleanroom observation window.
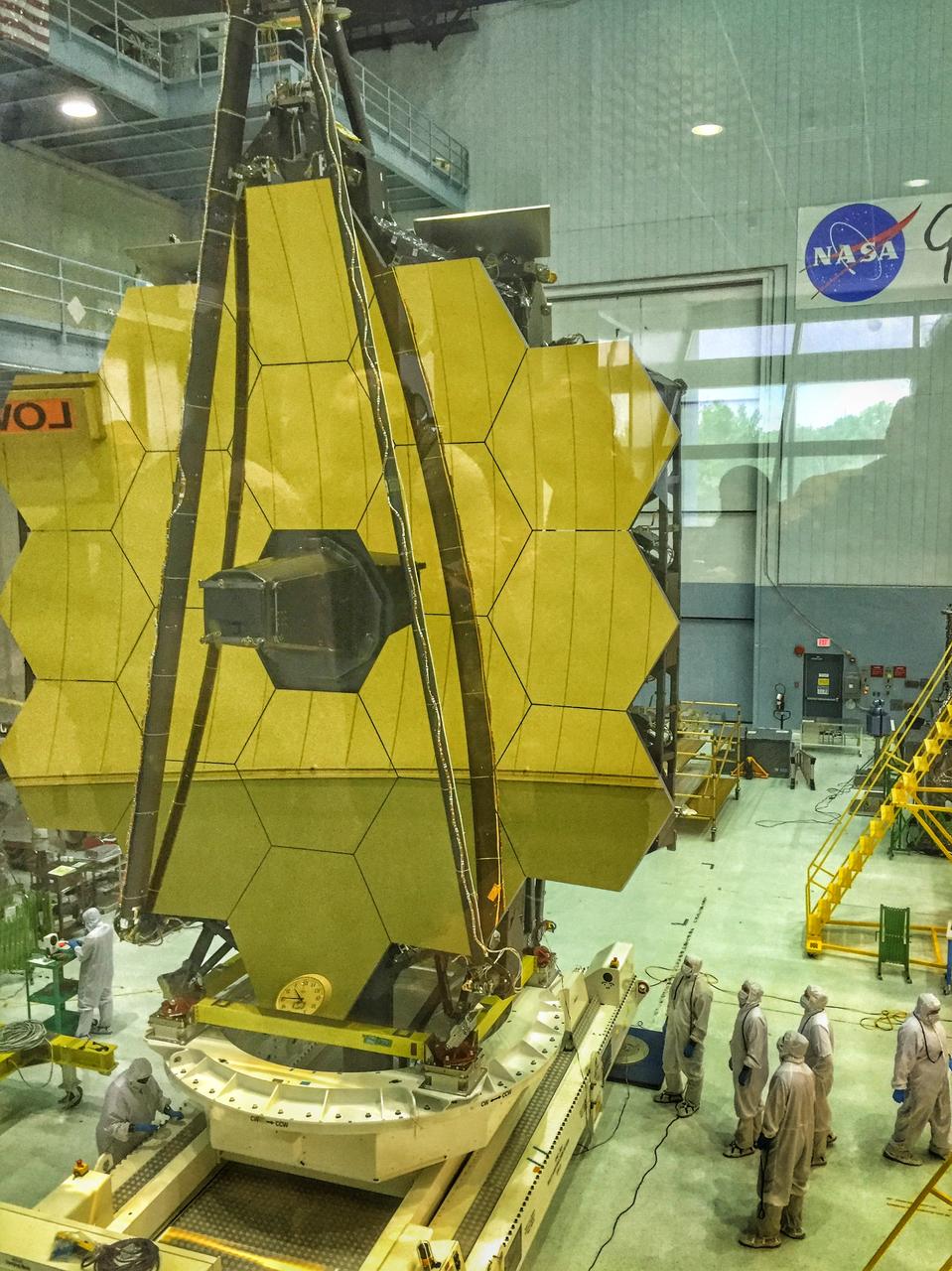

A rare view of the James Webb Space Telescope face-on, from the NASA Goddard cleanroom observation window.
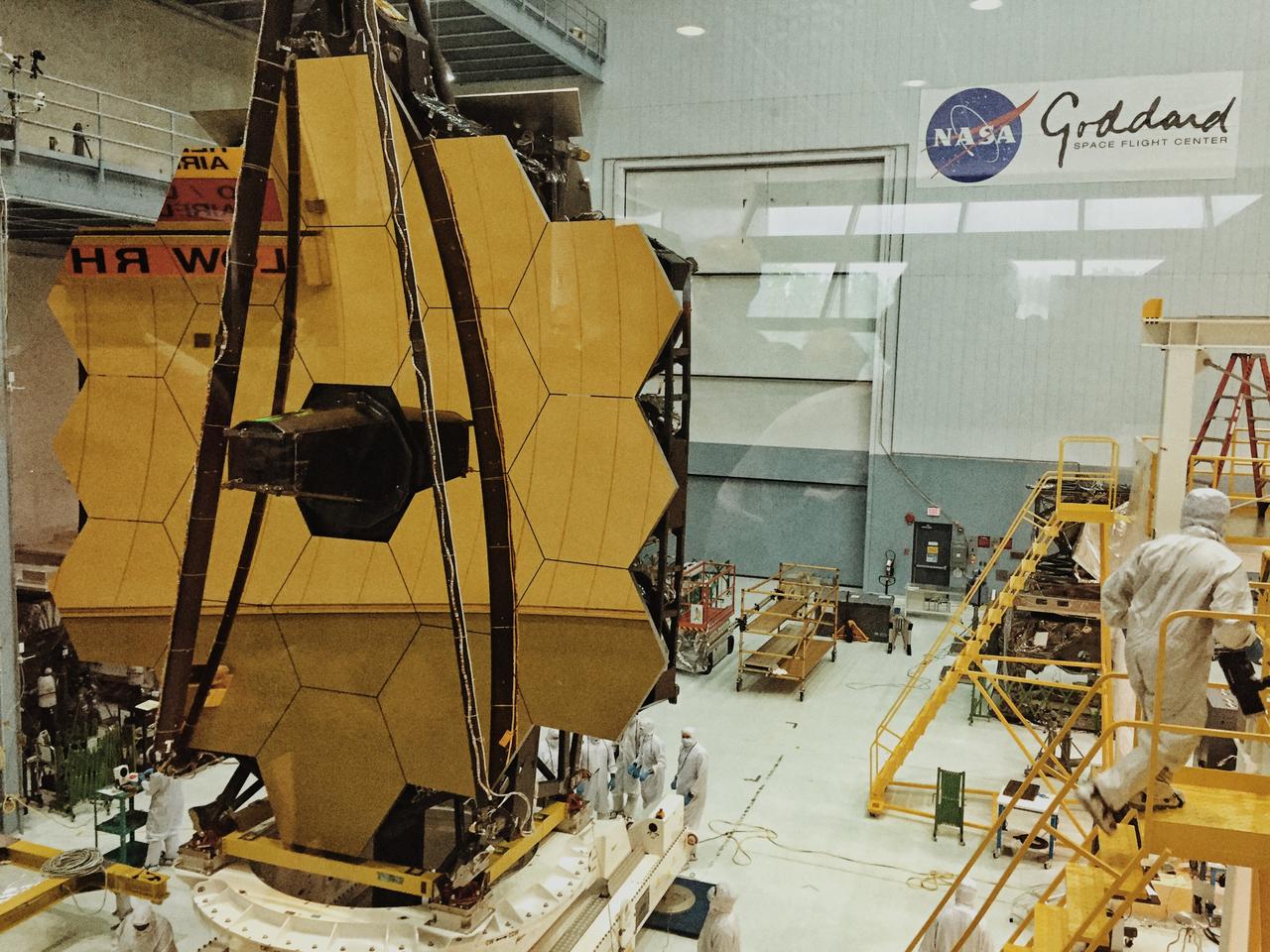

A rare view of the James Webb Space Telescope face-on, from the NASA Goddard cleanroom observation window. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth
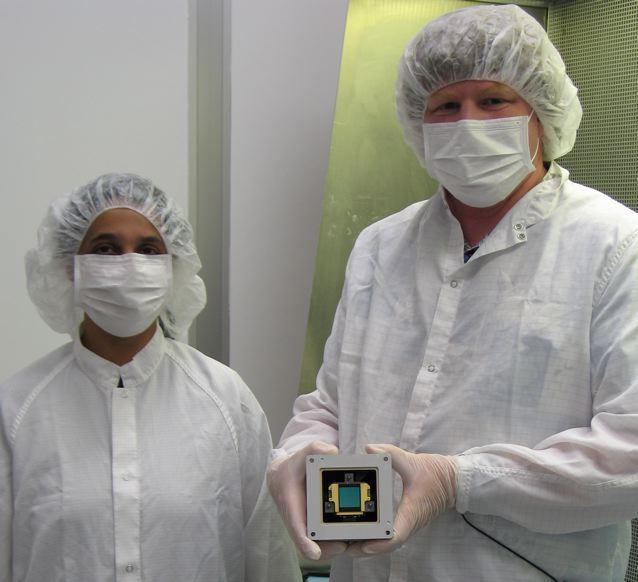

Mike Ressler right and Kalyani Sukhatme of NASA JPL pose in the clean room with a model component, called a focal plane module, of the Mid-Infrared Instrument on NASA James Webb Space Telescope.
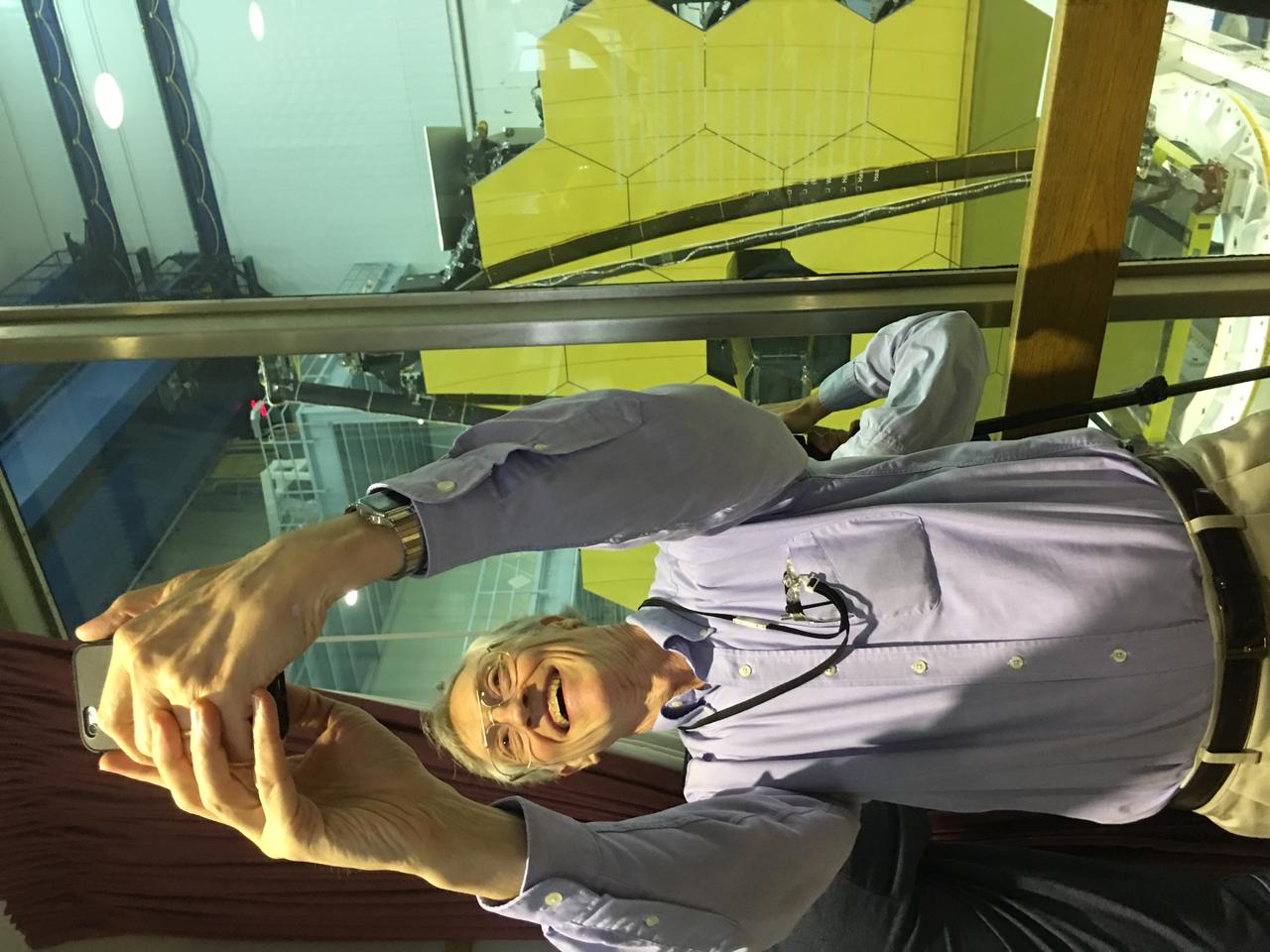

Nobel Laureate and James Webb Space Telescope project scientist Dr. John Mather takes a selfie with the telescope. May 4, 2016 was a rare day for JWST, as it briefly faced the cleanroom observation window. The telescope was eventually rotated face-down in prep for the installation of the flight instruments. Credit: Meredith Gibb

This photograph is a Hubble Space Telescope (HST) image of a sky full of glittering jewels. The HST peered into the Sagittarius star cloud, a narrow dust free region, providing this spectacular glimpse of a treasure chest full of stars.
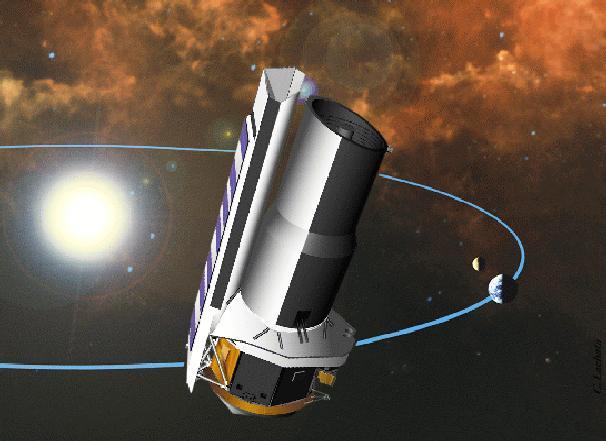
This image was used in a contest to rename the Space InfraRed Telescope Facility SIRTF, now known as the Spitzer Space Telescope.
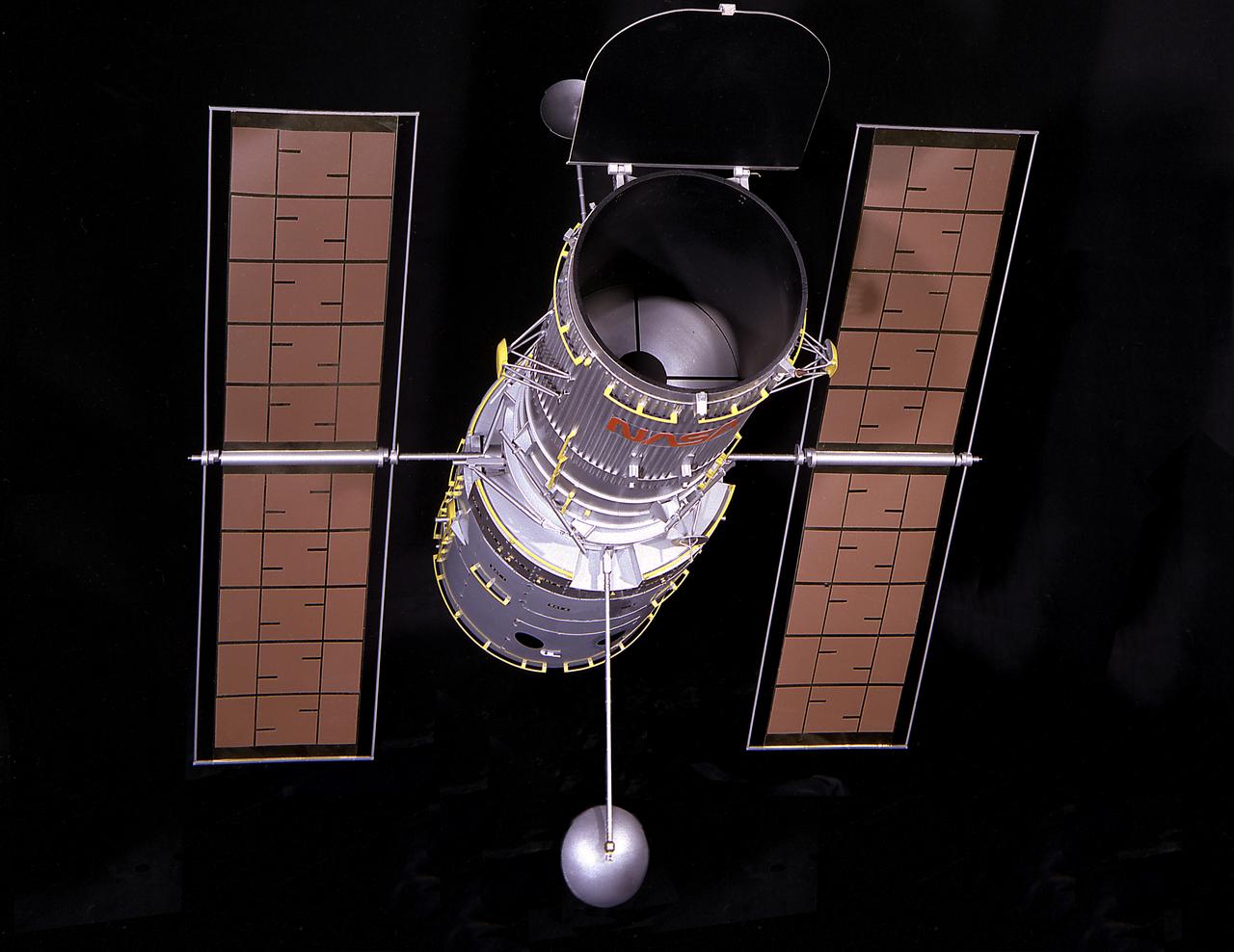
This is a photograph of a 1/15 scale model of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is 42.5-feet (13- meters) long and weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
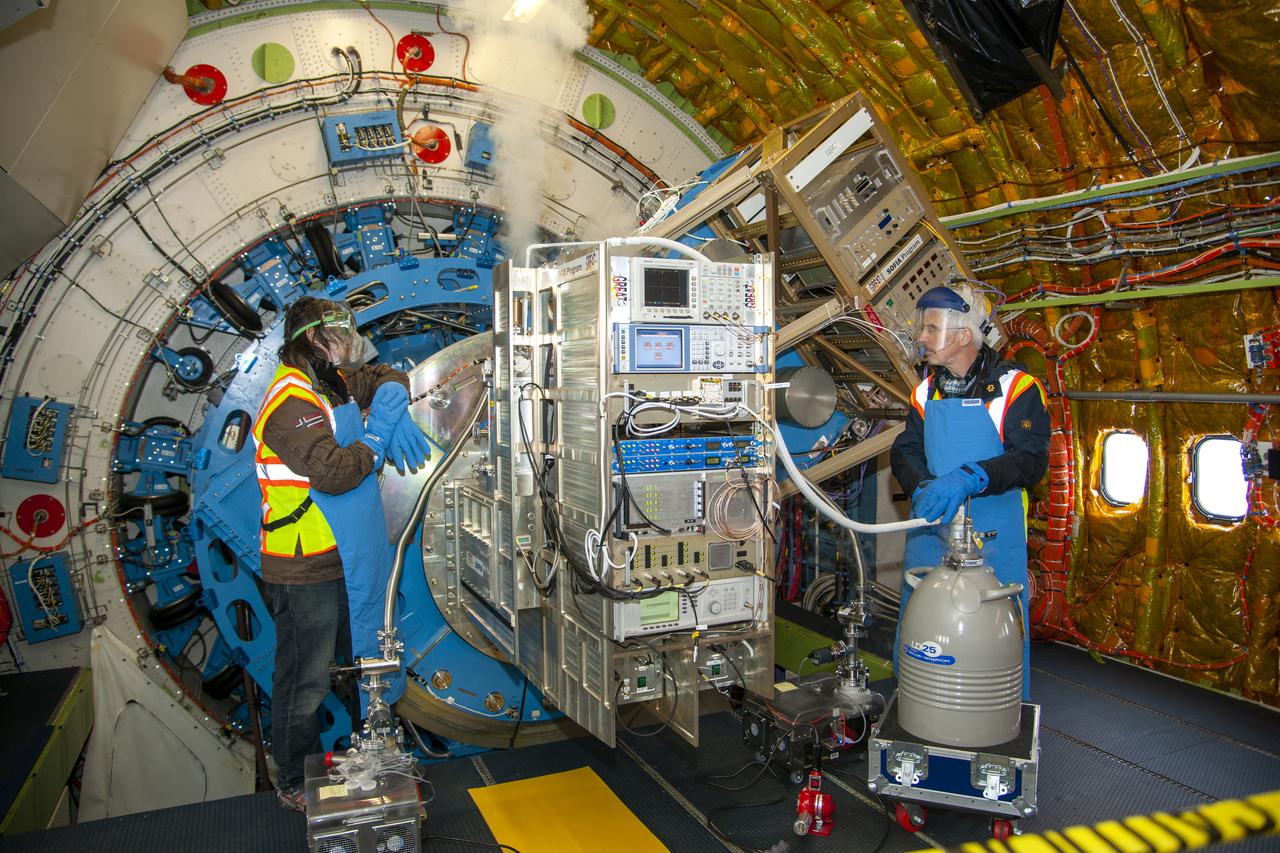

Technicians introduce liquid nitrogen to an instrument linked to SOFIA’s telescope. Detection of infrared wavelengths is greatly enhanced by removing as much heat from the telescope as possible.
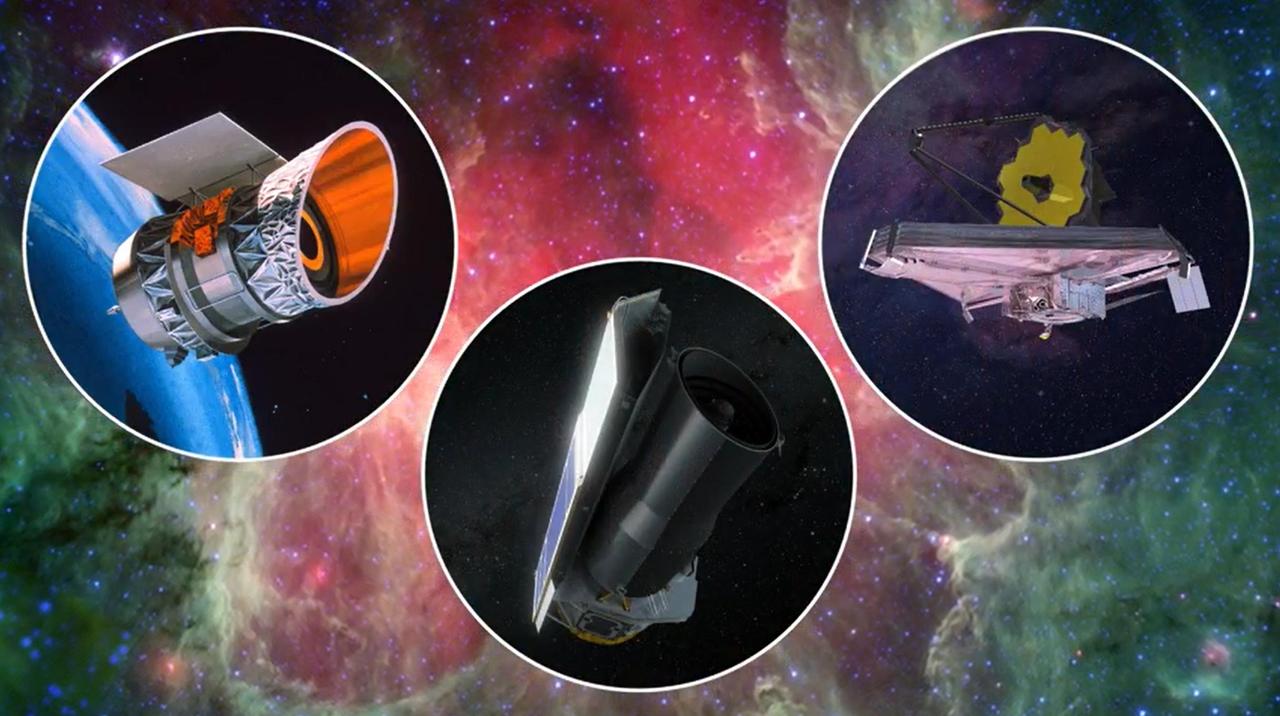

This artist's concept shows three space telescopes that observe infrared light, wavelengths slightly longer than what human eyes can see. On the right is NASA's James Webb Space Telescope. Launched in 2021, it is the largest and most powerful space observatory in history. On the left is NASA's Infrared Astronomical Satellite (IRAS), the first infrared telescope in Earth orbit, launched in 1983. In the middle is NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope, launched in 2003. The background image is from Spitzer and shows the Eagle Nebula. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25790
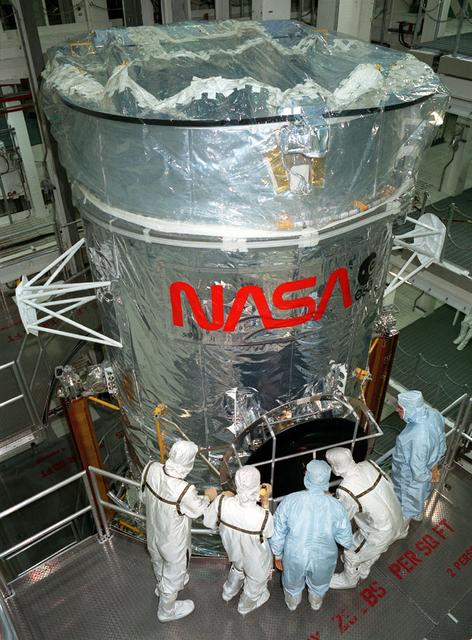

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) pictured in the Vertical Processing Facility (VPF) support fixture during final testing and verification at the Lockheed assembly plant.

Bob O'Connell, chair of the science oversight committee for the NASA Hubble Space Telescope Wide Field Camera 3 at the University of Virginia discusses newly released images from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope Wednesday, Sept. 9, 2009 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The images were from four of the telescopes' six operating science instruments. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Bob O'Connell, chair of the science oversight committee for the NASA Hubble Space Telescope Wide Field Camera 3 at the University of Virginia discusses newly released images from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope Wednesday, Sept. 9, 2009 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The images were from four of the telescopes' six operating science instruments. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) Town Hall -

James Webb Space Telescope Mirror Reveal

James Webb Space Telescope Mirror Reveal
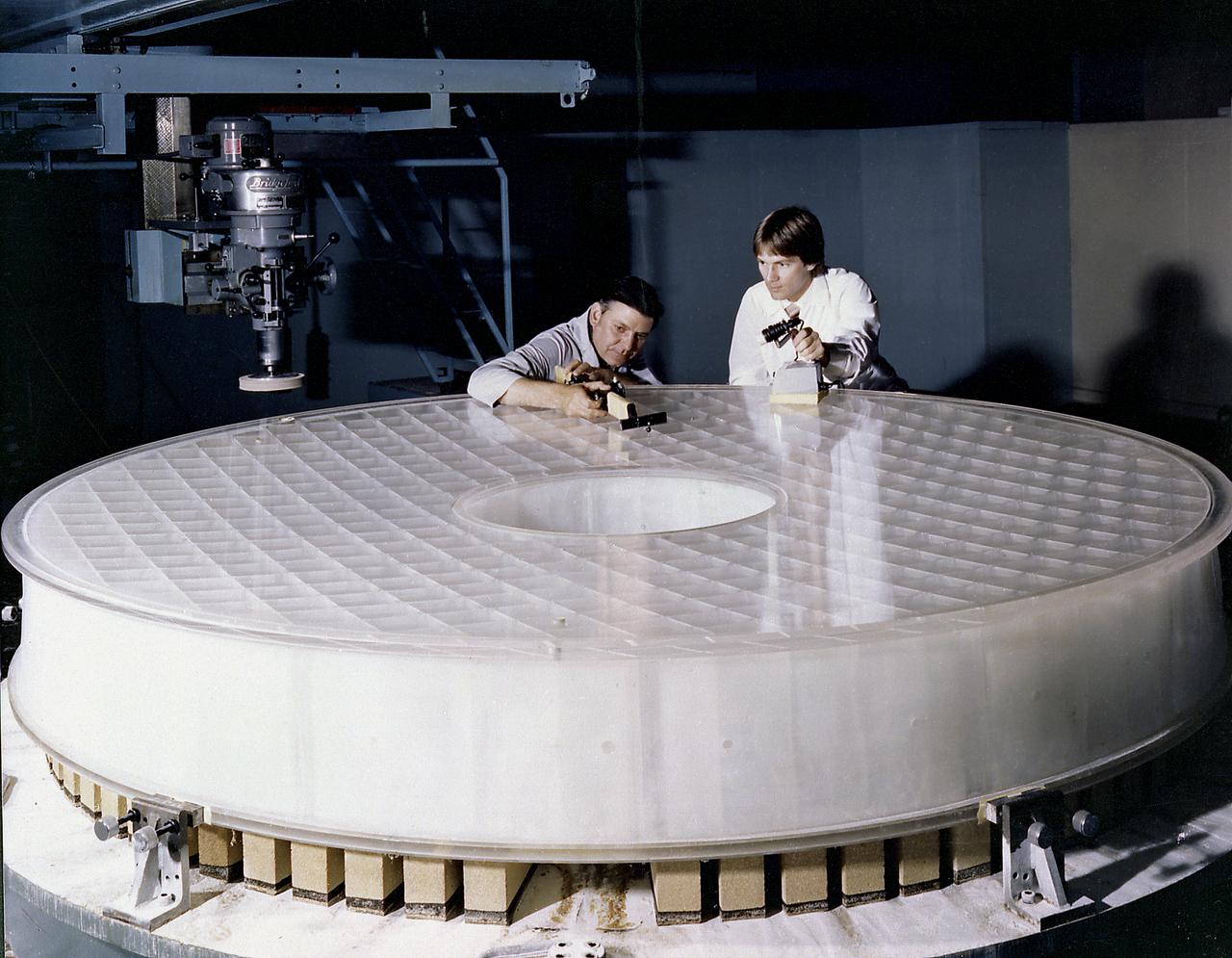

This photograph shows engineers inspecting the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) Primary Mirror at the Perkin-Elmer Corporation's large optics fabrication facility. After the 8-foot diameter mirror was ground to shape and polished, the glass surface was coated with a reflective layer of aluminum and a protective layer of magnesium fluoride, 0.1- and 0.025- micrometers thick, respectively. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST and the Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
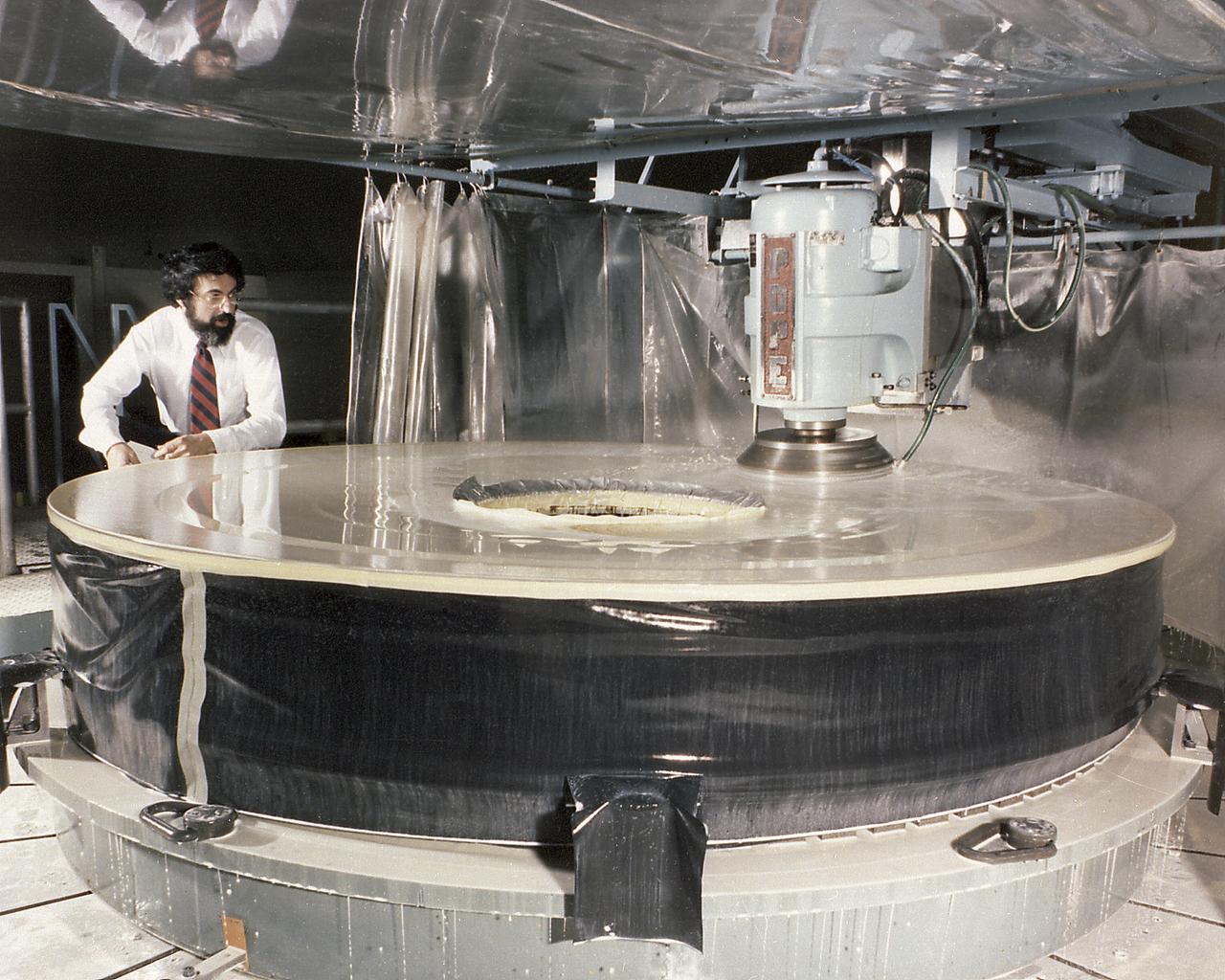

This photograph shows the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) Primary Mirror being ground at the Perkin-Elmer Corporation's large optics fabrication facility. After the 8-foot diameter mirror was ground to shape and polished, the glass surface was coated with a reflective layer of aluminum and a protective layer of magnesium fluoride, 0.1- and 0.025-micrometers thick, respectively. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST and the Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
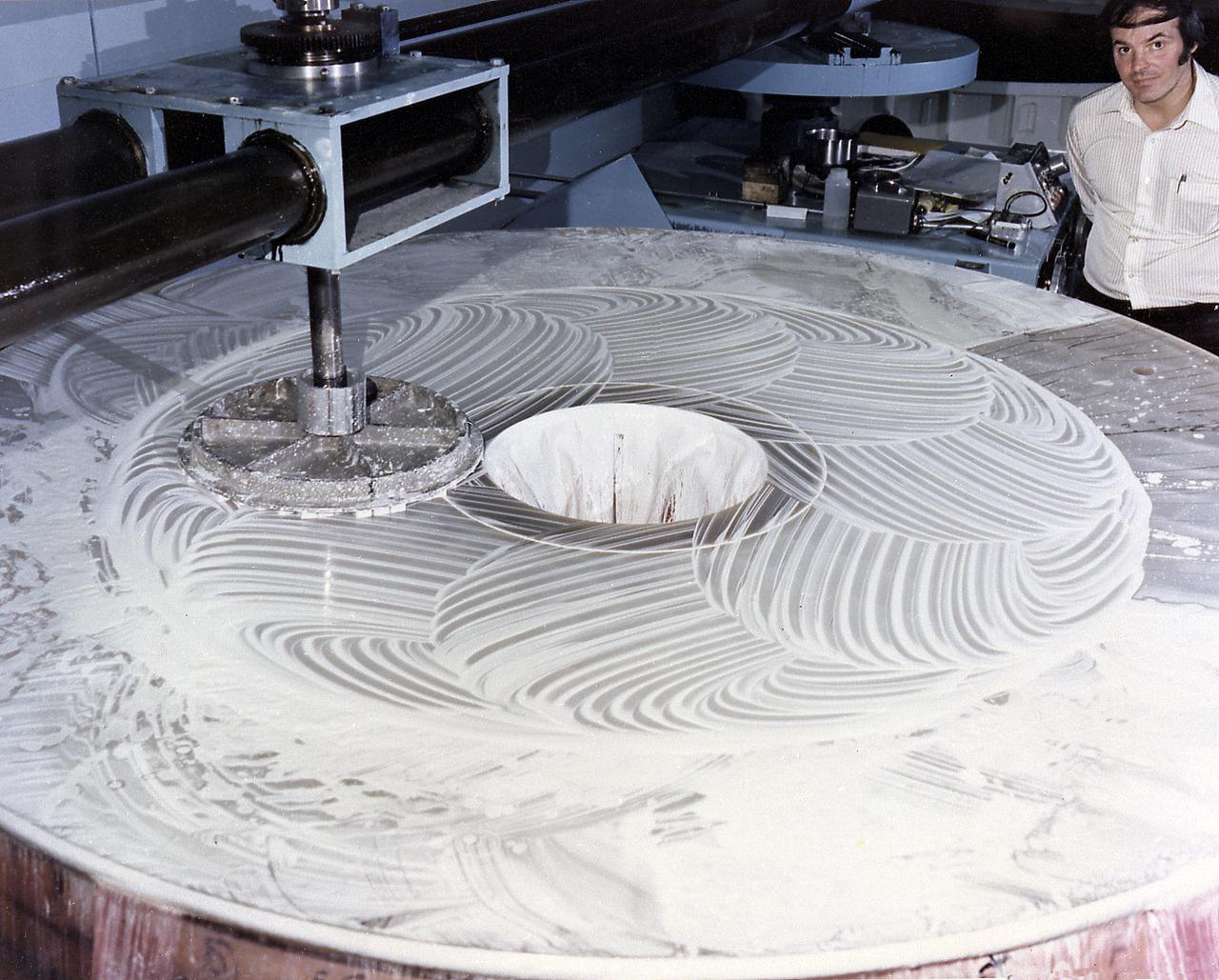

This photograph shows the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) Primary Mirror being polished at the the Perkin-Elmer Corporation's large optics fabrication facility. After the 8-foot diameter mirror was ground to shape and polished, the glass surface was coated with a reflective layer of aluminum and a protective layer of magnesium fluoride, 0.1- and 0.025-micrometers thick, respectively. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST and the Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
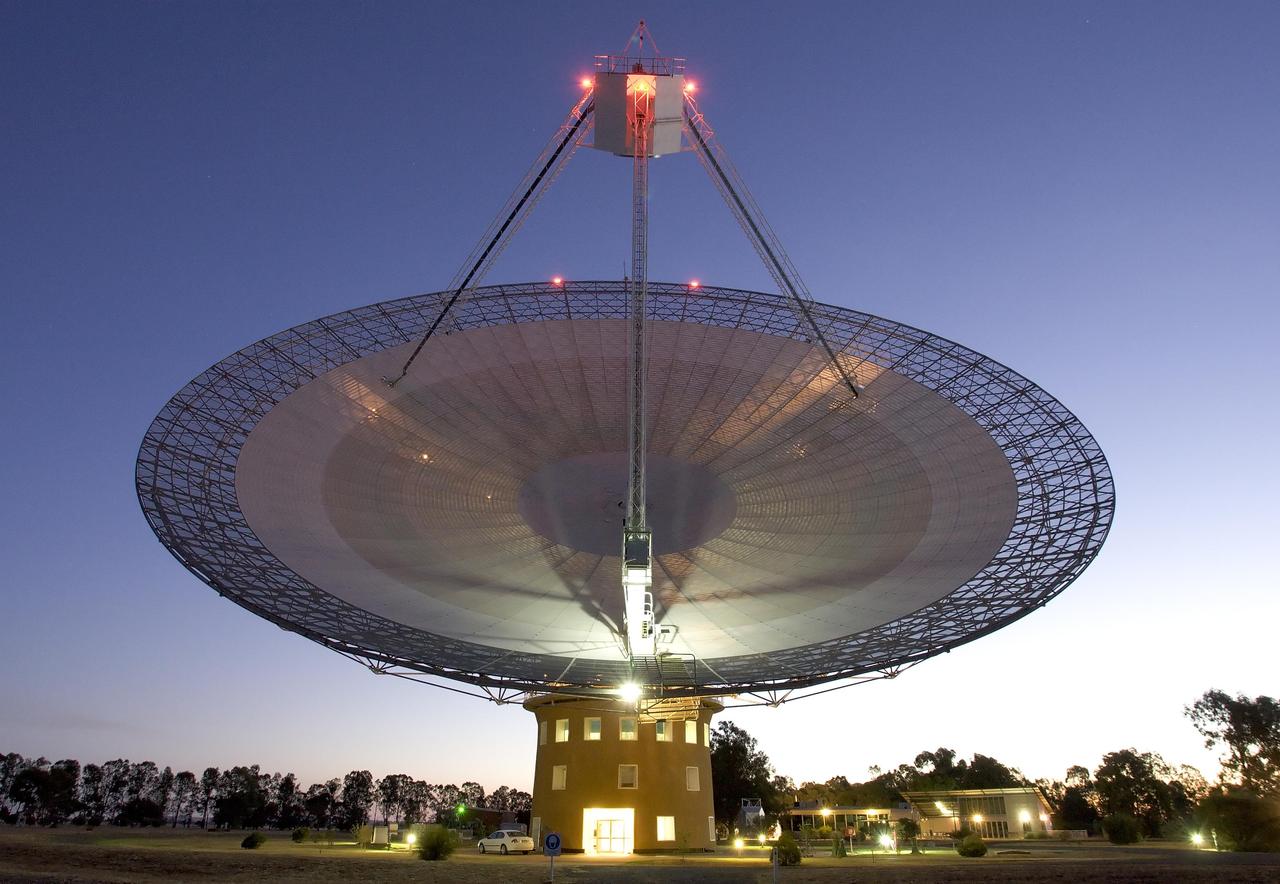

This image shows the Parkes telescope in Australia, part of the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization. Researchers used the telescope to detect the first population of radio bursts known to originate from beyond our galaxy.
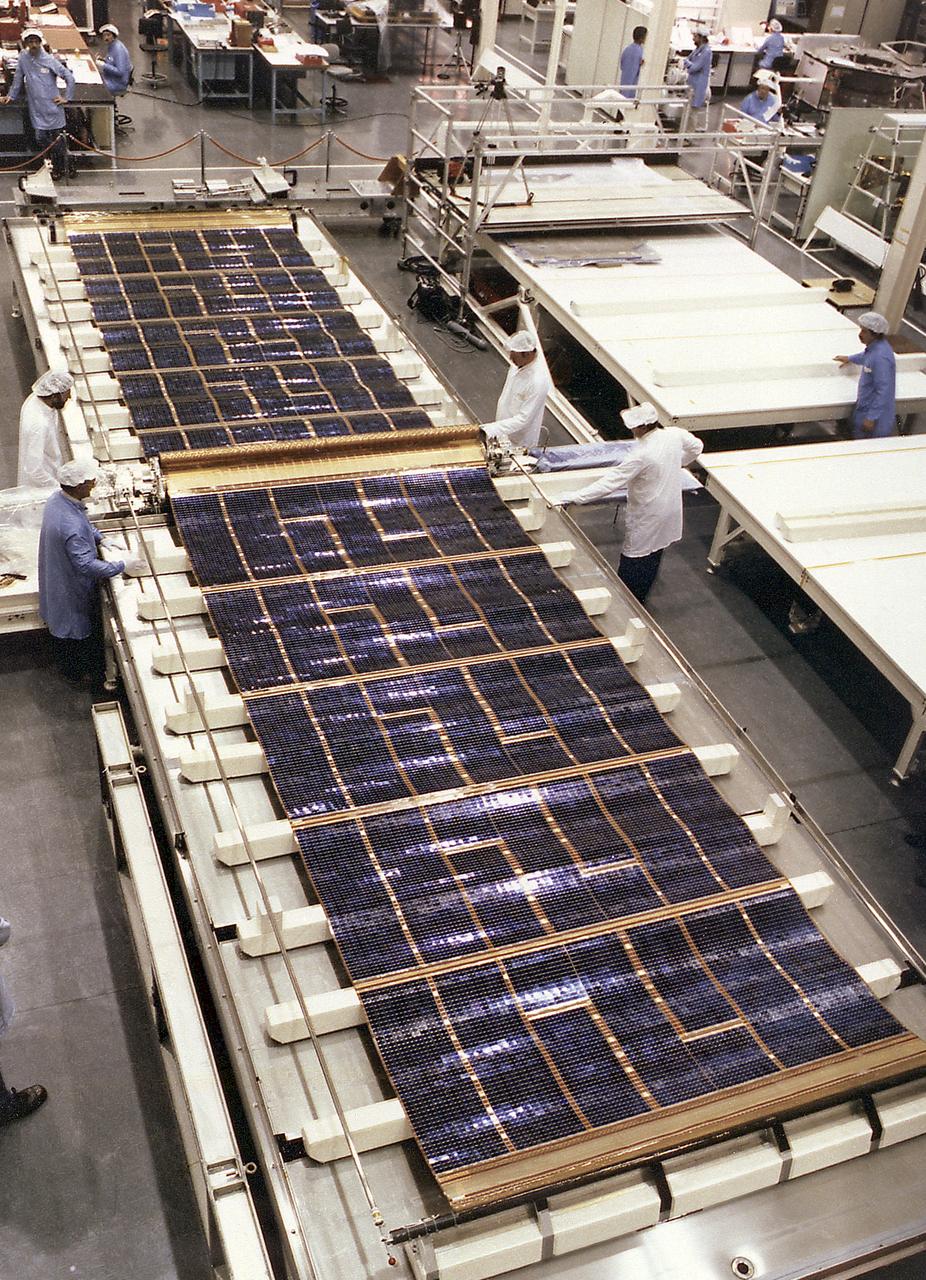

This is a view of a solar cell blanket deployed on a water table during the Solar Array deployment test. The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Solar Arrays provide power to the spacecraft. The arrays are mounted on opposite sides of the HST, on the forward shell of the Support Systems Module. Each array stands on a 4-foot mast that supports a retractable wing of solar panels 40-feet (12.1-meters) long and 8.2-feet (2.5-meters) wide, in full extension. The arrays rotate so that the solar cells face the Sun as much as possible to harness the Sun's energy. The Space Telescope Operations Control Center at the Goddard Space Center operates the array, extending the panels and maneuvering the spacecraft to focus maximum sunlight on the arrays. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST Solar Array was designed by the European Space Agency and built by British Aerospace. The Marshall Space Flight Center had overall responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST.
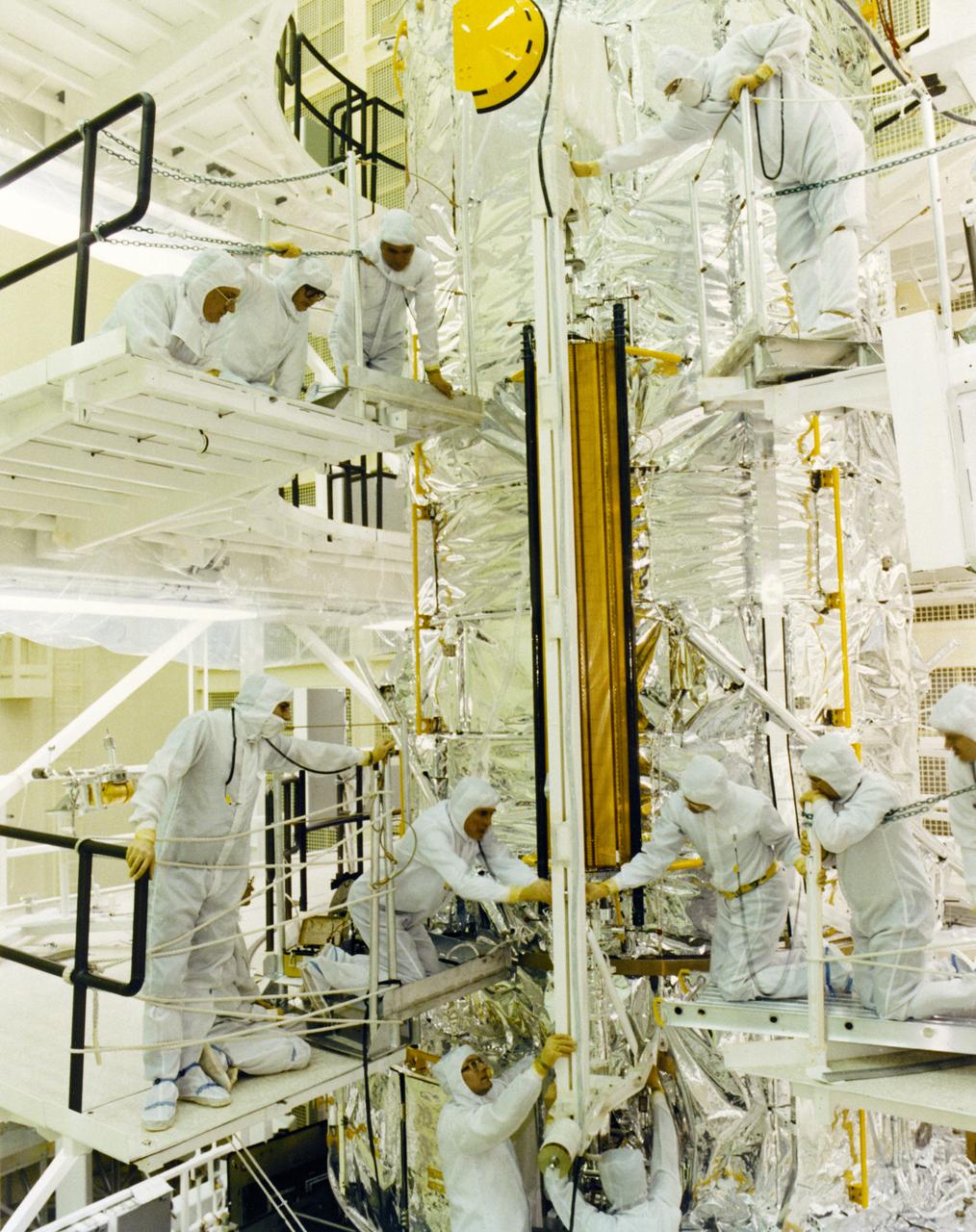

Engineers and technicians conduct a fit check of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Solar Array flight article in a clean room of the Lockheed Missile and Space Company. The Solar Array is 40- feet (12.1-meters) long and 8.2-feet (2.5-meters) wide, and provides power to the spacecraft. The HST is the first of NASA's great observatories and the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made. The purpose of the HST is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit by placing the telescope in space, enabling astronomers to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had overall responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company, Sunnyvale, California, produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
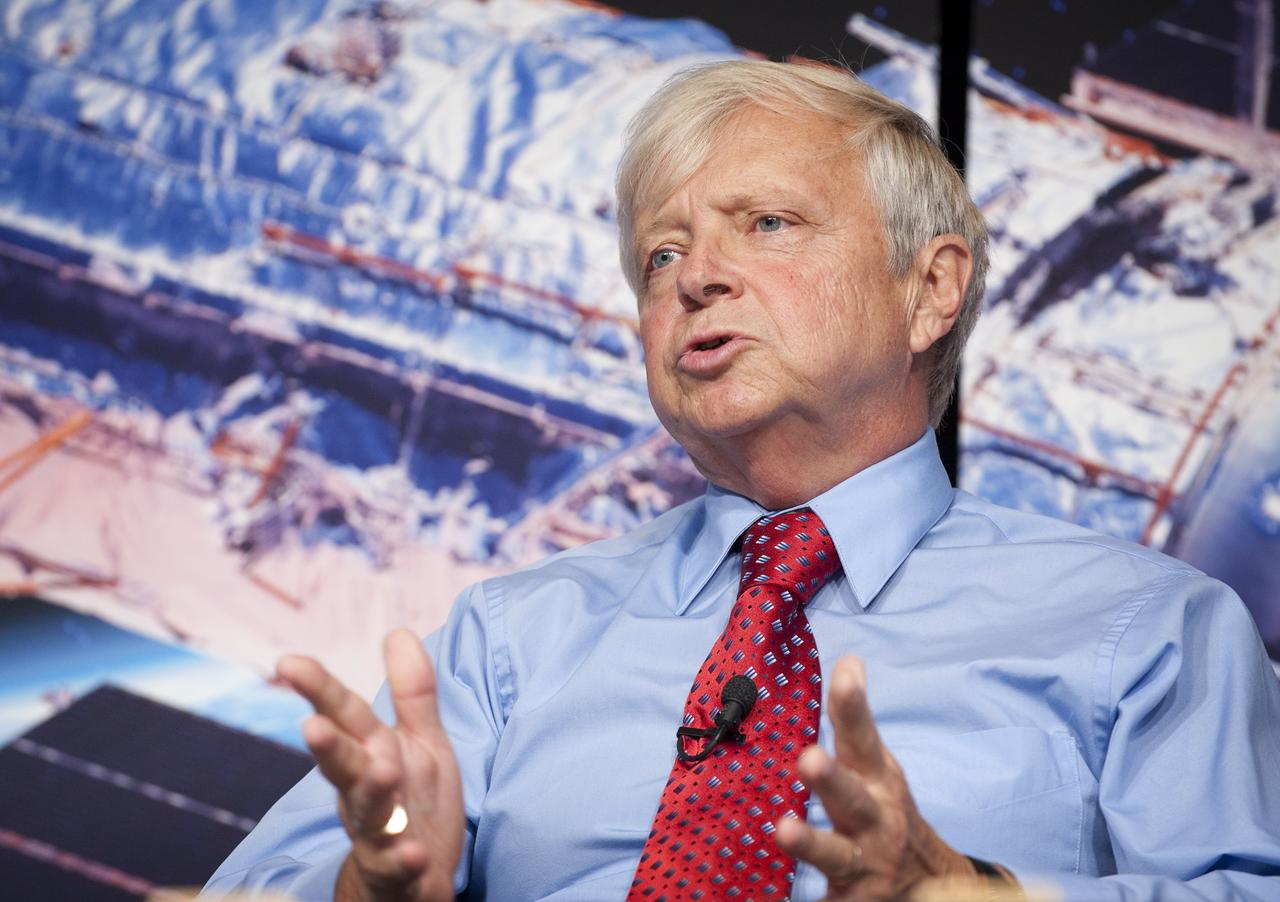

NASA Associate Administrator of the Science Mission Directorate Dr. Edward J. Weiler discusses newly released images from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope Wednesday, Sept. 9, 2009 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The images were from four of the telescopes' six operating science instruments. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
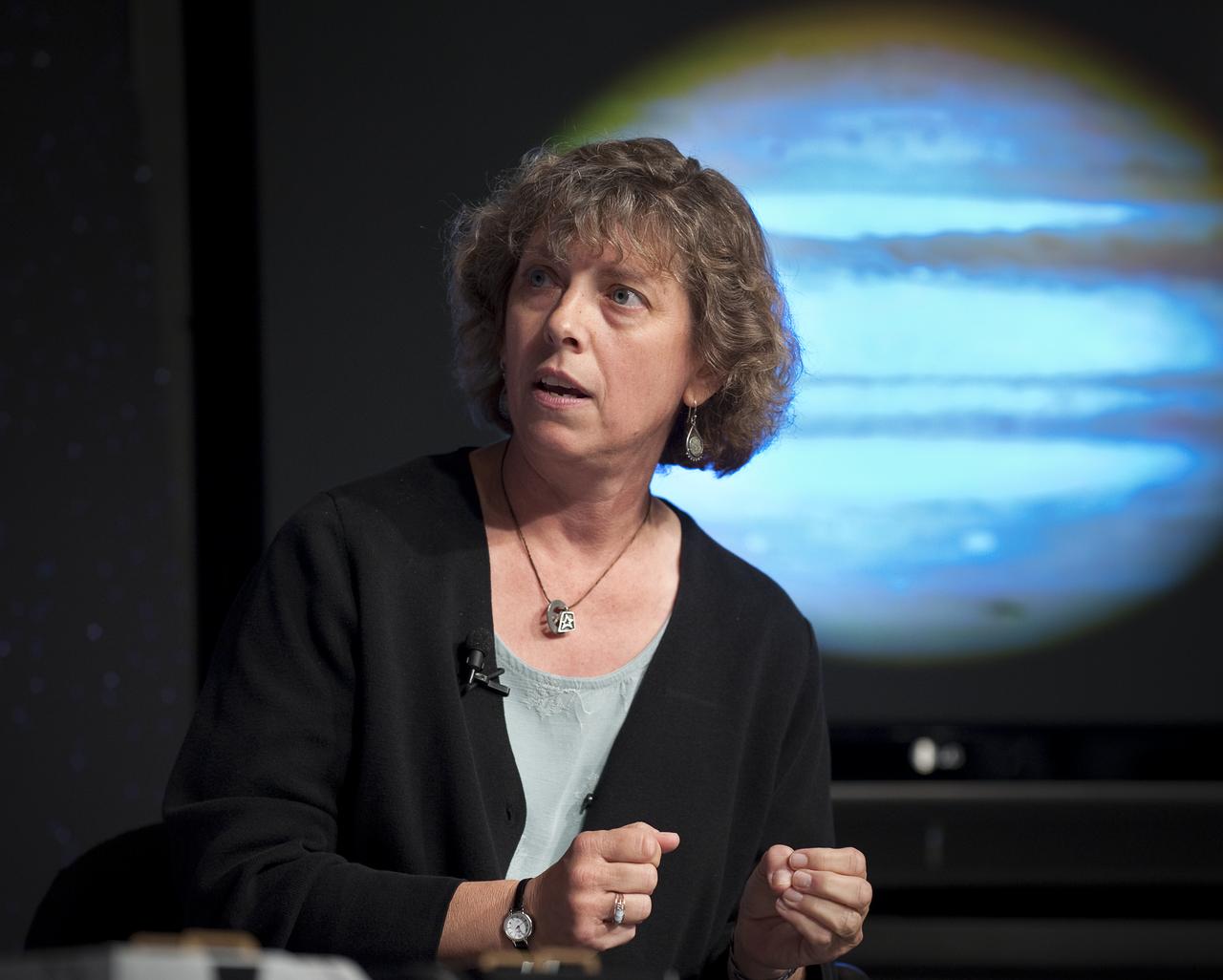

Heidi Hammel, senior research scientist at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colorado discusses newly released images from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope Wednesday, Sept. 9, 2009 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The images were from four of the telescopes' six operating science instruments. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
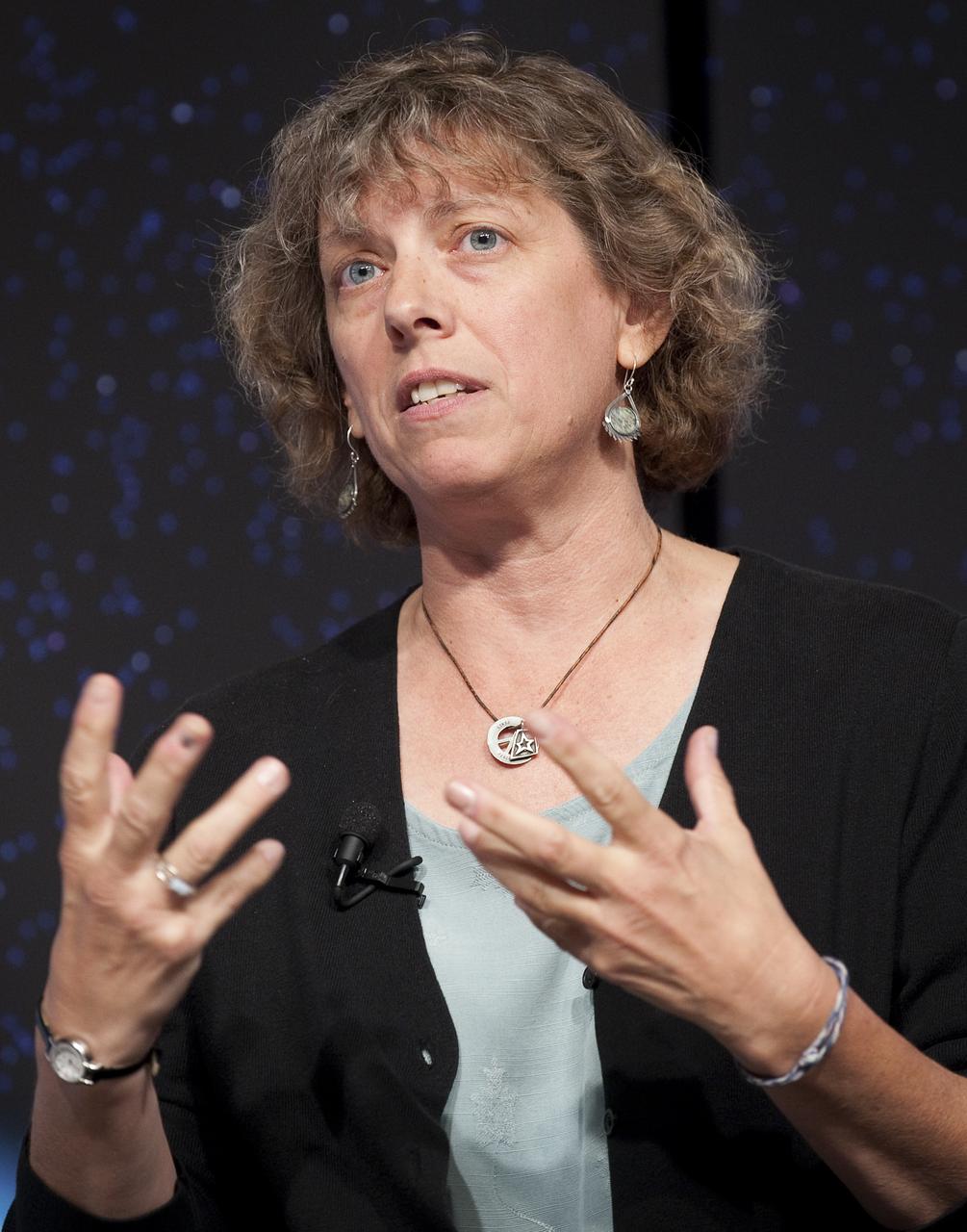

Heidi Hammel, senior research scientist at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colorado discusses newly released images from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope Wednesday, Sept. 9, 2009 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The images were from four of the telescopes' six operating science instruments. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Associate Administrator of the Science Mission Directorate Dr. Edward J. Weiler discusses newly released images from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope Wednesday, Sept. 9, 2009 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The images were from four of the telescopes' six operating science instruments. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
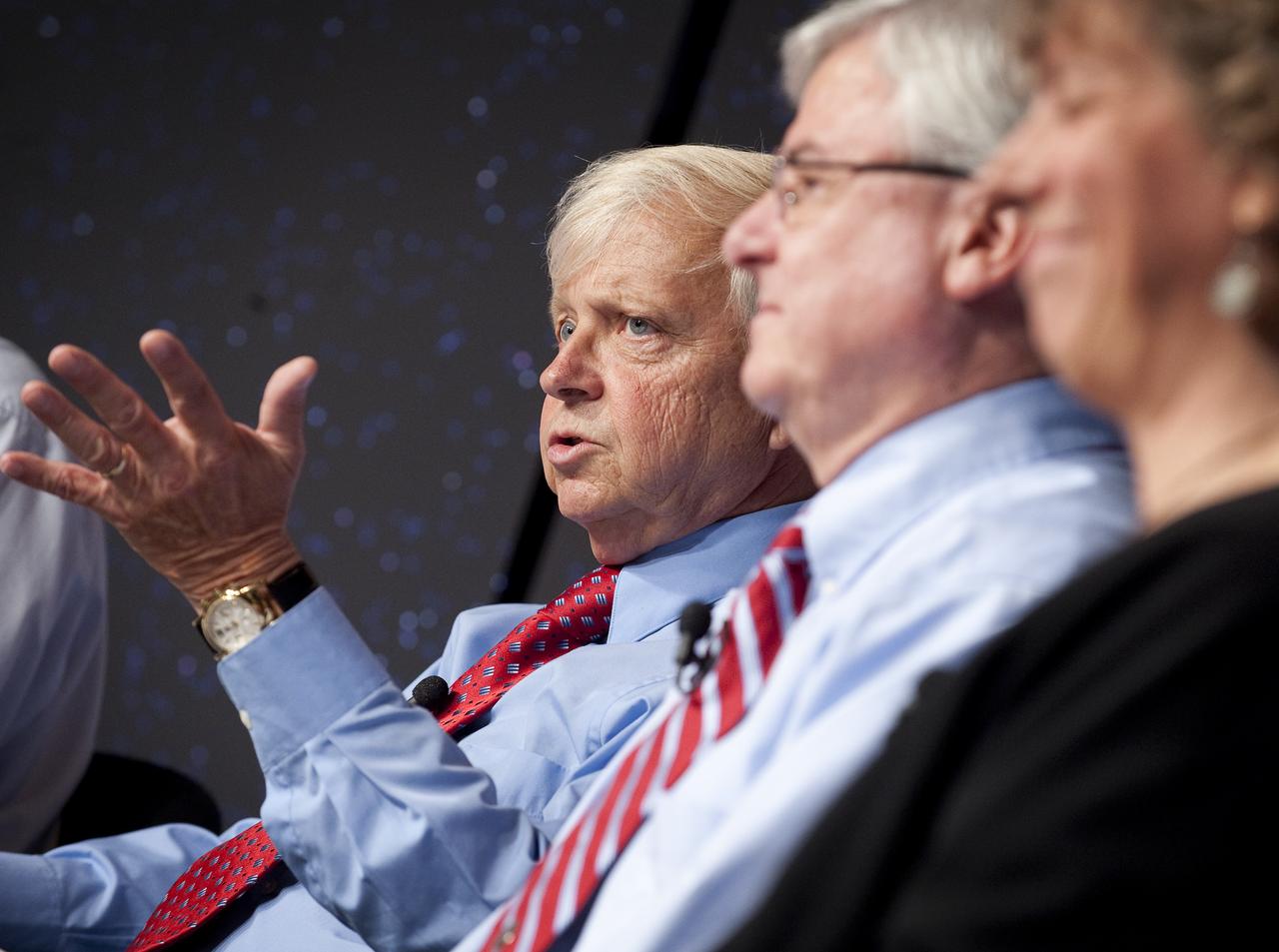

NASA Associate Administrator of the Science Mission Directorate Dr. Edward J. Weiler discusses newly released images from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope Wednesday, Sept. 9, 2009 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The images were from four of the telescopes' six operating science instruments. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
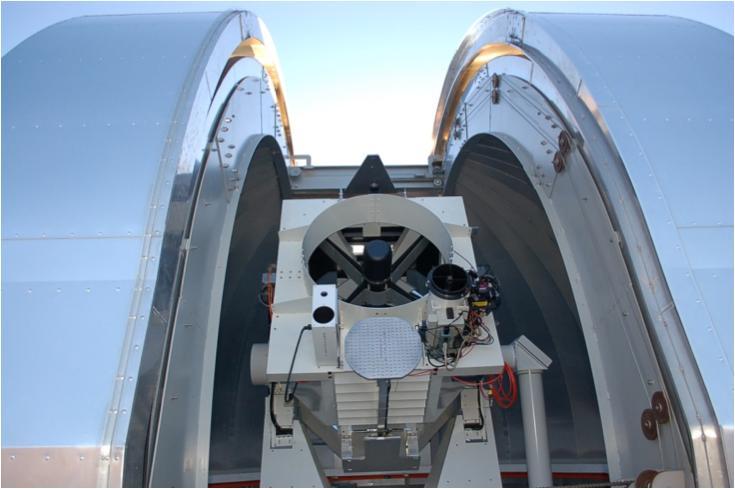

This is a 3-foot 1-meter aperture main telescope located at the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory Optical Communications Telescope Laboratory ground station.
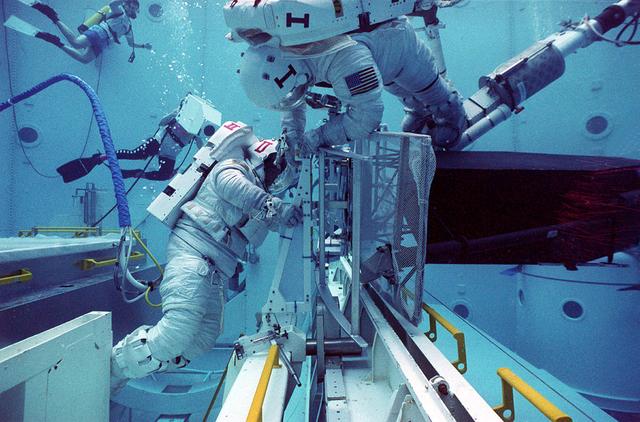
Astronauts Mark Lee and Rich Clifford perform test check-out procedures on the Hubble Space Telescope in the Marshall Space Flight Center's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS).
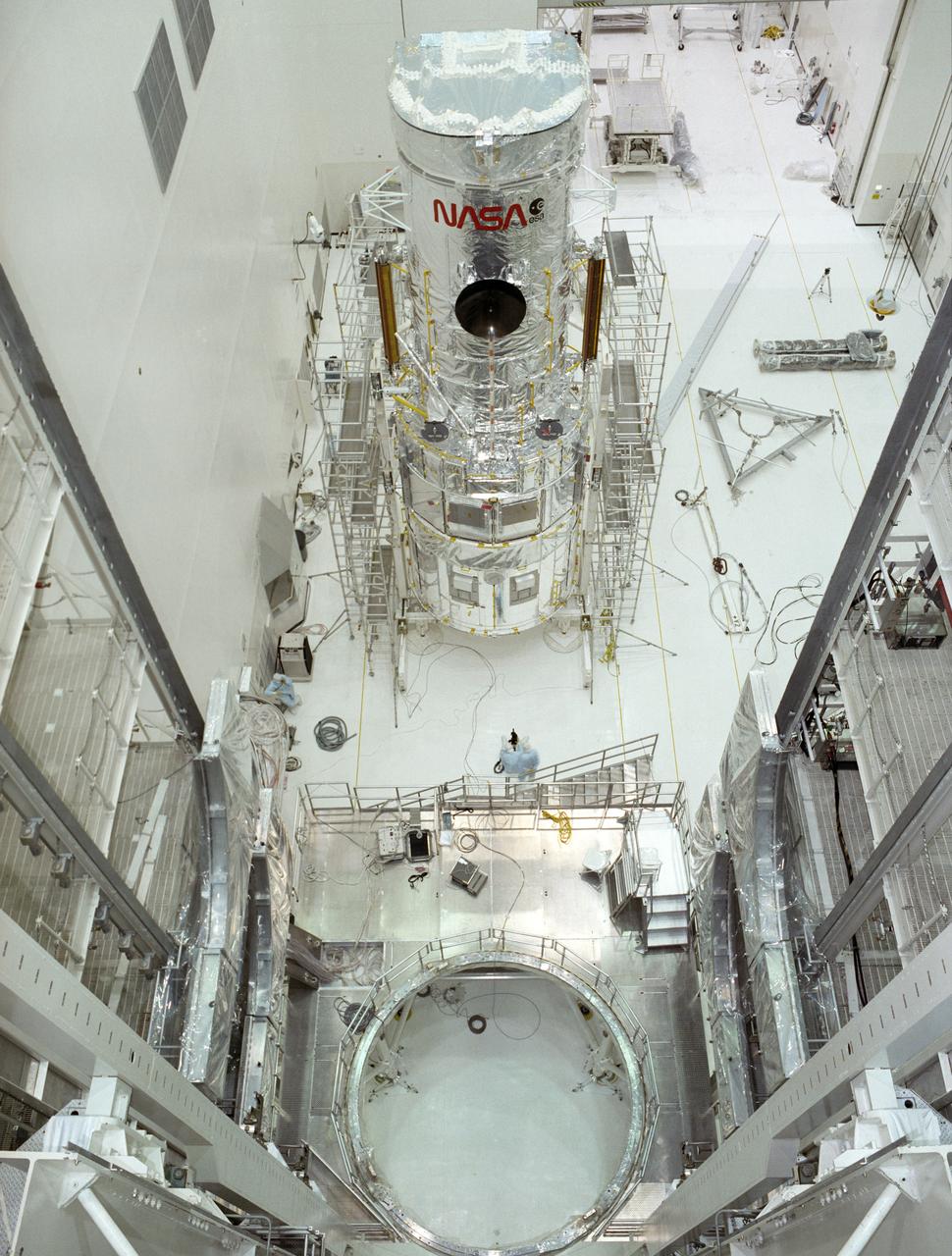

Ready for transportation to the Kennedy Space Center, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is pictured onboard the strongback dolly at the Vertical Processing Facility (VPF) at the Lockheed assembly plant upon completion of final testing and verification.
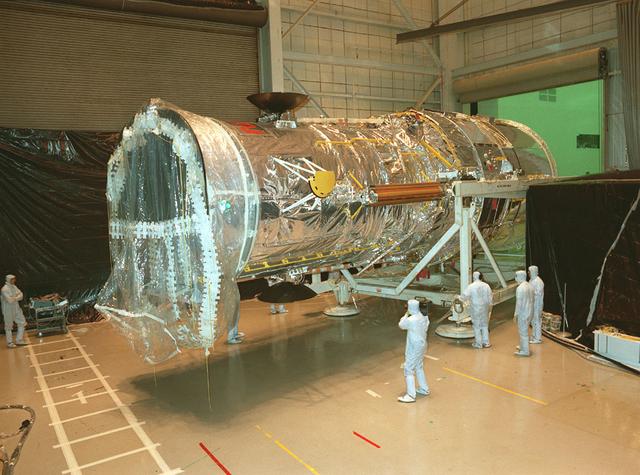

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) being transferred from the Vertical Assembly Test Area (VATA) to the High Bay at the Lockheed assembly plant in preparation for transport to the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) after final testing and verification.
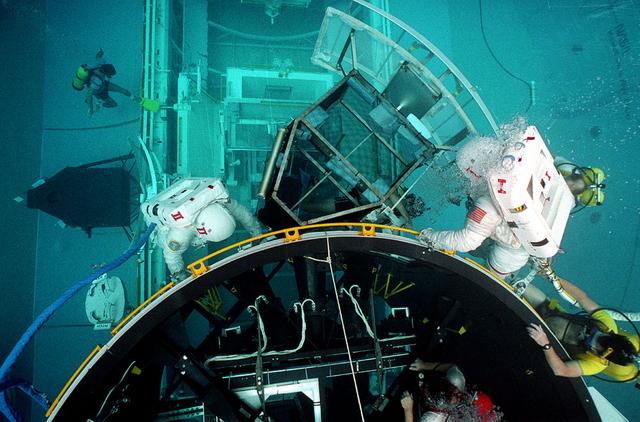

Astronauts Jim Voss and Jay Apt perform check-out procedures on a Hubble Space Telescope mock-up while working in the Marshall Space Flight Center's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS).

What look like giant twisters are spotted by the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). These images are, in actuality, pillars of gases that are in the process of the formation of a new star. These pillars can be billions of miles in length and may have been forming for millions of years. This one formation is located in the Lagoon Nebula and was captured by the Hubble's wide field planetary camera-2 (WFPC-2).
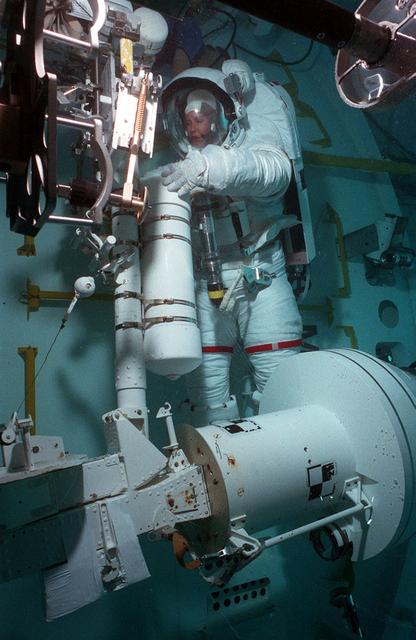

Astronaut Kathy Thornton conducts Hubble Space Telescope training in Marshall's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS).
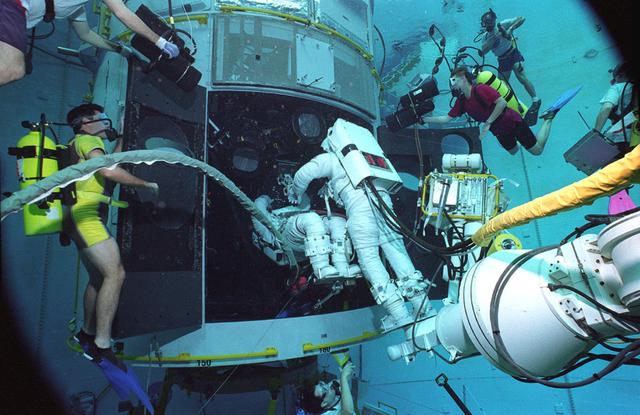

Astronauts Greg Harbaugh and Steve Smith conduct Hubble Space Telescope (HST) training in Marshall's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS).
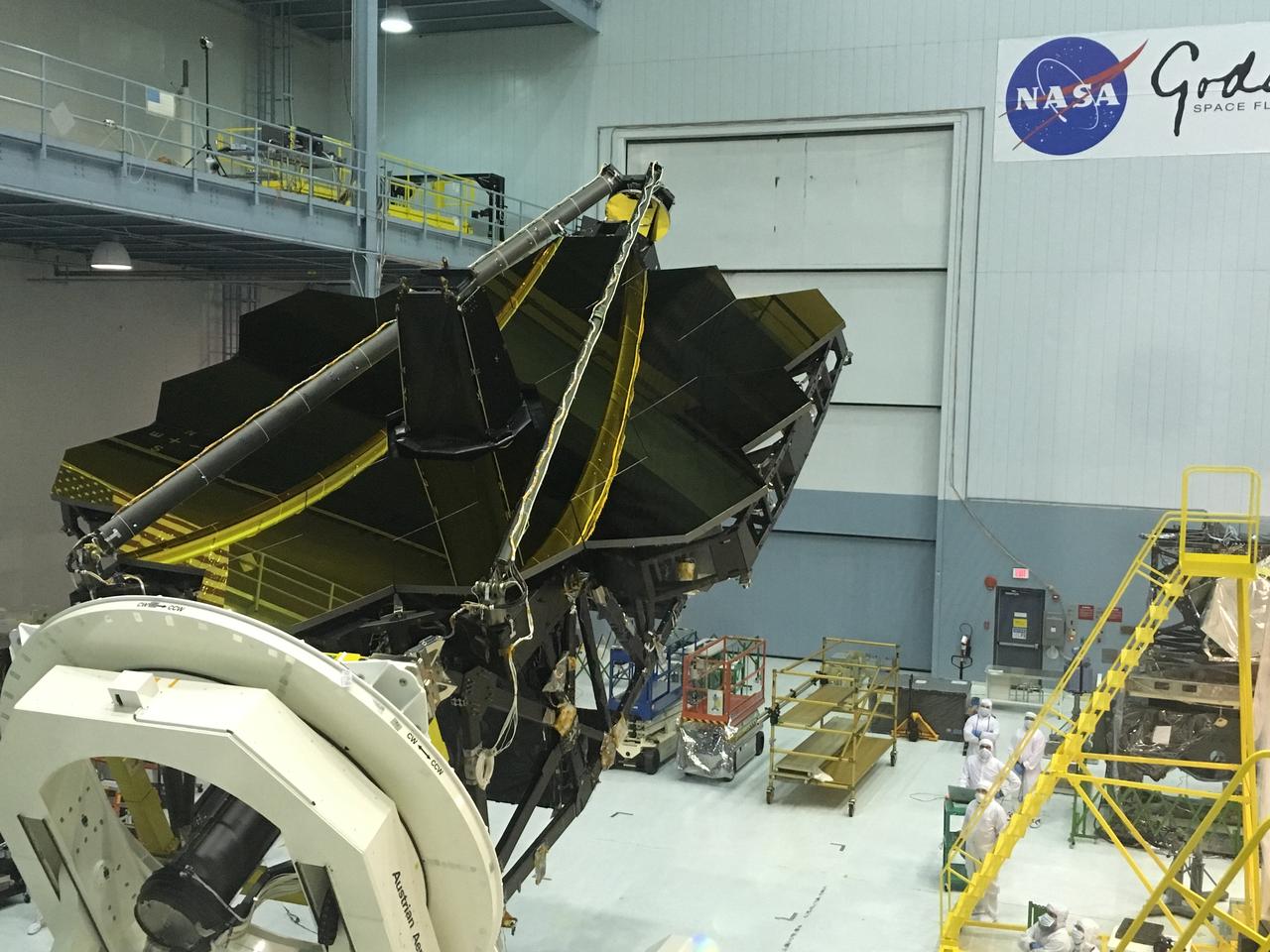

A rare view of the James Webb Space Telescope face-on, from the NASA Goddard cleanroom observation window.
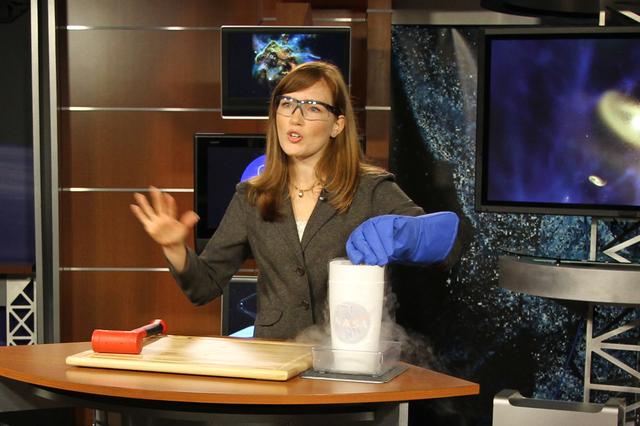

Amber Straughn talks about the extreme temperatures the Webb telescope must withstand in space.
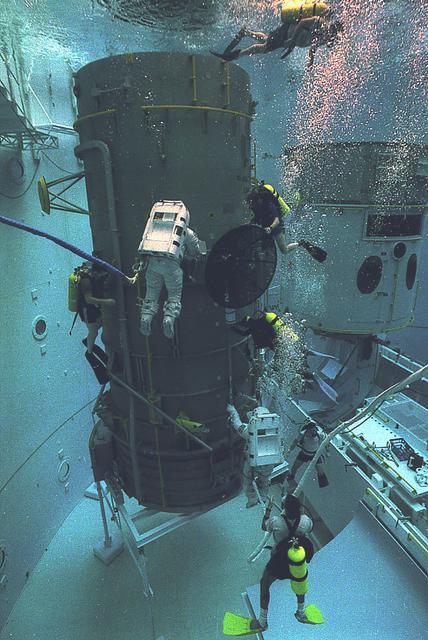

Underwater training is conducted in Marshall's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) in preparation for on-orbit Hubble Space Telescope operations.
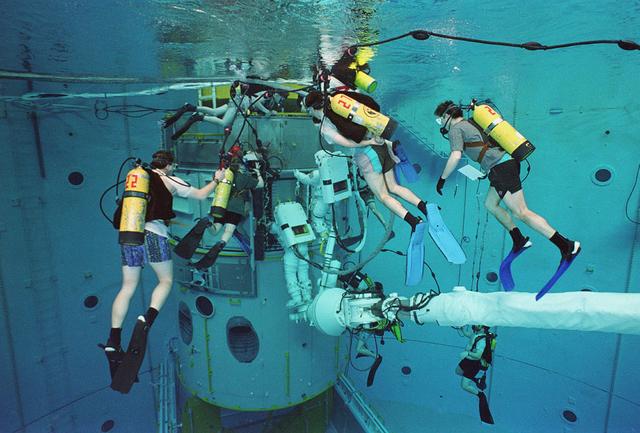

Underwater training is conducted in Marshall's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) in preparation for on-orbit Hubble Space Telescope operations.
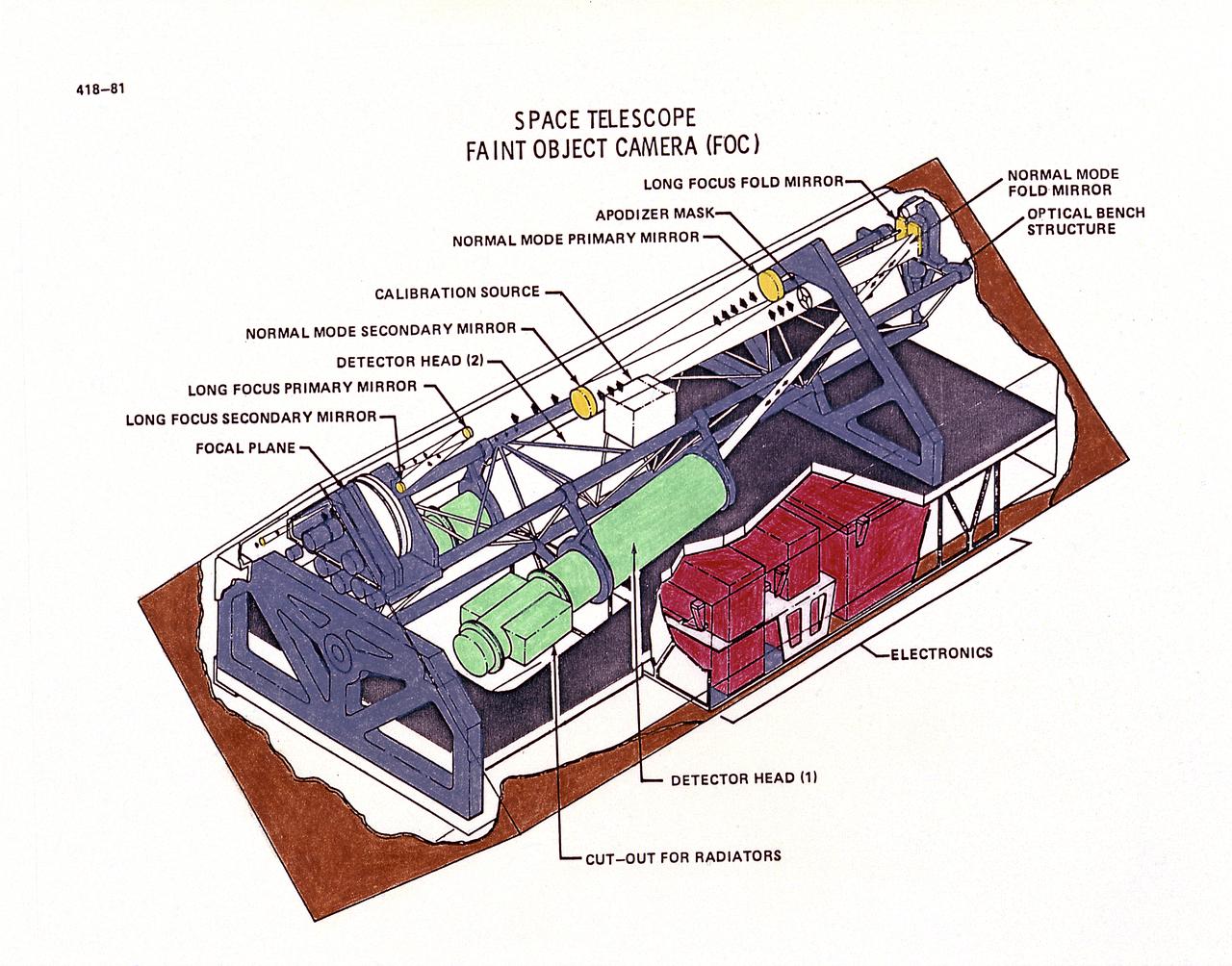
This drawing illustrates Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's), Faint Object Camera (FOC). The FOC reflects light down one of two optical pathways. The light enters a detector after passing through filters or through devices that can block out light from bright objects. Light from bright objects is blocked out to enable the FOC to see background images. The detector intensifies the image, then records it much like a television camera. For faint objects, images can be built up over long exposure times. The total image is translated into digital data, transmitted to Earth, and then reconstructed. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
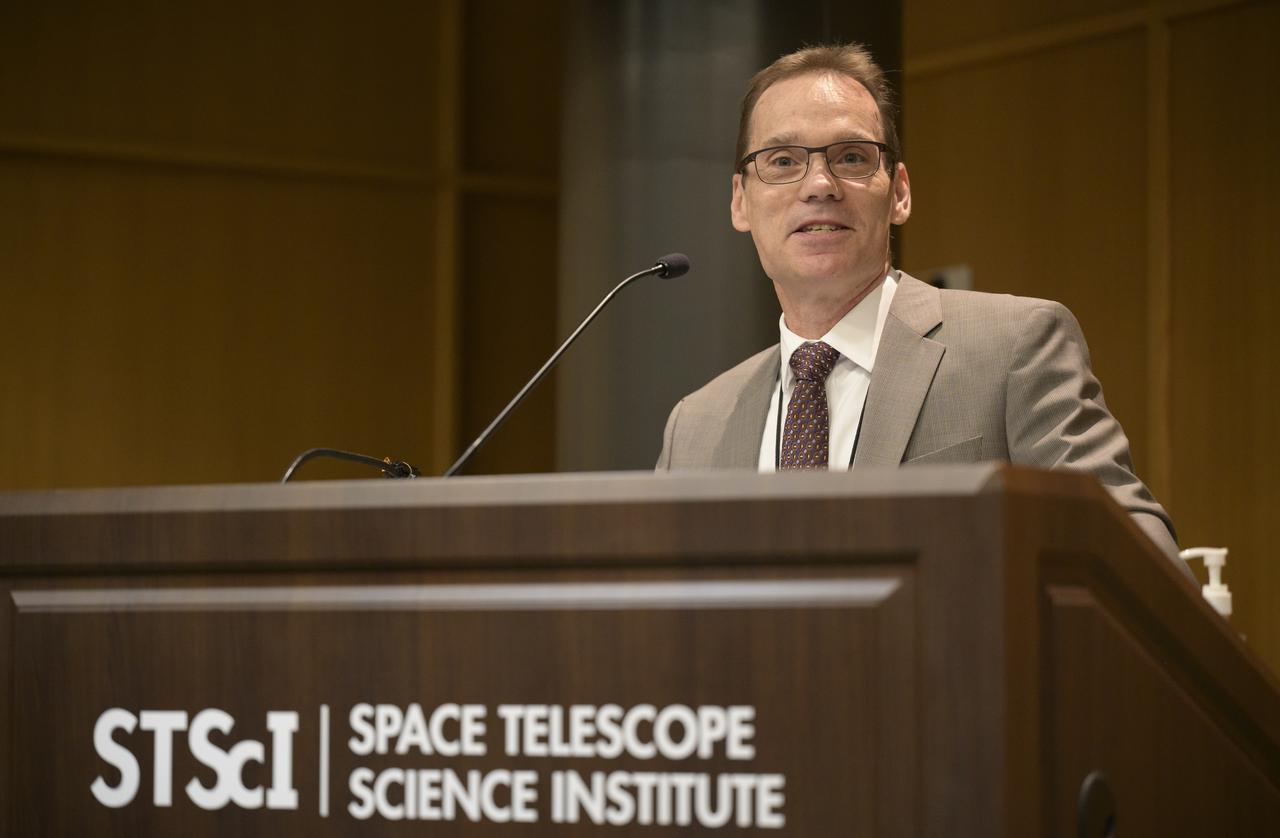

Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) Director Kenneth Sembach gives remarks during a briefing, Wednesday, June 29, 2022, at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore. The briefing focused on the status of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope in its final weeks of preparing for its science mission, as well as overviews of planned science for Webb’s first year of operations. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) Director Kenneth Sembach gives remarks during a briefing, Wednesday, June 29, 2022, at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore. The briefing focused on the status of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope in its final weeks of preparing for its science mission, as well as overviews of planned science for Webb’s first year of operations. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
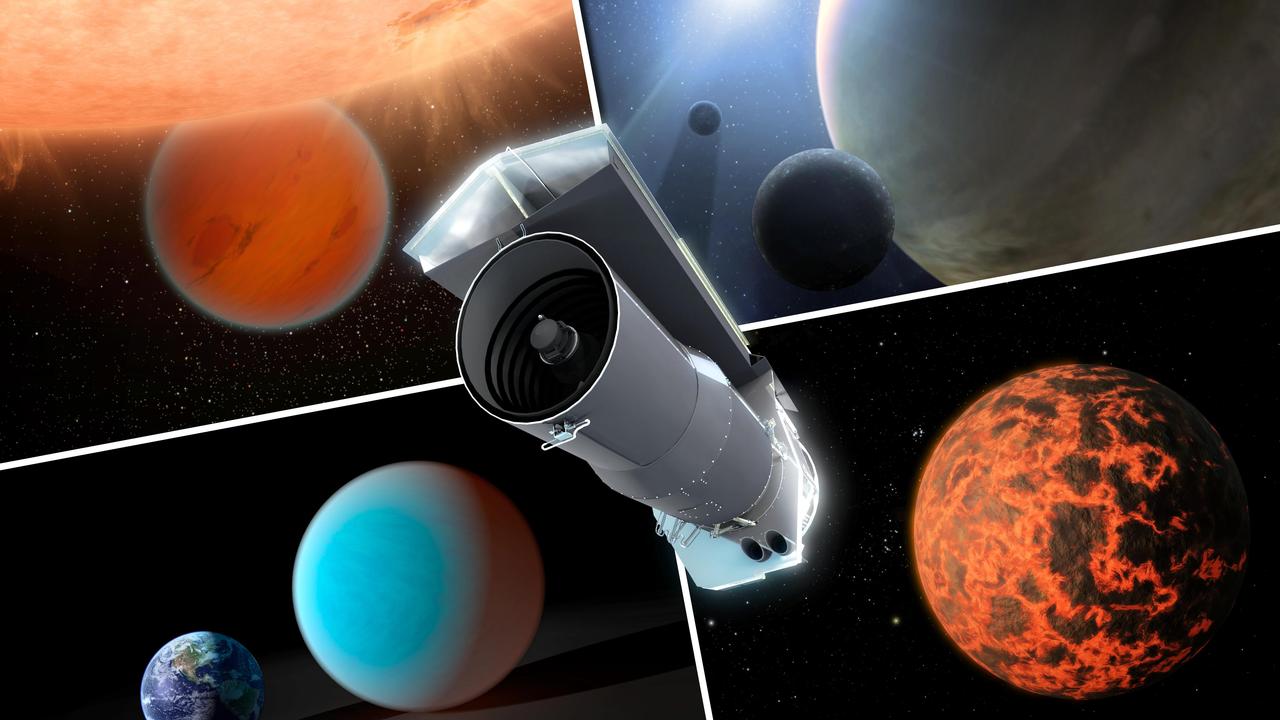

This artist concept shows NASA Spitzer Space Telescope surrounded by examples of exoplanets the telescope has examined in over its ten years in space.
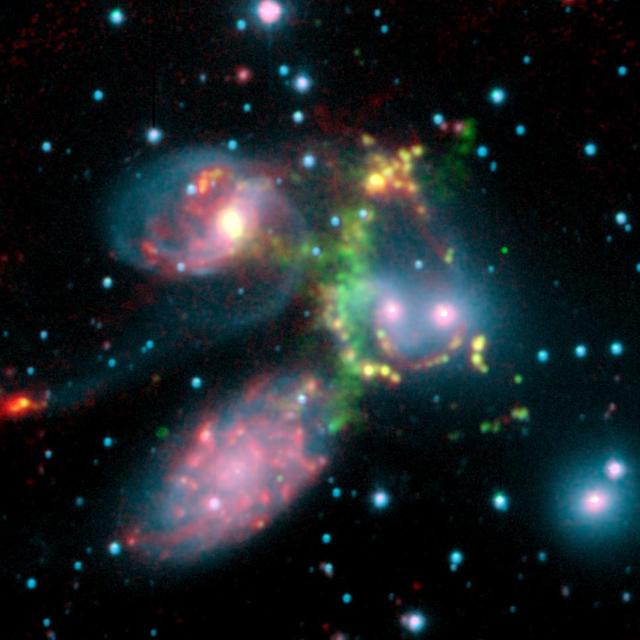

The false-color composite image of the Stephan’s Quintet galaxy cluster is made up of data from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope and a ground-based telescope in Spain.

This illustration depicts the design features of the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) Support Systems Module (SSM). The SSM is one of the three major elements of the HST and encloses the other two elements, the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA) and the Scientific Instruments (SI's). The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The spacecraft is 42.5-feet (13-meters) long and weighs 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). Two communication anternas, two solar array panels that collect energy for the HST, and storage bays for electronic gear are on the outside. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
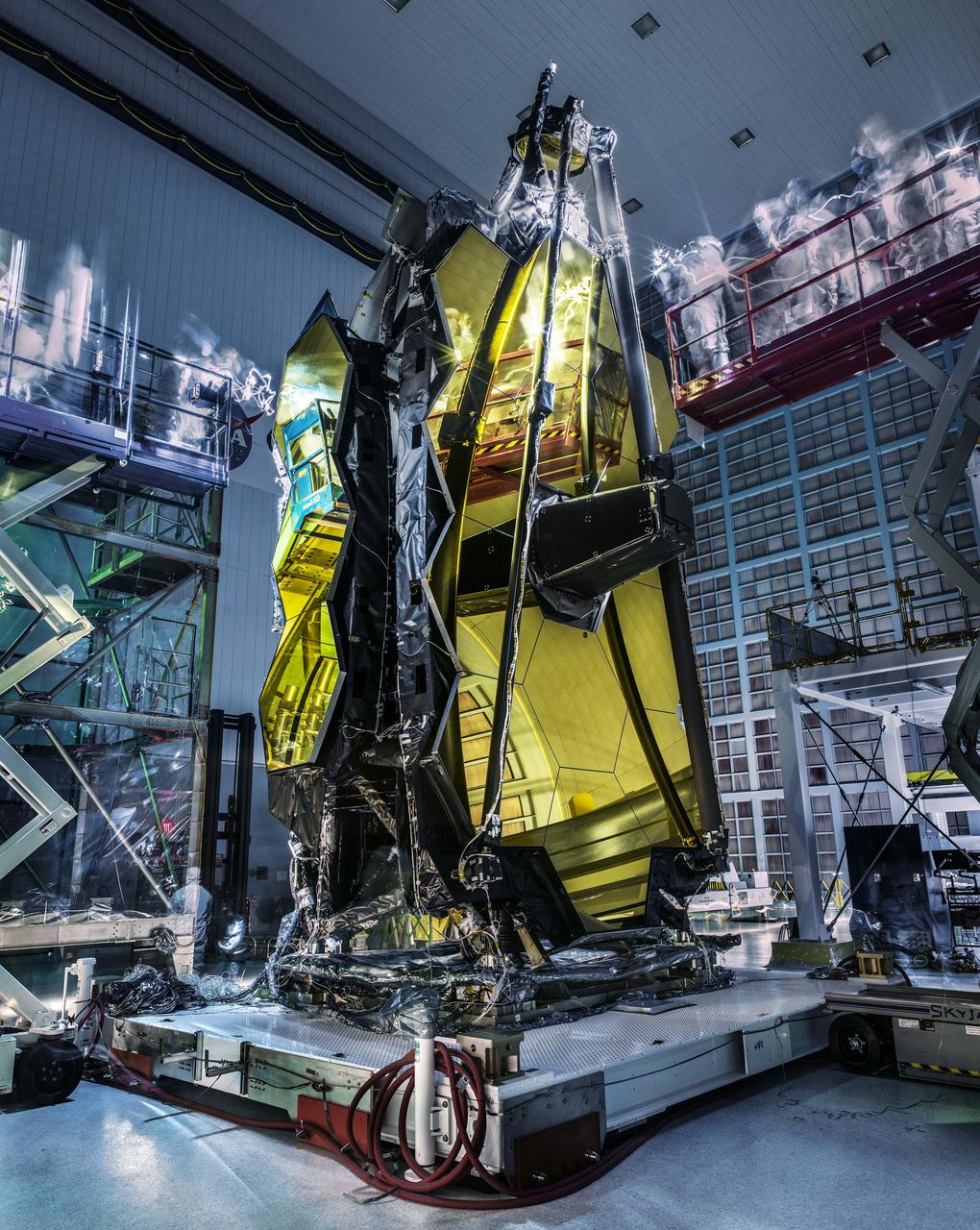

What happens when the lights are turned out in the enormous clean room that currently houses NASA's James Webb Space Telescope? The technicians who are inspecting the telescope and its expansive golden mirrors look like ghostly wraiths in this image as they conduct a "lights out inspection" in the Spacecraft Systems Development and Integration Facility (SSDIF) at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The clean room lights were turned off to inspect the telescope after it experienced vibration and acoustic testing. The contamination control engineer used a bright flashlight and special ultraviolet flashlights to inspect for contamination because it's easier to find in the dark. NASA photographer Chris Gunn said "The people have a ghostly appearance because it's a long exposure." He left the camera's shutter open for a longer than normal time so the movement of the technicians appear as a blur. He also used a special light "painting" technique to light up the primary mirror. The James Webb Space Telescope is the scientific successor to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. It will be the most powerful space telescope ever built. Webb is an international project led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and the Canadian Space Agency. For more information about the Webb telescope visit: <a href="http://www.jwst.nasa.gov" rel="nofollow">www.jwst.nasa.gov</a> or <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/webb" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/webb</a> Image Credit: NASA/Chris Gunn
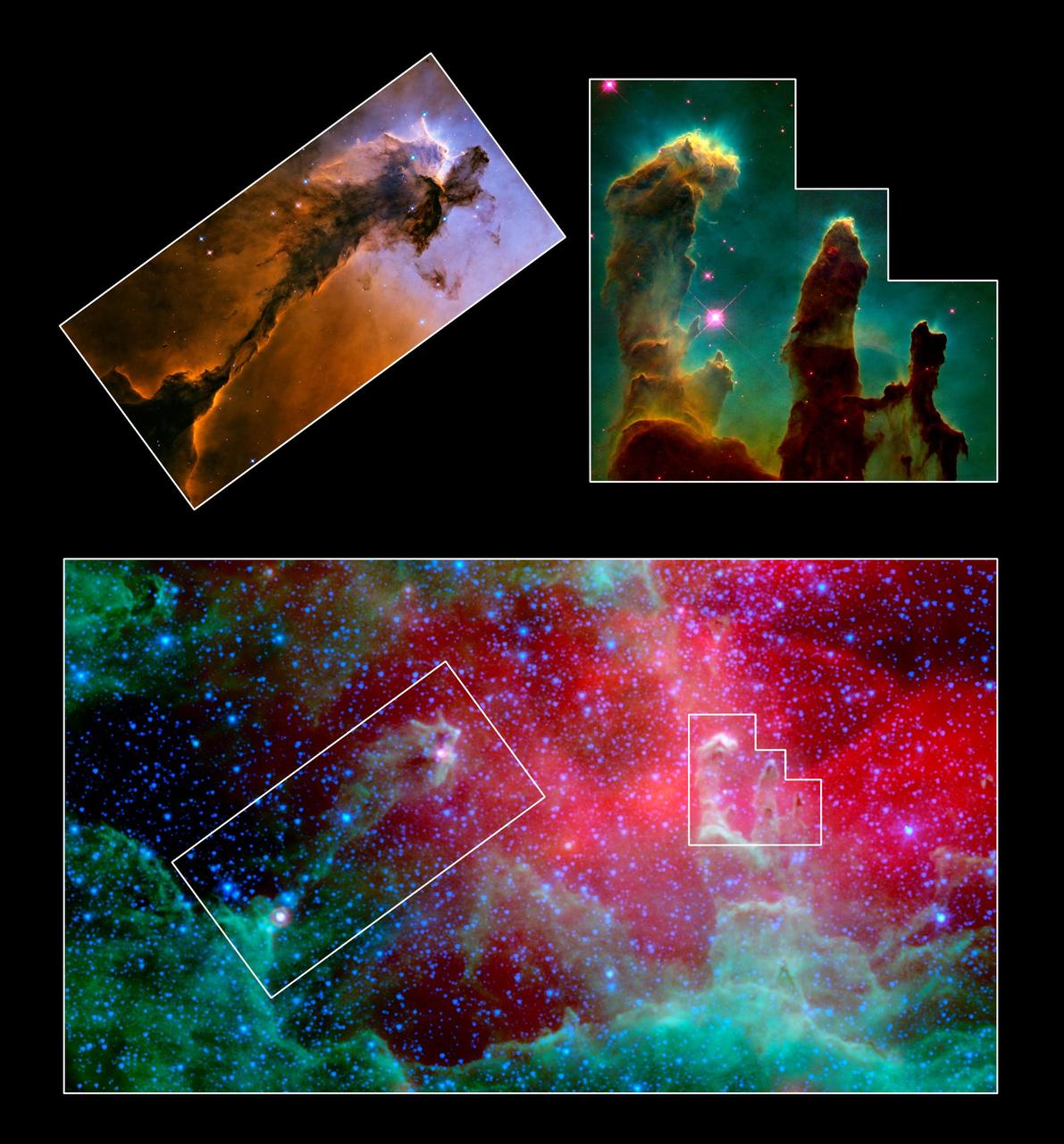

This image composite highlights the pillars of the Eagle nebula, as seen in infrared light by NASA Spitzer Space Telescope bottom and visible light by NASA Hubble Space Telescope top insets.
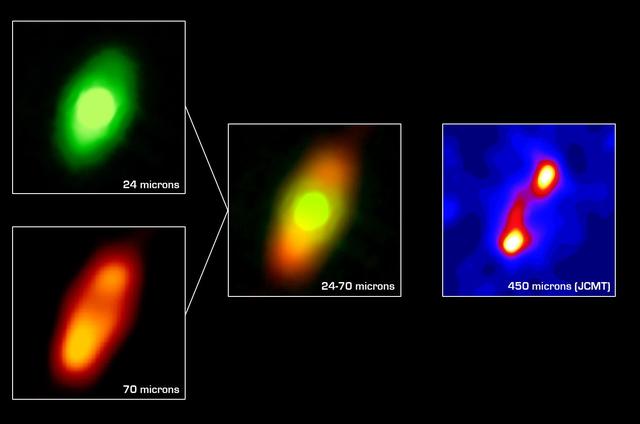
NASA Spitzer Space Telescope has obtained the first infrared images of the dust disc surrounding Fomalhaut, the 18th brightest star in the sky.
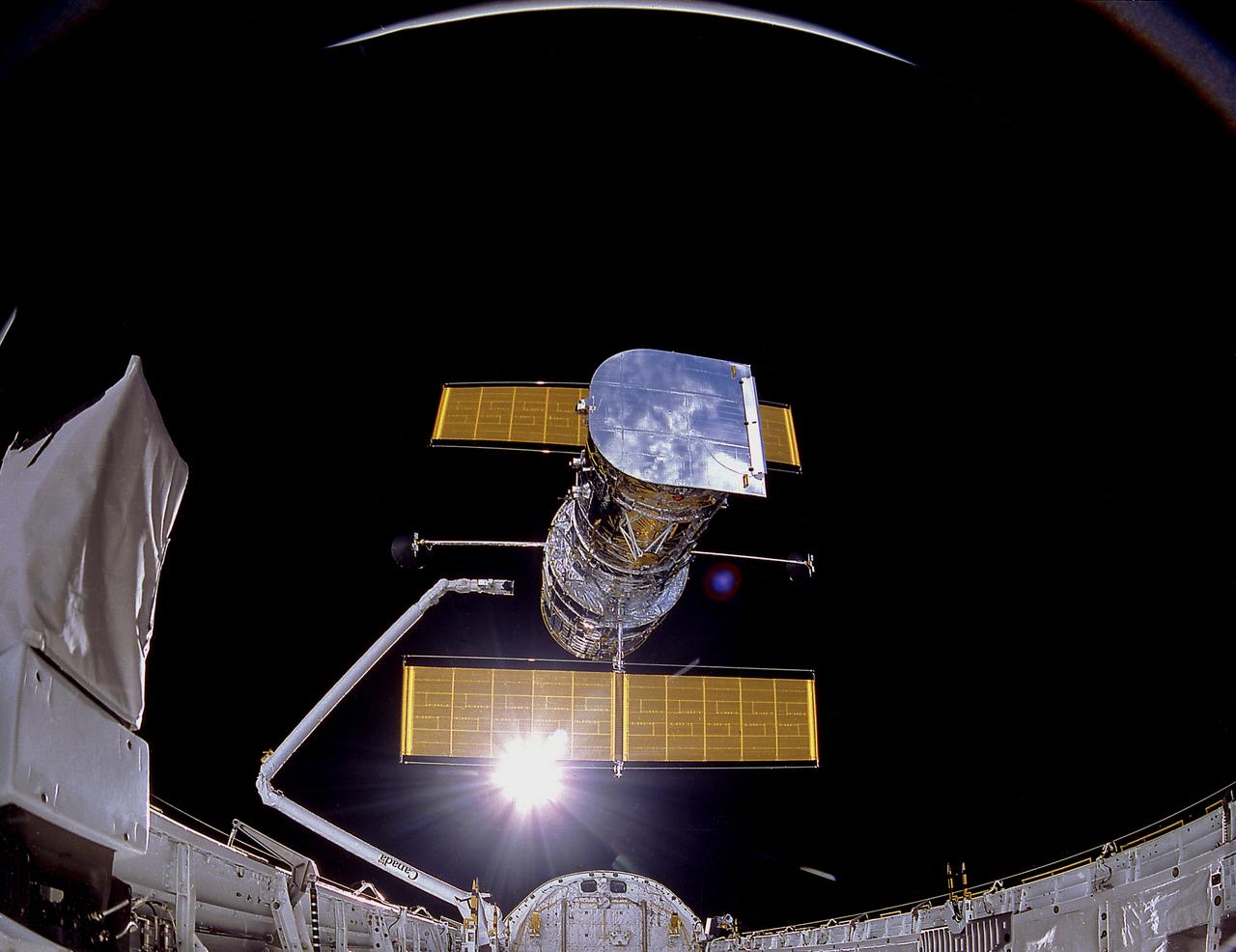

In this photograph, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was being deployed on April 25, 1990. The photograph was taken by the IMAX Cargo Bay Camera (ICBC) mounted in a container on the port side of the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery (STS-31 mission). The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit for 15 years or more. The HST provides fine detail imaging, produces ultraviolet images and spectra, and detects very faint objects. Two months after its deployment in space, scientists detected a 2-micron spherical aberration in the primary mirror of the HST that affected the telescope's ability to focus faint light sources into a precise point. This imperfection was very slight, one-fiftieth of the width of a human hair. A scheduled Space Service servicing mission (STS-61) in 1993 permitted scientists to correct the problem. During four spacewalks, new instruments were installed into the HST that had optical corrections. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. Photo Credit: NASA/Smithsonian Institution/Lockheed Corporation.

David Leckrone, senior project scientist for Hubble at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. discusses newly released images from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope Wednesday, Sept. 9, 2009 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The images were from four of the telescopes' six operating science instruments. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Charles F. Bolden delivers his remarks during a press conference where NASA unveiled new images from the Hubble Space Telescope Wednesday, Sept. 9, 2009 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The unveiled images were from four of the telescopes' six operating science instruments. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Associate Administrator of the Science Mission Directorate Dr. Edward J. Weiler listens to a reporters question during a press conference where NASA released images from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope Wednesday, Sept. 9, 2009 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The images were from four of the telescopes' six operating science instruments. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Charles F. Bolden delivers his remarks during a press conference where NASA unveiled new images from the Hubble Space Telescope Wednesday, Sept. 9, 2009 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The unveiled images were from four of the telescopes' six operating science instruments. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

David Leckrone, senior project scientist for Hubble at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. discusses newly released images from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope Wednesday, Sept. 9, 2009 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The images were from four of the telescopes' six operating science instruments. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Charles F. Bolden delivers his remarks during a press conference where NASA unveiled new images from the Hubble Space Telescope Wednesday, Sept. 9, 2009 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The unveiled images were from four of the telescopes' six operating science instruments. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
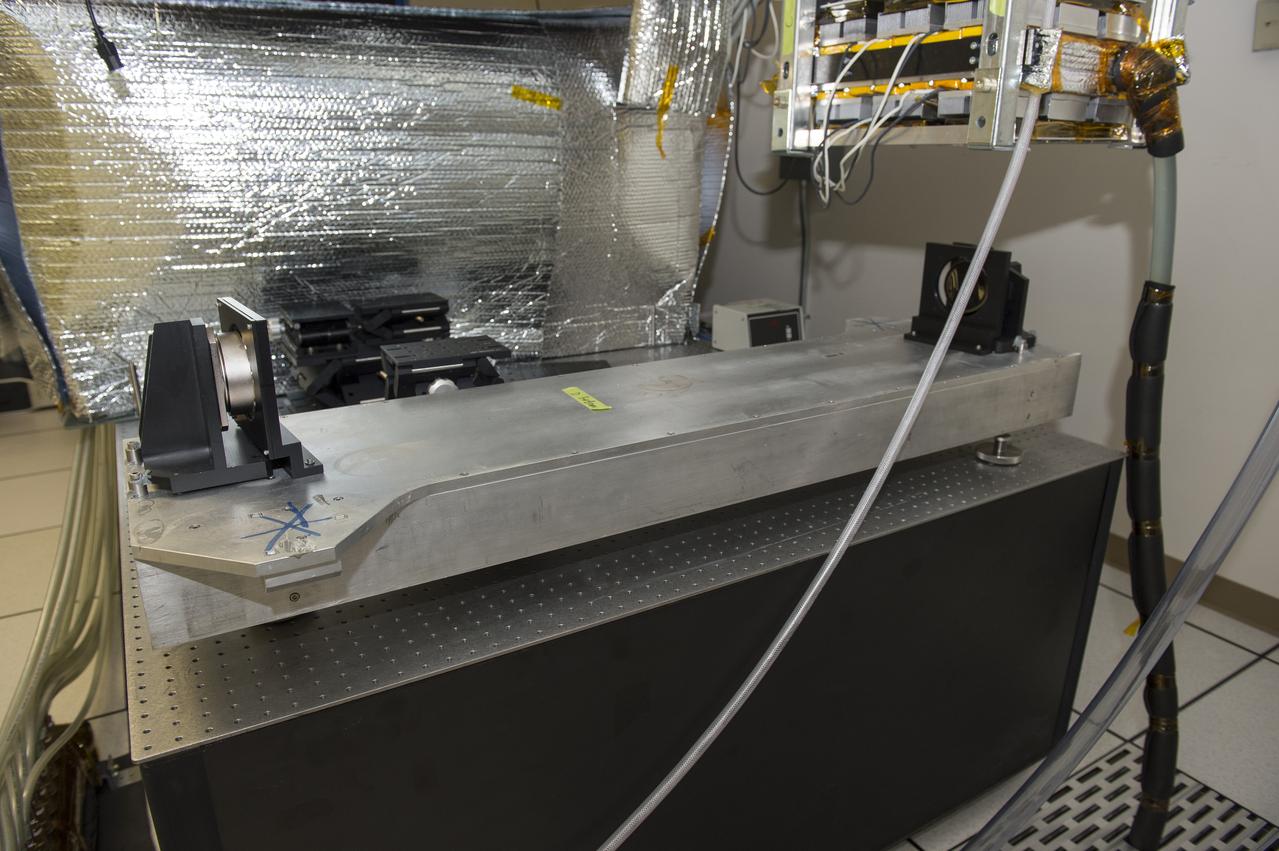
Next Generation PIAA mirrors were made by Tinsley and are inside the enclosure. Shows dummy set-up uning early PIAA mirors made by Axsys on loan to Ames from JPL.

The James Webb Space Telescope was lifted out of its assembly stand for the last time at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. In this photo, the telescope was hanging upside down as the lift crew were about to install it in the rollover fixture where it will be situated before moving on to its upcoming center of curvature test. Image credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn
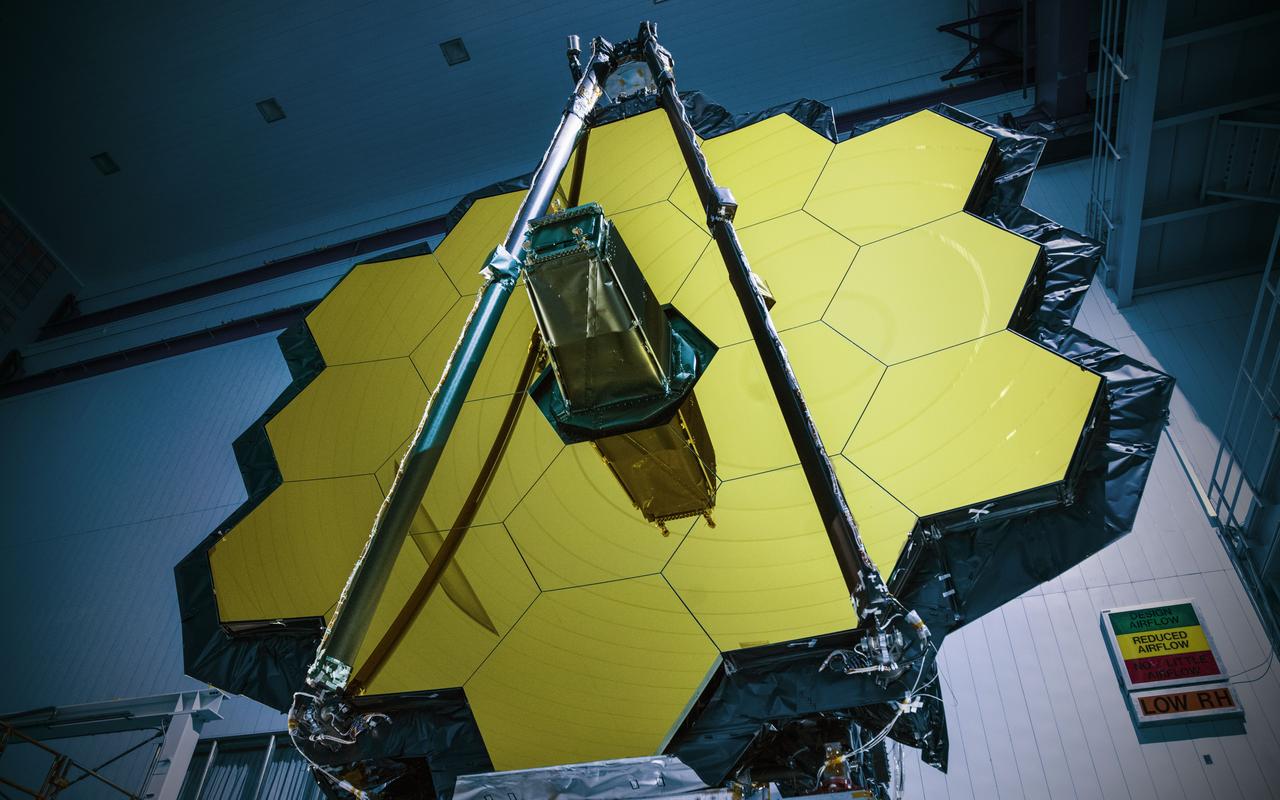

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has successfully passed the center of curvature test, an important optical measurement of Webb’s fully assembled primary mirror prior to cryogenic testing, and the last test held at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, before the spacecraft is shipped to NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston for more testing. After undergoing rigorous environmental tests simulating the stresses of its rocket launch, the Webb telescope team at Goddard analyzed the results from this critical optical test and compared it to the pre-test measurements. The team concluded that the mirrors passed the test with the optical system unscathed. “The Webb telescope is about to embark on its next step in reaching the stars as it has successfully completed its integration and testing at Goddard. It has taken a tremendous team of talented individuals to get to this point from all across NASA, our industry and international partners, and academia,” said Bill Ochs, NASA’s Webb telescope project manager. “It is also a sad time as we say goodbye to the Webb Telescope at Goddard, but are excited to begin cryogenic testing at Johnson.” Rocket launches create high levels of vibration and noise that rattle spacecraft and telescopes. At Goddard, engineers tested the Webb telescope in vibration and acoustics test facilities that simulate the launch environment to ensure that functionality is not impaired by the rigorous ride on a rocket into space. Before and after these environmental tests took place, optical engineers set up an interferometer, the main device used to measure the shape of the Webb telescope’s mirror. An interferometer gets its name from the process of recording and measuring the ripple patterns that result when different beams of light mix and their waves combine or “interfere.” Waves of visible light are less than a thousandth of a millimeter long and optics on the Webb telescope need to be shaped and aligned even more accurately than that to work correctly. Making measurements of the mirror shape and position by lasers prevents physical contact and damage (scratches to the mirror). So, scientists use wavelengths of light to make tiny measurements. By measuring light reflected off the optics using an interferometer, they are able to measure extremely small changes in shape or position that may occur after exposing the mirror to a simulated launch or temperatures that simulate the subfreezing environment of space. During a test conducted by a team from Goddard, Ball Aerospace of Boulder, Colorado, and the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, temperature and humidity conditions in the clean room were kept incredibly stable to minimize fluctuations in the sensitive optical measurements over time. Even so, tiny vibrations are ever-present in the clean room that cause jitter during measurements, so the interferometer is a “high-speed” one, taking 5,000 “frames” every second, which is a faster rate than the background vibrations themselves. This allows engineers to subtract out jitter and get good, clean results on any changes to the mirror's shape. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn Read more: <a href="https://go.nasa.gov/2oPqHwR" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2oPqHwR</a> NASA’s Webb Telescope Completes Goddard Testing
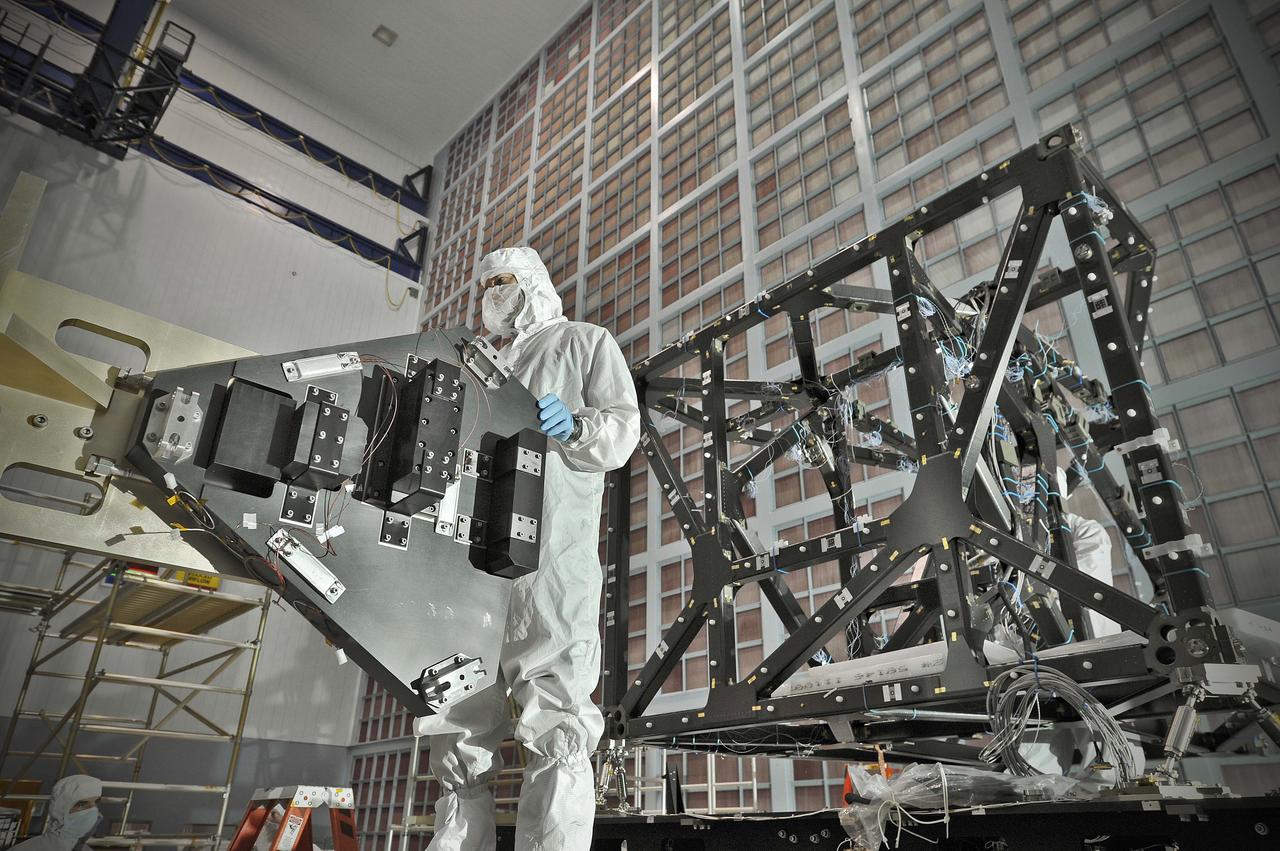

NASA image release September 17, 2010 In preparation for a cryogenic test NASA Goddard technicians install instrument mass simulators onto the James Webb Space Telescope ISIM structure. The ISIM Structure supports and holds the four Webb telescope science instruments : the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), the Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), the Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) and the Fine Guidance Sensor (FGS). Credit: NASA/GSFC/Chris Gunn To learn more about the James Webb Space Telescope go to: <a href="http://www.jwst.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">www.jwst.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> contributes to NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s endeavors by providing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
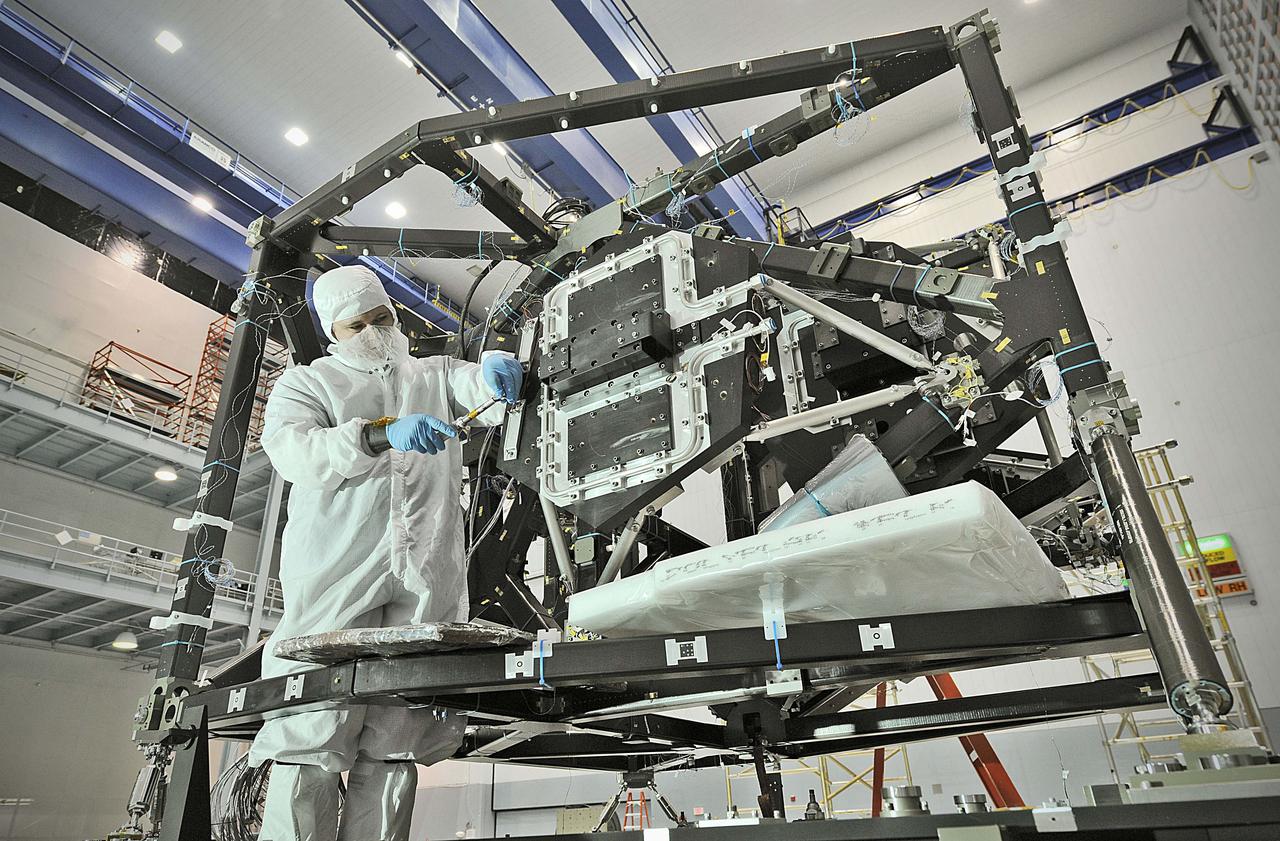

NASA image release September 17, 2010 In preparation for a cryogenic test NASA Goddard technicians install instrument mass simulators onto the James Webb Space Telescope ISIM structure. The ISIM Structure supports and holds the four Webb telescope science instruments : the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), the Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), the Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) and the Fine Guidance Sensor (FGS). Credit: NASA/GSFC/Chris Gunn To learn more about the James Webb Space Telescope go to: <a href="http://www.jwst.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">www.jwst.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> contributes to NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s endeavors by providing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

This infographic explains how NASA Spitzer Space Telescope can be used in tandem with a telescope on the ground to measure the distances to planets discovered using the microlensing technique. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19332
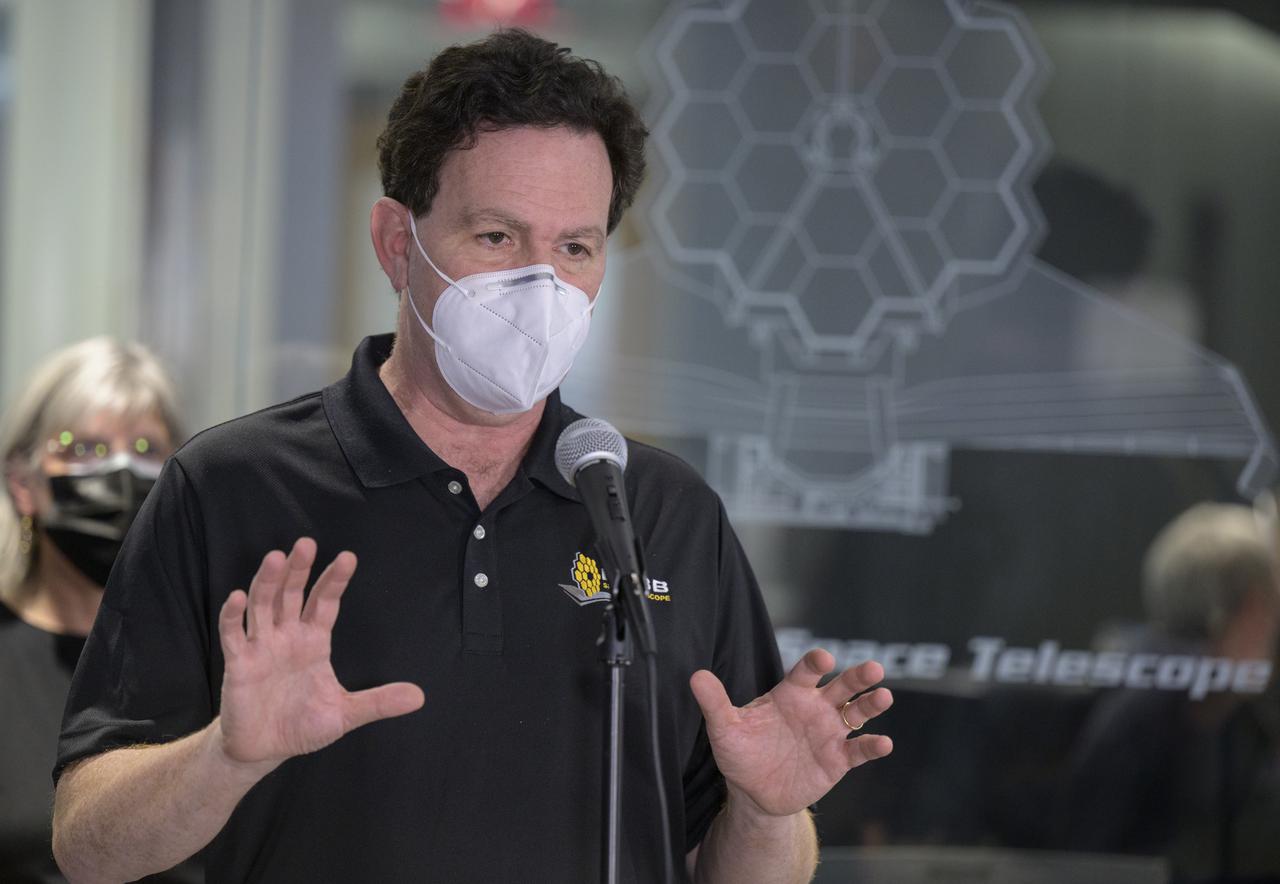

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Element Manager Lee Feinberg answers questions from the media during a briefing following the successful deployment of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope primary mirror, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from the Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. With Webb’s 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror fully deployed, the infrared observatory has completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Mission Systems Engineer Mike Menzel answers questions from the media during a briefing following the successful deployment of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope primary mirror, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from the Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. With Webb’s 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror fully deployed, the infrared observatory has completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Operations Project Scientist Jane Rigby answers questions from the media during a briefing following the successful deployment of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope primary mirror, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from the Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. With Webb’s 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror fully deployed, the infrared observatory has completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Commissioning Manager John Durning answers questions from the media during a briefing following the successful deployment of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope primary mirror, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from the Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. With Webb’s 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror fully deployed, the infrared observatory has completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Operations Project Scientist Jane Rigby answers questions from the media during a briefing following the successful deployment of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope primary mirror, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from the Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. With Webb’s 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror fully deployed, the infrared observatory has completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)