
USGS visit to Goddard

USGS visit to Goddard

USGS visit to Goddard

USGS visit to Goddard

USGS visit to Goddard

USGS visit to Goddard

USGS visit to Goddard

USGS visit to Goddard
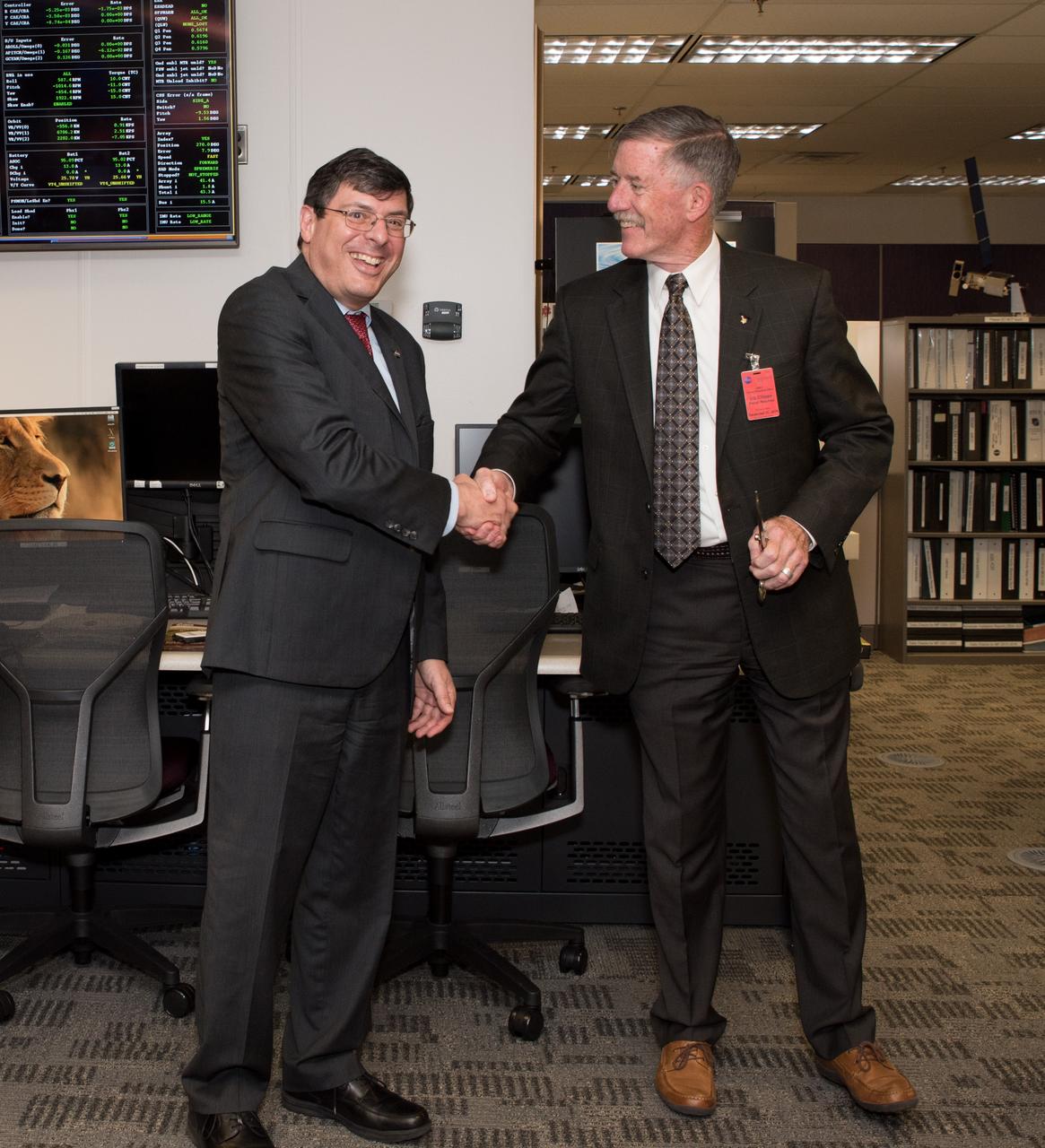

USGS visit to Goddard
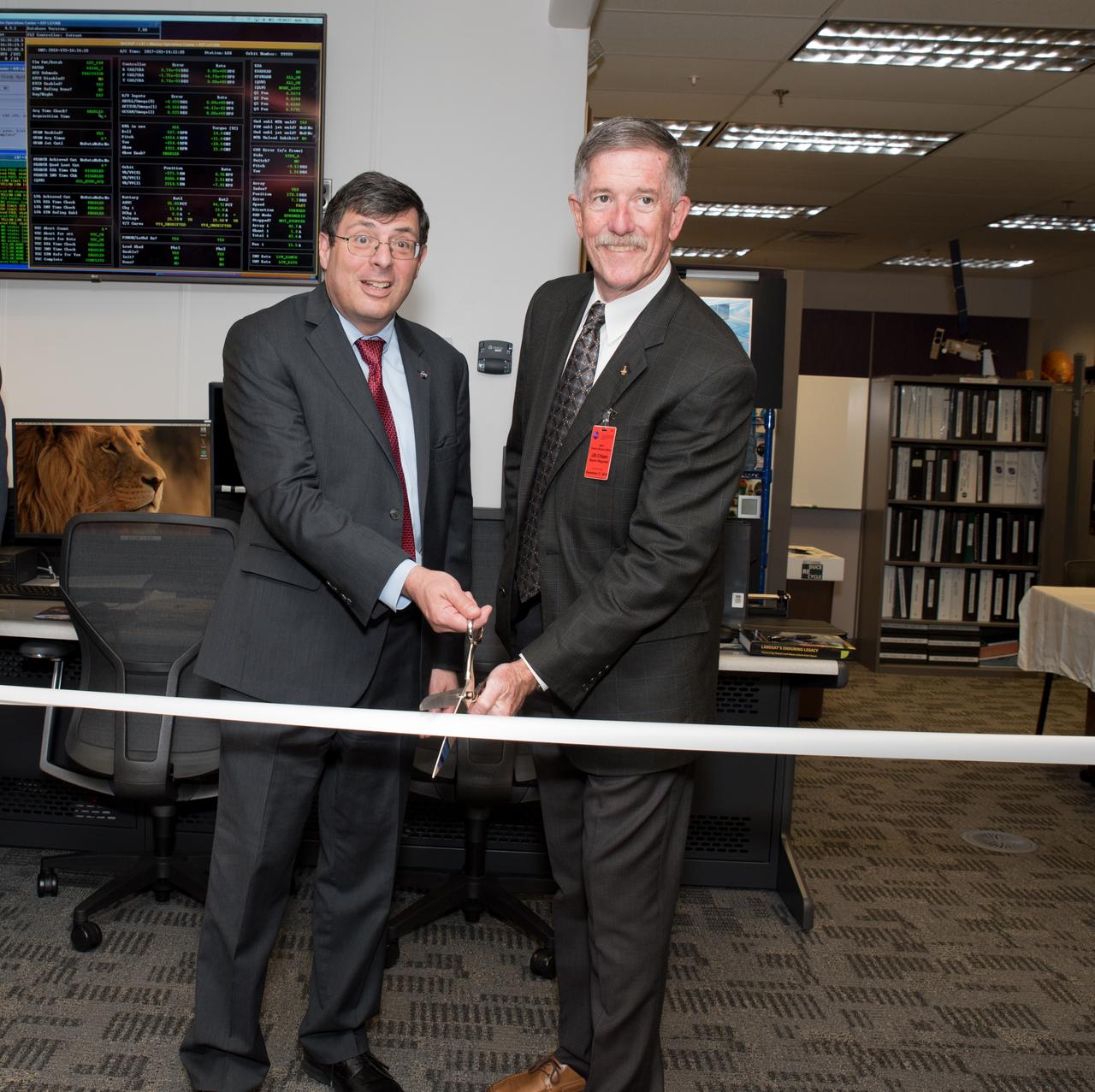

USGS visit to Goddard

USGS visit to Goddard

Artist illustration of the X-59 in flight over land (with cities and rural areas below). Satellite image from USGS/NASA Landsat.
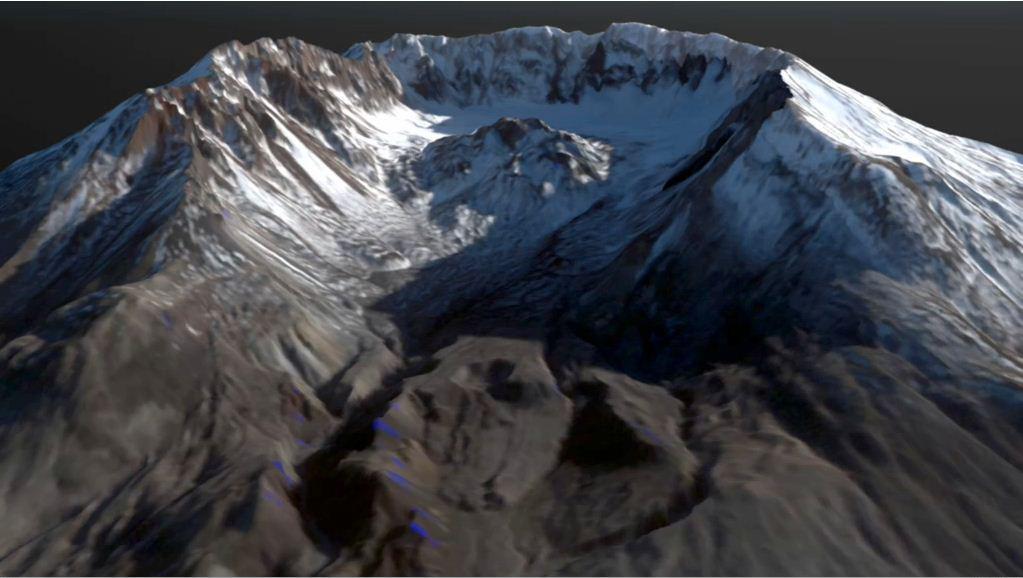
This frame from an animation depicts the growth of the lava dome at Mount St. Helens during the most recent period of activity. Lidar data courtesy USGS.
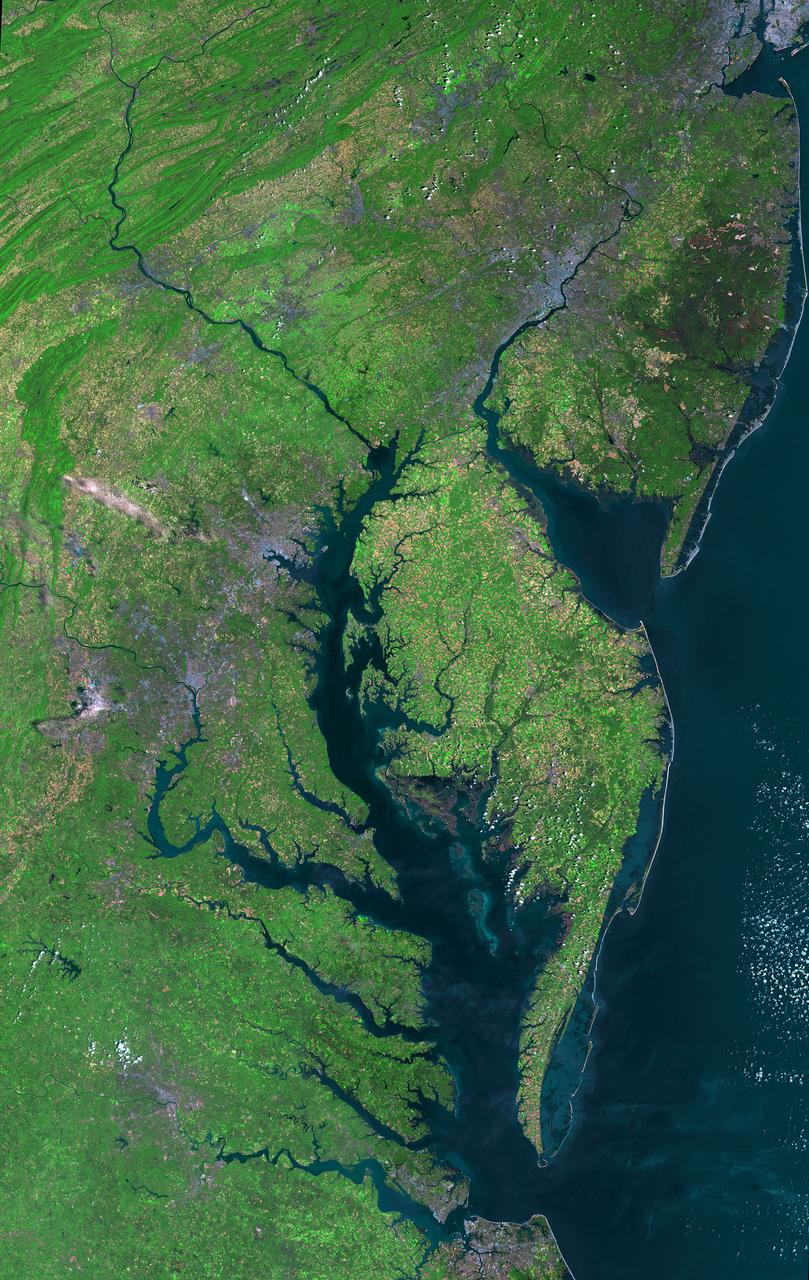

Aug 30, 2011 USGS has released a new mosaic of the Chesapeake Bay. Using six Landsat 5 images collected in July 2009 and 2011 a beautiful, seamless mosaic of the Chesapeake Bay region was created by the USGS Landsat team. The Washington D.C.-Baltimore-Philadelphia-New York City corridor can be clearly seen (look for silvery purple) as can the Chesapeake and Delaware Bays and the coastal Atlantic barrier islands from Fishermans Island, Virginia to Sandy Hook, New Jersey. To download the full high res go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/news/news-archive/news_0387.html" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/news/news-archive/news_0387.html</a> Credit: NASA/USGS/Landsat 5 <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dave Applegate, Director of the U.S. Geologic Survey (USGS), speaks before the ribbon cutting ceremony to open NASA’s Earth Information Center, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The Earth Information Center is new immersive experience that combines live data sets with cutting-edge data visualization and storytelling to allow visitors to see how our planet is changing. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
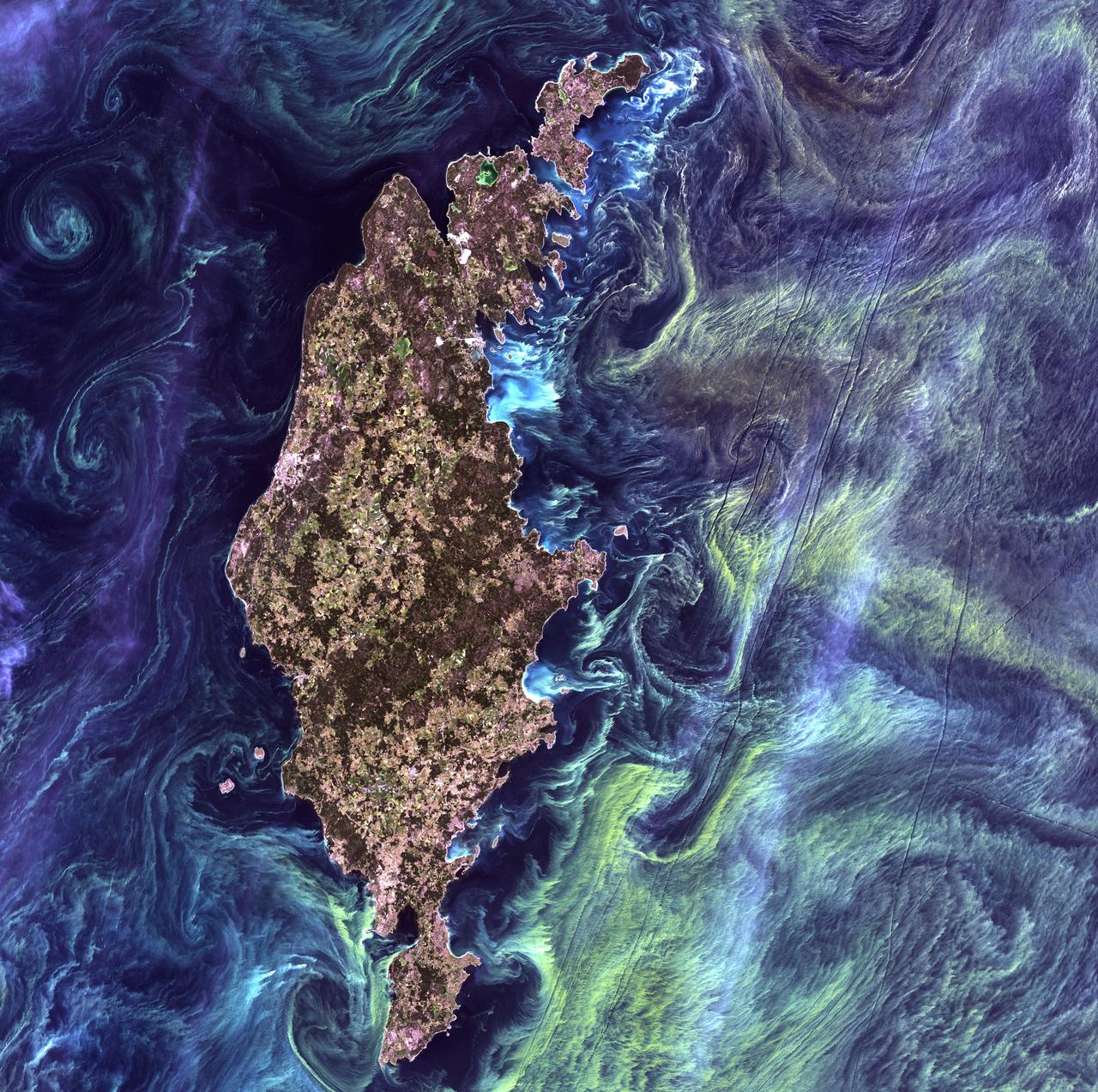
Van Gogh from Space - July 13th, 2005 Description: In the style of Van Gogh's painting "Starry Night," massive congregations of greenish phytoplankton swirl in the dark water around Gotland, a Swedish island in the Baltic Sea. Phytoplankton are microscopic marine plants that form the first link in nearly all ocean food chains. Population explosions, or blooms, of phytoplankton, like the one shown here, occur when deep currents bring nutrients up to sunlit surface waters, fueling the growth and reproduction of these tiny plants. Credit: USGS/NASA/Landsat 7 To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
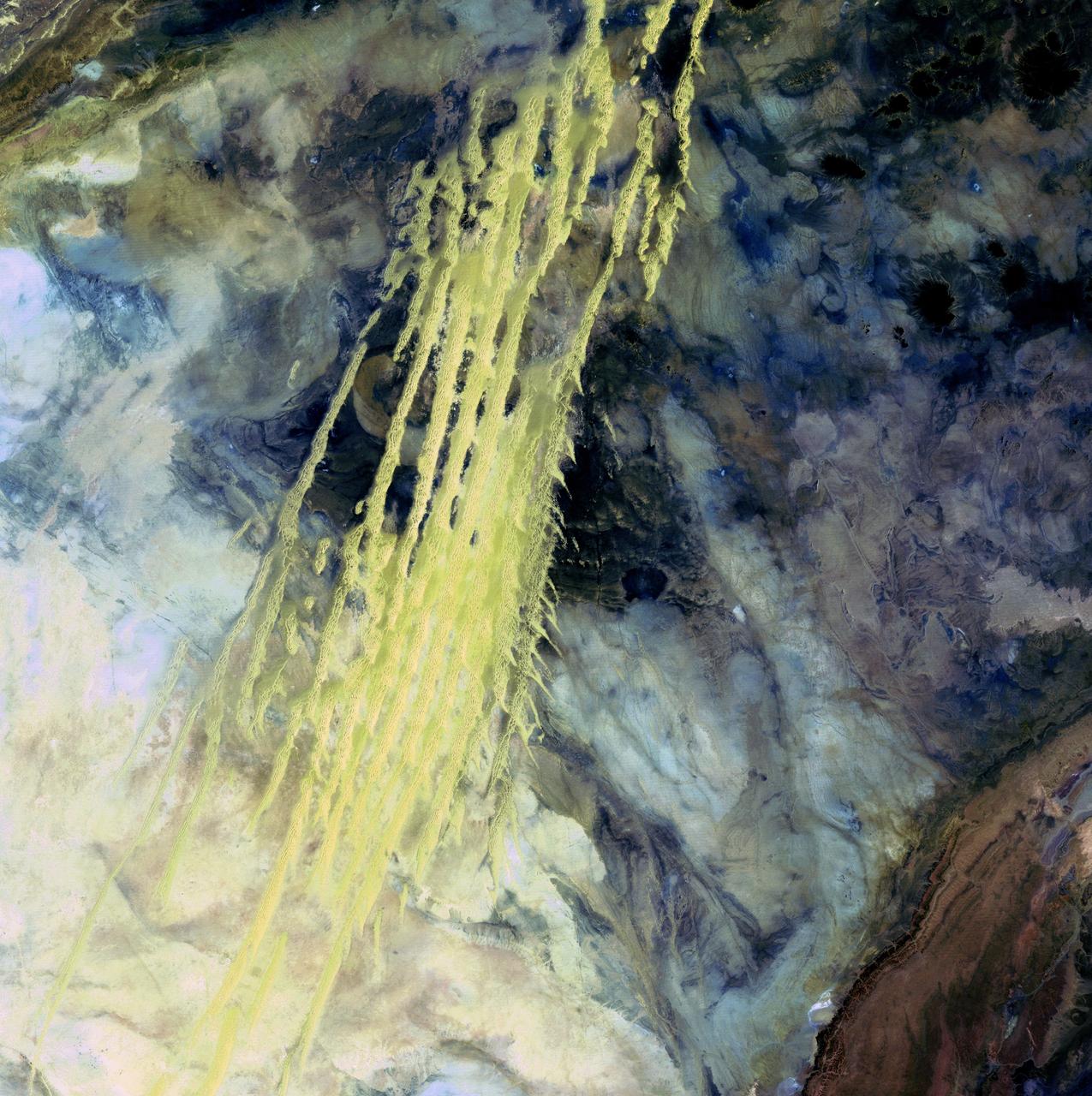

Algerian Abstract - April 8th, 1985 Description: What look like pale yellow paint streaks slashing through a mosaic of mottled colors are ridges of wind-blown sand that make up Erg Iguidi, an area of ever-shifting sand dunes extending from Algeria into Mauritania in northwestern Africa. Erg Iguidi is one of several Saharan ergs, or sand seas, where individual dunes often surpass 500 meters-nearly a third of a mile-in both width and height. Credit: USGS/NASA/Landsat 5 To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
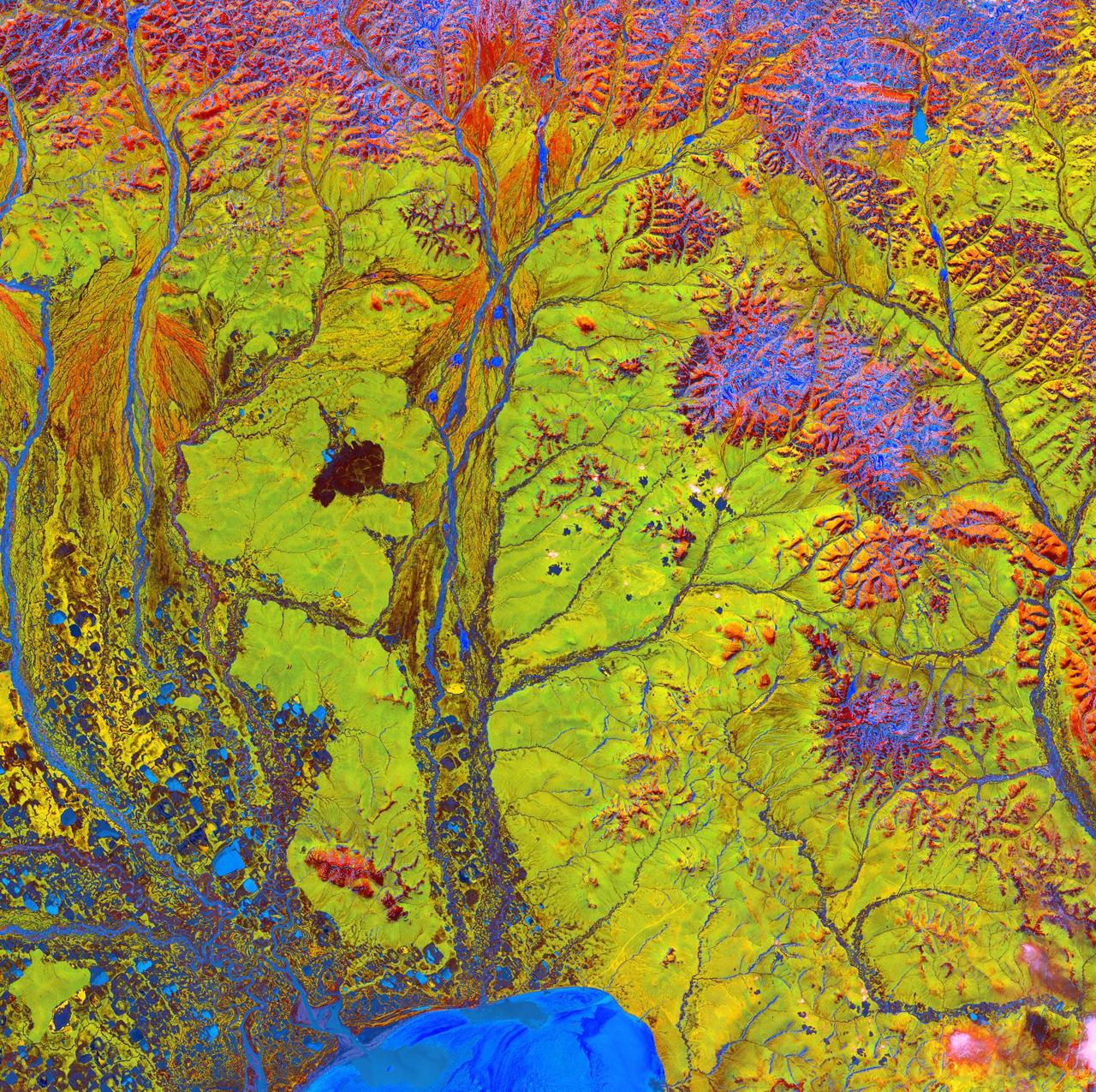
Siberian Ribbons - June 15th, 2005 Description: Vivid colors and bizarre shapes come together in an image that could be an imaginative illustration for a fantasy story. This labyrinth of exotic features is present along the edge of Russia's Chaunskaya Bay (vivid blue half circle) in northeastern Siberia. Two major rivers, the Chaun and Palyavaam, flow into the bay, which in turn opens into the Arctic Ocean. Ribbon lakes and bogs are present throughout the area, created by depressions left by receding glaciers. Credit: USGS/NASA/Landsat 5 To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

Meandering Mississippi - May 28th, 2003 Description: Small, blocky shapes of towns, fields, and pastures surround the graceful swirls and whorls of the Mississippi River. Countless oxbow lakes and cutoffs accompany the meandering river south of Memphis, Tennessee, on the border between Arkansas and Mississippi, USA. The "mighty Mississippi" is the largest river system in North America. Credit: USGS/NASA/Landsat 7 To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
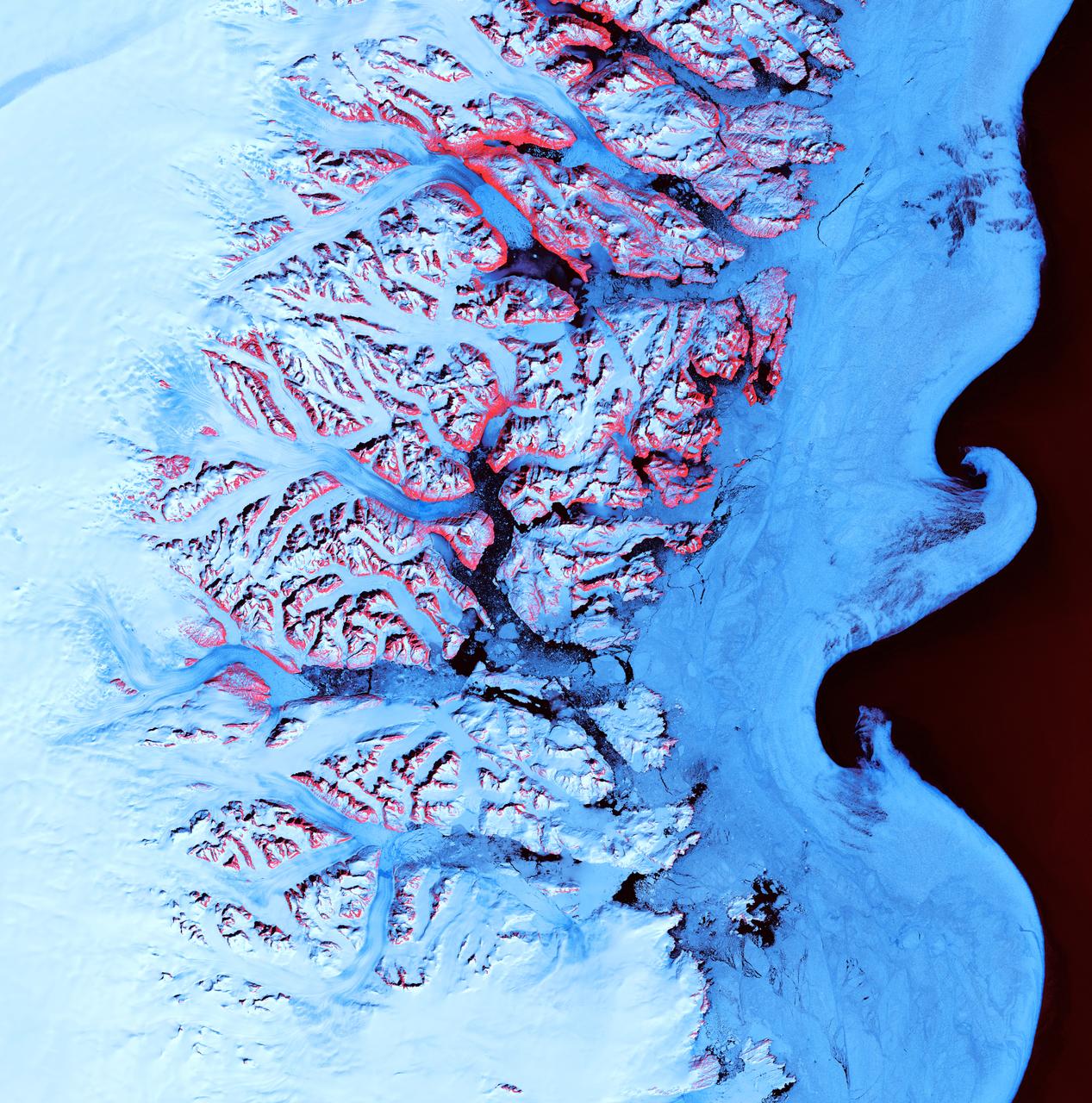

Ice Waves - May 21st, 2001 Description: Along the southeastern coast of Greenland, an intricate network of fjords funnels glacial ice to the Atlantic Ocean. During the summer melting season, newly calved icebergs join slabs of sea ice and older, weathered bergs in an offshore slurry that the southward-flowing East Greenland Current sometimes swirls into stunning shapes. Exposed rock of mountain peaks, tinted red in this image, hints at a hidden landscape. Credit: USGS/NASA/Landsat 7 To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
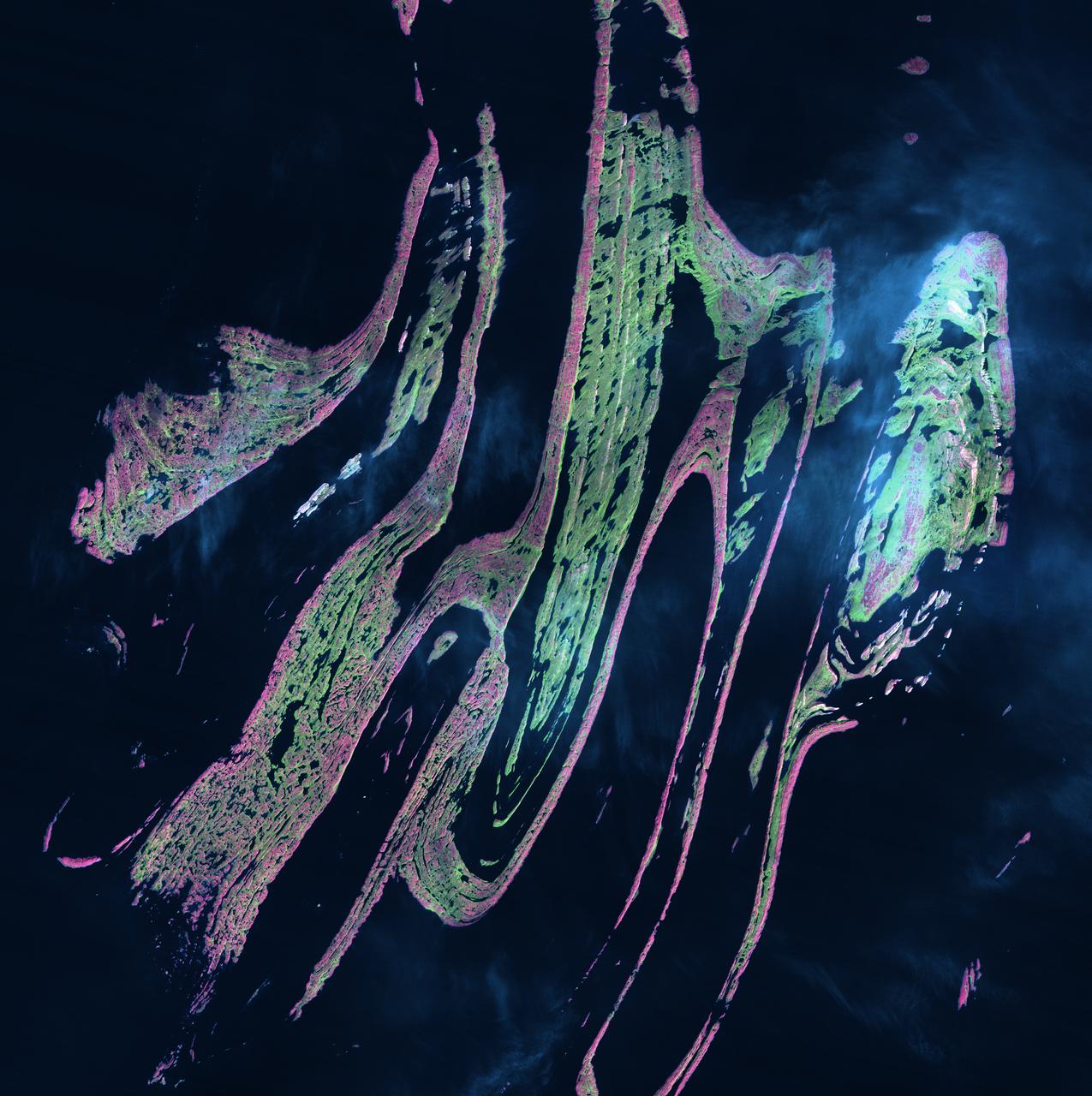
Belcher Islands - September 21st, 2001 Description: Like sweeping brushstrokes of pink and green, the Belcher Islands meander across the deep blue of Canada's Hudson Bay. The islands' only inhabitants live in the small town of Sanikiluaq, near the upper end of the middle island. Despite the green hues in this image, these rocky islands are too cold to sustain more than a smattering of low-growing vegetation. Credit: USGS/NASA/Landsat 5 To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
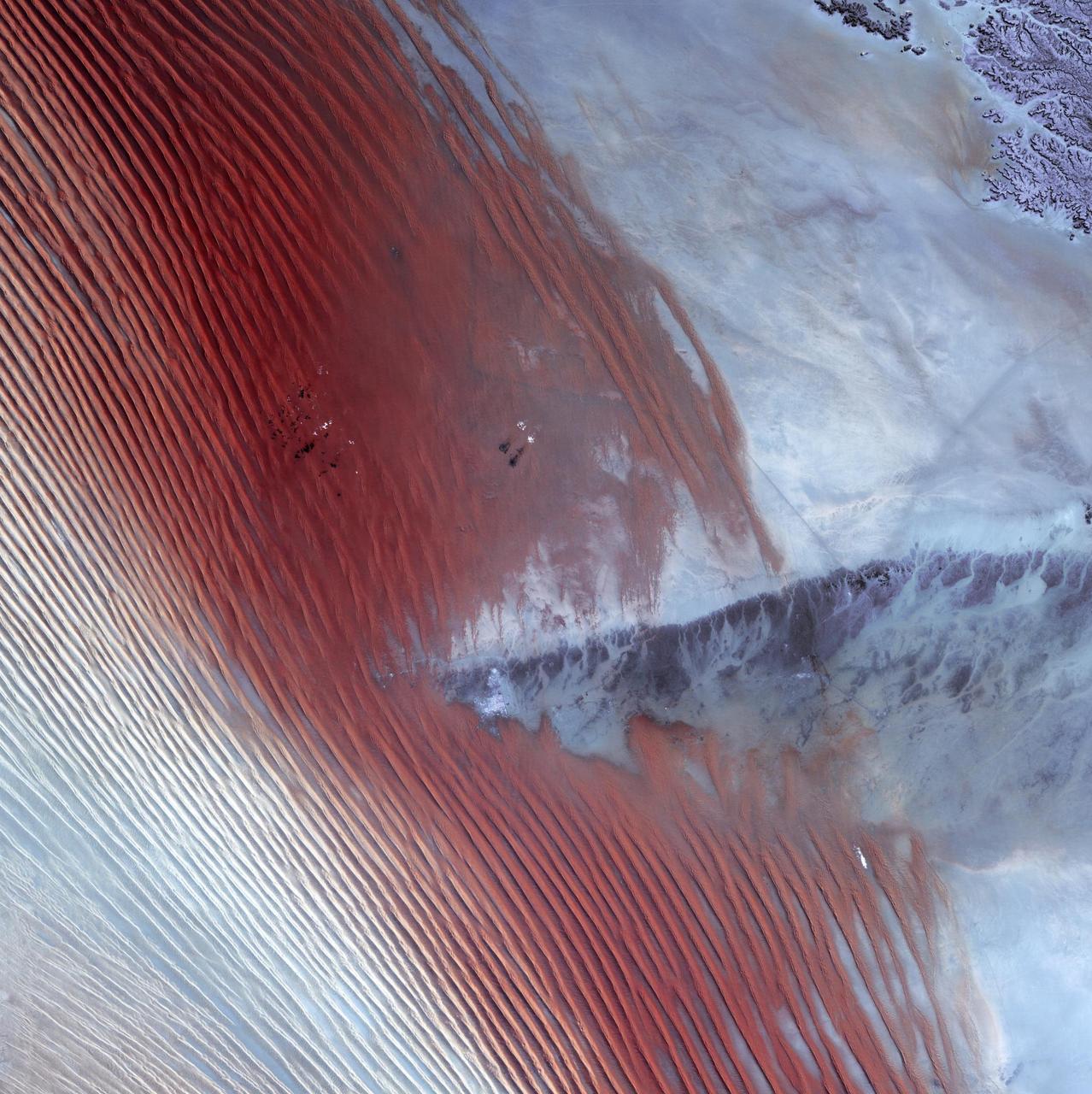
Empty Quarter - February 1st, 20003 Description: White pinpricks of cloud cast ebony shadows on the Rub' al Khali, or Empty Quarter, near the border between Saudi Arabia and Yemen. The lines of wind-sculpted sand are characteristic of immense sand deserts, or sand seas, and the Rub' al Khali is the largest desert of this type in the world. A highland ridge is just high enough to disturb the flow of the lines. In the center of that interruption lies the Saudi Arabian town of Sharurah. Credit: USGS/NASA/Landsat 7 To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
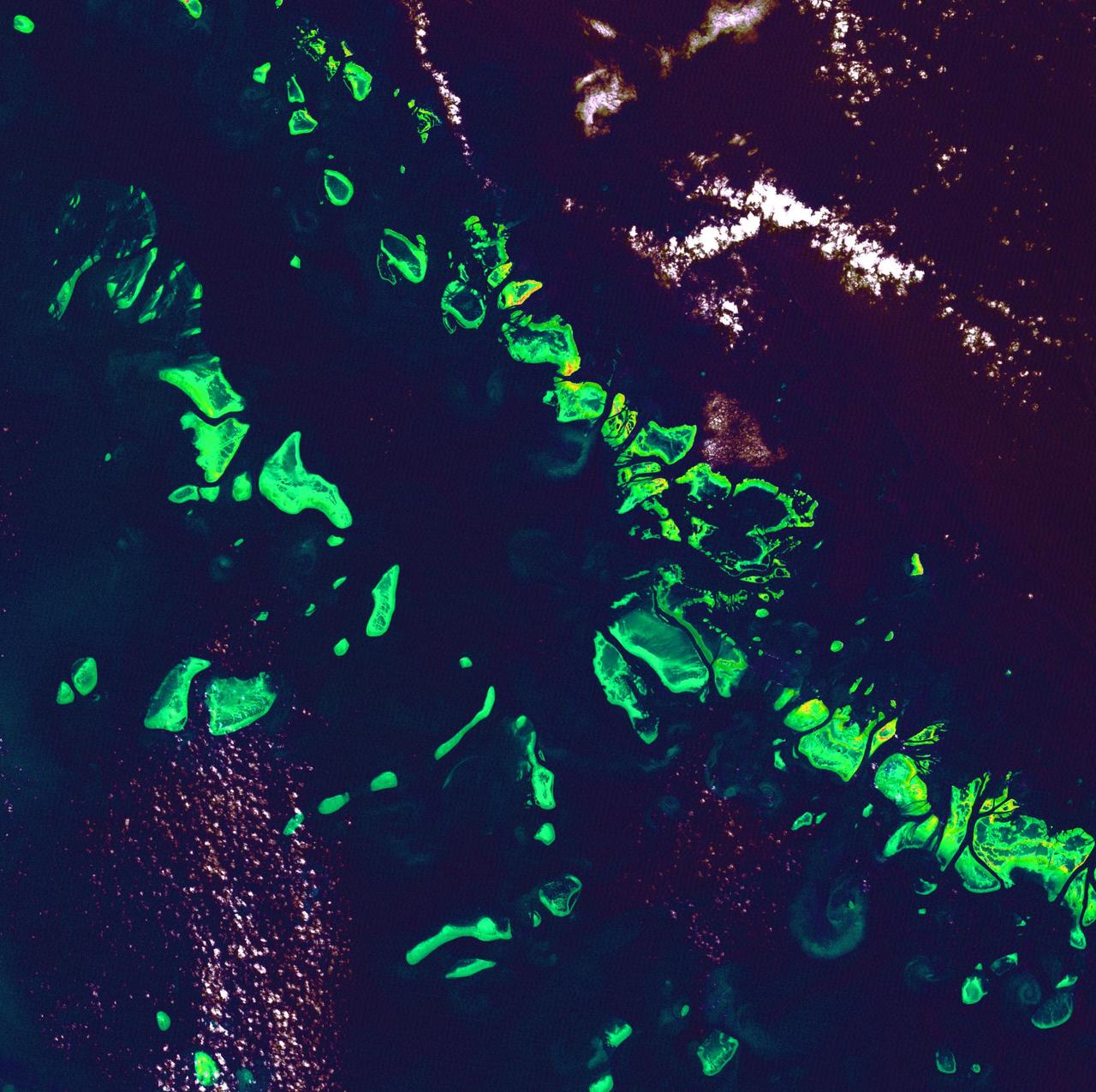

Great Barrier Reef - August 8th, 1999 Description: What might be mistaken for dinosaur bones being unearthed at a paleontological dig are some of the individual reefs that make up the Great Barrier Reef, the world's largest tropical coral reef system. The reef stretches more than 2,000 kilometers (1,240 miles) along the coast of Queensland, Australia. It supports astoundingly complex and diverse communities of marine life and is the largest structure on the planet built by living organisms. Credit: USGS/NASA/Landsat 7 To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
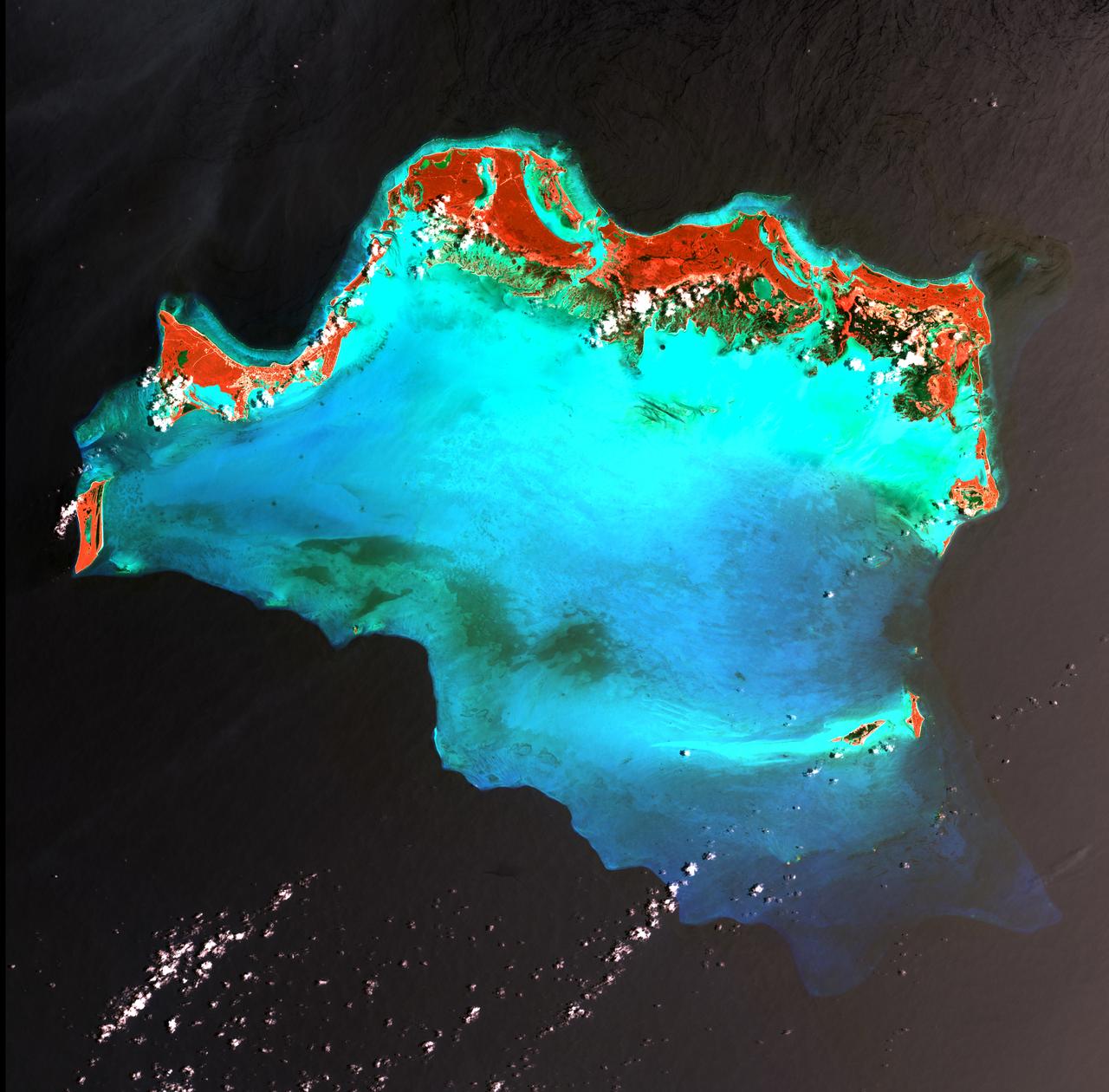

Caribbean Luxury - April 24th, 2003 Description: The Caicos Islands (pronounced KAY-kohss) in the northern Caribbean are a popular tourist attraction, renowned for their beautiful beaches, clear waters, scuba diving, and luxury resorts. The islands lie primarily along the northern perimeter of the submerged Caicos Bank (turquoise), a shallow limestone platform formed of sand, algae, and coral reefs covering 6,140 square kilometers (2,370 square miles). Credit: USGS/NASA/Landsat 7 To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
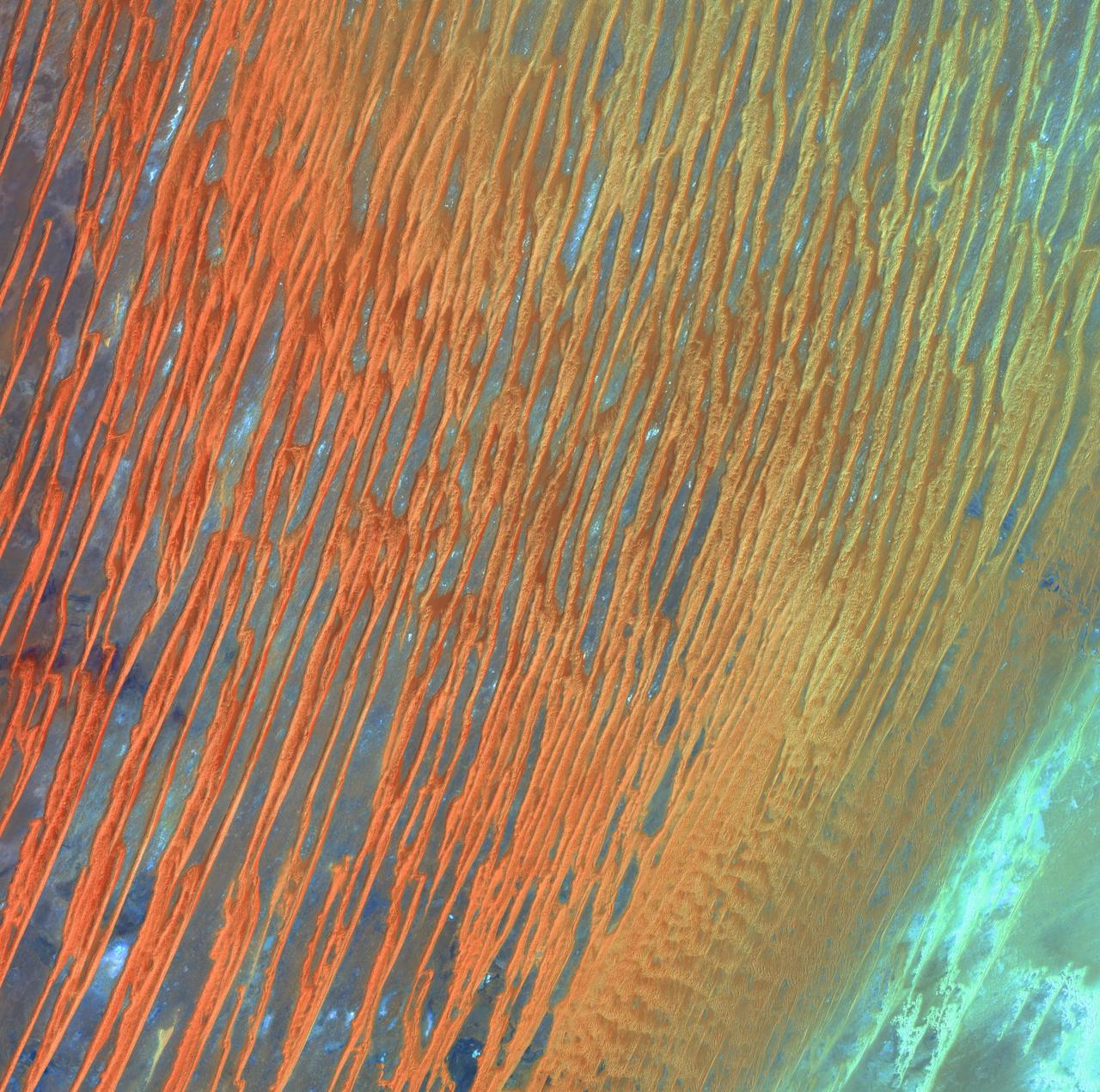
Desert Patterns - April 13th, 2003 Description: Seen through the "eyes" of a satellite sensor, ribbons of Saharan sand dunes seem to glow in sunset colors. These patterned stripes are part of Erg Chech, a desolate sand sea in southwestern Algeria, Africa, where the prevailing winds create an endlessly shifting collage of large, linear sand dunes. The term "erg" is derived from an Arabic word for a field of sand dunes. Credit: USGS/NASA/Landsat 7 To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
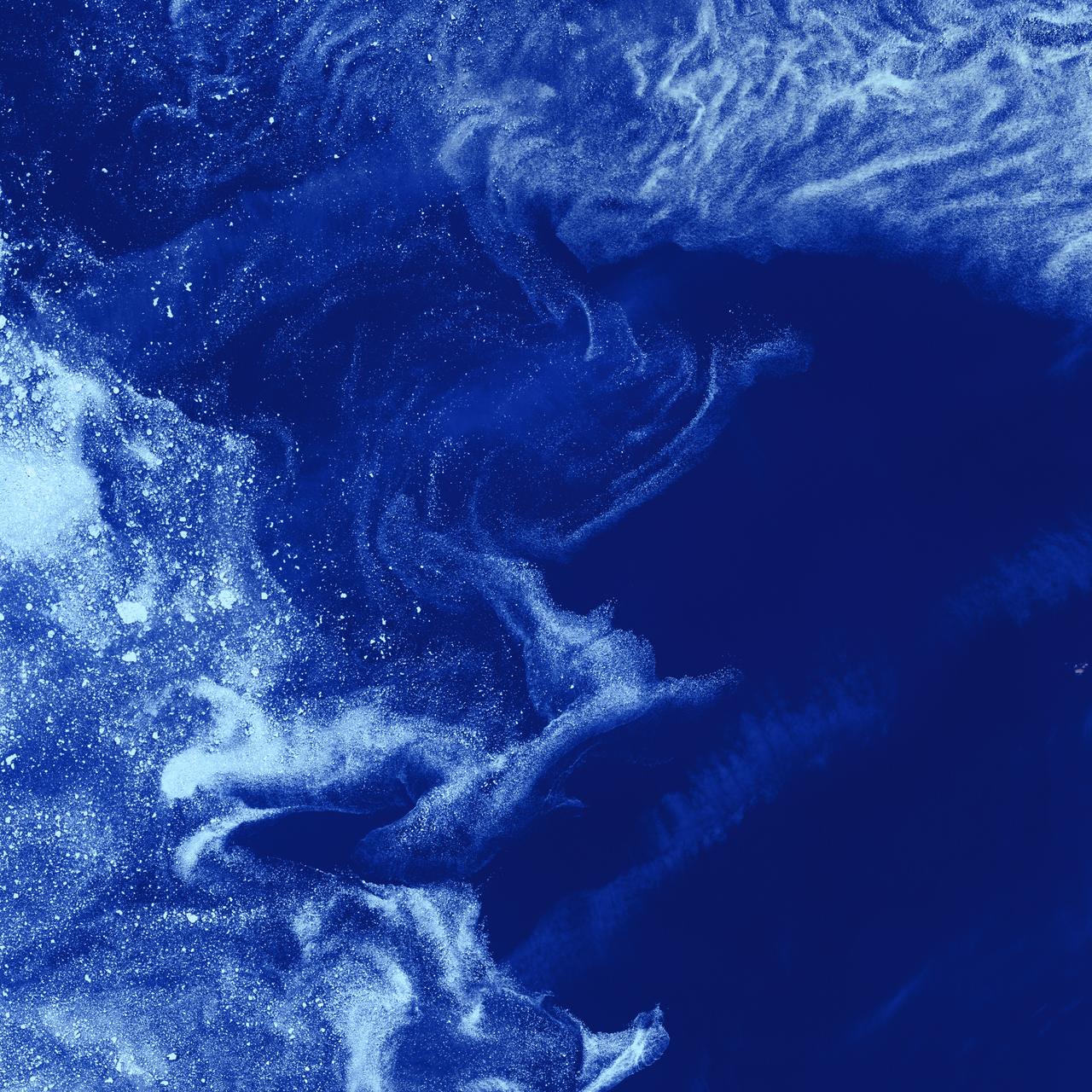
Ice Stars - August 4th, 2002 Description: Like distant galaxies amid clouds of interstellar dust, chunks of sea ice drift through graceful swirls of grease ice in the frigid waters of Foxe Basin near Baffin Island in the Canadian Arctic. Sea ice often begins as grease ice, a soupy slick of tiny ice crystals on the ocean's surface. As the temperature drops, grease ice thickens and coalesces into slabs of more solid ice. Credit: USGS/NASA/Landsat 7 To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
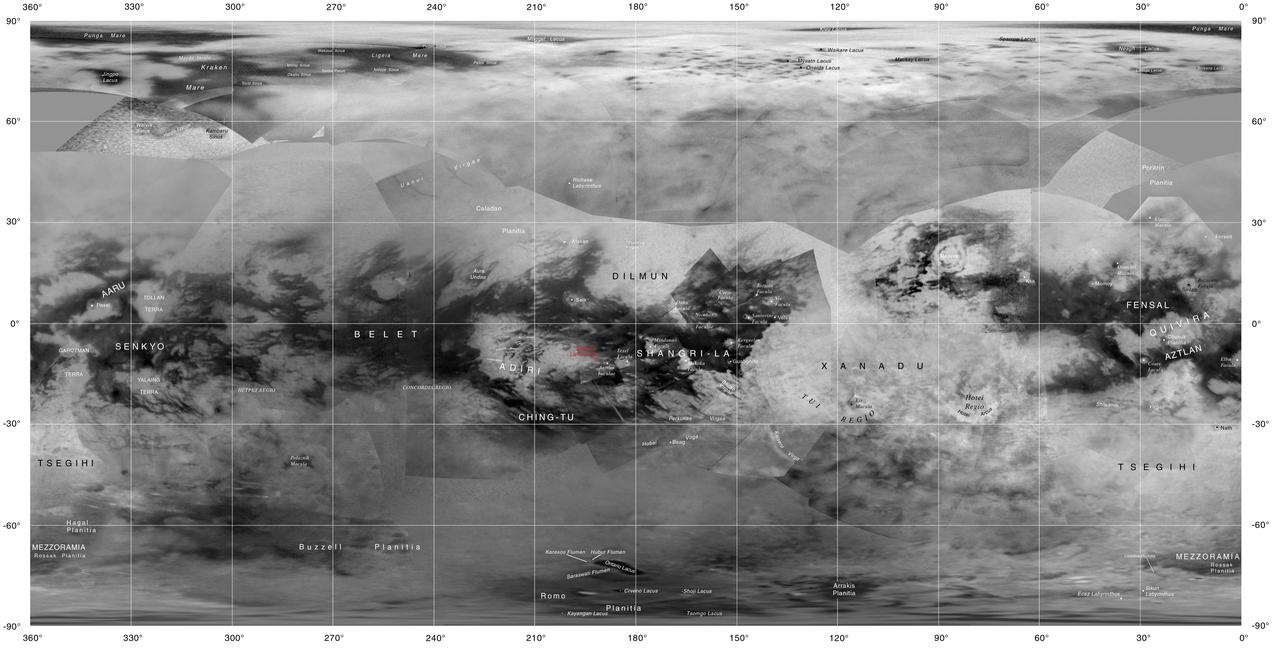
This map of Titan shows the names of many (but not all) features on the Saturnian moon that have been approved by the International Astronomical Union. This map was produced by the USGS Astrogeology Science Center for the International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20713
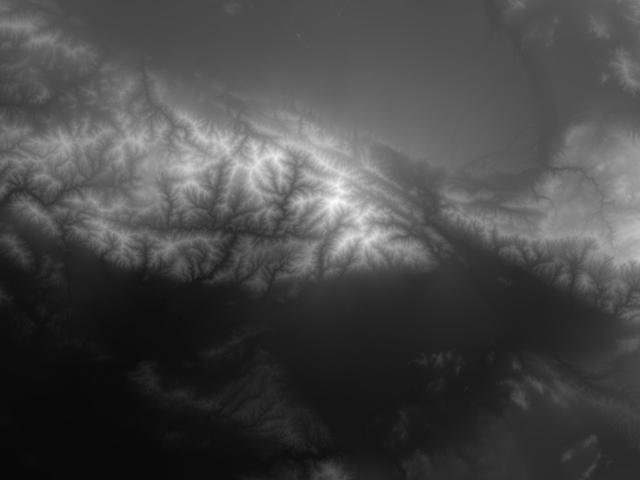
JSC2000E01553 (January 2000) --- This USGS elevation model showing increasing elevation as increasing brightness is included here for comparison purposes with the high-resolution topographic elevation map image in E01554. Both images depict the San Bernadino and San Gabriel Mountains in California, north of Los Angeles.
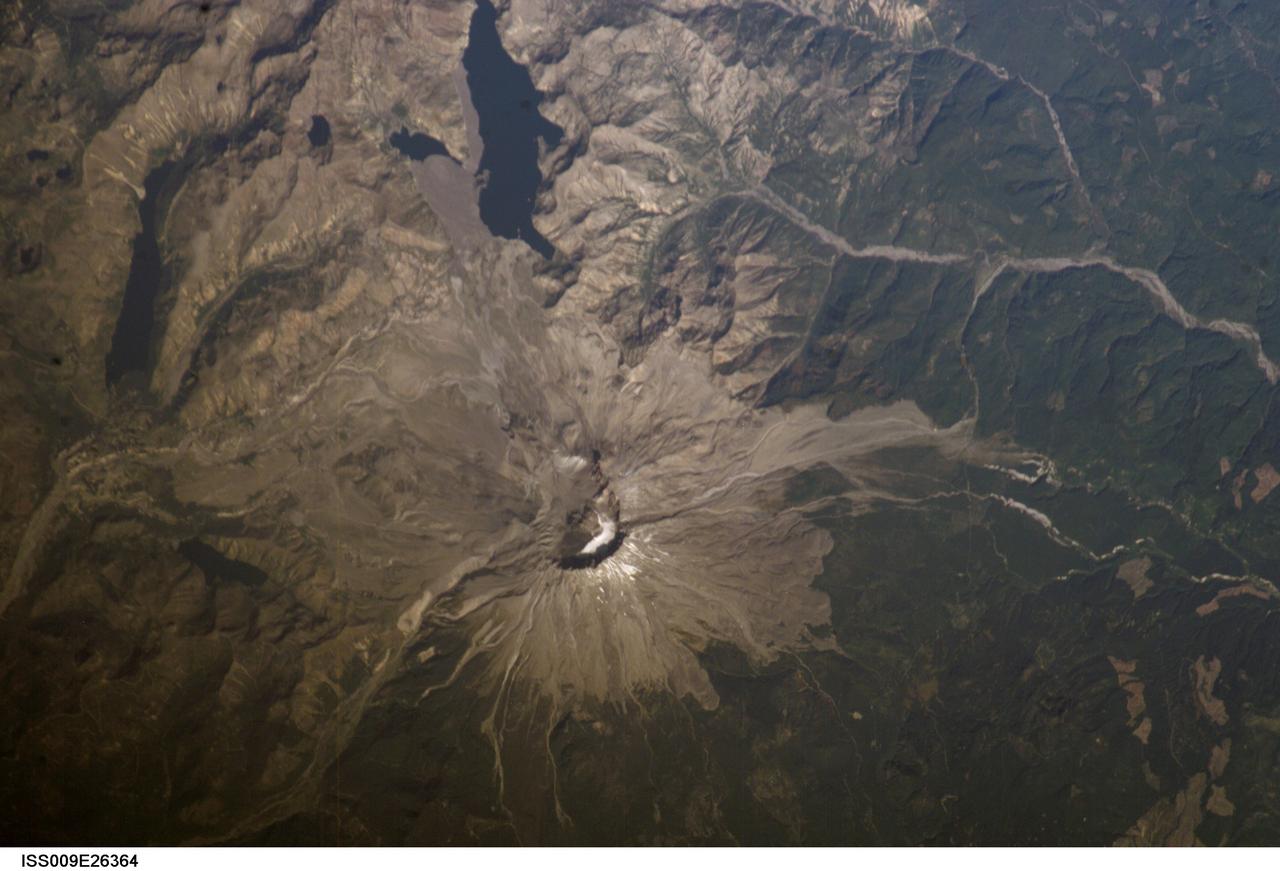
ISS009-E-26364 (1 October 2004) --- Mount Saint Helens, Washington, is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 9 crewmember on the International Space Station (ISS). The USGS has been monitoring Mount Saint Helens closely since last Thursday, when the volcano began to belch steam and swarms of tiny earthquakes were first recorded.
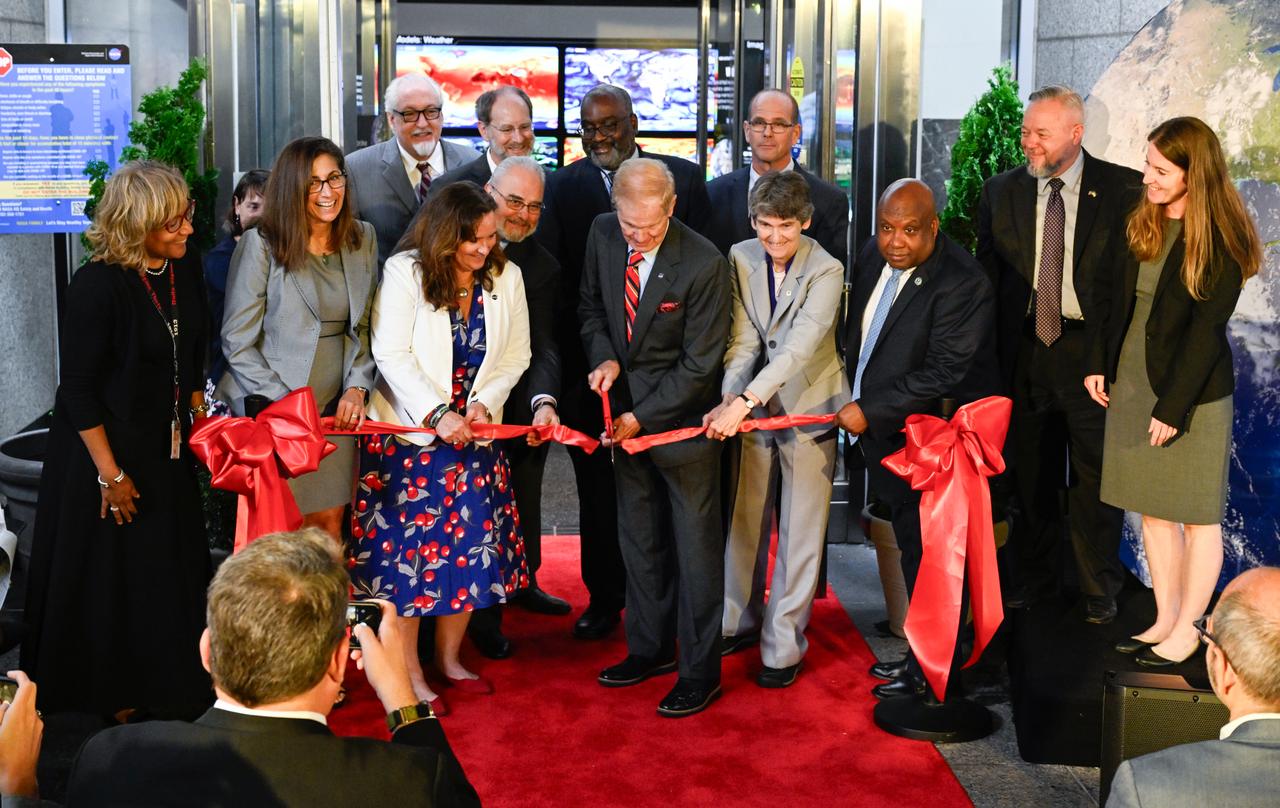

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, center, cuts the ribbon to open NASA’s Earth Information Center alongside agency leadership and leadership from NOAA, USGS, USDA, USAID, EPA, and FEMA, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The Earth Information Center is new immersive experience that combines live data sets with cutting-edge data visualization and storytelling to allow visitors to see how our planet is changing. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
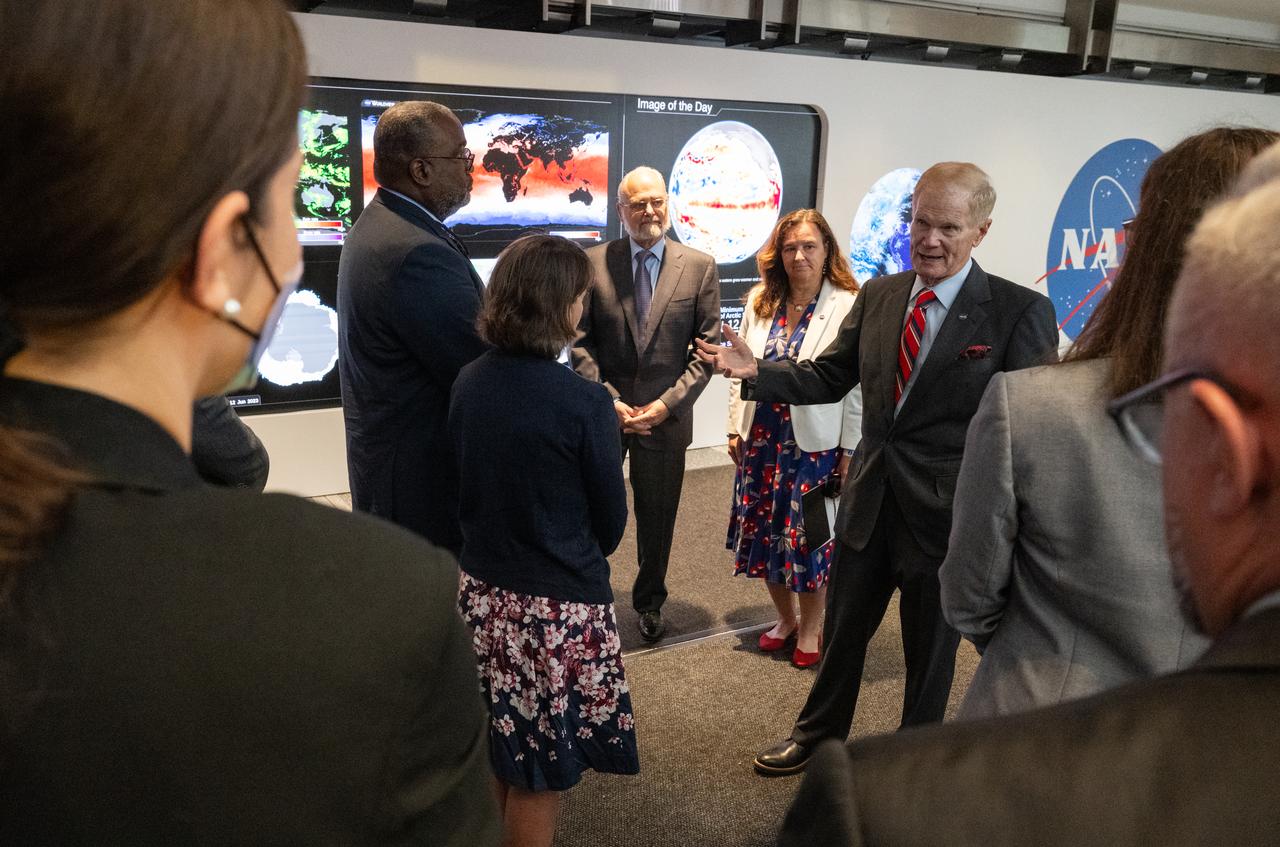

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson speaks to leadership from NOAA, USGS, USDA, USAID, EPA, and FEMA at the opening of NASA’s Earth Information Center, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The Earth Information Center is new immersive experience that combines live data sets with cutting-edge data visualization and storytelling to allow visitors to see how our planet is changing. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
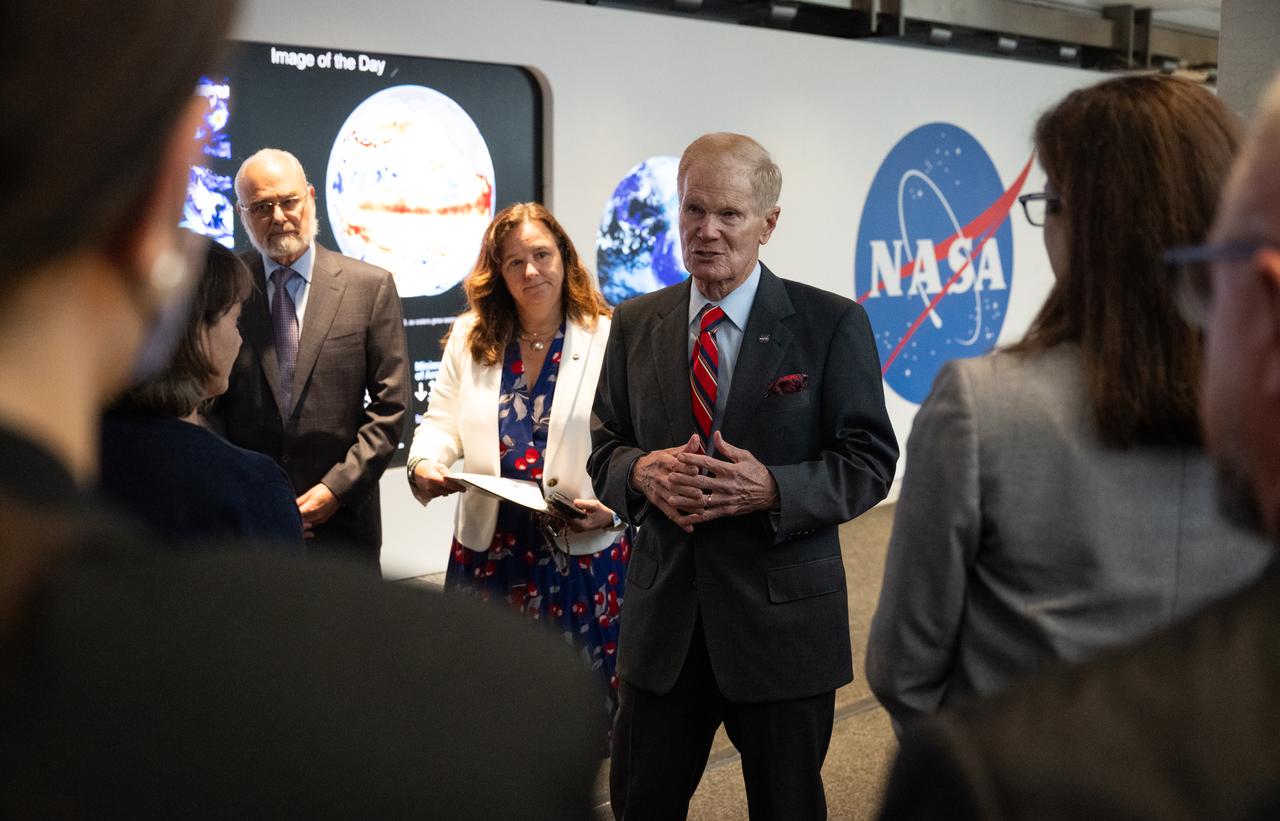

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson speaks to leadership from NOAA, USGS, USDA, USAID, EPA, and FEMA at the opening of NASA’s Earth Information Center, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The Earth Information Center is new immersive experience that combines live data sets with cutting-edge data visualization and storytelling to allow visitors to see how our planet is changing. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
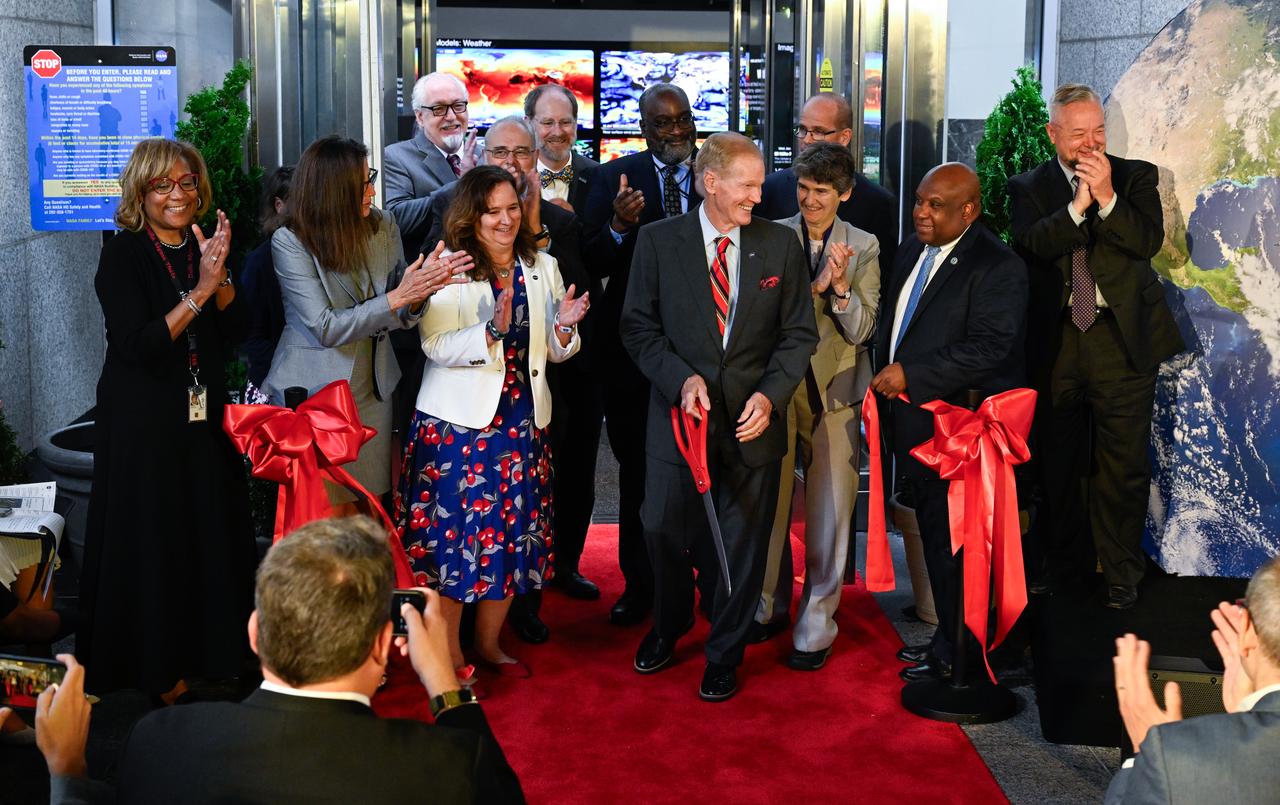

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, center, cuts the ribbon to open NASA’s Earth Information Center alongside agency leadership and leadership from NOAA, USGS, USDA, USAID, EPA, and FEMA, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The Earth Information Center is new immersive experience that combines live data sets with cutting-edge data visualization and storytelling to allow visitors to see how our planet is changing. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
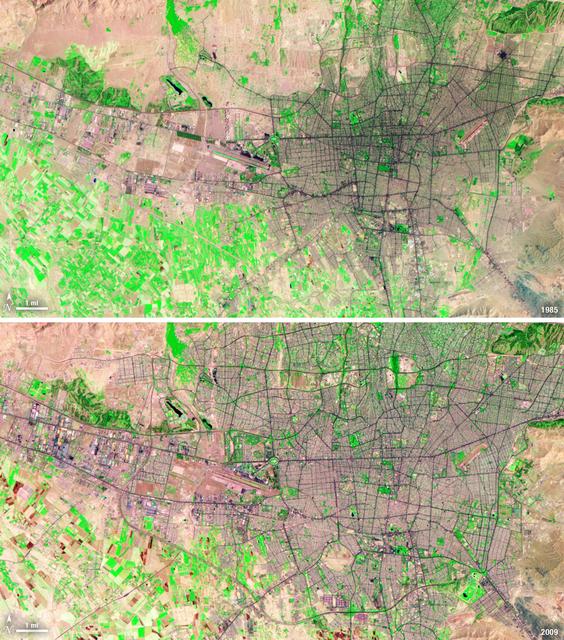
Between 1985 and 2009, the population of Tehran, Iran, grew from six million to just over seven million. The city's growth was spurred largely by migration from other parts of the country. In addition to being the hub of government and associated public sector jobs, Tehran houses more than half of Iran's industry. Landsat 5 acquired these false-color images of Tehran on August 2, 1985, and July 19, 2009. The city is a web of dark purple lines, vegetation is green and bare ground is pink and tan. The images were created using both infrared and visible light (band combination 7, 4, and 2) to distinguish urban areas from the surrounding desert. ---- NASA and the U.S. Department of the Interior through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) jointly manage Landsat, and the USGS preserves a 40-year archive of Landsat images that is freely available over the Internet. The next Landsat satellite, now known as the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) and later to be called Landsat 8, is scheduled for launch in 2013. In honor of Landsat’s 40th anniversary in July 2012, the USGS released the LandsatLook viewer – a quick, simple way to go forward and backward in time, pulling images of anywhere in the world out of the Landsat archive. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
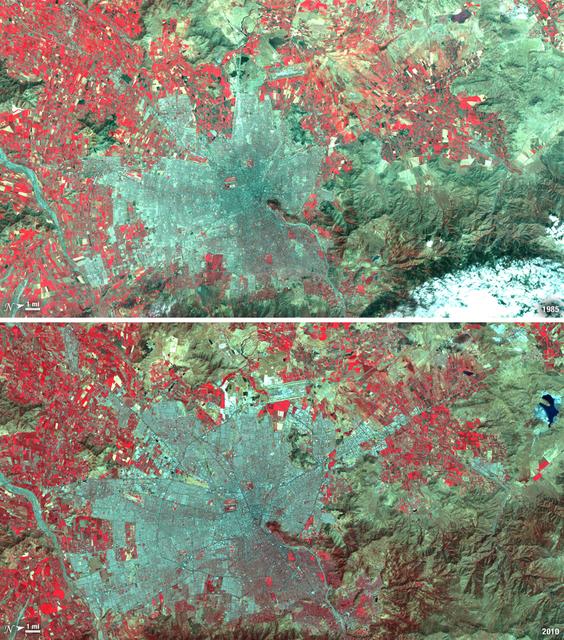

Santiago, Chile, ranks among the world's fastest growing cities. Chile is South America's fifth largest economy with strong export and tourism markets. More than a third of Chile's population lives in Santiago as of 2009. Taken on January 9, 1985, and January 30, 2010, this pair of images from the Landsat 5 satellite illustrates the city's steady growth. The images were made with infrared and visible light (Landsat bands 4, 3, and 2) so that plant-covered land is red. Bare or sparsely vegetated land is tan, and the city is dark silver. In the fifteen years that elapsed between 1985 and 2010, the city expanded away from the Andes Mountains along spoke-like lines, which are major roads. ---- NASA and the U.S. Department of the Interior through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) jointly manage Landsat, and the USGS preserves a 40-year archive of Landsat images that is freely available over the Internet. The next Landsat satellite, now known as the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) and later to be called Landsat 8, is scheduled for launch in 2013. In honor of Landsat’s 40th anniversary in July 2012, the USGS released the LandsatLook viewer – a quick, simple way to go forward and backward in time, pulling images of anywhere in the world out of the Landsat archive. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
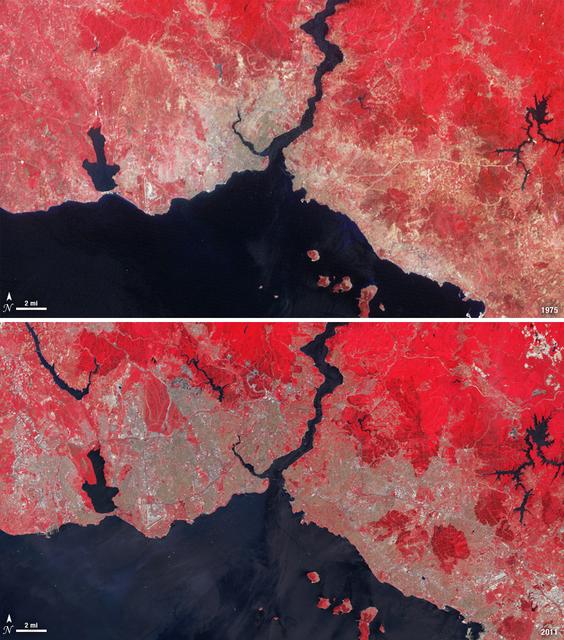

Istanbul has been a bustling trade city for thousands of years. In this 1975 image, taken by Landsat, the city centers on the Golden Horn the estuary that flows into the Bosporus Straight at the center of the scene. Shown in false color, vegetation is red, urban areas are gray, and water appears black. A bridge built in 1973 to connect the Asian and European sides of Istanbul is barely visible. By 2011, Istanbul's population had exploded from 2 to 13 million people, and the city has gone through a dramatic expansion. This Landsat 5 image shows densely packed urban areas stretching along the Sea of Marmara and up the Bosporus Straight where a second bridge built in 1988 now crosses the water. ---- NASA and the U.S. Department of the Interior through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) jointly manage Landsat, and the USGS preserves a 40-year archive of Landsat images that is freely available over the Internet. The next Landsat satellite, now known as the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) and later to be called Landsat 8, is scheduled for launch in 2013. In honor of Landsat’s 40th anniversary in July 2012, the USGS released the LandsatLook viewer – a quick, simple way to go forward and backward in time, pulling images of anywhere in the world out of the Landsat archive. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Over the last 25 years, Chandler, Arizona has traded its grid of fields for a grid of streets. Founded in 1912 on cotton, grains, alfalfa, and ostrich farms, brown and green irrigated fields still dominate the region southeast of Phoenix in this 1985 natural color image taken by Landsat 5. By 2011, the blue gray city streets in this Landsat 5 image have taken over. Chandler's economy has shifted from agriculture to manufacturing and electronics, and its population boomed from 30,000 people in 1980 to 236,000 in 2010. ---- Survey (USGS) jointly manage Landsat, and the USGS preserves a 40-year archive of Landsat images that is freely available over the Internet. The next Landsat satellite, now known as the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) and later to be called Landsat 8, is scheduled for launch in 2013. In honor of Landsat’s 40th anniversary in July 2012, the USGS released the LandsatLook viewer – a quick, simple way to go forward and backward in time, pulling images of anywhere in the world out of the Landsat archive. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
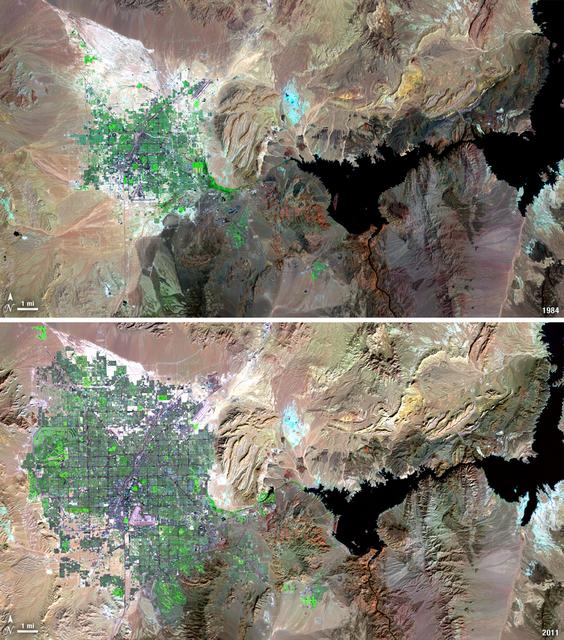
Over the years of the Landsat program, the desert city of Las Vegas has gone through a massive growth spurt. The outward expansion of the city over the last quarter of a century is shown here with two false-color Landsat 5 images (August 3, 1984, and November 2, 2011). The dark purple grid of city streets and the green of irrigated vegetation grow out in every direction into the surrounding desert. These images were created using reflected light from the shortwave infrared, near-infrared, and green portions of the electromagnetic spectrum (Landsat 5 TM bands 7,4,2). ---- NASA and the U.S. Department of the Interior through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) jointly manage Landsat, and the USGS preserves a 40-year archive of Landsat images that is freely available over the Internet. The next Landsat satellite, now known as the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) and later to be called Landsat 8, is scheduled for launch in 2013. In honor of Landsat’s 40th anniversary in July 2012, the USGS released the LandsatLook viewer – a quick, simple way to go forward and backward in time, pulling images of anywhere in the world out of the Landsat archive. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
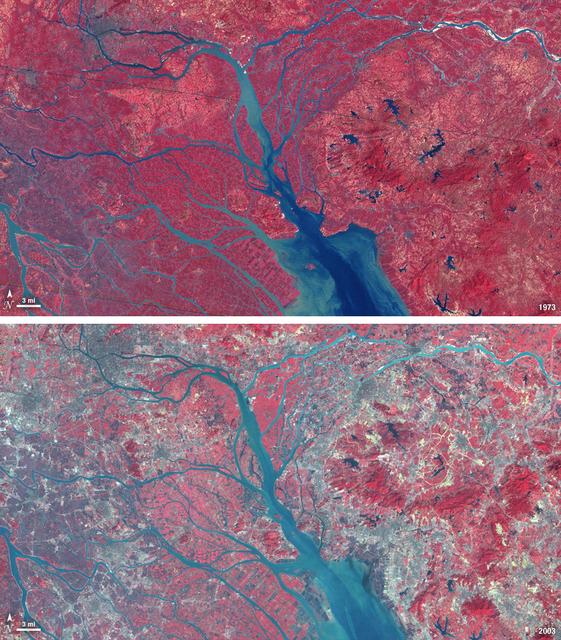

In 1979, China established two special economic zones around the Pearl River Delta, north of Hong Kong. This image, taken by Landsat 3 on October 19, 1973, shows that the region was rural when the zone was established. Plant-covered land, which is red in this false-color image, dominates the scene. Square grids are agriculture. By January 10, 2003, when Landsat 7 took this image, the Pearl River Delta was a densely populated urban corridor with several large cities. The urban areas are gray in this image. The region is a major manufacturing center with an economy the size of Taiwan’s. As of 2010, the Pearl River Economic Zone had a population of 36 million people. ---- NASA and the U.S. Department of the Interior through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) jointly manage Landsat, and the USGS preserves a 40-year archive of Landsat images that is freely available over the Internet. The next Landsat satellite, now known as the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) and later to be called Landsat 8, is scheduled for launch in 2013. In honor of Landsat’s 40th anniversary in July 2012, the USGS released the LandsatLook viewer – a quick, simple way to go forward and backward in time, pulling images of anywhere in the world out of the Landsat archive. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Tylar Greene, NASA Communications, moderates a mission and science briefing for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2021. Virtual participants (not shown) are Jeff Masek, Landsat 9 project scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center; Chris Crawford, Landsat 9 project scientist at USGS; Inbal Becker-Reshef, director of NASA’s Harvest food security and agriculture program; Del Jenstrom, Landsat 9 project manager at Goddard; Brian Sauer, Landsat 9 project manager at USGS; Sabrina Chapman, manager, system engineering, Northrop Grumman Space Systems; and Sarah Lipscy, OLI-2 senior engineer, Ball Aerospace & Technologies. Landsat 9 is scheduled to launch at 2:11 p.m. EDT (11:11 a.m. PDT) on Monday, Sept. 27, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg. The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests.

Tylar Greene, NASA Communications, moderates a mission and science briefing for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2021. Virtual participants (not shown) are Jeff Masek, Landsat 9 project scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center; Chris Crawford, Landsat 9 project scientist at USGS; Inbal Becker-Reshef, director of NASA’s Harvest food security and agriculture program; Del Jenstrom, Landsat 9 project manager at Goddard; Brian Sauer, Landsat 9 project manager at USGS; Sabrina Chapman, manager, system engineering, Northrop Grumman Space Systems; and Sarah Lipscy, OLI-2 senior engineer, Ball Aerospace & Technologies. Landsat 9 is scheduled to launch at 2:11 p.m. EDT (11:11 a.m. PDT) on Monday, Sept. 27, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg. The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests.
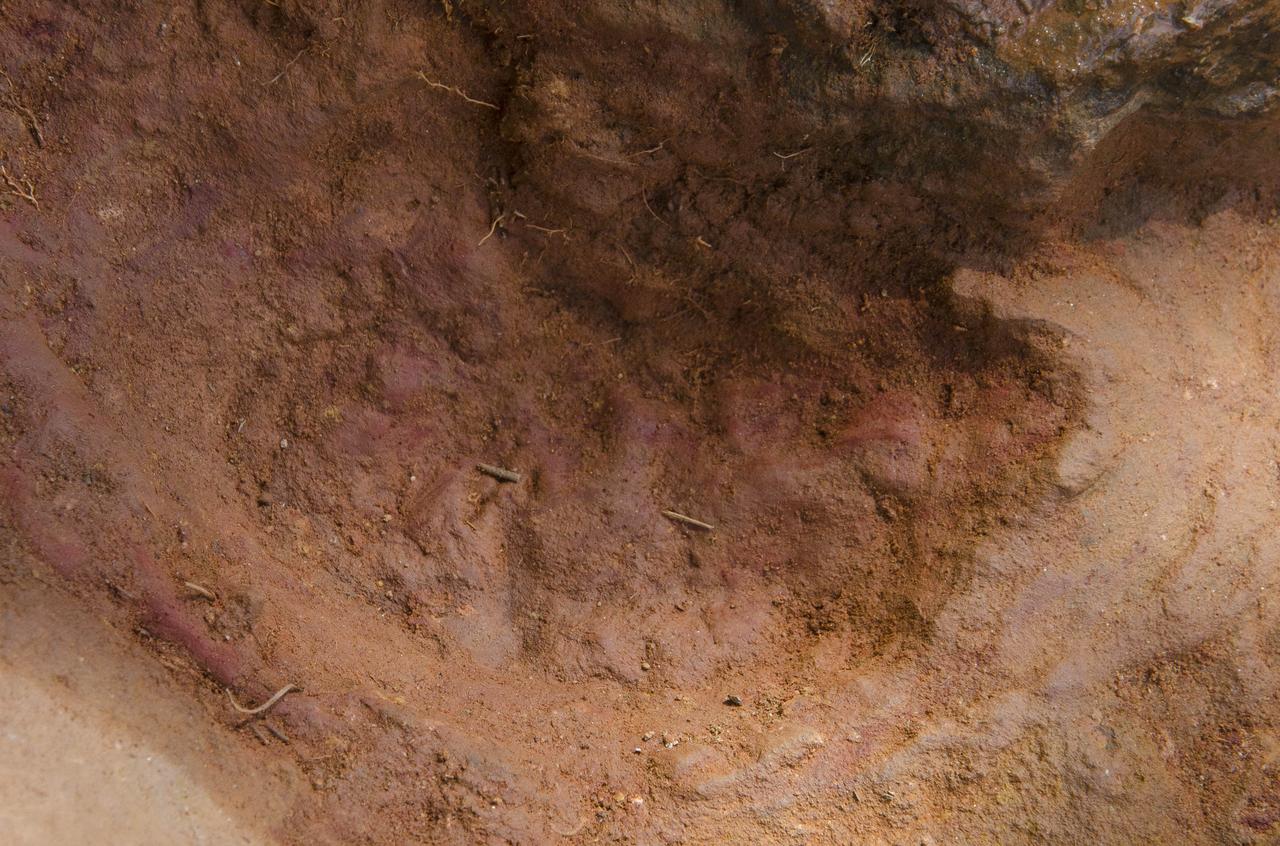

Not one, but two nodosaurs passed through the Goddard campus 110 to 112 million years ago, a USGS paleontologist confirmed. Pictured here the second track, overlapping the first, looks to be a young version of the same creature, perhaps following and sniffing along after, said Rob Weems, emeritus paleontologist and stratigrapher with the USGS. “It’s definitely a track.” To read more go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
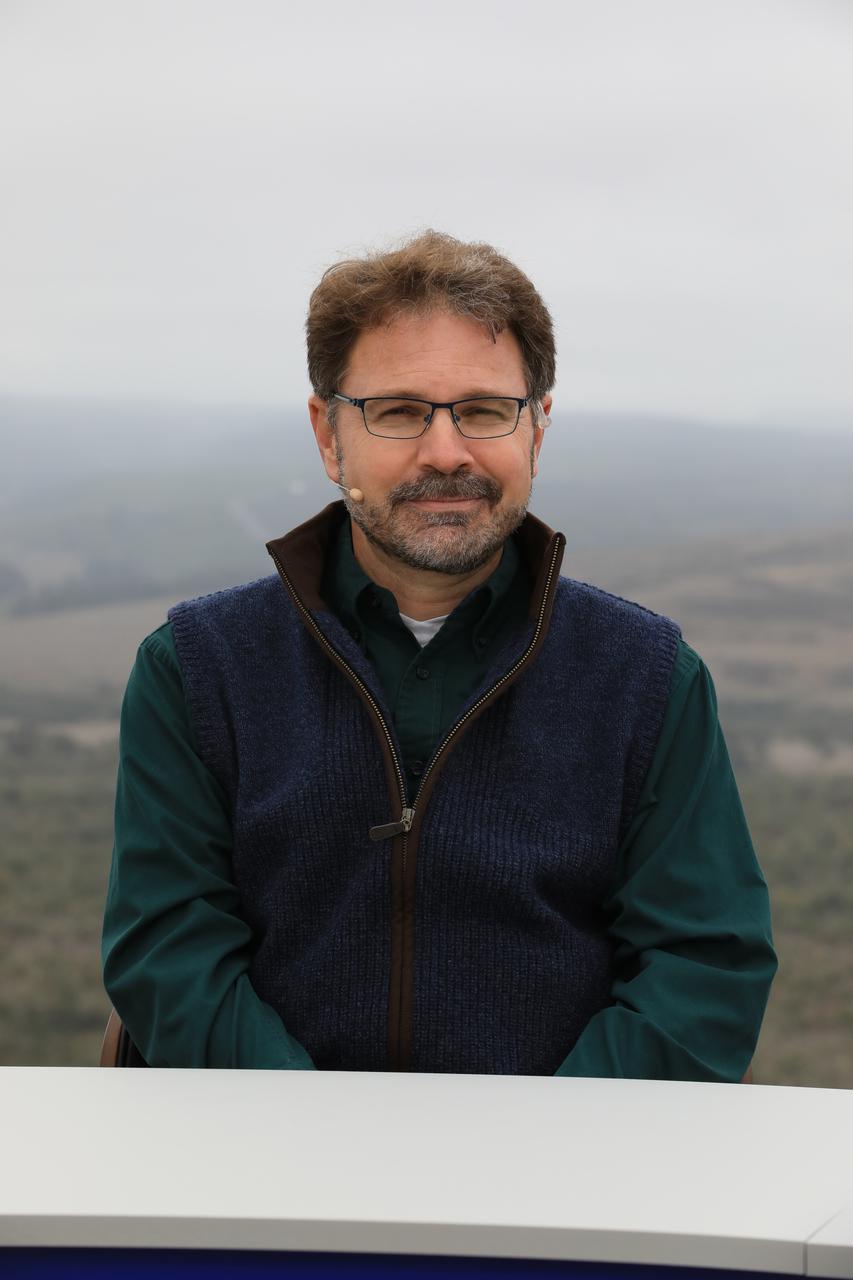

Dr. Pete Doucette, acting director, USGS Earth Resources, participates in the launch broadcast for the Landsat 9 mission on Sept. 27, 2021, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 3 at 2:12 p.m. EDT (11:12 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.
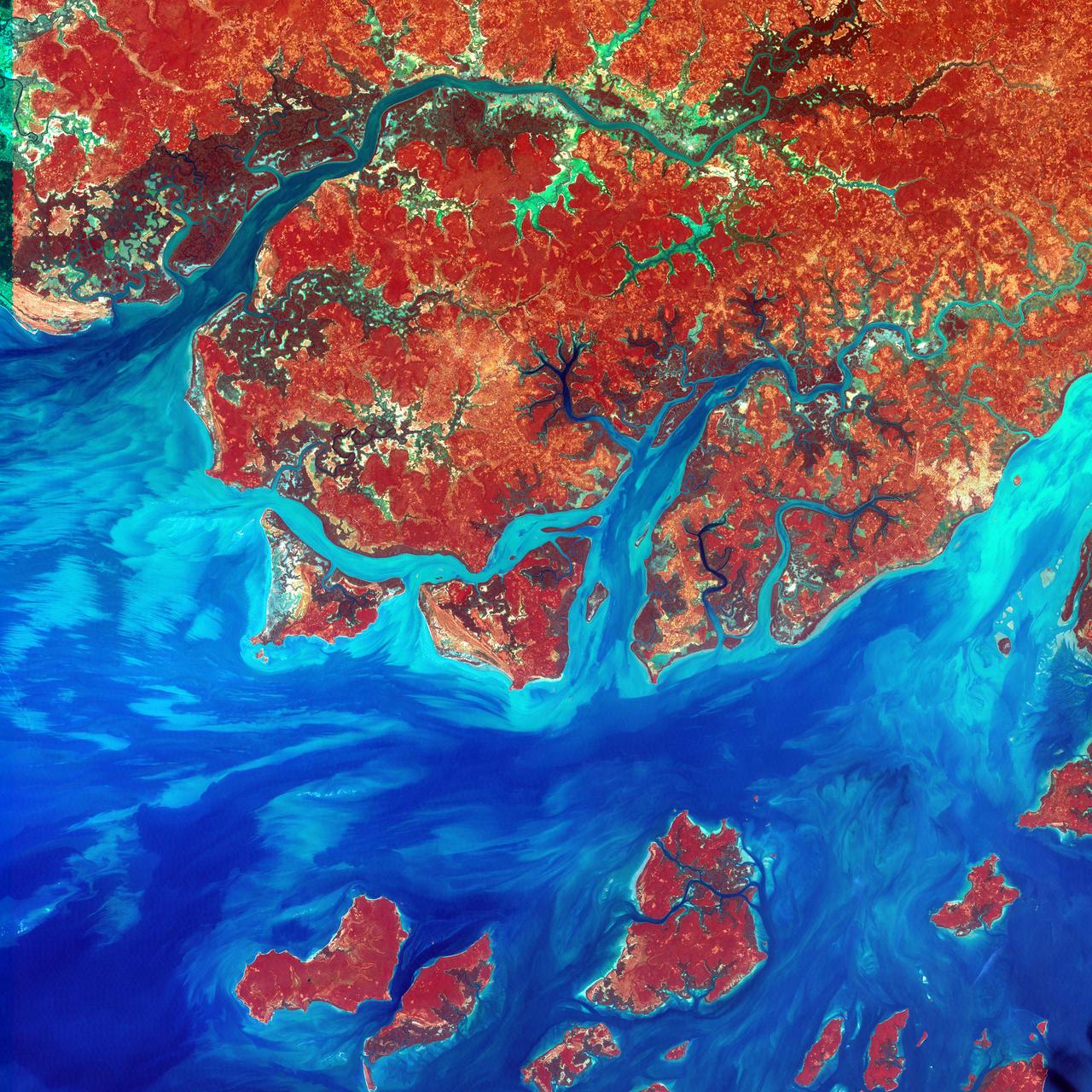

This Landsat 7 image of Guinea-Bissau, a small country in West Africa, shows the complex patterns of the country's shallow coastal waters, where silt carried by the Geba and other rivers washes out into the Atlantic Ocean. This is a false-color composite image made using infrared, red and blue wavelengths to bring out details in the silt was taken using Landsat 7's Enhanced Thematic Mapper plus (ETM+) sensor on Jan. 12, 2000. Image Credit: NASA/USGS EROS Data Center To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a>
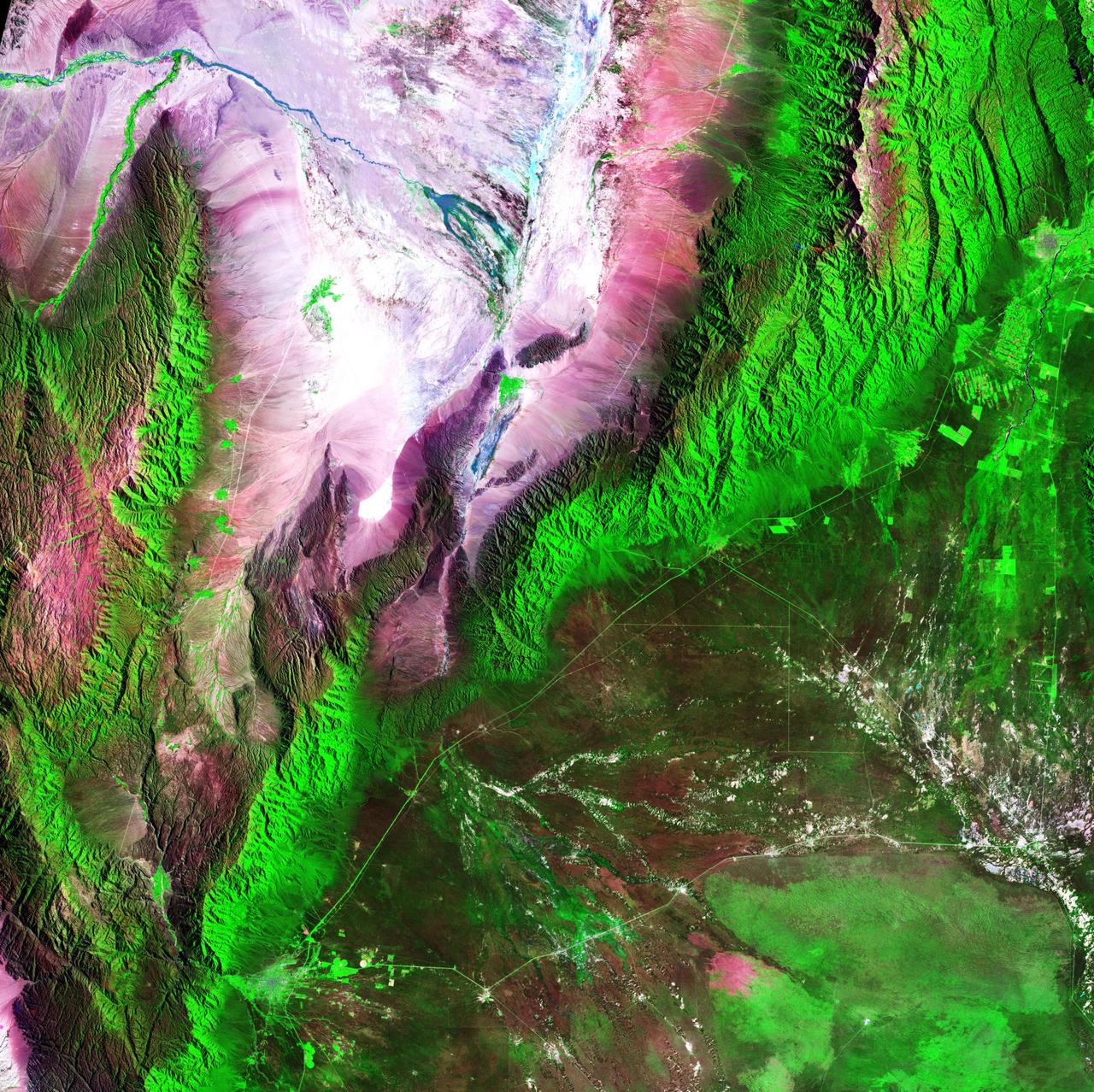
Acquisition Date: February 28, 1985 The Sierra de Velasco Mountains dominate this image in northern Argentina. The Catamarca province is in the northern part of the image, and the La Rioja province is to the south. The streams are fed by runoff from the snow in the Andes Mountains to the north. These intermittent streams can dry up rapidly. The larger urban area near the bottom of the image is La Rioja, the capital of the province of La Rioja. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Landsat/USGS To learn more about Landsat and to see the orginal high res file go to: <a href="http://landsat.usgs.gov/gallery_view.php?category=greenflag&thesort=mainTitle" rel="nofollow">landsat.usgs.gov/gallery_view.php?category=greenflag&...</a>

Image taken 1/11/2001: The so-called Richat Structure is a geological formation in the Maur Adrar Desert in the African country of Mauritania. Although it resembles an impact crater, the Richat Structure formed when a volcanic dome hardened and gradually eroded, exposing the onion-like layers of rock. The Richat Structure can be found on Landsat 7 WRS Path 203 Row 45, center: 21.68, -11.94. To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Landsat 7/USGS
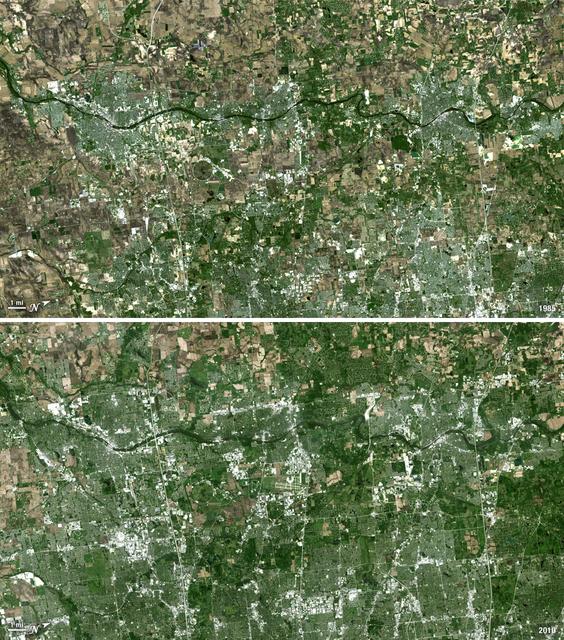

Forty miles west of downtown Chicago, the Fox River meanders its way through what has become the westernmost reaches of metropolitan Chicago, where the sprawling metropolis meets the hinterlands. While Chicago itself has seen a seven percent population decline during the last decade, the population of its metropolitan region, "Chicagoland," has steadily increased. These two natural-color Landsat 5 images acquired a quarter-century apart (on May 2, 1985, and May 23, 2010), stand witness to the soaring growth of this region. Aurora, Illinois’ second largest city, is the silvery-green region to the left hugging the Fox River, just south of the I-88 (North is to the right in this image); Carpentersville is found on the rightmost side, north of the I-90. From 1985 to 2010 a development explosion can been seen as the browns of pasture lands give way to silvery-green suburban areas and large white-colored business districts spring up along and east of the river. A major expansion of Dupage Airport appears in the middle of the 2010 image, and the circular-shaped region north of the I-88 and east of the Fox River, visible on both images, is the Department of Energy’s Fermilab. ---- NASA and the U.S. Department of the Interior through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) jointly manage Landsat, and the USGS preserves a 40-year archive of Landsat images that is freely available over the Internet. The next Landsat satellite, now known as the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) and later to be called Landsat 8, is scheduled for launch in 2013. In honor of Landsat’s 40th anniversary in July 2012, the USGS released the LandsatLook viewer – a quick, simple way to go forward and backward in time, pulling images of anywhere in the world out of the Landsat archive. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
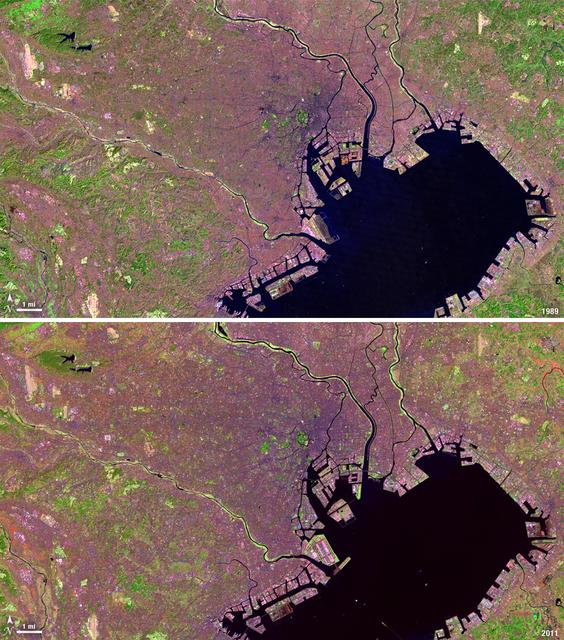

Tokyo is the world’s largest metropolitan region, home to nearly 37 million people. During the past two decades, Tokyo’s population has grown by more than 7 million. The city’s growth has continued despite Japan’s overall stagnating population, mainly due to a continued trend of centralization—citizens moving out of the country and into the city. Landsat 4 collected this first false-color image of Tokyo on Feb. 2, 1989. The upper half of Tokyo Bay is the large water body visible in a dark blue. In the middle of the image, central Tokyo appears a deep purple just north of the bay. Twenty-two years later, Landsat 5, captured this second image of Tokyo on April 5, 2011. The urban reaches of metropolitan Tokyo have grown in both distance and density, as seen where the green color of vegetation has turned to pink and purple shades of urbanization. A major expansion of Tokyo’s Haneda Airport, can be seen south of the city, on land built out into the bay. The constant circular spot of green in the dense city-center, visible on both images, is the Tokyo Imperial Palace and its gardens. (Landsat 5 TM Bands 7,4,2) ---- NASA and the U.S. Department of the Interior through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) jointly manage Landsat, and the USGS preserves a 40-year archive of Landsat images that is freely available over the Internet. The next Landsat satellite, now known as the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) and later to be called Landsat 8, is scheduled for launch in 2013. In honor of Landsat’s 40th anniversary in July 2012, the USGS released the LandsatLook viewer – a quick, simple way to go forward and backward in time, pulling images of anywhere in the world out of the Landsat archive. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
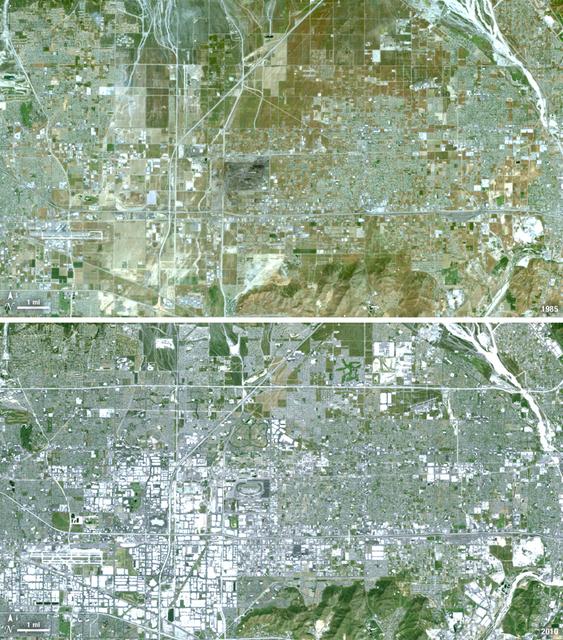
Thirty-five miles due east of downtown Los Angeles lies the city of Ontario, California. In 1881 two Canadian brothers established the town, naming it after their native city. By 1891 Ontario, Calif., was incorporated as a city. The farming-based economy (olives, citrus, dairy) of the city helped it grow to 20,000 by the 1960s. Subsequently, warehousing and freight trafficking took over as the major industry and the city’s population was over 160,000 by 2010. The L.A./Ontario International Airport is now America’s 15th busiest cargo airport. In these natural color Landsat 5 images, the massive growth of the city between 1985 and 2010 can be seen. The airport, found in the southwest portion of the images, added a number of runways and large warehousing structures now dominate the once rural areas surrounding the airport. In these images vegetation is green and brown and urban structures are bright white and gray. (Note there is a large dry riverbed in the northeast corner that is also bright white, but its nonlinear appearance sets it apart visually). ---- NASA and the U.S. Department of the Interior through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) jointly manage Landsat, and the USGS preserves a 40-year archive of Landsat images that is freely available over the Internet. The next Landsat satellite, now known as the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) and later to be called Landsat 8, is scheduled for launch in 2013. In honor of Landsat’s 40th anniversary in July 2012, the USGS released the LandsatLook viewer – a quick, simple way to go forward and backward in time, pulling images of anywhere in the world out of the Landsat archive. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
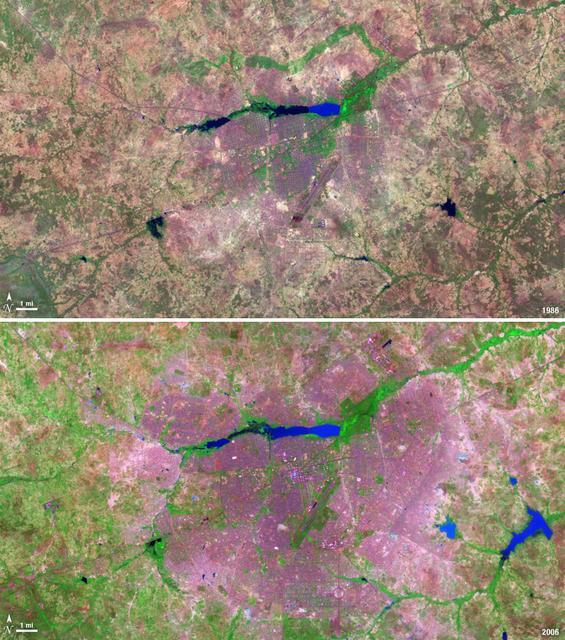

The landlocked western African nation of Burkina Faso experienced a 200 percent increase in urban population between 1975 and 2000. As a result, the area of the capital city Ouagadougou grew 14-fold during this period. These Landsat images show the city expanding outward from its center in the two decades between 1986 and 2006. On Nov. 18, 1986, the Landsat 5 satellite acquired this image of the capital. This false-color image shows vegetation in shades of green and gray, water in various shades of blue, and urban areas in pink and purple. The runway of the city’s airport can be seen as a long straight line that extends from southwest to northeast south of the large lake, Bois de Boulogne. Two decades later, on Oct. 16, 2006 Landsat 7 acquired this image of Ouagadougou. Growth radiated from the city center in all directions. The green strip of vegetation north of Bois de Boulogne has been paved over and a massive new development including a large thoroughfare and traffic circle can be seen south of the airport. ---- NASA and the U.S. Department of the Interior through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) jointly manage Landsat, and the USGS preserves a 40-year archive of Landsat images that is freely available over the Internet. The next Landsat satellite, now known as the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) and later to be called Landsat 8, is scheduled for launch in 2013. In honor of Landsat’s 40th anniversary in July 2012, the USGS released the LandsatLook viewer – a quick, simple way to go forward and backward in time, pulling images of anywhere in the world out of the Landsat archive. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
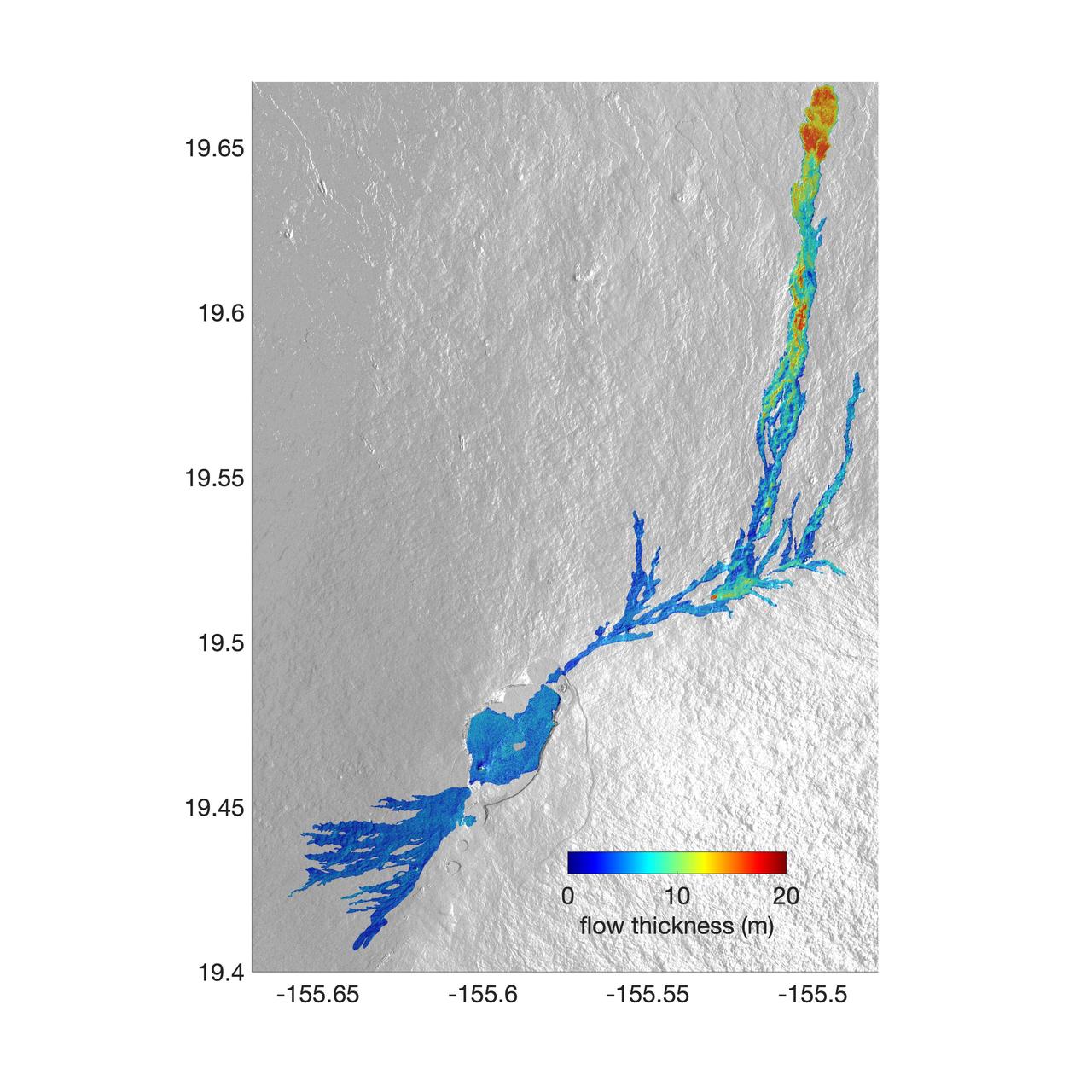
The world's largest active volcano – Hawaii's Mauna Loa – had been quiet for 38 years. But in 2022, the volcano began to stir, showing increased numbers of small earthquakes and subtle swelling of certain land surfaces in September. On November 27, fountains of lava began spurting from the mountain's Northeast Rift Zone and streams of molten rock flowed to the north. Ten days into the eruption, a NASA aircraft conducted its first flight over the erupting volcano. It carried NASA's Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar (UAVSAR) system, which was used to map the volcano's topography in fine detail with a Ka-band instrument called GLISTIN-A. Teams from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and the United States Geological Survey (USGS) used data from that sensor to map the thickness of those flows during a series of flights on December 7, 8, and 10. The map above shows the thickness of the lava flows during the flight on December 7, the day before USGS scientists noticed a significant decline in the pace of the eruption. A few days later, they declared the eruption had stopped. The map shows the thickness of the lava flows in the summit caldera, where the eruption began, and of lava flows on Mauna Loa's northeastern flank. The color variation from blue to orange indicates increasing lava flow thickness. A maximum thickness of roughly 25 meters (82 feet) is shown, though values exceeding 40 meters (131 feet) were observed in some areas. The thickening at the northern end of the flow is due to lava accumulating away from the vent, along with a flattening of the terrain at the saddle between the Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea volcanoes. By comparing to pre-eruption maps of this area's topography, including GLISTIN-A data collected in 2017, the USGS researchers were able to calculate the size and volume of the lava flow. Over the roughly 14-day eruption, Mauna Loa erupted more than 8.8 billion cubic feet (230 million cubic meters) along a lava flow that extended up to 16.5 miles (19.5 kilometers) from the vent, according to the USGS. The UAVSAR operates from a pod mounted beneath a crewed Gulfstream III jet from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California. Repeated topographic maps generated with each flight reveal the progression and thickening of lava with time – important information for scientific understanding of volcano processes and for emergency response. For the Mauna Loa science flights, the instrument suite featured an additional state-of-the-art imaging tool: the synthetic aperture radar-fusion optical short-wave infrared (SAR-Fusion Optical/SWIR) camera system. SAR-Fusion collects data over the same ground swath as GLISTIN-A to map land surface changes using optical/SWIR photogrammetry methods. GLISTIN-A was designed to provide all-weather, high-resolution surface topography not available through existing lidar or radar sensors. GLISTIN-A was originally demonstrated as a new radar technique for mapping ice surfaces. Science demonstration flights began in 2013 over alpine glaciers and sea ice in Alaska, and a floodplain in California. Its applications have since expanded to other areas, such as snow accumulation and volcano dynamics. The first time the instrument was deployed for volcano response was in 2018 during the three-month eruption of Kilauea. The success of that operation paved the way for deployment to Mauna Loa. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25526

A mural celebrating the 50 years of the Landsat mission is seen, Tuesday, Sept. 28, 2021, in Lompoc, California. On Monday, Sept. 27, 2021, the Landsat 9 satellite, a joint NASA/U.S. Geological Survey mission that will continue the legacy of monitoring Earth’s land and coastal regions, launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base, California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
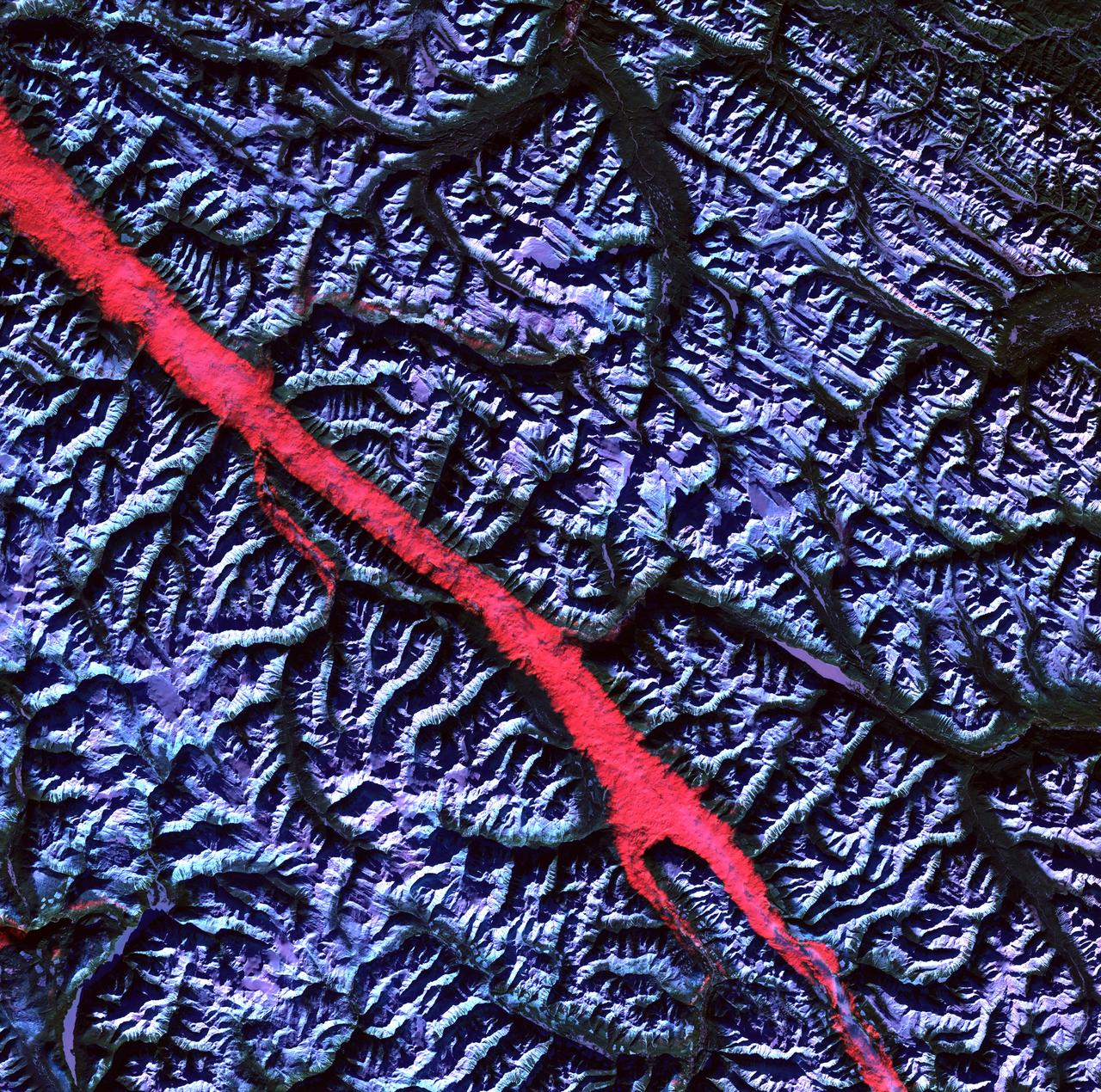

Acquisition Date: February 2004 The high reflectance of clouds compared to the surrounding land, coupled with the low sun elevation when this image was acquired, causes low clouds to appear red as they fill a portion of the Rocky Mountain Trench. Running parallel with the peaks of the Canadian Rockies and ranging from 2 to 10 miles (3 to 16 kilometers) wide and about 900 miles (1,448 kilometers) long, the Trench aligns with the Fraser River and makes its way past Mount Robson, the highest peak in the Canadian Rockies at 12,972 feet (3,954 meters). Mount Robson is near the center of this image. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Landsat/USGS To learn more about Landsat and to see the orginal high res file go to: <a href="http://landsat.usgs.gov/gallery_view.php?category=greenflag&thesort=mainTitle" rel="nofollow">landsat.usgs.gov/gallery_view.php?category=greenflag&...</a>

ISS022-E-035426 (22 Jan. 2010) --- Photographed from the International Space Station orbiting Earth at an altitude of 211 statute miles, this image of the Port au Prince area of Haiti from Jan. 22 is centered on the area that was heavily damaged by a magnitude 7.0 earthquake on Jan. 12. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Earthquake Center, a number of tremors of varying magnitudes up to 6.0 were recorded in ensuing days. Ships can be easily delineated in the harbor. The single runway of the airport, heavily damaged by the quake, is seen near center of the frame. The airport?s control tower was destroyed and has since been rebuilt and is now in service, thanks to part of the huge world-wide aid offered to the nation
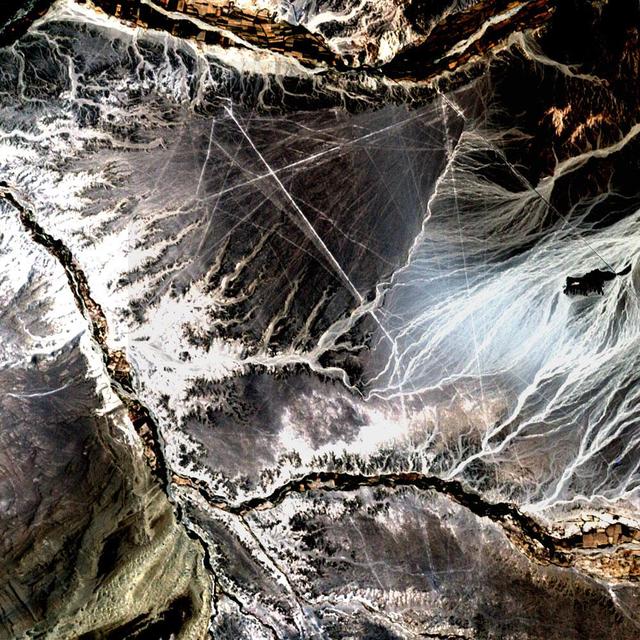

Acquisition Date: November 10, 2002 In the desert of southwest Peru, between the Andes Mountains and the Peruvian coast, lies a plateau with huge geometric patterns and spirals, animal figures including a monkey, a spider, and an 'owl man,' and thousands of perfectly straight lines. The last of these was drawn about a thousand years ago. Known as the Nazca lines, the drawings have mystified scientists since they were first discovered in the 1920s. Pictured here is all that can be seen of these lines by Landsat 7's 15 meter pan band, which has been used to sharpen the 30 meter Bands 3, 2, and 1. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Landsat/USGS To learn more about Landsat and to see the orginal high res file go to: <a href="http://landsat.usgs.gov/gallery_view.php?category=greenflag&thesort=mainTitle" rel="nofollow">landsat.usgs.gov/gallery_view.php?category=greenflag&...</a>
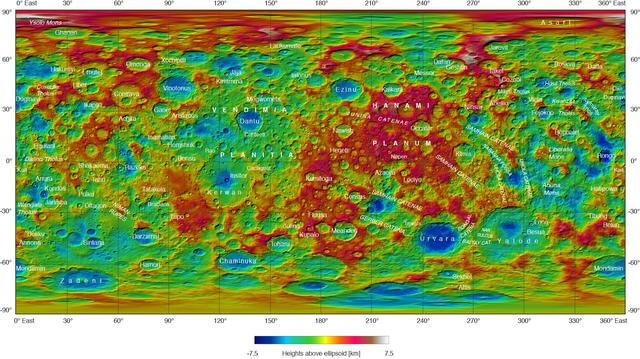
This topographical map of Ceres, made with images from NASA's Dawn spacecraft, shows all of the dwarf planet's named features as of September 2016. Dawn celebrated nine years since launch on September 27, 2016. To date, more than 110 places on Ceres have been named. These include craters such as Occator Crater, home of the brightest areas on the dwarf planet, as well as crater chains called catenae, mountains such as Ahuna Mons, and other geological features Among the most recently named features is Kwanzaa Tholus, named after the African-American winter holiday Kwanzaa, which is based on ancient African harvest festivals. A tholus is a small dome-shaped mountain or hill. There are a total of seven tholi named on Ceres. The latest list of features on Ceres can be found at the USGS Planetary Nomenclature website. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20918
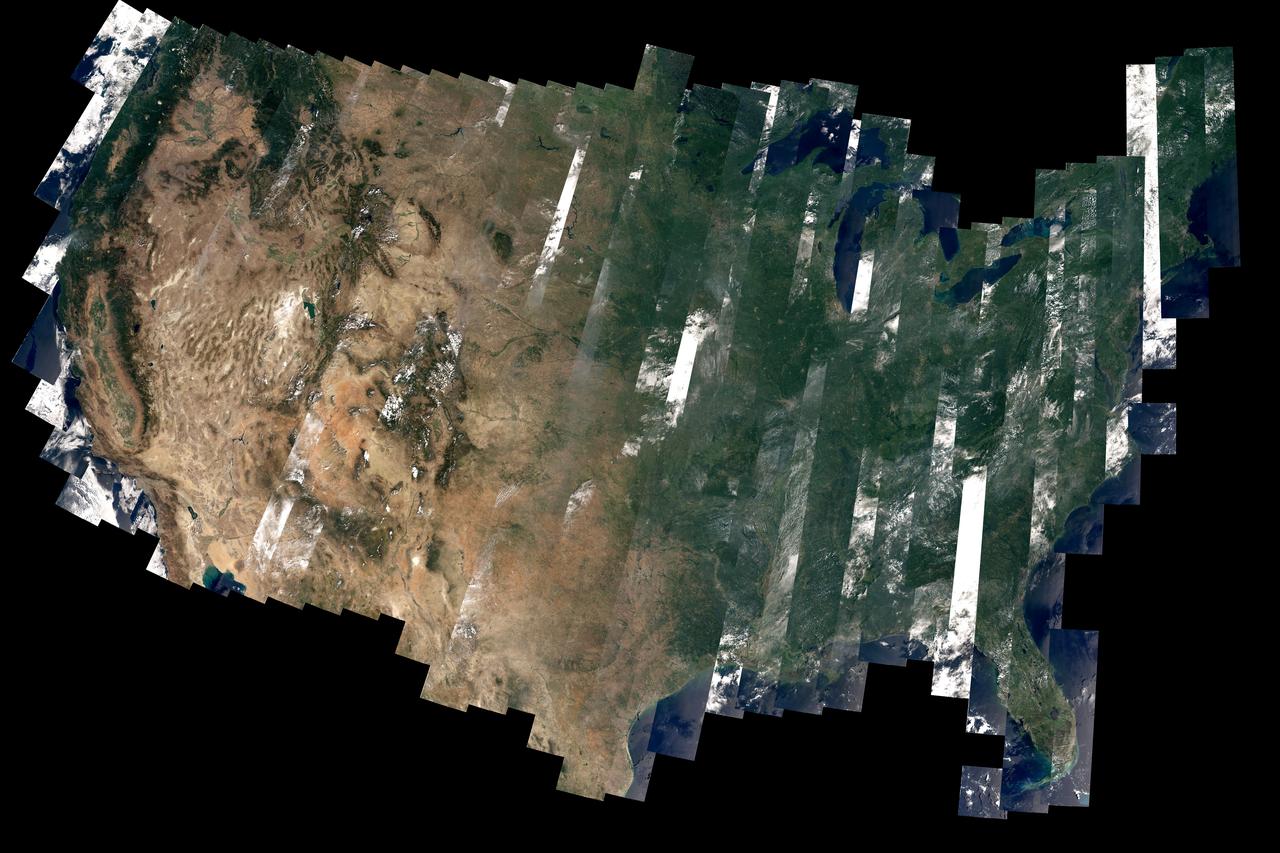

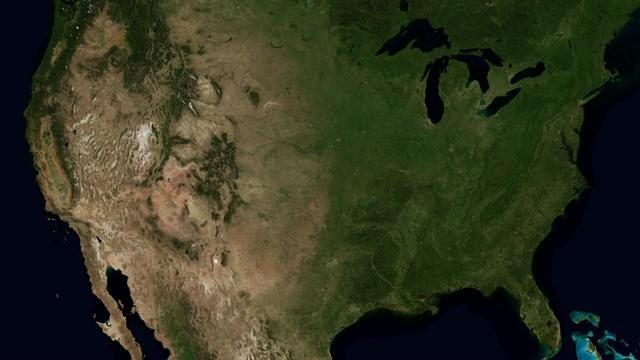
On February 11, 2013, the Landsat 8 satellite rocketed into a sunny California morning onboard a powerful Atlas V and began its life in orbit. In the year since launch, scientists have been working to understand the information the satellite has been sending back. Some have been calibrating the data—checking it against ground observations and matching it to the rest of the 42-year-long Landsat record. At the same time, the broader science community has been learning to use the new data. The map above—one of the first views of the United States from Landsat 8—is an example of how scientists are testing Landsat 8 data. David Roy, a co-leader of the USGS-NASA Landsat science team and researcher at South Dakota State University, made the map with observations taken during August 2013 by the satellite’s Operational Land Imager. Read more: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=83099" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=83099</a> Image courtesy David Roy, USGS-NASA WELD product. Caption by Holli Riebeek. Instrument: Landsat 8 - OLI Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
The Mississippi Watershed is the largest drainage basin in North America at 3.2 million square kilometers in area. The USGS has created a database of this area which indicates the direction of waterflow at each point. By assembling these directions into streamflows, it is possible to trace the path of water from every point of the area to the mouth of the Mississippi in the Gulf of Mexico. This animation starts with the points furthest from the Gulf and reveals the streams and rivers as a steady progression towards the mouth of the Mississippi until all the major rivers are revealed. The speed of the reveal of the rivers is not dependent on the actual speed of the water flow. The reveal proceeds at a constant velocity along each river path, timed so that all reveals reach the mouth of the Mississippi at the same time. This animation does not show actual flow rates of the rivers. All rivers are shown with identical rates. The river colors and widths correspond to the relative lengths of river segments. Credit: NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio/Horace Mitchell Go here to download this video: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/4493" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/4493</a>

The Landsat 9 instrument cover is removed from the spacecraft inside the Integrated Processing Facility (IPF) at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
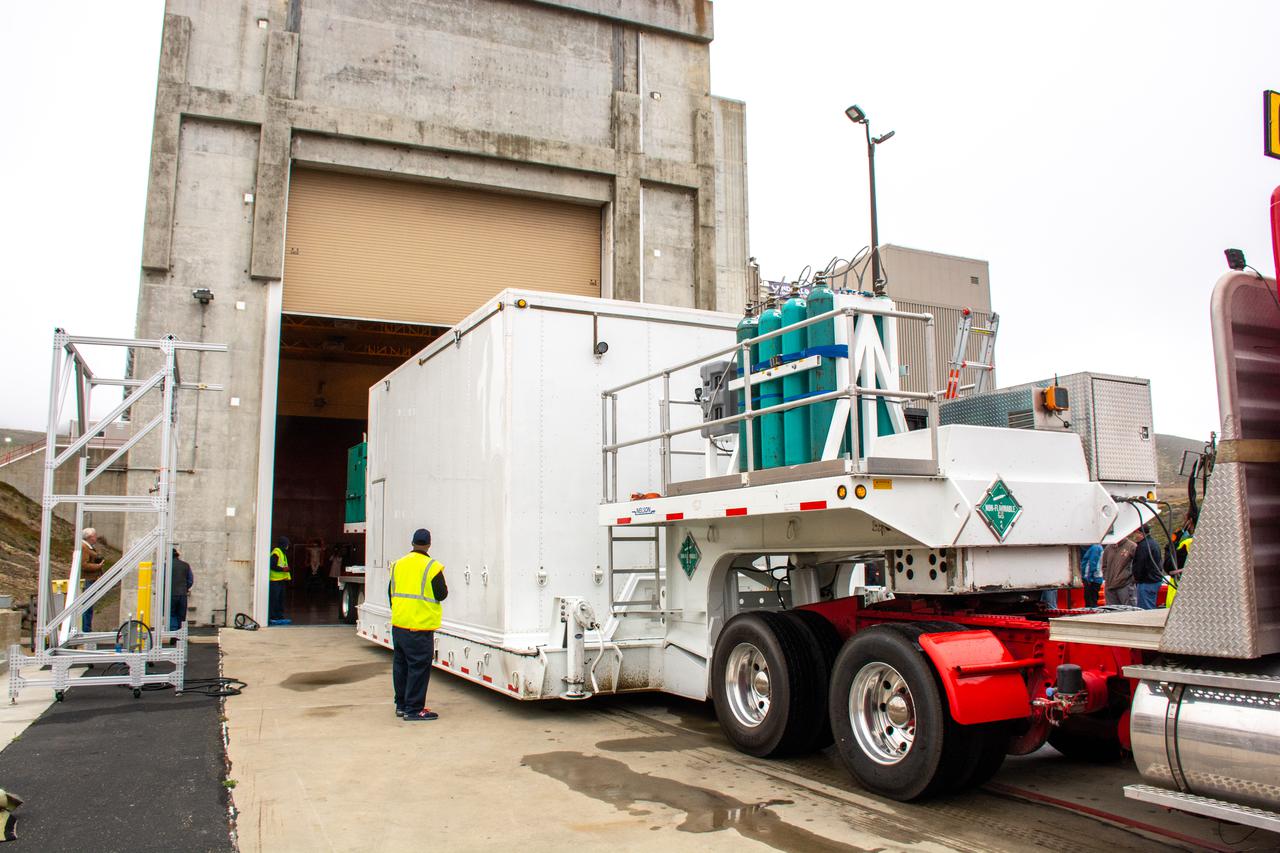

The satellite for the Landsat 9 mission, secured inside its shipping container, arrives at the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on July 7, 2021. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
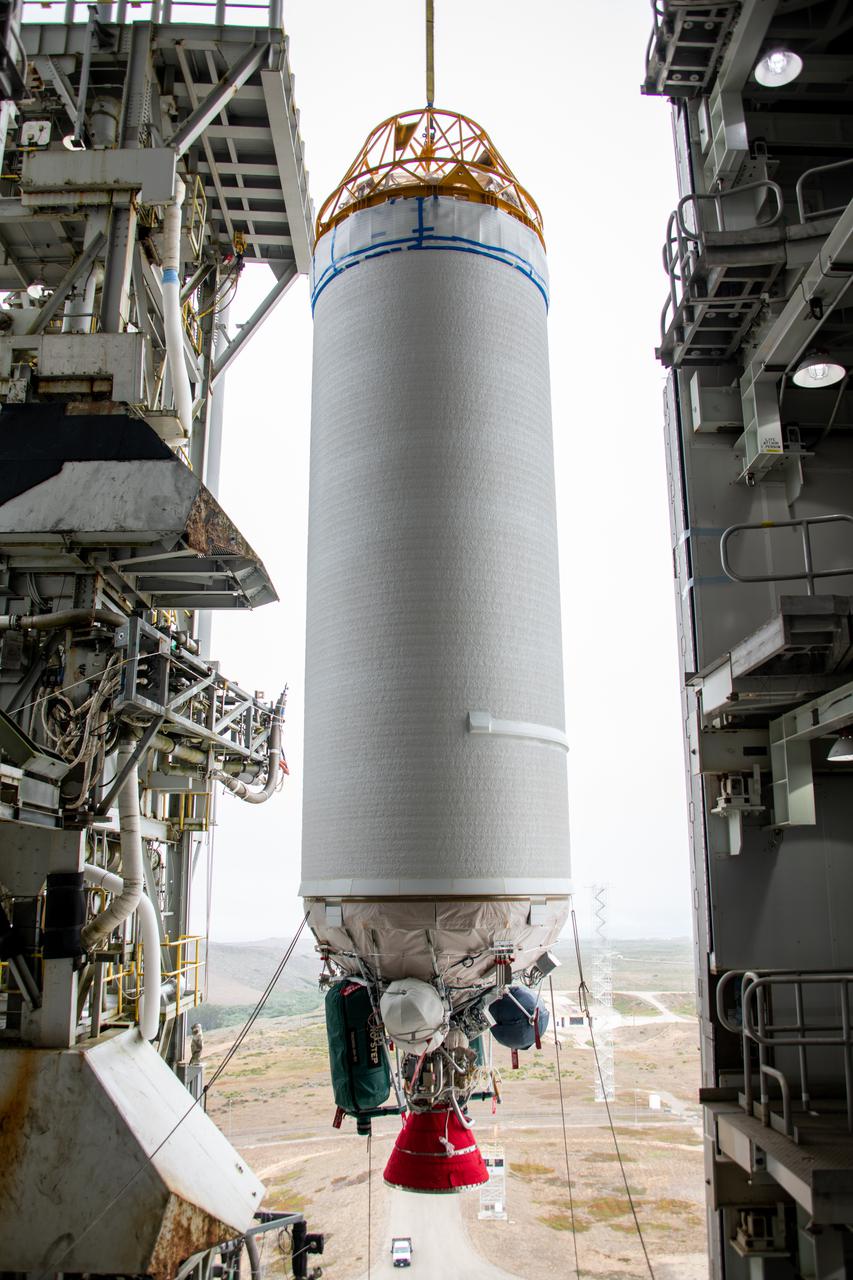

The United Launch Alliance Centaur second stage for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission seems suspended in midair in this view from inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on July 15, 2021. The Centaur will be moved into the integration facility and attached to the top of the Atlas V booster. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

Inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Source Base in California, workers help secure the interstage and assembly second stage adapters to the Centaur second stage of the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission on July 14, 2021. Landsat 9 will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, technicians with United Launch Alliance (ULA) remove the protective blankets from one payload fairing half for the Landsat 9 spacecraft on Aug. 2, 2021. The two halves of the ULA payload fairing will be secured around Landsat 9 to protect it during launch atop the ULA Atlas V rocket. Landsat 9 will launch on the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
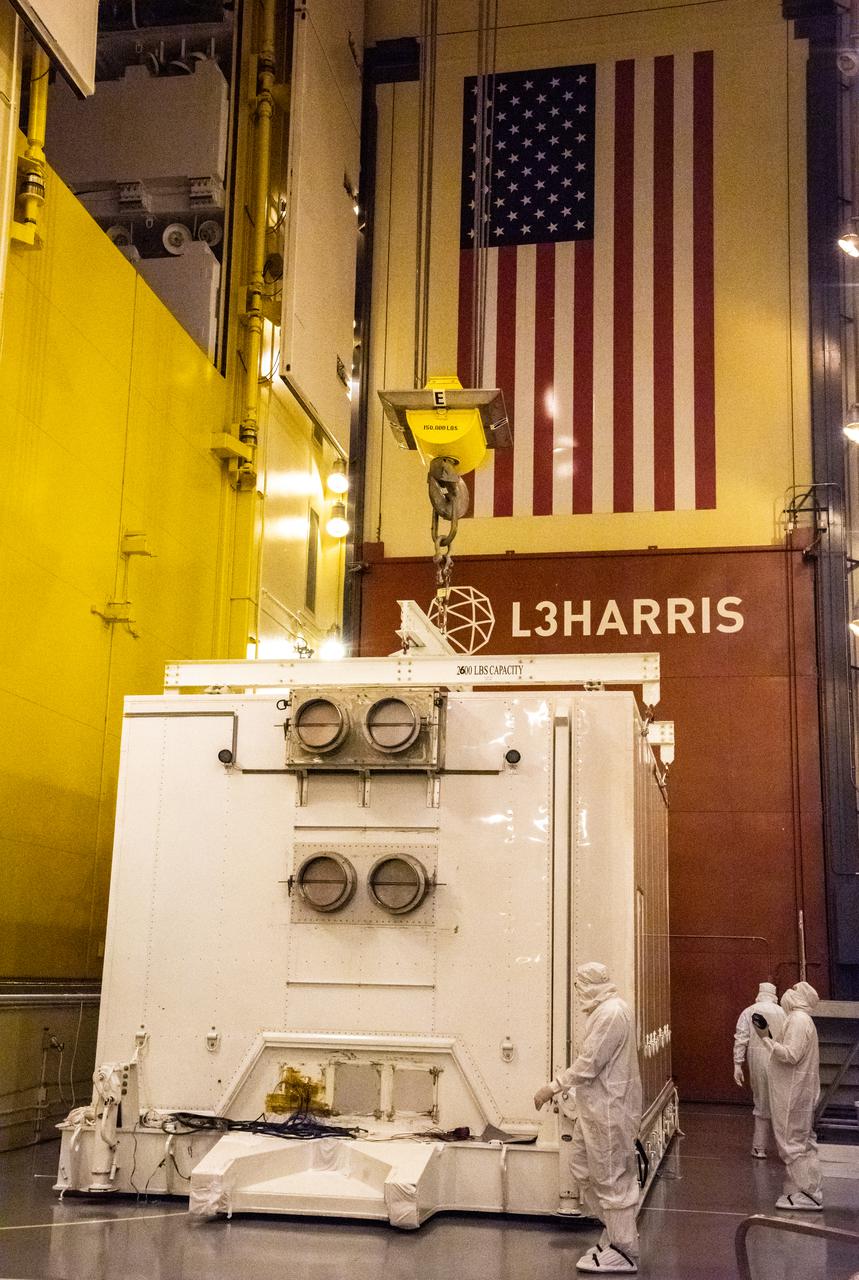

Technicians prepare to remove the satellite for the Landsat 9 mission from its shipping container following its arrival at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on July 7, 2021. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
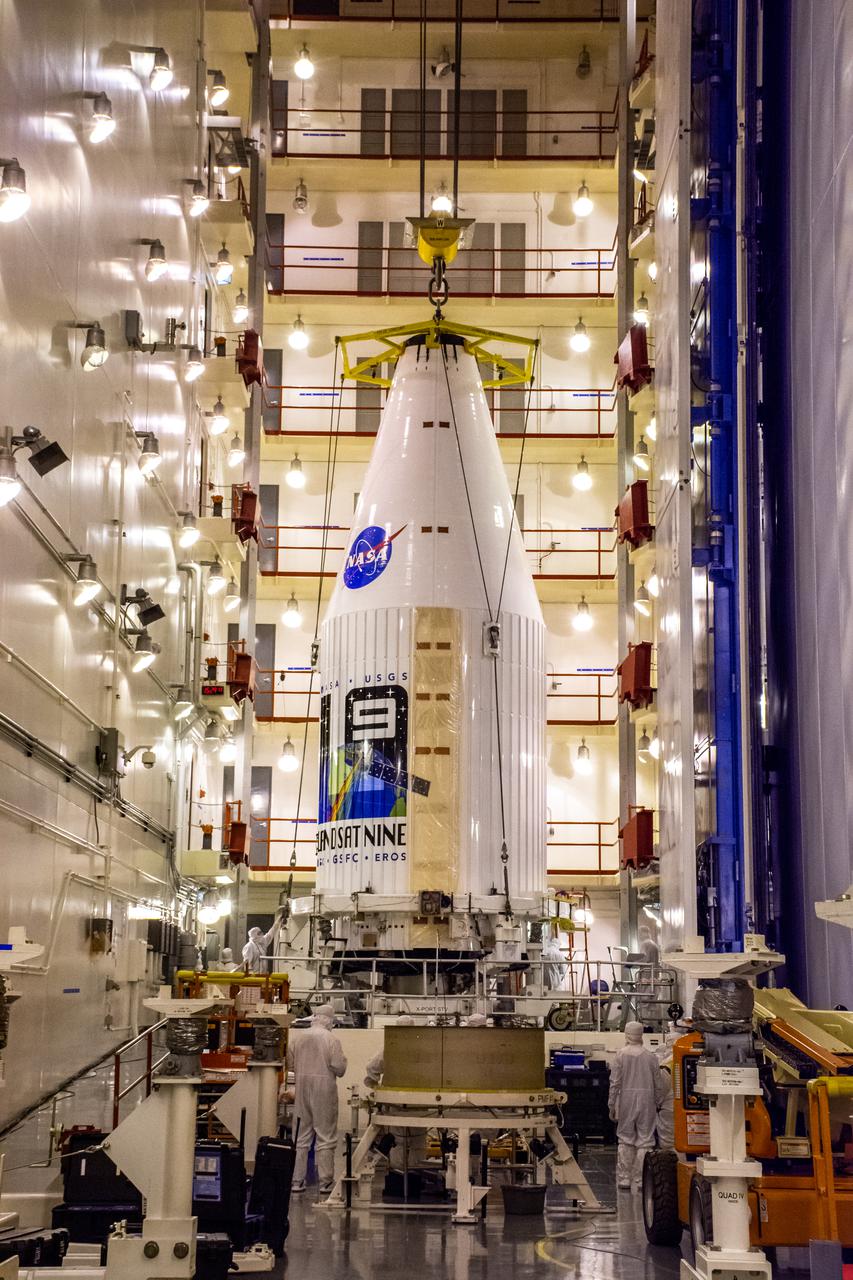

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, the Landsat 9 spacecraft, secured in the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing, is moved by crane into the transfer tower for closeout operations on Aug. 19, 2021. Landsat 9 will launch on a ULA Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
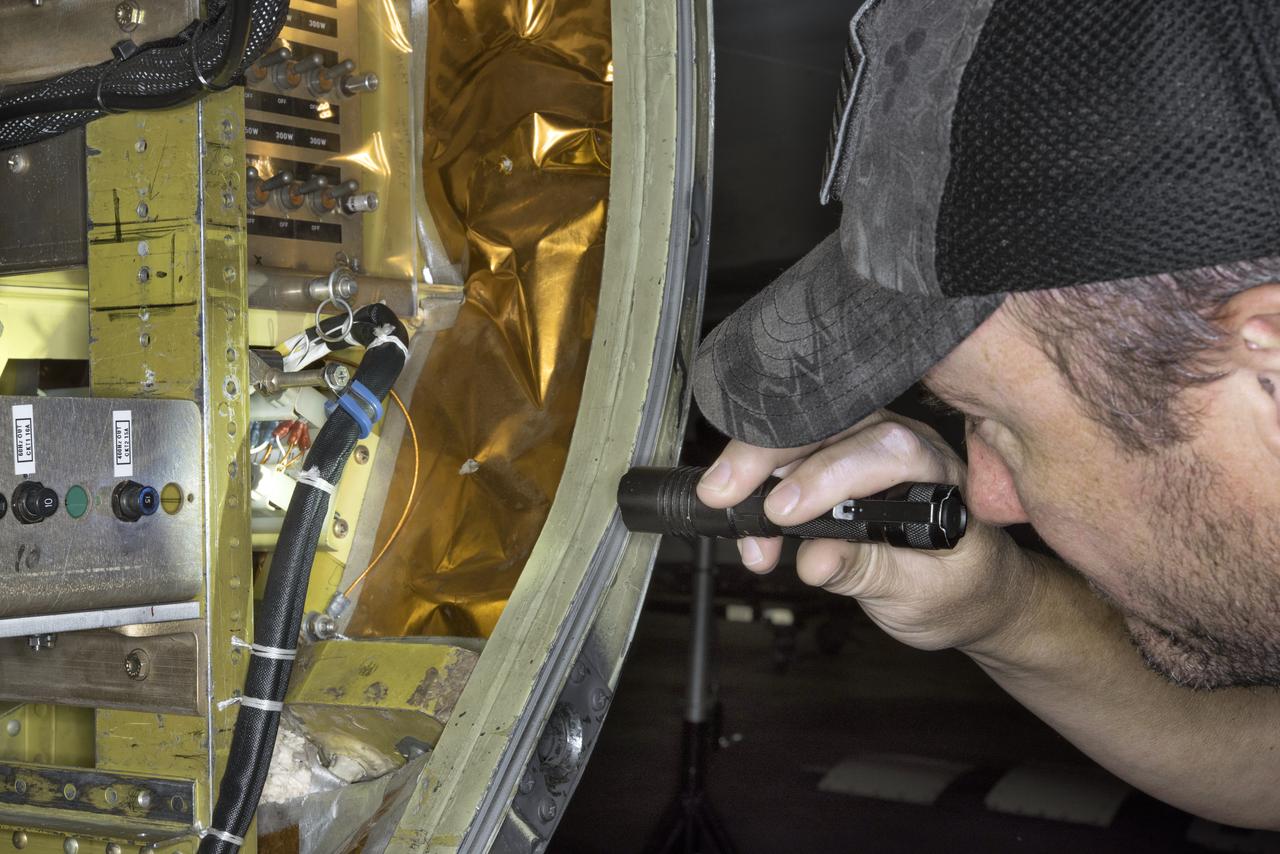

A ground crewman at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Palmdale, CA inspects the forward panel on the mid-body section of NASA’s ER2’s wingpod. The crew is preparing to fly the air-LUSI instrument aboard the ER2 to measure the Moon.
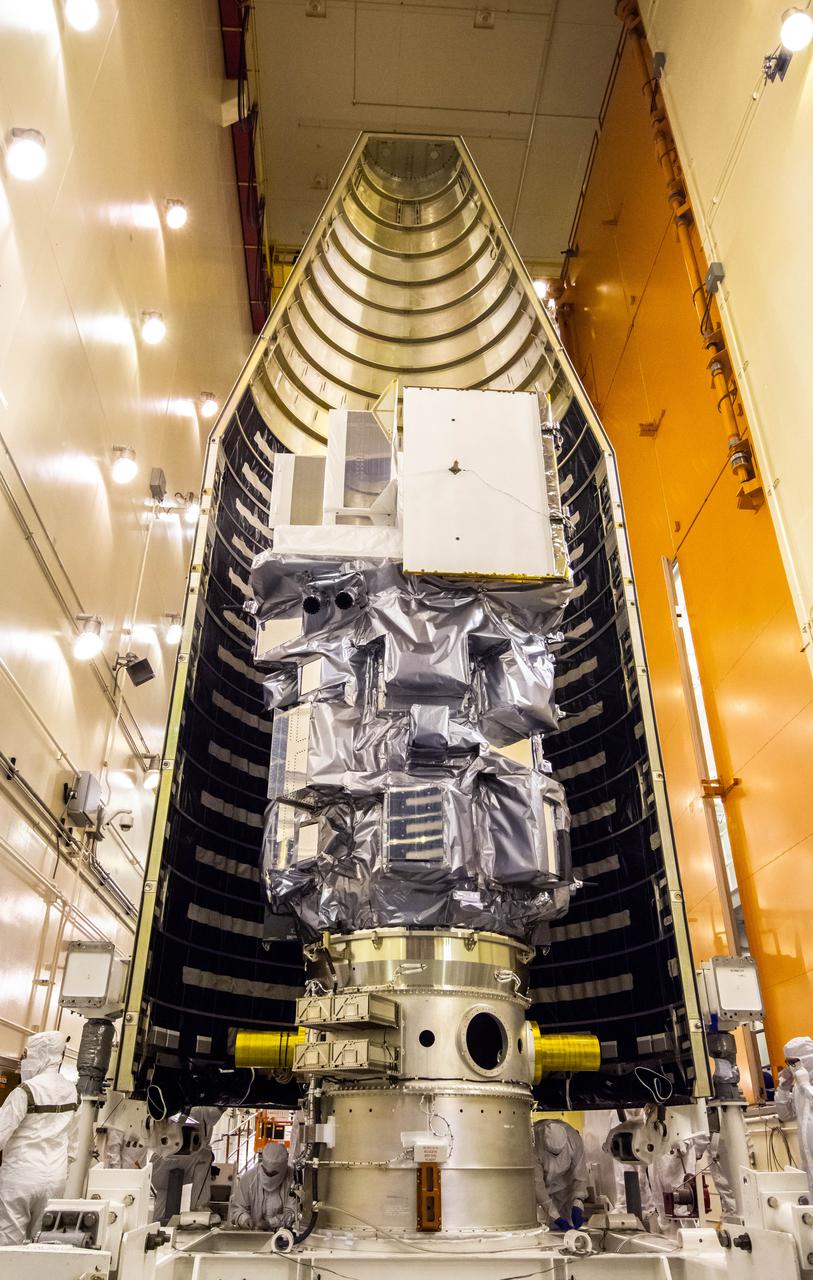

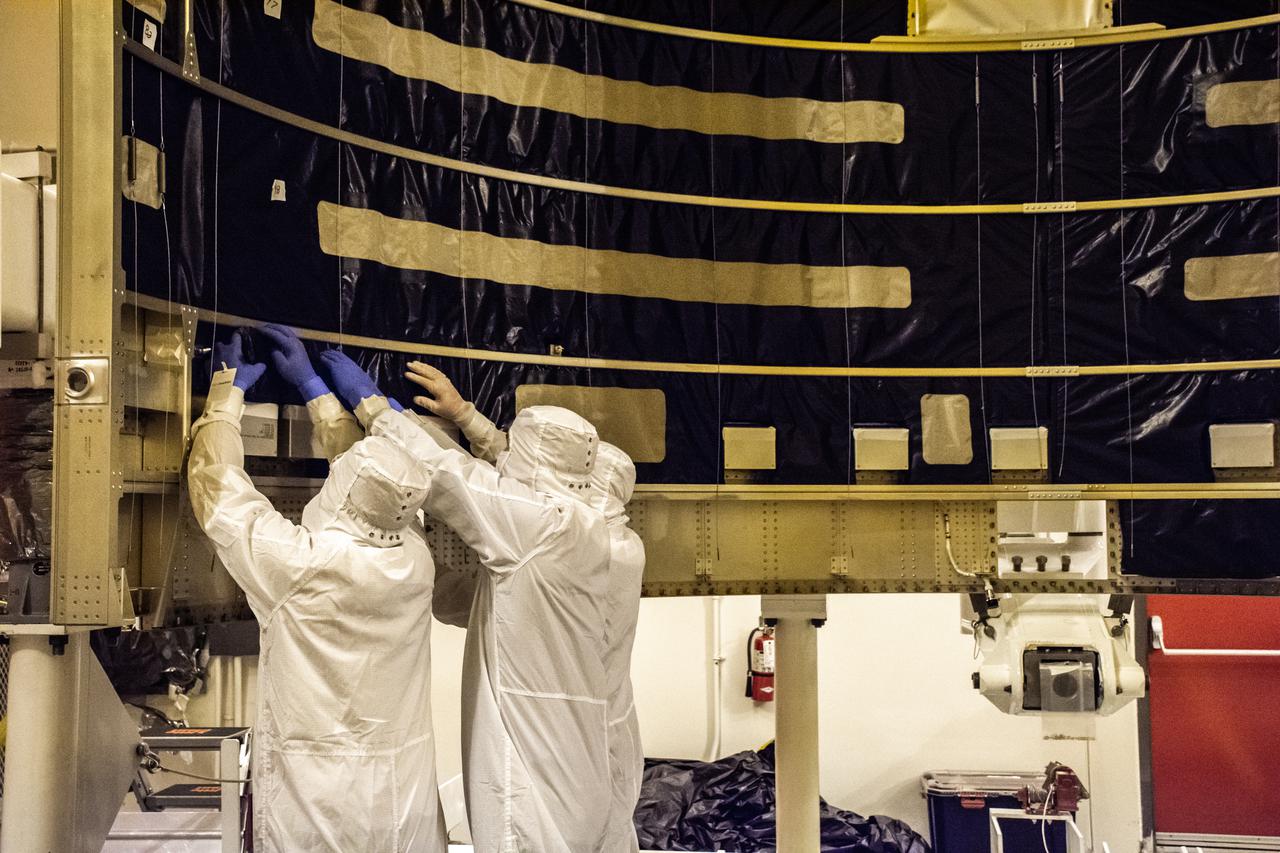
Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, the Landsat 9 spacecraft is moved into position for encapsulation on Aug. 16, 2021. The two halves of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing will surround and encase Landsat 9 to protect it during launch atop the ULA Atlas V rocket. Landsat 9 will launch on the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
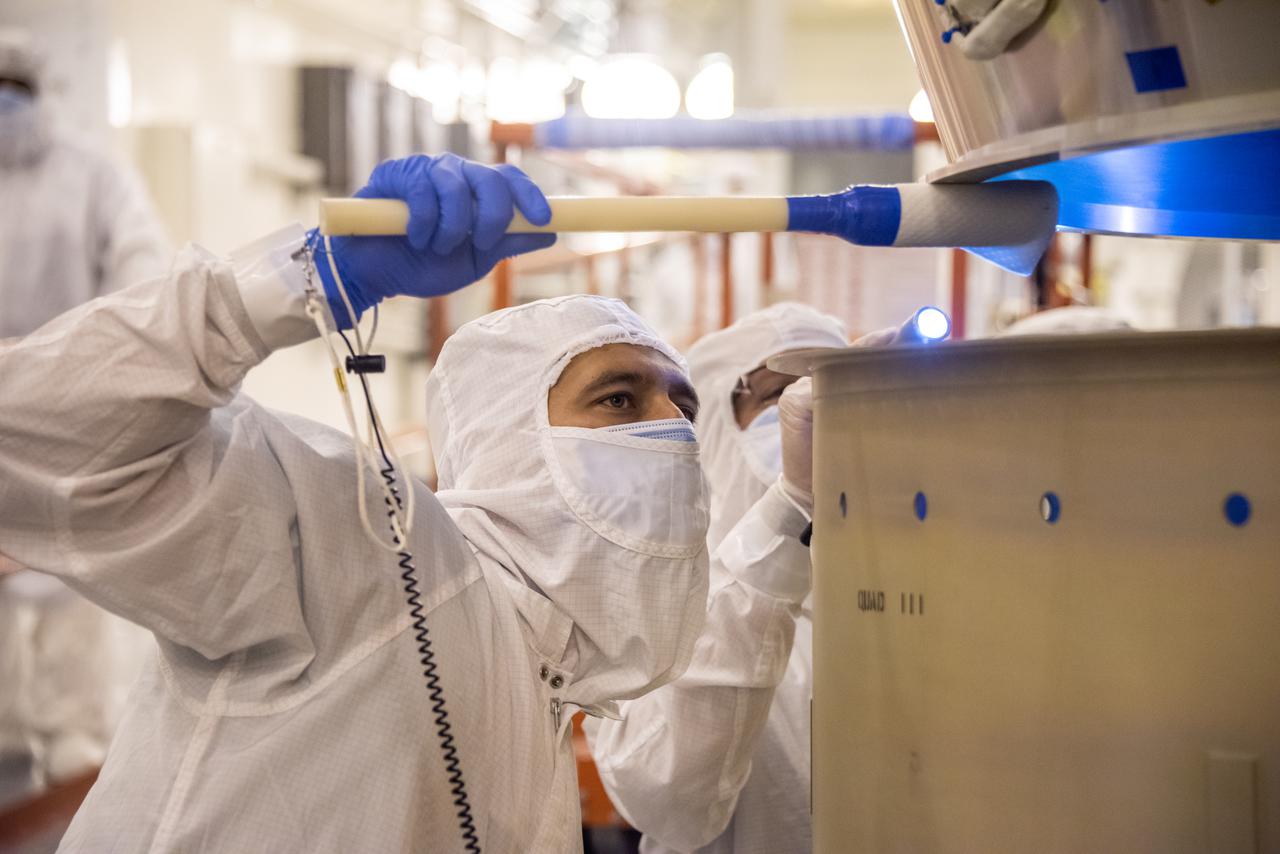

The Landsat 9 PSR to EFS C29 lift and mate inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, the Landsat 9 spacecraft is moved into position for encapsulation on Aug. 16, 2021. The two halves of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing will surround and encase Landsat 9 to protect it during launch atop the ULA Atlas V rocket. Landsat 9 will launch on the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
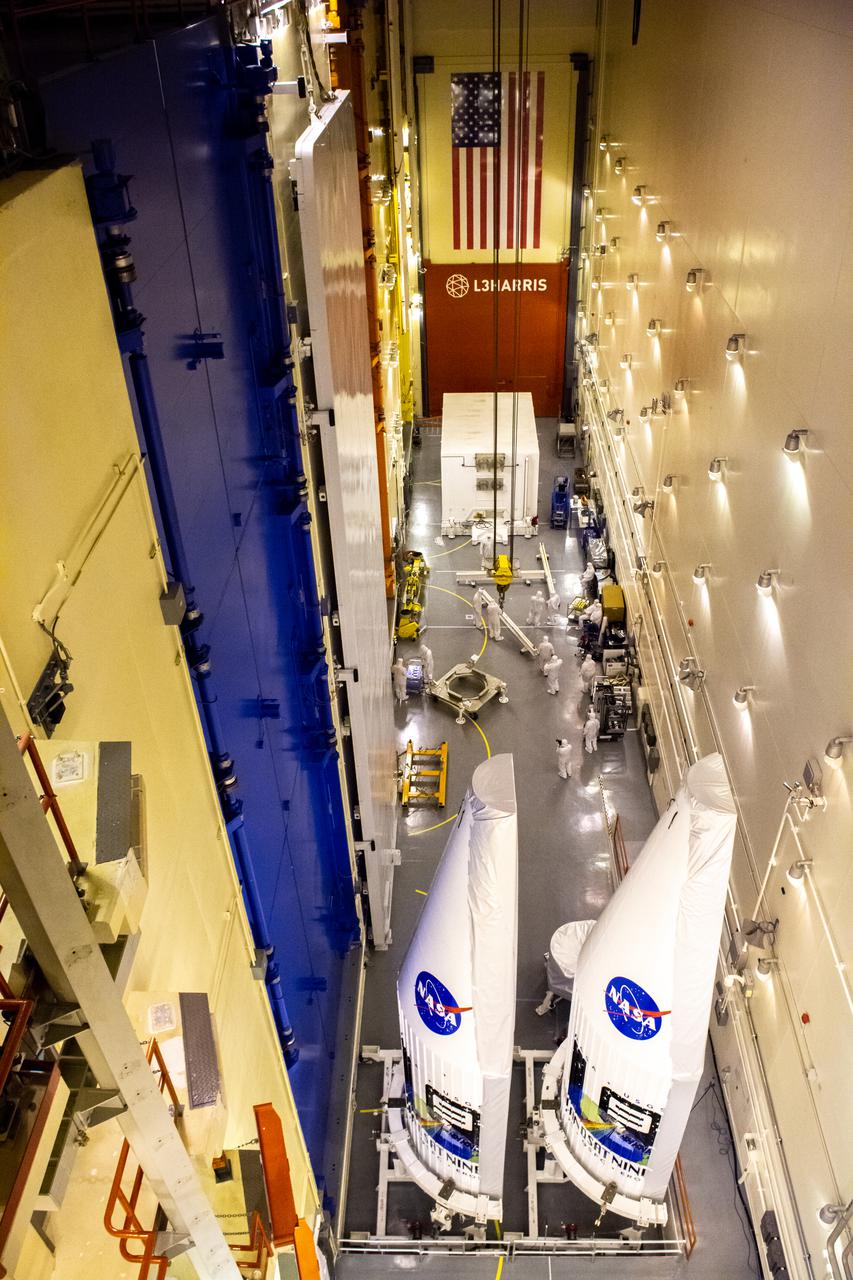

The two instruments that make up the satellite for the Landsat 9 mission are seen inside the protective payload fairings following their arrival at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on July 7, 2021. The fairings will encapsulate the satellite for its launch atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
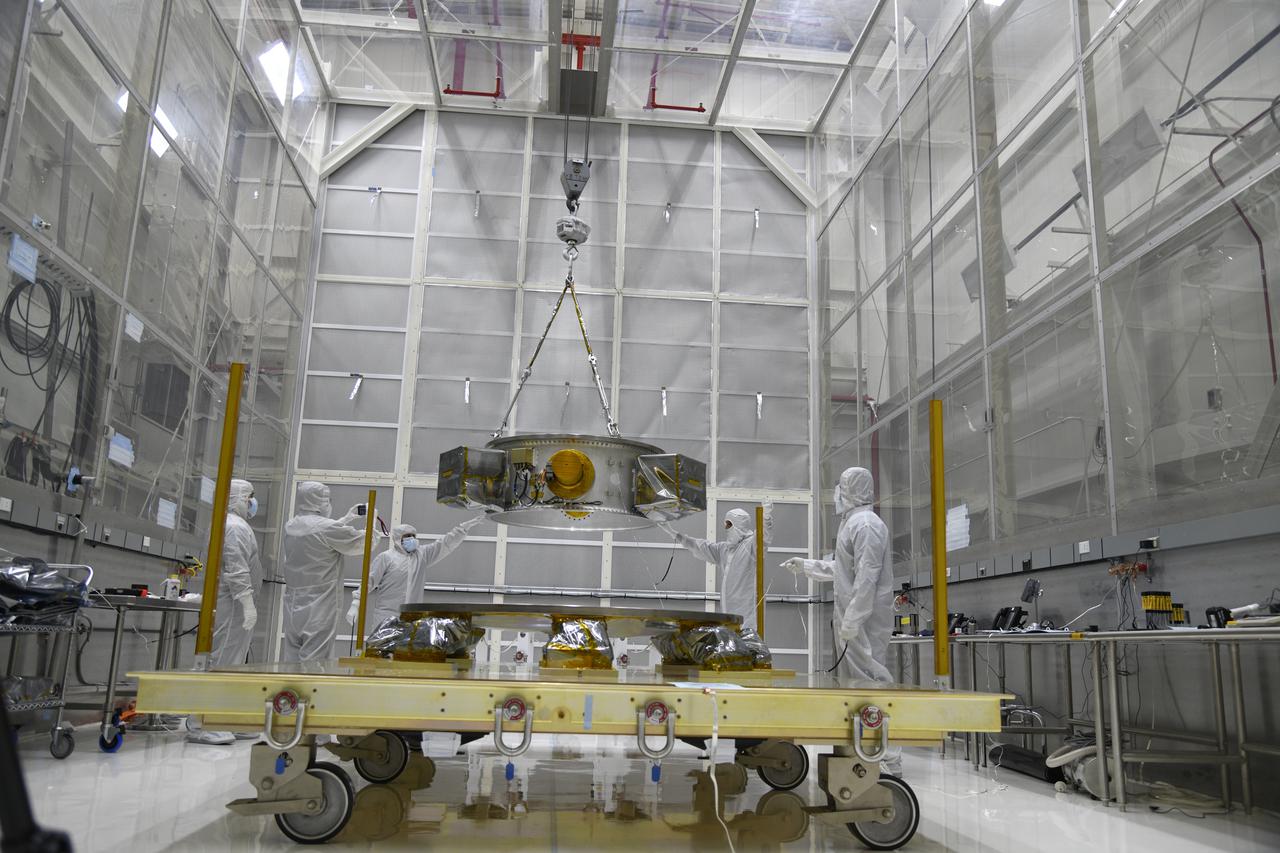

Technicians monitor the progress as a crane is used to lift the secondary payload adapter for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission onto a transporter stand at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on Aug. 4, 2021. The payload adapter will be transported to the Integrated Processing Facility. Several secondary payloads, called CubeSats, will launch with Landsat 9 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
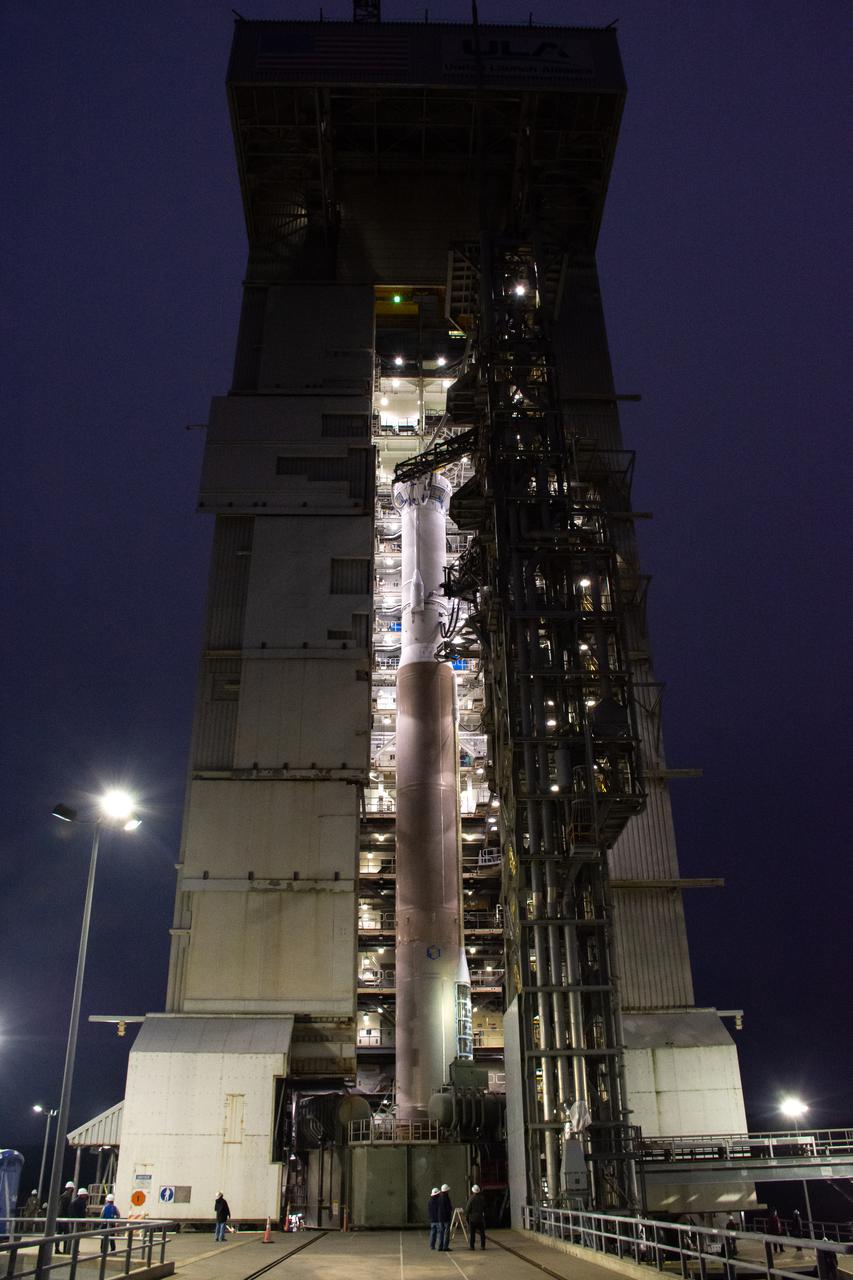

The Atlas V booster for the Landsat 9 satellite undergoes a dress rehearsal at Vandenberg Space Force Base’s Space Launch Complex 3 in California on Sept. 3, 2021. The Landsat 9 mission launch, which is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 27, 2021. Landsat 9 will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, the Landsat 9 spacecraft is moved into position for encapsulation on Aug. 16, 2021. The two halves of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing will surround and encase Landsat 9 to protect it during launch atop the ULA Atlas V rocket. Landsat 9 will launch on the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
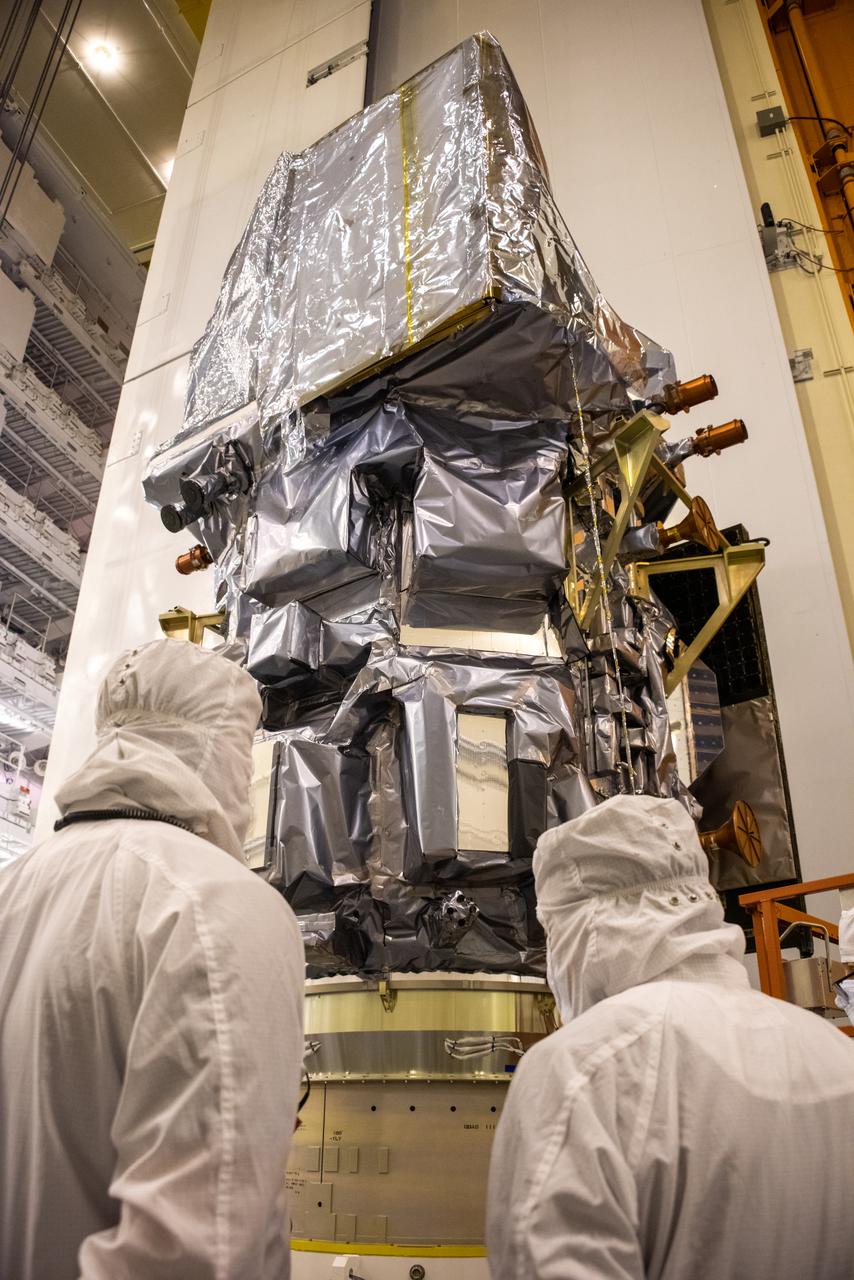

The Landsat 9 PSR to EFS C29 lift and mate inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
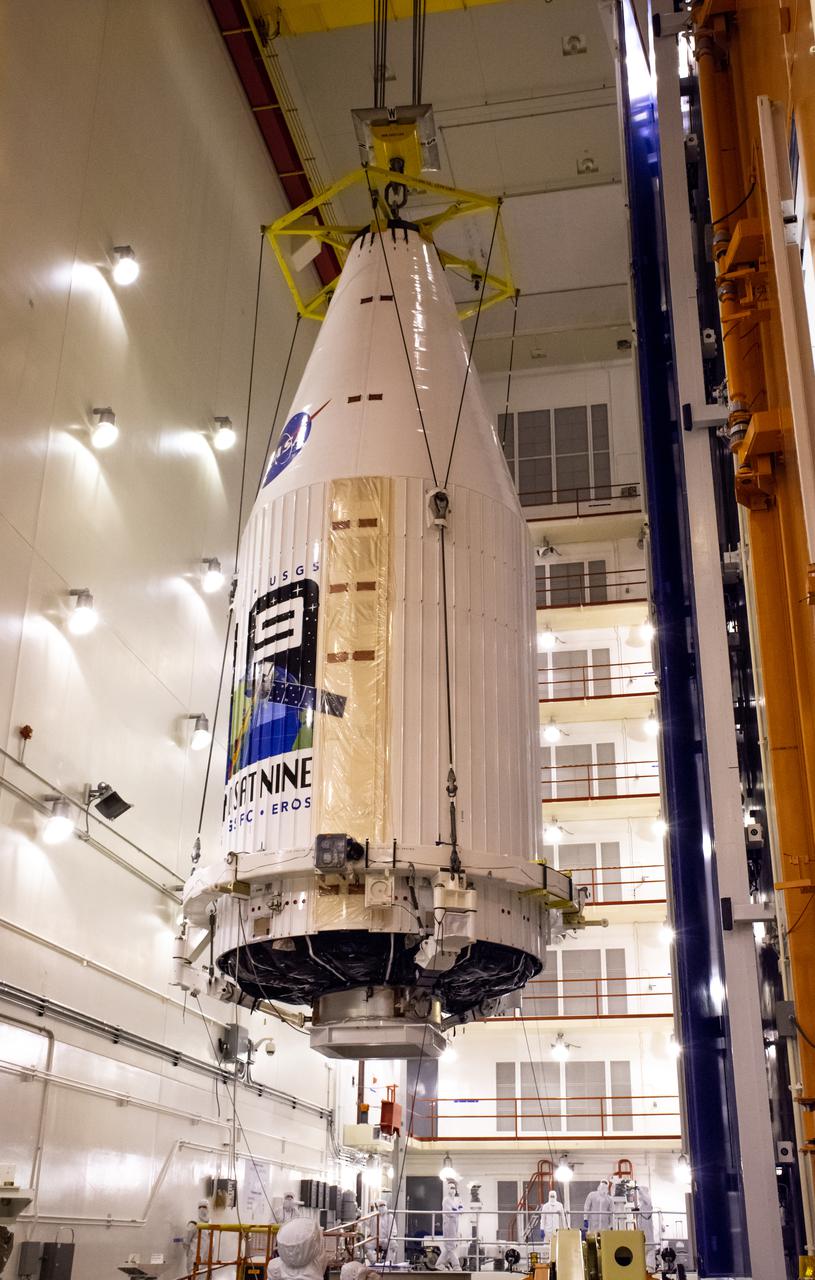

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, the Landsat 9 spacecraft, secured in the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing, is moved by crane toward the transfer tower for closeout operations on Aug. 19, 2021. Landsat 9 will launch on a ULA Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
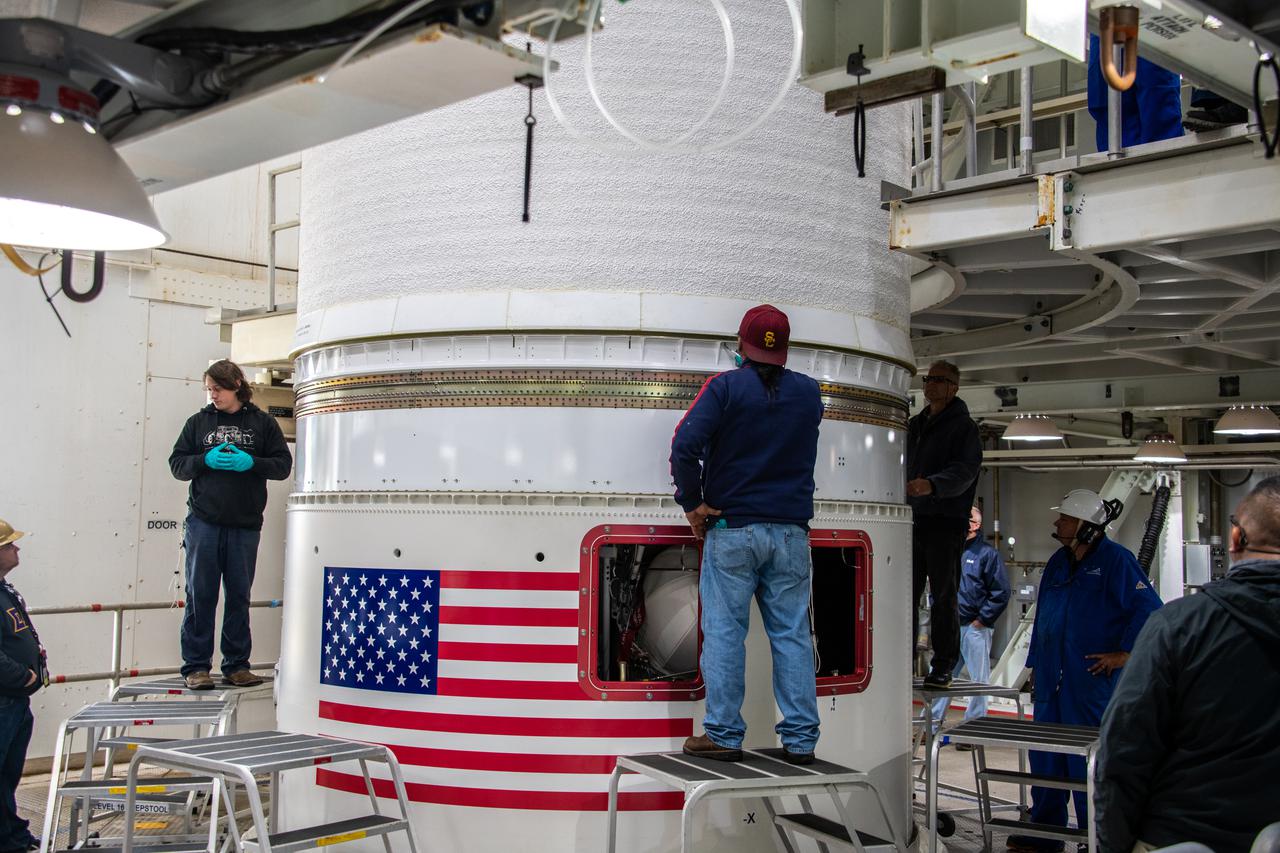

Inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, United Launch Alliance workers assist as the Centaur second stage for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission is lowered onto the Atlas V booster on July 15, 2021. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
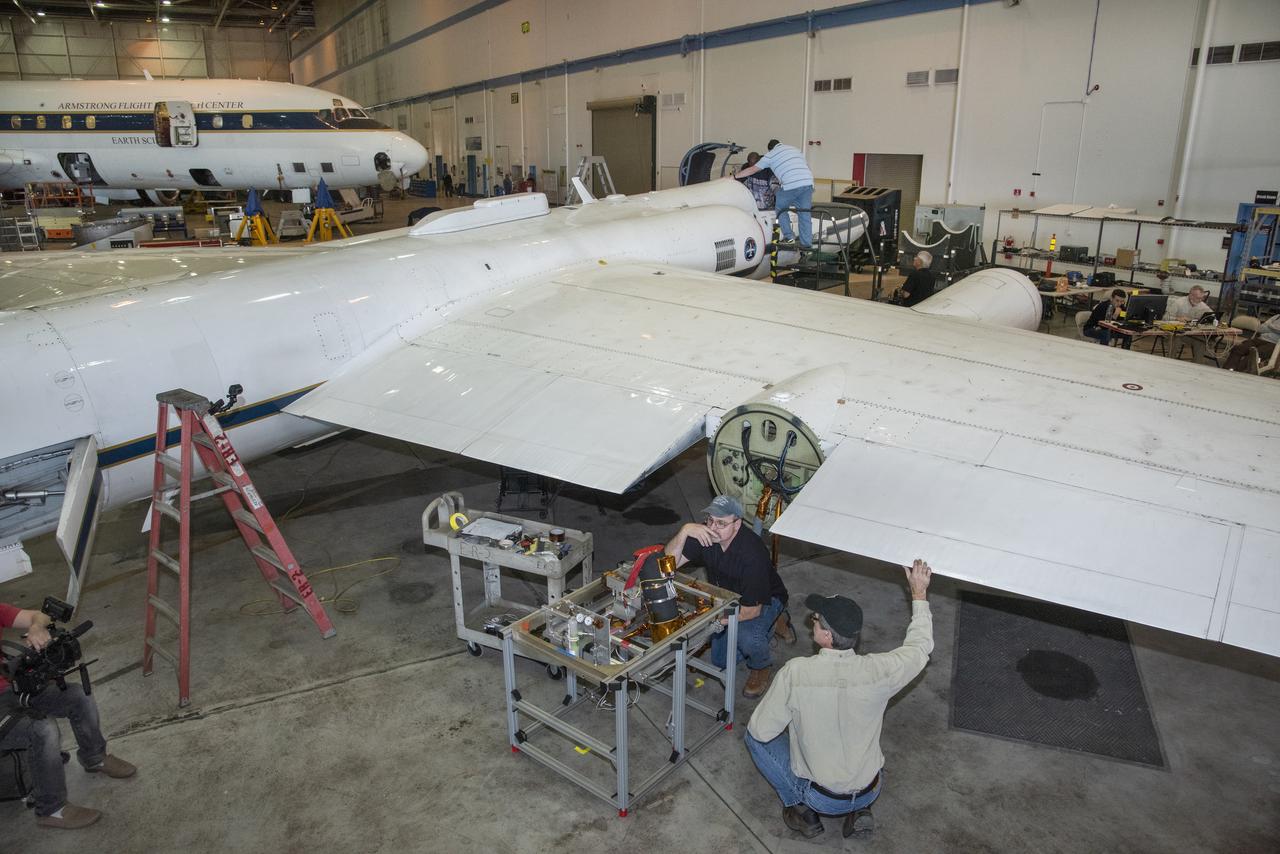

Steven Grantham (NIST) and John Woodward (NIST) contemplate cable management for air-LUSI’s Irradiance Instrument Subsystem telescope at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Palmdale, CA. It is critical that the delicate fiber optic cables move smoothly with the telescope.
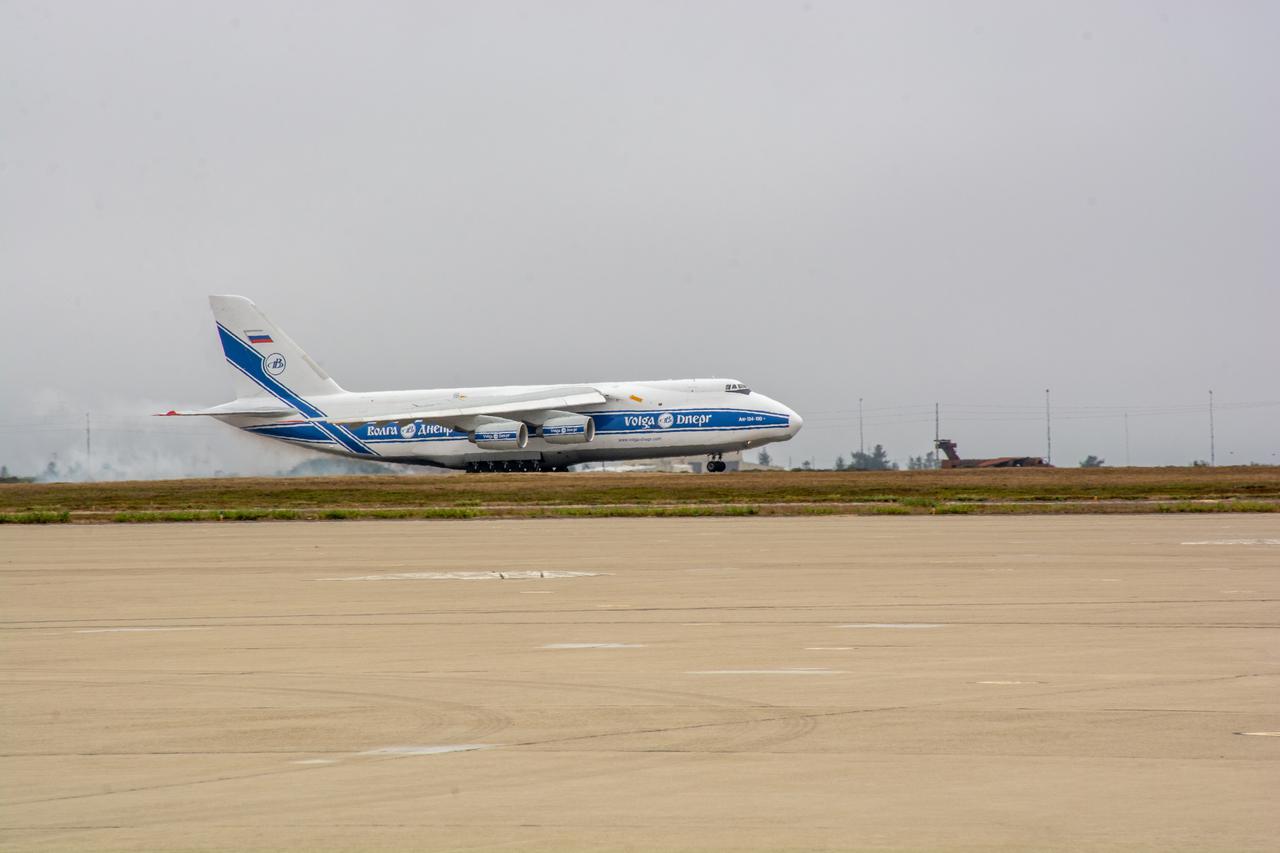

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission arrives aboard an Antonov 124 cargo aircraft at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on June 28, 2021. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop a ULA Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
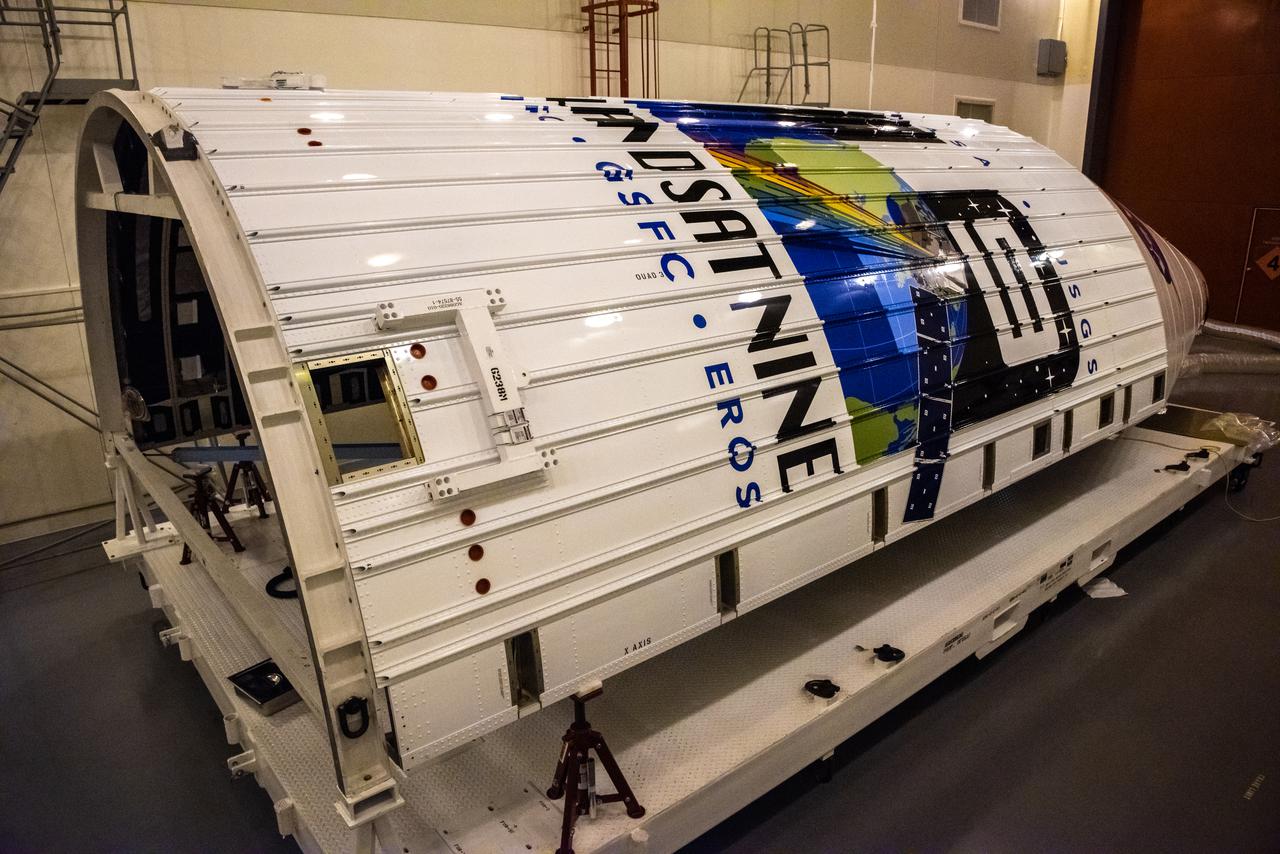

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, United Launch Alliance (ULA) technicians perform ultraviolet and white light inspections on one of two ULA Atlas V rocket payload fairings for NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite on June 17, 2021. The fairings will encapsulate the satellite for its launch atop the Atlas V from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near-infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
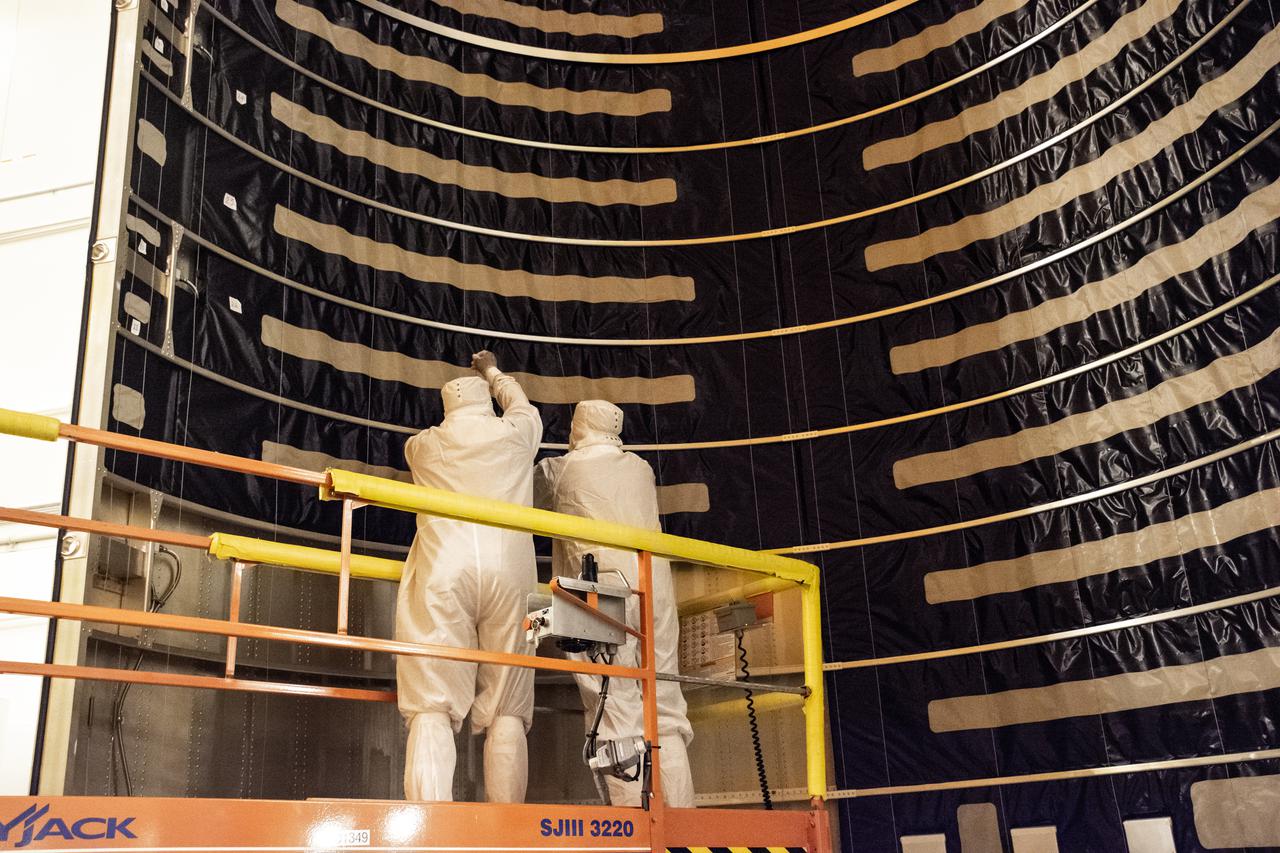

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, technicians with United Launch Alliance (ULA) remove the protective blankets from one payload fairing half for the Landsat 9 spacecraft on Aug. 2, 2021. The two halves of the ULA payload fairing will be secured around Landsat 9 to protect it during launch atop the ULA Atlas V rocket. Landsat 9 will launch on the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
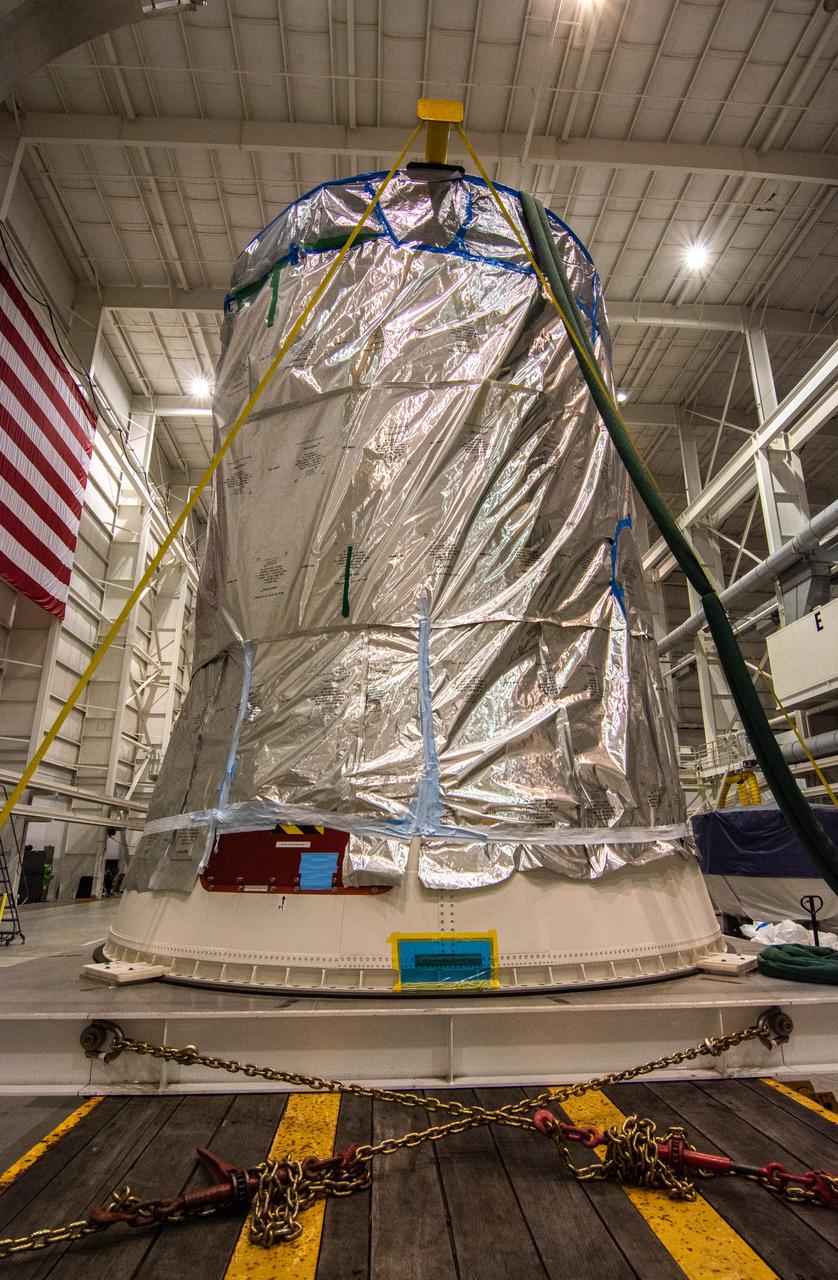

Preparations are underway to lift the interstage and assembly second stage adapters for the United Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on July 14, 2021. The adapters will be stacked atop the Centaur second stage in the Vertical Integration Facility near the launch pad. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
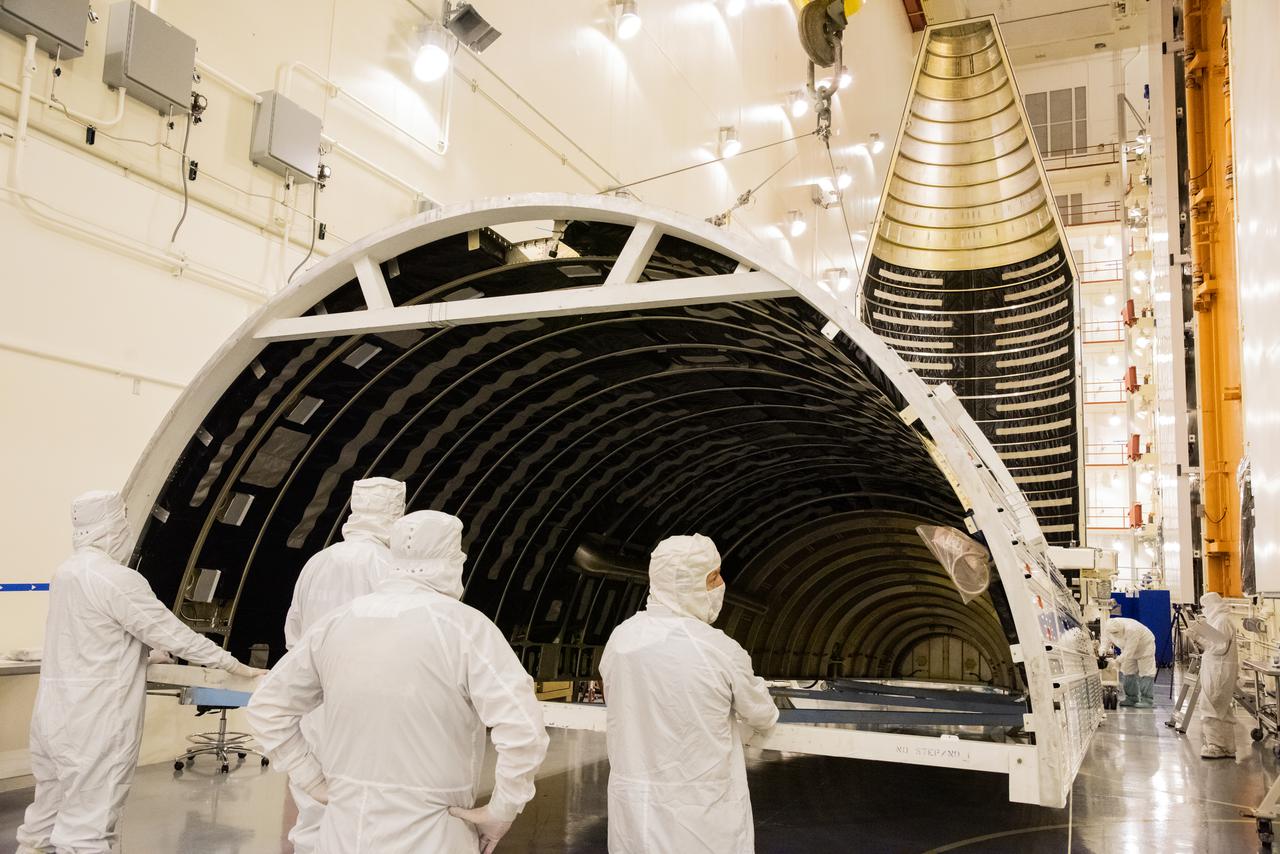

Preparations are underway to lift the second half of the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket payload fairing for NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite to the vertical position inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on June 21, 2021. The fairings will encapsulate the satellite for its launch atop the Atlas V from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near-infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
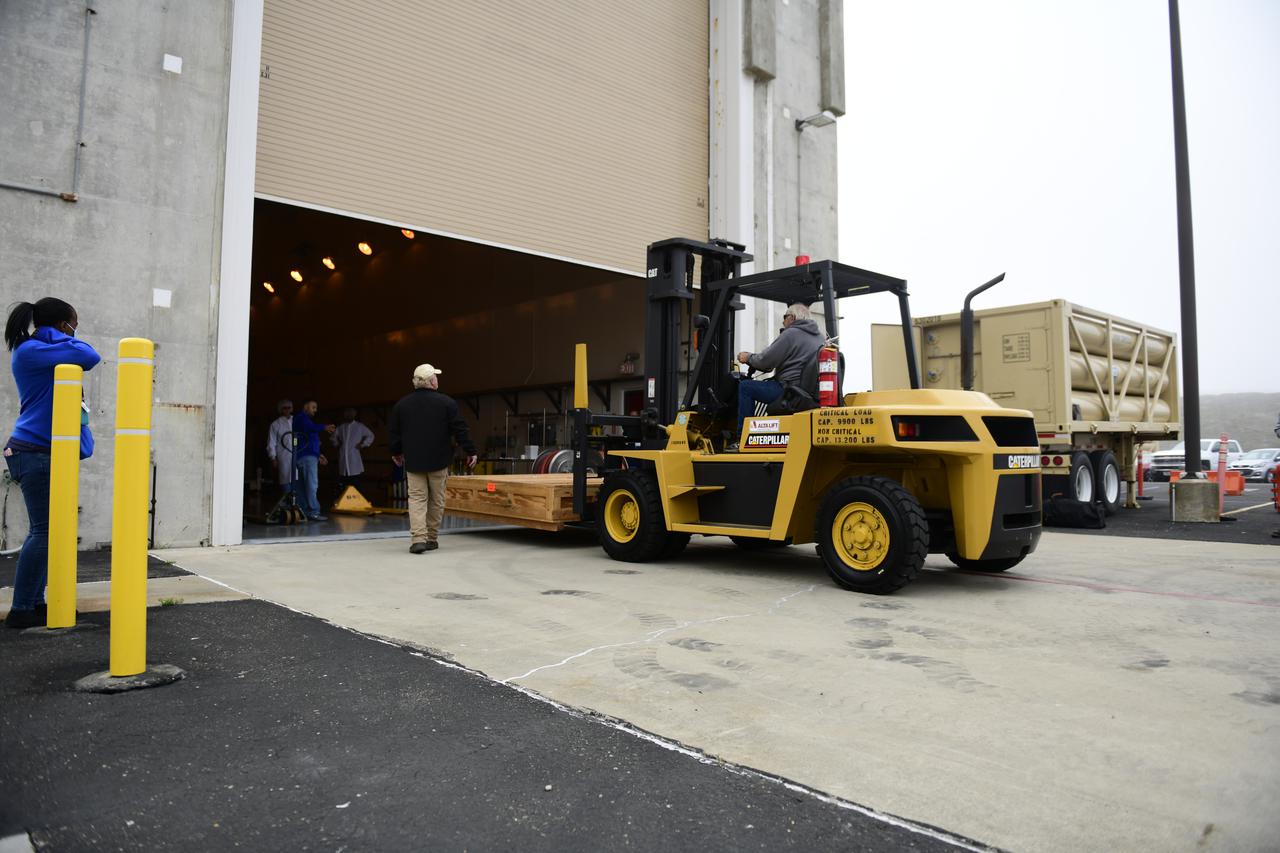

Containers of electrical ground support equipment for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission are moved inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on June 29, 2021. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
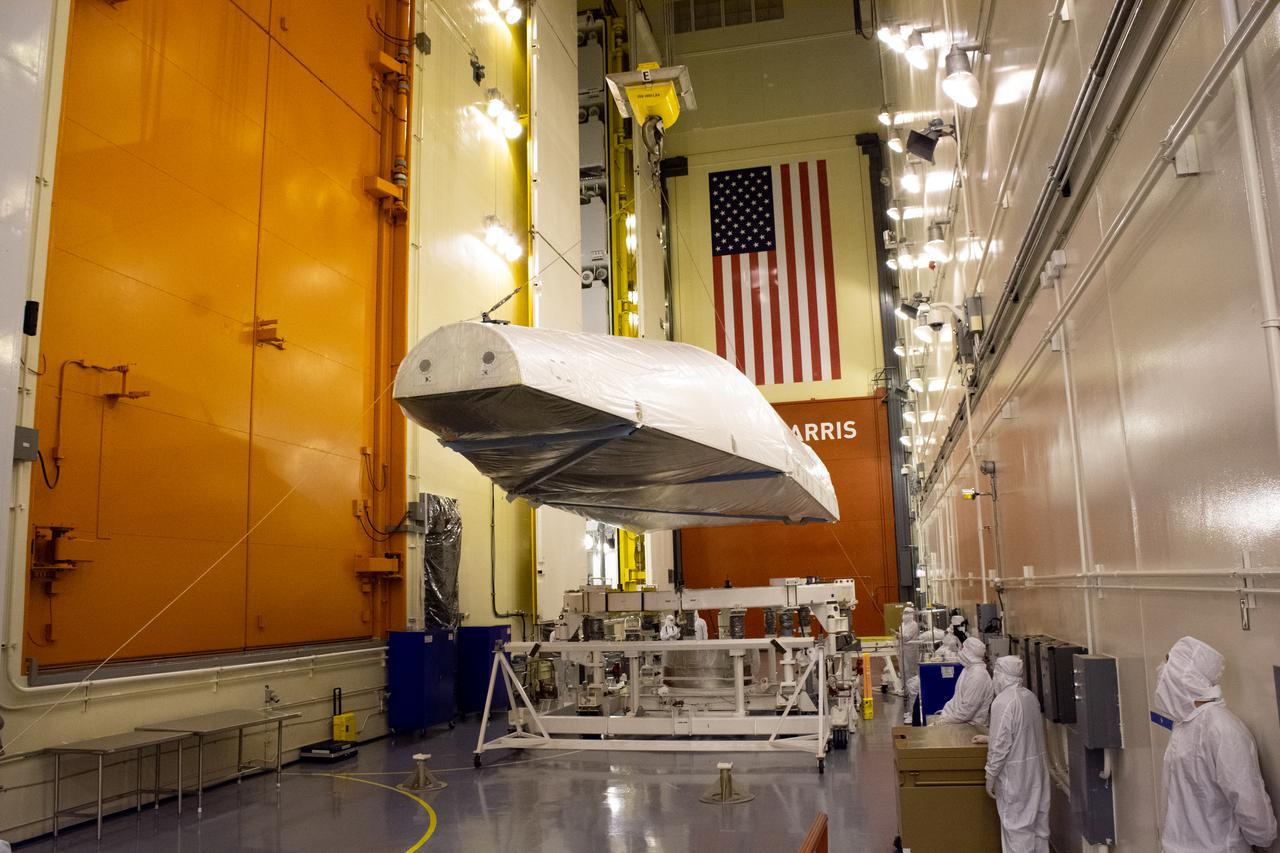

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, the first of two payload fairings for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is lifted by crane on June 3, 2021, to prepare it for NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite. The Atlas V will launch NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center. Landsat 9 will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, technicians monitor the progress as the Landsat 9 spacecraft is lifted by crane from the base of its protective container on July 8, 2021. Landsat 9 is being prepared for its launch atop the ULA Atlas V from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near-infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
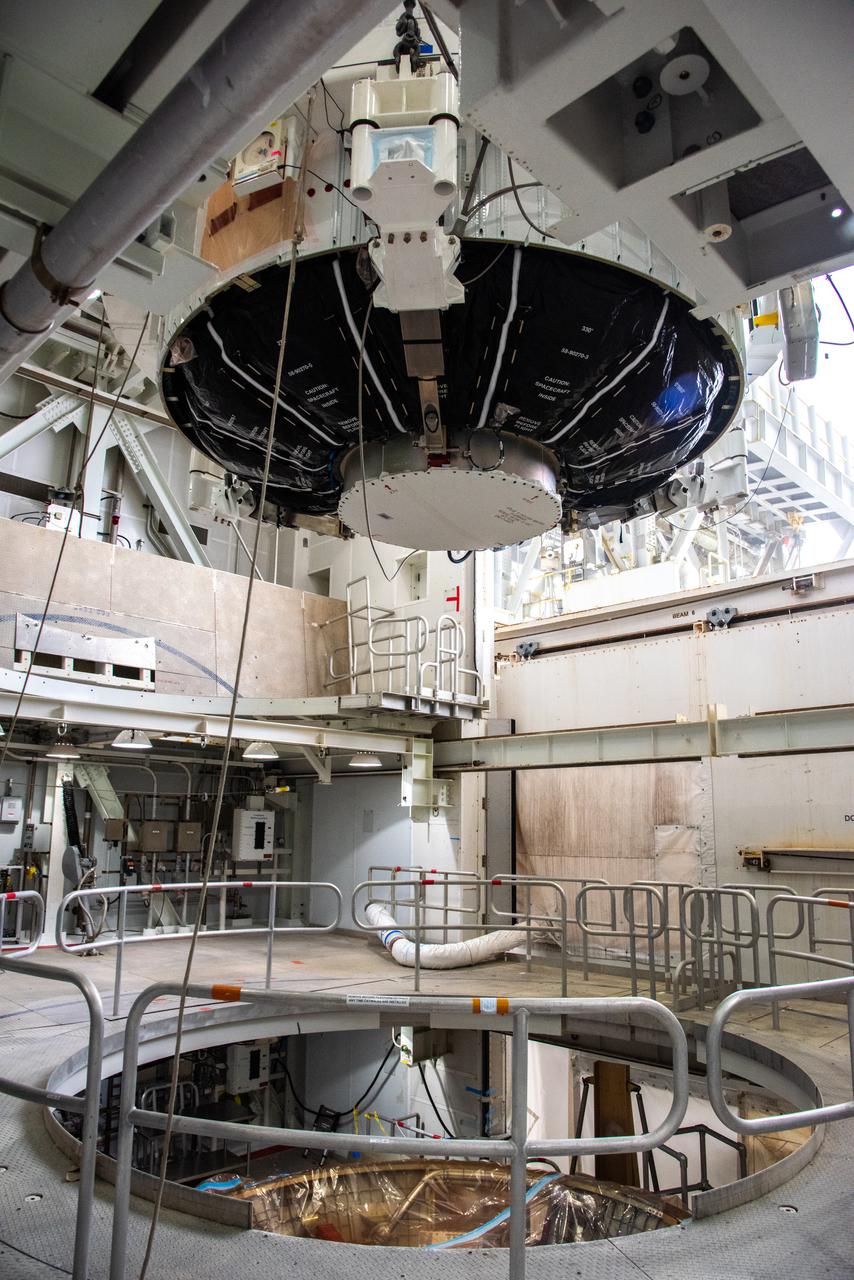

The Landsat 9 spacecraft is lifted and mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sept. 15, 2021, in preparation for liftoff no earlier than Sept. 27, 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
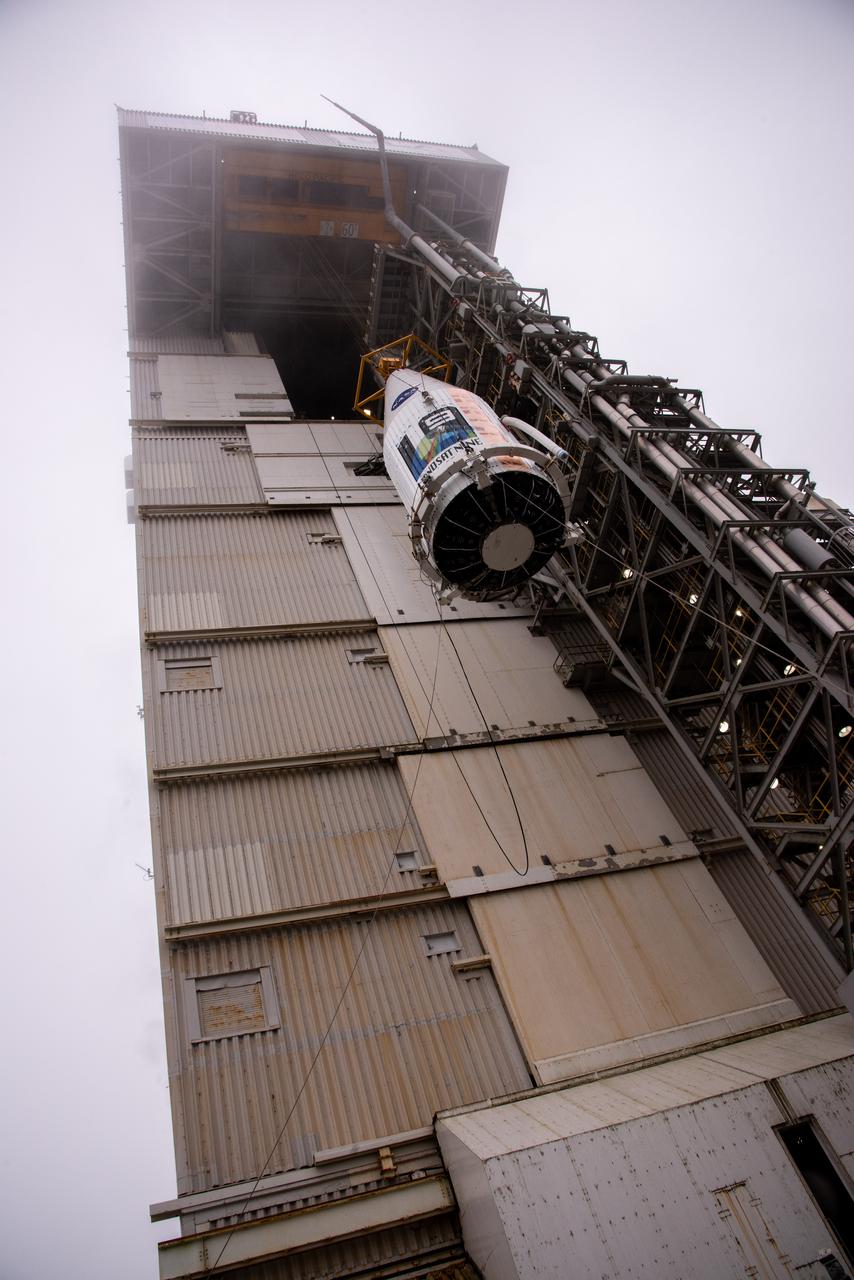

The Landsat 9 spacecraft is lifted and mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sept. 15, 2021, in preparation for liftoff no earlier than Sept. 27, 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
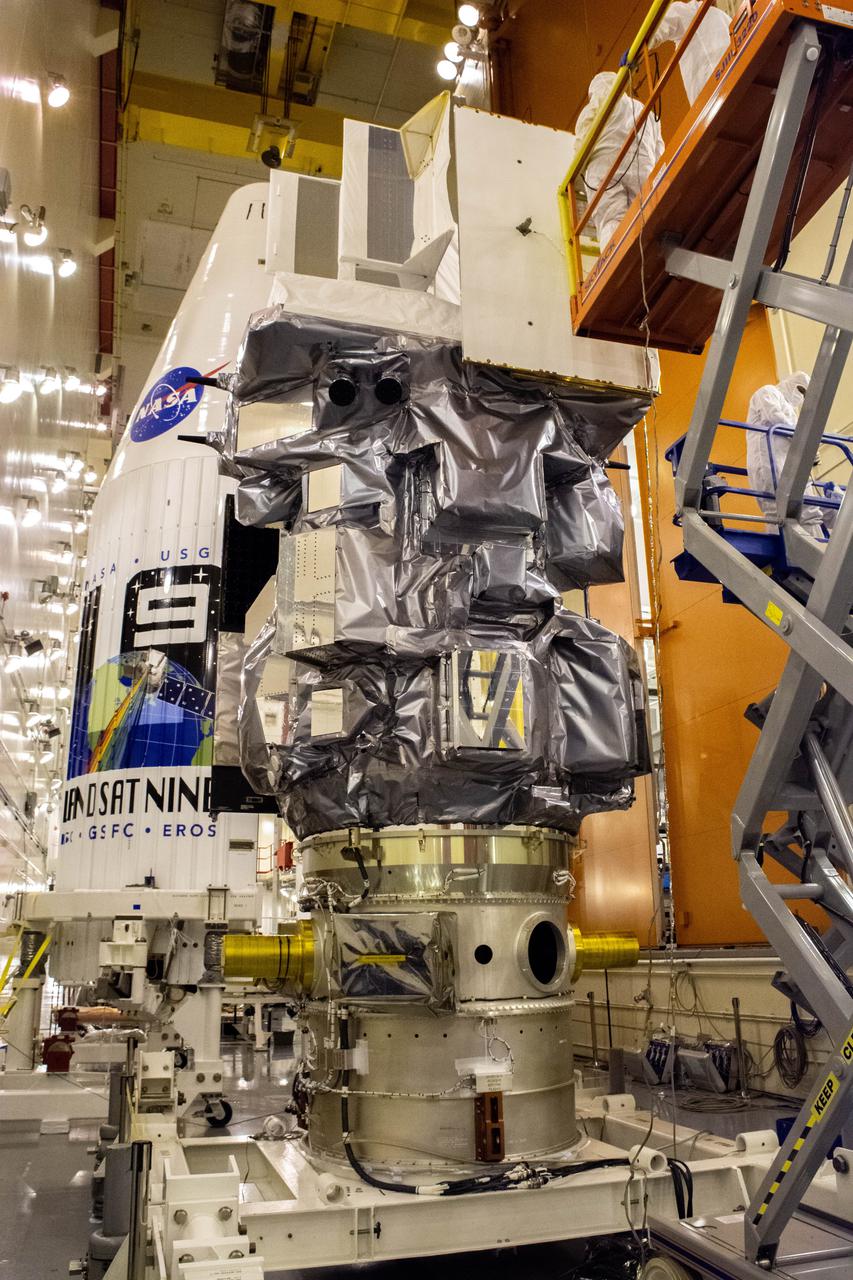

The Landsat 9 instrument cover is removed from the spacecraft inside the Integrated Processing Facility (IPF) at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
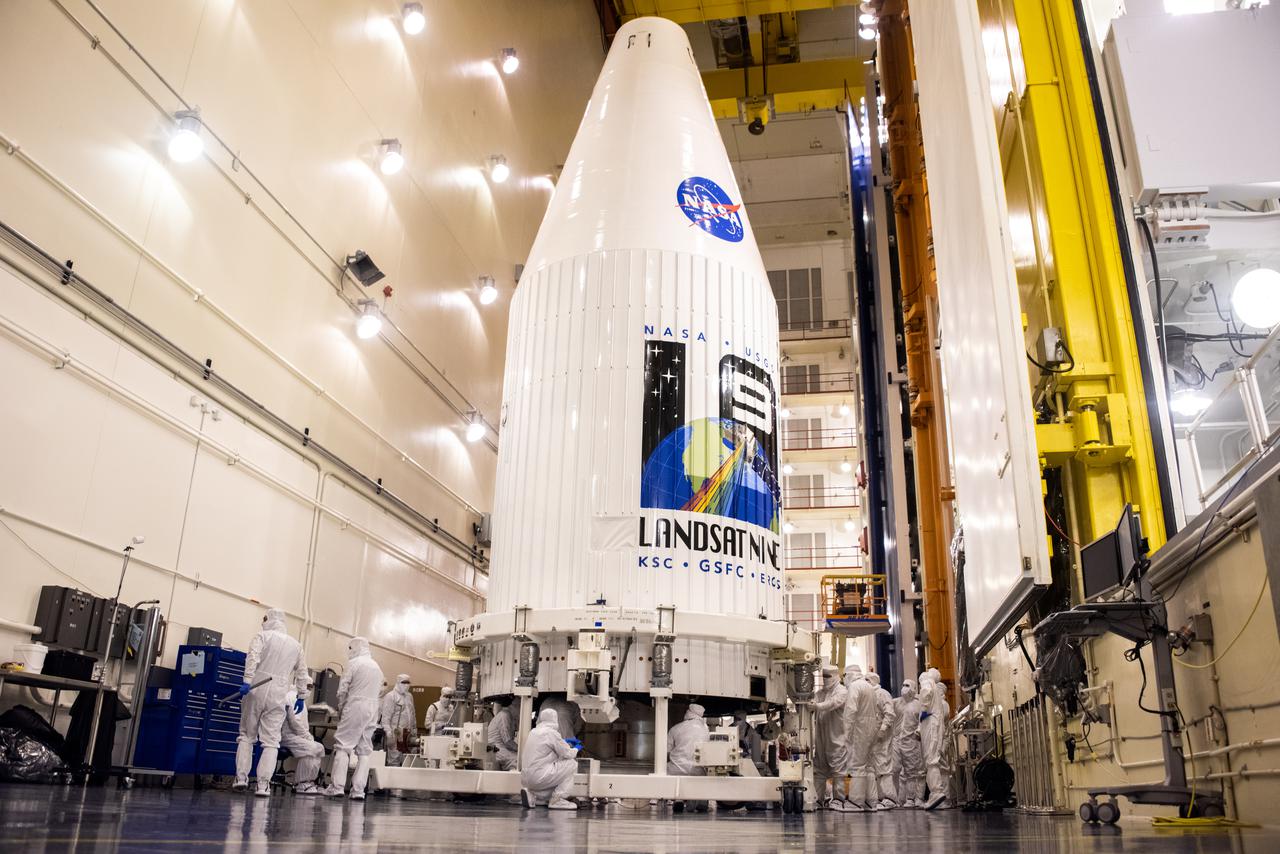

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, both United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairings are secured around the Landsat 9 spacecraft on Aug. 16, 2021. The fairings will encase and protect Landsat 9 during launch atop the ULA Atlas V rocket. Landsat 9 will launch on the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
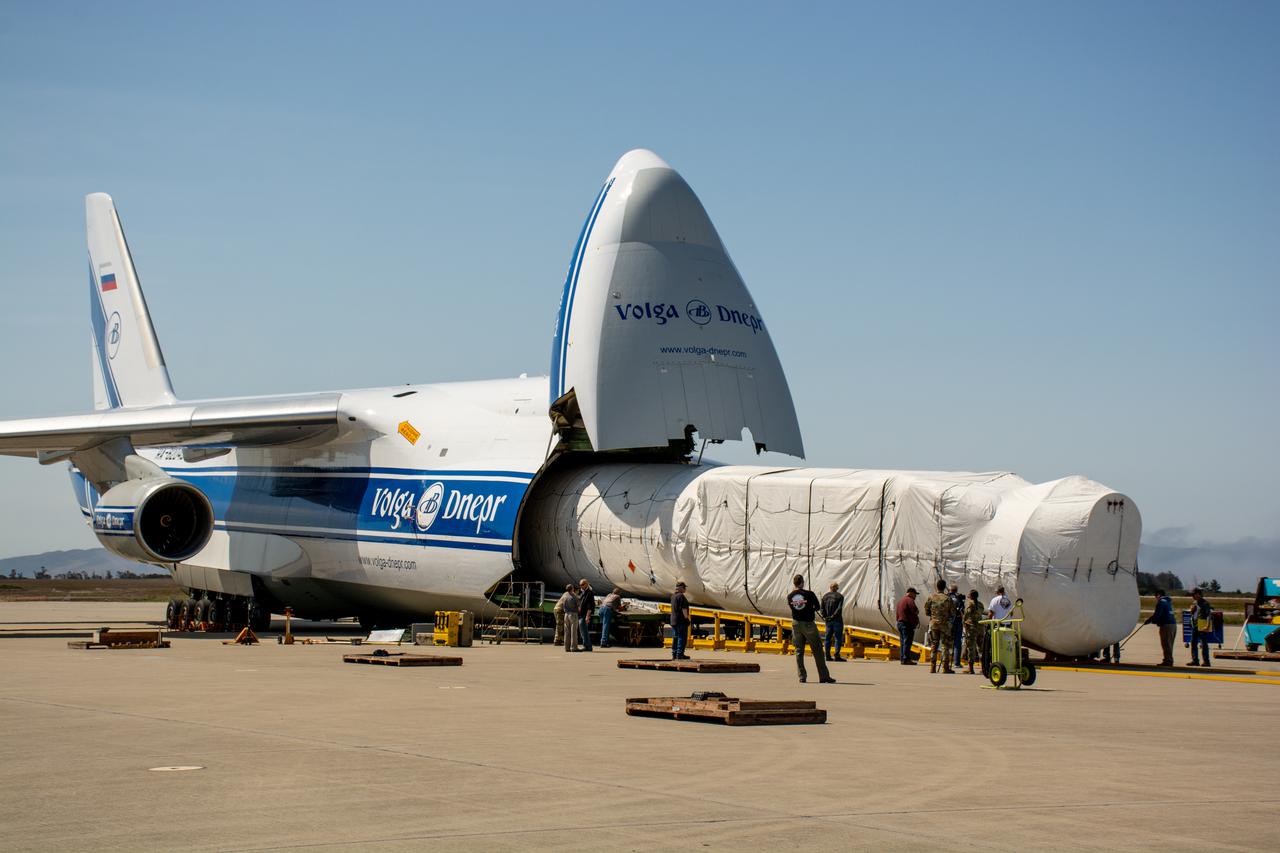

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission is offloaded from the Antonov 124 cargo aircraft at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on June 29, 2021. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop a ULA Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
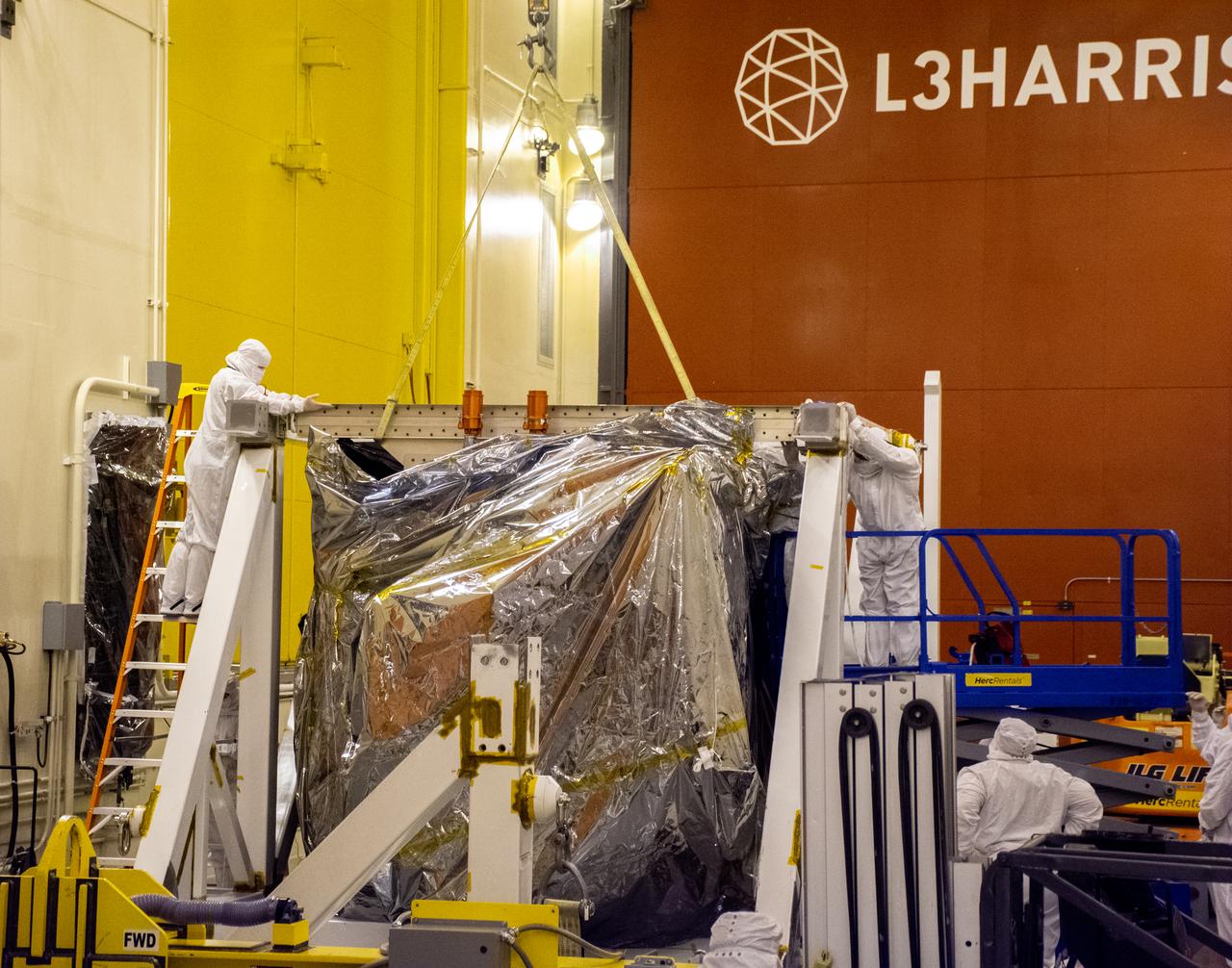

The Landsat 9 spacecraft (observatory) undergoes breakover operations inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
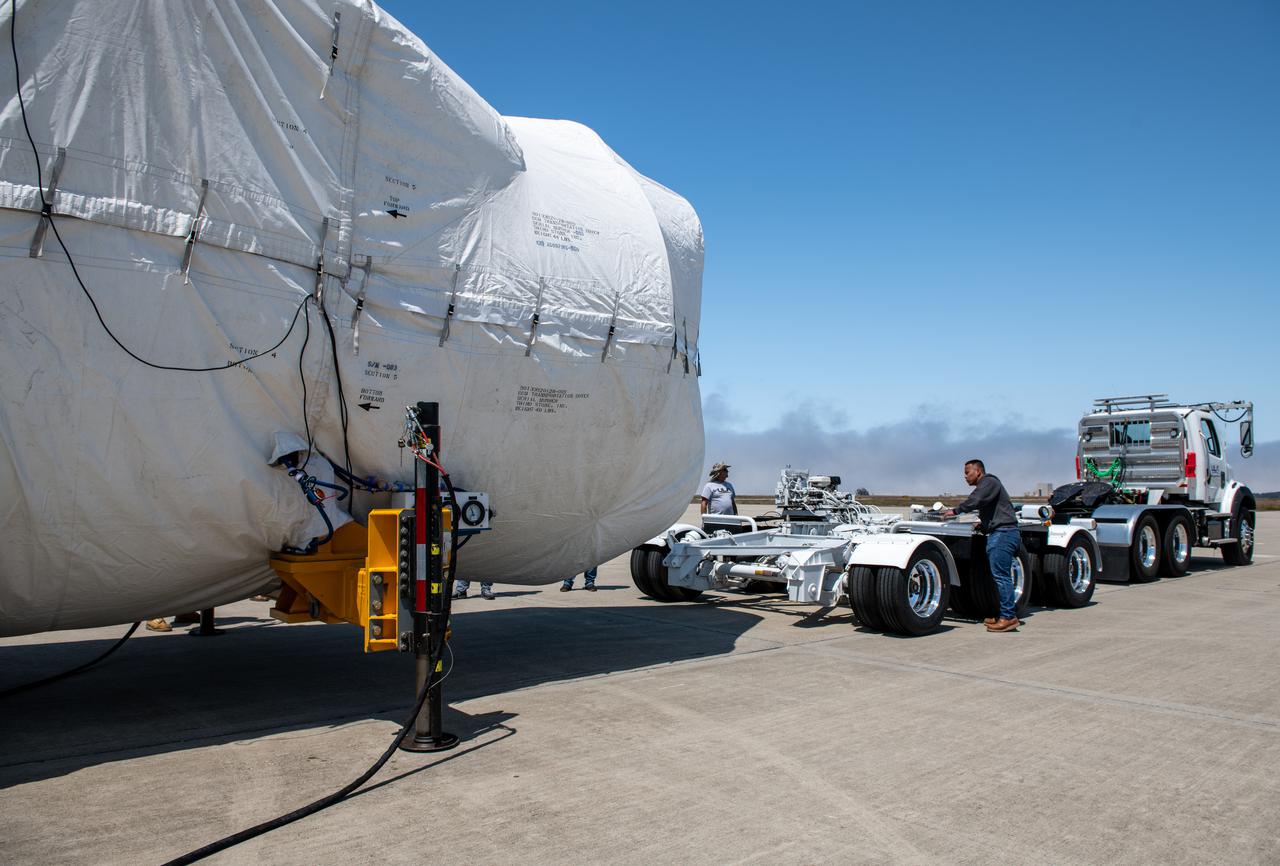

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission is offloaded from the Antonov 124 cargo aircraft at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on June 29, 2021 and prepared for transport to the Horizontal Integration Facility. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop a ULA Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

The Atlas V boat tail for the Landsat 9 mission is lifted and mated at Vandenberg Space Force Base’s Space Launch Complex 3 in California on July 17, 2021. The Landsat 9 mission launch, which is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 27, 2021. Landsat 9 will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

The satellite for the Landsat 9 mission, secured inside its shipping container, arrives at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on July 7, 2021. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
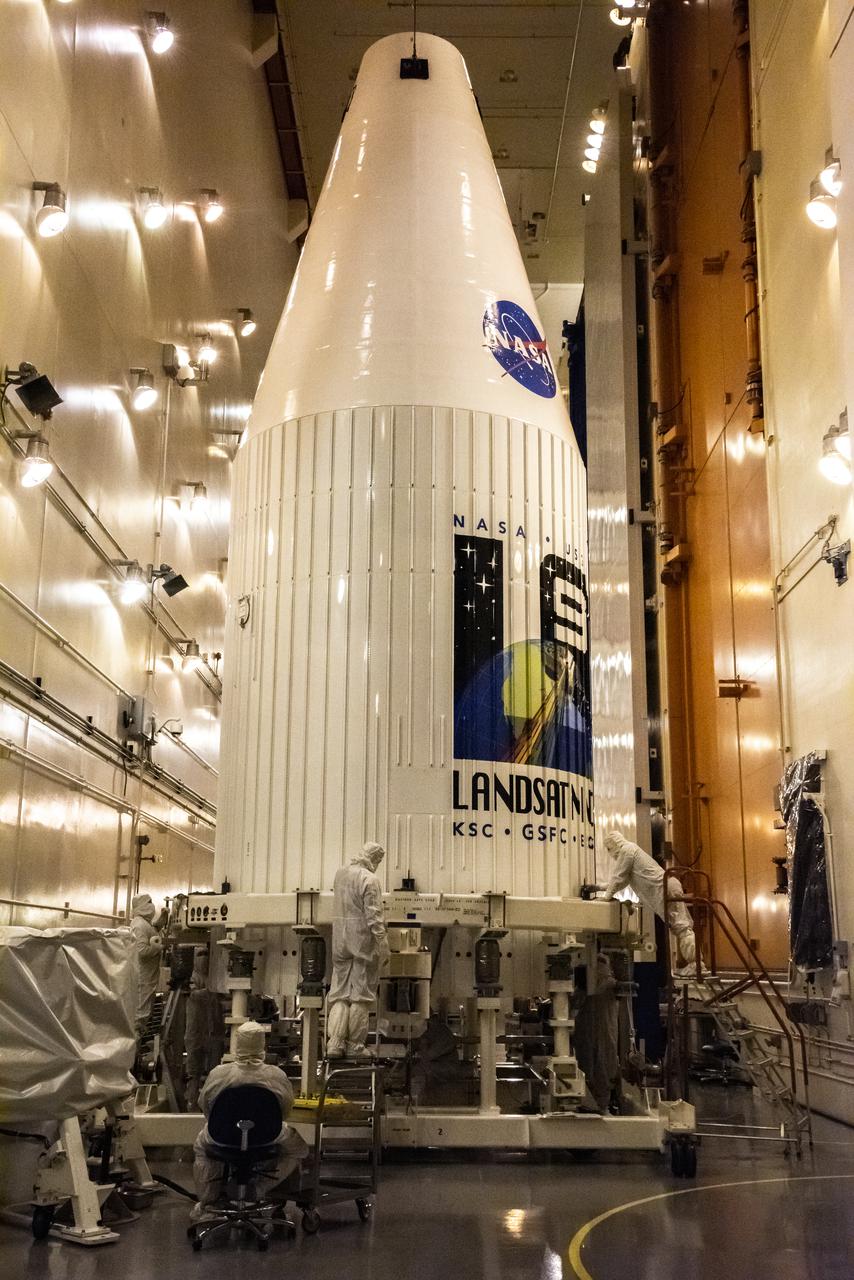

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, the second half of two United Launch Alliance Atlas V payload fairings for NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite is raised to the vertical position on June 21, 2021. The fairings will encapsulate the satellite for its launch atop the Atlas V from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near-infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
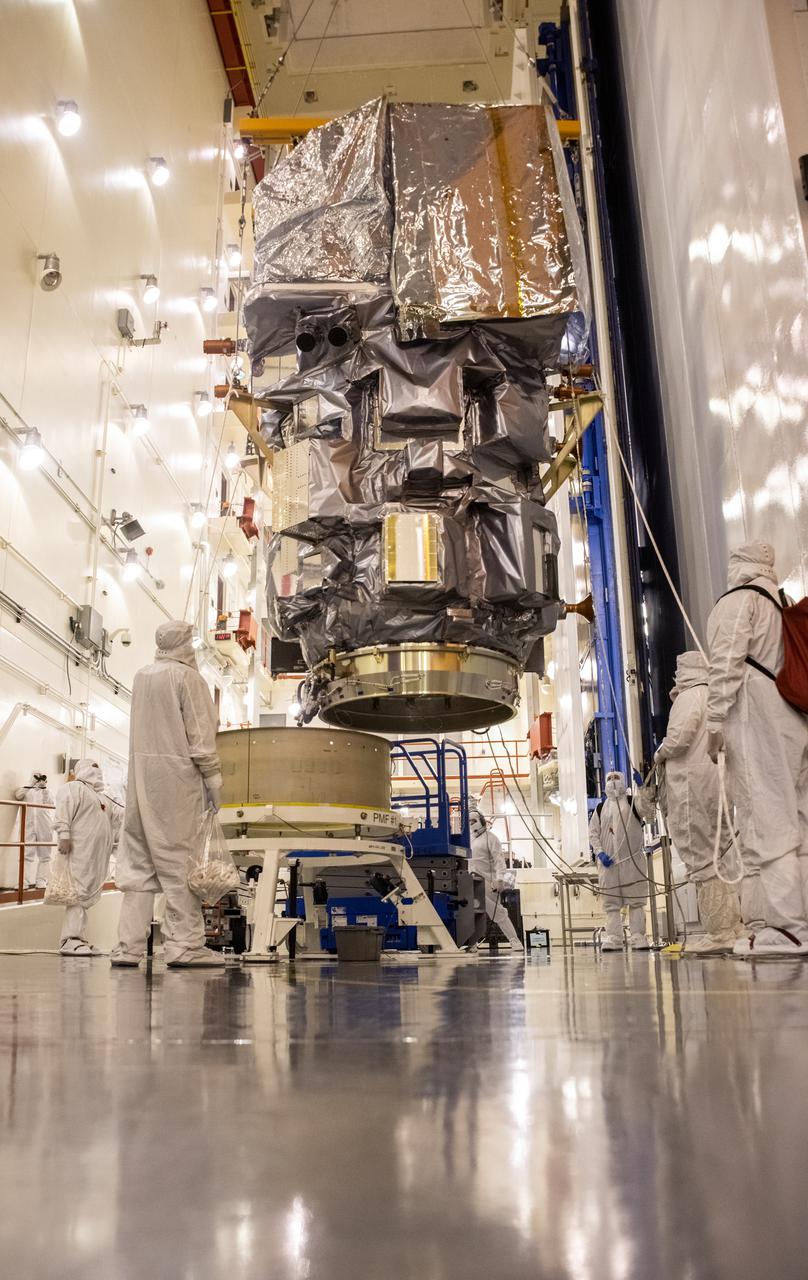

The Landsat 9 PSR to EFS C29 lift and mate inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
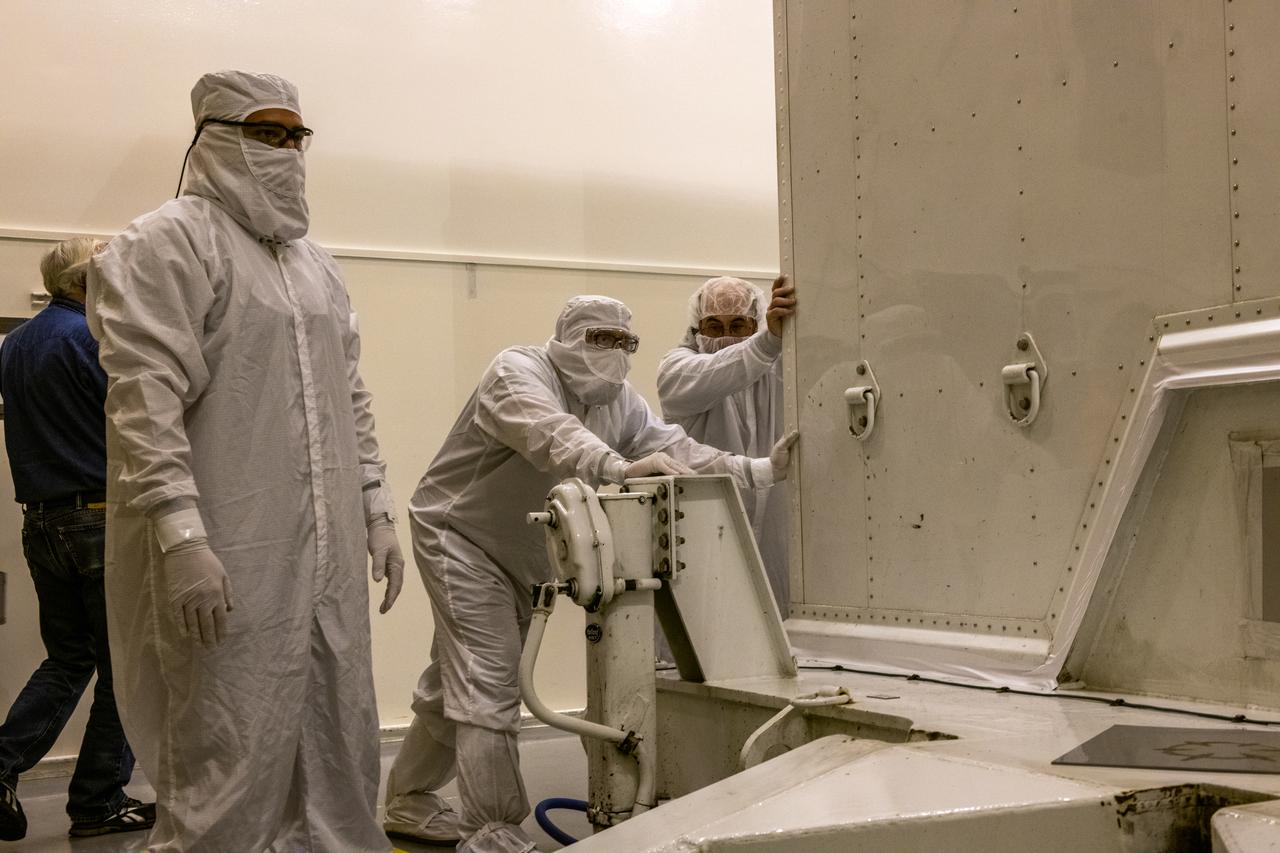

Technicians move the shipping container, carrying the satellite for the Landsat 9 mission, into a processing facility following its arrival at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on July 7, 2021. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
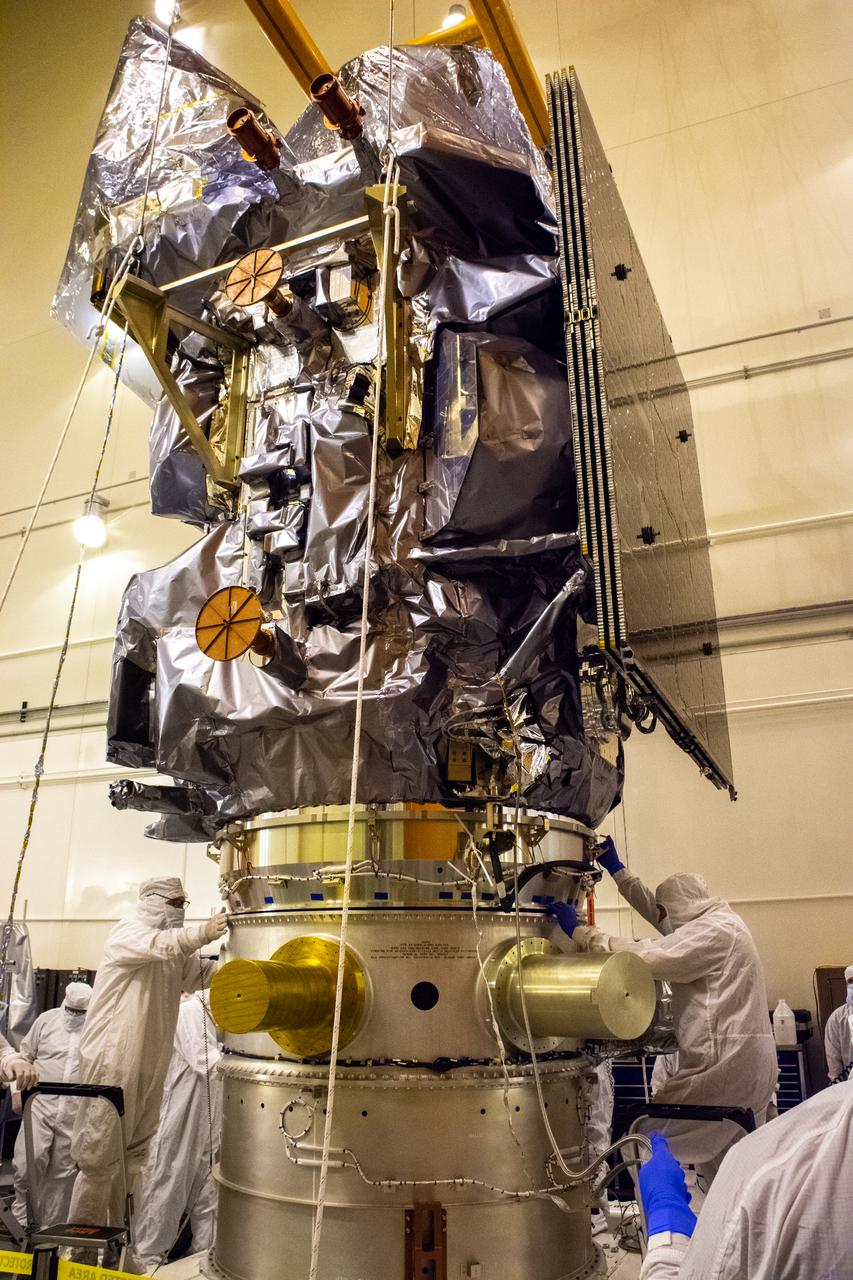
The Landsat 9 PSR to EFS C29 lift and mate inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
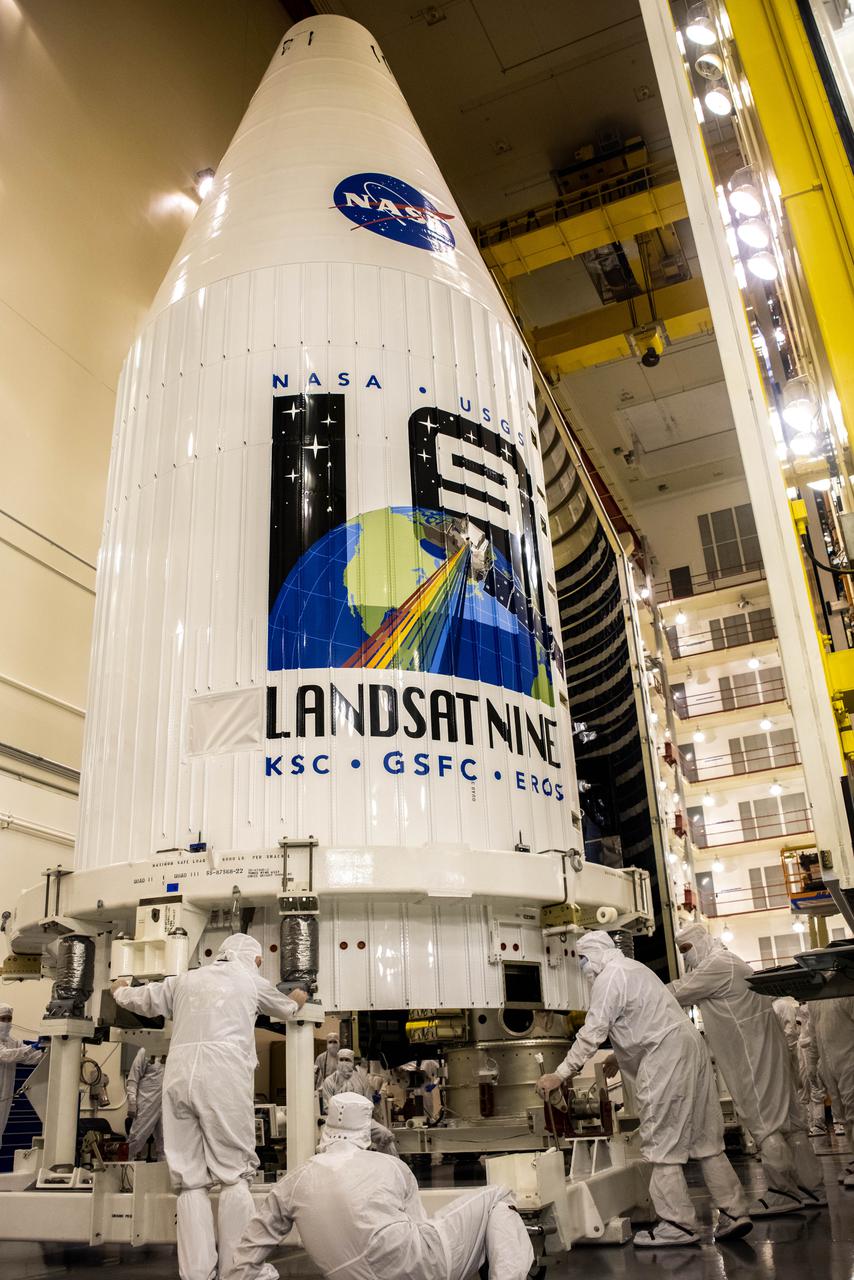

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, both halves of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing are slowly moved around the Landsat 9 spacecraft on Aug. 16, 2021. The payload fairing will be secured around Landsat 9 to protect it during launch atop the ULA Atlas V rocket. Landsat 9 will launch on the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
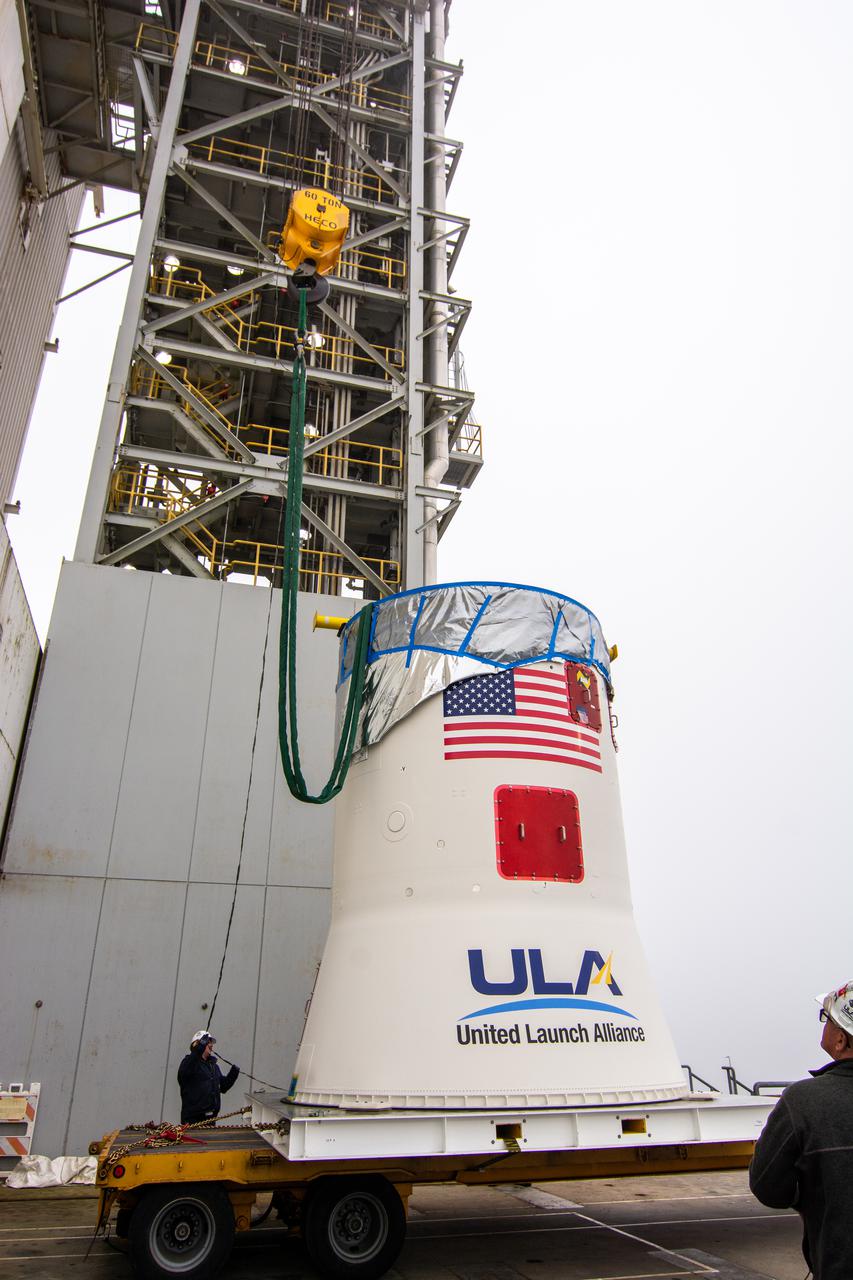

Preparations are underway to lift the interstage and assembly second stage adapters for the United Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on July 14, 2021. The adapters will be stacked atop the Centaur second stage in the Vertical Integration Facility near the launch pad. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.