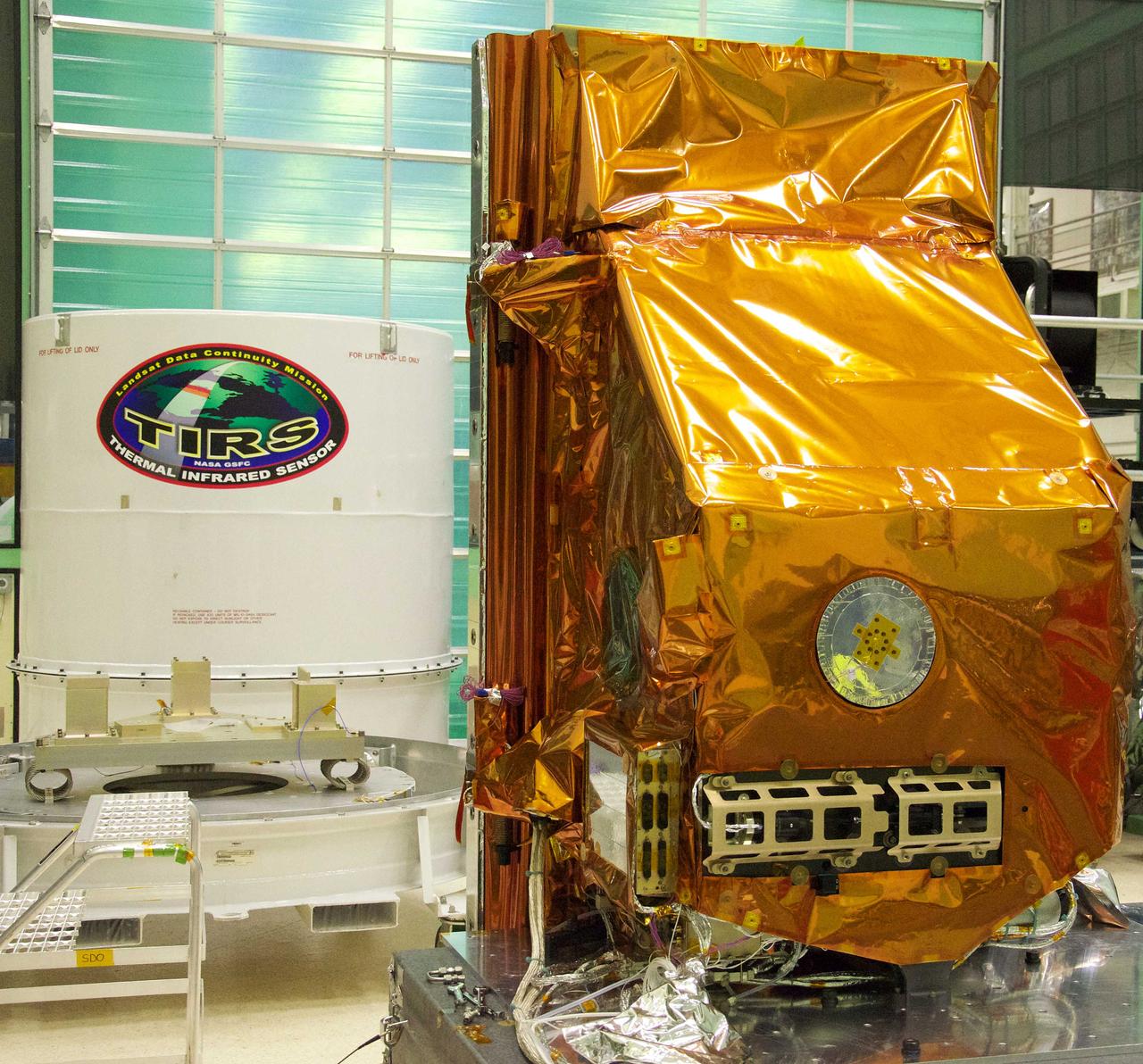

The TIRS instrument in the foreground with its shipping container waits in the background. The copper-color of TIRS is due to the gold-colored foil that coats the Multi-Layer Insulation blankets. The Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) will fly on the next Landsat satellite, the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM). TIRS was built on an accelerated schedule at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. and will now be integrated into the LDCM spacecraft at Orbital Science Corp. in Gilbert, Ariz. The Landsat Program is a series of Earth observing satellite missions jointly managed by NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey. Landsat satellites have been consistently gathering data about our planet since 1972. They continue to improve and expand this unparalleled record of Earth's changing landscapes for the benefit of all. For more information on Landsat, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/landsat" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/landsat</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
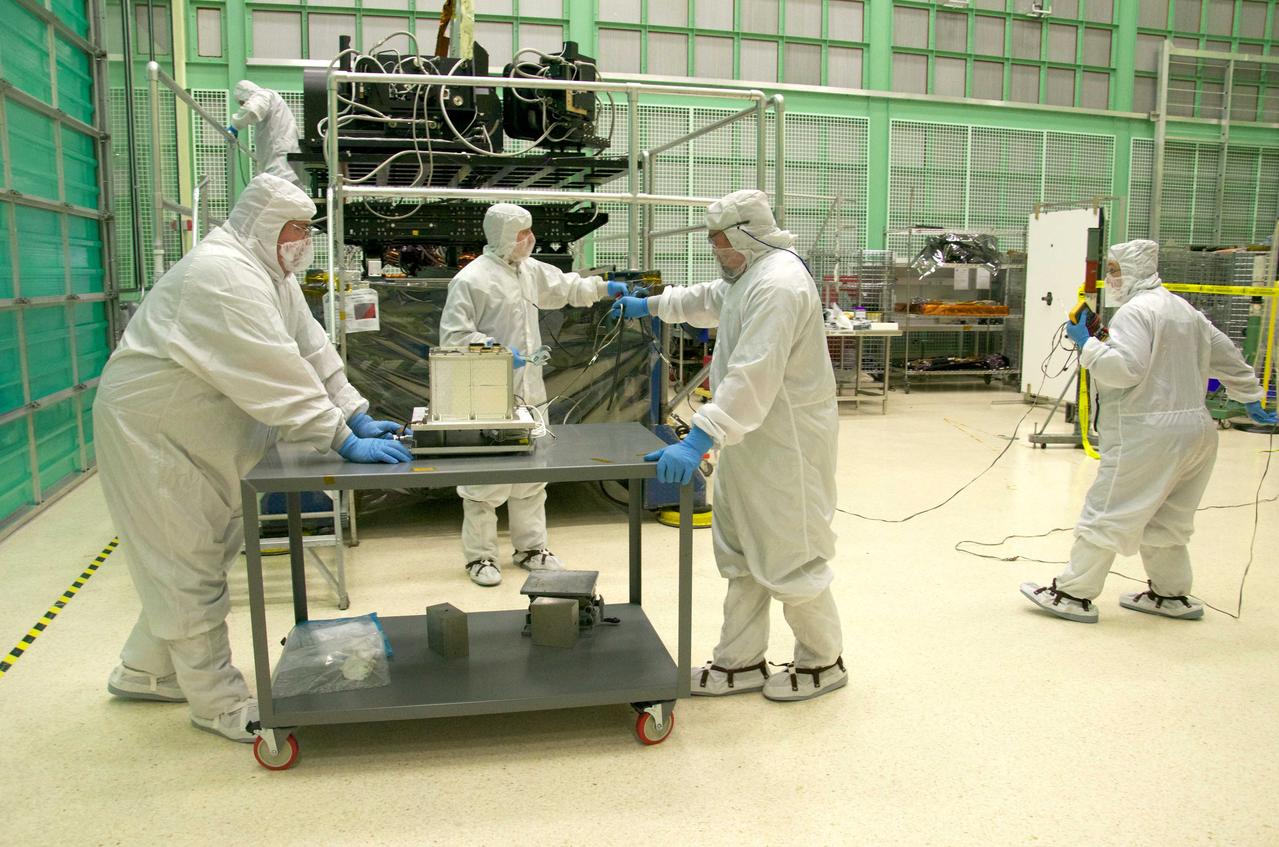

Pete Steigner, and Mike Golob (middle and right) assist an Chris Kolos in carefully moving a TIRS component across the clean room at Goddard. On the far right Robin Knight holds the component's 'grounding strap.' It's used to make sure that any static electricity that could possibly build up while the component is being moved doesn't affect the damage the sensitive electronics. The Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) will fly on the next Landsat satellite, the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM). TIRS was built on an accelerated schedule at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. and will now be integrated into the LDCM spacecraft at Orbital Science Corp. in Gilbert, Ariz. The Landsat Program is a series of Earth observing satellite missions jointly managed by NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey. Landsat satellites have been consistently gathering data about our planet since 1972. They continue to improve and expand this unparalleled record of Earth's changing landscapes for the benefit of all. For more information on Landsat, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/landsat" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/landsat</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
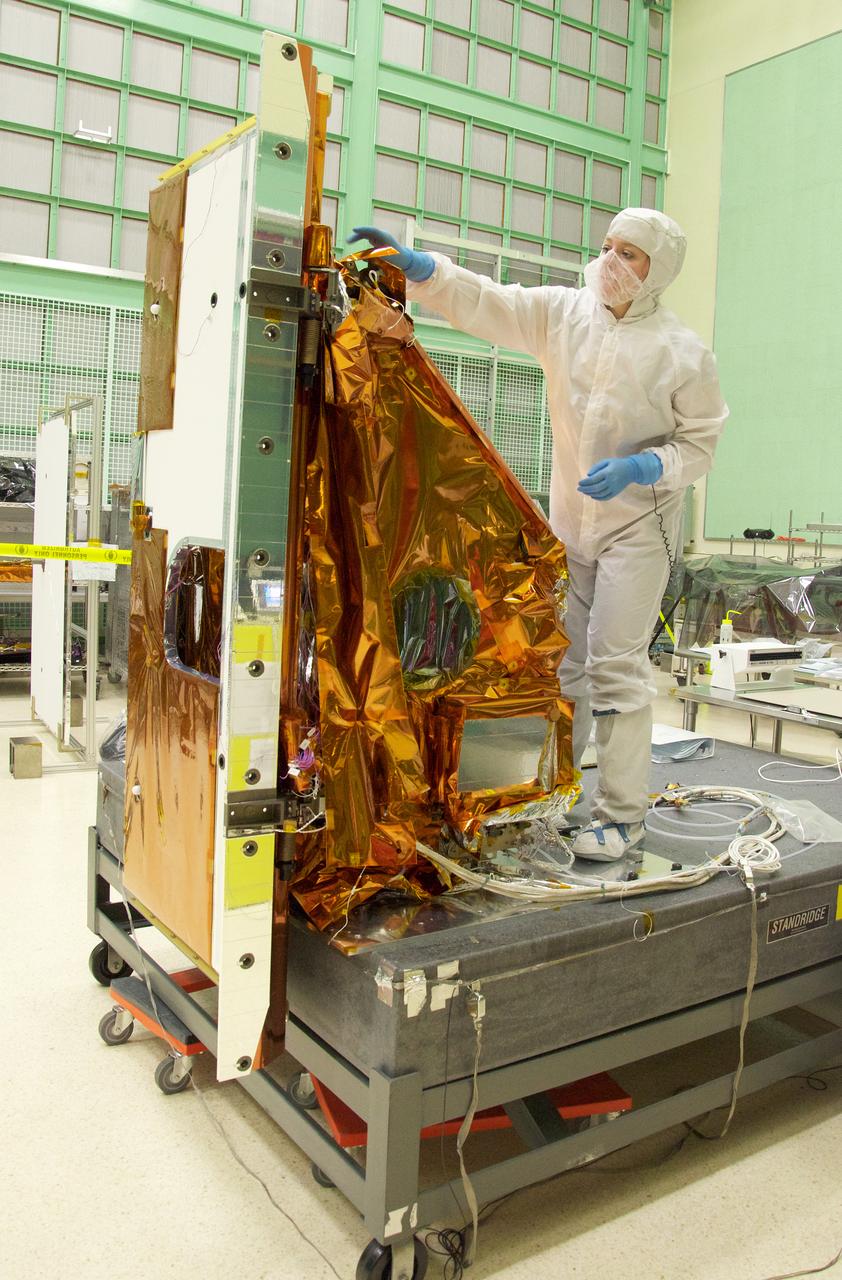

Aleksandra Bogunovic reaches across the instrument to affix the corners of a Multi-Layer Insulation blanket to the TIRS instrument. The Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) will fly on the next Landsat satellite, the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM). TIRS was built on an accelerated schedule at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. and will now be integrated into the LDCM spacecraft at Orbital Science Corp. in Gilbert, Ariz. The Landsat Program is a series of Earth observing satellite missions jointly managed by NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey. Landsat satellites have been consistently gathering data about our planet since 1972. They continue to improve and expand this unparalleled record of Earth's changing landscapes for the benefit of all. For more information on Landsat, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/landsat" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/landsat</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Aleksandra Bogunovic (left) and Veronica Otero (right) look on while Pete Steigner (in the middle) adds a flow tube that will make sure that nitrogen gas flows through the instrument while it's being shipped. The gas will keep contaminating particles from infiltrating the instrument. The Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) will fly on the next Landsat satellite, the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM). TIRS was built on an accelerated schedule at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. and will now be integrated into the LDCM spacecraft at Orbital Science Corp. in Gilbert, Ariz. The Landsat Program is a series of Earth observing satellite missions jointly managed by NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey. Landsat satellites have been consistently gathering data about our planet since 1972. They continue to improve and expand this unparalleled record of Earth's changing landscapes for the benefit of all. For more information on Landsat, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/landsat" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/landsat</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
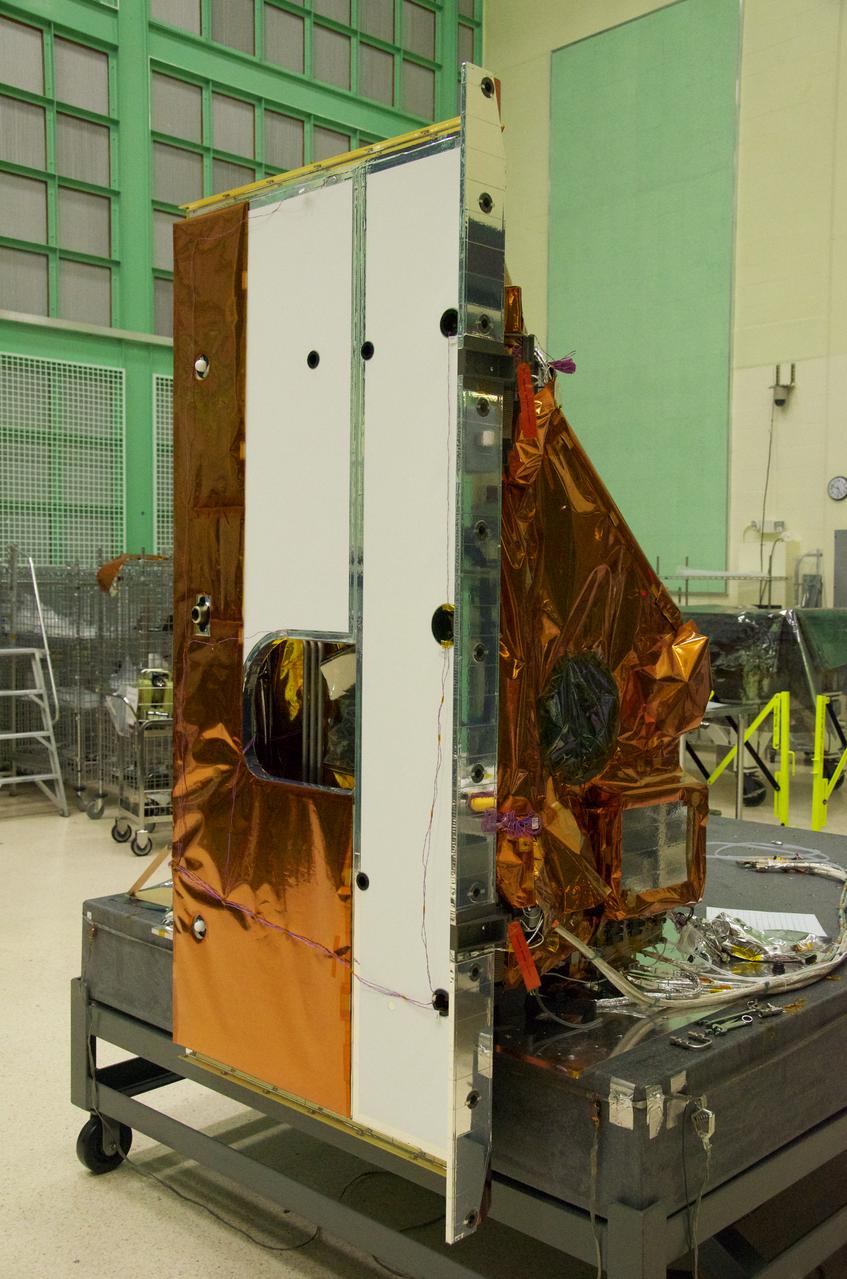

The Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) will fly on the next Landsat satellite, the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM). The right side of the instrument is what's called the 'nadir side,' that's the side that points toward Earth when the instrument is in space. The black circle visible on the right side is where the optics for the instrument are located. In that area are the lens and the detectors. The white area is a radiator that radiates heat to keep the telescope and the detector cool. The black hole on the white area on the left is what the satellite operators point to deep space when they calibrate the instrument to the cold temperatures of space. TIRS was built on an accelerated schedule at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. and will now be integrated into the LDCM spacecraft at Orbital Science Corp. in Gilbert, Ariz. The Landsat Program is a series of Earth observing satellite missions jointly managed by NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey. Landsat satellites have been consistently gathering data about our planet since 1972. They continue to improve and expand this unparalleled record of Earth's changing landscapes for the benefit of all. For more information on Landsat, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/landsat" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/landsat</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
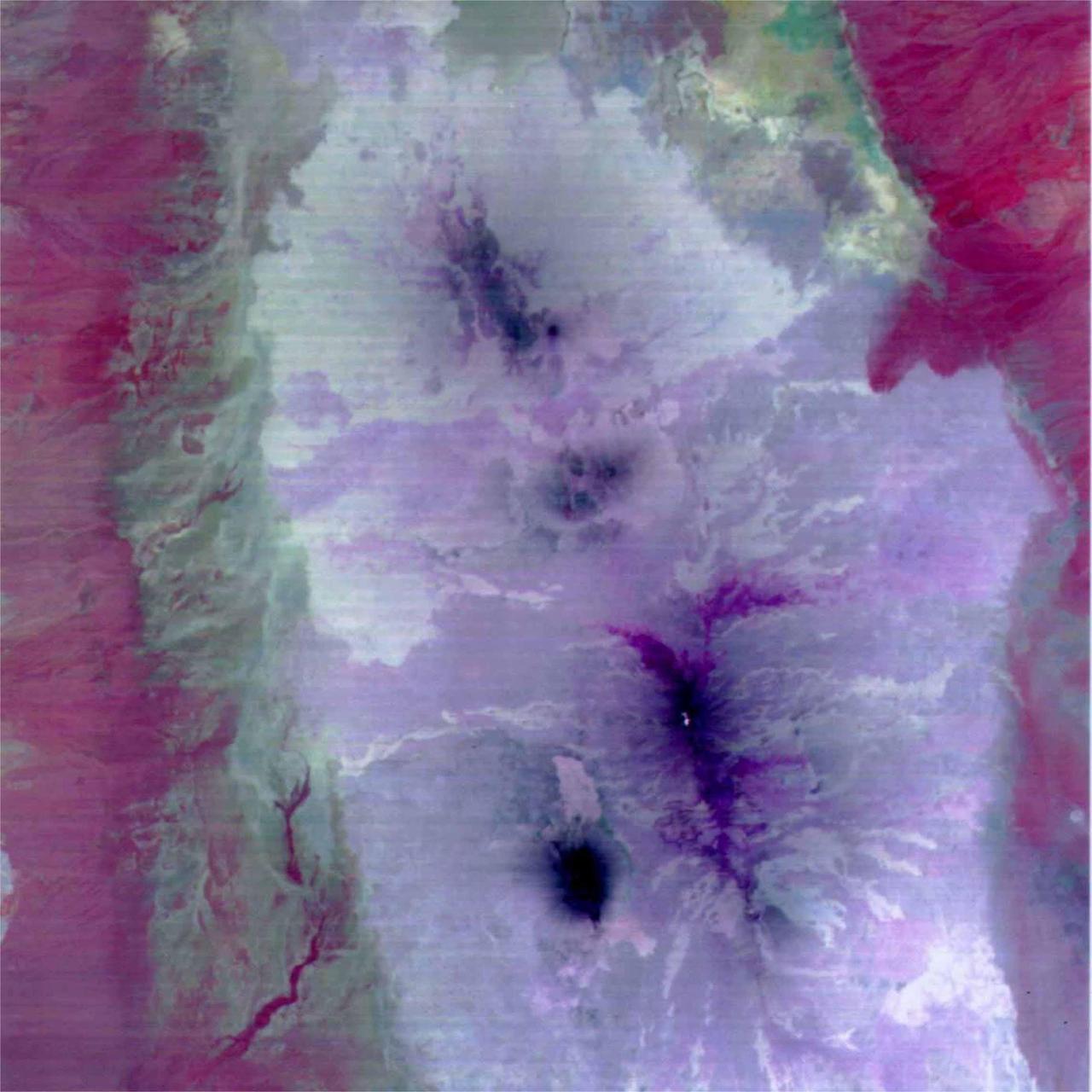

This image is a color composite covering the Rift Valley inland area of Ethiopia (south of the region shown in PIA02452). The color difference of this image reflects the distribution of different rocks with different amounts of silicon dioxide. It is inferred that the area with whitish color is covered with basalt and the pinkish area in the center contain sandesite. This is the first spaceborne, multi-band TIR image in history that enables geologists to distinguish between rocks with similar compositions. The size of image: 60 km x 60 km approx., ground resolution 90 m x 90 m approximately. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02453
ASTER succeeded in acquiring this image at night, which is something Visible/Near Infrared VNIR) and Shortwave Infrared (SWIR) sensors cannot do. The scene covers the Red Sea coastline to an inland area of Ethiopia. White pixels represent areas with higher temperature material on the surface, while dark pixels indicate lower temperatures. This image shows ASTER's ability as a highly sensitive, temperature-discerning instrument and the first spaceborne TIR multi-band sensor in history. The size of image: 60 km x 60 km approx., ground resolution 90 m x 90 m approximately. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02452
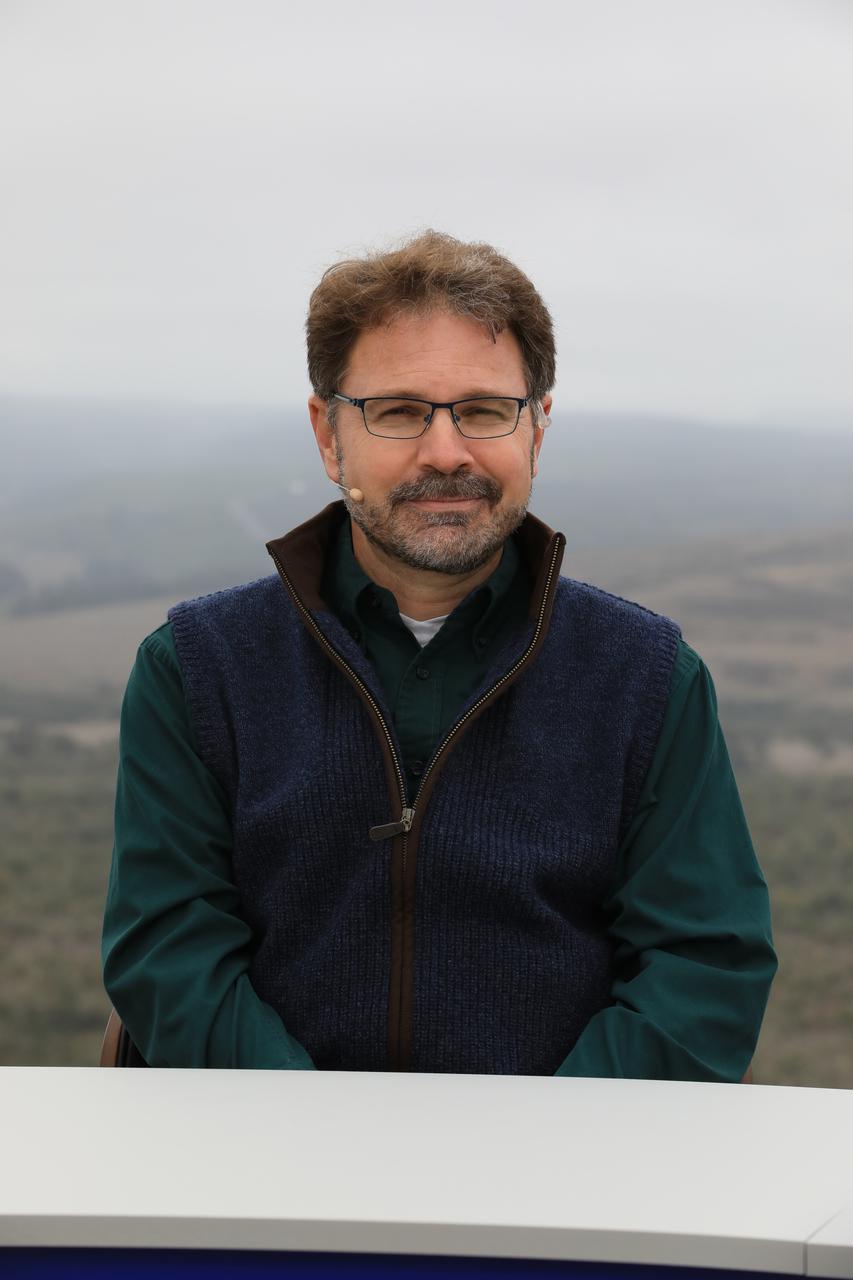

Dr. Pete Doucette, acting director, USGS Earth Resources, participates in the launch broadcast for the Landsat 9 mission on Sept. 27, 2021, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 3 at 2:12 p.m. EDT (11:12 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.

Omar Baez, NASA senior launch director, participates in the launch broadcast for the Landsat 9 mission on Sept. 27, 2021, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 3 at 2:12 p.m. EDT (11:12 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.
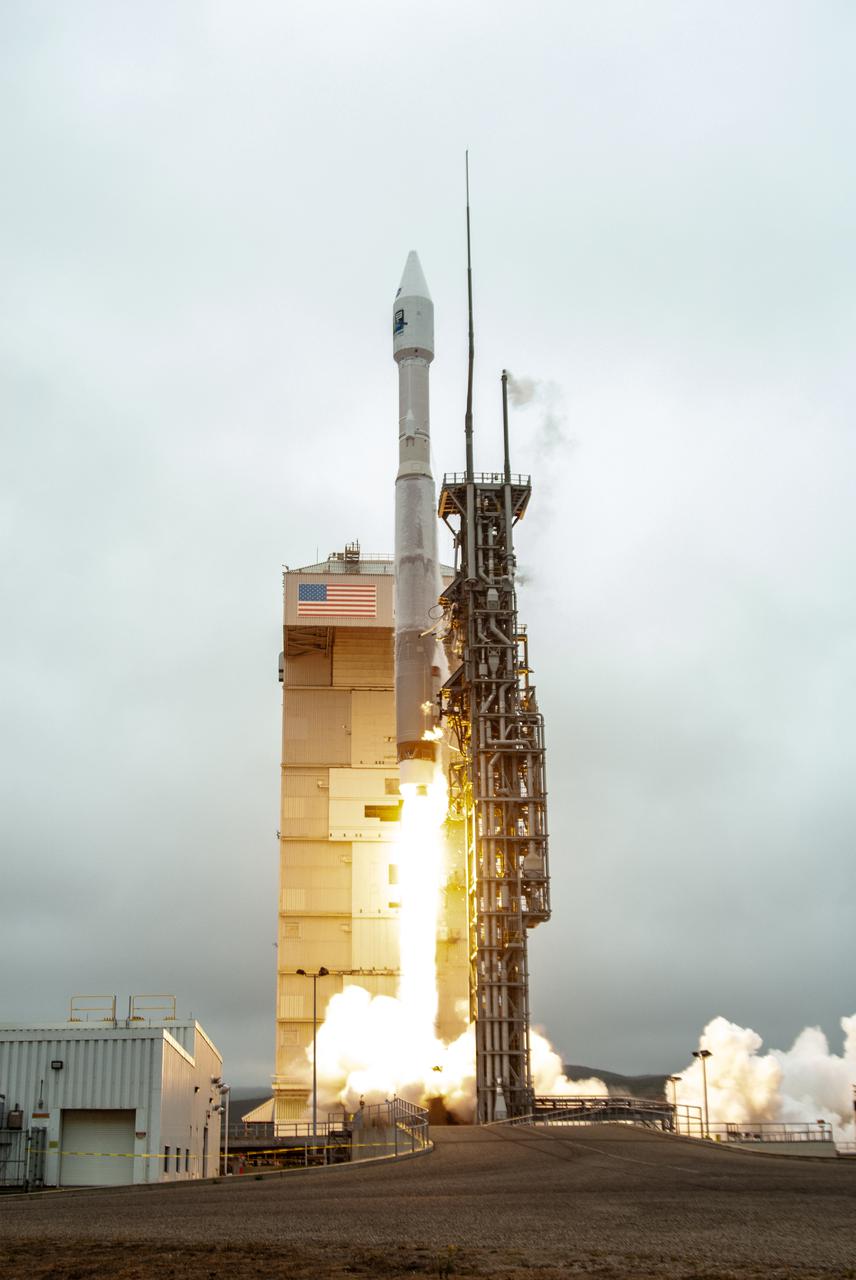

NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launches on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Station in California on Sept. 27, 2021. Launch time was 2:11 p.m. EDT (11:11 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.
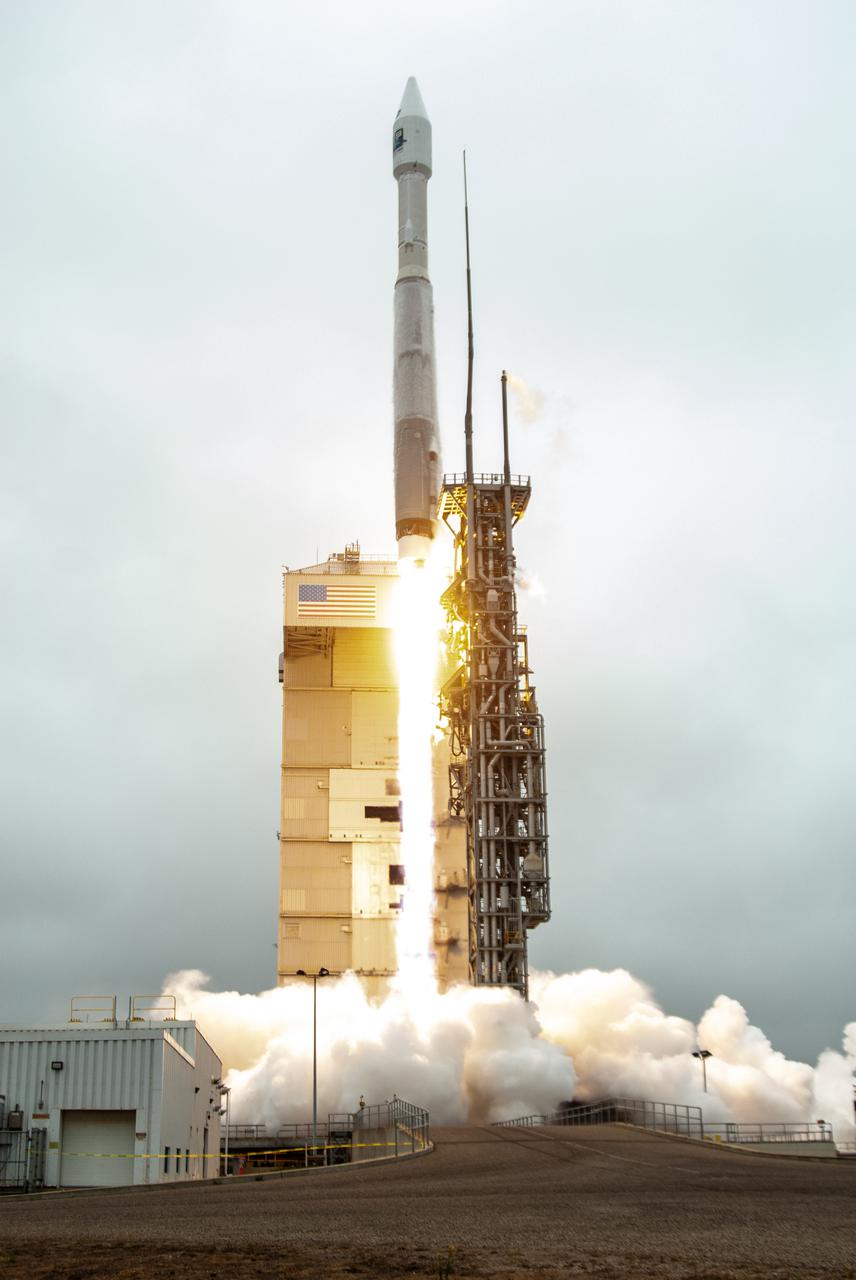

NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launches on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Station in California on Sept. 27, 2021. Launch time was 2:11 p.m. EDT (11:11 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.

Jeff Masek, Landsat 9 project scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, participates in the launch broadcast for the Landsat 9 mission on Sept. 27, 2021, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 3 at 2:12 p.m. EDT (11:12 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.
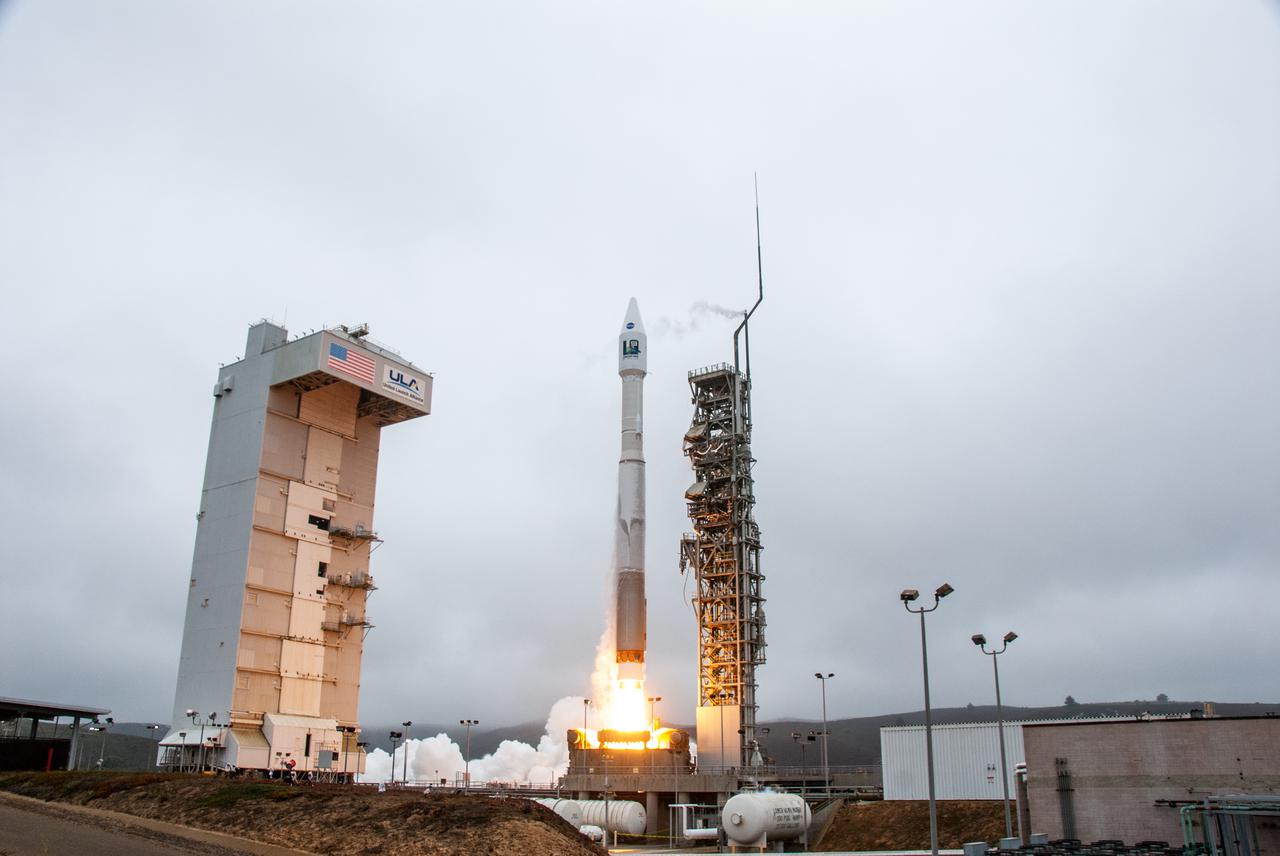

NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launches on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Station in California on Sept. 27, 2021. Launch time was 2:11 p.m. EDT (11:11 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.

Marie Lewis, NASA Communications, moderates the launch broadcast for the Landsat 9 mission on Sept. 27, 2021, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 3 at 2:12 p.m. EDT (11:12 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.
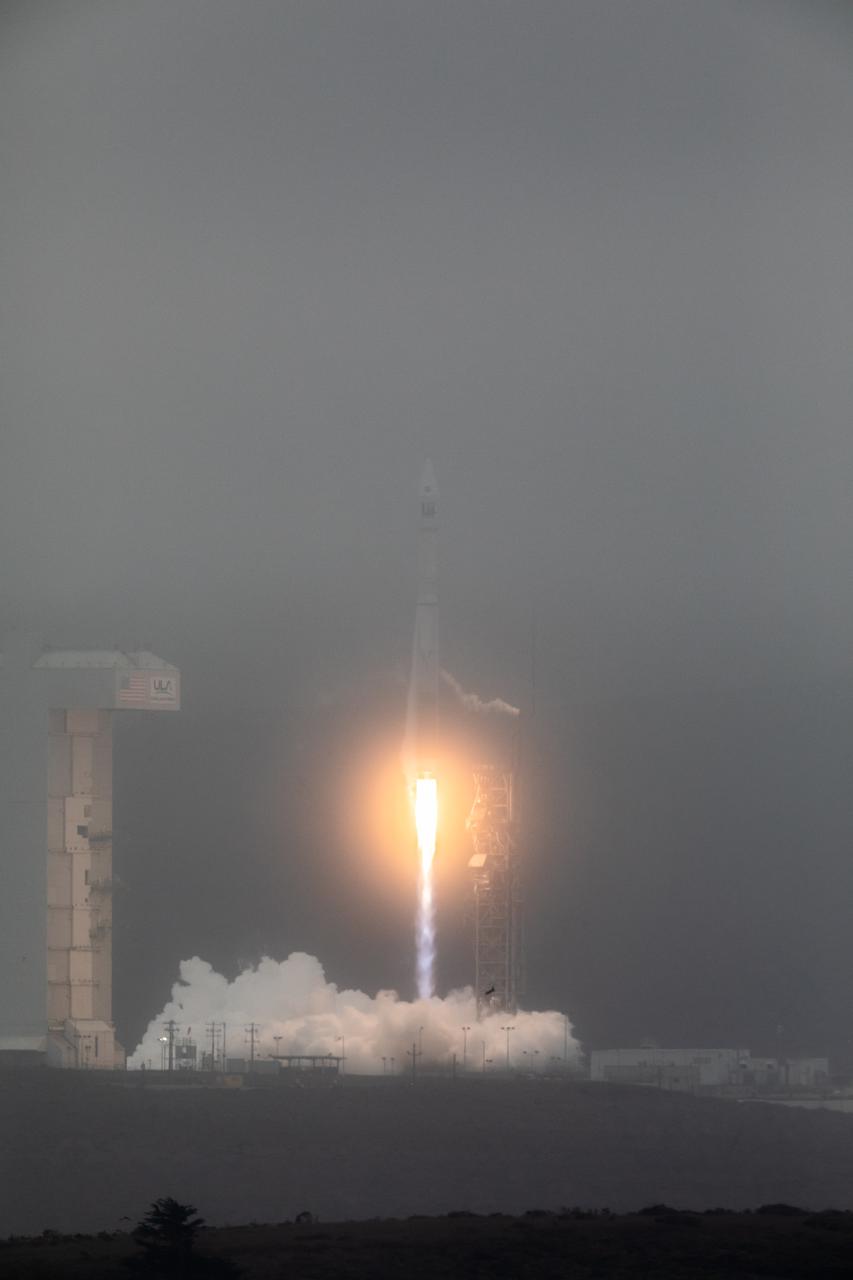

NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launches on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Station in California on Sept. 27, 2021. Launch time was 2:12 p.m. EDT (11:12 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.
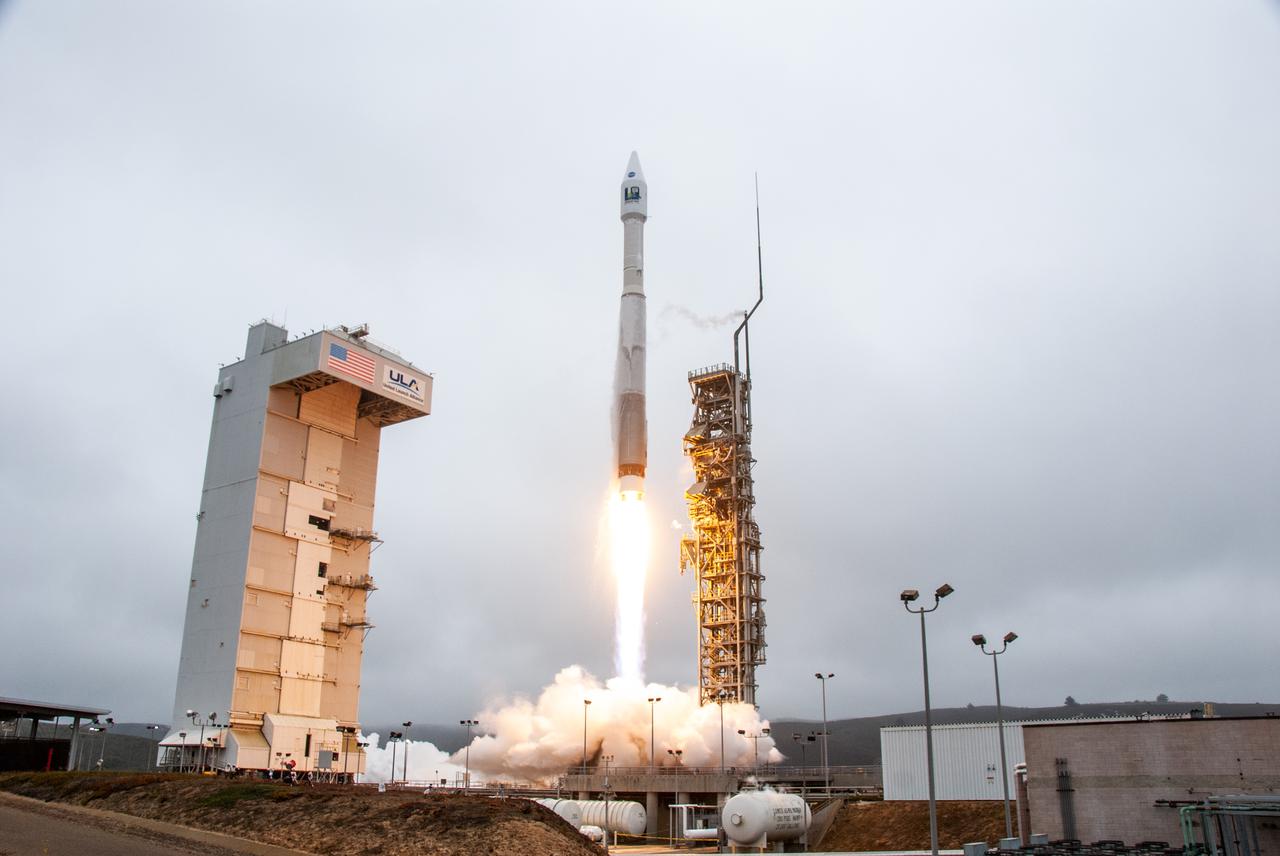

NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launches on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Station in California on Sept. 27, 2021. Launch time was 2:11 p.m. EDT (11:11 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.
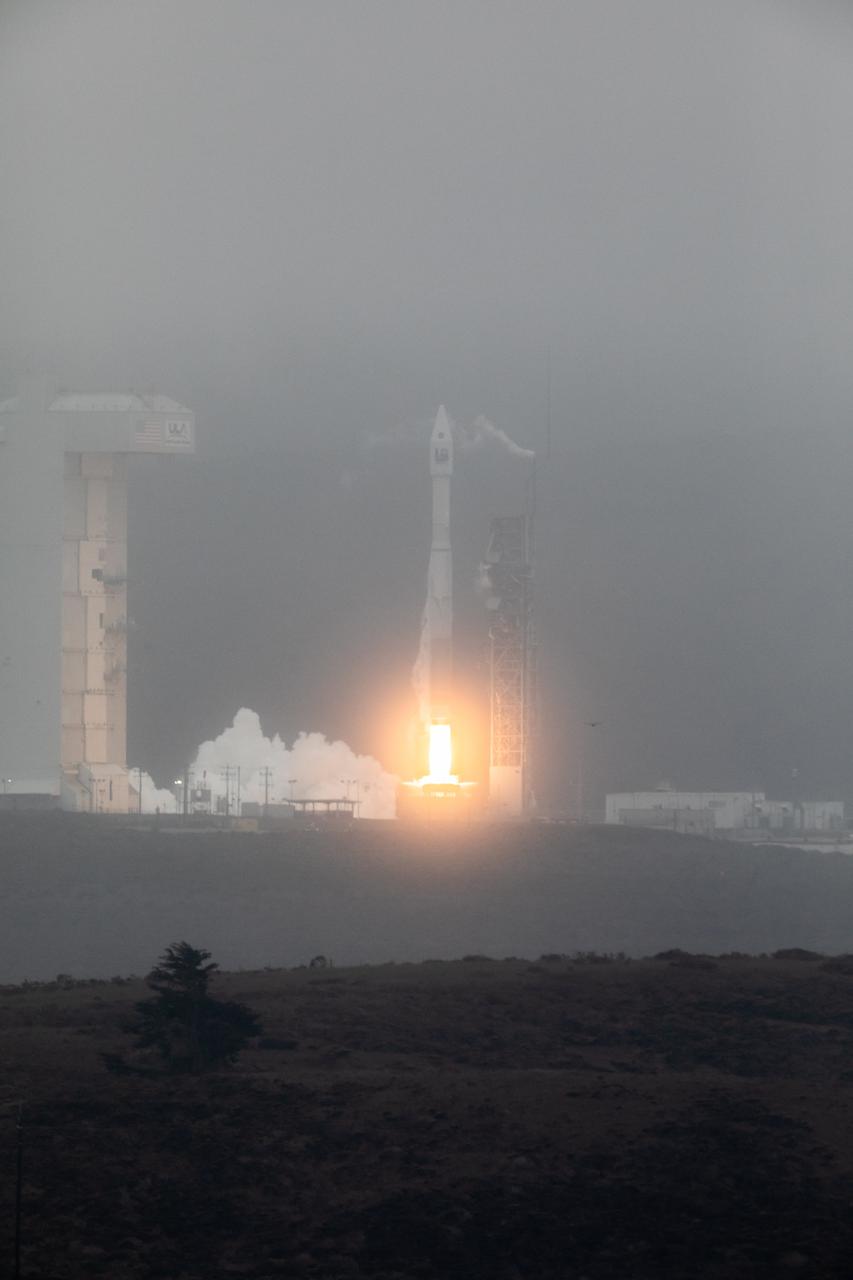

NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launches on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Station in California on Sept. 27, 2021. Launch time was 2:12 p.m. EDT (11:12 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.
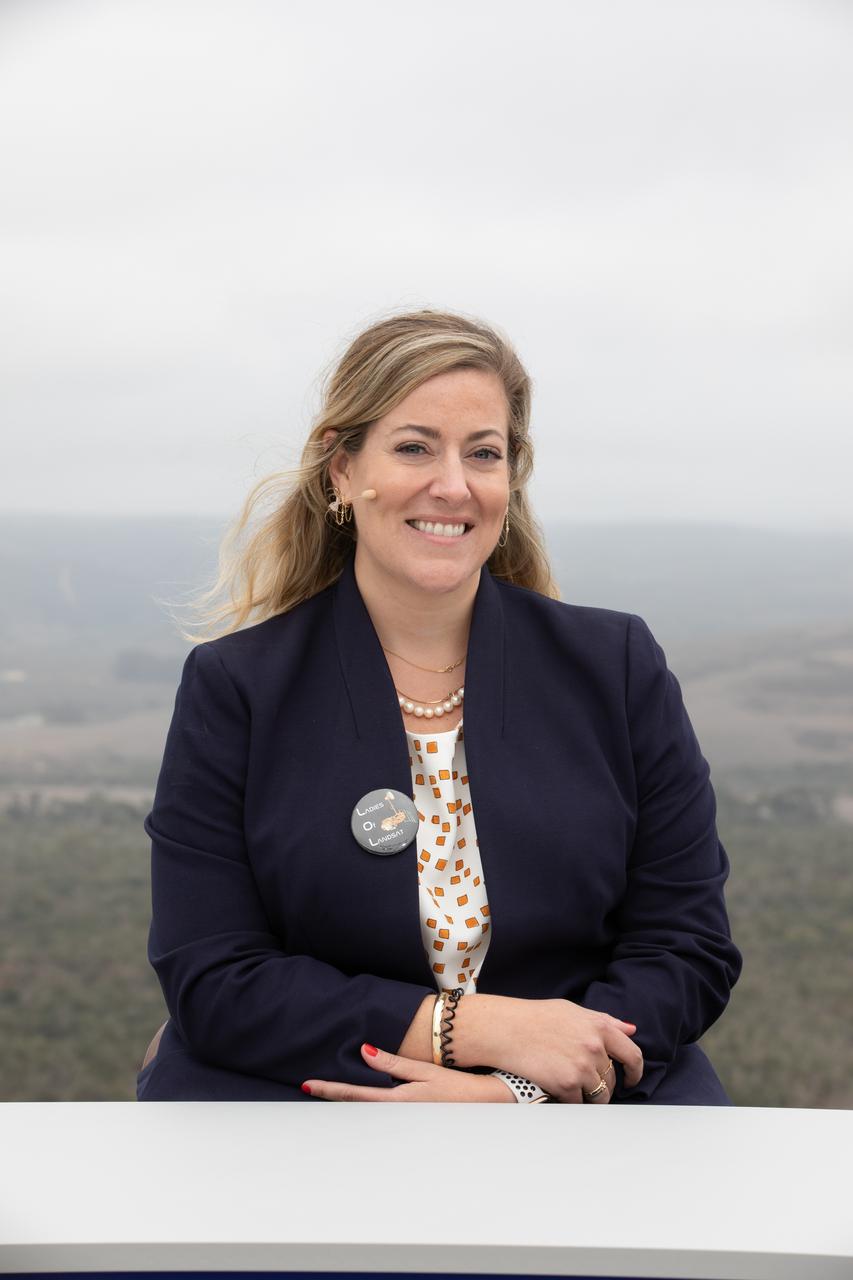

Dr. Kate Frickas, cofounder of "Ladies of Landsat", participates in the launch broadcast for the Landsat 9 mission on Sept. 27, 2021, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 3 at 2:12 p.m. EDT (11:12 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.
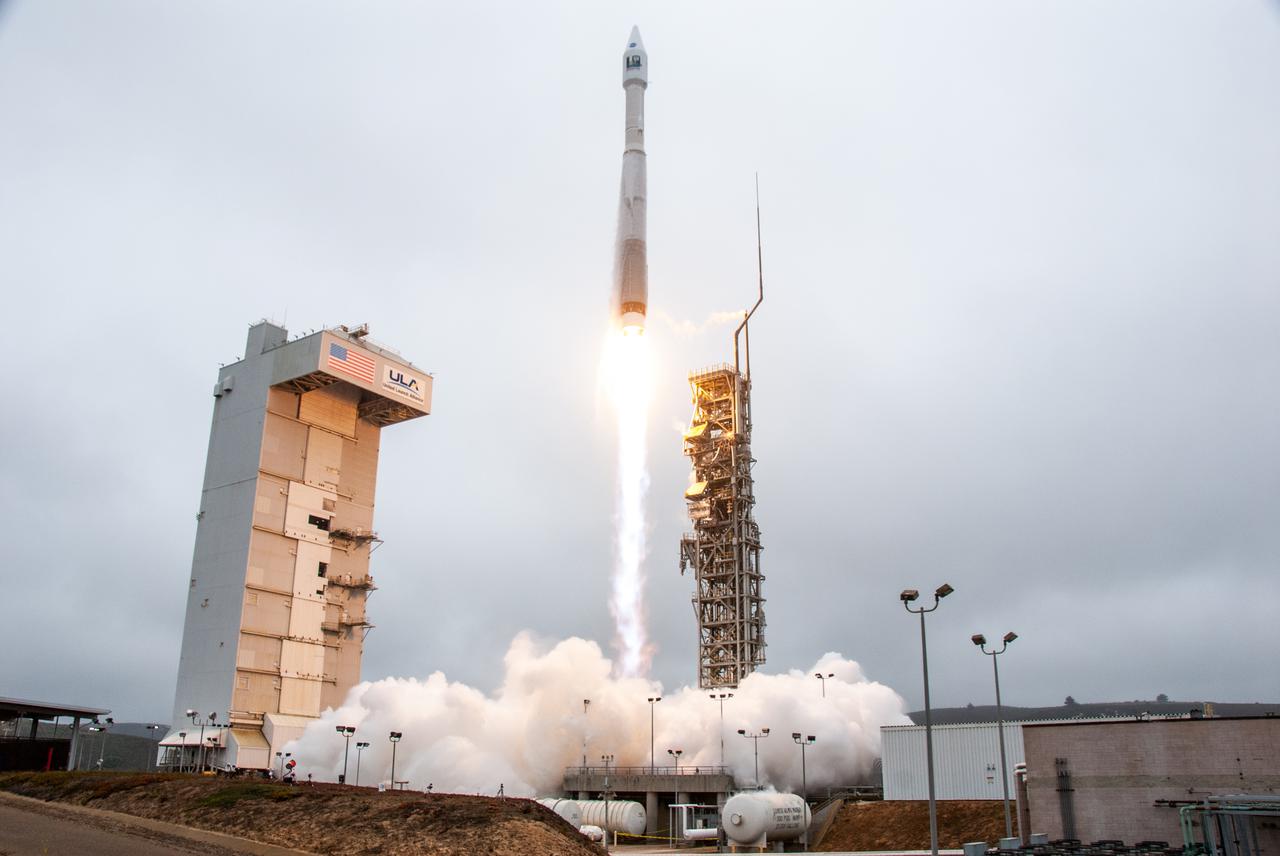

NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launches on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Station in California on Sept. 27, 2021. Launch time was 2:11 p.m. EDT (11:11 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.
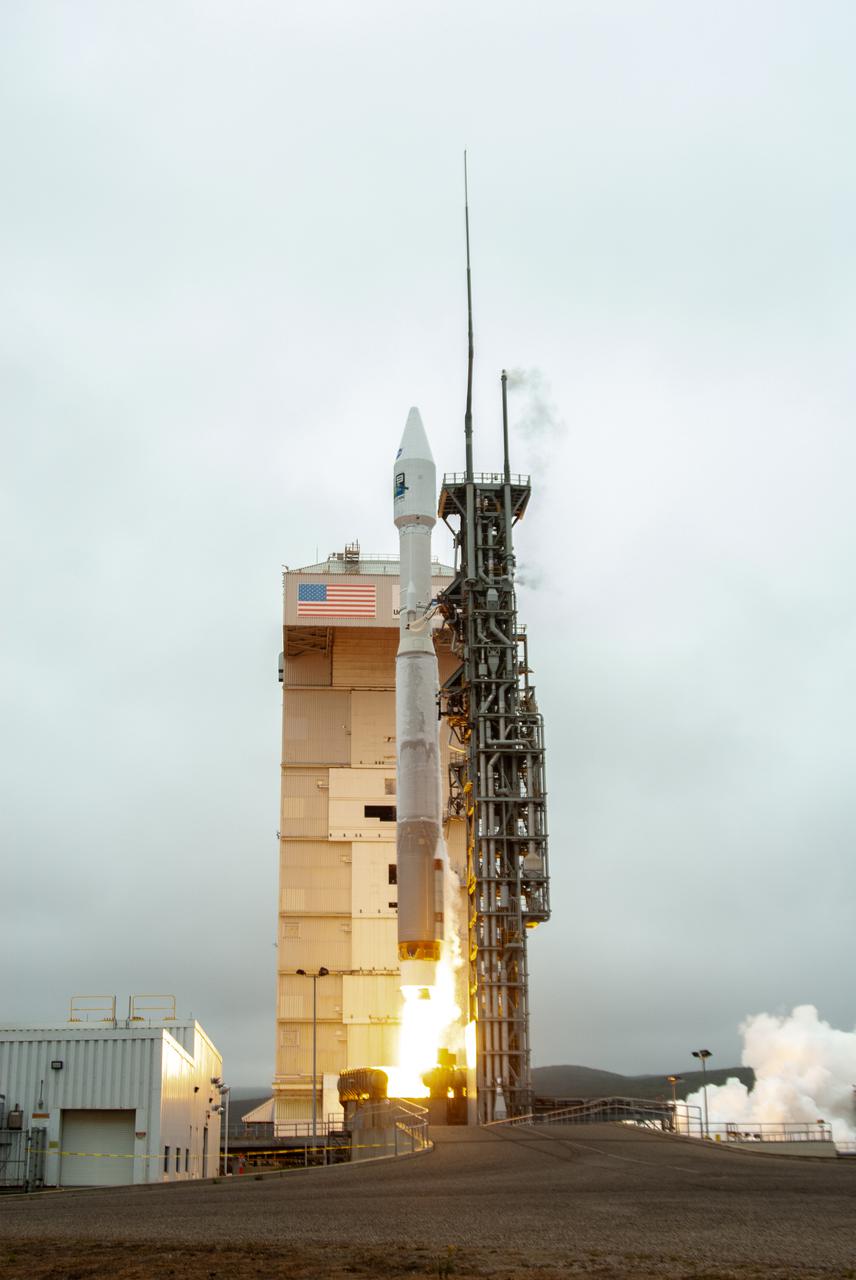

NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launches on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Station in California on Sept. 27, 2021. Launch time was 2:11 p.m. EDT (11:11 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.
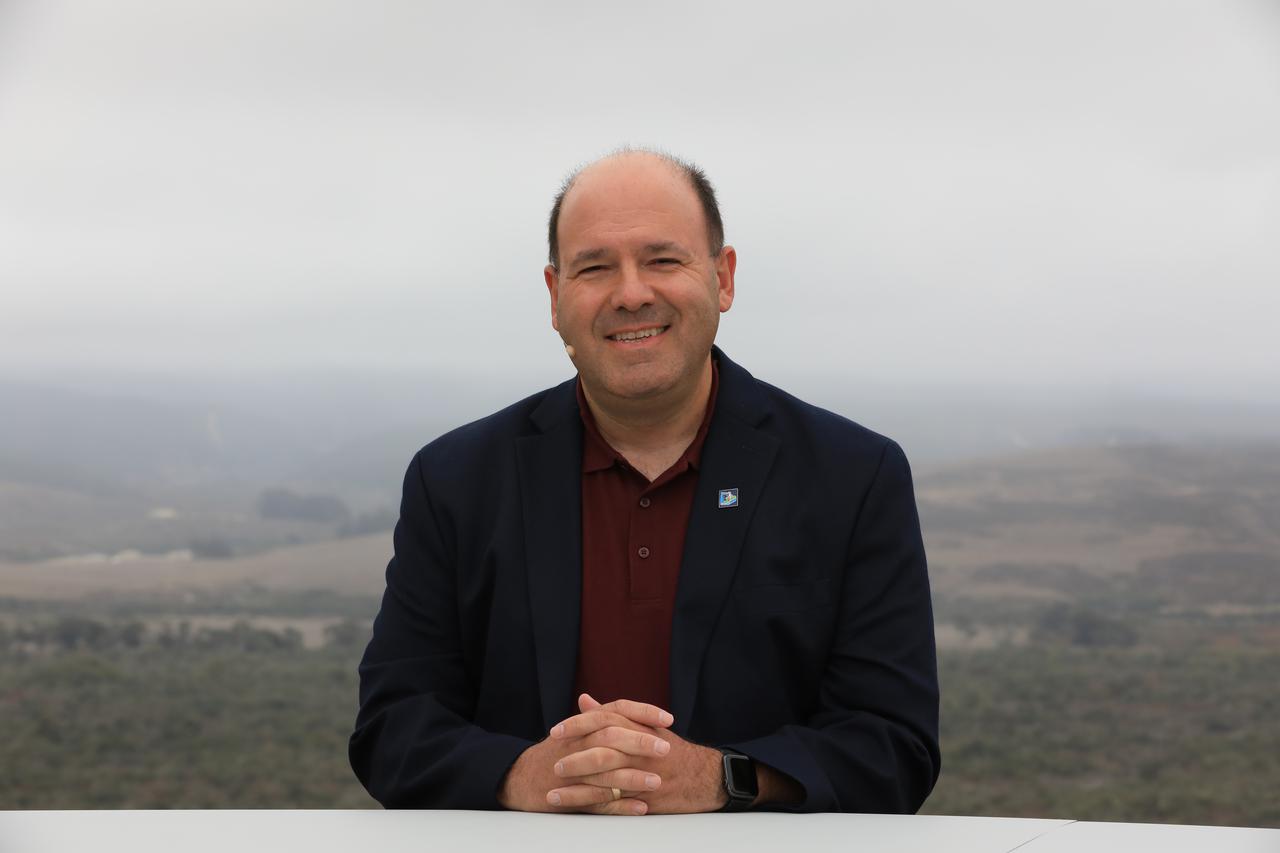

Frank DeMauro, vice president, Northrop Grumman Tactical Space Systems, participates in the launch broadcast for the Landsat 9 mission on Sept. 27, 2021, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 3 at 2:12 p.m. EDT (11:12 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.
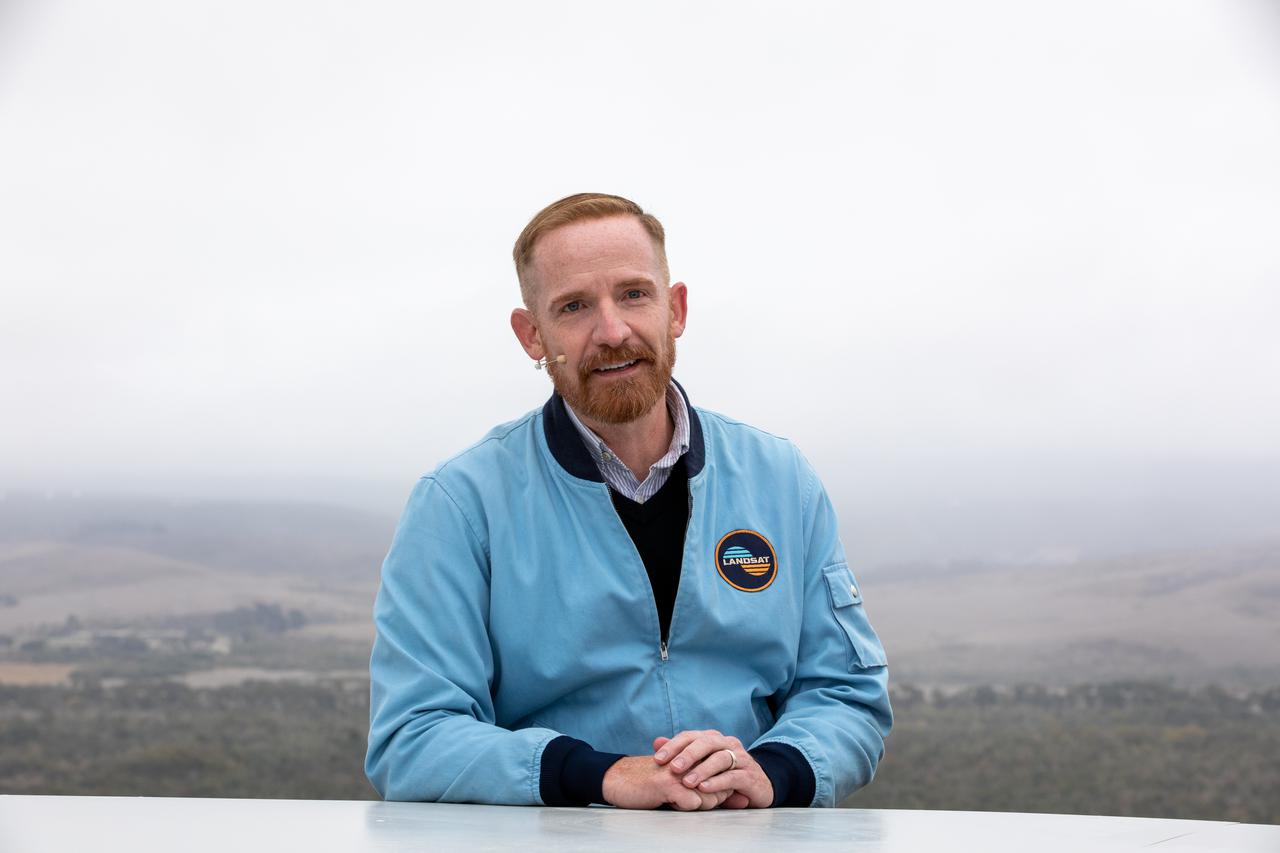

Marc Evan Jackson, actor, "Landsat Steve" in Kong: Skull Island, participates in the launch broadcast for the Landsat 9 mission on Sept. 27, 2021, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 3 at 2:12 p.m. EDT (11:12 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.
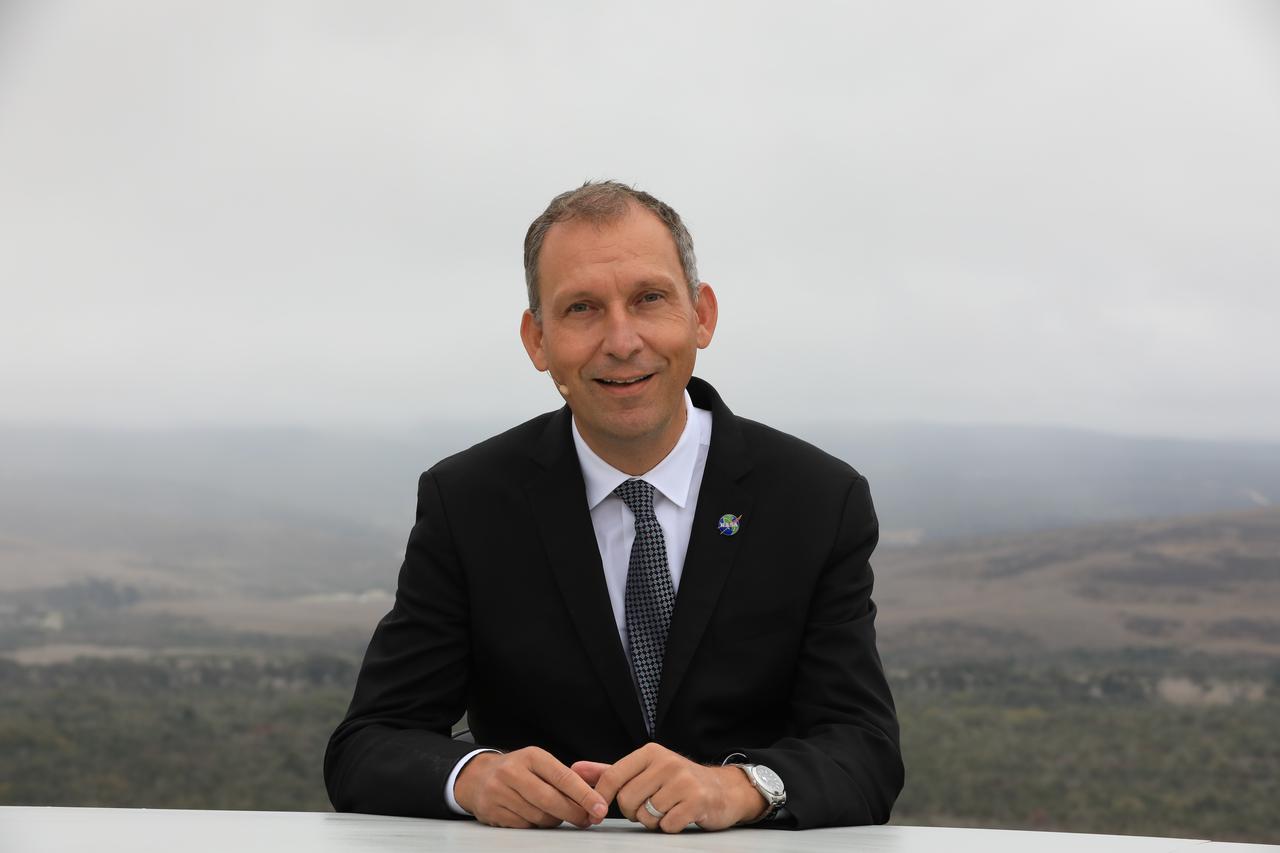

Dr. Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator, NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, participates in the launch broadcast for the Landsat 9 mission on Sept. 27, 2021, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 3 at 2:12 p.m. EDT (11:12 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.
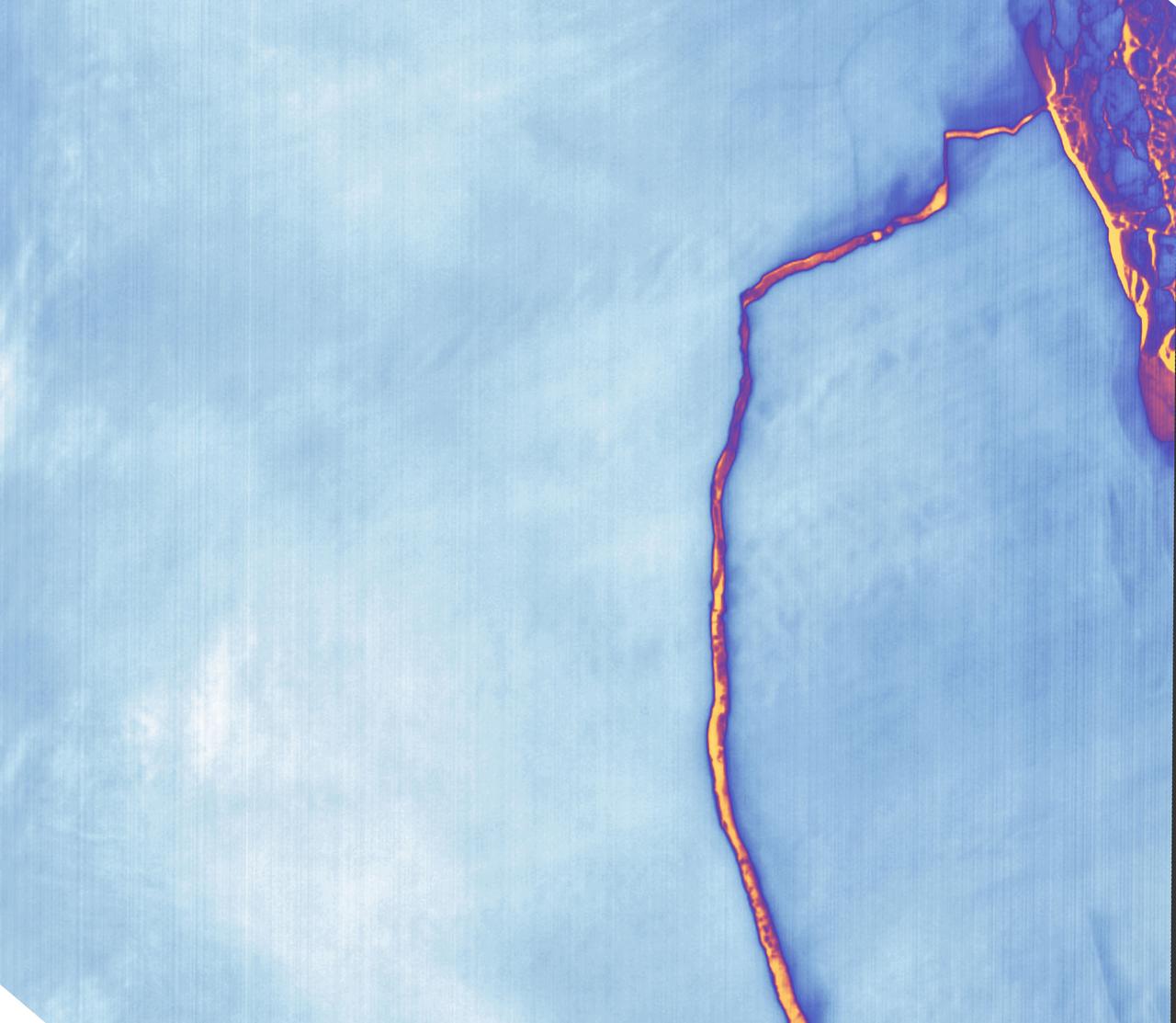
Sometime between July 10 and July 12, an iceberg about the size of Delaware split off from Antarctica’s Larsen C ice shelf. Now that nearly 5,800 square kilometers (2,200 square miles) of ice has broken away, the Larsen C shelf area has shrunk by approximately 10 percent. This false-color image was captured by Landsat’s Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS). It shows the relative warmth or coolness of the landscape. Orange indicates where the surface is the warmest, most notably the mélange between the new berg and the ice shelf. Light blues and whites are the coldest areas, including the ice shelf and the iceberg. On July 13, the U.S. National Ice Center issued a press release confirming the new iceberg and officially naming it A-68. Credit: NASA Earth Observatory images by Joshua Stevens, using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

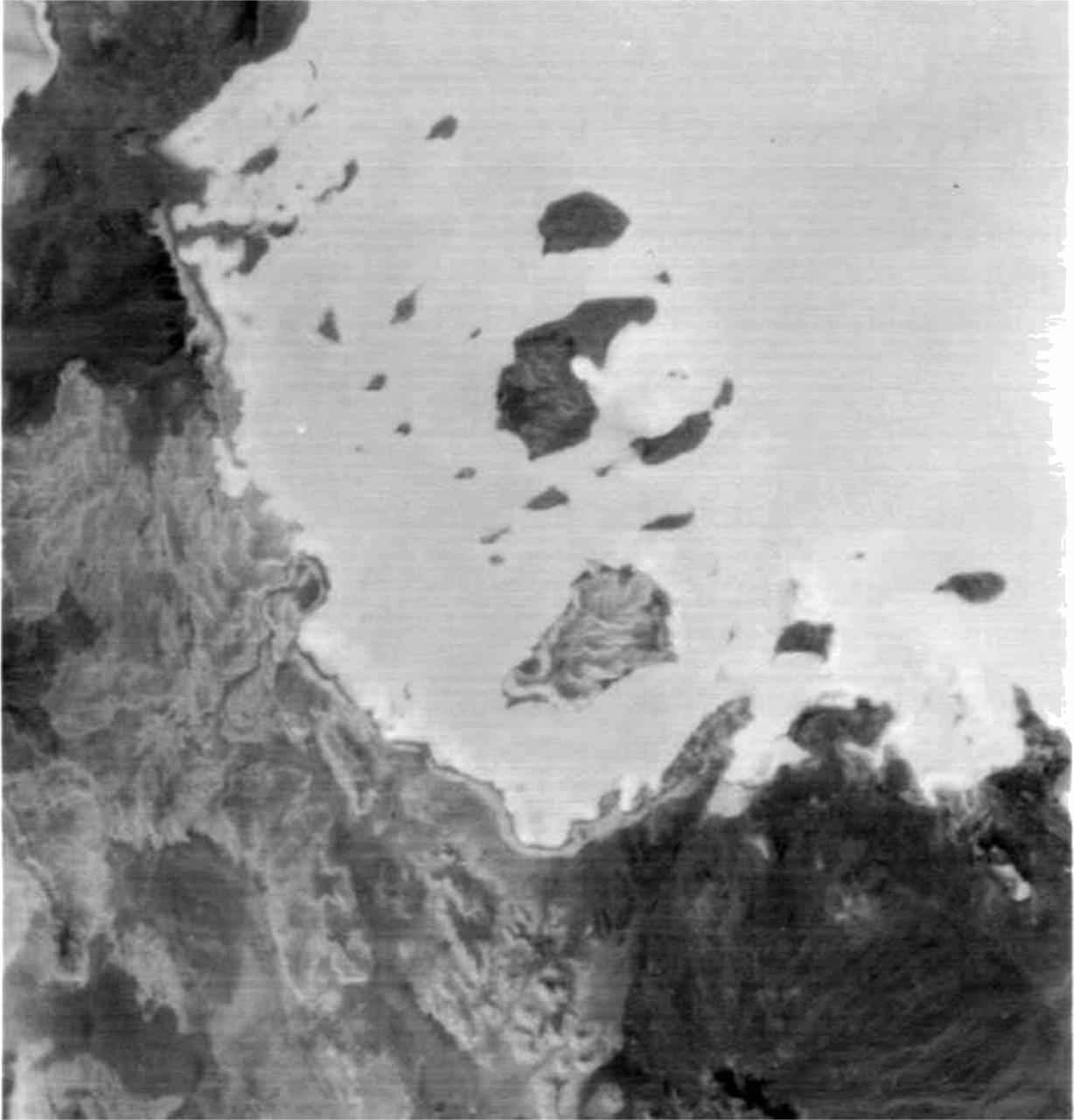
As Antarctica remains shrouded in darkness during the Southern Hemisphere winter, the Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) on Landsat 8 captured a new snap of the 2,240-square-mile iceberg that split off from the Antarctic Peninsula’s Larsen C ice shelf on July 10-12. The satellite imagery is a composite of Landsat 8 as it past on July 14 and July 21 and shows that the main berg, A-68, has already lost several smaller pieces. The A-68 iceberg is being carried by currents northward out of its embayment on the Larsen C ice shelf. The latest imagery also details a group of three small, not yet released icebergs at the north end of the embayment. Credits: NASA Goddard/UMBC JCET, Christopher A. Shuman <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>