
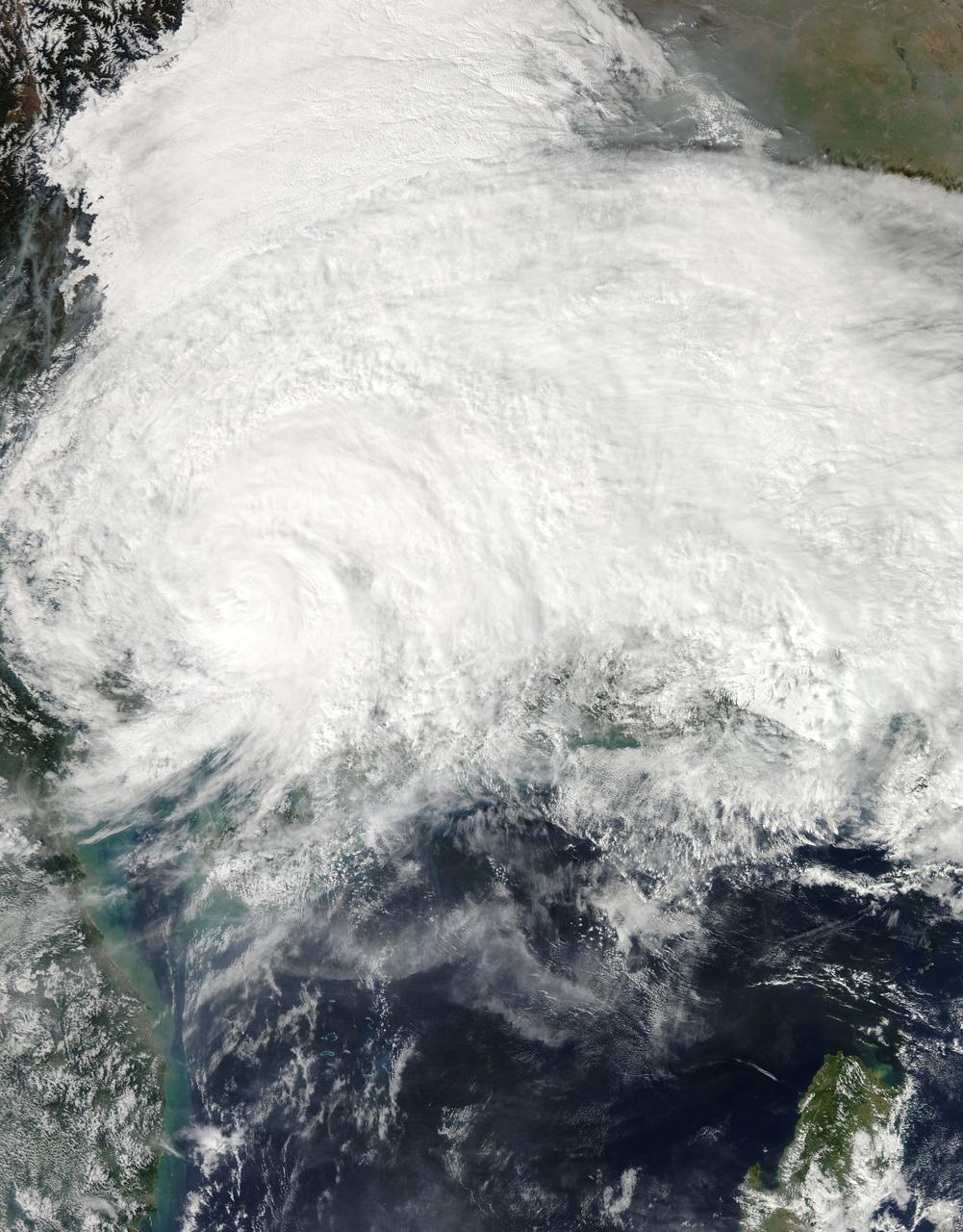
Like dancers pirouetting in opposite directions, the rotational patterns of two different tropical storms are contrasted in this pair of MISR nadir-camera images. The left-hand image is of Tropical Storm Bud, acquired on June 17, 2000 (Terra orbit 2656) as the storm was dissipating. Bud was situated in the eastern Pacific Ocean between Socorro Island and the southern tip of Baja California. South of the storm's center is a vortex pattern caused by obstruction of the prevailing flow by tiny Socorro Island. Sonora, Mexico and Baja California are visible at the top of the image. The right-hand image is of Tropical Cyclone Dera, acquired on March 12, 2001 (Terra orbit 6552). Dera was located in the Indian Ocean, south of Madagascar. The southern end of this large island is visible in the top portion of this image. Northern hemisphere tropical storms, like Bud, rotate in a counterclockwise direction, whereas those in the southern hemisphere, such as Dera, rotate clockwise. The opposite spins are a consequence of Earth's rotation. Each image covers a swath approximately 380 kilometers wide. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA03400
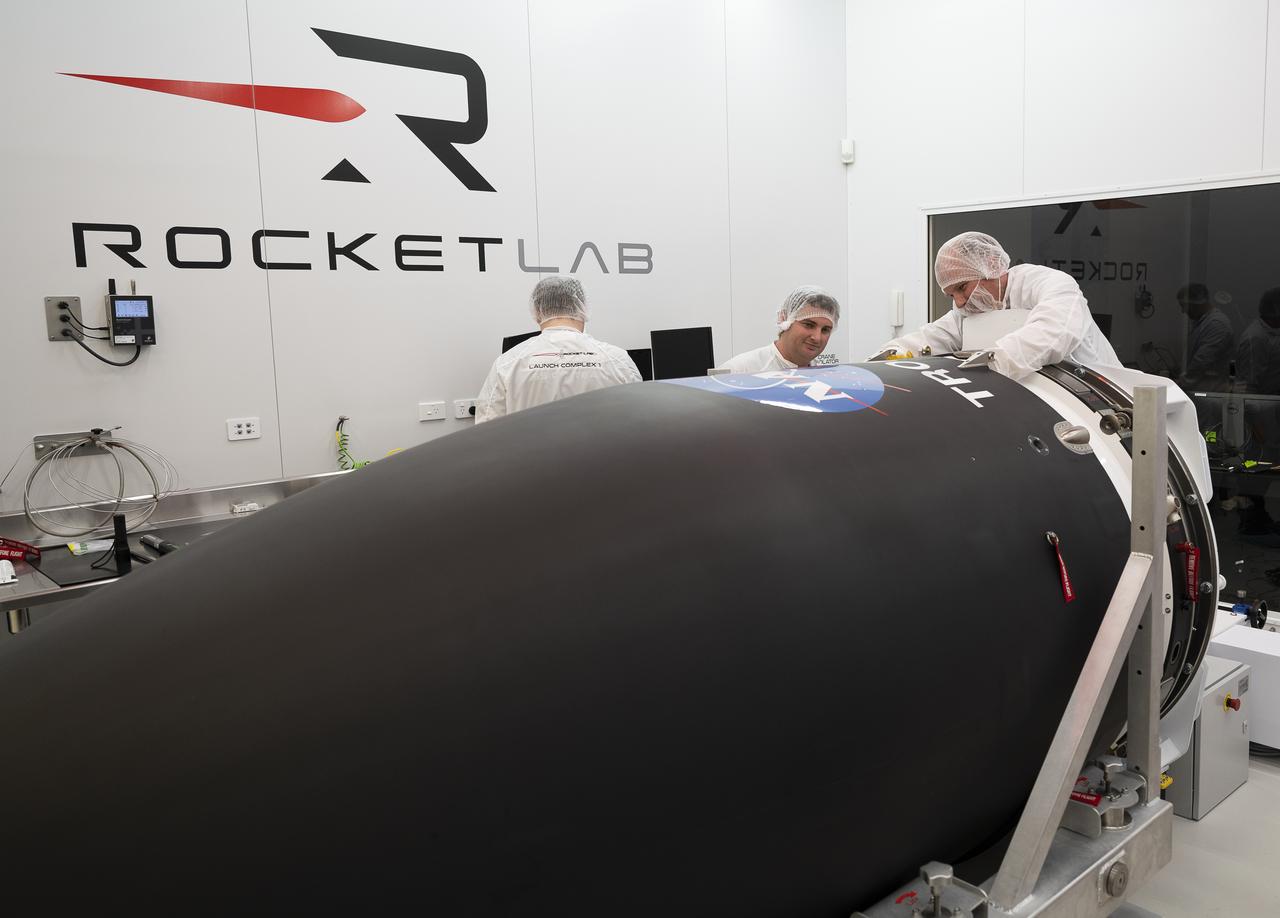

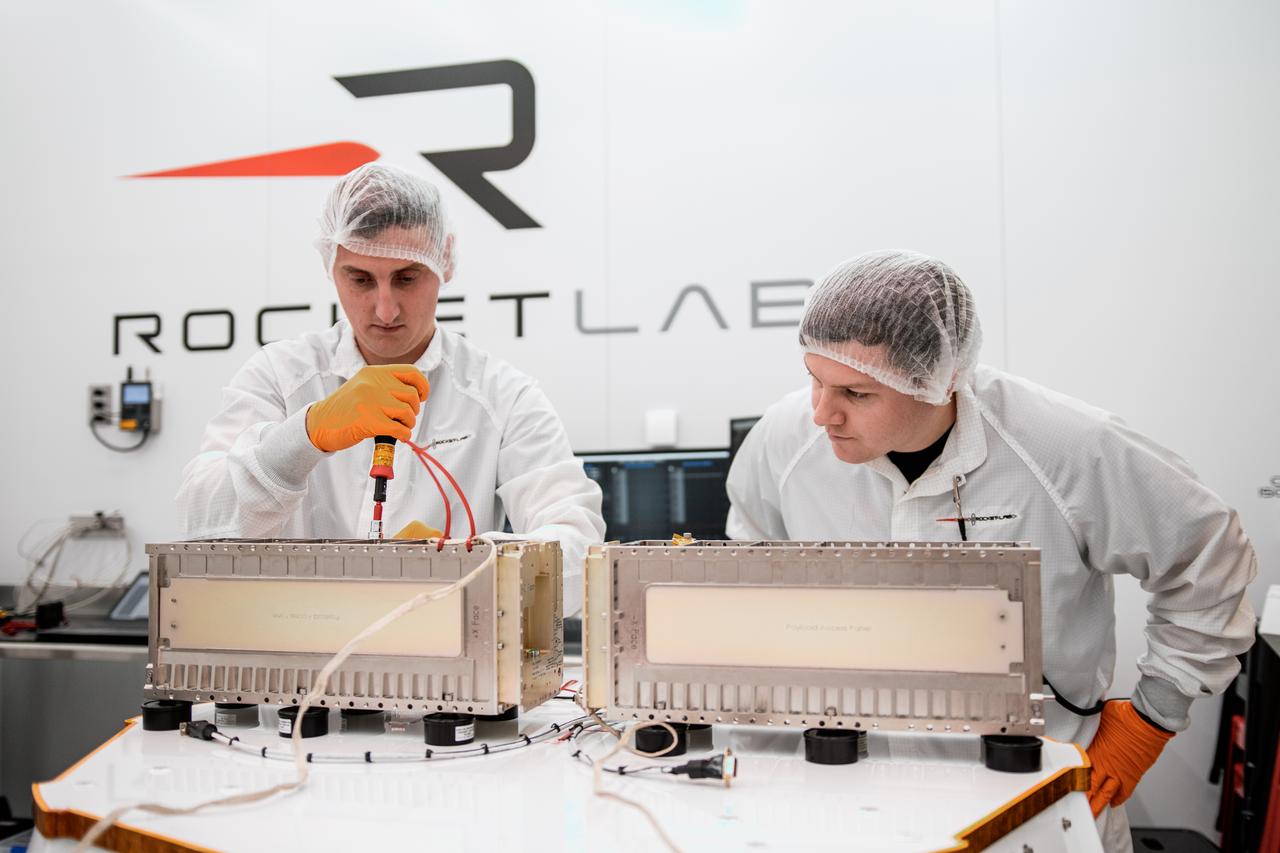
NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are encapsulated inside Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing in a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Technicians prepare NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats for encapsulation in Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing in a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
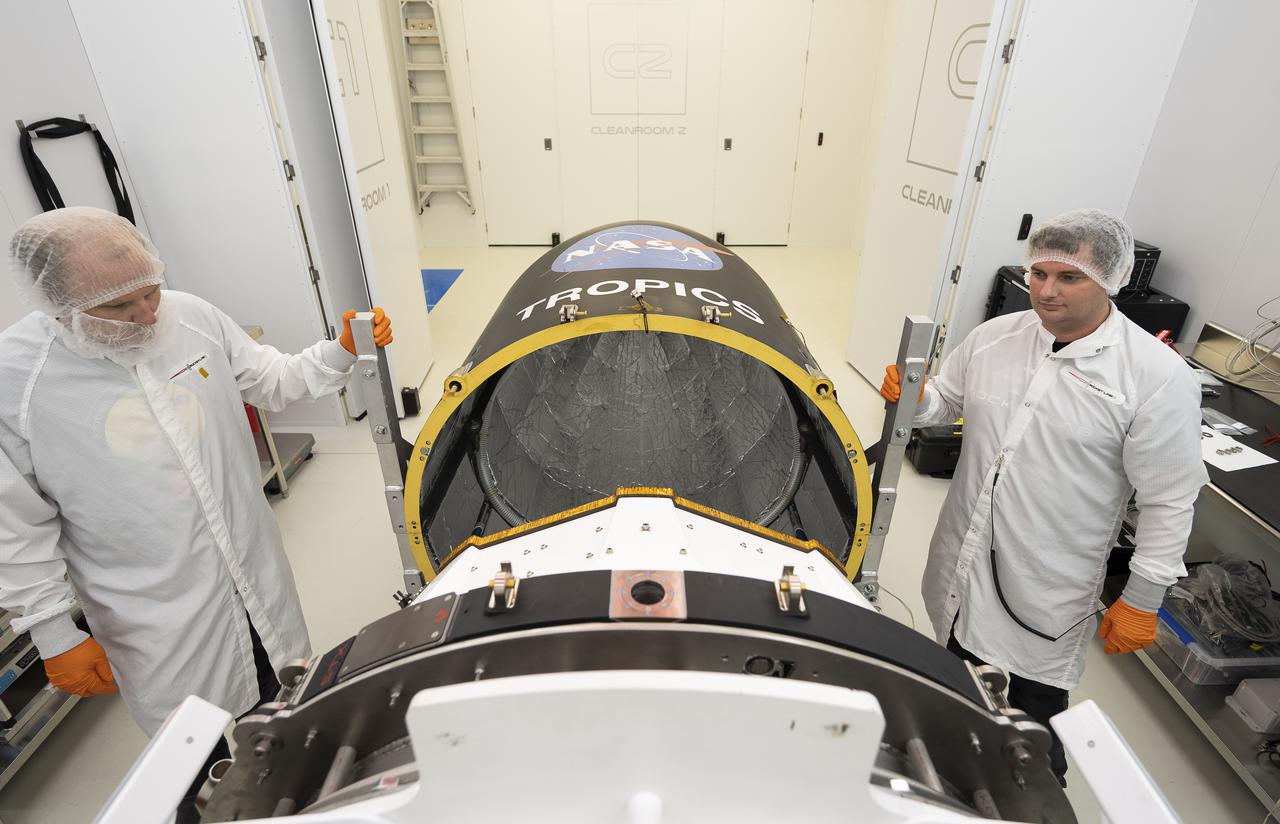

Technicians place NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats in Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing in a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
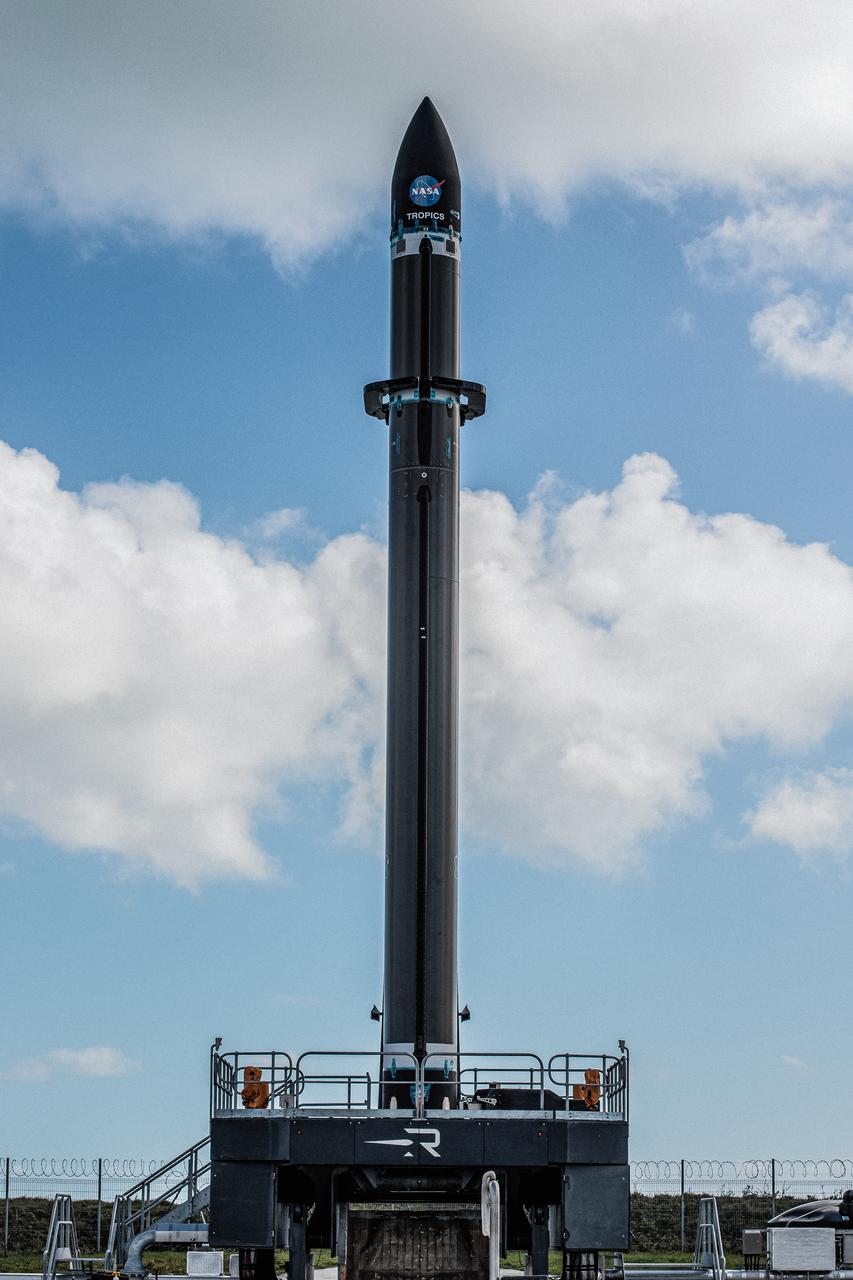

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
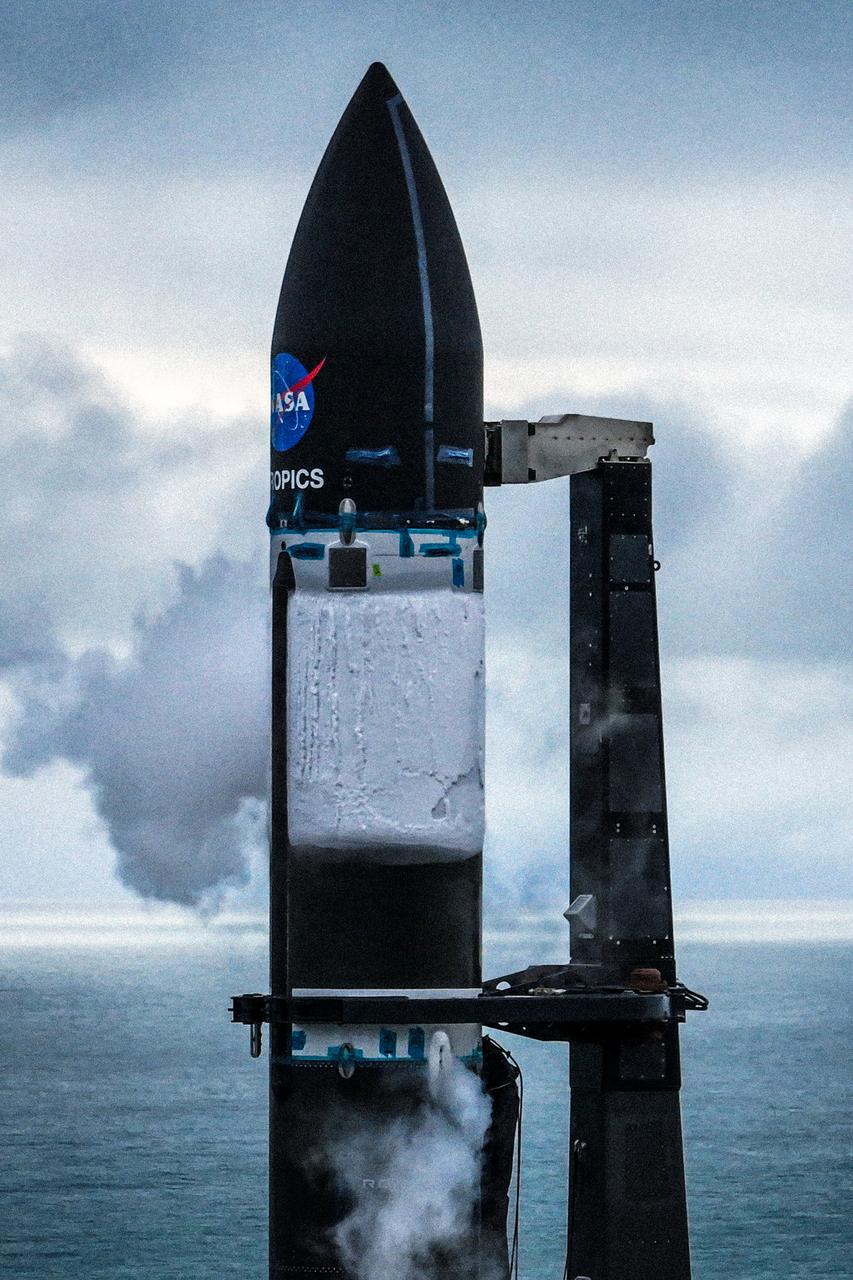

A wet dress rehearsal is underway for Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand on April 28, 2023. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
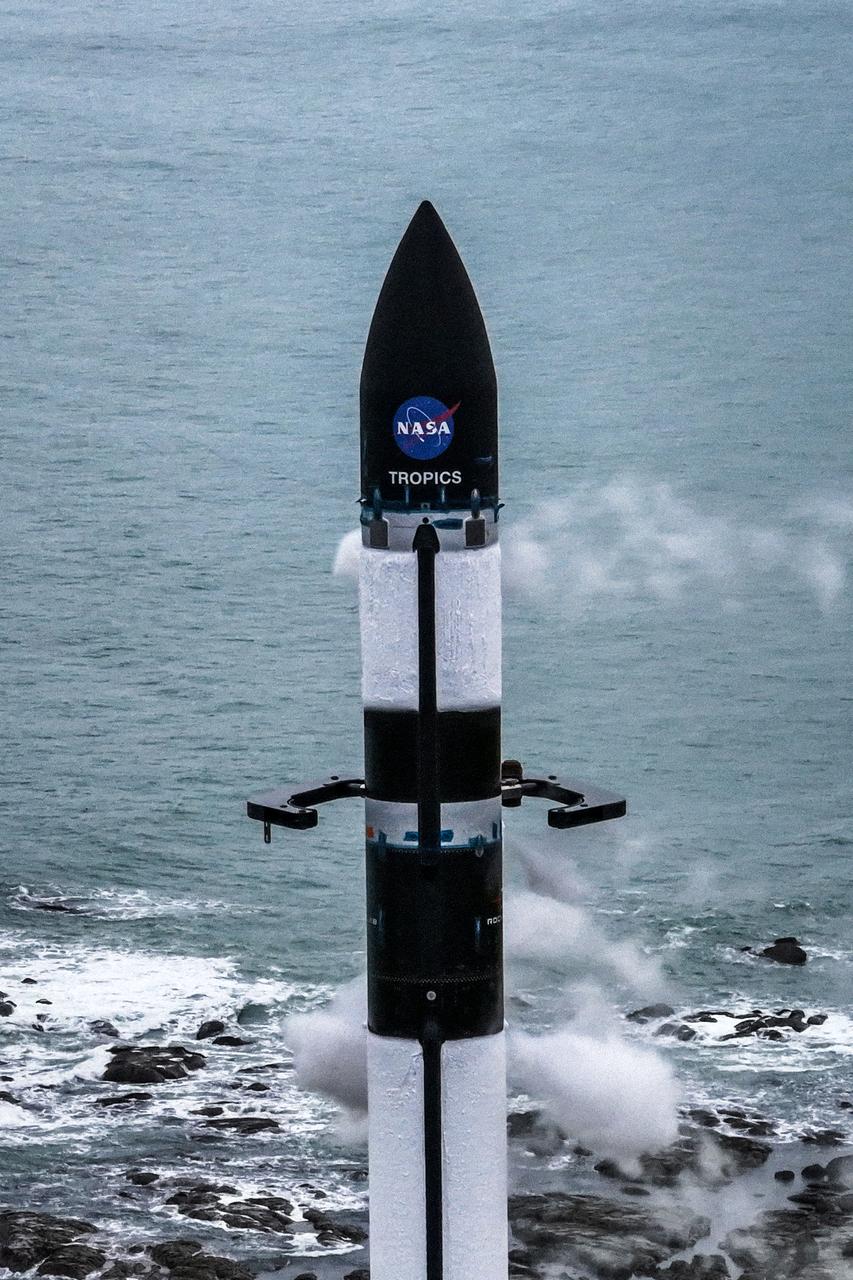

A wet dress rehearsal is underway for Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand on April 28, 2023. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
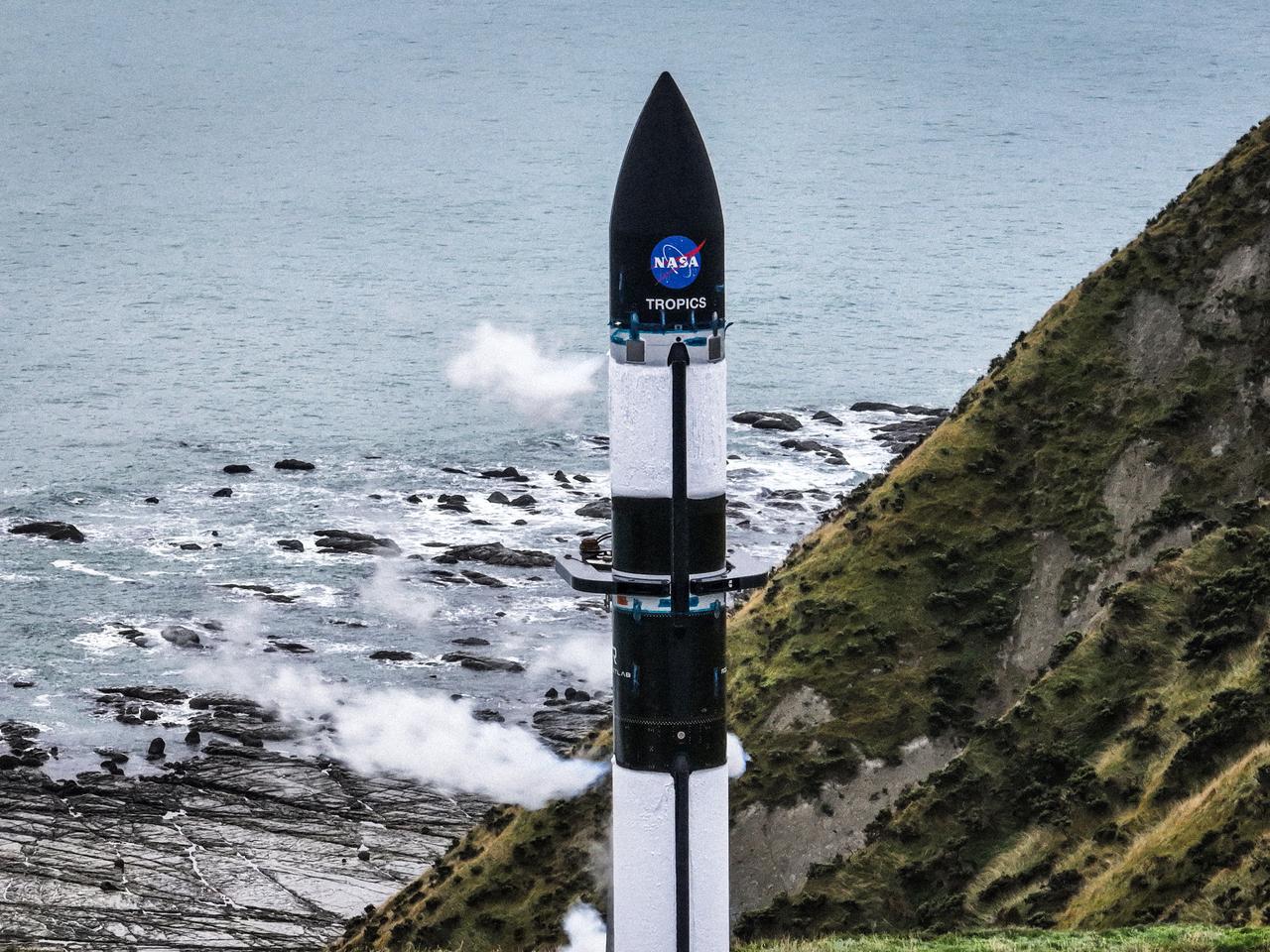

A wet dress rehearsal is underway for Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand on April 28, 2023. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing is in view inside a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats have been encapsulated inside the payload fairing. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Technicians check Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing inside a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats have been encapsulated inside the payload fairing. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing is in view inside a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats have been encapsulated inside the payload fairing. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
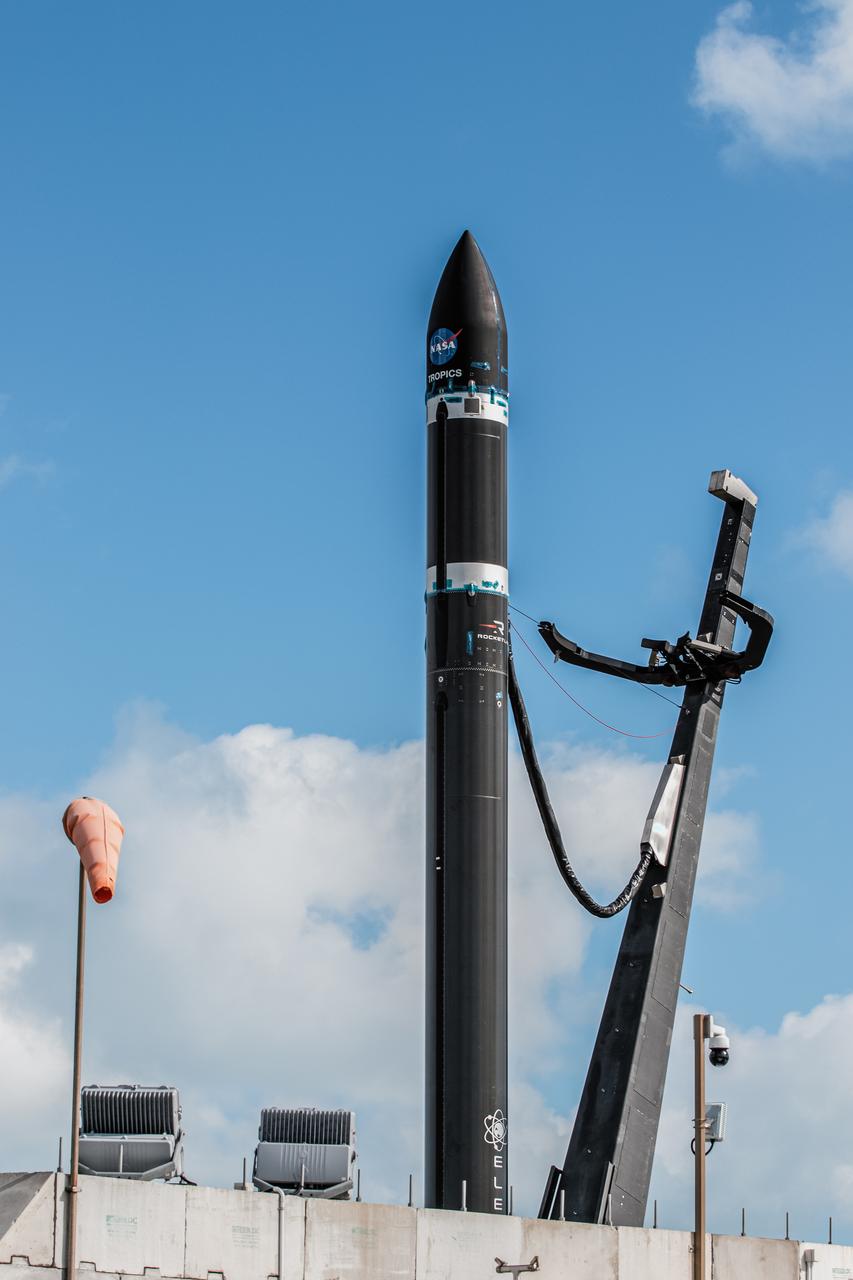

With the umbilical tower in view, Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
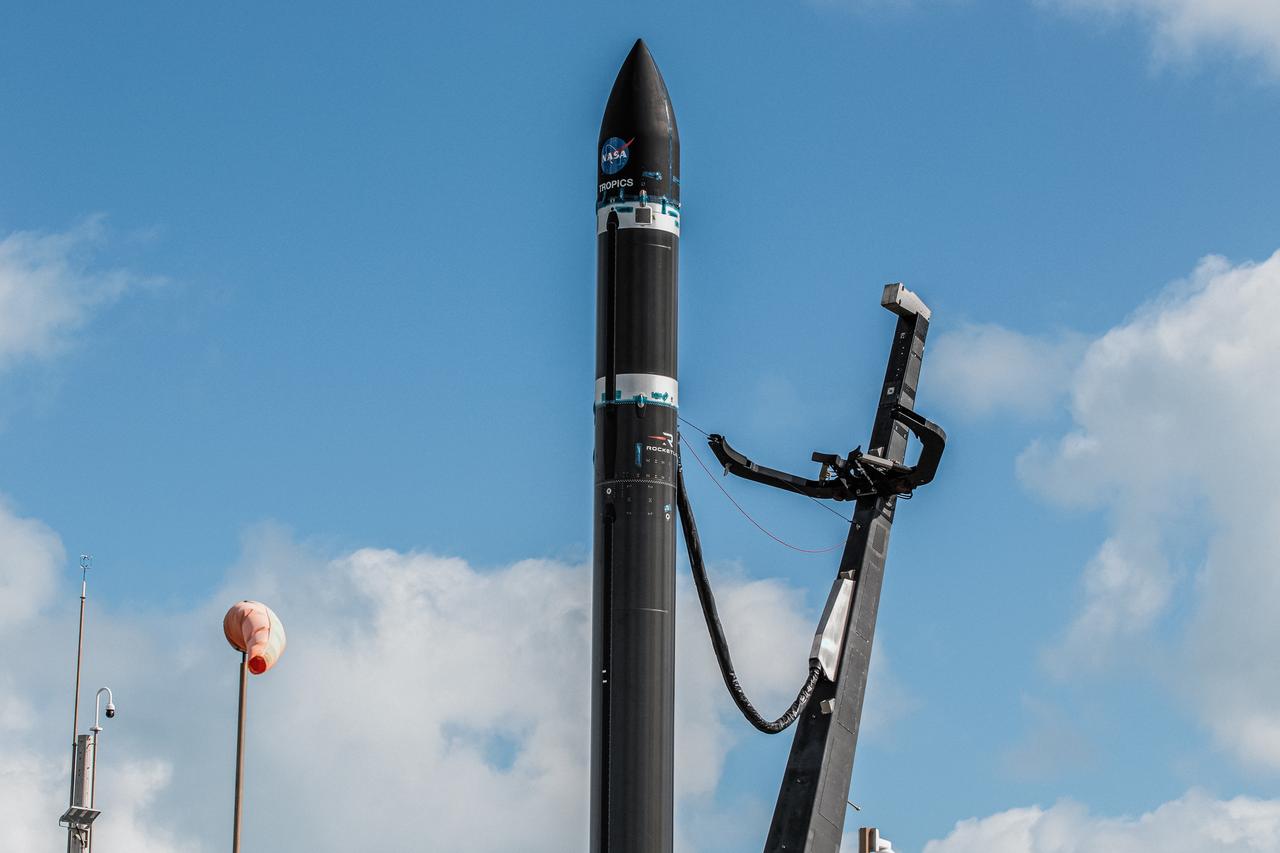

With the umbilical tower in view, Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
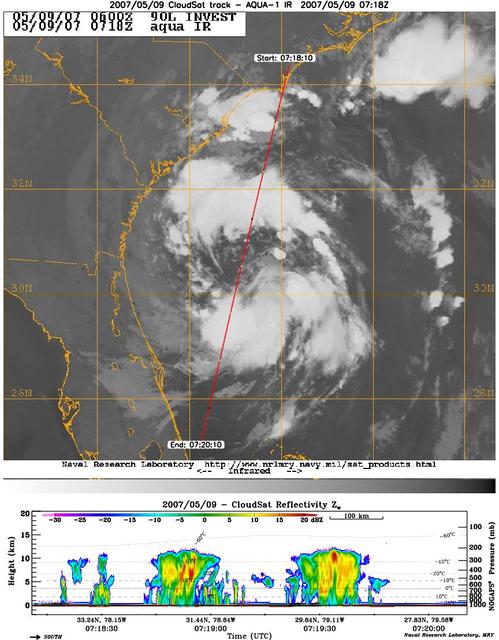
CloudSat's Cloud Profiling Radar captured a profile across Tropical Storm Andrea on Wednesday, May 9, 2007, near the South Carolina/Georgia/Florida Atlantic coast. The upper image shows an infrared view of Tropical Storm Andrea from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer instrument on NASA's Aqua satellite, with CloudSat's ground track shown as a red line. The lower image is the vertical cross section of radar reflectivity along this path, where the colors indicate the intensity of the reflected radar energy. CloudSat orbits approximately one minute behind Aqua in a satellite formation known as the A-Train. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA09379
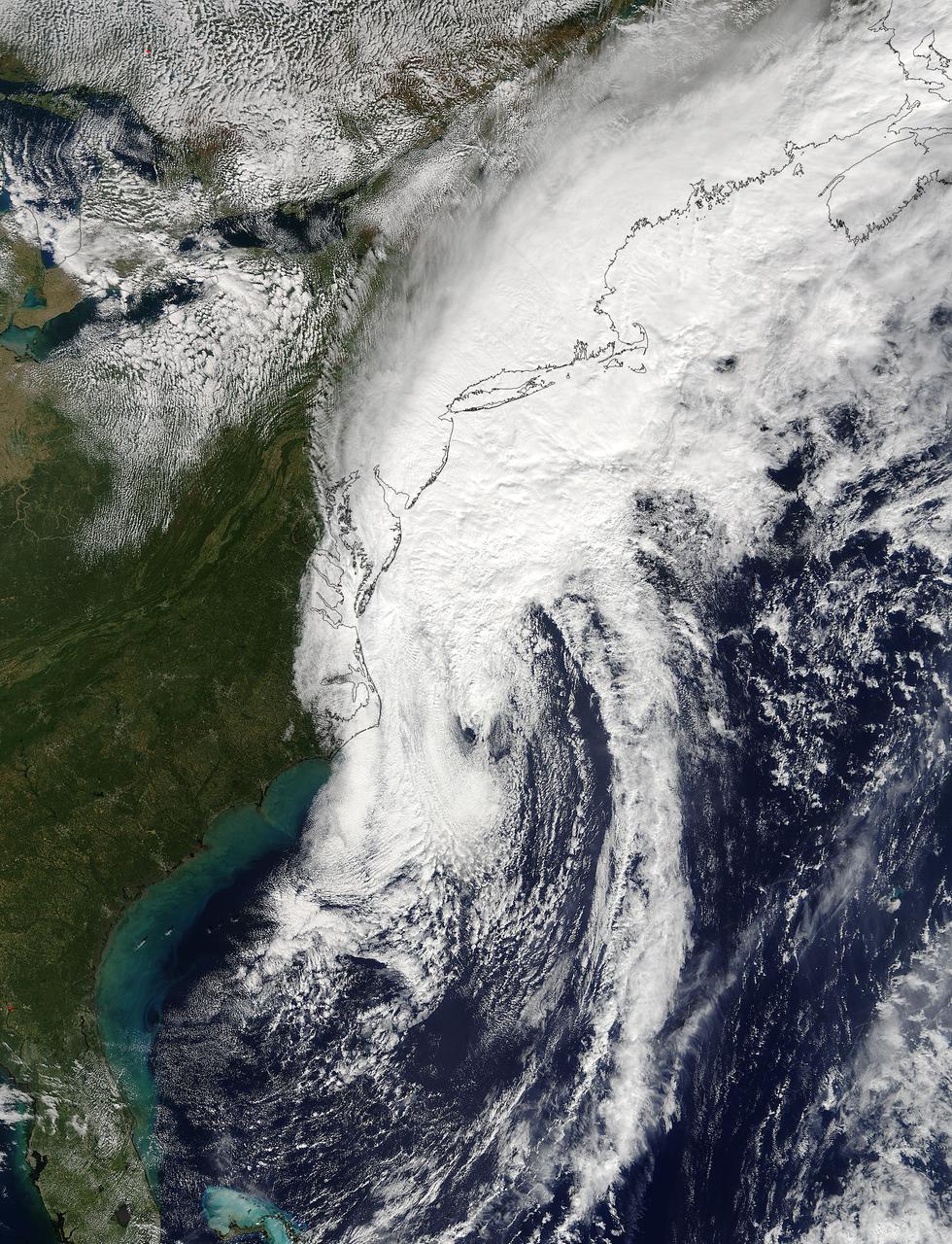

NASA Gets a Last Look at Post-Tropical Cyclone Matthew Before It was Swallowed Up Post-Tropical Cyclone Matthew was swallowed up or absorbed by a cold front on Oct. 10, but NASA's Terra satellite captured a last look at the storm before that happened. On Sunday, Oct. 9, 2016 at 11:45 a.m. EDT (1545 UTC) NASA's Terra satellite captured a last look at Post-Tropical Cyclone Matthew as it was being absorbed by a cold front along the U.S. Eastern Seaboard. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2dfhQg9" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2dfhQg9</a> Credits: NASA Goddard MODIS Rapid Response Team
Tropical storm Bonnie, Gulf of Mexico, captured on August 11 at 1:30am CDT. Located in the Gulf of Mexico, the center of the storm is positioned about 280 miles south-southwest of the mouth of the Mississippi River. Bonnie is a small tropical storm with wind speeds sustained at 45 mph and extending 30 miles from the storm center. It is moving northward at 5 mph. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00441
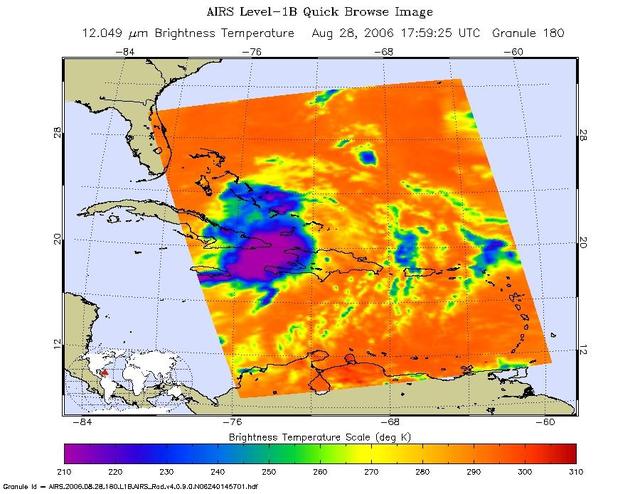
This infrared image shows Tropical Storm Ernesto over Cuba, from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder AIRS on NASA Aqua satellite in August, 2006. Because infrared radiation does not penetrate through clouds, AIRS infrared images show either the temperature of the cloud tops or the surface of the Earth in cloud-free regions. The lowest temperatures (in purple) are associated with high, cold cloud tops that make up the top of the storm. In cloud-free areas the AIRS instrument will receive the infrared radiation from the surface of the Earth, resulting in the warmest temperatures (orange/red). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00510

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket soars upward after liftoff from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
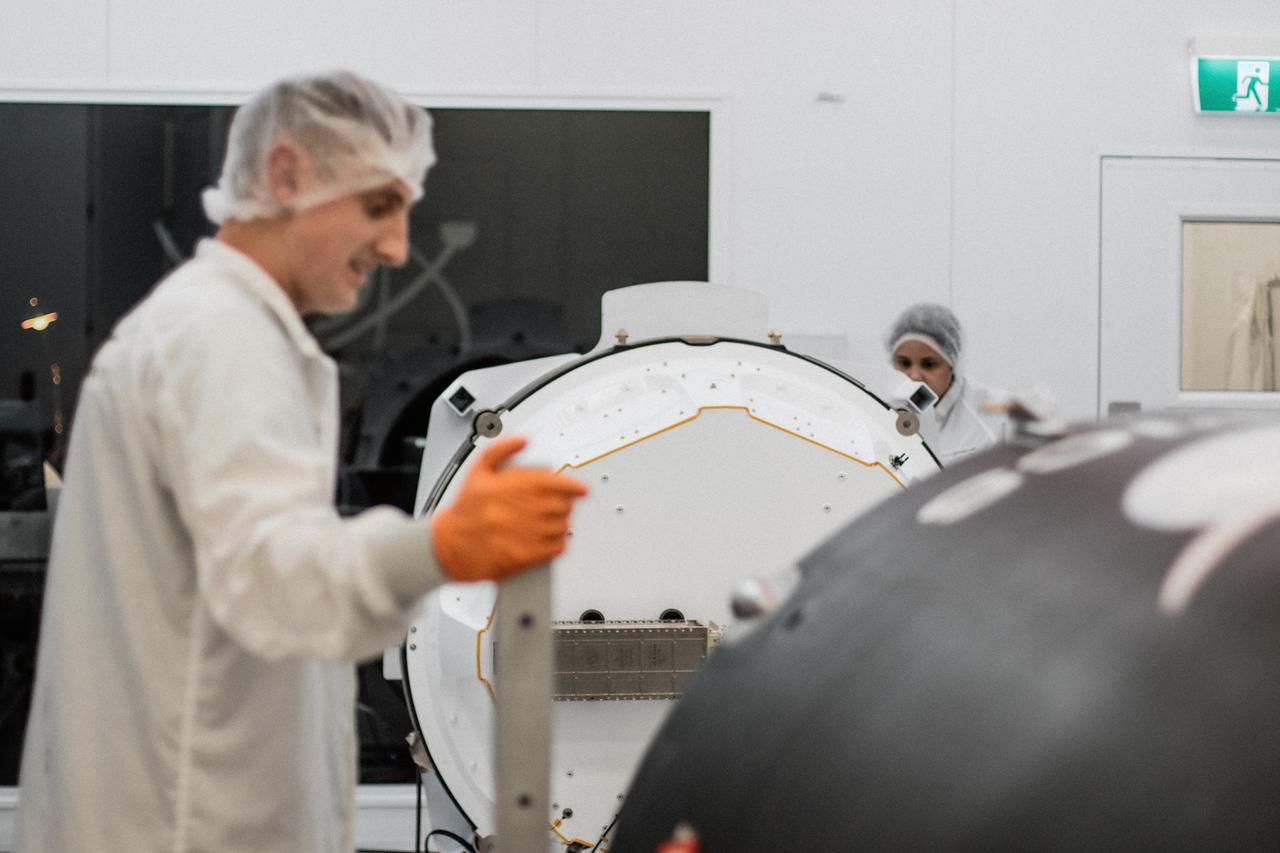

Two CubeSats are encapsulated at the Rocket Lab facility in Mahia, New Zealand, on April 24, 2023, in preparation for NASA’s second TROPICS (Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), for liftoff of the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.

Two CubeSats are encapsulated at the Rocket Lab facility in Mahia, New Zealand, on April 24, 2023, in preparation for NASA’s second TROPICS (Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), for liftoff of the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
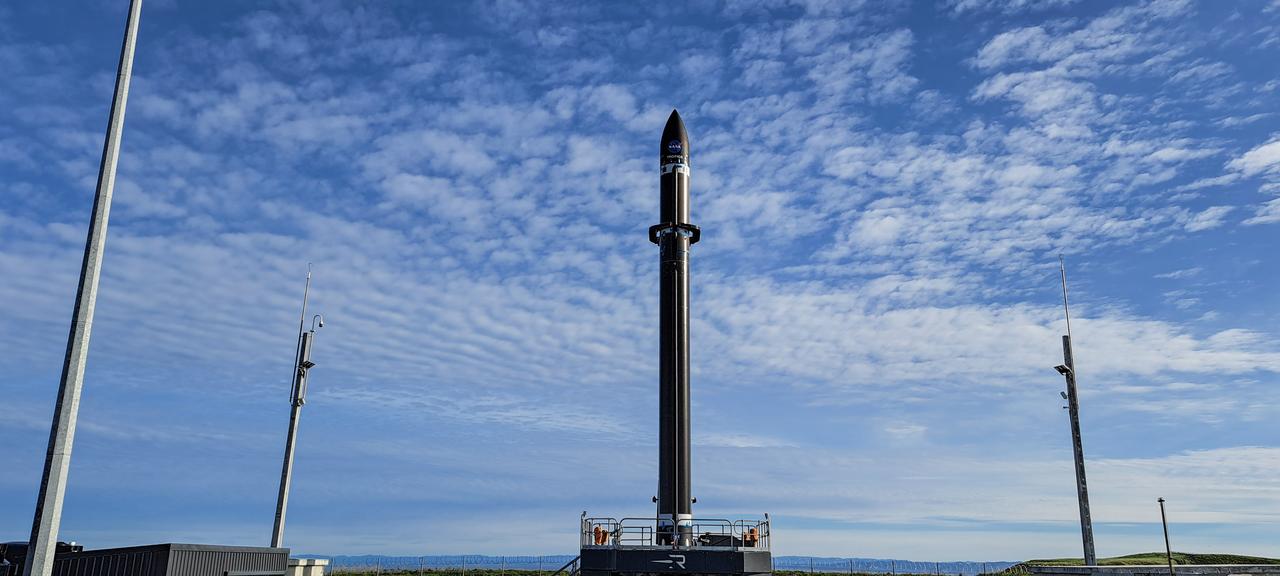

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, during a May 18, 2023, wet dress rehearsal for NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), to launch the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.

Two CubeSats are encapsulated at the Rocket Lab facility in Mahia, New Zealand, on April 24, 2023, in preparation for NASA’s second TROPICS (Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), for liftoff of the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
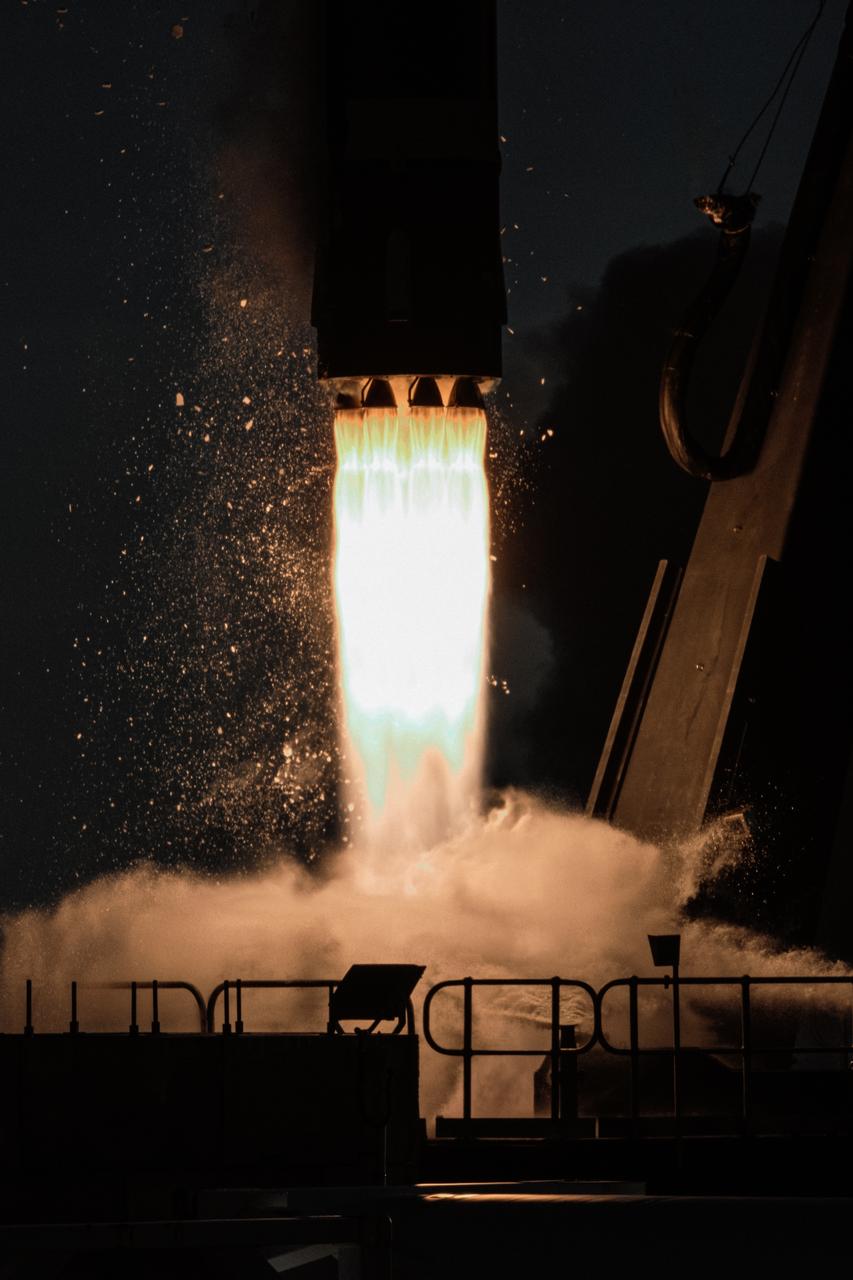

The first stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket ignites at liftoff from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
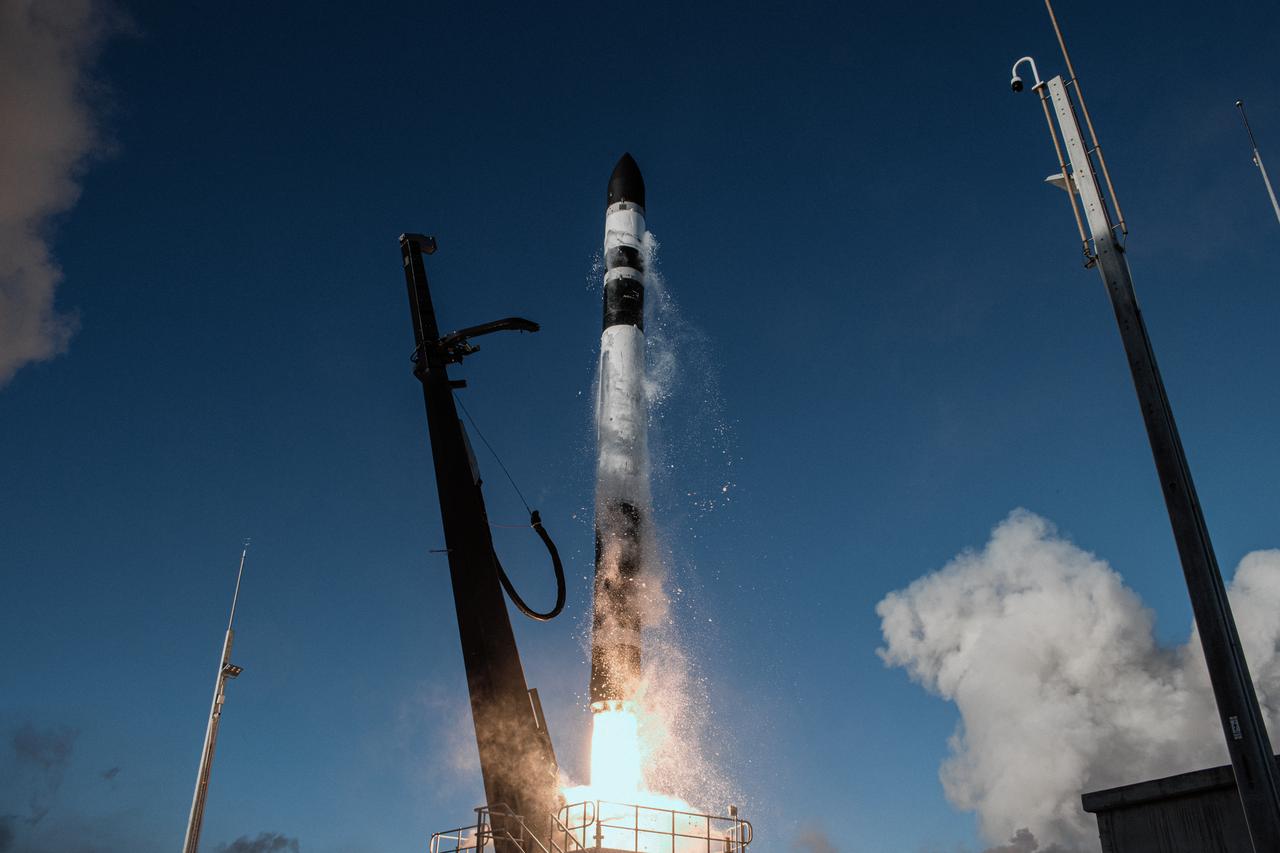

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
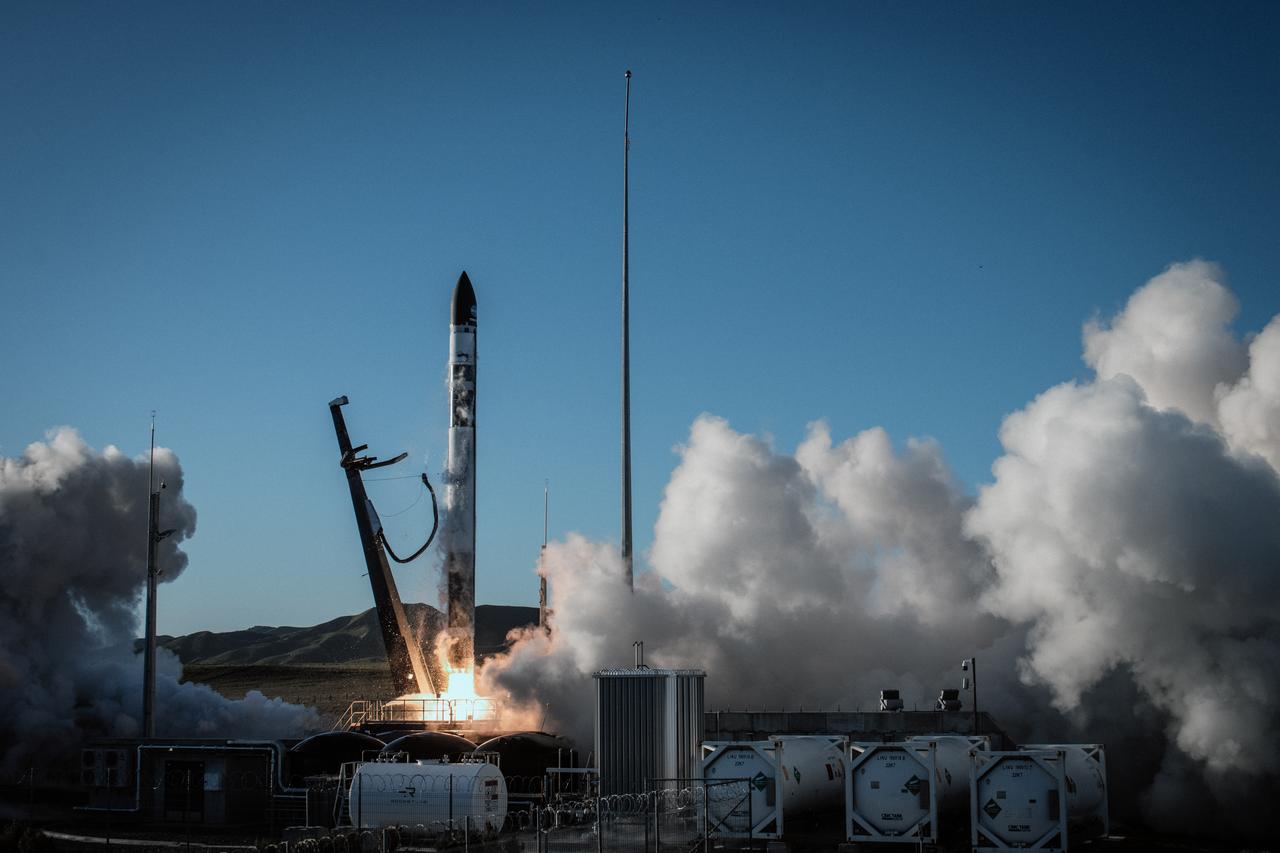

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
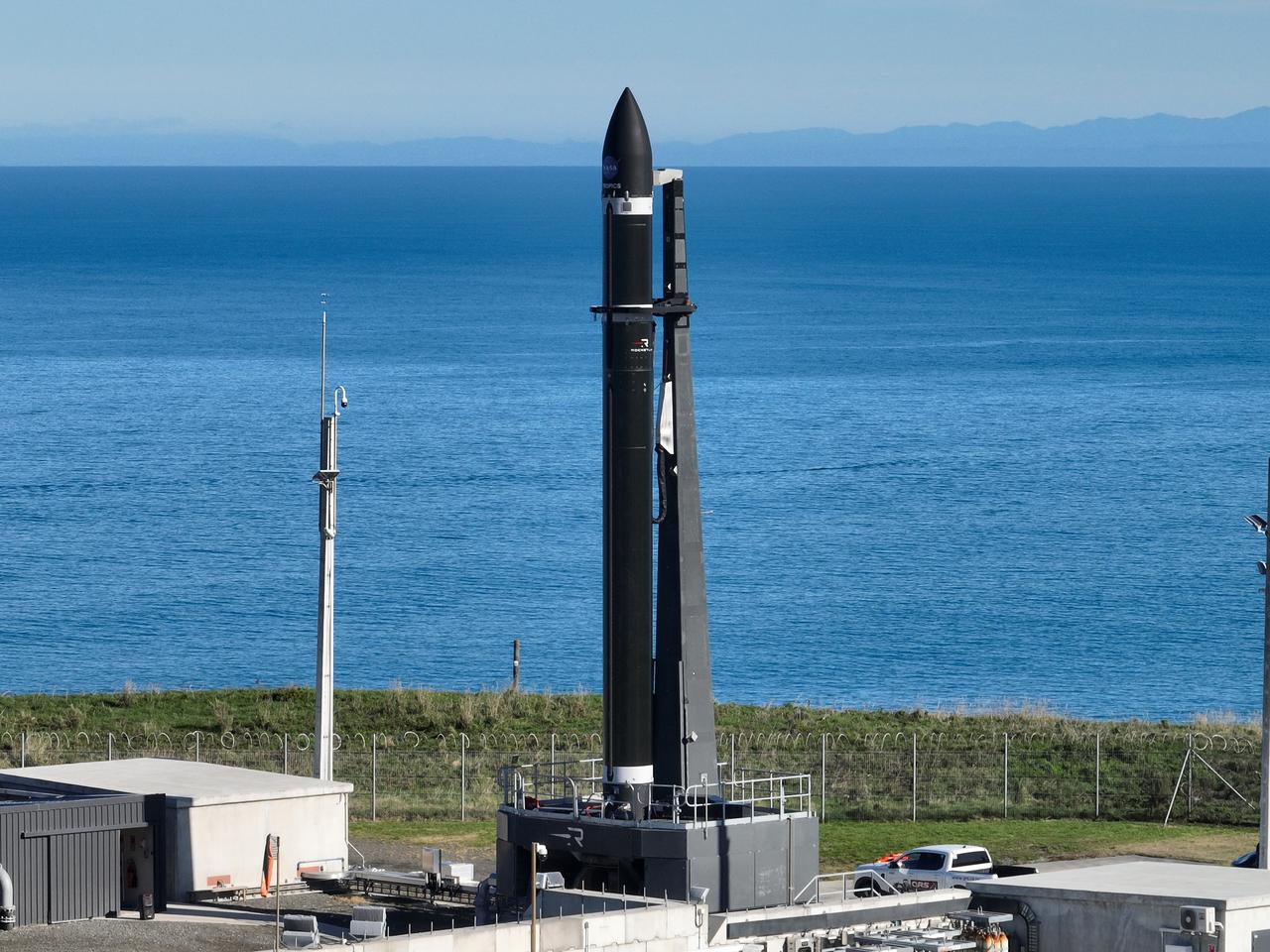

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
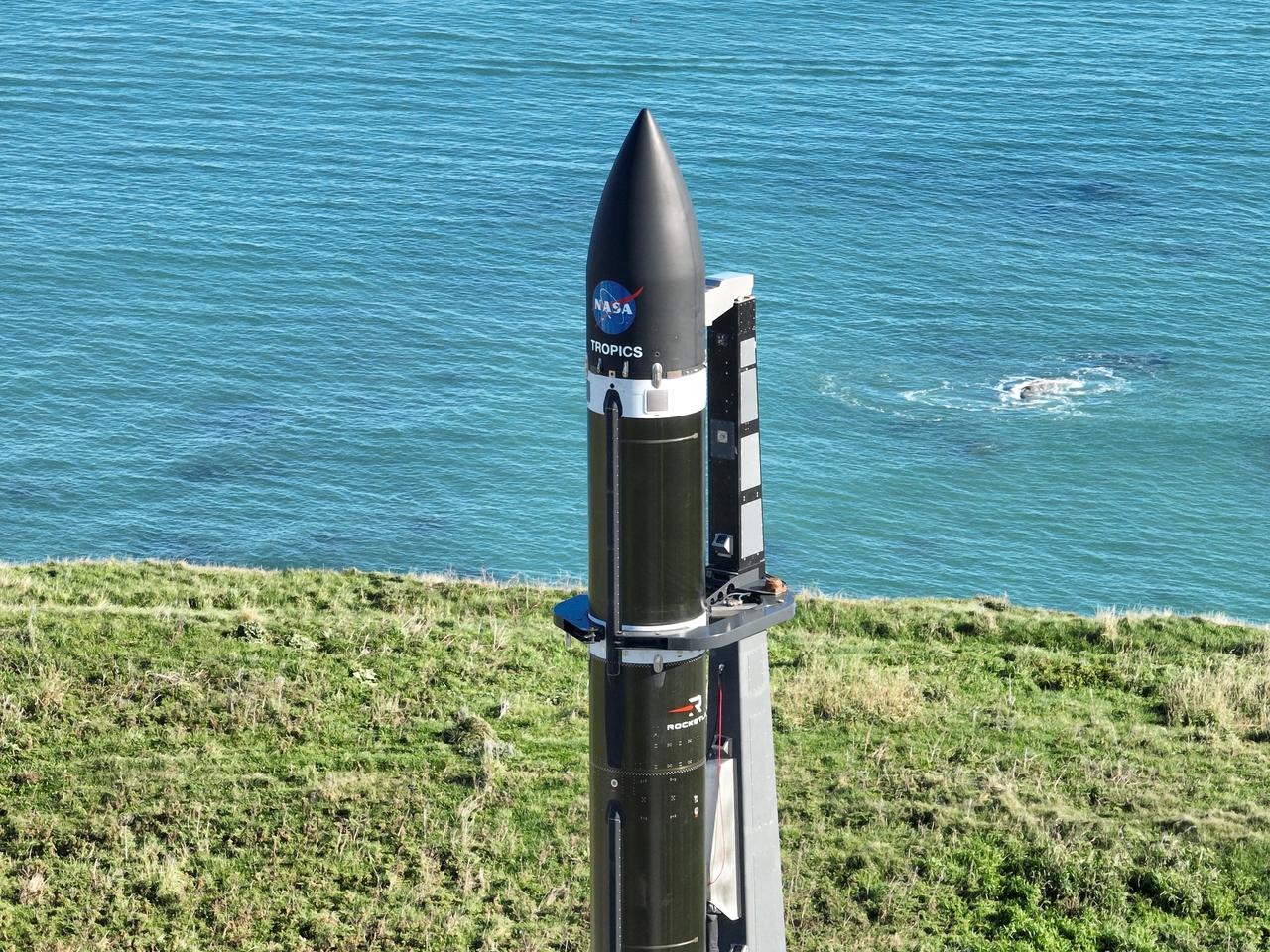

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
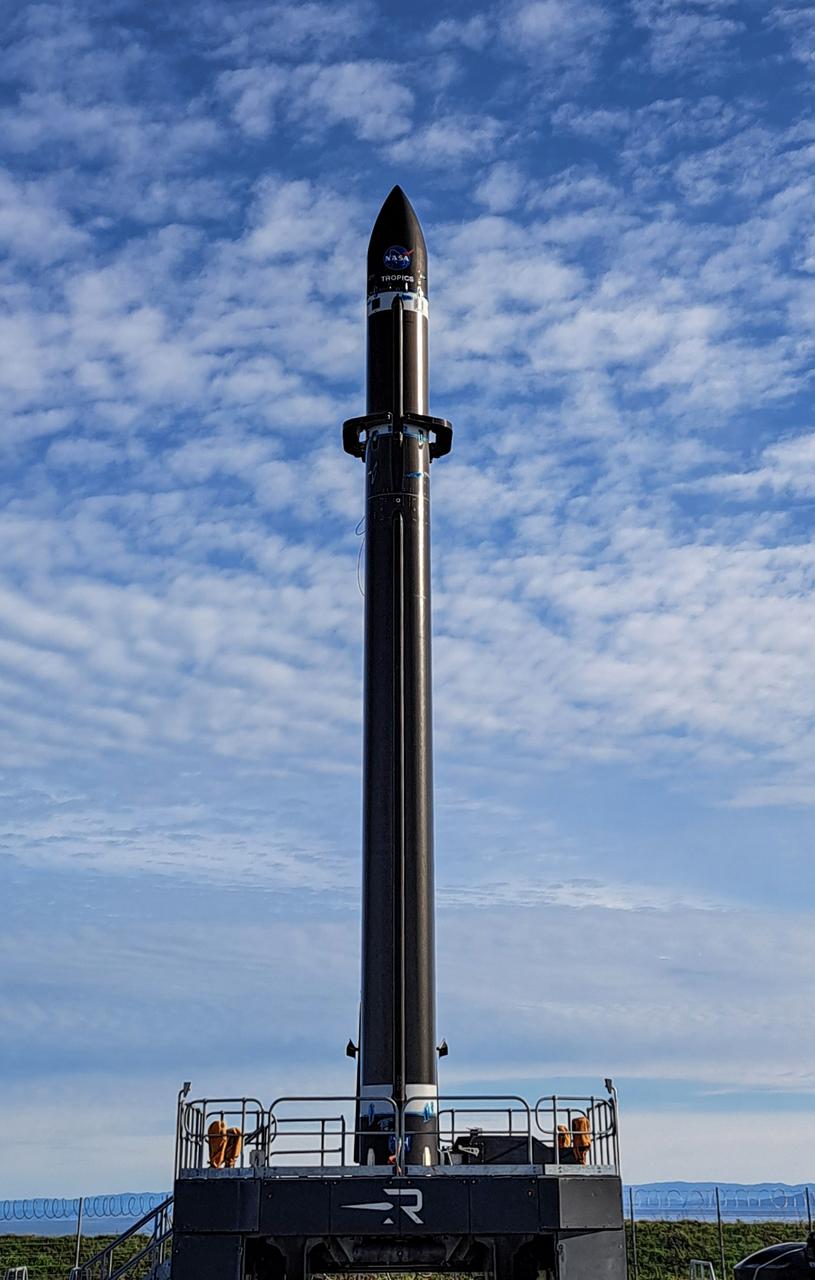

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, during a May 18, 2023, wet dress rehearsal for NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), to launch the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
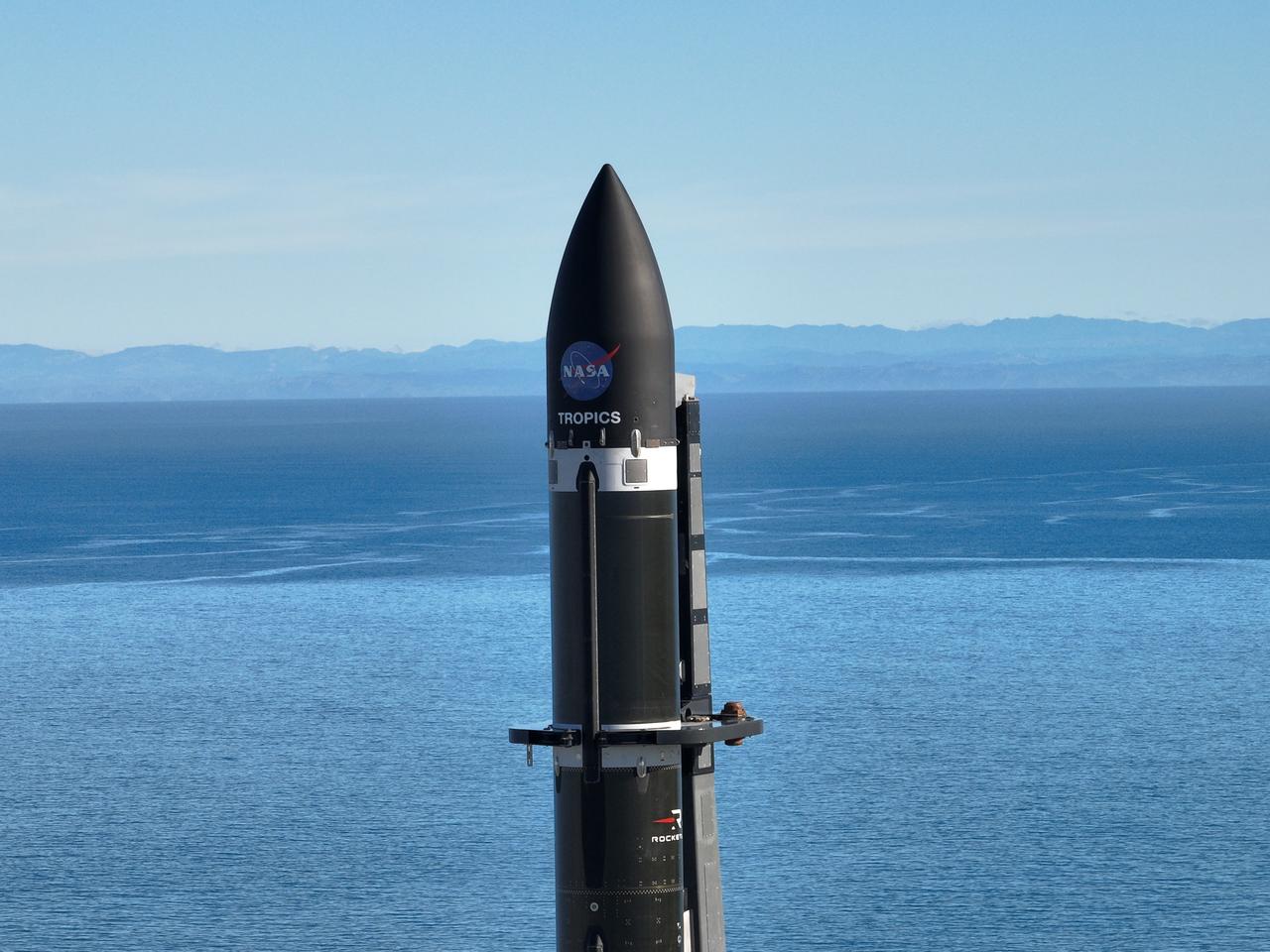

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
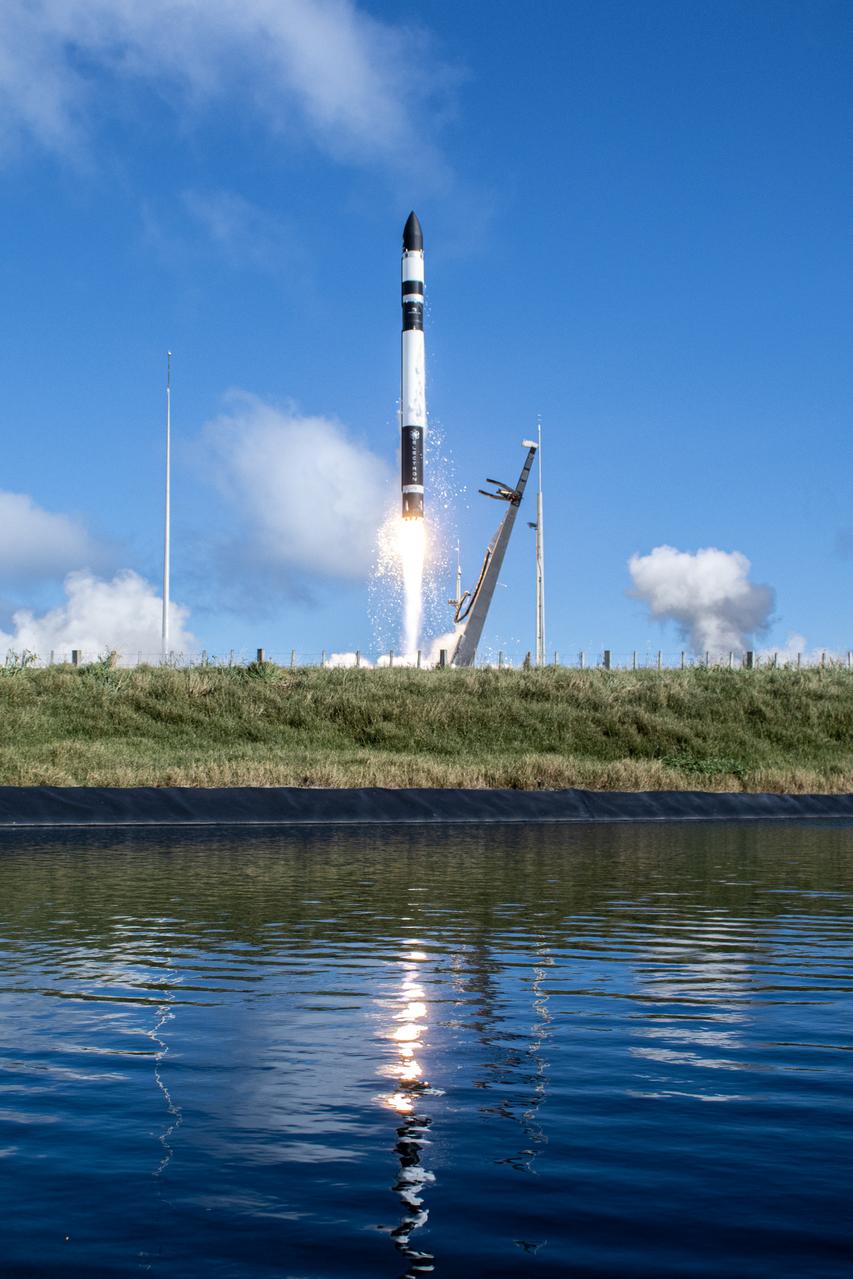

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
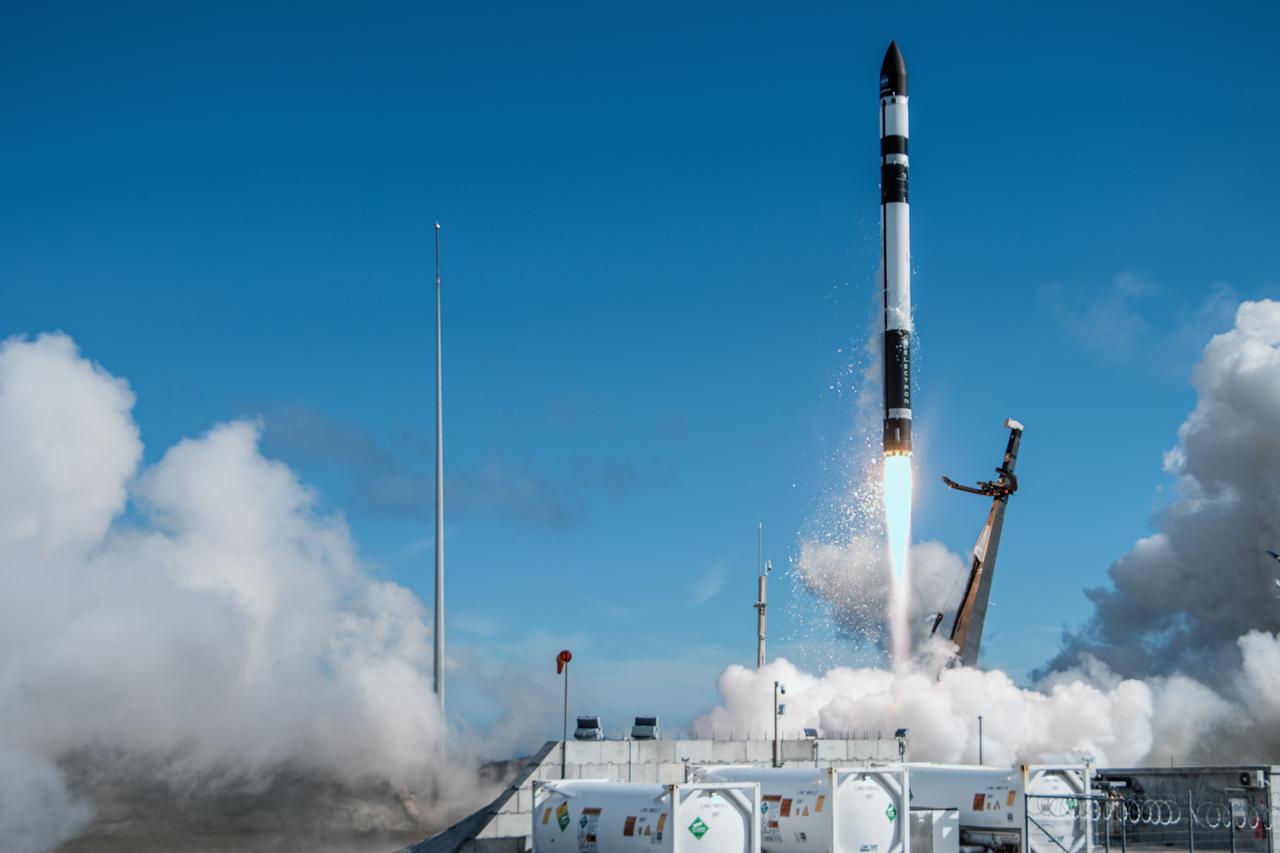

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
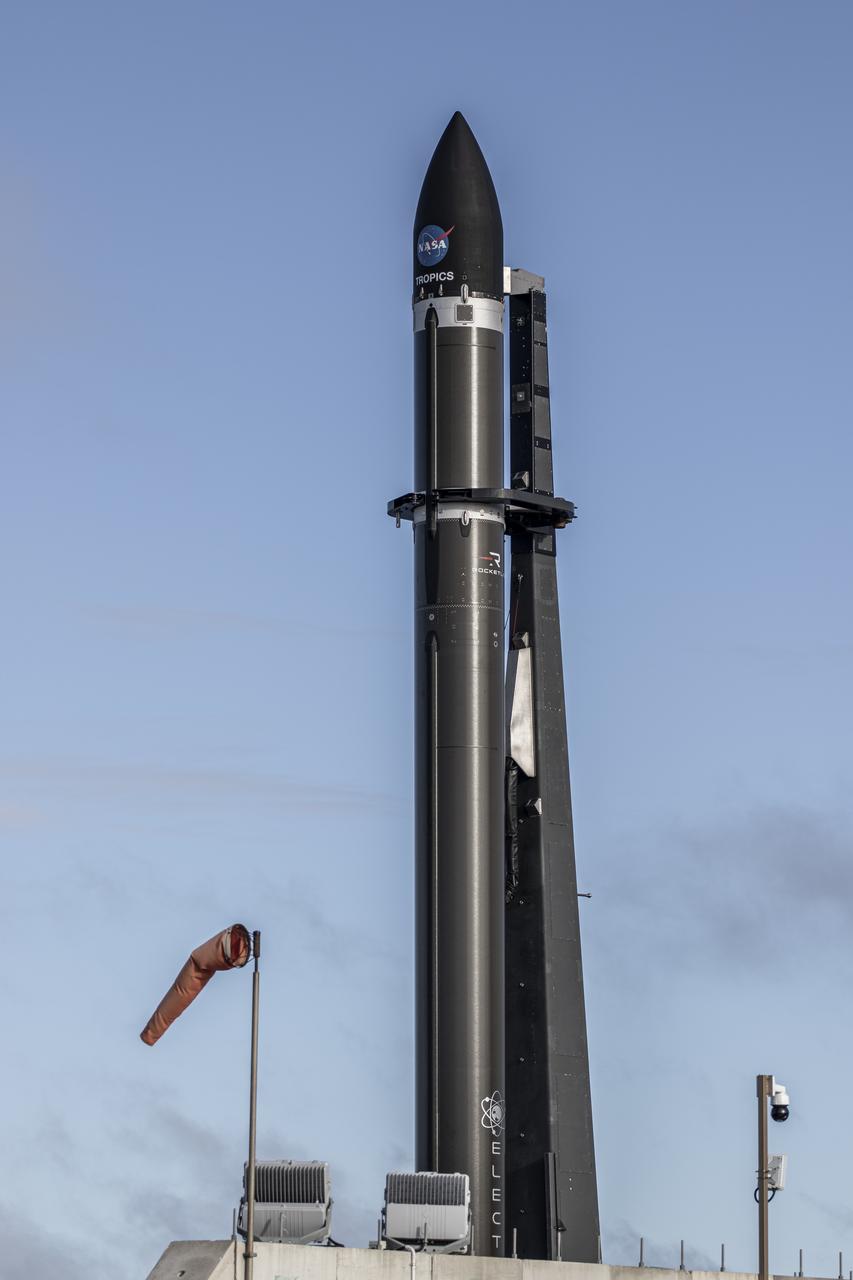

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket is poised for launch atop Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand. Launch time is May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT). The Electron rocket is carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
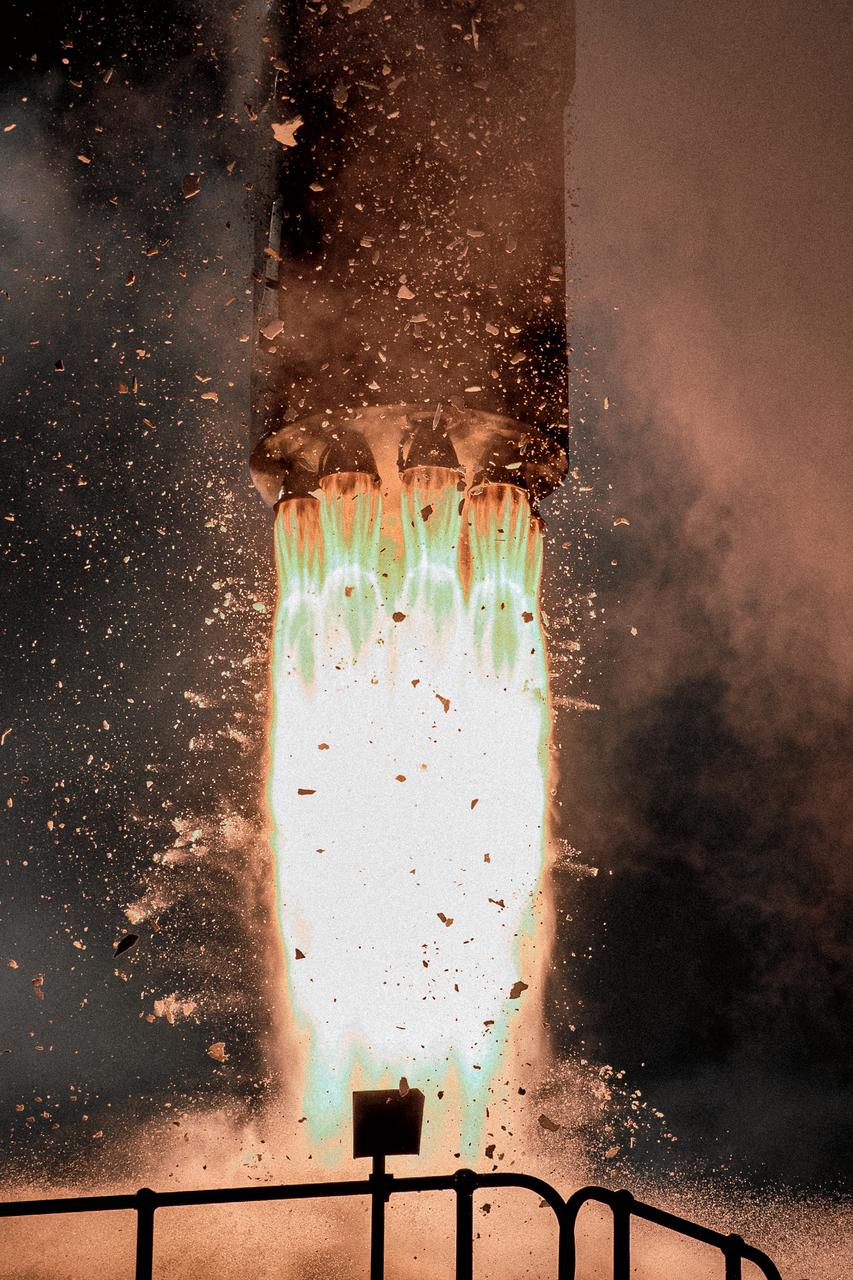

The engines of the first stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket ignite as the rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
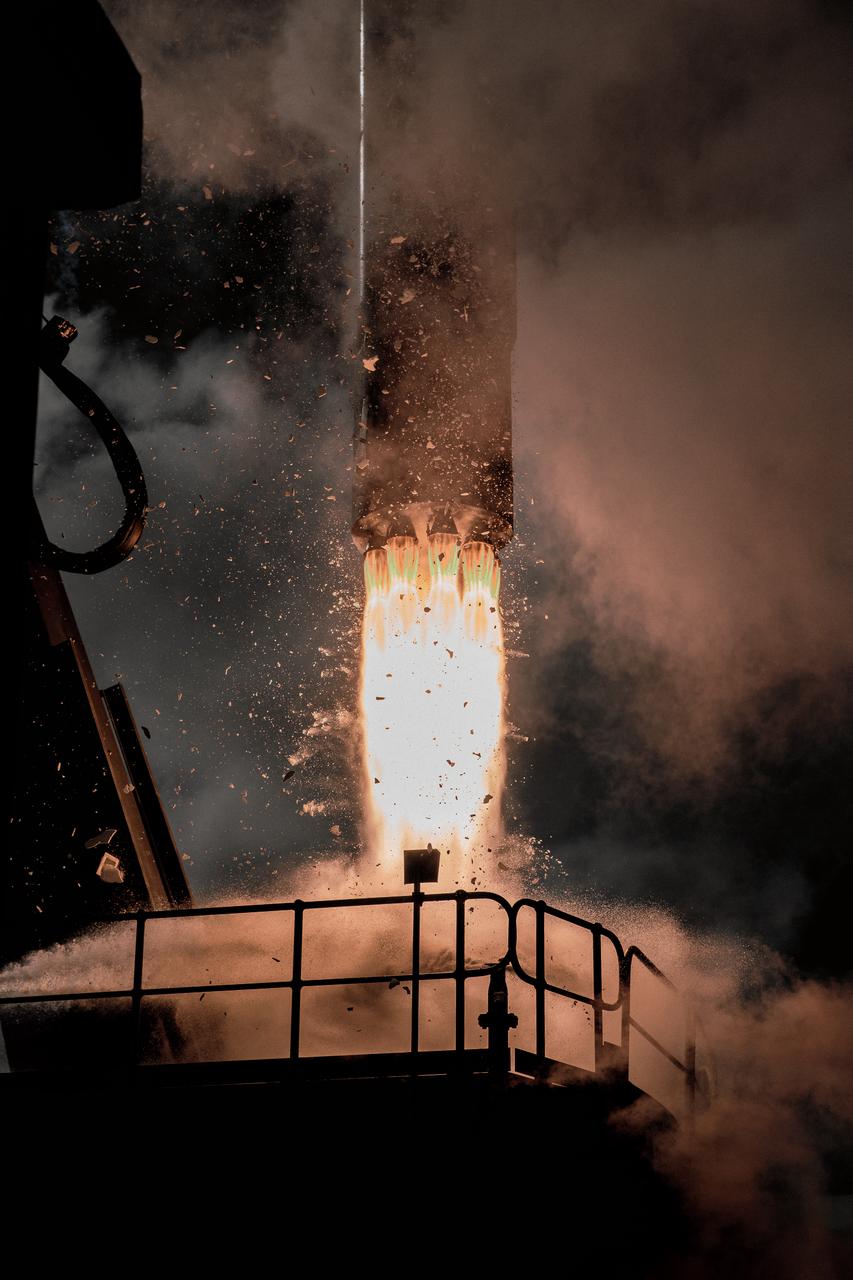

The engines of the first stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket ignite as the rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
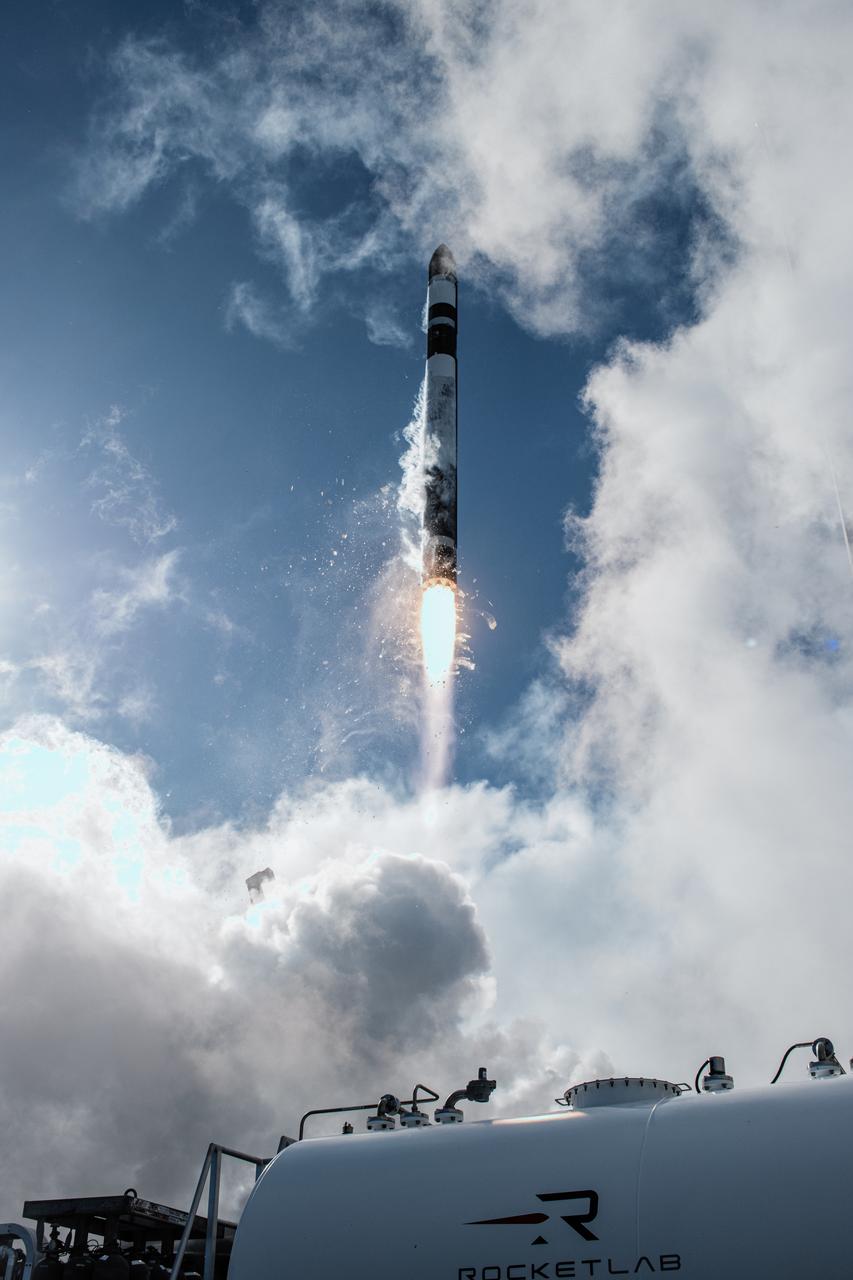

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket soars upward after liftoff from Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
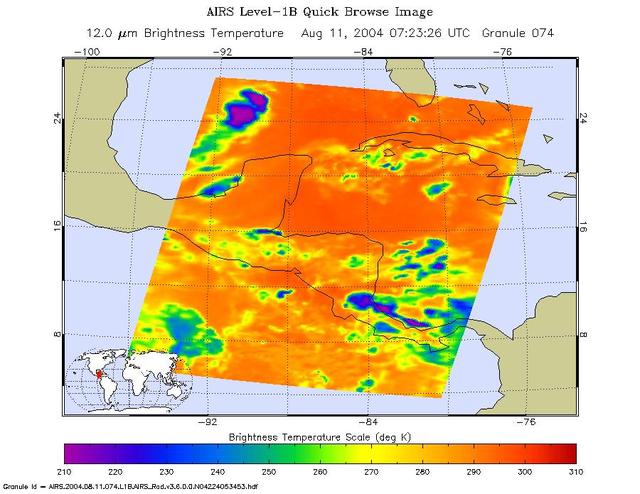
Tropical Storm Blas as observed by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder AIRS onboard NASA Aqua in the year 2004. The major contribution to radiation (infrared light) that AIRS channels sense comes from different levels in the atmosphere, depending upon the channel wavelength. To create the movie, a set of AIRS channels were selected which probe the atmosphere at progressively deeper levels. If there were no clouds, the color in each frame would be nearly uniform until the Earth's surface is encountered. The tropospheric air temperature warms at a rate of 6 K (about 11 F) for each kilometer of descent toward the surface. Thus the colors would gradually change from cold to warm as the movie progresses. Clouds block the infrared radiation. Thus wherever there are clouds we can penetrate no deeper in infrared. The color remains fixed as the movie progresses, for that area of the image is "stuck" to the cloud top temperature. The coldest temperatures around 220 K (about -65 F) come from altitudes of about 10 miles. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00436
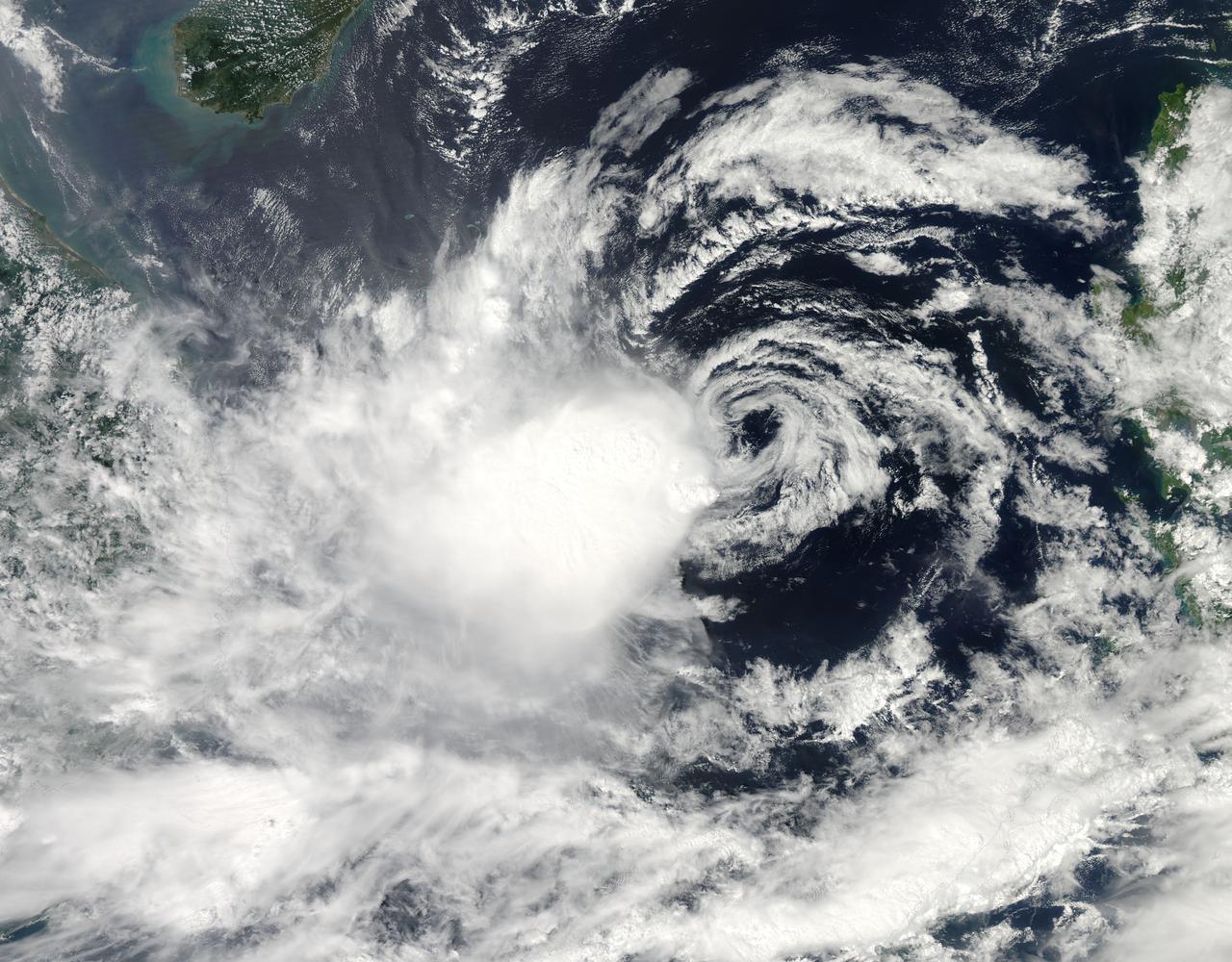
It is easy to see the effect of the strong northeasterly wind shear battering Tropical Storm Gaemi in satellite imagery from NASA. This true-color image acquired on Oct. 5 shows a large oval-shaped area of showers and thunderstorms associated with the storm, southwest of the exposed center of circulation. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Gaemi as it was approaching Vietnam on Oct. 5, 2012 at 0550 UTC (1:50 a.m. EDT). A true-color image of the storm was captured by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument and shows bulk of showers and thunderstorms were clearly to the southwest of the center. The circulation center appears as a ring of concentric bands of clouds northeast of the large rounded area of clouds and showers associated with the storm. On Tuesday, October 5, 2012 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), Tropical Storm Gaemi still had maximum sustained winds near 35 knots (40 mph/65 km/h) as it did 24 hours before. It was located 425 nautical miles (489 miles/787 km) east of Hue, Vietnam near 14.7 North latitude and 117.7 East longitude. Early on October 7, Tropical Storm Gaemi made landfall over Vietnam with wind speeds reported at 34 mph (55 mph), and bringing rainfall of more than 4 inches in some areas of Vietnam. Once ashore, the storm quickly moved inland and rapidly weakened as it headed towards Cambodia. With winds reduced, Gaemi served primarily as a rainmaker, but the rain may bring flooding and landslides to the region. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
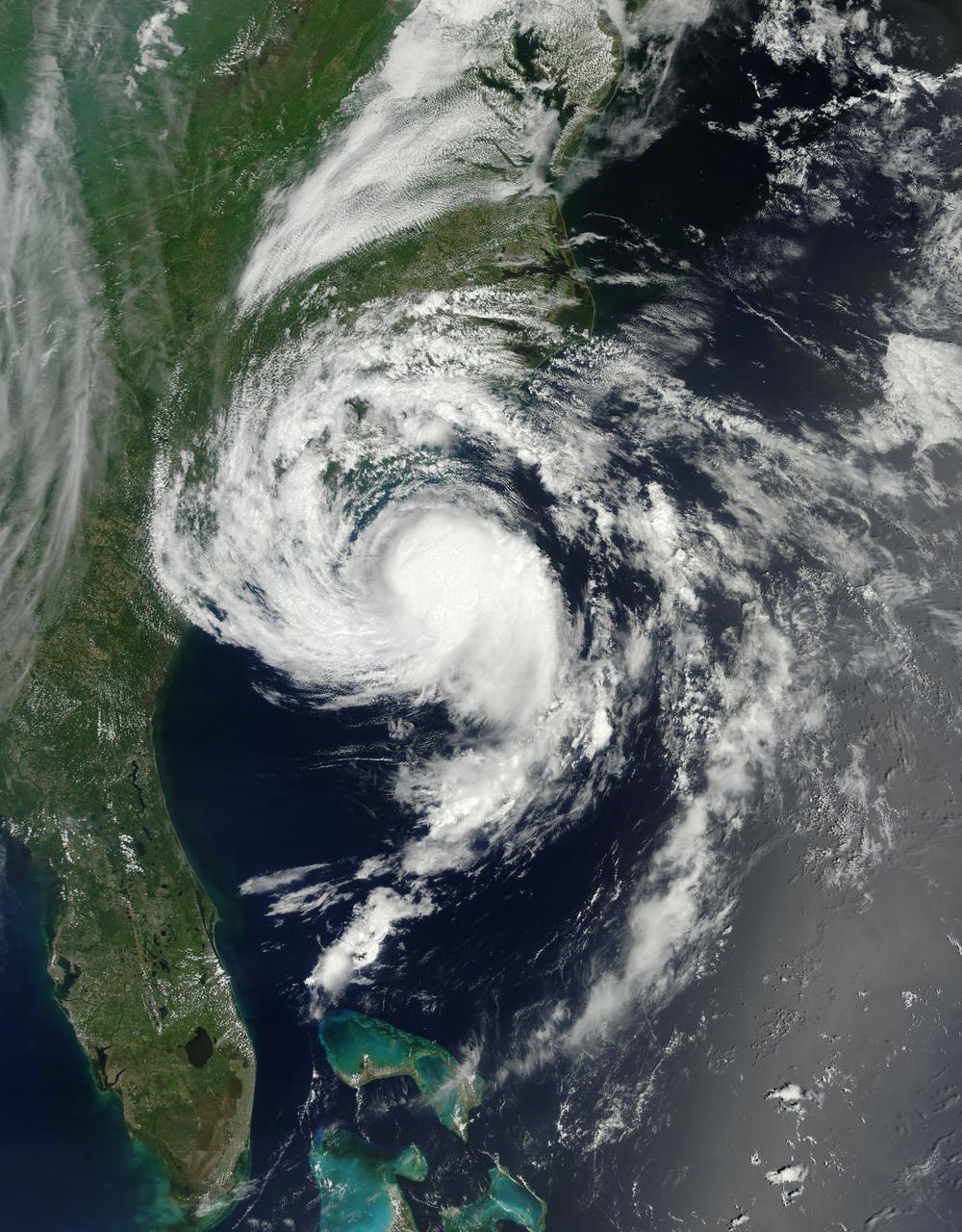

At about 6:00 a.m. EDT (10:00 UTC) on May 10, 2015, Tropical Storm Ana made landfall between Myrtle Beach and North Myrtle Beach, South Carolina. One day earlier, on the morning of May 9, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite acquired this true-color image of the storm off the coast of the Carolinas. At the time, Ana had just evolved from a subtropical storm to a tropical storm with maximum sustained winds of 93 kilometers (58 miles) per hour. Ana’s life ashore was brief – the storm was downgraded to a tropical depression at 2:00 p.m. EDT (14:00 UTC) on May 10. During that time, parts of South Carolina and eastern North Carolina was drenched with heavy rain – some areas reported over 6 inches of rainfall – and heavy winds. A water spout was reported in Dare County, North Carolina, and the storm contributed to significant beach erosion along the coast. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
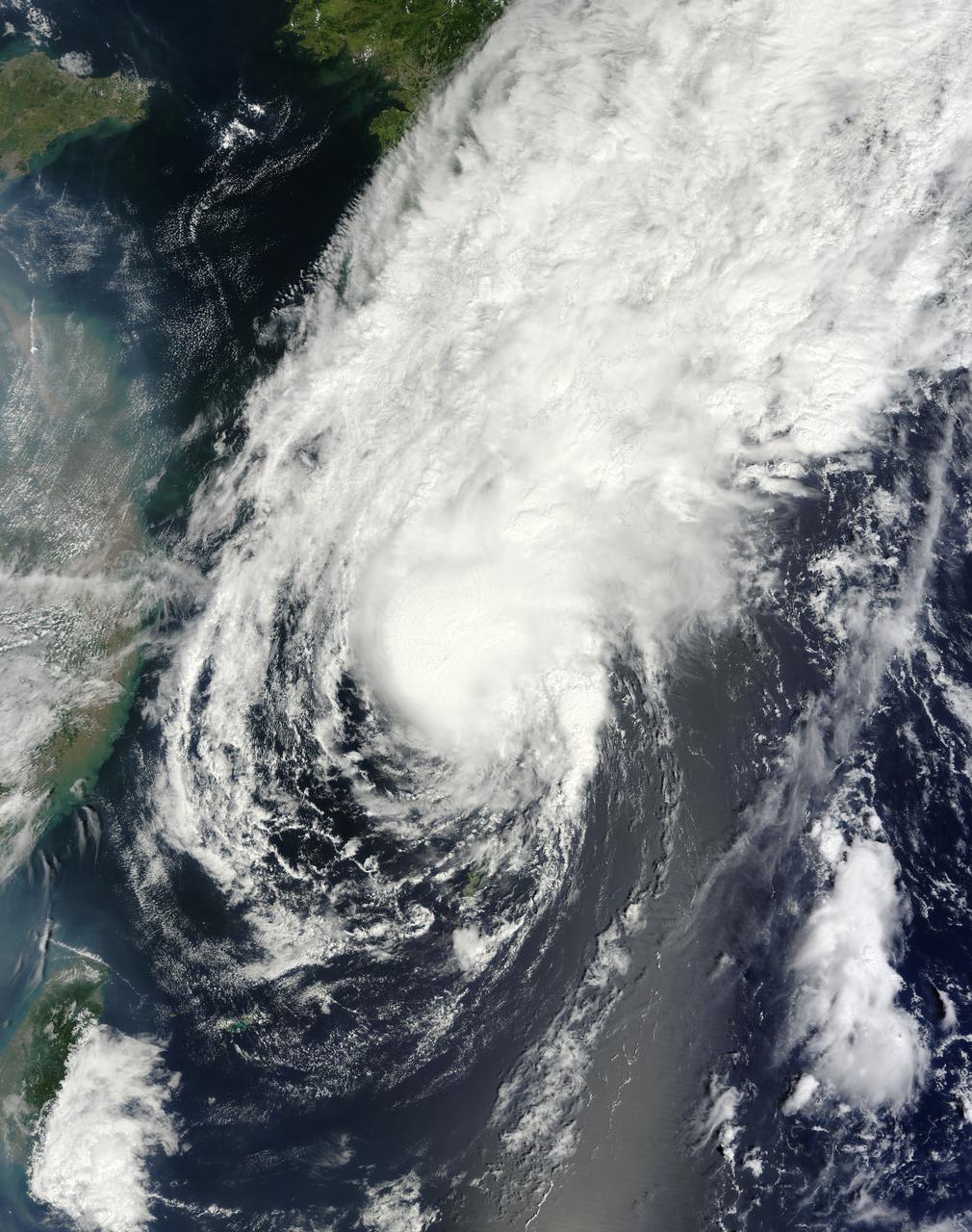

Tropical Storm Toraji Approaching Japan, 09/03/2013 at 02:10 UTC. Terra/MODIS <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
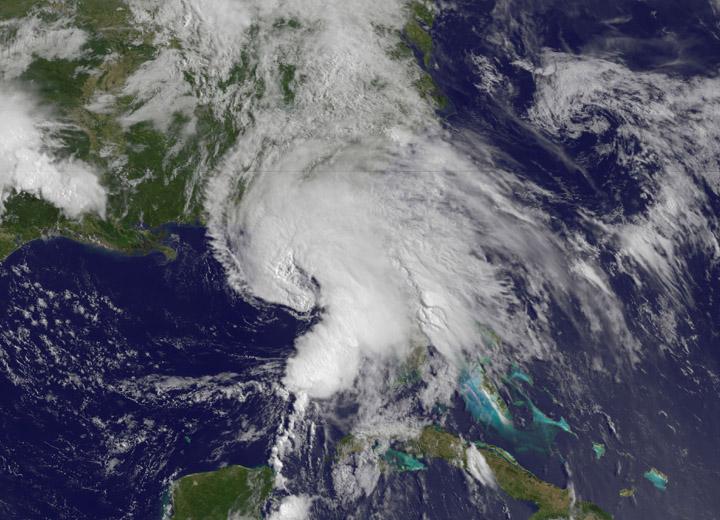

This NOAA GOES-East satellite animation shows the development of System 91L into Tropical Storm Andrea over the course of 3 days from June 4 to June 6, just after Andrea was officially designated a tropical storm. Credit: NASA's GOES Project --- NASA Sees Heavy Rainfall in Tropical Storm Andrea NASA’s TRMM satellite passed over Tropical Storm Andrea right after it was named, while NASA’s Terra satellite captured a visible image of the storm’s reach hours beforehand. TRMM measures rainfall from space and saw that rainfall rates in the southern part of the storm was falling at almost 5 inches per hour. NASA’s Terra satellite passed over Tropical Storm Andrea on June 5 at 16:25 UTC (12:25 p.m. EDT) and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument, captured a visible image of the storm. At that time, Andrea’s clouds had already extended over more than half of Florida. At 8 p.m. EDT on Wednesday, June 5, System 91L became the first tropical storm of the Atlantic Ocean hurricane season. Tropical Storm Andrea was centered near 25.5 North and 86.5 West, about 300 miles (485 km) southwest of Tampa, Fla. At the time Andrea intensified into a tropical storm, its maximum sustained winds were near 40 mph (65 kph). Full updates can be found at NASA's Hurricane page: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/hurricane" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/hurricane</a> Rob Gutro NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center

This GOES-West satellite image shows four tropical cyclones in the North Western, Central and Eastern Pacific Ocean on September 1, 2015. In the Western Pacific (far left) is Typhoon Kilo. Moving east (to the right) into the Central Pacific is Hurricane Ignacio (just east of Hawaii), and Hurricane Jimena. The eastern-most storm is Tropical Depression 14E in the Eastern Pacific. Credit: NASA/NOAA GOES Project <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
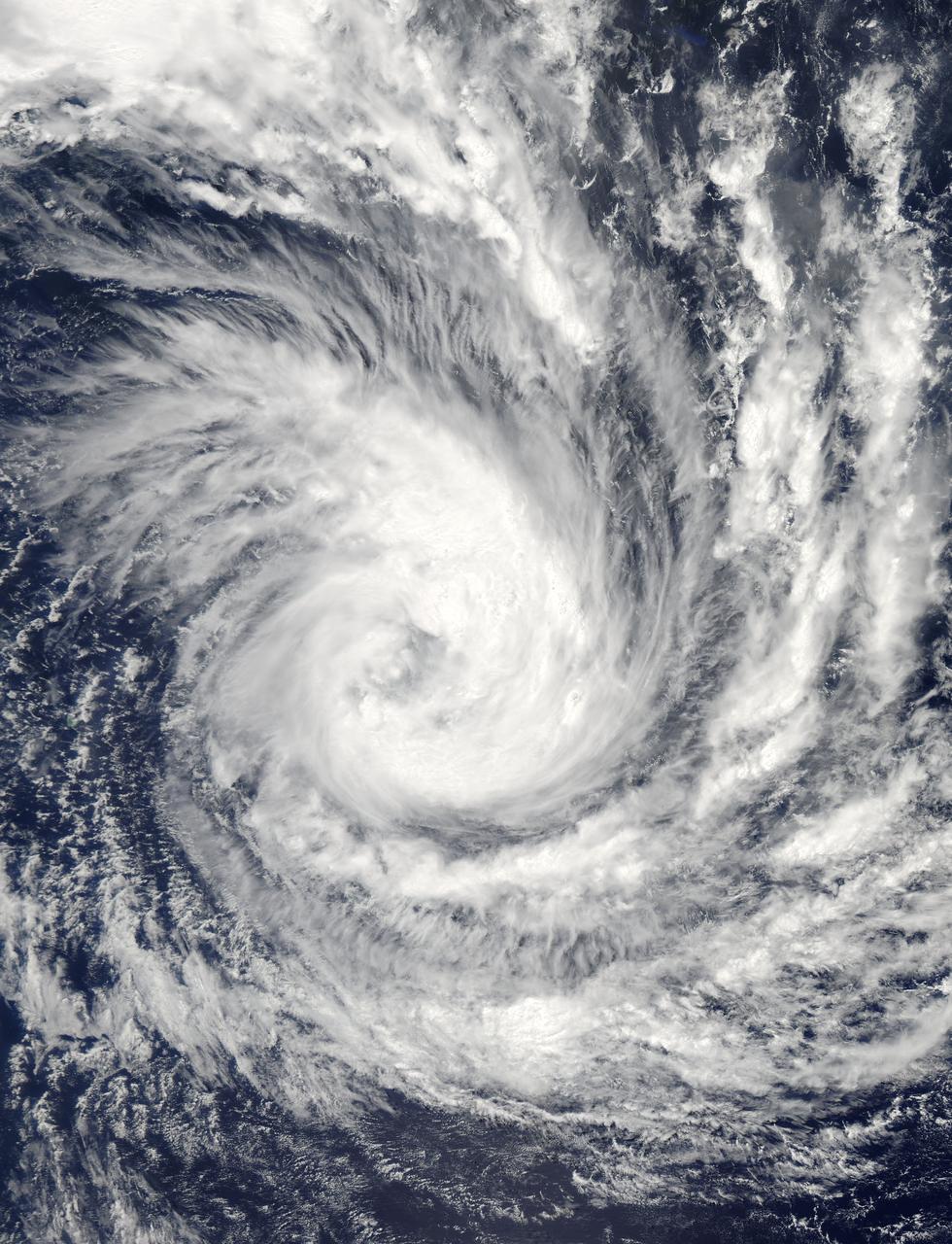
Tropical Cyclone Glenda took a five day tour of the Southern Indian Ocean in late February, 2015. The storm formed from a low pressure system, System 90S on February 24, when maximum sustained winds reached 40 mph (64 km/h). The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite captured this true-color image of Tropical Storm Glenda on February 25 at 08:55 UTC (3:55 a.m. EST). At that time bands of thunderstorms wrapped into the low-level center of circulation. An eye was beginning to form. At 0900 UTC (4 a.m. EST) on February 25, Glenda's maximum sustained winds were near 63.2 mph (102 km/h). It was centered near 17.6 south latitude and 69.1 east longitude, about 760 miles (1,224 km) south-southwest of Diego Garcia. Glenda was moving to the west-southwest at 8 mph (13 km/h). At that time, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center expect Glenda to strengthen to near 109 mph (176 km/h) before beginning to weaken. However, strong wind shear began to affect the storm. By the afternoon of February 26 Tropical Cyclone Glenda’s winds had dropped to about 58 mph (93 km/h), and by February 28 the storm had transitioned to an extra-tropical storm. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
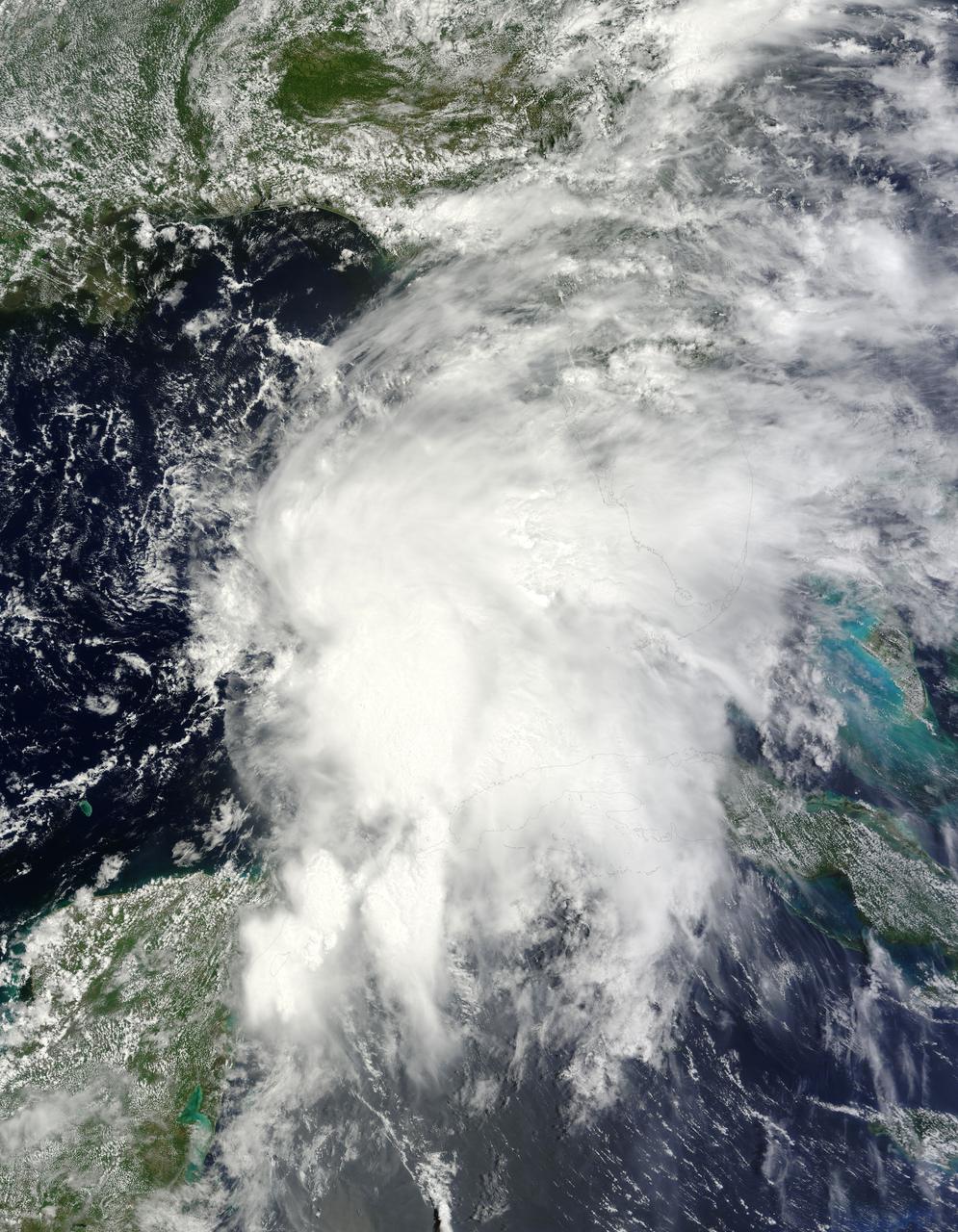

NASA’s Terra satellite passed over Tropical Storm Andrea on June 5 at 16:25 UTC (12:25 p.m. EDT) and the MODIS instrument captured this visible image of the storm. Andrea’s clouds had already extended over more than half of Florida. Credit: NASA Goddard MODIS Rapid Response Team --- NASA Sees Heavy Rainfall in Tropical Storm Andrea NASA’s TRMM satellite passed over Tropical Storm Andrea right after it was named, while NASA’s Terra satellite captured a visible image of the storm’s reach hours beforehand. TRMM measures rainfall from space and saw that rainfall rates in the southern part of the storm was falling at almost 5 inches per hour. NASA’s Terra satellite passed over Tropical Storm Andrea on June 5 at 16:25 UTC (12:25 p.m. EDT) and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument, captured a visible image of the storm. At that time, Andrea’s clouds had already extended over more than half of Florida. At 8 p.m. EDT on Wednesday, June 5, System 91L became the first tropical storm of the Atlantic Ocean hurricane season. Tropical Storm Andrea was centered near 25.5 North and 86.5 West, about 300 miles (485 km) southwest of Tampa, Fla. At the time Andrea intensified into a tropical storm, its maximum sustained winds were near 40 mph (65 kph). Full updates can be found at NASA's Hurricane page: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/hurricane" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/hurricane</a> Rob Gutro NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center

On Nov. 11 at 05:45 UTC, the MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured this image of Tropical Storm Haiyan over mainland China. Credit: NASA Goddard MODIS Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
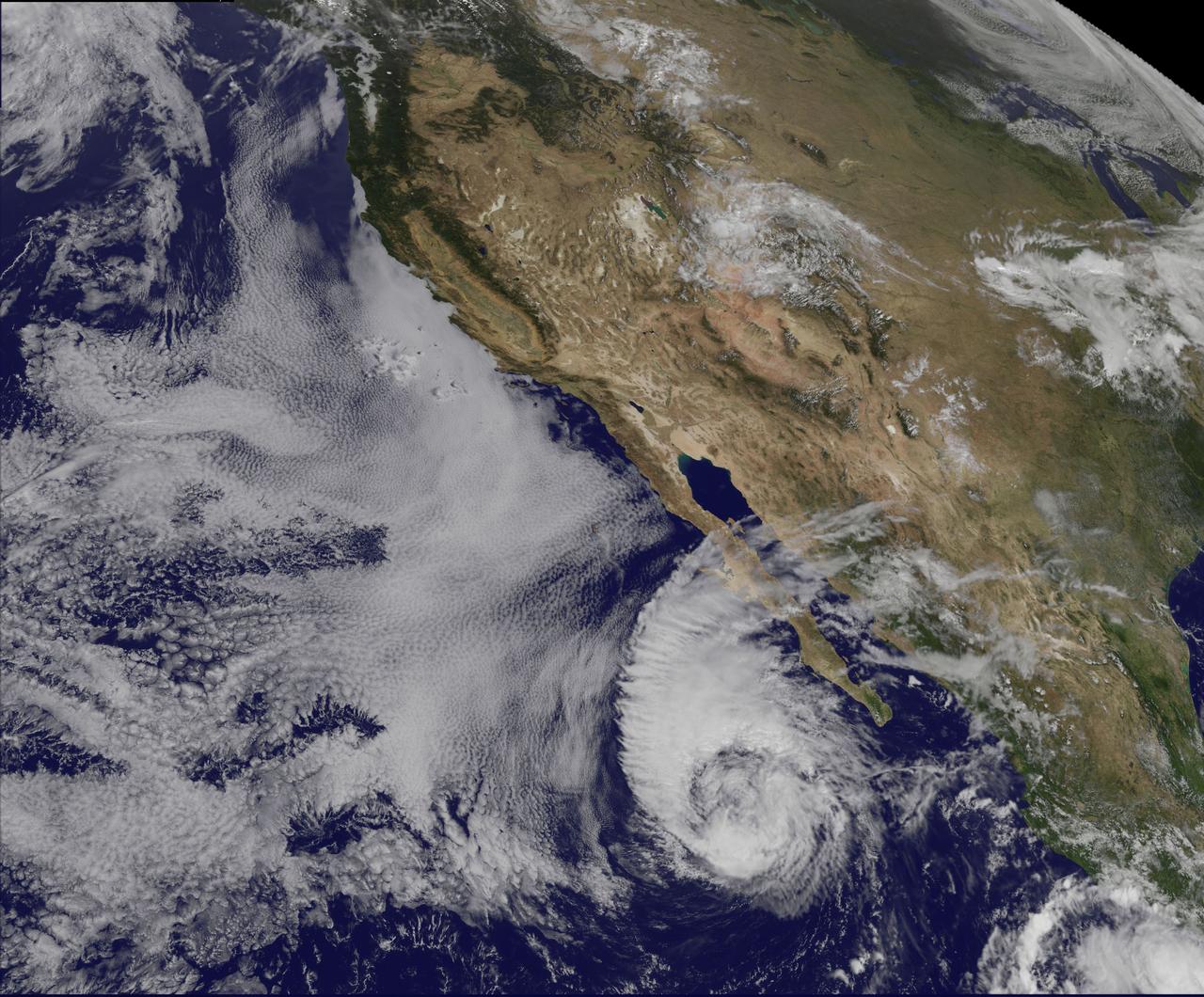

This visible image of Tropical Storm Miriam was captured by NOAA's GOES-15 satellite on Sept. 26, 2012 at 10:45 a.m. EDT off the coast of Baja California. The strongest thunderstorms were in a large band of thunderstorms north and northwest of the center. Miriam is banked to the north and west by an extensive field of stratocumulus clouds. Credit: NASA/NOAA GOES Project ---- Once a powerful hurricane, Miriam is now a tropical storm off the coast of Baja California, Mexico. Tropical Storm Miriam was seen in the Eastern Pacific Ocean by NOAA's GOES-15 satellite, and the visible image revealed that the strongest part of the storm was north and west of the center. NOAA's GOES-15 satellite sits in a fixed position over the western U.S. that allows it to monitor the Eastern Pacific Ocean and it captured a visible image of Tropical Storm Miriam on Sept. 26, 2012 at 10:45 a.m. EDT off the coast of Baja California. The strongest thunderstorms were north and northwest of the center in a large band, wrapping around the center of the tropical storm. Miriam is banked to the north and west by an extensive field of stratocumulus clouds Wind shear is taking its toll on Miriam. The National Hurricane Center noted there is an increasing "separation between the low- to mid-level centers of the storm (think of the storm as having multiple layers) due to 20-25 knots of southwesterly shear associated with a shortwave trough (elongated area of low pressure) rotating around the northwestern side of the storm. At 11 a.m. EDT on Sept. 26, Tropical Storm Miriam had maximum sustained winds near 65 mph (100 kph), dropping from 70 mph (100 kmh) just six hours before. It was located about 425 miles (680 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California Miriam was moving slowly at 6 mph (9 kmh) to the north-northwest and away from the coast. Miriam's minimum central pressure was near 992 millibars. A Miriam continues to pull away from Baja California, rough ocean swells will keep affecting the south and west coasts today, Sept. 26, and tomorrow, Sept. 27. By Sept. 28, Friday, the ocean swells will gradually begin to subside. Miriam is moving into a region where wind shear is forecast to increase and sea surface temperatures will fall. Those are two factors that will contribute to the weakening of the tropical storm over the next several days. Rob Gutro NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center Image: NASA GOES Project <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Although there's only one formed tropical cyclone in the Atlantic: Hurricane Cristobal, there are three other developing areas of low pressure and all were captured in this panoramic image from NOAA's GOES-East satellite today at 8 a.m. EDT. Cristobal is a hurricane located east of the U.S. East coast and is forecast to move up toward eastern Canada tonight (and stay off-shore). The image was made at NASA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Low #1. A weak area of low pressure near the coast of South Texas is producing disorganized showers and thunderstorms. Significant development of this system is unlikely before it moves inland over South Texas and northern Mexico today. It has a ten percent chance of development into a tropical depression in the next 2 days. Low #2. A tropical wave located over the eastern Caribbean Sea continues to produce disorganized cloudiness and showers. Upper-level winds are expected to remain unfavorable for development during the next couple of days while the system moves across the eastern and central Caribbean Sea. However, environmental conditions could become conducive for some development when the system moves over the northwestern Caribbean Sea on Sunday and into the southwestern Gulf of Mexico early next week. It has a near zero chance to develop in the next 2 days. Low #3. A tropical wave is forecast to move off the west coast of Africa on Friday. Environmental conditions could be conducive for some gradual development of this system while it moves westward at 10 to 15 mph across the eastern Atlantic early next week. This has a near zero chance of development in the next two days. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
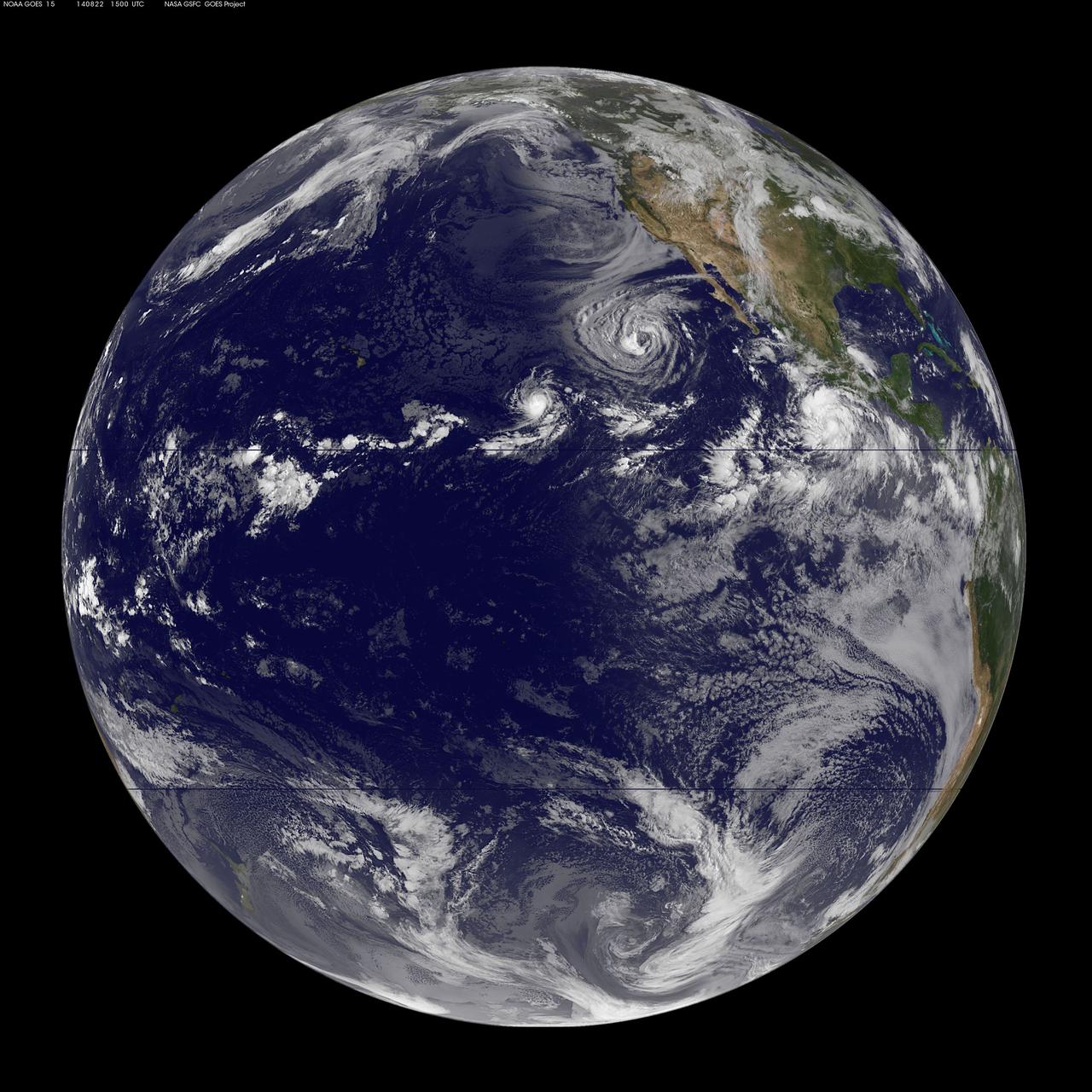
NASA and NOAA satellites are studying the triple tropical tempests that are now romping through the Eastern Pacific Ocean. NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured Tropical Storm Karina, Tropical Storm Lowell and newly formed Tropical Storm Marie on August 22. NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured all three storms in an infrared image at 0900 UTC (5 a.m. EDT), and Tropical Lowell clearly dwarfs Karina to its west, and Marie to the east. The infrared image was created at NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. For more information about Lowell, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/12e-eastern-pacific-ocean/" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/12e-eastern-pacific-ocean/</a> For more information about Karina, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/karina-eastern-pacific/" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/karina-eastern-pacific/</a> Rob Gutro NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
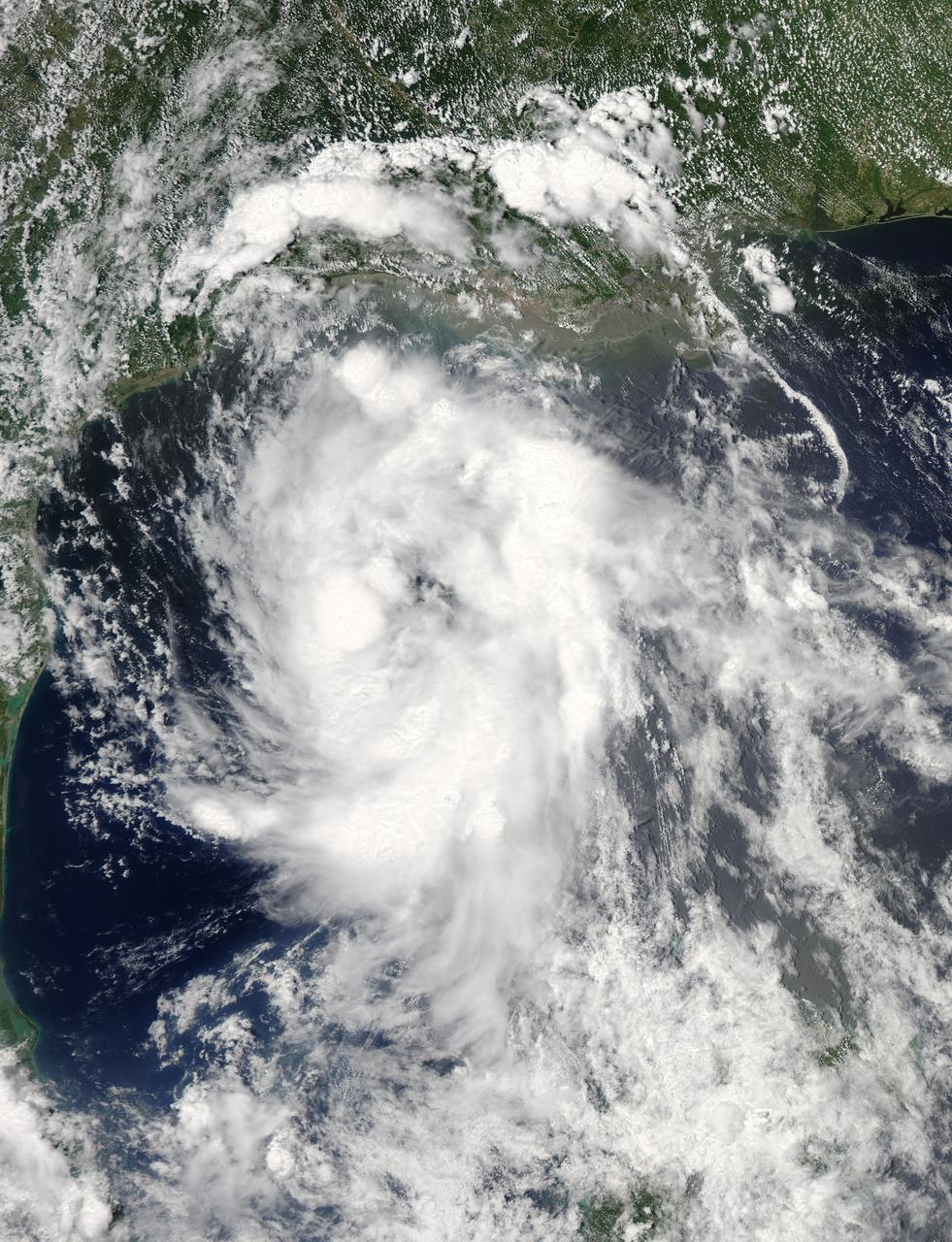

On June 15 at 19:15 UTC (3:15 p.m. EDT) the MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Storm Bill approaching Texas and Louisiana. Powerful thunderstorms circled the center in fragmented bands. At 11 a.m. CDT on June 16, a Tropical Storm Warning was in effect from Baffin Bay to High Island Texas as Bill was making landfall. The National Hurricane Center noted that Bill is expected to produce total rain accumulations of 4 to 8 inches over eastern Texas and eastern Oklahoma and 2 to 4 inches over western Arkansas and southern Missouri, with possible isolated maximum amounts of 12 inches in eastern Texas. In eastern Texas and far western Louisiana today and tonight, isolated tornadoes are also possible, as with any landfalling tropical storm. Tropical storm conditions are expected to continue into the evening in the warning area. Along the coasts, the combination of a storm surge and the tide will cause normally dry areas near the coast to be flooded by rising waters. The water could reach the following heights above ground if the peak surge occurs at the time of high tide. The NHC noted that the Upper Texas coast could experience 2 to 4 feet, and the western Louisiana coast between 1 to 2 feet. At 10 a.m. CDT (1500 UTC), the center of Tropical Storm Bill was located near latitude 28.2 North, longitude 96.4 West. Bill was moving toward the northwest near 10 mph (17 kph) and that general motion is expected to continue today. The latest minimum central pressure reported by an Air Force Reserve Hurricane Hunter aircraft was 997 millibars. Reports from an Air Force Reserve reconnaissance aircraft indicate that maximum sustained winds remain near 60 mph (95 kph) with higher gusts. Unlike Carlos, Bill is not a compact storm. Tropical-storm-force winds extend outward up to 150 miles (240 km) from the center. Between 9 and 10 a.m. CDT, an automated observing station at Port O'Connor also reported a sustained wind of 44 mph (70 kph) and a gust to 53 mph (85 kph). For updated forecasts, watches and warnings, visit the National Hurricane Center webpage at <a href="http://www.nhc.noaa.gov" rel="nofollow">www.nhc.noaa.gov</a>. For local forecasts and advisories, visit: <a href="http://www.weather.gov" rel="nofollow">www.weather.gov</a>. Bill is forecast to continue moving inland and is expected to be a tropical depression by Wednesday, June 17, west of Dallas. The remnants of Bill are forecast to move into the Midwest later in the week. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
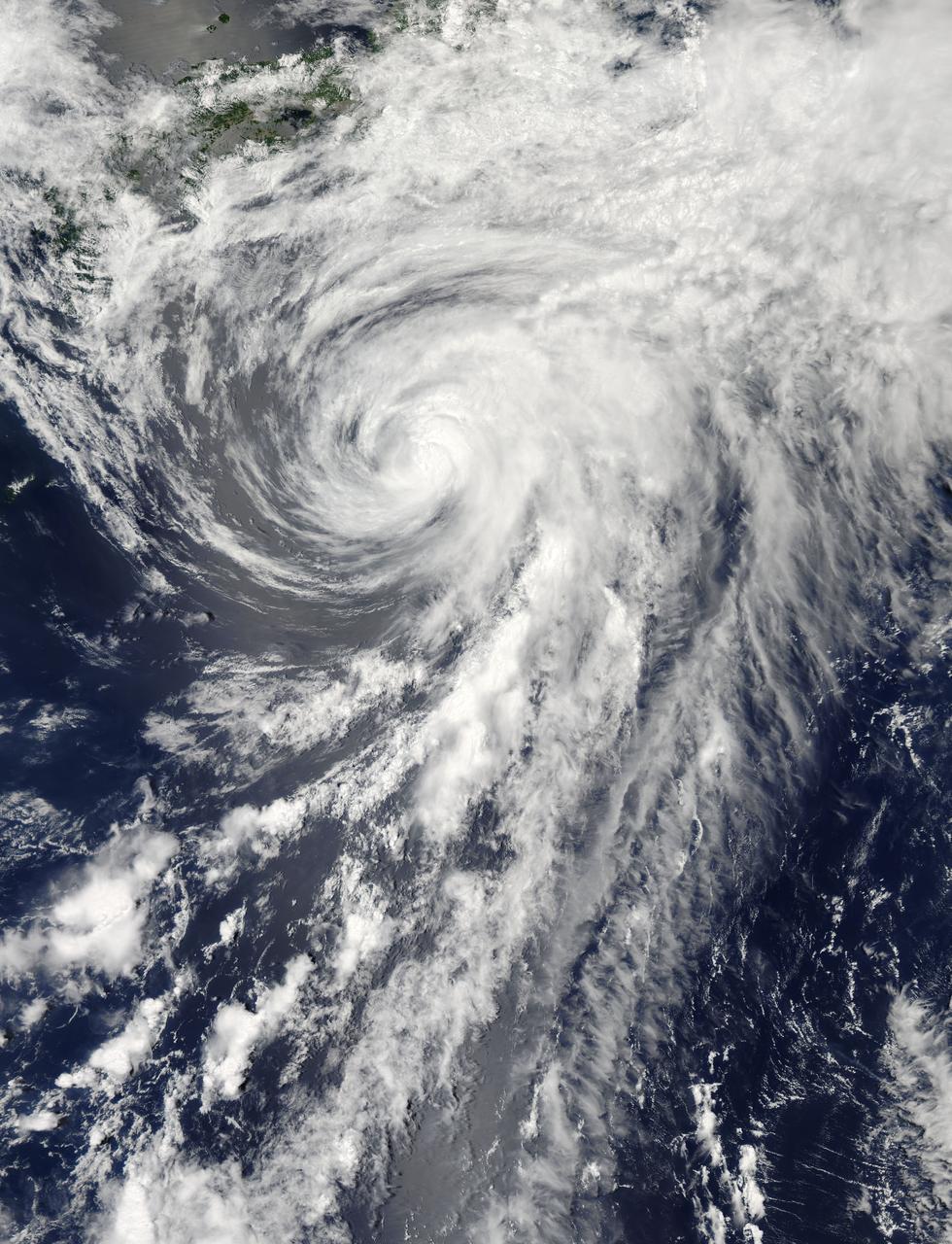
On Tuesday, June 11, 2013 Tropical Storm Yagi spun in the North Pacific Ocean just south of Japan. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite captured this beautiful true-color image of the storm on that same date at 4:10 UTC (1:10 p.m. Japan local time). The image shows a clear apostrophe-shaped cyclone, with a closed eye and somewhat elliptical shape. The clouds associated with the northern fringes of the storm draped over southeastern coastal Japan, and a long “tail” (or band) of thunderstorms fed into the center from the south. Multispectral imagery also showed tight bands of thunderstorms wrapping into the center of the storm, although the building of thunderstorms was weakening around the center. Near the same time as the image was captured, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center announced that vertical wind shear was starting to take a toll on Yagi. Northwesterly wind shear had caused the system to tilt slightly with the upper-level center displaced about 20 nautical miles east of the low-level center. Tropical Storm Yagi developed from Tropical Depression 03W in the Western North Pacific Ocean on June 6, and intensified the weekend of June 8-9, when it reached Tropical Storm status and was given the name Yagi. Also known as Dante, the storm reached the maximum wind speeds on June 10 and 11, after which it began to weaken as it moved into cooler waters. On June 14, Yagi’s remnants passed about 200 miles south of Tokyo, and brought soaking rains to the coastline of Japan’s Honshu Island. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
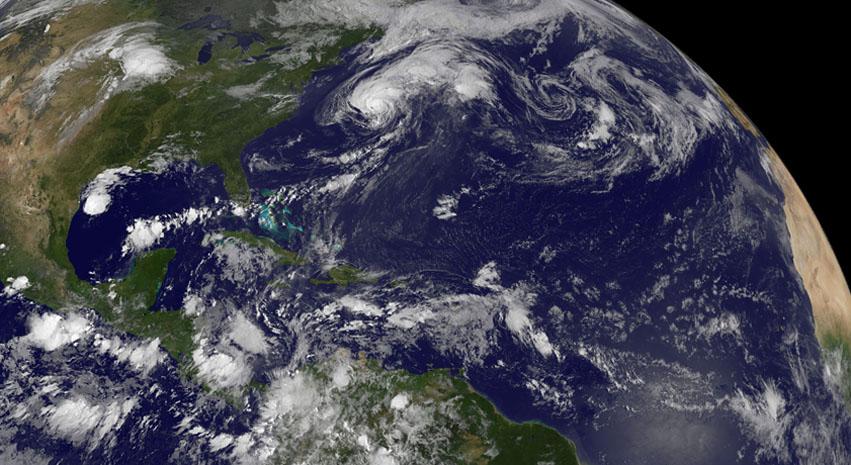

Although there's only one formed tropical cyclone in the Atlantic: Hurricane Cristobal, there are three other developing areas of low pressure and all were captured in this panoramic image from NOAA's GOES-East satellite today at 8 a.m. EDT. Cristobal is a hurricane located east of the U.S. East coast and is forecast to move up toward eastern Canada tonight (and stay off-shore). The image was made at NASA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Low #1. A weak area of low pressure near the coast of South Texas is producing disorganized showers and thunderstorms. Significant development of this system is unlikely before it moves inland over South Texas and northern Mexico today. It has a ten percent chance of development into a tropical depression in the next 2 days. Low #2. A tropical wave located over the eastern Caribbean Sea continues to produce disorganized cloudiness and showers. Upper-level winds are expected to remain unfavorable for development during the next couple of days while the system moves across the eastern and central Caribbean Sea. However, environmental conditions could become conducive for some development when the system moves over the northwestern Caribbean Sea on Sunday and into the southwestern Gulf of Mexico early next week. It has a near zero chance to develop in the next 2 days. Low #3. A tropical wave is forecast to move off the west coast of Africa on Friday. Environmental conditions could be conducive for some gradual development of this system while it moves westward at 10 to 15 mph across the eastern Atlantic early next week. This has a near zero chance of development in the next two days. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
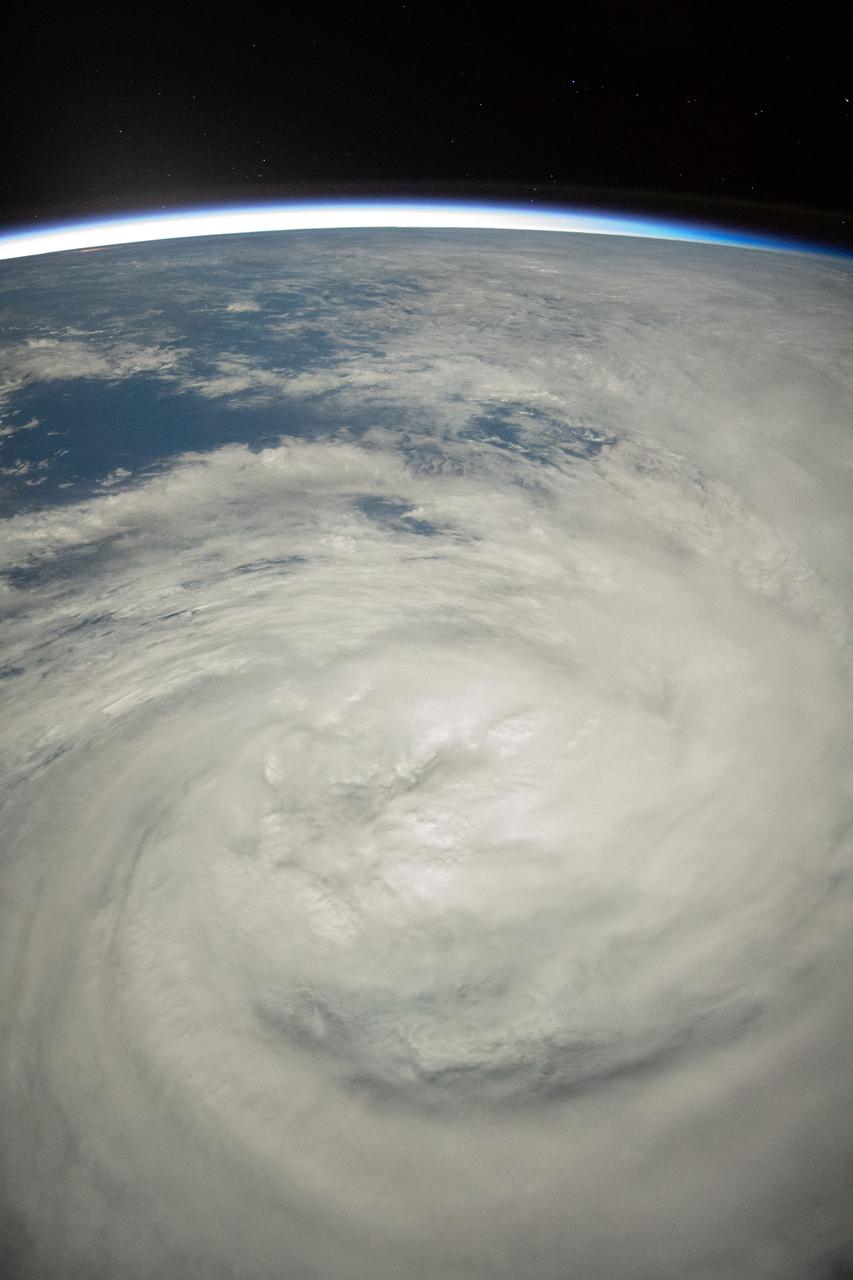

iss058e023922 (Feb. 20, 2019) --- Tropical Cyclone Oma is pictured as the International Space Station orbited 256 miles above the Coral Sea off the coast of Queensland, Australia.

The outflow from Tropical Storm Toraji spawned tornadoes that caused injuries and property damage in Koshigaya, Saitama Prefecture, Japan, just northeast of Tokyo, on September 2, 2013. This image was taken by the Suomi NPP satellite's VIIRS instrument around 0425Z on September 2, 2013. Credit: NASA/NOAA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Tropical Storm Hagupit's low level circulation center is being obscured by its deep central convection and intensities are hard to pinpoint as the storm interacts with land. Once clear over the waters of the South China Sea Hagupit is forecast to continue weakening as it approaches the southern coast of Vietnam. This image was taken by the Suomi NPP satellite's VIIRS instrument around 0510Z on December 8, 2014. NASA/NOAA/NPP Credit: NASA/NOAA via <b><a href="www.nnvl.noaa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NOAA Environmental Visualization Laboratory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
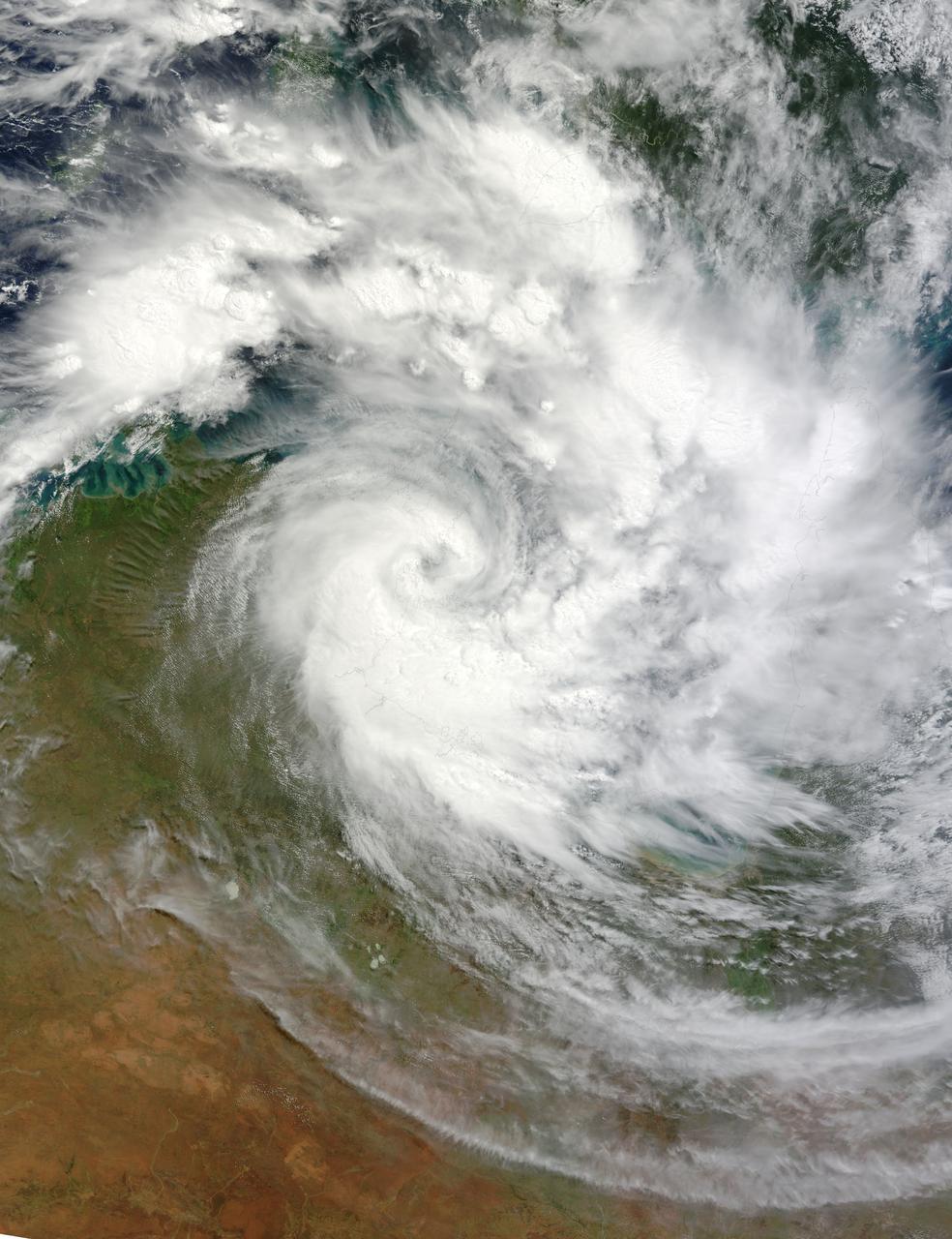

NASA image March 29, 2010 Tropical Cyclone Paul spanned the ocean waters between Australia and New Guinea on March 29, 2010. The MODIS on NASA’s Terra satellite captured this natural-color image the same day. The center of the cyclone is along the coast of Northern Territory’s Arnhem Land. Clouds run counter-clockwise across the Gulf of Carpentaria and Cape York Peninsula, over New Guinea’s Pulau Dolok, and over the Arafura Sea. On March 29, 2010, the U.S. Navy’s Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) reported that Tropical Cyclone Paul storm had maximum sustained winds of 60 knots (110 kilometers per hour) and gusts up to 75 knots (140 kilometers per hour). The storm was located roughly 315 nautical miles (585 kilometers) east of Darwin. The storm had moved slowly toward the southwest over the previous several hours. The JTWC forecast that the storm would likely maintain its current intensity for several more hours before slowly dissipating over land. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS To learn more about this image go to: <a href="http://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/individual.php?db_date=2010-03-30" rel="nofollow">modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/individual.php?db_date=2010-0...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
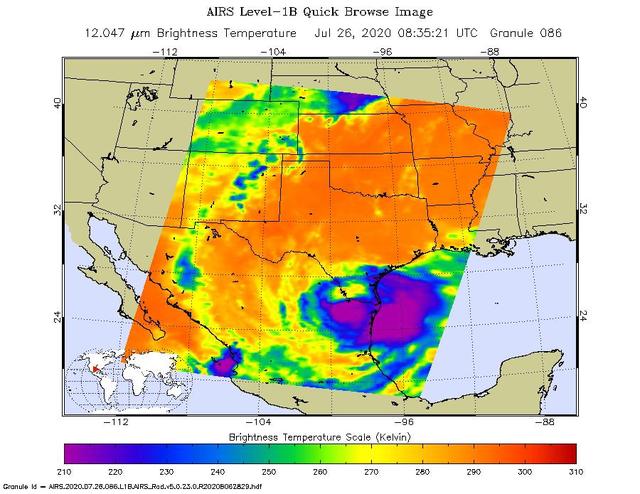
NASA's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) was monitoring Tropical Storm Hanna as it took aim at southern Texas on July 26. Perched on NASA's Aqua satellite, AIRS is an instrument that studies Earth's weather and climate. Hanna made landfall as a Category 1 hurricane around 5 p.m. local time over Padre Island, Texas, on July 25. Since then, the storm has lost steam, weakening to a tropical storm in the early morning hours of July 26, and then to a tropical depression by the afternoon. The purple areas in the AIRS image — taken at 1:35 a.m. local time on July 26 — show regions within the tropical storm with cold clouds high in Earth's atmosphere that tend to produce heavy rainfall. The National Hurricane Center predicts that Hanna will continue over northeastern Mexico, where it will dissipate by late in the day on July 27. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23784

NASA image acquired January 28, 2011 Tropical Cyclone Bianca continued moving southward along the coast of Western Australia on January 28, 2011. At 5:00 a.m. on January 28 local time (21:00 UTC on January 27), the U.S. Navy’s Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) reported that Bianca was located about 135 nautical miles (250 kilometers) west of Learmonth, Western Australia. The storm had maximum sustained winds of 90 knots (165 kilometers per hour) and gusts up to 110 knots (205 kilometers per hour), having intensified over the previous day. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite captured this natural-color image at 2:30 p.m. Western Australia time (6:30 UTC) on January 28, 2011. Bianca spans hundreds of kilometers, and the storm’s eye appears west-southwest of Learmonth. The JTWC forecast that Bianca would continue strengthening for about 12 more hours then begin to weaken, thanks to reduced sea surface temperatures and increased vertical wind shear. NASA image by Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team at NASA GSFC. Caption by Michon Scott. Instrument: Aqua - MODIS To view more images of this event go to: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/event.php?id=48914" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/event.php?id=48914</a> Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
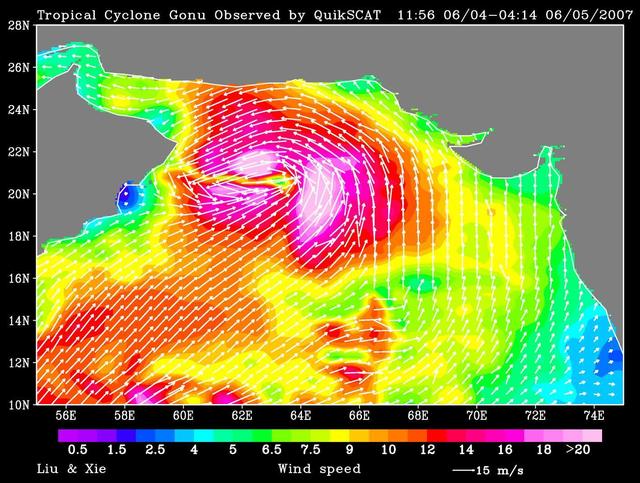
NASA QuikScat observed a rare tropical cyclone in the northern part of the Arabian Sea, threatening the petroleum shipping lanes and the Gulf States e.g. Oman that are unprepared for such an event.
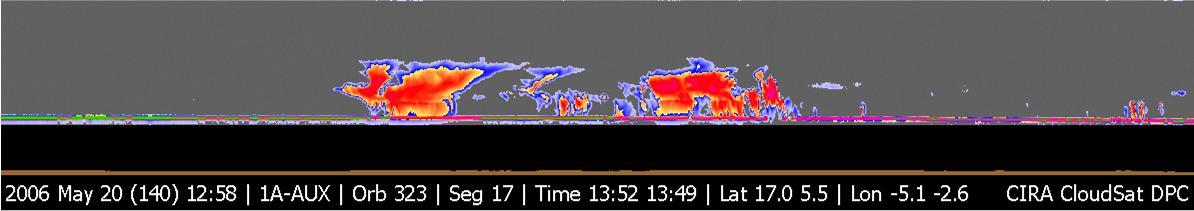
NASA CloudSat image of a horizontal cross-section of tropical clouds and thunderstorms over east Africa.
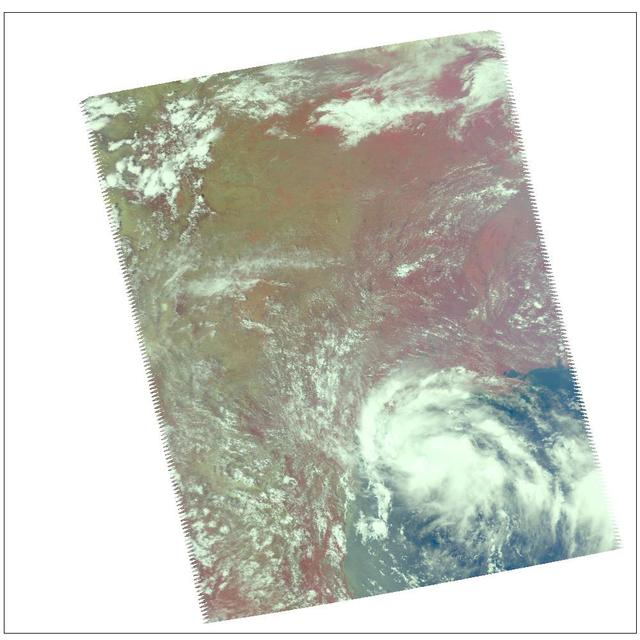
Visible image of Tropical Storm Erin, the Atlantic Ocean 210 miles south of Galveston, Texas, August, 2007, from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder AIRS on NASA Aqua satellite.
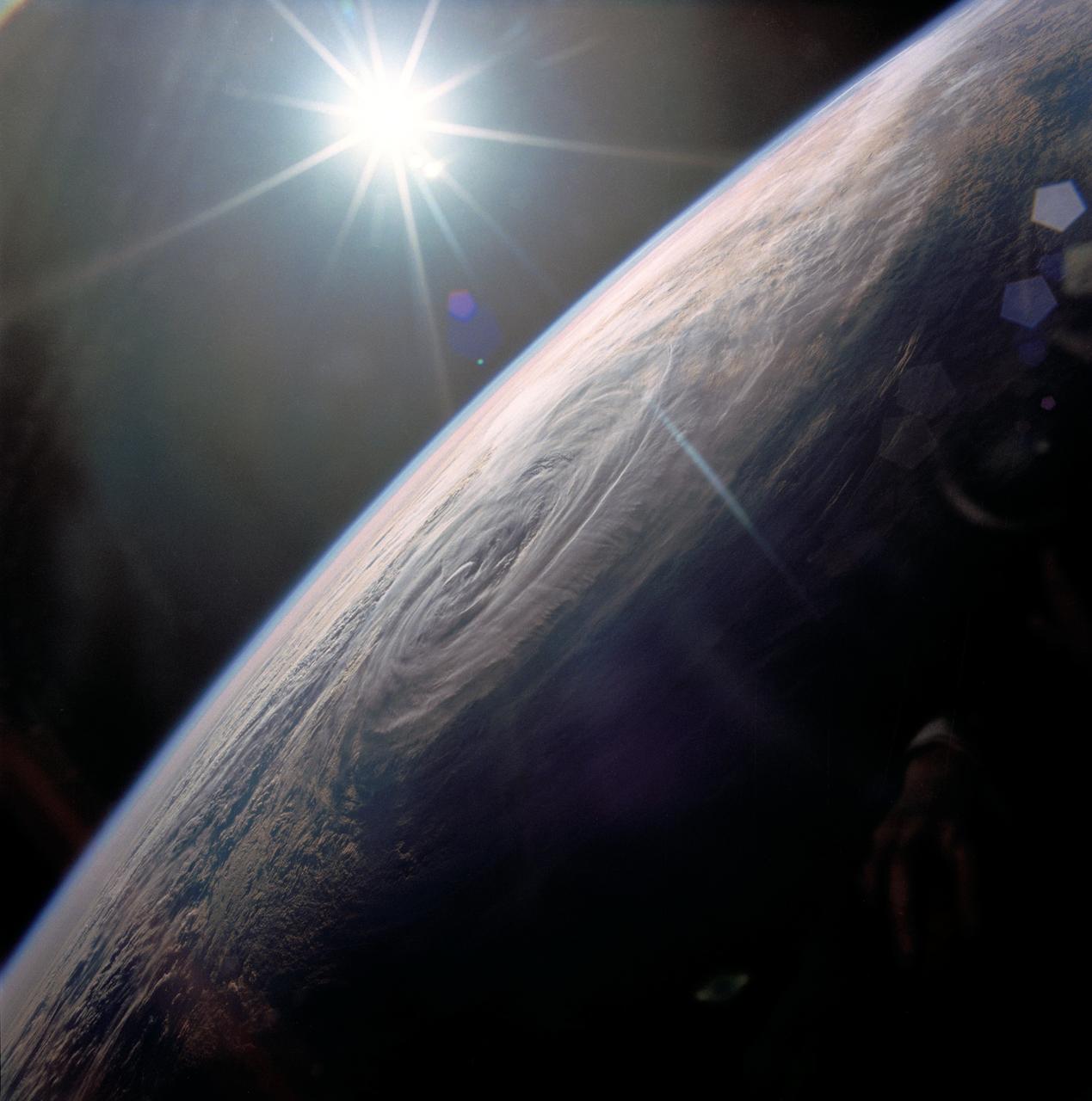

STS032-80-036 (9-20 Jan. 1990) --- This oblique view of Tropical Storm Sam in the eastern Indian Ocean off the western coast of Australia was photographed with a 70mm camera by the astronauts. Tropical Storm Sam (known as Willy-Willy in Australia) was born in the eastern Indian Ocean near the islands of Timor and Sumba in Indonesia. The storm tracked southwestward attaining sustained winds in excess of 60 knots (70 miles per hour). Other than on Christmas Island and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands south of Java, and for strong swells along the western Australia coast, the storm had little impact on land areas. At the time this photograph was taken, the storm was beginning to dissipate in the south Indian Ocean. The eye of the storm is still visible near center, with the swirling bands of the storm propagating in a clockwise direction toward the center. Winds aloft have begun to shear the tops of thunderstorms associated with the storm, forming a high cirrus cloud cover over the center portions of the storm. This picture was used by the crew at their January 30, 1990 Post-Flight Press Conference (PFPC).

NASA image acquired January 28, 2011 High res file here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5400445475">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5400445475</a> Tropical Cyclone Bianca continued moving southward along the coast of Western Australia on January 28, 2011. At 5:00 a.m. on January 28 local time (21:00 UTC on January 27), the U.S. Navy’s Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) reported that Bianca was located about 135 nautical miles (250 kilometers) west of Learmonth, Western Australia. The storm had maximum sustained winds of 90 knots (165 kilometers per hour) and gusts up to 110 knots (205 kilometers per hour), having intensified over the previous day. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite captured this natural-color image at 2:30 p.m. Western Australia time (6:30 UTC) on January 28, 2011. Bianca spans hundreds of kilometers, and the storm’s eye appears west-southwest of Learmonth. The JTWC forecast that Bianca would continue strengthening for about 12 more hours then begin to weaken, thanks to reduced sea surface temperatures and increased vertical wind shear. NASA image by Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team at NASA GSFC. Caption by Michon Scott. Instrument: Aqua - MODIS To view more images of this event go to: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/event.php?id=48914" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/event.php?id=48914</a> Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
NASA image acquired Sept 6, 2010 at 16 :45 UTC Tropical Storm Hermine (10L) in the Gulf of Mexico Satellite: Terra Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team To learn more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hurricanes/archives/2010/h2010_Hermine.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hurricanes/archives/2010/h2010...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

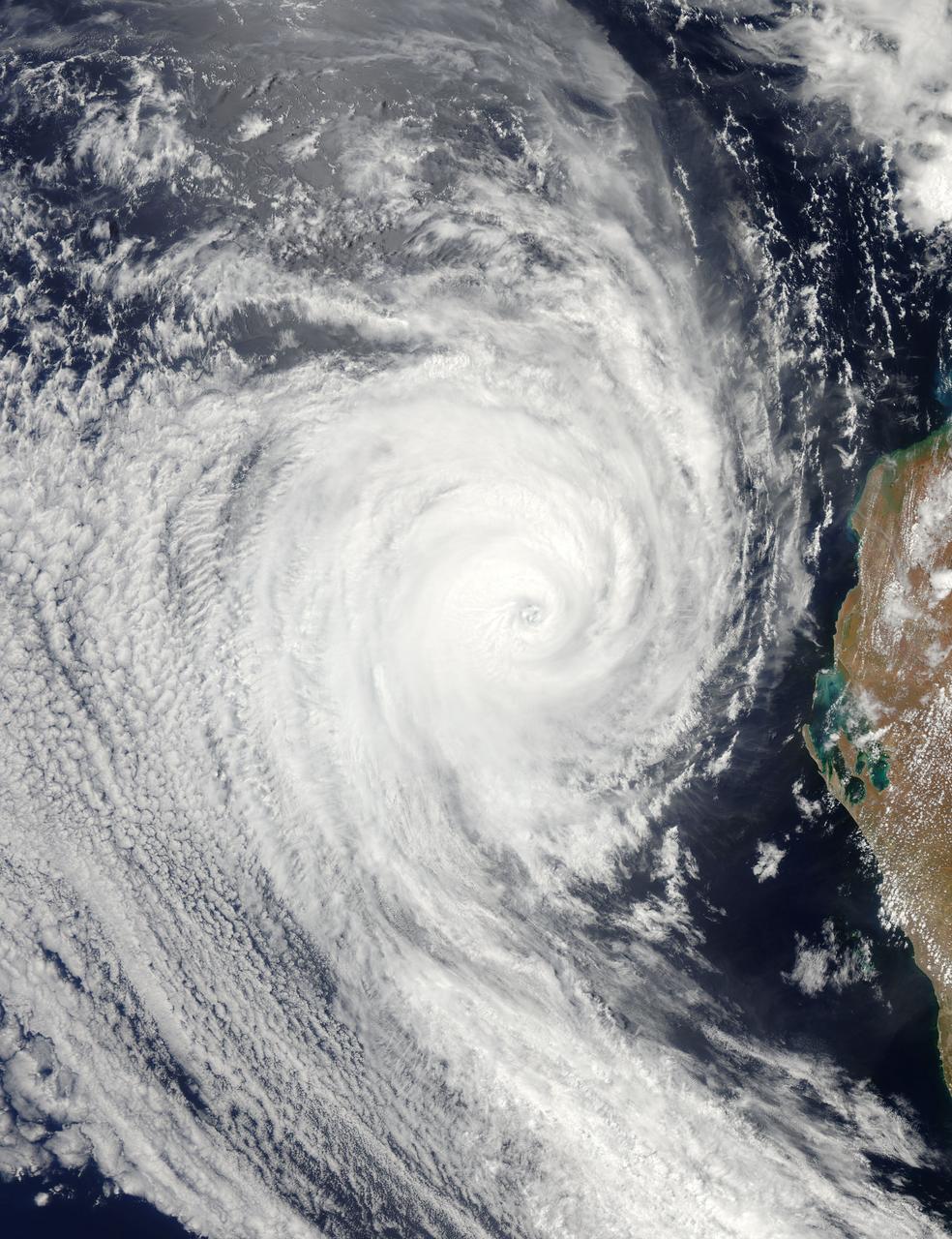
Image acquired February 19, 2010: Tropical Cyclone Gelane had sustained winds of 125 knots (230 kilometers per hour) and gusts up to 150 knots (275 kilometers per hour), according to a report from the U.S. Navy’s Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) on February 19, 2010. The JTWC reported that Gelane was roughly 315 nautical miles (585 kilometers) east-northeast of Port Louis, Mauritius, and was forecast to travel toward the southwest, weakening slightly as it moved. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite captured this true-color image on February 19, 2010. Gelane’s spiral arms span hundreds of kilometers over the open ocean. Credit: NASA image by Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team, Goddard Space Flight Center. Caption by Michon Scott. Instrument: Aqua - MODIS..For more details and a higher res file of this image go to: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=42767" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=42767</a>

A south tropical disturbance that has just passed Jupiter's iconic Great Red Spot is captured in this color-enhanced image from NASA's Juno spacecraft. Threads of orange haze are pulled from the Great Red Spot by the turbulence of the south tropical disturbance. The image was taken at 3:04 a.m. PDT (6:04 p.m. EDT) on April 1, 2018, as the spacecraft performed its 12th close flyby of Jupiter. Citizen scientist Kevin M. Gill created this image using data from the spacecraft's JunoCam imager. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22938. - Enhanced image by Kevin M. Gill (CC-BY) based on images provided courtesy of NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS
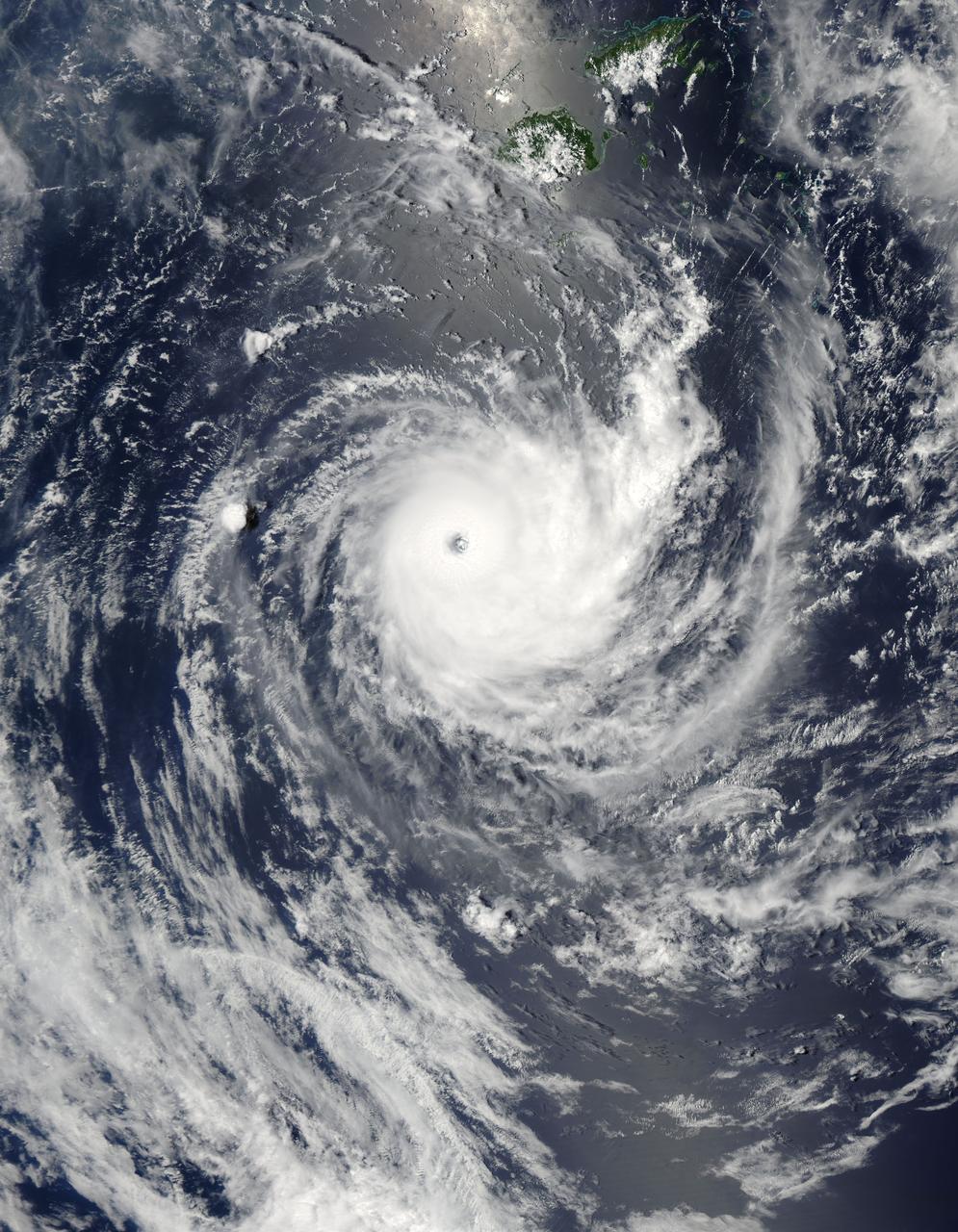

NASA image acquired January 26,02011 Tropical Cyclone Wilma raged over the Pacific Ocean in late January 2011. At 8:00 p.m. New Caledonia time (9:00 UTC) on January 26, the U.S. Navy’s Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) reported that Wilma was located some 555 nautical miles (1,030 kilometers) east of Noumea, New Caledonia. Wilma packed maximum sustained winds of 115 knots (215 kilometers per hour) with gusts up to 140 knots (260 kilometers per hour). The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite captured this natural-color image at 12:45 p.m. New Caledonia time (1:45 UTC) on January 26, 2011. Wilma has a tightly coiled configuration and a well-defined eye. The storm hovers over the Pacific Ocean just south of Fiji. According to the JTWC, Wilma would remain strong for a day or so, then would being to gradually weaken, thanks to greater vertical wind shear and lower sea surface temperatures. NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
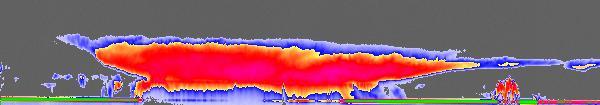
NASA new CloudSat satellite captured its first tropical storm, Alberto, as it spun over the Gulf of Mexico the morning of June 12, 2006.
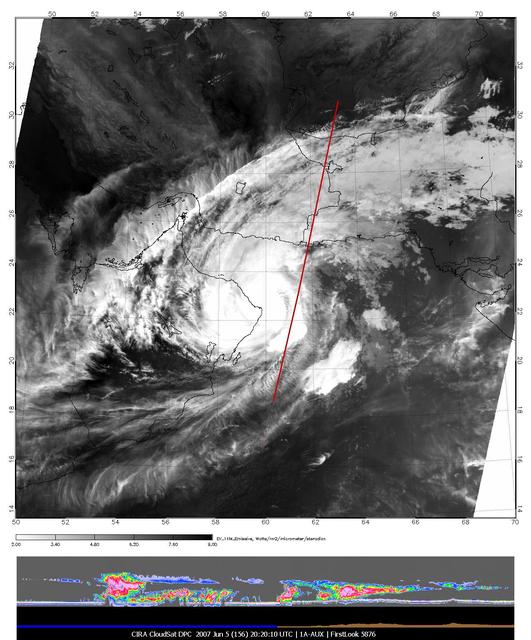
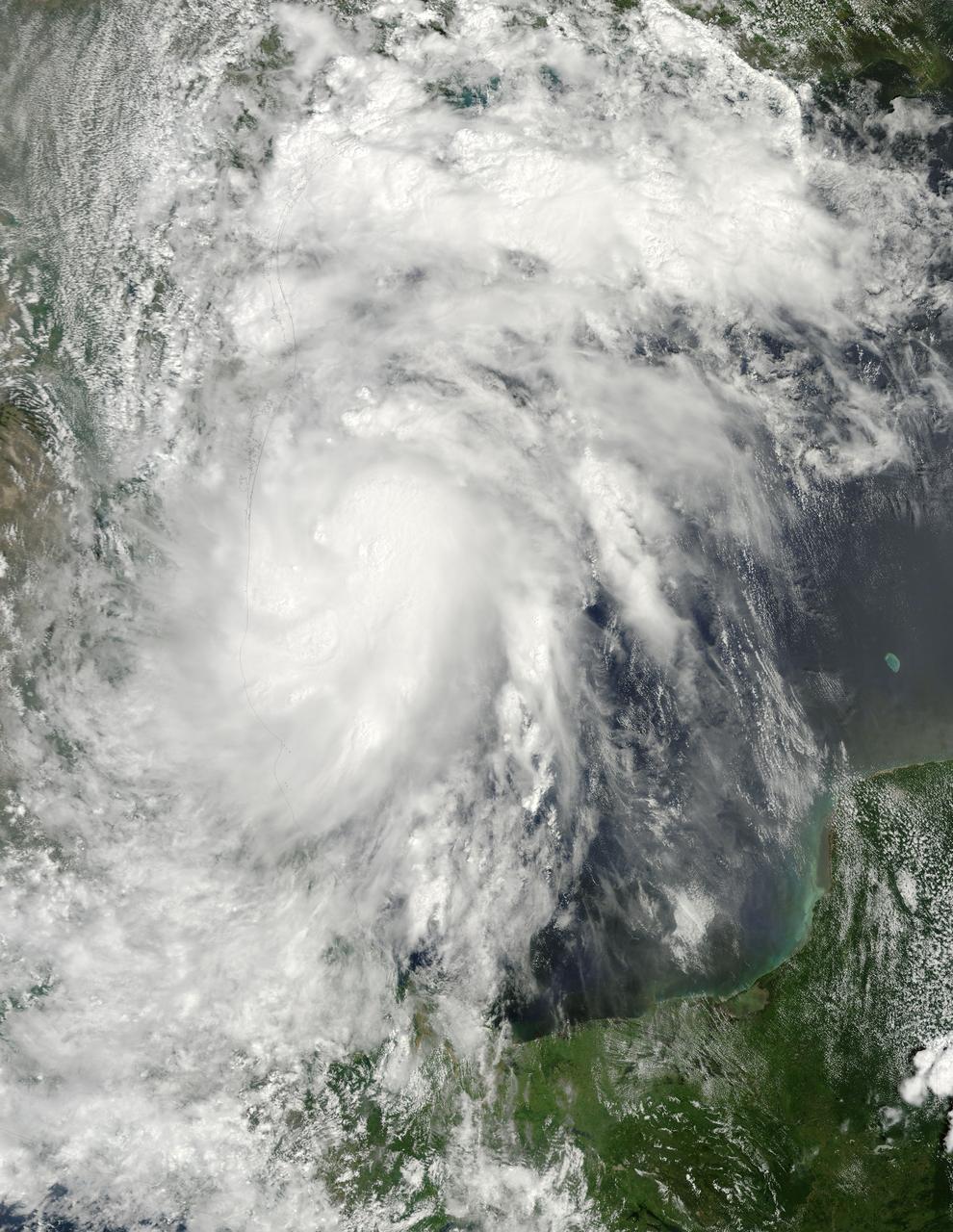
The image of Tropical Cyclone Gonu in the upper panel was taken by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer MODIS instrument on NASA Aqua satellite on June 5, 2007, at approximately 20:20 UTC.
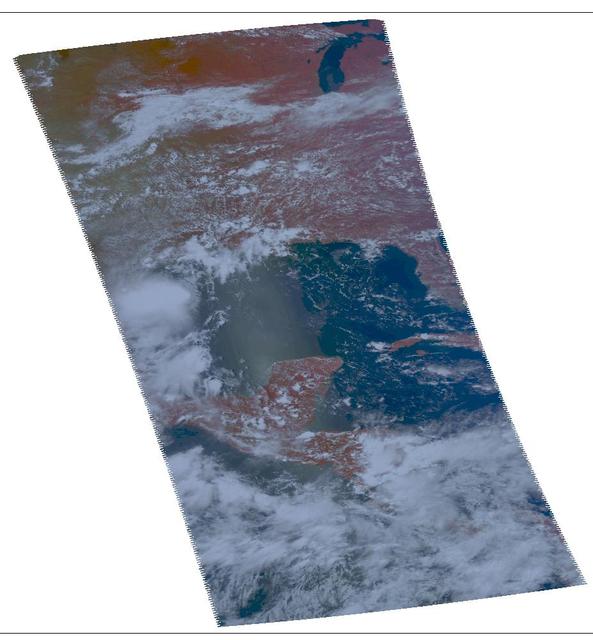
NASA Aqua spacecraft passed over Tropical Storm Don at 8:17 UTC 1:17 a.m. EDT on July 29, 2011. Texas is experiencing exceptional drought conditions; Tropical Storm Don may bring relief.
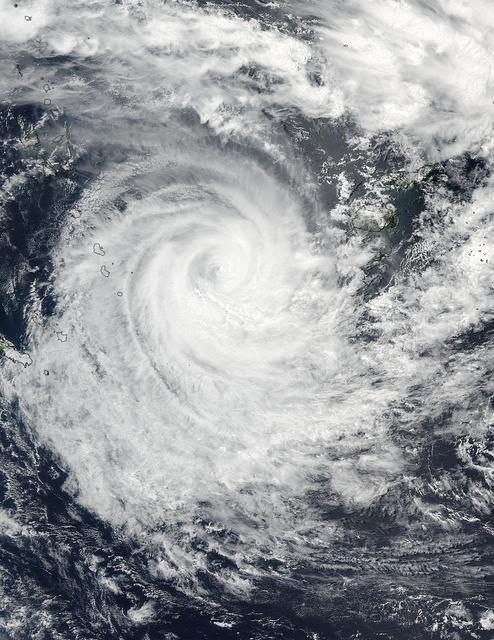

NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite saw that Tropical Cyclone Winston maintained a pinhole eye as it tracked east of southern Vanuatu's islands in the Southern Pacific Ocean on Feb. 23. Infrared imagery showed bands of strong thunderstorms were wrapping into the low-level center of the storm. Tropical Cyclone Winston was moving past Vanuatu in the South Pacific Ocean on Feb. 23 at 0140 UTC when NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured this image of the storm. Credits: NOAA/NASA Goddard Rapid Response Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/winston-southwestern-pacific-ocean" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/winston-southwestern-pa...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
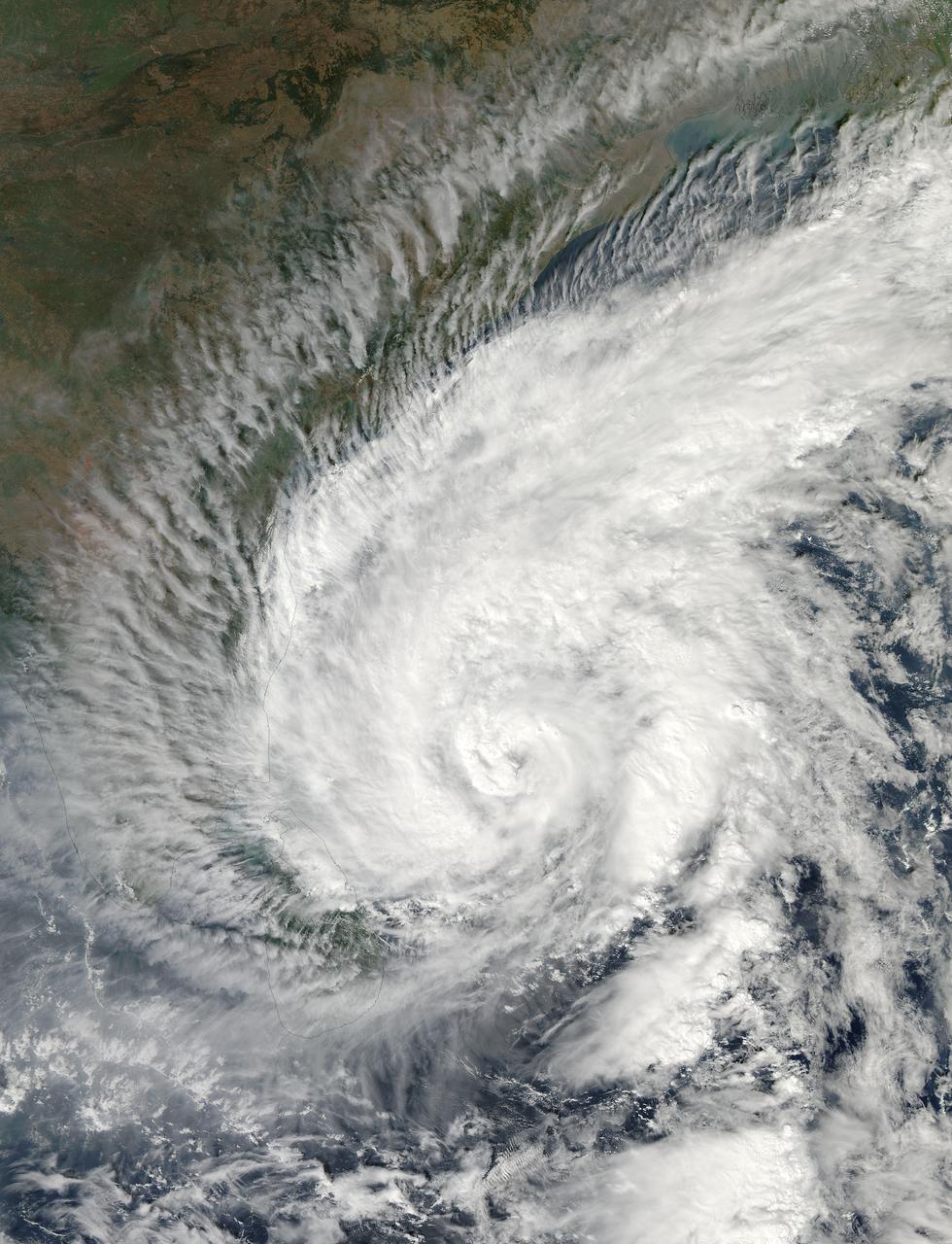
Tropical Cyclone Madi approaching India. Acquired by Aqua/MODIS on 12/07/2013 at 07:55 UTC. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
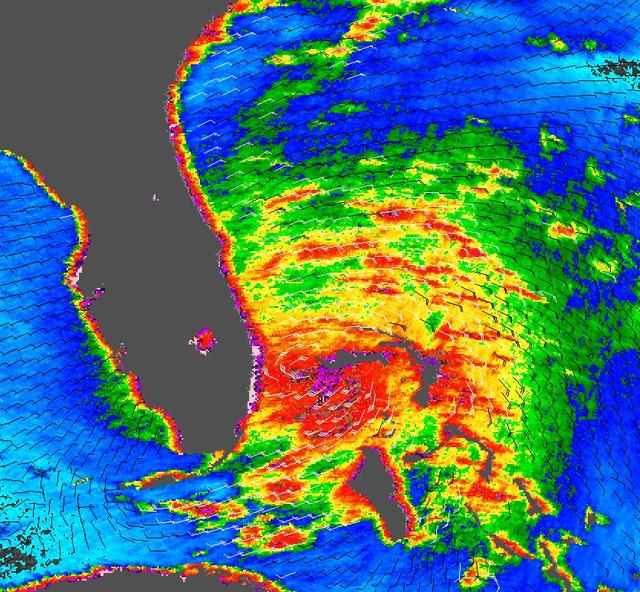
Tropical Storm Katrina is shown here as observed by NASA QuikScatsatellite on August 25, 2005, at 08:37 UTC 4:37 a.m. in Florida. At this time, the storm had 80 kilometers per hour 50 miles per hour; 43 knots sustained winds.
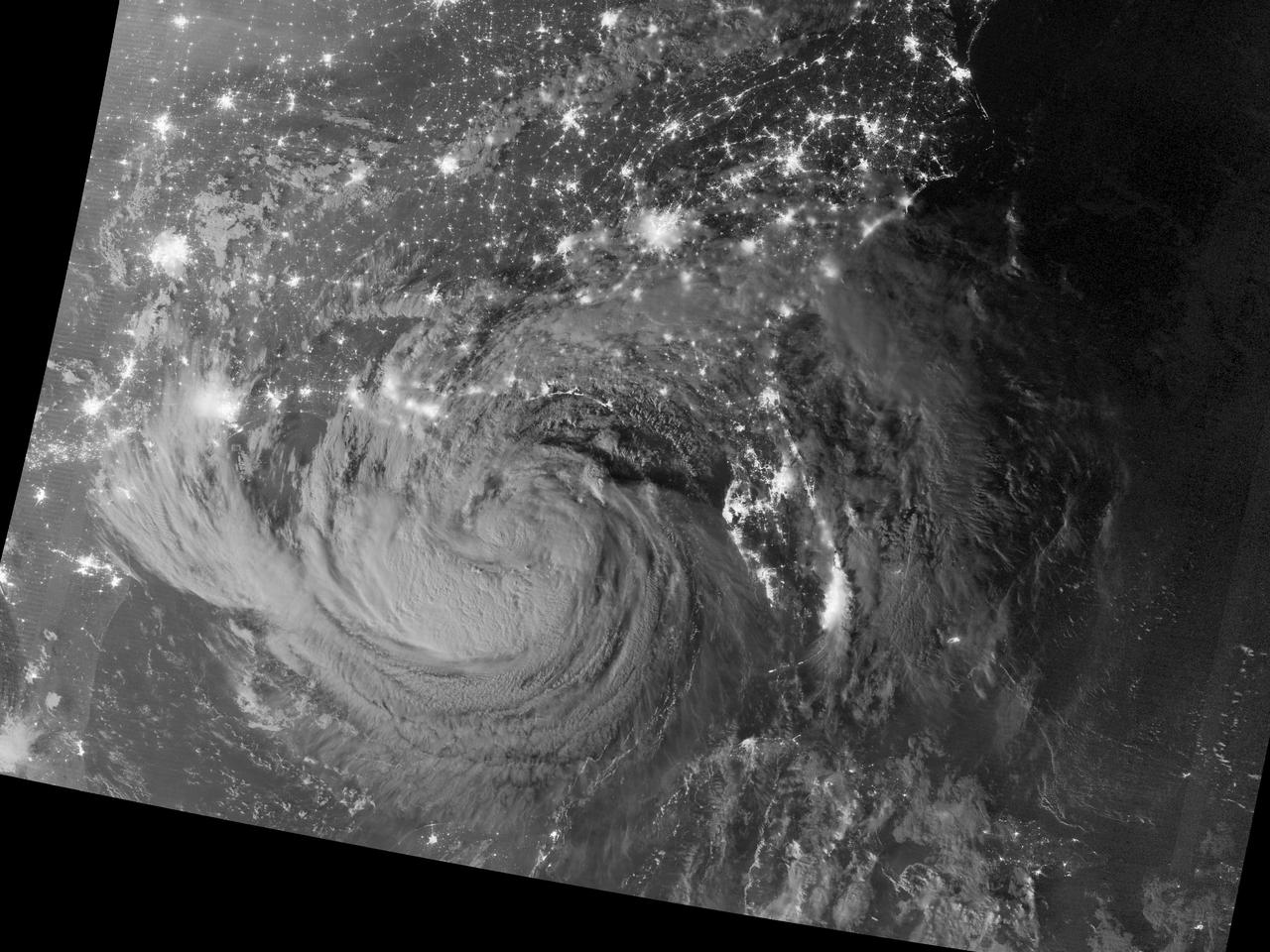
NASA image acquired August 28, 2012 Early on August 28, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi-NPP satellite captured this nighttime view of Tropical Storm Isaac and the cities near the Gulf Coast of the United States. The image was acquired just after local midnight by the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses light intensification to enable the detection of dim signals. In this case, the clouds of Isaac were lit by moonlight. Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day Night Band data. Caption by Mike Carlowicz. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
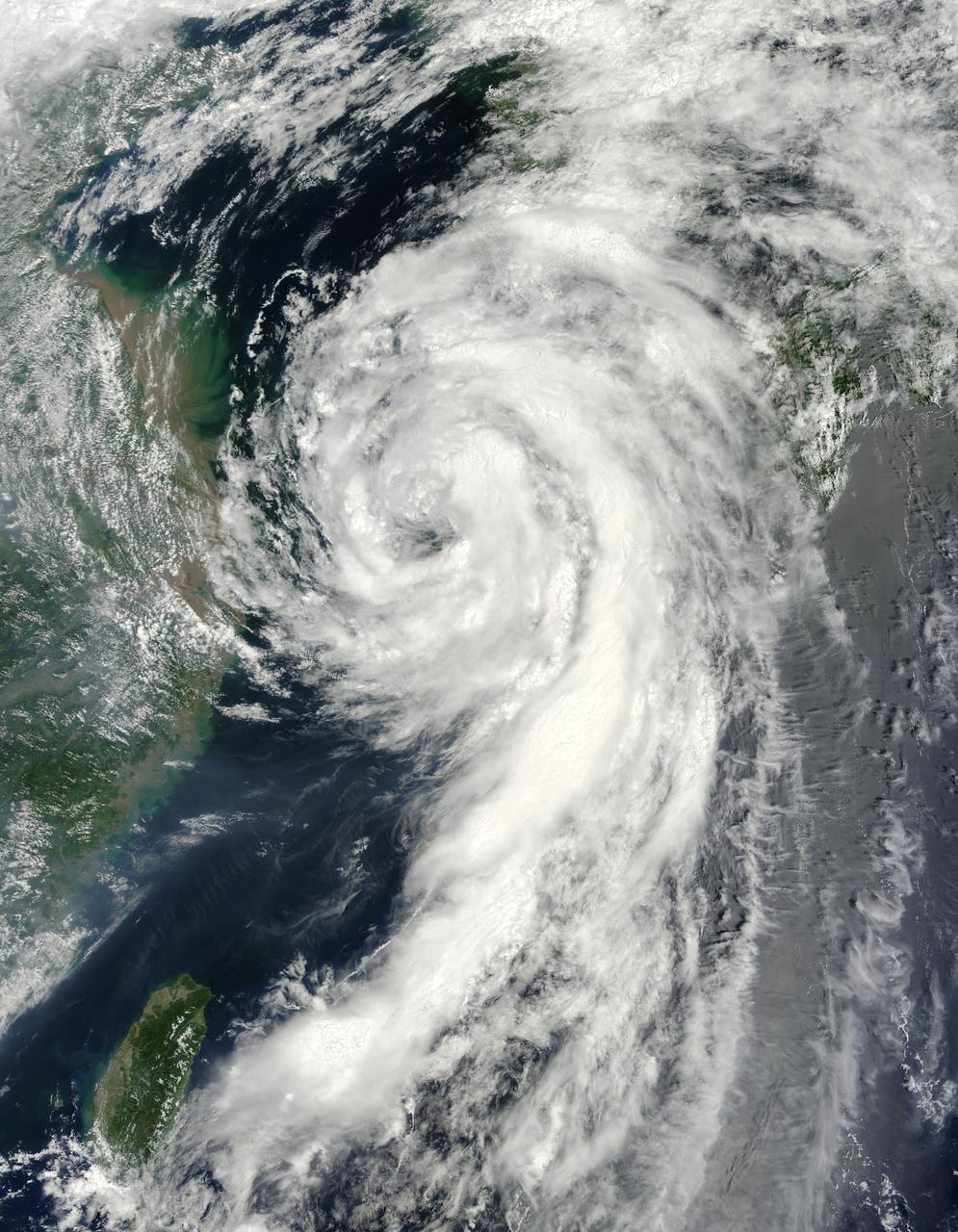

NASA image acquired August 10, 2010 Tropical Storm Dianmu blew over the East China Sea in early August 2010, traveling slowly toward the Korean Peninsula. On August 10, 2010, the U.S. Navy’s Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) reported that Dianmu had winds of 55 knots (100 kilometers per hour) with gusts up to 70 knots (130 kilometers per hour). JTWC stated that the storm was roughly 270 nautical miles (500 kilometers) south-southwest of Seoul. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite captured this natural-color image on August 10. The storm, which sports a distinct eye, stretches primarily north-south, sending spiral clouds hundreds of kilometers southward over the East China Sea. Storm clouds skirt China’s eastern coast. NASA image by Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team at NASA GSFC. Caption by Michon Scott. Instrument: Terra - MODIS <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a><b></b></b>
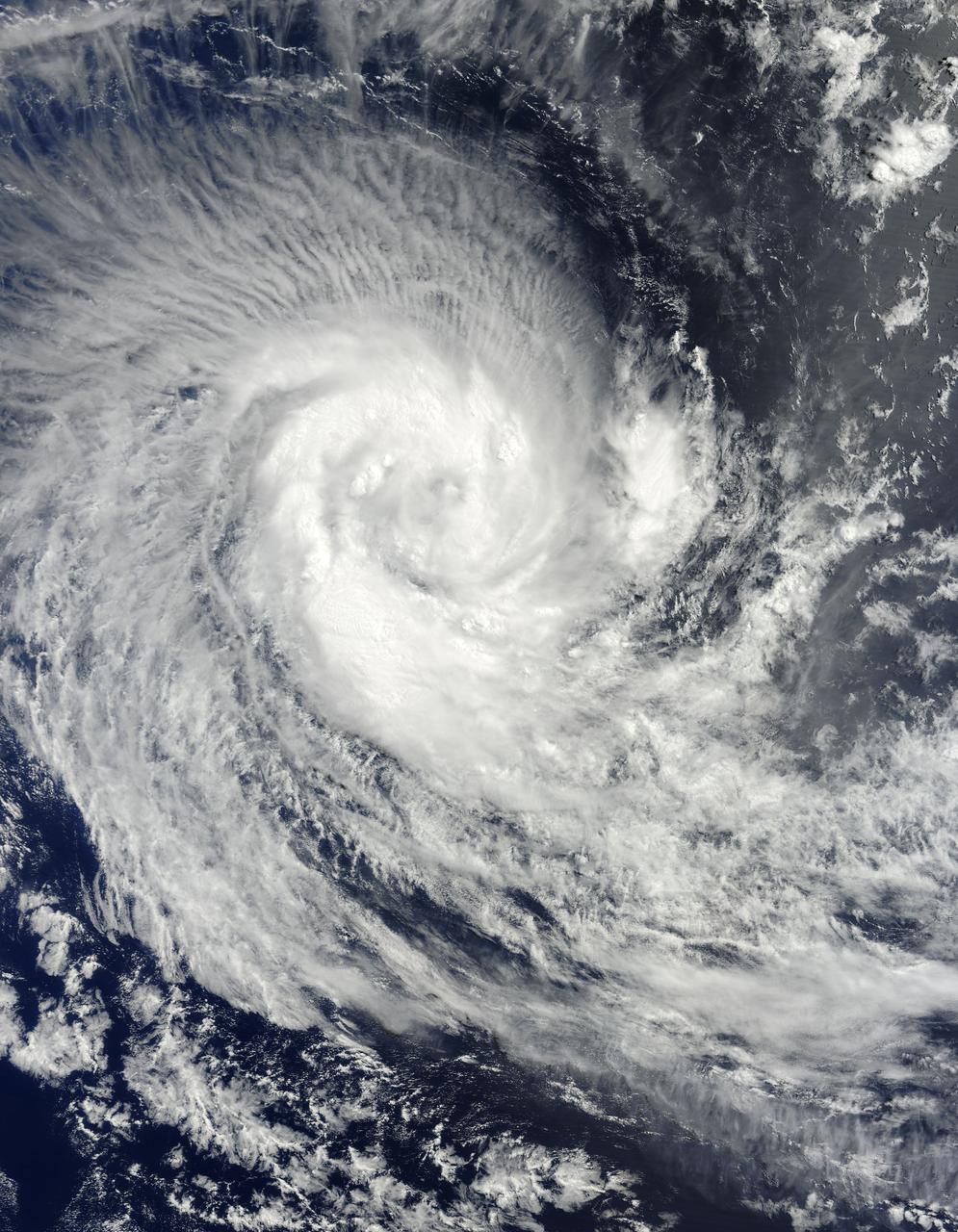
NASA image acquired March 24, 2010. Tropical Cyclone Imani swirled over the Southern Indian Ocean on March 24, 2010. The same day, the U.S. Navy’s Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) reported that the storm had maximum sustained winds of 55 knots (100 kilometers per hour) and gusts up to 70 knots (130 kilometers per hour). The storm was located roughly 745 nautical miles (1,380 kilometers) west-southwest of Cocos Island, having traveled toward the south-southwest for several hours. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite captured this natural-color image of the storm on March 24, 2010. Imani spans several hundred kilometers over the Southern Indian Ocean, producing thin, radial clouds on its northern margin. The storm occurs far from any major landmass. The JTWC forecast that Imani would continue traveling toward the south-southwest until reaching mid-latitude. The storm was expected to eventually turn southward and weaken. NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team at NASA GSFC. Caption by Michon Scott. Instrument: Terra - MODIS To learn more about this image go to: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=43225" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=43225</a> For more information about Goddard Space Flight Center go here: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html</a>
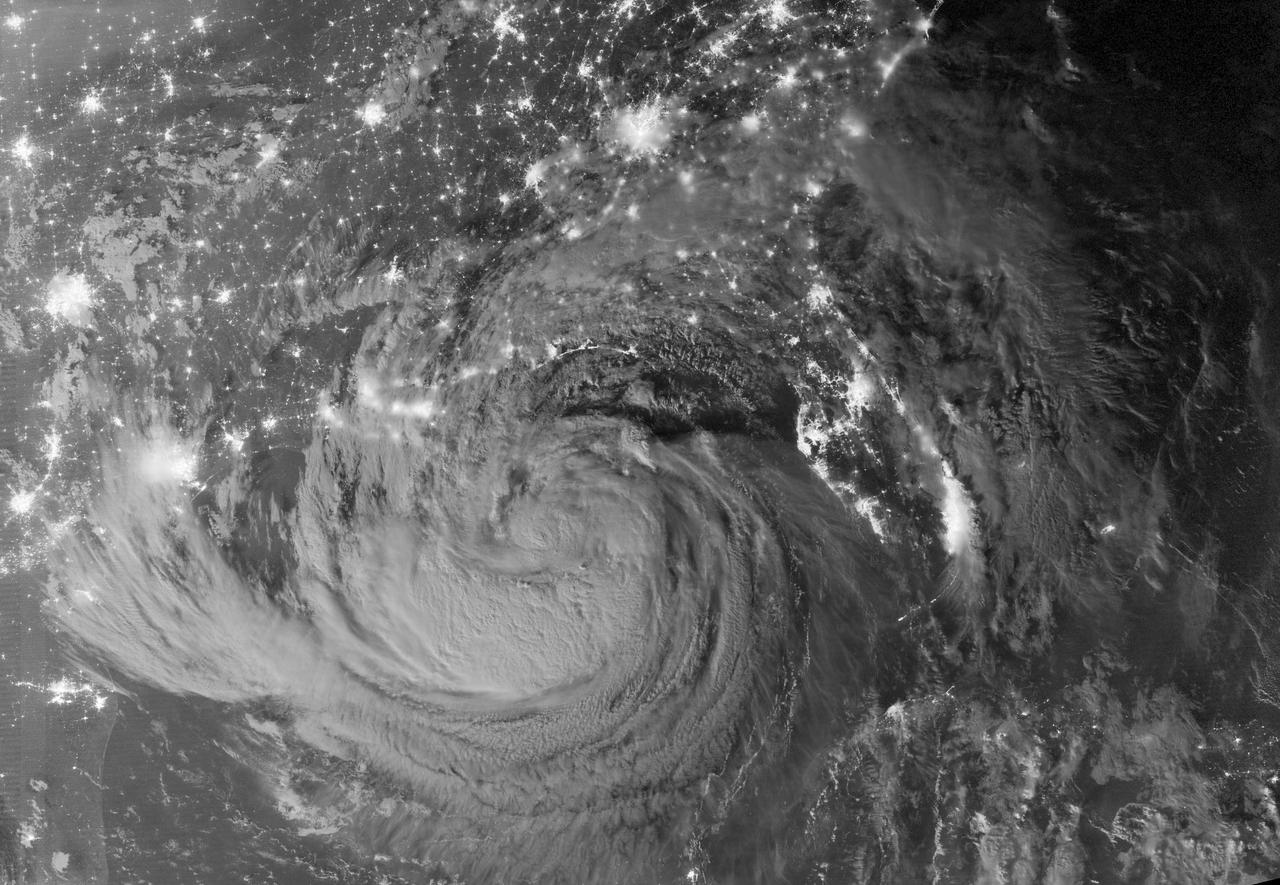

NASA image acquired August 28, 2012 Early on August 28, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi-NPP satellite captured this nighttime view of Tropical Storm Isaac and the cities near the Gulf Coast of the United States. The image was acquired just after local midnight by the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses light intensification to enable the detection of dim signals. In this case, the clouds of Isaac were lit by moonlight. Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day Night Band data. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
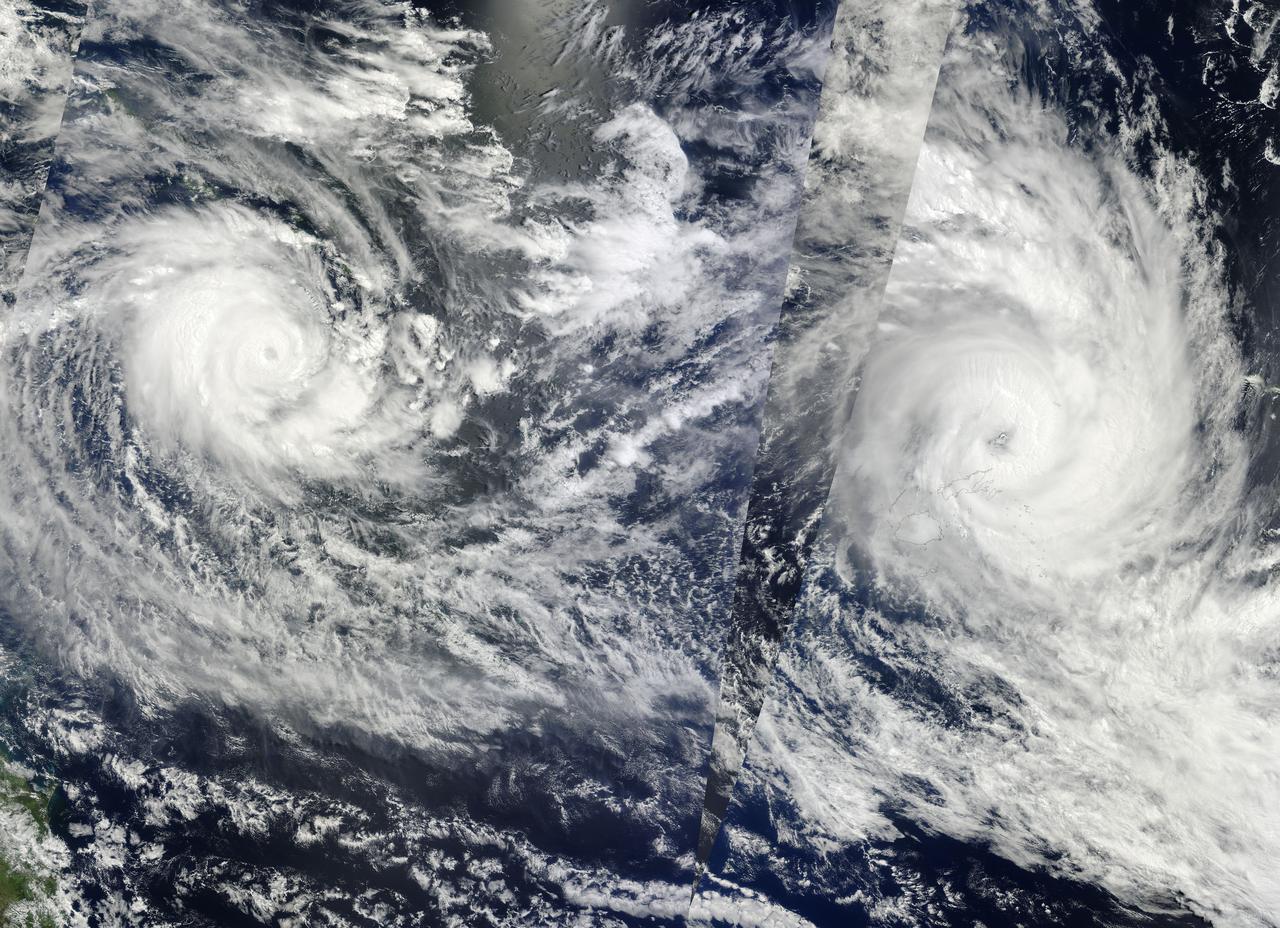
NASA Image acquired March 14 - 15, 2010 Two fierce tropical cyclones raged over the South Pacific Ocean in mid-March 2010, the U.S. Navy’s Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) reported. Over the Solomon Islands, Tropical Cyclone Ului had maximum sustained winds of 130 knots (240 kilometers per hour, 150 miles per hour) and gusts up to 160 knots (300 km/hr, 180 mph). Over Fiji, Tropical Cyclone Tomas had maximum sustained winds of 115 knots (215 km/hr, 132 mph) and gusts up to 140 knots (260 km/hr, 160 mph). The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra and Aqua satellites captured both storms in multiple passes over the South Pacific on March 15, 2010, local time. The majority of the image is from the morning of March 15 (late March 14, UTC time) as seen by MODIS on the Terra satellite, with the right portion of the image having been acquired earliest. The wedge-shaped area right of center is from Aqua MODIS, and it was taken in the early afternoon of March 15 (local time). Although it packs less powerful winds, according to the JTWC, Tomas stretches across a larger area. It was moving over the northern Fiji islands when Terra MODIS captured the right portion of the image. According to early reports, Tomas forced more than 5,000 people from their homes while the islands sustained damage to crops and buildings. The JTWC reported that Tomas had traveled slowly toward the south and was passing over an area of high sea surface temperatures. (Warm seas provide energy for cyclones.) This storm was expected to intensify before transitioning to an extratropical storm. Ului is more compact and more powerful. A few hours before this image was taken, the storm had been an extremely dangerous Category 5 cyclone with sustained winds of 140 knots (260 km/hr, 160 mph). Ului degraded slightly before dealing the southern Solomon Islands a glancing blow. Initial news reports say that homes were damaged on the islands, but no one was injured. Like Tomas, Ului had been moving westward over an area of high sea surface temperatures. This storm was expected to continue moving westward before turning south and eventually weakening. The high-resolution image provided above is at 500 meters per pixel. The MODIS Rapid Response System provides this image at additional resolutions. NASA image by Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team, Goddard Space Flight Center. Caption by Michon Scott and Holli Riebeek. Instrument: Terra - MODIS To learn more about this image go here: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=43154." rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=43154.</a>.
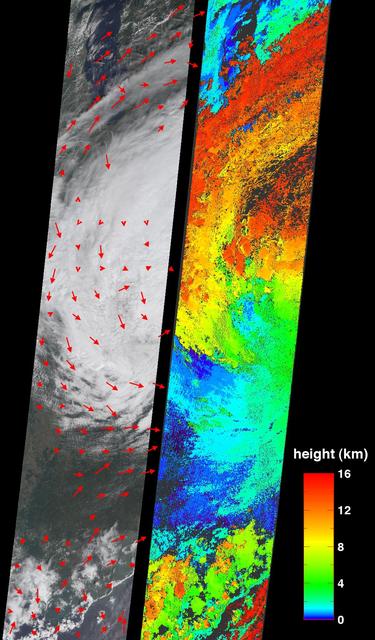
On Tuesday, August 30, 2005, NASA Terra spacecraft retrieved cloud-top heights and cloud-tracked wind velocities for Tropical Storm Katrina, as the center of the storm was situated over the Tennessee Valley.
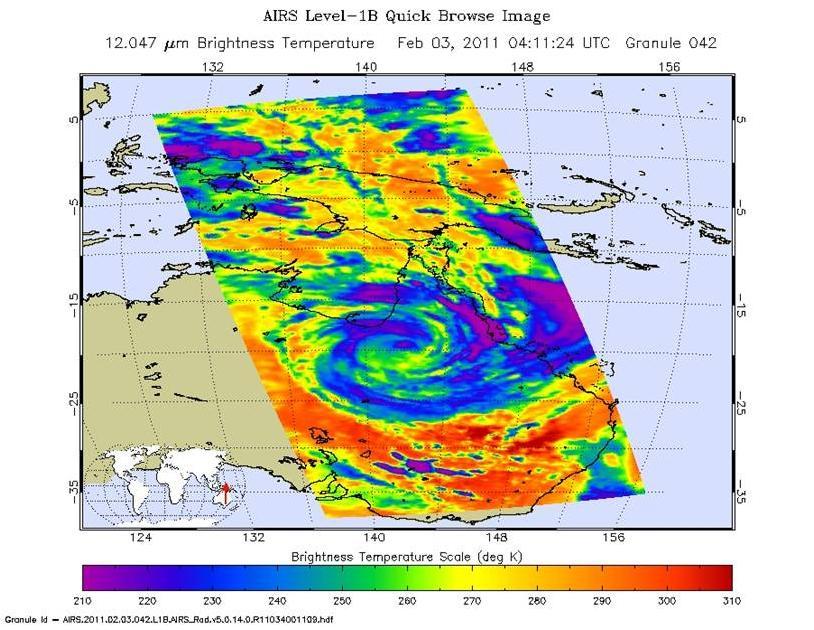
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder AIRS instrument onboard NASA Aqua spacecraft captured this infrared image of Tropical Cyclone Yasi on Feb. 2, 2011 as the storm passed over Australia Great Dividing Range.
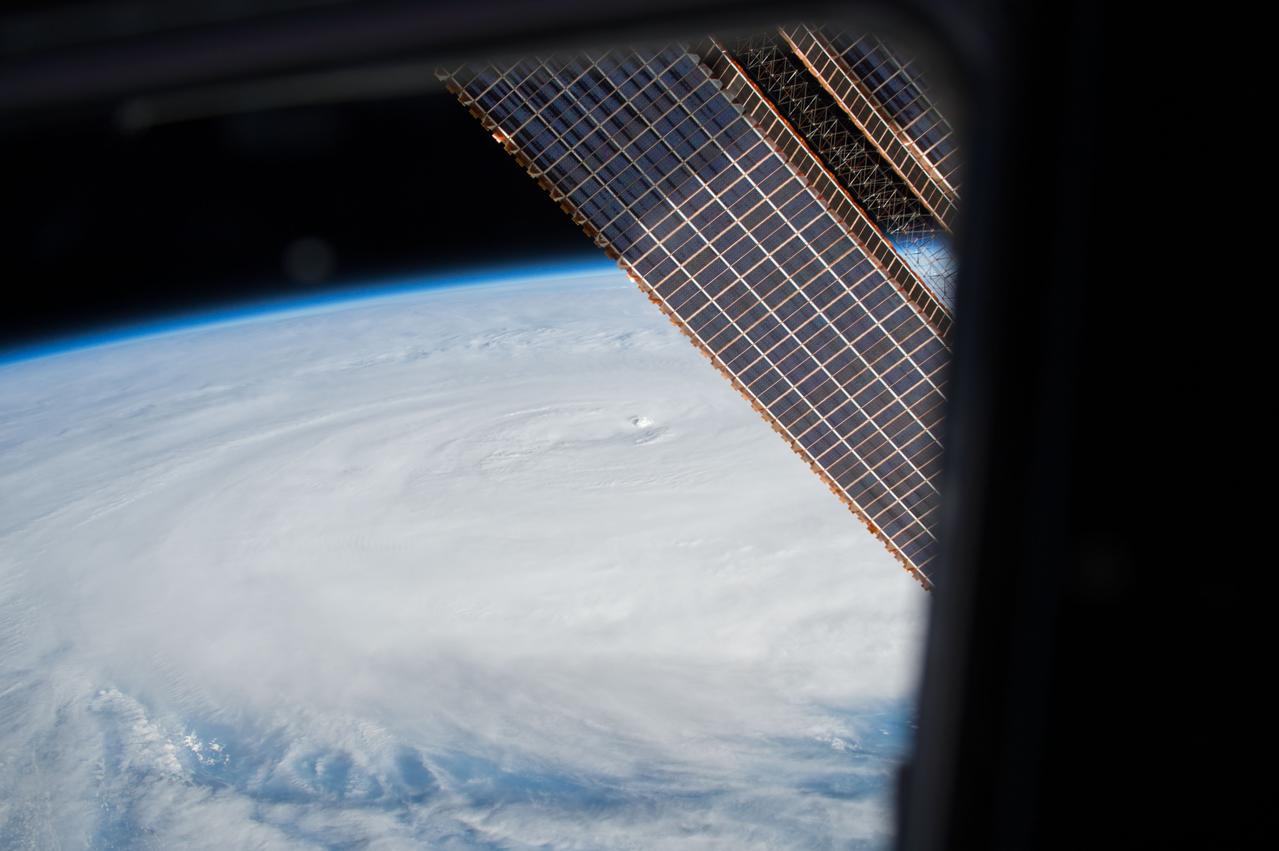

iss050e060444 (03/27/2017) --- Tropical Cyclone Debbie as photographed by crewmembers aboard the International Space Station on March 27, 2017. The large storm made landfall across the northeastern coast of Australia on March 28.
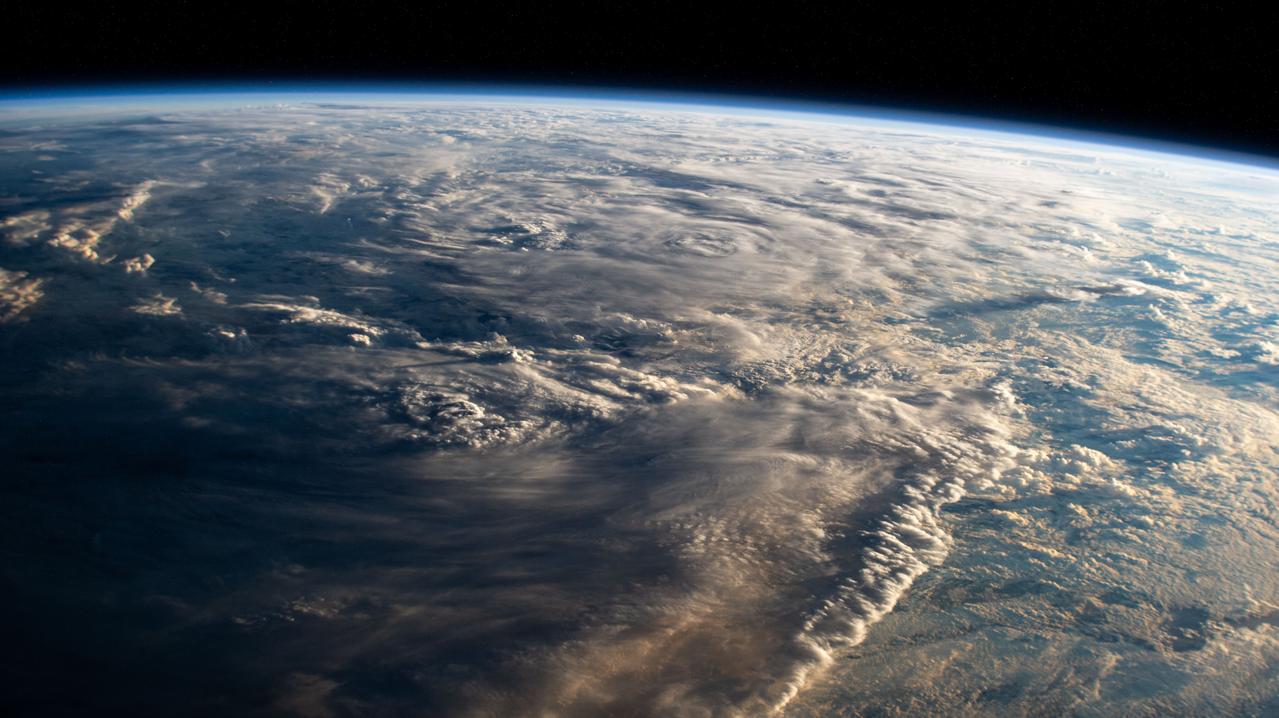

iss071e6649782 (Sept. 12, 2024) --- A tropical depression in the Atlantic Ocean in between Africa and South America is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 259 miles above.
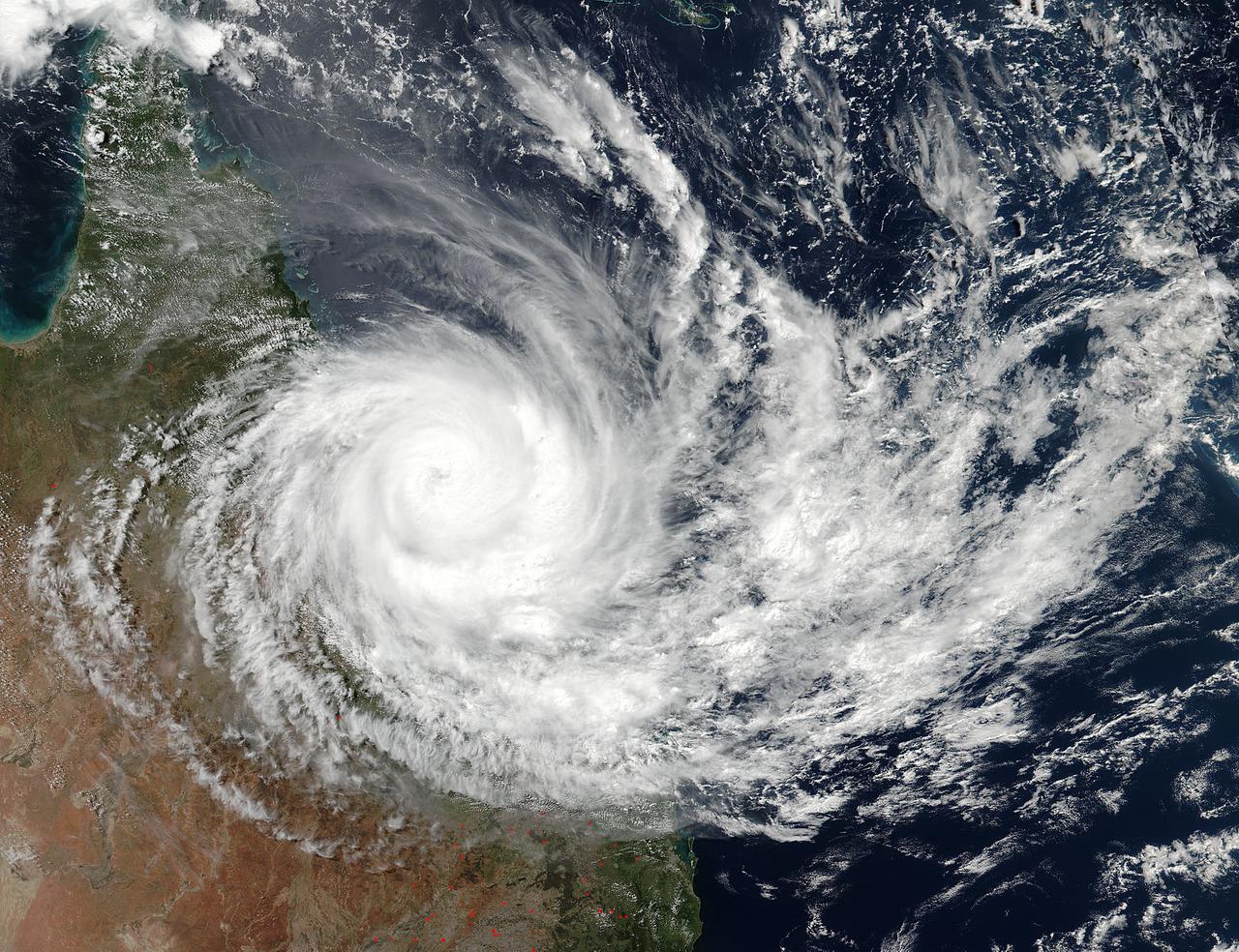
Tropical Cyclone Debbie made landfall in Queensland bringing heavy rainfall, hurricane-force winds, rough seas, and flooding. NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite provided a visible look at the storm from space while NASA's Aqua satellite analyzed cloud temperatures to determine the location of the strongest storms within. Read more: <a href="https://go.nasa.gov/2o29Sxh" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2o29Sxh</a> Credit: NASA/NOAA/Suomi NPP <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
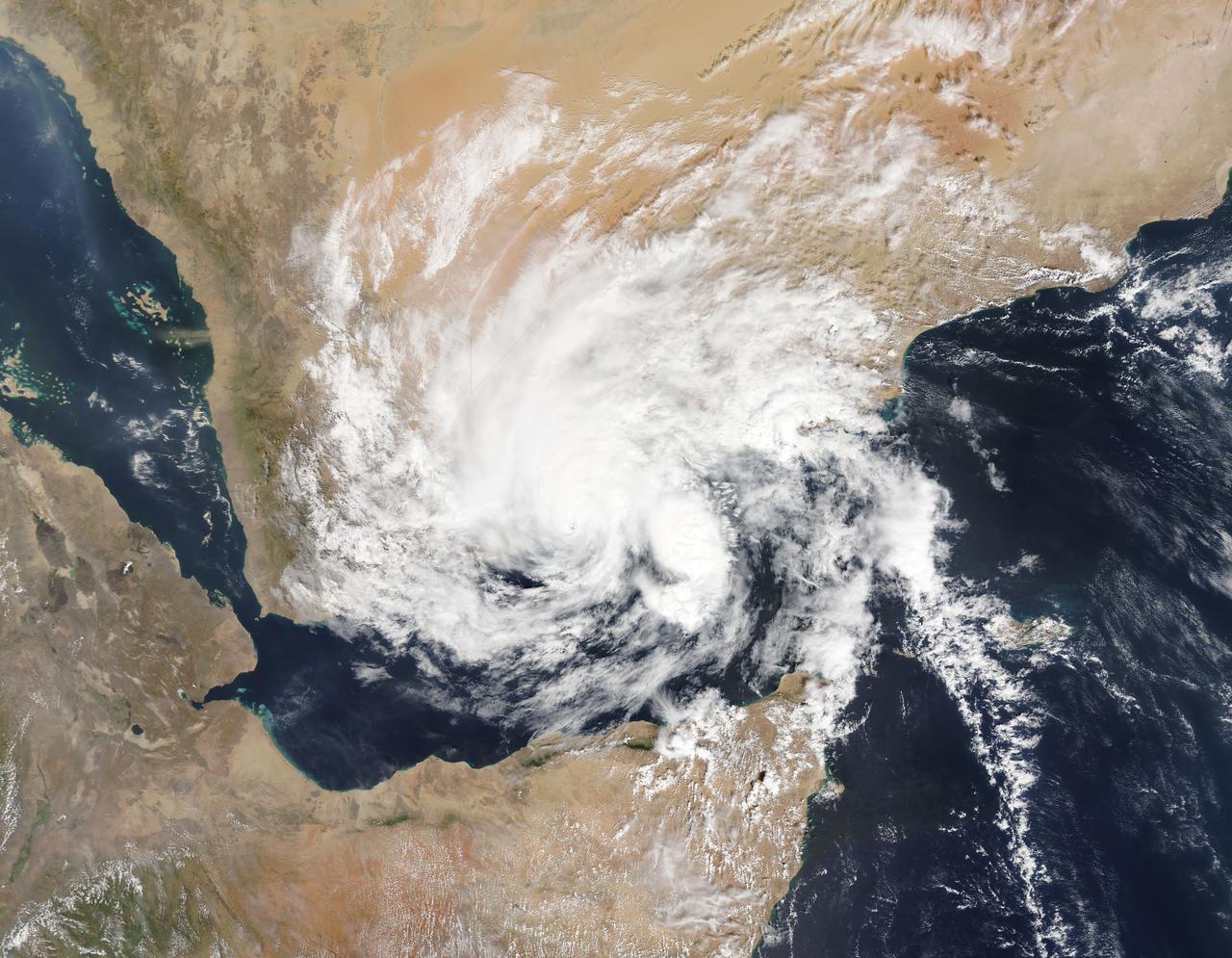
On Nov. 3, 2015 at 07:20 UTC (2:20 a.m. EDT) the MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured this image of Tropical Cyclone Chapala over Yemen. Credit: NASA Goddard MODIS Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
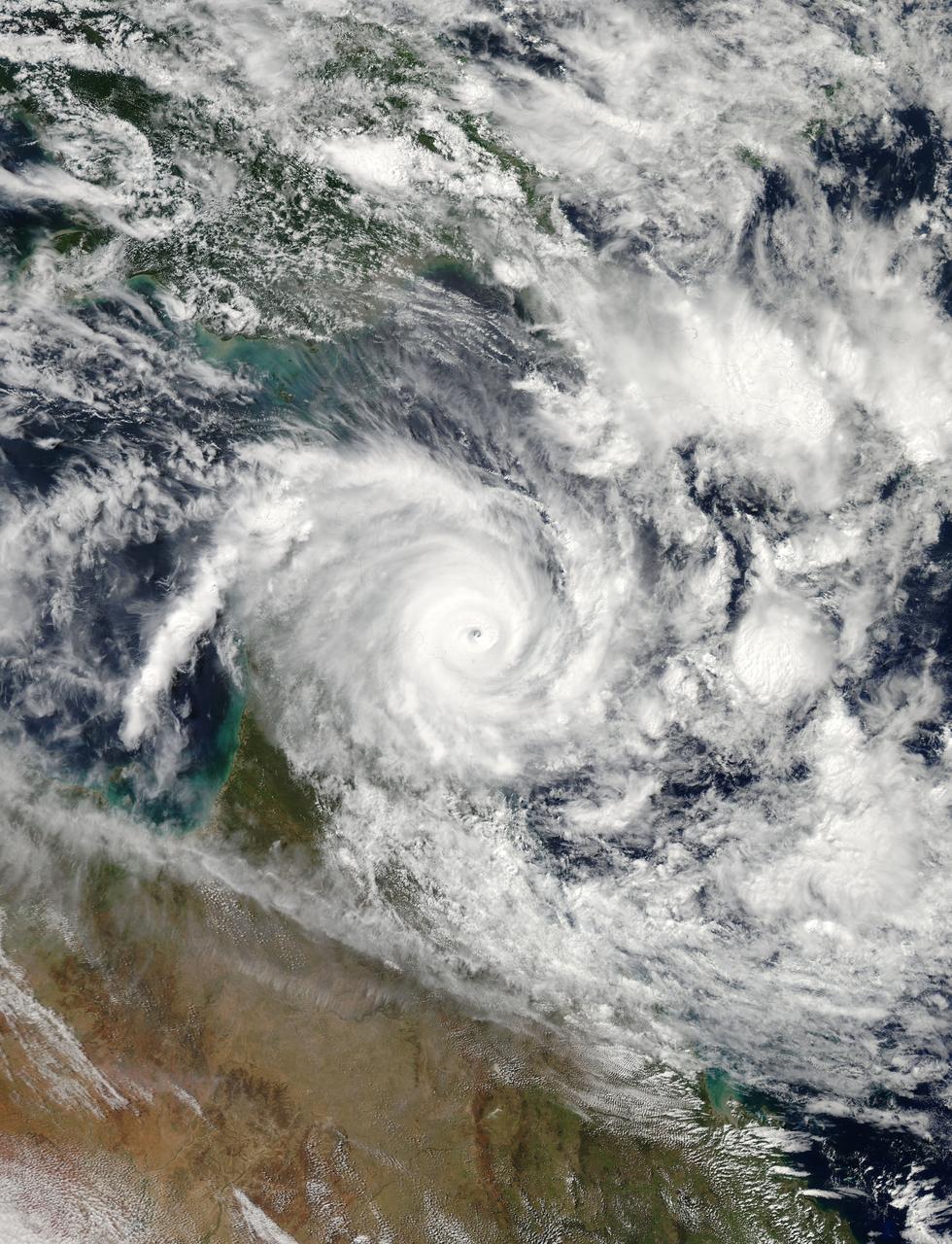
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Cyclone Ita as it began making landfall on the Eastern Cape York Peninsula of Queensland, Australia, today, April 11, 2014. Ita officially made landfall at Cape Flattery about 9:00 p.m. local AEST time as a Category 4 storm according to reports from the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC). The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer that flies aboard Aqua captured an image of the Category 4 storm on April 11 at 12:00 a.m. EDT (4 a.m. UTC). Satellite imagery indicates the eye is 9.2 miles wide (8 nautical miles, or 14.8 km). Warnings and watches remain in effect as the center of Ita is expected to remain at hurricane strength as it moves in a southerly direction, staying just west of Cairns over the next day. A tropical cyclone warning is in effect between Coen and Innisfail, including Cooktown, Port Douglas, Cairns, extending inland to Kalinga, Palmerville, Mareeba and Chillagoe. A tropical cyclone watch is in effect between Innisfail to Cardwell, extending inland. ABC reported that the strongest maximum sustained winds around the center of circulation were near 142.9 mph (124.2 knots, or 230 kph) and many trees have been downed and homes damaged. According to ABC, preliminary reports suggest that power may be out for a month in some areas. On April 11 at 5 a.m. EDT (9 a.m. UTC), Tropical Cyclone Ita had maximum sustained winds near 143.8 mph (125 knots, or 231.5 kph). It was centered near 14.8 degrees south latitude and 145.3 degrees east longitude, about 168 miles (146 nautical miles, or 288 km) north of Cairns, Australia, and has tracked south-southwestward at 10.3 mph (9 knots, or 16.6 kph). Ita is moving around a subtropical ridge (elongated area) of high pressure and the Joint Typhoon Warning Center expects Ita to start curving to the southeast around that ridge in the next day before heading back out into the Coral Sea. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team Rob Gutro, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
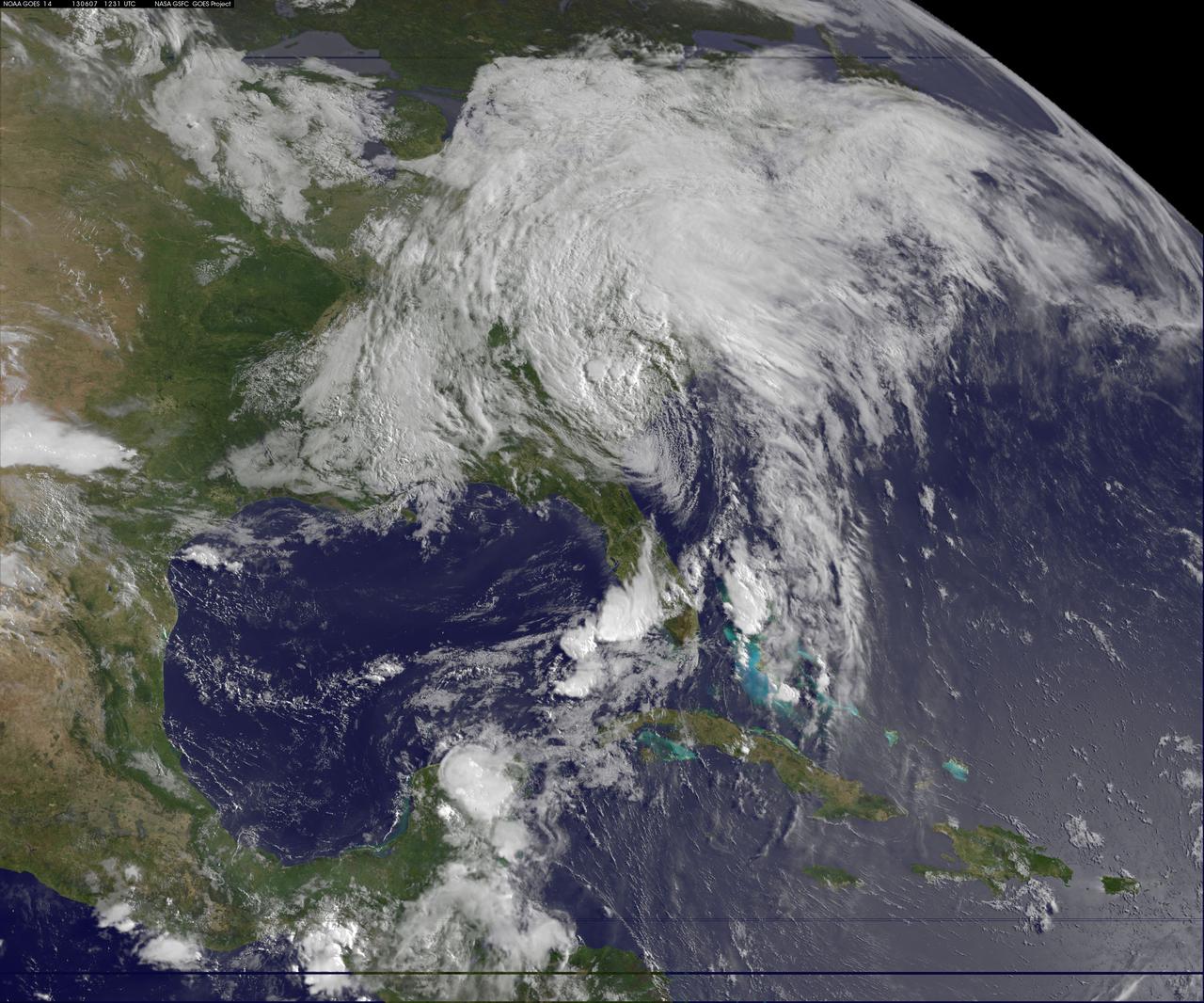
This image of tropical storm Andrea was assembled from data collected by NOAA's GOES-14 satellite at 8:31 a.m. EDT on June 7, when the storm's center was about 35 miles north-northwest of Charleston, S.C. Credit: NASA/NOAA GOES Project <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
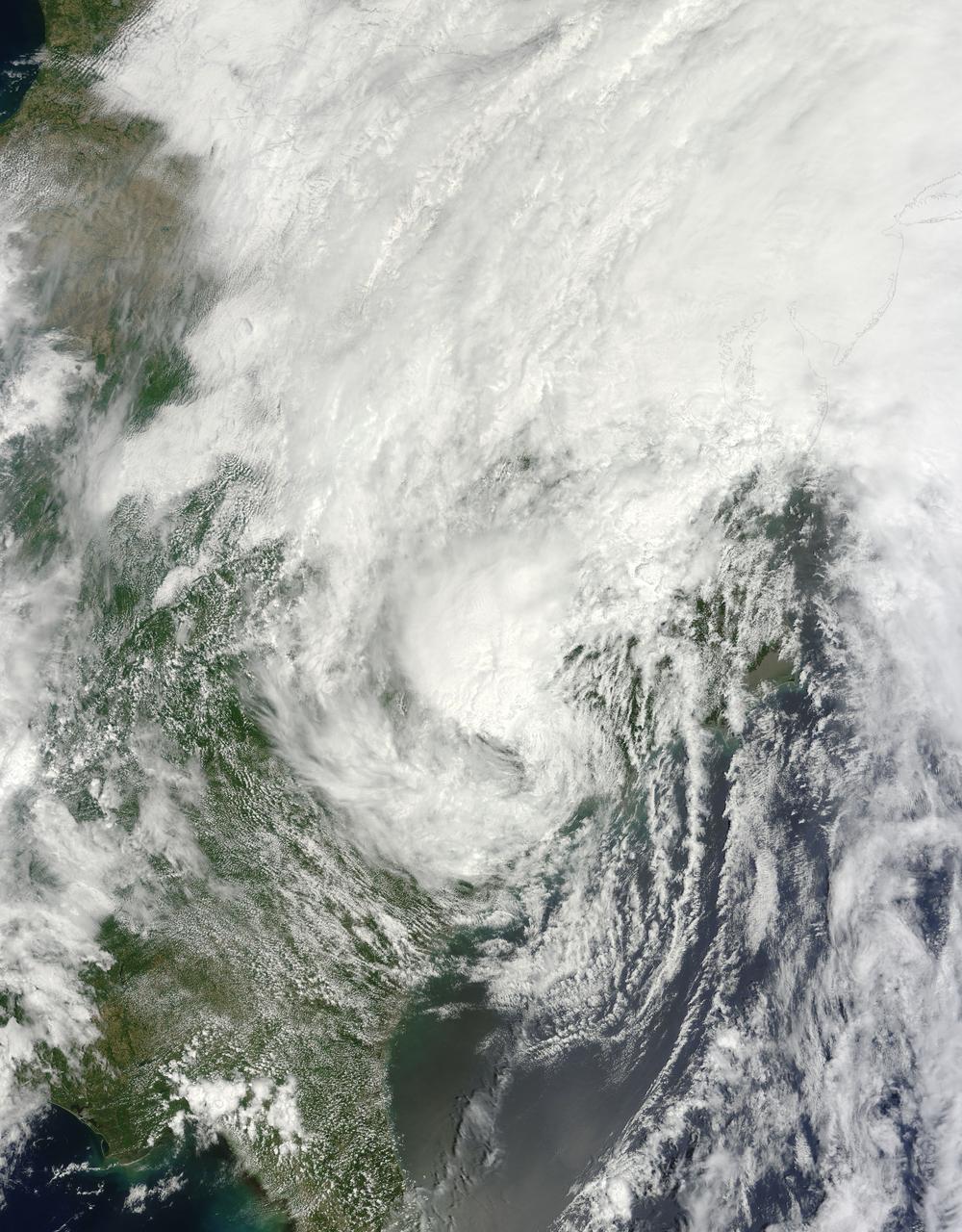
This is a satellite image from the MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite of Tropical Storm Andrea that was captured today, June 7 at 12:10 p.m. EDT- as Andrea makes its way up the U.S. East coast. At this time, Andrea was centered over North Carolina. Credit: NASA Goddard MODIS Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Radar and satellite imagery indicate that the convective organization of the cyclone has improved, and the cyclone is being upgraded based on a sustained wind report of 33 kt from Settlement Point, Grand Bahama Island earlier this morning. Low shear conditions and warm sea-surface temperatures should allow for at least steady strengthening, and the cyclone is expected to become a hurricane by 72 hours. This image was taken by GOES East at 1445Z on July 1, 2014. <b><a href="http://goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">Credit: NOAA/NASA GOES Project</a></b> Caption: NOAA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
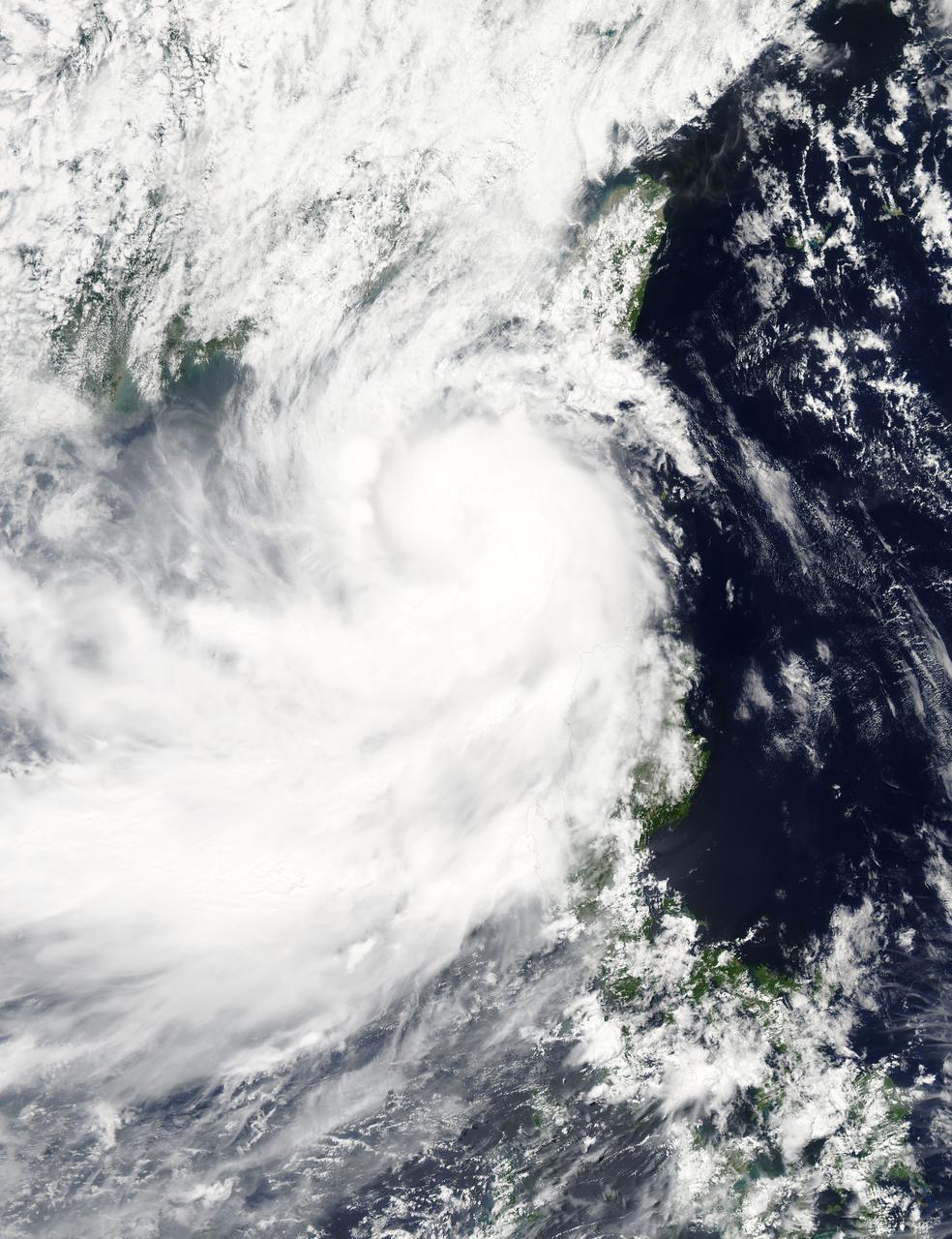
NASA's Aqua satellite captured a picture of Tropical Storm Linfa in the South China Sea on July 7 when it was between southern Taiwan and the northern Philippines. Aqua passed over Linfa on July 7 at 05:25 UTC (1:25 a.m. EDT) and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument captured a visible image of the storm. Bands of thunderstorms wrapping into the center of circulation from the south, draped over western Luzon. The MODIS image showed the tight concentration of thunderstorms around Linfa's center were located over the South China Sea. Fragmented bands of thunderstorms north of the center were brushing over Southern Taiwan while clouds from another band of fragmented thunderstorms stretched northwest through the Taiwan Strait. On July 7 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), Tropical Storm Linfa's maximum sustained winds had increased to 50 knots (57.5 mph/92.6 kph), up from 45 knots (51.7 mph/83.3 kph) six hours before. Linfa strengthened in the warm waters of the South China Sea now that its center has moved away from the northern Philippines and was no longer over land. Linfa was centered near 21.0 North latitude and 118.8 East longitude, about 277 nautical miles (319 miles/513.3 km) east-southeast of Hong Kong, China. Linfa has tracked northward at 3 knots (3.5 mph/5.5 kph). China's National Meteorological Centre has (CNMC) issued a yellow category warning of typhoon at 6:00 a.m. July 7, Beijing Time. CNMC noted that Linfa is the tenth typhoon this year and at that time it was centered about 430 km (267.2 miles) southeast of border between Fujian and Guangdong For updated warnings and watches from the China Meteorological Service, visit: <a href="http://www.cma.gov.cn/en/WeatherWarnings/" rel="nofollow">www.cma.gov.cn/en/WeatherWarnings/</a>. Linfa is moving north between Luzon and Taiwan. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center expects Linfa to strengthen to 60 knots (69 mph/111 kph) by mid-day on July 9, before weakening and then making landfall in mainland China. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
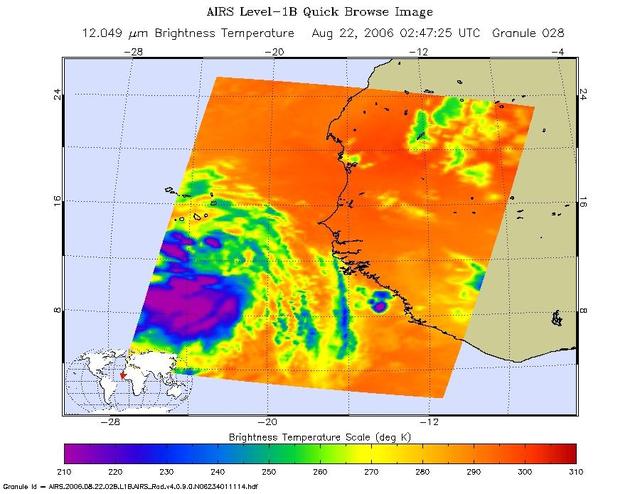
These images show Tropical Depression Debbie in the Atlantic, from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) on NASA's Aqua satellite on August 22, 2006. This AIRS image shows the temperature of the cloud tops or the surface of the Earth in cloud-free regions. The lowest temperatures (in purple) are associated with high, cold cloud tops that make up the top of the storm. The infrared signal does not penetrate through clouds. Where there are no clouds the AIRS instrument reads the infrared signal from the surface of the Earth, revealing warmer temperatures (red). At the time the data were taken from which these images were made the eye had not yet opened but the storm is now well organized. The location of the future eye appears as a circle at 275 K brightness temperature in the microwave image just to the SE of the Azores. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00508

A south tropical disturbance has just passed Jupiter's iconic Great Red Spot and is captured stealing threads of orange haze from the Great Red Spot in this series of color-enhanced images from NASA's Juno spacecraft. From left to right, this sequence of images was taken between 2:57 a.m. and 3:36 a.m. PDT (5:57 a.m. and 6:36 a.m. EDT) on April 1, 2018, as the spacecraft performed its 12th close flyby of Jupiter. Citizen scientists Gerald Eichstädt and Seán Doran created this image using data from the spacecraft's JunoCam imager. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22937 ** Image Credit: Enhanced Image by Gerald Eichstädt and Seán Doran (CC BY-NC-SA) based on images provided courtesy of NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS
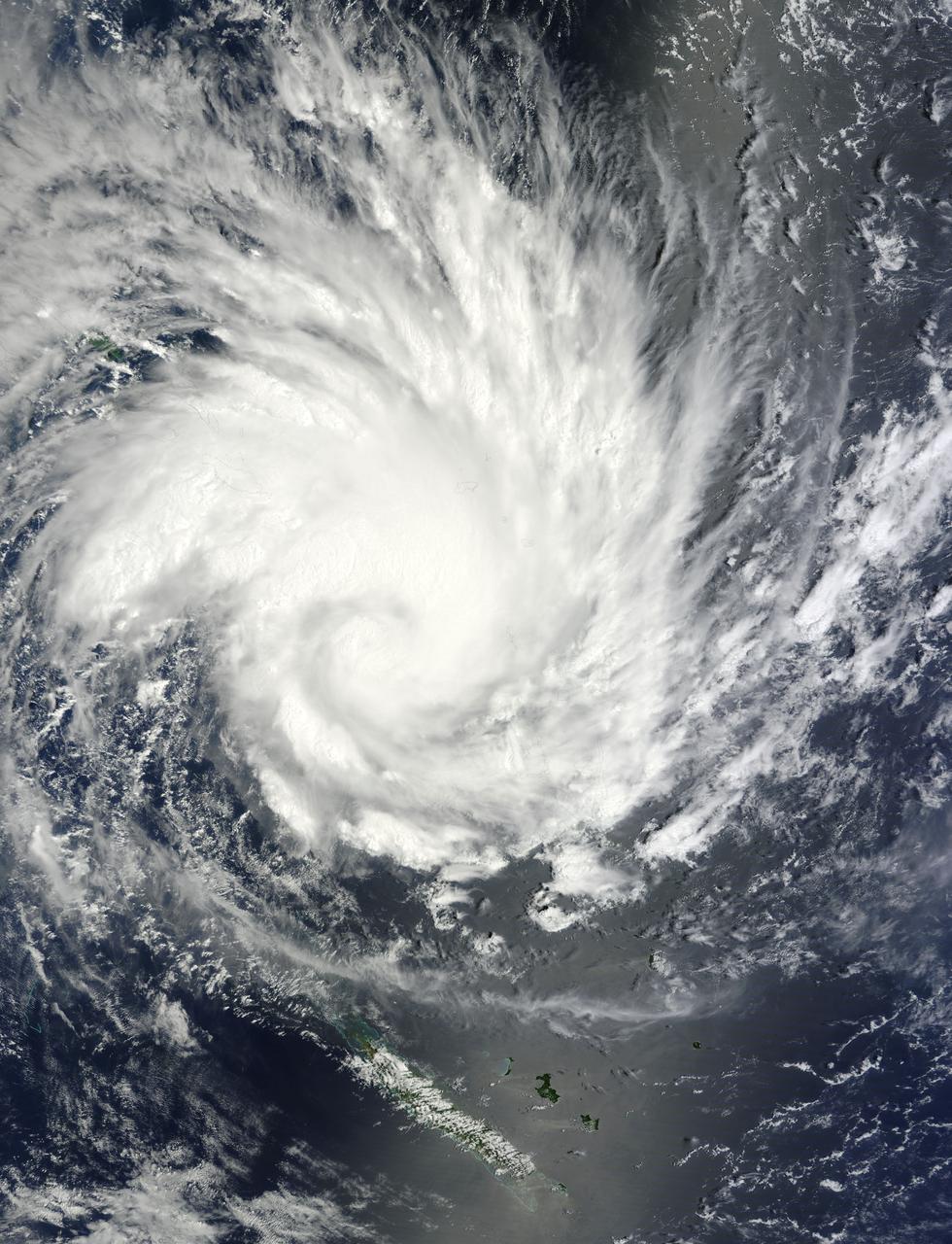

NASA image acquired January 30, 2011 at 23:20 UTC. Satellite: Terra <b> Click here to see the most recent image captured Feb. 1: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5407540724/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5407540724/</a></b> Tropical Storm Anthony made landfall in Queensland, Australia this past weekend, and now the residents are watching a larger, more powerful cyclone headed their way. NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of the large Tropical Cyclone Yasi late yesterday as it makes its way west through the Coral Sea toward Queensland. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured an image of Cyclone Yasi on Jan. 30 at 23:20 UTC (6:20 p.m. EST/09:20 a.m., Monday, January 31 in Australia/Brisbane local time). Although the image did not reveal a visible eye, the storm appears to be well-formed and also appears to be strengthening. Warnings and watches are already in effect throughout the Coral Sea. The Solomon Islands currently have a Tropical Cyclone warning for the provinces of Temotu, Rennell & Bellona, Makira and Guadalcanal. The Australian Bureau of Meteorology has already posted a Tropical Cyclone Watch from Cooktown to Yeppoon and inland to between Georgetown and Moranbah in Queensland, Australia. The Australian Bureau of Meteorology expects damaging winds to develop in coastal and island communities between Cooktown and Yeppoon Wednesday morning, and inland areas on Wednesday afternoon. Updates from the Australian Bureau of Meteorology can be monitored at the Bureau's website at <a href="http://www.bom.gov.au" rel="nofollow">www.bom.gov.au</a>. On January 31 at 1500 UTC (10 a.m. EST/ 1:00 a.m. Tuesday February 1, 2011 in Australia/Brisbane local time), Tropical Cyclone Yasi had maximum sustained winds near 90 knots (103 mph/166 kmh). Yasi is a Category Two Cyclone on the Saffir-Simpson Scale. It was centered about 875 miles E of Cairns, Australia, near 13.4 South latitude and 160.4 East longitude. It was moving west near 19 knots (22 mph/35 kmh). Cyclone-force winds extend out to 30 miles (48 km) from the center. Animated infrared satellite imagery, such as that from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite, showed deep convective (thunderstorm) bands wrapping tighter into the low level circulation center. Wrapping bands of thunderstorms indicate strengthening. Yasi is forecast to move west then southwestward into an area of low vertical wind shear (strong wind shear can weaken a storm). Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) expect Yasi to continue strengthening over the next 36 hours. JTWC forecasts a landfall just south of Cairns as a large 100-plus knot (115 mph/185 kmh)n system by Wednesday. Residents along the Queensland coast should now be making preparations now for the storm's arrival. Rob Gutro NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team Click here to see more images from <b><a href="http://rapidfire.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/?latest" rel="nofollow">MODIS</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
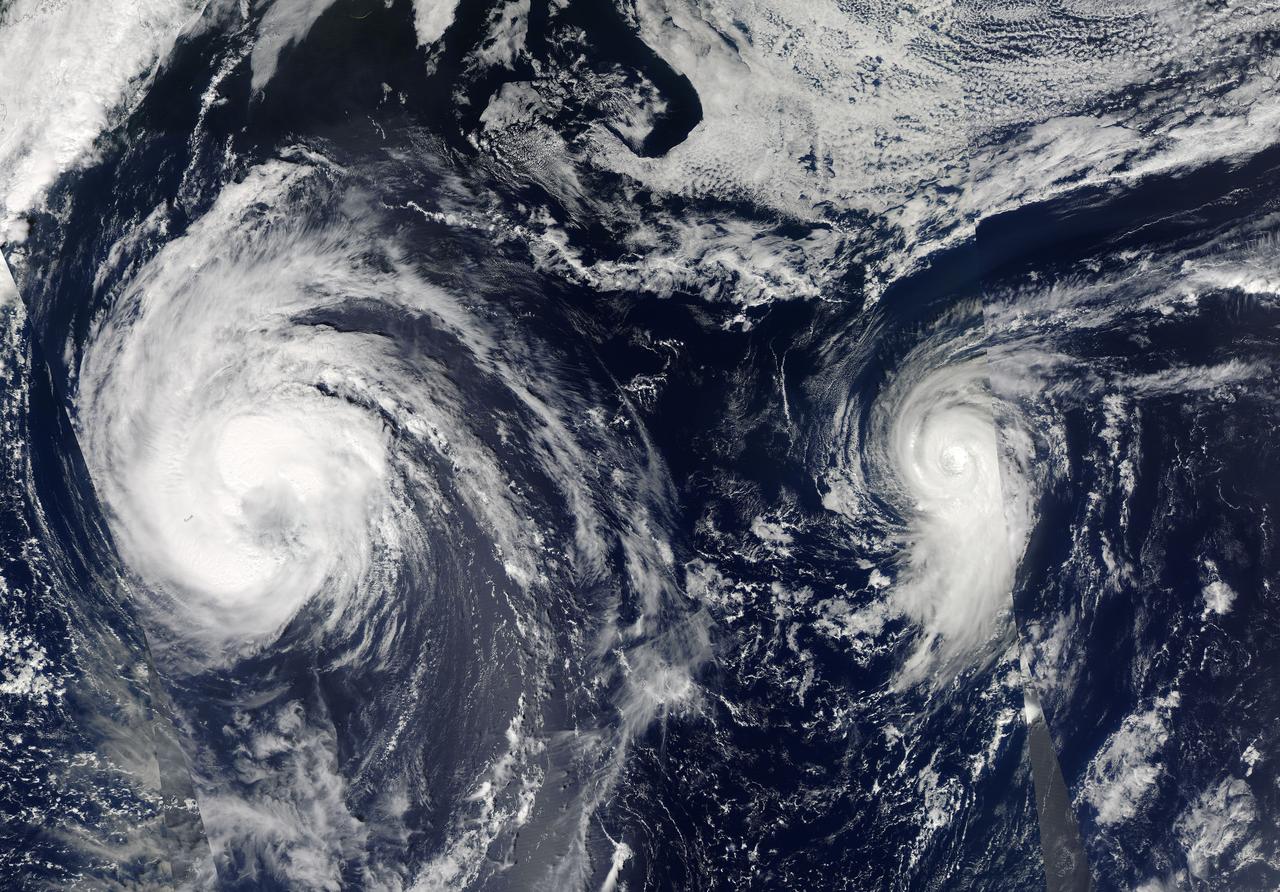

This visible image of Tropical Storm Leslie and Hurricane Michael was taken by the MODIS instrument aboard both NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites on Sept. 9 at 12:50 p.m. EDT. Credit: NASA Goddard/MODIS Rapid Response Team -- Satellite images from two NASA satellites were combined to create a full picture of Tropical Storm Leslie and Hurricane Michael spinning in the Atlantic Ocean. Imagery from NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites showed Leslie now past Bermuda and Michael in the north central Atlantic, and Leslie is much larger than the smaller, more powerful Michael. Images of each storm were taken by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS instrument that flies onboard both the Aqua and Terra satellites. Both satellites captured images of both storms on Sept. 7 and Sept. 10. The image from Sept. 7 showed a much more compact Michael with a visible eye. By Sept. 10, the eye was no longer visible in Michael and the storm appeared more elongated from south to north. To continue reading go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/NkUPqn" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/NkUPqn</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
This infrared image shows Tropical Depression 6 Florence in the Atlantic, from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder AIRS on NASA Aqua satellite in September, 2006. Because infrared radiation does not penetrate through clouds, AIRS infrared images show either the temperature of the cloud tops or the surface of the Earth in cloud-free regions. The lowest temperatures (in purple) are associated with high, cold cloud tops that make up the top of the storm. In cloud-free areas the AIRS instrument will receive the infrared radiation from the surface of the Earth, resulting in the warmest temperatures (orange/red). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00512
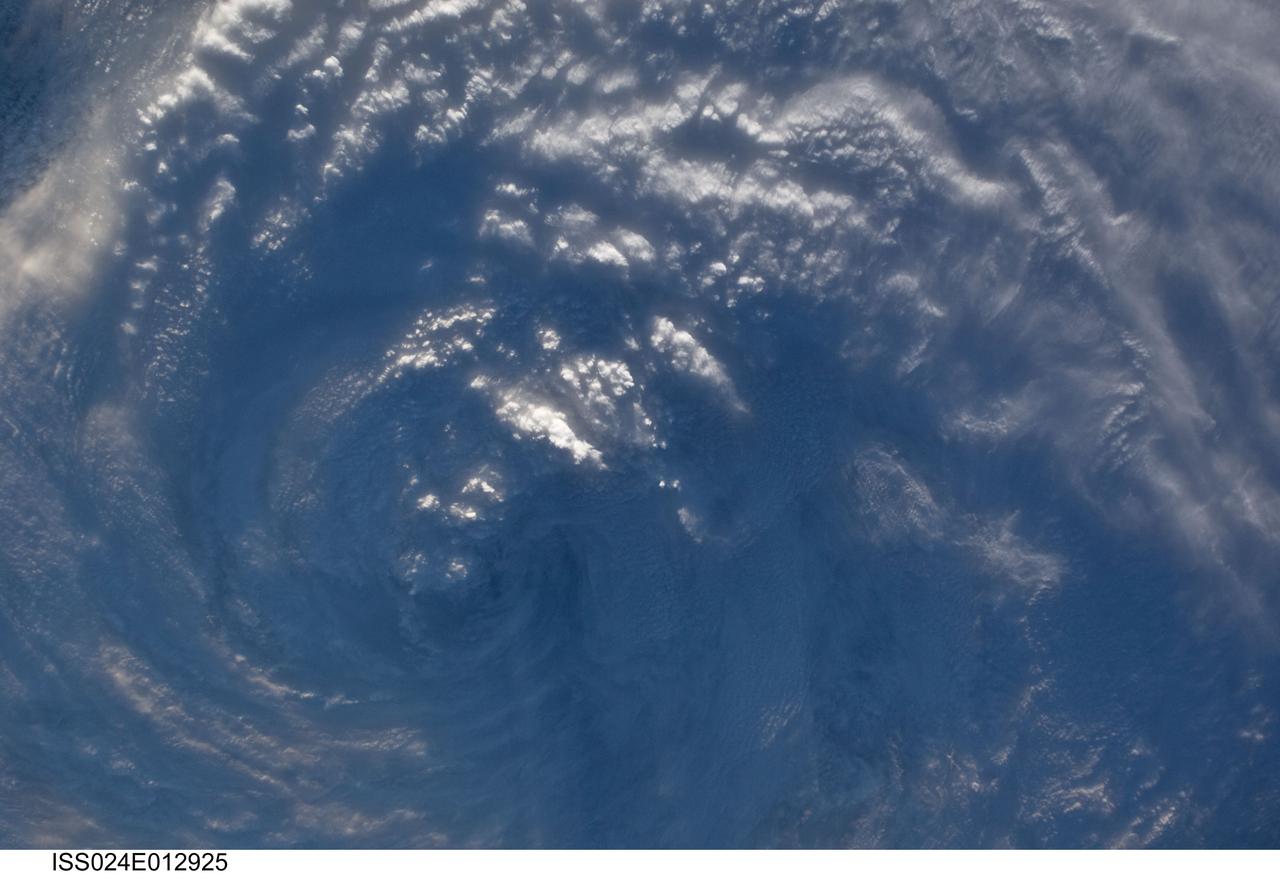
ISS024-E-012925 (30 Aug. 2010) --- Tropical Storm Danielle is featured in this Aug. 30 image photographed by an Expedition 24 crew member on the International Space Station.
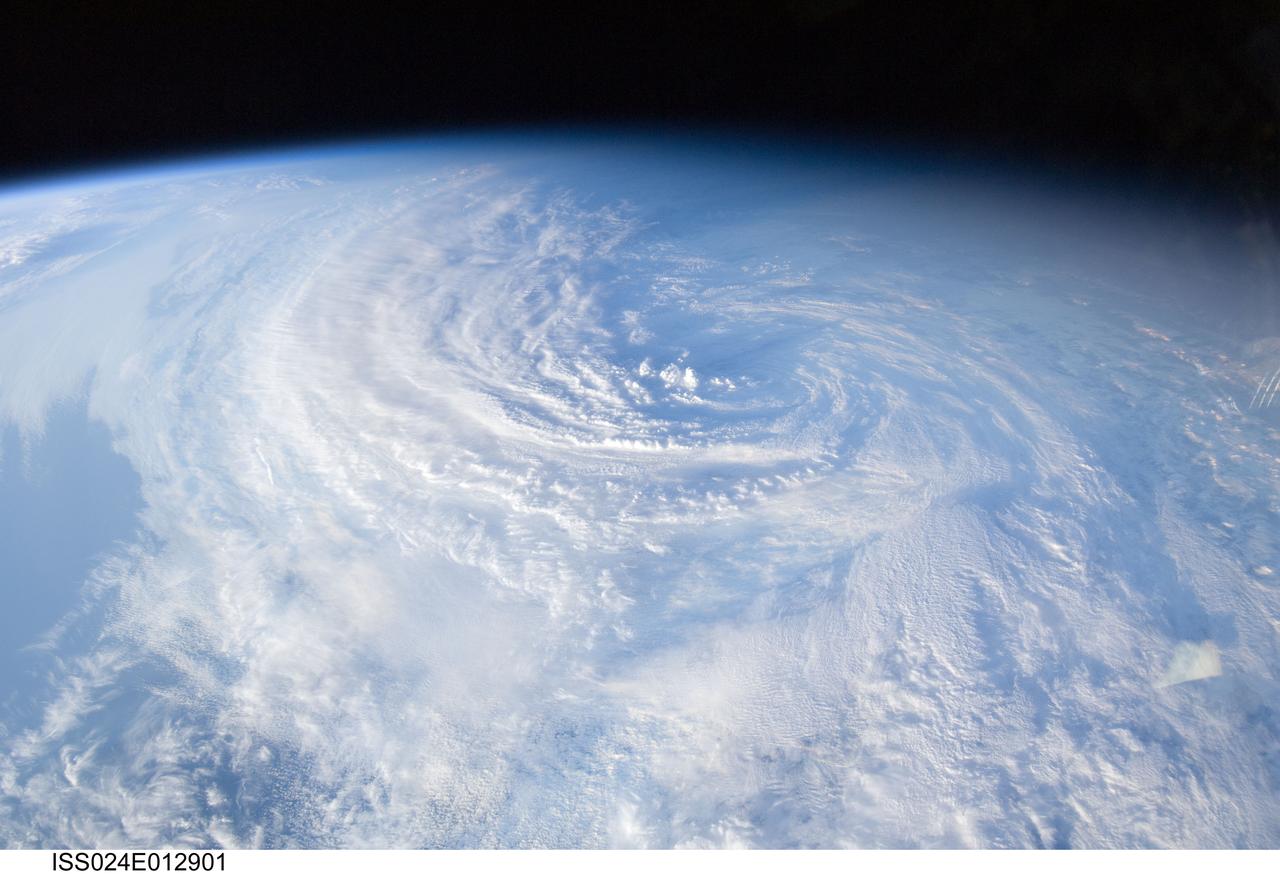

ISS024-E-012901 (30 Aug. 2010) --- Tropical Storm Danielle is featured in this Aug. 30 image photographed by an Expedition 24 crew member on the International Space Station.
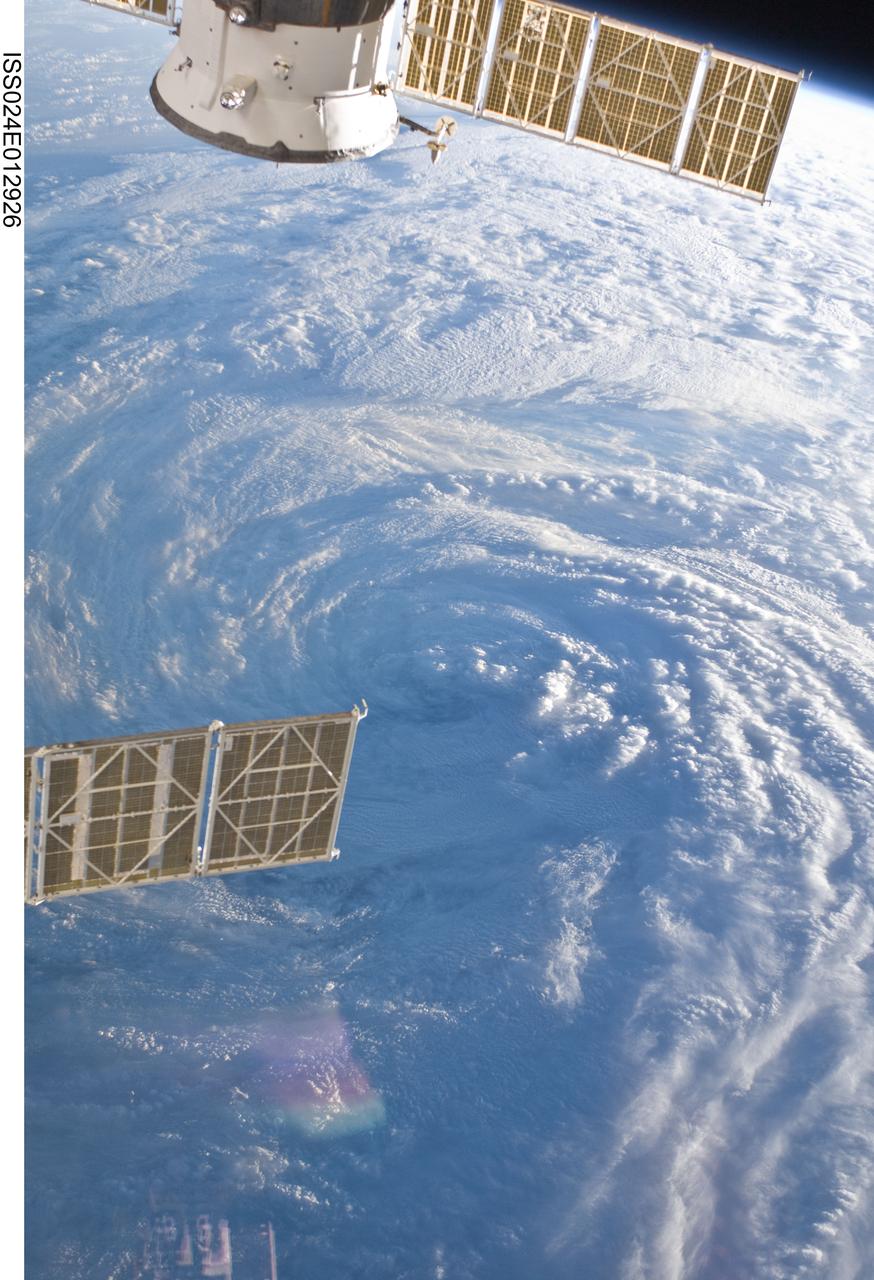

ISS024-E-012926 (30 Aug. 2010) --- Tropical Storm Danielle is featured in this Aug. 30 image photographed by an Expedition 24 crew member on the International Space Station.
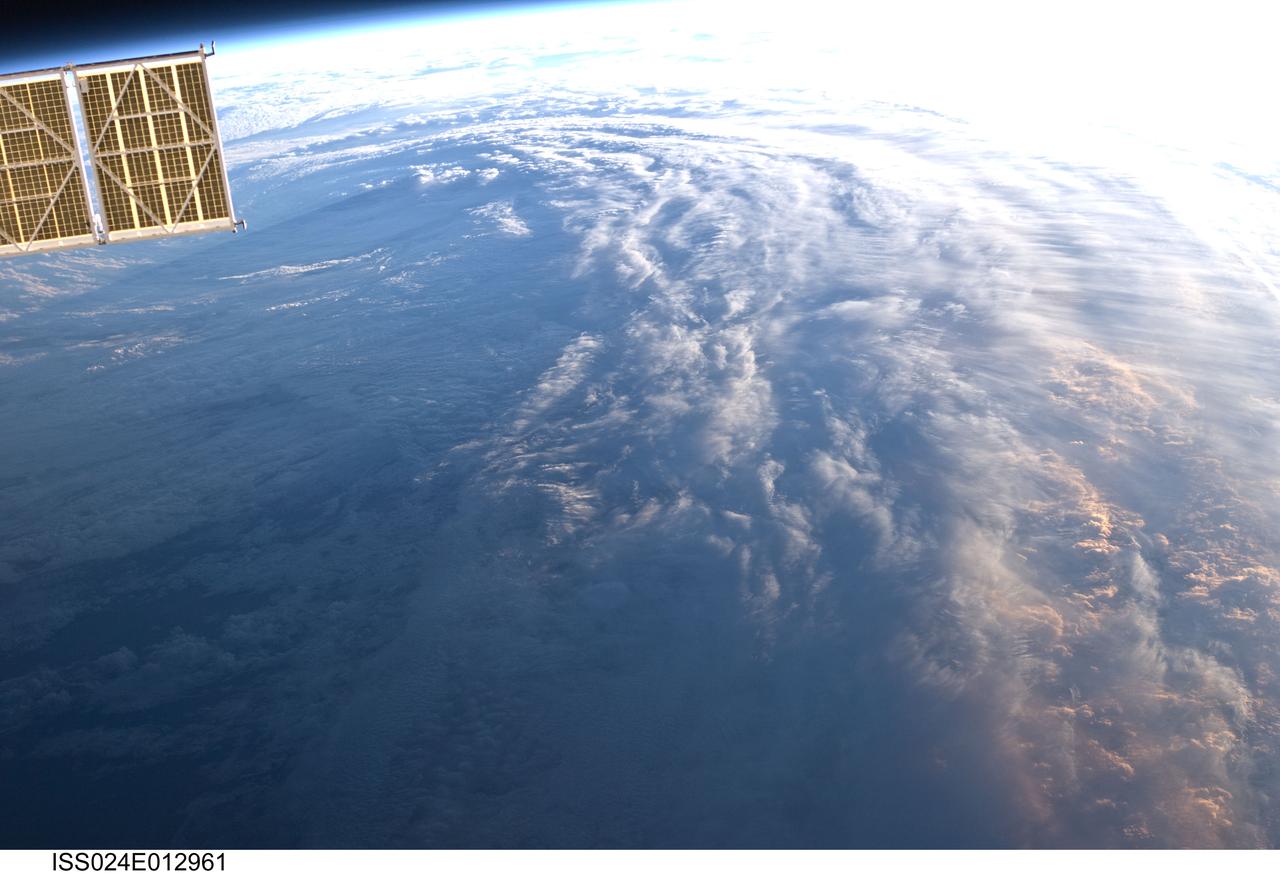

ISS024-E-012961 (30 Aug. 2010) --- Tropical Storm Danielle is featured in this Aug. 30 image photographed by an Expedition 24 crew member on the International Space Station.

ISS024-E-012930 (30 Aug. 2010) --- Tropical Storm Danielle is featured in this Aug. 30 image photographed by an Expedition 24 crew member on the International Space Station.
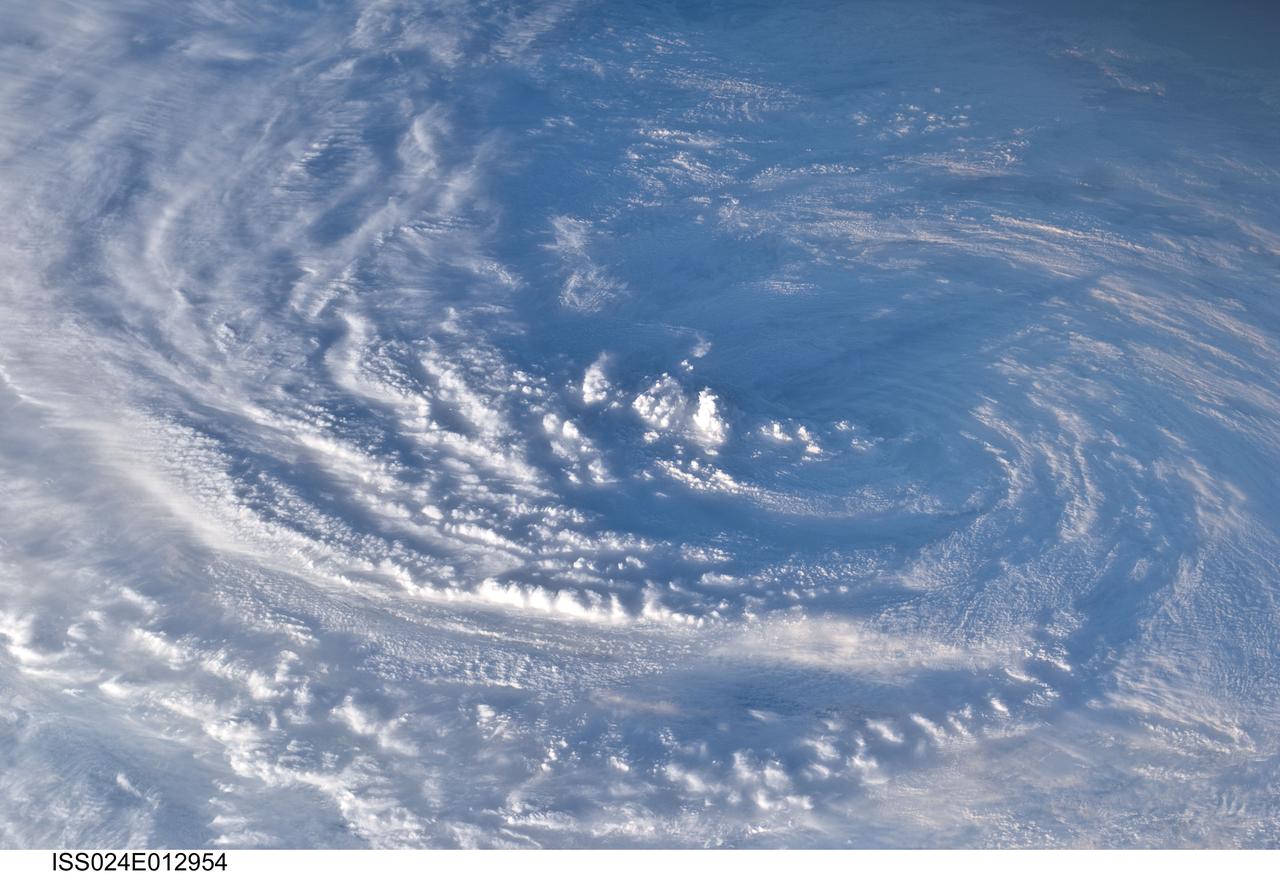

ISS024-E-012954 (30 Aug. 2010) --- Tropical Storm Danielle is featured in this Aug. 30 image photographed by an Expedition 24 crew member on the International Space Station.