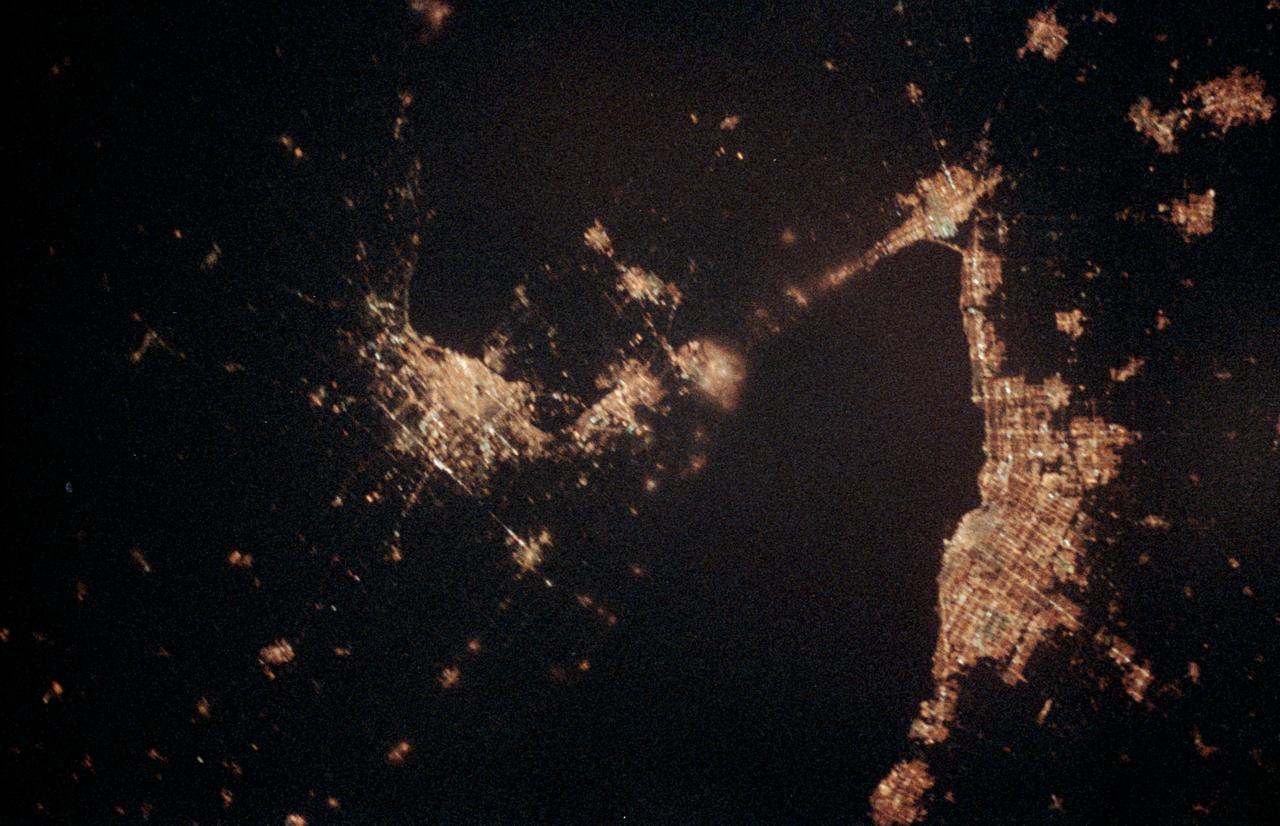

STS060-06-037 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- The city lights of Buffalo and Toronto outline the shores of the east end of Lake Erie and the west end of Lake Ontario in this night scene of western New York and southern Ontario. Between the two major cities are the cities of Niagara Falls, New York and Niagara Falls, Canada, which straddle the Niagara River just north of the actual falls. This photograph was taken with a special ASA-1600 film that is normally used for night-time photography of aurora, noctilucent clouds, biomass burning, and city lights.

Earth observation taken during a night pass by an Expedition 36 crew member on board the International Space Station (ISS). Per Twitter message this is labeled as: Detroit, Cleveland, Toronto and a blue hint of sunrise.
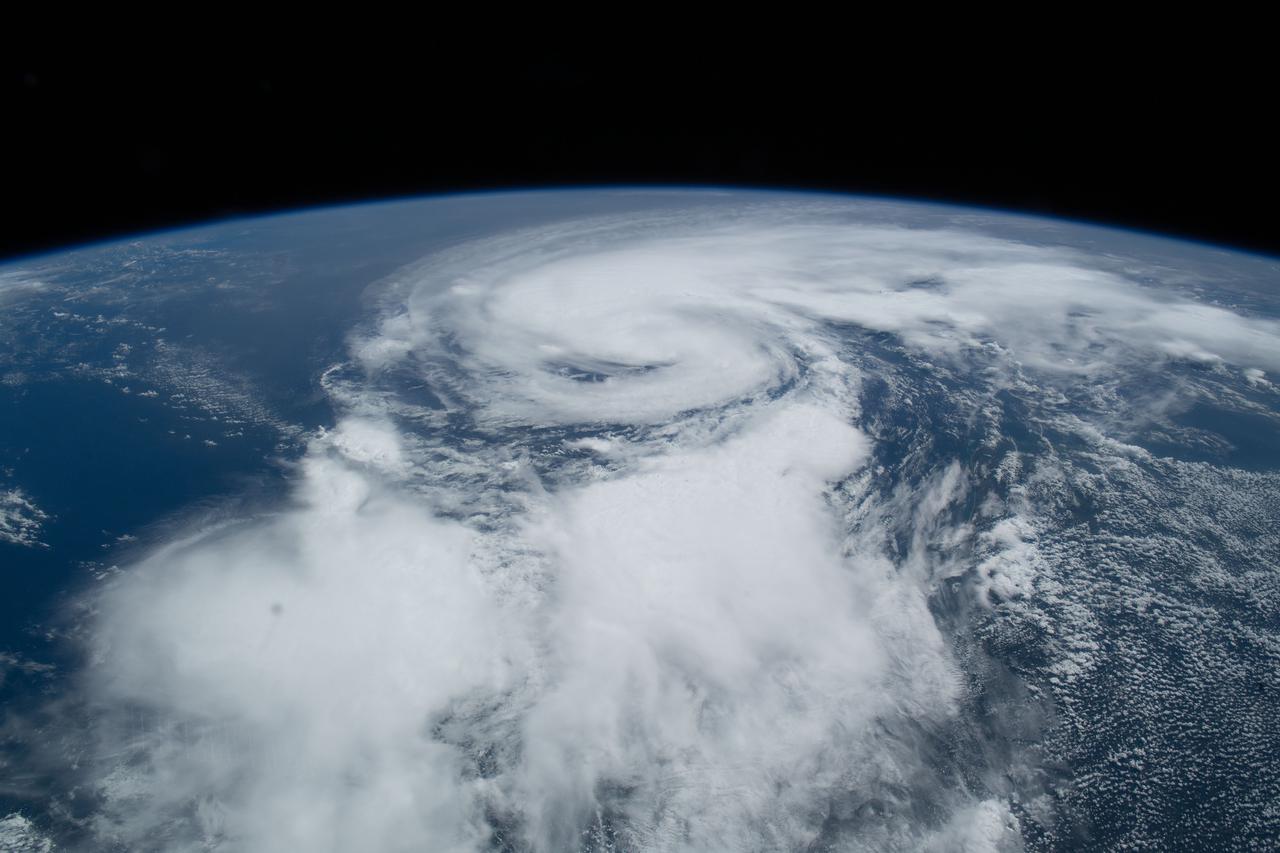

iss065e281869 (Aug. 21, 2021) --- Hurricane Henri is pictured off the eastern coast of the United States from the International Space Station as it orbited 264 miles above Toronto, Canada.
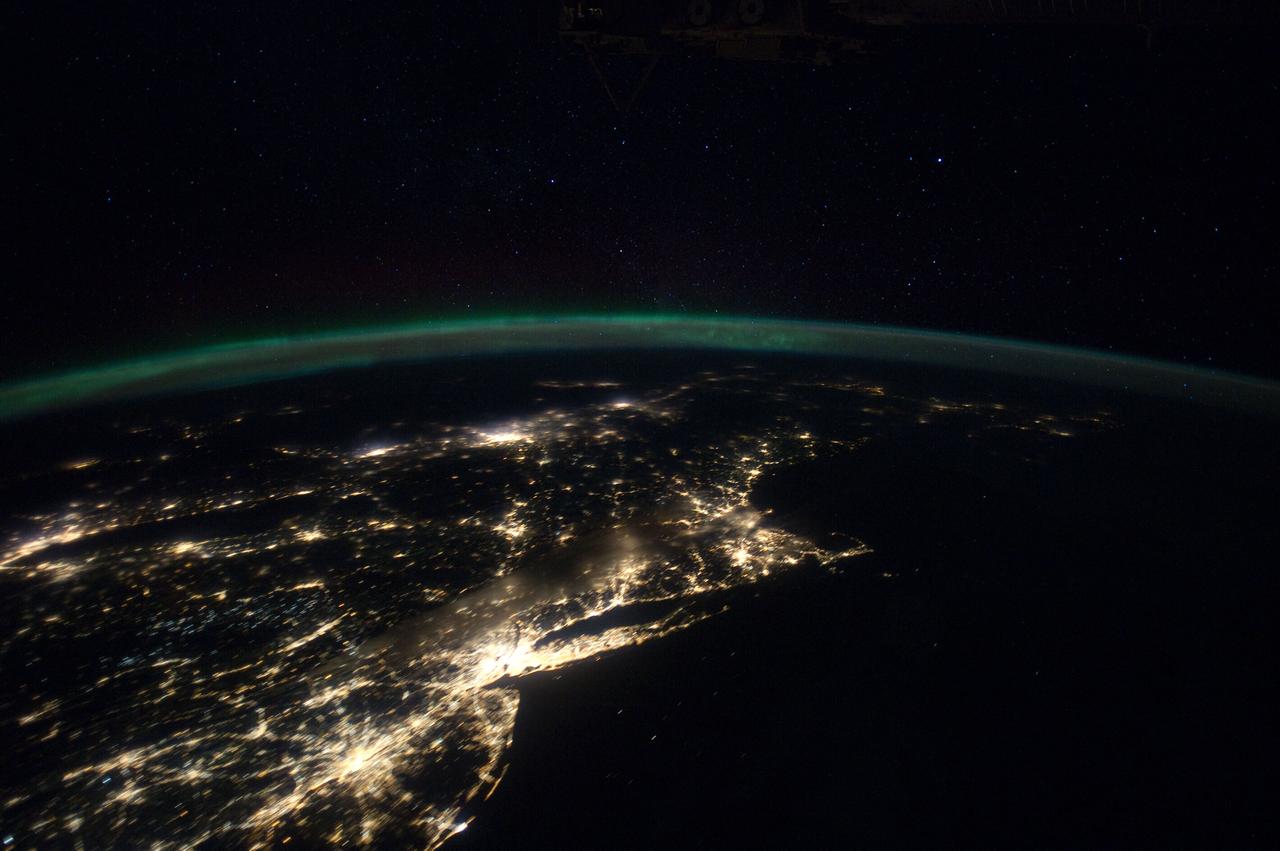

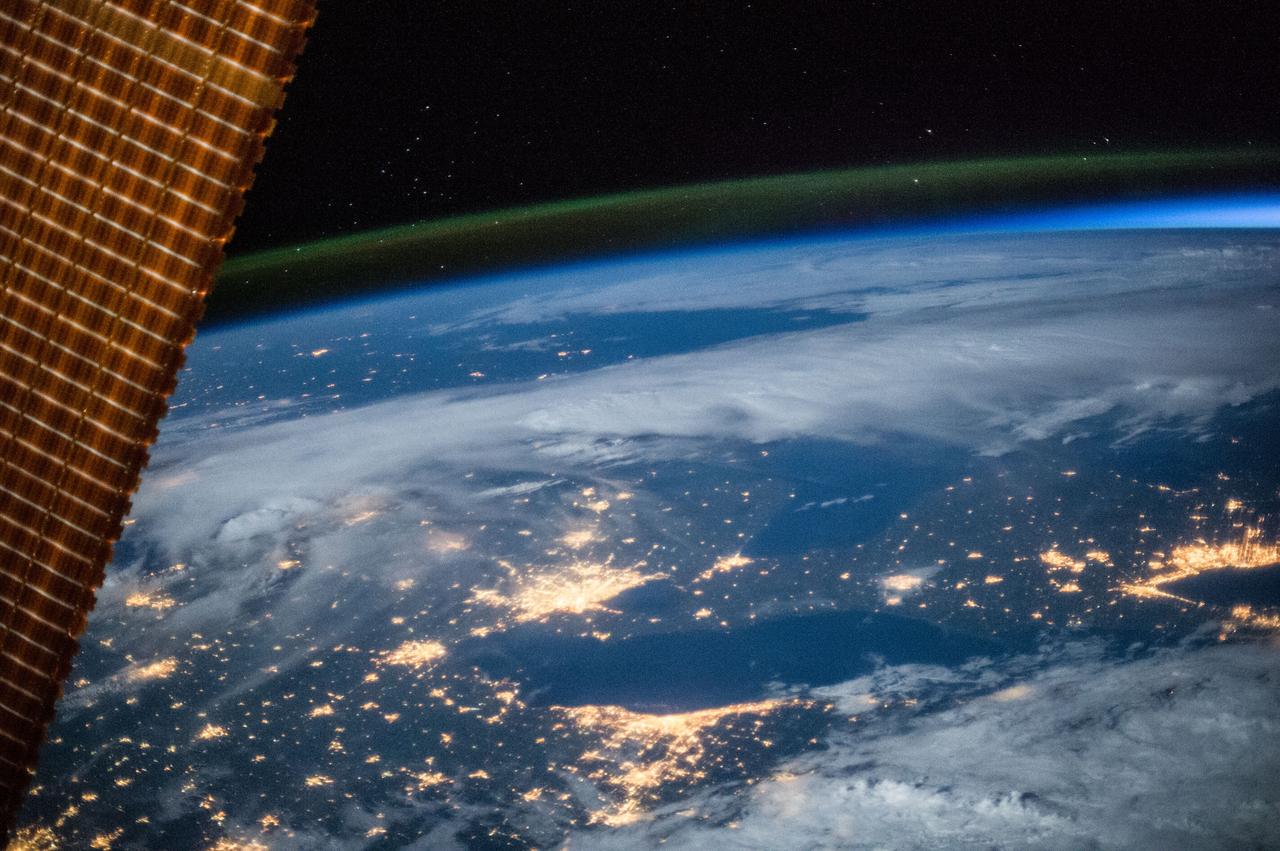
ISS030-E-055791 (29 Jan. 2012) --- This Jan. 29 panorama of much of the East Coast, photographed by one of the Expedition 30 crew members aboard the International Space Station, provides a look generally northeastward: Philadelphia-New York City-Boston corridor (bottom-center); western Lake Ontario shoreline with Toronto (left edge); Montreal (near center). An optical illusion in the photo makes the atmospheric limb and light activity from Aurora Borealis appear “intertwined.”
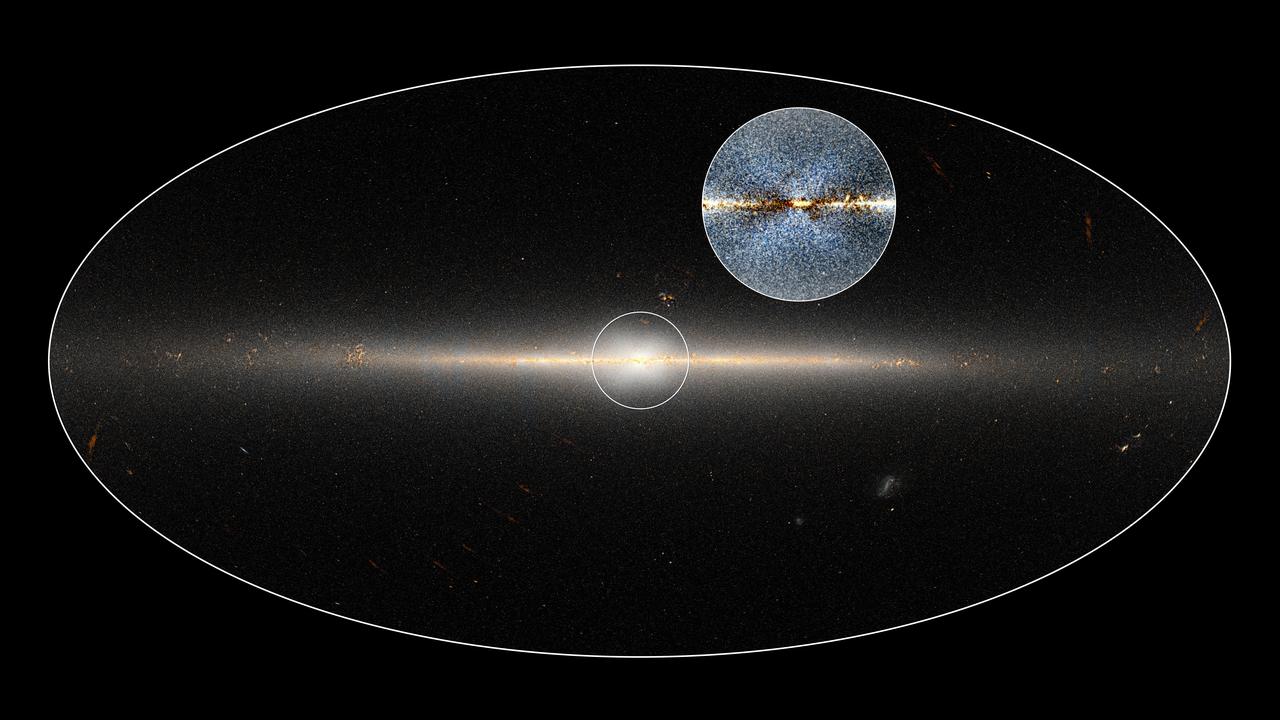
In 2010, NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) mission observed the entire sky twice. Astronomers used these data to point out the X-shaped structure in the bulge of the Milky Way, contained in the small circle at center, as well as the inset image. The circled central portion covers roughly the area of sky that would be blocked by a basketball when held out at arm's length. Dustin Lang, an astronomer at the Dunlap Institute of the University of Toronto, used these data to make this map, which shows the full 360-degree panorama of the sky as seen by WISE. Lang collaborated with Melissa Ness, postdoctoral researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Germany, http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20699
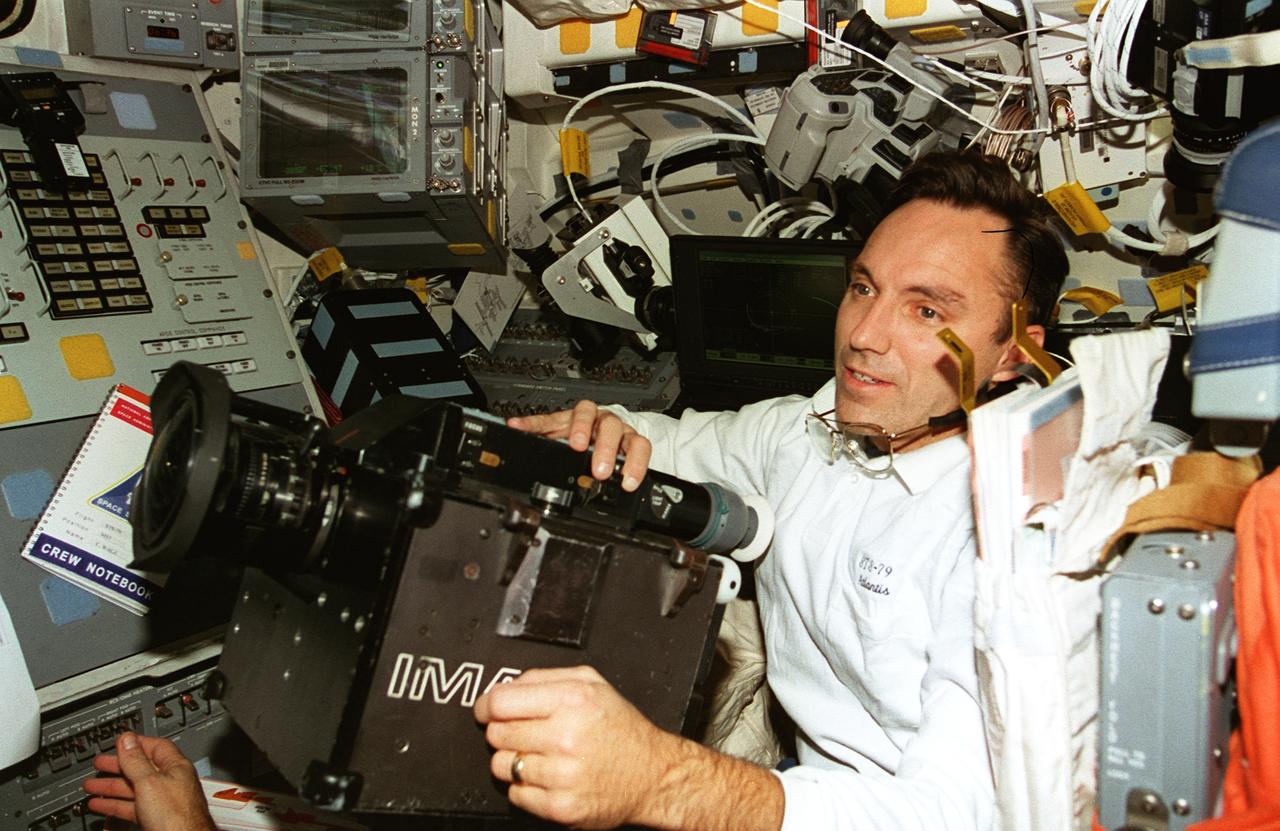

STS079-362-023 (16-26 Sept. 1996) --- Astronaut Carl E. Walz, mission specialist, positions the IMAX camera for a shoot on the flight deck of the Space Shuttle Atlantis. The IMAX project is a collaboration among NASA, the Smithsonian Institution's National Air and Space Museum, IMAX Systems Corporation and the Lockheed Corporation to document in motion picture format significant space activities and promote NASA's educational goals using the IMAX film medium. This system, developed by IMAX of Toronto, uses specially designed 65mm cameras and projectors to record and display very high definition color motion pictures which, accompanied by six-channel high fidelity sound, are displayed on screens in IMAX and OMNIMAX theaters that are up to ten times larger than a conventional screen, producing a feeling of "being there." The 65mm photography is transferred to 70mm motion picture films for showing in IMAX theaters. IMAX cameras have been flown on 14 previous missions.
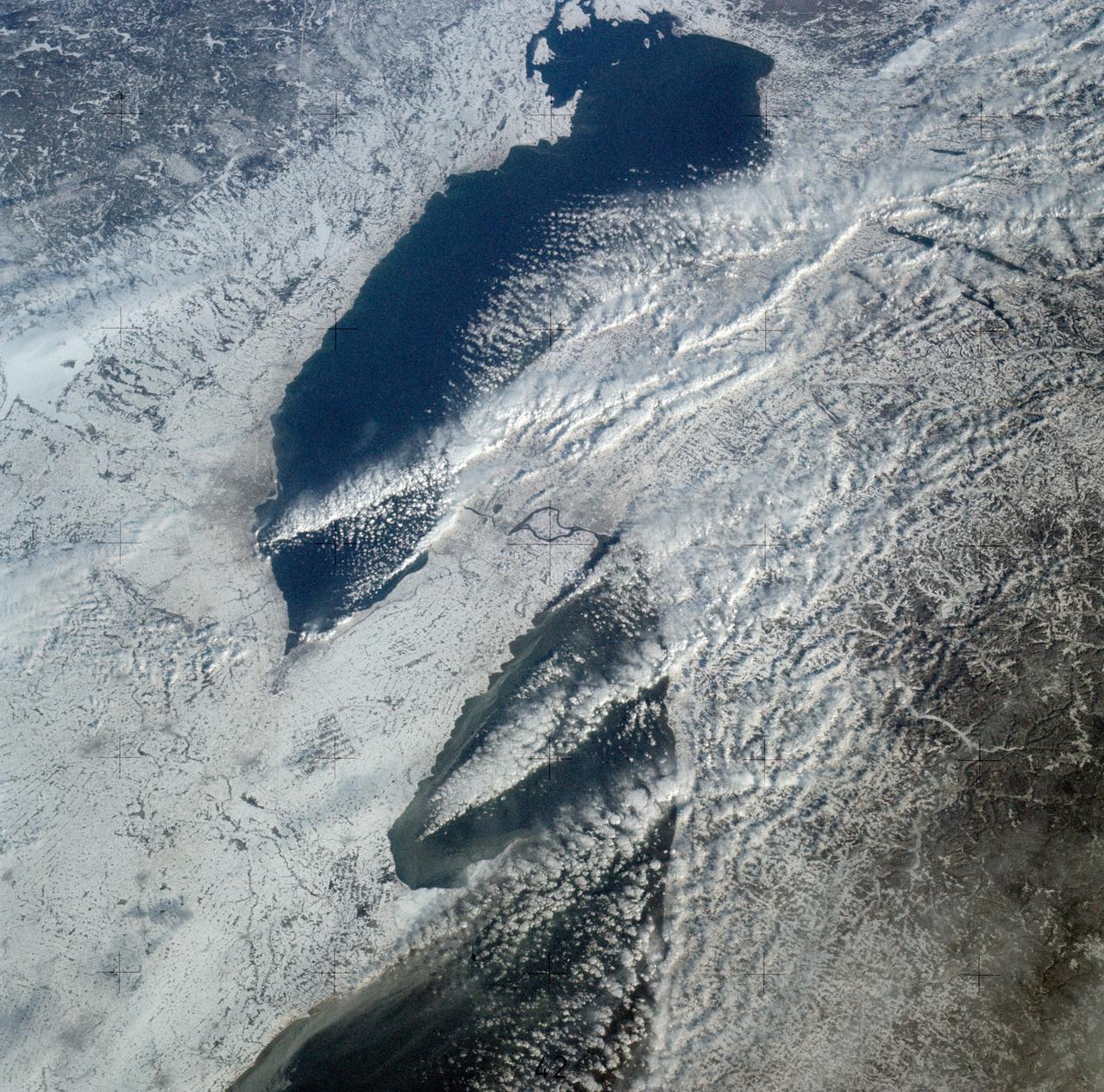

SL4-139-3989 (February 1974) --- An oblique view of a portion of the Great Lakes area as seen from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. This picture was taken with a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad camera. Lake Erie is in the foreground; and Lake Ontario is in the background. The Niagara Falls area is in the center of the photograph. Portions of Pennsylvania, New York, and Ontario, Canada are visible, but under nearly complete snow cover. Major structural features, drainage patterns, road systems and the cities of Buffalo and Toronto are easily distinguished and actually enhanced by the snow. At the time this picture was taken, these two Great Lakes had no observable ice, although cloud formations partially mask the southern shores of the two bodies of water. James Barnes, a snow-pattern expert, will analyze Skylab photographs like this one to gain further knowledge of snow cover over land masses. Photo credit: NASA
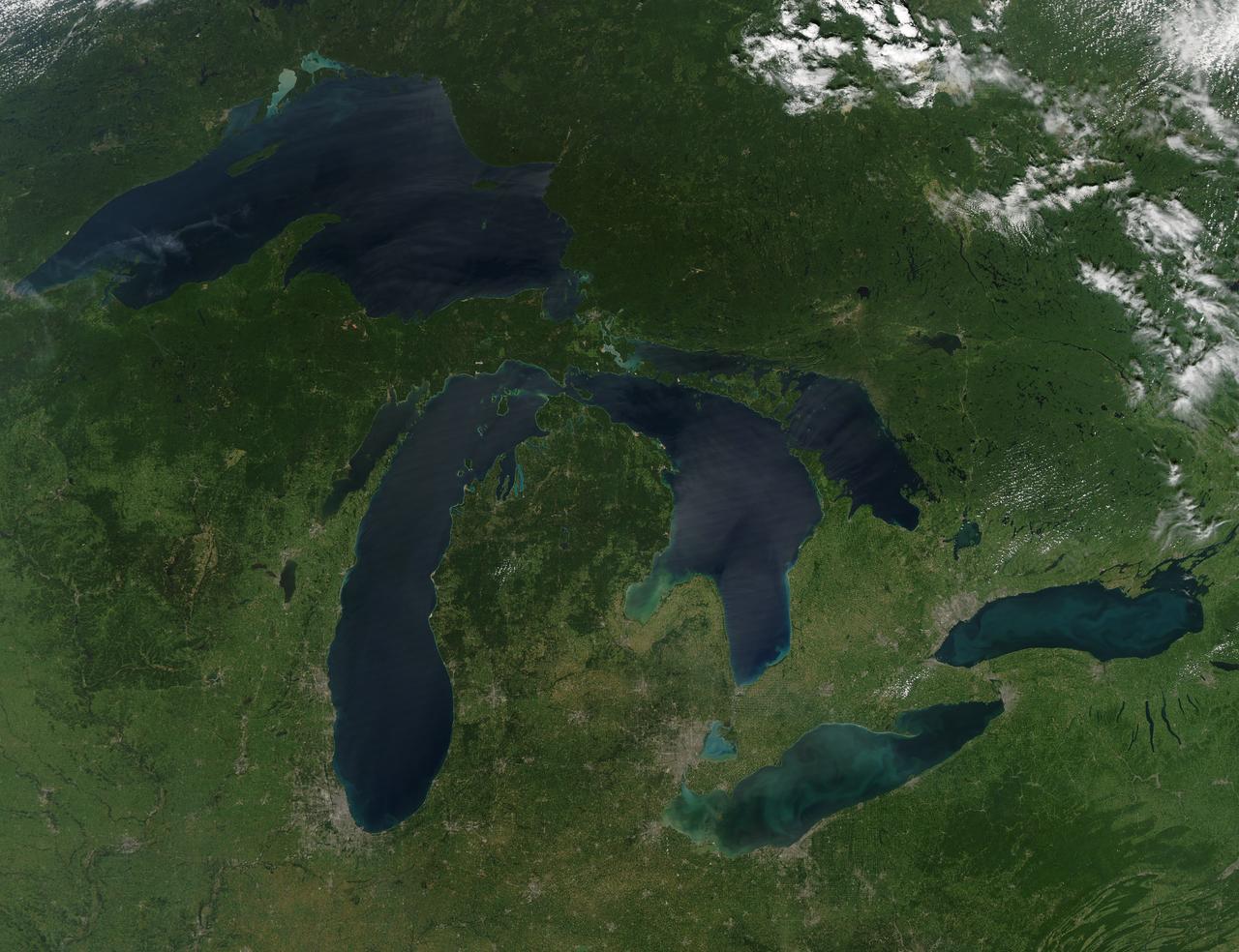
NASA image acquired August 28, 2010 Late August 2010 provided a rare satellite view of a cloudless summer day over the entire Great Lakes region. North Americans trying to sneak in a Labor Day weekend getaway on the lakes were hoping for more of the same. The Great Lakes comprise the largest collective body of fresh water on the planet, containing roughly 18 percent of Earth's supply. Only the polar ice caps contain more fresh water. The region around the Great Lakes basin is home to more than 10 percent of the population of the United States and 25 percent of the population of Canada. Many of those people have tried to escape record heat this summer by visiting the lakes. What they found, according to The Hamilton Spectator, was record-breaking water temperatures fueled by record-breaking air temperatures in the spring and summer. By mid-August, the waters of Lake Superior were 6 to 8°C (11 to 14°F) above normal. Lake Michigan set records at about 4°C (7°F) above normal. The other three Great Lakes – Huron, Erie, and Ontario -- were above normal temperatures, though no records were set. The image was gathered by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite at 1:30 p.m. Central Daylight Time (18:30 UTC) on August 28. Open water appears blue or nearly black. The pale blue and green swirls near the coasts are likely caused by algae or phytoplankton blooms, or by calcium carbonate (chalk) from the lake floor. The sweltering summer temperatures have produced an unprecedented bloom of toxic blue-green algae in western Lake Erie, according to the Cleveland Plain Dealer. NASA image by Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team, Goddard Space Flight Center. Caption by Mike Carlowicz. Instrument: Aqua - MODIS Click here to see more images from <b><a href="#//earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Goddard’s Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

ISS026-E-012474 (24 Dec. 2010) --- A night view of the Montreal metropolitan area is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 26 crew member on the International Space Station. This photograph of the Montreal, Quebec, Canada metropolitan area (center) illustrates the extent of urbanization made clearly visible by city lights at night. Major roadways and industrial areas are traced by bright white lighting, while the adjacent residential and commercial land uses are characterized by more diffuse yellow-gold lighting. Rivers and other water bodies appear black, while the surrounding rural countryside is faintly illuminated by moonlight. Blurry areas at top and bottom left are caused by cloud cover. Montreal is the largest city in the dominantly French-speaking Province of Quebec. The metropolitan area is the country?s second-largest, having been surpassed by Toronto in 1976. While the city of Montreal proper is located on?and almost completely covers?the Island of Montreal at the confluence of the St. Lawrence (center) and Ottawa Rivers (not visible), the city takes its name from Mont Royal located at the city?s center . Several smaller urban areas form a loose ring around the Montreal metro region: Sorel-Tracy, Saint-Hyacinthe, Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu, Salaberry-de-Valleyfield, Saint-Jerome, and Joliette are among those that can be readily identified. The International Space Station was located over the Pennsylvania-New York border (near Warren, PA) at the time this image was taken?a ground distance of approximately 600 kilometers southwest of Montreal. This distance from the camera target, coupled with the oblique (inclined) viewing angle from the ISS, results in the foreshortened appearance of urban areas in the image.
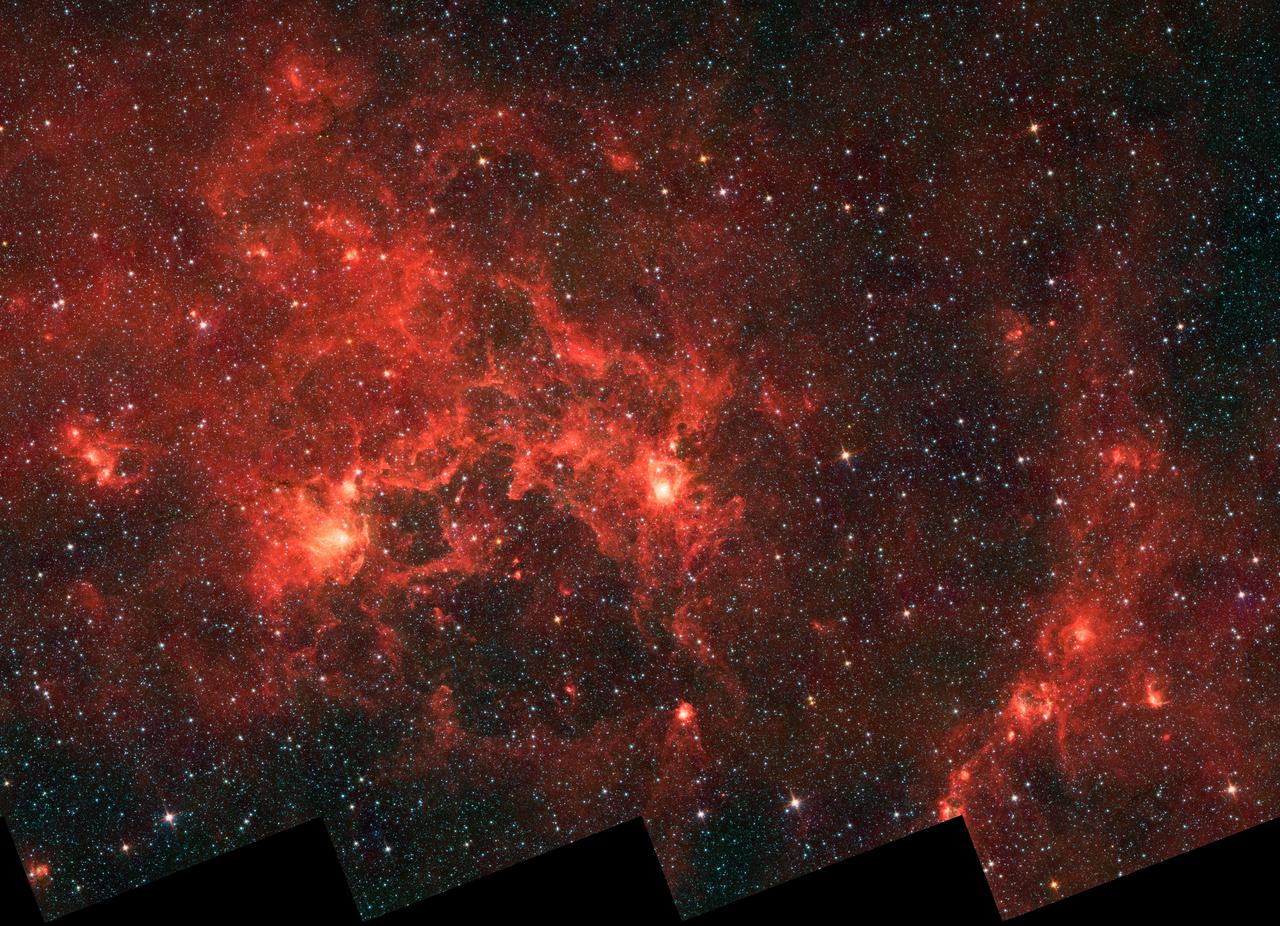

This infrared image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope shows the nebula nicknamed the Dragonfish. This turbulent region, jam-packed with stars, is home to some of the most luminous massive stars in our Milky Way galaxy.
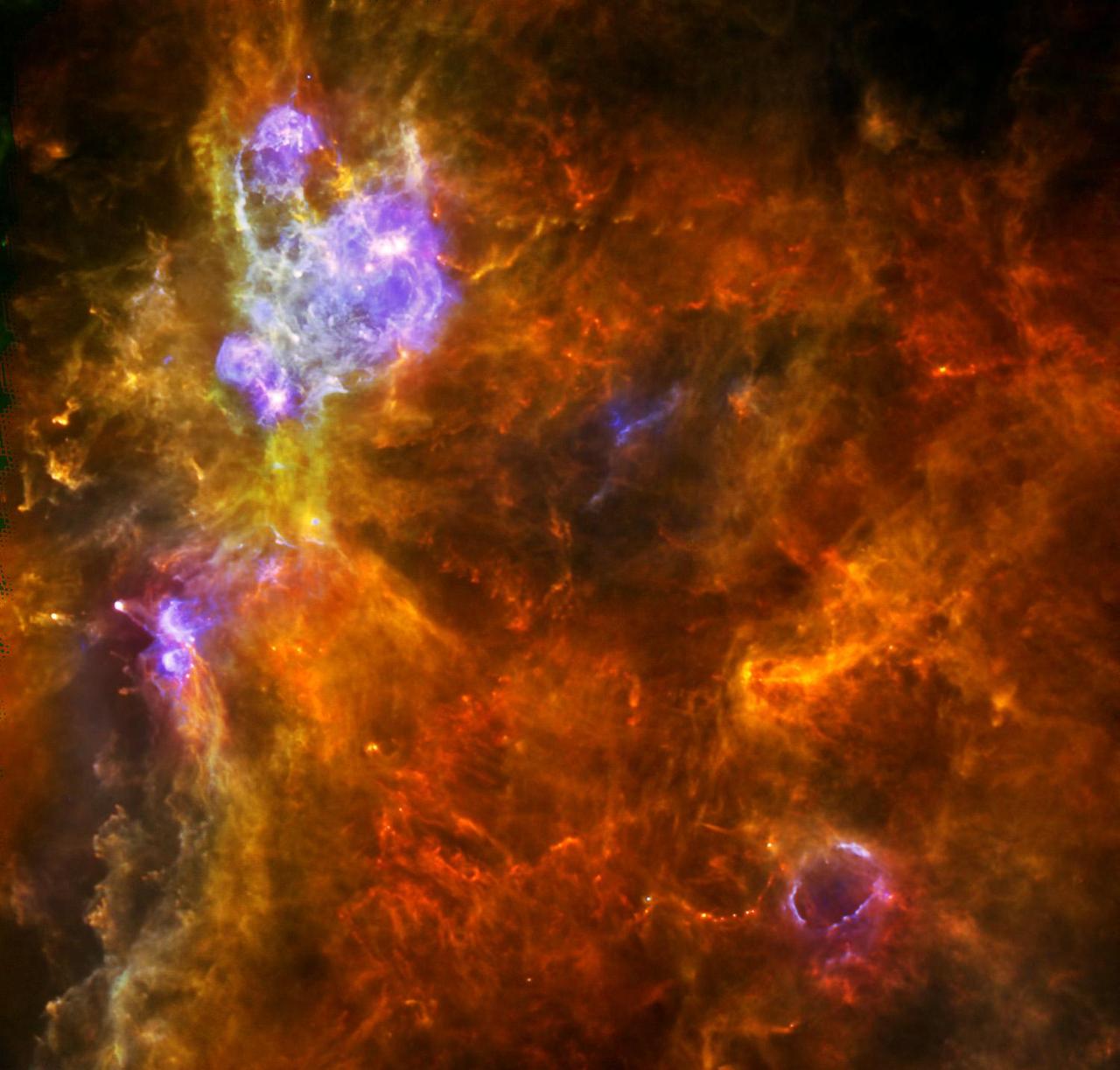

W3 is an enormous stellar nursery about 6,200 light-years away in the Perseus Arm, one of the Milky Way galaxy main spiral arms as seen by ESA Herschel space observatory.