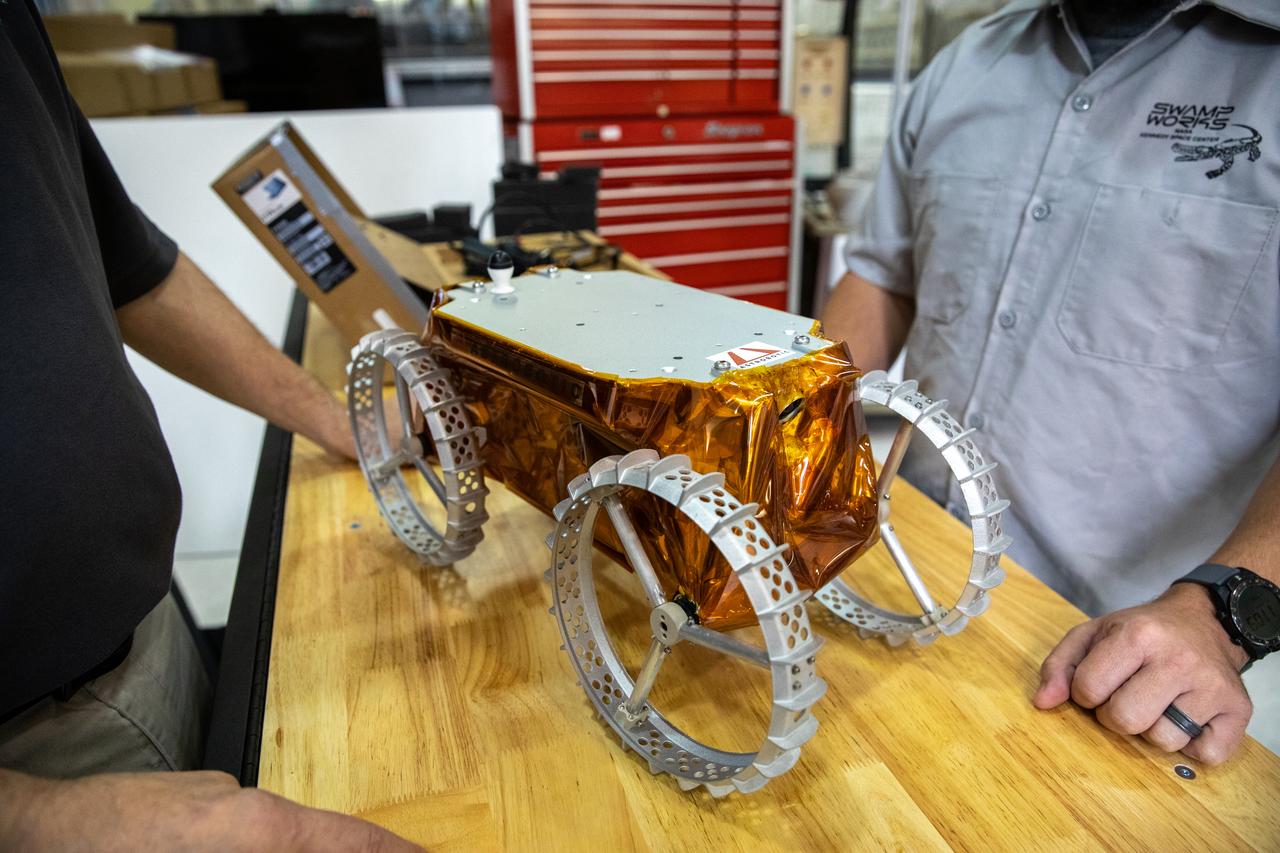

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
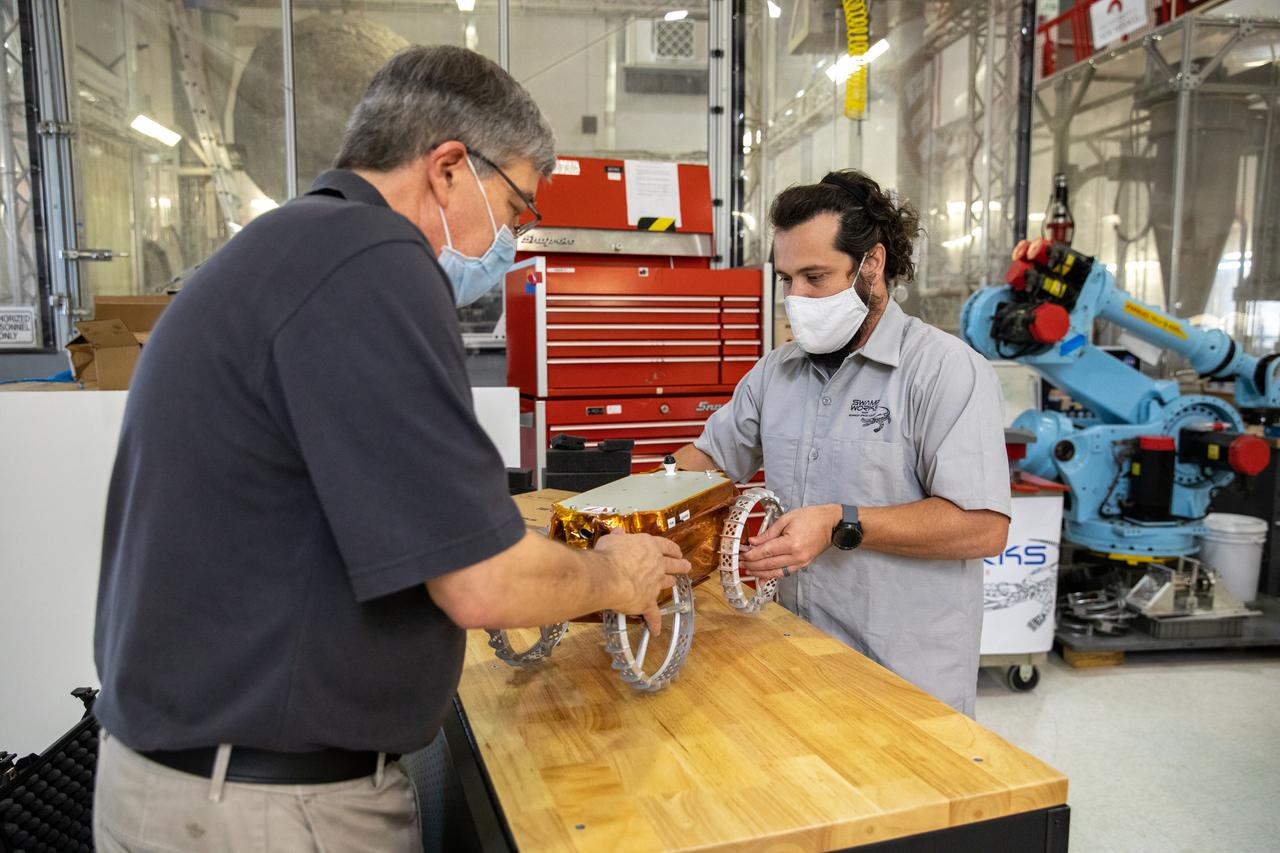

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
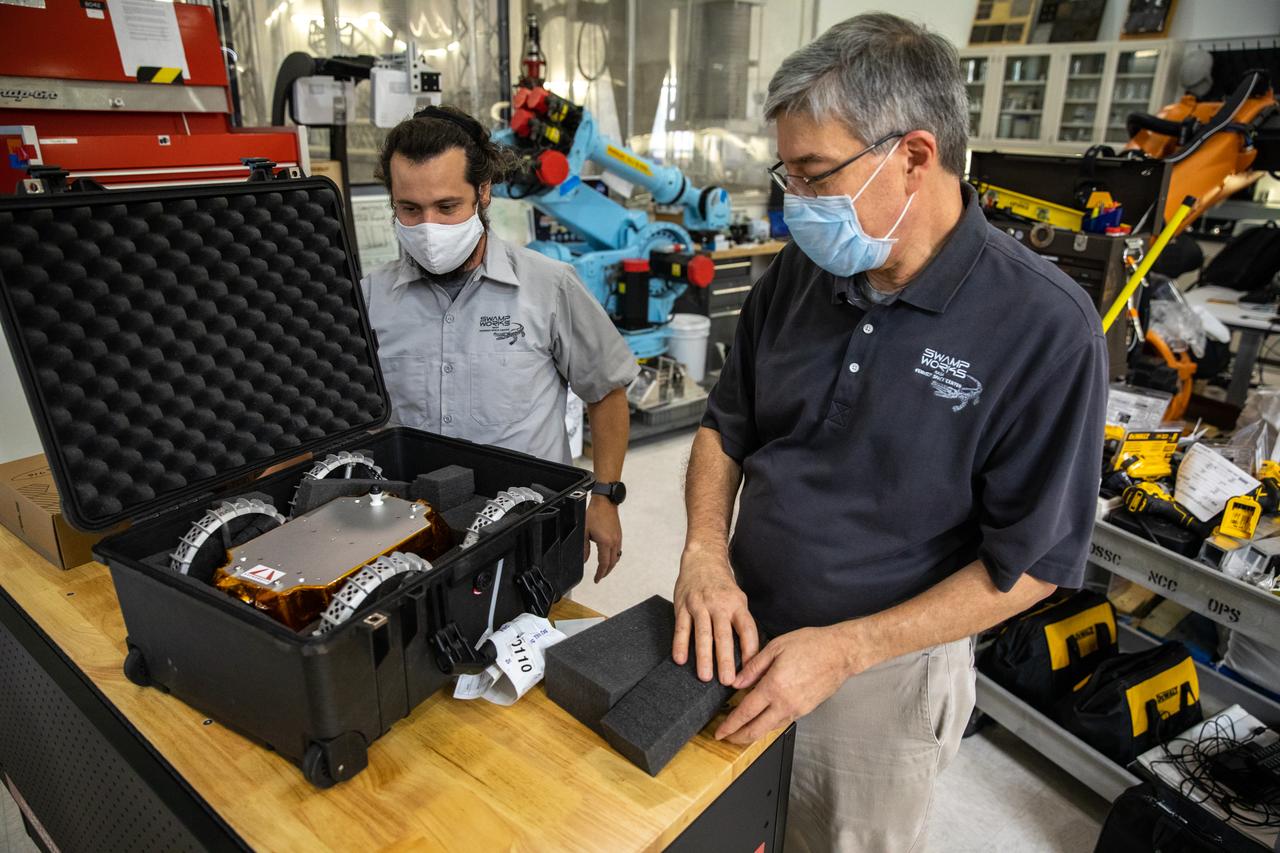

A.J. Nick, left, and Jim Mantovani, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
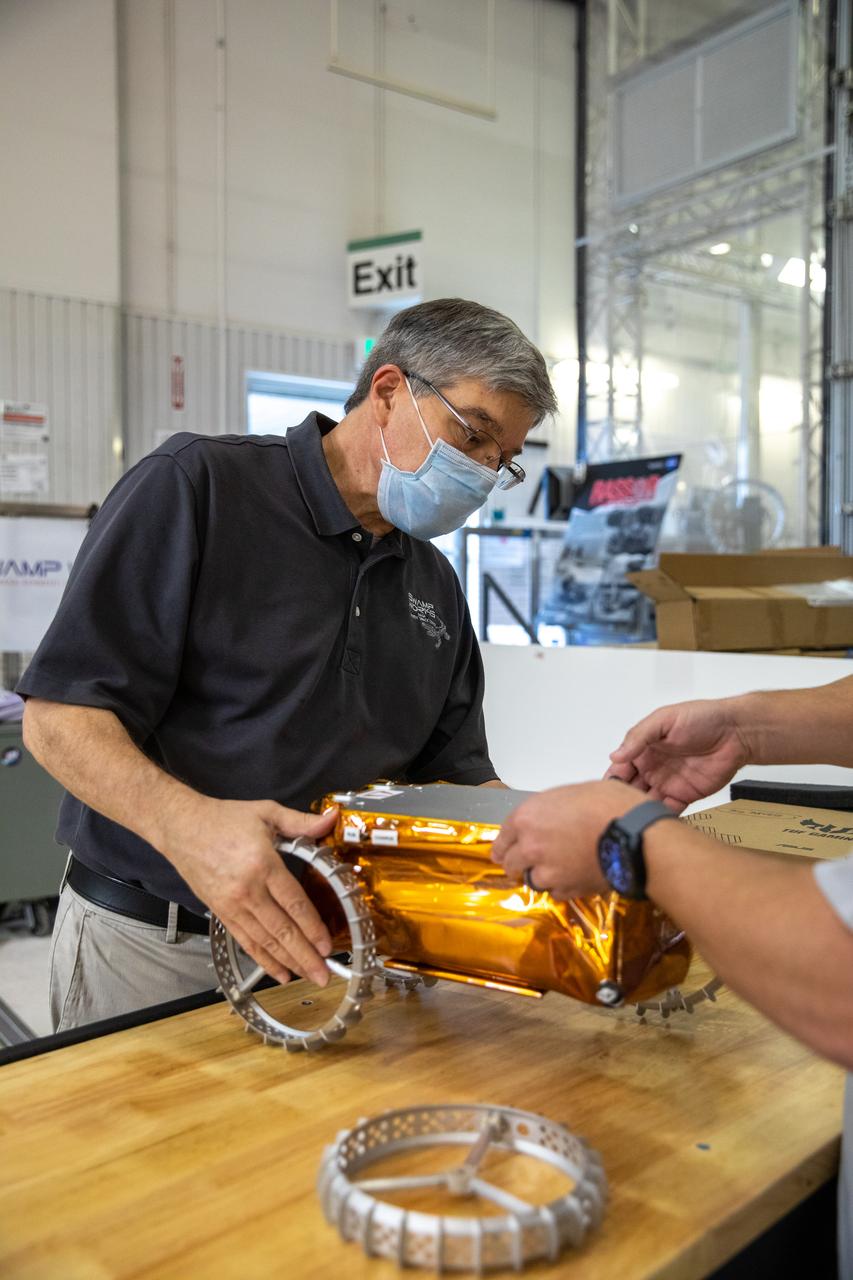

Jim Mantovani, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unboxes a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Kennedy’s A.J. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
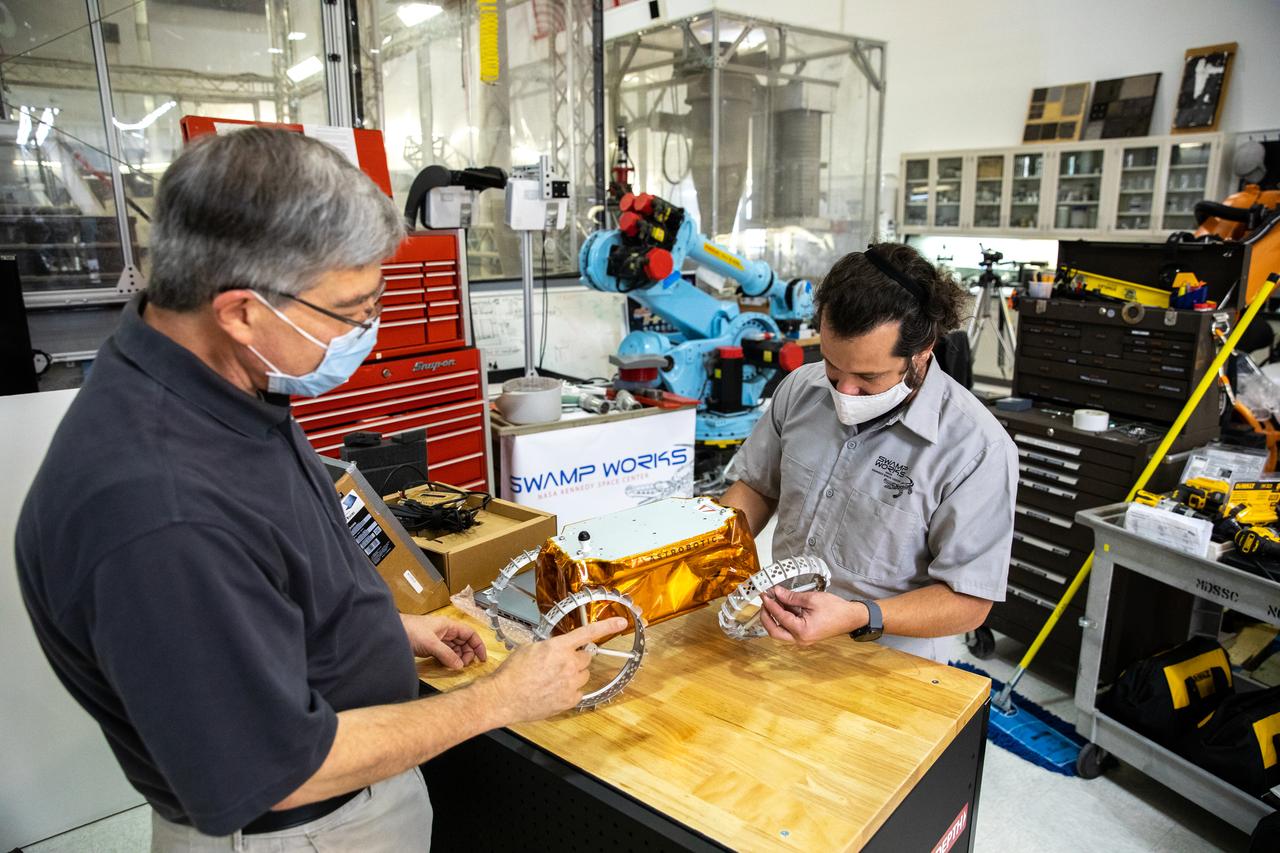

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
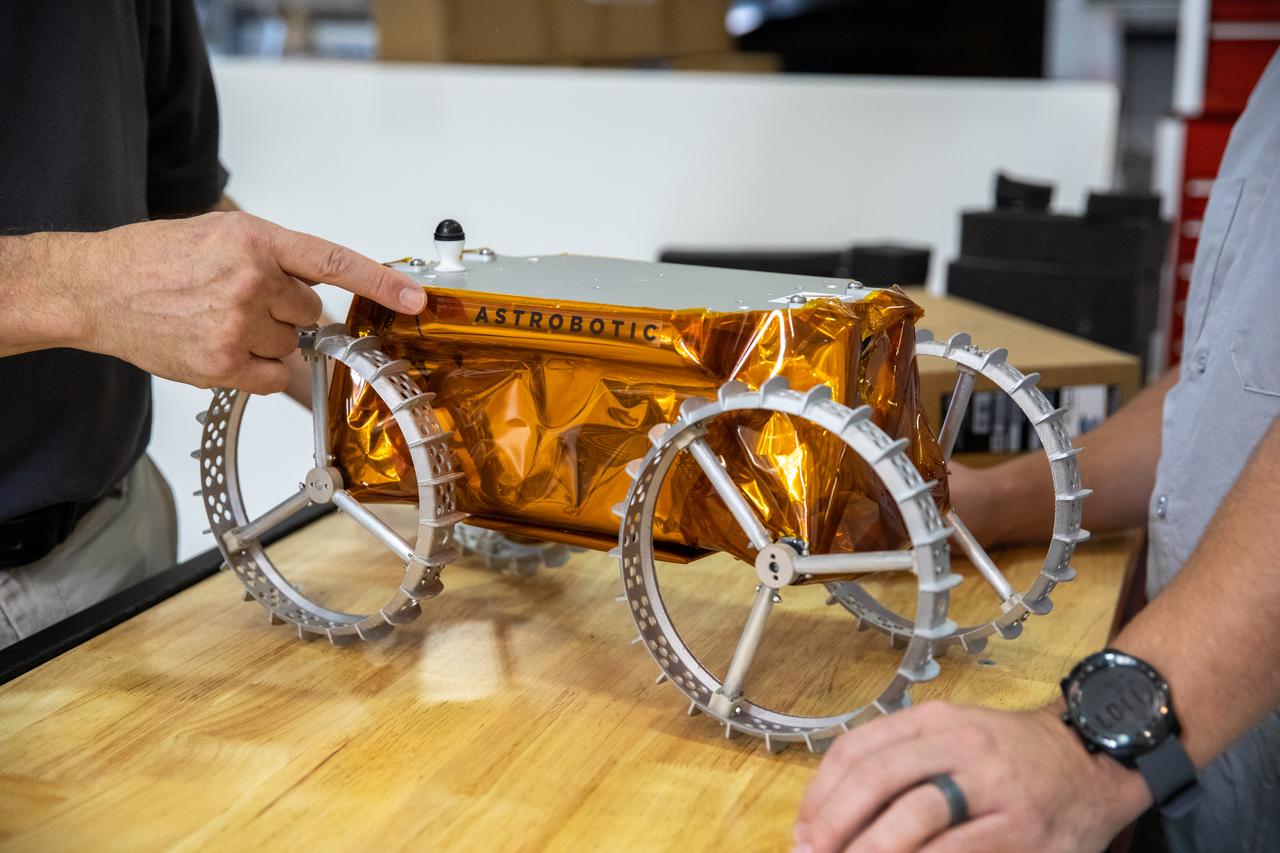

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
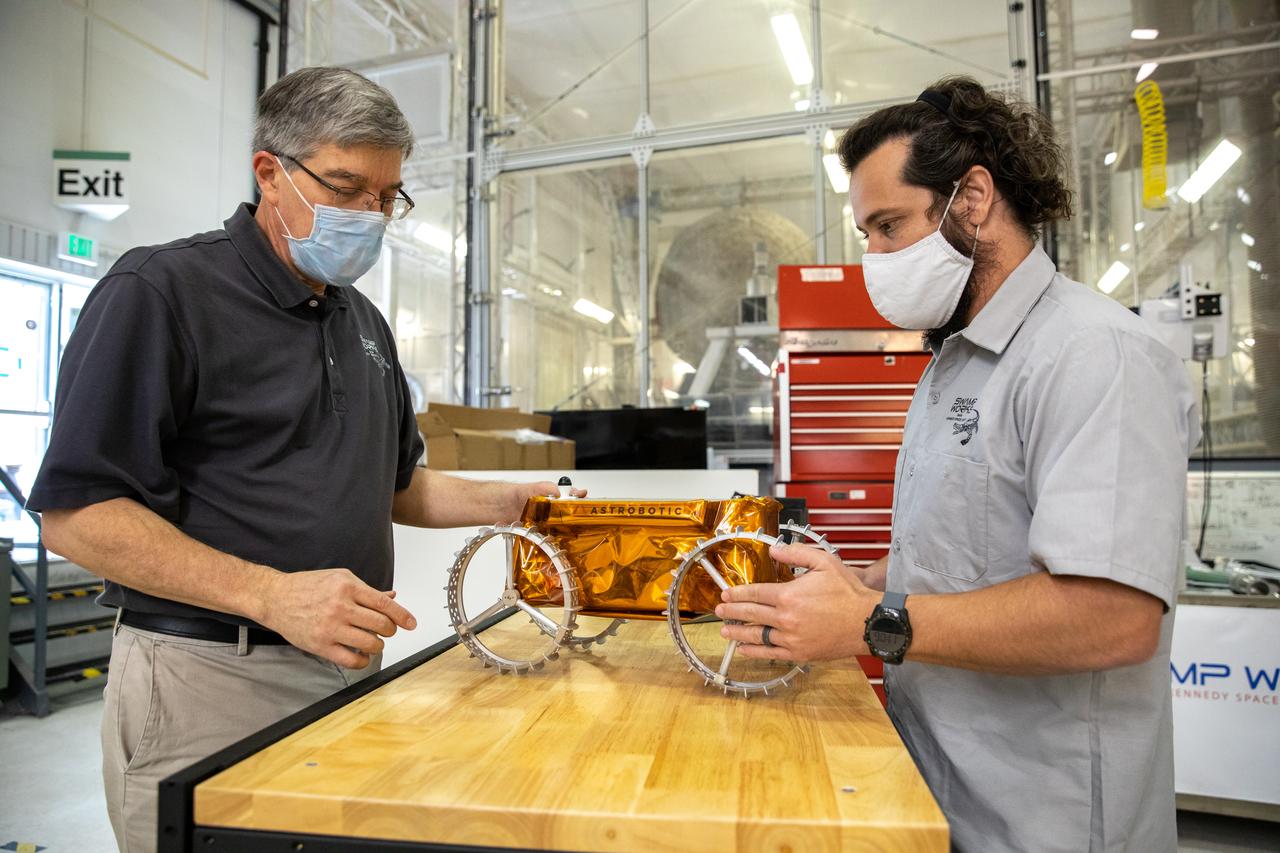

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.

A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unboxes a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
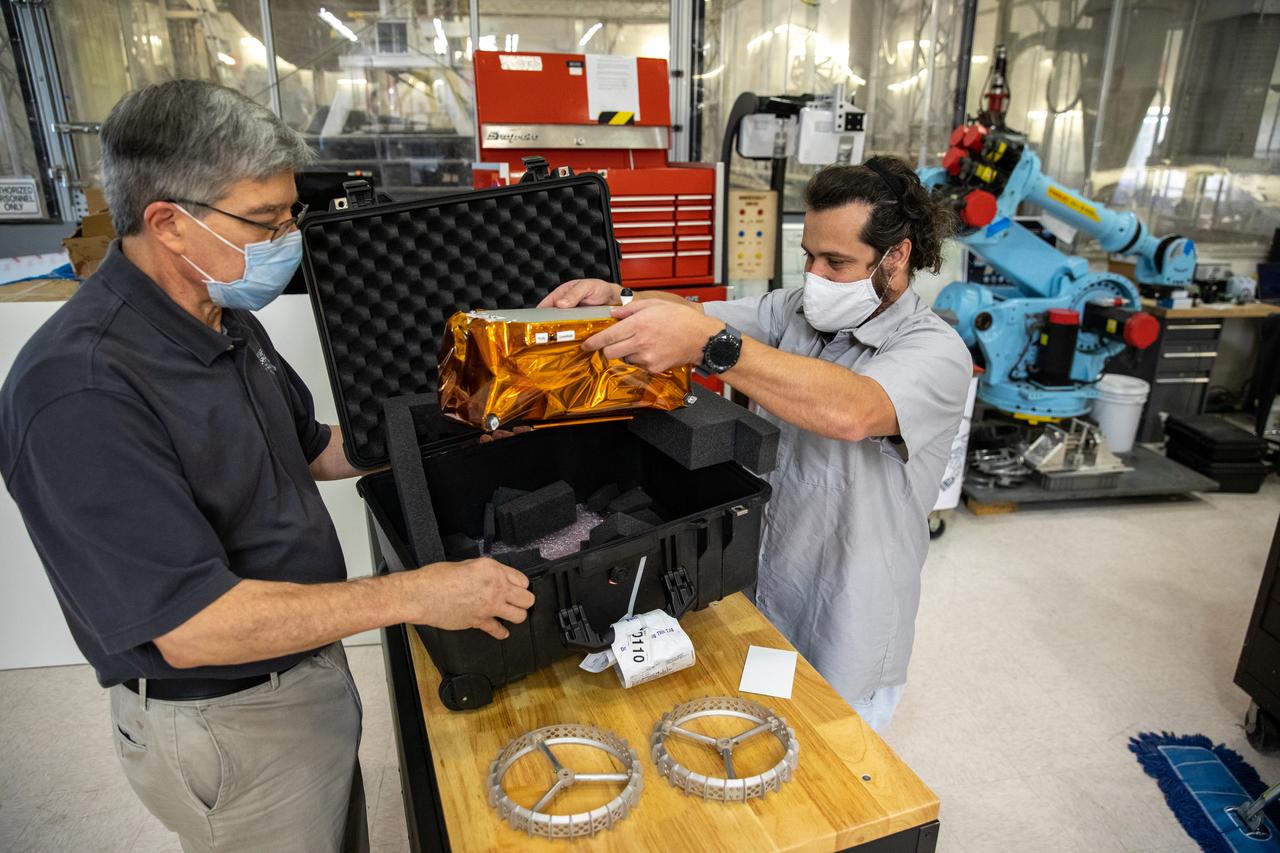

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
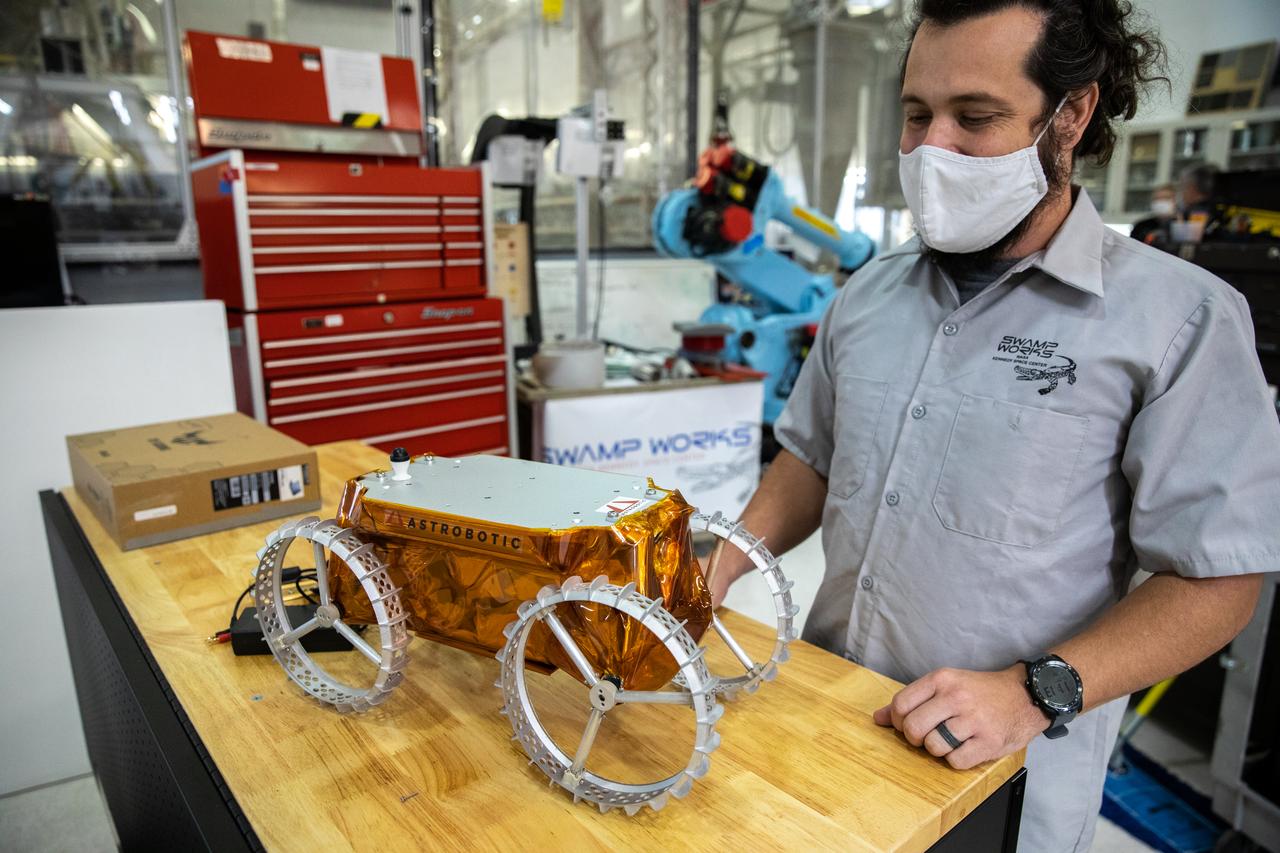

A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unboxes a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
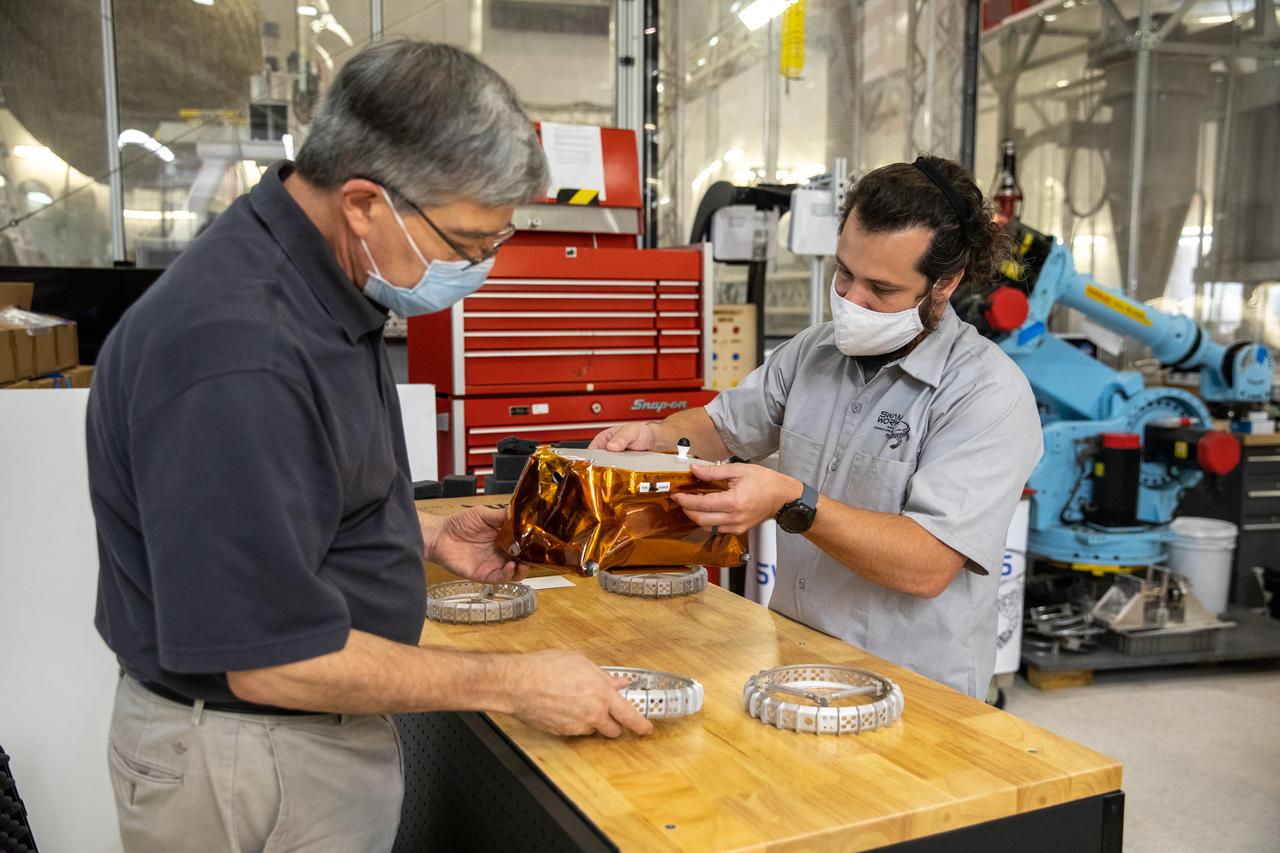

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
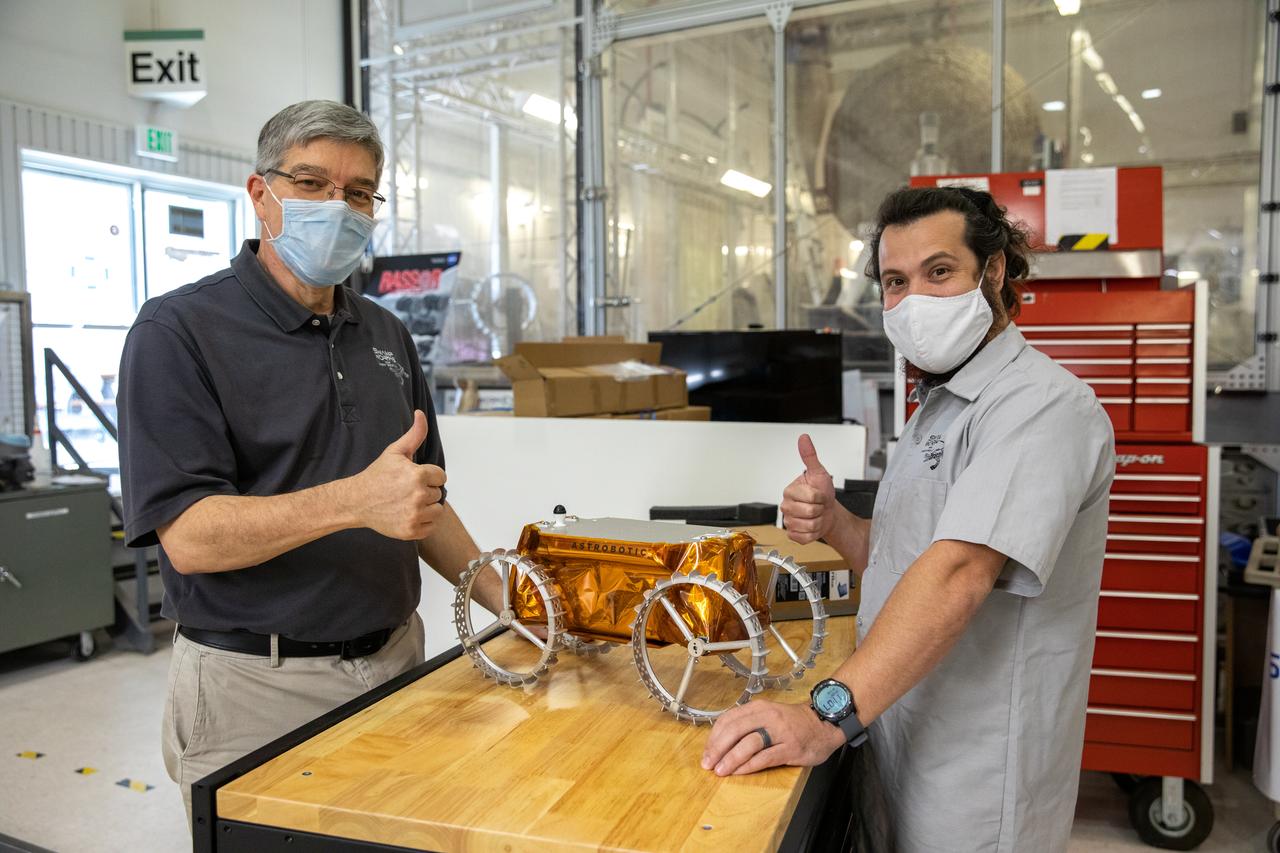

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
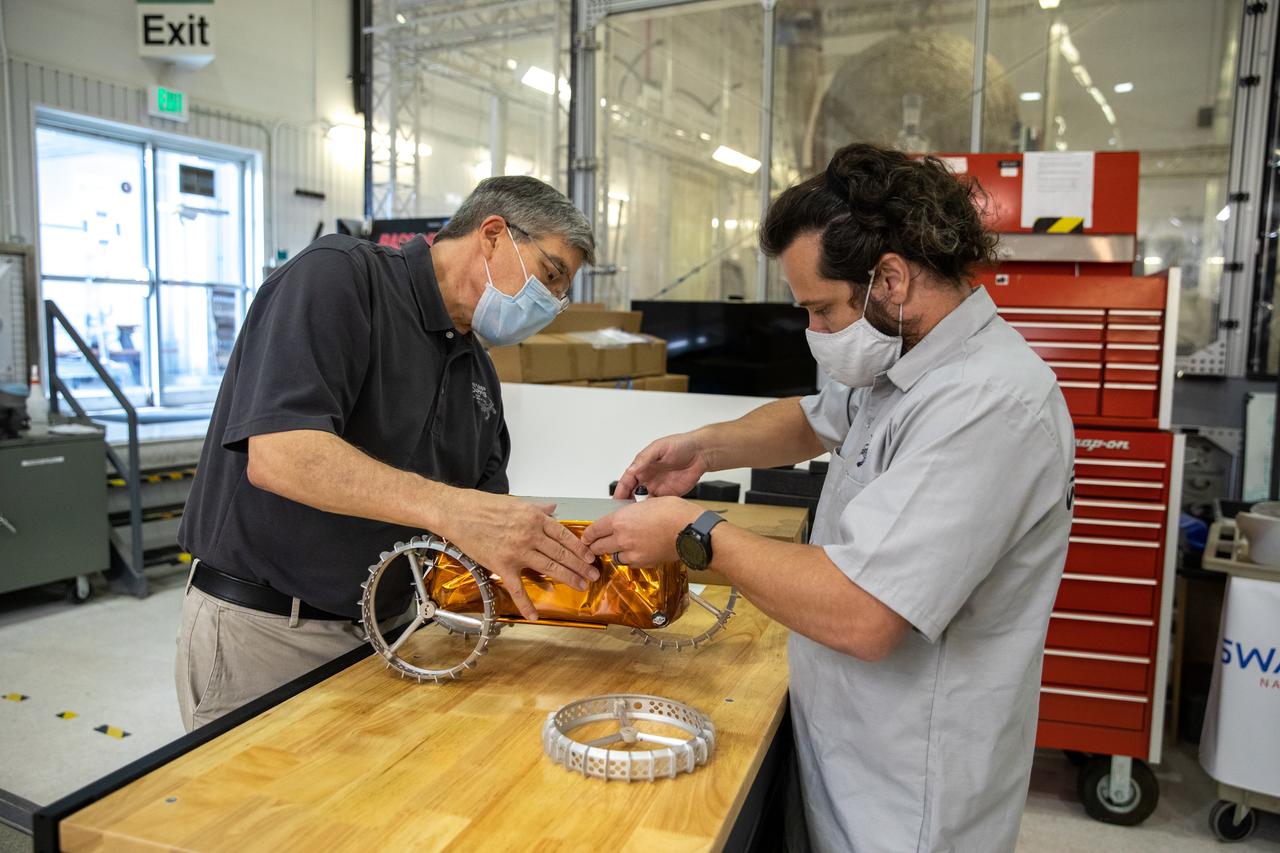

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
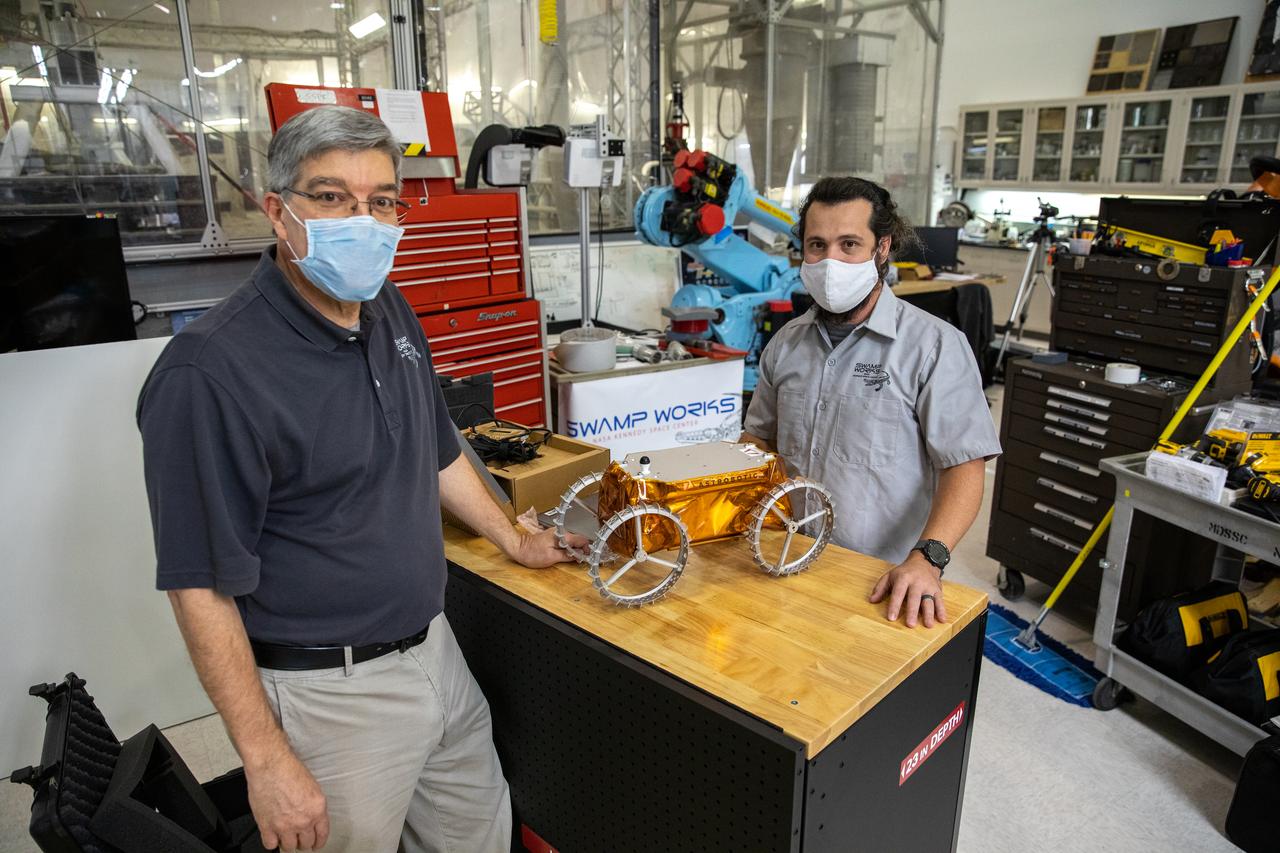

Jim Mantovani, left, and A.J. Nick, with Kennedy Space Center’s Exploration and Research and Technology programs, unbox a CubeRover at the Florida spaceport on Oct. 9, 2020. The rover was delivered by Pittsburgh-based space robotics company Astrobotic, as part of a Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award from NASA. Nick will lead CubeRover testing in the coming months in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) Laboratory’s regolith bin, which holds approximately 120 tons of lunar regolith simulant at Kennedy’s Swamp Works. In 2019, NASA announced a $2 million Tipping Point award to develop more mature CubeRover’s payload interfaces and increase its capabilities.
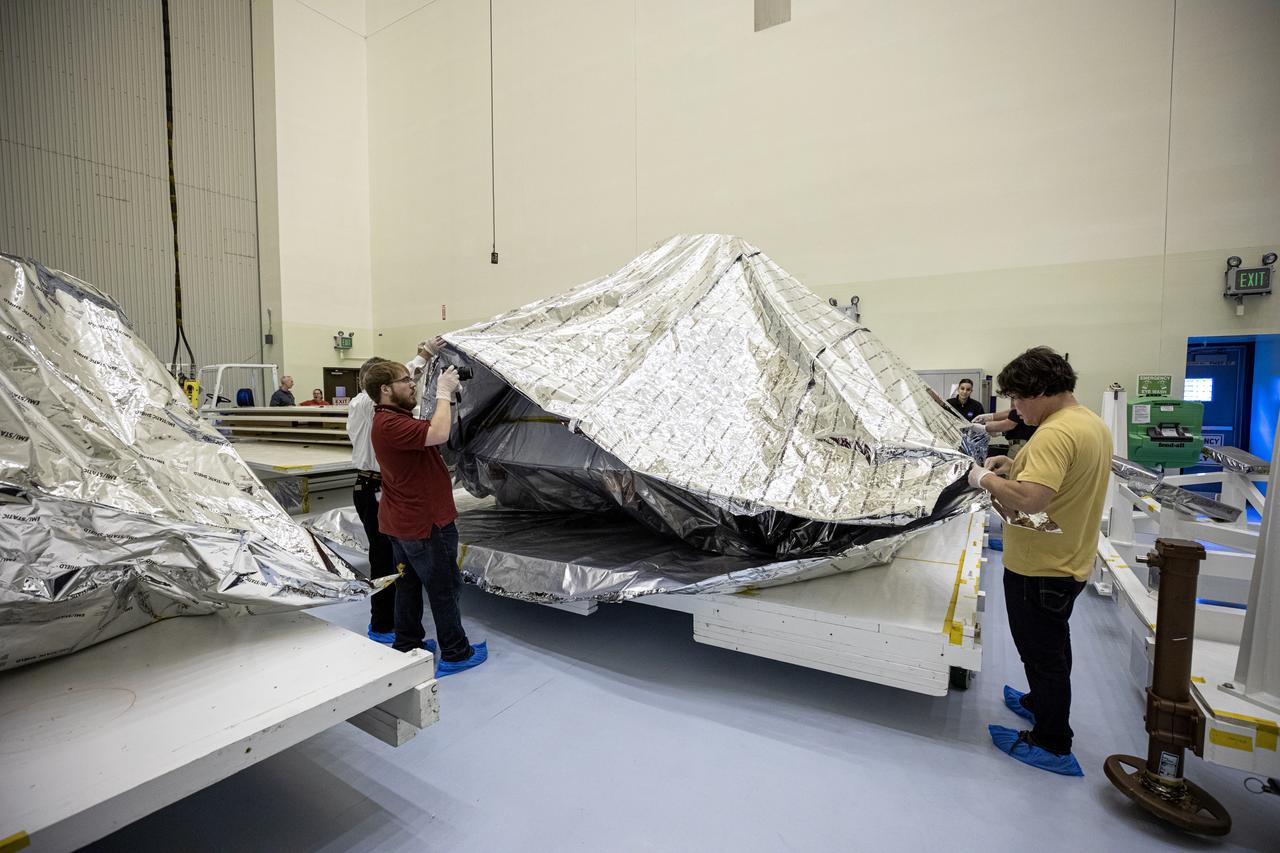

The heat shield and back shell for the Mars 2020 rover are unboxed inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Dec. 13, 2019. The two integral pieces of equipment, which were flown to the Florida spaceport from Lockheed Martin Space in Denver, Colorado, will protect the rover during its passage to Mars. The Mars 2020 rover is being manufactured at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. When completed, the rover will be delivered to Kennedy in mid-February, 2020, with the mission scheduled to launch in the summer of 2020.
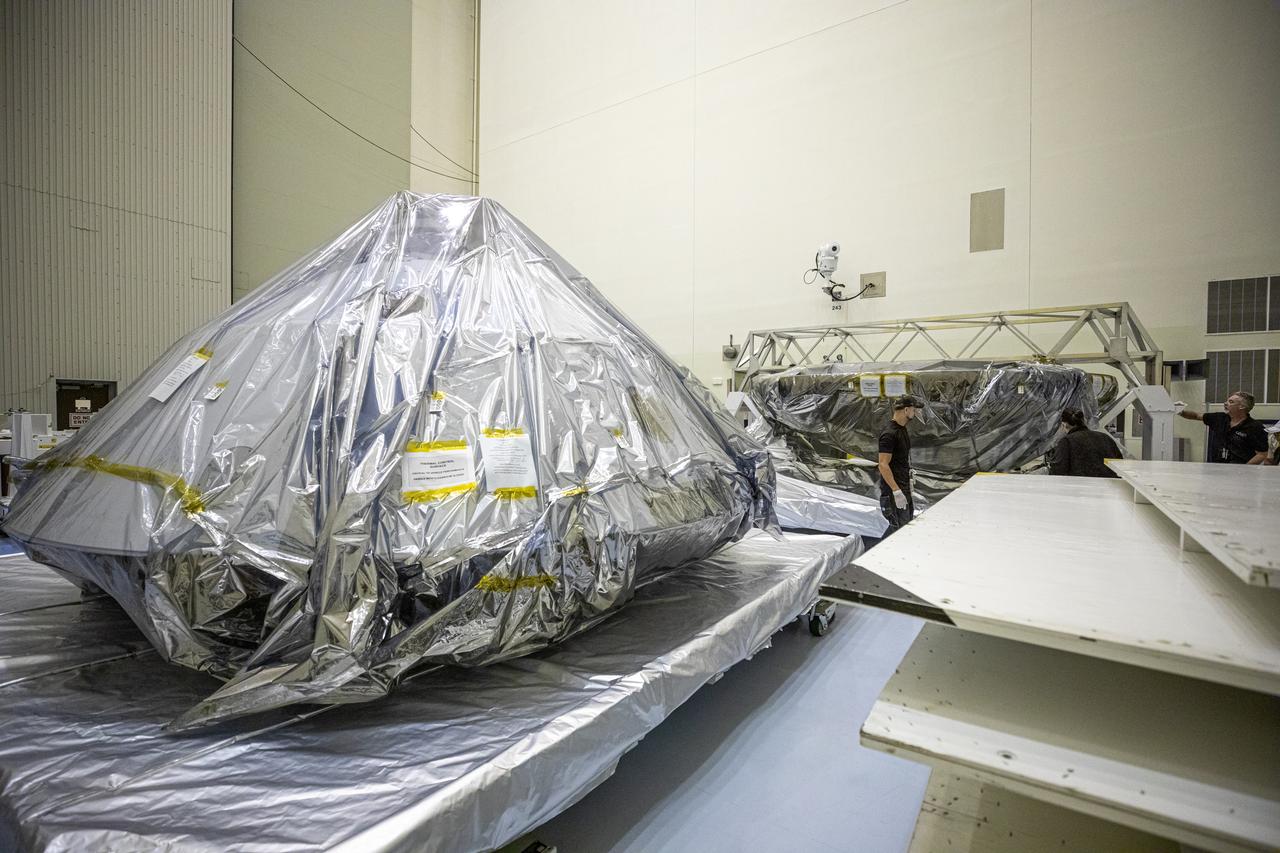

The heat shield and back shell for the Mars 2020 rover are unboxed inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Dec. 13, 2019. The two integral pieces of equipment, which were flown to the Florida spaceport from Lockheed Martin Space in Denver, Colorado, will protect the rover during its passage to Mars. The Mars 2020 rover is being manufactured at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. When completed, the rover will be delivered to Kennedy in mid-February, 2020, with the mission scheduled to launch in the summer of 2020.
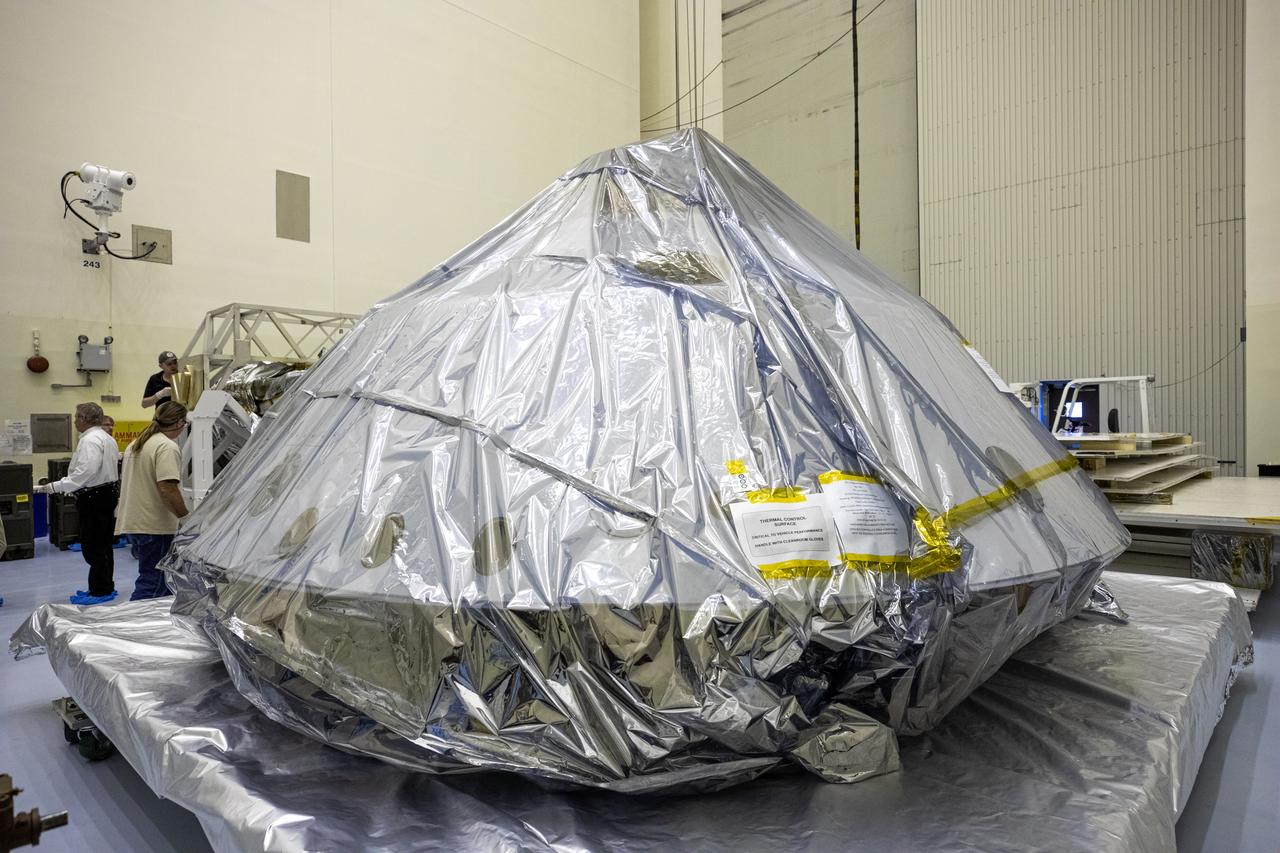

The heat shield and back shell for the Mars 2020 rover are unboxed inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Dec. 13, 2019. The two integral pieces of equipment, which were flown to the Florida spaceport from Lockheed Martin Space in Denver, Colorado, will protect the rover during its passage to Mars. The Mars 2020 rover is being manufactured at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. When completed, the rover will be delivered to Kennedy in mid-February, 2020, with the mission scheduled to launch in the summer of 2020.
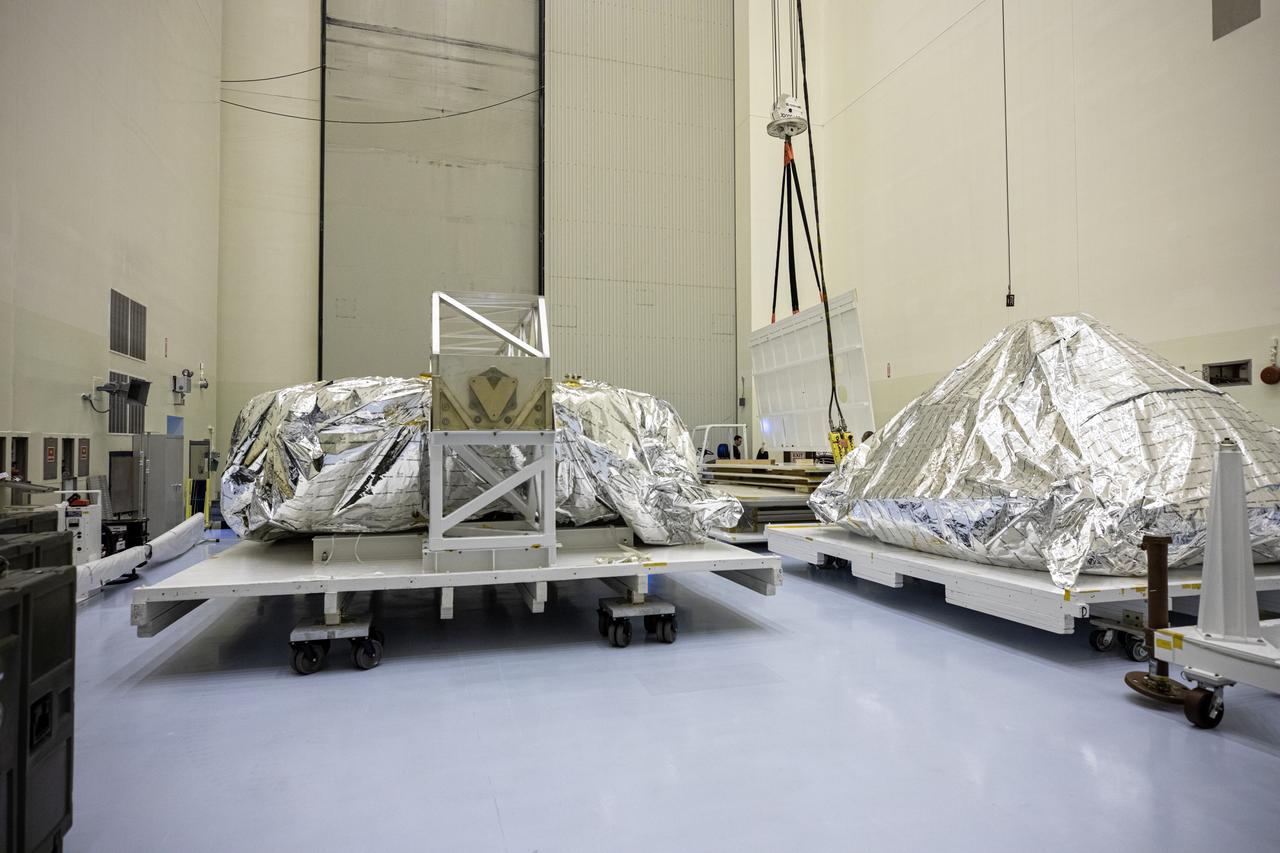

The heat shield and back shell for the Mars 2020 rover are unboxed inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Dec. 13, 2019. The two integral pieces of equipment, which were flown to the Florida spaceport from Lockheed Martin Space in Denver, Colorado, will protect the rover during its passage to Mars. The Mars 2020 rover is being manufactured at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. When completed, the rover will be delivered to Kennedy in mid-February, 2020, with the mission scheduled to launch in the summer of 2020.
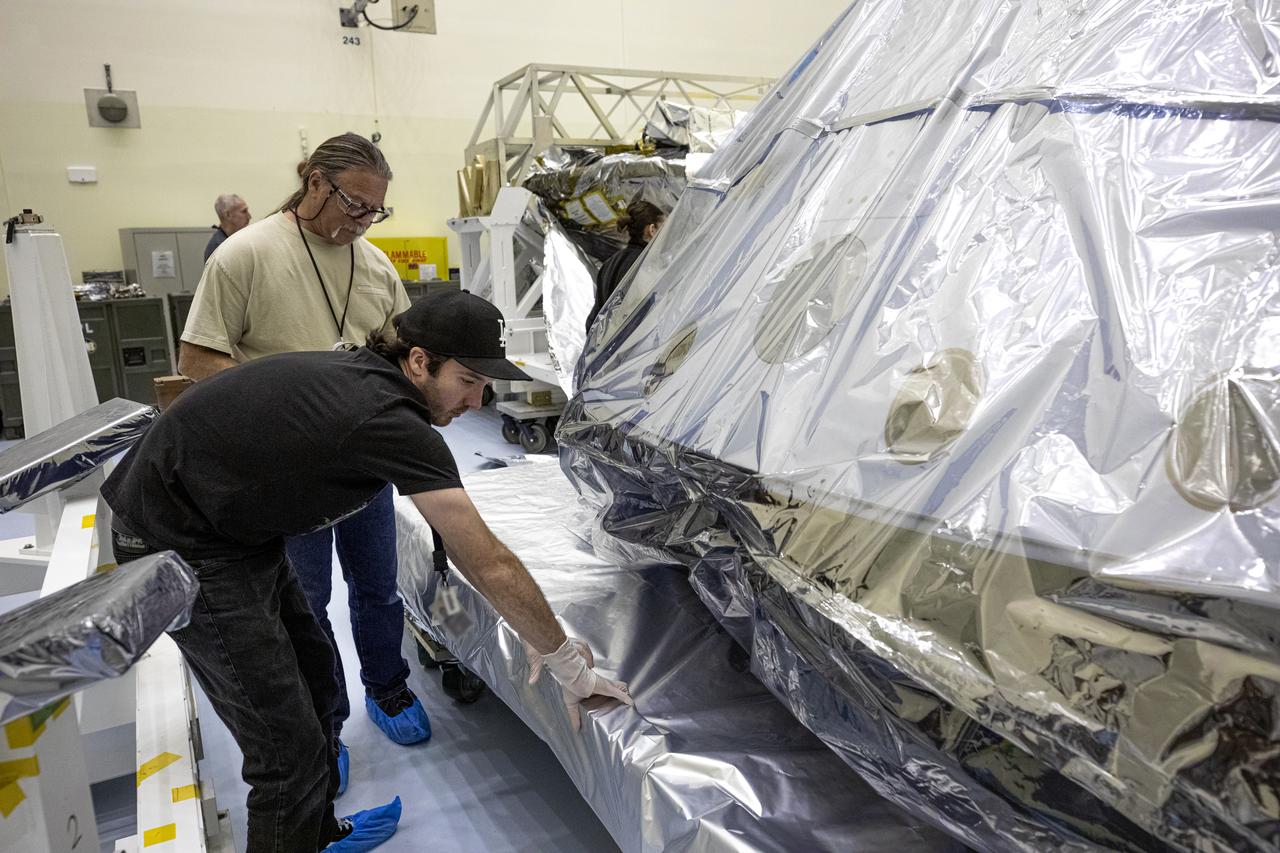

The heat shield and back shell for the Mars 2020 rover are unboxed inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Dec. 13, 2019. The two integral pieces of equipment, which were flown to the Florida spaceport from Lockheed Martin Space in Denver, Colorado, will protect the rover during its passage to Mars. The Mars 2020 rover is being manufactured at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. When completed, the rover will be delivered to Kennedy in mid-February, 2020, with the mission scheduled to launch in the summer of 2020.
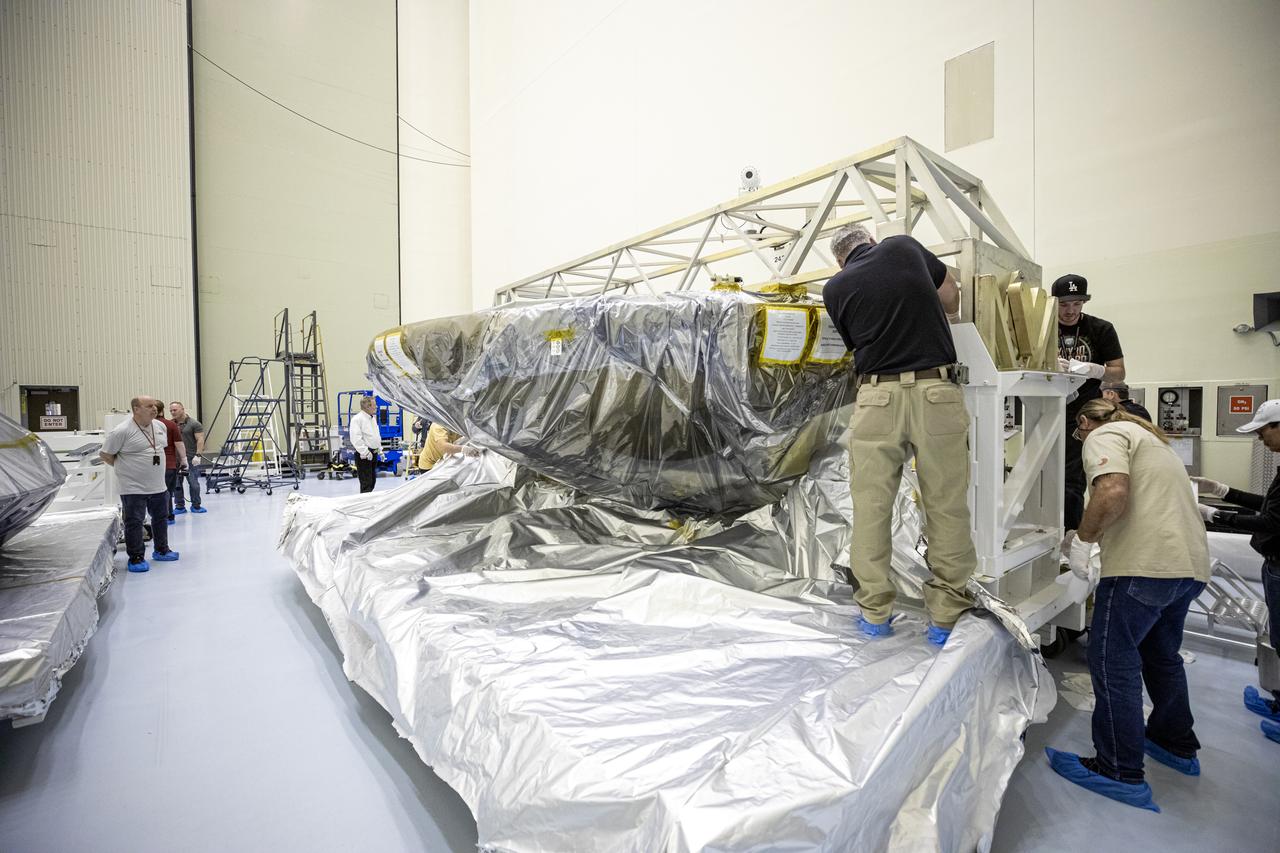

The heat shield and back shell for the Mars 2020 rover are unboxed inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Dec. 13, 2019. The two integral pieces of equipment, which were flown to the Florida spaceport from Lockheed Martin Space in Denver, Colorado, will protect the rover during its passage to Mars. The Mars 2020 rover is being manufactured at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. When completed, the rover will be delivered to Kennedy in mid-February, 2020, with the mission scheduled to launch in the summer of 2020.
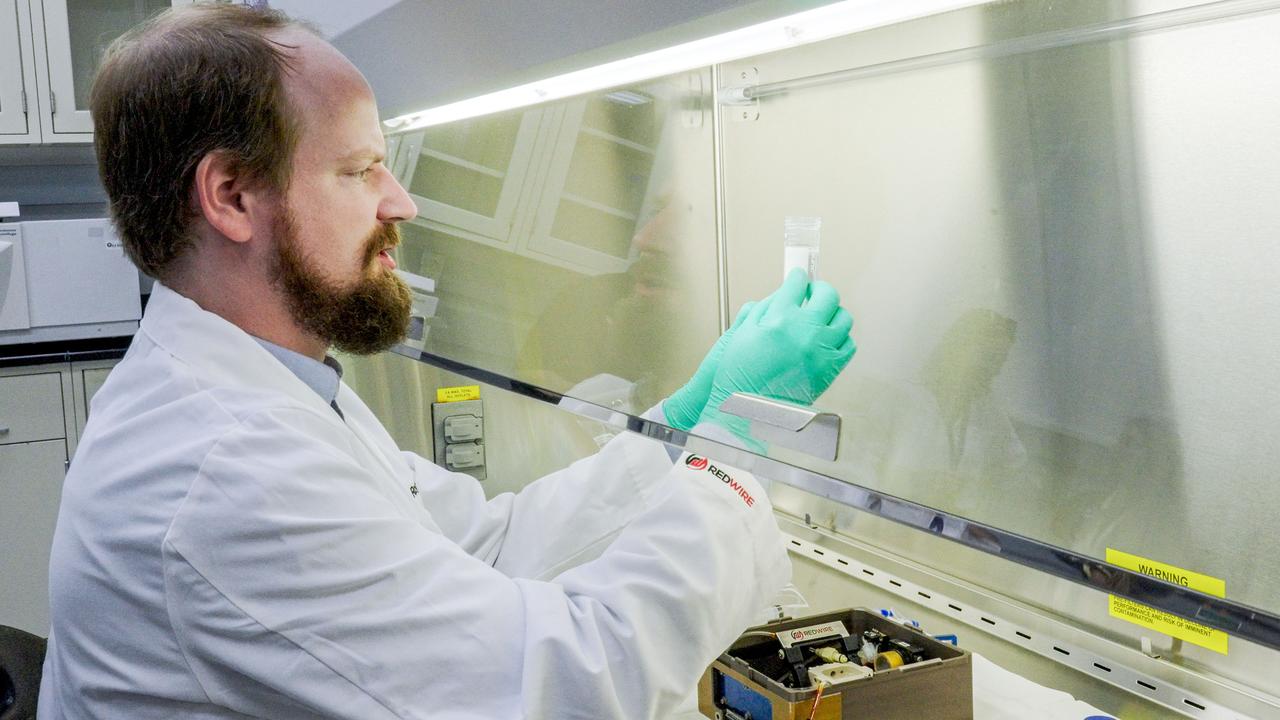

jsc2023e052854 (9/6/2023) --- Dr. Aaron Rodgers unboxes the BFF-Meniscus-2 investigation after its return from the International Space Station. The first human knee meniscus has been successfully 3D bioprinted in orbit using the BioFabrication Facility. This is a significant step towards developing solutions to promote recovery from musculoskeletal injuries. Image courtesy of Redwire.
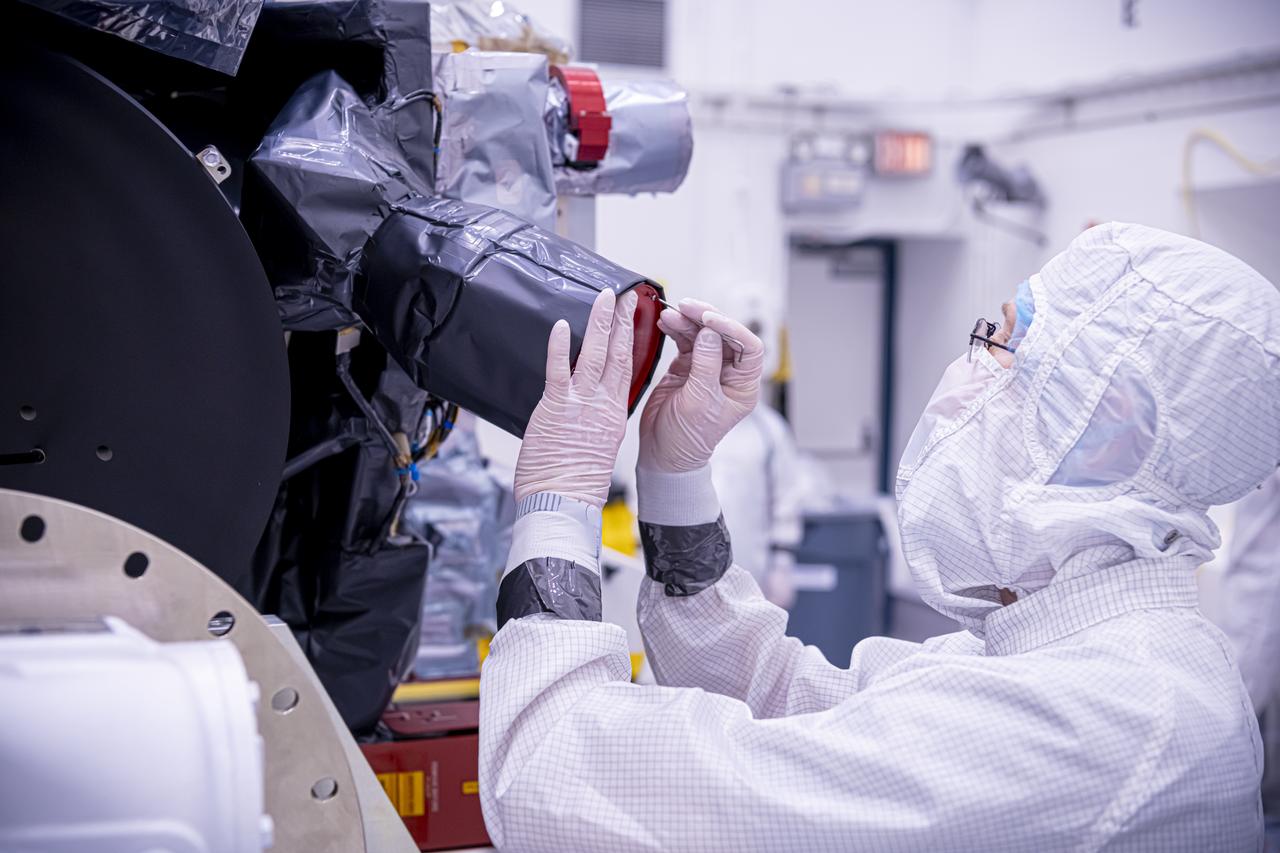

Technicians inspect the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory on Thursday, July 24, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.

Technicians inspect the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory on Thursday, July 24, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
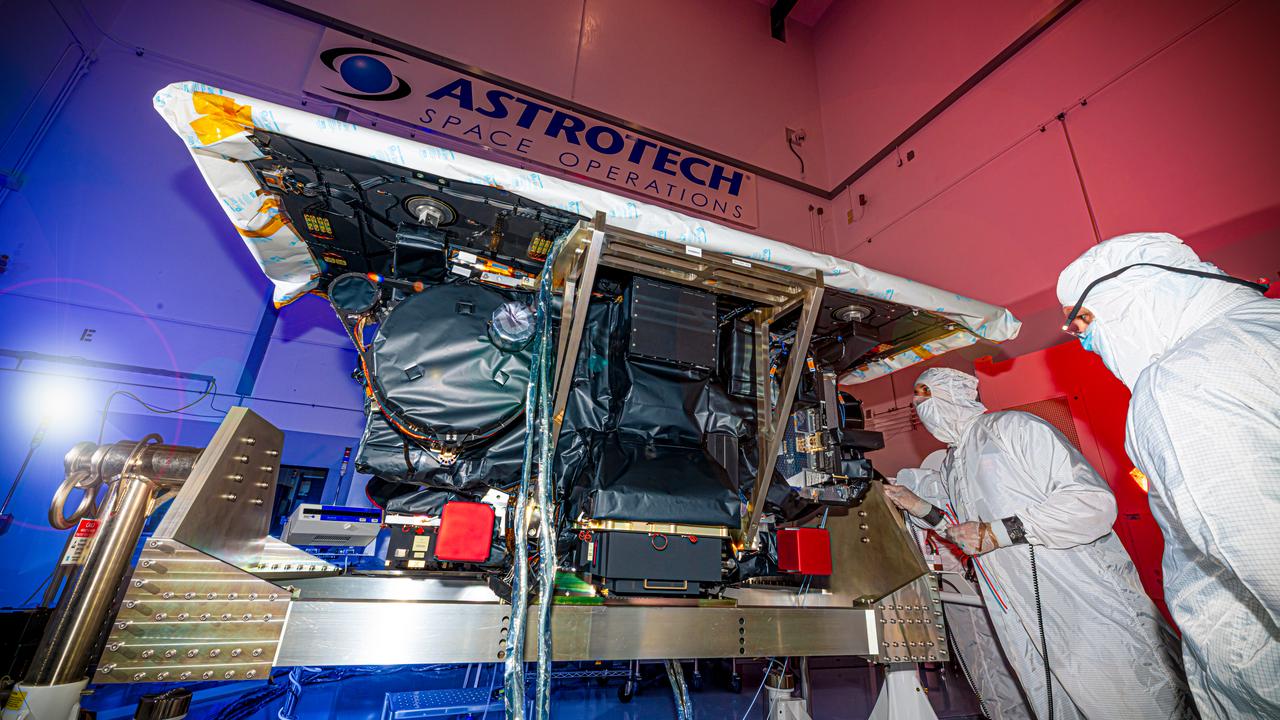

Technicians inspect the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory on Thursday, July 24, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
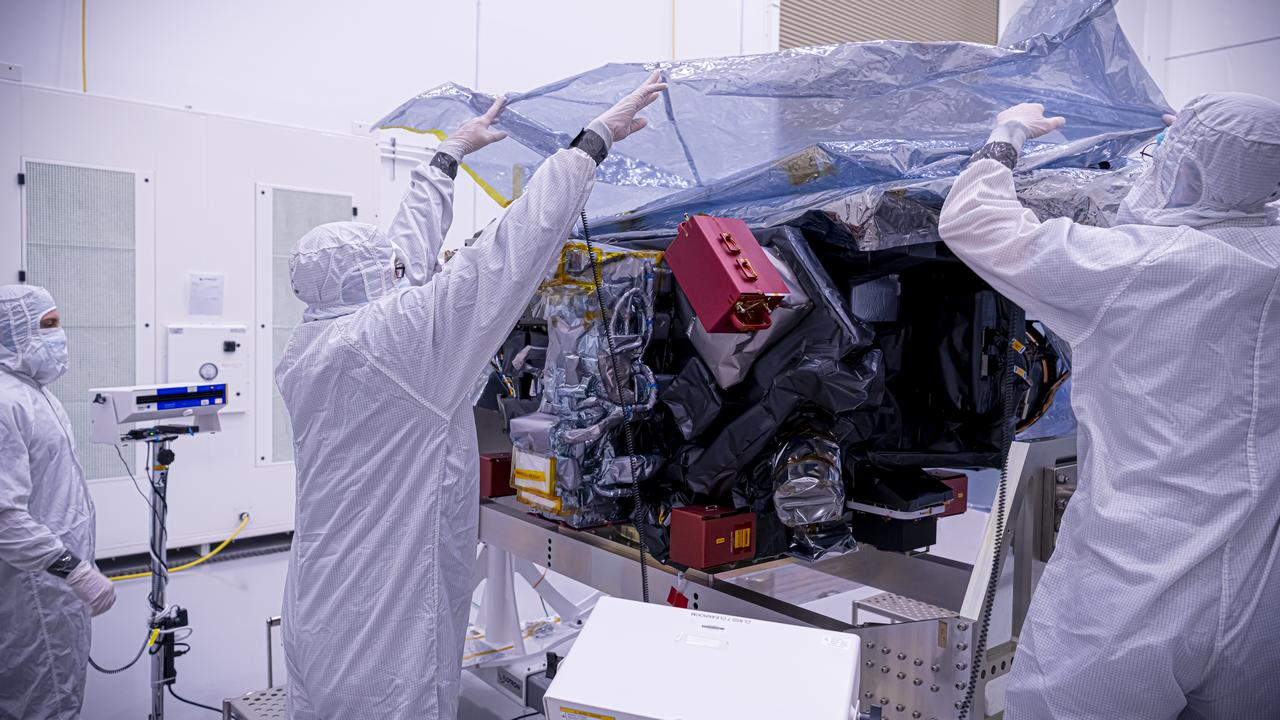

Technicians inspect the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory on Thursday, July 24, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
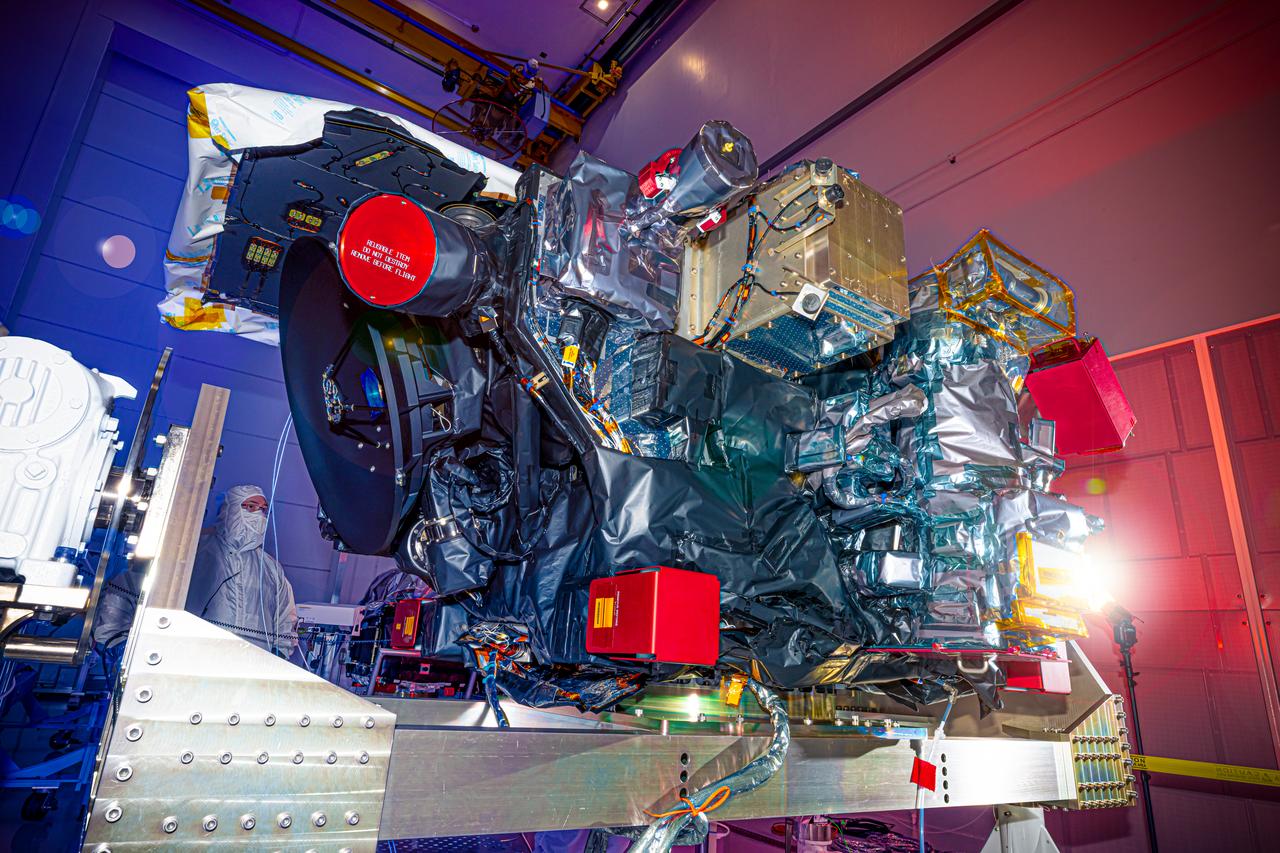

Technicians inspect the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory on Thursday, July 24, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.

jsc2023e052853 (9/6/2023) --- Dr. Aaron Rodgers unboxes the BFF-Meniscus-2 investigation after its return from the International Space Station. The first human knee meniscus has been successfully 3D bioprinted in orbit using the BioFabrication Facility. This is a significant step towards developing solutions to promote recovery from musculoskeletal injuries. Image courtesy of Redwire.
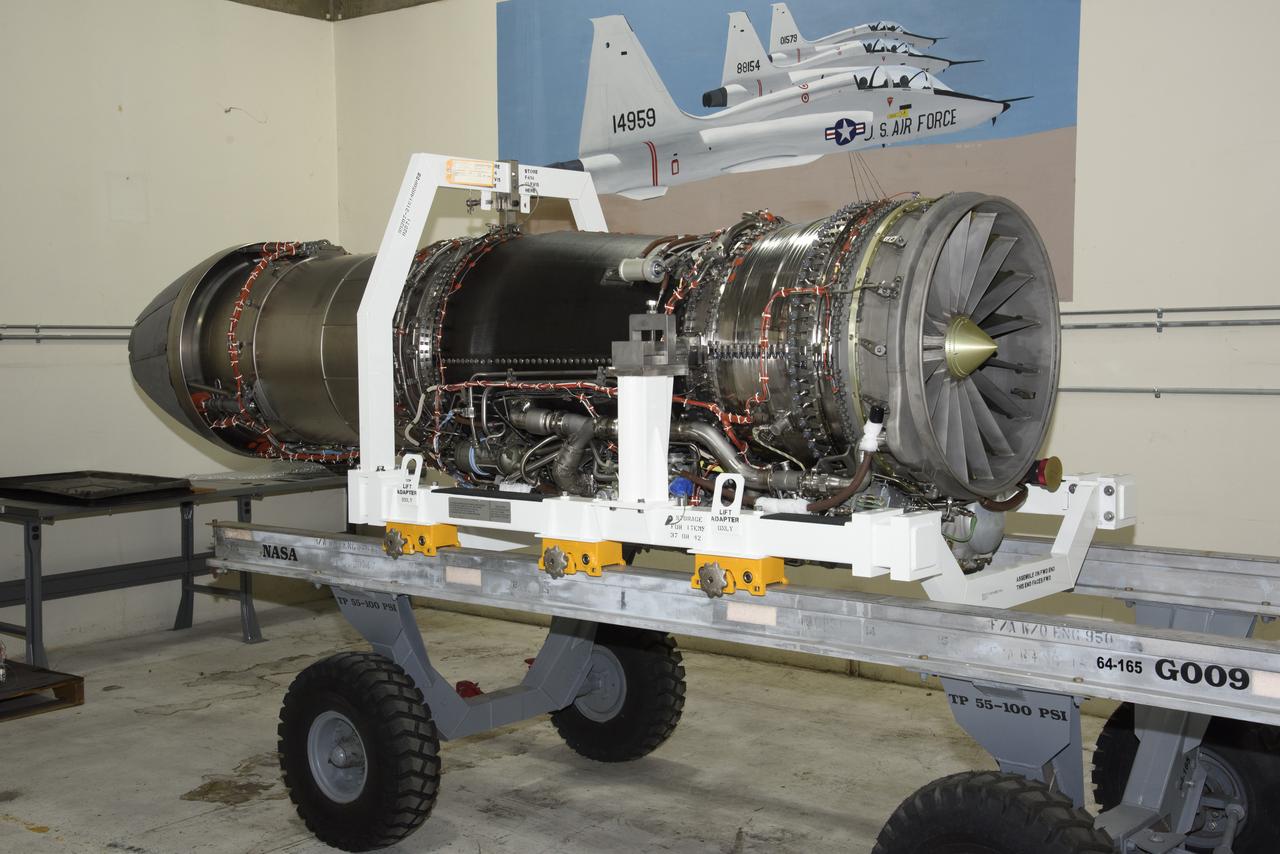

The F414-GE-100 engine, which will power NASA’s X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology X-plane (QueSST) in flight, is unboxed at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The engine, one of two delivered by GE, is approximately 13 feet long, and will power X-59 on missions to gather information about how the public perceives the sounds of quieter supersonic flight.
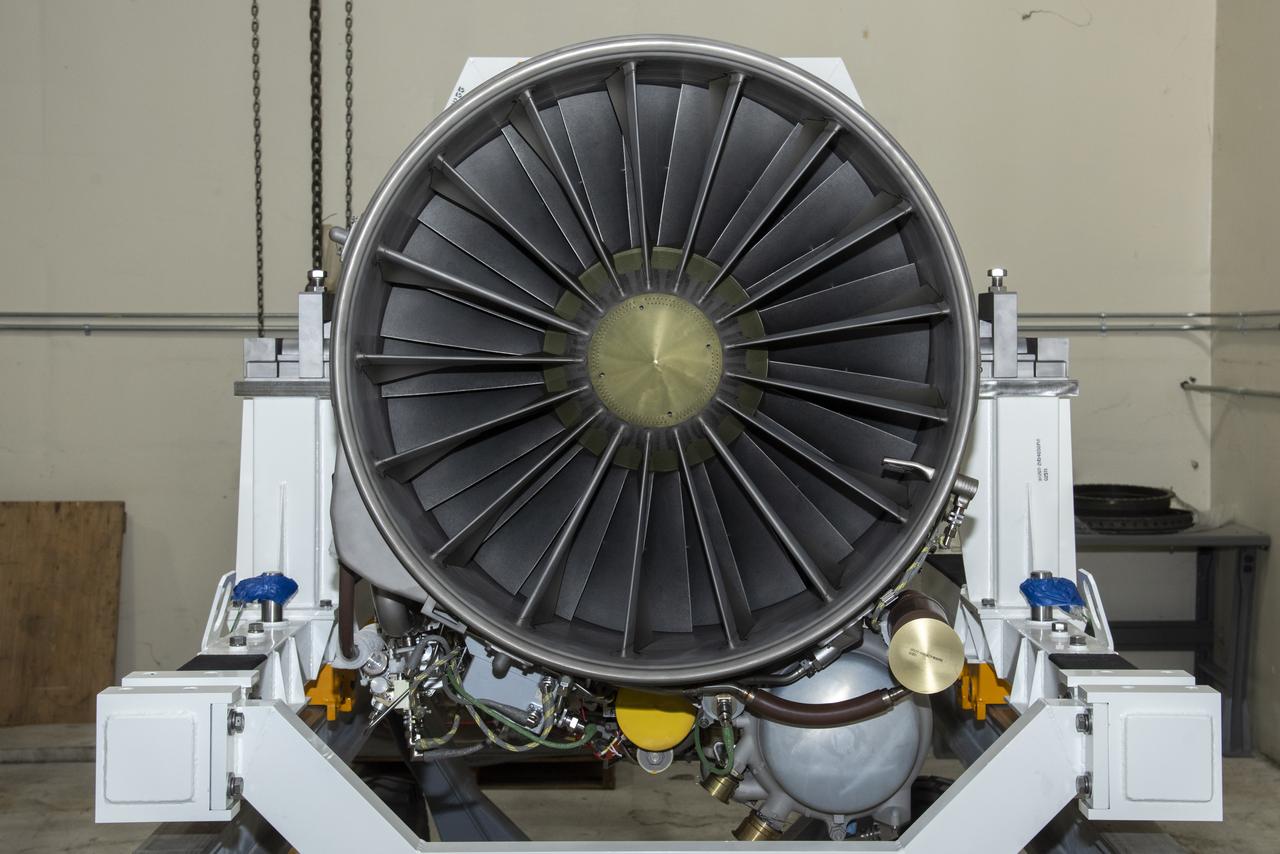

The F414-GE-100 engine, which will power NASA’s X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology X-plane (QueSST) in flight, is unboxed at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The engine, one of two delivered by GE, is approximately 13 feet long, and will power X-59 on missions to gather information about how the public perceives the sounds of quieter supersonic flight.

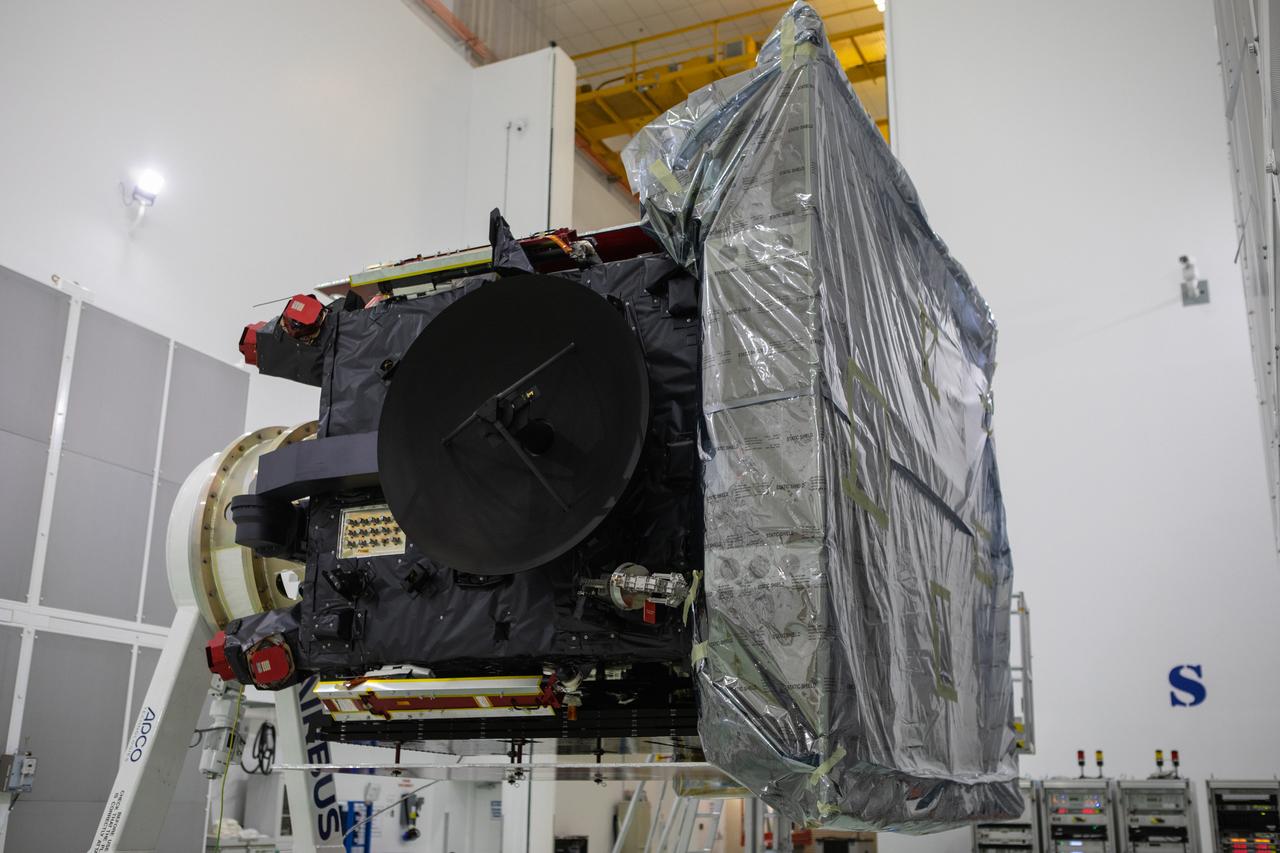
Employees with BAE Systems pose for a photo following the arrival of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Jan. 14, 2025. BAE Systems (formerly Ball Aerospace) built the telescope and the spacecraft bus. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. Riding along with SPHEREx, NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) mission will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind. Liftoff aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for 10:09 p.m. EST (7:09 p.m. PST), Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025, from Space Launch Complex 4 East.
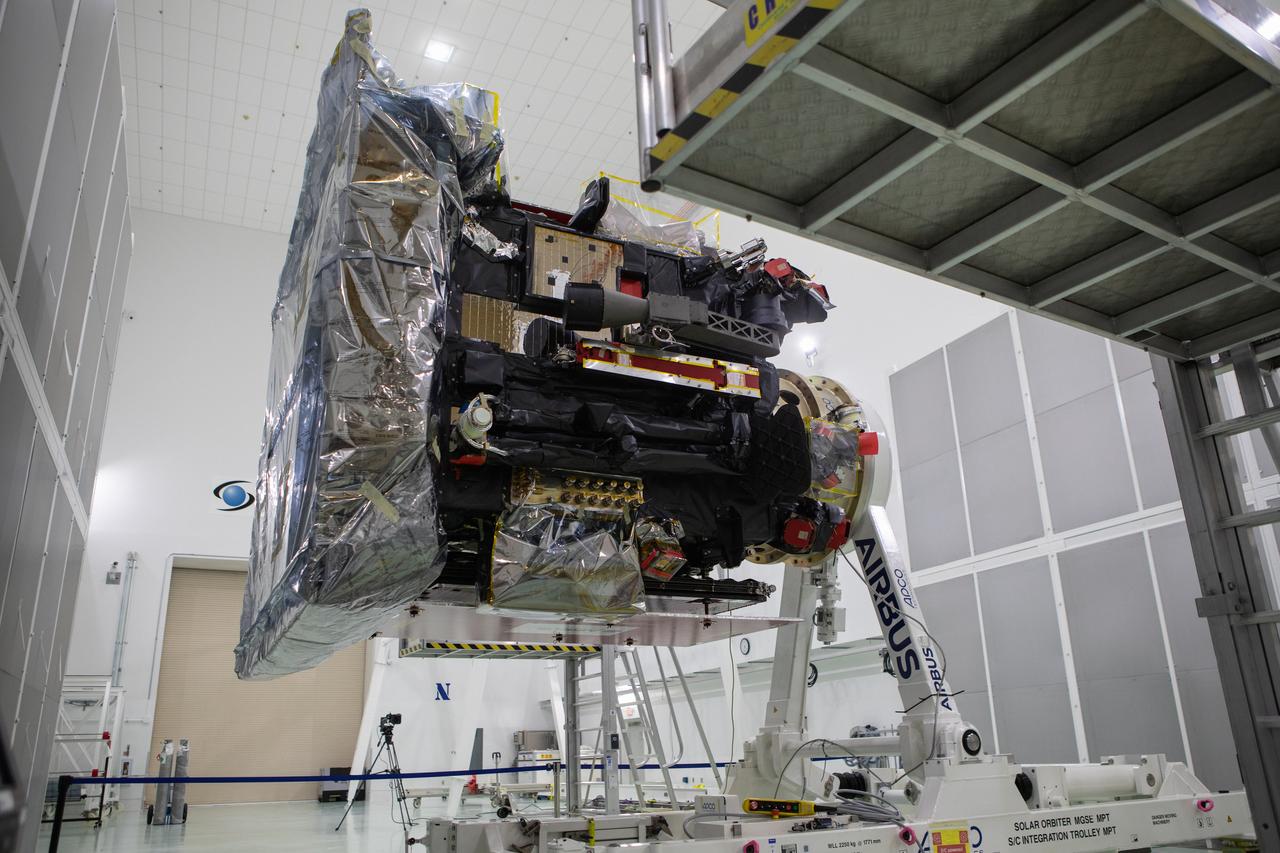

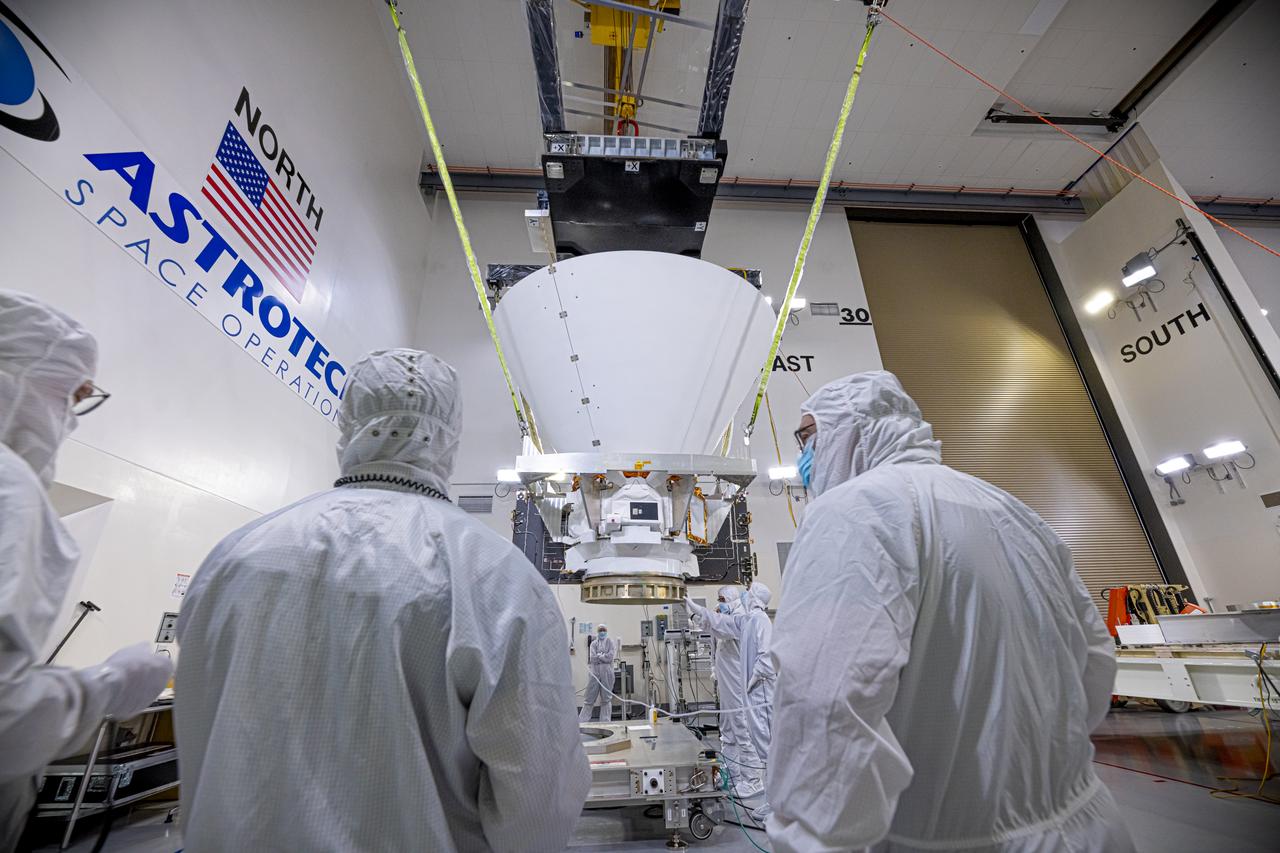
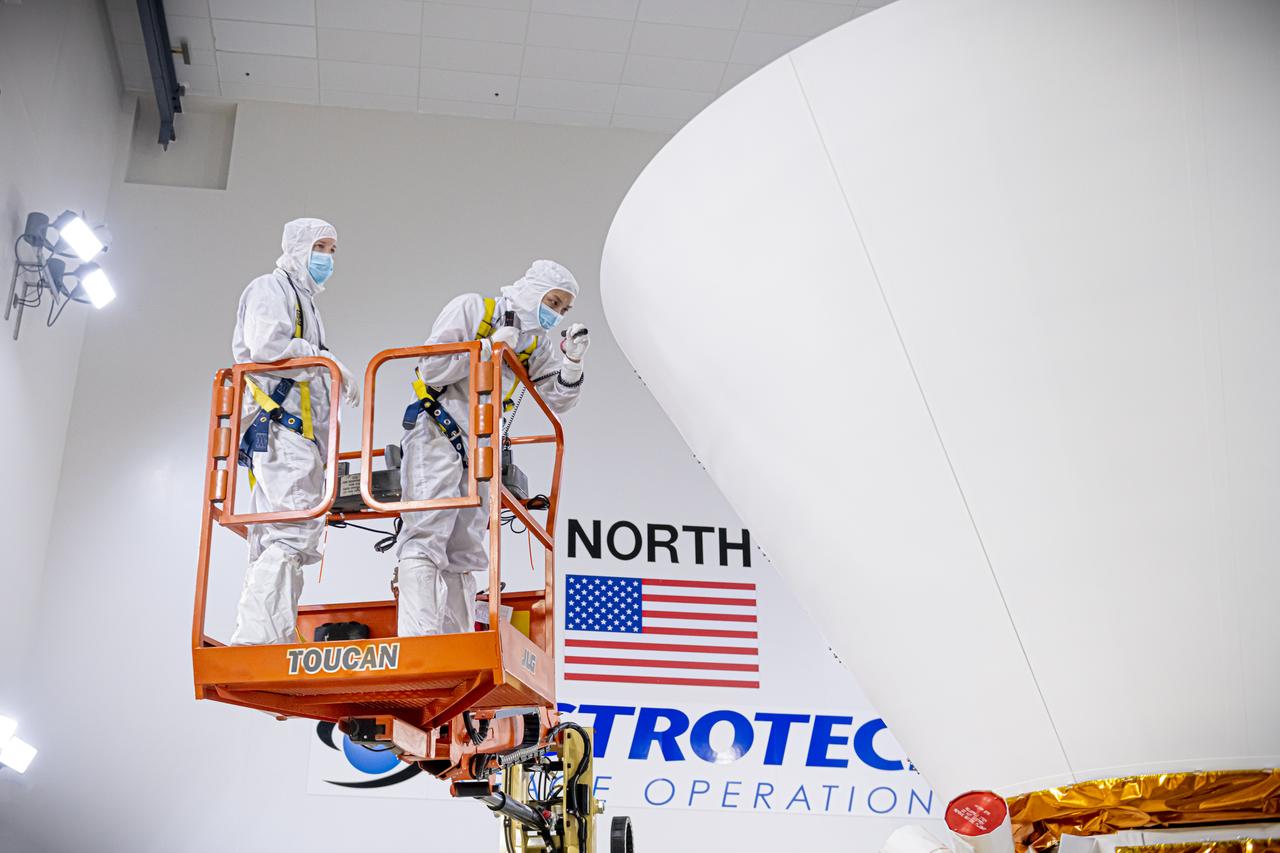
The Solar Orbiter spacecraft has been removed from its shipping container inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Nov. 18, 2019. The spacecraft was flown aboard an Antonov cargo aircraft from Munich, Germany, arriving at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Nov. 1, 2019. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
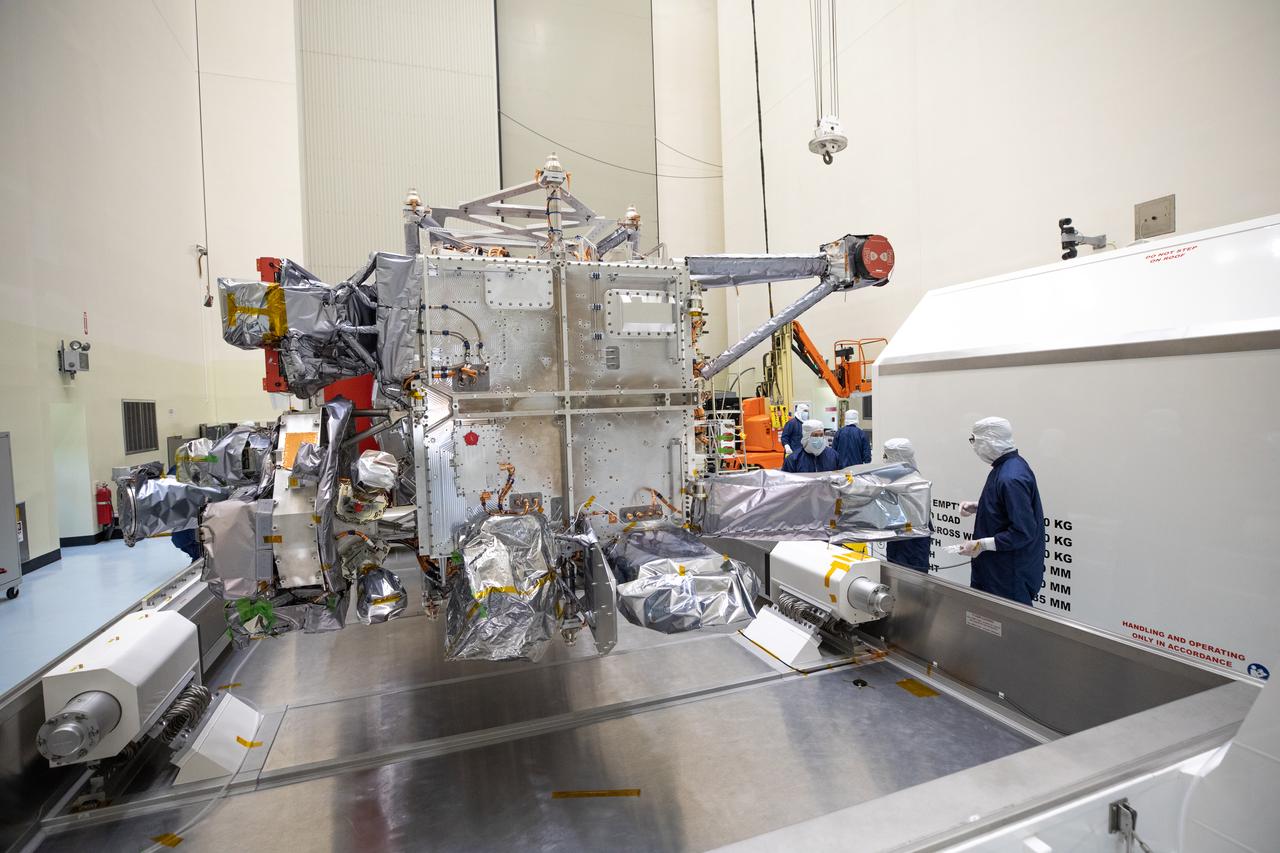

As part of prelaunch processing, crews inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida uncrate the agency’s largest planetary mission spacecraft, Europa Clipper, on Tuesday, May 28, 2024. Slated to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket later this year from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, Europa Clipper will help determine if conditions exist below the surface Jupiter’s fourth largest moon, Europa, that could support life.
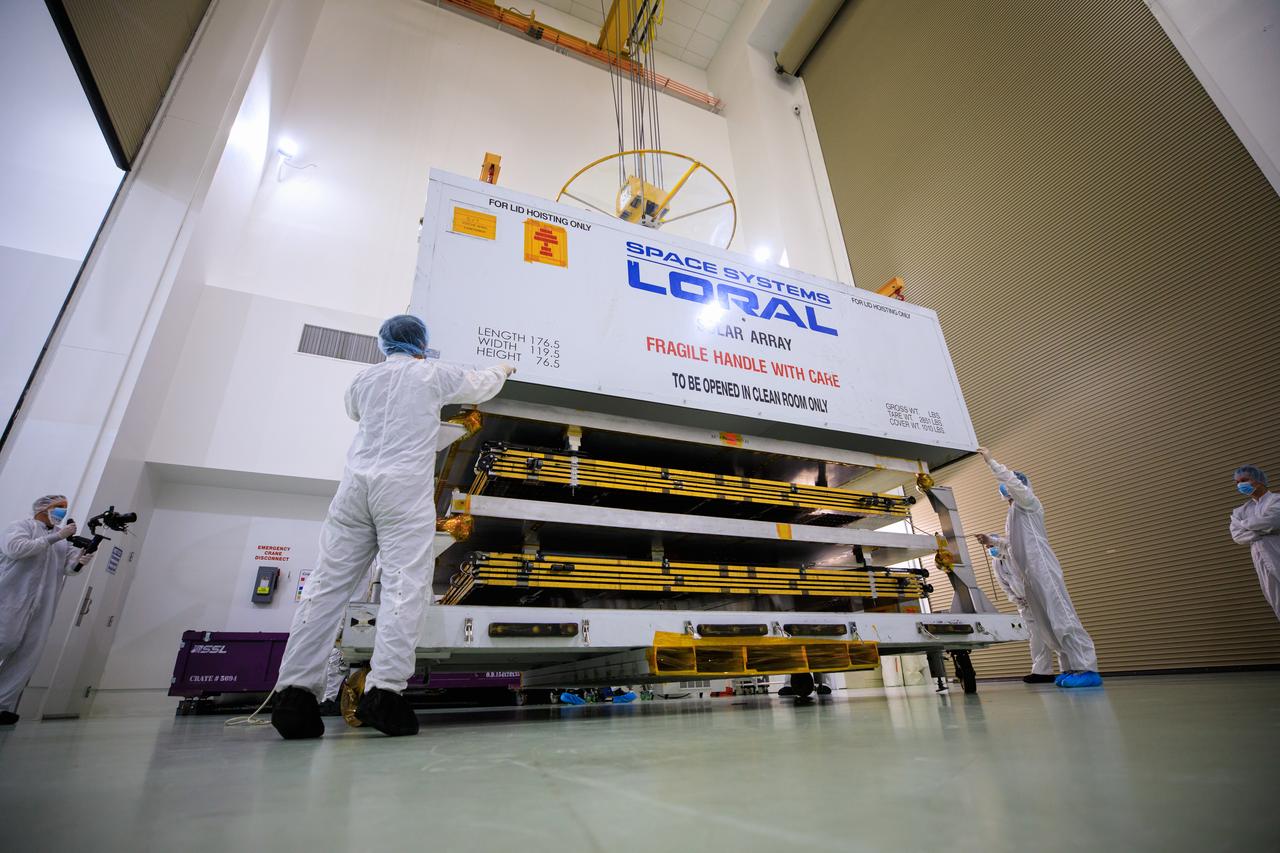

A NASA team uncrates the twin solar arrays for the agency’s Psyche spacecraft at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 18, 2023. The solar arrays were shipped from Maxar Technologies, in San Jose, California. They are part of the solar electric propulsion system, provided by Maxar, that will power the spacecraft on its journey to explore a metal-rich asteroid. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for Oct. 5, 2023. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.
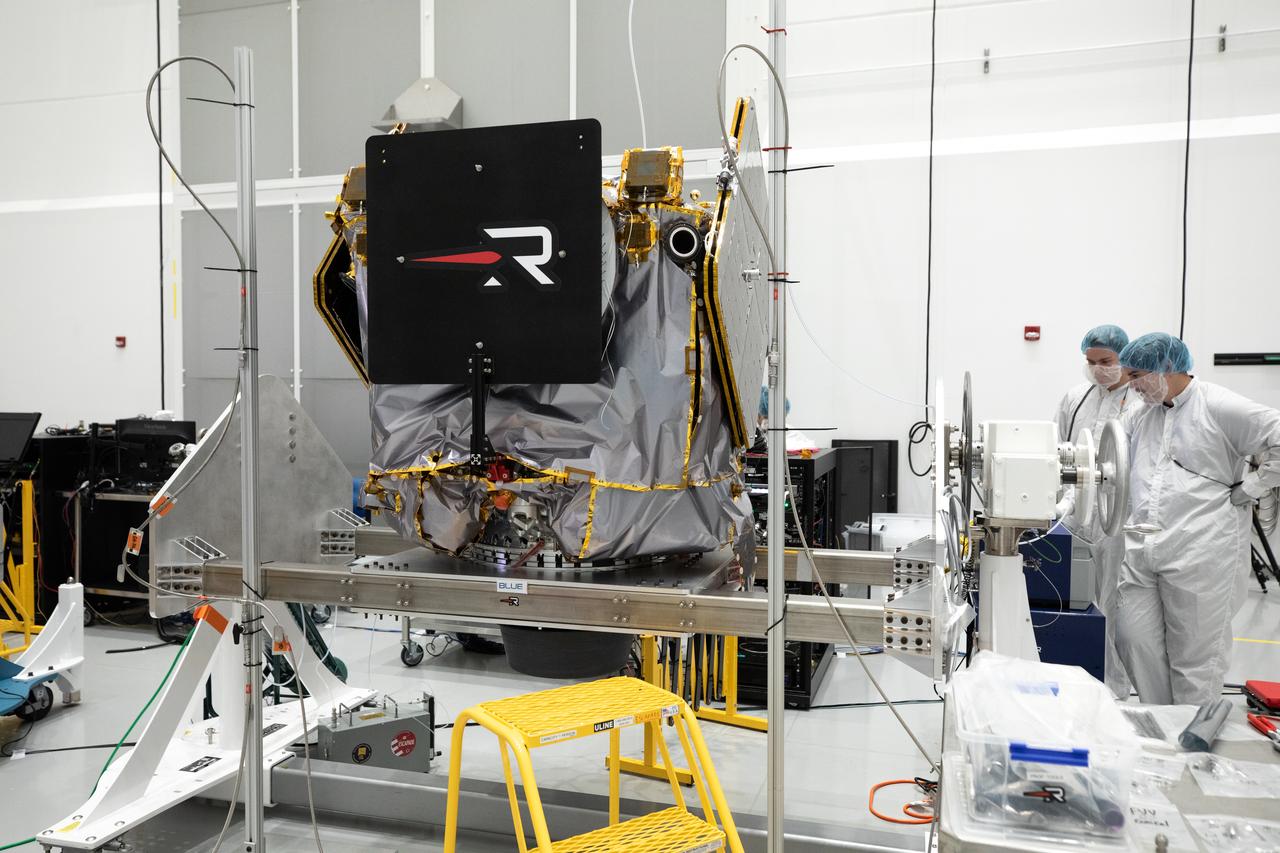

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
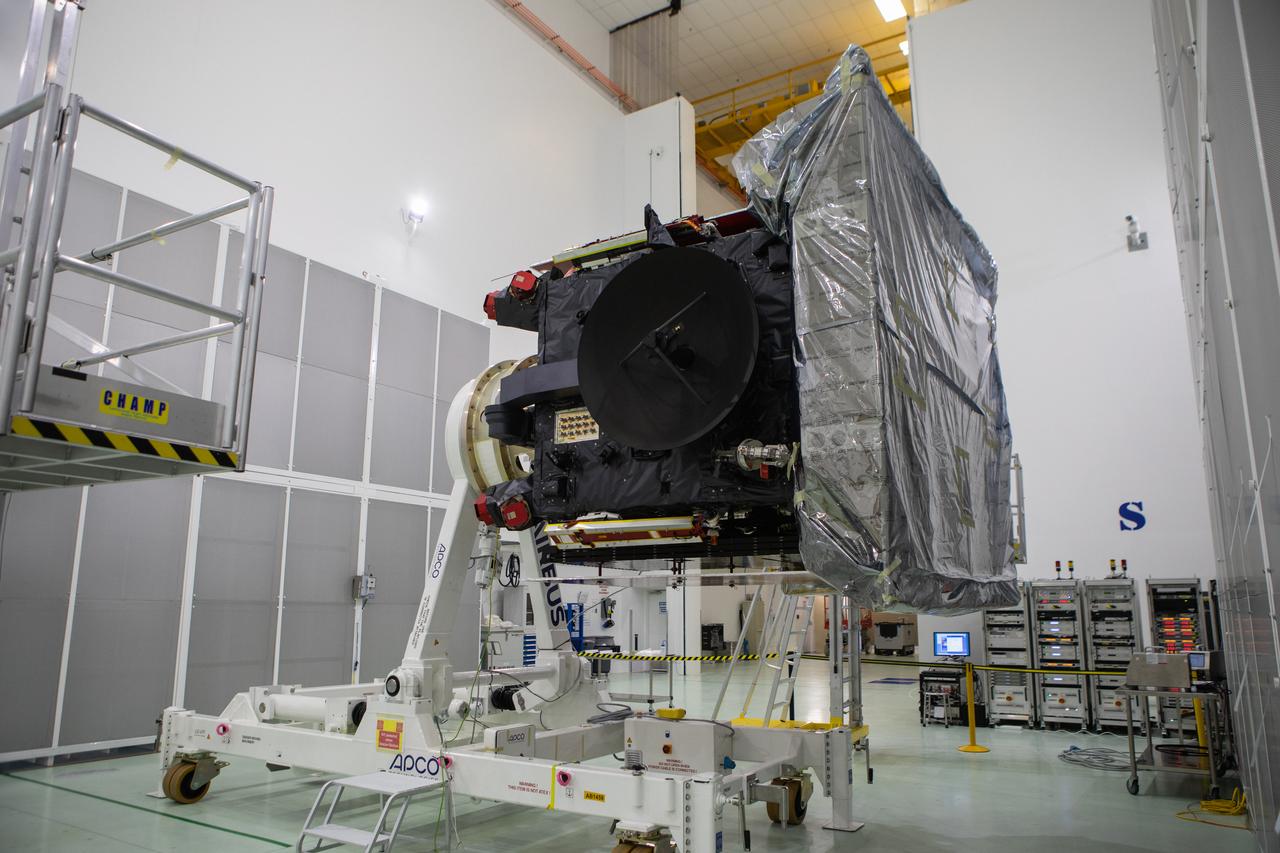

The Solar Orbiter spacecraft has been removed from its shipping container inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Nov. 18, 2019. The spacecraft was flown aboard an Antonov cargo aircraft from Munich, Germany, arriving at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Nov. 1, 2019. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
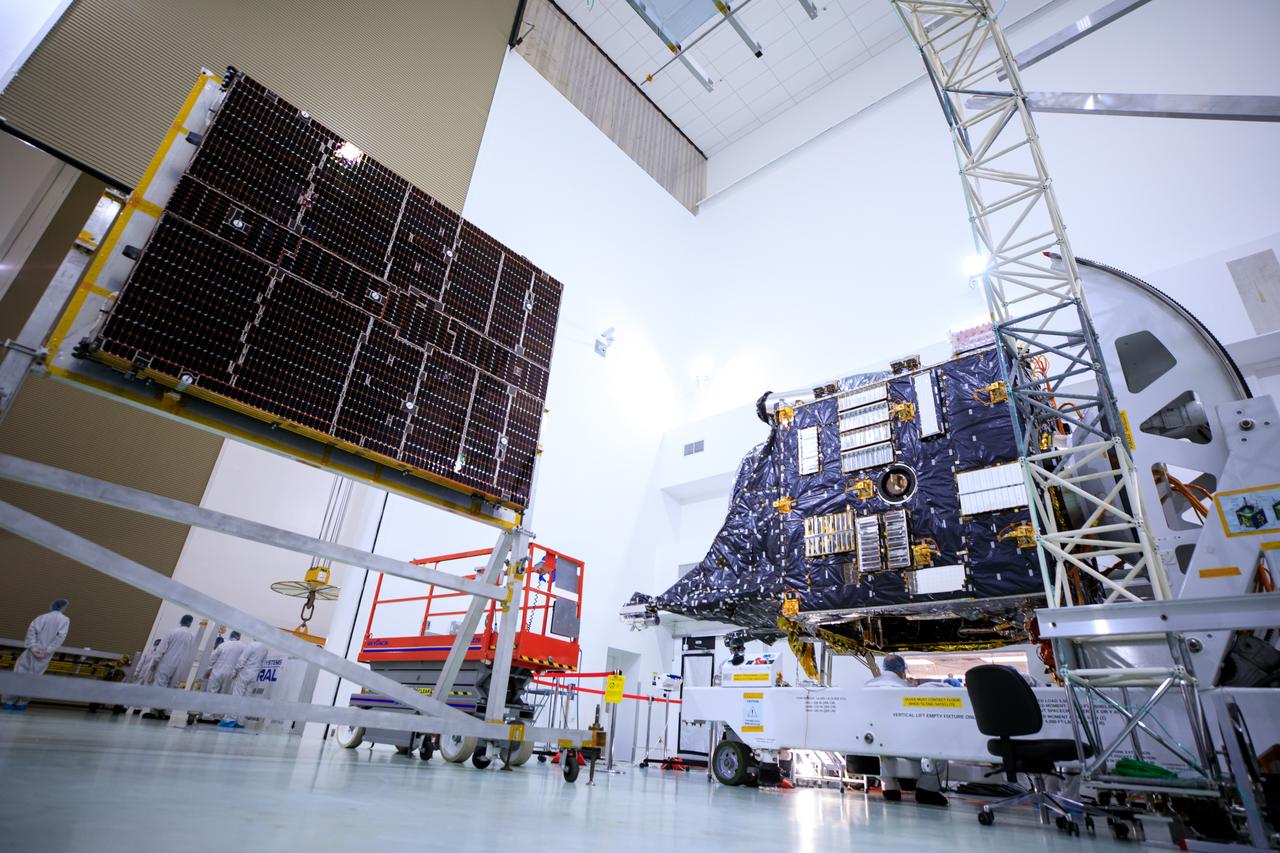

Solar arrays for the agency’s Psyche spacecraft is attached to a stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 18, 2023. The solar arrays were shipped from Maxar Technologies, in San, Jose, California. They are part of the solar electric propulsion system, provided by Maxar, that will power the spacecraft on its journey to explore a metal-rich asteroid. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for Oct. 5, 2023. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.
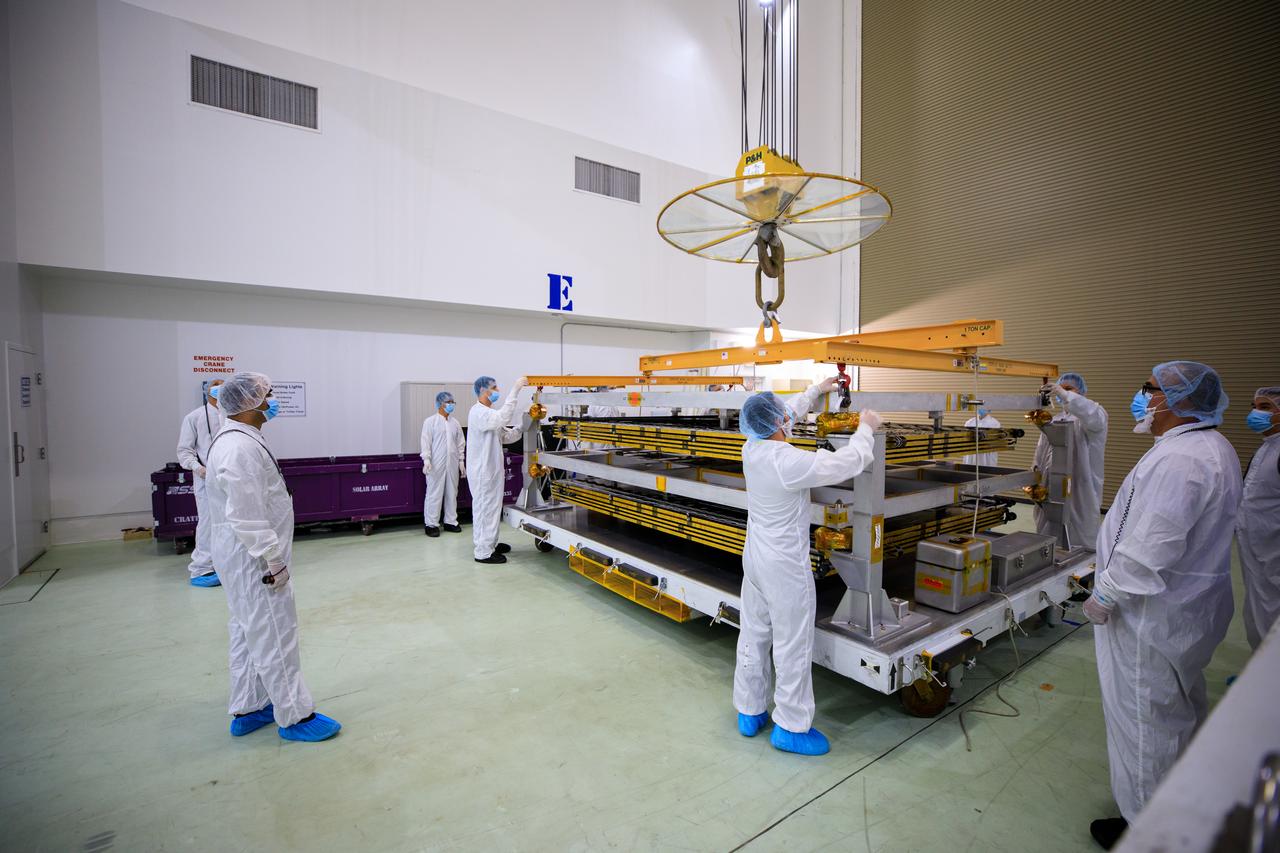

A NASA team uses a crane to lift the twin solar arrays for NASA’s Psyche spacecraft up from their shipping base at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 18, 2023. The solar arrays were shipped from Maxar Technologies, in San Jose, California. They are part of the solar electric propulsion system, provided by Maxar, that will power the spacecraft on its journey to explore a metal-rich asteroid. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for Oct. 5, 2023. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.
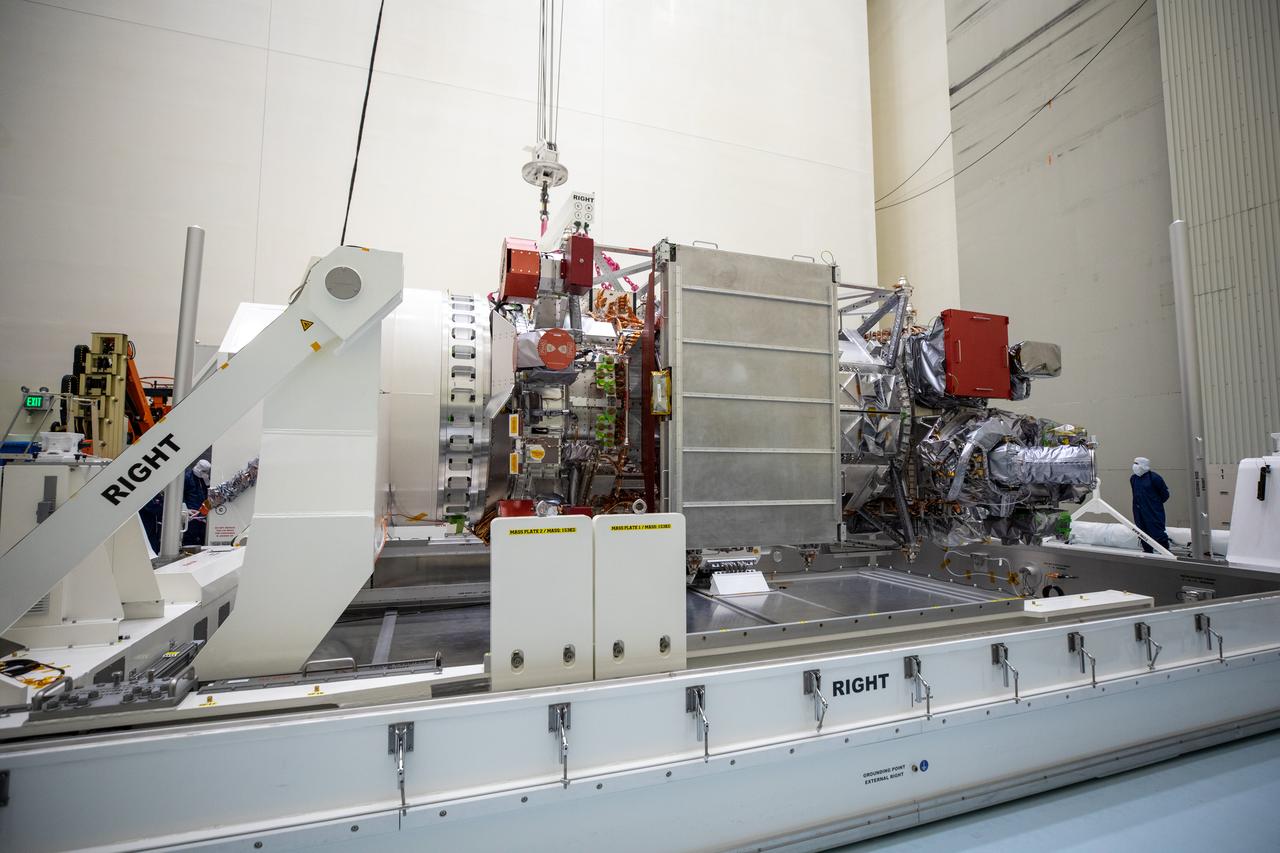
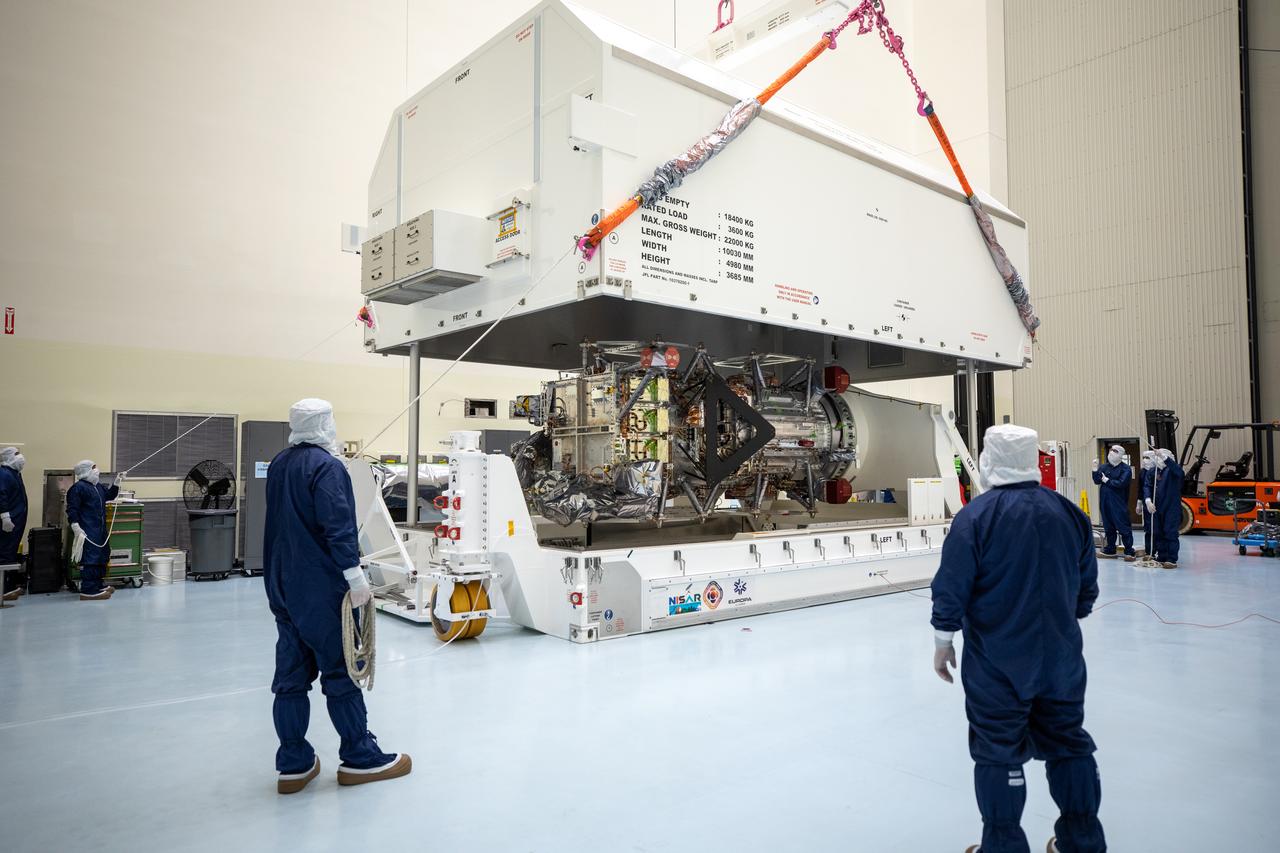
As part of prelaunch processing, crews inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida uncrate the agency’s largest planetary mission spacecraft, Europa Clipper, on Tuesday, May 28, 2024. Slated to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket later this year from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, Europa Clipper will help determine if conditions exist below the surface Jupiter’s fourth largest moon, Europa, that could support life.

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
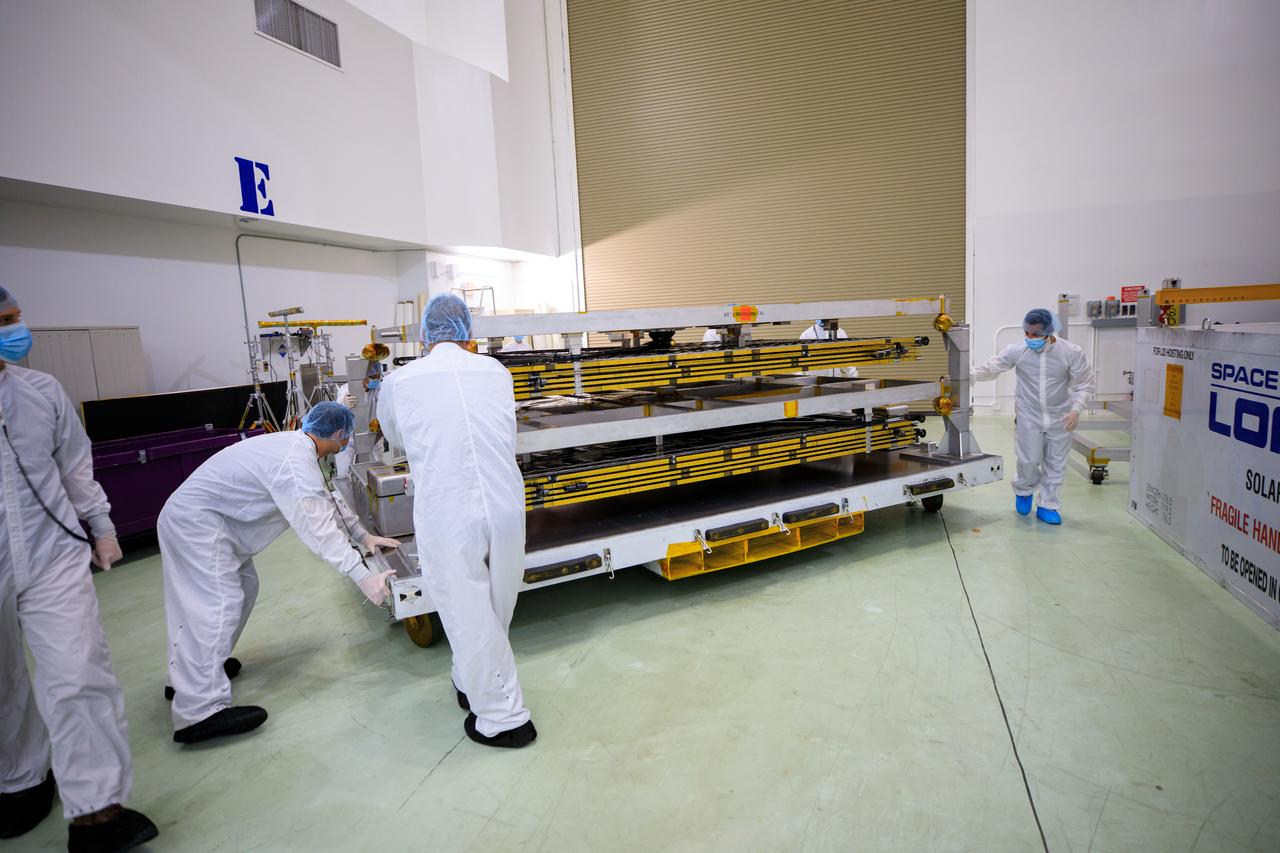

A NASA team uncrates the twin solar arrays for NASA’s Psyche spacecraft at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 18, 2023. The solar arrays were shipped from Maxar Technologies, in California. They are part of the solar electric propulsion system, provided by Maxar, that will power the spacecraft on its journey to explore a metal-rich asteroid. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for Oct. 5, 2023. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.

A NASA team lifts the cover off the twin solar arrays for NASA’s Psyche spacecraft at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 18, 2023. The solar arrays were shipped from Maxar Technologies, in San Jose, in California. They are part of the solar electric propulsion system, provided by Maxar, that will power the spacecraft on its journey to explore a metal-rich asteroid. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for Oct. 5, 2023. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.

Technicians remove NASA’s largest planetary mission spacecraft, Europa Clipper, from its protective shipping container inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, May 28, 2024. Slated to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket later this year from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, Europa Clipper will help determine if conditions exist below the surface Jupiter’s fourth largest moon, Europa that could support life.
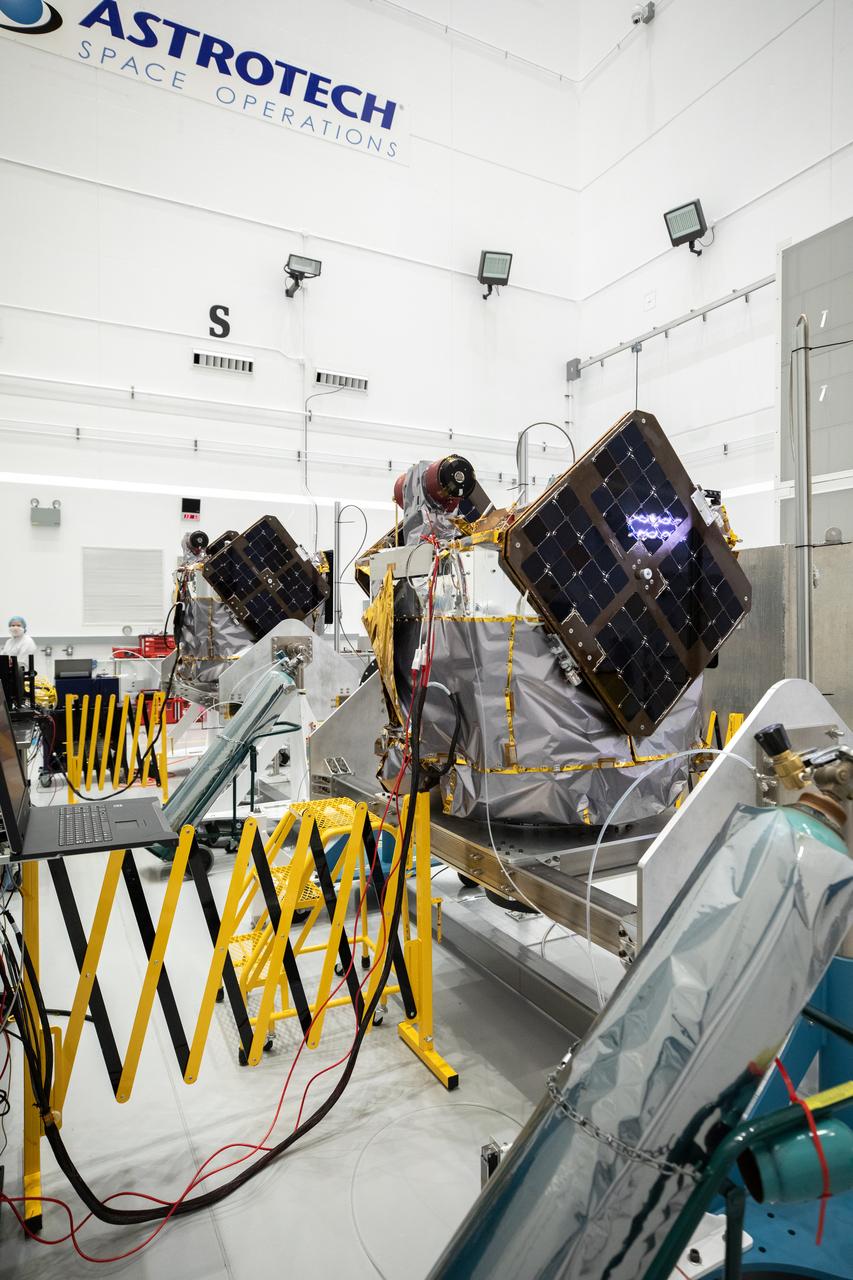

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
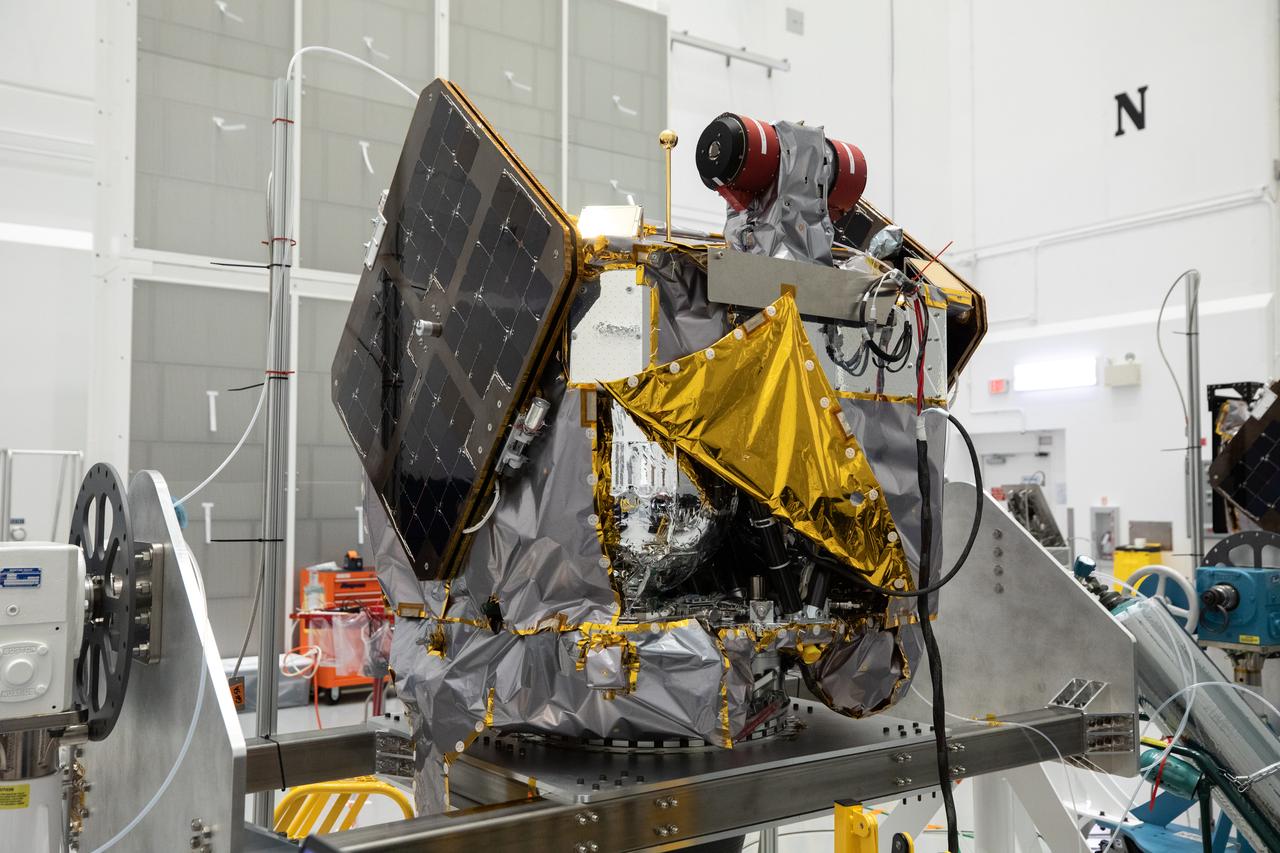

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
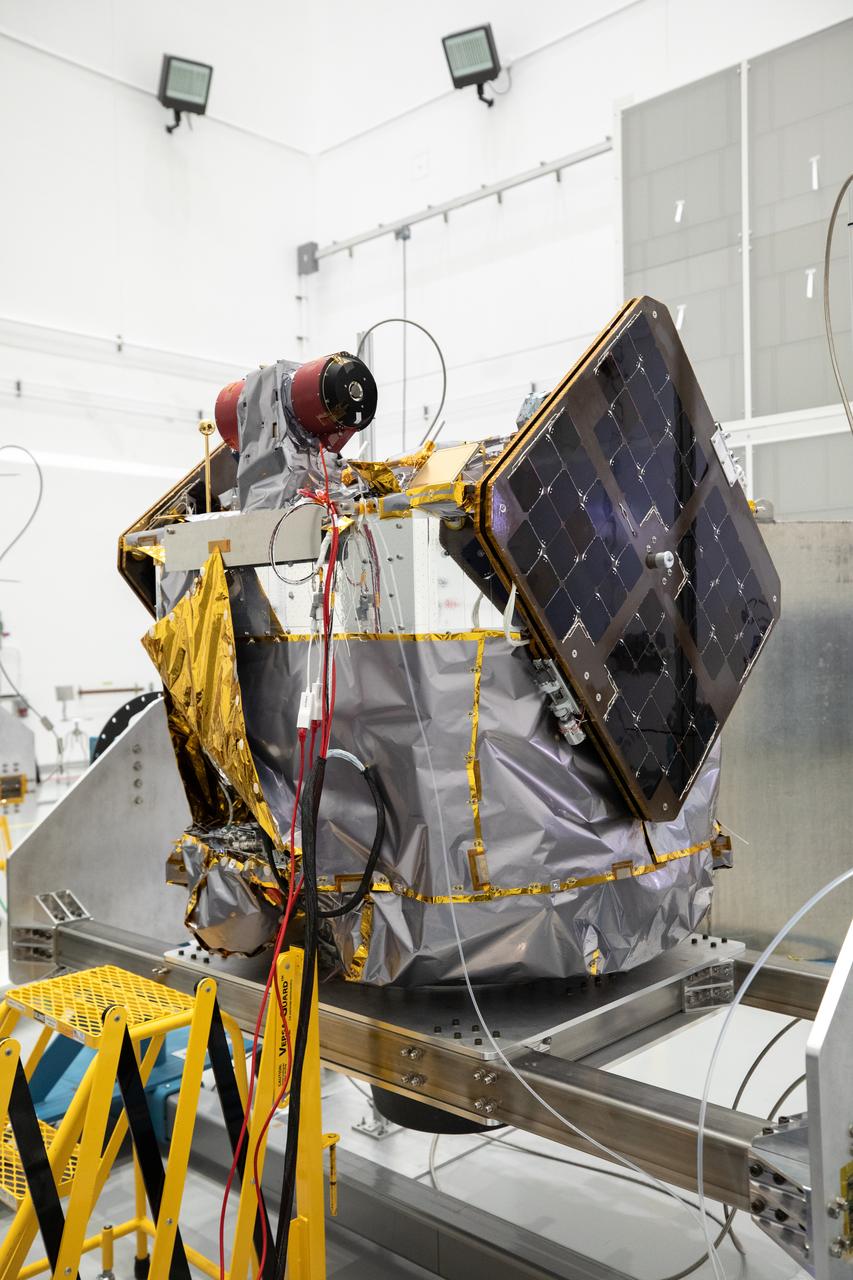

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
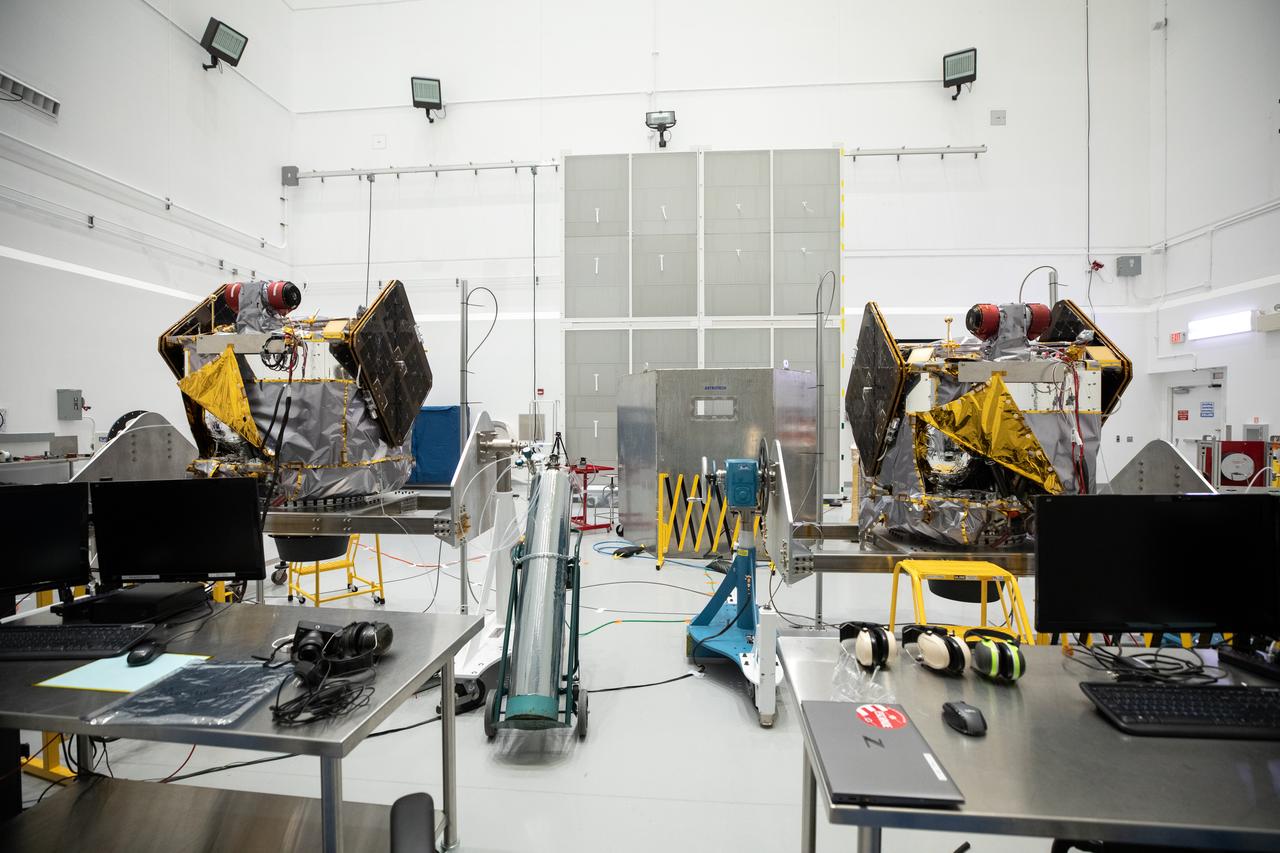

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
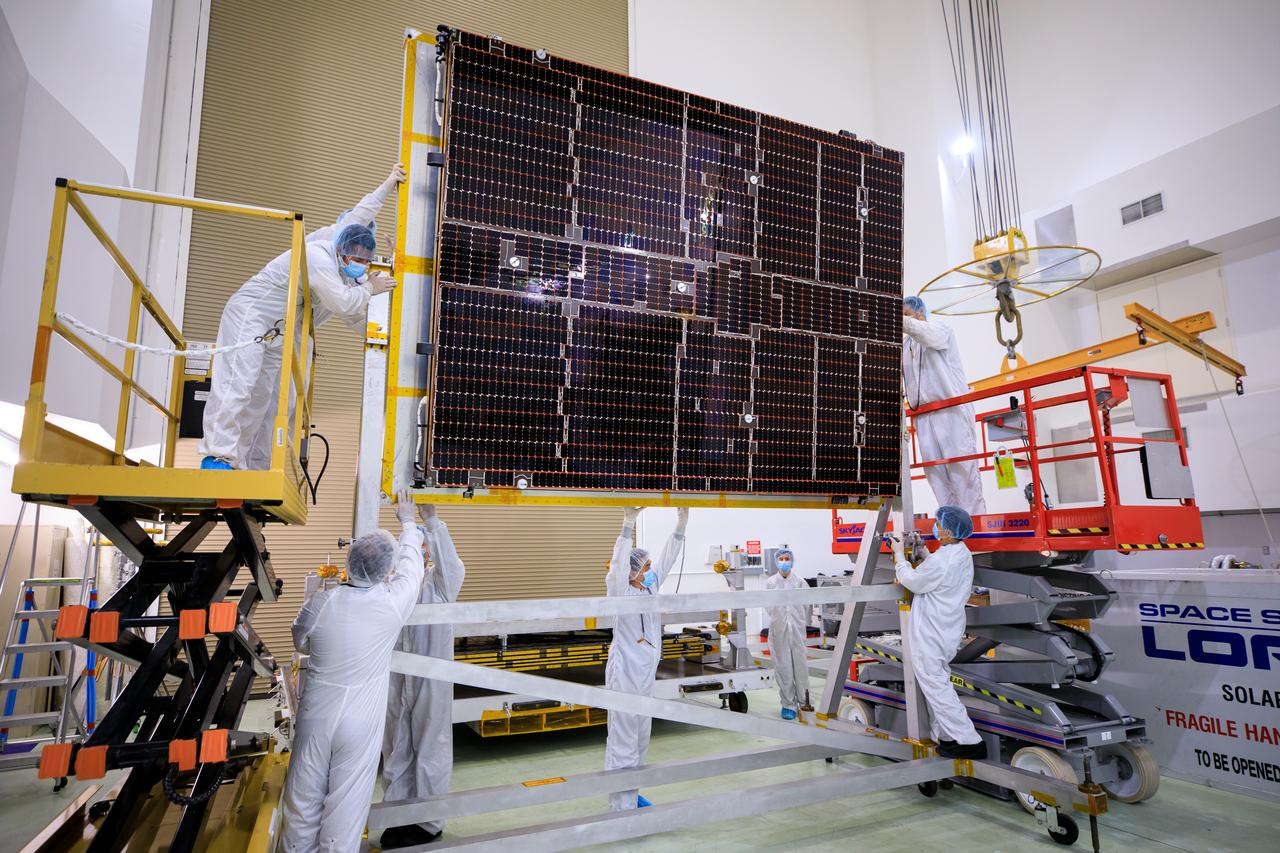

A NASA team helps attach solar arrays for the agency’s Psyche spacecraft onto a stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 18, 2023. The solar arrays were shipped from Maxar Technologies, in San, Jose, California. They are part of the solar electric propulsion system, provided by Maxar, that will power the spacecraft on its journey to explore a metal-rich asteroid. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for Oct. 5, 2023. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.
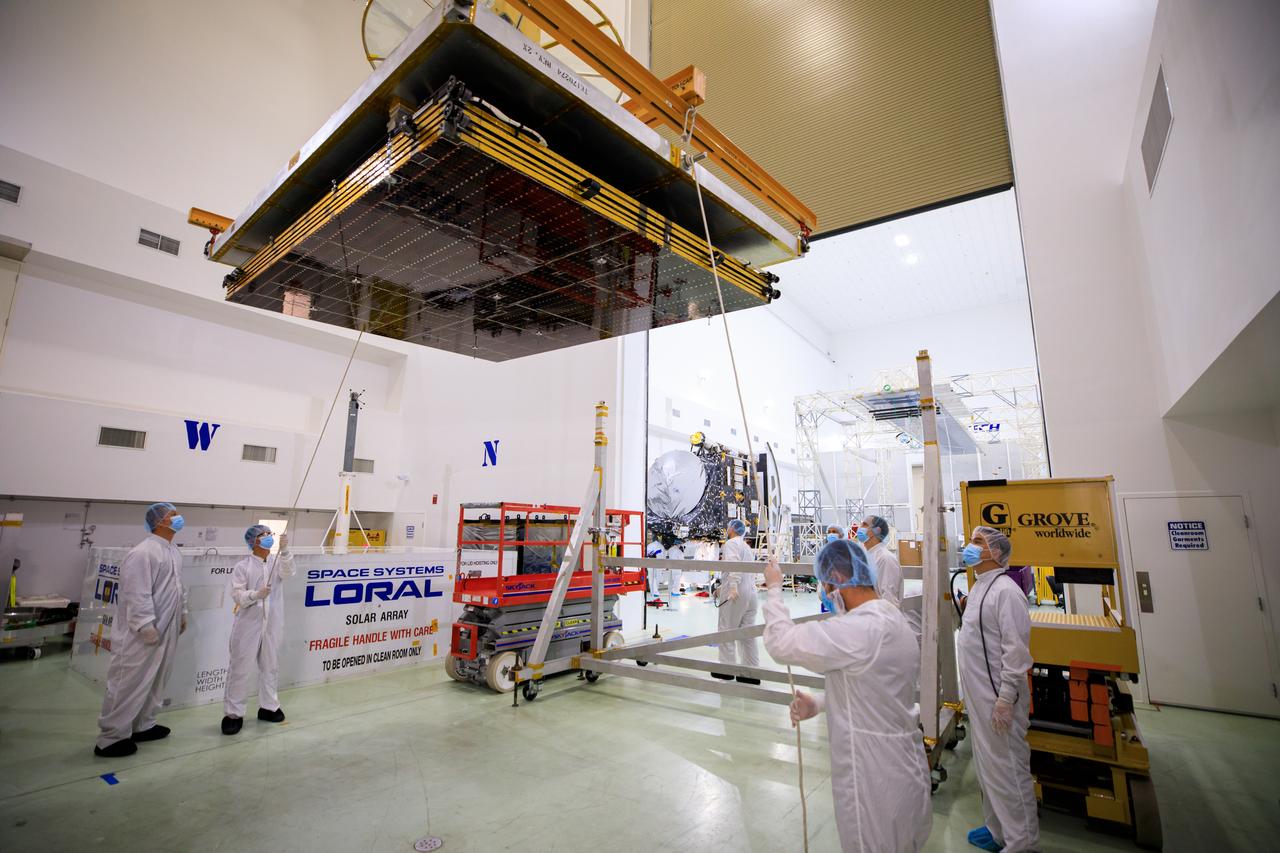

A NASA team assists as a crane is used to move the twin solar arrays for the agency’s Psyche spacecraft along the high bay inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 18, 2023. The solar arrays were shipped from Maxar Technologies, in San, Jose, California. They are part of the solar electric propulsion system, provided by Maxar, that will power the spacecraft on its journey to explore a metal-rich asteroid. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for Oct. 5, 2023. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.
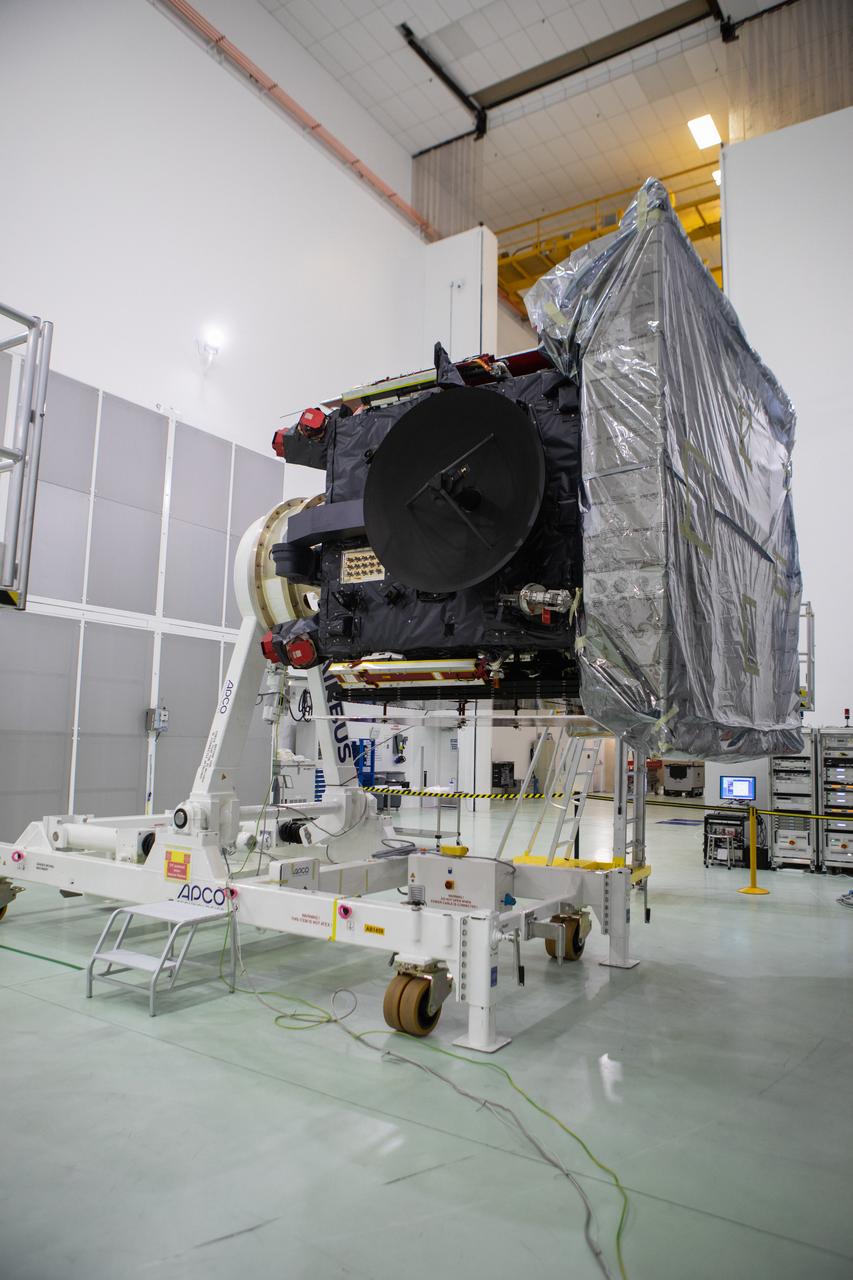

The Solar Orbiter spacecraft was removed from its shipping container inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Nov. 18, 2019. The spacecraft was flown aboard an Antonov cargo aircraft from Munich, Germany, arriving at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Nov. 1, 2019. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
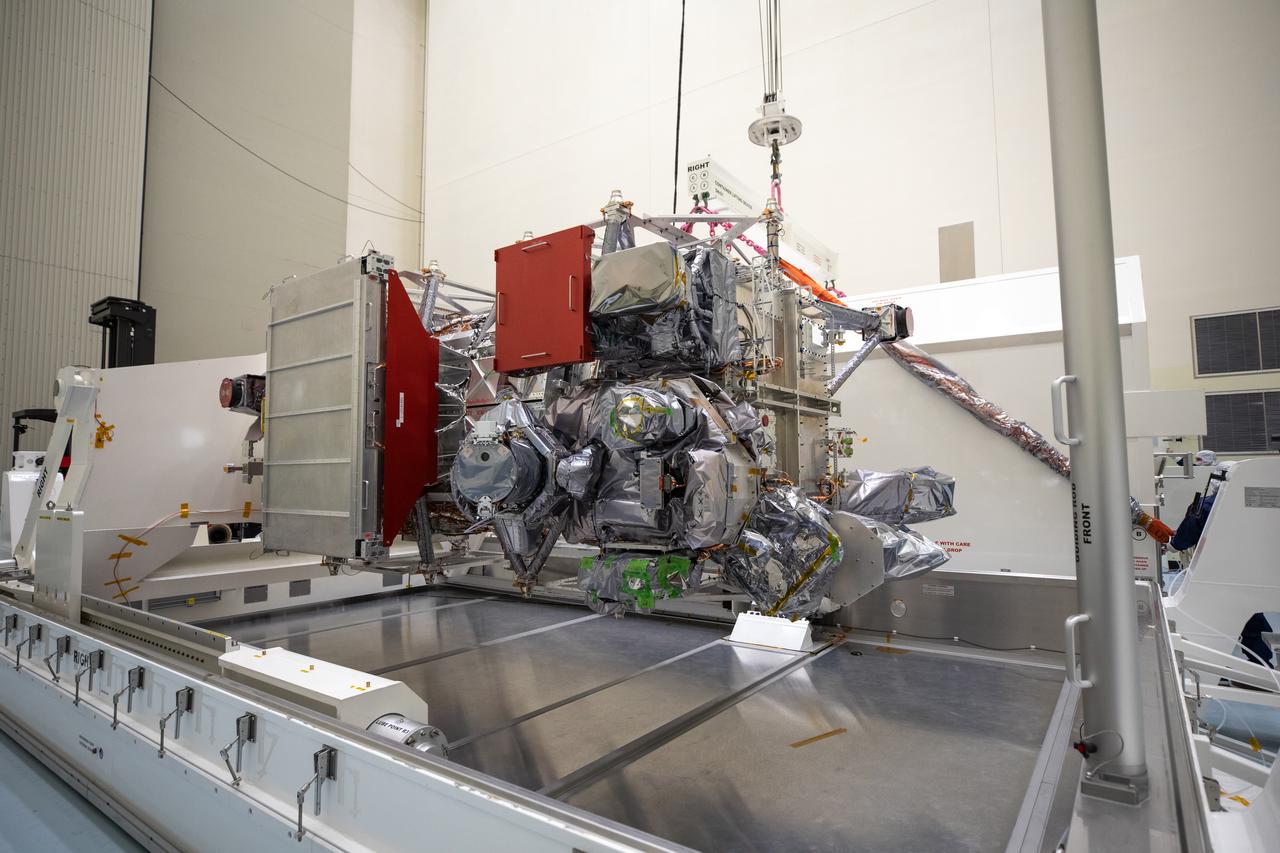

As part of prelaunch processing, crews inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida uncrate the agency’s largest planetary mission spacecraft, Europa Clipper, on Tuesday, May 28, 2024. Slated to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket later this year from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, Europa Clipper will help determine if conditions exist below the surface Jupiter’s fourth largest moon, Europa, that could support life.
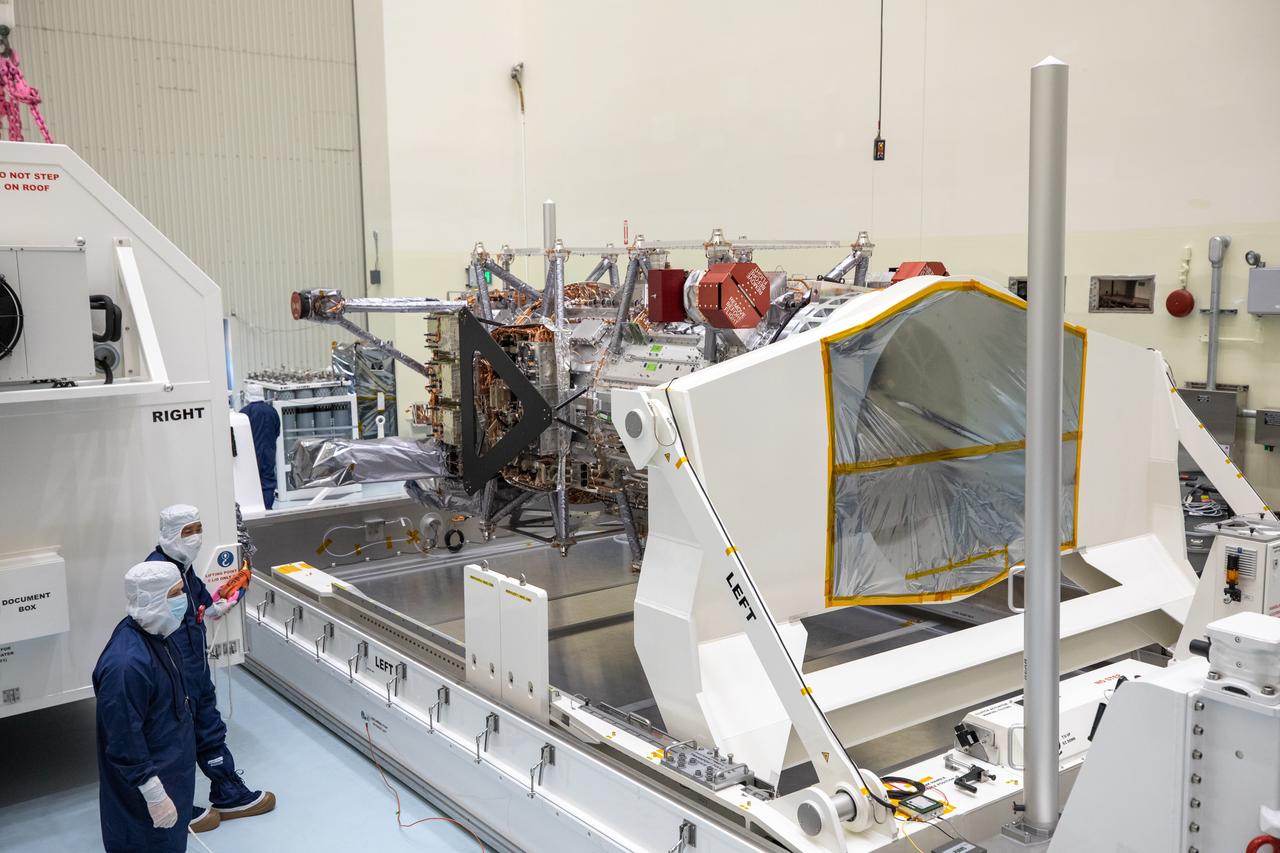

As part of prelaunch processing, crews inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida uncrate the agency’s largest planetary mission spacecraft, Europa Clipper, on Tuesday, May 28, 2024. Slated to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket later this year from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, Europa Clipper will help determine if conditions exist below the surface Jupiter’s fourth largest moon, Europa, that could support life.
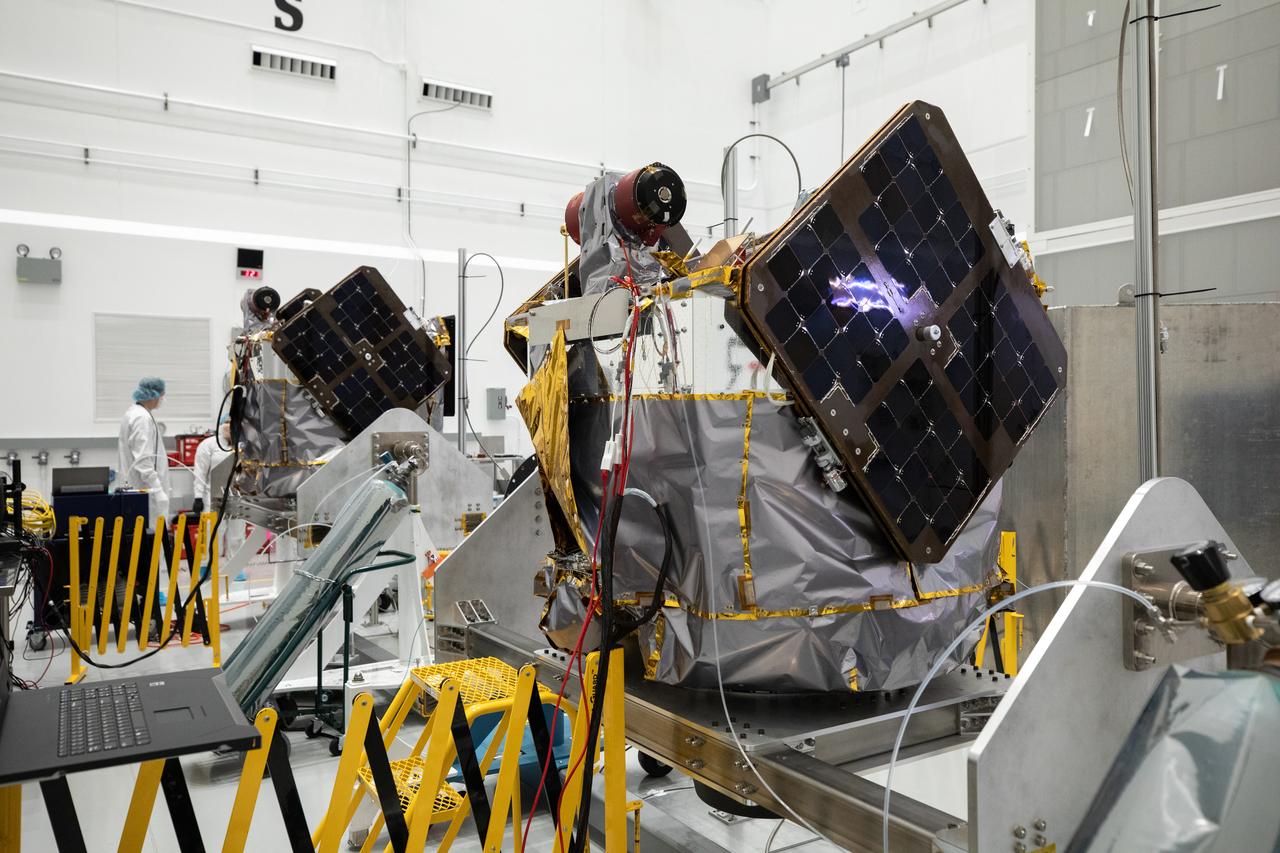

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
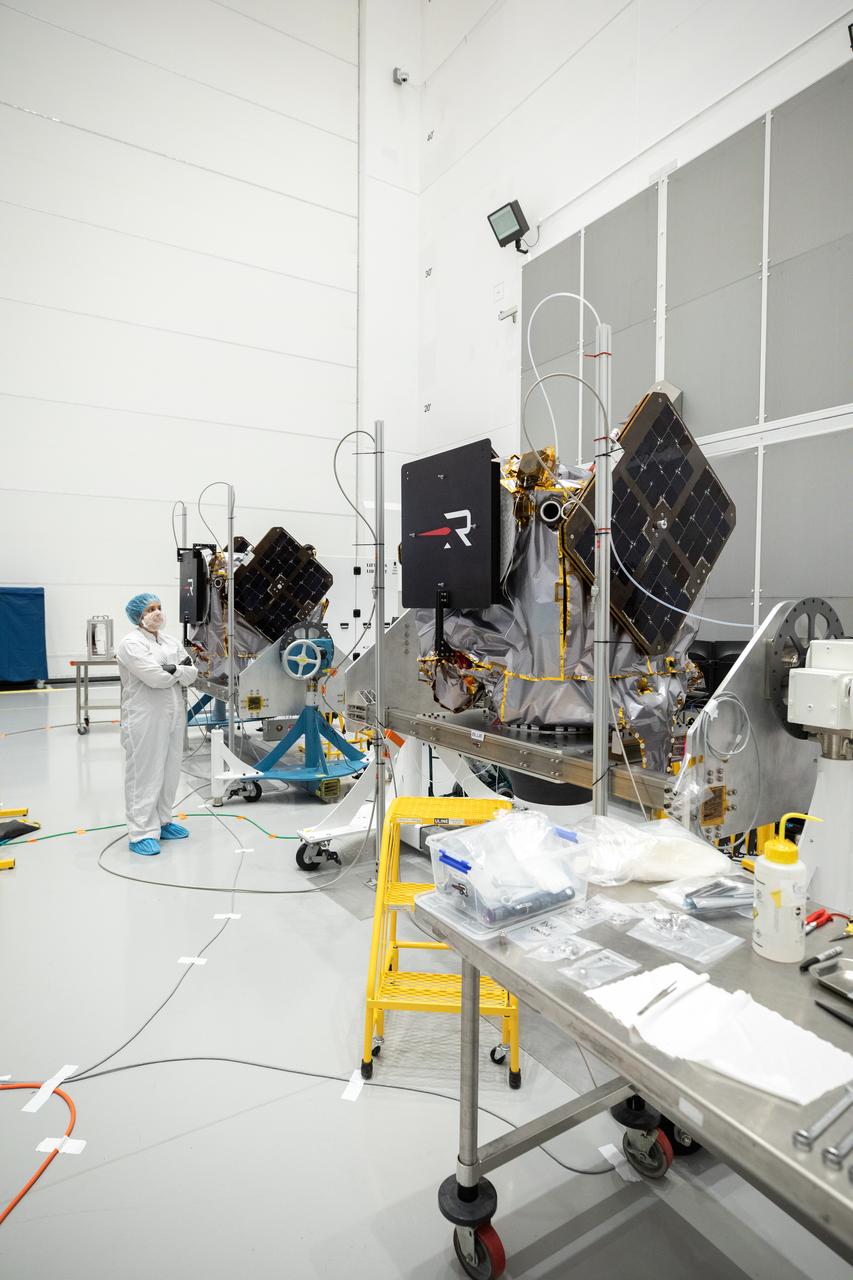

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.

Technicians remove NASA’s largest planetary mission spacecraft, Europa Clipper, from its protective shipping container inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, May 28, 2024. Slated to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket later this year from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, Europa Clipper will help determine if conditions exist below the surface Jupiter’s fourth largest moon, Europa that could support life.
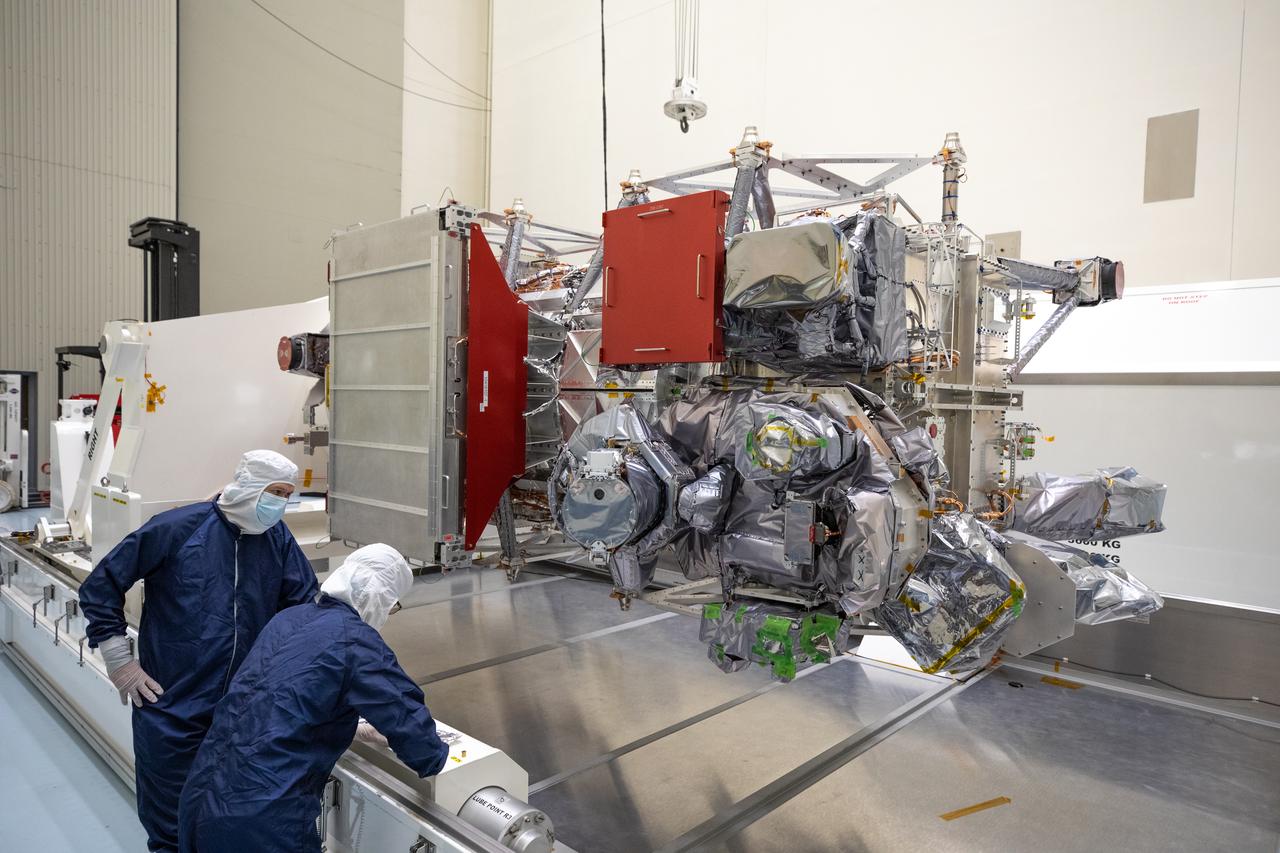

As part of prelaunch processing, crews inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida uncrate the agency’s largest planetary mission spacecraft, Europa Clipper, on Tuesday, May 28, 2024. Slated to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket later this year from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, Europa Clipper will help determine if conditions exist below the surface Jupiter’s fourth largest moon, Europa, that could support life.

Employees with BAE Systems conduct spacecraft processing of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Jan. 16, 2025. BAE Systems (formerly Ball Aerospace) built the telescope and the spacecraft bus. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. Riding along with SPHEREx, NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) mission will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind. Liftoff aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for 10:09 p.m. EST (7:09 p.m. PST), Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025, from Space Launch Complex 4 East.
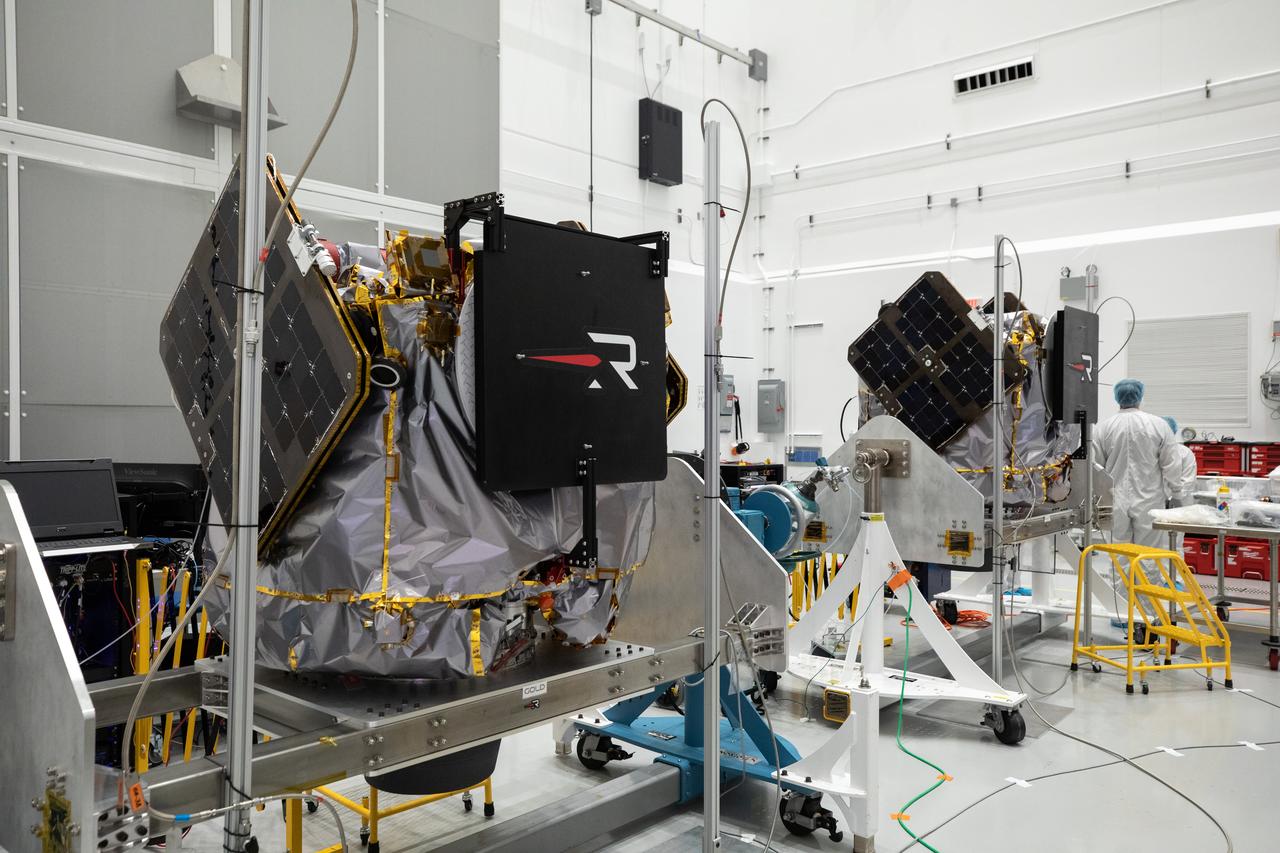

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
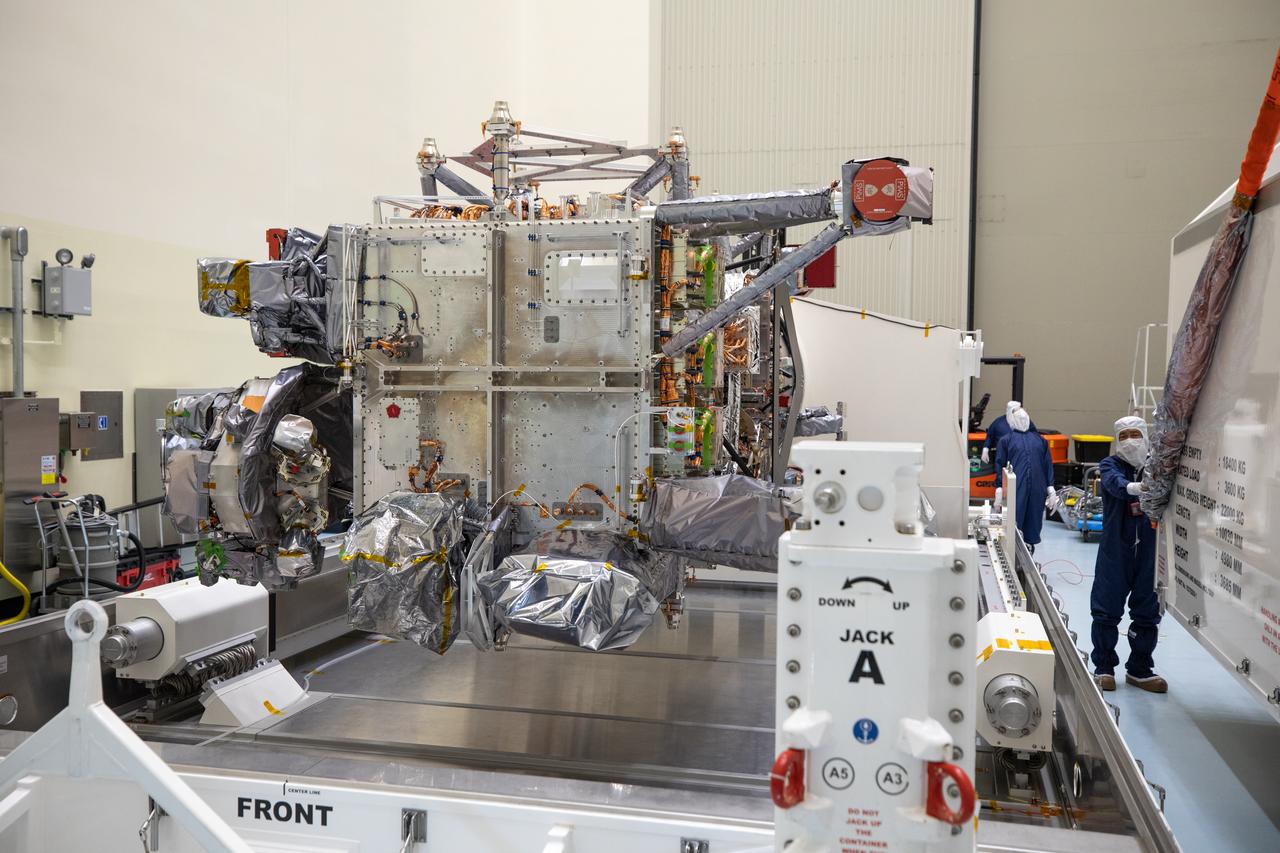
As part of prelaunch processing, crews inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida uncrate the agency’s largest planetary mission spacecraft, Europa Clipper, on Tuesday, May 28, 2024. Slated to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket later this year from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, Europa Clipper will help determine if conditions exist below the surface Jupiter’s fourth largest moon, Europa, that could support life.

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
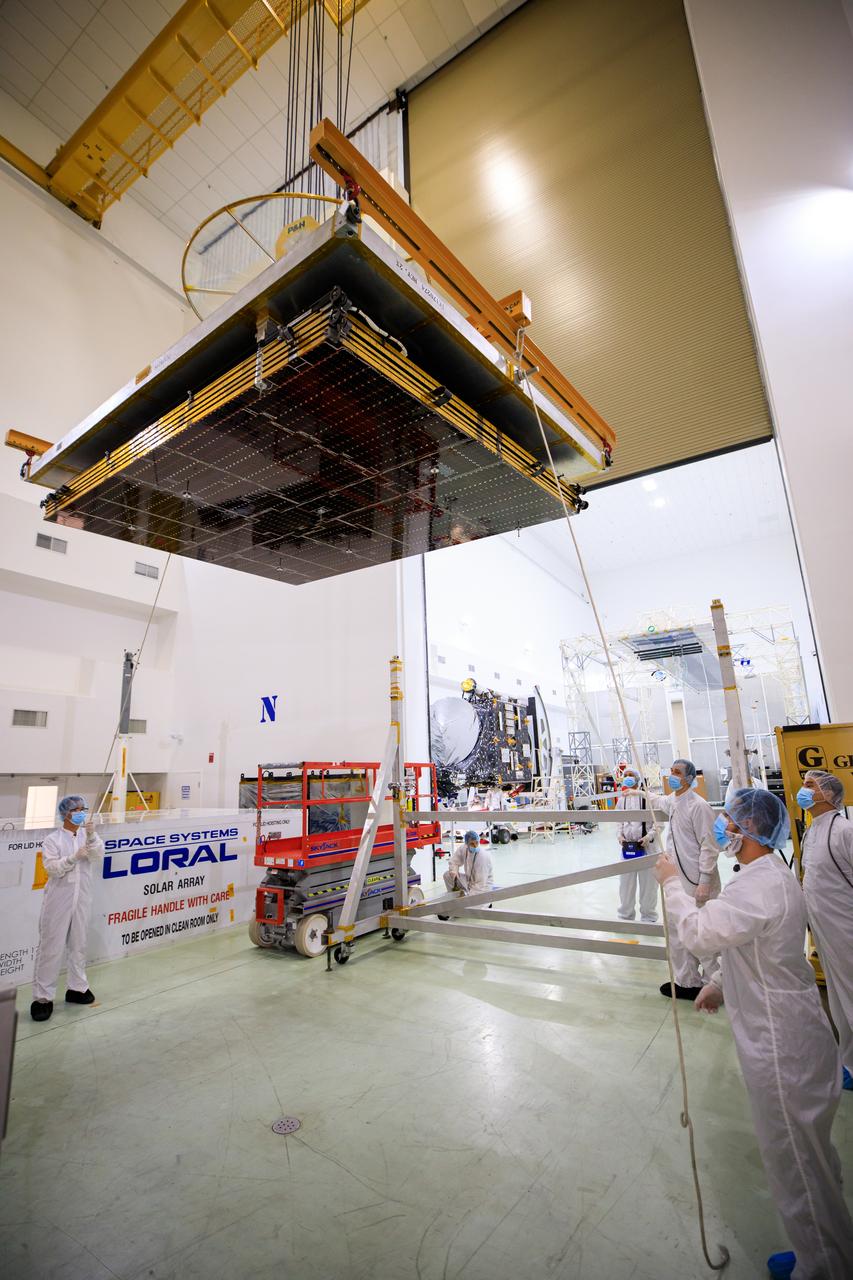

A NASA team assists as a crane is used to move the twin solar arrays for the agency’s Psyche spacecraft along the high bay inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 18, 2023. The solar arrays were shipped from Maxar Technologies, in San, Jose, California. They are part of the solar electric propulsion system, provided by Maxar, that will power the spacecraft on its journey to explore a metal-rich asteroid. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for Oct. 5, 2023. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.

Employees with BAE Systems conduct spacecraft processing of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Jan. 16, 2025. BAE Systems (formerly Ball Aerospace) built the telescope and the spacecraft bus. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. Riding along with SPHEREx, NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) mission will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind. Liftoff aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for 10:09 p.m. EST (7:09 p.m. PST), Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025, from Space Launch Complex 4 East.

The Solar Orbiter spacecraft has been removed from its shipping container inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Nov. 18, 2019. The spacecraft was flown aboard an Antonov cargo aircraft from Munich, Germany, arriving at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Nov. 1, 2019. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.

Employees with BAE Systems conduct spacecraft processing of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Jan. 16, 2025. BAE Systems (formerly Ball Aerospace) built the telescope and the spacecraft bus. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. Riding along with SPHEREx, NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) mission will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind. Liftoff aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for 10:09 p.m. EST (7:09 p.m. PST), Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025, from Space Launch Complex 4 East.
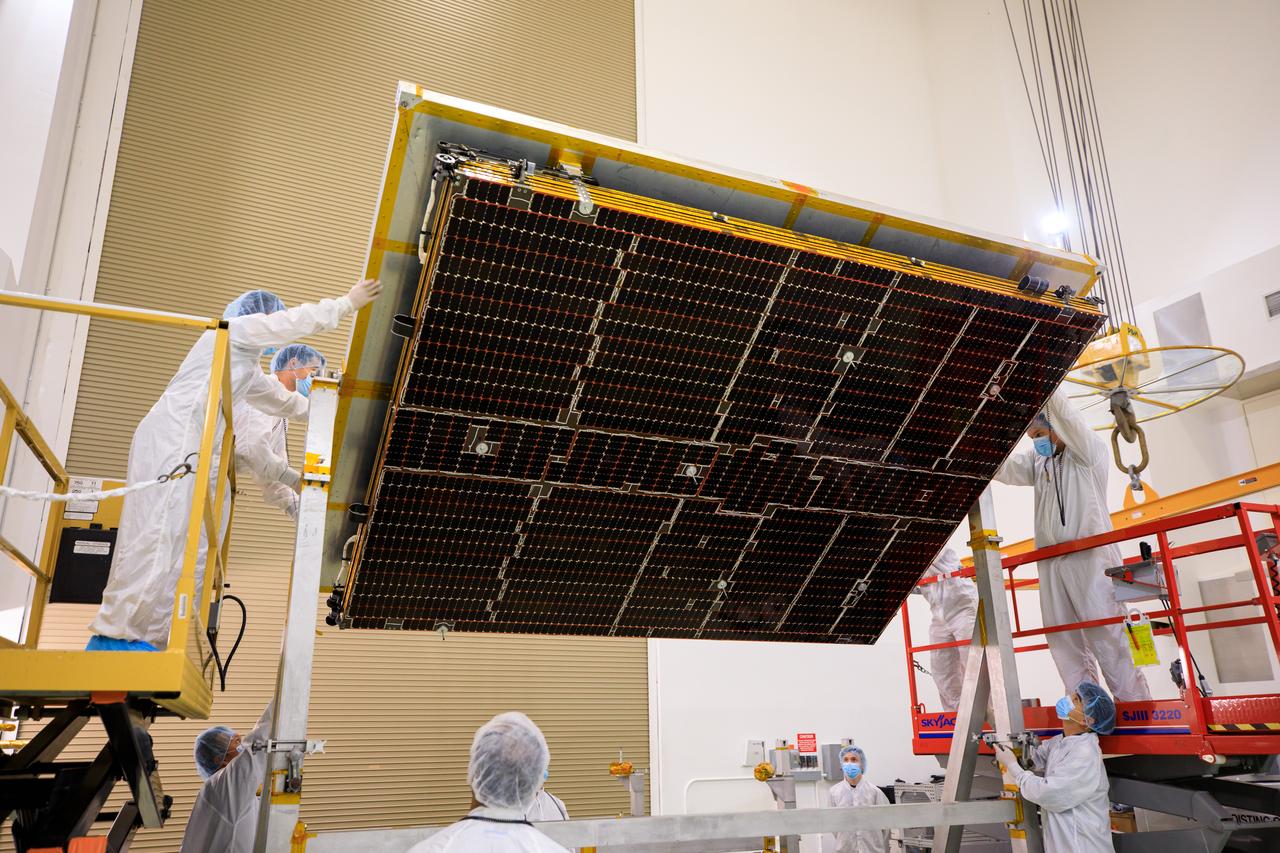

A NASA team helps lower one of two solar arrays for the agency’s Psyche spacecraft onto a stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 18, 2023. The solar arrays were shipped from Maxar Technologies, in San, Jose, California. They are part of the solar electric propulsion system, provided by Maxar, that will power the spacecraft on its journey to explore a metal-rich asteroid. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for Oct. 5, 2023. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.
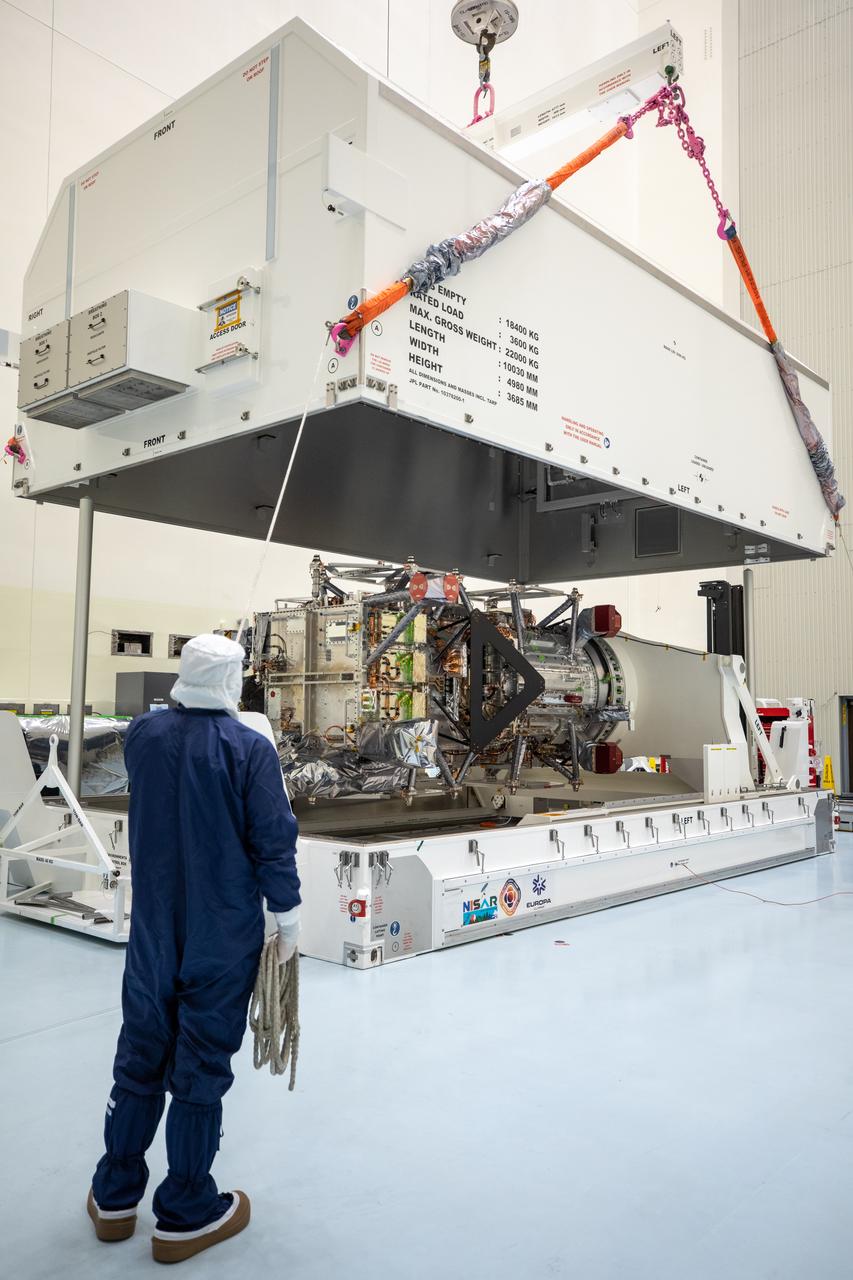

Technicians remove NASA’s largest planetary mission spacecraft, Europa Clipper, from its protective shipping container inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, May 28, 2024. Slated to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket later this year from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, Europa Clipper will help determine if conditions exist below the surface Jupiter’s fourth largest moon, Europa that could support life.
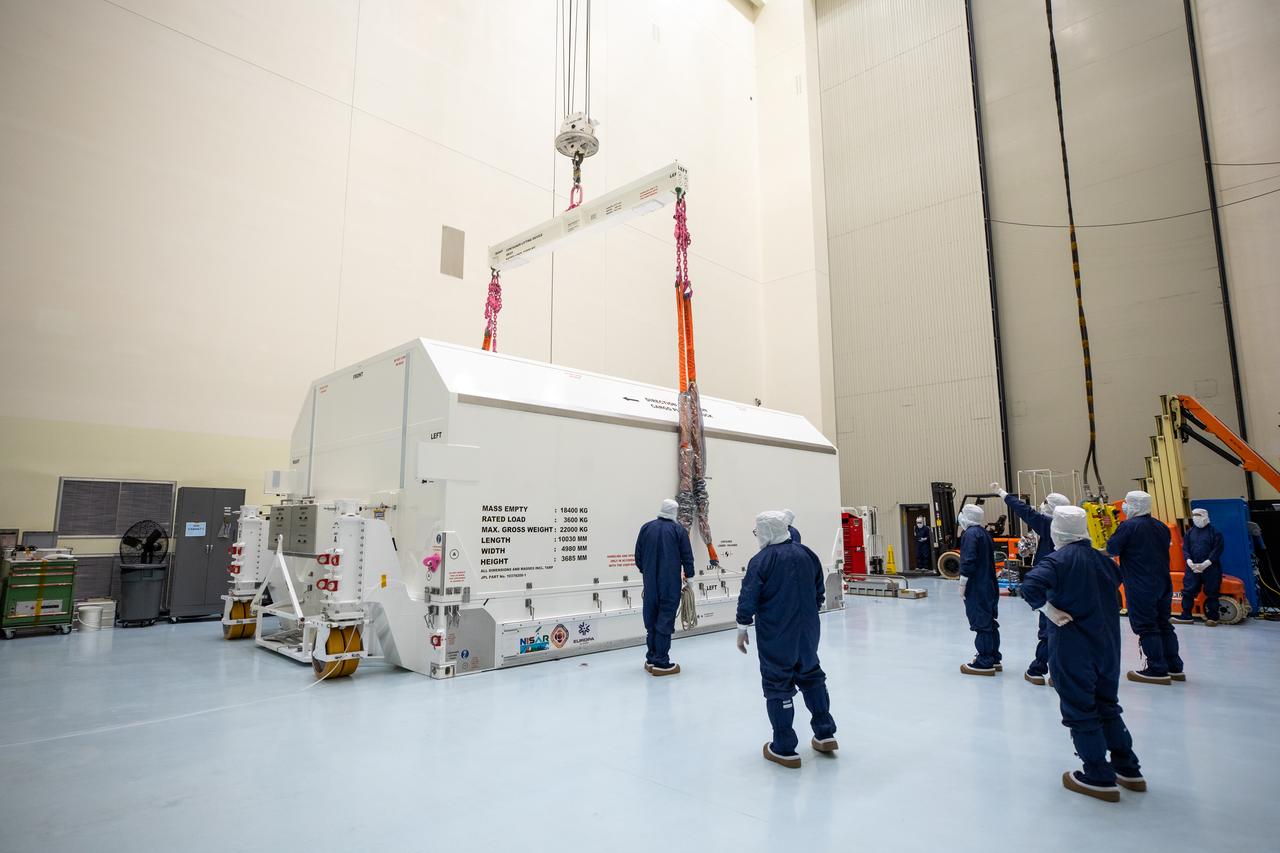

Technicians remove NASA’s largest planetary mission spacecraft, Europa Clipper, from its protective shipping container inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, May 28, 2024. Slated to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket later this year from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, Europa Clipper will help determine if conditions exist below the surface Jupiter’s fourth largest moon, Europa that could support life.
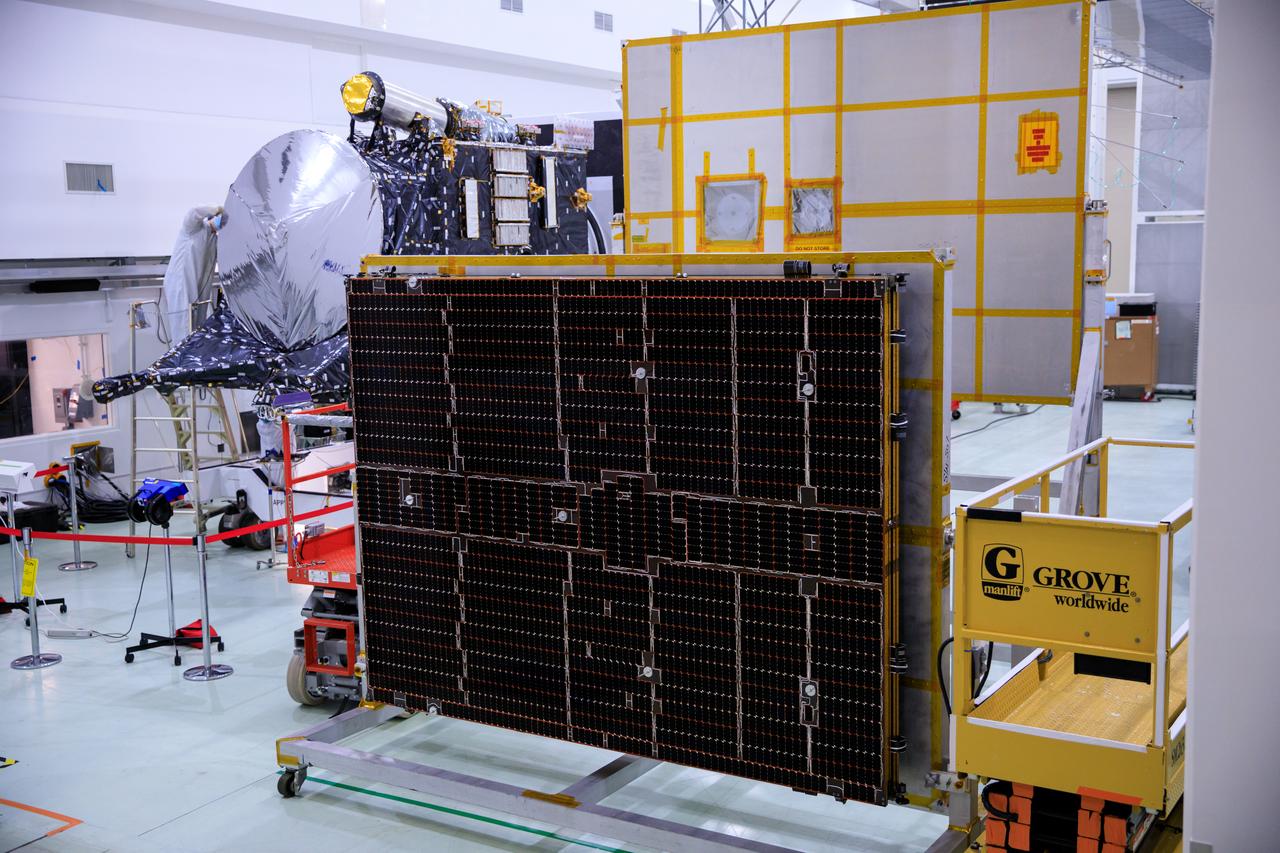

Solar arrays for the agency’s Psyche spacecraft is attached to a stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 18, 2023. The solar arrays were shipped from Maxar Technologies, in San, Jose, California. They are part of the solar electric propulsion system, provided by Maxar, that will power the spacecraft on its journey to explore a metal-rich asteroid. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for Oct. 5, 2023. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.
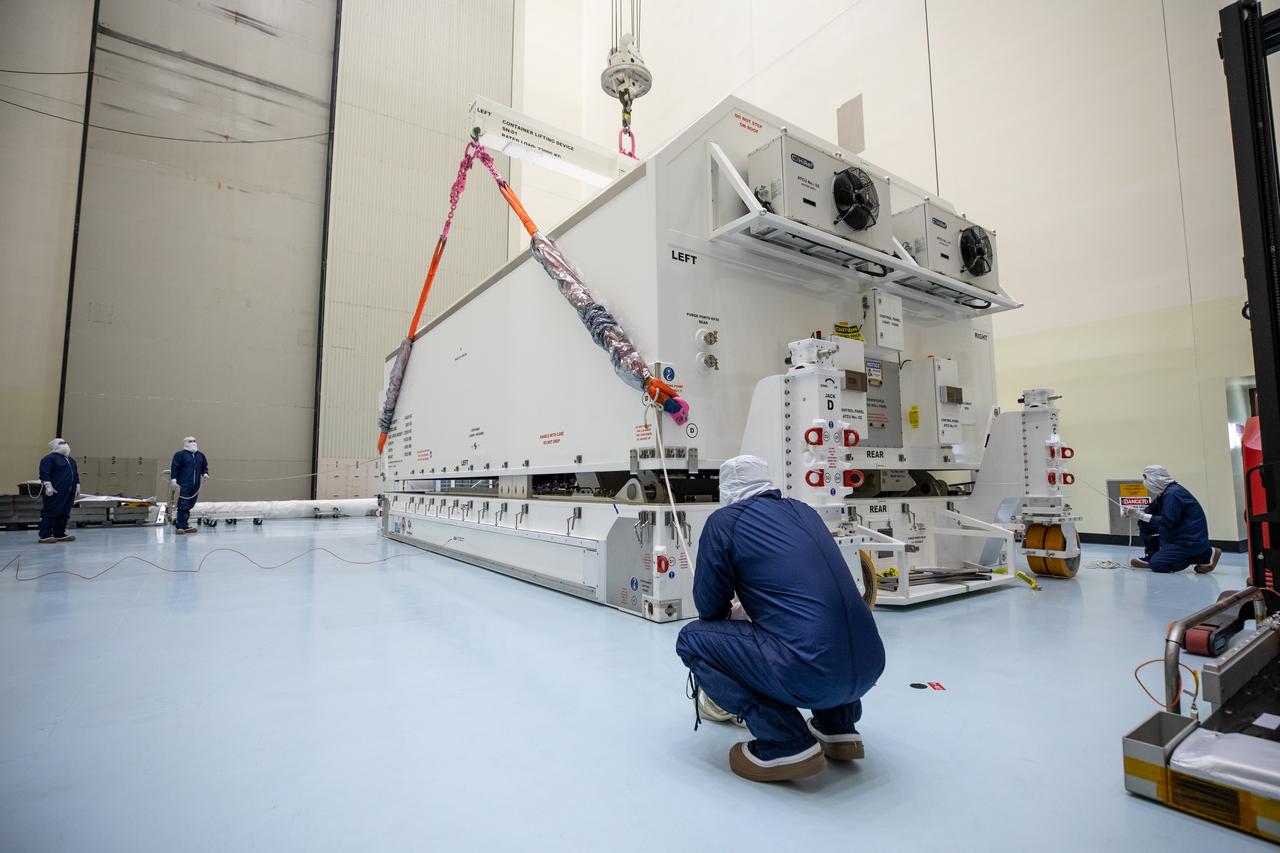

Technicians remove NASA’s largest planetary mission spacecraft, Europa Clipper, from its protective shipping container inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, May 28, 2024. Slated to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket later this year from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, Europa Clipper will help determine if conditions exist below the surface Jupiter’s fourth largest moon, Europa that could support life.
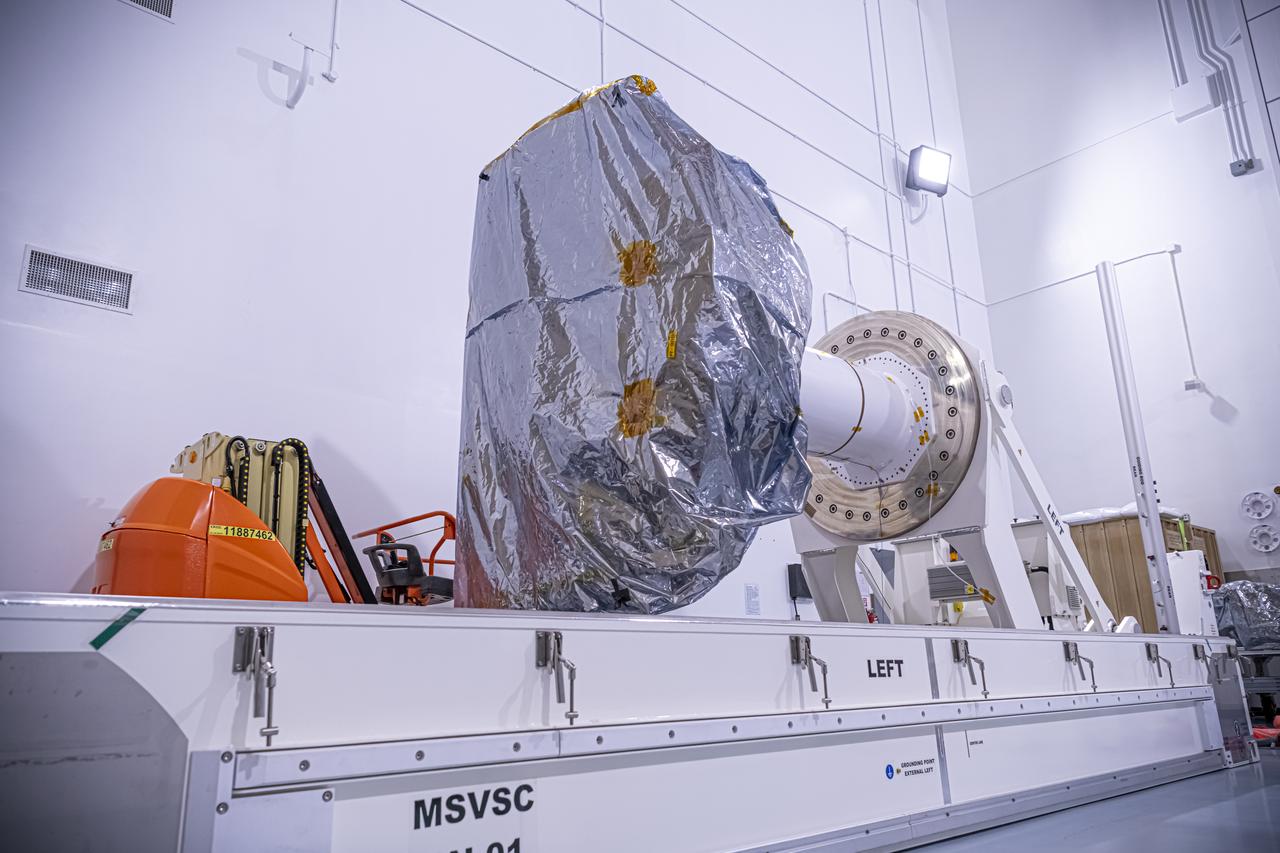

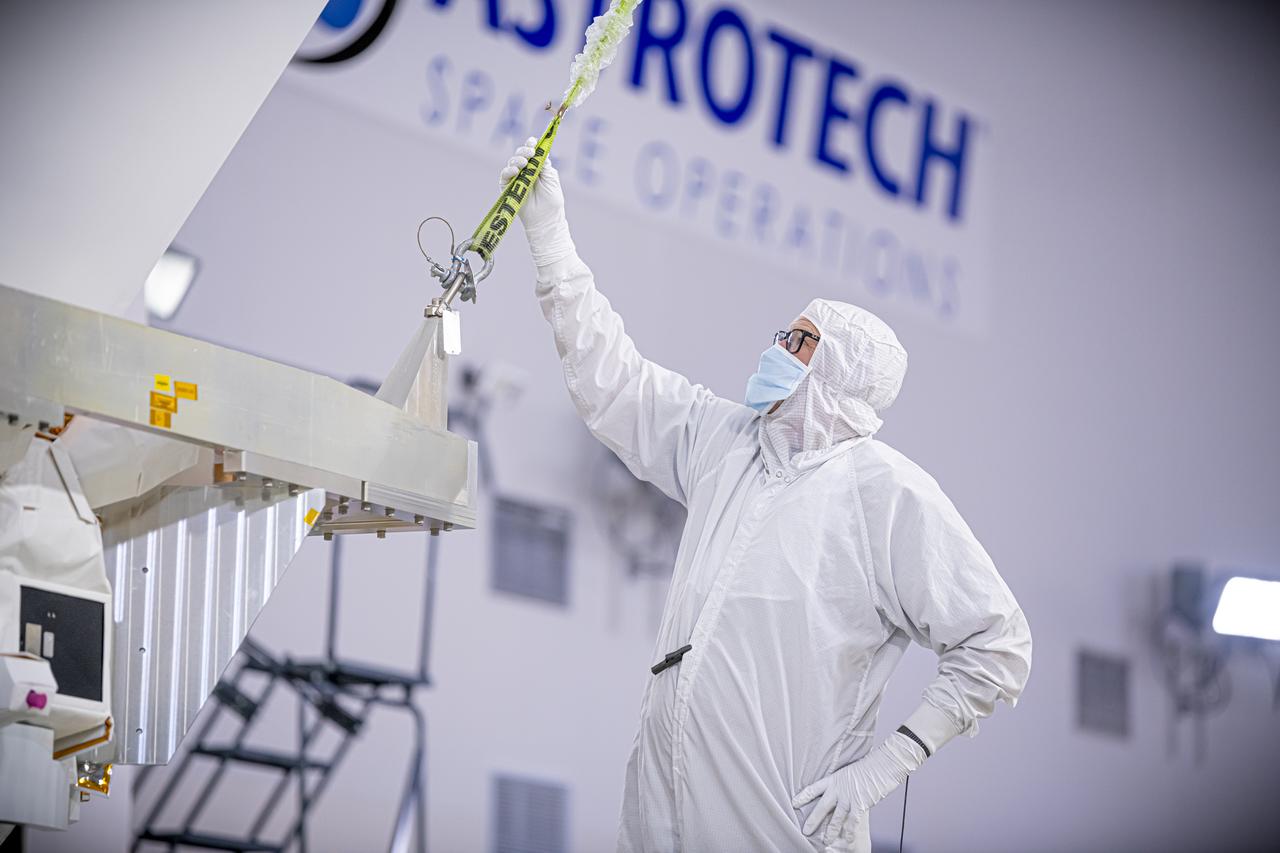
A photographer captures the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory laying horizontal on Tuesday, July 22, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
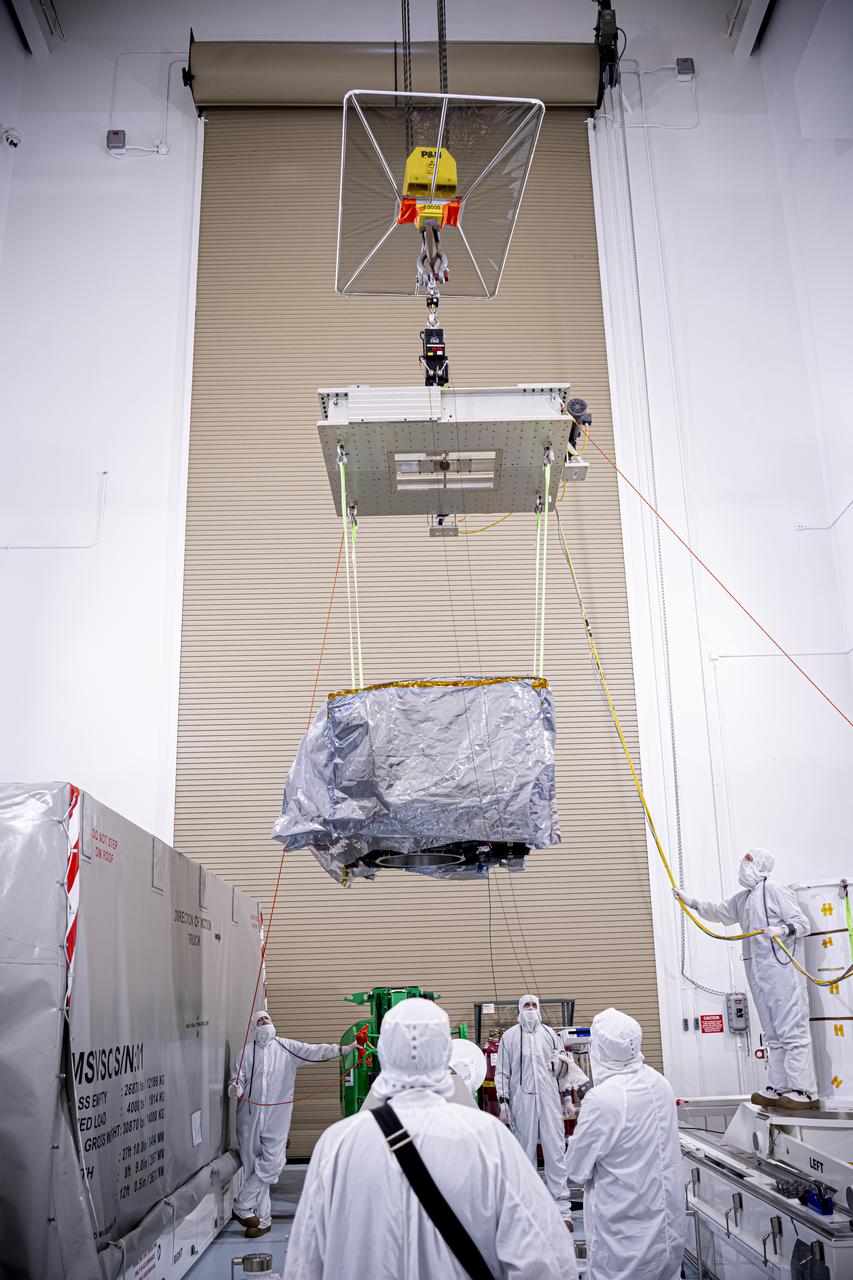

Technicians rotate the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory vertically and use a crane to lift it from its transport container on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.

Technicians rotate the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory vertically and use a crane to lift it from its transport container on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.

Technicians rotate the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory vertically and use a crane to lift it from its transport container on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
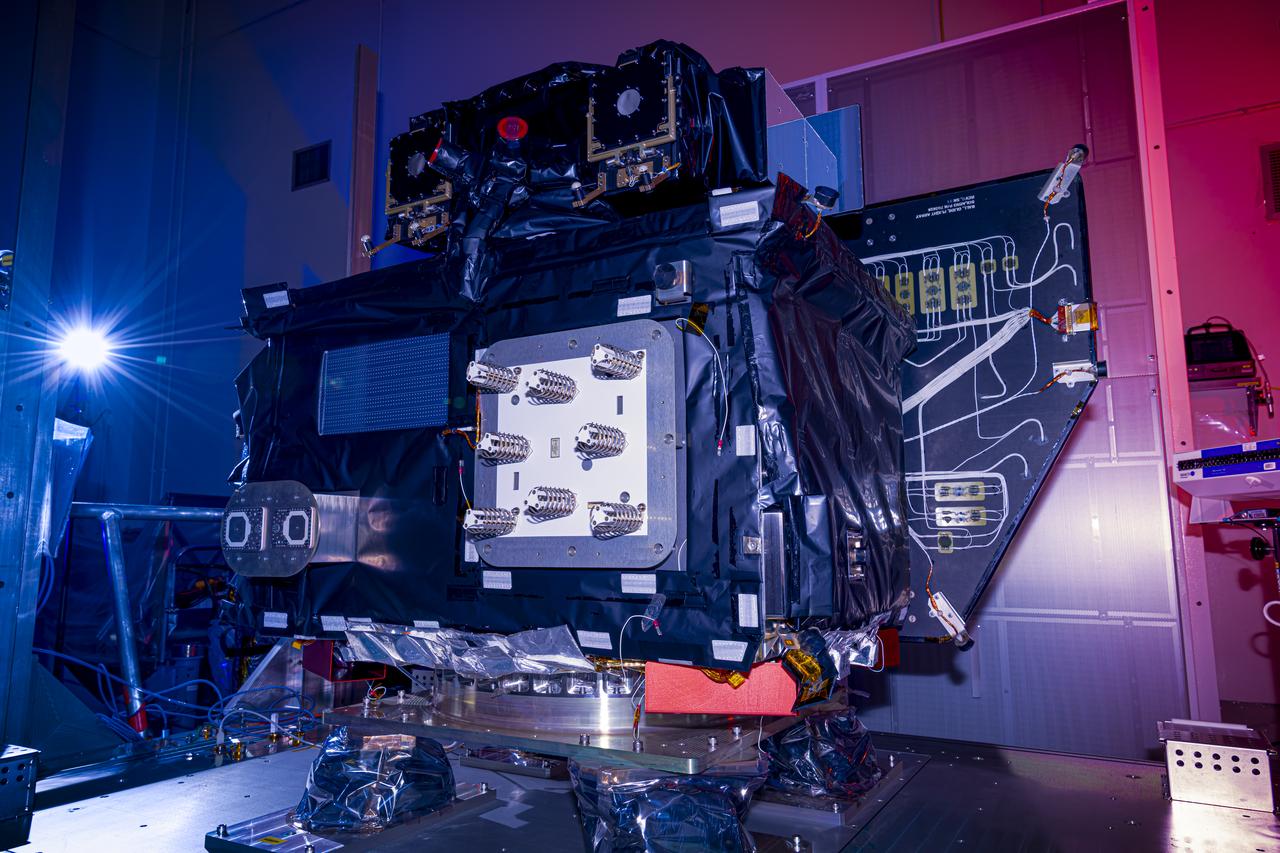
A photographer captures a photo of NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, following arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Carruthers Geocorona Observatory is a small satellite set to operate at Lagrange Point 1 (L1), an orbit point between the Earth and Sun about one million miles away. Carruthers will use its ultraviolet cameras to monitor how space weather from the Sun impacts the exosphere, the outermost part of Earth’s atmosphere. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.

Technicians inspect NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, following arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Carruthers Geocorona Observatory is a small satellite set to operate at Lagrange Point 1 (L1), an orbit point between the Earth and Sun about one million miles away. Carruthers will use its ultraviolet cameras to monitor how space weather from the Sun impacts the exosphere, the outermost part of Earth’s atmosphere. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.

Technicians inspect NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, following arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Carruthers Geocorona Observatory is a small satellite set to operate at Lagrange Point 1 (L1), an orbit point between the Earth and Sun about one million miles away. Carruthers will use its ultraviolet cameras to monitor how space weather from the Sun impacts the exosphere, the outermost part of Earth’s atmosphere. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
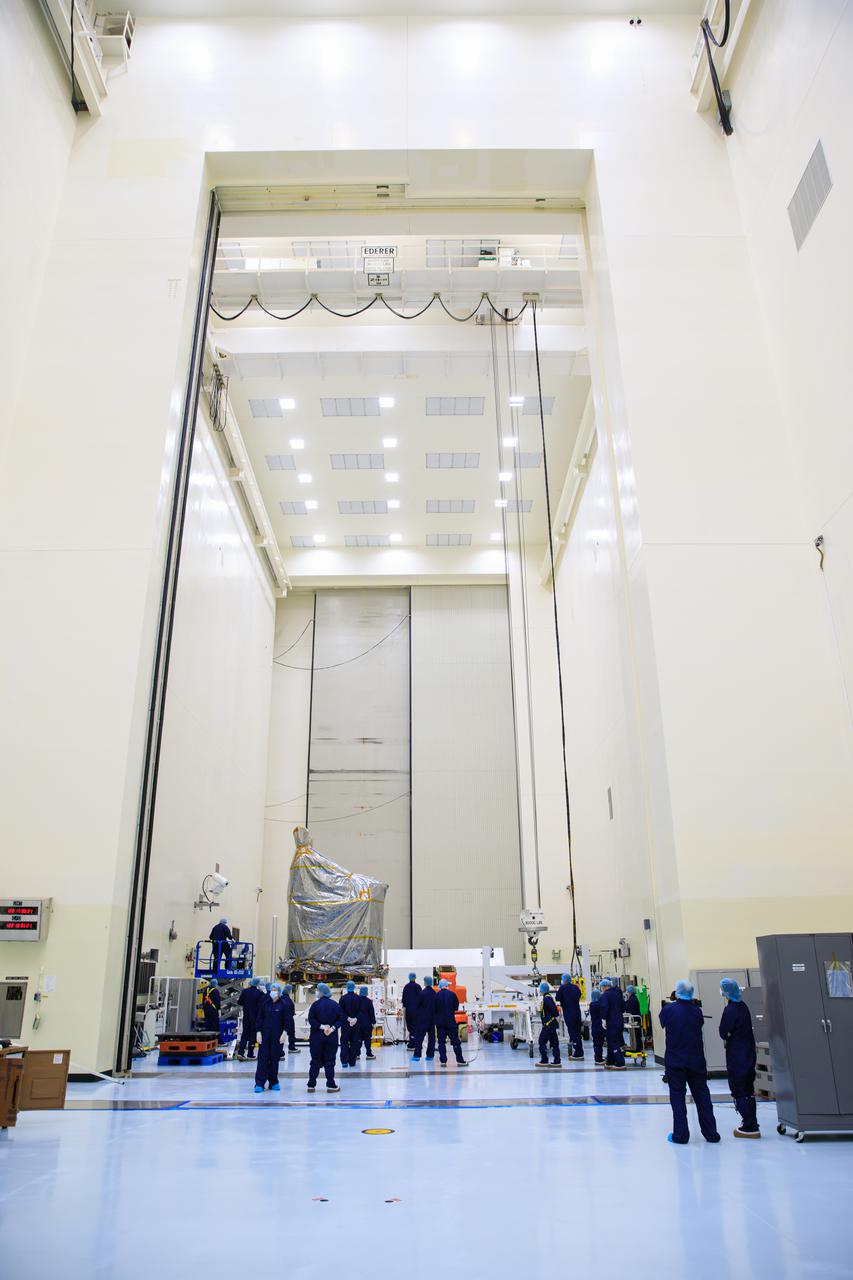

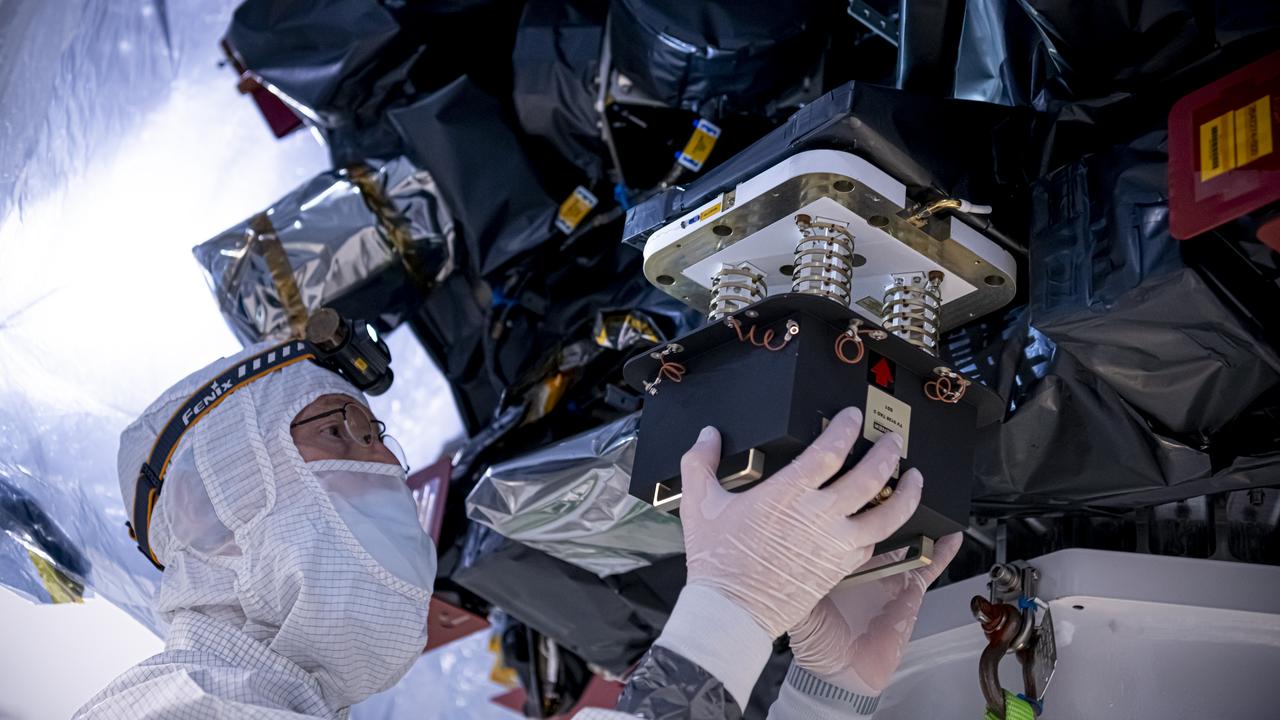
Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians prepare to move the agency’s Psyche spacecraft – recently removed from its shipping container and inside a protective covering – to a work stand on May 2, 2022. Psyche is scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.
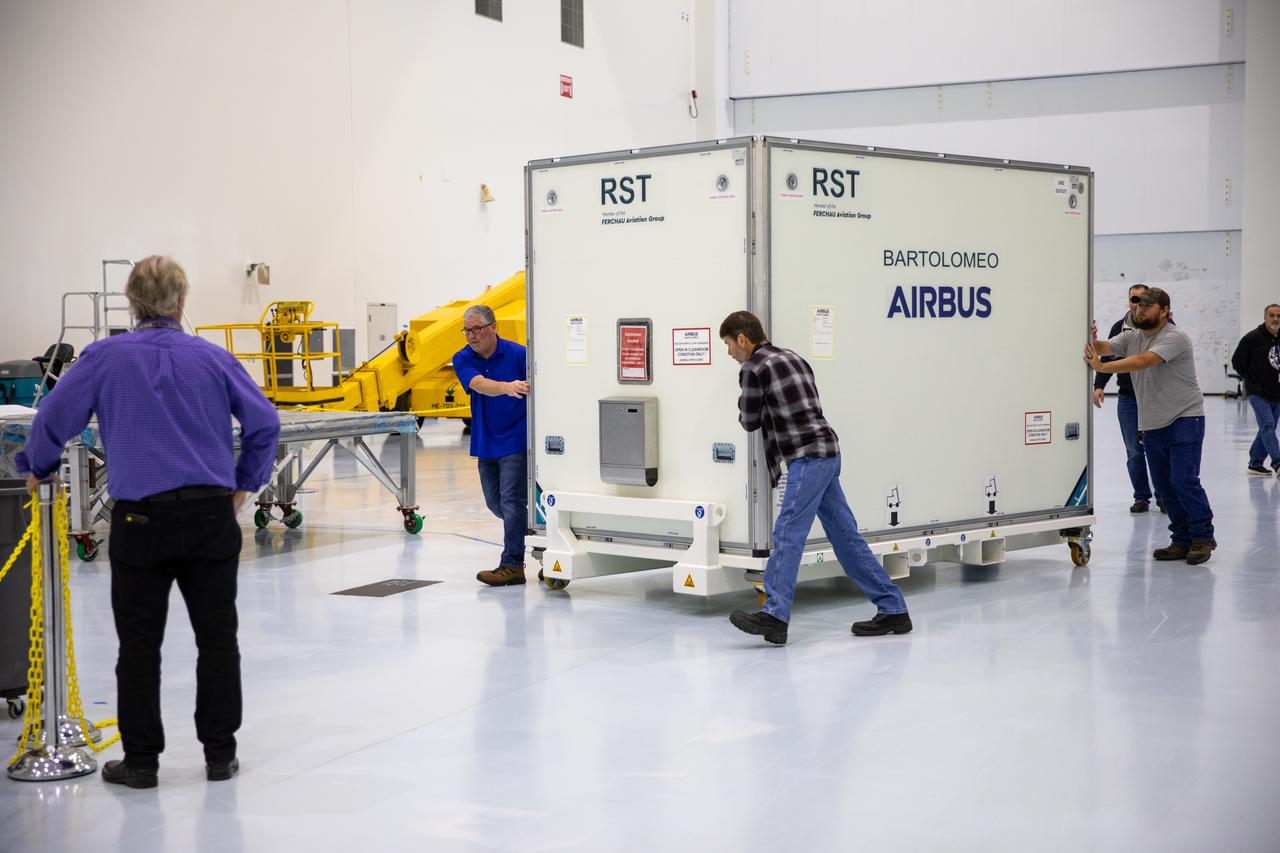

The Bartolomeo platform that will be carried to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s 20th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-20) mission for NASA is moved in its shipping container inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 30, 2020. Bartolomeo was manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. The platform will attach to the exterior of the space station’s European Columbus Module. Named for the younger brother of Christopher Columbus, the platform has the capability to host external payloads in low-Earth orbit on the station. CRS-20 is scheduled to launch aboard SpaceX’s Dragon cargo spacecraft atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket in March 2020.

The Bartolomeo platform that will be carried to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s 20th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-20) mission for NASA is inside its shipping container in the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 30, 2020. Bartolomeo was manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. The platform will attach to the exterior of the space station’s European Columbus Module. Named for the younger brother of Christopher Columbus, the platform has the capability to host external payloads in low-Earth orbit on the station. CRS-20 is scheduled to launch aboard SpaceX’s Dragon cargo spacecraft atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket in March 2020.
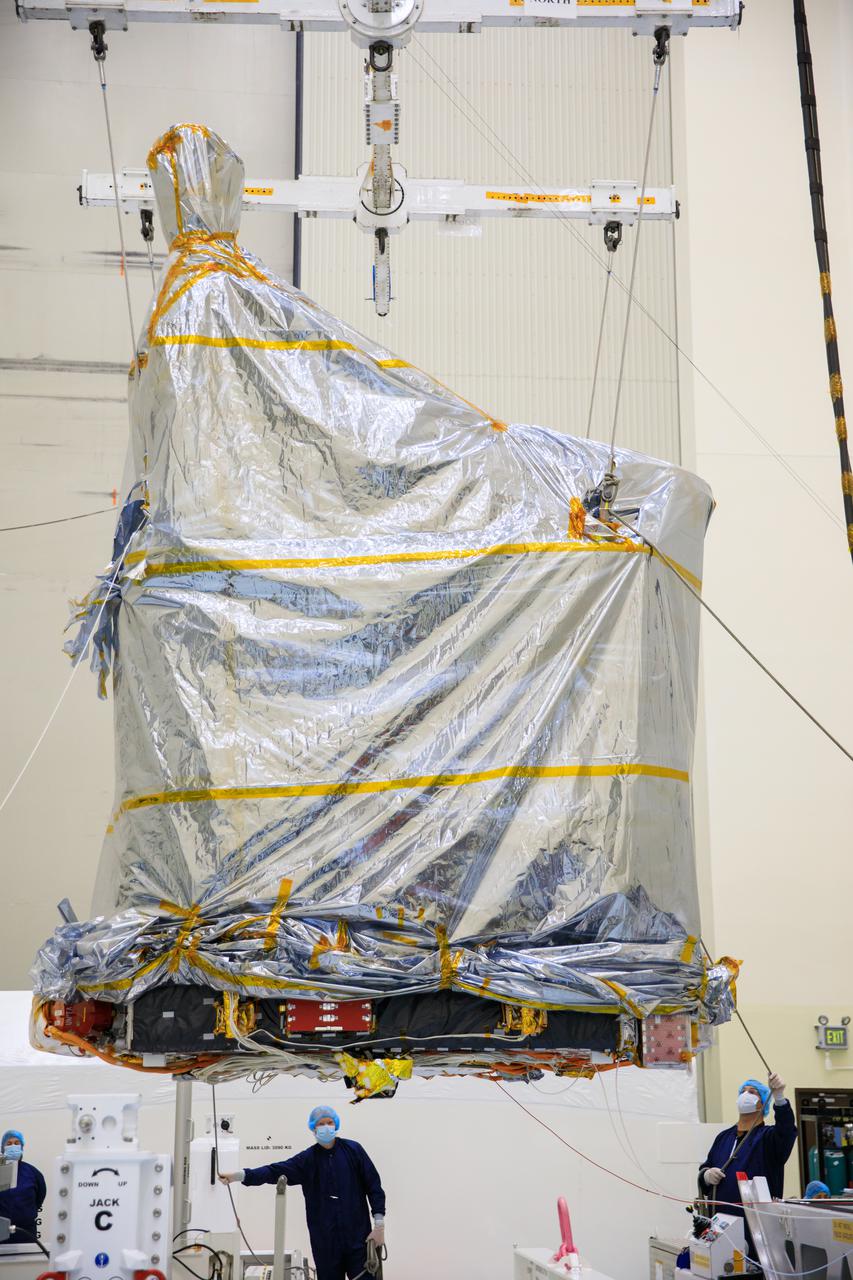

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the agency’s Psyche spacecraft – recently removed from its shipping container and inside a protective covering – is moved by crane to a work stand on Monday, May 2, 2022. Psyche is scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.
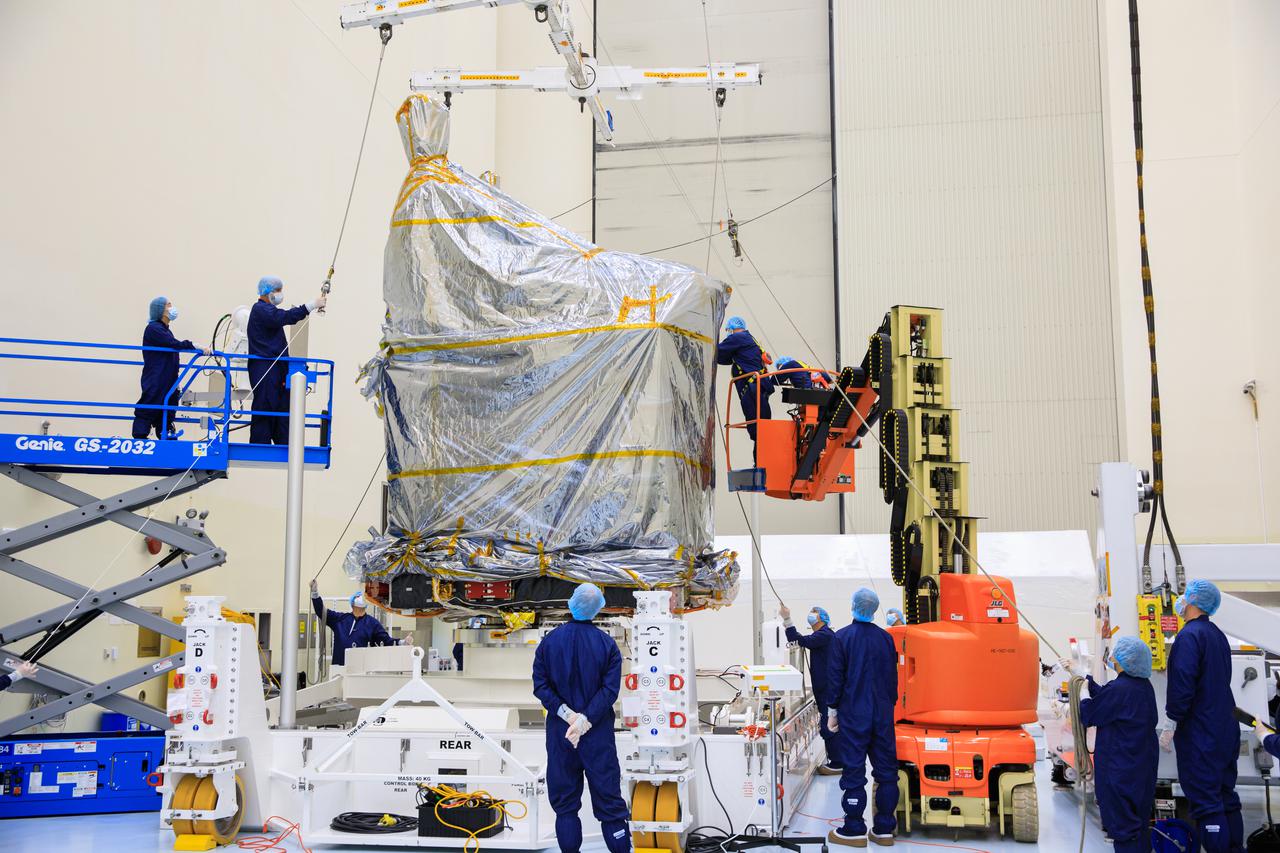

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the agency’s Psyche spacecraft – recently removed from its shipping container and inside a protective covering – is moved by crane to a work stand on Monday, May 2, 2022. Psyche is scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.

Airbus workers inspect the Bartolomeo platform after it was unpacked from its shipping container in the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 30, 2020. Bartolomeo was manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. The platform will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s 20th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-20) mission for the agency. The platform will attach to the exterior of the space station’s European Columbus Module. Named for the younger brother of Christopher Columbus, the platform has the capability to host external payloads in low-Earth orbit on the station. CRS-20 is scheduled to launch aboard SpaceX’s Dragon cargo spacecraft atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket in March 2020.
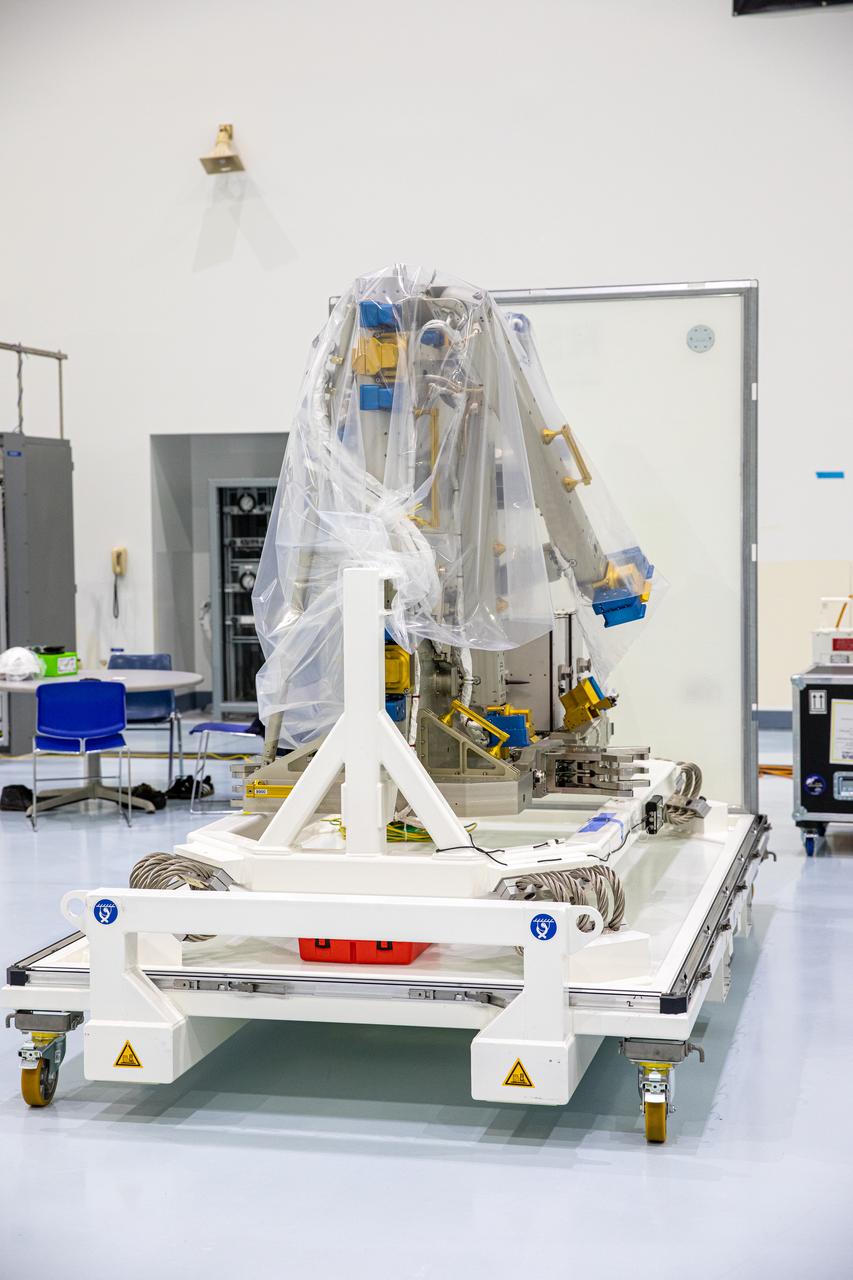

The Bartolomeo platform that will be delivered to the International Space Station is unpacked from its shipping container inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 30, 2020. Bartolomeo was manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. The platform will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s 20th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-20) mission for the agency. The platform will attach to the exterior of the space station’s European Columbus Module. Named for the younger brother of Christopher Columbus, the platform has the capability to host external payloads in low-Earth orbit on the station. CRS-20 is scheduled to launch aboard SpaceX’s Dragon cargo spacecraft atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket in March 2020.
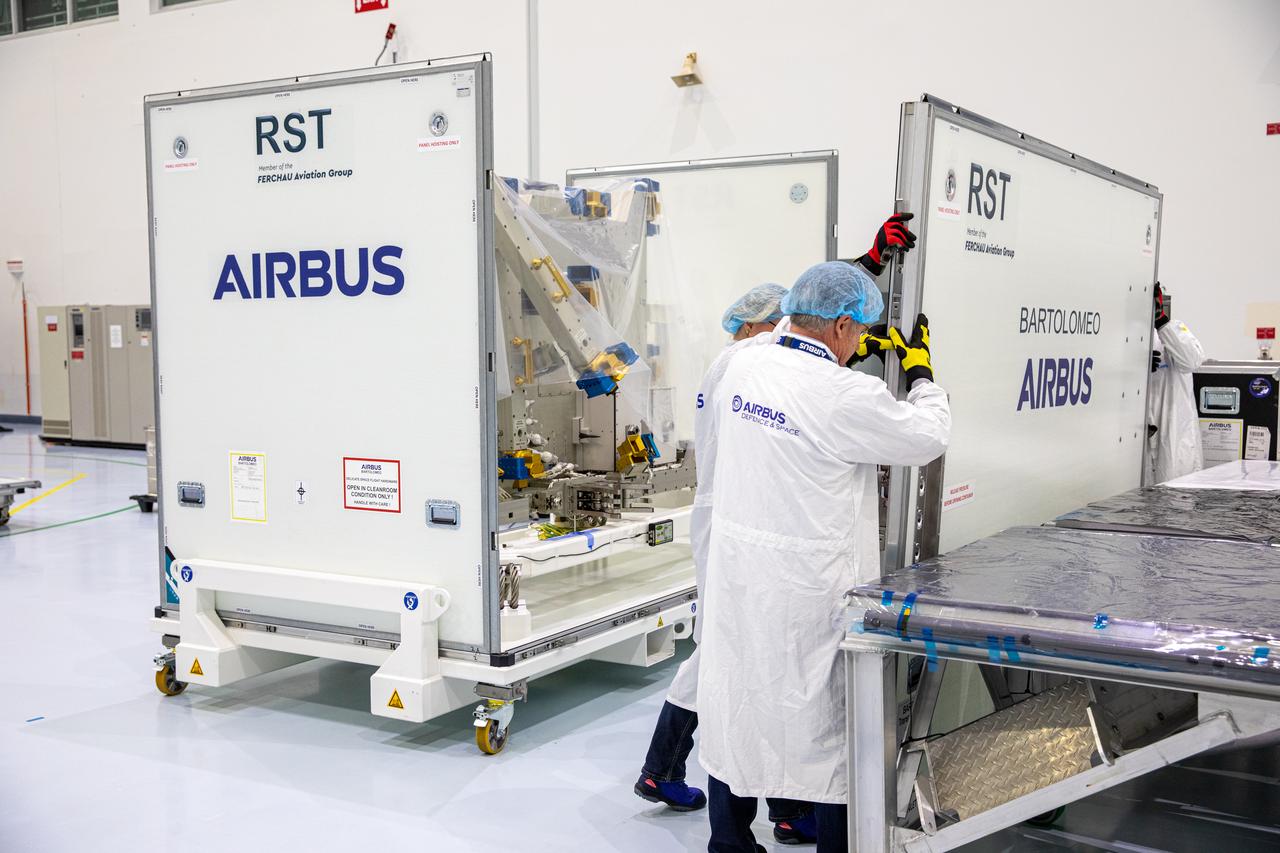

Airbus workers unpack the Bartolomeo platform in the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 30, 2020. Bartolomeo was manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. The platform will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s 20th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-20) mission for the agency. The platform will attach to the exterior of the space station’s European Columbus Module. Named for the younger brother of Christopher Columbus, the platform has the capability to host external payloads in low-Earth orbit on the station. CRS-20 is scheduled to launch aboard SpaceX’s Dragon cargo spacecraft atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket in March 2020.
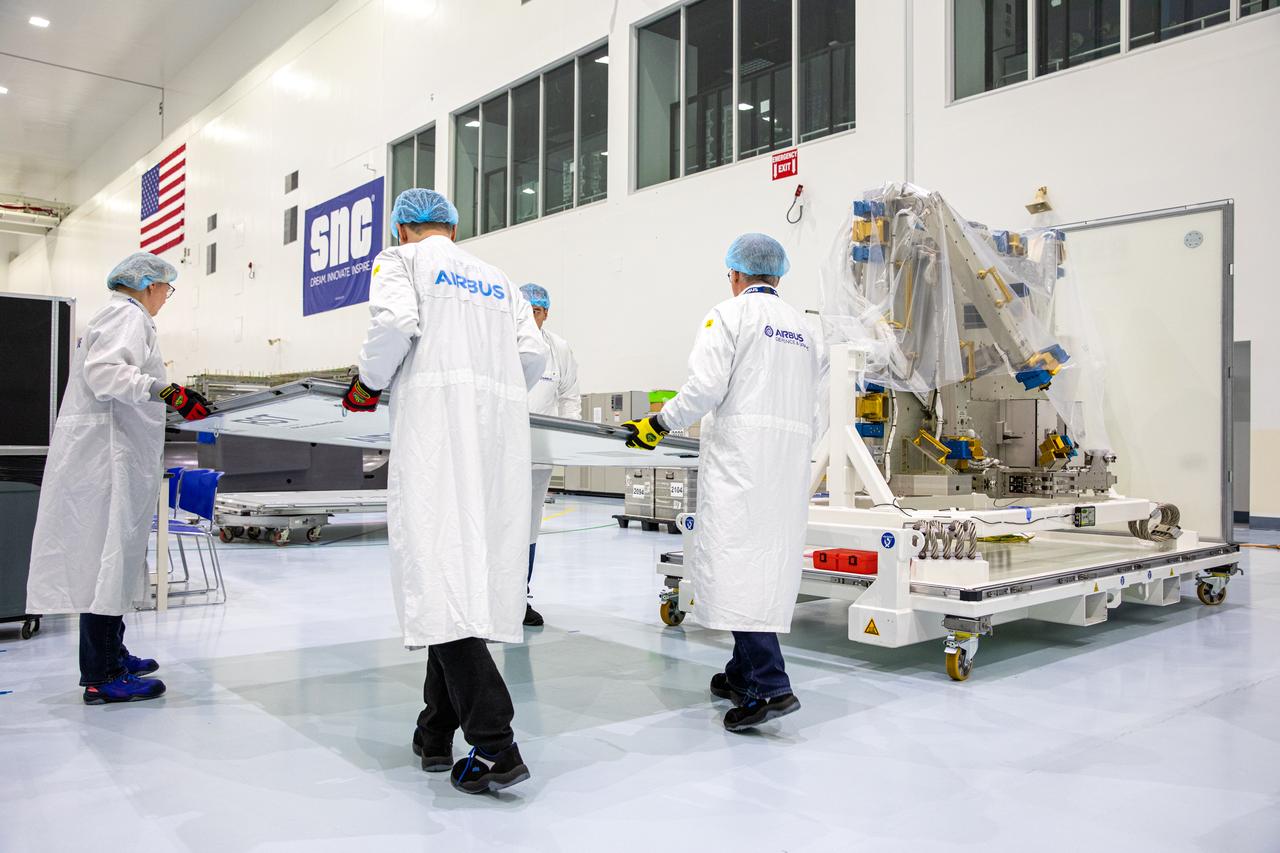

Airbus workers unpack the Bartolomeo platform in the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 30, 2020. Bartolomeo was manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. The platform will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s 20th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-20) mission for the agency. The platform will attach to the exterior of the space station’s European Columbus Module. Named for the younger brother of Christopher Columbus, the platform has the capability to host external payloads in low-Earth orbit on the station. CRS-20 is scheduled to launch aboard SpaceX’s Dragon cargo spacecraft atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket in March 2020.
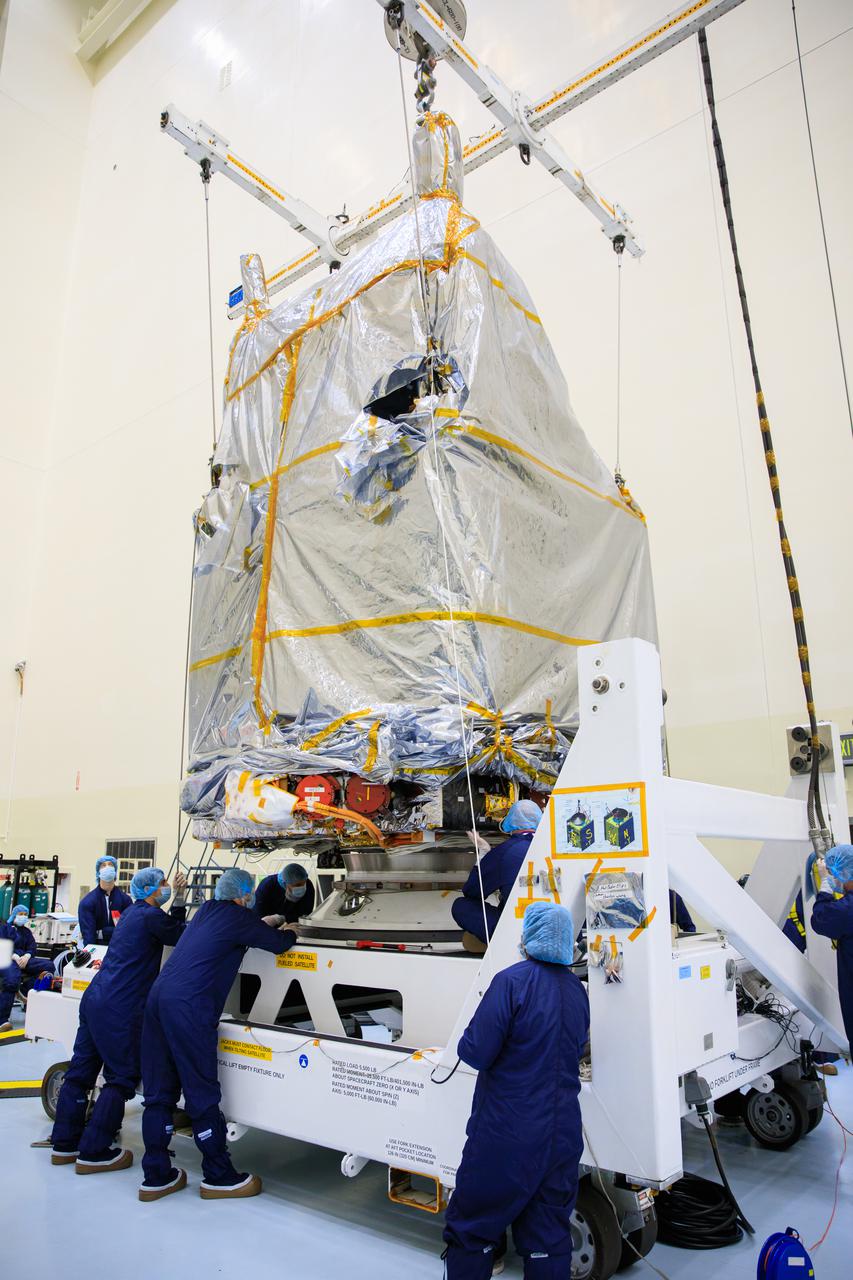

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the agency’s Psyche spacecraft – recently removed from its shipping container and inside a protective covering – is moved by crane to a work stand on Monday, May 2, 2022. Psyche is scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.
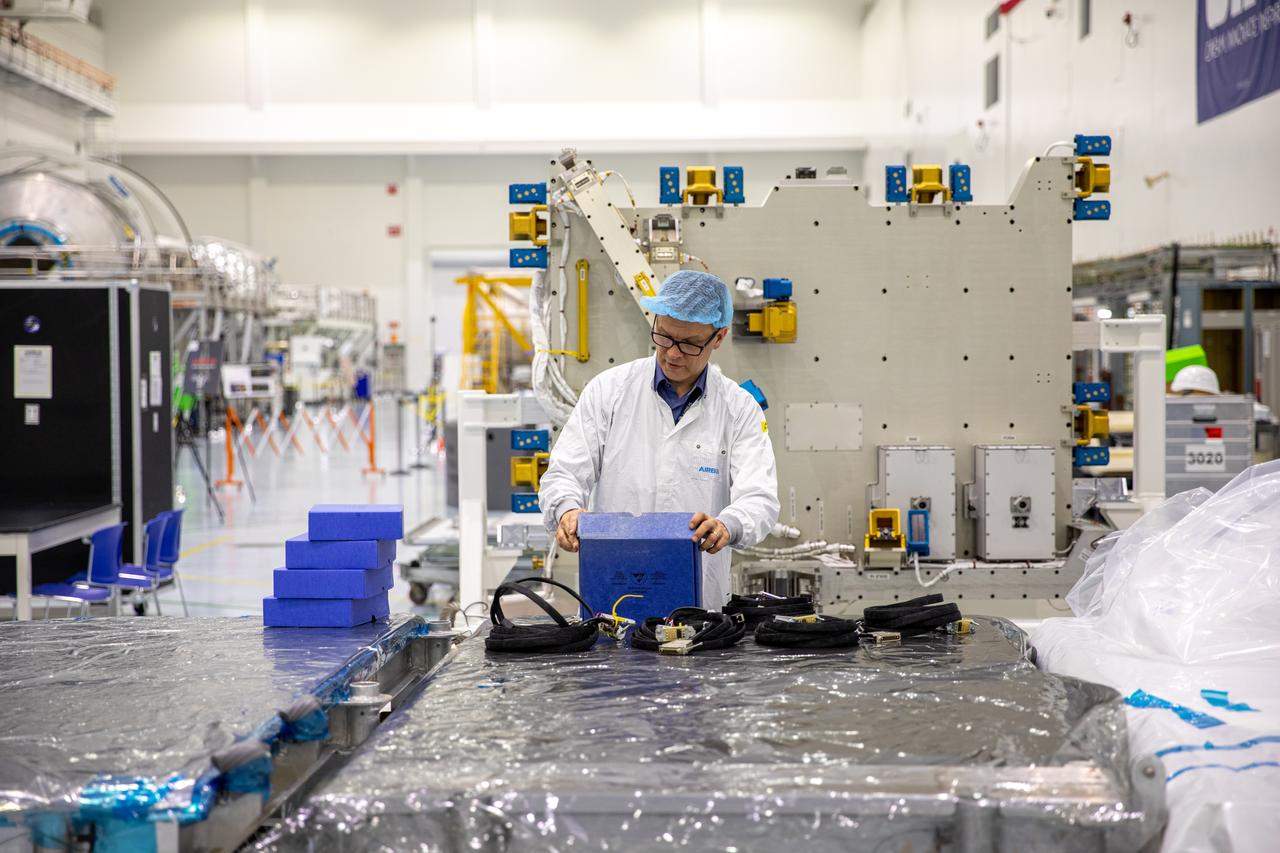

Airbus workers inspects parts for the Bartolomeo platform after it was unpacked from its shipping container in the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 30, 2020. Bartolomeo was manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. The platform will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s 20th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-20) mission for the agency. The platform will attach to the exterior of the space station’s European Columbus Module. Named for the younger brother of Christopher Columbus, the platform has the capability to host external payloads in low-Earth orbit on the station. CRS-20 is scheduled to launch aboard SpaceX’s Dragon cargo spacecraft atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket in March 2020.
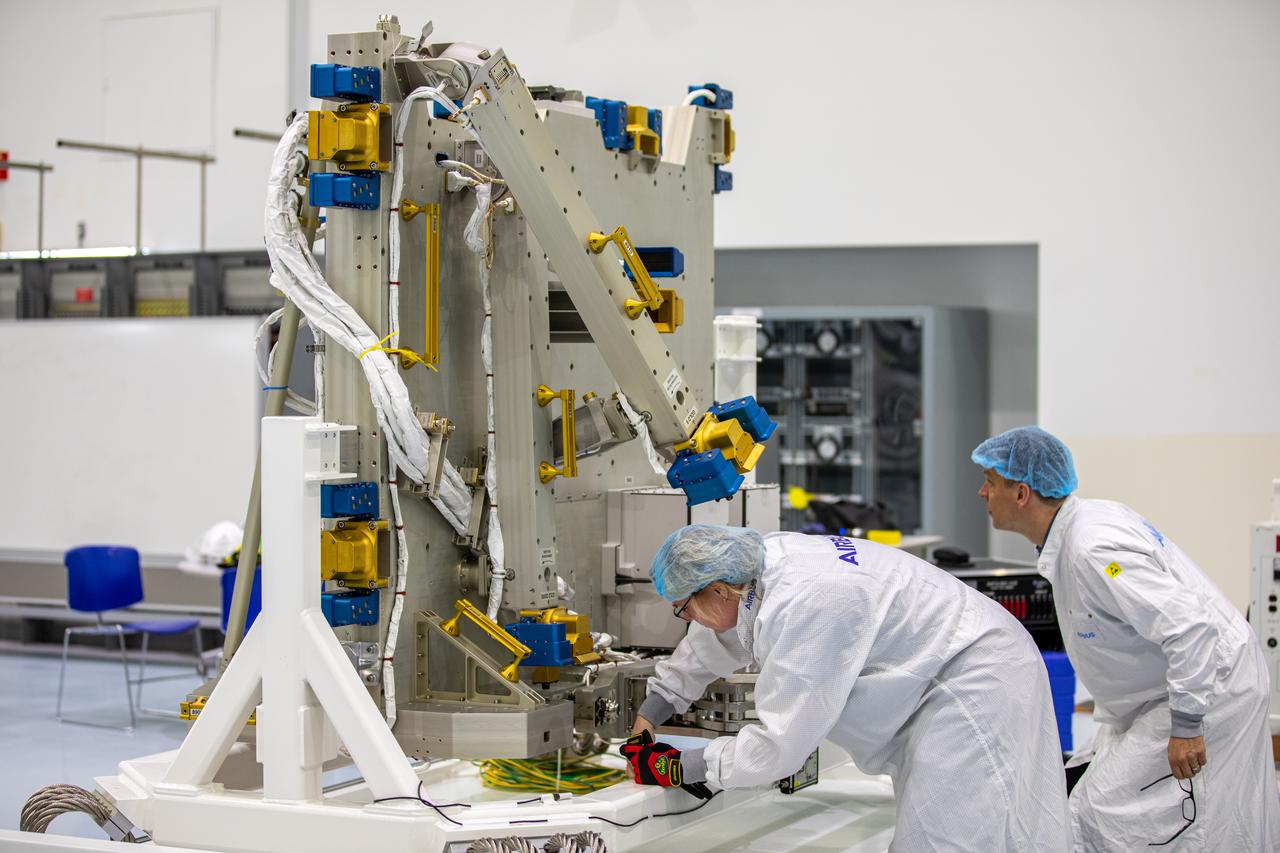

Airbus workers unpack the Bartolomeo platform in the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 30, 2020. Bartolomeo was manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. The platform will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s 20th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-20) mission for the agency. The platform will attach to the exterior of the space station’s European Columbus Module. Named for the younger brother of Christopher Columbus, the platform has the capability to host external payloads in low-Earth orbit on the station. CRS-20 is scheduled to launch aboard SpaceX’s Dragon cargo spacecraft atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket in March 2020.
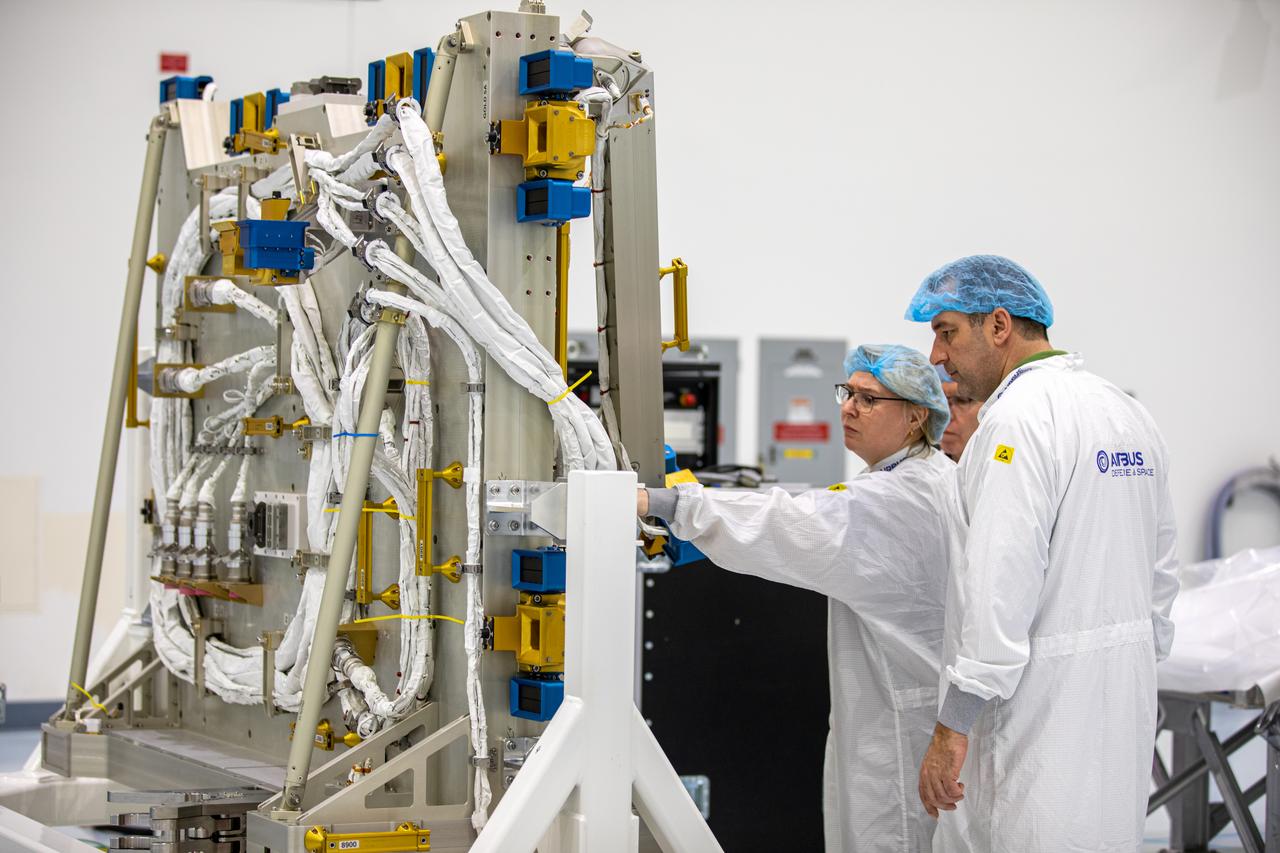

Airbus workers inspect the Bartolomeo platform after it was unpacked from its shipping container in the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 30, 2020. Bartolomeo was manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. The platform will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s 20th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-20) mission for the agency. The platform will attach to the exterior of the space station’s European Columbus Module. Named for the younger brother of Christopher Columbus, the platform has the capability to host external payloads in low-Earth orbit on the station. CRS-20 is scheduled to launch aboard SpaceX’s Dragon cargo spacecraft atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket in March 2020.
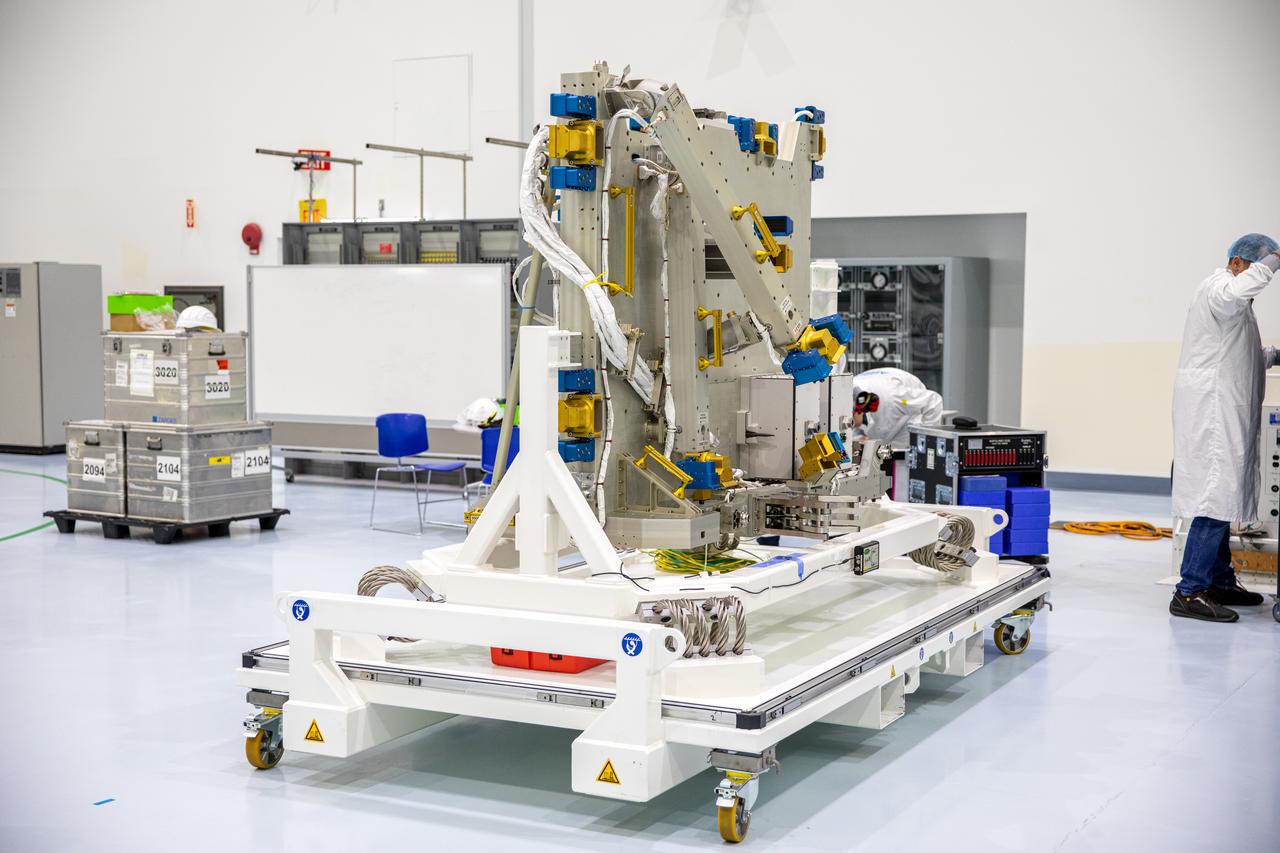

Airbus workers unpack the Bartolomeo platform in the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 30, 2020. Bartolomeo was manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. The platform will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s 20th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-20) mission for the agency. The platform will attach to the exterior of the space station’s European Columbus Module. Named for the younger brother of Christopher Columbus, the platform has the capability to host external payloads in low-Earth orbit on the station. CRS-20 is scheduled to launch aboard SpaceX’s Dragon cargo spacecraft atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket in March 2020.

Technicians remove the protective casing covering NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory on Monday, July 21, 2025, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Carruthers Geocorona Observatory is a small satellite set to operate at Lagrange Point 1 (L1), an orbit point between the Earth and Sun about one million miles away. Carruthers will use its ultraviolet cameras to monitor how space weather from the Sun impacts the exosphere, the outermost part of Earth’s atmosphere. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
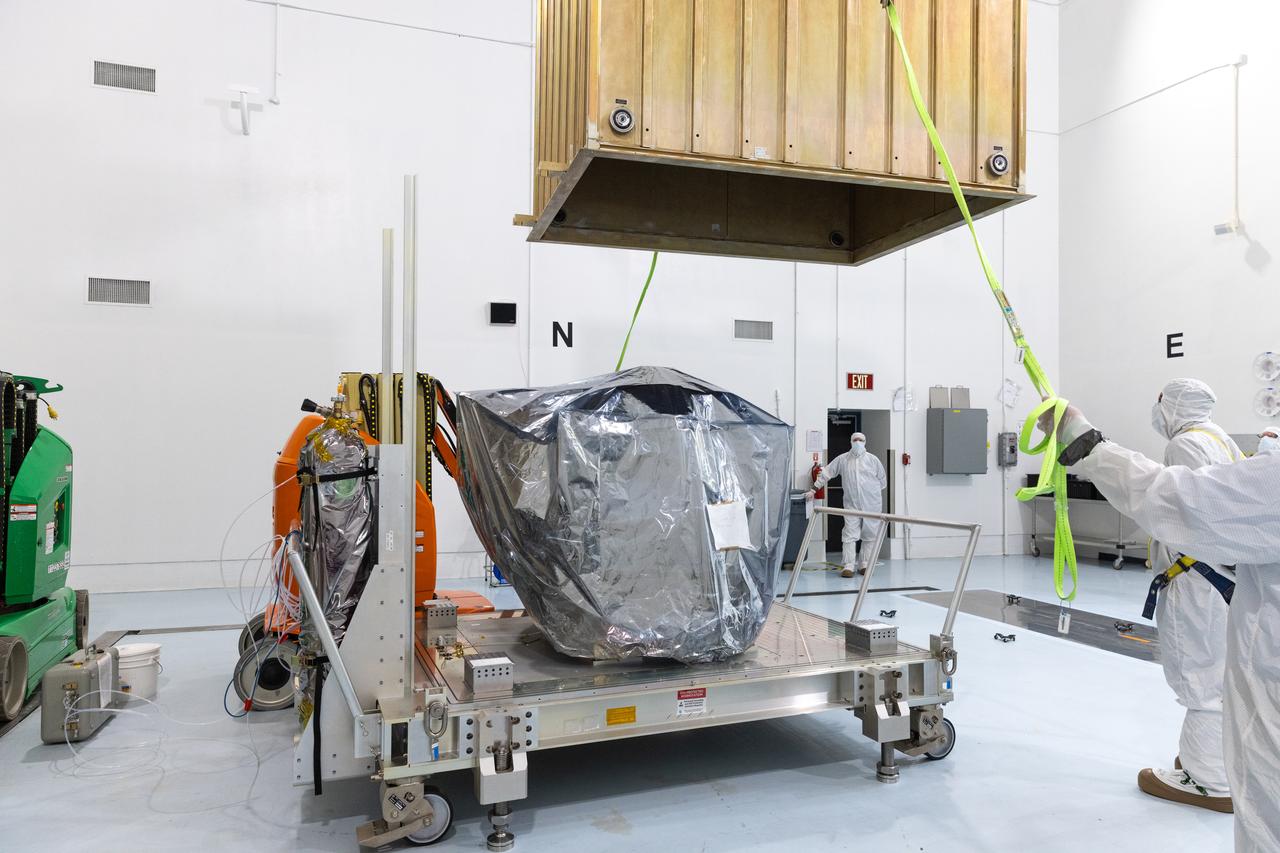

Technicians remove the protective casing covering NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory on Monday, July 21, 2025, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Carruthers Geocorona Observatory is a small satellite set to operate at Lagrange Point 1 (L1), an orbit point between the Earth and Sun about one million miles away. Carruthers will use its ultraviolet cameras to monitor how space weather from the Sun impacts the exosphere, the outermost part of Earth’s atmosphere. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
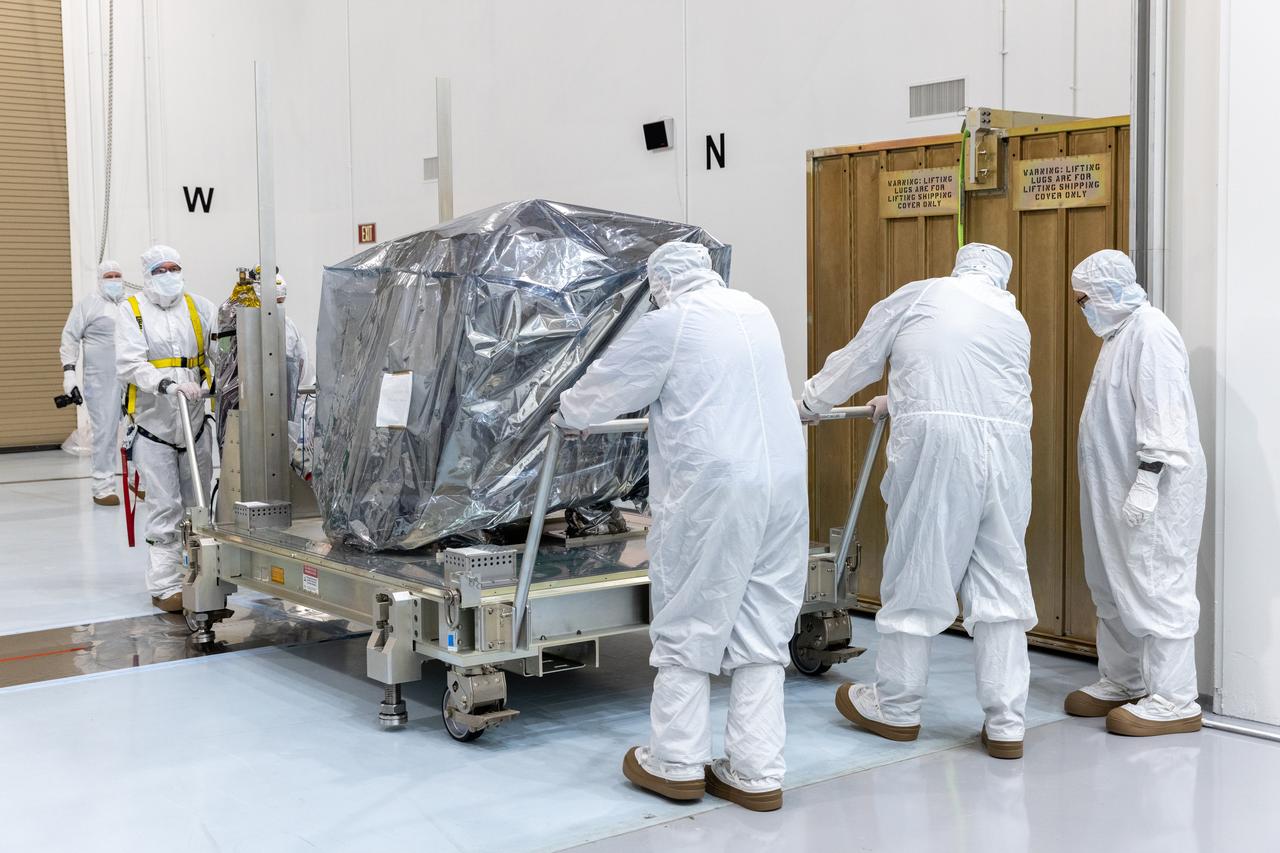

Technicians remove the protective casing covering NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory on Monday, July 21, 2025, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Carruthers Geocorona Observatory is a small satellite set to operate at Lagrange Point 1 (L1), an orbit point between the Earth and Sun about one million miles away. Carruthers will use its ultraviolet cameras to monitor how space weather from the Sun impacts the exosphere, the outermost part of Earth’s atmosphere. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
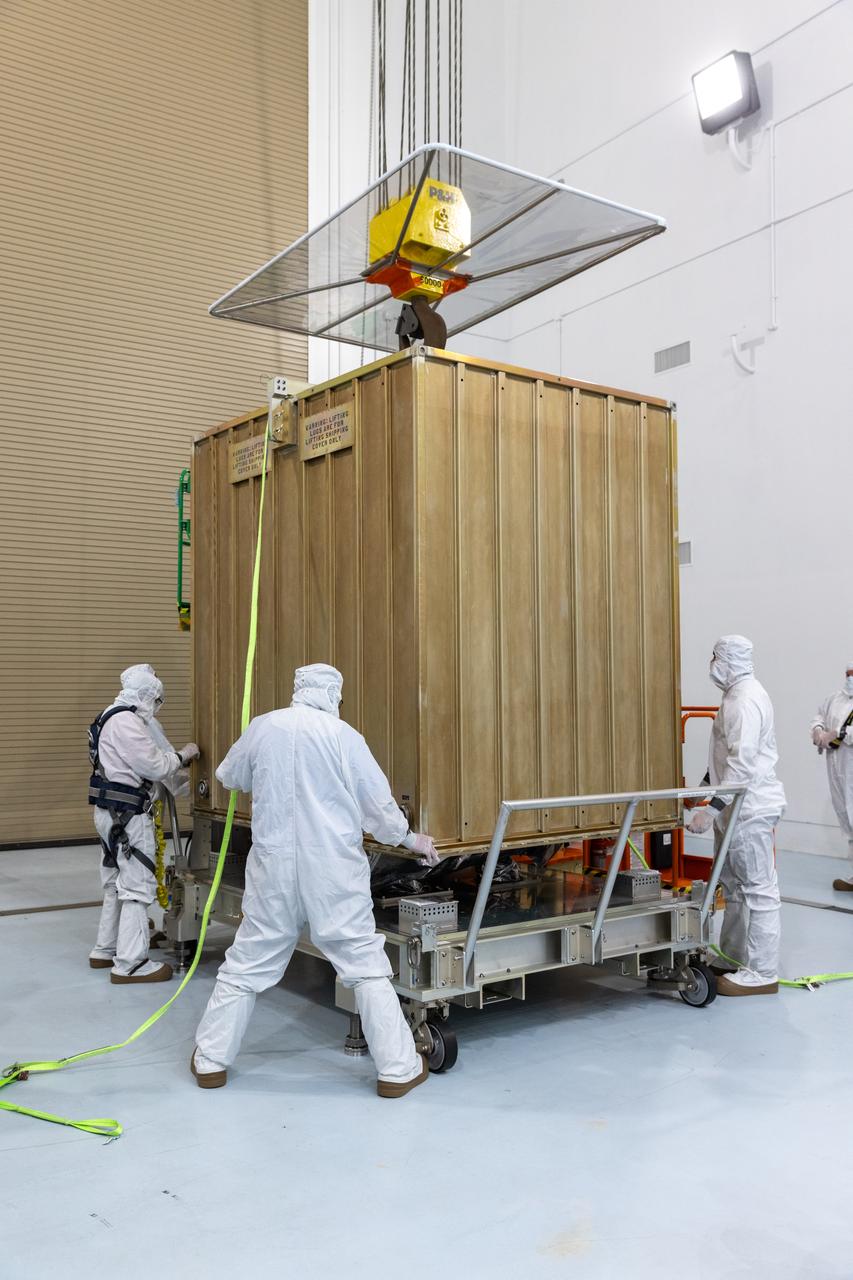

Technicians prepare to remove the protective casing covering NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory on Monday, July 21, 2025, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Carruthers Geocorona Observatory is a small satellite set to operate at Lagrange Point 1 (L1), an orbit point between the Earth and Sun about one million miles away. Carruthers will use its ultraviolet cameras to monitor how space weather from the Sun impacts the exosphere, the outermost part of Earth’s atmosphere. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
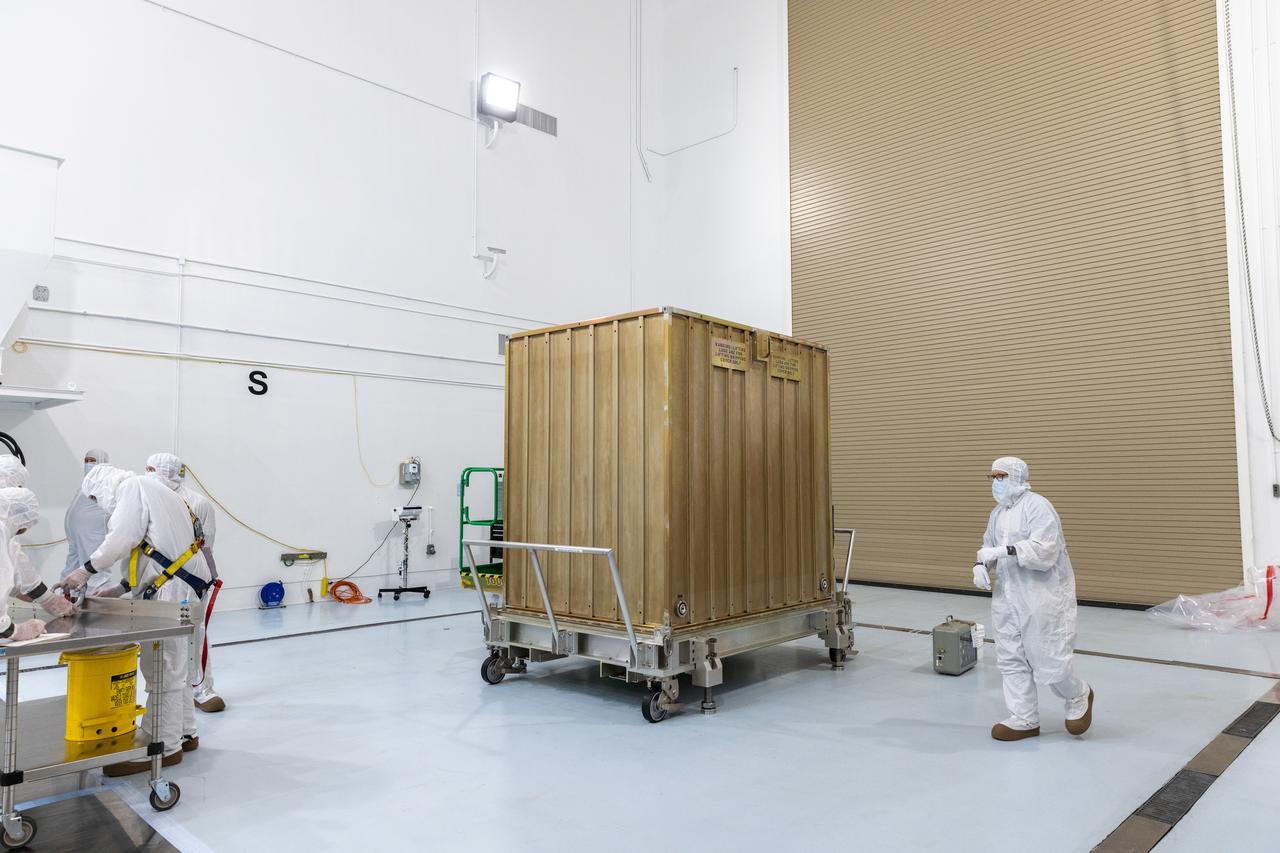

Technicians prepare to remove the protective casing covering NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory on Monday, July 21, 2025, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Carruthers Geocorona Observatory is a small satellite set to operate at Lagrange Point 1 (L1), an orbit point between the Earth and Sun about one million miles away. Carruthers will use its ultraviolet cameras to monitor how space weather from the Sun impacts the exosphere, the outermost part of Earth’s atmosphere. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
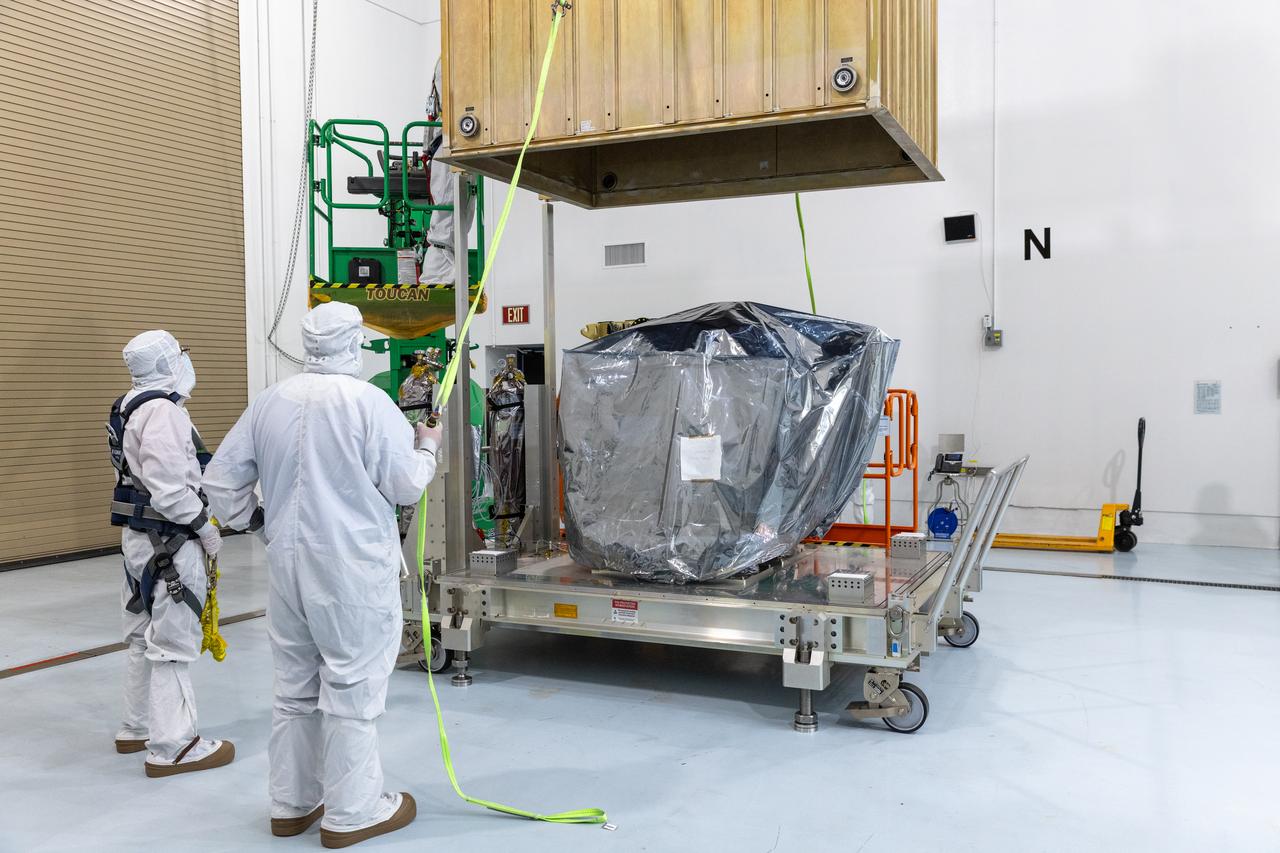

Technicians remove the protective casing covering NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory on Monday, July 21, 2025, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Carruthers Geocorona Observatory is a small satellite set to operate at Lagrange Point 1 (L1), an orbit point between the Earth and Sun about one million miles away. Carruthers will use its ultraviolet cameras to monitor how space weather from the Sun impacts the exosphere, the outermost part of Earth’s atmosphere. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
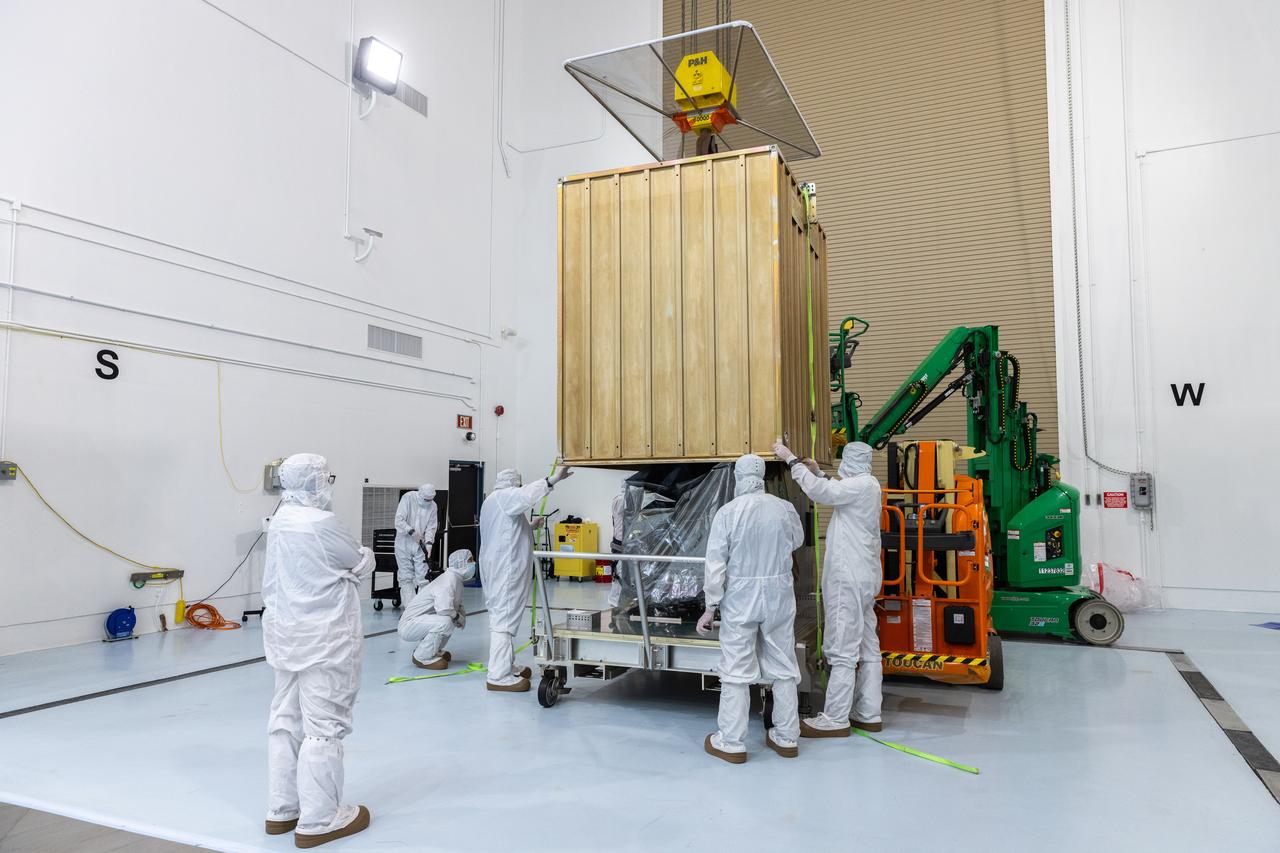

Technicians prepare to remove the protective casing covering NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory on Monday, July 21, 2025, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Carruthers Geocorona Observatory is a small satellite set to operate at Lagrange Point 1 (L1), an orbit point between the Earth and Sun about one million miles away. Carruthers will use its ultraviolet cameras to monitor how space weather from the Sun impacts the exosphere, the outermost part of Earth’s atmosphere. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
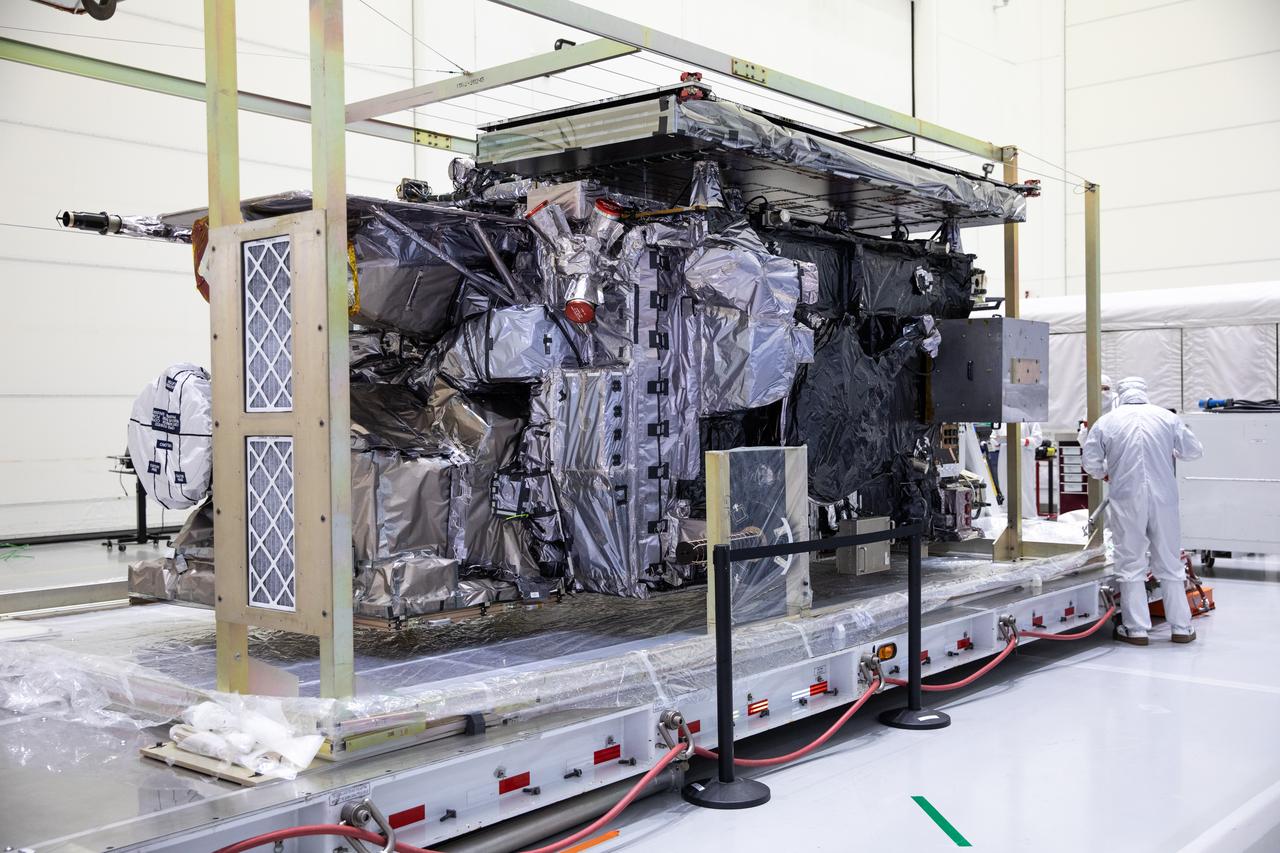

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is uncrated for prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the final in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

The mission insignia of NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) mission is pictured in front of the satellite in a vertical position on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

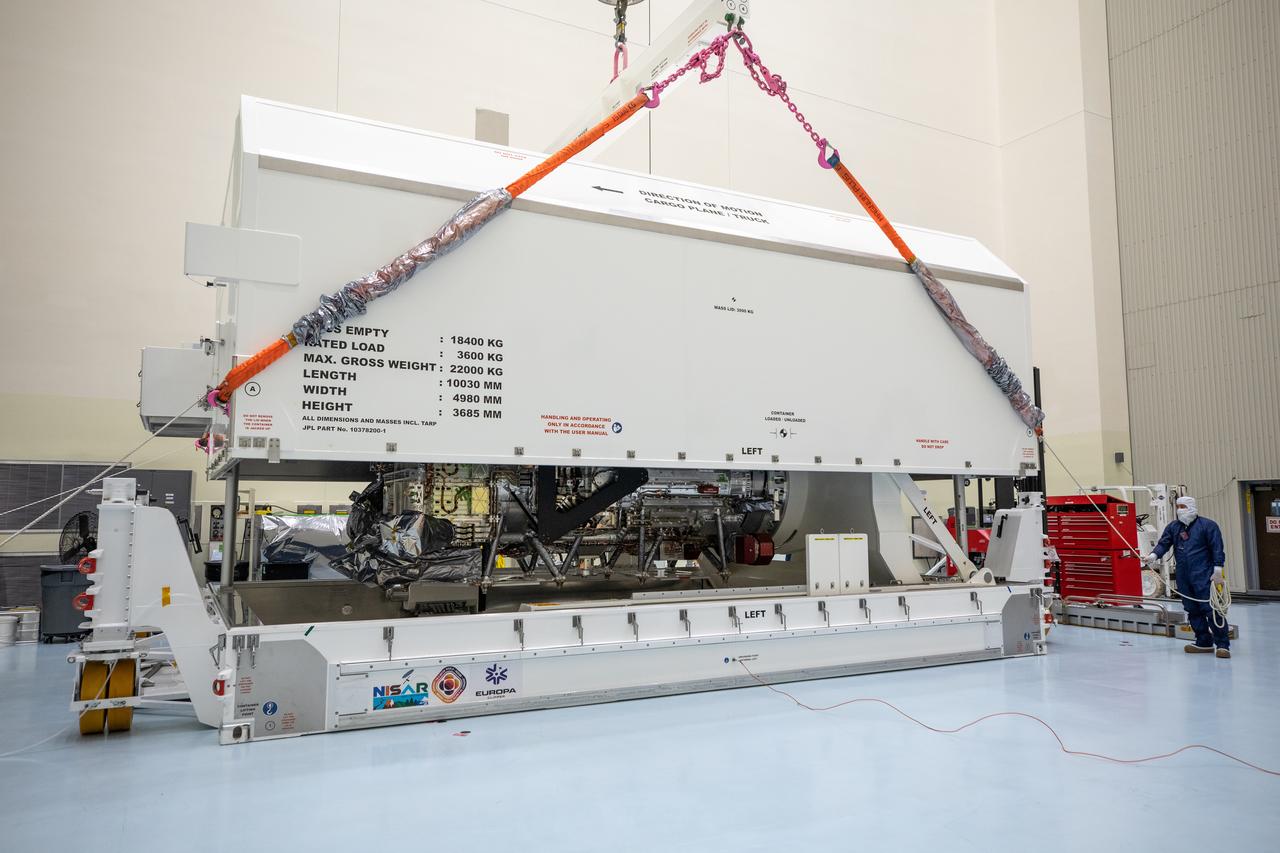
NASA’s largest planetary mission spacecraft, Europa Clipper, arrives at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, May 24, 2024. Slated to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket later this year from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, Europa Clipper will help determine if conditions exist below the surface Jupiter’s fourth largest moon, Europa, that could support life.
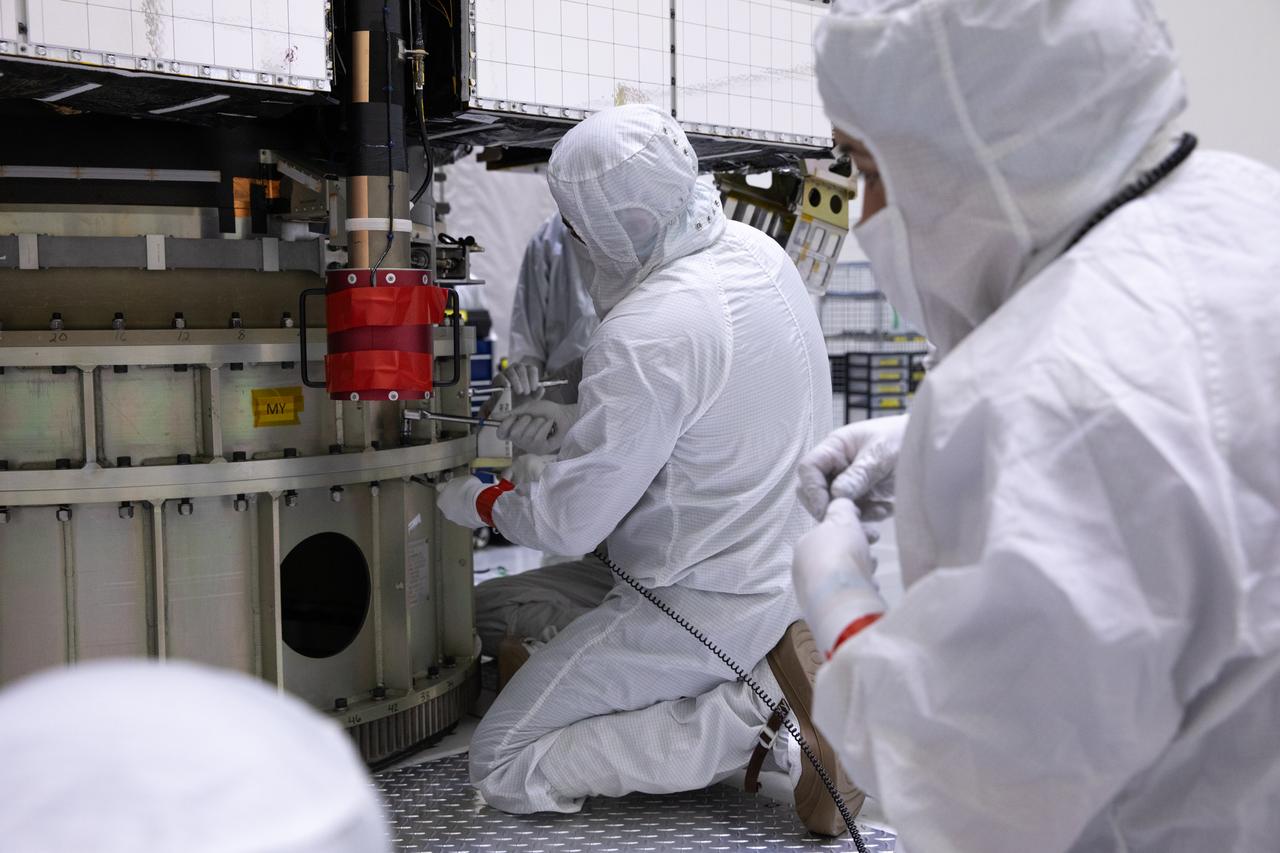

Technicians monitor movement and guide NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) as a crane hoists it on to a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.