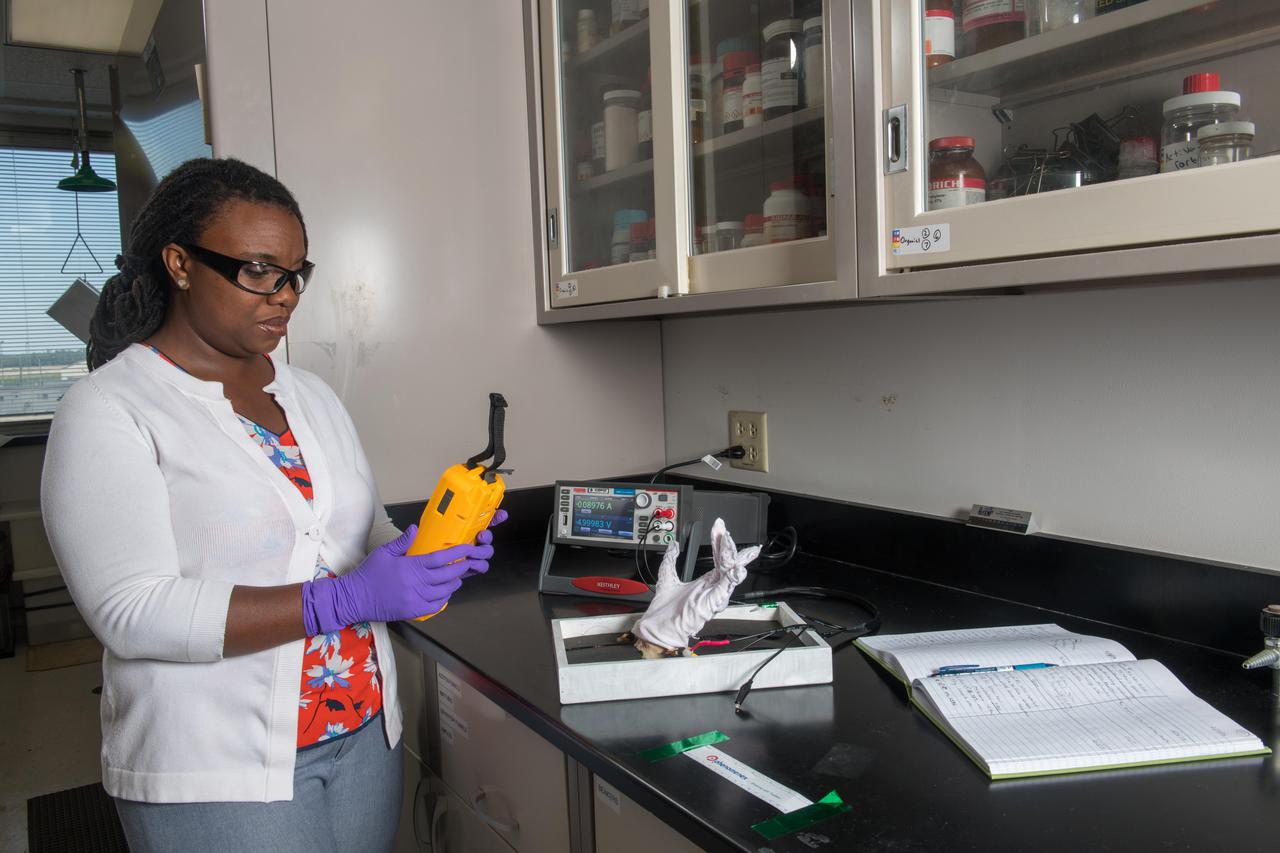

Development of Lightweight, Electrically Conductive, Multi-functional Textiles and Composites
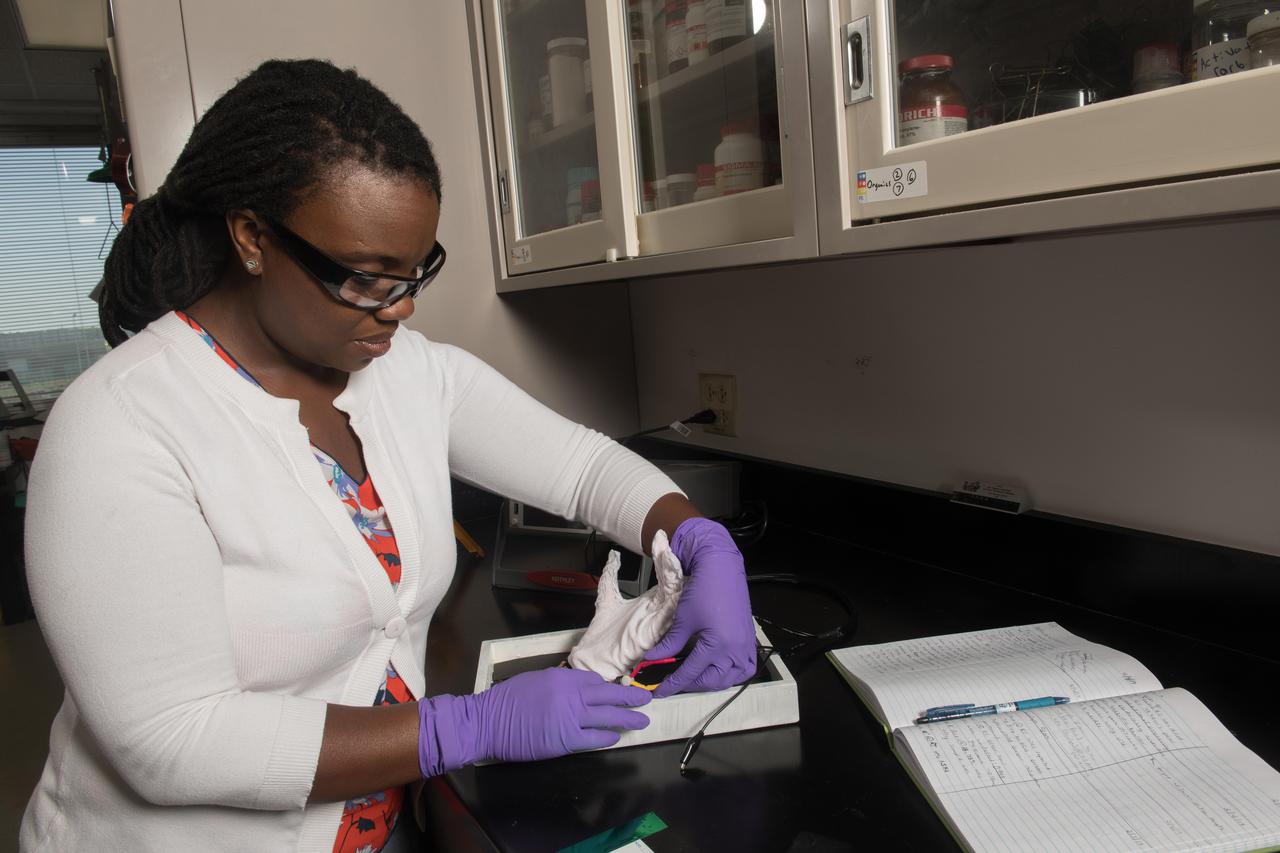

Development of Lightweight, Electrically Conductive, Multi-functional Textiles and Composites
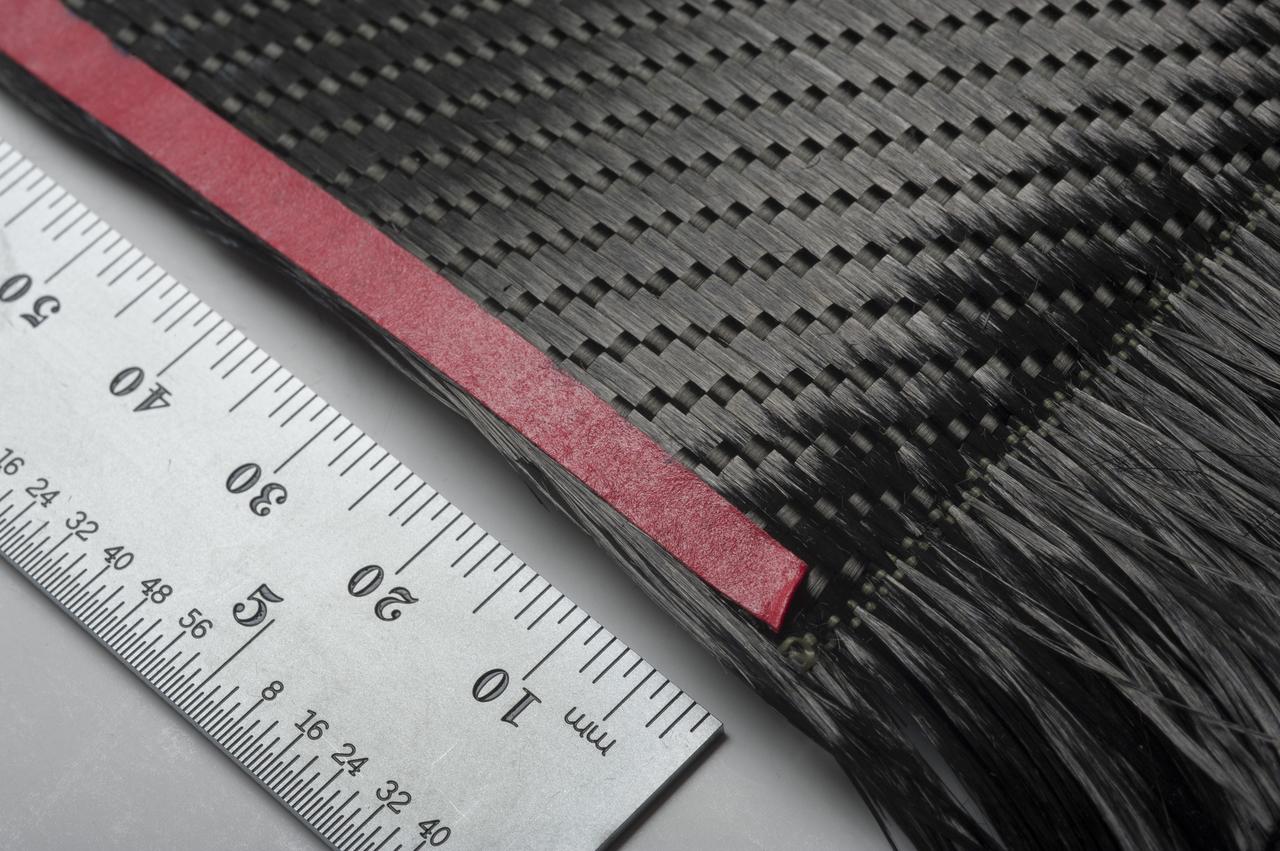

MITSUBISHI K13D2U PITCH-BASED CARBON FIBERS COMMERCIALLY WOVEN BY T.E.A.M., INC. (TEXTILE ENGINEERING AND MANUFACTURING
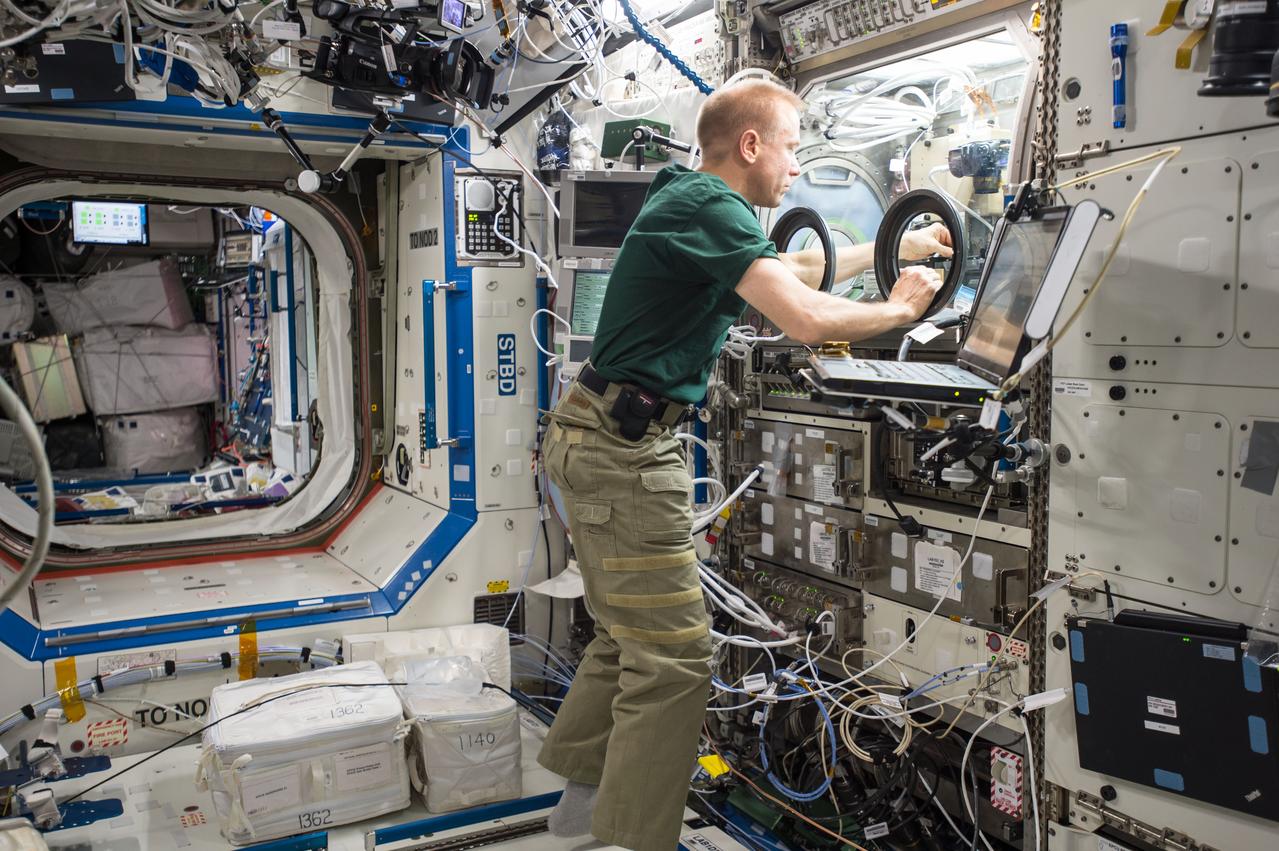

ISS046e025945 (01/27/2016) --- NASA astronaut Tim Kopra sets up hardware for the Burning and Suppression of Solids – Milliken, or BASS-M, experiment. The BASS-M investigation tests flame-retardant cotton fabrics to determine how well they resist burning in microgravity. Results benefit research on flame-retardant textiles that can be used on Earth and in space
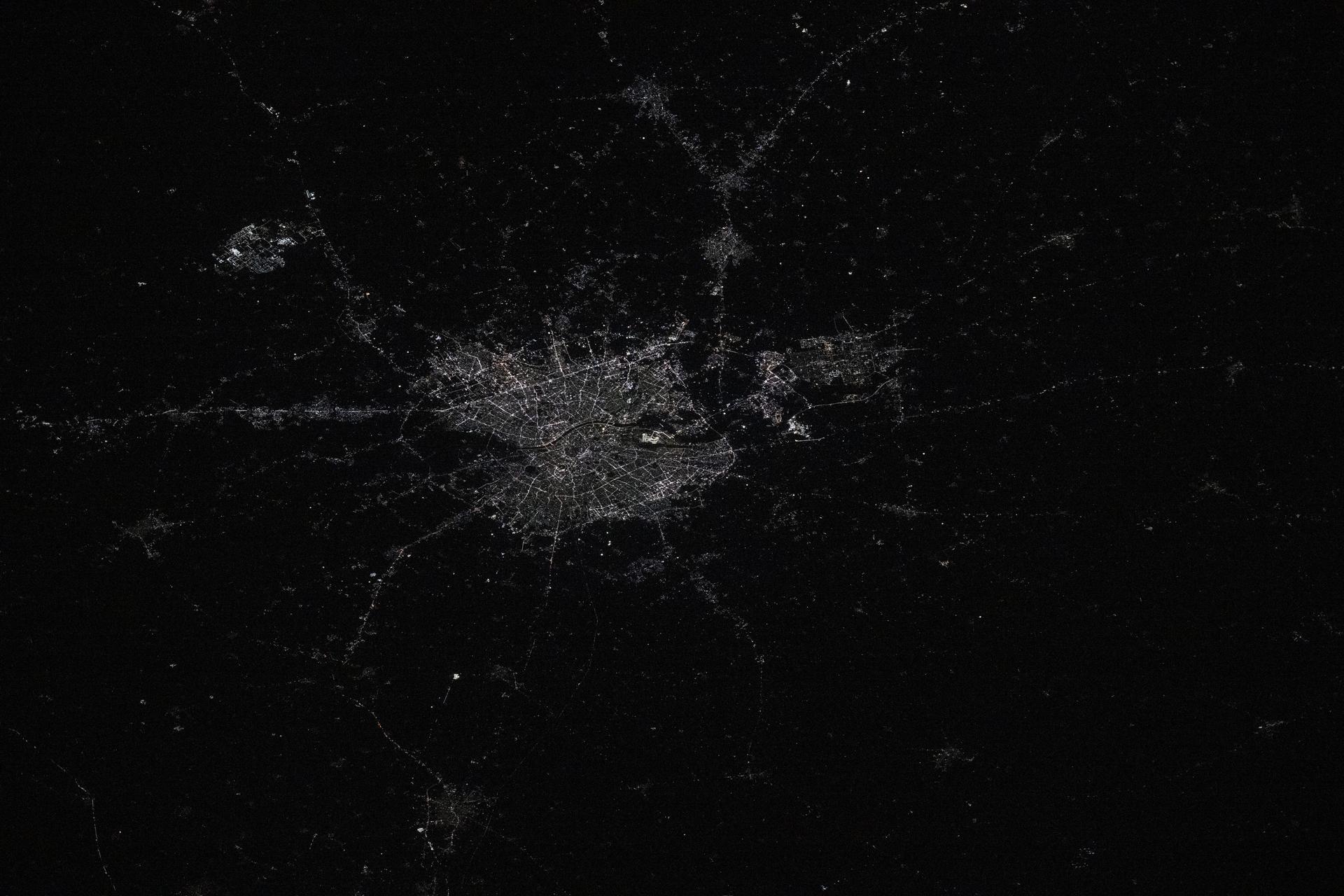

iss072e757408 (March 6, 2025) --- Ahmadebad, India—with a metropolitan population of about 9.3 million residents and split by the Sabarmati River—is pictured from the International Space Station at approximately 9:40 p.m. local time as it orbited 258 miles above the South Asian nation. Founded over 600 years ago, India’s first UNESCO World Heritage City is renowned for its thriving textile industry and vibrant street food culture.
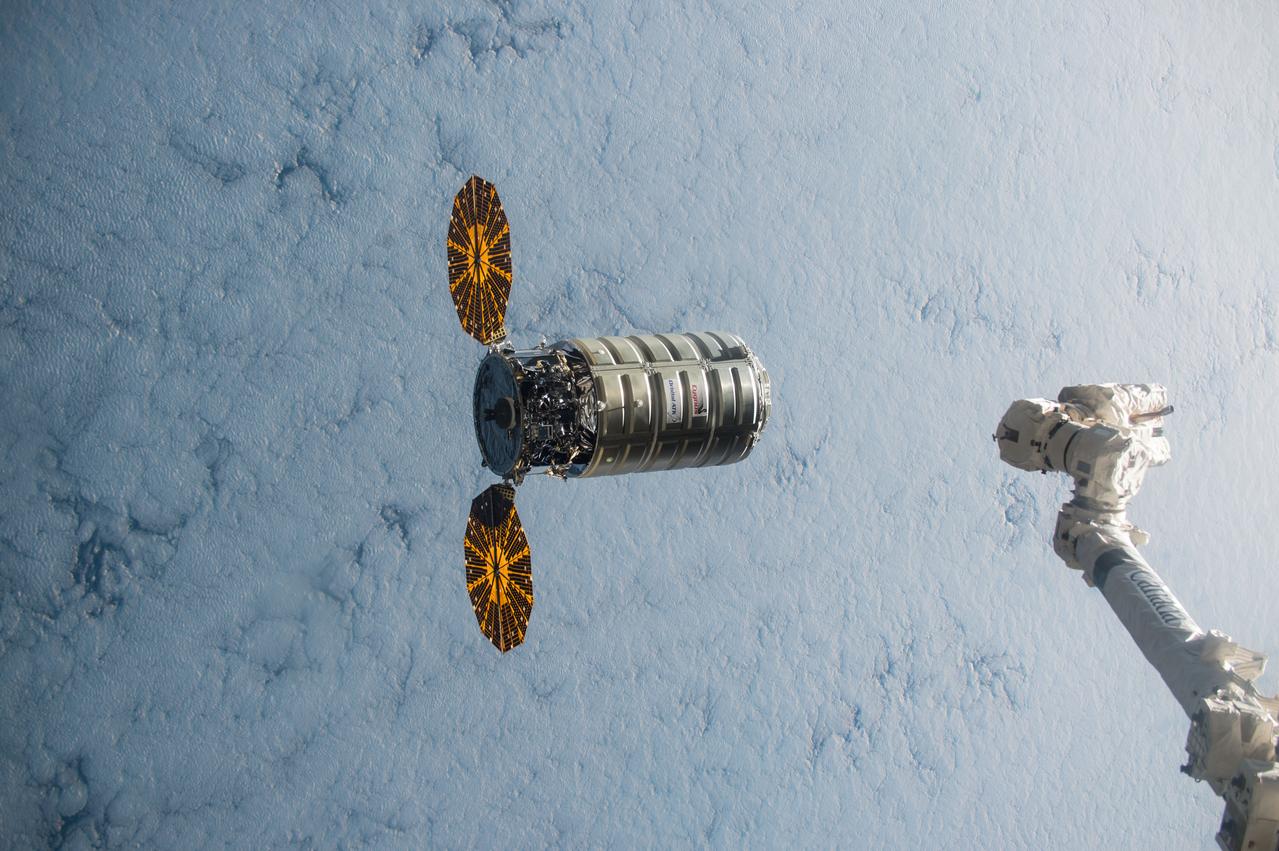

ISS045e176110 (12/09/2015) --- Using the International Space Station’s robotic arm, Canadarm2 (right) NASA Flight Engineer Kjell Lindgren prepares to capture Orbital ATK’s Cygnus cargo vehicle Dec. 09, 2015. The space station crew and the robotics officer in mission control in Houston will position Cygnus for installation to the orbiting laboratory’s Earth-facing port of the Unity module. Among the more than 7,000 pounds of supplies aboard Cygnus are numerous science and research investigations and technology demonstrations, including a new life science facility that will support studies on cell cultures, bacteria and other microorganisms; a microsatellite deployer and the first microsatellite that will be deployed from the space station; several other educational and technology demonstration CubeSats; and experiments that will study the behavior of gases and liquids, clarify the thermo-physical properties of molten steel, and evaluate flame-resistant textiles.
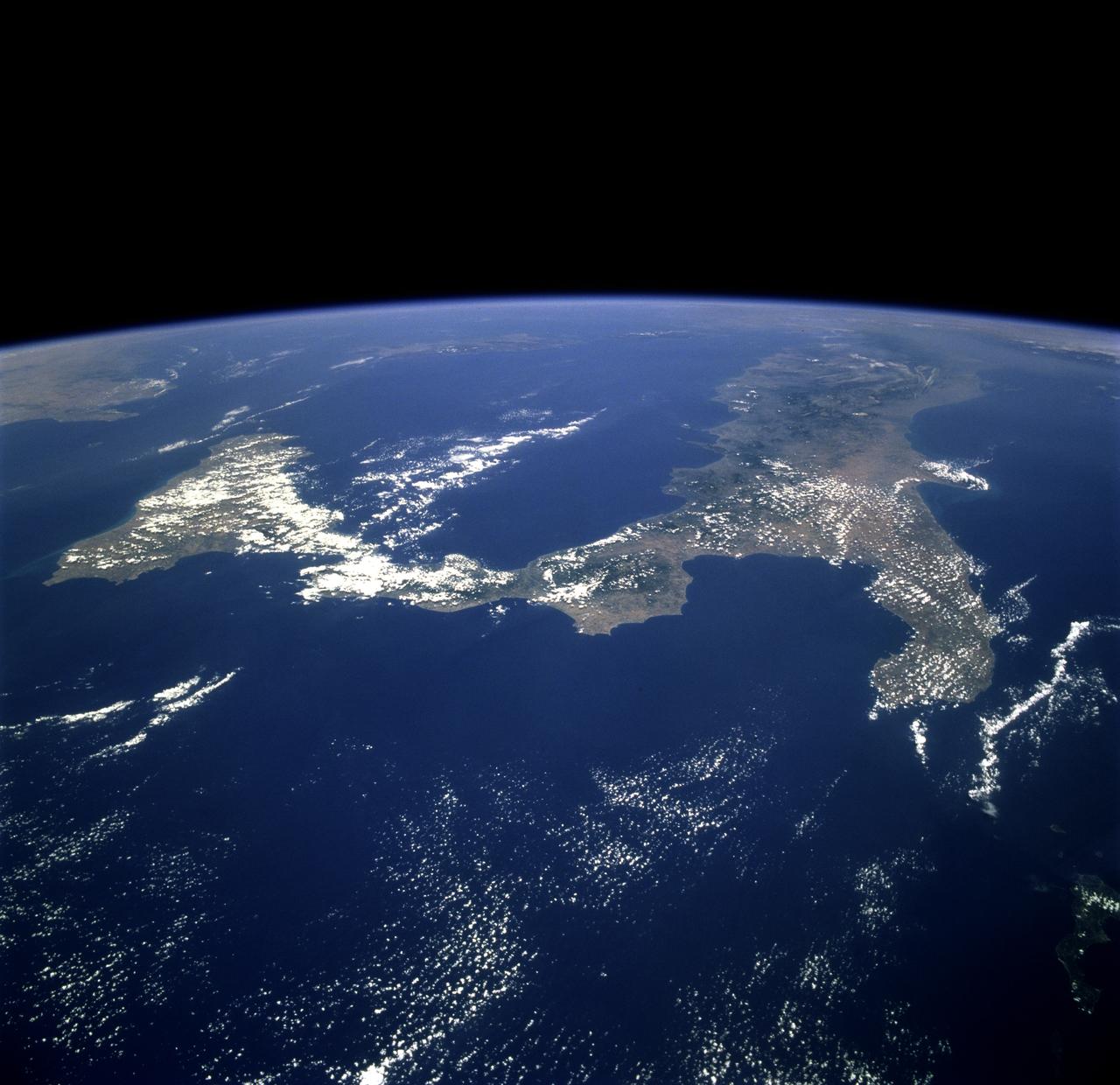

STS078-751-012 (20 June-7 July 1996) --- The international crew of the Life and Microgravity Spacelab (LMS-1) mission onboard the Space Shuttle Columbia photographed this oblique view of the "toe" of Italy and the island of Sicily. Southern Italy is known as the Mezzogiorno because of the intensity of sunshine there at midday (Mezzogiorno is the Italian term for "midday" or "noon"). Mezzogiorno is a mainland subregion consisting of the modern southern Italian regions of Abruzzi, Molise, Campania, Puglia, Basilicata, and Calabria and an insular subregion composed of Sicily and Sardinia. Southern Italy is dominated by the Apennine Range, seen in the photo on the west side, and up to one-half of the land is too steep for any form of cultivation. Coastal plains are generally narrow and poorly drained and are limited to the environs of the cities of Naples and Salerno, Foggia, and Taranto. Chief crops in this region include wheat, olives, grapes, peaches, apricots, pears, and various vegetables. Iron, steel, machine tools, agricultural machinery, and petrochemicals are produced in the industrial triangle of Bari, Brindisi, and Taranto; industries around Naples are more diversified and produce textiles and various consumer goods, iron, steel, Olivetti office machinery, Pirelli cables, Alfa Romeo automobiles, and ships. The Adriatic Sea on the east separates it from the Balkans, and the Mediterranean Sea on the south separates it from North Africa. Three major tectonic plates, converging from the south, the west, and the northeast, create geologically unstable conditions throughout southern Italy and Sicily. The most famous of southern Italy's four active volcanoes is Mount Vesuvius, whose eruption in AD 79 destroyed Pompeii. Sicily's Mount Etna and Stromboli, on an island north of Sicily, were active during this Space Shuttle mission.
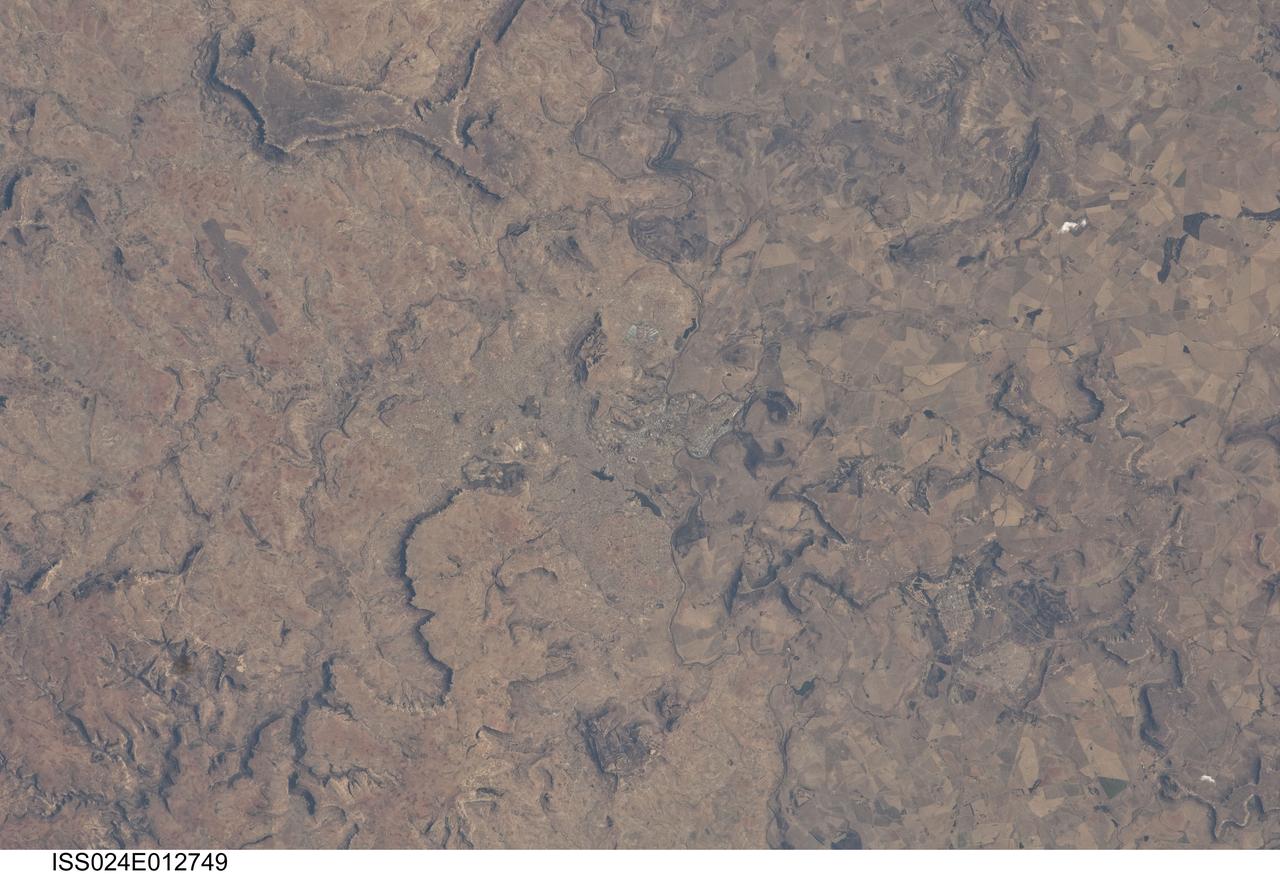

ISS024-E-012749 (28 Aug. 2010) --- Maseru, Lesotho is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 24 crew member on the International Space Station. Maseru is the capital city of the Kingdom of Lesotho and is located along the northwestern border of the country with the Republic of South Africa. The footprint of the urban area, recognizable by street grids and distinctive blue-roofed industrial buildings at center, is only just visible against the surrounding landscape. The city has expanded eightfold (to 230,000 today) since independence from the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in 1966, and is now home to one in five inhabitants in the country. The Caledon (or Mohokare) River flows adjacent to Maseru and forms a part of the border between Lesotho and South Africa. Locally, the border extends from approximately top center left to bottom center right, with the cities of Ladybrand and Manyatseng located in South Africa. Moshoeshoe I International Airport (left) provides access to the capital. Major industries in the city include flour mills, and footwear and textile companies. Tourism is also a growing part of the local economy. The Kingdom of Lesotho is completely landlocked by the surrounding Republic of South Africa. Major landforms visible in the image near Maseru include the Qeme and Berea Plateaus to the south and east respectively; these are erosional remnants of widespread horizontally layered sedimentary rocks that formed in the Karoo Basin during the Upper Triassic Period (approximately 200–229 million years ago), according to scientists.
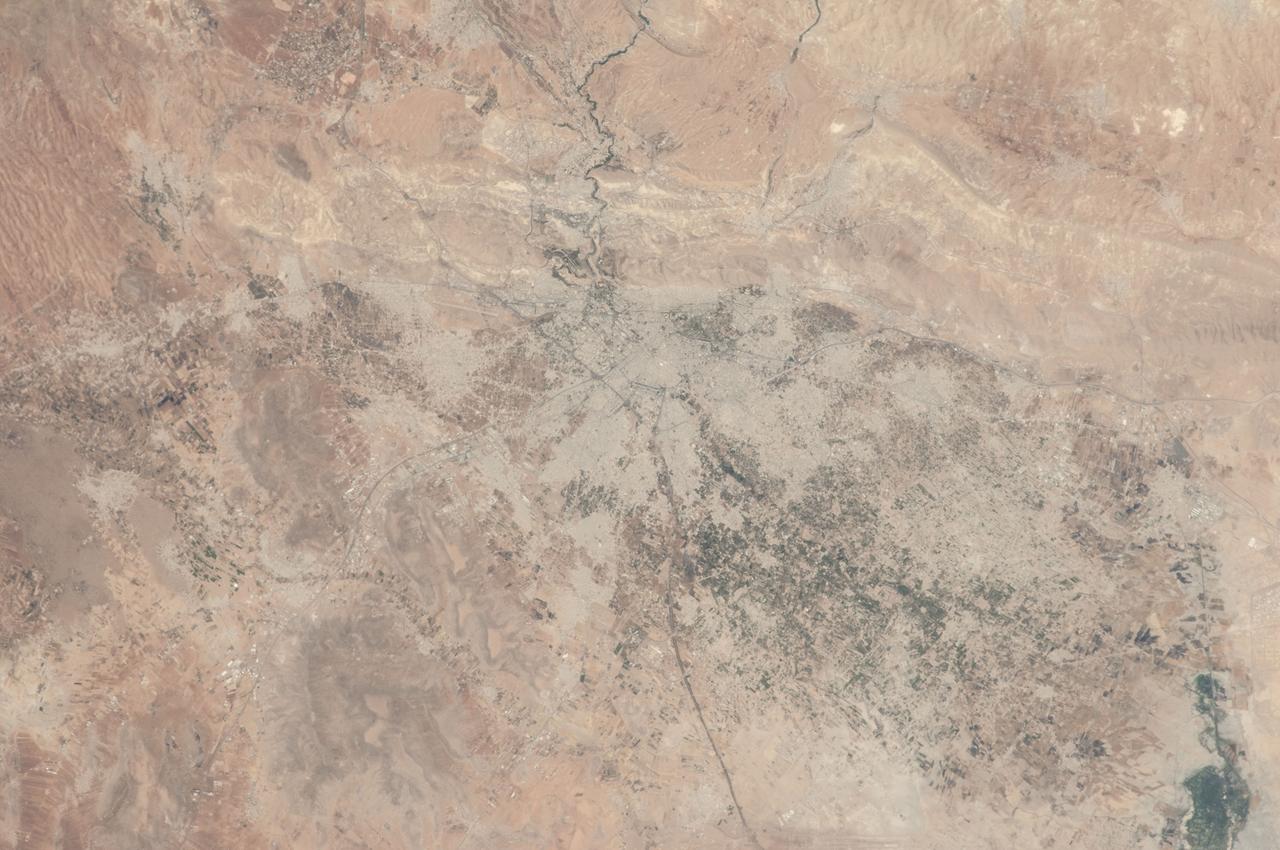

ISS036-E-012047 (26 June 2013) --- Damascus, Syria is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 36 crew member on the International Space Station. The capital city of the Syrian Arab Republic, Damascus, and its surrounding metropolitan area is highlighted in this photograph from the space station. Damascus is one of the oldest cities in the Middle East, with evidence of human habitation extending back to 8,000-10,000 BC. During medieval times, the city was well known as a craft and trade center specializing in the production of swords and lace; ?Damascus steel? became a watchword for high-quality blades through the 19th century due to its superior properties and characteristic visual appearance. Urban areas are readily recognizable as gray-white regions contrasting with surrounding brown to tan semi-arid landscape. The Barada River runs through Damascus, and is visible entering the metropolitan area at top center. The Ghouta oasis, fed by the Barada River, once encircled Damascus but urban expansion has converted much of the oasis from agricultural to other land uses. A large region of agriculture extends to the southeast of Damascus, visible as extensive green fields at lower right. Today, the city is the center of a metropolitan area with a population of over 2.6 million (based on 2004 information from the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics). Current industries include textiles, food processing, and chemicals, with traditional artisan handcrafts still produced in the old core of Damascus. Most recently, the city has experienced unrest, military conflict, and loss of life stemming from the ongoing Syrian Civil War.
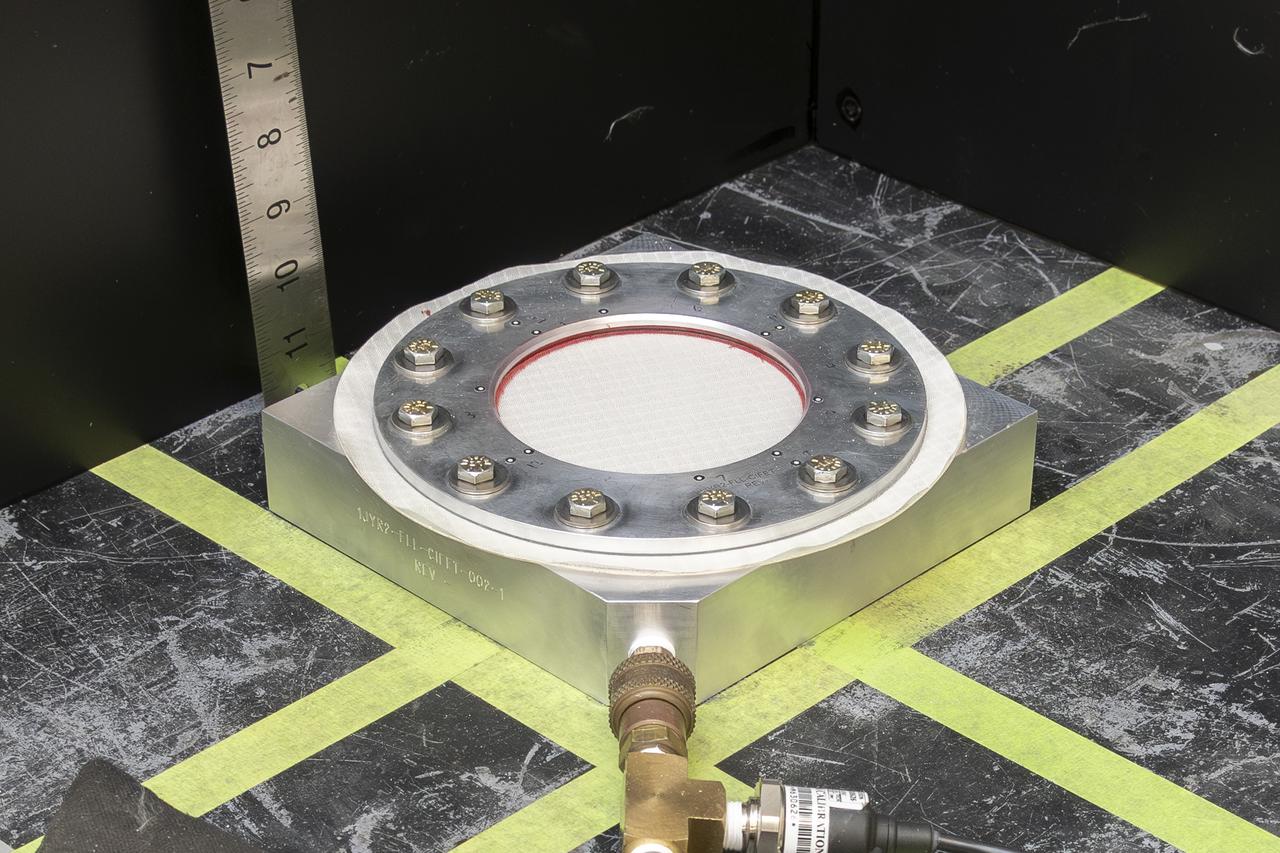
The test team prepares a test fixture with a nylon fabric sample at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The fabric in the test fixture forms a bubble when pressure is applied to the silicone bladder underneath. A similar test can be performed with a sensor on the fabric to verify the sensor will work when stretched in three dimensions.
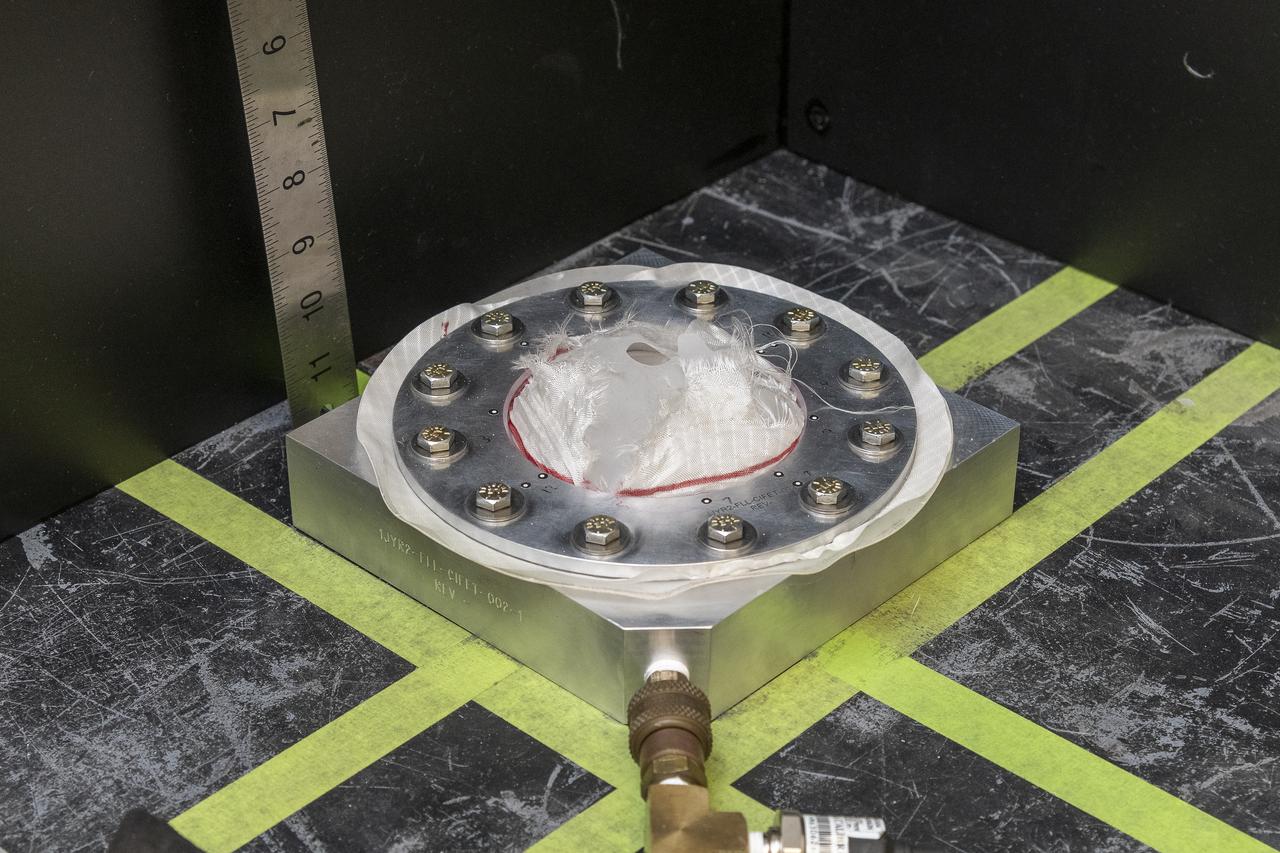
Pressure is applied to a test fixture with a nylon fabric sample until it fails at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The fabric in the test fixture forms a bubble when pressure is applied to the silicone bladder underneath. In this frame, the silicone bladder is visible underneath the torn fabric after it was inflated to failure. A similar test can be performed with a sensor on the fabric to verify the sensor will work when stretched in three dimensions.
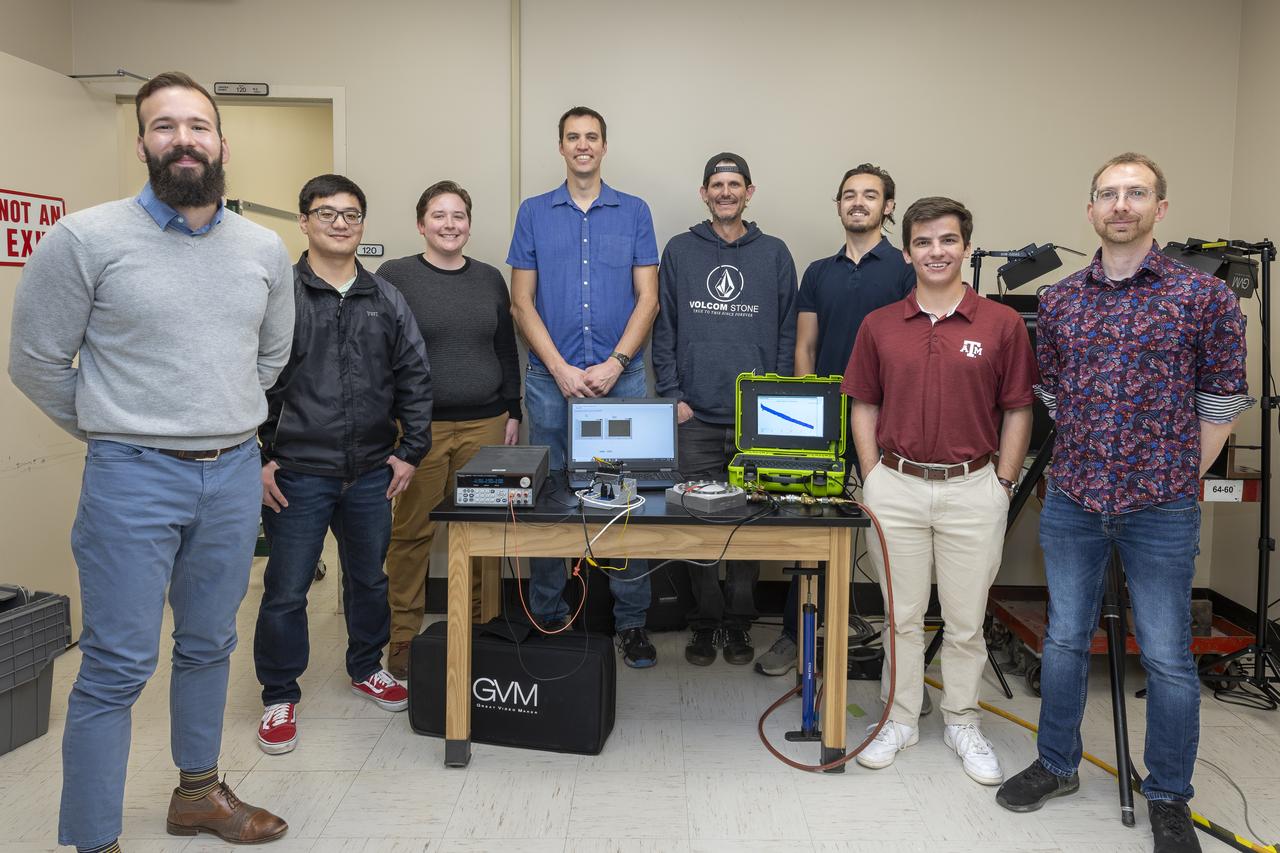

Erick Rossi De La Fuente, from left, John Rudy, L. J. Hantsche, Adam Curry, Jeff Howell, Coby Asselin, Benjamin Mayeux, and Paul Bean pose with a test fixture, material, sensor, and data acquisition systems at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The sensor tests seek to quantify the limits of the material to improve computer models and make more reliable supersonic parachutes.
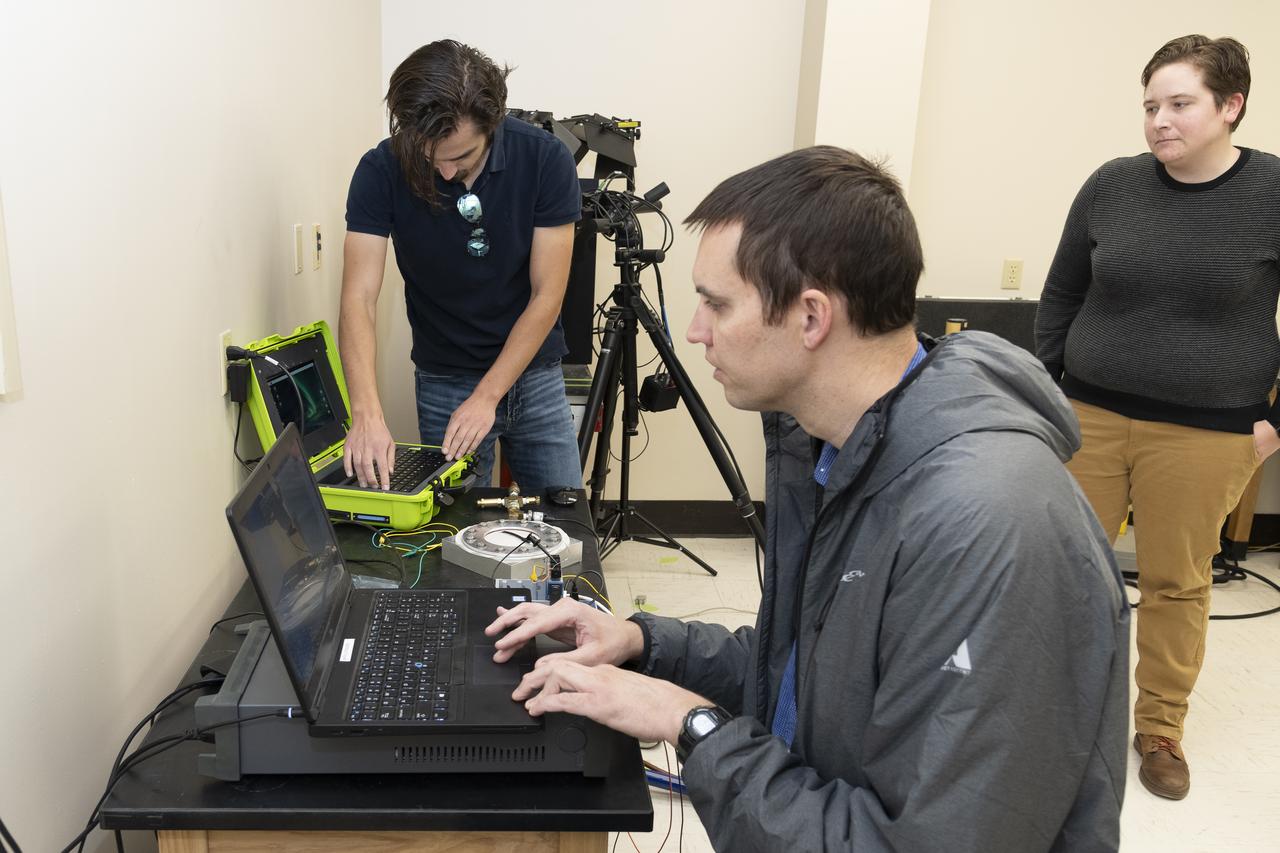

Coby Asselin, from left, Adam Curry, and L. J. Hantsche set up the data acquisition systems used during testing of a senor to determine parachute canopy material strength at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The sensor tests seek to quantify the limits of the material to improve computer models and make more reliable supersonic parachutes.