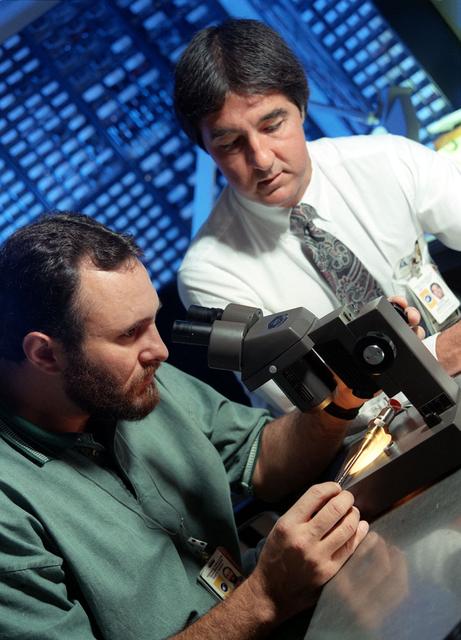

A rugged, highly accurate, low-temperature sensor is developed by NASA researchers. A new sensor allows accurate, quick low-temperature measurements in rugged environments. This is especially useful in piping with very cold liquids under high pressure, and high flow rate conditions.
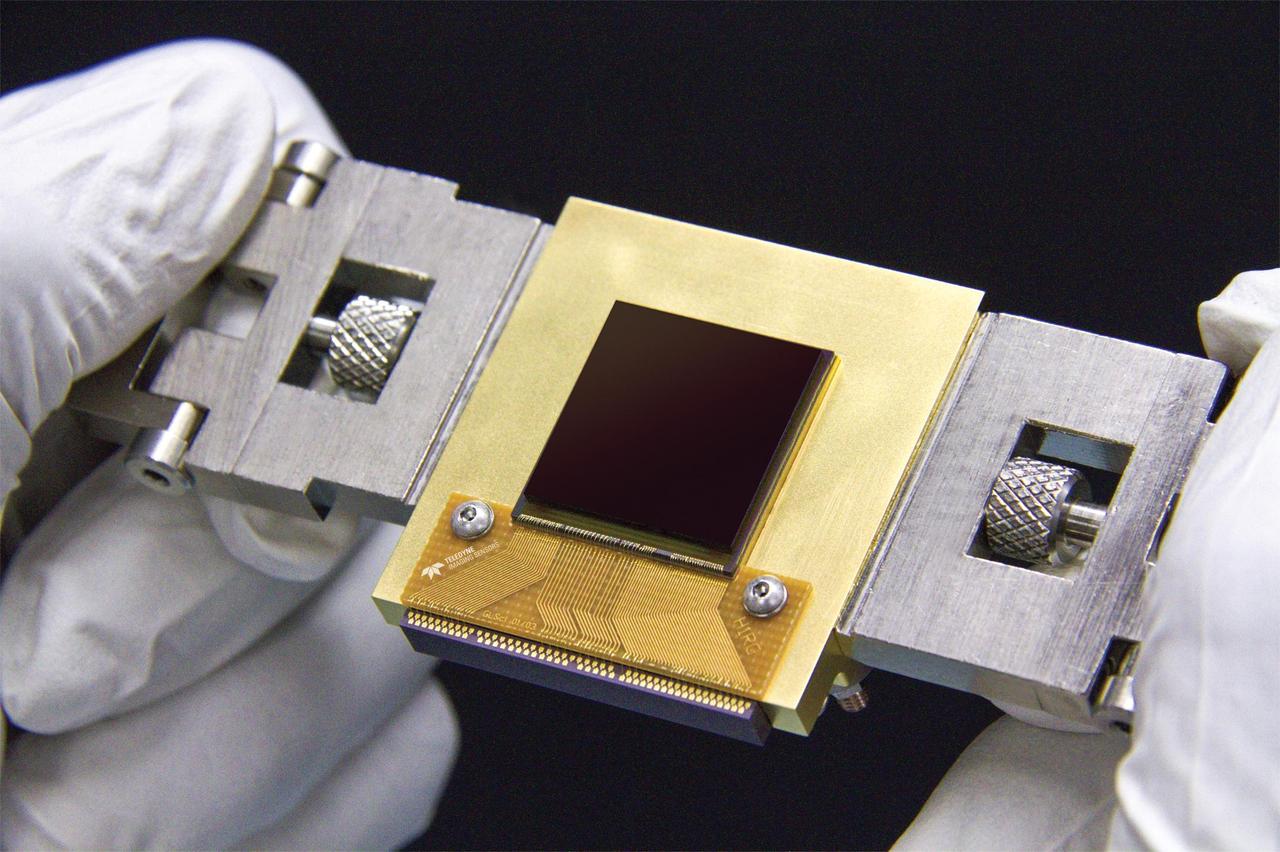
The NEOCam chip is the first megapixel sensor capable of detecting infrared wavelengths at temperatures achievable in deep space without refrigerators or cryogens.
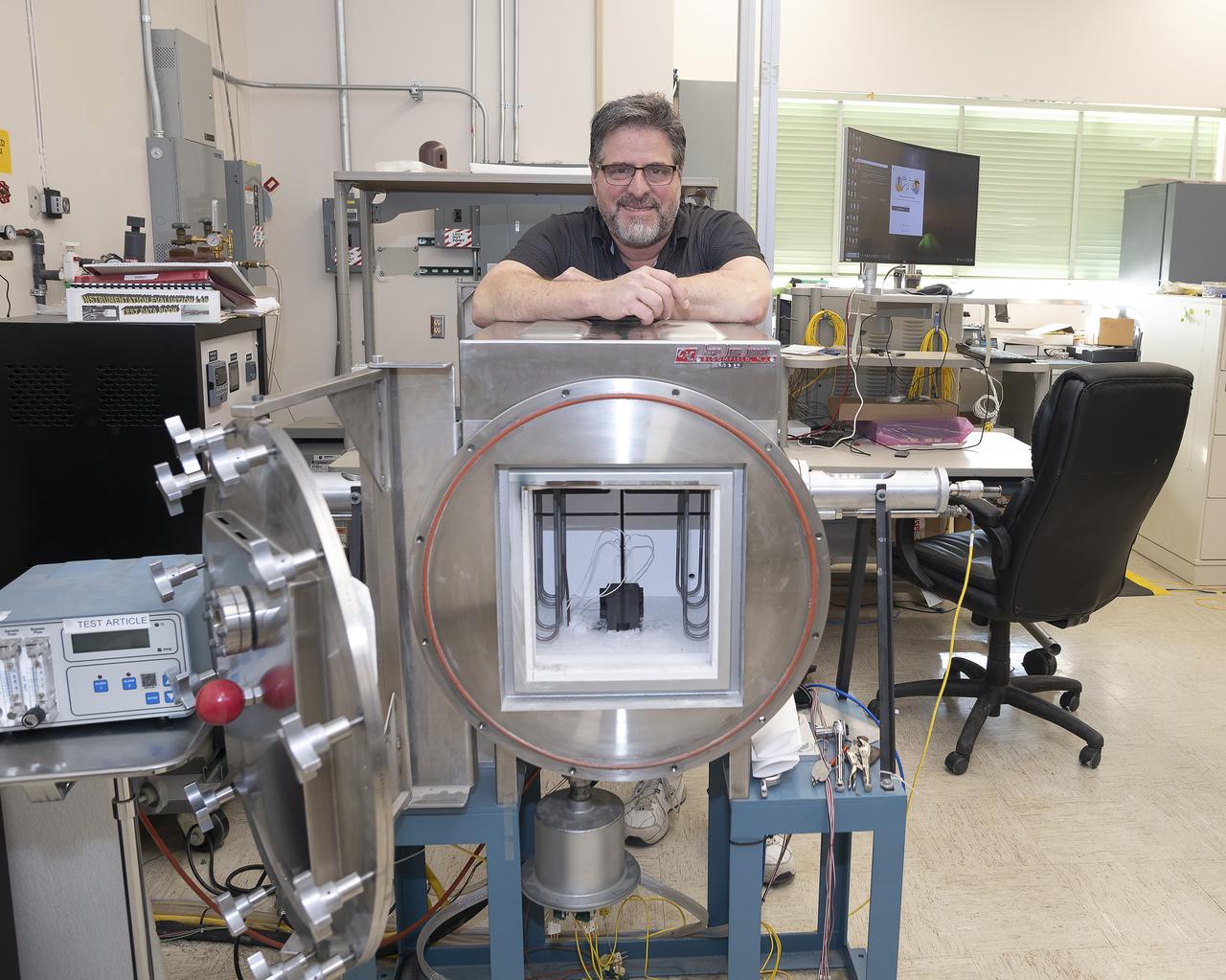

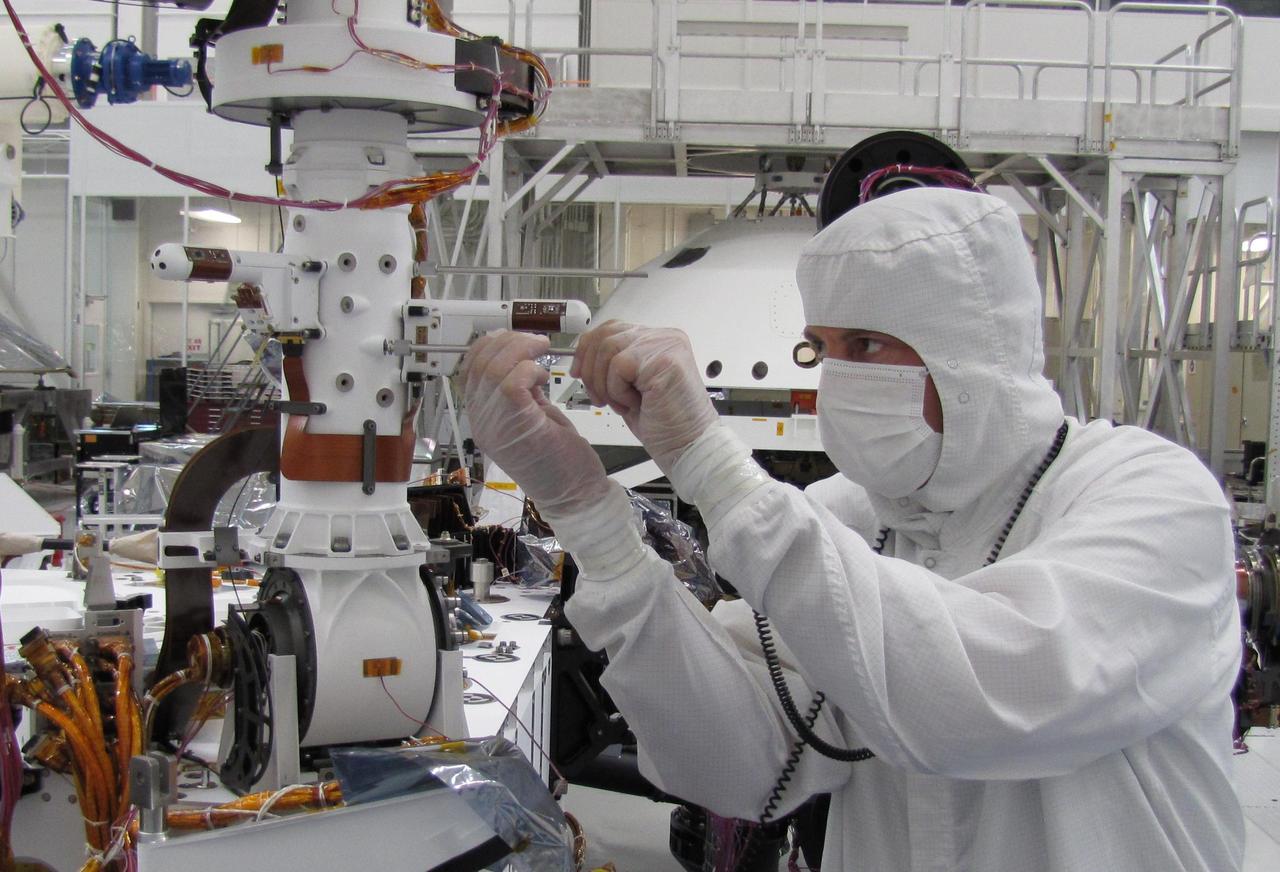
Anthony piazza, a researcher at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research center in Edwards, California, works with high-temperature strain sensors. This test article is a bending load bar, which enables high-temperature optical strain sensor research up to 1,800 degrees Fahrenheit.
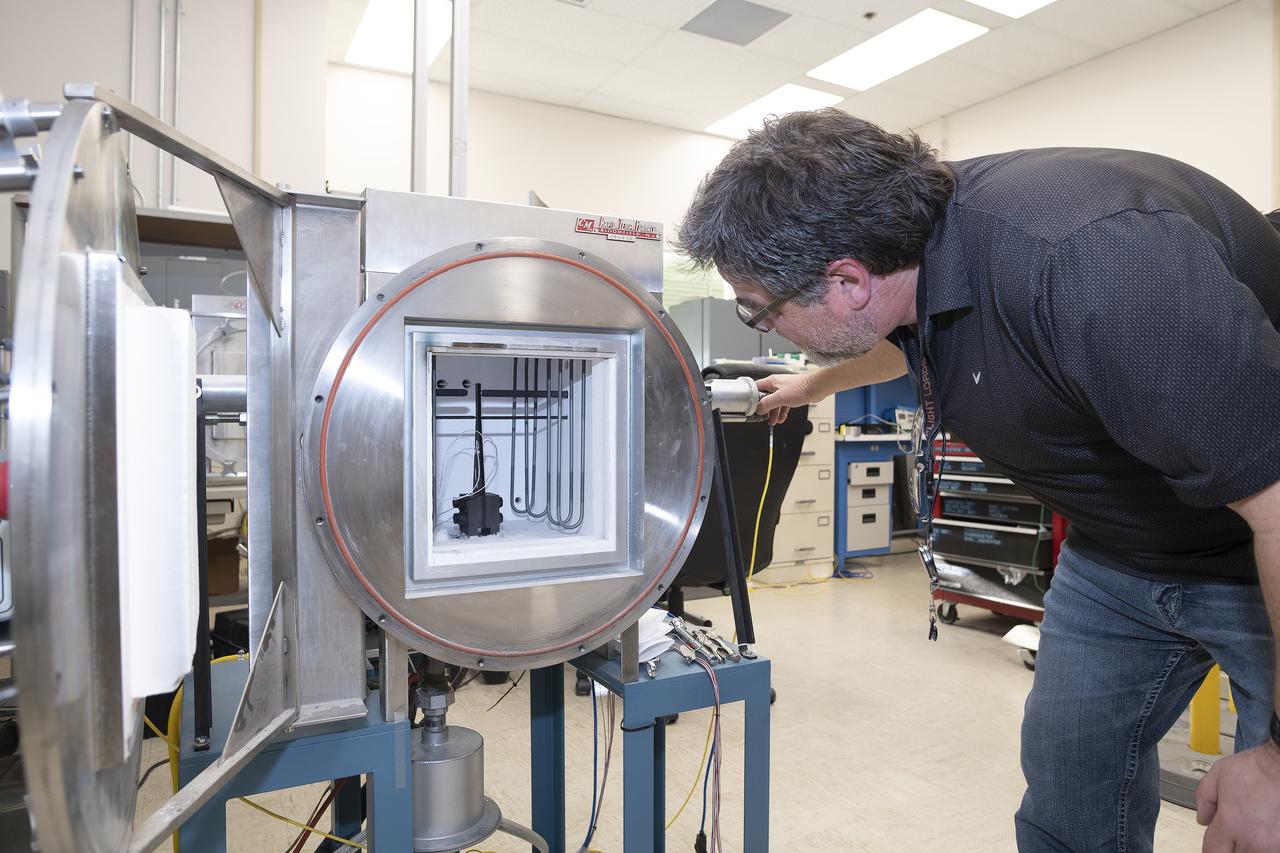

Anthony piazza, a researcher at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research center in Edwards, California, works with high-temperature strain sensors. This test article is a bending load bar, which enables high-temperature optical strain sensor research up to 1,800 degrees Fahrenheit.
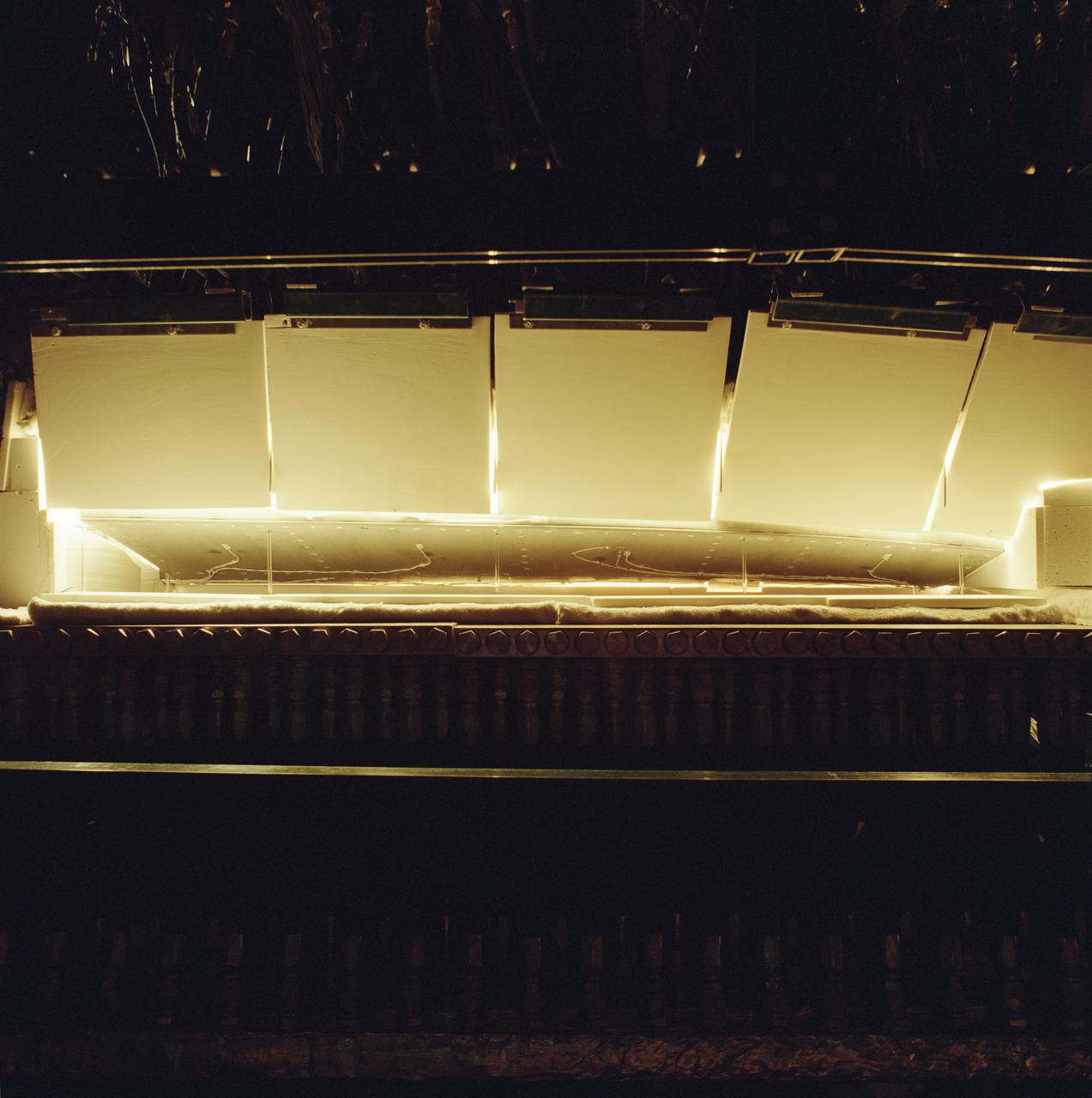

The X-37 advanced technology demonstrator flaperon unit was one of the first ever thermal and mechanical qualification tests of a carbon-carbon control surface designed for space flight. The test also featured extensive use of high-temperature fiber optic strain sensors. Peak temperatures reached 2,500 degrees Fahrenheit.
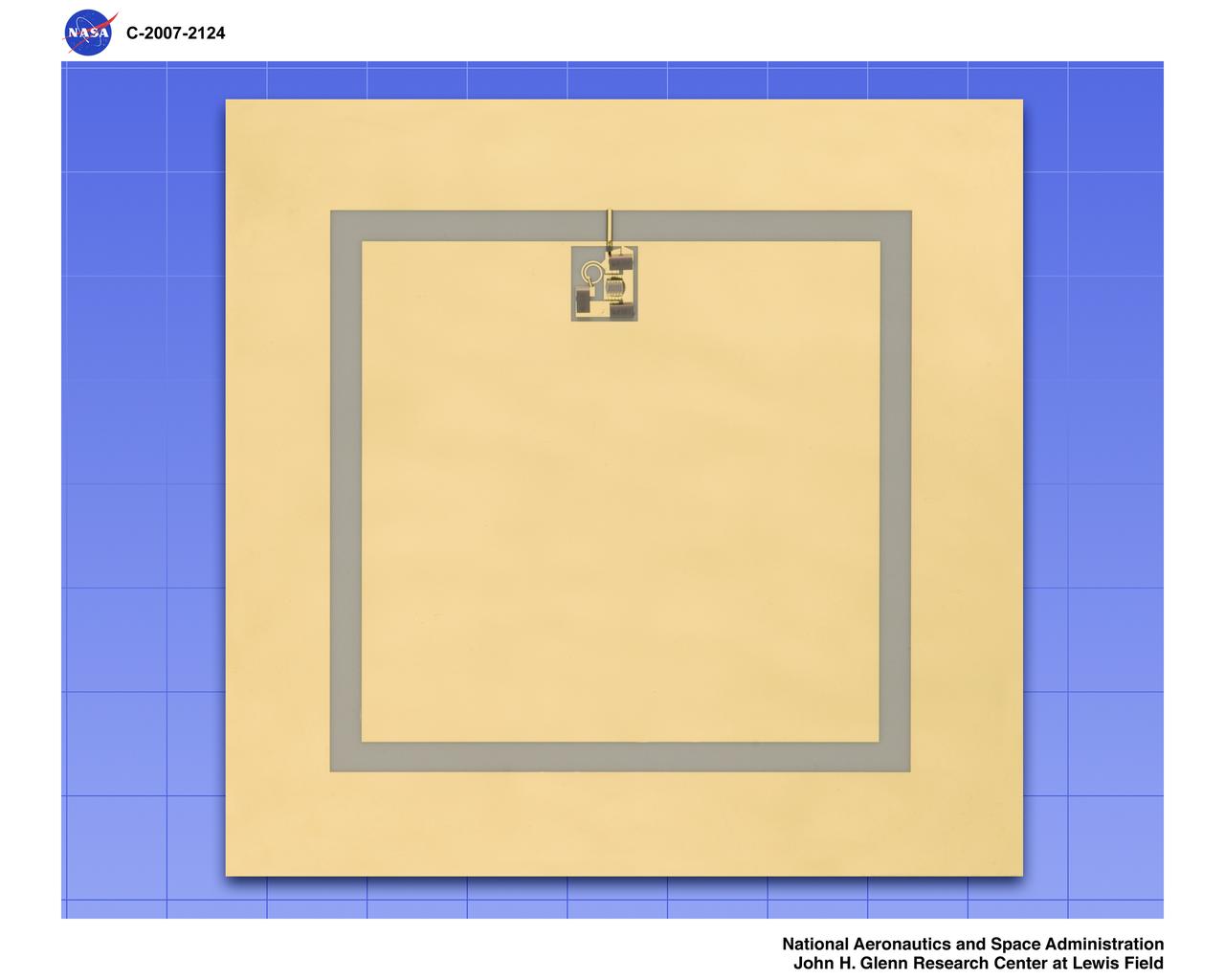
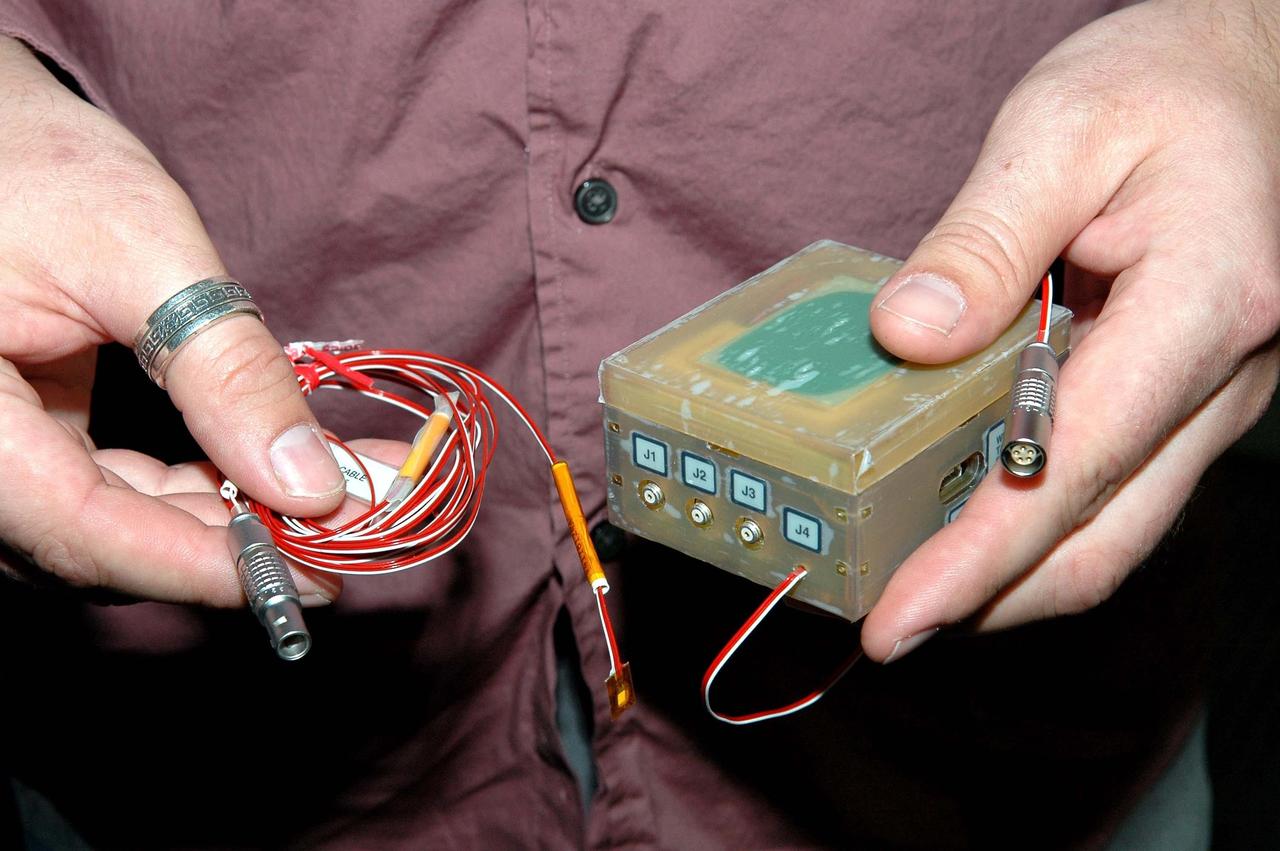
Oscillator / Antenna for High Temperature Wireless Sensor

The Rover Environmental Monitoring Station (REMS) on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover includes temperature and humidity sensors mounted on the rover's mast. One of the REMS booms extends to the left from the mast in this view. Spain provided REMS to NASA's Mars Science Laboratory Project. The monitoring station has provided information about air pressure, relative humidity, air temperature, ground temperature, wind and ultraviolet radiation in all Martian seasons and at all times of day or night. This view is a detail from a January 2015 Curiosity self-portrait. The self-portrait, at PIA19142, was assembled from images taken by Curiosity's Mars Hand Lens Imager. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19164
Here is a closeup of some of the X-59’s wiring and instrumentation system. Displayed here is the remote instrumentation encoder, which can be found in the wing of the aircraft. This encoder communicates with the plane’s other instrumentation systems like pressure and temperature sensors within the X-59.

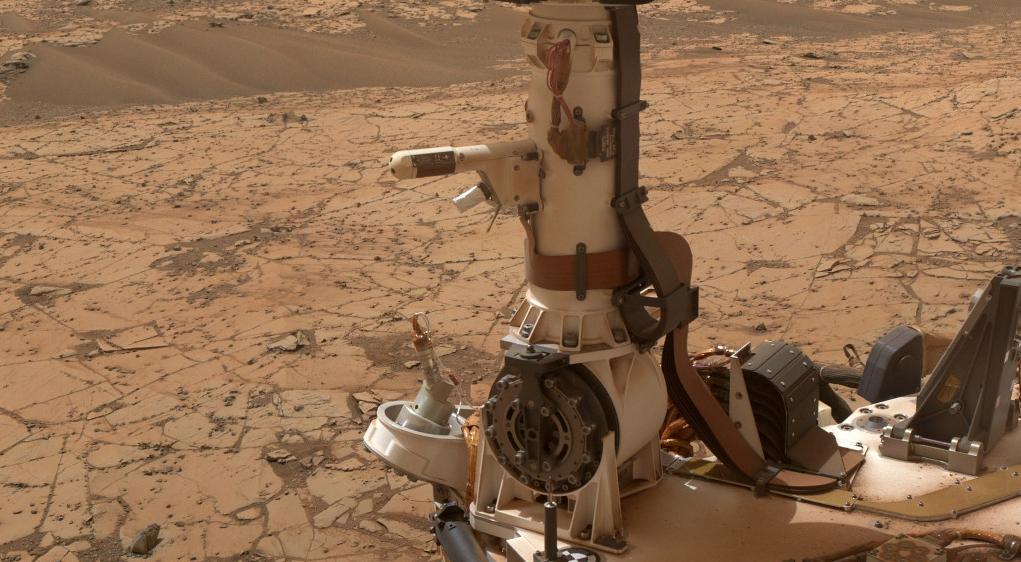
Sensors on two finger-like mini-booms extending horizontally from the mast of NASA Mars rover Curiosity will monitor wind speed, wind direction and air temperature; image taken during installation of the instrument inside a clean room at NASA JPL.

This artist's concept shows NASA's InSight lander with its instruments deployed on the Martian surface. InSight's package of weather sensors, called the Auxiliary Payload Subsystem (APSS), includes an air pressure sensor inside the lander -- its inlet is visible on InSight's deck -- and two air temperature and wind sensors on the deck. Under the deck's edge is a magnetometer, provided by UCLA, to measure changes in the local magnetic field that could also influence SEIS. InSight's air temperature and wind sensors are actually refurbished spares built for Curiosity's Rover Environmental Monitoring Station (REMS). Called Temperature and Wind for InSight, or TWINS, these two east- and west-facing booms sit on the lander's deck and were provided by Spain's Centro de Astrobiología (CAB). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22957
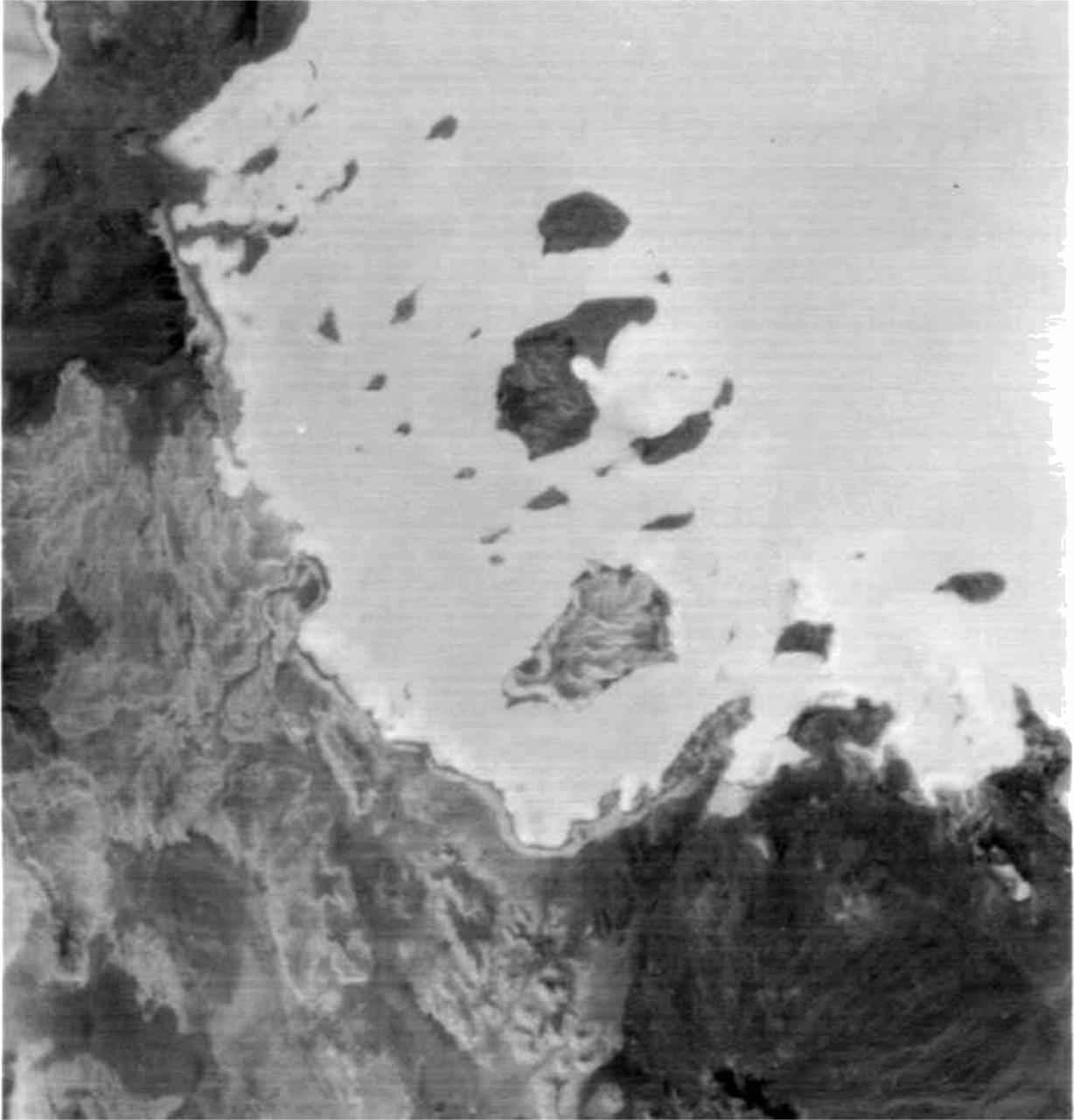
ASTER succeeded in acquiring this image at night, which is something Visible/Near Infrared VNIR) and Shortwave Infrared (SWIR) sensors cannot do. The scene covers the Red Sea coastline to an inland area of Ethiopia. White pixels represent areas with higher temperature material on the surface, while dark pixels indicate lower temperatures. This image shows ASTER's ability as a highly sensitive, temperature-discerning instrument and the first spaceborne TIR multi-band sensor in history. The size of image: 60 km x 60 km approx., ground resolution 90 m x 90 m approximately. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02452
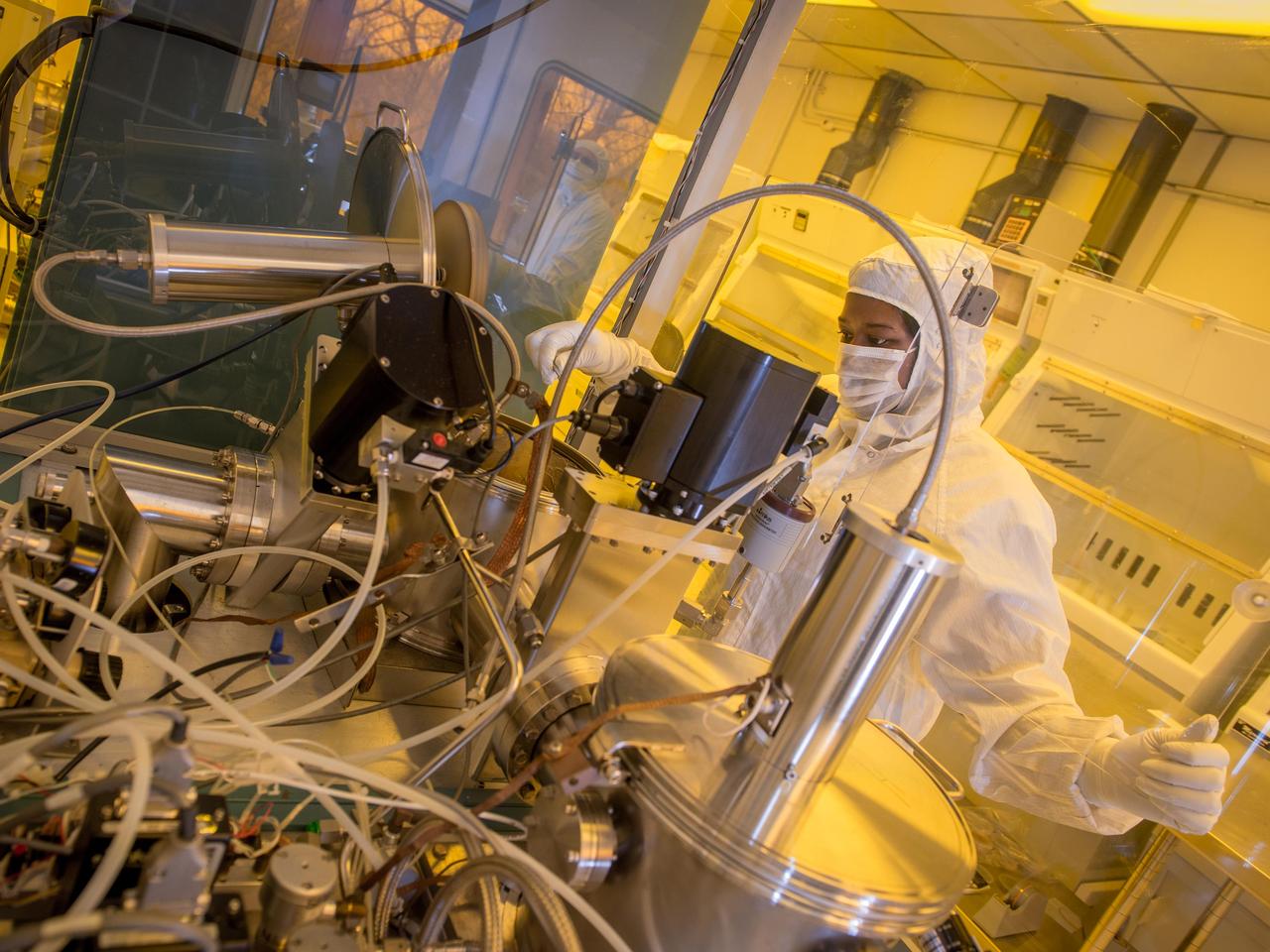

NASA Glenn technician Ariana Miller prepares an ultrahigh vacuum chamber used to test the materials used in silicon carbide based sensors and electronics that can operate at extremely high temperatures (500 degrees Celsius and higher) for applications such as sensor systems for aircraft engines and Venus exploration.
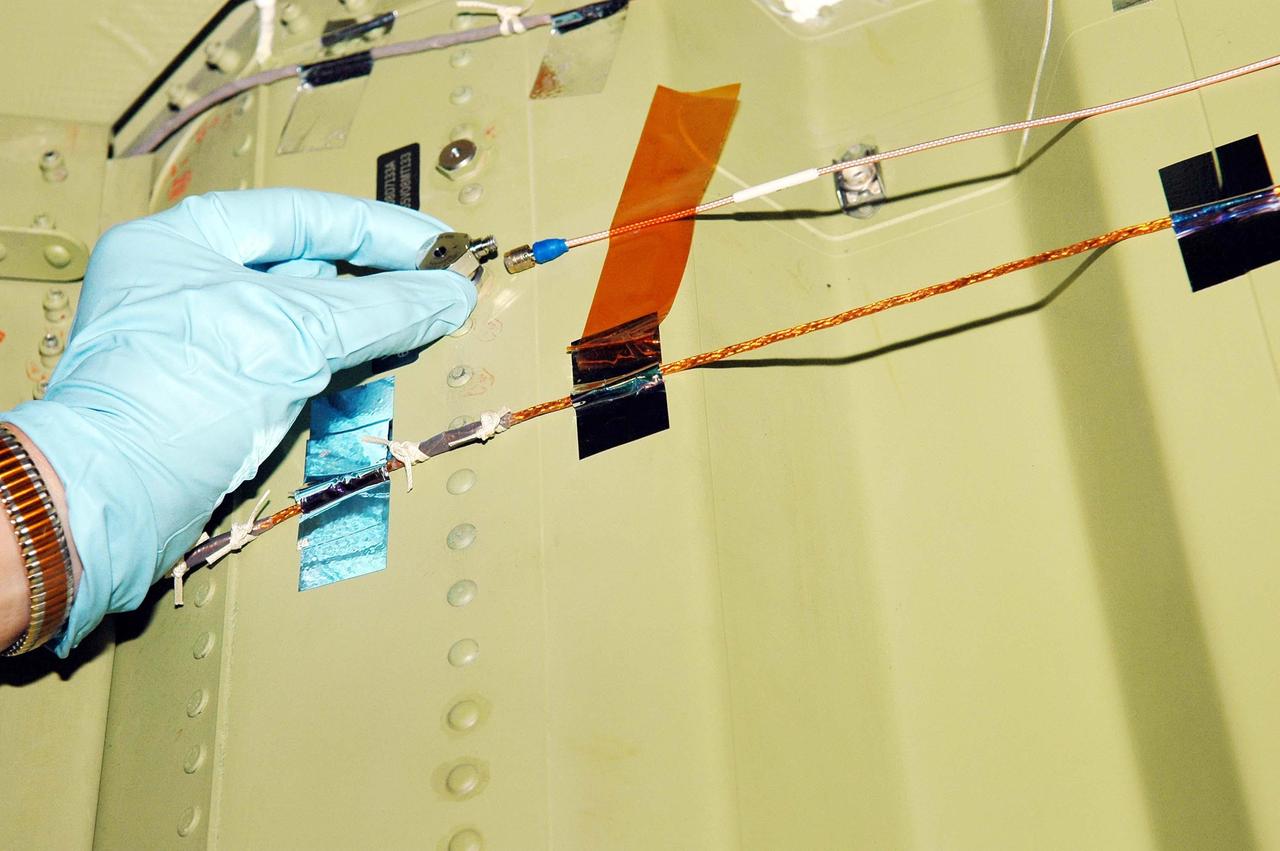
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In an installation demonstration in the Orbiter Processing Facility, a sensor is placed on the wing leading edge of orbiter Discovery. The sensors are part of the Wing Leading Edge Impact Detection System, a new safety measure added for all future Space Shuttle missions. The system also includes accelerometers that monitor the orbiter's wings for debris impacts during launch and while in orbit. There are 22 temperature sensors and 66 accelerometers on each wing. Sensor data will flow from the wing to the crew compartment, where it will be transmitted to Earth.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In an installation demonstration the Orbiter Processing Facility, a sensor is placed on the wing leading edge of orbiter Discovery. The sensors are part of the Wing Leading Edge Impact Detection System, a new safety measure added for all future Space Shuttle missions. The system also includes accelerometers that monitor the orbiter's wings for debris impacts during launch and while in orbit. There are 22 temperature sensors and 66 accelerometers on each wing. Sensor data will flow from the wing to the crew compartment, where it will be transmitted to Earth.
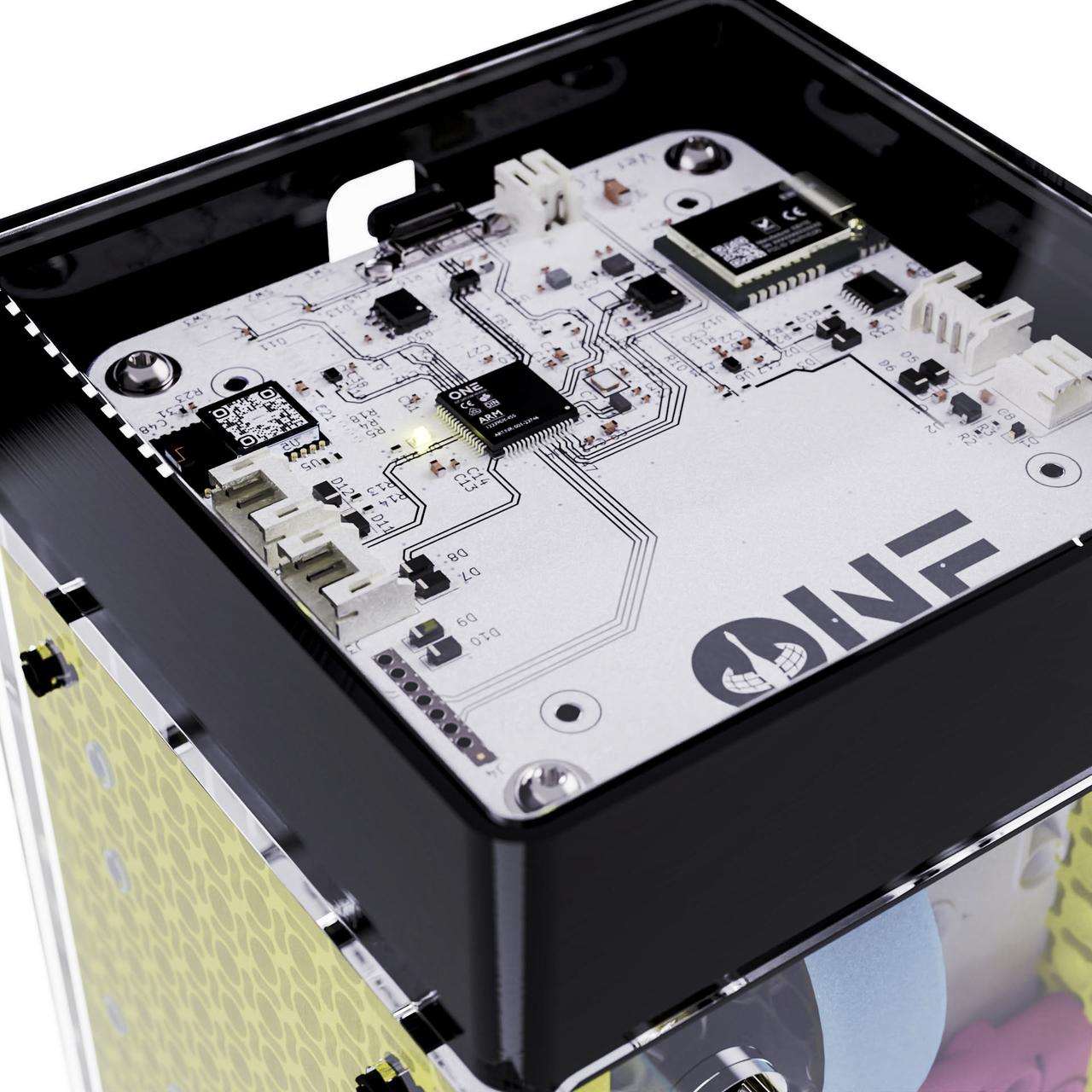
jsc2023e053550 (7/27/2023) --- The denMACH ONE IoT modem complete with inbuilt sensors to measure temperature, humidity, CO2, barometric pressure, compass points, accelerometer, GPS. Image courtesy SpaceTech denMACH.
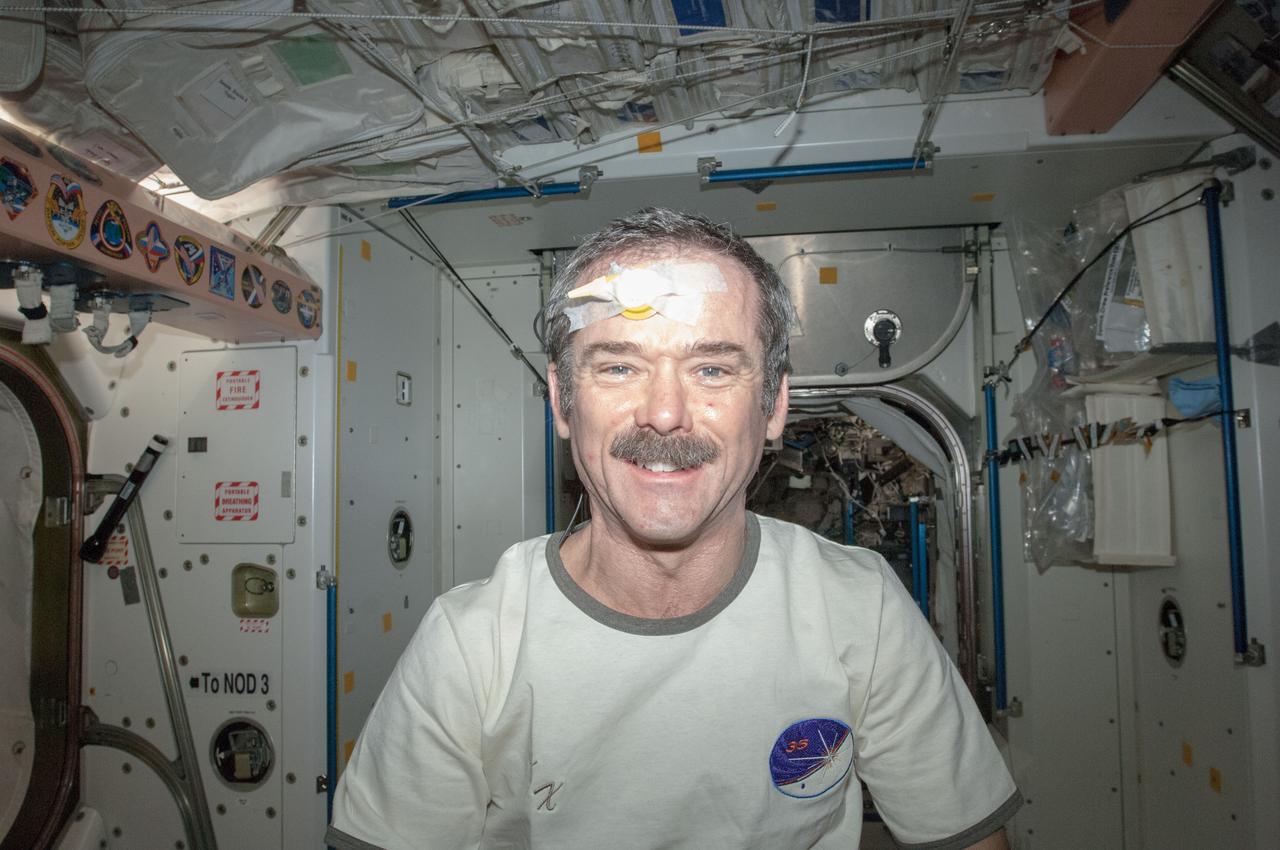

Expedition 35 commander and Canadian Space Agency astronaut Chris Hadfield (with a temperature sensor taped to his forehead) poses for a photo in the Unity Node 1 before getting a haircut.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - During an installation demonstration the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance technician Lisa Campbell handles components of the sensor system being placed on the wing leading edge of orbiter Discovery. The sensors are part of the Wing Leading Edge Impact Detection System, a new safety measure added for all future Space Shuttle missions. The system also includes accelerometers that monitor the orbiter's wings for debris impacts during launch and while in orbit. There are 22 temperature sensors and 66 accelerometers on each wing. Sensor data will flow from the wing to the crew compartment, where it will be transmitted to Earth.
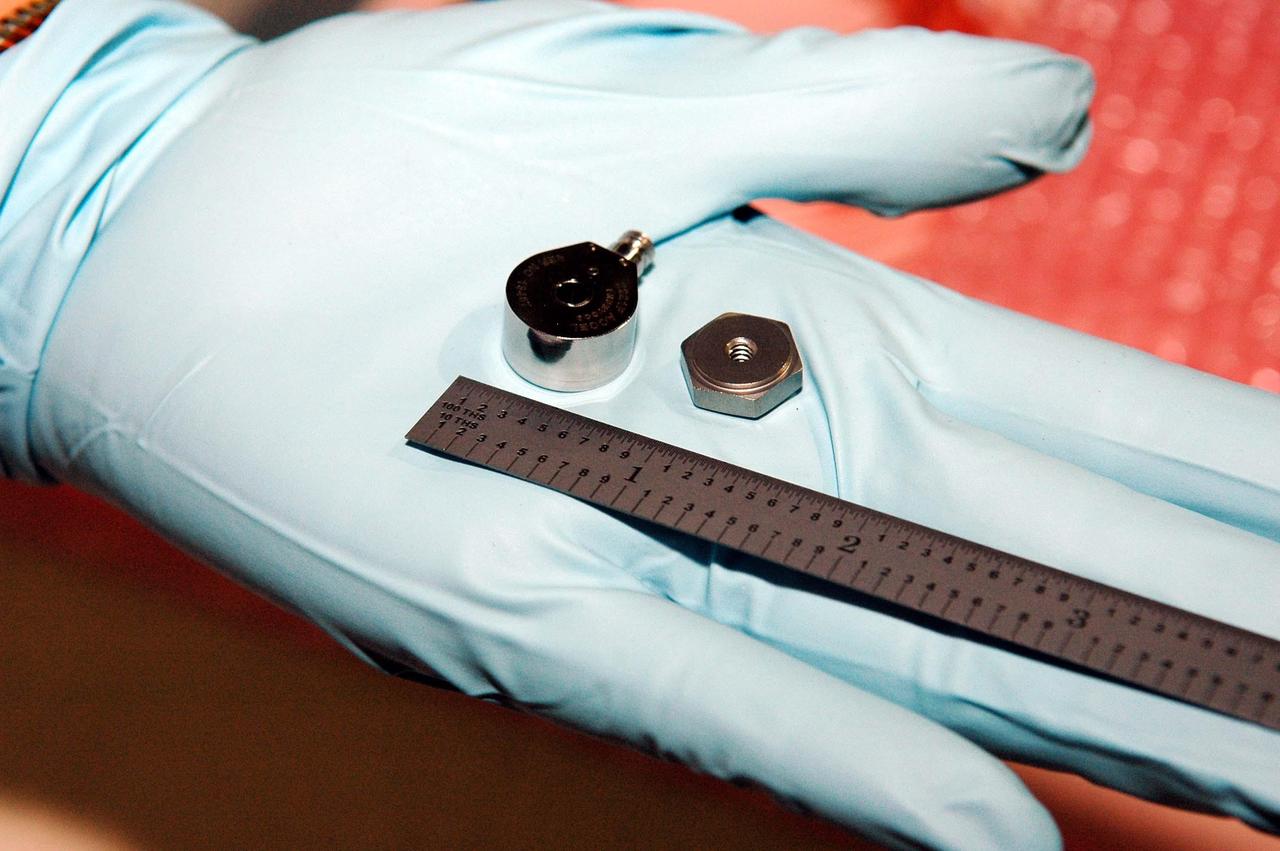
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This photo shows the size of the sensors being placed on the wing leading edge of orbiter Discovery. In her hand, United Space Alliance technician Lisa Campbell holds an accelerometer (left), which will eventually be installed on a mounting nut. The sensors are part of the Wing Leading Edge Impact Detection System, a new safety measure added for all future Space Shuttle missions. The system also includes accelerometers that monitor the orbiter's wings for debris impacts during launch and while in orbit. There are 22 temperature sensors and 66 accelerometers on each wing. Sensor data will flow from the wing to the crew compartment, where it will be transmitted to Earth.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - During an installation demonstration the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance technician Lisa Campbell works with components of the sensor system being placed on the wing leading edge of orbiter Discovery. The sensors are part of the Wing Leading Edge Impact Detection System, a new safety measure added for all future Space Shuttle missions. The system also includes accelerometers that monitor the orbiter's wings for debris impacts during launch and while in orbit. There are 22 temperature sensors and 66 accelerometers on each wing. Sensor data will flow from the wing to the crew compartment, where it will be transmitted to Earth.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - During an installation demonstration the Orbiter Processing Facility, Robert Early, lead instrument engineer with United Space Alliance, holds components of the sensor system being placed on the wing leading edge of orbiter Discovery. The sensors are part of the Wing Leading Edge Impact Detection System, a new safety measure added for all future Space Shuttle missions. The system also includes accelerometers that monitor the orbiter's wings for debris impacts during launch and while in orbit. There are 22 temperature sensors and 66 accelerometers on each wing. Sensor data will flow from the wing to the crew compartment, where it will be transmitted to Earth.
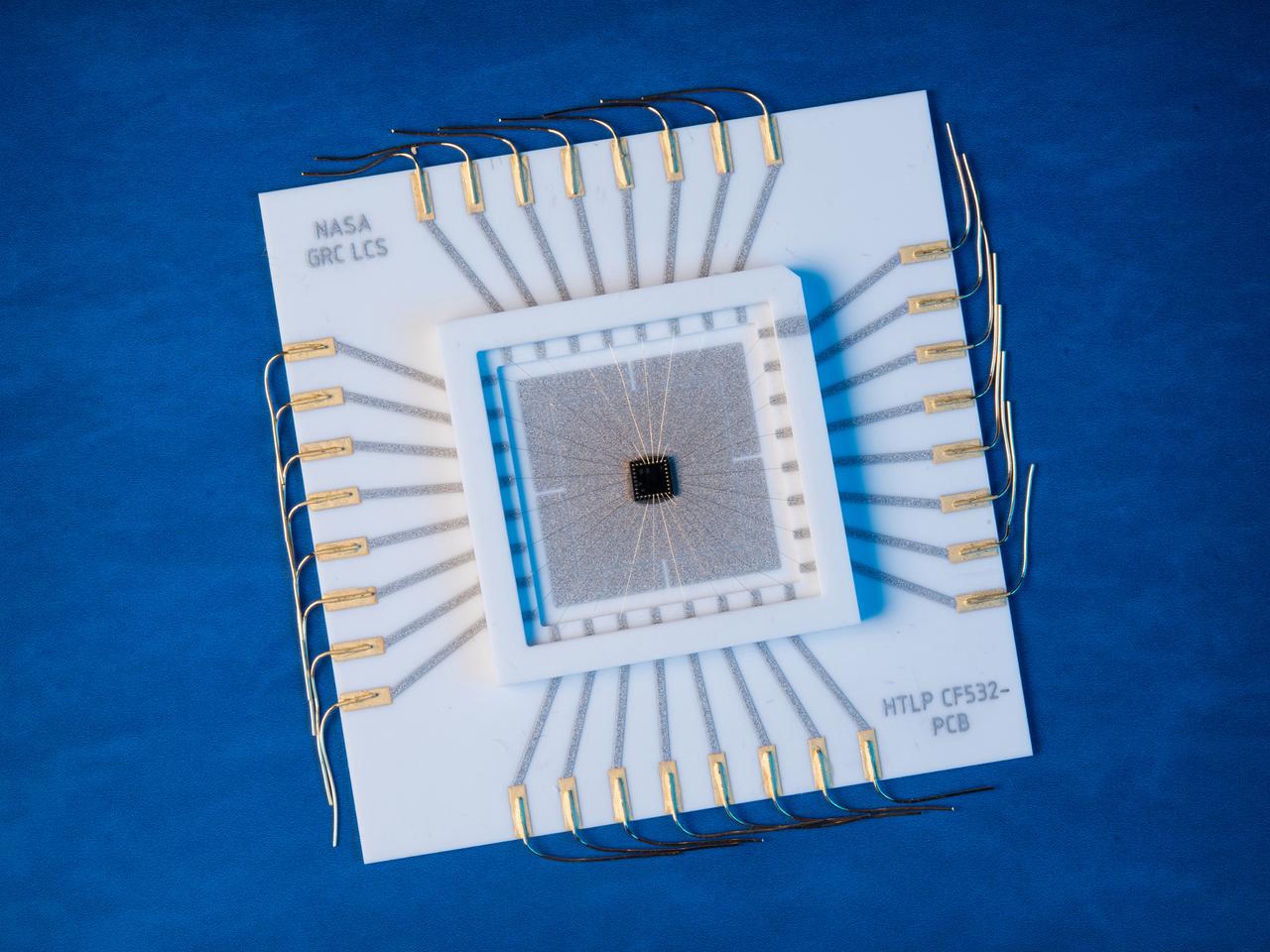
A multilevel interconnect silicon carbide integrated circuit chip with co-fired ceramic package and circuit board recently developed at the NASA GRC Smart Sensors and Electronics Systems Branch for high temperature applications. High temperature silicon carbide electronics and compatible packaging technologies are elements of instrumentation for aerospace engine control and long term inner-solar planet explorations.
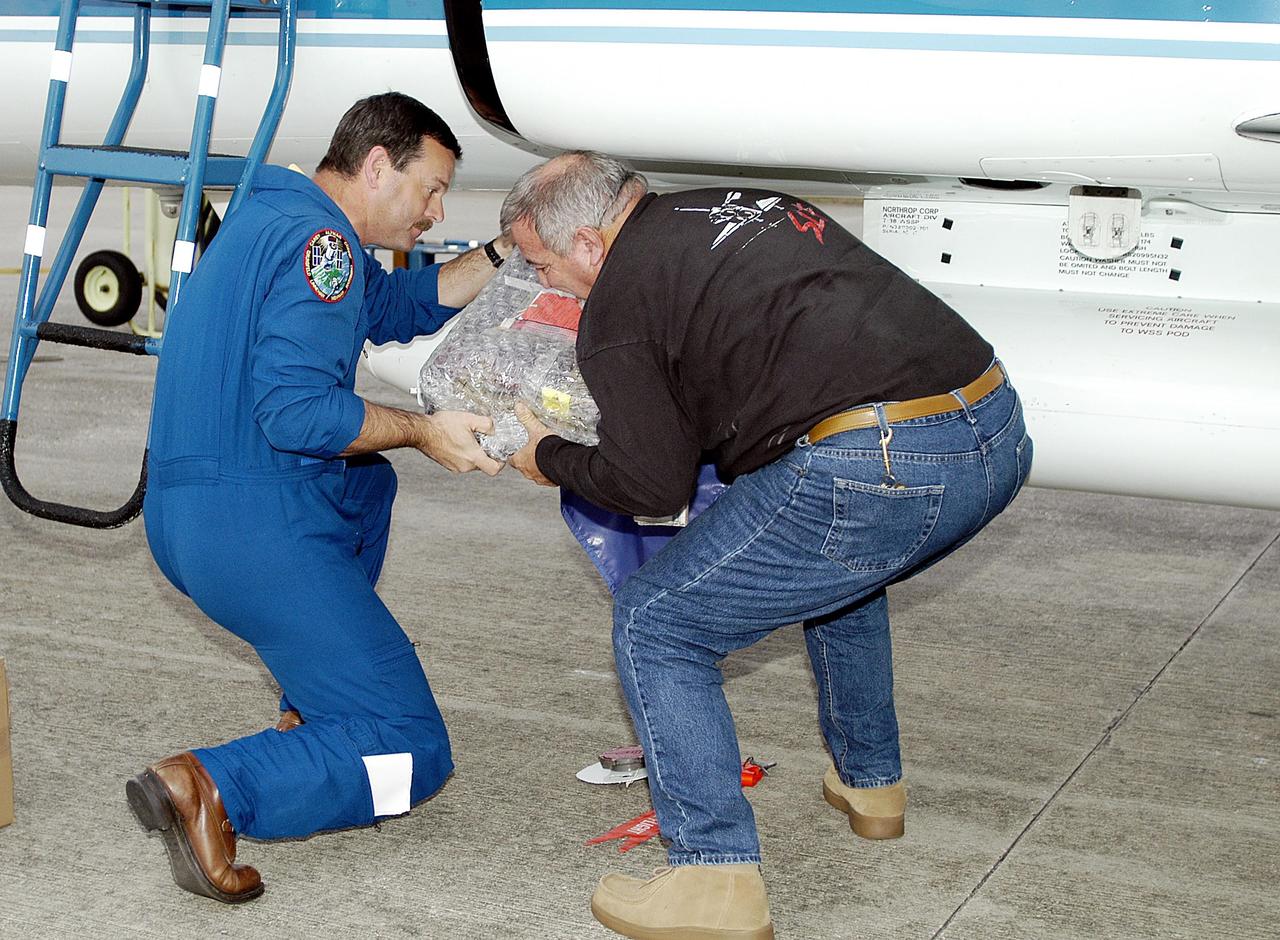

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Orbiter Experiment Support System (OEX) recorder from Columbia is removed from the T-38 jet aircraft that brought it to KSC. Search teams near Hemphill, Texas, recovered the recorder, which stores sensor information about temperature, aerodynamic pressure, vibrations and other data from dozens of sensor locations on the orbiter, operating only during launch and re-entry. The OEX uses magnetic tape to record data that is not sent to the ground by telemetry.
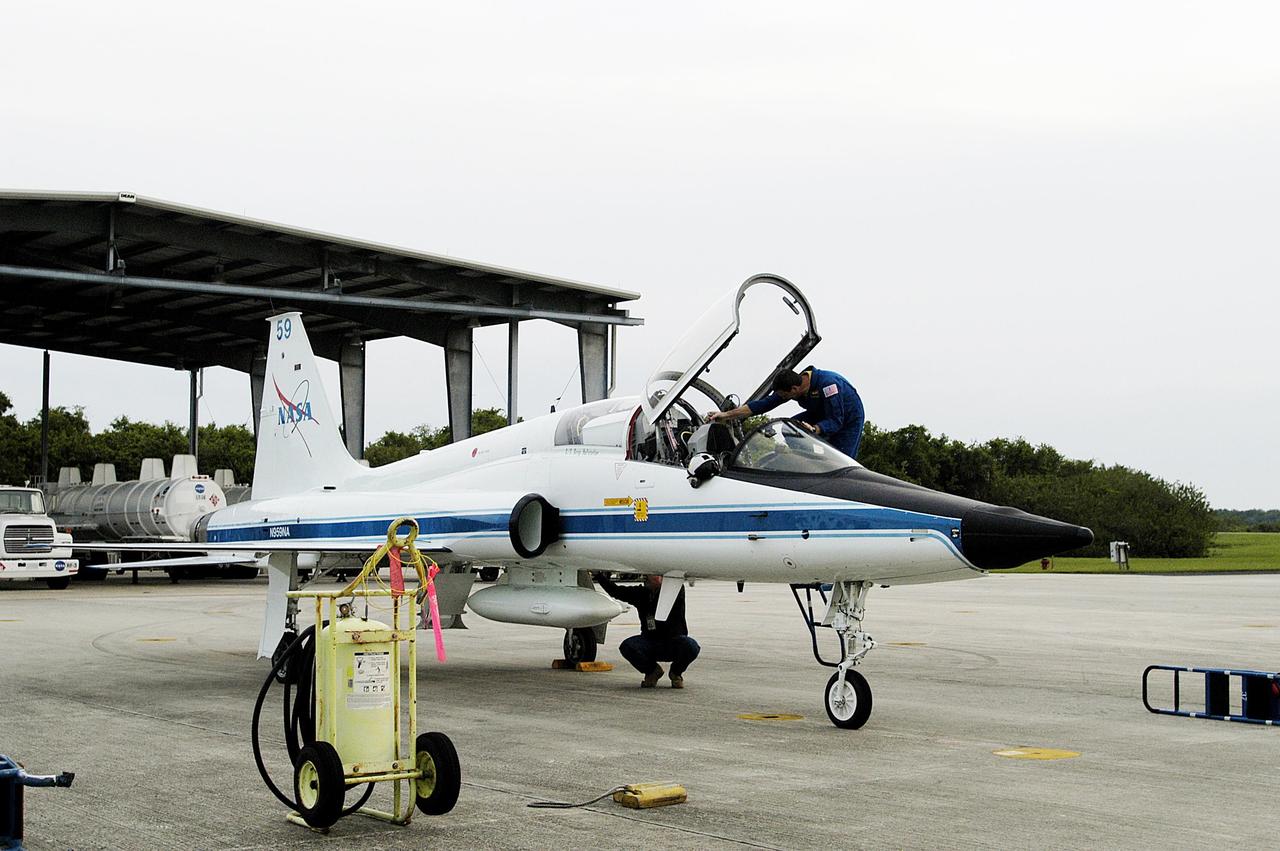

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A T-38 jet aircraft carrying the Orbiter Experiment Support System (OEX) recorder from Columbia arrives at the Shuttle Landing Facility. Search teams near Hemphill, Texas, recovered the recorder, which stores sensor information about temperature, aerodynamic pressure, vibrations and other data from dozens of sensor locations on the orbiter, operating only during launch and re-entry. The OEX uses magnetic tape to record data that is not sent to the ground by telemetry.
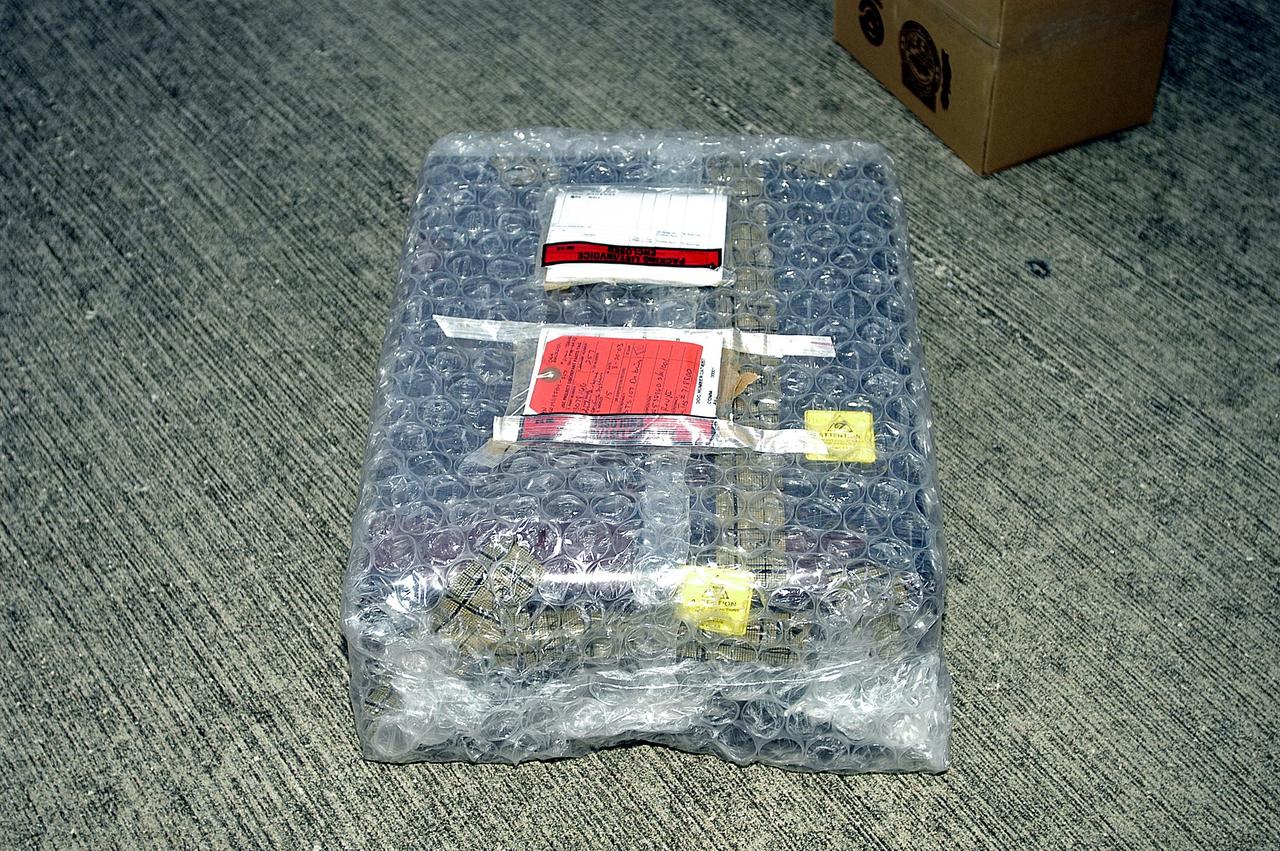

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Orbiter Experiment Support System (OEX) recorder from Columbia, in protective covering, sits on the pavement after its arrival at KSC aboard a T-38 jet aircraft. Search teams near Hemphill, Texas, recovered the recorder, which stores sensor information about temperature, aerodynamic pressure, vibrations and other data from dozens of sensor locations on the orbiter, operating only during launch and re-entry. The OEX uses magnetic tape to record data that is not sent to the ground by telemetry.
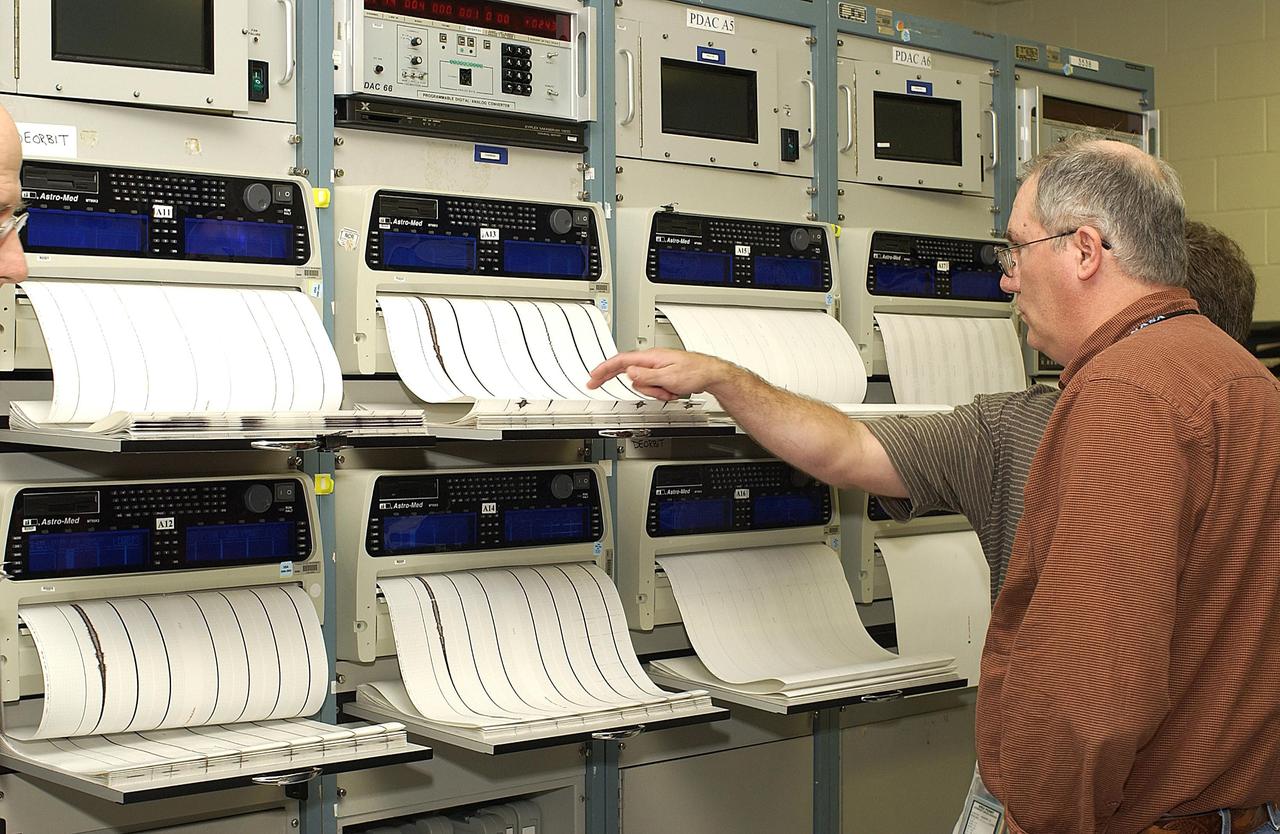

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the KSC Launch Control Center look at the printout from Columbia's Orbiter Experiment Support System (OEX) recorder. After duplication the tape will be reviewed at the Johnson Space Center in Houston and other facilities. No actual sensor data on that tape has been reviewed at this time. Search teams near Hemphill, Texas recovered the recorder, which stores sensor information about temperature, aerodynamic pressure, vibrations and other data from dozens of sensor locations on the orbiter, operating only during launch and re-entry. The OEX uses magnetic tape to record data that is not sent to the ground by telemetry.
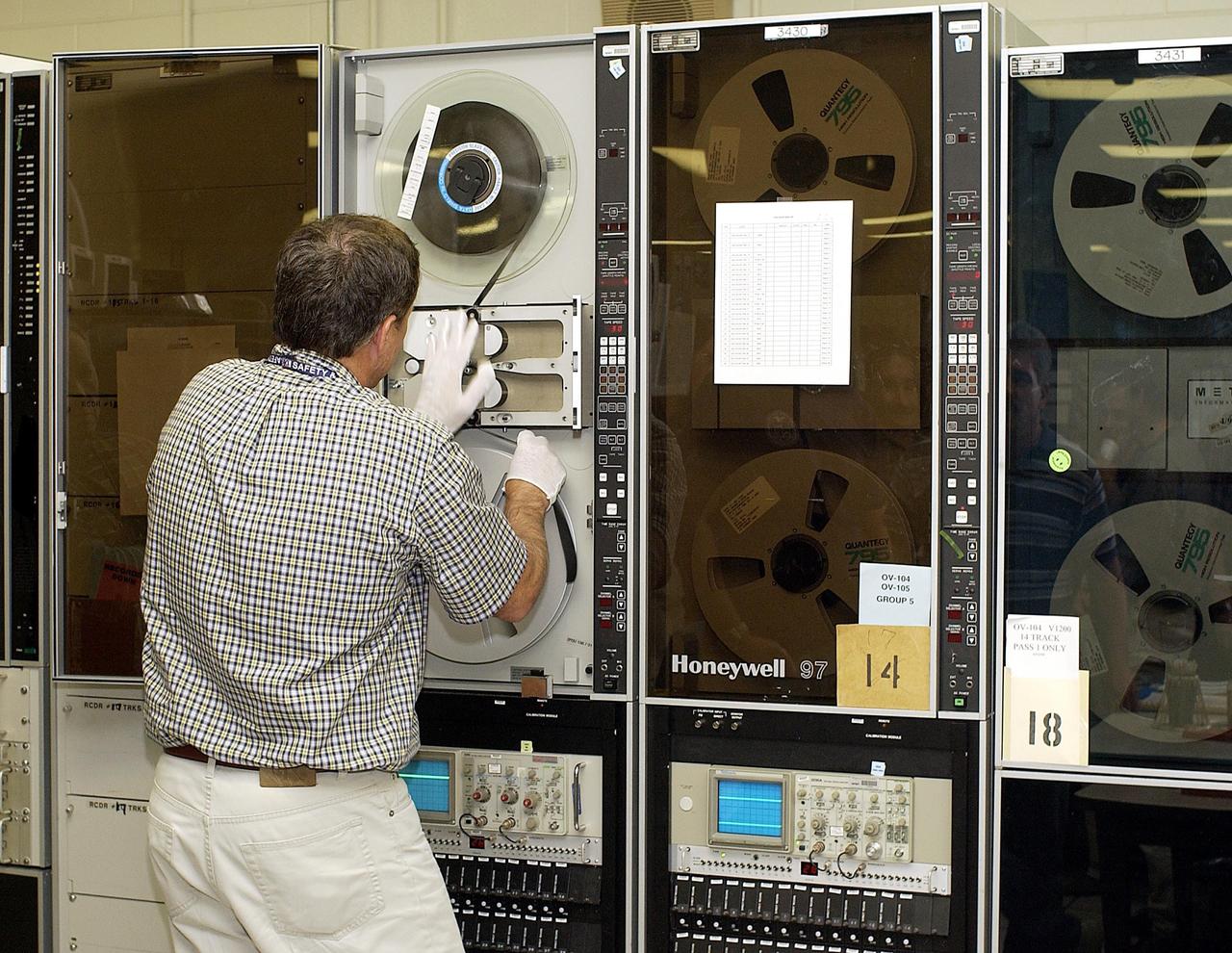

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Columbia's Orbiter Experiment Support System (OEX) recorder is put on taping equipment in the KSC Launch Control Center. The recorder tape is being duplicated and will be reviewed at the Johnson Space Center in Houston and other facilities. No actual sensor data on that tape has been reviewed at this time, Search teams near Hemphill, Texas recovered the recorder, which stores sensor information about temperature, aerodynamic pressure, vibrations and other data from dozens of sensor locations on the orbiter, operating only during launch and re-entry. The OEX uses magnetic tape to record data that is not sent to the ground by telemetry.
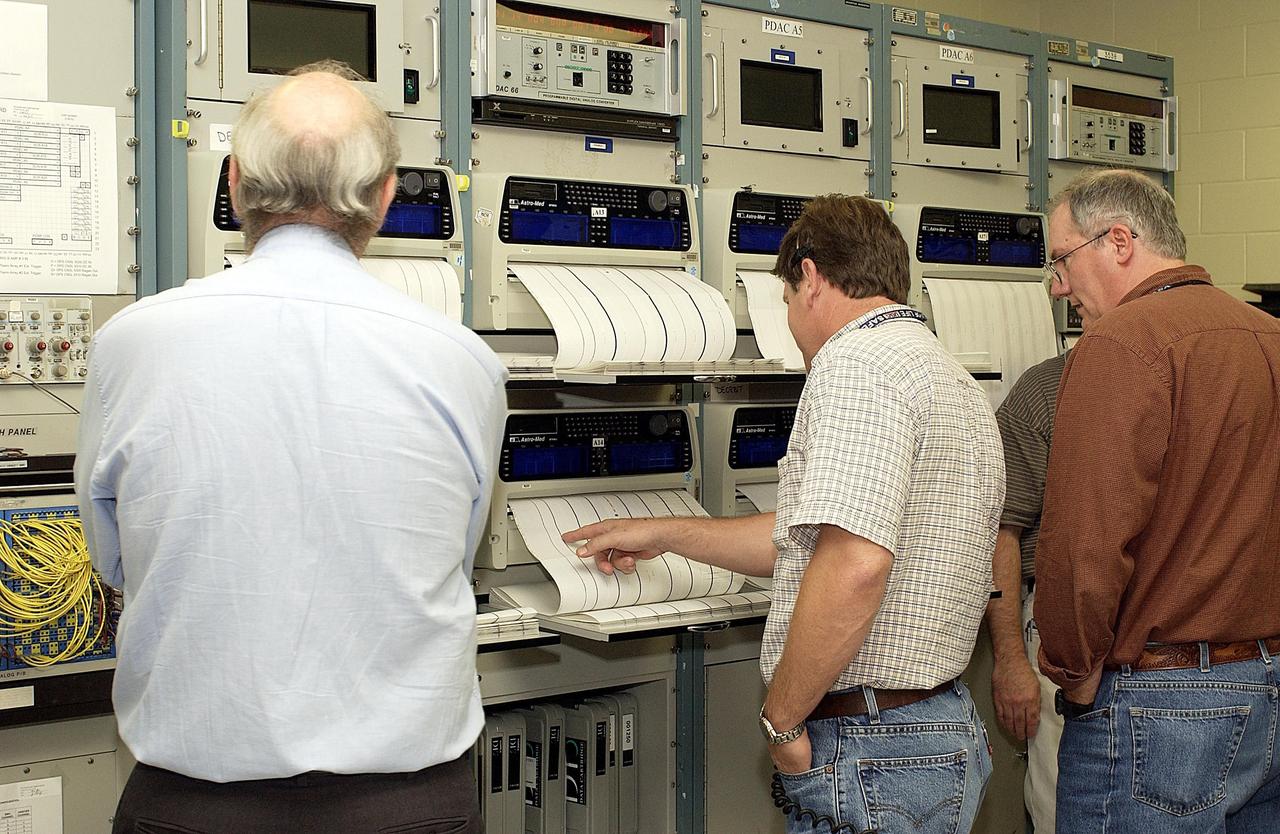

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the KSC Launch Control Center look at the printout from Columbia's Orbiter Experiment Support System (OEX) recorder. After duplication the tape will be reviewed at the Johnson Space Center in Houston and other facilities. No actual sensor data on that tape has been reviewed at this time. Search teams near Hemphill, Texas recovered the recorder, which stores sensor information about temperature, aerodynamic pressure, vibrations and other data from dozens of sensor locations on the orbiter, operating only during launch and re-entry. The OEX uses magnetic tape to record data that is not sent to the ground by telemetry.
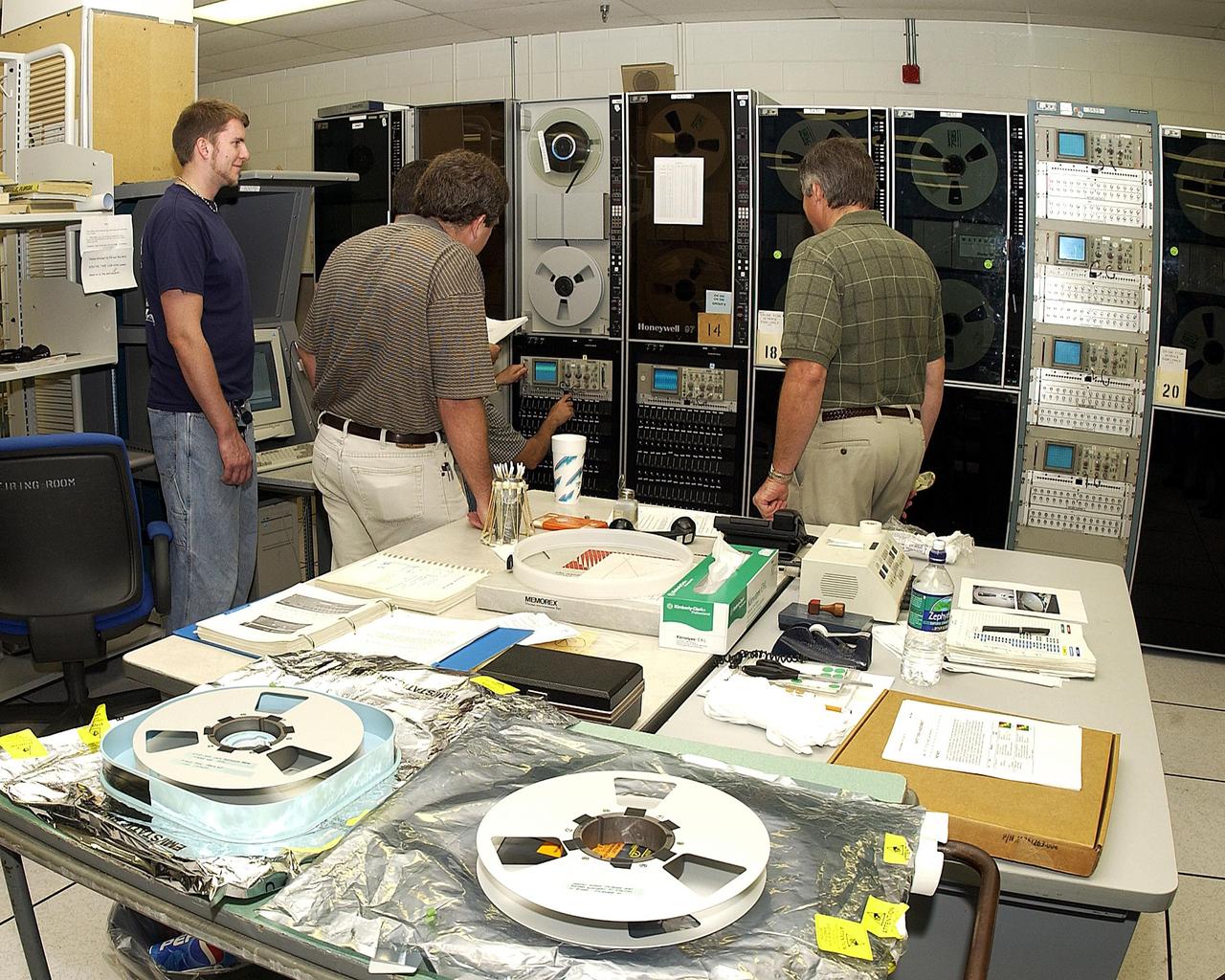

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the KSC Launch Control Center watch the taping operation involving Columbia's Orbiter Experiment Support System (OEX) recorder. After duplication the tape will be reviewed at the Johnson Space Center in Houston and other facilities. No actual sensor data on that tape has been reviewed at this time. Search teams near Hemphill, Texas recovered the recorder, which stores sensor information about temperature, aerodynamic pressure, vibrations and other data from dozens of sensor locations on the orbiter, operating only during launch and re-entry. The OEX uses magnetic tape to record data that is not sent to the ground by telemetry.

jsc2021e033556 (8/4/2021) --- Thermo-Mini device with integrated sensor system and data storage - Placed on the head, Thermo-Mini monitors continuously the core body temperature of the astronaut (36 hrs measurement) before, during and after the ISS-mission.
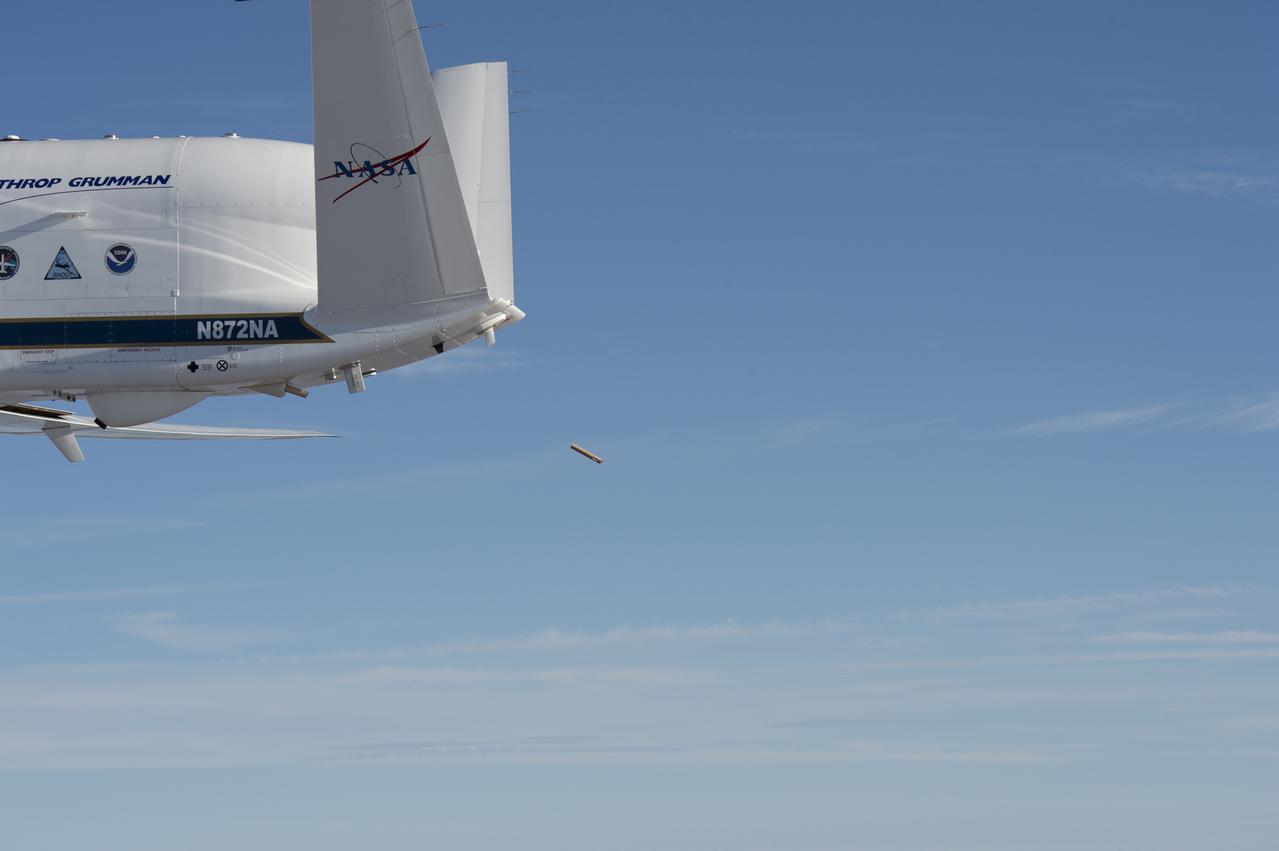

NASA’s Global Hawk aircraft deploys a dropsonde during a test flight over the Dryden Aeronautical Test Range in August 2015. The small, tube-shaped sensor will transmit data on temperature, humidity, and wind speed, which will be used to help improve weather model forecasts
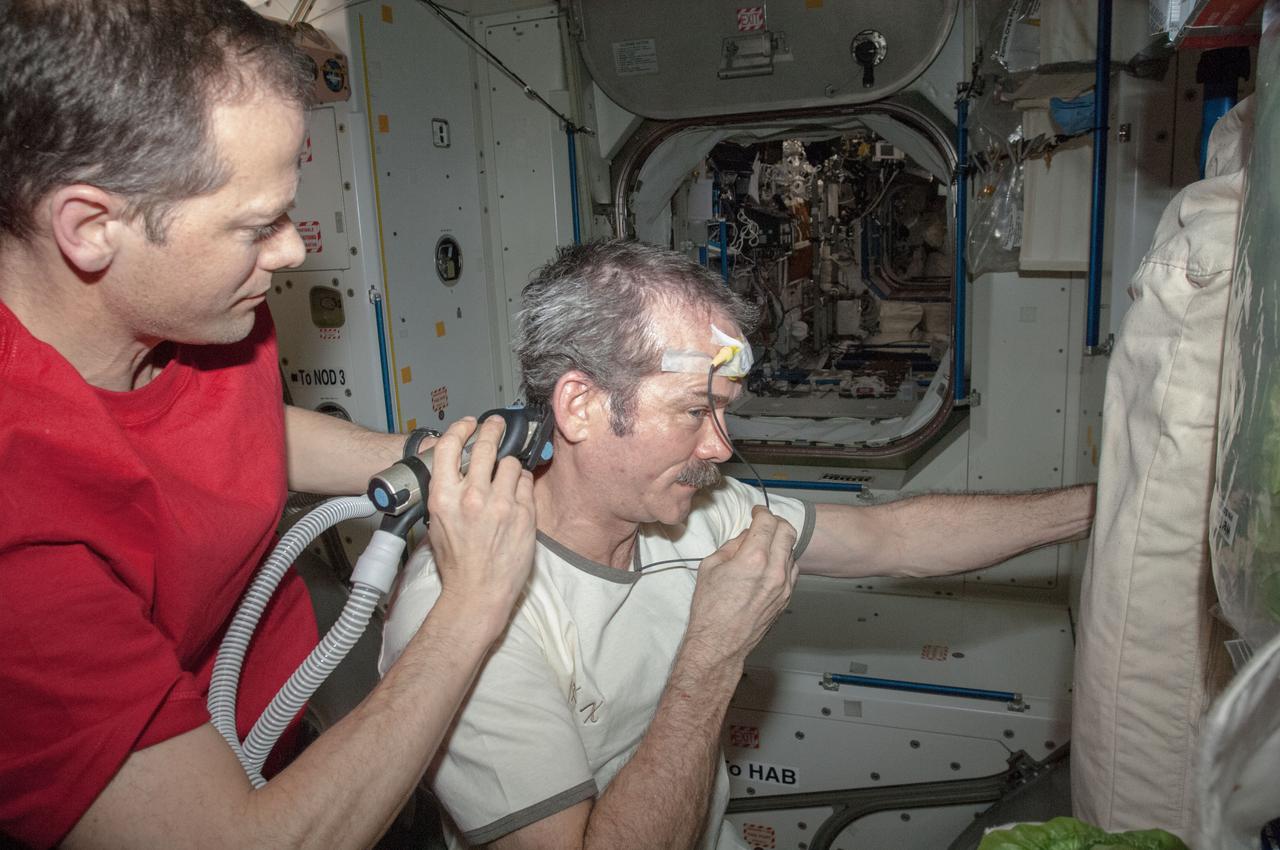

Expedition 35 flight engineer Tom Marshburn gives commander Chris Hadfield a haircut (using clippers attached to a vacuum hose) in the Unity Node 1. Hadfield (a Canadian Space Agency astronaut) has a temperature sensor taped to his forehead.

Jonathan Lopez and Allen Parker confer on the hypersonic Fiber Optic Sensor System at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, on February 13, 2025. The system measures strain and temperature, critical safety data for hypersonic vehicles that travel five time the speed of sound.
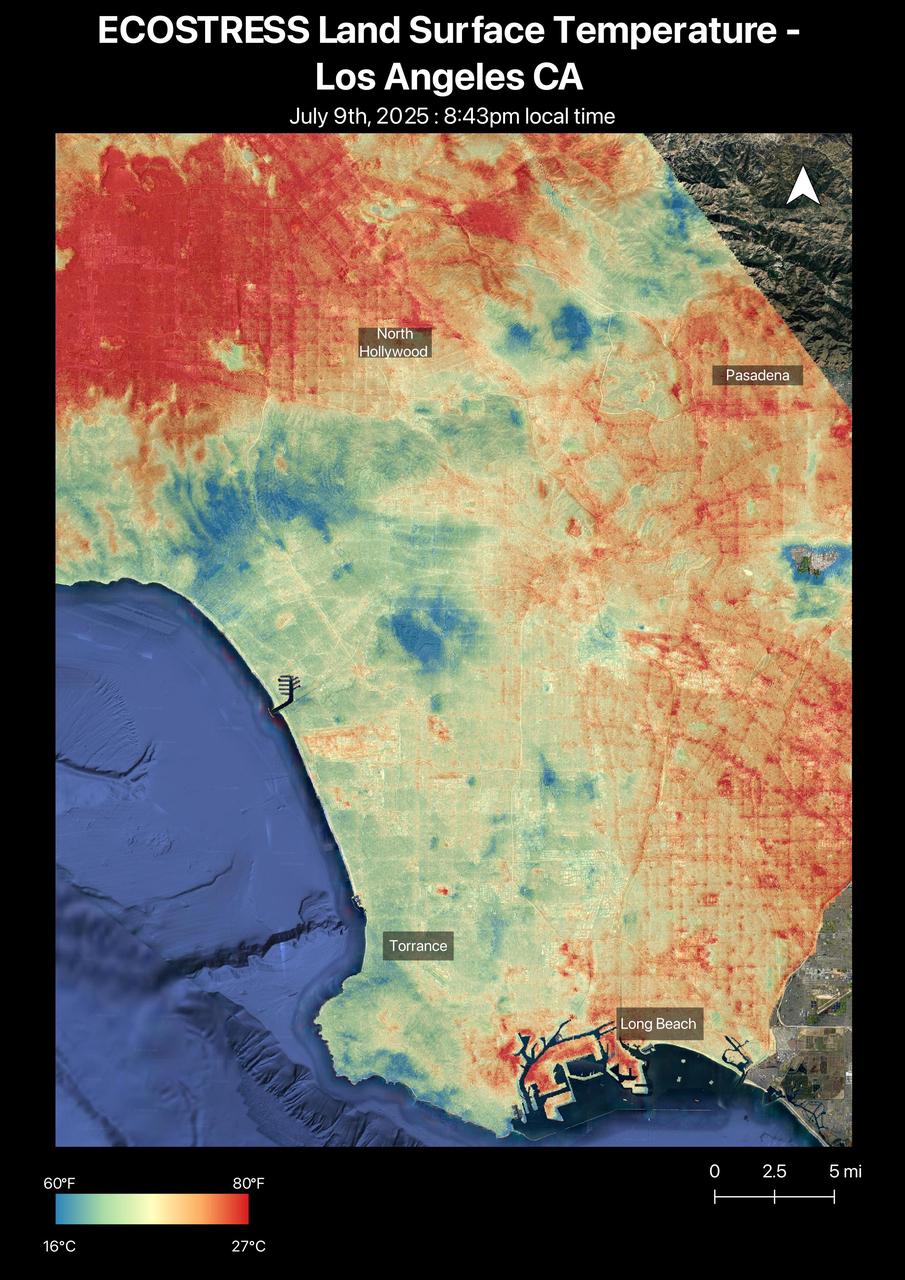
A short-lived heat wave that hit the Los Angeles area the week of July 7, 2025, was the first of summer. The heat lingered into the evening hours, as captured by NASA's Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station (ECOSTRESS) instrument. By nearly 8:45 p.m. local time July 9, surface temperatures in the San Fernando Valley were still over 80 degrees Fahrenheit (27 degrees Celsius). The ECOSTRESS sensor recorded similar temperatures for downtown Pasadena (Figure A) and parts of Altadena, east of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which manages the mission. In these data visualizations, dark red indicates higher temperatures, while areas in blue and green are cooler. Coastal regions remained significantly cooler than inland areas. The ECOSTRESS instrument measures thermal infrared emissions from Earth's surface. This enables researchers to monitor plant health, the progress of wildfires, land surface temperatures, and the burn risk to people from hot surfaces such as asphalt. Land surface temperatures are hotter than air temperatures during the day. Air temperatures, which are measured out of direct sunlight, are usually what meteorologists report in a weather forecast. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26651
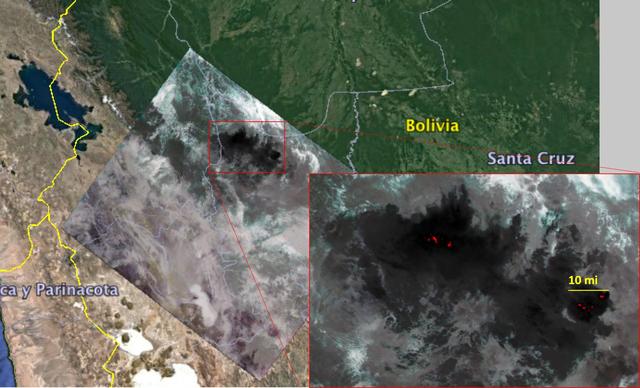
NASA's Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station (ECOSTRESS) captured new imagery of fires in the Amazon regions of Brazil and Bolivia on Aug. 23, 2019. The red areas are where surface temperatures exceeded the maximum measureable temperature of the instrument's sensor (approximately 220 degrees Fahrenheit or 104 degrees Celsius), highlighting the burning areas along the fire fronts. The dark wispy areas indicate thick smoke — thick enough that it obscures much of the fire from view. The measurements cover areas of about 77 by 77 yards (70 by 70 meters) each, or about the size of a football field. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23357
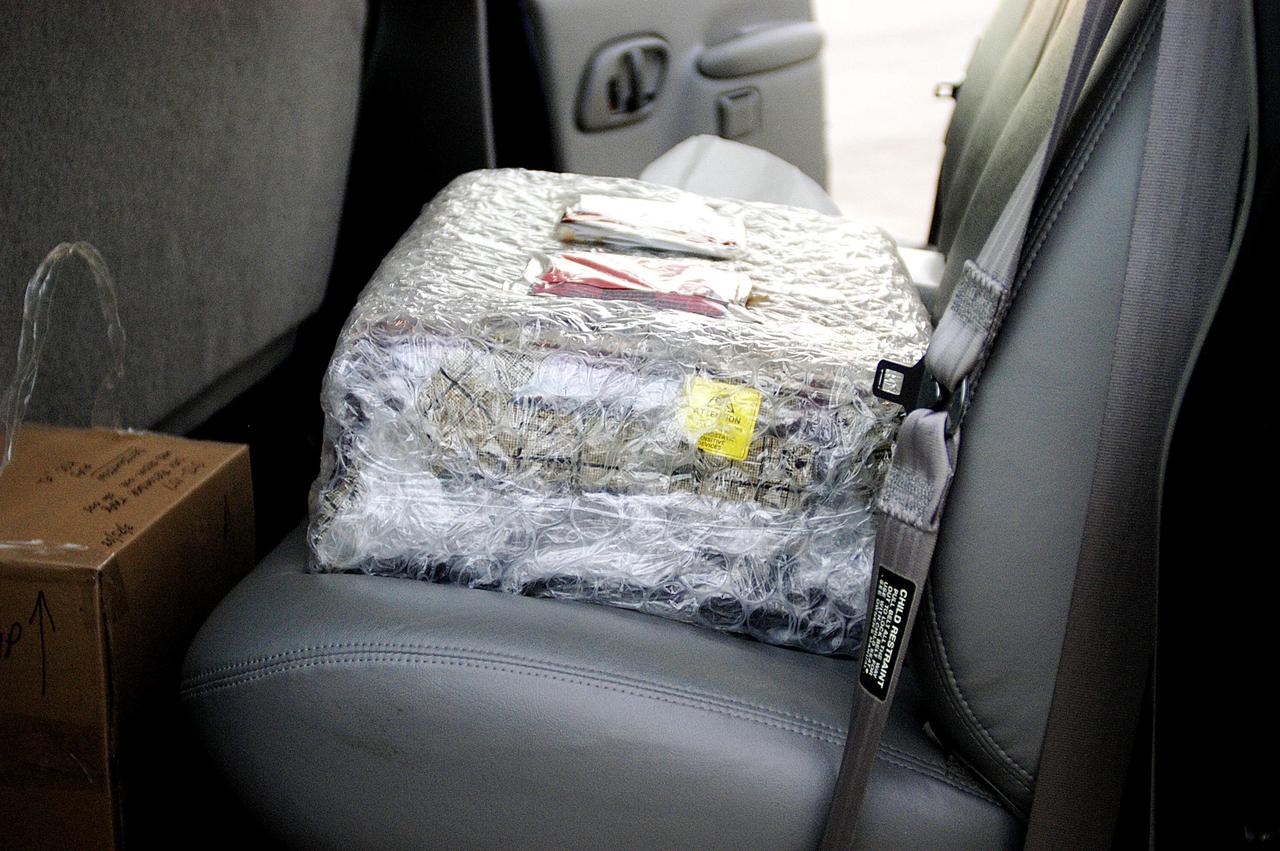

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Orbiter Experiment Support System (OEX) recorder from Columbia, in protective covering, rests inside a transport vehicle after its arrival at KSC aboard a T-38 jet aircraft. Search teams near Hemphill, Texas, recovered the recorder, which stores sensor information about temperature, aerodynamic pressure, vibrations and other data from dozens of sensor locations on the orbiter, operating only during launch and re-entry. The OEX uses magnetic tape to record data that is not sent to the ground by telemetry.
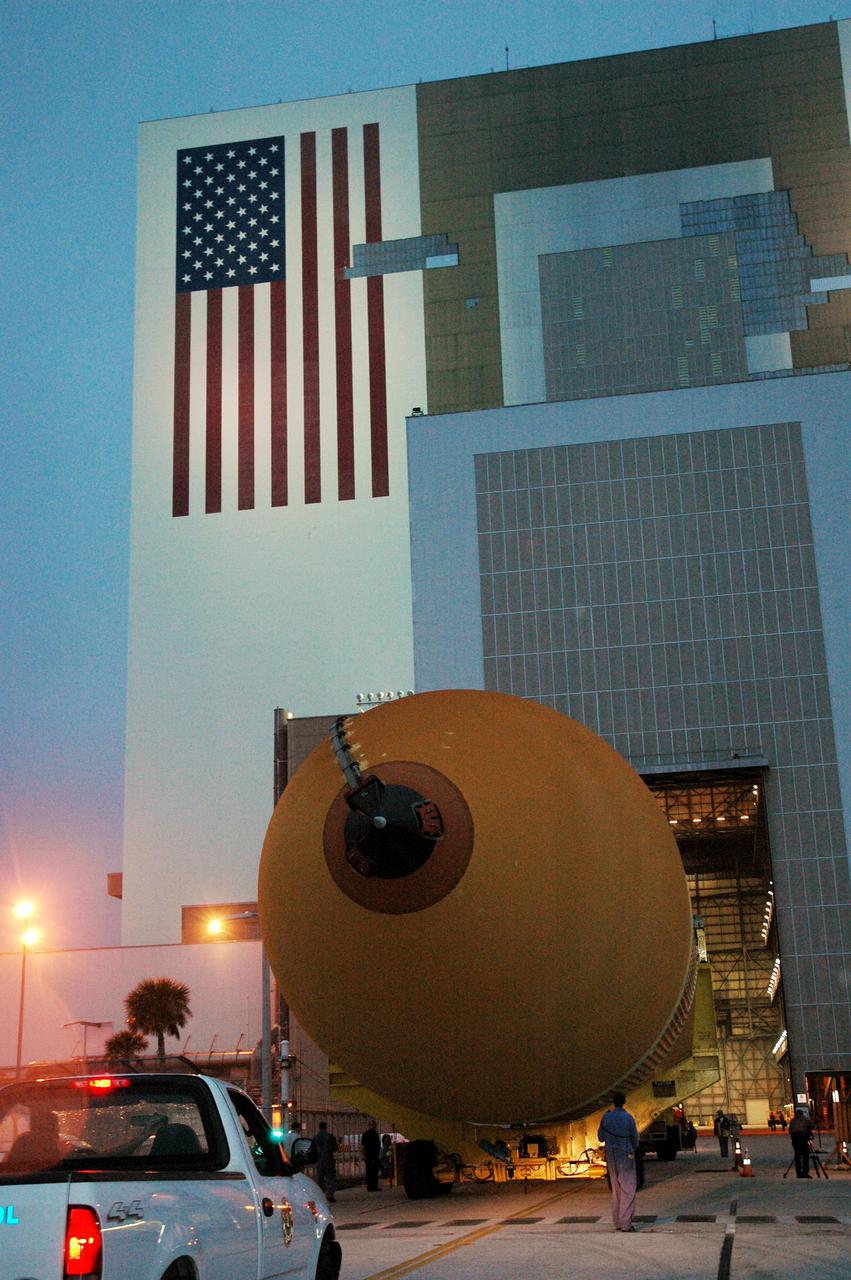
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The second redesigned External Tank (ET-121) moves toward the open doors in the Vehicle Assembly Building. The tank recently arrived at the Turn Basin after its 900-mile journey at sea from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In addition to the Return to Flight modifications, this tank has been outfitted with temperature sensors and accelerometers, used to measure vibration. These sensors will gather information about how the tank performs during flight. The tank is designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-121, which has a launch window of July 12 to July 31, 2005.
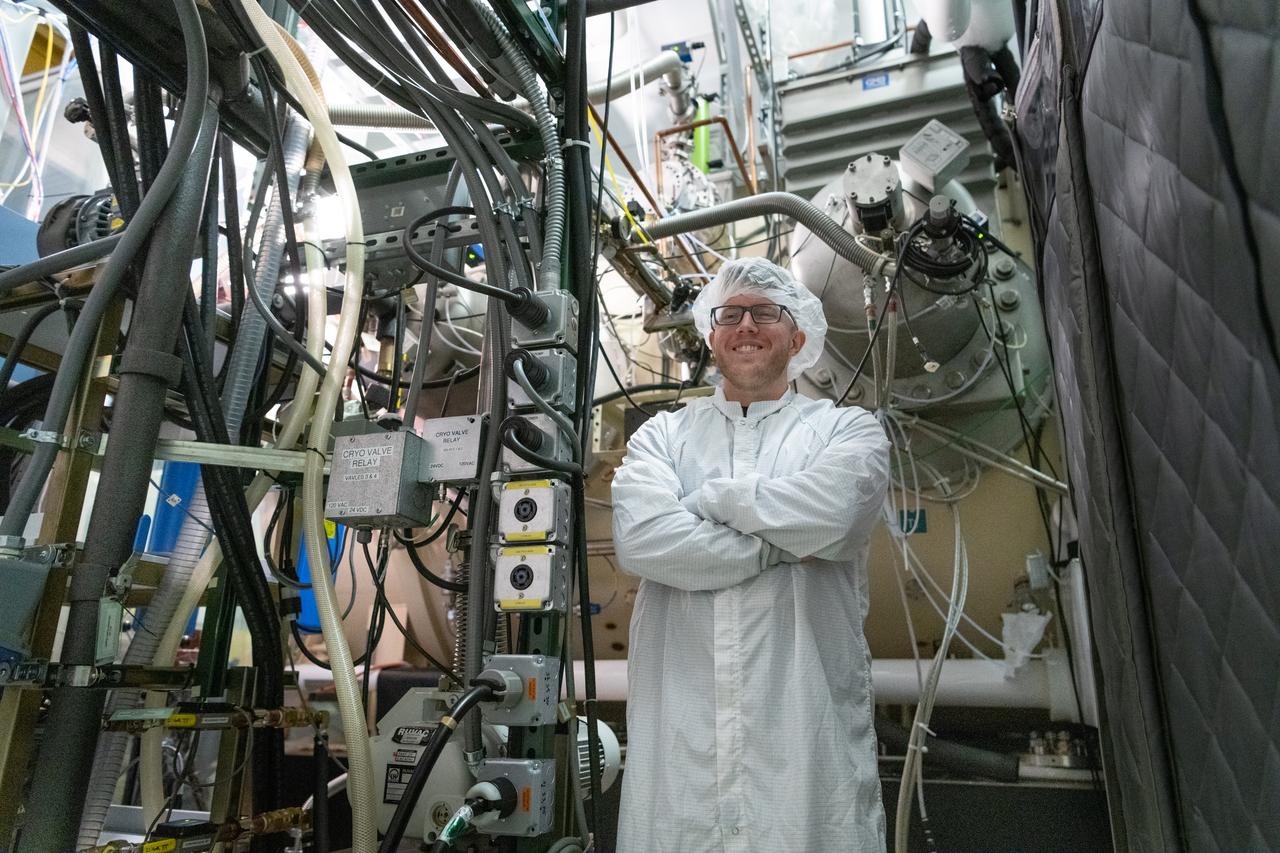

Thermal vacuum technician, Sean Cook, monitors the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) thermal vacuum chamber temperatures during the environmental test campaign. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
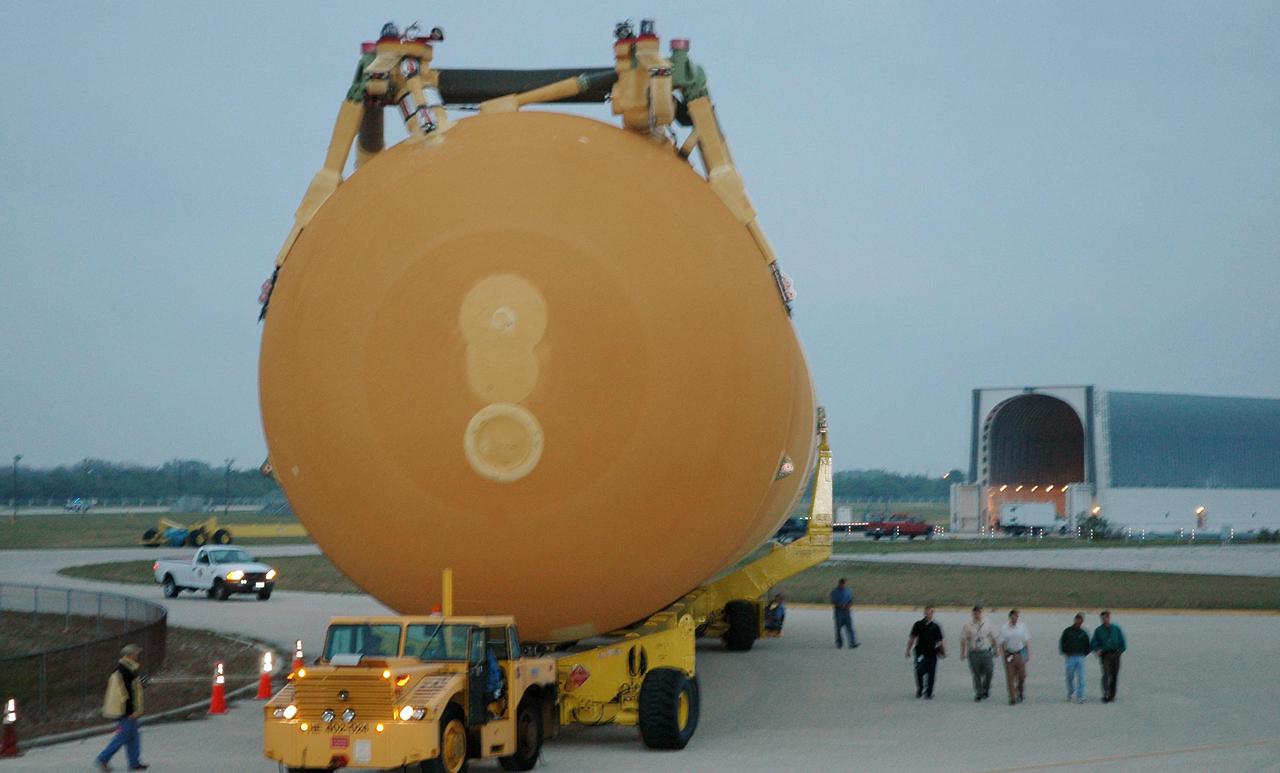

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The second redesigned External Tank (ET-121) dwarfs the workers accompanying it on its way to the Vehicle Assembly Building. The tank recently arrived at the Turn Basin aboard the barge in the background after its 900-mile journey at sea from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In addition to the Return to Flight modifications, this tank has been outfitted with temperature sensors and accelerometers, used to measure vibration. These sensors will gather information about how the tank performs during flight. The tank is designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-121, which has a launch window of July 12 to July 31, 2005.

This concept illustrates Skylab Earth observation studies, an Earth Resources Experiment Package (EREP). EREP was designed to explore the use of the widest possible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum for Earth resource investigations with sensors that recorded data in the visible, infrared, and microwave spectral regions. Resources subject to this study included a capability of mapping Earth resources and land uses, crop and forestry cover, health of vegetation, types of soil, water storage in snow pack, surface or near-surface mineral deposits, sea surface temperature, and the location of likely feeding areas for fish, etc. A significant feature of EREP was the ability of man to operate the sensors in a laboratory fashion.
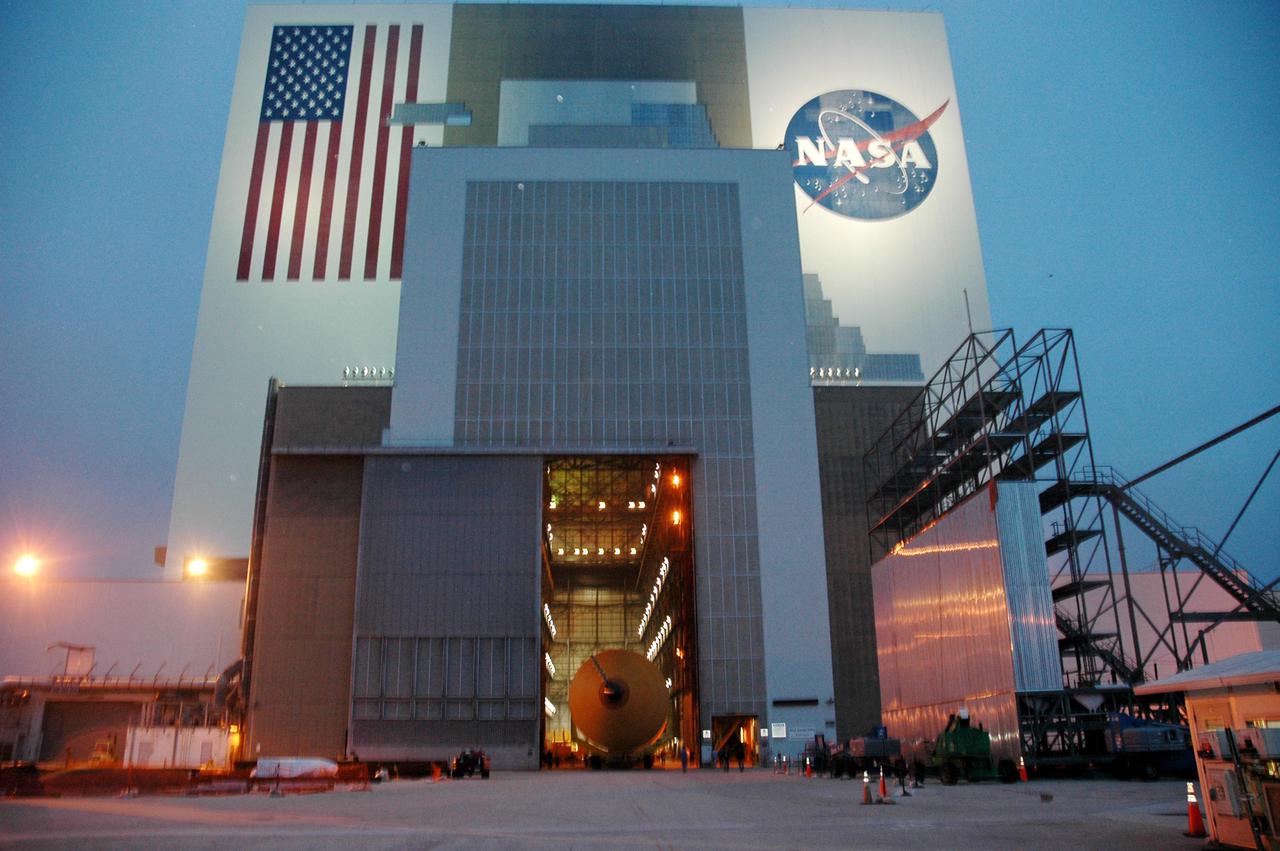

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Through the open doors of the Vehicle Assembly Building can be seen the second redesigned External Tank (ET-121). The tank recently arrived at the Turn Basin after its 900-mile journey at sea from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In addition to the Return to Flight modifications, this tank has been outfitted with temperature sensors and accelerometers, used to measure vibration. These sensors will gather information about how the tank performs during flight. The tank is designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-121, which has a launch window of July 12 to July 31, 2005.
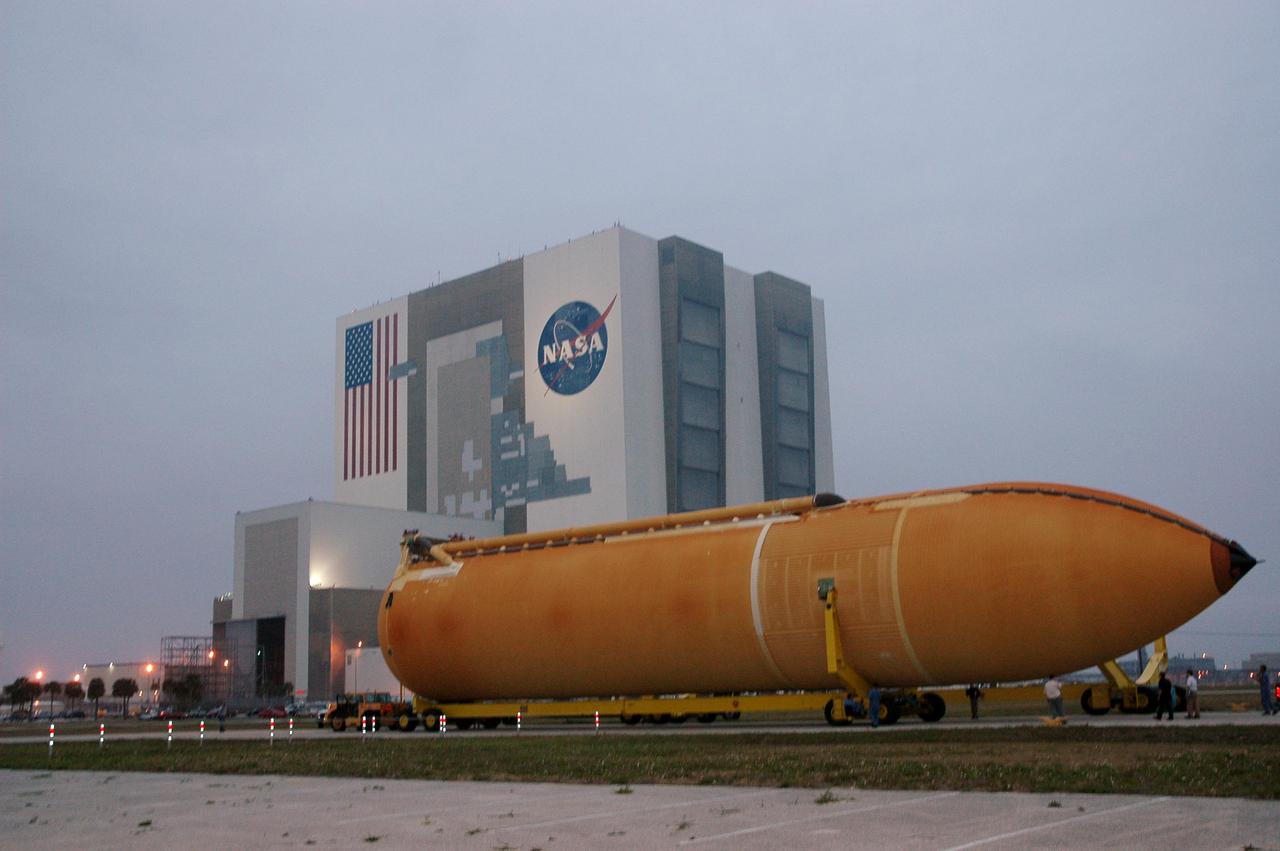

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -The second redesigned External Tank (ET-121) moves slowly on the road from the Turn Basin to the Vehicle Assembly Building in the background. The tank recently arrived at the Turn Basin aboard a barge after its 900-mile journey at sea from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In addition to the Return to Flight modifications, this tank has been outfitted with temperature sensors and accelerometers, used to measure vibration. These sensors will gather information about how the tank performs during flight. The tank is designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-121, which has a launch window of July 12 to July 31, 2005.
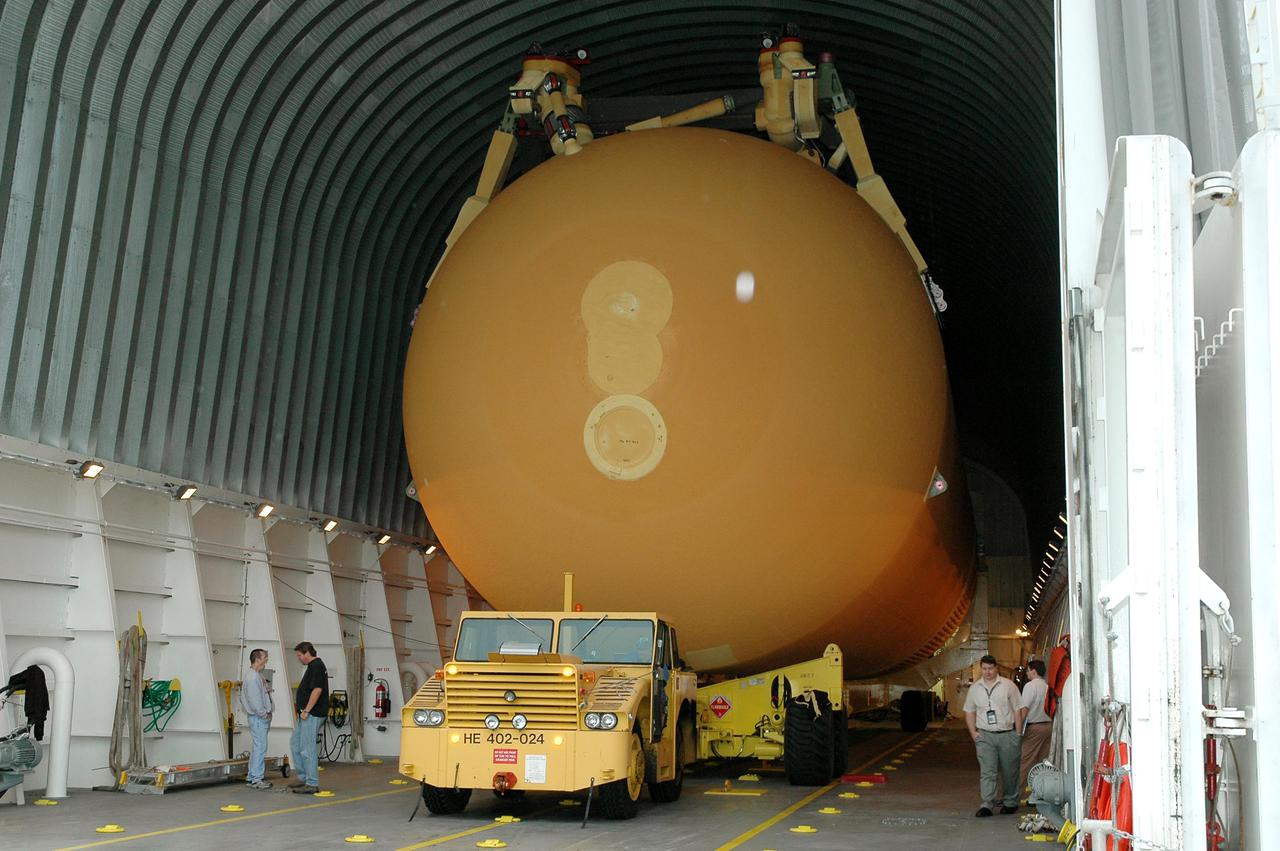

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The second redesigned External Tank (ET-121) is ready to leave the barge at the Turn Basin near the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) after its 900-mile journey at sea from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. It will then be offloaded and transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In addition to the Return to Flight modifications, this tank has been outfitted with temperature sensors and accelerometers, used to measure vibration. These sensors will gather information about how the tank performs during flight. The tank is designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-121, which has a launch window of July 12 to July 31, 2005.
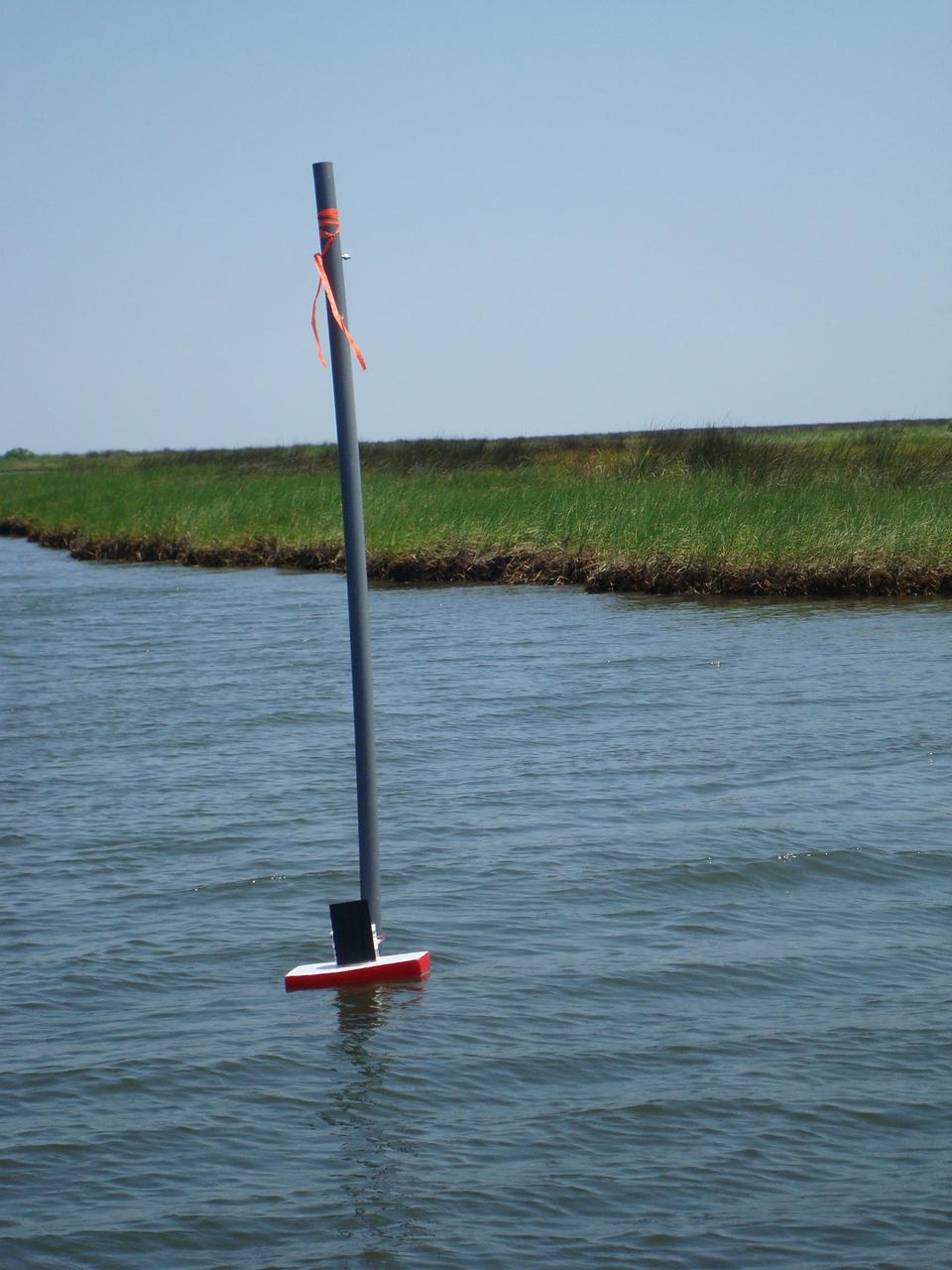

Once tethered in place in Gulf Coast waters, a DRIFTER sensor device is able to transmit valuable information about water temperature and conductivity. The Applied Science and Technology Project Office at Stennis Space Center designed the DRIFTER as an inexpensive device that can be used for science projects in local schools. Two of the devices, deployed in coastal waters, survived Hurricane Isaac, continuing to transmit valuable data regarding the storm.
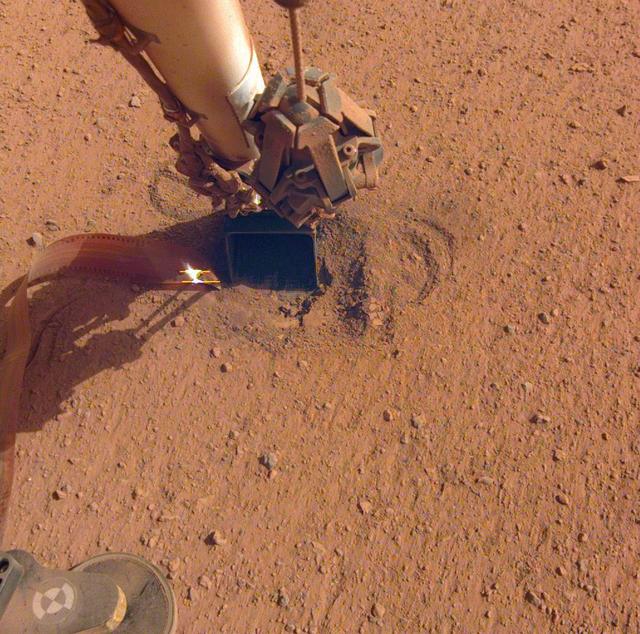

NASA's InSight lander retracted its robotic arm on Oct. 3, 2020, revealing the spot where the self-digging "mole" is attempting to burrow into the planet's surface. Attached to the mole is the copper-colored ribbon, which is laden with temperature sensors designed to measure the heat flow within Mars. In the months to come, the scoop seen on the end of the arm will be used to scrape and tamp down soil on top of the mole, in hopes of helping it dig. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24098
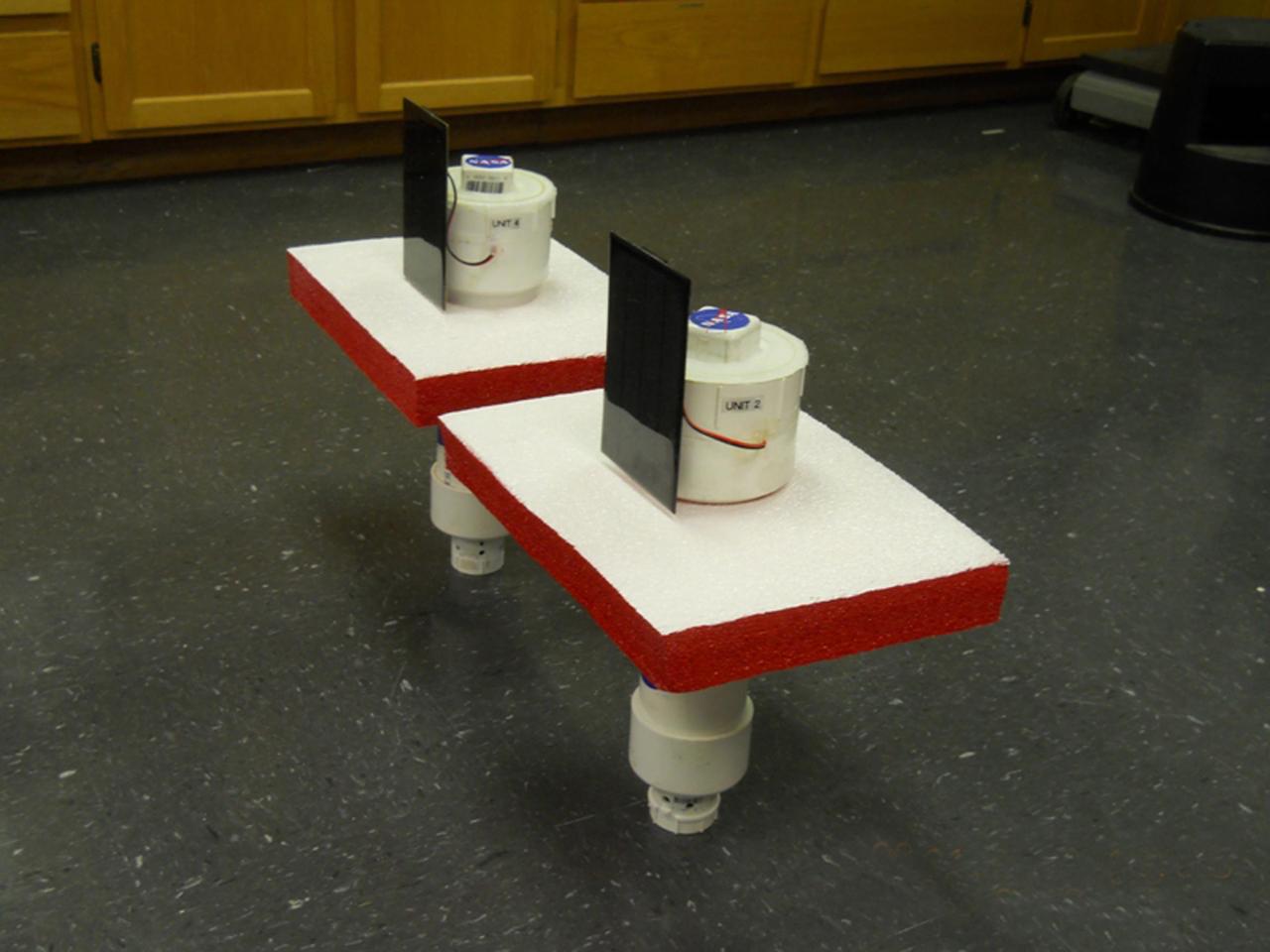

DRIFTER sensor devices were designed by the Applied Science and Technology Project Office as inexpensive tools that can be used for science projects in local schools. The devices transmit information about water temperature and conductivity for use by Gulf Coast researchers. The DRIFTER project began as an effort to help Gulf Coast oyster fishermen dealing with the effects of fresh water intrusion.
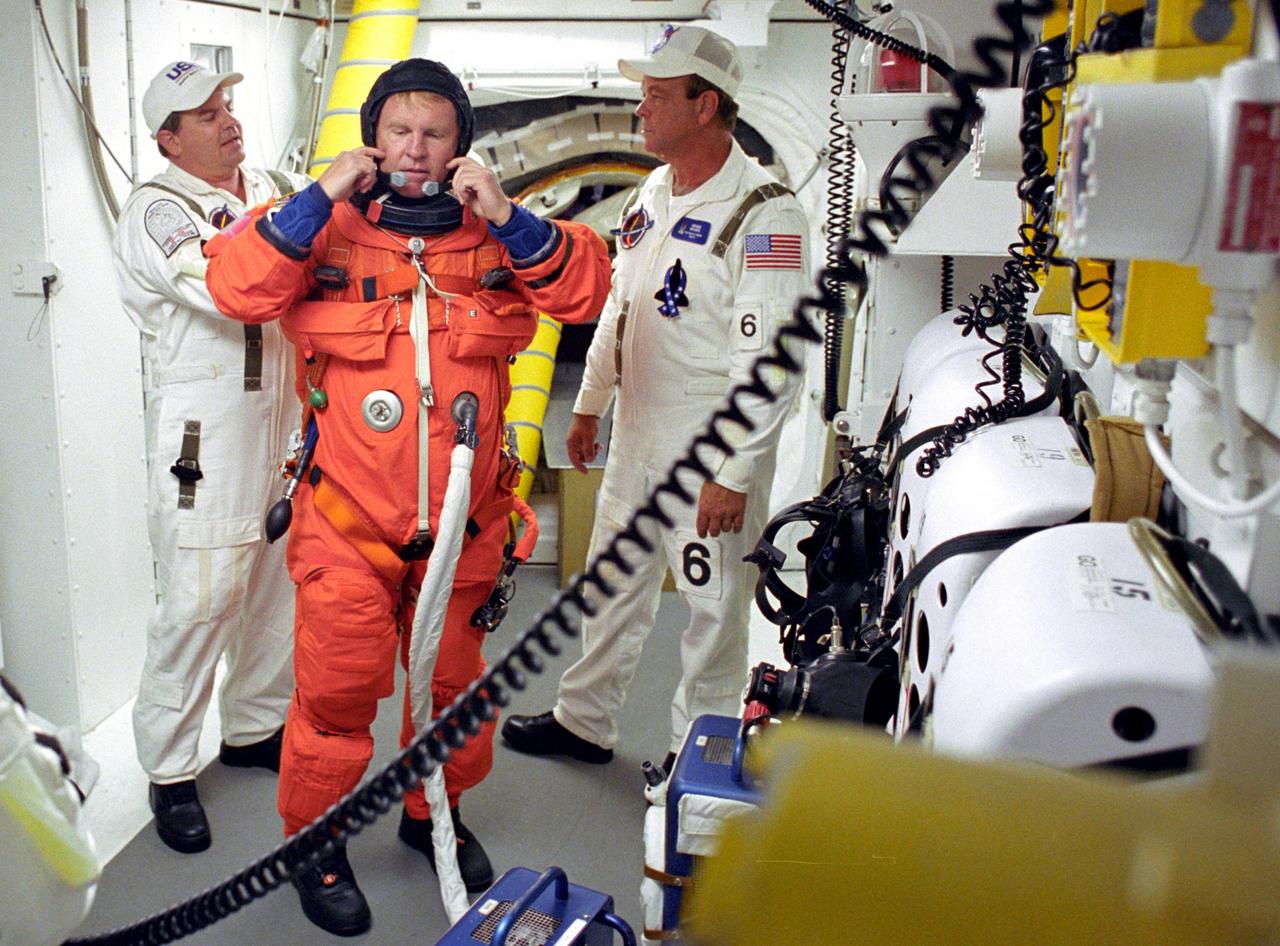

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Mission Specialist Andrew Thomas is helped by the Closeout Crew with his launch and entry suit before entering Space Shuttle Discovery. The Return to Flight mission to the International Space Station carries the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure and Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, housing 15 tons of hardware and supplies that will be transferred to the Station after the Shuttle docks to the complex . On this mission, the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay.
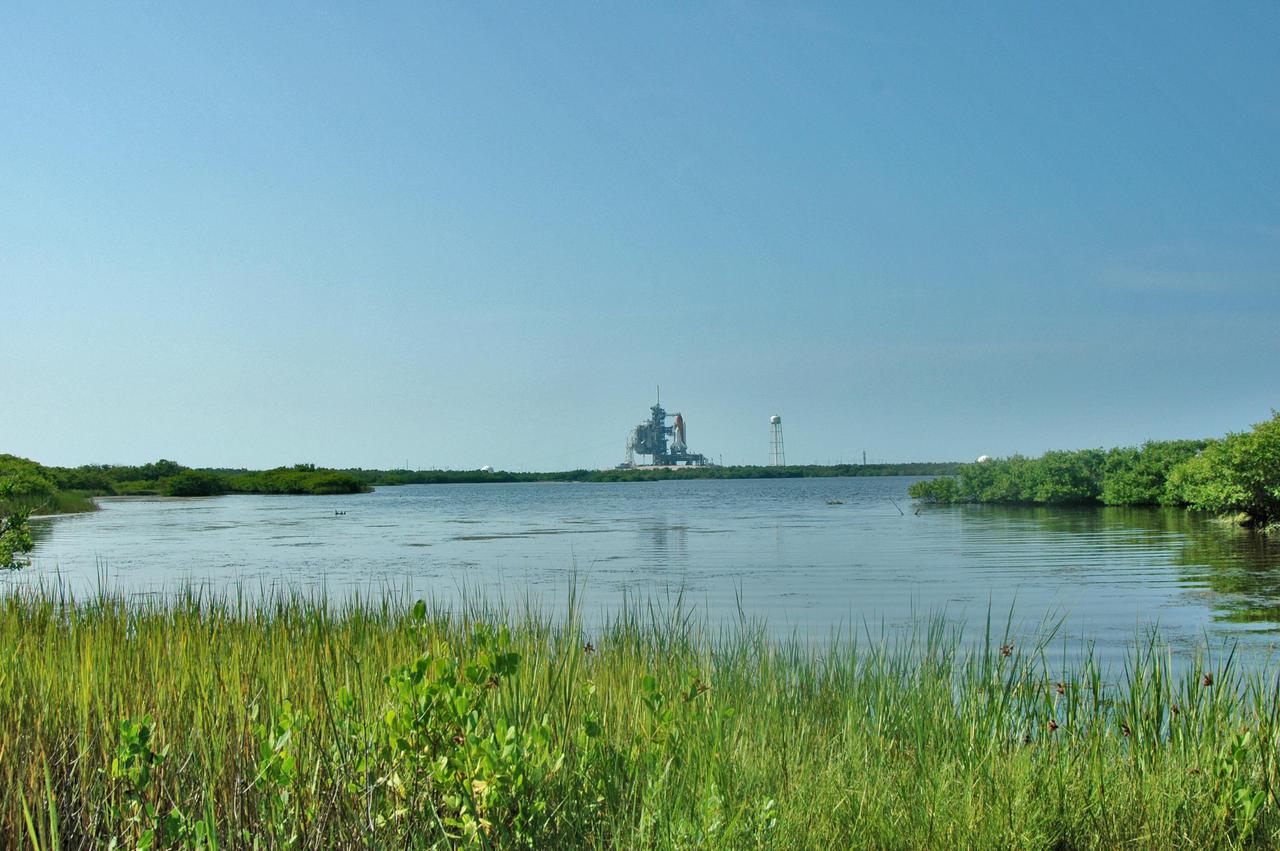

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A pristine view to Launch Pad 39B at NASA Kennedy Space Center shows the Space Shuttle Discovery as it waits for launch.Discovery is scheduled to lift off on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114 at 10:39 a.m. EDT July 26 with a crew of seven. On the mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.
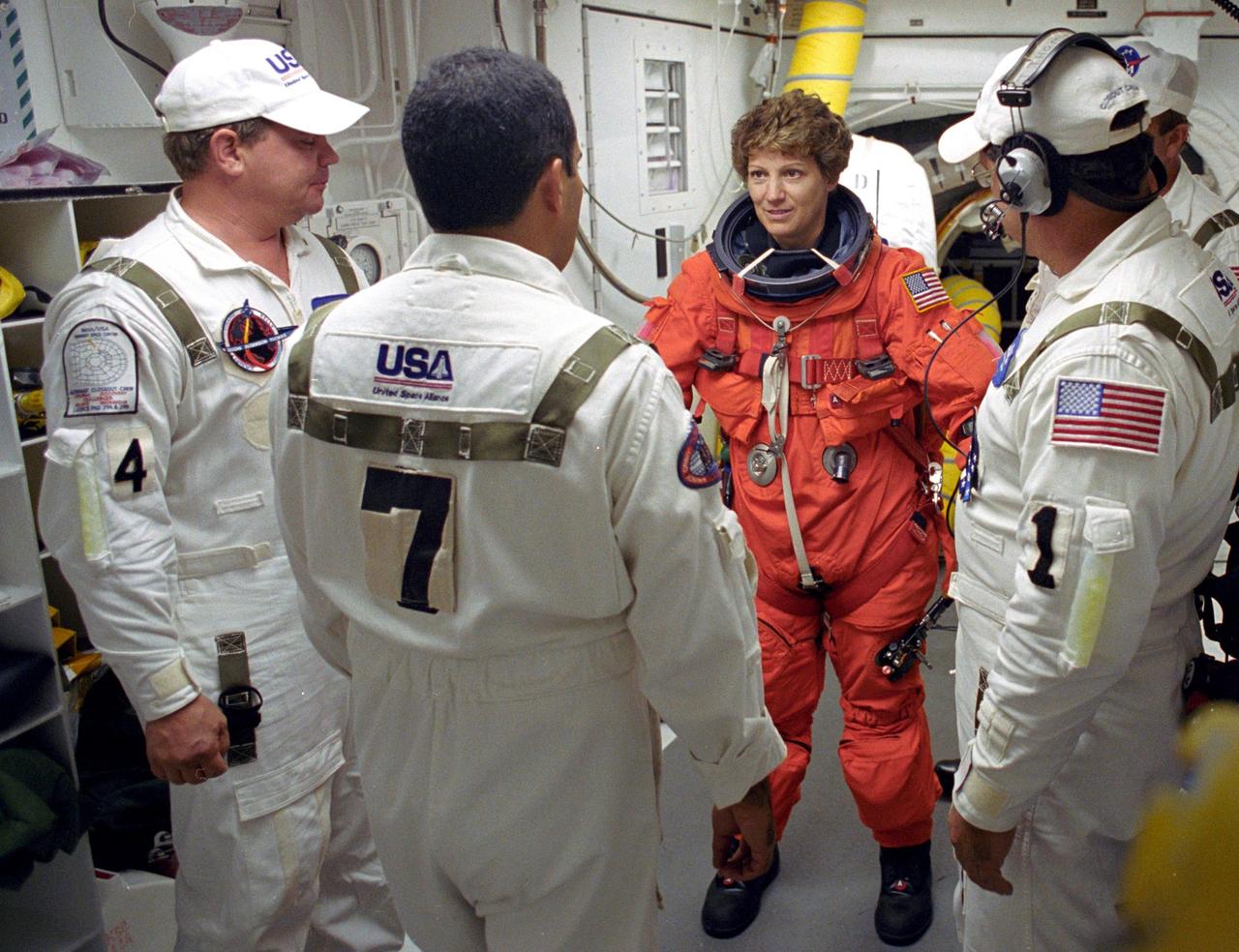

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Mission Commander Eileen Collins is helped by the Closeout Crew with her launch and entry suit before entering Space Shuttle Discovery. The Return to Flight mission to the International Space Station carries the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure and Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, housing 15 tons of hardware and supplies that will be transferred to the Station after the Shuttle docks to the complex . On this mission, the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay.
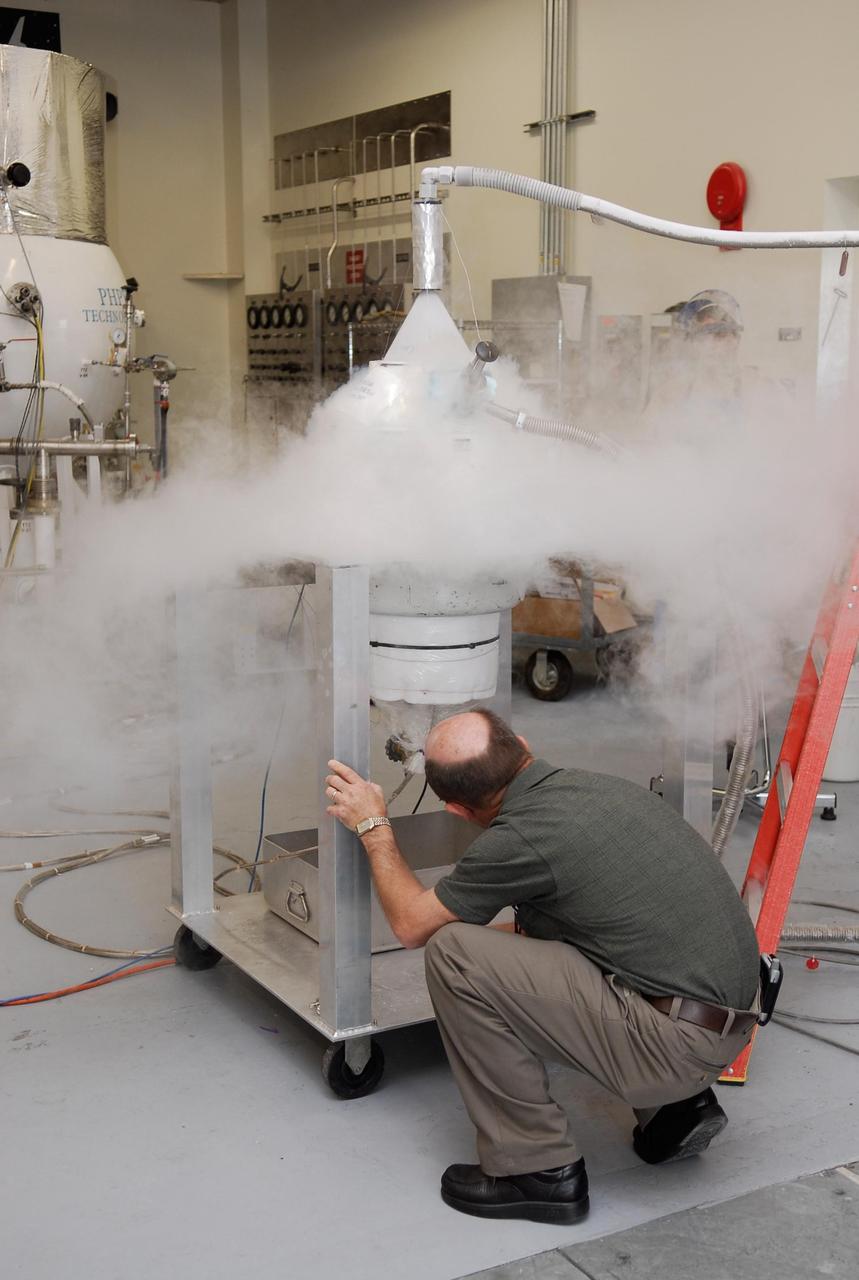

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the cryogenic test bed facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Time Domain Reflectometry, or TDR, instrumentation is being exposed to "wet" super-cold temperatures for identifying the signature of a cryogenic environment and calibrating the TDR equipment. The equipment will be used at the launch pad to test a procedure identical to a tanking test on space shuttle Atlantis' external tank planned for Dec. 18. The shuttle's planned launches on Dec. 6 and Dec. 9 were postponed because of false readings from the part of the engine cut-off, or ECO, sensor system that monitors the liquid hydrogen section of the tank. The liftoff date from NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Florida, is now targeted for Jan. 10, depending on the resolution of the problem in the fuel sensor system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
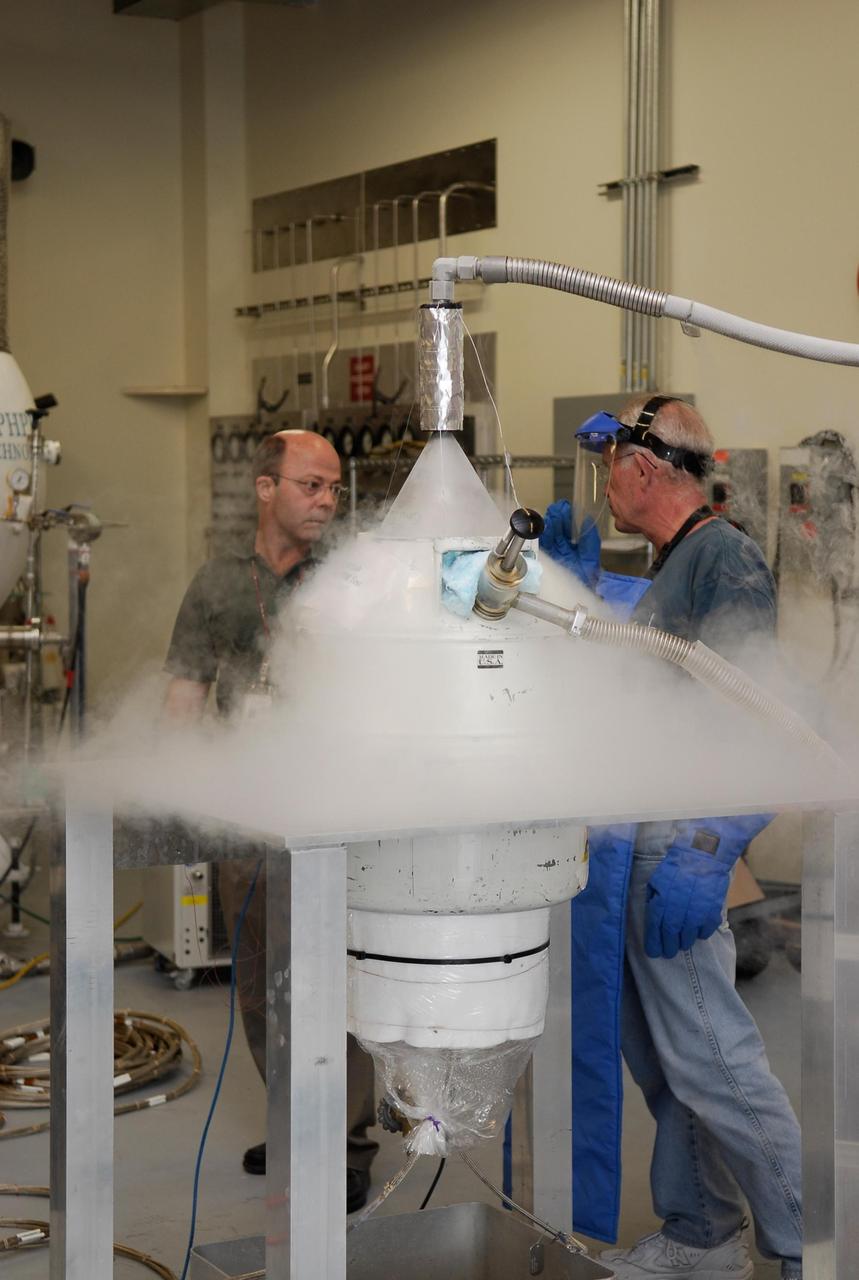

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the cryogenic test bed facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Time Domain Reflectometry, or TDR, instrumentation is being exposed to "wet" super-cold temperatures for identifying the signature of a cryogenic environment and calibrating the TDR equipment. The equipment will be used at the launch pad to test a procedure identical to a tanking test on space shuttle Atlantis' external tank planned for Dec. 18. The shuttle's planned launches on Dec. 6 and Dec. 9 were postponed because of false readings from the part of the engine cut-off, or ECO, sensor system that monitors the liquid hydrogen section of the tank. The liftoff date from NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Florida, is now targeted for Jan. 10, depending on the resolution of the problem in the fuel sensor system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
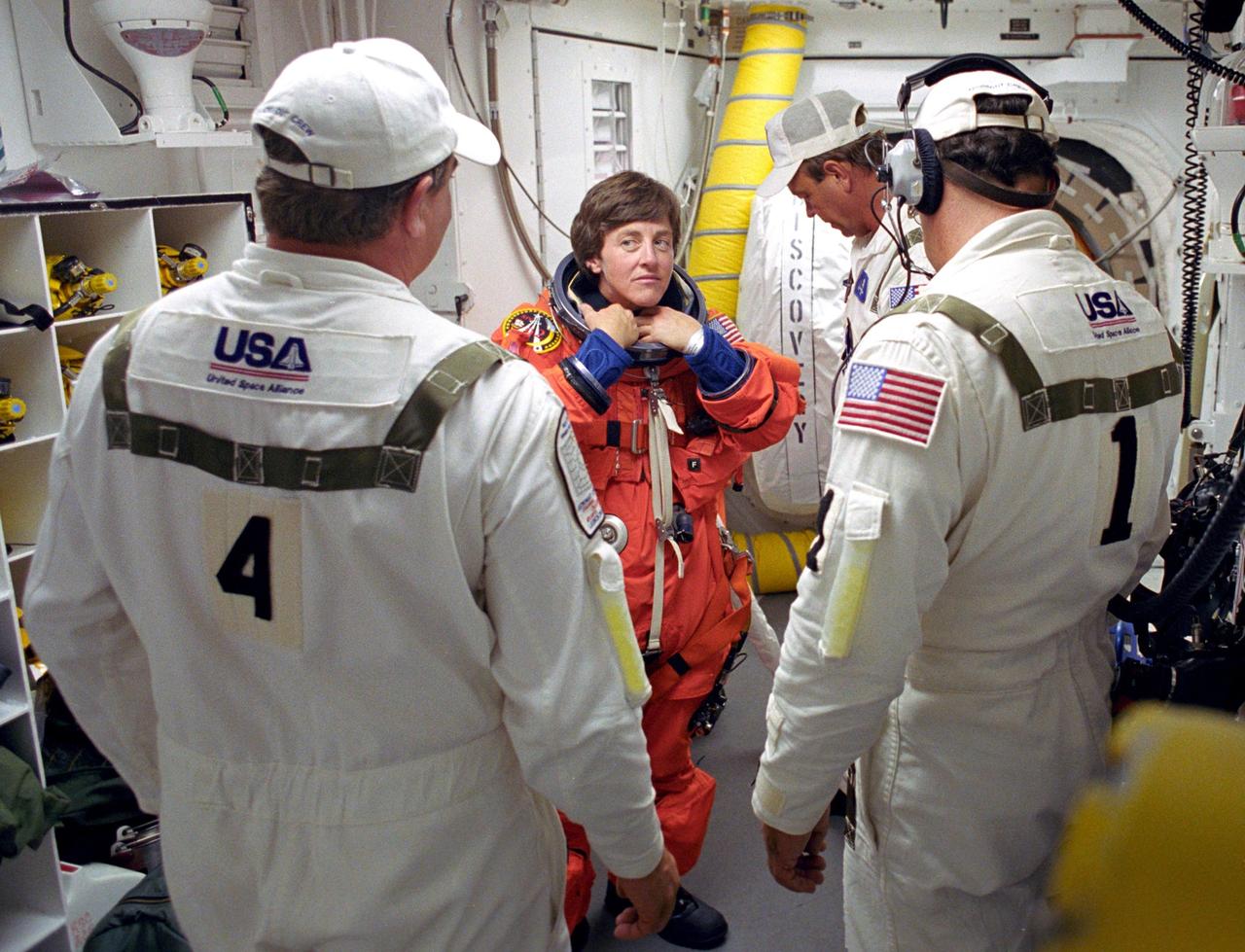

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Mission Specialist Wendy Lawrence is helped with her launch and entry suit by the Closeout Crew before entering Space Shuttle Discovery. The Return to Flight mission to the International Space Station carries the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure and Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, housing 15 tons of hardware and supplies that will be transferred to the Station after the Shuttle docks to the complex . On this mission, the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay.
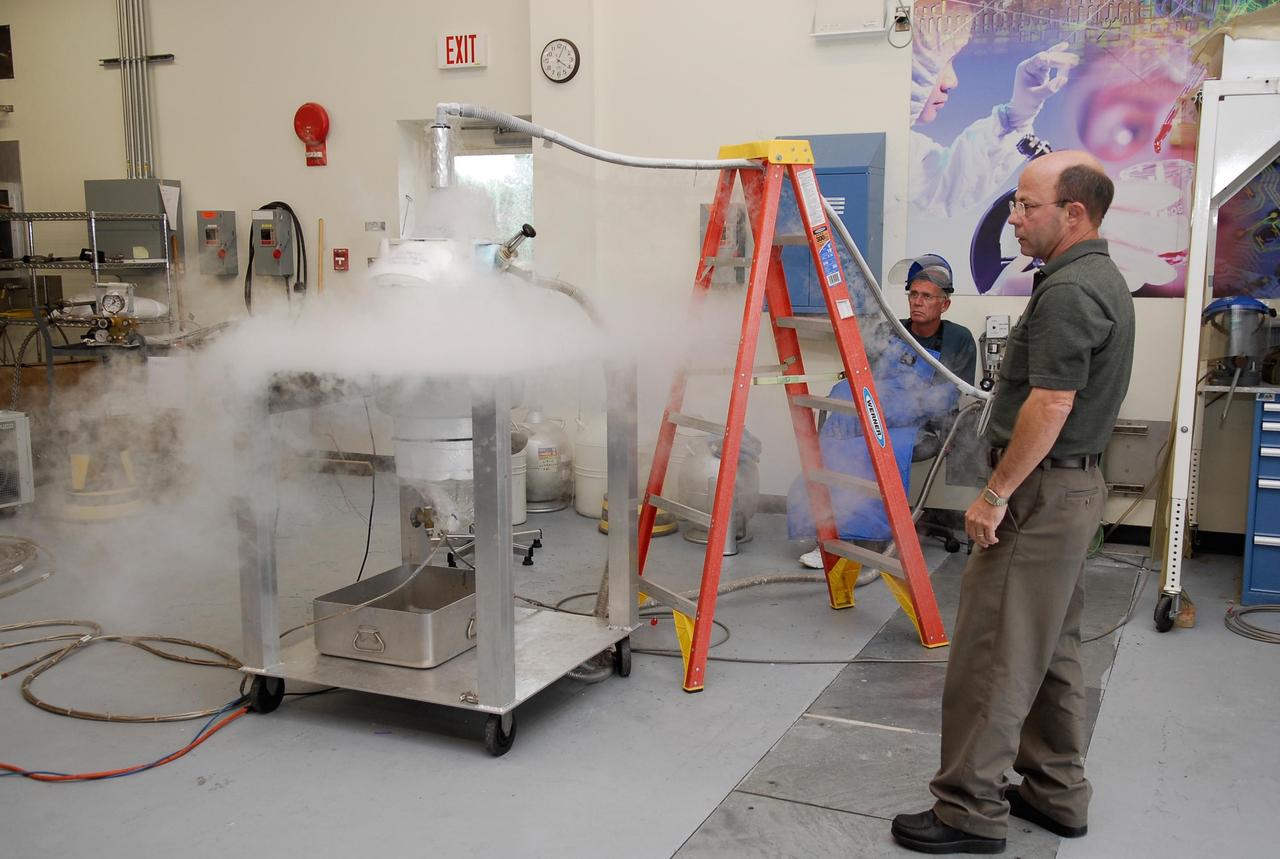

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the cryogenic test bed facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Time Domain Reflectometry, or TDR, instrumentation is being exposed to "wet" super-cold temperatures for identifying the signature of a cryogenic environment and calibrating the TDR equipment. The equipment will be used at the launch pad to test a procedure identical to a tanking test on space shuttle Atlantis' external tank planned for Dec. 18. The shuttle's planned launches on Dec. 6 and Dec. 9 were postponed because of false readings from the part of the engine cut-off, or ECO, sensor system that monitors the liquid hydrogen section of the tank. The liftoff date from NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Florida, is now targeted for Jan. 10, depending on the resolution of the problem in the fuel sensor system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
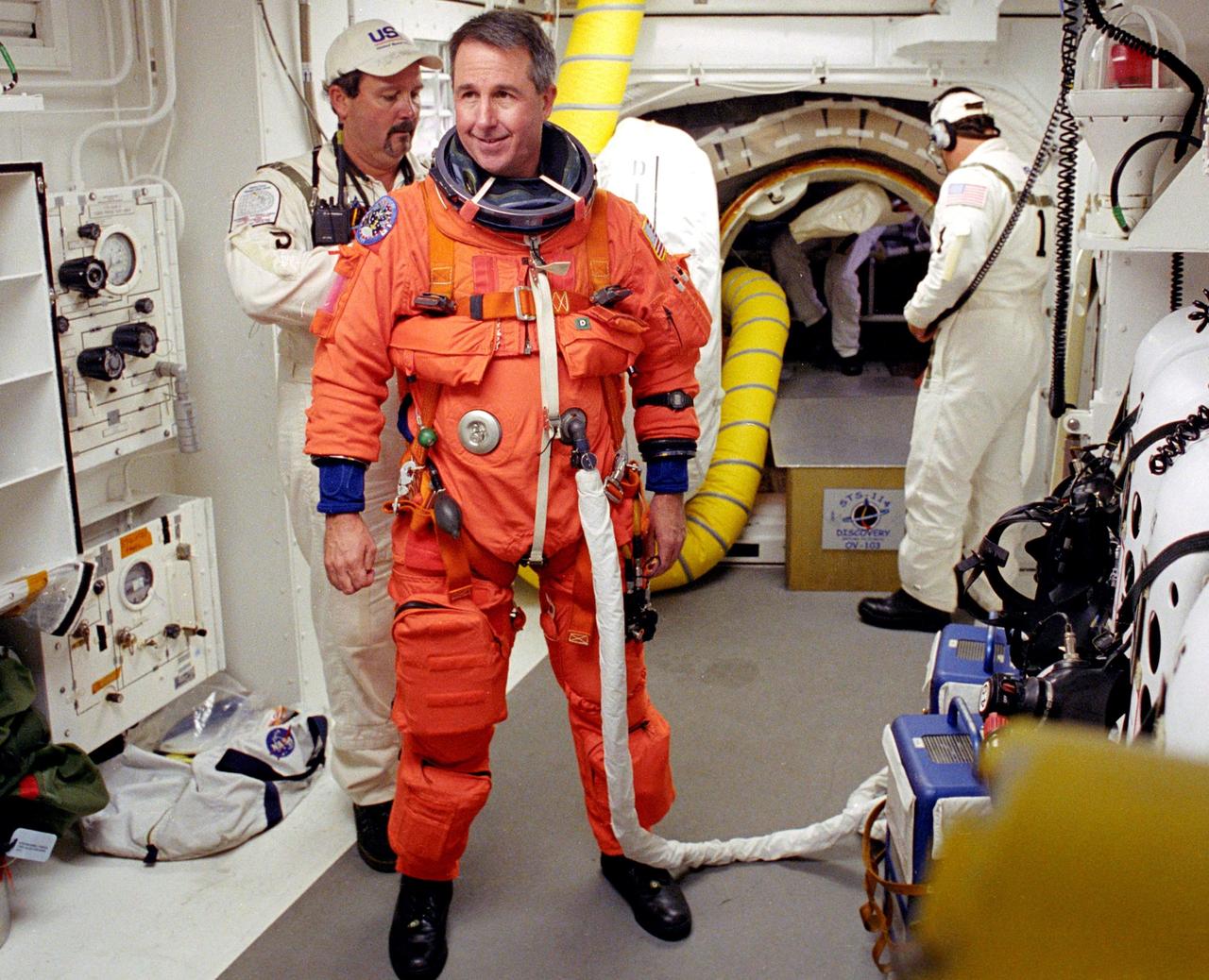

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Mission Specialist Stephen Robinson is helped by the Closeout Crew with his launch and entry suit before entering Space Shuttle Discovery. The Return to Flight mission to the International Space Station carries the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure and Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, housing 15 tons of hardware and supplies that will be transferred to the Station after the Shuttle docks to the complex . On this mission, the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay.
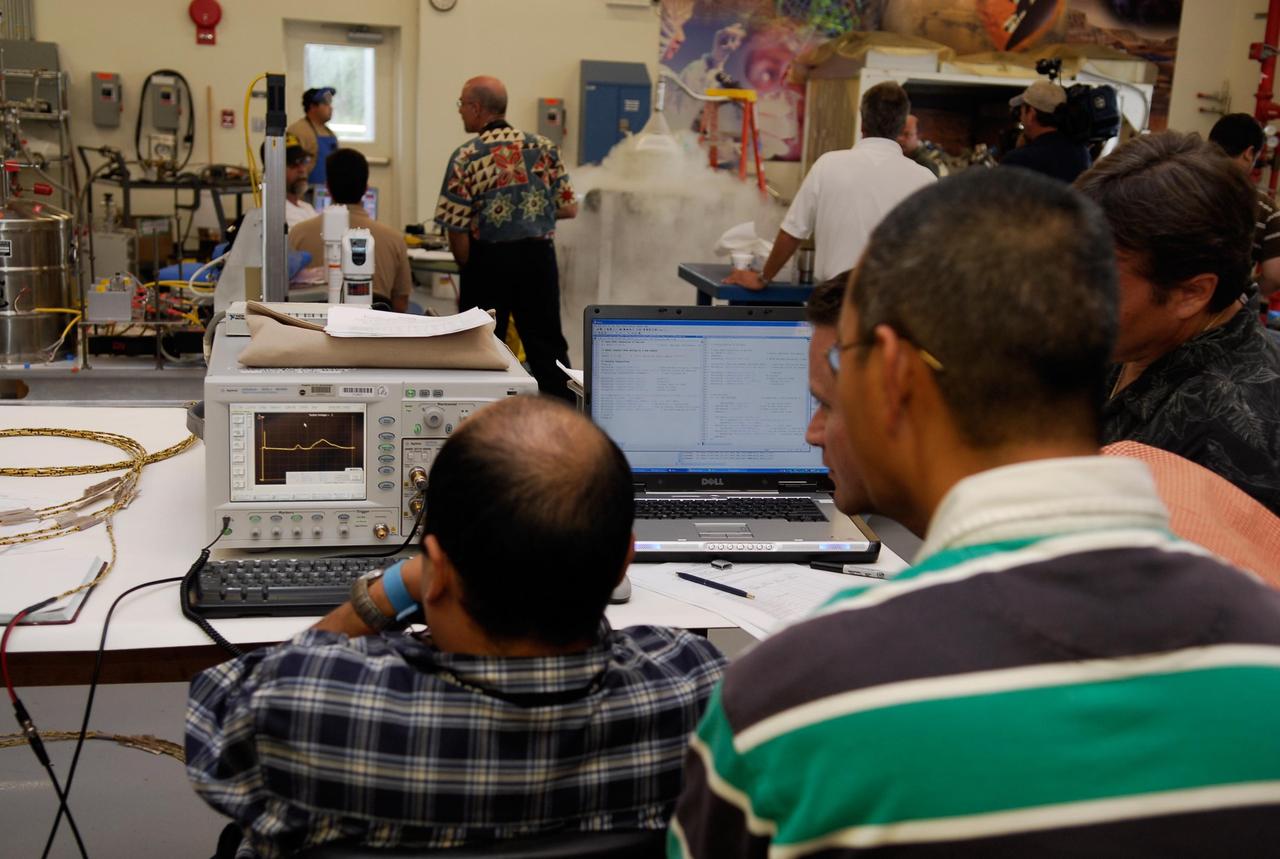

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the cryogenic test bed facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians monitor readings during a test exposing Time Domain Reflectometry, or TDR, instrumentation to "wet" super-cold temperatures for identifying the signature of a cryogenic environment and calibrating the TDR equipment. The equipment will be used at the launch pad to test a procedure identical to a tanking test on space shuttle Atlantis' external tank planned for Dec. 18. The shuttle's planned launches on Dec. 6 and Dec. 9 were postponed because of false readings from the part of the engine cut-off, or ECO, sensor system that monitors the liquid hydrogen section of the tank. The liftoff date from NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Florida, is now targeted for Jan. 10, depending on the resolution of the problem in the fuel sensor system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
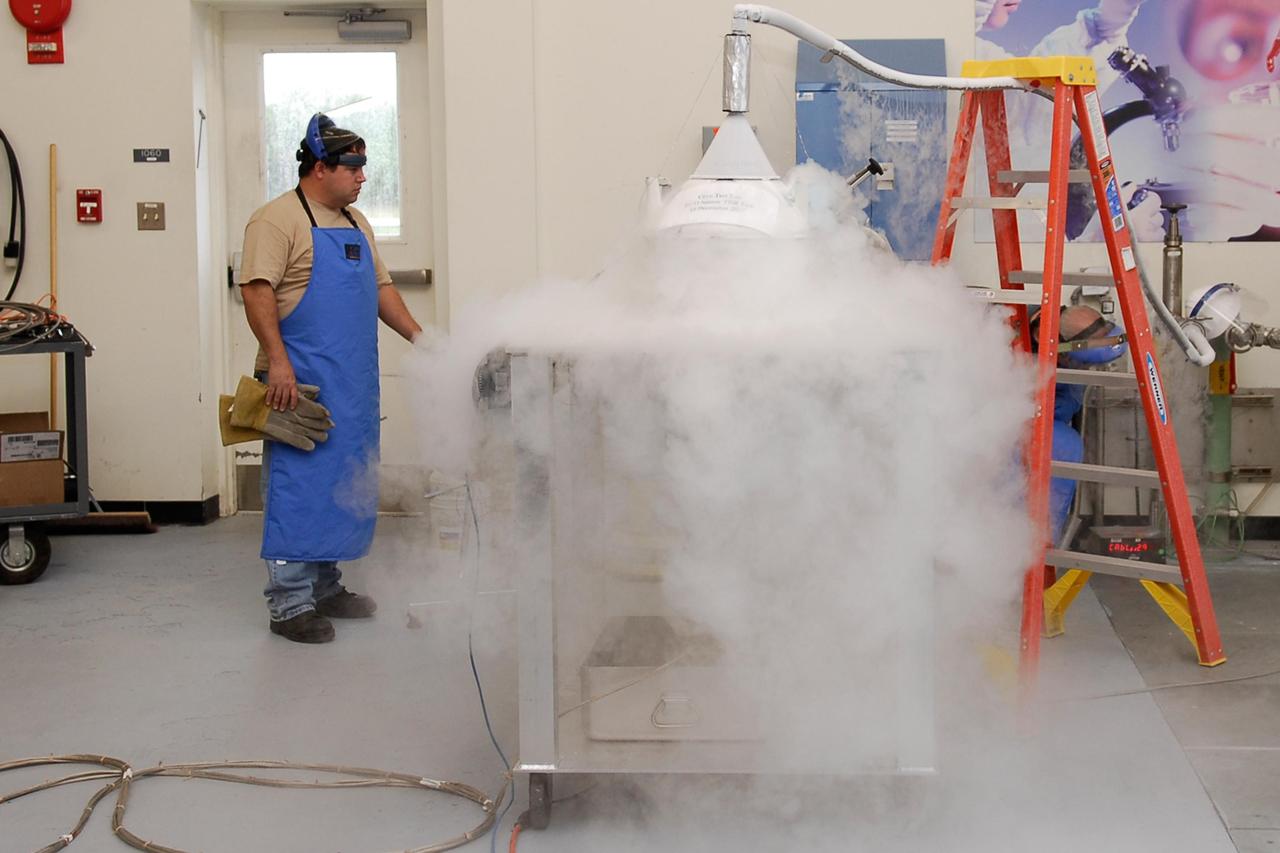

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the cryogenic test bed facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Time Domain Reflectometry, or TDR, instrumentation is being exposed to "wet" super-cold temperatures for identifying the signature of a cryogenic environment and calibrating the TDR equipment. The equipment will be used at the launch pad to test a procedure identical to a tanking test on space shuttle Atlantis' external tank planned for Dec. 18. The shuttle's planned launches on Dec. 6 and Dec. 9 were postponed because of false readings from the part of the engine cut-off, or ECO, sensor system that monitors the liquid hydrogen section of the tank. The liftoff date from NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Florida, is now targeted for Jan. 10, depending on the resolution of the problem in the fuel sensor system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
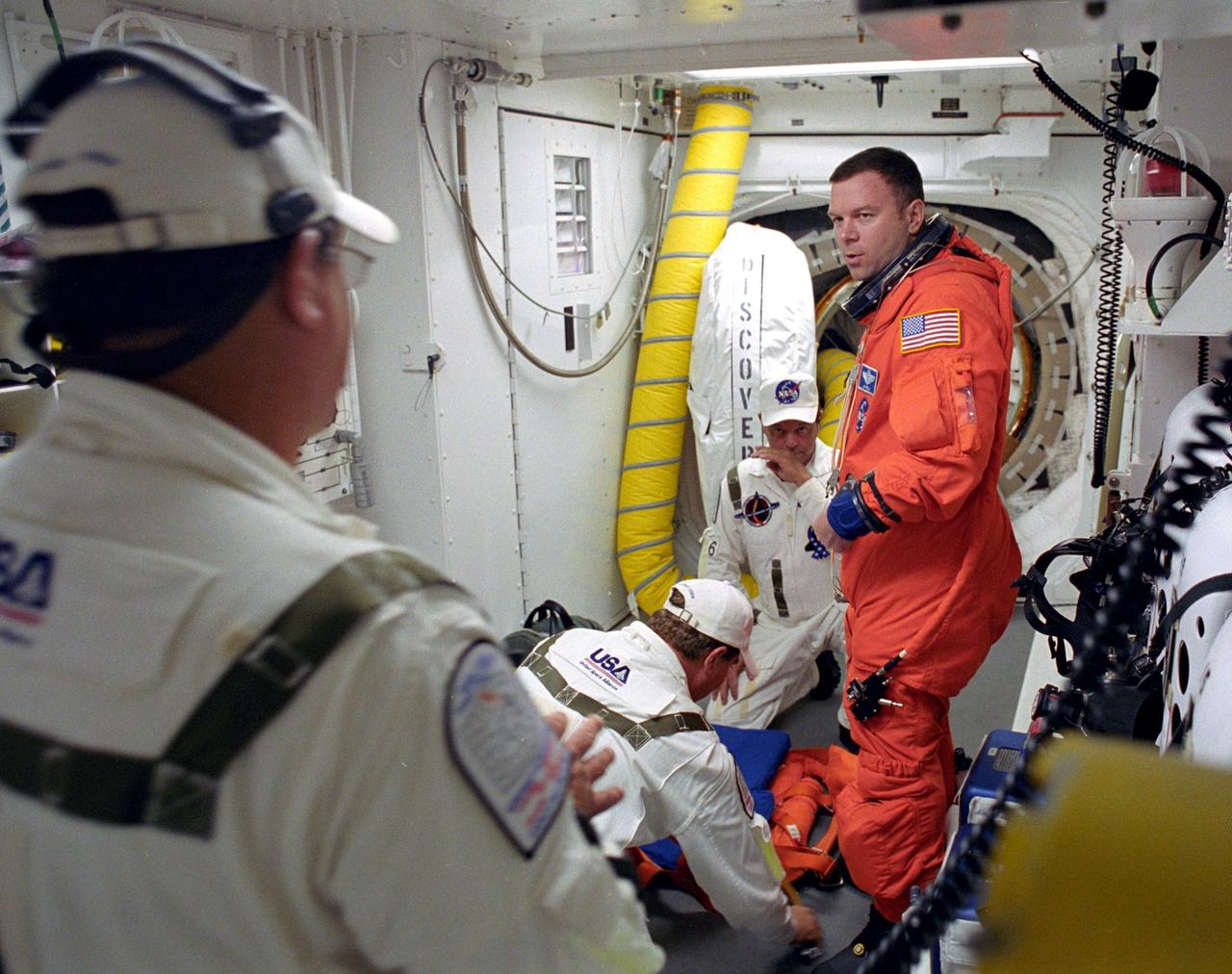

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Pilot James Kelly is helped by the Closeout Crew with his launch and entry suit before entering Space Shuttle Discovery.The Return to Flight mission to the International Space Station carries the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure and Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, housing 15 tons of hardware and supplies that will be transferred to the Station after the Shuttle docks to the complex . On this mission, the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay.
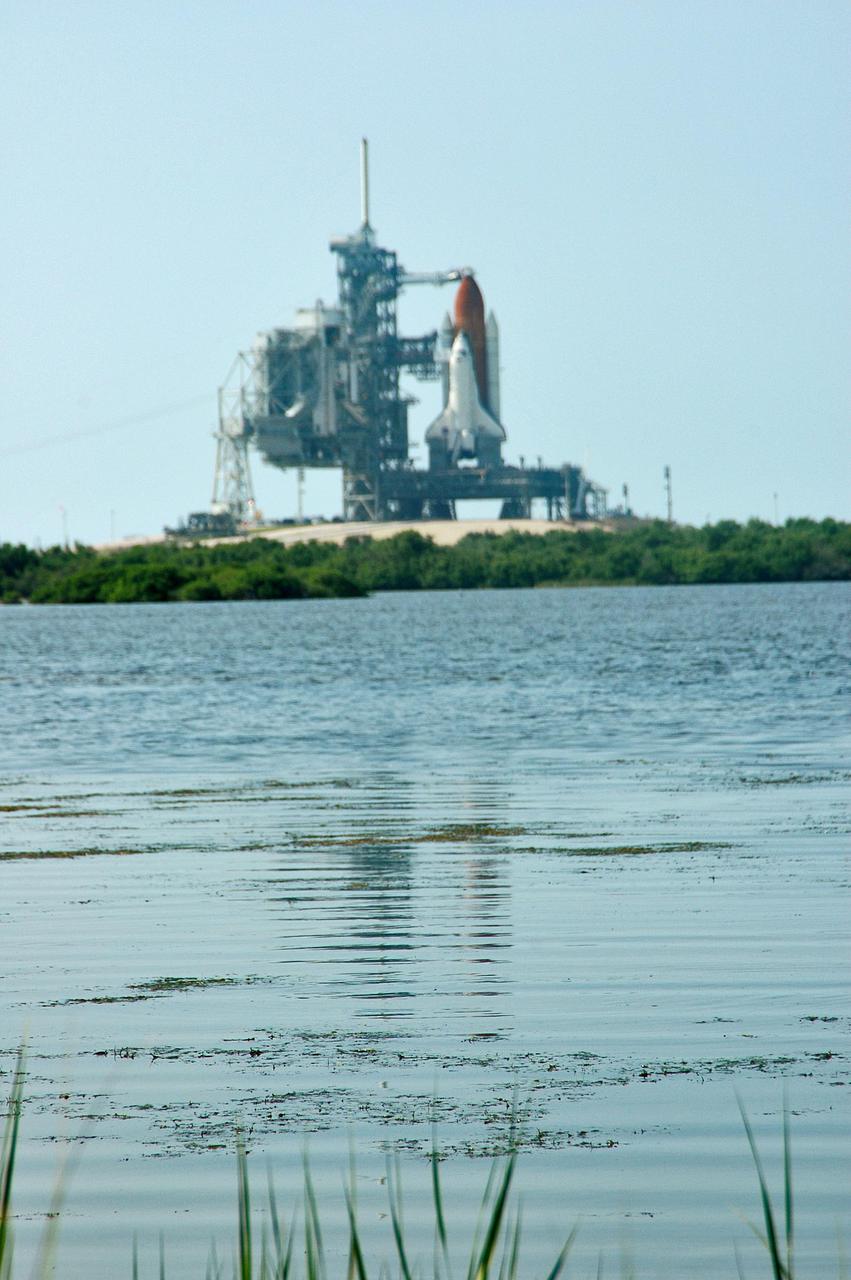

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A pristine view to Launch Pad 39B at NASA Kennedy Space Center shows the Space Shuttle Discovery as it waits for launch. Discovery is scheduled to lift off on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114 at 10:39 a.m. EDT July 26 with a crew of seven. On the mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.
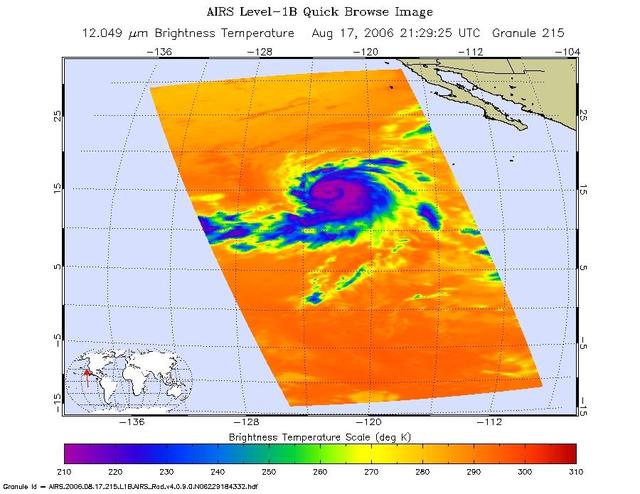
Infrared, microwave, and visible/near-infrared images of Hurricane Hector in the eastern Pacific were created with data from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) on NASA's Aqua satellite on August 17, 2006. The infrared AIRS image shows the temperature of the cloud tops or the surface of the Earth in cloud-free regions. The lowest temperatures (in purple) are associated with high, cold cloud tops that make up the top of the hurricane. The infrared signal does not penetrate through clouds. Where there are no clouds the AIRS instrument reads the infrared signal from the surface of the Earth, revealing warmer temperatures (red). At the time the data were taken from which these images were made, Hector is a well organized storm, with the strongest convection in the SE quadrant. The increasing vertical wind shear in the NW quadrant is appearing to have an effect. Maximum sustained winds are at 85 kt, gusts to 105 kt. Estimated minimum central pressure is 975 mbar. The microwave image is created from microwave radiation emitted by Earth's atmosphere and received by the instrument. It shows where the heaviest rainfall is taking place (in blue) in the storm. Blue areas outside of the storm where there are either some clouds or no clouds, indicate where the sea surface shines through. The "visible" image is created from data acquired by the visible light/near-infrared sensor on the AIRS instrument. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00507
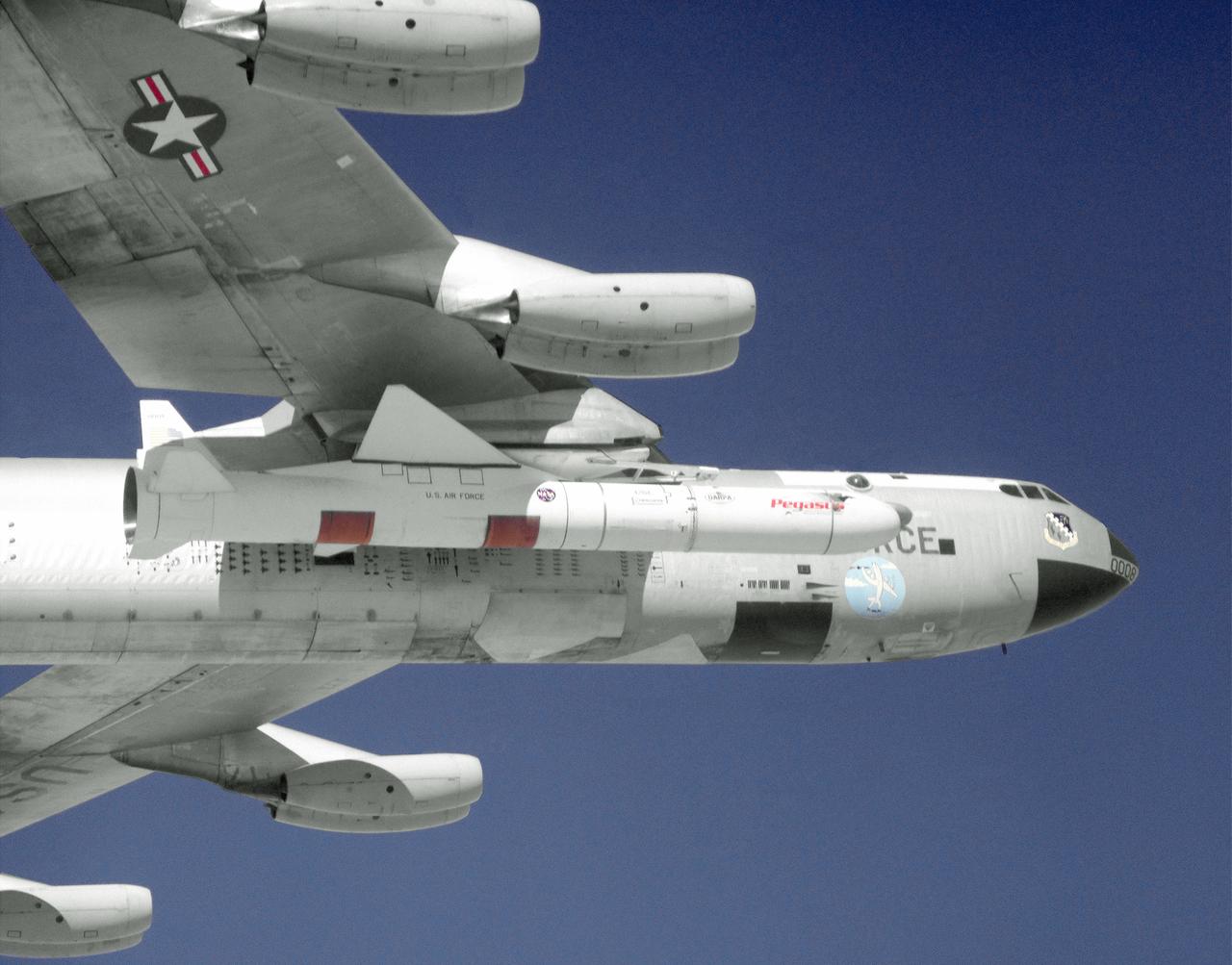

The Pegasus air-launched space booster is carried aloft under the right wing of NASA's B-52 carrier aircraft on its first captive flight from the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The first of two scheduled captive flights was completed on November 9, 1989. Pegasus is used to launch satellites into low-earth orbits cheaply. In 1997, a Pegasus rocket booster was also modified to test a hypersonic experiment (PHYSX). An experimental "glove," installed on a section of its wing, housed hundreds of temperature and pressure sensors that sent hypersonic flight data to ground tracking facilities during the experiment’s flight.
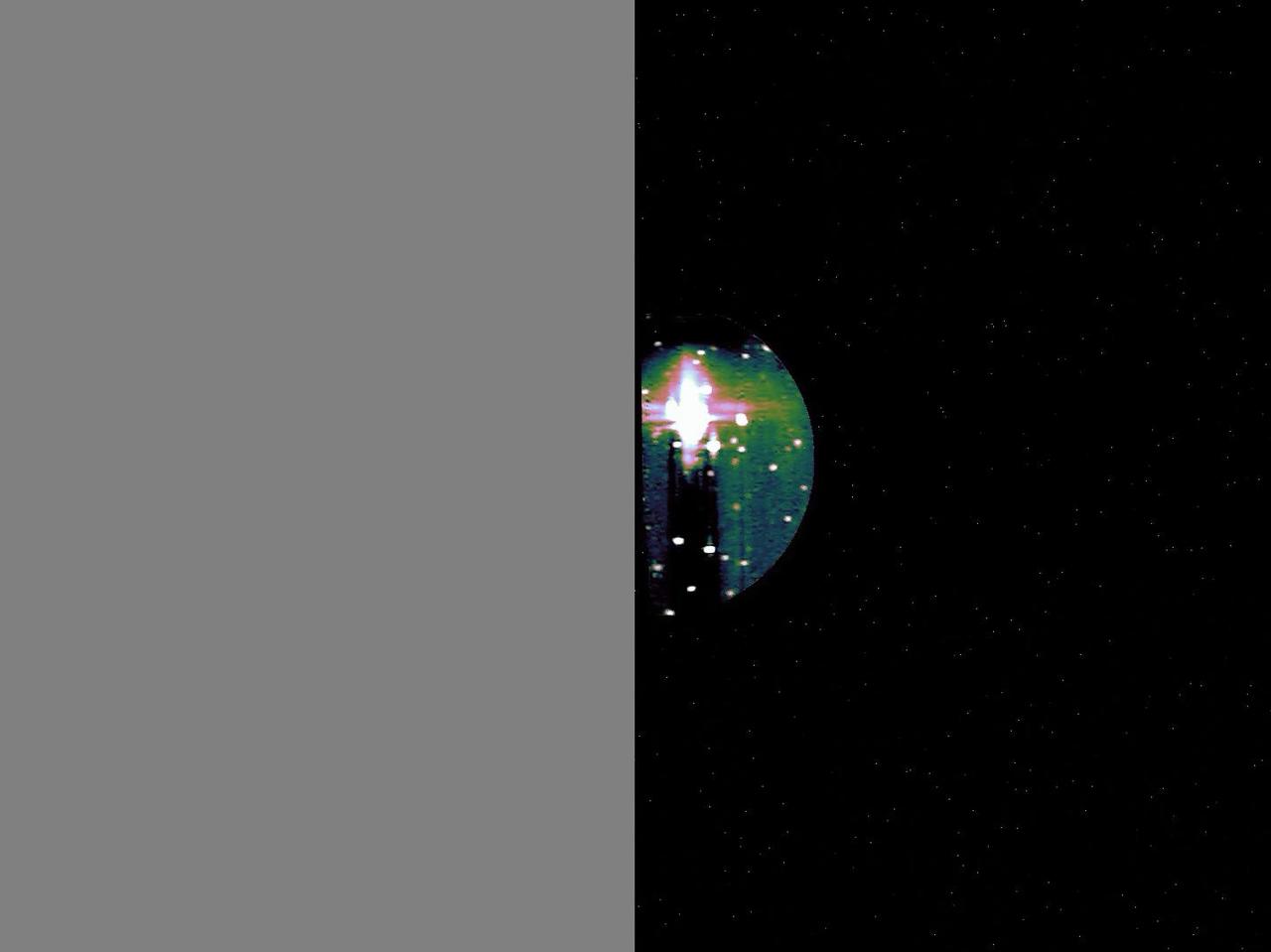
The JIRAM (Jovian Infrared Auroral Mapper) instrument aboard NASA's Juno spacecraft captured this view of the south polar region of Jupiter's volcanic moon Io during a flyby on Dec. 27, 2024. JIRAM "sees" infrared light not visible to the human eye. This animation shows actual data from JIRAM, with minimal processing. The bright spots indicate locations with higher temperatures caused by volcanic activity, including an area with such a strong signal that it saturated the sensor. The gray areas resulted when Io left JIRAM's field of view during the observation. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26594
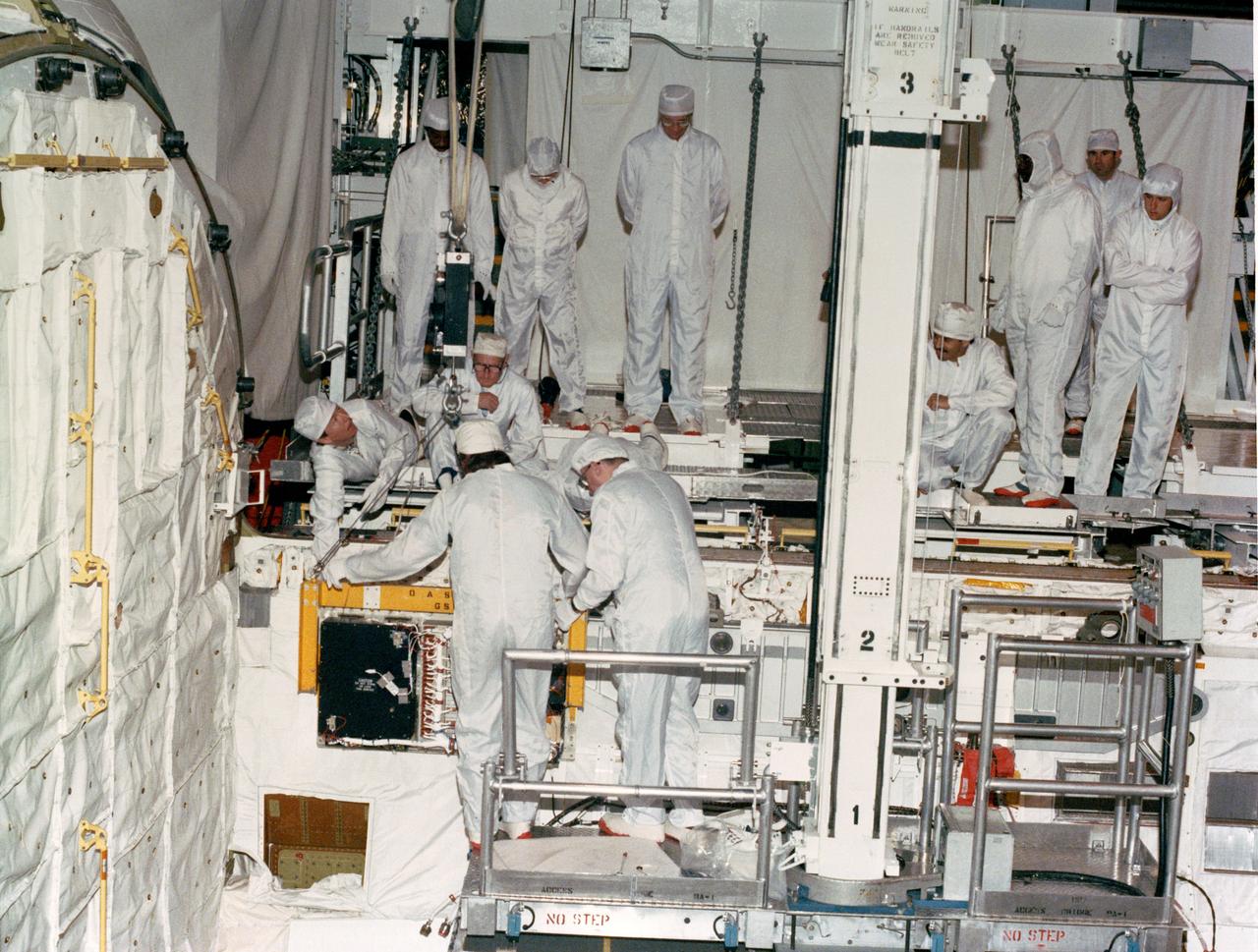

S88-37764 (18 April 1988) --- OASIS, instrumentation which will record the environment experienced by Discovery during the STS-26 Space Shuttle mission, is lowered into position for attachment to the orbiter's aft port sill. Instrumentation sensors in the payload bay which are connected to the tape recorder module will document a variety of environmental measurements during various phases of the flight including temperature, pressure, vibration, sounds, acceleration, stress, and strain. OASIS will also record data during the Flight Readiness Firing. NASA is flying OASIS aboard Discovery in support of the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) program office of the Air Force Space Division. The system was developed by Lockheed under a NASA contract, funded by the Air Force.

The Laminar Soot Processes (LSP) experiment under way during the Microgravity Sciences Lab-1 mission in 1997. LSP-2 will fly in the STS-107 Research 1 mission in 2001. The principal investigator is Dr. Gerard Faeth of the University of Michigan. LSP uses a small jet burner, similar to a classroom butane lighter, that produces flames up to 60 mm (2.3 in) long. Measurements include color TV cameras and a temperature sensor, and laser images whose darkness indicates the quantity of soot produced in the flame. Glenn Research in Cleveland, OH, manages the project.

Ultrasonic Measurement System. Ultrasonic measurement system will enable simultaneous measurement of temperature, velocity and density fields through a grid of ultrasonic sensors. This method incorporates a theoretical approach and machine learning techniques to develop a physics-informed data-driven calibration and operation workflow. This allows at least ten times faster data processing times as well as potential capability of transient measurements and solid particle detection. The system can also be utilized for health monitoring. This measurement technique is in line with the “air-breathing propulsion” core competency of GRC. However it can also enables next generation space data processing with higher performance computing capable of operating in harsh deep space environments.
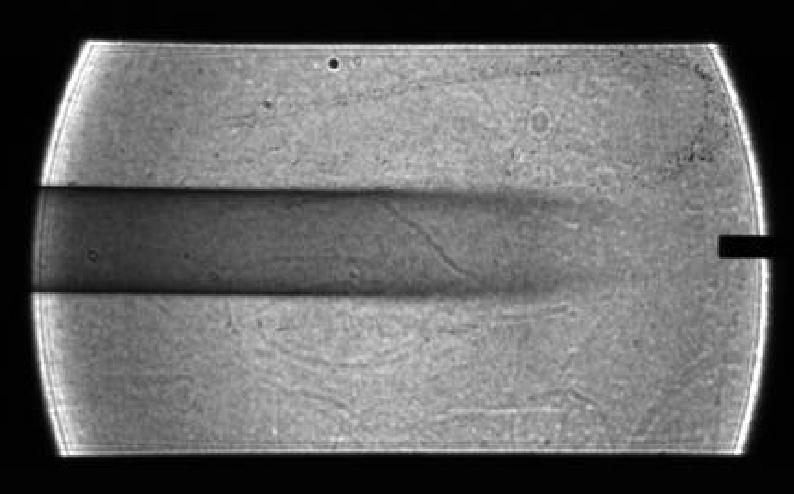
Image of soot (smoke) plume made for the Laminar Soot Processes (LSP) experiment during the Microgravity Sciences Lab-1 mission in 1997. LSP-2 will fly in the STS-107 Research 1 mission in 2002. The principal investigator is Dr. Gerard Faeth of the University of Michigan. LSP uses a small jet burner, similar to a classroom butane lighter, that produces flames up to 60 mm (2.3 in) long. Measurements include color TV cameras and a temperature sensor, and laser images whose darkness indicates the quantity of soot produced in the flame. Glenn Research in Cleveland, OH, manages the project.

This 1970 photograph shows Skylab's Multispectral Scanner, one of the major components of an Earth Resources Experiment Package (EREP). It was designed to evaluate the on-orbit use of multispectral scanning of Earth resources. Investigators could evaluate the usefulness of spacecraft multispectral data for crop identification, vegetation mapping, soil moisture measurements, identification of contaminated areas in large bodies of water, and surface temperature mapping. The overall purpose of the EREP was to test the use of sensors that operated in the visible, infrared, and microwave portions of the electromagnetic spectrum to monitor and study Earth resources. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
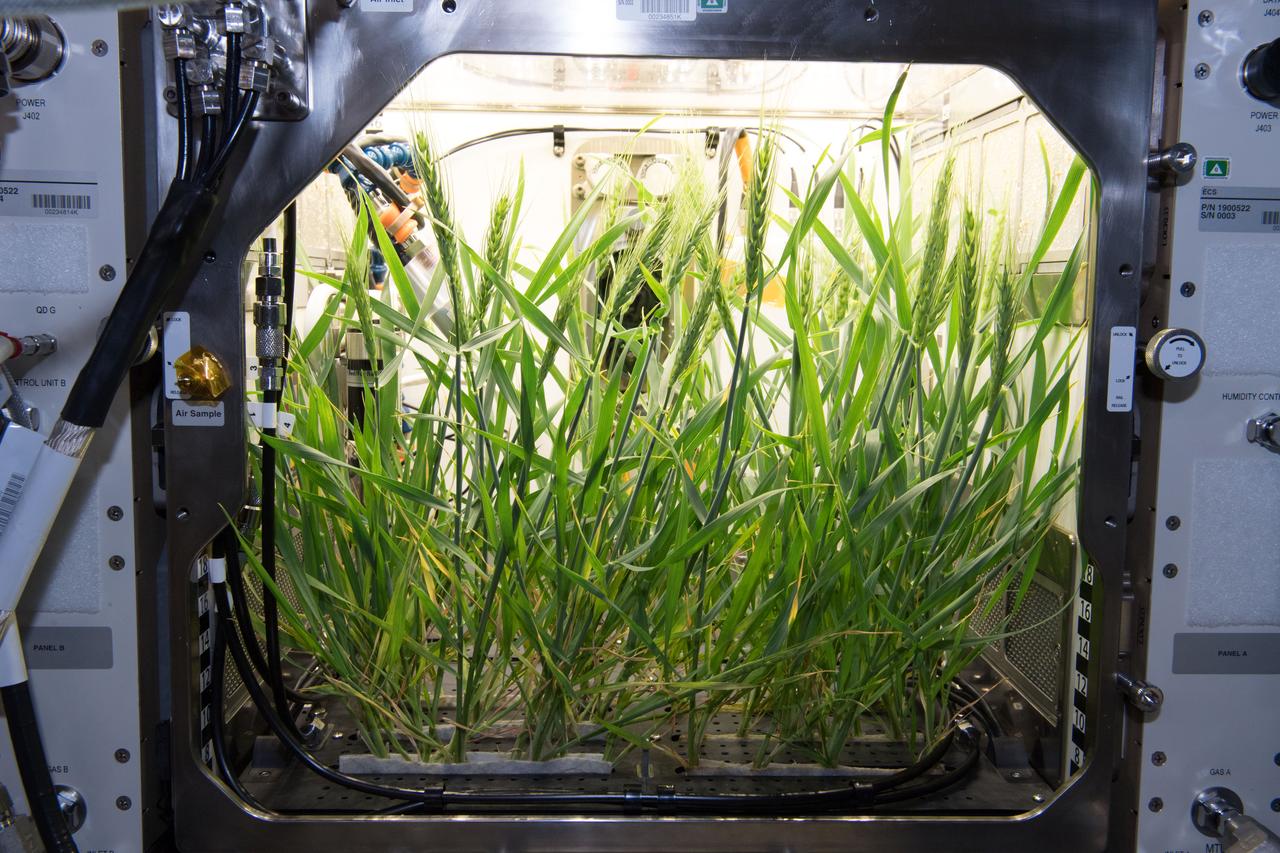

The first growth test of crops in the Advanced Plant Habitat aboard the International Space Station yielded great results. Arabidopsis seeds – small flowering plants related to cabbage and mustard – grew for about six weeks and the dwarf wheat for five weeks. The APH is now ready to support large plant testing on ISS. APH is a fully enclosed, closed-loop system with an environmentally controlled growth chamber. It uses red, blue and green LED lights, and broad spectrum white LED lights. The system's more than 180 sensors will relay real-time information, including temperature, oxygen content and moisture levels back to the team at Kennedy Space Center.

A model of a tiny, wedge-shaped robot designed to explore subsurface oceans of icy moons, right, sits beside a large waterproof capsule containing electronics and sensors for testing below glacial ice at the Juneau Icefield in Alaska in July 2023. The model, about 5 inches (12 centimeters) long, was 3D-printed to show the final envisioned size of a futuristic NASA mission concept called SWIM, short for Sensing With Independent Micro-swimmers. Led by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory from spring 2021 to fall 2024, SWIM envisions a swarm of dozens of self-propelled, cellphone-size robots exploring the waters of icy moons like Jupiter's Europa and Saturn's Enceladus. Delivered to the subsurface ocean by an ice-melting cryobot, the tiny robots would zoom away to look for chemical and temperature signals that could point to life. The capsule shown here contains the first generation of an ocean composition sensor built for the SWIM robots by a team at Georgia Tech. The final version of the sensor would enable each robot to simultaneously measure temperature, pressure, acidity or alkalinity, conductivity, and chemical makeup. During the Alaska field test, the team lowered the capsule through a borehole in the ice and measured pressure and conductivity down to a depth of 164 feet (50 meters). This field test was conducted as part of a JPL-managed project called ORCAA (Ocean Worlds Reconnaissance and Characterization of Astrobiological Analogs). Known as an analog mission, ORCAA is working to answer science questions and test technology in preparation for a potential future mission to explore the surface or subsurface of icy moons. ORCAA is funded by NASA's Planetary Science and Technology from Analog Research program. SWIM was supported by Phase I and II funding from NASA's Innovative Advanced Concepts program under the agency's Space Technology Mission Directorate. JPL is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, California. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26424
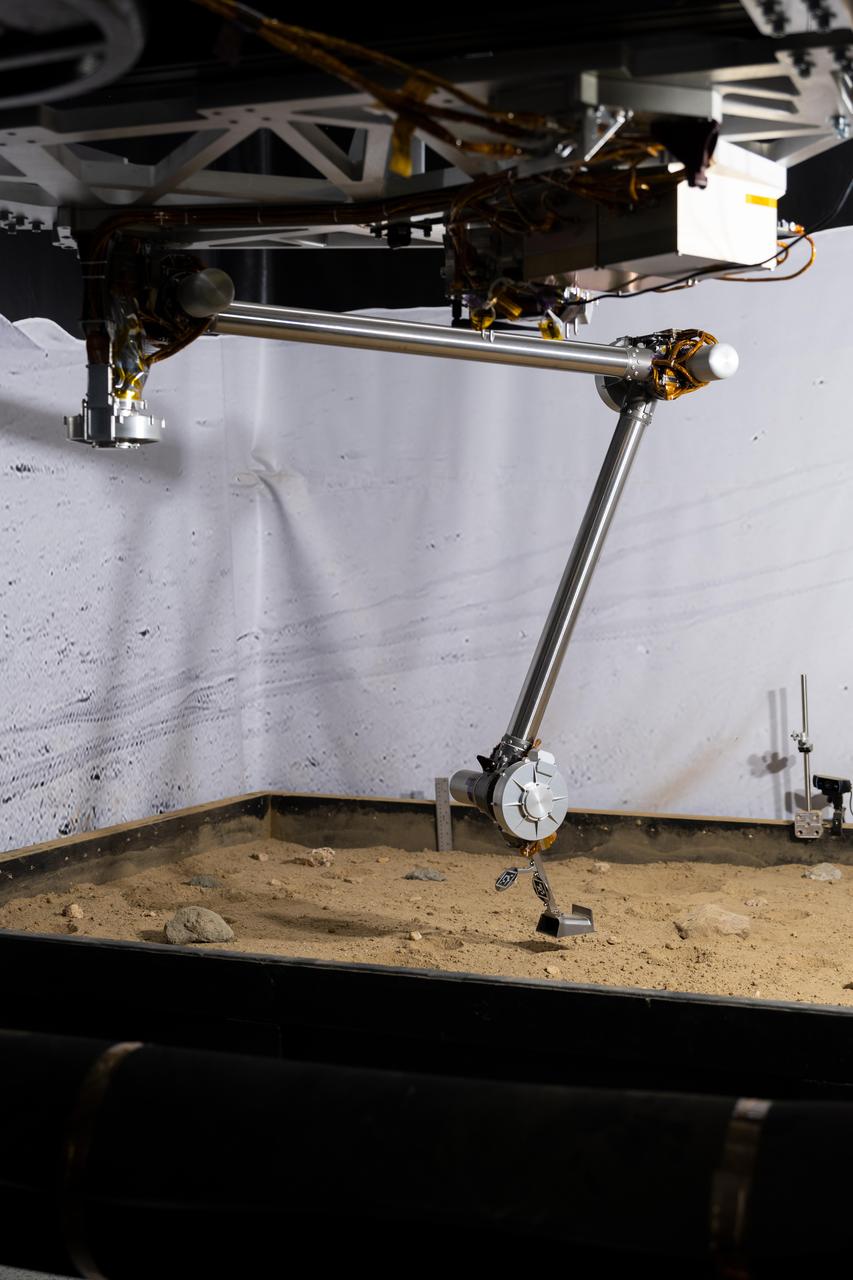
The 3D-printed titanium scoop of the Cold Operable Lunar Deployable Arm (COLDArm) robotic arm system is poised above a test bed filled with material to simulate lunar regolith (broken rocks and dust) at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. COLDArm can function in temperatures as cold as minus 280 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 173 degrees Celsius). COLDArm is designed to go on a Moon lander and operate during lunar night, a period that lasts about 14 Earth days. Frigid temperatures during lunar night would stymie current spacecraft, which must rely on energy-consuming heaters to stay warm. To operate in the cold, the 6-foot-6-inch (2-meter) arm combines several key new technologies: gears made of bulk metallic glass that require no lubrication or heating, cold motor controllers that don't need to be kept warm in an electronics box near the core of the spacecraft, and a cryogenic six-axis force torque sensor that lets the arm "feel" what it's doing and make adjustments. A variety of attachments and small instruments could go on the end of the arm, including the scoop, which could be used for collecting samples from a planet's surface. Like the arm on NASA's InSight Mars lander, COLDArm could deploy science instruments to the surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25317
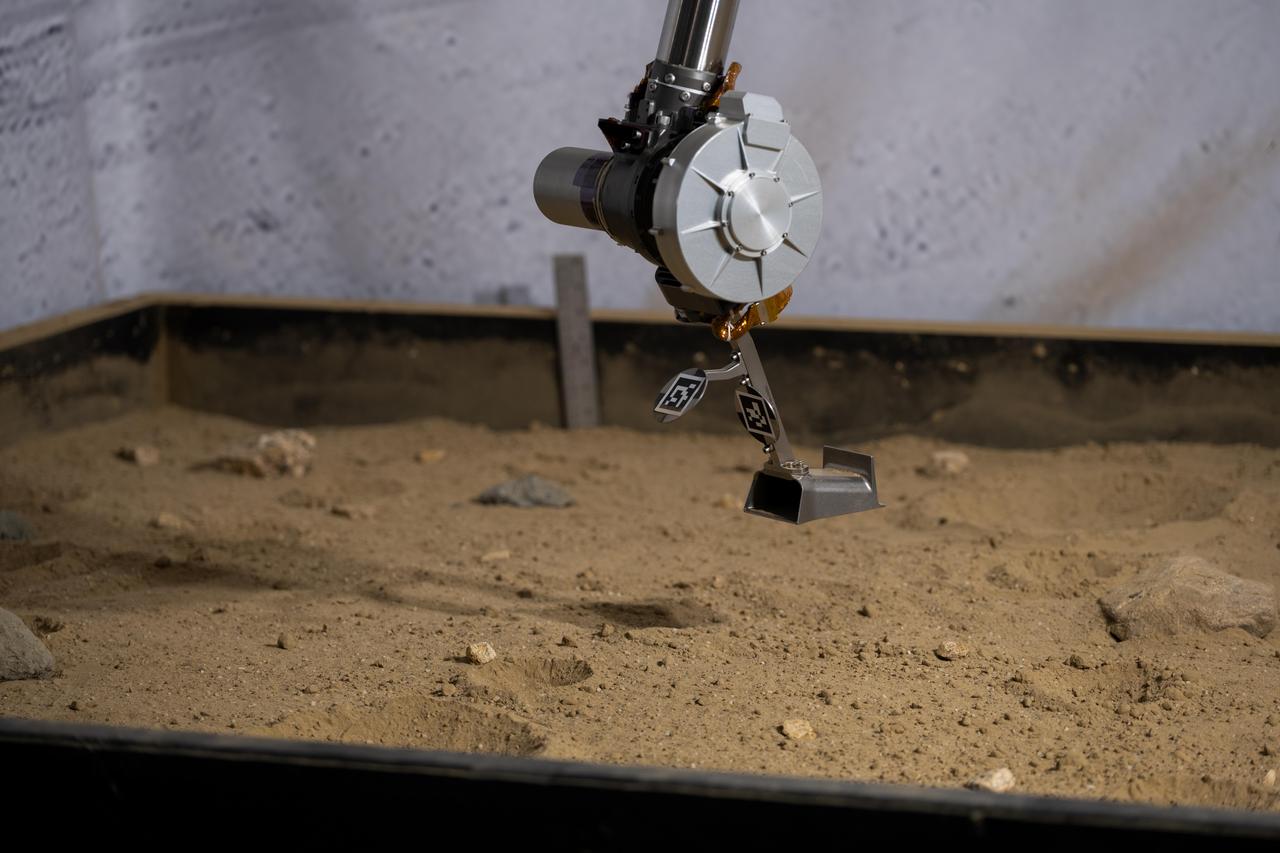

The 3D-printed titanium scoop of the Cold Operable Lunar Deployable Arm (COLDArm) robotic arm system is poised above a test bed filled with material to simulate lunar regolith (broken rocks and dust) at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. COLDArm can function in temperatures as cold as minus 280 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 173 degrees Celsius). COLDArm is designed to go on a Moon lander and operate during lunar night, a period that lasts about 14 Earth days. Frigid temperatures during lunar night would stymie current spacecraft, which must rely on energy-consuming heaters to stay warm. To operate in the cold, the 6-foot-6-inch (2-meter) arm combines several key new technologies: gears made of bulk metallic glass that require no lubrication or heating, cold motor controllers that don't need to be kept warm in an electronics box near the core of the spacecraft, and a cryogenic six-axis force torque sensor that lets the arm "feel" what it's doing and make adjustments. A variety of attachments and small instruments could go on the end of the arm, including the scoop, which could be used for collecting samples from a planet's surface. Like the arm on NASA's InSight Mars lander, COLDArm could deploy science instruments to the surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25318
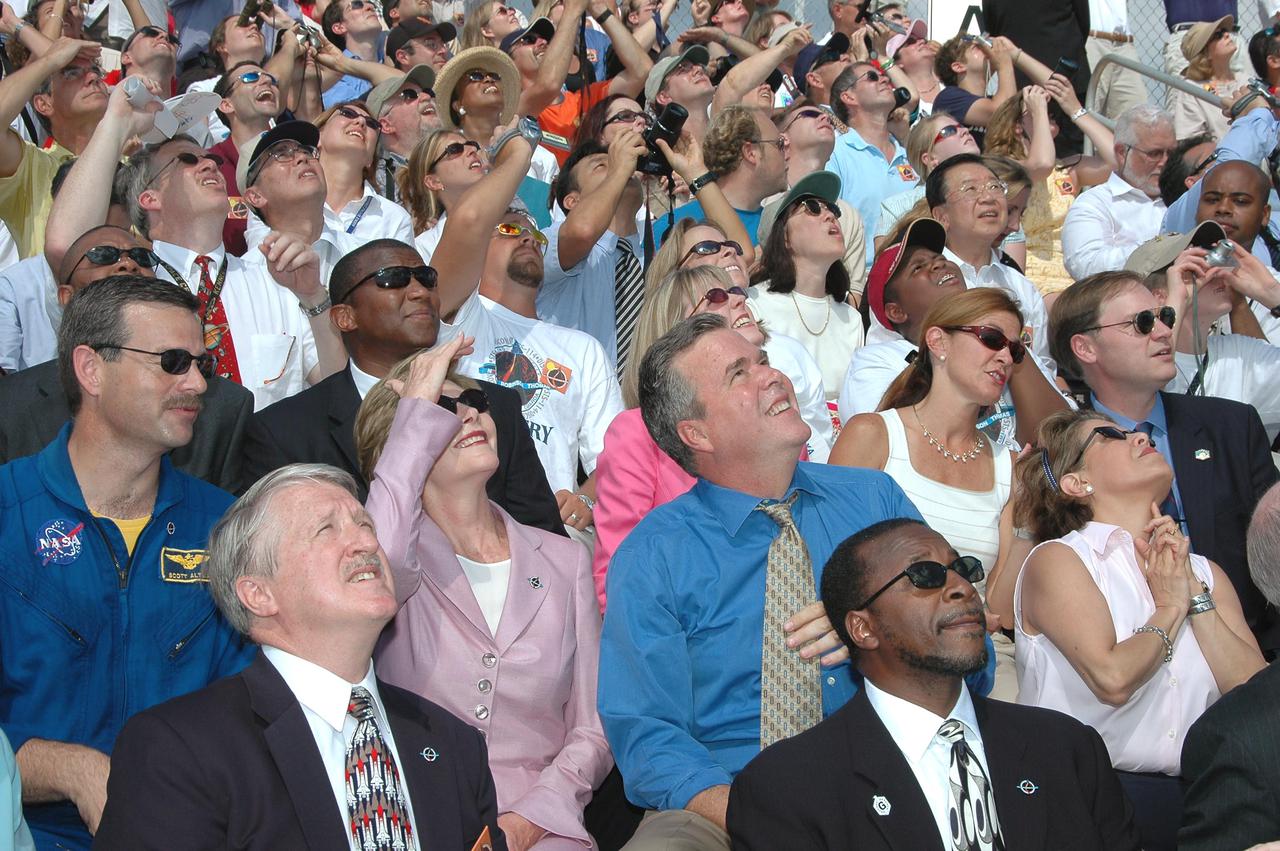

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the stands at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Banana Creek viewing site, First Lady Laura Bush and other guests follow path of Space Shuttle Discovery as it successfully launches on Return to Flight mission STS-114 at 10:39 a.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39B. At right of Mrs. Bush is Florida Gov. Jeb Bush. KSC Deputy Director Woodrow Whitlow Jr. is in front of the governor. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7.

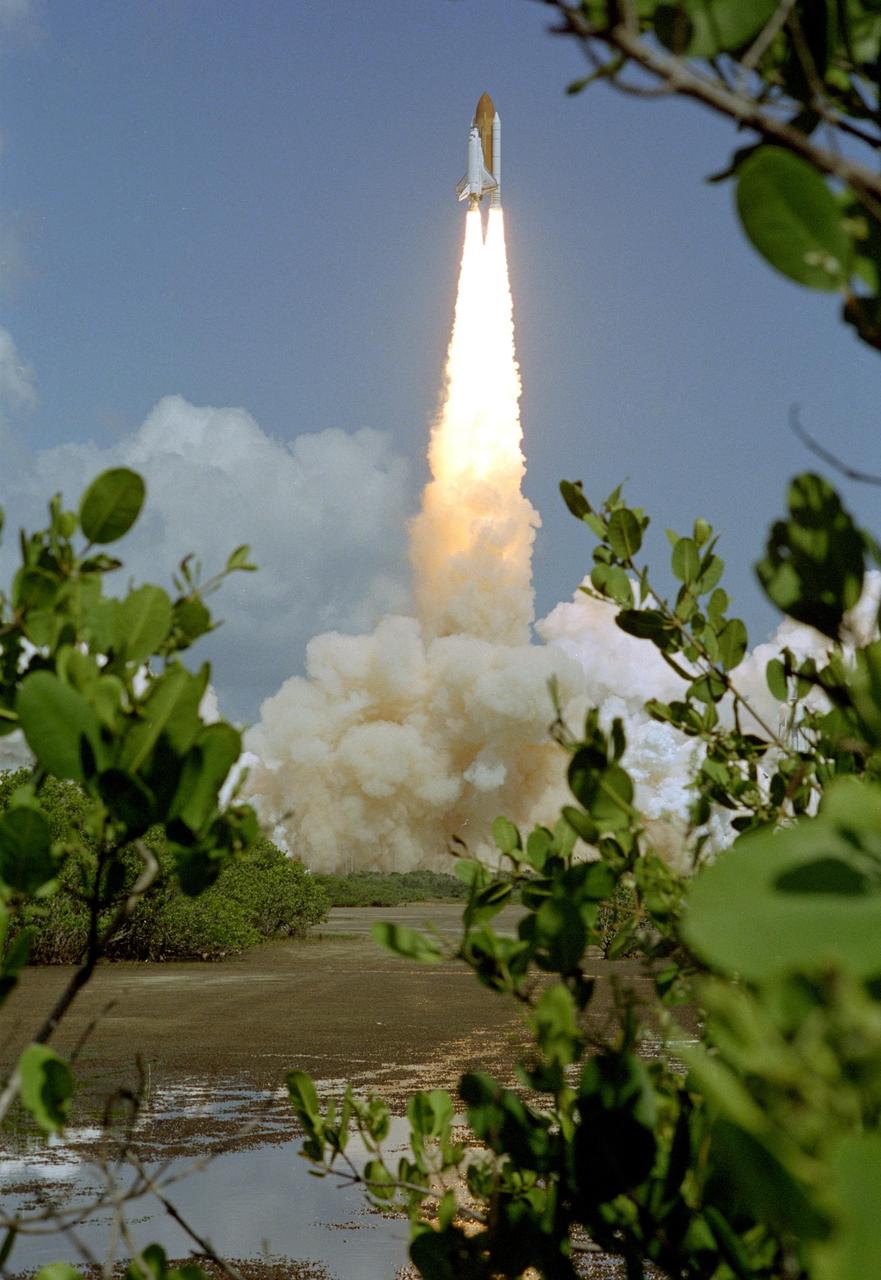
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Multiple cameras on the perimeter of Launch Pad 39B capture the launch of Space Shuttle Discovery as it rises above the lightning mast (left side) on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114. It is the 114th flight in the Space Shuttle Program and the 31st for Discovery. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure. (Photo Credit: Scott Andrews)
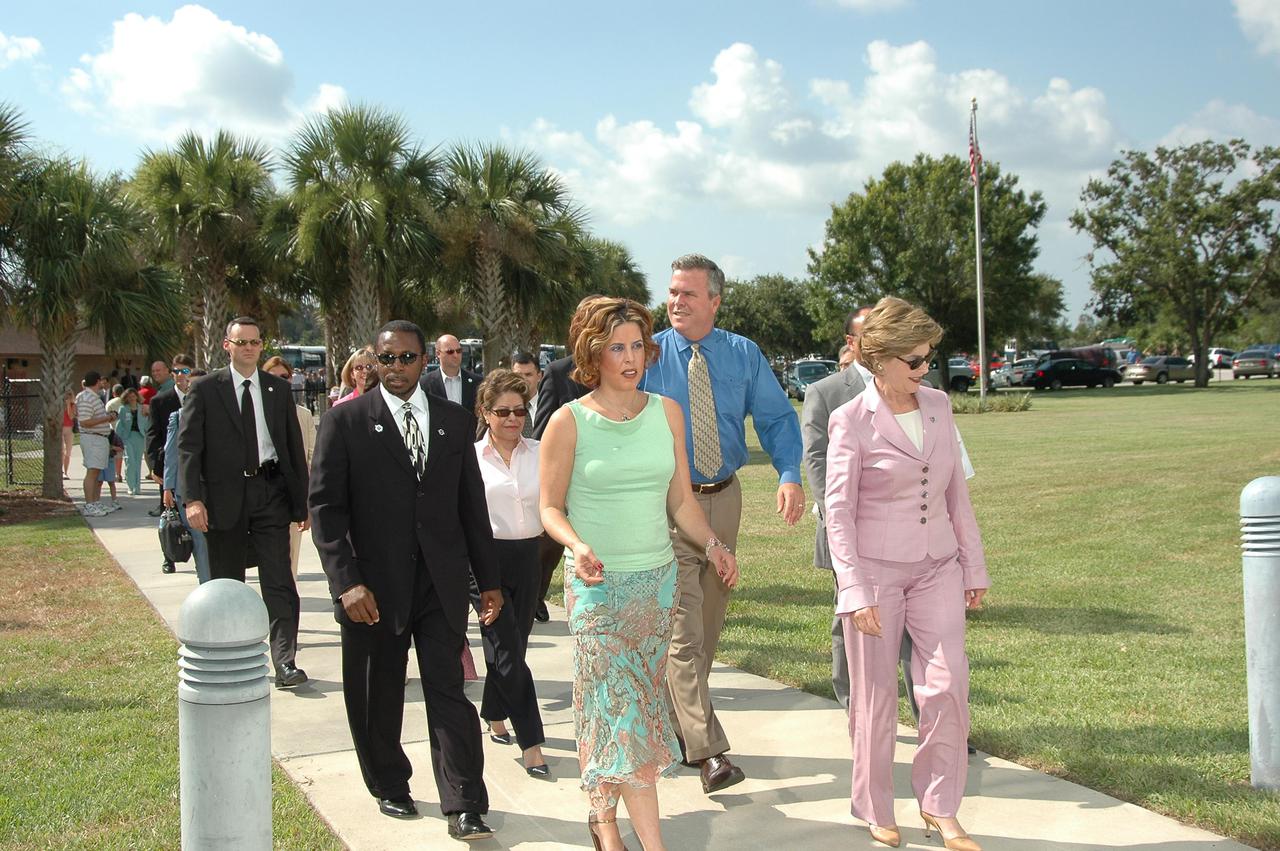

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - KSC Deputy Director Woodrow Whitlow Jr. (left) escorts distinguished guests to the VIP viewing site at NASA Kennedy Space Center. First Lady Laura Bush is in front (right) with Noelle Bush, the daughter of Florida Gov. Jeb Bush and Columba Bush behind her. They are attending the historic launch of Space Shuttle Discovery on Return to Flight mission STS-114, scheduled to lift off at 10:39 a.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39B with a crew of seven. Mrs. Bush is only the third First Lady to witness a Space Shuttle launch at KSC. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7.

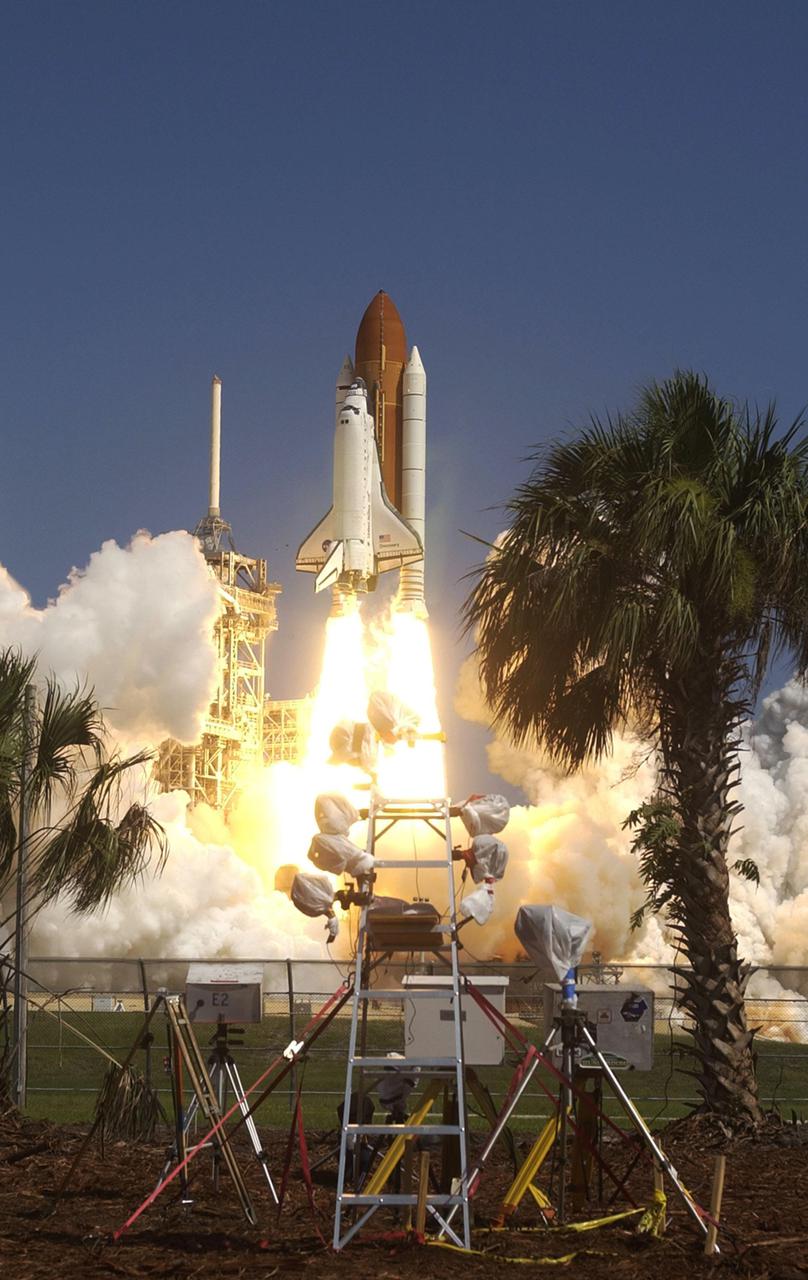
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Viewed from a camera in the midst of Florida greenery across the marshy water, Space Shuttle Discovery leaps through billows of smoke and steam on Launch Pad 39B on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114. Liftoff occurred at 10:39 a.m. EDT. This is the 114th Space Shuttle flight and the 31st for Discovery. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.
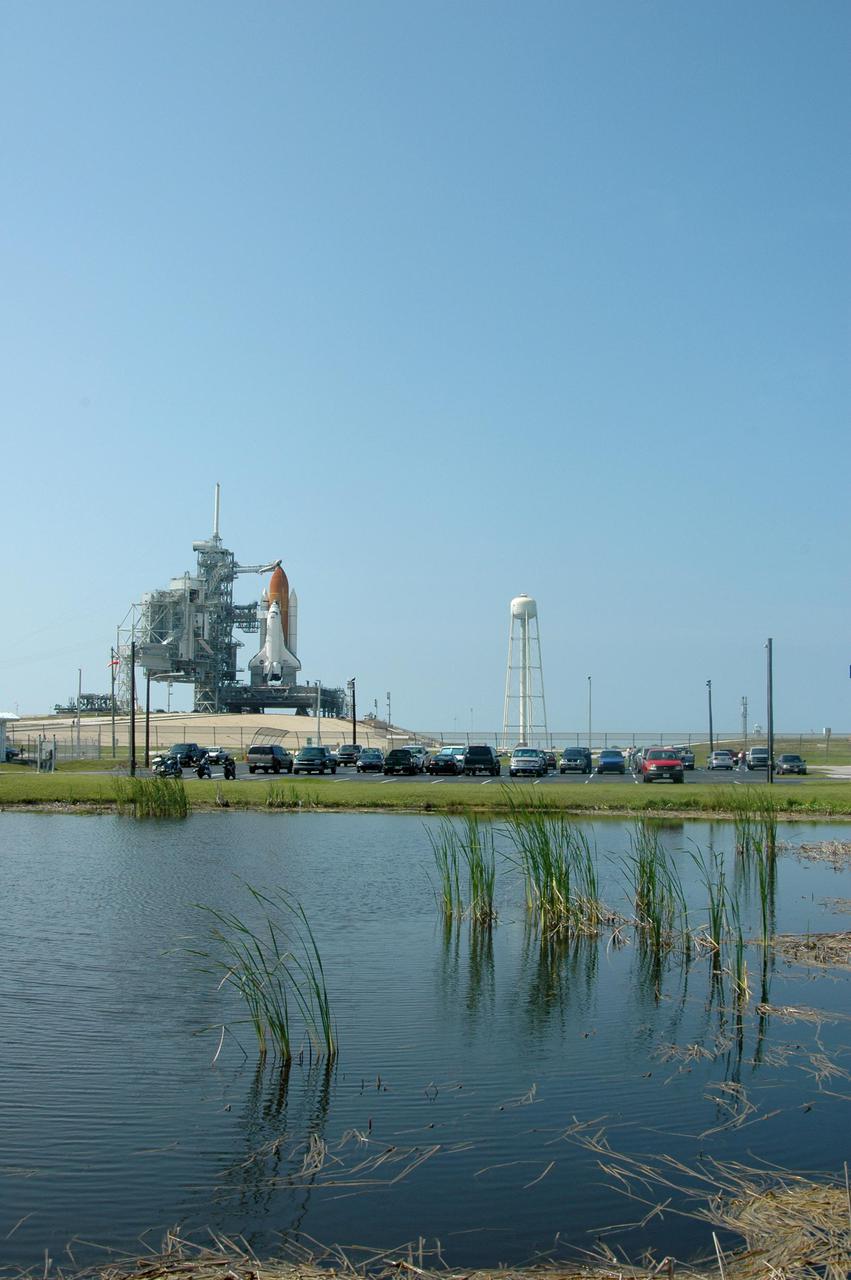

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Cameras at the edge of a pond have a pristine view to Launch Pad 39B at NASA Kennedy Space Center where the Space Shuttle Discovery waits for launch. On the right of the Shuttle is the 290-foot-tall water tower that holds 300,000 gallons of water, part of the sound suppression system during a launch. Discovery is scheduled to lift off on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114 at 10:39 a.m. EDT July 26 with a crew of seven. On the mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.
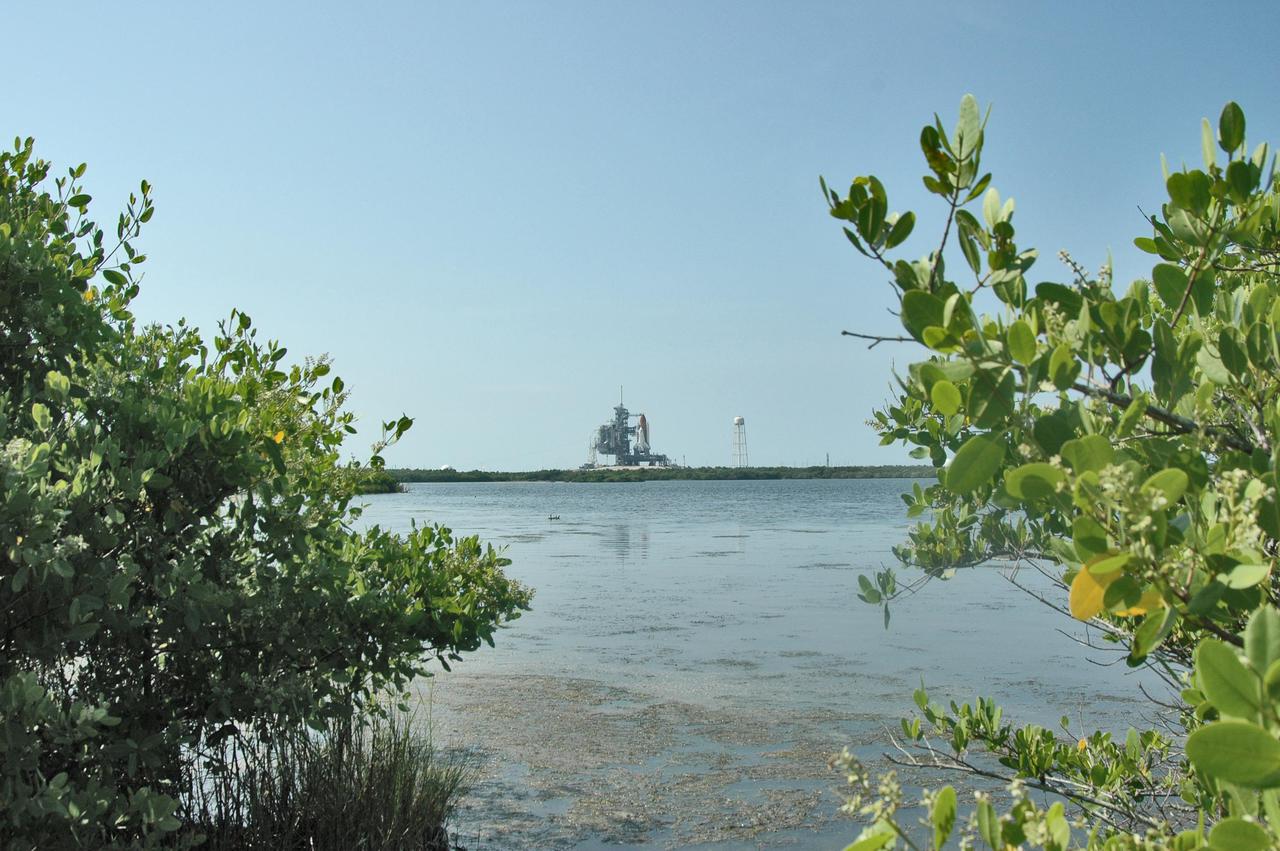

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Seen after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure, and framed by marsh greenery, a fully revealed Space Shuttle Discovery on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Pad 39B rises from the horizon beyond the pond. Discovery is scheduled to lift off on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114 at 10:39 a.m. EDT July 26 with a crew of seven. On the mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.
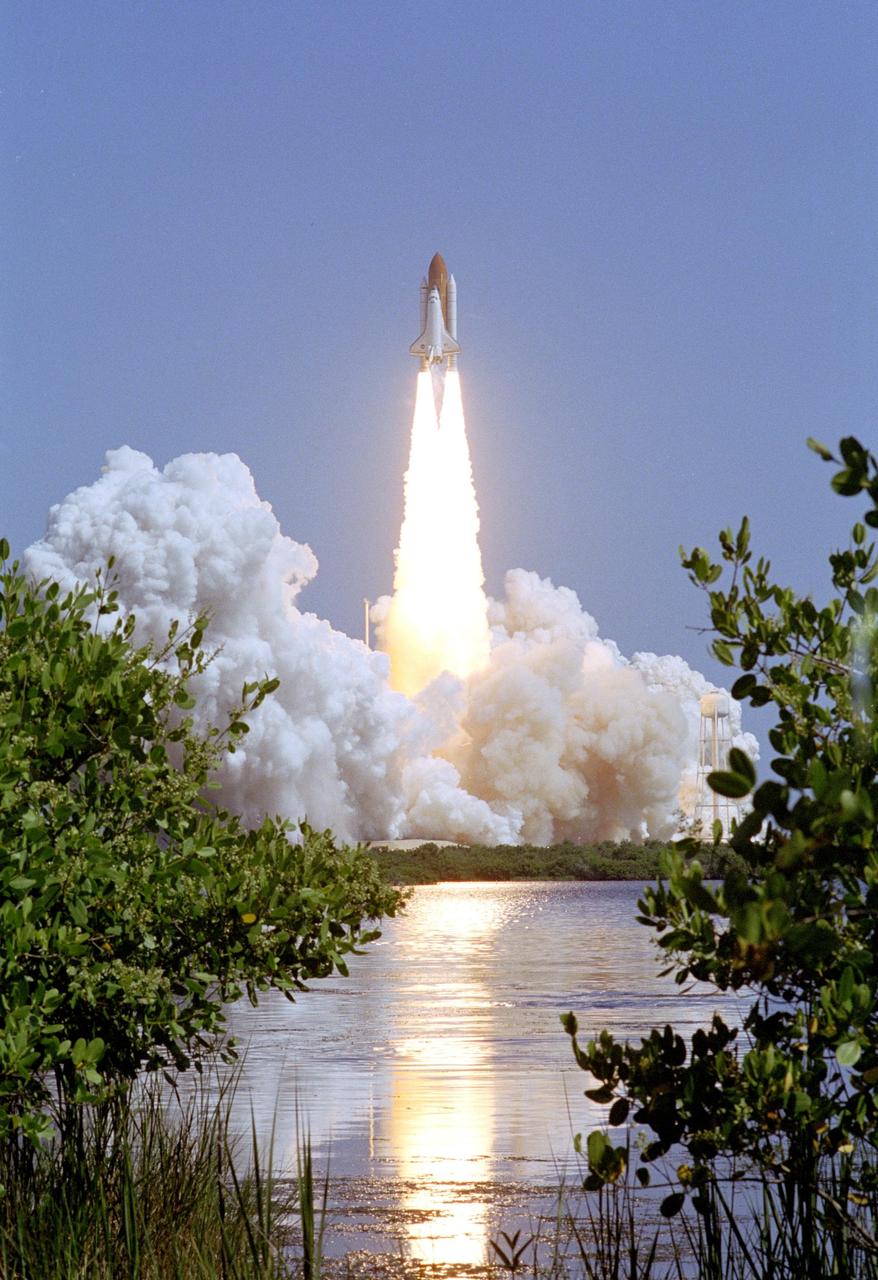

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The flames of Space Shuttle Discovery’s Solid Rocket Boosters are reflected in the water next to Launch Pad 39B as the Shuttle leaps from the pad on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114. Liftoff occurred at 10:39 a.m. EDT. It is the 114th Space Shuttle flight and the 31st for Discovery. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.
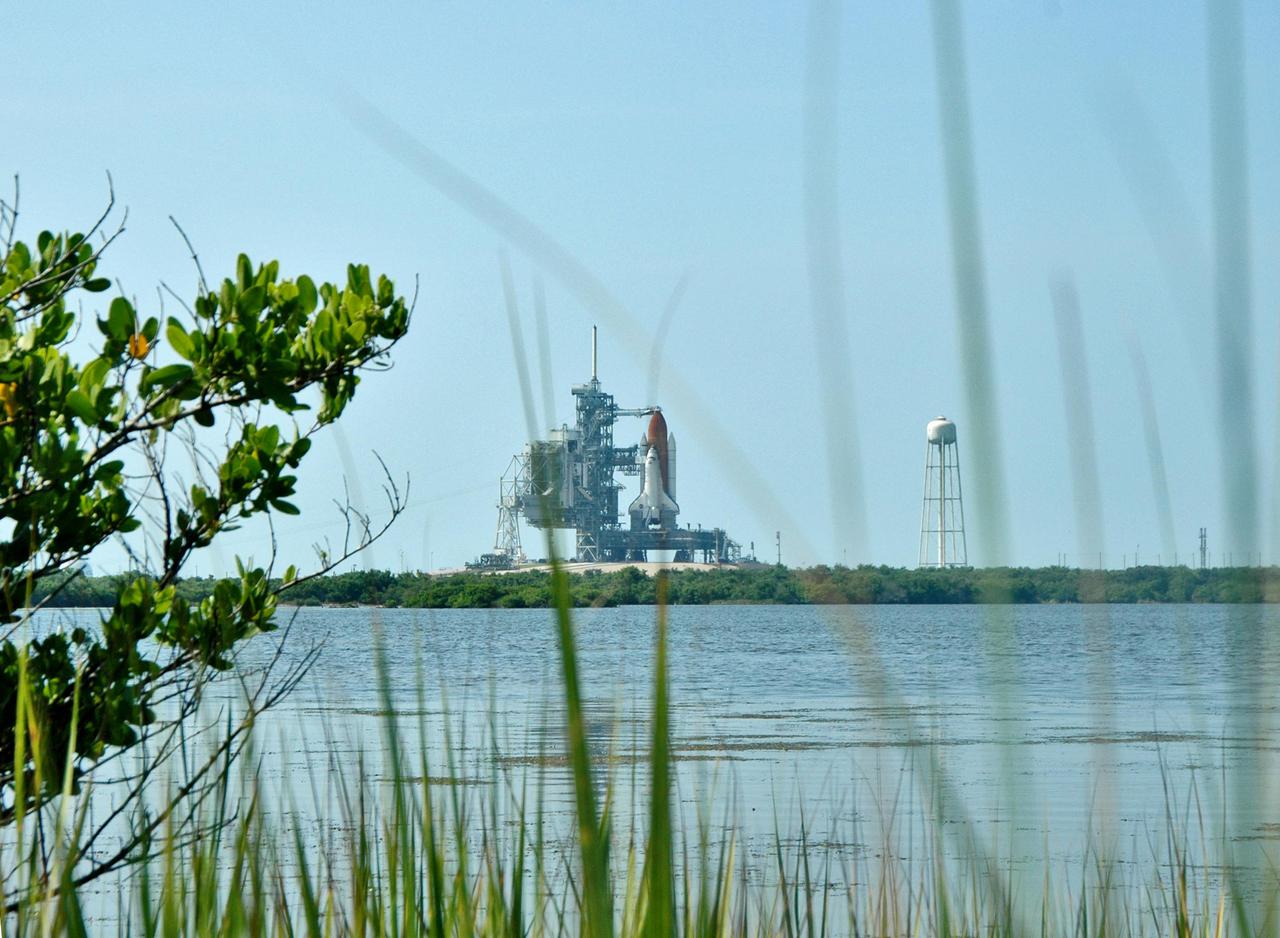

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the edge of a pond across from Launch Pad 39B, only long grasses stand between the camera and Space Shuttle Discovery as it waits for launch. Discovery is scheduled to lift off on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114 at 10:39 a.m. EDT July 26 with a crew of seven. On the mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.
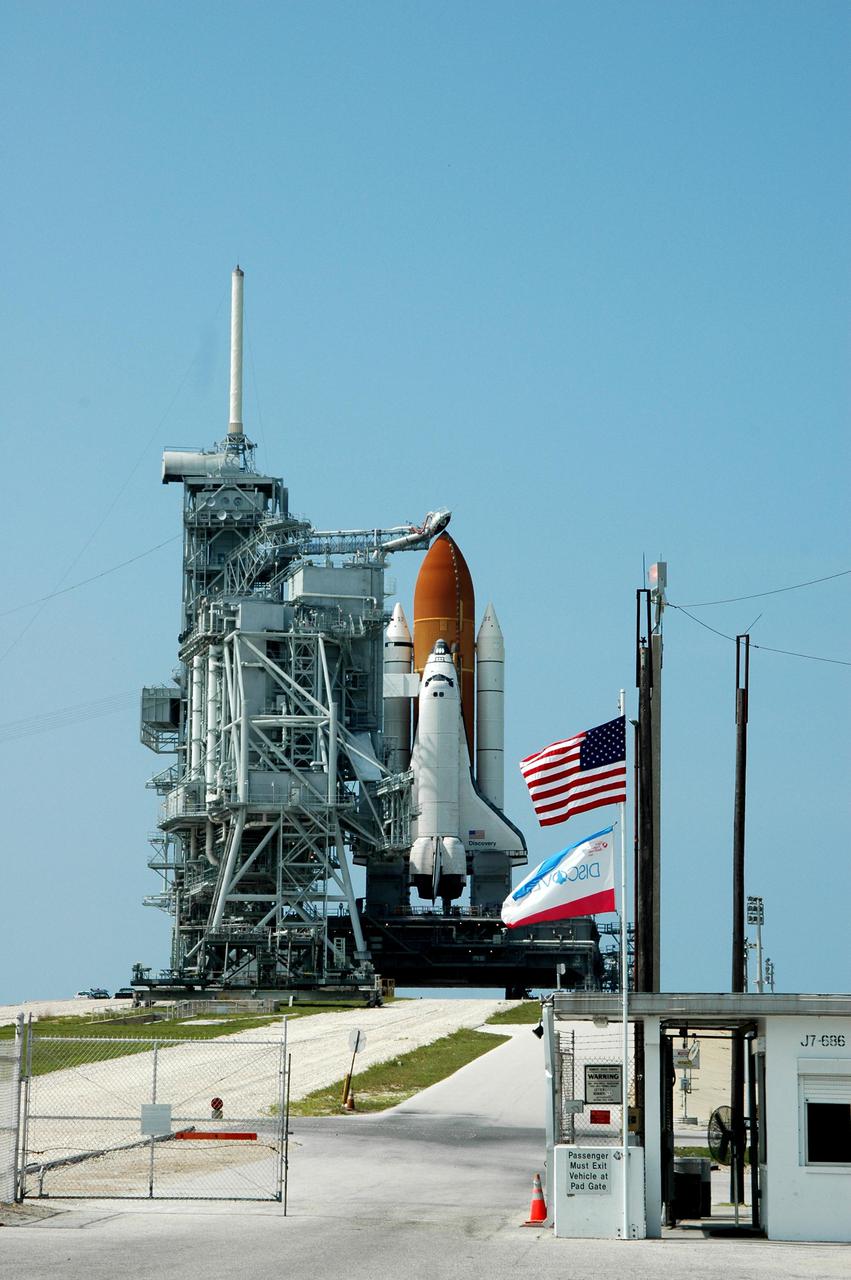

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Flags are flying on Launch Pad 39B at NASA Kennedy Space Center as Space Shuttle Discovery is ready on the pad for launch after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure. Rollback of the RSS is a major preflight milestone, typically occurring during the T-11-hour hold on L-1 (the day before launch). Discovery is scheduled to lift off on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114 at 10:39 a.m. EDT July 26 with a crew of seven. On the mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.
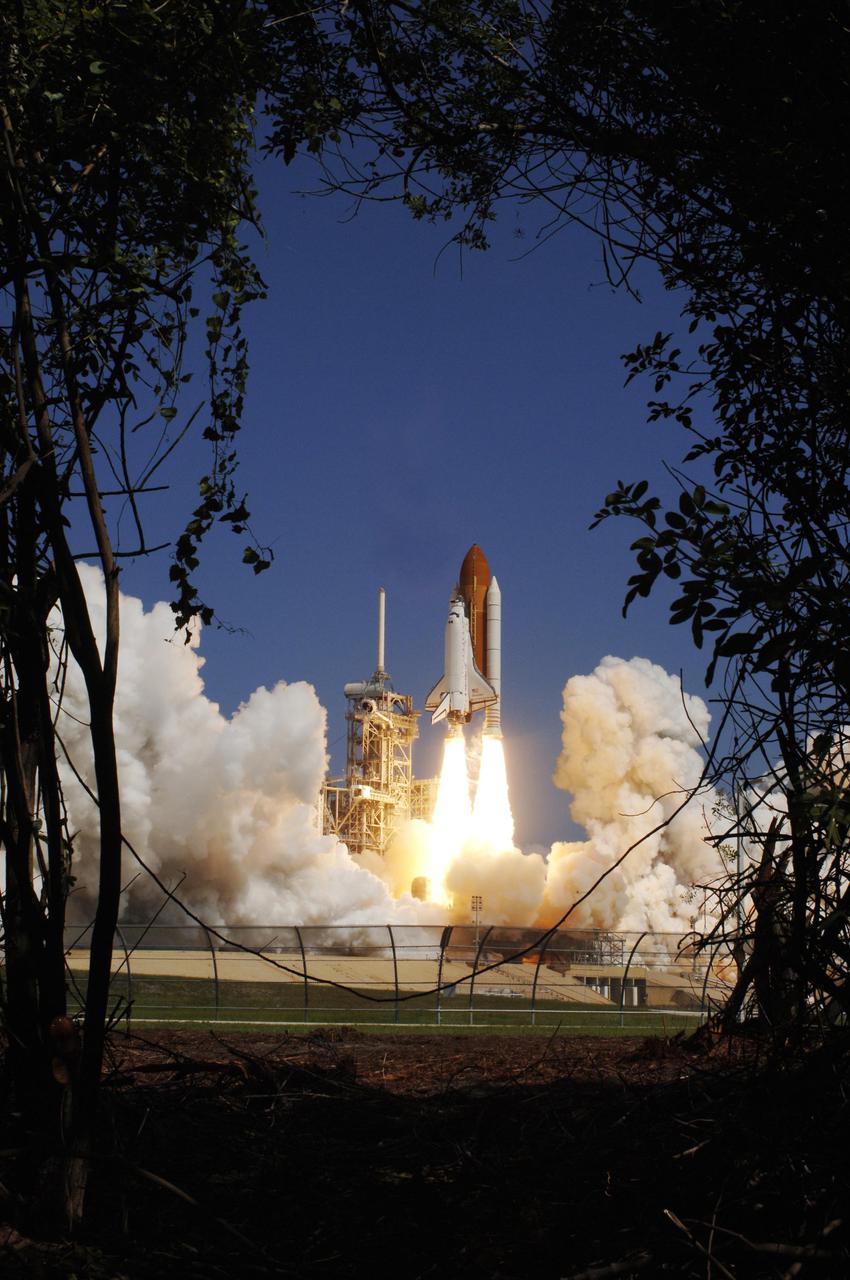

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Framed by Florida greenery, Space Shuttle Discovery lifts off Launch Pad 39B at 10:39 a.m. EDT on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114. It is the 114th Space Shuttle flight and the 31st for Discovery. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Launch Control Center at NASA Kennedy Space Center, First Lady Laura Bush thanks NASA Administrator for his hospitality. At far left is Center Director Jim Kennedy. Mrs. Bush witnessed the historic launch of Space Shuttle Discovery on Return to Flight mission STS-114. She is only the third First Lady to witness a Space Shuttle launch at KSC.On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7.
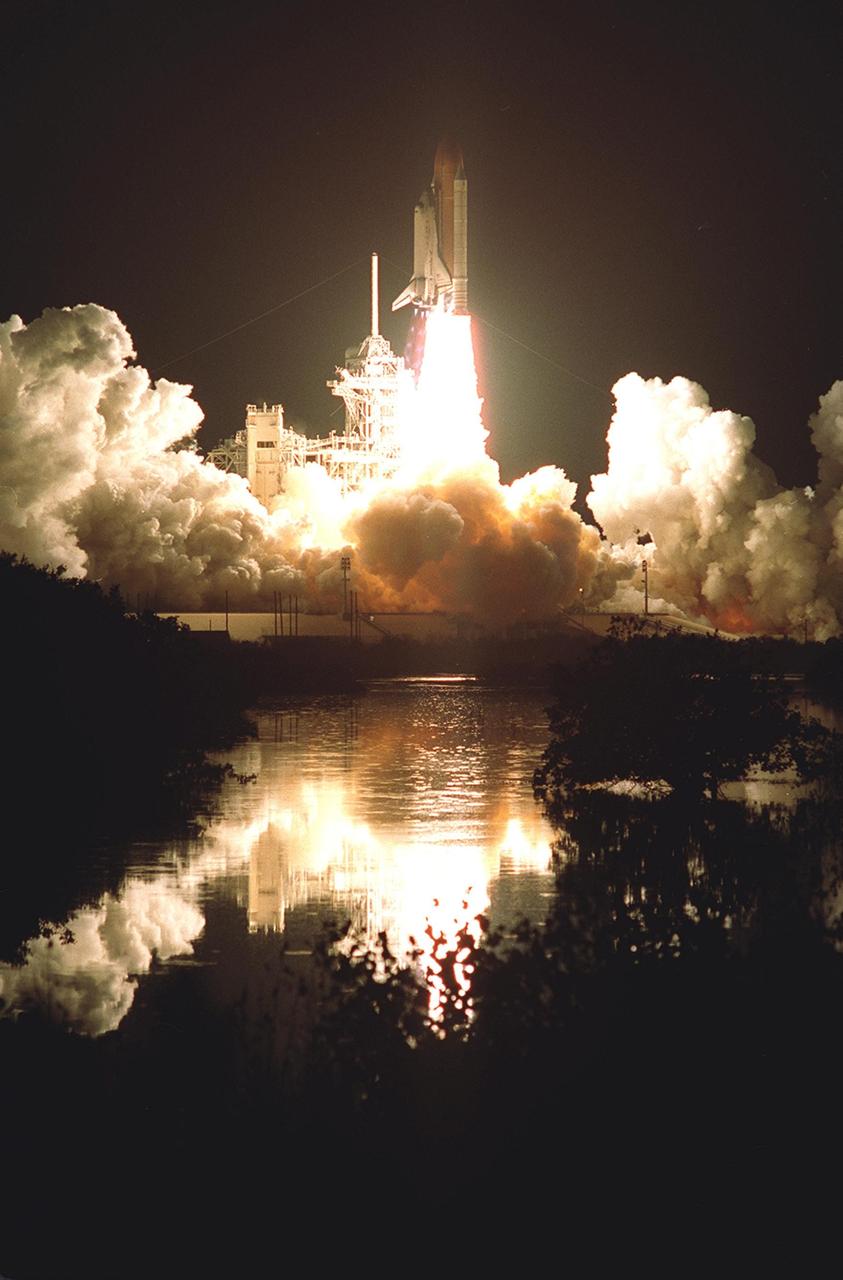

Turning night into day, the brilliance of Space Shuttle Discovery's launch is reflected in the waters nearby. Liftoff occurred at 7:50 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. On board are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. STS-103 is a Hubble Servicing Mission, with three planned space walks designed to install new equipment and replace old. The primary objective is to replace the gyroscopes that make up the three Rate Sensor Units. Extravehicular activities include installing a new computer, changing out one of the Fine Guidance Sensors, replacing a tape recorder with a new solid state recorder, and installing a voltage/temperature improvement kit, and begin repairing the insulation on the telescope's outer surface. After the 7-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 27, at about 5:24 p.m. EST. This is the 27th flight of Discovery and the 96th mission in the Space Shuttle Program. It is the third launch at Kennedy Space Center in 1999
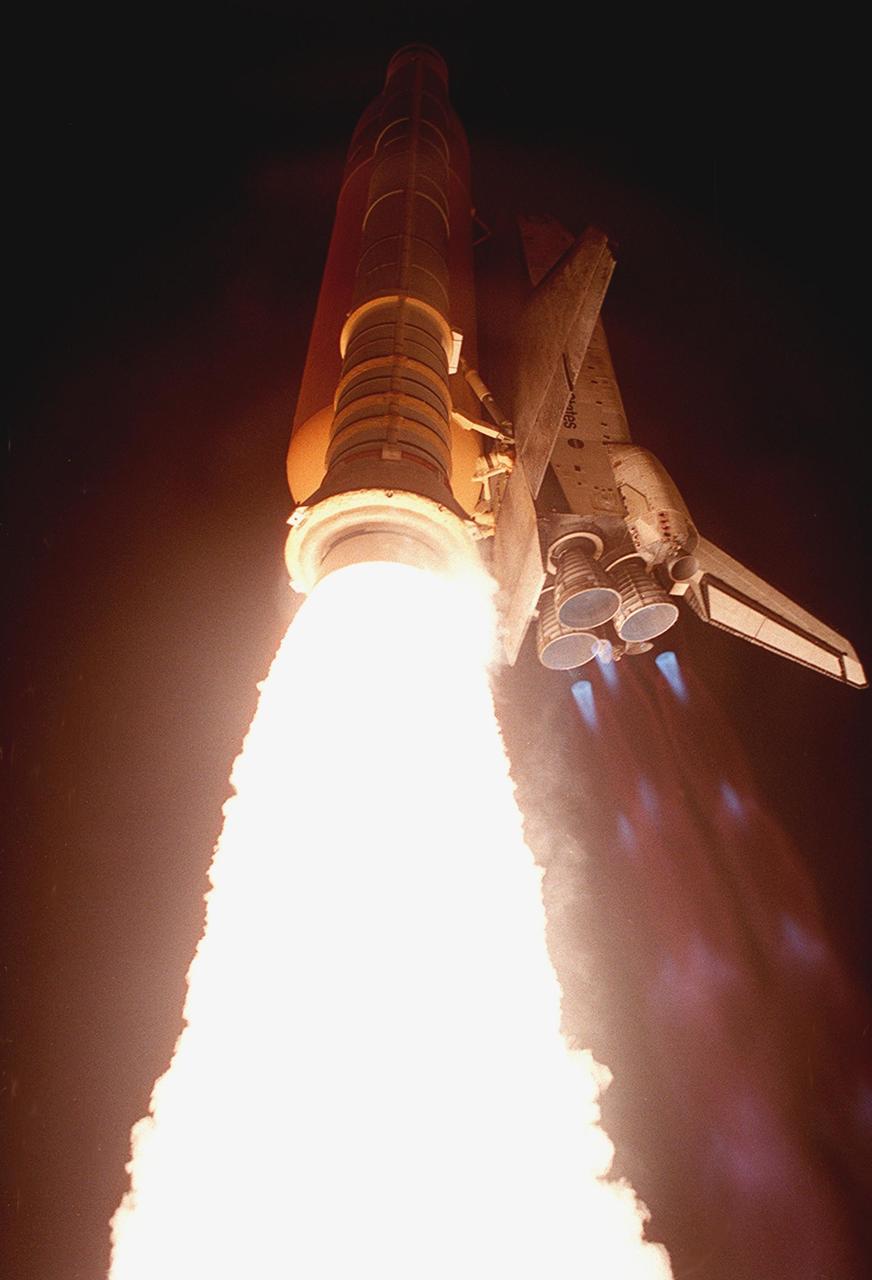

Like a roman candle, Space Shuttle Discovery roars into the clear night sky trailing brilliant exhaust from the solid rocket boosters (center) and blue mach diamonds from the main engine nozzles. Liftoff occurred at 7:50 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. On board are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. STS-103 is a Hubble Servicing Mission, with three planned space walks designed to install new equipment and replace old. The primary objective is to replace the gyroscopes that make up the three Rate Sensor Units. Extravehicular activities include installing a new computer, changing out one of the Fine Guidance Sensors, replacing a tape recorder with a new solid state recorder, and installing a voltage/temperature improvement kit, and begin repairing the insulation on the telescope's outer surface. After the 7-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 27, at about 5:24 p.m. EST. This is the 27th flight of Discovery and the 96th mission in the Space Shuttle Program. It is the third launch at Kennedy Space Center in 1999
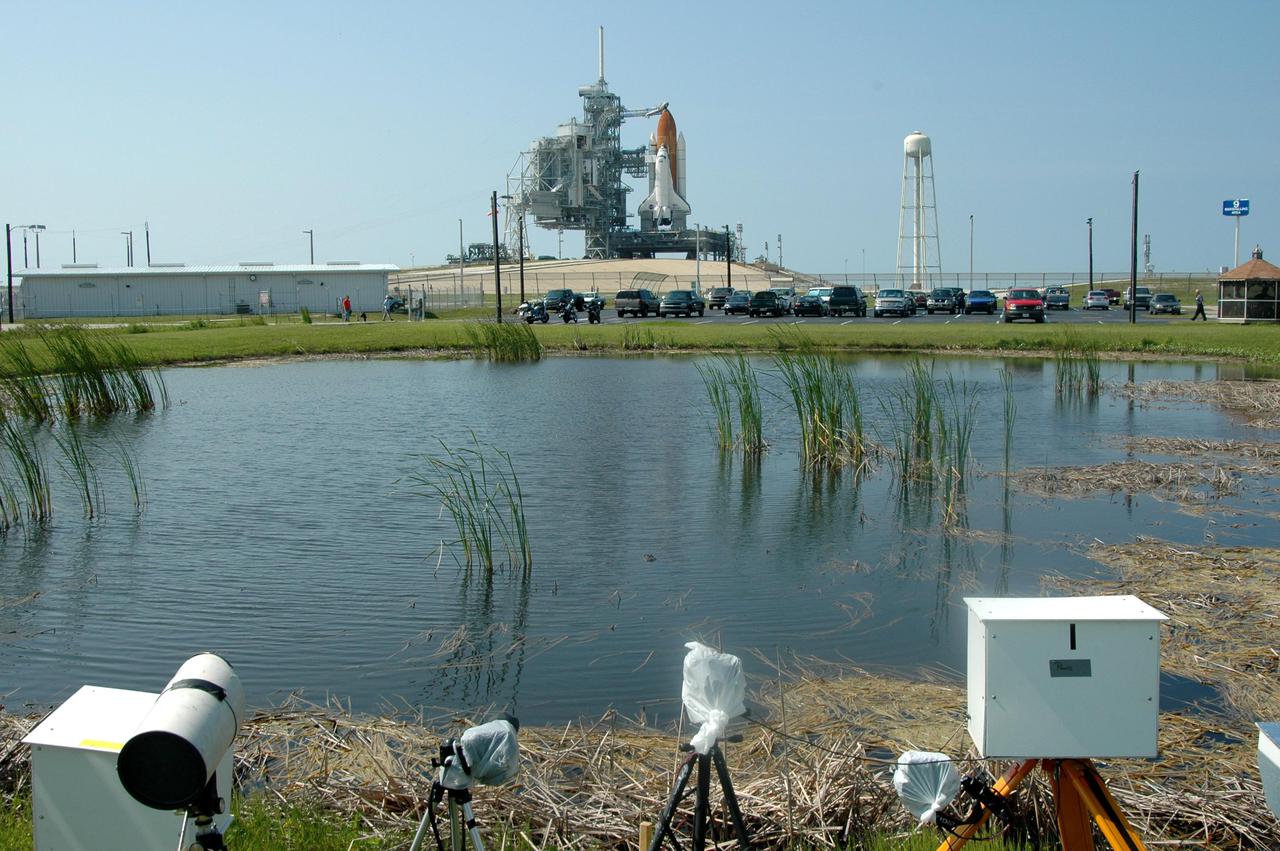

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Cameras at the edge of a pond have a pristine view to Launch Pad 39B at NASA Kennedy Space Center where the Space Shuttle Discovery waits for launch. On the right of the Shuttle is the 290-foot-tall water tower that holds 300,000 gallons of water, part of the sound suppression system during a launch. Discovery is scheduled to lift off on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114 at 10:39 a.m. EDT July 26 with a crew of seven. On the mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.
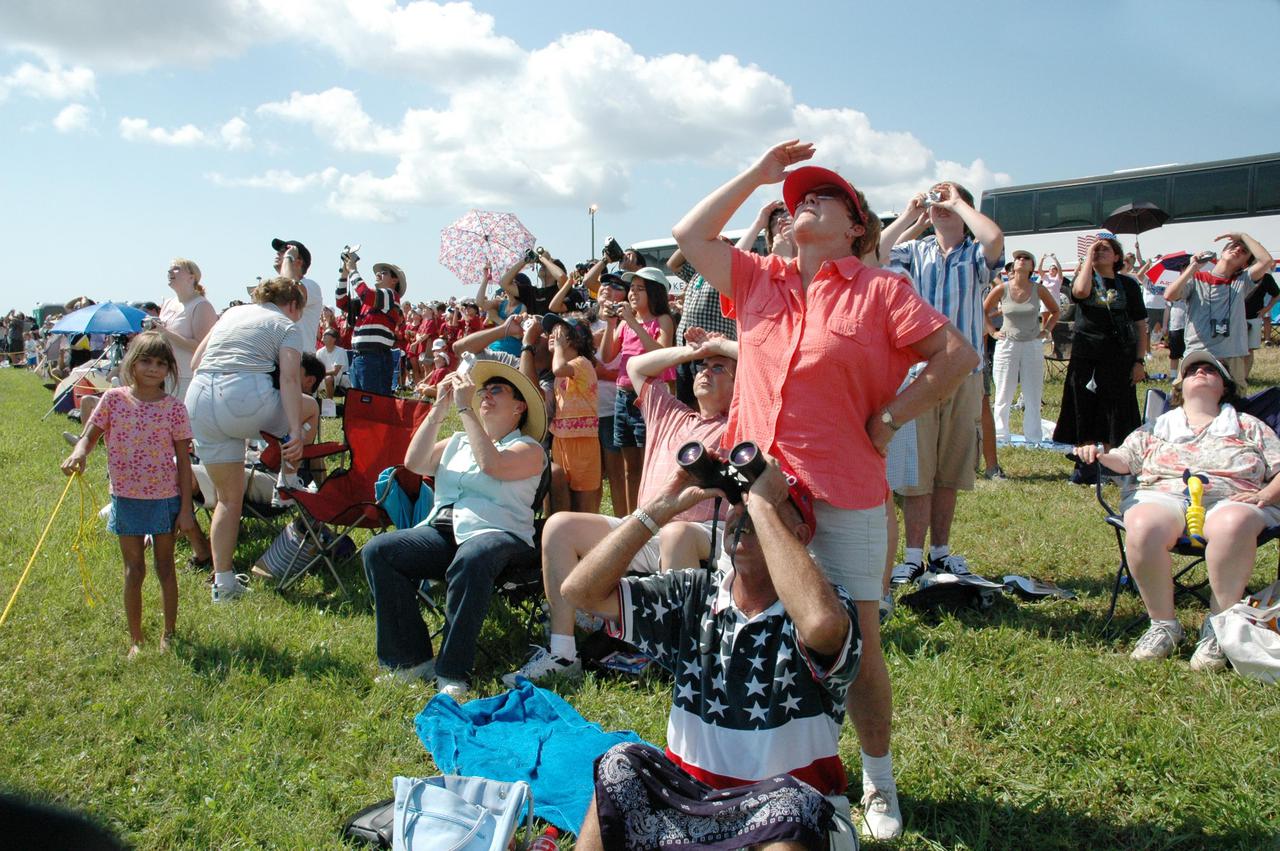

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Spectators fill the grounds near NASA Kennedy Space Center to witness the launch of Space Shuttle Discovery on Return to Flight mission STS-114. They were among thousands of spectators attending the historic return of the Space Shuttle to space. It is the 114th Space Shuttle flight and the 31st for Discovery. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Into a clear blue sky Space Shuttle Discovery lifts off at 10:39 a.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39B on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114. It is the 114th Space Shuttle flight and the 31st for Discovery. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.
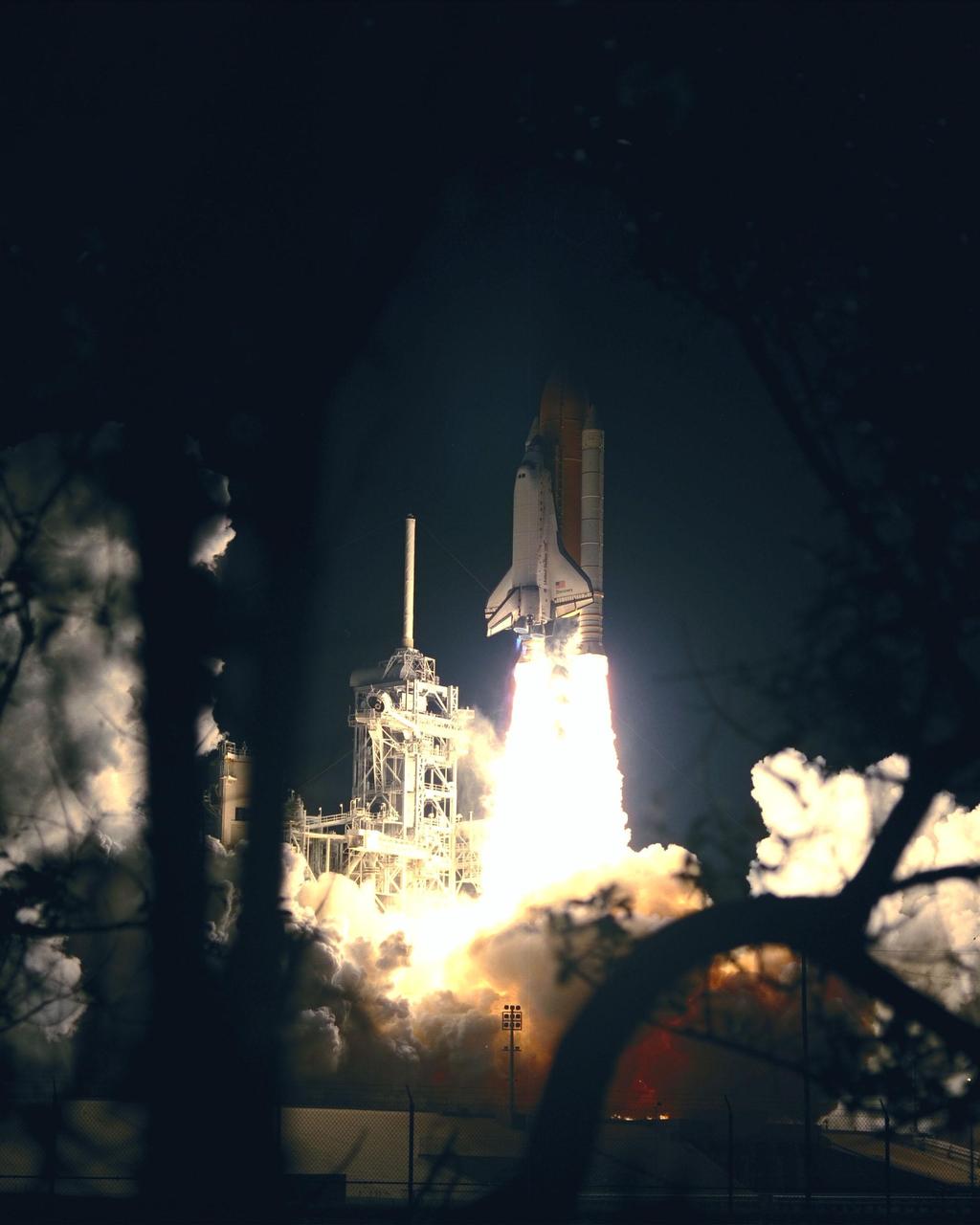

The successful liftoff of Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-103 illuminates the night sky. Liftoff occurred at 7:50 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. On board are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. STS-103 is a Hubble Servicing Mission, with three planned space walks designed to install new equipment and replace old. The primary objective is to replace the gyroscopes that make up the three Rate Sensor Units. Extravehicular activities include installing a new computer, changing out one of the Fine Guidance Sensors, replacing a tape recorder with a new solid state recorder, and installing a voltage/temperature improvement kit, and begin repairing the insulation on the telescope's outer surface. After the 7-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 27, at about 5:24 p.m. EST. This is the 27th flight of Discovery and the 96th mission in the Space Shuttle Program. It is the third launch at Kennedy Space Center in 1999
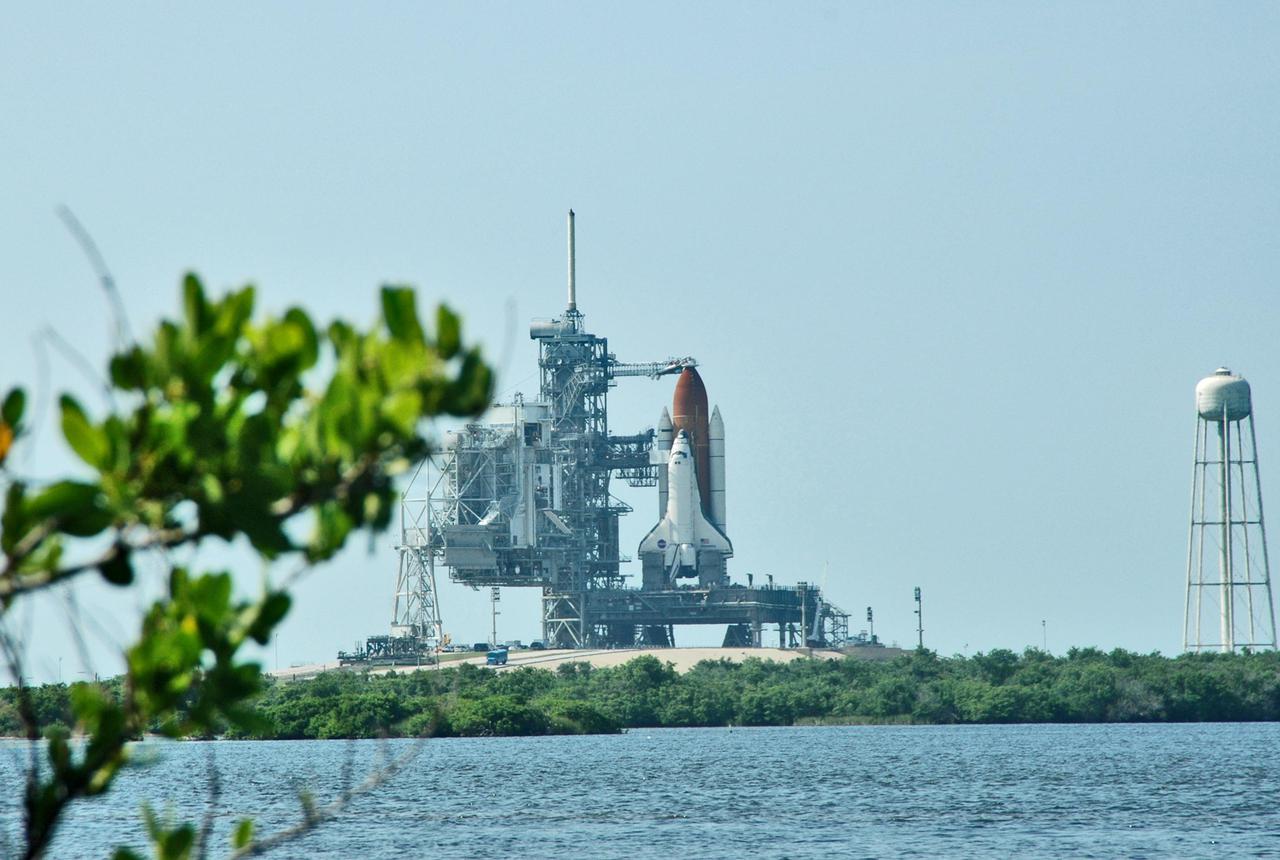

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Seen after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure, and framed by marsh greenery, a fully revealed Space Shuttle Discovery on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Pad 39B erupts on the horizon beyond the pond. Discovery is scheduled to lift off on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114 at 10:39 a.m. EDT July 26 with a crew of seven. On the mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.
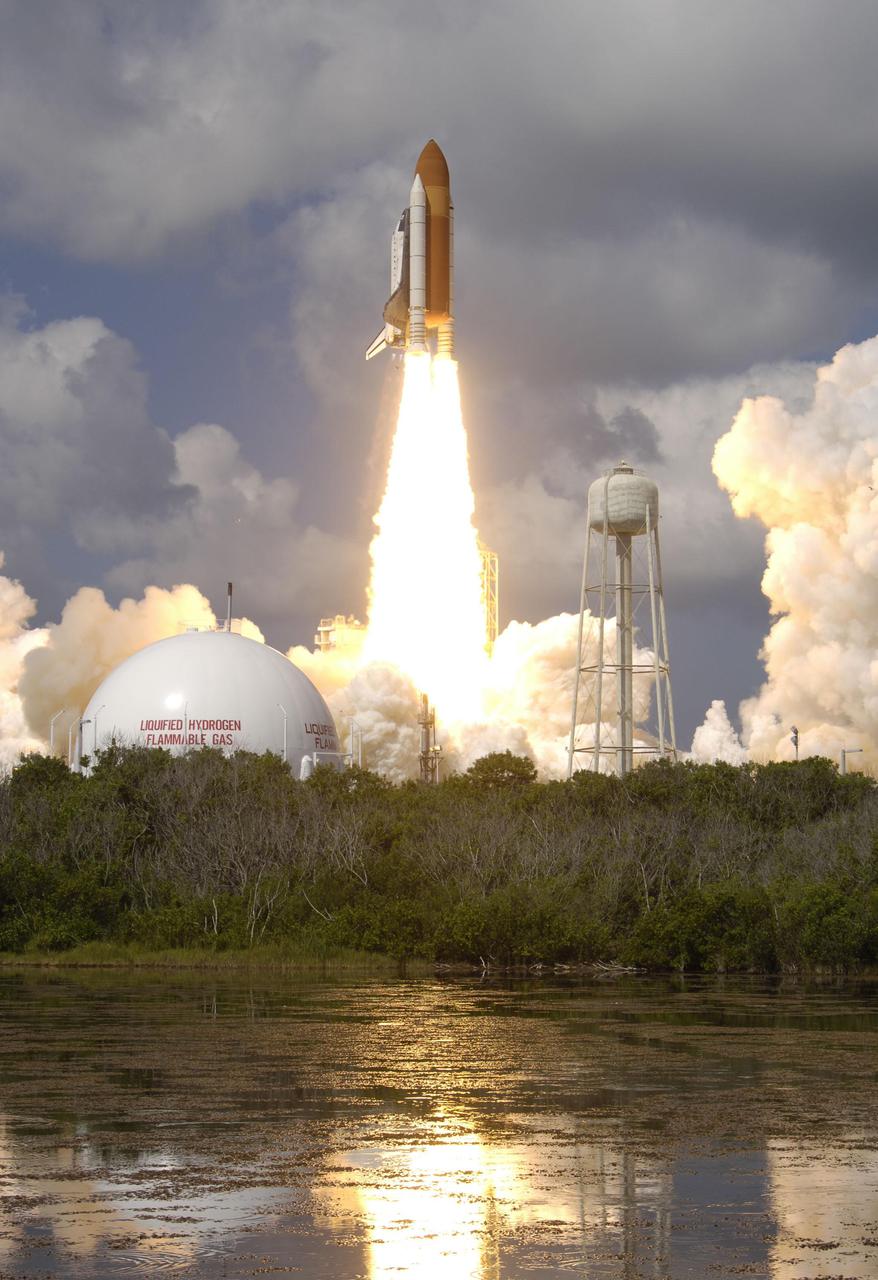

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Seeming to erupt from between the liquefied hydrogen gas tank on the left and 290-foot water tower on the right, Space Shuttle Discovery roars into the cloud-filled sky from Launch Pad 39B. Discovery is launching on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114. It is the 114th flight in the Space Shuttle Program and the 31st for Discovery. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure. (Photo Credit: Scott Andrews)
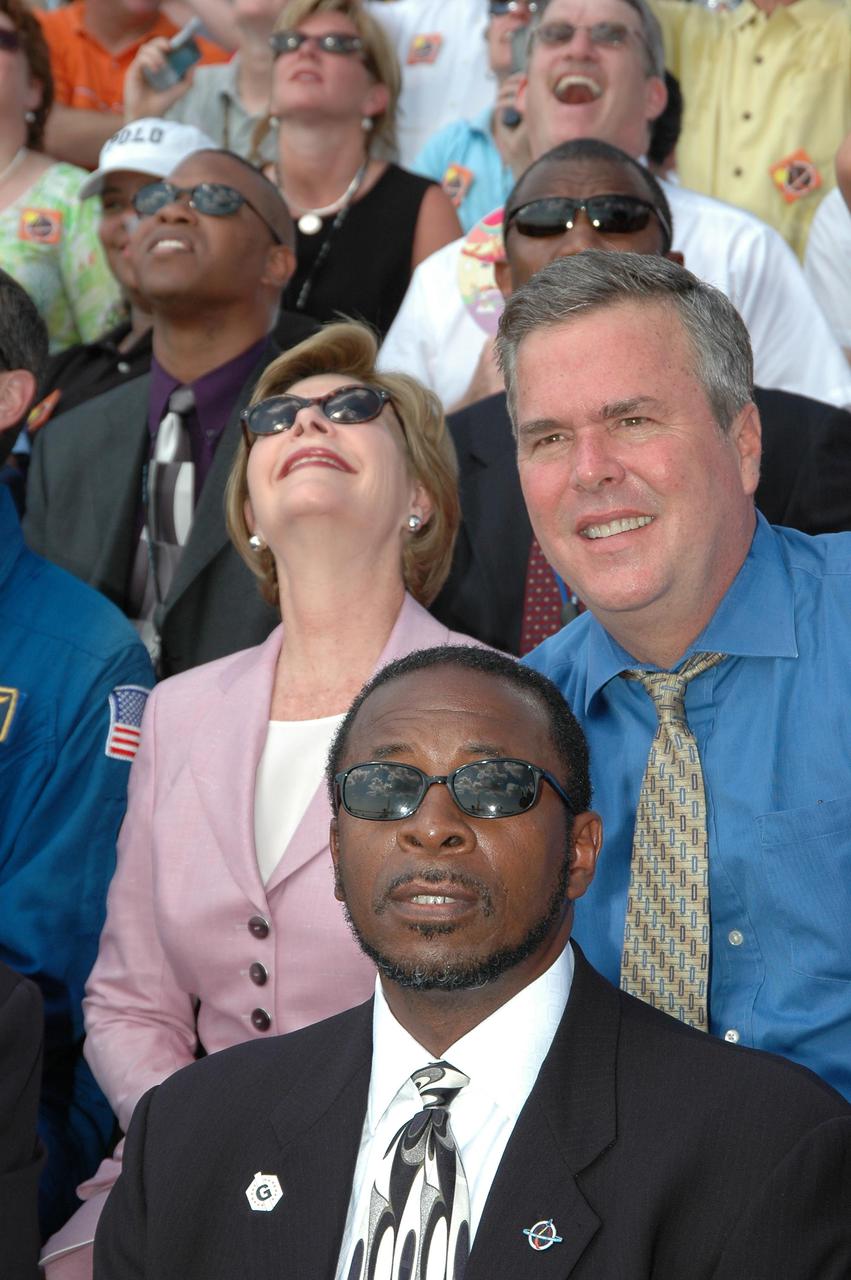

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the stands at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Banana Creek viewing site, First Lady Laura Bush follows the path of Space Shuttle Discovery as it successfully launches on Return to Flight mission STS-114 at 10:39 a.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39B. At right is Florida Gov. Jeb Bush. KSC Deputy Director Woodrow Whitlow Jr. is in front of the governor. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7.
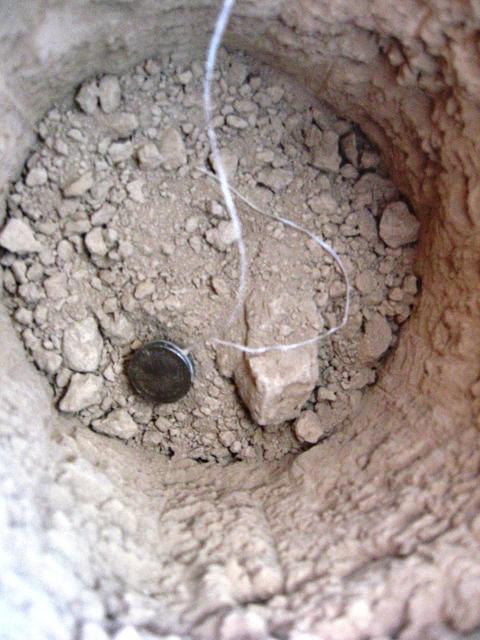

This is a Hygrochron sensor. Sensors were buried at different depths, to see how the temperature and moisture levels in the ground changed close to and farther from the surface. Special permission from the National Park Service is needed to dig at Racetrack Playa. Photo credit: NASA/GSFC/Maggie McAdam To read a feature story on the Racetrack Playa go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/earth/features/roving-rocks.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/earth/features/roving-rocks.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a><b></b></b>
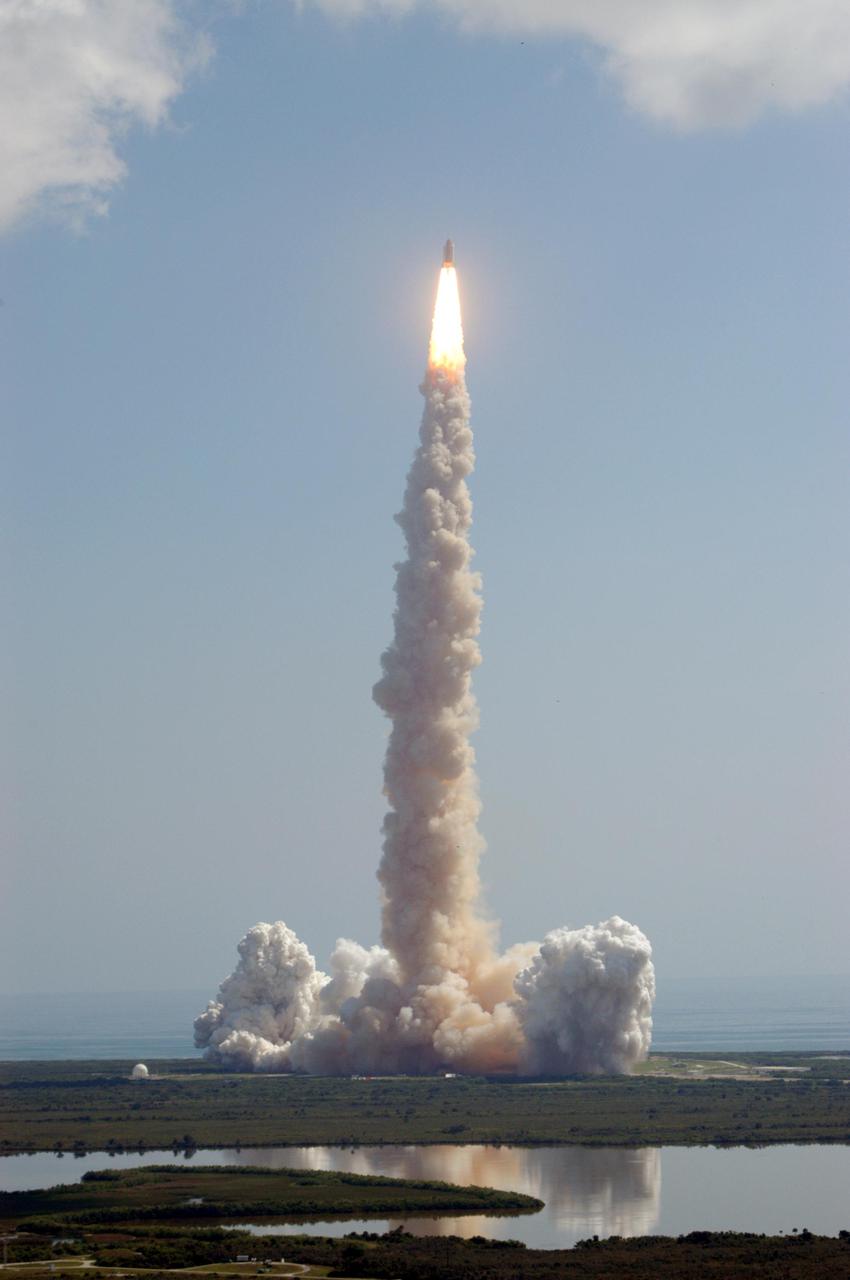

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Looking like a roman candle rising off Launch Pad 39B at NASA Kennedy Space Center, Space Shuttle Discovery roars into the path of a stray cloud after liftoff at 10:39 a.m. EDT on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114. It is the 114th Space Shuttle flight and the 31st for Discovery. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.

(Nikon camera D1 test)Amid billows of smoke and steam, Space Shuttle Discovery lights up the clear night sky as it lifts off on time at 7:50:00.069 EST from Launch Pad 39B on mission STS-103. On board are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. STS-103 is a Hubble Servicing Mission, with three planned space walks designed to install new equipment and replace old. The primary objective is to replace the gyroscopes that make up the three Rate Sensor Units. Extravehicular activities include installing a new computer, changing out one of the Fine Guidance Sensors, replacing a tape recorder with a new solid state recorder, and installing a voltage/temperature improvement kit, and begin repairing the insulation on the telescope's outer surface. After the 7-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 27, at about 5:24 p.m. EST. This is the 27th flight of Discovery and the 96th mission in the Space Shuttle Program. It is the third launch at Kennedy Space Center in 1999

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A busload of children eagerly wait on the roadside at NASA Kennedy Space Center for the launch of Space Shuttle Discovery on Return to Flight mission STS-114. They were among thousands of spectators attending the historic return of the Space Shuttle to space. It is the 114th Space Shuttle flight and the 31st for Discovery. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.
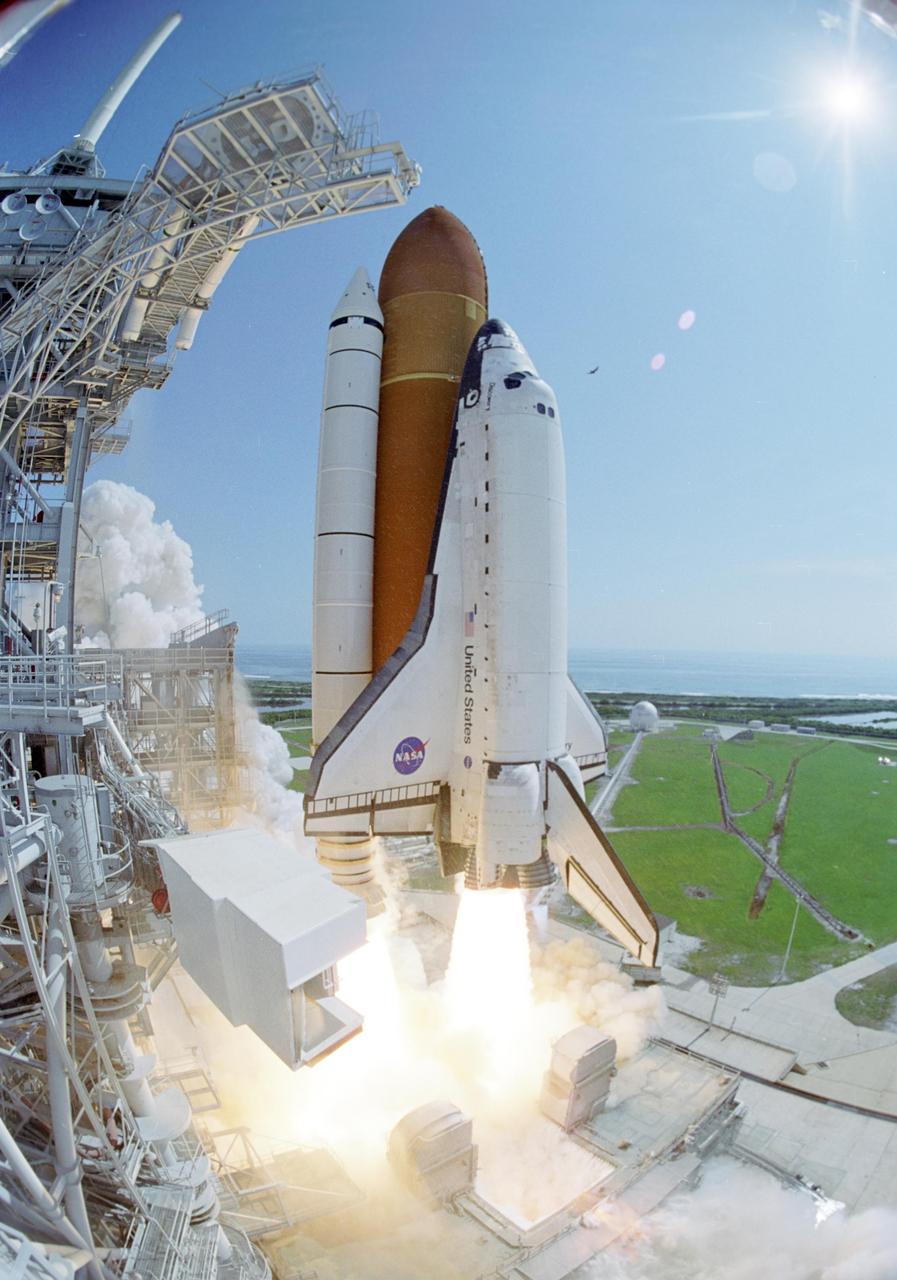

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A fish-eye view shows Space Shuttle Discovery moments after liftoff from Launch Pad 39B on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114. At left is the Fixed Service Structure with the White Room appearing to be suspended in mid-air. The White Room provides the astronauts access into the orbiter. The liftoff occurred at 10:39 a.m. EDT. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7.
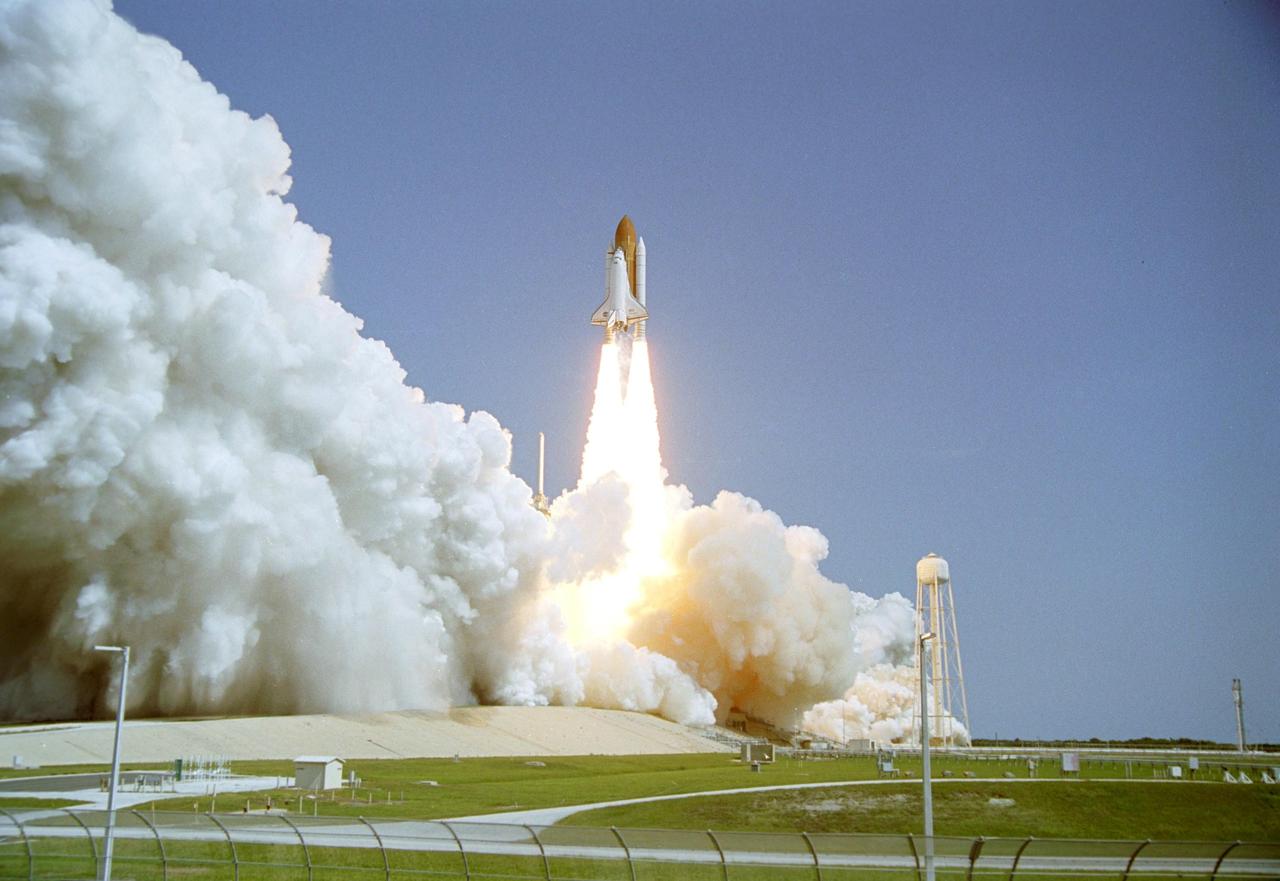

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - As billows of smoke and steam roll away, Space Shuttle Discovery leaps from Launch Pad 39B on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114. Liftoff occurred at 10:39 a.m. EDT. At right is the 290-foot water tower that holds the 300,000 gallons of water that flood the pad for sound suppression. This is the 114th Space Shuttle flight and the 31st for Discovery. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.
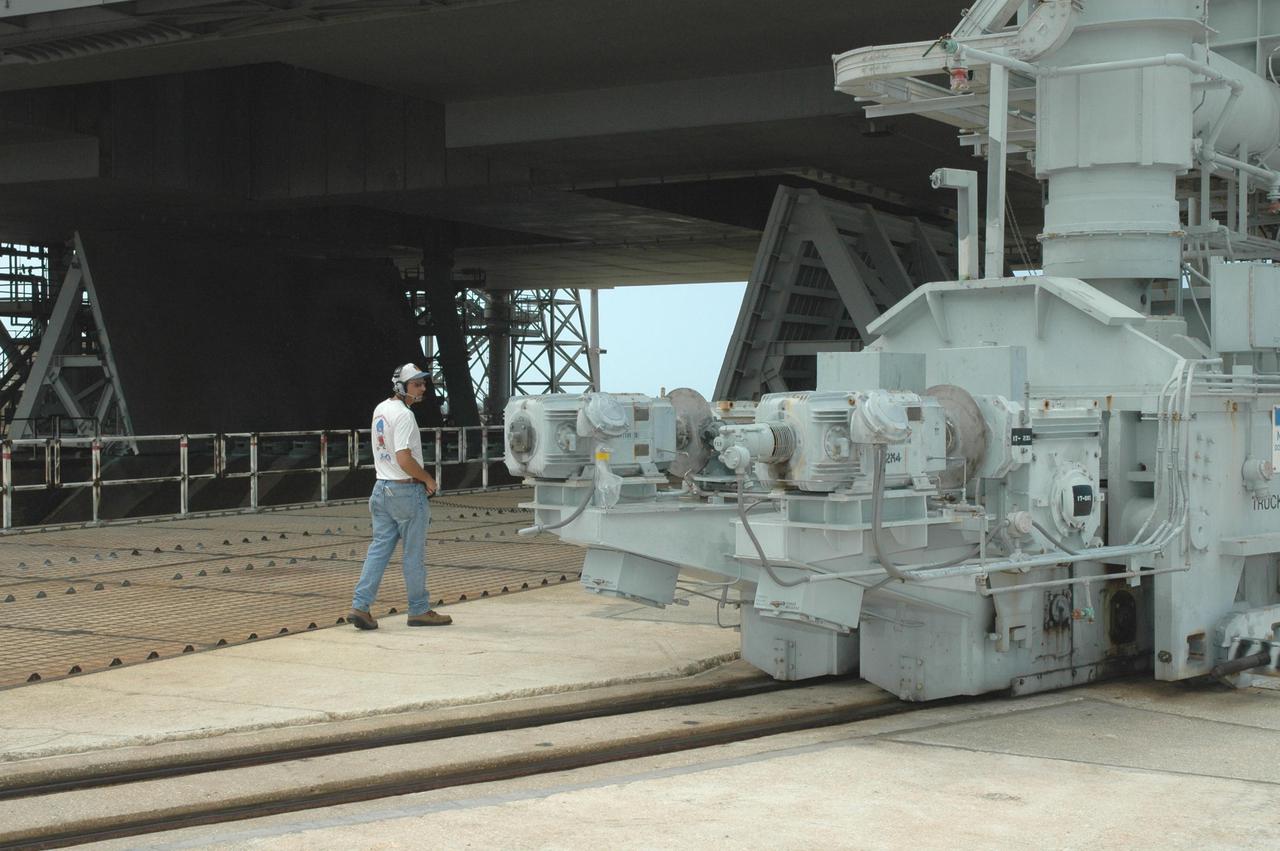

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A worker on Launch Pad 39B at NASA Kennedy Space Center walks alongside the track of the Rotating Service Structure as it begins rolling back from its position around Space Shuttle Discovery. Rollback of the RSS is a major preflight milestone, typically occurring during the T-11-hour hold on L-1 (the day before launch). Discovery is scheduled to lift off on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114 at 10:39 a.m. EDT July 26 with a crew of seven. On the mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.
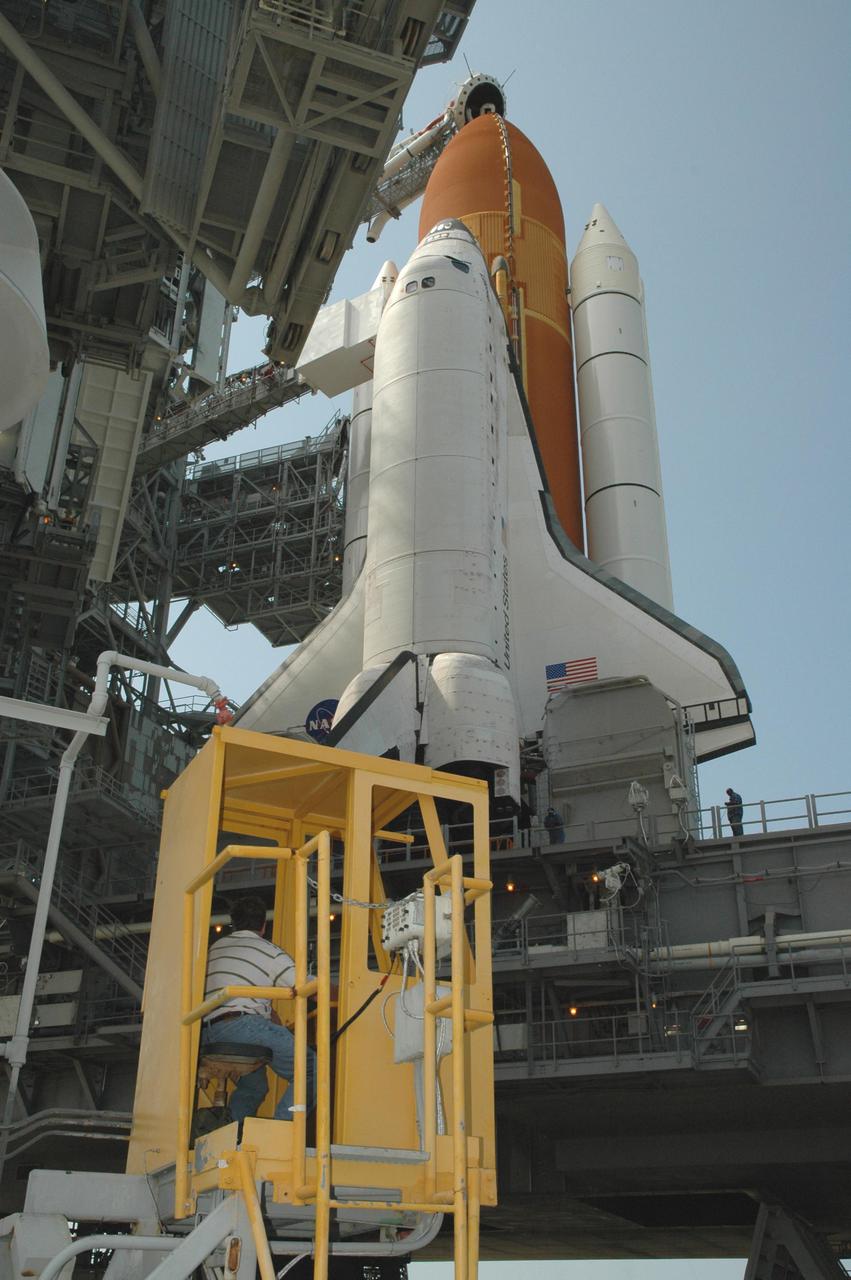

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A worker on Launch Pad 39B at NASA Kennedy Space Center sits in the control cab of the Rotating Service Structure as it begins rolling back from its position around Space Shuttle Discovery. Rollback of the RSS is a major preflight milestone, typically occurring during the T-11-hour hold on L-1 (the day before launch). Discovery is scheduled to lift off on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114 at 10:39 a.m. EDT July 26 with a crew of seven. On the mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.
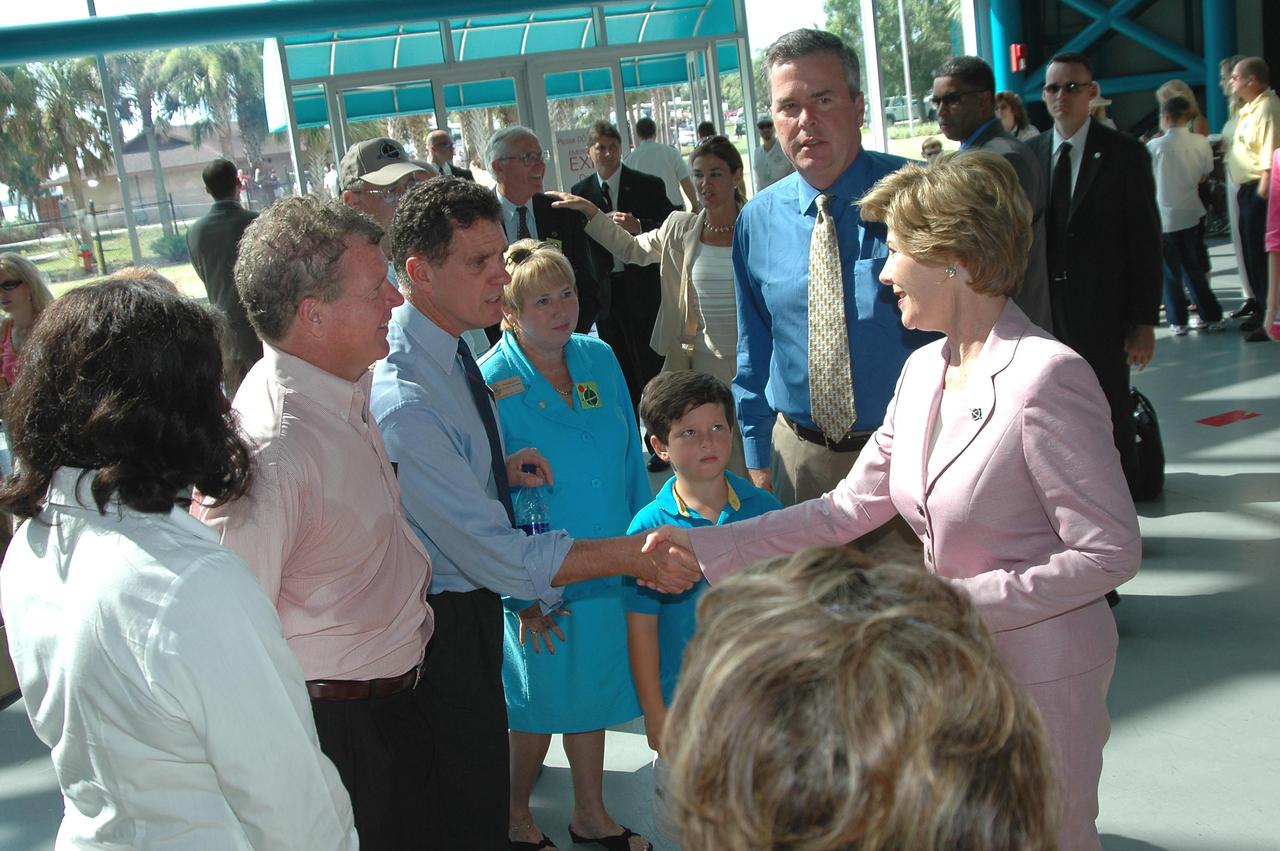

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Apollo_Saturn V Center, First Lady Laura Bush (right) greets Florida Congressman Dave Weldon (shaking hands) and Congressman Tom Feeney. They are attending the historic launch of Space Shuttle Discovery on Return to Flight mission STS-114, scheduled to lift off at 10:39 a.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39B with a crew of seven. Mrs. Bush is only the third First Lady to witness a Space Shuttle launch at KSC. Behind Mrs. Bush is Florida Gov. Jeb Bush. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7.
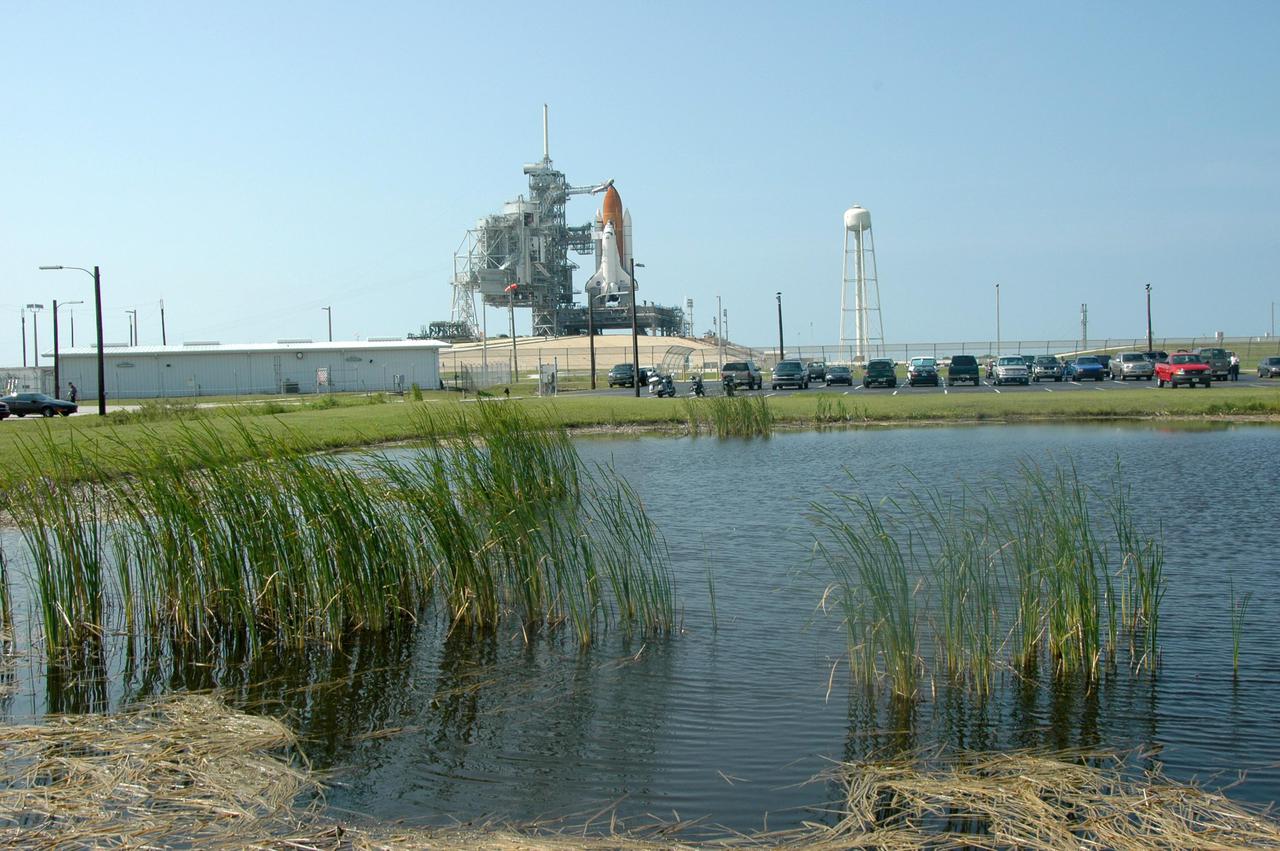

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the edge of a pond across from Launch Pad 39B, only long grasses stand between the camera and Space Shuttle Discovery as it waits for launch. Discovery is scheduled to lift off on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114 at 10:39 a.m. EDT July 26 with a crew of seven. On the mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure.
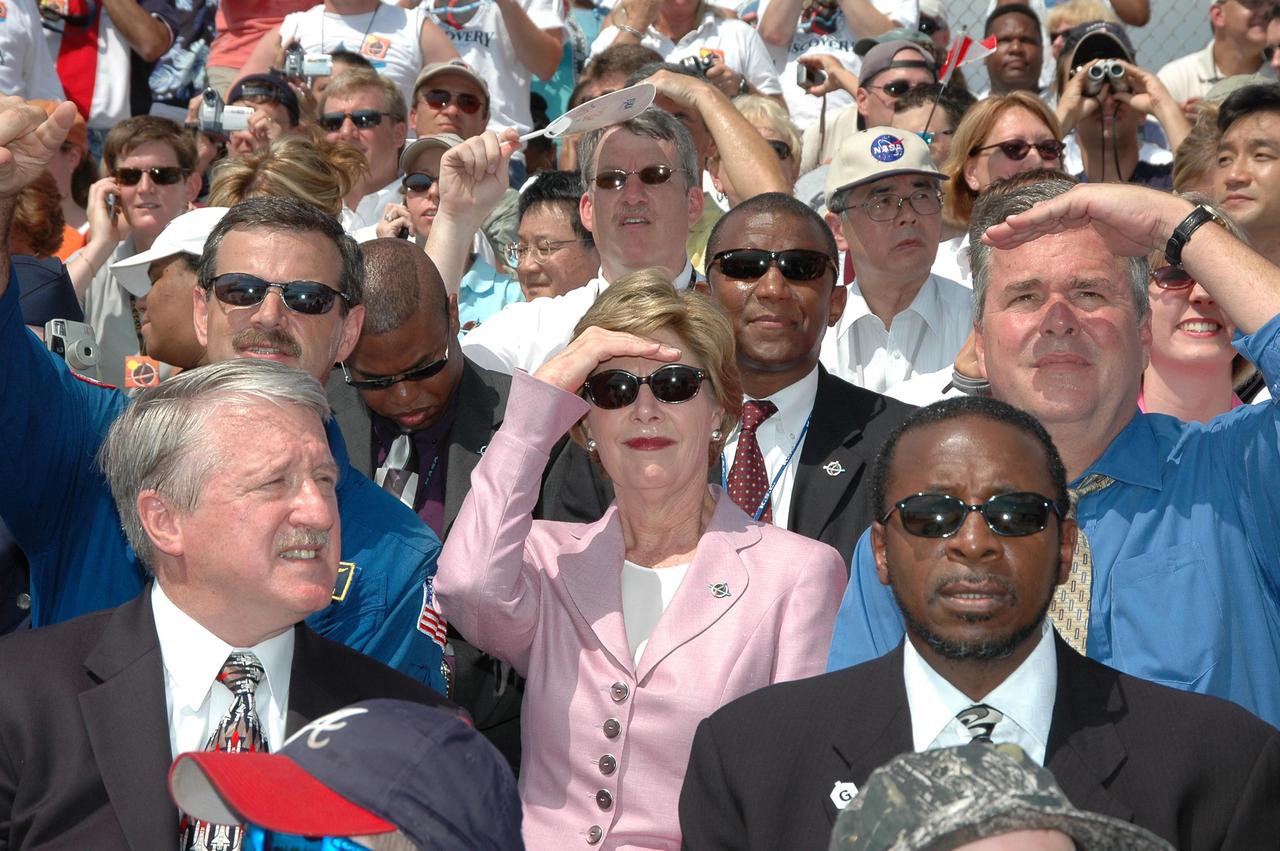

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the stands at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Banana Creek viewing site, First Lady Laura Bush (center) watches Launch Pad 39B for the liftoff of Space Shuttle Discovery on Return to Flight mission STS-114, scheduled to lift off at 10:39 a.m. EDT. She is flanked by astronaut Scott Altmann at left and Florida Gov. Jeb Bush at right. In front of her are Michael O’Brien (left), assistant administrator for External Relations, and Woodrow Whitlow Jr. (right), KSC deputy director. Mrs. Bush is only the third First Lady to witness a Space Shuttle launch at KSC. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7.