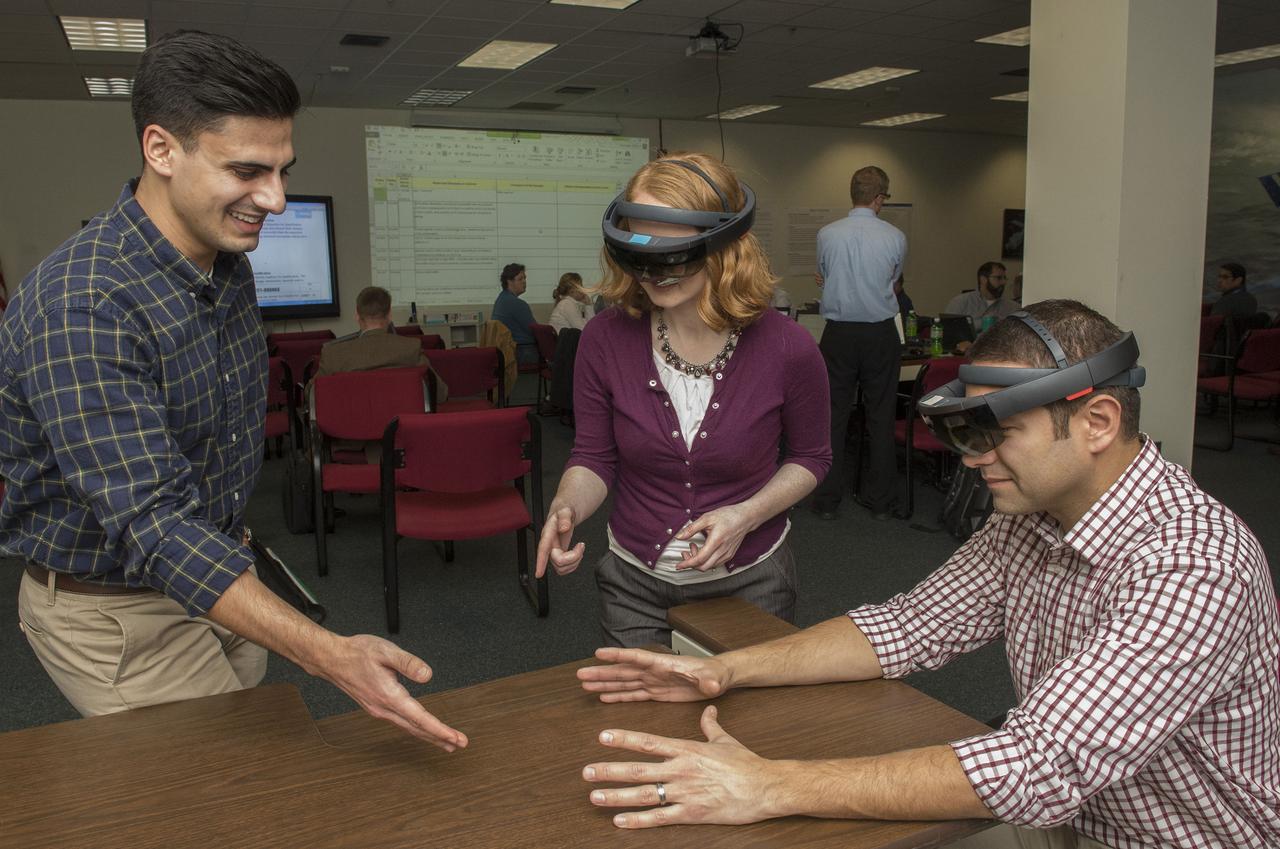

BOEING AND MARSHALL ENGINEERS SHARE VIRTUAL REALITY TECHNOLOGY FOR SLS DESIGN PLANNING.

Telepresence Virtual Reality (Mars)
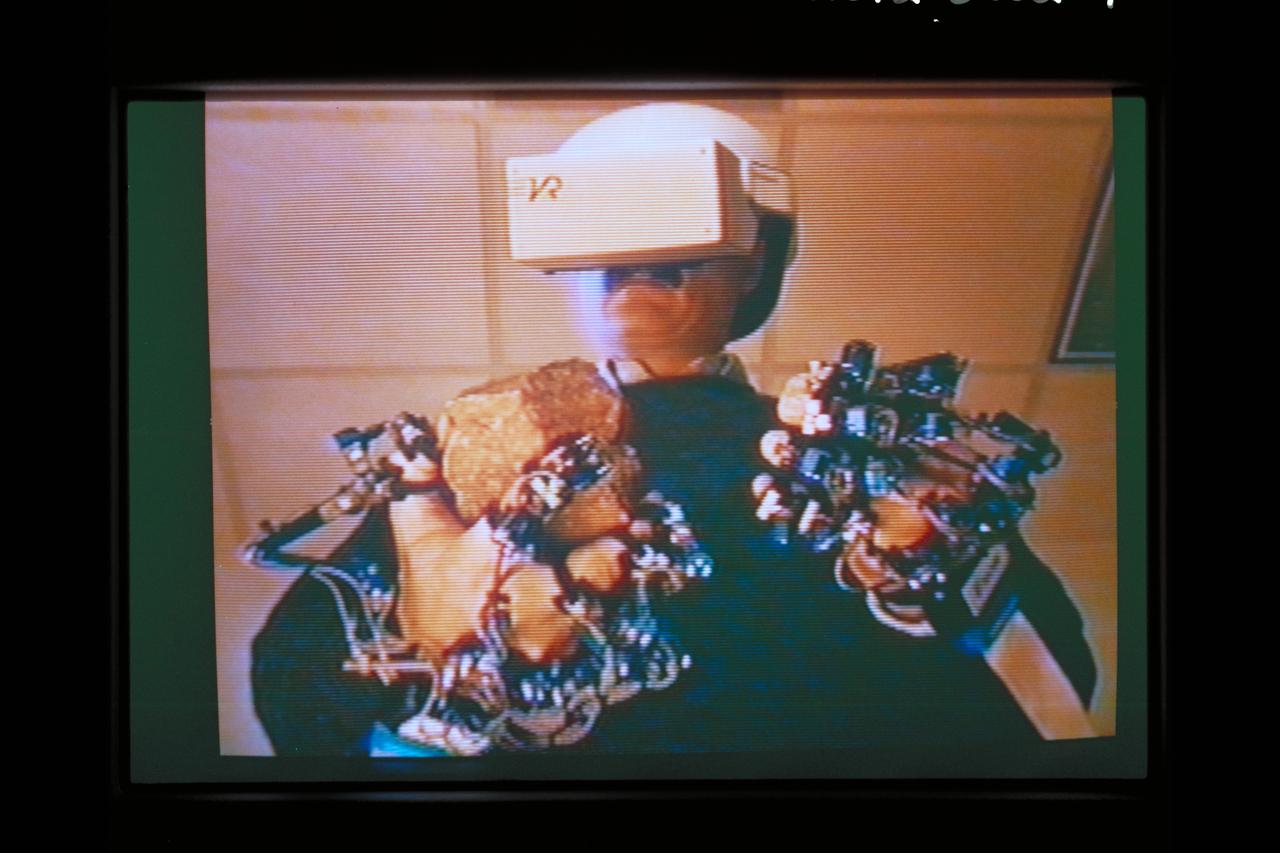

Telepresence Virtual Reality (Mars)
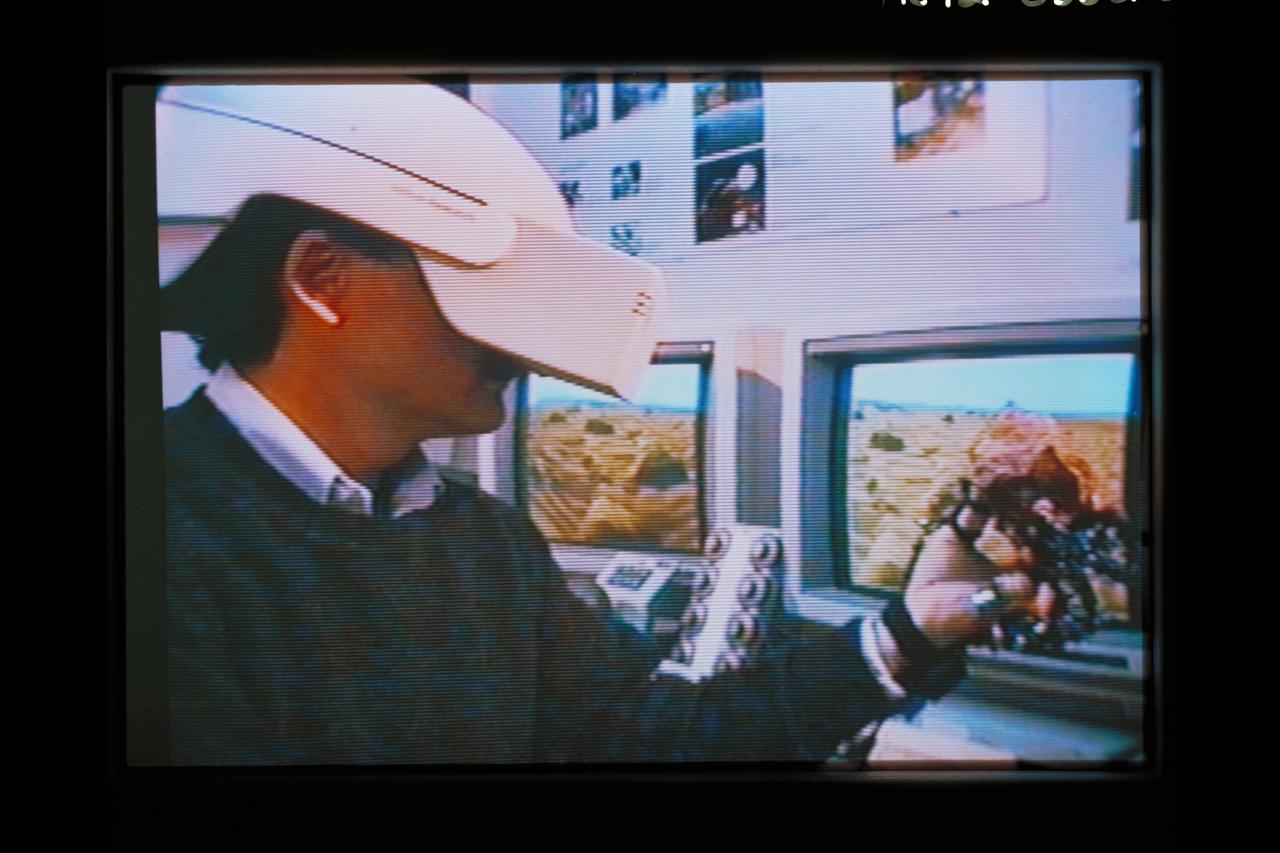

Telepresence Virtual Reality (Mars)
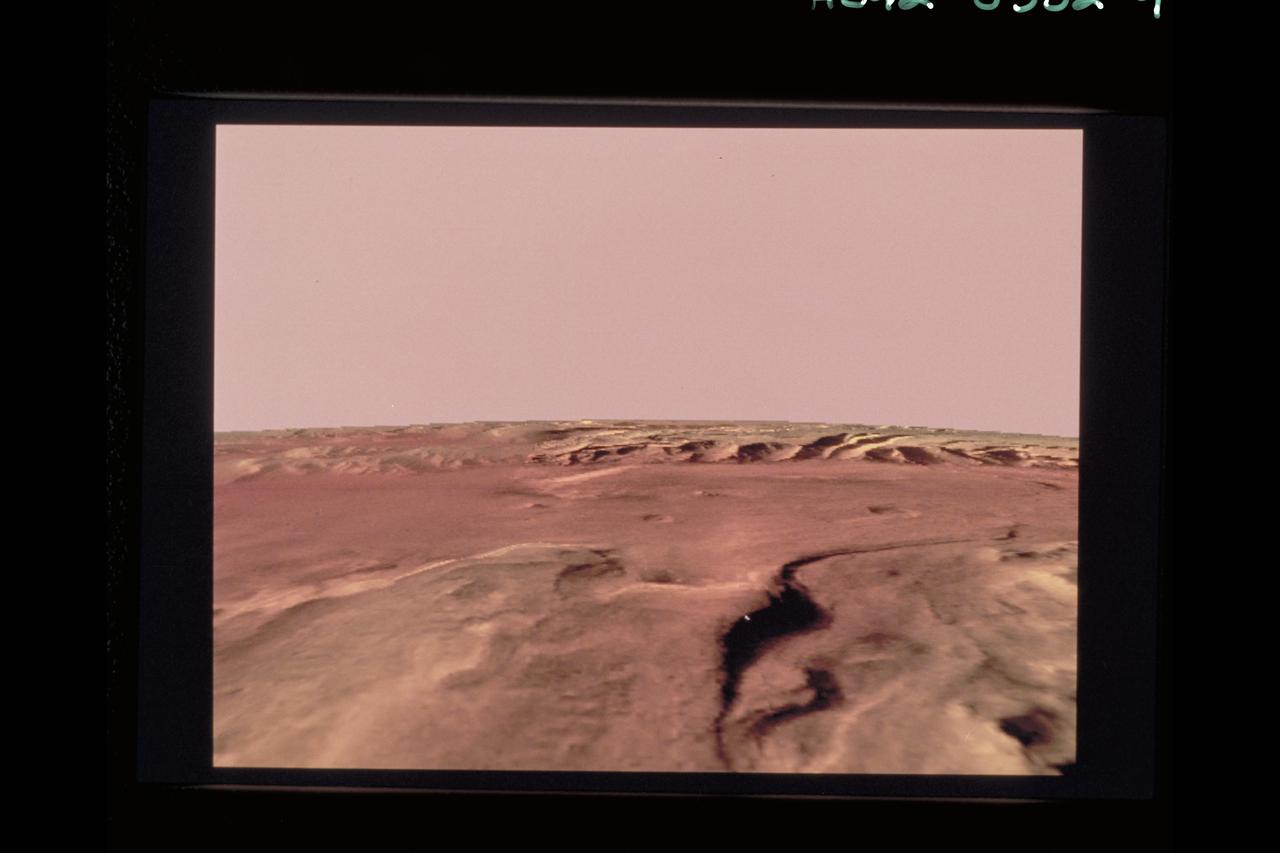

Telepresence Virtual Reality (Mars Surface)
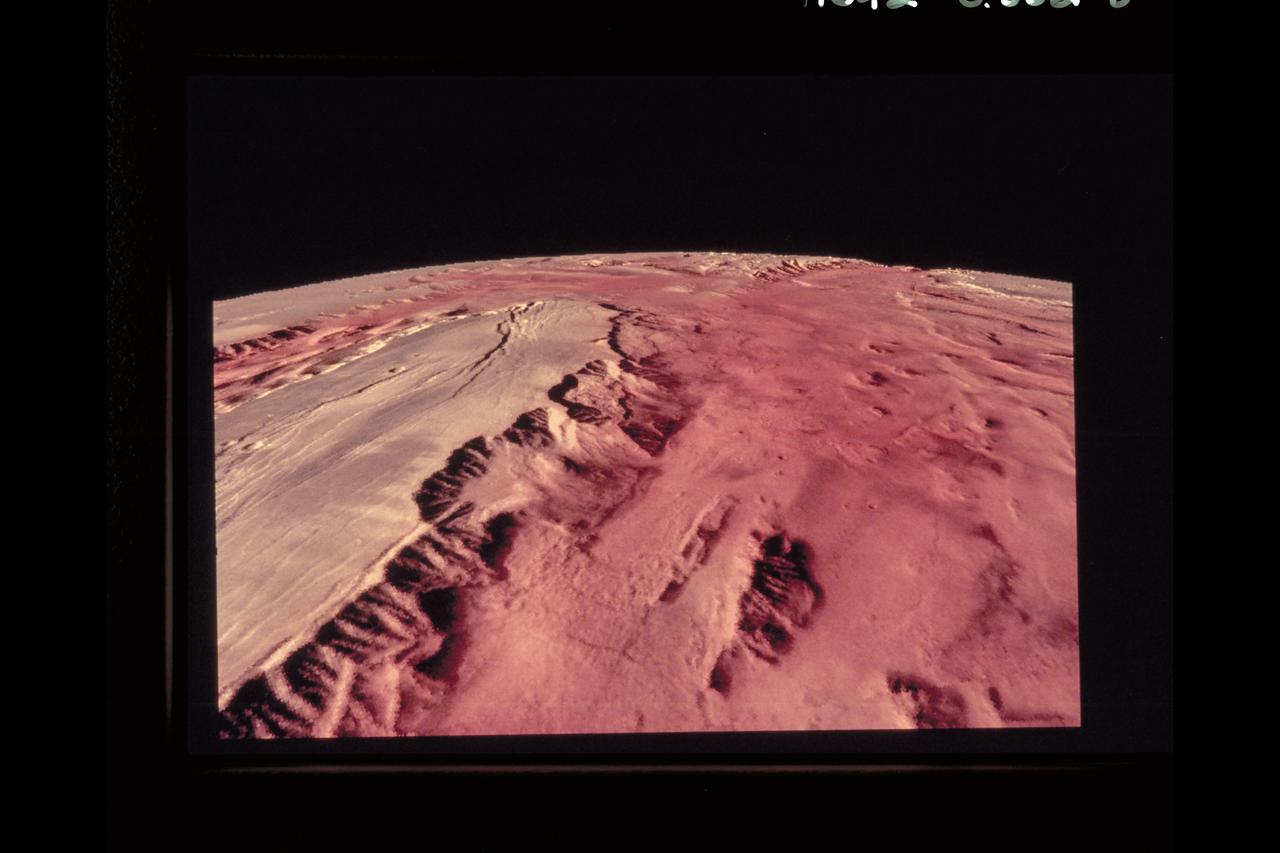

Telepresence Virtual Reality (Mars Surface)
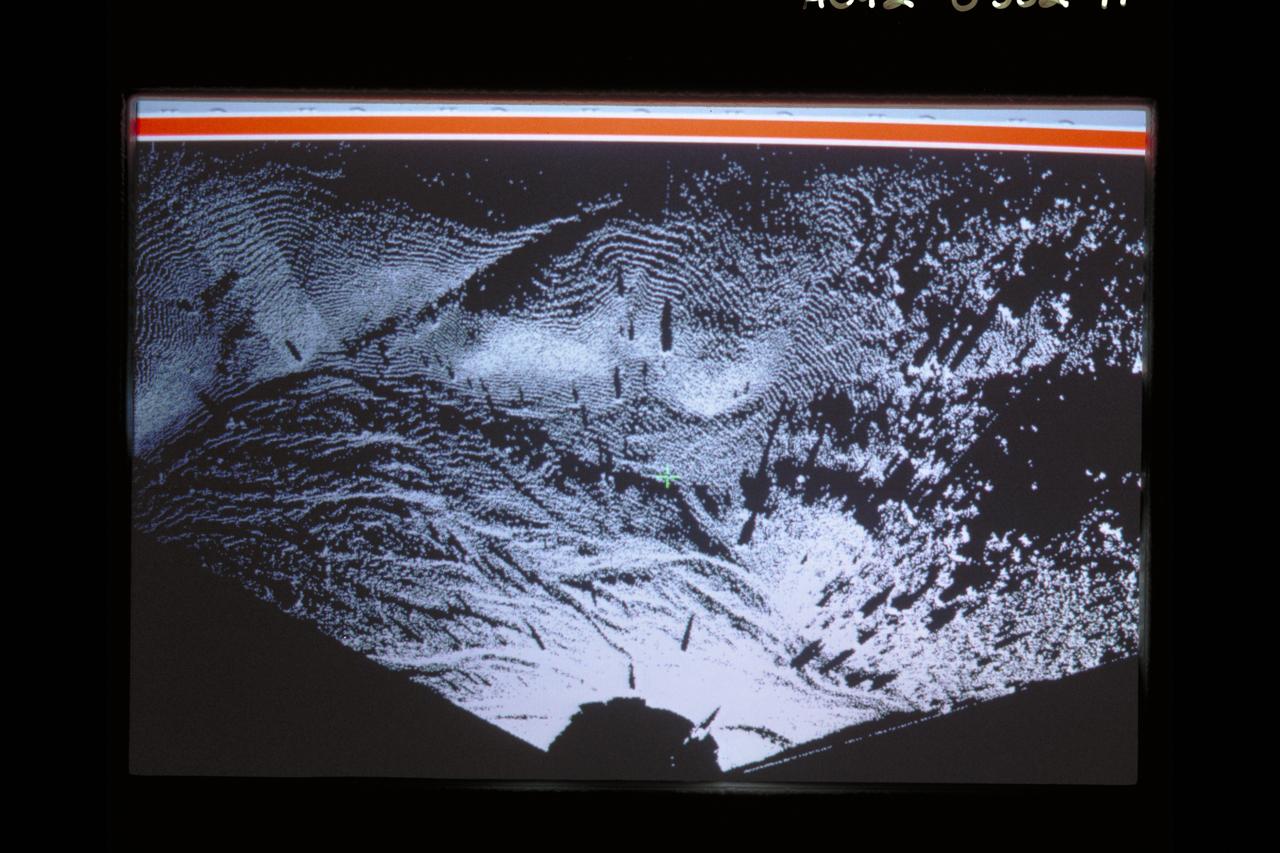
Telepresence Virtual Reality (Mars Surface)
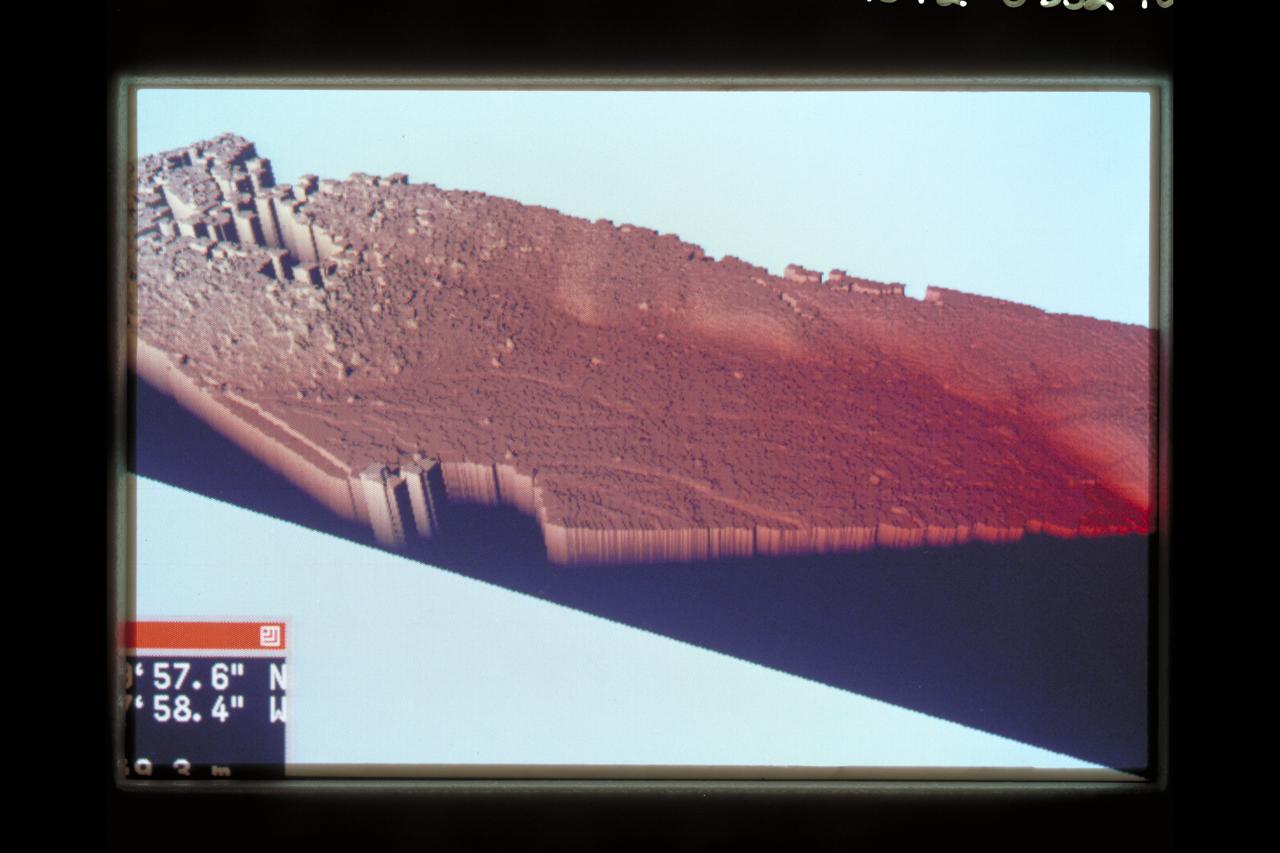

Telepresence Virtual Reality (Mars Surface)
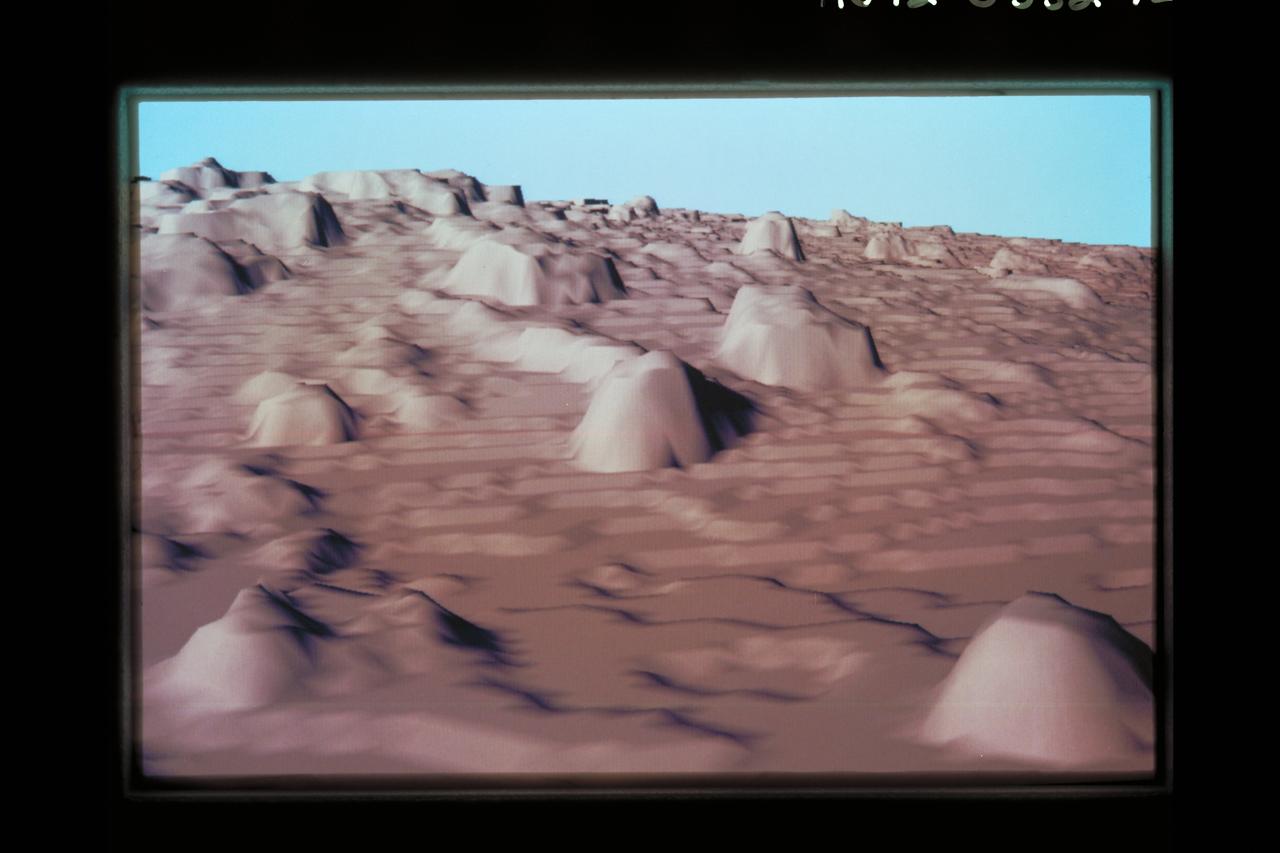

Telepresence Virtual Reality (Mars Surface)
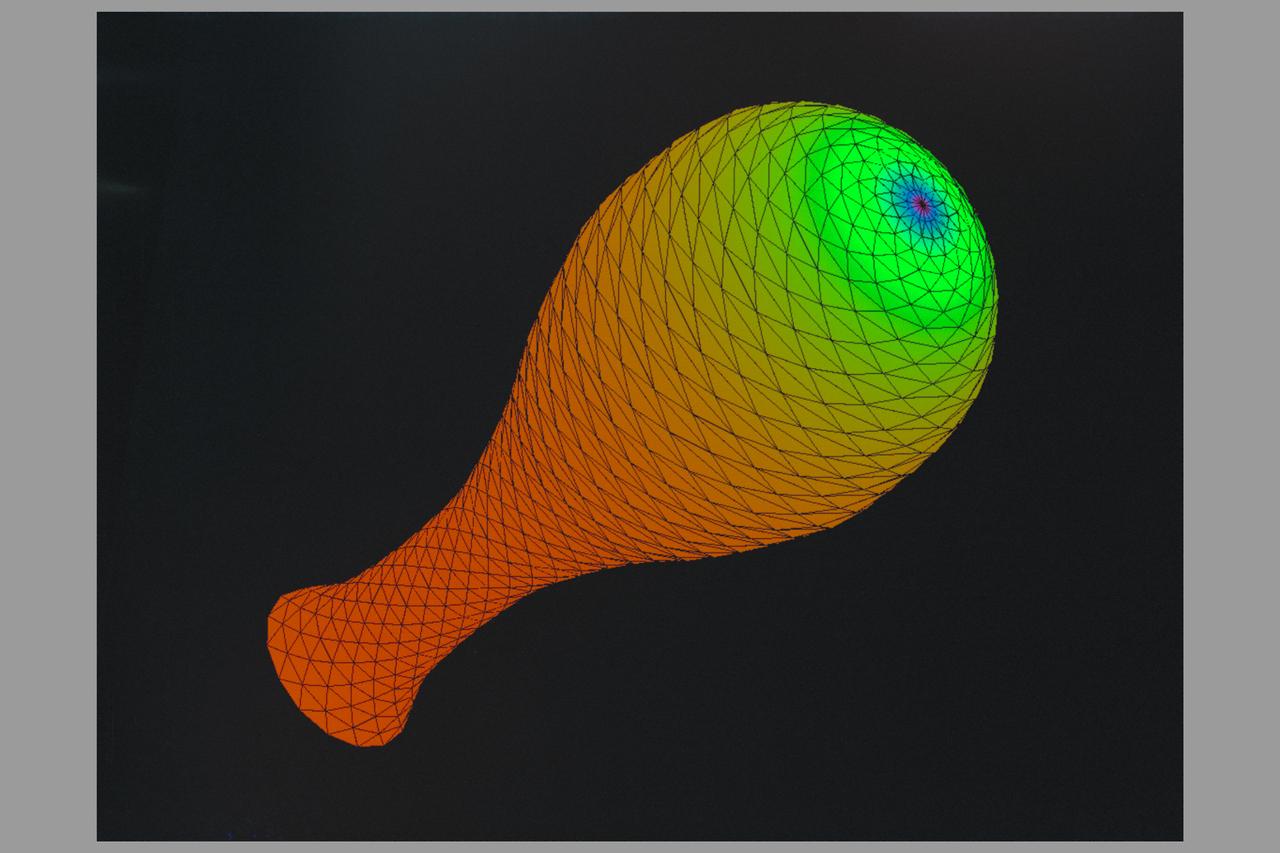
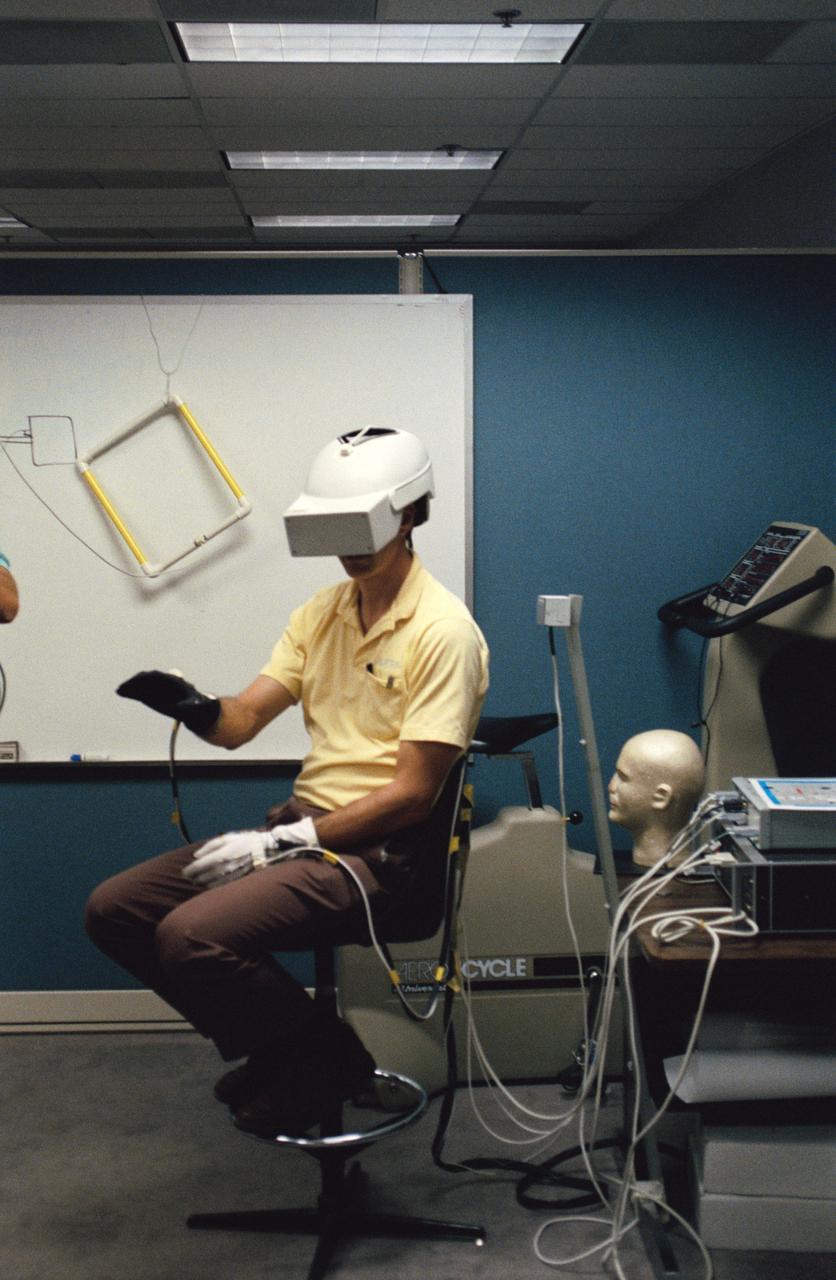
Virtual Reality Application for Neuroscience Research Biocomputation in the study of space motion sickness and balance (inner ear)
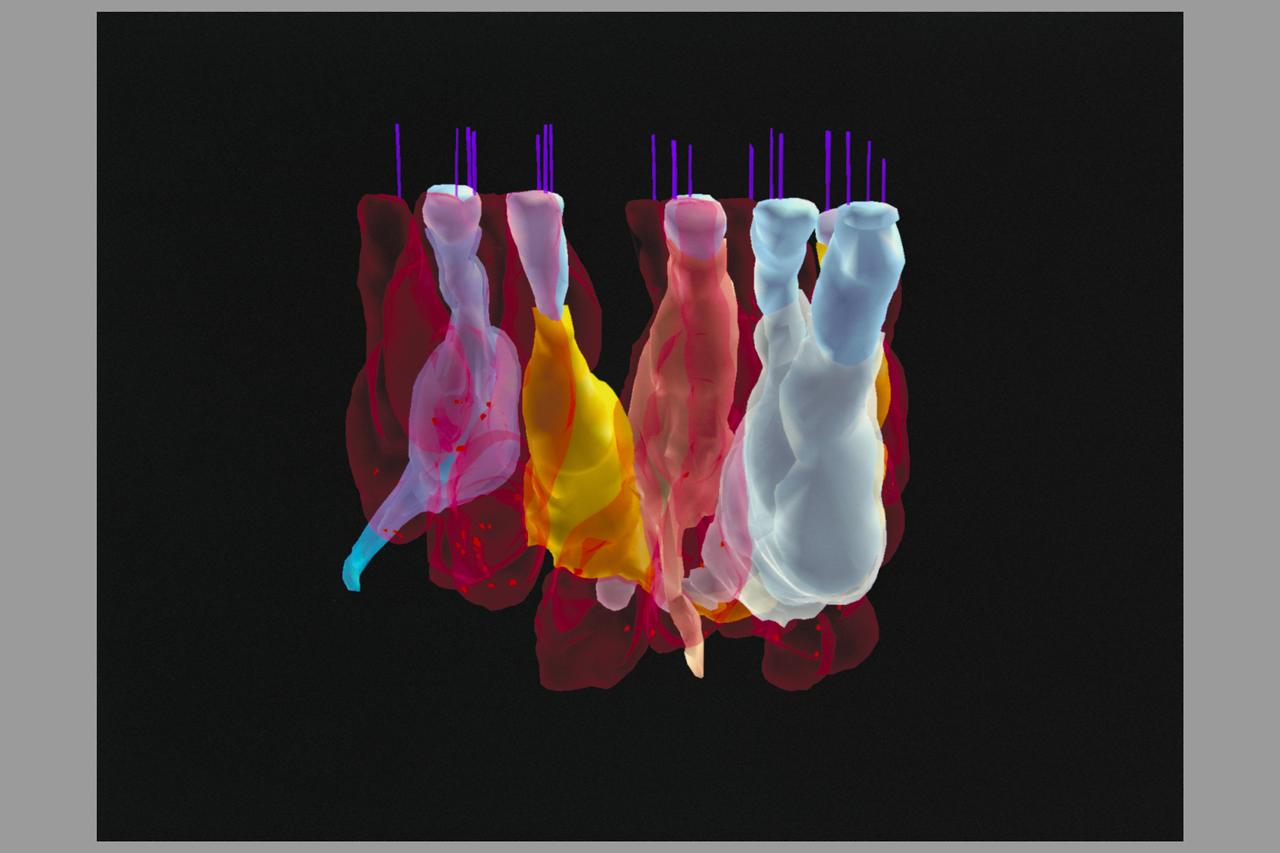

Virtual Reality Application for Neuroscience Research Biocomputation in the study of space motion sickness and balance (inner ear)
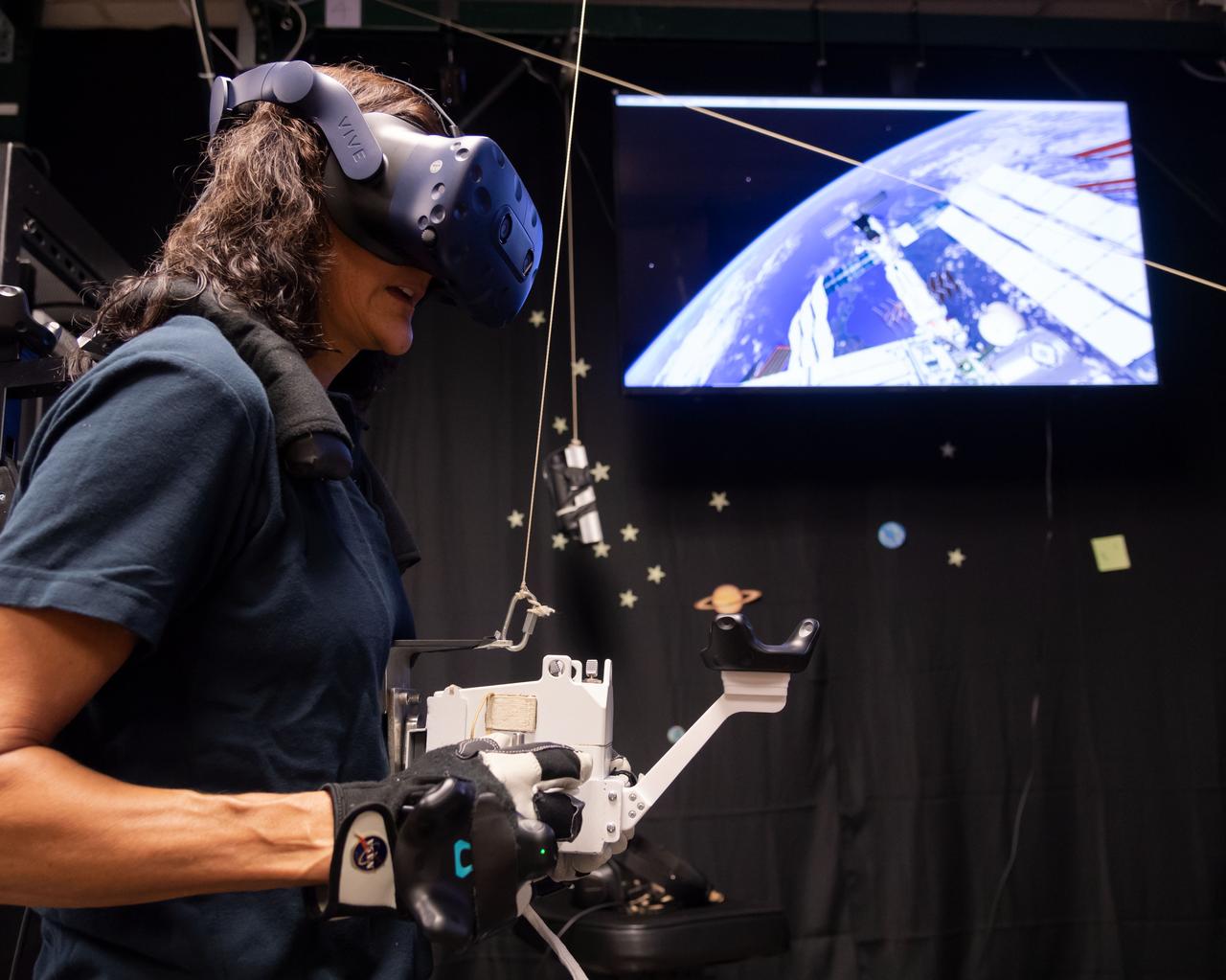

The Virtual Reality Lab at Johnson Space Center in Houston provides real-time graphics and motion simulators to replicate the space environment. Commercial Crew Astronaut Suni Williams practices spacewalking in preparation for a mission to the International Space Station in 2019. Williams is assigned to Boeing’s first operational mission after the company’s test flight with crew.
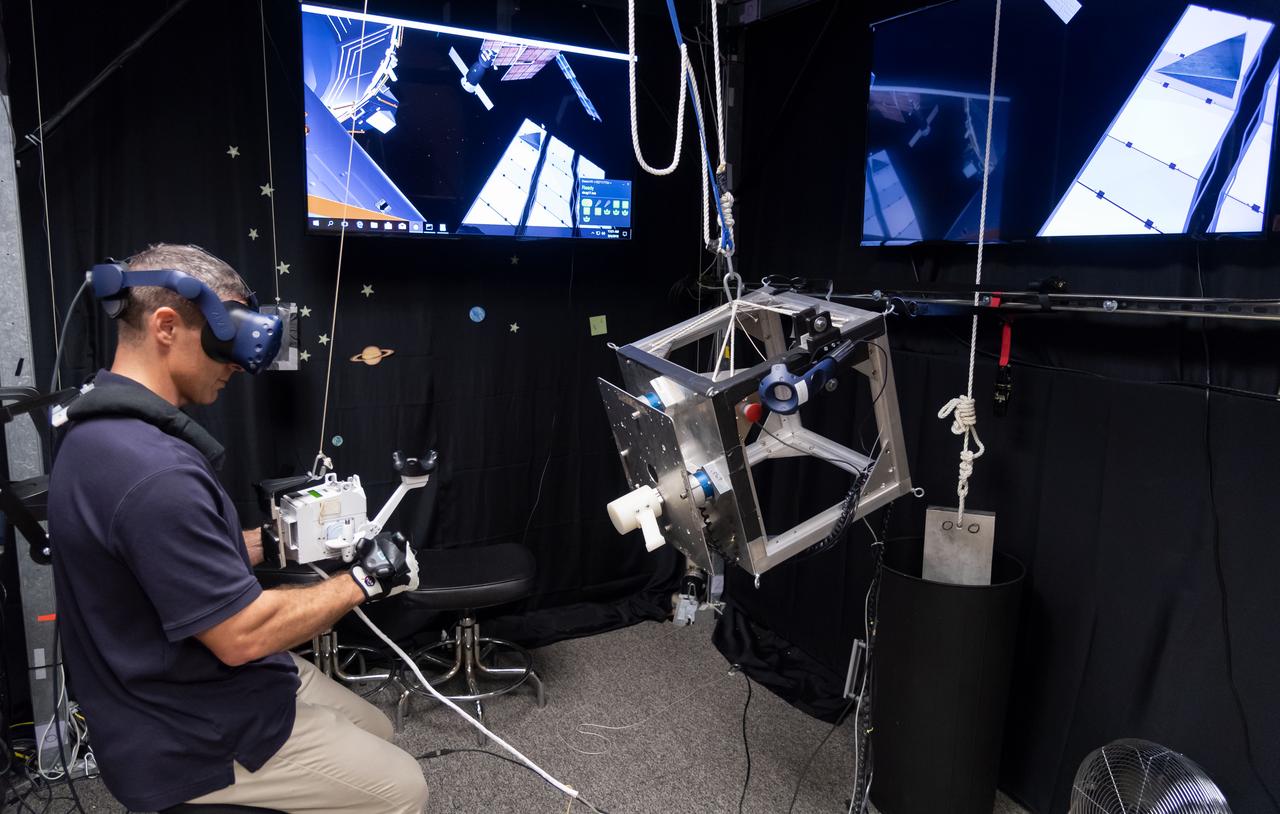

The Virtual Reality Lab at Johnson Space Center in Houston provides real-time graphics and motion simulators to replicate the space environment. Commercial Crew Astronaut Mike Hopkins practices spacewalking in preparation for a mission to the International Space Station. Hopkins is assigned to SpaceX’s first operational mission after the company’s test flight with crew.

Telepresence Virtual Reality (Mars) Underwater, TROV (Telepresence Controlled REmote Vehicle)
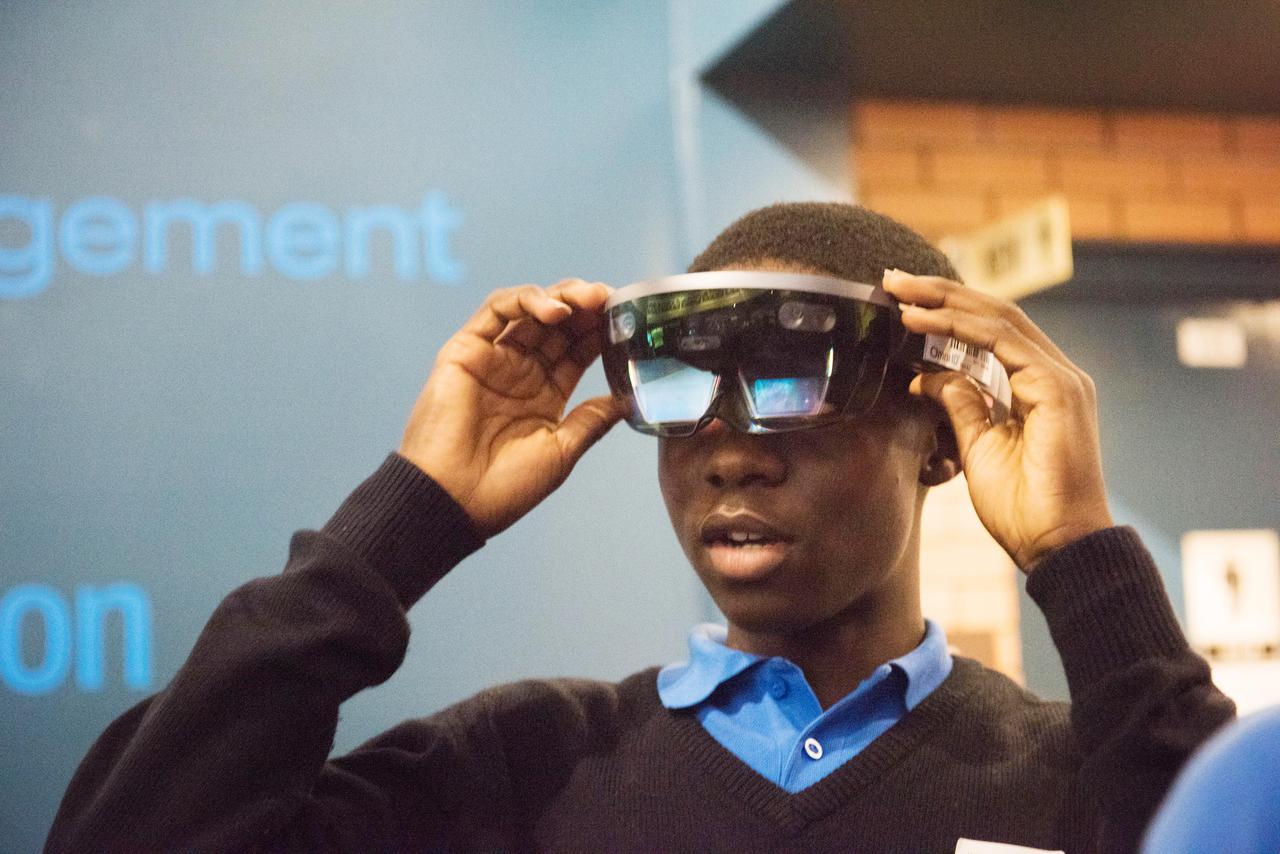

During Avaiation Day, 2018, a Participant uses a Microsoft HoloLens Virtual Reality Headset to view a NASA Created Immersive Visualization
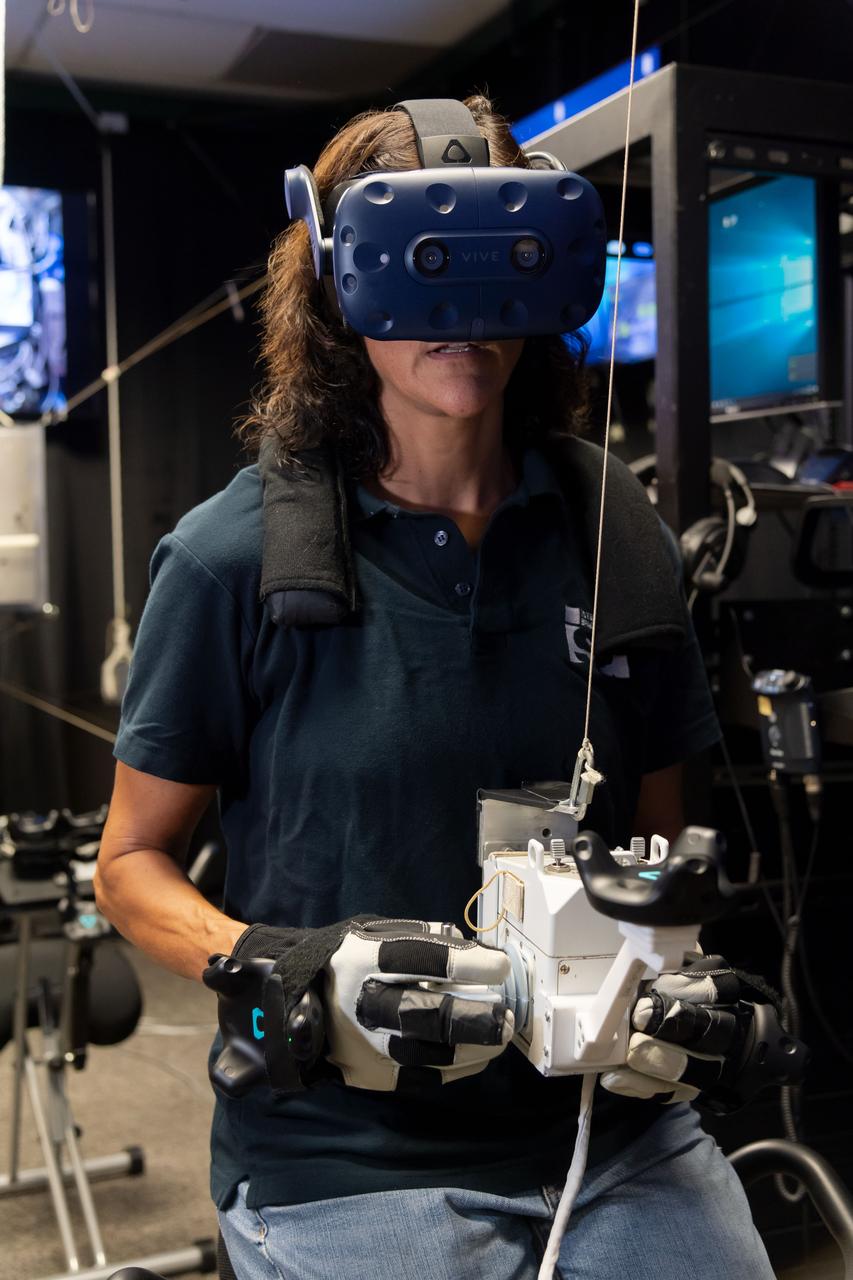

Commercial Crew Astronaut Suni Williams practices spacewalking in the Virtual Reality Lab at Johnson Space Center in Houston. The training provides real-time graphics and motion simulators to replicate the space environment. NASA’s Commercial Crew Program is working with Boeing and SpaceX to return human spaceflight launches to the United States in 2019. Williams is assigned to Boeing’s first operational mission after the company’s test flight with crew.

Commercial Crew Astronaut Mike Hopkins practices spacewalking in the Virtual Reality Lab at Johnson Space Center in Houston. The training provides real-time graphics and motion simulators to replicate the space environment. NASA’s Commercial Crew Program is working with Boeing and SpaceX to return human spaceflight launches to the United States in 2019. Hopkins is assigned to SpaceX’s first operational mission after the company’s test flight with crew.

A person observes the computational Fluid Dynamics solution for cryogenic storage tank mixing inside the Glenn Reconfigurable User-interface and Virtual Reality Exploration on October 18, 2023. The GRUVE Lab provides a fully interactive virtual reality space in which to observe and analyze data and environments. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)

jsc2024e076628 – Tess Caswell, a crew stand-in for the Artemis III Virtual Reality Mini-Simulation, executes a moonwalk in the Prototype Immersive Technology (PIT) lab at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. The simulation was a test of using VR as a training method for flight controllers and science teams’ collaboration on science-focused traverses on the lunar surface. Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz

Astronauts John M. Grunsfeld (left), STS-109 payload commander, and Nancy J. Currie, mission specialist, use the virtual reality lab at Johnson Space Center to train for upcoming duties aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. This type of computer interface paired with virtual reality training hardware and software helps to prepare the entire team to perform its duties for the fourth Hubble Space Telescope Servicing mission. The most familiar form of virtual reality technology is some form of headpiece, which fits over your eyes and displays a three dimensional computerized image of another place. Turn your head left and right, and you see what would be to your sides; turn around, and you see what might be sneaking up on you. An important part of the technology is some type of data glove that you use to propel yourself through the virtual world. Currently, the medical community is using the new technologies in four major ways: To see parts of the body more accurately, for study, to make better diagnosis of disease and to plan surgery in more detail; to obtain a more accurate picture of a procedure during surgery; to perform more types of surgery with the most noninvasive, accurate methods possible; and to model interactions among molecules at a molecular level.
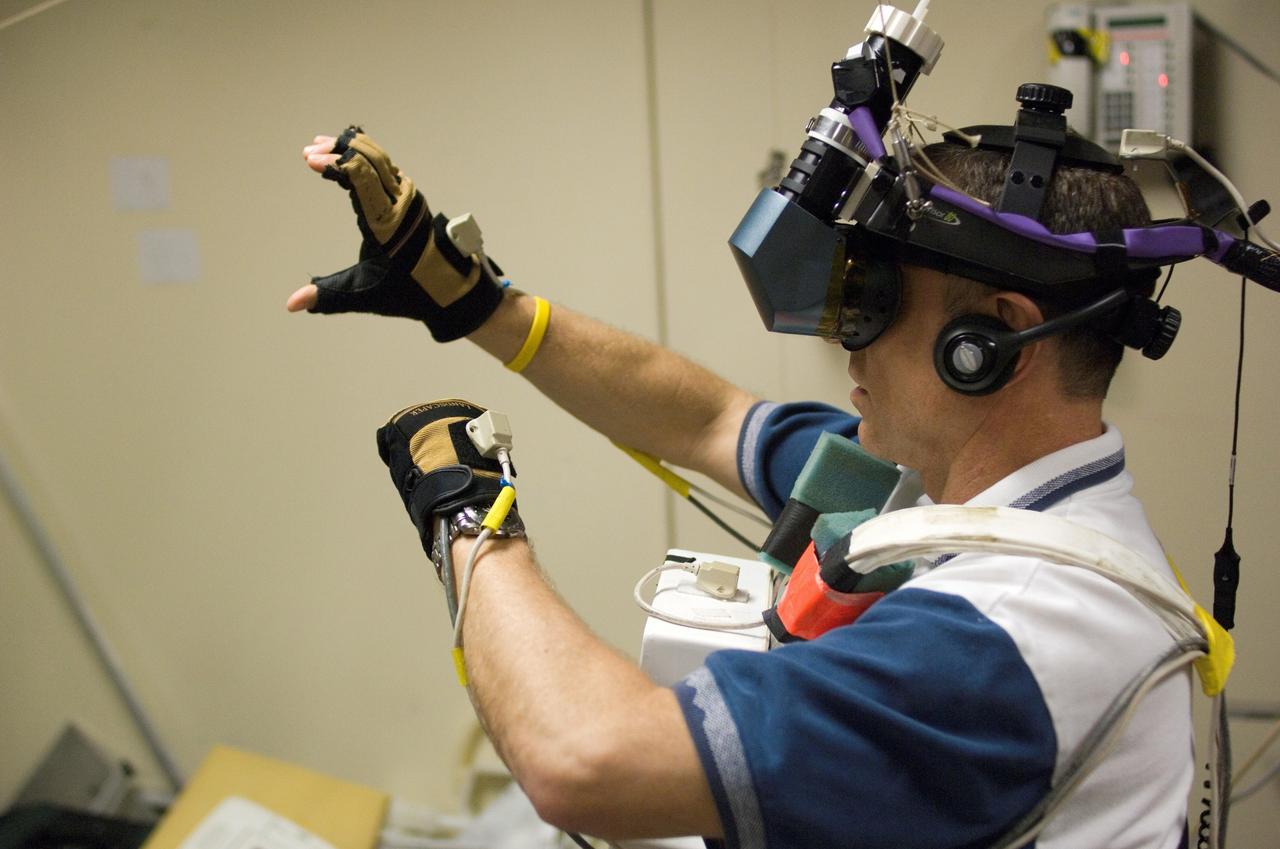

STS-118 astronaut and mission specialist Dafydd R. “Dave” Williams, representing the Canadian Space Agency, uses Virtual Reality Hardware in the Space Vehicle Mock Up Facility at the Johnson Space Center to rehearse some of his duties for the upcoming mission. This type of virtual reality training allows the astronauts to wear special gloves and other gear while looking at a computer that displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the station hardware which with they will be working.
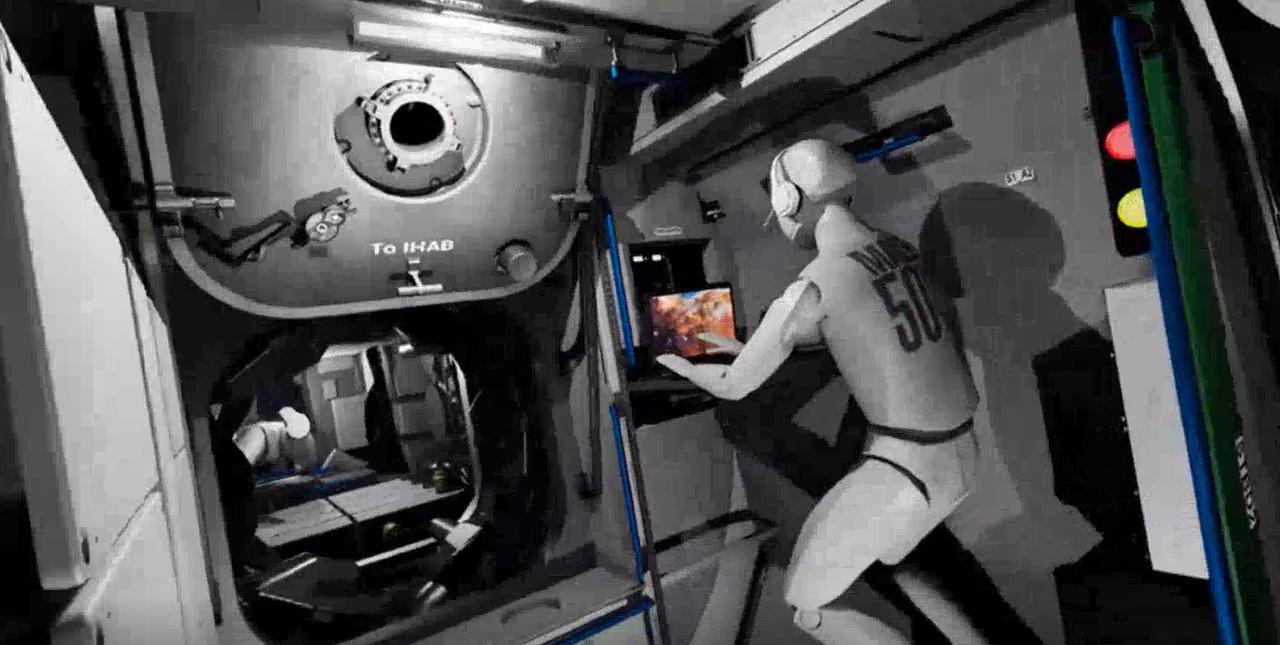

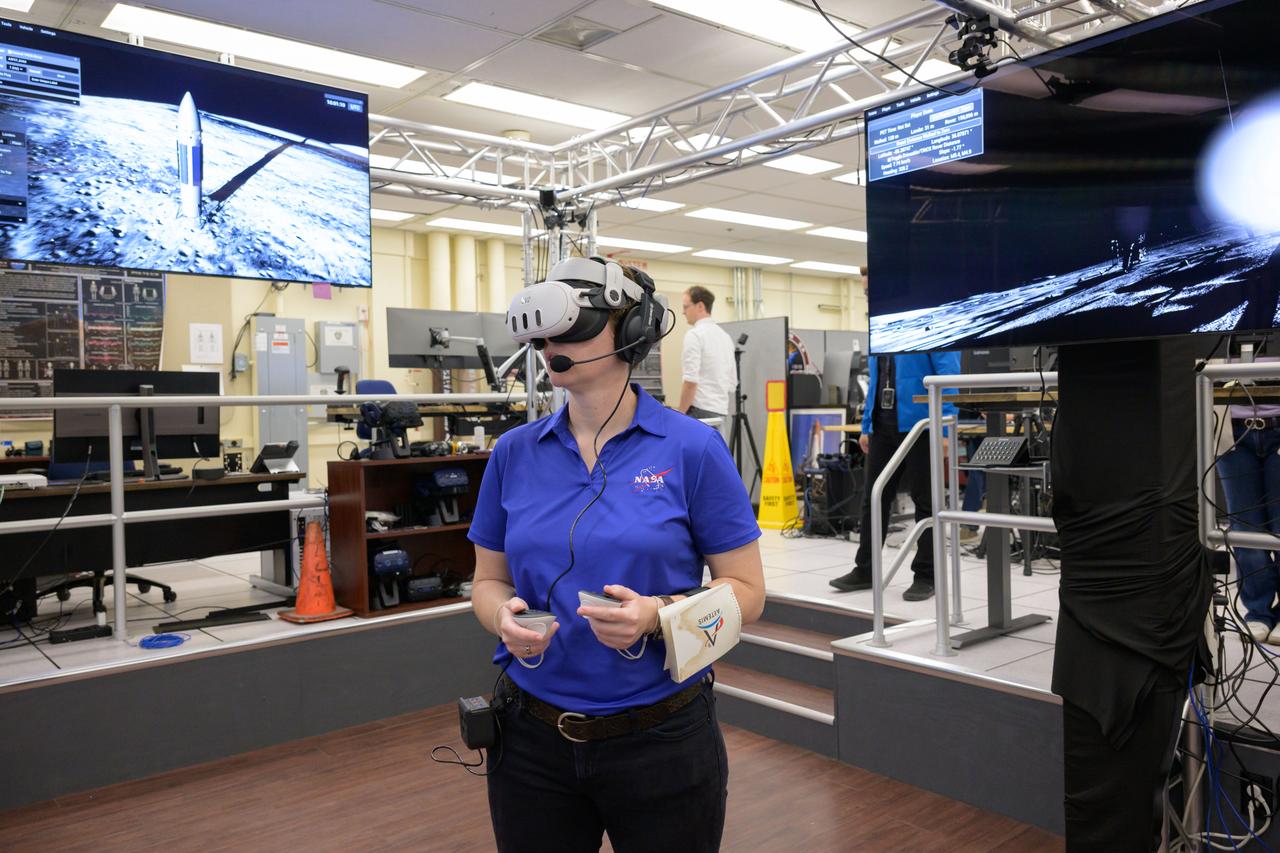
What astronauts see as they tour the Gateway lunar space station in virtual reality.
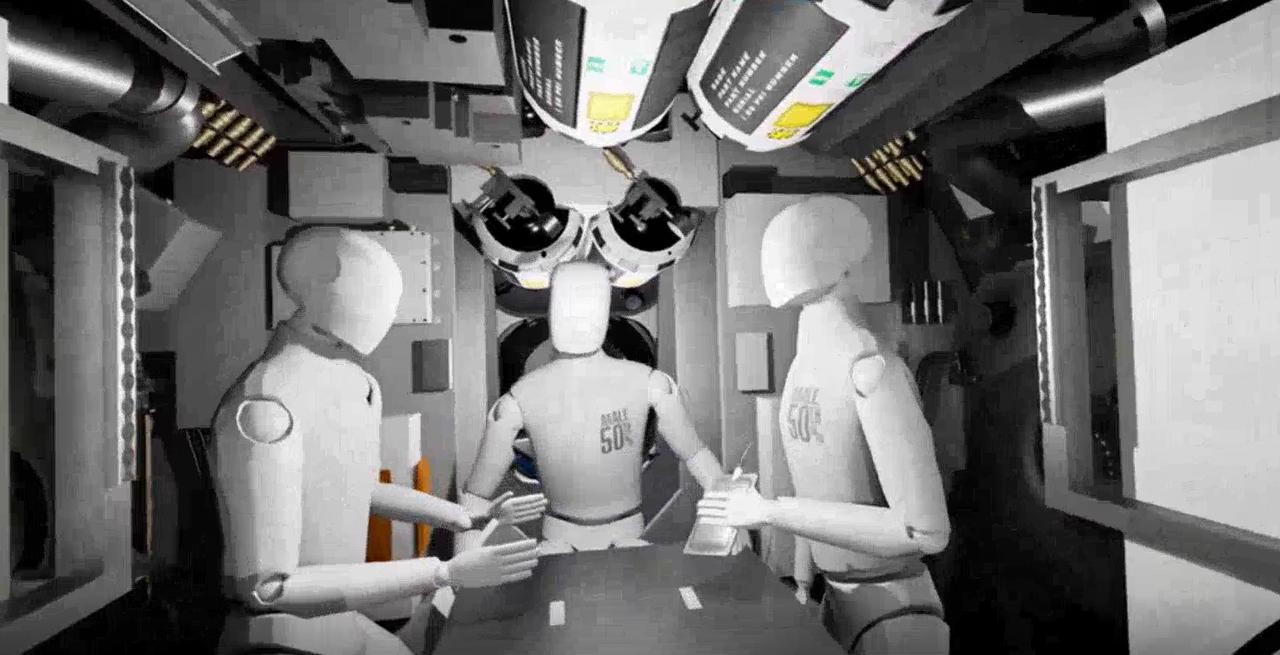

What astronauts see as they tour the Gateway lunar space station in virtual reality.
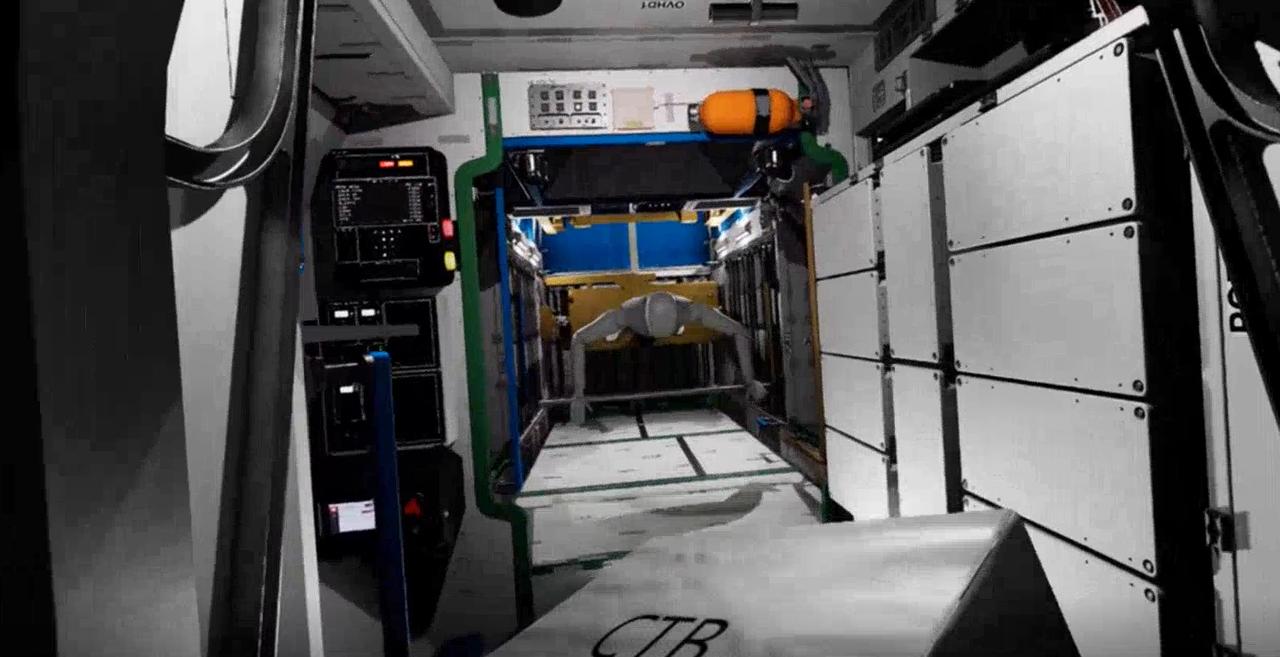

What astronauts see as they tour the Gateway lunar space station in virtual reality.

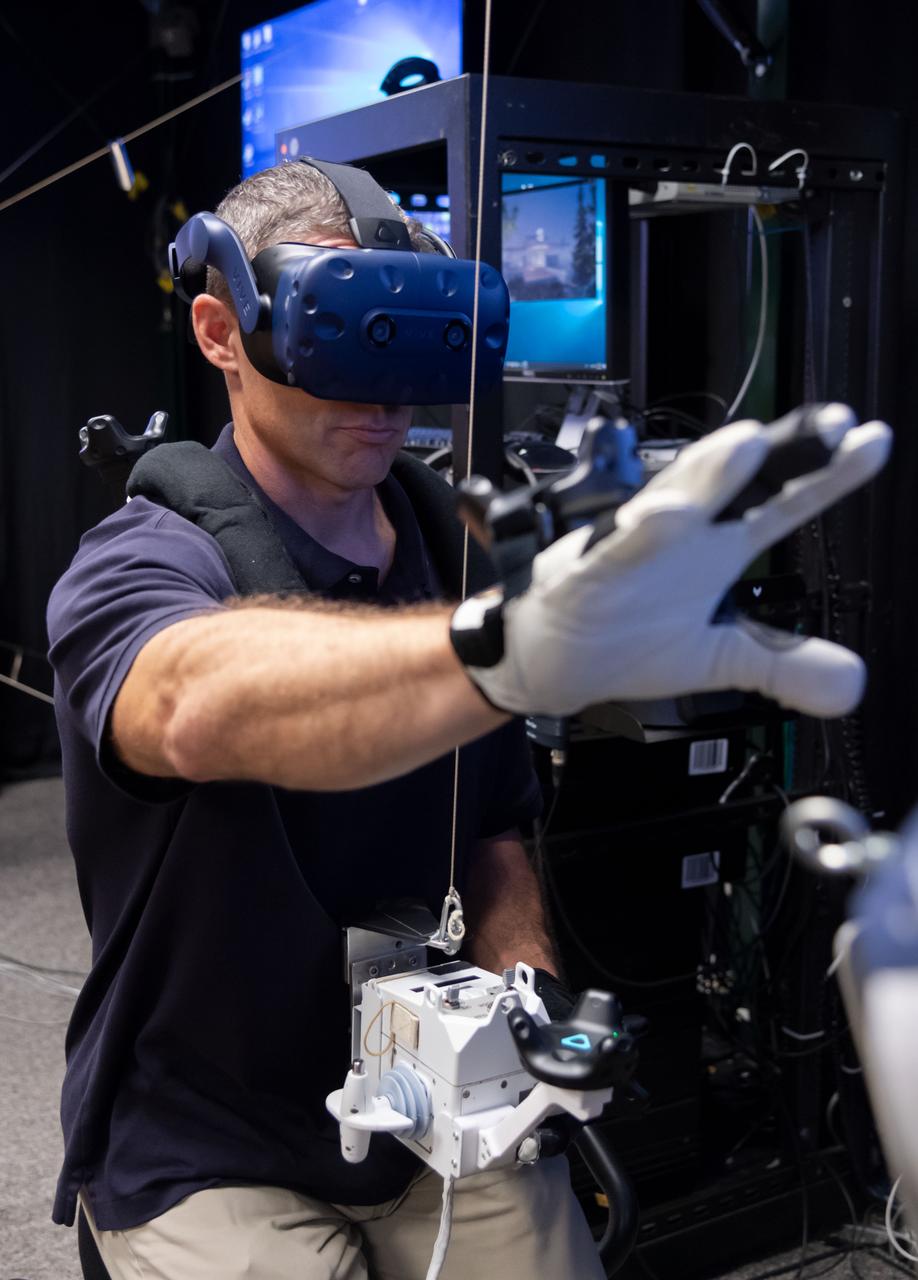
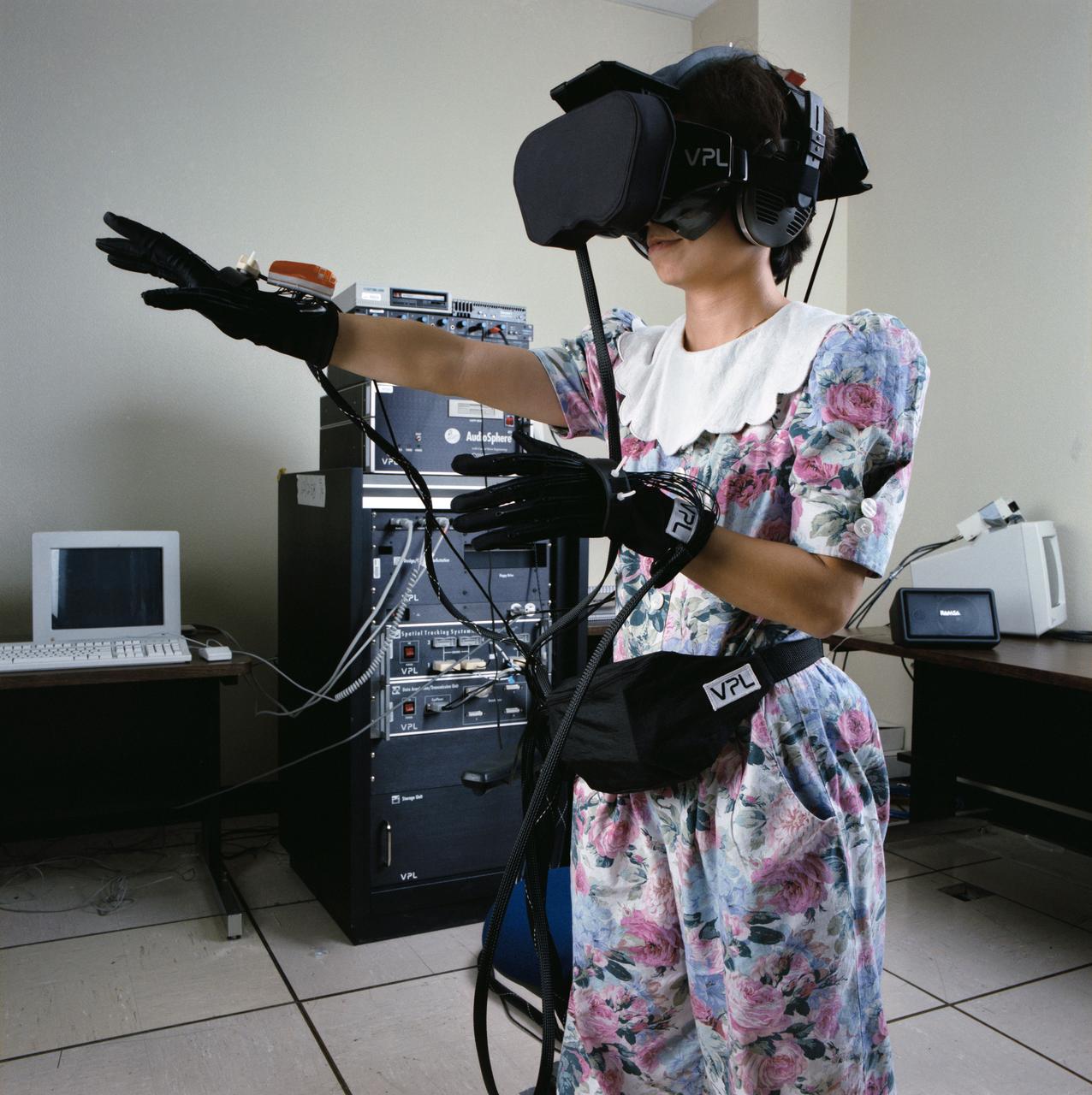
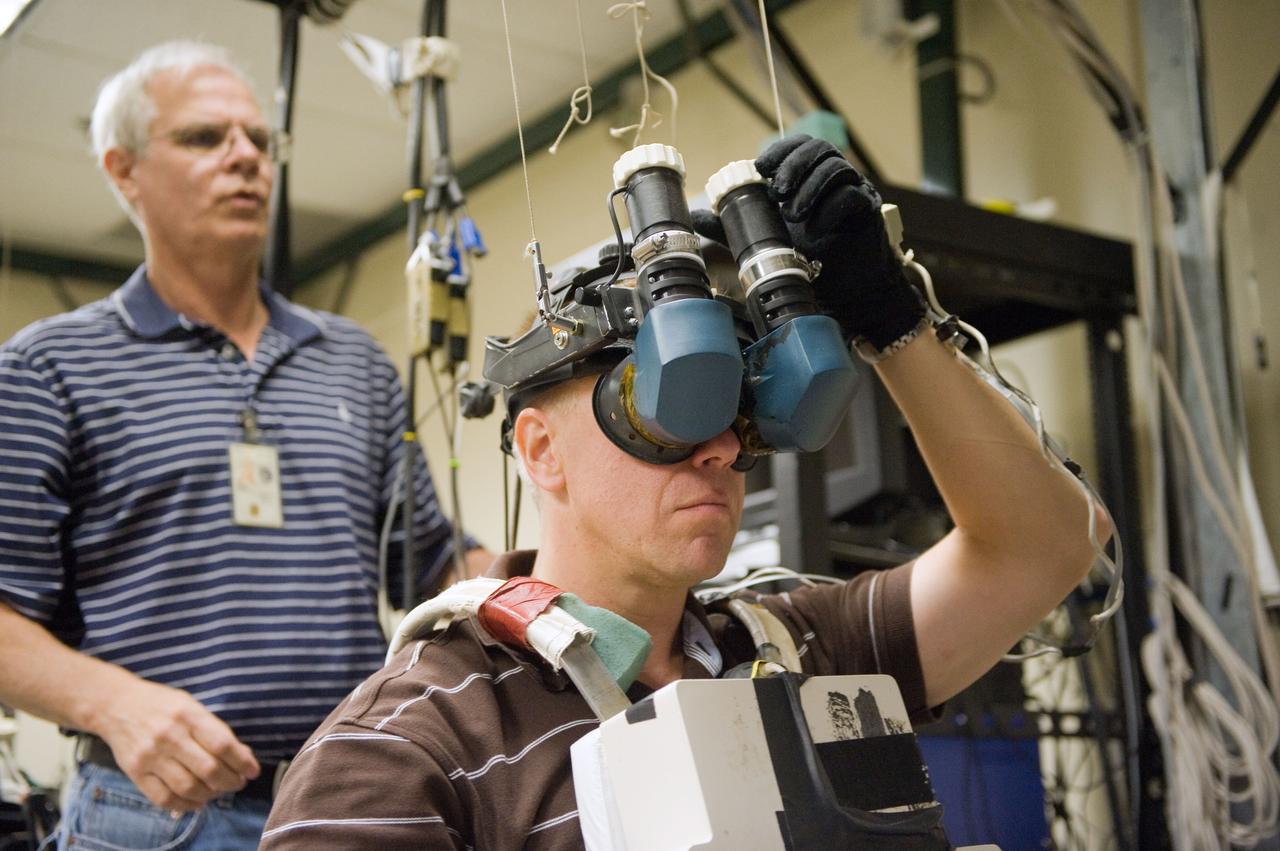
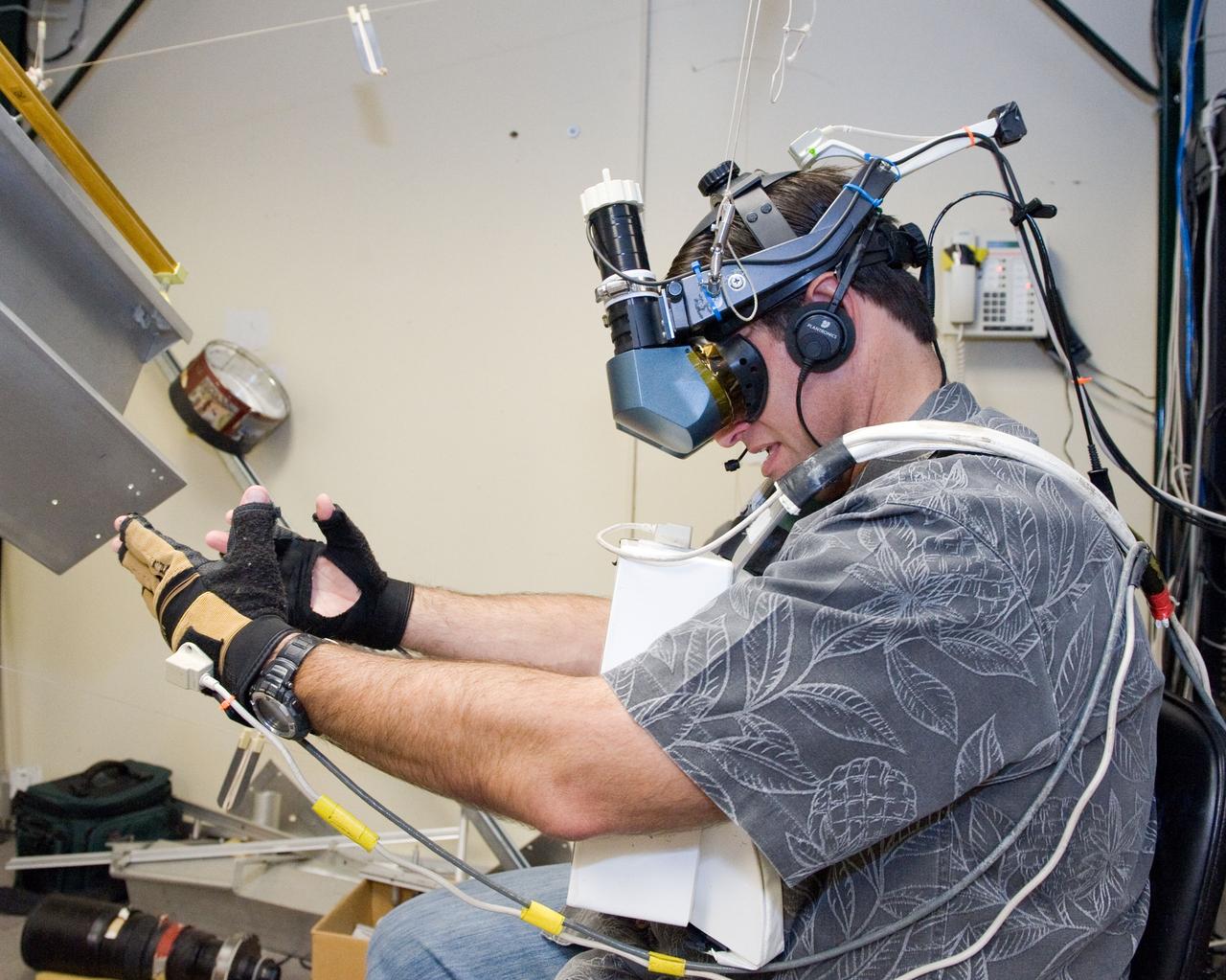
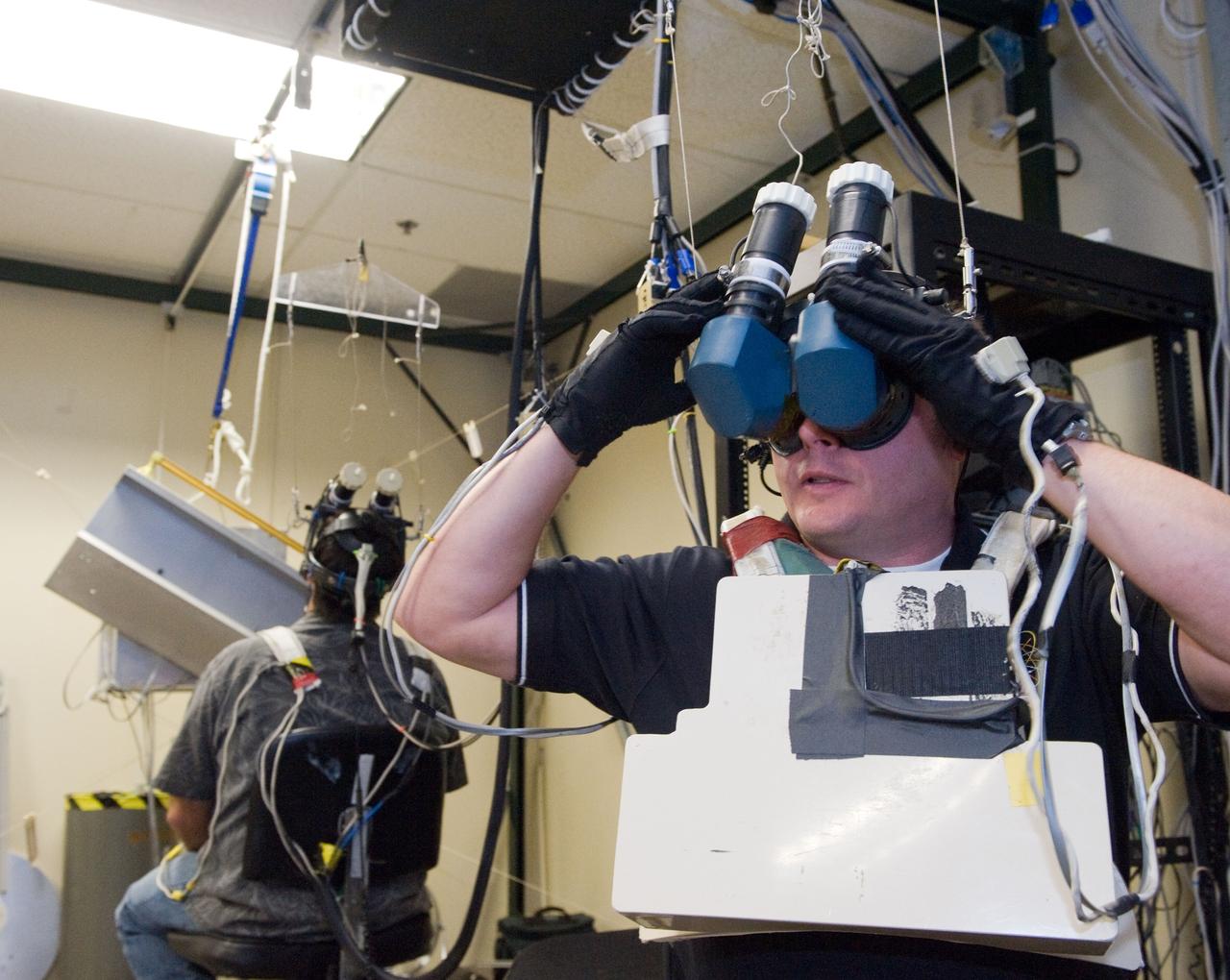
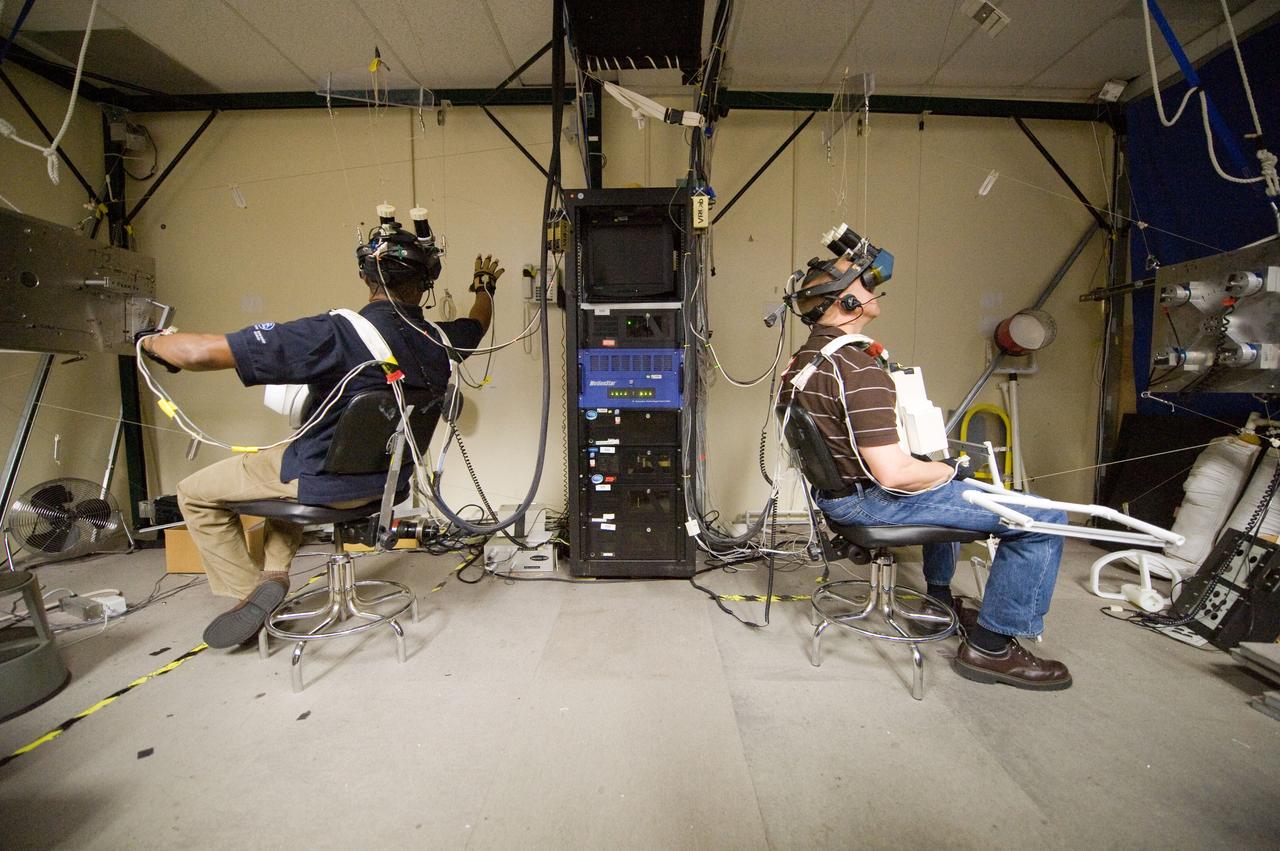
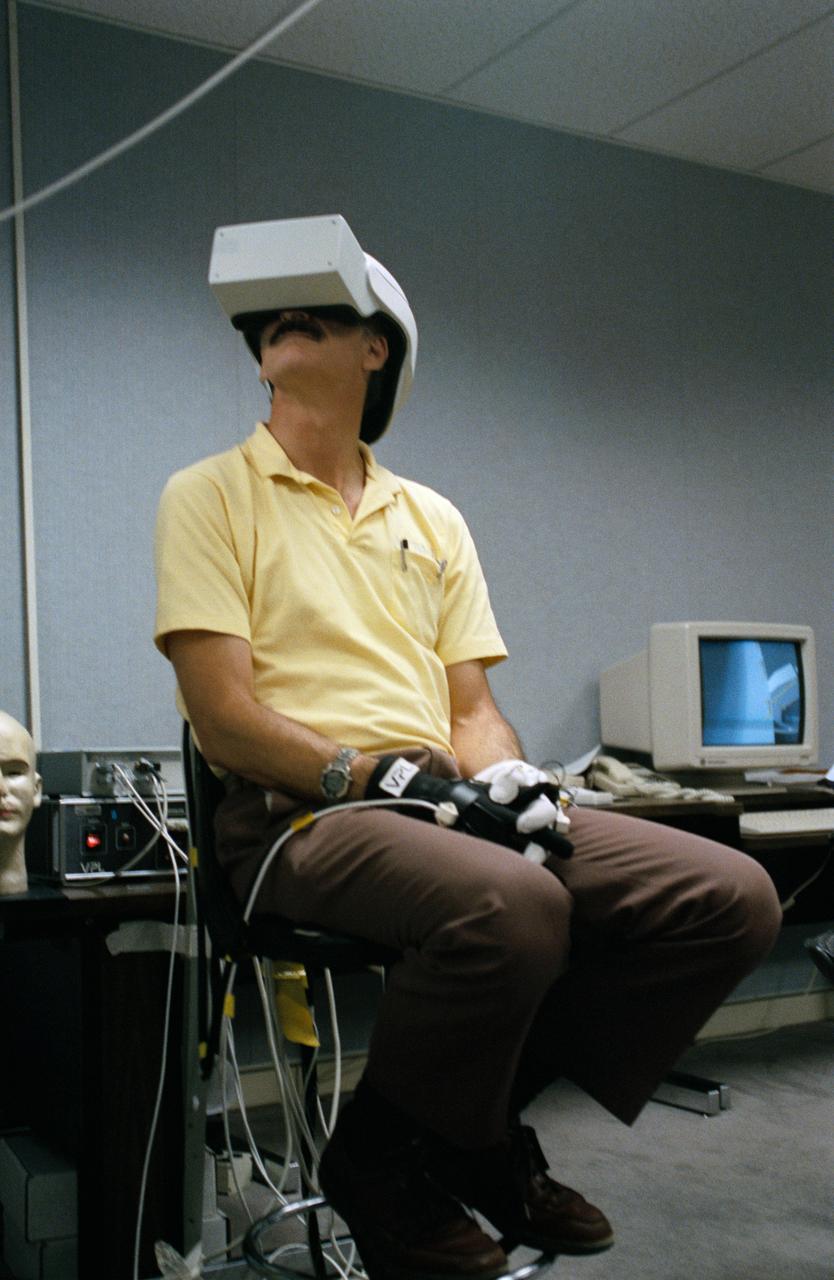
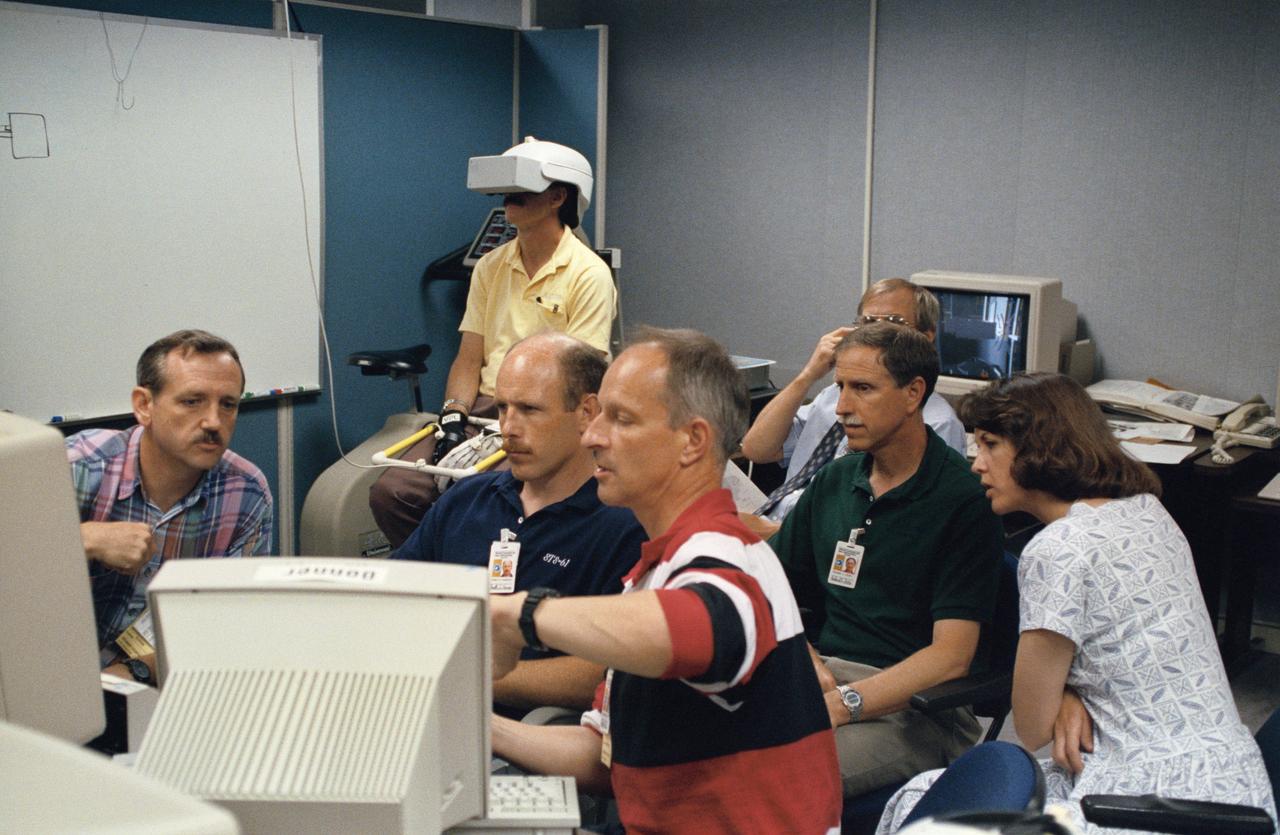
Virtual Reality (VR) can provide cost effective methods to design and evaluate components and systems for maintenance and refurbishment operations. Marshall SPace Flight Center (MSFC) is begirning to utilize VR for design analysis in the X-34 experimental reusable space vehicle. Analysts at MSFC's Computer Applications and Virtual Environments (CAVE) used Head Mounted Displays (HMD) (pictured), spatial trackers and gesture inputs as a means to animate or inhabit a properly sized virtual human model. These models are used in a VR scenario as a way to determine functionality of space and maintenance requirements for the virtual X-34. The primary functions of the virtual X-34 mockup is to support operations development and design analysis for engine removal, the engine compartment and the aft fuselage. This capability provides general visualization support to engineers and designers at MSFC and to the System Design Freeze Review at Orbital Sciences Corporation (OSC).

Virtual Reality (VR) can provide cost effective methods to design and evaluate components and systems for maintenance and refurbishment operations. Marshall Spce Flight Center (MSFC) is begirning to utilize VR for design analysis in the X-34 experimental reusable space vehicle. Analysts at MSFC's Computer Applications and Virtual Environments (CAVE) used Head Mounted Displays (HMD) (pictured), spatial trackers and gesture inputs as a means to animate or inhabit a properly sized virtual human model. These models are used in a VR scenario as a way to determine functionality of space and maintenance requirements for the virtual X-34. The primary functions of the virtual X-34 mockup is to support operations development and design analysis for engine removal, the engine compartment and the aft fuselage. This capability provides general visualization support to engineers and designers at MSFC and to the System Design Freeze Review at Orbital Sciences Corporation (OSC).
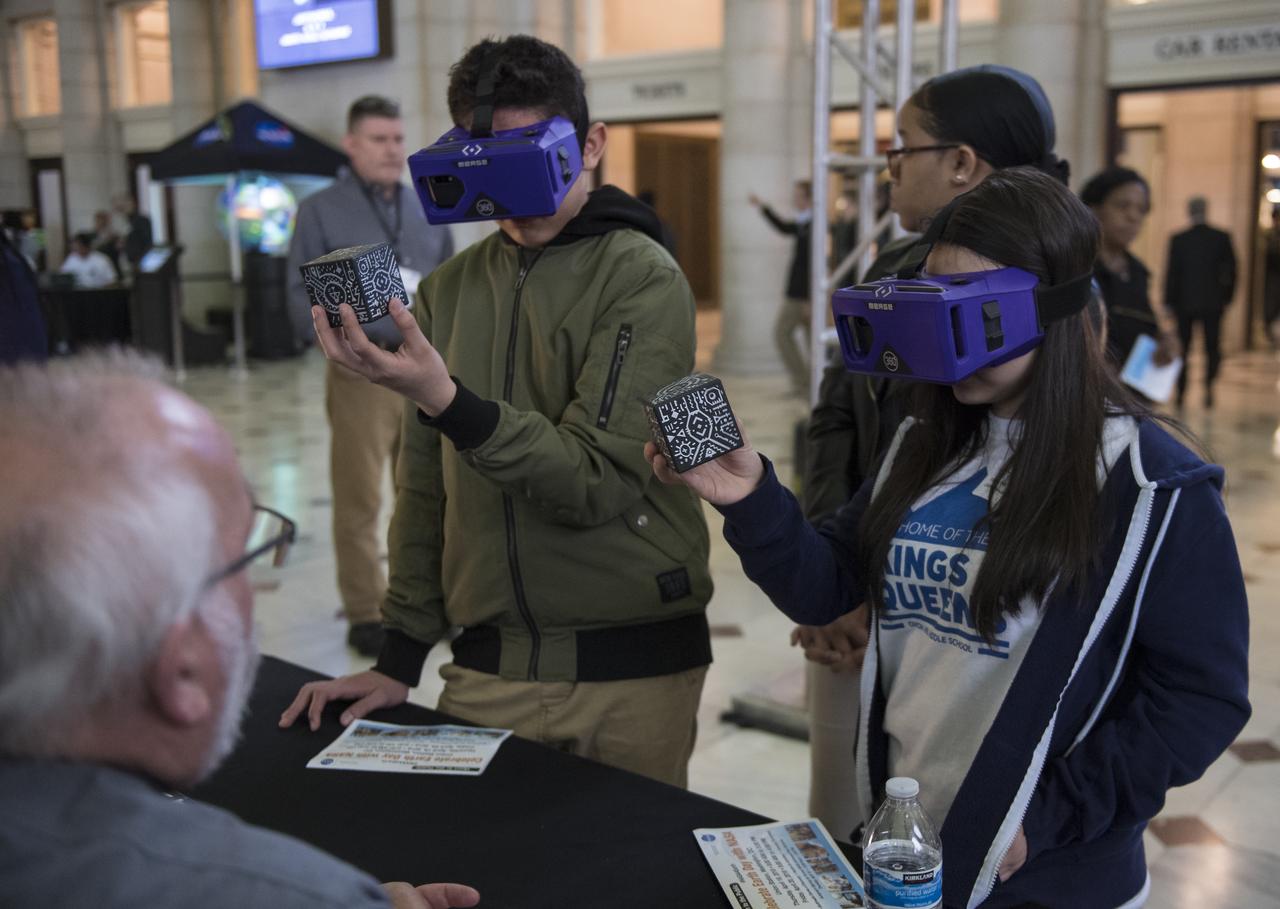

Visitors look through virtual reality goggles at one of NASA's exhibits at the Earth Day event on Thursday, April 19, 2018 at Union Station in Washington, D.C. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
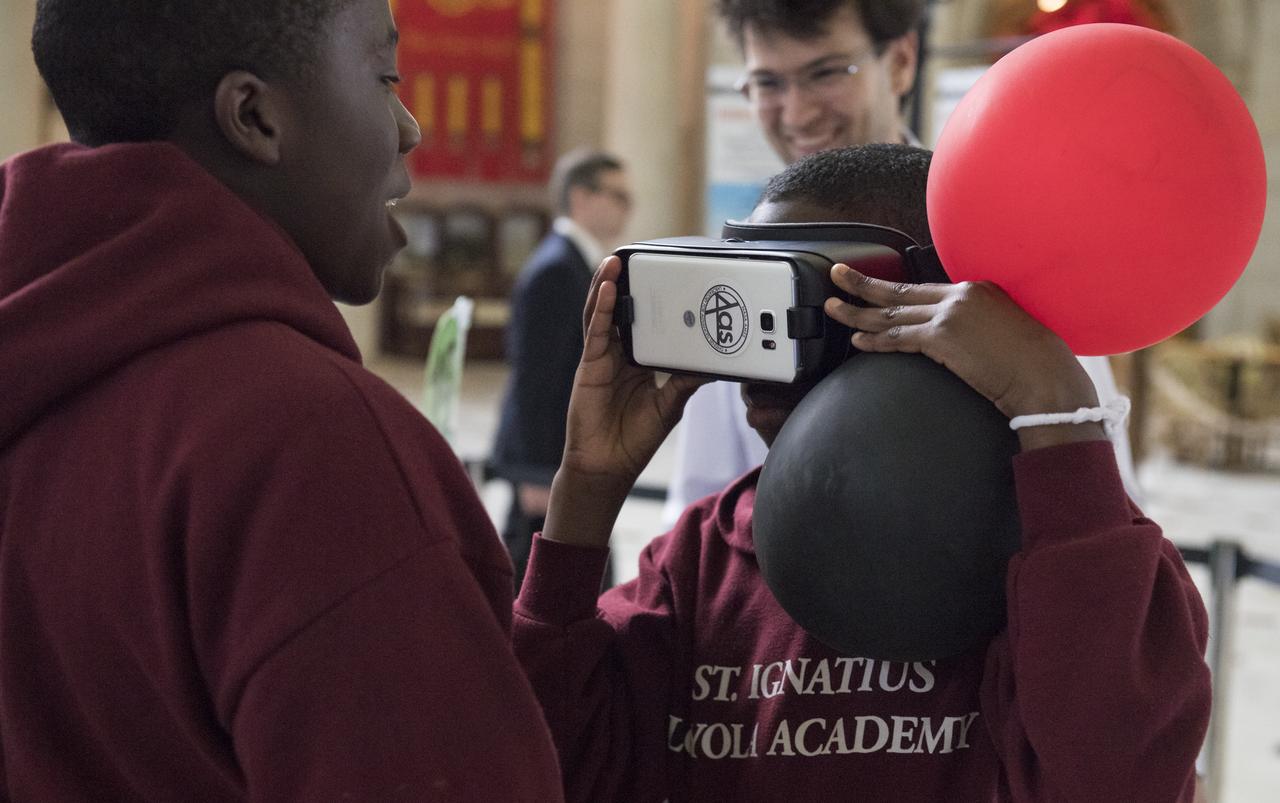

A visitor looks through virtual reality viewers at one of NASA's exhibits at the Earth Day event on Thursday, April 19, 2018 at Union Station in Washington, D.C. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

S91-50404 (1 Nov 1991) --- Bebe Ly of the Information Systems Directorate's (ISD) Software Technology Branch at the Johnson Space Center (JSC) gives virtual reality a try. The stereo video goggles and head[phones allow her to see and hear in a computer-generated world and the gloves allow her to move around and grasp objects. Ly is a member of the team that developed the C Language Integrated production System (CLIPS) which has been instrumental in developing several of the systems to be demonstrated in an upcoming Software Technology Exposition at JSC.

JSC2006-E-41641 (25 Sept. 2006) --- Cosmonaut Oleg V. Kotov, Expedition 15 flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, participates in a camera review training session in the virtual reality lab in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at Johnson Space Center.

JSC2006-E-41640 (25 Sept. 2006) --- Cosmonaut Fyodor N. Yurchikhin, Expedition 15 commander representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, participates in a camera review training session in the virtual reality lab in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at Johnson Space Center.

JSC2010-E-121049 (27 Aug. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Andrew Feustel (foreground), STS-134 mission specialist, uses the virtual reality lab in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to train for some of his duties aboard the space shuttle and space station. This type of computer interface, paired with virtual reality training hardware and software, helps to prepare crew members for dealing with space station elements. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
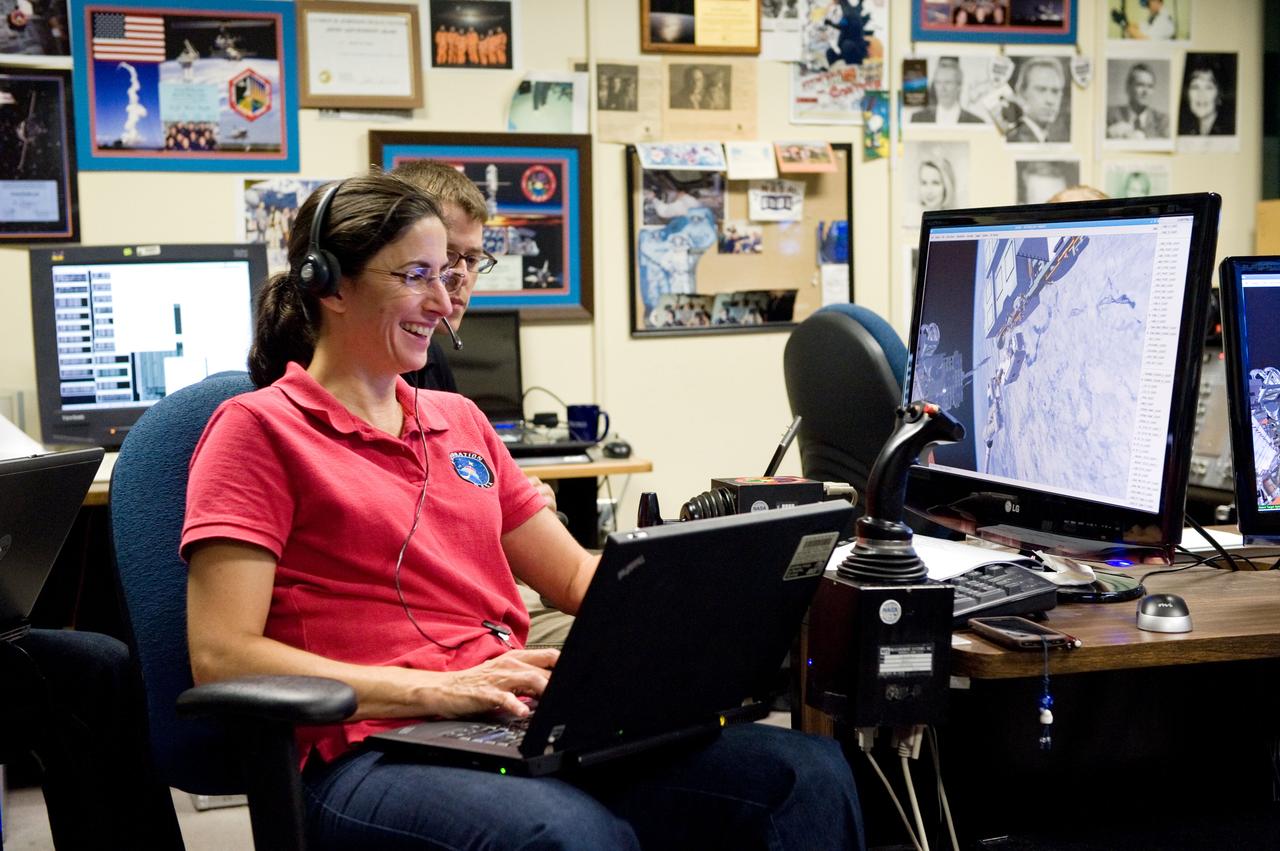

JSC2010-E-170882 (1 Oct. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Nicole Stott, STS-133 mission specialist, uses the virtual reality lab in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to train for some of her duties aboard the space shuttle and space station. This type of computer interface, paired with virtual reality training hardware and software, helps to prepare crew members for dealing with space station elements. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

JSC2010-E-170878 (1 Oct. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Michael Barratt, STS-133 mission specialist, uses the virtual reality lab in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to train for some of his duties aboard the space shuttle and space station. This type of computer interface, paired with virtual reality training hardware and software, helps to prepare crew members for dealing with space station elements. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
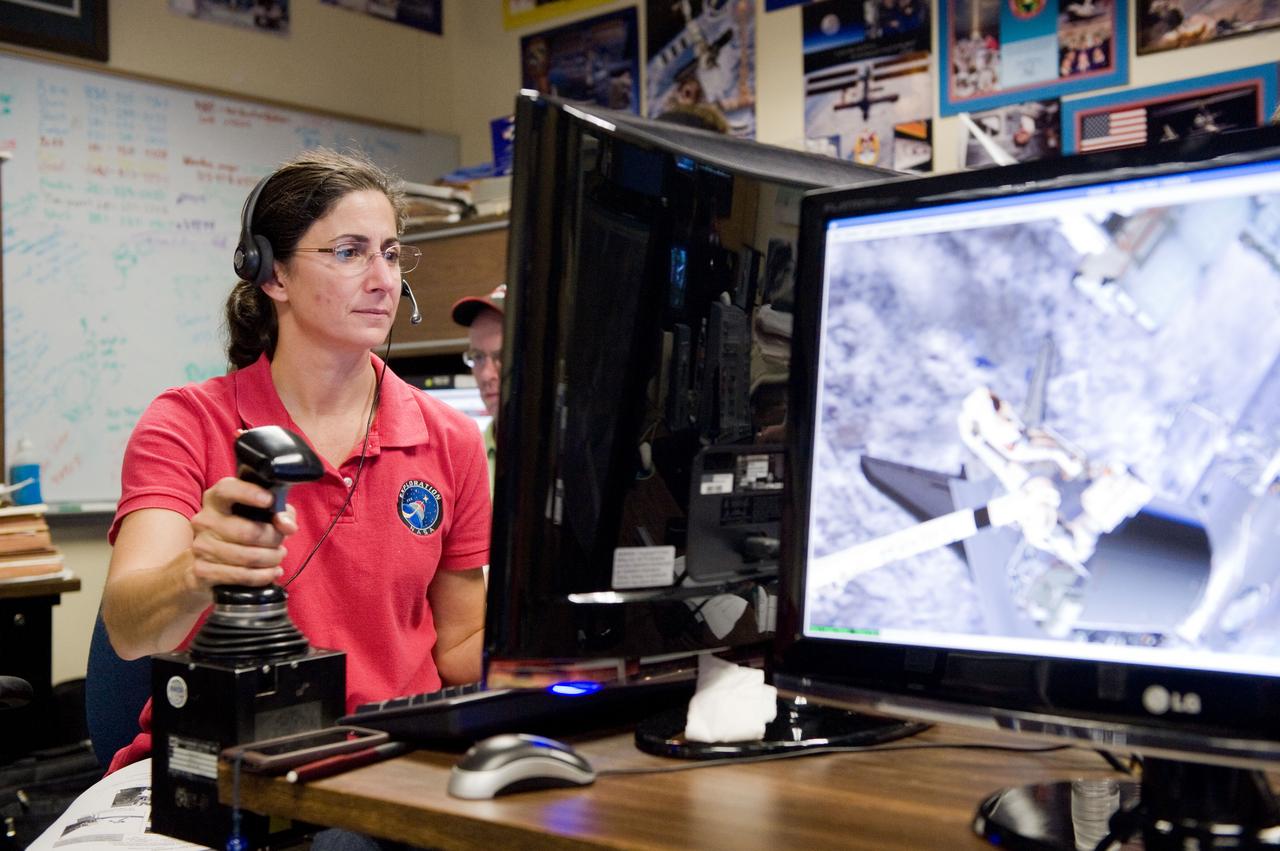

JSC2010-E-170888 (1 Oct. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Nicole Stott, STS-133 mission specialist, uses the virtual reality lab in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to train for some of her duties aboard the space shuttle and space station. This type of computer interface, paired with virtual reality training hardware and software, helps to prepare crew members for dealing with space station elements. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

JSC2010-E-121056 (27 Aug. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Gregory H. Johnson, STS-134 pilot, uses the virtual reality lab in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to train for some of his duties aboard the space shuttle and space station. This type of computer interface, paired with virtual reality training hardware and software, helps to prepare crew members for dealing with space station elements. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

JSC2010-E-170871 (1 Oct. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Tim Kopra, STS-133 mission specialist, uses virtual reality hardware in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to rehearse some of his duties on the upcoming mission to the International Space Station. This type of virtual reality training allows the astronauts to wear a helmet and special gloves while looking at computer displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the station hardware with which they will be working. Crew trainer David Homan assisted Kopra. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
JSC2010-E-170897 (1 Oct. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Tim Kopra, STS-133 mission specialist, uses virtual reality hardware in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to rehearse some of his duties on the upcoming mission to the International Space Station. This type of virtual reality training allows the astronauts to wear a helmet and special gloves while looking at computer displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the station hardware with which they will be working. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

JSC2010-E-121058 (27 Aug. 2010) --- NASA astronauts Michael Fincke (foreground) and Greg Chamitoff, both STS-134 mission specialists, use virtual reality hardware in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to rehearse some of their duties on the upcoming mission to the International Space Station. This type of virtual reality training allows the astronauts to wear a helmet and special gloves while looking at computer displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the station hardware with which they will be working. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
JSC2010-E-121055 (27 Aug. 2010) --- NASA astronauts Michael Fincke (right) and Greg Chamitoff, both STS-134 mission specialists, use virtual reality hardware in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to rehearse some of their duties on the upcoming mission to the International Space Station. This type of virtual reality training allows the astronauts to wear a helmet and special gloves while looking at computer displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the station hardware with which they will be working. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

JSC2010-E-170892 (1 Oct. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Alvin Drew, STS-133 mission specialist, uses virtual reality hardware in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to rehearse some of his duties on the upcoming mission to the International Space Station. This type of virtual reality training allows the astronauts to wear a helmet and special gloves while looking at computer displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the station hardware with which they will be working. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

JSC2010-E-121053 (27 Aug. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Greg Chamitoff, STS-134 mission specialist, uses virtual reality hardware in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to rehearse some of his duties on the upcoming mission to the International Space Station. This type of virtual reality training allows the astronauts to wear a helmet and special gloves while looking at computer displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the station hardware with which they will be working. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

JSC2010-E-121052 (27 Aug. 2010) --- NASA astronauts Michael Fincke (foreground) and Greg Chamitoff, both STS-134 mission specialists, use virtual reality hardware in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to rehearse some of their duties on the upcoming mission to the International Space Station. This type of virtual reality training allows the astronauts to wear a helmet and special gloves while looking at computer displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the station hardware with which they will be working. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

JSC2010-E-170885 (1 Oct. 2010) --- NASA astronauts Alvin Drew (left) and Tim Kopra, both STS-133 mission specialists, use virtual reality hardware in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to rehearse some of their duties on the upcoming mission to the International Space Station. This type of virtual reality training allows the astronauts to wear a helmet and special gloves while looking at computer displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the station hardware with which they will be working. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

JSC2010-E-170873 (1 Oct. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Tim Kopra, STS-133 mission specialist, uses virtual reality hardware in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to rehearse some of his duties on the upcoming mission to the International Space Station. This type of virtual reality training allows the astronauts to wear a helmet and special gloves while looking at computer displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the station hardware with which they will be working. Crew trainer David Homan assisted Kopra. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
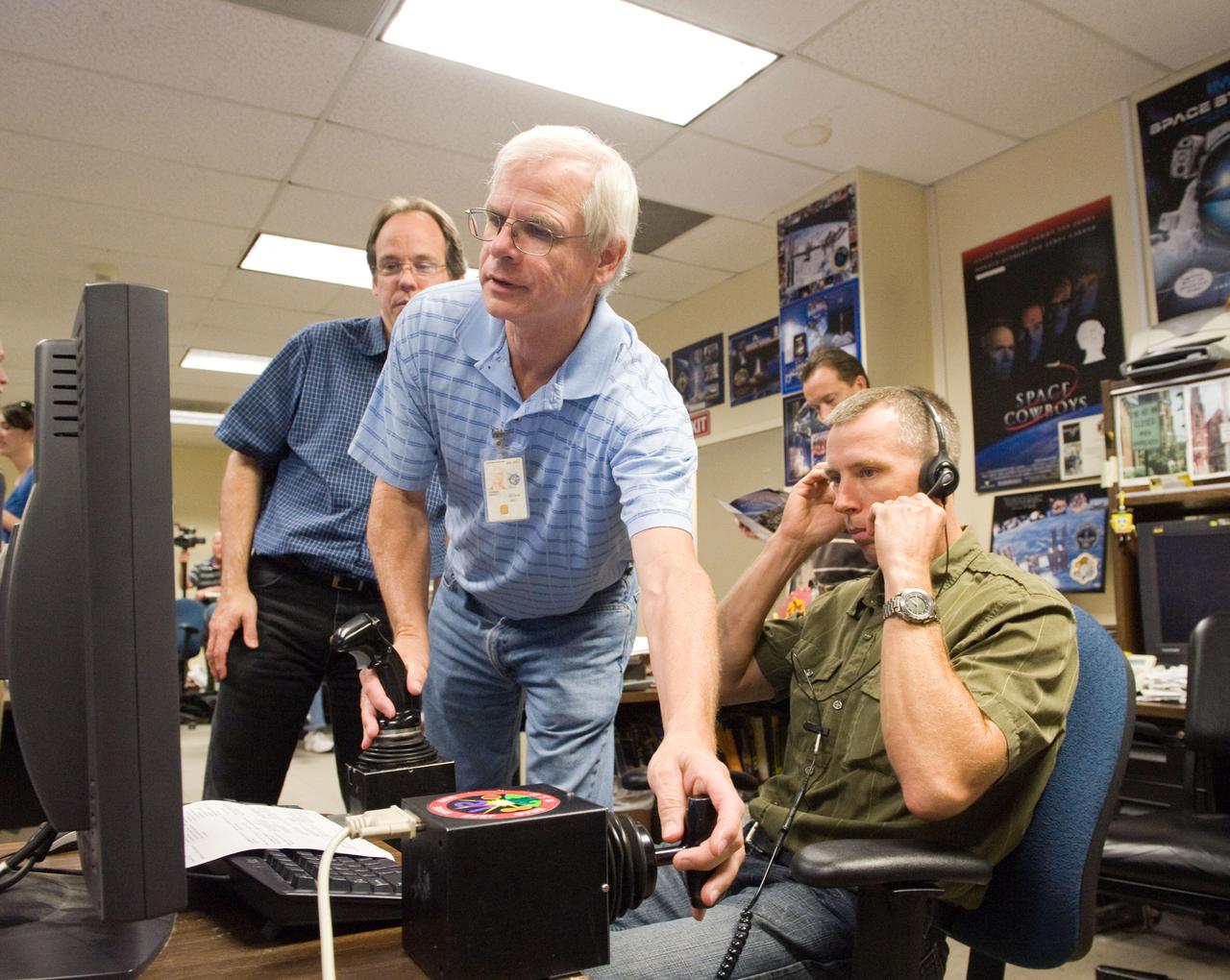

JSC2010-E-121045 (27 Aug. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Andrew Feustel (right), STS-134 mission specialist, uses the virtual reality lab in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to train for some of his duties aboard the space shuttle and space station. This type of computer interface, paired with virtual reality training hardware and software, helps to prepare crew members for dealing with space station elements. David Homan assisted Feustel. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
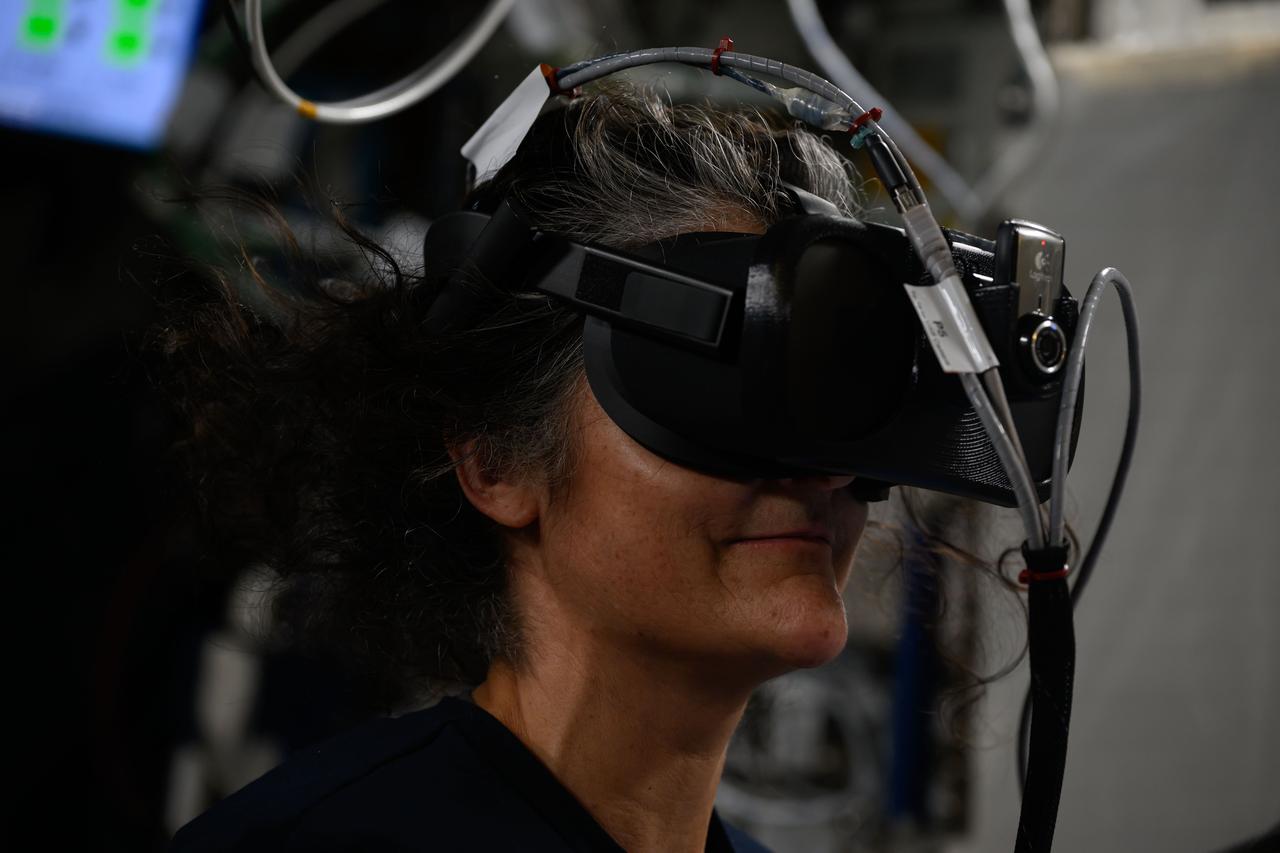

iss072e422431 (Dec. 27, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Commander Suni Williams wears a virtual reality headset and practices emergency maneuvers a spacewalker would use in the unlikely event they became untethered from the International Space Station. During spacewalks astronauts wear U.S. spacesuits with a jetpack installed called a SAFER, or Simplified Aid for EVA (Extra Vehicular Activity) Rescue, that contains a controller and thrusters used to guide a crew member back to the safety of the orbital outpost.

iss072e422426 (Dec. 27, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Commander Suni Williams wears a virtual reality headset and practices emergency maneuvers a spacewalker would use in the unlikely event they became untethered from the International Space Station. During spacewalks astronauts wear U.S. spacesuits with a jetpack installed called a SAFER, or Simplified Aid for EVA (Extra Vehicular Activity) Rescue, that contains a controller and thrusters used to guide a crew member back to the safety of the orbital outpost.
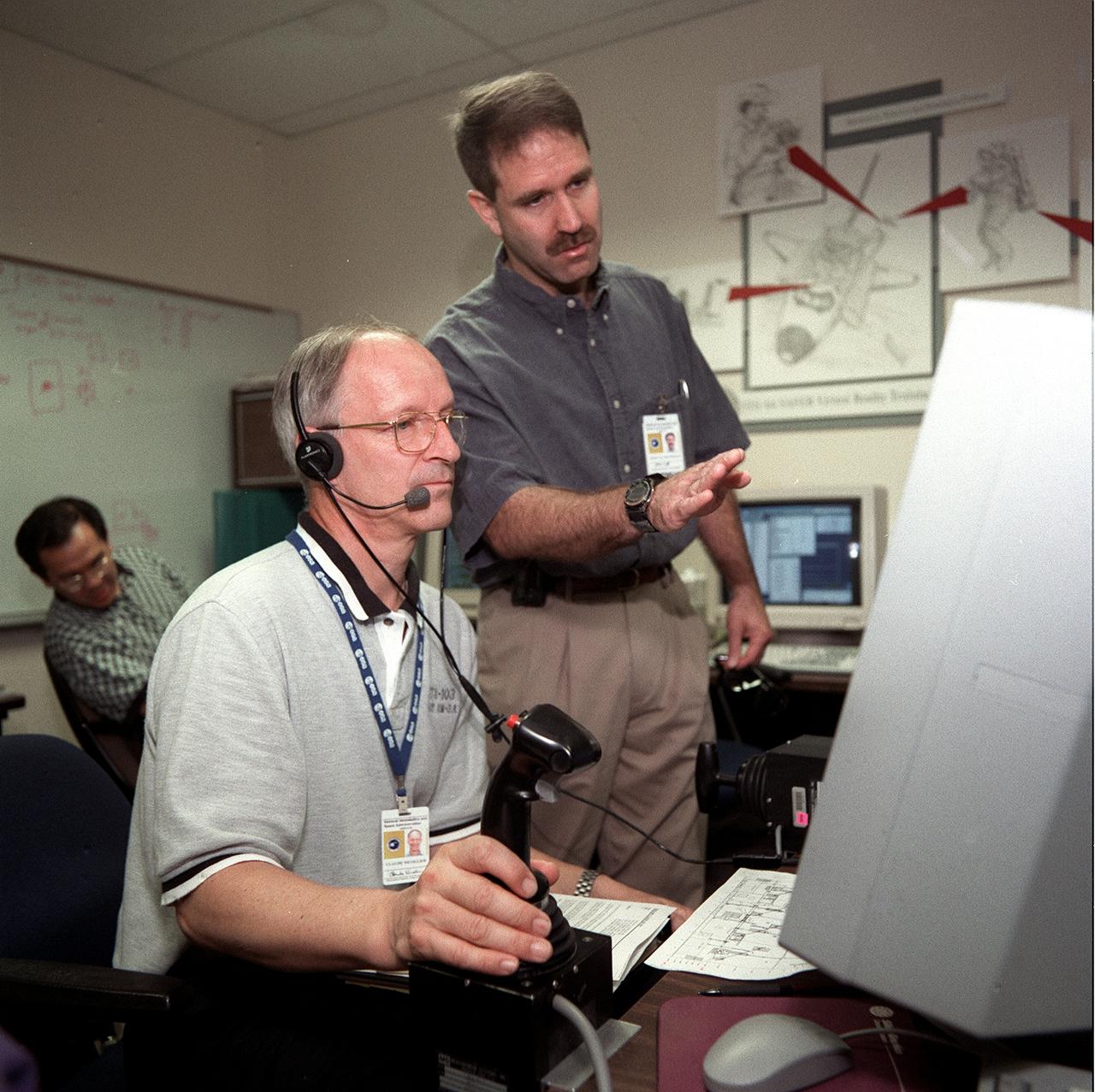

S99-05679 (24 May 1999) --- Astronauts Claude Nicollier (seated), representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and John M. Grunsfeld use virtual reality hardware to rehearse some of their duties for the upcoming STS-103 mission, NASA's third servicing visit to the Earth-orbiting Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The two mission specialists will be joined by five other astronauts, including a second ESA representative, for the STS-103 mission, scheduled for autumn of this year.
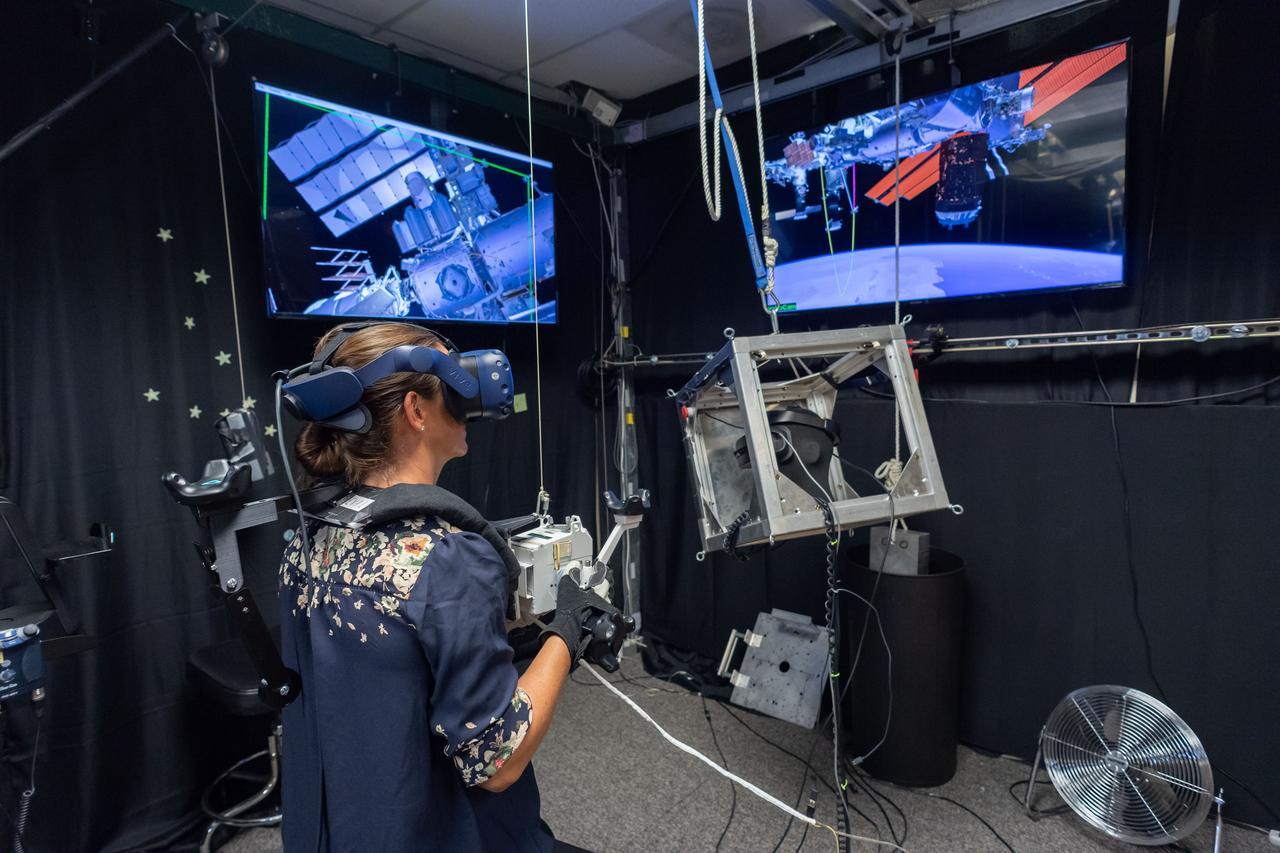

Commercial Crew Program astronaut and Boeing Crew Flight Test crew member Nicole Mann in SAFER Skills training in VR Lab.
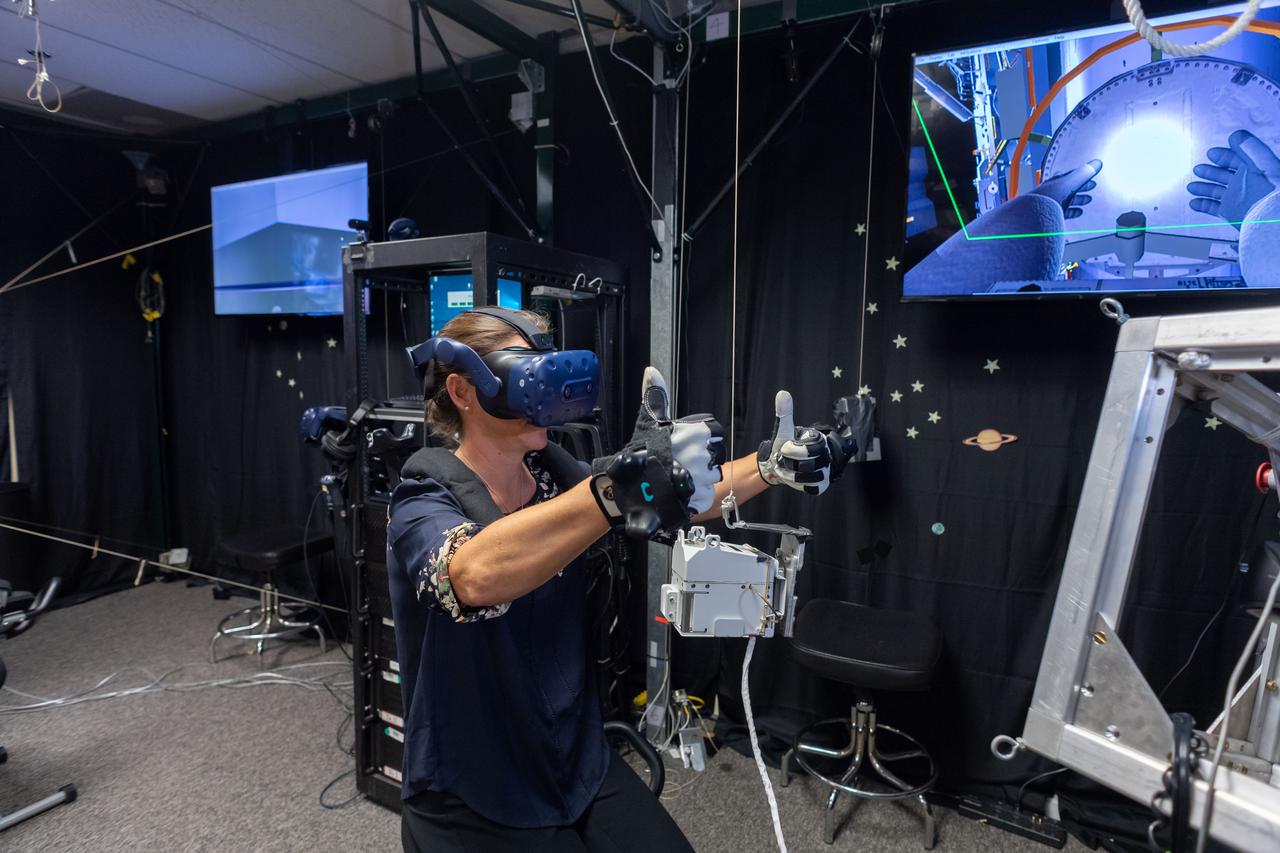

Commercial Crew Program astronaut and Boeing Crew Flight Test crew member Nicole Mann in SAFER Skills training in VR Lab.
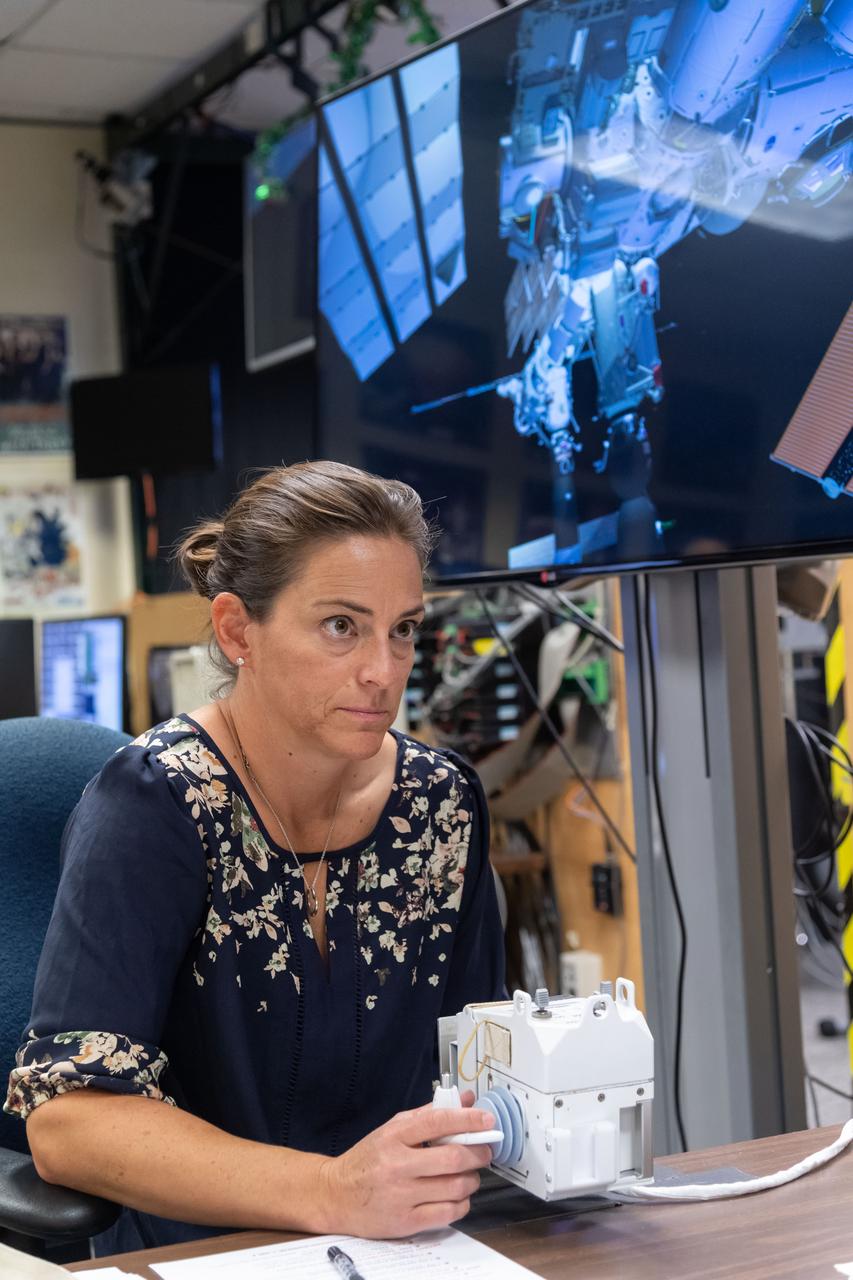

Commercial Crew Program astronaut and Boeing Crew Flight Test crew member Nicole Mann in SAFER Skills training in VR Lab.
Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).
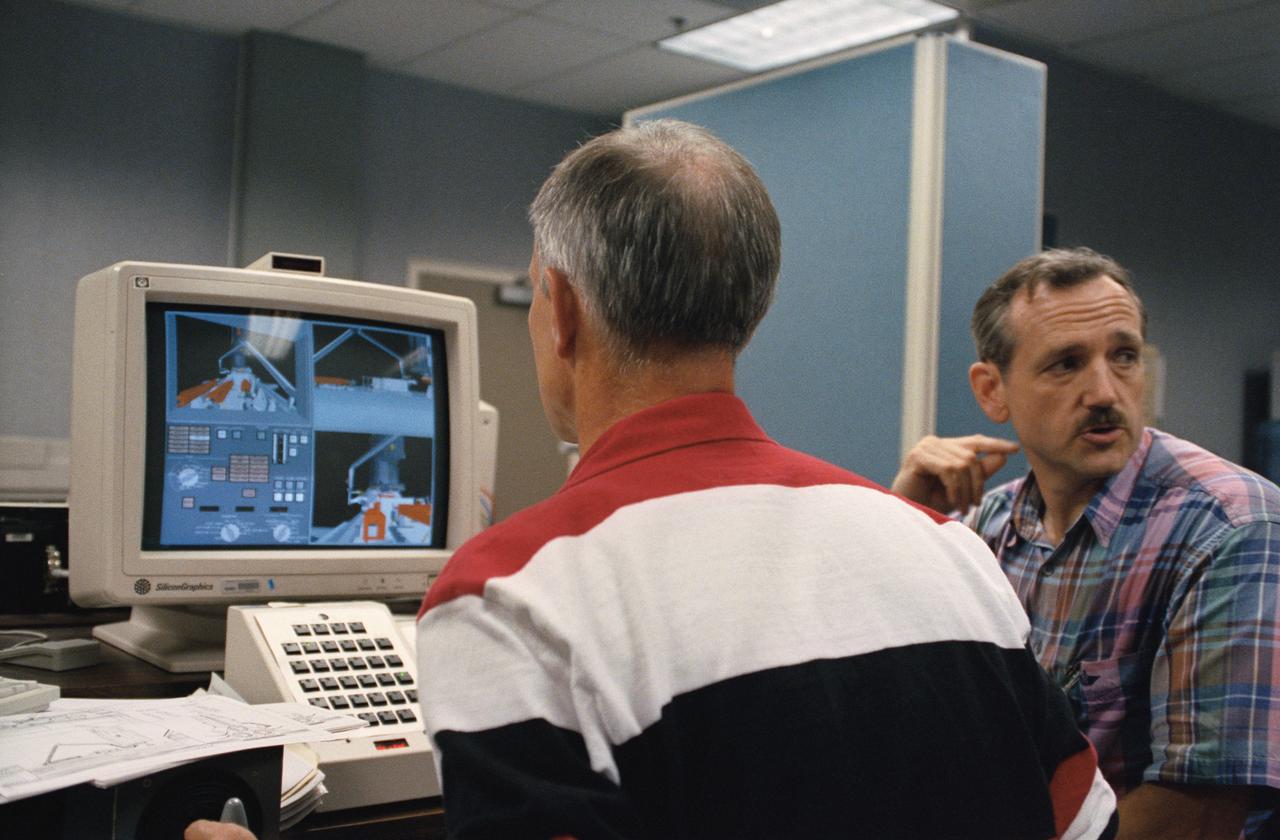

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).
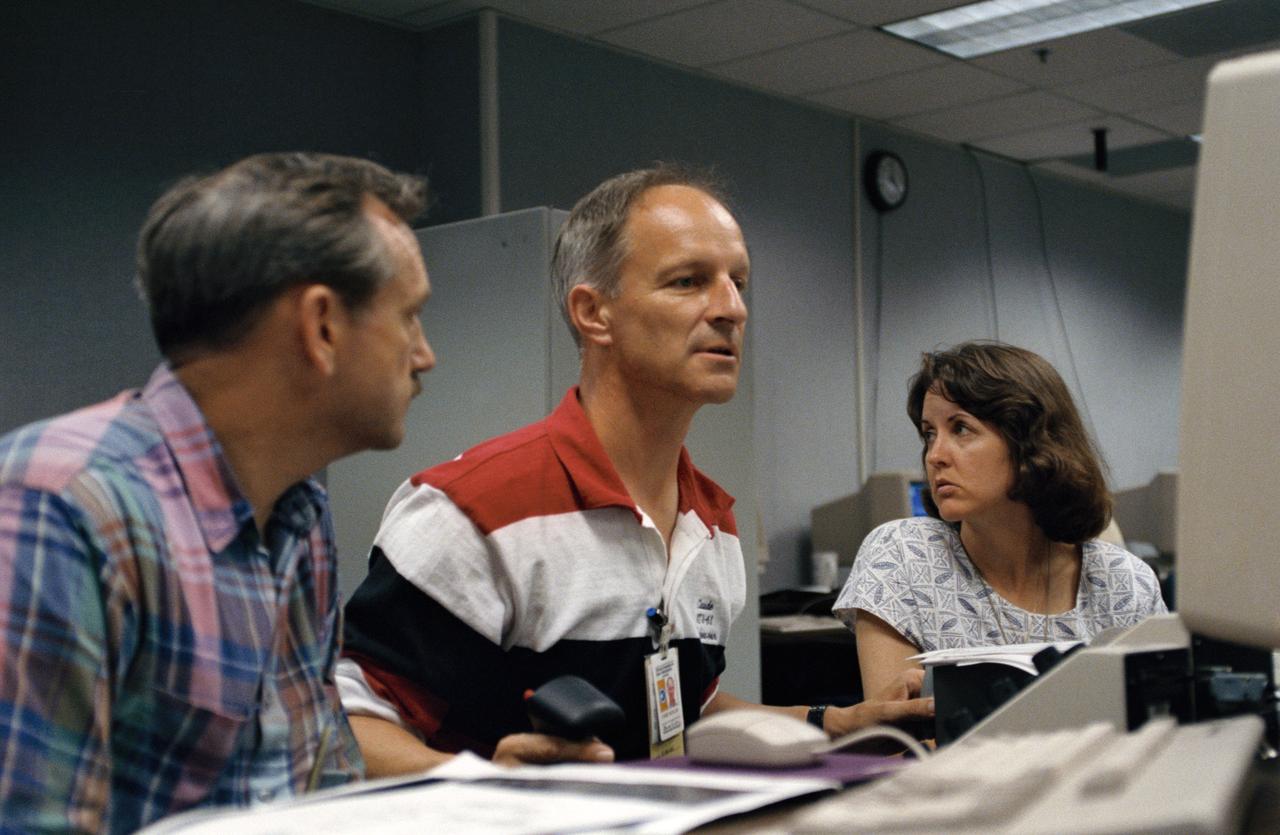

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).
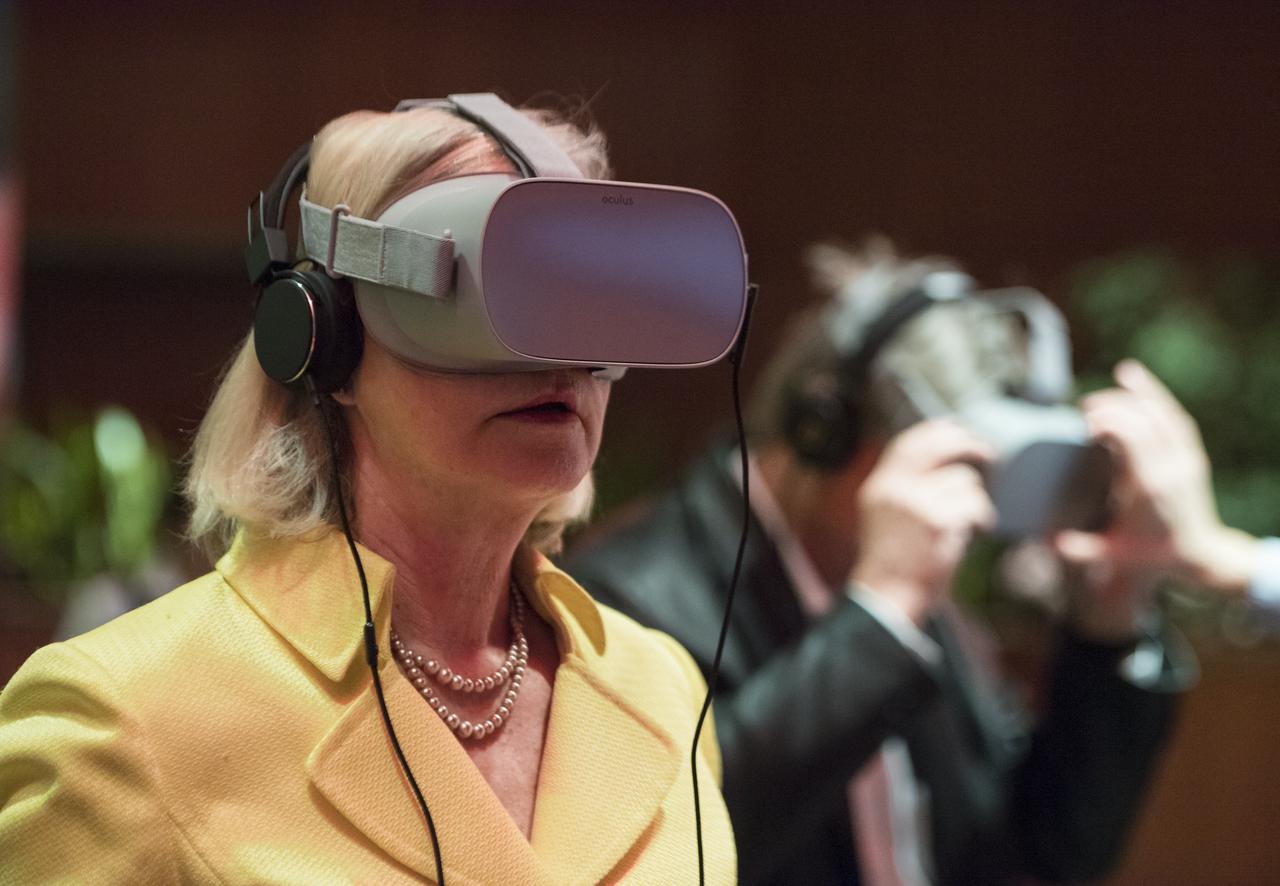

A guest uses some virtual reality viewers before a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films winners and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
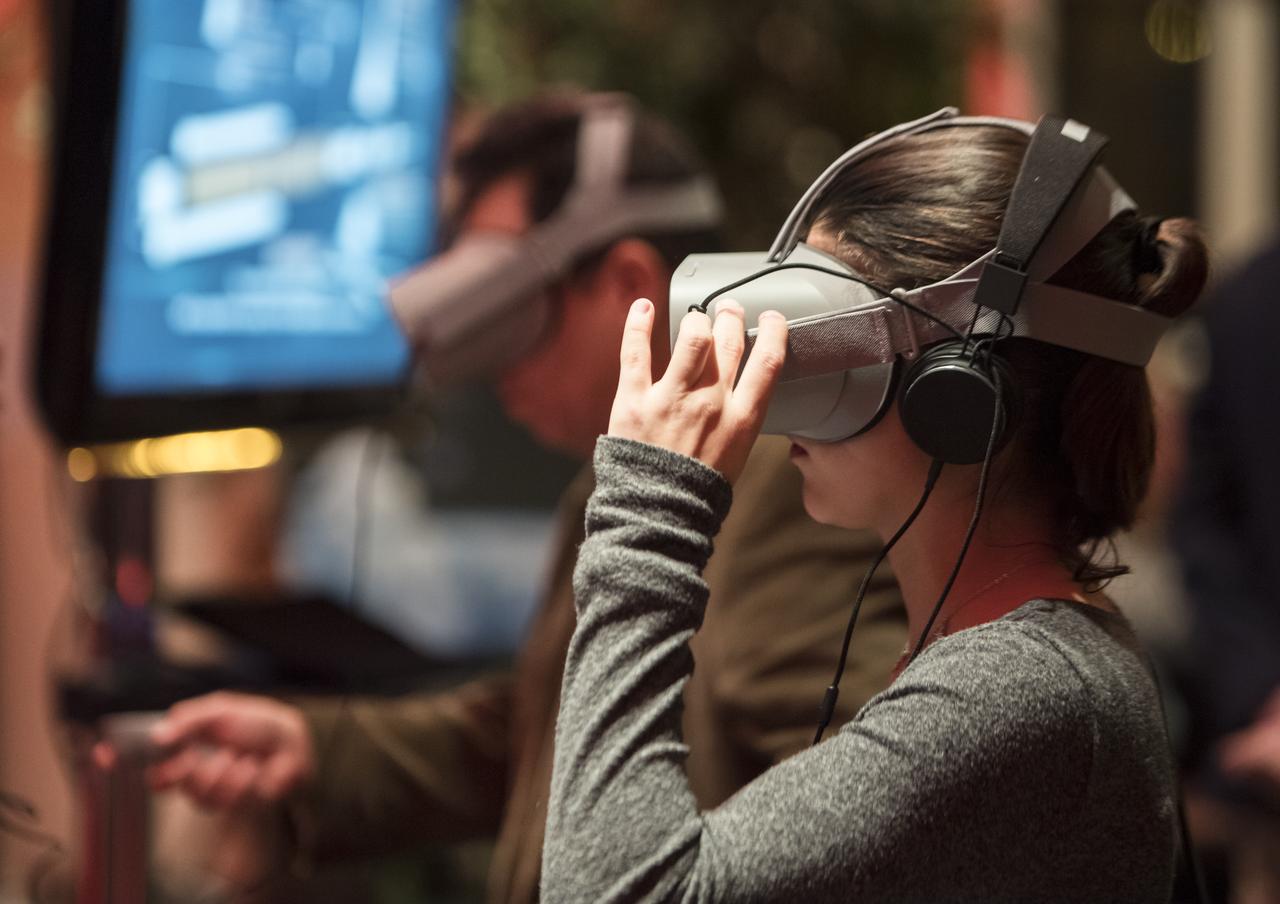

A guest uses some virtual reality viewers before a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films winners and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
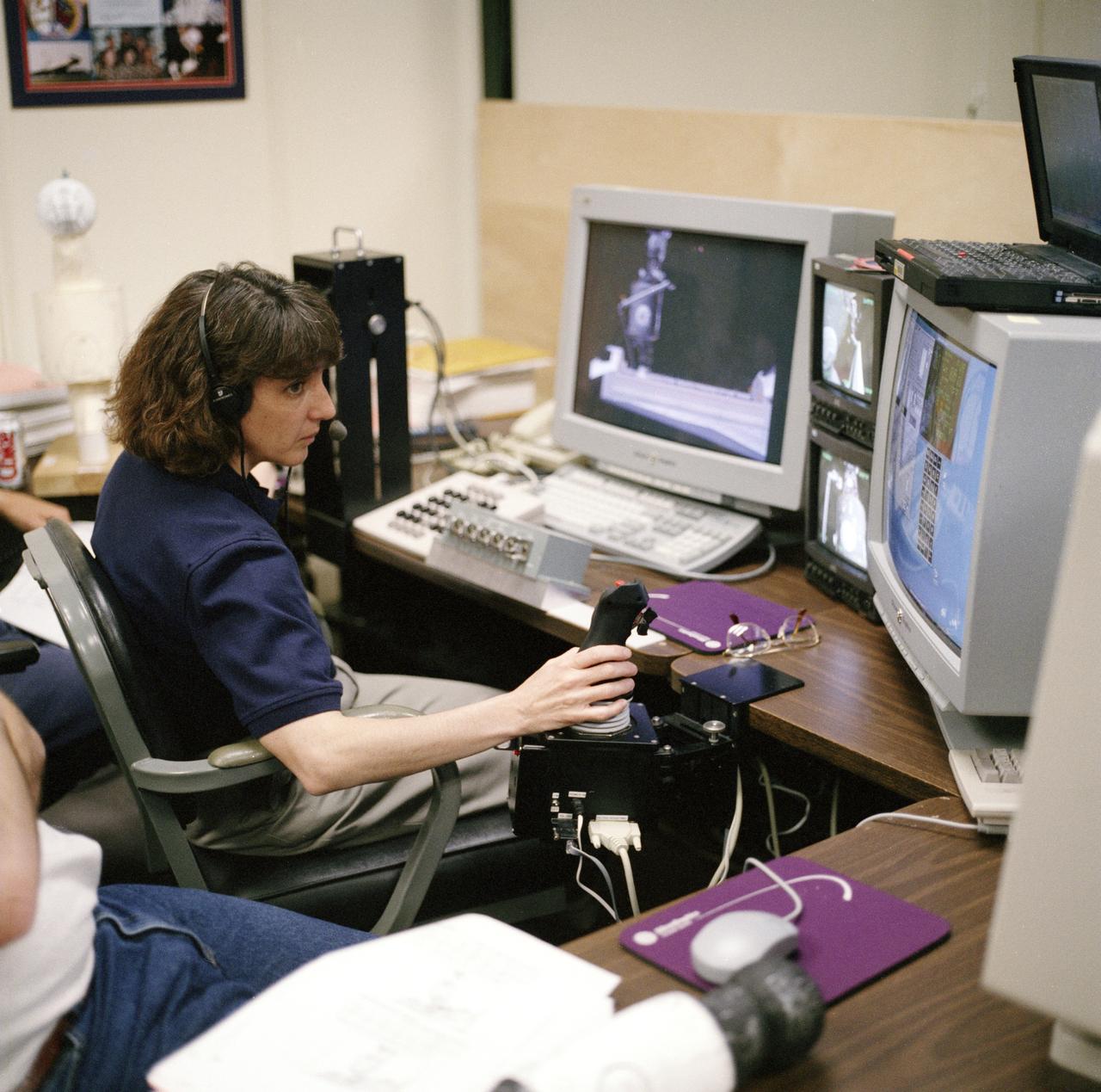

S98-05075 (8 Apr. 1998) --- Astronaut Nancy J. Currie, assigned as a mission specialist for the mission, uses hardware in the virtual reality lab at the Johnson Space Center (JSC) to train for her duties aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. This type computer interface paired with virtual reality training hardware for the assigned space-walking astronauts -- in this case, Jerry L. Ross and James H. Newman -- helps to prepare the entire team for dealing with International Space Station (ISS) elements. One of those elements will be the Functional Cargo Block (FGB), which will have been launched a couple of weeks prior to STS-88. Once the FGB is captured using the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) of the Endeavour, Currie will maneuver the robot arm to dock the FGB to the conical mating adapter at the top of Node 1, to be carried in the Endeavour?s cargo bay. In ensuing days, three Extravehicular Activity?s (EVA) by Ross and Newman will be performed to make power, data and utility connections between the two modules.
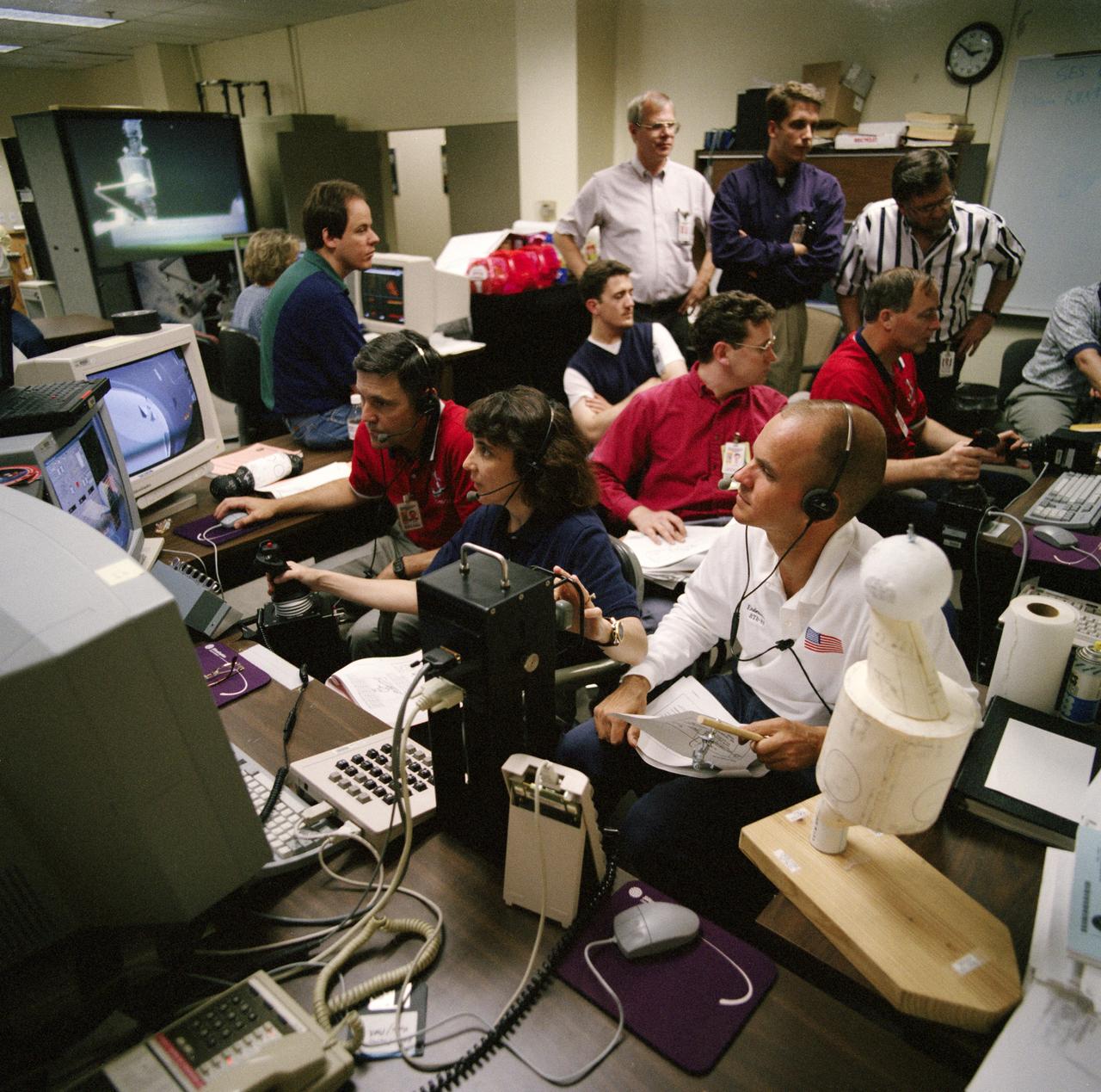

S98-05077 (8 Apr. 1998) --- With crew mates looking on, astronaut Nancy J. Currie, mission specialist, uses hardware in the virtual reality lab at the Johnson Space Center (JSC) to train for her duties aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. She is flanked by astronaut Robert Cabana (left), commander; and Frederick W. Sturckow (right), pilot. This type computer interface paired with virtual reality training hardware for the assigned space-walking astronauts -- Jerry L. Ross and James H. Newman -- helps to prepare the entire team for dealing with International Space Station (ISS) elements. One of those elements will be the Functional Cargo Block (FGB), which will have been launched a couple of weeks prior to STS-88. Once the FGB is captured using the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) of the Endeavour, Currie will maneuver the robot arm to dock the FGB to the conical mating adapter at the top of Node 1, to be carried in the Endeavour's cargo bay. In ensuing days, three Extravehicular Activity?s (EVA) by Ross and Newman will be performed to make power, data and utility connections between the two modules. Looking on is Scott A. Bleisath (behind Currie), with the EVA Systems Group at JSC.

S98-05078 (8 Apr. 1998) --- With crew mates looking on, astronaut Nancy J. Currie, mission specialist, uses hardware in the virtual reality lab at the Johnson Space Center (JSC) to train for her duties aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. She is flanked by astronaut Robert Cabana (left), commander; and Frederick W. Sturckow (right), pilot. This type computer interface paired with virtual reality training hardware for the assigned space-walking astronauts -- Jerry L. Ross and James H. Newman -- helps to prepare the entire team for dealing with International Space Station (ISS) elements. One of those elements will be the Functional Cargo Block (FGB), which will have been launched a couple of weeks prior to STS-88. Once the FGB is captured using the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) of the Endeavour, Currie will maneuver the robot arm to dock the FGB to the conical mating adapter at the top of Node 1, to be carried in the Endeavour's cargo bay. In ensuing days, three Extravehicular Activity?s (EVA) by Ross and Newman will be performed to make power, data and utility connections between the two modules. Looking on is Scott A. Bleisath (behind Currie), with the EVA Systems Group at JSC.

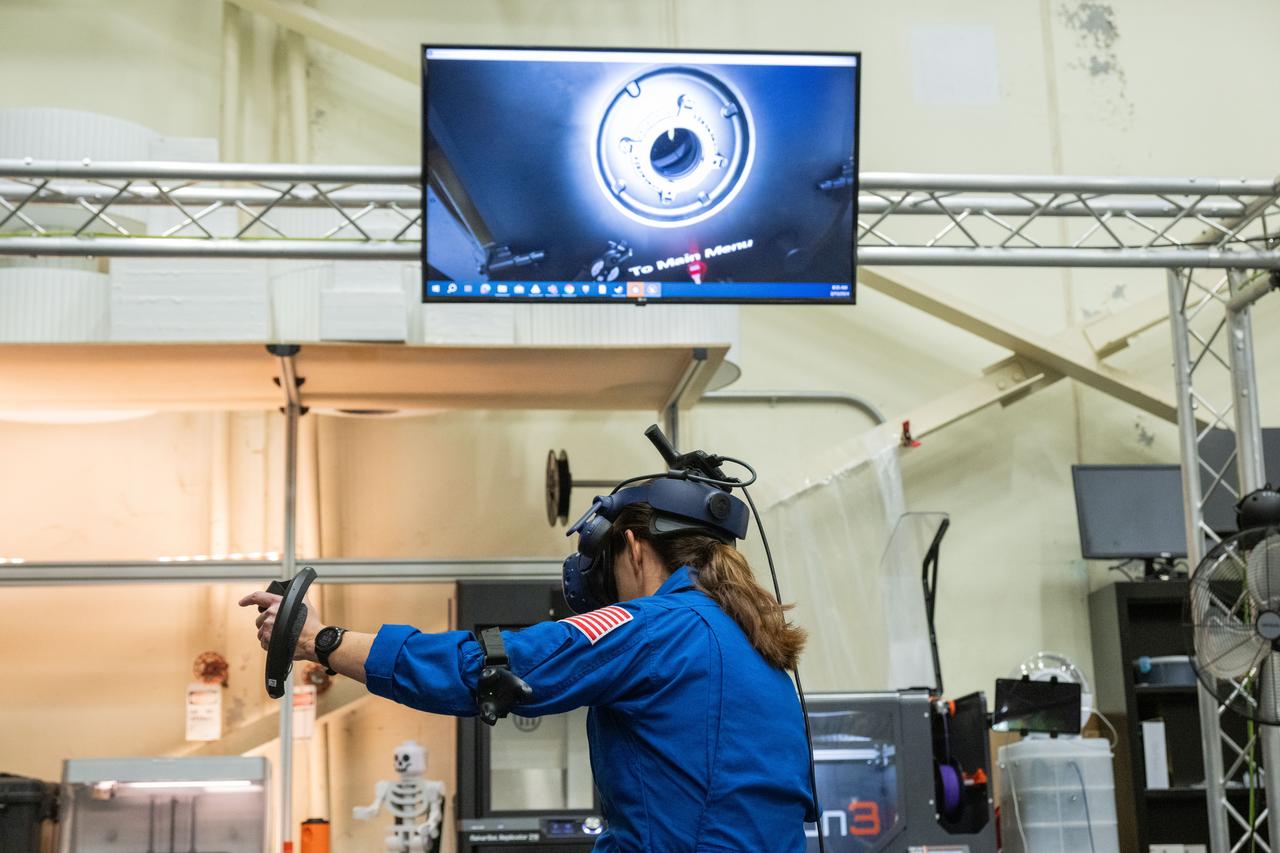
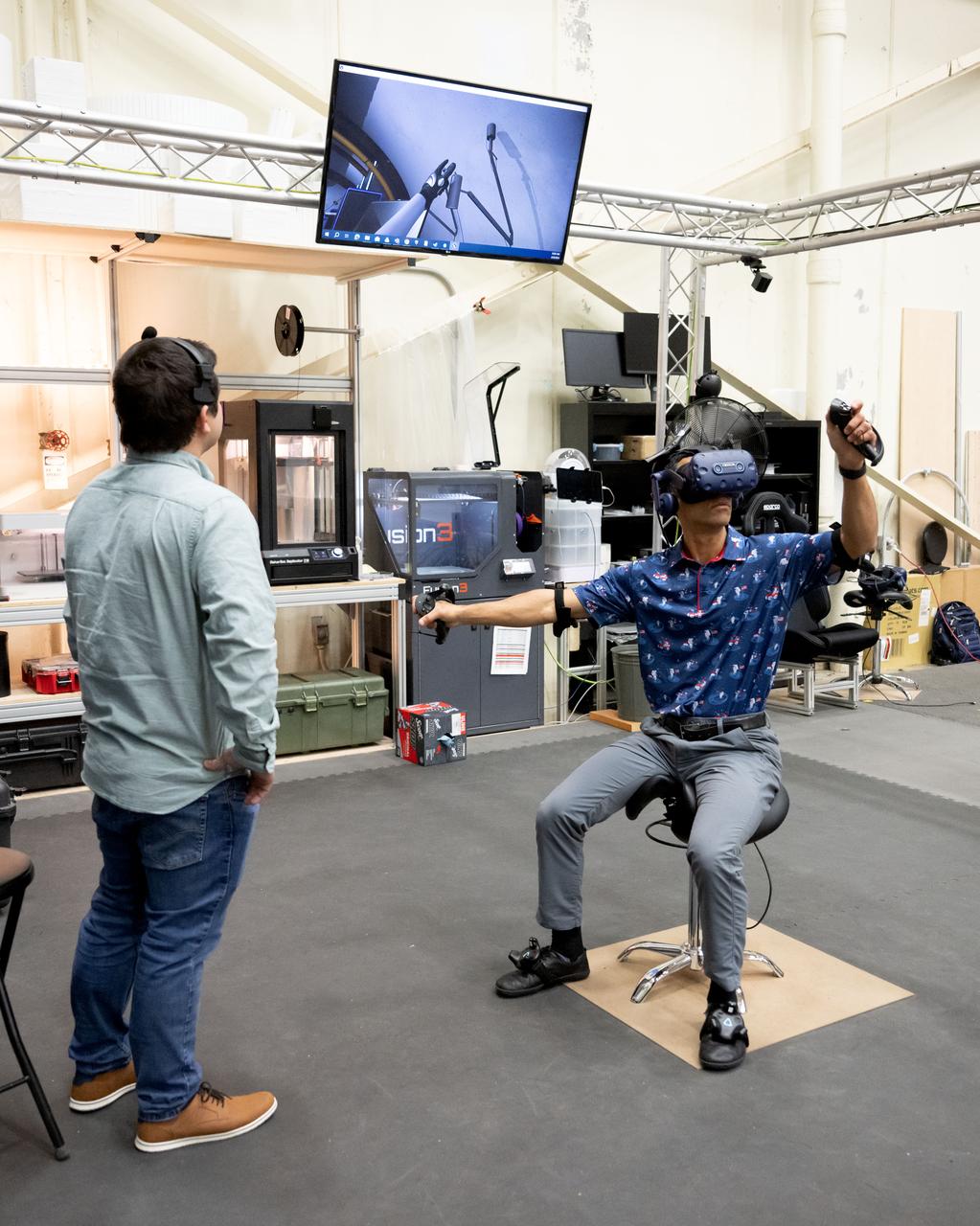
JSC2010-E-170877 (1 Oct. 2010) --- A large monitor is featured in this image during STS-133 crew members? training activities in the virtual reality laboratory in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
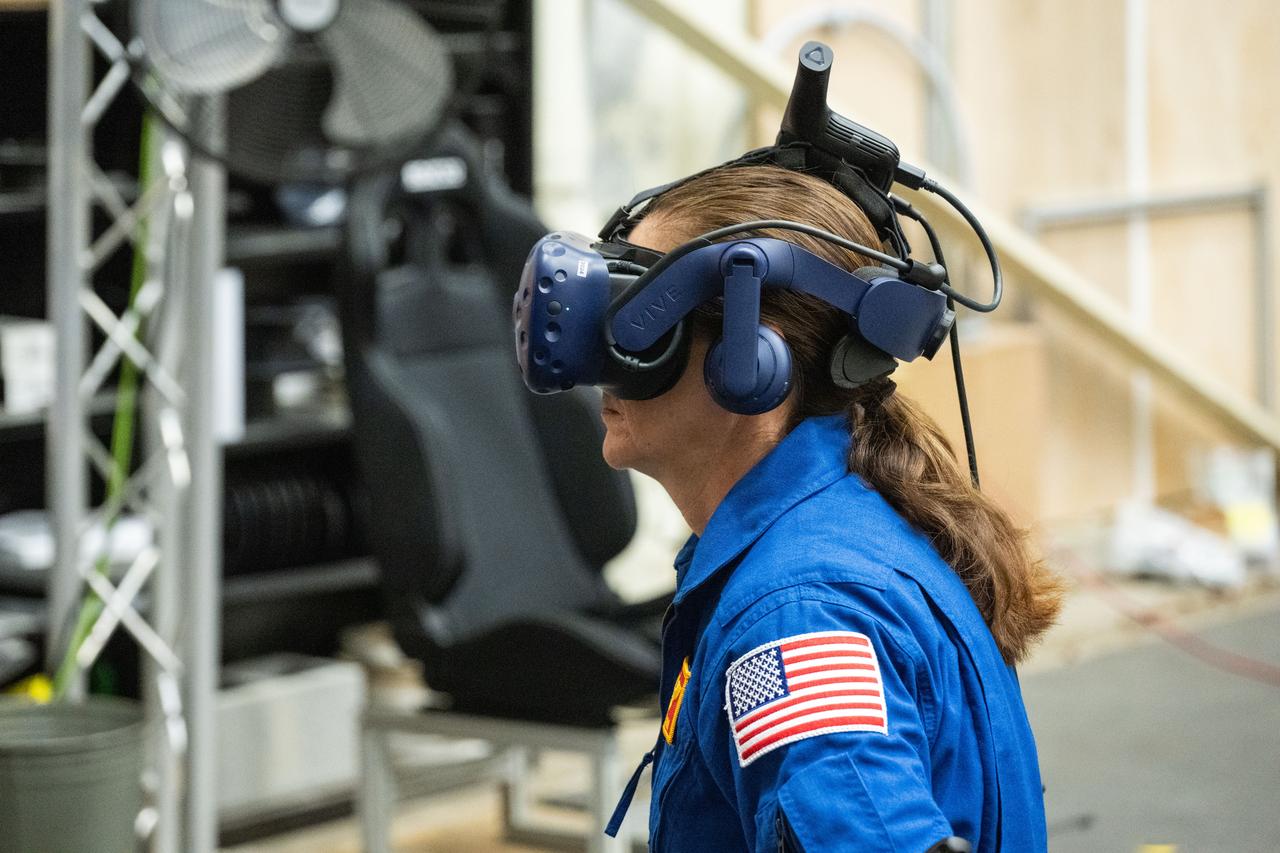

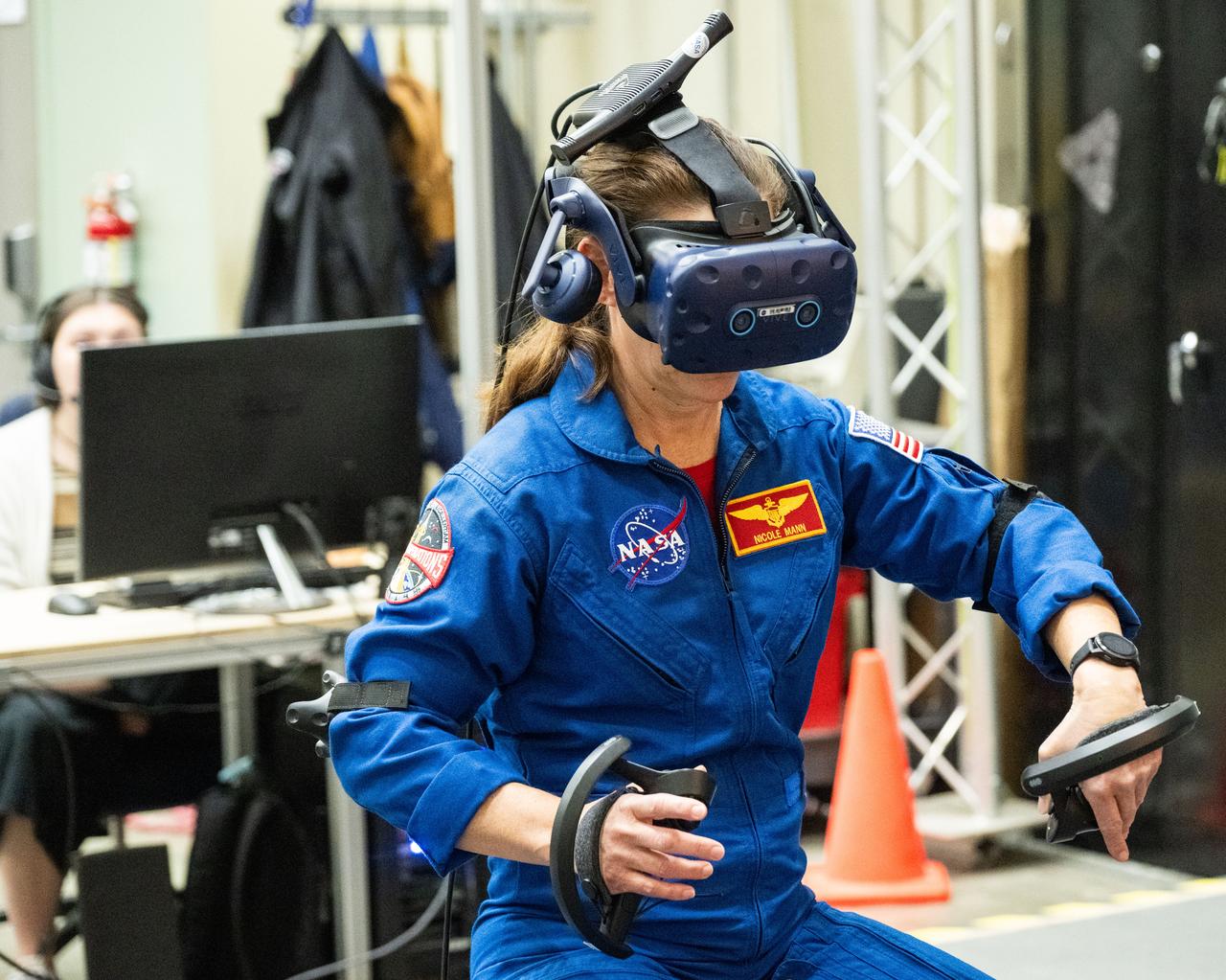
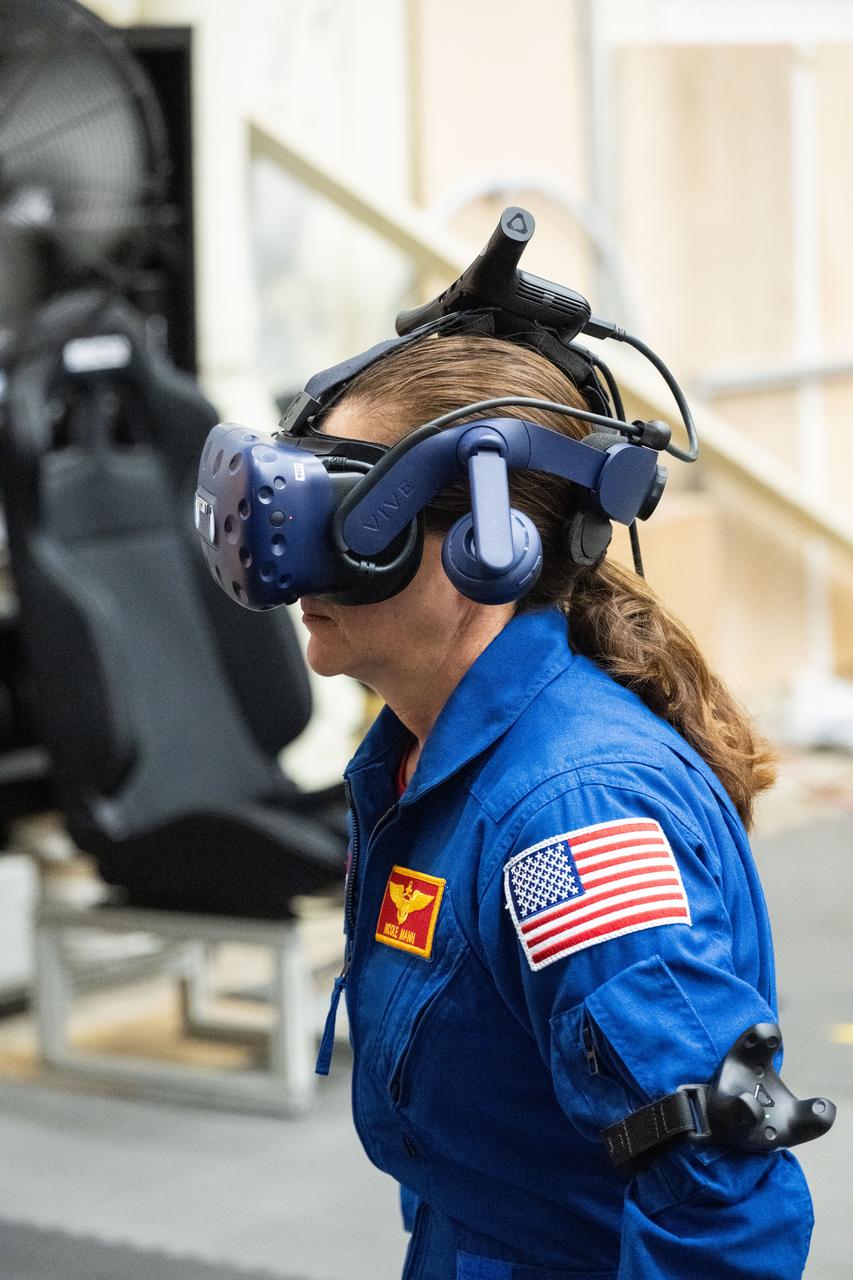
NASA astronaut Nicole Mann participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: 02-13-24 LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: Photographic support for Gateway Web Feature: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Nicole Mann PHOTOGRAPHER: Photo Credit: NASA / Bill Stafford
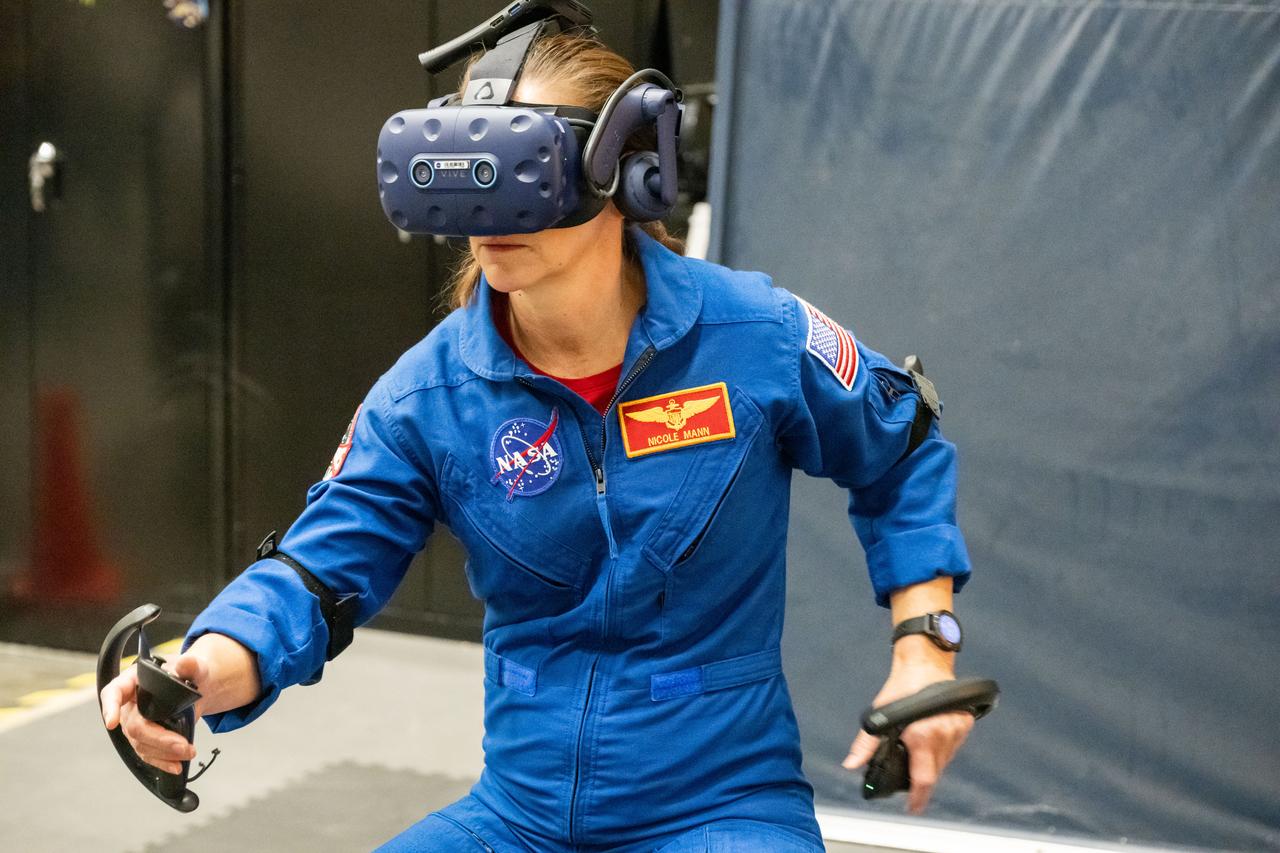

NASA astronaut Nicole Mann participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: 02-13-24 LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: Photographic support for Gateway Web Feature: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Nicole Mann PHOTOGRAPHER: Photo Credit: NASA / Bill Stafford

NASA astronaut Nicole Mann participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: 02-13-24 LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: Photographic support for Gateway Web Feature: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Nicole Mann PHOTOGRAPHER: Photo Credit: NASA / Bill Stafford

NASA astronaut Raja Chari participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: February 09, 2022. LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Raja Chari. Photo Credit: NASA / Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Raja Chari participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: February 09, 2022. LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Raja Chari. Photo Credit: NASA / Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Raja Chari participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: February 09, 2022. LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Raja Chari. Photo Credit: NASA / Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Raja Chari participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: February 09, 2022. LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Raja Chari. Photo Credit: NASA / Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Nicole Mann participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: 02-13-24 LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: Photographic support for Gateway Web Feature: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Nicole Mann PHOTOGRAPHER: Photo Credit: NASA / Bill Stafford

NASA astronaut Raja Chari participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: February 09, 2022. LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Raja Chari. Photo Credit: NASA / Josh Valcarcel
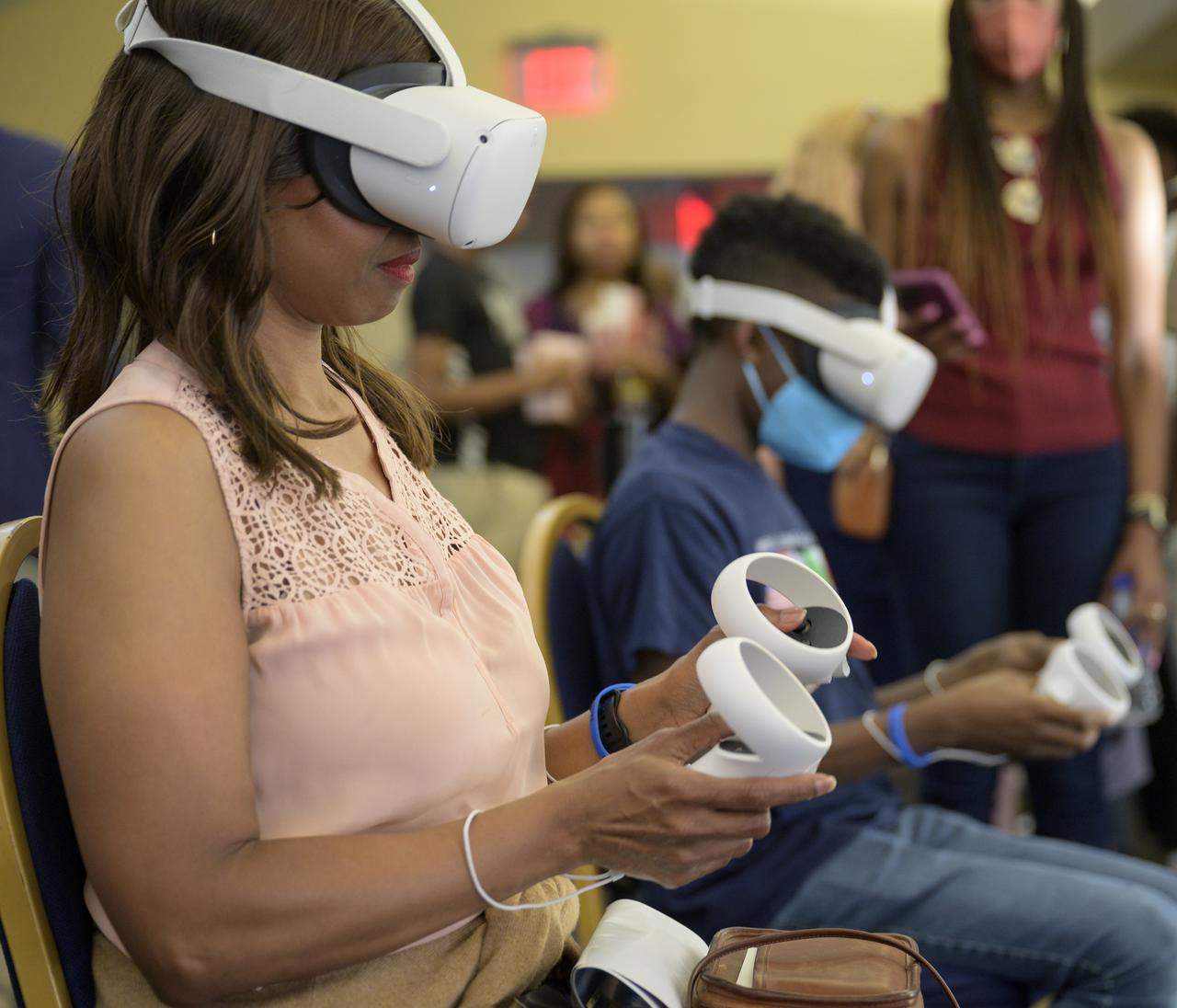

Attendees try on Oculus headsets and experience the International Space Station using virtual reality prior to the screening of the NASA produced documentary “The Color of Space” at Howard University’s Cramton Auditorium in Washington, Saturday, June 18, 2022. Premiering on Juneteenth, the federal holiday commemorating the end of slavery in the United States, “The Color of Space” is an inspirational documentary that tells the stories of NASA’s Black astronauts determined to reach the stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA astronaut Nicole Mann participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: 02-13-24 LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: Photographic support for Gateway Web Feature: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Nicole Mann PHOTOGRAPHER: Photo Credit: NASA / Bill Stafford

NASA astronaut Raja Chari participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: February 09, 2022. LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Raja Chari. Photo Credit: NASA / Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Nicole Mann participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: 02-13-24 LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: Photographic support for Gateway Web Feature: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Nicole Mann PHOTOGRAPHER: Photo Credit: NASA / Bill Stafford
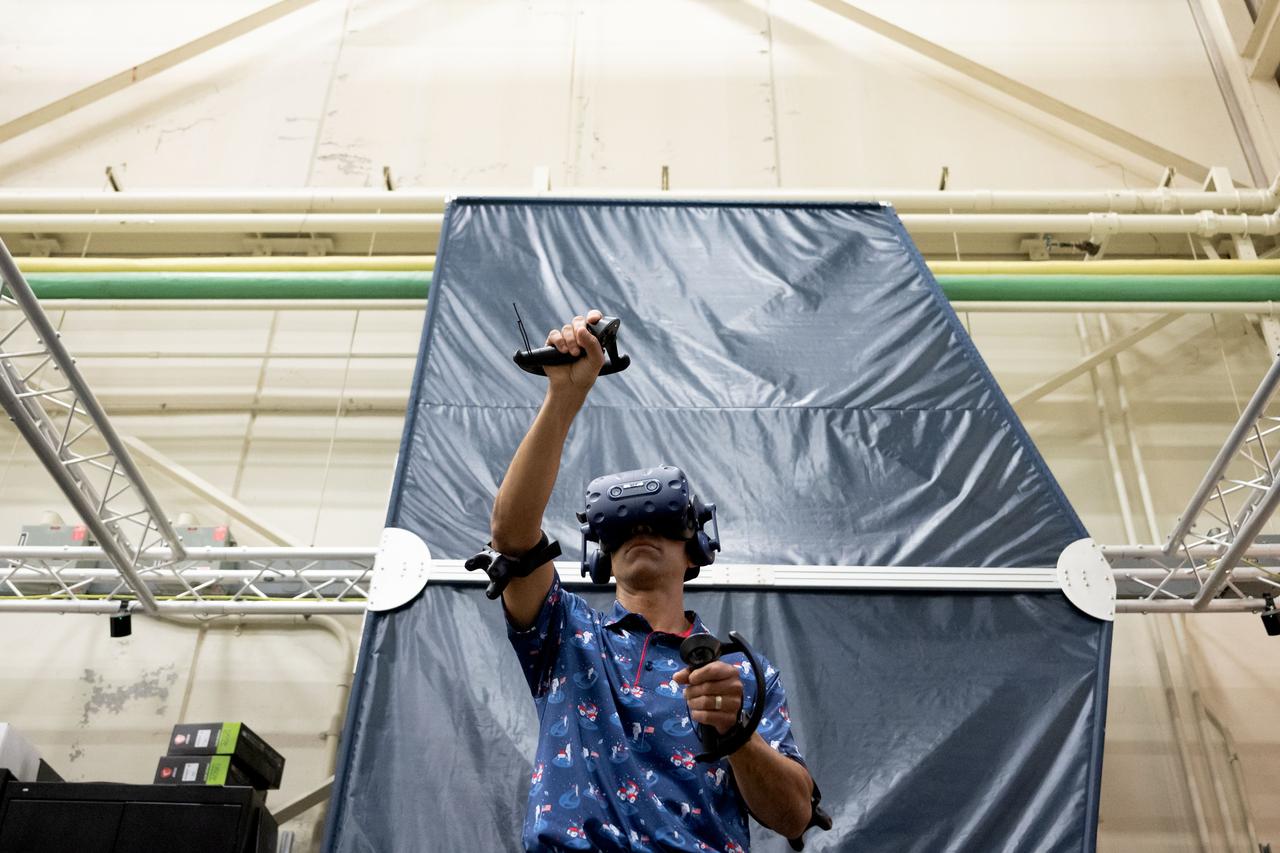

NASA astronaut Raja Chari participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: February 09, 2022. LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Raja Chari. Photo Credit: NASA / Josh Valcarcel
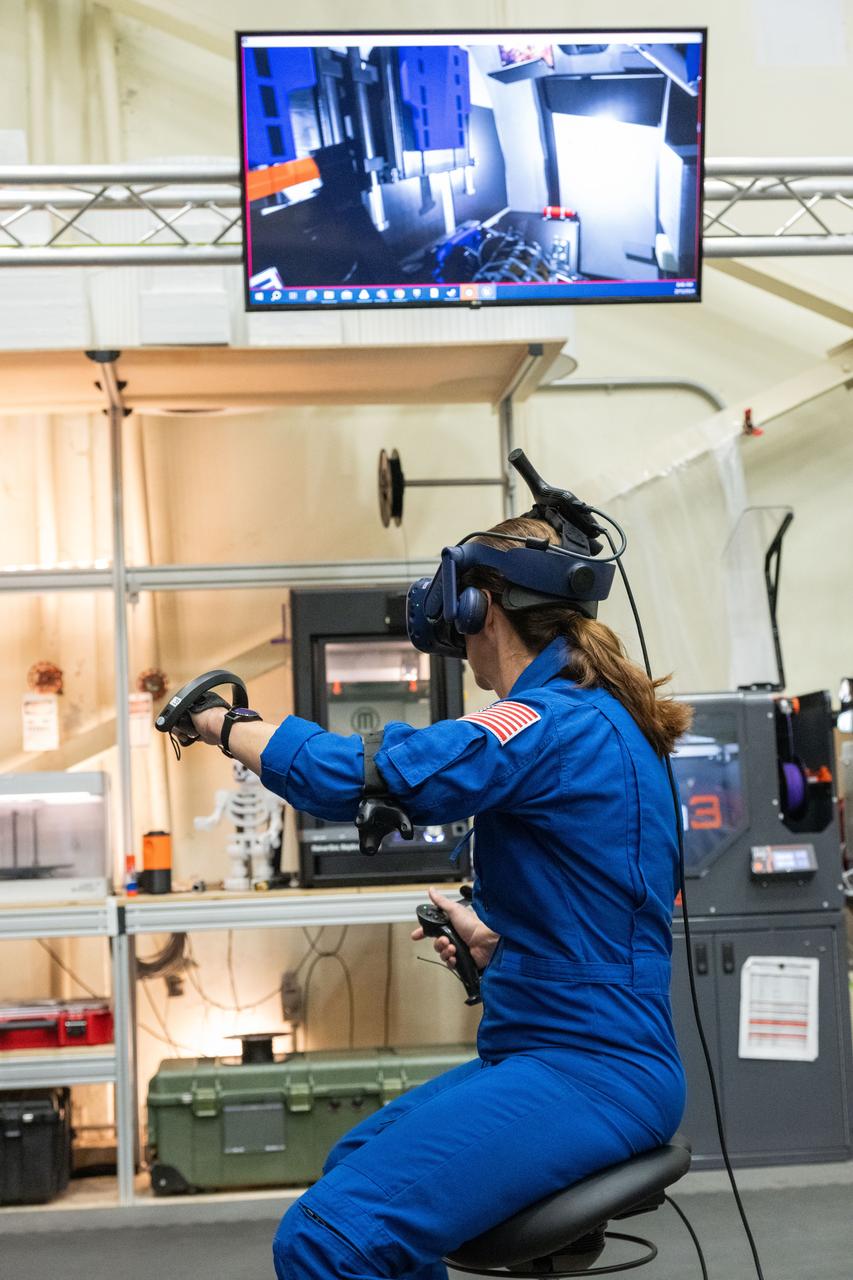

NASA astronaut Nicole Mann participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: 02-13-24 LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: Photographic support for Gateway Web Feature: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Nicole Mann PHOTOGRAPHER: Photo Credit: NASA / Bill Stafford
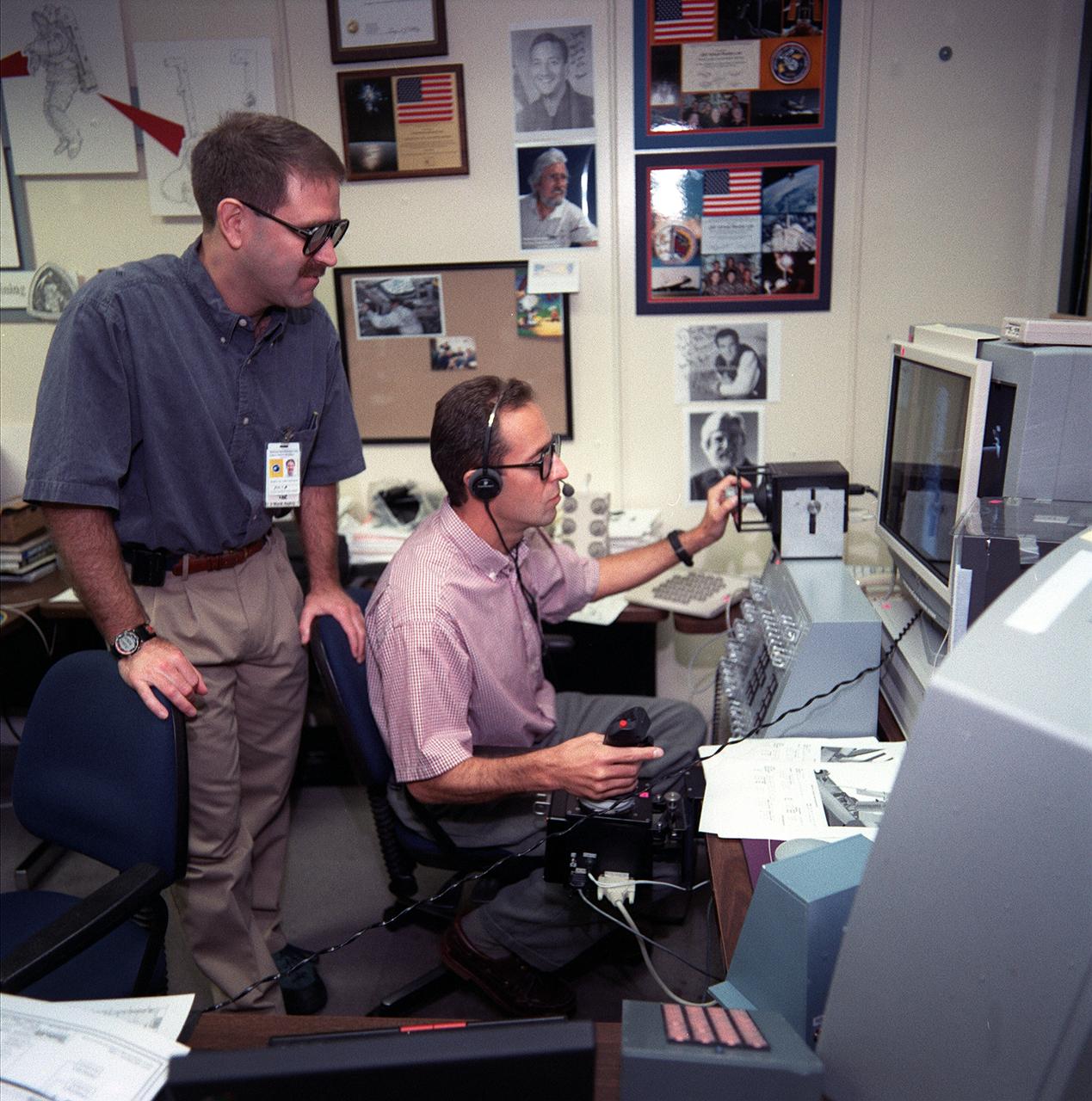

S99-05678 (24 May 1999)--- Astronaut Jean-Francois Clervoy (right), STS-103 mission specialist representing the European Space Agency (ESA), "controls" the shuttle's remote manipulator system (RMS) during a simulation using virtual reality type hardware at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Looking on is astronaut John M. Grunsfeld, mission specialist. Both astronauts are assigned to separate duties supporting NASA's third Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission. Clervoy will be controlling Discovery's RMS and Grunsfeld is one of four astronauts that will be paired off for a total of three spacewalks on the mission.
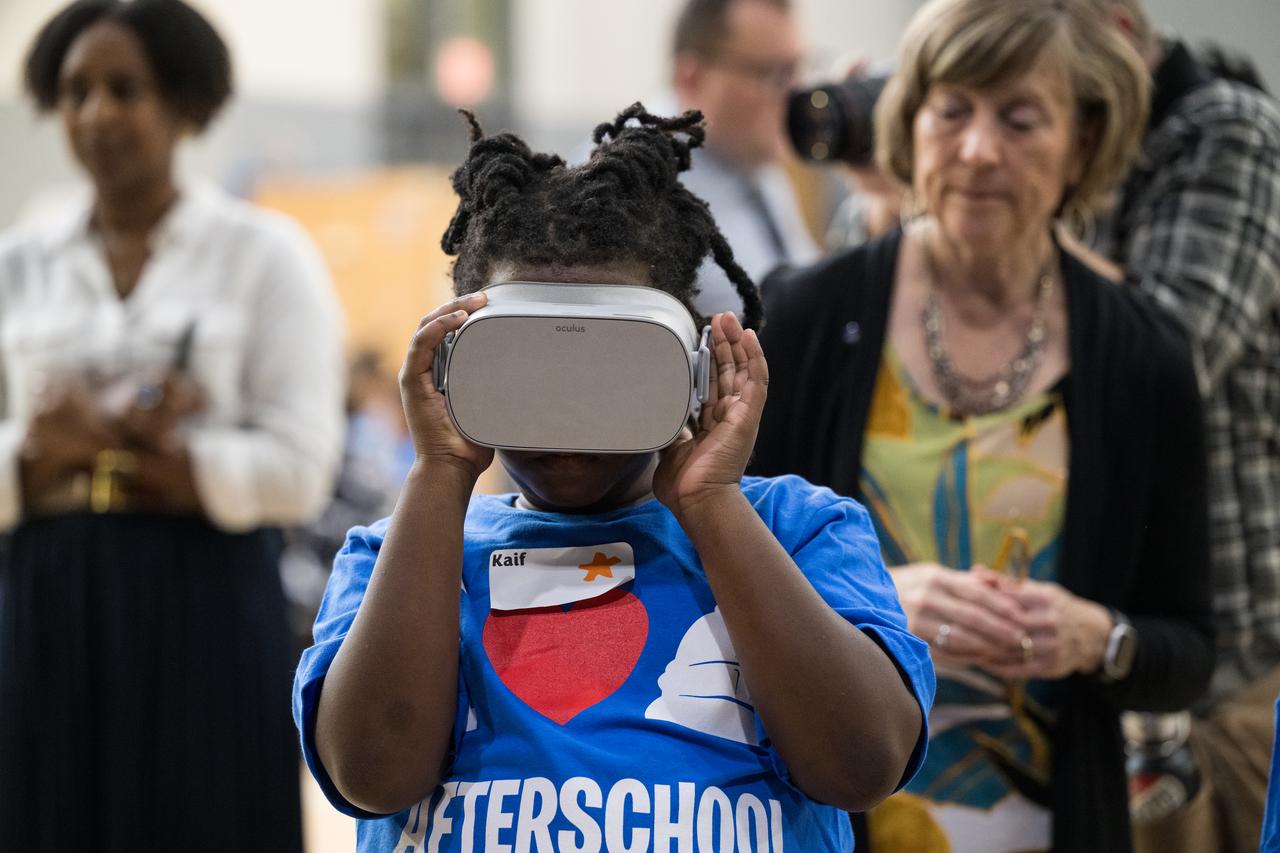

Students at Wheatley Education Campus participate in a virtual reality tour of NASA’s Neutral Buoyancy Lab during a kickoff event for the 21st Century Community Learning Centers NASA and Department of Education partnership, Monday, Sept. 23, 2024 at Wheatley Education Campus in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
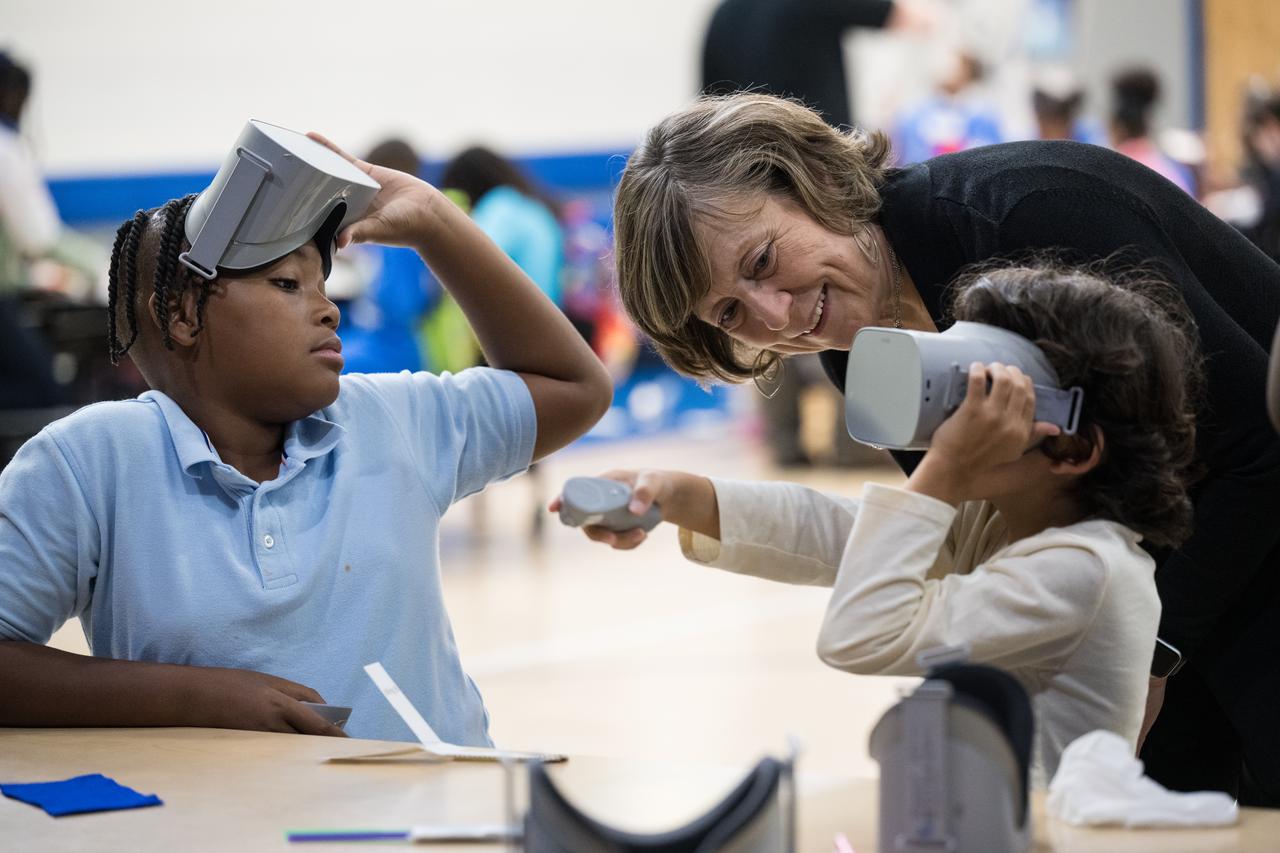

Students at Wheatley Education Campus participate in a virtual reality tour of NASA’s Neutral Buoyancy Lab during a kickoff event for the 21st Century Community Learning Centers NASA and Department of Education partnership, Monday, Sept. 23, 2024 at Wheatley Education Campus in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
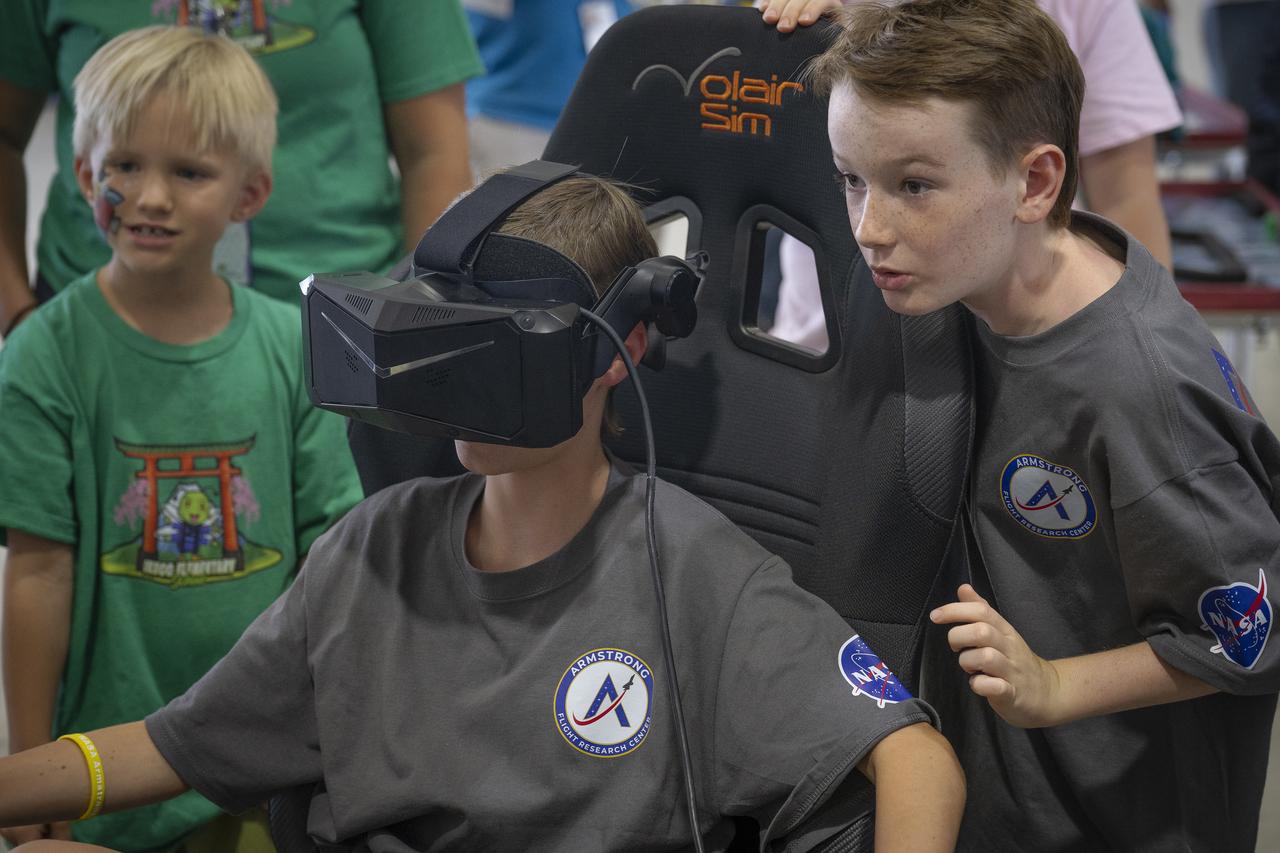

Children explore a virtual reality flight simulator during Bring Kids to Work Day on June 17, 2025, at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The immersive experience introduced participants to aerospace engineering and flight research in an engaging, hands-on environment.
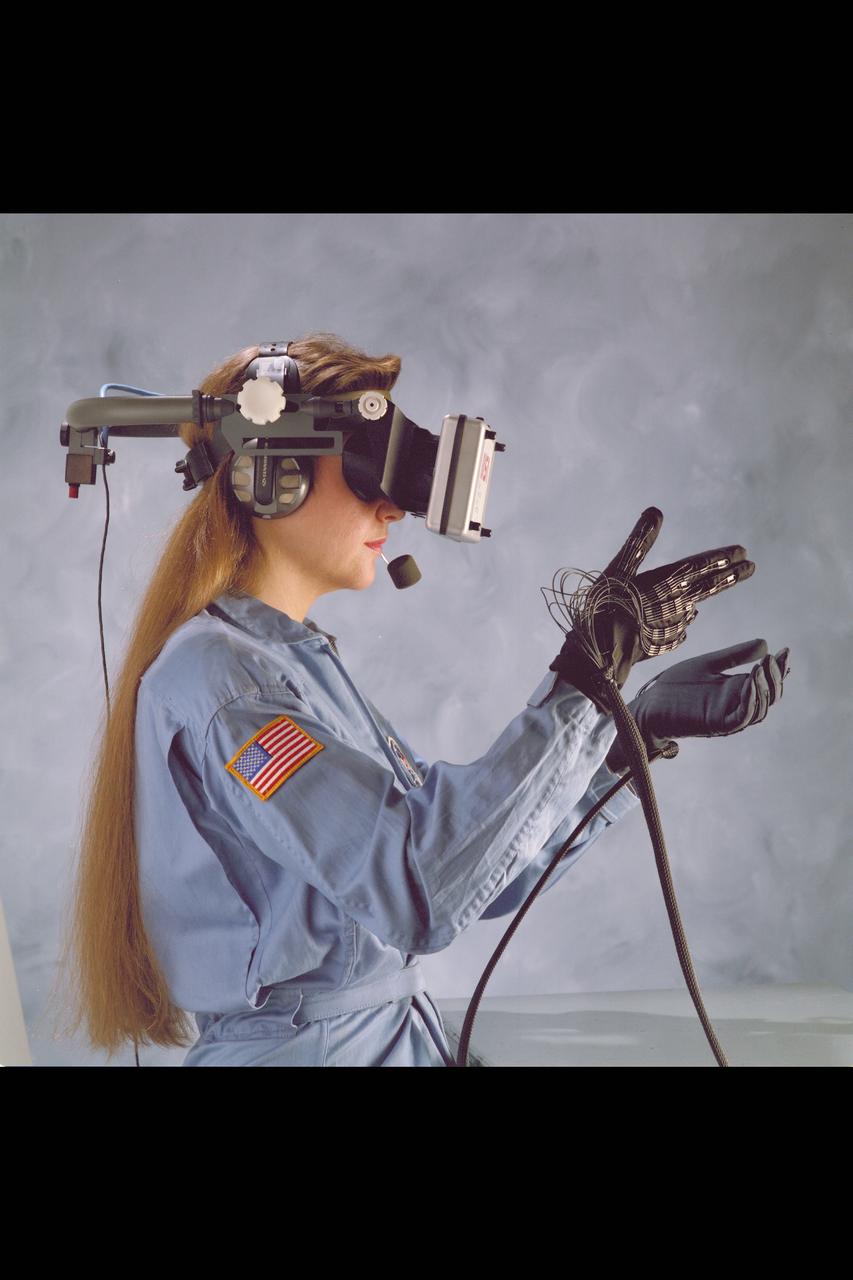

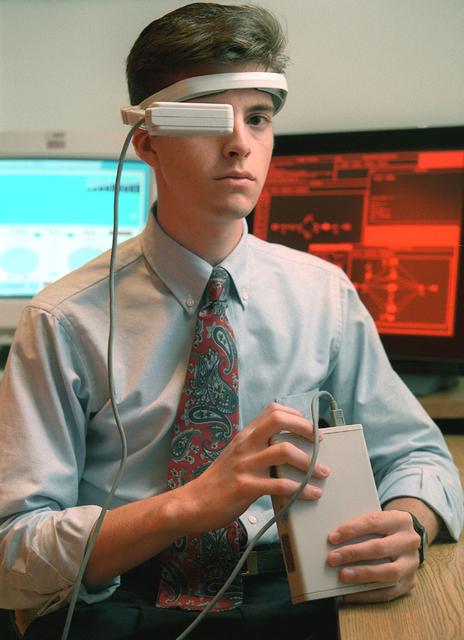
Virtual Environment Reality workstation technology (helmet & gloves)
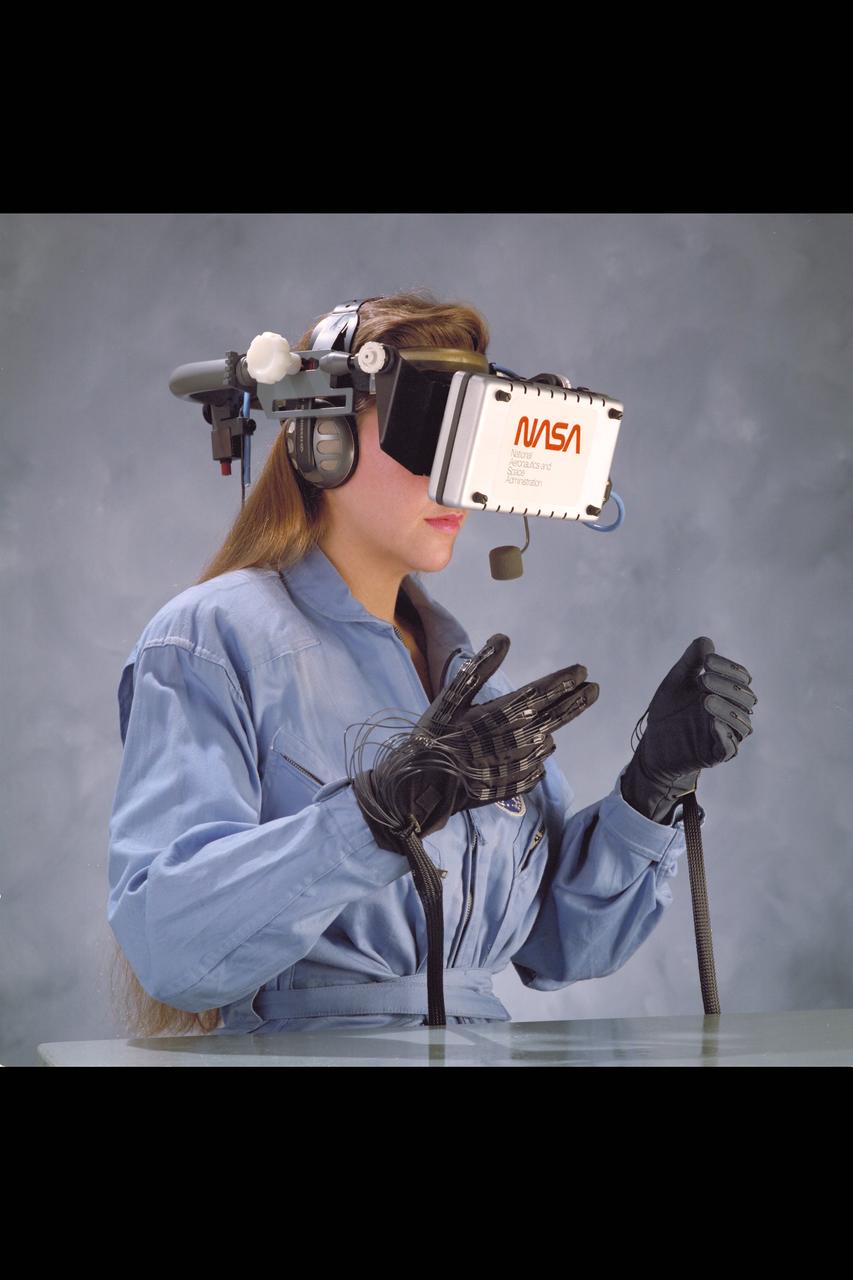

Virtual Environment Reality workstation technology (helmet & gloves)
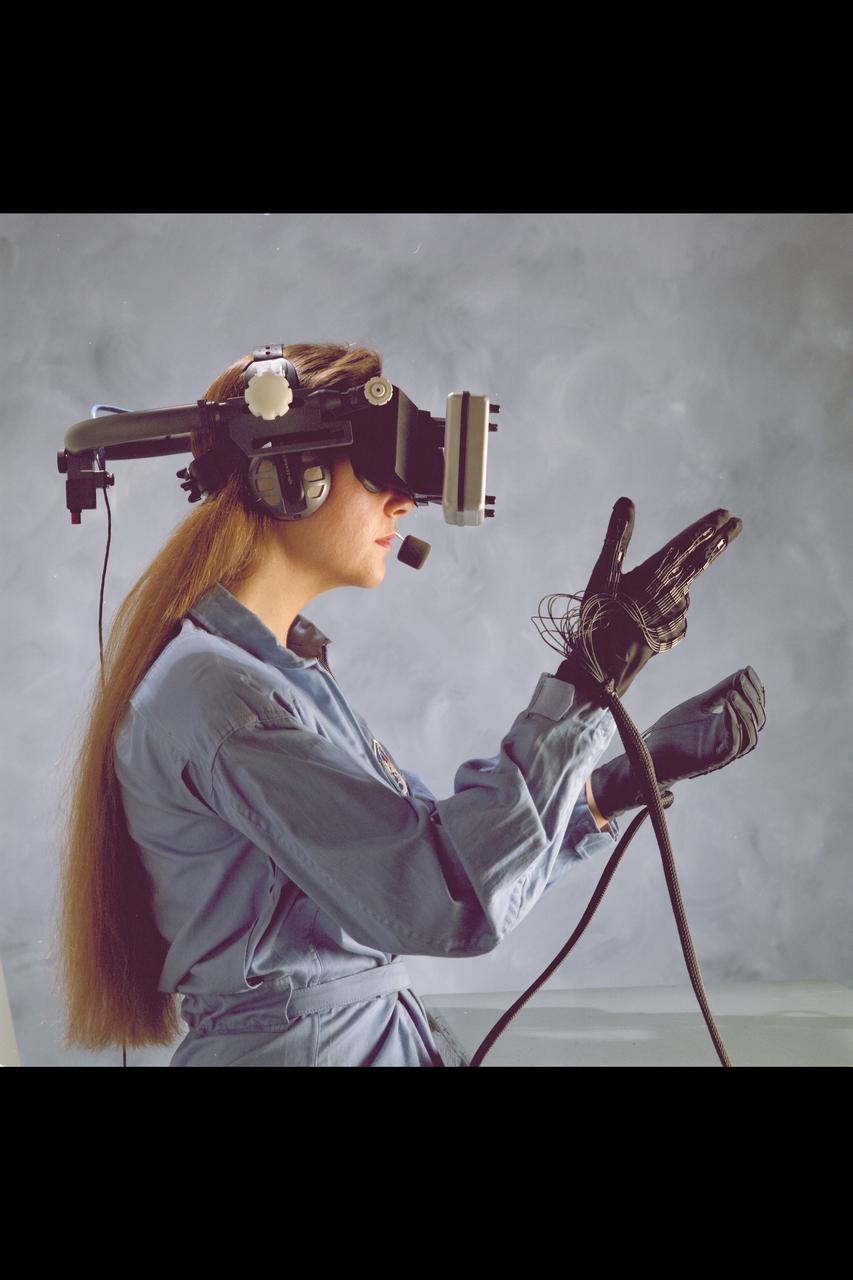

Virtual Environment Reality workstation helmet and gloves
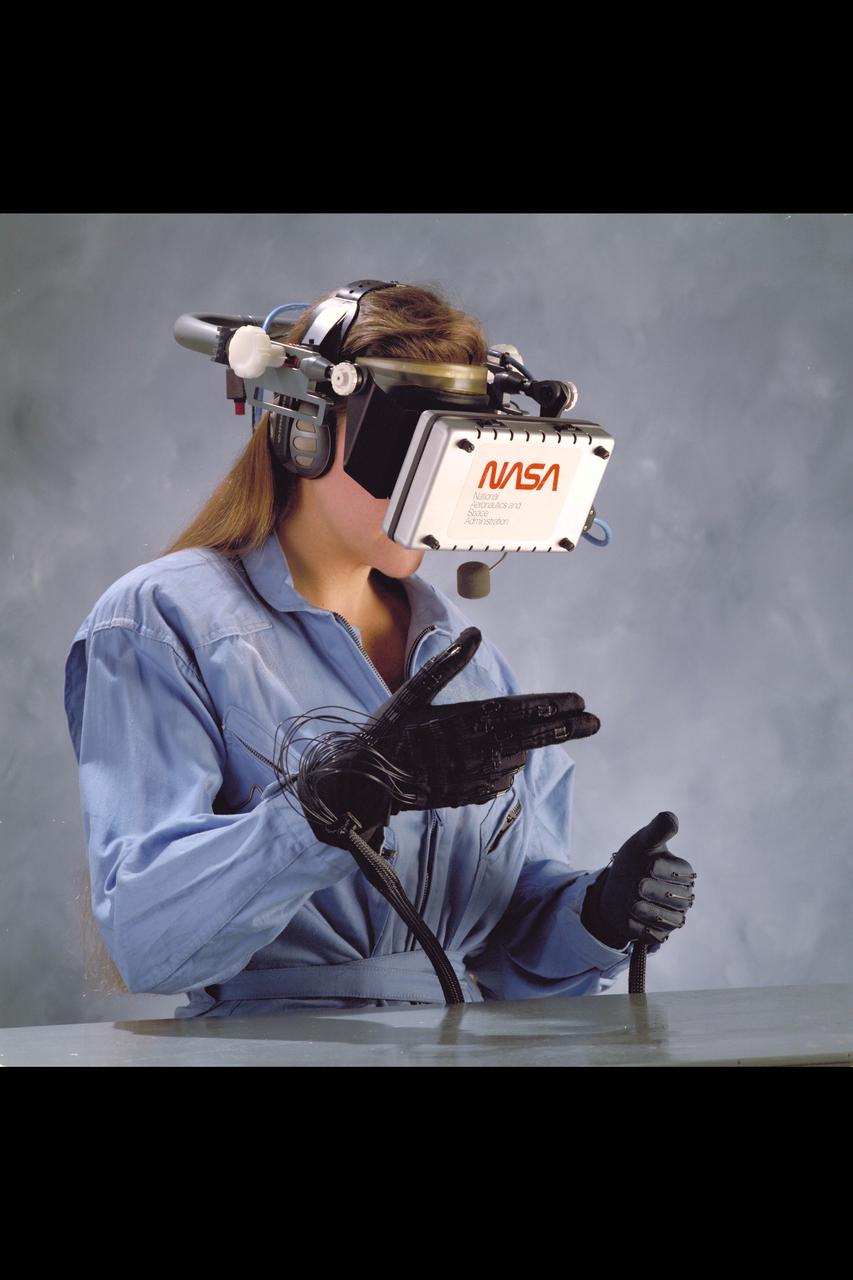

Virtual Environment Reality workstation technology (helmet & gloves)
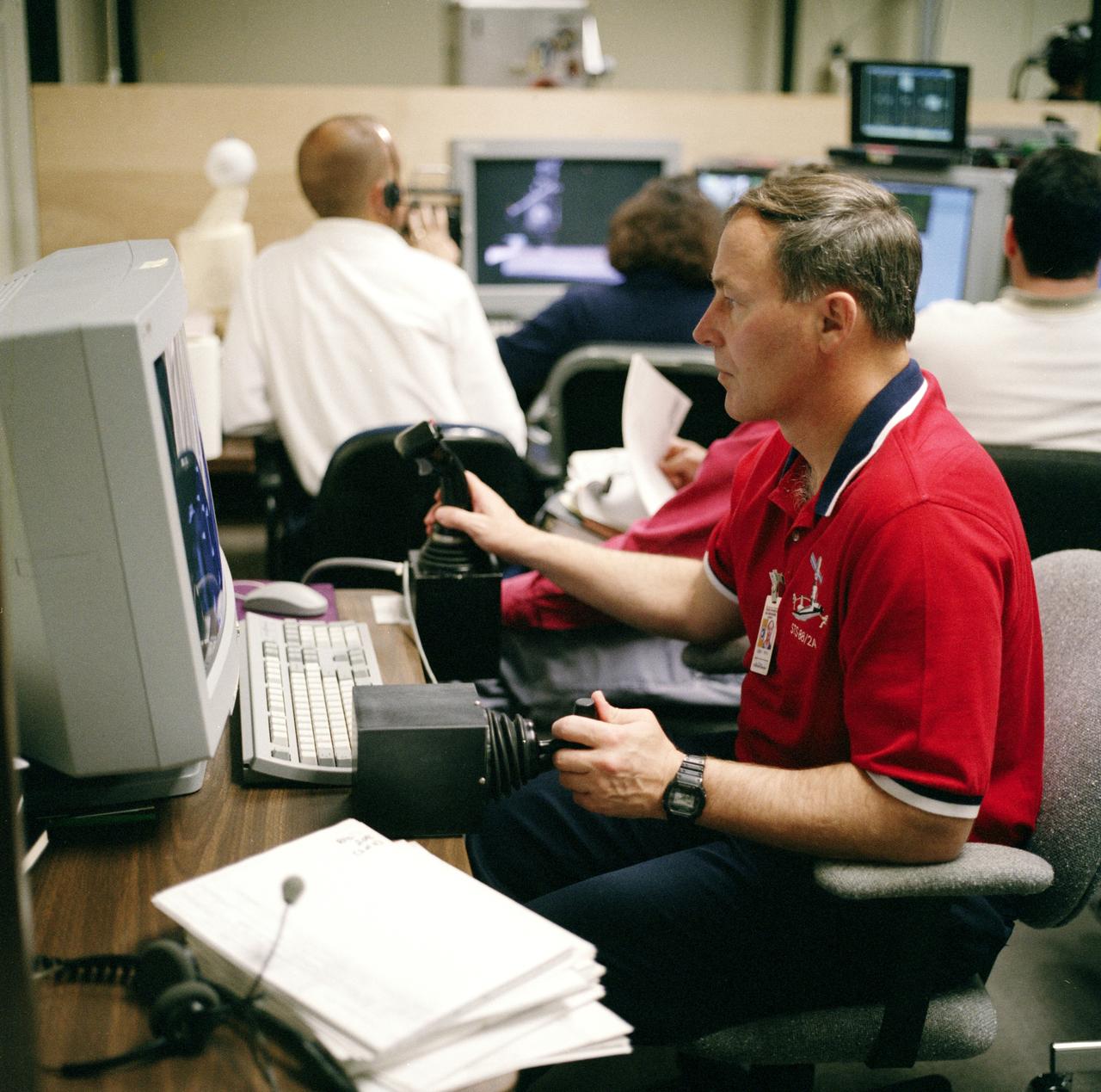

S98-05074 (8 Apr. 1998) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, assigned as a mission specialist for the mission, uses special gear and software to train for his duties aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. This type virtual reality training supplements practice for each of the assigned space-walking astronauts -- Ross and James H. Newman -- during which they wear a helmet and special gloves to look at computer displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the early International Space Station (ISS) hardware with which they'll be working. One of those elements will be the Functional Cargo Block (FGB), which will have been launched a couple of weeks prior to STS-88. Once the FGB is captured using the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) of the Endeavour, astronaut Nancy J. Currie will maneuver the robot arm to dock the FGB to the conical mating adapter at the top of Node 1, to be carried in the Shuttle's cargo bay. In ensuing days, three space walks by Ross and Newman will be performed to make power, data and utility connections between the two modules. Currie also uses this same lab to train for her RMS controlling duties.
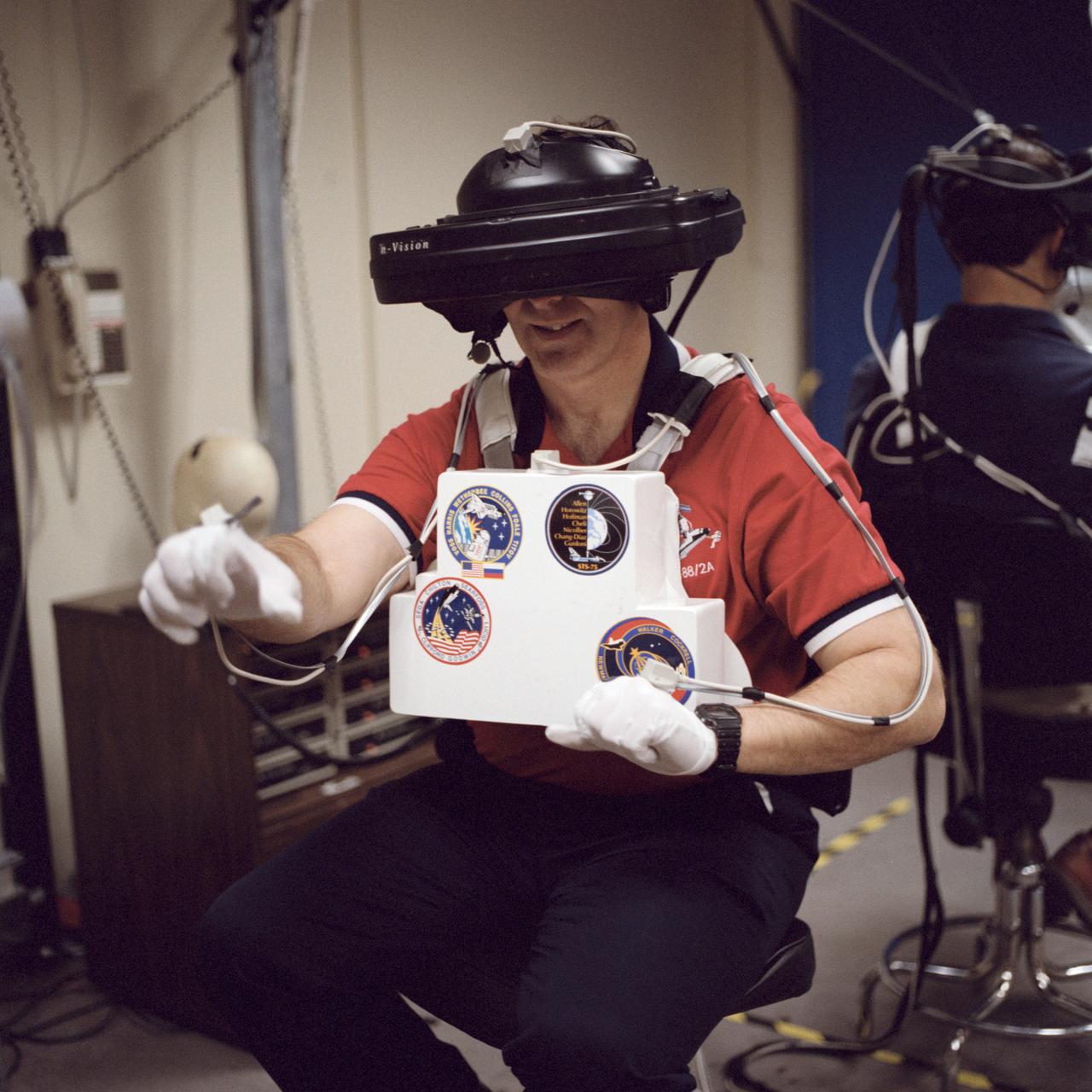

S98-05079 (8 Apr. 1998) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, assigned as a mission specialist for the mission, uses specialized gear to train for his duties aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. This type virtual reality training allows each of the assigned Extravehicular Activity (EVA) astronauts -- Ross and James H. Newman -- to wear a helmet and special gloves to look at computer displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the International Space Station (ISS) hardware with which they'll be working. One of those elements will be the Functional Cargo Block (FGB), which will have been launched a couple of weeks prior to STS-88. Once the FGB is captured using the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) of the Endeavour, astronaut Nancy J. Currie will maneuver the robot arm to dock the FGB to the conical mating adapter at the top of Node 1, to be carried in the Shuttle's cargo bay. In ensuing days, three EVA space walks by Ross and Newman will be performed to make power, data and utility connections between the two modules. Currie also uses this same lab to train for her RMS controlling duties.
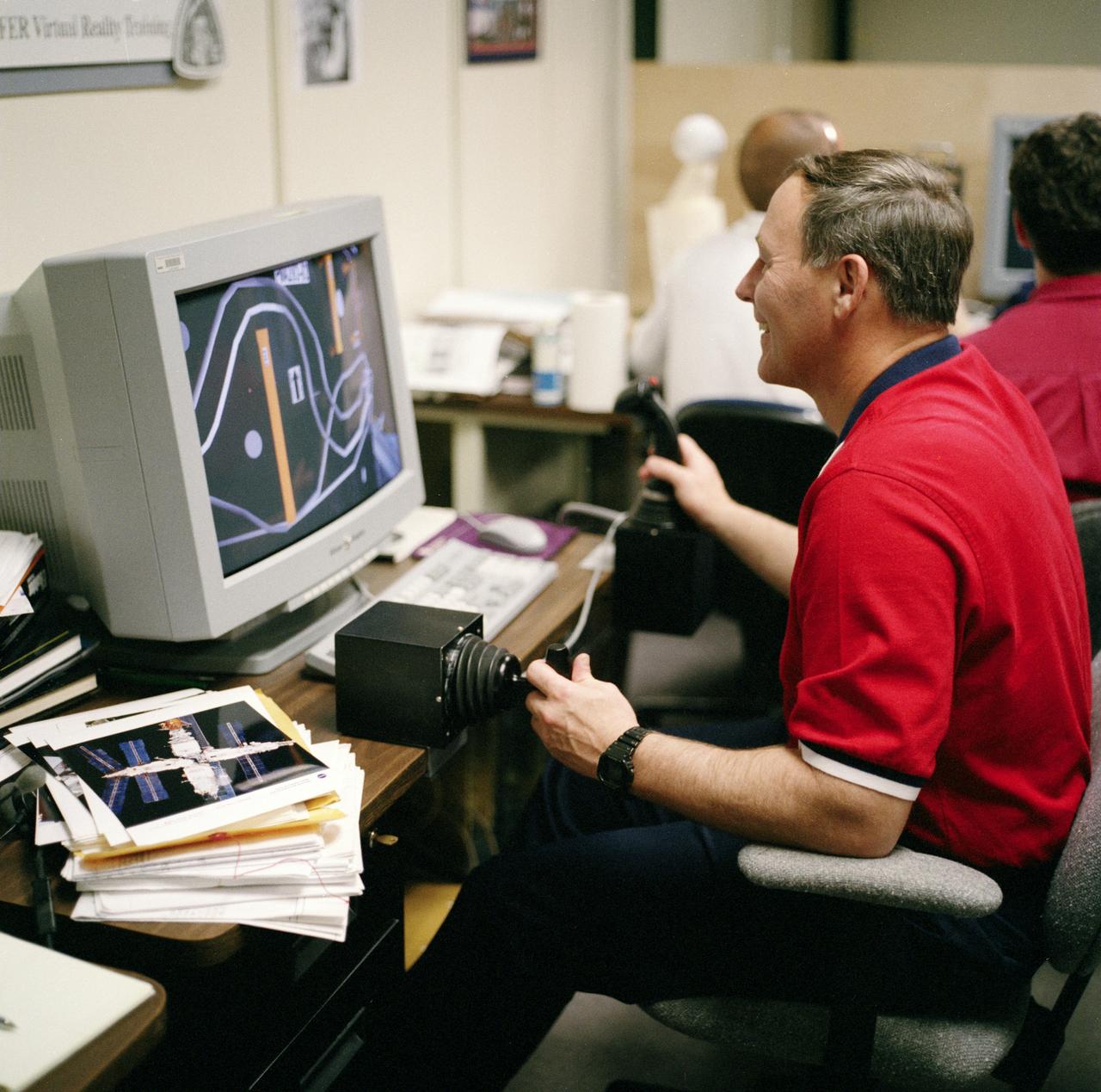

S98-05076 (8 Apr. 1998) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, assigned as a mission specialist for the mission, uses special gear and software to train for his duties aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. This type virtual reality training supplements practice for each of the assigned space-walking astronauts -- Ross and James H. Newman -- during which they wear a helmet and special gloves to look at computer displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the early International Space Station (ISS) hardware with which they'll be working. One of those elements will be the Functional Cargo Block (FGB), which will have been launched a couple of weeks prior to STS-88. Once the FGB is captured using the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) of the Endeavour, astronaut Nancy J. Currie will maneuver the robot arm to dock the FGB to the conical mating adapter at the top of Node 1, to be carried in the Shuttle's cargo bay. In ensuing days, three space walks by Ross and Newman will be performed to make power, data and utility connections between the two modules. Currie also uses this same lab to train for her RMS controlling duties.
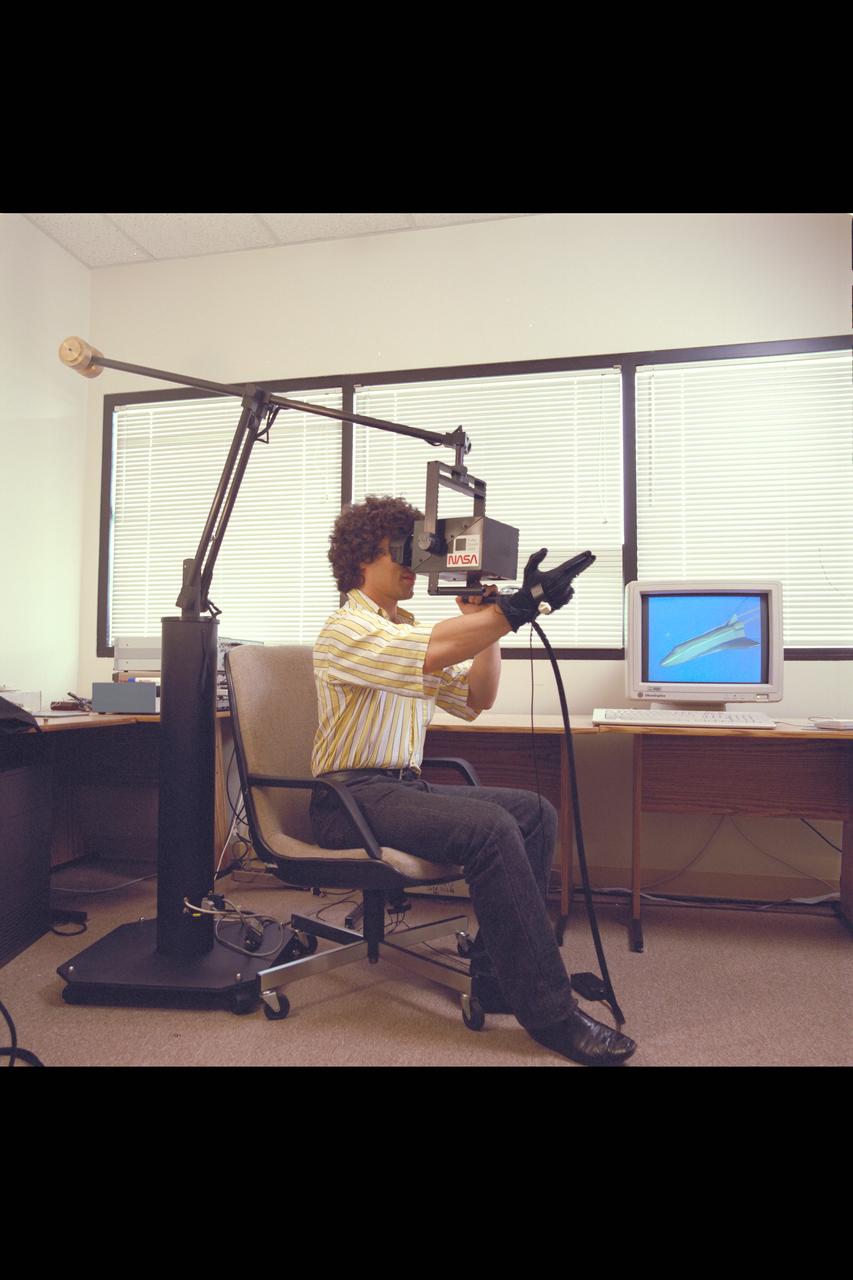

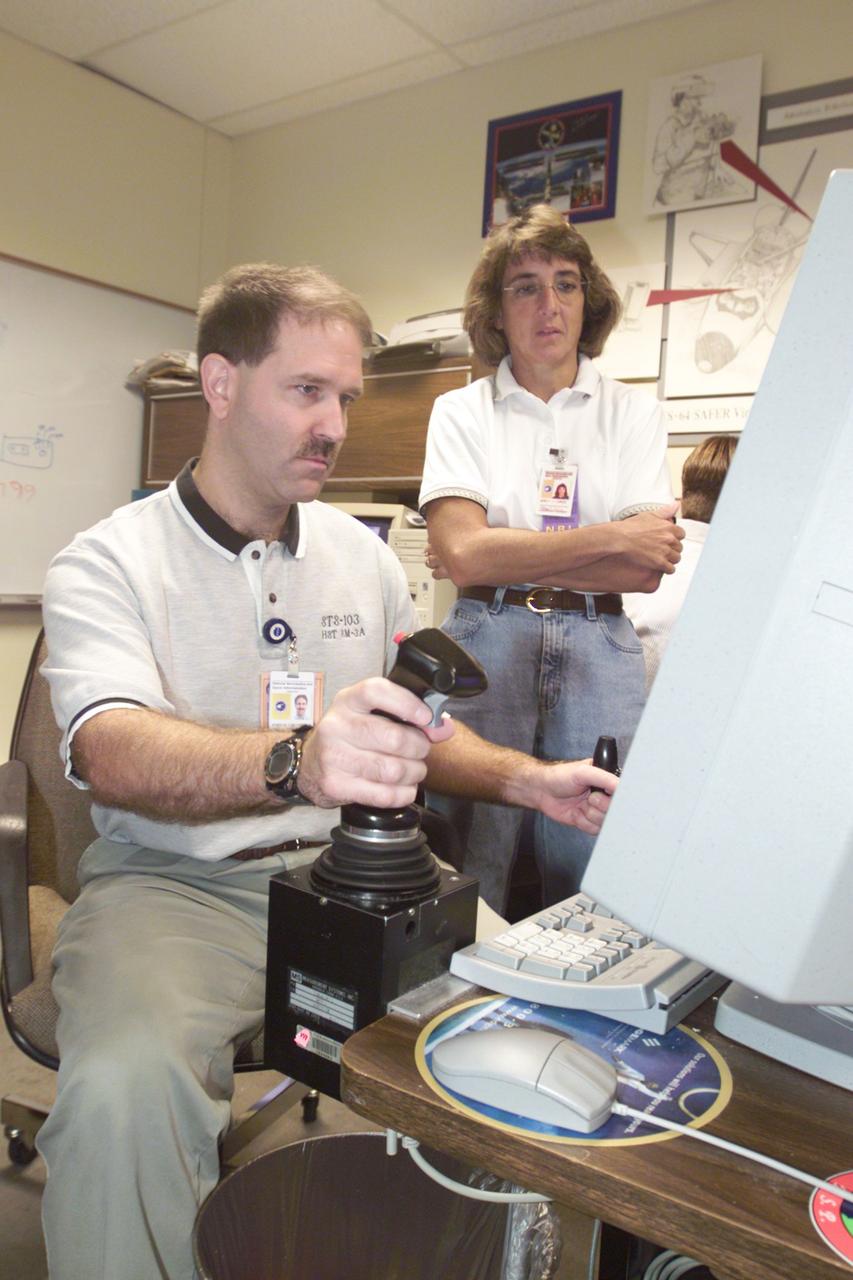
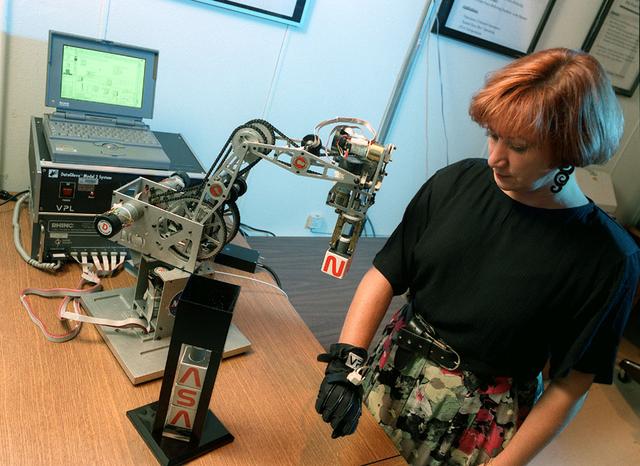
N-258 NAS facility virtual reality workstation, hand-held maneuvering unit , test and virtual environment simulation by Creon Levitt

Expedition 11 Training with Krikalev/Henderson as their continued their training in the Virtual Reality Laboratory in building 9. View includes: Sergei Krikalev and Henderson using the virtual optics to view the International Space Station.

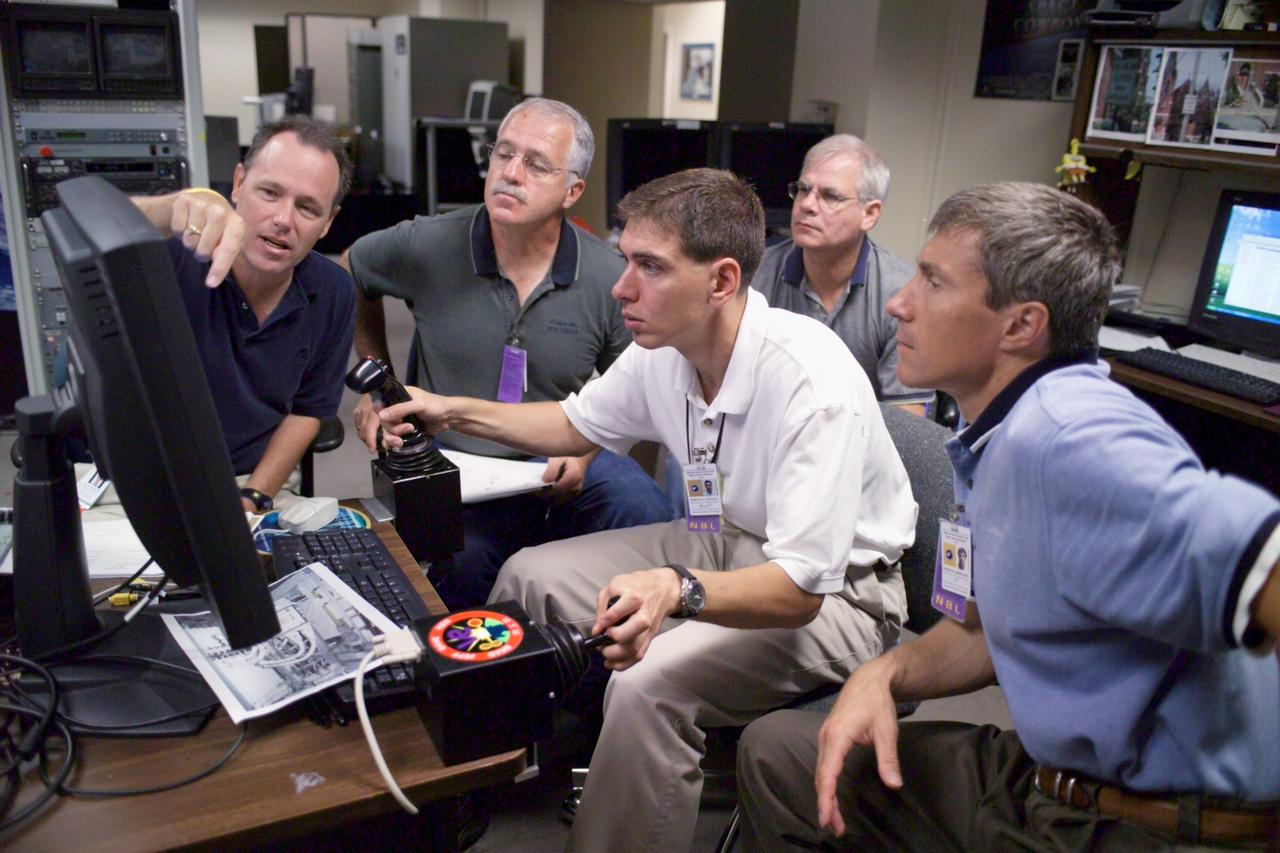
JSC2010-E-043673 (25 March 2010) --- NASA astronauts Gregory H. Johnson, STS-134 pilot; and Shannon Walker, Expedition 24/25 flight engineer, use the virtual reality lab in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to train for some of their duties aboard the space shuttle and space station. This type of computer interface, paired with virtual reality training hardware and software, helps to prepare crew members for dealing with space station elements.
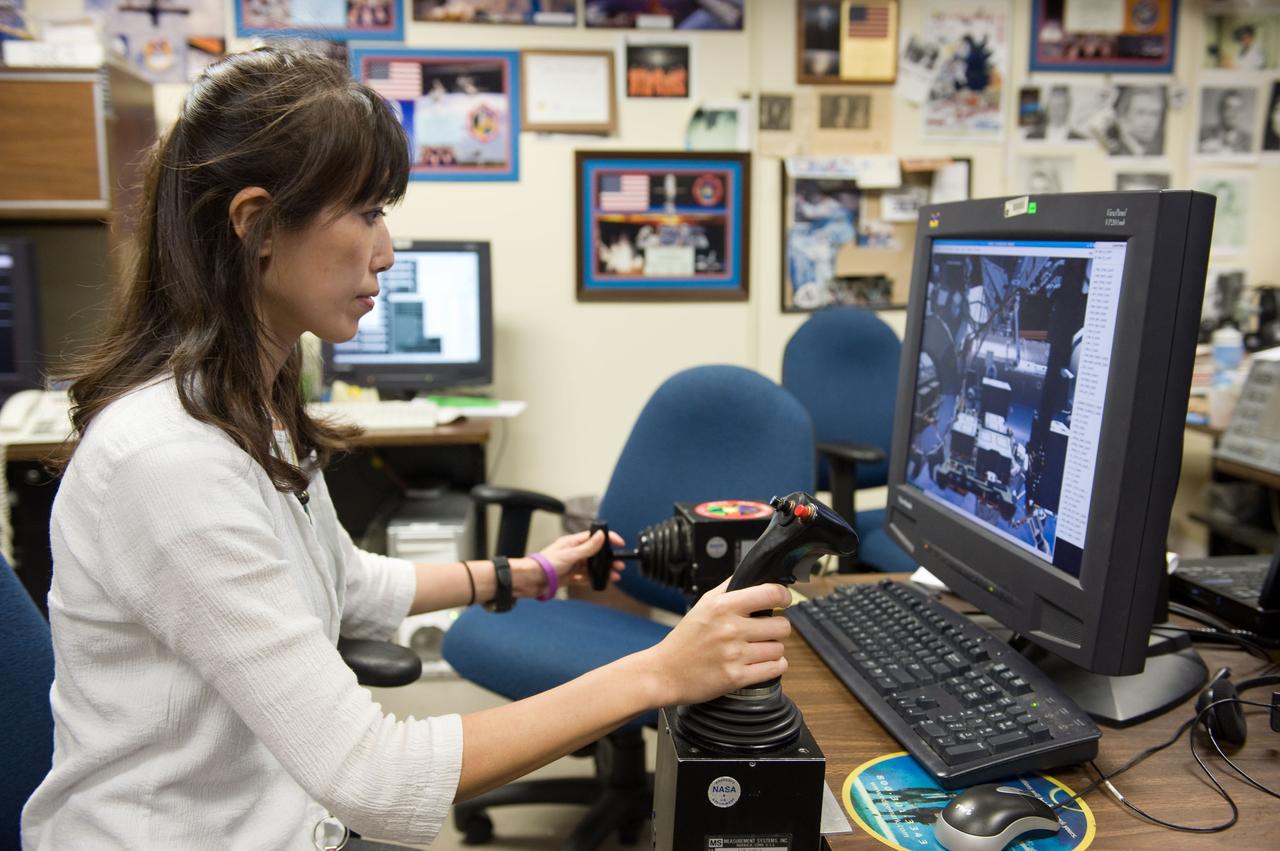

JSC2009-E-214328 (25 Sept. 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Naoko Yamazaki, STS-131 mission specialist, uses the virtual reality lab in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to train for some of her duties aboard the space shuttle and space station. This type of computer interface, paired with virtual reality training hardware and software, helps to prepare the entire team for dealing with space station elements.
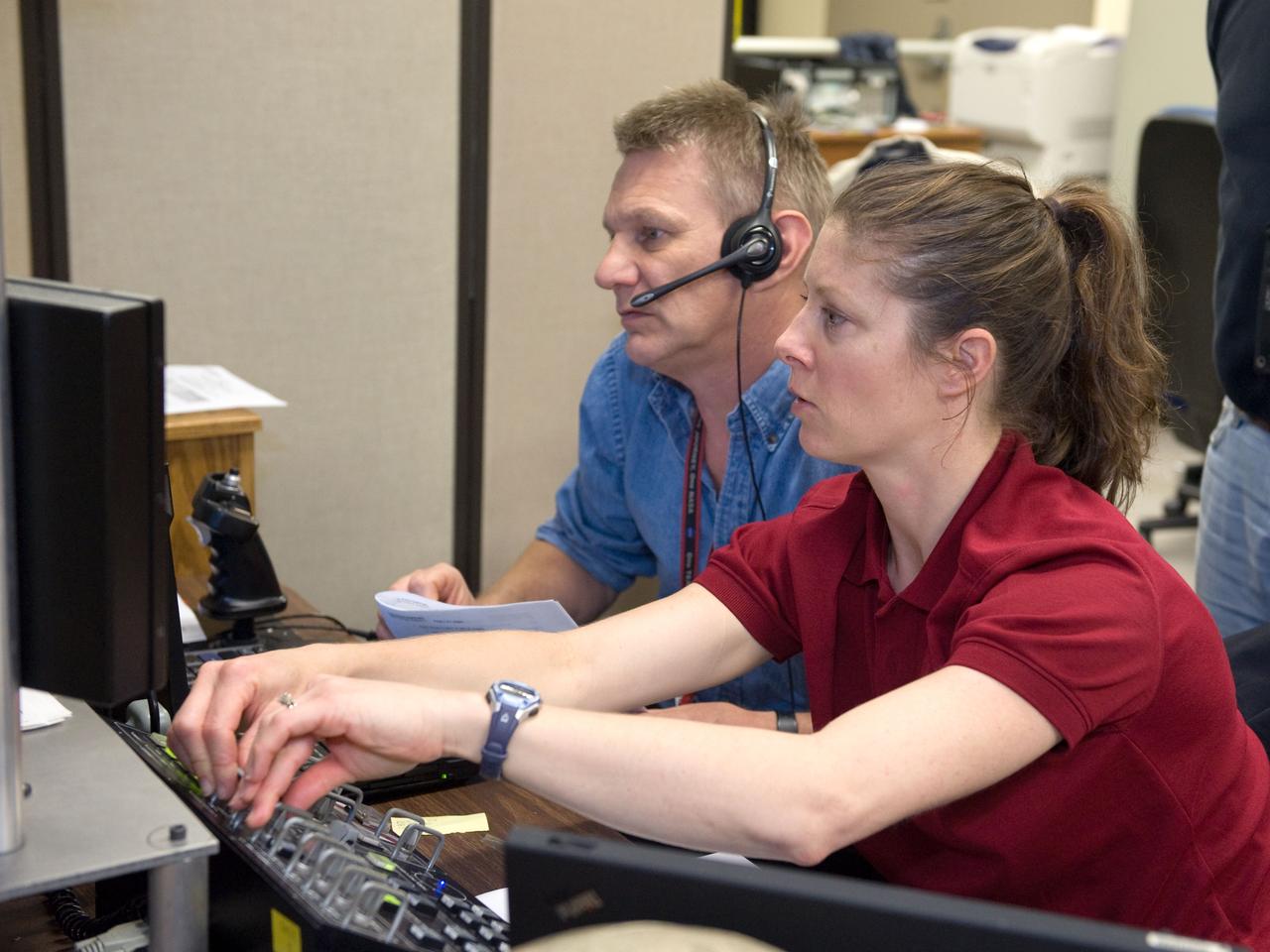

JSC2010-E-014953 (28 Jan. 2010) --- NASA astronauts Piers Sellers, STS-132 mission specialist; and Tracy Caldwell Dyson, Expedition 23/24 flight engineer, use the virtual reality lab in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to train for some of their duties aboard the space shuttle and space station. This type of computer interface, paired with virtual reality training hardware and software, helps to prepare crew members for dealing with space station elements.
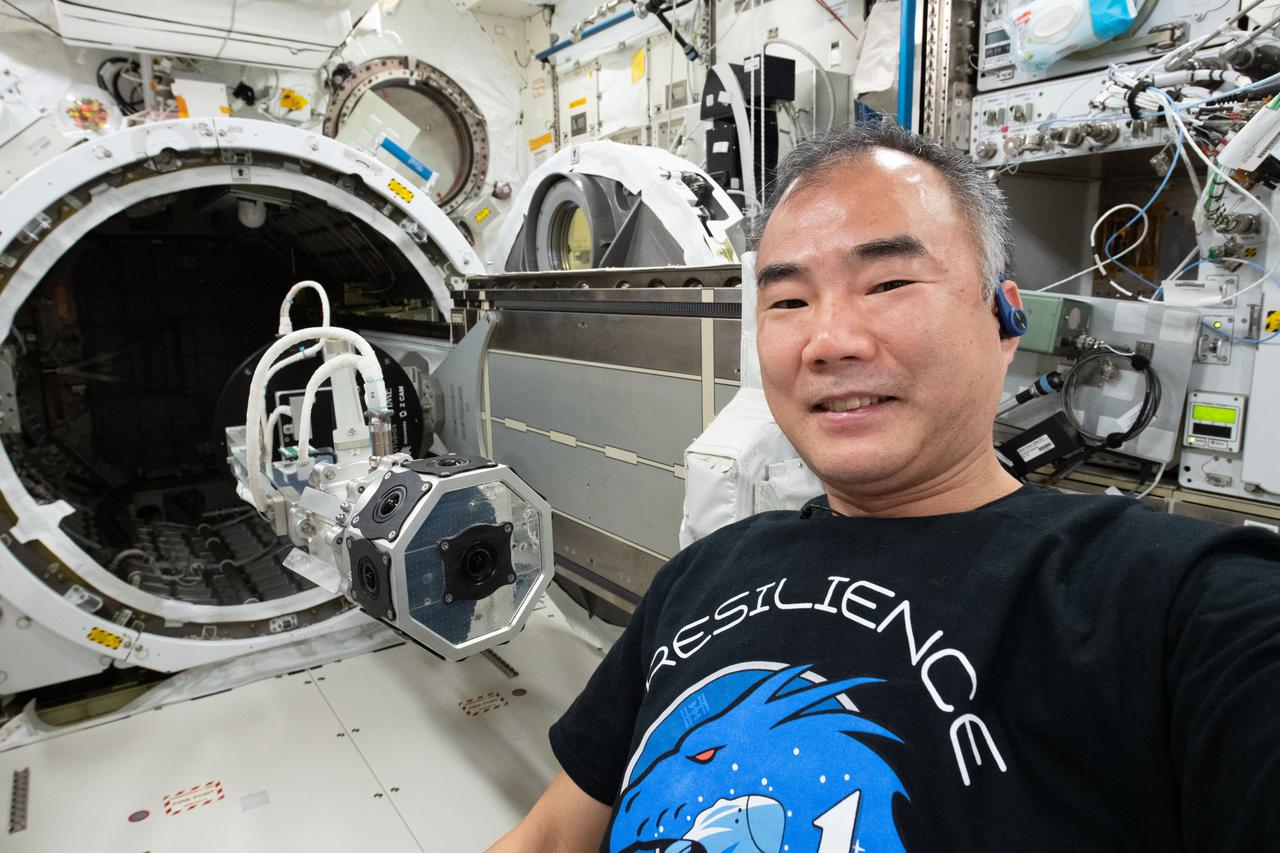

iss064e035270 (Feb. 23, 2021) --- JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut and Expedition 64 Flight Engineer Soichi Noguchi is pictured after installing a three-dimensional virtual reality camera on the Kibo laboratory module's airlock slide table. The camera films activities aboard the orbiting lab in cinematic virtual reality to document living and working in space for audiences on Earth as part of the ISS Experience investigation.

JSC2010-E-043662 (25 March 2010) --- NASA astronauts Gregory H. Johnson, STS-134 pilot; and Shannon Walker, Expedition 24/25 flight engineer, use the virtual reality lab in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center to train for some of their duties aboard the space shuttle and space station. This type of computer interface, paired with virtual reality training hardware and software, helps to prepare crew members for dealing with space station elements.
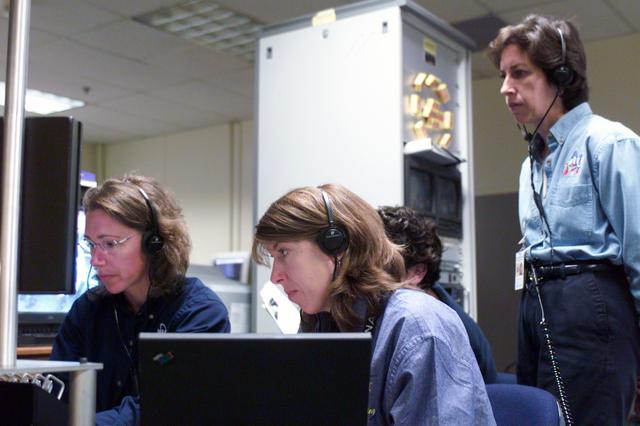

JSC2002-E-34625 (21 Aug. 2002) --- Astronaut Sandra H. Magnus (left), STS-112 mission specialist, uses the virtual reality lab at NASA?s Johnson Space Center (JSC) to train for her duties aboard the space shuttle Atlantis. This type of computer interface paired with virtual reality training hardware and software helps to prepare the entire team for dealing with ISS elements. Lead SSRMS instructor Elizabeth C. Bloomer assisted Magnus. Astronaut Ellen Ochoa (standing) looks on. Photo credit: NASA
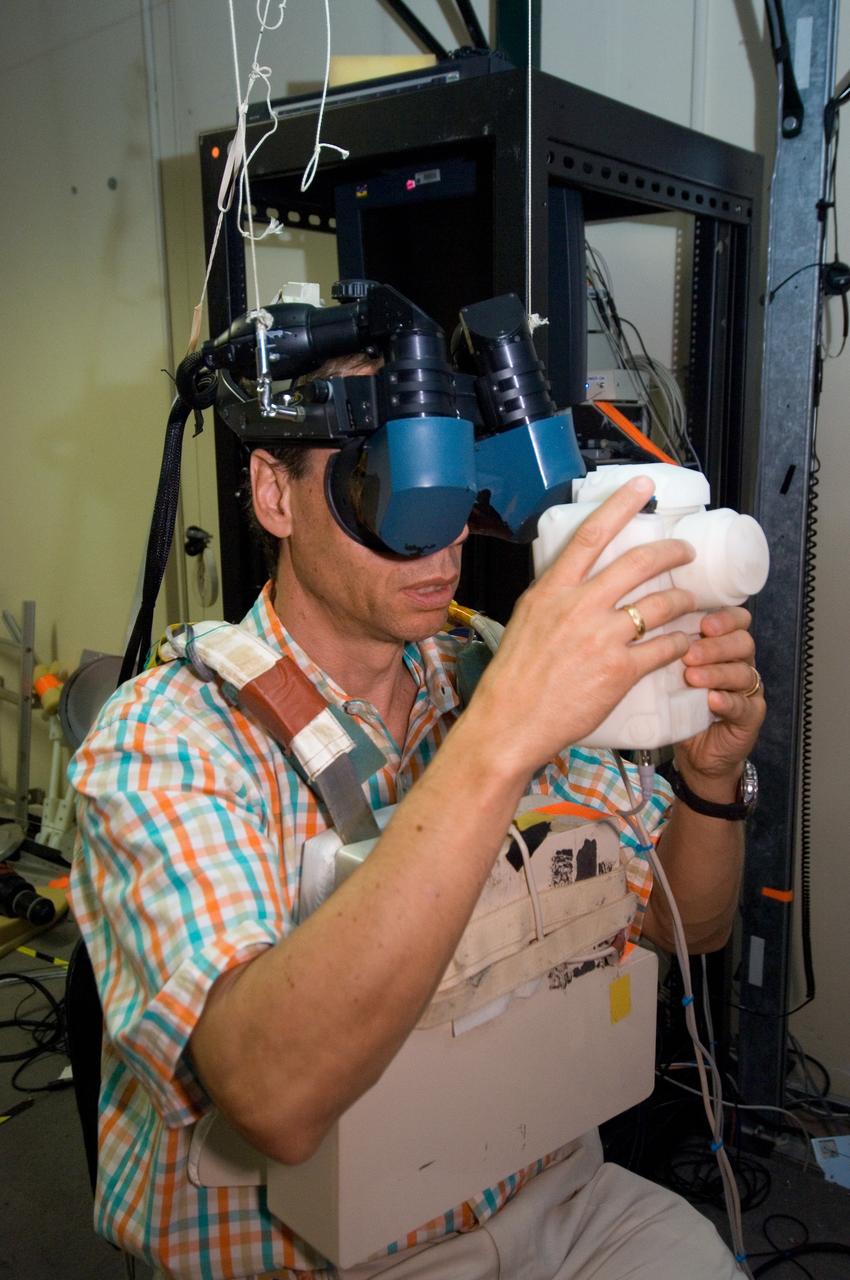

JSC2006-E-33309 (7 Aug. 2006) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Christer Fuglesang, STS-116 mission specialist, uses virtual reality hardware in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center to rehearse some of his duties on the upcoming mission to the International Space Station. This type of virtual reality training allows the astronauts to wear a helmet and special gloves while looking at computer displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the station hardware with which they will be working.