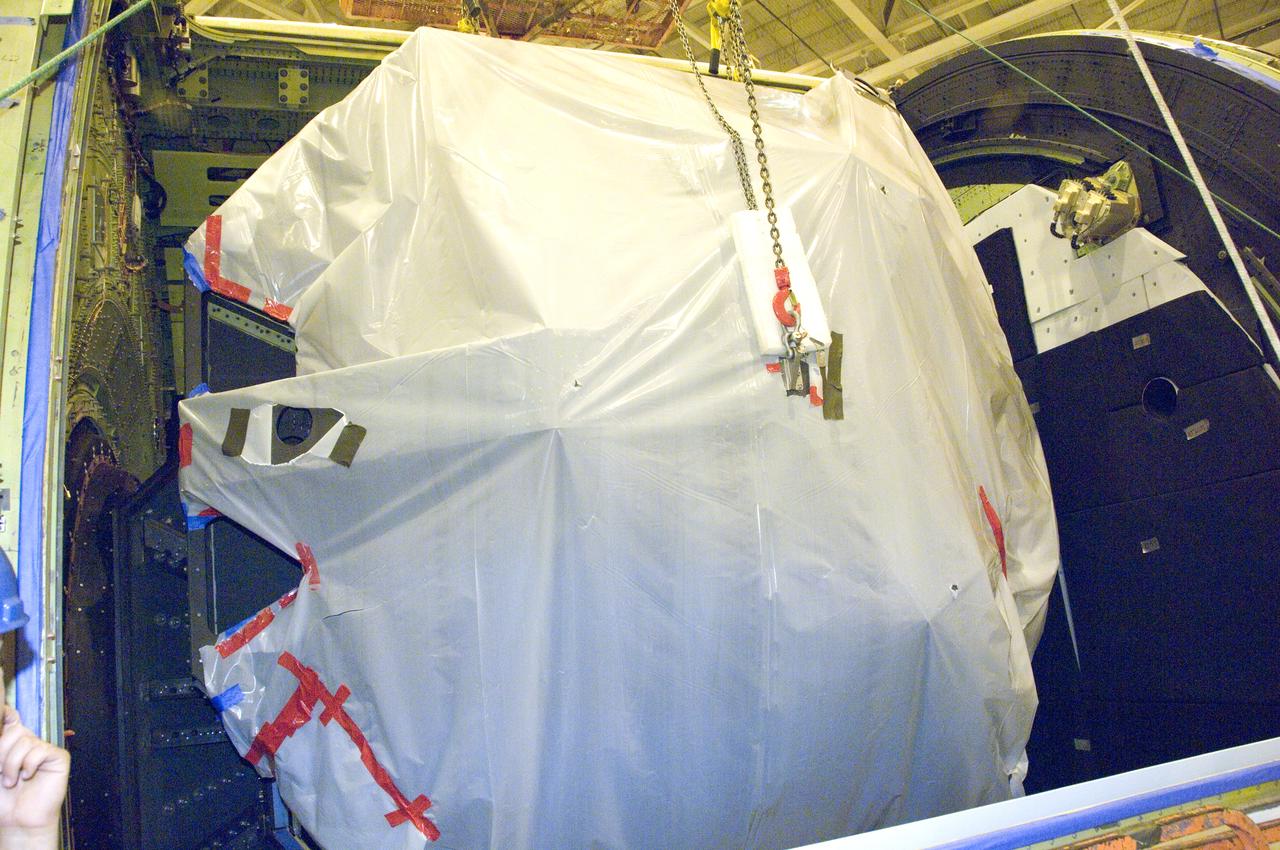

SOFIA's primary mirror is placed in the telescope cavity for reinstallation prior to telescope adjustments preparing SOFIA for first science.
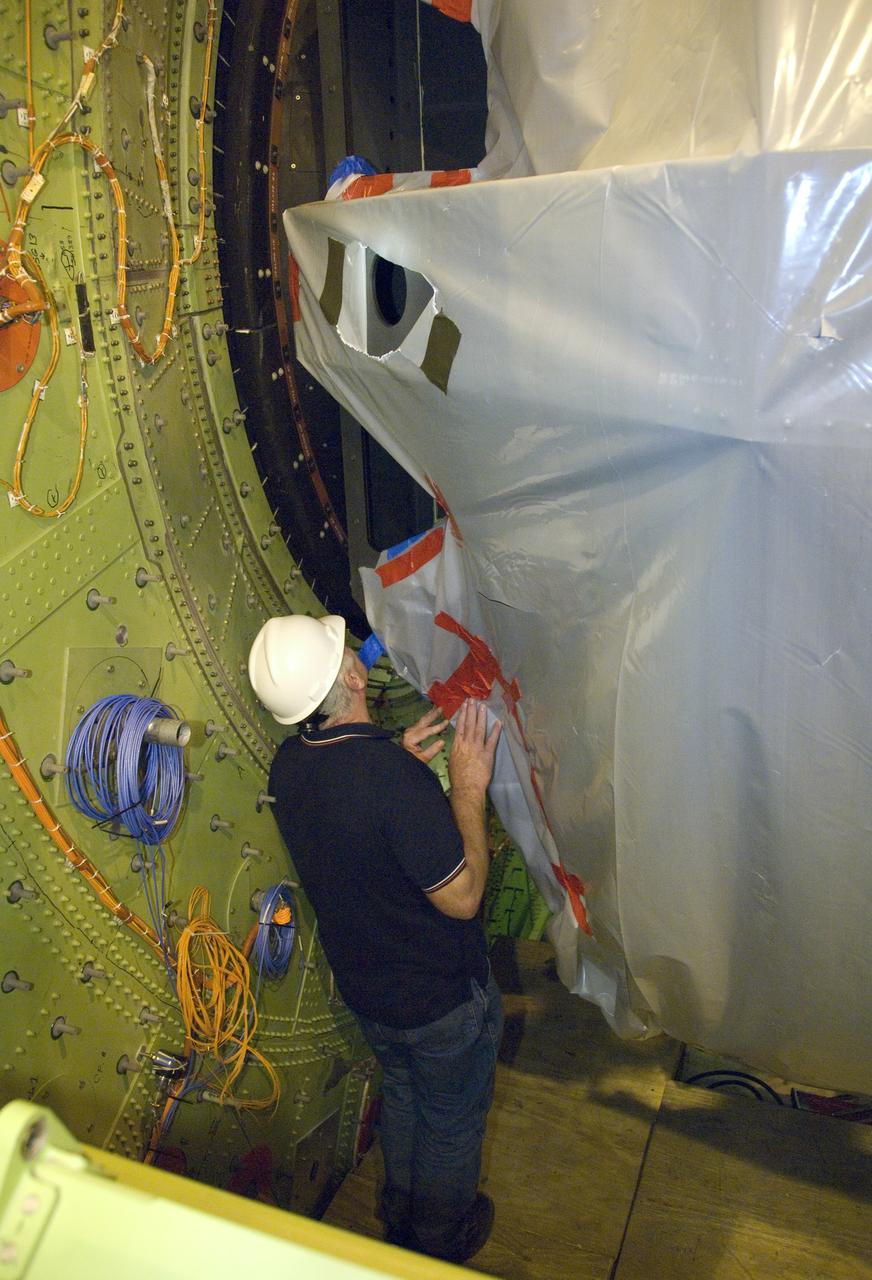

A technician guides SOFIA's primary mirror assembly into the aircraft's telescope cavity completing the mirror reinstallation following its initial coating.
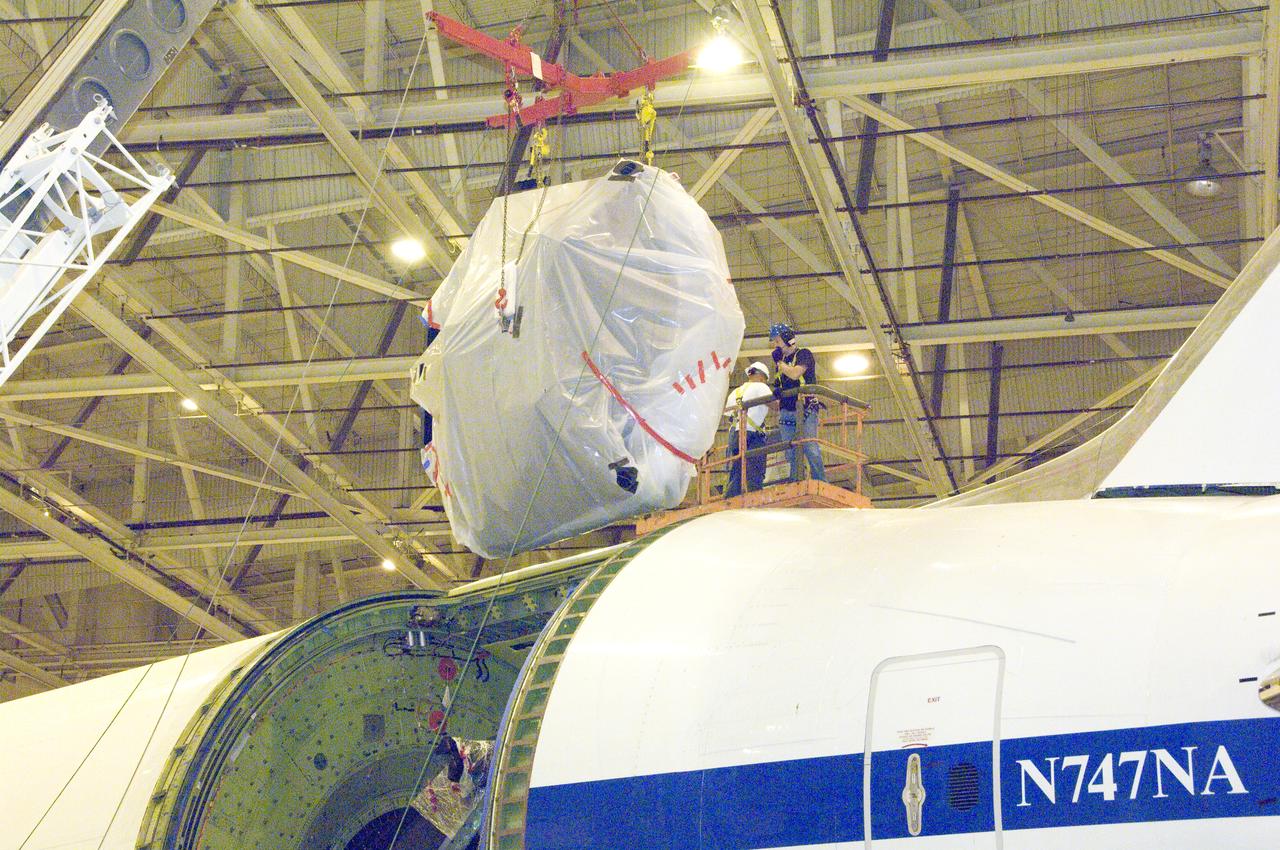

echnicians lift SOFIA's primary mirror assembly above NASA's 747SP airborne astronomy aircraft just prior to installation in the telescope cavity.
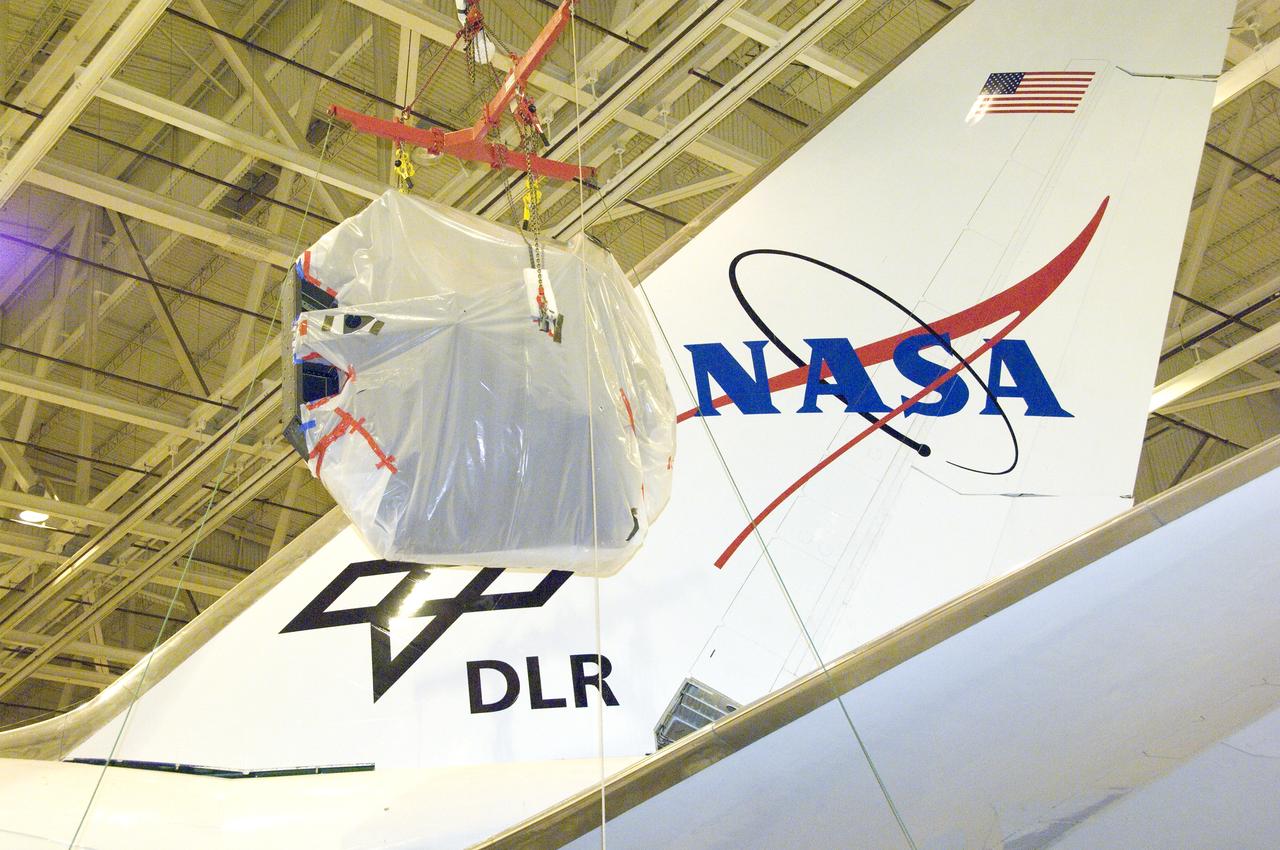

SOFIA's primary mirror assembly is lifted above wing level prior to its reinstallation in the telescope cavity of NASA's 747 airborne observatory Oct. 8, 2008.
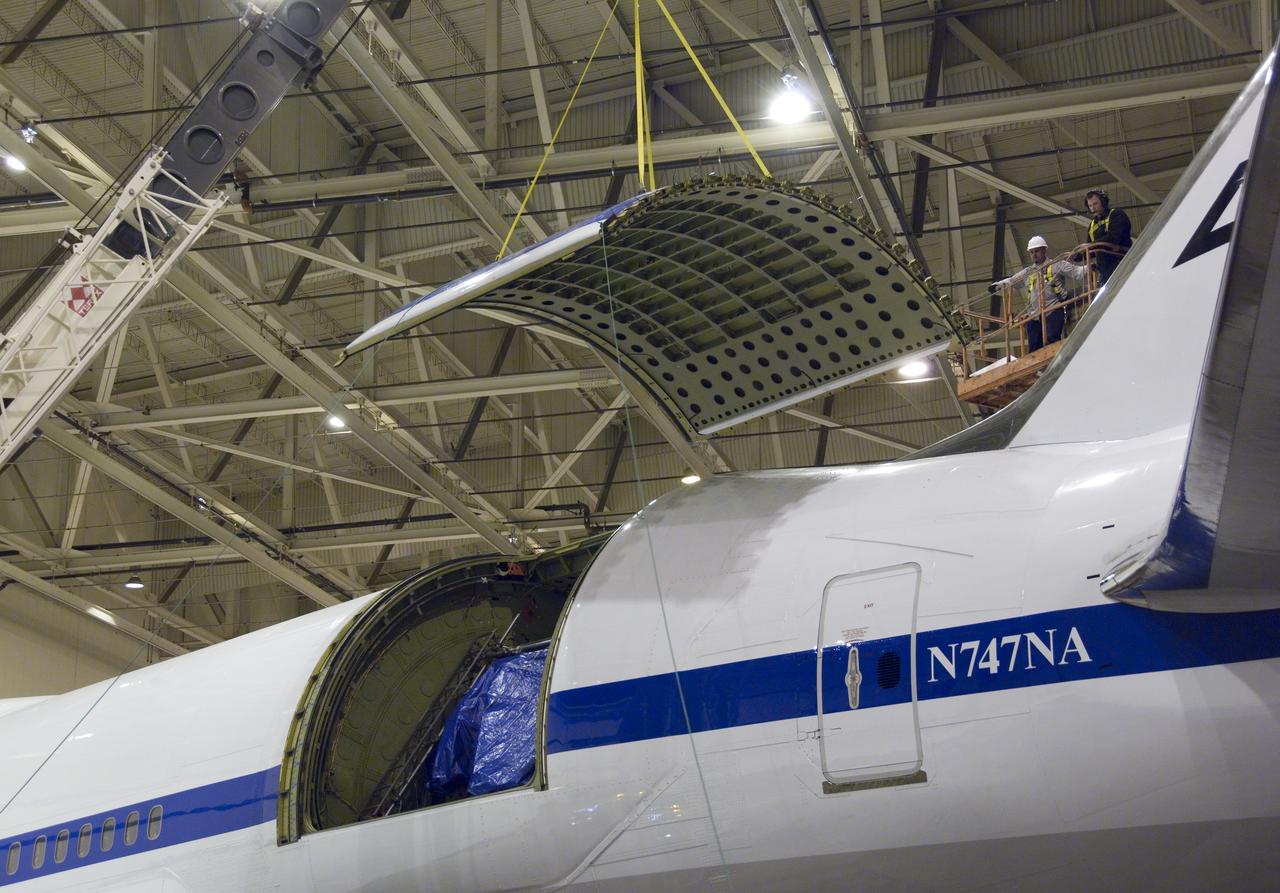

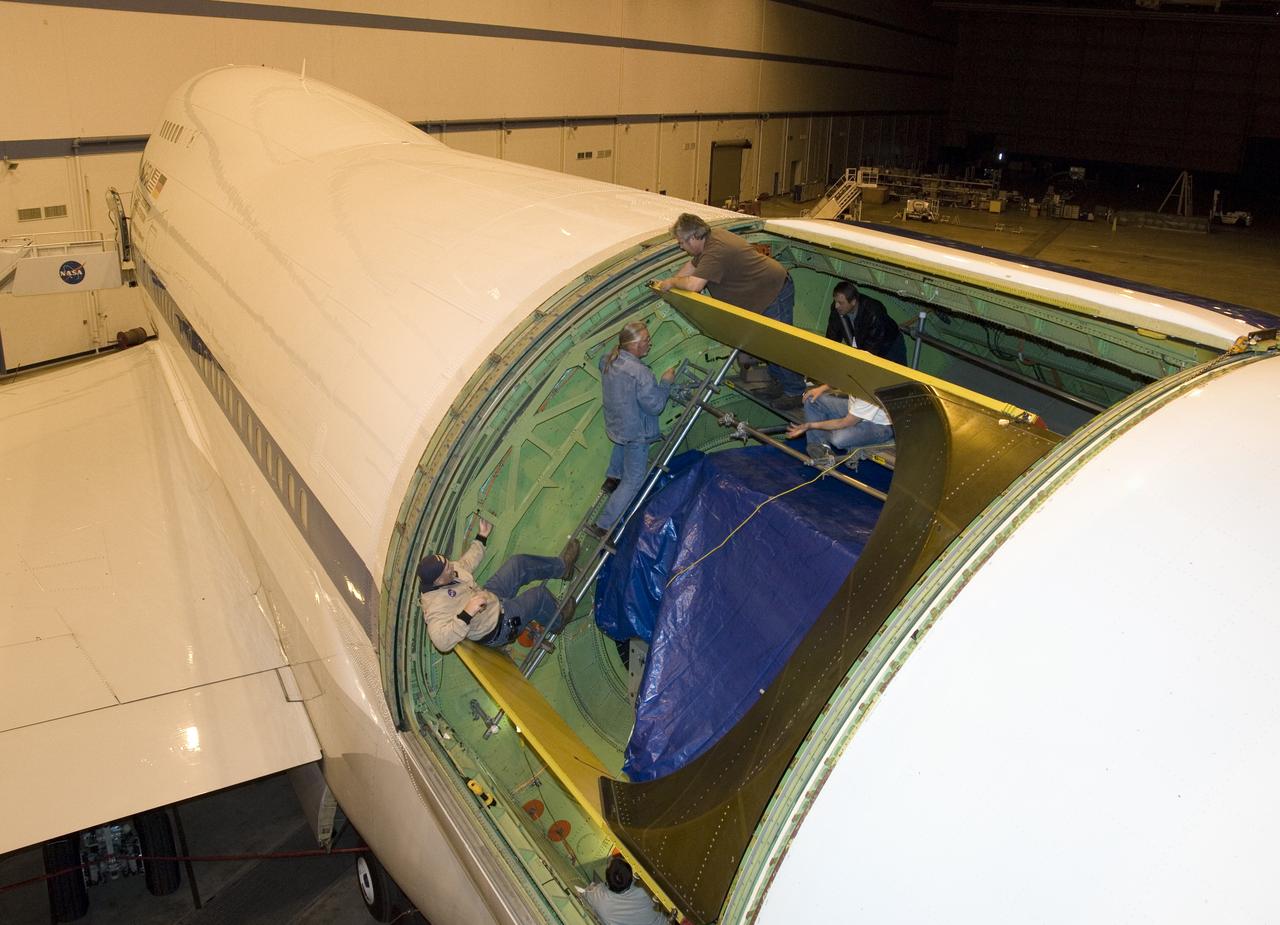
Technicians guide removal of the upper rigid door assembly that covers the telescope cavity on NASA's SOFIA 747SP in preparation for primary mirror removal.
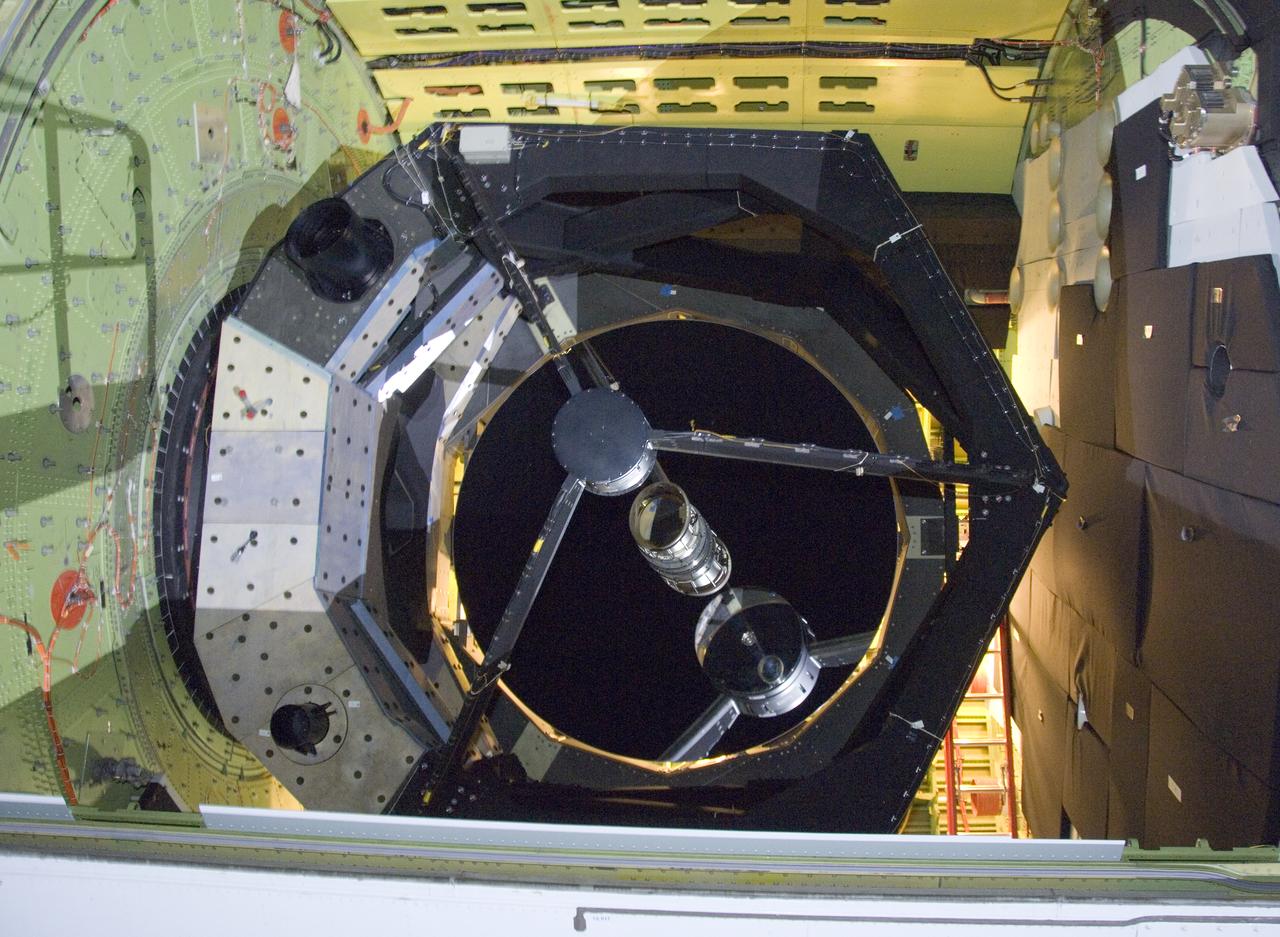

The 2.5-meter infrared telescope peers out from its cavity in the SOFIA airborne observatory during nighttime line operations testing at Palmdale, Calif.

The SOFIA airborne observatory's 2.5-meter infrared telescope peers out from its cavity in the SOFIA rear fuselage during nighttime line operations testing.

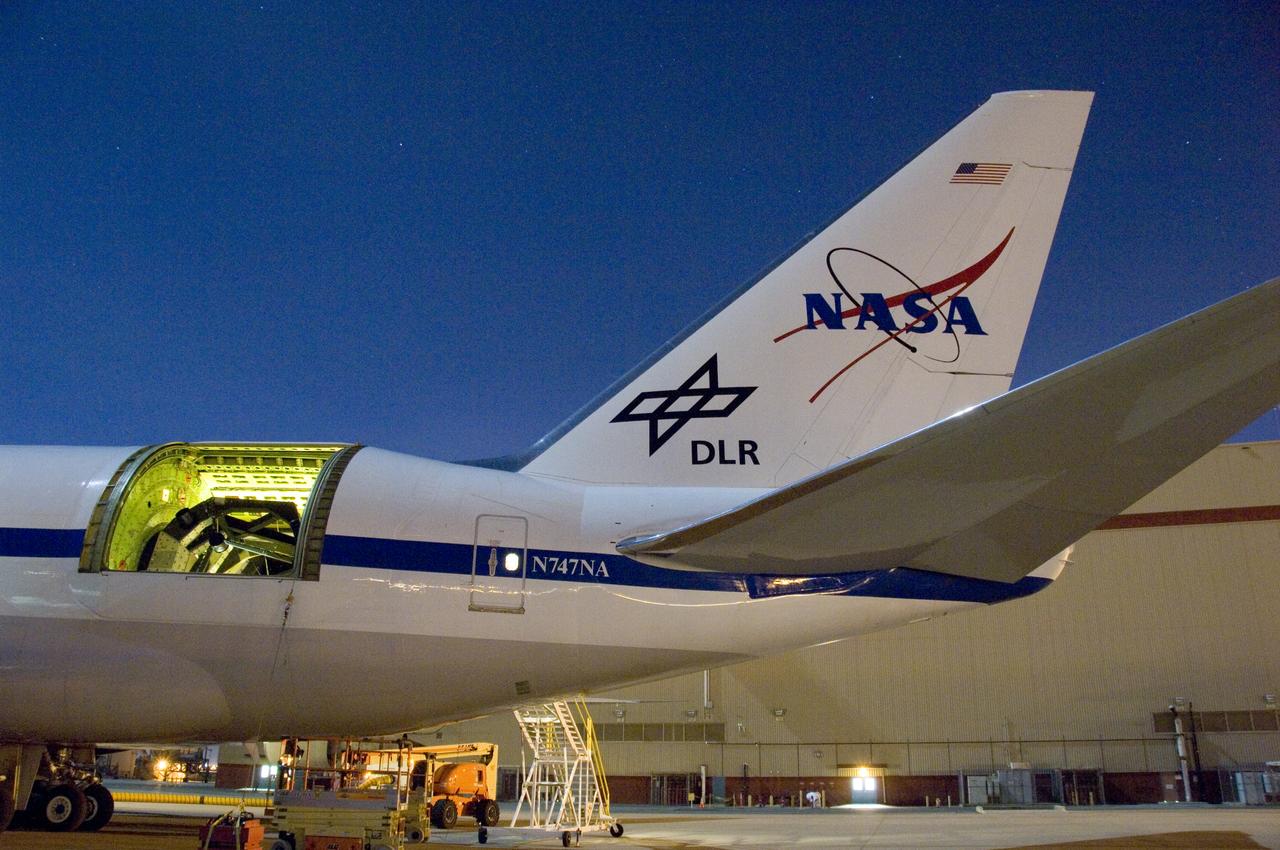
A rotating external door (white) was installed over the telescope cavity in the rear fuselage of NASA's SOFIA Boeing 747SP during modifications in Waco, Texas.
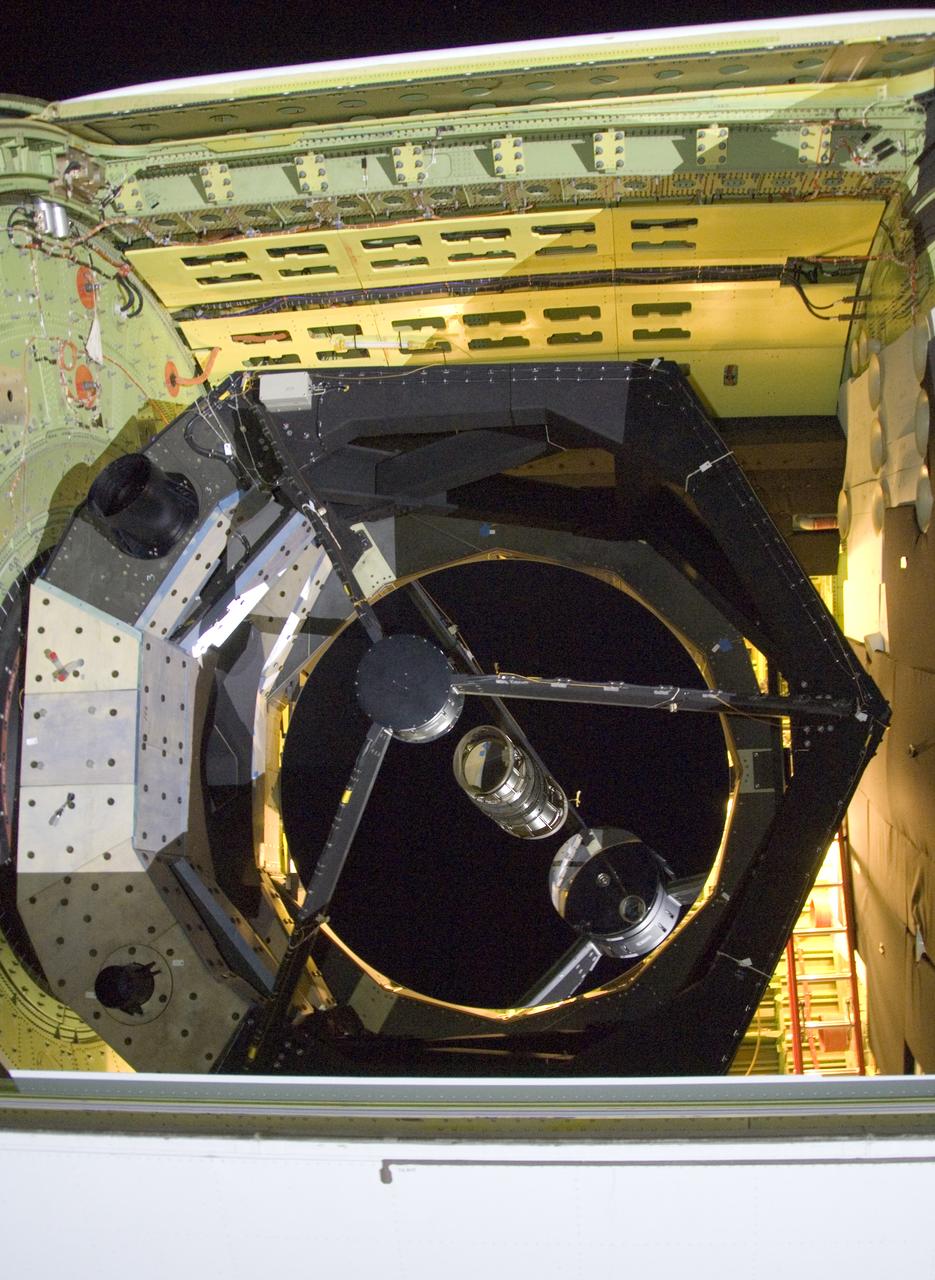
he SOFIA airborne observatory's 2.5-meter infrared telescope peers out from its cavity in the SOFIA rear fuselage during nighttime line operations testing.
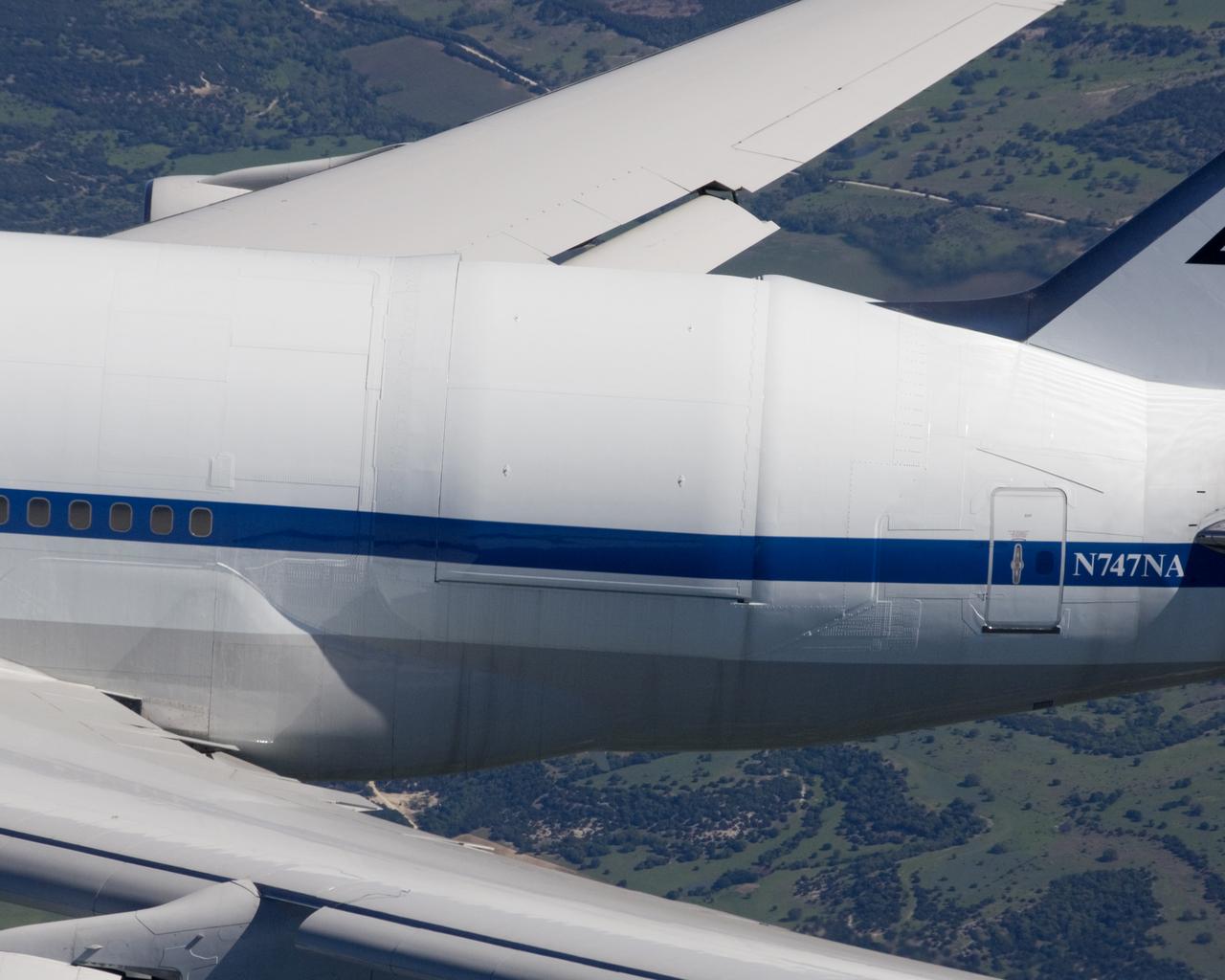

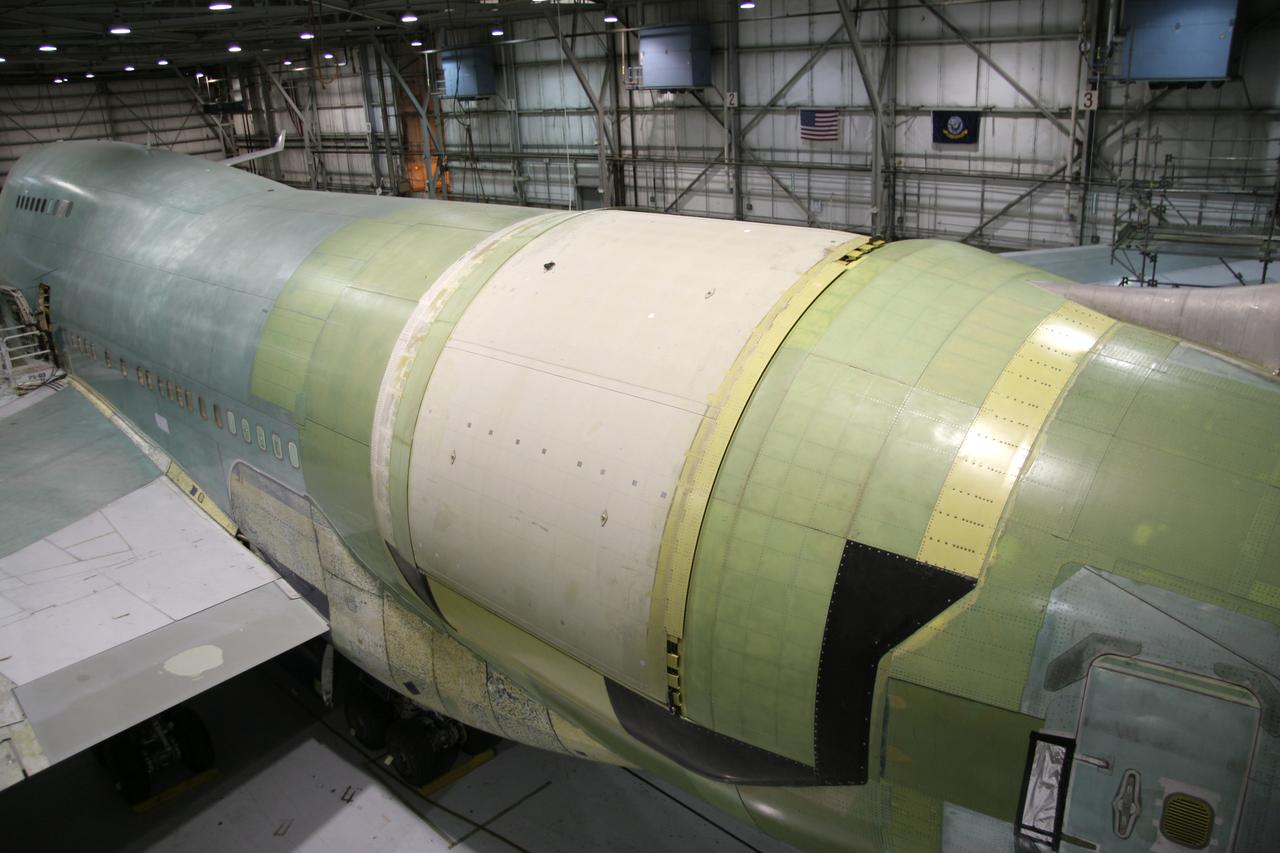
NASA's SOFIA 747SP shows evidence of modification to its aft fuselage contours to accommodate a 16-foot-tall cavity door for its 45,000-pound infrared telescope.

Generations of stars can be seen in this new infrared portrait from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. In this wispy star-forming region, called W5, the oldest stars can be seen as blue dots in the centers of the two hollow cavities.

A bubbling cauldron of star birth is highlighted in this image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. Massive stars have blown bubbles, or cavities, in the dust and gas -- a violent process that triggers both the death and birth of stars.
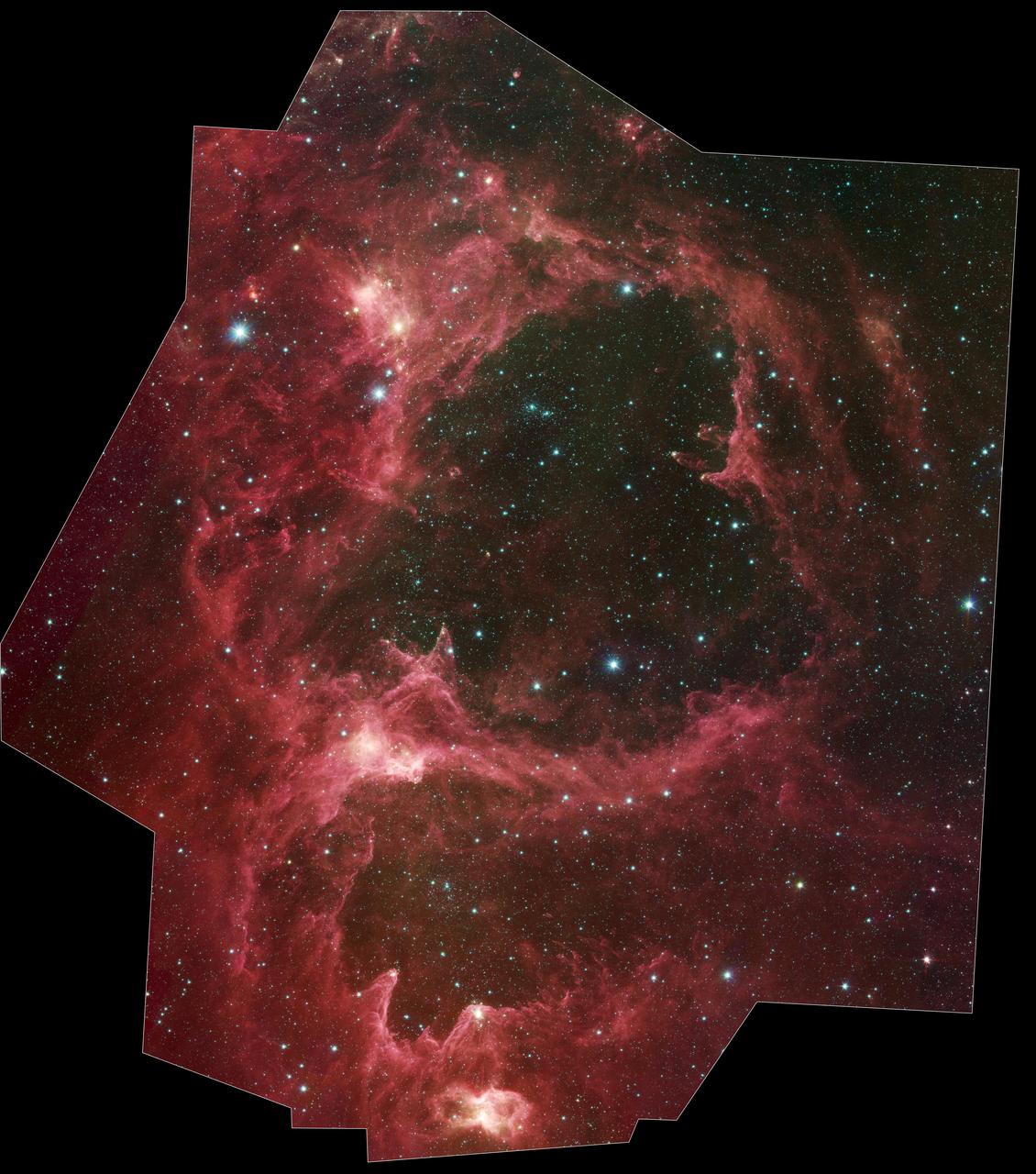

Generations of stars can be seen in this new infrared portrait from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. In this wispy star-forming region, called W5, the oldest stars can be seen as blue dots in the centers of the two hollow cavities.
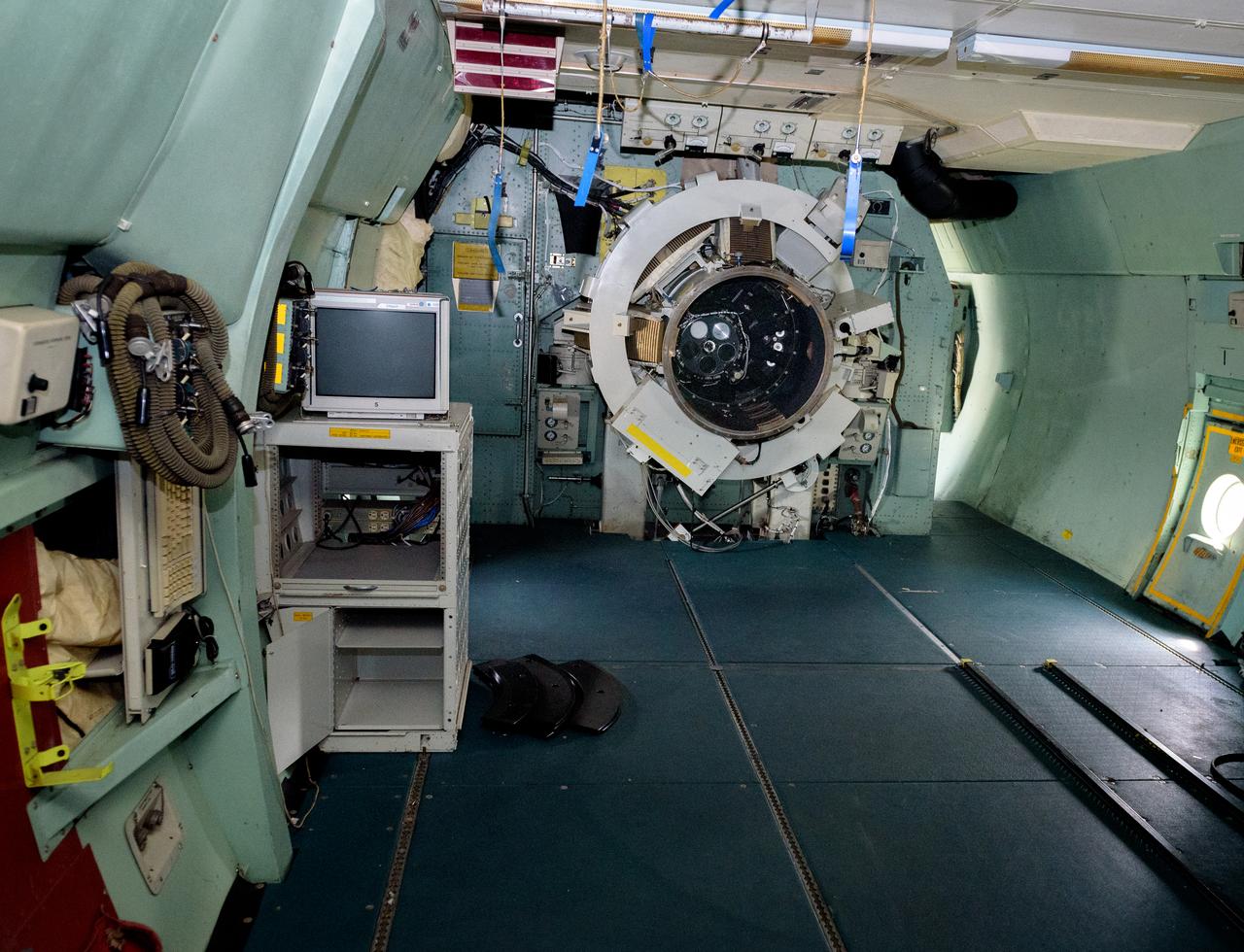

The science instrument mount/telescope flange leading to the telescope cavity. The port work area is where science instruments were connected to the telescope. Astronomers and the science team sat immediately to the left in the port work area on the modified C-141 Kuiper Airborne Observatory, (KAO) (NASA-714), (seats have been removed).
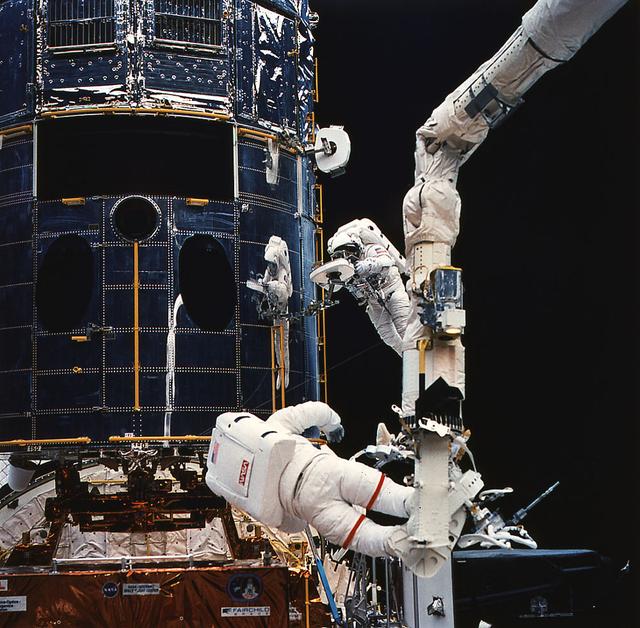

Anchored on the end of orbiter Endeavour's remote manipulator system arm, astronaut Jeffrey Hoffman (foreground) prepares to install the new wide field planetary camera into the empty cavity of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Astronaut Story Musgrave works with a portable foot restraint.
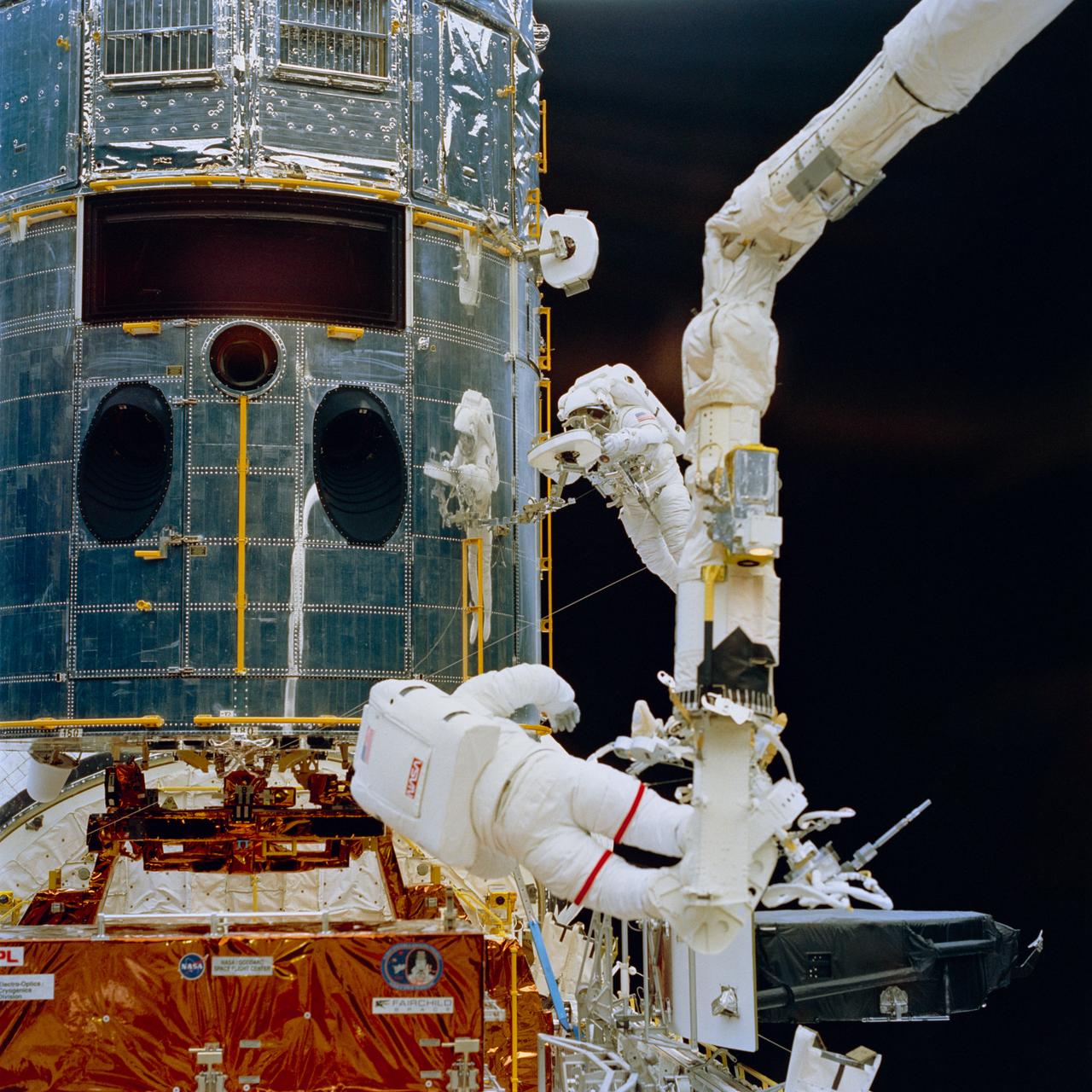
STS061-74-046 (7 Dec 1993) --- Anchored on the end of the Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman (foreground) prepares to install the new Wide Field\Planetary Camera (WFPC II) into the empty cavity (top left) on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). WFPC I is seen temporarily stowed at bottom right. Astronaut F. Story Musgrave works with a Portable Foot Restraint (PFR) at frame center, as his image is reflected in the shiny surface of the telescope. Hoffman and Musgrave shared chores on three of the five extravehicular activity?s (EVA) during the mission.
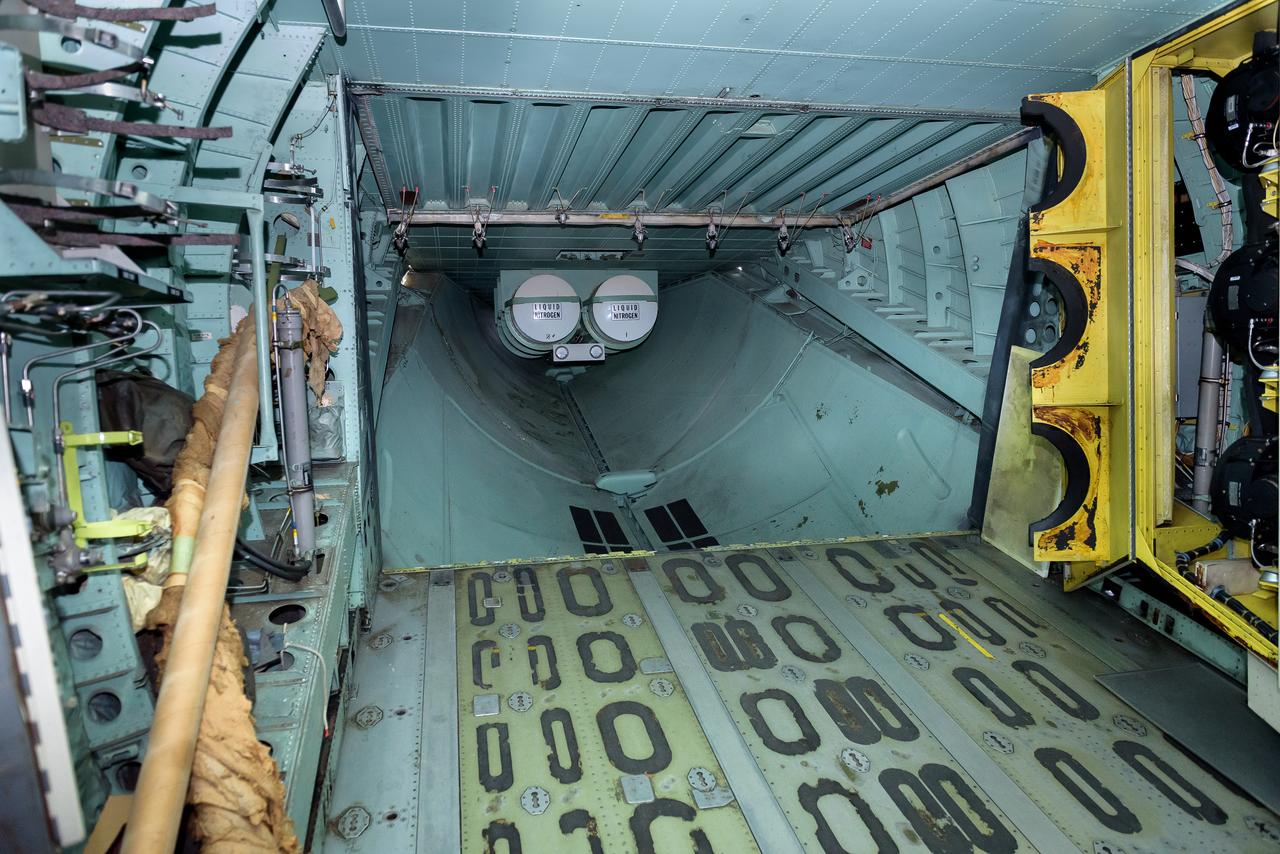

Two nitrogen, LN2, tanks mounted in the aft section of the modified C-141 Kuiper Airborne Observatory, (KAO) (NASA-714), used to cool and purge moisture from the telescope cavity. The aft pressure door, hinged at top, was closed during flight; the clamshell cargo doors in the aft fuselage could also lower the aft ramp to allow supplies to be driven aboard.
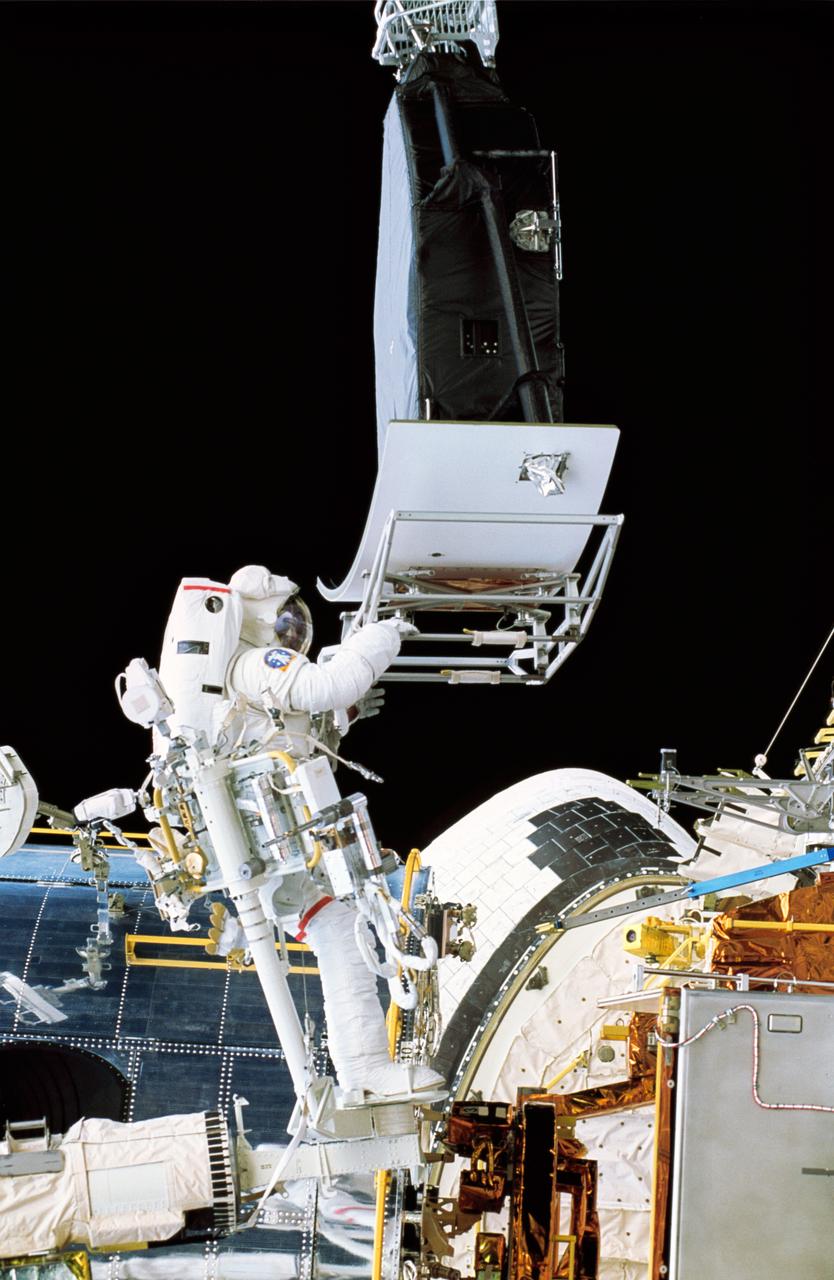

STS061-37-011 (7 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman with Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC 1) during changeout operations. WF/PC-2 has already been installed in cavity (out of frame). Astronauts Hoffman and Story Musgrave are performing Extravehicular Activities (EVA) to repair the Hubble Space Telescope (HST).
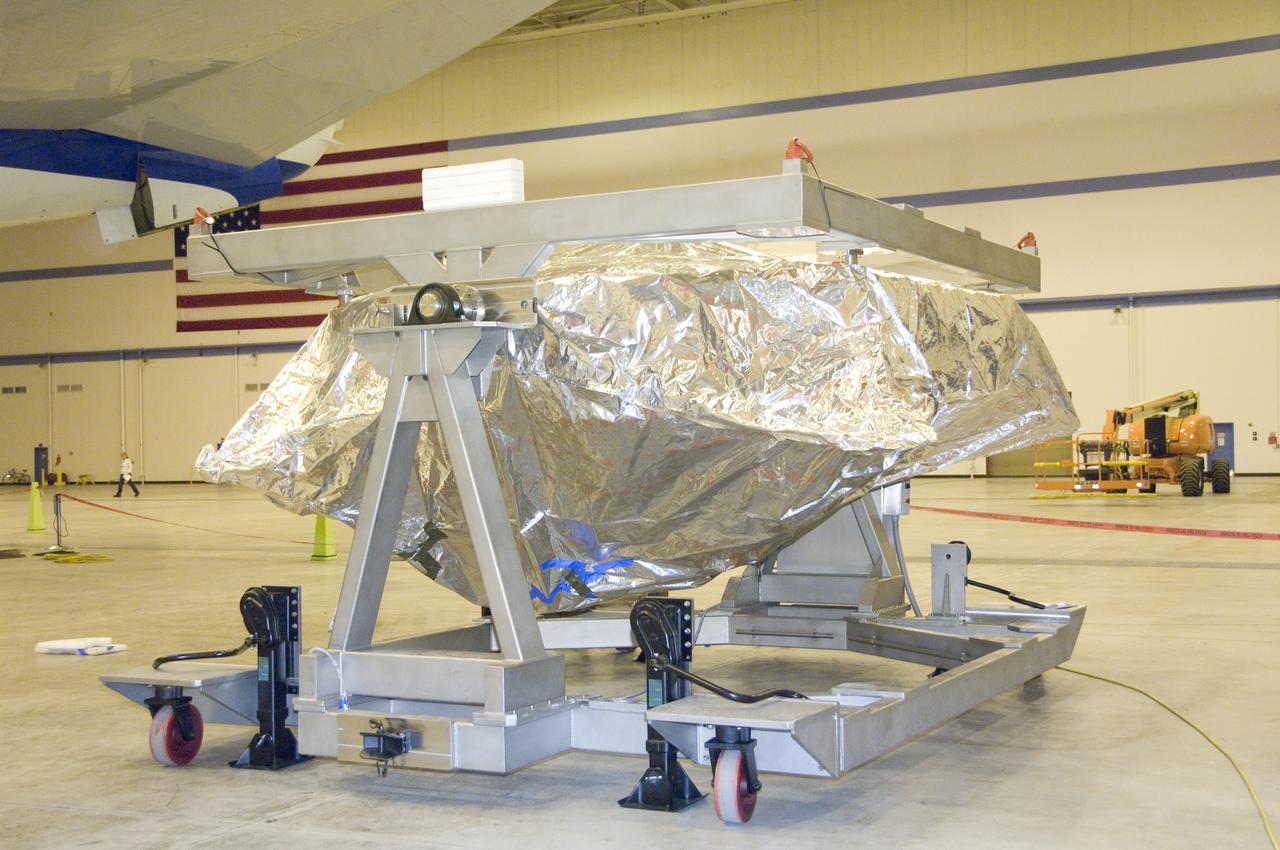

SOFIA's primary mirror assembly rests in its transportation cradle prior to reinstallation in NASA's airborne laboratory on Oct. 8, 2008.
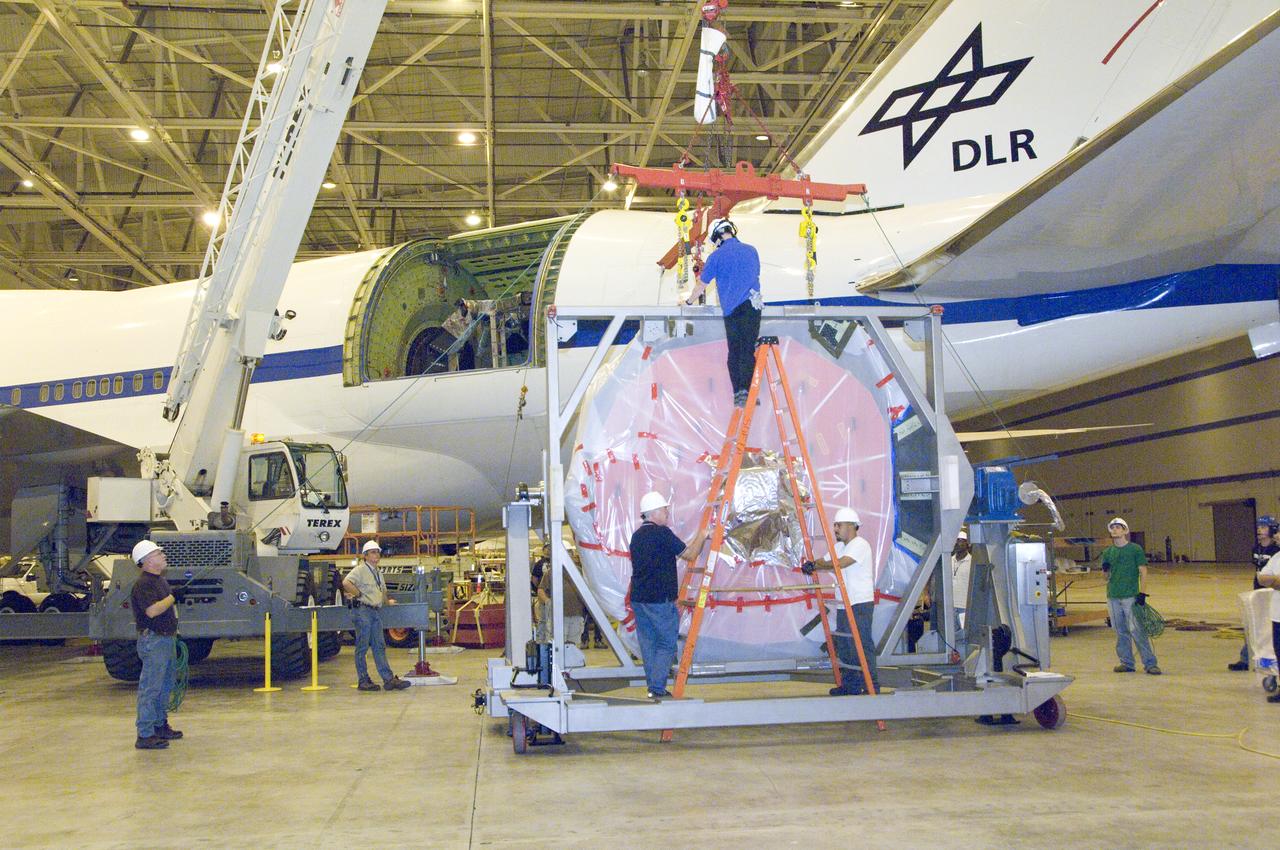

Engineers and technicians prepare SOFIA's German-built primary mirror assembly for reinstallation into NASA's 747SP airborne observatory.

This new image of the Orion Nebula produced using previously released data from three telescopes shows two enormous caverns carved out by unseen giant stars that can release up to a million times more light than our Sun. All that radiation breaks apart dust grains there, helping to create the pair of cavities. Much of the remaining dust is swept away when the stars produce wind or when they die explosive deaths as supernovae. This infrared image shows dust but no stars. Blue light indicates warm dust heated by unseen massive stars. Observed in infrared light – a range of wavelengths outside what human eyes can detect – the views were provided by NASA's retired Spitzer Space Telescope and the Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE), which now operates under the moniker NEOWISE. Spitzer and WISE were both managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, which is a division of Caltech. Around the edge of the two cavernous regions, the dust that appears green is slightly cooler. Red indicates cold dust that reaches temperatures of about minus 440 Fahrenheit (minus 260 Celsius). The cold dust appears mostly on the outskirts of the dust cloud, away from the regions where stars form. The red and green light shows data from the now-retired Herschel Space Telescope, an ESA (European Space Agency) observatory that captured wavelengths in the far-infrared and microwave ranges, where cold dust radiates. In between the two hollow regions are orange filaments where dust condenses and forms new stars. Over time, these filaments may produce new giant stars that will once again reshape the region. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25434

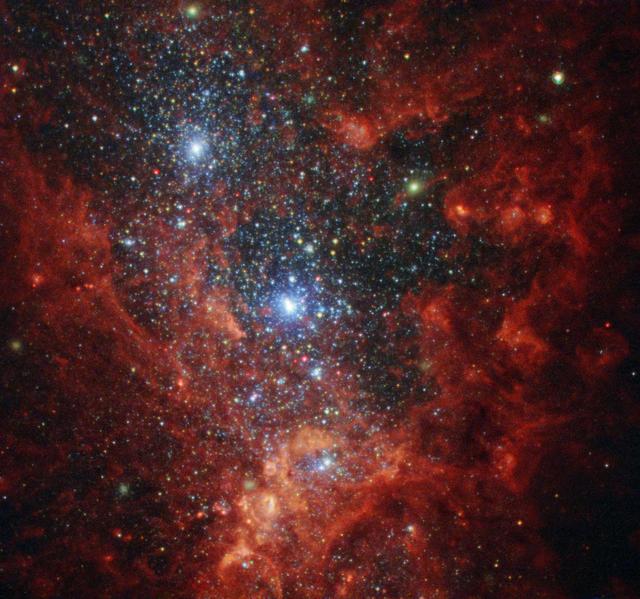
NASA image release June 6, 2010 Like a July 4 fireworks display a young, glittering collection of stars looks like an aerial burst. The cluster is surrounded by clouds of interstellar gas and dust - the raw material for new star formation. The nebula, located 20,000 light-years away in the constellation Carina, contains a central cluster of huge, hot stars, called NGC 3603. This environment is not as peaceful as it looks. Ultraviolet radiation and violent stellar winds have blown out an enormous cavity in the gas and dust enveloping the cluster, providing an unobstructed view of the cluster. Most of the stars in the cluster were born around the same time but differ in size, mass, temperature, and color. The course of a star's life is determined by its mass, so a cluster of a given age will contain stars in various stages of their lives, giving an opportunity for detailed analyses of stellar life cycles. NGC 3603 also contains some of the most massive stars known. These huge stars live fast and die young, burning through their hydrogen fuel quickly and ultimately ending their lives in supernova explosions. Star clusters like NGC 3603 provide important clues to understanding the origin of massive star formation in the early, distant universe. Astronomers also use massive clusters to study distant starbursts that occur when galaxies collide, igniting a flurry of star formation. The proximity of NGC 3603 makes it an excellent lab for studying such distant and momentous events. This Hubble Space Telescope image was captured in August 2009 and December 2009 with the Wide Field Camera 3 in both visible and infrared light, which trace the glow of sulfur, hydrogen, and iron. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc. in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, R. O'Connell (University of Virginia), F. Paresce (National Institute for Astrophysics, Bologna, Italy), E. Young (Universities Space Research Association/Ames Research Center), the WFC3 Science Oversight Committee, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.

What looks much like craggy mountains on a moonlit evening is actually the edge of a nearby, young, star-forming region NGC 3324 in the Carina Nebula. Captured in infrared light by the Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) on NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, this image reveals previously obscured areas of star birth. Called the Cosmic Cliffs, the region is actually the edge of a gigantic, gaseous cavity within NGC 3324, roughly 7,600 light-years away. The cavernous area has been carved from the nebula by the intense ultraviolet radiation and stellar winds from extremely massive, hot, young stars located in the center of the bubble, above the area shown in this image. The high-energy radiation from these stars is sculpting the nebula’s wall by slowly eroding it away. NIRCam – with its crisp resolution and unparalleled sensitivity – unveils hundreds of previously hidden stars, and even numerous background galaxies. Several prominent features in this image are described below. • The “steam” that appears to rise from the celestial “mountains” is actually hot, ionized gas and hot dust streaming away from the nebula due to intense, ultraviolet radiation. • Dramatic pillars rise above the glowing wall of gas, resisting the blistering ultraviolet radiation from the young stars. • Bubbles and cavities are being blown by the intense radiation and stellar winds of newborn stars. • Protostellar jets and outflows, which appear in gold, shoot from dust-enshrouded, nascent stars. • A “blow-out” erupts at the top-center of the ridge, spewing gas and dust into the interstellar medium. • An unusual “arch” appears, looking like a bent-over cylinder. This period of very early star formation is difficult to capture because, for an individual star, it lasts only about 50,000 to 100,000 years – but Webb’s extreme sensitivity and exquisite spatial resolution have chronicled this rare event. Located roughly 7,600 light-years away, NGC 3324 was first catalogued by James Dunlop in 1826. Visible from the Southern Hemisphere, it is located at the northwest corner of the Carina Nebula (NGC 3372), which resides in the constellation Carina. The Carina Nebula is home to the Keyhole Nebula and the active, unstable supergiant star called Eta Carinae. NIRCam was built by a team at the University of Arizona and Lockheed Martin’s Advanced Technology Center.
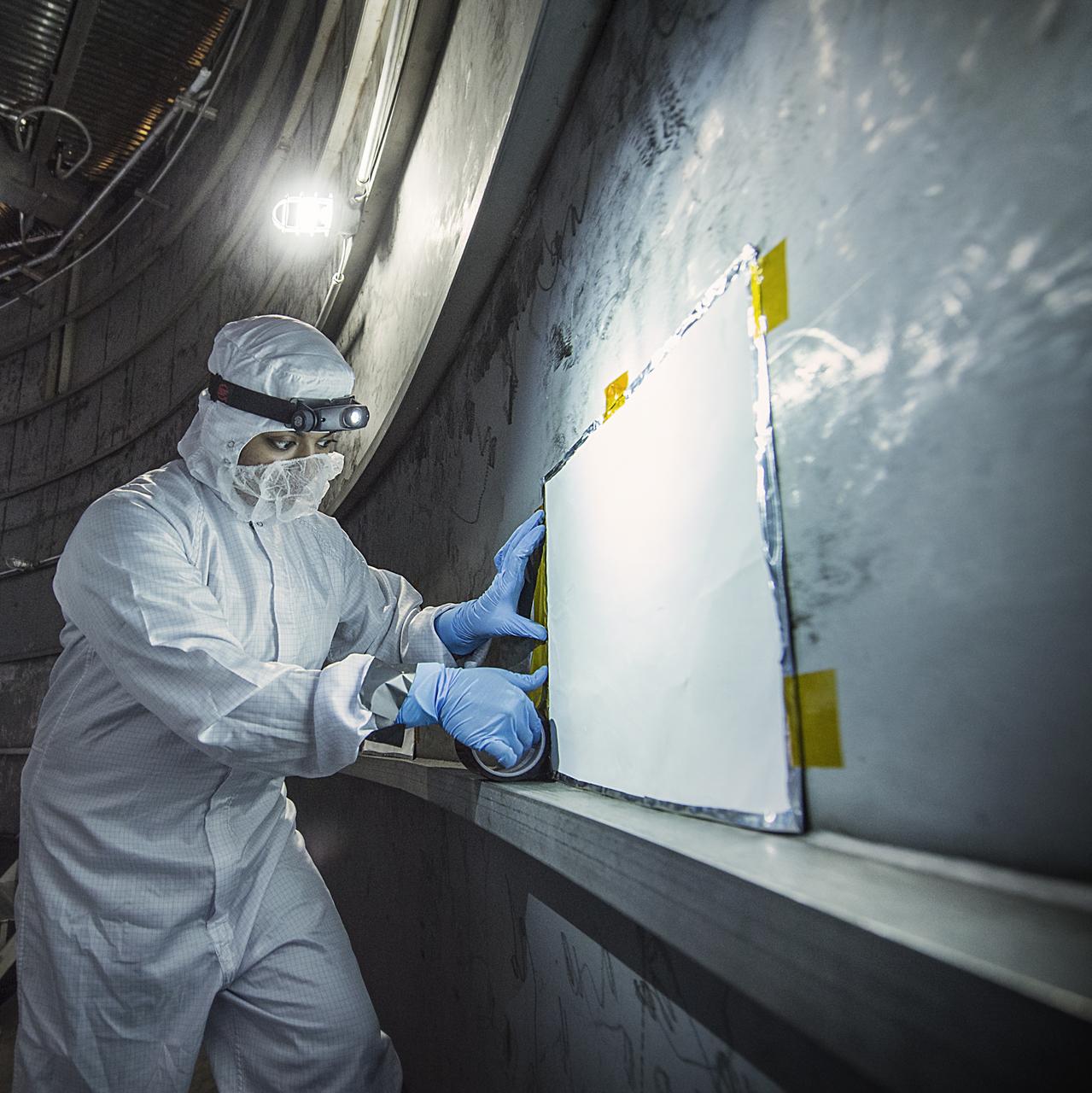

Contamination from organic molecules can harm delicate instruments and engineers are taking special care at NASA to prevent that from affecting the James Webb Space Telescope (and all satellites and instruments). Recently, Nithin Abraham, a Thermal Coatings Engineer placed Molecular Adsorber Coating or "MAC" panels in the giant chamber where the Webb telescope will be tested. This contamination can occur through a process when a vapor or odor is emitted by a substance. This is called "outgassing." The "new car smell" is an example of that, and is unhealthy for people and sensitive satellite instruments. So, NASA engineers have created a new way to protect those instruments from the damaging effects of contamination coming from outgassing. "The Molecular Adsorber Coating (MAC) is a NASA Goddard coatings technology that was developed to adsorb or entrap outgassed molecular contaminants for spaceflight applications," said Nithin Abraham, Thermal Coatings Engineer at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. MAC is currently serving as an innovative contamination mitigation tool for Chamber A operations at NASA Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. MAC can be used to keep outgassing from coming in from outside areas or to capture outgassing directly from hardware, components, and within instrument cavities. In this case, MAC is helping by capturing outgassed contaminants outside the test chamber from affecting the Webb components. MAC is expected to capture the outgassed contaminants that exist in the space of the vacuum chamber (not from the Webb components). Credit: NASA/GoddardChris Gunn Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/nasa-technology-protects-webb-telescope-from-contamination" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/nasa-technology-protects-web...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
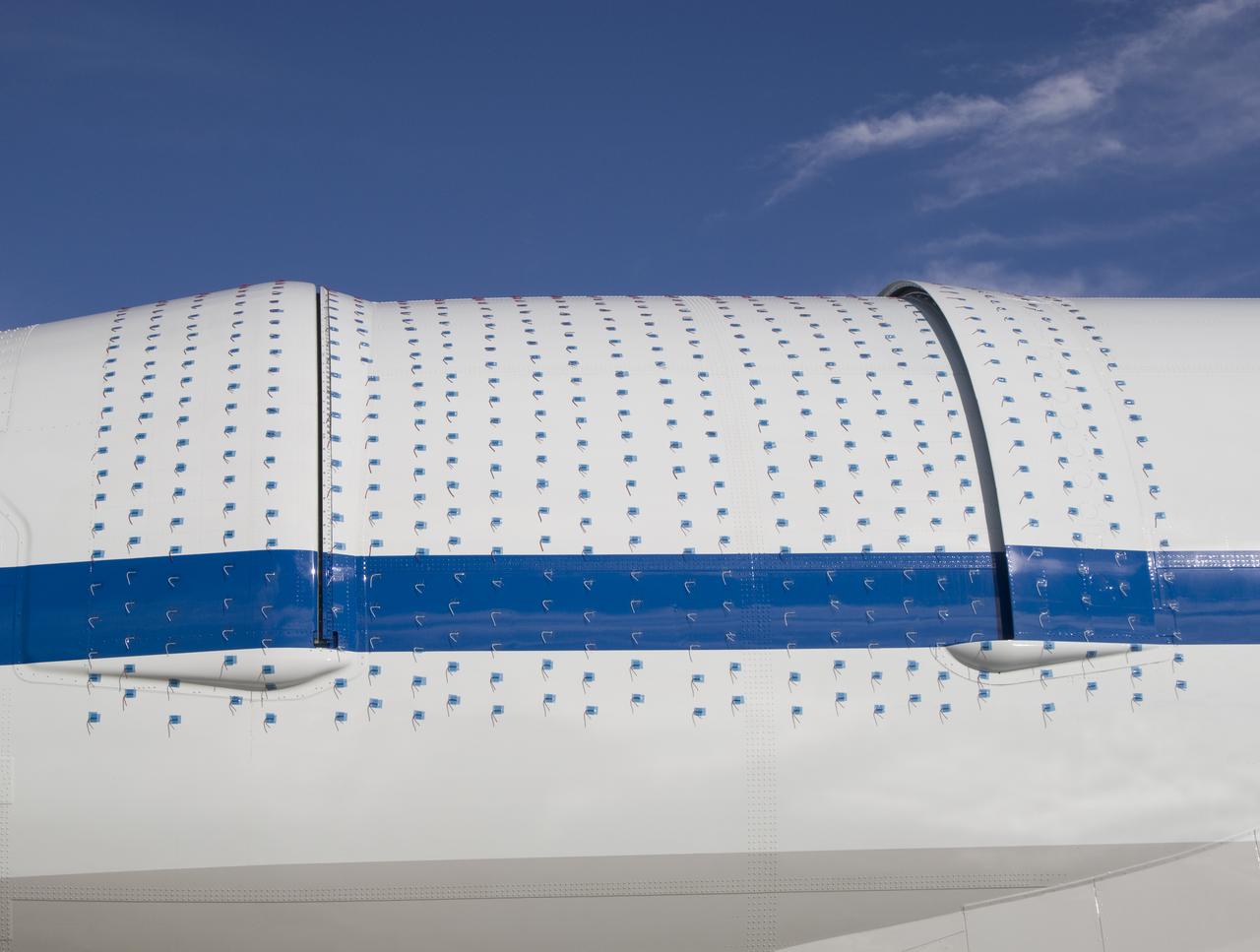

NASA's Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, or SOFIA, arrived at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. on May 31, 2007. The heavily modified Boeing 747SP was ferried to Dryden from Waco, Texas, where L-3 Communications Integrated Systems installed a German-built 2.5-meter infrared telescope and made other major modifications over the past several years. SOFIA is scheduled to undergo installation and integration of mission systems and a multi-phase flight test program at Dryden over the next three years that is expected to lead to a full operational capability to conduct astronomy missions in about 2010. During its expected 20-year lifetime, SOFIA will be capable of "Great Observatory" class astronomical science, providing astronomers with access to the visible, infrared and sub-millimeter spectrum with optimized performance in the mid-infrared to sub-millimeter range.

This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image reveals the iridescent interior of one of the most active galaxies in our local neighbourhood — NGC 1569, a small galaxy located about eleven million light-years away in the constellation of Camelopardalis (The Giraffe). This galaxy is currently a hotbed of vigorous star formation. NGC 1569 is a starburst galaxy, meaning that — as the name suggests — it is bursting at the seams with stars, and is currently producing them at a rate far higher than that observed in most other galaxies. For almost 100 million years, NGC 1569 has pumped out stars over 100 times faster than the Milky Way! As a result, this glittering galaxy is home to super star clusters, three of which are visible in this image — one of the two bright clusters is actually the superposition of two massive clusters. Each containing more than a million stars, these brilliant blue clusters reside within a large cavity of gas carved out by multiple supernovae, the energetic remnants of massive stars. In 2008, Hubble observed the galaxy's cluttered core and sparsely populated outer fringes. By pinpointing individual red giant stars, Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys enabled astronomers to calculate a new — and much more precise — estimate for NGC 1569’s distance. This revealed that the galaxy is actually one and a half times further away than previously thought, and a member of the IC 342 galaxy group. Astronomers suspect that the IC 342 cosmic congregation is responsible for the star-forming frenzy observed in NGC 1569. Gravitational interactions between this galactic group are believed to be compressing the gas within NGC 1569. As it is compressed, the gas collapses, heats up and forms new stars.

This NASA Hubble Space Telescope image, taken in near-infrared light, transforms the pillars into eerie, wispy silhouettes, which are seen against a background of myriad stars. The near-infrared light can penetrate much of the gas and dust, revealing stars behind the nebula as well as hidden away inside the pillars. Some of the gas and dust clouds are so dense that even the near-infrared light cannot penetrate them. New stars embedded in the tops of the pillars, however, are apparent as bright sources that are unseen in the visible image. The ghostly bluish haze around the dense edges of the pillars is material getting heated up by the intense ultraviolet radiation from a cluster of young, massive stars and evaporating away into space. The stellar grouping is above the pillars and cannot be seen in the image. At the top edge of the left-hand pillar, a gaseous fragment has been heated up and is flying away from the structure, underscoring the violent nature of star-forming regions. Astronomers used filters that isolate the light from newly formed stars, which are invisible in the visible-light image. At these wavelengths, astronomers are seeing through the pillars and even through the back wall of the nebula cavity and can see the next generations of stars just as they're starting to emerge from their formative nursery. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1HGfkqr" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1HGfkqr</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Peering deep into the core of the Crab Nebula, this close-up image reveals the beating heart of one of the most historic and intensively studied remnants of a supernova, an exploding star. The inner region sends out clock-like pulses of radiation and tsunamis of charged particles embedded in magnetic fields. The neutron star at the very center of the Crab Nebula has about the same mass as the sun but compressed into an incredibly dense sphere that is only a few miles across. Spinning 30 times a second, the neutron star shoots out detectable beams of energy that make it look like it's pulsating. The NASA Hubble Space Telescope snapshot is centered on the region around the neutron star (the rightmost of the two bright stars near the center of this image) and the expanding, tattered, filamentary debris surrounding it. Hubble's sharp view captures the intricate details of glowing gas, shown in red, that forms a swirling medley of cavities and filaments. Inside this shell is a ghostly blue glow that is radiation given off by electrons spiraling at nearly the speed of light in the powerful magnetic field around the crushed stellar core. The neutron star is a showcase for extreme physical processes and unimaginable cosmic violence. Bright wisps are moving outward from the neutron star at half the speed of light to form an expanding ring. It is thought that these wisps originate from a shock wave that turns the high-speed wind from the neutron star into extremely energetic particles. When this "heartbeat" radiation signature was first discovered in 1968, astronomers realized they had discovered a new type of astronomical object. Now astronomers know it's the archetype of a class of supernova remnants called pulsars - or rapidly spinning neutron stars. These interstellar "lighthouse beacons" are invaluable for doing observational experiments on a variety of astronomical phenomena, including measuring gravity waves. Observations of the Crab supernova were recorded by Chinese astronomers in 1054 A.D. The nebula, bright enough to be visible in amateur telescopes, is located 6,500 light-years away in the constellation Taurus. Credits: NASA and ESA, Acknowledgment: J. Hester (ASU) and M. Weisskopf (NASA/MSFC) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Fireworks shows are not just confined to Earth’s skies. NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has captured a spectacular fireworks display in a small, nearby galaxy, which resembles a July 4th skyrocket. A firestorm of star birth is lighting up one end of the diminutive galaxy Kiso 5639. The dwarf galaxy is shaped like a flattened pancake, but because it is tilted edge-on, it resembles a skyrocket, with a brilliant blazing head and a long, star-studded tail. Kiso 5639 is a rare, nearby example of elongated galaxies that occur in abundance at larger distances, where we observe the universe during earlier epochs. Astronomers suggest that the frenzied star birth is sparked by intergalactic gas raining on one end of the galaxy as it drifts through space. “I think Kiso 5639 is a beautiful, up-close example of what must have been common long ago,” said lead researcher Debra Elmegreen of Vassar College, in Poughkeepsie, New York. “The current thinking is that galaxies in the early universe grow from accreting gas from the surrounding neighborhood. It’s a stage that galaxies, including our Milky Way, must go through as they are growing up.” Observations of the early universe, such as Hubble’s Ultra-Deep Field, reveal that about 10 percent of all galaxies have these elongated shapes, and are collectively called “tadpoles.” But studies of the nearby universe have turned up only a few of these unusual galaxies, including Kiso 5639. The development of the nearby star-making tadpole galaxies, however, has lagged behind that of their peers, which have spent billions of years building themselves up into many of the spiral galaxies seen today. Elmegreen used Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 to conduct a detailed imaging study of Kiso 5639. The images in different filters reveal information about an object by dissecting its light into its component colors. Hubble’s crisp resolution helped Elmegreen and her team analyze the giant star-forming clumps in Kiso 5639 and determine the masses and ages of the star clusters. The international team of researchers selected Kiso 5639 from a spectroscopic survey of 10 nearby tadpole galaxies, observed with the Grand Canary Telescope in La Palma, Spain, by Jorge Sanchez Almeida and collaborators at the Instituto de Astrofisica de Canarias. The observations revealed that in most of those galaxies, including Kiso 5639, the gas composition is not uniform. The bright gas in the galaxy’s head contains fewer heavier elements (collectively called “metals”), such as carbon and oxygen, than the rest of the galaxy. Stars consist mainly of hydrogen and helium, but cook up other “heavier” elements. When the stars die, they release their heavy elements and enrich the surrounding gas. “The metallicity suggests that there has to be rather pure gas, composed mostly of hydrogen, coming into the star-forming part of the galaxy, because intergalactic space contains more pristine hydrogen-rich gas,” Elmegreen explained. “Otherwise, the starburst region should be as rich in heavy elements as the rest of the galaxy.” Hubble offers a detailed view of the galaxy’s star-making frenzy. The telescope uncovered several dozen clusters of stars in the galaxy’s star-forming head, which spans 2,700 light-years across. These clusters have an average age of less than 1 million years and masses that are three to six times larger than those in the rest of the galaxy. Other star formation is taking place throughout the galaxy but on a much smaller scale. Star clusters in the rest of the galaxy are between several million to a few billion years old. “There is much more star formation going on in the head than what you would expect in such a tiny galaxy,” said team member Bruce Elmegreen of IBM’s Thomas J. Watson’s Research Center, in Yorktown Heights, New York. “And we think the star formation is triggered by the ongoing accretion of metal-poor gas onto a part of an otherwise quiescent dwarf galaxy.” Hubble also revealed giant holes peppered throughout the galaxy’s starburst head. These cavities give the galaxy’s head a Swiss-cheese appearance because numerous supernova detonations – like firework aerial bursts – have carved out holes of rarified superheated gas. The galaxy, located 82 million light-years away, has taken billions of years to develop because it has been drifting through an isolated “desert” in the universe, devoid of much gas. What triggered the starburst in such a backwater galaxy? Based on simulations by Daniel Ceverino of the Center for Astronomy at Heidelberg University in Germany, and other team members, the observations suggest that less than 1 million years ago, Kiso 5639’s leading edge encountered a filament of gas. The filament dropped a large clump of matter onto the galaxy, stoking the vigorous star birth. Debra Elmegreen expects that in the future other parts of the galaxy will join in the star-making fireworks show. “Galaxies rotate, and as Kiso 5639 continues to spin, another part of the galaxy may receive an infusion of new gas from this filament, instigating another round of star birth,” she said. The team’s results have been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal. Other team members include Casiana Munoz-Tunon and Mercedes Filho (Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Canary Islands), Jairo Mendez-Abreu (University of St. Andrews, United Kingdom), John Gallagher (University of Wisconsin-Madison), and Marc Rafelski (NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland). The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C.
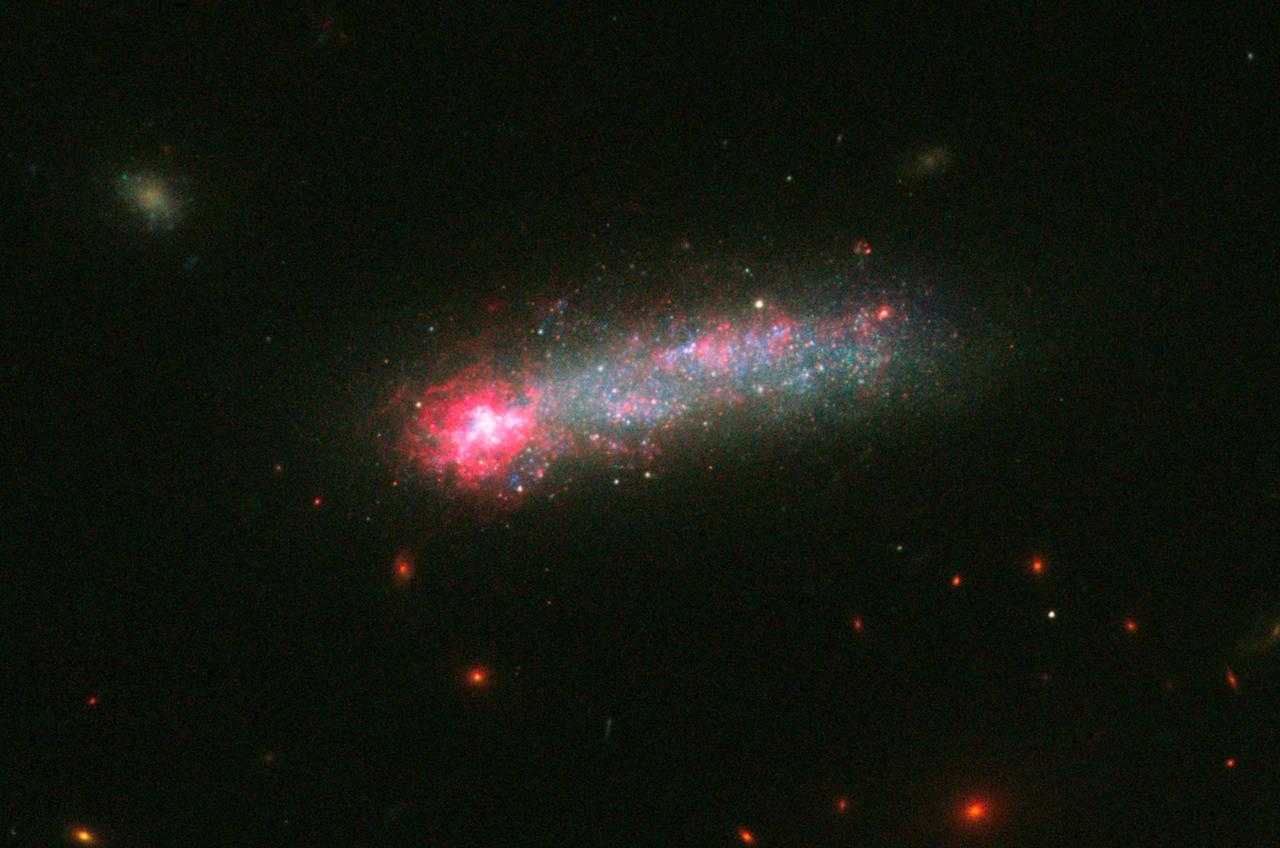

Fireworks shows are not just confined to Earth’s skies. NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has captured a spectacular fireworks display in a small, nearby galaxy, which resembles a July 4th skyrocket. A firestorm of star birth is lighting up one end of the diminutive galaxy Kiso 5639. The dwarf galaxy is shaped like a flattened pancake, but because it is tilted edge-on, it resembles a skyrocket, with a brilliant blazing head and a long, star-studded tail. Kiso 5639 is a rare, nearby example of elongated galaxies that occur in abundance at larger distances, where we observe the universe during earlier epochs. Astronomers suggest that the frenzied star birth is sparked by intergalactic gas raining on one end of the galaxy as it drifts through space. “I think Kiso 5639 is a beautiful, up-close example of what must have been common long ago,” said lead researcher Debra Elmegreen of Vassar College, in Poughkeepsie, New York. “The current thinking is that galaxies in the early universe grow from accreting gas from the surrounding neighborhood. It’s a stage that galaxies, including our Milky Way, must go through as they are growing up.” Observations of the early universe, such as Hubble’s Ultra-Deep Field, reveal that about 10 percent of all galaxies have these elongated shapes, and are collectively called “tadpoles.” But studies of the nearby universe have turned up only a few of these unusual galaxies, including Kiso 5639. The development of the nearby star-making tadpole galaxies, however, has lagged behind that of their peers, which have spent billions of years building themselves up into many of the spiral galaxies seen today. Elmegreen used Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 to conduct a detailed imaging study of Kiso 5639. The images in different filters reveal information about an object by dissecting its light into its component colors. Hubble’s crisp resolution helped Elmegreen and her team analyze the giant star-forming clumps in Kiso 5639 and determine the masses and ages of the star clusters. The international team of researchers selected Kiso 5639 from a spectroscopic survey of 10 nearby tadpole galaxies, observed with the Grand Canary Telescope in La Palma, Spain, by Jorge Sanchez Almeida and collaborators at the Instituto de Astrofisica de Canarias. The observations revealed that in most of those galaxies, including Kiso 5639, the gas composition is not uniform. The bright gas in the galaxy’s head contains fewer heavier elements (collectively called “metals”), such as carbon and oxygen, than the rest of the galaxy. Stars consist mainly of hydrogen and helium, but cook up other “heavier” elements. When the stars die, they release their heavy elements and enrich the surrounding gas. “The metallicity suggests that there has to be rather pure gas, composed mostly of hydrogen, coming into the star-forming part of the galaxy, because intergalactic space contains more pristine hydrogen-rich gas,” Elmegreen explained. “Otherwise, the starburst region should be as rich in heavy elements as the rest of the galaxy.” Hubble offers a detailed view of the galaxy’s star-making frenzy. The telescope uncovered several dozen clusters of stars in the galaxy’s star-forming head, which spans 2,700 light-years across. These clusters have an average age of less than 1 million years and masses that are three to six times larger than those in the rest of the galaxy. Other star formation is taking place throughout the galaxy but on a much smaller scale. Star clusters in the rest of the galaxy are between several million to a few billion years old. “There is much more star formation going on in the head than what you would expect in such a tiny galaxy,” said team member Bruce Elmegreen of IBM’s Thomas J. Watson’s Research Center, in Yorktown Heights, New York. “And we think the star formation is triggered by the ongoing accretion of metal-poor gas onto a part of an otherwise quiescent dwarf galaxy.” Hubble also revealed giant holes peppered throughout the galaxy’s starburst head. These cavities give the galaxy’s head a Swiss-cheese appearance because numerous supernova detonations – like firework aerial bursts – have carved out holes of rarified superheated gas. The galaxy, located 82 million light-years away, has taken billions of years to develop because it has been drifting through an isolated “desert” in the universe, devoid of much gas. What triggered the starburst in such a backwater galaxy? Based on simulations by Daniel Ceverino of the Center for Astronomy at Heidelberg University in Germany, and other team members, the observations suggest that less than 1 million years ago, Kiso 5639’s leading edge encountered a filament of gas. The filament dropped a large clump of matter onto the galaxy, stoking the vigorous star birth. Debra Elmegreen expects that in the future other parts of the galaxy will join in the star-making fireworks show. “Galaxies rotate, and as Kiso 5639 continues to spin, another part of the galaxy may receive an infusion of new gas from this filament, instigating another round of star birth,” she said. The team’s results have been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal. Other team members include Casiana Munoz-Tunon and Mercedes Filho (Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Canary Islands), Jairo Mendez-Abreu (University of St. Andrews, United Kingdom), John Gallagher (University of Wisconsin-Madison), and Marc Rafelski (NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland). The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. For images and more information about Kiso 5639 and Hubble, visit: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/news/2016/23" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/news/2016/23</a> <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/hubble" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/hubble</a> Image credit: NASA, ESA, and D. Elmegreen (Vassar College) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
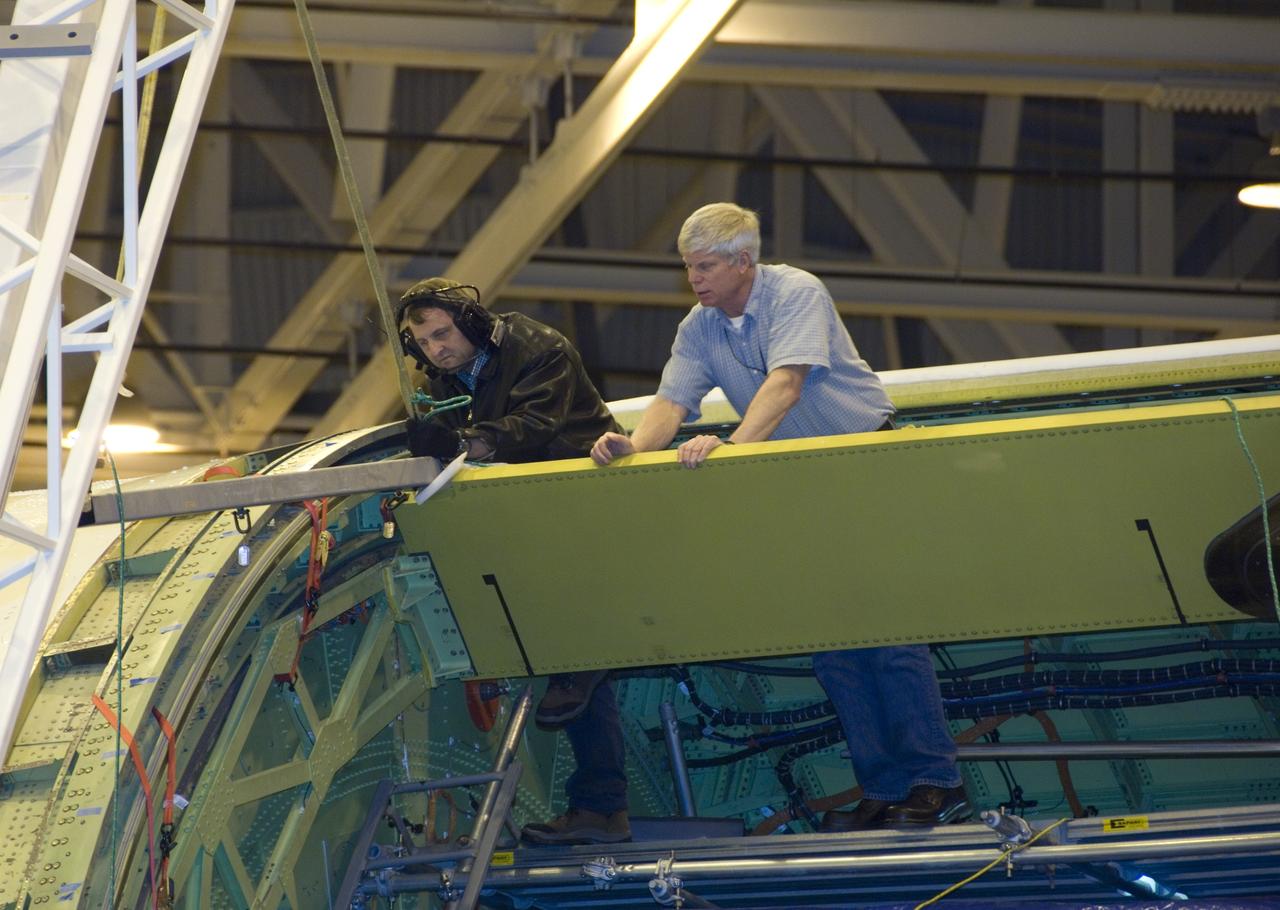

Technicians carefully maneuver a spreader bar into place before removing the telescope aperture assembly from NASA's SOFIA infrared observatory Boeing 747SP.

Technicians carefully disassemble portions of the aperture mounting assembly from NASA's SOFIA aircraft in preparation for removal of the telescope.
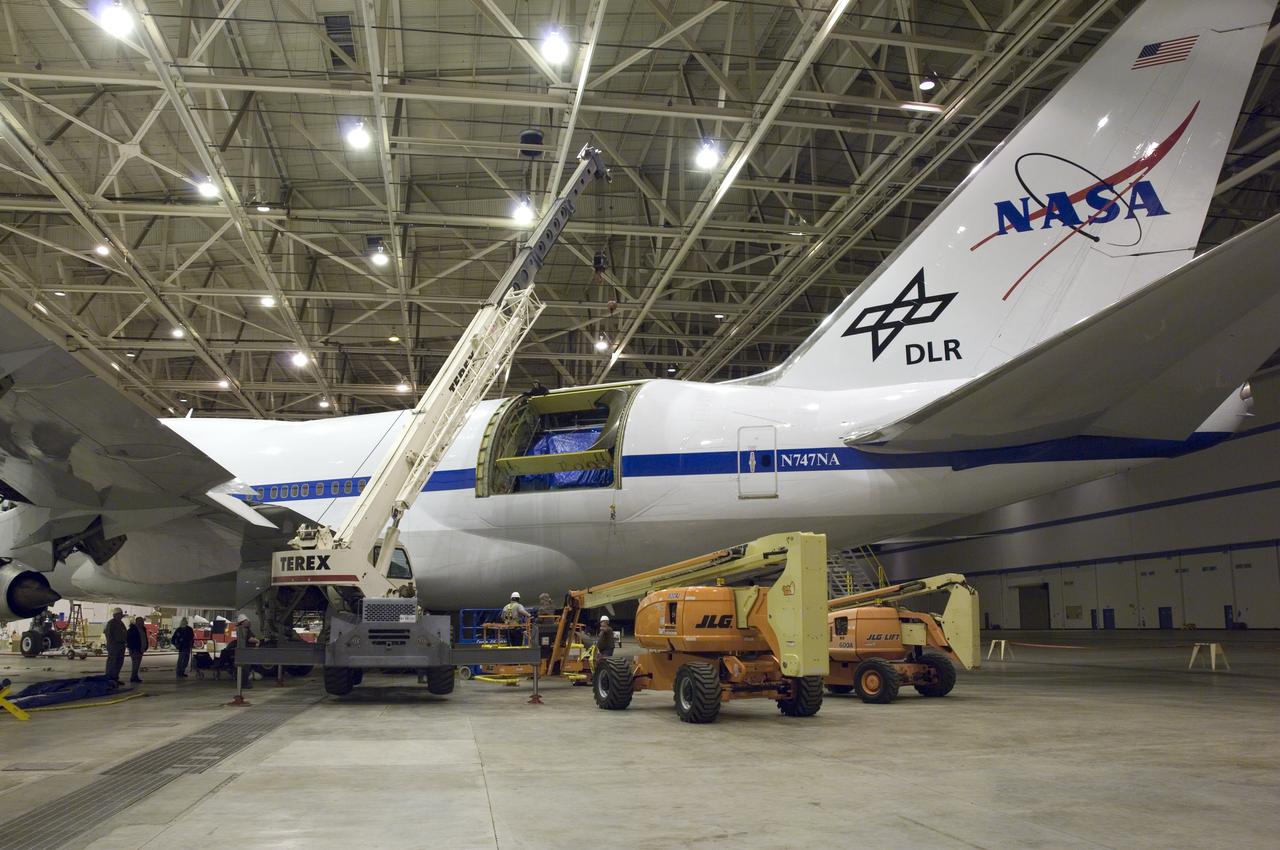

A large mobile crane and hi-lift are maneuvered into place for removal of the aperture assembly and cavity doors from NASA's SOFIA observatory aircraft.