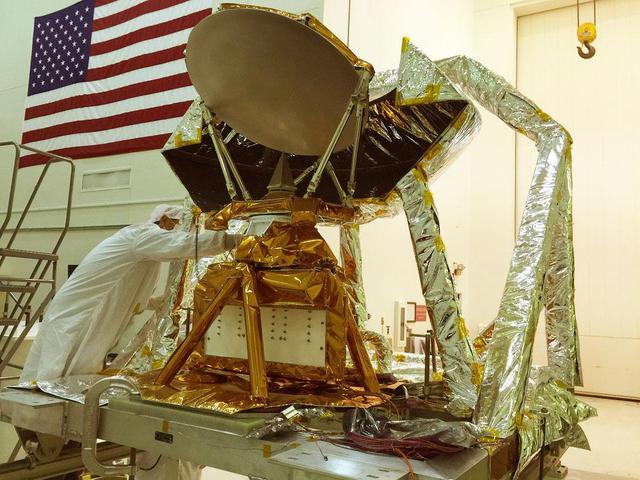

The COWVR instrument (center, wrapped in gold foil) in JPL's Environmental Test Laboratory during vibration testing. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24981
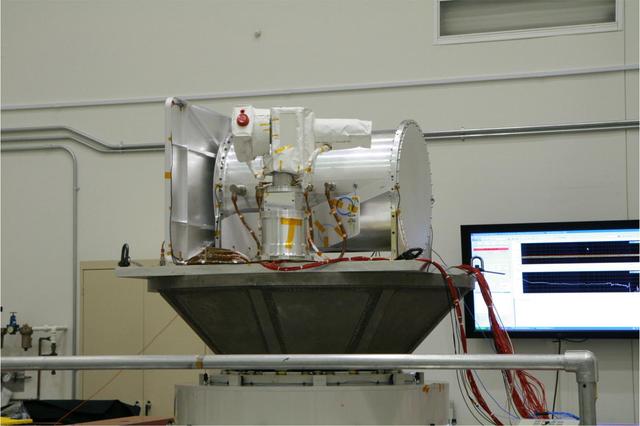

The Optical PAyload for Lasercomm Science OPALS undergoes vibration testing at NASa Jet Propulsion Laboratory in December 2012.
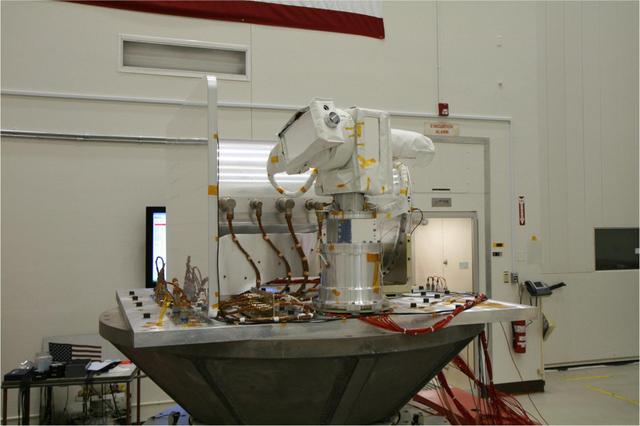

The Optical PAyload for Lasercomm Science OPALS undergoes vibration testing at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory in December 2012.

Vibration testing of the horizontal axis of the spacecraft. Credit: NASA/Goddard The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission is an international partnership co-led by NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) that will provide next-generation global observations of precipitation from space. GPM will study global rain, snow and ice to better understand our climate, weather, and hydrometeorological processes. As of Novermber 2013 the GPM Core Observatory is in the final stages of testing at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. The satellite will be flown to Japan in the fall of 2013 and launched into orbit on an HII-A rocket in early 2014. For more on the GPM mission, visit <a href="http://gpm.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">gpm.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a>. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
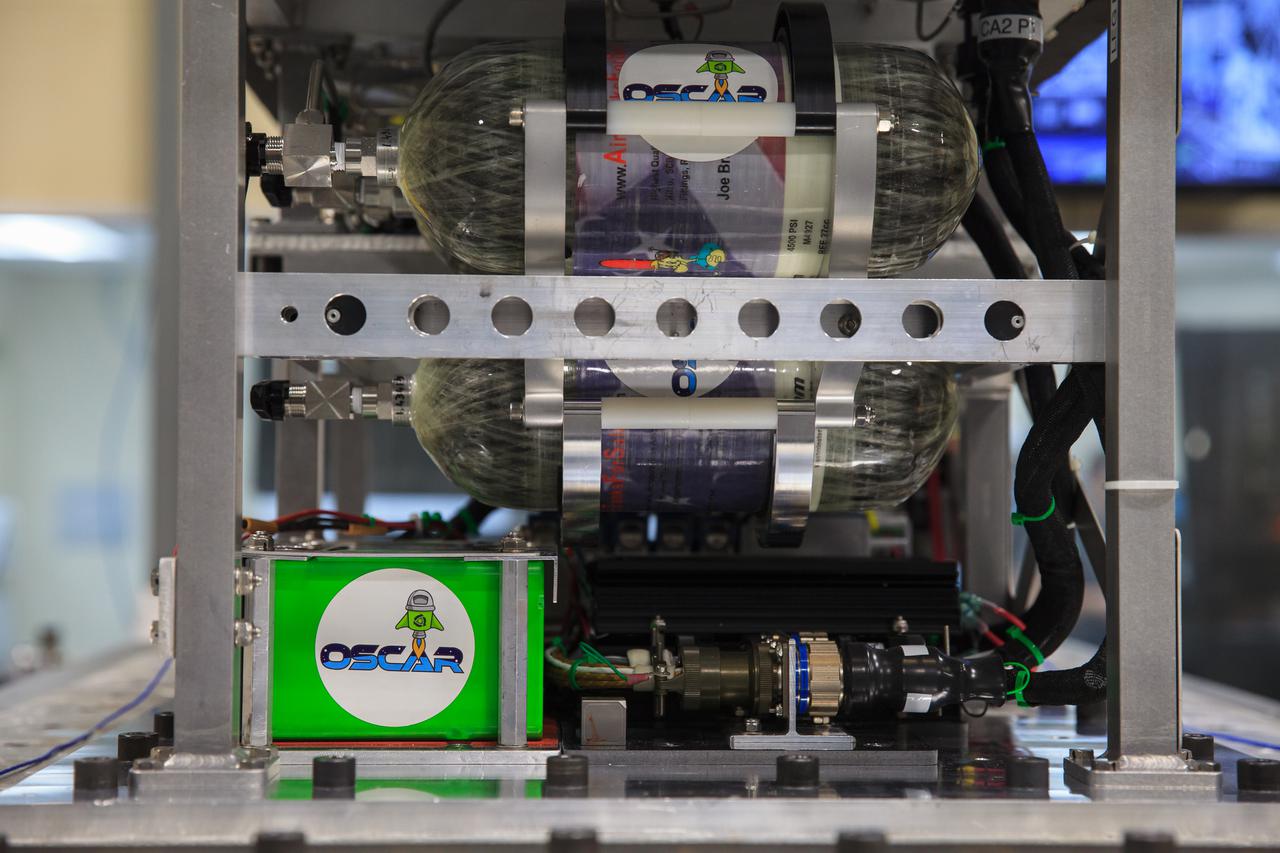
NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, undergoes vibration testing inside the Vibration Test Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The tests are part of ongoing preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.
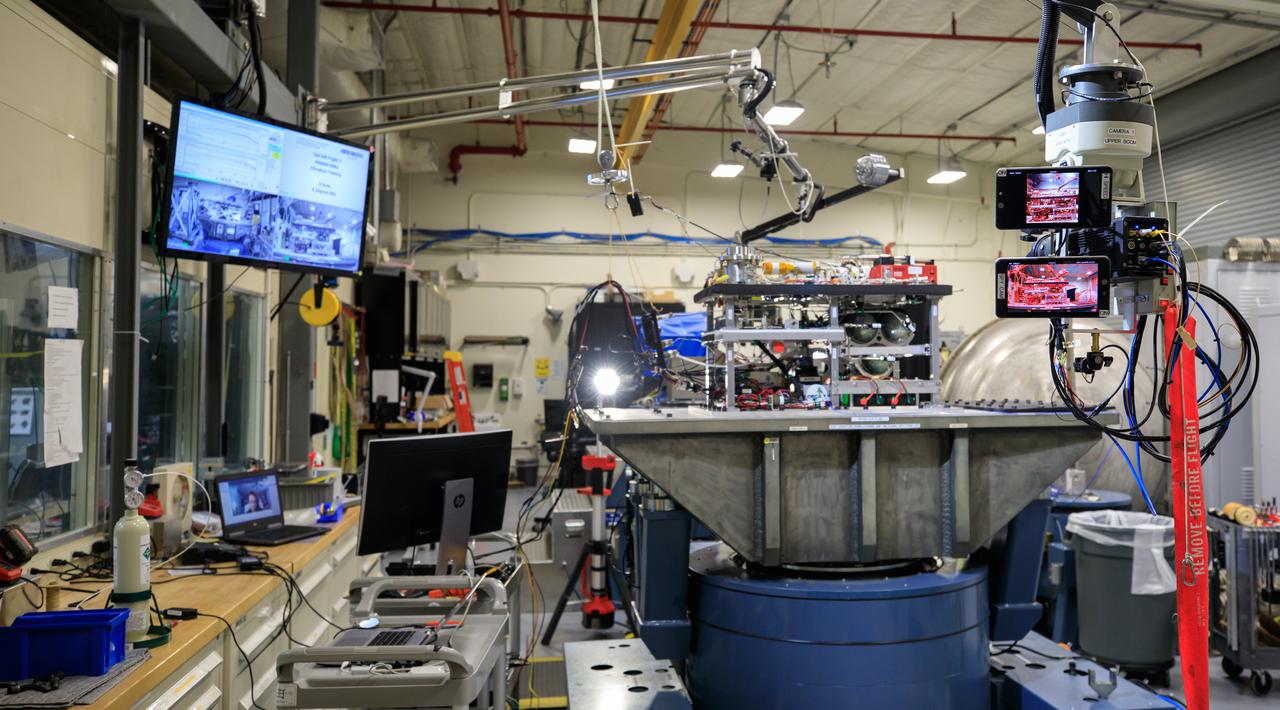

NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, undergoes vibration testing inside the Vibration Test Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The tests are part of ongoing preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.

Inside the Vibration Test Lab at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) undergoes vibration testing on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.
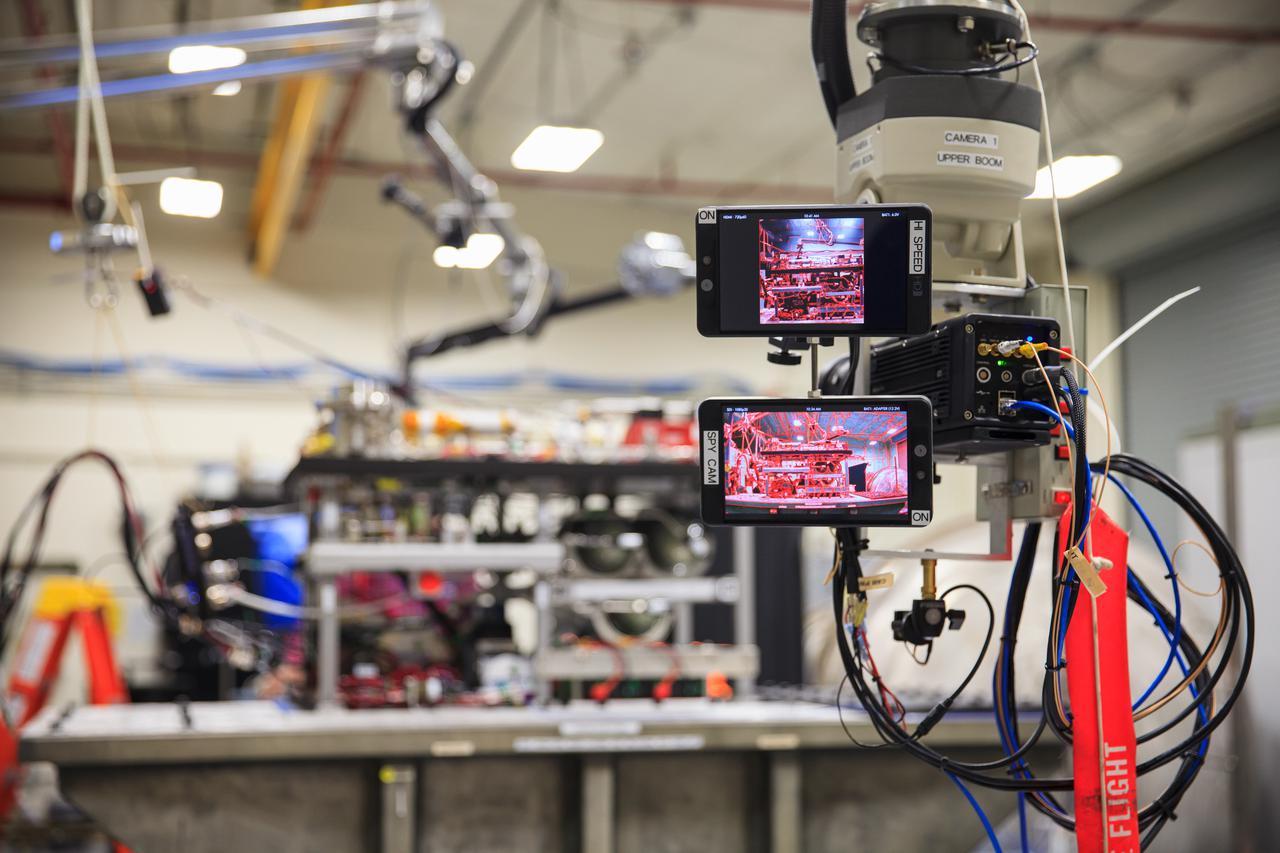

NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, undergoes vibration testing inside the Vibration Test Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.
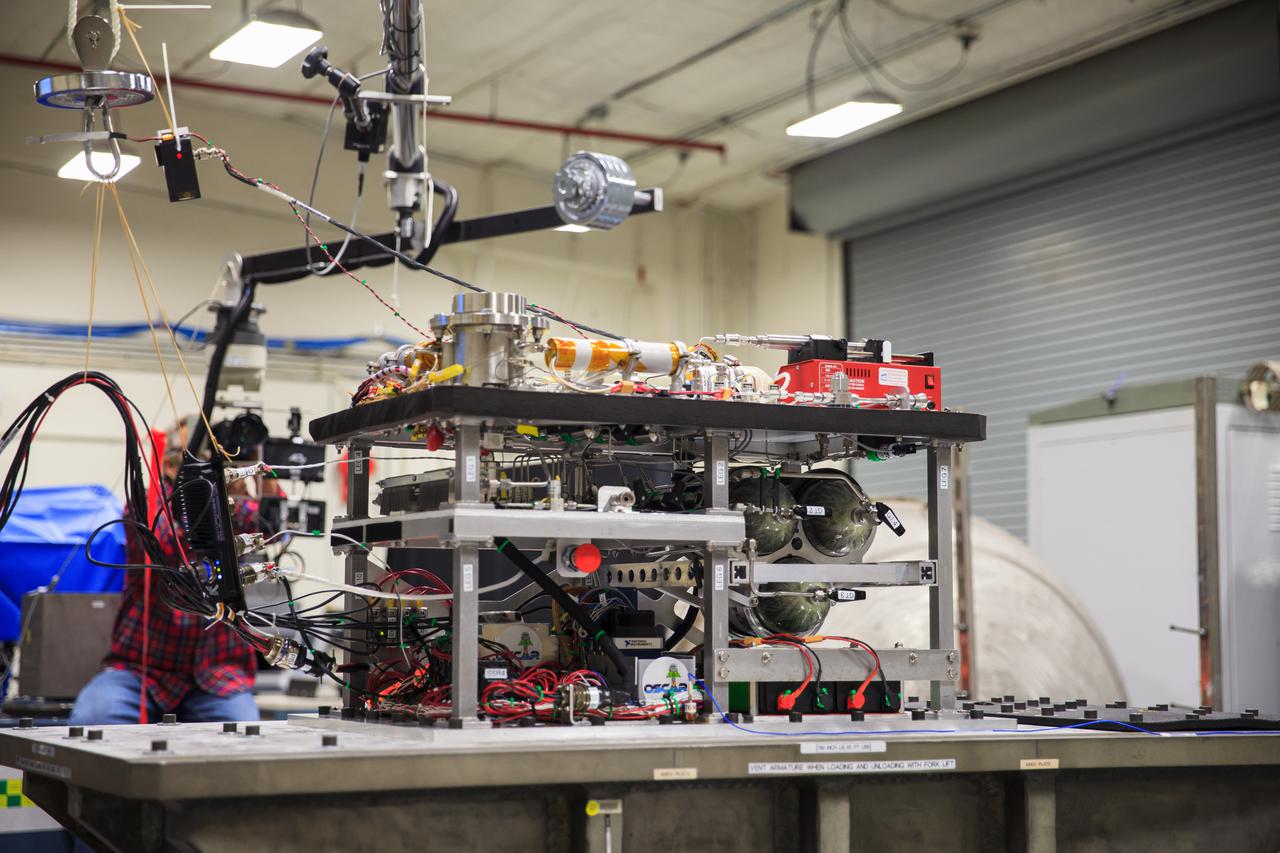

NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, undergoes vibration testing inside the Vibration Test Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.

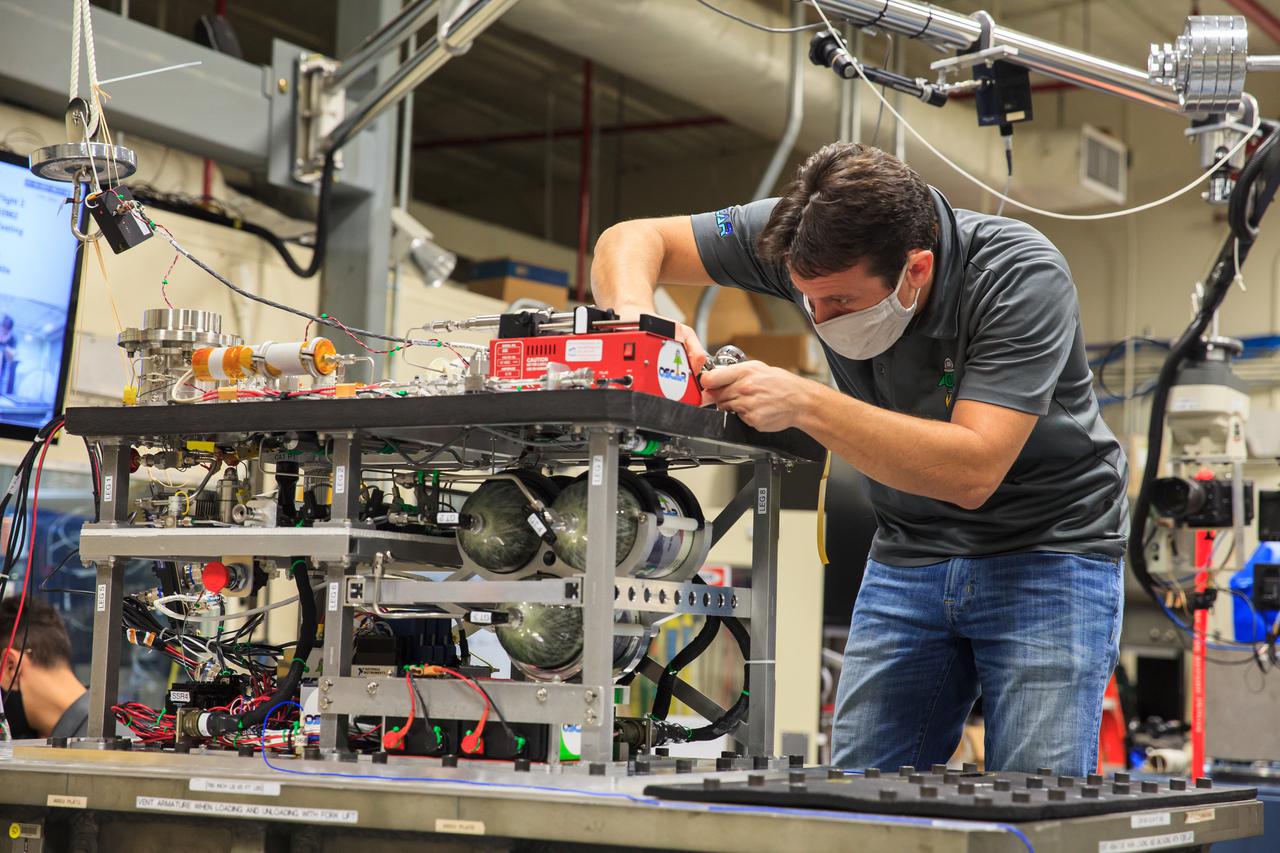
Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR), prepares OSCAR for vibration tests inside the Vibration Test Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The tests are part of ongoing preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.
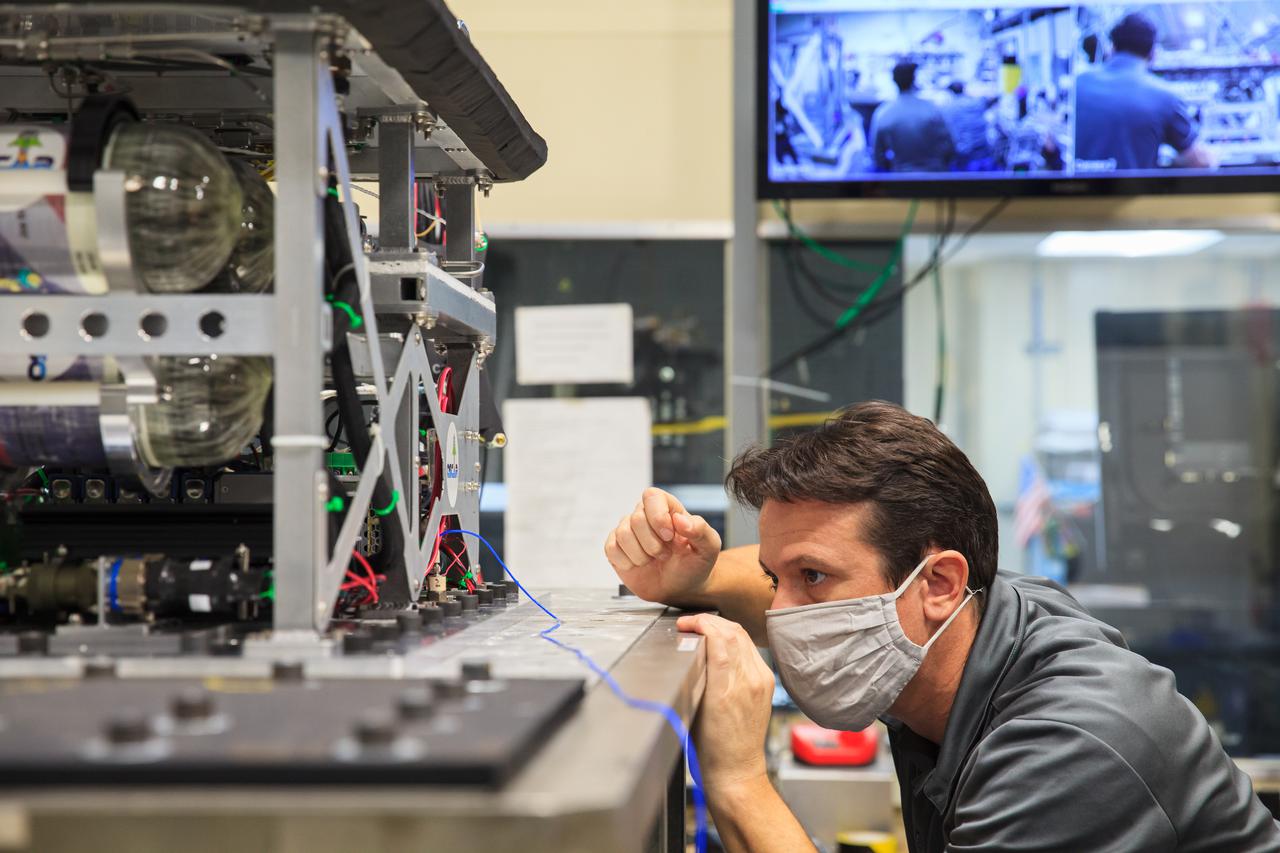

Gino Carro, a pressure vessels and systems engineer for Kennedy Space Center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, prepares NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) for vibration tests inside the Vibration Test Lab at the Florida spaceport on Jan. 14, 2021. The tests are part of ongoing preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.
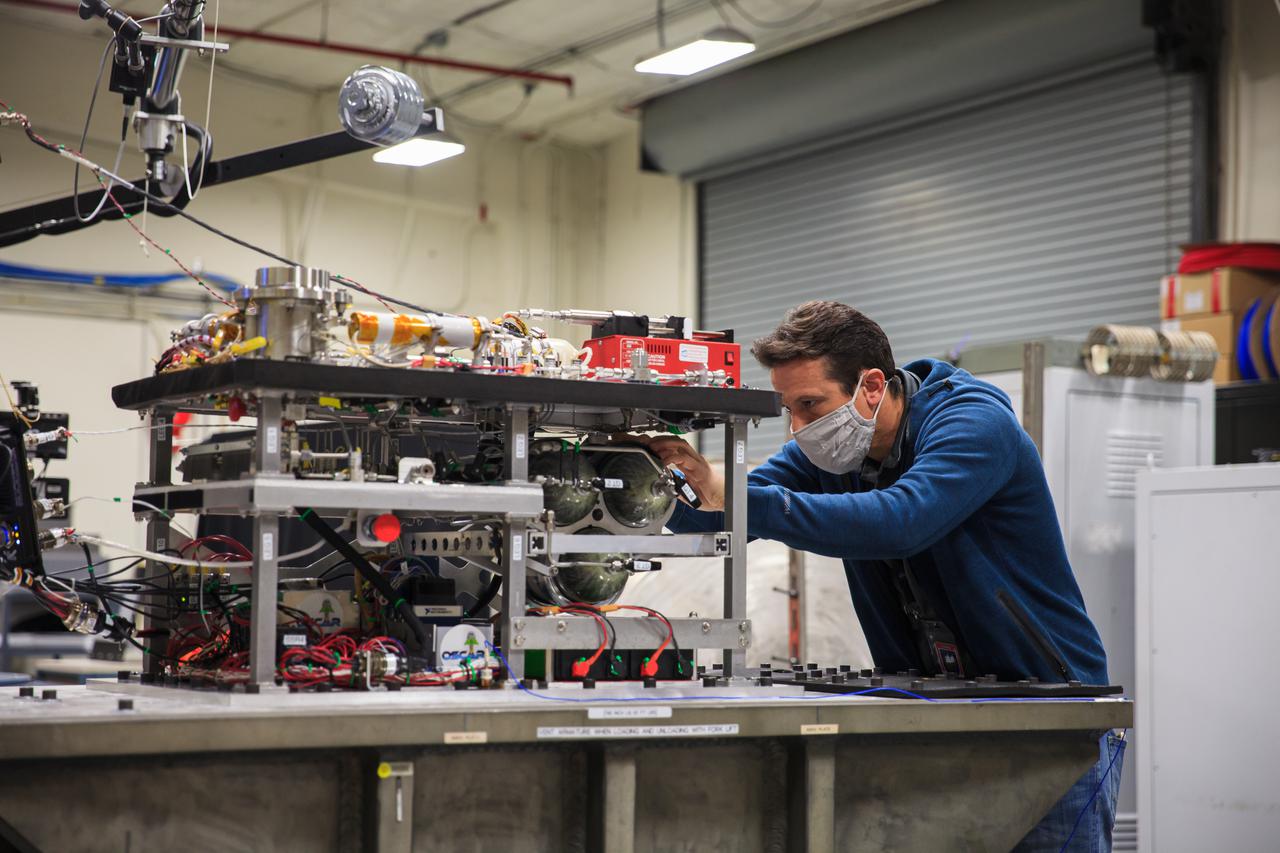

Gino Carro, a pressure vessels and systems engineer for Kennedy Space Center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, prepares NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) for vibration tests inside the Vibration Test Lab at the Florida spaceport on Jan. 14, 2021. The tests are part of ongoing preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.
Gino Carro, a pressure vessels and systems engineer for Kennedy Space Center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, prepares NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) for vibration tests inside the Vibration Test Lab at the Florida spaceport on Jan. 14, 2021. The tests are part of ongoing preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.
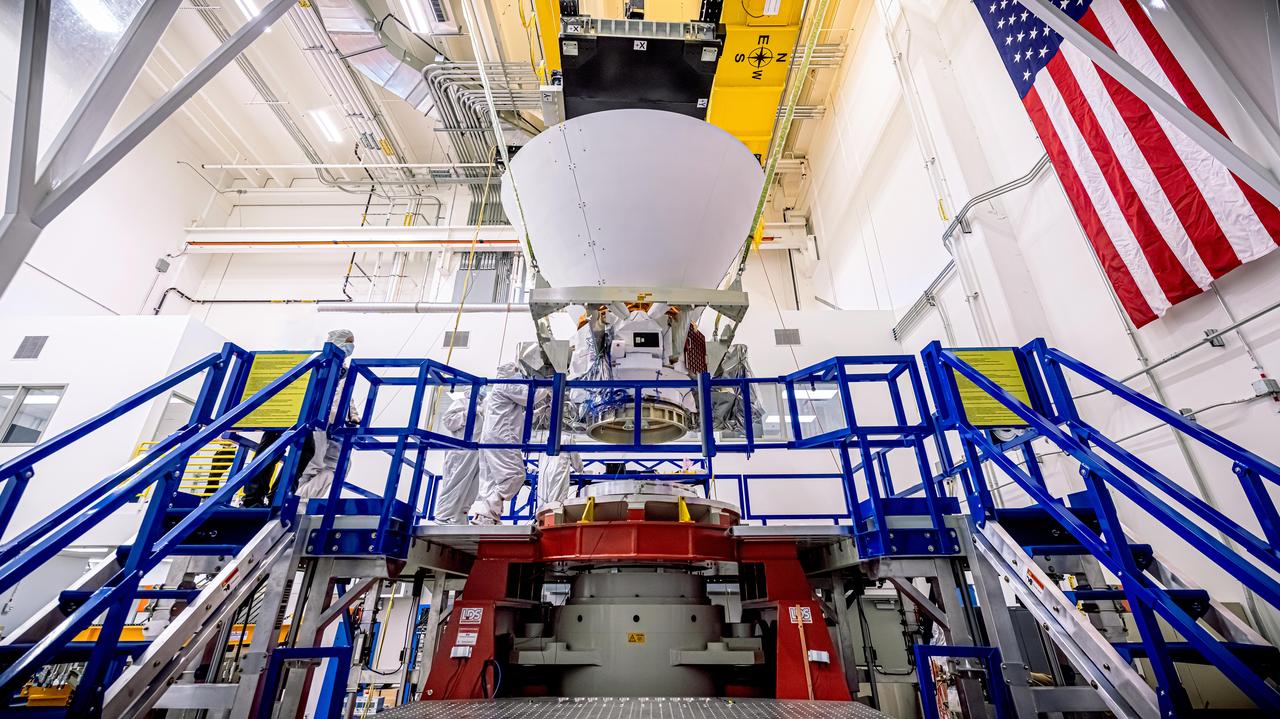

NASA's SPHEREx observatory is lifted and installed onto a vibration table in the Z-axis configuration at BAE Systems in Boulder, Colorado, in August 2024. In this test, the spacecraft is subjected to vibrations in all three axes separately. The test was successfully completed Aug. 16, 2024. Short for Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer, SPHEREx will create a map of the cosmos like no other. Using a technique called spectroscopy to image the entire sky in 102 wavelengths of infrared light, SPHEREx will gather information about the composition of and distance to millions of galaxies and stars. With this map, scientists will study what happened in the first fraction of a second after the big bang, how galaxies formed and evolved, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26539
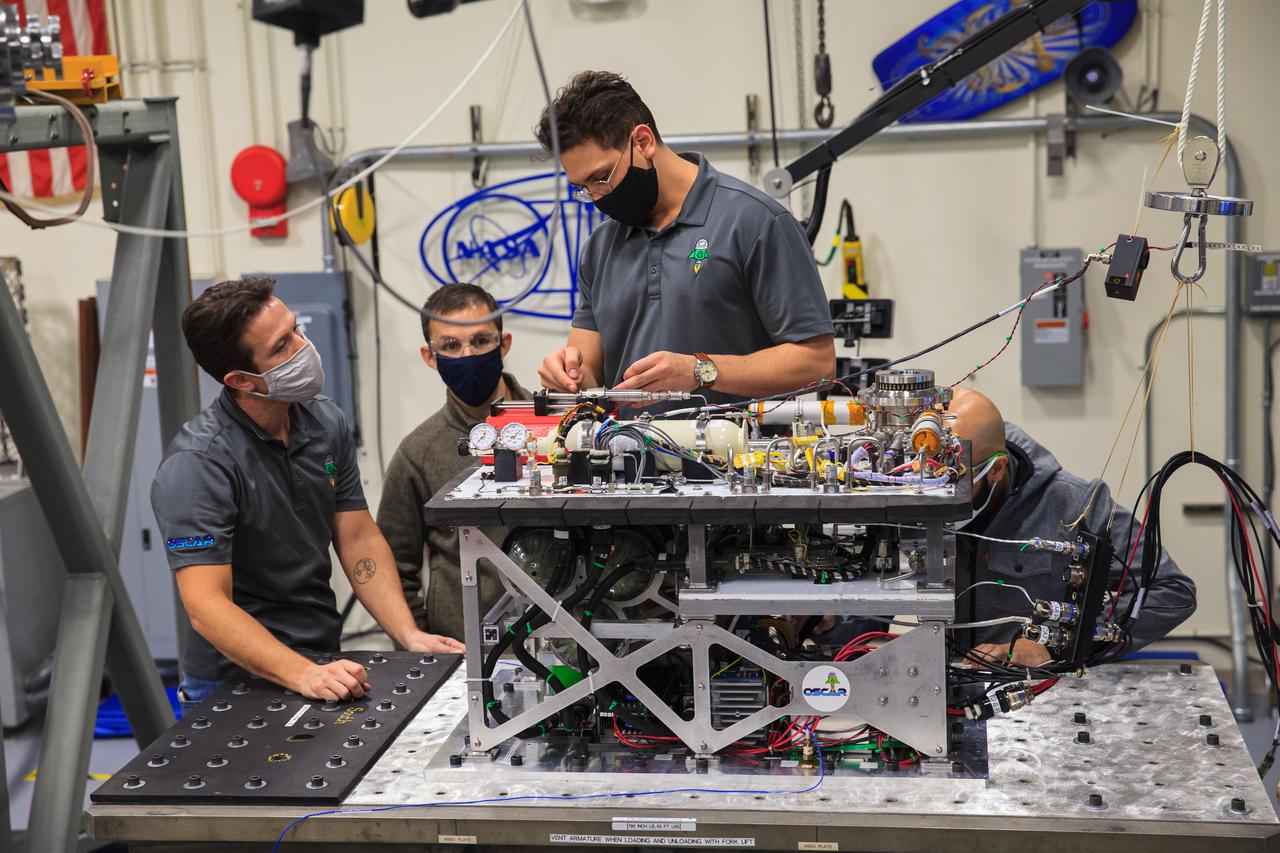
Kennedy Space Center engineers conduct vibration tests inside the Florida spaceport’s Vibration Test Lab on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for the suborbital flight of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, slated for later this year. From left are Gino Carro, a pressure vessels and systems engineer for the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract; David Rinderknecht, NASA chemical engineer; Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for OSCAR; and Malay Shah, NASA thermal/fluid analysis engineer. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
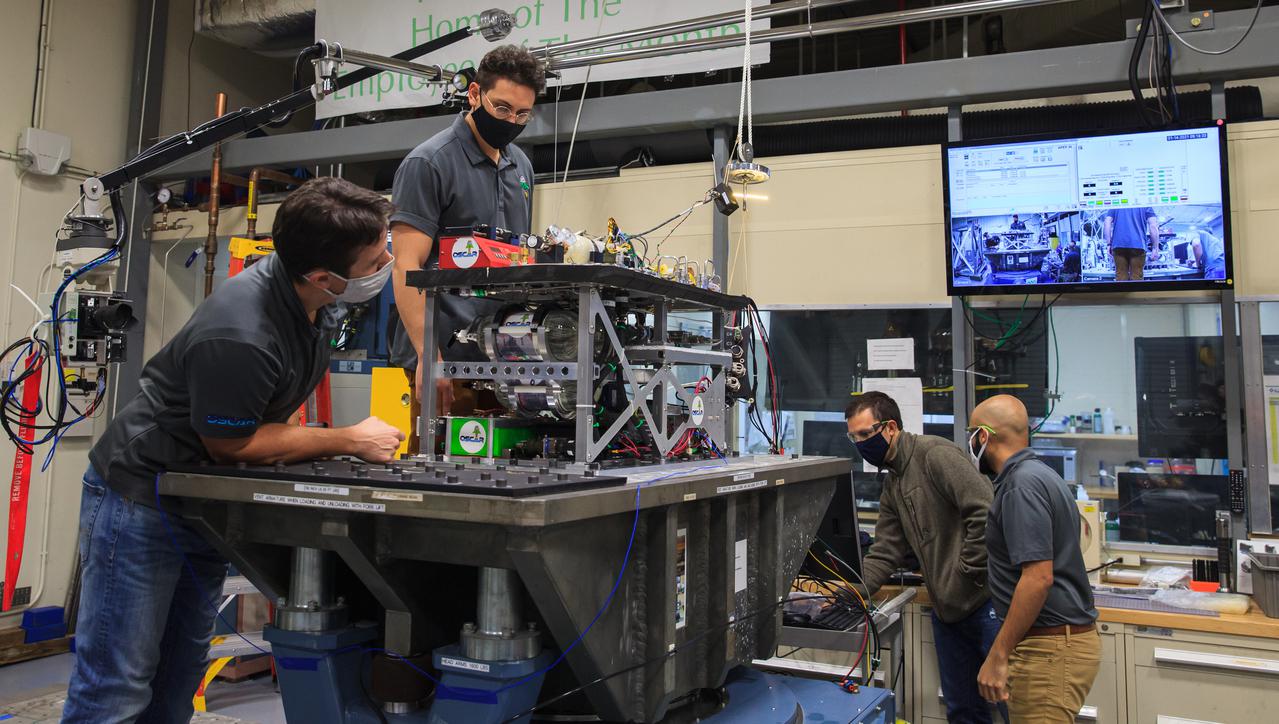
Kennedy Space Center engineers conduct vibration tests inside the Florida spaceport’s Vibration Test Lab on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for the suborbital flight of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, slated for later this year. From left are Gino Carro, a pressure vessels and systems engineer for the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract; Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for OSCAR; David Rinderknecht, NASA chemical engineer; and Malay Shah, NASA thermal/fluid analysis engineer. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.

Engineers and technicians prepare the Carbon Mapper imaging spectrometer, which will measure the greenhouse gases methane and carbon dioxide from space, for vibration testing at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in August 2023. This test is one of a series meant to ensure that the instrument can withstand the rigors of launch and the harsh conditions of space. Engineers subjected the spectrometer to intense vibrations similar to what it will endure atop a rocket blasting into orbit. The instrument was shipped from JPL to Planet Labs PBC in San Francisco on Sept. 12, 2023, where it will be integrated into a Tanager satellite. Designed and built by JPL, imaging spectrometer will be part of an effort led by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper organization to collect data on greenhouse gas point-source emissions. The information will help locate and quantify "super-emitters" – the small percentage of individual sources responsible for a significant fraction of methane and carbon dioxide emissions around the world. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26093
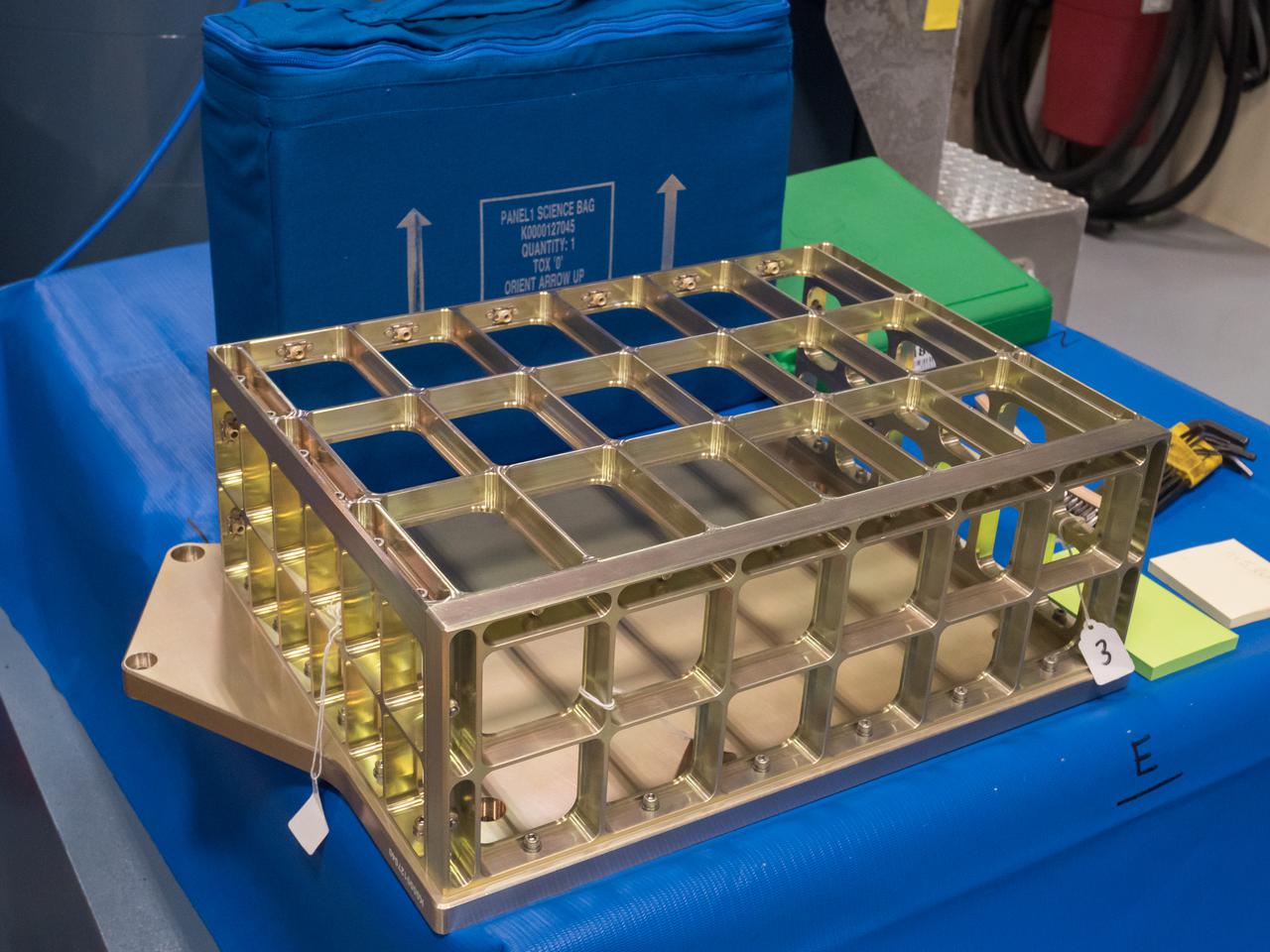
NASA’s BioExperiment-1 is being prepared for testing in the Vibration Laboratory at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 13, 2021. BioExpt-1 is a space biology pathfinder, which will carry plant, algae, yeast, and fungi for biology research beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO). NASA will install the BioExpt-1 payload container assembles onto panels inside the Orion capsule. BioExpt-1 will return these science payloads to Earth to provide critical and unique data about life beyond LEO for the first time in more than 40 years. Artemis I is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions that will enable human exploration of the Moon and eventually on to Mars.
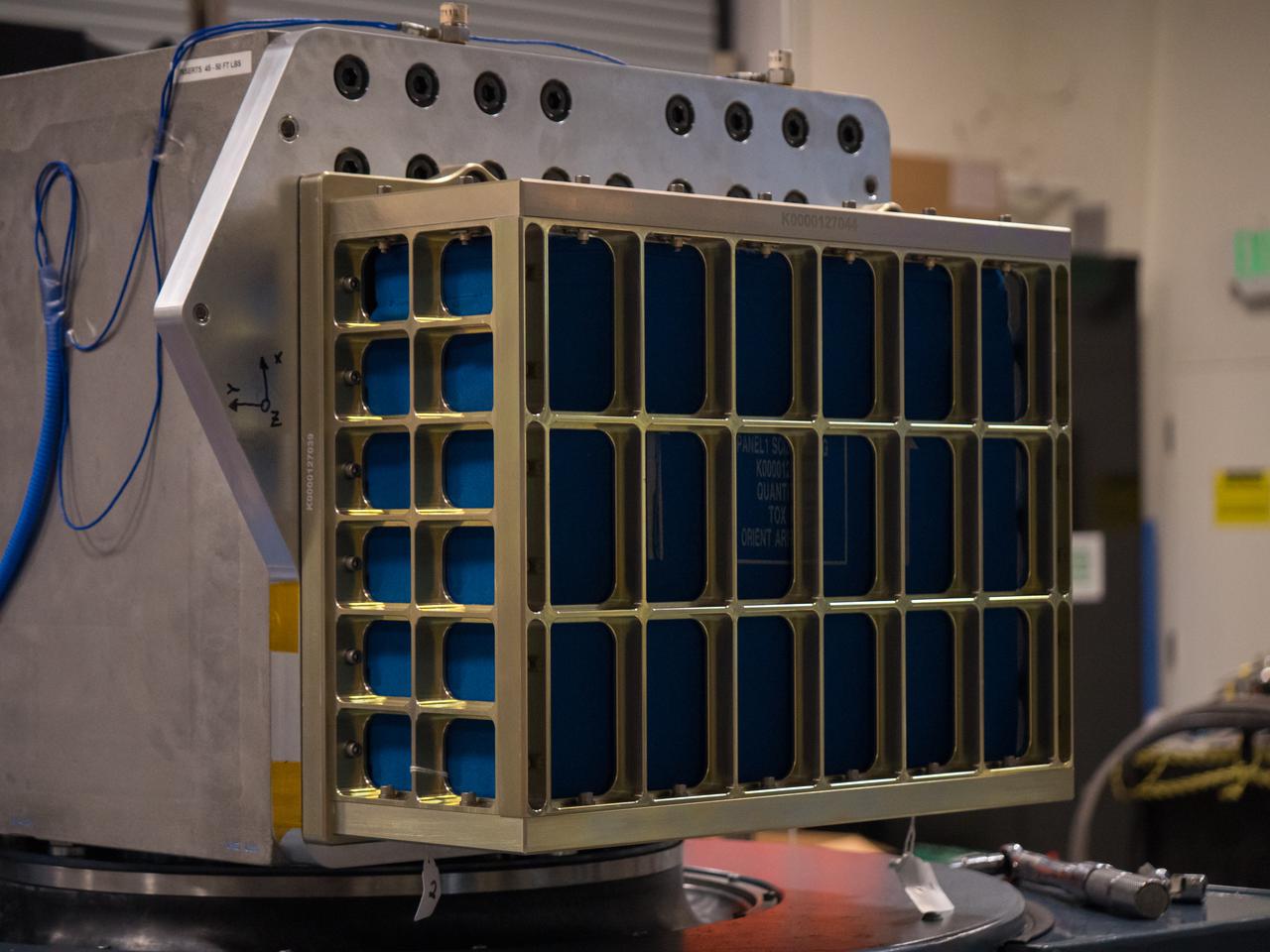
NASA’s Biology Experiment-1 (BioExpt-1) undergoes testing in the Vibration Laboratory at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 13, 2021. BioExpt-1 is a space biology pathfinder, which will carry plants, algae, yeast, and fungi for biology research beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO). NASA will install the BioExpt-1 payload container assembles onto panels inside the Orion capsule. BioExpt-1 will return these science payloads to Earth to provide critical and unique data about life beyond LEO for the first time in more than 40 years. Artemis I is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions that will enable human exploration of the Moon and eventually on to Mars.
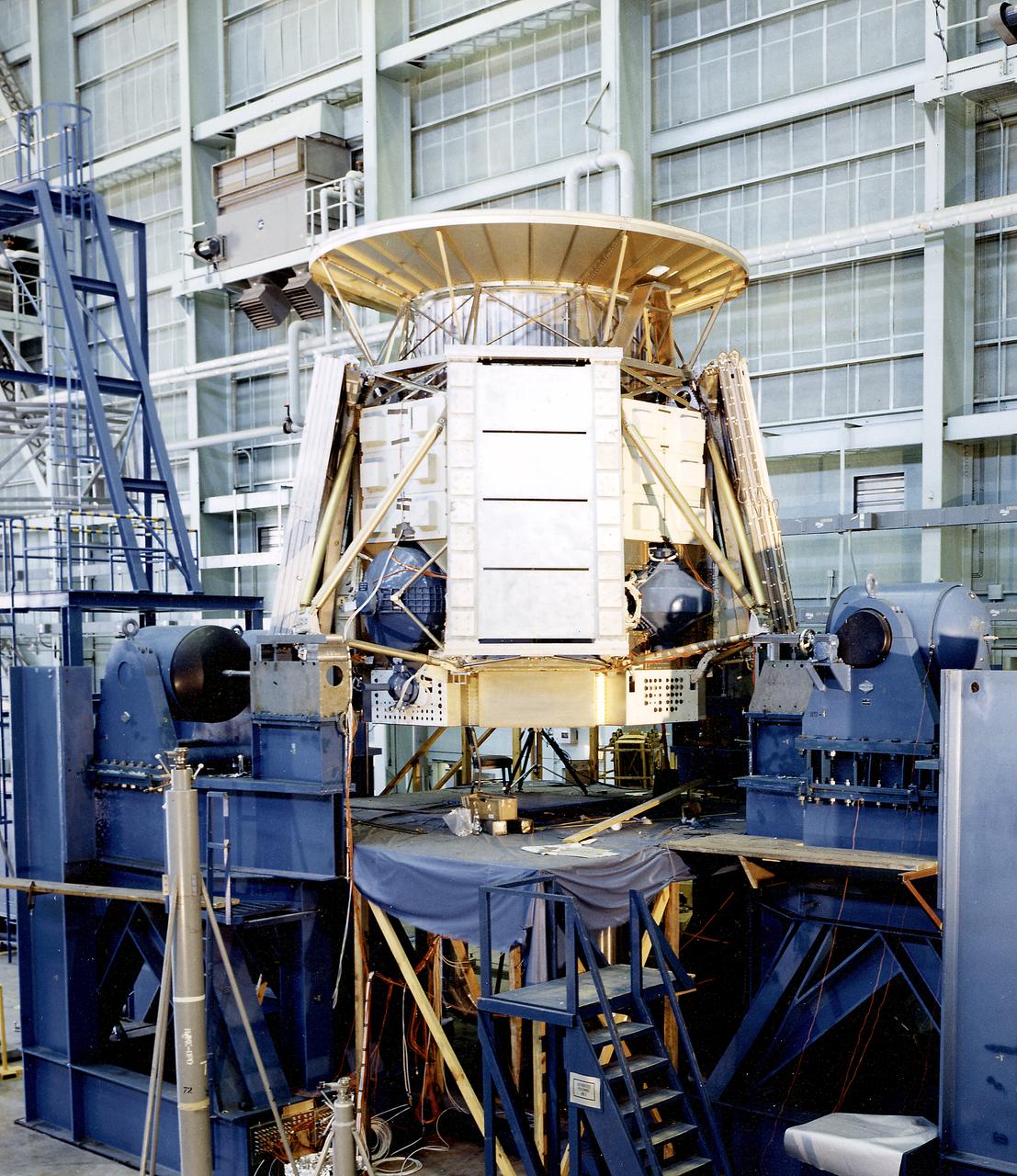

The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), one of four major components comprising the Skylab, was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. In this image, the ATM is shown undergoing horizontal vibration testing in a vibration test unit.
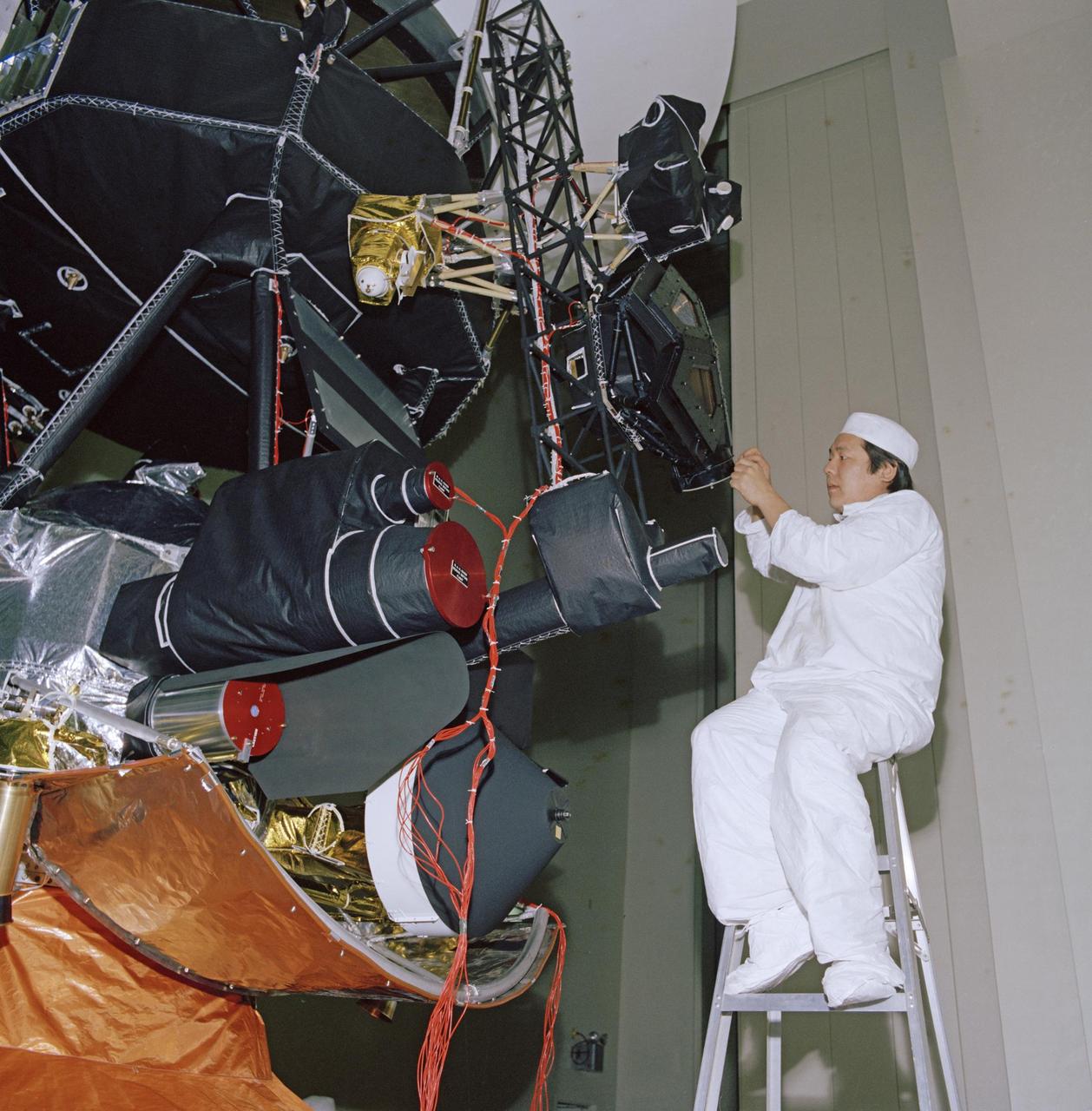
An engineer works on vibration acoustics and pyro shock testing for one of NASA's Voyager spacecraft on November 18, 1976. Several of the spacecraft's science instruments are visible at left. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21733

Dave Flowers, the project manager for NASA’s Biology Experiment-1 (BioExpt-1) in Exploration Research and Technology Programs, prepares it for testing in the Vibration Laboratory at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 13, 2021. BioExpt-1 is a space biology pathfinder, which will carry plants, algae, yeast, and fungi for biology research beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO). NASA will install the BioExpt-1 payload container assembles onto panels inside the Orion capsule. BioExpt-1 will return these science payloads to Earth to provide critical and unique data about life beyond LEO for the first time in more than 40 years. Artemis I is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions that will enable human exploration of the Moon and eventually on to Mars.
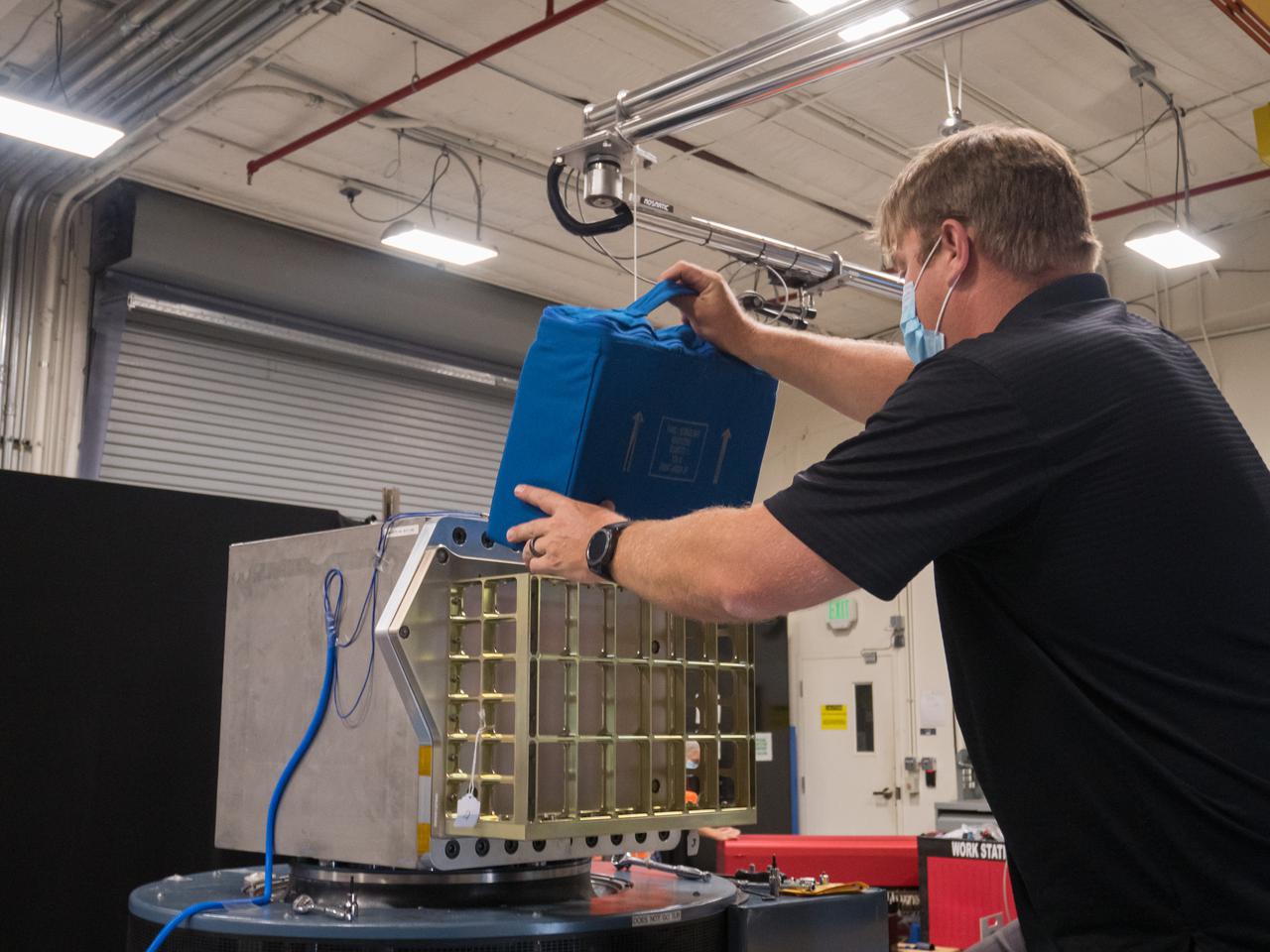

Adam Chaney, a mechanical engineer with the Laboratory Support Services and Operations (LASSO) contract at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares NASA’s Biology Experiment-1 (BioExpt-1) for testing in the Vibration Laboratory at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 13, 2021. BioExpt-1 is a space biology pathfinder, which will carry plants, algae, yeast, and fungi for biology research beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO). NASA will install the BioExpt-1 payload container assembles onto panels inside the Orion capsule. BioExpt-1 will return these science payloads to Earth to provide critical and unique data about life beyond LEO for the first time in more than 40 years. Artemis I is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions that will enable human exploration of the Moon and eventually on to Mars.
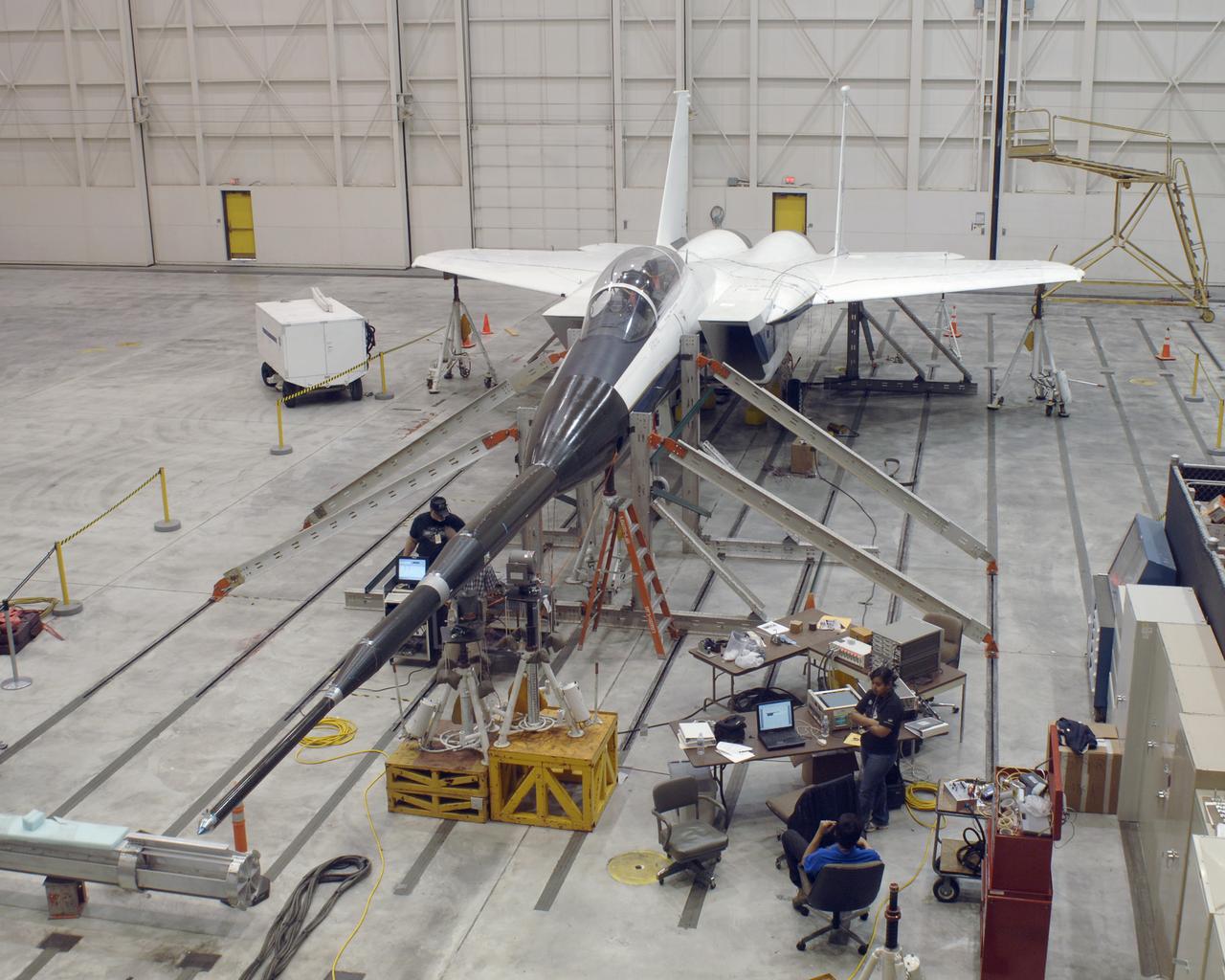

NASA Dryden's F-15B testbed aircraft with the Gulfstream Quiet Spike sonic boom mitigator attached undergoes ground vibration testing in preparation for test flights. The project seeks to verify the structural integrity of the multi-segmented, articulating spike attachment designed to reduce and control a sonic boom.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 . Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 . Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 .Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 . Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 . Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 .Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 .Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 . Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 .Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 . Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 .Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
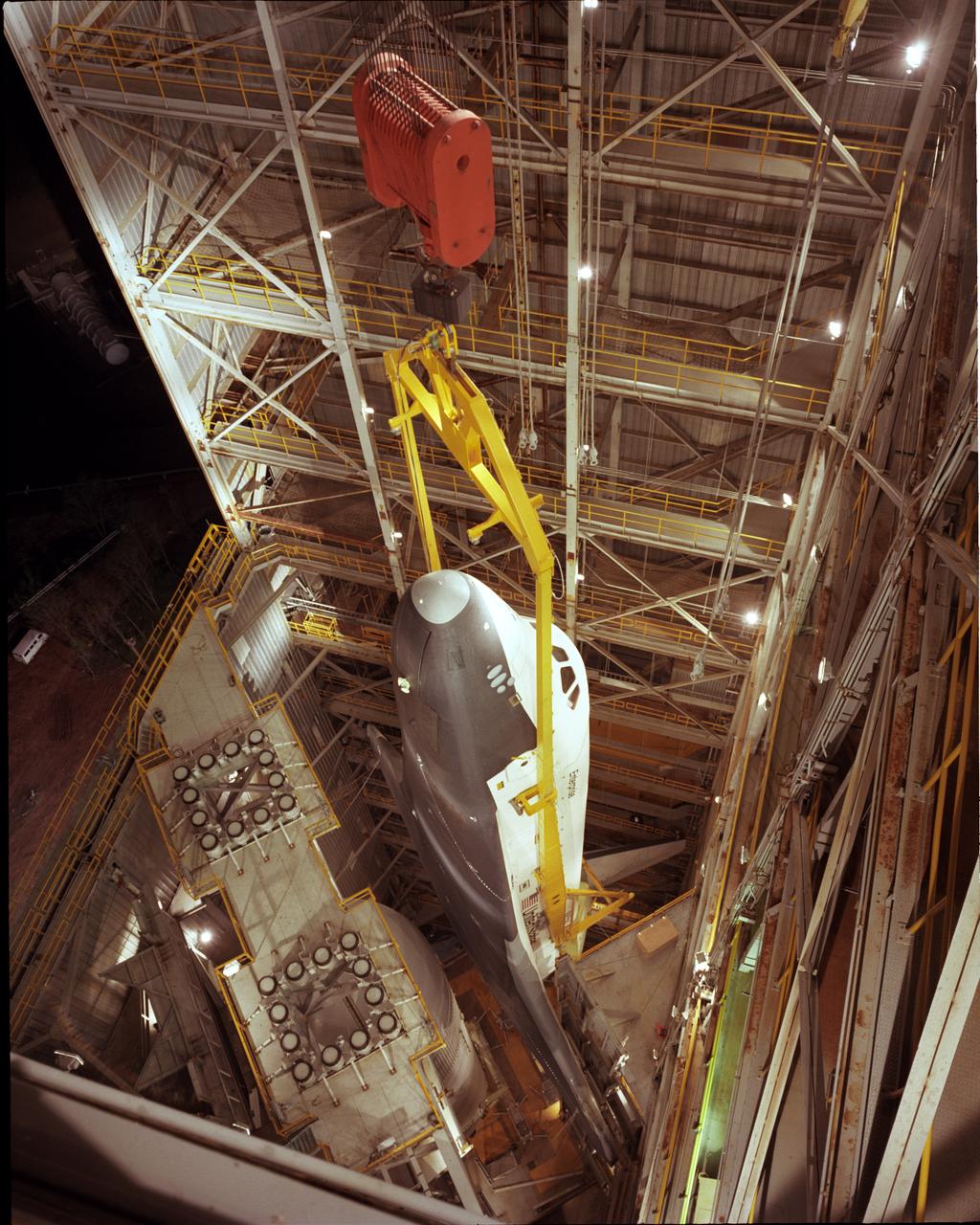

The Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise is lowered into the Dynamic Test Stand for Mated Vertical Ground Vibration tests (MVGVT) at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The tests marked the first time ever that the entire shuttle complement (including Orbiter, external tank, and solid rocket boosters) were mated vertically.
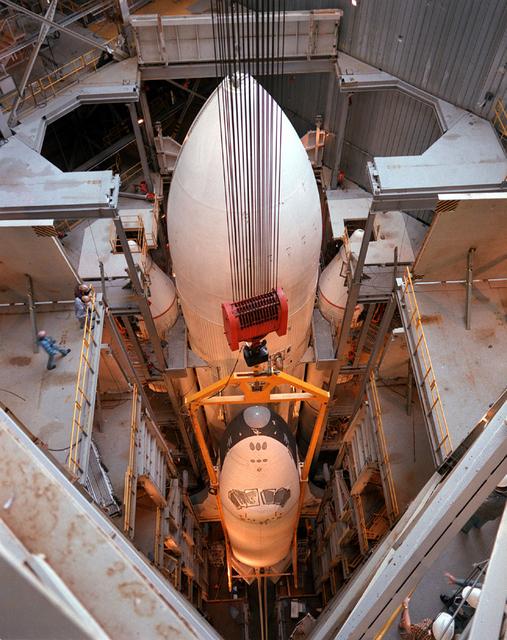

The Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise inside of Marshall Space Flight Center's Dynamic Test Stand for Mated Vertical Ground Vibration tests (MVGVT). The tests marked the first time ever that the entire shuttle complement including Orbiter, external tank, and solid rocket boosters were vertically mated.
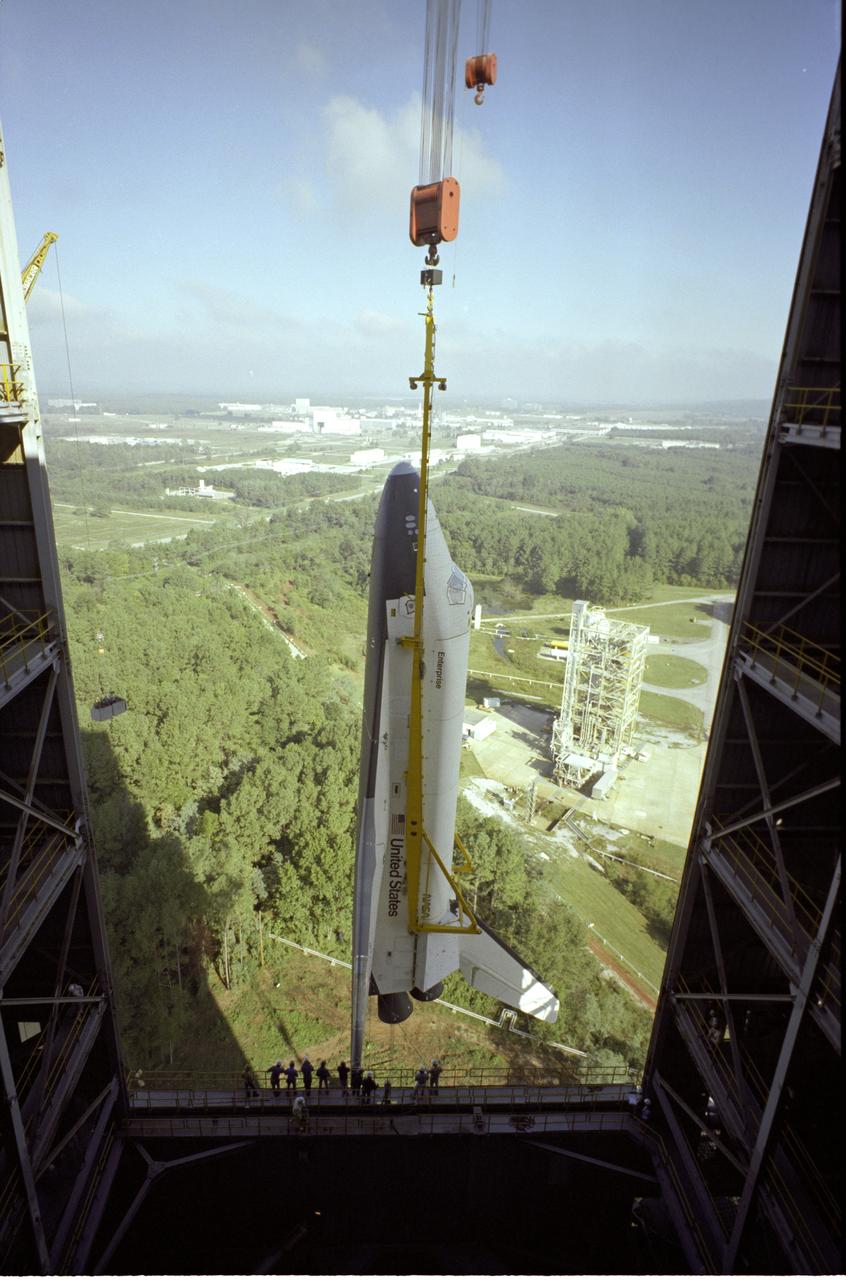

The Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise is being installed into liftoff configuration at Marshall Space Flight Center's Dynamic Test Stand for Mated Vertical Ground Vibration tests (MVGVT). The tests marked the first time ever that the entire shuttle complement (including Orbiter, external tank, and solid rocket boosters) were mated vertically.
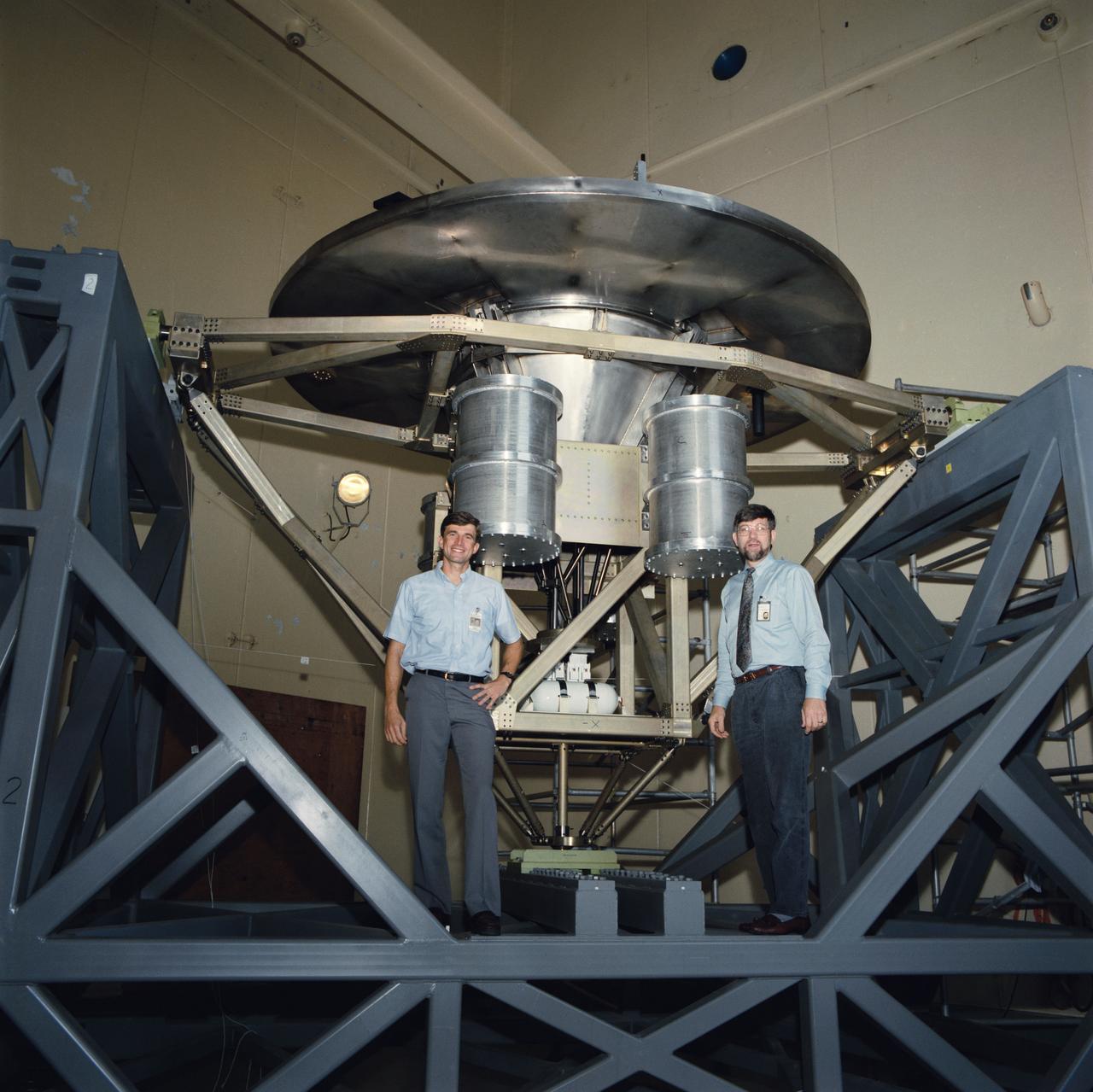

The Wake Shield Facility is displayed on a test stand at JSC. Astronaut Ronald M. Sega, mission specialist for STS-60, is seen with the facility during a break in testing in the acoustic and vibration facility at JSC.
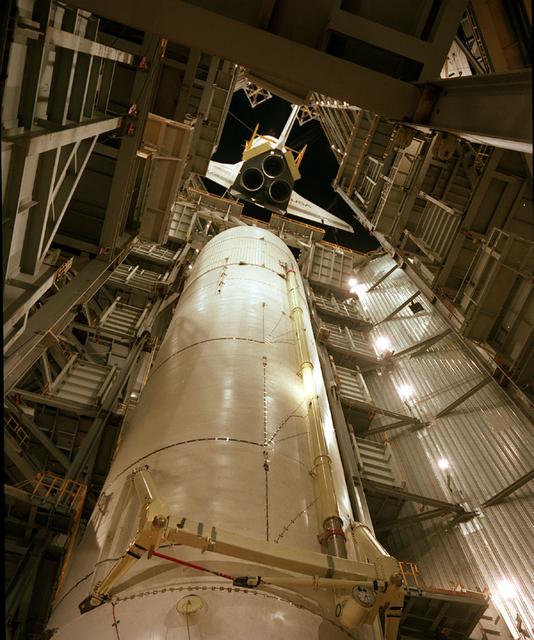

This is an interior ground level view of the Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise being lowered for mating to External Tank (ET) inside Marshall Space Flight Center's Dynamic Test Stand for Mated Vertical Ground Vibration tests (MVGVT). The tests marked the first time ever that the entire shuttle complement (including Orbiter, external tank, and solid rocket boosters) were mated vertically.
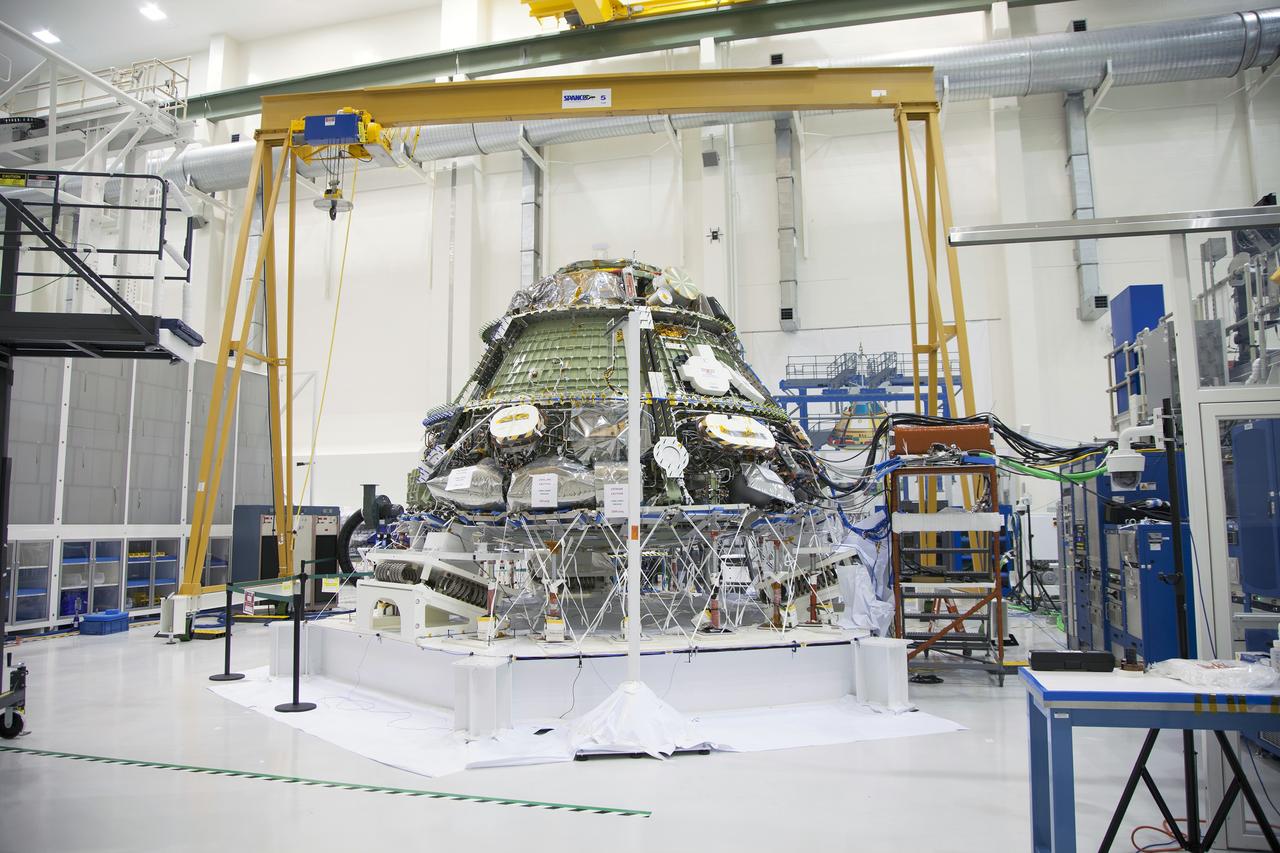

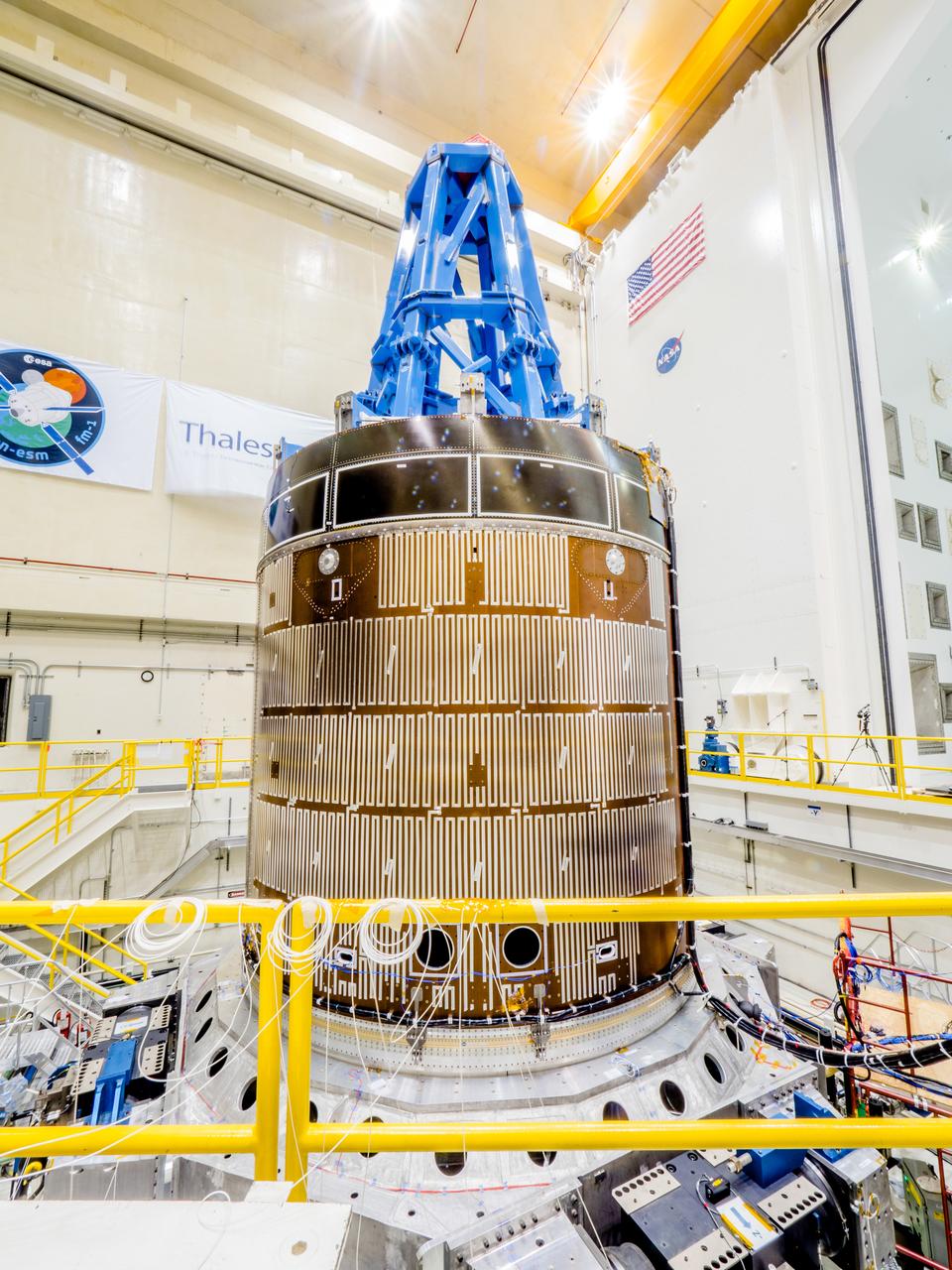
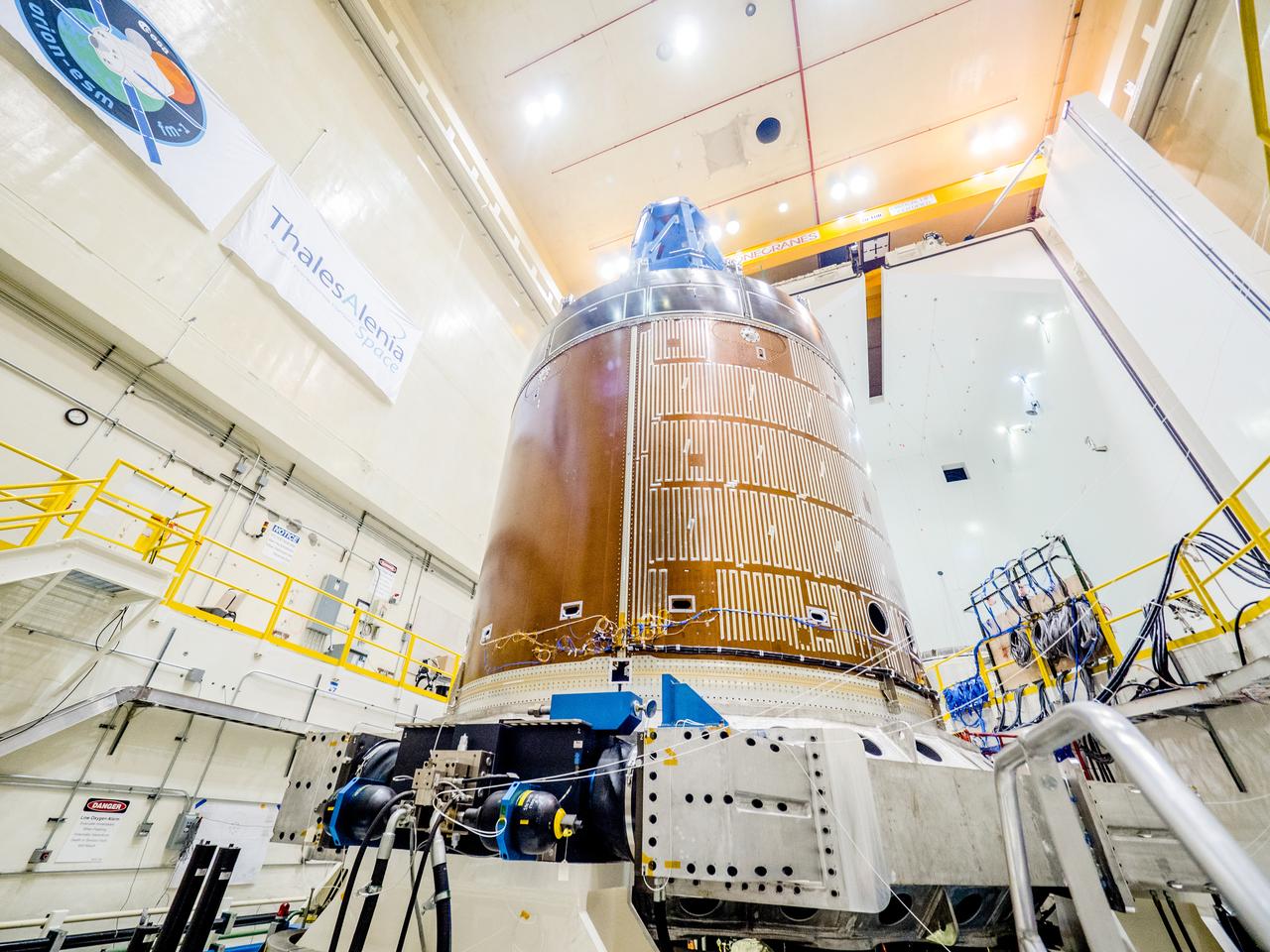
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion crew module is positioned on a special portable test chamber and prepared for a multi-point random vibration test. Accelerometers and strain gages have been attached to Orion in various locations. During a series of tests, each lasting only 30 seconds, Orion will be subjected to gradually increasing levels of vibrations that represent levels the vehicle would experience during launch, orbit and descent. The data is reviewed in order to assess the health of the crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
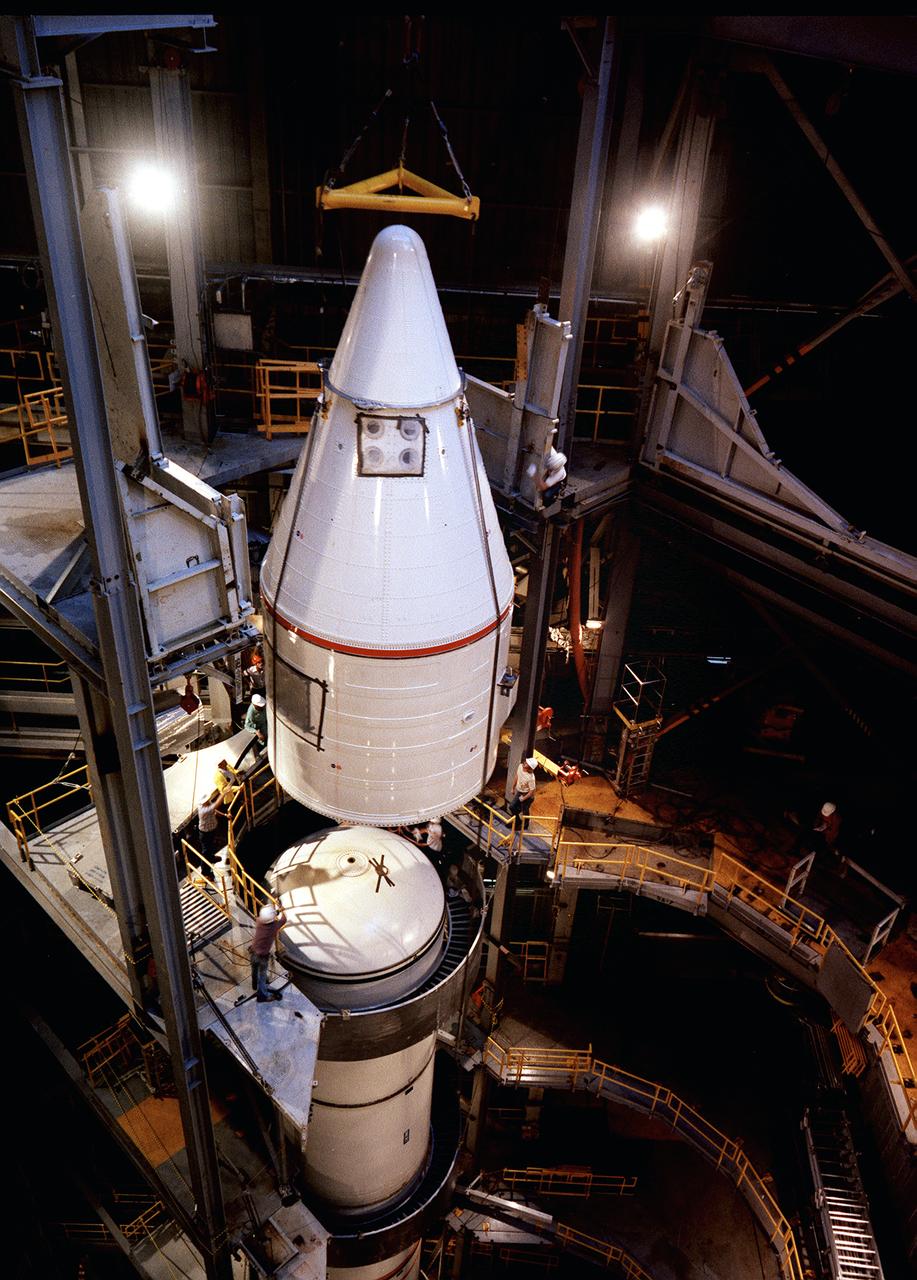

Workmen in the Dynamic Test Stand lowered the nose cone into place to complete stacking of the left side of the solid rocket booster (SRB) in the Dynamic Test Stand at the east test area of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The SRB would be attached to the external tank (ET) and then the orbiter later for the Mated Vertical Ground Vibration Test (MVGVT), that resumed in October 1978. The stacking of a complete Shuttle in the Dynamic Test Stand allowed test engineers to perform ground vibration testing on the Shuttle in its liftoff configuration. The purpose of the MVGVT was to verify that the Space Shuttle would perform as predicted during launch. The platforms inside the Dynamic Test Stand were modified to accommodate two SRB'S to which the ET was attached.
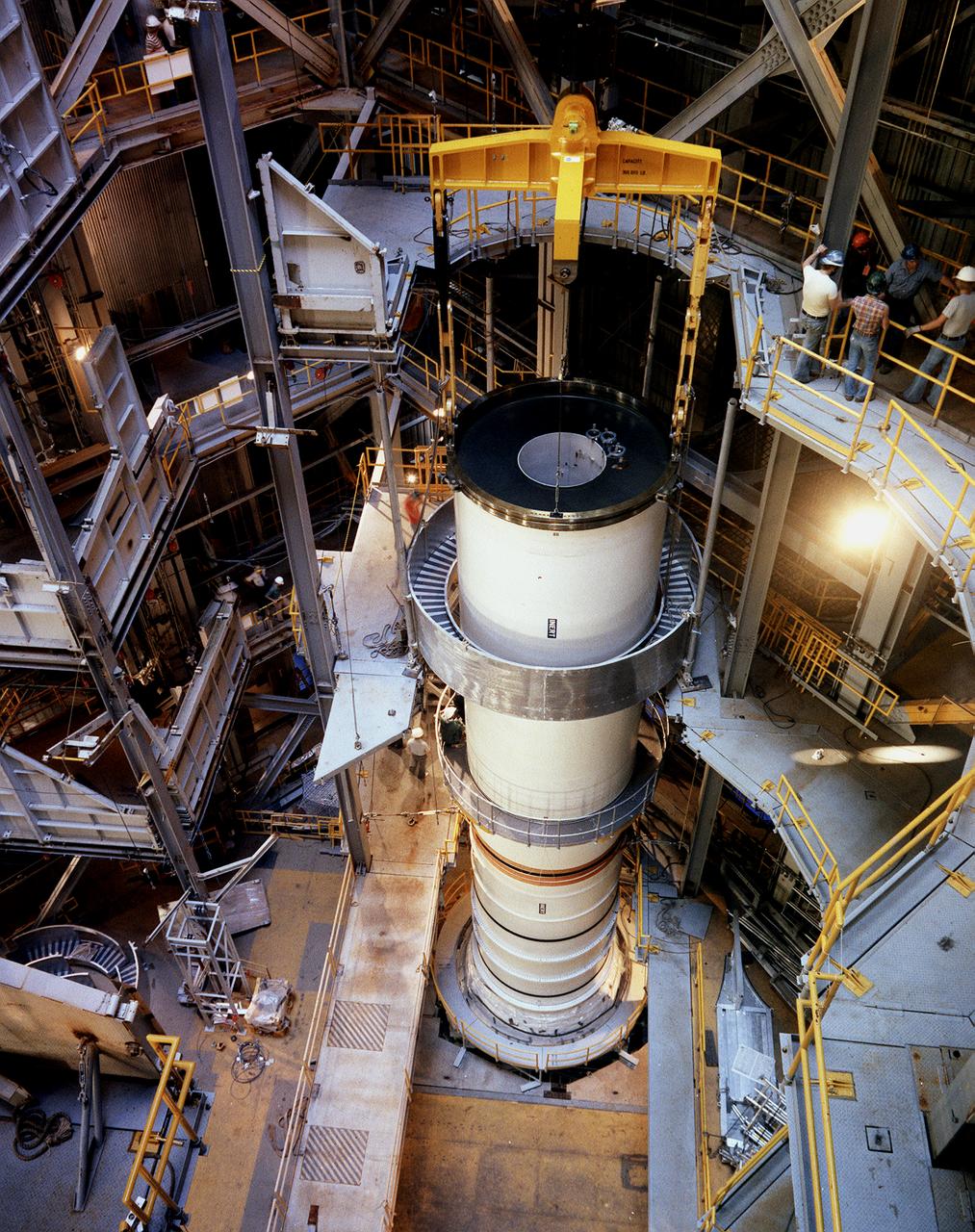

This photograph shows stacking of the left side of the solid rocket booster (SRB) segments in the Dynamic Test Stand at the east test area of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Staging shown here are the aft skirt, aft segment, and aft center segment. The SRB was attached to the external tank (ET) and then the orbiter later for the Mated Vertical Ground Vibration Test (MVGVT), that resumed in October 1978. The stacking of a complete Shuttle in the Dynamic Test Stand allowed test engineers to perform ground vibration testing on the Shuttle in its liftoff configuration. The purpose of the MVGVT is to verify that the Space Shuttle would perform as predicted during launch. The platforms inside the Dynamic Test Stand were modified to accommodate two SRB's to which the ET was attached.
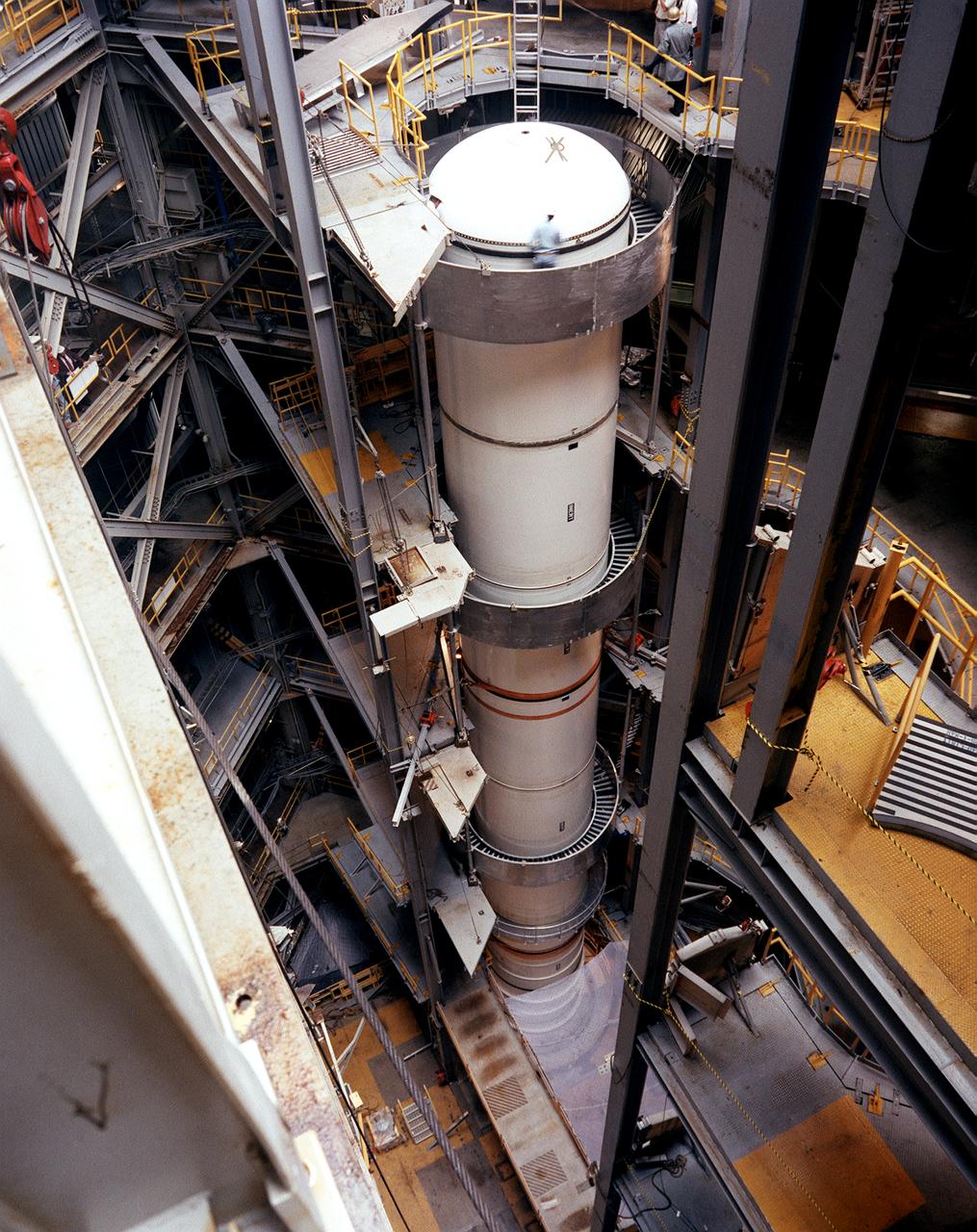
This photograph shows the left side of the solid rocket booster (SRB) segment as it awaits being mated to the nose cone and forward skirt in the Dynamic Test Stand at the east test area of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The SRB would be attached to the external tank (ET) and then the orbiter later for the Mated Vertical Ground Vibration Test (MVGVT), that resumed in October 1978. The stacking of a complete Shuttle in the Dynamic Test Stand allowed test engineers to perform ground vibration testing on the Shuttle in its liftoff configuration. The purpose of the MVGVT was to verify that the Space Shuttle would perform as predicted during launch. The platforms inside the Dynamic Test Stand were modified to accommodate two SRB's to which the ET was attached.
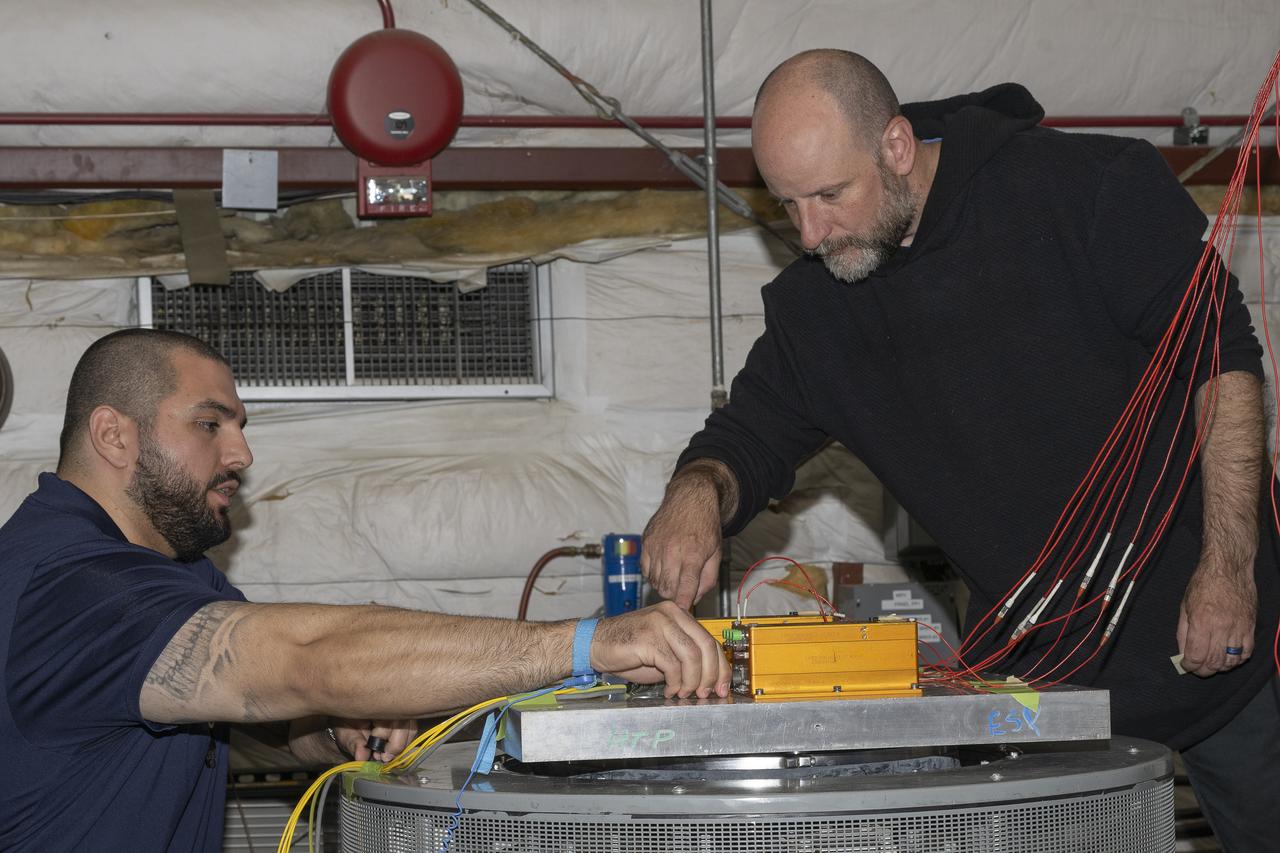

Jonathan Lopez and Nathan Rick prepare the hypersonic Fiber Optic Sensing System for vibration tests in the Environmental Laboratory at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. Testing on a machine called a shaker proved that the system could withstand the severe vibration it will endure in hypersonic flight, or travel at five times the speed of sound.
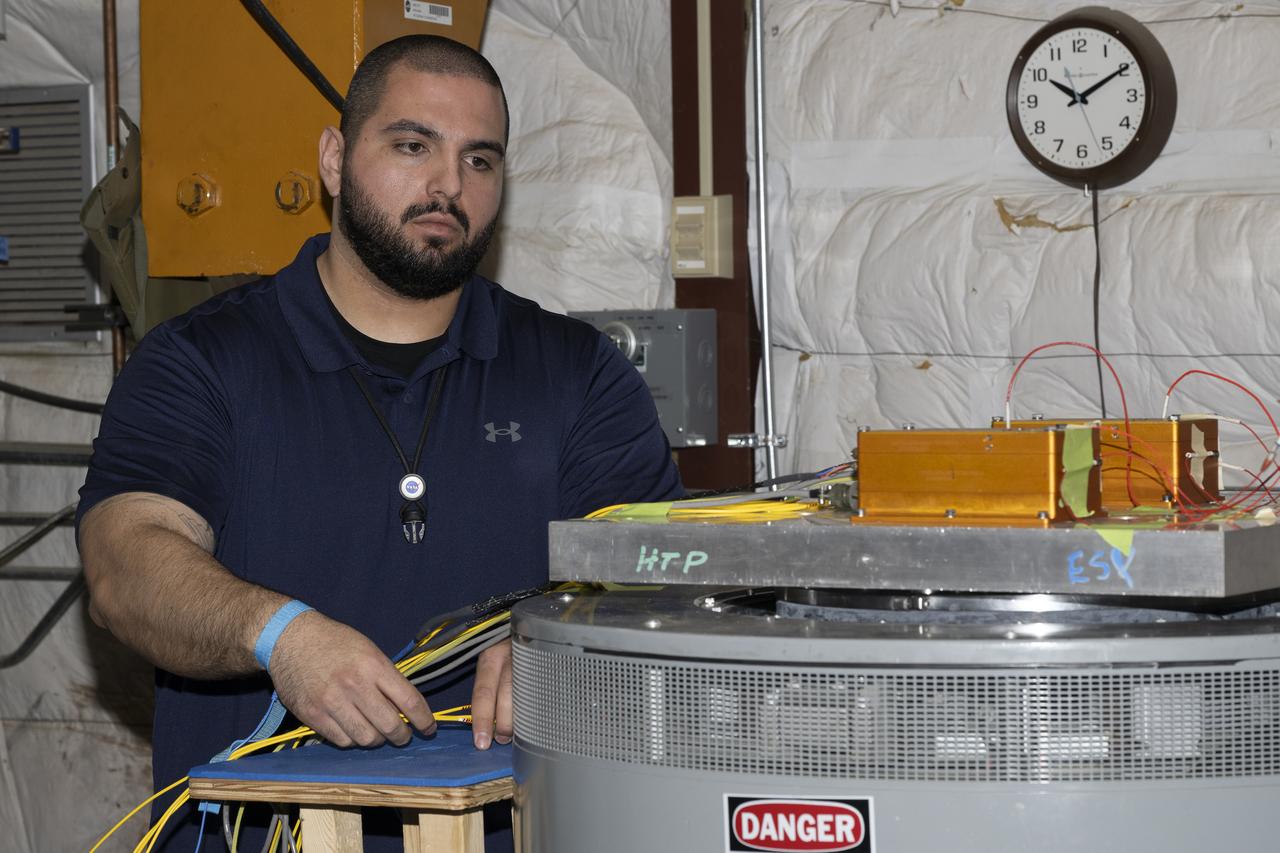

Jonathan Lopez prepares the hypersonic Fiber Optic Sensing System for vibration tests in the Environmental Laboratory at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. Testing on a machine called a shaker proved that the system could withstand the severe vibration it will endure in hypersonic flight, or travel at five times the speed of sound.
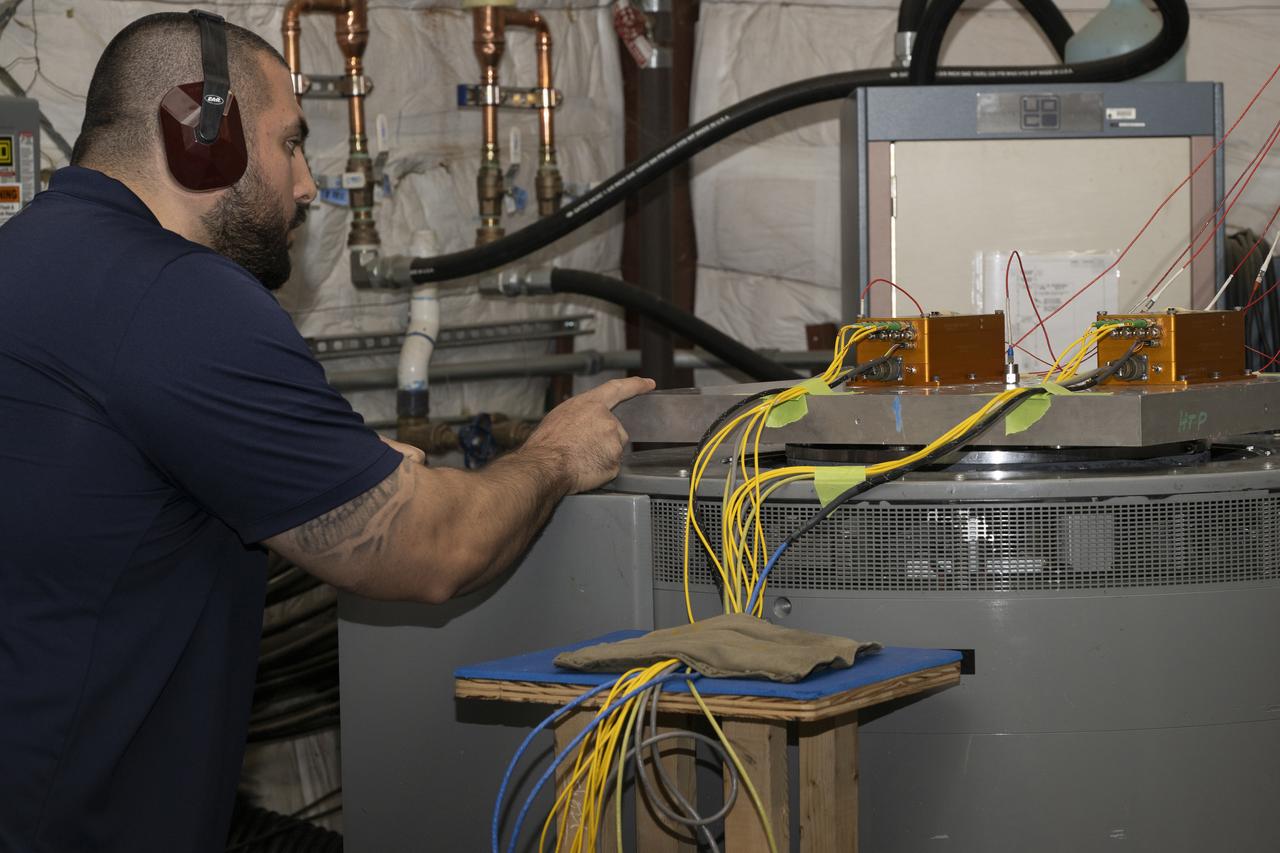

Jonathan Lopez prepares the hypersonic Fiber Optic Sensing System for vibration tests in the Environmental Laboratory at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. Testing on a machine called a shaker proved that the system could withstand the severe vibration it will endure in hypersonic flight, or travel at five times the speed of sound.
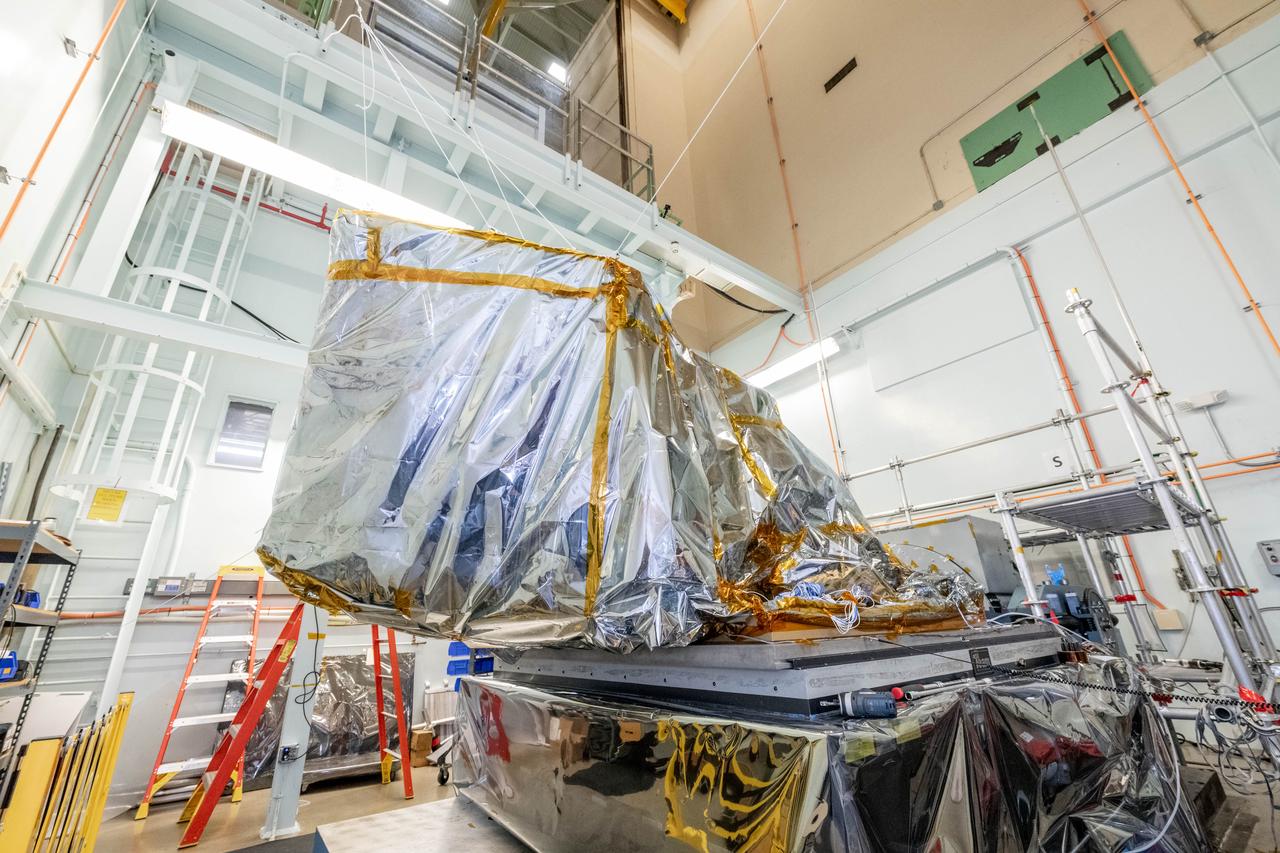

The Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) is configured for vibration testing. OCI is bagged with Dun-Shield to protect the instrument from contamination outside of a cleanroom environment, and also provides protection from static electricity. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
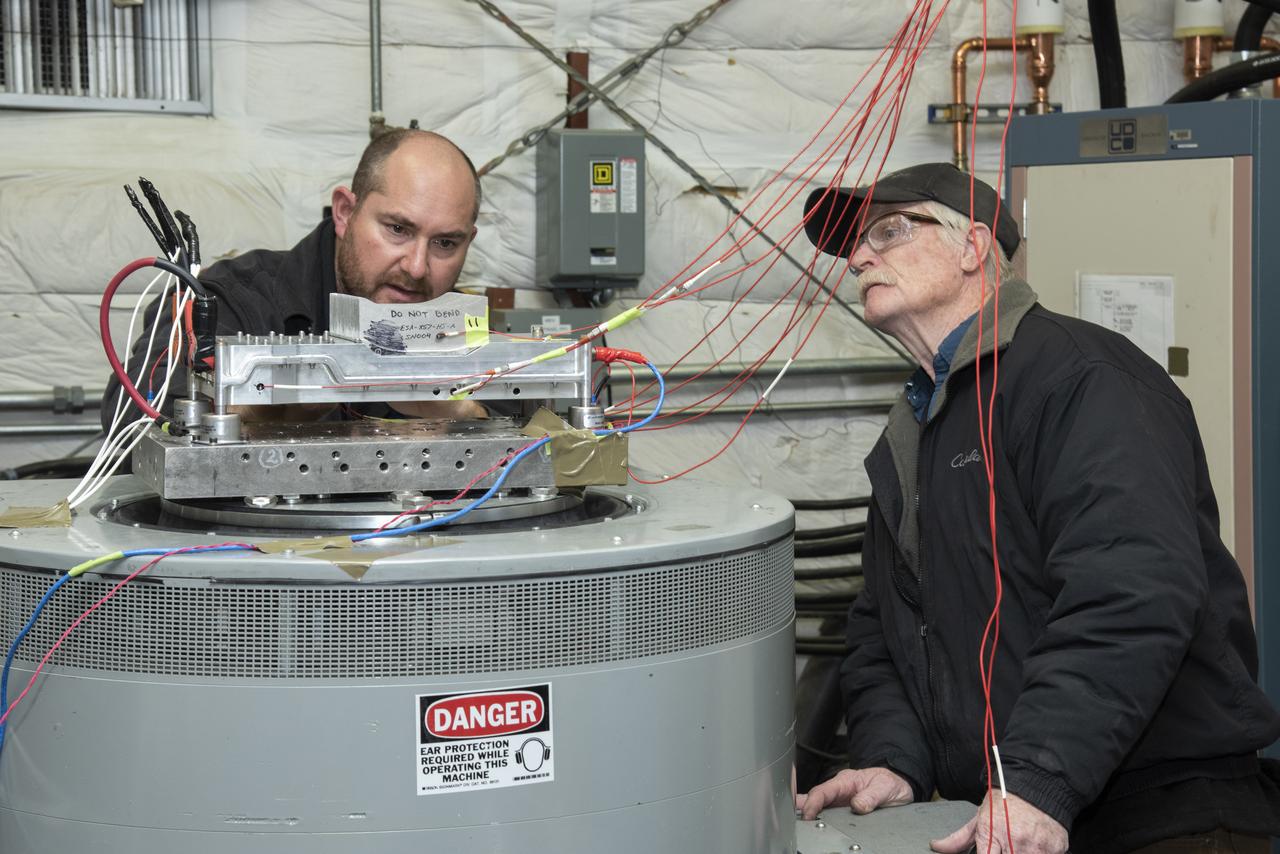

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASAs first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
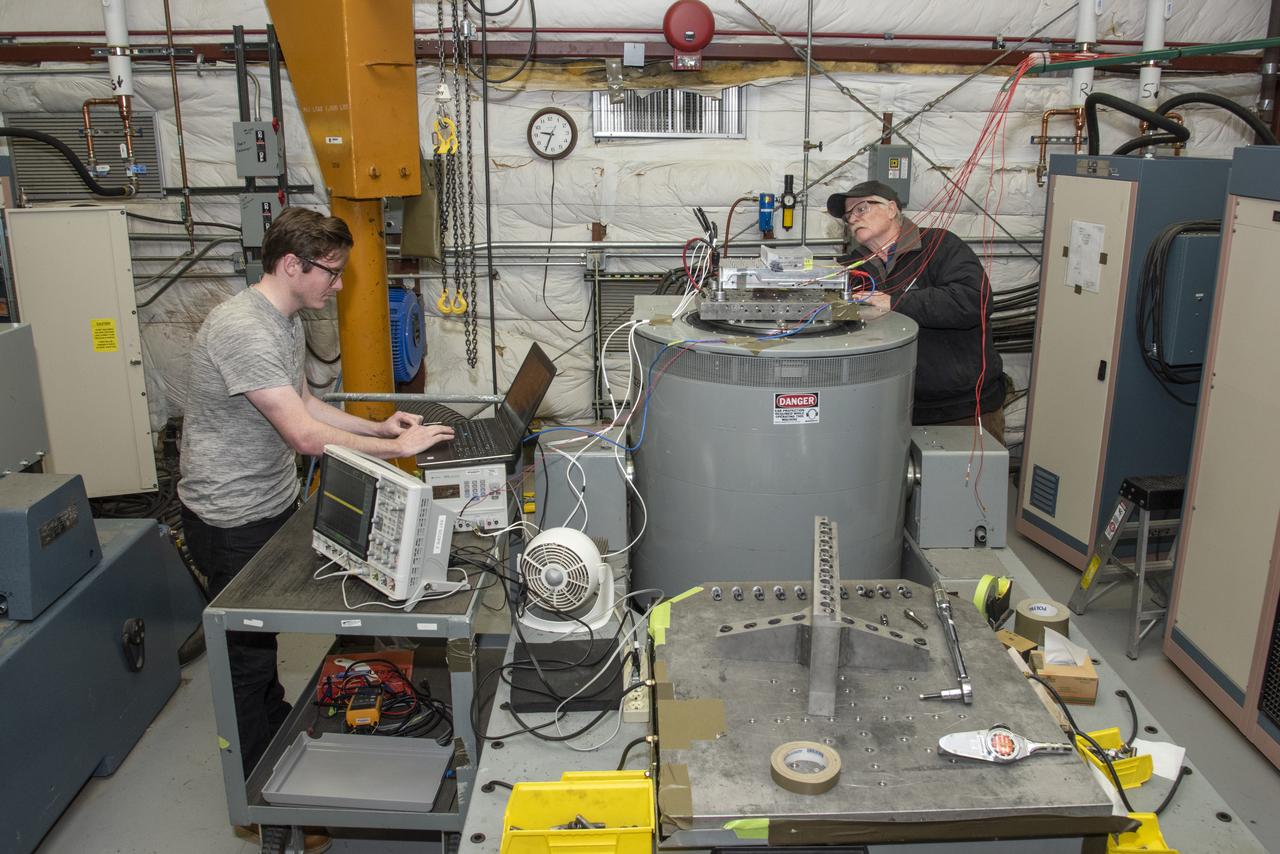

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
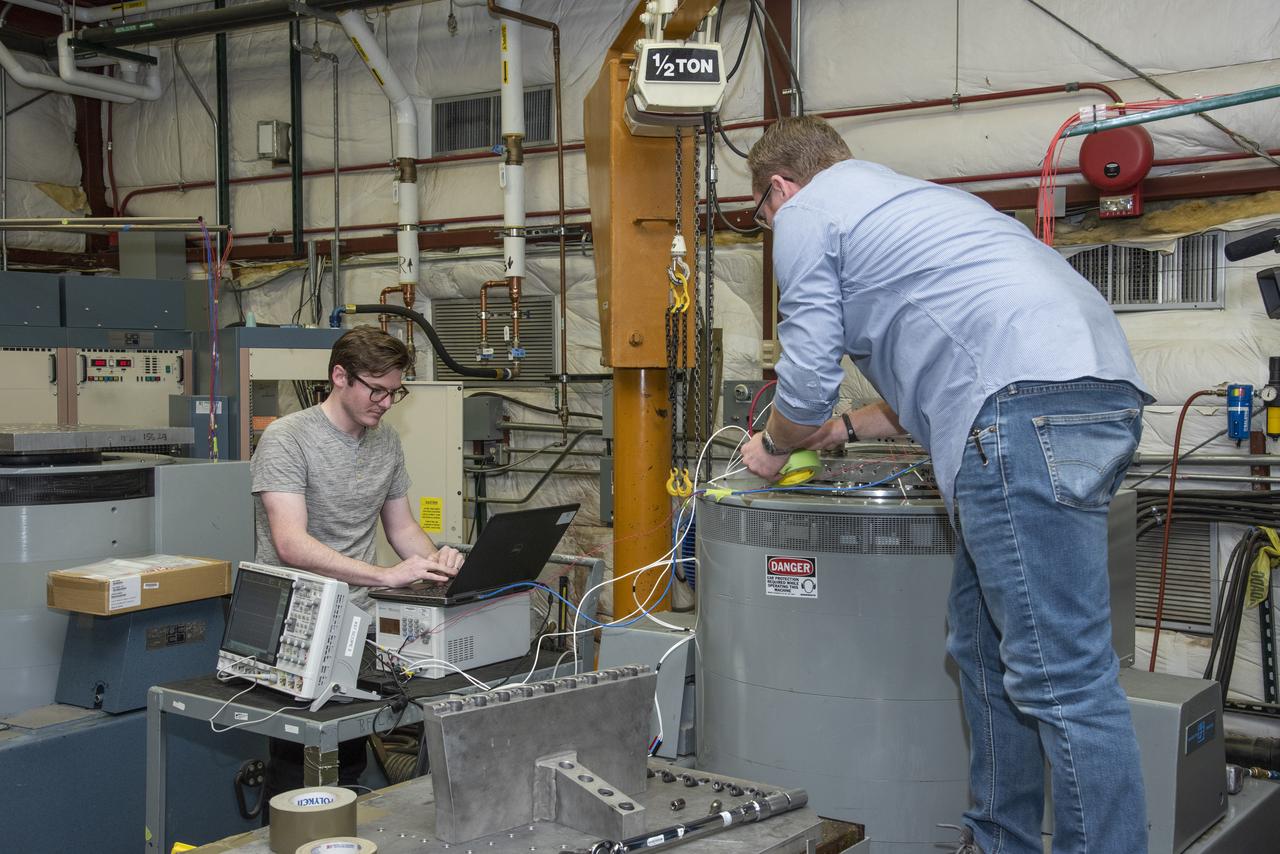

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
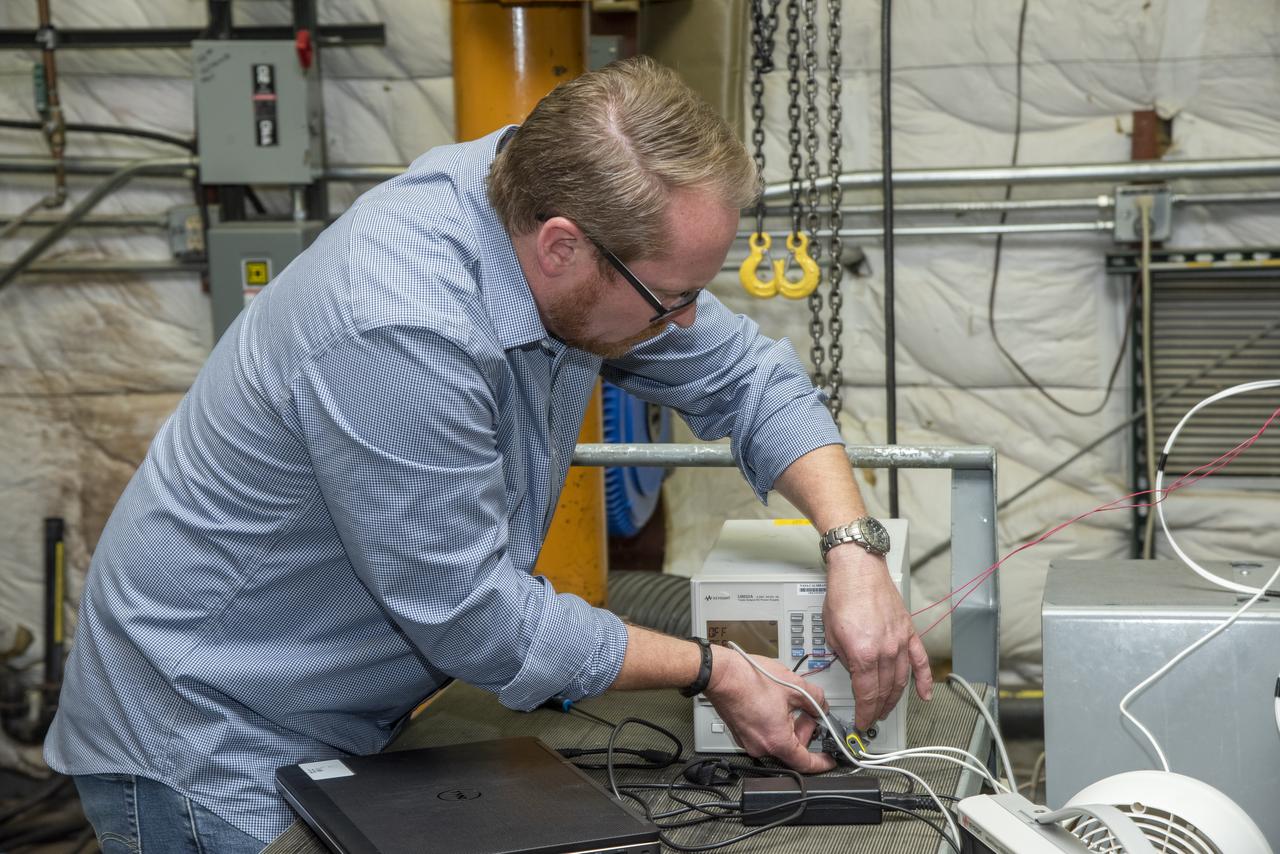

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
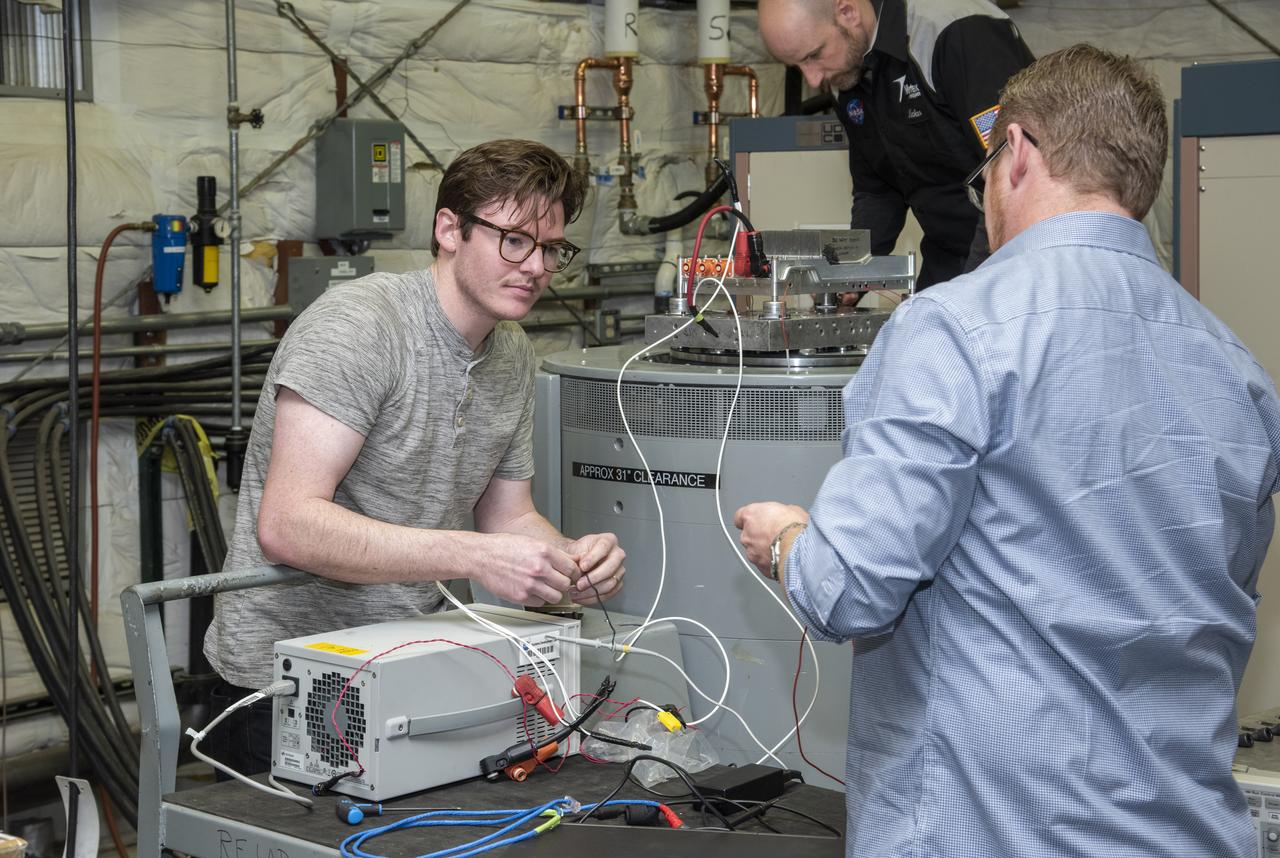
Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
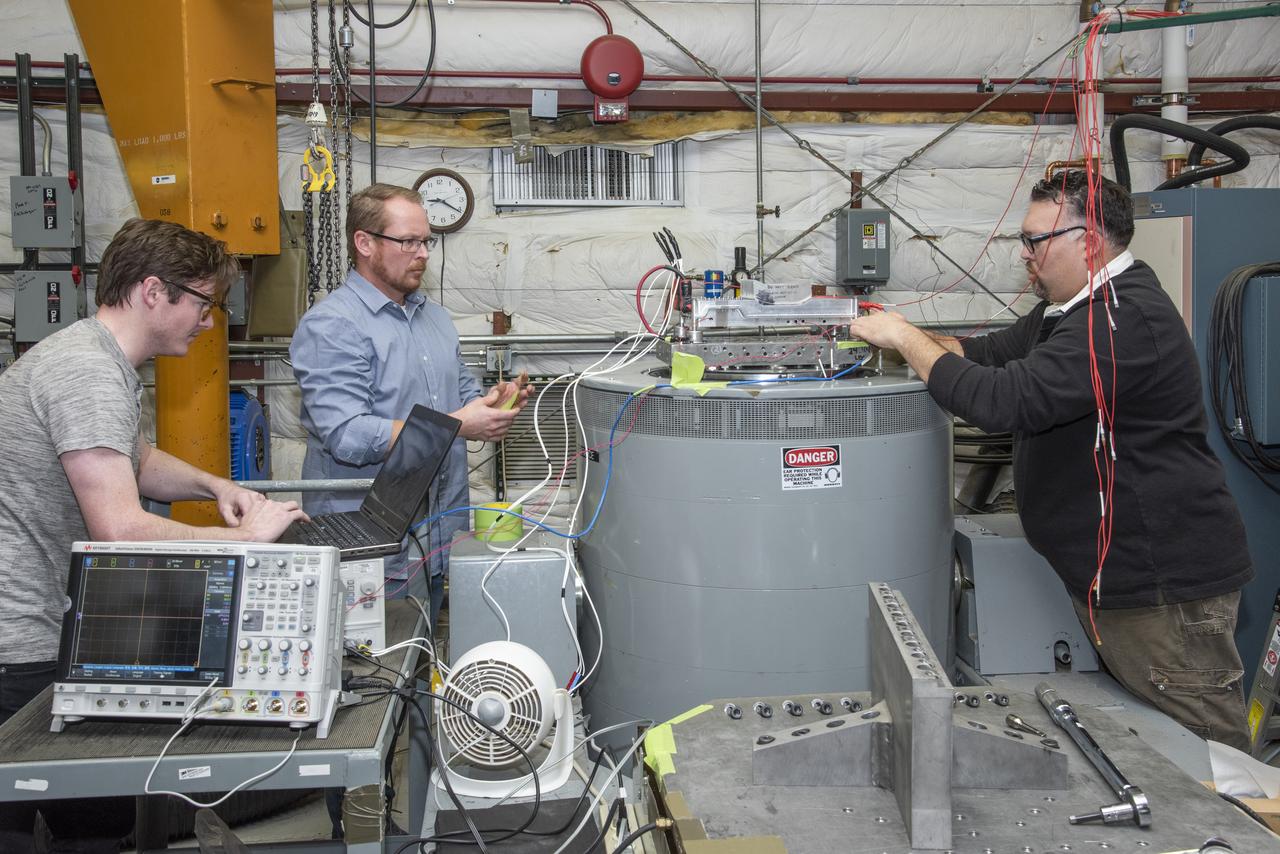

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
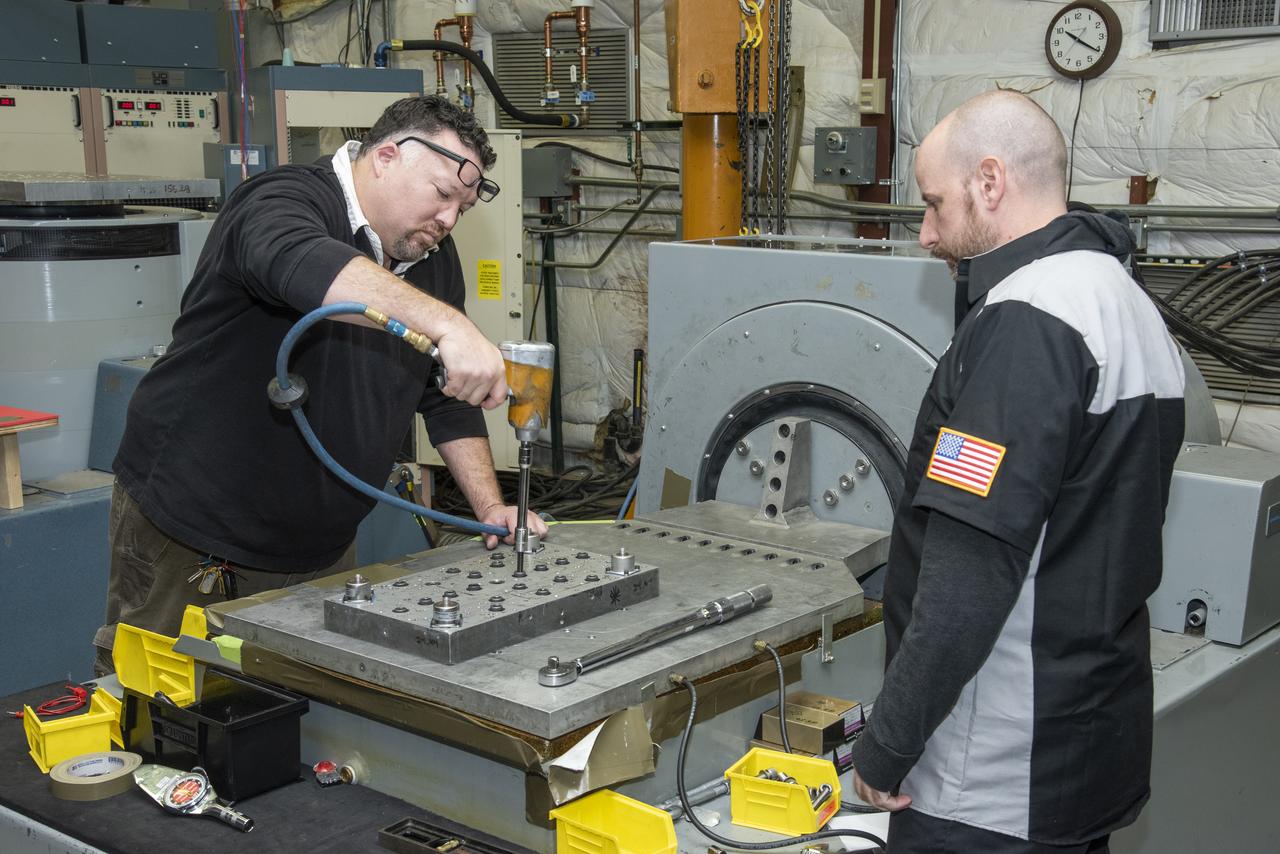

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
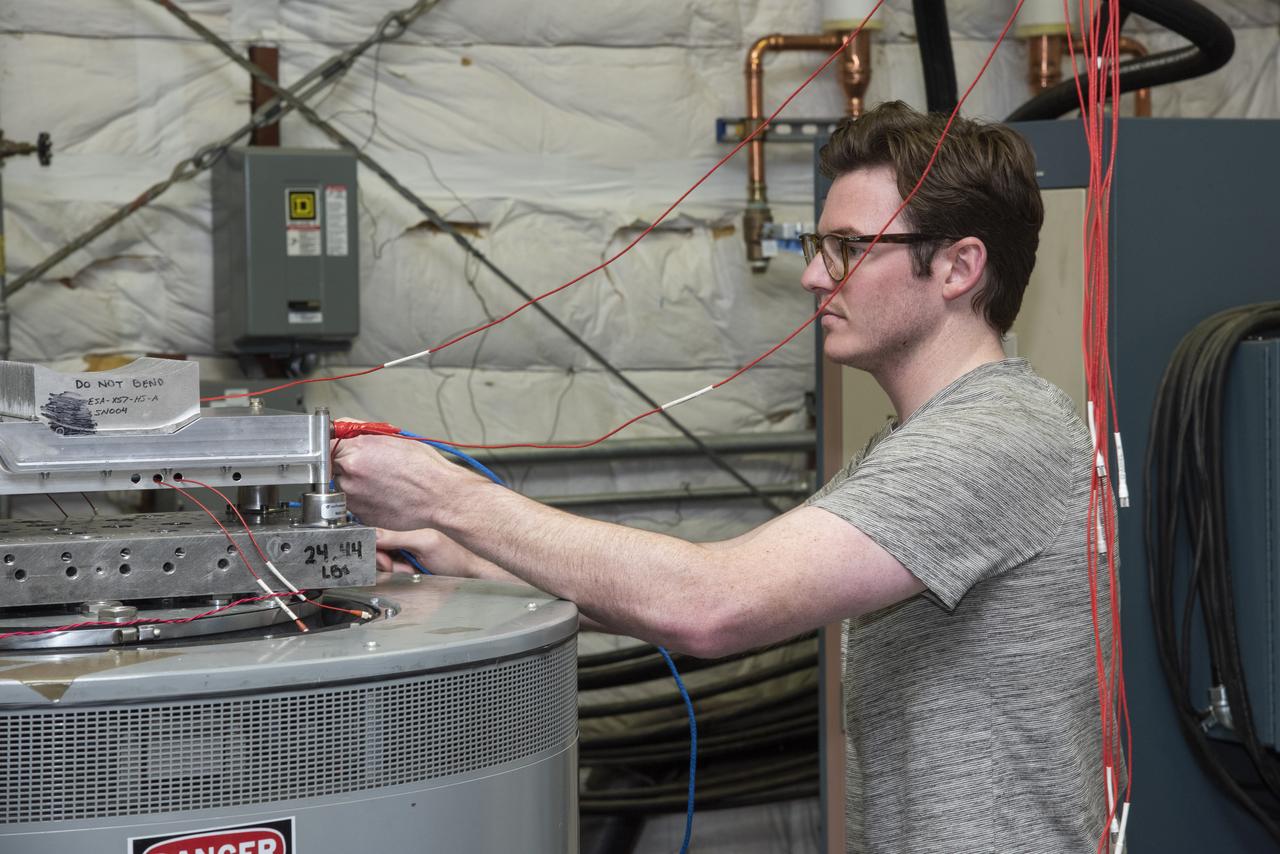

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
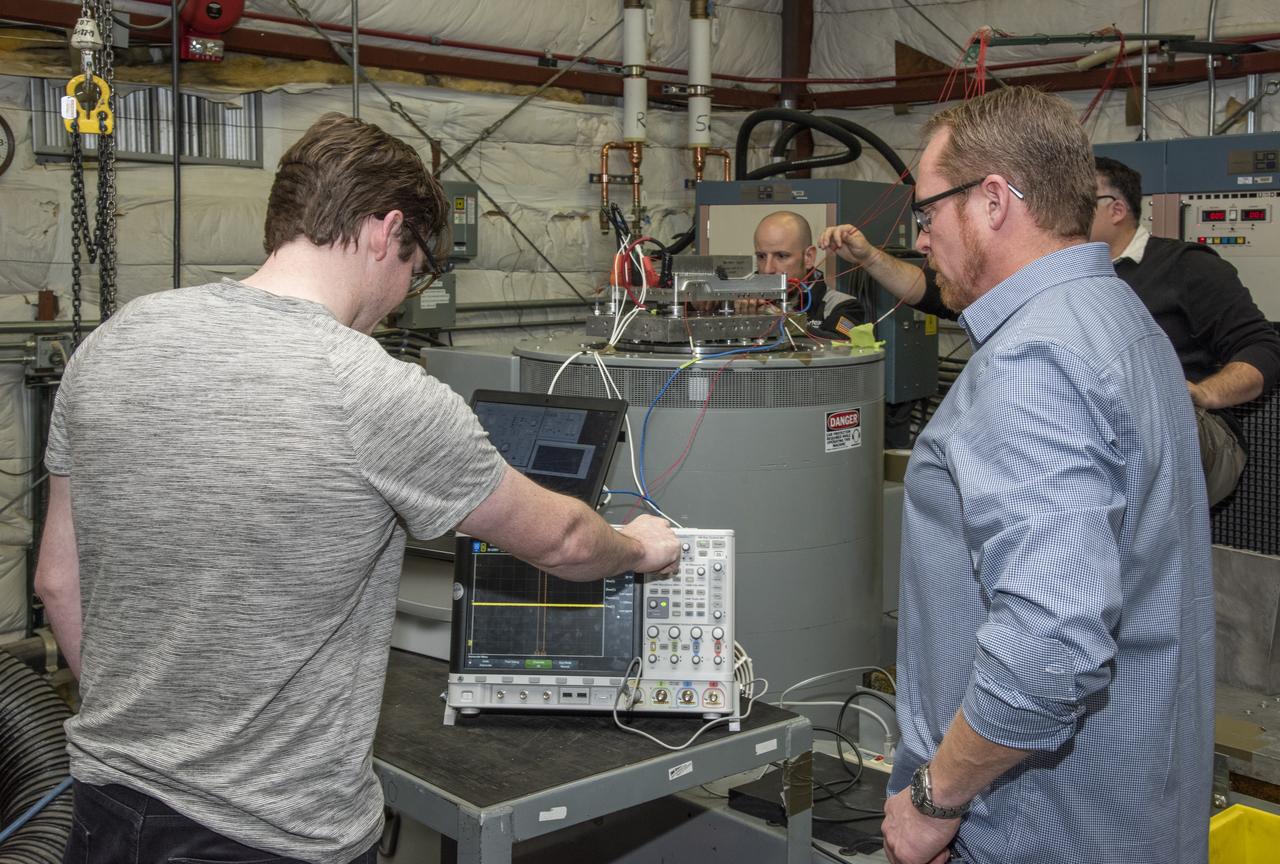

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
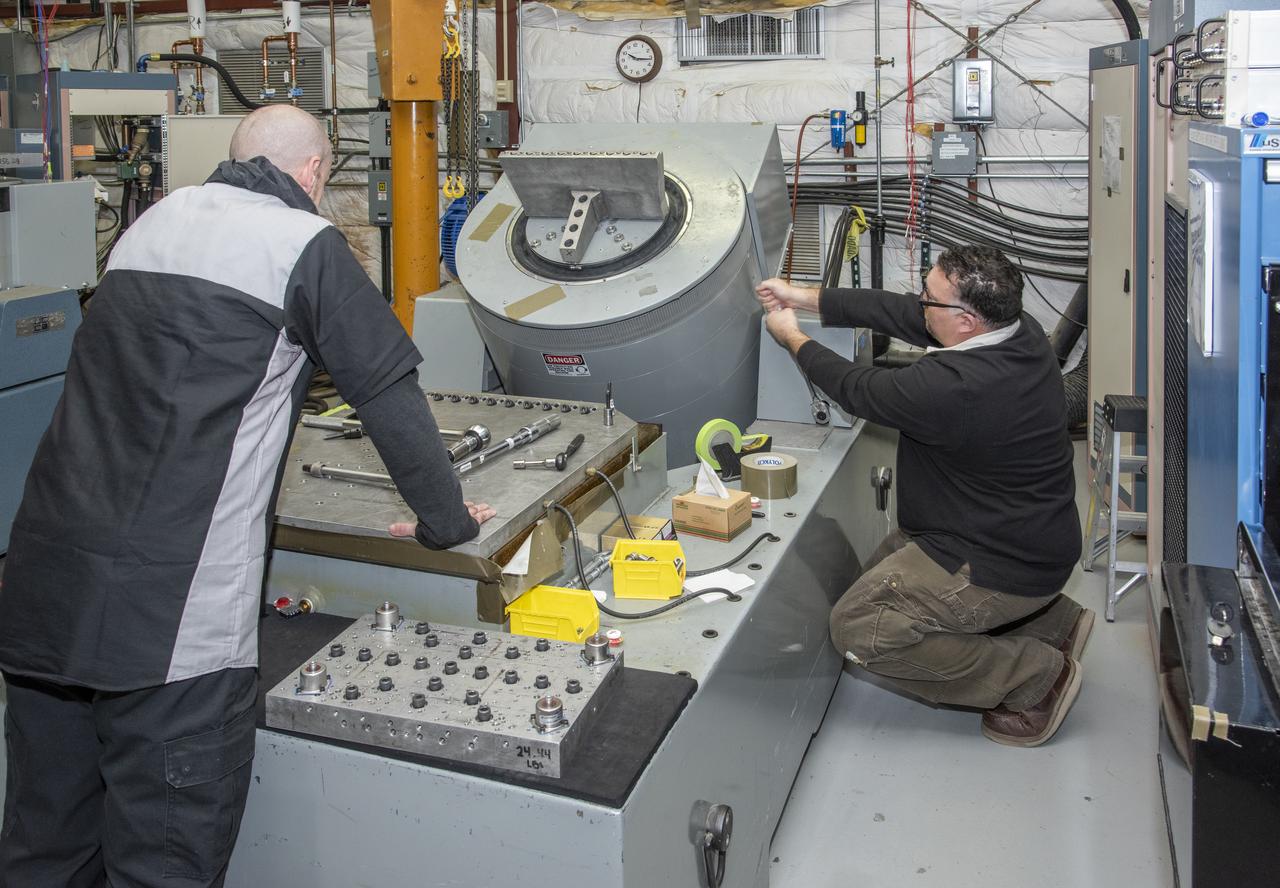

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
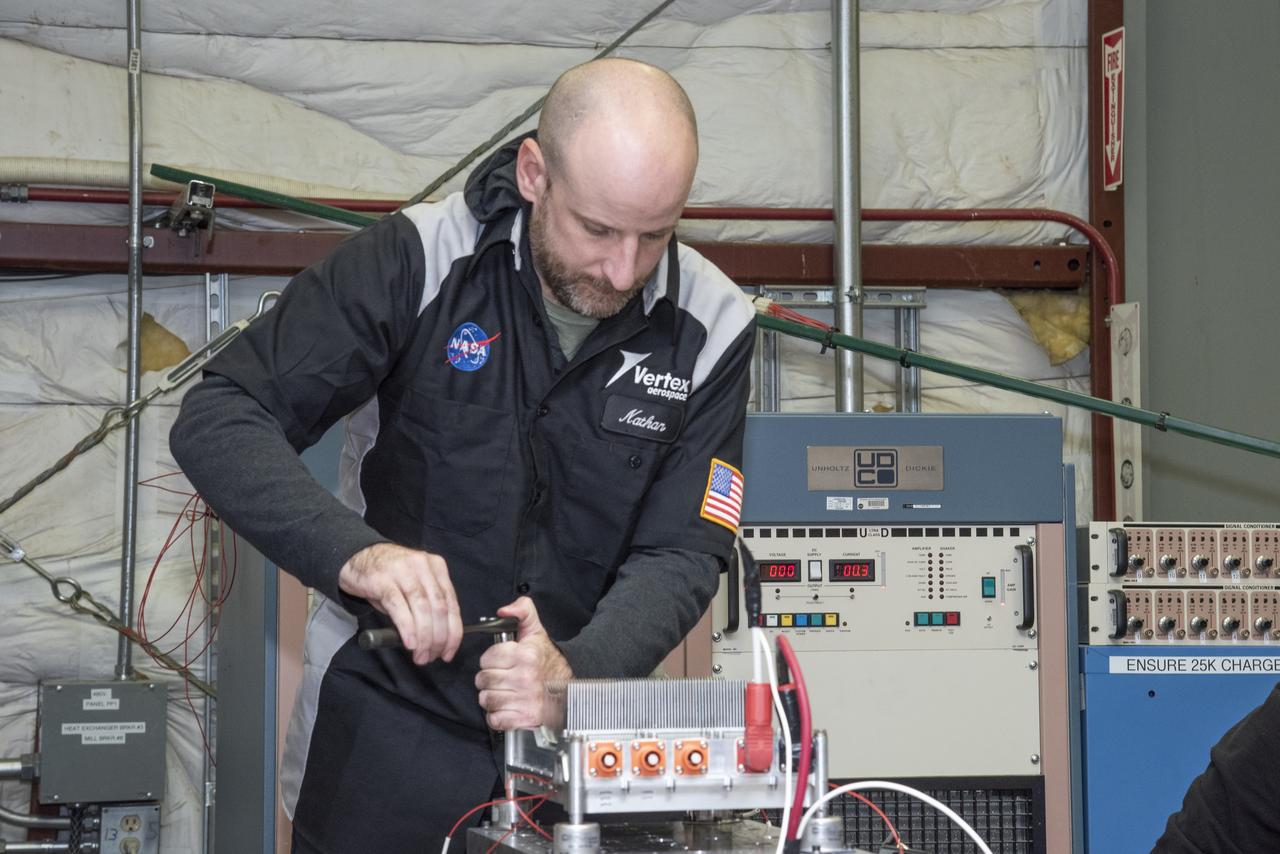

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
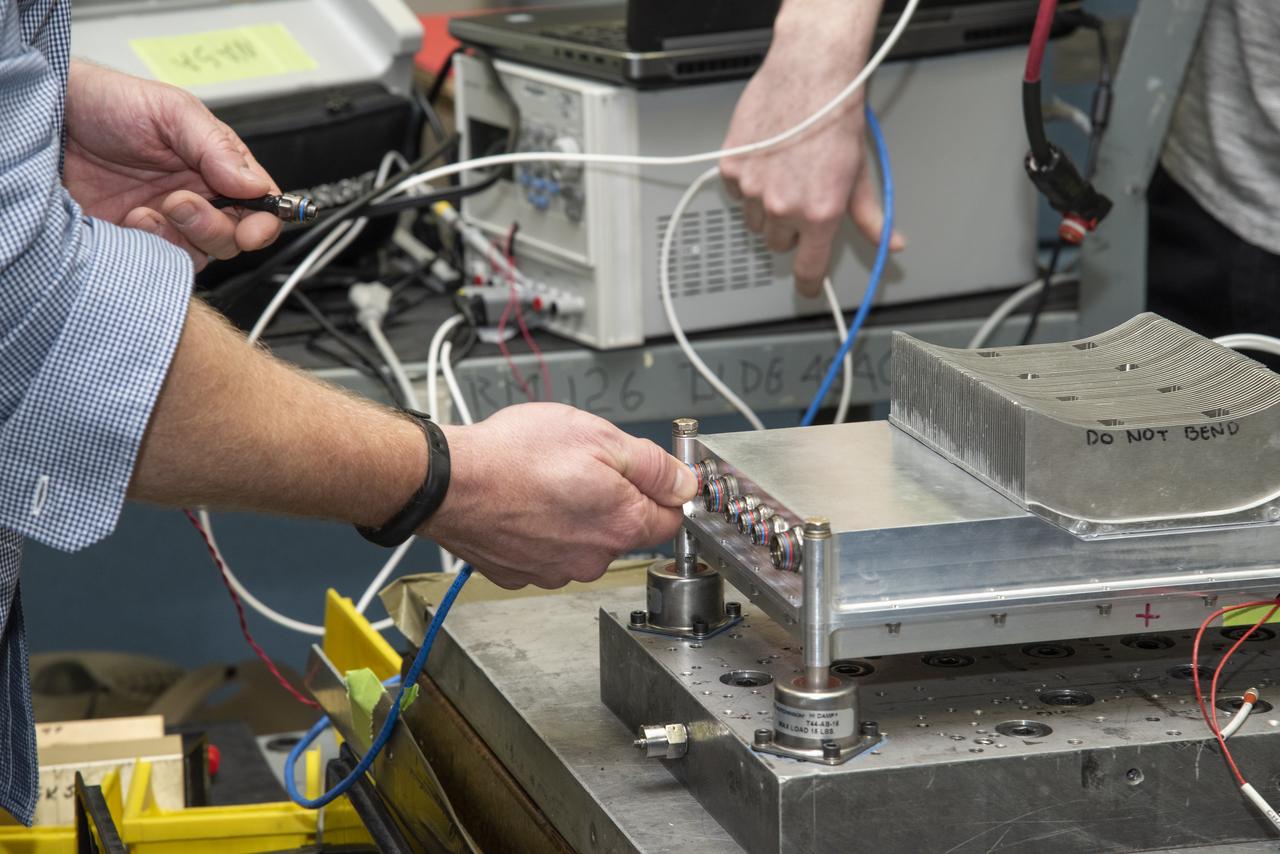
Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
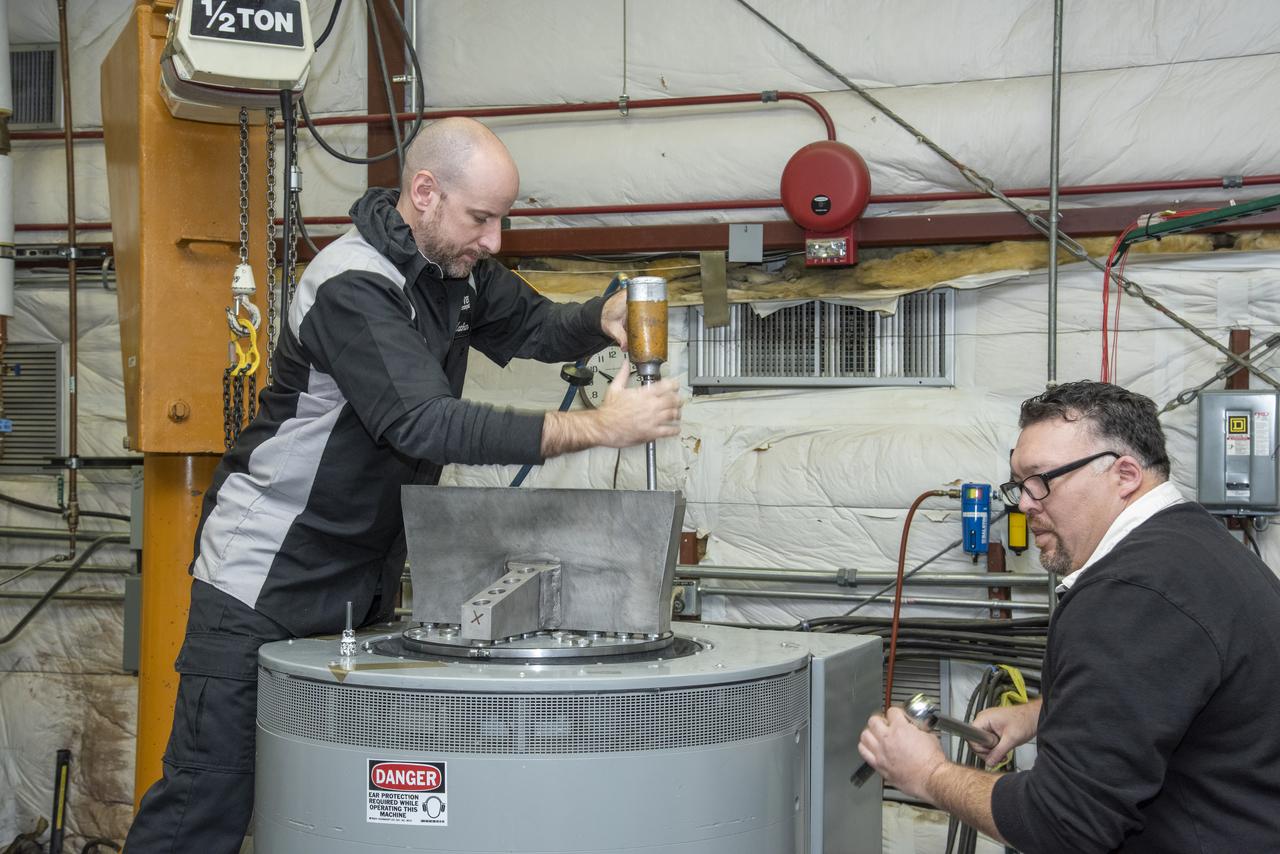

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
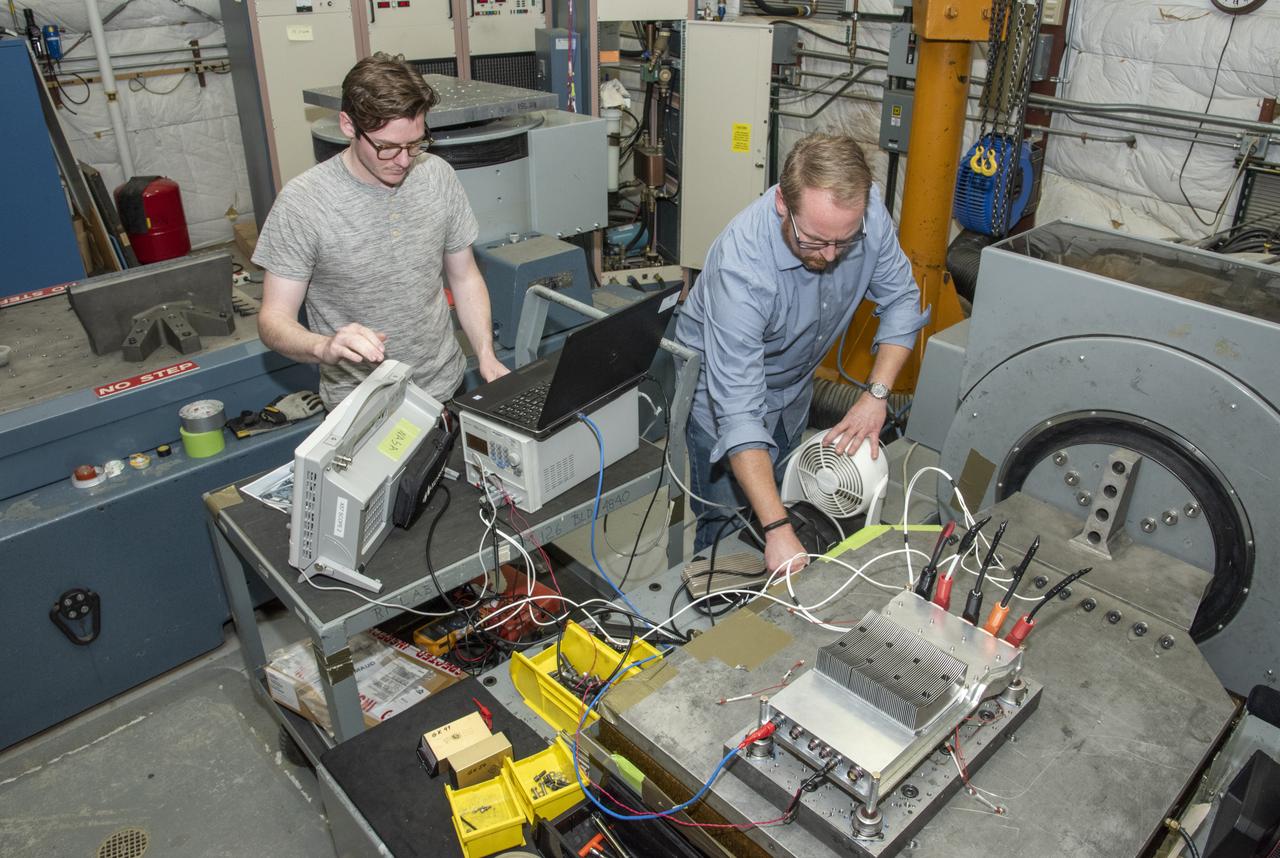

Engineers from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA’s all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong’s environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project’s first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA’s first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
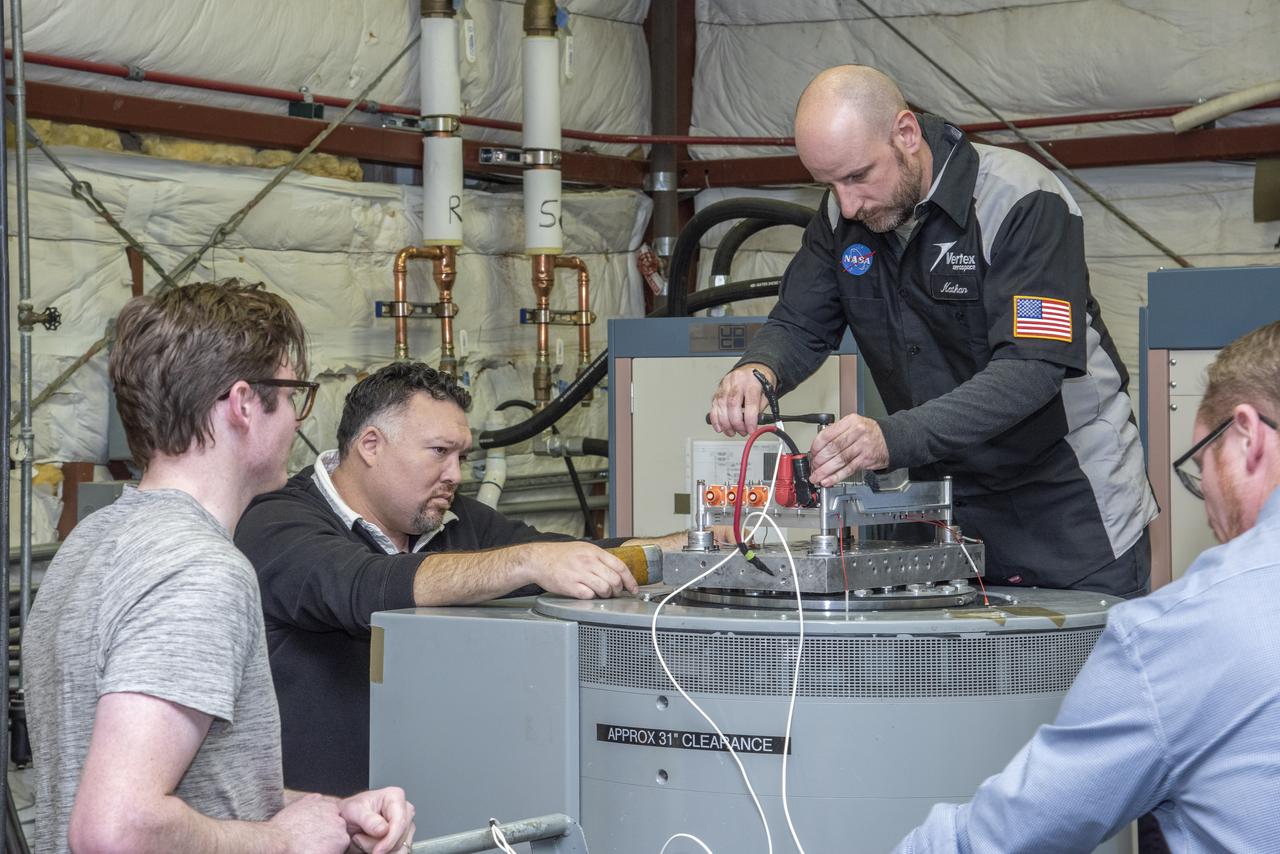

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
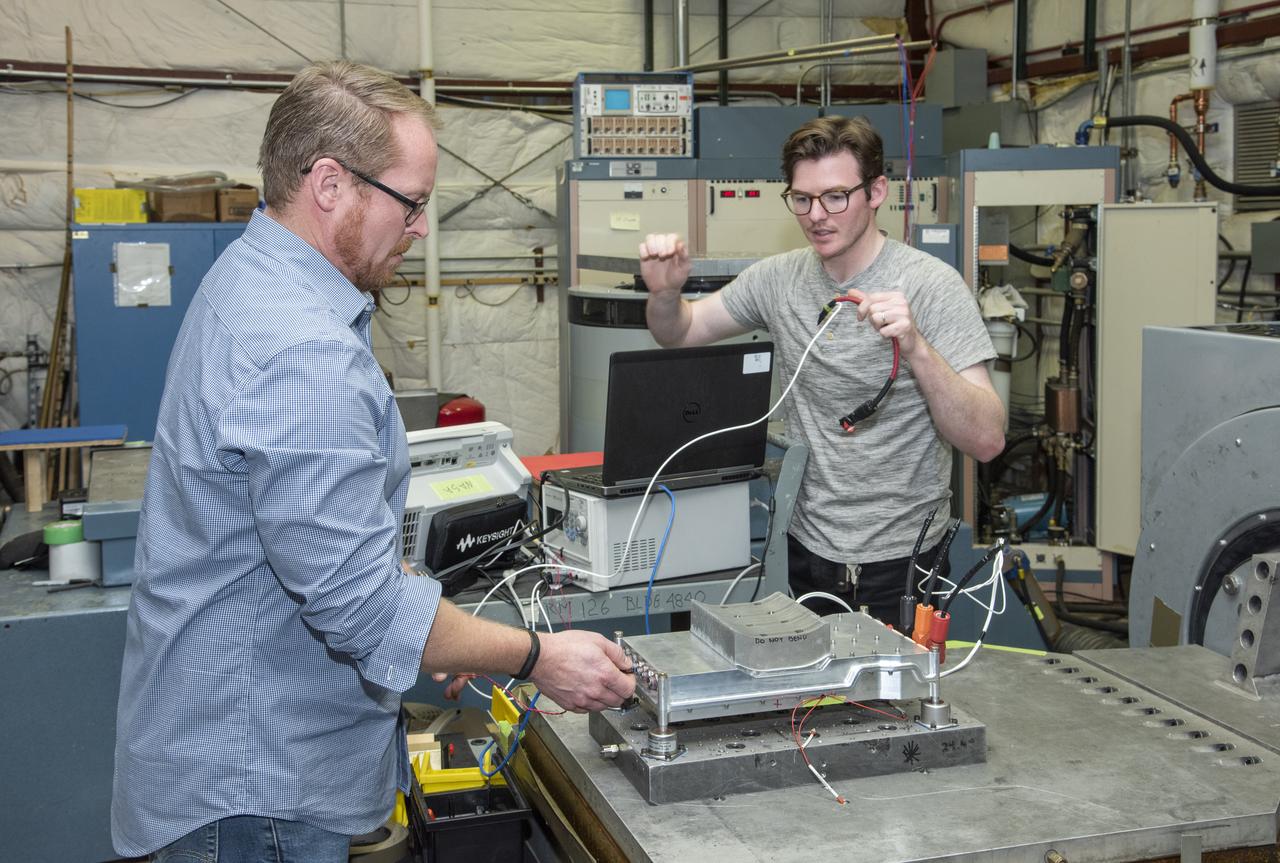

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
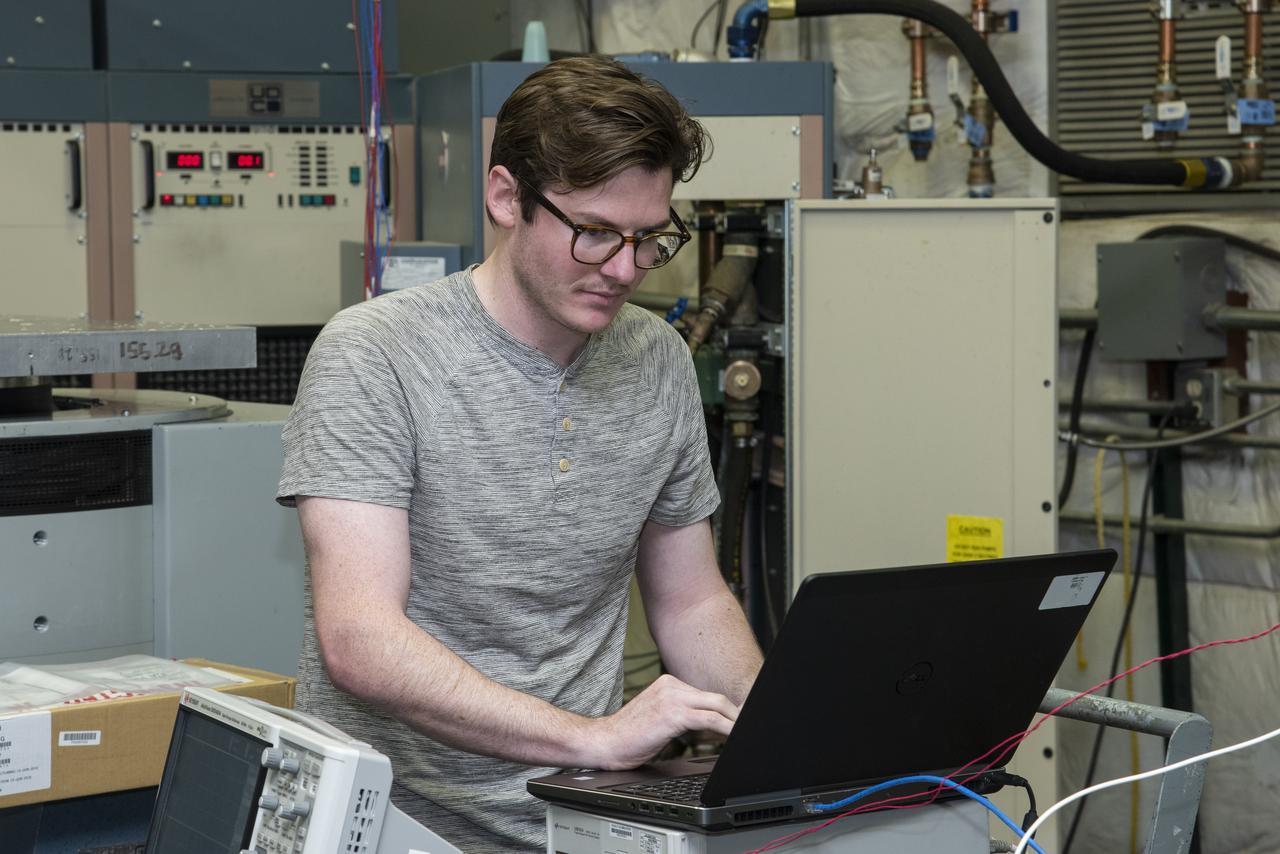

Engineers from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA’s all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong’s environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project’s first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA’s first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
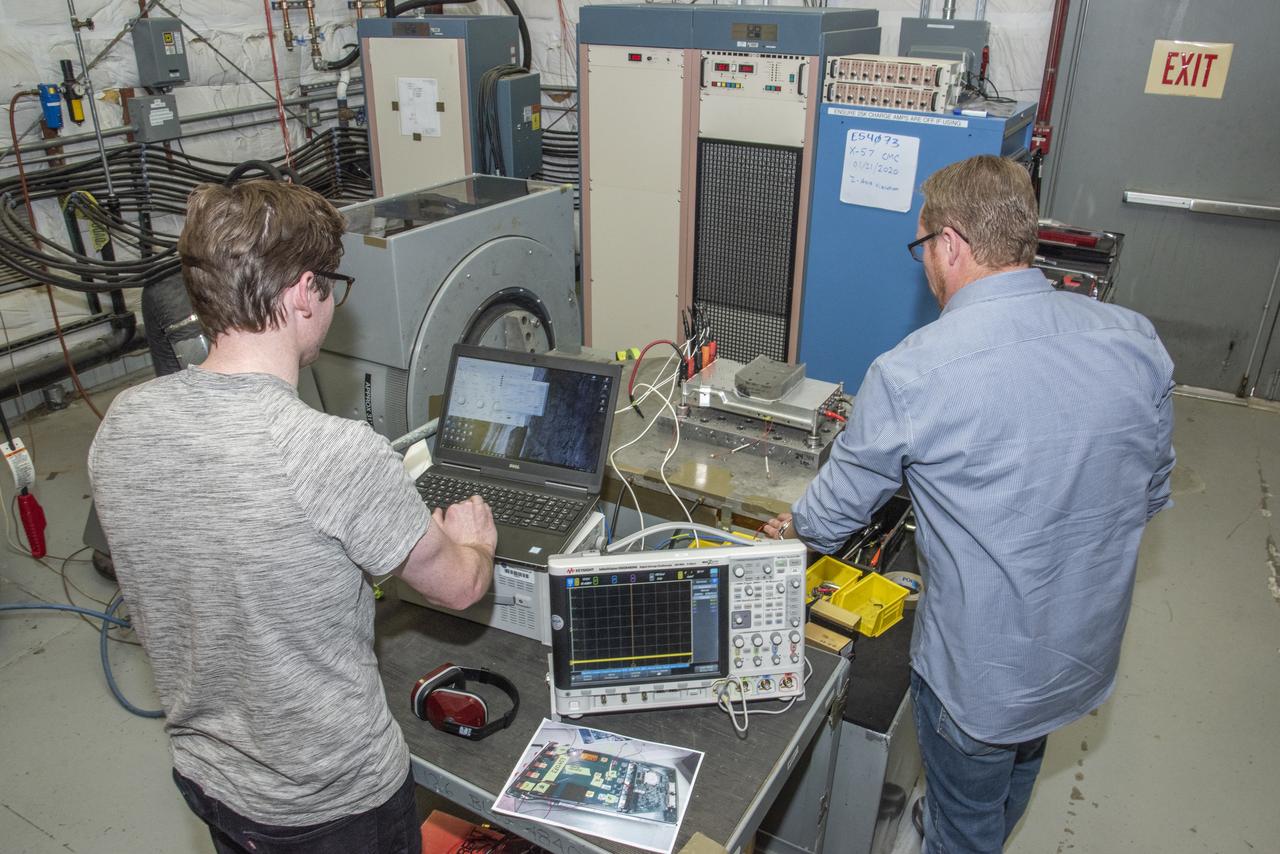

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
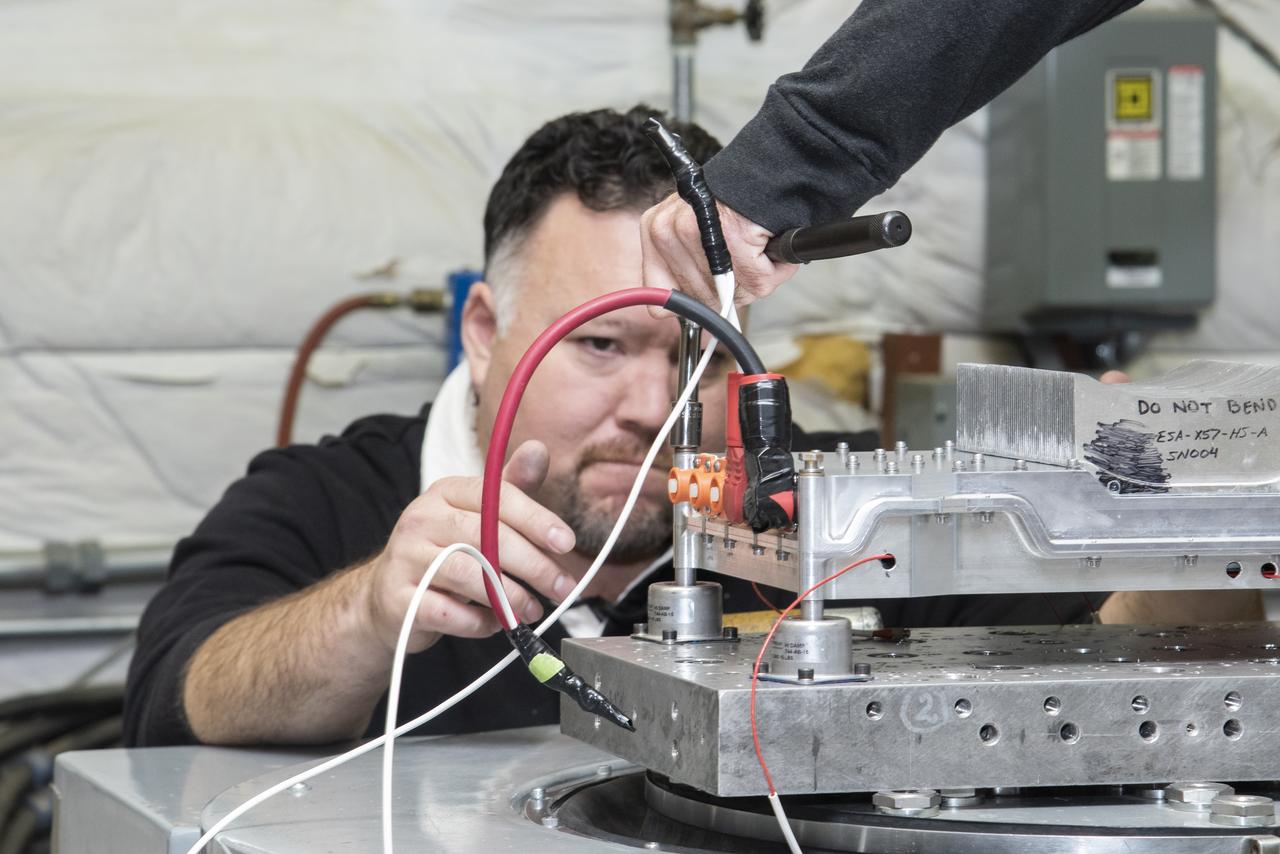

Engineers from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA’s all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong’s environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project’s first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA’s first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
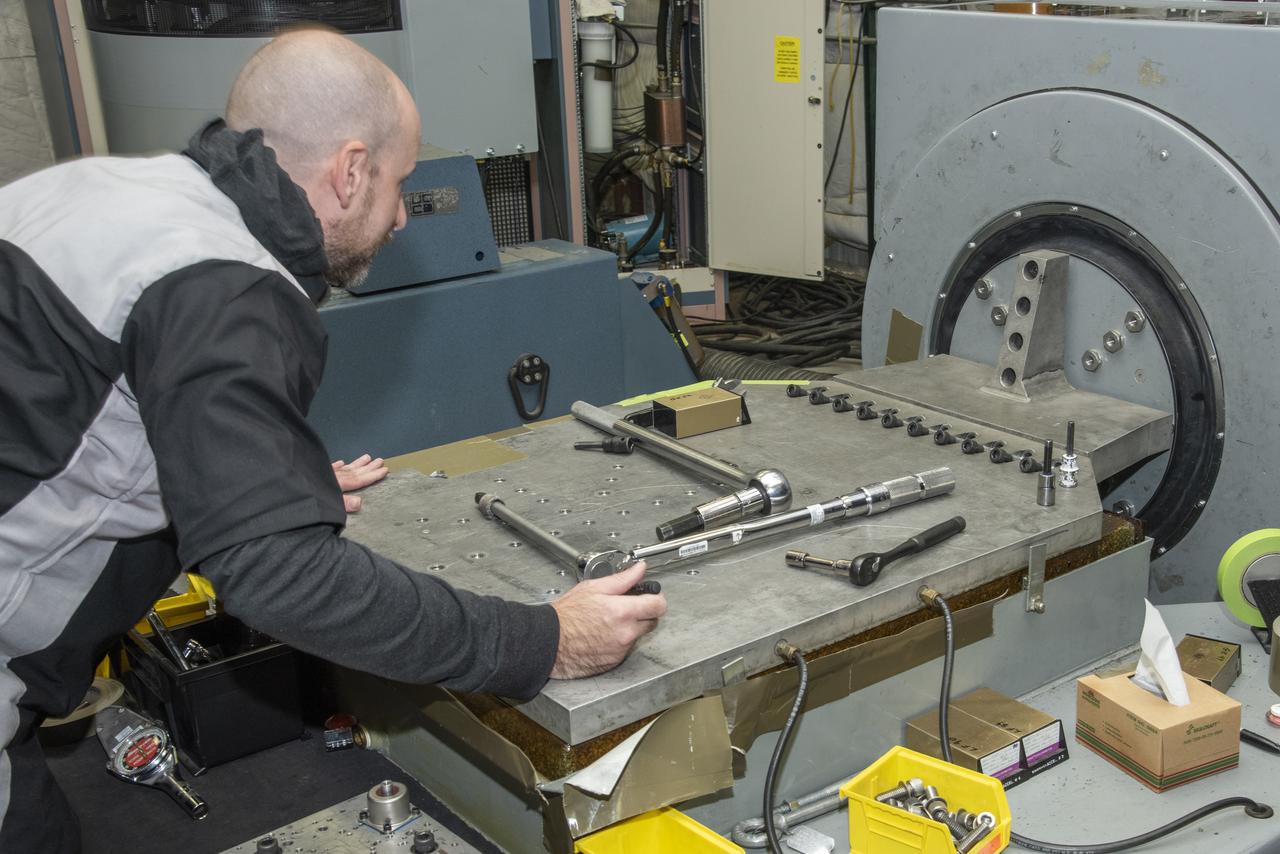

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
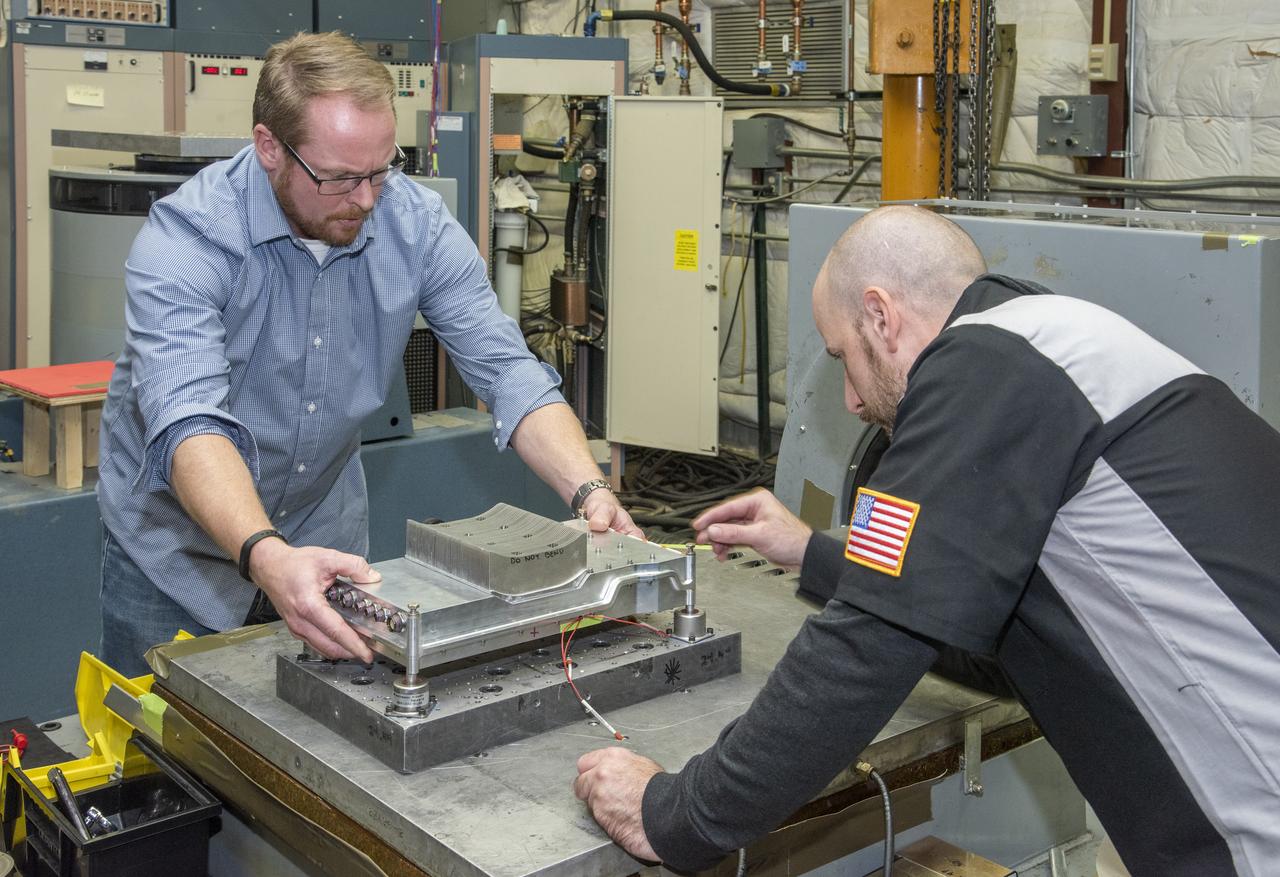

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
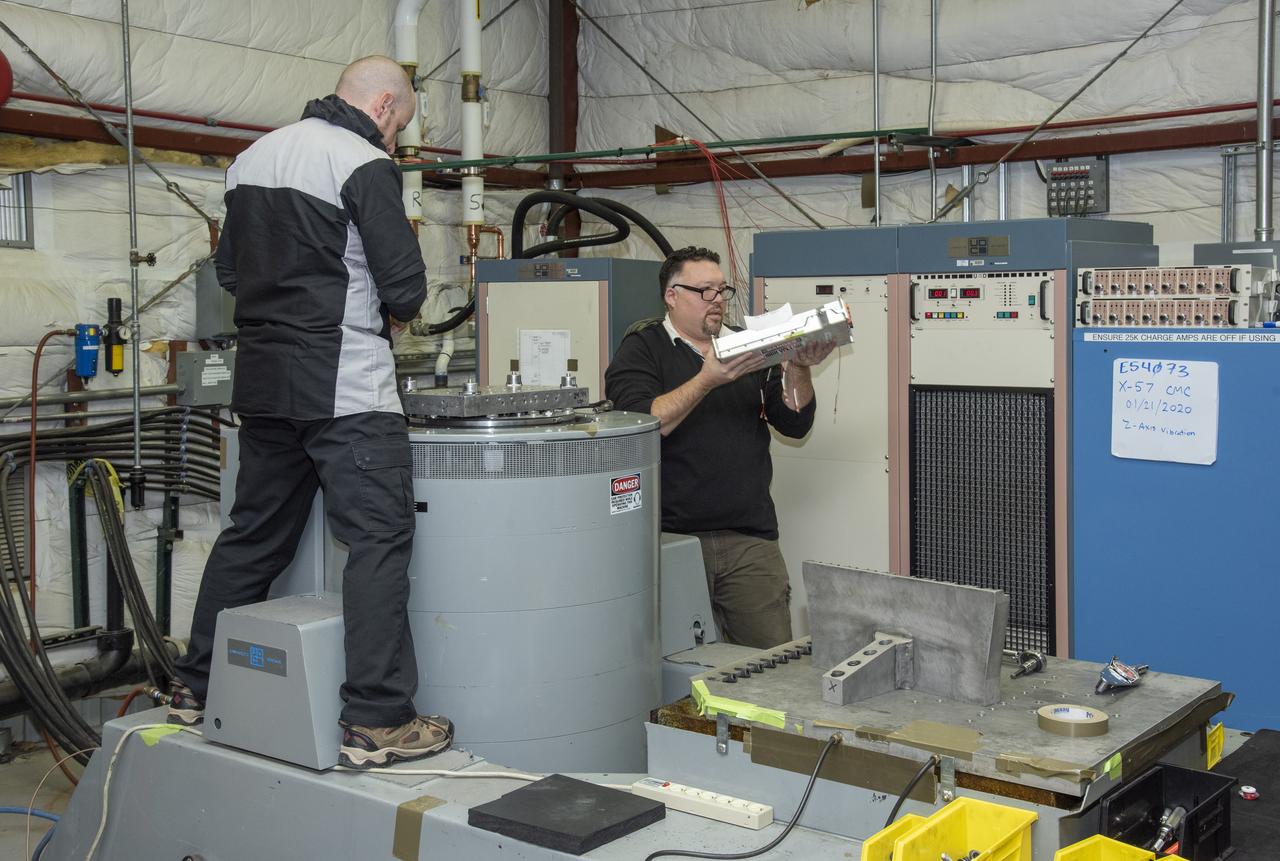

Engineers from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA’s all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong’s environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project’s first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA’s first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
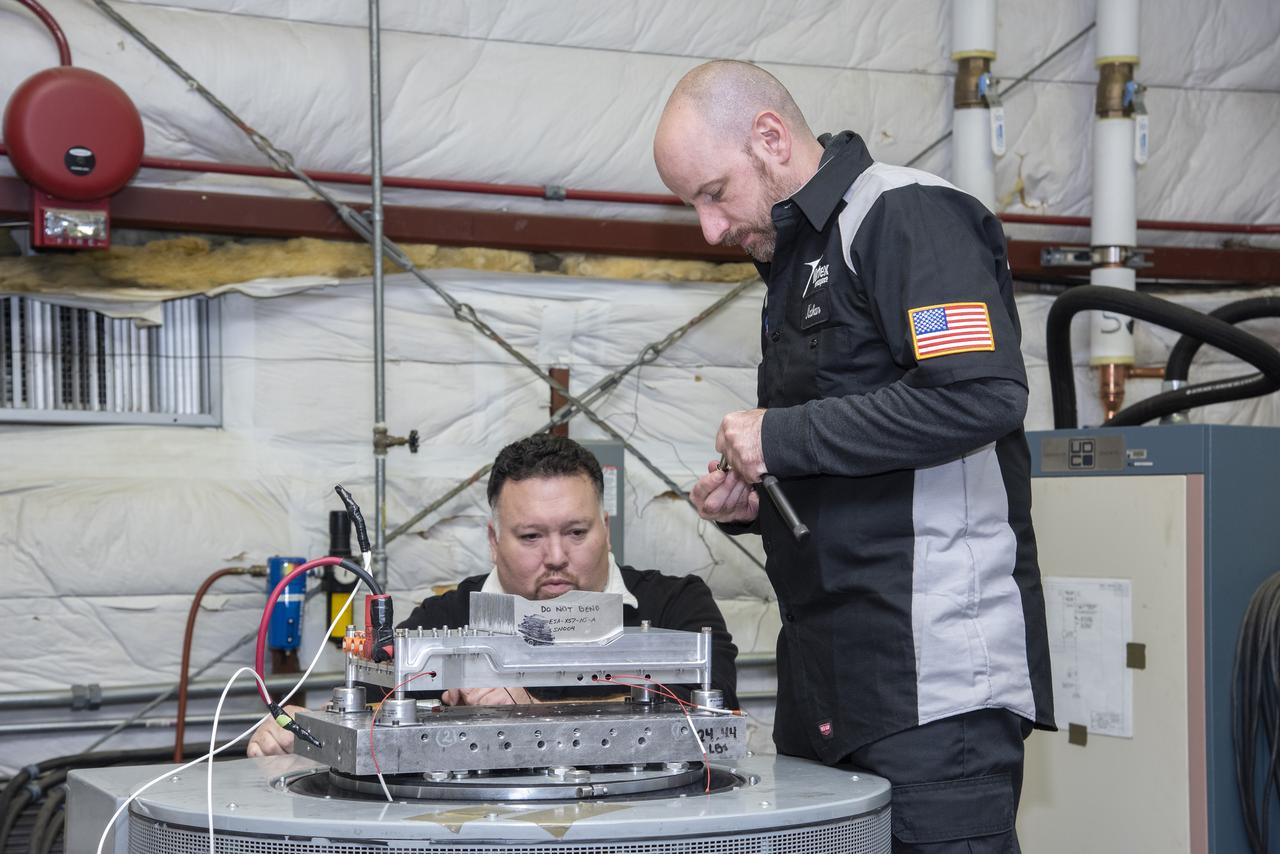

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
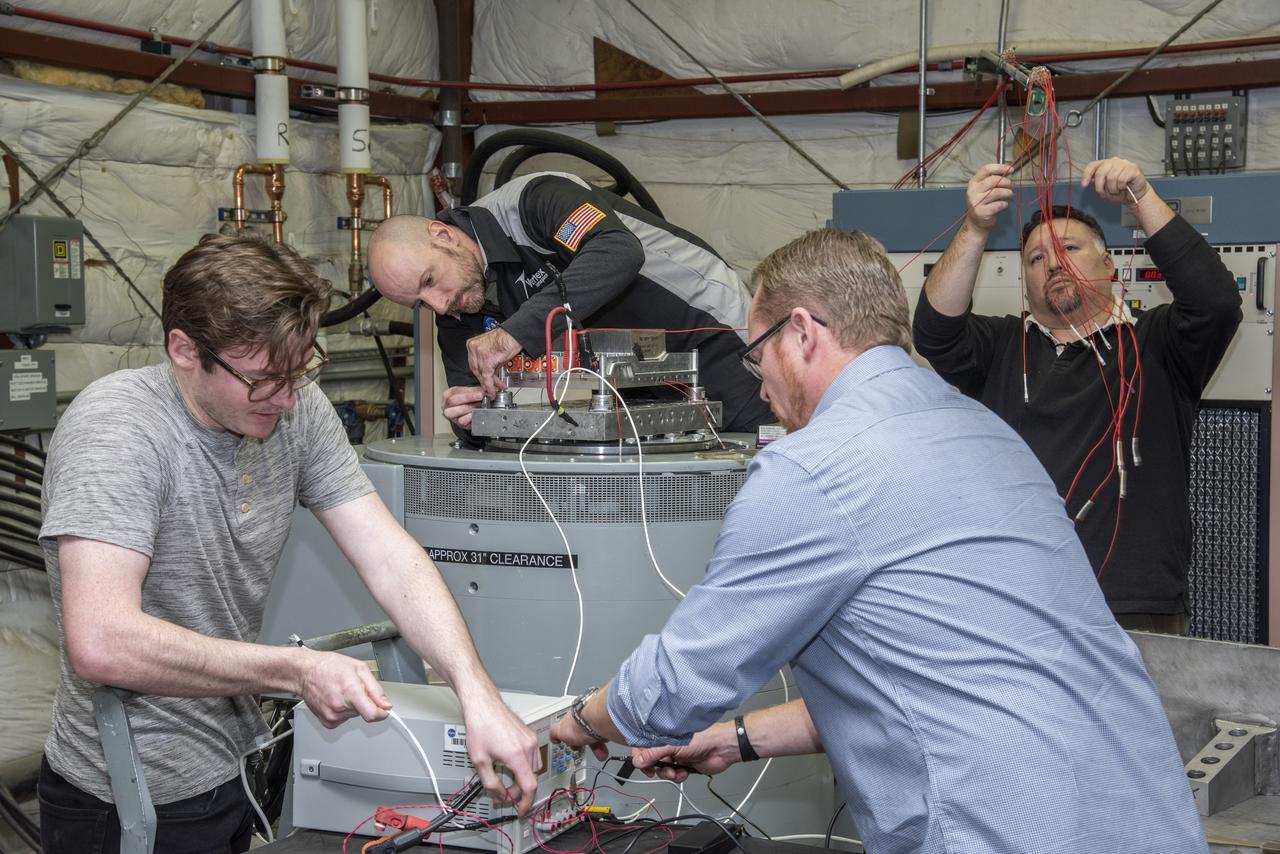

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
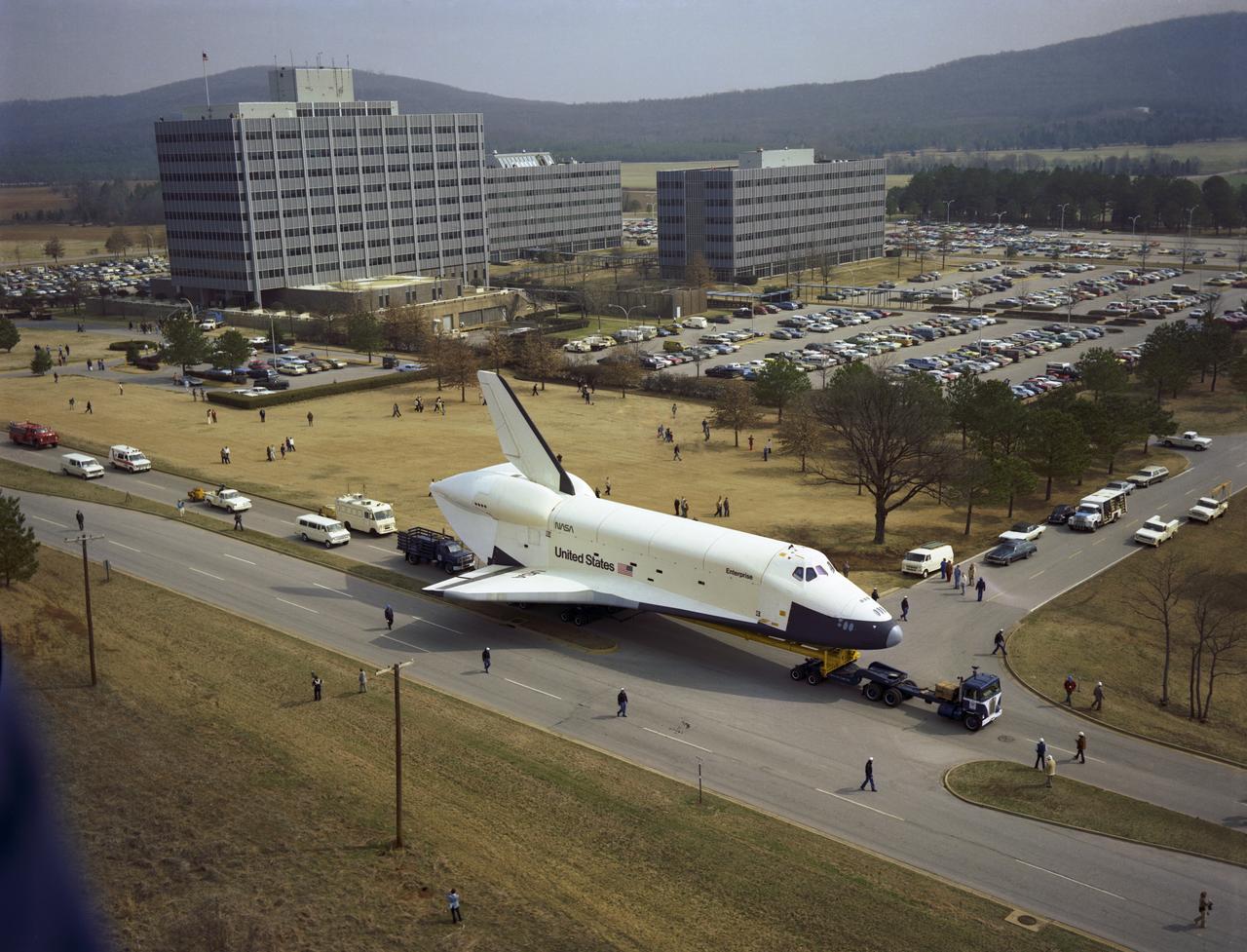

In this view, the Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise is seen heading South on Rideout Road with Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC'S) administrative 4200 Complex in the background, as it is being transported to MSFC's building 4755 for later Mated Vertical Ground Vibration tests (MVGVT) at MSFC's Dynamic Test Stand. The tests marked the first time ever that the entire shuttle complement (including Orbiter, external tank, and solid rocket boosters) were mated vertically.
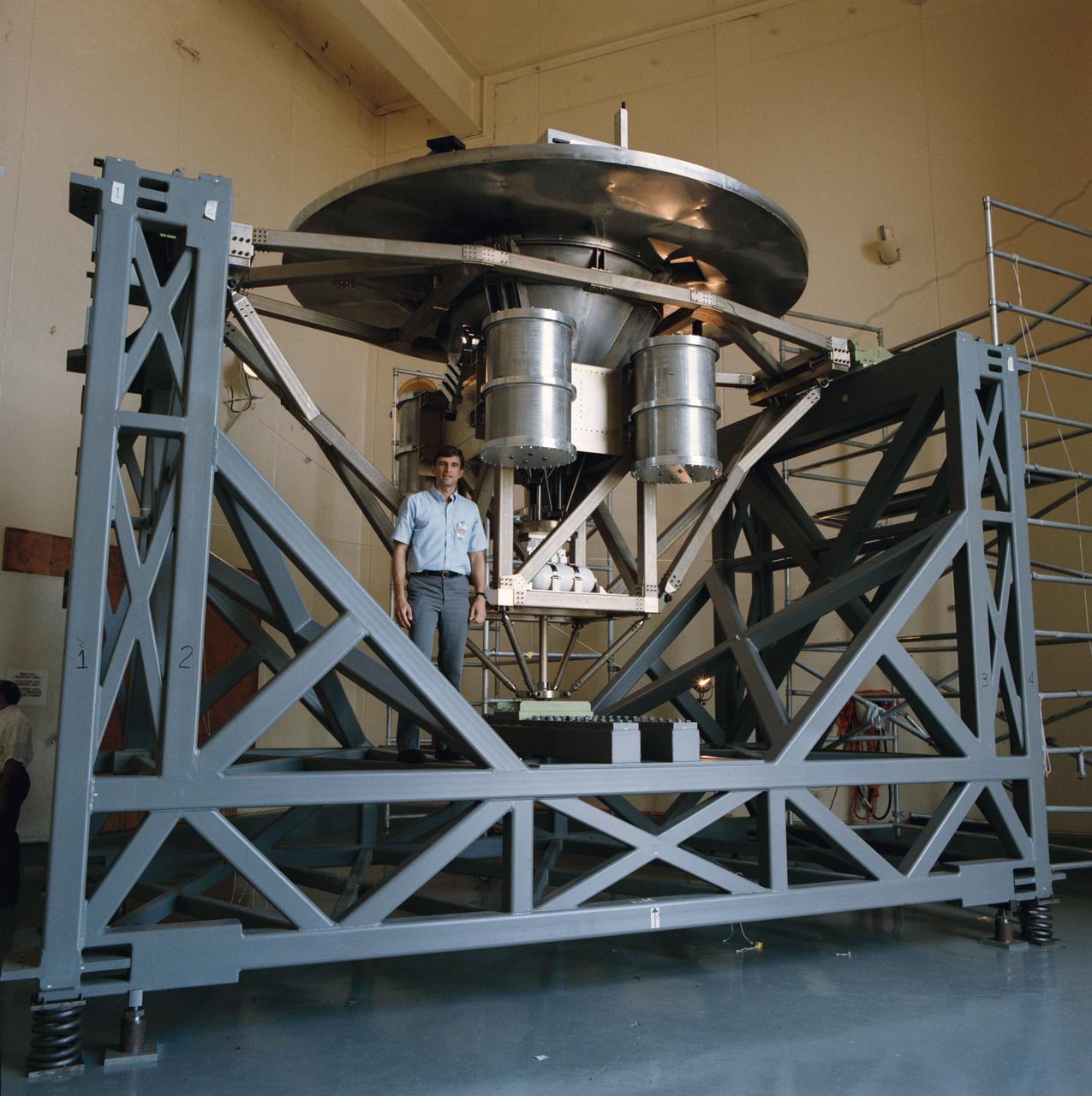

Astronaut Ronald M. Sega stands beside the University of Houston's Wake Shield Facility before it undergoes a Modal Survey Test in the Vibration and Acoustic Test Facility Building 49, prior to being flown on space shuttle mission STS-60.
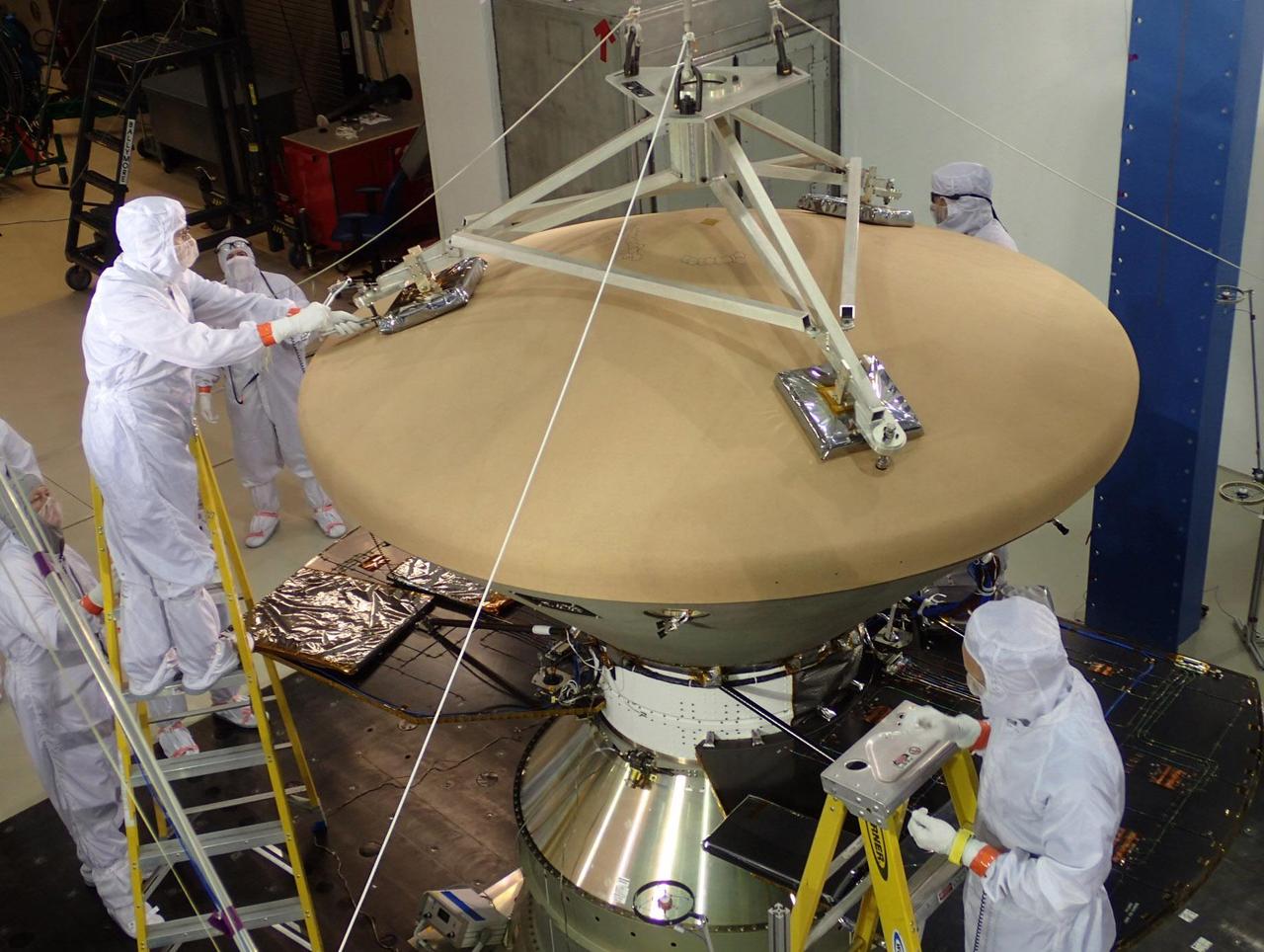

Spacecraft specialists at Lockheed Martin Space Systems, Denver, prepare NASA's InSight spacecraft for vibration testing as part of assuring that it is ready for the rigors of launch from Earth and flight to Mars. The spacecraft is oriented with its heat shield facing up in this July 13, 2015, photograph. InSight, for Interior Exploration Using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, is scheduled for launch in March 2016 and landing in September 2016. It will study the deep interior of Mars to advance understanding of the early history of all rocky planets, including Earth. Note: After thorough examination, NASA managers have decided to suspend the planned March 2016 launch of the Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) mission. The decision follows unsuccessful attempts to repair a leak in a section of the prime instrument in the science payload. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19815
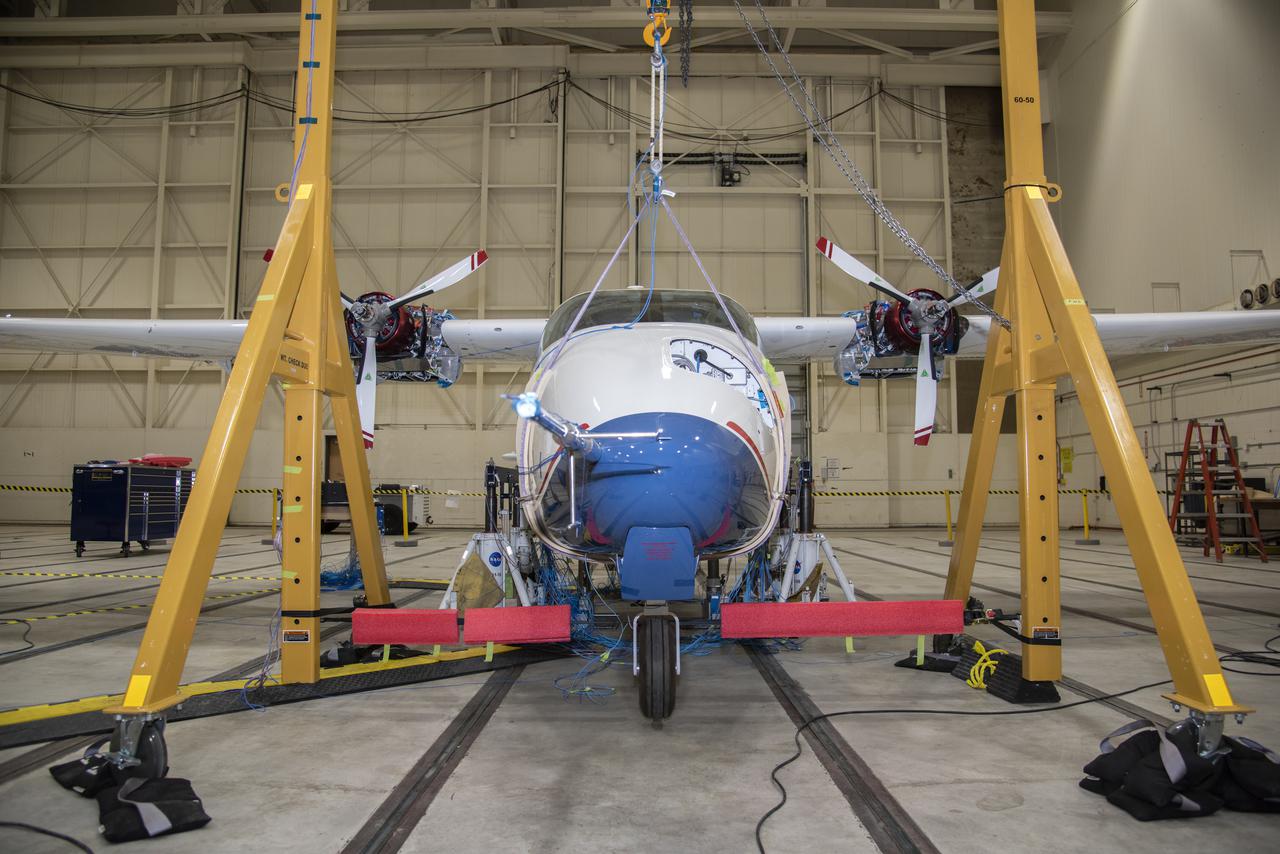

NASA’s all-electric X-57 Maxwell prepares for ground vibration testing, or GVT, at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California. Done in parallel with cruise motor controller testing, the GVT tested the vehicle at various vibration levels, helping engineers to examine and validate the integrity of the vehicle for flight conditions. A goal of X-57 is to help the Federal Aviation Administration set certification standards for emerging electric aircraft markets.
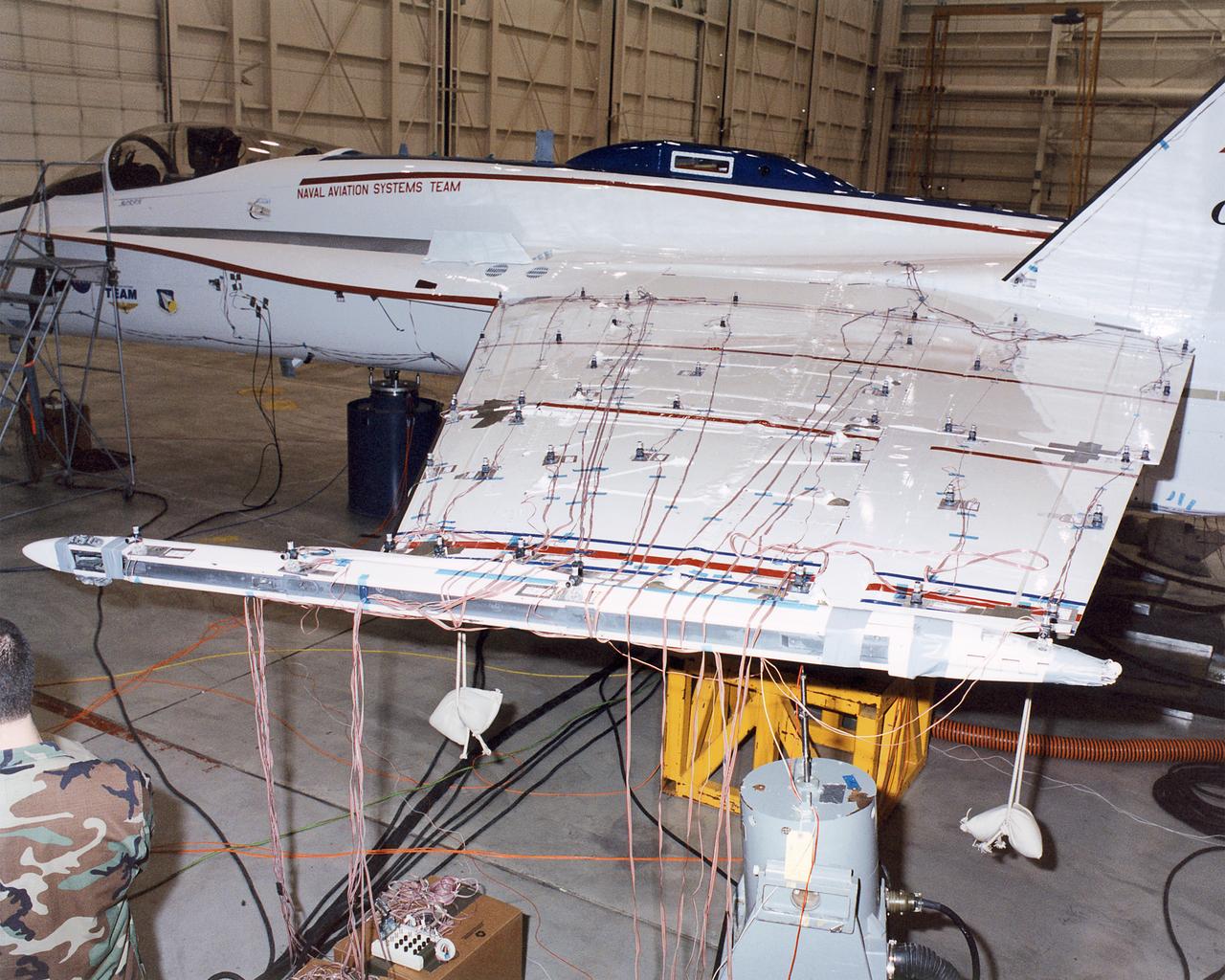

The upper wing surfaces of the Active Aeroelastic Wing F/A-18 test aircraft are covered with accelerometers and other sensors during ground vibration tests at NASA Dryden Flight Research Center.

From left, April Torres and Karen Estes watch incoming data from vibration tests on the hypersonic Fiber Optic Sensing System at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards California. Testing on a machine called a shaker proved that the system could withstand the severe vibration it will endure in hypersonic flight, or travel at five times the speed of sound.

Researchers test a 10-foot Mock Truss-Braced Wing at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. From left, ground vibration test director Ben Park, Natalie Spivey, and Samson Truong, prepare for a vibration test. The aircraft concept involves a wing braced on an aircraft using diagonal struts that also add lift and could result in significantly improved aerodynamics.
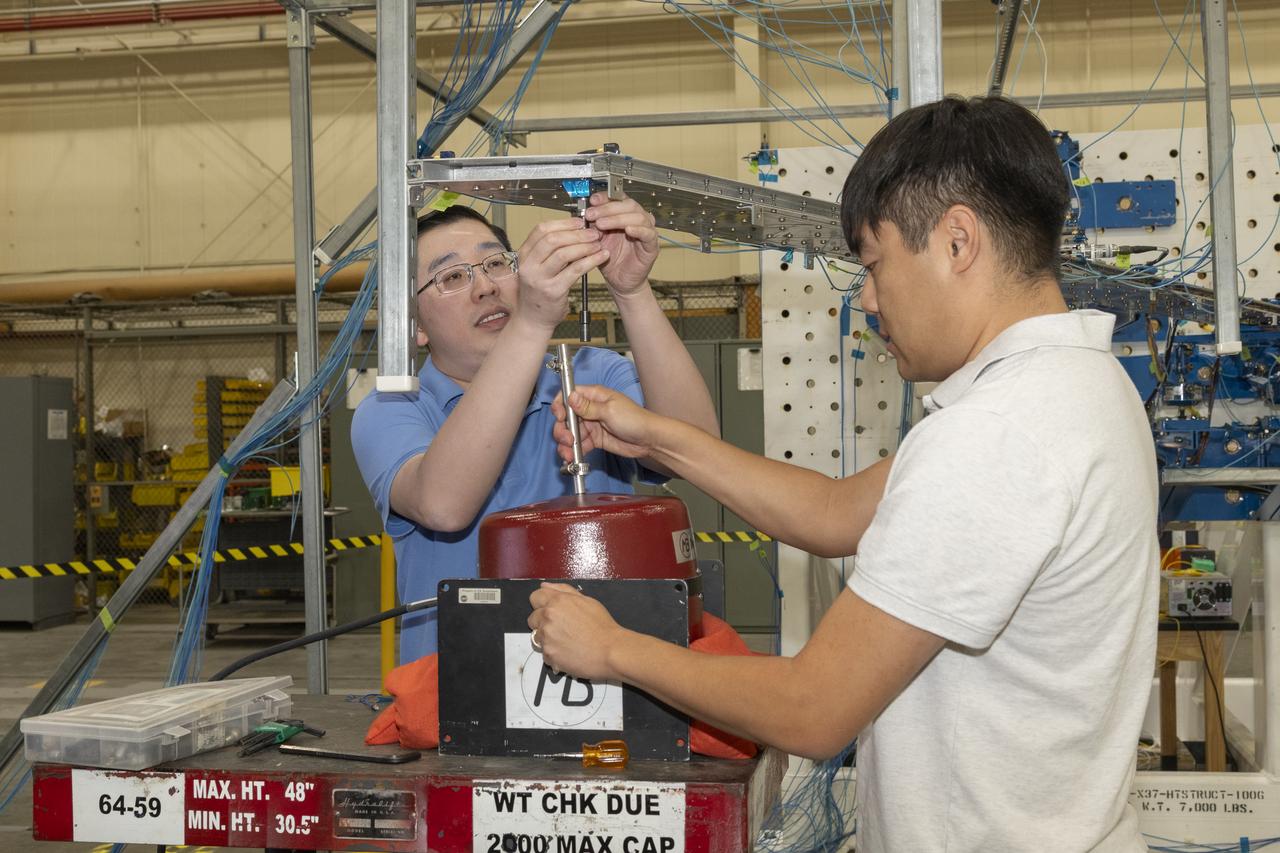

Researchers test a 10-foot Mock Truss-Braced Wing at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. Samson Truong, from left, and Ben Park, NASA mock wing ground vibration test director, prepare for a vibration test. The aircraft concept involves a wing braced on an aircraft using diagonal struts that also add lift and could result in significantly improved aerodynamics.

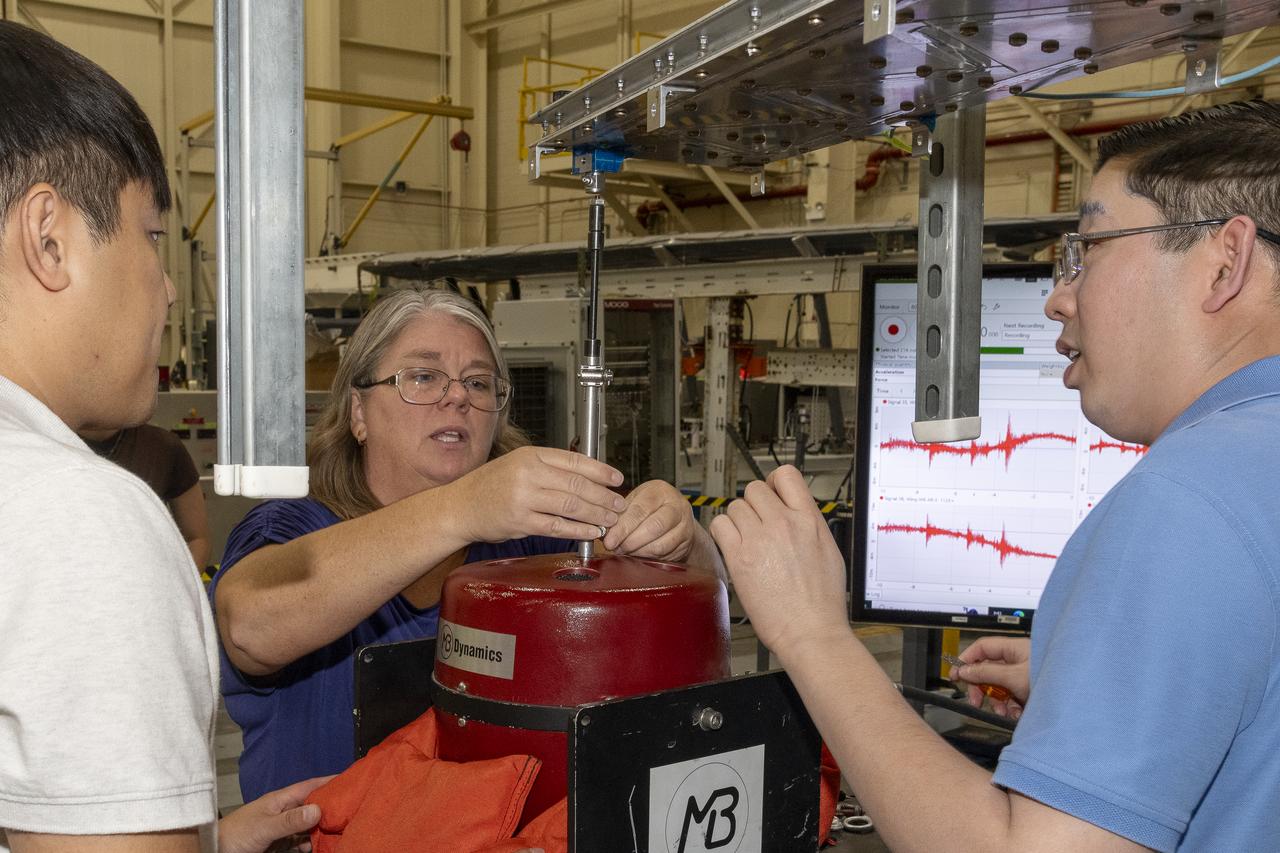
Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.

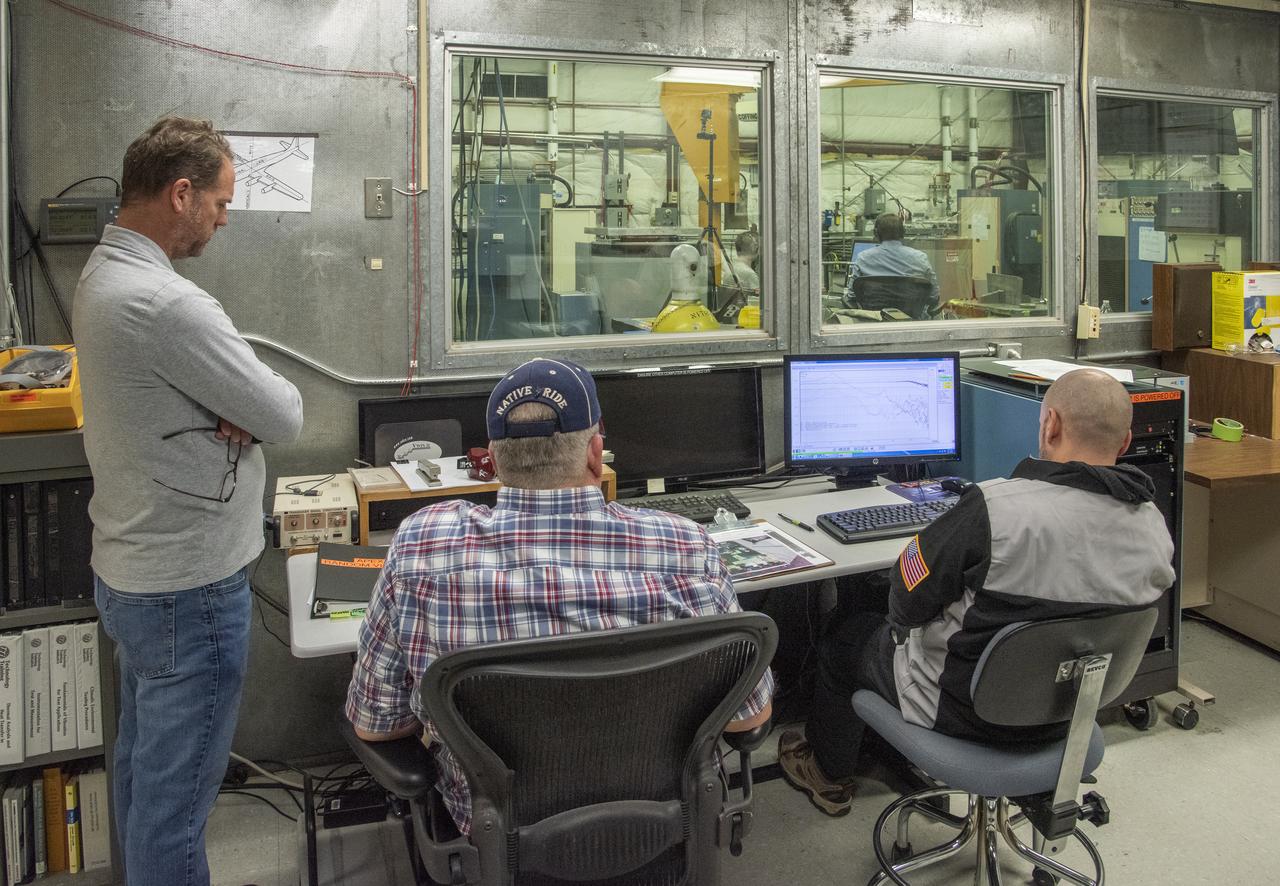
Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
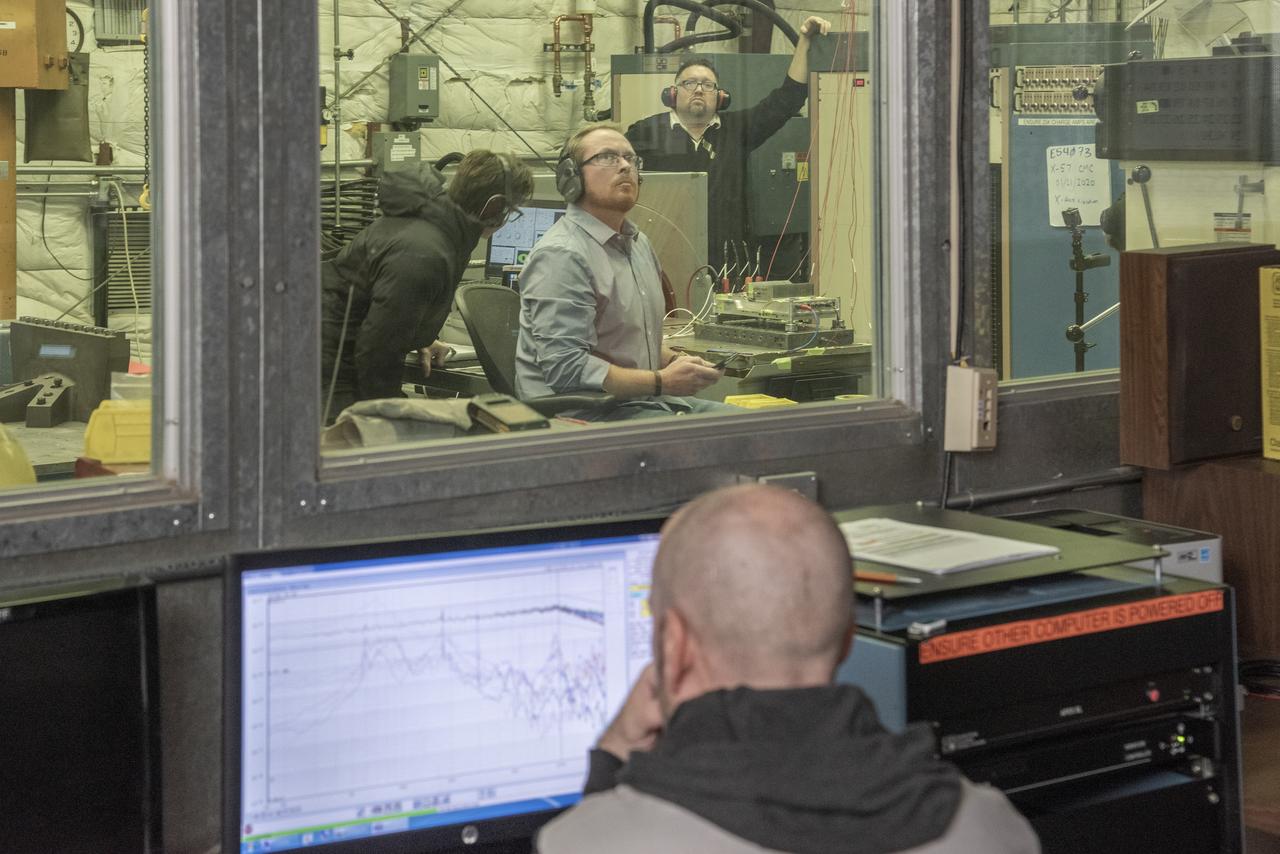

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.

A cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane, undergoes vibration testing at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s environmental lab. The cruise motor controller is exposed to two levels of vibration on three different axes, helping NASA to examine the integrity of the controller for flight conditions. The cruise motor controller will be a critical component for providing power to X-57’s motors when the aircraft takes to the skies in 2020.

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
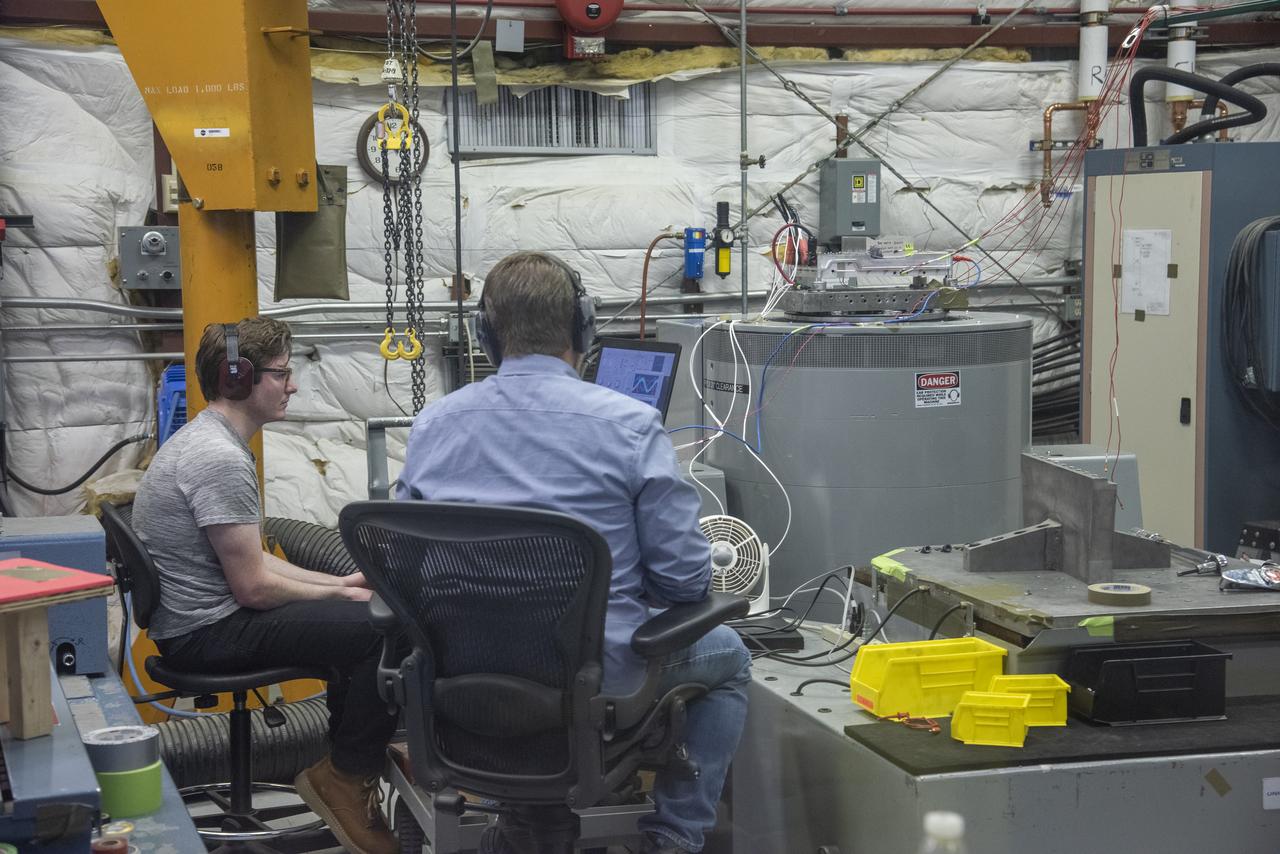
A cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane, undergoes vibration testing at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab. The cruise motor controller is exposed to two levels of vibration on three different axes, helping NASA to examine the integrity of the controller for flight conditions. The cruise motor controller will be a critical component for providing power to X-57's motors when the aircraft takes to the skies in 2020.

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
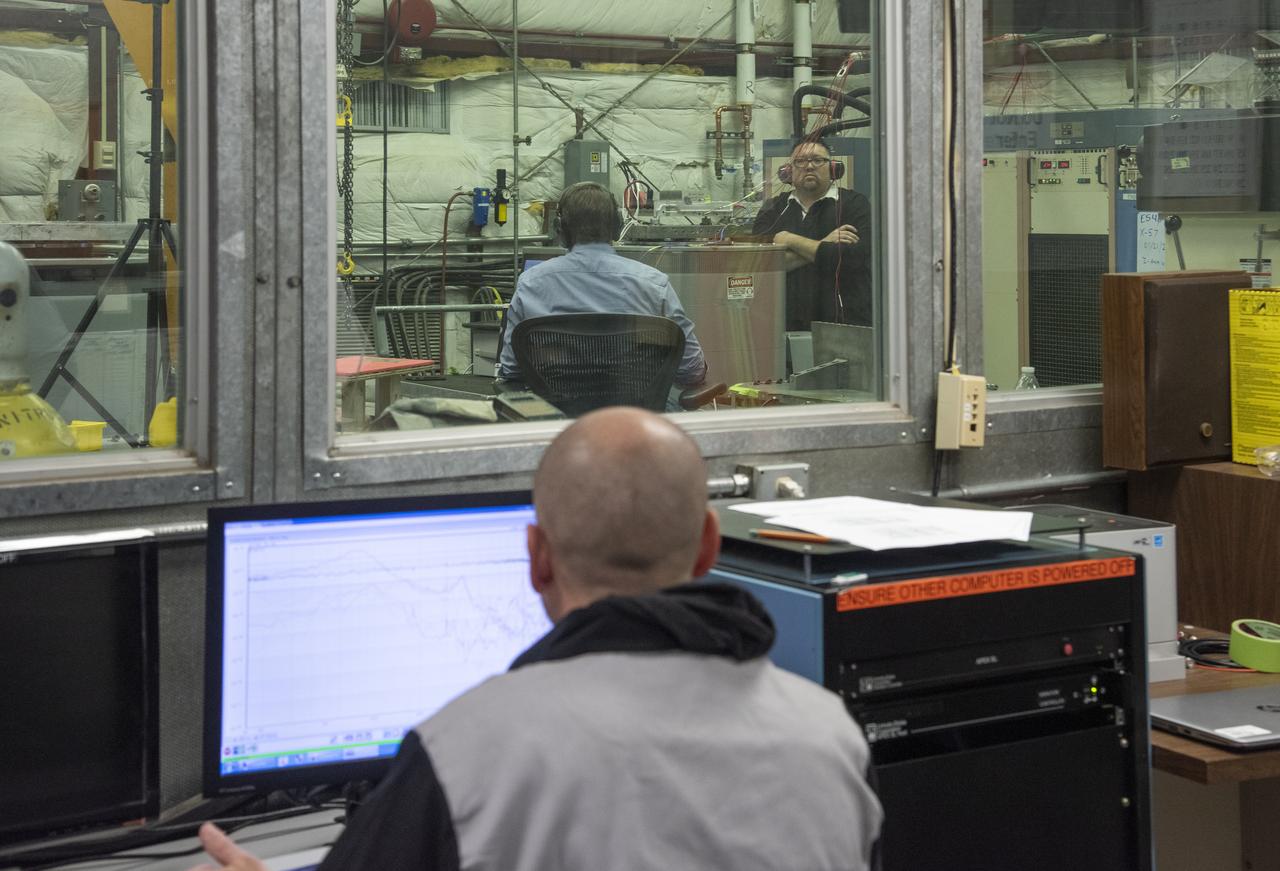

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
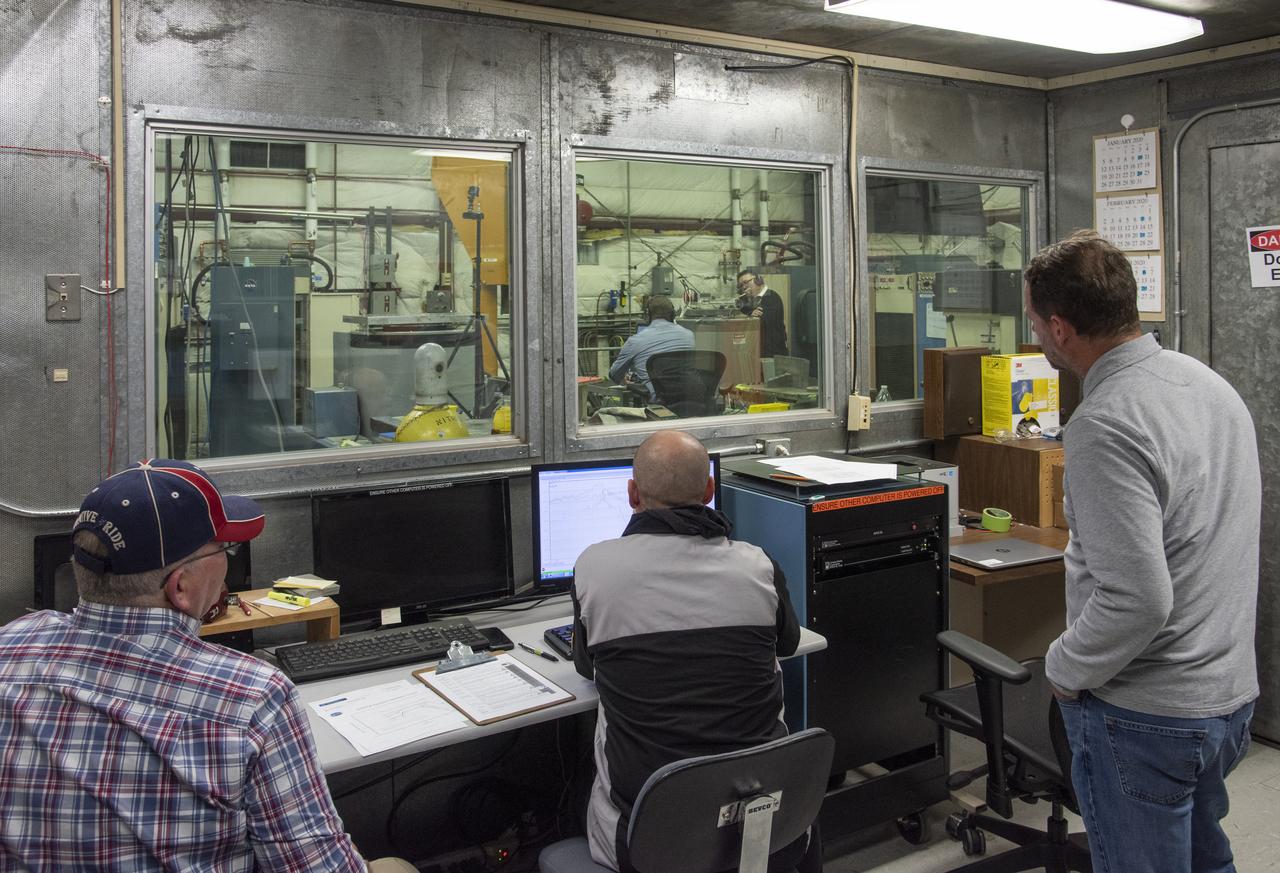

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
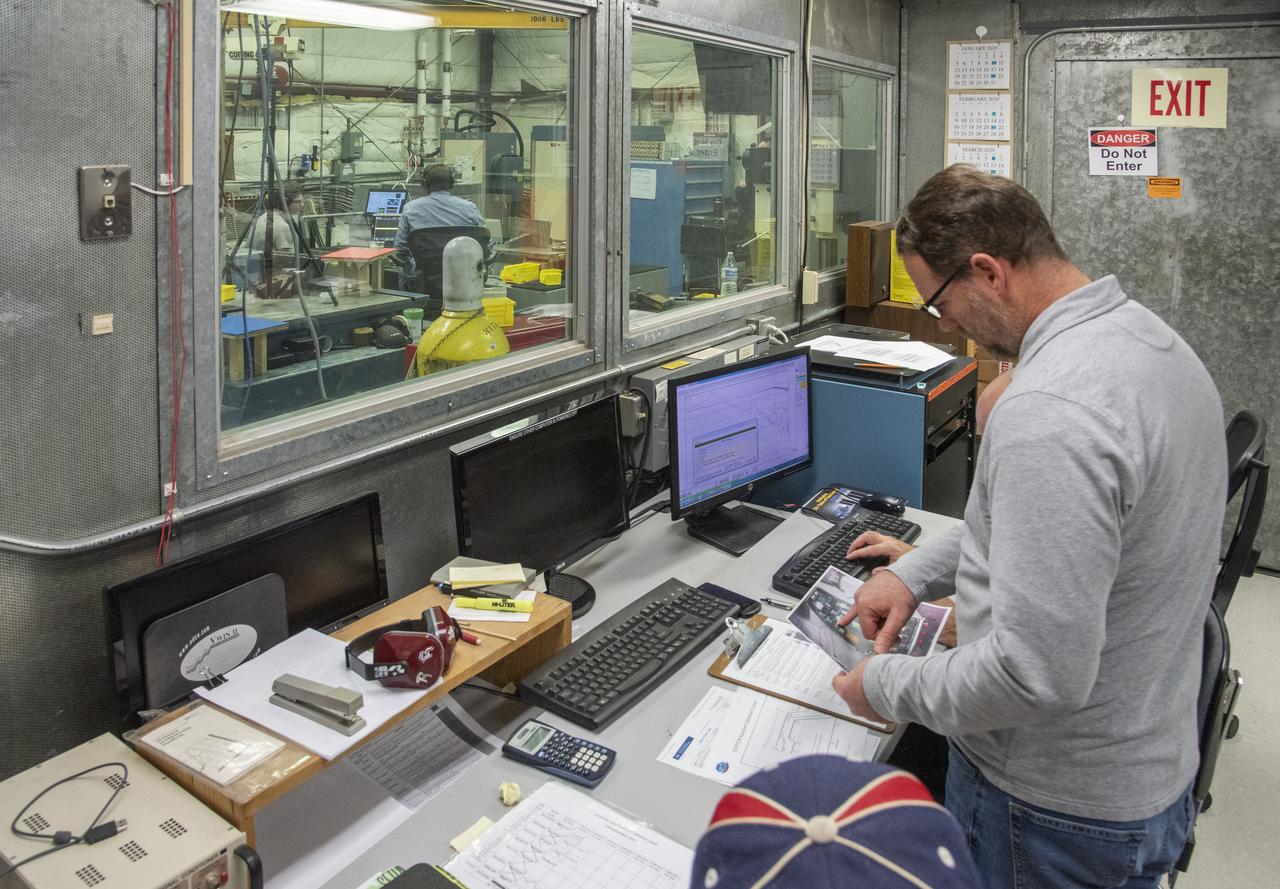

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
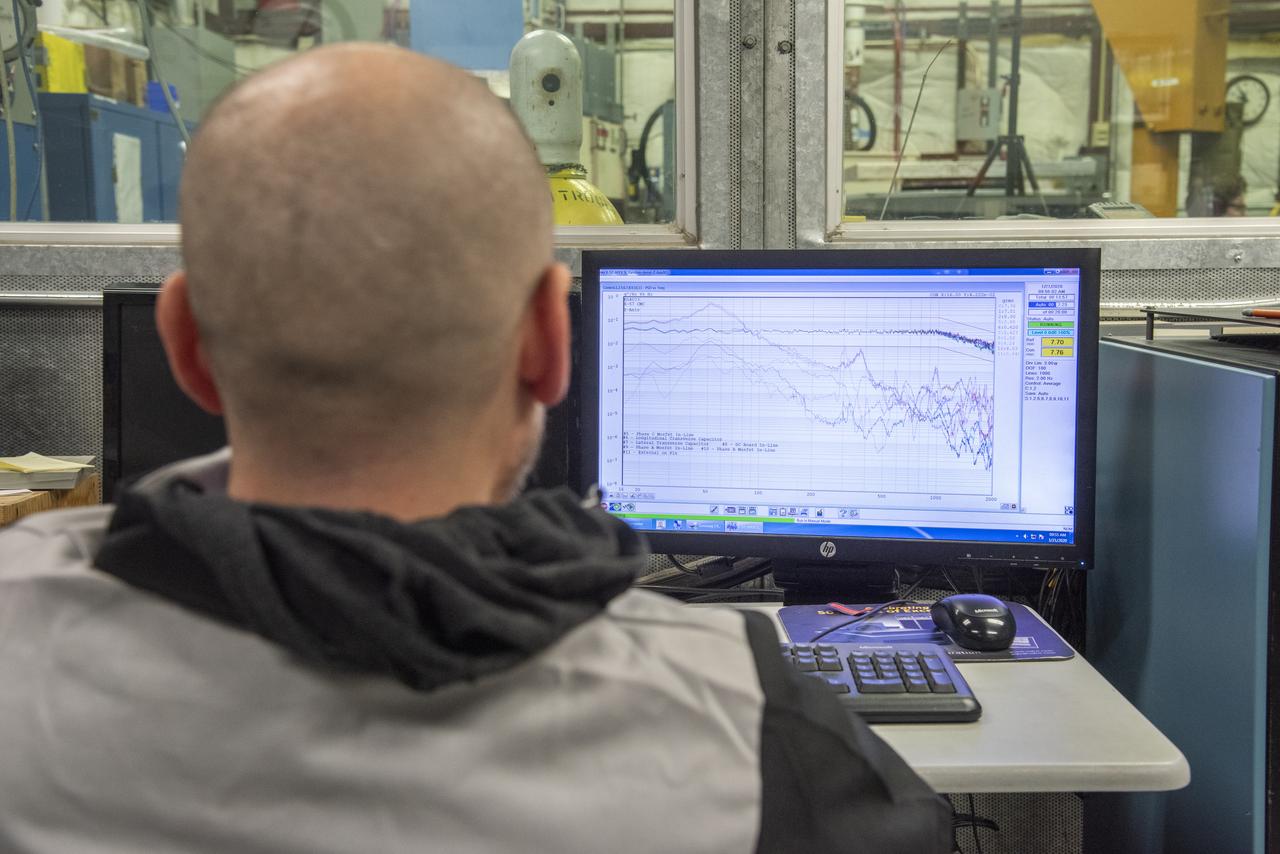

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
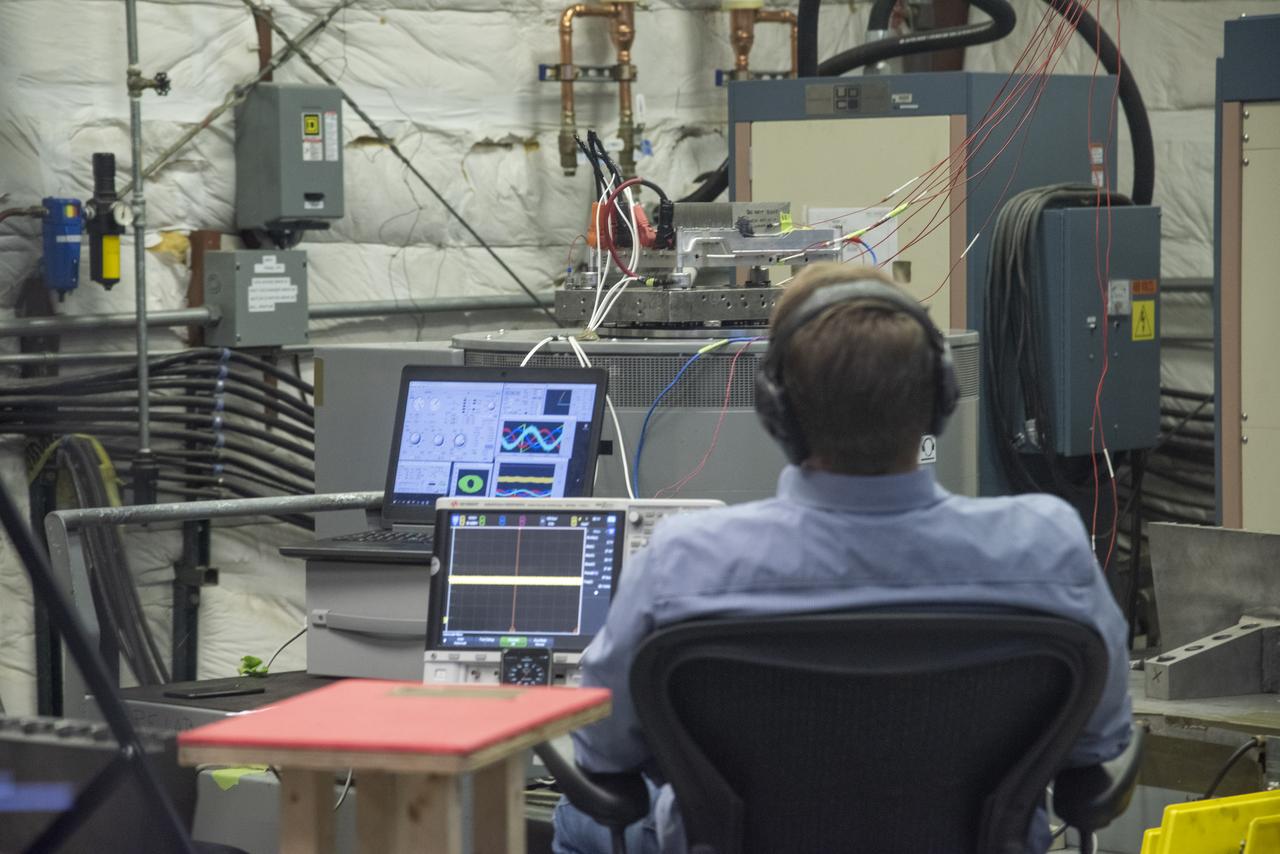

A cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane, undergoes vibration testing at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab. The cruise motor controller is exposed to two levels of vibration on three different axes, helping NASA to examine the integrity of the controller for flight conditions. The cruise motor controller will be a critical component for providing power to X-57's motors when the aircraft takes to the skies in 2020.
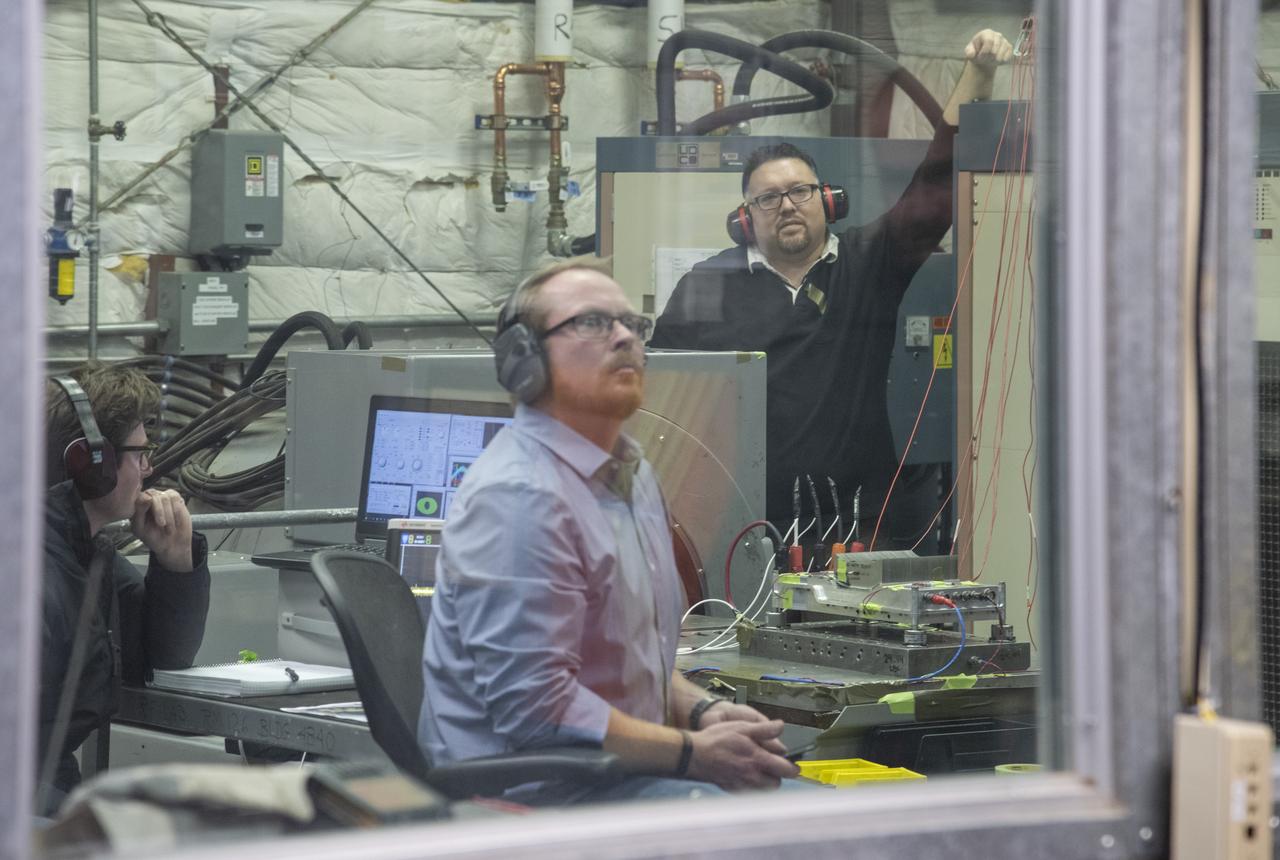

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
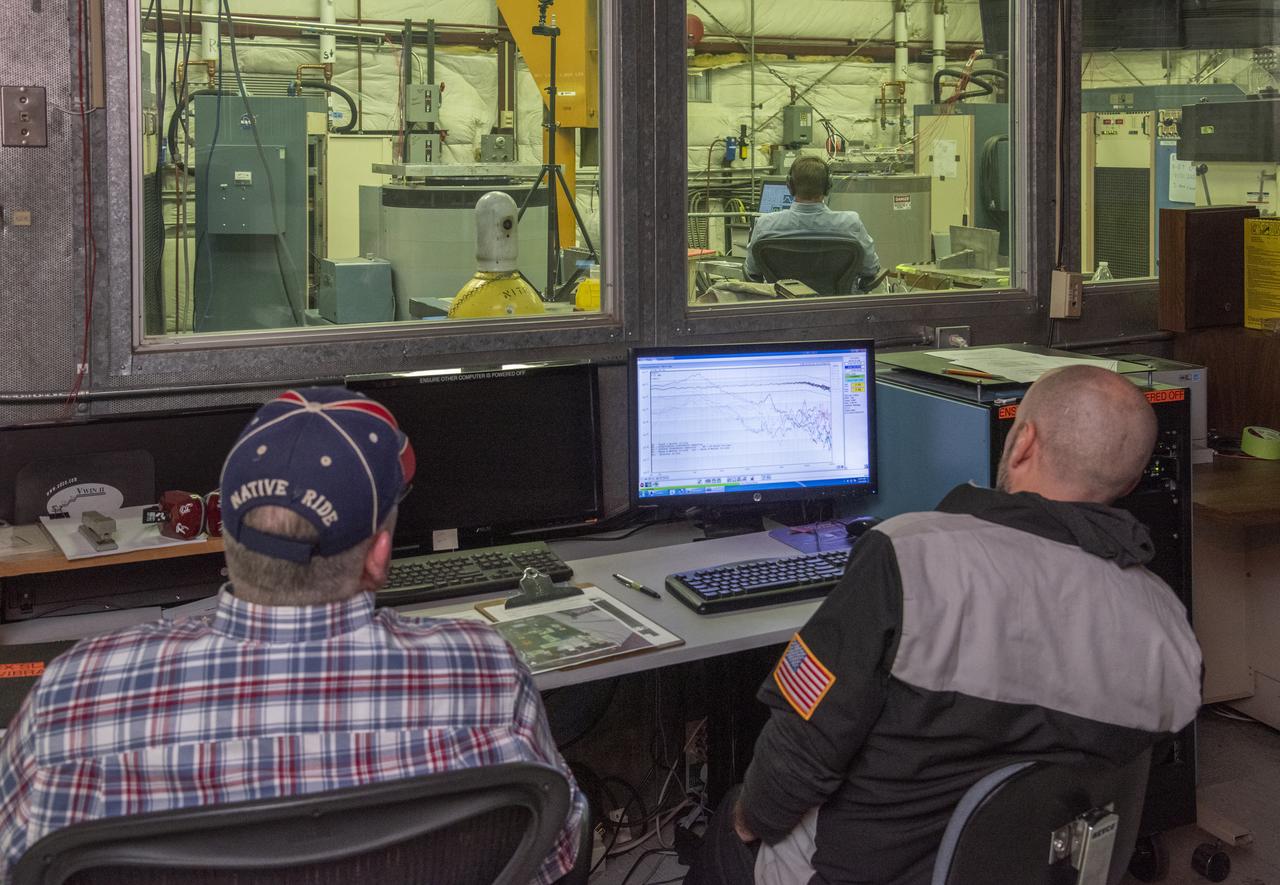

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
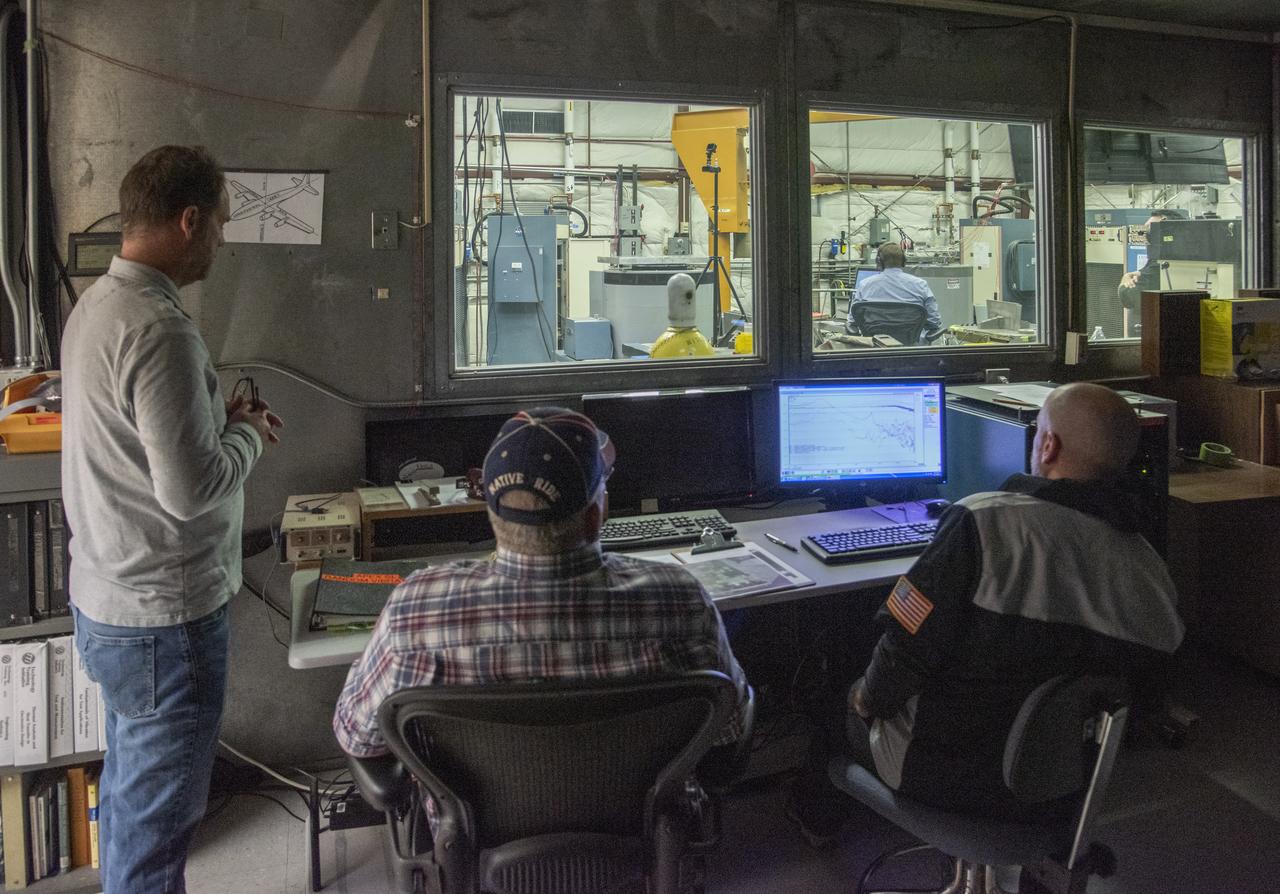

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
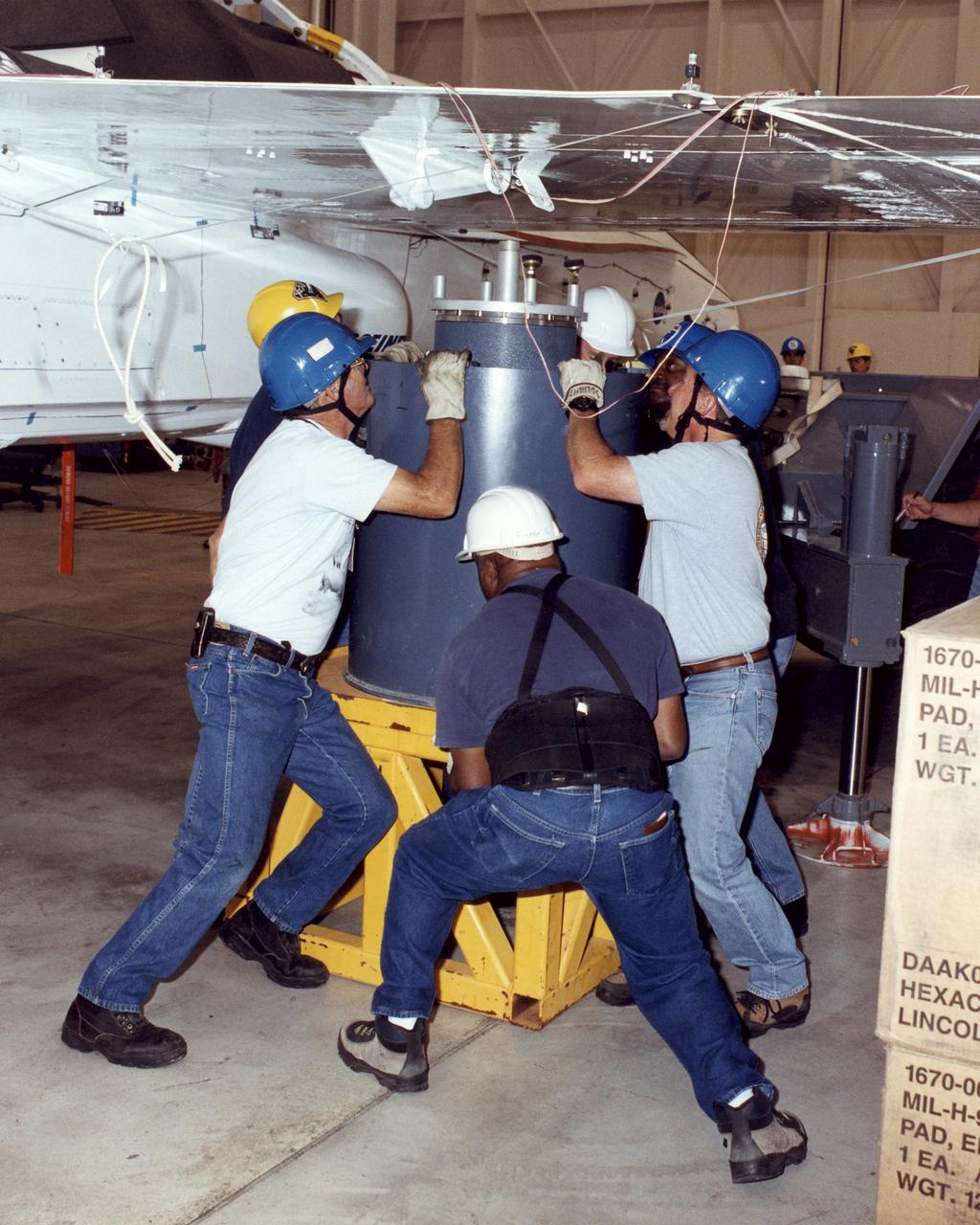

NASA Dryden technicians (Dave Dennis, Freddy Green and Jeff Doughty) position a support cylinder under the right wing of the Active Aeroelastic Wing F/A-18 test aircraft prior to ground vibration tests.
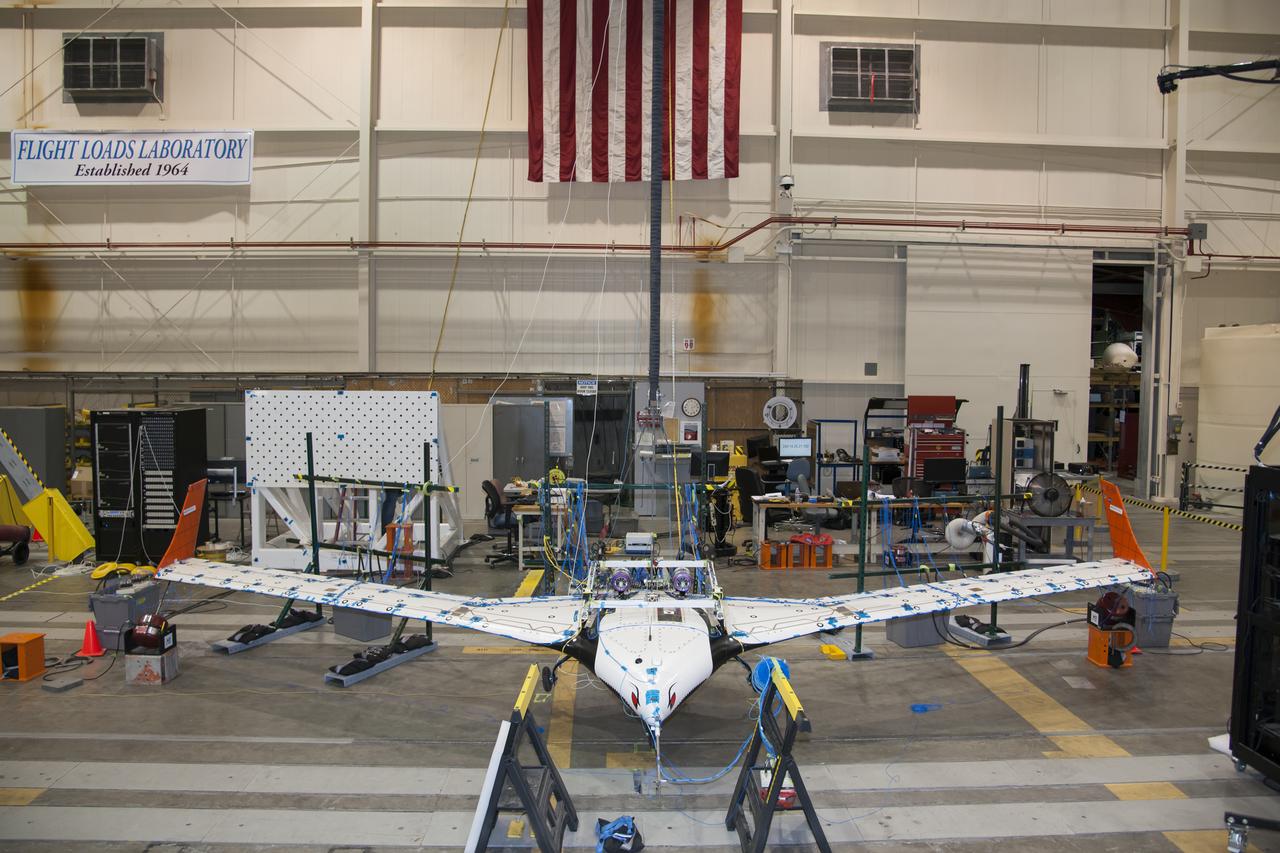

The X-56 Multi-Utility Technology Testbed (MUTT) undergoes ground vibration tests in Armstrong's Flight Loads Laboratory.
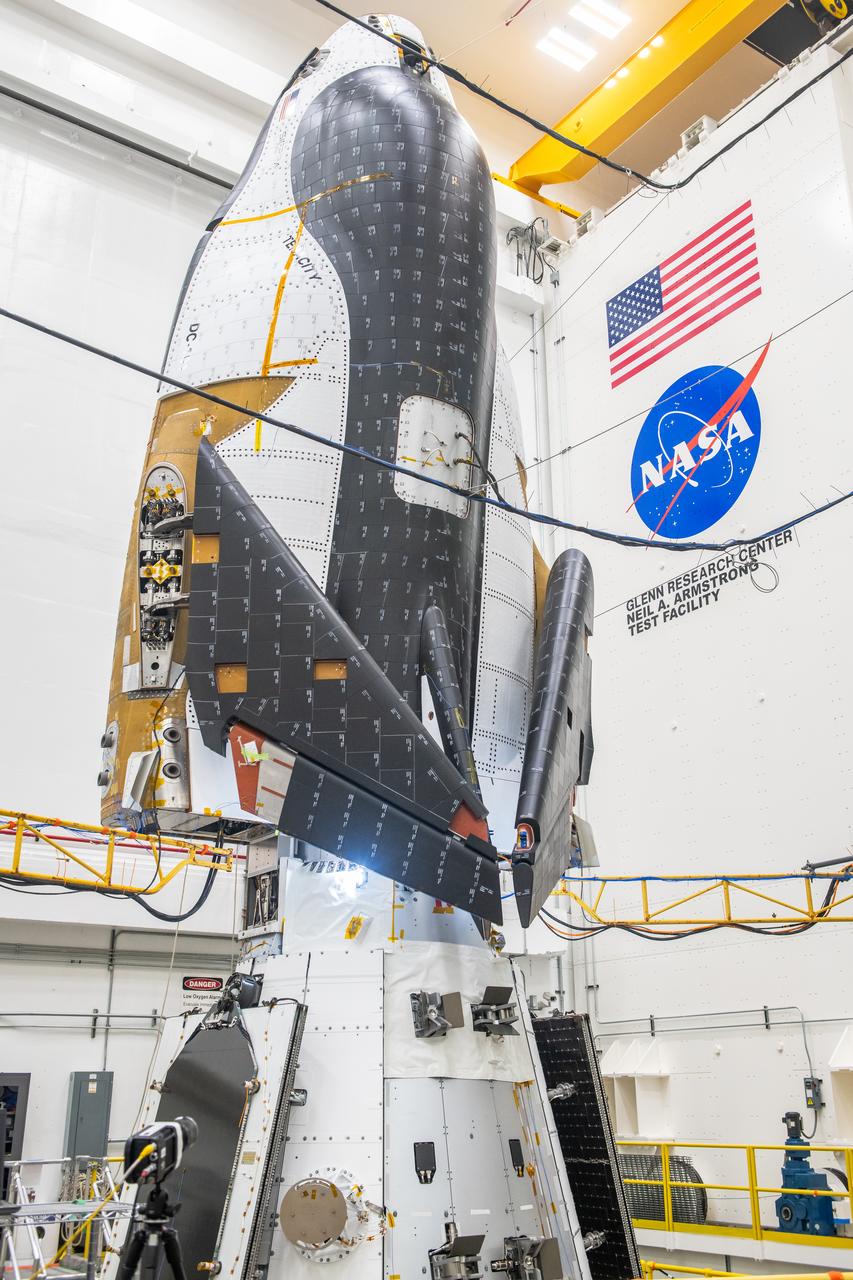

The Neil Armstrong Test Facility, part of NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, is home to multiple test facilities, including the Space Environments Complex and the In-Space Propulsion Facility, both stops for Dream Chaser. The complex is home to the Mechanical Vibration Facility, which subjects test articles to the rigorous conditions of launch. While at Armstrong, the Dream Chaser winged spacecraft was stacked atop its Shooting Star cargo module on the vibration table to experience vibrations like those during launch and re-entry to the Earth’s atmosphere.
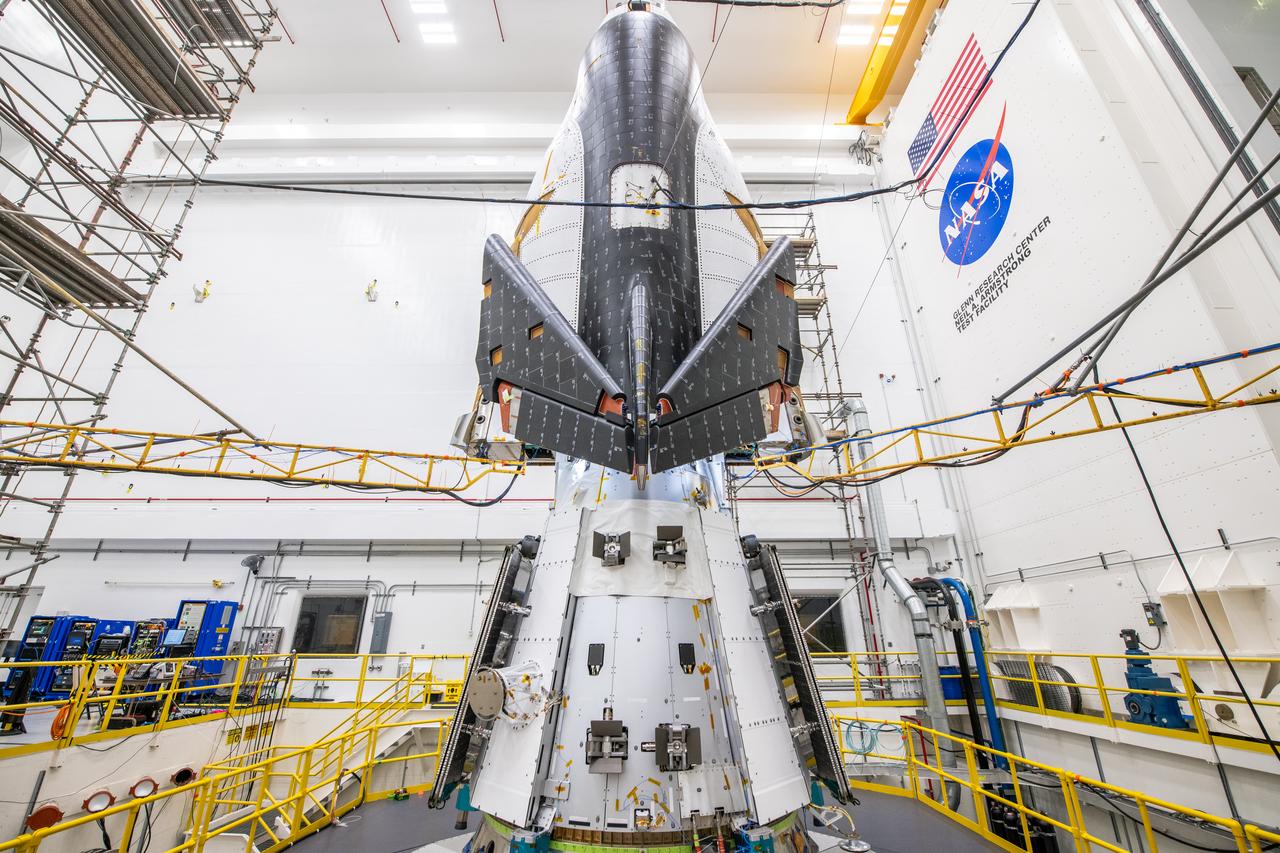

The Neil Armstrong Test Facility, part of NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, is home to multiple test facilities, including the Space Environments Complex and the In-Space Propulsion Facility, both stops for Dream Chaser. The complex is home to the Mechanical Vibration Facility, which subjects test articles to the rigorous conditions of launch. While at Armstrong, the Dream Chaser winged spacecraft was stacked atop its Shooting Star cargo module on the vibration table to experience vibrations like those during launch and re-entry to the Earth’s atmosphere.