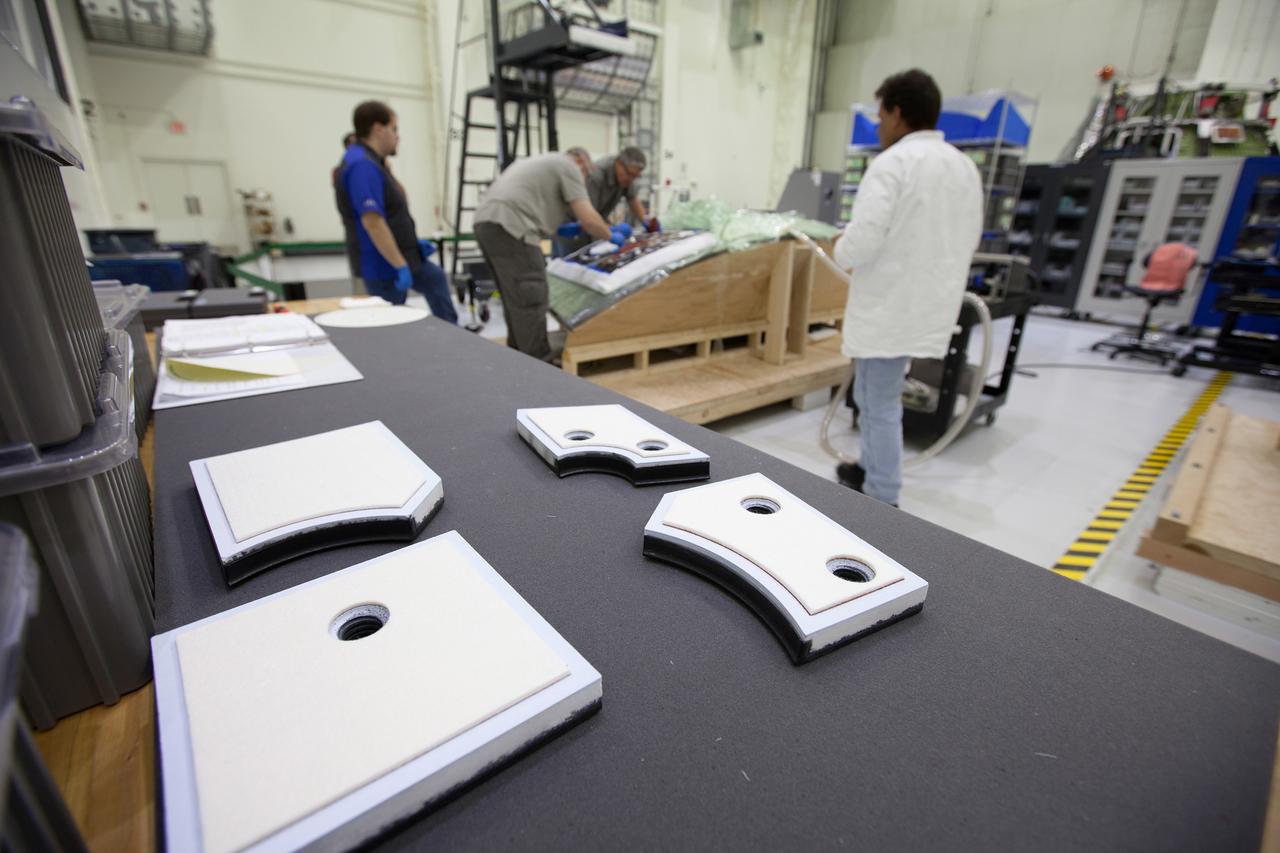

At Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians bond thermal protection system tiles to Orion's backshell panels on July 8, 2016...While similar to those used on the space shuttle, Orion only requires about 1,300 tiles compared to more than 24,000 on the shuttle. The tiles, along with the spacecraft’s heat shield, will protect Orion from the 5,000 degree Fahrenheit heat of re-entry.

At Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians bond thermal protection system tiles to Orion's backshell panels on July 8, 2016...While similar to those used on the space shuttle, Orion only requires about 1,300 tiles compared to more than 24,000 on the shuttle. The tiles, along with the spacecraft’s heat shield, will protect Orion from the 5,000 degree Fahrenheit heat of re-entry.
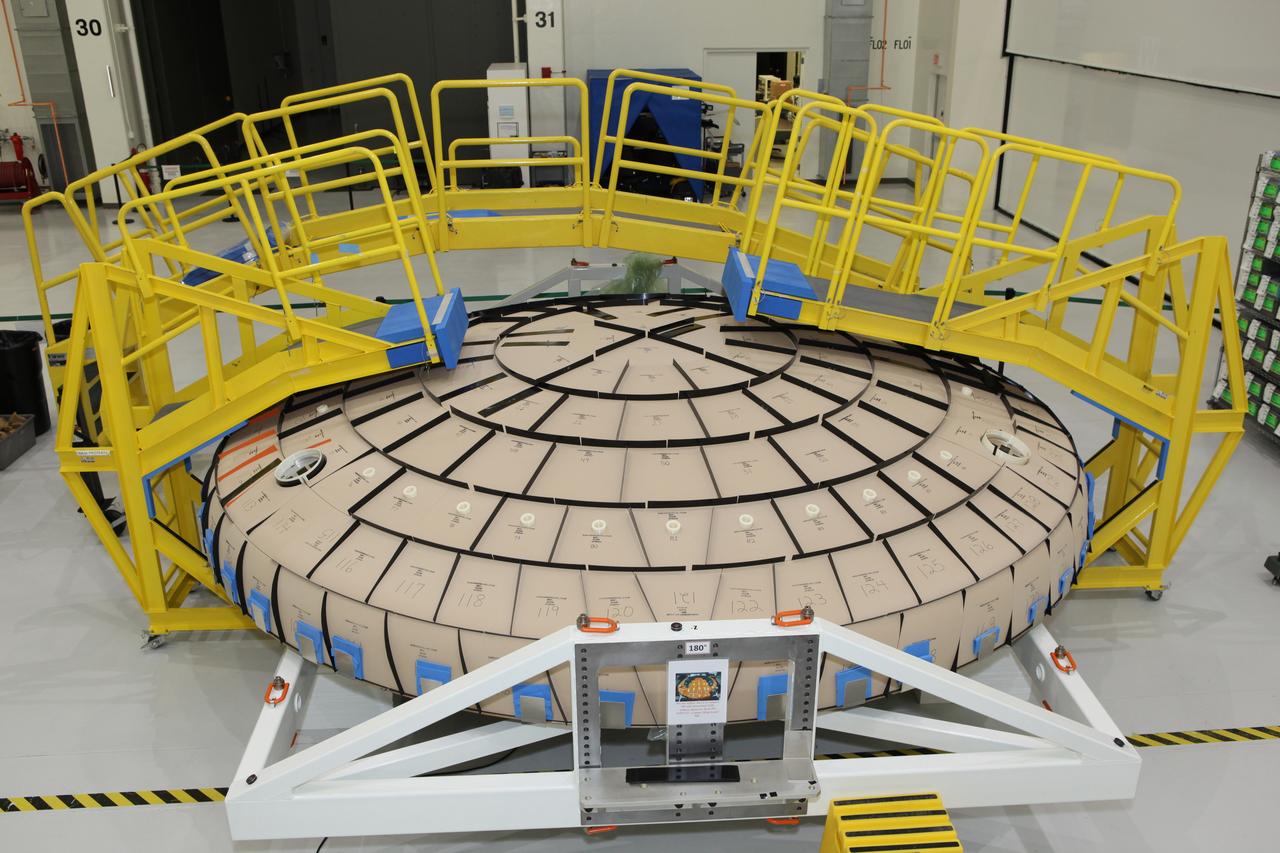
Tile blocks are prefitted around the heat shield for the Orion crew module inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 24, 2016. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

A small piece of thermal insulation tile floats in space near the Shuttle Columbia. The cloudy surface of the earth is used as a background.
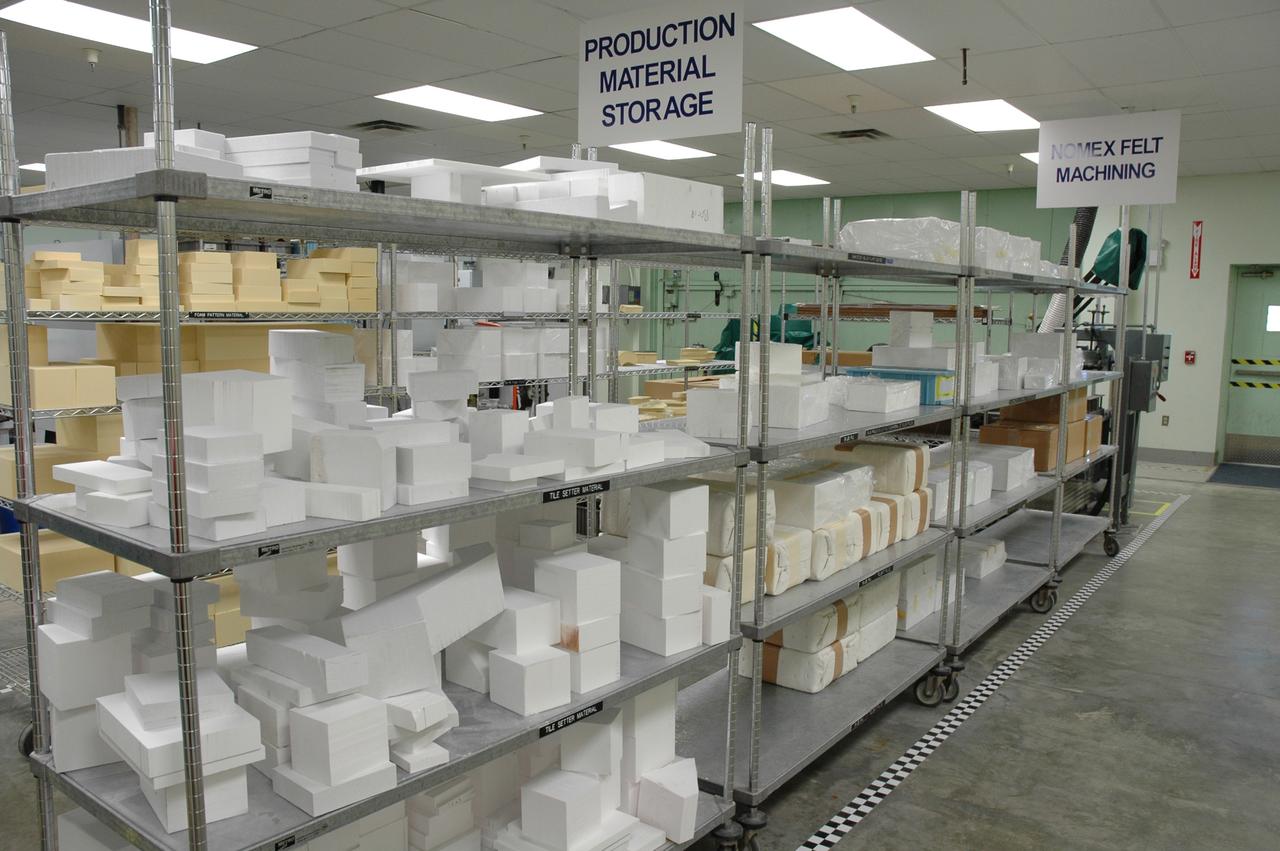

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Tile Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, shelves are stacked with Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tiles. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high. These areas include the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
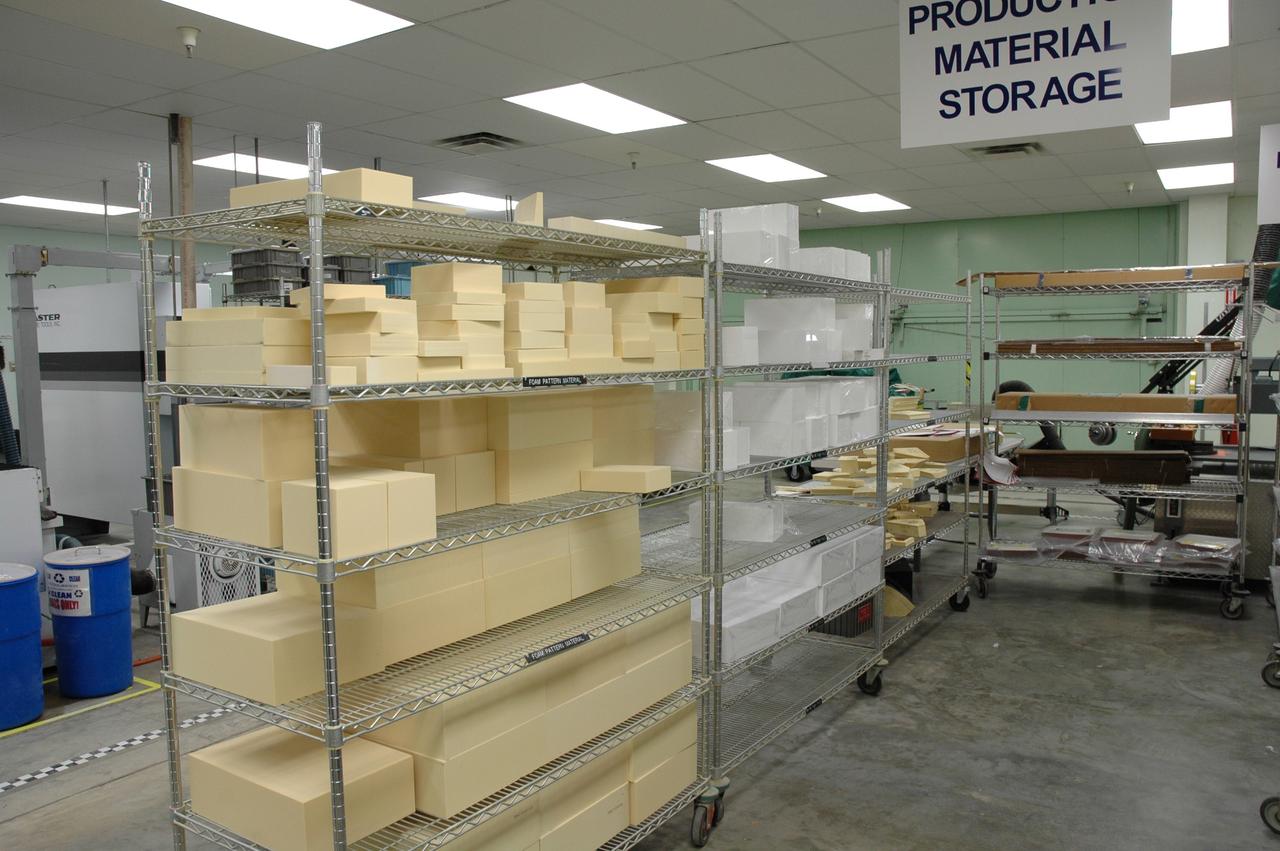

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Tile Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, shelves are stacked with Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tiles. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high. These areas include the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a United Space Alliance technician installs Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile on space shuttle Endeavour during processing activities. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station on its STS-126 mission. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a United Space Alliance technician installs Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile on space shuttle Endeavour during processing activities. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station on its STS-126 mission. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
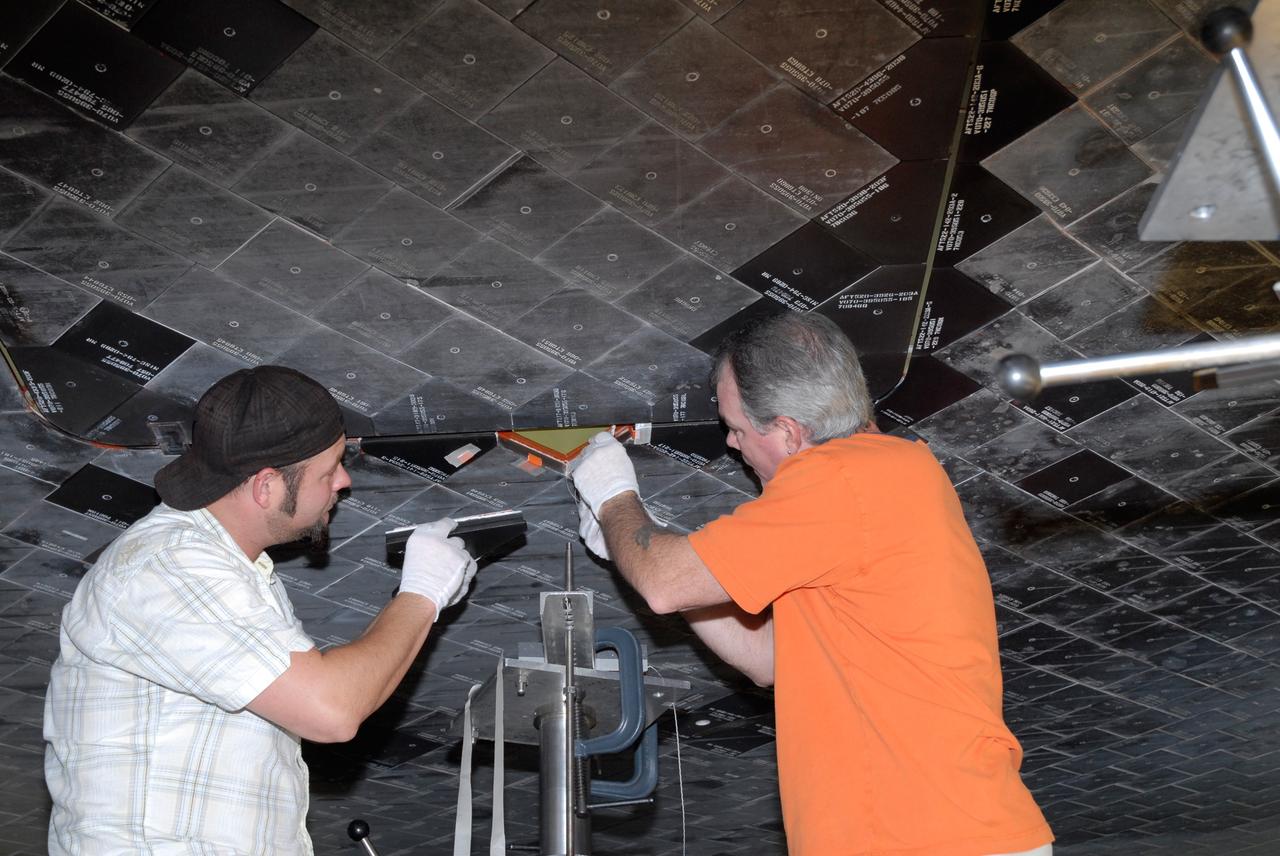

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, United Space Alliance technicians install Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile on space shuttle Endeavour during processing activities. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station on its STS-126 mission. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
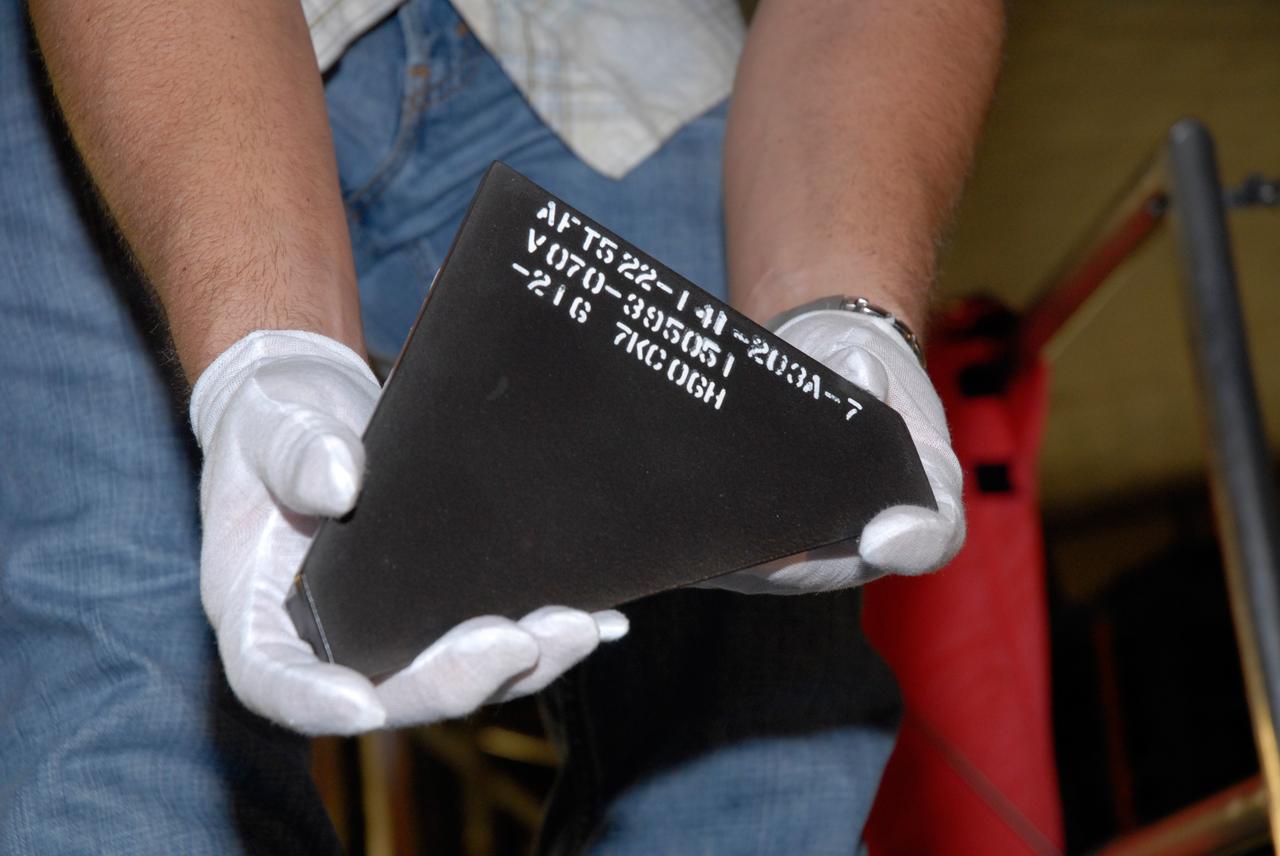

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a United Space Alliance technician holds one of the Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile that will be installed on space shuttle Endeavour during processing activities. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station on its STS-126 mission. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
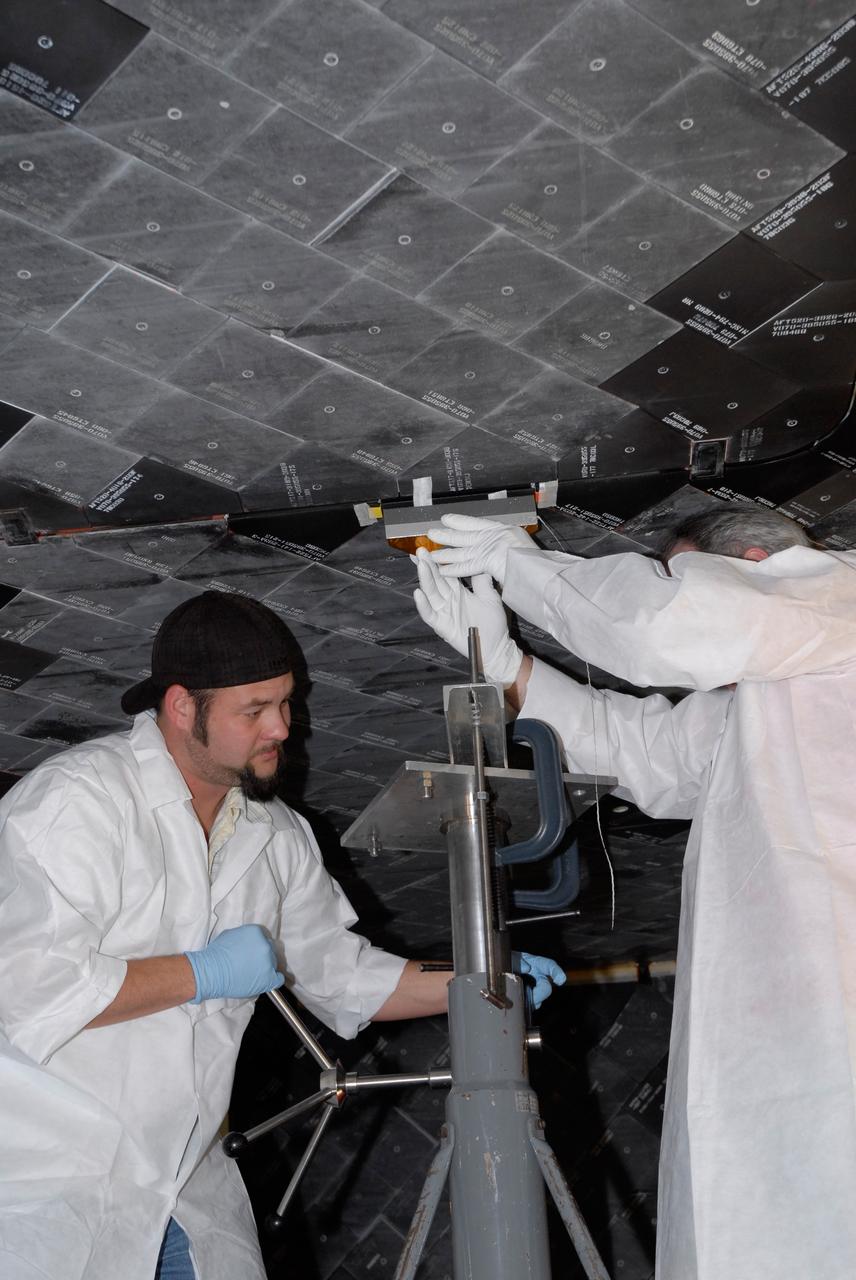

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, United Space Alliance technicians install Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile on space shuttle Endeavour during processing activities. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station on its STS-126 mission. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
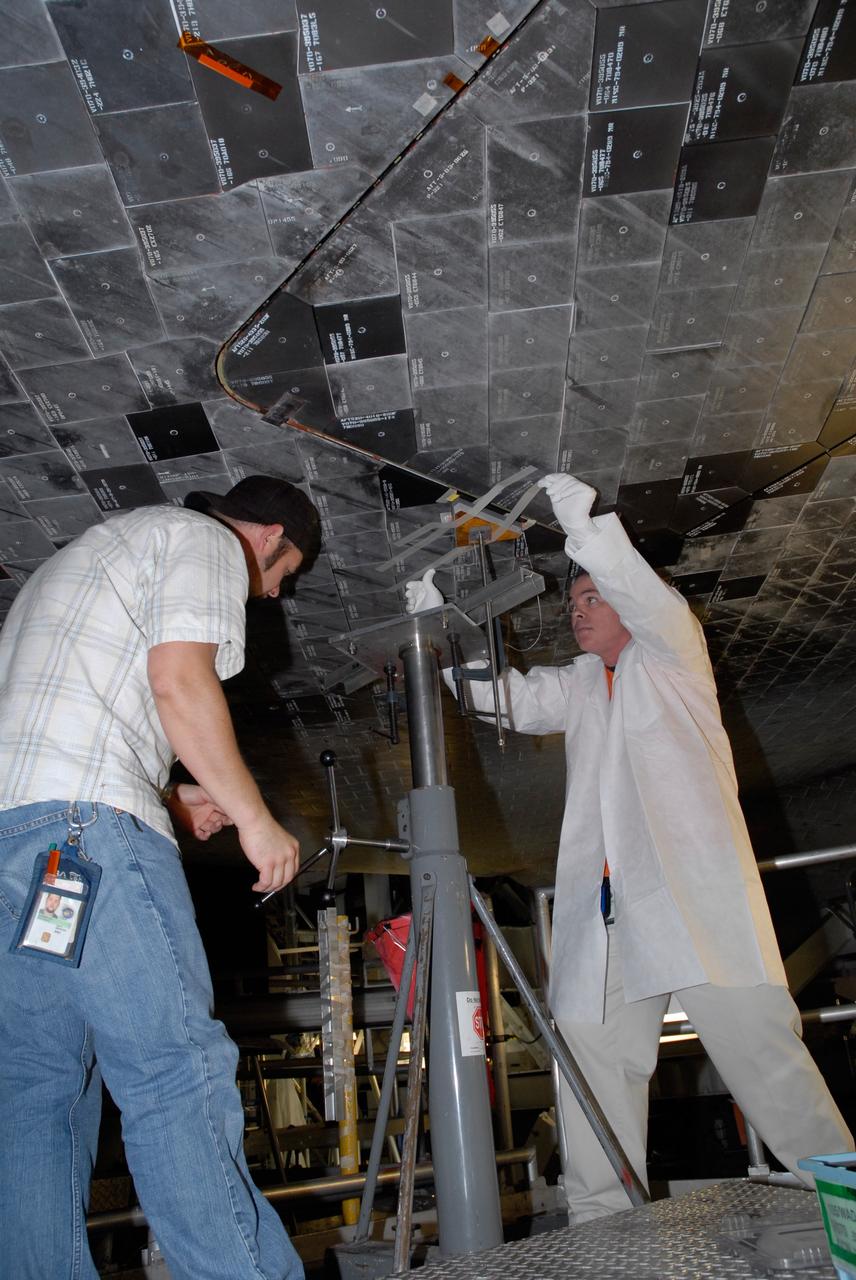

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, United Space Alliance technicians install Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile on space shuttle Endeavour during processing activities. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station on its STS-126 mission. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
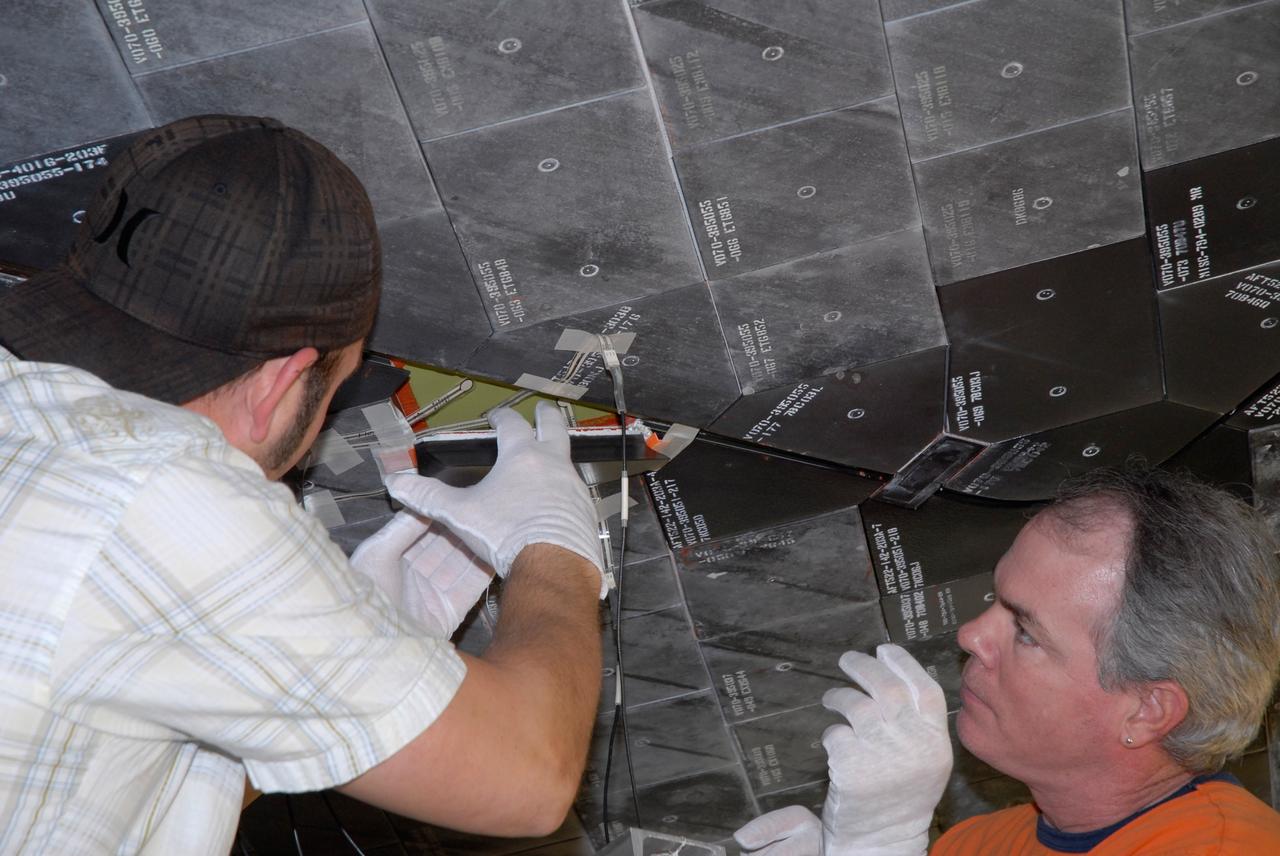

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, United Space Alliance technicians install Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile on space shuttle Endeavour during processing activities. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station on its STS-126 mission. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
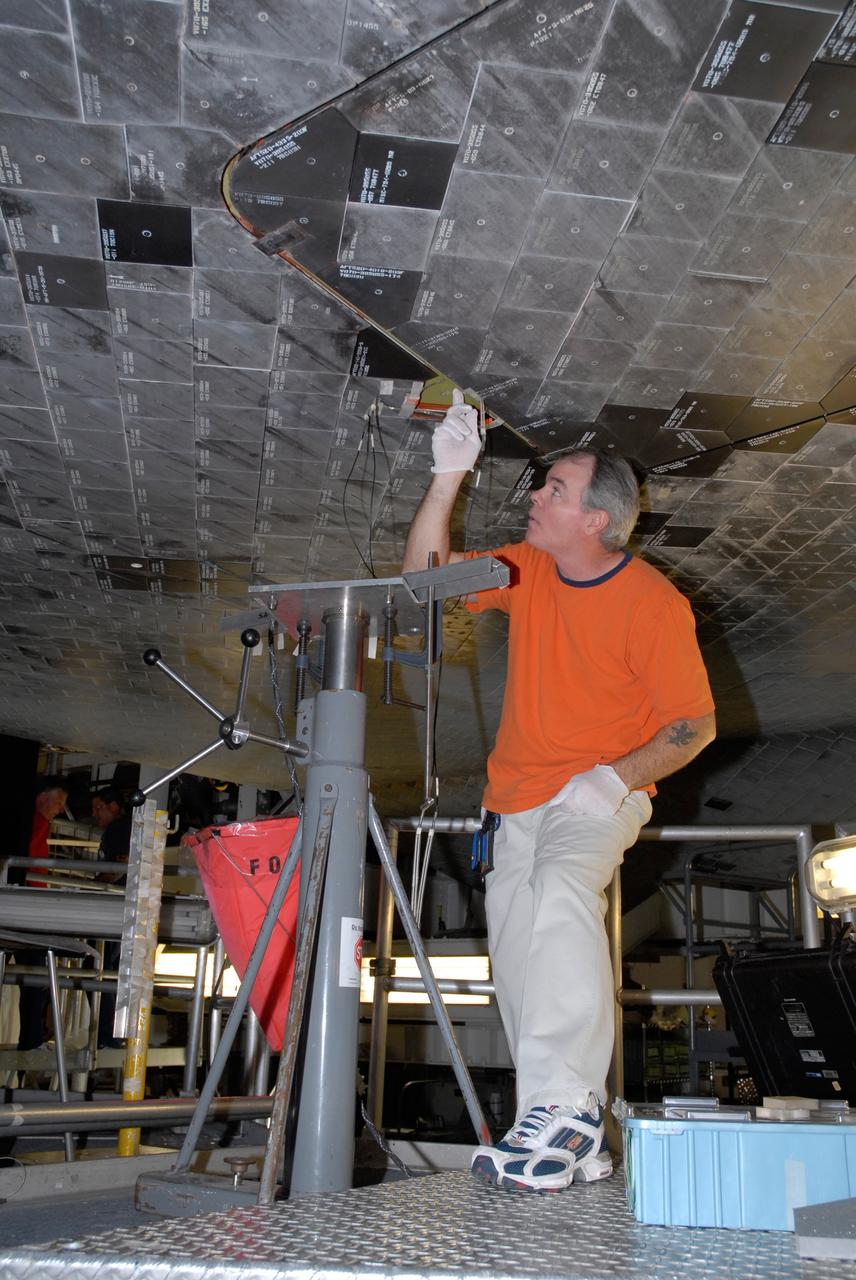

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a United Space Alliance technician installs Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile on space shuttle Endeavour during processing activities. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station on its STS-126 mission. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
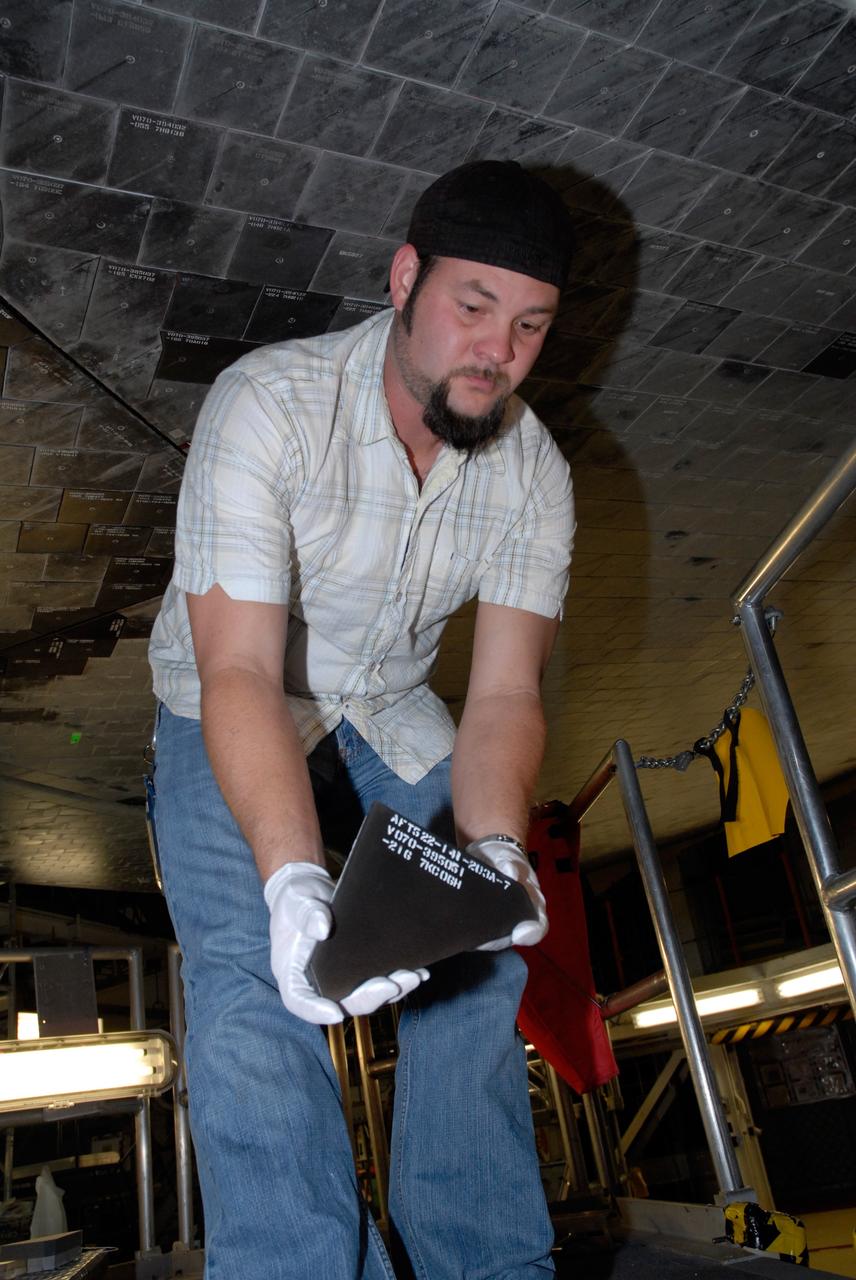

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a United Space Alliance technician holds one of the Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile that will be installed on space shuttle Endeavour during processing activities. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station on its STS-126 mission. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
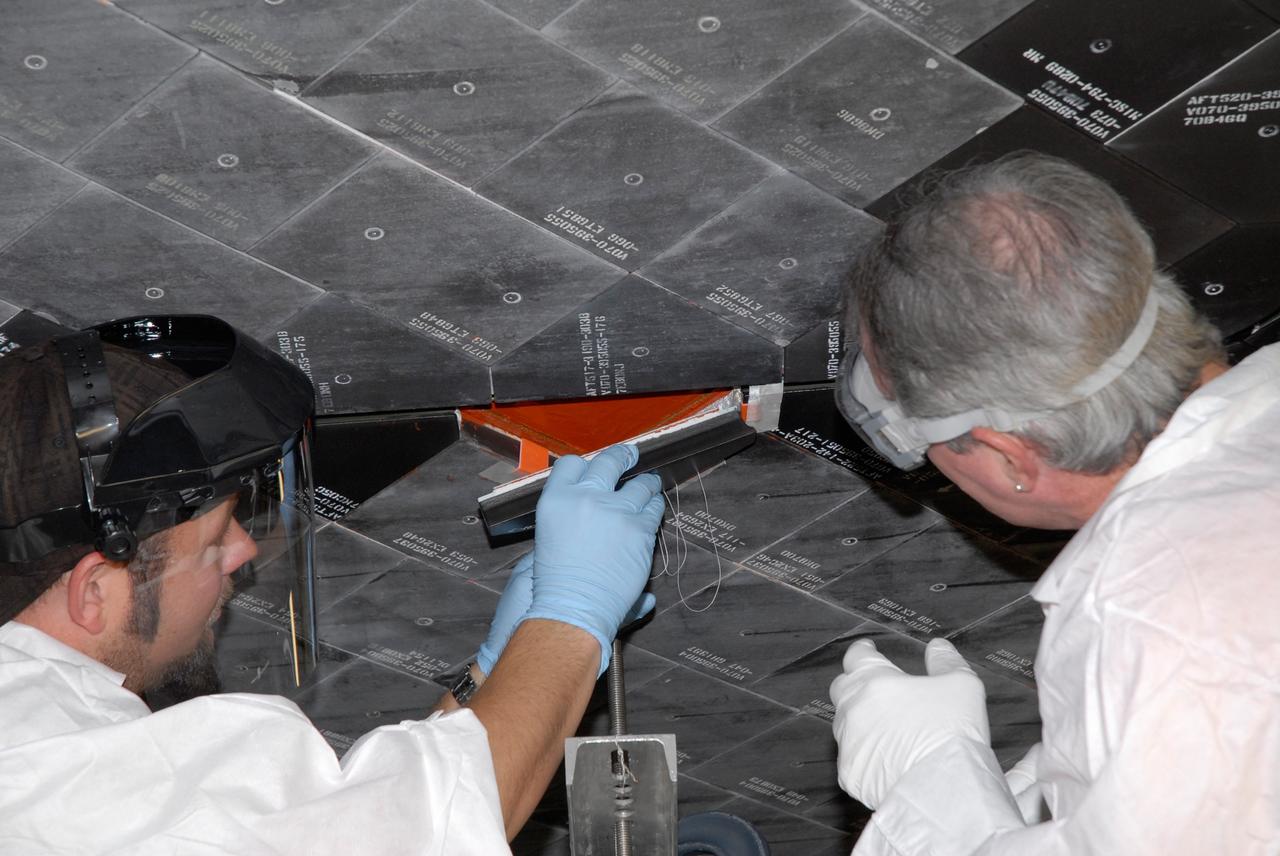

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, United Space Alliance technicians install Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile on space shuttle Endeavour during processing activities. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station on its STS-126 mission. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
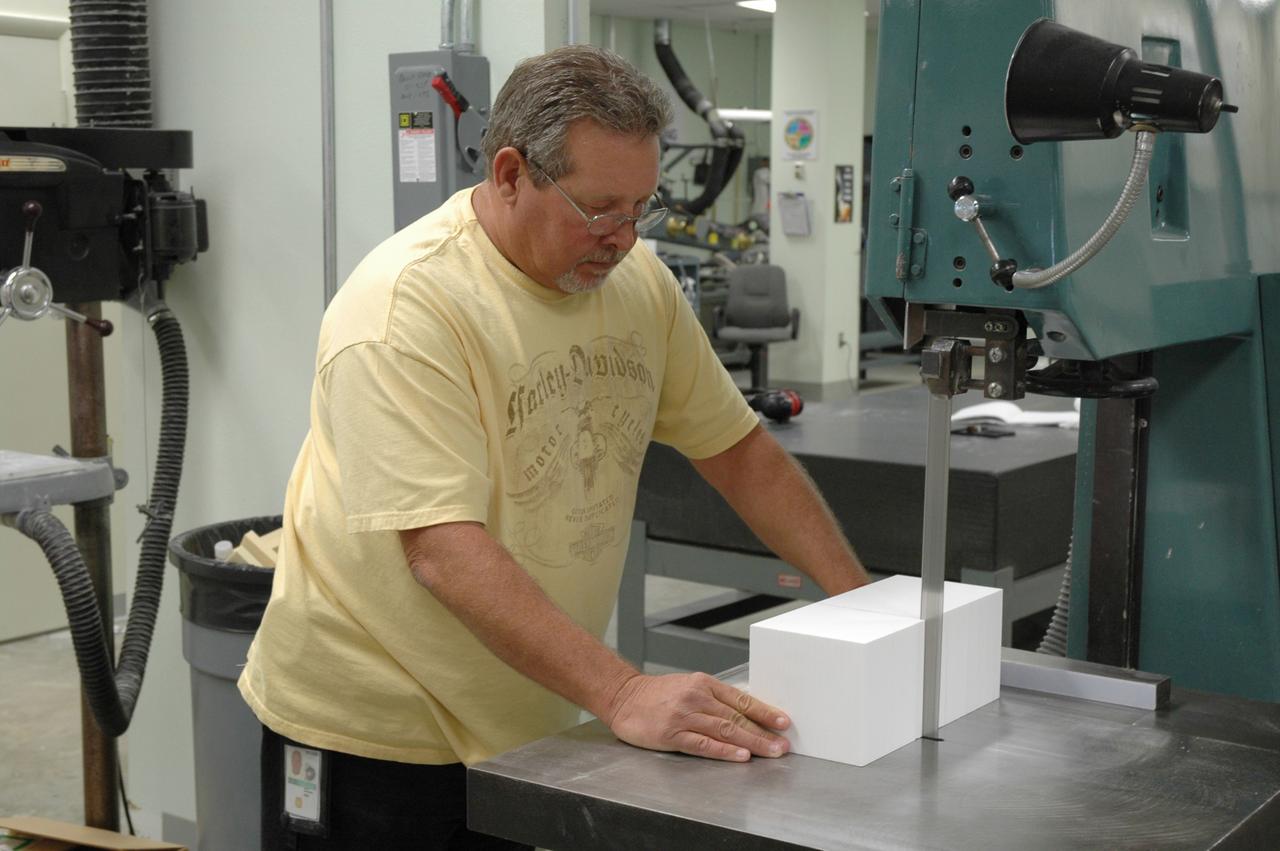

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Tile Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a United Space Alliance technician cuts a block of Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tile. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high. These areas include the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
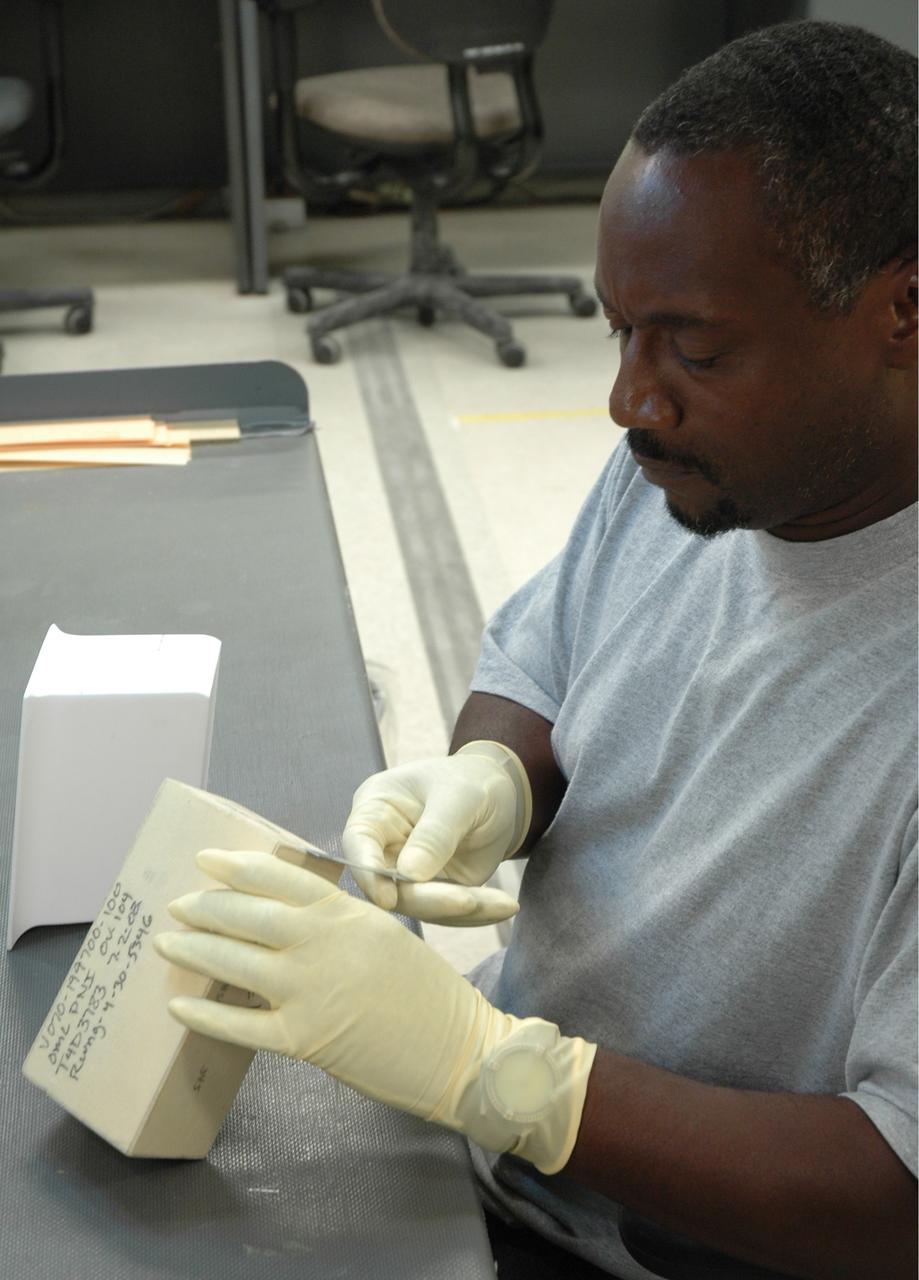

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Tile Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a United Space Alliance technician checks a Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tile. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high. These areas include the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
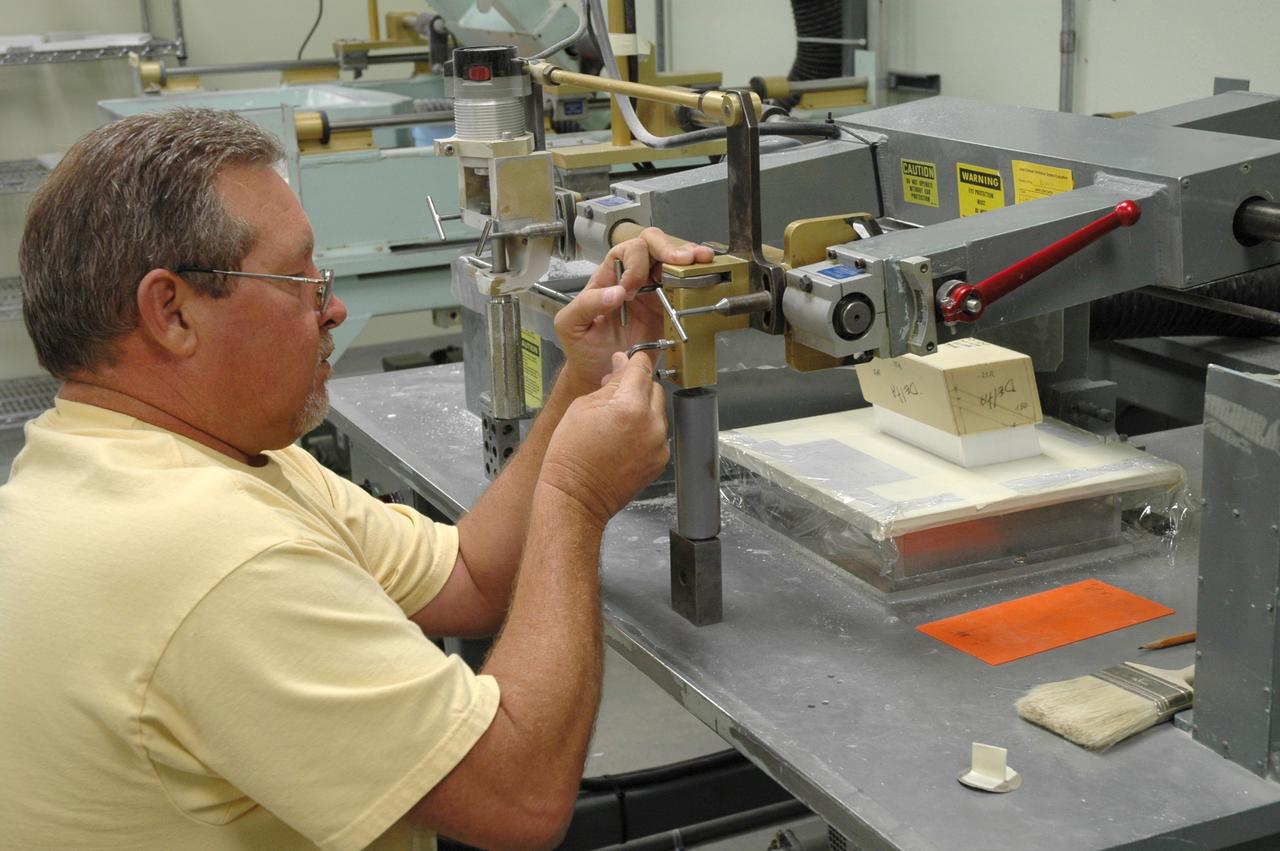

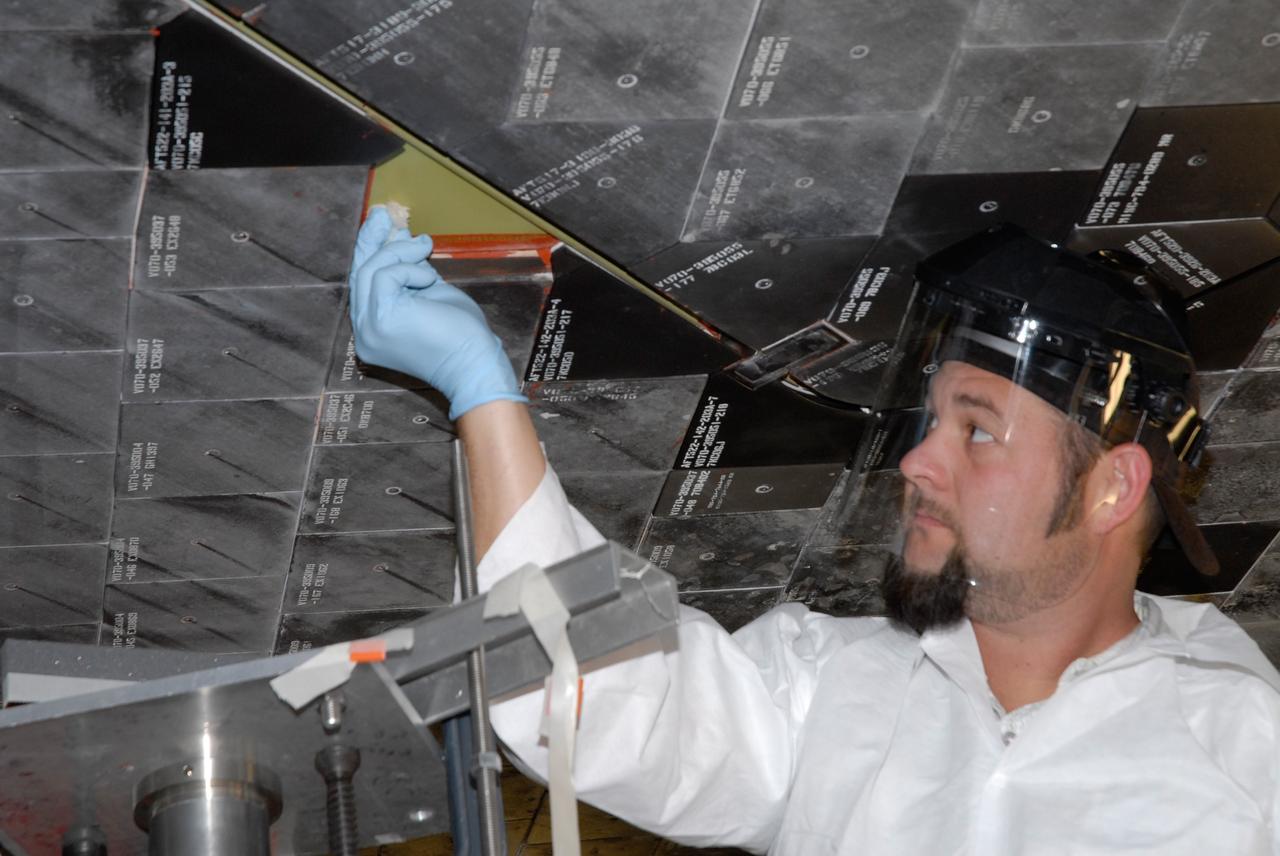
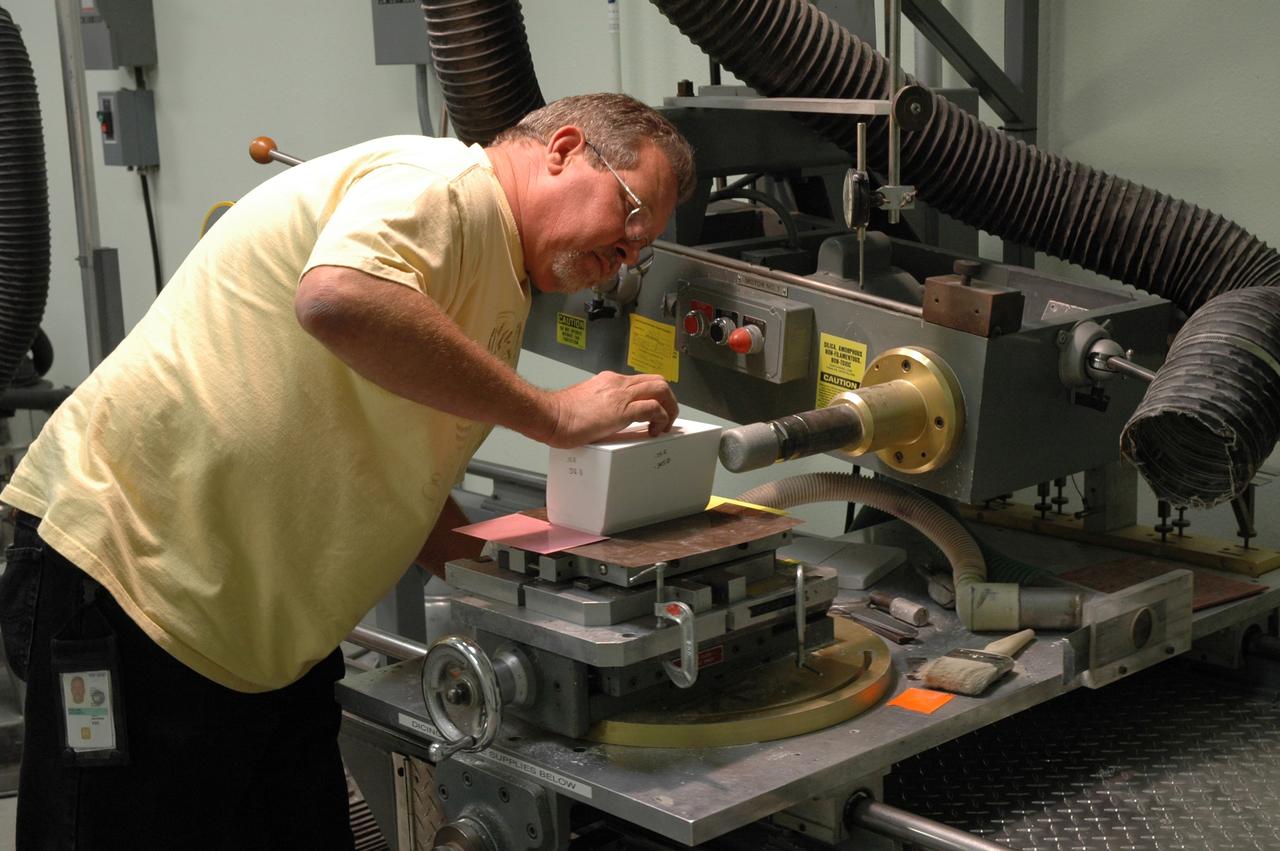
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Tile Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a United Space Alliance machinist, Tony Rollins, is setting up the tracer mill to machine the Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tile. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high. These areas include the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
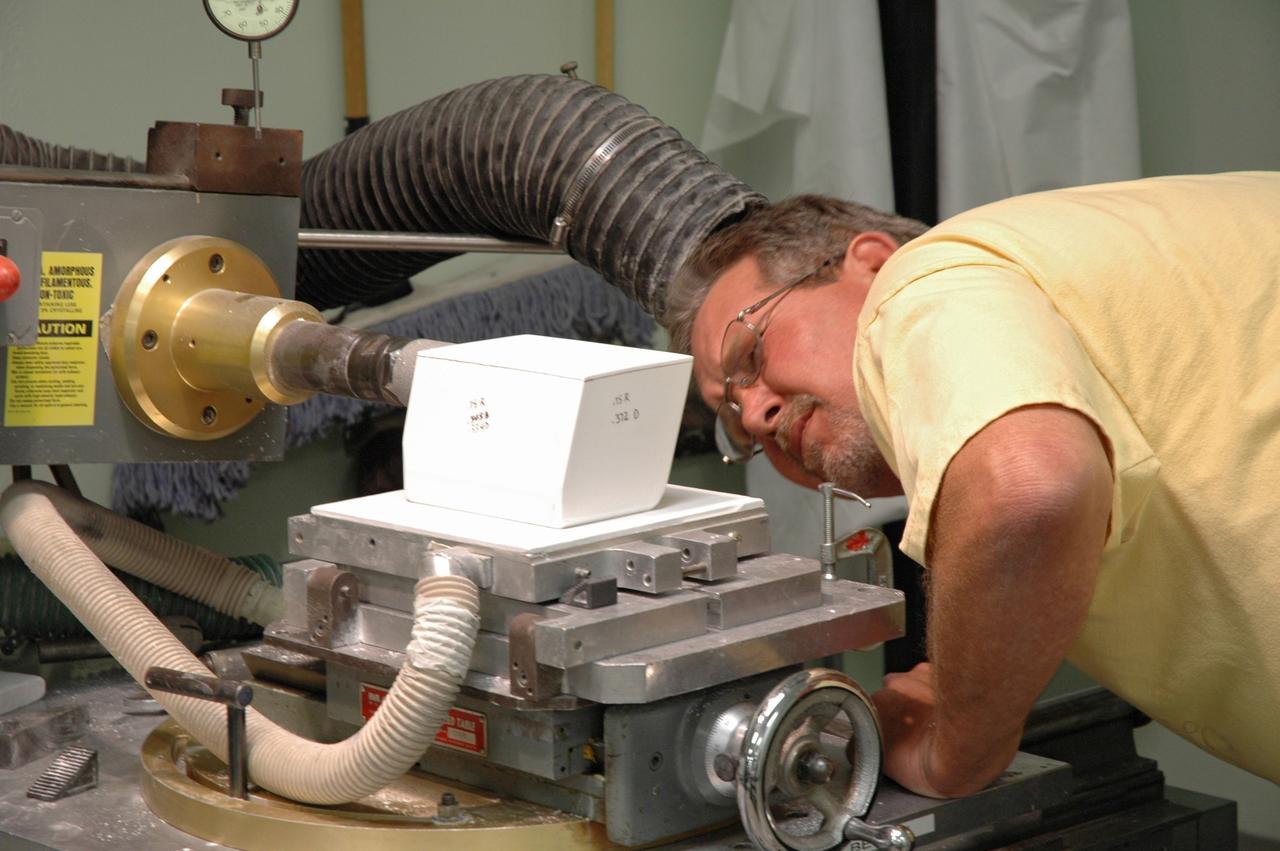

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Tile Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a United Space Alliance technician checks the shape of Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tile he cut. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high. These areas include the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Tile Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a United Space Alliance technician checks the Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tile he cut. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high. These areas include the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
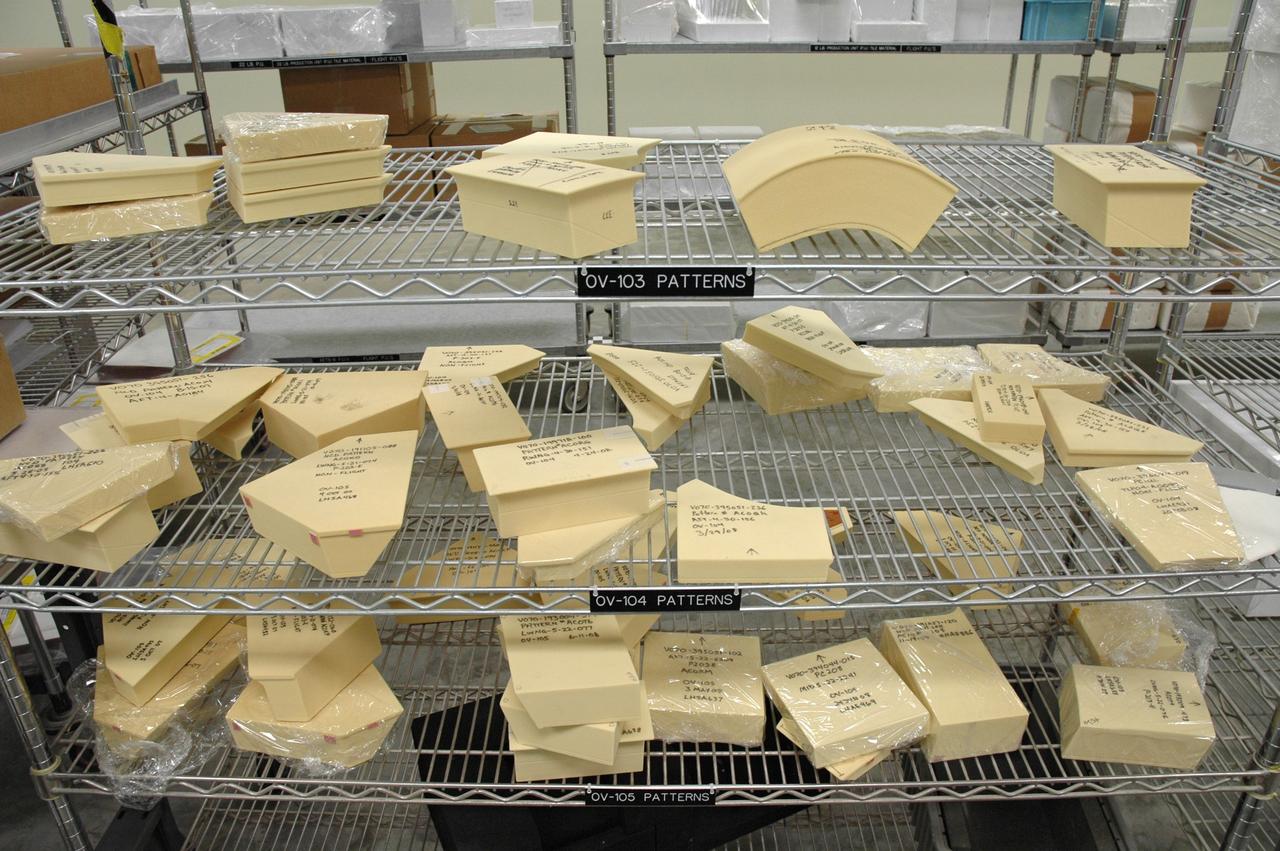

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Tile Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tiles of different shapes await use on the three orbiters: Discovery, Atlantis and Endeavour. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high. These areas include the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
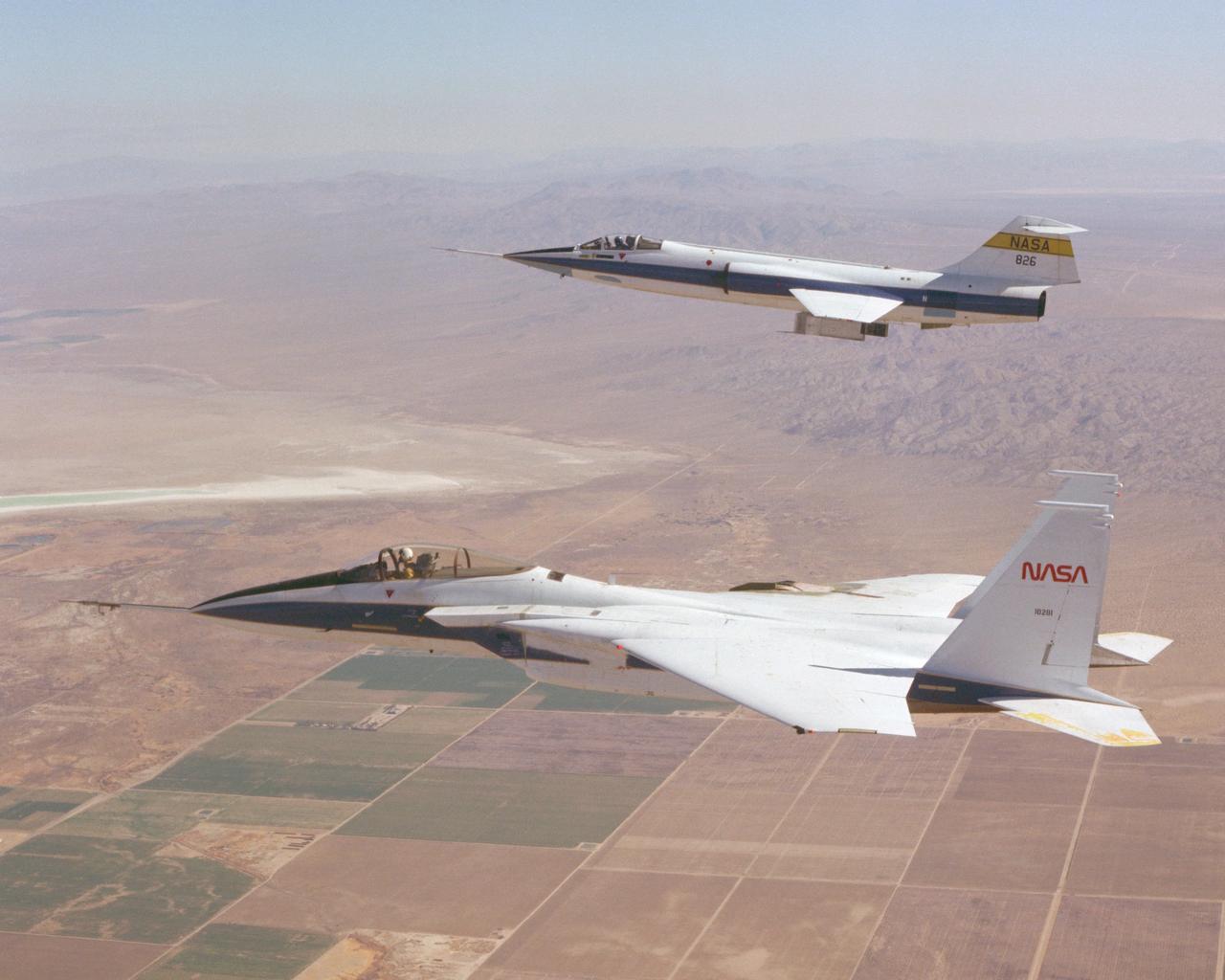

F-15 #281 and F-104 #826 fly in formation during Space Shuttle tile testing. Note the tiles mounted on the right wing of the F-15 and the centerline test fixture of the F-104.
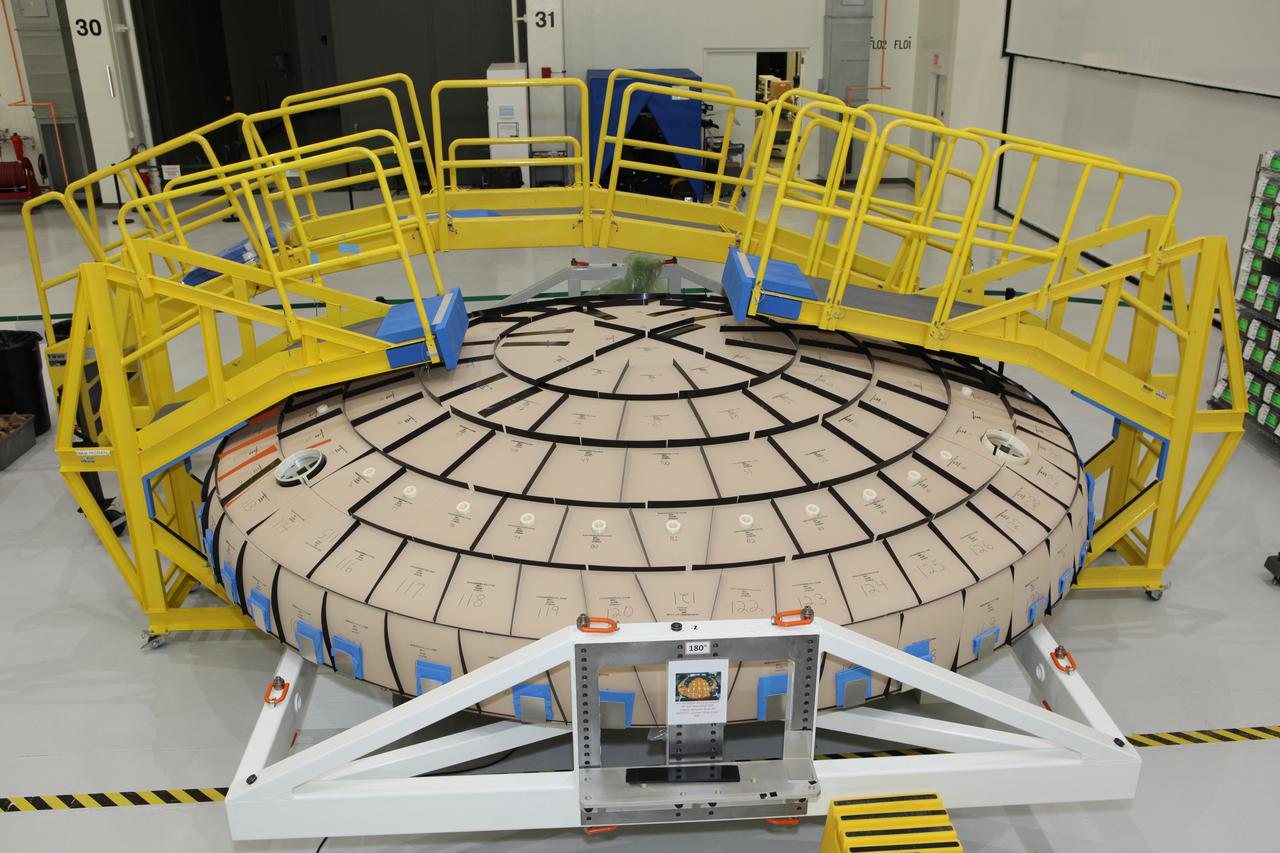
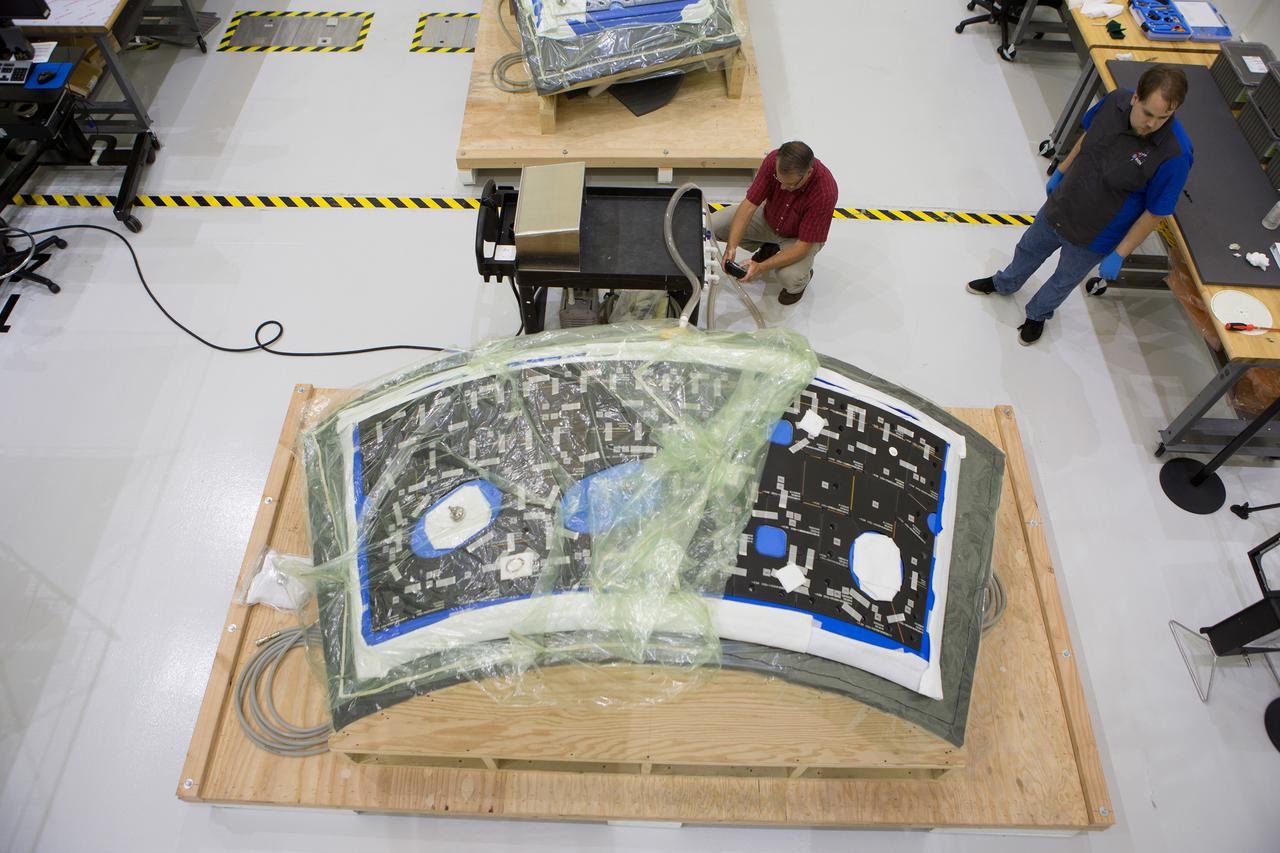
Tile blocks have been prefitted around the heat shield for the Orion crew module inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The heat shield is one of the most critical elements of Orion and protects it and the future astronauts inside from searing temperatures experienced during reentry through Earth’s atmosphere when they return home. For Exploration Mission-1, the top layer of Orion’s heat shield that is primarily responsible for helping the crew module endure reentry heat will be composed of approximately 180 blocks, which are made of an ablative material called Avcoat designed to wear away as it heats up. Orion is being prepared for its flight on the agency’s Space Launch System for Exploration Mission-1 in late 2018. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and NASA’s Journey to Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion.
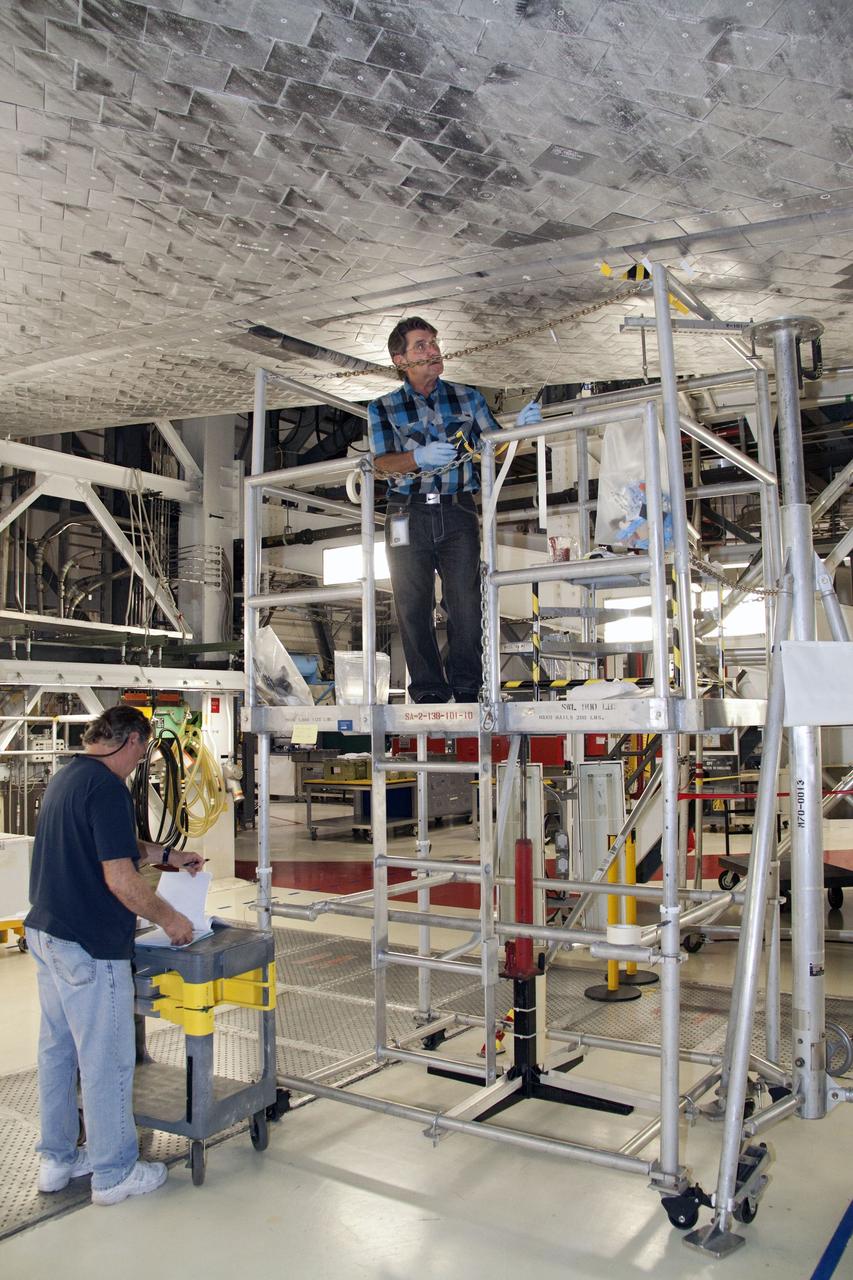

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician is preparing to work on replacing some of space shuttle Atlantis' heat shield tiles. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System that protects the shuttle against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will carry the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last flight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
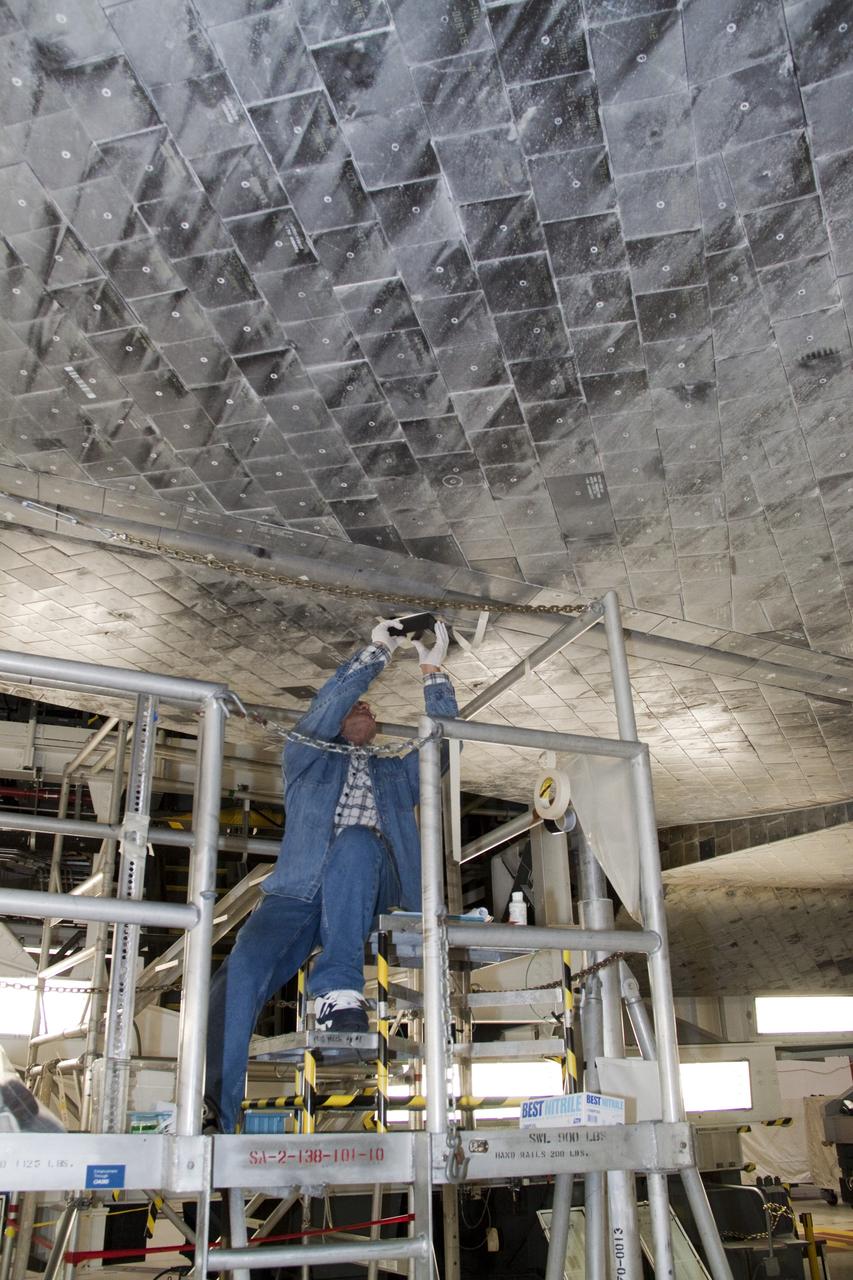

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician is replacing a heat shield tile under space shuttle Atlantis. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System, thermal shields to protect against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last spaceflight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
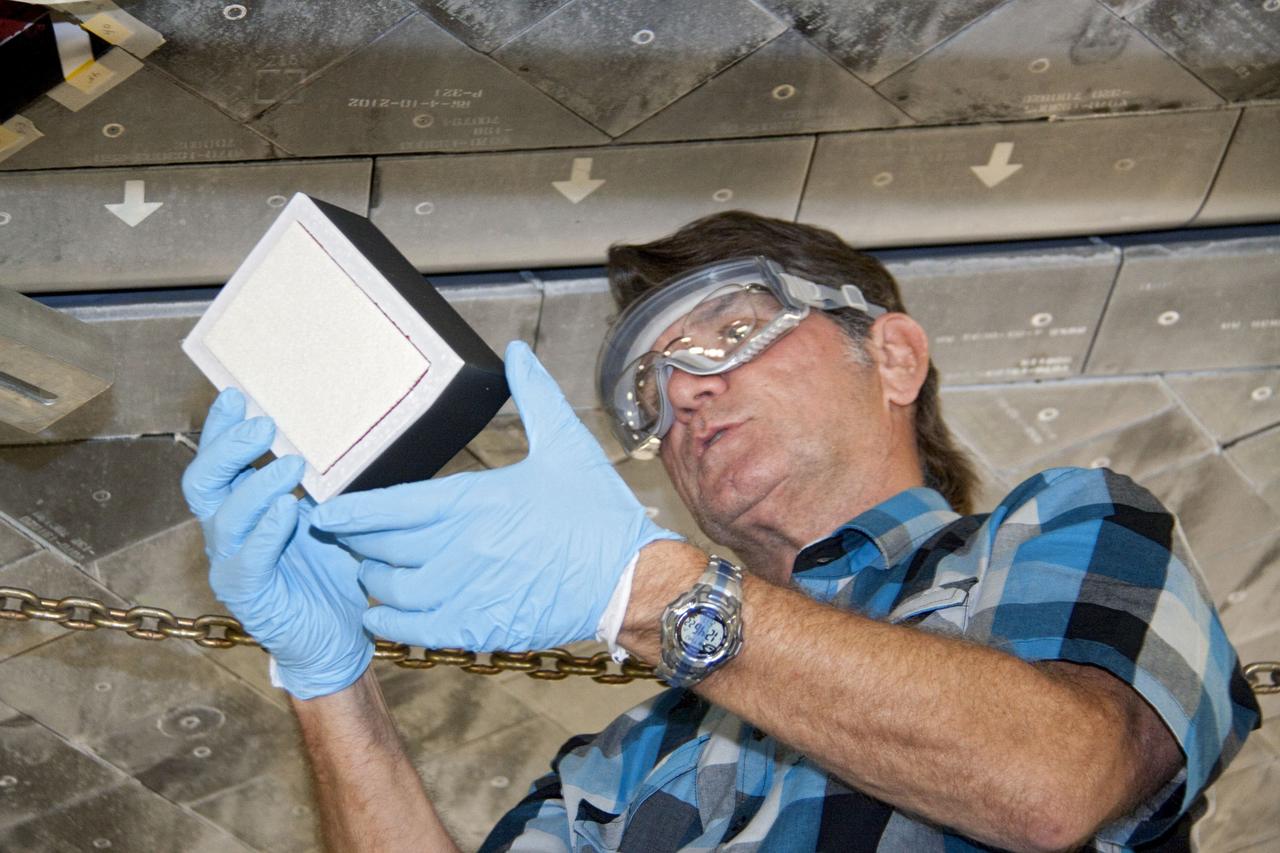

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician closely inspects a heat shield tile for space shuttle Atlantis before securing it into position. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System that protects the shuttle against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will carry the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last flight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
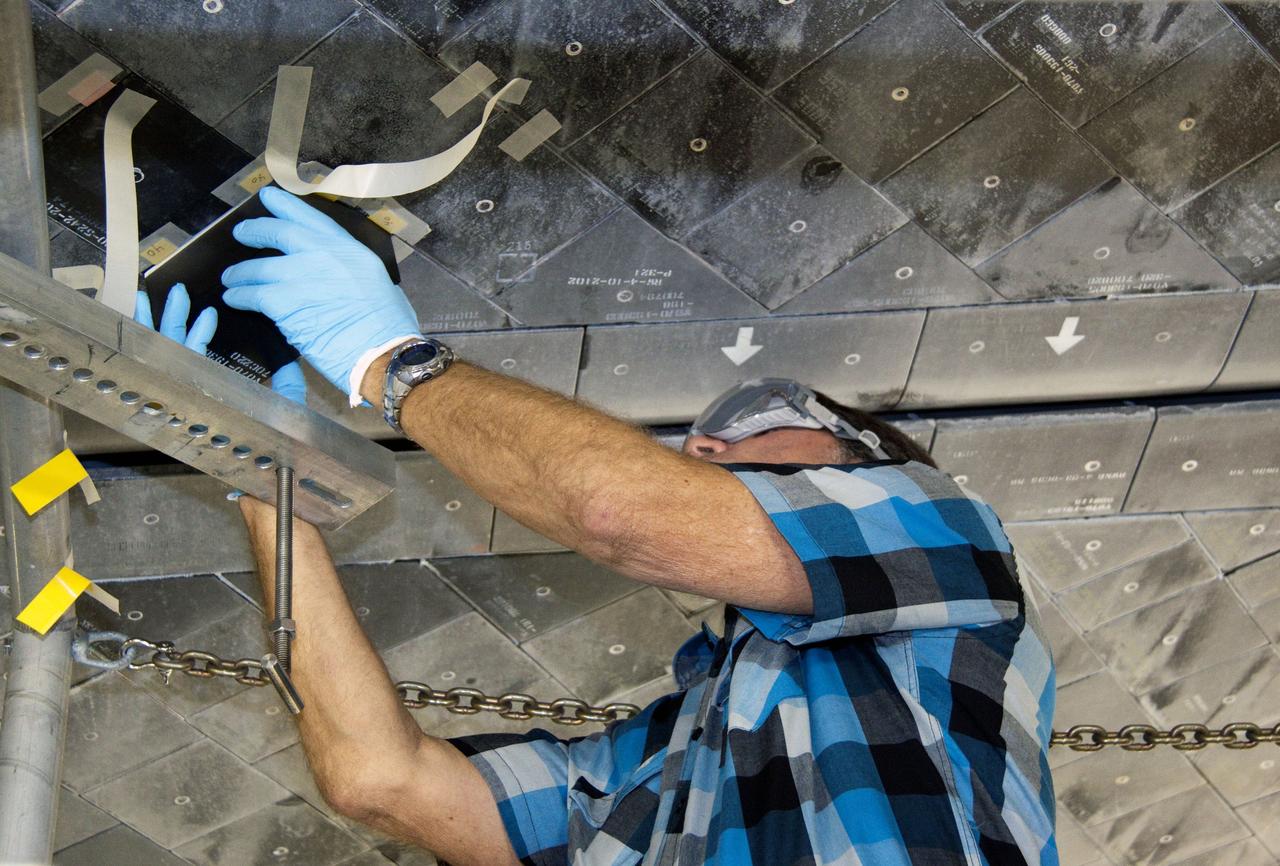

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician places a heat shield tile into position under space shuttle Atlantis. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System that protects the shuttle against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will carry the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last flight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
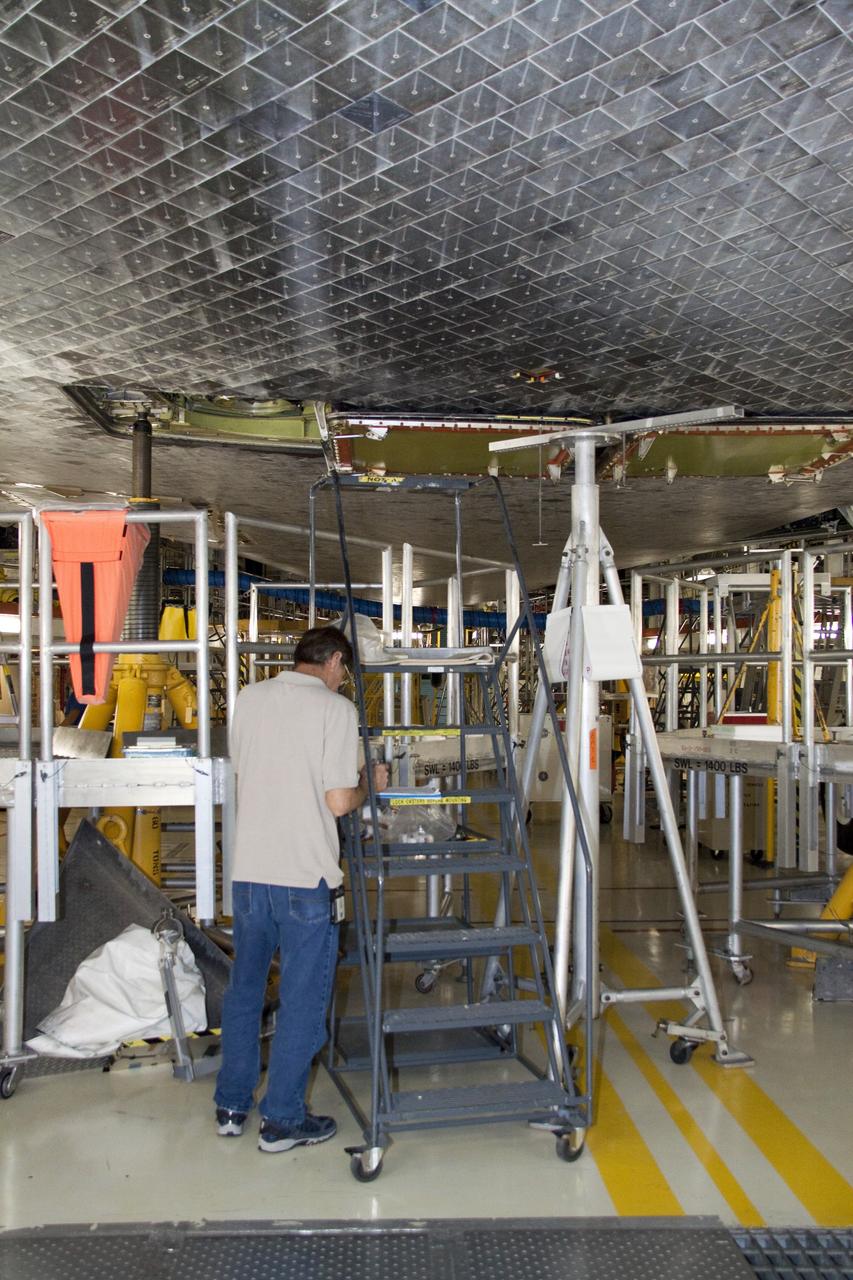

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician is ready to work on replacing some of space shuttle Atlantis' heat shield tiles. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System, thermal shields to protect against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last spaceflight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
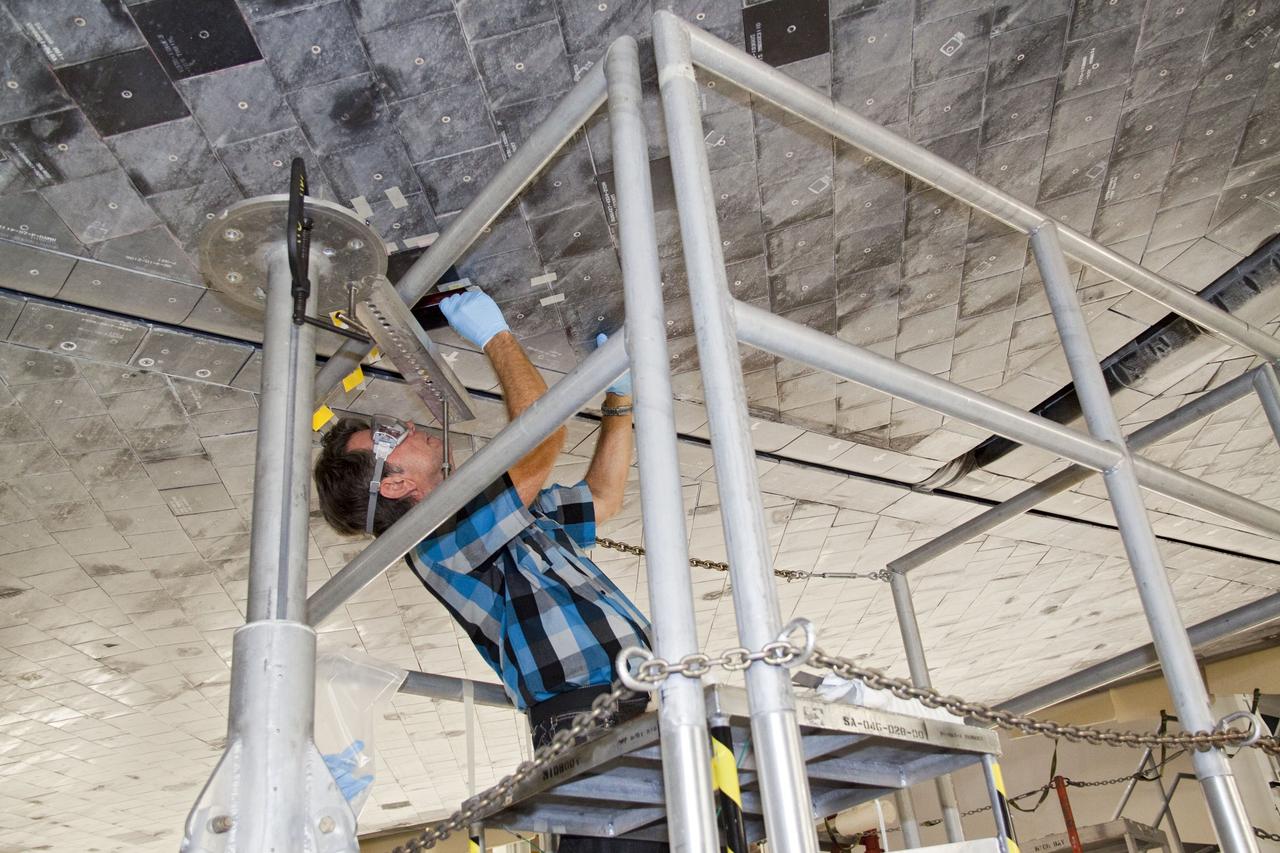

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician inspects the area on space shuttle Atlantis' underside before a heat shield tile is installed. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System that protects the shuttle against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will carry the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last flight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
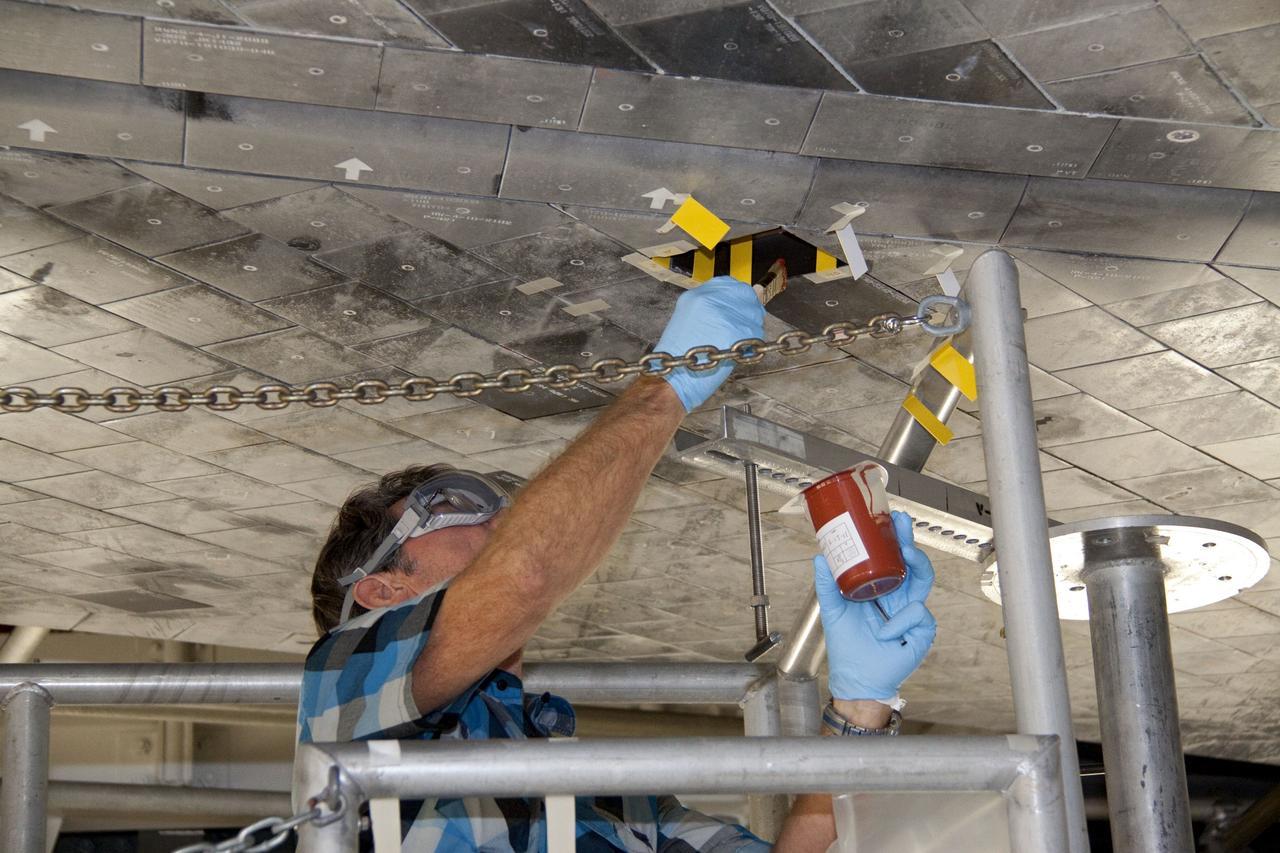

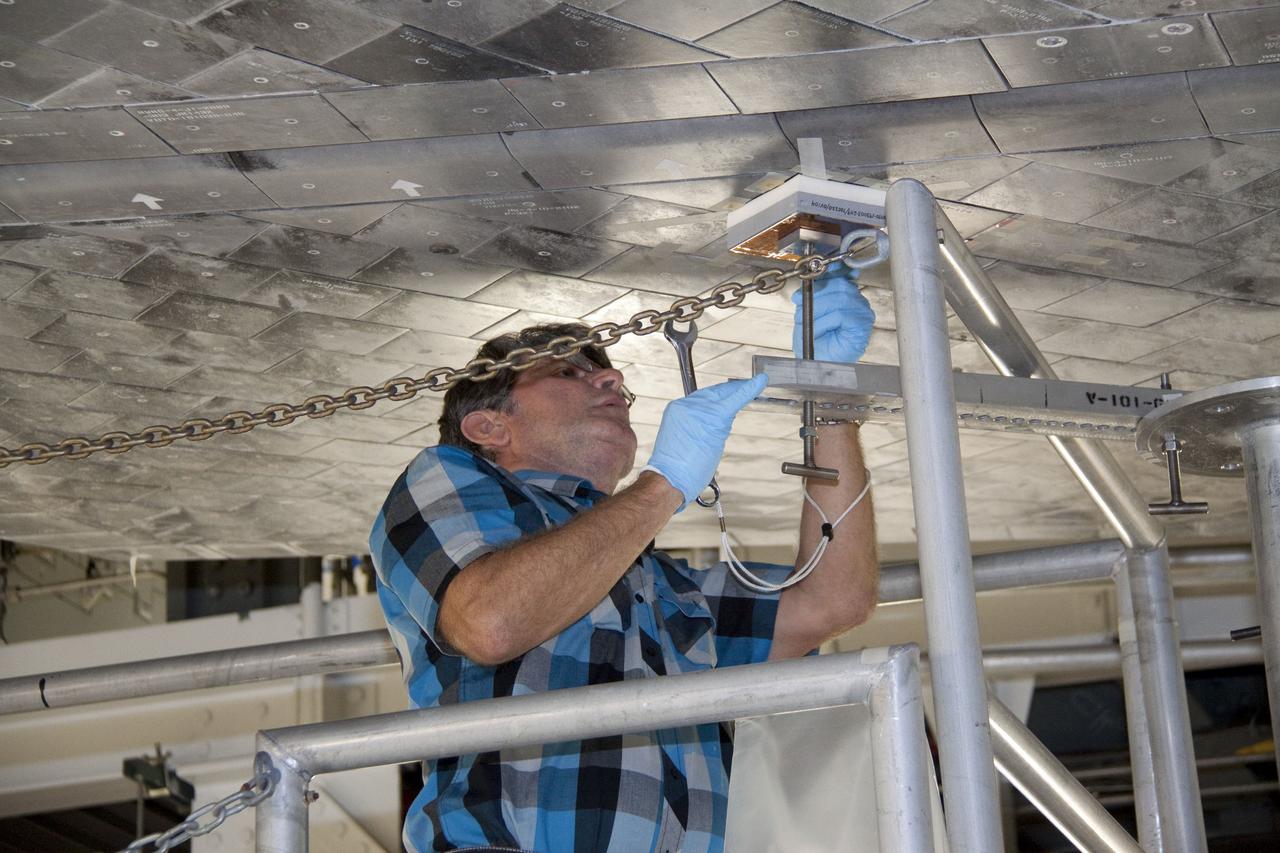
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician applies a bonding agent to an area on space shuttle Atlantis' underside where a heat shield tile will be installed. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System that protects the shuttle against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will carry the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last flight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
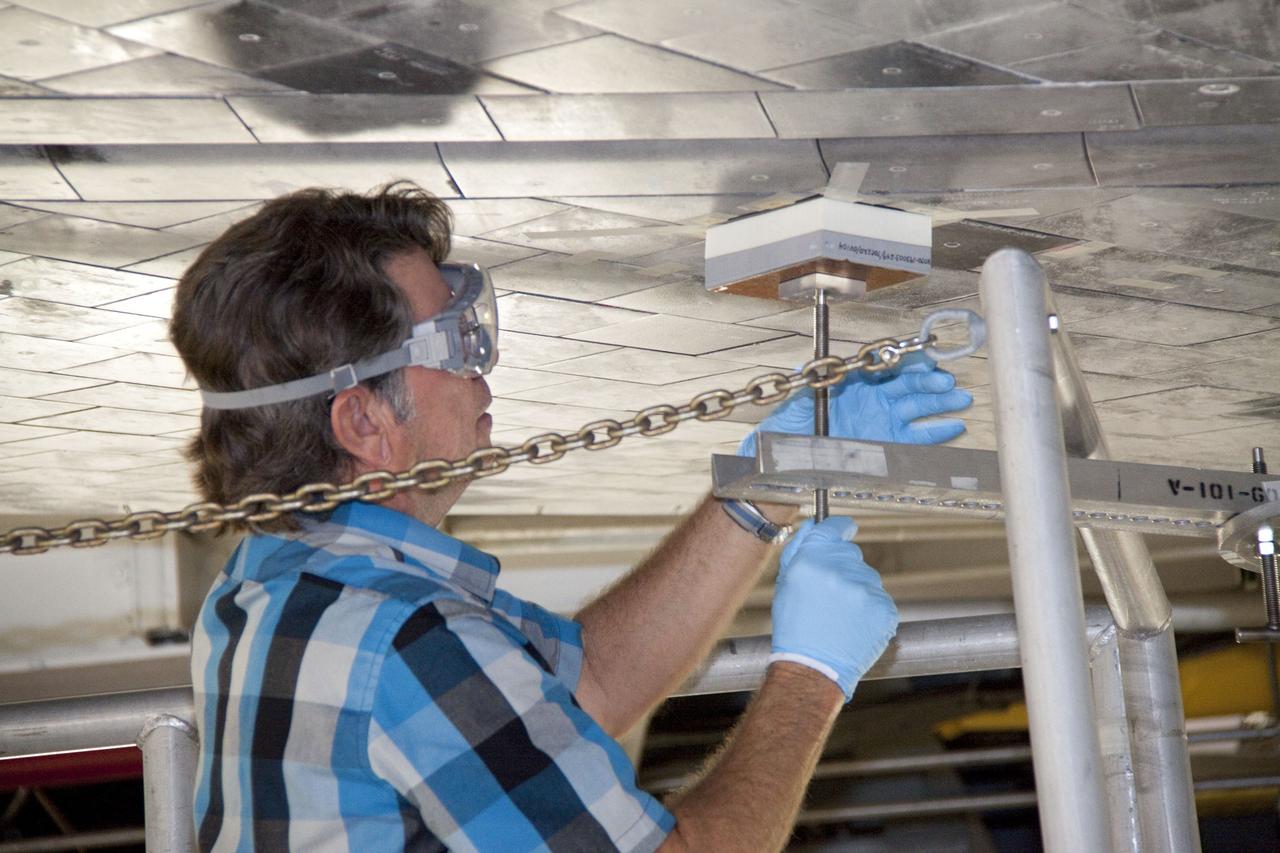

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician secures a newly installed heat shield tile in place under space shuttle Atlantis with a pressure fitting to ensure a tight bond. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System that protects the shuttle against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will carry the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last flight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
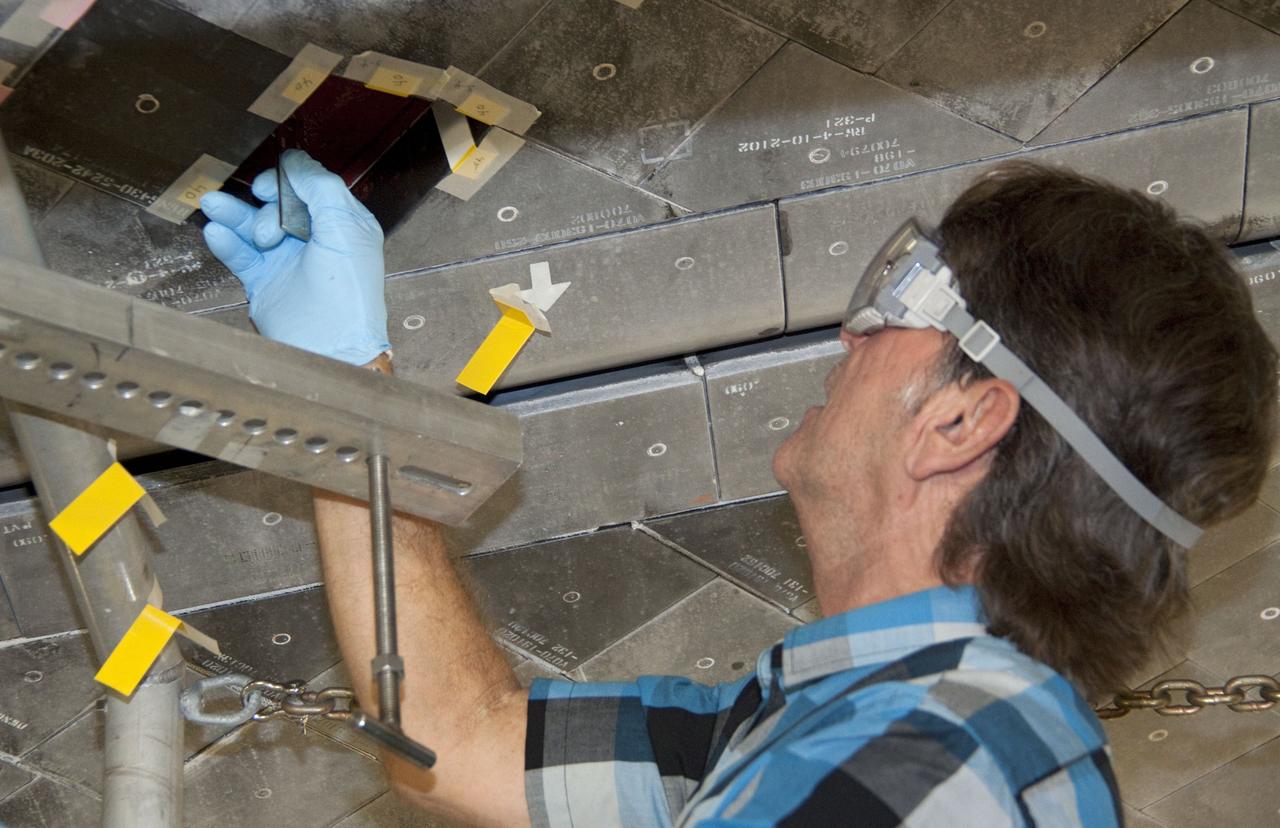

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician installs a gap filler in the area on space shuttle Atlantis' underside before a heat shield tile is installed. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System that protects the shuttle against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will carry the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last flight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
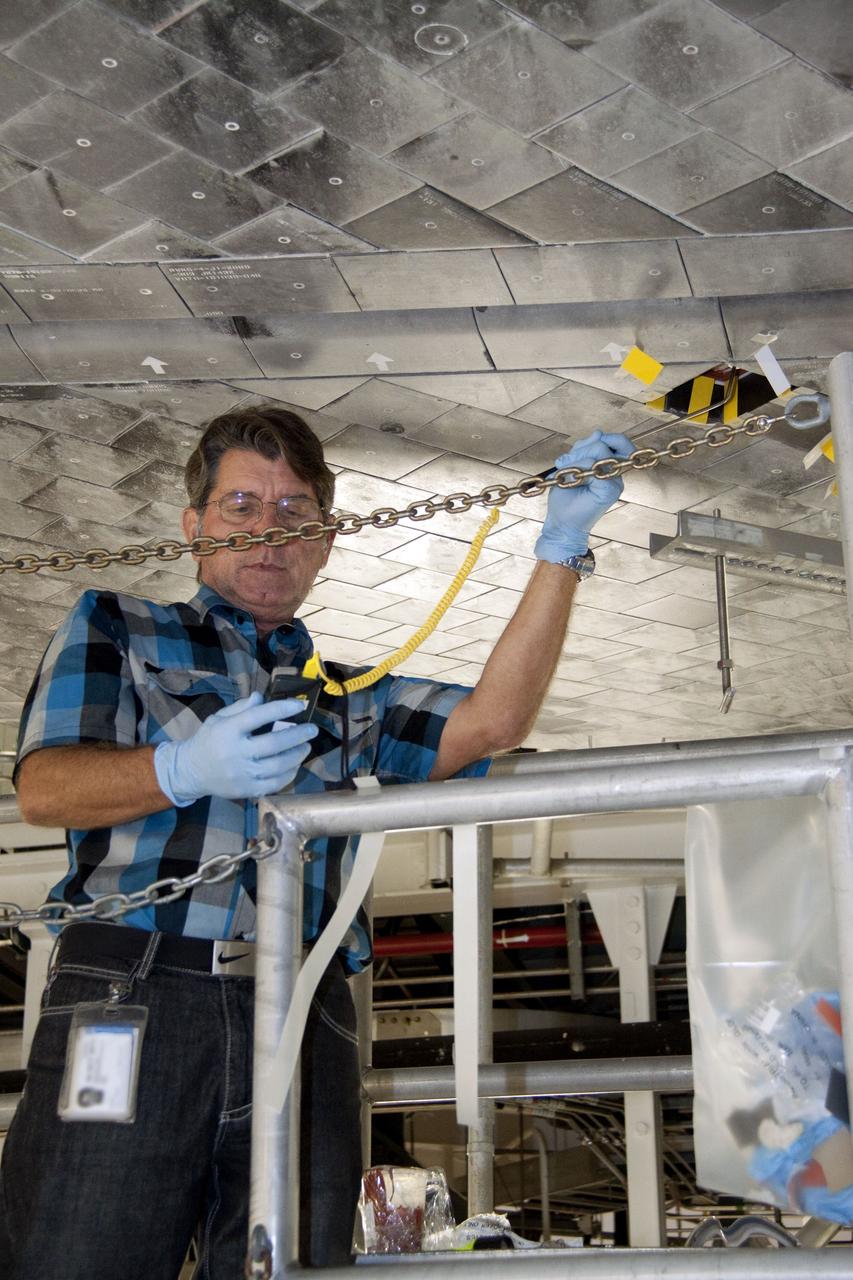

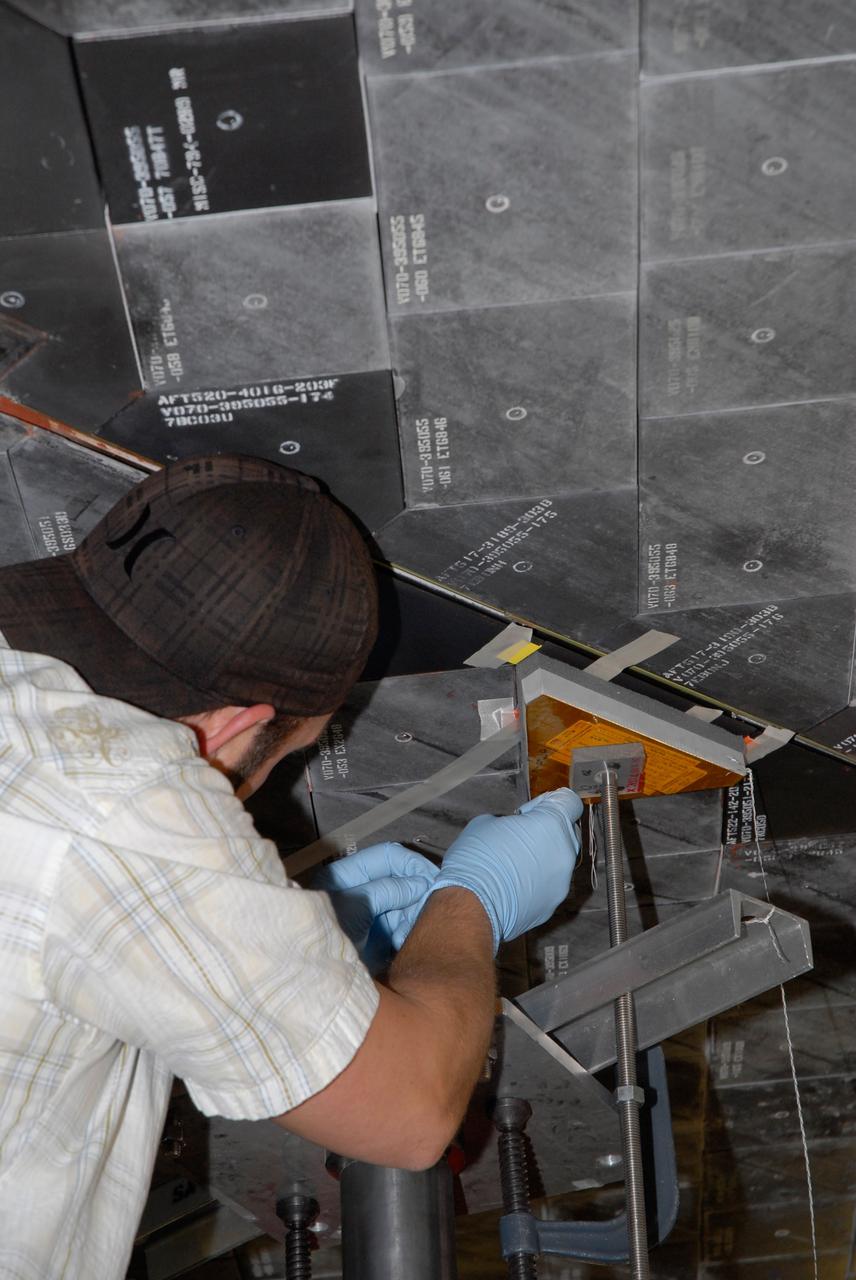
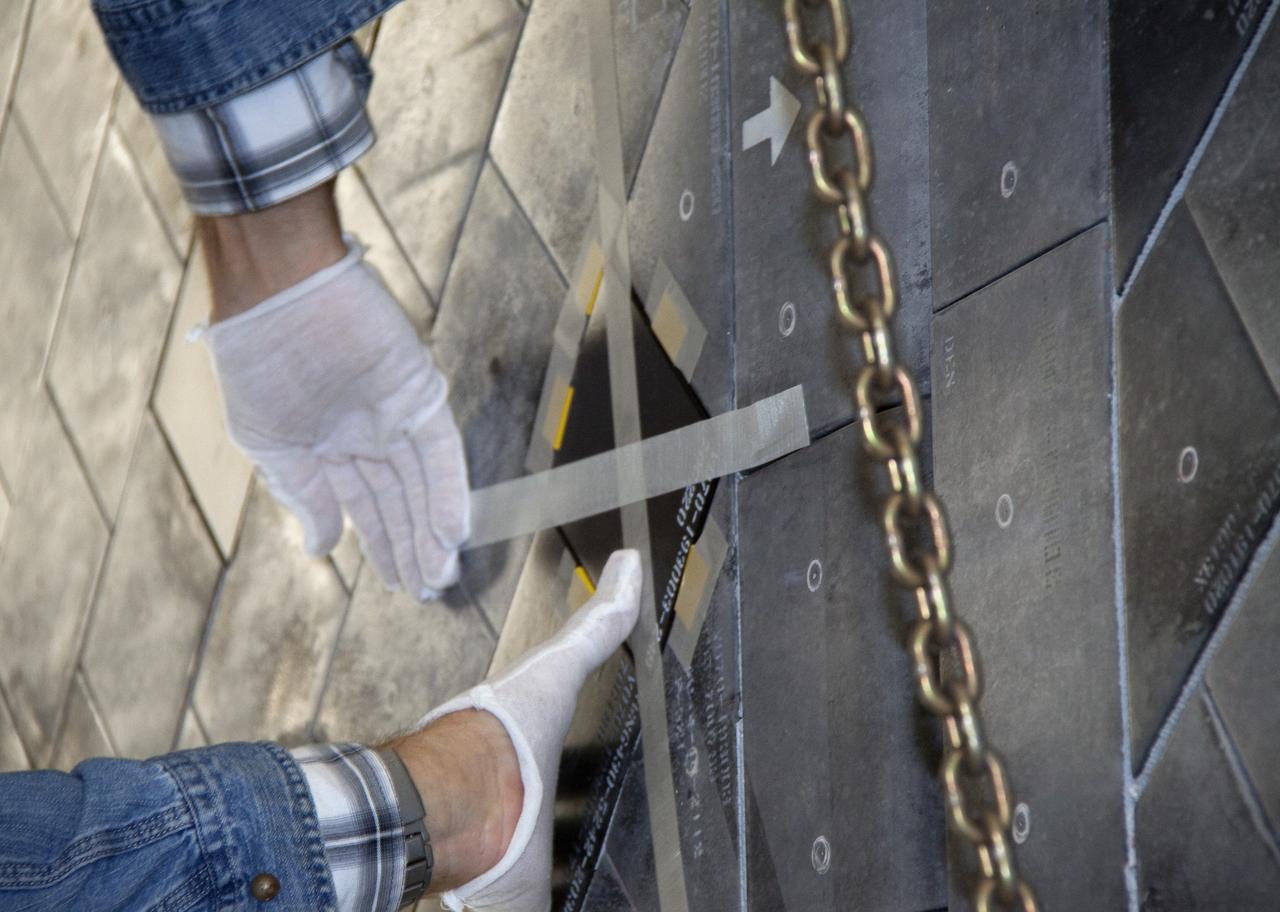
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician takes a measurement of the surface in the area on space shuttle Atlantis' underside where a heat shield tile will be installed. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System that protects the shuttle against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will carry the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last flight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
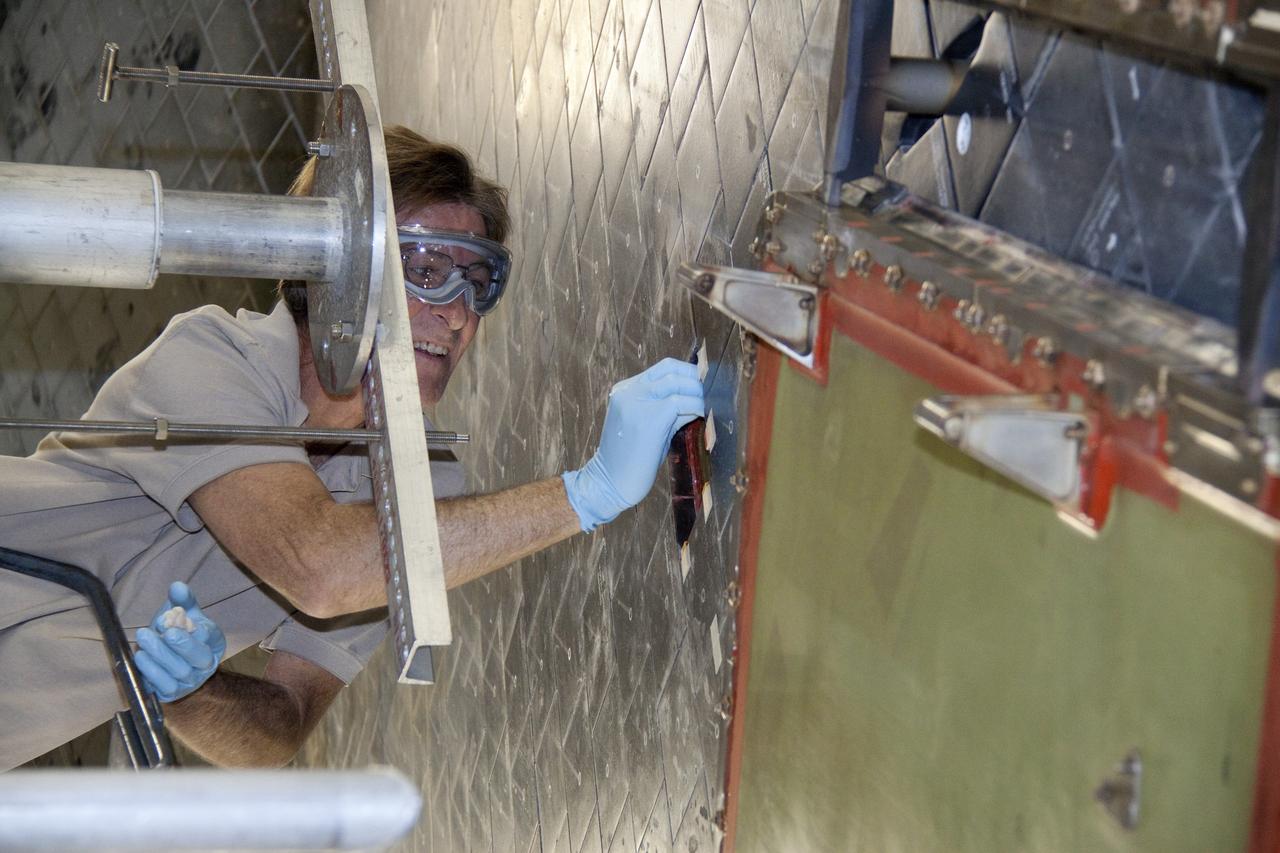

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician prepares the surface under space shuttle Atlantis before installing a heat shield tile. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System, thermal shields to protect against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last spaceflight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
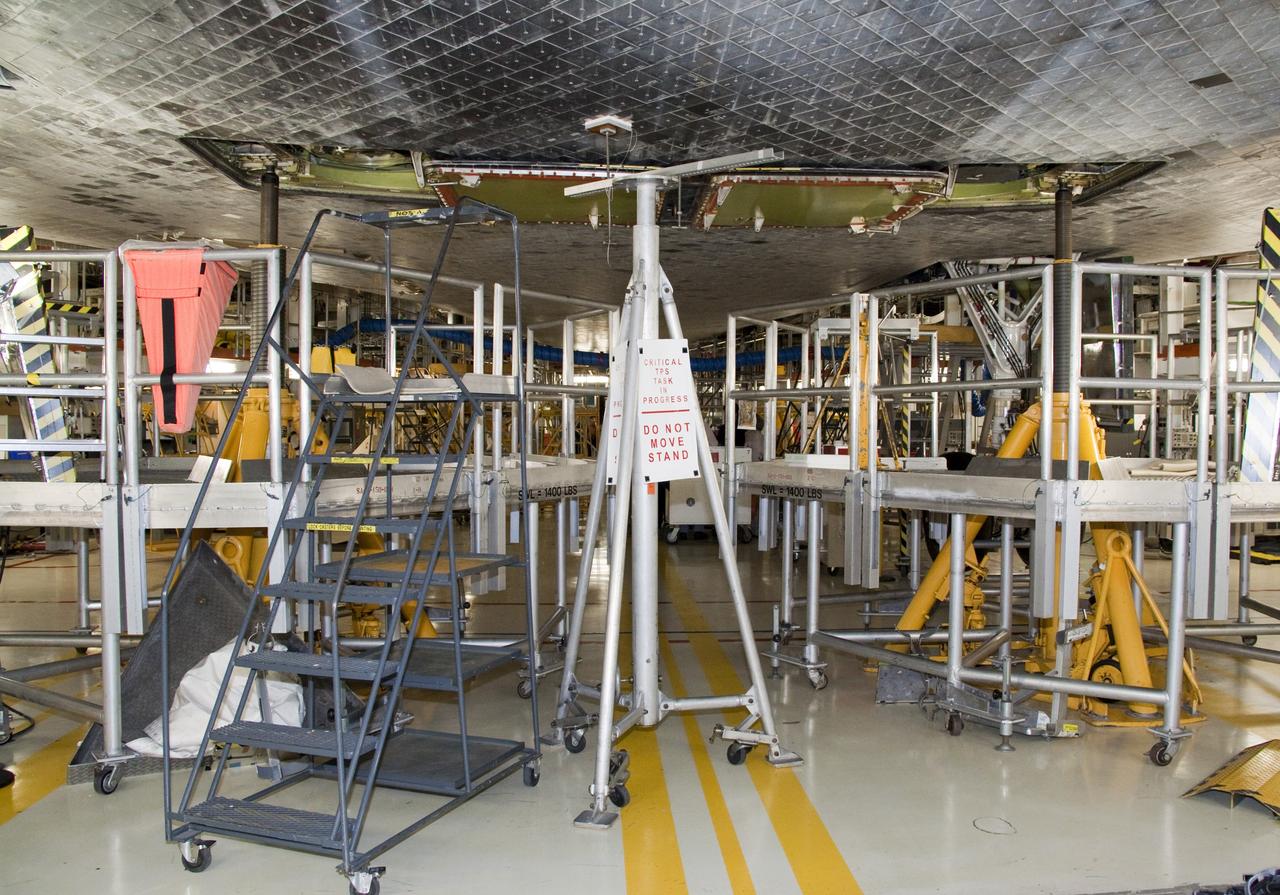

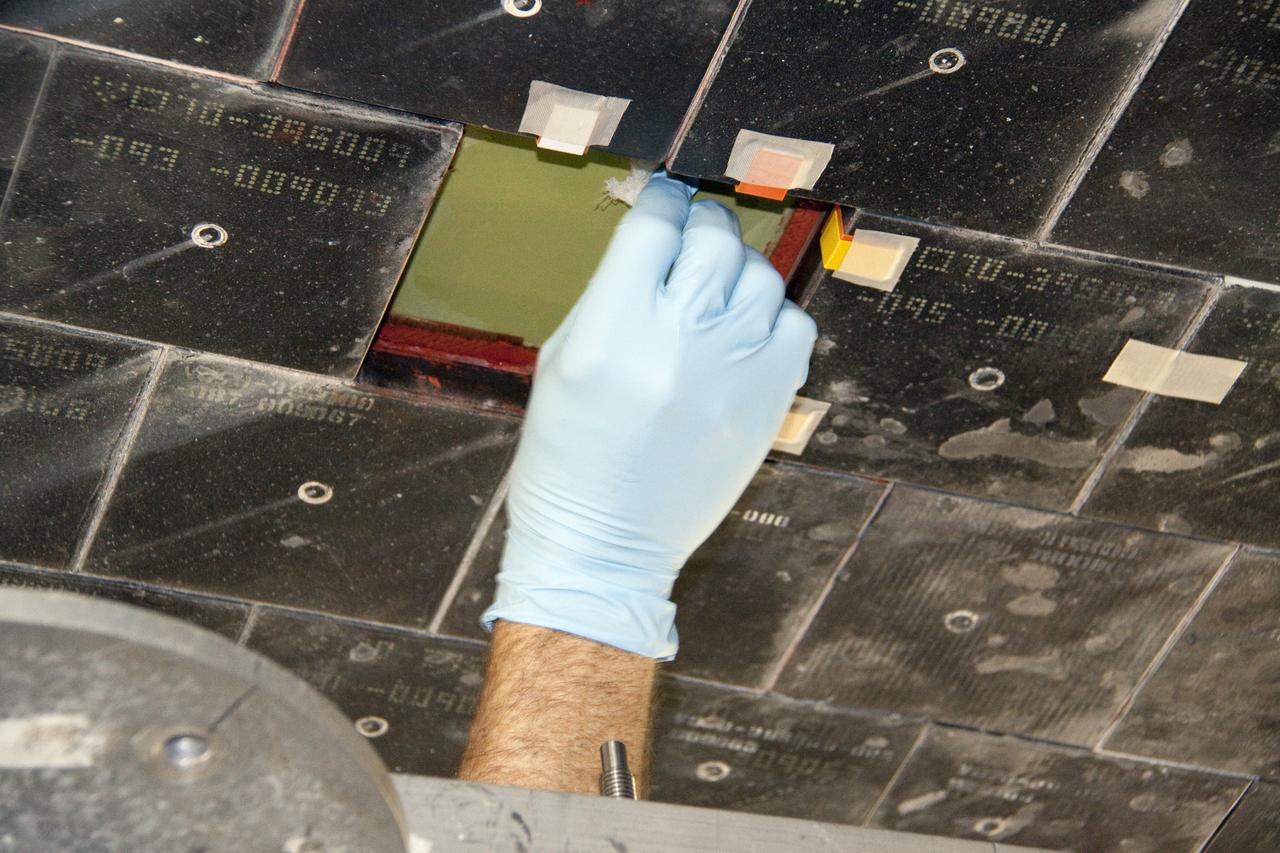
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician has secured a newly installed heat shield tile in place under space shuttle Atlantis with a pressure fitting to ensure a tight bond. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System, thermal shields to protect against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last spaceflight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician prepares the surface under space shuttle Atlantis before installing a heat shield tile. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System, thermal shields to protect against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last spaceflight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
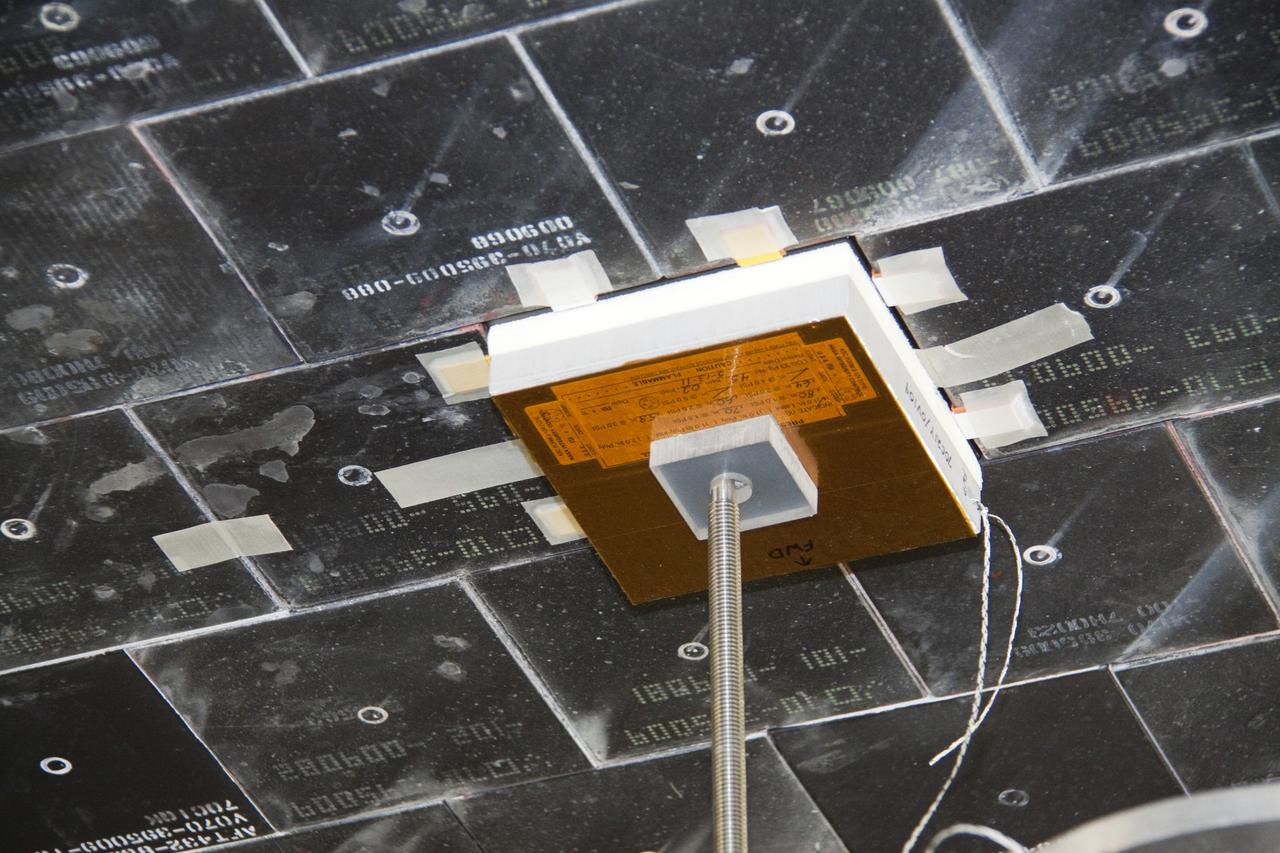
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician has secured a newly installed heat shield tile in place under space shuttle Atlantis with a pressure fitting to ensure a tight bond. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System, thermal shields to protect against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last spaceflight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician secures a newly installed heat shield tile in place under space shuttle Atlantis with a pressure fitting to ensure a tight bond. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System that protects the shuttle against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will carry the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last flight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician secures a newly installed heat shield tile in place under space shuttle Atlantis. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System, thermal shields to protect against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last spaceflight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
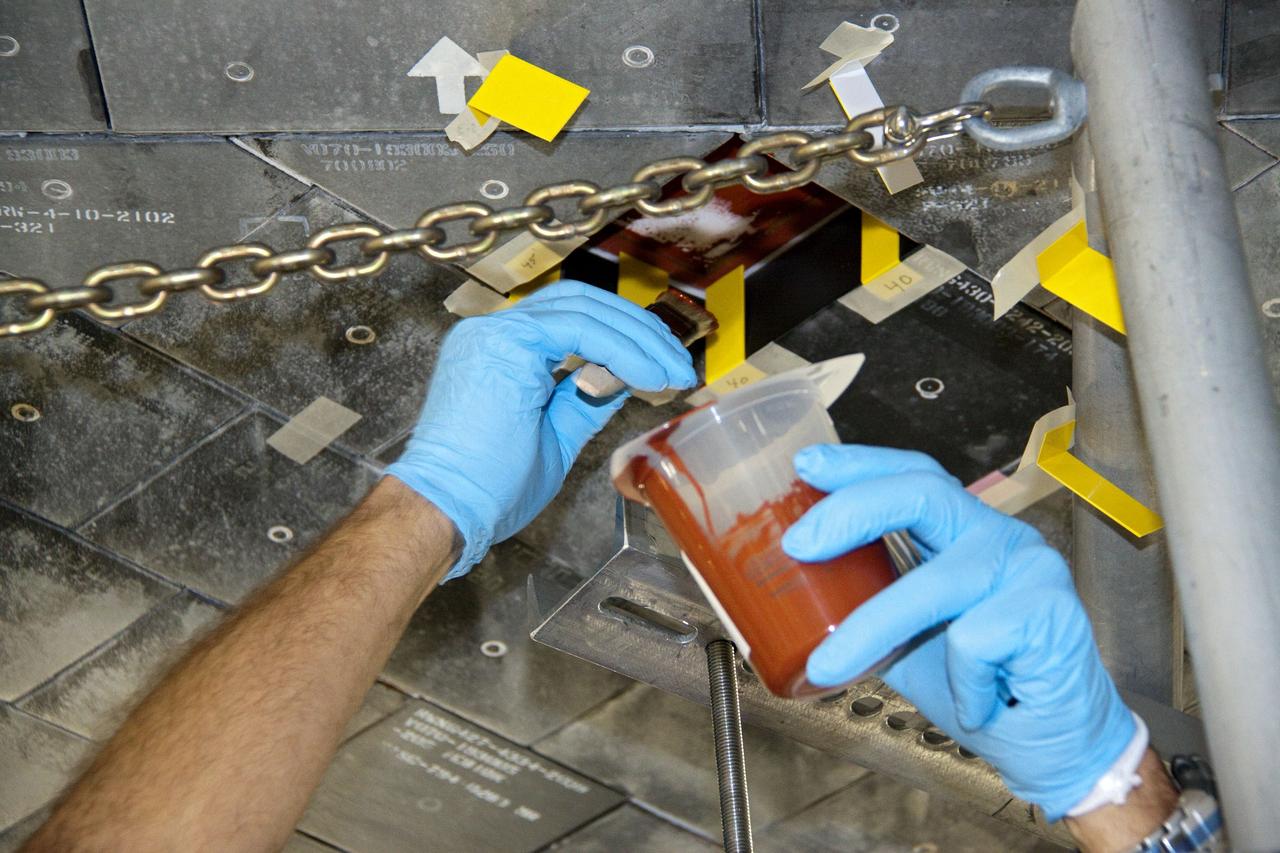

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician applies a bonding agent to an area on space shuttle Atlantis' underside where a heat shield tile will be installed. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System that protects the shuttle against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will carry the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last flight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
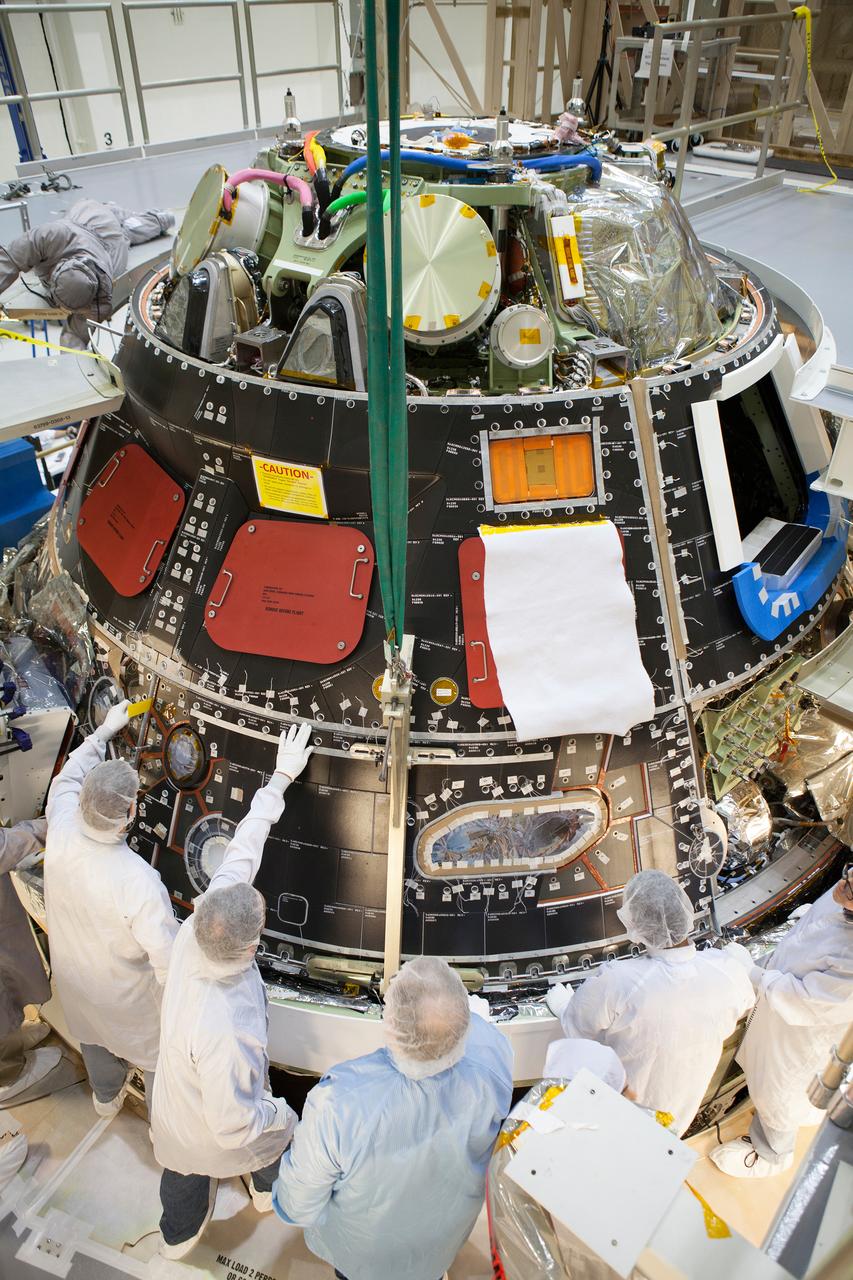

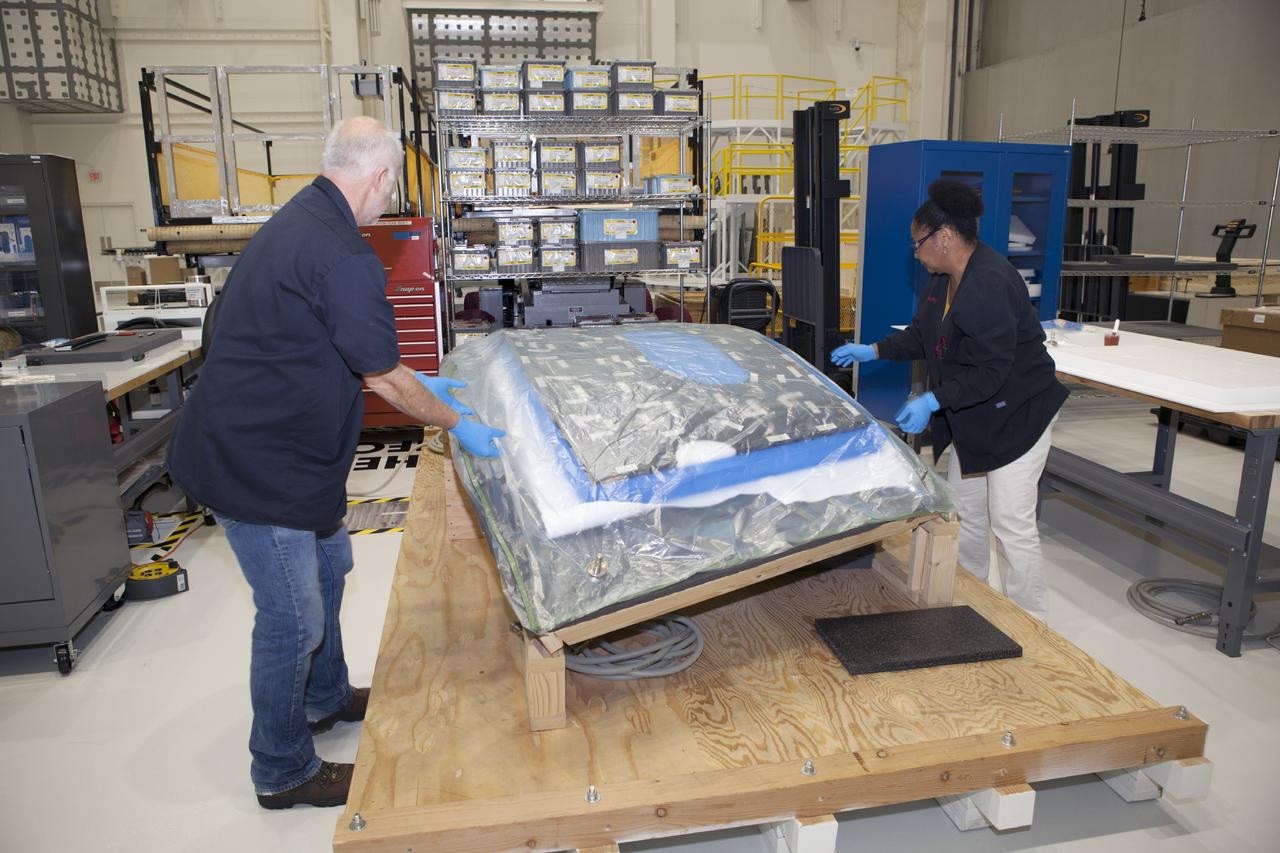
Inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians dressed in clean-room suits have installed a back shell tile panel onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) crew module and check the fit next to the middle back shell tile panel on Aug. 7, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
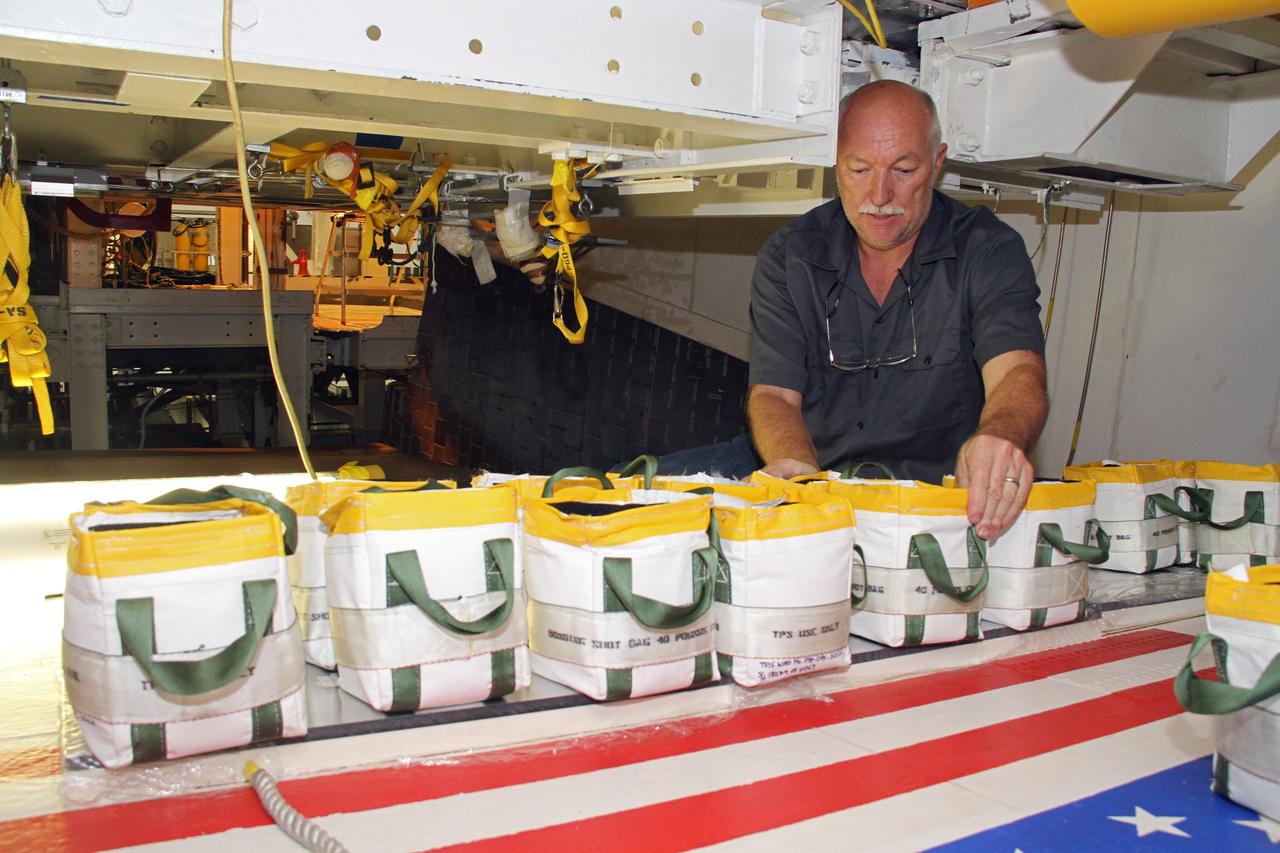

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mike Williams, a thermal protection system technician with United Space Alliance, arranges weights atop a freshly installed section of tile on the right wing of space shuttle Endeavour at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The weights will hold the section in place while the adhesive hardens beneath. Ongoing transition and retirement activities are preparing the spacecraft for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Endeavour flew 25 missions during its 19-year career. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
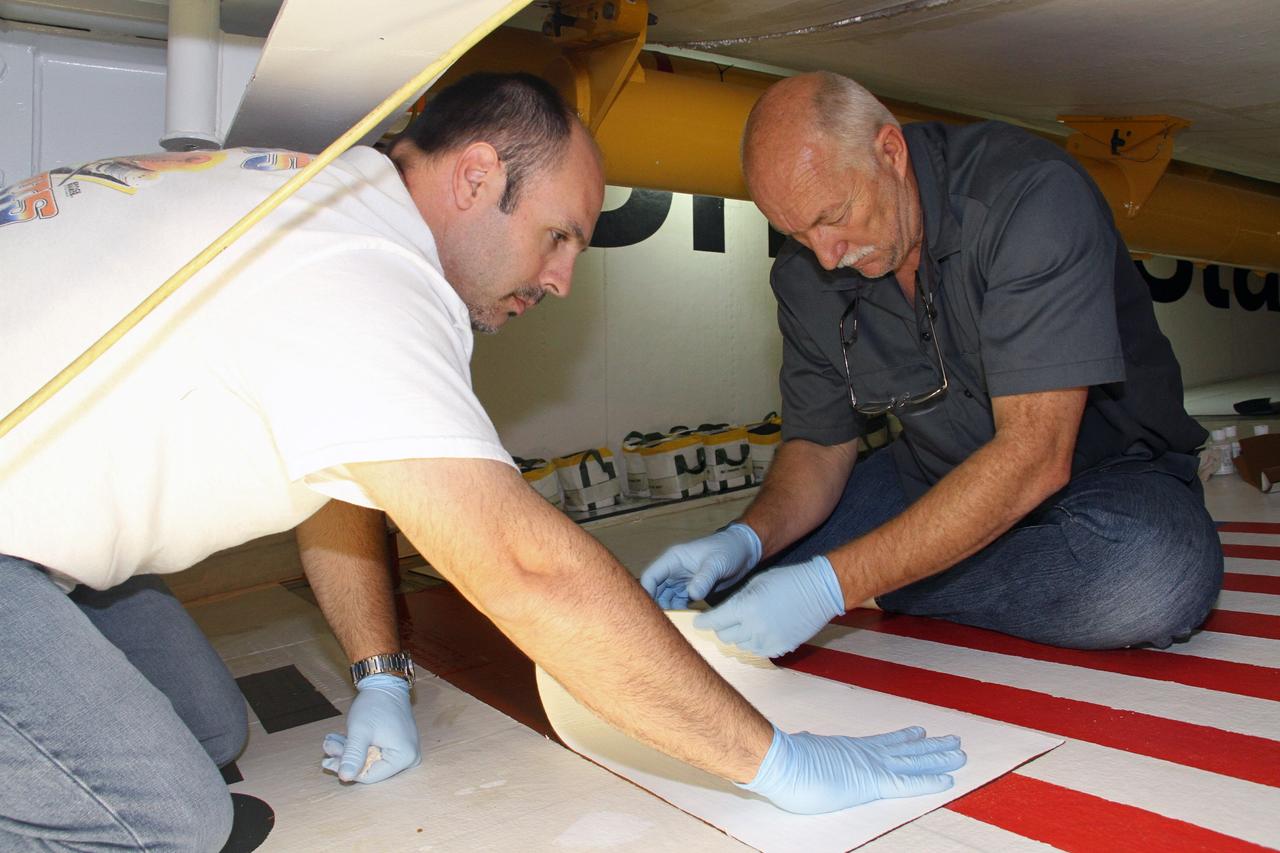

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Jeremy Schwarz, left, quality assurance technician, and Mike Williams, right, a thermal protection system technician, both with United Space Alliance, affix a section of tile to the right wing of space shuttle Endeavour at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ongoing transition and retirement activities are preparing the spacecraft for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Endeavour flew 25 missions during its 19-year career. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
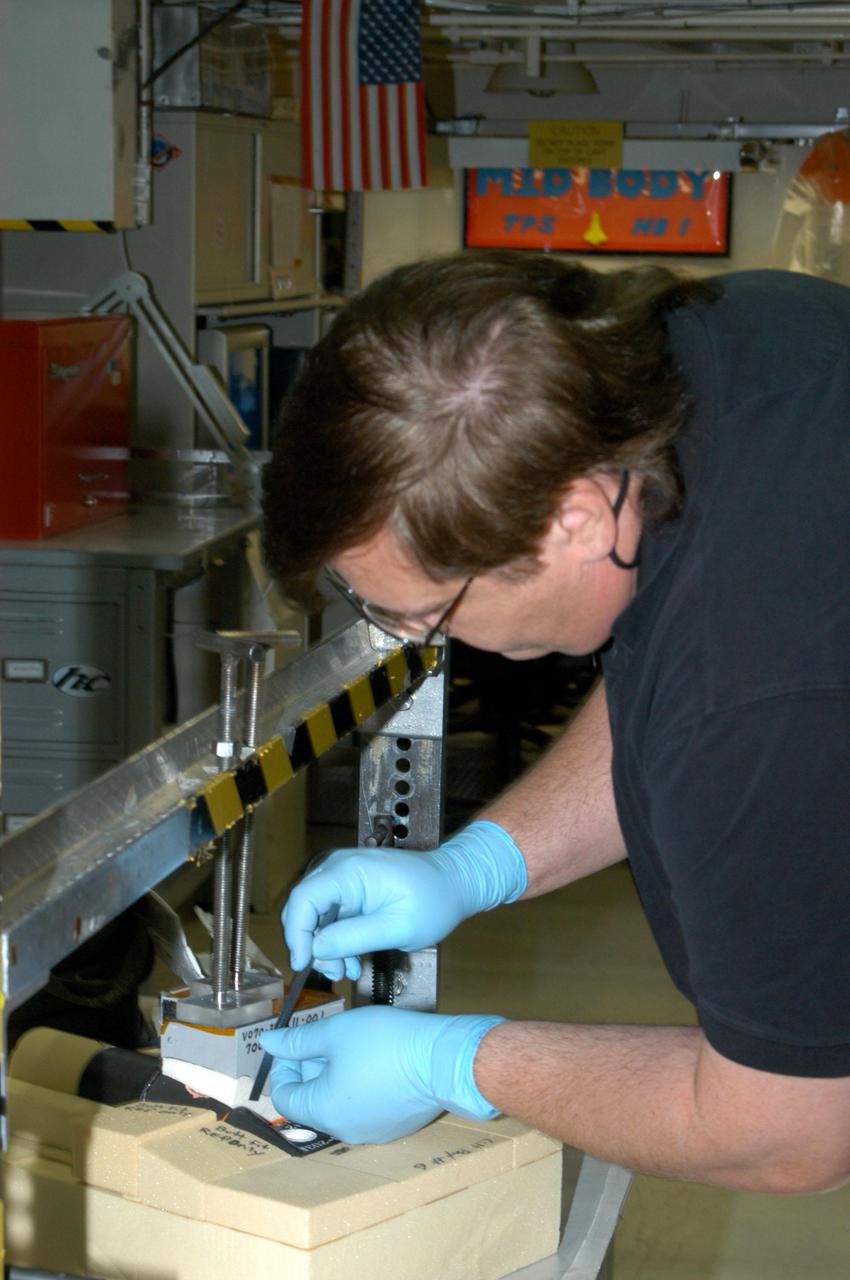

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, United Space Alliance technician George Arnett works on tile bonding for the orbiter Atlantis. The orbiter is scheduled to fly on Return to Flight mission STS-121 in July. STS-121 is a Return to Flight Utilities and Logistics Flight (ULF-2) to the International Space Station.
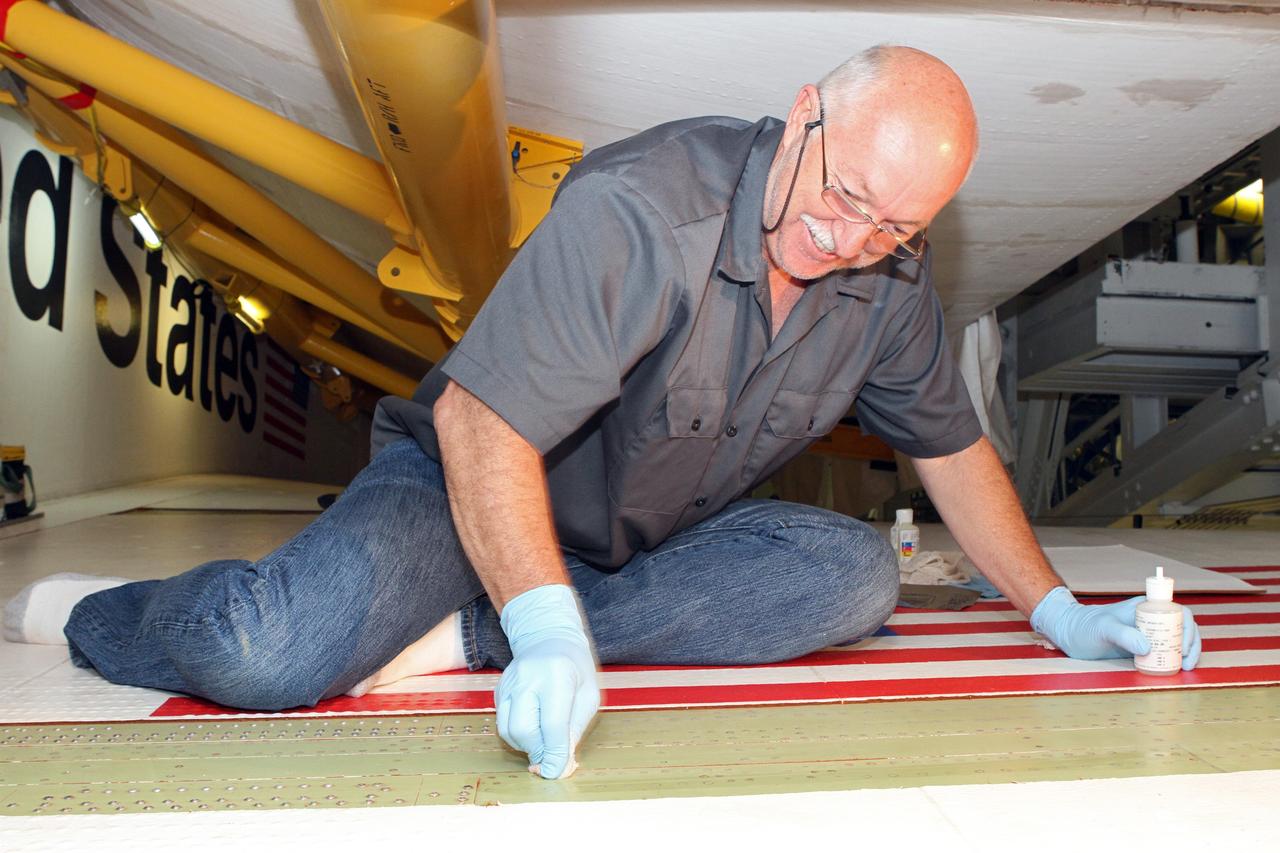

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Mike Williams, a thermal protection system technician with United Space Alliance, crouches on space shuttle Endeavour's right wing as he prepares the wing surface for tile bonding. Ongoing transition and retirement activities are preparing the spacecraft for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Endeavour flew 25 missions during its 19-year career. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
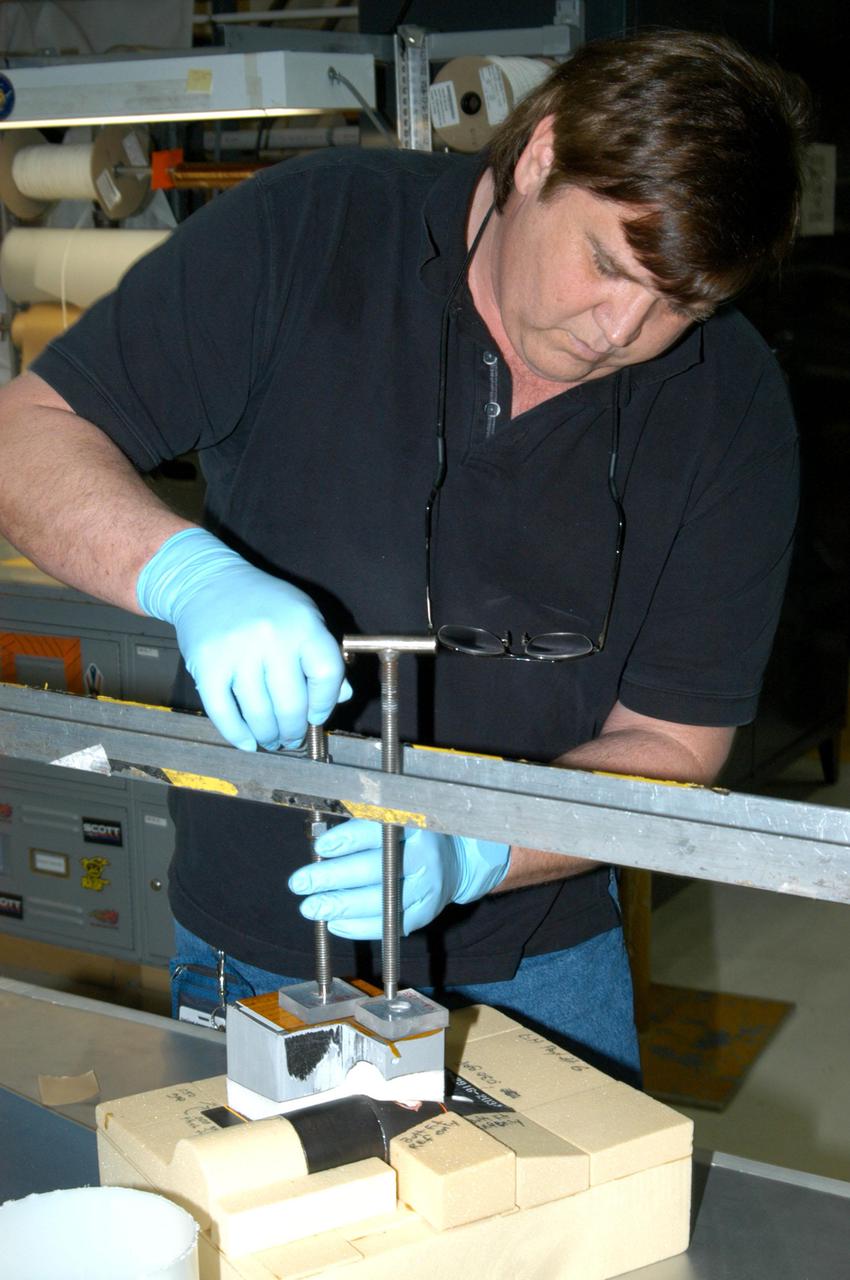

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, United Space Alliance technician George Arnett works on tile bonding for the orbiter Atlantis. The orbiter is scheduled to fly on Return to Flight mission STS-121 in July. STS-121 is a Return to Flight Utilities and Logistics Flight (ULF-2) to the International Space Station.
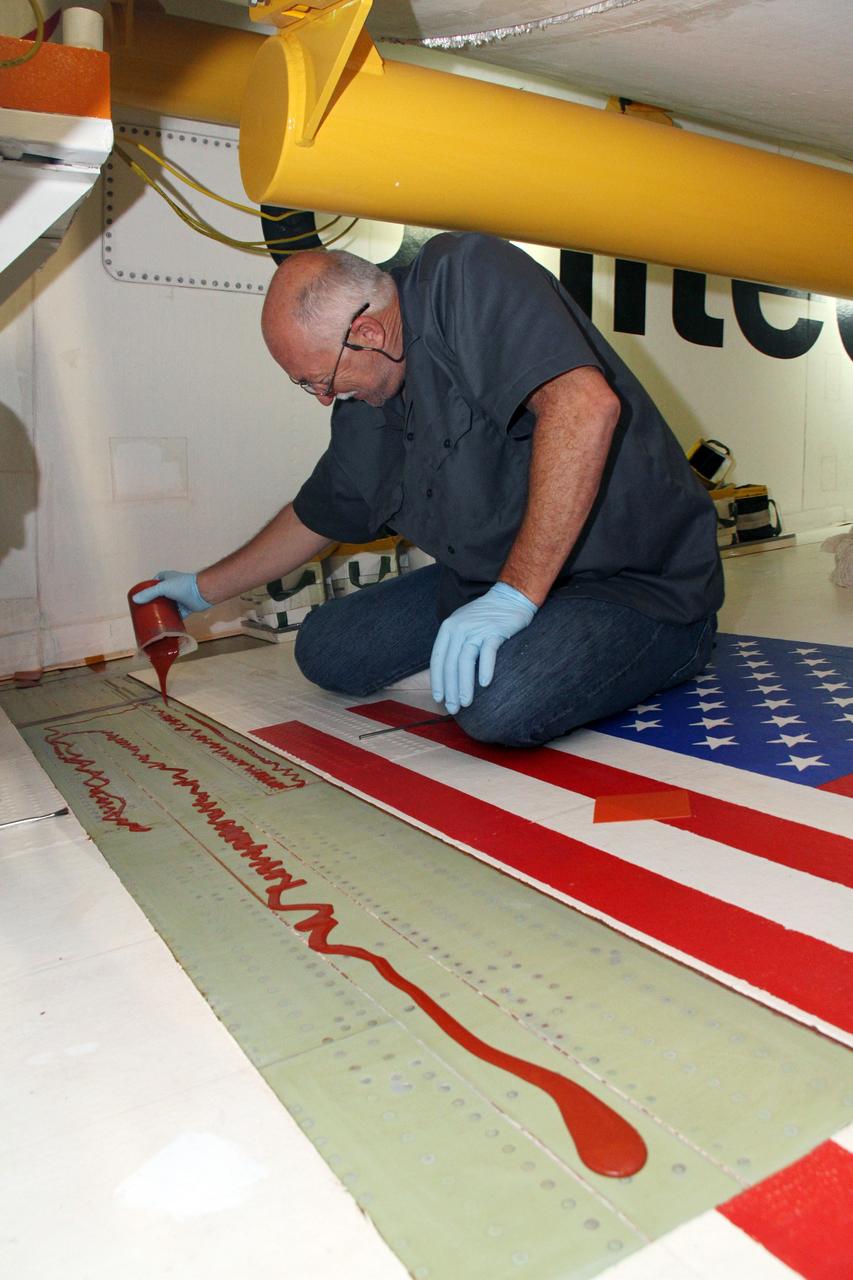

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Mike Williams, a thermal protection system technician with United Space Alliance, applies adhesive to the right wing of space shuttle Endeavour in preparation for tile bonding. Ongoing transition and retirement activities are preparing the spacecraft for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Endeavour flew 25 missions during its 19-year career. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
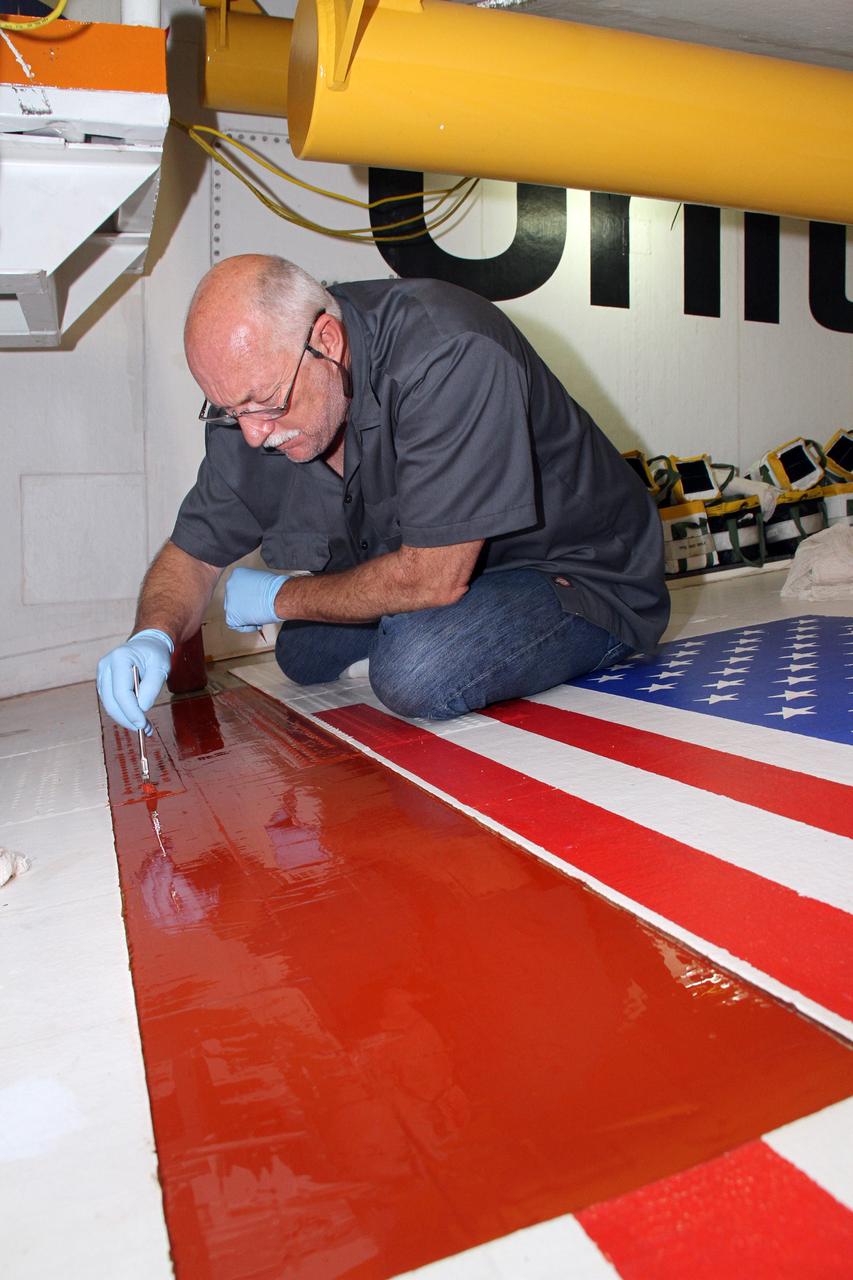

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Mike Williams, a thermal protection system technician with United Space Alliance, puts the finishing touches on a layer of adhesive applied to the right wing of space shuttle Endeavour. The work is being done in preparation for tile bonding. Ongoing transition and retirement activities are preparing the spacecraft for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Endeavour flew 25 missions during its 19-year career. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
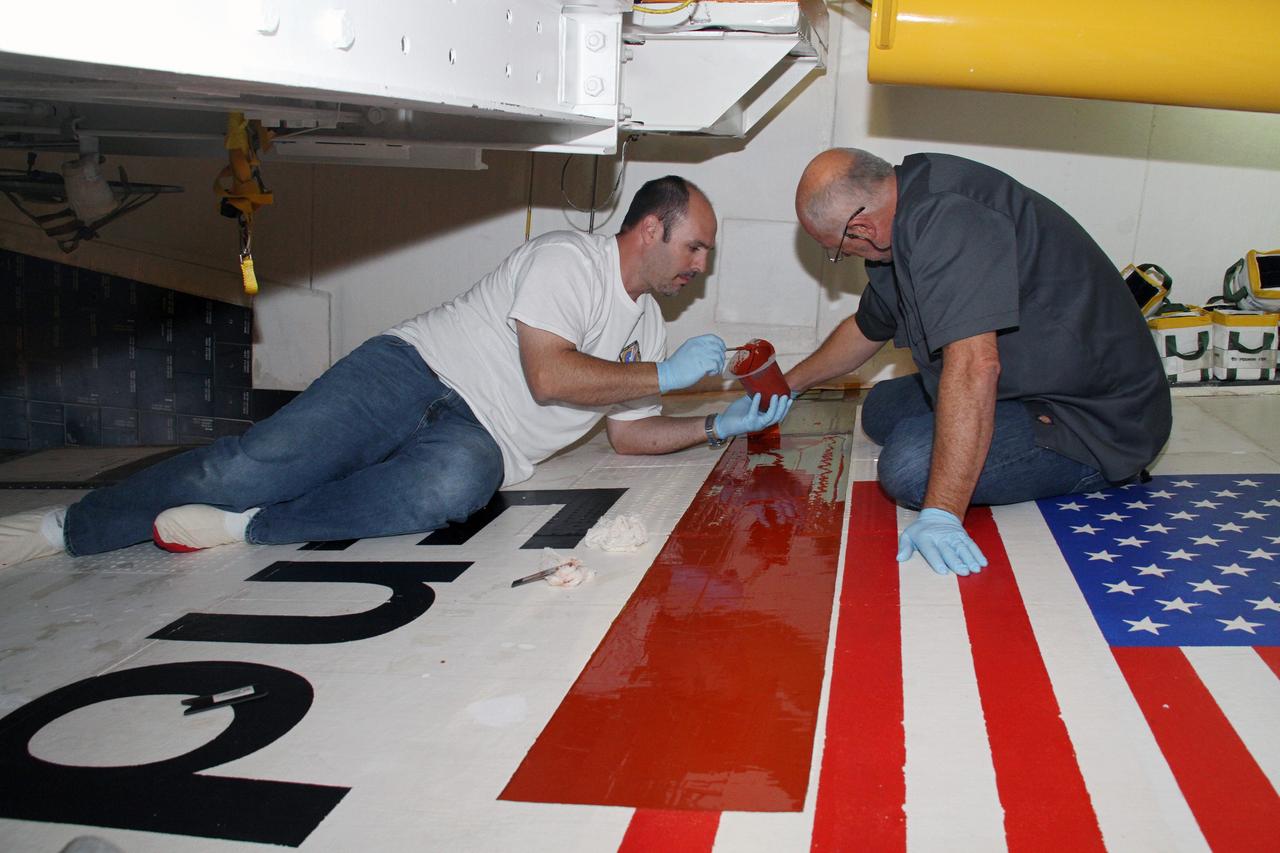

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Jeremy Schwarz, left, quality assurance technician, and Mike Williams, right, a thermal protection system technician, both with United Space Alliance, apply adhesive to space shuttle Endeavour's right wing. The work is being done in preparation for tile bonding. Endeavour is inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ongoing transition and retirement activities are preparing the spacecraft for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Endeavour flew 25 missions during its 19-year career. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
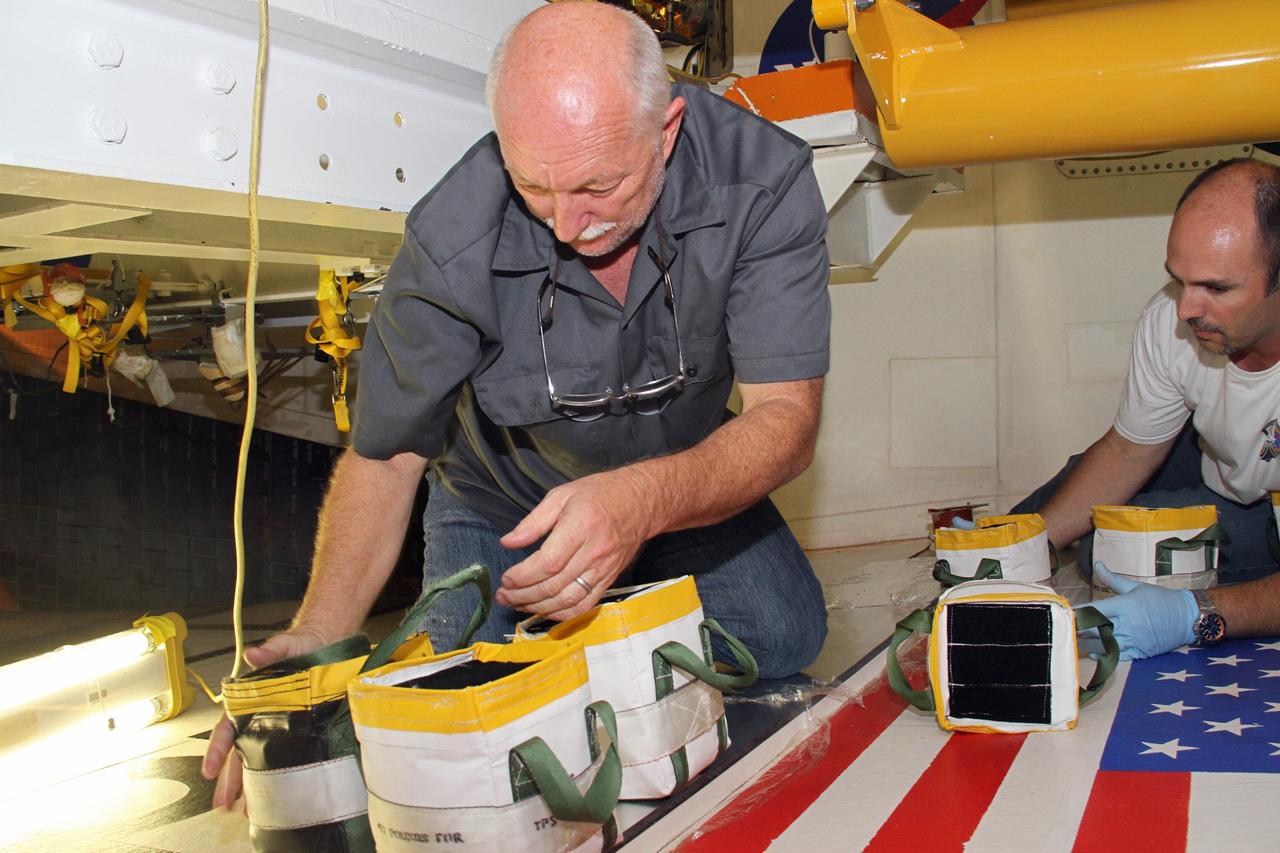

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mike Williams, left, a thermal protection system technician, and Jeremy Schwarz, right, quality assurance technician, both with United Space Alliance, set weights atop a newly installed section of tile on the right wing of space shuttle Endeavour at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The weights will hold the section in place while the adhesive hardens beneath. Ongoing transition and retirement activities are preparing the spacecraft for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Endeavour flew 25 missions during its 19-year career. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
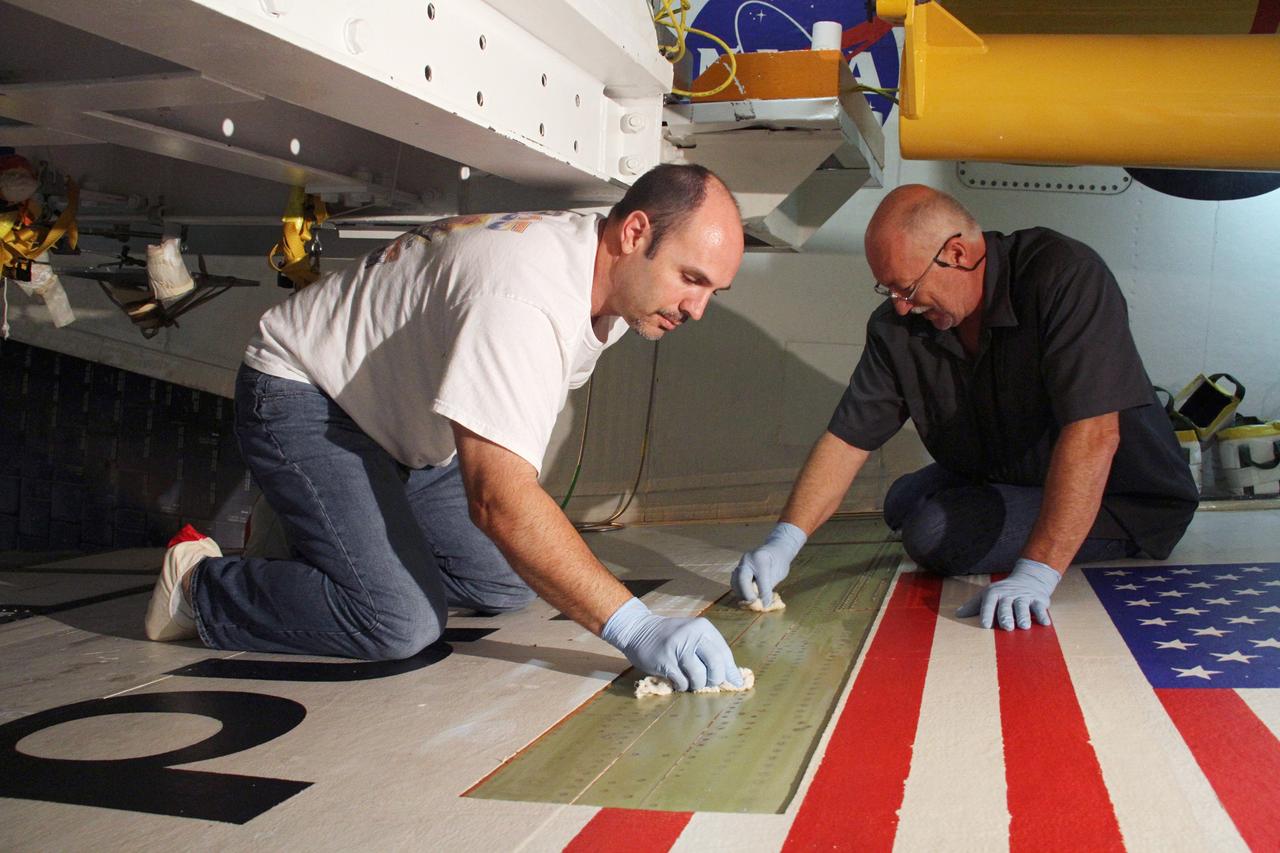

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Jeremy Schwarz, left, quality assurance technician, and Mike Williams, right, a thermal protection system technician, both with United Space Alliance, prepare the right wing of space shuttle Endeavour for tile bonding. Endeavour is inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ongoing transition and retirement activities are preparing the spacecraft for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Endeavour flew 25 missions during its 19-year career. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

Wall tiles from Kennedy Space Center’s former headquarters building are presented to Kennedy Director Janet Petro inside the Florida spaceport’s Central Campus Headquarters Building on May 3, 2022. The two 15-pound sections from the building were preserved by Maverick Constructors LLC, the construction company that completed demolition of the structure. The company’s presentation of the tiles is in honor of the many civil servants and contractors who dedicated their lives to working for and supporting NASA in this building.

Wall tiles from Kennedy Space Center’s former headquarters building are presented to Kennedy Director Janet Petro inside the Florida spaceport’s Central Campus Headquarters Building on May 3, 2022. The two 15-pound sections from the building were preserved by Maverick Constructors LLC, the construction company that completed demolition of the structure. The company’s presentation of the tiles is in honor of the many civil servants and contractors who dedicated their lives to working for and supporting NASA in this building.
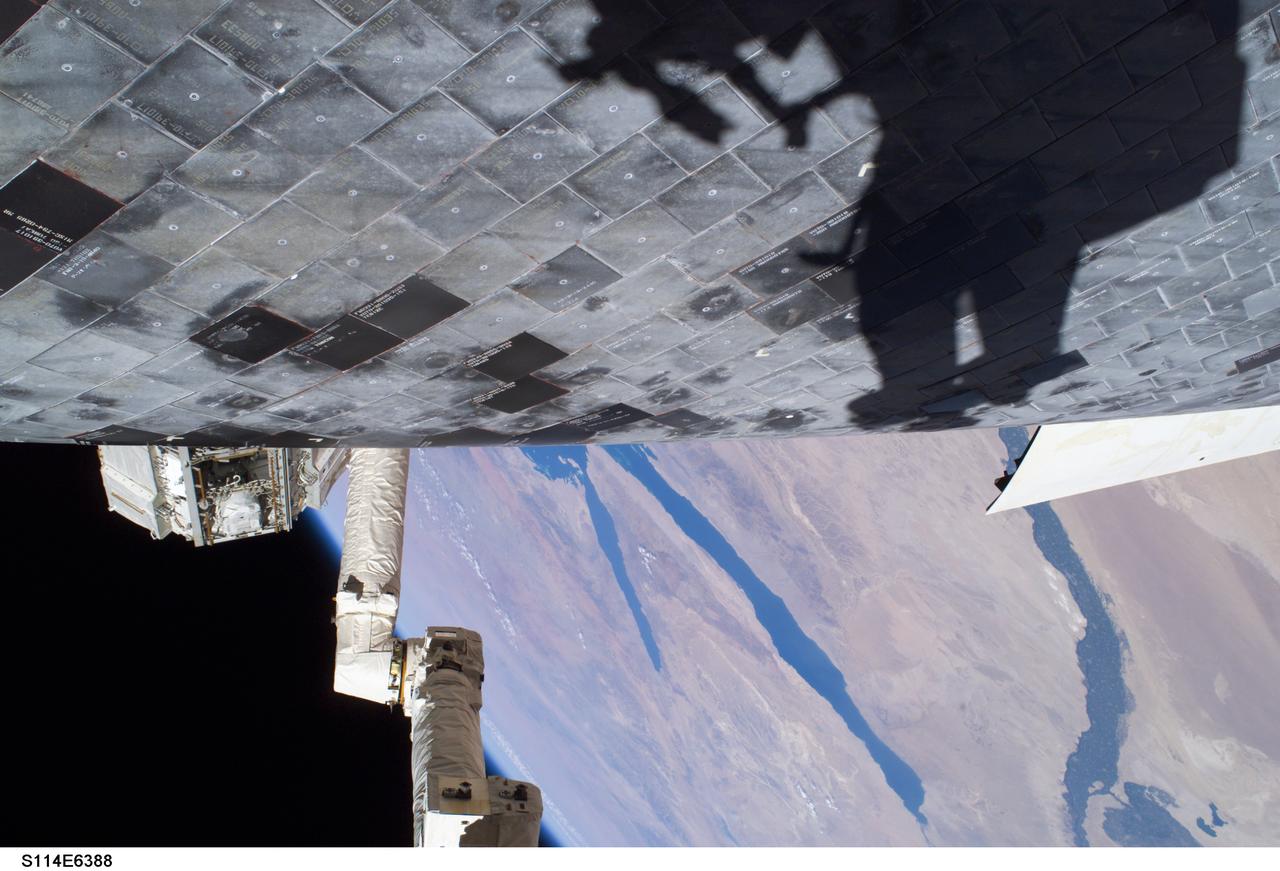

S114-E-6388 (3 August 2005) --- A close-up view of a portion of the thermal protection tiles on Space Shuttle Discovery’s underside is featured in this image photographed by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, during the mission’s third session of extravehicular activities (EVA). Robinson’s shadow is visible on the thermal protection tiles and a portion of the Canadian-built remote manipulator system (RMS) robotic arm and the Nile River is visible at bottom.
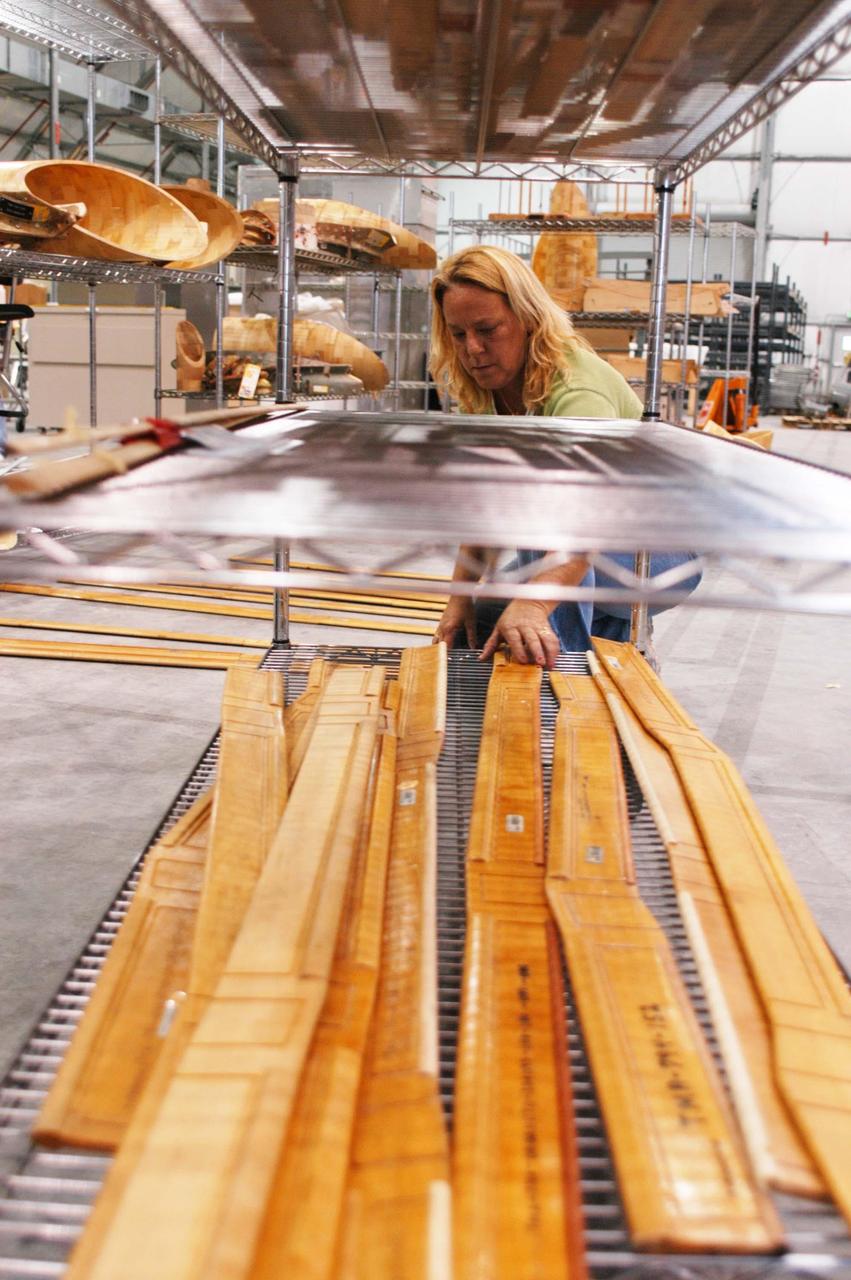

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - United Space Alliance worker Janet Mills works on equipment in the temporary tile shop set up in the RLV hangar at KSC. The hurricane-ravaged Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF), which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. Undamaged equipment was removed from the TPSF and stored in the hangar. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A temporary tile shop has been set up in the RLV hangar at KSC after equipment was removed from the hurricane-ravaged Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF). Here United Space Alliance worker Bab Jarosz works with the 30-needle sewing machines. The TPSF, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.

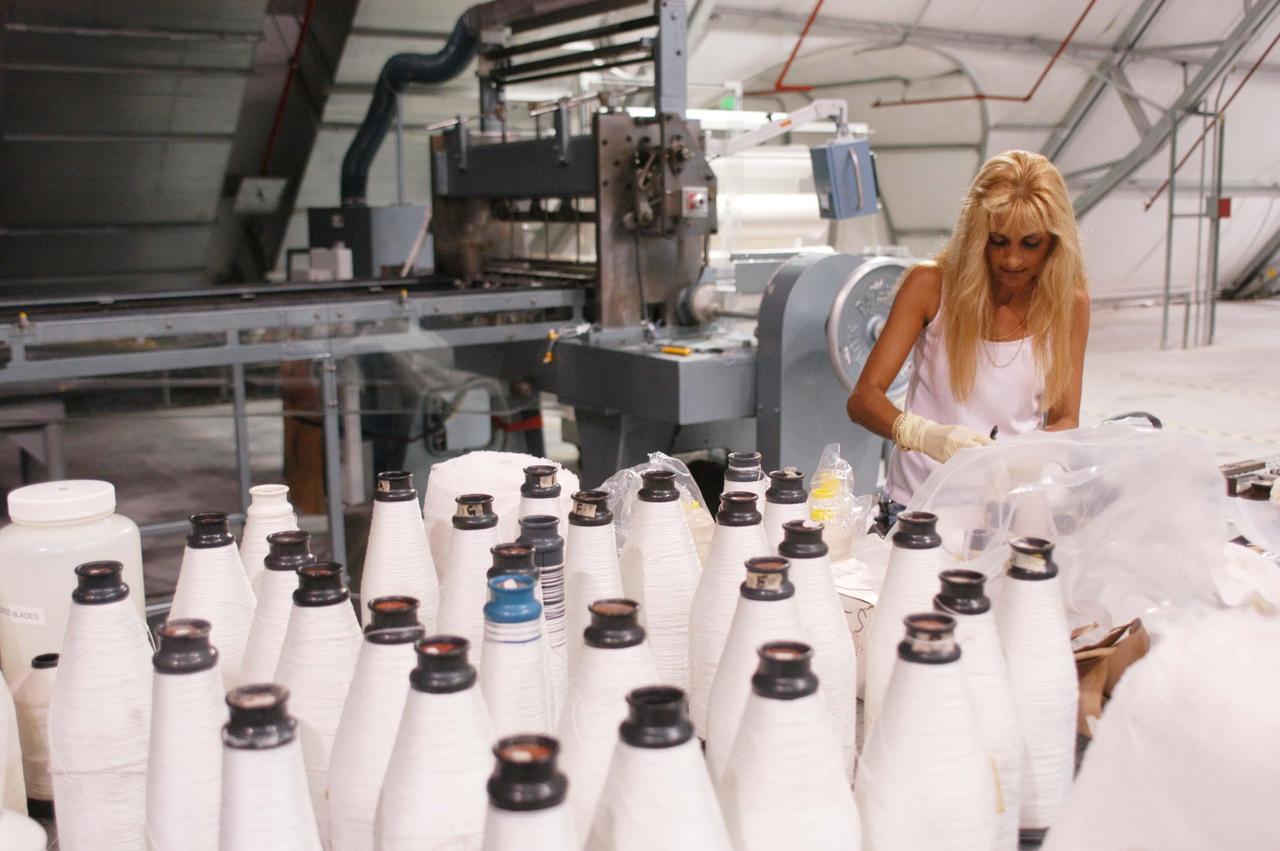
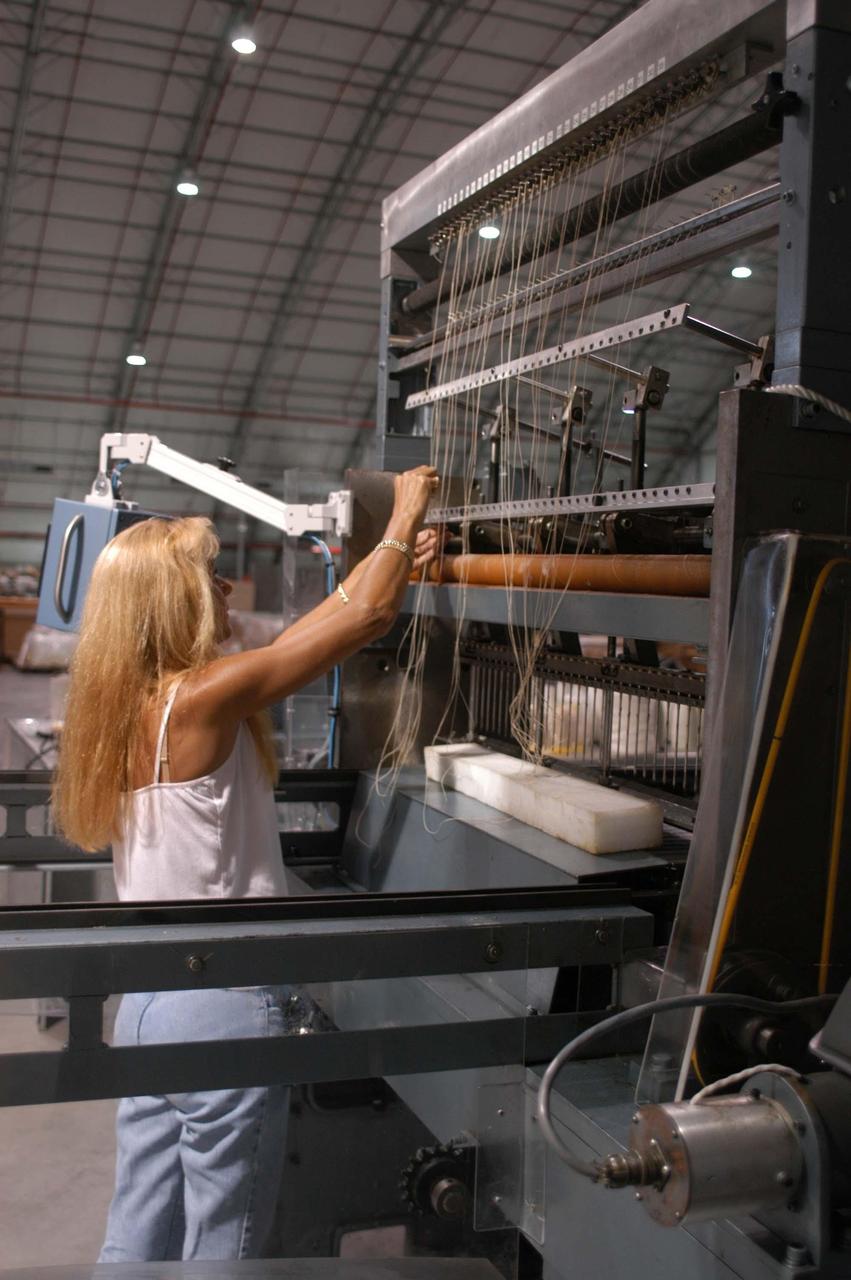
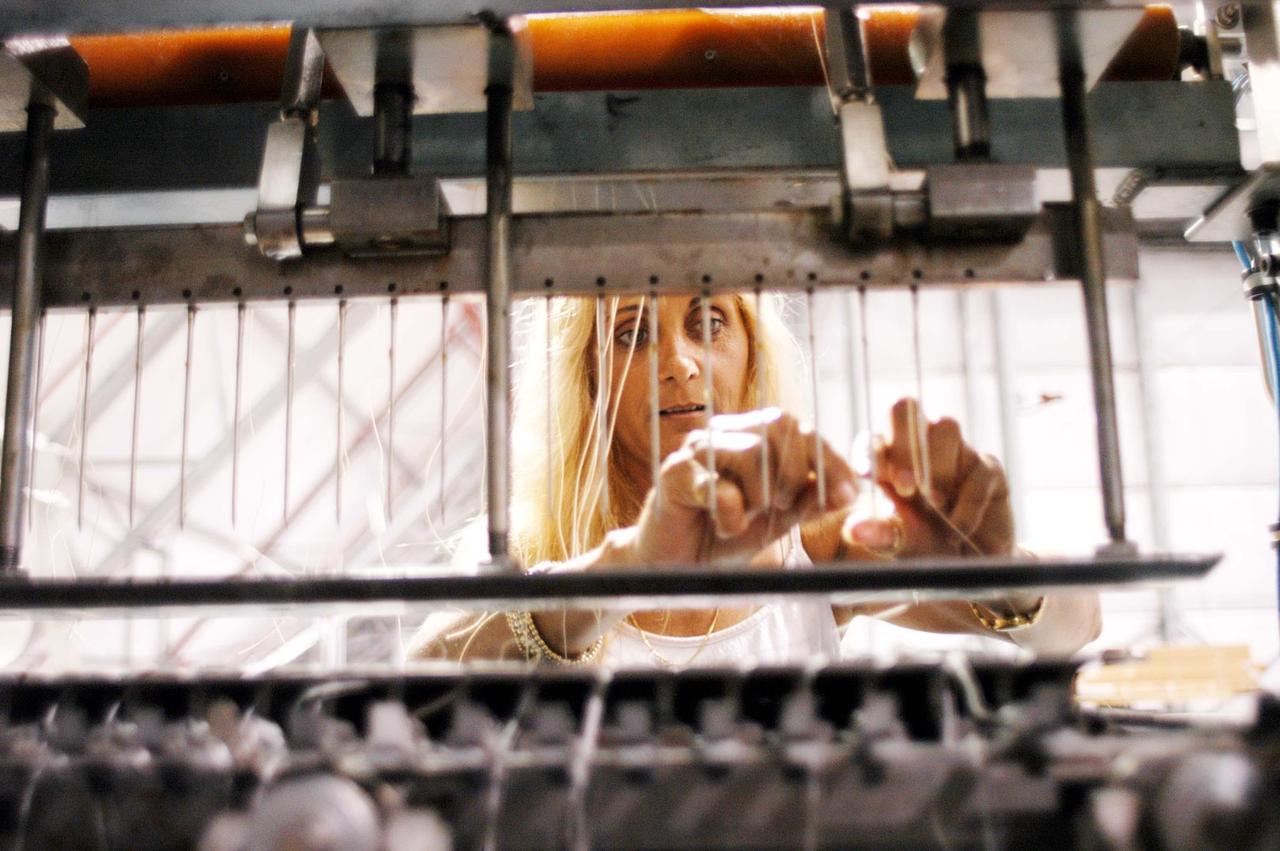
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a tile technician places spacers between the thermal protection system tiles that will be installed on the Orion crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

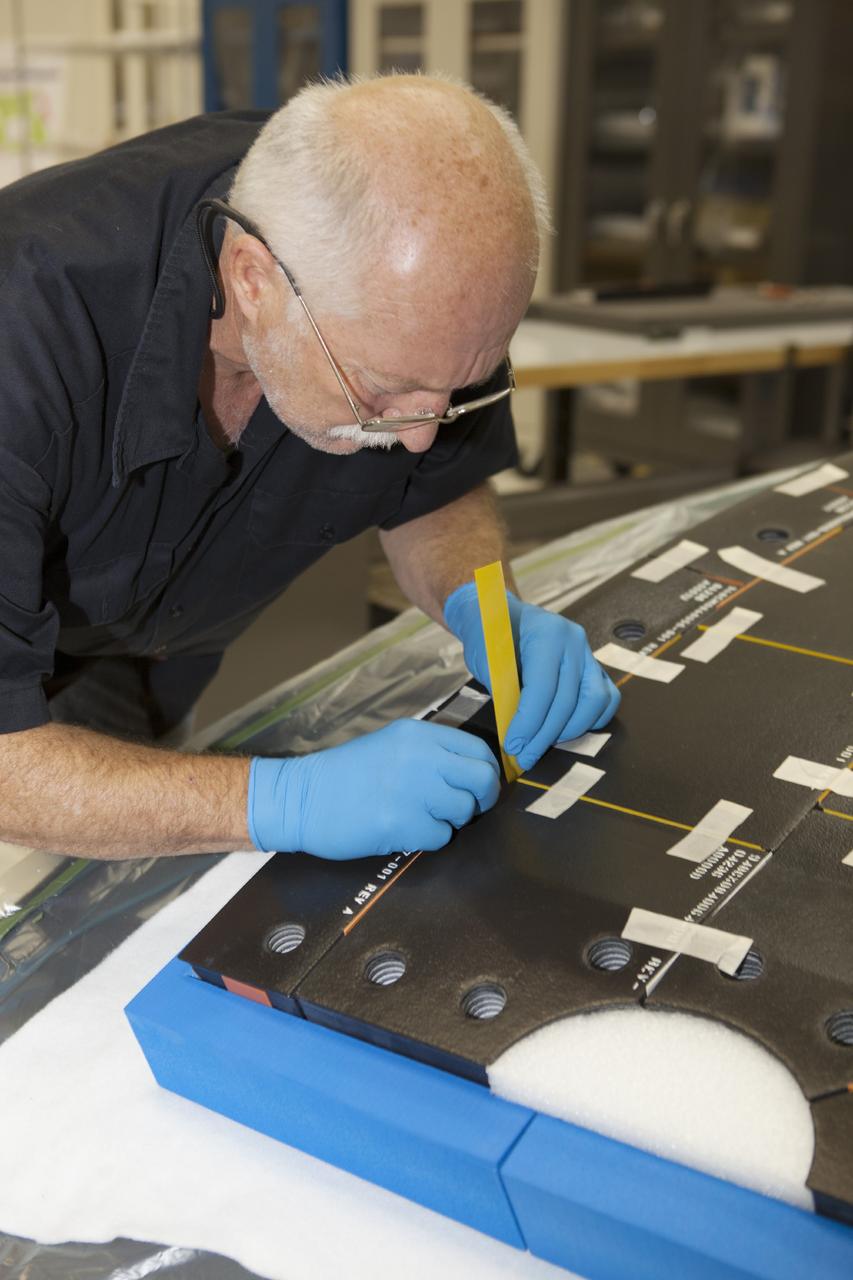
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a tile technician works on a section of thermal protection system tiles that will be installed on the Orion crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - United Space Alliance worker Kathy Evans works on equipment in the temporary tile shop set up in the RLV hangar at KSC. The hurricane-ravaged Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF), which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. Undamaged equipment was removed from the TPSF and stored in the hangar. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - United Space Alliance worker Bab Jarosz works with the 30-needle sewing machines from the Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF). A temporary tile shop has been set up in the RLV hangar at KSC after equipment was removed from the hurricane-ravaged facility. The TPSF, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - United Space Alliance worker Bab Jarosz works with the 30-needle sewing machines from the Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF). A temporary tile shop has been set up in the RLV hangar at KSC after equipment was removed from the hurricane-ravaged facility. The TPSF, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.

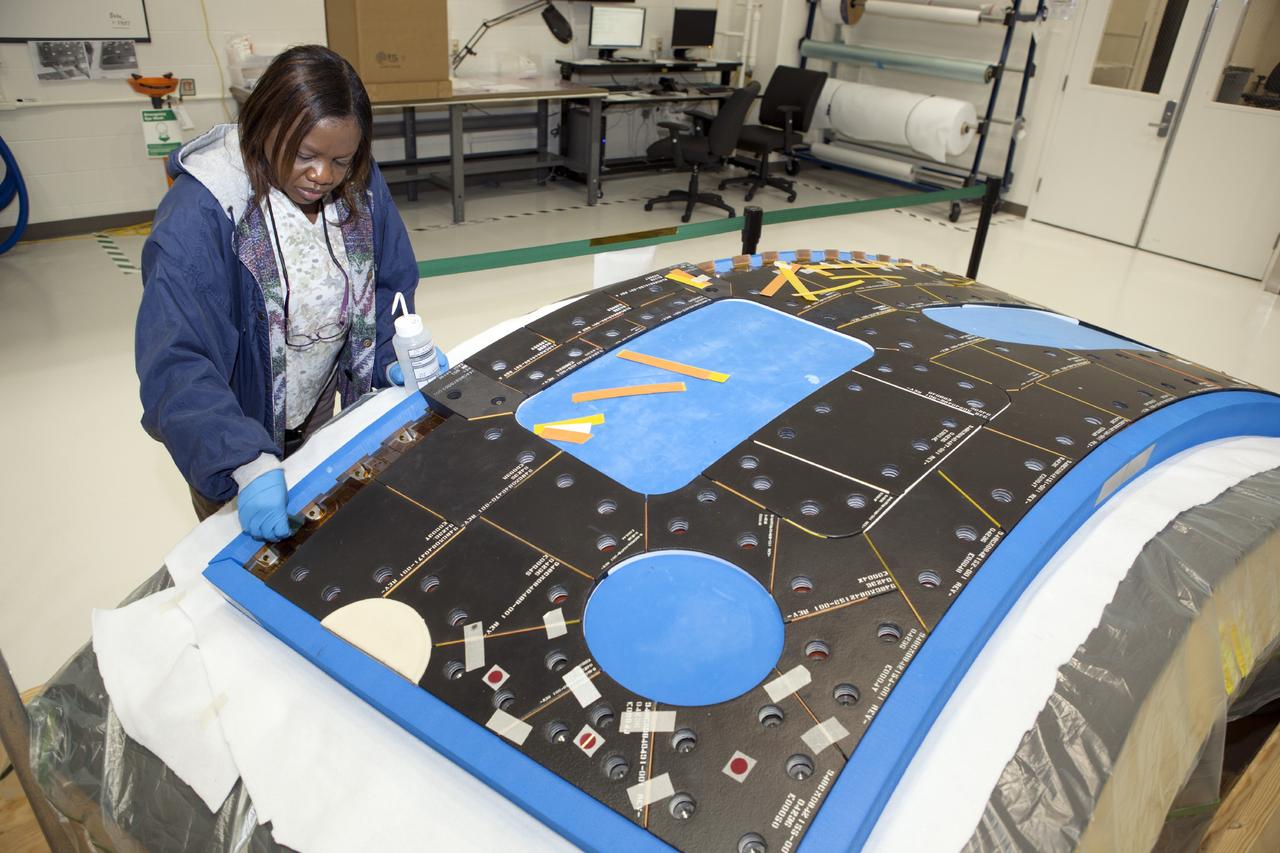
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, two tile technicians wrap a section of the thermal protection system tiles that will be installed on the Orion crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
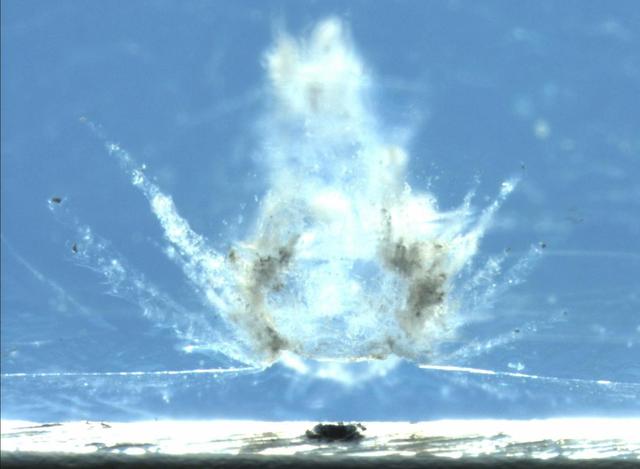
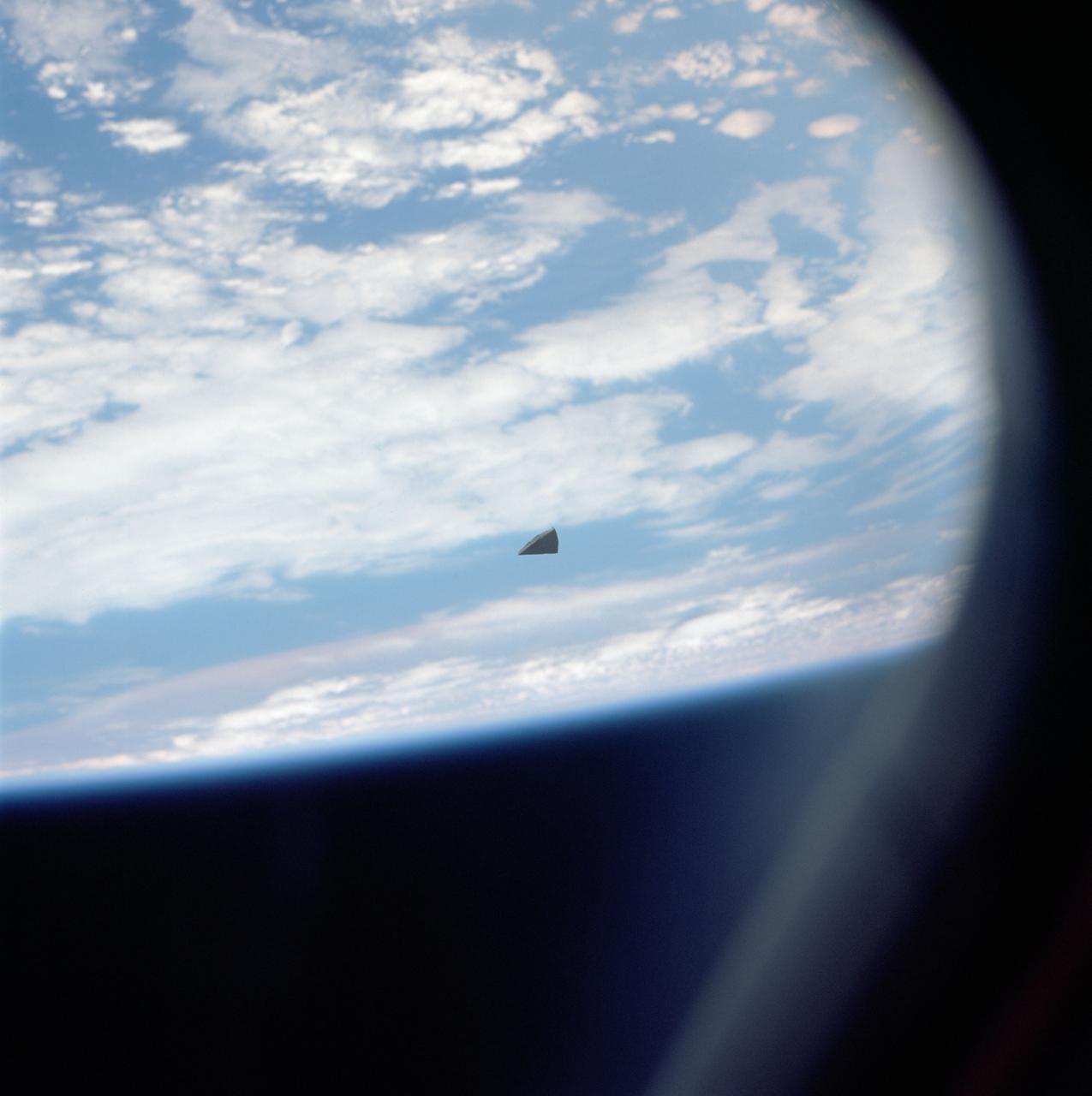
This image from NASA shows a particle impact on the aluminum frame that holds the aerogel tiles. The debris from the impact shot into the adjacent aerogel tile producing the explosion pattern of ejecta framents captured in the material.

Wall tiles from Kennedy Space Center’s former headquarters building are presented to Kennedy Director Janet Petro inside the Florida spaceport’s Central Campus Headquarters Building on May 3, 2022. The two 15-pound sections from the building were preserved by Maverick Constructors LLC, the construction company that completed demolition of the structure. The company’s presentation of the tiles is in honor of the many civil servants and contractors who dedicated their lives to working for and supporting NASA in this building. Shown in the photo are Maverick East Coast division manager Ralph Kennedy and Sheri LaShier.

Wall tiles from Kennedy Space Center’s former headquarters building are presented to Kennedy Director Janet Petro inside the Florida spaceport’s Central Campus Headquarters Building on May 3, 2022. The two 15-pound sections from the building were preserved by Maverick Constructors LLC, the construction company that completed demolition of the structure. The company’s presentation of the tiles is in honor of the many civil servants and contractors who dedicated their lives to working for and supporting NASA in this building. Shown in the photo are Maverick East Coast division manager Ralph Kennedy and Sheri LaShier.
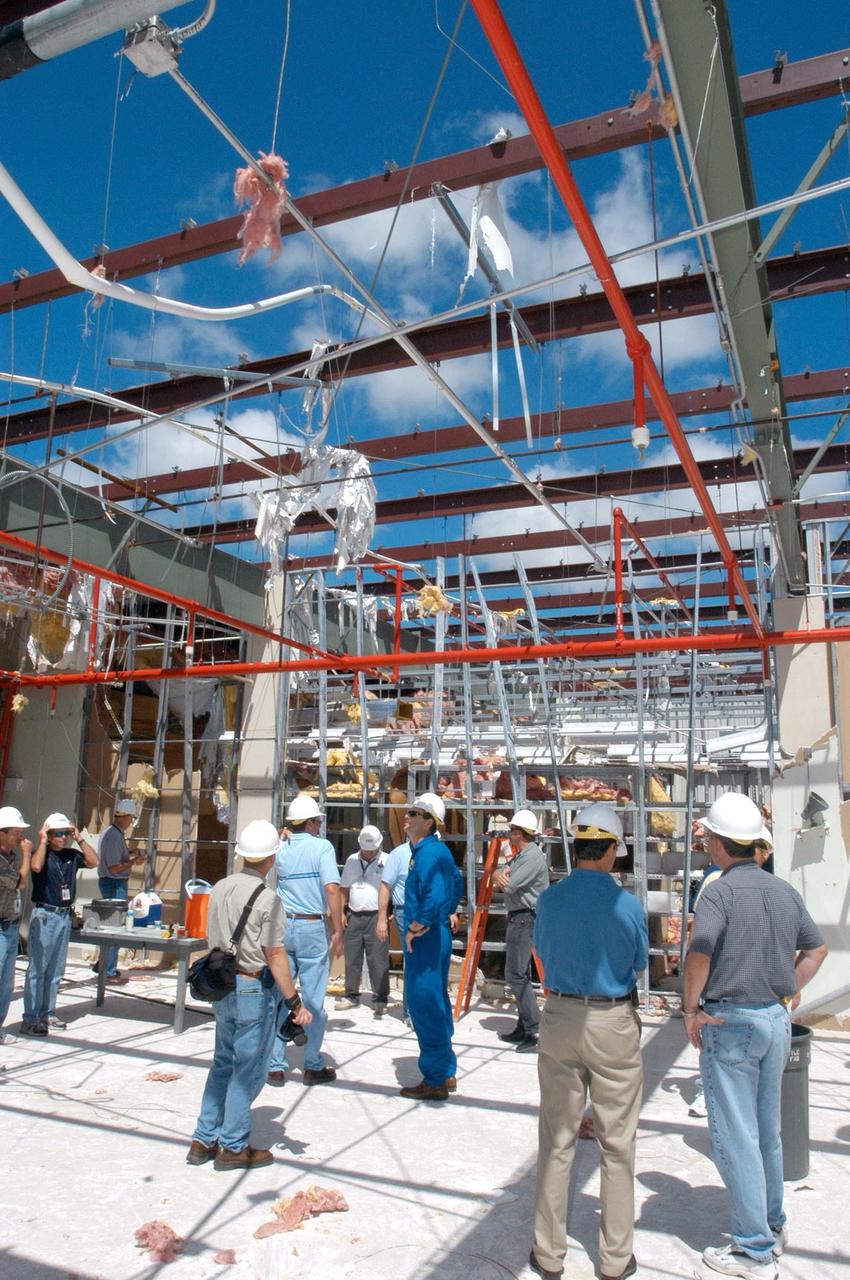

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Members of a hurricane assessment team from Johnson Space Center and Marshall Space Flight Center observe the damage to the roof of the Thermal Protection System (TPS) Facility at KSC after Hurricane Frances hit the east coast of Central Florida and Kennedy Space Center. Near the center is astronaut Scott Altmann, a member of the team. The facility, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof. Equipment and materials that survived the storm have been relocated to the RLV hangar near the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility.
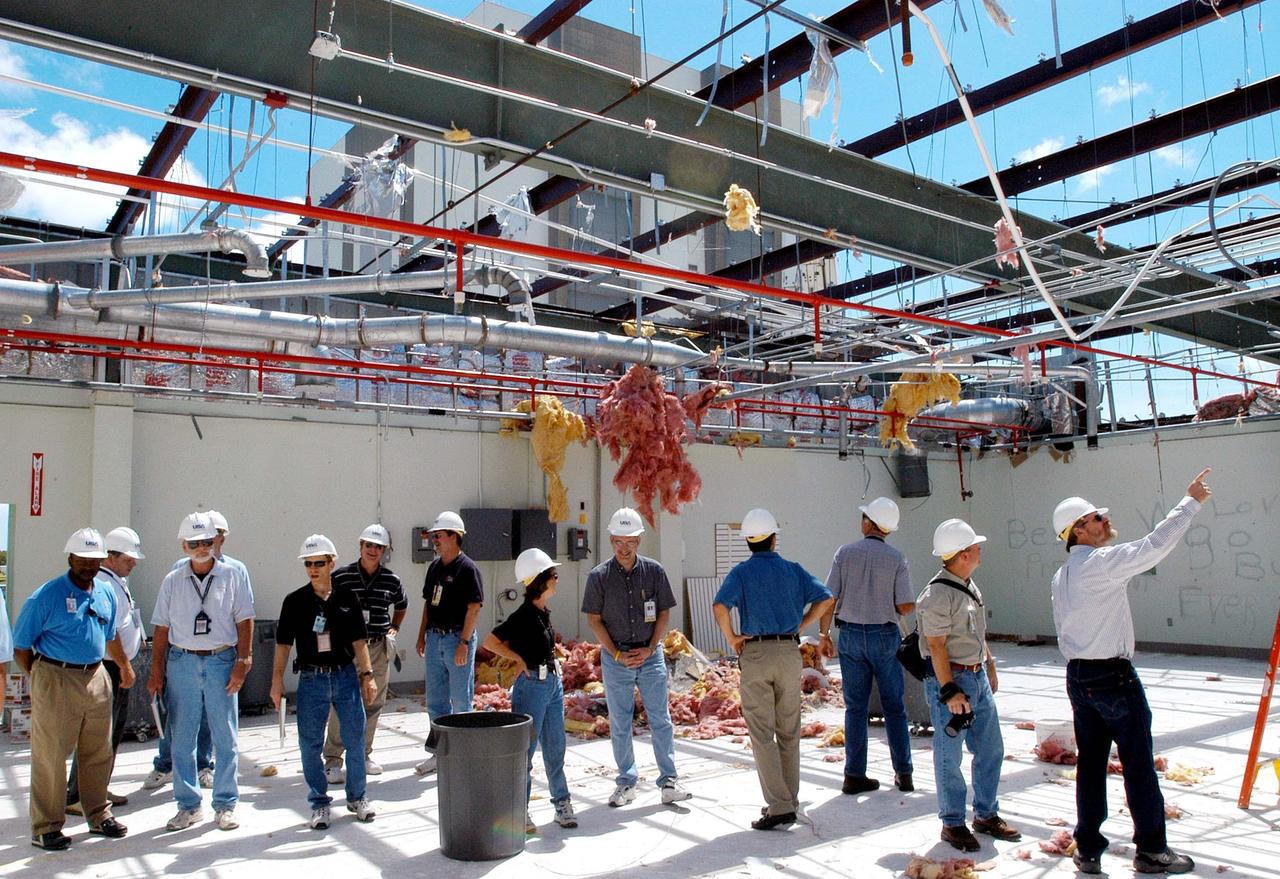

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Members of a hurricane assessment team from Johnson Space Center and Marshall Space Flight Center observe the damage to the roof of the Thermal Protection System (TPS) Facility at KSC after Hurricane Frances hit the east coast of Central Florida and Kennedy Space Center. The facility, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof. Equipment and materials that survived the storm have been relocated to the RLV hangar near the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility.

S114-E-6412 (3 August 2005) --- Space Shuttle Discovery’s underside thermal protection tiles are featured in this image photographed by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, during the mission’s third session of extravehicular activities (EVA).
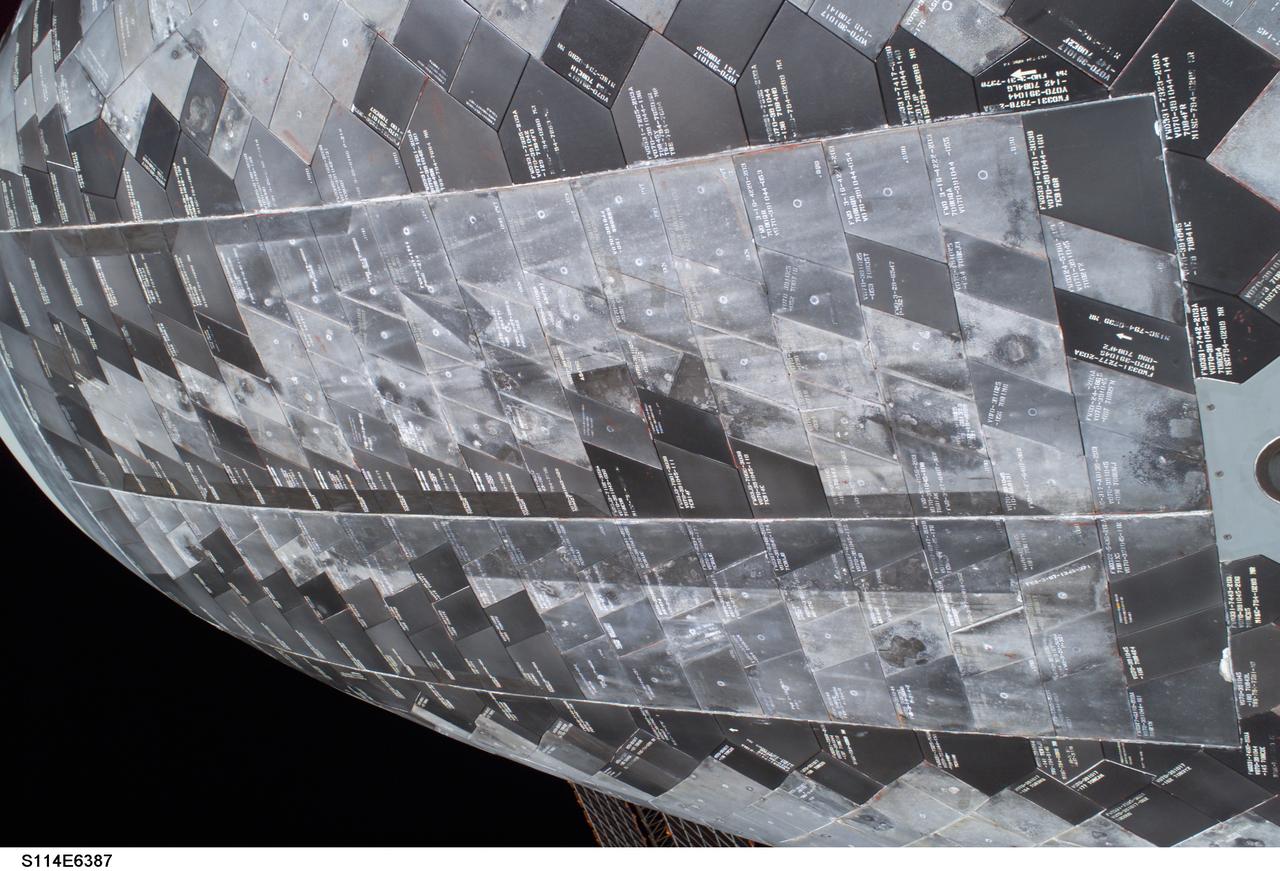

S114-E-6387 (3 August 2005) --- A close-up view of a portion of the thermal protection tiles on Space Shuttle Discovery’s underside is featured in this image photographed by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, during the mission’s third session of extravehicular activities (EVA).
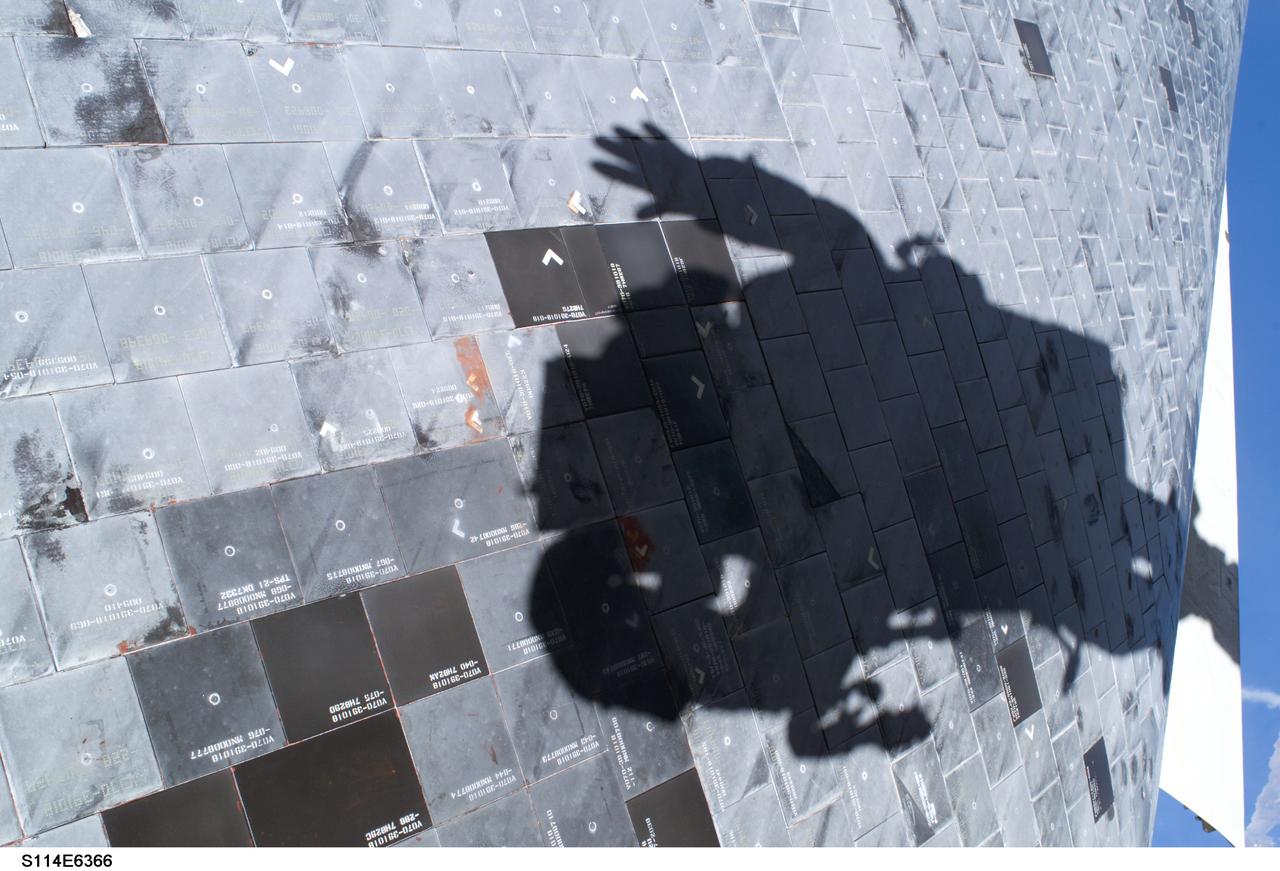

S114-E-6366 (3 August 2005) --- Space Shuttle Discovery’s underside is featured in this image photographed by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, during today’s extravehicular activities (EVA). Robinson’s shadow is visible on the thermal protection tiles.

Launched on July 26 2005, from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-114 was classified as Logistics Flight 1. Among the Station-related activities of the mission were the delivery of new supplies and the replacement of one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 also carried the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. A major focus of the mission was the testing and evaluation of new Space Shuttle flight safety, which included new inspection and repair techniques. Upon its approach to the International Space Station (ISS), the Space Shuttle Discovery underwent a photography session in order to assess any damages that may have occurred during its launch and/or journey through Space. The mission’s third and final Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA) included taking a close-up look and the repair of the damaged heat shield. Gap fillers were removed from between the orbiter’s heat-shielding tiles located on the craft’s underbelly. Never before had any repairs been done to an orbiter while still in space. This close up of the thermal tiles was taken by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist (out of frame). Astronaut Soichi Noguchi, STS-114 mission specialist representing the Japan Aerospace Exploration (JAXA), can be seen in the background perched on a Space Station truss.
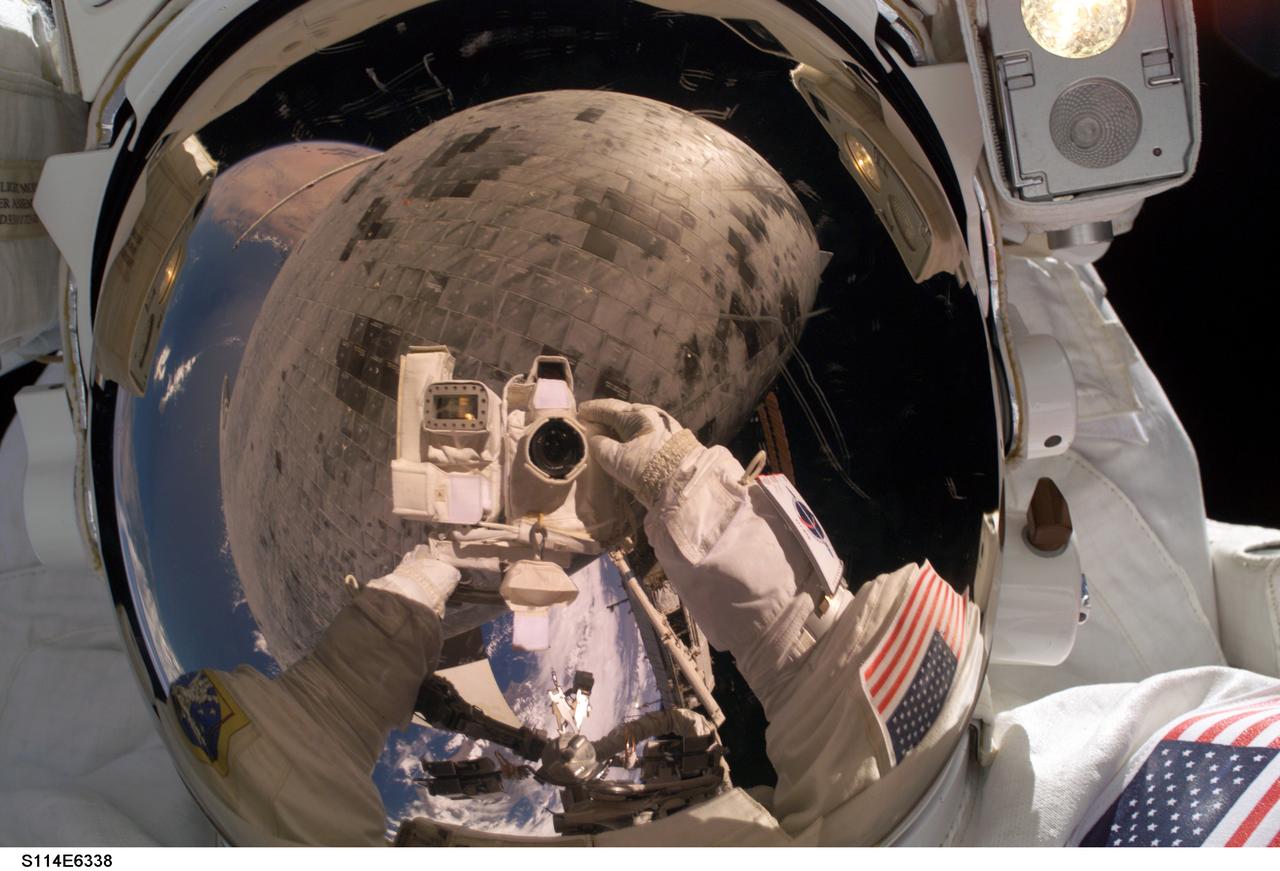

Launched on July 26, 2005 from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-114 was classified as Logistics Flight 1. Among the Station-related activities of the mission were the delivery of new supplies and the replacement of one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 also carried the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. A major focus of the mission was the testing and evaluation of new Space Shuttle flight safety, which included new inspection and repair techniques. Upon its approach to the International Space Station (ISS), the Space Shuttle Discovery underwent a photography session in order to assess any damages that may have occurred during its launch and/or journey through Space. The mission’s third and final Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA) included taking a close-up look and the repair of the damaged heat shield. Gap fillers were removed from between the orbiter’s heat-shielding tiles located on the craft’s underbelly. Never before had any repairs been done to an orbiter while still in space. Astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, used the pictured still digital camera to expose a photo of his helmet visor during the EVA. Also visible in the reflection are thermal protection tiles on Discovery’s underside.
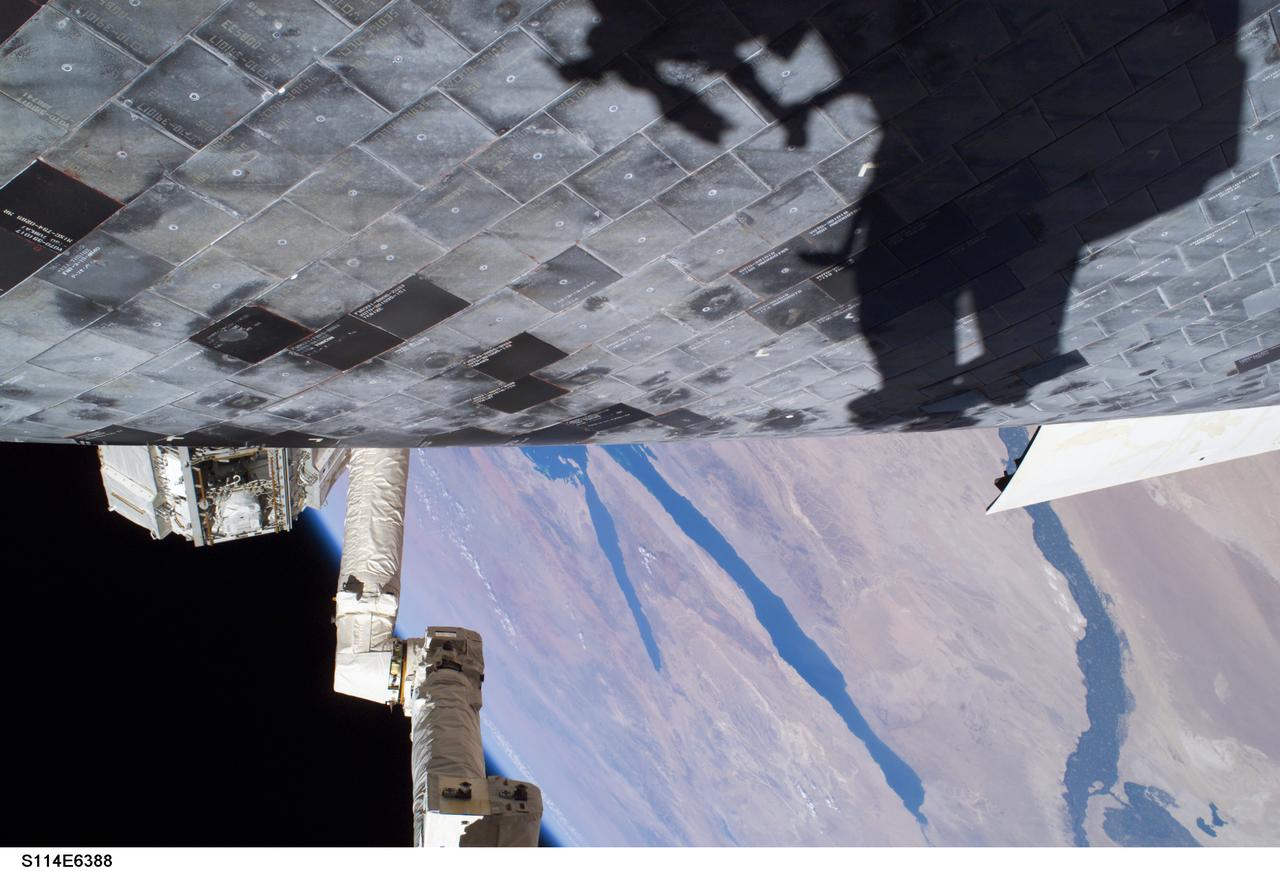

Launched on July 26, 2005 from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-114 was classified as Logistics Flight 1. Among the Station-related activities of the mission were the delivery of new supplies and the replacement of one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 also carried the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. A major focus of the mission was the testing and evaluation of new Space Shuttle flight safety, which included new inspection and repair techniques. Upon its approach to the International Space Station (ISS), the Space Shuttle Discovery underwent a photography session in order to assess any damages that may have occurred during its launch and/or journey through Space. The mission’s third and final Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA) included taking a close-up look and the repair of the damaged heat shield. Gap fillers were removed from between the orbiter’s heat-shielding tiles located on the craft’s underbelly. Never before had any repairs been done to an orbiter while still in space. This particular photo was taken by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, whose shadow is visible on the thermal protection tiles, and a portion of the Canadian built Remote Manipulator System (RMS) robotic arm and the Nile River is visible at the bottom.
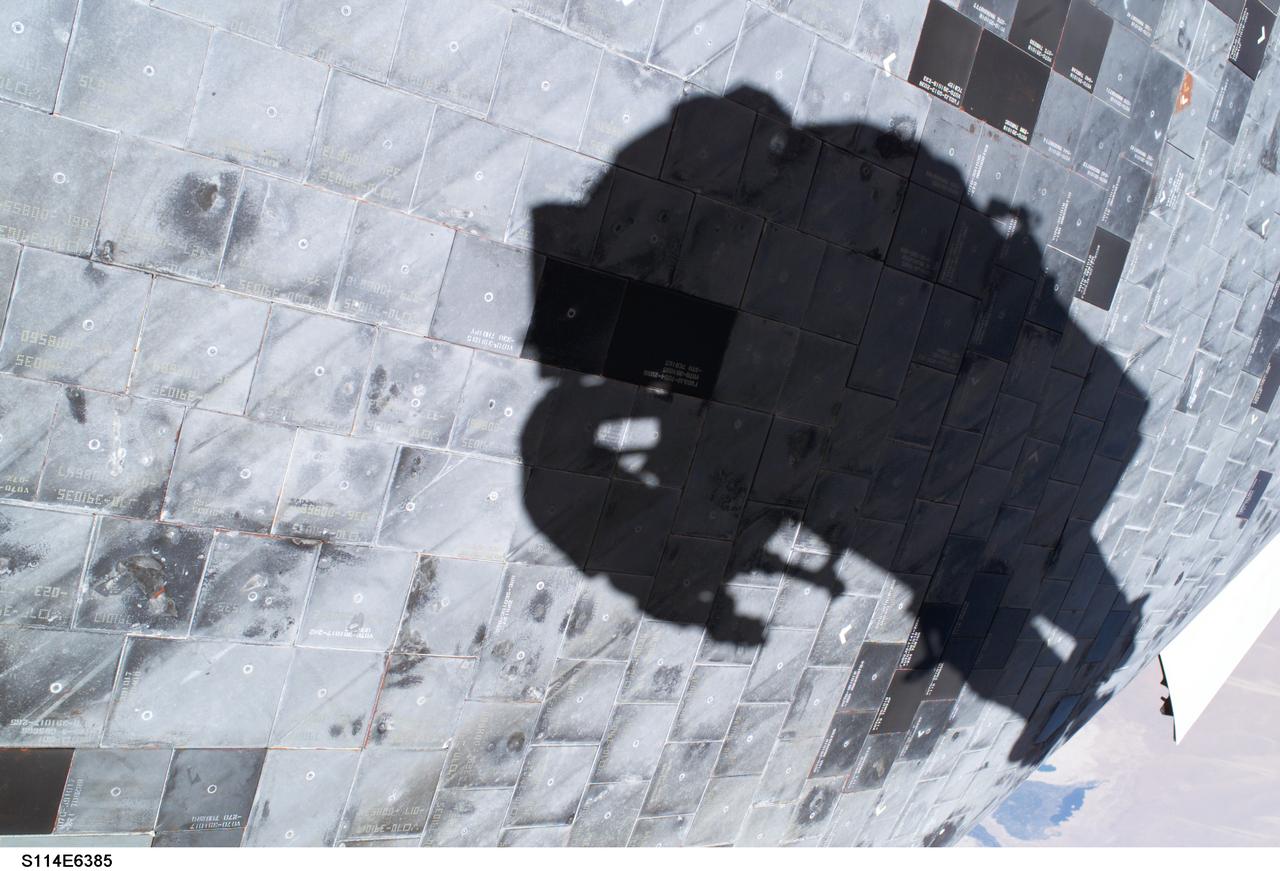

Launched on July 26, 2005 from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-114 was classified as Logistics Flight 1. Among the Station-related activities of the mission were the delivery of new supplies and the replacement of one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 also carried the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. A major focus of the mission was the testing and evaluation of new Space Shuttle flight safety, which included new inspection and repair techniques. Upon its approach to the International Space Station (ISS), the Space Shuttle Discovery underwent a photography session in order to assess any damages that may have occurred during its launch and/or journey through Space. The mission’s third and final Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA) included taking a close-up look and the repair of the damaged heat shield. Gap fillers were removed from between the orbiter’s heat-shielding tiles located on the craft’s underbelly. Never before had any repairs been done to an orbiter while still in space. This particular photo was taken by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, whose shadow is visible on the thermal protection tiles.
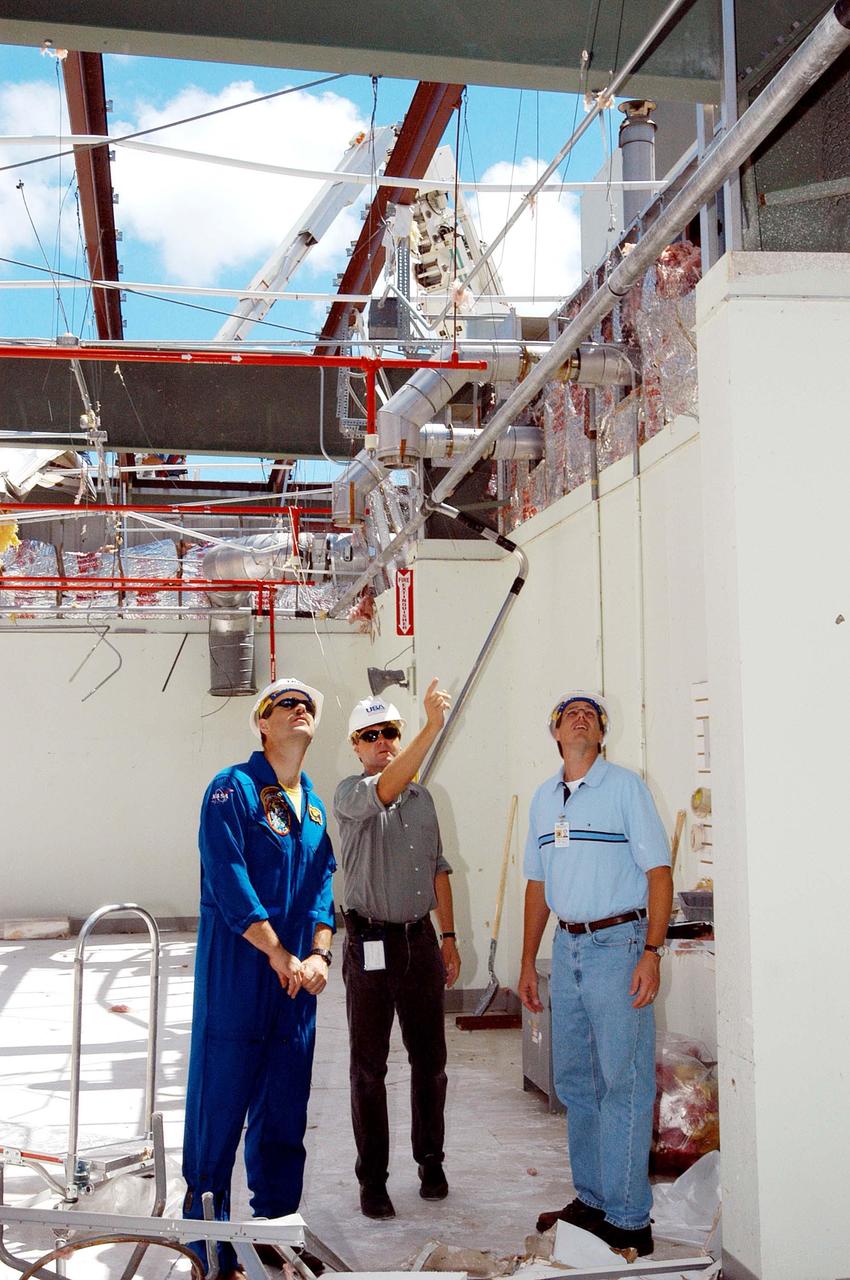

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Members of a hurricane assessment team from Johnson Space Center and Marshall Space Flight Center observe the damage to the roof of the Thermal Protection System (TPS) Facility at KSC after Hurricane Frances hit the east coast of Central Florida and Kennedy Space Center. At left is astronaut Scott Altmann, a member of the team, and at center is Martin Wilson, manager of the TPS operations. The facility, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof. Equipment and materials that survived the storm have been relocated to the RLV hangar near the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility.
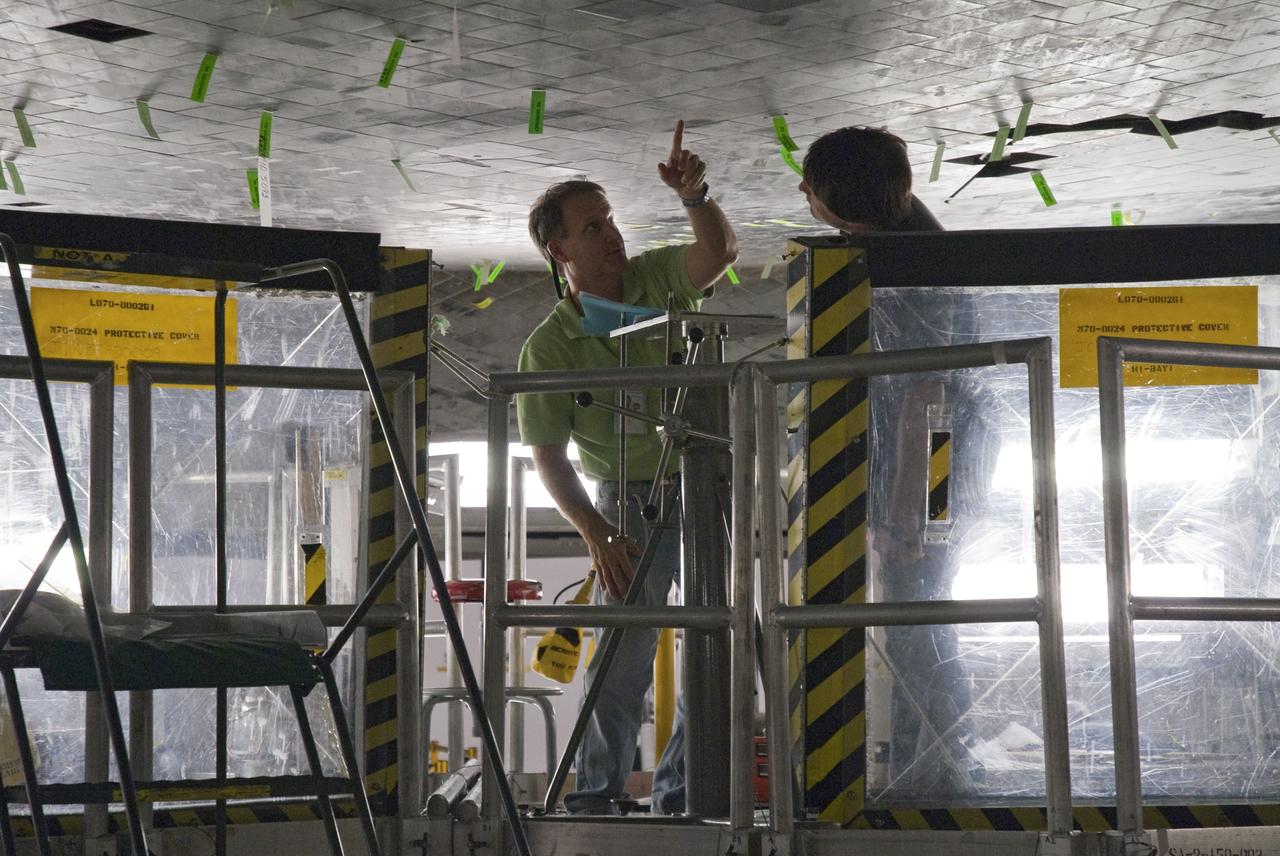

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician points to an area on space shuttle Endeavour's underside that may require tile replacement. As the final planned mission of the Space Shuttle Program, Endeavour and its crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, as well as critical spare components to the station on the STS-134 mission targeted for launch Feb. 26, 2011. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, thermal protection system technicians work on replacing some of space shuttle Endeavour's heat shield tiles. As the final planned mission of the Space Shuttle Program, Endeavour and its crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, as well as critical spare components to the station on the STS-134 mission targeted for launch Feb. 26, 2011. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
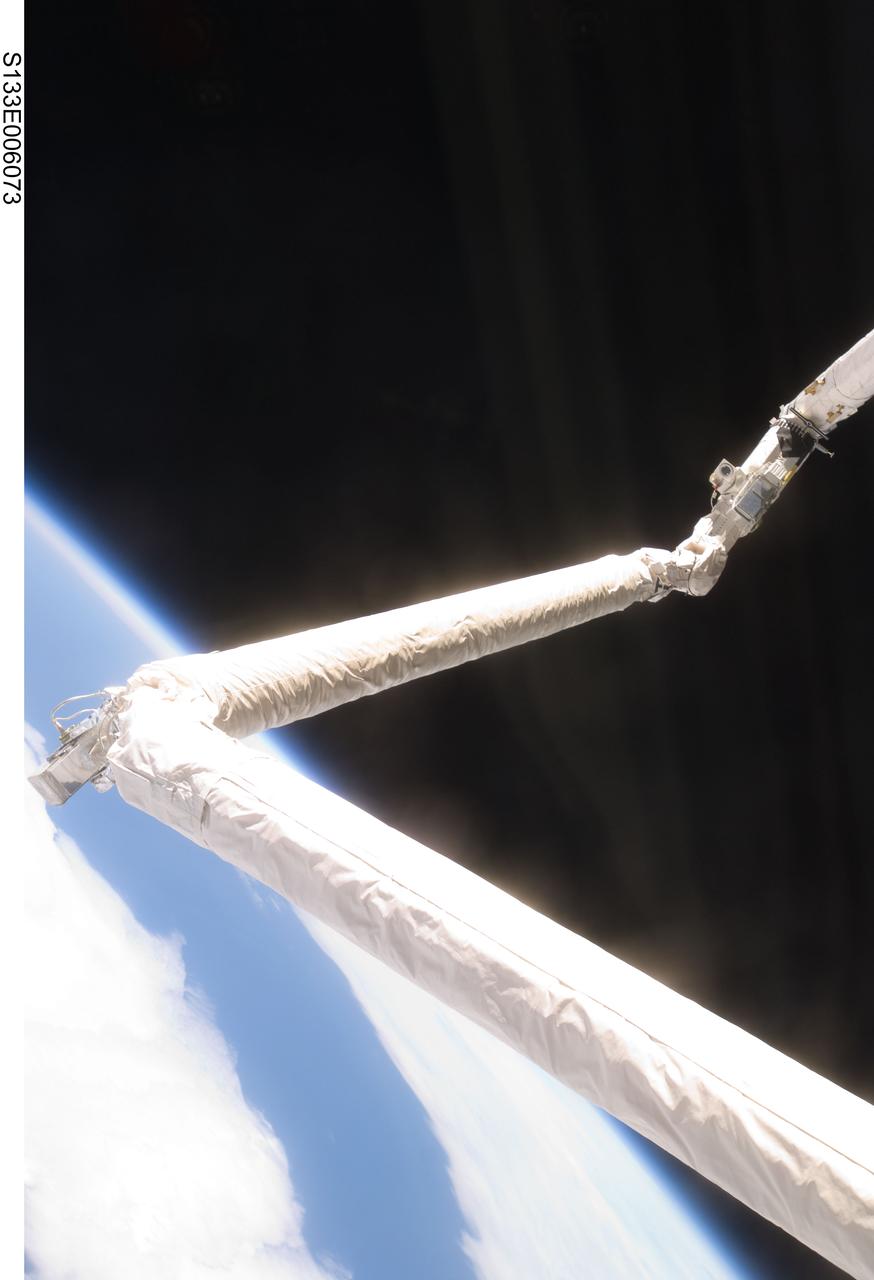

S133-E-006073 (25 Feb. 2011) --- Controlled by the STS-133 astronauts inside Discovery's cabin, the Remote Manipulator System/Orbiter Boom Sensor System (RMS/OBSS) equipped with special cameras, begins to conduct thorough inspections of the shuttle’s thermal tile system on flight day 2. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
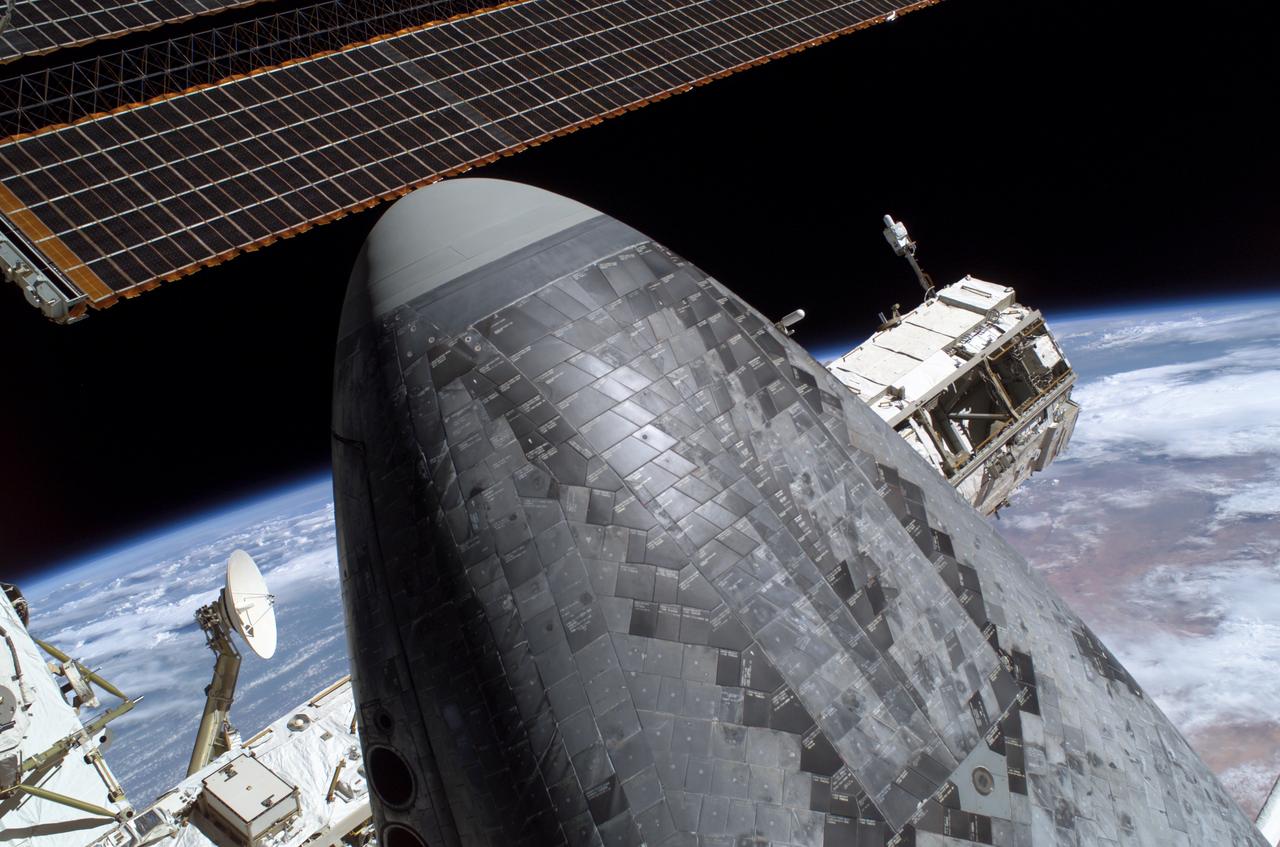

S114-E-6405 (3 August 2005) --- Space Shuttle Discovery’s underside nosecone thermal protection tiles are featured in this image photographed by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, during the mission’s third session of extravehicular activities (EVA). Part of the P1 truss and a solar array are visible in the background. The blackness of space and a blue and white Earth form the backdrop for the image.
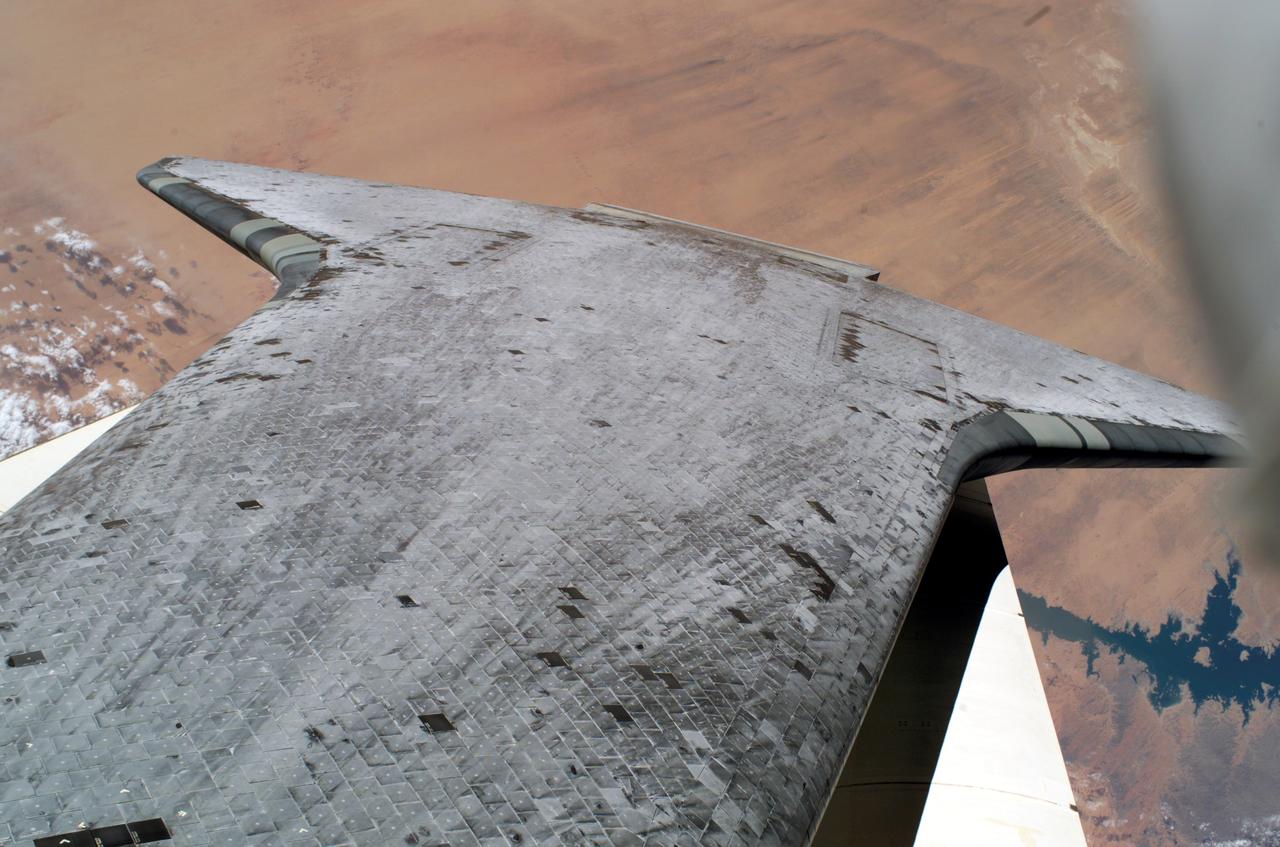

S114-E-6396 (3 August 2005) --- Space Shuttle Discovery’s underside thermal protection tiles are featured in this image photographed by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, during the mission’s third session of extravehicular activities (EVA). Lake Nasser along the Nile River, Egypt is visible near Discovery’s starboard wing.
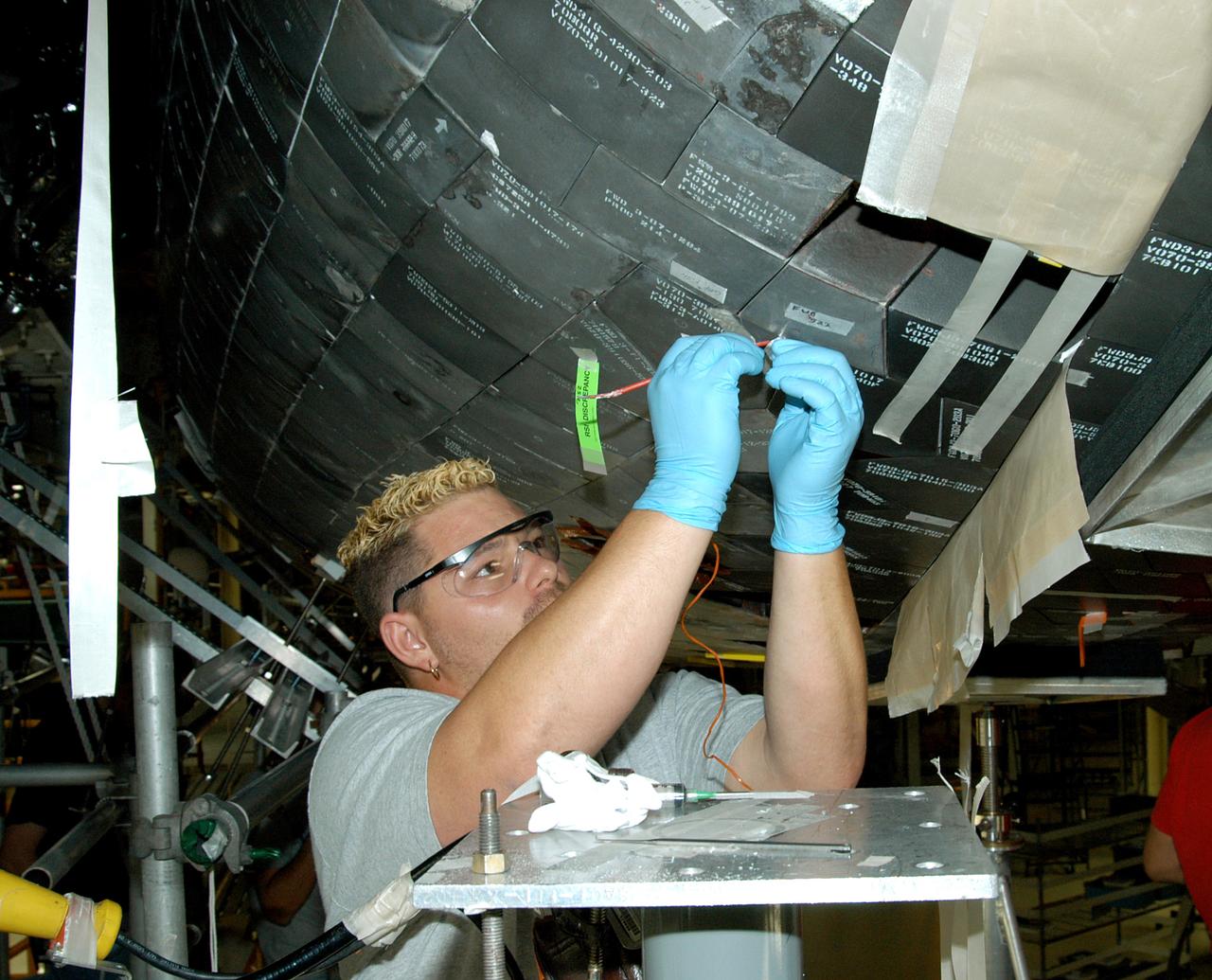

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, KSC employee Chris Moore repairs tile on the forward area of the orbiter Discovery. The vehicle has undergone Orbiter Major Modifications in the past year, which includes tile check and repair. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System, thermal shields to protect against temperatures as high as 3,000° Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Discovery is scheduled to fly on mission STS-121 to the International Space Station.

This photo shows the Shuttle tile flight test fixture under the wing of a National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration WP-3D aircraft.
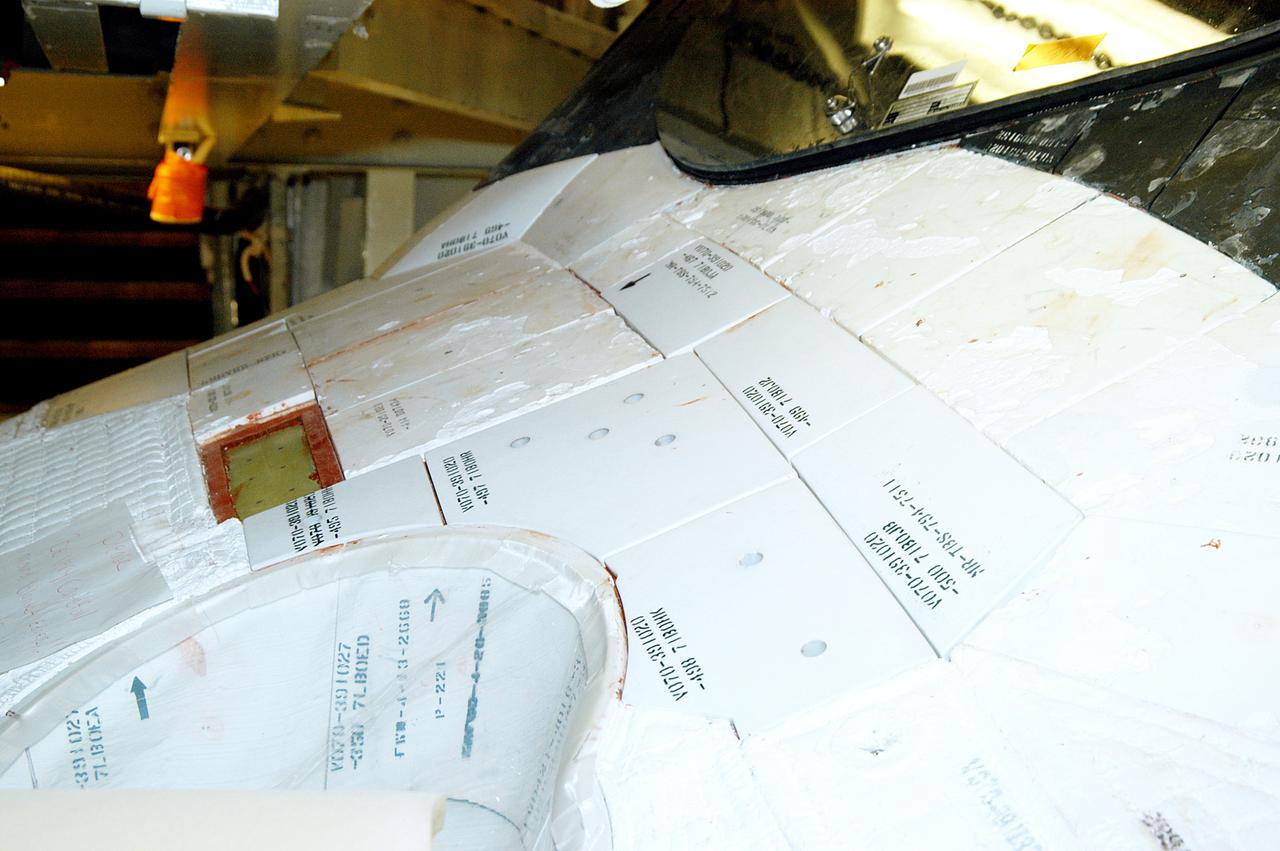

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This view shows the tiles below the windshield on the orbiter Atlantis. A gap test is being performed on the tiles as part of return-to-flight activities. Atlantis is scheduled for mission STS-114, a return-to-flight test mission to the International Space Station.
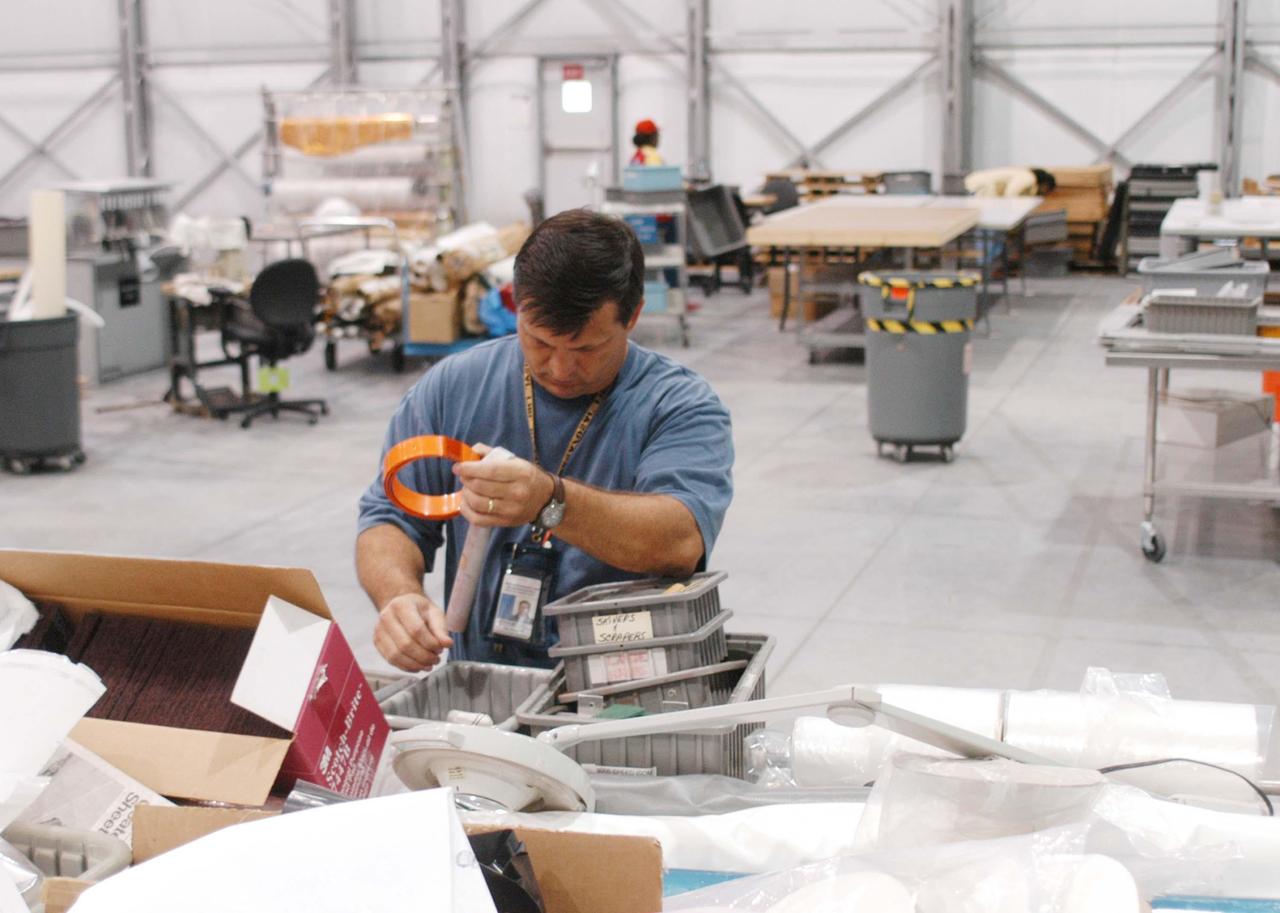

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the RLV hangar at KSC, United Space Alliance worker Steve Mitchell unpacks equipment that was removed from the hurricane-ravaged Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF). The facility, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.
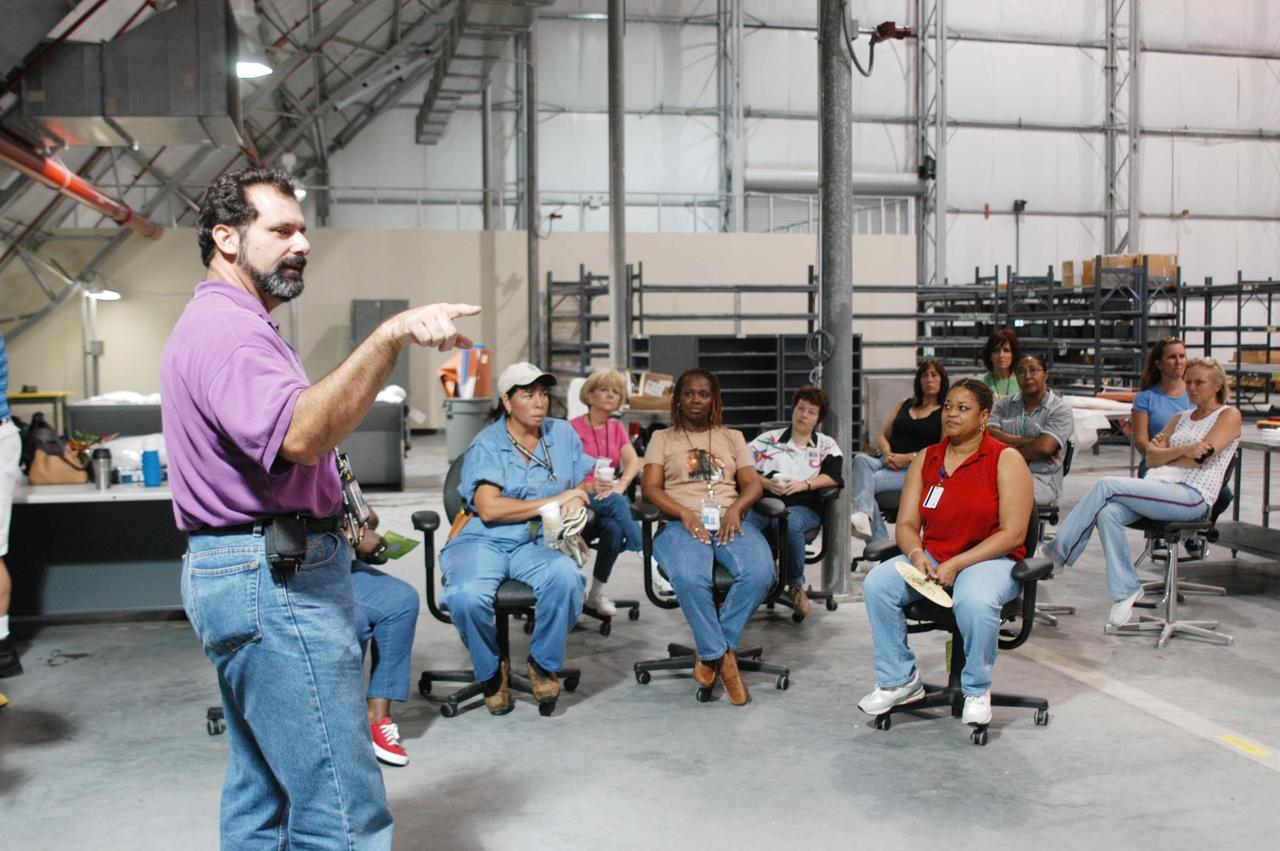

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the RLV hangar at KSC, Steve Harrington talks to workers about the equipment removed from the hurricane-ravaged Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF) now being stored in the hangar. The facility, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the RLV hangar at KSC, Kevin Harrington, manager of Softgoods Production, talks to workers about the equipment removed from the hurricane-ravaged Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF) now being stored in the hangar. The facility, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the RLV hangar at KSC, United Space Alliance workers Frank Rhodes and Lynn Rosenbauer look at wrapped material removed from the hurricane-ravaged Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF). The facility, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the RLV hangar at KSC, United Space Alliance workers Beth Smith (left) and Theresa Haygood unwrap equipment removed from the hurricane-ravaged Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF). The facility, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - United Space Alliance workers Dallas Lewis (left) and Damon Petty carry out equipment from the Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF). The TPSF, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. Undamaged equipment is being moved to the RLV hangar at KSC. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the RLV hangar at KSC, Steve Harrington talks to workers about the equipment removed from the hurricane-ravaged Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF) now being stored in the hangar. The facility, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - United Space Alliance workers Dallas Lewis (left) and Damon Petty clean up hurricane debris inside the Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF). Much of the roof was torn off by Hurricane Frances as it passed over Central Florida during the Labor Day weekend. Undamaged equipment has been moved to the RLV hangar at KSC. The TPSF, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the RLV hangar at KSC, United Space Alliance workers set up shelves for equipment removed from the hurricane-ravaged Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF) and now being stored in the hangar. The facility, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - United Space Alliance worker Janet Mills stores equipment removed from the hurricane-ravaged Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF) in the RLV hangar at KSC. The TPSF, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. Undamaged equipment has been moved to the hangar. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Columbia debris hangar at KSC, a United Space Alliance worker lines up air heaters salvaged from the hurricane-ravaged Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF) in order to dry them out. The TPSF, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. Undamaged equipment has been moved to the RLV hangar at KSC. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.
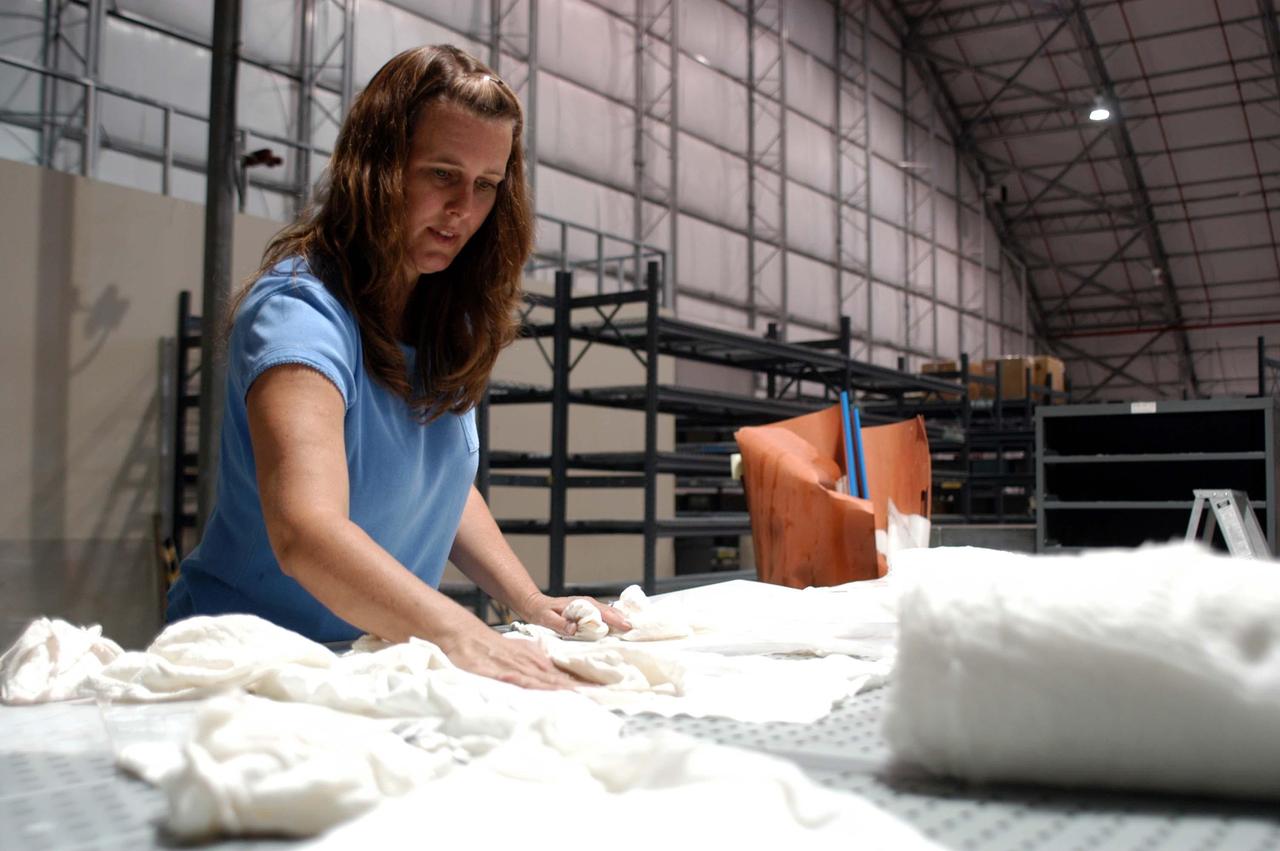

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the RLV hangar at KSC, Terri McCall cleans up equipment removed from the hurricane-ravaged Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF). The facility, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.
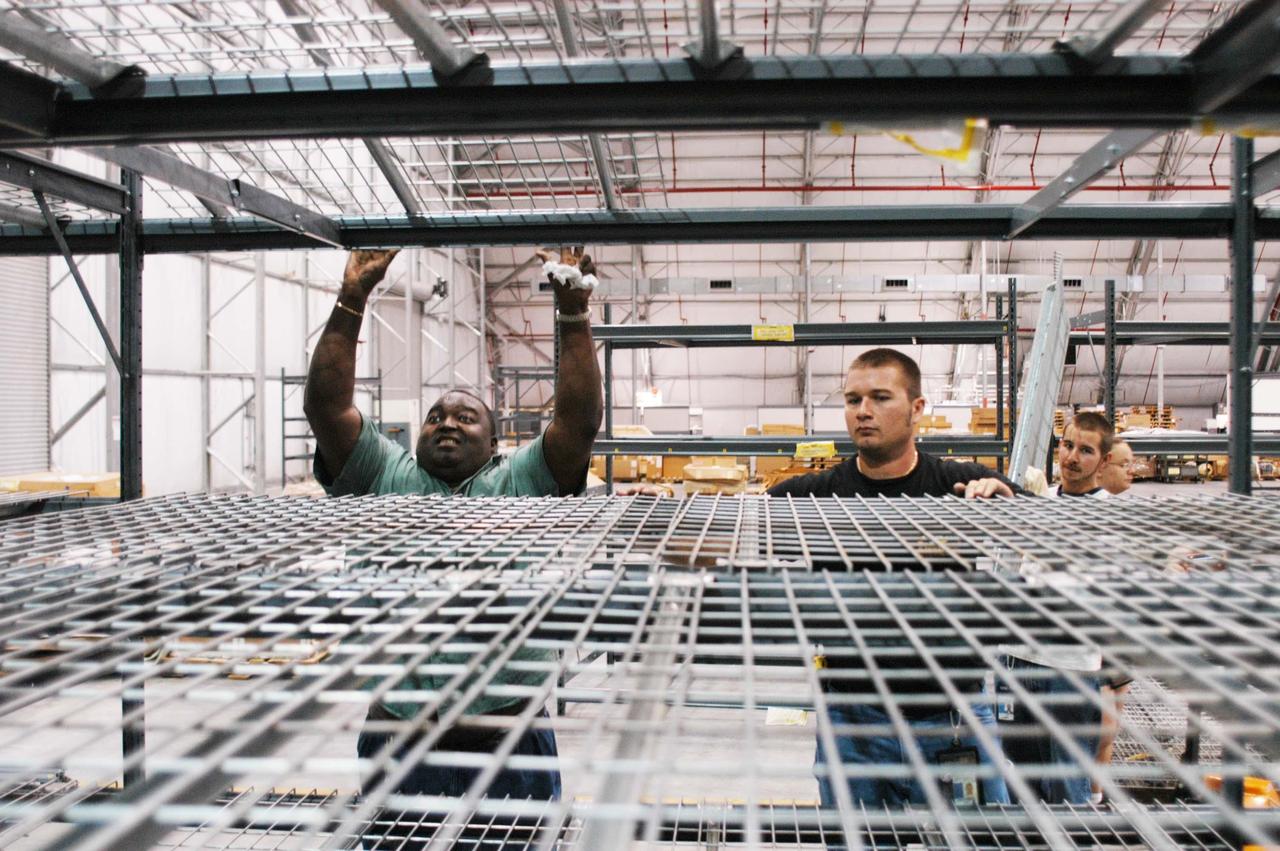

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the RLV hangar at KSC, United Space Alliance workers Matt Carter (left) and Mike Sherman set up racks to hold equipment removed from the hurricane-ravaged Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF). The facility, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, is almost totally unserviceable at this time after losing approximately 35 percent of its roof due to Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4-5. The maximum wind at the surface from Hurricane Frances was 94 mph from the northeast at 6:40 a.m. on Sunday, September 5. It was recorded at a weather tower located on the east shore of the Mosquito Lagoon near the Cape Canaveral National Seashore. The highest sustained wind at KSC was 68 mph.
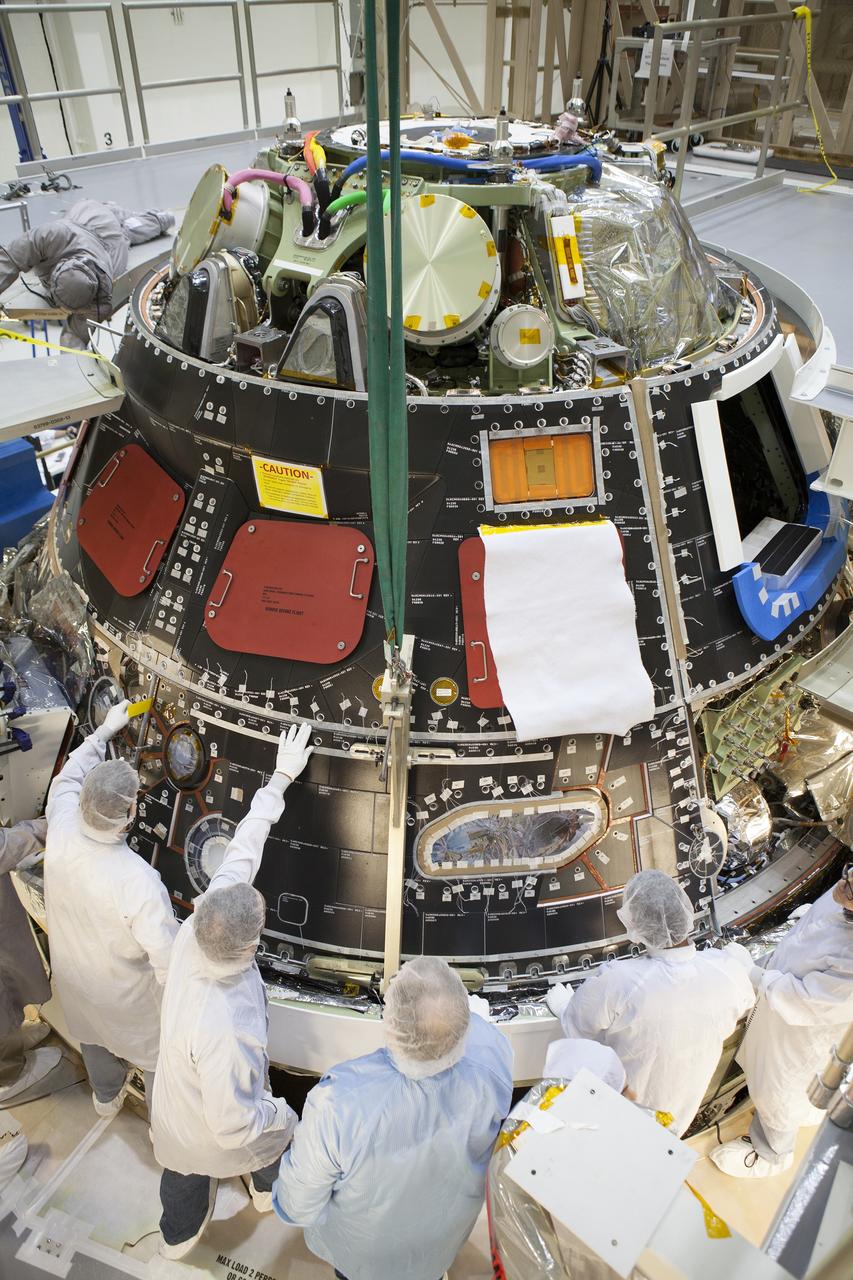

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians dressed in clean-room suits have installed a back shell tile panel onto the Orion crew module and are checking the fit next to the middle back shell tile panel. Preparations are underway for Exploration Flight Test-1, or EFT-1. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

Kennedy Space Center Director Janet Petro, second from left, poses with Maverick Constructors LLC employees, from left, Carlos Rodriguez, president, Ralph Kennedy, East Coast division manager, Liz McGrath, Sheri LaShier, and Stephanie Liquori inside Kennedy’s Central Campus Headquarters Building on May 3, 2022. Maverick, the construction company that completed the demolition of Kennedy’s former headquarters, presented Petro with two preserved sections of the building. The presentation of the 15-pound wall tiles is in honor of the many civil servants and contractors who dedicated their lives to working for and supporting NASA in this building.
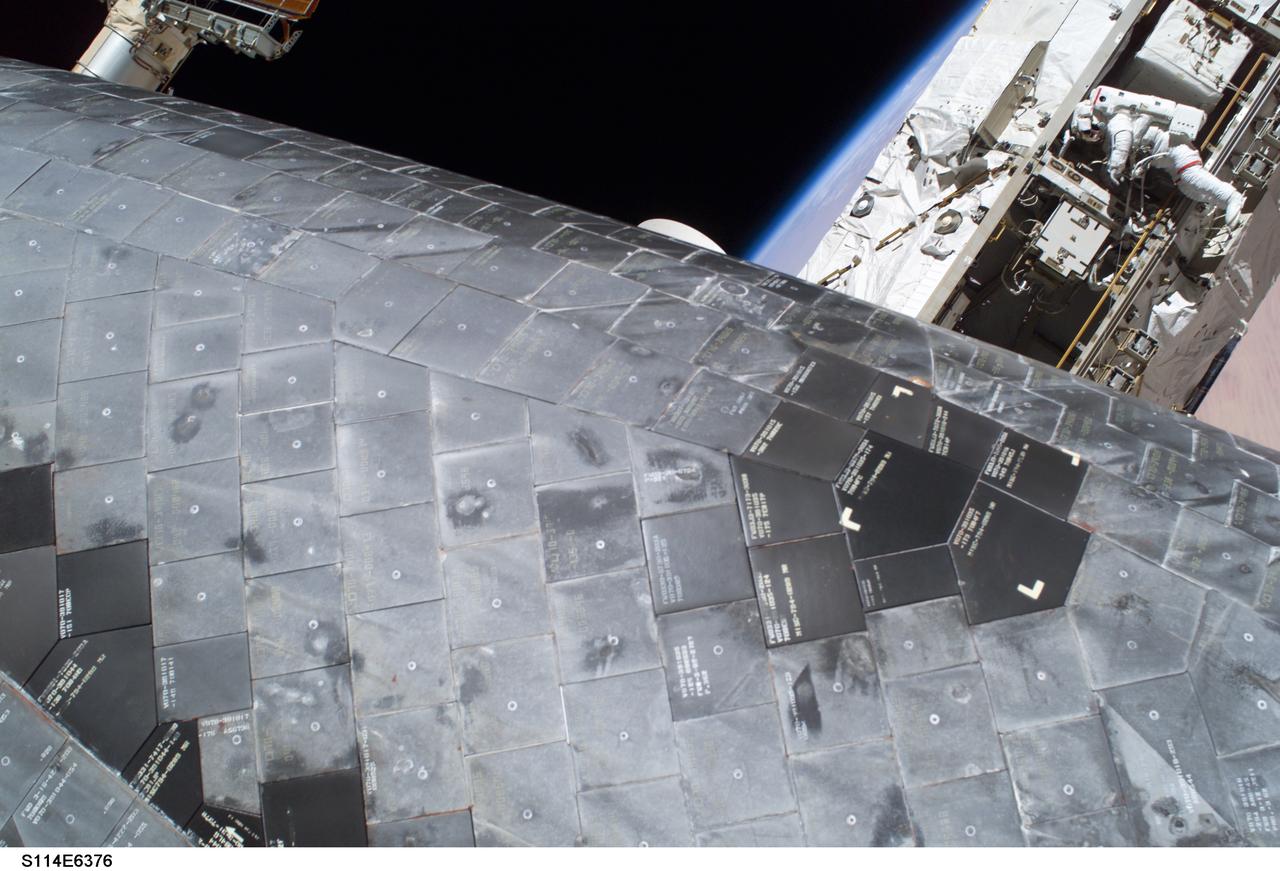

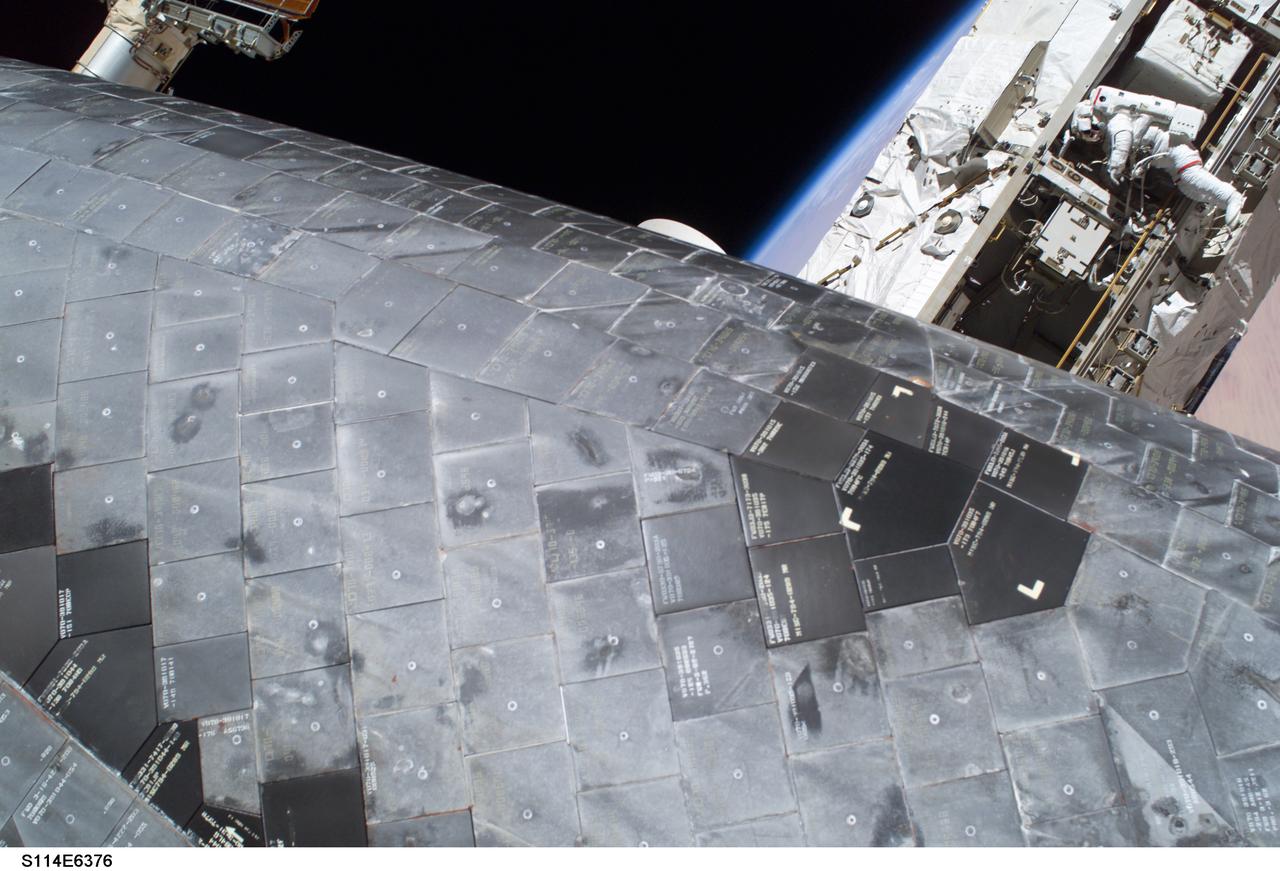
S114-E-6376 (3 August 2005) --- A close-up view of a portion of the thermal protection tiles on Space Shuttle Discovery’s underside is featured in this image photographed by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson (out of frame), STS-114 mission specialist, during the mission’s third session of extravehicular activities (EVA). While perched on a Space Station truss, astronaut Soichi Noguchi (background), mission specialist representing Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), acts as observer and communication relay station between fellow spacewalker Robinson and astronaut Andrew S. W. Thomas aboard Discovery.