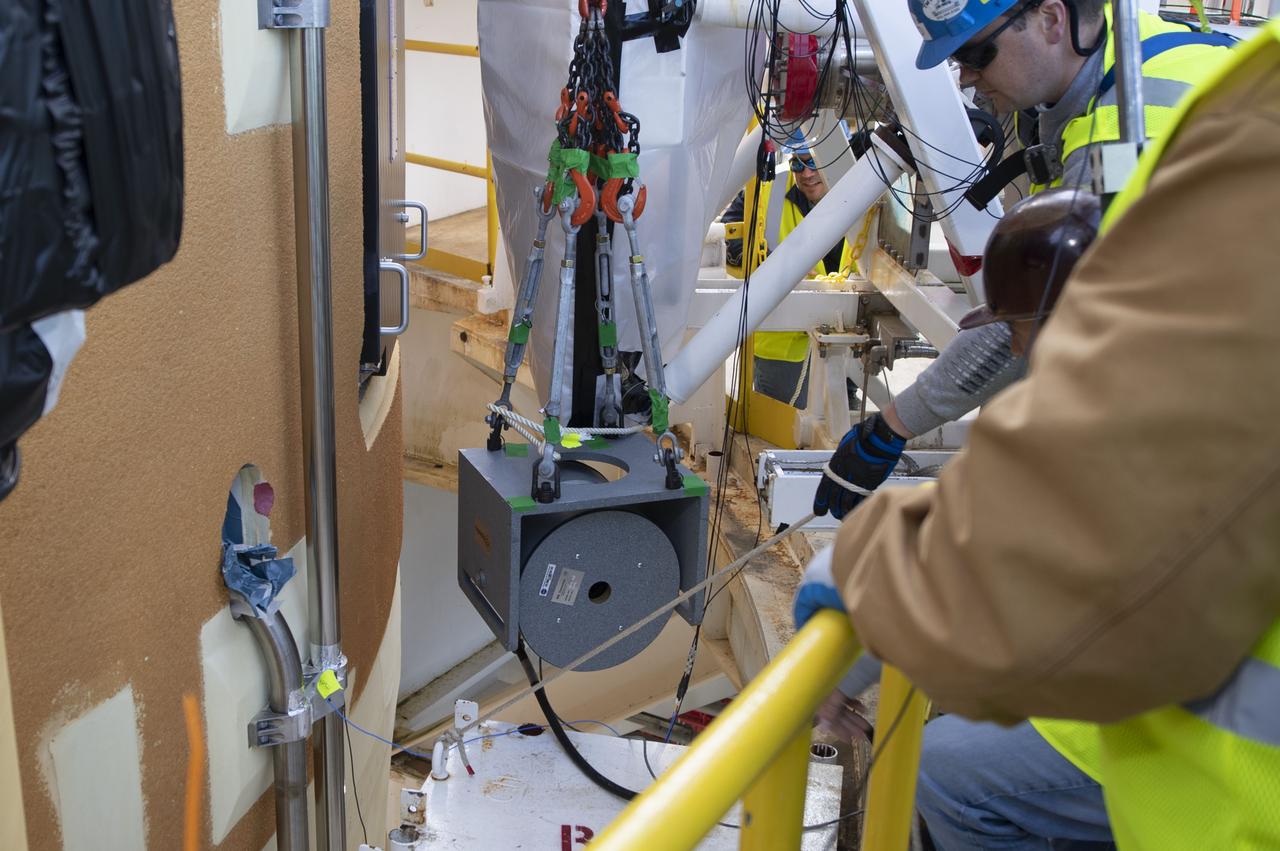

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
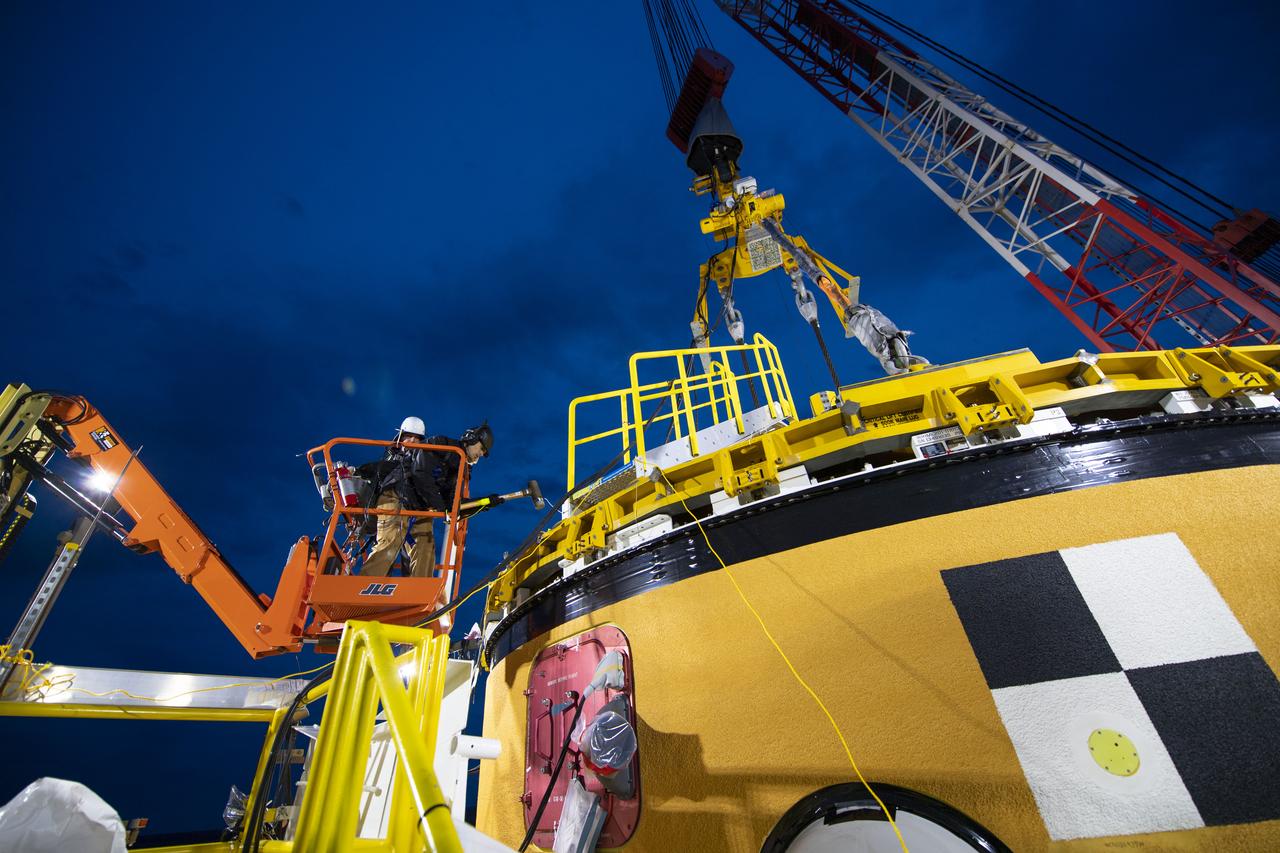

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
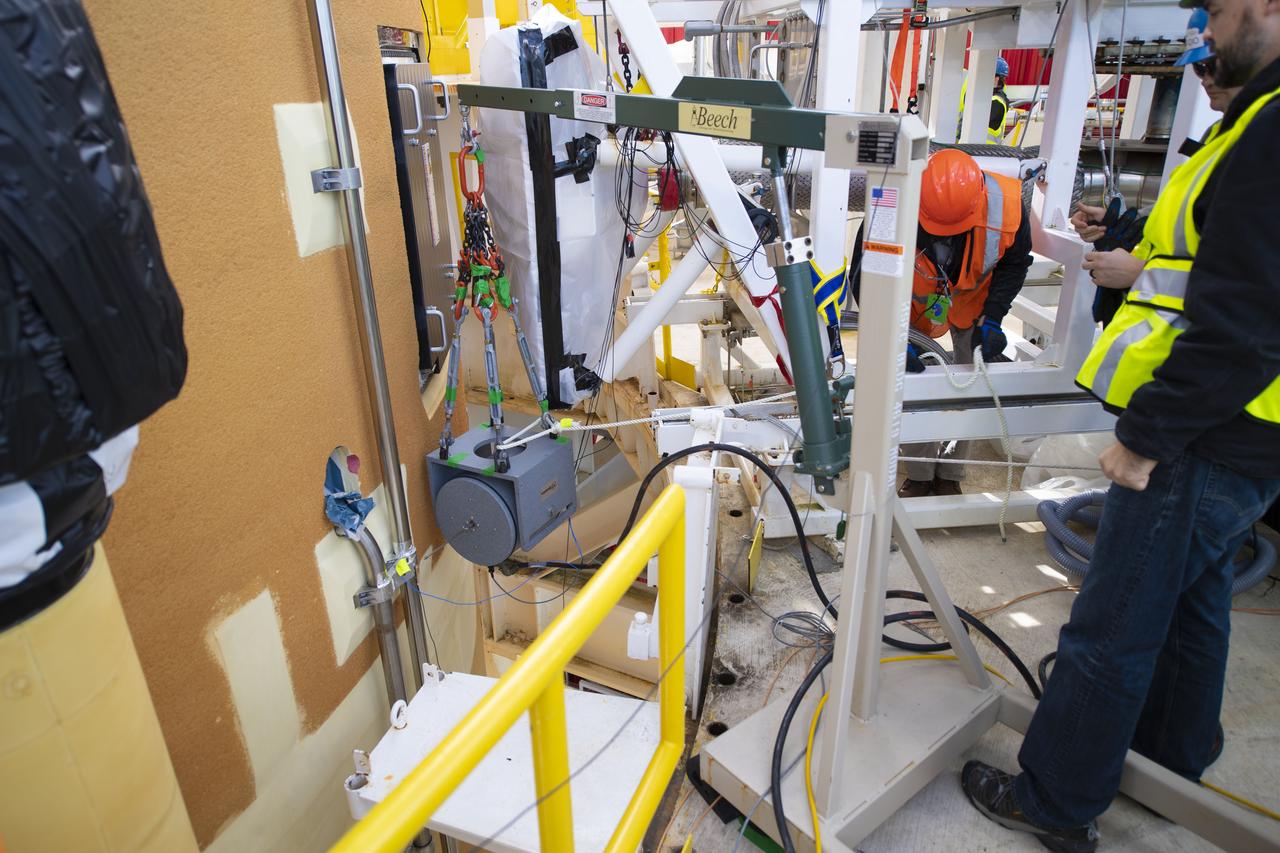

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
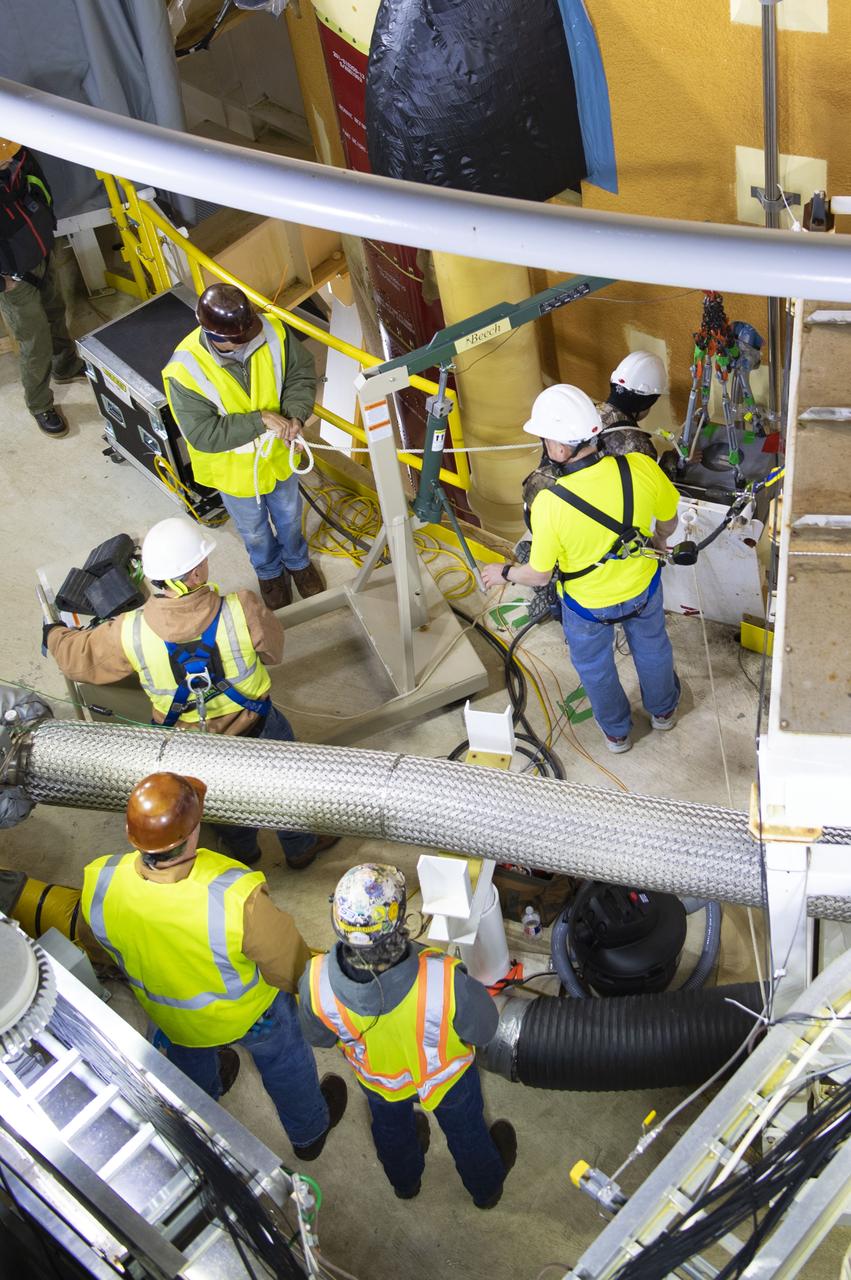

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
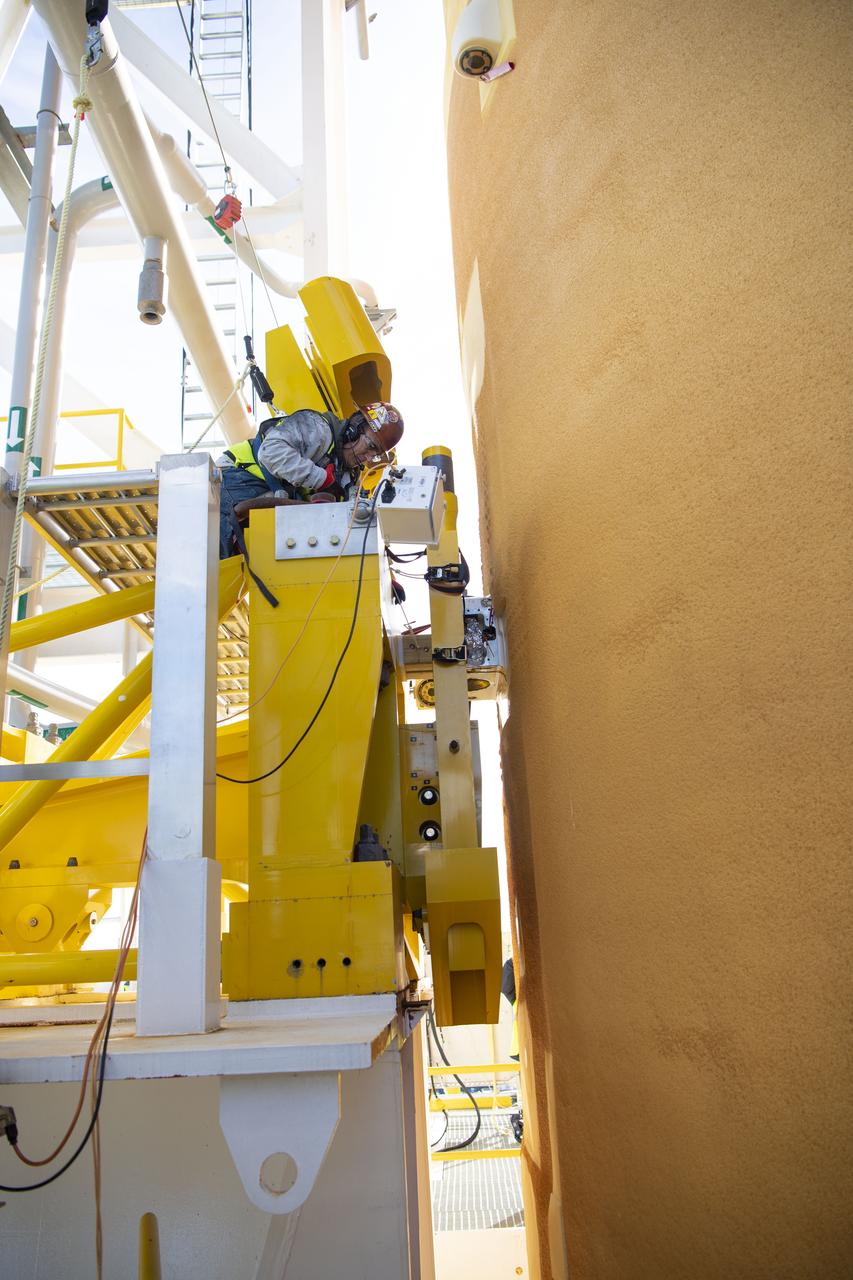

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
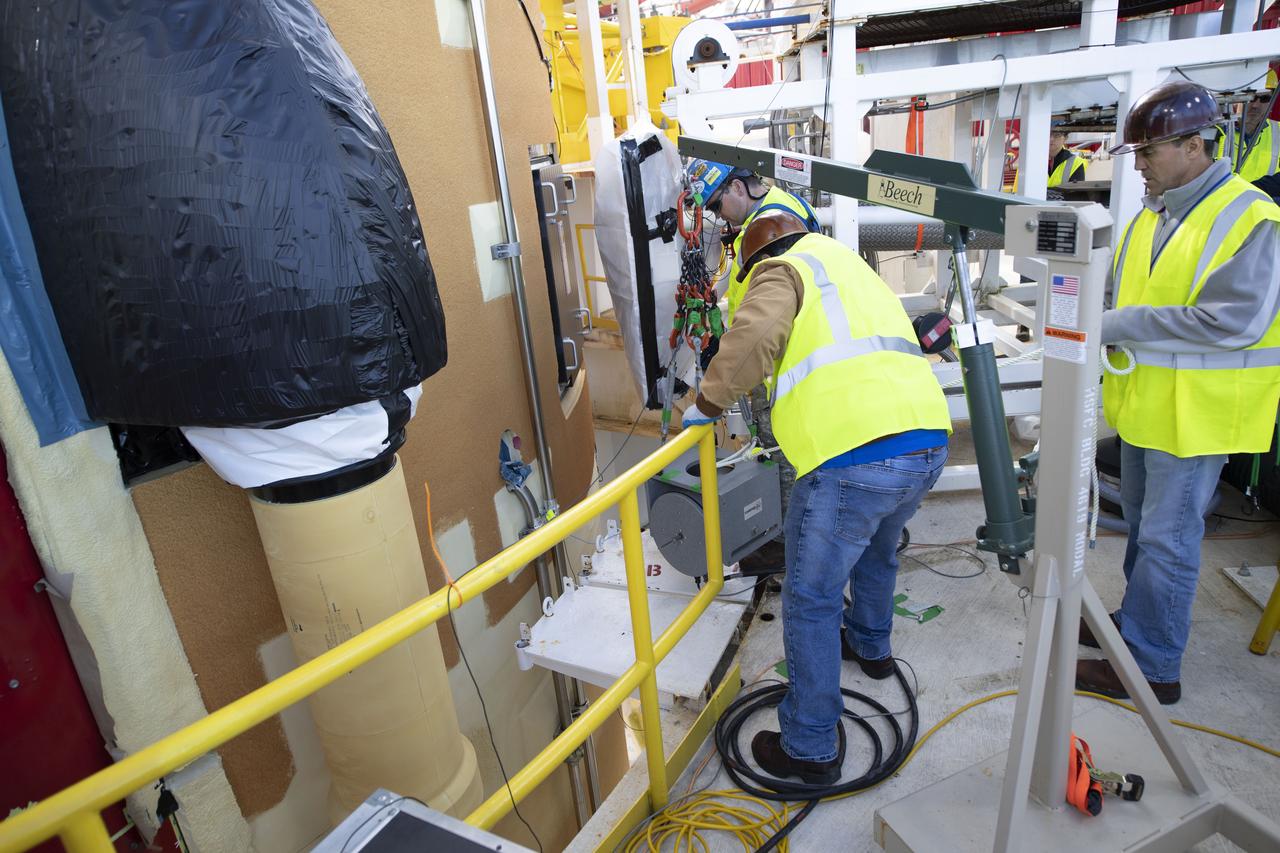

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
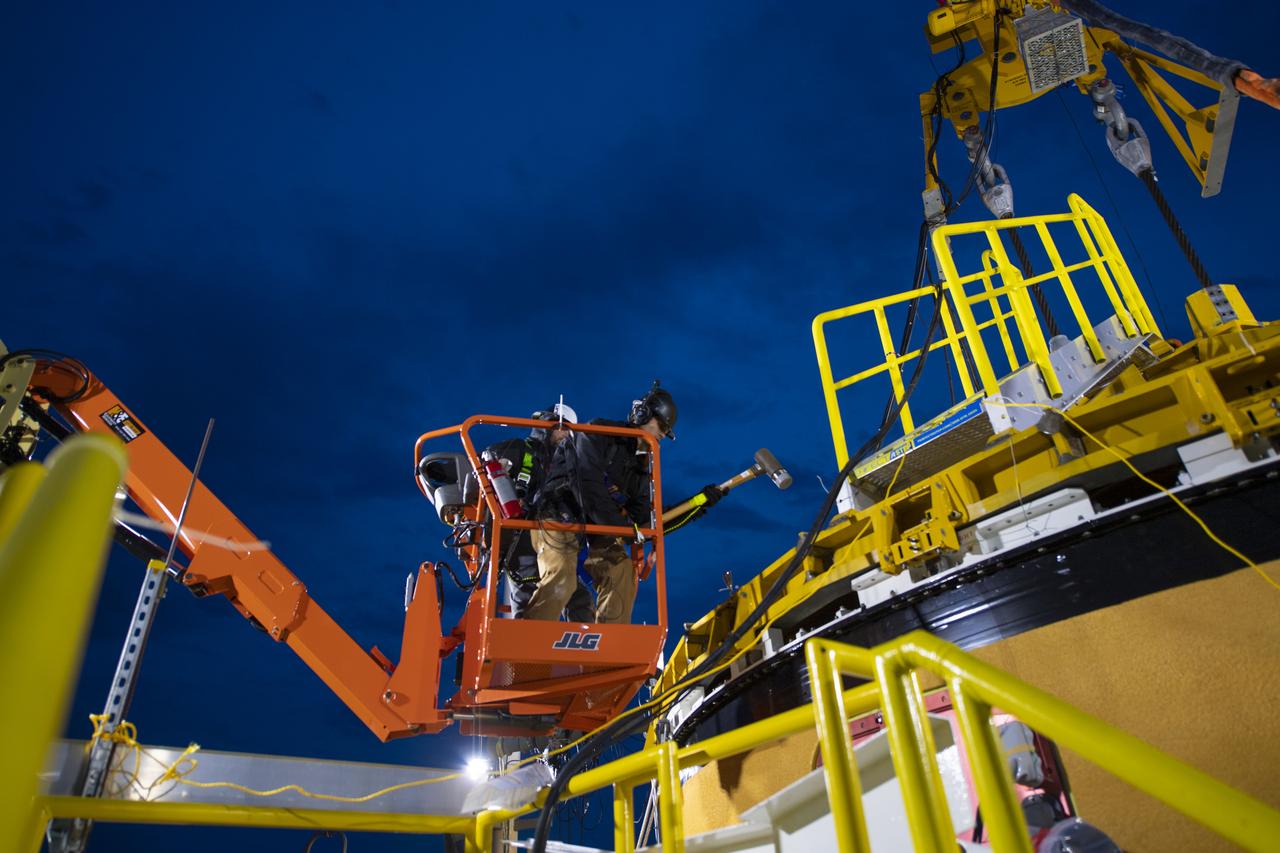

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
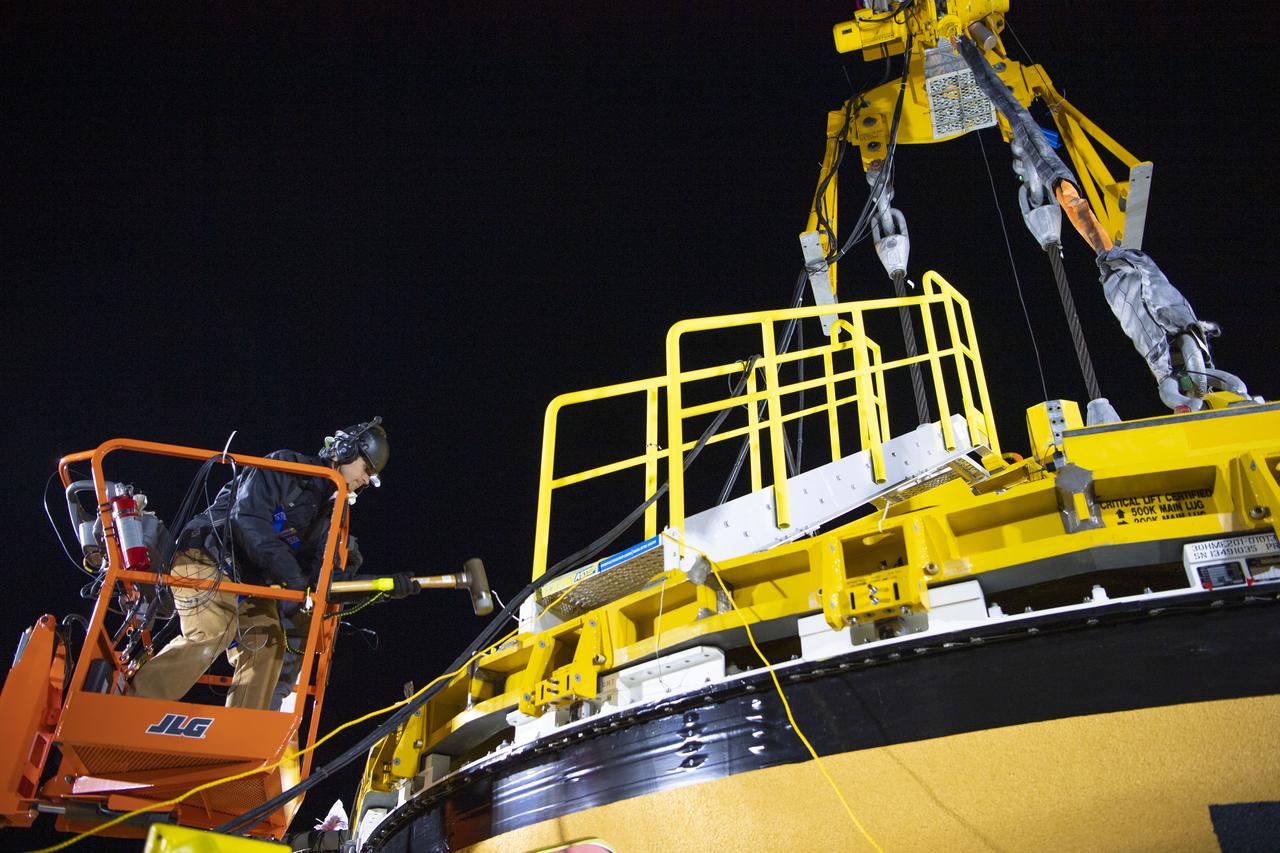

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
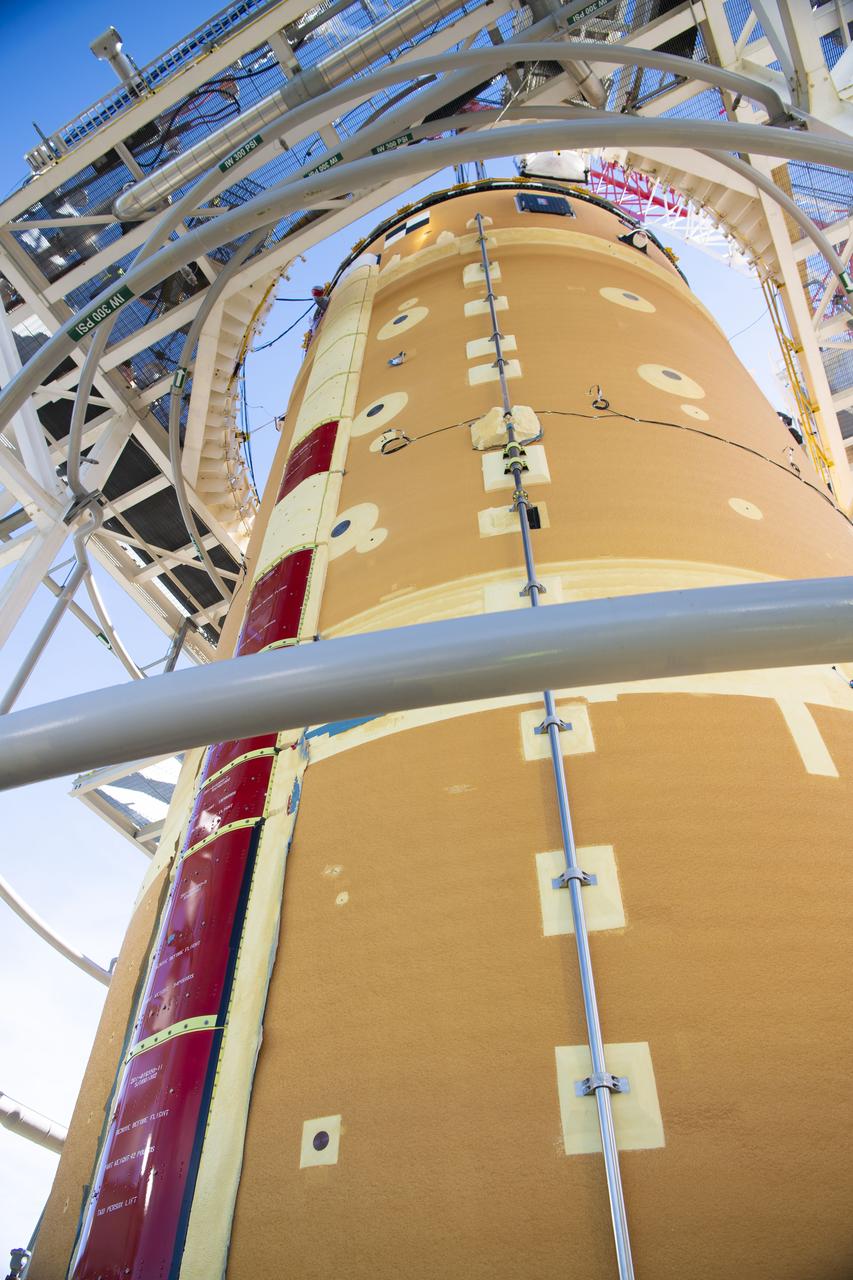

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
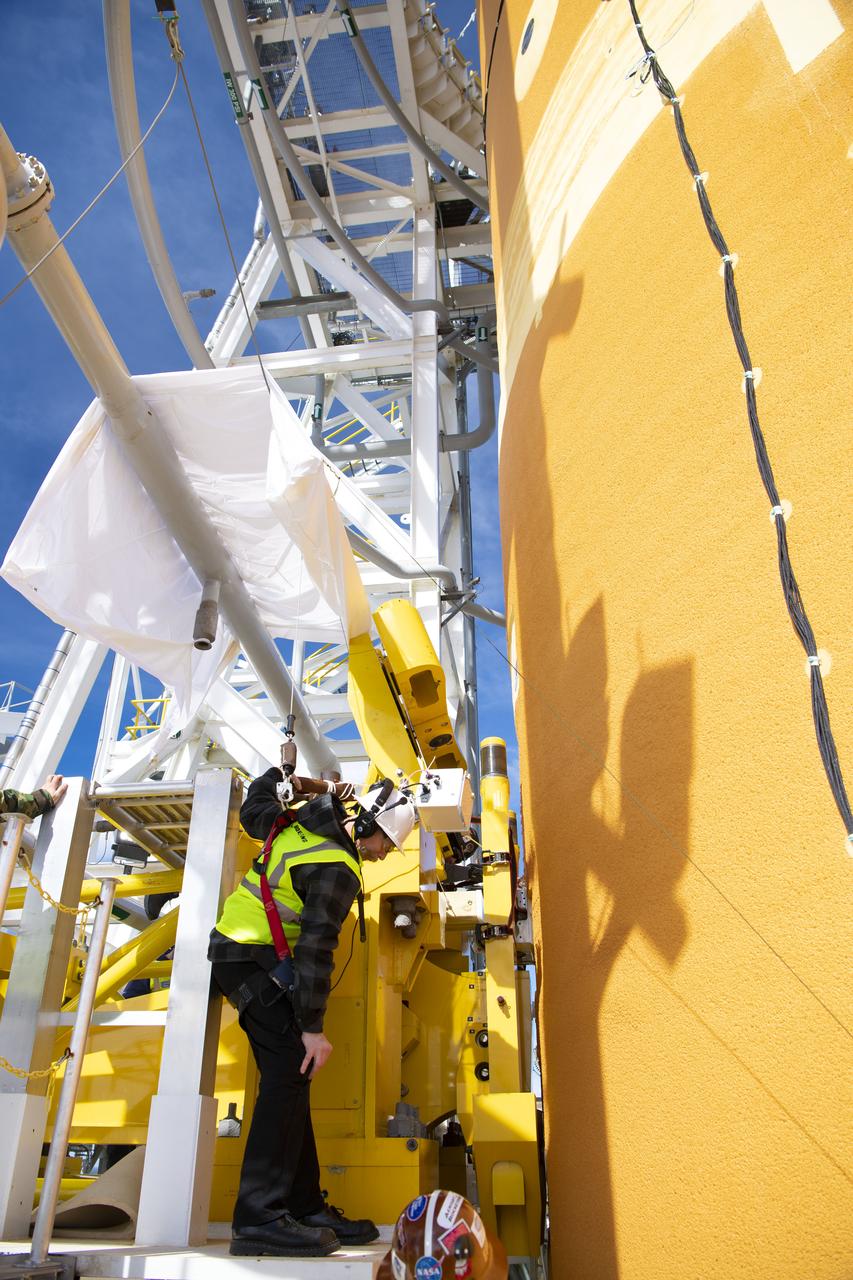

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
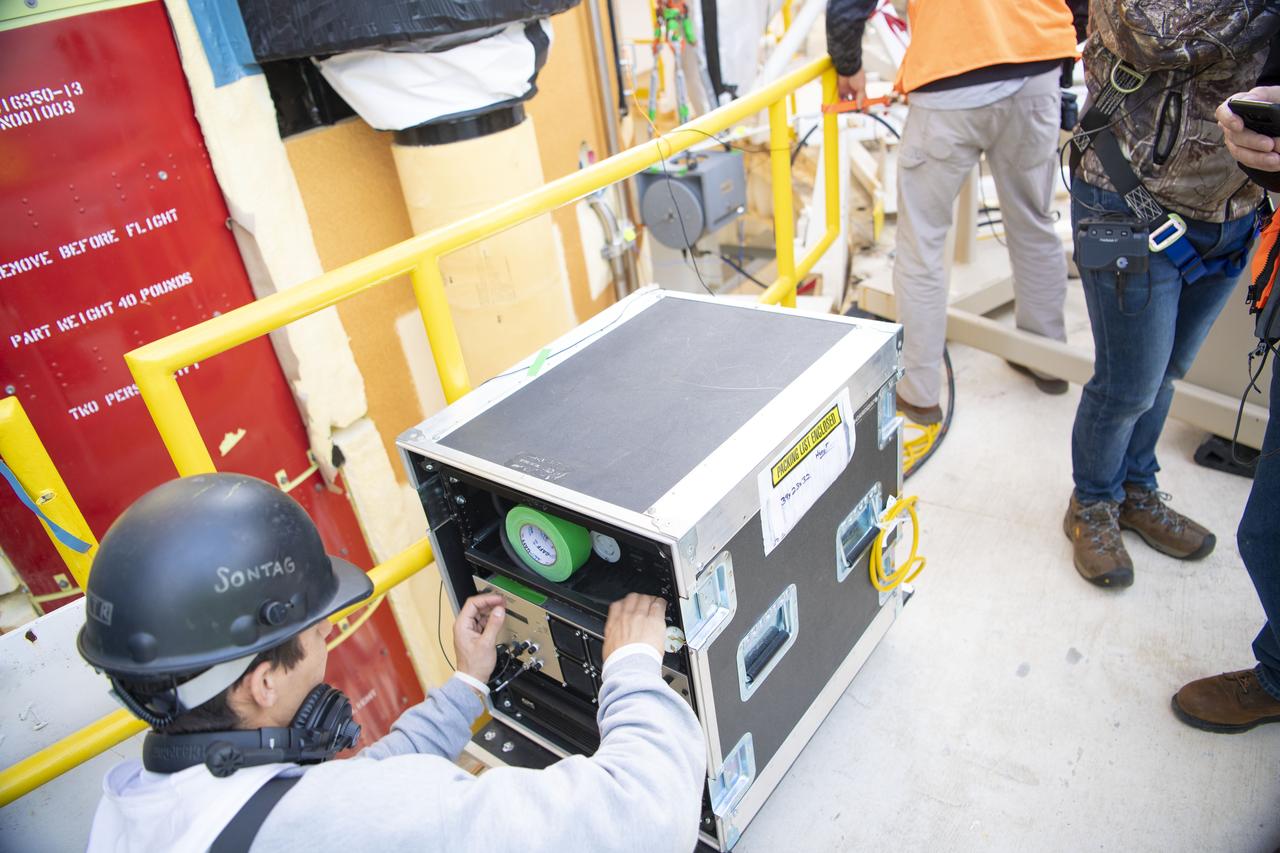

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
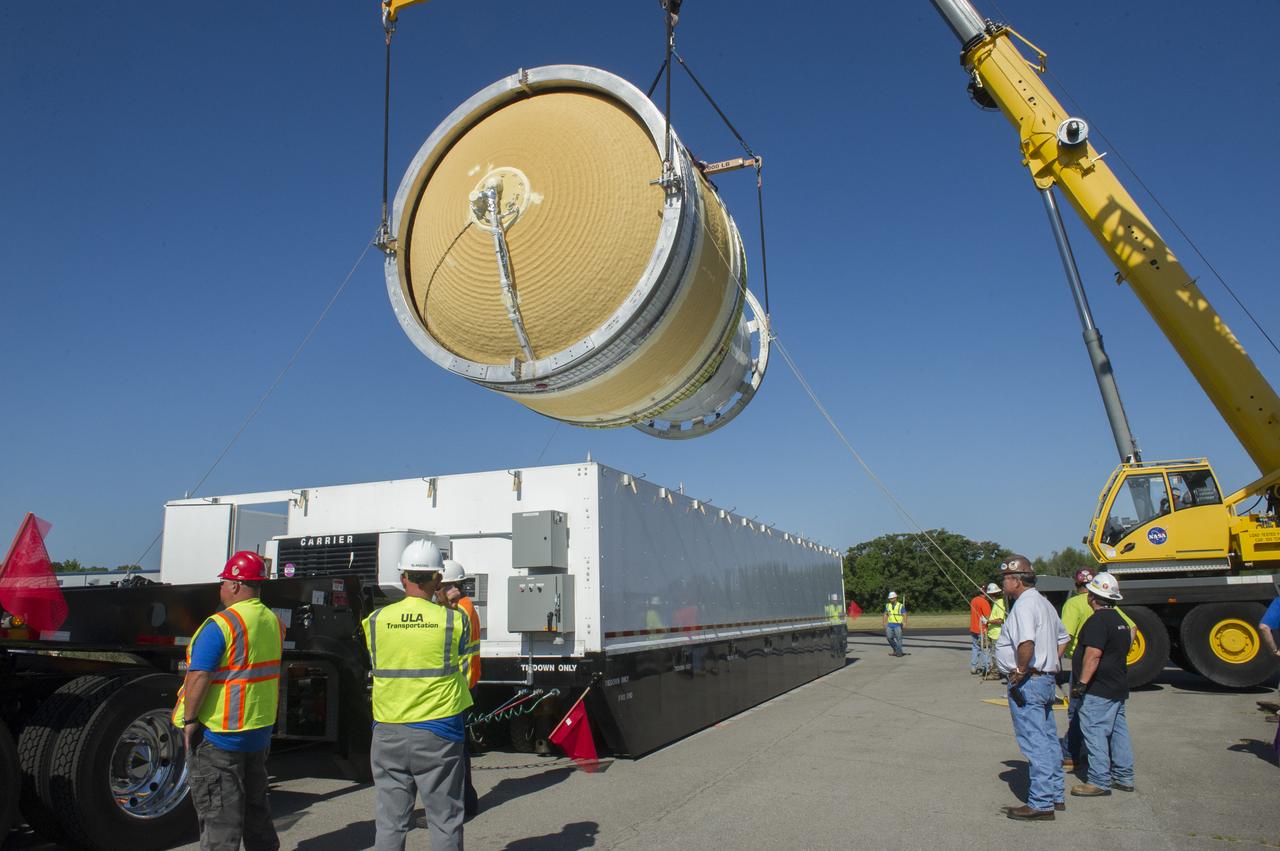

TWO CRANES LIFT THE APPROXIMATELY 8,000-POUND INTERIM CRYOGENIC PROPULSION STAGE TEST ARTICLE OUT OF ITS CRATE AT MARSHALL.
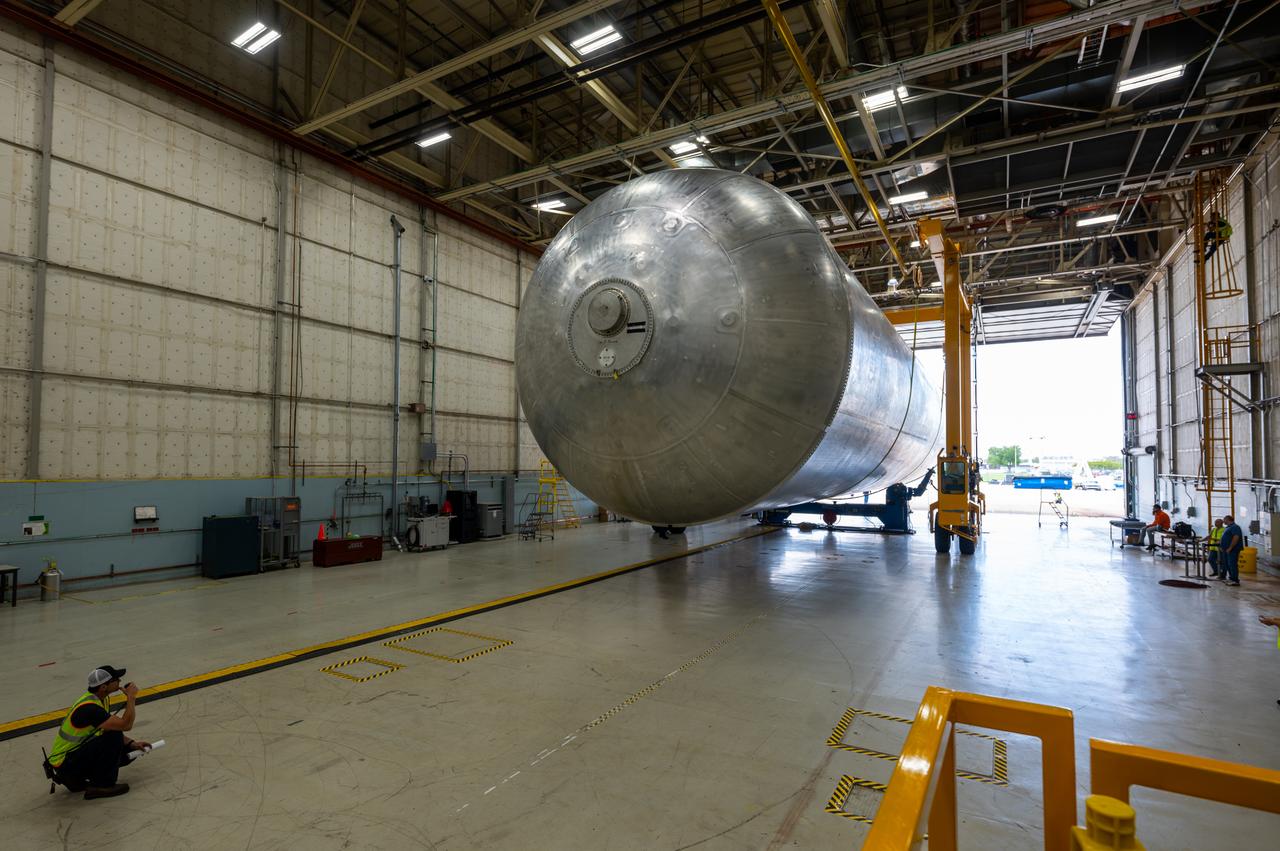

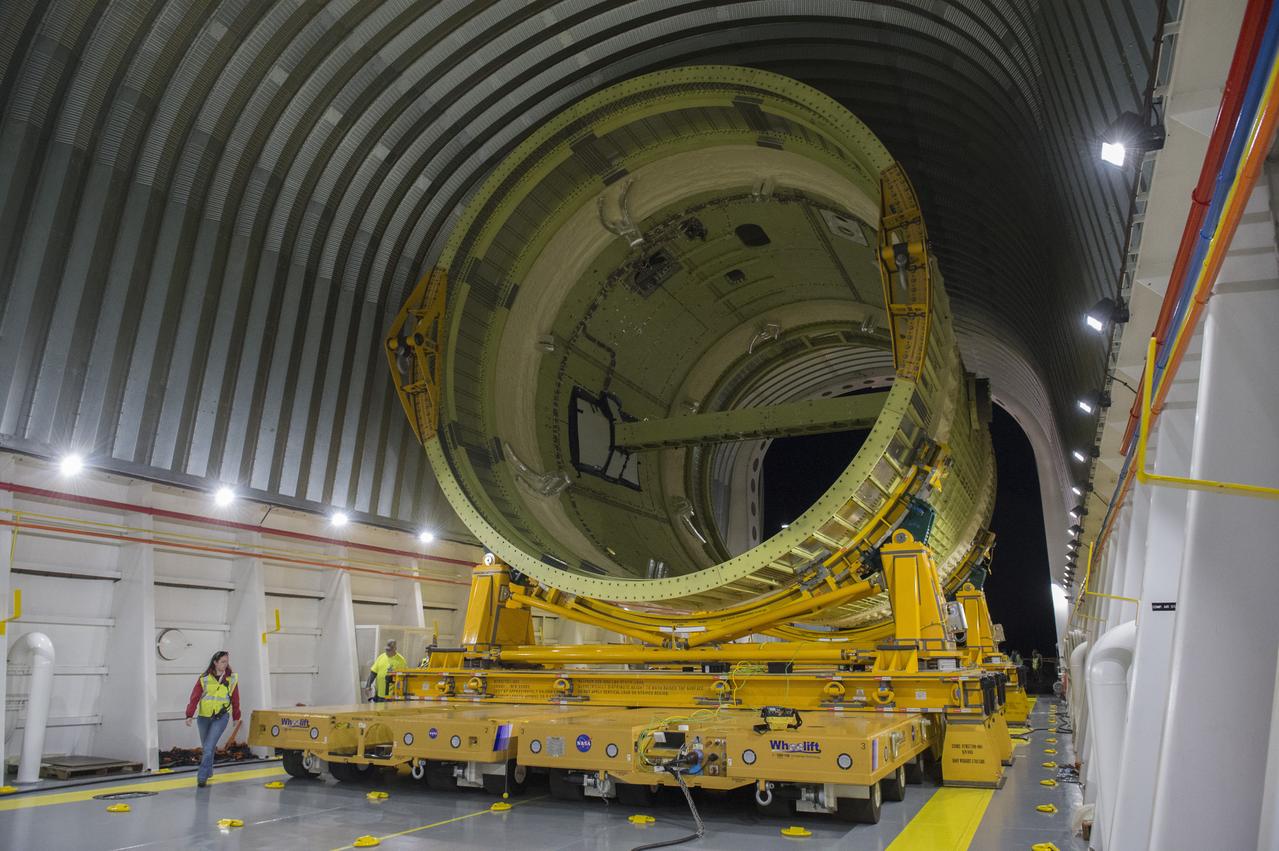
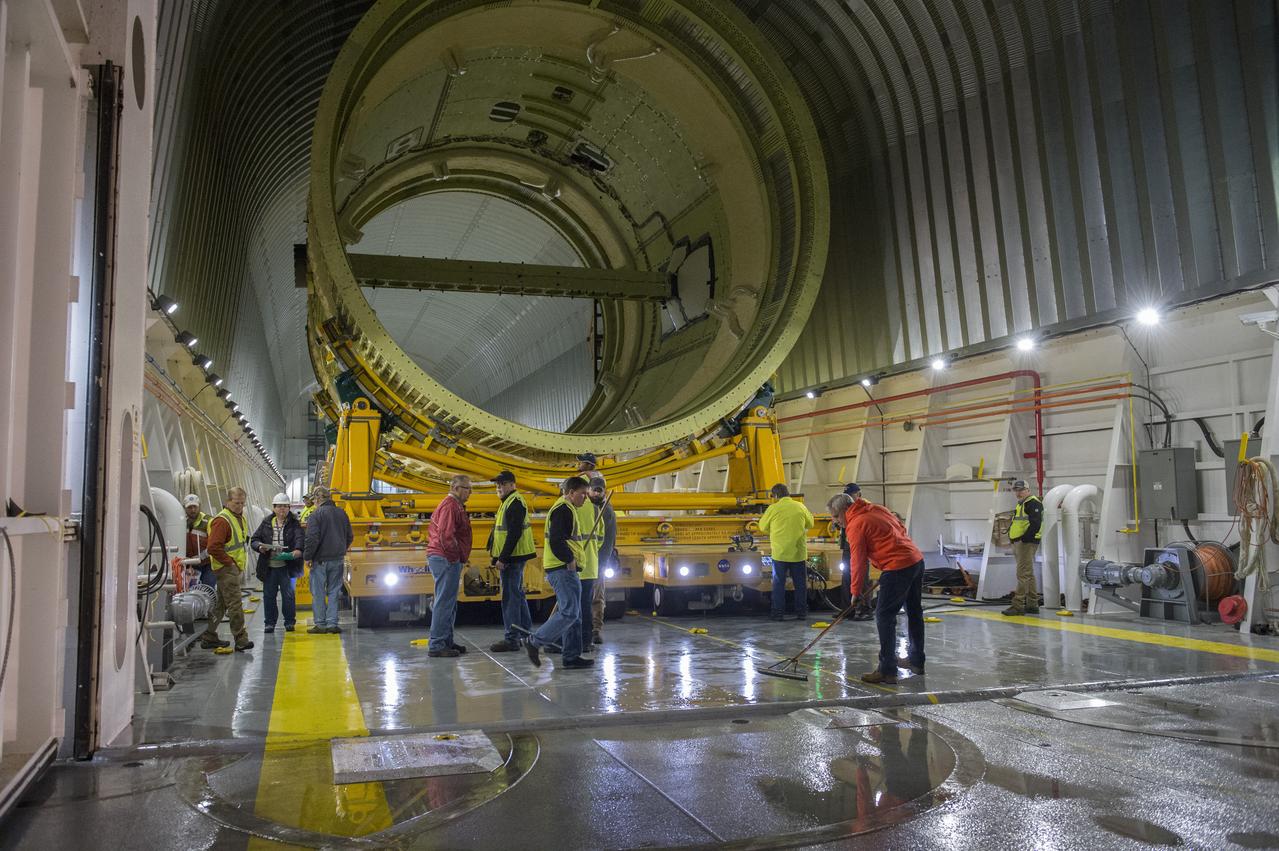
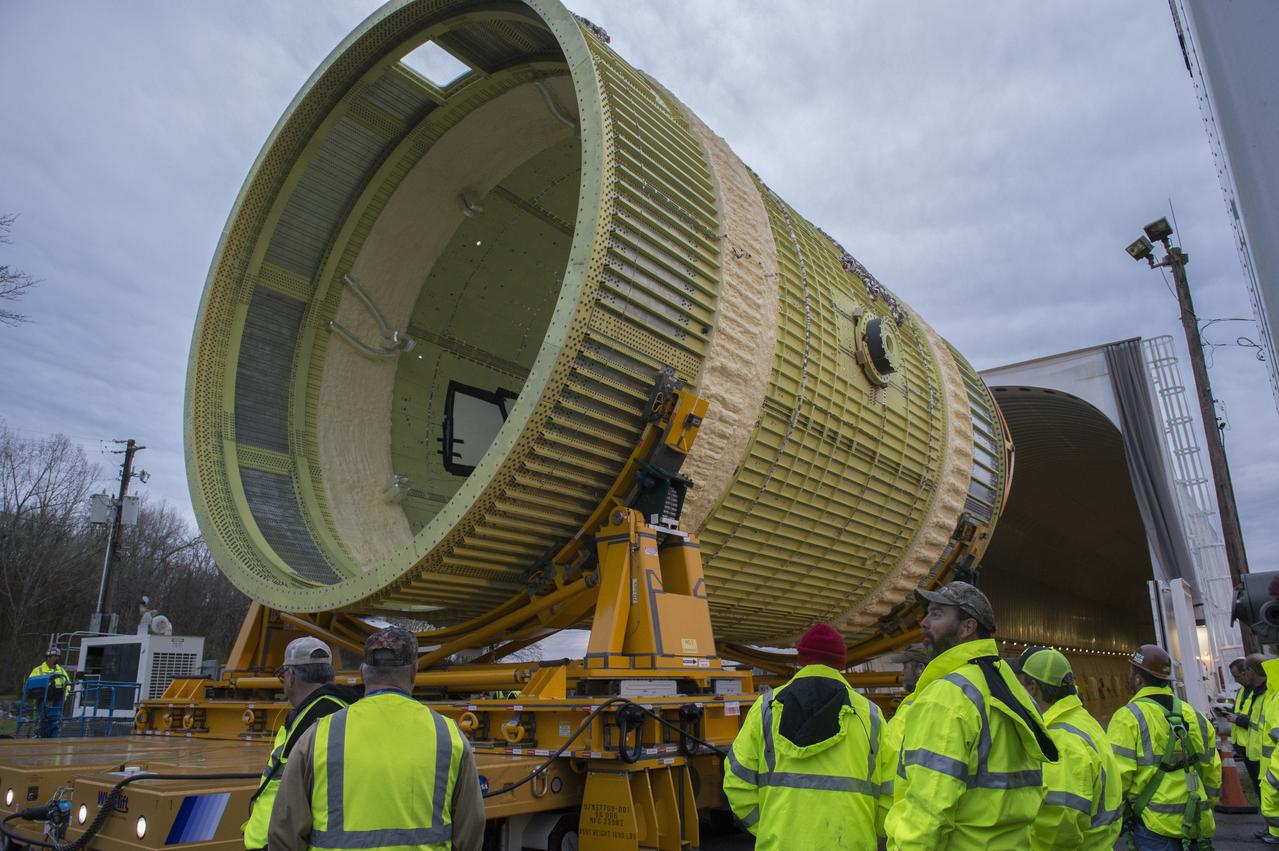
The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface.
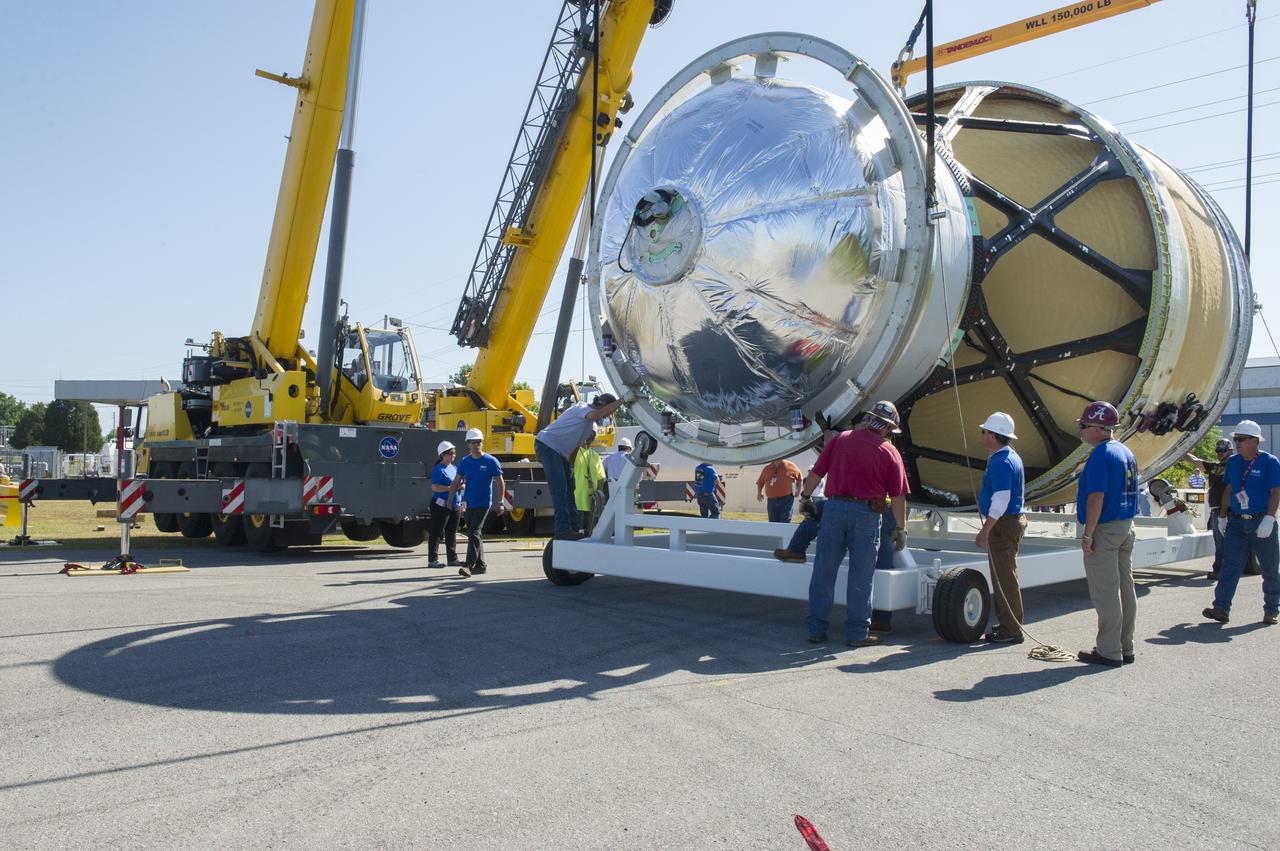

TWO CRANES LIFT THE APPROXIMATELY 8,000-POUND INTERIM CRYOGENIC PROPULSION STAGE TEST ARTICLE OUT OF ITS CRATE AT MARSHALL. THE TEST ARTICLE ARRIVED AT MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER VIA BARGE ON THE TENNESSEE RIVER AND WAS TRANSPORTED TO BUILDING 4649 WHERE TESTING WILL BEGIN.
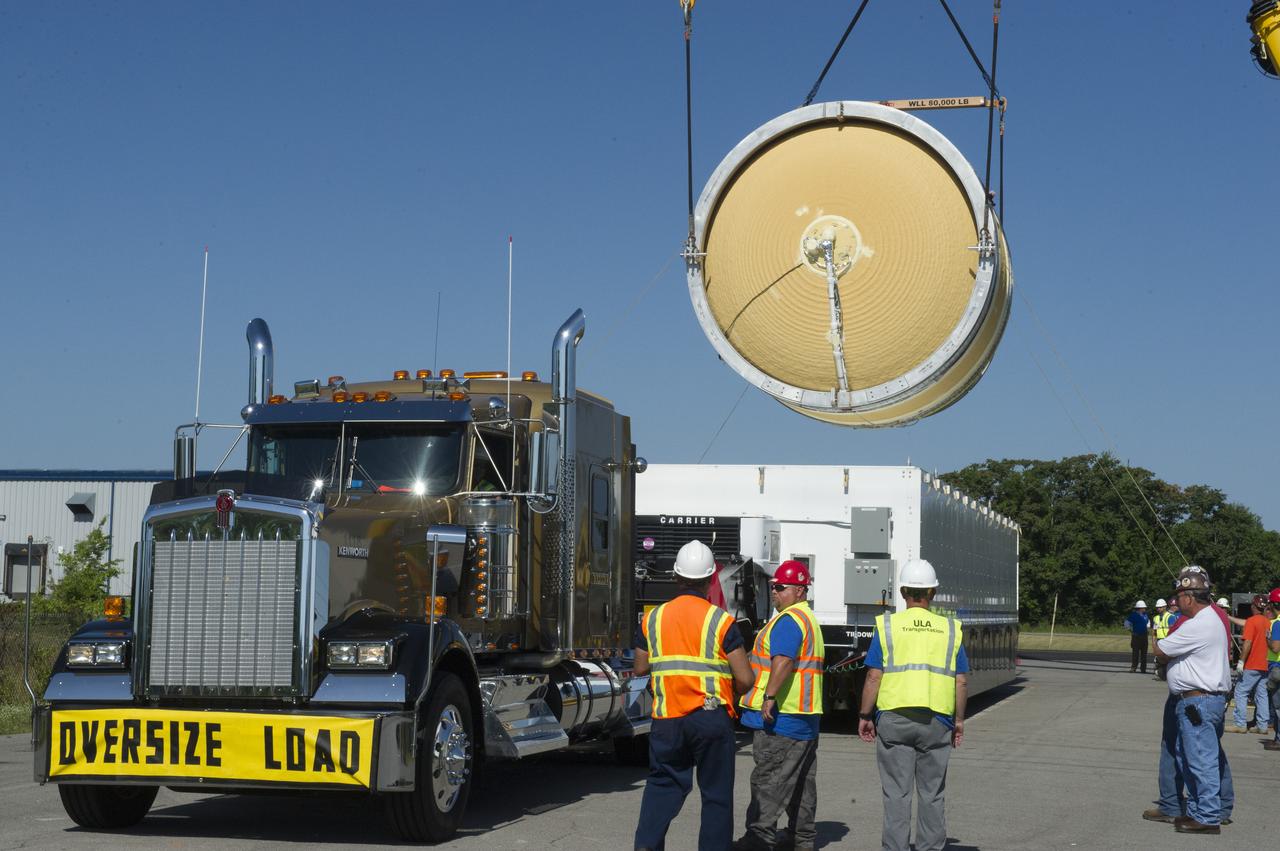

TWO CRANES LIFT THE APPROXIMATELY 8,000-POUND INTERIM CRYOGENIC PROPULSION STAGE TEST ARTICLE OUT OF ITS CRATE AT MARSHALL. THE TEST ARTICLE ARRIVED AT MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER VIA BARGE ON THE TENNESSEE RIVER AND WAS TRANSPORTED TO BUILDING 4649 WHERE TESTING WILL BEGIN.
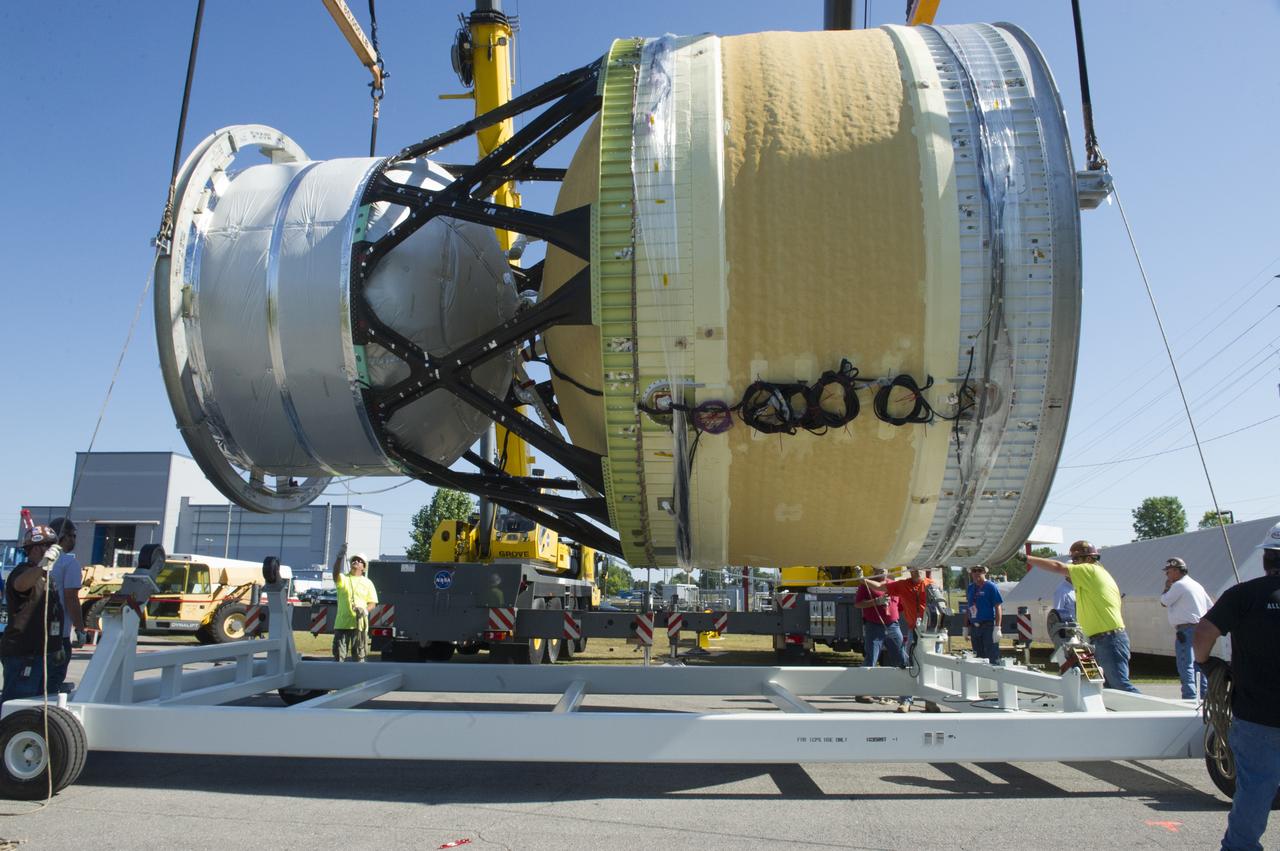

TWO CRANES LIFT THE APPROXIMATELY 8,000-POUND INTERIM CRYOGENIC PROPULSION STAGE TEST ARTICLE OUT OF ITS CRATE AT MARSHALL. THE TEST ARTICLE ARRIVED AT MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER VIA BARGE ON THE TENNESSEE RIVER AND WAS TRANSPORTED TO BUILDING 4649 WHERE TESTING WILL BEGIN.
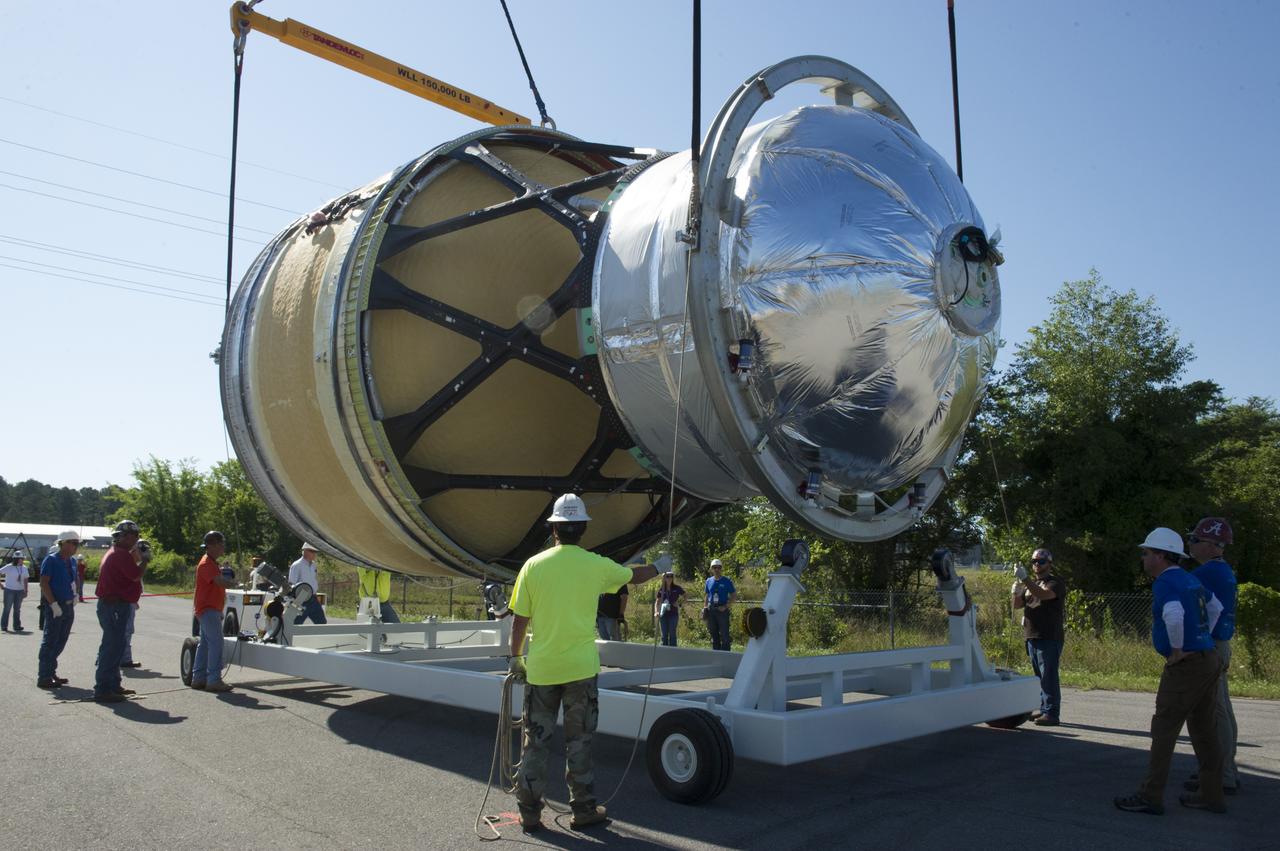

TWO CRANES LIFT THE APPROXIMATELY 8,000-POUND INTERIM CRYOGENIC PROPULSION STAGE TEST ARTICLE OUT OF ITS CRATE AT MARSHALL. THE TEST ARTICLE ARRIVED AT MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER VIA BARGE ON THE TENNESSEE RIVER AND WAS TRANSPORTED TO BUILDING 4649 WHERE TESTING WILL BEGIN.
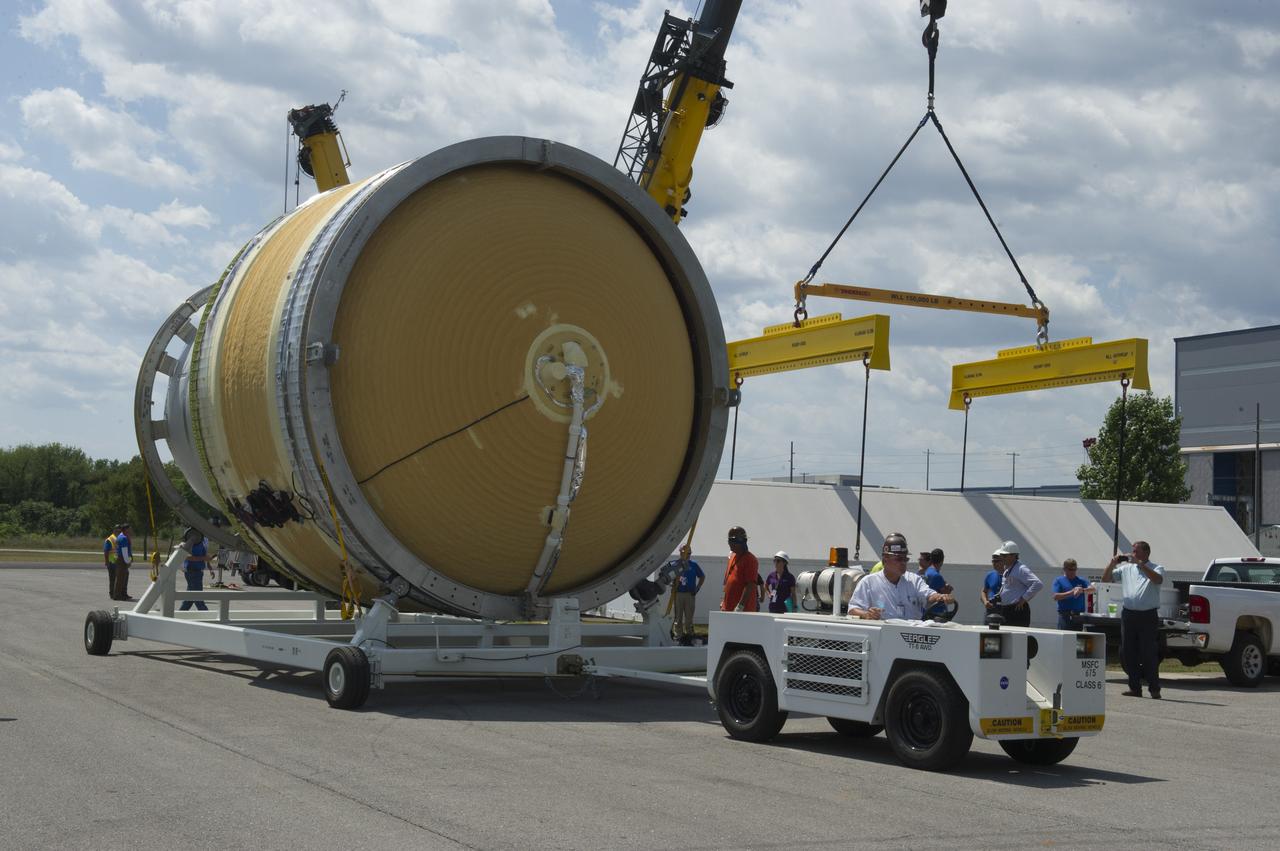

TWO CRANES LIFT THE APPROXIMATELY 8,000-POUND INTERIM CRYOGENIC PROPULSION STAGE TEST ARTICLE OUT OF ITS CRATE AT MARSHALL. THE TEST ARTICLE ARRIVED AT MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER VIA BARGE ON THE TENNESSEE RIVER AND WAS TRANSPORTED TO BUILDING 4649 WHERE TESTING WILL BEGIN.
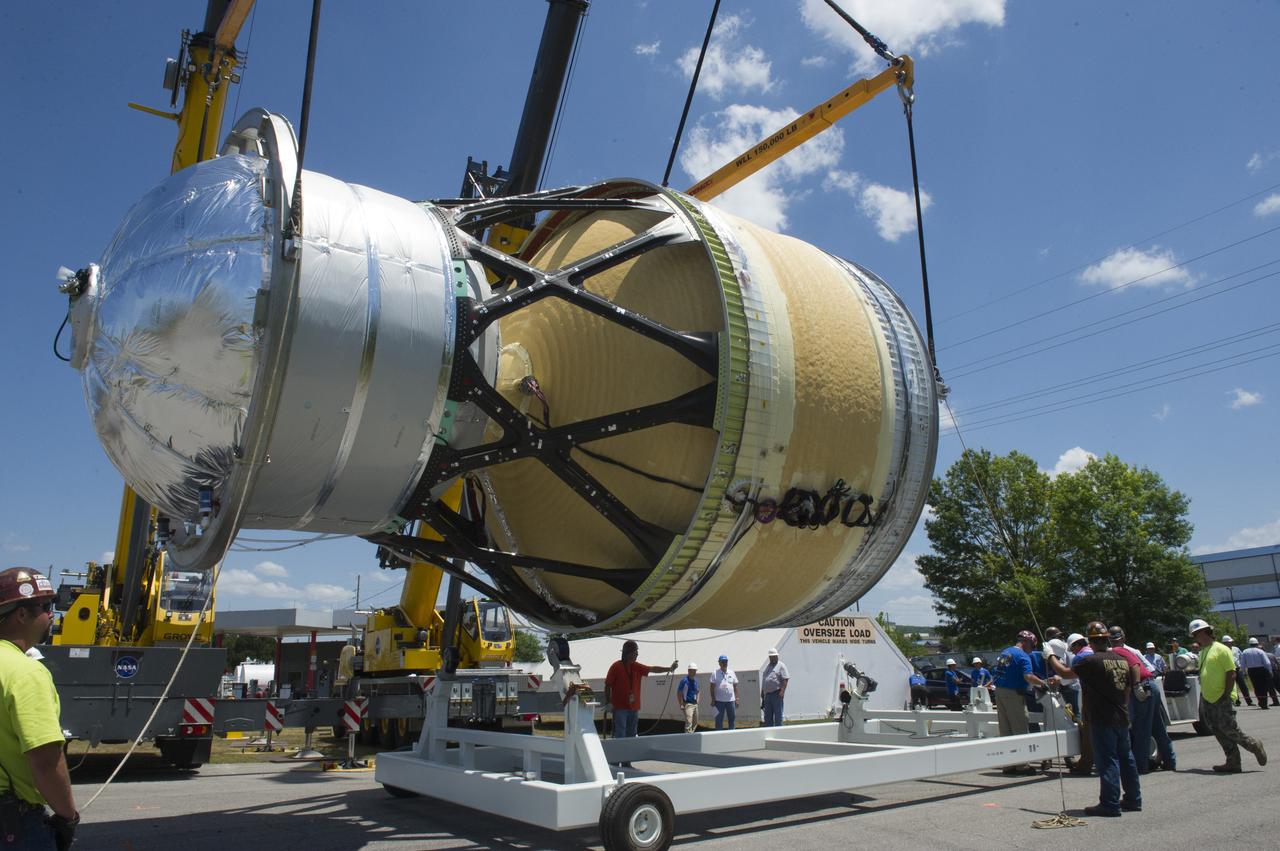

TWO CRANES LIFT THE APPROXIMATELY 8,000-POUND INTERIM CRYOGENIC PROPULSION STAGE TEST ARTICLE OUT OF ITS CRATE AT MARSHALL. THE TEST ARTICLE ARRIVED AT MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER VIA BARGE ON THE TENNESSEE RIVER AND WAS TRANSPORTED TO BUILDING 4649 WHERE TESTING WILL BEGIN.
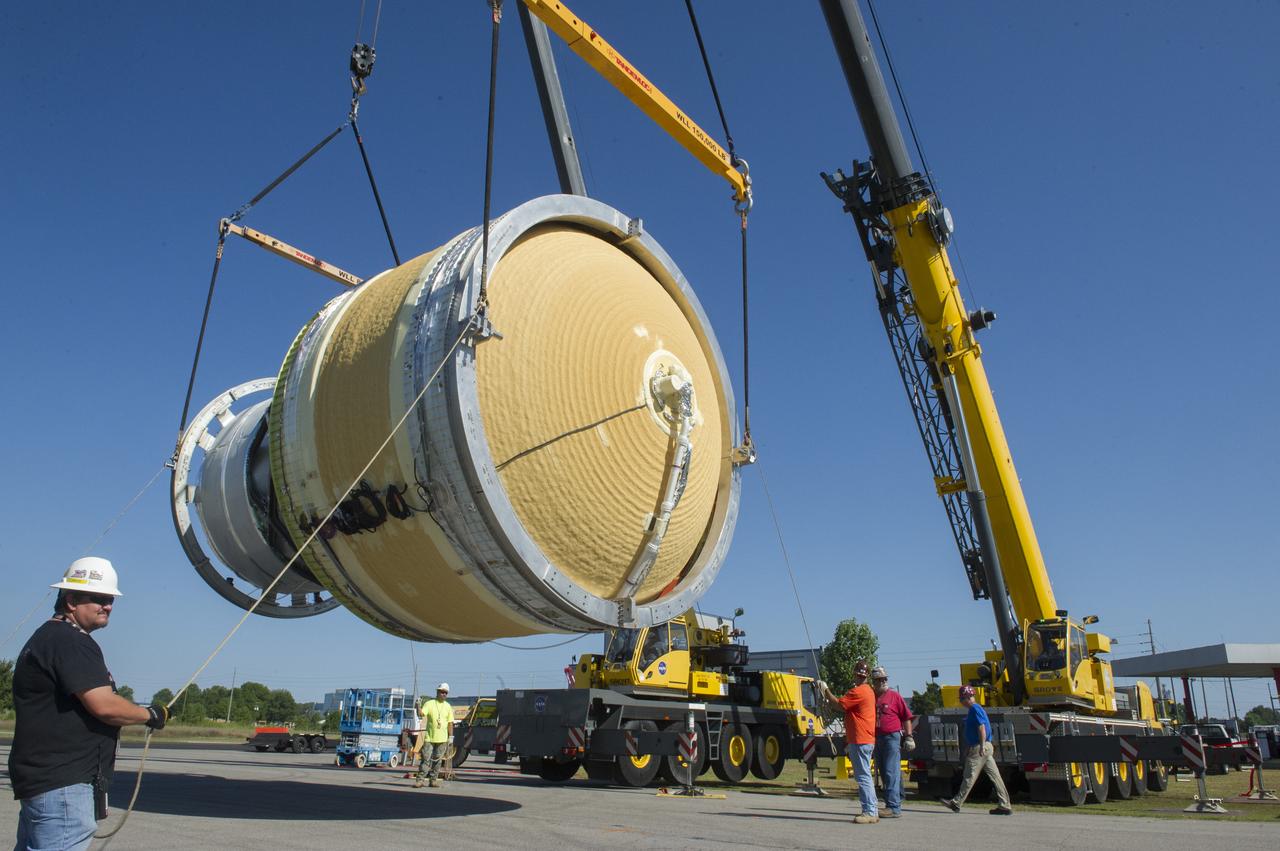

TWO CRANES LIFT THE APPROXIMATELY 8,000-POUND INTERIM CRYOGENIC PROPULSION STAGE TEST ARTICLE OUT OF ITS CRATE AT MARSHALL. THE TEST ARTICLE ARRIVED AT MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER VIA BARGE ON THE TENNESSEE RIVER AND WAS TRANSPORTED TO BUILDING 4649 WHERE TESTING WILL BEGIN.
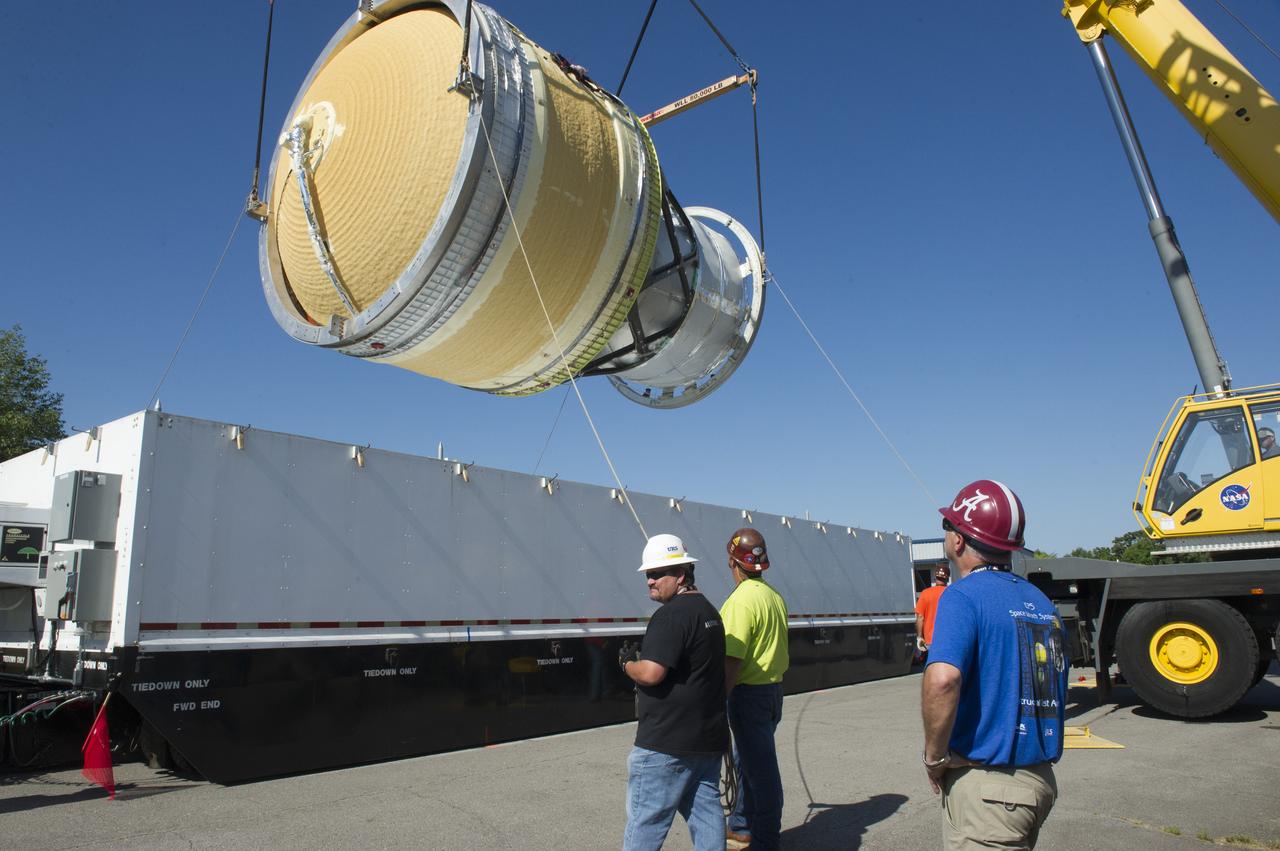

TWO CRANES LIFT THE APPROXIMATELY 8,000-POUND INTERIM CRYOGENIC PROPULSION STAGE TEST ARTICLE OUT OF ITS CRATE AT MARSHALL. THE TEST ARTICLE ARRIVED AT MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER VIA BARGE ON THE TENNESSEE RIVER AND WAS TRANSPORTED TO BUILDING 4649 WHERE TESTING WILL BEGIN.
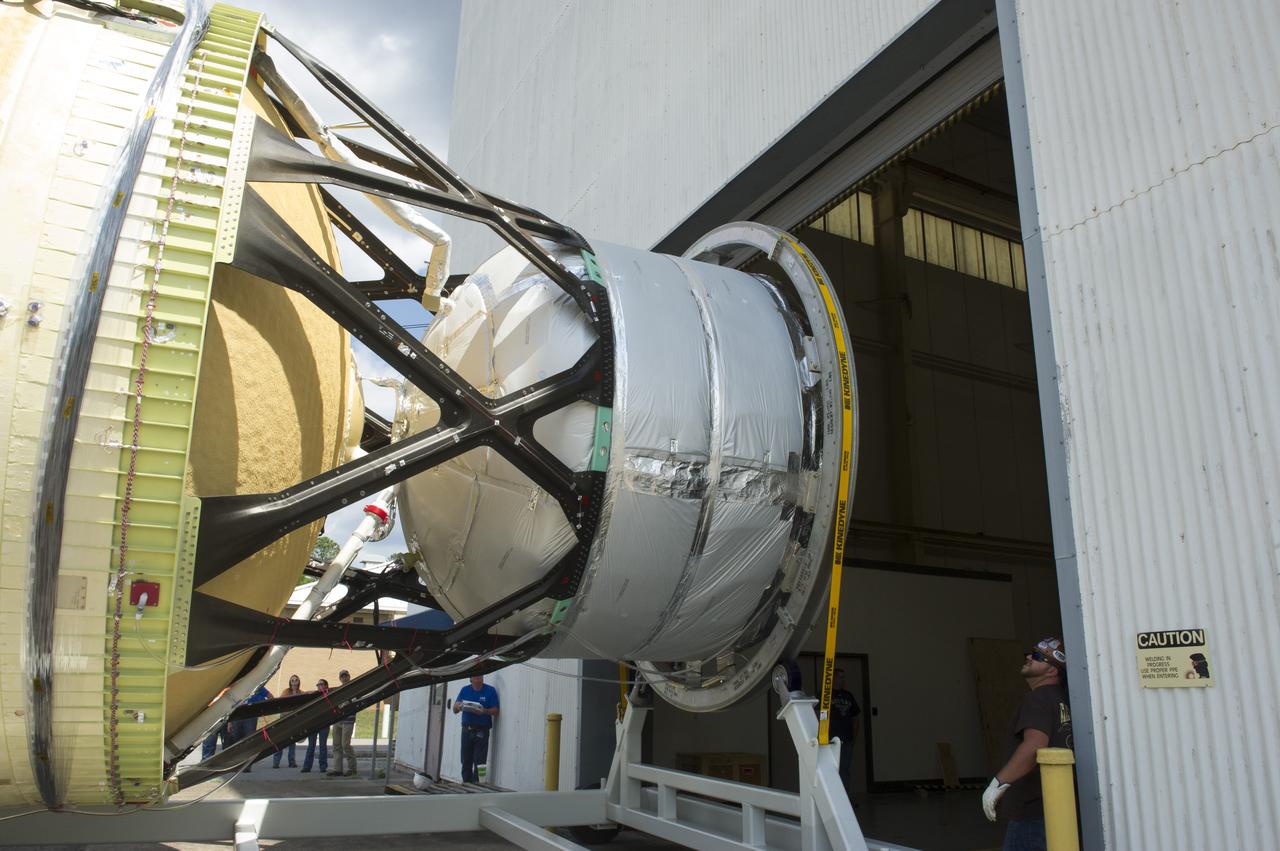

TWO CRANES LIFT THE APPROXIMATELY 8,000-POUND INTERIM CRYOGENIC PROPULSION STAGE TEST ARTICLE OUT OF ITS CRATE AT MARSHALL. THE TEST ARTICLE ARRIVED AT MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER VIA BARGE ON THE TENNESSEE RIVER AND WAS TRANSPORTED TO BUILDING 4649 WHERE TESTING WILL BEGIN.
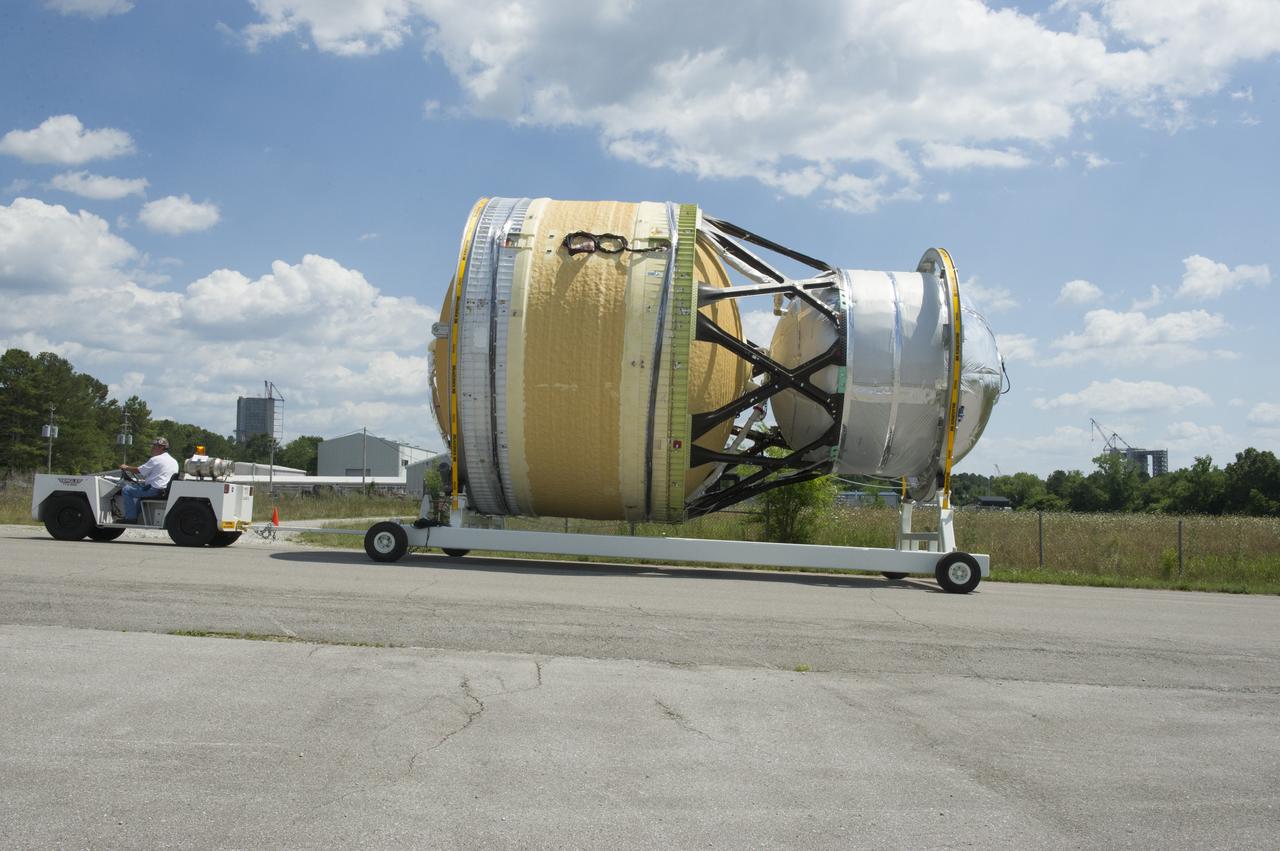

TWO CRANES LIFT THE APPROXIMATELY 8,000-POUND INTERIM CRYOGENIC PROPULSION STAGE TEST ARTICLE OUT OF ITS CRATE AT MARSHALL. THE TEST ARTICLE ARRIVED AT MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER VIA BARGE ON THE TENNESSEE RIVER AND WAS TRANSPORTED TO BUILDING 4649 WHERE TESTING WILL BEGIN.
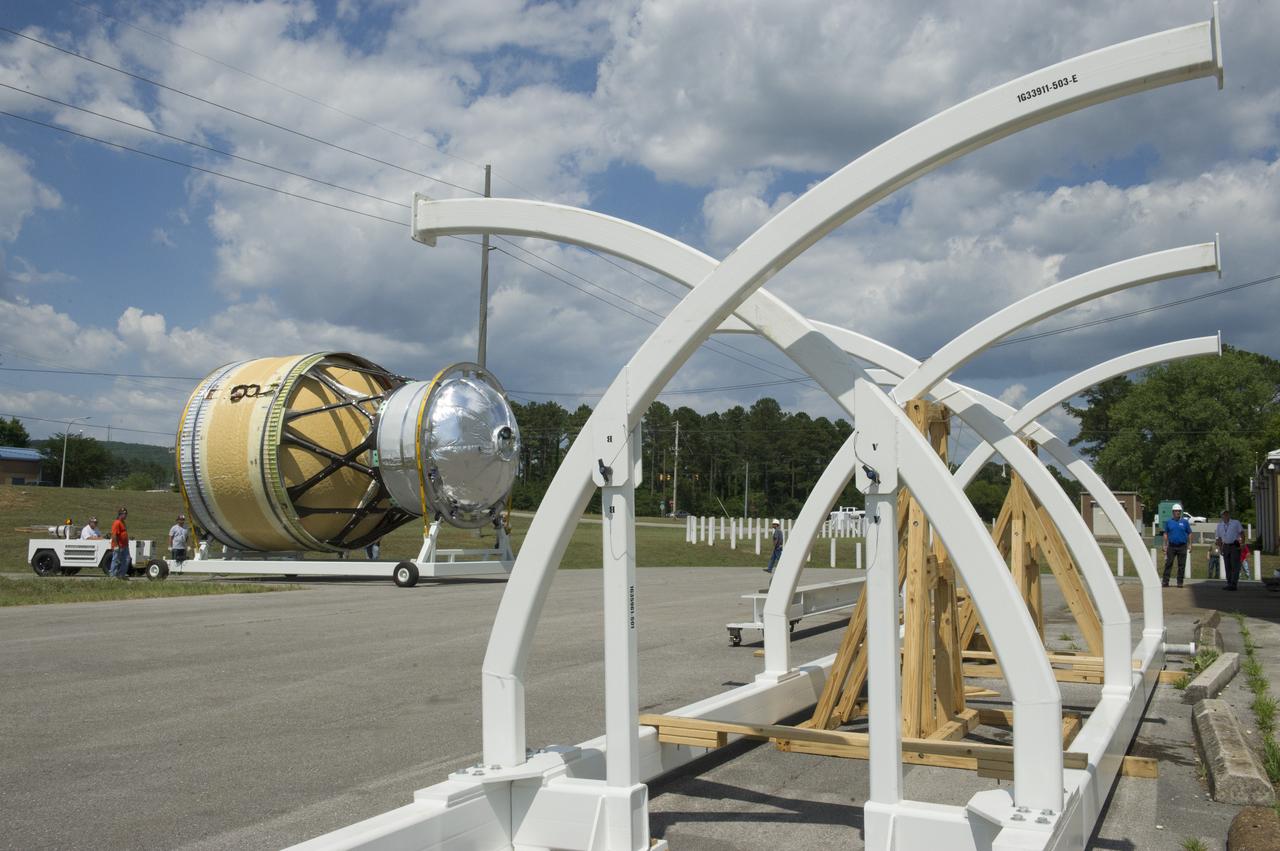

TWO CRANES LIFT THE APPROXIMATELY 8,000-POUND INTERIM CRYOGENIC PROPULSION STAGE TEST ARTICLE OUT OF ITS CRATE AT MARSHALL. THE TEST ARTICLE ARRIVED AT MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER VIA BARGE ON THE TENNESSEE RIVER AND WAS TRANSPORTED TO BUILDING 4649 WHERE TESTING WILL BEGIN.
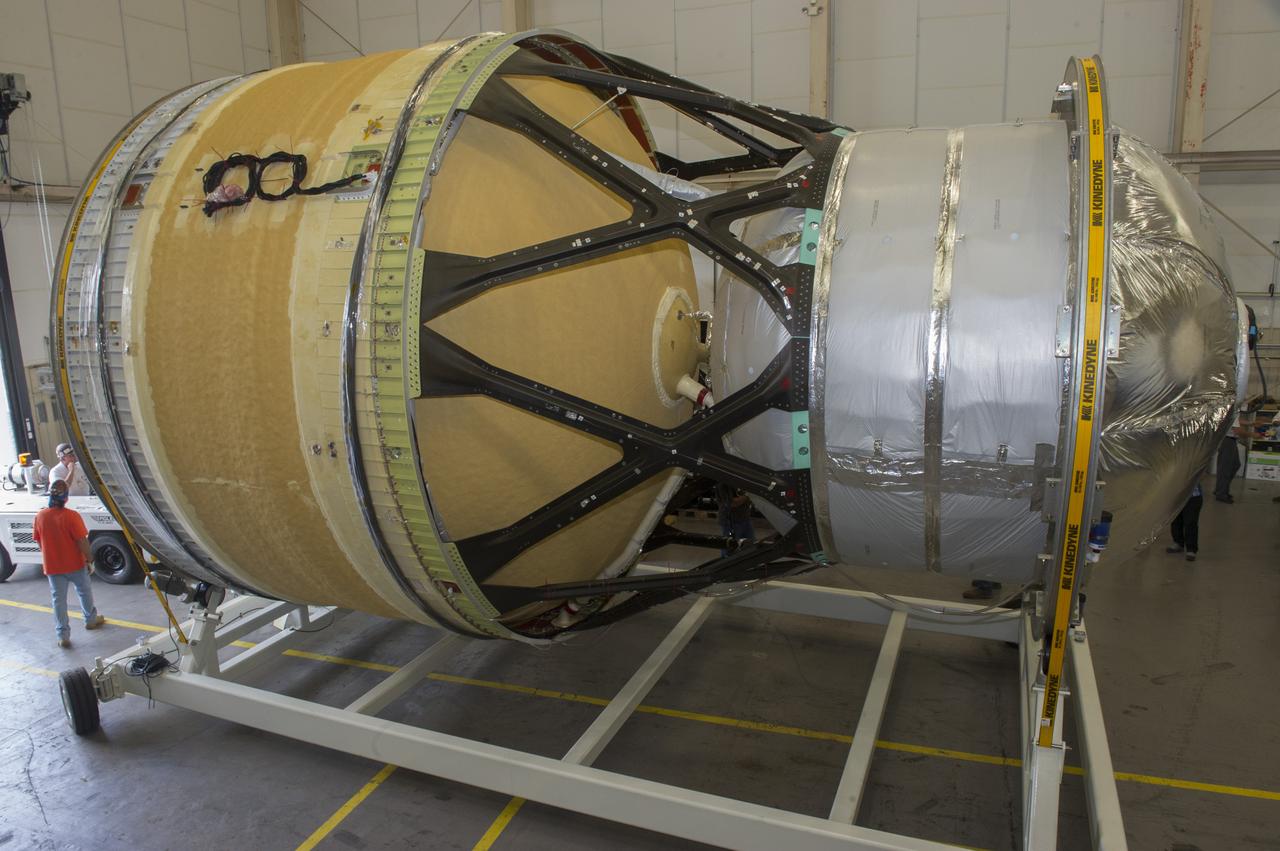

TWO CRANES LIFT THE APPROXIMATELY 8,000-POUND INTERIM CRYOGENIC PROPULSION STAGE TEST ARTICLE OUT OF ITS CRATE AT MARSHALL. THE TEST ARTICLE ARRIVED AT MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER VIA BARGE ON THE TENNESSEE RIVER AND WAS TRANSPORTED TO BUILDING 4649 WHERE TESTING WILL BEGIN.

TWO CRANES LIFT THE APPROXIMATELY 8,000-POUND INTERIM CRYOGENIC PROPULSION STAGE TEST ARTICLE OUT OF ITS CRATE AT MARSHALL. THE TEST ARTICLE ARRIVED AT MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER VIA BARGE ON THE TENNESSEE RIVER AND WAS TRANSPORTED TO BUILDING 4649 WHERE TESTING WILL BEGIN.

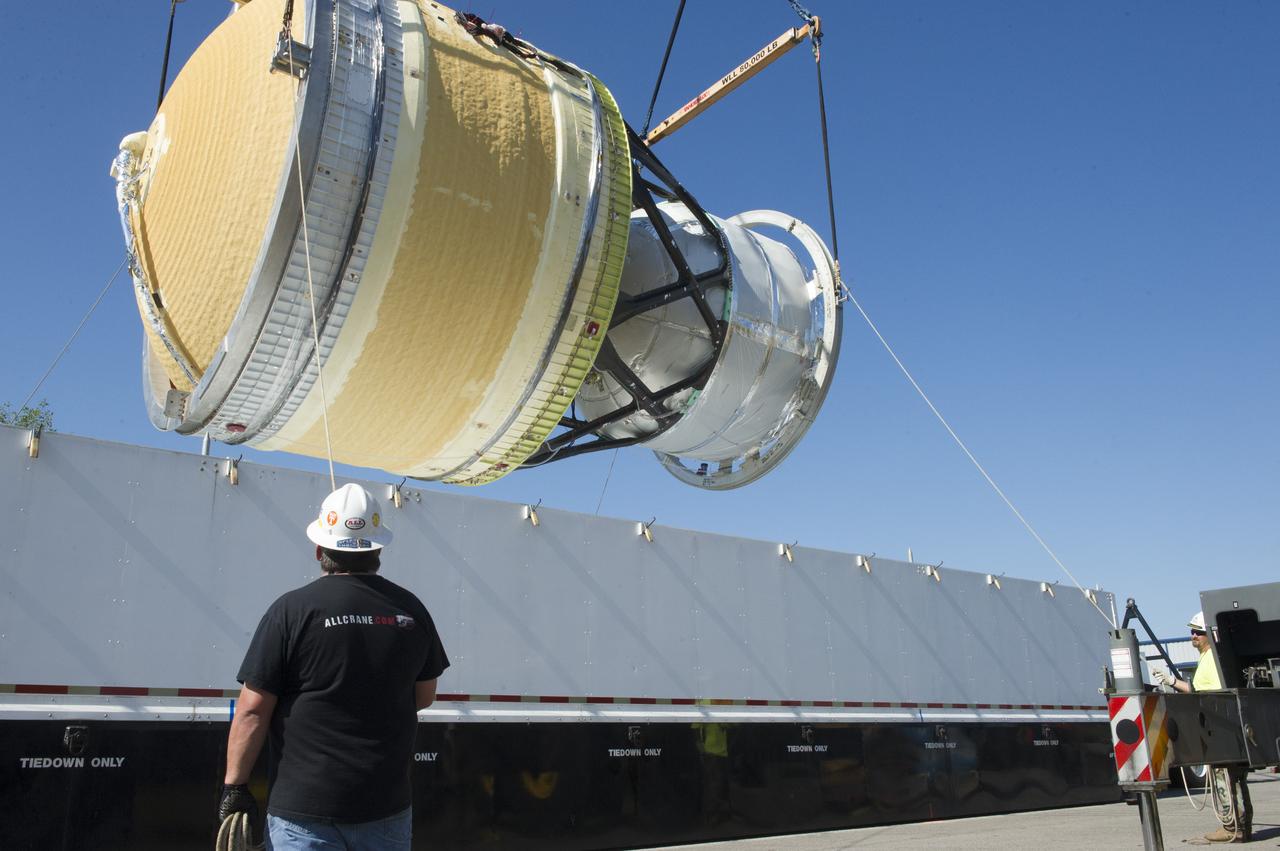
The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing

The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing
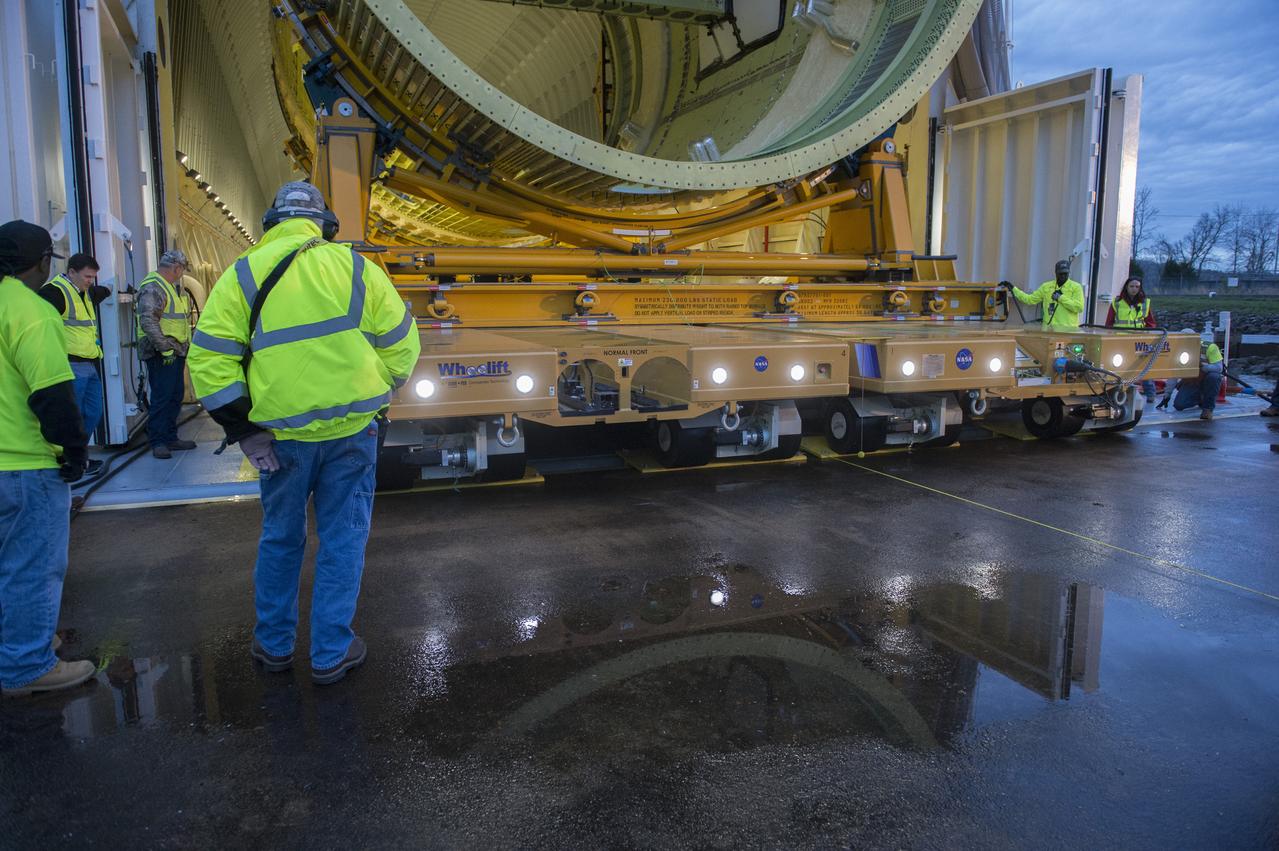

The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing
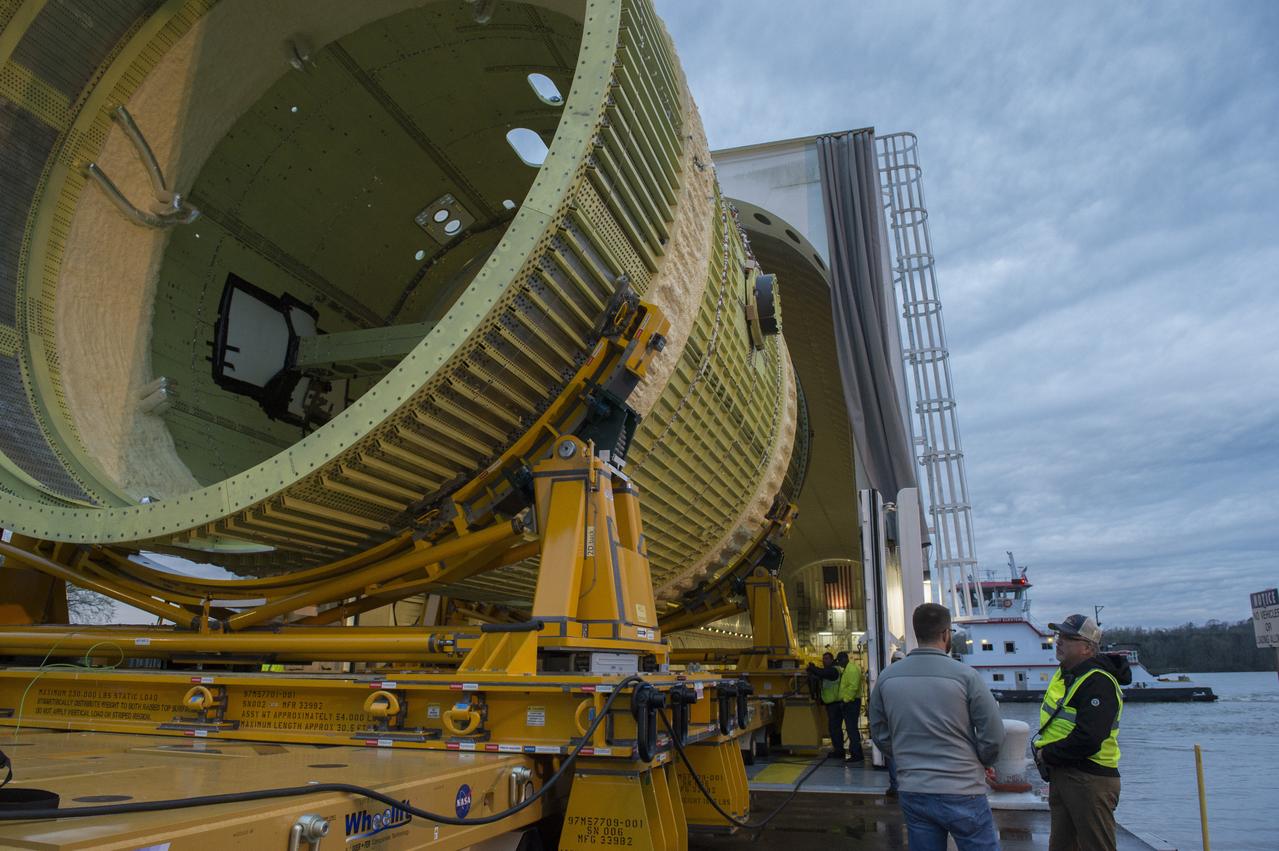

The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing
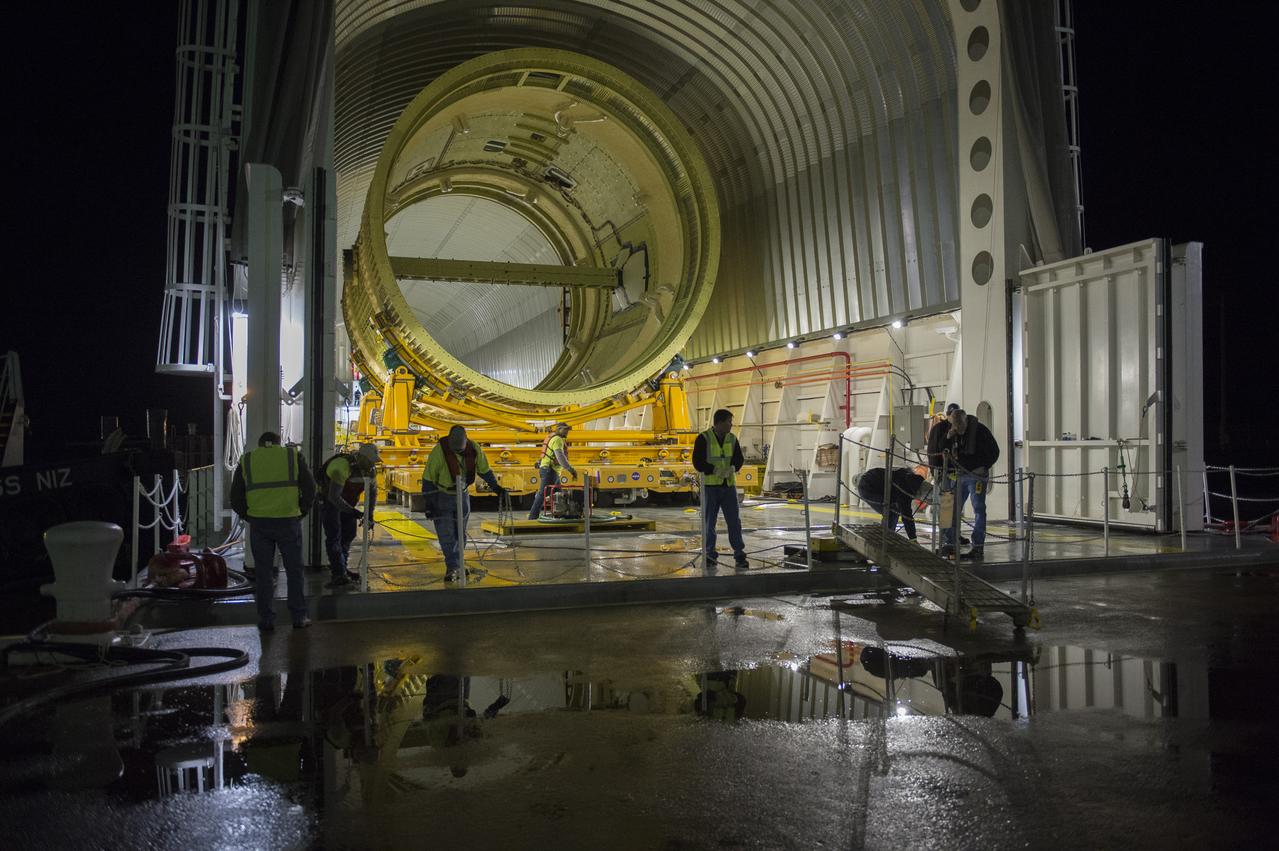

The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing
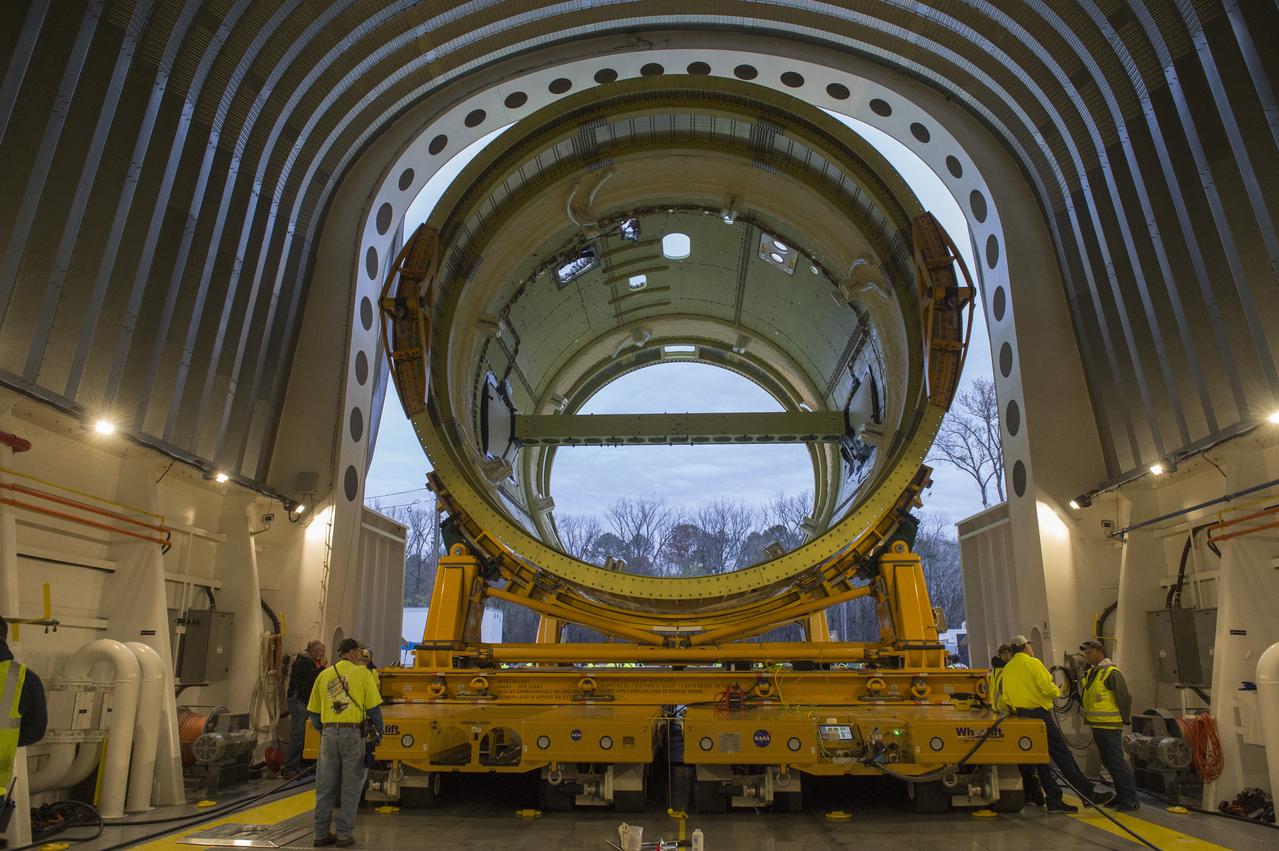

The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing
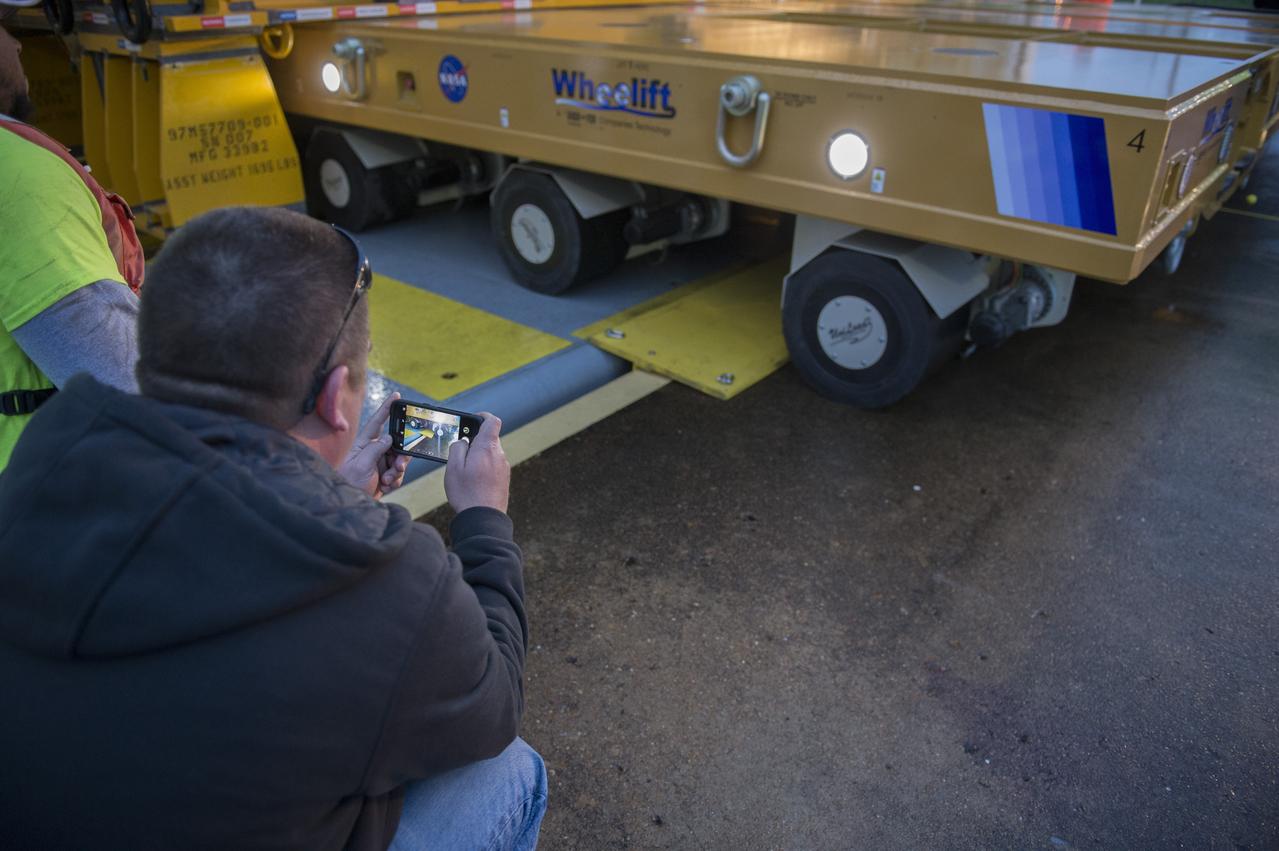

The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing

The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing

The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing

The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing
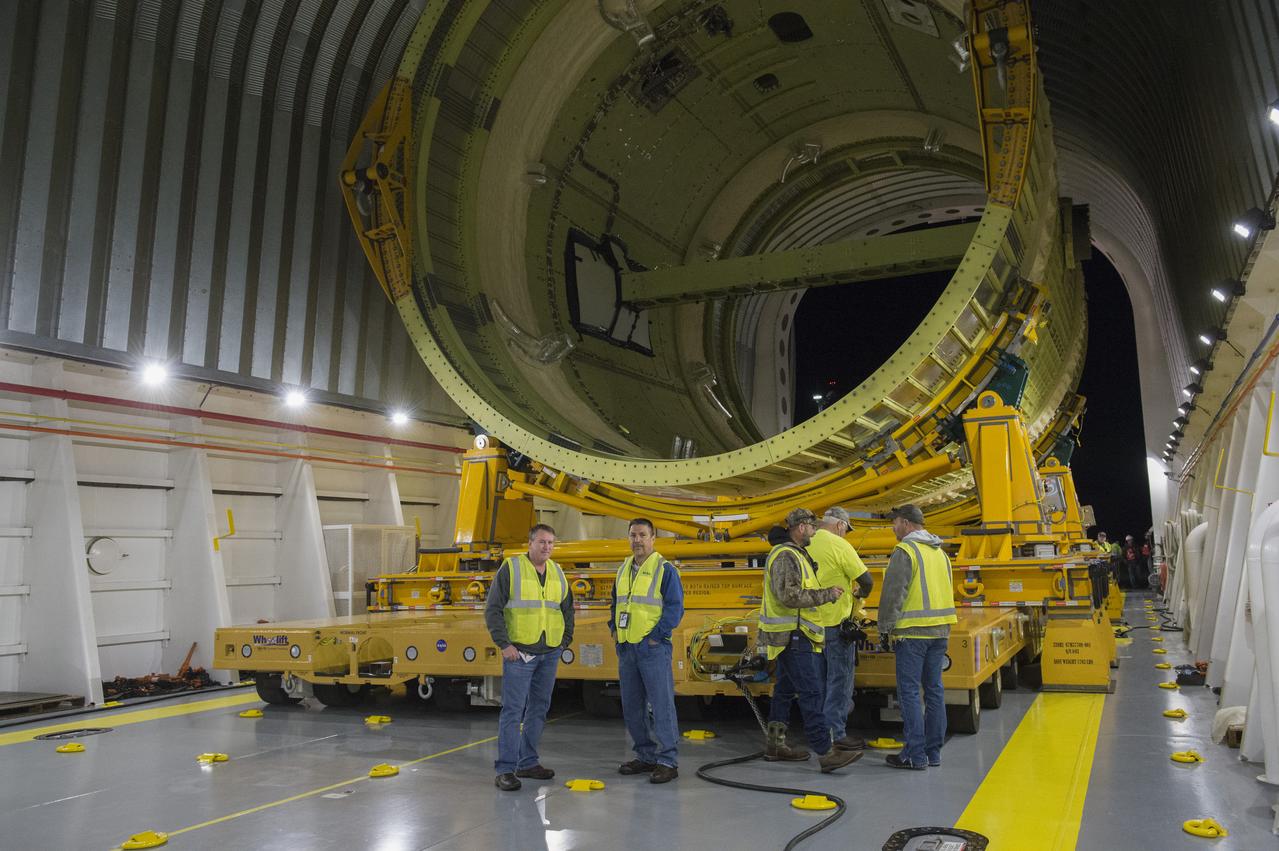

The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing
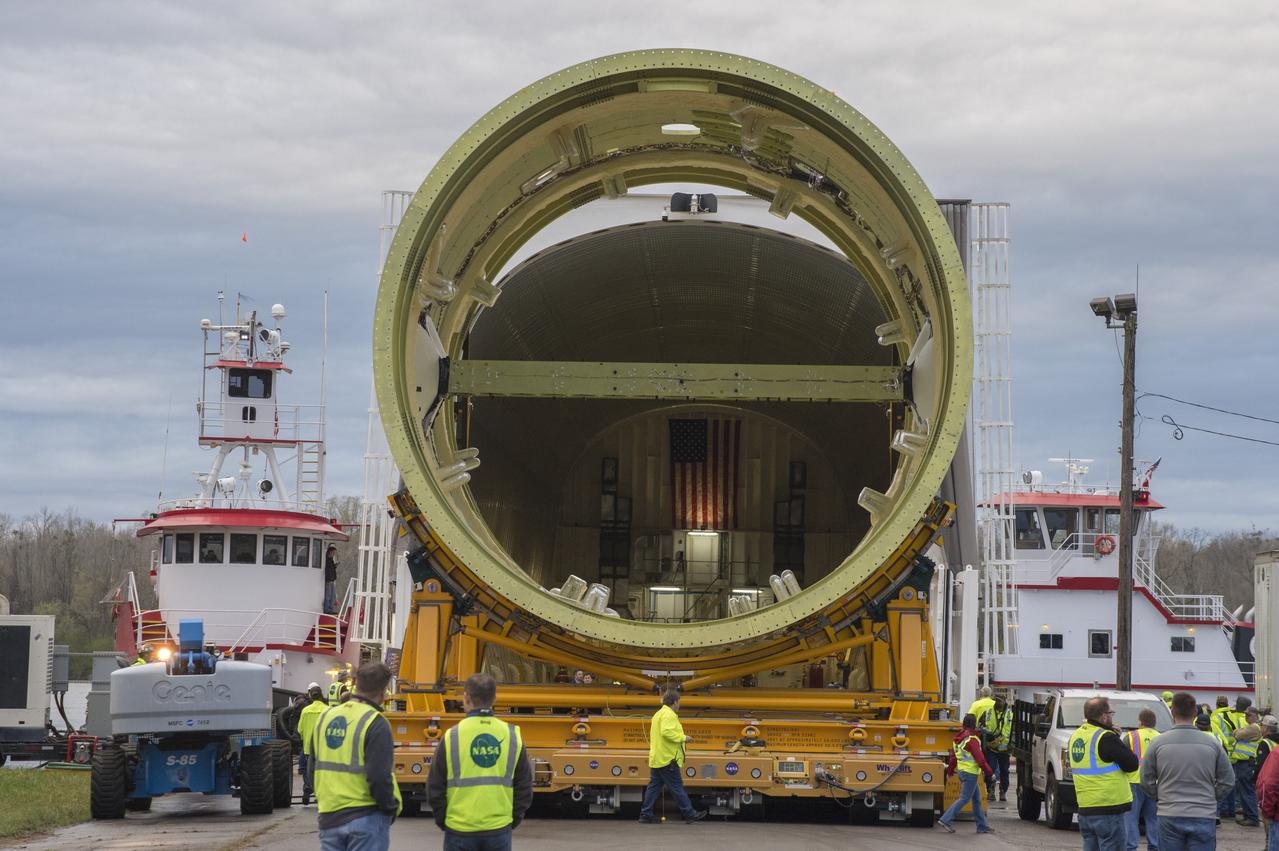

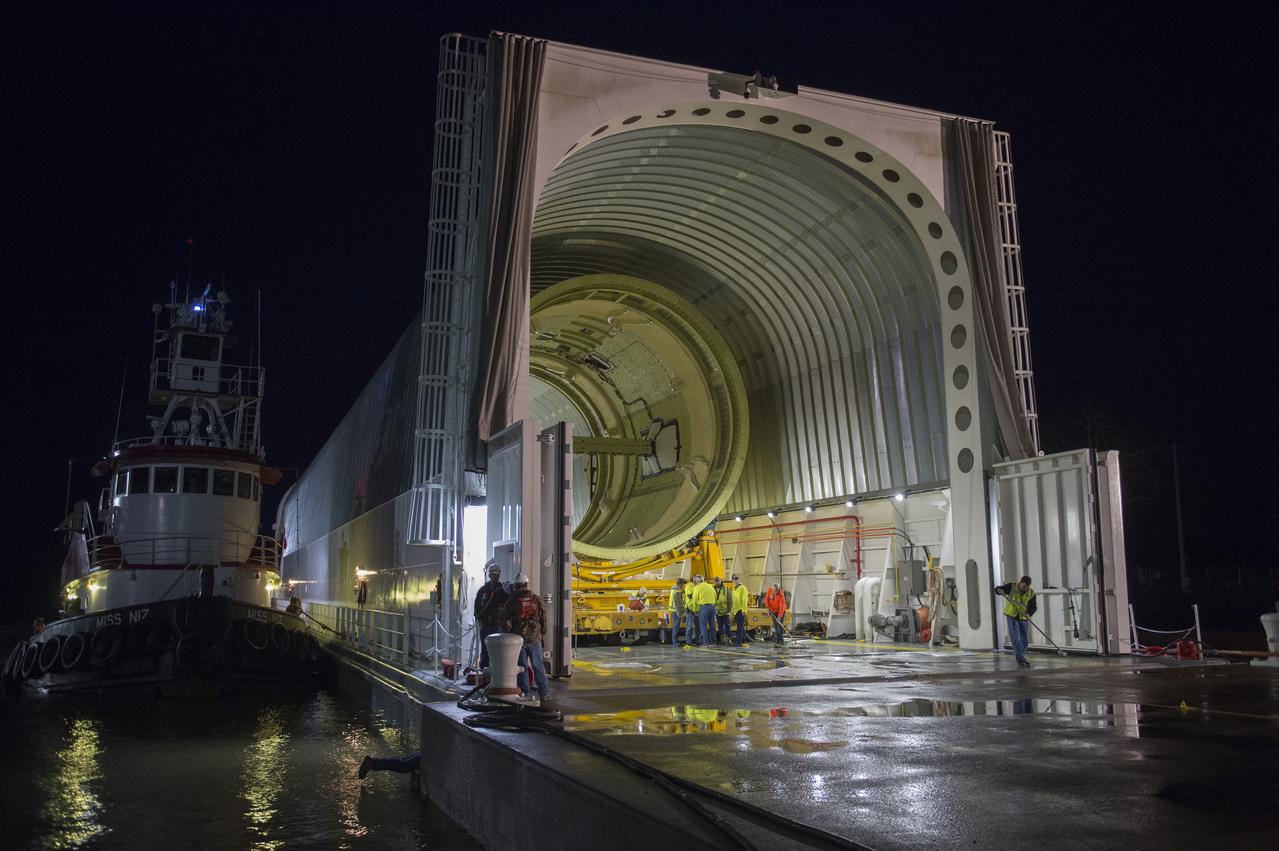
The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing. STA hardware completely free of barge and flanked by tug boats.
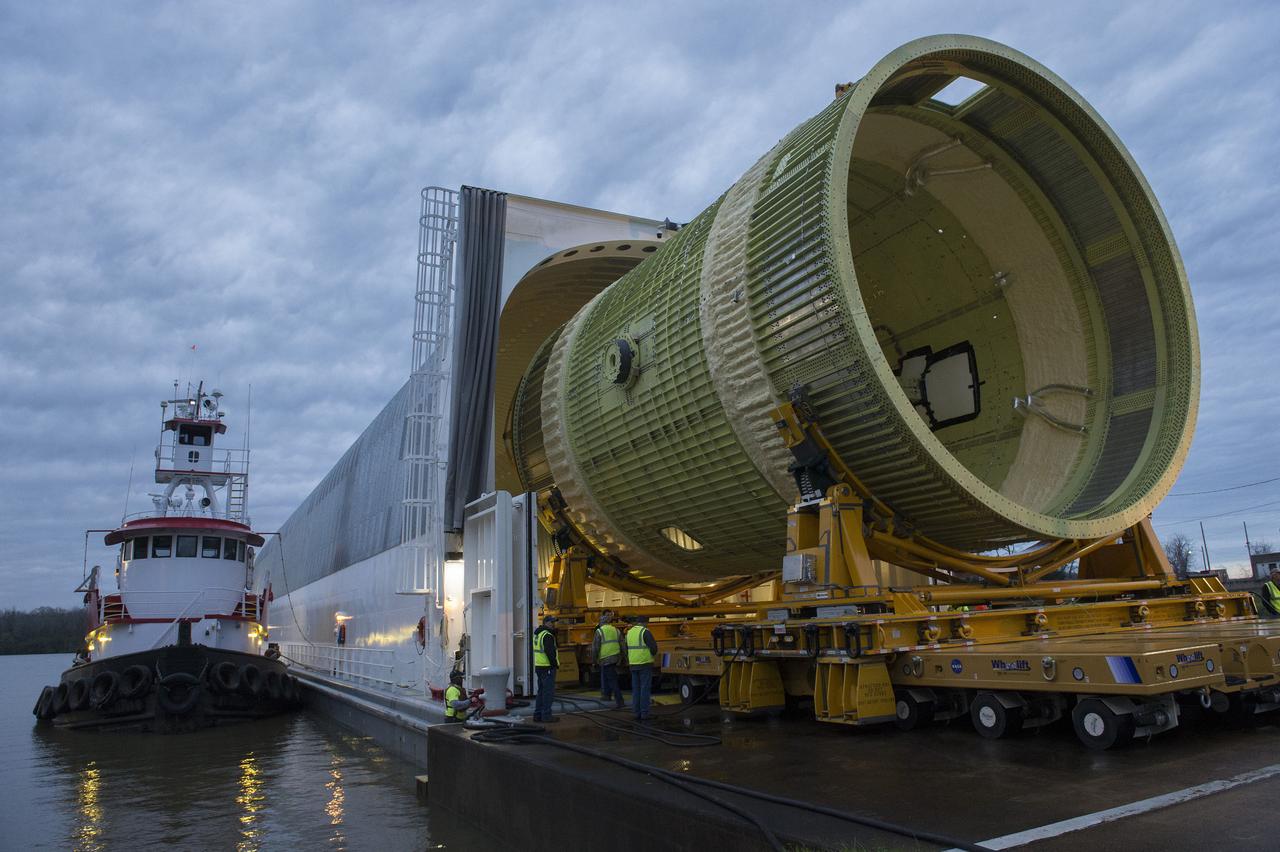

The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing. STA emerges from Barge Pegasus.
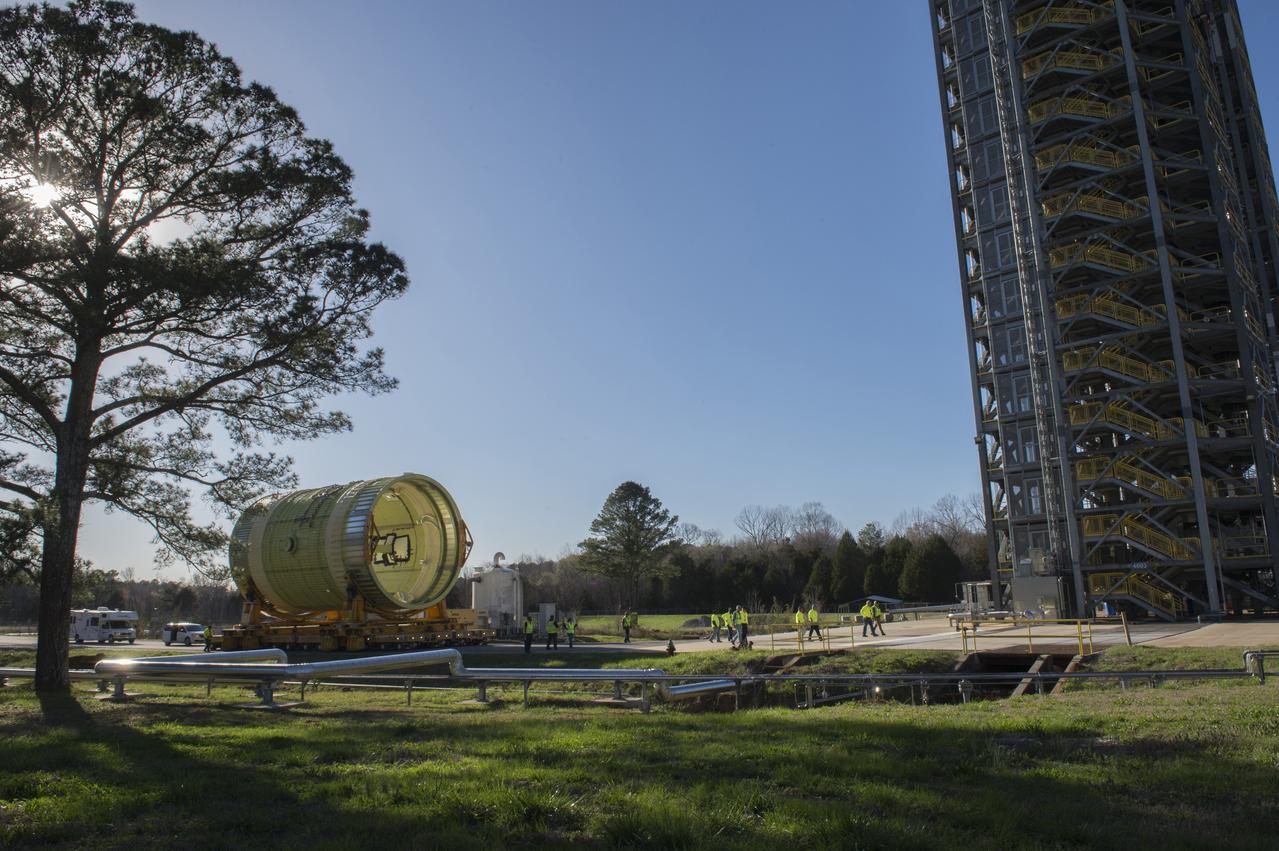

The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing via MSFC West Test Area. STA approaches Test Stand 4693, SLS LH2 test Stand, on way to Bldg. 4619

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand ahead of a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Friday, Jan. 15, 2021 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
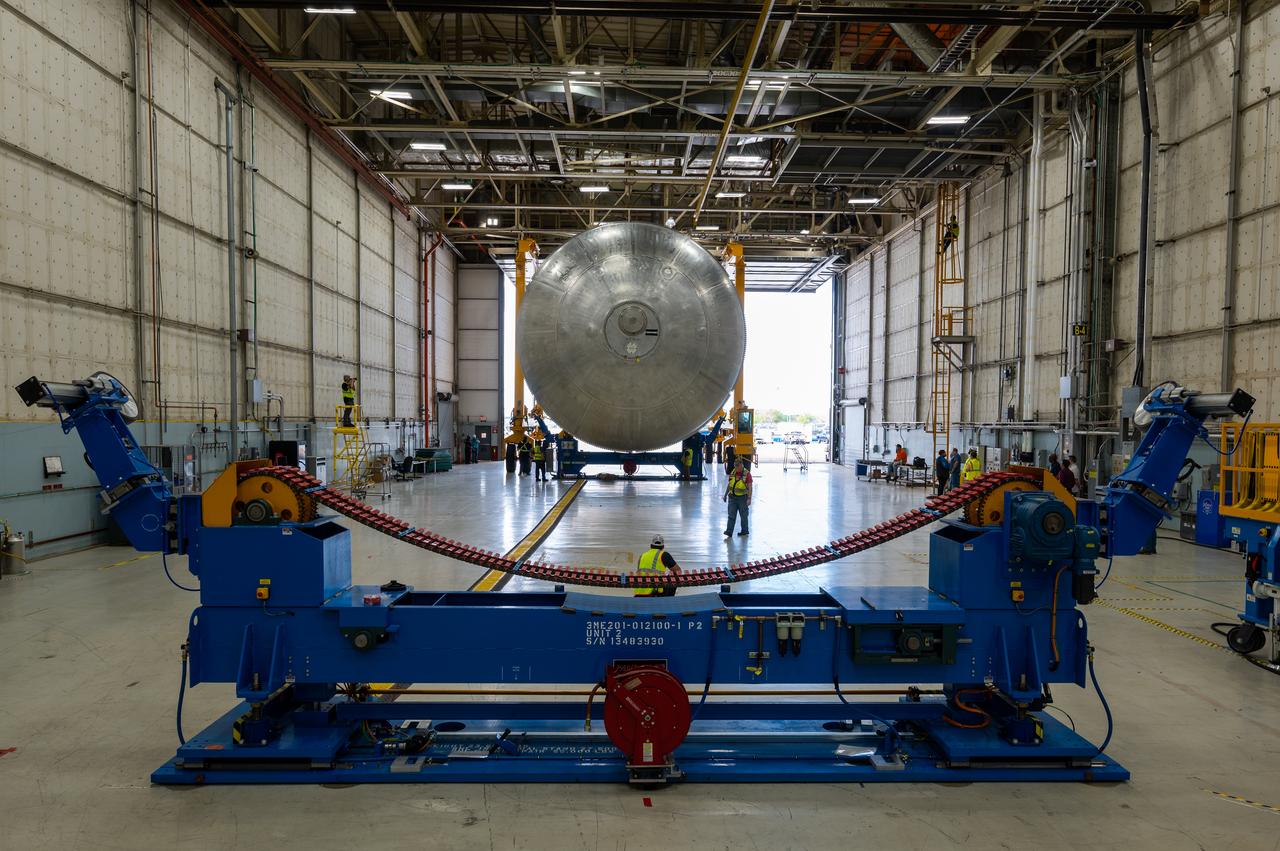

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface.
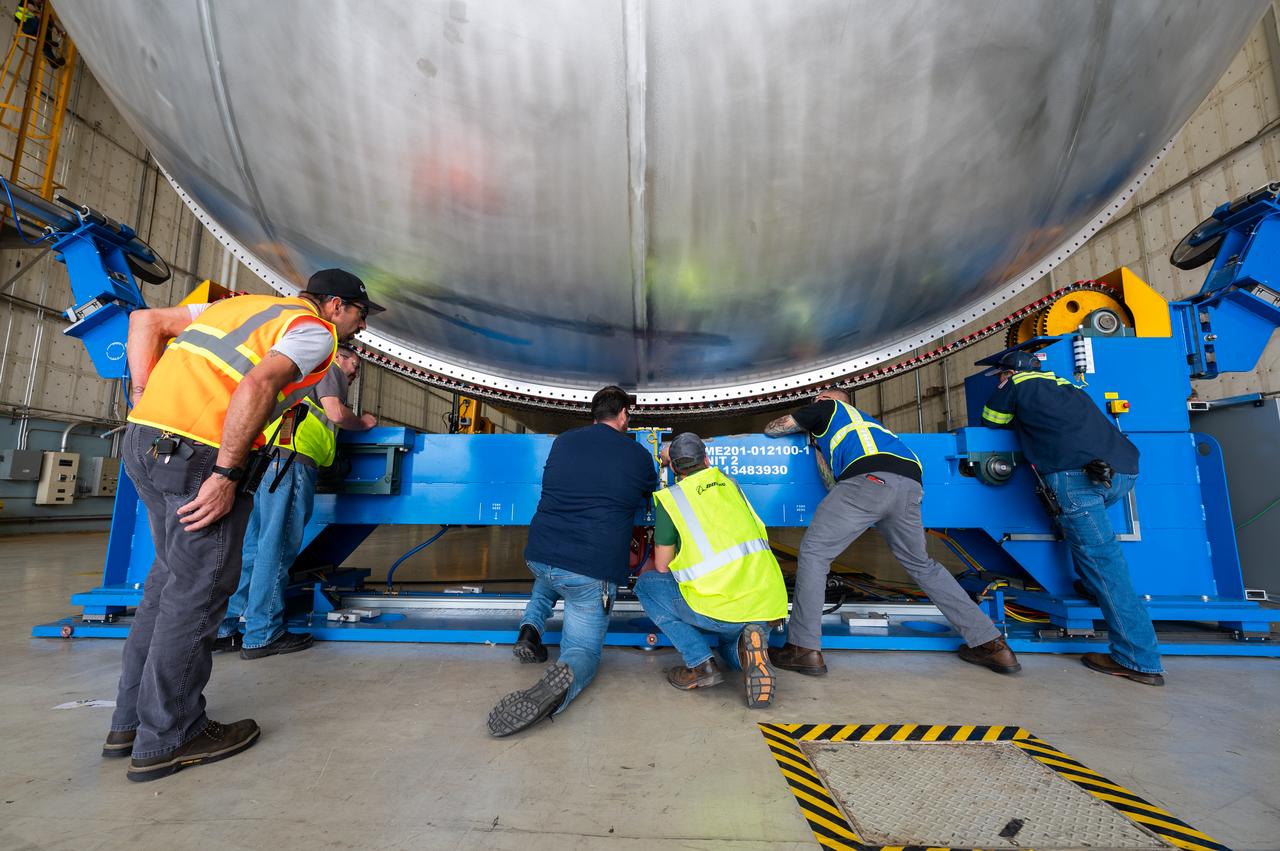

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface.
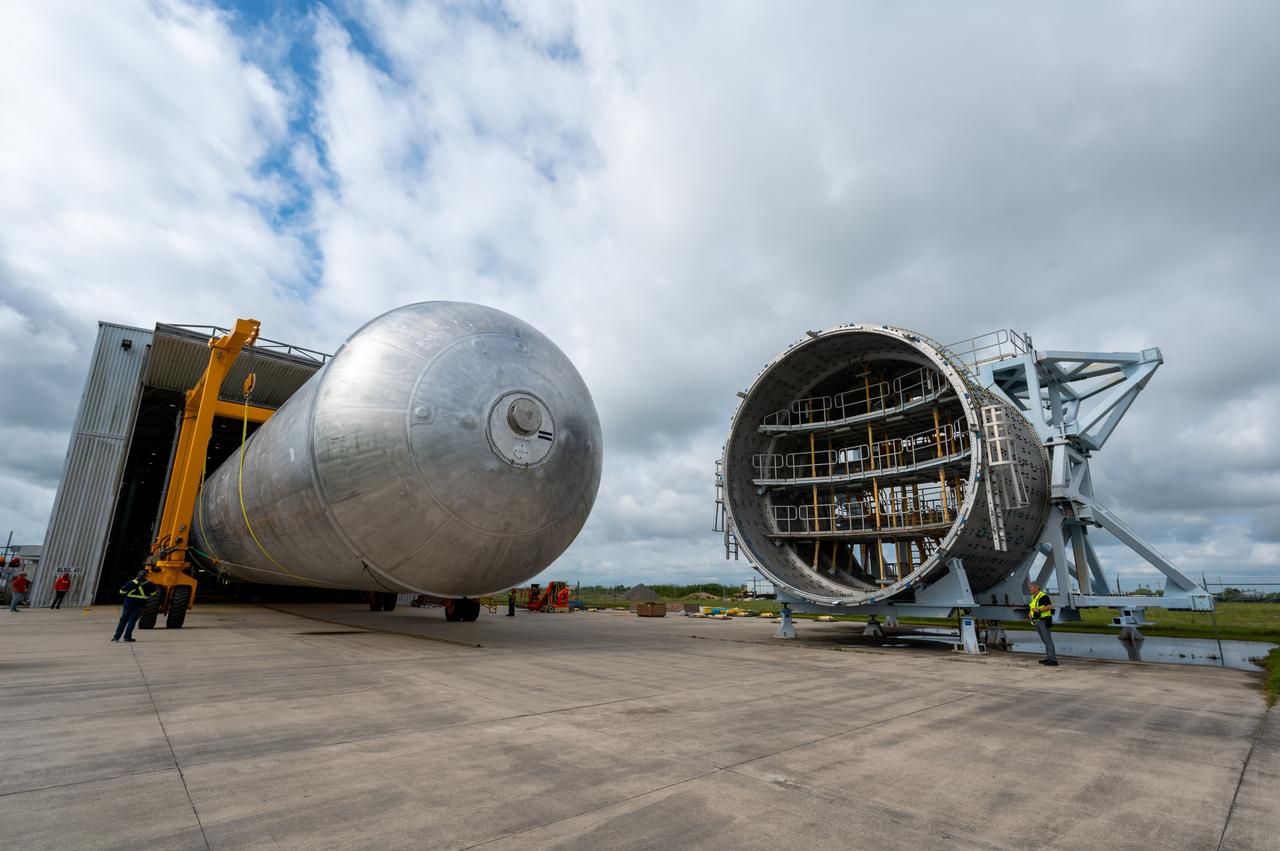

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface.
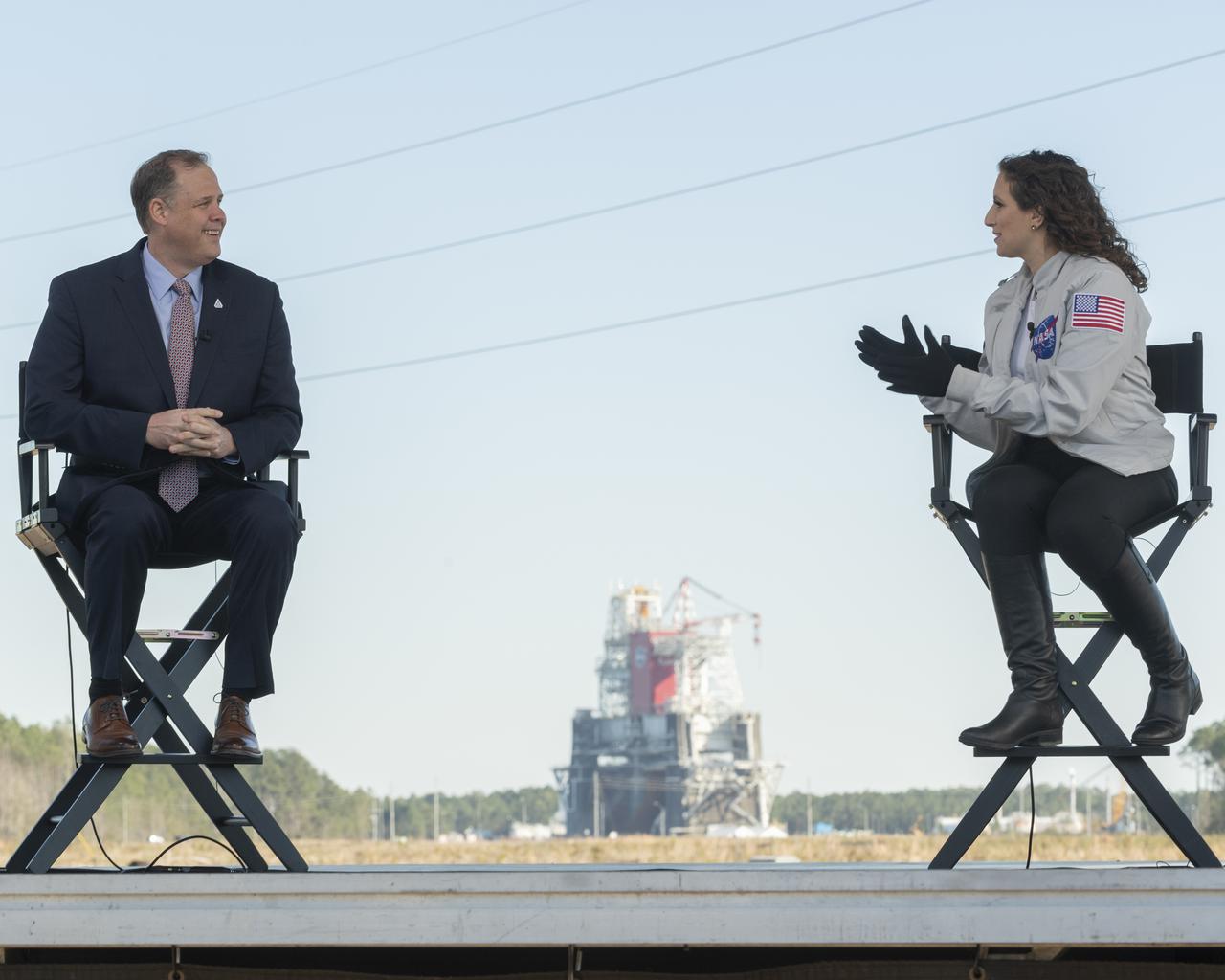

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine discusses the upcoming Green Run hot fire test on NASA television with Leigh D’Angelo of NASA, Saturday, January 16, 2021, at NASA's Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. In the background, the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand ahead of a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
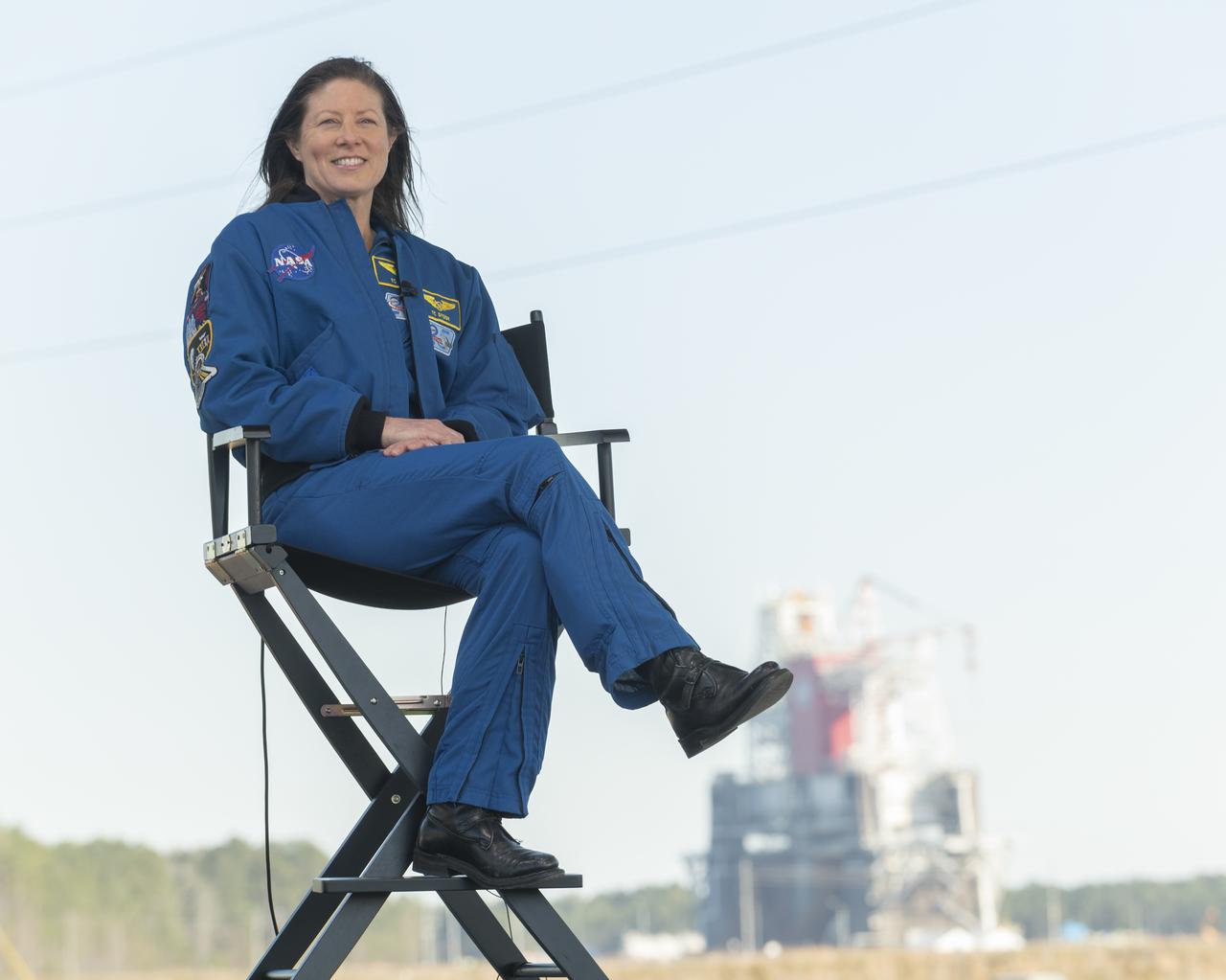

NASA astronaut Tracy Caldwell Dyson discusses the upcoming Green Run hot fire test on NASA television, Saturday, January 16, 2021, at NASA's Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. In the background, the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand ahead of a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
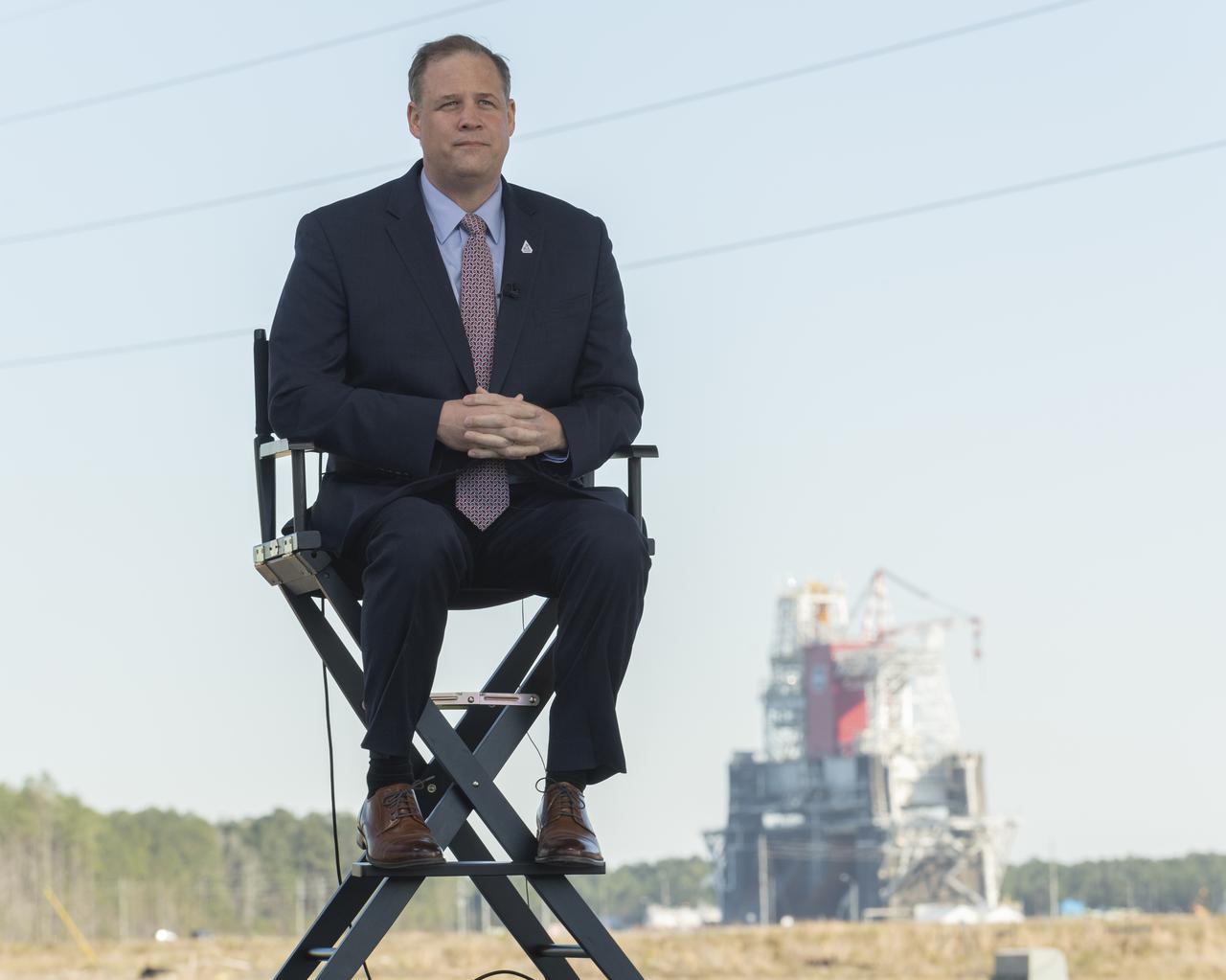

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine discusses the upcoming Green Run hot fire test on NASA television, Saturday, January 16, 2021, at NASA's Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. In the background, the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand ahead of a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
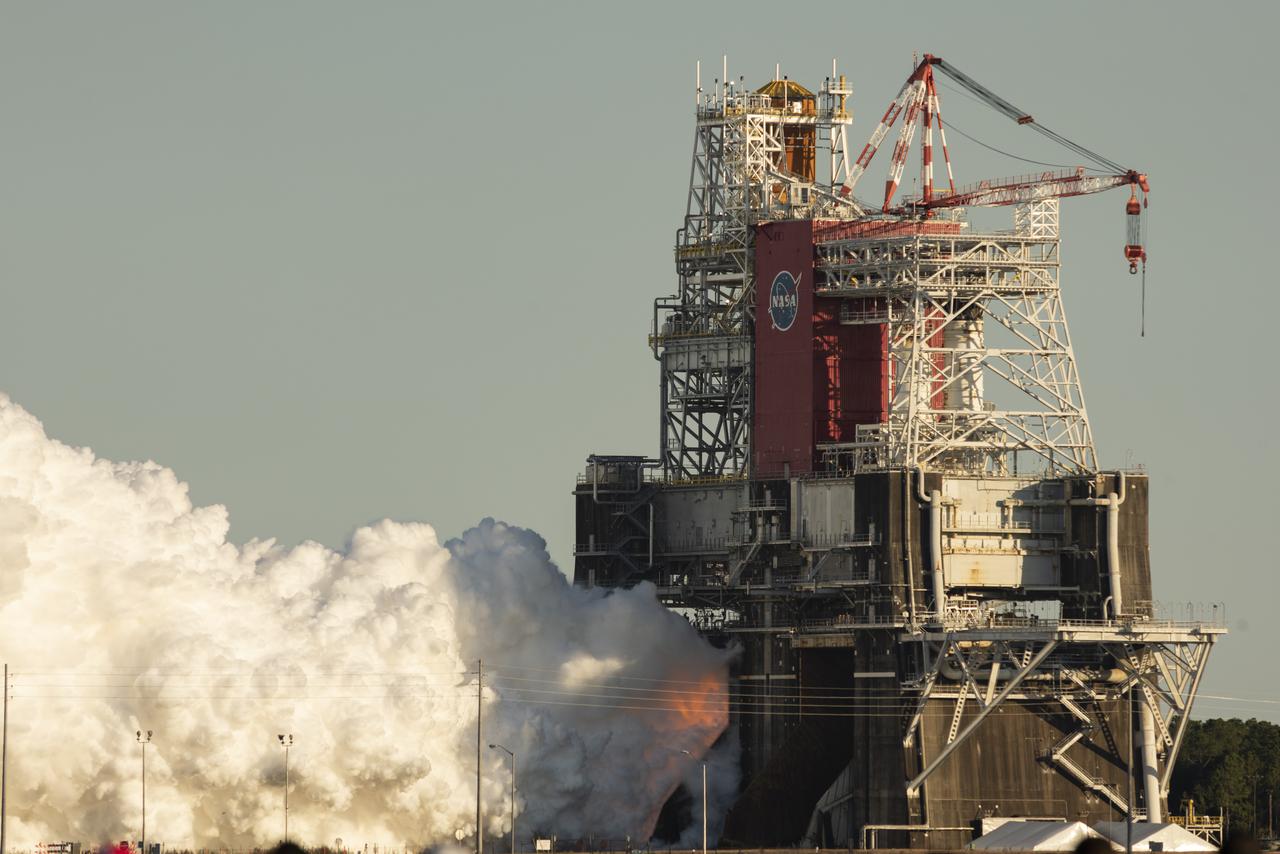

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
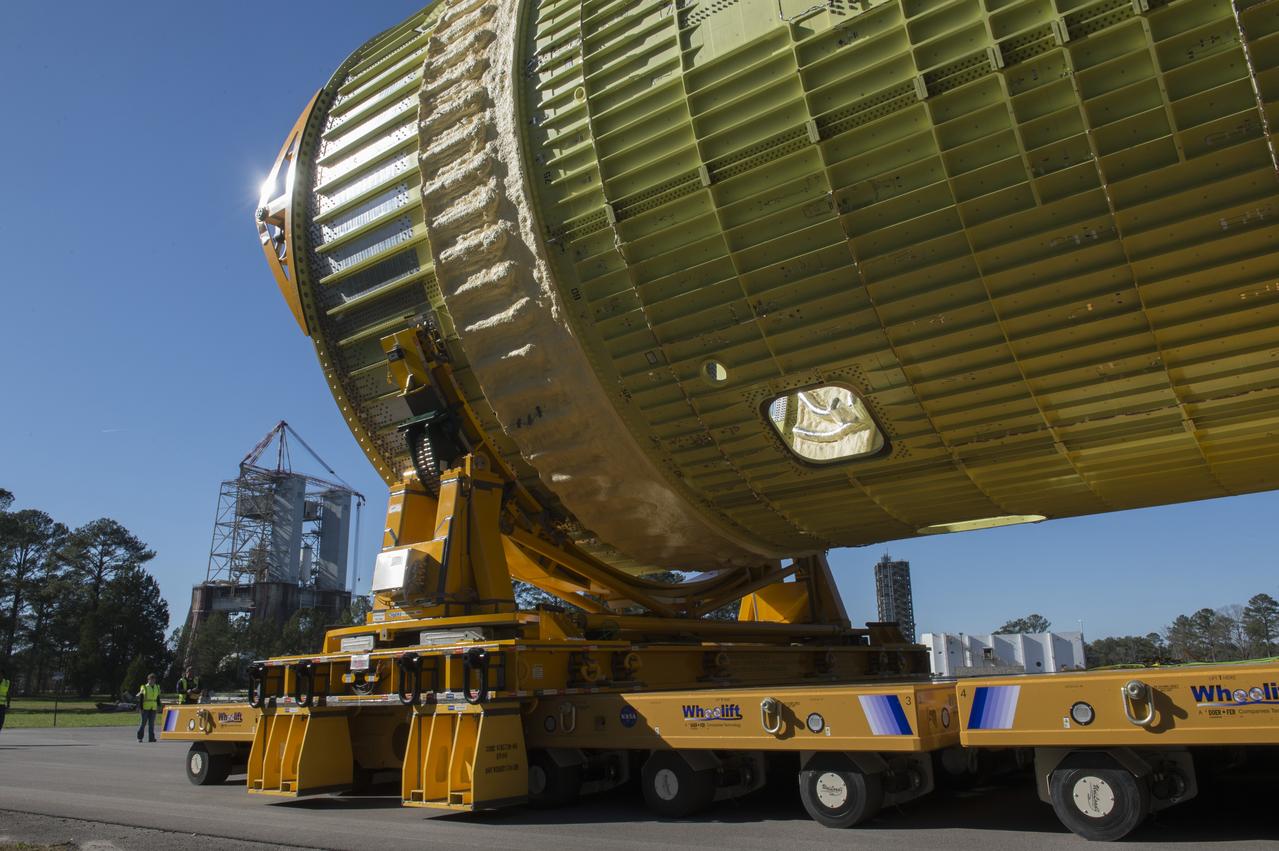

The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing via MSFC West Test Area. Historic Saturn 1-C test stand on far left, blockhouse 4670 on far right, SLS LH2 test stand, 4693, in center.
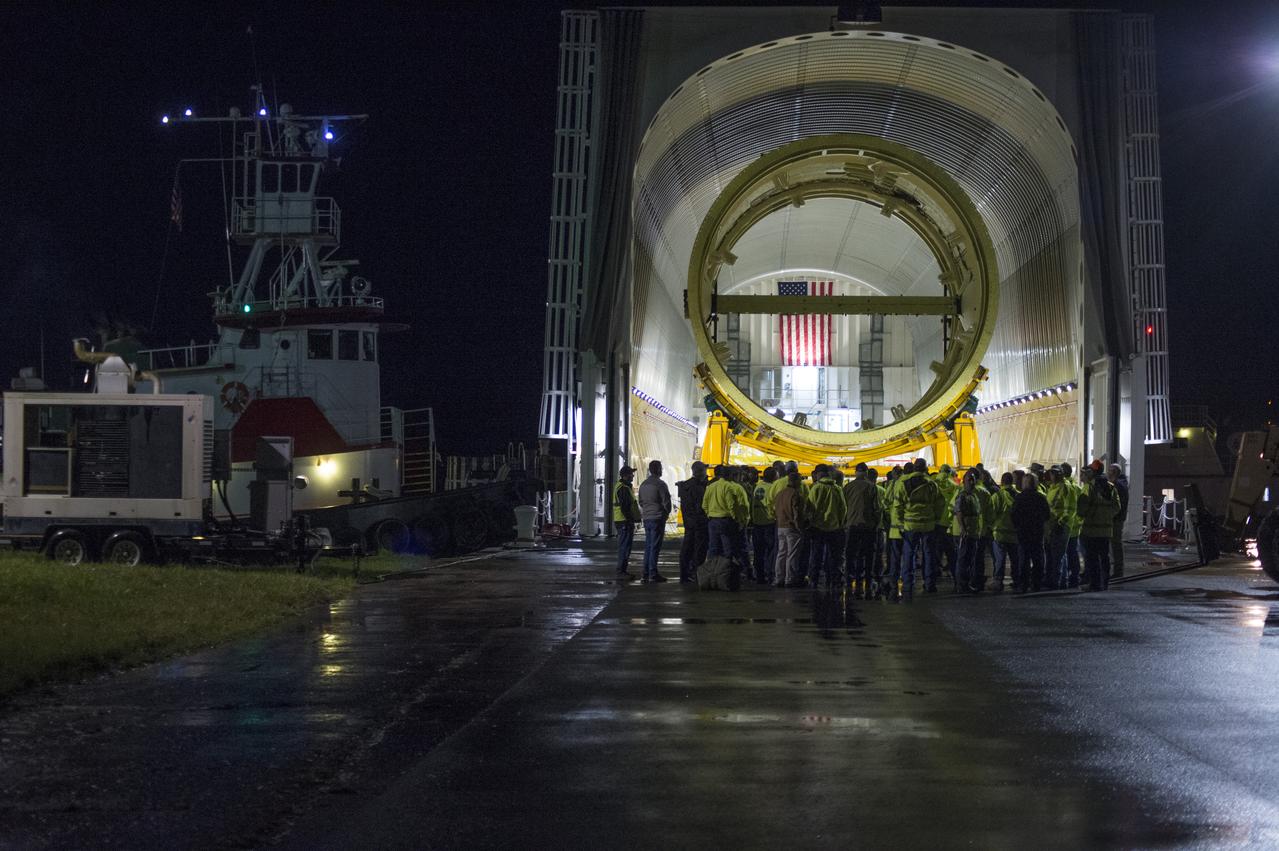

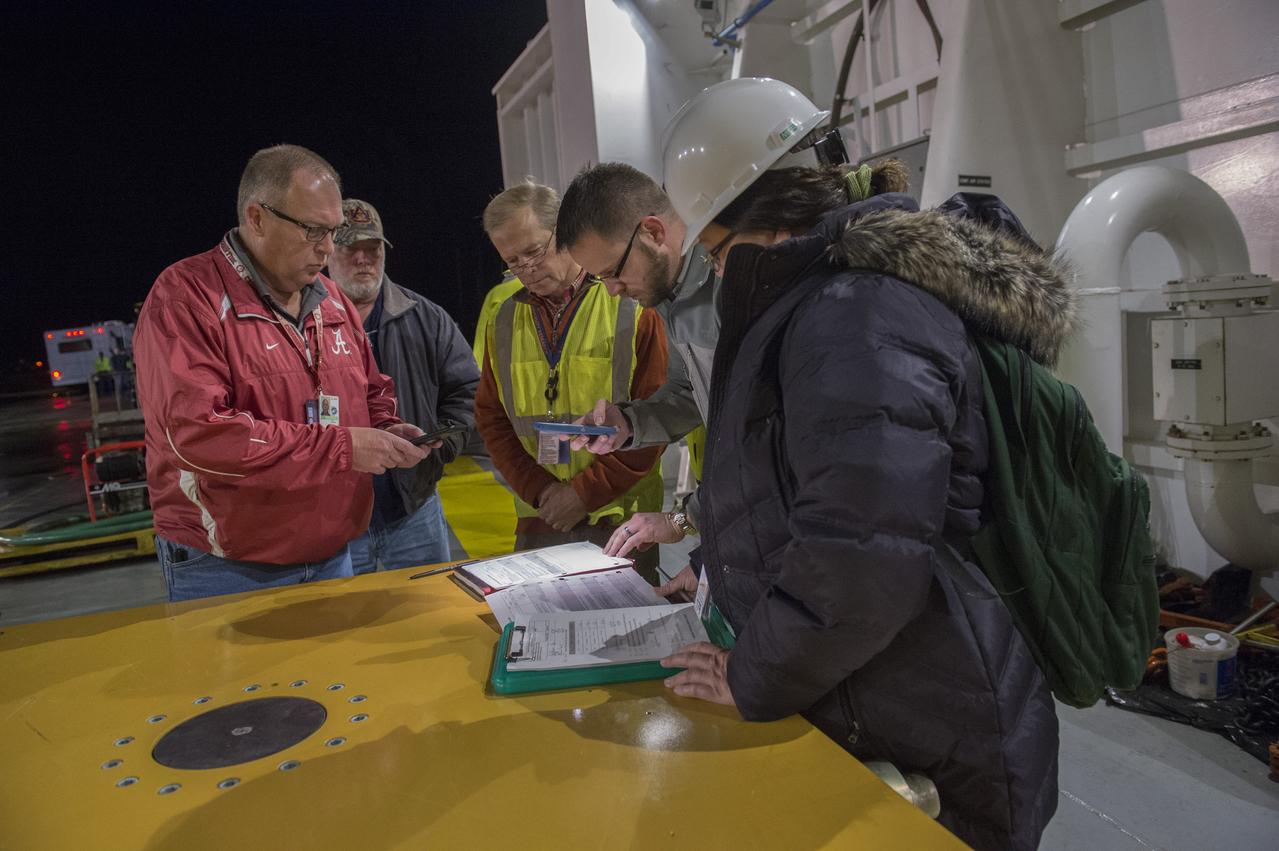
The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing. Members of MSFC Logistics Office and Move Team members gather for last minute instructions and safety briefing before off-loading STA hardware.
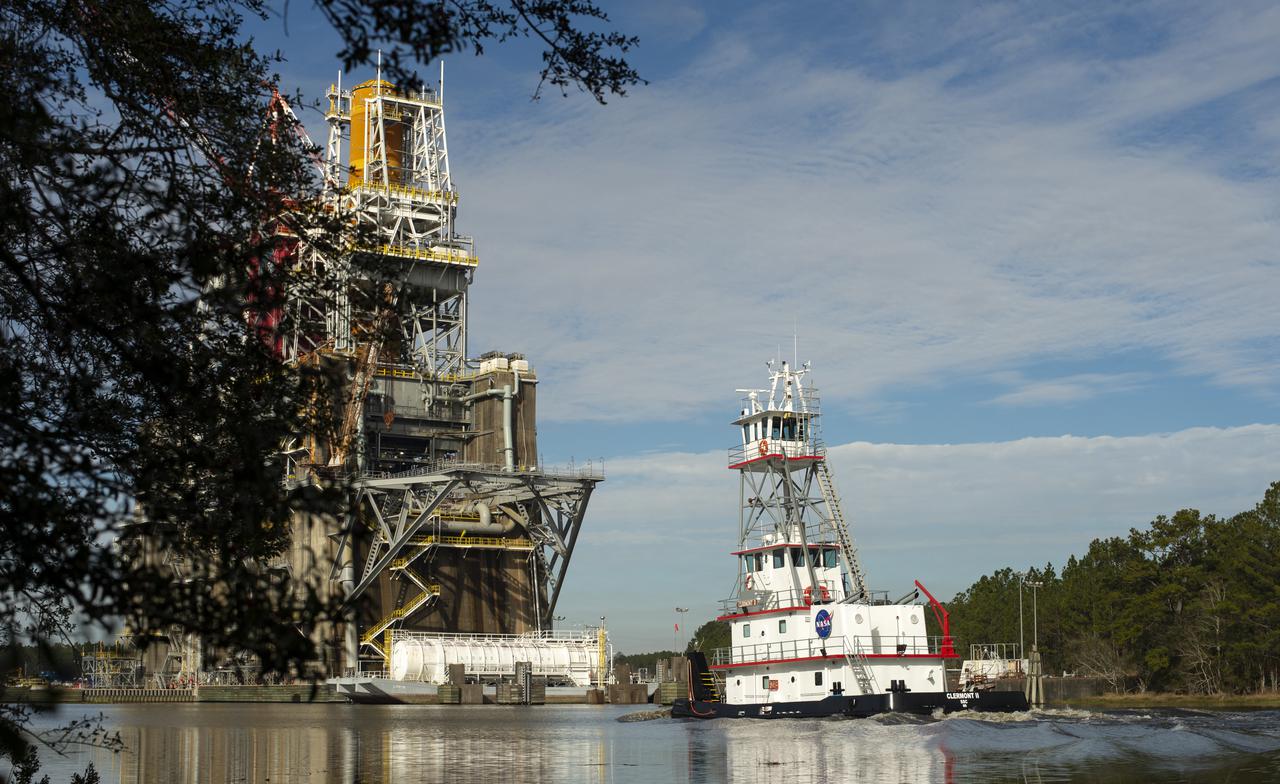

NASA tugboat Clermont II arrives at the B-2 Test Stand the day after a hot fire test of the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. During the test the four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
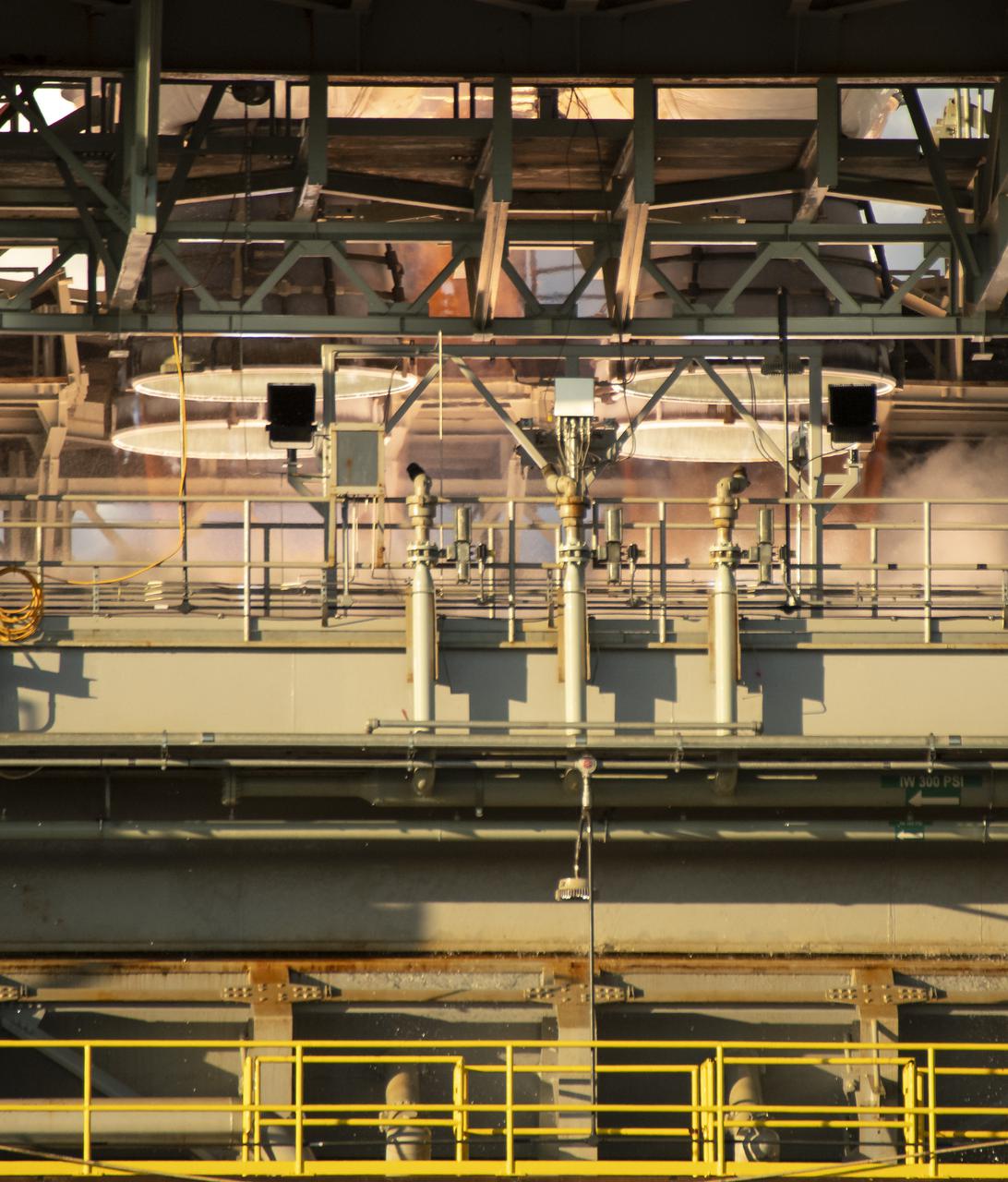

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
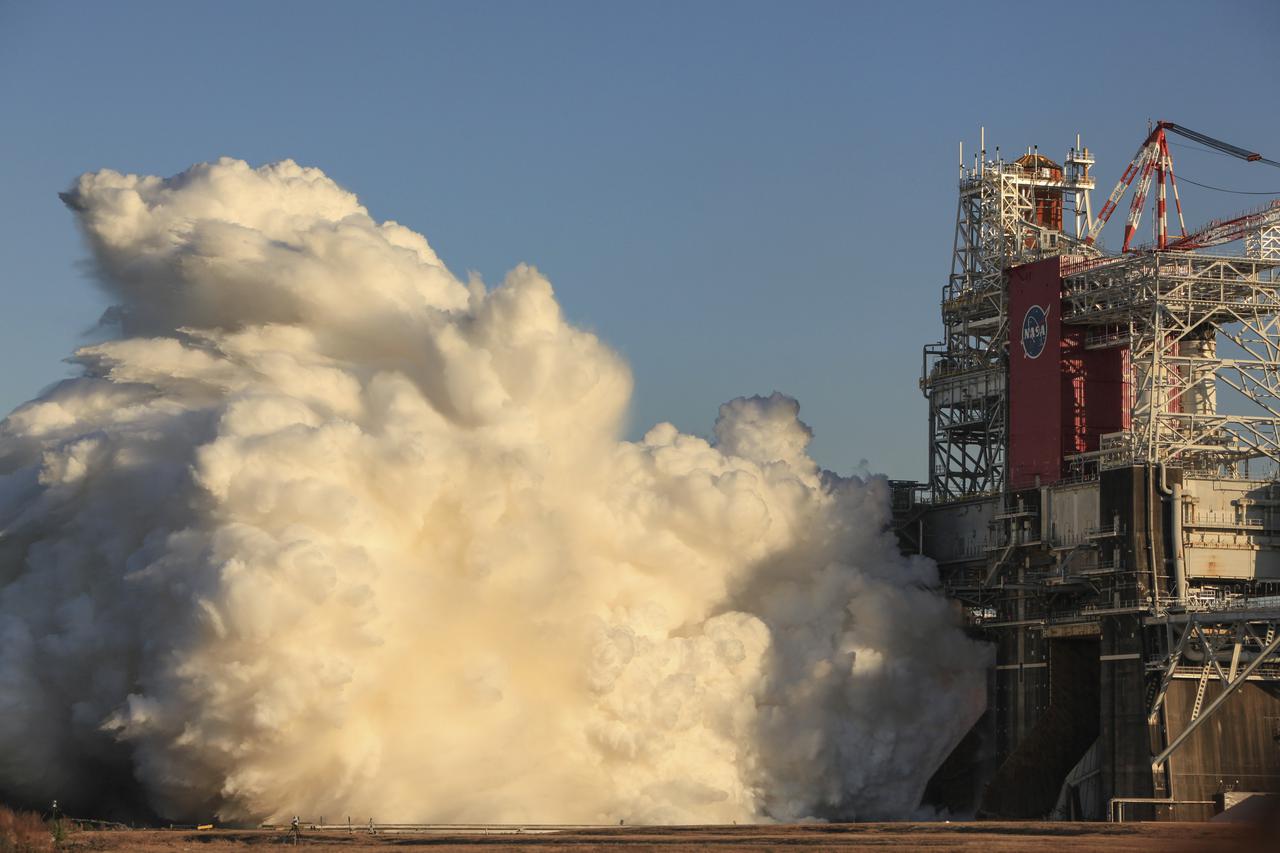

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
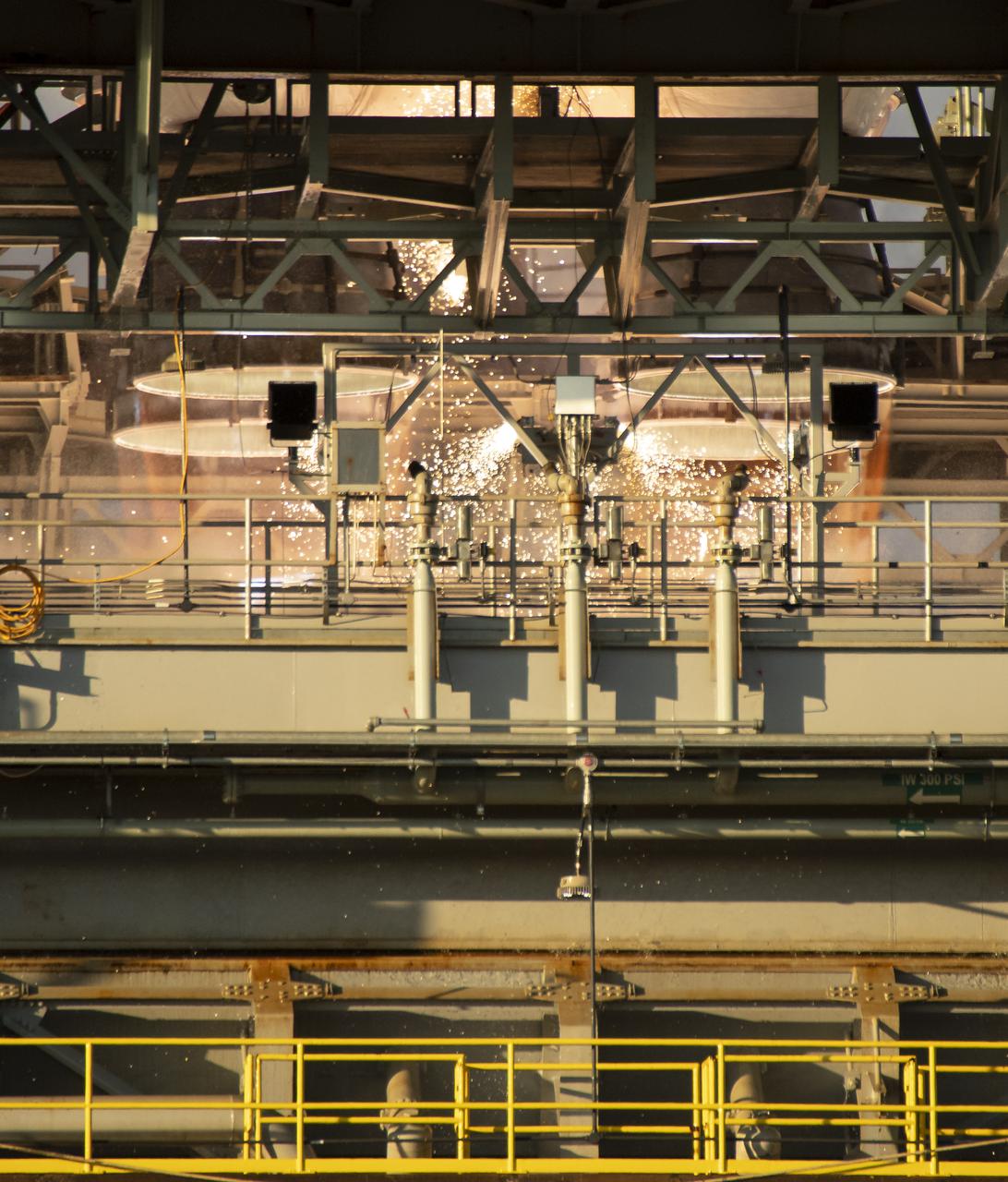

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
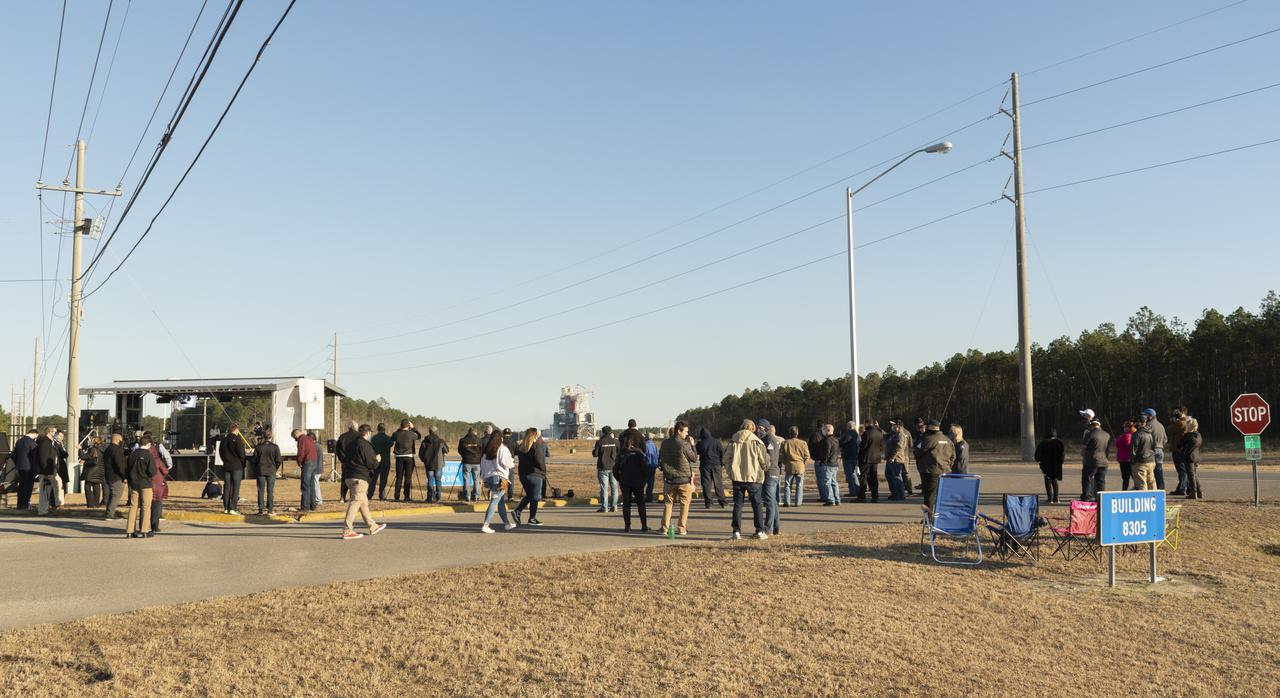

NASA guests gather to watch as the core stage for the first flight of NASA's Space Launch System rocket undergoes a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test in the B-2 Test Stand, January 16, 2021, at NASA's Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)

Invited media gather to report as the core stage for the first flight of NASA's Space Launch System rocket undergoes a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test in the B-2 Test Stand, Saturday, January 16, 2021, at NASA's Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
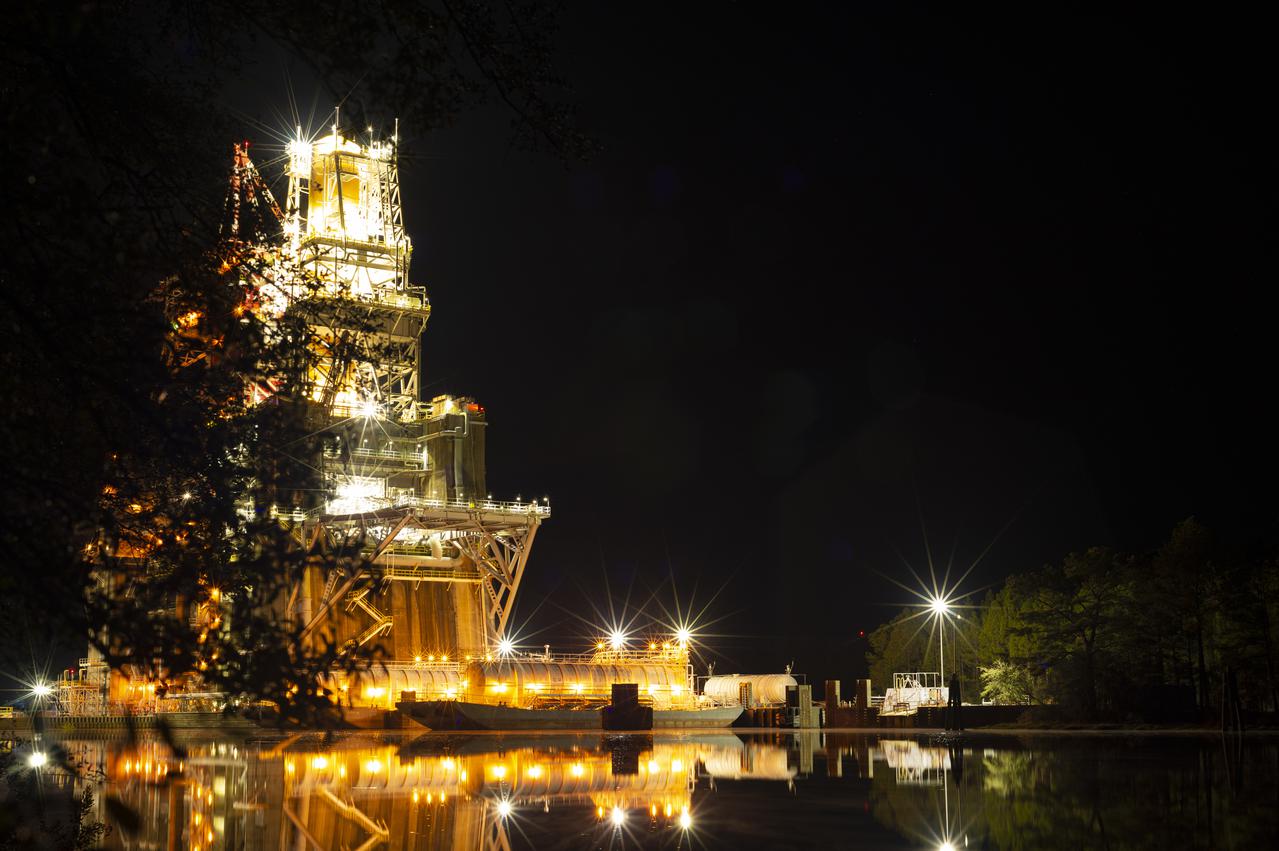

The B-2 Test Stand with the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in later in the evening after a hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
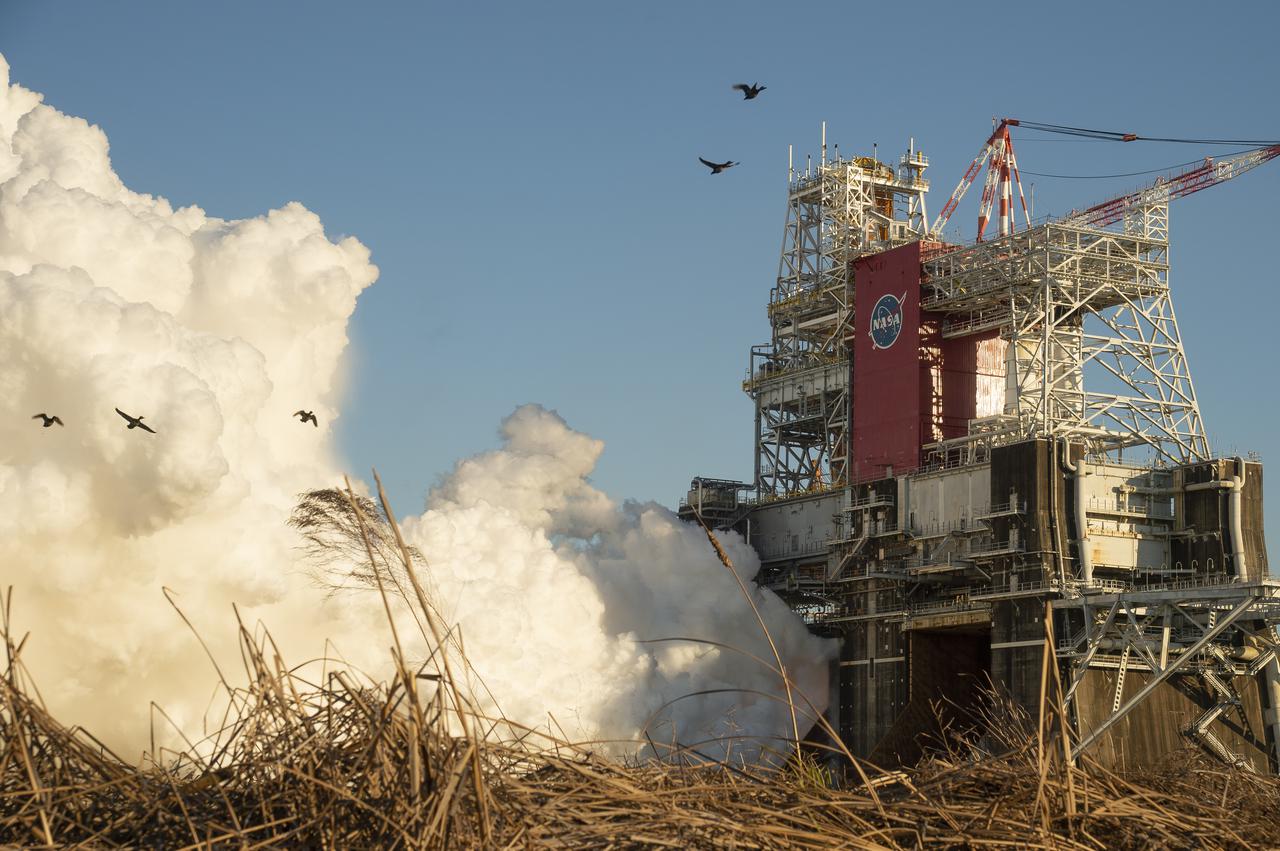

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
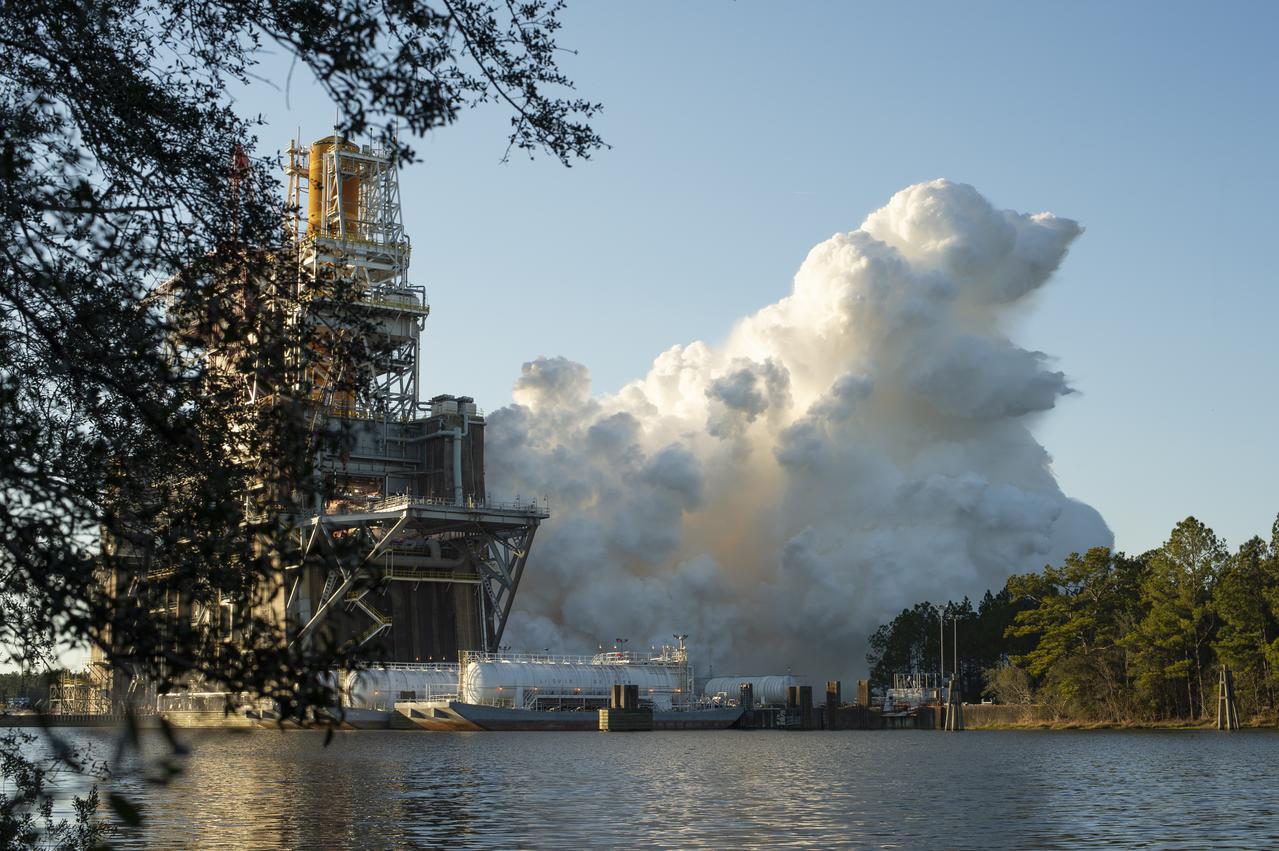

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
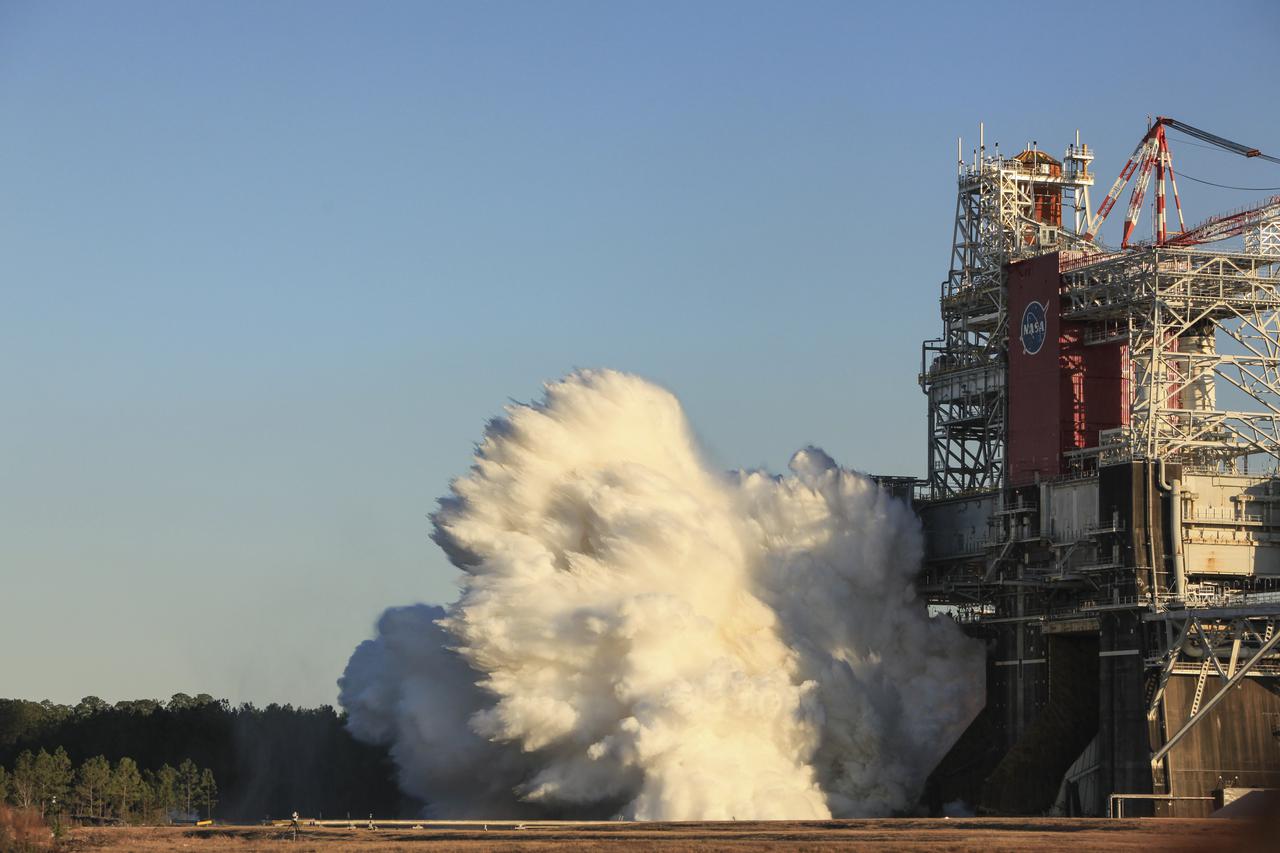

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
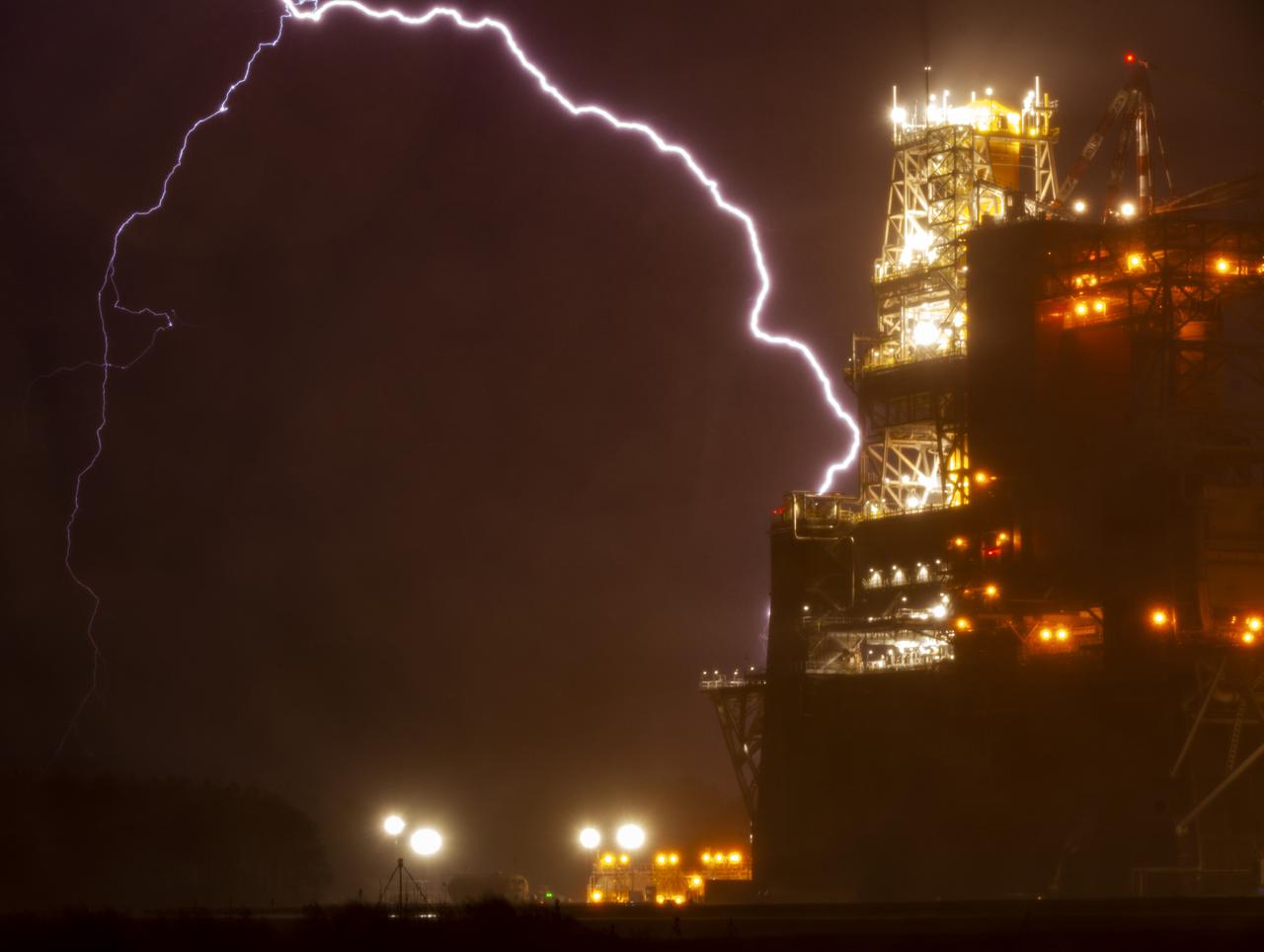

A bolt of lightning is seen near the B-2 Test Stand the night before a second hot fire test of the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket, Wednesday, March 17, 2021 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
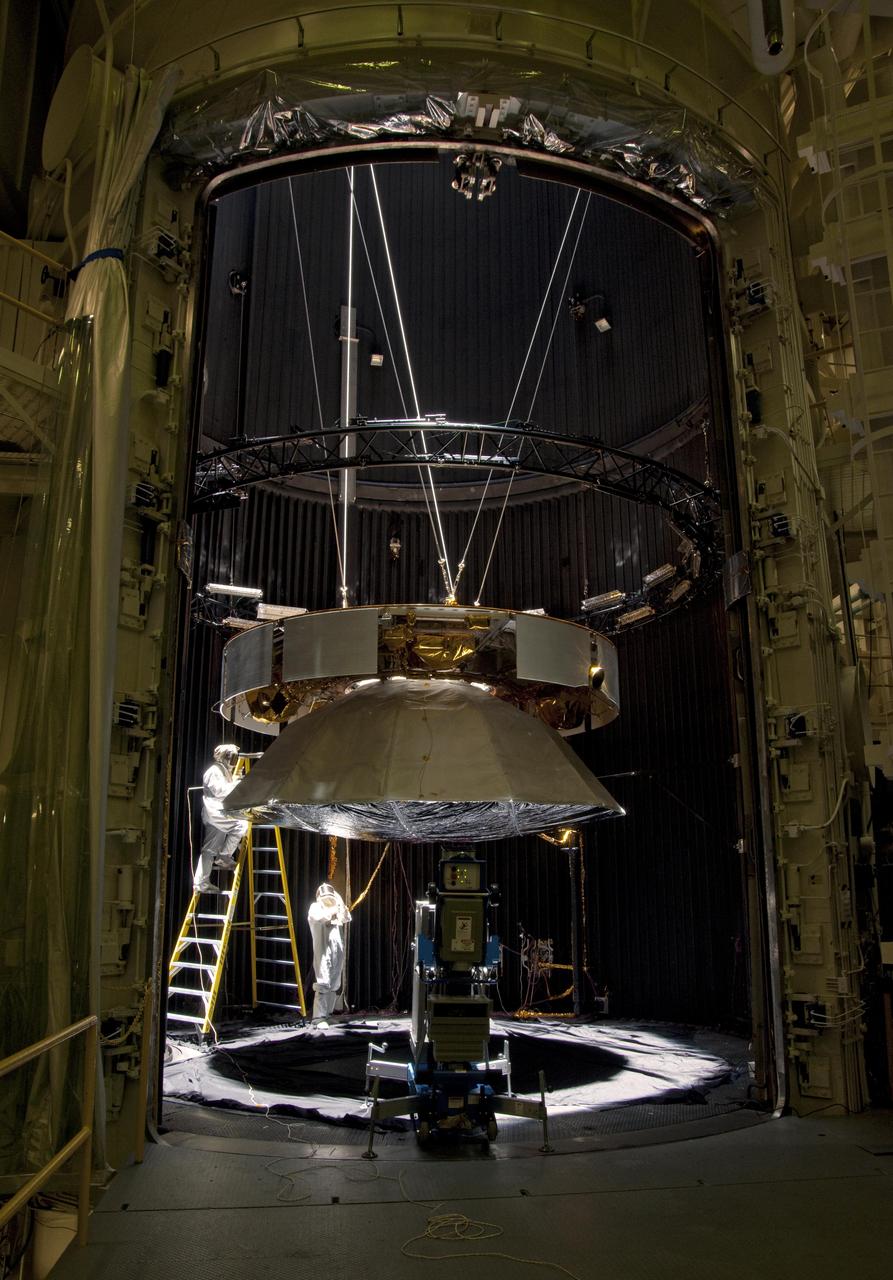

Testing of the cruise stage for NASA Mars Science Laboratory in August 2010 included a session in a facility that simulates the environment found in interplanetary space. Spacecraft technicians at JPL prepare a space-simulation test.
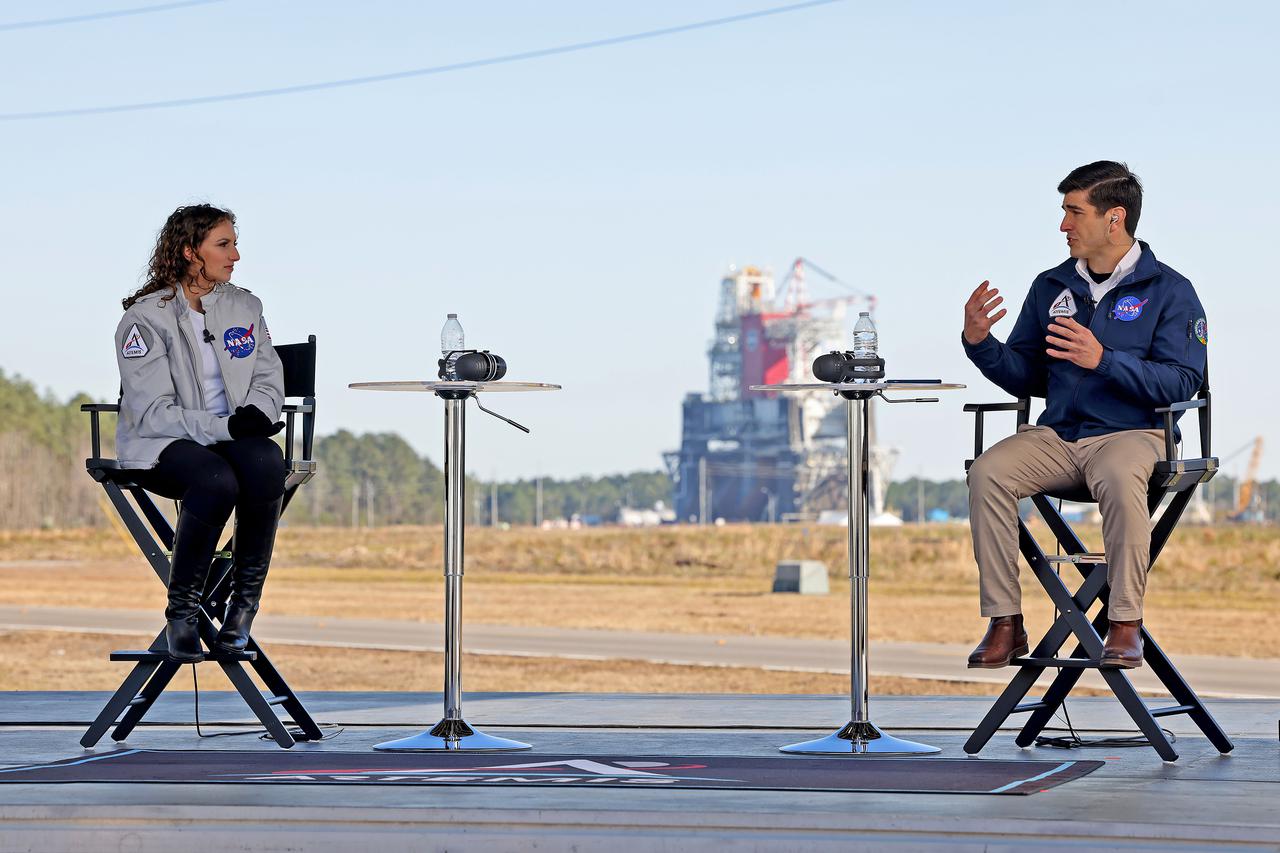

Host Leigh D’Angelo (left) talks with NASA Space Launch System core stage engineer Alex Cagnola from Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, during NASA TV live coverage from Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Jan. 16, 2021. D’Angelo, also from Michoud Assembly Facility, hosted the NASA TV coverage prior to the hot fire test of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
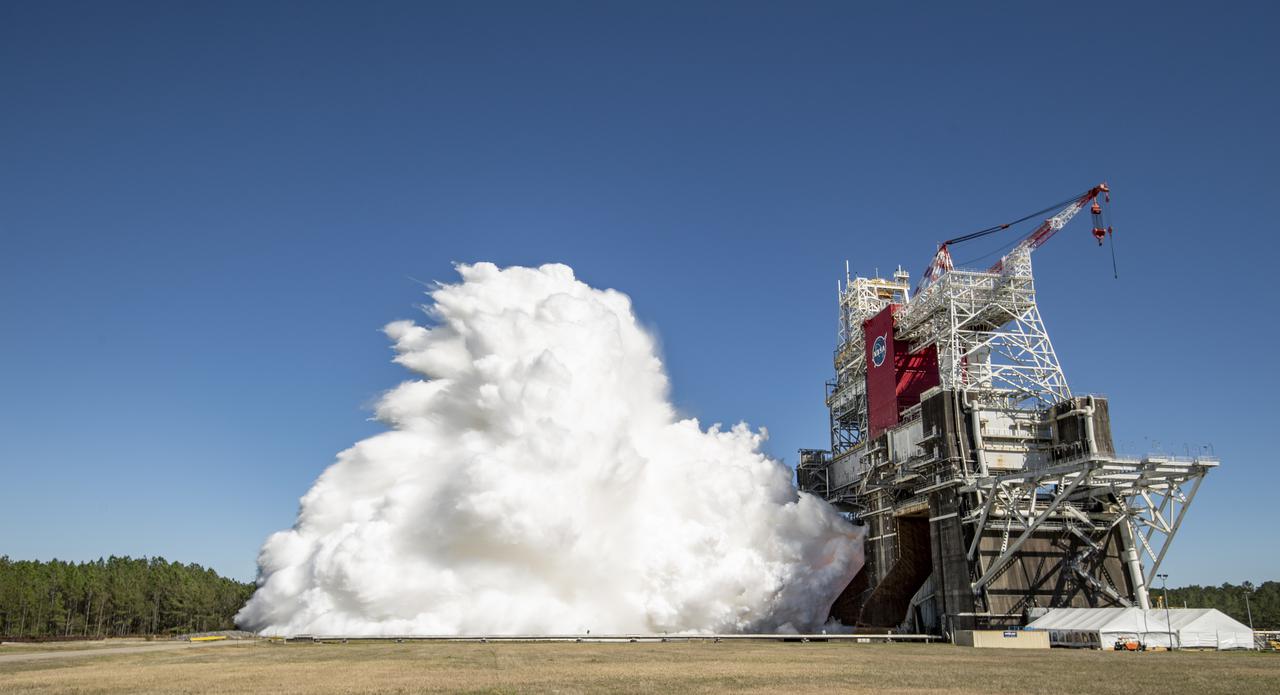

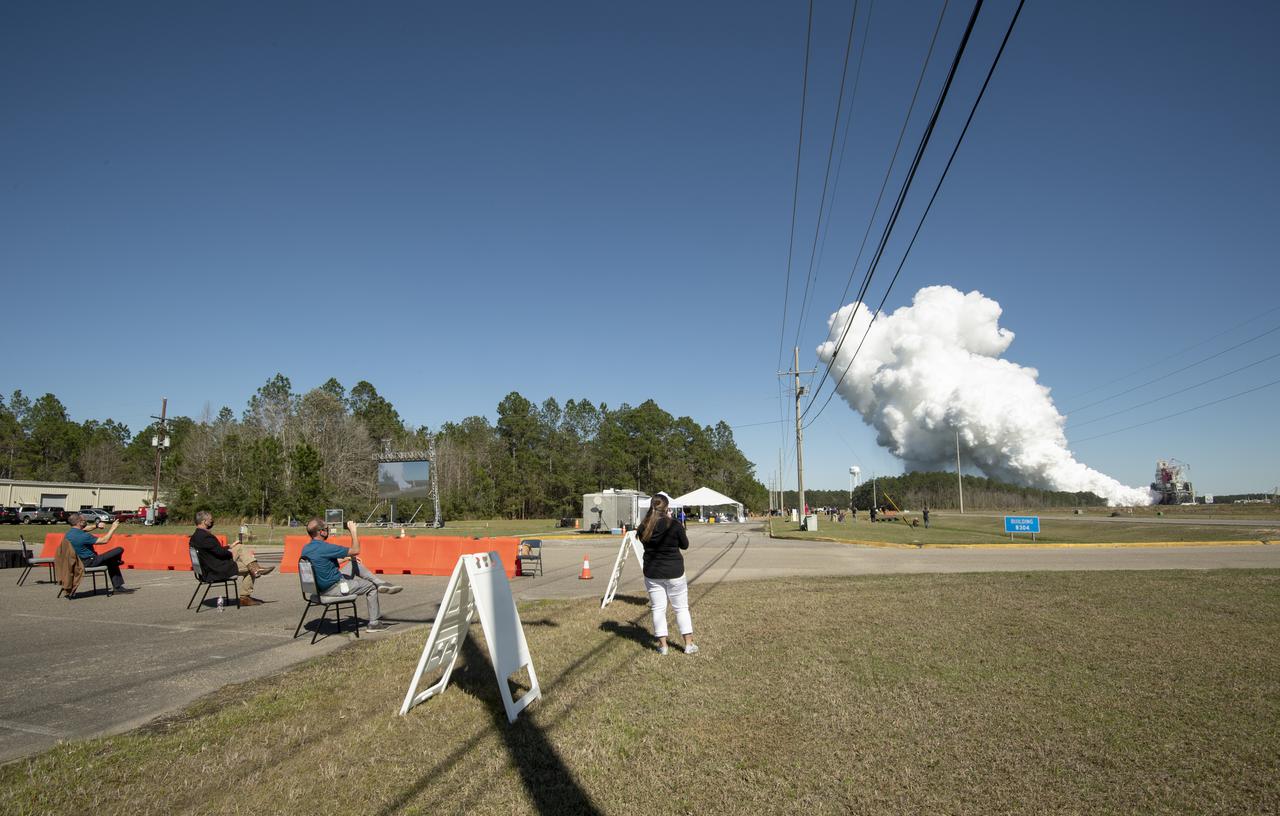
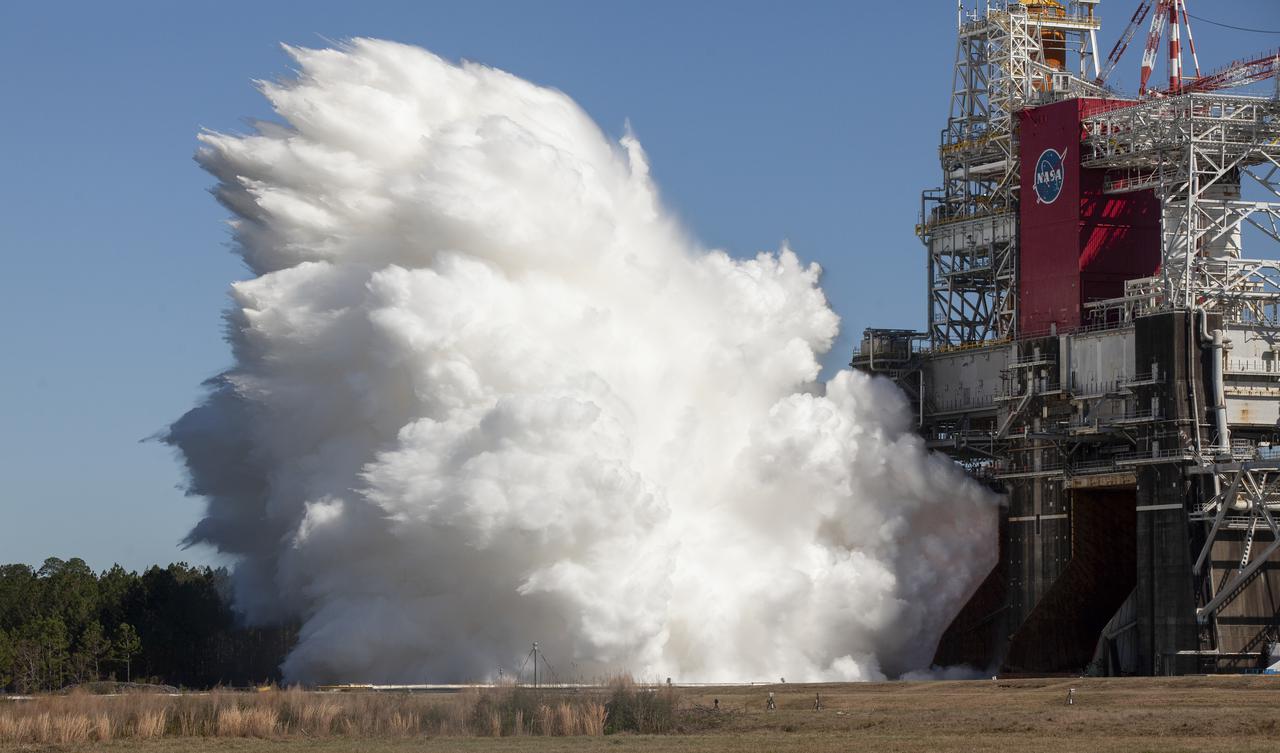
The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
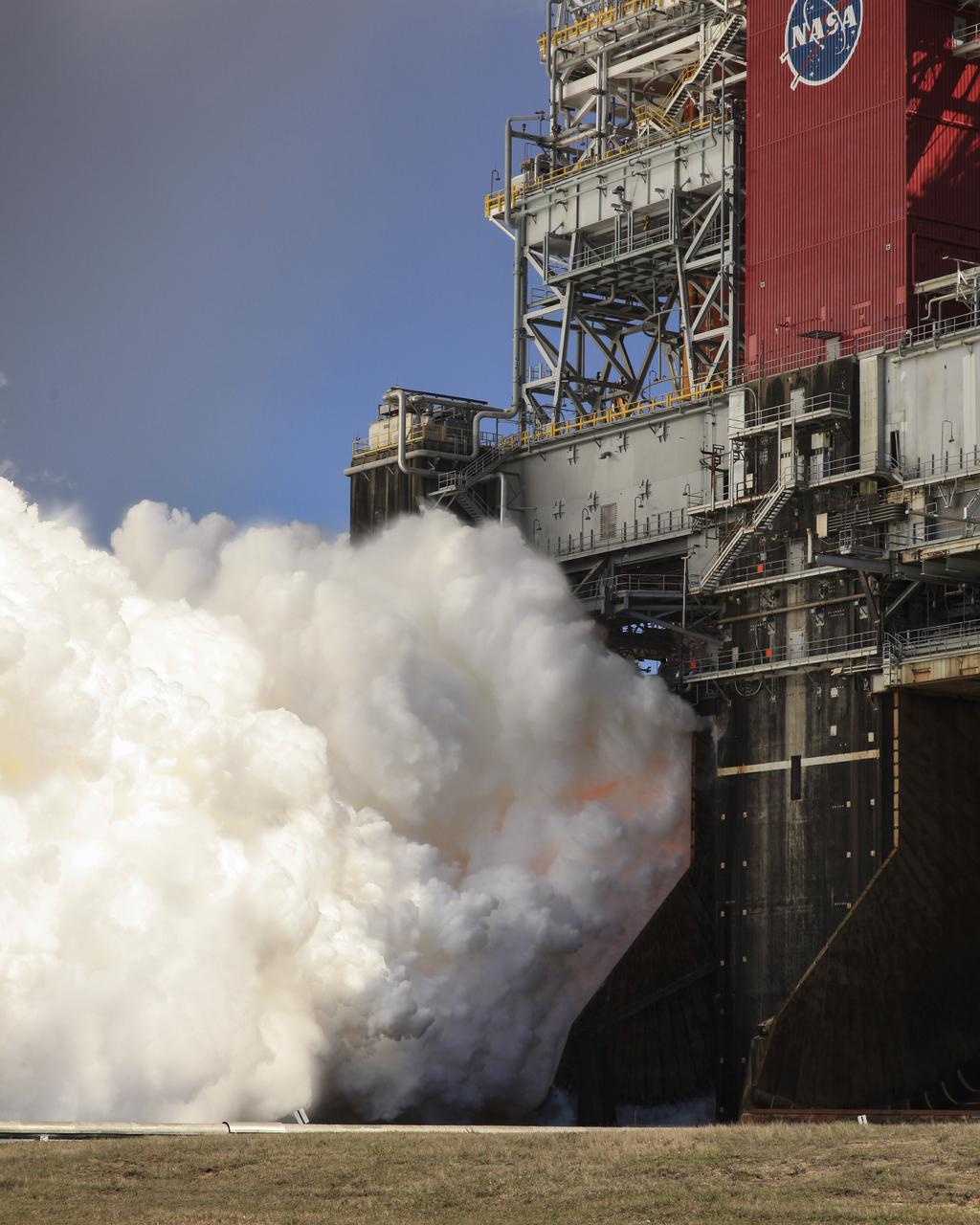

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
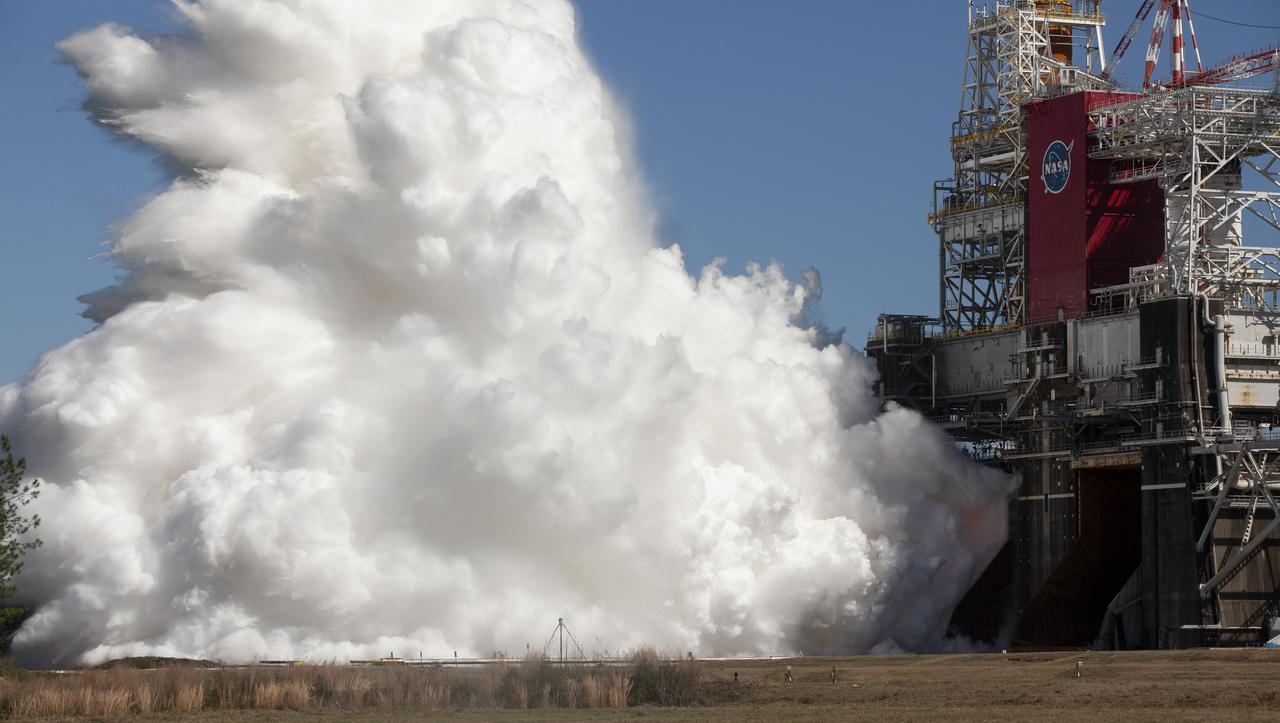

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
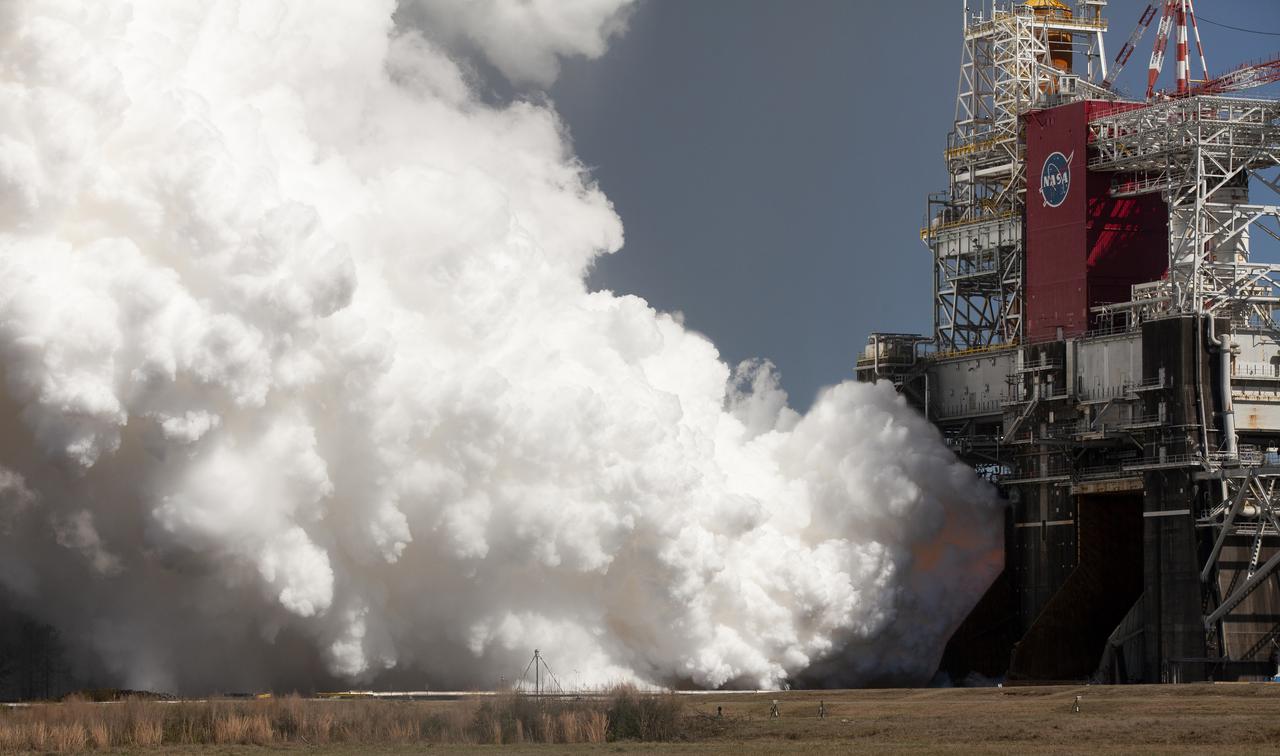

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
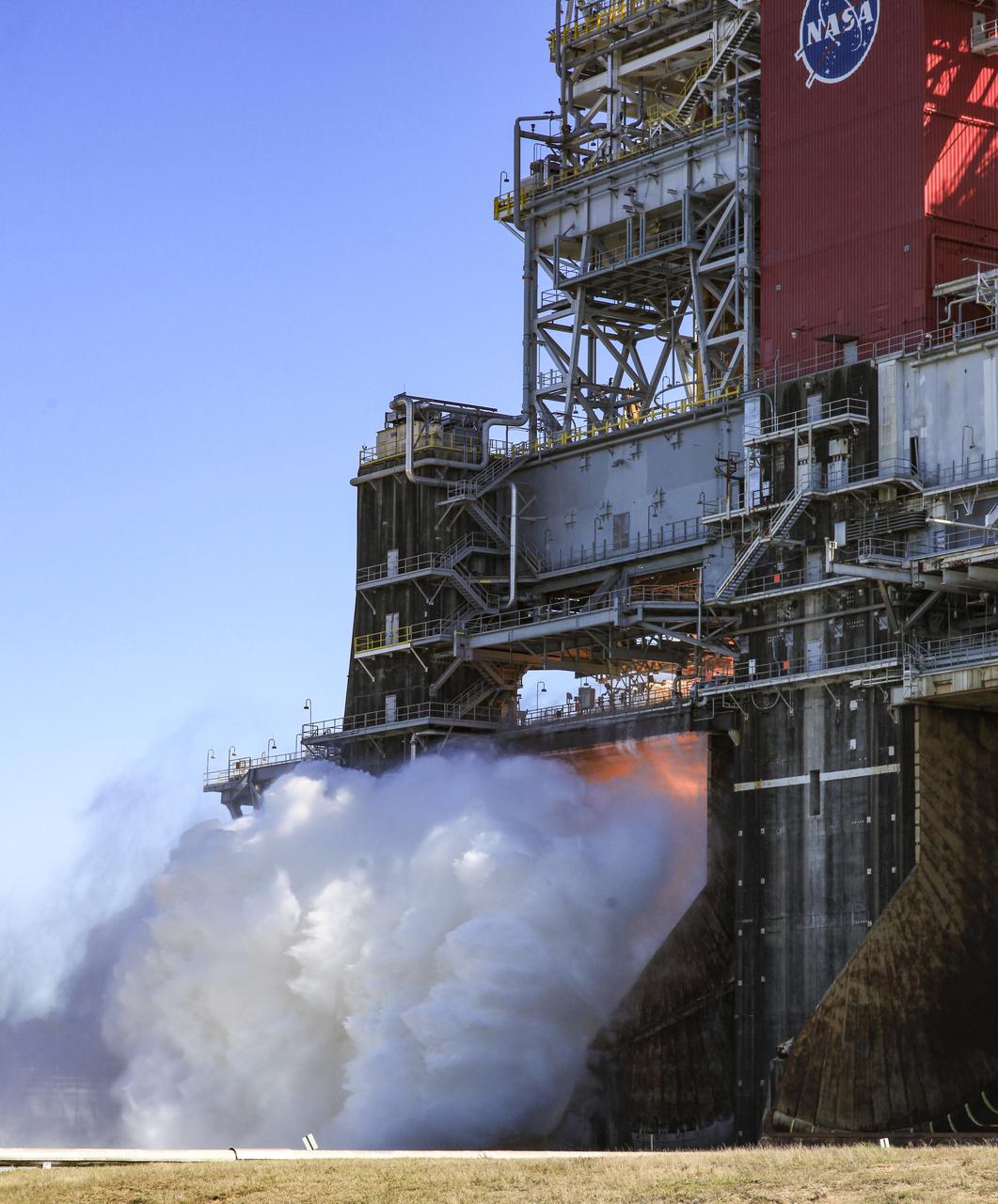

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
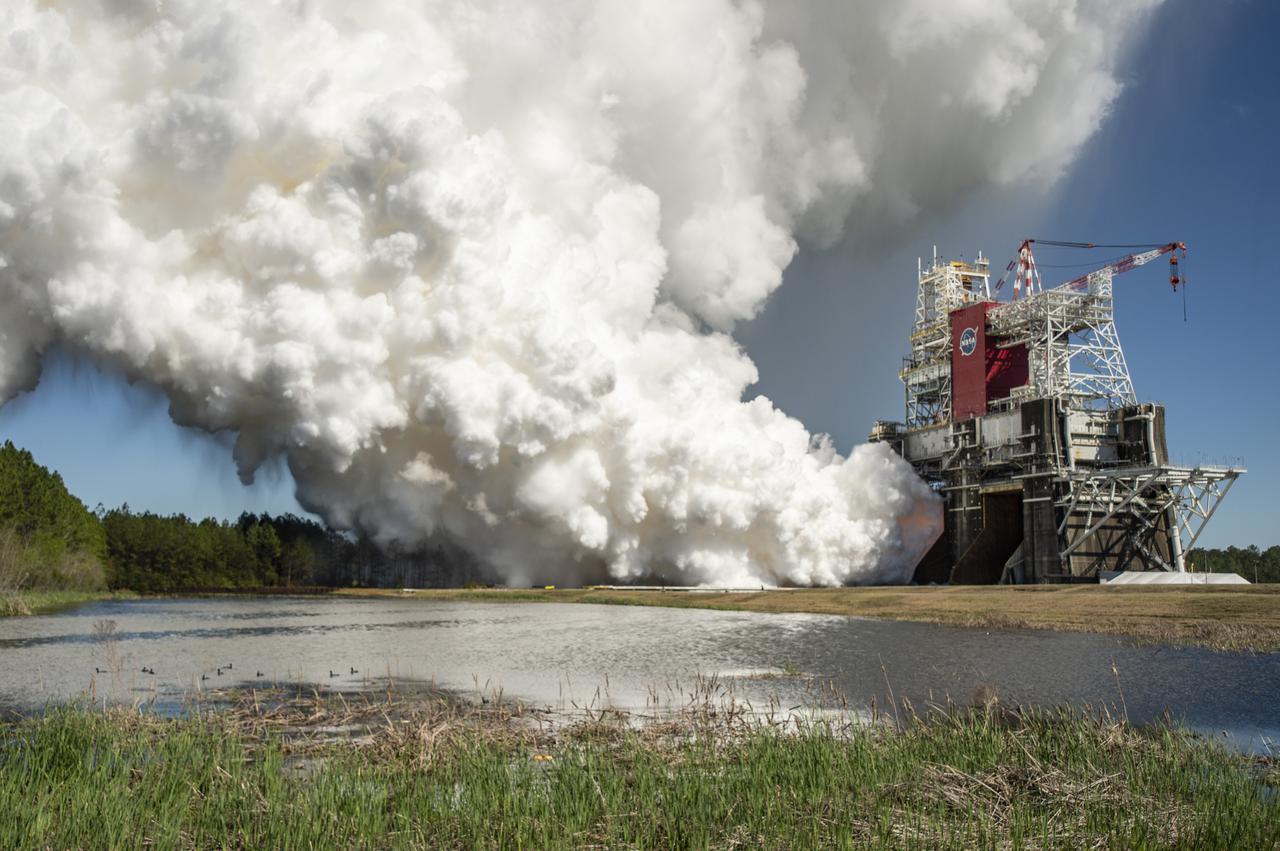

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
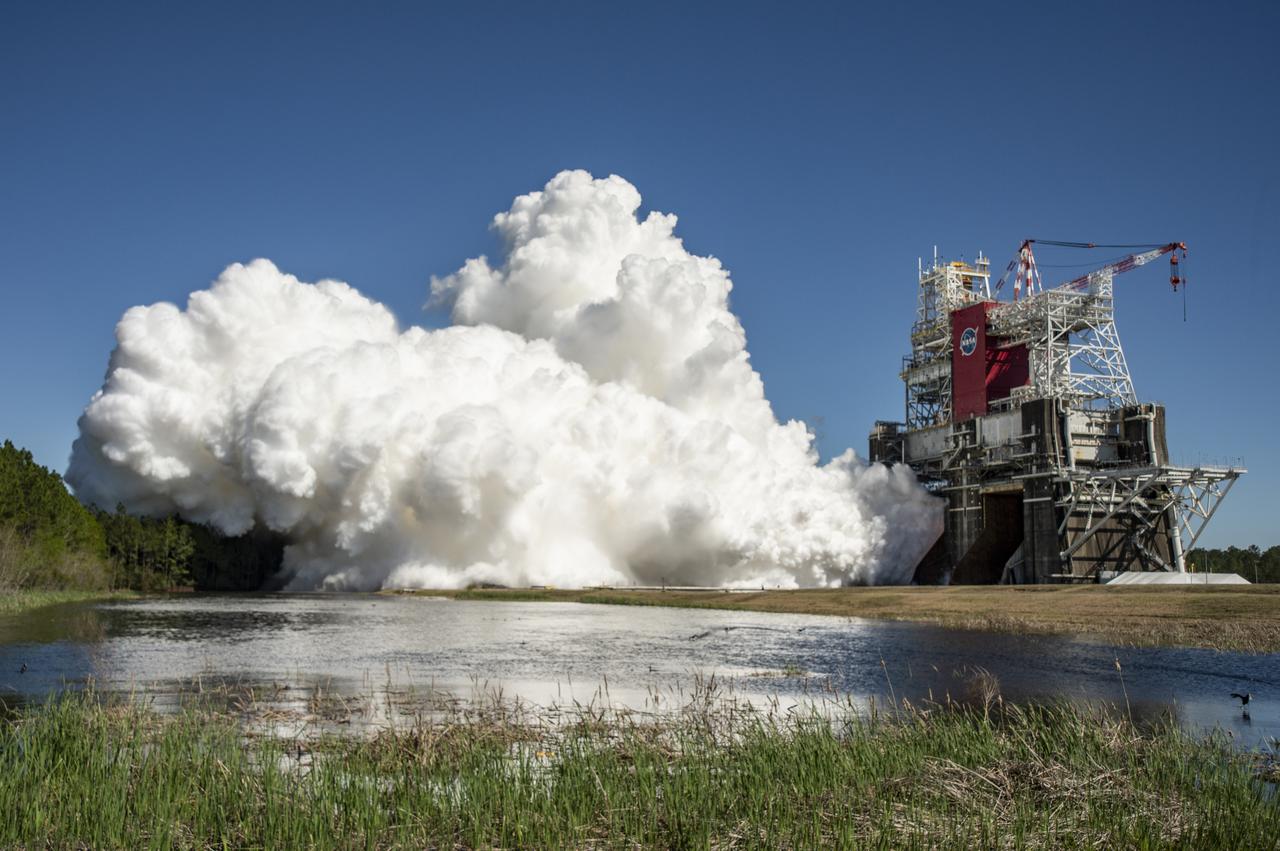

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
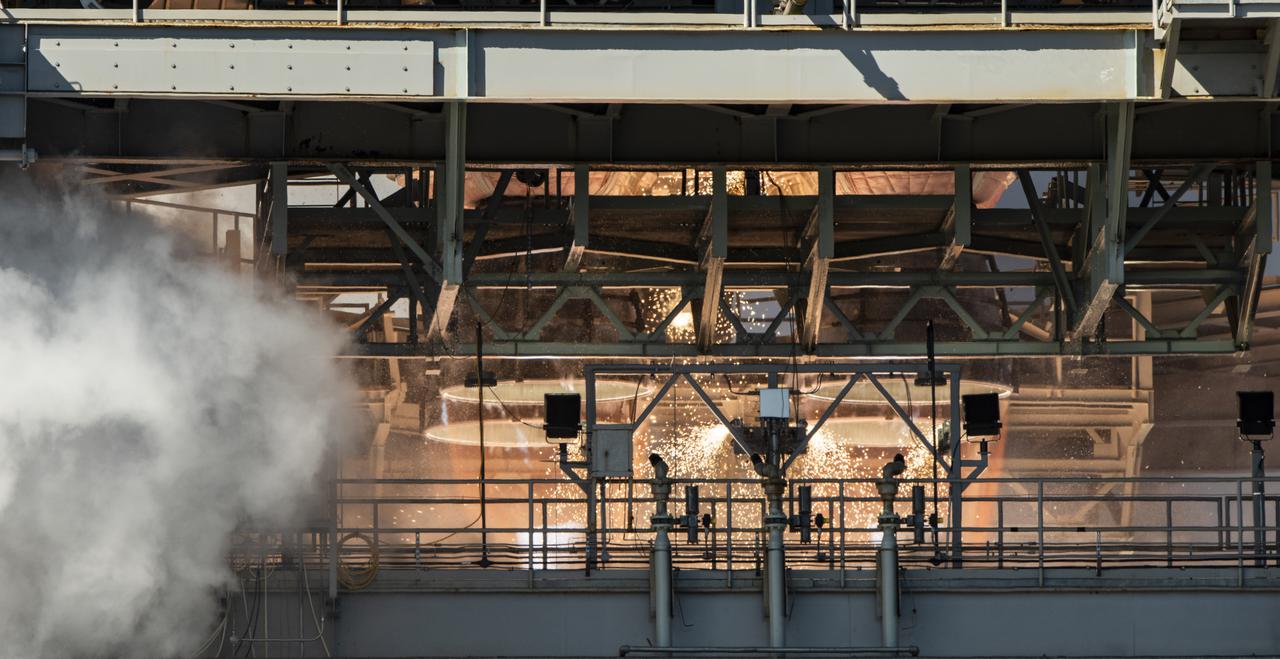

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)

Invited guests watch as the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket undergoes a second hot fire test in the B-2 Test Stand, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
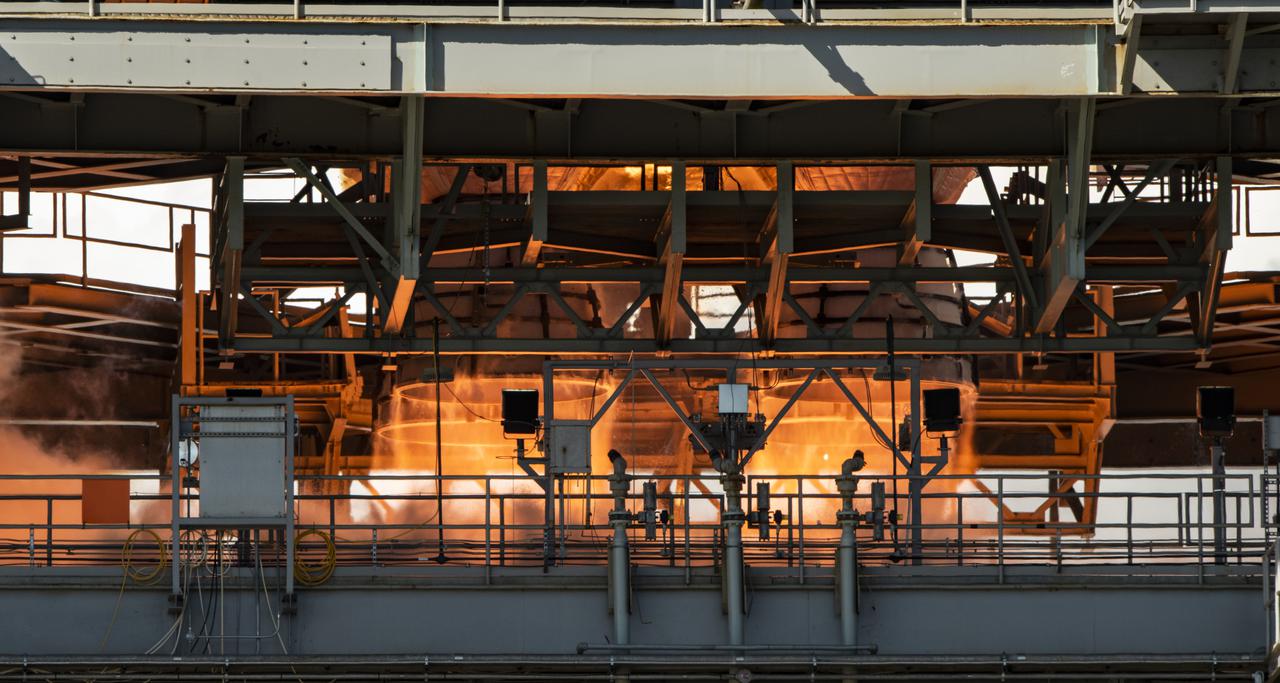

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
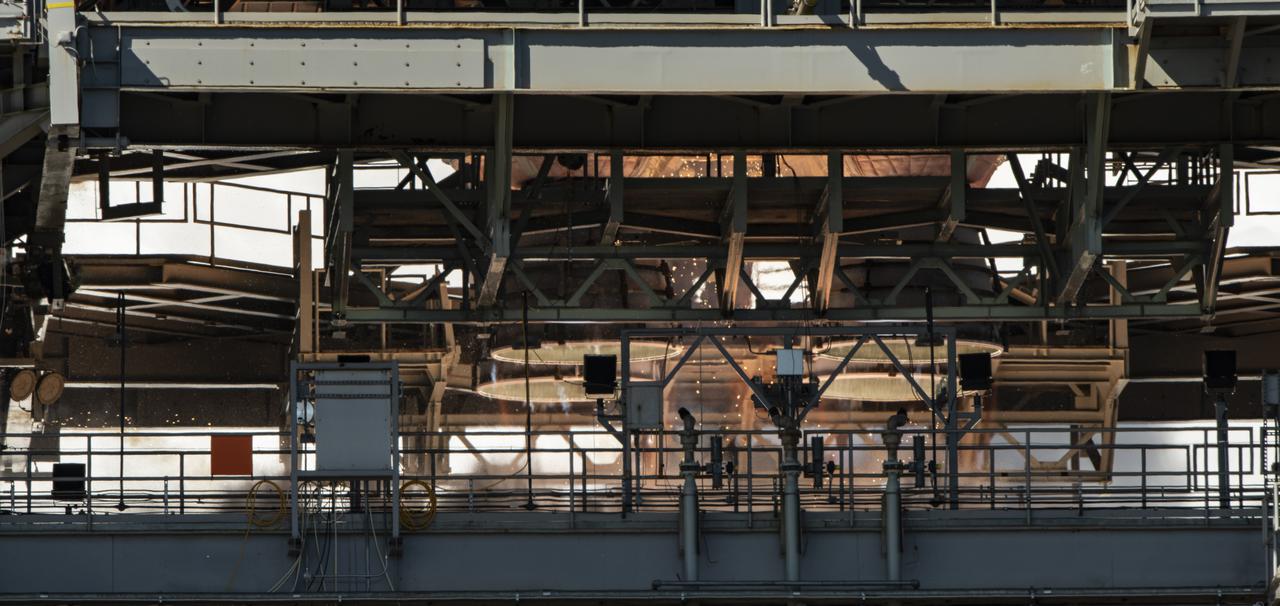

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
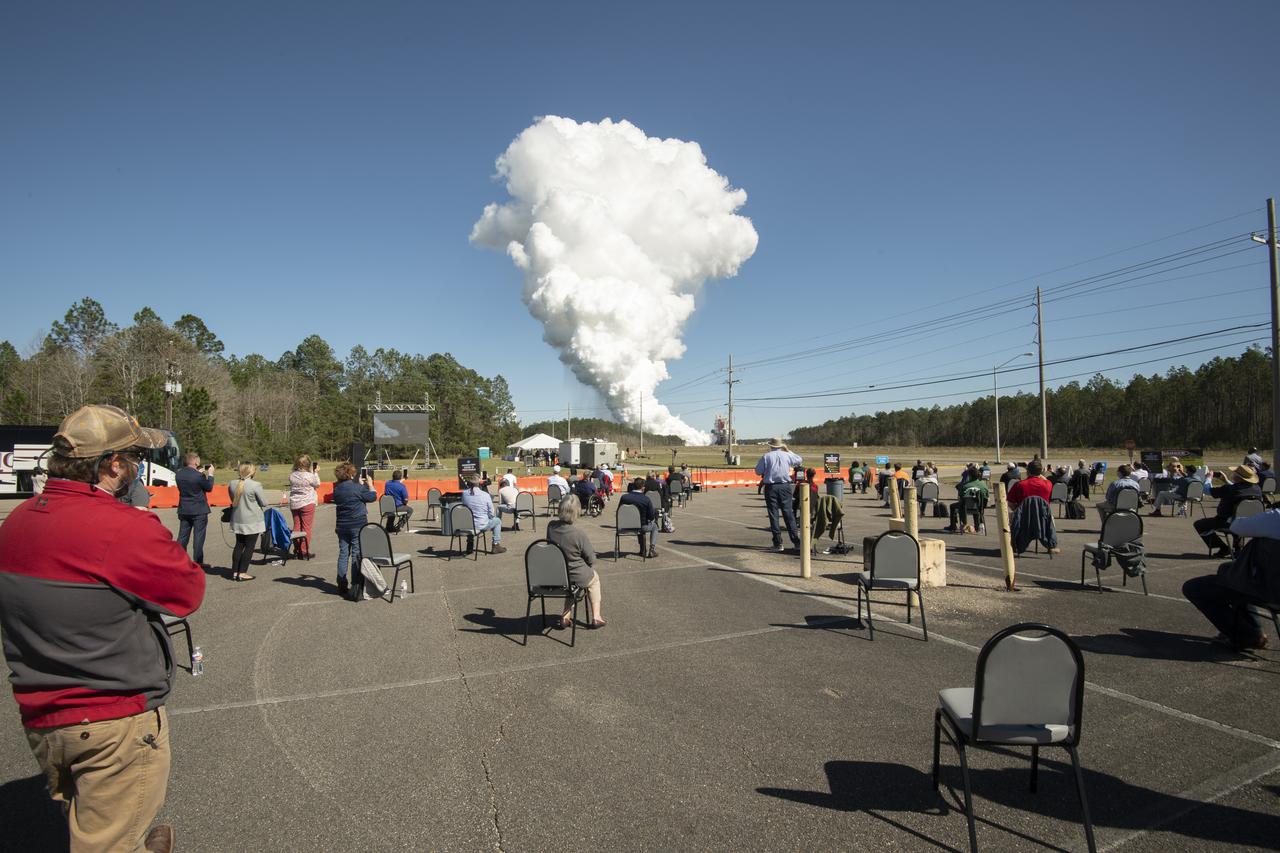

Invited guests watch as the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket undergoes a second hot fire test in the B-2 Test Stand, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
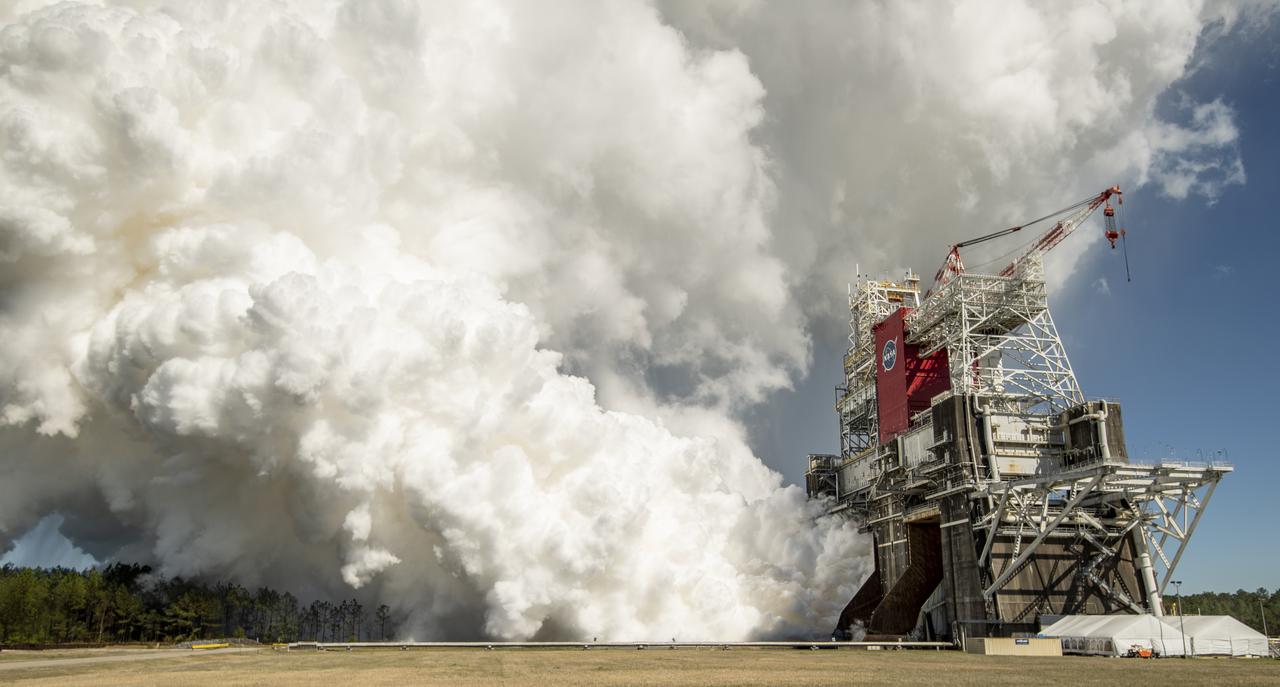

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
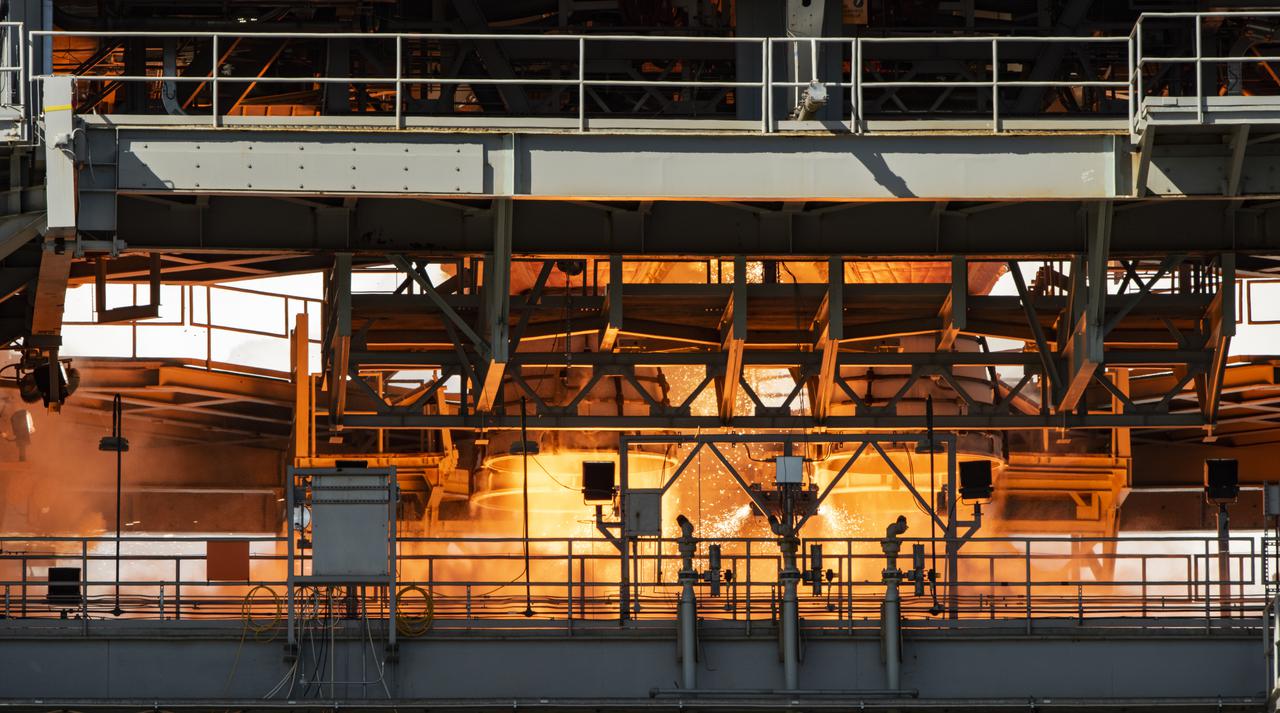

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
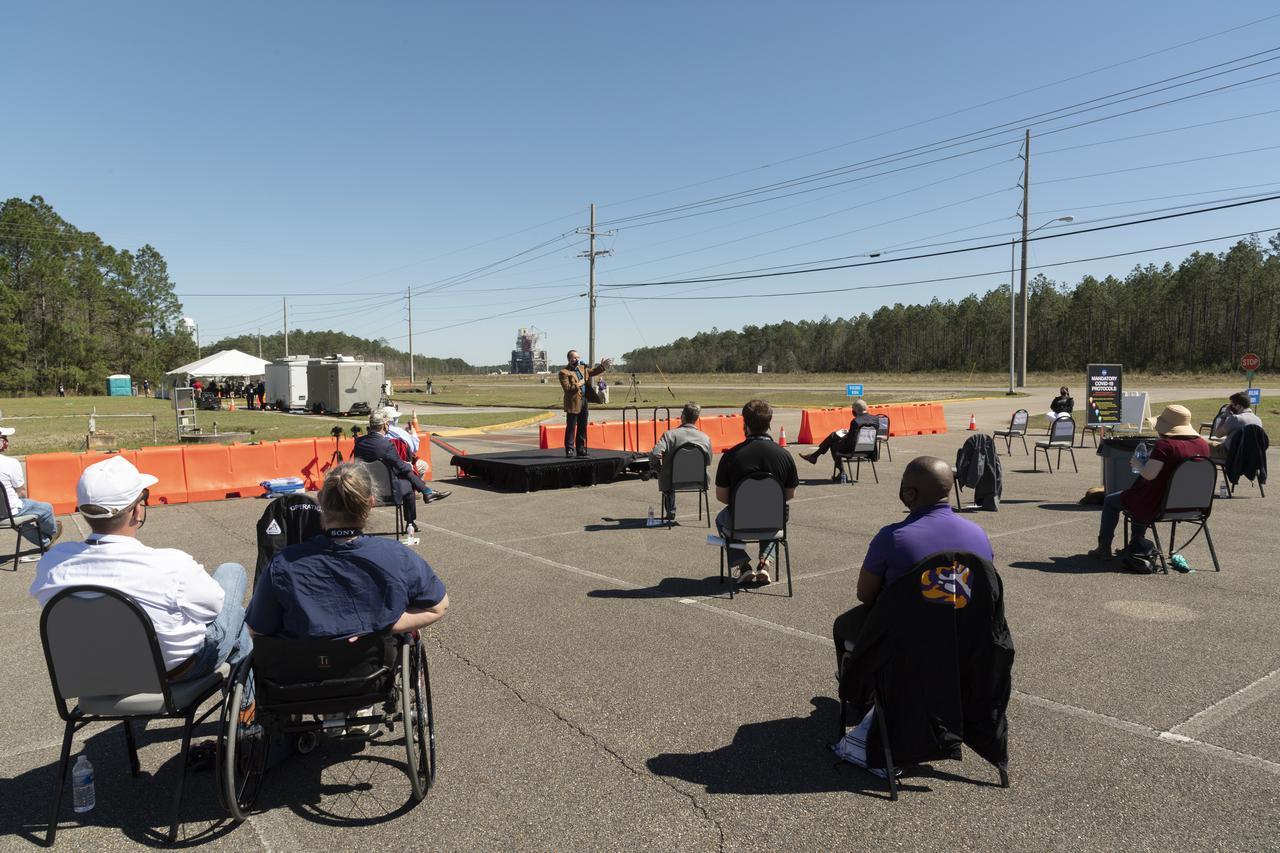

Rick Gilbrech, director of NASA's Stennis Space Center, speaks to invited guests ahead of a second hot fire test of the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket in the B-2 Test Stand, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
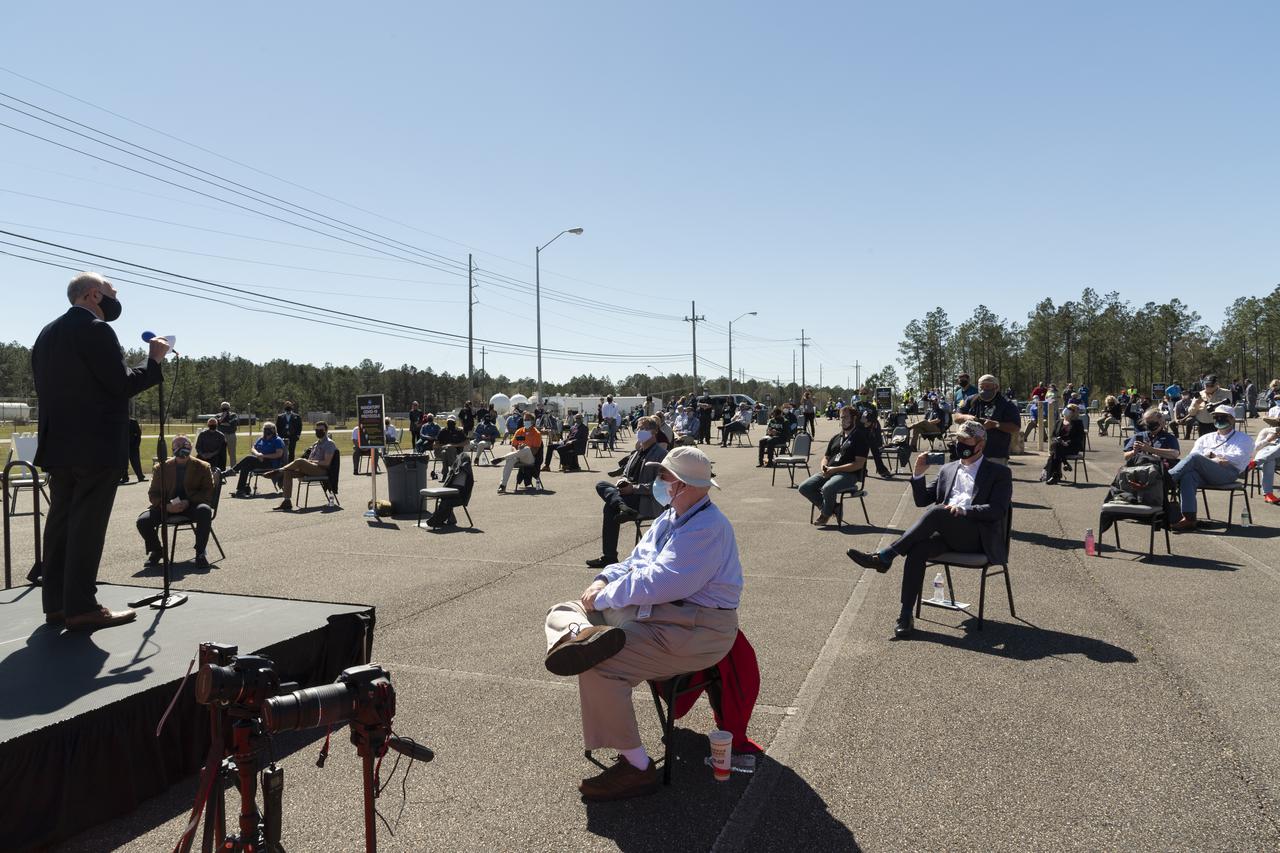

Acting NASA Administrator Steve Jurczyk speaks to invited guests ahead of a second hot fire test of the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket in the B-2 Test Stand, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
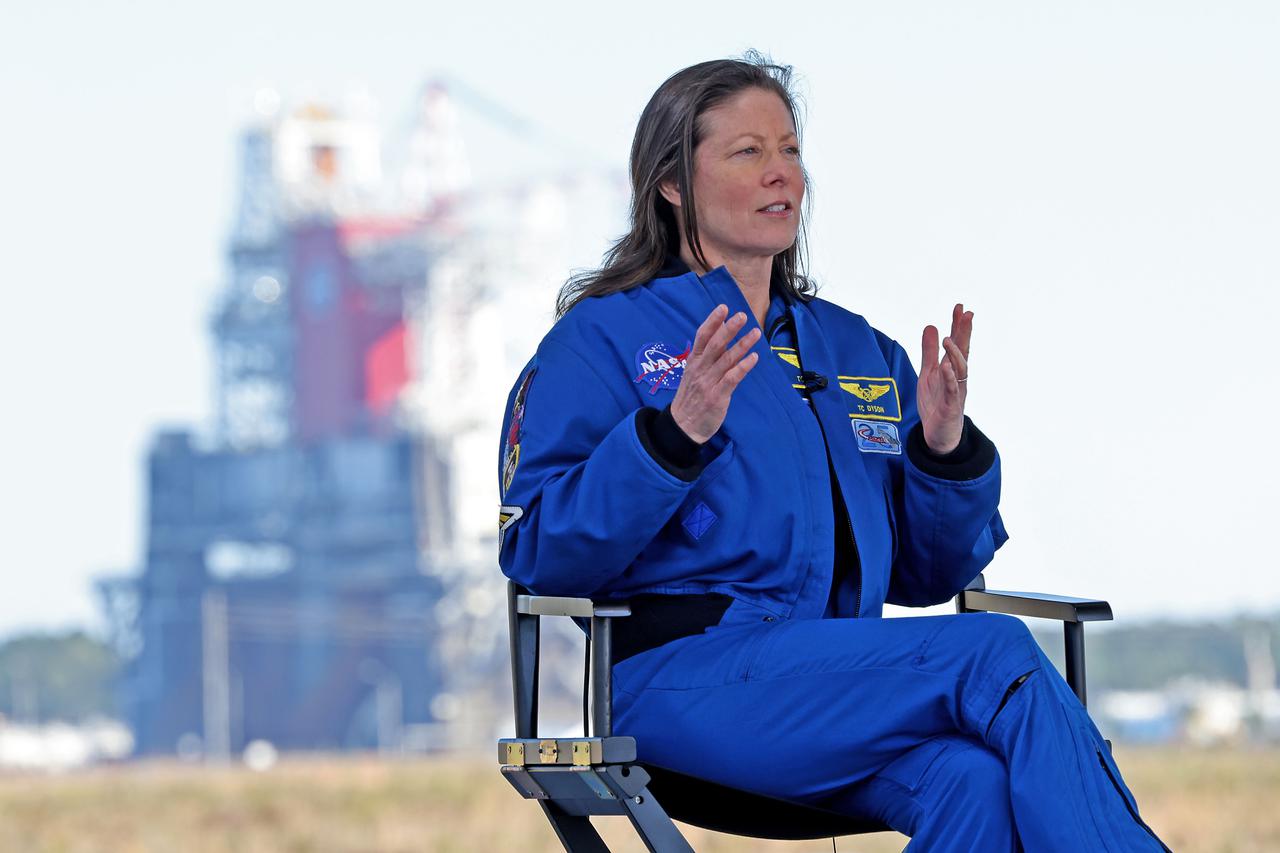

Astronaut Tracy Caldwell Dyson speaks on NASA TV prior to the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Saturday, January 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
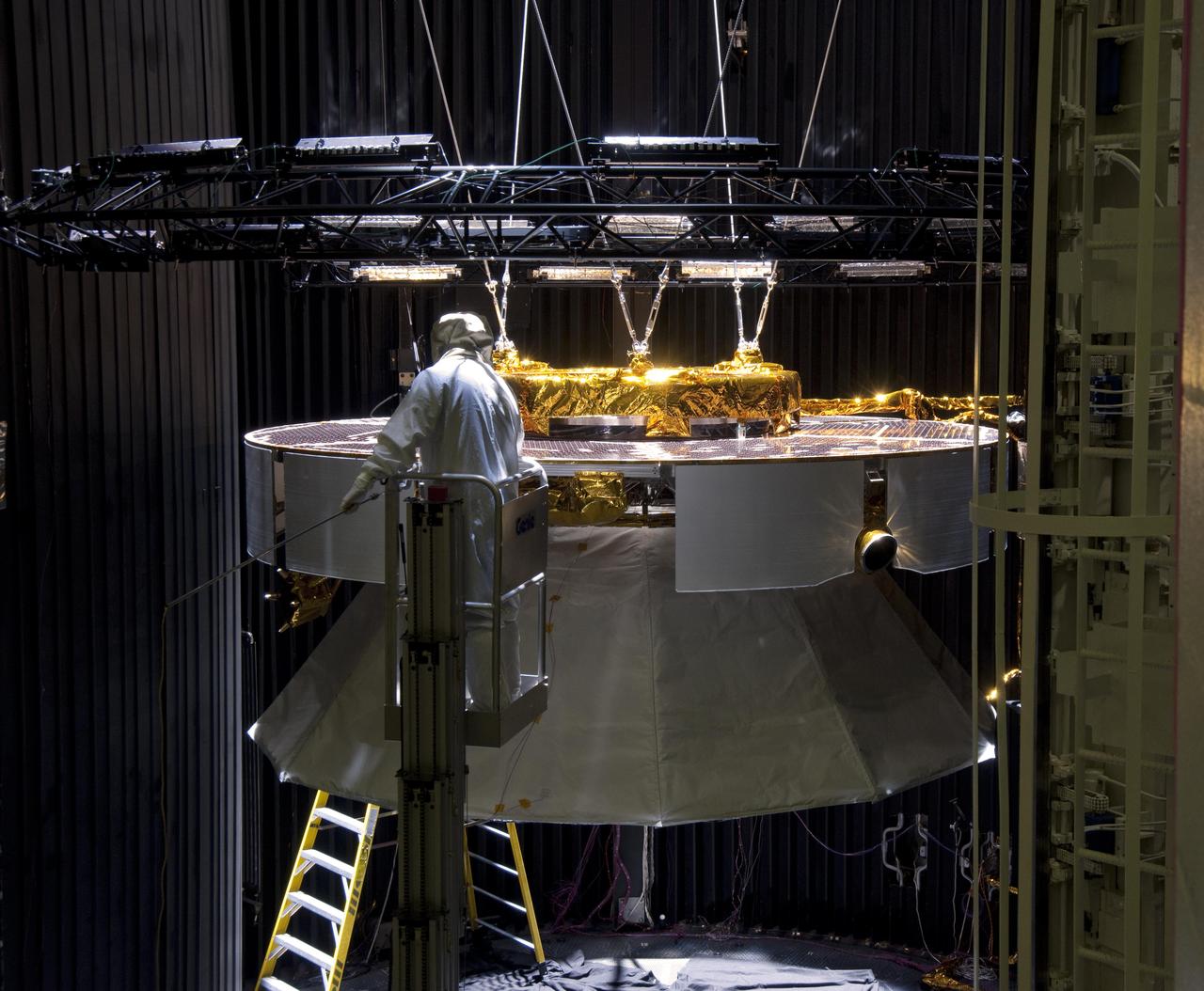

Testing of the cruise stage for NASA Mars Science Laboratory in August 2010 included a session in a facility that simulates the environment found in interplanetary space.
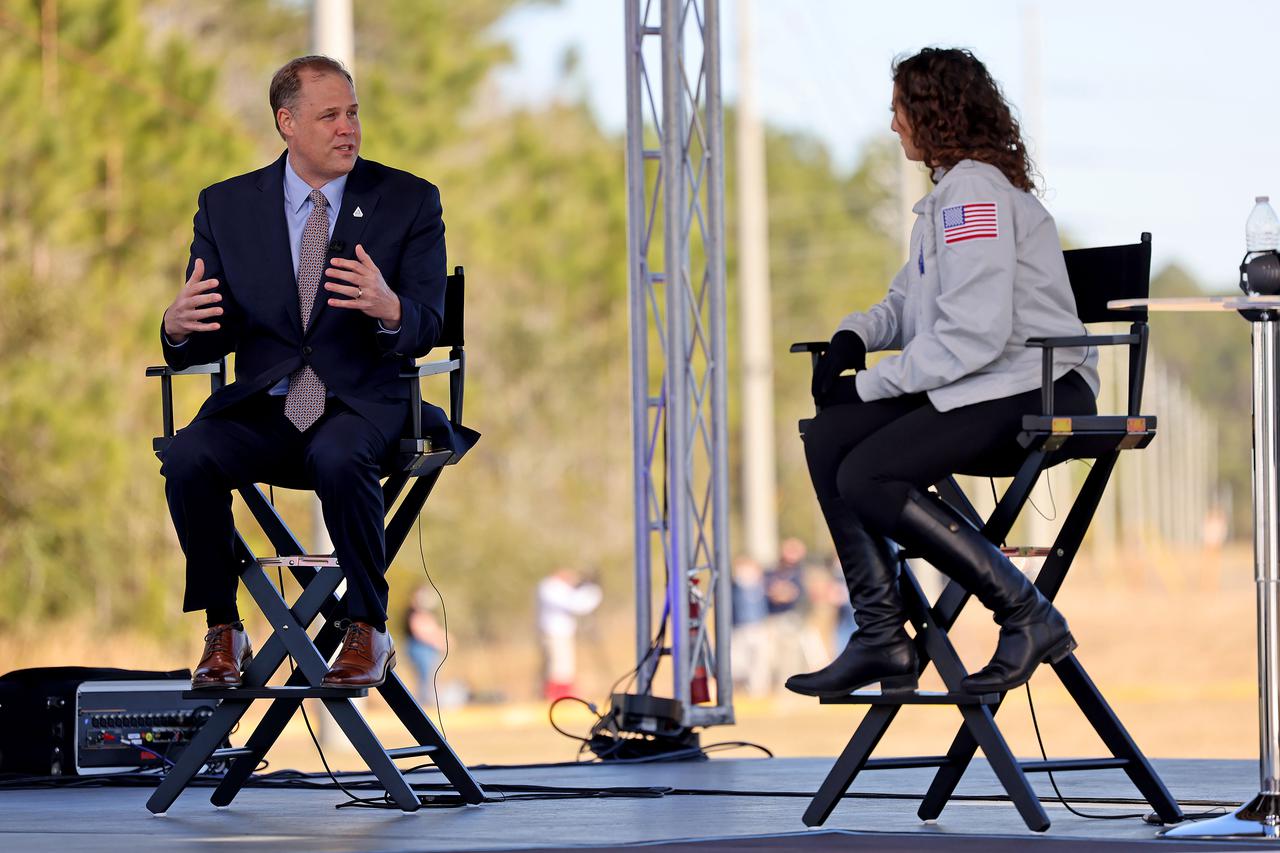

Outgoing NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine (left) talks with host Leigh D’Angelo during NASA TV live coverage from Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Jan. 16, 2021. D’Angelo, from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in nearby New Orleans, hosted the NASA TV coverage prior to the hot fire test of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

This photograph shows a test firing of a Saturn V second stage (S-II) on the S-IC test stand at the Propulsion Test Facility near New Orleans, Louisiana. This second stage component was used in the unmarned test flight of Apollo 4.

THIS IS A TEST OF THE 1ST STAGE RE-ENTRY VEHICLE. HEAT TESTING OF A 3% MODEL TO SUPPORT THE ARES/ CLV FIRST STAGE RE-ENTRY. THIS TEST OCCURRED AT ARNOLD AIR FORCE BASE, TENNESSEE. THIS TESTING SUPPORTS THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE CONSTELLATION/ARES PROJECT. THIS IMAGE IS EXTRACTED FROM A HIGH DEFINITION VIDEO FILE AND IS THE HIGHEST RESOLUTION AVAILABLE.
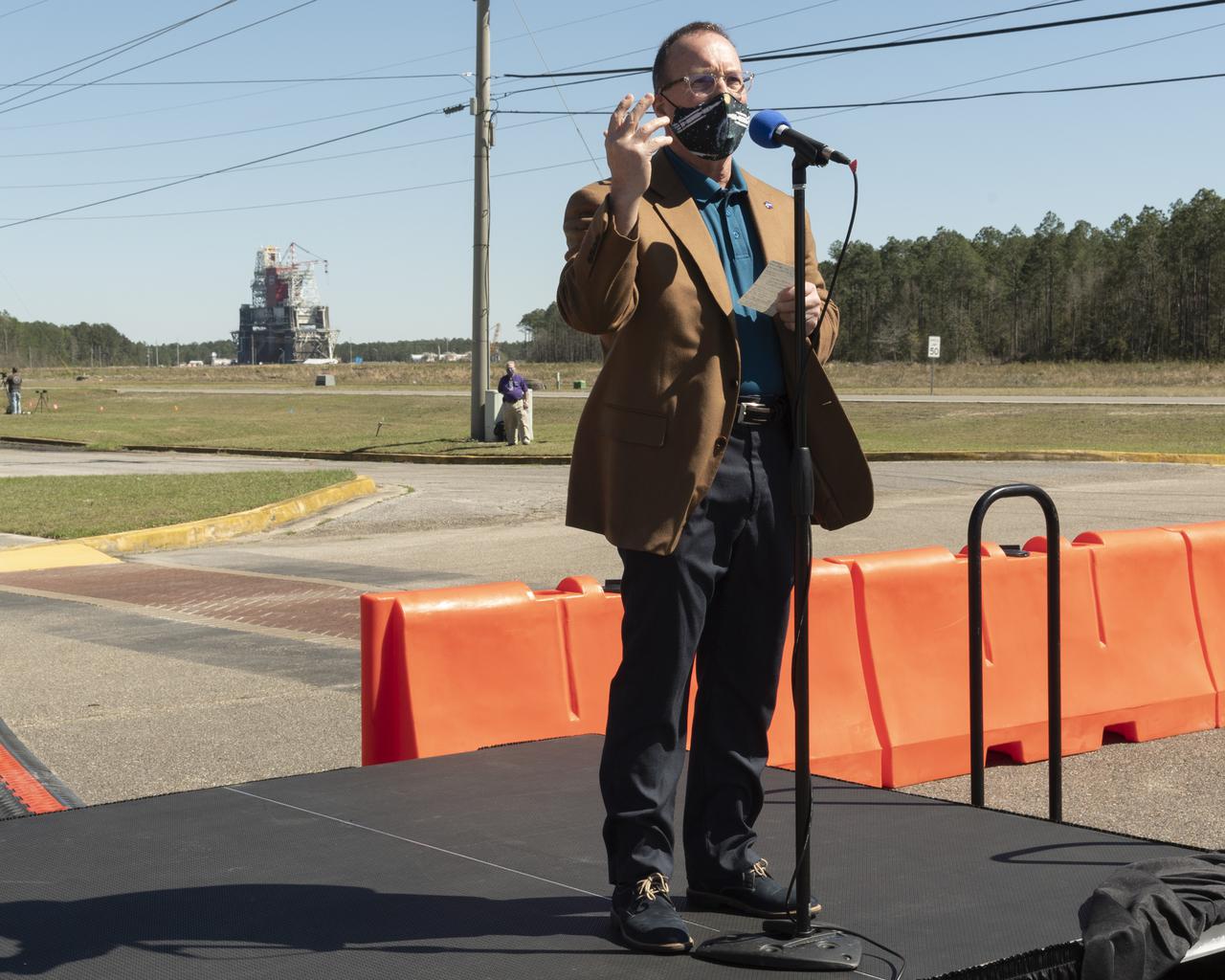

Rick Gilbrech, director of NASA's Stennis Space Center, speaks to invited guests ahead of a second hot fire test of the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket in the B-2 Test Stand, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
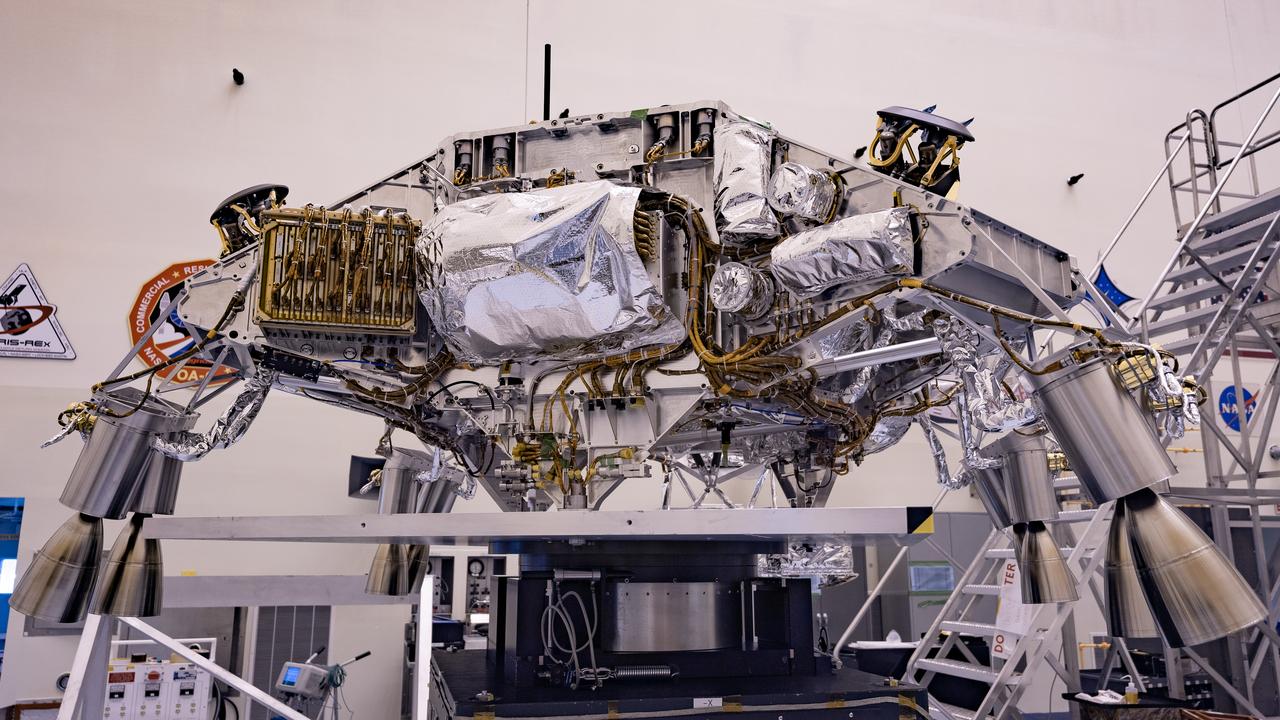
Engineers perform mass properties testing on the rocket-powered descent stage of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center on April 12, 2020. The testing to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides, was performed inside the Florida spaceport’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The descent stage will lower the rover through the thin Martian atmosphere and onto the surface on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The rover will seek signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for possible return to Earth.
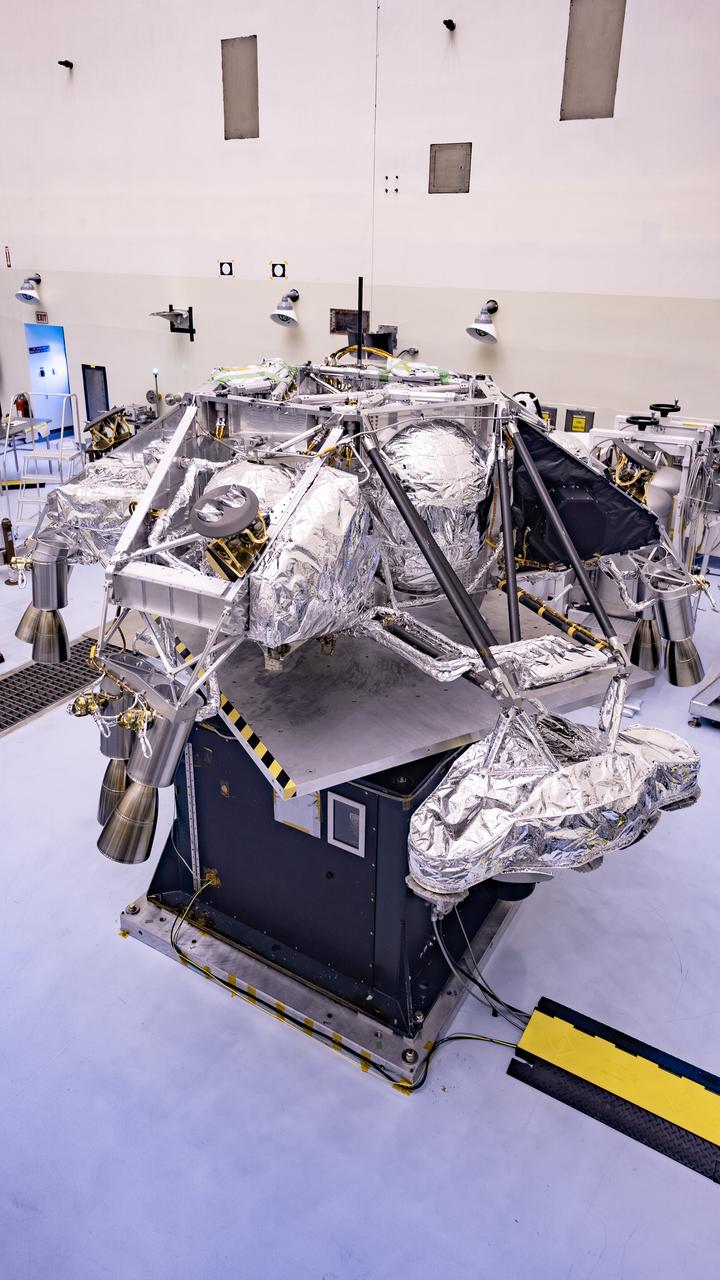

Engineers perform mass properties testing on the rocket-powered descent stage of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center on April 12, 2020. The testing to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides, was performed inside the Florida spaceport’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The descent stage will lower the rover through the thin Martian atmosphere and onto the surface on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The rover will seek signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for possible return to Earth.
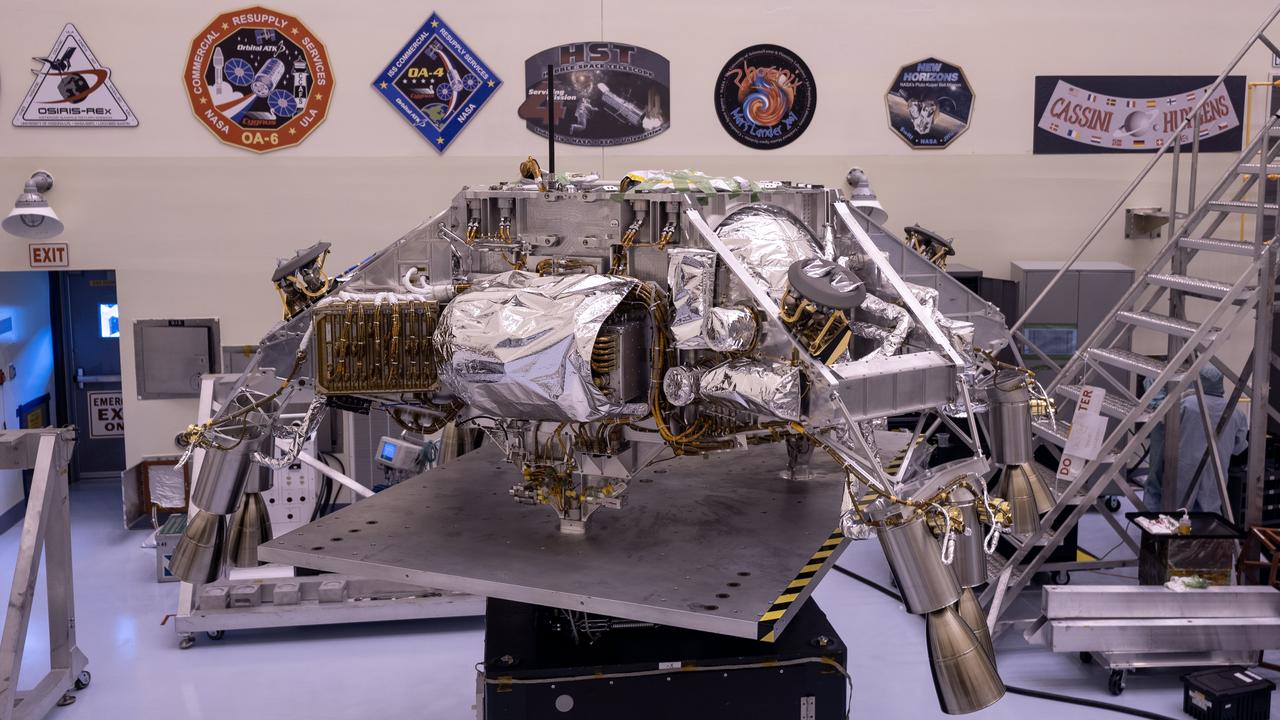

Engineers perform mass properties testing on the rocket-powered descent stage of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center on April 12, 2020. The testing to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides, was performed inside the Florida spaceport’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The descent stage will lower the rover through the thin Martian atmosphere and onto the surface on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The rover will seek signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for possible return to Earth.
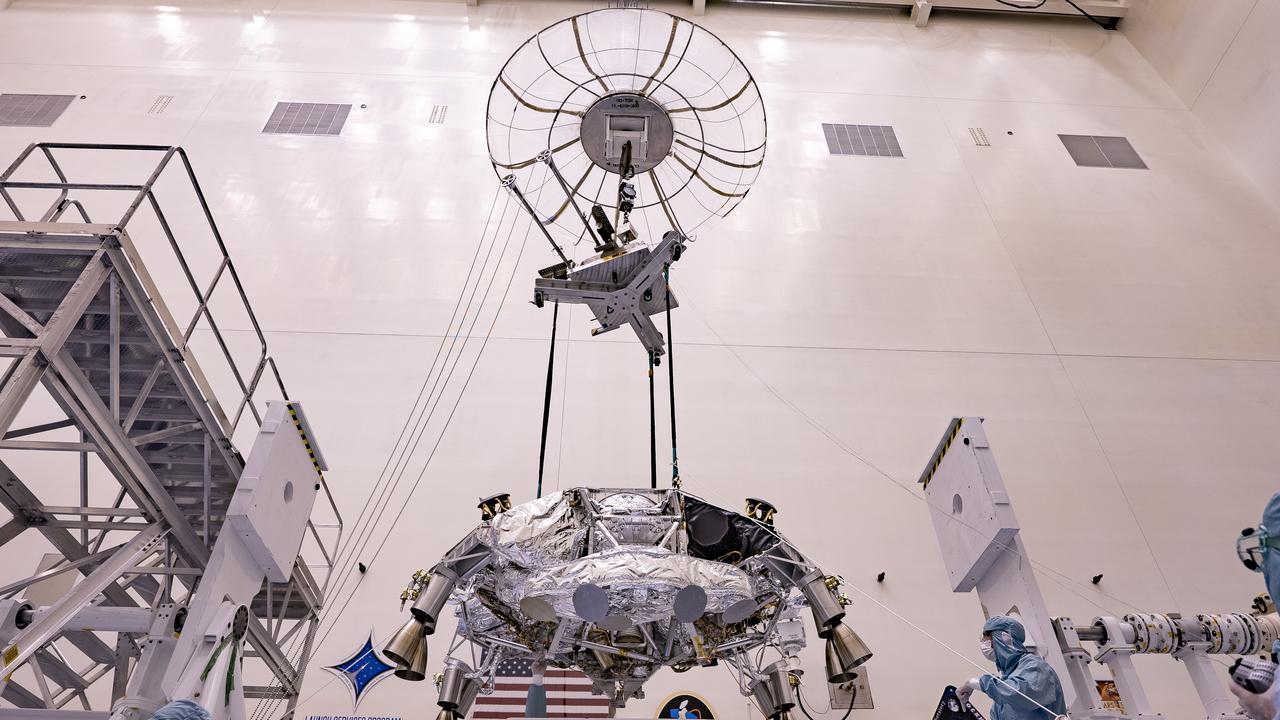
Engineers perform mass properties testing on the rocket-powered descent stage of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center on April 9, 2020. The testing to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides, was performed inside the Florida spaceport’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The descent stage will lower the rover through the thin Martian atmosphere and onto the surface on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The rover will seek signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for possible return to Earth.
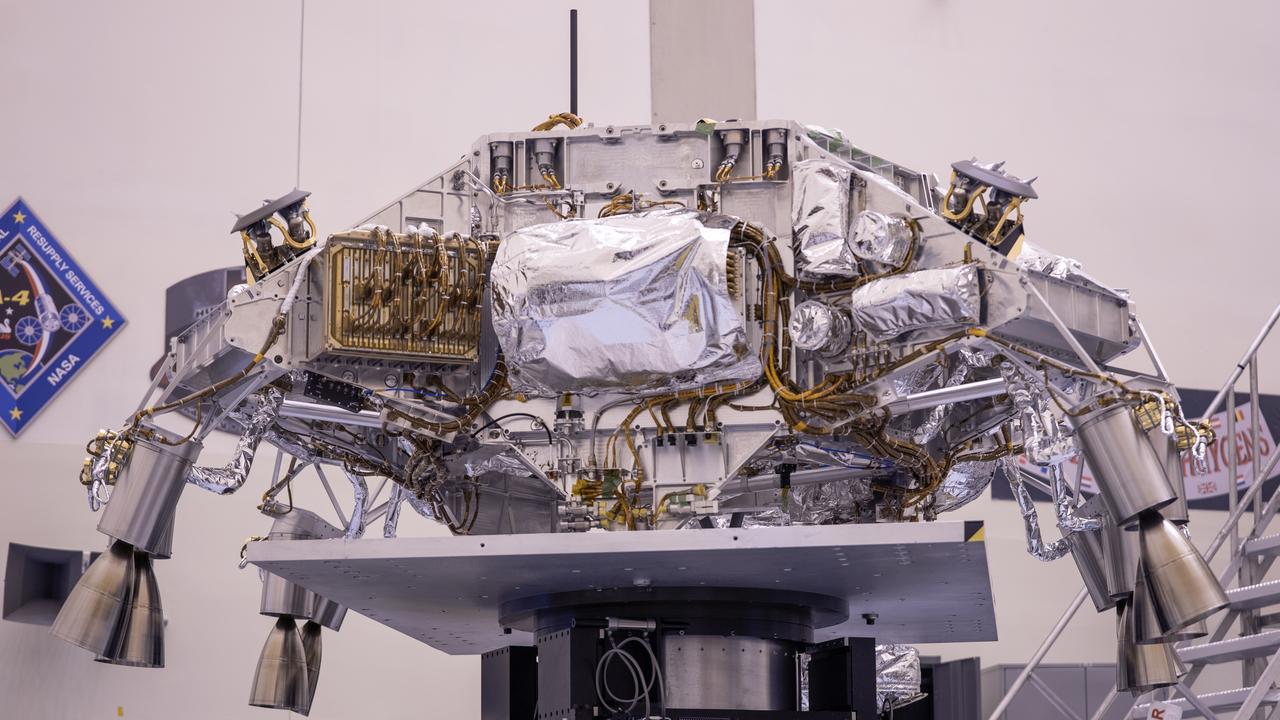
Engineers perform mass properties testing on the rocket-powered descent stage of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center on April 12, 2020. The testing to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides, was performed inside the Florida spaceport’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The descent stage will lower the rover through the thin Martian atmosphere and onto the surface on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The rover will seek signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for possible return to Earth.
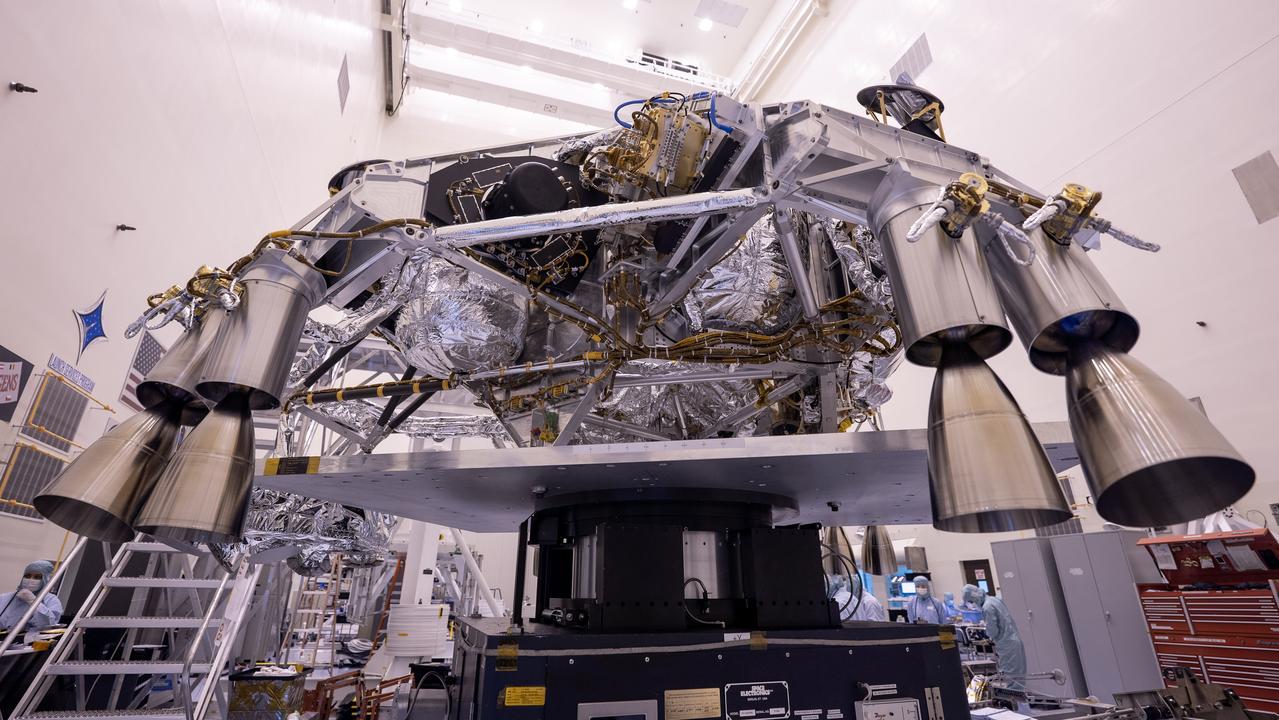

Engineers perform mass properties testing on the rocket-powered descent stage of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center on April 12, 2020. The testing to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides, was performed inside the Florida spaceport’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The descent stage will lower the rover through the thin Martian atmosphere and onto the surface on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The rover will seek signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for possible return to Earth.
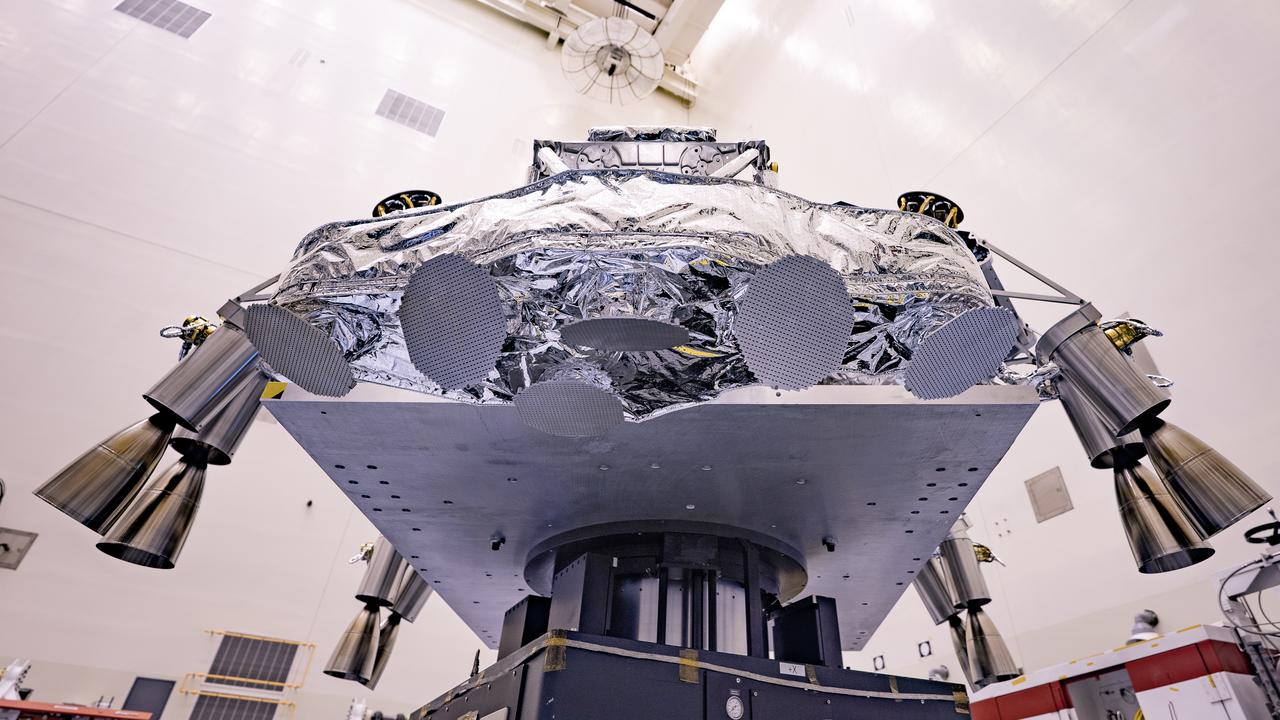

Engineers perform mass properties testing on the rocket-powered descent stage of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center on April 12, 2020. The testing to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides, was performed inside the Florida spaceport’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The descent stage will lower the rover through the thin Martian atmosphere and onto the surface on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The rover will seek signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for possible return to Earth.
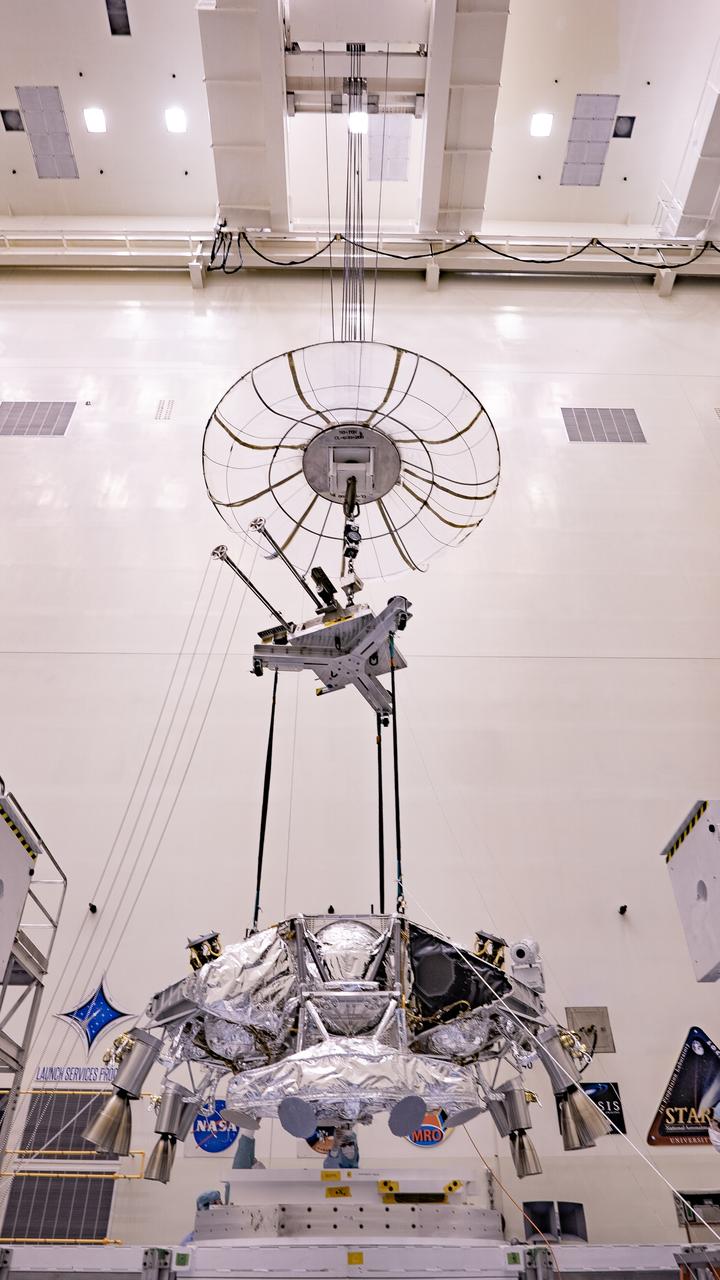

Engineers perform mass properties testing on the rocket-powered descent stage of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center on April 9, 2020. The testing to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides, was performed inside the Florida spaceport’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The descent stage will lower the rover through the thin Martian atmosphere and onto the surface on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The rover will seek signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for possible return to Earth.
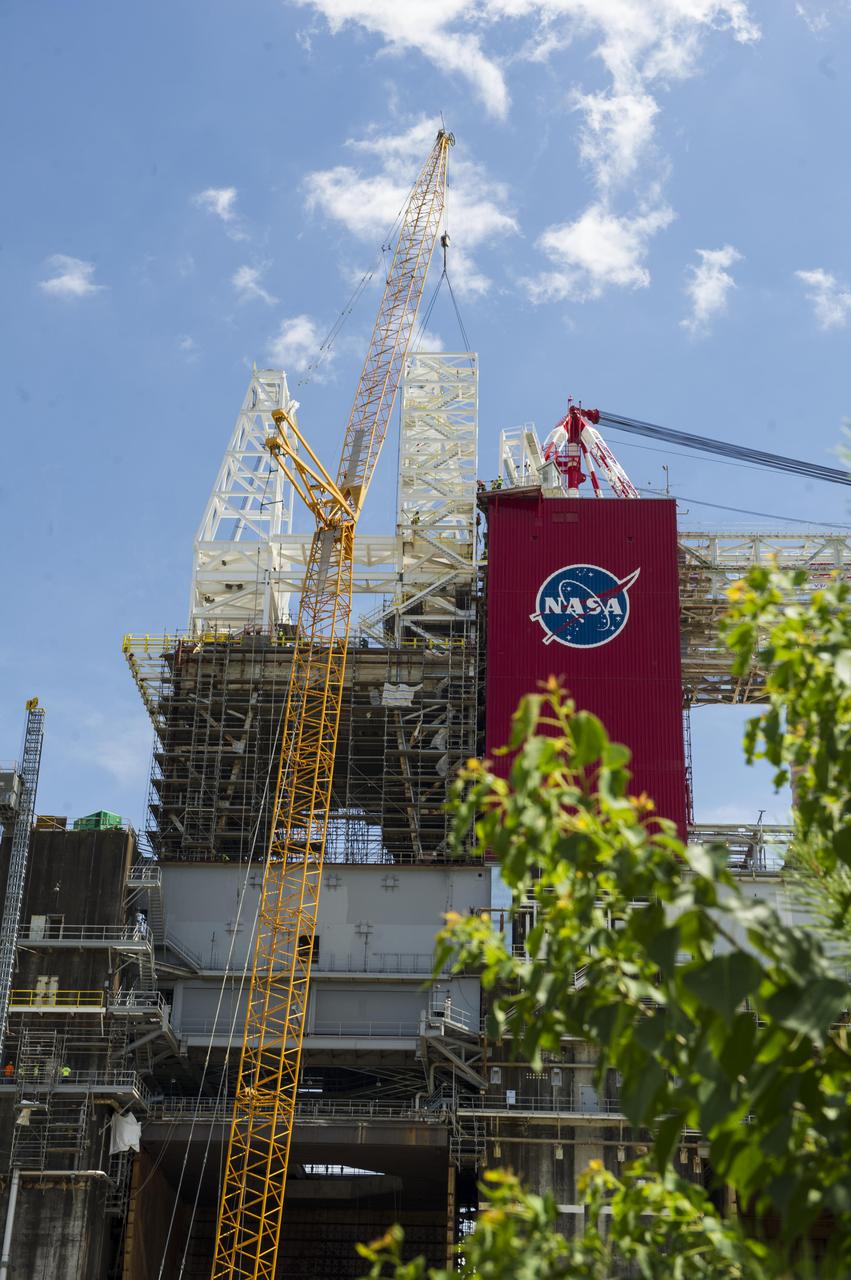

A structural steel section is lifted into place atop the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center as part of modification work to prepare for testing the core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System. The section is part of the Main Propulsion Test Article (MPTA) framework, which will support the SLS core stage for testing. The existing framework was installed on the stand in the late 1970s to test the shuttle MPTA. However, that framework had to be repositioned and modified to accommodate the larger SLS stage. About 1 million pounds of structural steel has been added, extending the framework about 100 feet higher and providing a new look to the Stennis skyline. Stennis will test the actual flight core stage for the first uncrewed SLS mission, Exploration Mission-1.
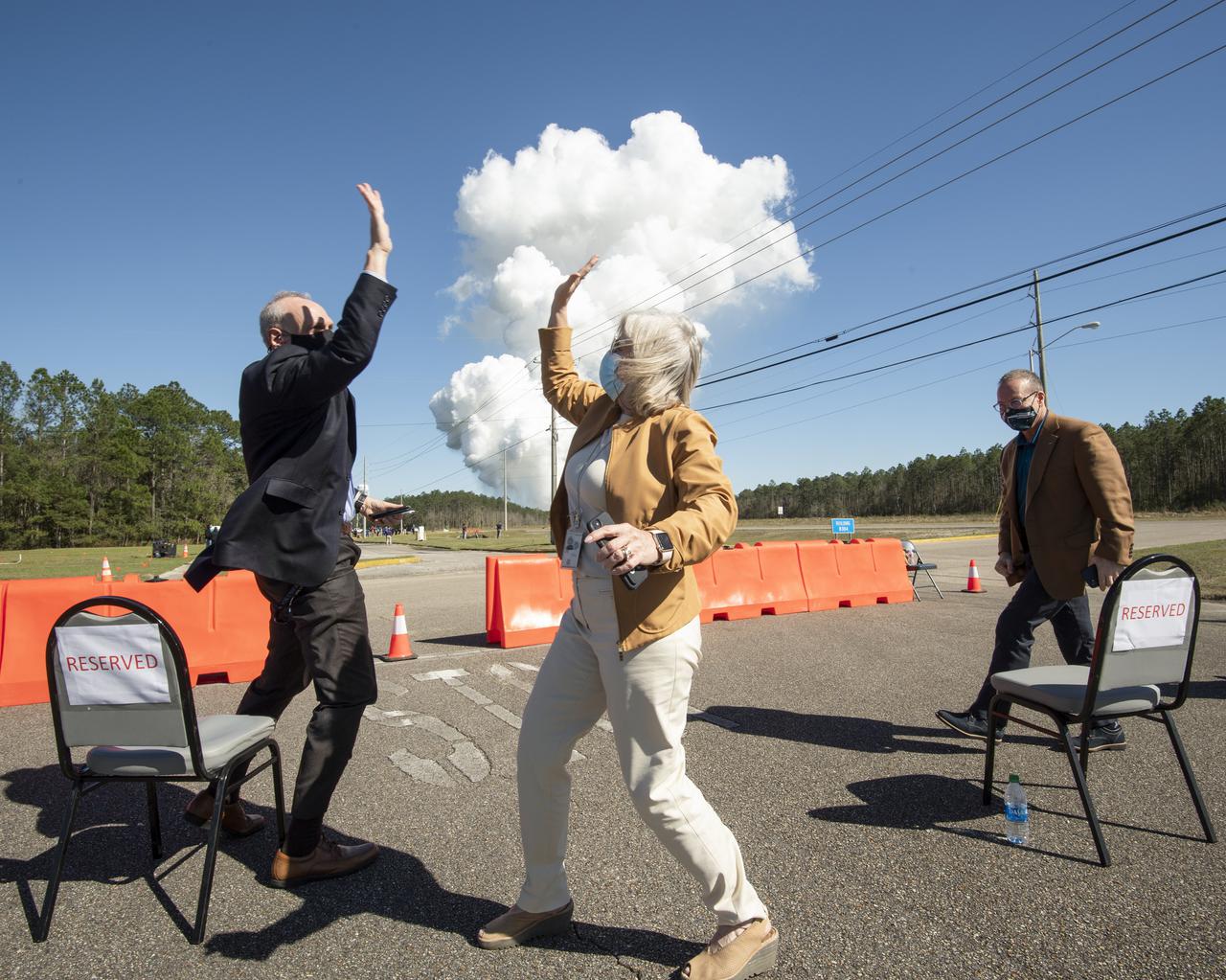

Acting NASA Administrator Steve Jurczyk, left, and Jody Singer, director of NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, right, high five following a second hot fire test of the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket in the B-2 Test Stand, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
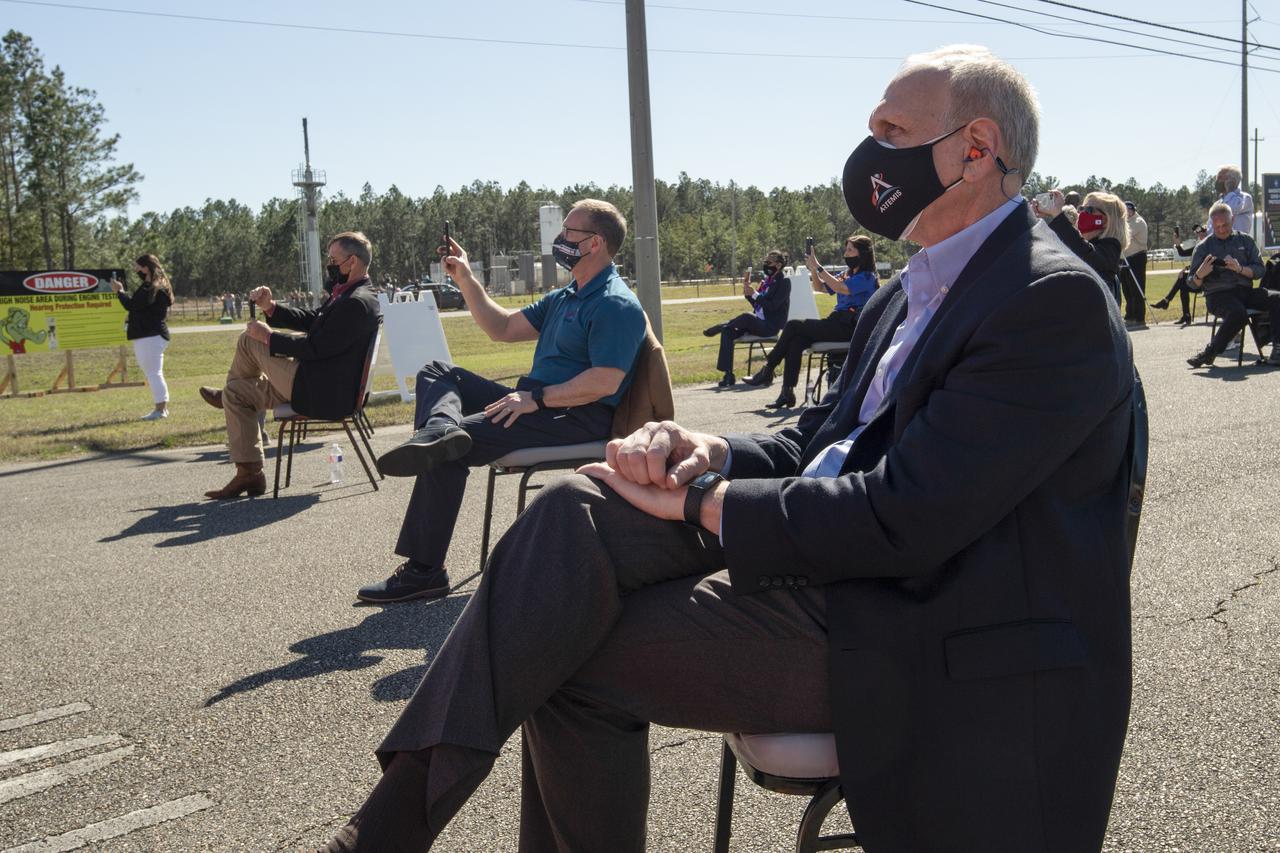

Acting NASA Administrator Steve Jurczyk, right, and Rick Gilbrech, director of NASA's Stennis Space Center, center, watch as the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket undergoes a second hot fire test in the B-2 Test Stand, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
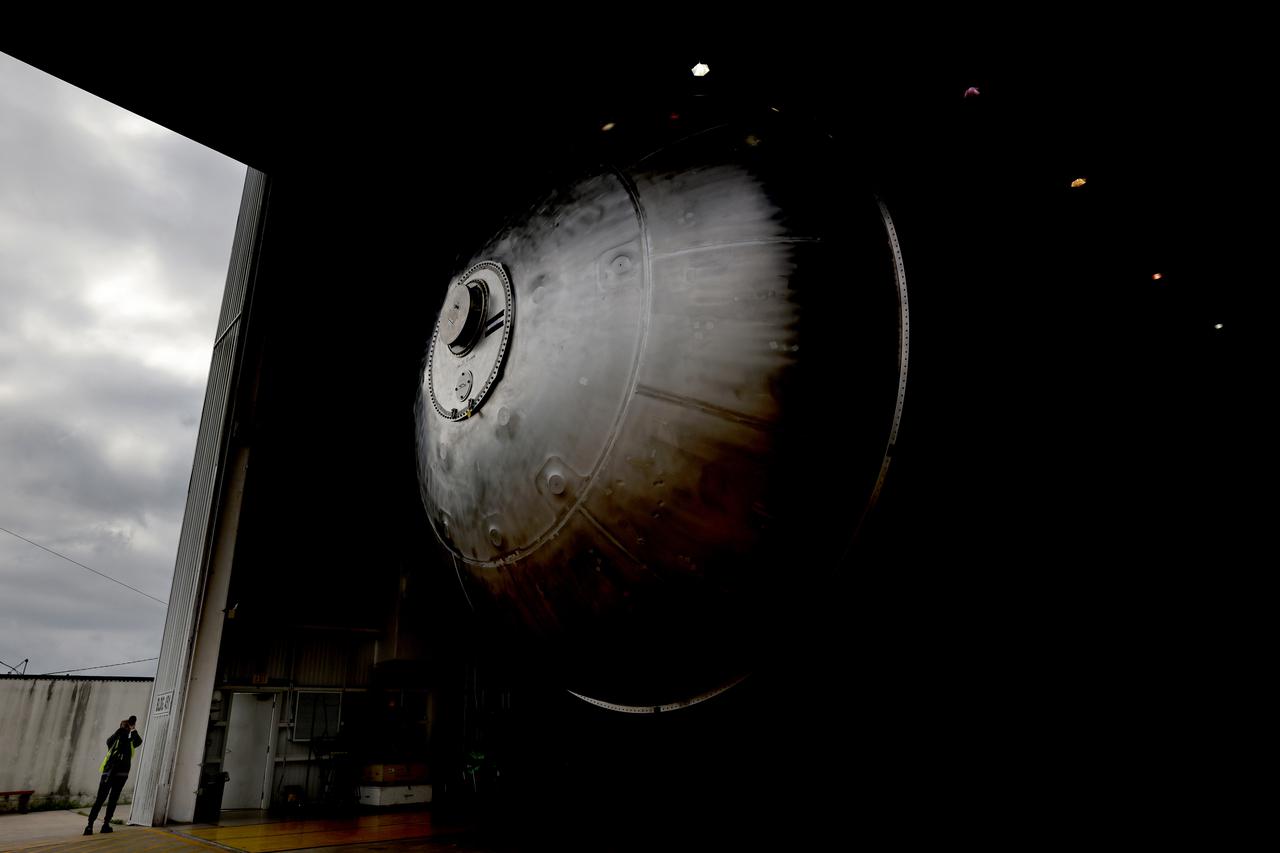

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface. Photographed on Monday, April 18, 2022. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker