
A dark, smooth, relatively uncratered area on Mercury was photographed two hours after NASA Mariner 10 flew by the planet. The prominent, sharp crater with a central peak is 30 kilometers 19 miles across.
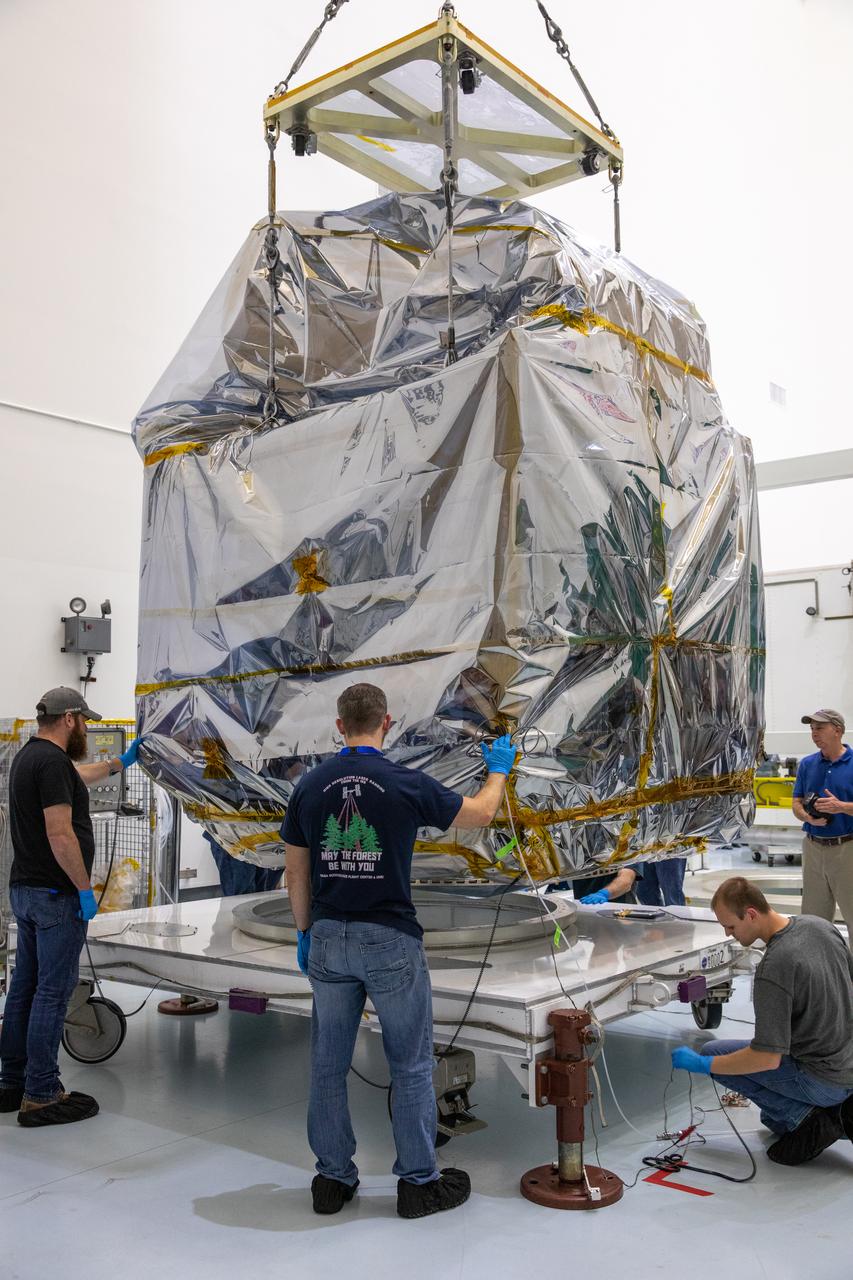

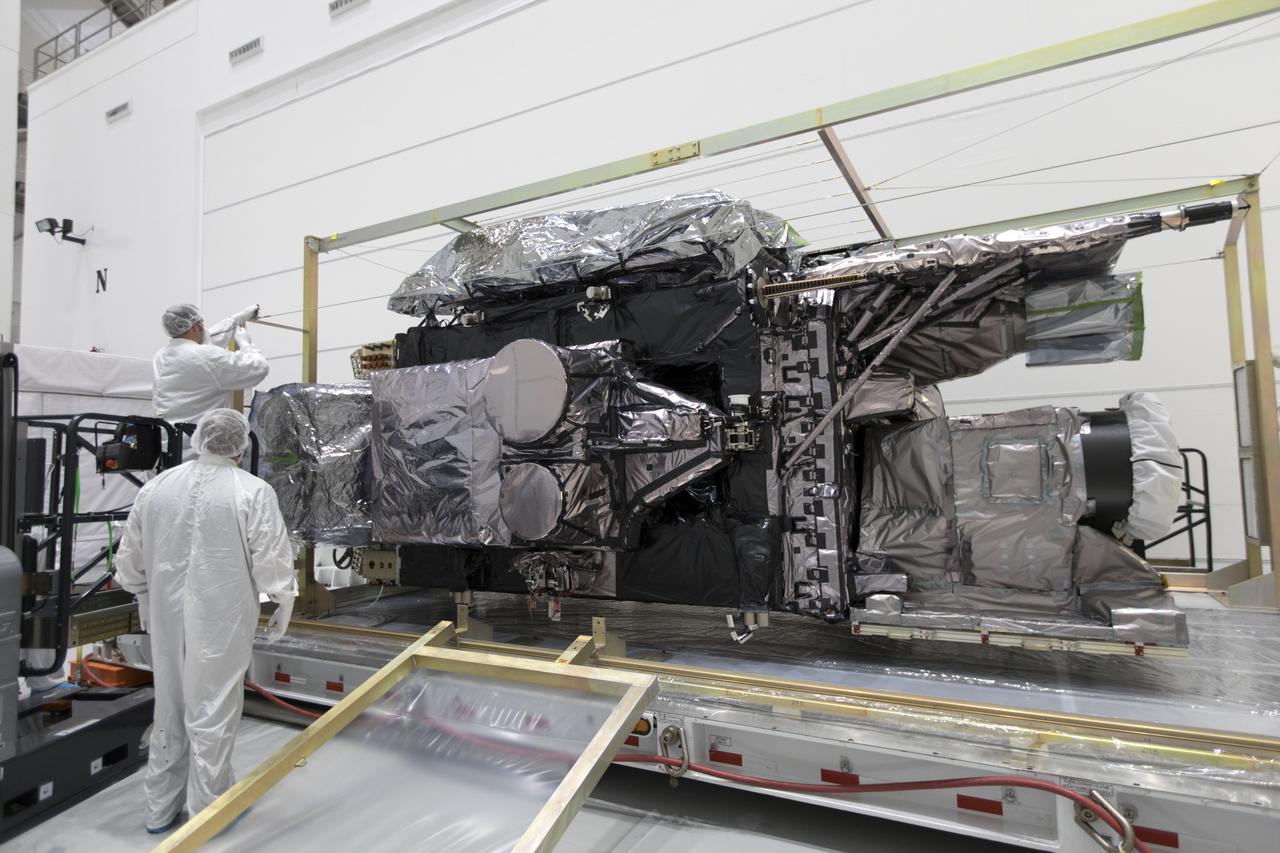
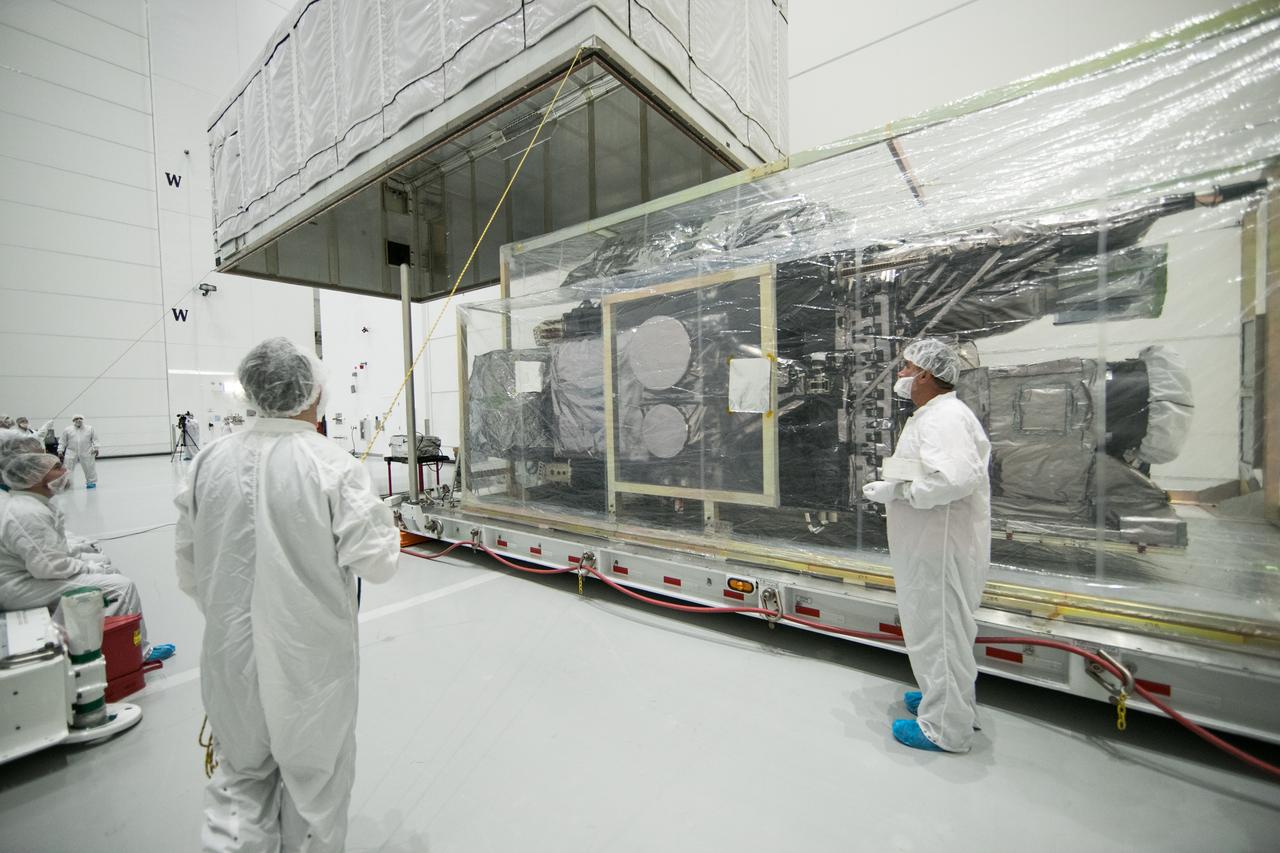
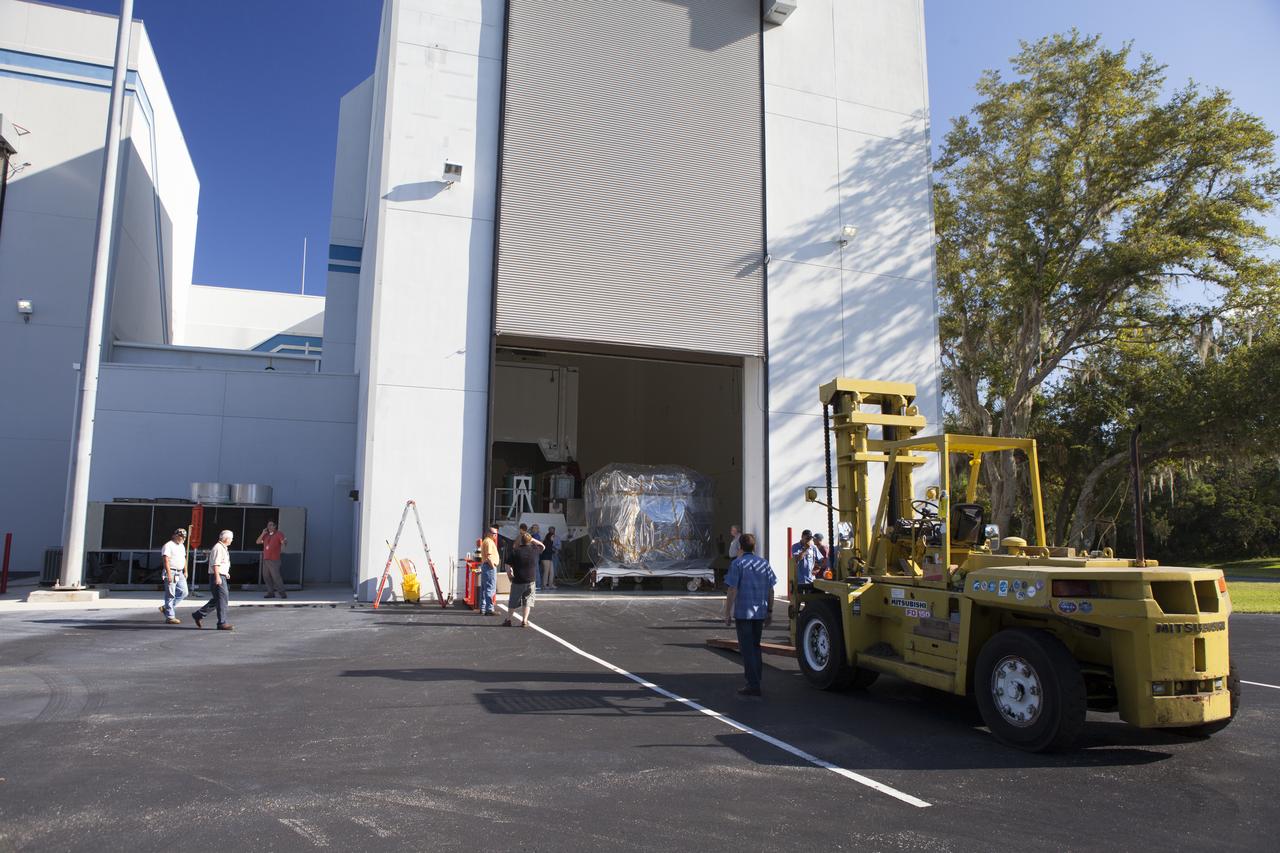
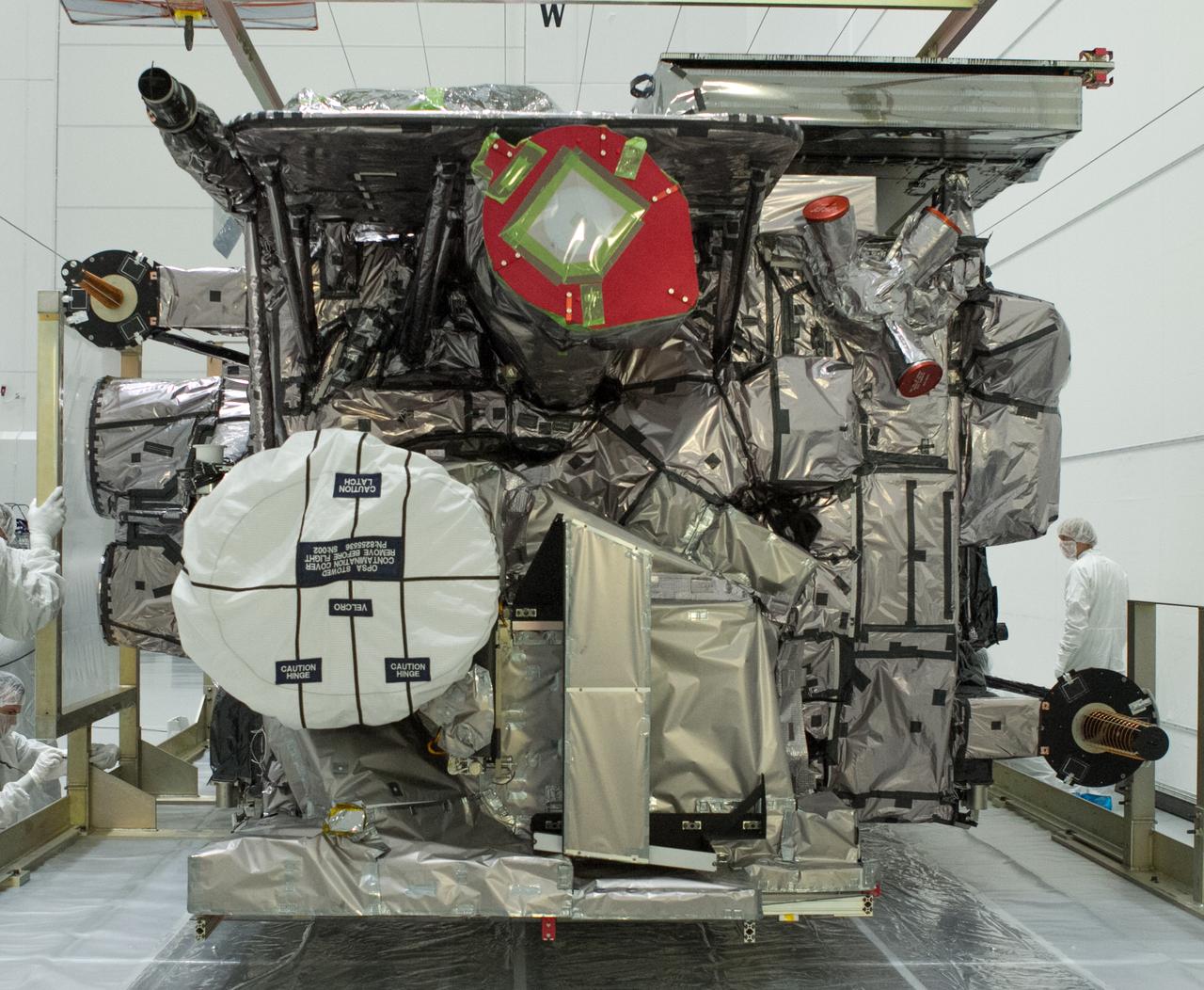
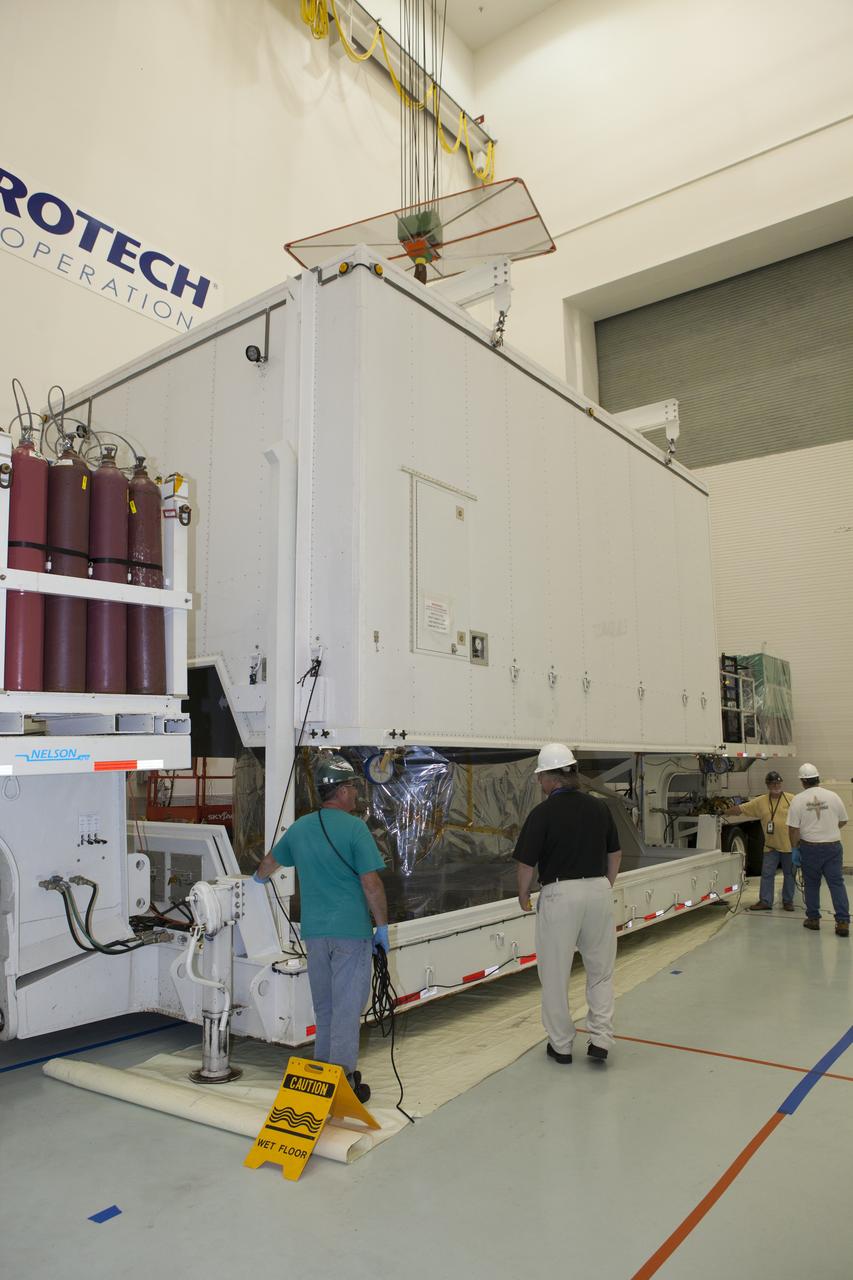
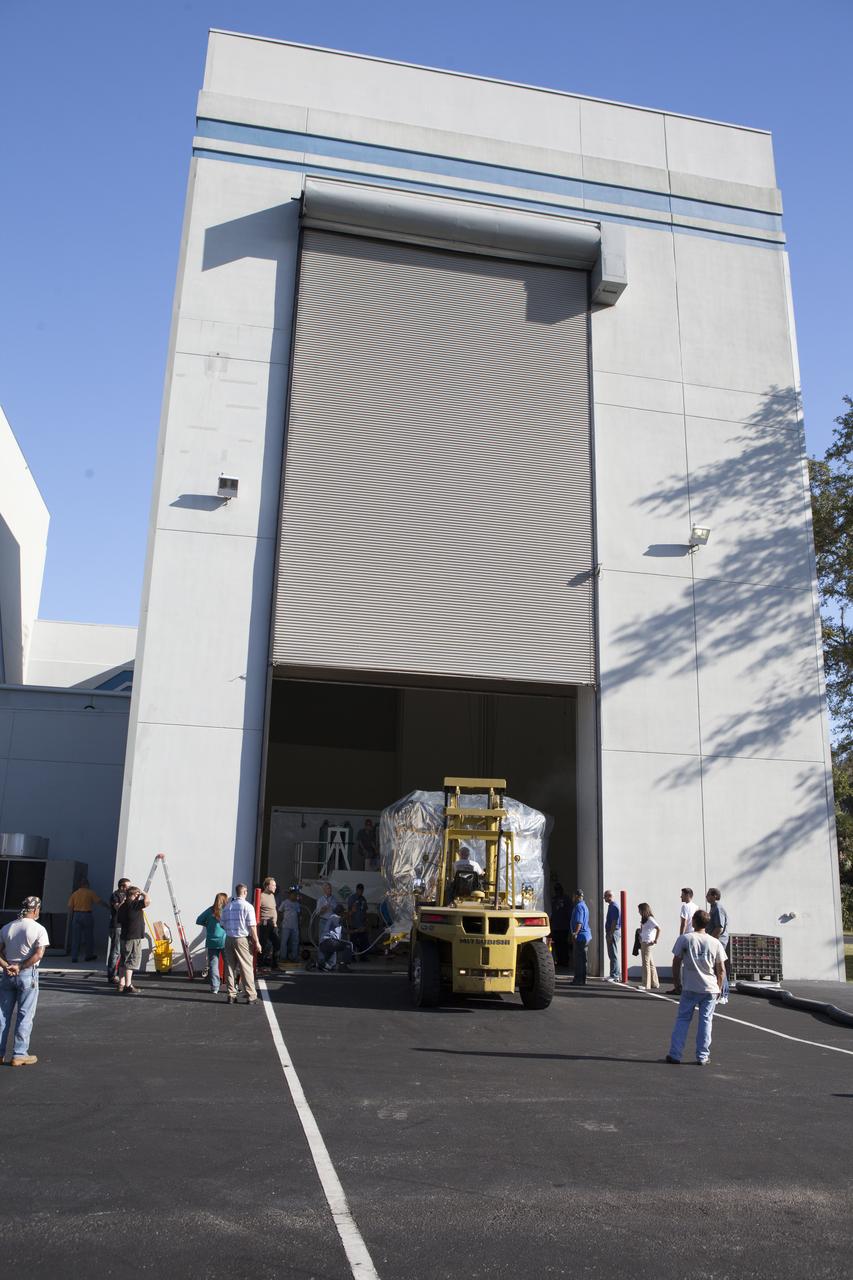
NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft is uncrated for prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 15, 2023. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web. PACE will be encapsulated for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
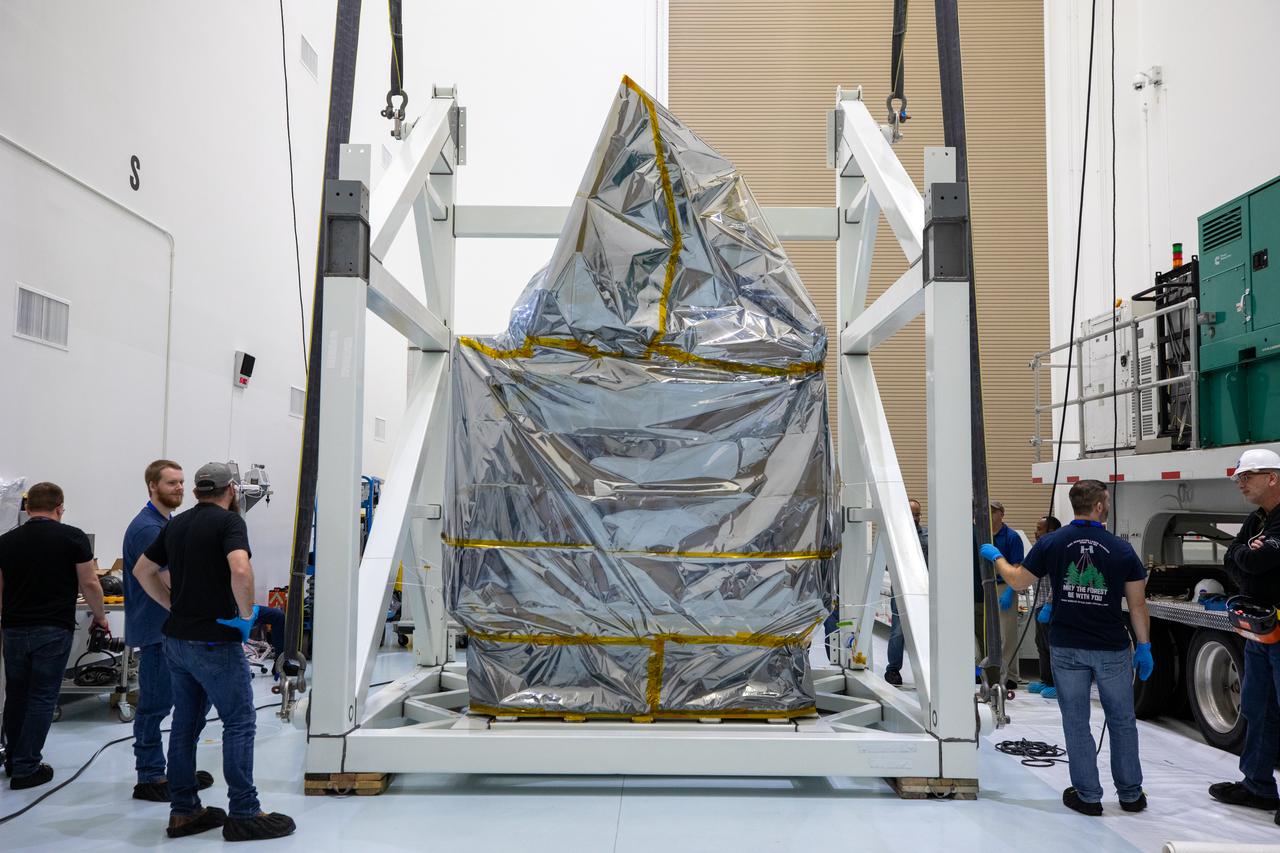

NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft is uncrated for prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 15, 2023. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web. PACE will be encapsulated for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
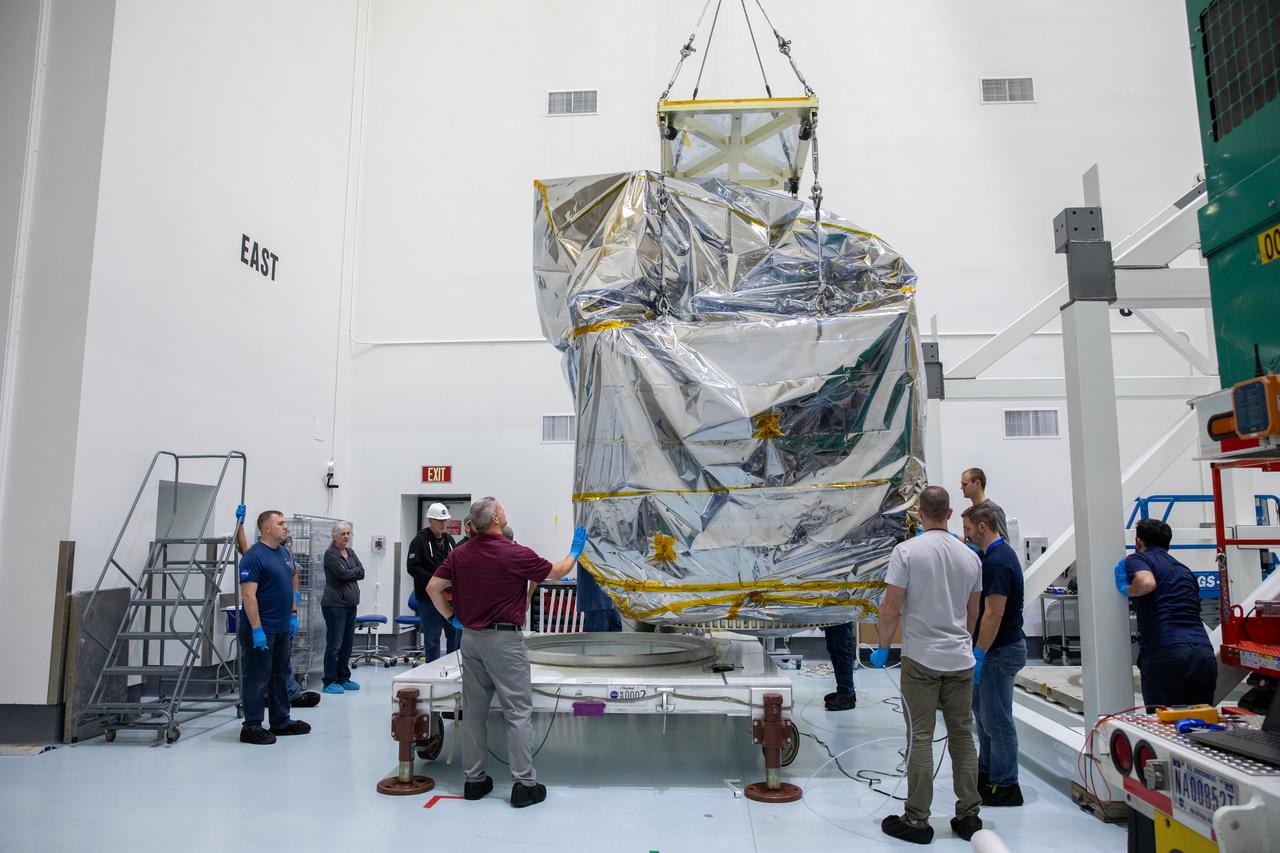

NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft is uncrated for prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 15, 2023. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web. PACE will be encapsulated for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
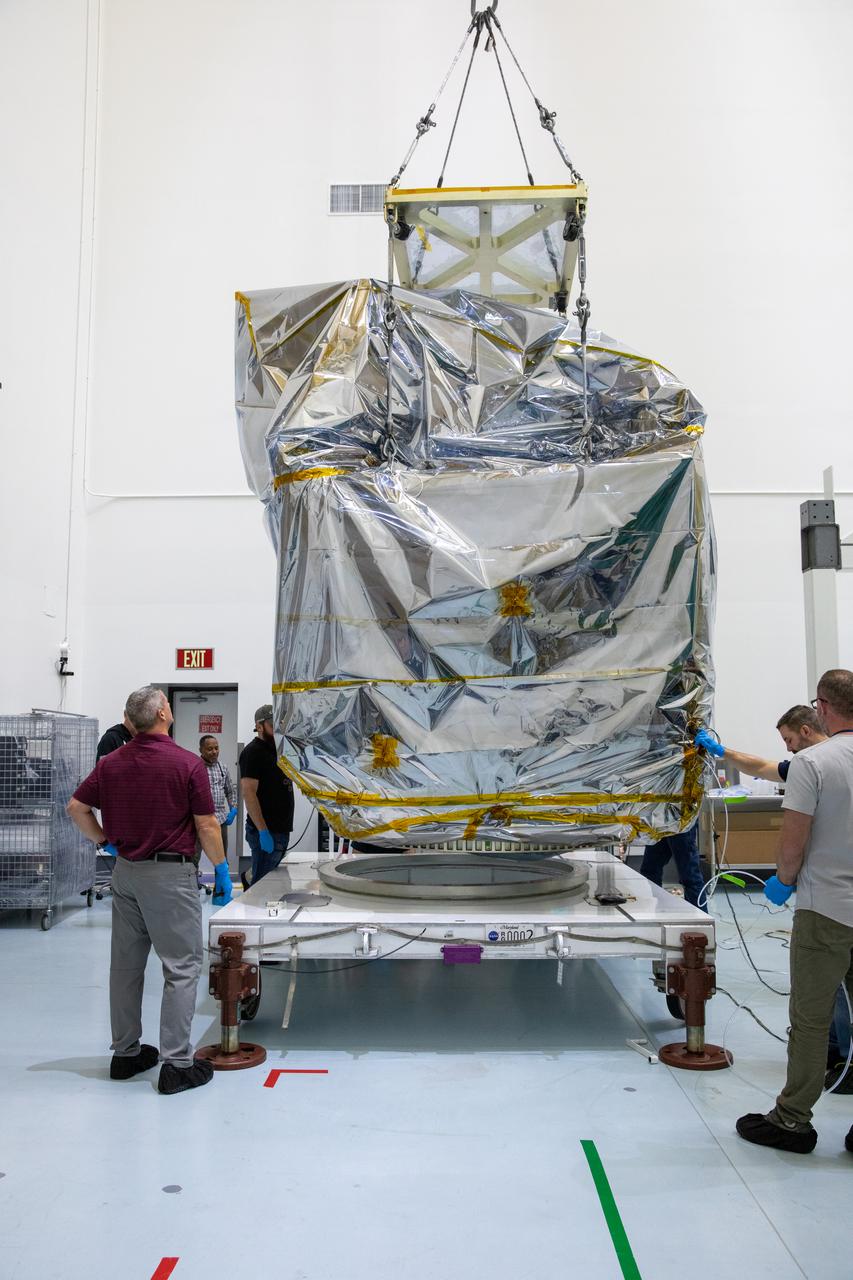

NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft is uncrated for prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 15, 2023. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web. PACE will be encapsulated for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
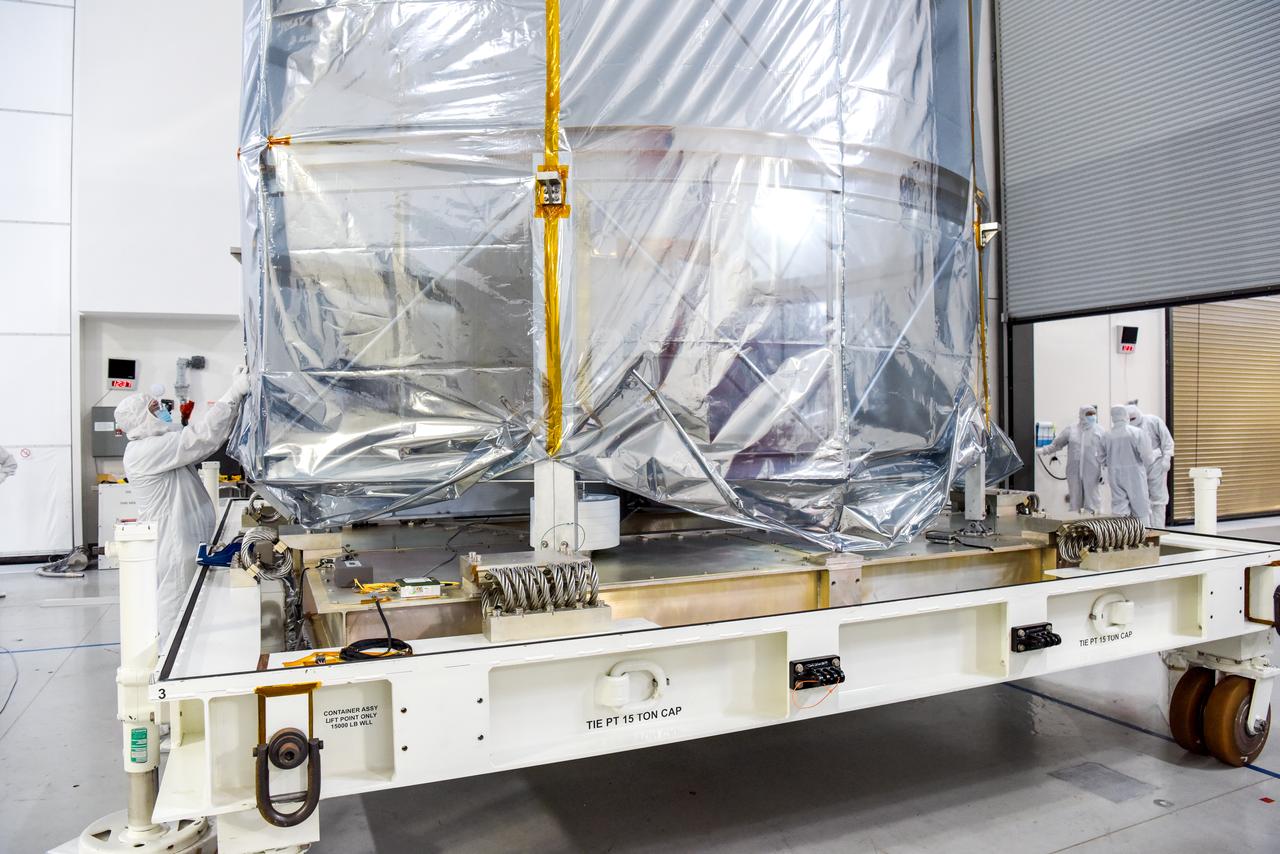

NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) is uncrated for prelaunch processing at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 15, 2025. SPHEREx will enter a polar orbit around Earth and create a 3D map of the entire sky, gathering information about millions of galaxies for scientists to study what happened after the big bang, the history of galaxy evolution, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. SPHEREx will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.

The GOES-R spacecraft is revealed following its uncrating inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.
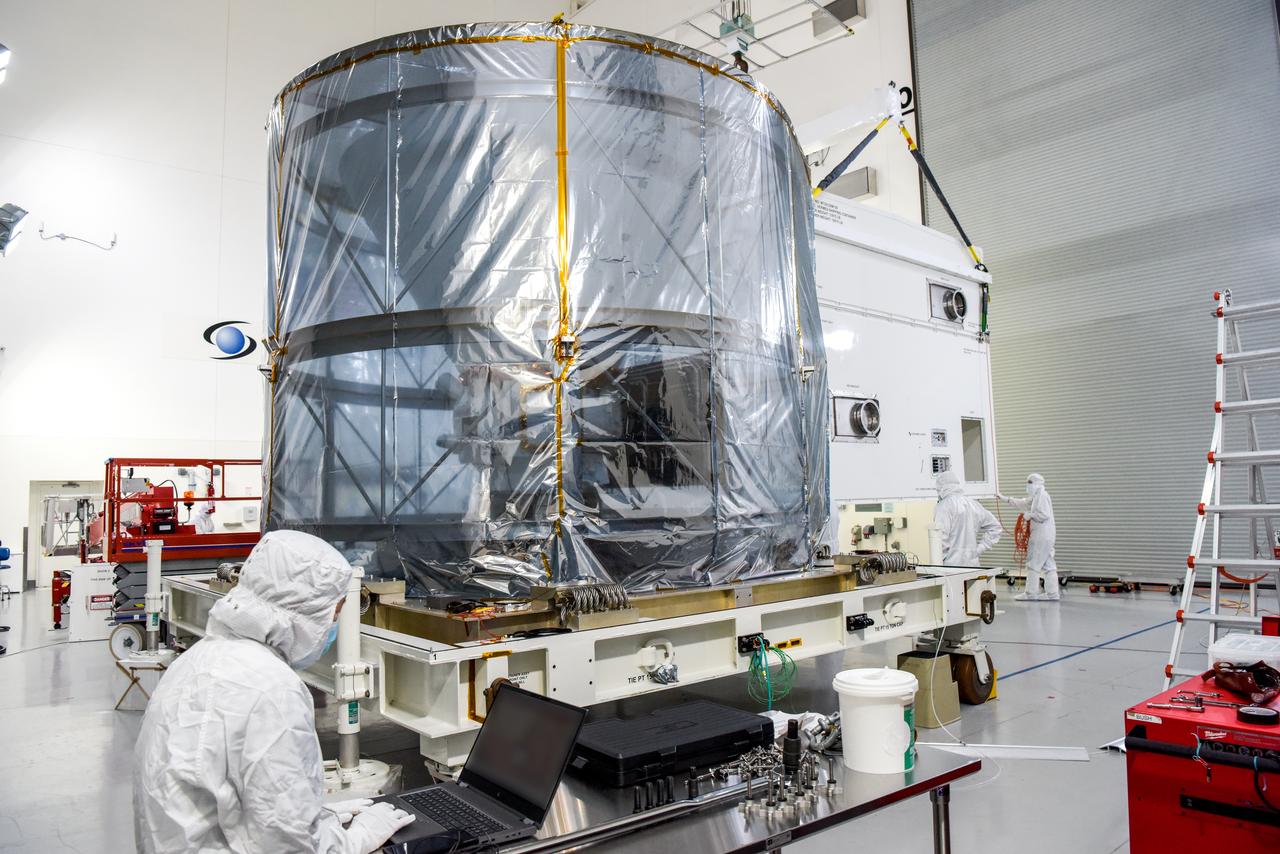

NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) is uncrated for prelaunch processing at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 15, 2025. SPHEREx will enter a polar orbit around Earth and create a 3D map of the entire sky, gathering information about millions of galaxies for scientists to study what happened after the big bang, the history of galaxy evolution, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. SPHEREx will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
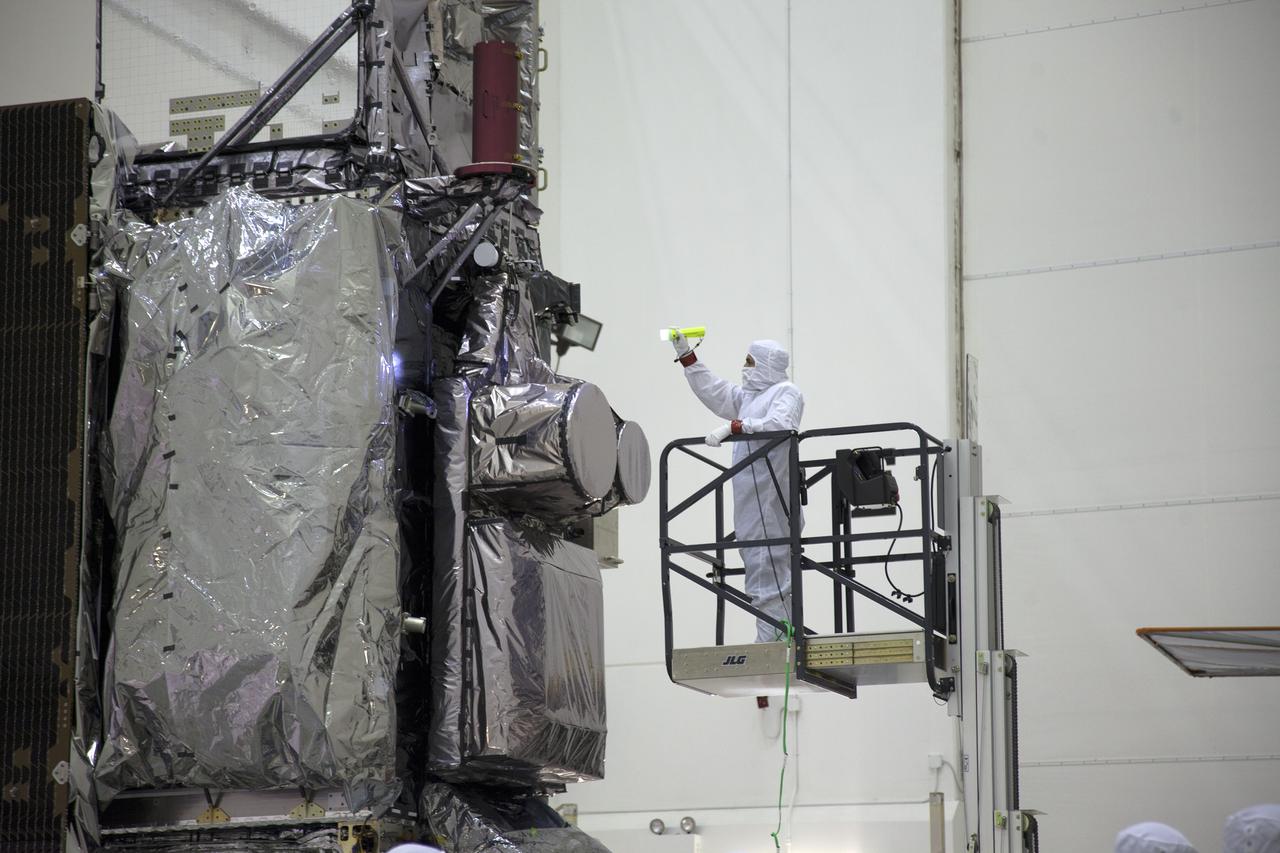

The GOES-R spacecraft is inspected after being uncrated and raised to vertical inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.
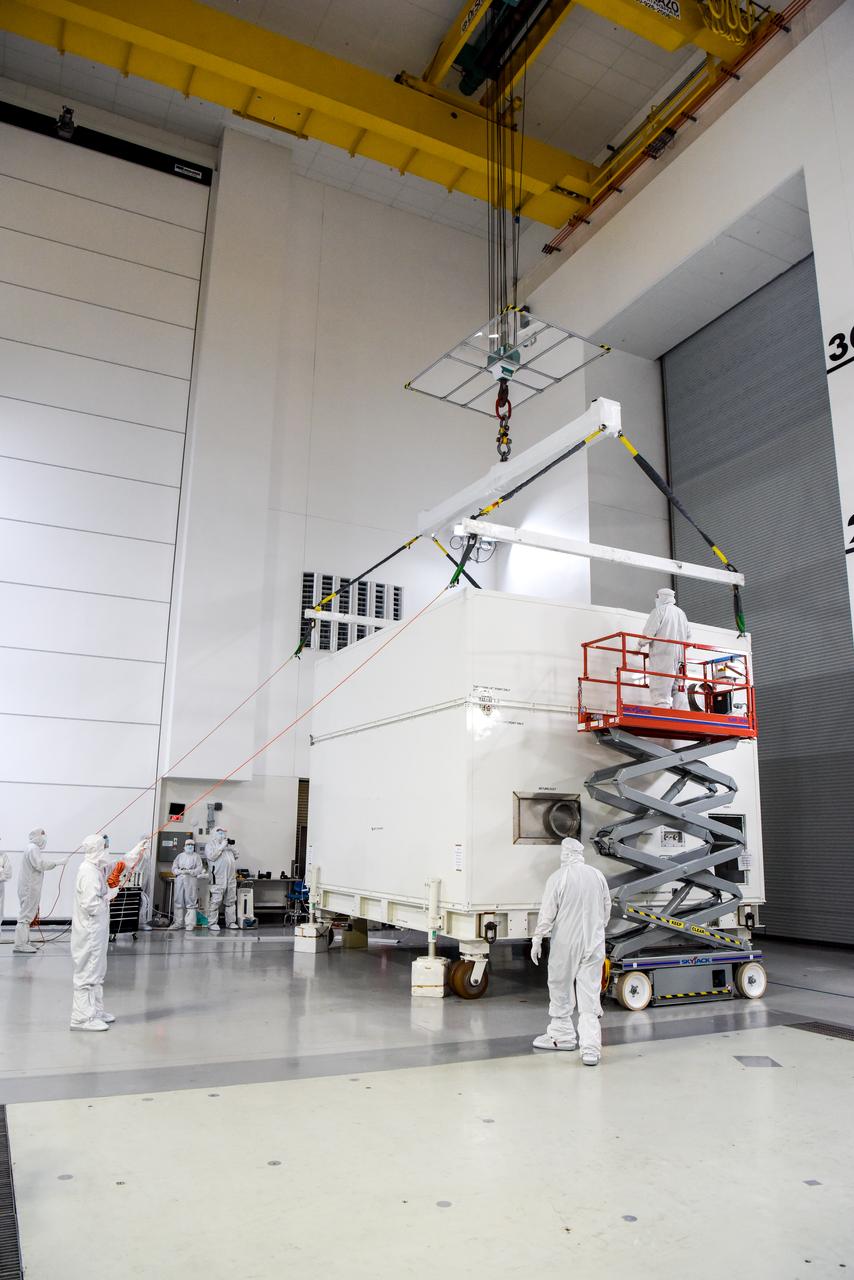

NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) is uncrated for prelaunch processing at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 15, 2025. SPHEREx will enter a polar orbit around Earth and create a 3D map of the entire sky, gathering information about millions of galaxies for scientists to study what happened after the big bang, the history of galaxy evolution, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. SPHEREx will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
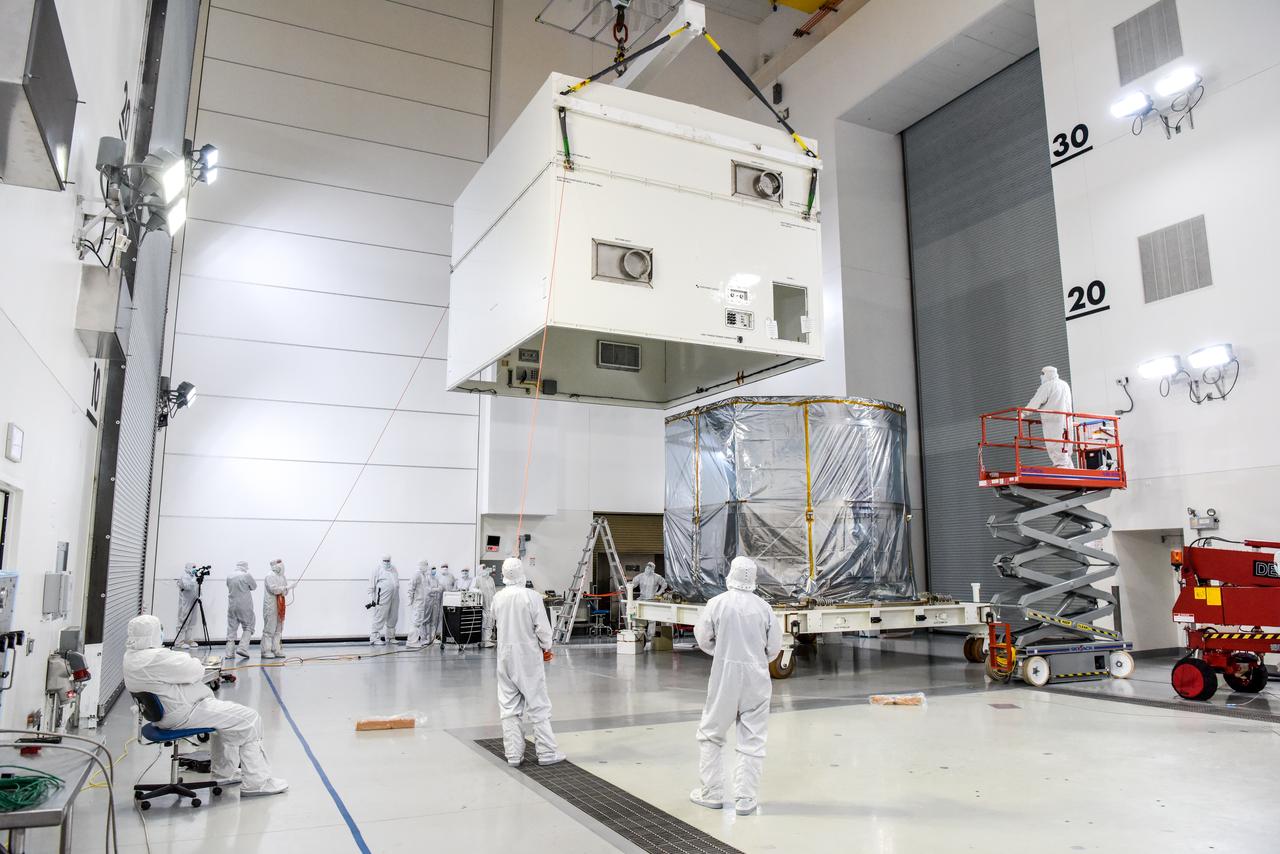

NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) is uncrated for prelaunch processing at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 15, 2025. SPHEREx will enter a polar orbit around Earth and create a 3D map of the entire sky, gathering information about millions of galaxies for scientists to study what happened after the big bang, the history of galaxy evolution, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. SPHEREx will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
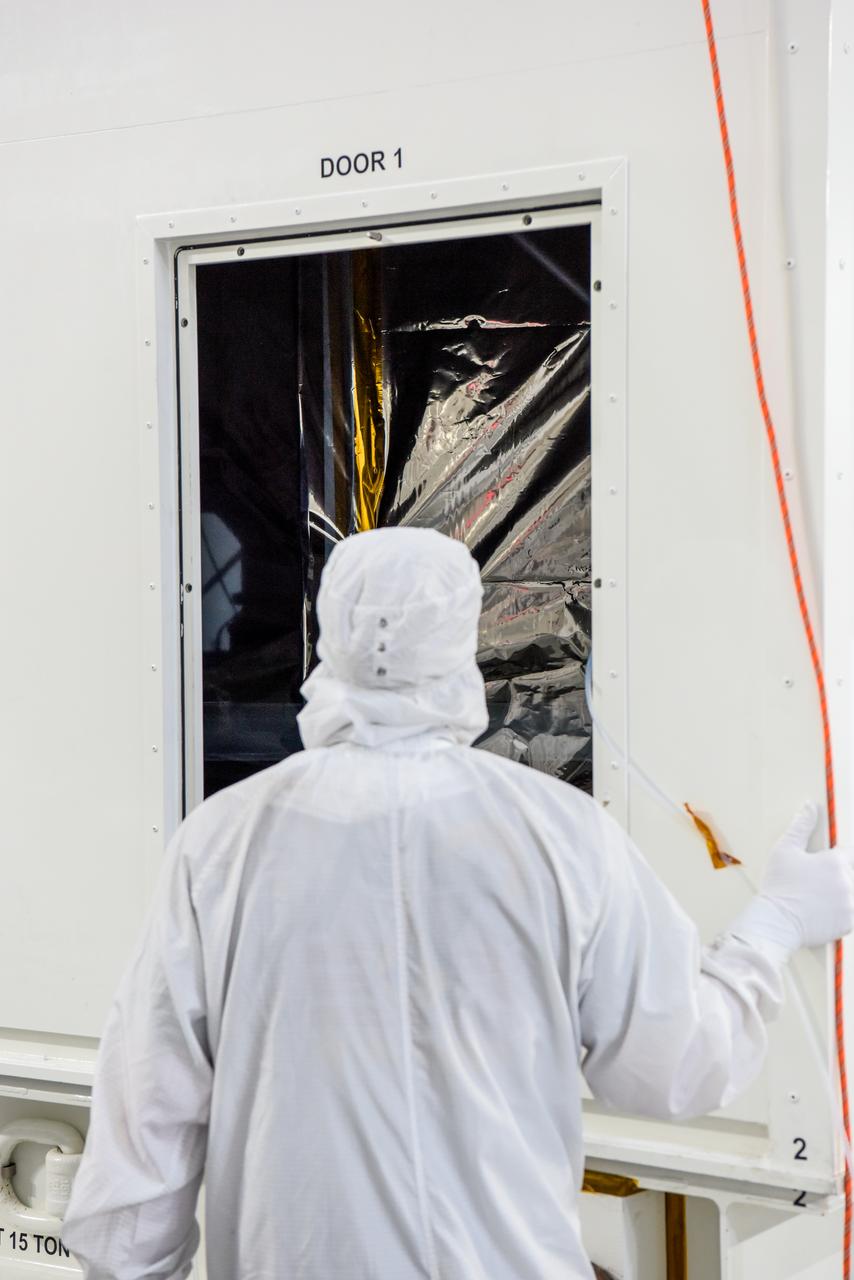

NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) is uncrated for prelaunch processing at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 15, 2025. SPHEREx will enter a polar orbit around Earth and create a 3D map of the entire sky, gathering information about millions of galaxies for scientists to study what happened after the big bang, the history of galaxy evolution, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. SPHEREx will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
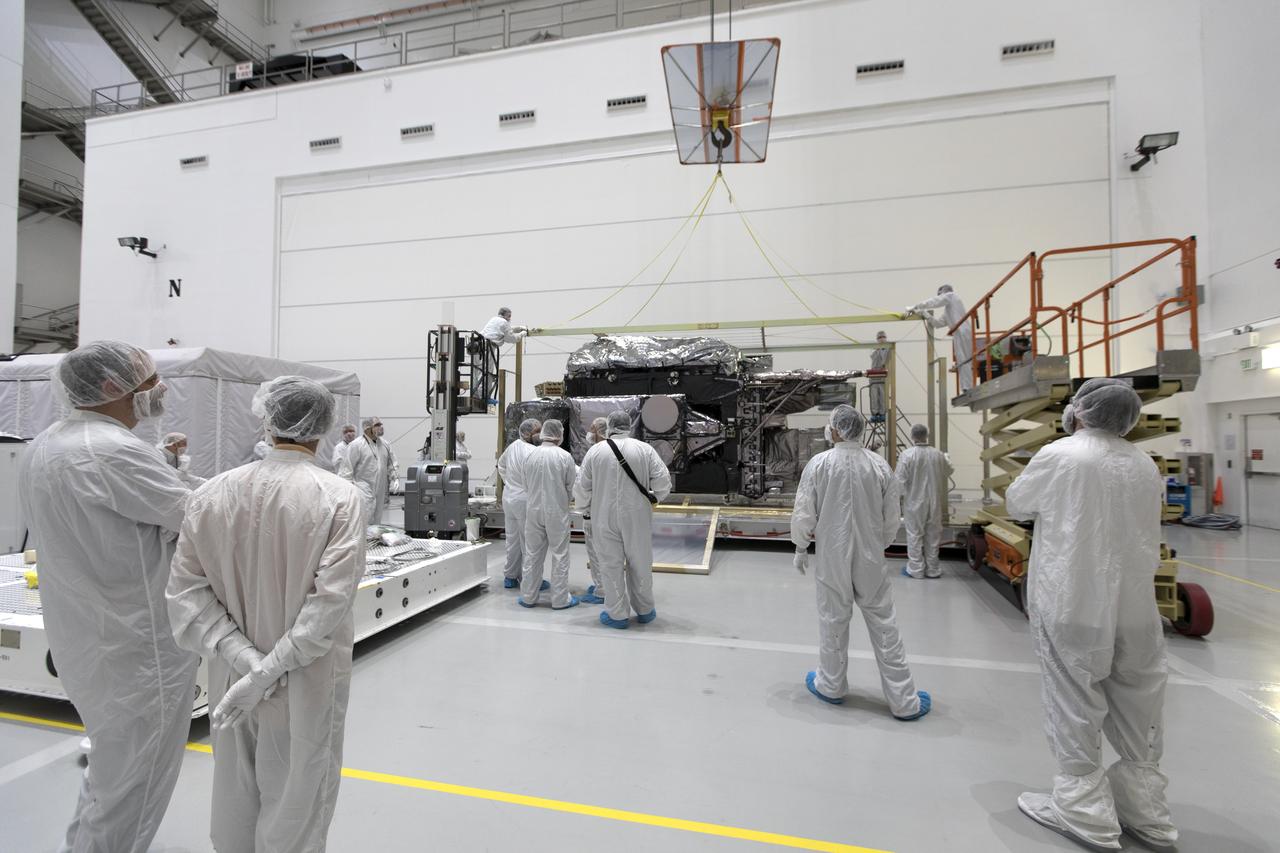

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technician and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
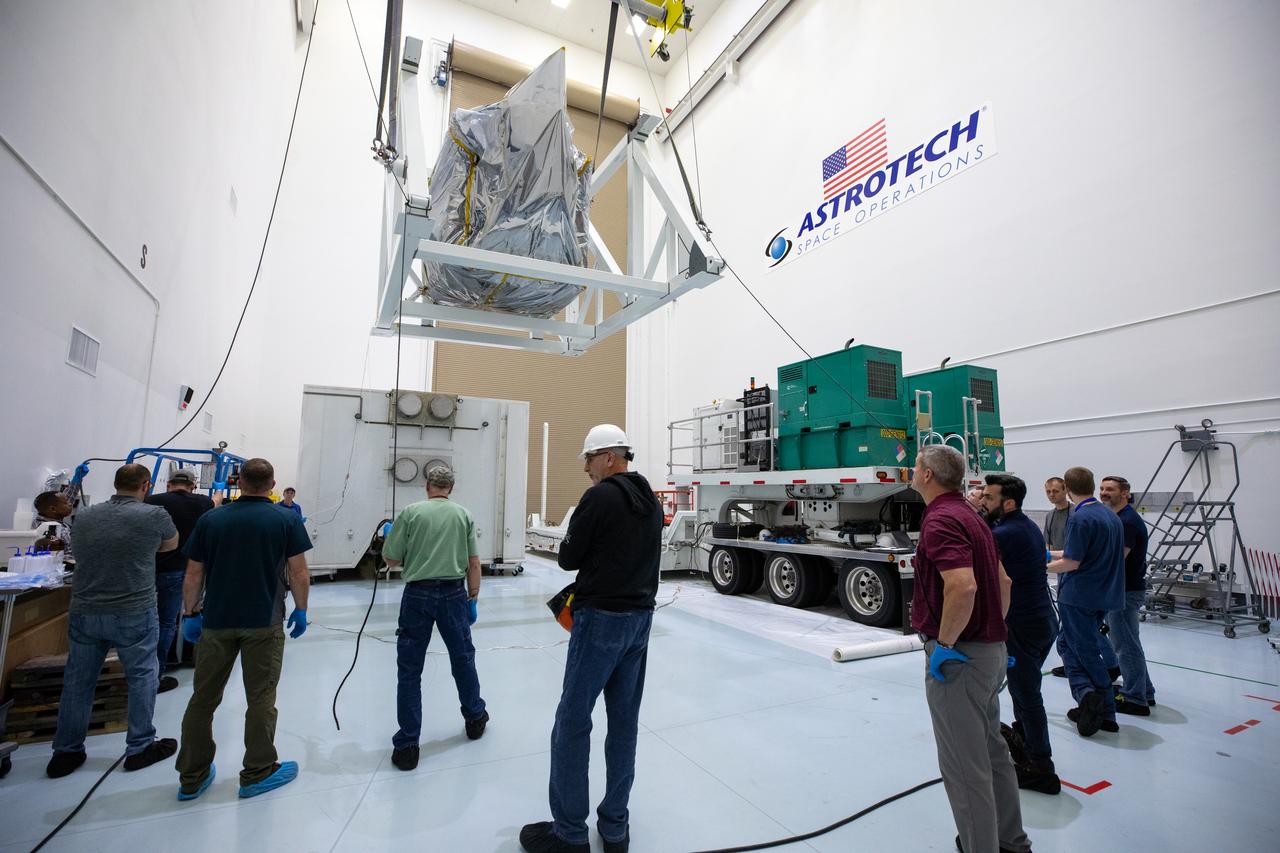

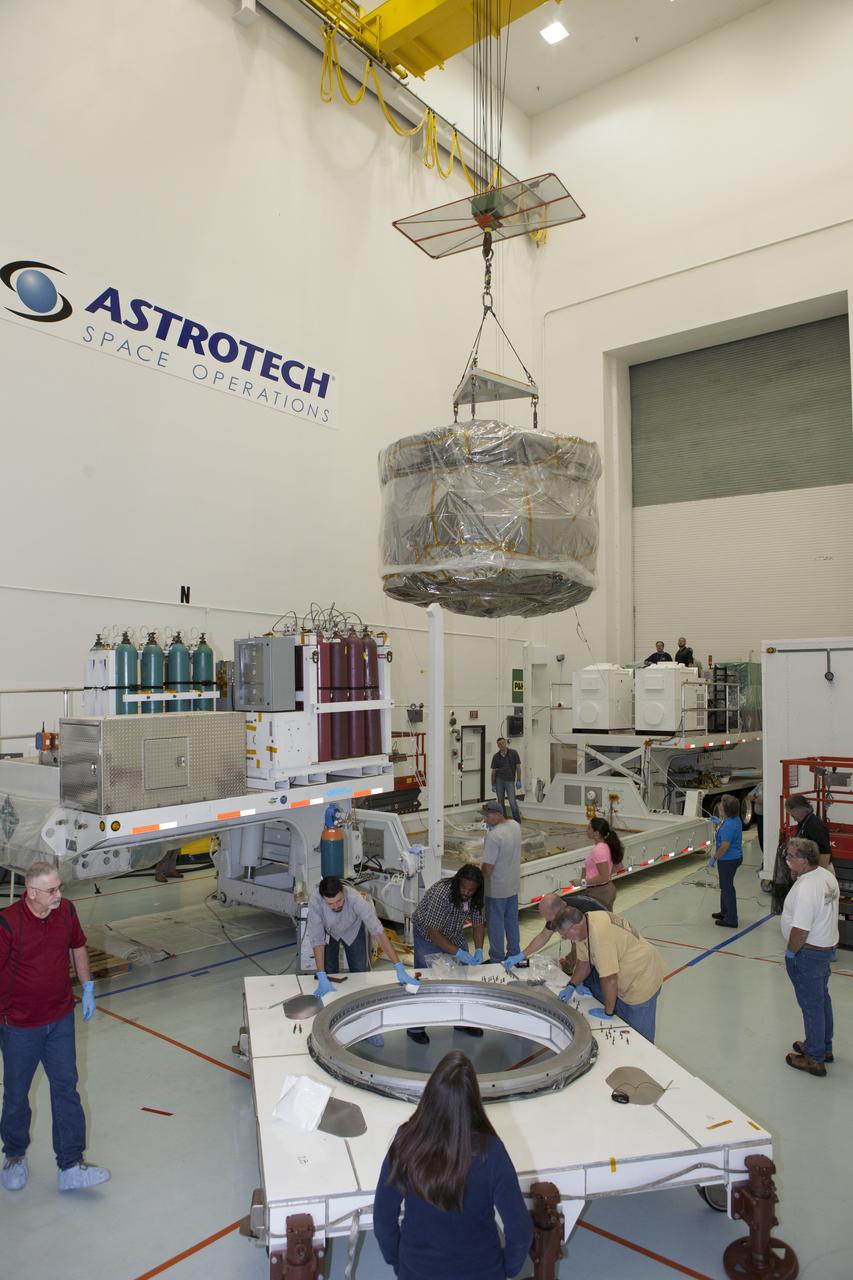
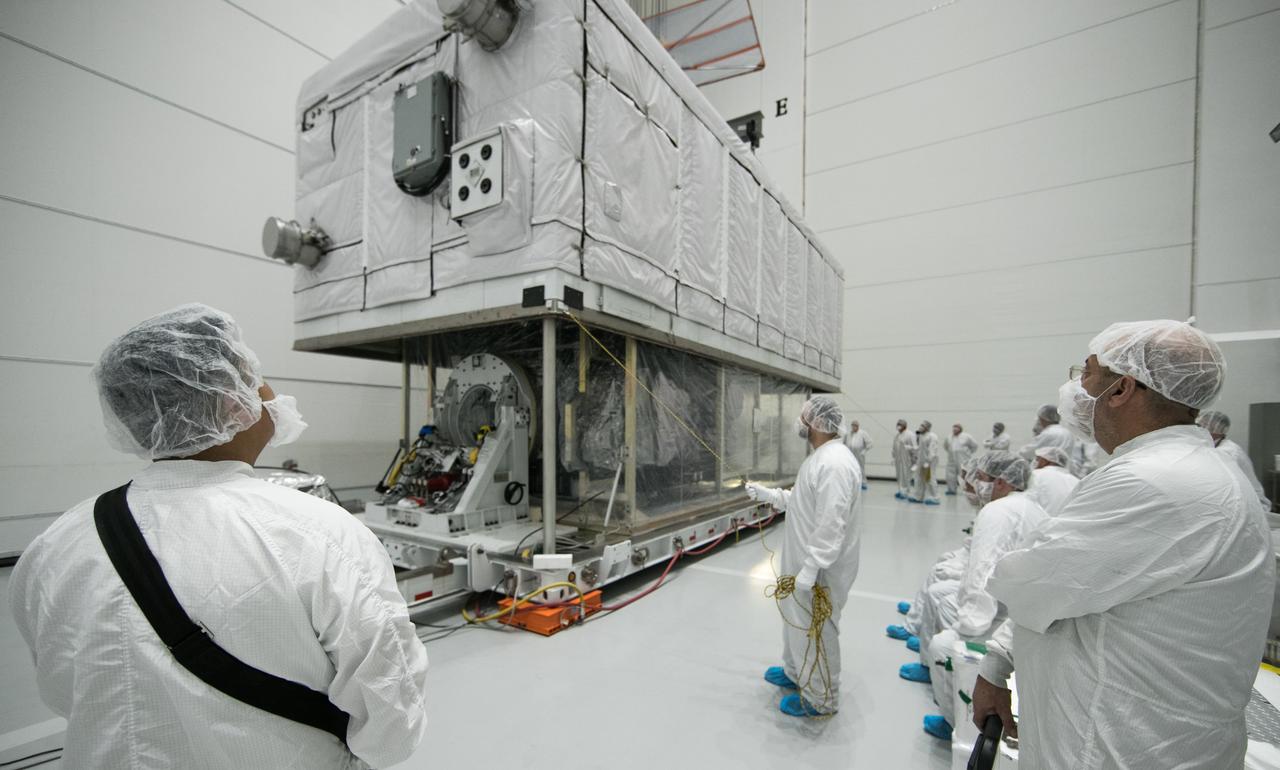
Technicians monitor movement as a crane hoists NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft after being uncrated on Wednesday, Nov. 15, 2023, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web. PACE will be encapsulated for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
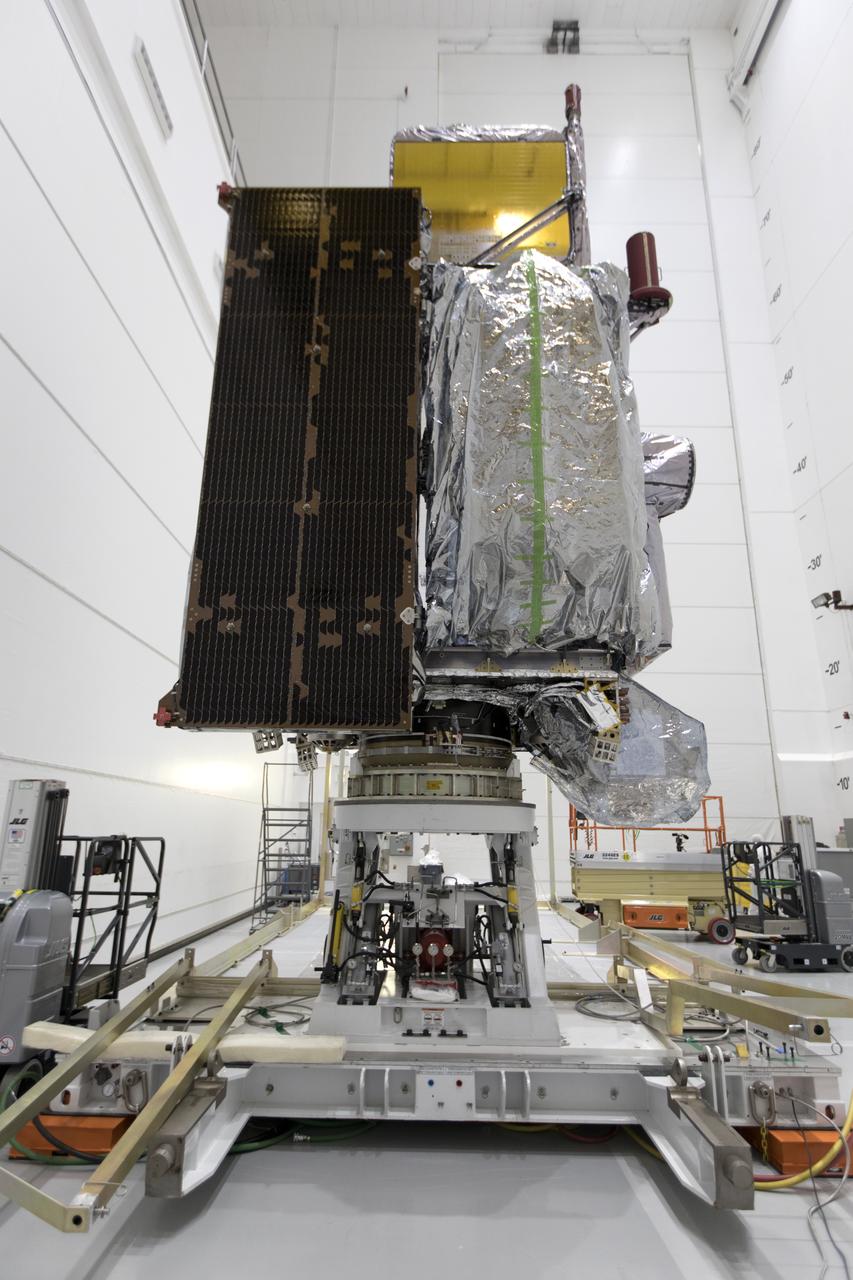

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
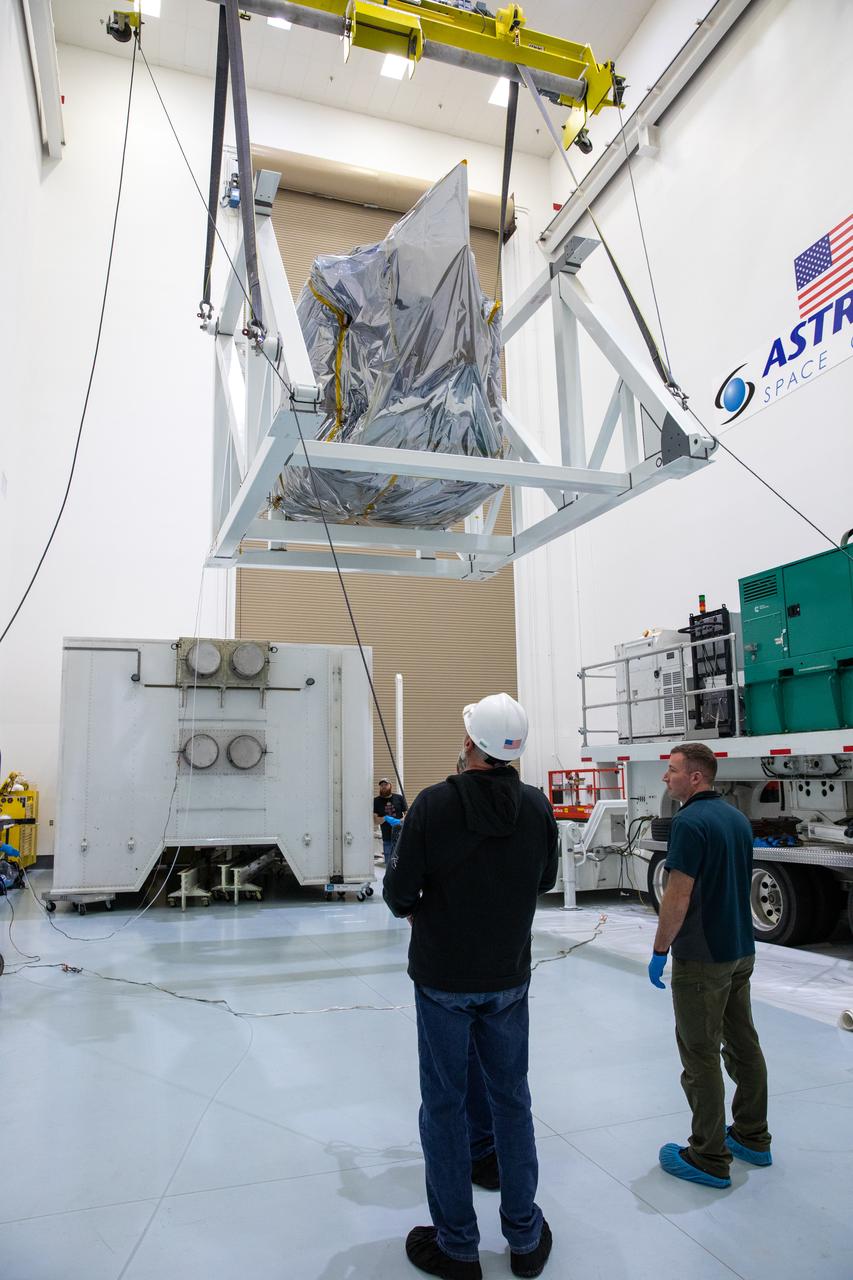

Technicians monitor movement as a crane hoists NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft after being uncrated on Wednesday, Nov. 15, 2023, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web. PACE will be encapsulated for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.

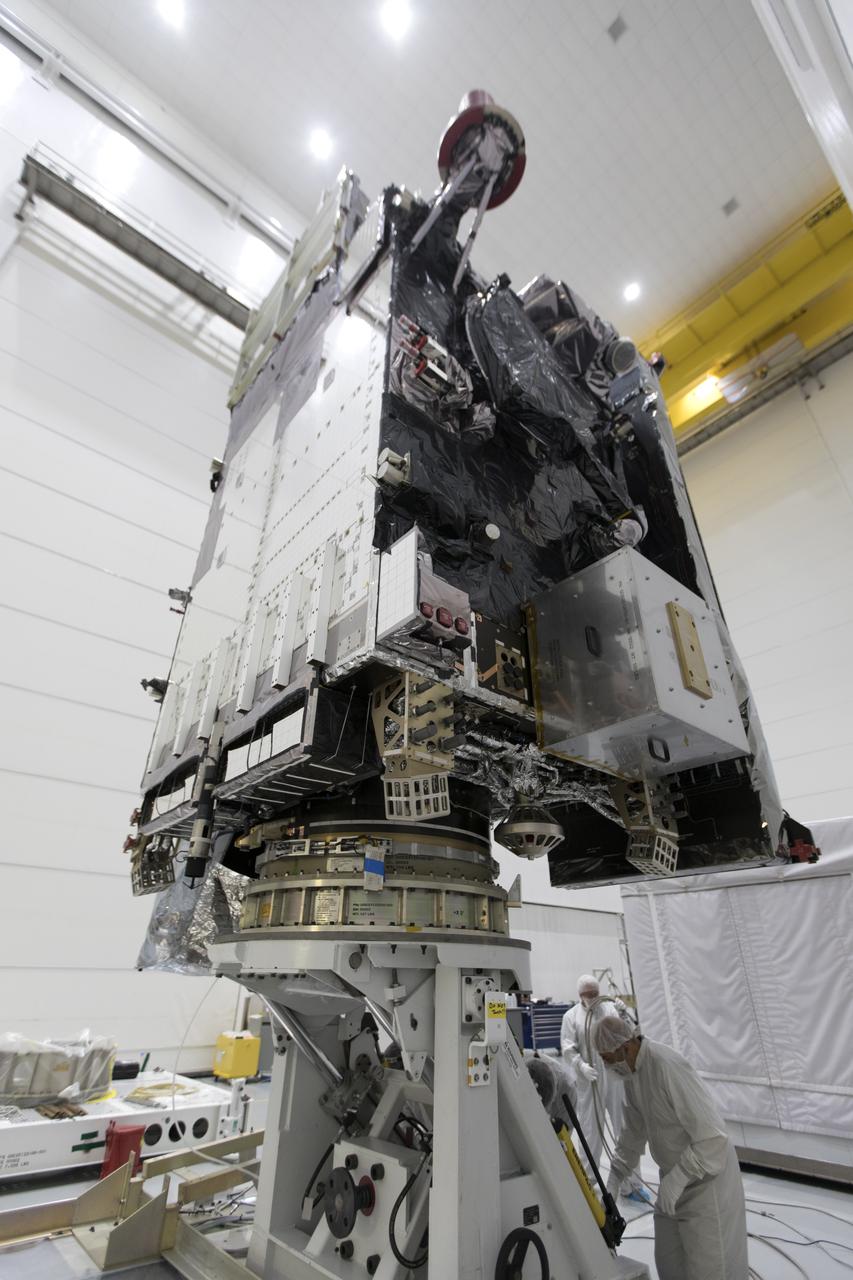
At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, a technician inspects NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
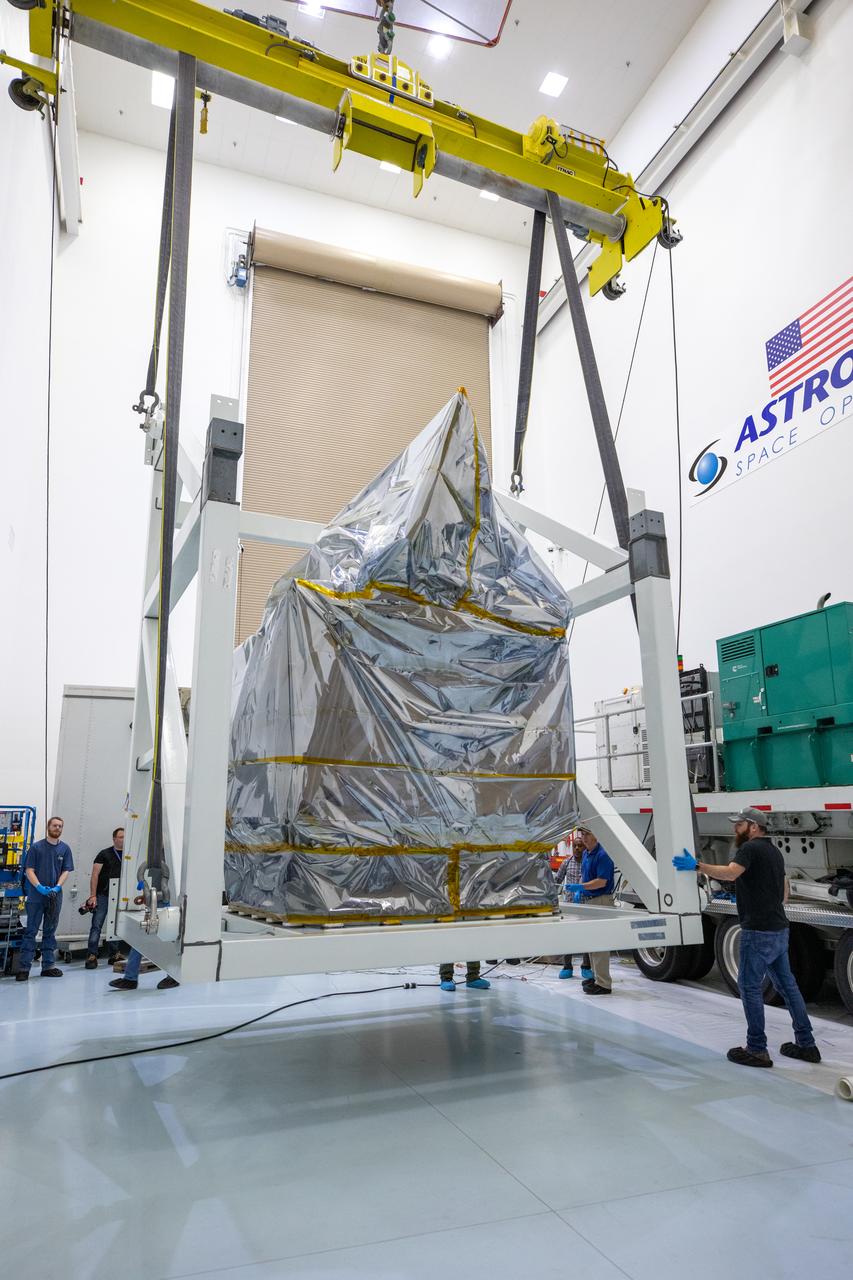

Technicians monitor movement as a crane hoists NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft after being uncrated on Wednesday, Nov. 15, 2023, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web. PACE will be encapsulated for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
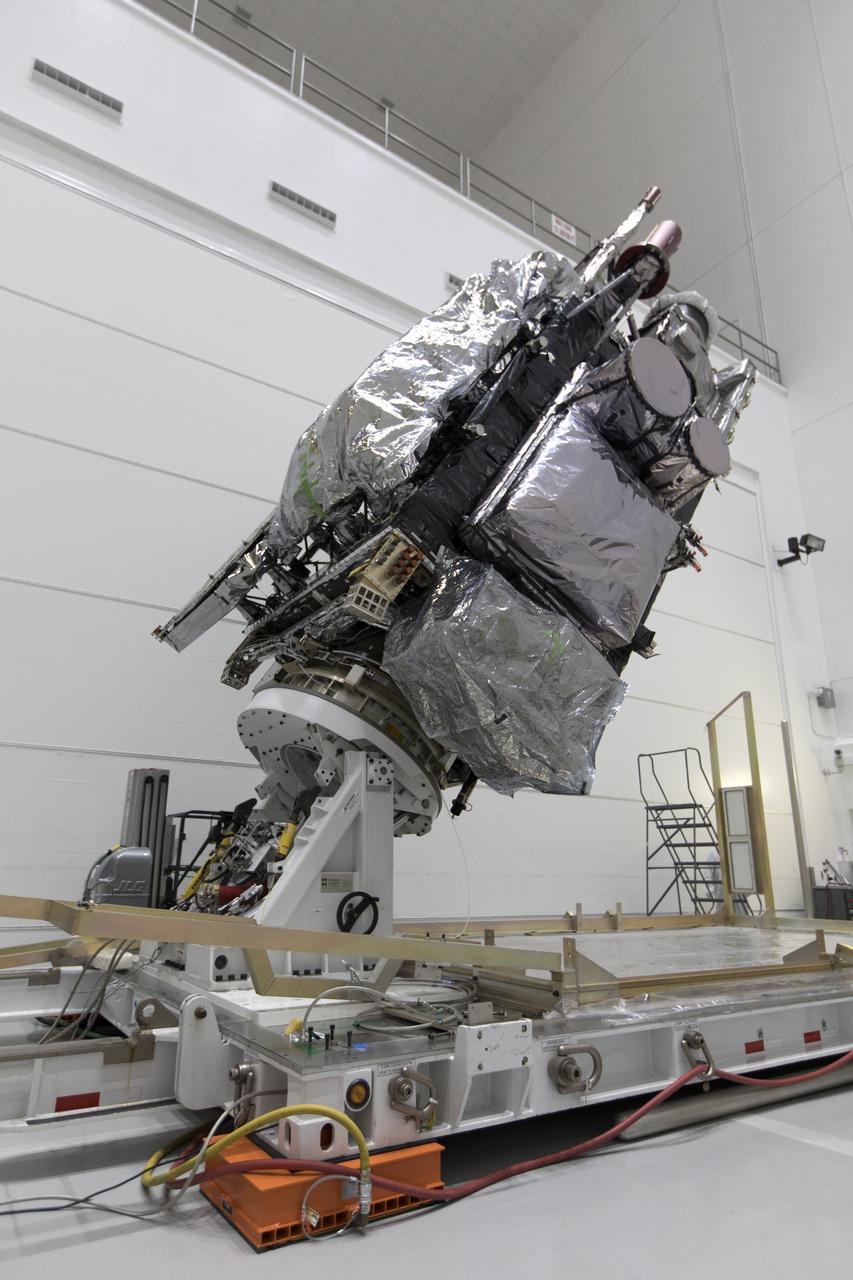

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
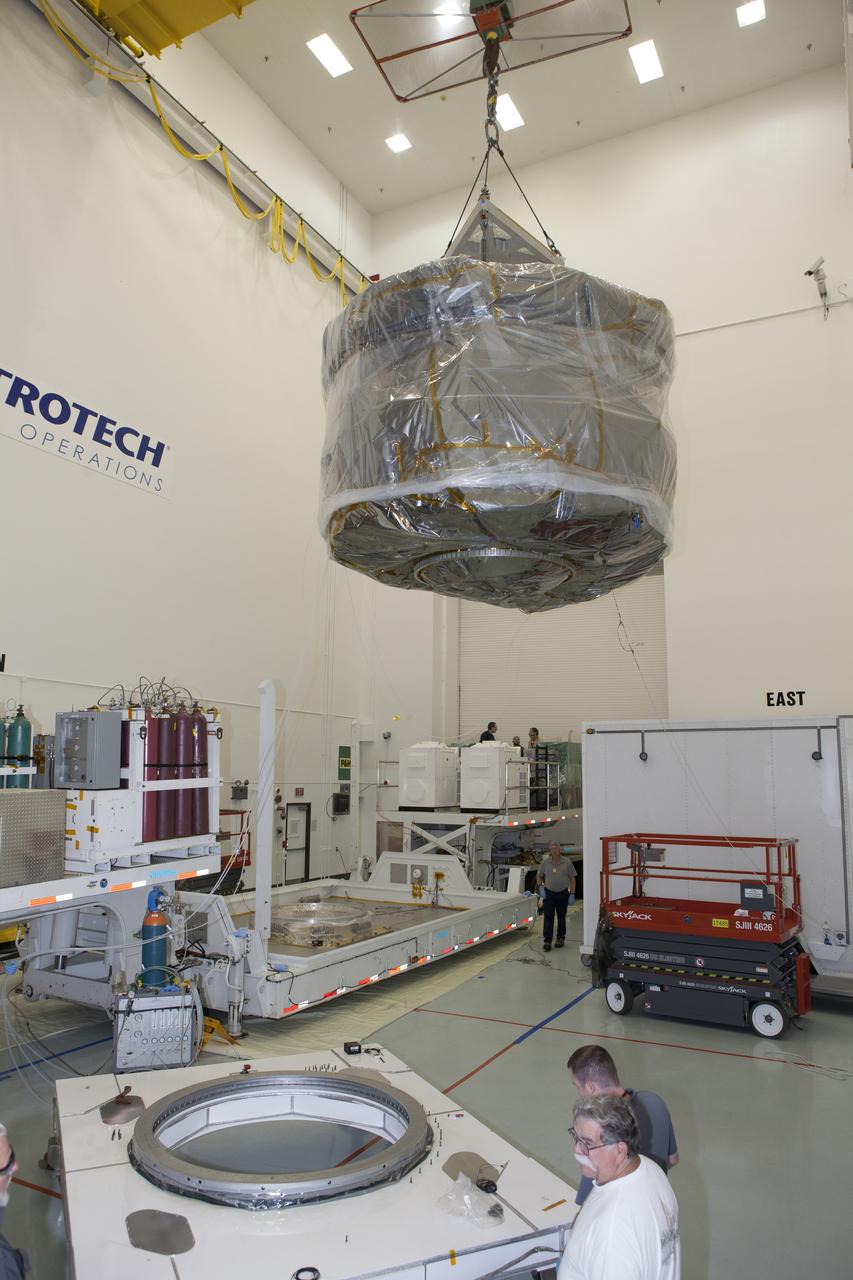

Two of the observatories, the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory are suspended over a payload dolly during uncrating operations in the Building 2 south encapsulation bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
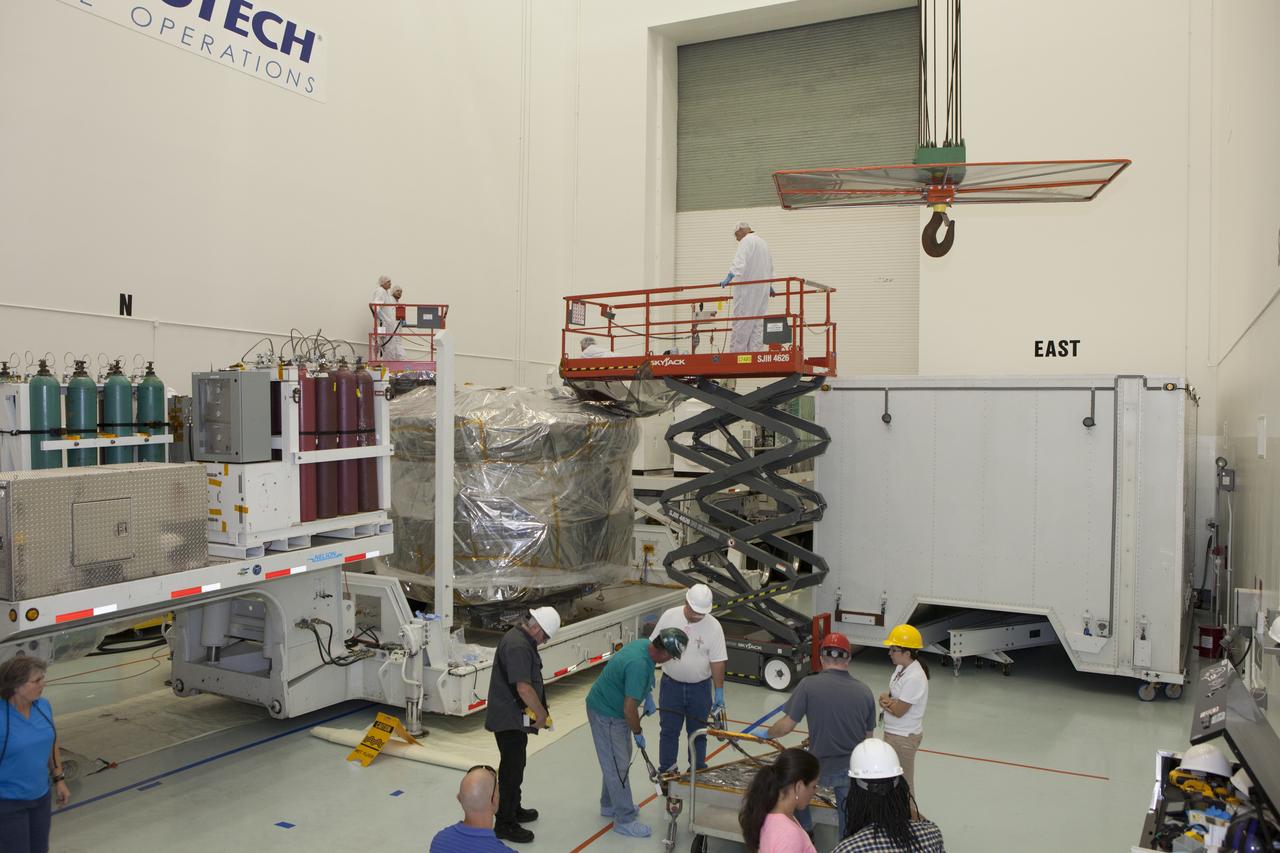

Workers prepare a payload dolly for the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, two of the observatories for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, during uncrating operations in the Building 2 south encapsulation bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
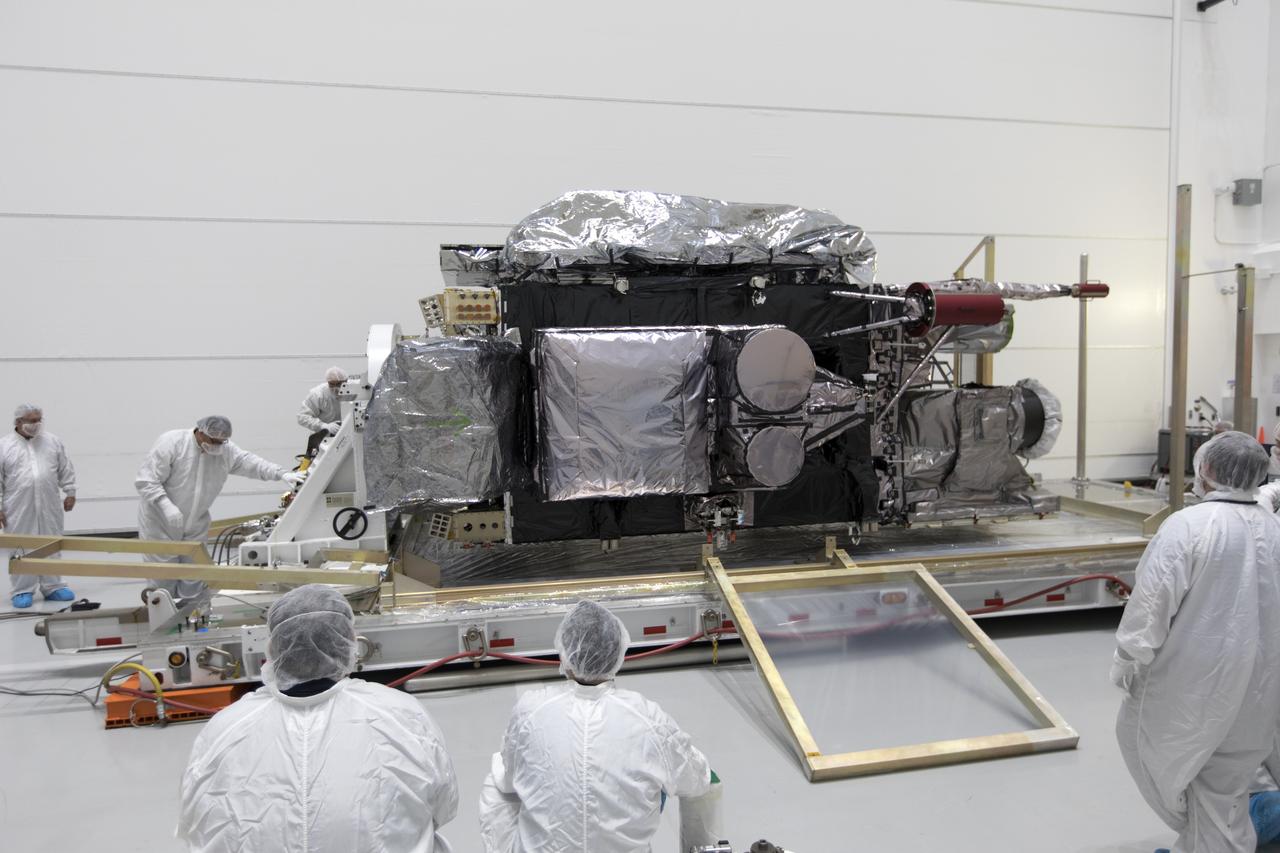

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technician and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
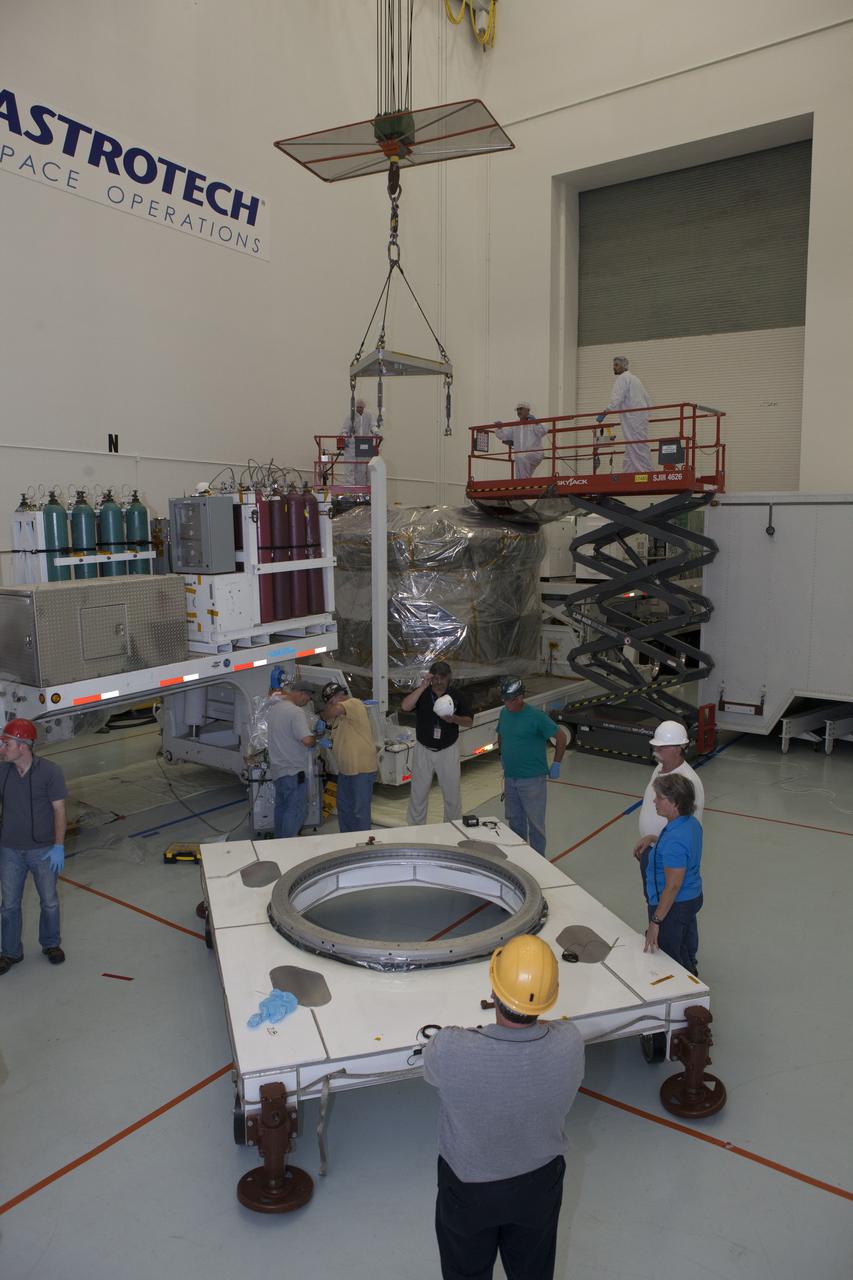

A crane is lowered toward the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, two of the observatories for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, during uncrating operations in the Building 2 south encapsulation bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
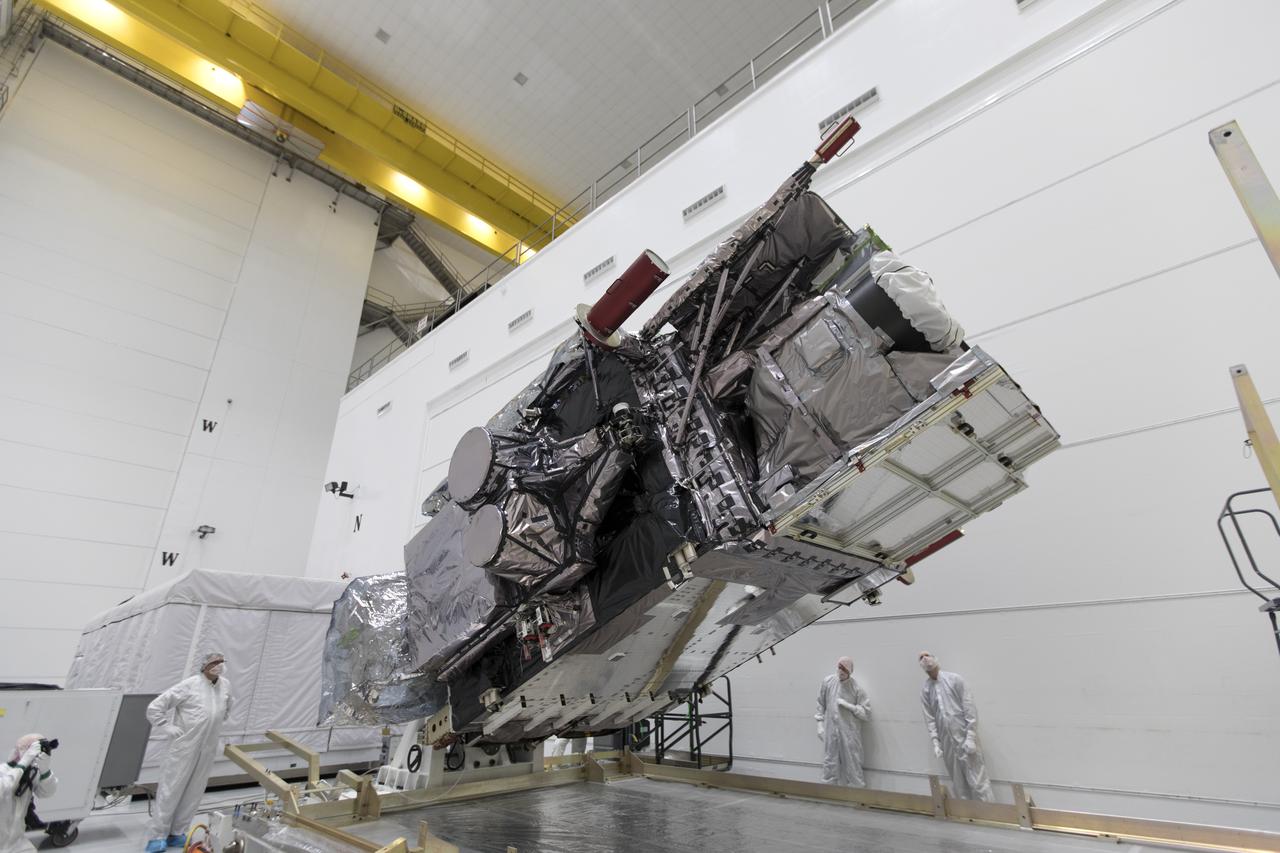

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
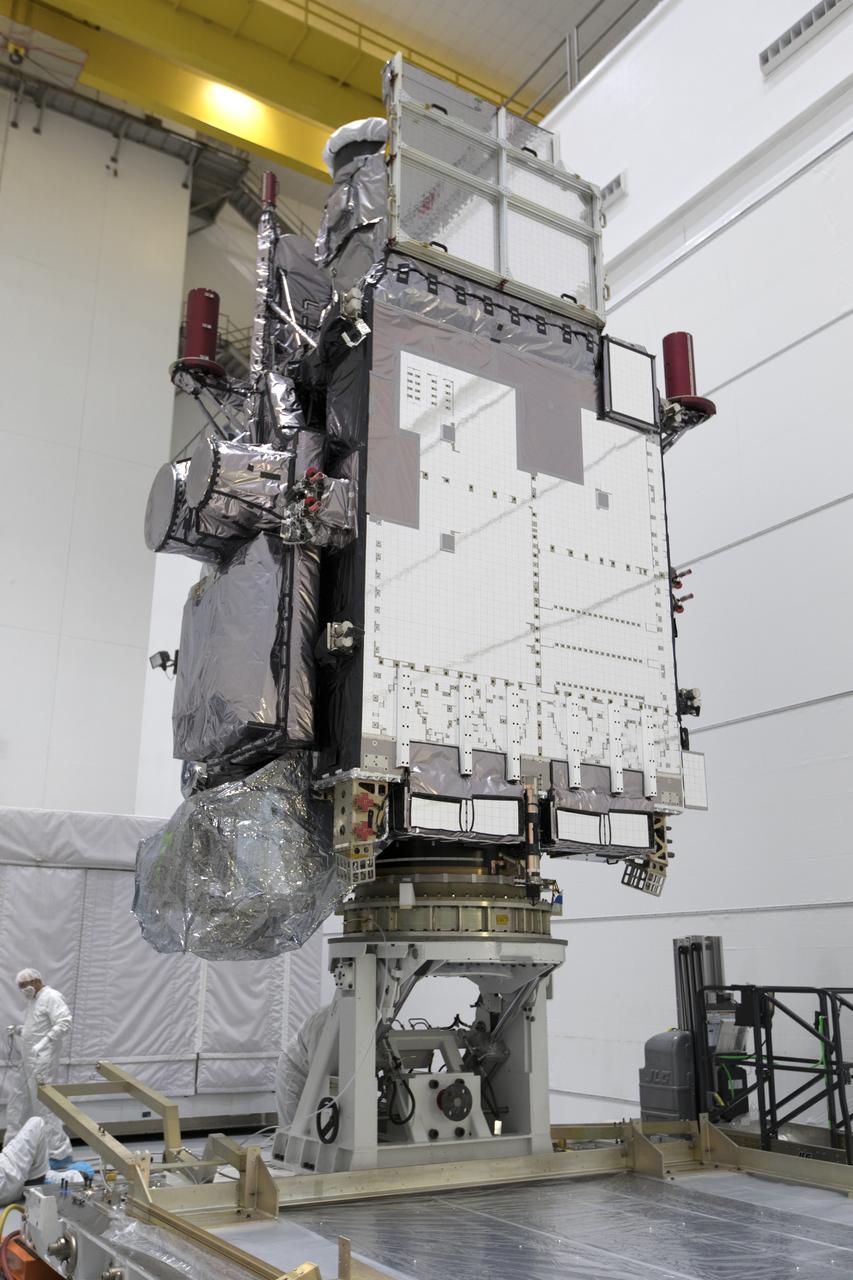

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

Two of the observatories, the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, glides toward a payload dolly during uncrating operations in the Building 2 south encapsulation bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
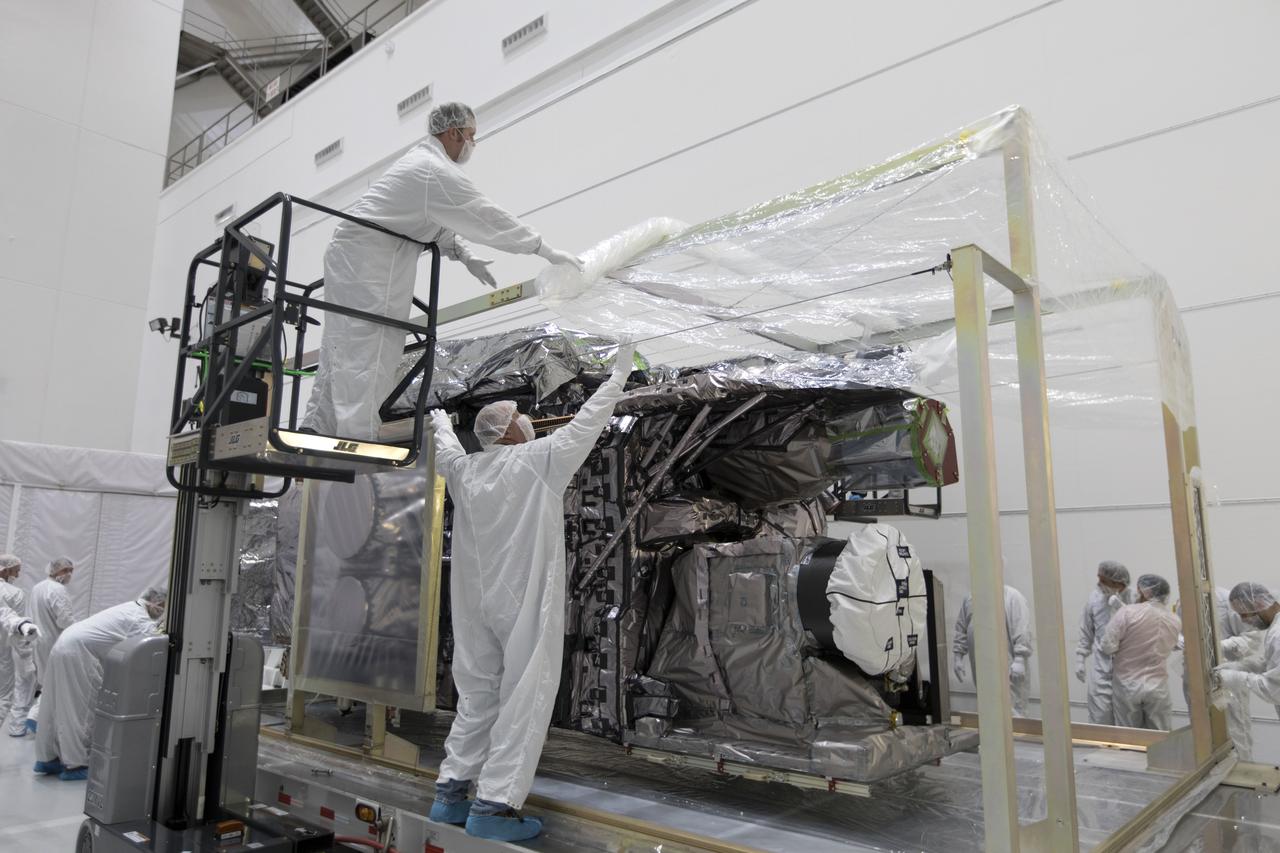

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technician and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
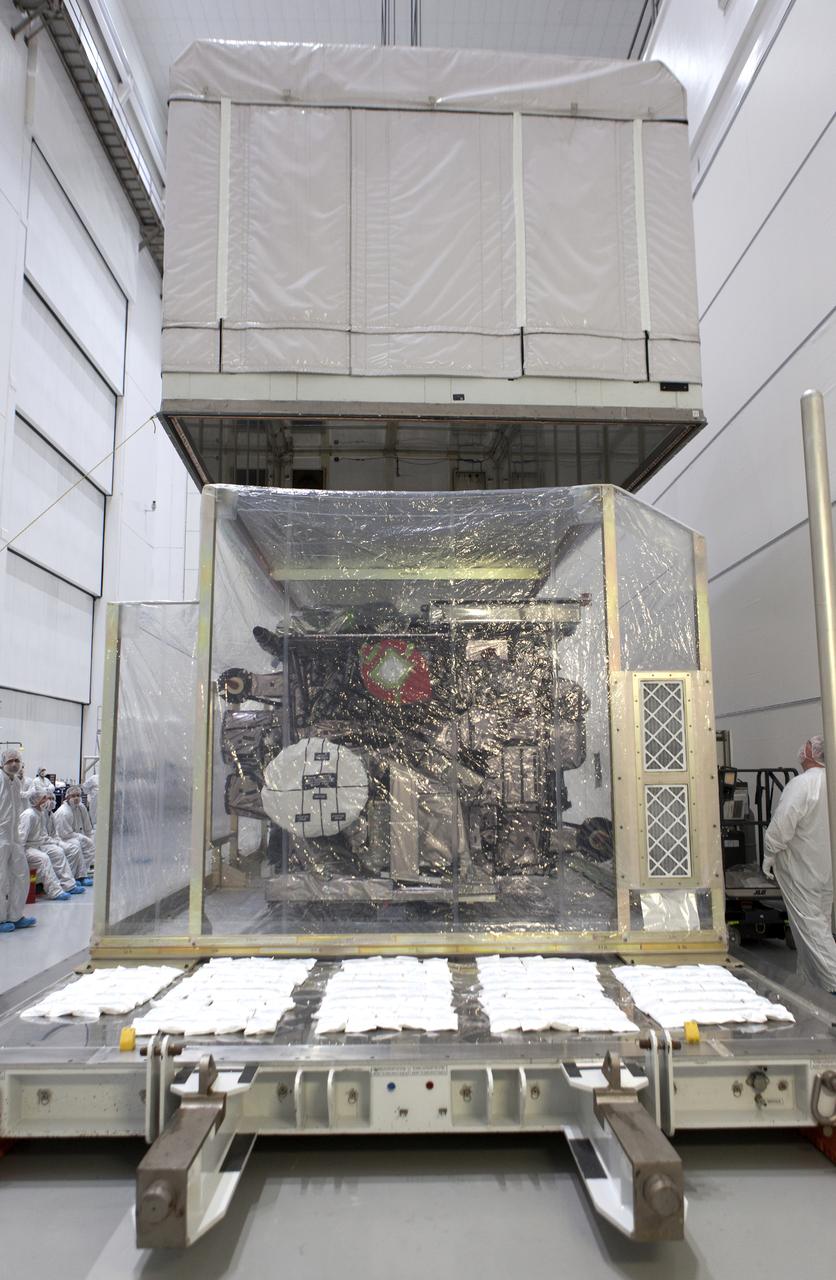

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
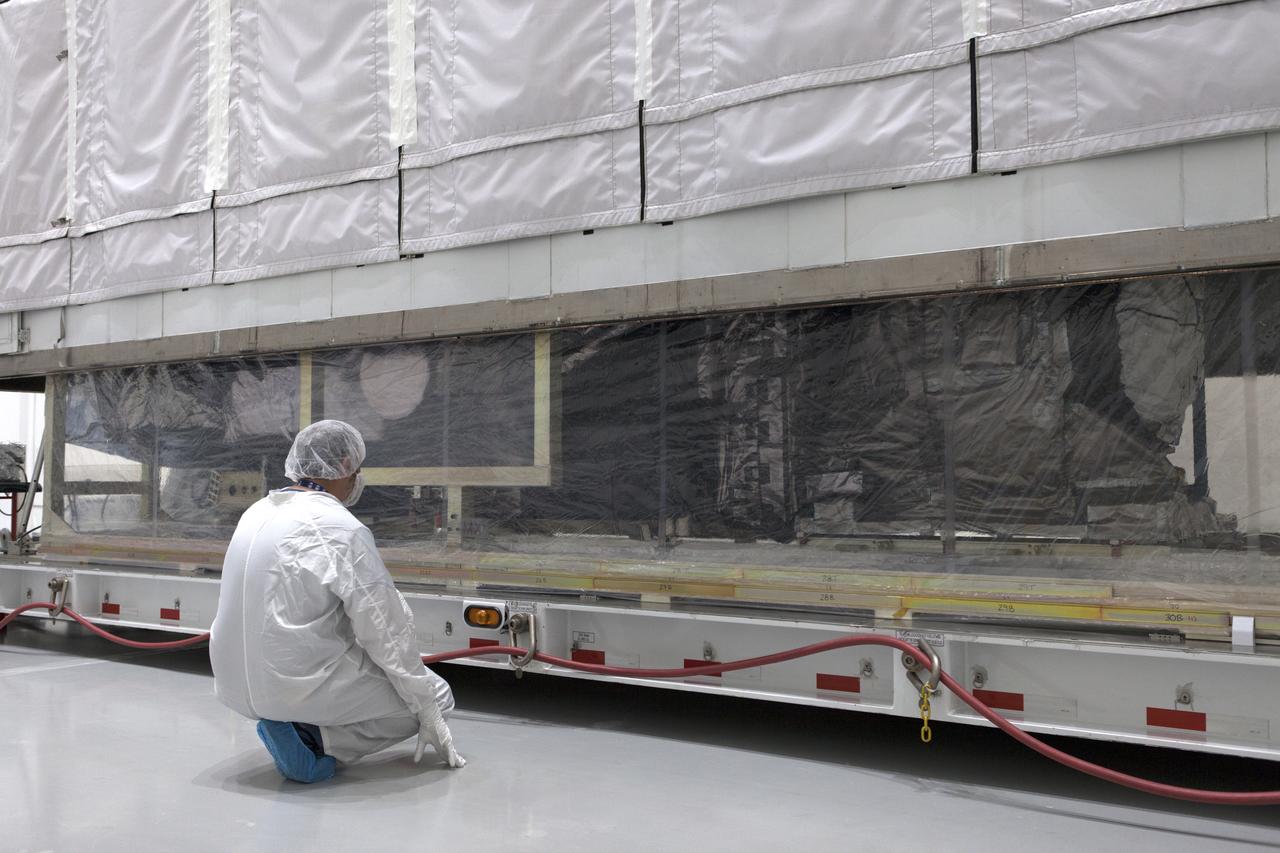

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, a technician watches as NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
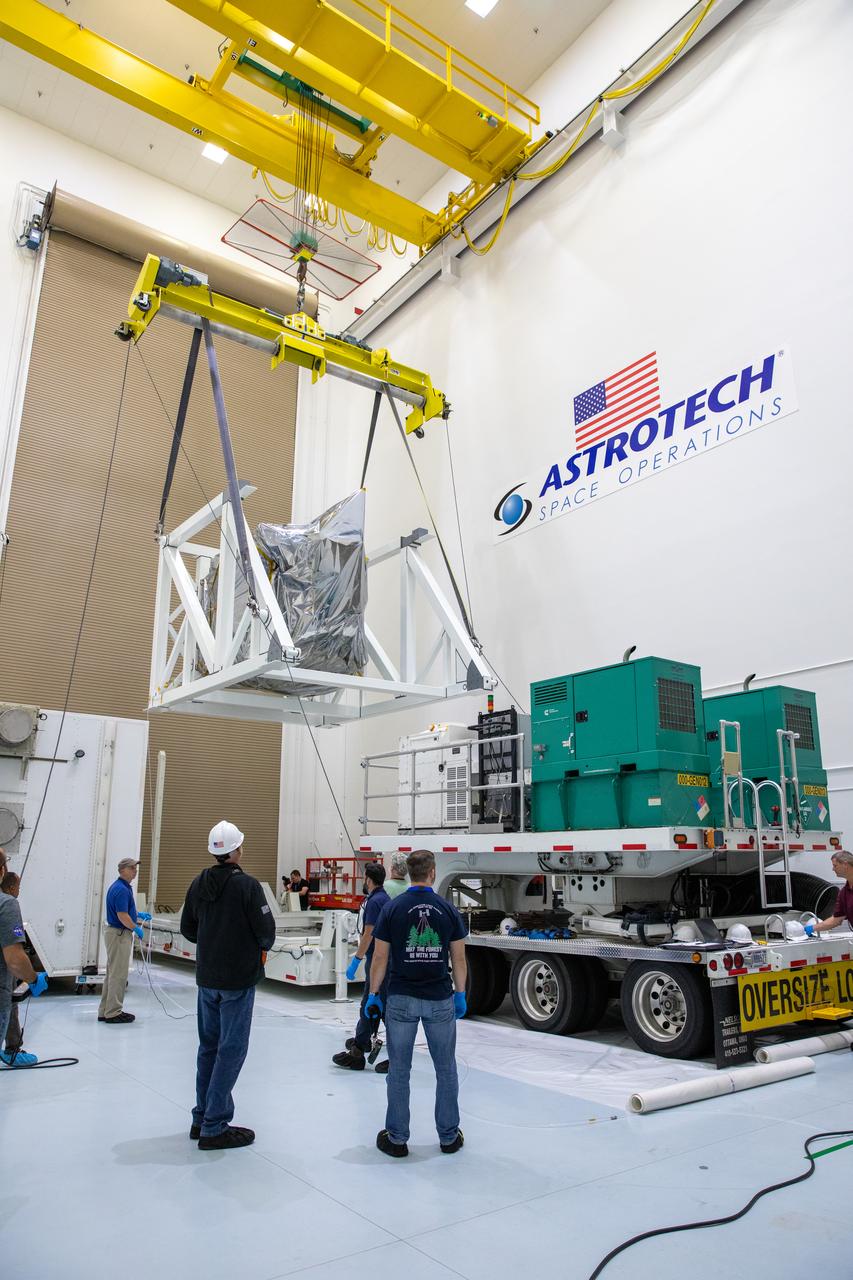

Technicians monitor movement as a crane hoists NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft after being uncrated on Wednesday, Nov. 15, 2023, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web. PACE will be encapsulated for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
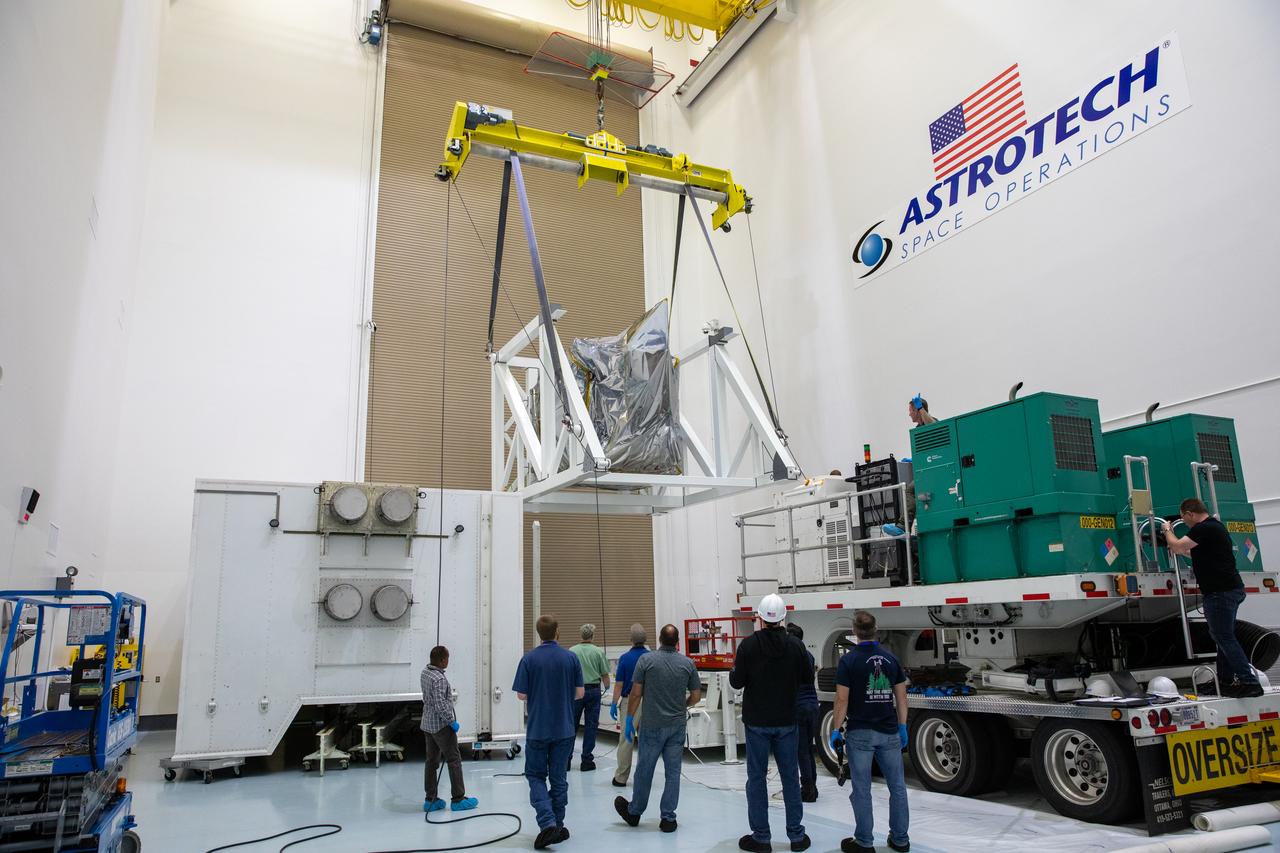

Technicians monitor movement as a crane hoists NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft after being uncrated on Wednesday, Nov. 15, 2023, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web. PACE will be encapsulated for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
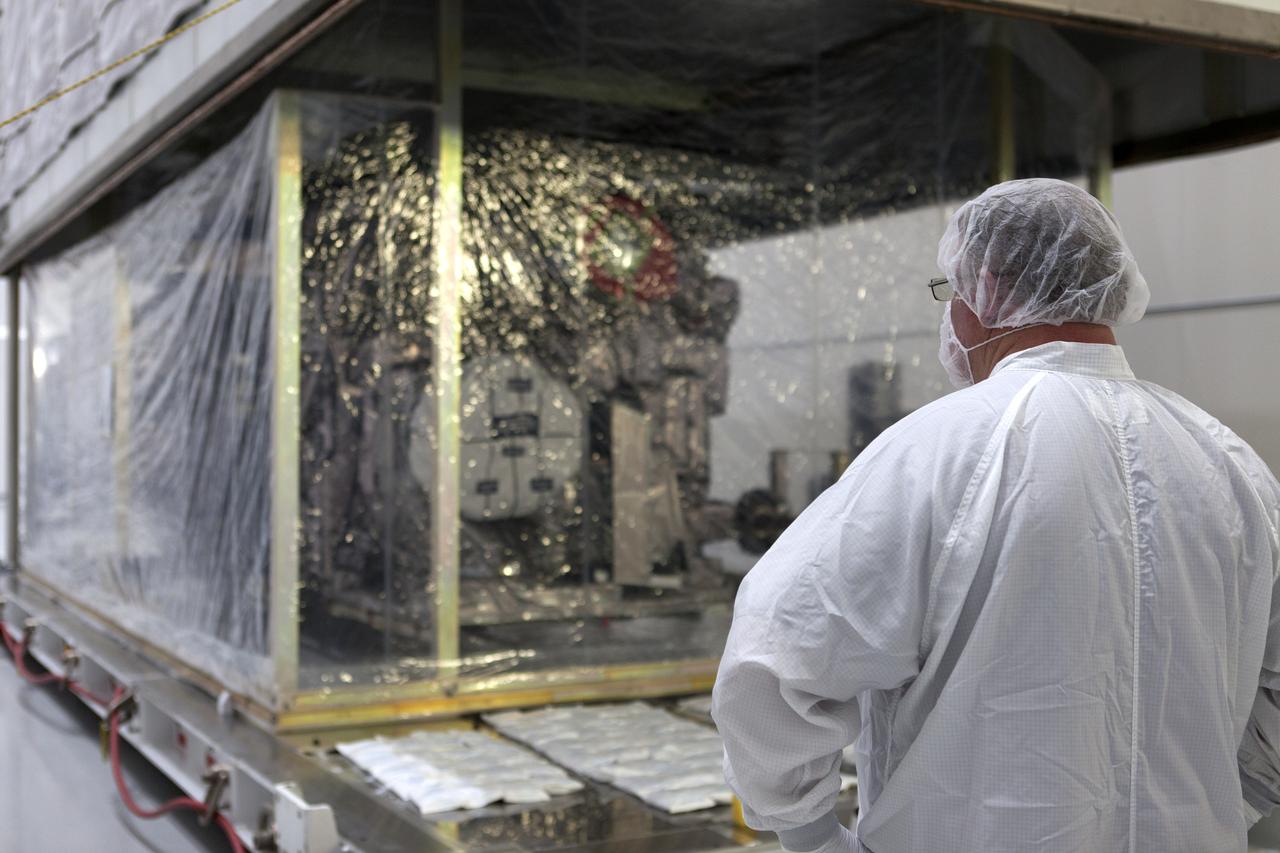

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, a technician watches as NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
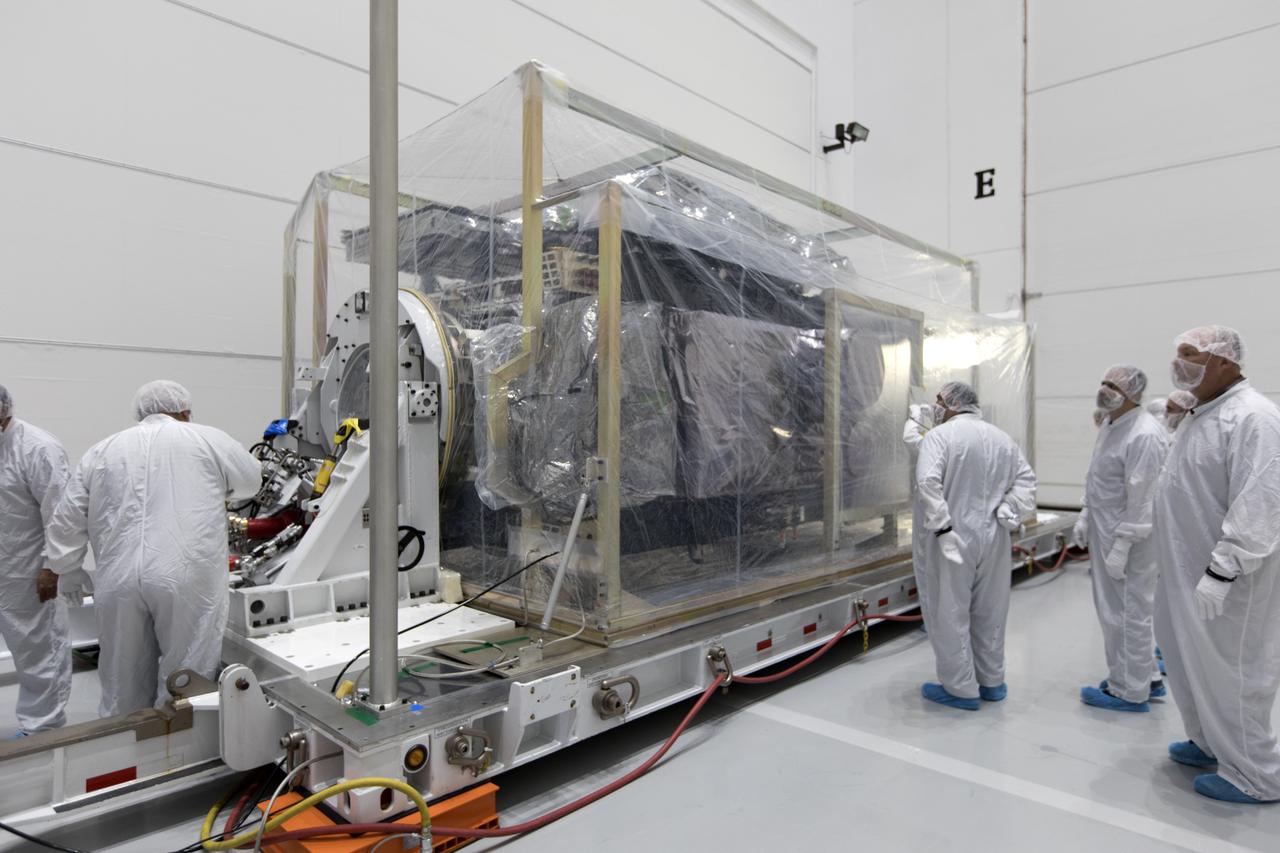

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technician and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
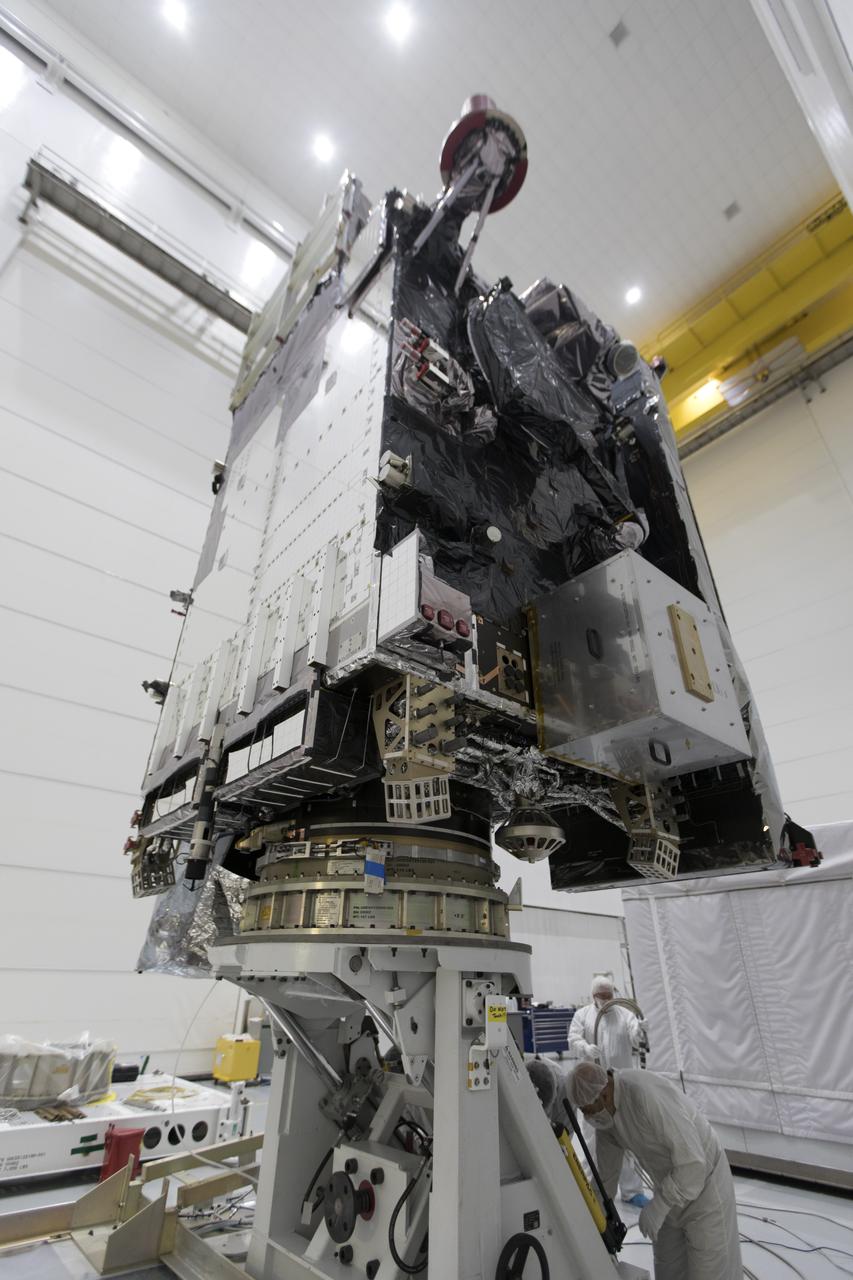

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
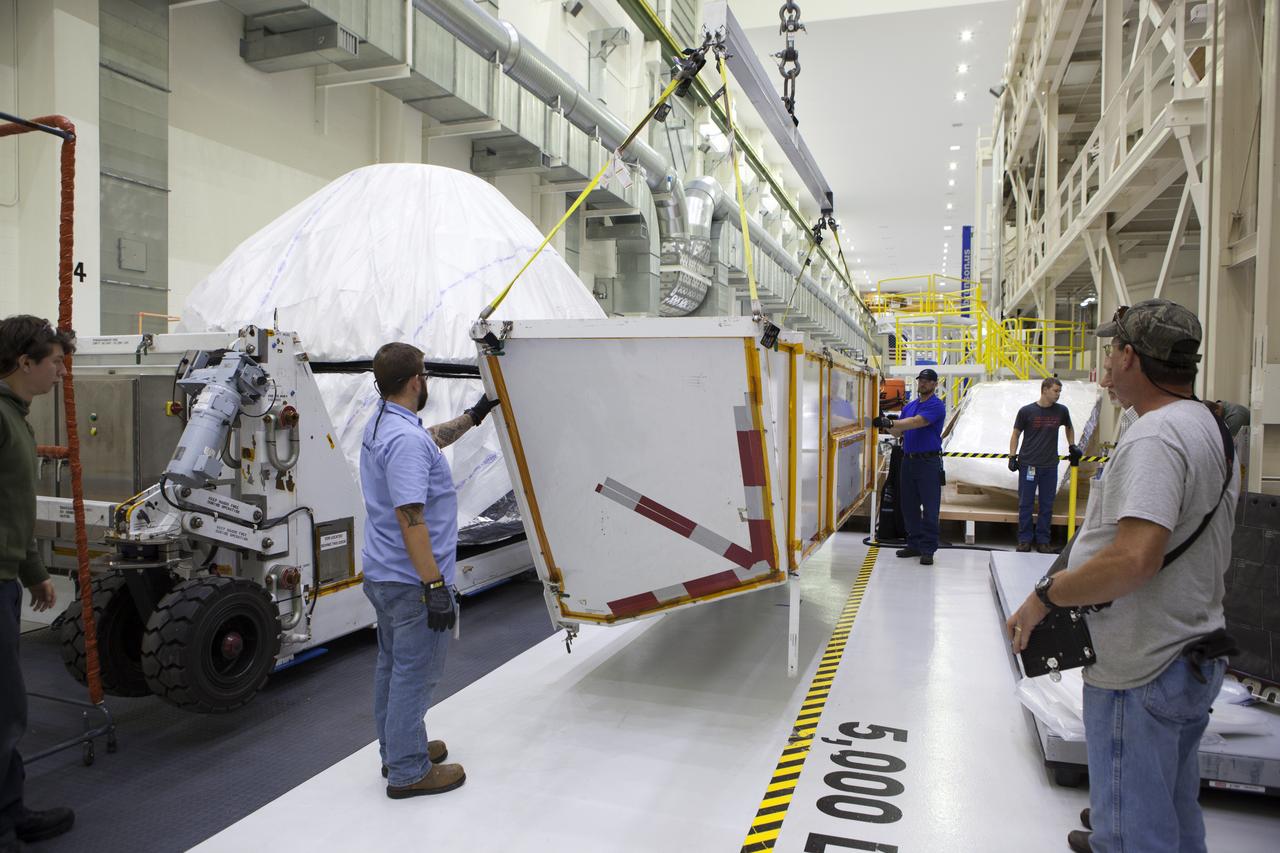

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians with Lockheed Martin assist as a crane lifts the cover away from the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article was moved inside the facility's high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
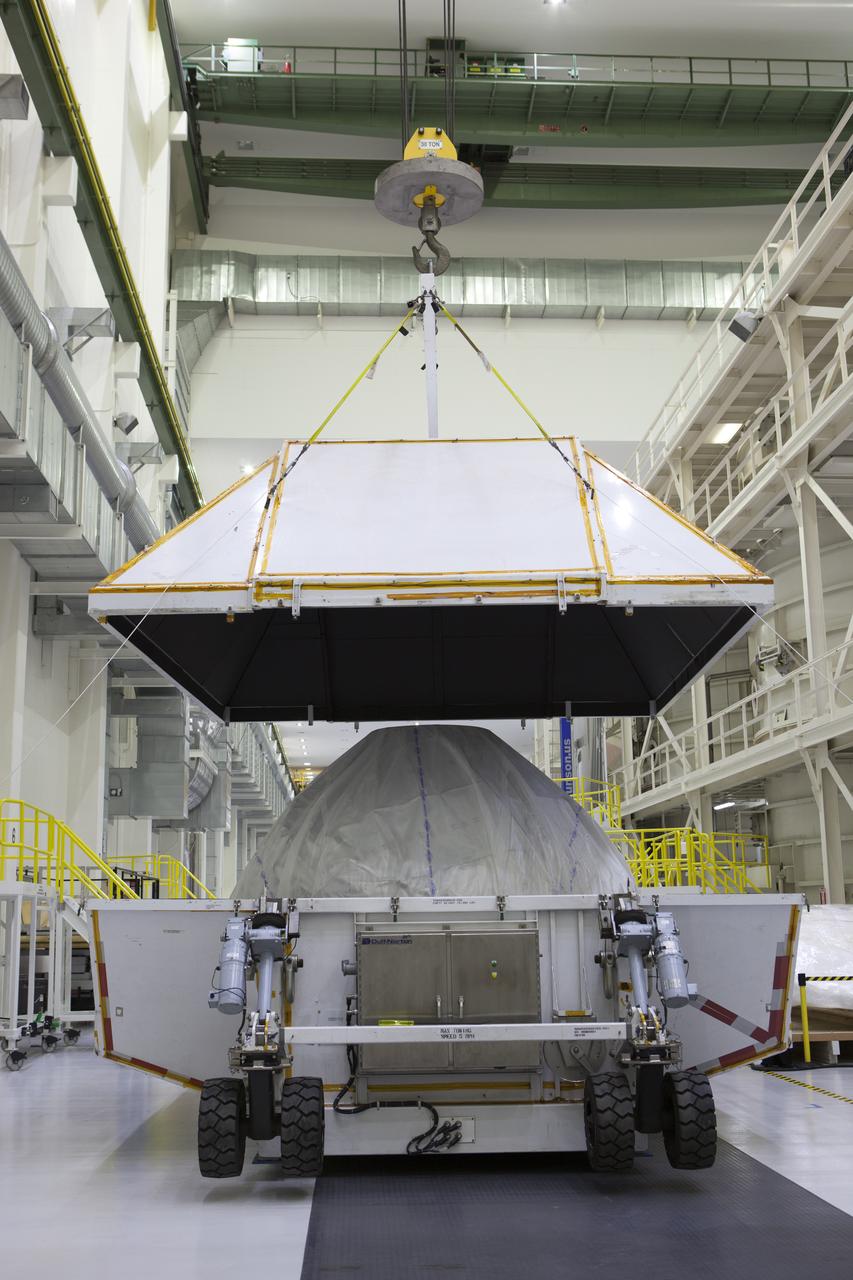

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts the cover up from the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article was moved inside the facility's high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
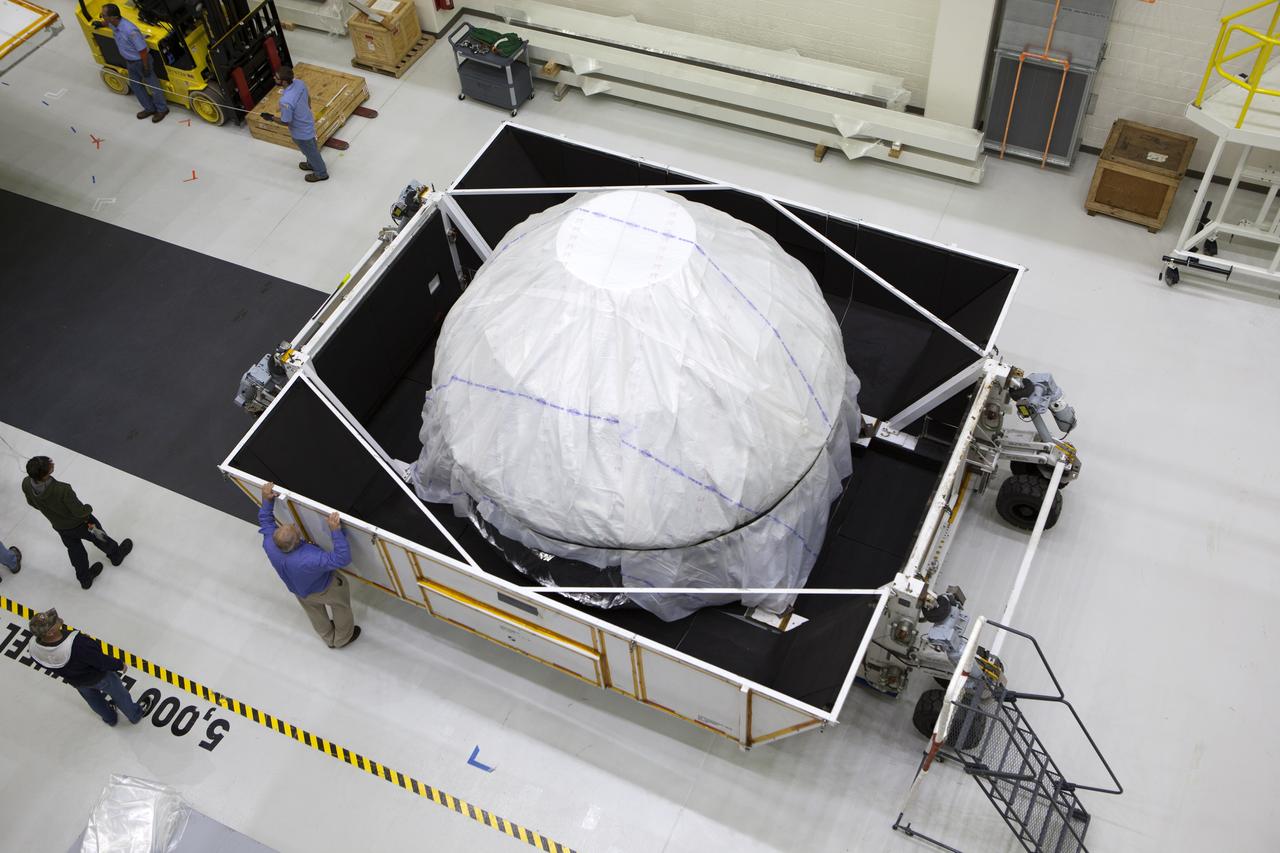

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the cover has been removed from the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article was moved inside the facility's high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
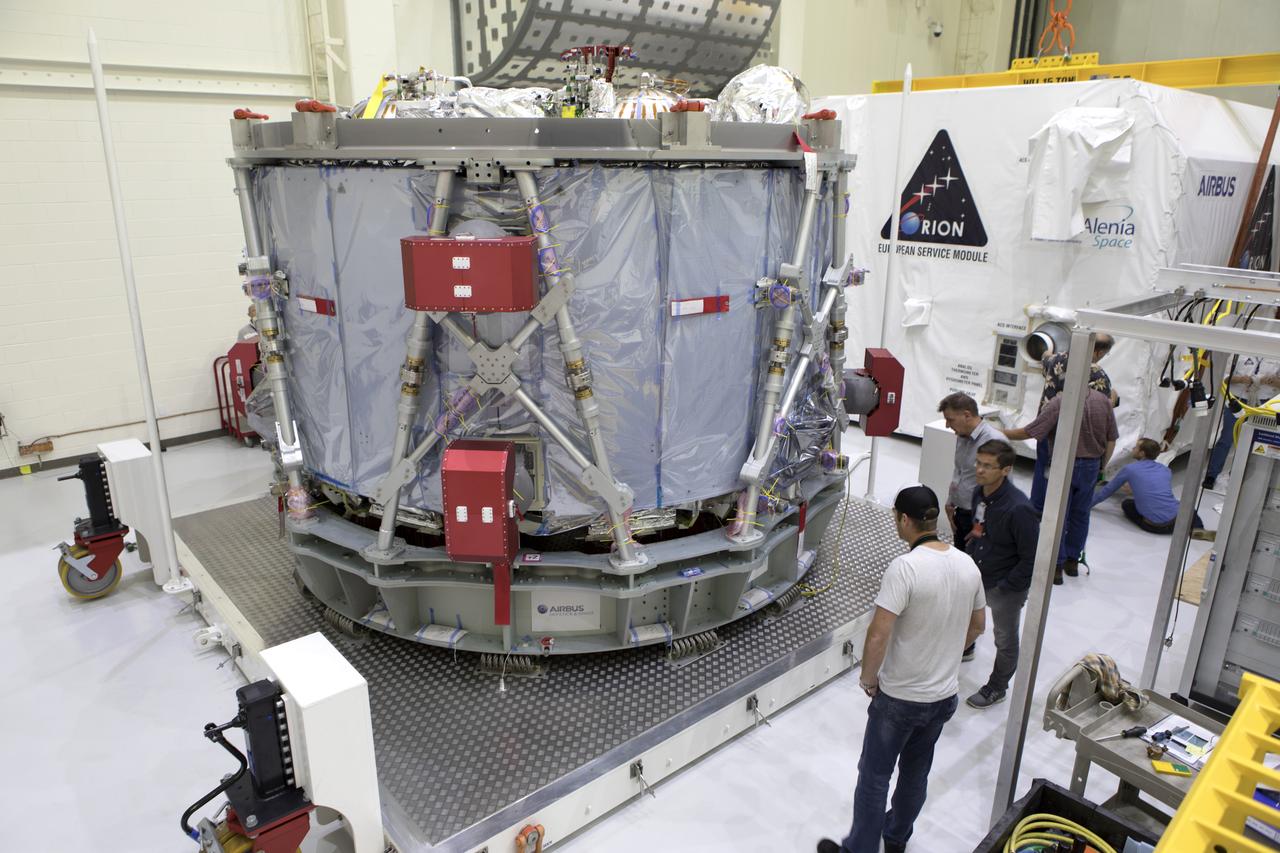

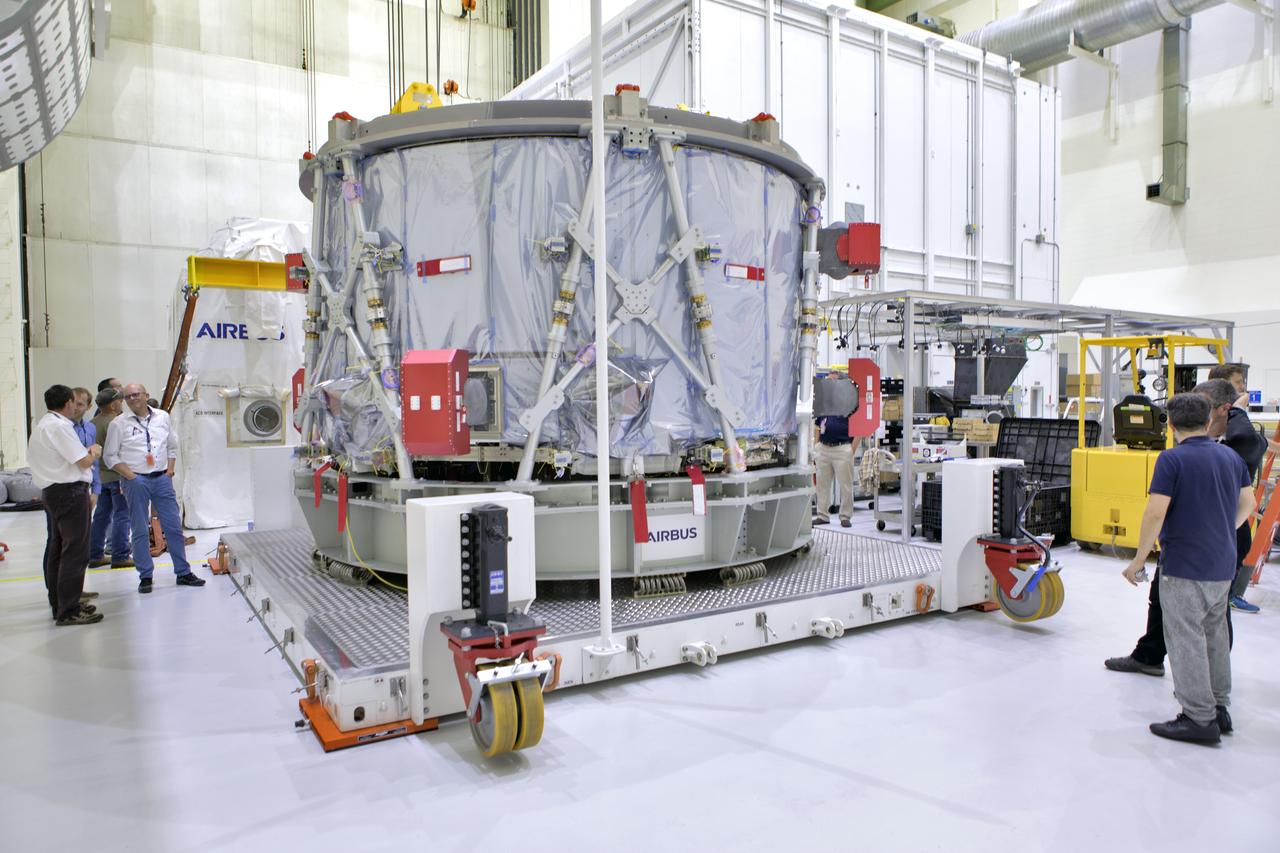
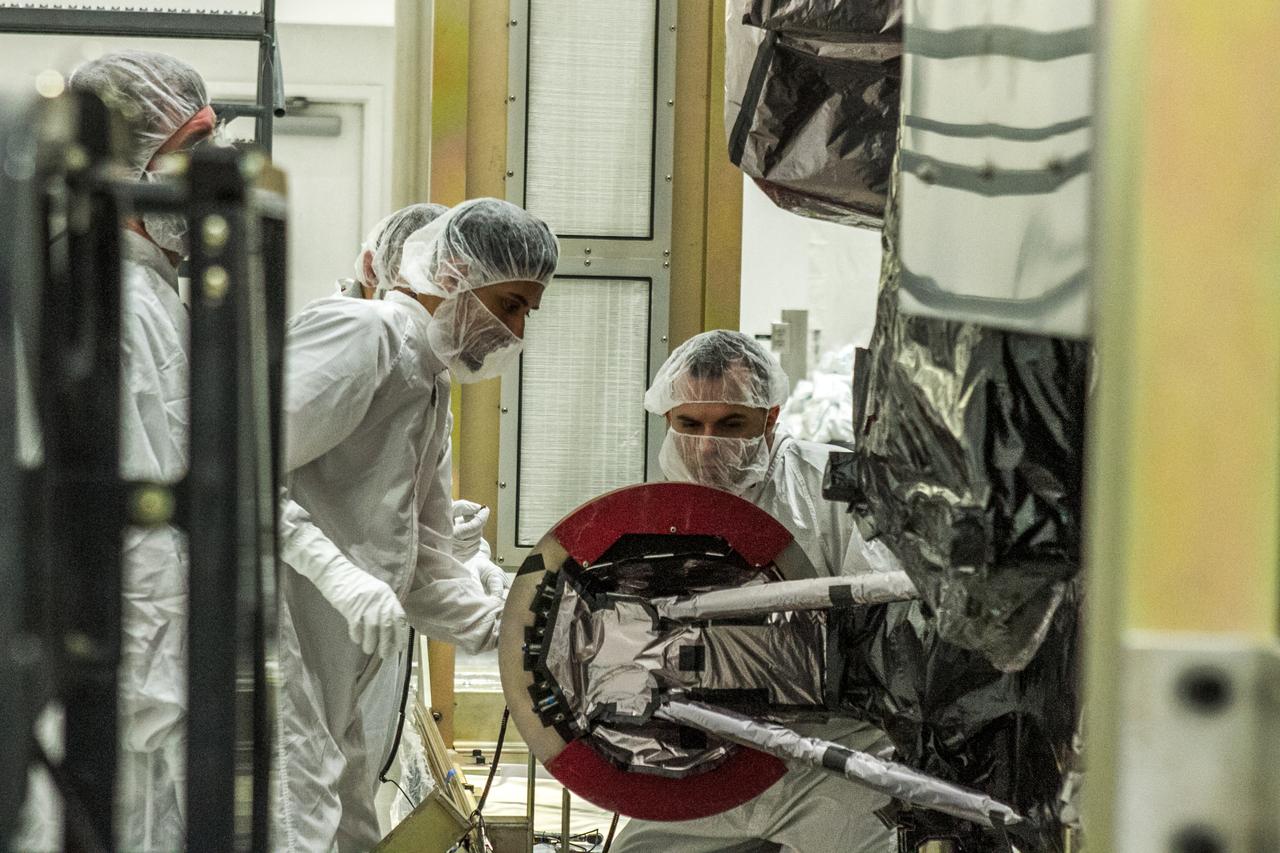
Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) is uncrated at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.

Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) is uncrated at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.

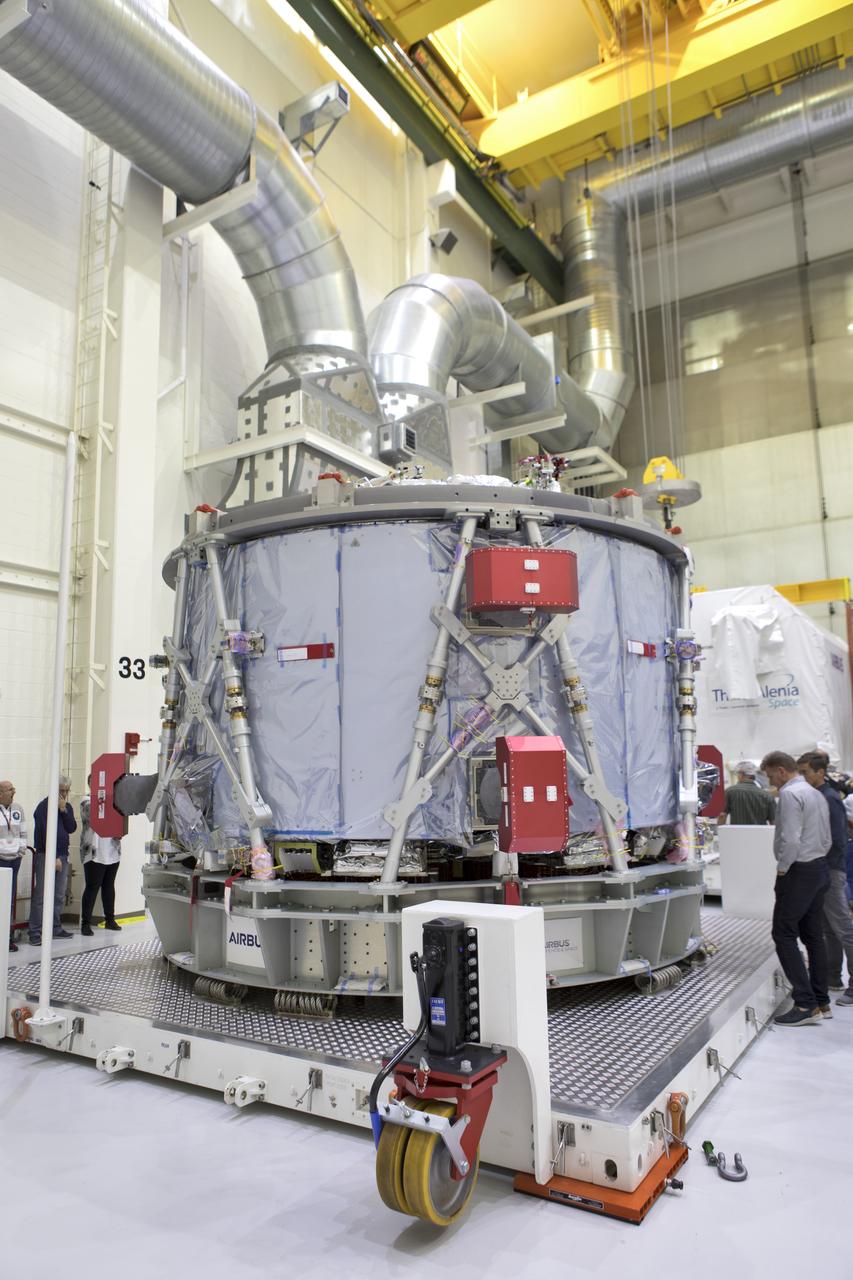
Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay On Nov. 6, 2018, a crane is used to uncrate the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
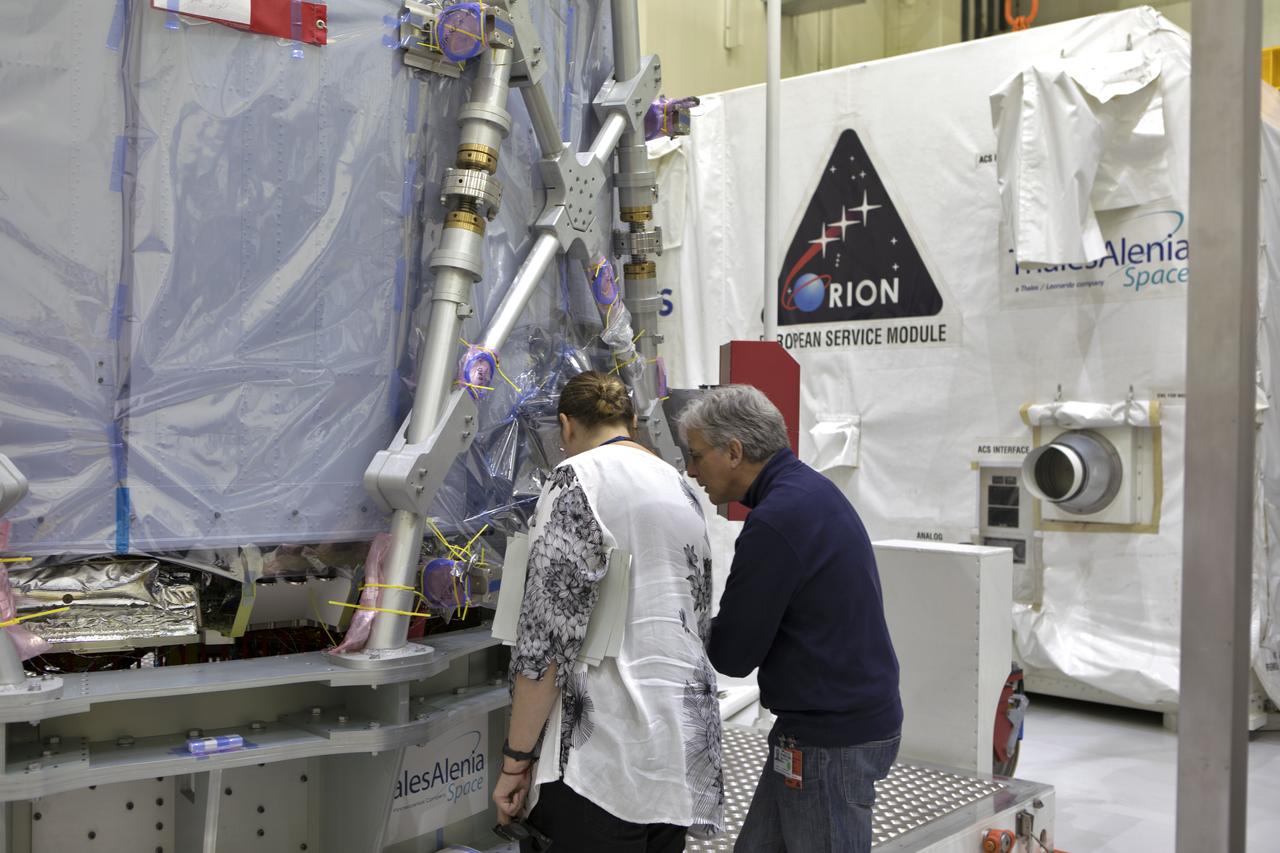

Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, European Space Agency (ESA) and Airbus engineers check the ESA European Service Module (ESM) after it is uncrated at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.

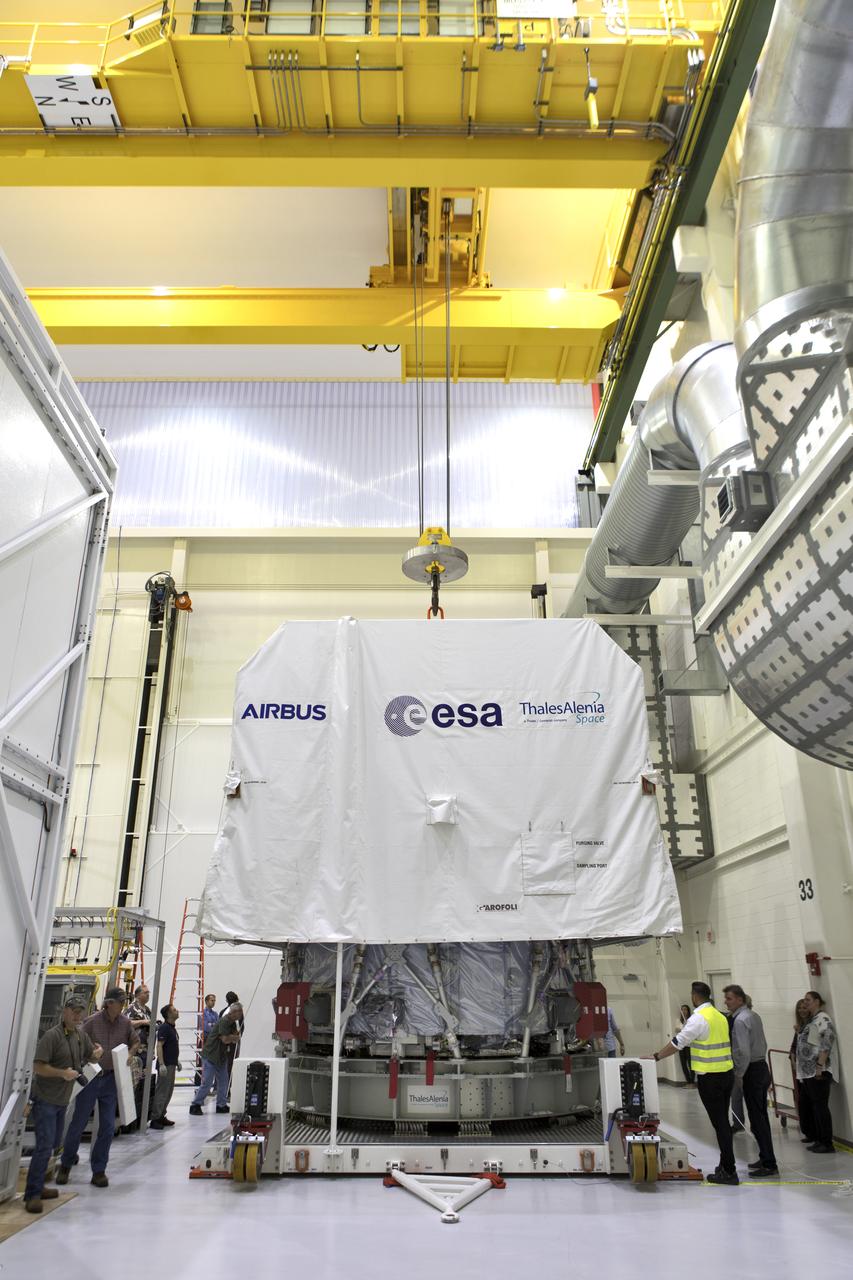
Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) is uncrated and ready for its move to the high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.

Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, European Space Agency (ESA) and Airbus technicians begin to uncrate the ESA's European Service Module (ESM) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
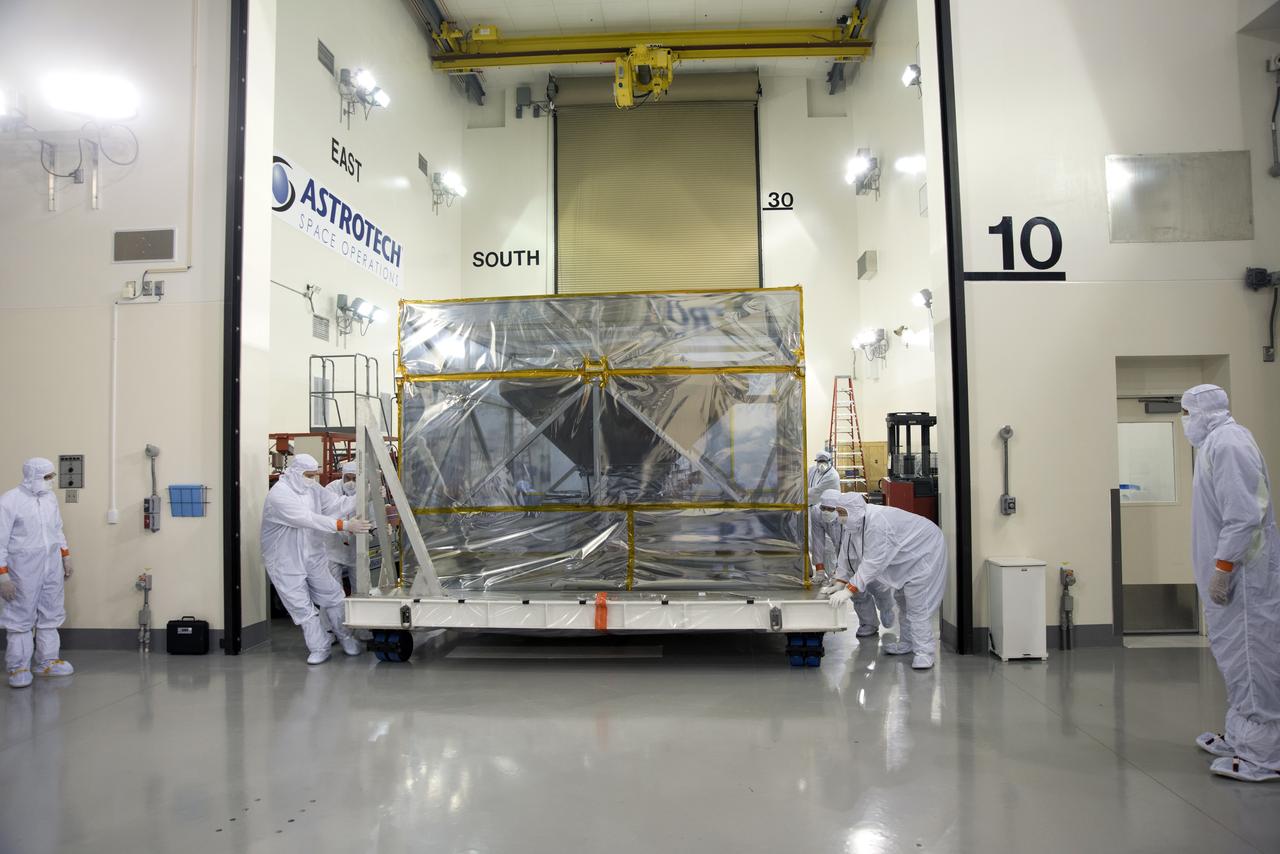

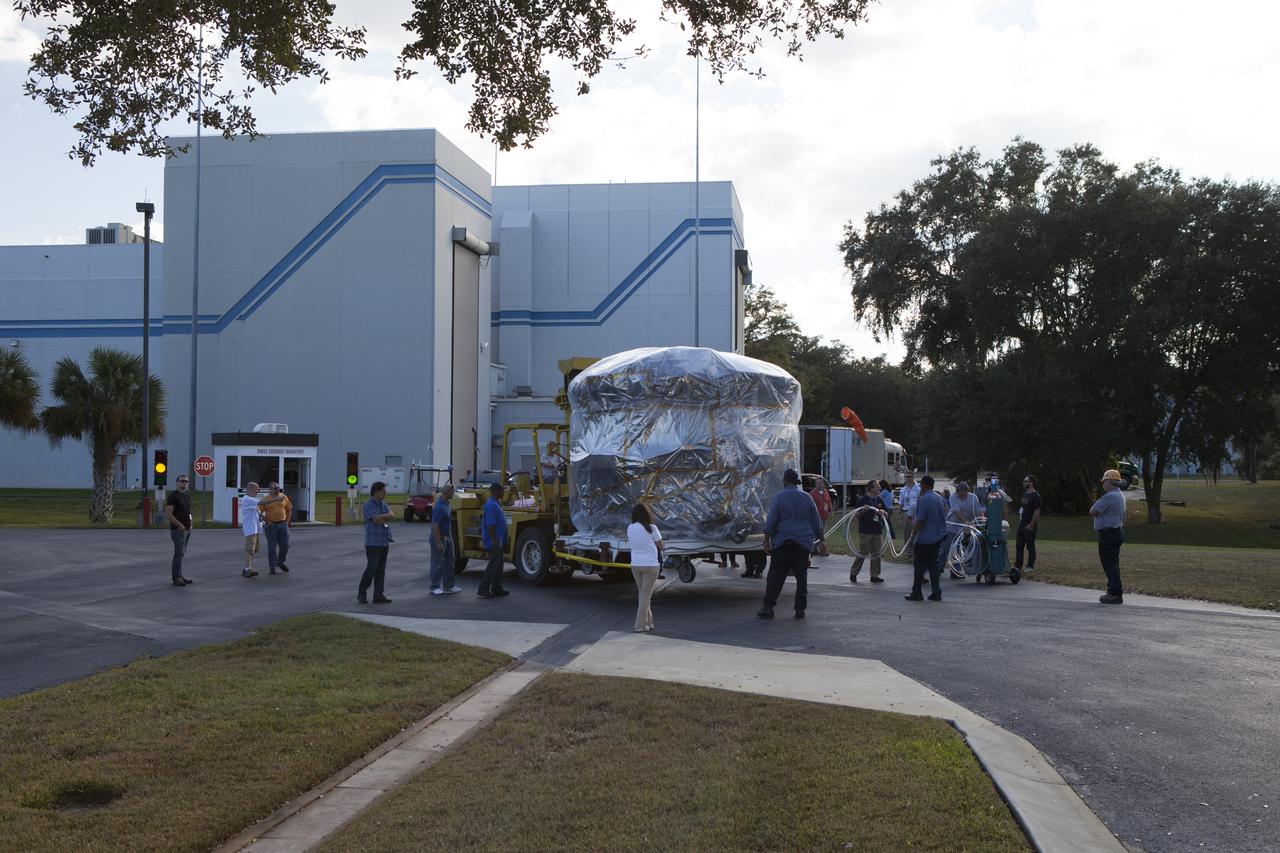
At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft is uncrated inside the Astrotech processing facility. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft is uncrated inside the Astrotech processing facility. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
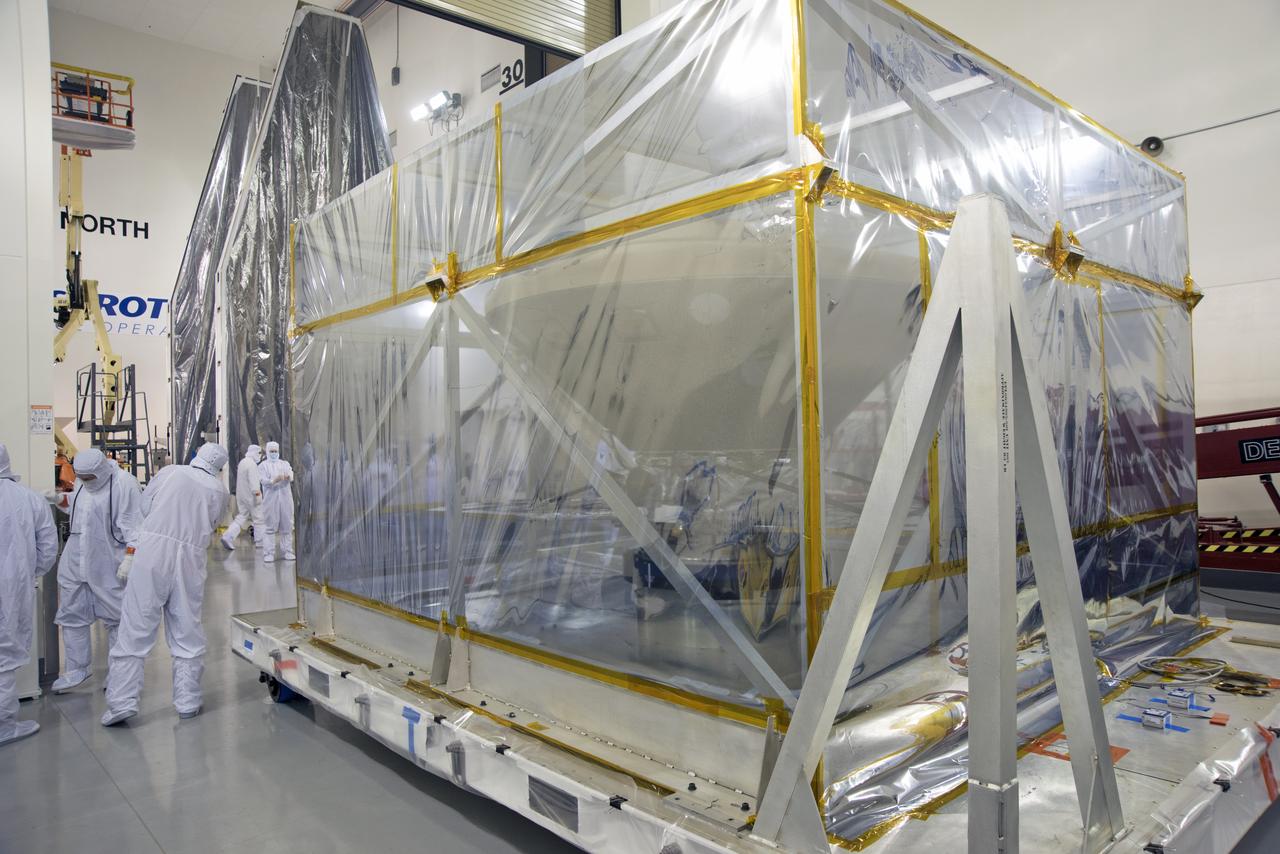

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft is uncrated inside the Astrotech processing facility. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
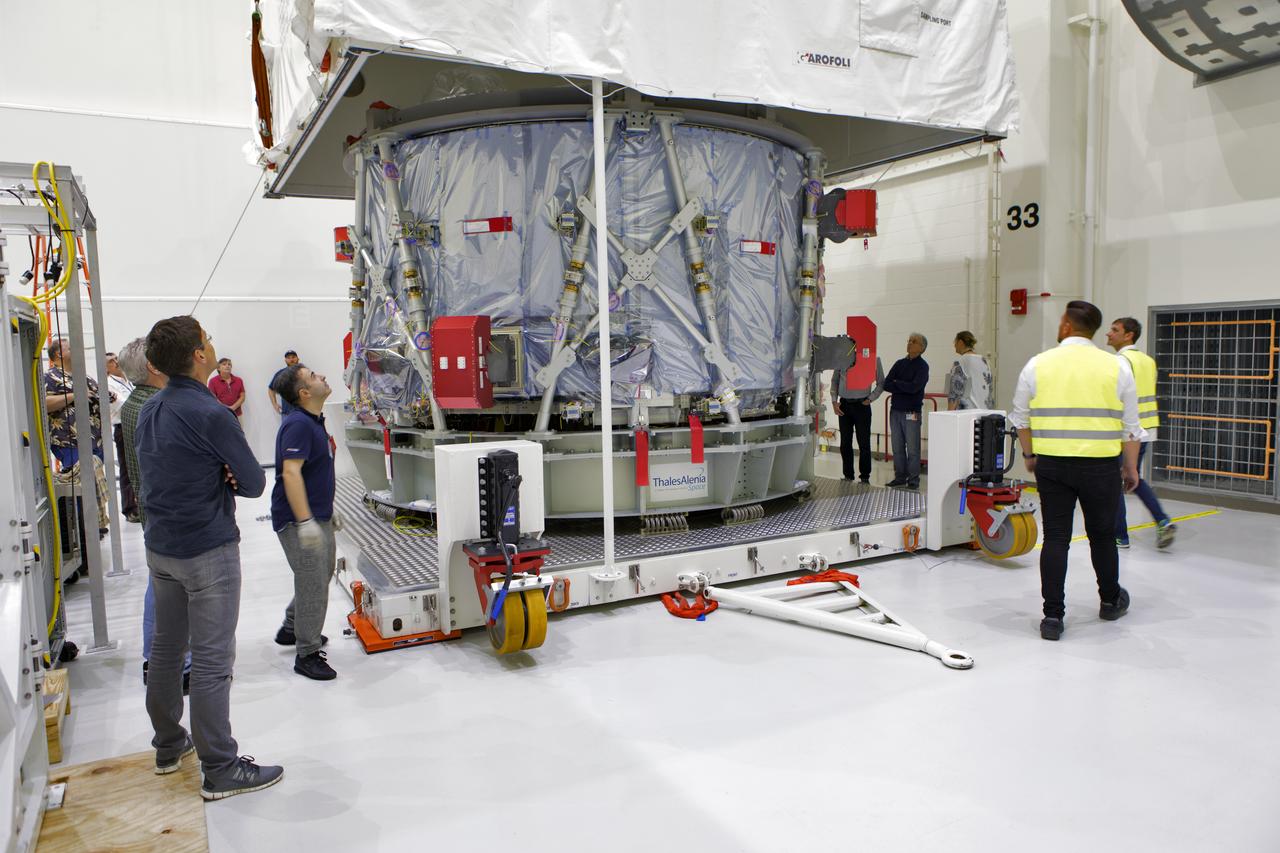

Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay On Nov. 6, 2018, European Space Agency (ESA) and Airbus engineers and technicians watch as a crane is used to uncrate the ESA's European Service Module (ESM) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
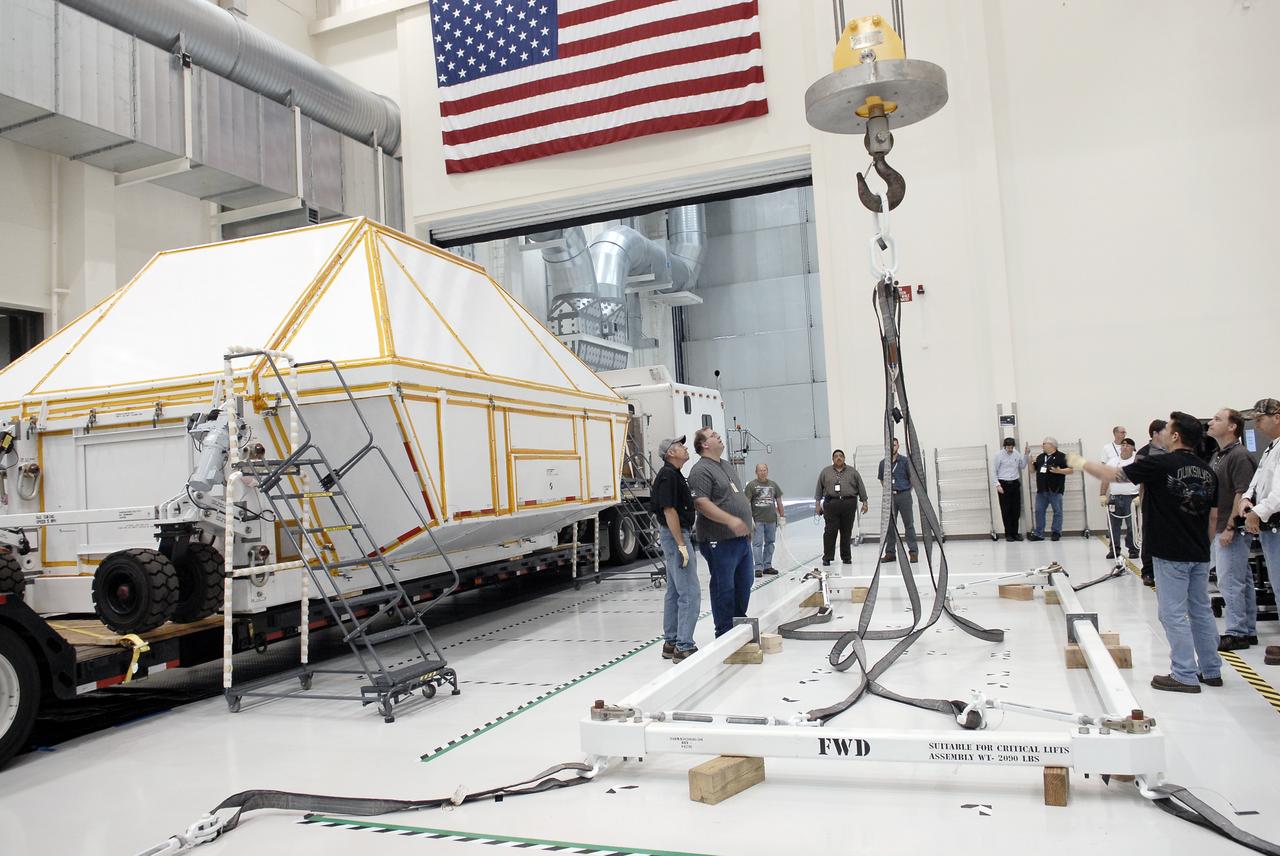

Orion EFT-1 Crew Module Uncrating
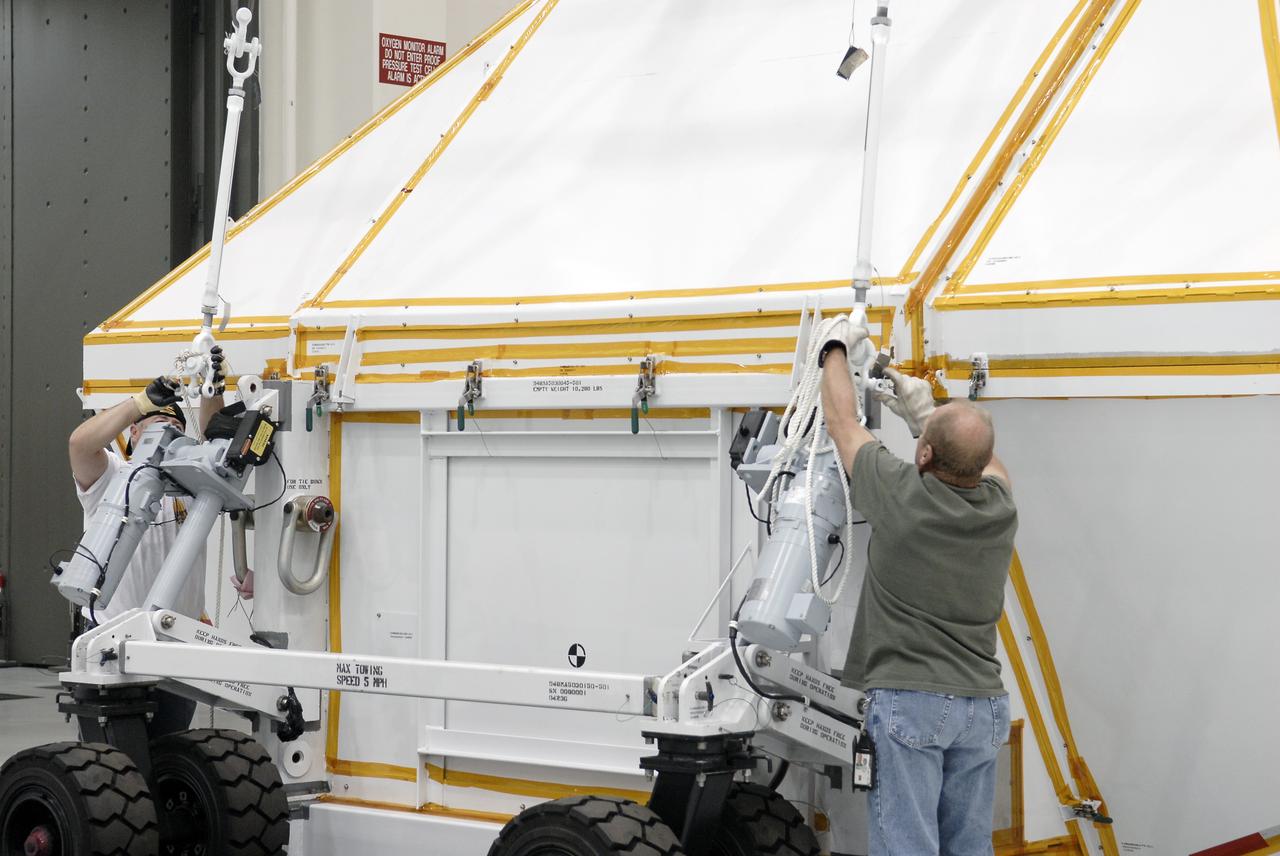

Orion EFT-1 Crew Module Uncrating
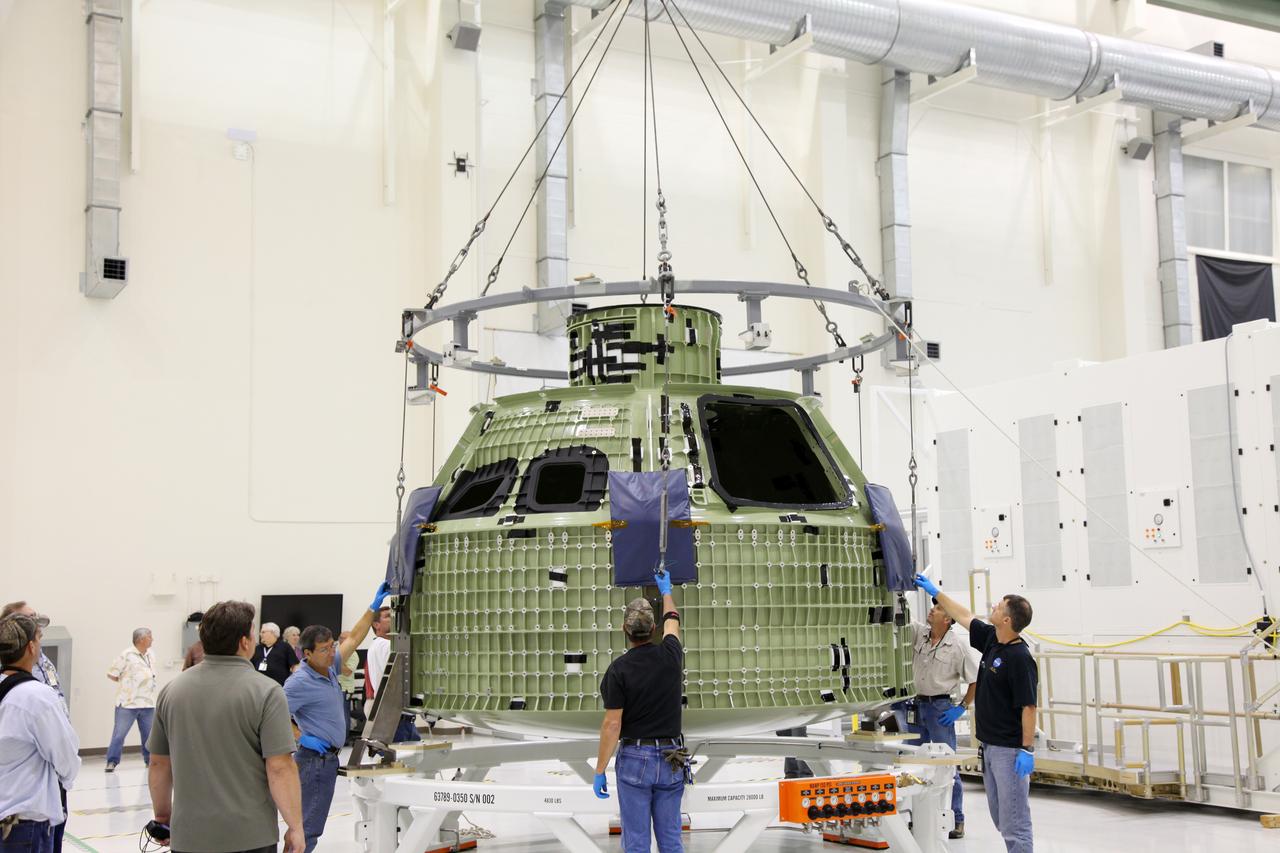

Orion EFT-1 Crew Module Being Uncrated
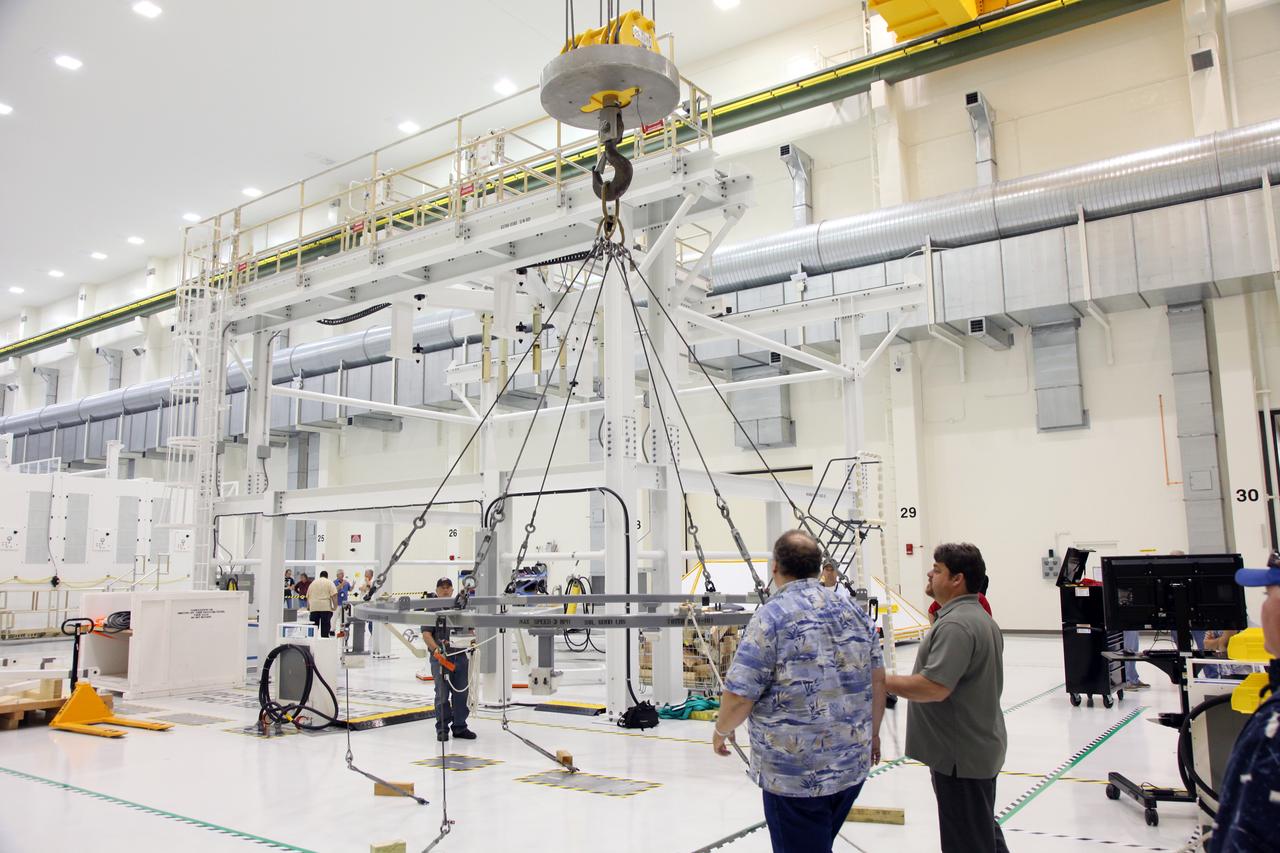

Orion EFT-1 Crew Module Being Uncrated
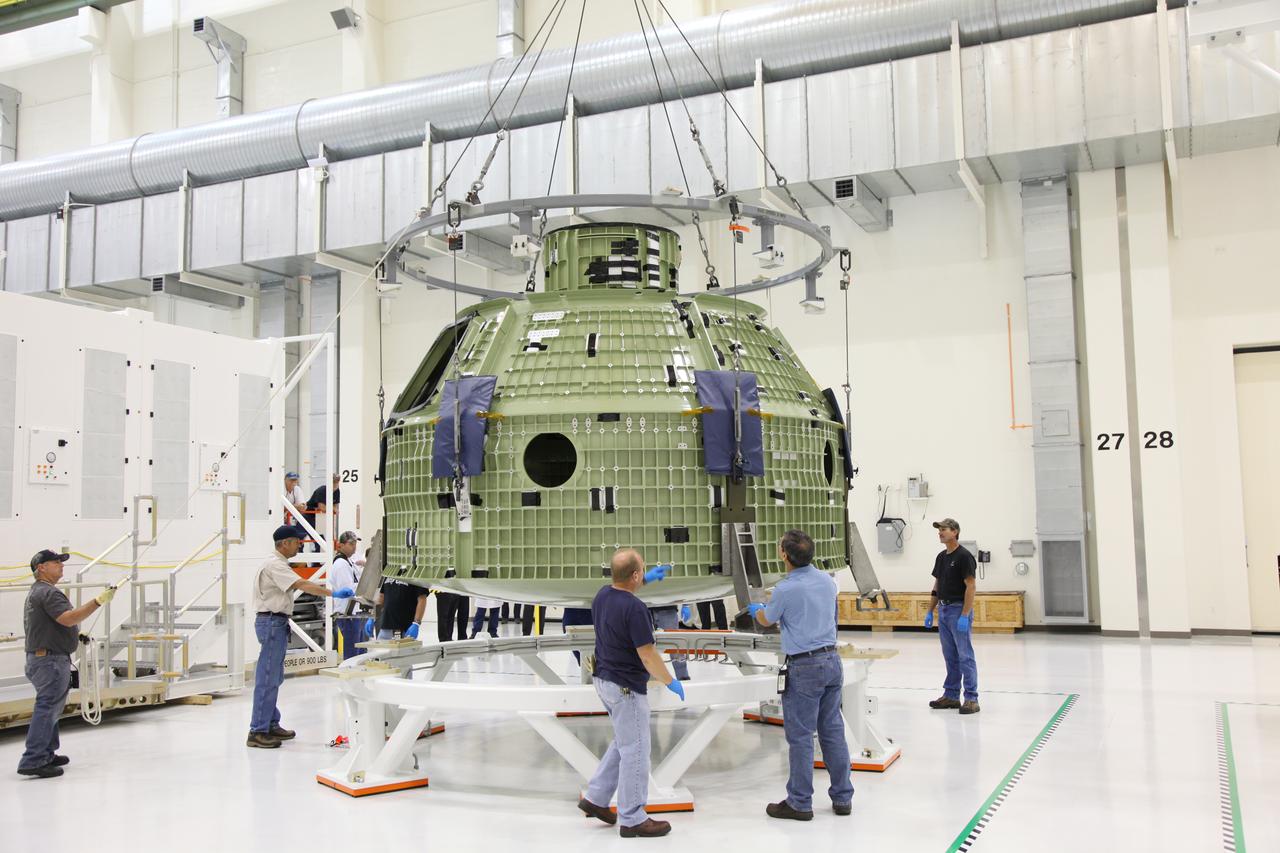

Orion EFT-1 Crew Module Being Uncrated
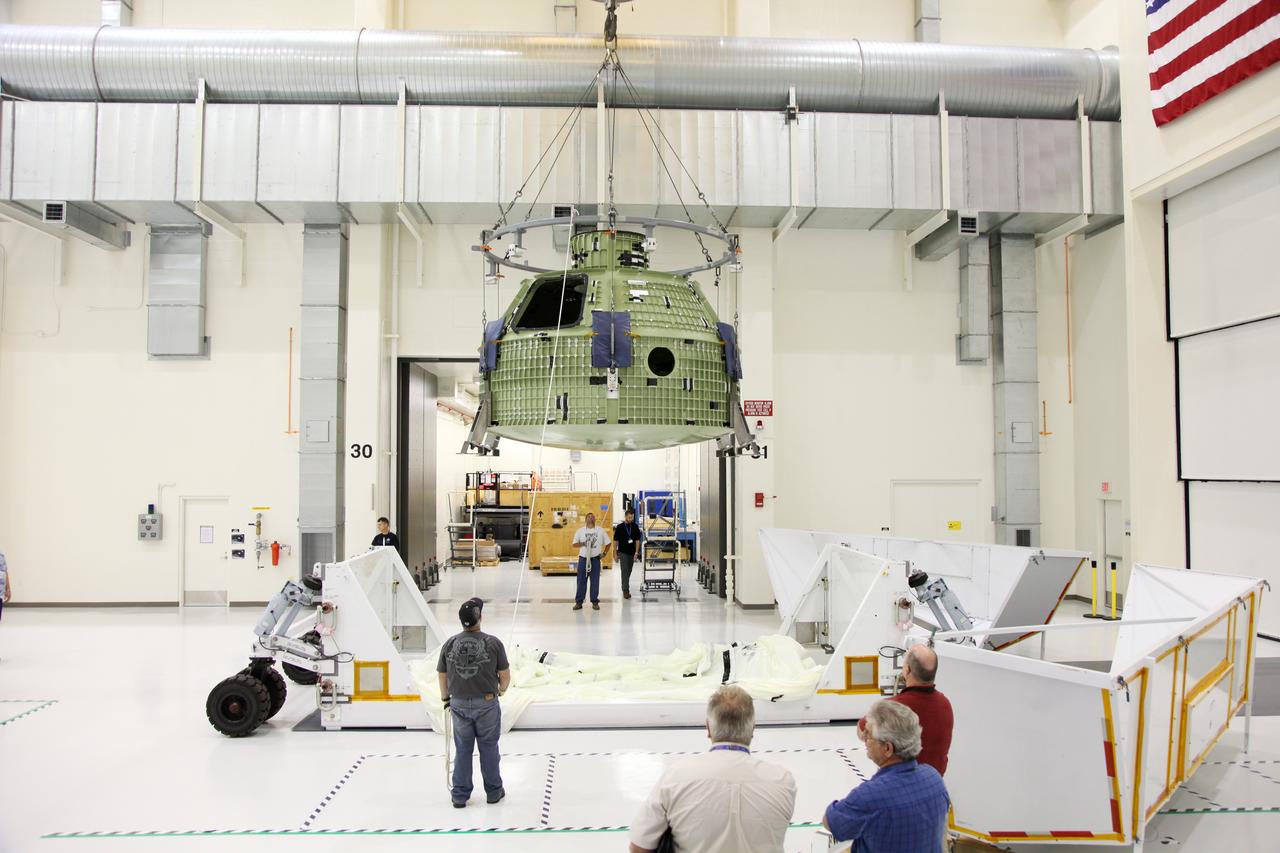

Orion EFT-1 Crew Module Being Uncrated
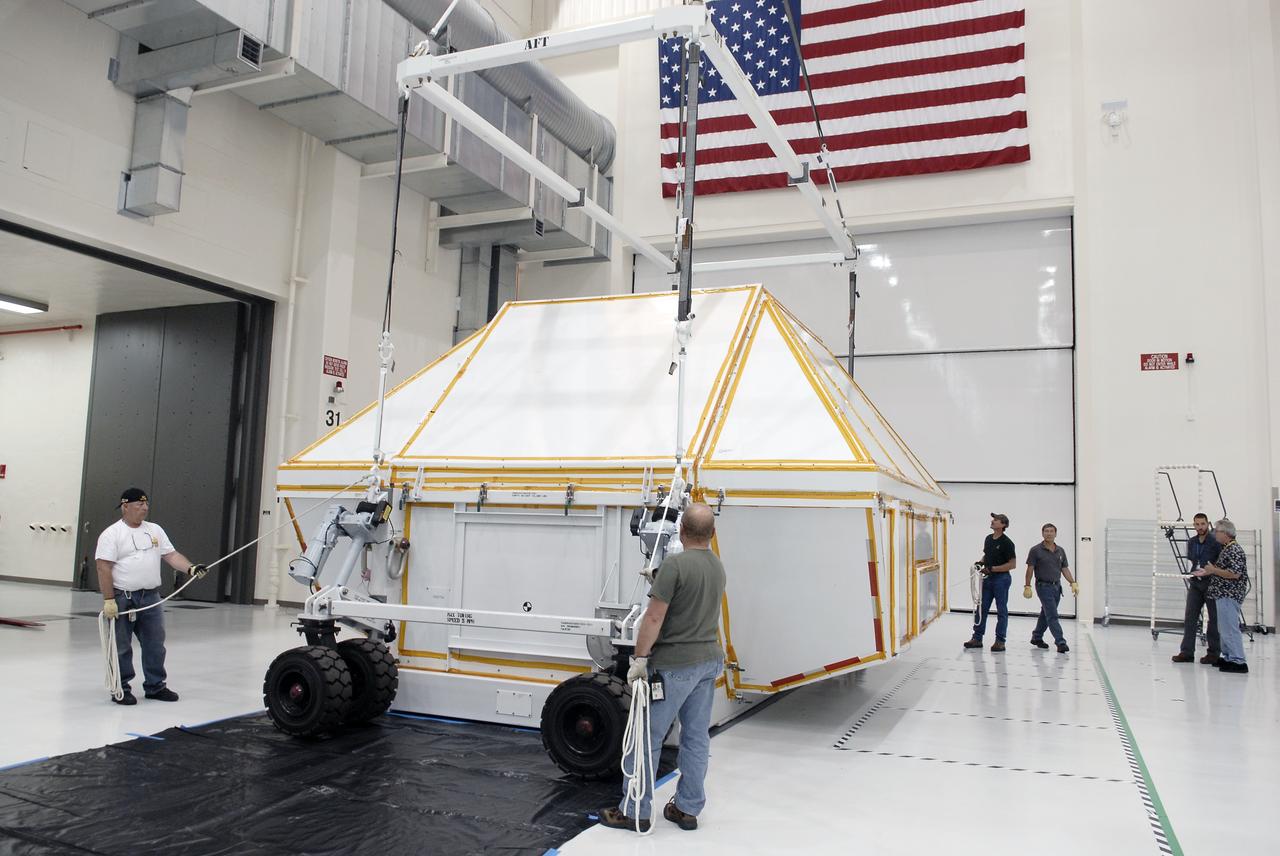

Orion EFT-1 Crew Module Uncrating
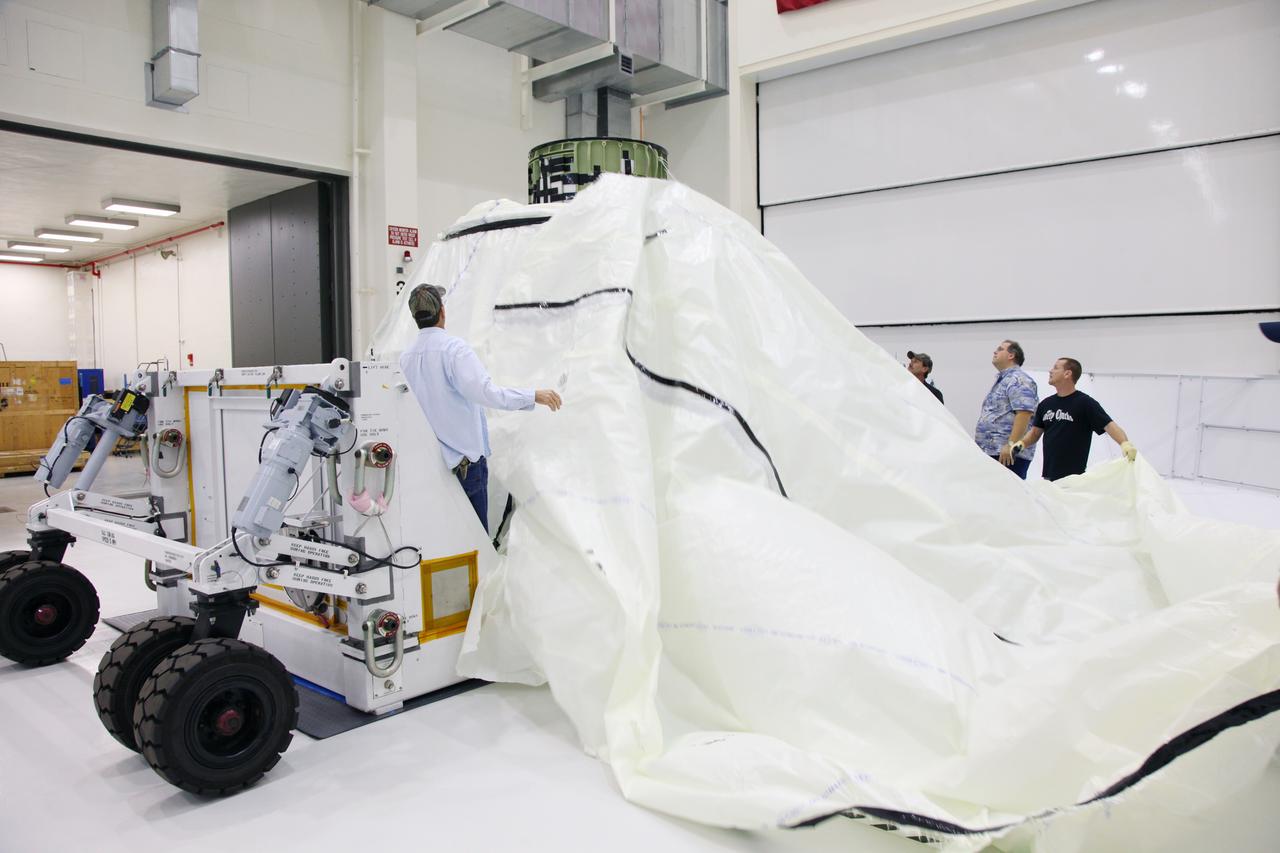

Orion EFT-1 Crew Module Being Uncrated
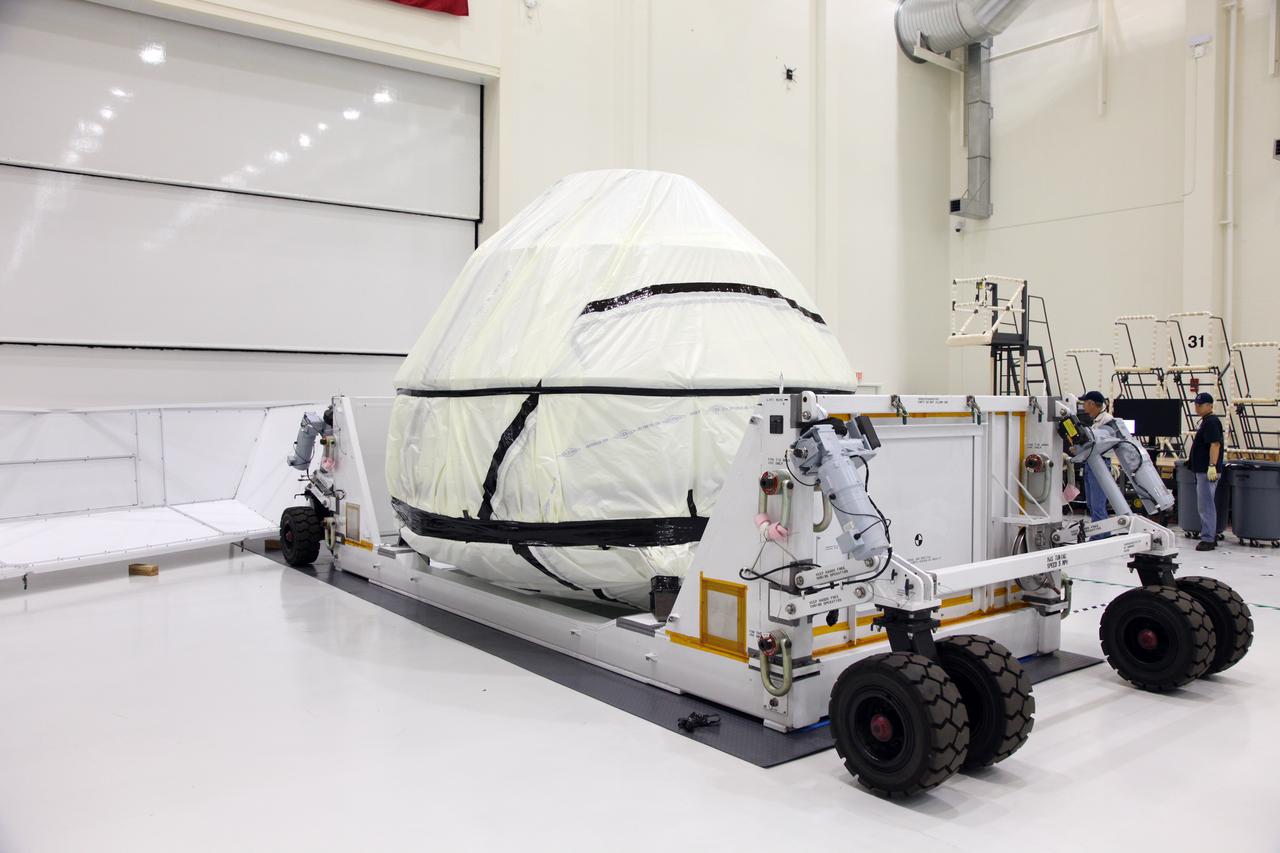

Orion EFT-1 Crew Module Being Uncrated
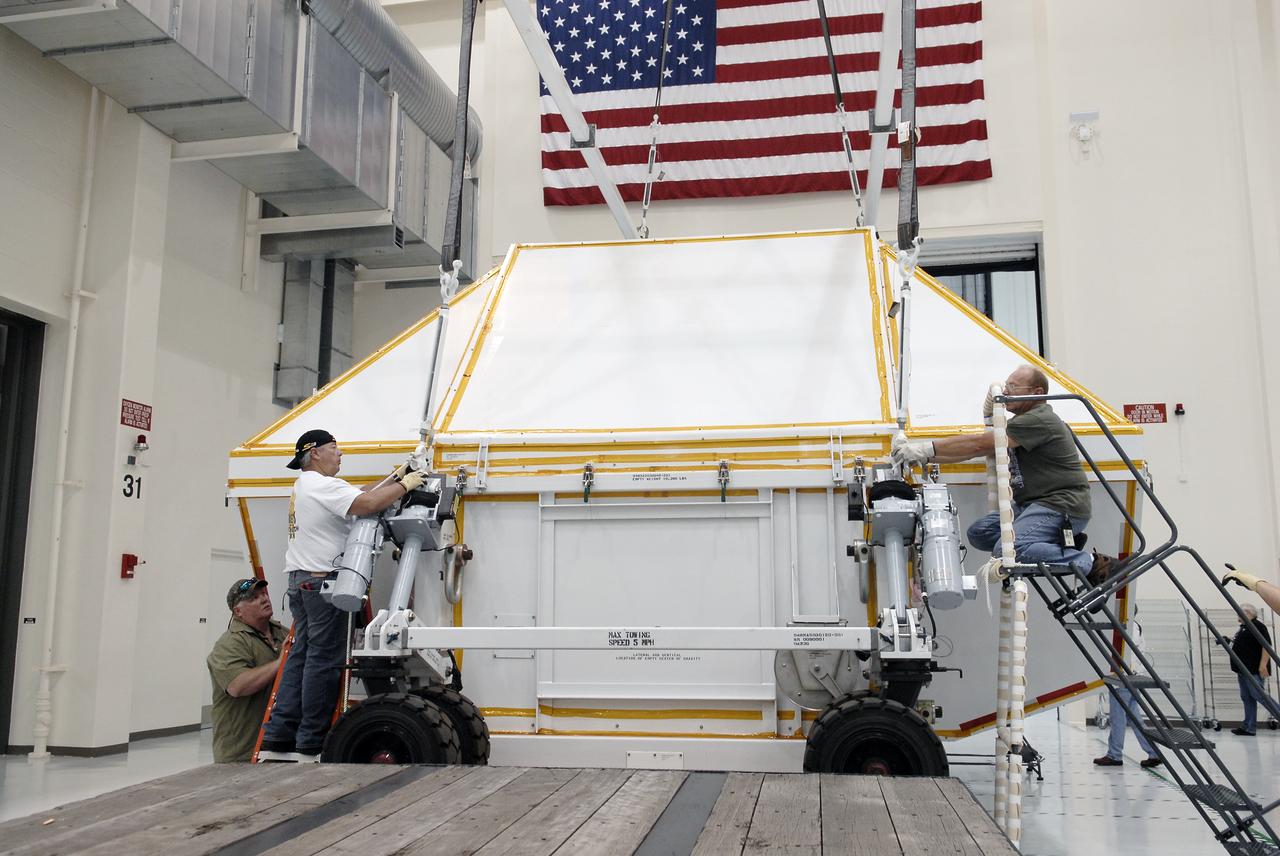

Orion EFT-1 Crew Module Uncrating
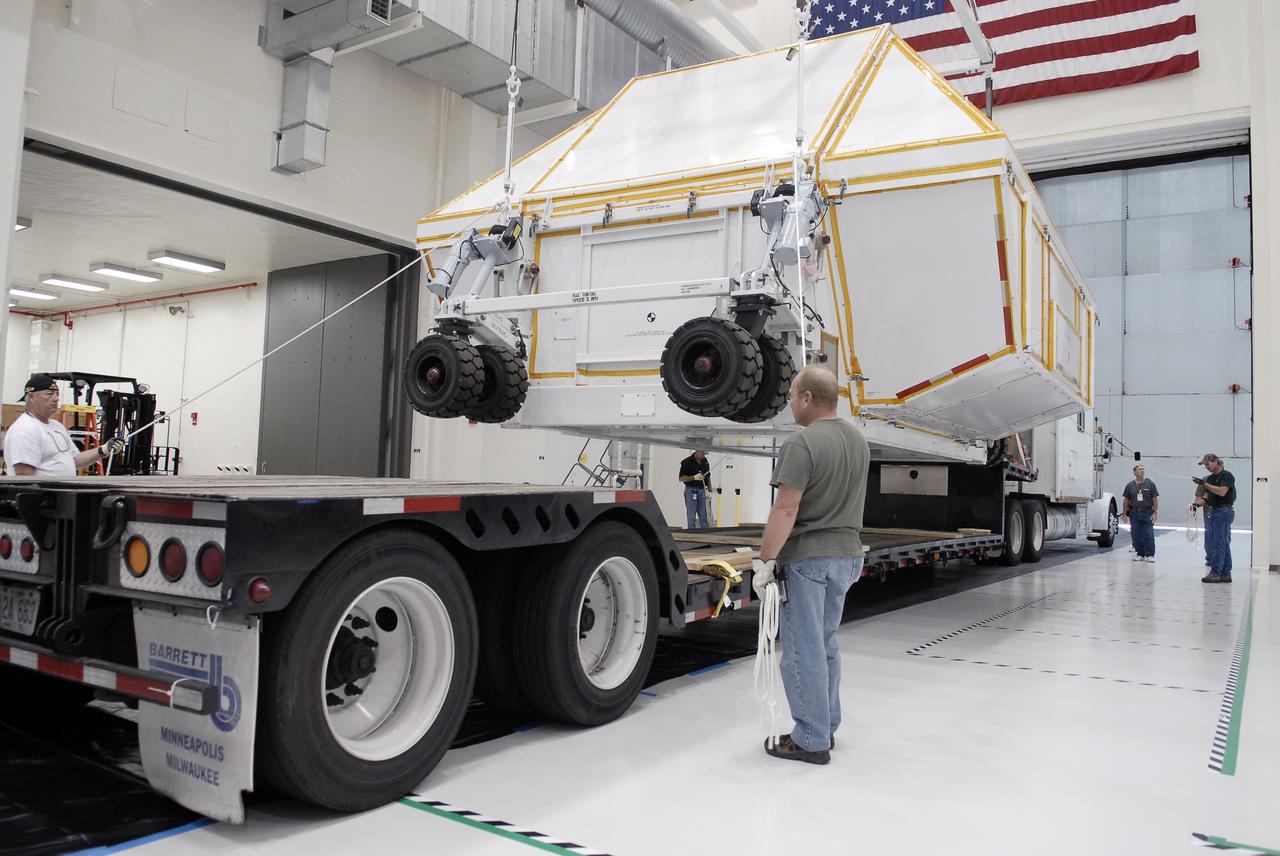

Orion EFT-1 Crew Module Uncrating
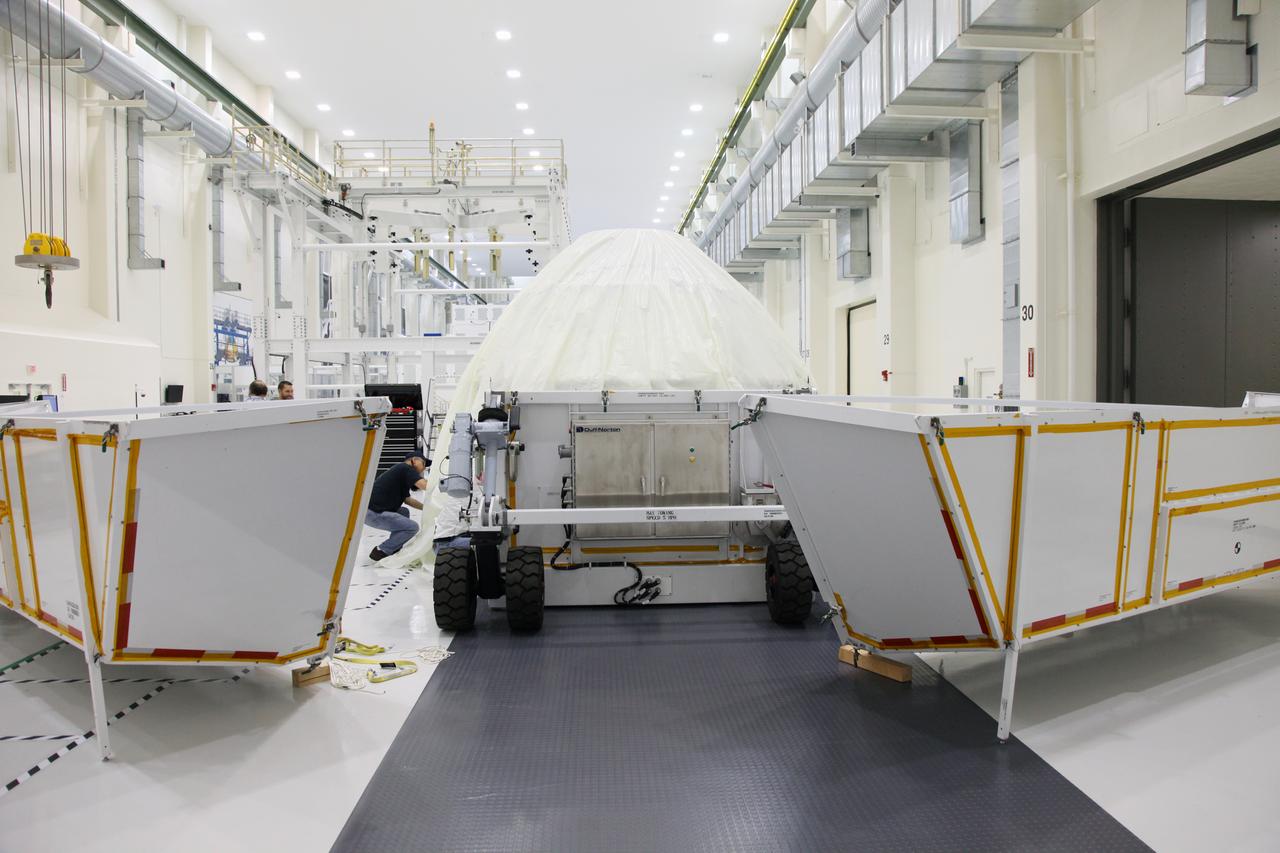

Orion EFT-1 Crew Module Being Uncrated
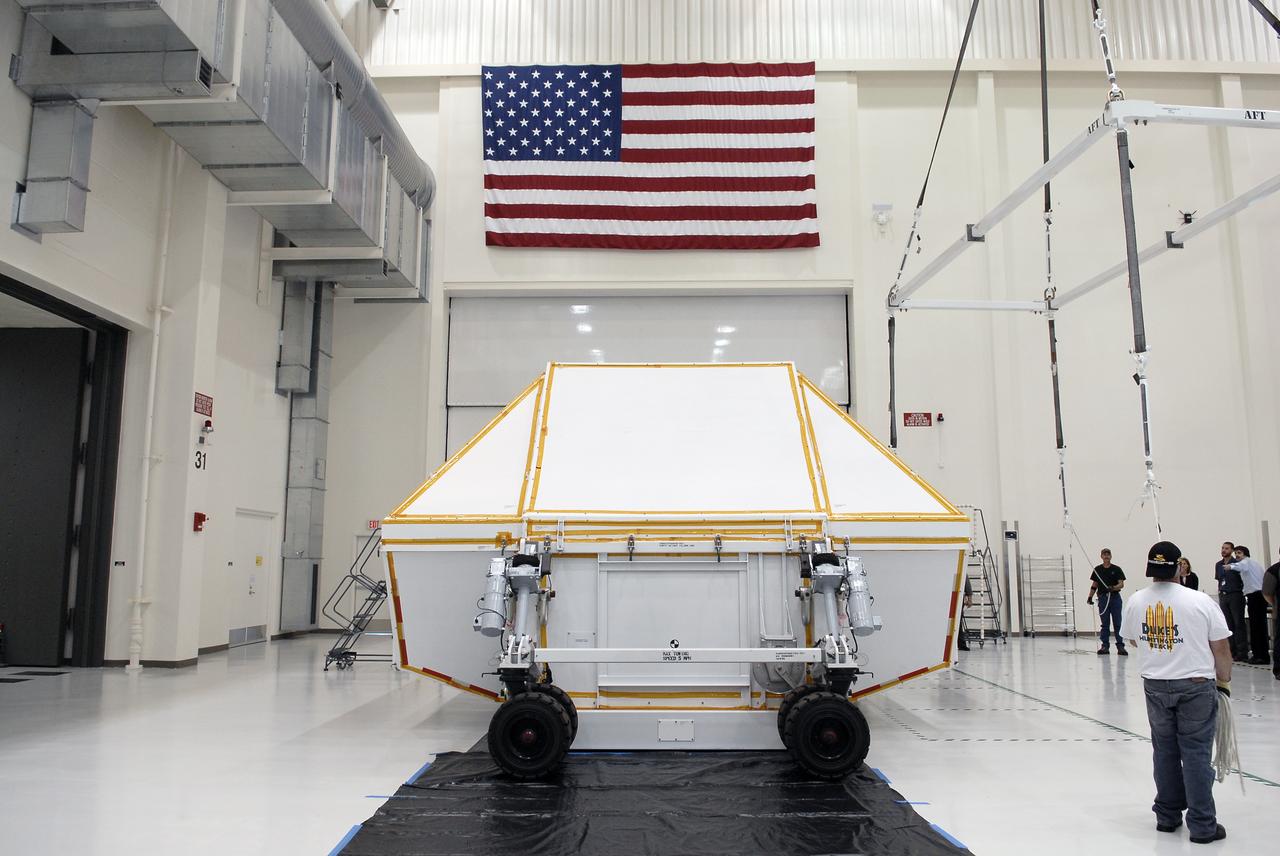

Orion EFT-1 Crew Module Uncrating
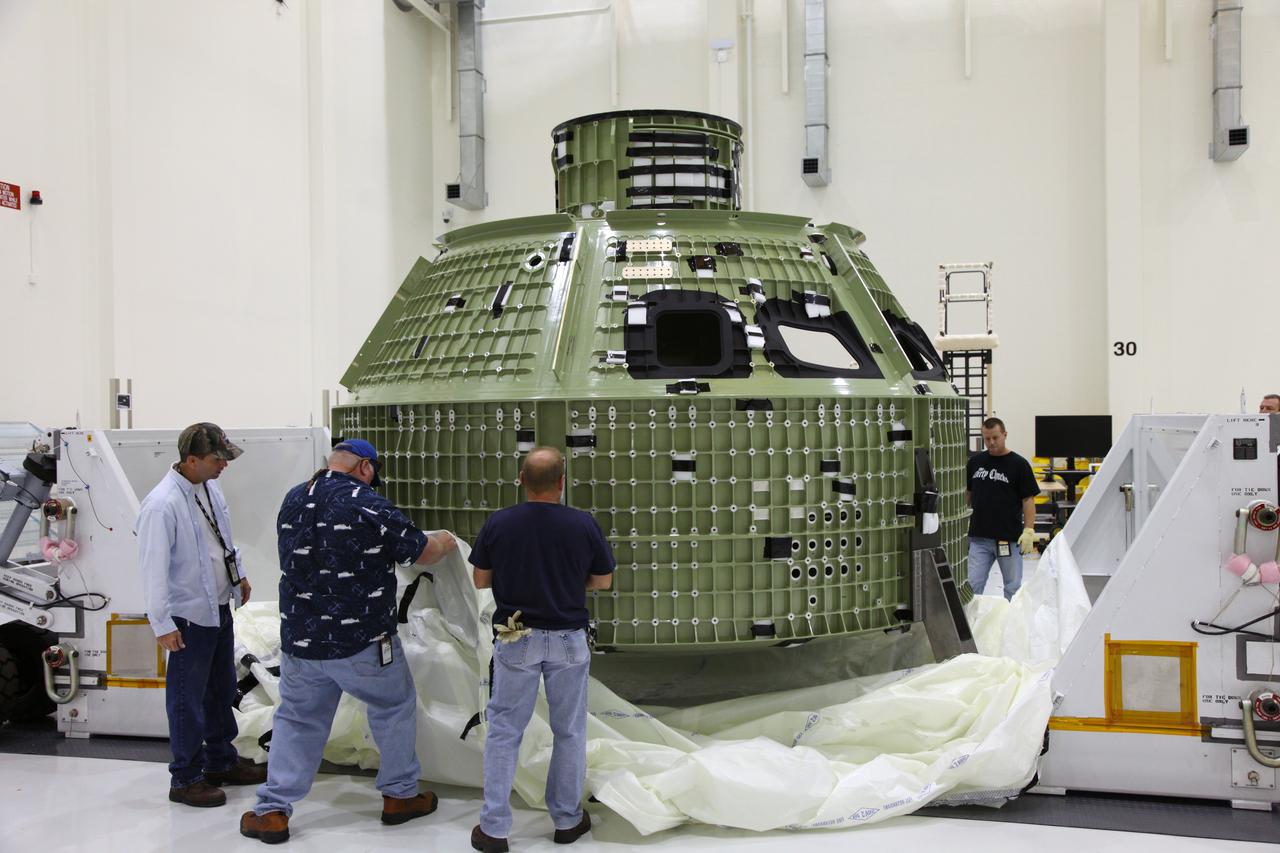

Orion EFT-1 Crew Module Being Uncrated
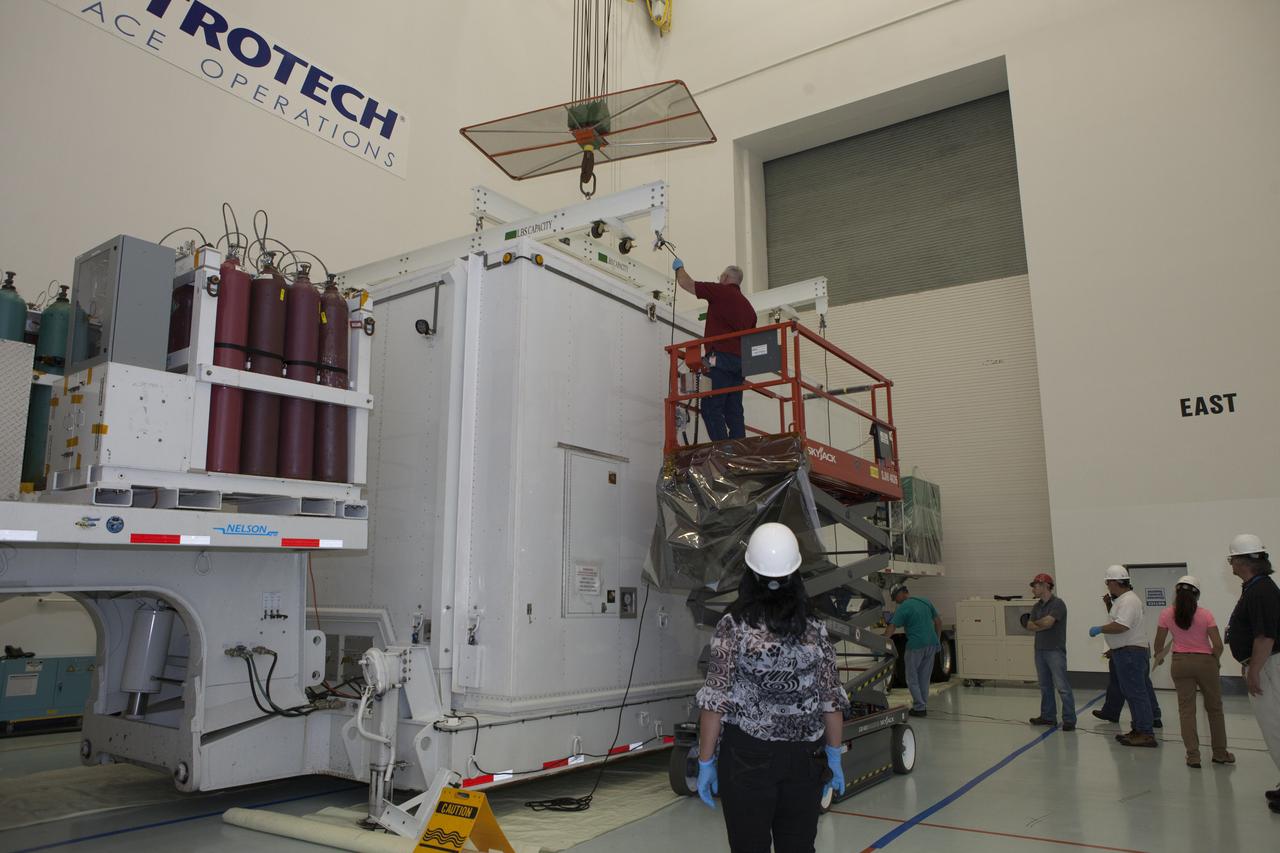

Workers attach a crane to the protective shipping container to prepare to uncover the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, two of the observatories for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS. They were delivered to the Building 2 south encapsulation bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
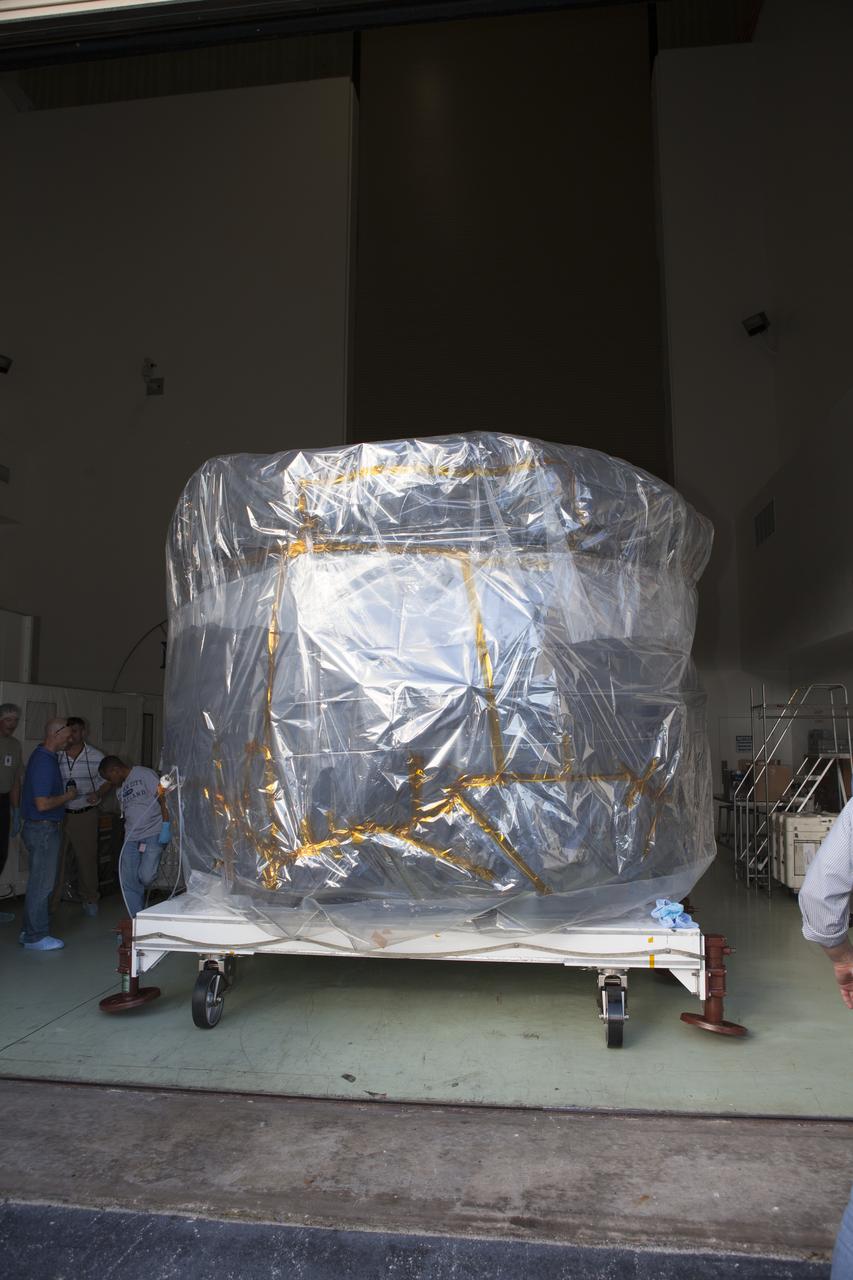

Two of the observatories, the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, arrive in the Building 1 airlock at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers remove NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) from its shipping container. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

Workers position two of the observatories, the lower stack, mini-stack number 1 for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, onto a payload dolly in the Building 2 south encapsulation bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after removal from its shipping container. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers remove NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) from its shipping container. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

Preparations are underway to tow two of the observatories, the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, from the Building 2 south encapsulation bay to the Building 1 high bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

Two of the observatories, the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, roll into the Building 1 airlock at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been removed from its shipping container. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

The protective shipping container is lifted from the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, two of the observatories for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, in the Building 2 south encapsulation bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

Two of the observatories for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, begin the trip from the Building 2 south encapsulation bay to the Building 1 high bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
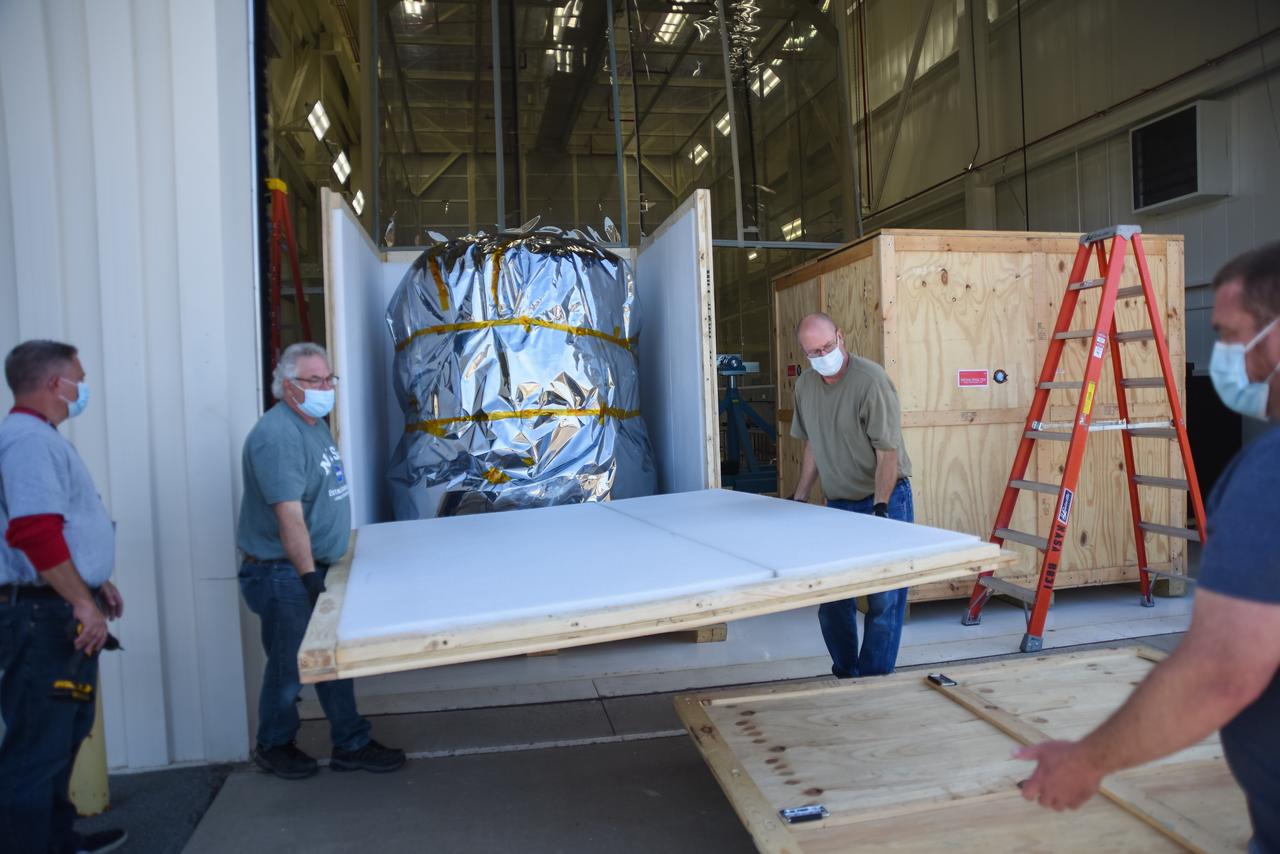

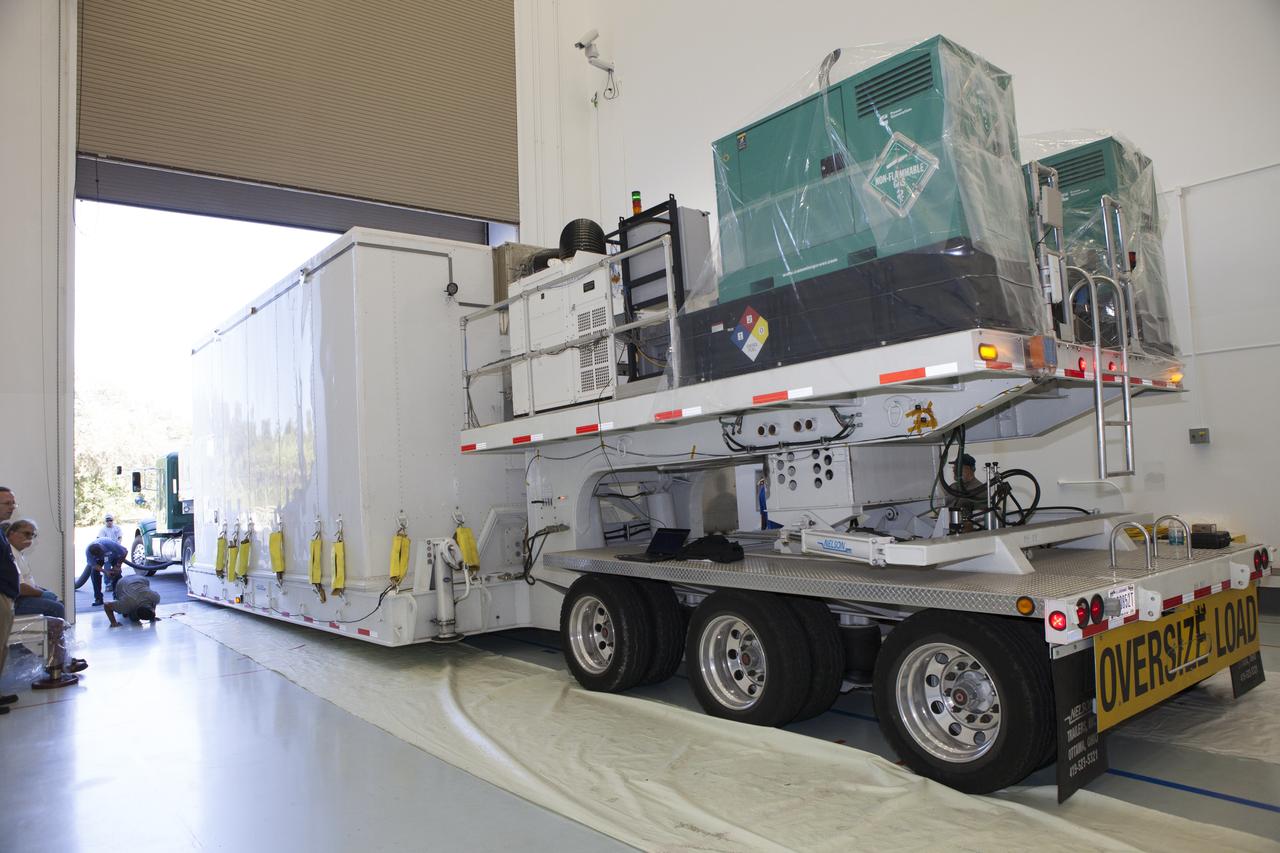
Teams working at Building 836 on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California remove NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) from its shipping container on Monday, Aug. 15, 2022. LOFTID is a rideshare launching with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite. The technology demonstration mission is slated to test new capabilities for landing payloads, including in a thinner atmosphere like that on Mars.
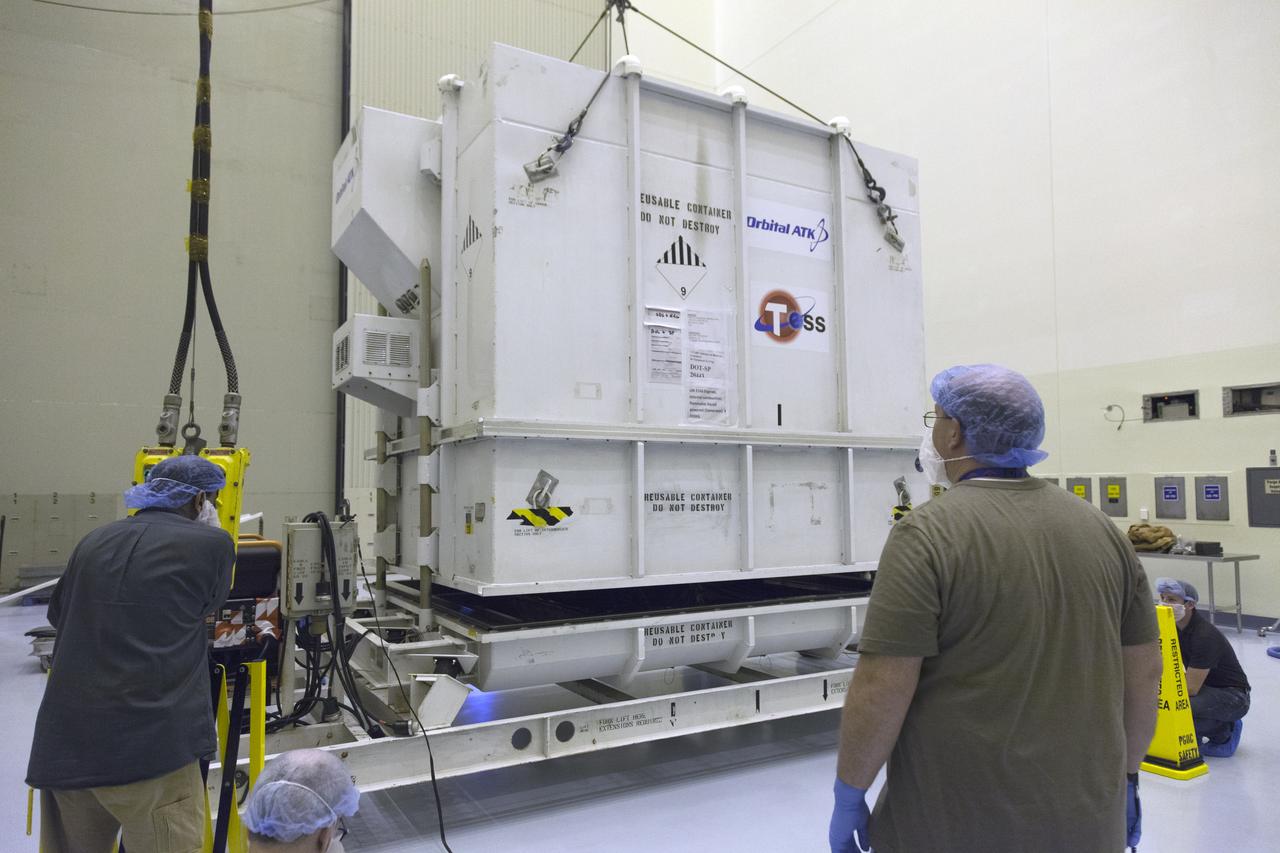

The shipping container with NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) arrives inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the PHSF, TESS will be unpacked, lifted up and moved to a test stand for processing. TESS is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. TESS is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
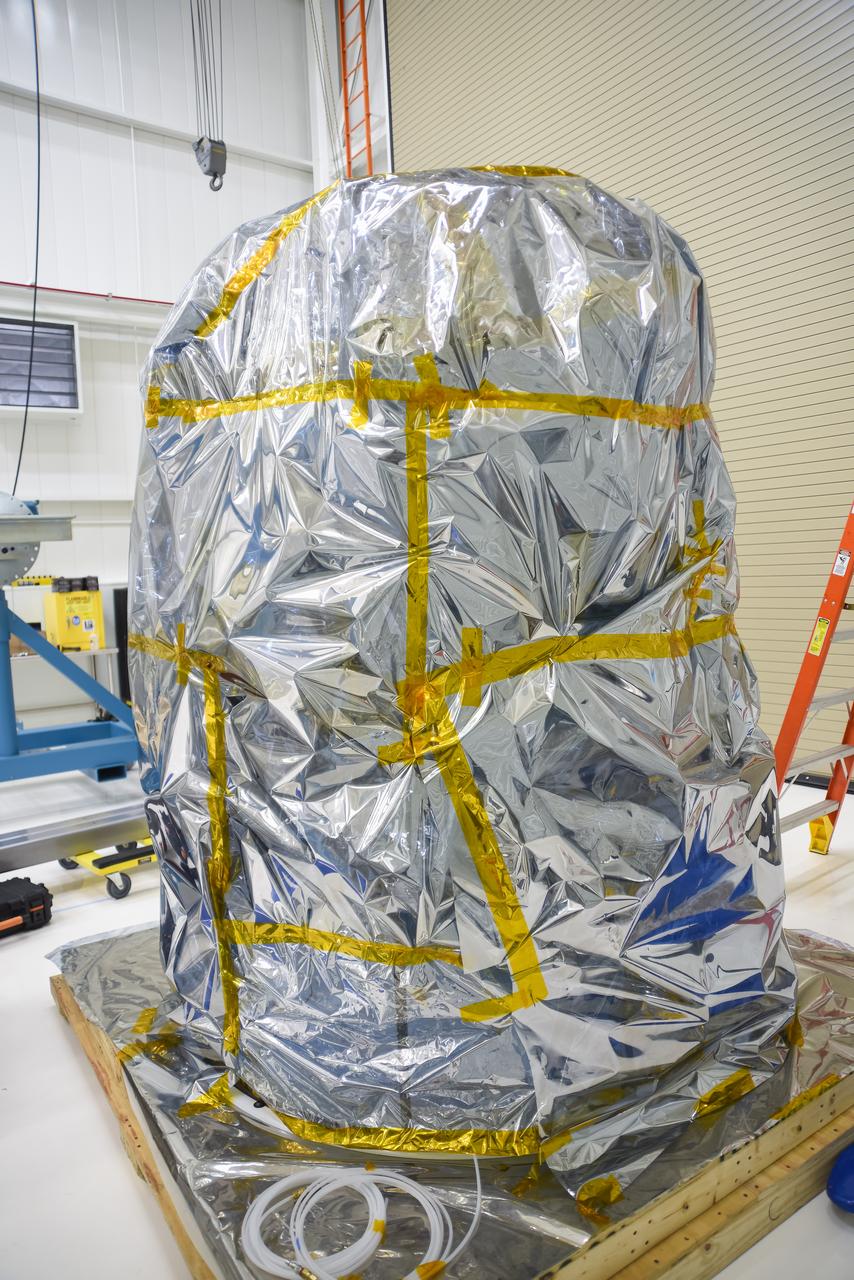

NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) arrives for processing inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California Monday, Aug. 15, 2022. LOFTID is a rideshare launching with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite. Teams working at Astrotech will prepare LOFTID to mate it with JPSS-2. After that a team will stack the encapsulated spacecraft and re-entry vehicle on a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 401 rocket. The technology demonstration mission is slated to test new capabilities for landing payloads, including in a thinner atmosphere like that on Mars. NASA is targeting launch for Tuesday, Nov. 1, from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex-3.
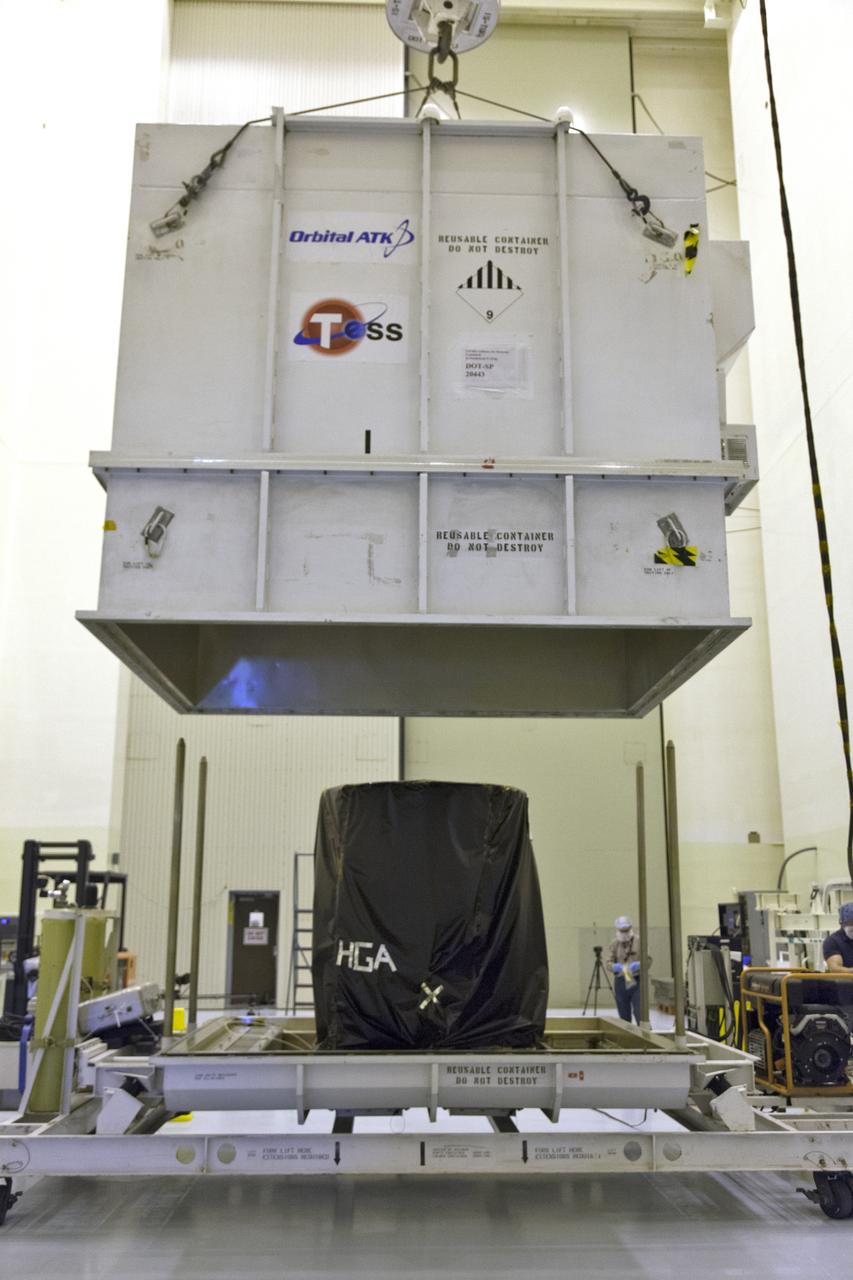

The top of the shipping container is lifted up by crane from NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. TESS will be unpacked, lifted up by crane and moved to a test stand for processing. TESS is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. TESS is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.

NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) arrives for processing inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California Monday, Aug. 15, 2022. LOFTID is a rideshare launching with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite. Teams working at Astrotech will prepare LOFTID to mate it with JPSS-2. After that a team will stack the encapsulated spacecraft and re-entry vehicle on a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 401 rocket. The technology demonstration mission is slated to test new capabilities for landing payloads, including in a thinner atmosphere like that on Mars. NASA is targeting launch for Tuesday, Nov. 1, from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex-3.

Preparations are underway to remove the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, two of the observatories for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, from their protective shipping container in the Building 2 south encapsulation bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

Workers surround two of the observatories, the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, on their trip from the Building 2 south encapsulation bay to the Building 1 high bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

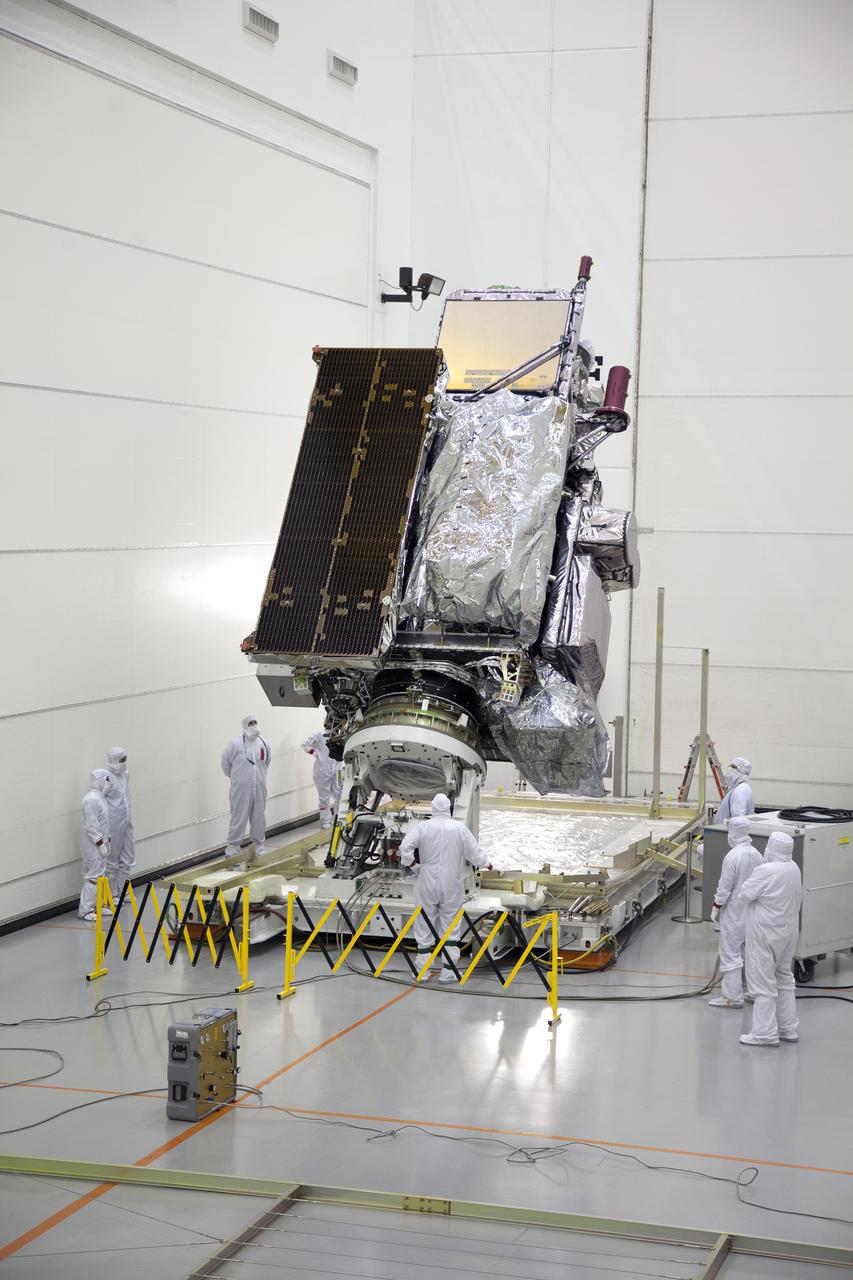
Team members monitor progress as the GOES-R spacecraft is lifted from horizontal to vertical inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.
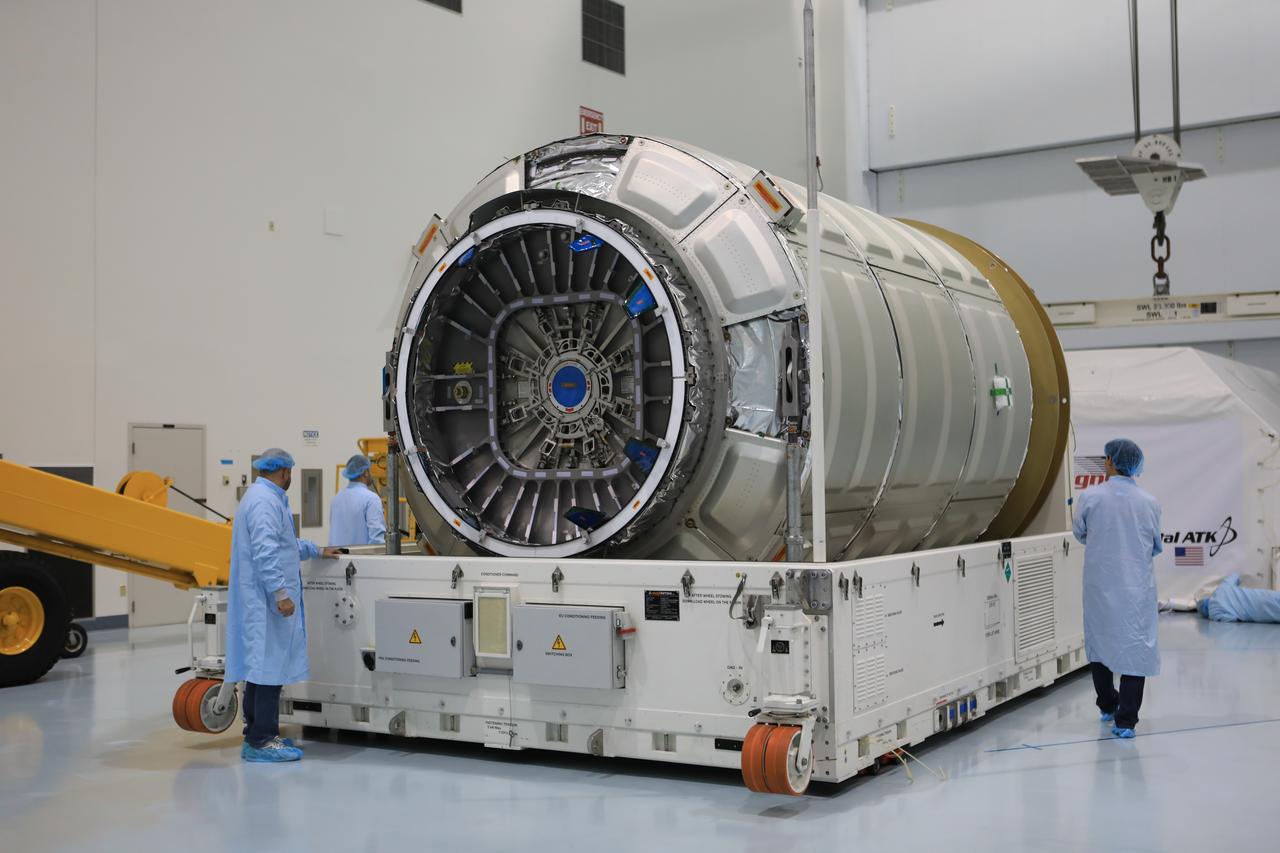

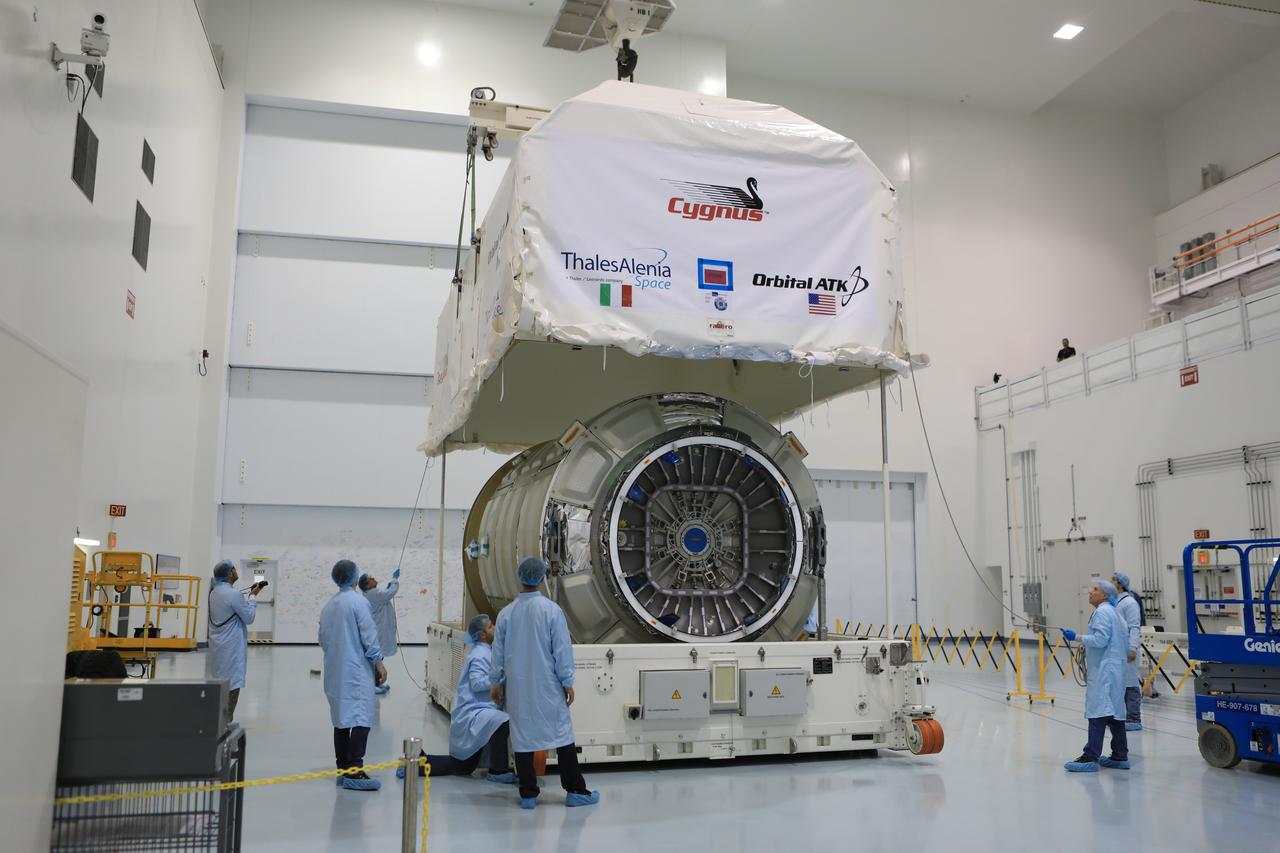
Inside the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida engineers and technicians remove the Orbital ATK OA-7 Cygnus spacecraft's pressurized cargo module (PCM) from its environmentally controlled shipping container. Scheduled to launch on March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK OA-7 mission will lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
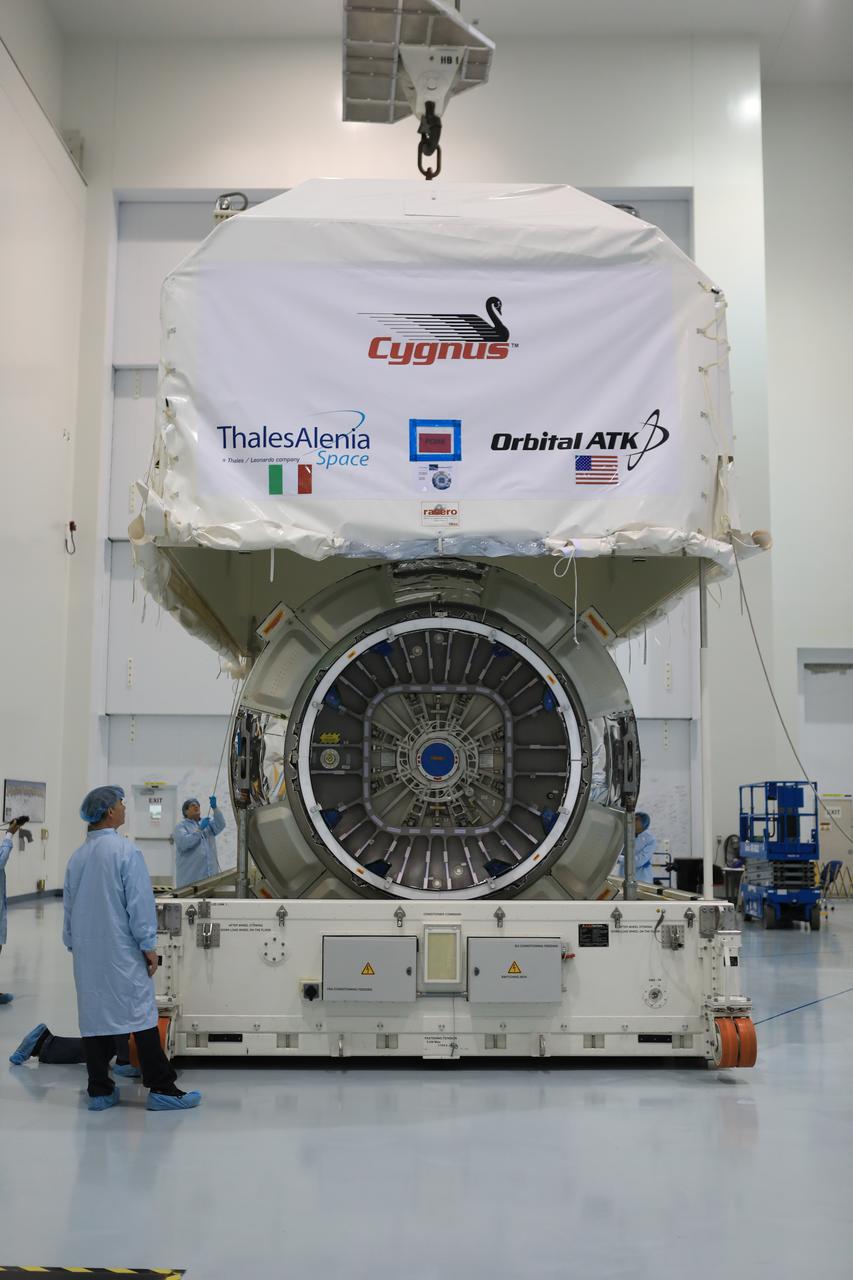

Inside the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida engineers and technicians remove the Orbital ATK OA-7 Cygnus spacecraft's pressurized cargo module (PCM) from its environmentally controlled shipping container. Scheduled to launch on March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK OA-7 mission will lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.

Team members remove a protective plastic covering from the GOES-R spacecraft inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.
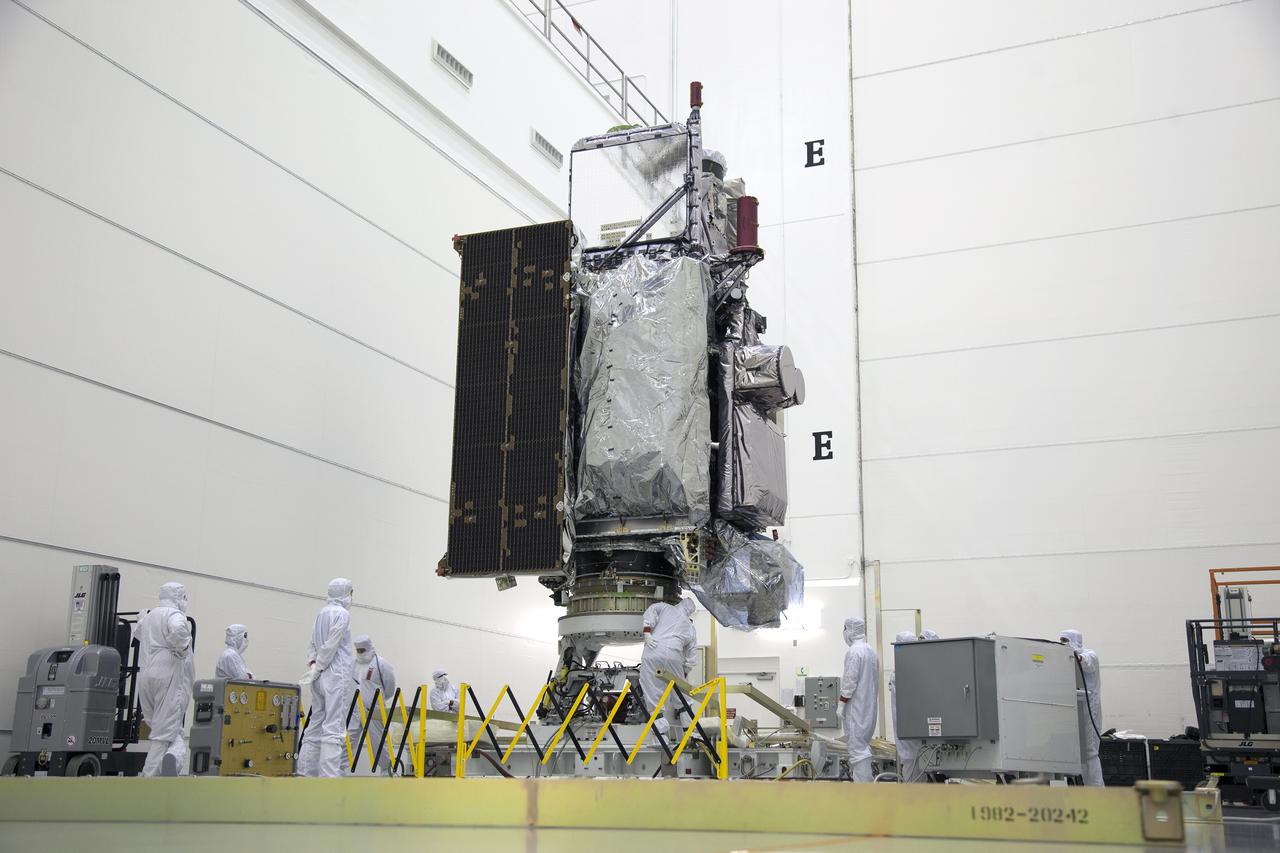

The GOES-R spacecraft stands vertically inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.
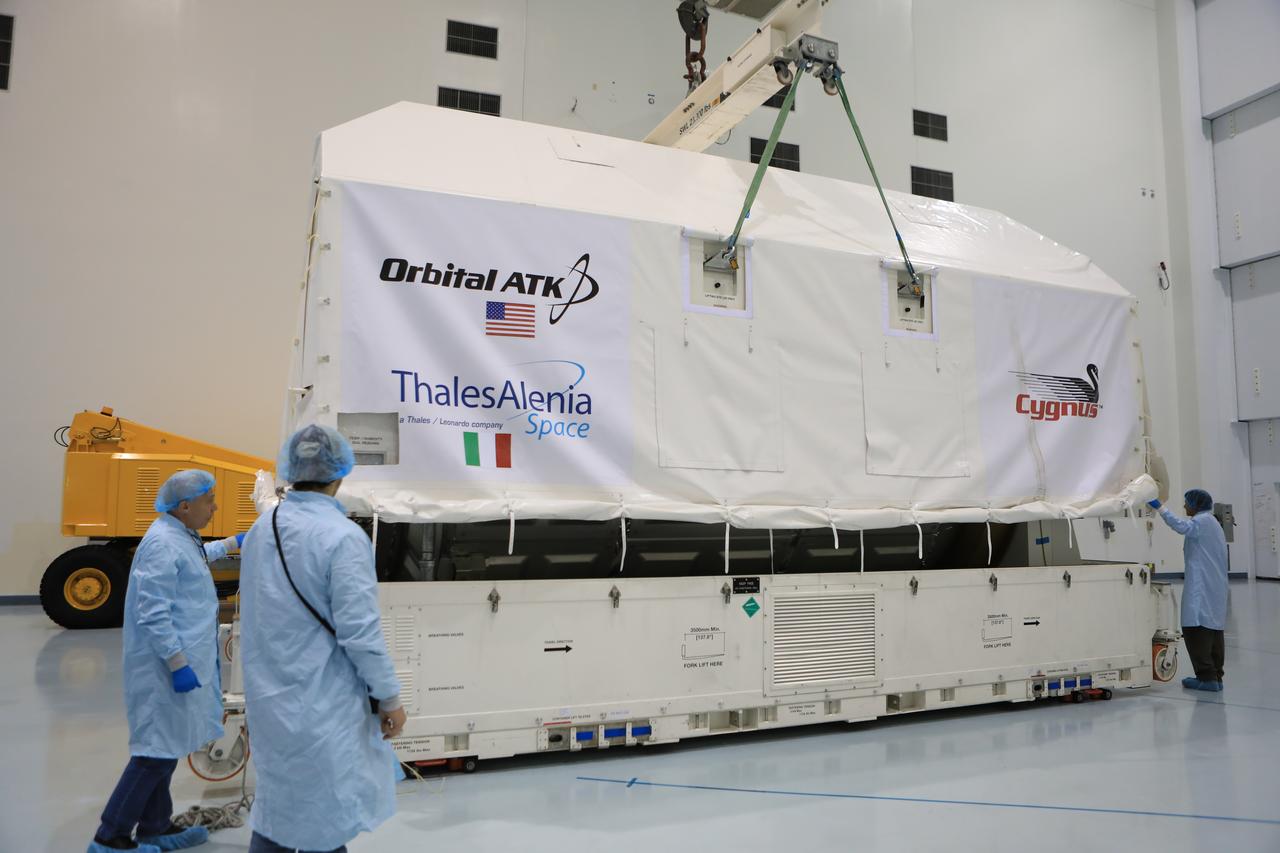

Inside the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida engineers and technicians remove the Orbital ATK OA-7 Cygnus spacecraft's pressurized cargo module (PCM) from its environmentally controlled shipping container. Scheduled to launch on March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK OA-7 mission will lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
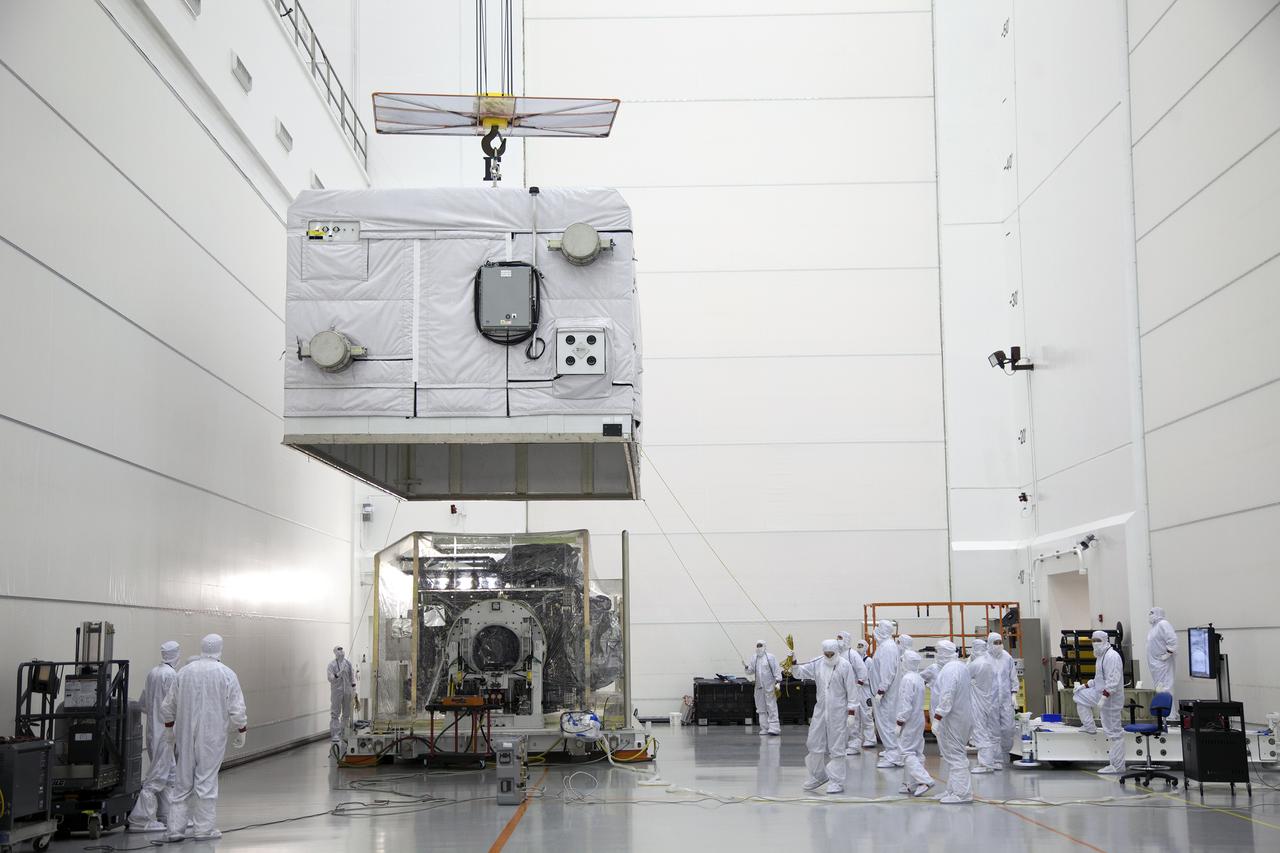

The shipping container is lifted off the GOES-R spacecraft inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.
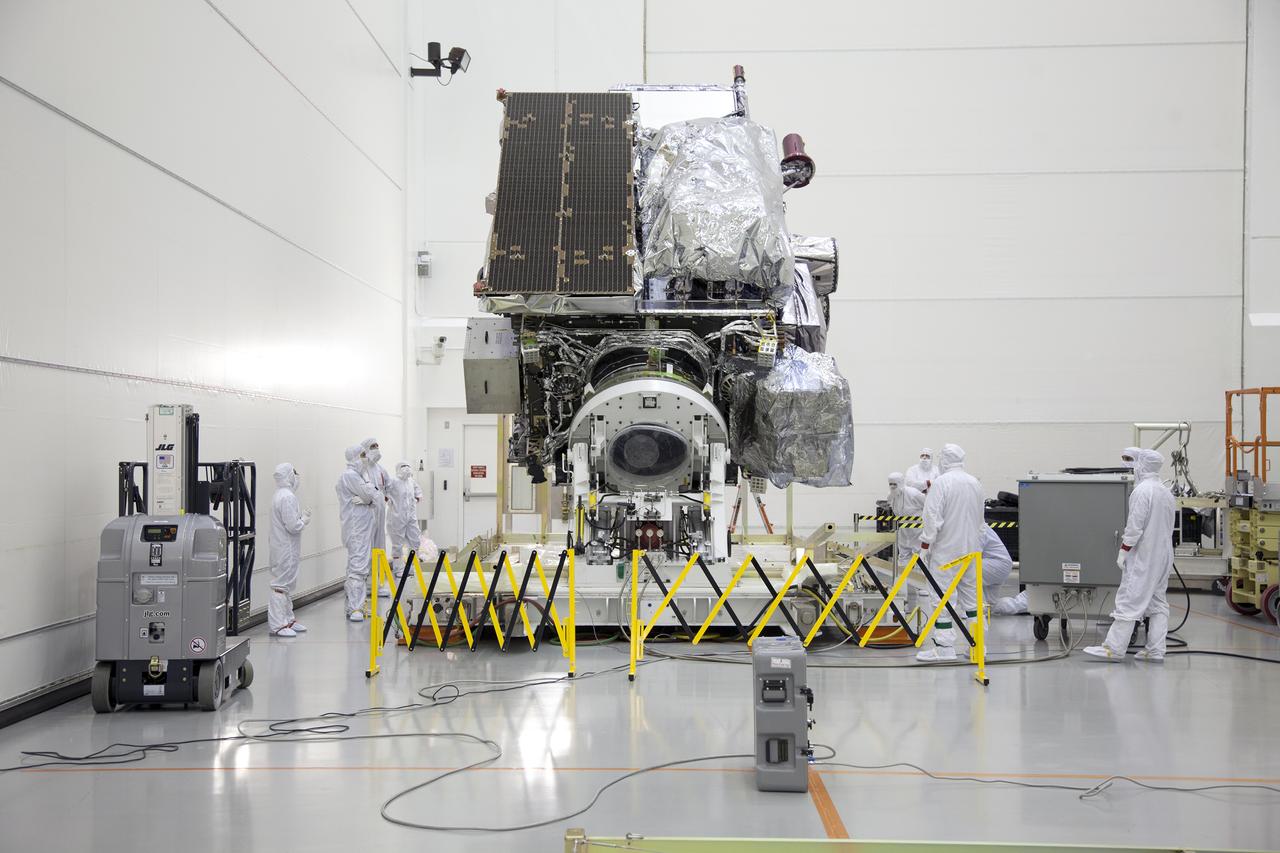
Team members monitor progress as the GOES-R spacecraft is lifted from horizontal to vertical inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.

Team members monitor progress as the GOES-R spacecraft is raised to vertical inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.
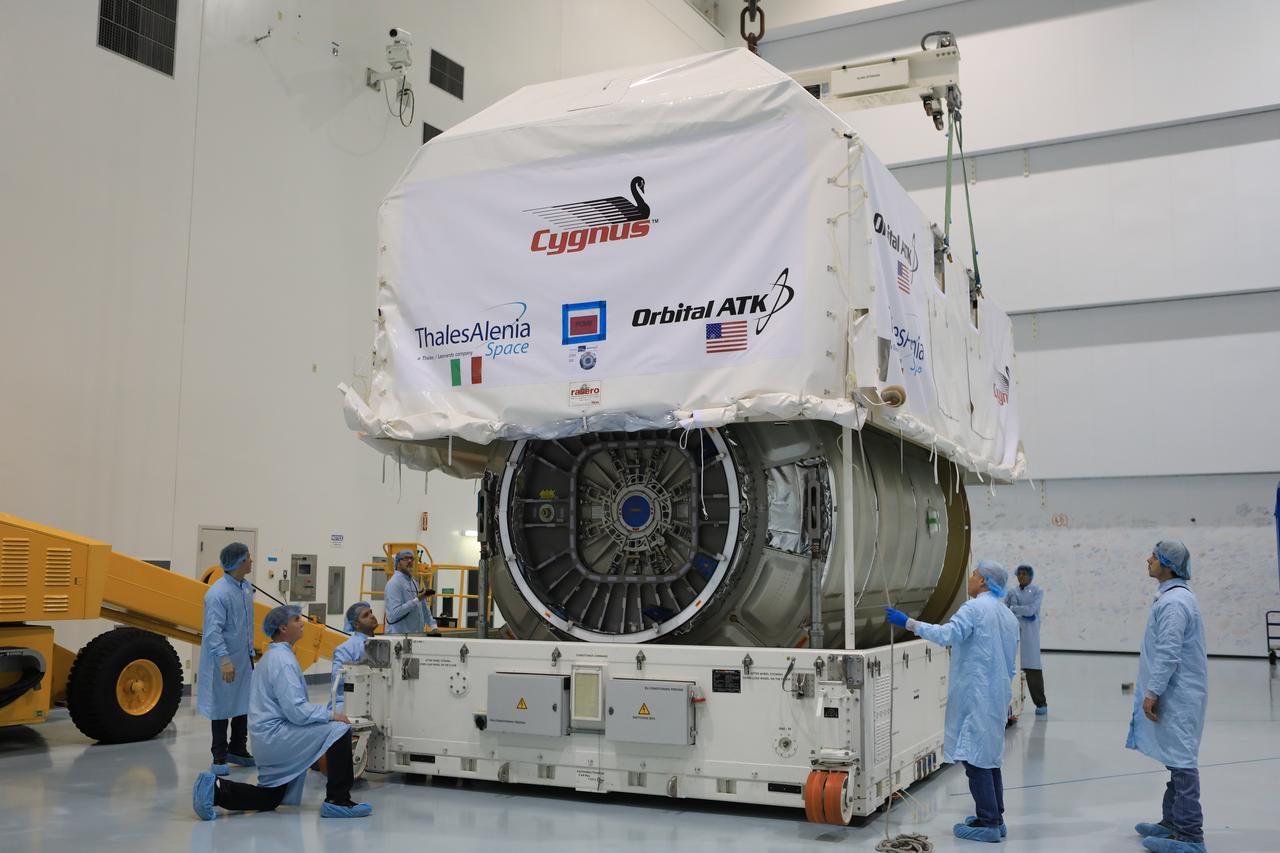

Inside the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida engineers and technicians remove the Orbital ATK OA-7 Cygnus spacecraft's pressurized cargo module (PCM) from its environmentally controlled shipping container. Scheduled to launch on March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK OA-7 mission will lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.

Inside the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida engineers and technicians remove the Orbital ATK OA-7 Cygnus spacecraft's pressurized cargo module (PCM) from its environmentally controlled shipping container. Scheduled to launch on March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK OA-7 mission will lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
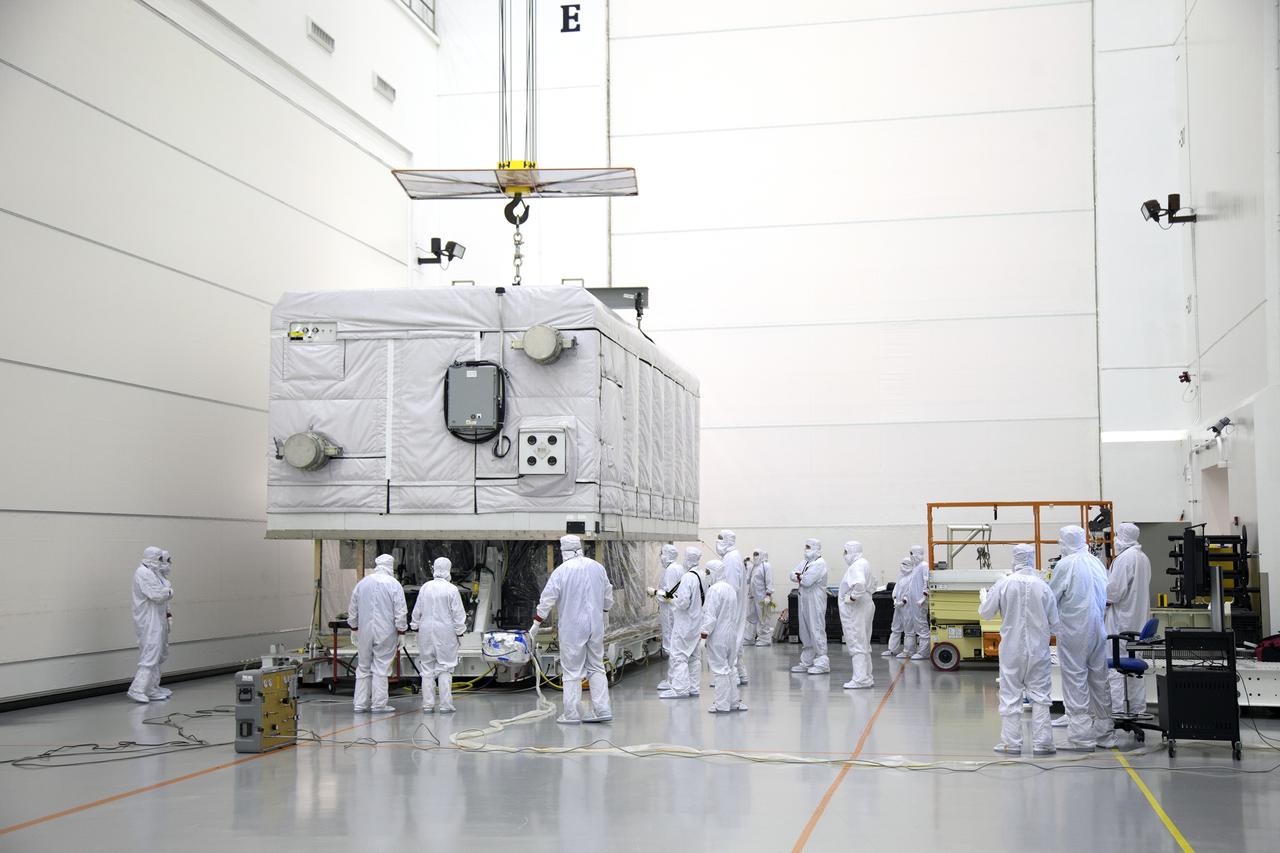

The shipping container is lifted off the GOES-R spacecraft inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.
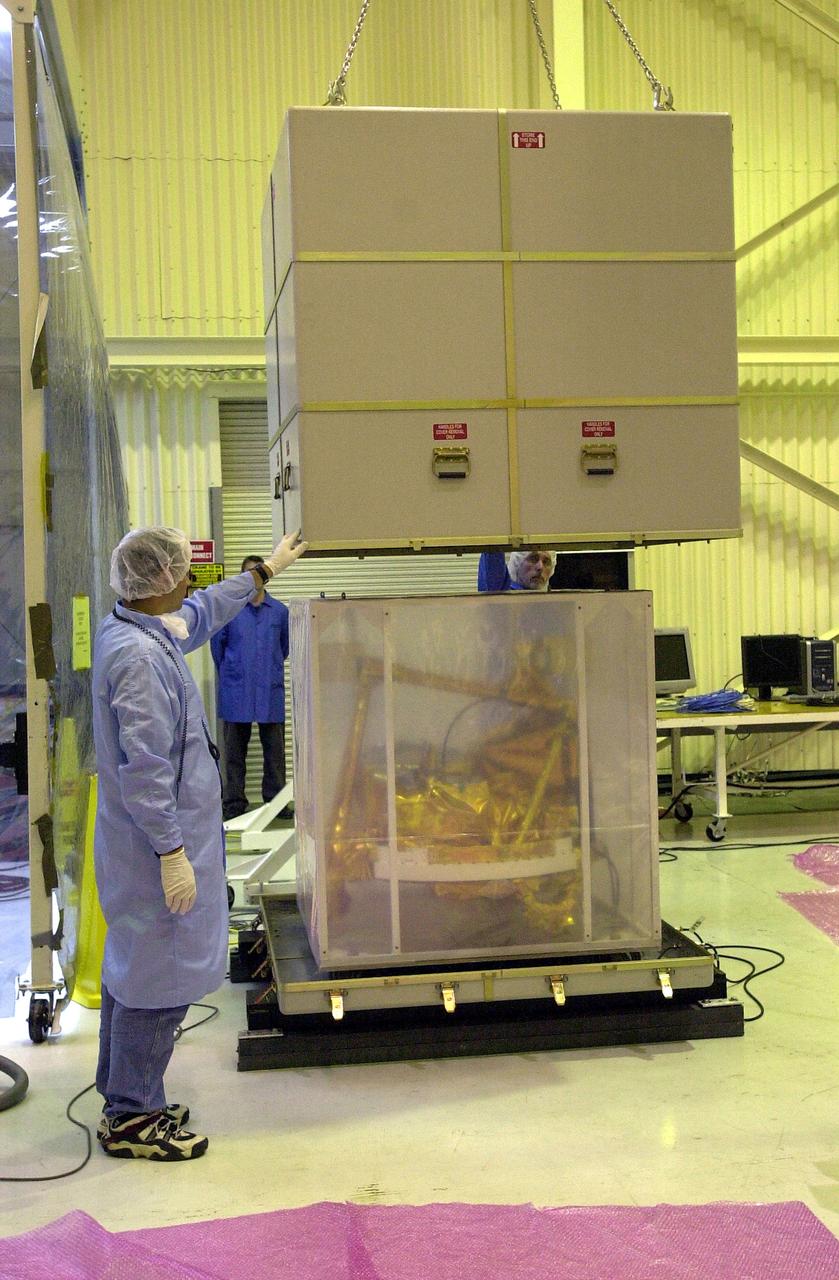

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The SciSat-1 spacecraft is uncrated at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. SciSat-1 weighs approximately 330 pounds and will be placed in a 400-mile-high polar orbit to investigate processes that control the distribution of ozone in the upper atmosphere. The scientific mission of SciSat-1 is to measure and understand the chemical processes that control the distribution of ozone in the Earth’s atmosphere, particularly at high altitudes. The data from the satellite will provide Canadian and international scientists with improved measurements relating to global ozone processes and help policymakers assess existing environmental policy and develop protective measures for improving the health of our atmosphere, preventing further ozone depletion. The mission is designed to last two years.
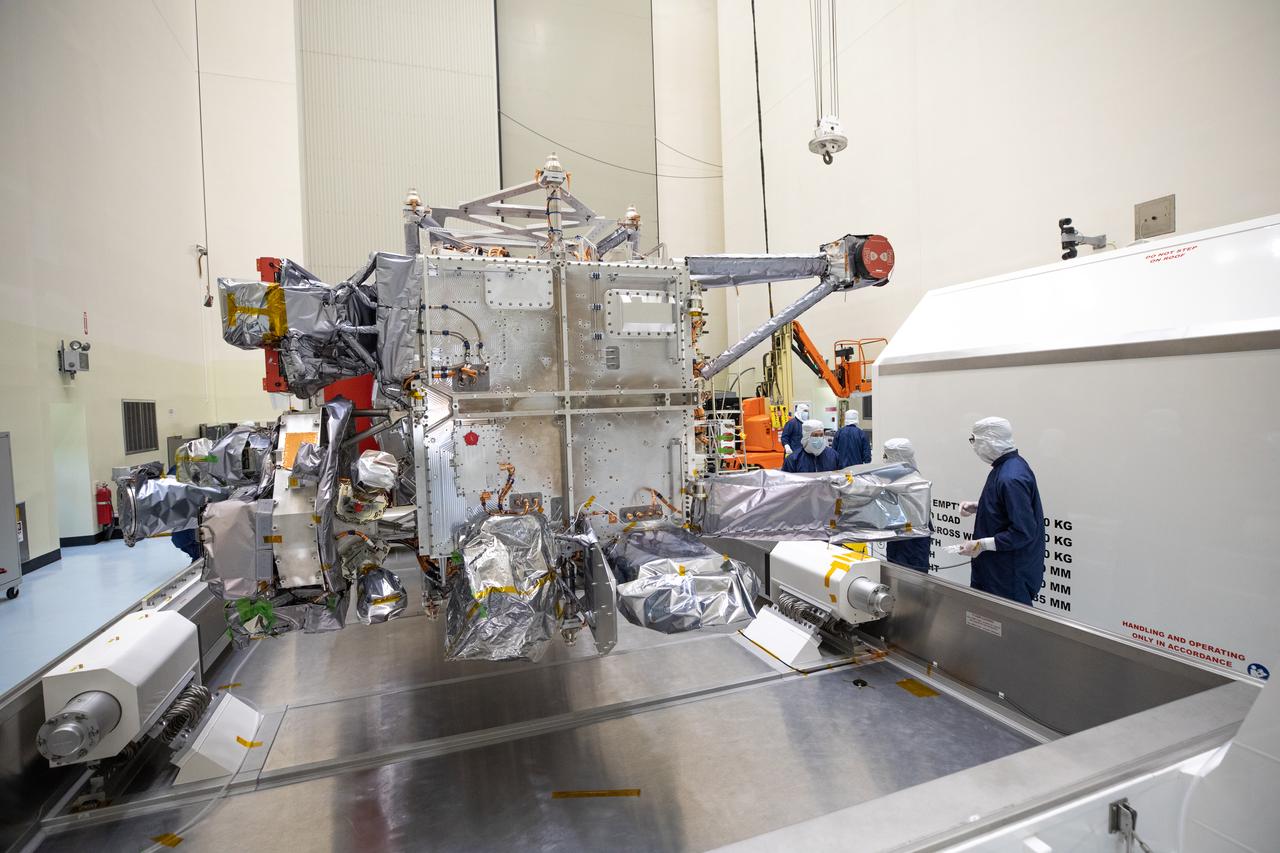

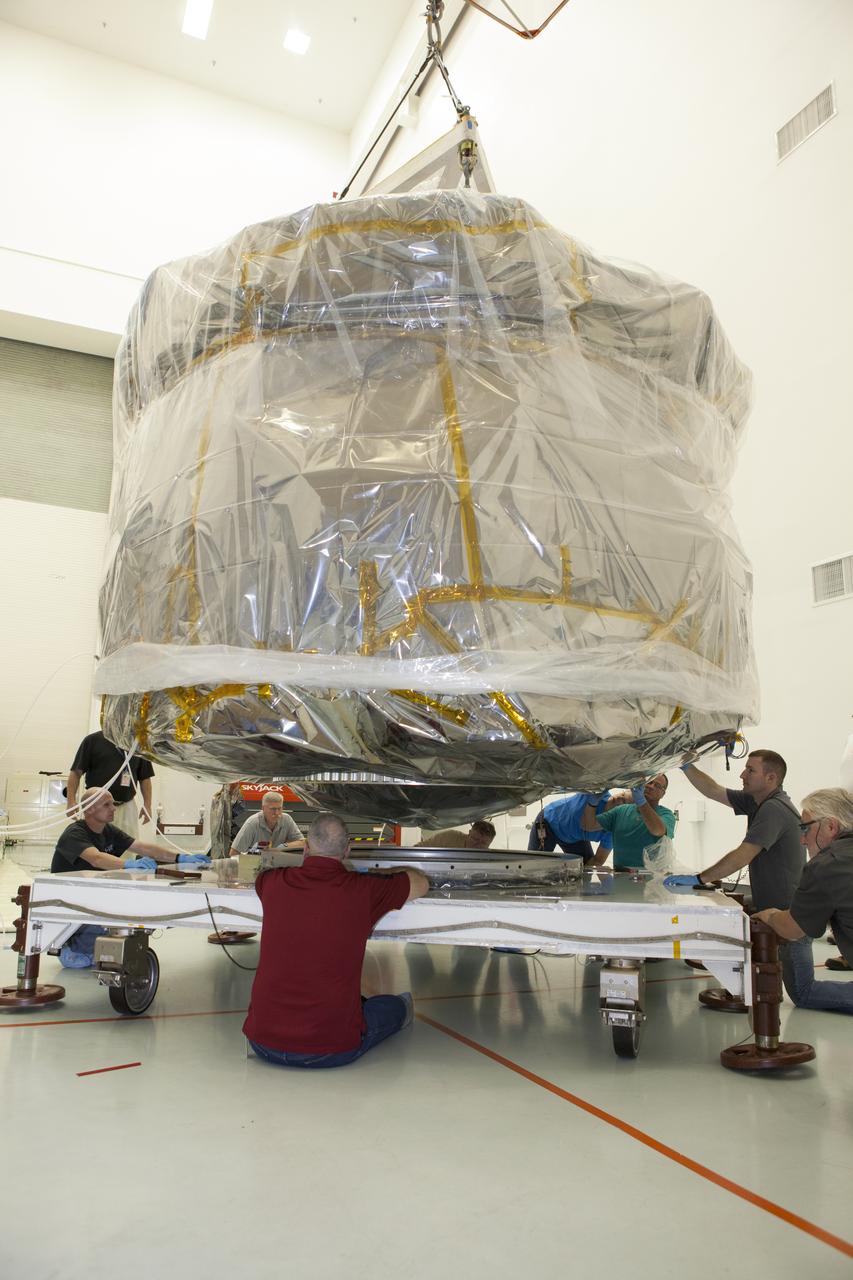
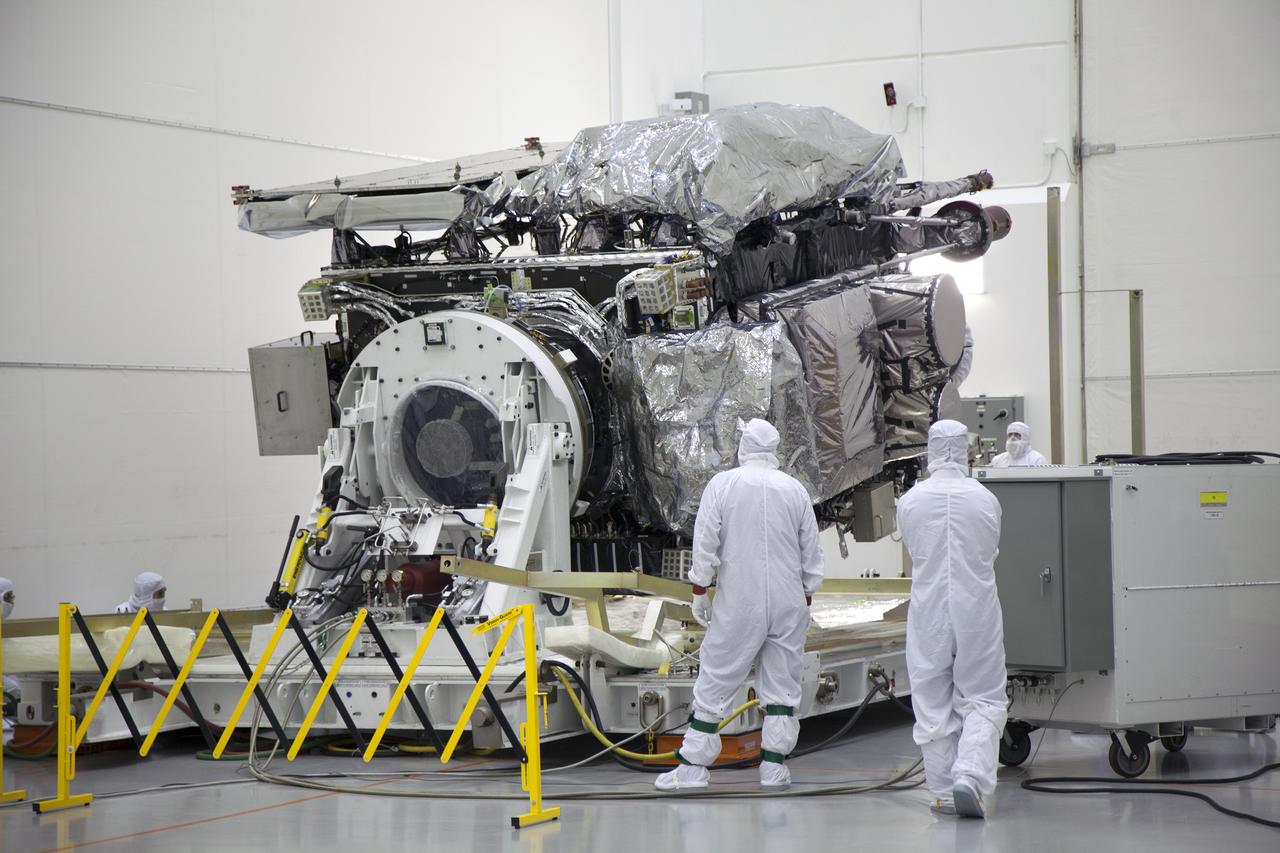
As part of prelaunch processing, crews inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida uncrate the agency’s largest planetary mission spacecraft, Europa Clipper, on Tuesday, May 28, 2024. Slated to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket later this year from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, Europa Clipper will help determine if conditions exist below the surface Jupiter’s fourth largest moon, Europa, that could support life.
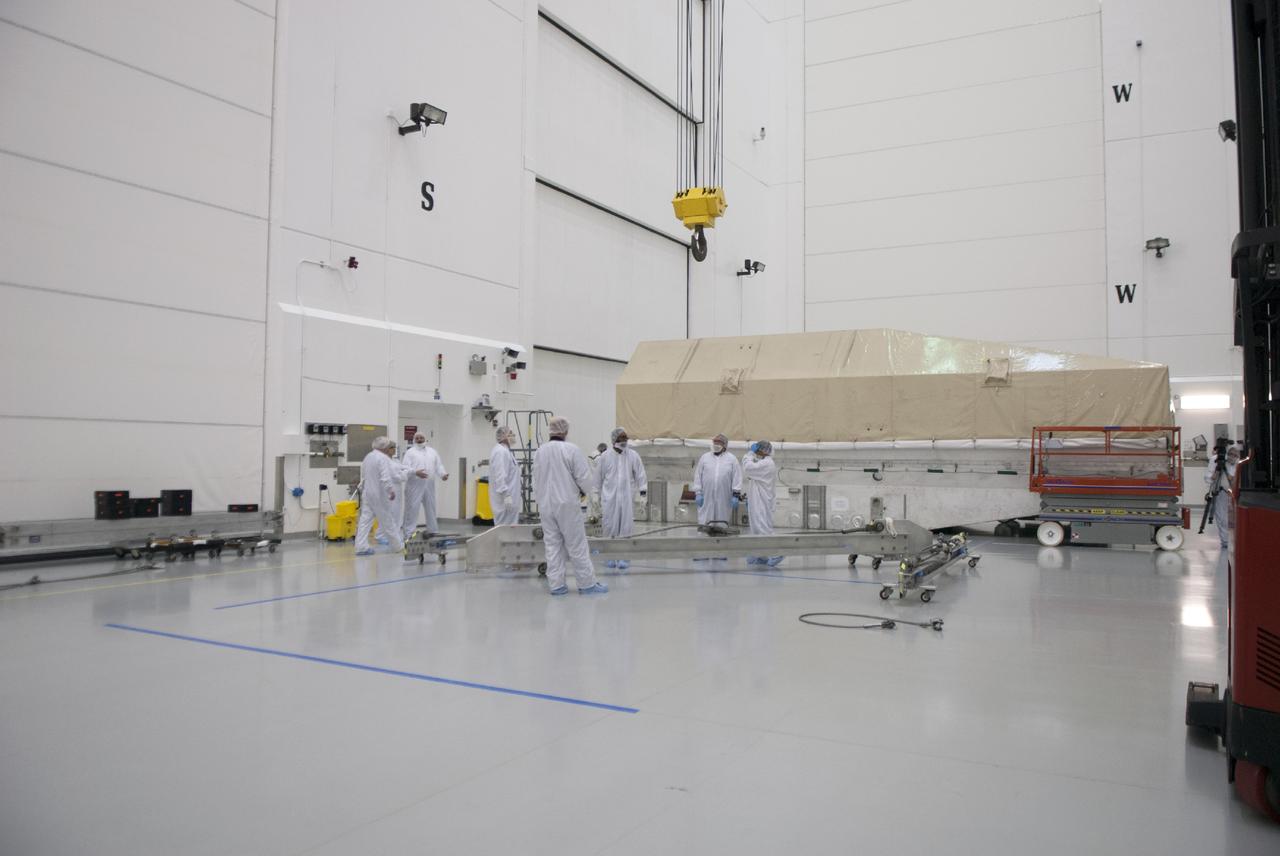

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Engineers prepare to uncrate NASA's TDRS-L satellite inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville for launch processing. The TDRS is the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
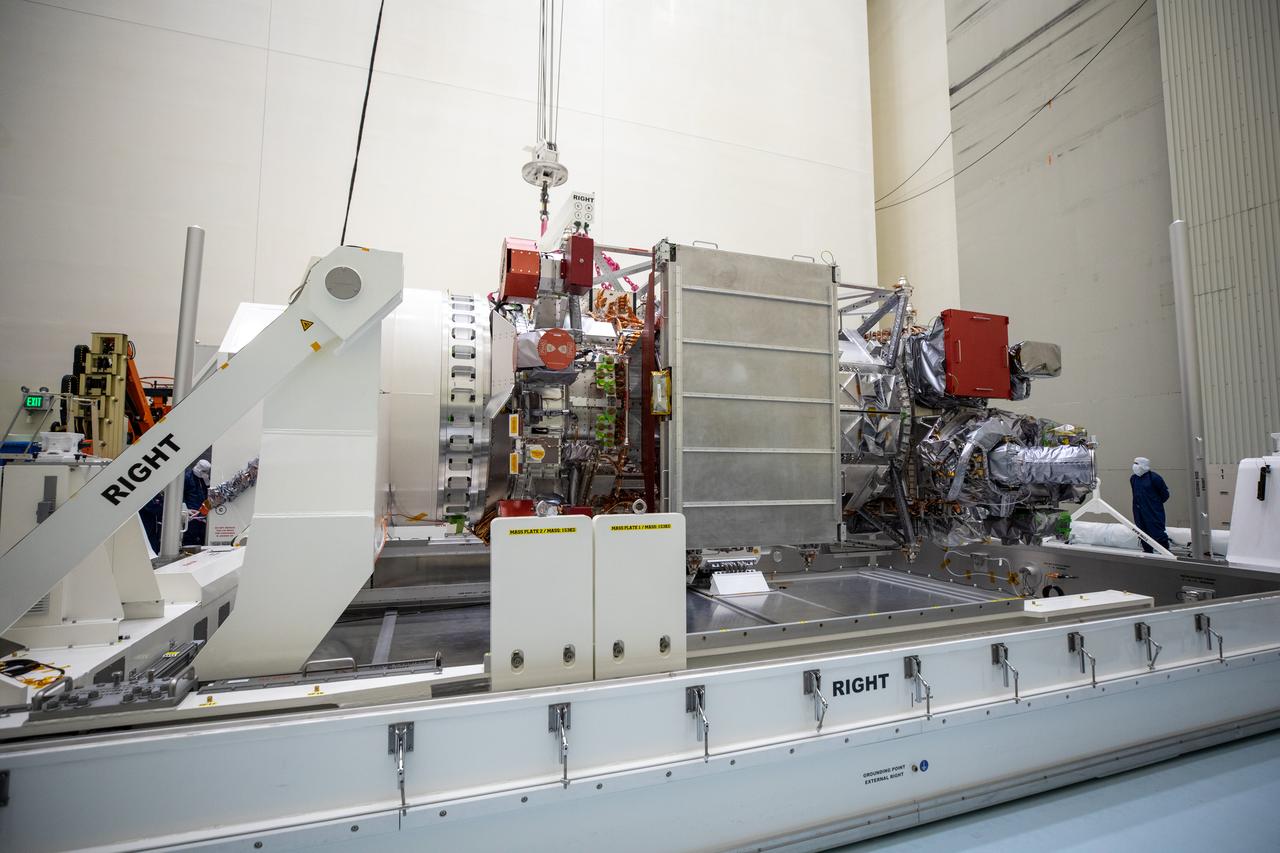
As part of prelaunch processing, crews inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida uncrate the agency’s largest planetary mission spacecraft, Europa Clipper, on Tuesday, May 28, 2024. Slated to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket later this year from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, Europa Clipper will help determine if conditions exist below the surface Jupiter’s fourth largest moon, Europa, that could support life.
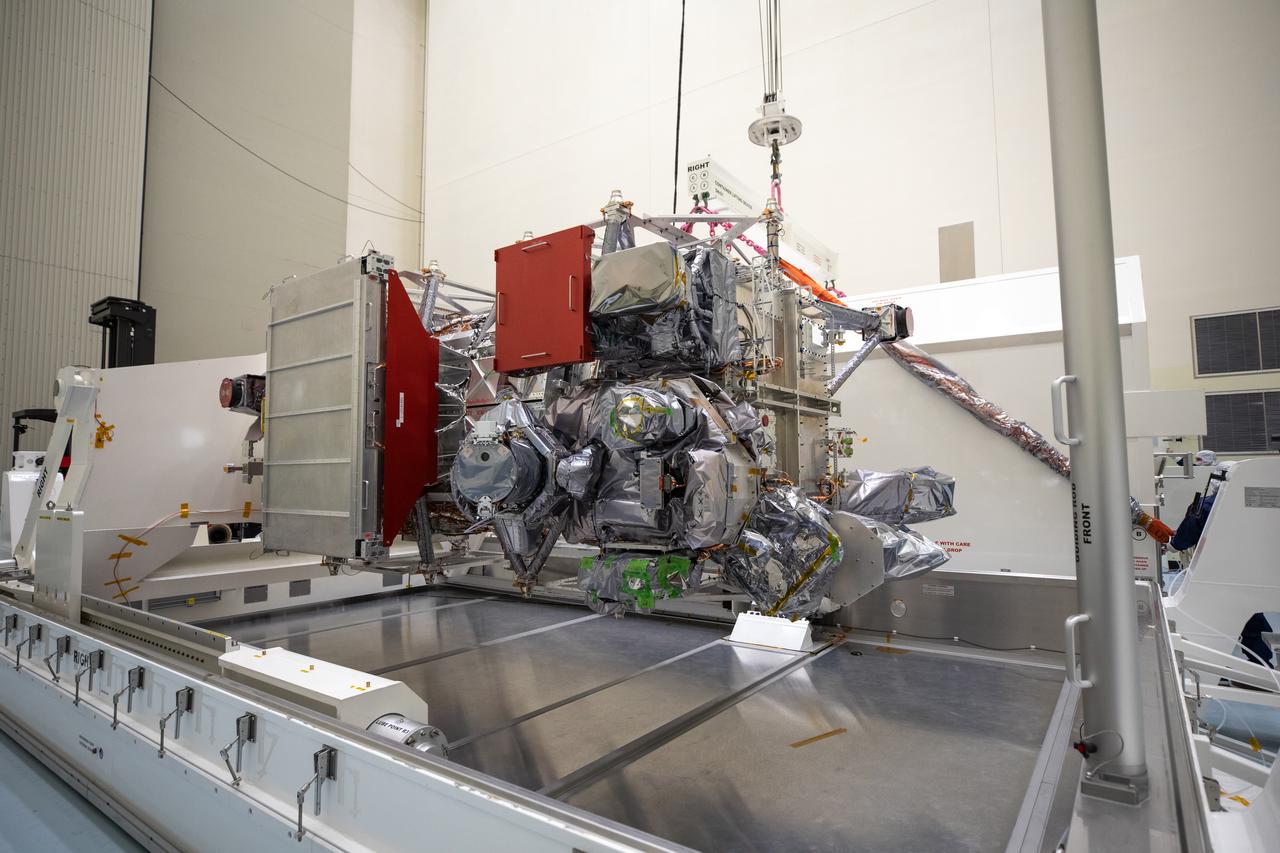

As part of prelaunch processing, crews inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida uncrate the agency’s largest planetary mission spacecraft, Europa Clipper, on Tuesday, May 28, 2024. Slated to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket later this year from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, Europa Clipper will help determine if conditions exist below the surface Jupiter’s fourth largest moon, Europa, that could support life.
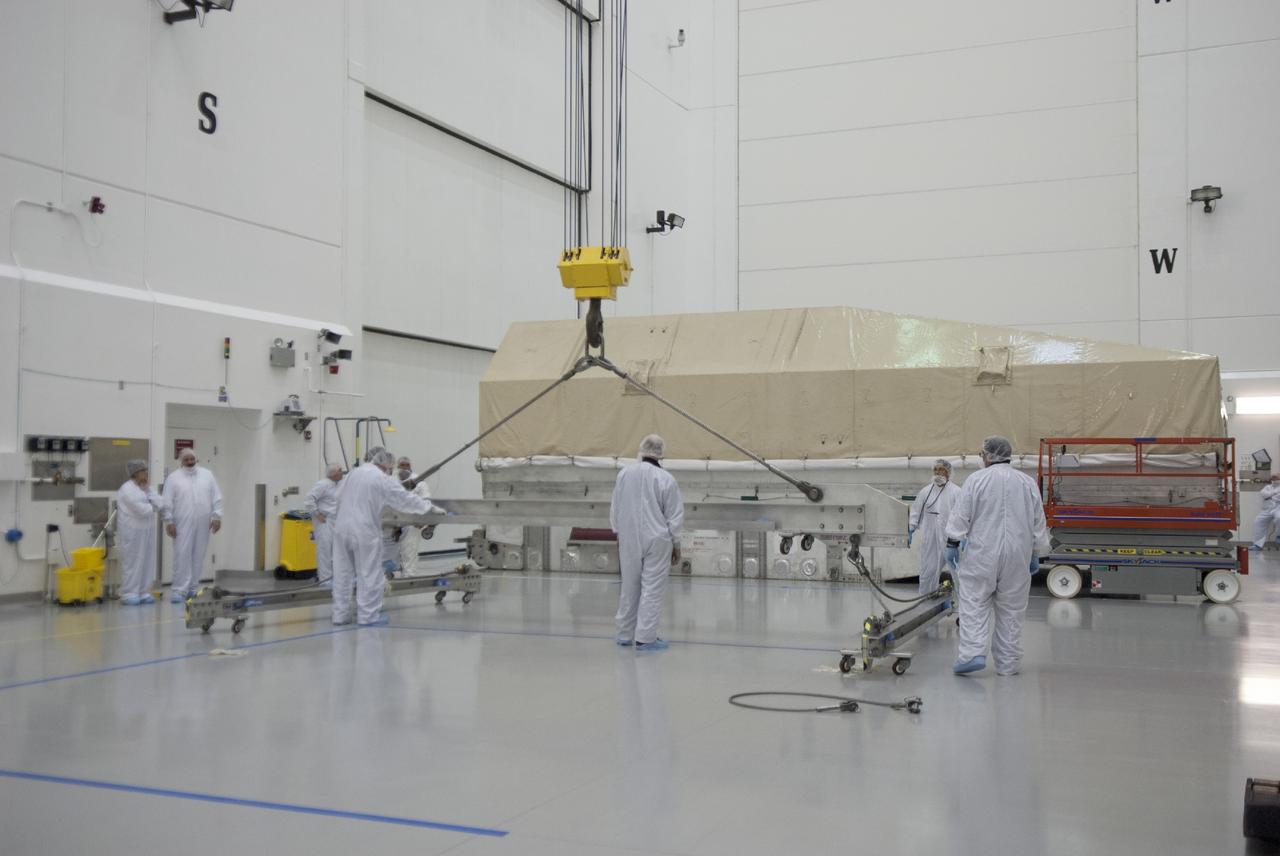

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Engineers prepare to uncrate NASA's TDRS-L satellite inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville for launch processing. The TDRS is the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
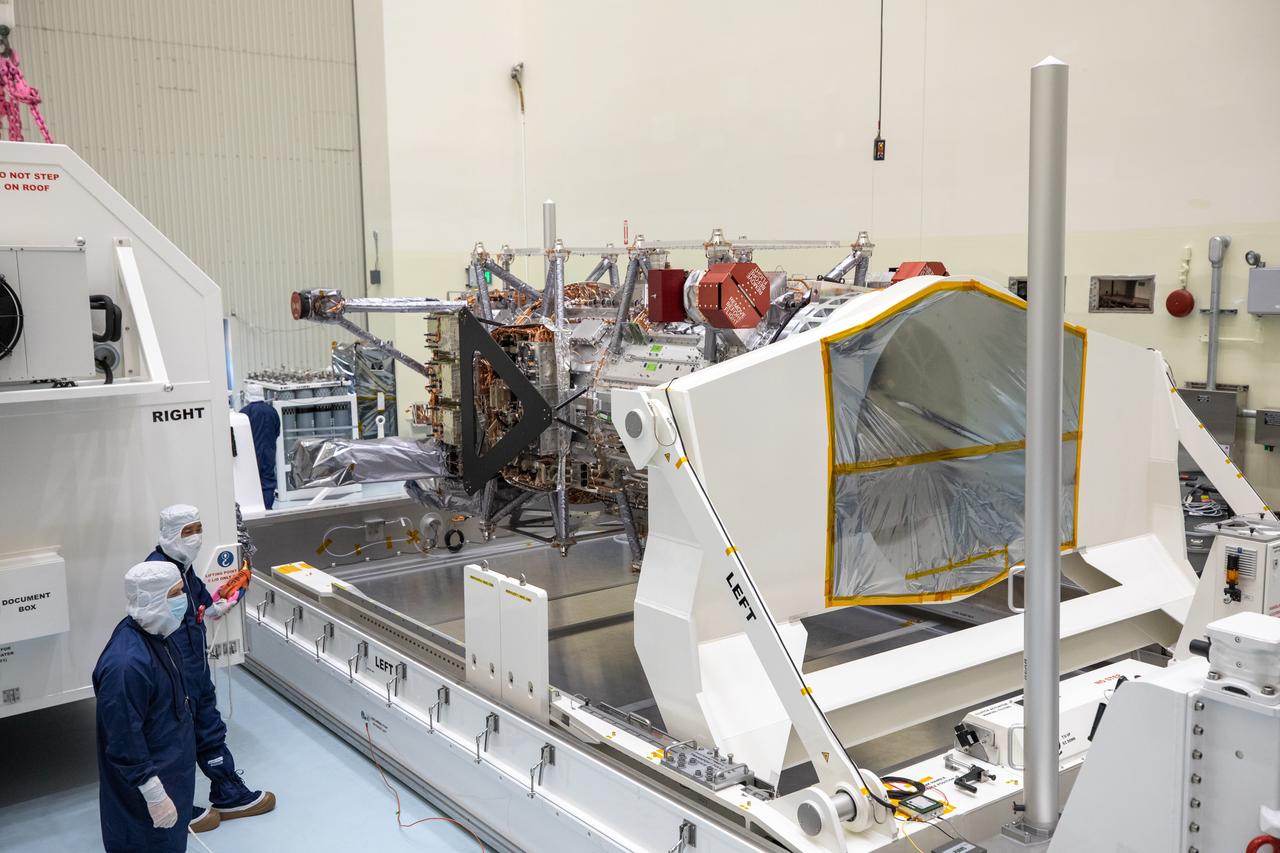

As part of prelaunch processing, crews inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida uncrate the agency’s largest planetary mission spacecraft, Europa Clipper, on Tuesday, May 28, 2024. Slated to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket later this year from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, Europa Clipper will help determine if conditions exist below the surface Jupiter’s fourth largest moon, Europa, that could support life.