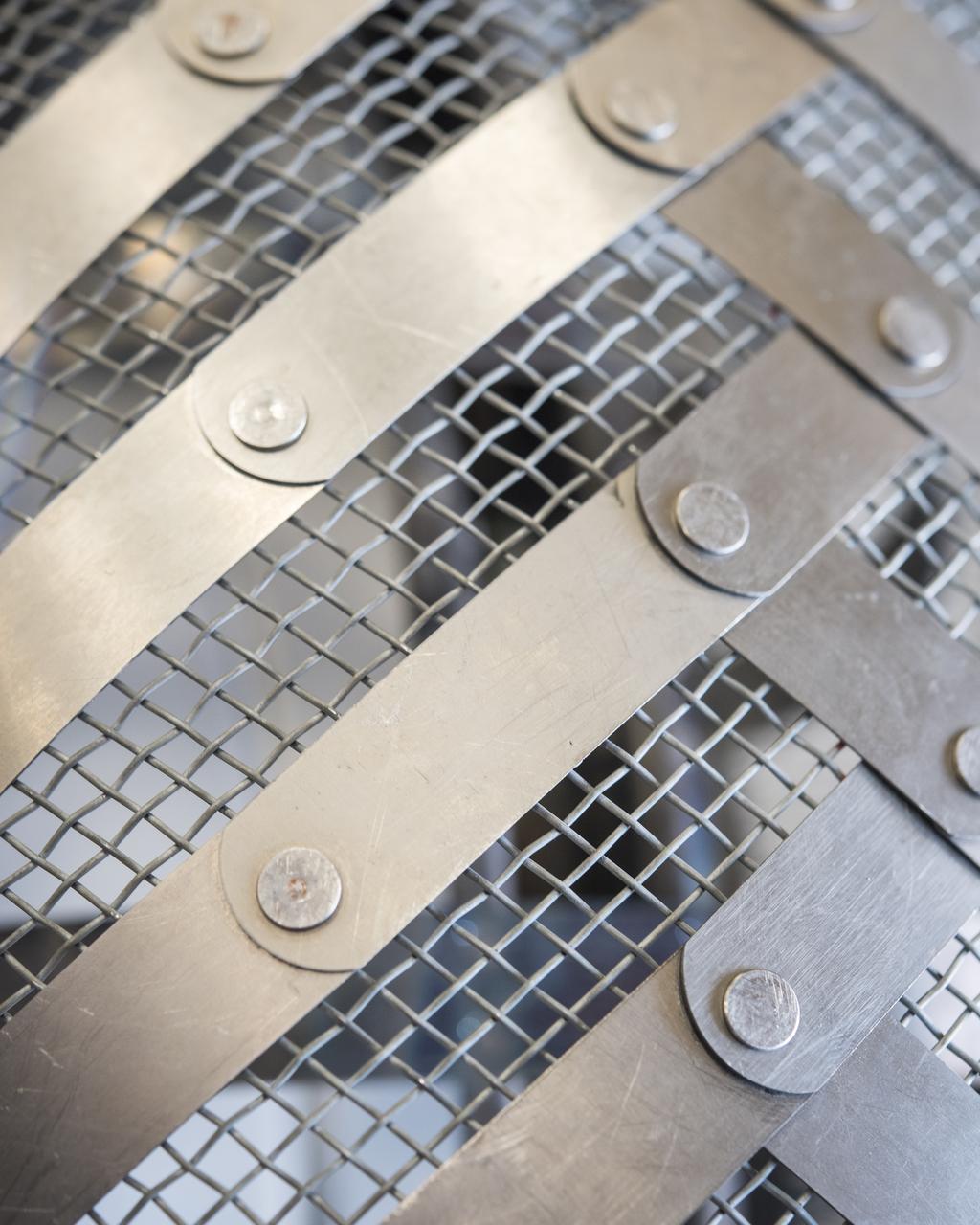
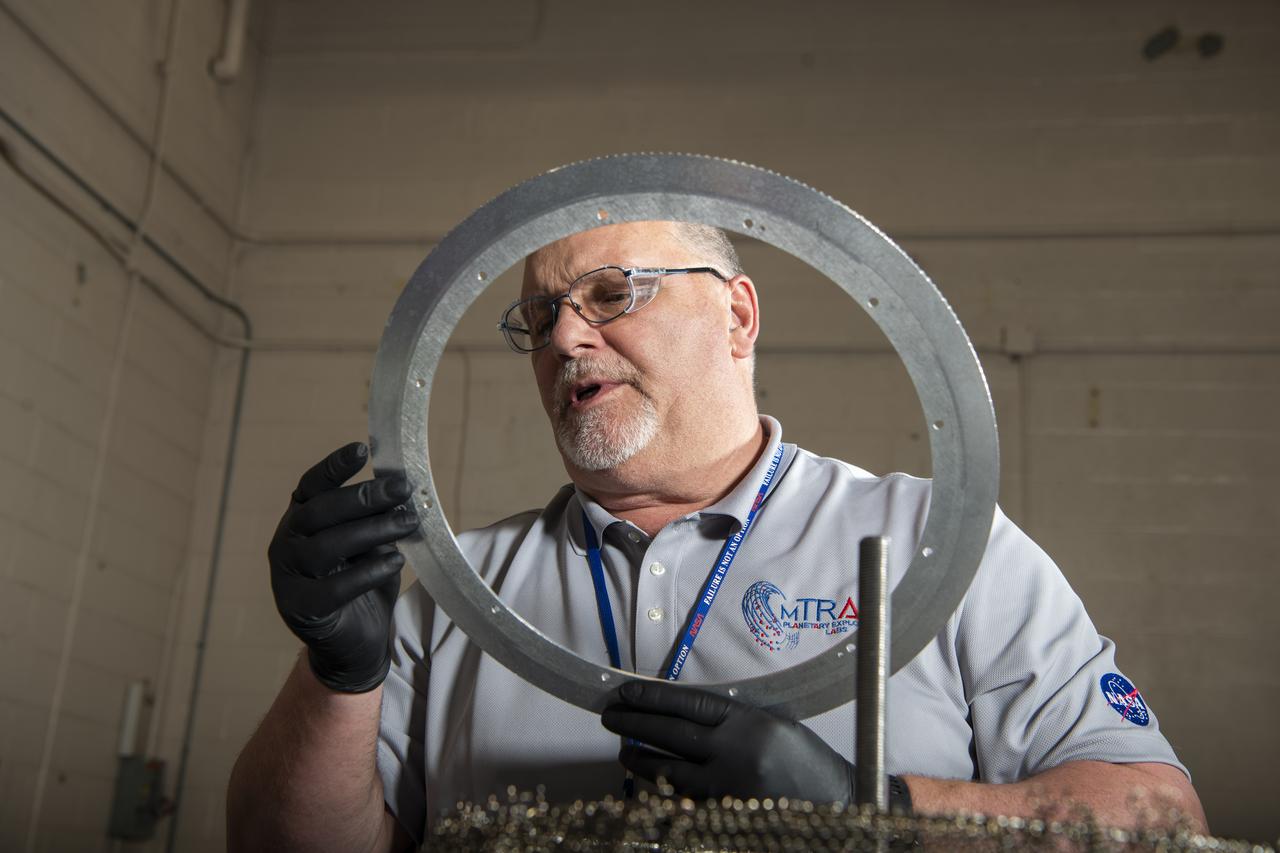
This is a close-up of an exact replica of the Apollo-era Lunar Roving Vehicle Wheel, of which twelve originals still rest on the surface of the Moon. The tire was designed to flex under load, without air, and was formed from a mesh of plated piano wire. Metal straps were hand riveted onto the mesh to reduce sinking into loose lunar soils. These replica wheels were tested in NASA Glenn's SLOPE Lab to establish a baseline for future improvements.
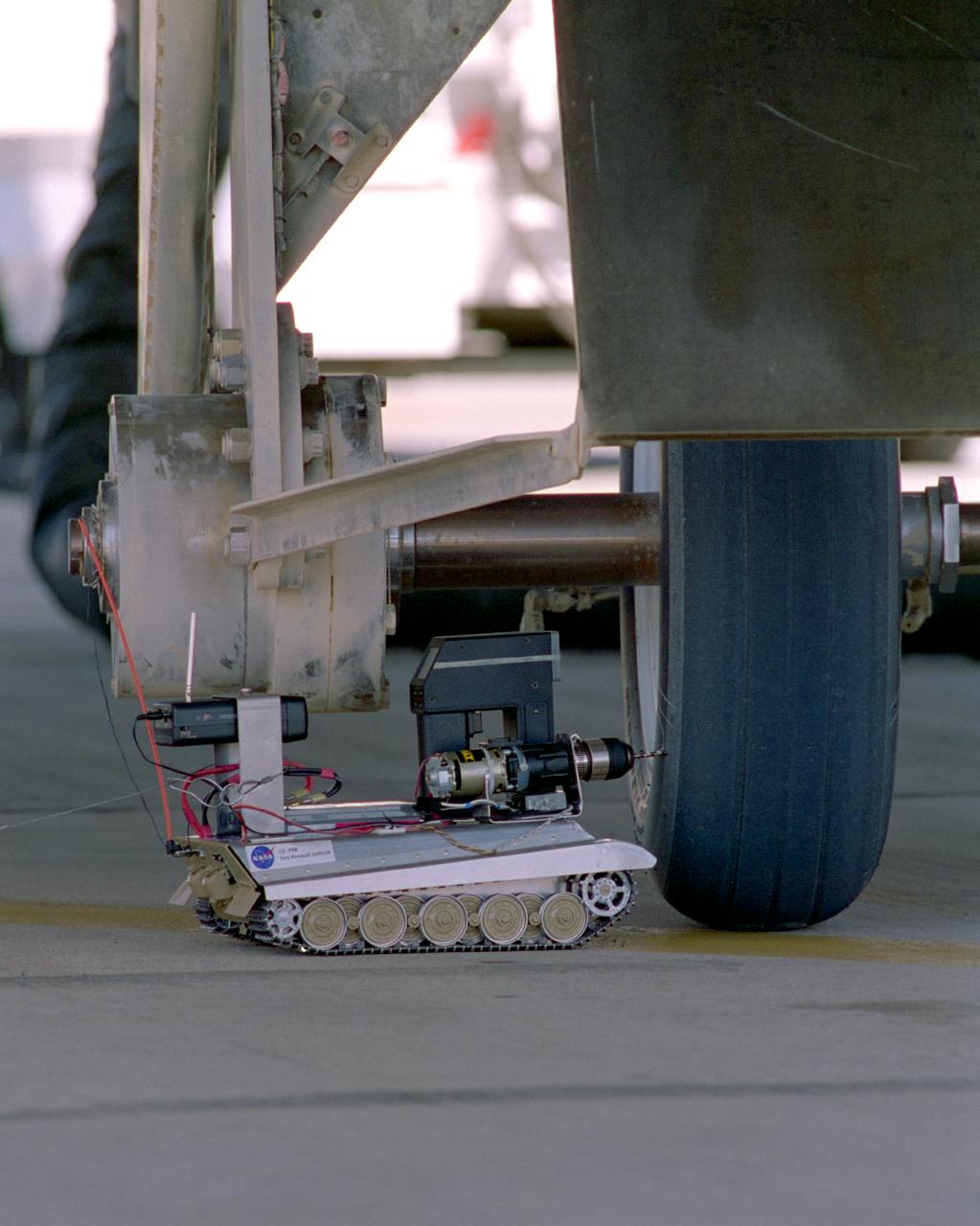
Created from a 1/16th model of a German World War II tank, the TAV (Tire Assault Vehicle) was an important safety feature for the Convair 990 Landing System Research Aircraft, which tested space shuttle tires. It was imperative to know the extreme conditions the shuttle tires could tolerate at landing without putting the shuttle and its crew at risk. In addition, the CV990 was able to land repeatedly to test the tires. The TAV was built from a kit and modified into a radio controlled, video-equipped machine to drill holes in aircraft test tires that were in imminent danger of exploding because of one or more conditions: high air pressure, high temperatures, and cord wear. An exploding test tire releases energy equivalent to two and one-half sticks of dynamite and can cause severe injuries to anyone within 50 ft. of the explosion, as well as ear injury - possibly permanent hearing loss - to anyone within 100 ft. The degree of danger is also determined by the temperature pressure and cord wear of a test tire. The TAV was developed by David Carrott, a PRC employee under contract to NASA.
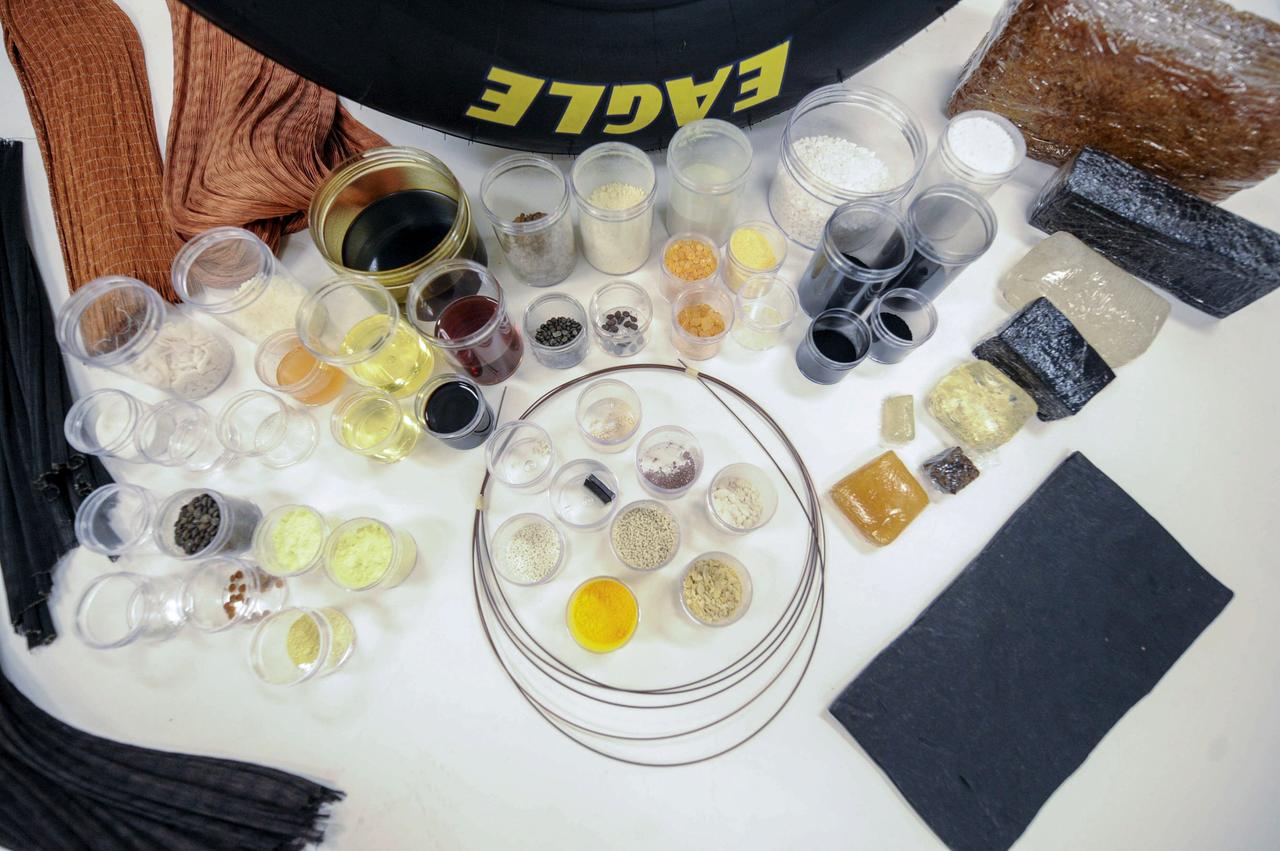

jsc2019e040131 (7/17/2019) --- Tires are comprised of up to 60 different components, ranging from chemicals and fillers to multiple types of rubber and reinforcing cords. The Pushing the Limits of Silica Fillers for Tire Applications (Goodyear Tire) investigation evaluates creation of novel silica forms and structures, or morphologies, using traditional techniques to form silica fillers in microgravity. The space environment may yield results not possible in ground-based environments. Better understanding of silica morphology and the relationship between silica structure and properties may improve the silica design process as well as silica rubber formulation and tire manufacturing and performance on the ground. (Image courtesy of: The Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company)
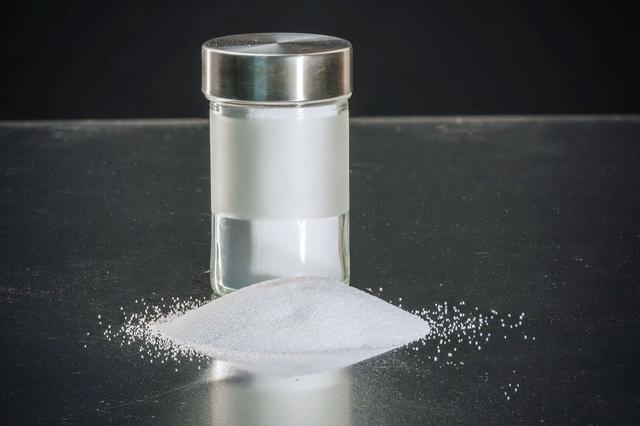

jsc2019e040132 (3/10/2015) --- Preflight image of silica, a common element used in tires to help enhance performance in areas such as fuel efficiency and wet traction. The Pushing the Limits of Silica Fillers for Tire Applications (Goodyear Tire) investigation evaluates creation of novel silica forms and structures, or morphologies, using traditional techniques to form silica fillers in microgravity. The space environment may yield results not possible in ground-based environments. Better understanding of silica morphology and the relationship between silica structure and properties may improve the silica design process as well as silica rubber formulation and tire manufacturing and performance on the ground. (Image courtesy of: The Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company)
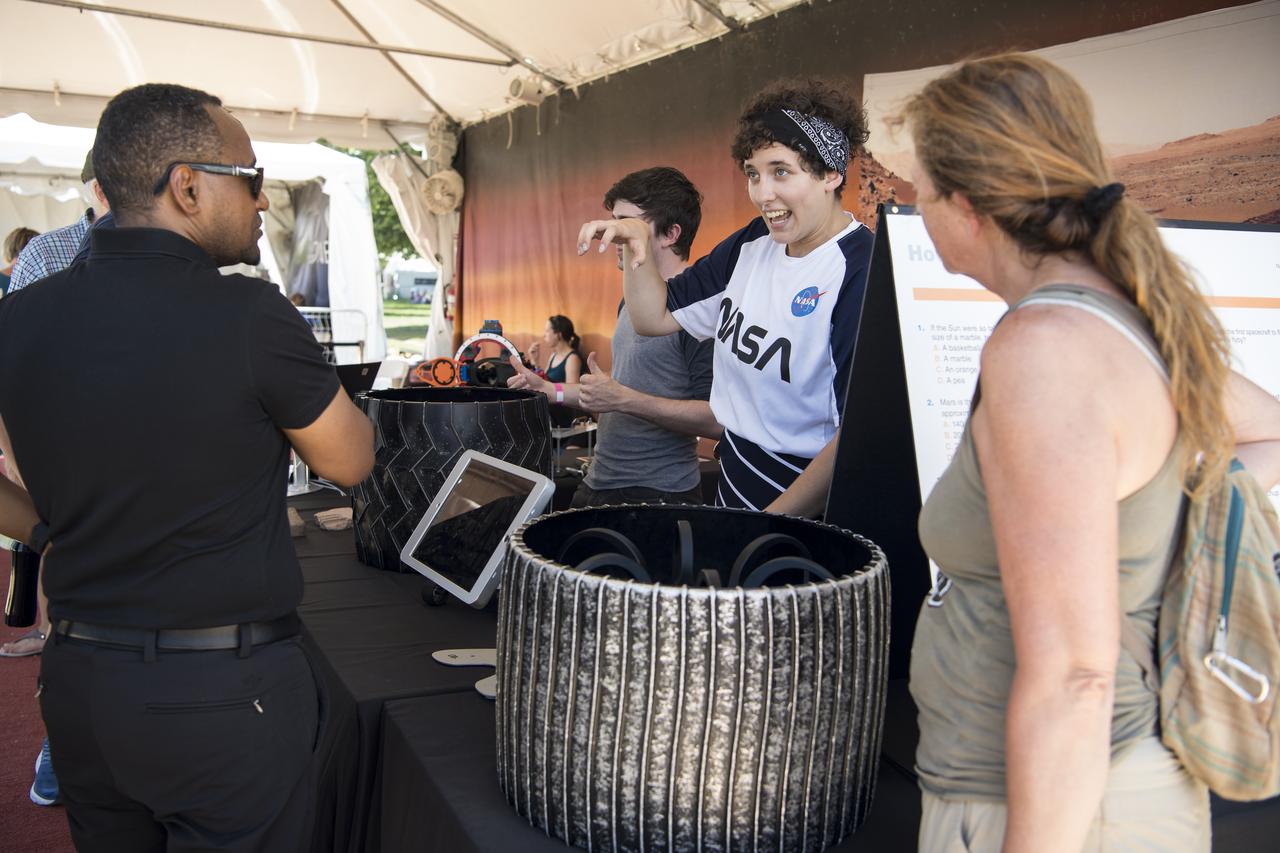

Visitors learn about rover tires at the Apollo 11 50th Anniversary celebration on the National Mall, Friday, July 19, 2019 in Washington. Apollo 11 was the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon and launched on July 16, 1969 with astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
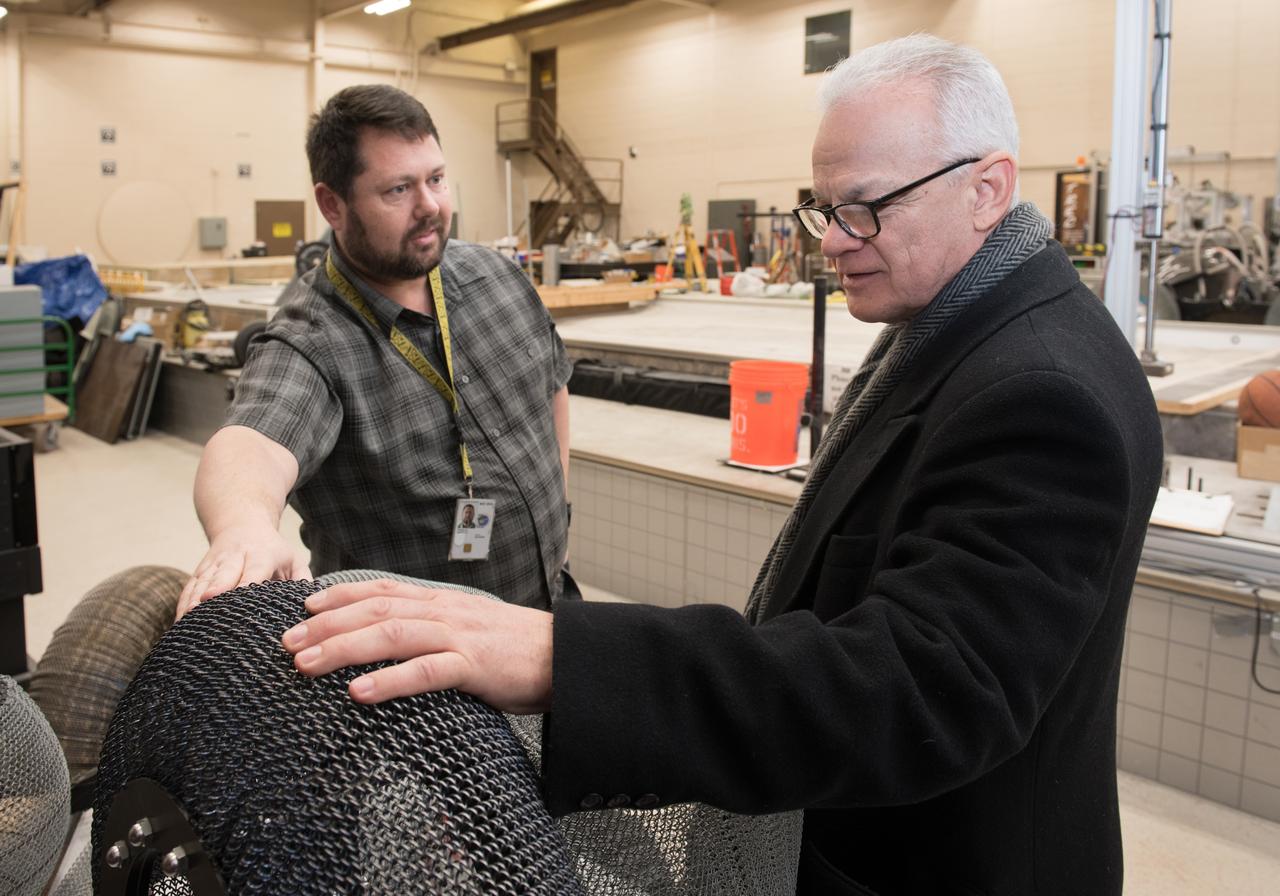

A Co-inventor of the Shape Memory Alloy, Spring Tire, shows the NASA Chief Technologist the first SMA Spring Tire Prototype during a tour of the Glenn Research Center, Simulated Lunar Operations Laboratory (SLOPE).
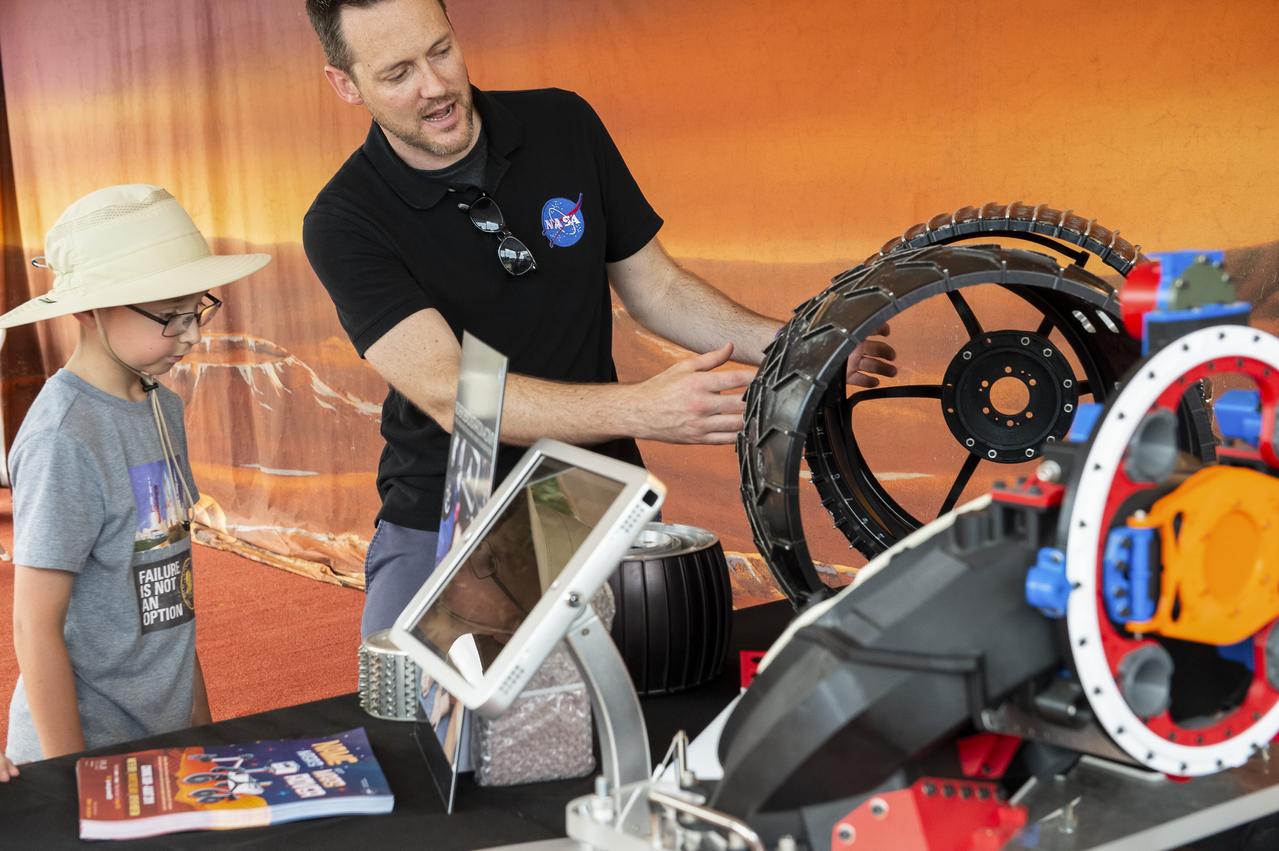

Visitors learn about rover tires at the Apollo 11 50th Anniversary celebration on the National Mall, Thursday, July 18, 2019 in Washington. Apollo 11 was the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon and launched on July 16, 1969 with astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin. Photo Credit: (NASA/Connie Moore)
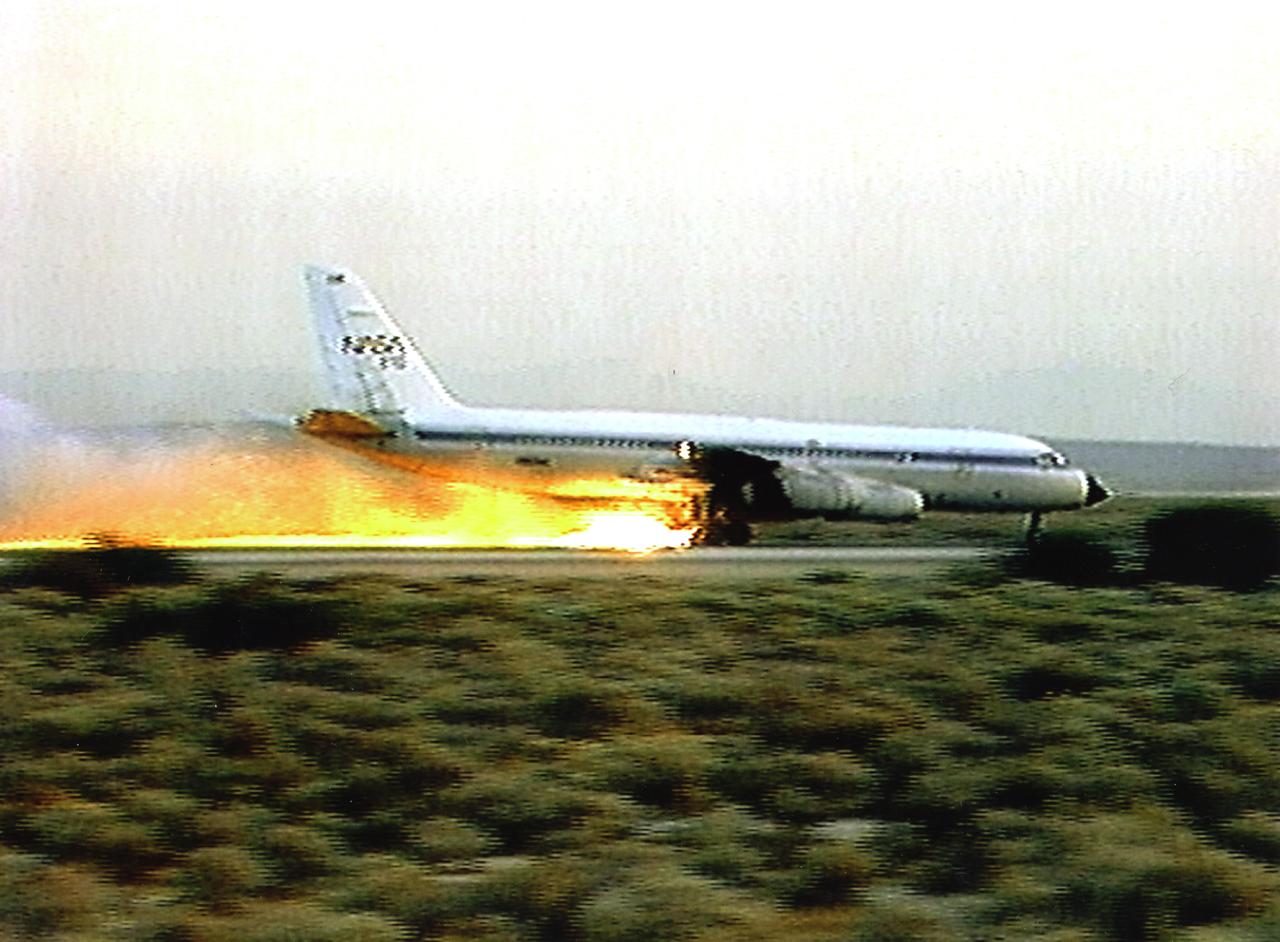

A NASA CV-990, modified as a Landing Systems Research Aircraft (LSRA), lands on the Edwards AFB main runway in test of the space shuttle landing gear system. In this case, the shuttle tire failed, bursting into flame during the rollout. The space shuttle landing gear test unit, operated by a high-pressure hydraulic system, allowed engineers to assess and document the performance of space shuttle main and nose landing gear systems, tires and wheel assemblies, plus braking and nose wheel steering performance. The series of 155 test missions for the space shuttle program provided extensive data about the life and endurance of the shuttle tire systems and helped raise the shuttle crosswind landing limits at Kennedy. The CV-990 used as the LSRA was built in 1962 by the Convair Division of General Dynamics Corp., Ft. Worth, Texas, served as a research aircraft at Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California, before it came to Dryden.
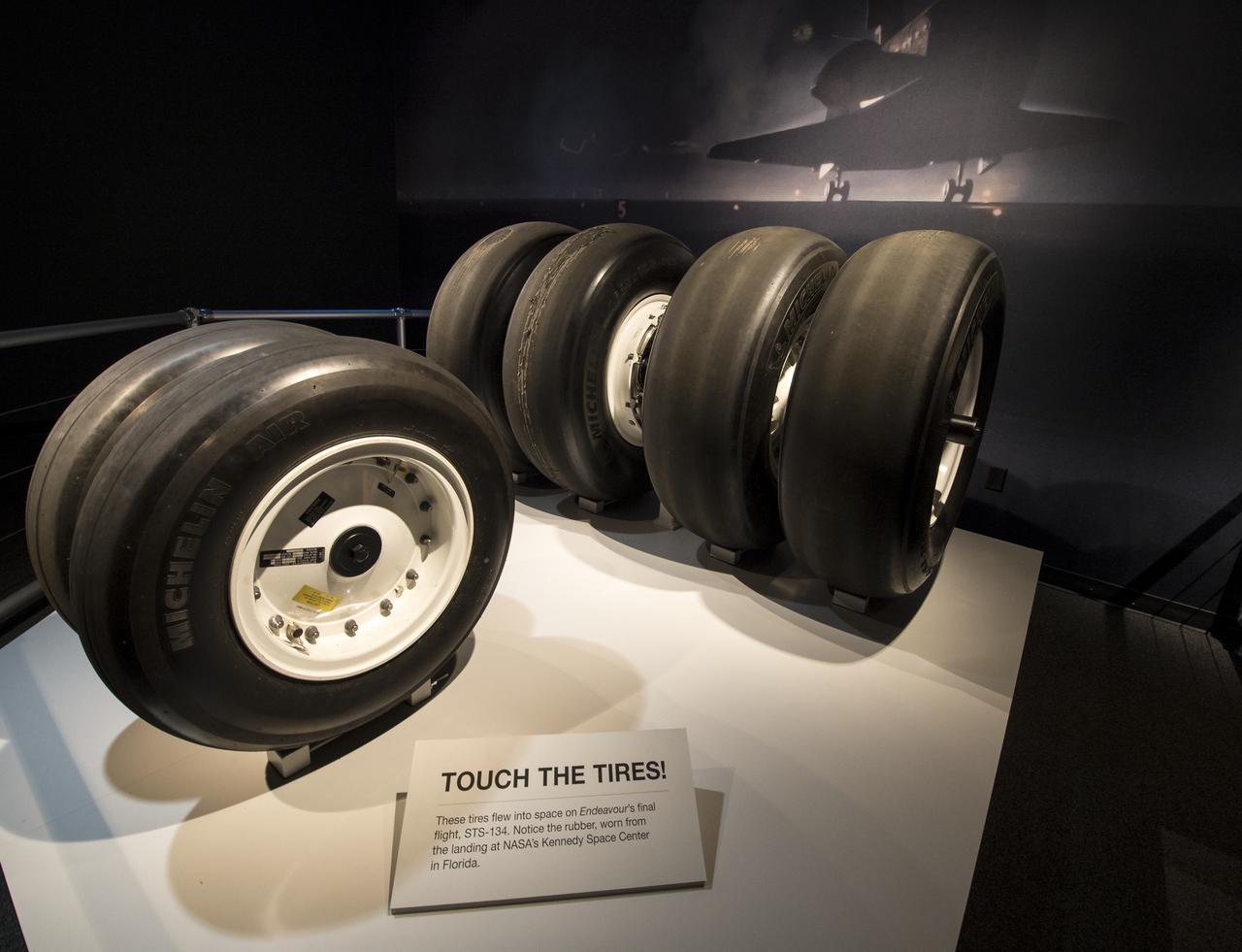

Tires from space shuttle Endeavour's final flight are on display at the California Science Center's, California Experience gallery, Tuesday, Oct. 30, 2012, in Los Angeles. The grand opening ceremony for the California Science center's Samuel Oschin Space Shuttle Endeavour Display Pavilion took place on Tuesday, Oct. 30, 2012. Endeavour, built as a replacement for space shuttle Challenger, completed 25 missions, spent 299 days in orbit, and orbited Earth 4,671 times while traveling 122,883,151 miles. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
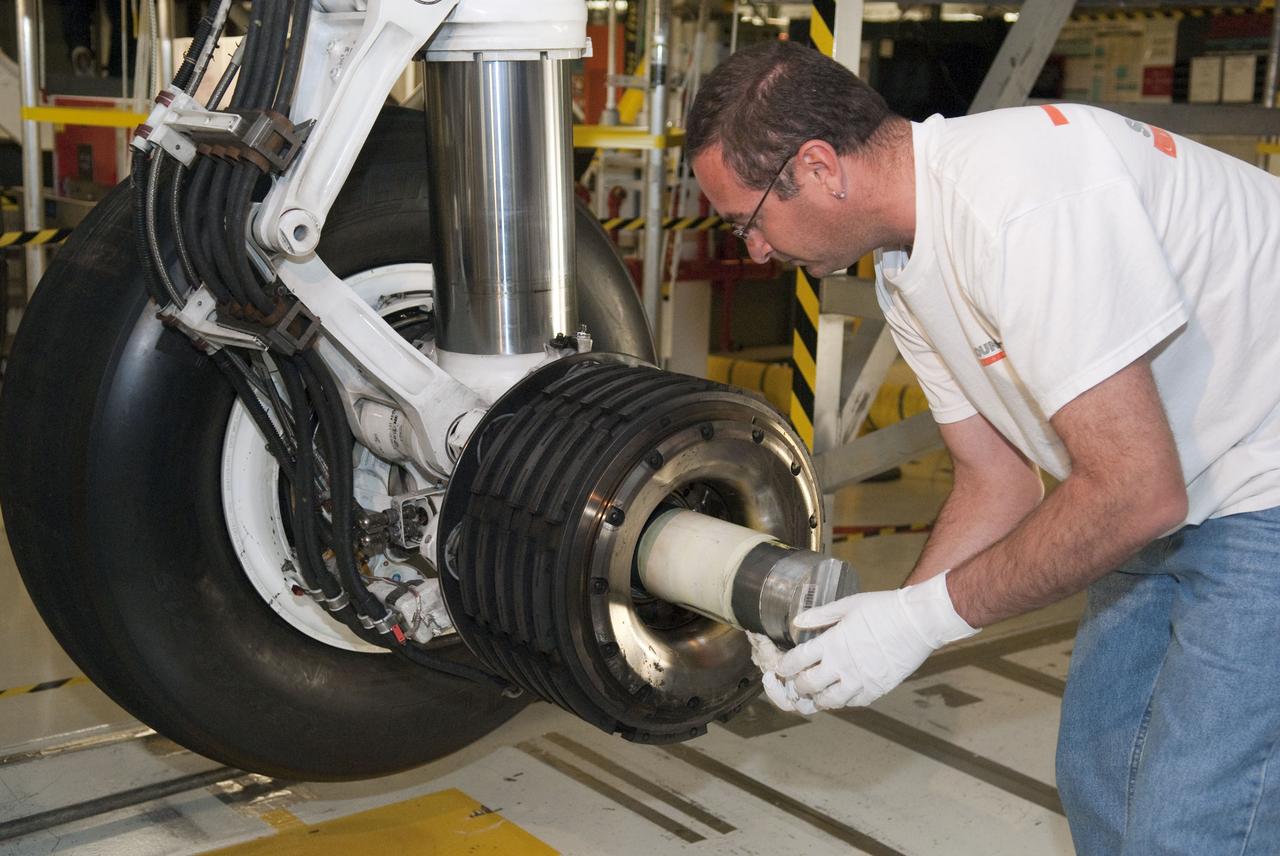

STS-133 ENDEAVOUR TIRES AND BRAKES REMOVAL

STS-133 ENDEAVOUR TIRES AND BRAKES REMOVAL
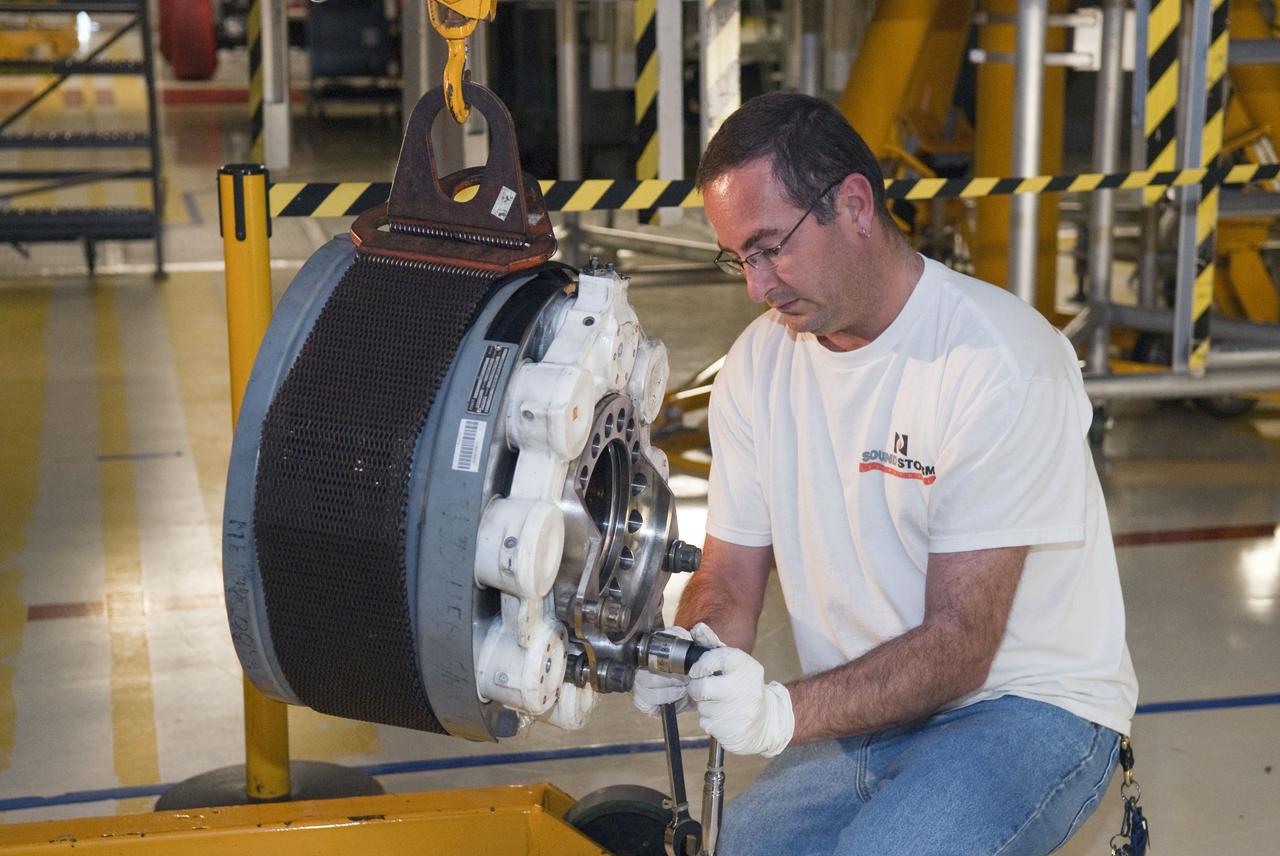

STS-133 ENDEAVOUR TIRES AND BRAKES REMOVAL
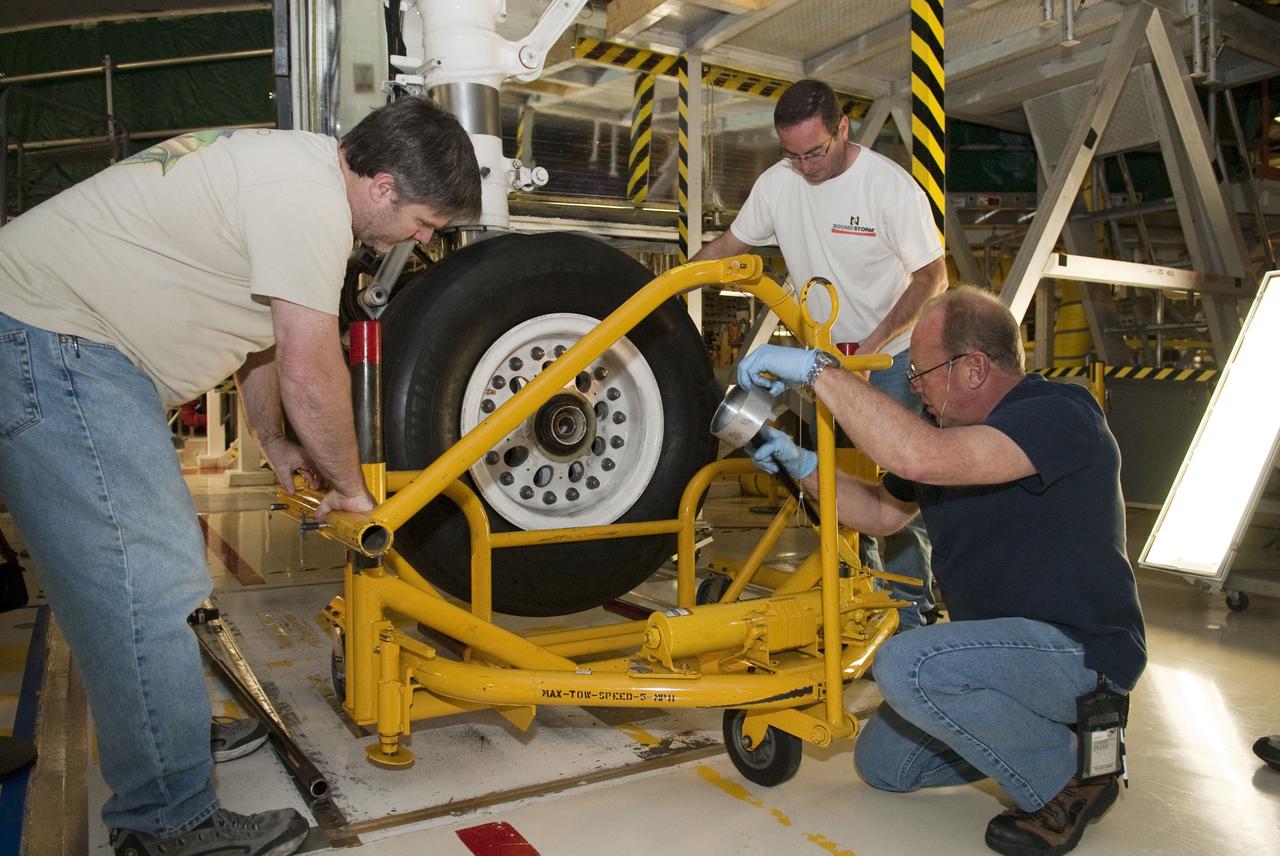

STS-133 ENDEAVOUR TIRES AND BRAKES REMOVAL
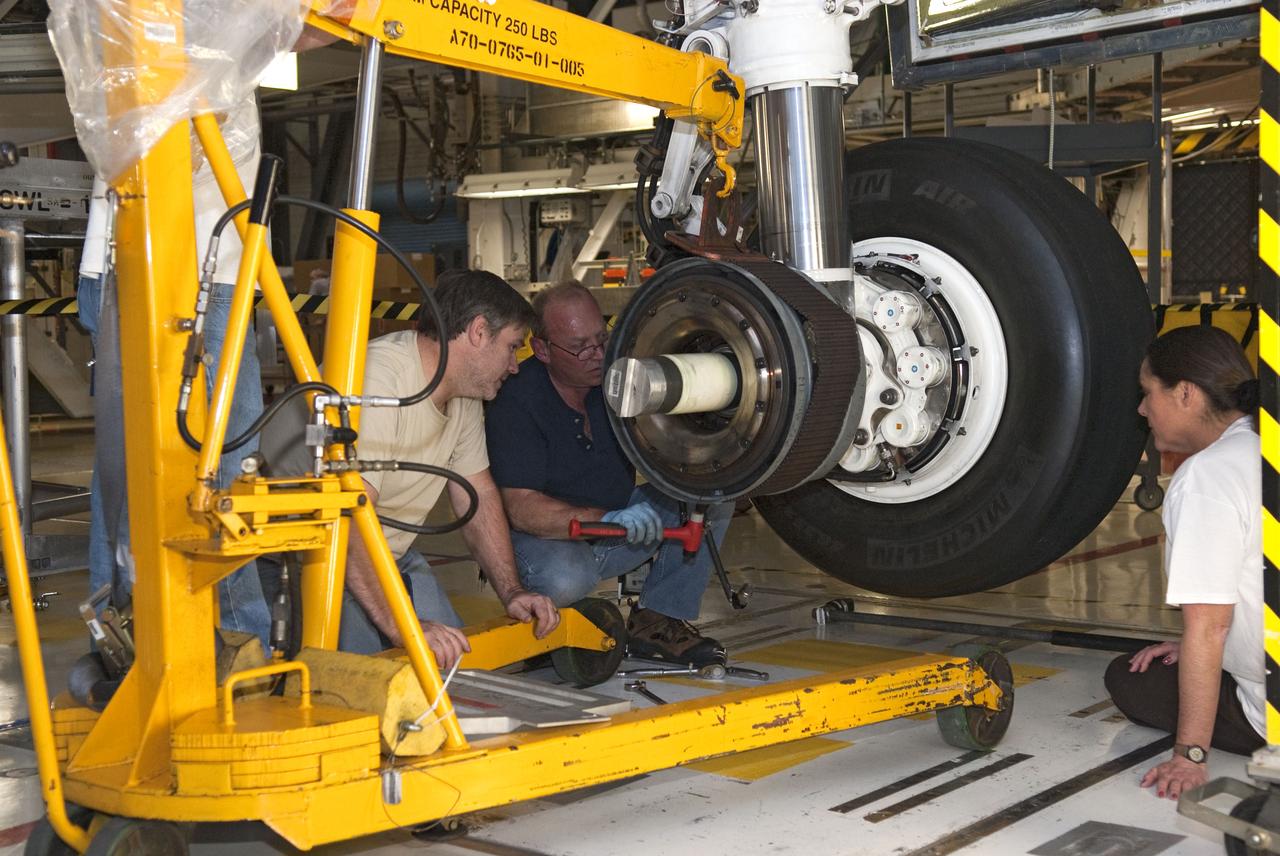

STS-133 ENDEAVOUR TIRES AND BRAKES REMOVAL
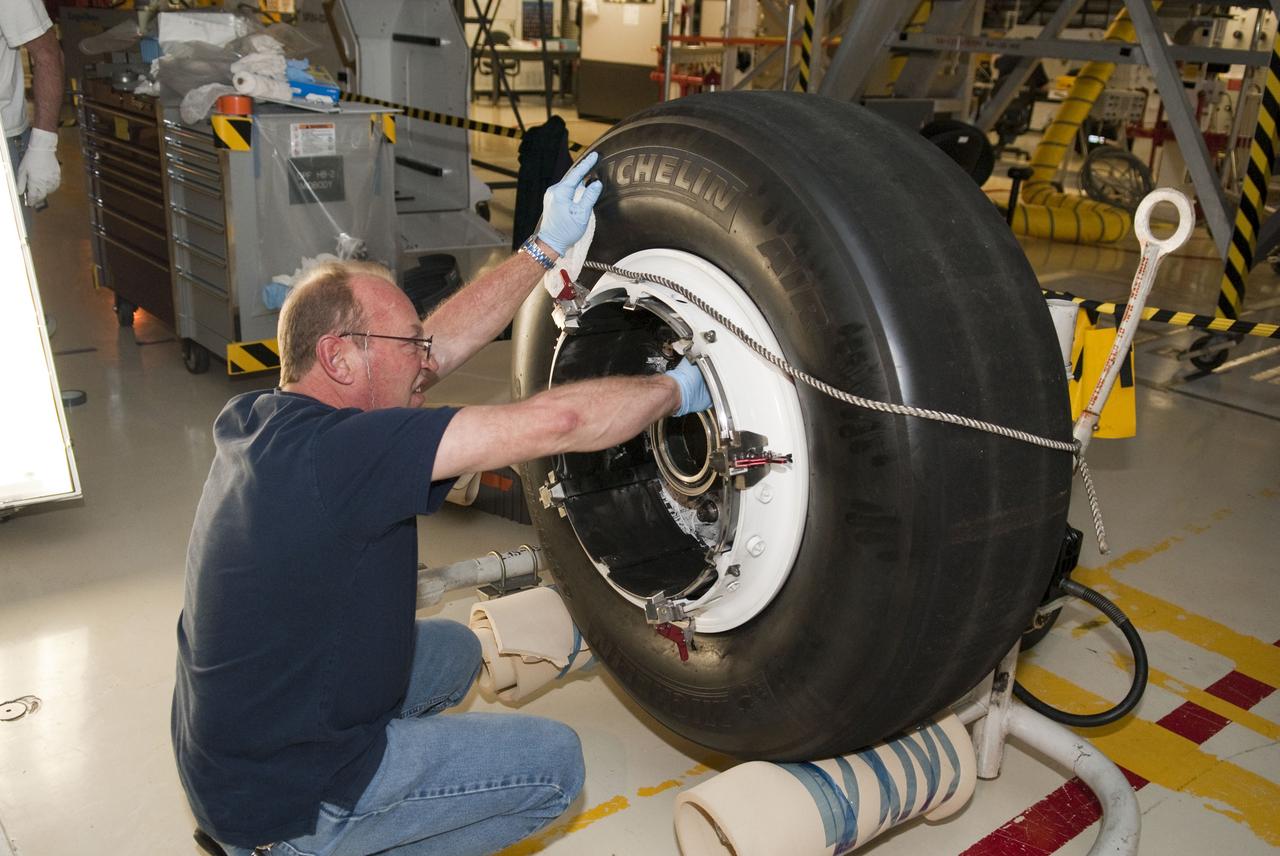

STS-133 ENDEAVOUR TIRES AND BRAKES REMOVAL
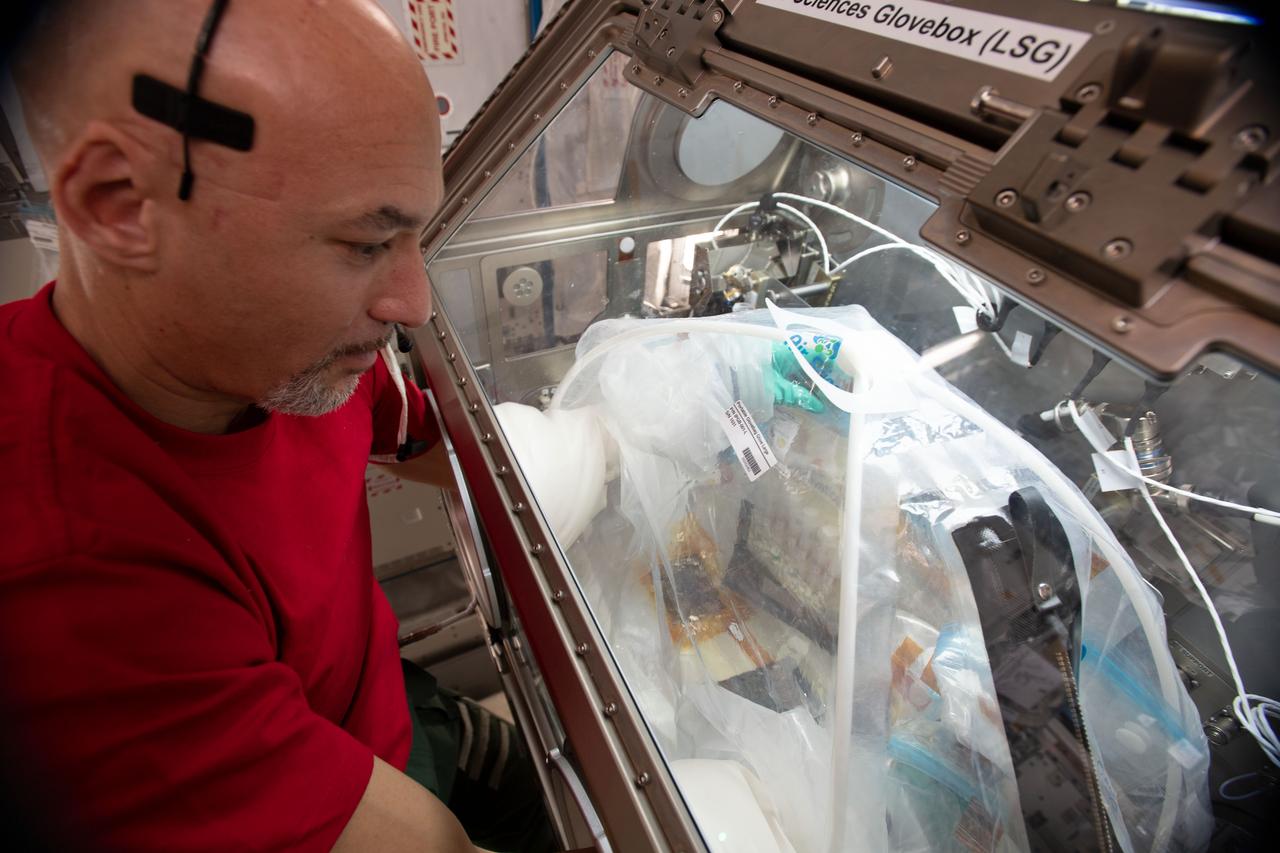

iss060e043690 (8/22/2019) --- (Aug. 22, 2019) ---European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Luca Parmitano conducts science operations in the Life Sciences Glovebox aboard the International Space Station (ISS). He is working on the Goodyear Tire experiment that is exploring ways to manufacture safer, more fuel-efficient tires on Earth.
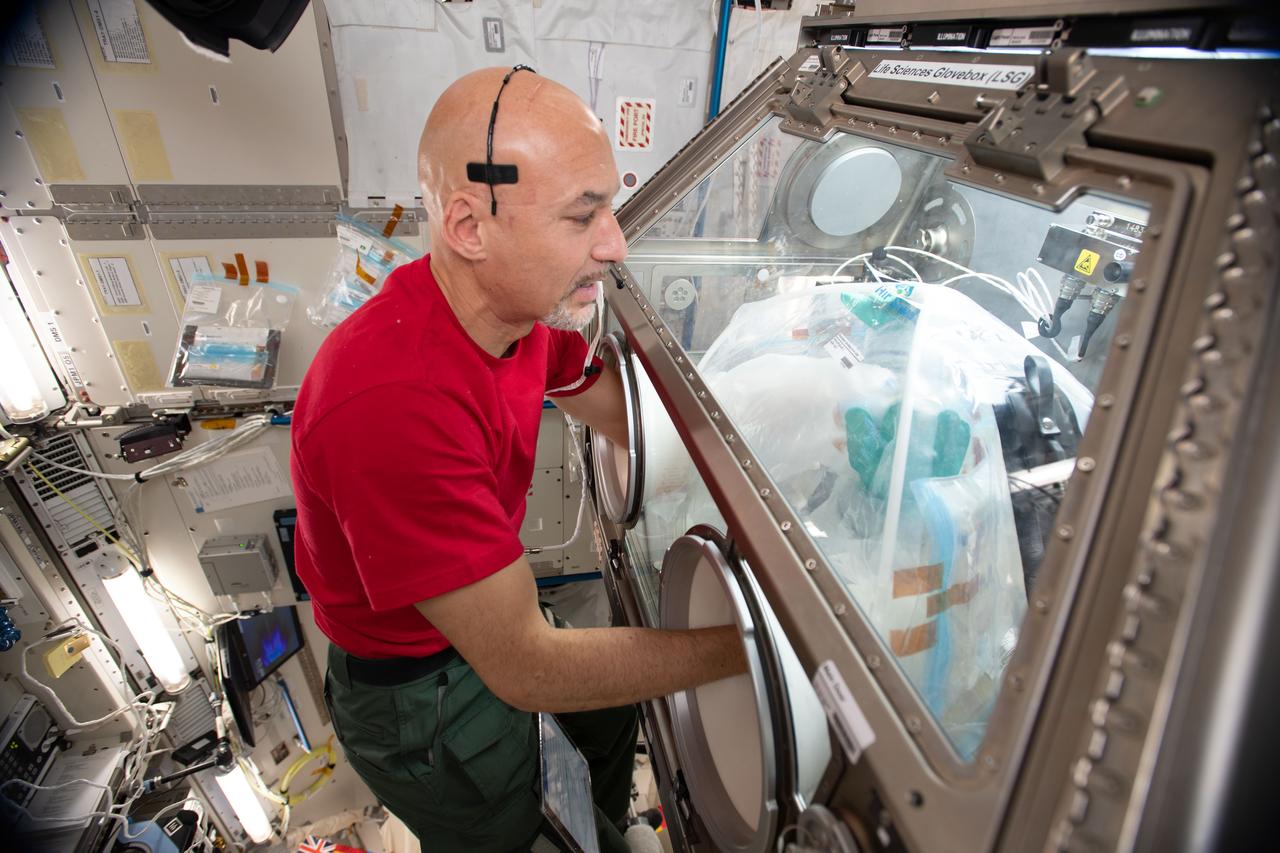

iss060e043685 (Aug. 22, 2019) --- Expedition 60 Flight Engineer Luca Parmitano of ESA (European Space Agency) conducts science operations in the Life Sciences Glovebox. He is working on the Goodyear Tire experiment that is exploring ways to manufacture safer, more fuel-efficient tires on Earth.
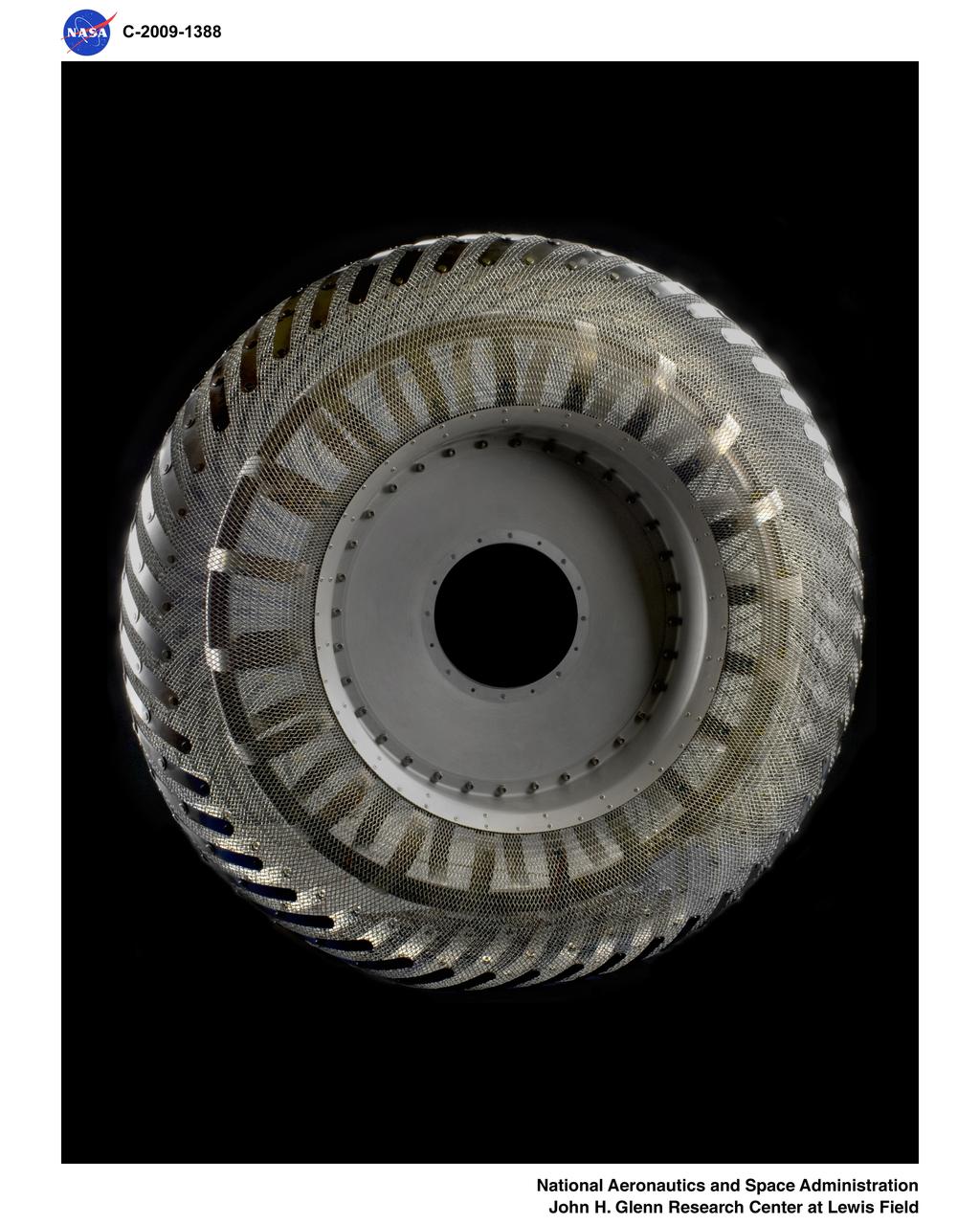

Wire Mesh Tire from the Simulated Lunar Operations Laboratory (SLOPE Lab)
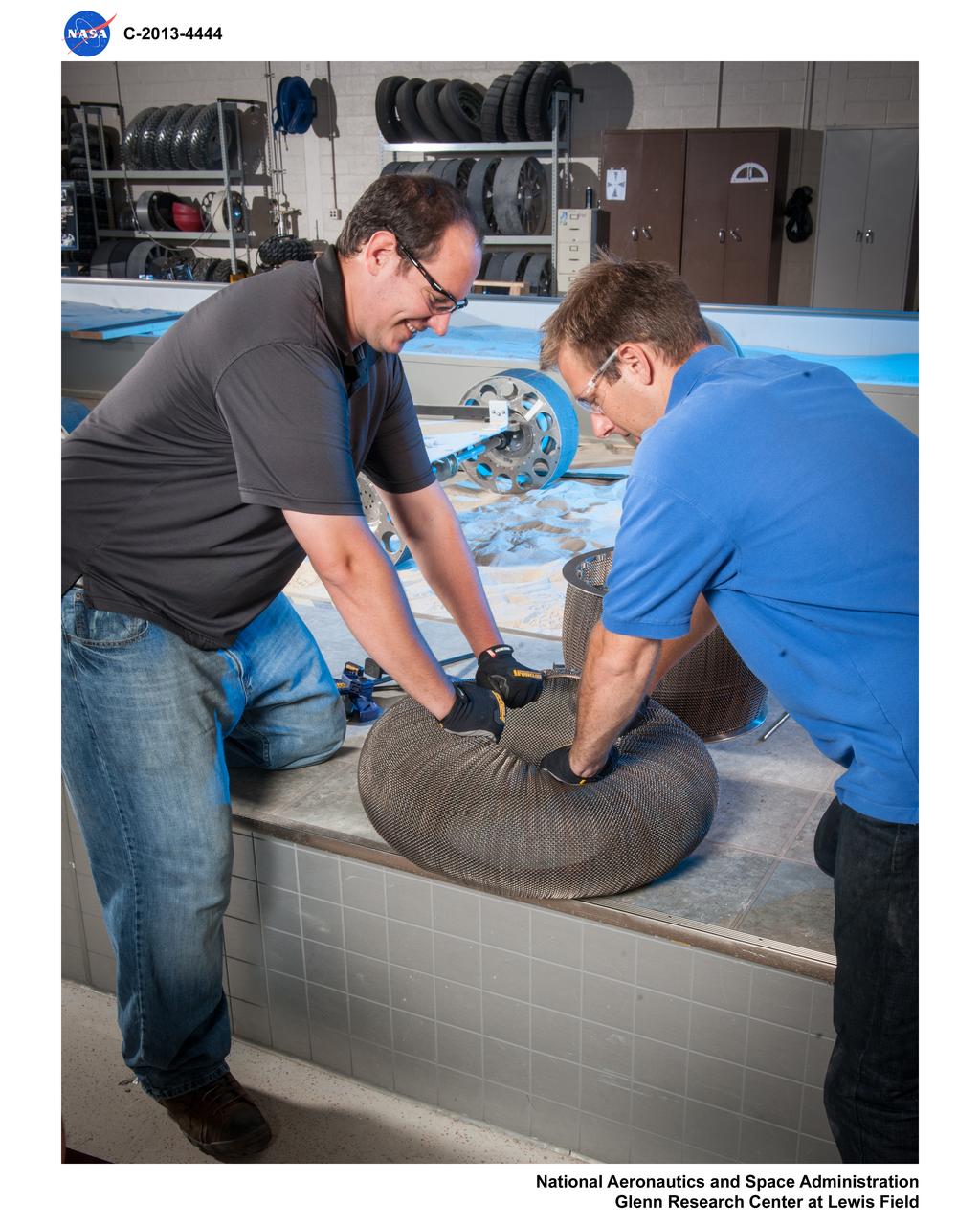

Fabrication of rover spring tires in the Simulated Lunar Operations, SLOPe Lab, Laboratory
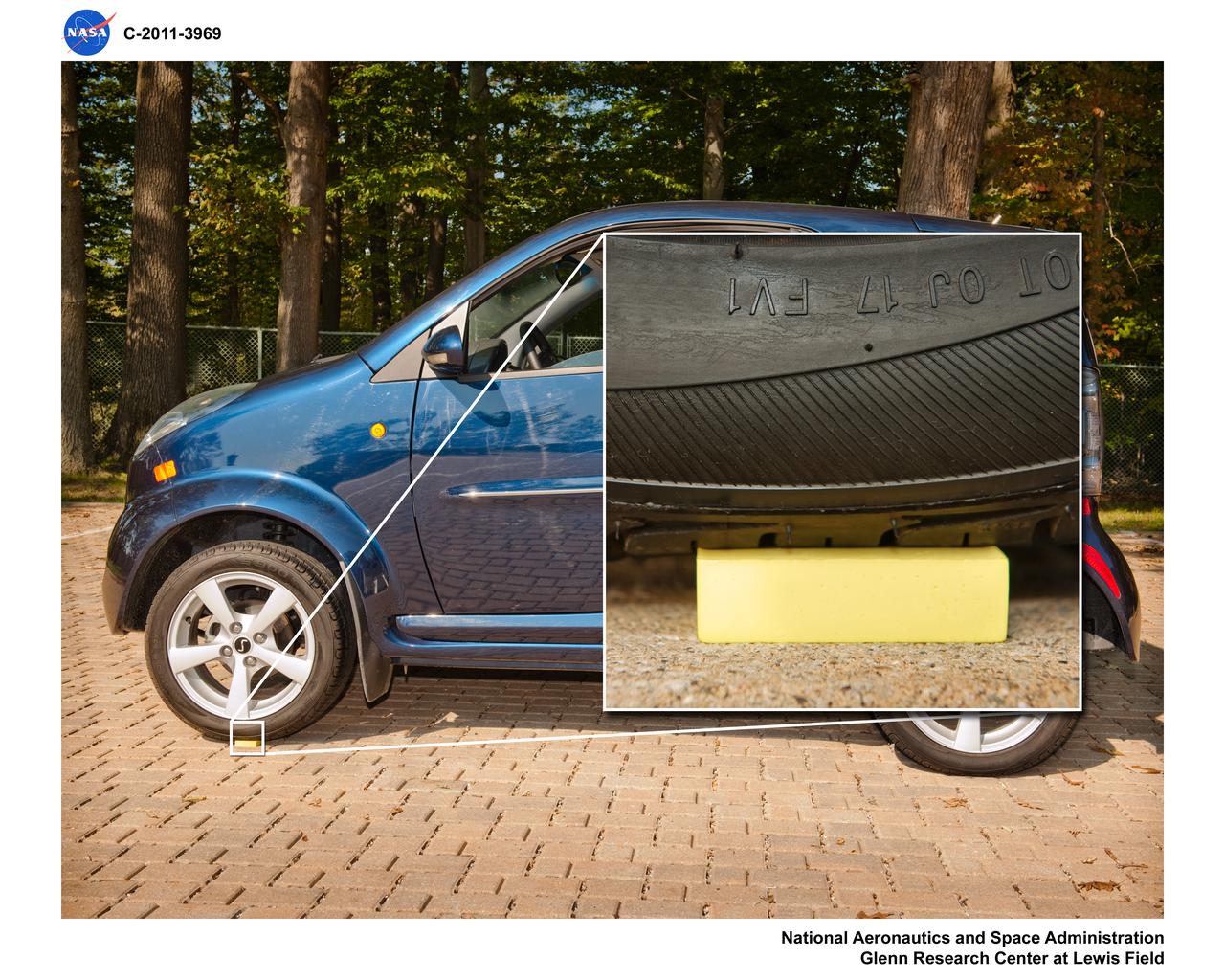

Polyimide Aerogel Material Sample under the weight of an Automobile Tire
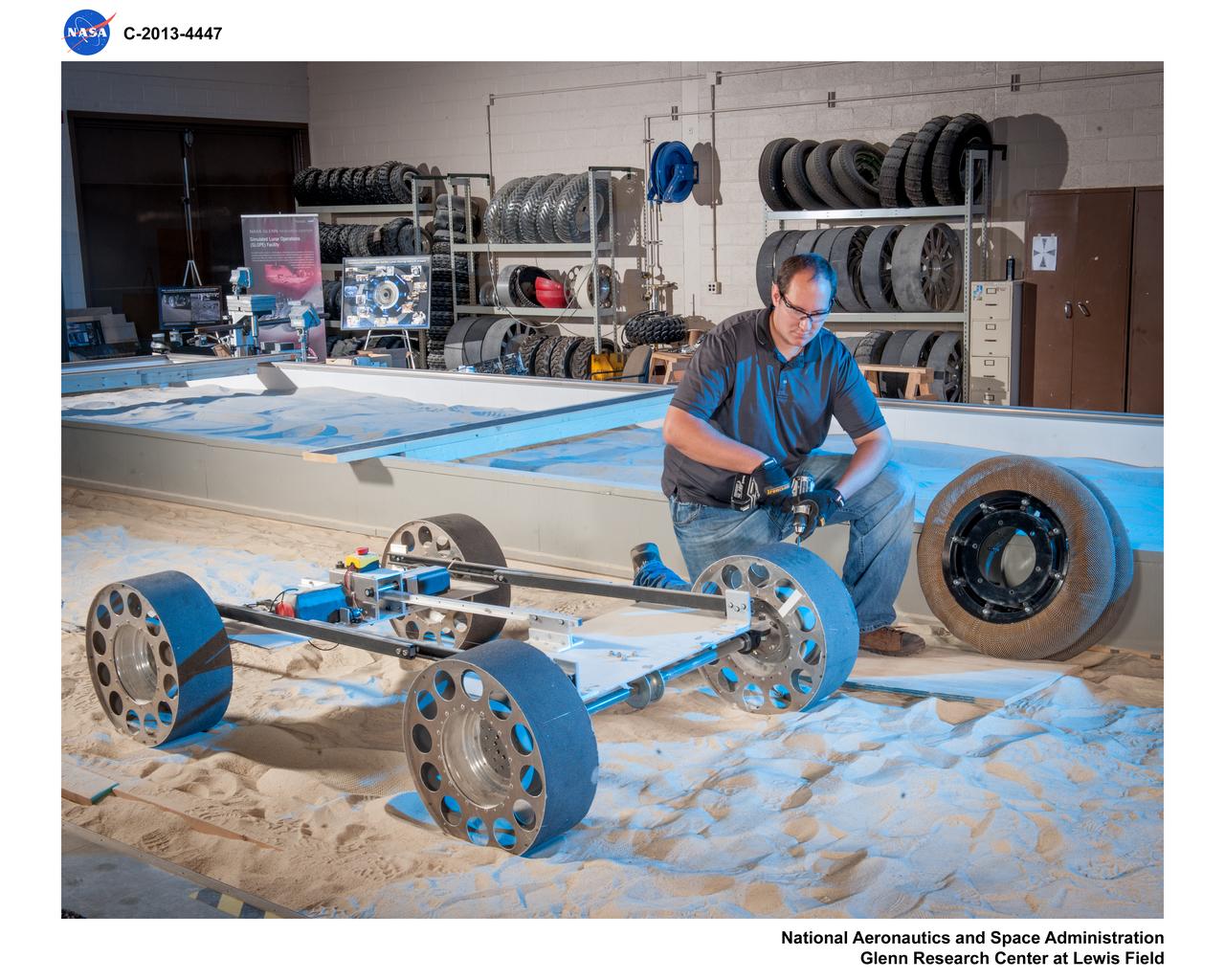

Fabrication of rover spring tires in the Simulated Lunar Operations, SLOPe Lab, Laboratory

Fabrication of rover spring tires in the Simulated Lunar Operations, SLOPe Lab, Laboratory
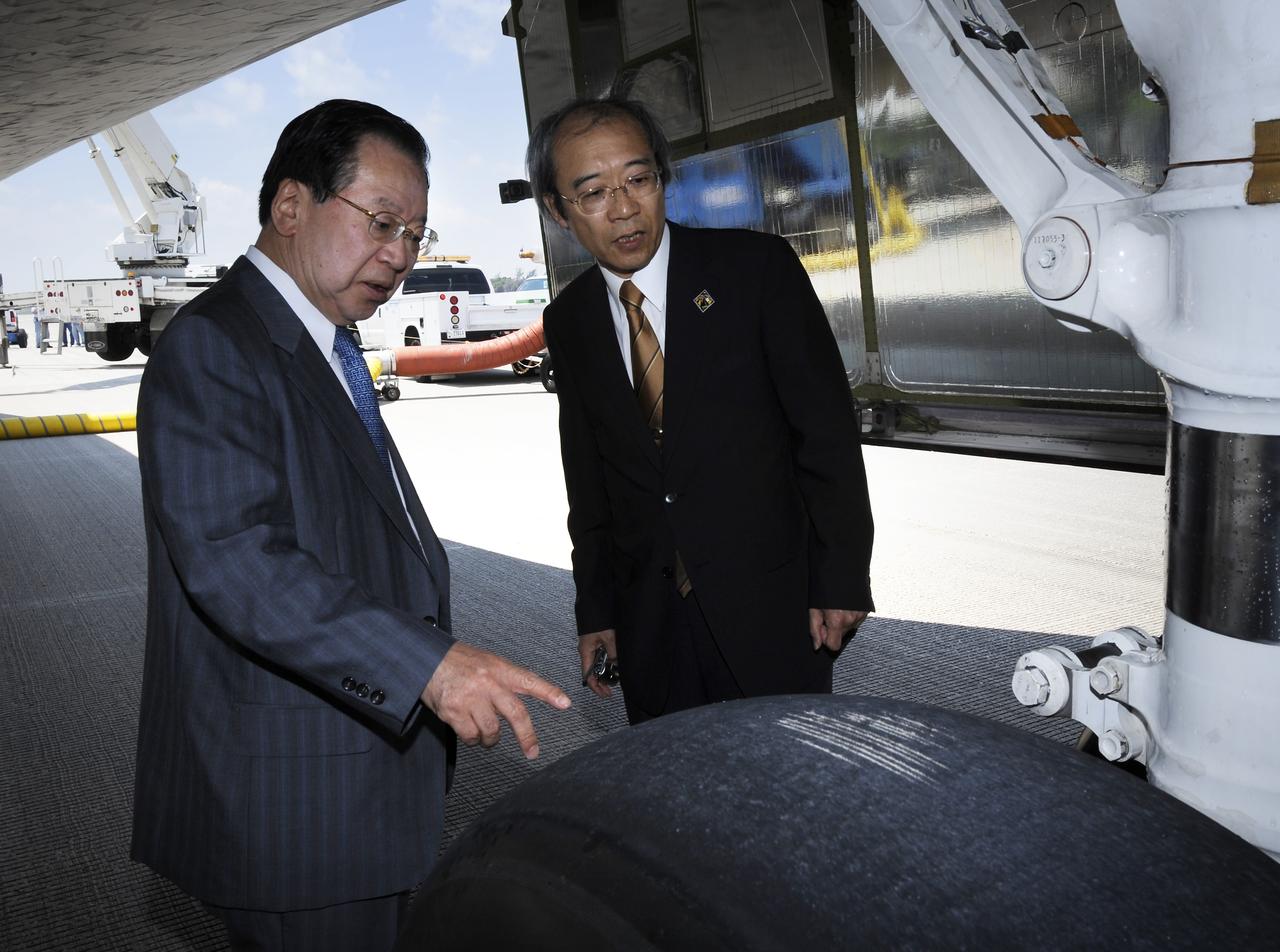

Vice President of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Mr. Kaoru Mamiya, left, and Mr. Yuichi Yamaura of JAXA look at one of the space shuttle Discovery tires shortly after Discovery touched down at 11:15 a.m., Saturday, June 14, 2008, at the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida. During the 14-day STS-124 mission Discovery's crew installed the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's large Kibo laboratory and its remote manipulator system leaving a larger space station and one with increased science capabilities. Discovery also brought home NASA astronaut Garrett Reisman after his 3 month mission onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
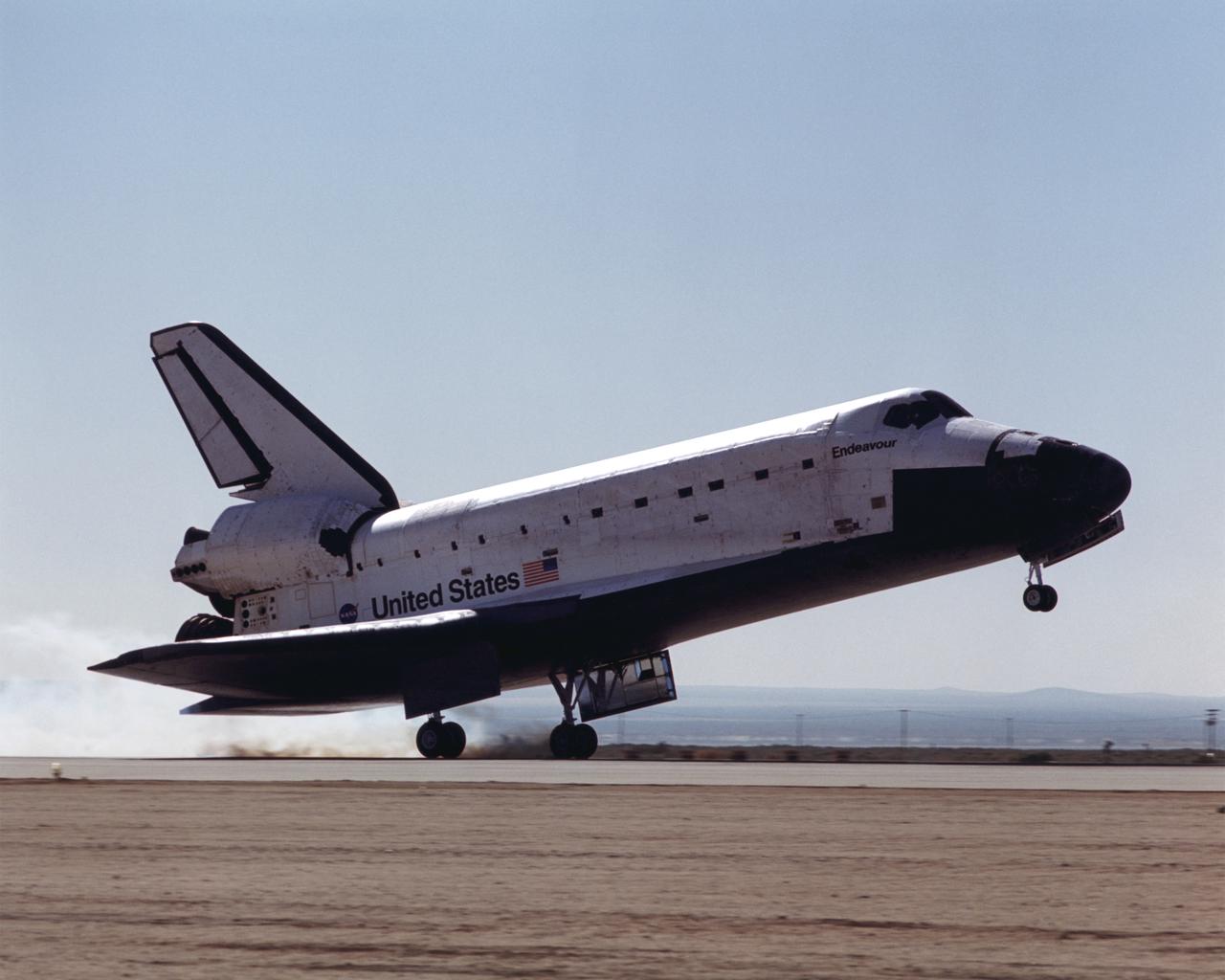

Space Shuttle Endeavour's tires produced a momentary puff of smoke as Mission STS-100 landed at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center on Edwards Air Force Base, California, May 1, 2001.
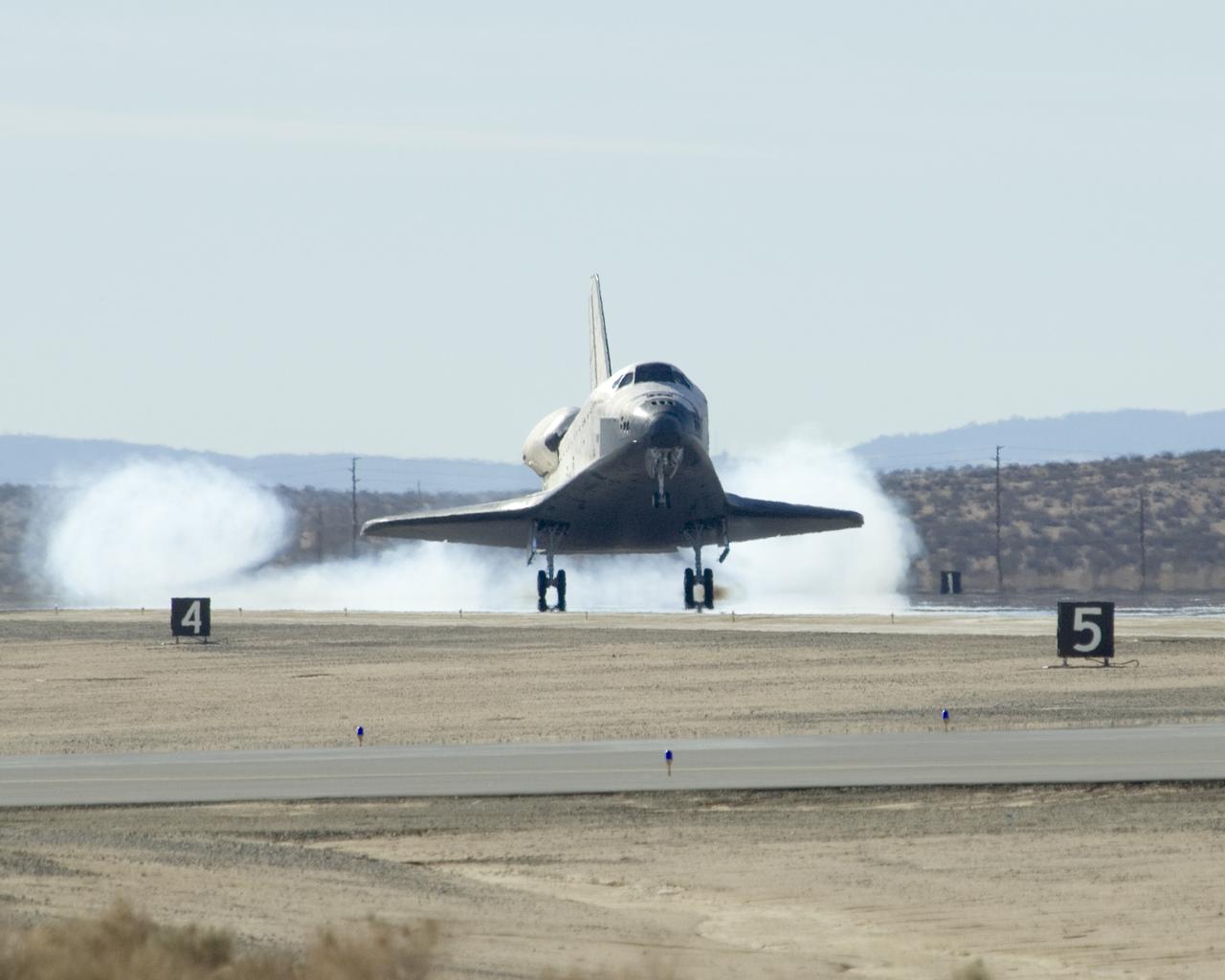

Smoke swirls as Space Shuttle Endeavour's tires strike the runway at Edwards Air Force Base Nov. 30 to conclude mission STS-126 to the International Space Station.
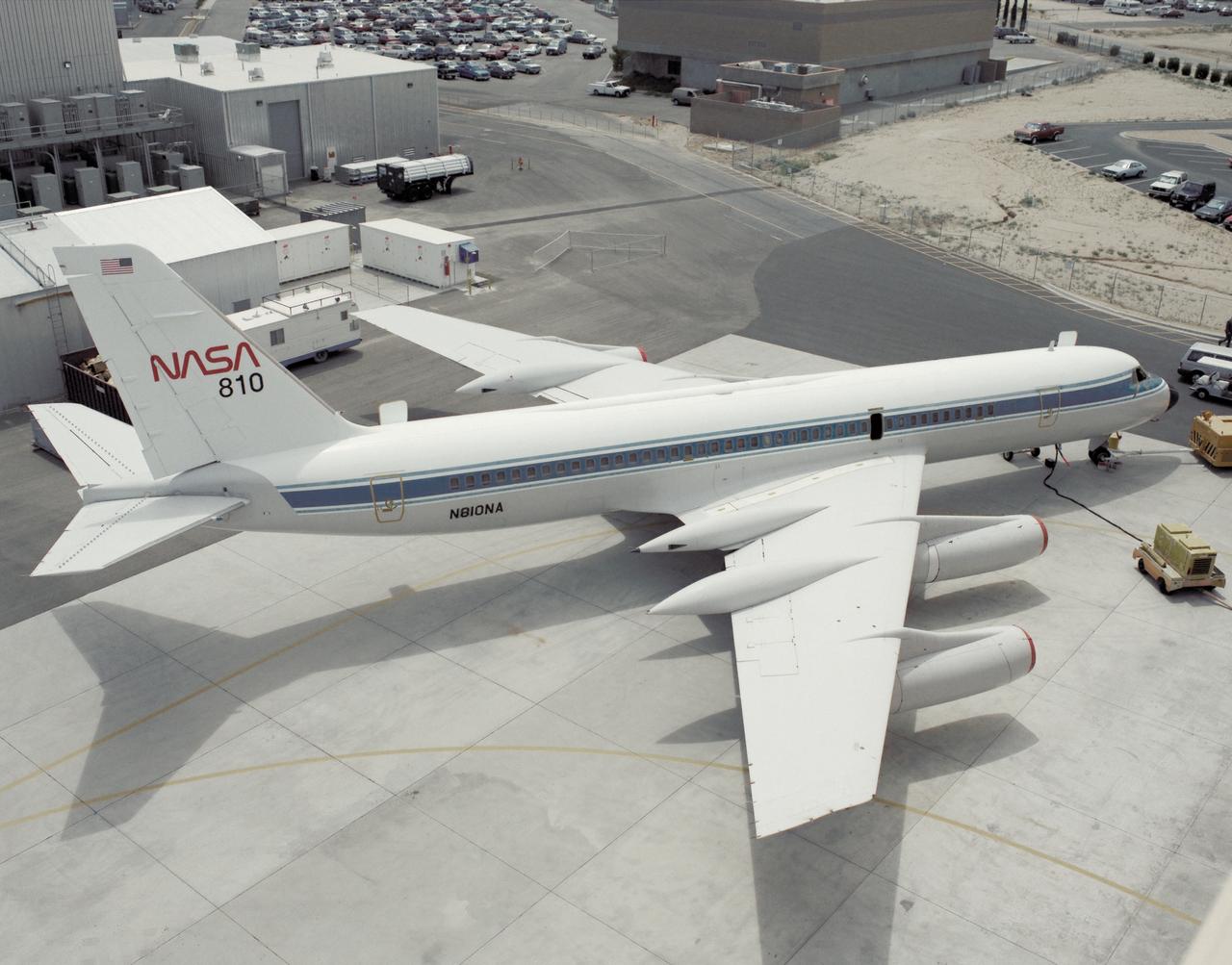

A NASA CV-990, modified as a Landing Systems Research Aircraft (LSRA), is serviced on the ramp at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, before a test of the space shuttle landing gear system. The space shuttle landing gear test unit, operated by a high-pressure hydraulic system, allowed engineers to assess and document the performance of space shuttle main and nose landing gear systems, tires and wheel assemblies, plus braking and nose wheel steering performance. The series of 155 test missions for the space shuttle program provided extensive data about the life and endurance of the shuttle tire systems and helped raise the shuttle crosswind landing limits at Kennedy.
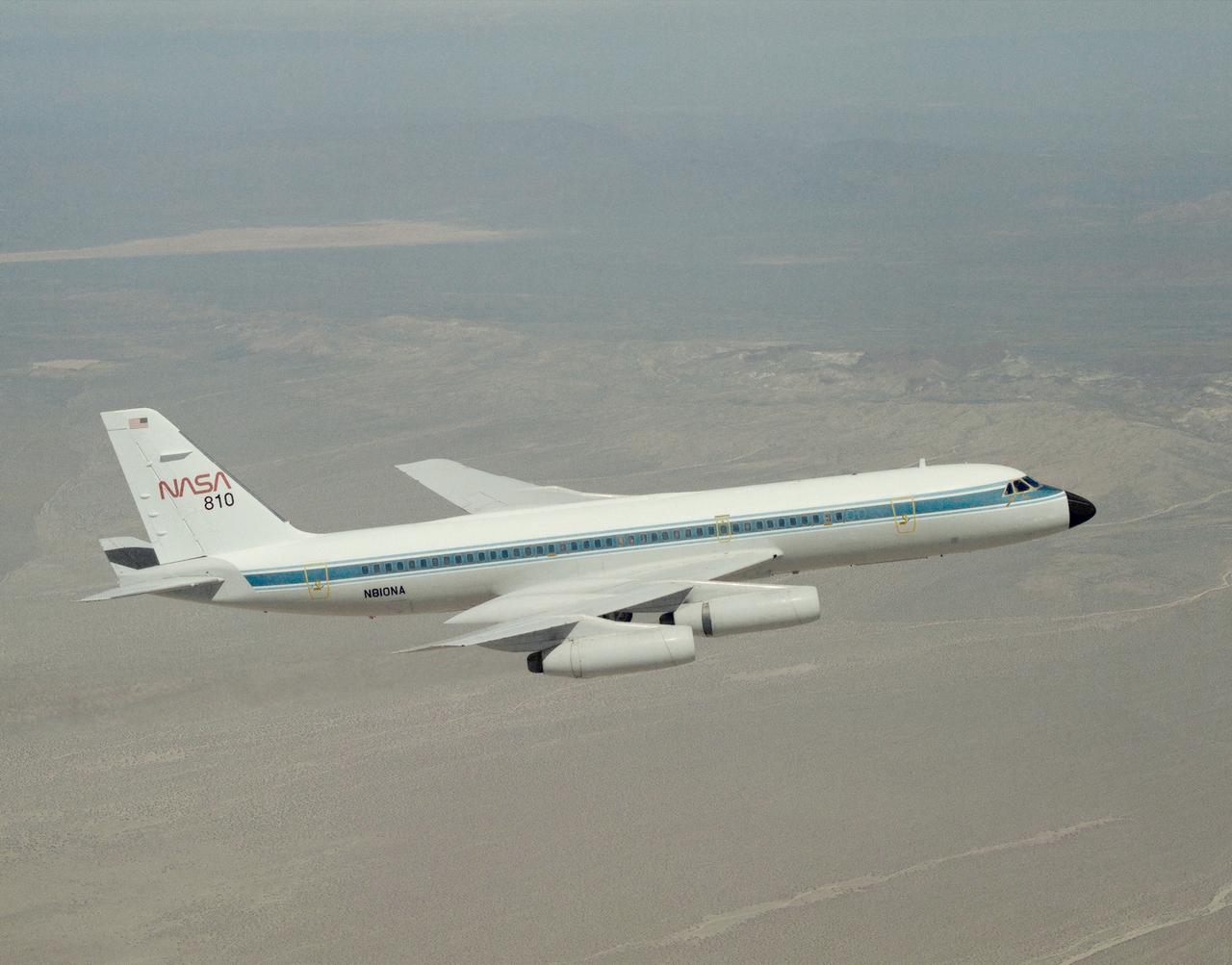

A NASA CV-990, modified as a Landing Systems Research Aircraft (LSRA), in flight over NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, for a test of the space shuttle landing gear system. The space shuttle landing gear test unit, operated by a high-pressure hydraulic system, allowed engineers to assess and document the performance of space shuttle main and nose landing gear systems, tires and wheel assemblies, plus braking and nose wheel steering performance. The series of 155 test missions for the space shuttle program provided extensive data about the life and endurance of the shuttle tire systems and helped raise the shuttle crosswind landing limits at Kennedy.
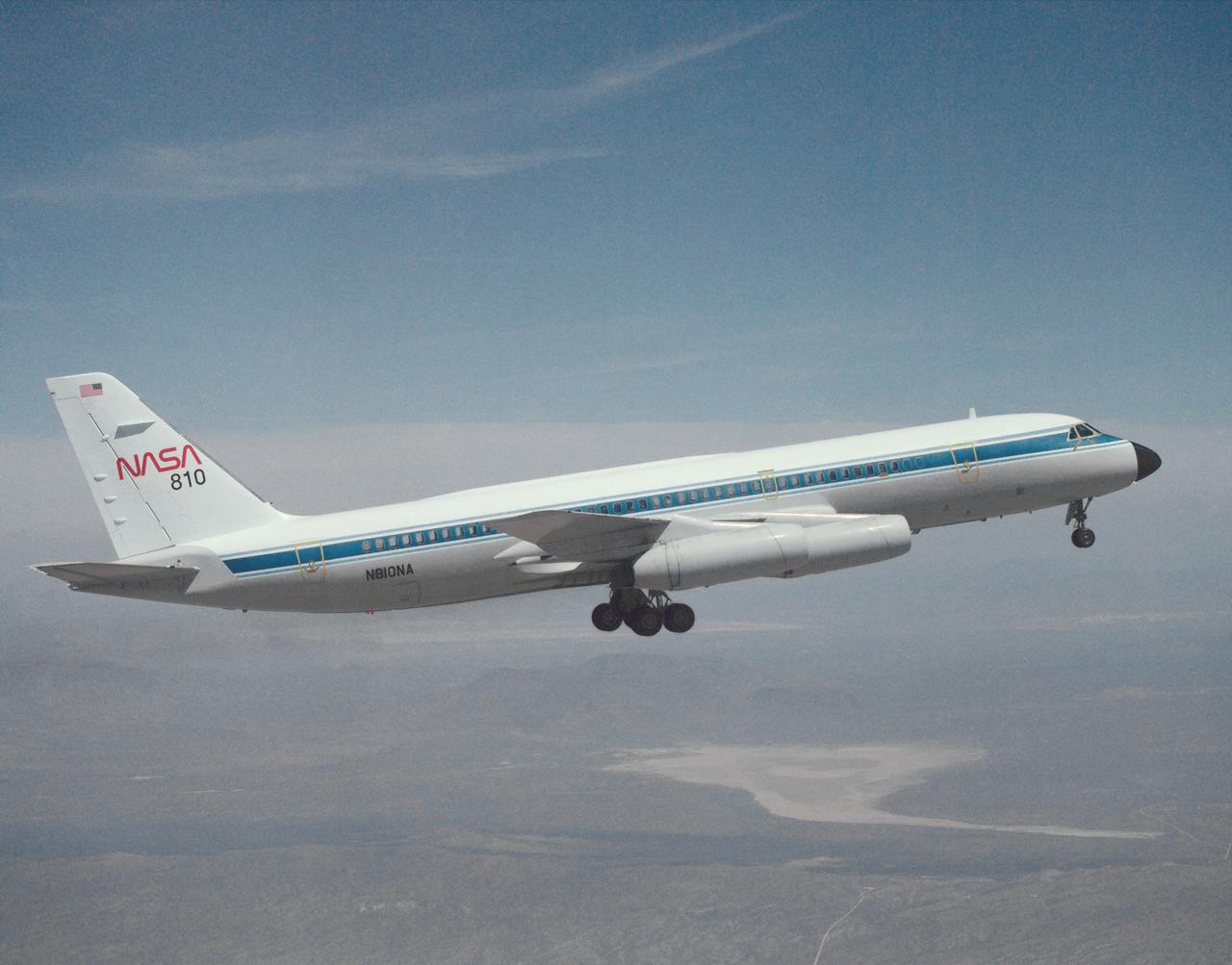

A NASA CV-990, modified as a Landing Systems Research Aircraft (LSRA), in flight over NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, for a test of the space shuttle landing gear system. The space shuttle landing gear test unit, operated by a high-pressure hydraulic system, allowed engineers to assess and document the performance of space shuttle main and nose landing gear systems, tires and wheel assemblies, plus braking and nose wheel steering performance. The series of 155 test missions for the space shuttle program provided extensive data about the life and endurance of the shuttle tire systems and helped raise the shuttle crosswind landing limits at Kennedy.
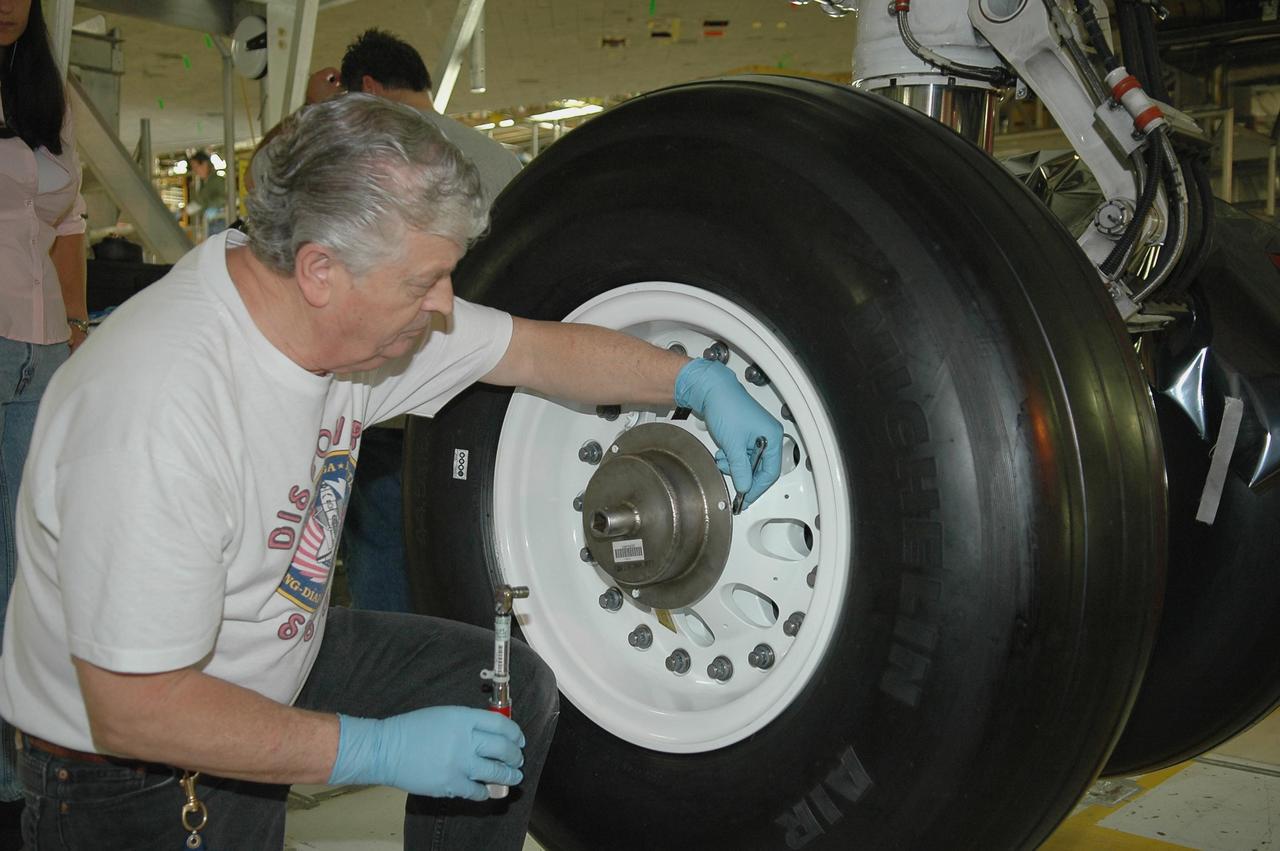

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In NASA’s Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3, United Space Alliance senior shuttle machinist Jake Jackson checks the torque on a newly installed flight tire on Discovery. Discovery processing is under way for the second return to flight test mission, STS-121.
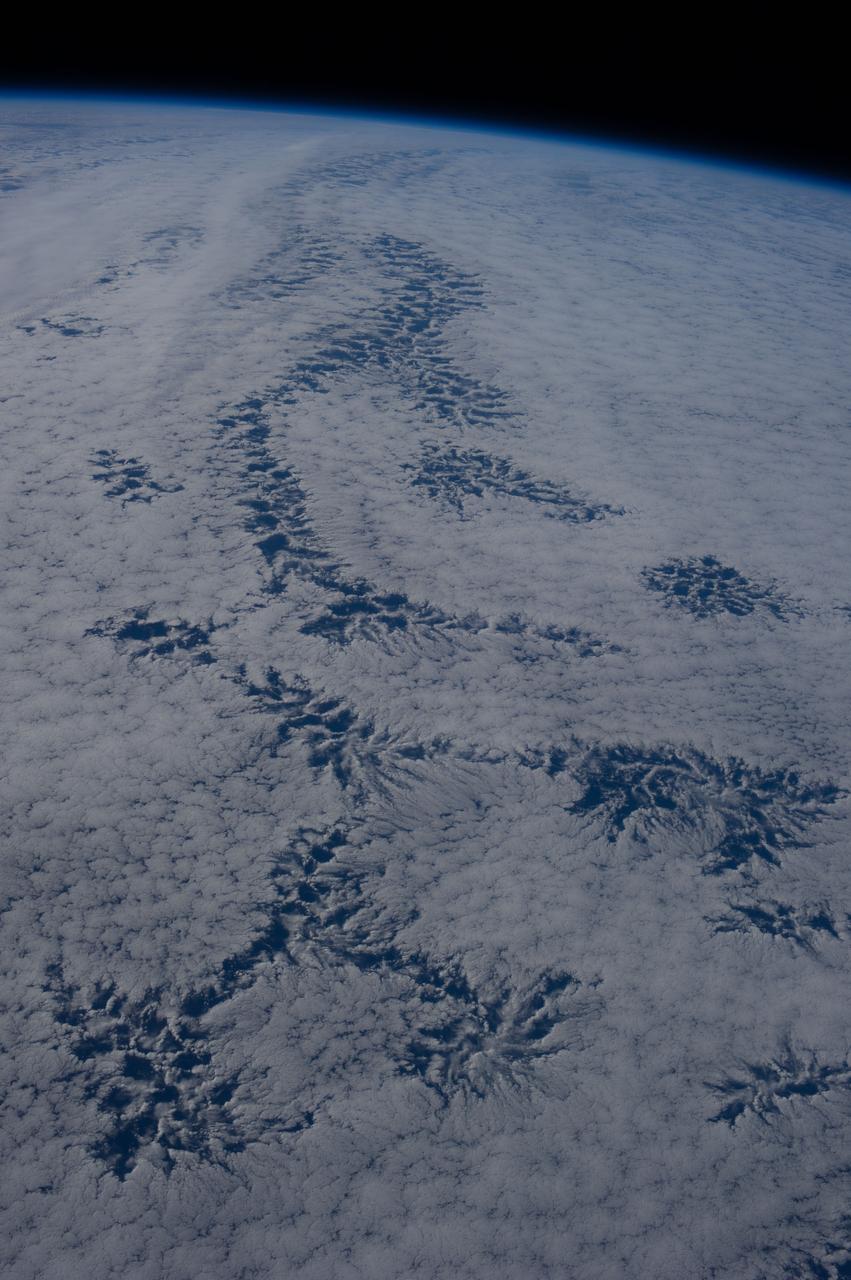

Earth observation taken during day pass by an Expedition 36 crew member on board the International Space Station (ISS). Per Twitter message: Never tire of finding shapes in the clouds! These look very botanical to me. Simply perfect.
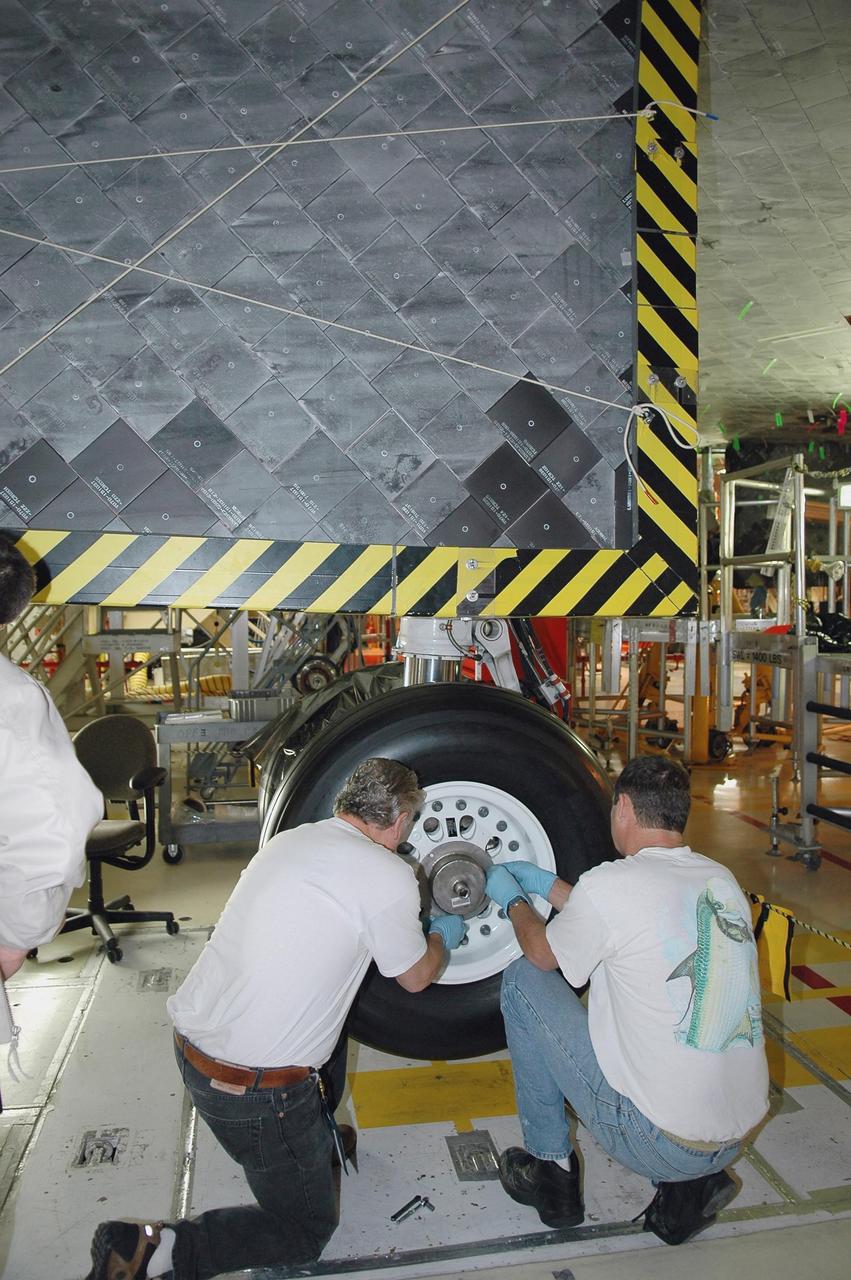

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In NASA’s Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3, United Space Alliance senior shuttle machinist Jake Jackson (left) installs and torques flight tires on Discovery. Discovery processing is under way for the second return to flight test mission, STS-121.
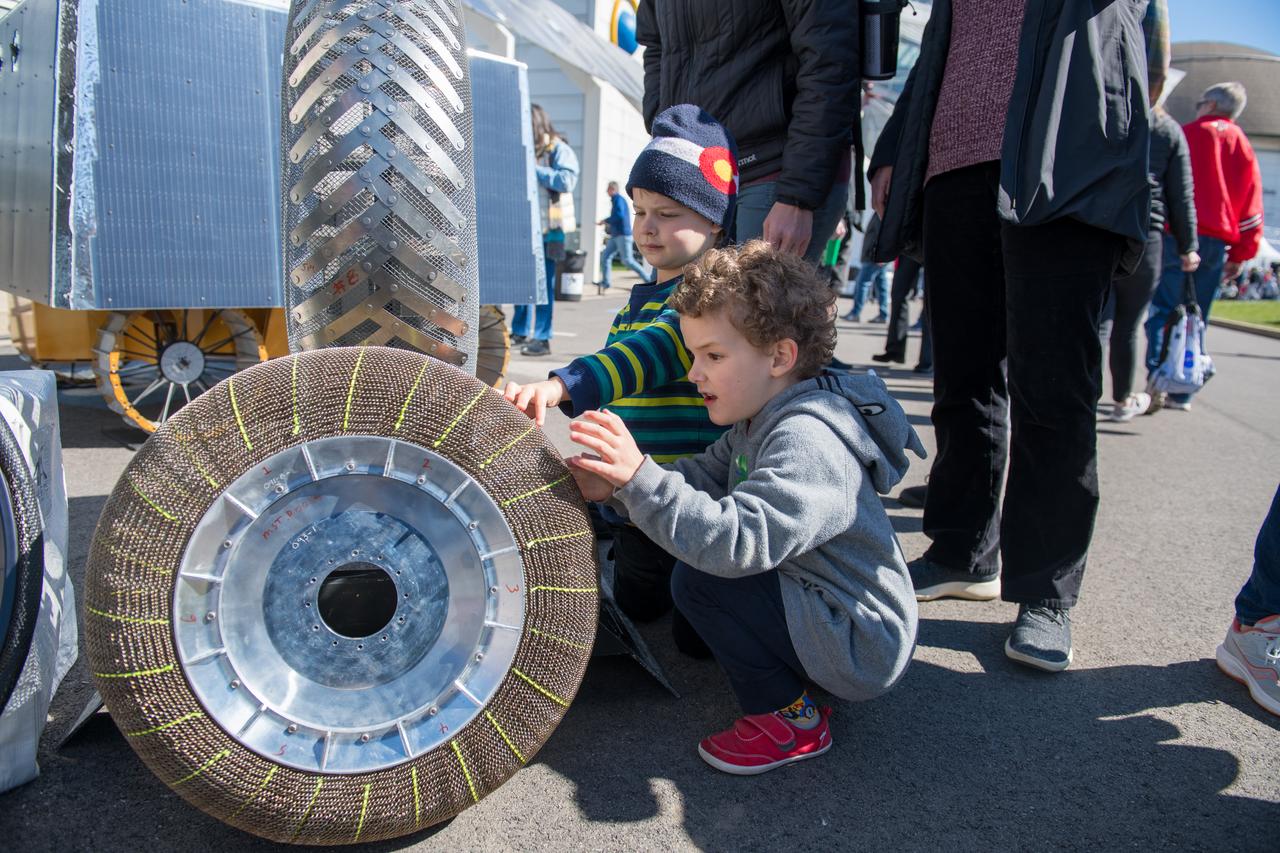

An event attendee checks out a rover tire made with shape memory alloys at the Total Eclipse Fest at the Great Lakes Science Center in Cleveland, OH on April 7, 2024. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the North American continent from Mexico’s Pacific coast to the Atlantic coast of Newfoundland, Canada. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of Central America and Europe.
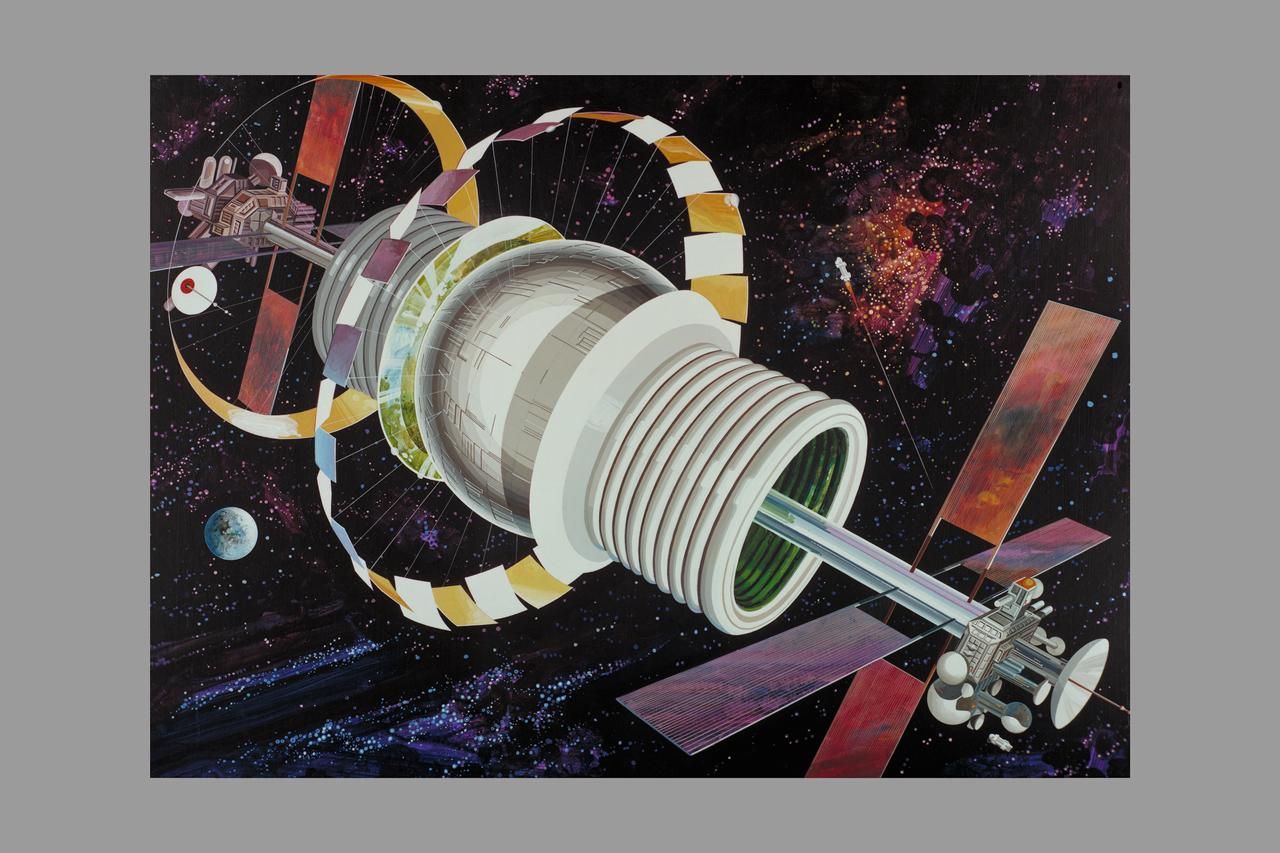
Artist: Rick Guidice Space Colonization - Bernal Sphere - The residential area is in the central sphere. Farming regions are in the 'tires.' Mirrors reflect sunlight into the habitat and farms. The large flat panels radiate away extra heat into space, and panels of solar cells provide electricity. Factories and docks for spaceships are at either end of the long central tube. (NOTE: art printed in Book 'Space Colony - Frontier of the 21st Century by Franklyn M. Branley)
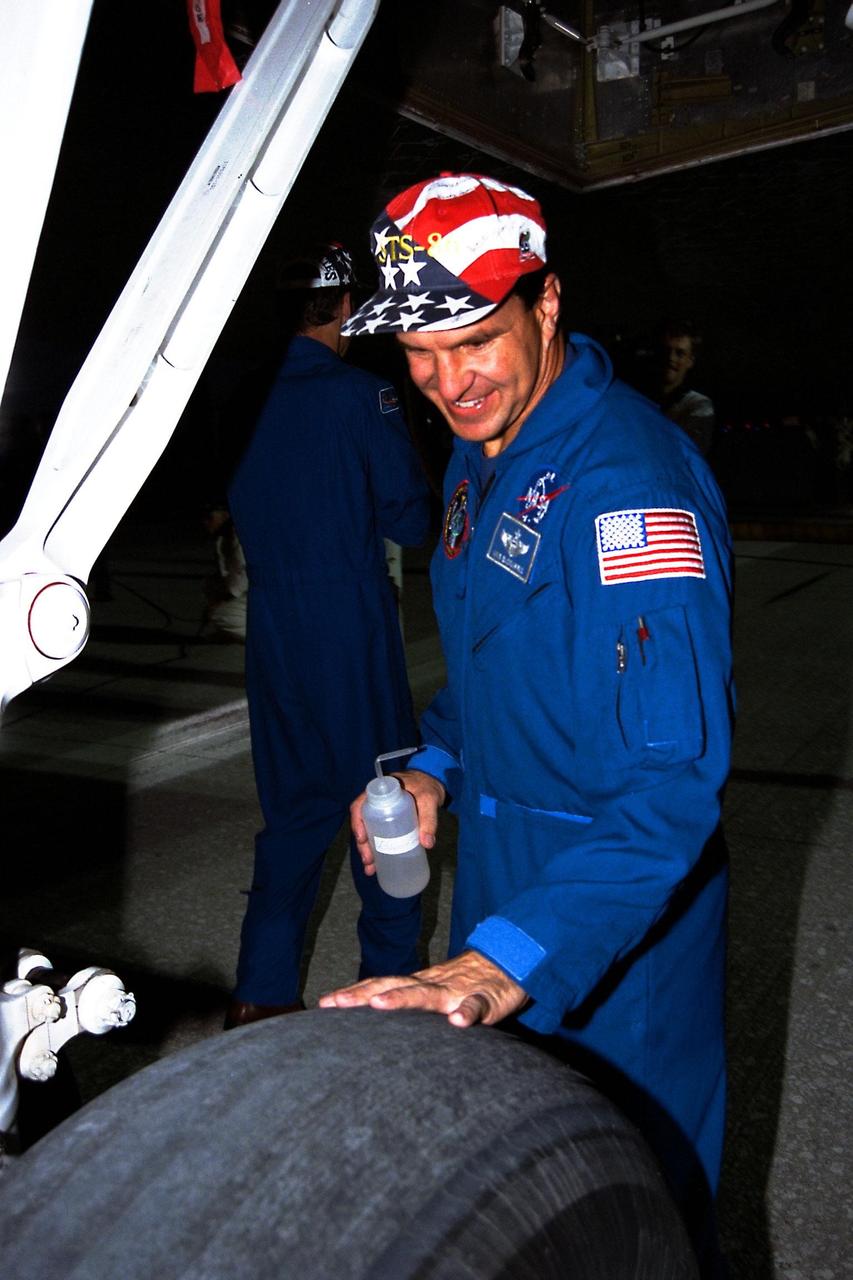

STS-86 Pilot Michael J. Bloomfield, the only space rookie on the crew, feels the heat from a tire on the orbiter Atlantis more than an hour after the landing on KSC’s Runway 15. The nearly 11-day mission ended with main gear touchdown at 5:55:09 p.m. EDT, Oct. 6, 1997. STS-86 was the seventh docking of the Space Shuttle with the Russian Space Station Mir
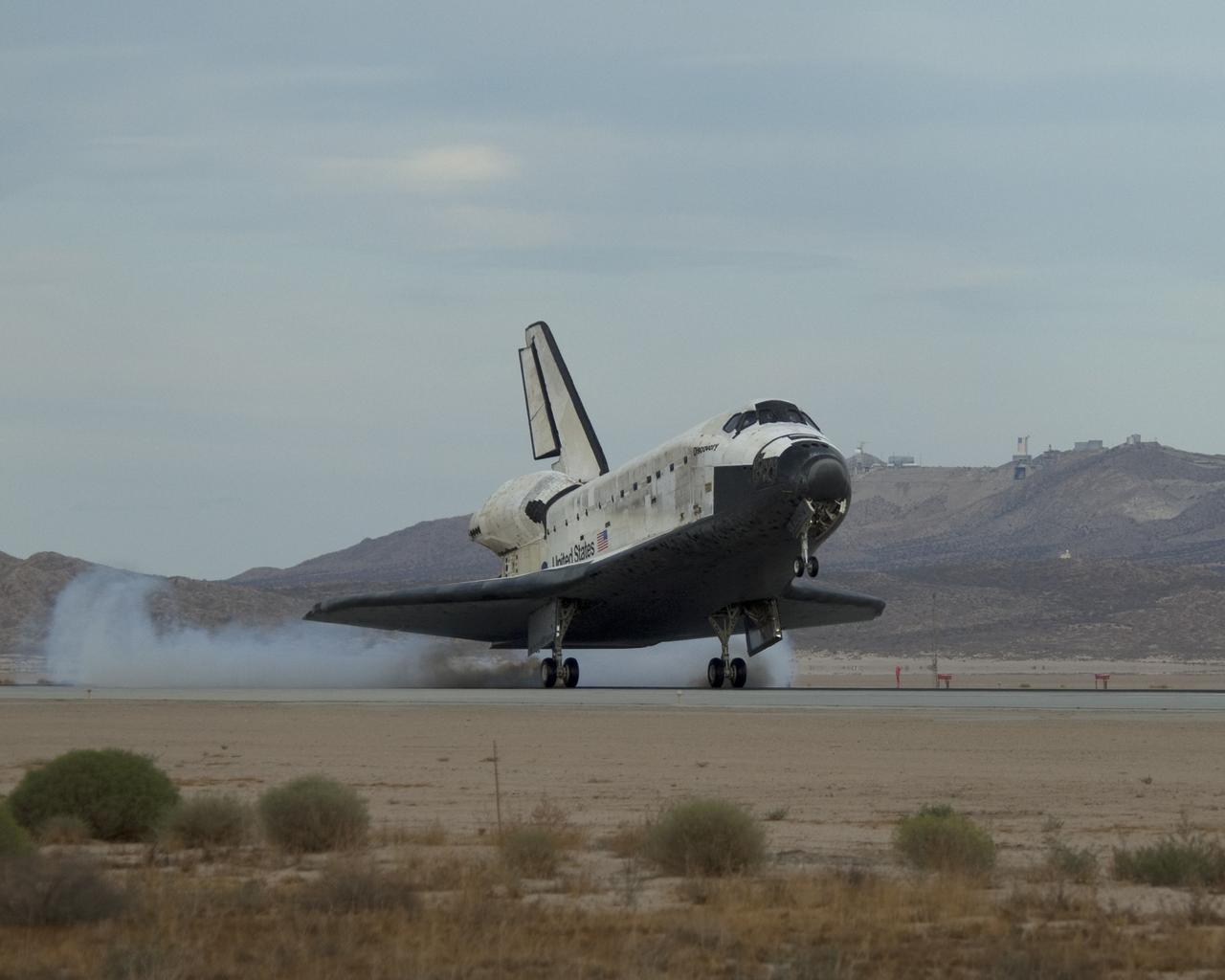

EDWARDS AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- (ED09-0253-01) Streams of smoke trail from the main landing gear tires as Space Shuttle Discovery touches down on Runway 22L at Edwards Air Force Base to conclude the almost 14-day STS-128 mission to the International Space Station. (NASA photo / Jim Ross)
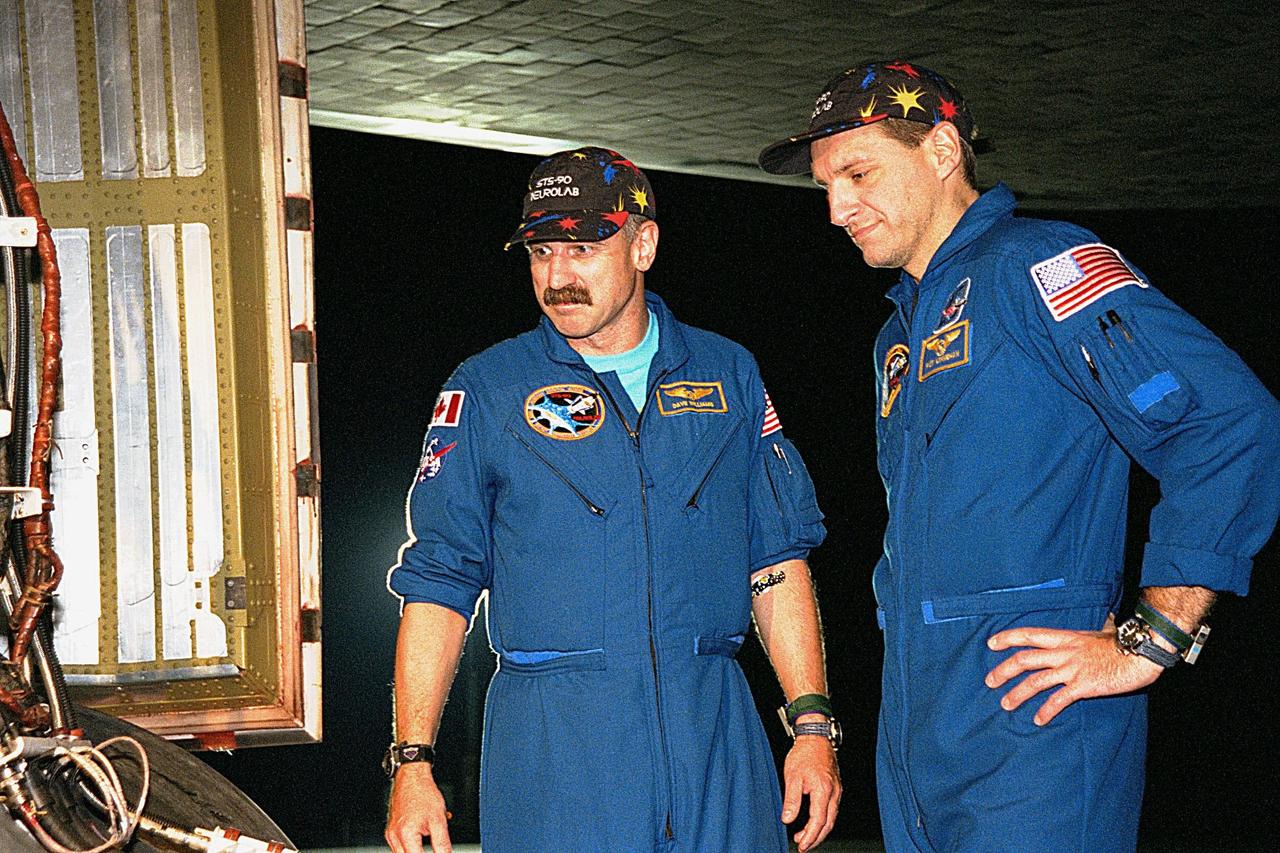

STS-90 Mission Specialists Dafydd (Dave) Williams, M.D., with the Canadian Space Agency (left) and Richard Linnehan, D.V.M., inspect the orbiter Columbia's tires in the evening after their midday arrival on May 3, ending their nearly 16-day Neurolab mission. The 90th Shuttle mission was Columbia's 13th landing at the space center and the 43rd KSC landing in the history of the Space Shuttle program. During the mission, the crew conducted research to contribute to a better understanding of the human nervous system
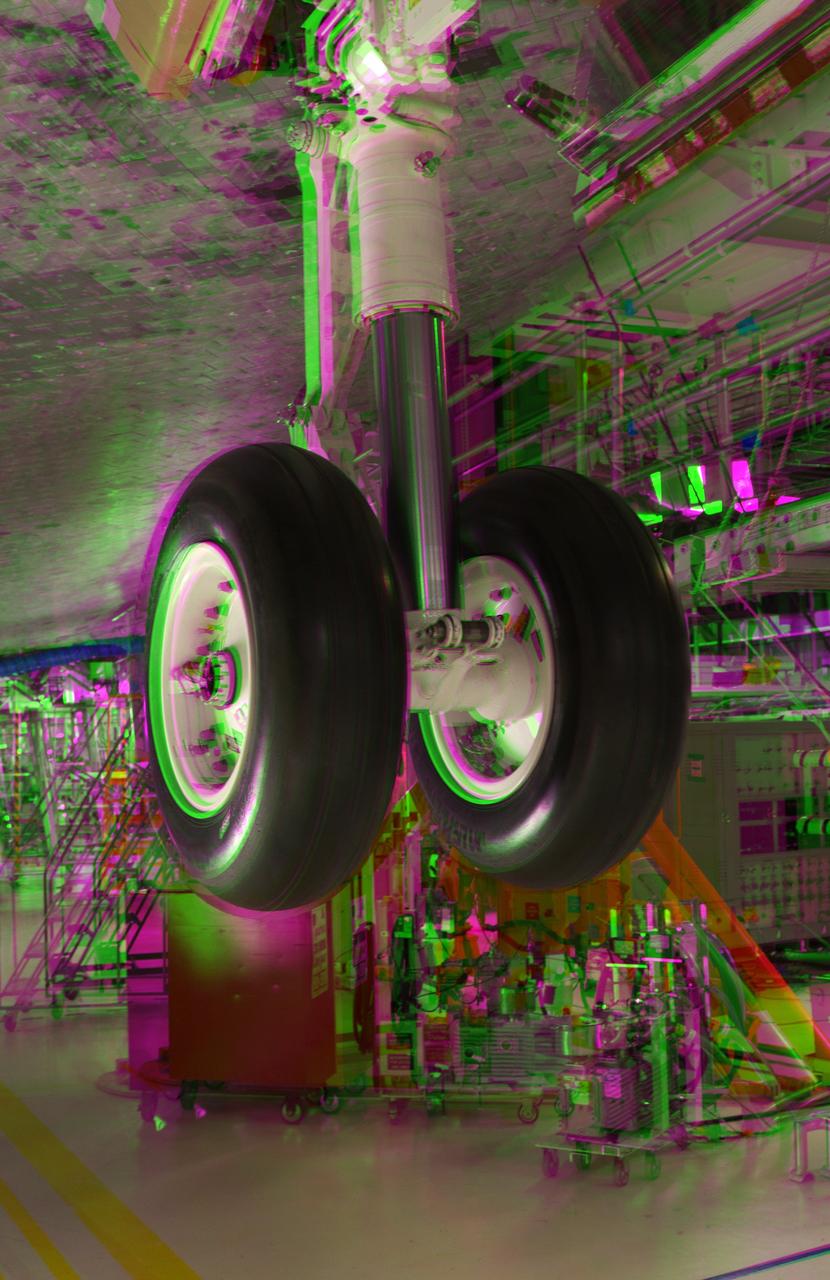

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This 3-D image was taken in Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after crews installed the final tire on space shuttle Discovery. This is part of the spacecraft's transition and retirement processing and work performed on Discovery is expected to help rocket designers build next-generation spacecraft and prepare the shuttle for future public display. To view this image, use green and magenta 3-D glasses. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
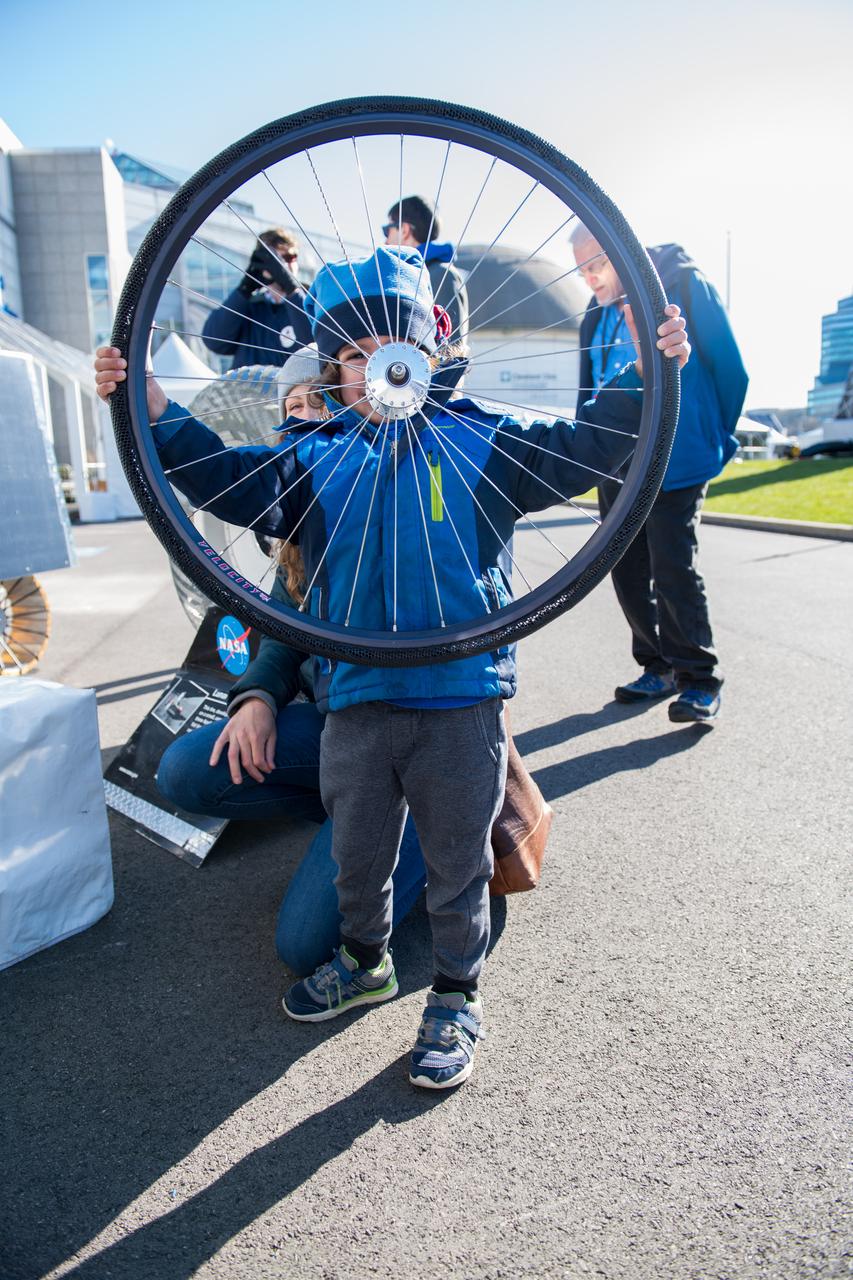

An event attendee holds a bike tire made with shape memory alloys at the Total Eclipse Fest at the Great Lakes Science Center in Cleveland, OH on April 7, 2024. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the North American continent from Mexico’s Pacific coast to the Atlantic coast of Newfoundland, Canada. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of Central America and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jef Janis)
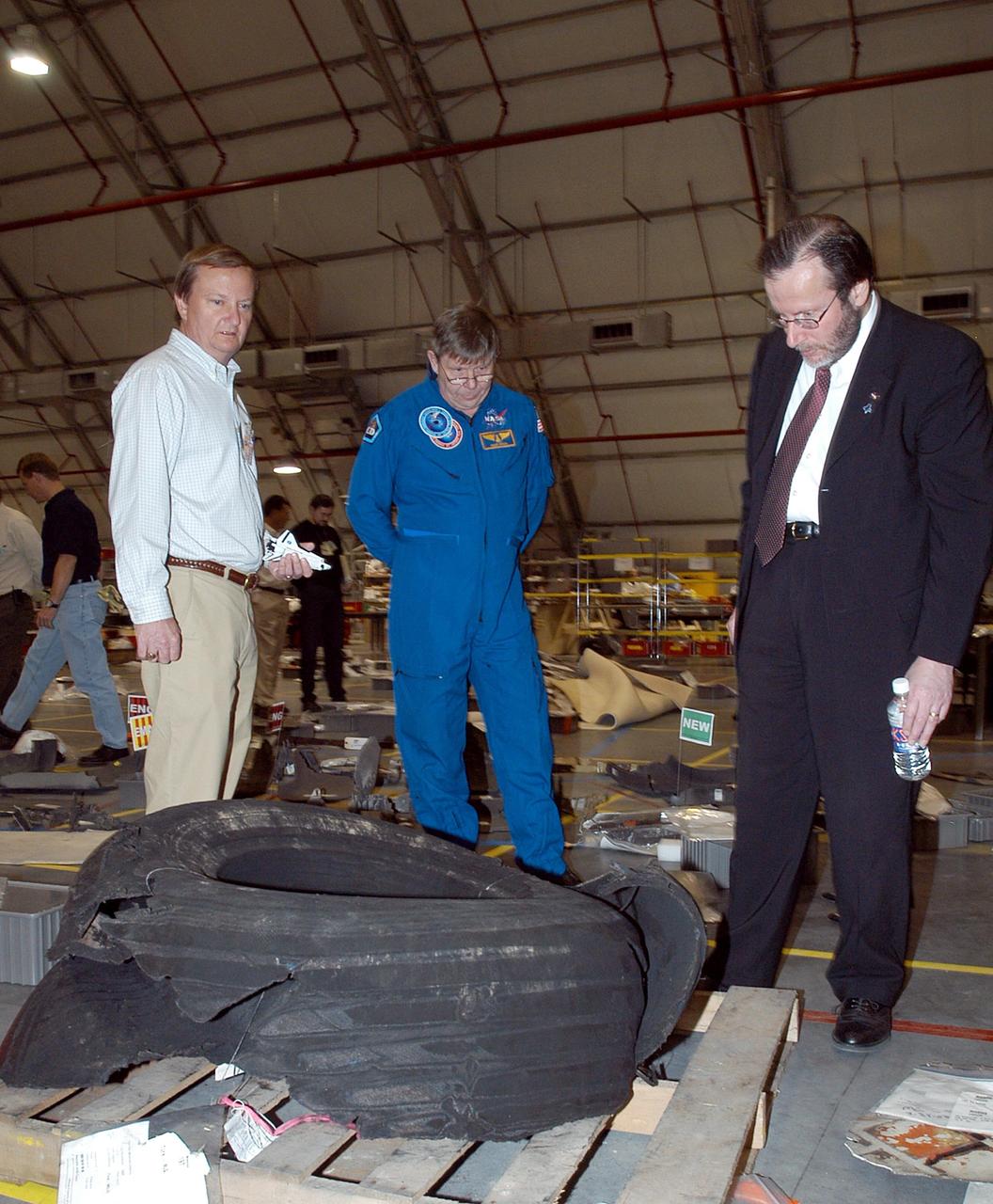

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the RLV Hangar at KSC, Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach (left), former payload specialist Dr. Roger Crouch (center) and NASA Chief of Staff and White House liaison Courtney Stadd look at one of Space Shuttle Columbia's tires. The debris is one of more than 35,000 pieces collected so far. More than 1,218 pieces have been identified. The search of more than 500,000 acres of primary recovery area for Columbia material has passed the halfway mark. To date about 28 percent of Columbia, by weight, has been delivered to the hangar.
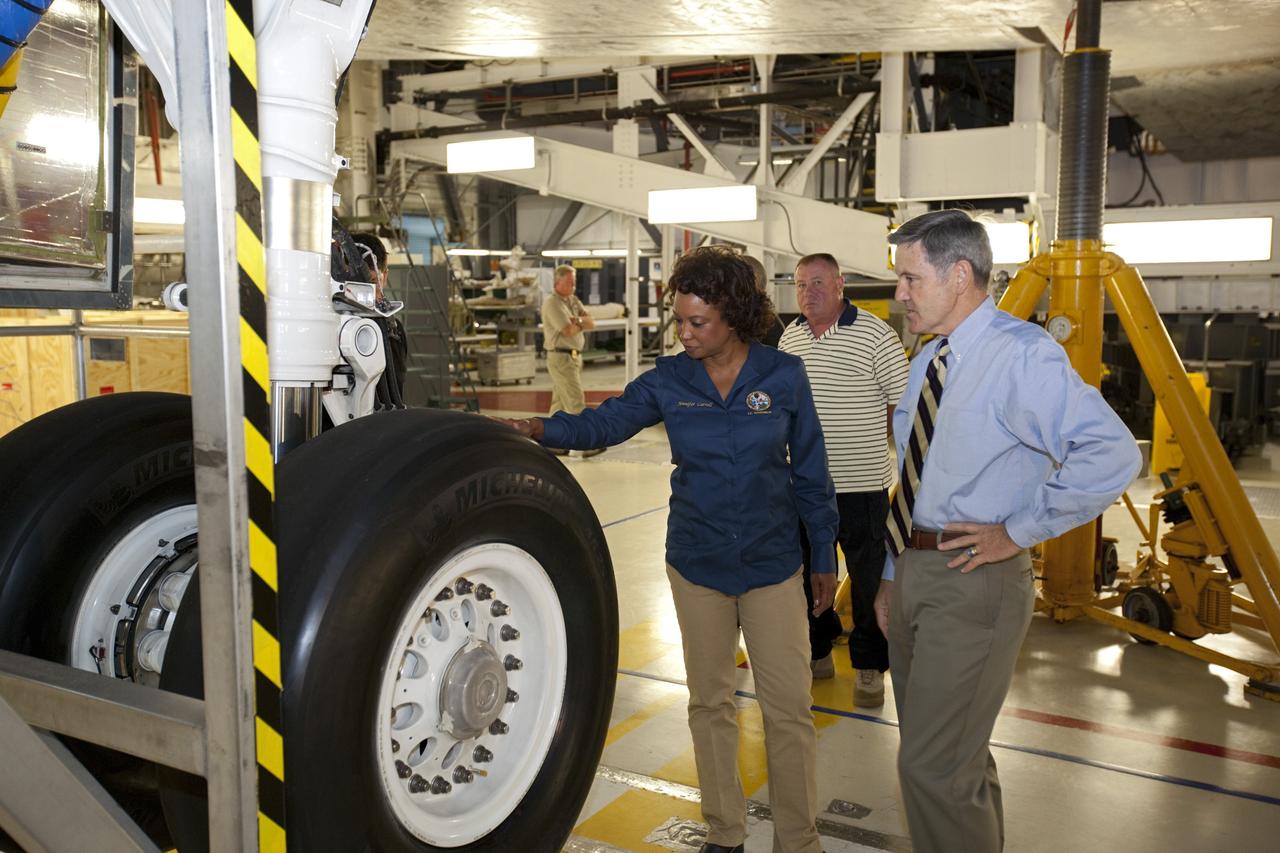

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Florida’s Lt. Gov. Jennifer Carroll, left, examines one of the tires on space shuttle Atlantis during a tour of Kennedy Space Center’s Orbiter Processing Facility-1. Kennedy’s Director Bob Cabana, at right, is her guide. The tour coincided with Carroll’s visit to Kennedy for a meeting with Cabana. Atlantis is being prepared for public display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in 2013. The groundbreaking for Atlantis’ exhibit hall took place in January Atlantis is scheduled to be moved to the visitor complex in November. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
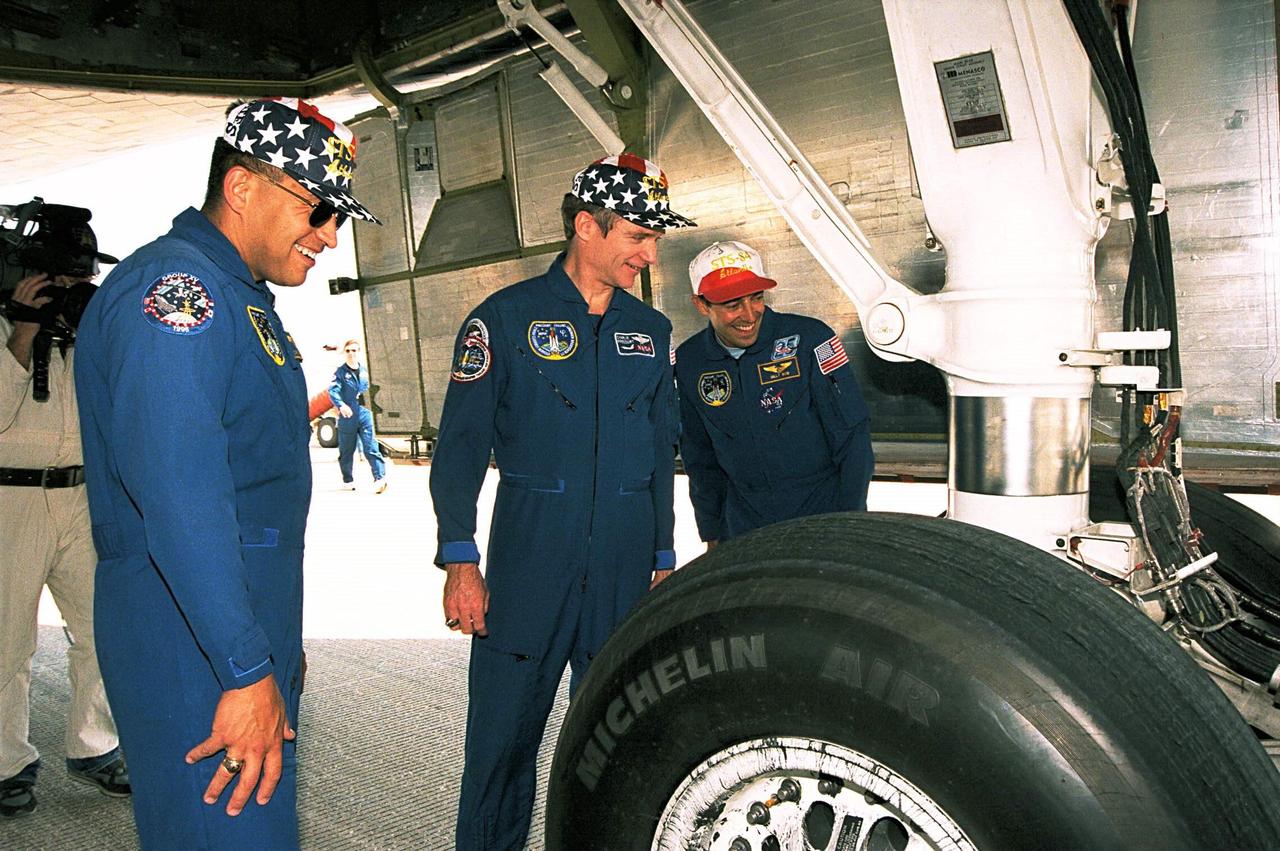

STS-84 crew members, from left, Mission Specialist Carlos I. Noriega, Commander Charles J. Precourt and Mission Specialist Jean-Francois Clervoy examine the tires of the Space Shuttle Atlantis after landing. Atlantis traveled about 3.6 million miles during the nine-day mission, which was the sixth of nine planned dockings of the Space Shuttle with the Russian Space Station Mir. The mission also included the exchange of STS-84 Mission Specialist C. Michael Foale for astronaut and Mir 23 crew member, Jerry M. Linenger, who spent the last four months on the Russian space station
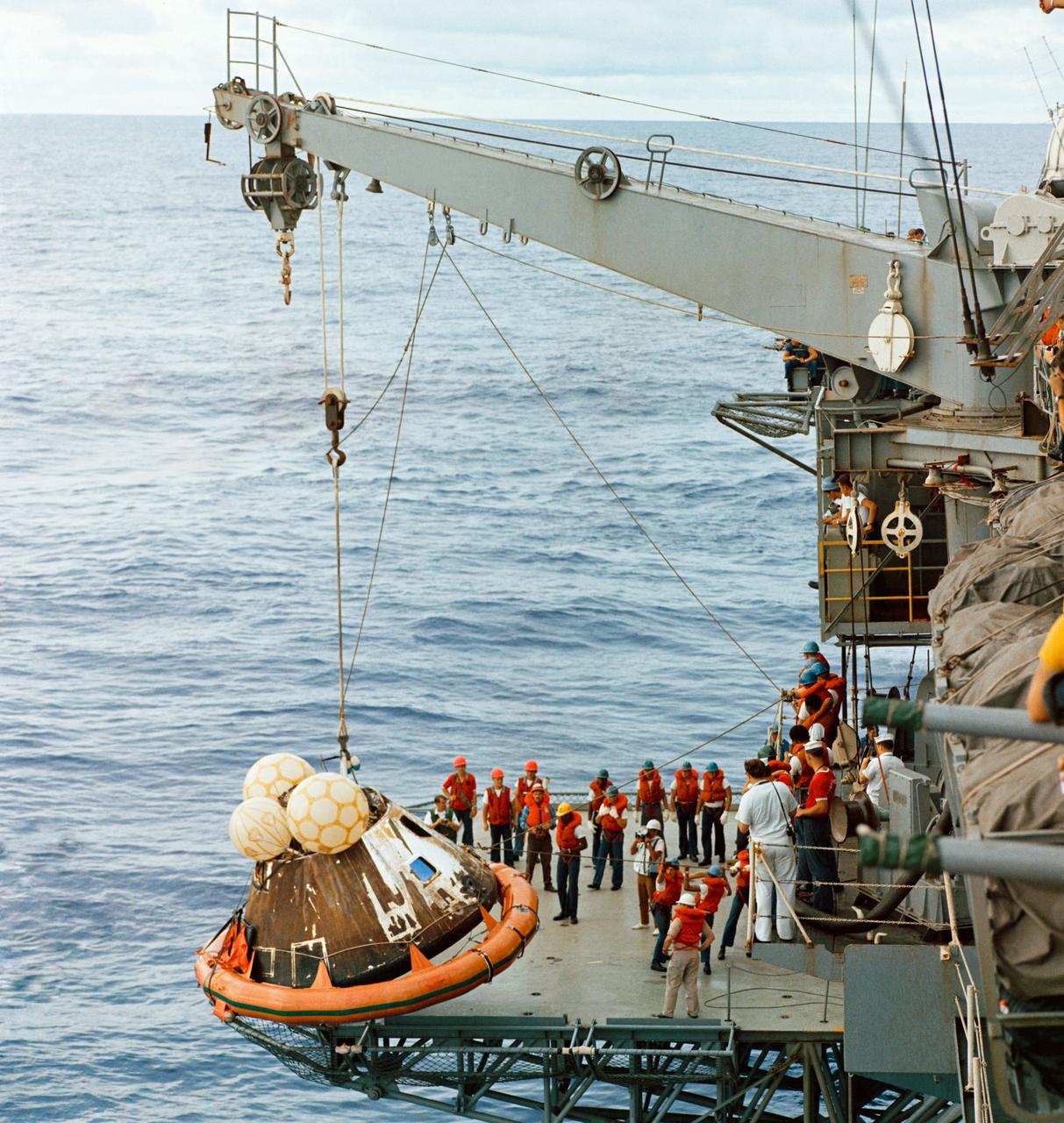

S70-15530 (17 April 1970) --- Crew men aboard the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 13 mission, hoist the Command Module (CM) aboard ship. The Apollo 13 crew men, astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., John L. Swigert Jr. and Fred W. Haise Jr., were already aboard the Iwo Jima when this photograph was taken. The CM, with the three tired crew men aboard, splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, only about four miles from the recovery vessel in the South Pacific Ocean.
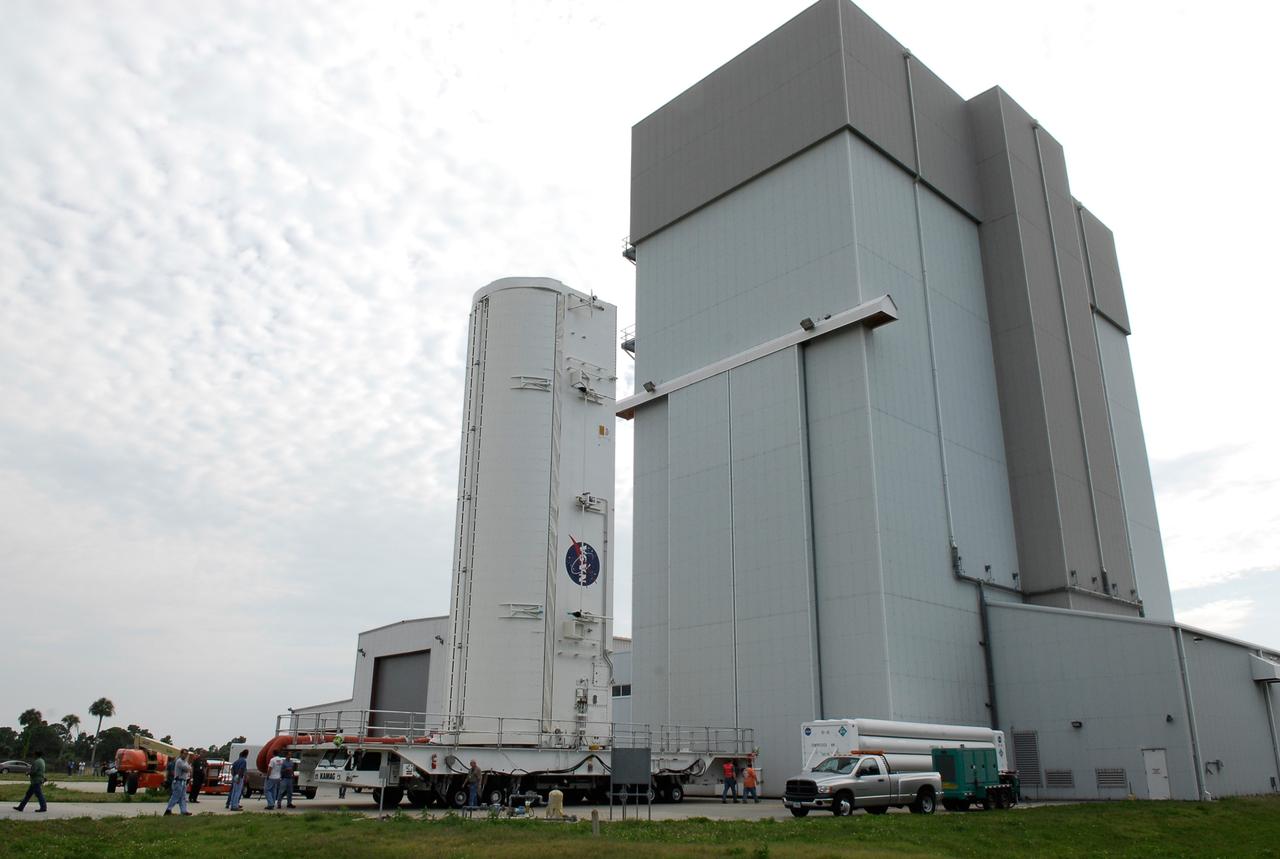

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Positioned on its 12-wheeled, 24-tire transporter, the payload canister with the STS-124 mission payload, Japanese Experiment Module - Pressurized Module and the Japanese Remote Manipulator System, or RMS, inside, begins its slow journey to Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. At the pad, the payload will be transferred into the payload changeout room on the rotating service structure. The transporter is 65 feet long and 23 feet wide. The transporter’s wheels are independently steerable, permitting it to move forward, backward, sideways or diagonally and to turn on its own axis like a carousel. It is equipped with pneumatic-actuated braking and hydrostat¬ic leveling and drive systems. It is steered from a two-seat operator cab mounted at one end. From the payload changeout room, the pressurized module and RMS then will be transferred into space shuttle Discovery’s payload bay. Launch is targeted for May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
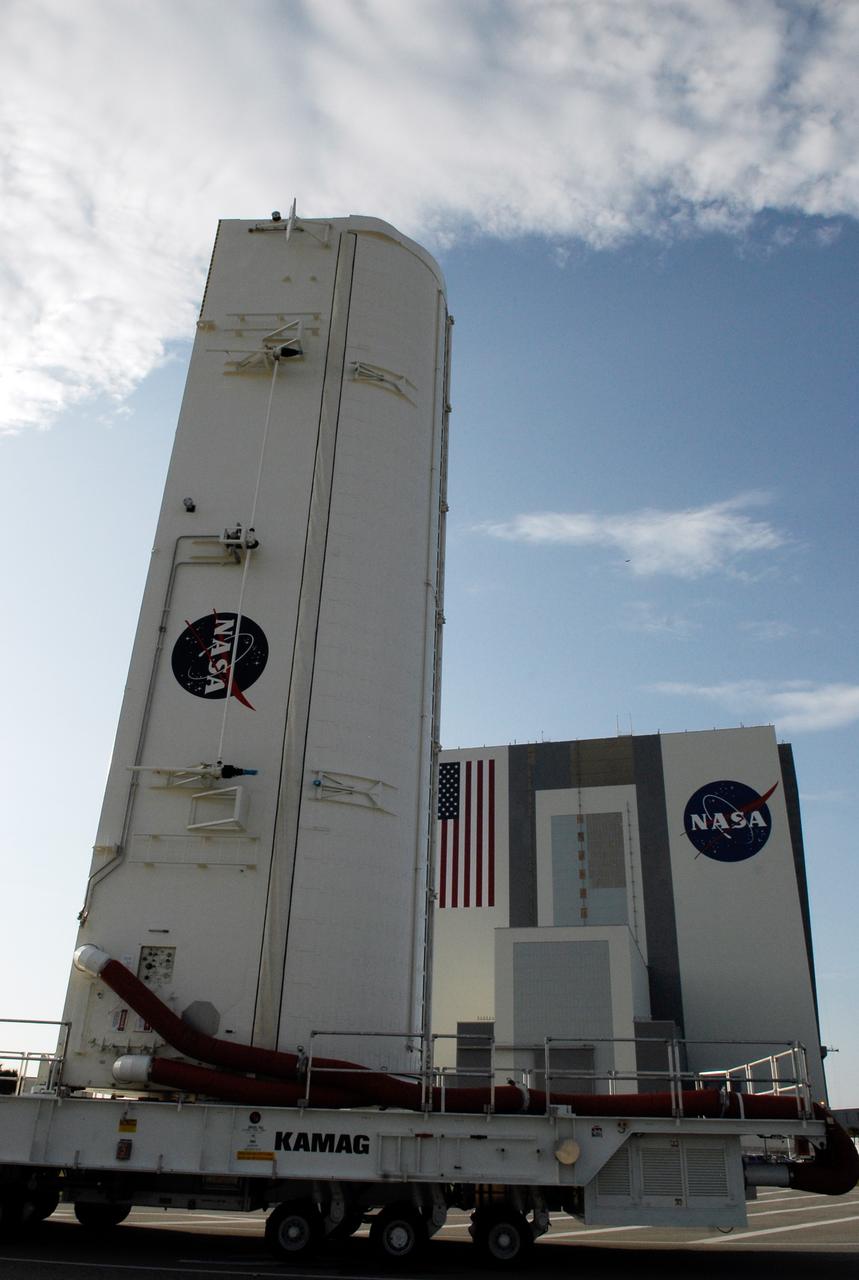

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Positioned on its 12-wheeled, 24-tire transporter, the payload canister with the STS-124 mission payload, Japanese Experiment Module - Pressurized Module and the Japanese Remote Manipulator System, or RMS, inside, slowly passes the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on its journey to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the payload will be transferred into the payload changeout room on the rotating service structure. The transporter is 65 feet long and 23 feet wide. The transporter’s wheels are independently steerable, permitting it to move forward, backward, sideways or diagonally and to turn on its own axis like a carousel. It is equipped with pneumatic-actuated braking and hydrostat¬ic leveling and drive systems. It is steered from a two-seat operator cab mounted at one end. From the payload changeout room, the pressurized module and RMS then will be transferred into space shuttle Discovery’s payload bay. Launch is targeted for May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This photo shows the leaking hydraulic seal in space shuttle Discovery's right main-gear strut. United Space Alliance and B.F. Goodrich technicians are working to replace the seal. The struts act as shock absorbers during the shuttle's landing. Engineers determined the observed leak of hydraulic fluid in the main landing gear strut exceeded specification and could not be reduced to an acceptable rate. Removing the strut and replacing seals require disconnecting and replacing the brakes and tires, disconnecting and reconnecting instruments and other requirements to allow access to the strut. Discovery had been scheduled to roll over Sept. 19 from its processing hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. A new rollover date will be set after technicians determine how long replacing the seal will take. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
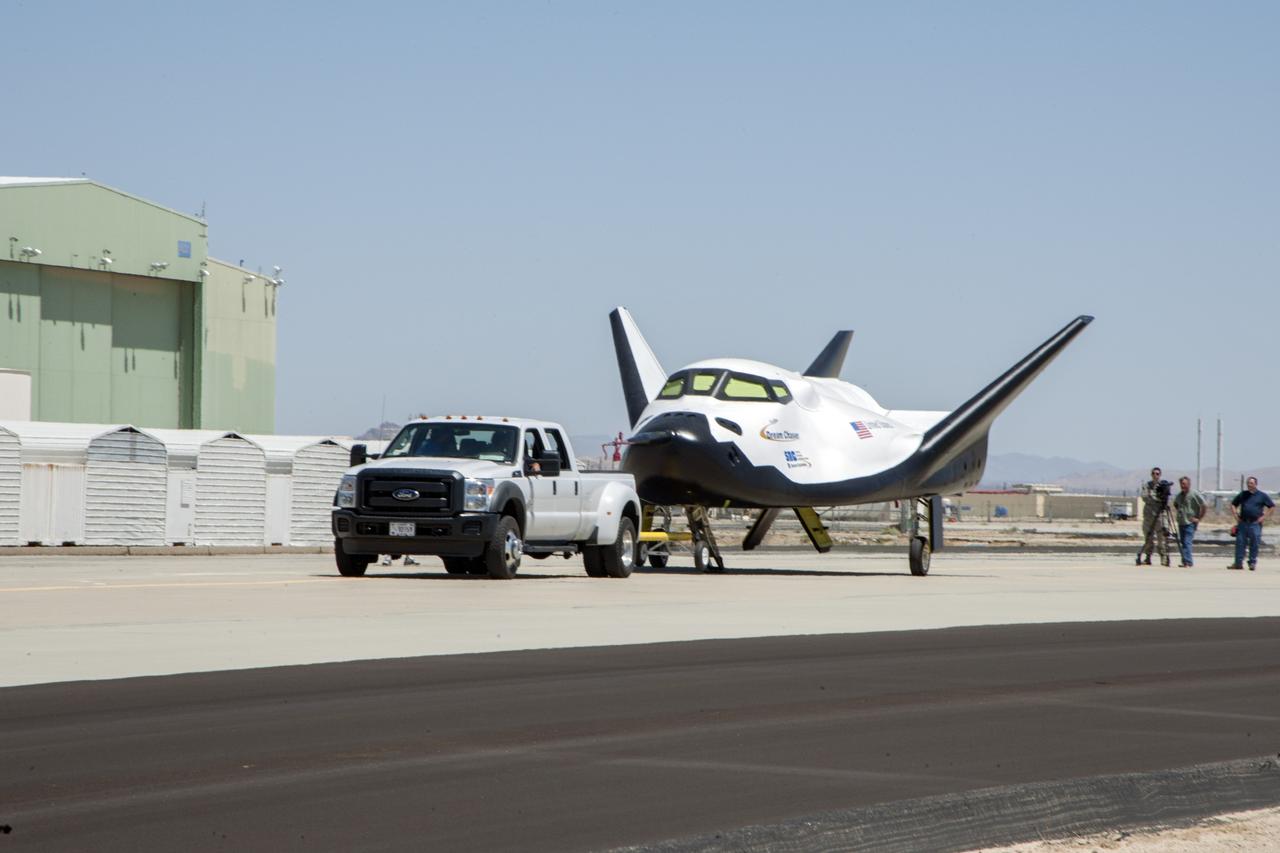

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-164-34 - Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC Space Systems' team members tow the Dream Chaser flight vehicle out to a concrete runway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California for range and taxi tow tests. The ground testing will validate the performance of the spacecraft's nose skid, brakes, tires and other systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-92 crew look over a tire on the landing gear of orbiter Discovery in the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1. From left to right are Mission Specialists Jeff Wisoff (pointing) and Leroy Chiao, Commander Brian Duffy and Mission Specialist Koichi Wakata, who is with the Japanese space agency. Standing behind them is Mission Specialist Michael Lopez-Alegria. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. Others taking part are Pilot Pam Melroy and Mission Specialist Bill McArthur. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 on Shuttle Discovery from Launch Pad 39A on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. Discovery will carry the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1, Pressurized Mating Adapter 3 (PMA-3), Ku-band Communications System, and Control Moment Gyros (CMGs)

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This photo reveals the area of a seal on space shuttle Discovery's right main-gear strut that was determined to be leaking. United Space Alliance and B.F. Goodrich technicians are replacing the seal. The struts act as shock absorbers during the shuttle's landing. Engineers determined the observed leak of hydraulic fluid in the main landing gear strut exceeded specification and could not be reduced to an acceptable rate. Removing the strut and replacing seals require disconnecting and replacing the brakes and tires, disconnecting and reconnecting instruments and other requirements to allow access to the strut. Discovery had been scheduled to roll over Sept. 19 from its processing hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. A new rollover date will be set after technicians determine how long replacing the seal will take. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
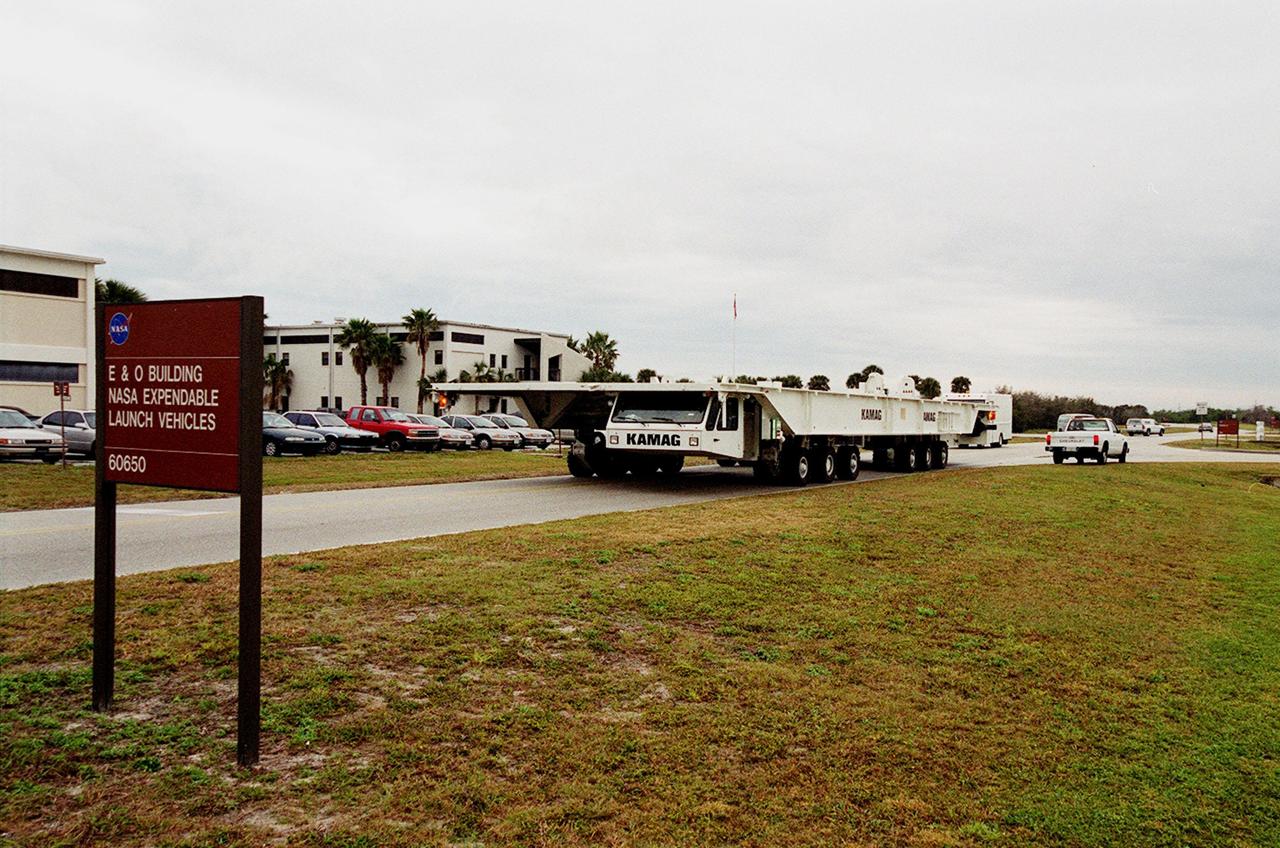

One of two new payload transporters for Kennedy Space Center moves through Cape Canaveral Air Station after being unloaded from a barge at Port Canaveral. The transporters, manufactured by the KAMAG Transporttechnick, GmbH, of Ulm, Germany, are replacing the existing Payload Canister Transporter system, which is 20 years old. Each transporter is 65 feet long and 22 feet wide and has 24 tires divided between its two axles. The transporter travels 10 miles per hour unloaded, 5 miles per hour when loaded; it weighs up to 172,000 pounds when the canister with payloads rides atop. The transporters will be outfitted with four subsystems for monitoring the environment inside the canister during the payload moves: the Electrical Power System, Environmental Control System, Instrumentation and Communications System, and the Fluids and Gases System. Engineers and technicians are being trained on the transporter's operation and maintenance

This is a von Braun 1952 space station concept. In a 1952 series of articles written in Collier's, Dr. Wernher von Braun, then Technical Director of the Army Ordnance Guided Missiles Development Group at Redstone Arsenal, wrote of a large wheel-like space station in a 1,075-mile orbit. This station, made of flexible nylon, would be carried into space by a fully reusable three-stage launch vehicle. Once in space, the station's collapsible nylon body would be inflated much like an automobile tire. The 250-foot-wide wheel would rotate to provide artificial gravity, an important consideration at the time because little was known about the effects of prolonged zero-gravity on humans. Von Braun's wheel was slated for a number of important missions: a way station for space exploration, a meteorological observatory and a navigation aid. This concept was illustrated by artist Chesley Bonestell.
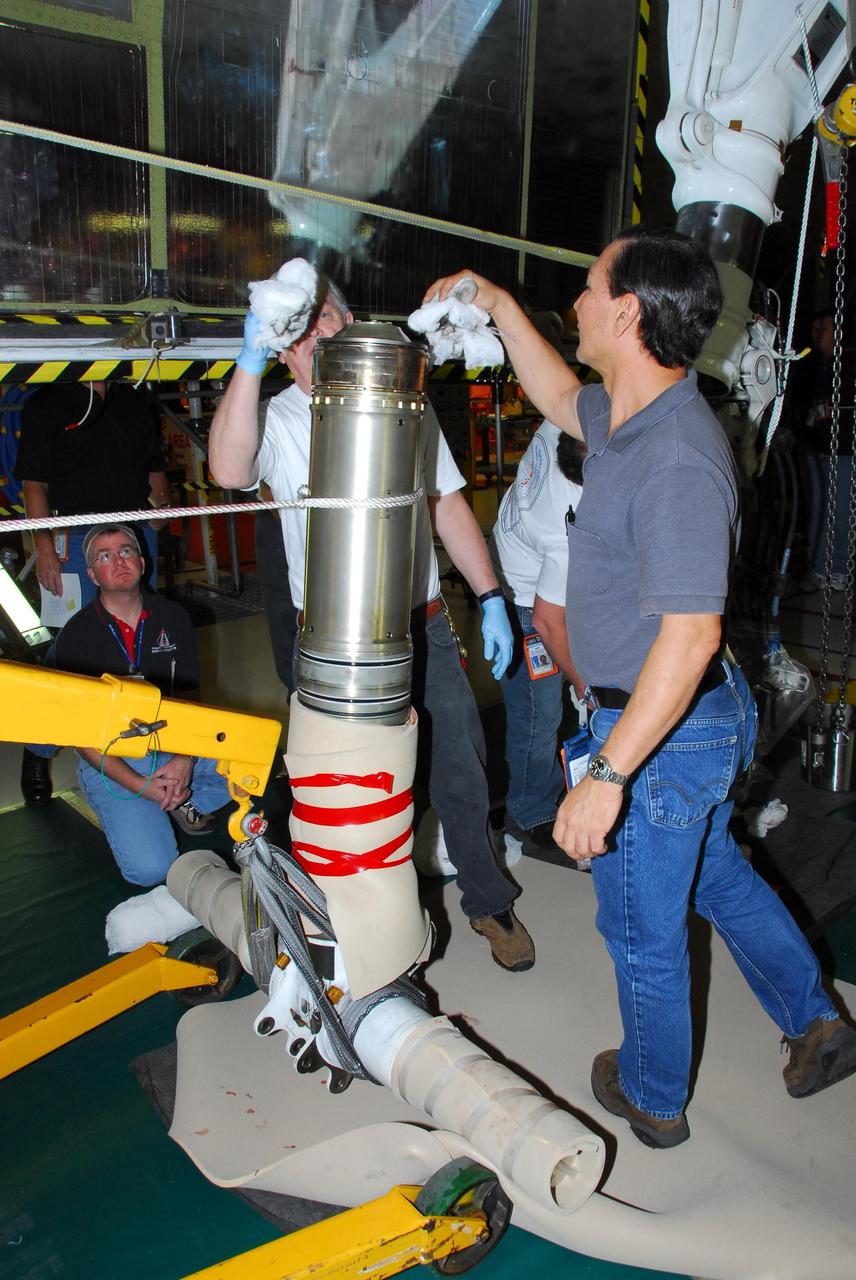

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, United Space Alliance and B.F. Goodrich technicians work on the starboard landing gear assembly of space shuttle Discovery. They will replace a leaking dynamic seal in Discovery's right main-gear strut. The struts act as shock absorbers during the shuttle's landing. Engineers determined the observed leak of hydraulic fluid in the main landing gear strut exceeded specification and could not be reduced to an acceptable rate. Removing the strut and replacing seals require disconnecting and replacing the brakes and tires, disconnecting and reconnecting instruments and other requirements to allow access to the strut. Discovery had been scheduled to roll over Sept. 19 from its processing hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. A new rollover date will be set after technicians determine how long replacing the seal will take. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
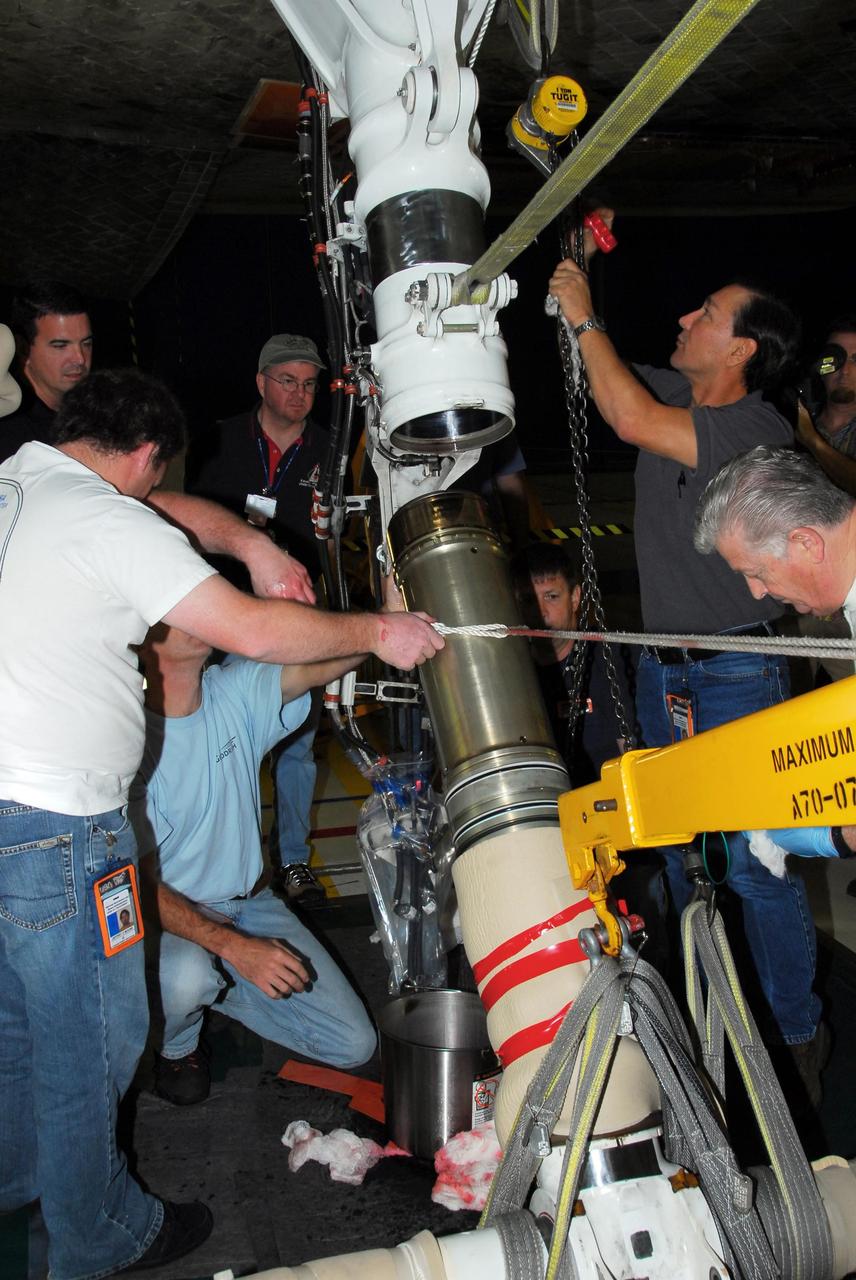

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, United Space Alliance and B.F. Goodrich technicians work on the starboard landing gear assembly of space shuttle Discovery. They will replace a leaking dynamic seal in Discovery's right main-gear strut. The struts act as shock absorbers during the shuttle's landing. Engineers determined the observed leak of hydraulic fluid in the main landing gear strut exceeded specification and could not be reduced to an acceptable rate. Removing the strut and replacing seals require disconnecting and replacing the brakes and tires, disconnecting and reconnecting instruments and other requirements to allow access to the strut. Discovery had been scheduled to roll over Sept. 19 from its processing hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. A new rollover date will be set after technicians determine how long replacing the seal will take. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
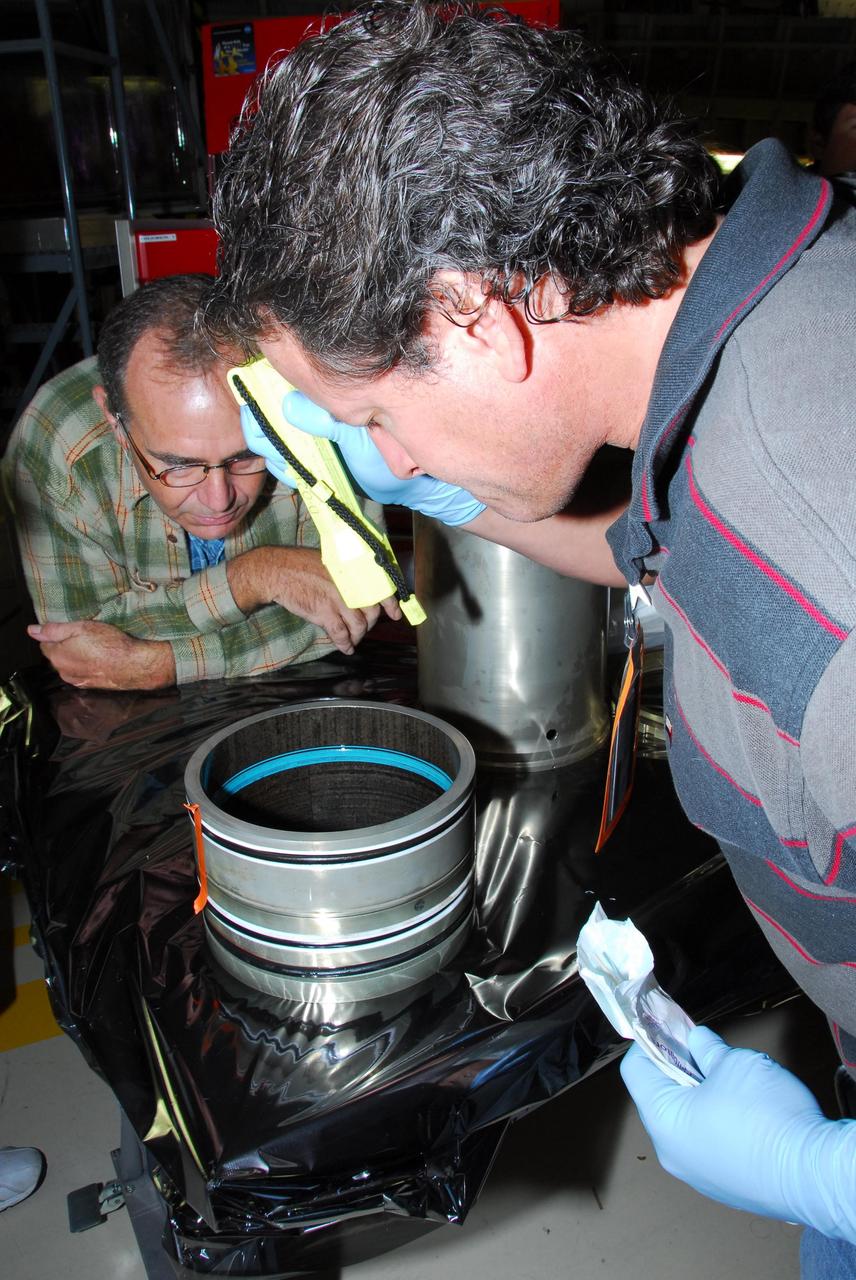

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, United Space Alliance and B.F. Goodrich technicians look inside part of space shuttle Discovery's right main-gear strut where a leaking seal has been found. The struts act as shock absorbers during the shuttle's landing. The seal will be replaced. Engineers determined the observed leak of hydraulic fluid in the main landing gear strut exceeded specification and could not be reduced to an acceptable rate. Removing the strut and replacing seals require disconnecting and replacing the brakes and tires, disconnecting and reconnecting instruments and other requirements to allow access to the strut. Discovery had been scheduled to roll over Sept. 19 from its processing hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. A new rollover date will be set after technicians determine how long replacing the seal will take. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
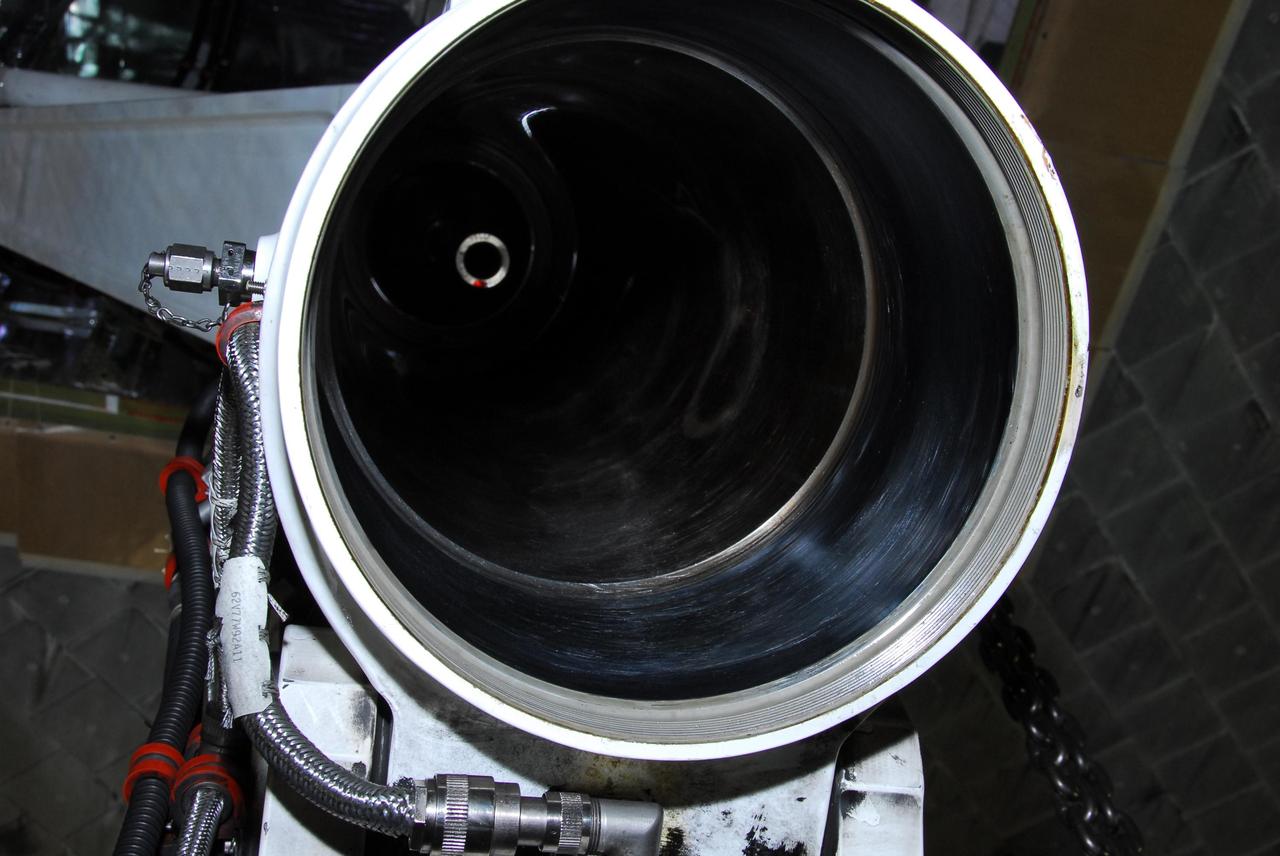

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This photo looks inside space shuttle Discovery's right main-gear strut where a leaking seal has been found. United Space Alliance and B.F. Goodrich technicians will replace a leaking dynamic seal in Discovery's right main-gear strut. The struts act as shock absorbers during the shuttle's landing. Engineers determined the observed leak of hydraulic fluid in the main landing gear strut exceeded specification and could not be reduced to an acceptable rate. Removing the strut and replacing seals require disconnecting and replacing the brakes and tires, disconnecting and reconnecting instruments and other requirements to allow access to the strut. Discovery had been scheduled to roll over Sept. 19 from its processing hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. A new rollover date will be set after technicians determine how long replacing the seal will take. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
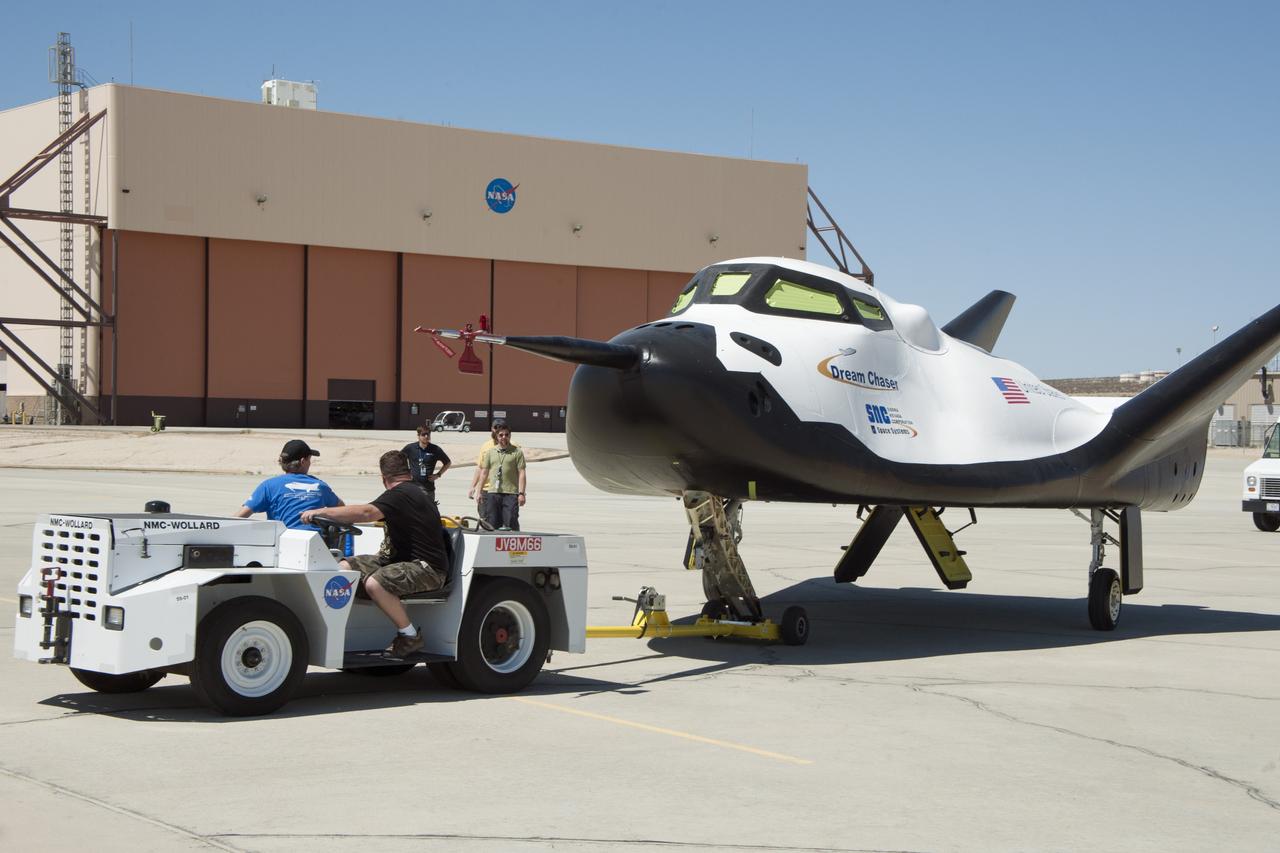

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-164-33 - Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC Space Systems' team members tow the Dream Chaser flight vehicle out to a concrete runway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California for range and taxi tow tests. The ground testing will validate the performance of the spacecraft's nose skid, brakes, tires and other systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
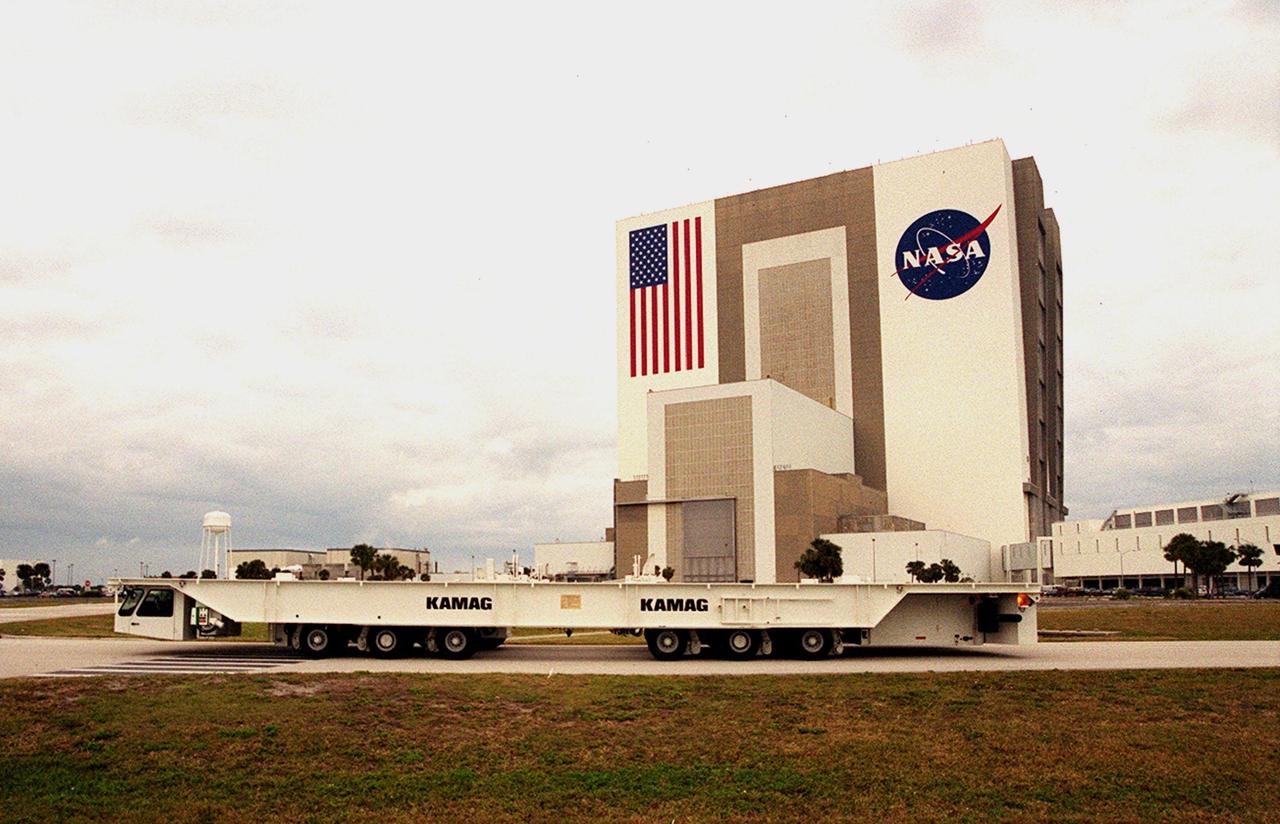
One of two new payload transporters for Kennedy Space Center moves past the Vehicle Assembly Building (left) and Launch Control Center (right) after being unloaded from a barge at Port Canaveral. The transporters, manufactured by the KAMAG Transporttechnick, GmbH, of Ulm, Germany, are replacing the existing Payload Canister Transporter system, which is 20 years old. Each transporter is 65 feet long and 22 feet wide and has 24 tires divided between its two axles. The transporter travels 10 miles per hour unloaded, 5 miles per hour when loaded; it weighs up to 172,000 pounds when the canister with payloads rides atop. The transporters will be outfitted with four subsystems for monitoring the environment inside the canister during the payload moves: the Electrical Power System, Environmental Control System, Instrumentation and Communications System, and the Fluids and Gases System. Engineers and technicians are being trained on the transporter's operation and maintenance
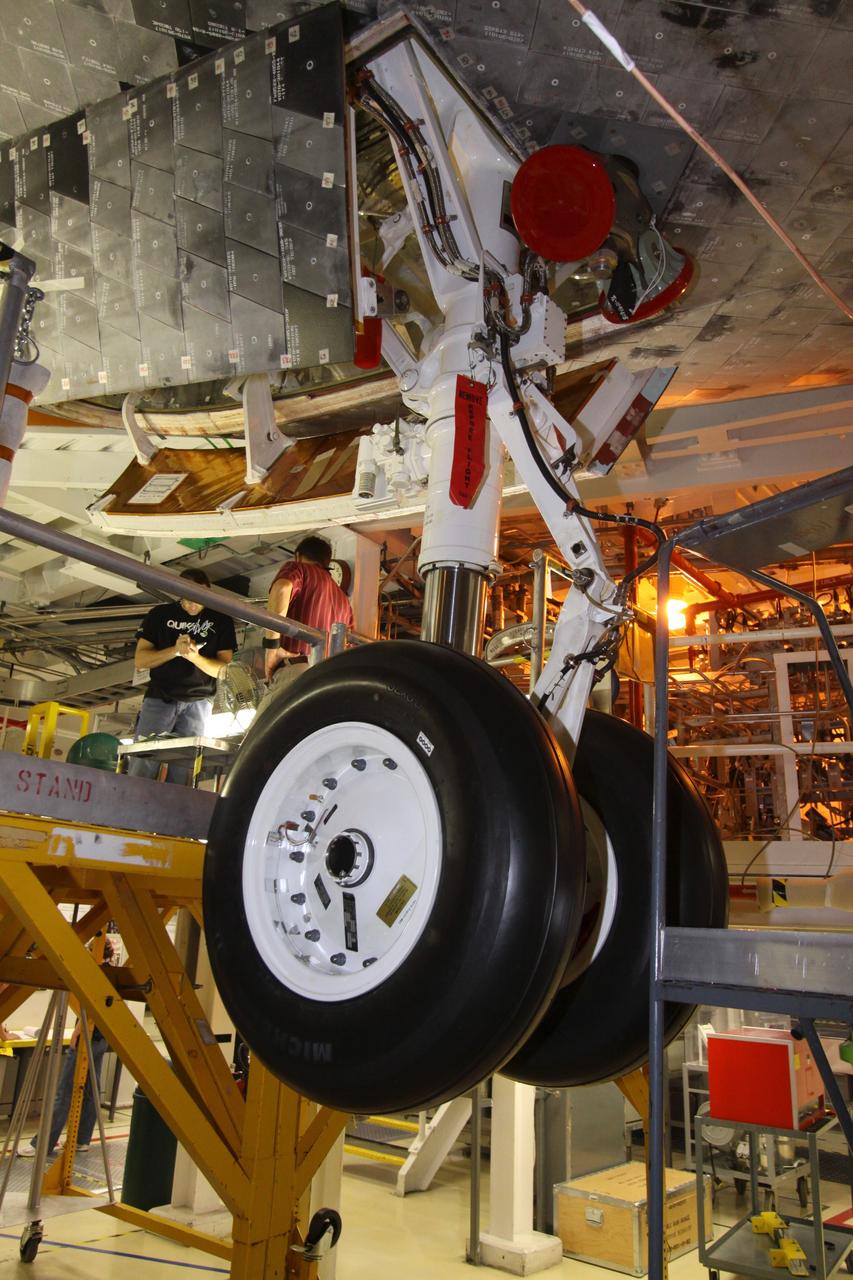

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers verify that the processing of space shuttle Endeavour is complete, its payload bay doors are closed, and it is ready for its move to the Vehicle Assembly Building. This close-up is of Endeavour's nose-wheel landing gear and tires. The move, or "rollover," is targeted for Dec. 12. The Tranquility module, the payload for Endeavour's STS-130 mission to the International Space Station, will be installed in the payload bay after the shuttle has reached the pad. Endeavour's launch is targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. For information on the STS-130 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts130/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
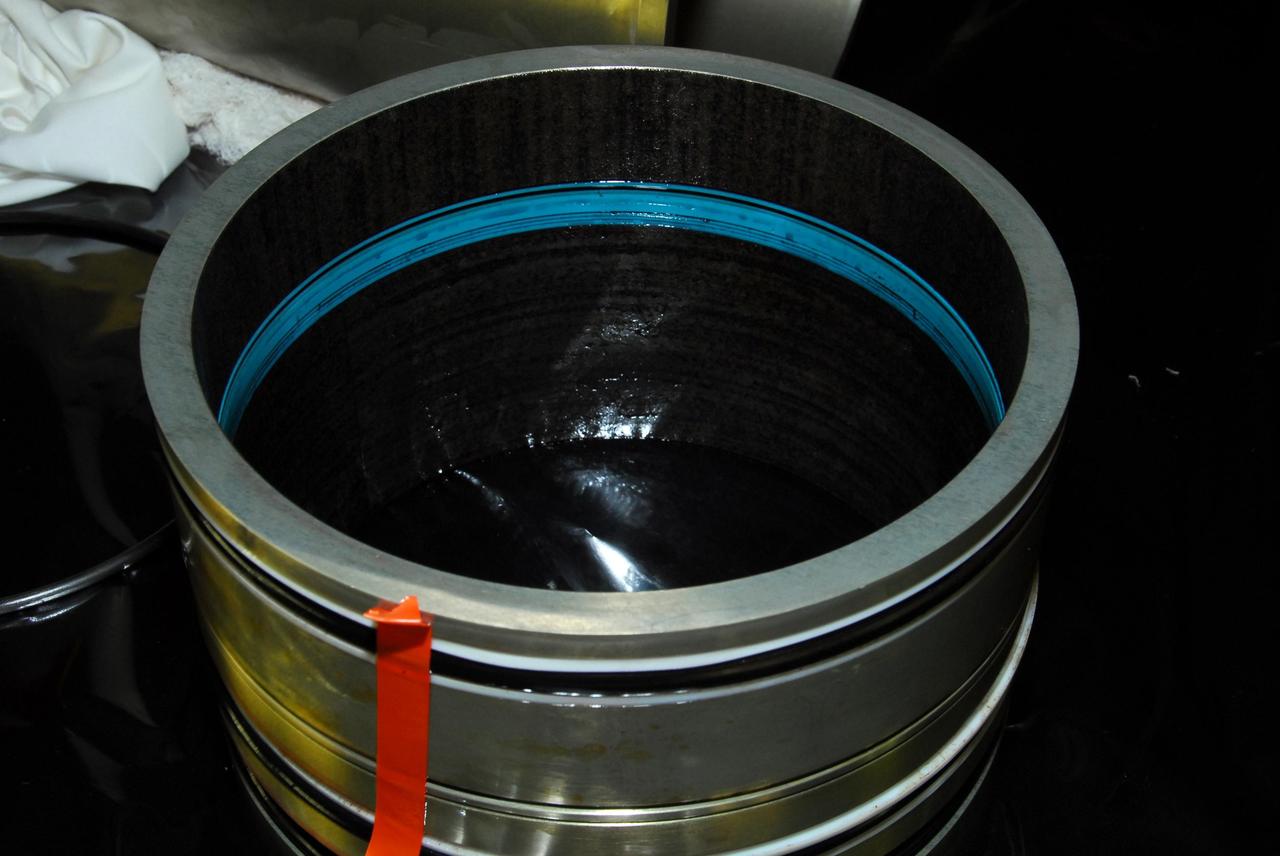

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This photo looks inside space shuttle Discovery's right main-gear strut where a leaking seal has been found. United Space Alliance and B.F. Goodrich technicians will replace the seal. The struts act as shock absorbers during the shuttle's landing. Engineers determined the observed leak of hydraulic fluid in the main landing gear strut exceeded specification and could not be reduced to an acceptable rate. Removing the strut and replacing seals require disconnecting and replacing the brakes and tires, disconnecting and reconnecting instruments and other requirements to allow access to the strut. Discovery had been scheduled to roll over Sept. 19 from its processing hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. A new rollover date will be set after technicians determine how long replacing the seal will take. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
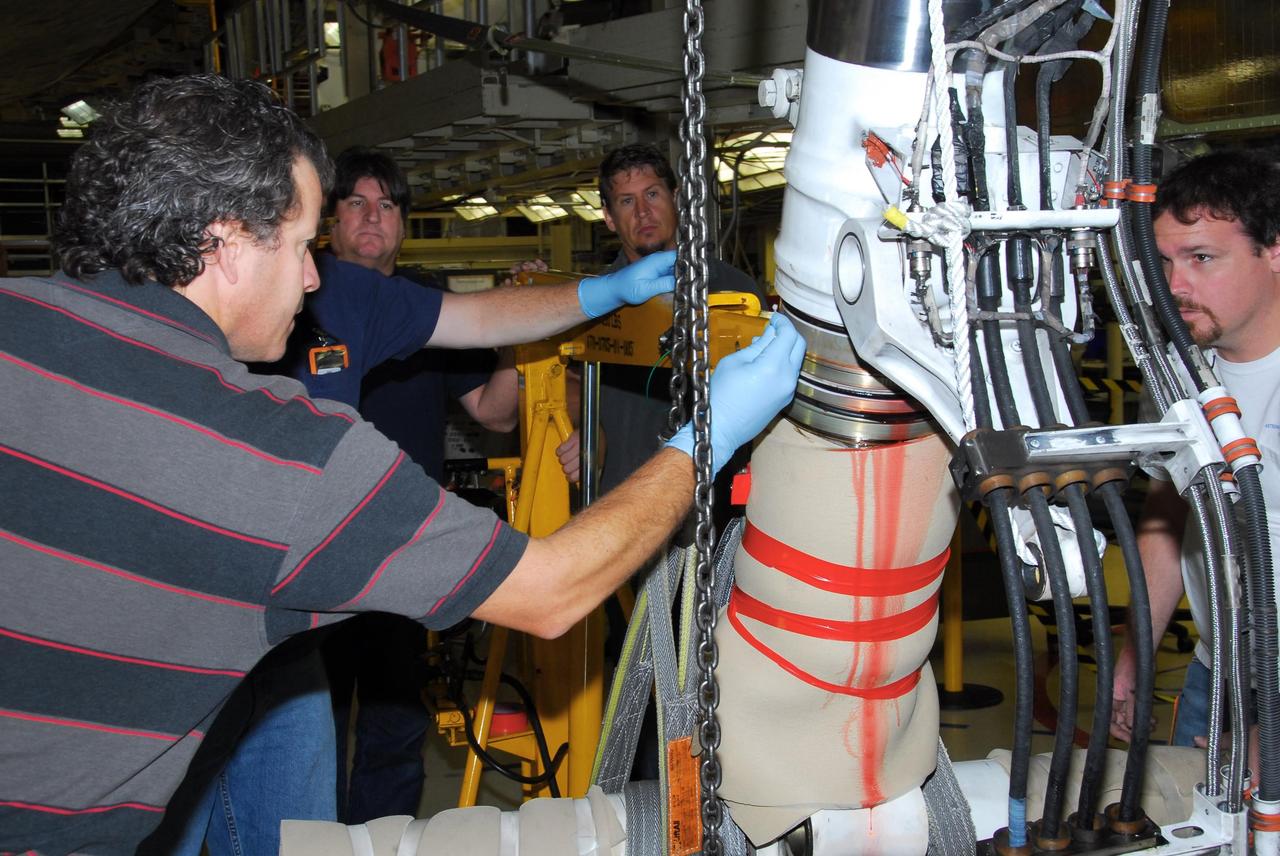

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, United Space Alliance and B.F. Goodrich technicians begin work on the starboard landing gear assembly of space shuttle Discovery. They will replace a leaking dynamic seal in Discovery's right main-gear strut. The struts act as shock absorbers during the shuttle's landing. Engineers determined the observed leak of hydraulic fluid in the main landing gear strut exceeded specification and could not be reduced to an acceptable rate. Removing the strut and replacing seals require disconnecting and replacing the brakes and tires, disconnecting and reconnecting instruments and other requirements to allow access to the strut. Discovery had been scheduled to roll over Sept. 19 from its processing hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. A new rollover date will be set after technicians determine how long replacing the seal will take. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
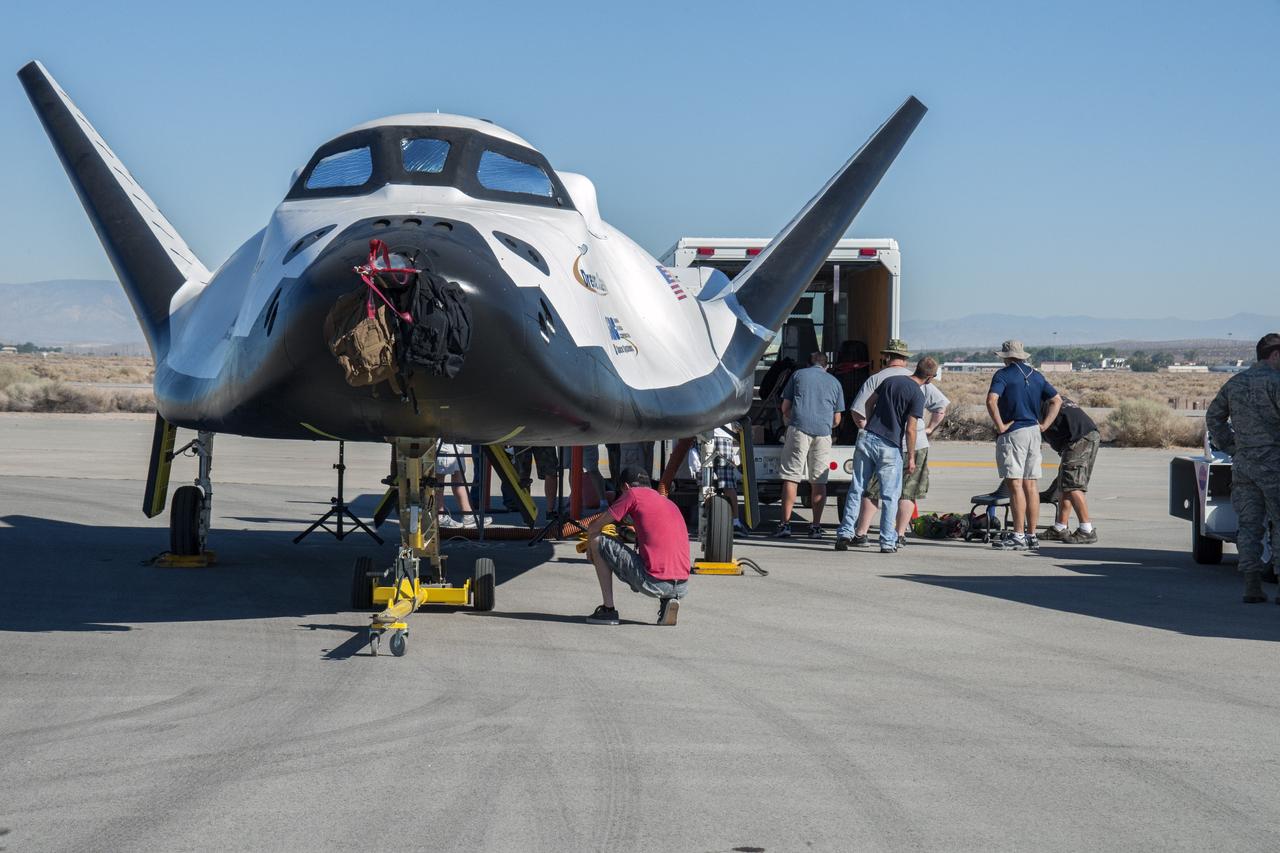

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0215-024 - Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC Space Systems' team members prepare to tow the Dream Chaser flight vehicle along a concrete runway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California for range and taxi tow tests. The ground testing will validate the performance of the spacecraft's nose skid, brakes, tires and other systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
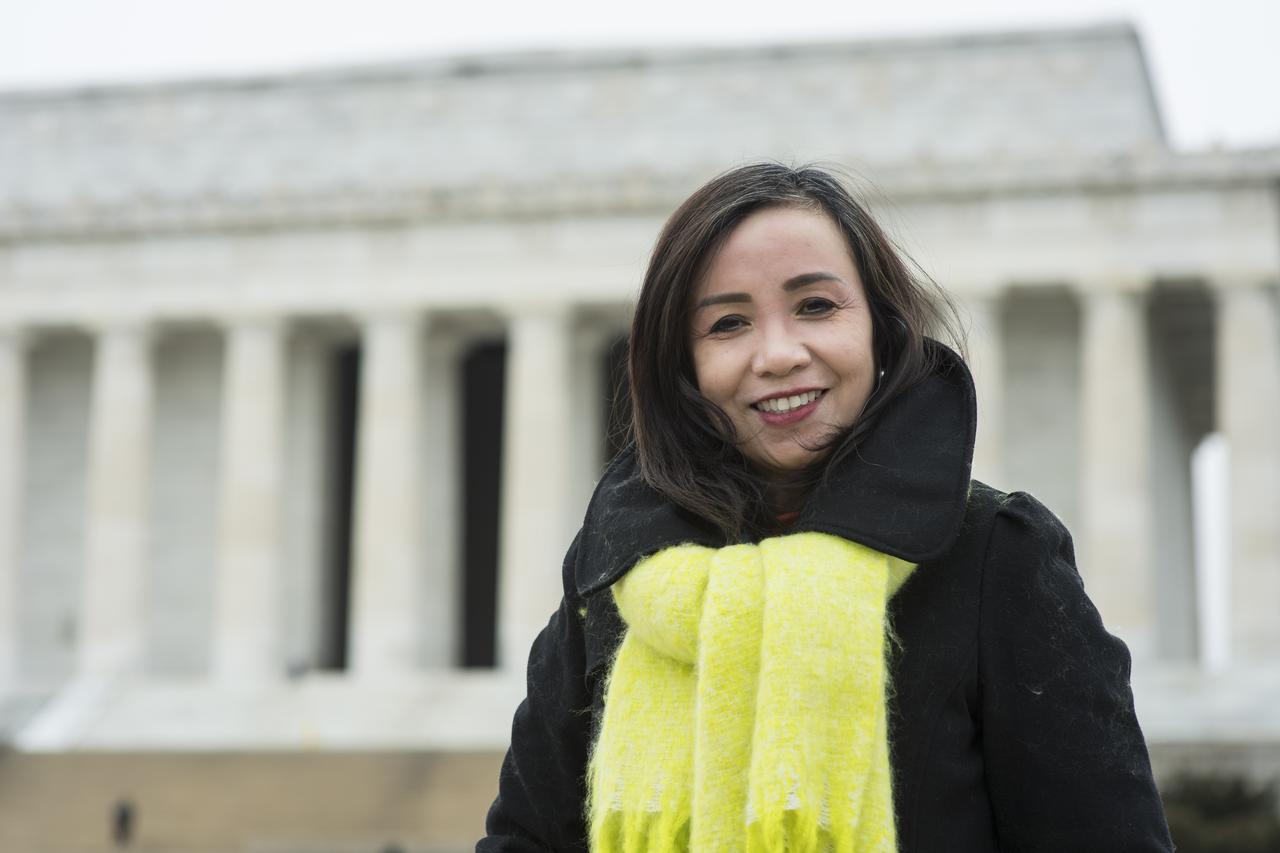

“Especially right now during the pandemic crisis, I love to occupy my mind. People say that they’re tired of being at home, but I don’t feel that. I practice yoga. I love decorating our house and working in the backyard during the summer time. If I don’t like where something is, I have to change it. That’s what I love. It’s the same thing with my work —I go outside the box to get ideas. I think about, how do I solve this? I apply the same skills to my creative passions and my current job. I create strategies for a better way of doing business for NASA. And I set the tone to keep me motivated and more productive.” NASA Senior Program Analyst, Jenny Acebron-Carlos, poses for a portrait at the Lincoln Memorial, Friday, Feb. 12, 2021 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
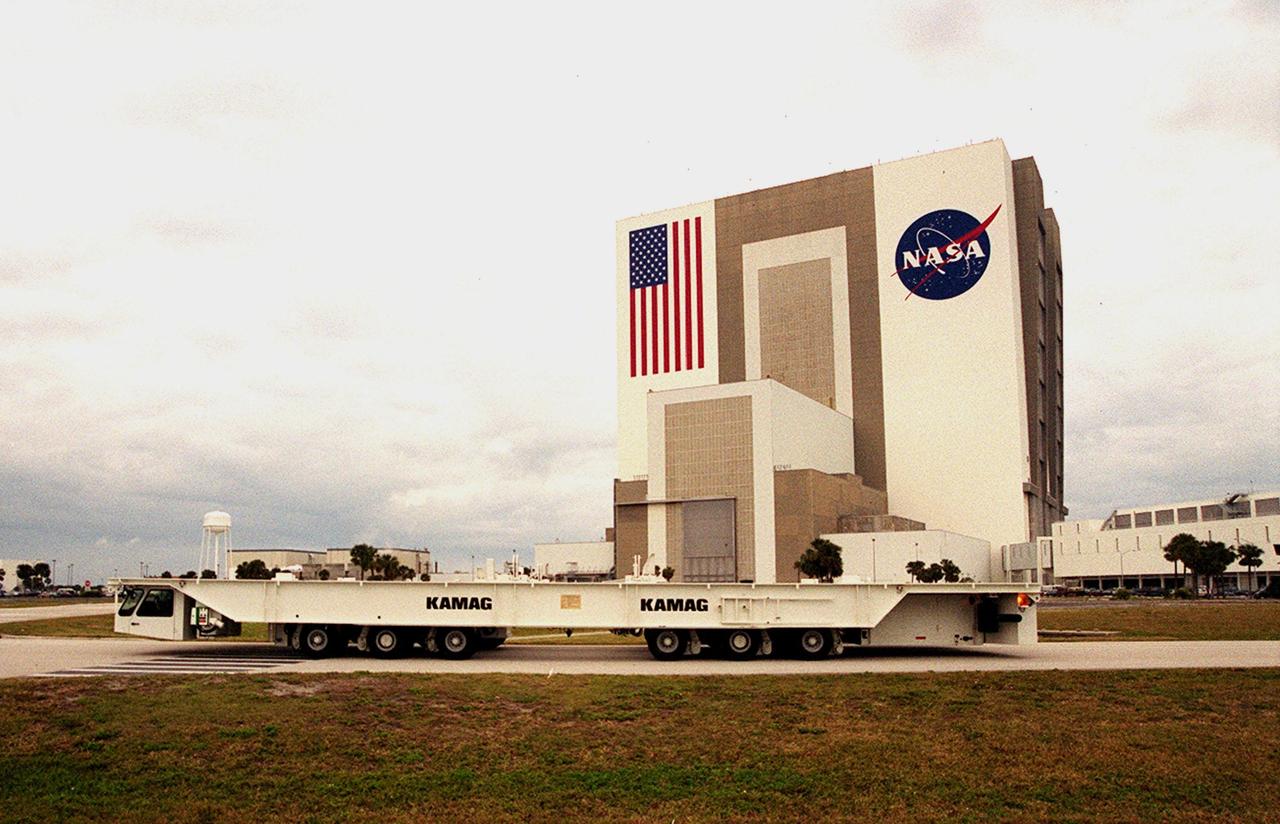
One of two new payload transporters for Kennedy Space Center moves past the Vehicle Assembly Building (left) and Launch Control Center (right) after being unloaded from a barge at Port Canaveral. The transporters, manufactured by the KAMAG Transporttechnick, GmbH, of Ulm, Germany, are replacing the existing Payload Canister Transporter system, which is 20 years old. Each transporter is 65 feet long and 22 feet wide and has 24 tires divided between its two axles. The transporter travels 10 miles per hour unloaded, 5 miles per hour when loaded; it weighs up to 172,000 pounds when the canister with payloads rides atop. The transporters will be outfitted with four subsystems for monitoring the environment inside the canister during the payload moves: the Electrical Power System, Environmental Control System, Instrumentation and Communications System, and the Fluids and Gases System. Engineers and technicians are being trained on the transporter's operation and maintenance
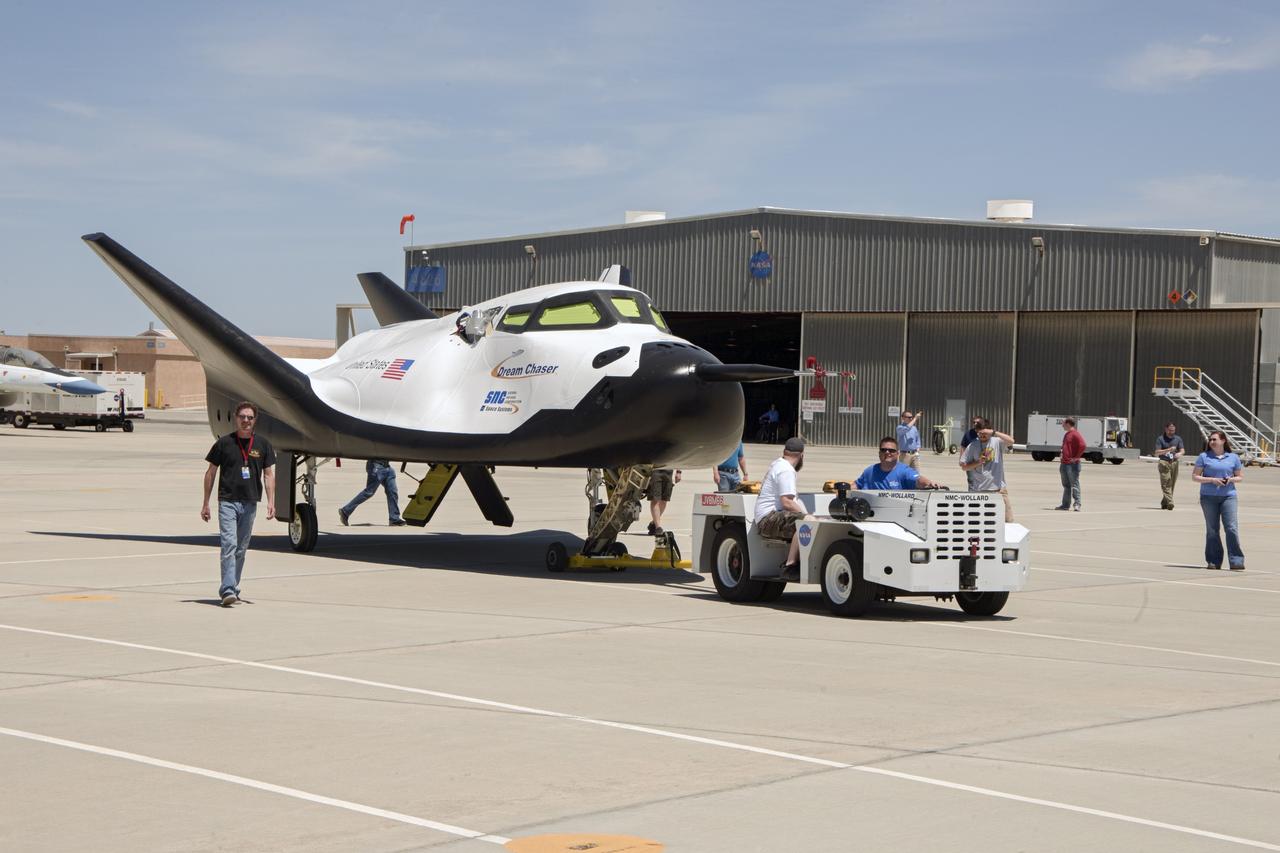

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-161-35 - Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC Space Systems' team members tow the Dream Chaser flight vehicle out to a concrete runway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California for range and taxi tow tests. The ground testing will validate the performance of the spacecraft's nose skid, brakes, tires and other systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich

One of two new payload transporters for Kennedy Space Center moves through Cape Canaveral Air Station after being unloaded from a barge at Port Canaveral. The transporters, manufactured by the KAMAG Transporttechnick, GmbH, of Ulm, Germany, are replacing the existing Payload Canister Transporter system, which is 20 years old. Each transporter is 65 feet long and 22 feet wide and has 24 tires divided between its two axles. The transporter travels 10 miles per hour unloaded, 5 miles per hour when loaded; it weighs up to 172,000 pounds when the canister with payloads rides atop. The transporters will be outfitted with four subsystems for monitoring the environment inside the canister during the payload moves: the Electrical Power System, Environmental Control System, Instrumentation and Communications System, and the Fluids and Gases System. Engineers and technicians are being trained on the transporter's operation and maintenance
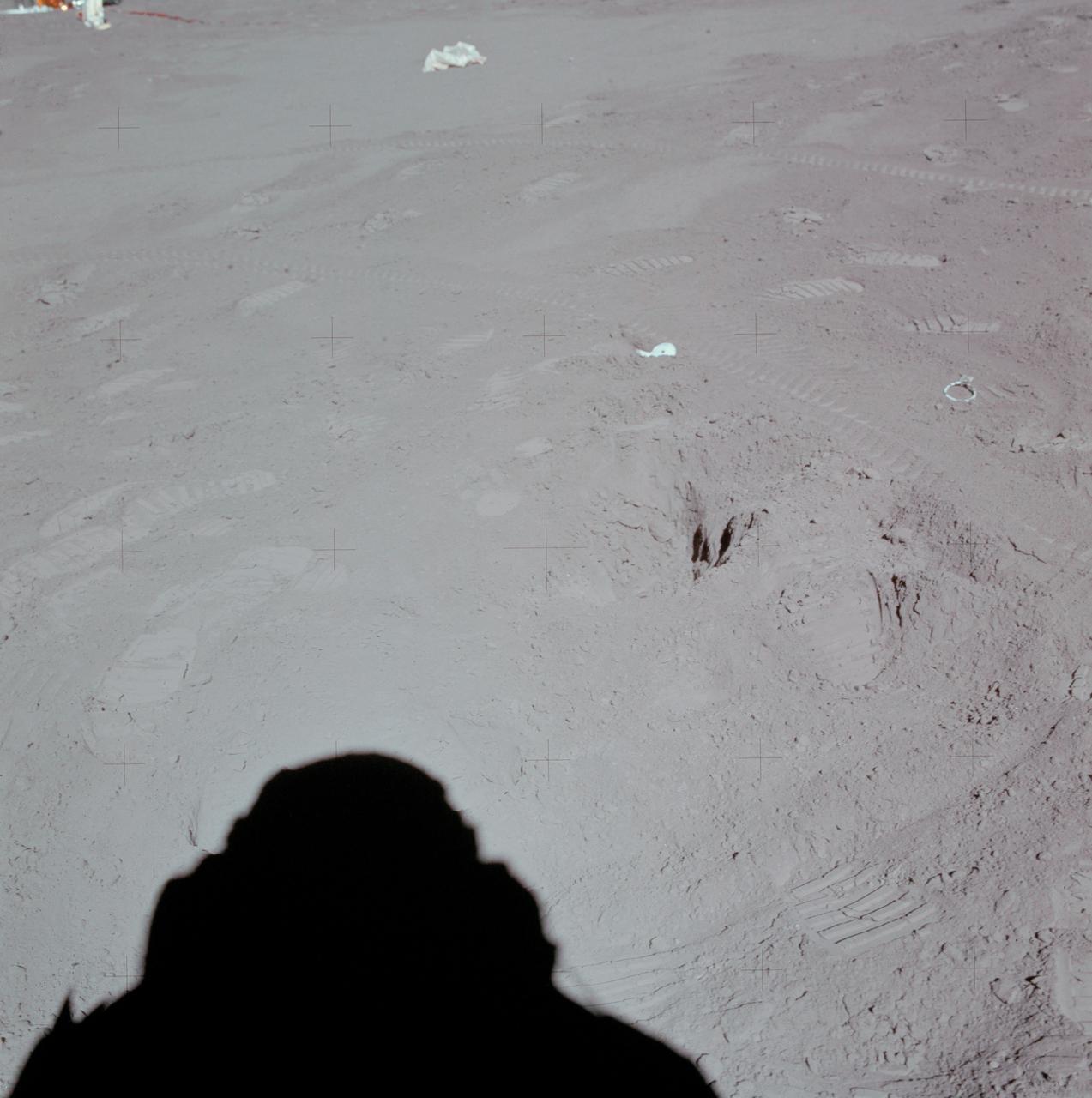

AS15-88-11872 (31 July 1971) --- This north-looking view at Station 8 near the Hadley-Apennine landing site was photographed by one of the missions two moon explorer's (see shadow, foreground) during the third Apollo 15 extravehicular activity (EVA). Prints from the boots of astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, as well as tire tracks from the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) are scattered throughout the view. A small part of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) is in the upper left corner. Lunar samples 15252 and 15253 were removed from this area and returned to Earth for analysis by scientists. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
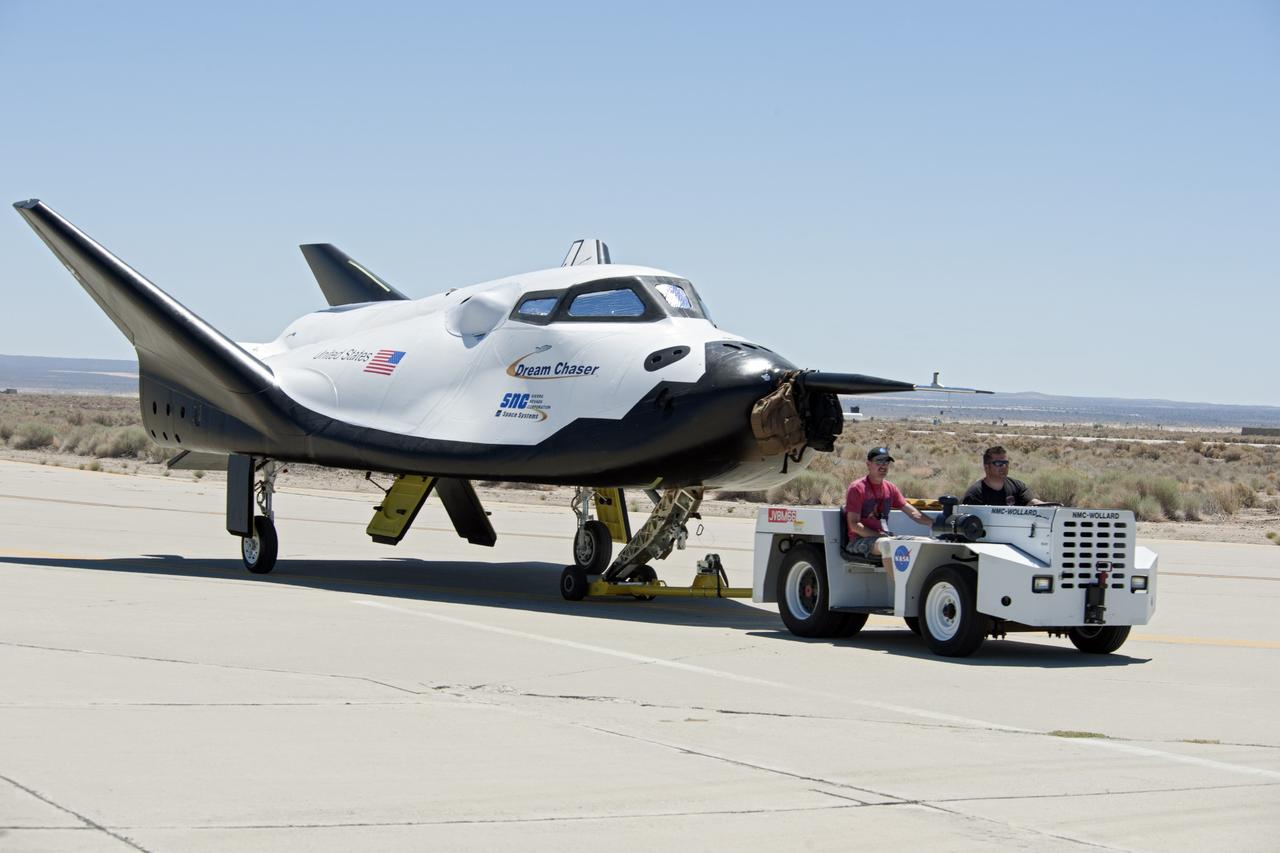

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0215-072 - Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC Space Systems' team members tow the Dream Chaser flight vehicle along a concrete runway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California for range and taxi tow tests. The ground testing will validate the performance of the spacecraft's nose skid, brakes, tires and other systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
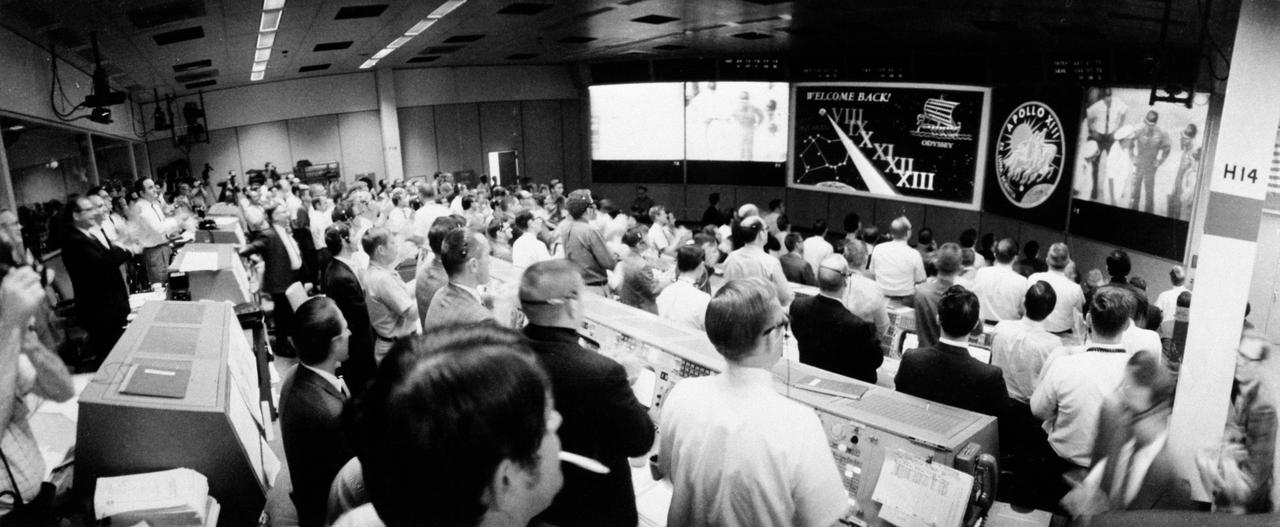

S70-35472 (17 April 1970) --- Overall view of the crowded Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center (MCC) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) during post-recovery ceremonies aboard the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 13 mission. The Apollo 13 spacecraft, with astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, aboard, splashed down in the South Pacific at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970. The smooth splashdown and recovery operations brought an end to a perilous spaceflight for the crewmembers, and a tiring one for ground crew in MCC.
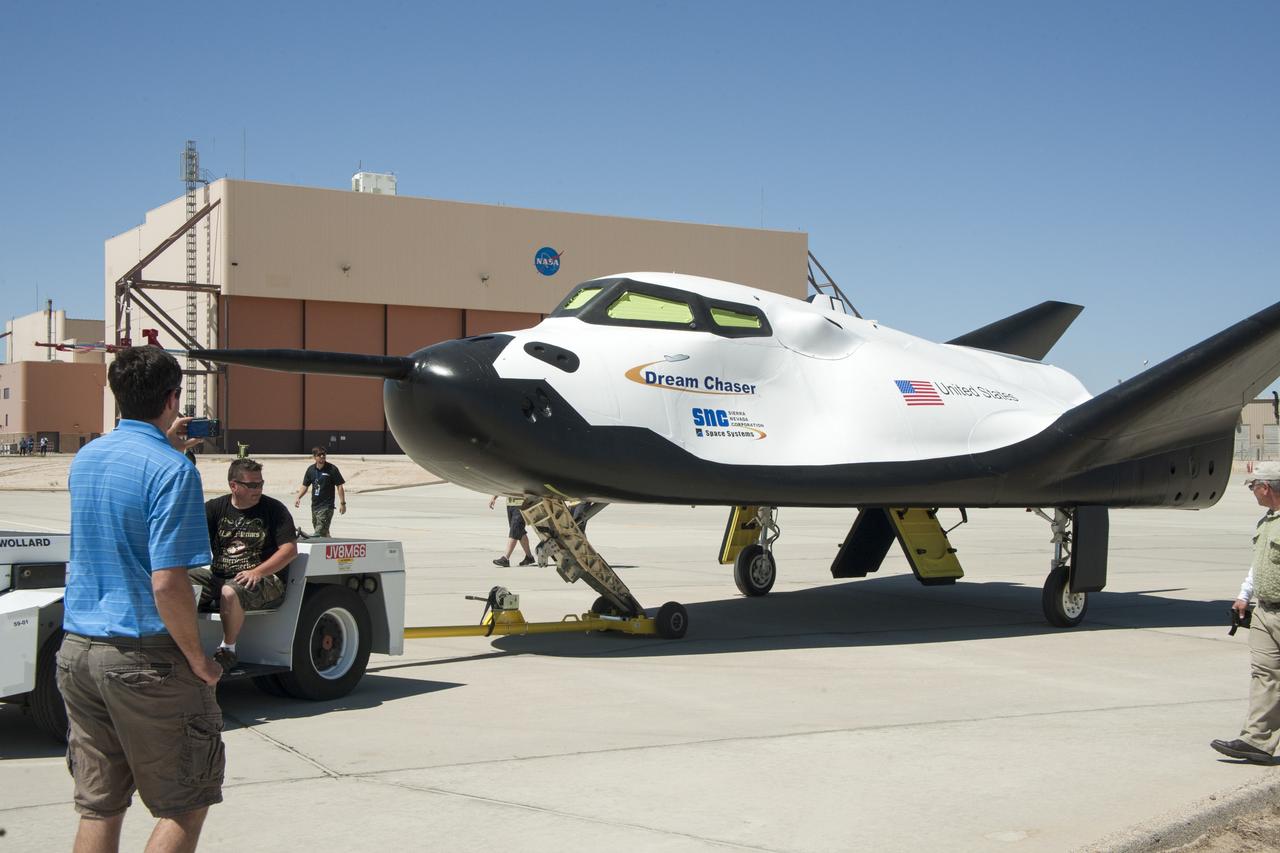

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-164-32 - Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC Space Systems' team members tow the Dream Chaser flight vehicle out to a concrete runway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California for range and taxi tow tests. The ground testing will validate the performance of the spacecraft's nose skid, brakes, tires and other systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
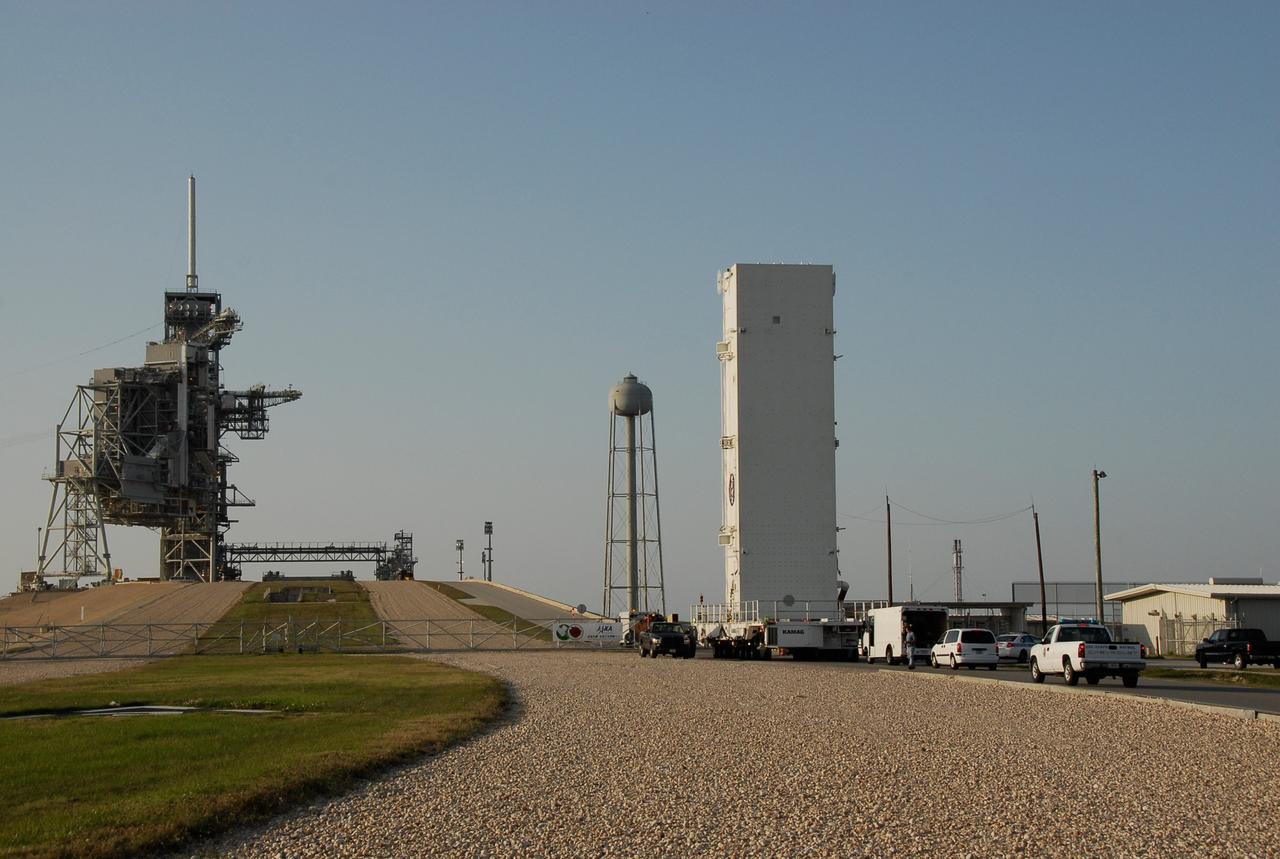

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Positioned on its 12-wheeled, 24-tire transporter, the payload canister with the STS-124 mission payload, Japanese Experiment Module - Pressurized Module and the Japanese Remote Manipulator System, or RMS, inside, approaches the ramp to Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The transporter is 65 feet long and 23 feet wide. The transporter’s wheels are independently steerable, permitting it to move forward, backward, sideways or diagonally and to turn on its own axis like a carousel. It is equipped with pneumatic-actuated braking and hydrostat¬ic leveling and drive systems. It is steered from a two-seat operator cab mounted at one end. From the payload changeout room, the pressurized module and RMS will be transferred into space shuttle Discovery’s payload bay. Launch is targeted for May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
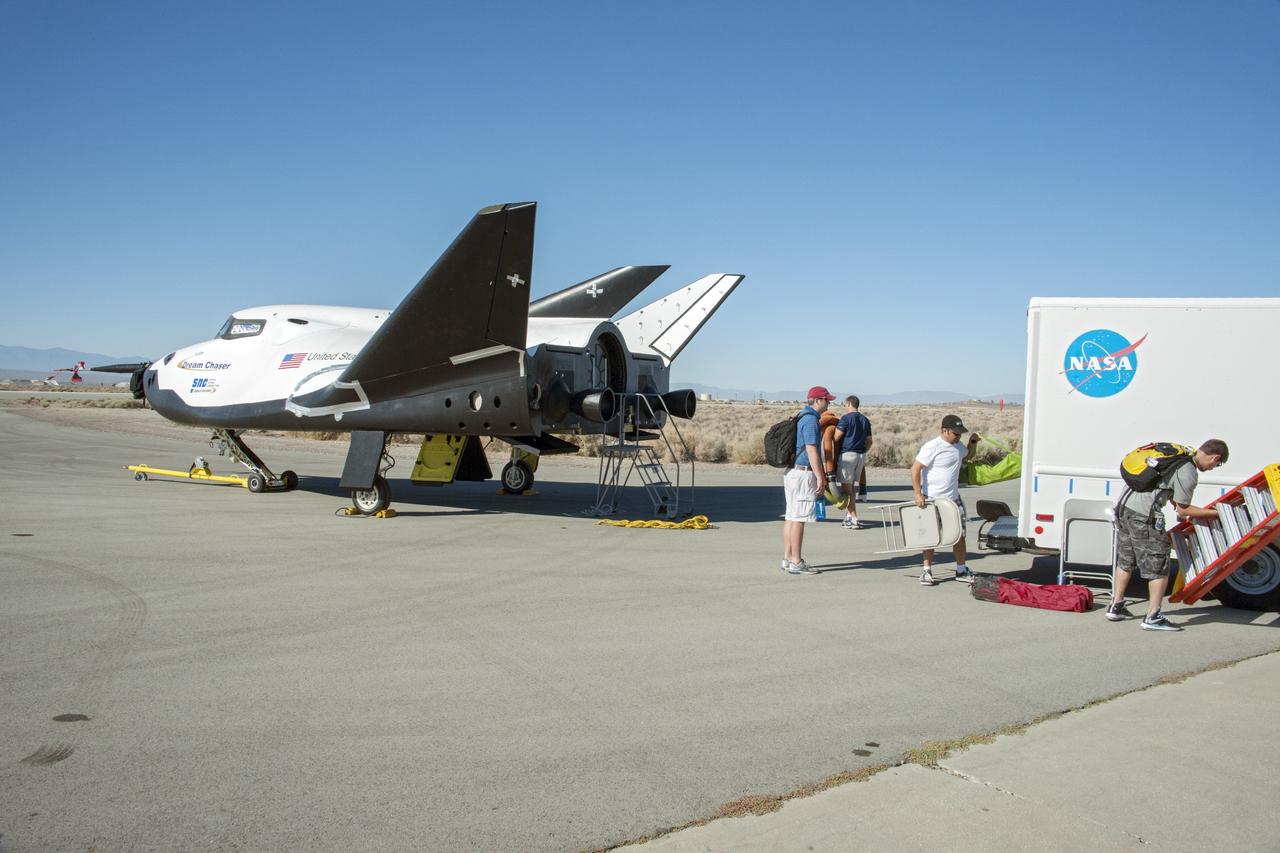

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0215-016 - Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC Space Systems' team members prepare to tow the Dream Chaser flight vehicle along a concrete runway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California for range and taxi tow tests. The ground testing will validate the performance of the spacecraft's nose skid, brakes, tires and other systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
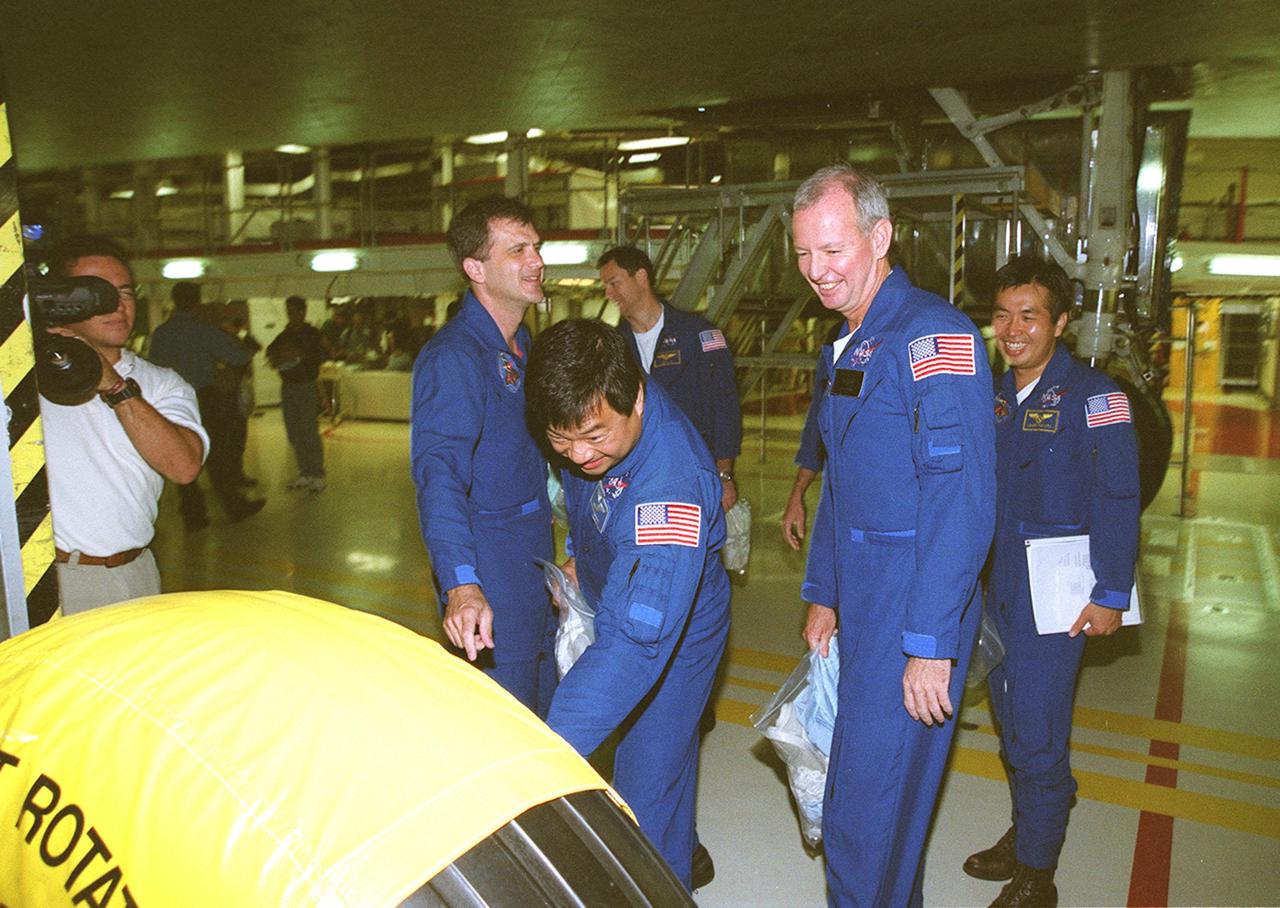

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-92 crew look over a tire on the landing gear of orbiter Discovery in the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1. From left to right are Mission Specialists Jeff Wisoff (pointing) and Leroy Chiao, Commander Brian Duffy and Mission Specialist Koichi Wakata, who is with the Japanese space agency. Standing behind them is Mission Specialist Michael Lopez-Alegria. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. Others taking part are Pilot Pam Melroy and Mission Specialist Bill McArthur. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 on Shuttle Discovery from Launch Pad 39A on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. Discovery will carry the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1, Pressurized Mating Adapter 3 (PMA-3), Ku-band Communications System, and Control Moment Gyros (CMGs)

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, United Space Alliance and B.F. Goodrich technicians remove part of space shuttle Discovery's right main-gear strut where a leaking seal has been found. They will replace the seal. The struts act as shock absorbers during the shuttle's landing. Engineers determined the observed leak of hydraulic fluid in the main landing gear strut exceeded specification and could not be reduced to an acceptable rate. Removing the strut and replacing seals require disconnecting and replacing the brakes and tires, disconnecting and reconnecting instruments and other requirements to allow access to the strut. Discovery had been scheduled to roll over Sept. 19 from its processing hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. A new rollover date will be set after technicians determine how long replacing the seal will take. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, United Space Alliance and B.F. Goodrich technicians begin work on the starboard landing gear assembly of space shuttle Discovery. They will replace a leaking dynamic seal in Discovery's right main-gear strut. The struts act as shock absorbers during the shuttle's landing. Engineers determined the observed leak of hydraulic fluid in the main landing gear strut exceeded specification and could not be reduced to an acceptable rate. Removing the strut and replacing seals require disconnecting and replacing the brakes and tires, disconnecting and reconnecting instruments and other requirements to allow access to the strut. Discovery had been scheduled to roll over Sept. 19 from its processing hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. A new rollover date will be set after technicians determine how long replacing the seal will take. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
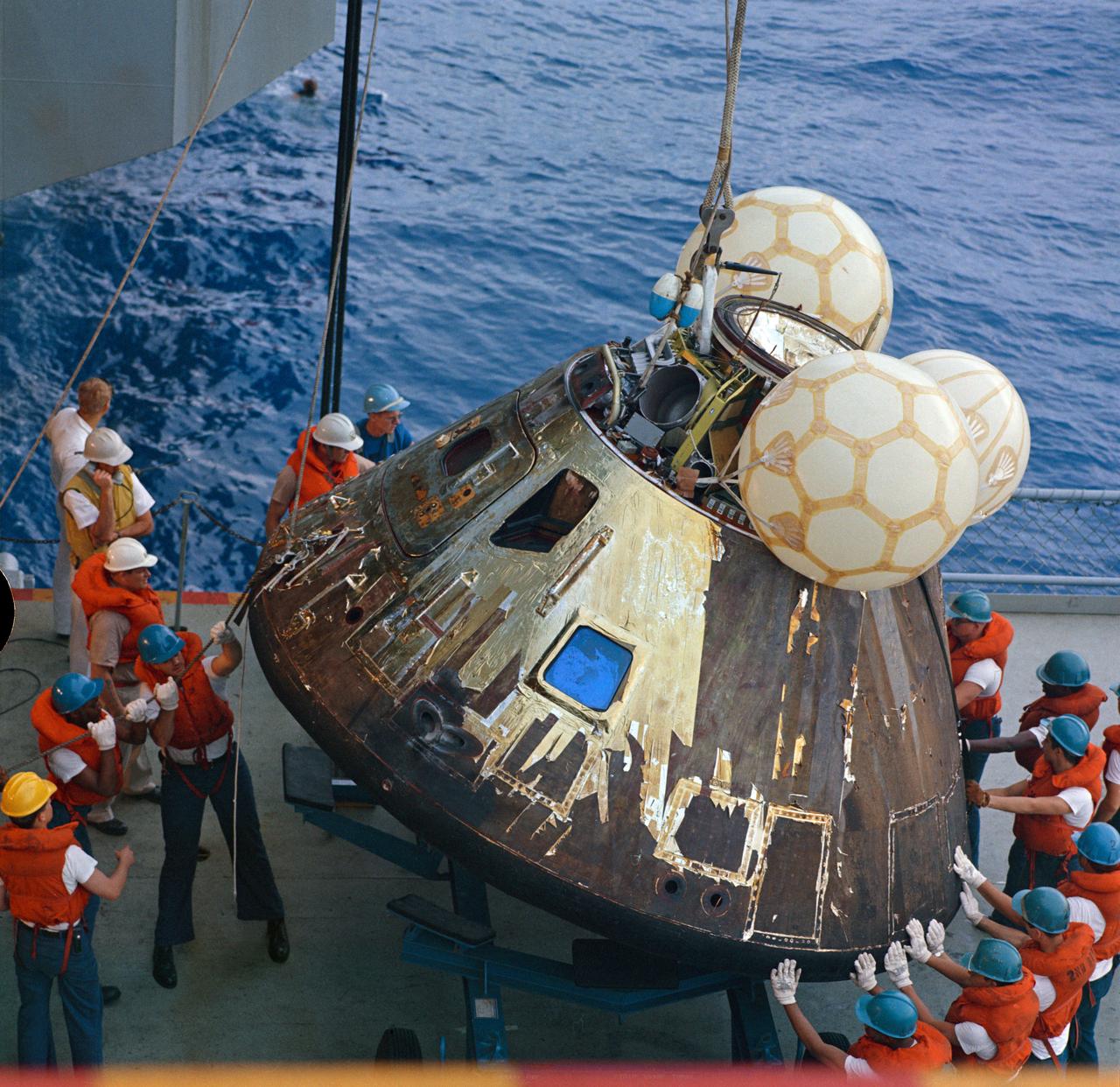

S70-35632 (17 April 1970) --- Crewmen aboard the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 13 mission, guide the Command Module (CM) atop a dolly onboard the ship. The CM is connected by strong cable to a hoist on the vessel. The Apollo 13 crewmembers, astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, were already aboard the USS Iwo Jima when this photograph was made. The CM, with the three tired crewmen aboard, splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, only about four miles from the recovery vessel in the South Pacific Ocean.
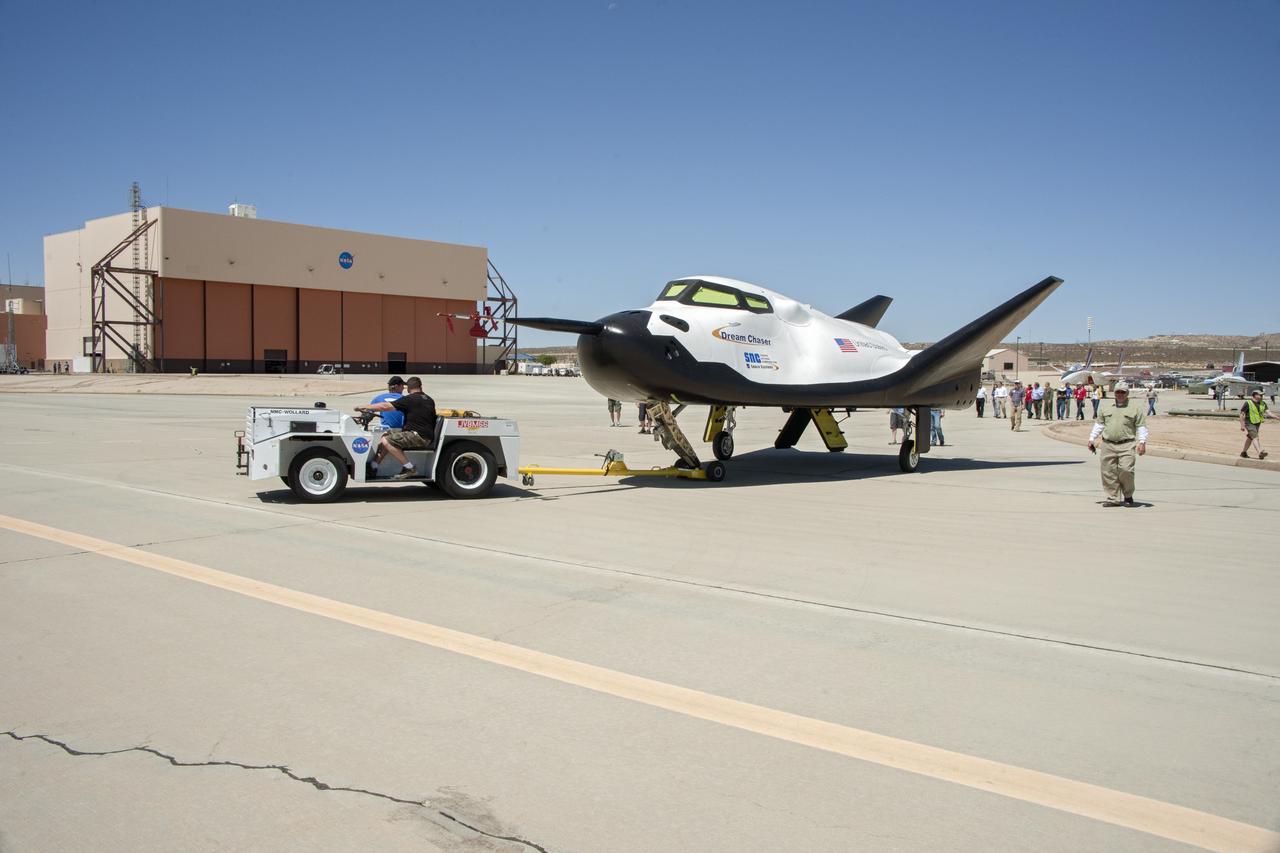

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-164-34 - Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC Space Systems' team members tow the Dream Chaser flight vehicle out to a concrete runway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California for range and taxi tow tests. The ground testing will validate the performance of the spacecraft's nose skid, brakes, tires and other systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
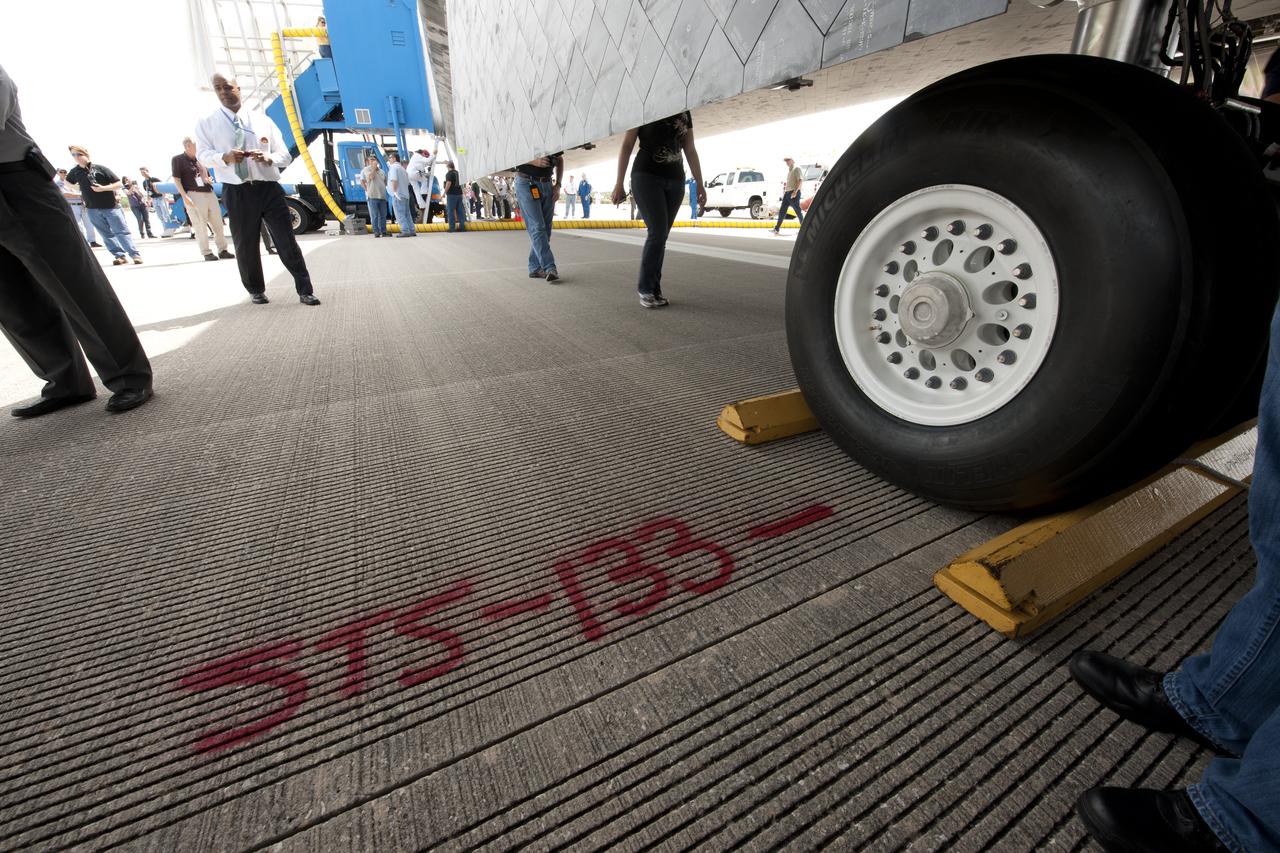

The runway of the Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) is marked to show where the wheels stopped for the space shuttle Discovery (STS-133) shortly after it landed, Wednesday, March 9, 2011, at Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Fla., completing its 39th and final flight. Since 1984, Discovery flew 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited Earth 5,830 times and traveled 148,221,675 miles. Photo credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Streams of smoke trail from the main landing gear tires as space shuttle Atlantis touches down on Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after 11 days in space, completing the 4.5-million-mile STS-129 mission on orbit 171. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Aboard Atlantis are Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Carl Winebarger
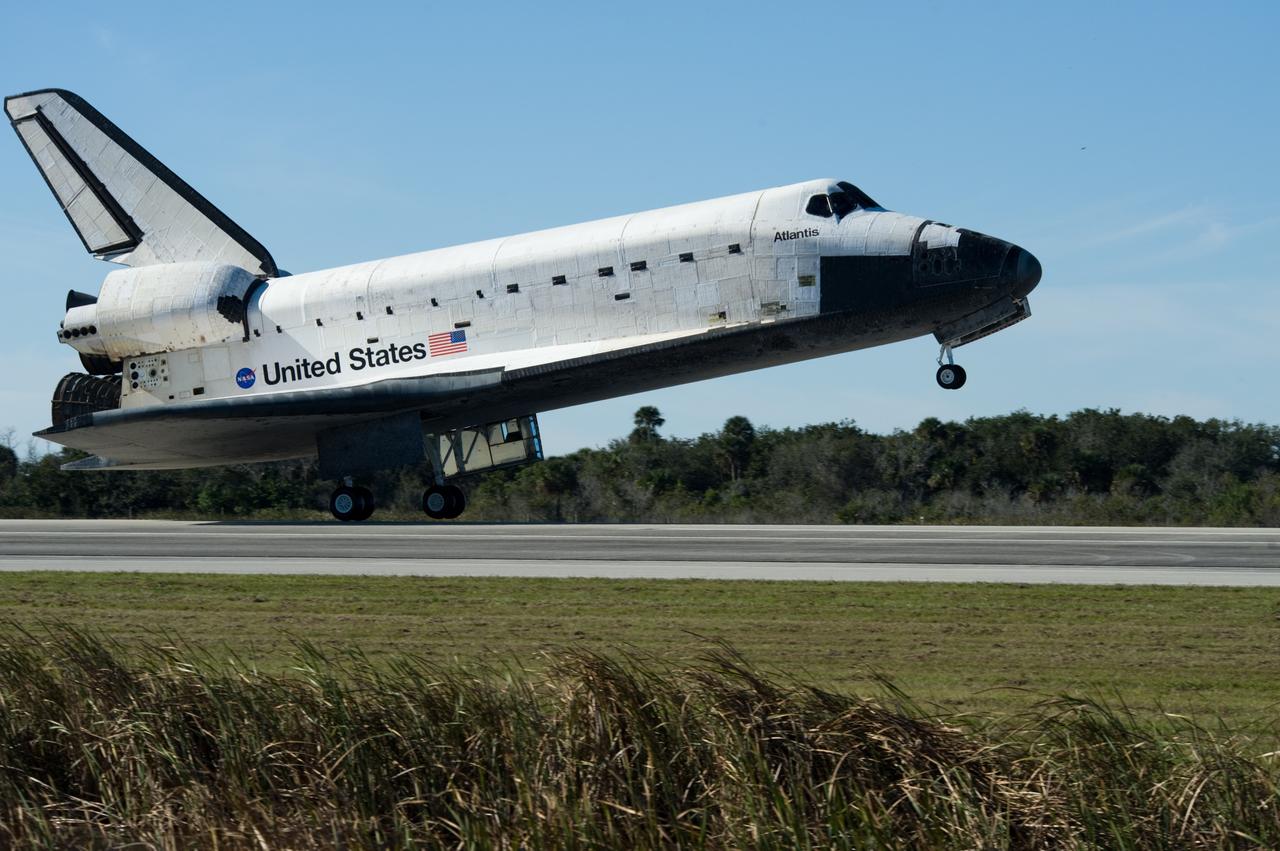

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space shuttle Atlantis' main landing gear tires near contact with Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after 11 days in space, completing the 4.5-million mile STS-129 mission on orbit 171. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Aboard Atlantis are Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Carl Winebarger

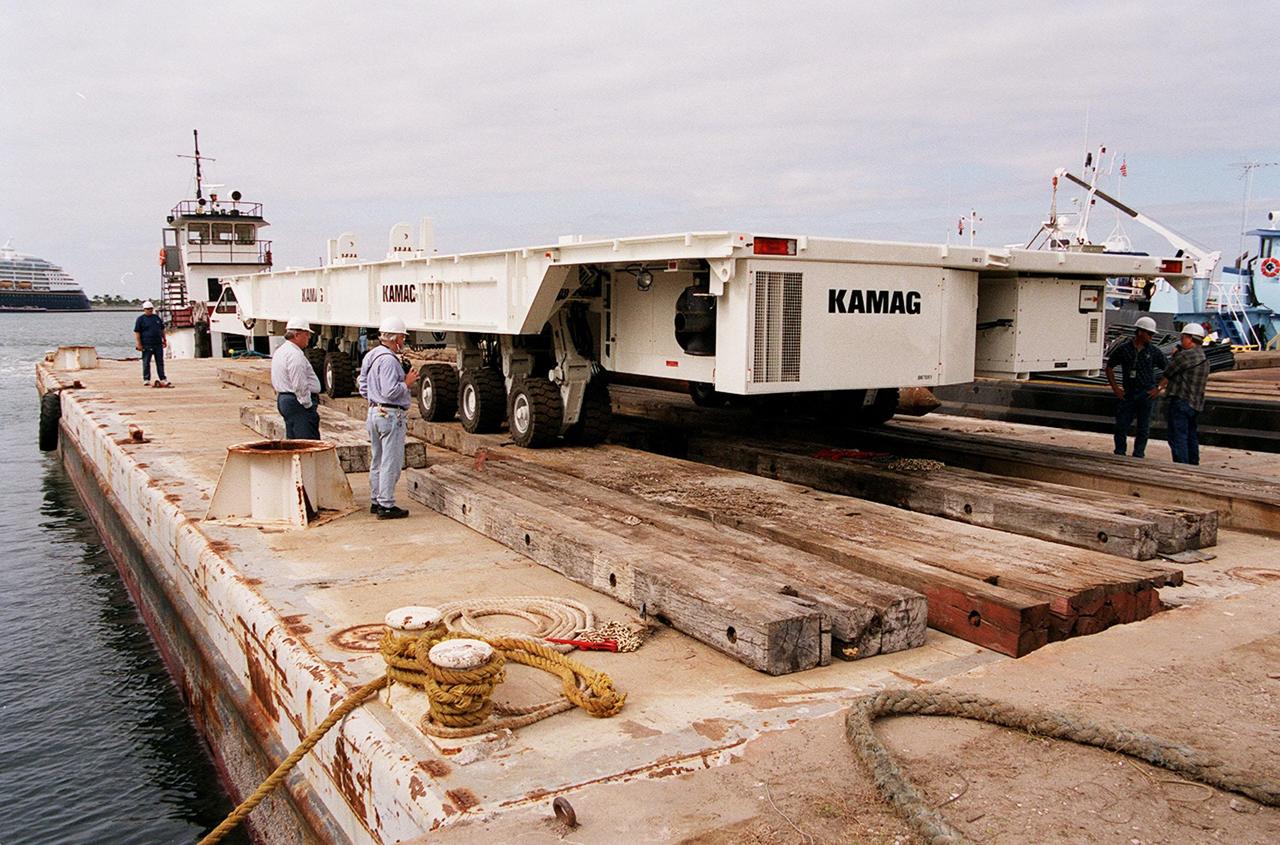
One of two new payload transporters for Kennedy Space Center arrives at Port Canaveral. In the background is a cruise ship docked at the Port. The transporters were shipped by barge from their manufacturer, the KAMAG Company of Ulm, Germany. They are used to carry spacecraft and International Space Station elements from payload facilities to and from the launch pads and orbiter hangars. Each transporter is 65 feet long and 22 feet wide and has 24 tires divided between its two axles. The transporter travels 10 miles per hour unloaded, 5 miles per hour when loaded; it weighs up to 172,000 pounds when the canister with payloads rides atop. The transporters will be outfitted with four subsystems for monitoring the environment inside the canister during the payload moves: the Electrical Power System, Environmental Control System, Instrumentation and Communications System, and the Fluids and Gases System. Engineers and technicians are being trained on the transporter's operation and maintenance. The new transporters are replacing the 20-year-old existing Payload Canister Transporter system
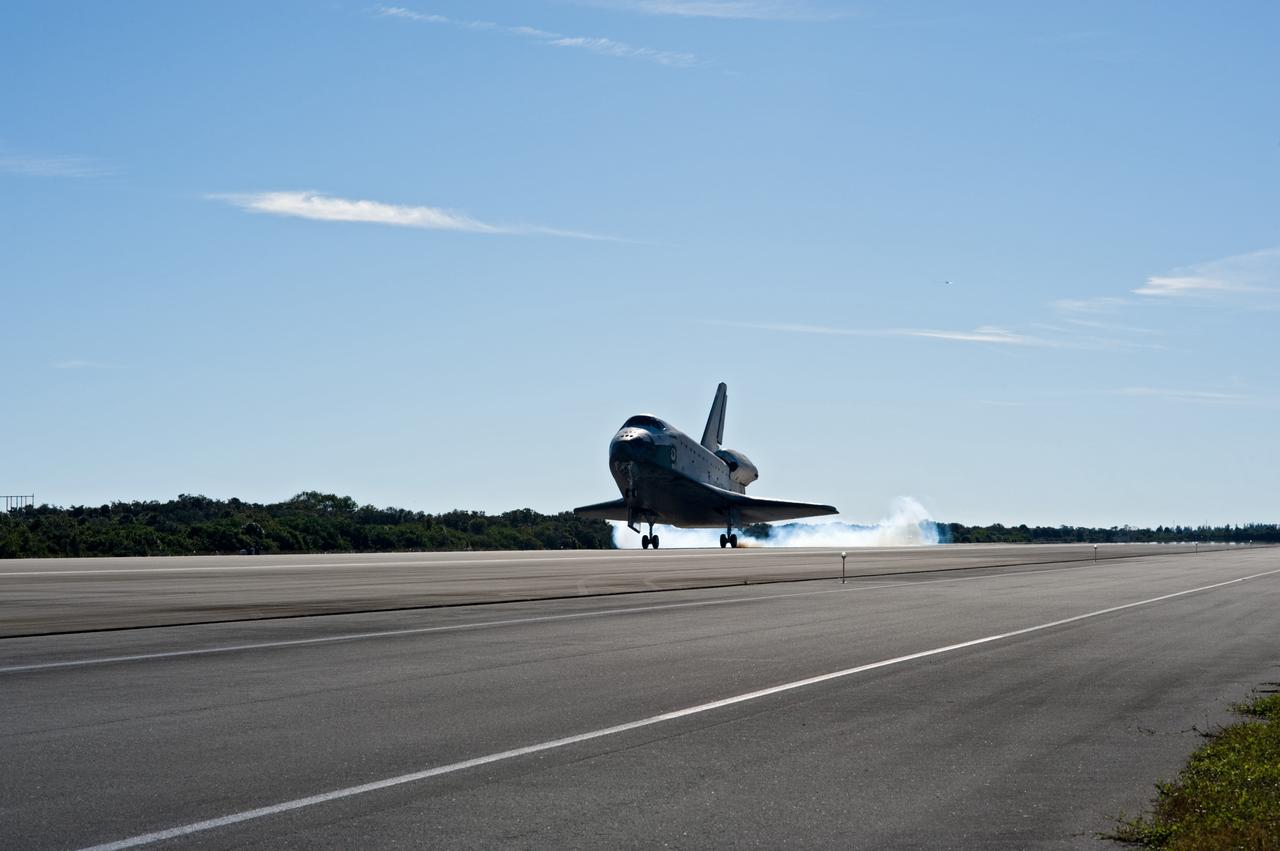

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Streams of smoke trail from the main landing gear tires as space shuttle Atlantis touches down on Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after 11 days in space, completing the 4.5-million-mile STS-129 mission on orbit 171. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Aboard Atlantis are Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell and Rick Prickett
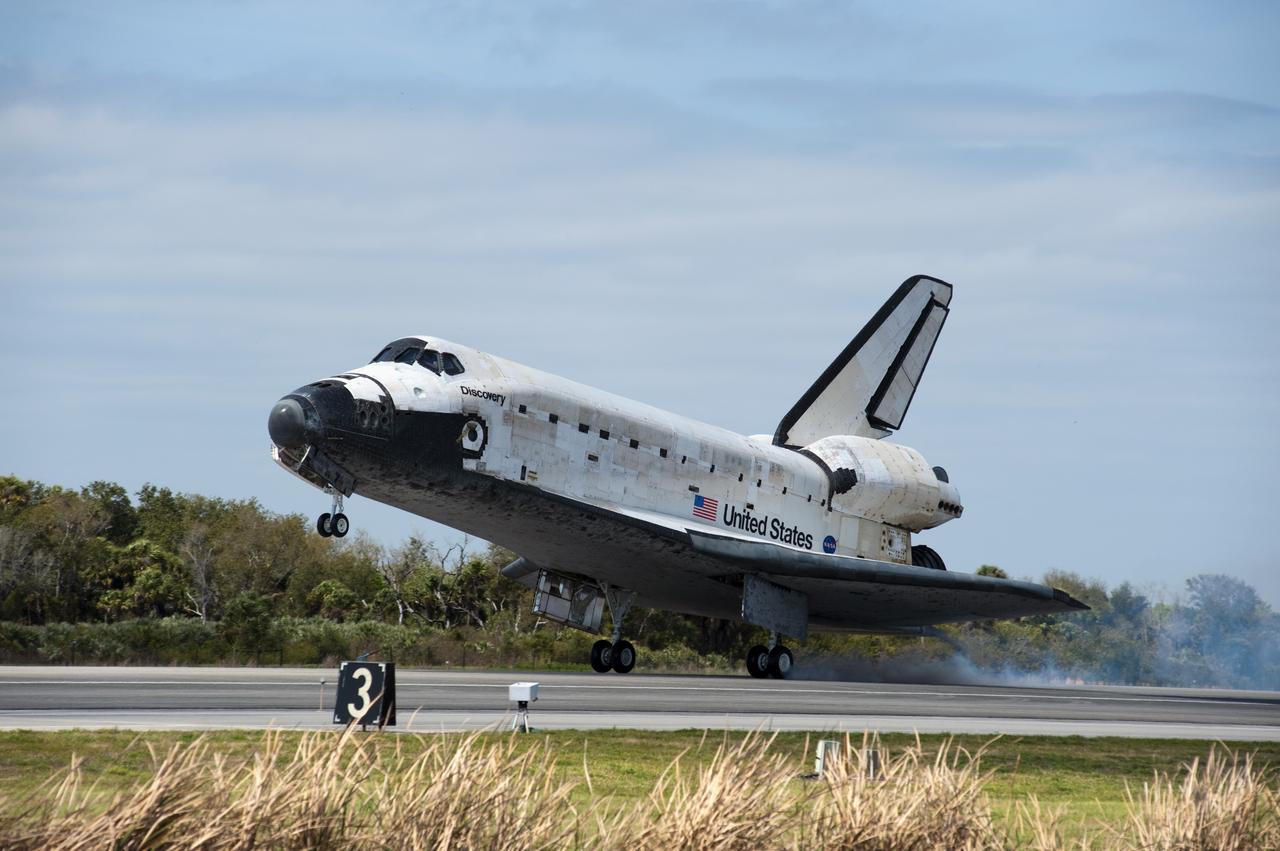

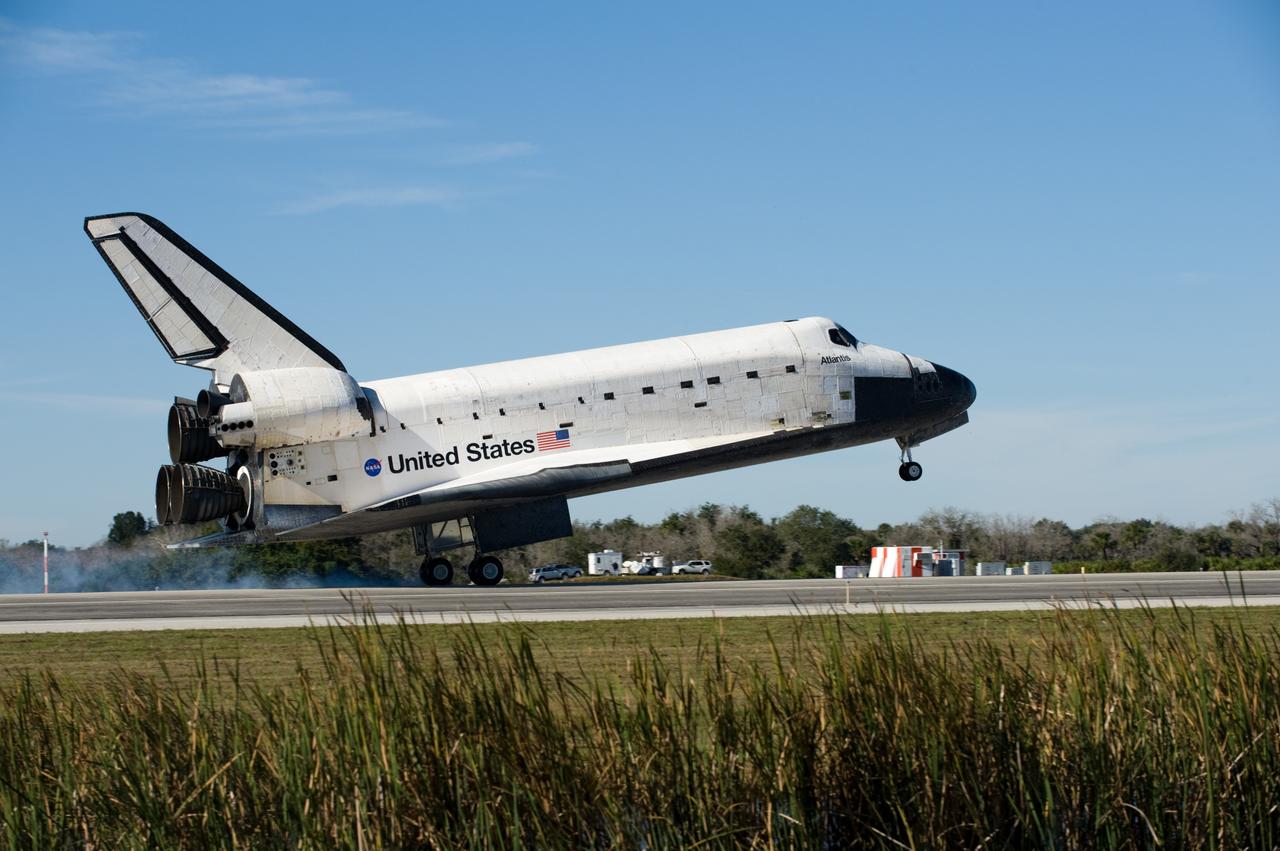
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Streams of smoke trail from the main landing gear tires as space shuttle Discovery touches down on Runway 15 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after 13-days in space, completing the 5.3-million-mile STS-133 mission. Main gear touchdown was at 11:57:17 a.m., followed by nose gear touchdown at 11:57:28, and wheelstop at 11:58:14 a.m. On board are Commander Steve Lindsey, Pilot Eric Boe, and Mission Specialists Nicole Stott, Michael Barratt, Alvin Drew and Steve Bowen. Discovery and its six-member crew delivered the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. STS-133 was Discovery's 39th and final mission. This was the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. Photo credit: NASA/Linda Perry
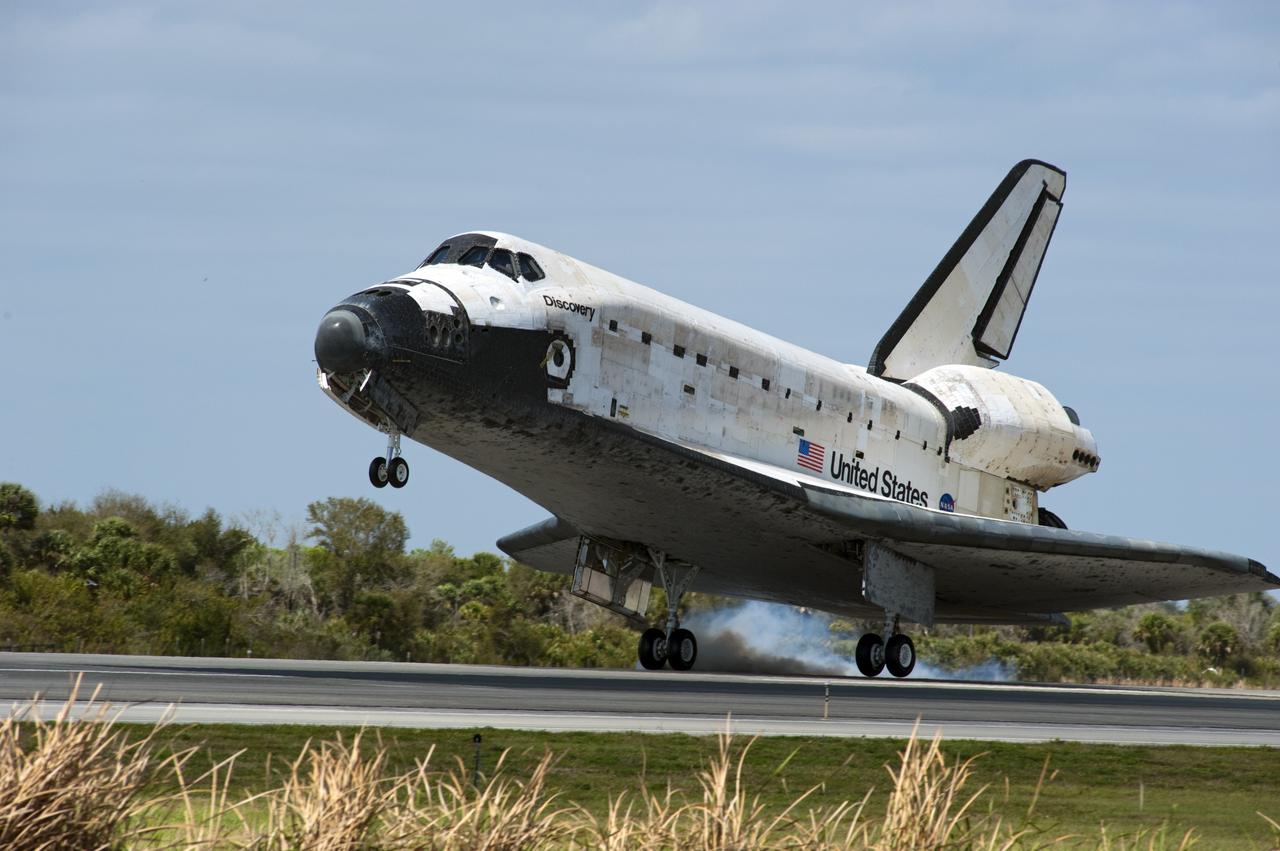

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Streams of smoke trail from the main landing gear tires as space shuttle Discovery touches down on Runway 15 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landing was at 11:57 a.m. EST, completing the 13-day STS-133 mission to the International Space Station. Main gear touchdown was at 11:57:17 a.m., followed by nose gear touchdown at 11:57:28, and wheelstop at 11:58:14 a.m. On board are Commander Steve Lindsey, Pilot Eric Boe, and Mission Specialists Nicole Stott, Michael Barratt, Alvin Drew and Steve Bowen. Discovery and its six-member crew delivered the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. STS-133 was Discovery's 39th and final mission. This was the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Streams of smoke trail from the main landing gear tires as space shuttle Endeavour touches down on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. EDT, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. On board are STS-134 Commander Mark Kelly, Pilot Greg H. Johnson, and Mission Specialists Mike Fincke, Drew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and the European Space Agency's Roberto Vittori. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray
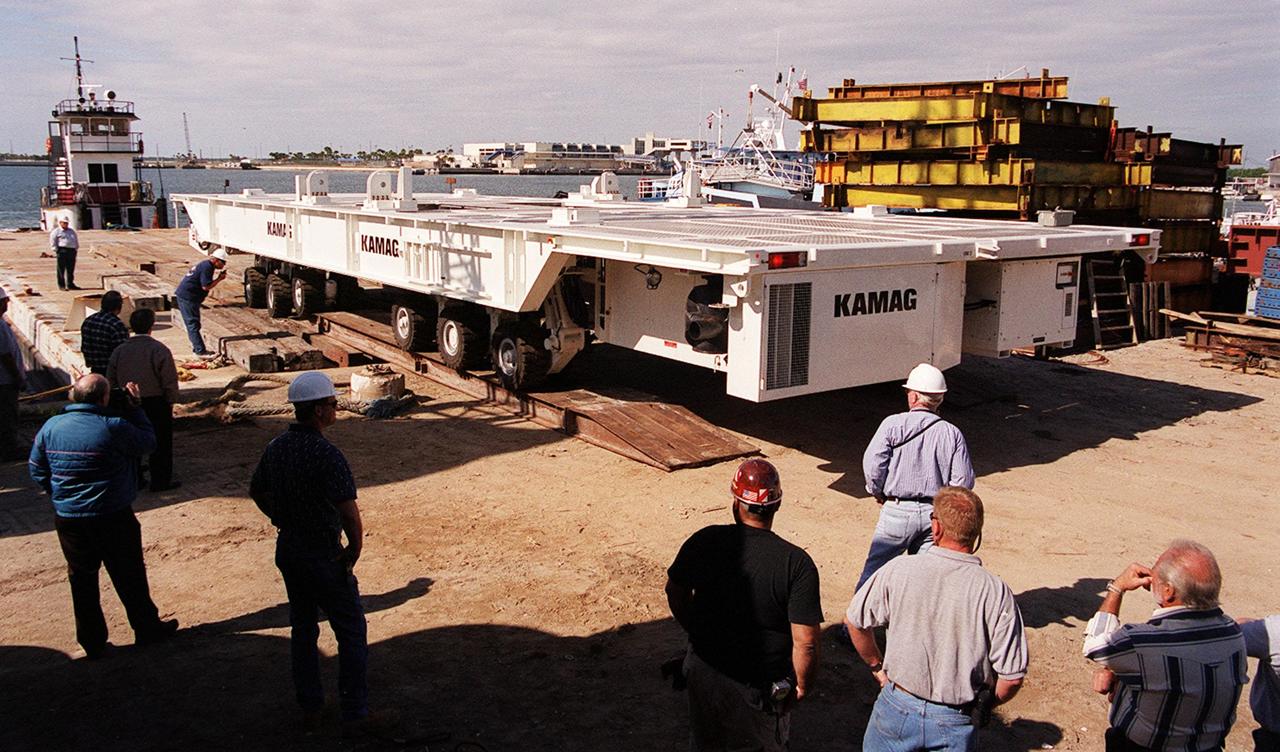

One of two new payload transporters for Kennedy Space Center arrives at Port Canaveral. They were shipped by barge from their manufacturer, the KAMAG Company of Ulm, Germany. The transporters are used to carry spacecraft and International Space Station elements from payload facilities to and from the launch pads and orbiter hangars. Each transporter is 65 feet long and 22 feet wide and has 24 tires divided between its two axles. The transporter travels 10 miles per hour unloaded, 5 miles per hour when loaded; it weighs up to 172,000 pounds when the canister with payloads rides atop. The transporters will be outfitted with four subsystems for monitoring the environment inside the canister during the payload moves: the Electrical Power System, Environmental Control System, Instrumentation and Communications System, and the Fluids and Gases System. Engineers and technicians are being trained on the transporter's operation and maintenance. The new transporters are replacing the 20-year-old existing Payload Canister Transporter system

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The tires of space shuttle Atlantis' main landing gear make contact with Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after 11 days in space, completing the 4.5-million mile STS-129 mission on orbit 171. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Aboard Atlantis are Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Thomas Farrar Jr.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Touchdown is apparent by the cloud of dust kicked up by space shuttle Atlantis as its main landing gear tires contact Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After 11 days in space, Atlantis' 4.5-million-mile STS-129 mission is completed on orbit 171. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Aboard Atlantis are Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell and Rick Prickett

One of two new payload transporters for Kennedy Space Center sits on the dock at Port Canaveral. In the background is a cruise ship docked at the Port. The transporters were shipped by barge from their manufacturer, the KAMAG Company of Ulm, Germany. They are used to carry spacecraft and International Space Station elements from payload facilities to and from the launch pads and orbiter hangars. Each transporter is 65 feet long and 22 feet wide and has 24 tires divided between its two axles. The transporter travels 10 miles per hour unloaded, 5 miles per hour when loaded; it weighs up to 172,000 pounds when the canister with payloads rides atop. The transporters will be outfitted with four subsystems for monitoring the environment inside the canister during the payload moves: the Electrical Power System, Environmental Control System, Instrumentation and Communications System, and the Fluids and Gases System. Engineers and technicians are being trained on the transporter's operation and maintenance. The new transporters are replacing the 20-year-old existing Payload Canister Transporter system
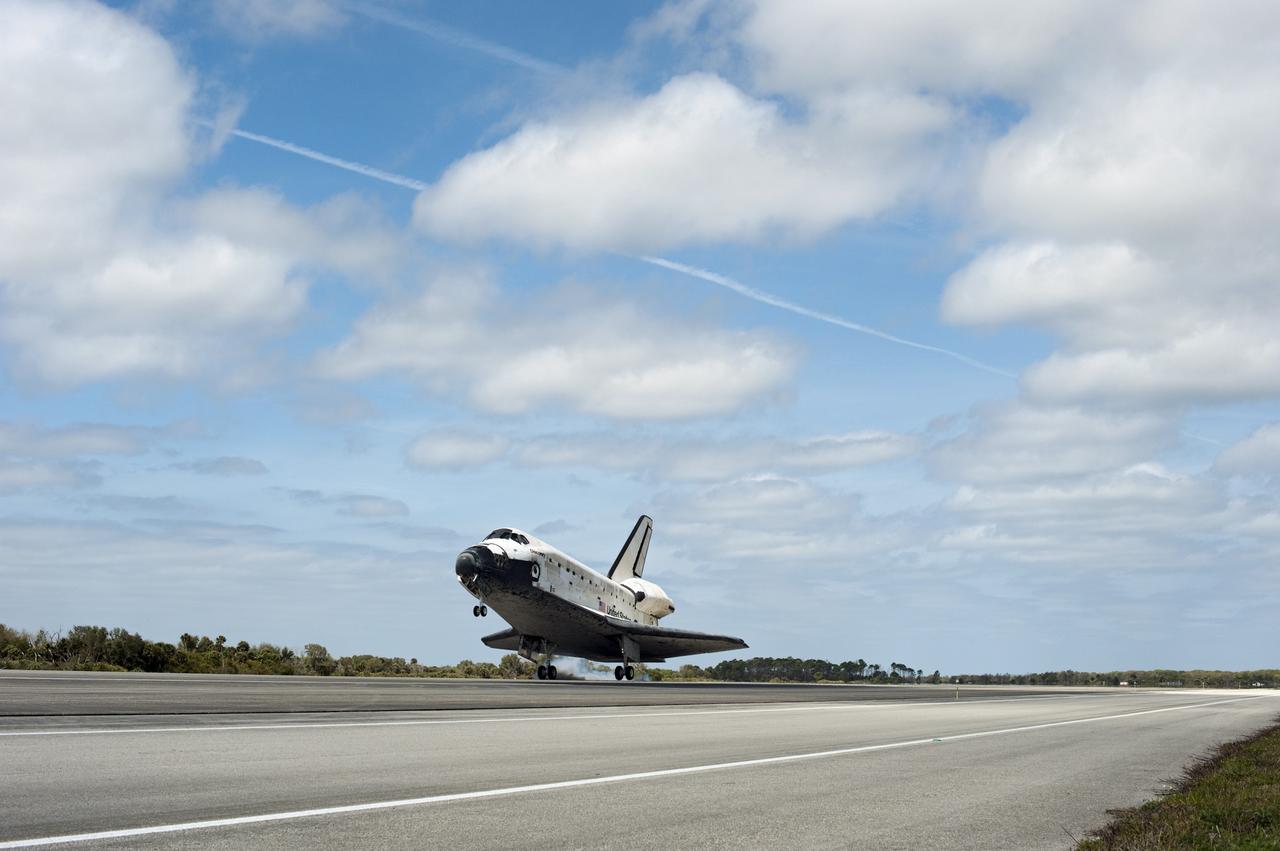

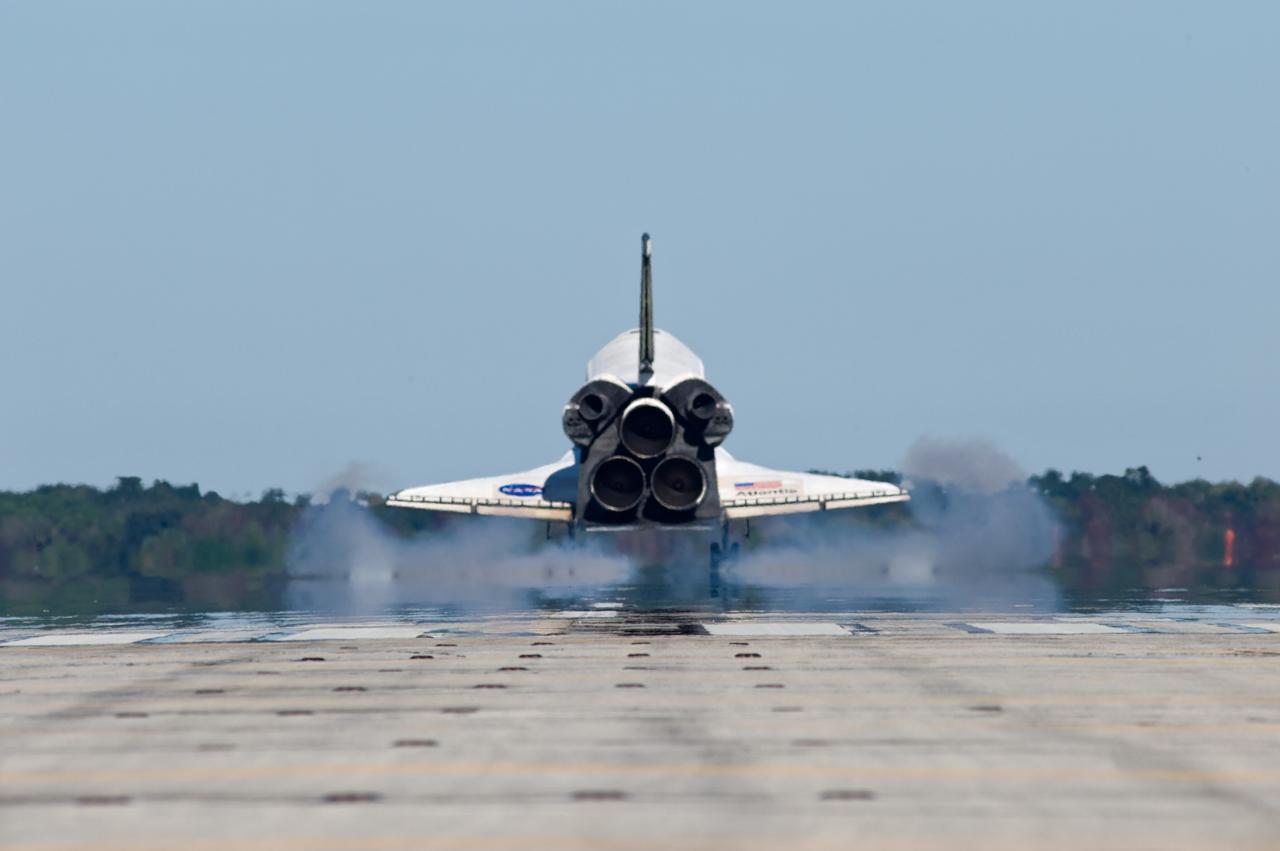
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A puff of smoke from space shuttle Discovery's tires follows their contact with Runway 15 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Discovery's final return from space completed the 13-day, 5.3-million-mile STS-133 mission. Main gear touchdown was at 11:57:17 a.m., followed by nose gear touchdown at 11:57:28, and wheelstop at 11:58:14 a.m. On board are Commander Steve Lindsey, Pilot Eric Boe, and Mission Specialists Nicole Stott, Michael Barratt, Alvin Drew and Steve Bowen. Discovery and its six-member crew delivered the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. STS-133 was Discovery's 39th and final mission. This was the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
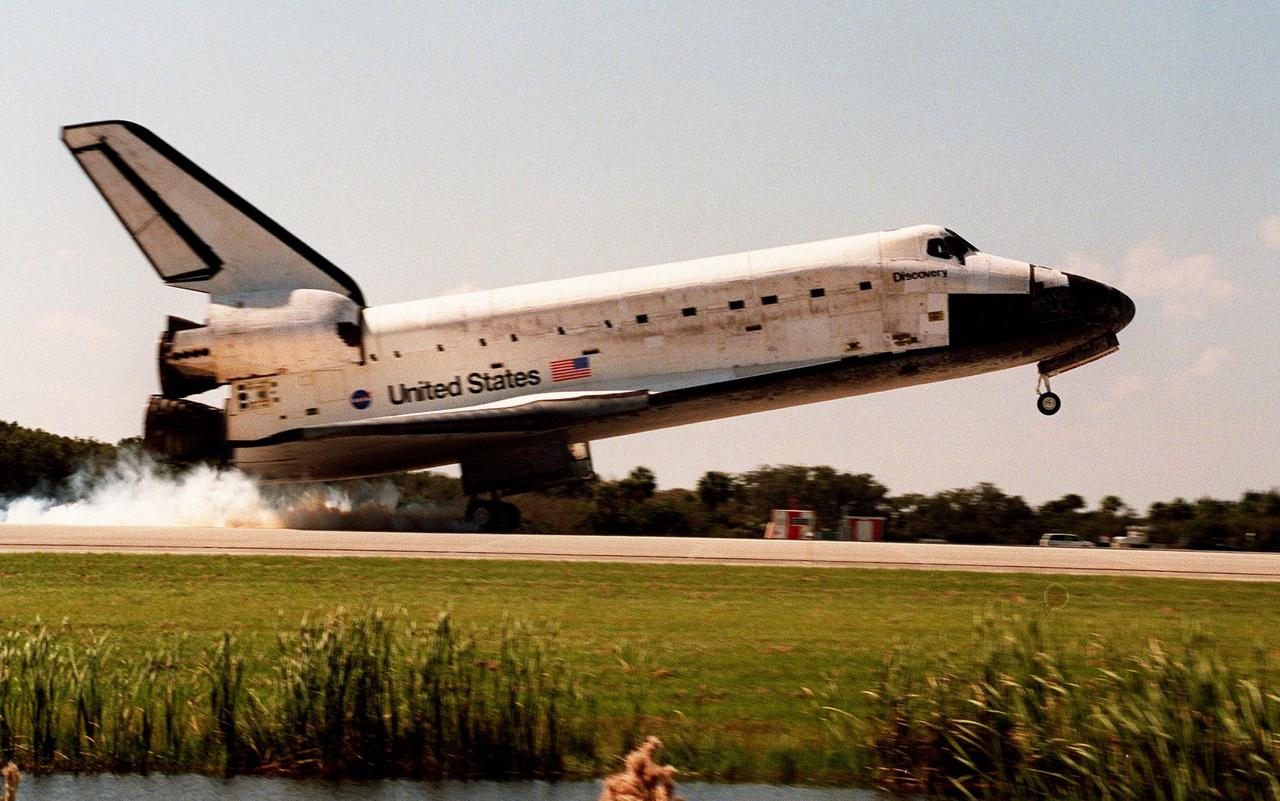

Orbiter Discovery smokes its tires as it touches down on runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown was at 12:04 p.m. EST, landing on orbit 135. Discovery returns to Earth with its crew of seven after successfully completing mission STS-95, lasting nearly nine days and 3.6 million miles. The crew consists of Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr.; Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski; Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio; Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, with the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai,M.D., with the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The mission included research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
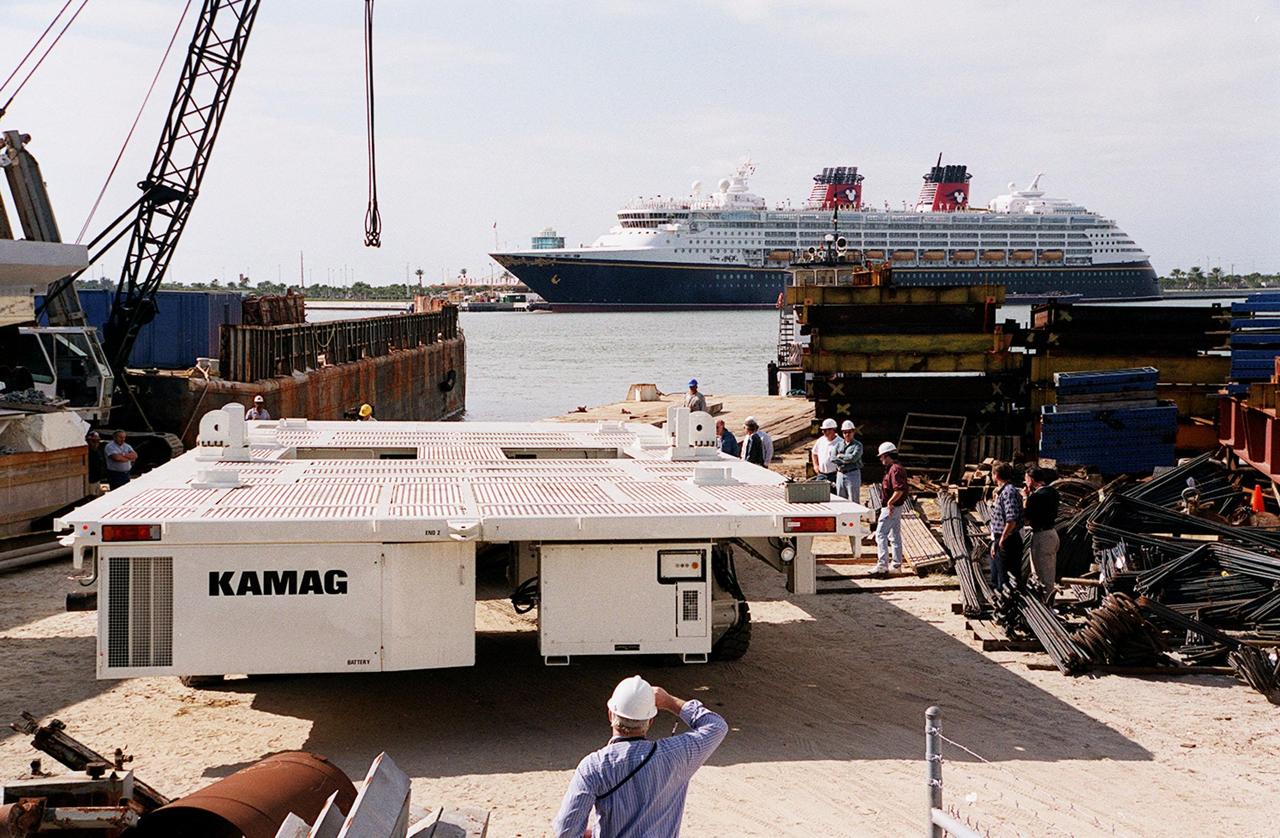

One of two new payload transporters for Kennedy Space Center arrives at Port Canaveral. In the background is a cruise ship docked at the Port. The transporters were shipped by barge from their manufacturer, the KAMAG Company of Ulm, Germany. They are used to carry spacecraft and International Space Station elements from payload facilities to and from the launch pads and orbiter hangars. Each transporter is 65 feet long and 22 feet wide and has 24 tires divided between its two axles. The transporter travels 10 miles per hour unloaded, 5 miles per hour when loaded; it weighs up to 172,000 pounds when the canister with payloads rides atop. The transporters will be outfitted with four subsystems for monitoring the environment inside the canister during the payload moves: the Electrical Power System, Environmental Control System, Instrumentation and Communications System, and the Fluids and Gases System. Engineers and technicians are being trained on the transporter's operation and maintenance. The new transporters are replacing the 20-year-old existing Payload Canister Transporter system
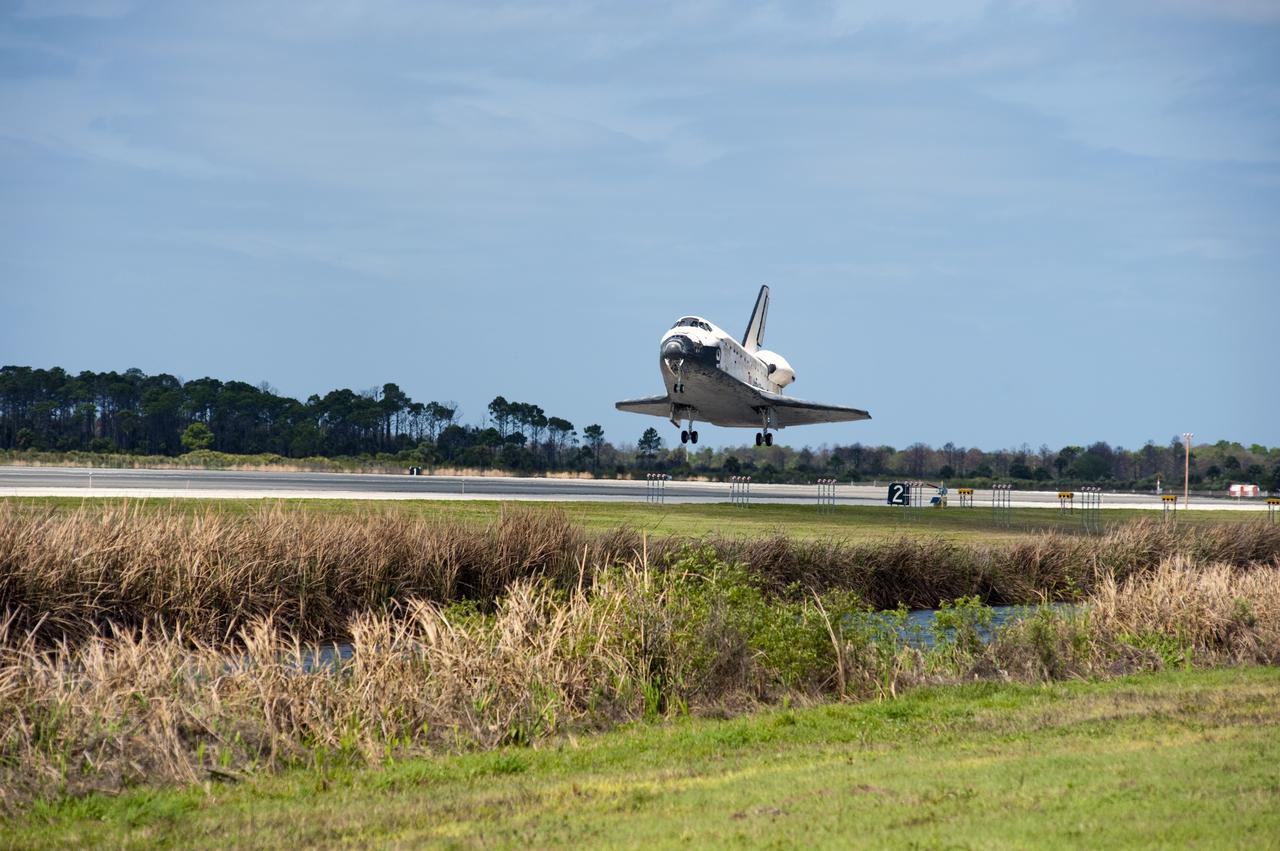

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space shuttle Discovery's main landing gear tires are down as the spacecraft approaches Runway 15 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Discovery's final return from space completed the 13-day, 5.3-million-mile STS-133 mission. Main gear touchdown was at 11:57:17 a.m., followed by nose gear touchdown at 11:57:28, and wheelstop at 11:58:14 a.m. On board are Commander Steve Lindsey, Pilot Eric Boe, and Mission Specialists Nicole Stott, Michael Barratt, Alvin Drew and Steve Bowen. Discovery and its six-member crew delivered the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. STS-133 was Discovery's 39th and final mission. This was the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. Photo credit: NASA/Linda Perry
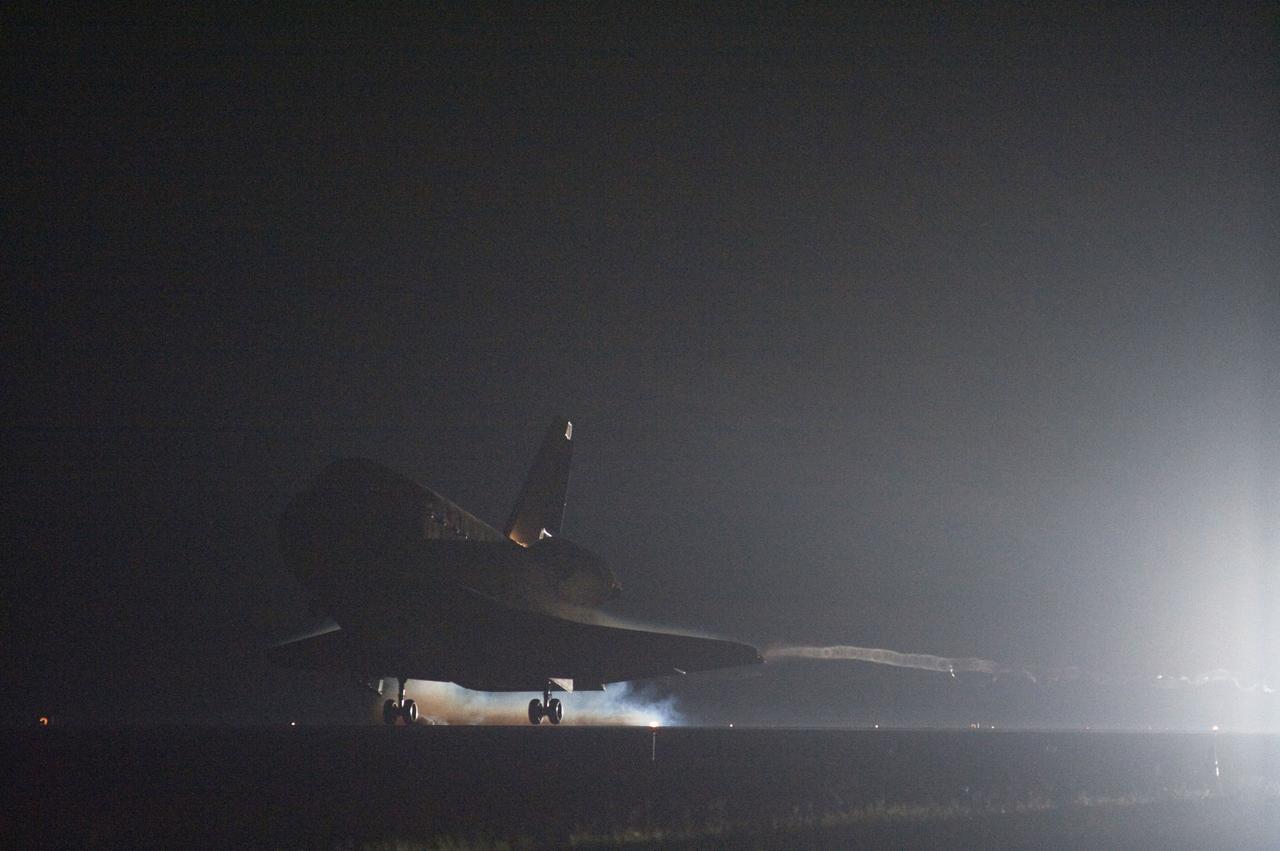

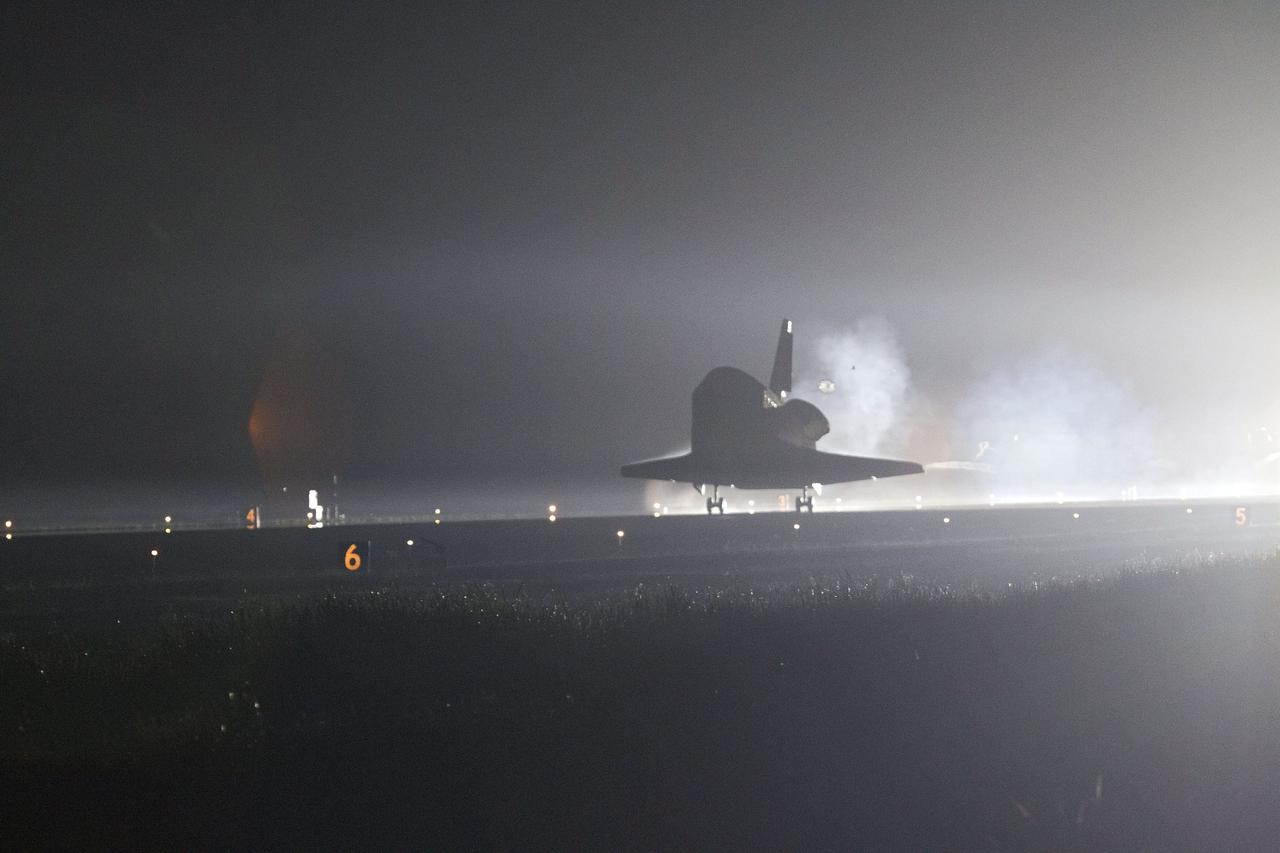
STS134-S-109 (1 June 2011) --- Streams of smoke trail from the main landing gear tires as space shuttle Endeavour touches down on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time marking the 24th night landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
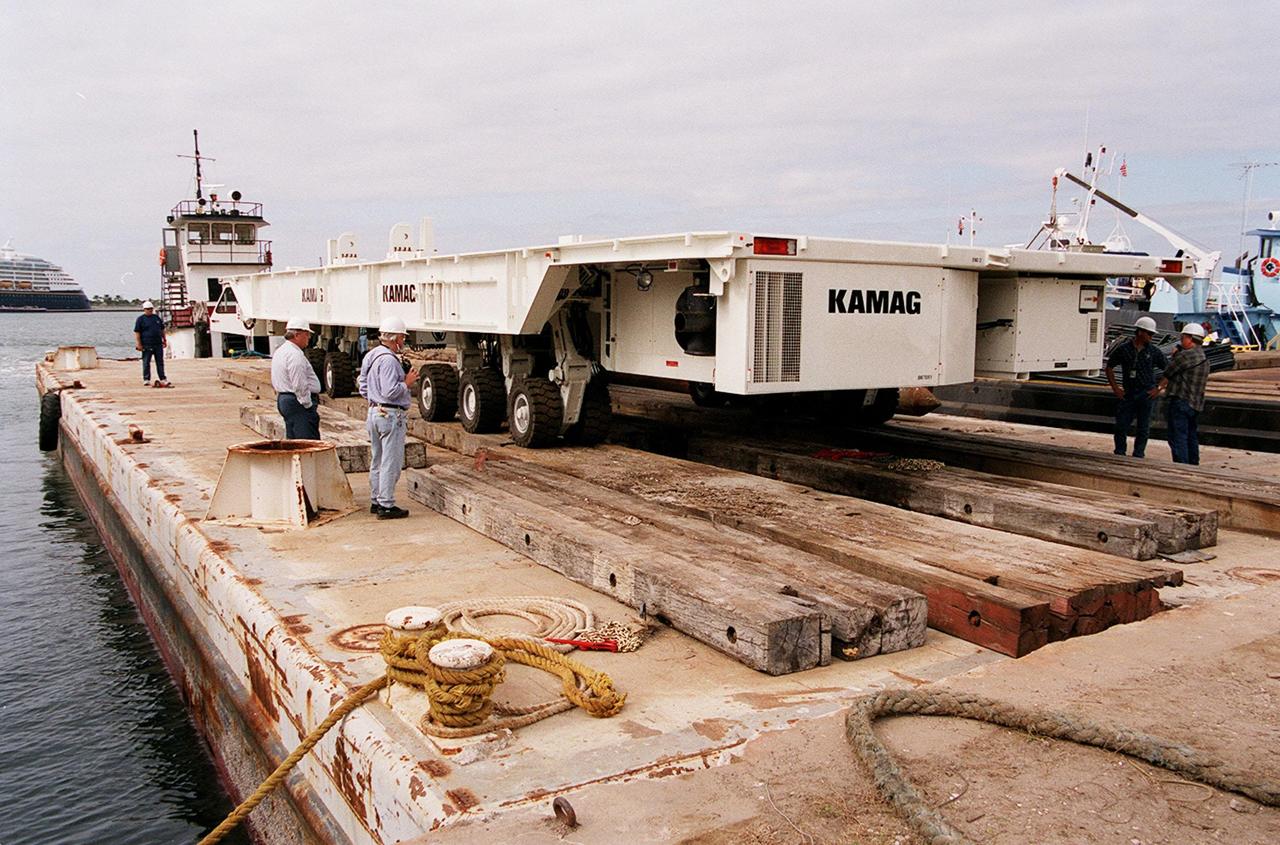

One of two new payload transporters for Kennedy Space Center sits on the dock at Port Canaveral. In the background is a cruise ship docked at the Port. The transporters were shipped by barge from their manufacturer, the KAMAG Company of Ulm, Germany. They are used to carry spacecraft and International Space Station elements from payload facilities to and from the launch pads and orbiter hangars. Each transporter is 65 feet long and 22 feet wide and has 24 tires divided between its two axles. The transporter travels 10 miles per hour unloaded, 5 miles per hour when loaded; it weighs up to 172,000 pounds when the canister with payloads rides atop. The transporters will be outfitted with four subsystems for monitoring the environment inside the canister during the payload moves: the Electrical Power System, Environmental Control System, Instrumentation and Communications System, and the Fluids and Gases System. Engineers and technicians are being trained on the transporter's operation and maintenance. The new transporters are replacing the 20-year-old existing Payload Canister Transporter system
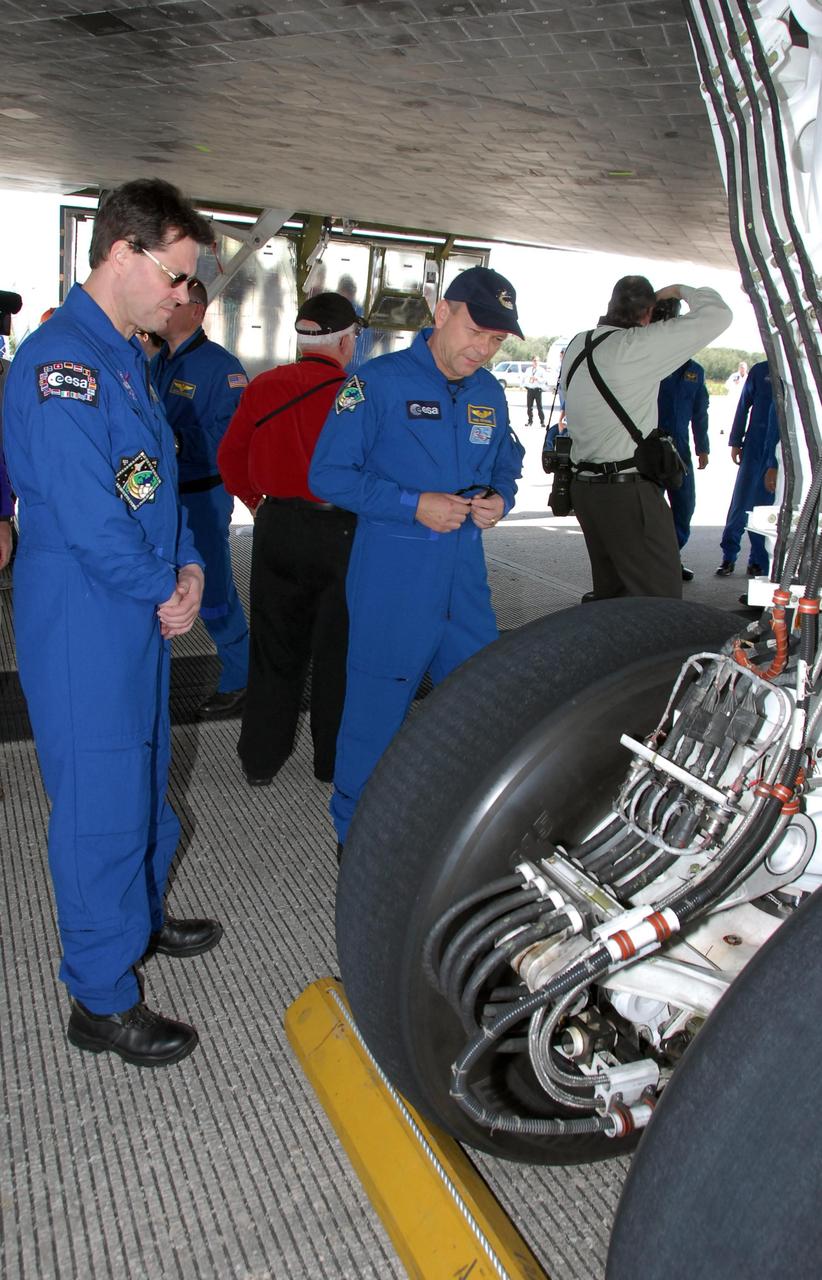

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After exiting the crew transport vehicle, STS-122 Mission Specialists Rex Walheim and Hans Schlegel check the tire on space shuttle Atlantis' landing gear. After a round trip of nearly 5.3 million miles, space shuttle Atlantis and crew returned to Earth with a landing at 9:07 a.m. EST. The shuttle landed on orbit 202 to complete the 13-day STS-122 mission. Main gear touchdown was 9:07:10 a.m. Nose gear touchdown was 9:07:20 a.m. Wheel stop was at 9:08:08 a.m. Mission elapsed time was 12 days, 18 hours, 21 minutes and 44 seconds. During the mission, Atlantis' crew installed the new Columbus laboratory, leaving a larger space station and one with increased science capabilities. The Columbus Research Module adds nearly 1,000 cubic feet of habitable volume and affords room for 10 experiment racks, each an independent science lab. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
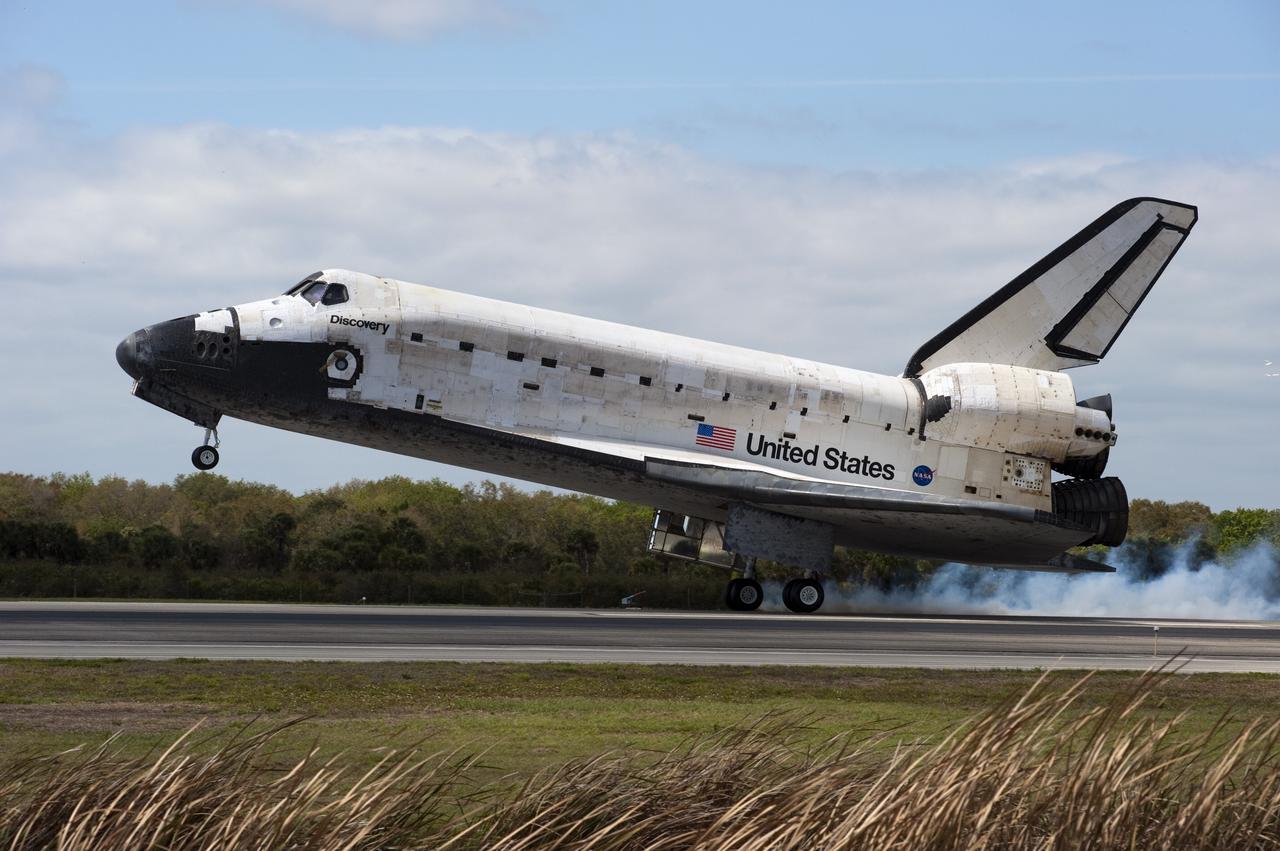

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Streams of smoke trail from the main landing gear tires as space shuttle Discovery touches down on Runway 15 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after 13-days in space, completing the 5.3-million-mile STS-133 mission. Main gear touchdown was at 11:57:17 a.m., followed by nose gear touchdown at 11:57:28, and wheelstop at 11:58:14 a.m. On board are Commander Steve Lindsey, Pilot Eric Boe, and Mission Specialists Nicole Stott, Michael Barratt, Alvin Drew and Steve Bowen. Discovery and its six-member crew delivered the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. STS-133 was Discovery's 39th and final mission. This was the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Cooper
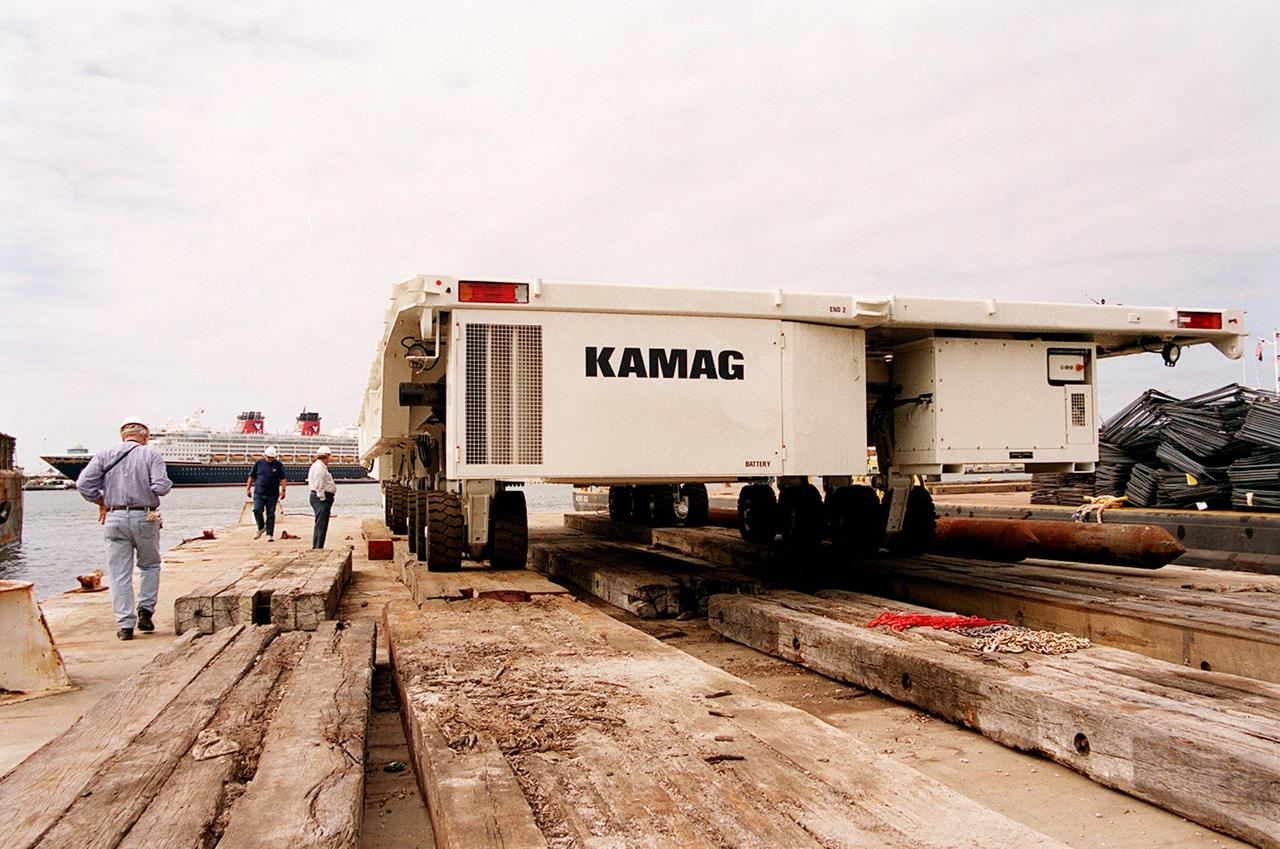

One of two new payload transporters for Kennedy Space Center sits on the dock at Port Canaveral. In the background is a cruise ship docked at the Port. The transporters were shipped by barge from their manufacturer, the KAMAG Company of Ulm, Germany. They are used to carry spacecraft and International Space Station elements from payload facilities to and from the launch pads and orbiter hangars. Each transporter is 65 feet long and 22 feet wide and has 24 tires divided between its two axles. The transporter travels 10 miles per hour unloaded, 5 miles per hour when loaded; it weighs up to 172,000 pounds when the canister with payloads rides atop. The transporters will be outfitted with four subsystems for monitoring the environment inside the canister during the payload moves: the Electrical Power System, Environmental Control System, Instrumentation and Communications System, and the Fluids and Gases System. Engineers and technicians are being trained on the transporter's operation and maintenance. The new transporters are replacing the 20-year-old existing Payload Canister Transporter system
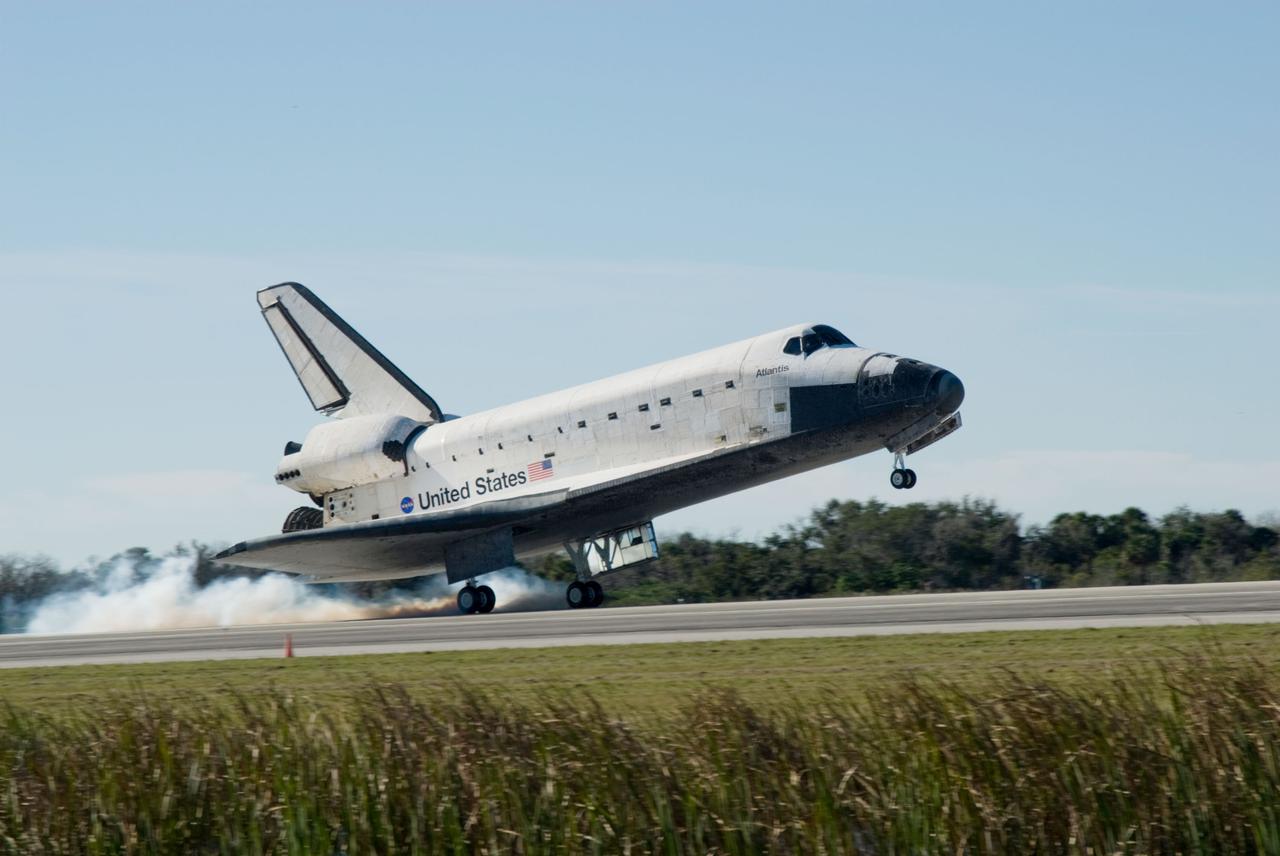

PHOTO CREDIT: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Streams of smoke trail from the main landing gear tires as space shuttle Atlantis touches down on Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after 11 days in space, completing the 4.5-million-mile STS-129 mission on orbit 171. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EDT. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Aboard Atlantis are Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
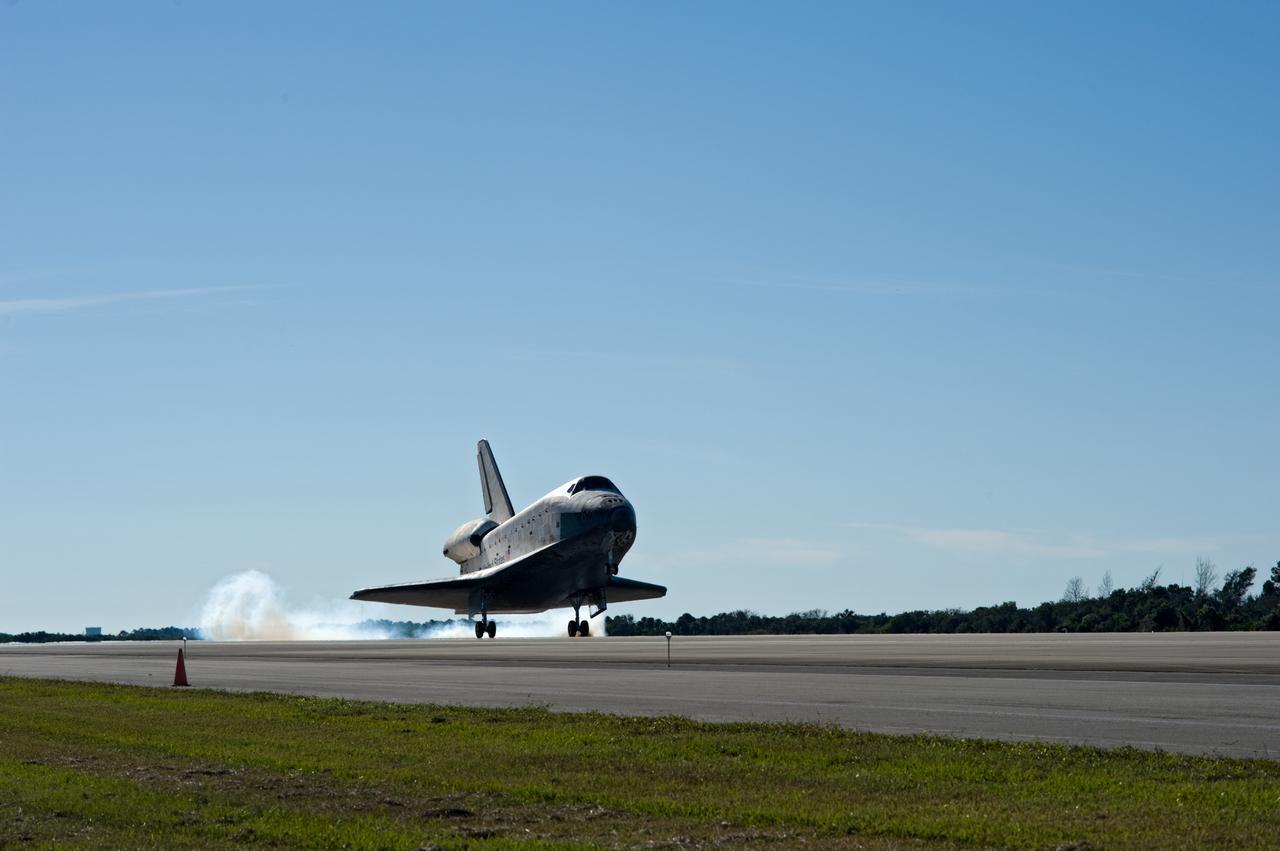

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Touchdown is apparent by the streams of smoke trailing space shuttle Atlantis as its main landing gear tires contact Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After 11 days in space, Atlantis' 4.5-million-mile STS-129 mission is completed on orbit 171. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Aboard Atlantis are Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell and Rick Prickett
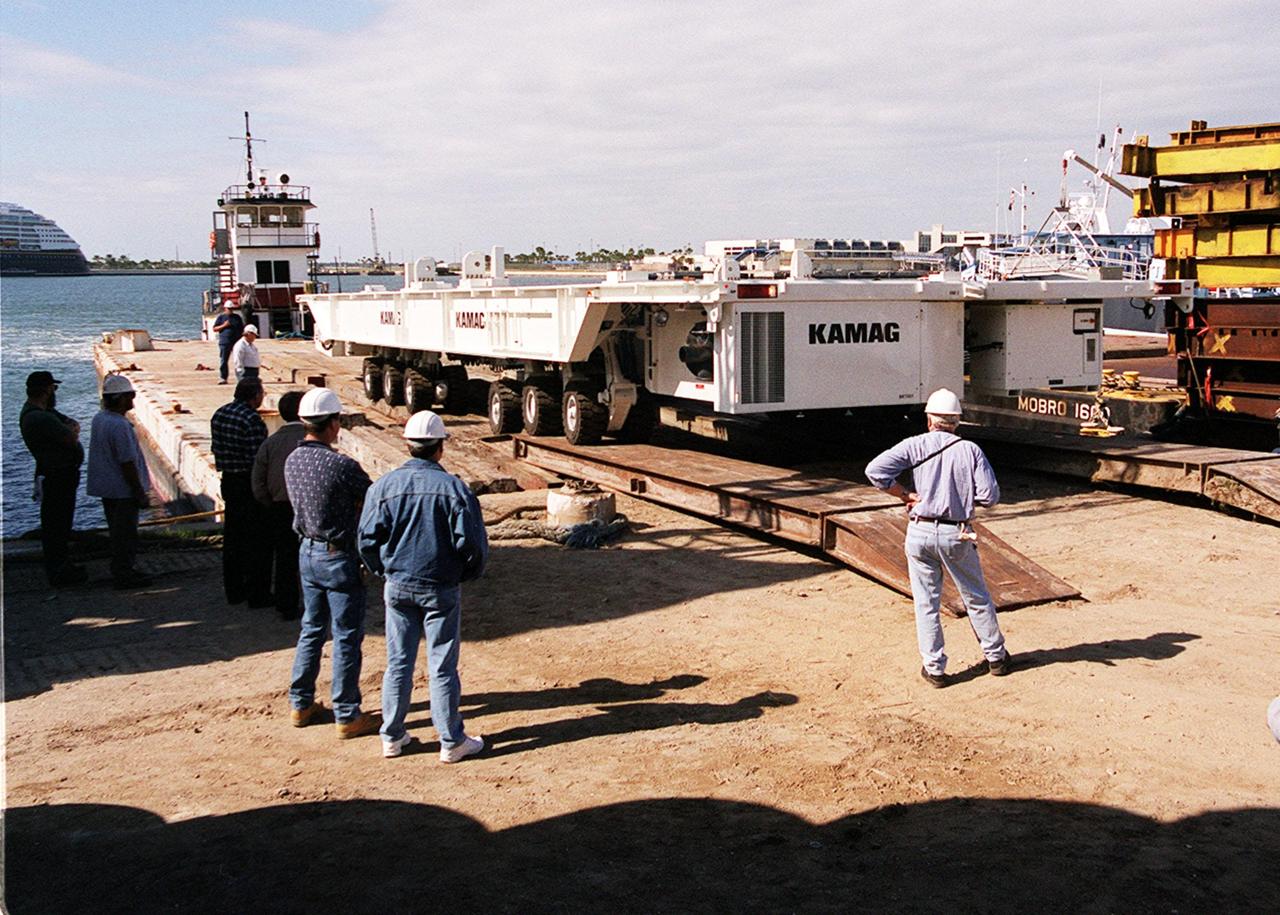

The first of two new payload transporters for Kennedy Space Center arrives at Port Canaveral. They were shipped by barge from their manufacturer, the KAMAG Company of Ulm, Germany. The transporters are used to carry spacecraft and International Space Station elements from payload facilities to and from the launch pads and orbiter hangars. Each transporter is 65 feet long and 22 feet wide and has 24 tires divided between its two axles. The transporter travels 10 miles per hour unloaded, 5 miles per hour when loaded; it weighs up to 172,000 pounds when the canister with payloads rides atop. The transporters will be outfitted with four subsystems for monitoring the environment inside the canister during the payload moves: the Electrical Power System, Environmental Control System, Instrumentation and Communications System, and the Fluids and Gases System. Engineers and technicians are being trained on the transporter's operation and maintenance. The new transporters are replacing the 20-year-old existing Payload Canister Transporter system
