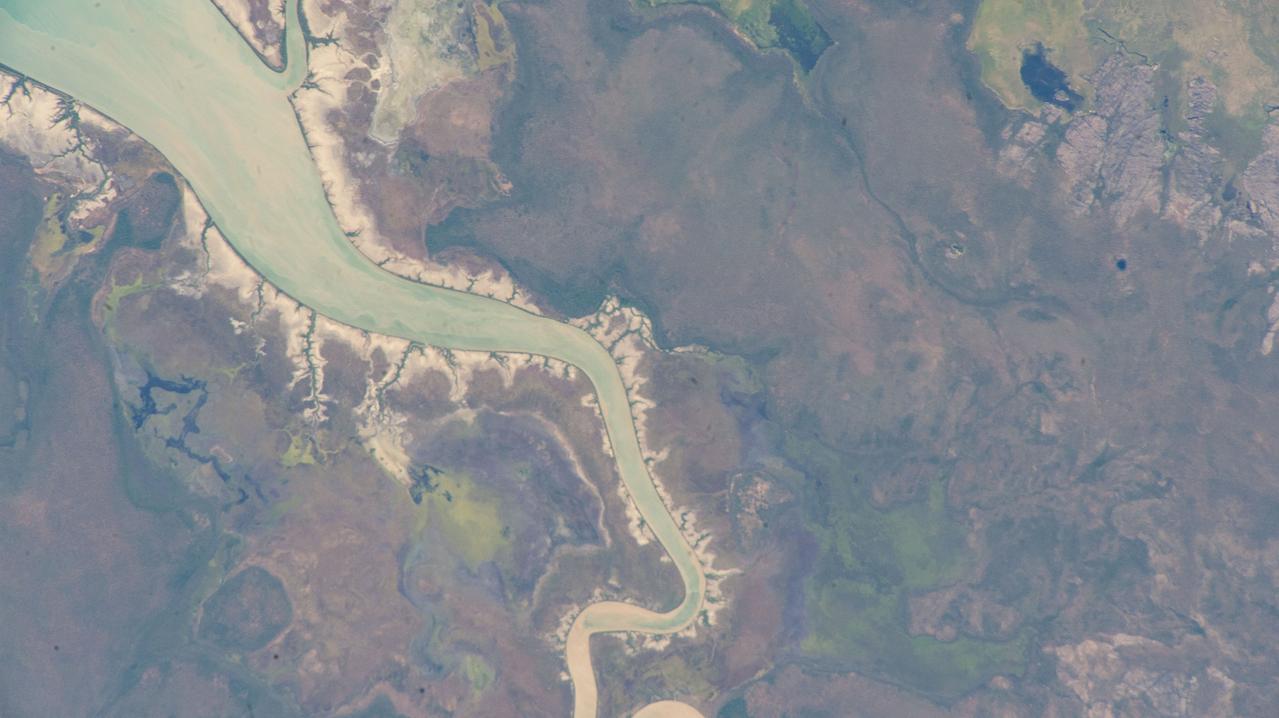

iss073e0078217 (May 22, 2025) --- The Kakadu waterway, with its fractal-like tributaries, in the savanna region of Australia's Northern Territory near Van Diemen Gulf is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 262 miles above.
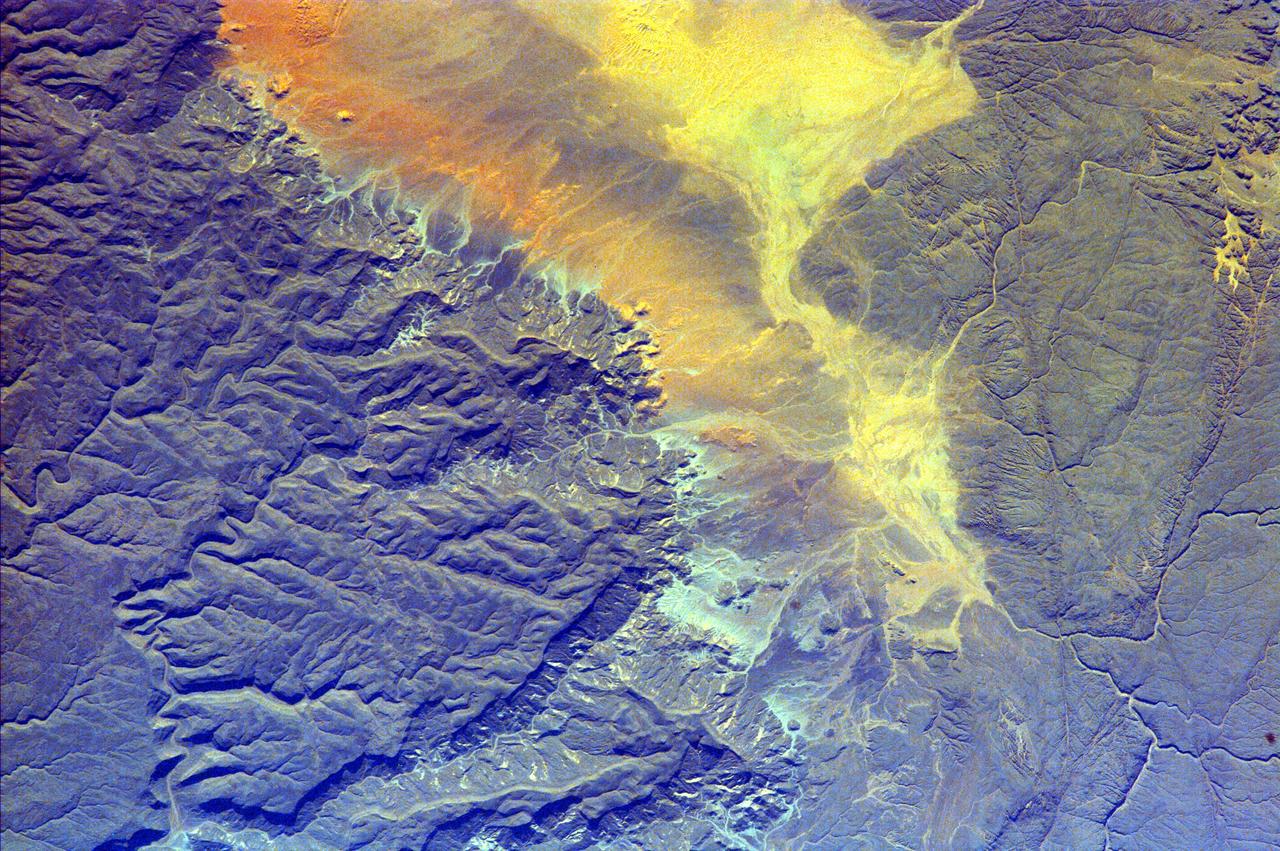

The impermanent waterways shown here from NASA EarthKAM are part of Oued Irharrhar, which appear to be carrying sulfur yellow and iron red deposits. The city of Amguid is located on these waterways, and all lie in the Mouydir Mountains in Algeria.

While the quiet supersonic dive maneuver produces a quieter version of the sonic boom in a necessary area, it produces a loud sonic boom out over the ocean. Doing so over the busiest waterway in the country makes it necessary to provide high levels of situational awareness to vessels below, through communications between NASA public affairs officers and the U.S. Coast Guard command center.
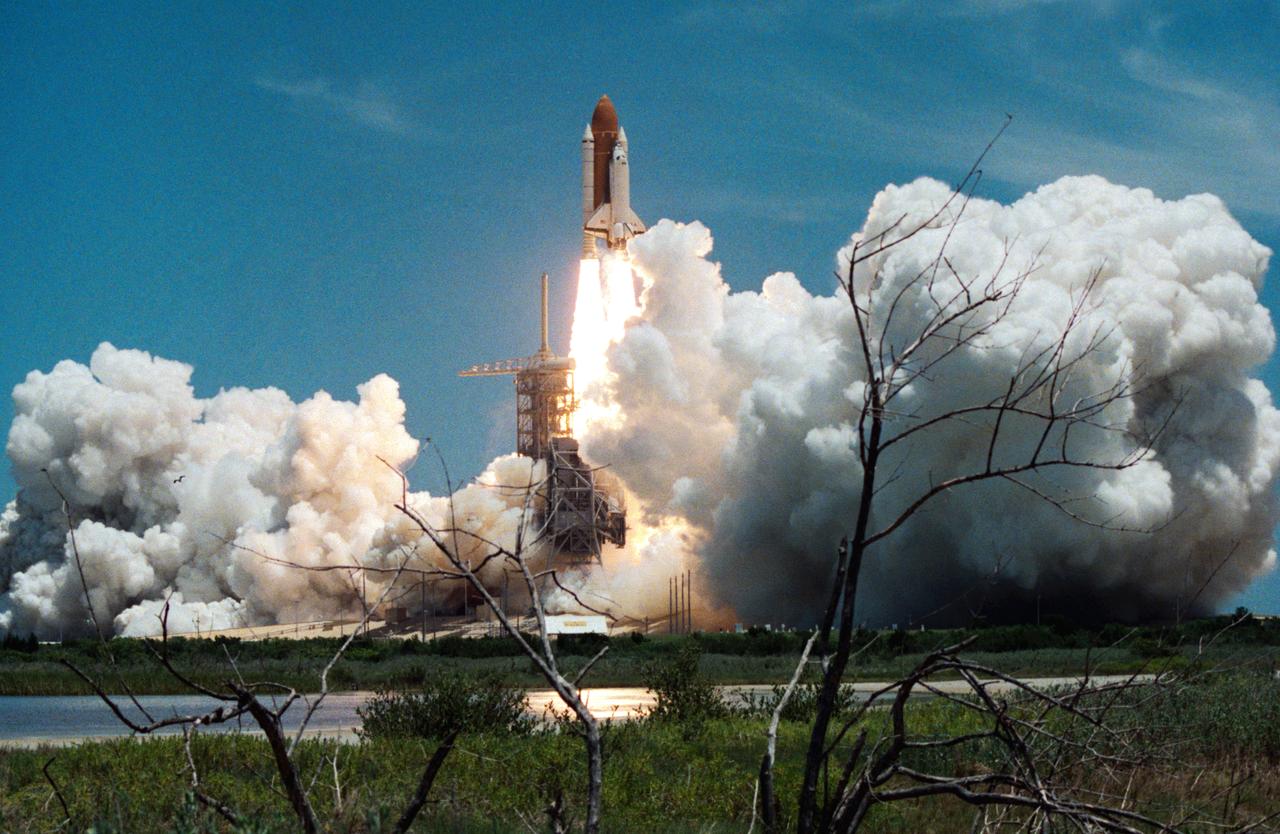

Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, begins its roll maneuver after clearing the fixed service structure (FSS) tower as it rises above Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39A. In the foreground of this horizontal scene is Florida brush and a waterway. Beyond the brush, the shuttle's exhaust cloud envelops the immediate launch pad area. Launch occurred at 12:43 pm Eastern Daylight Time (EDT). The glow of the space shuttle main engine (SSME) and solid rocket booster (SRB) firings is reflected in the nearby waterway. Once in Earth orbit, STS-65's six NASA astronauts and a Japanese Payload Specialist aboard OV-102 will begin two weeks of experimentation in support of the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2).
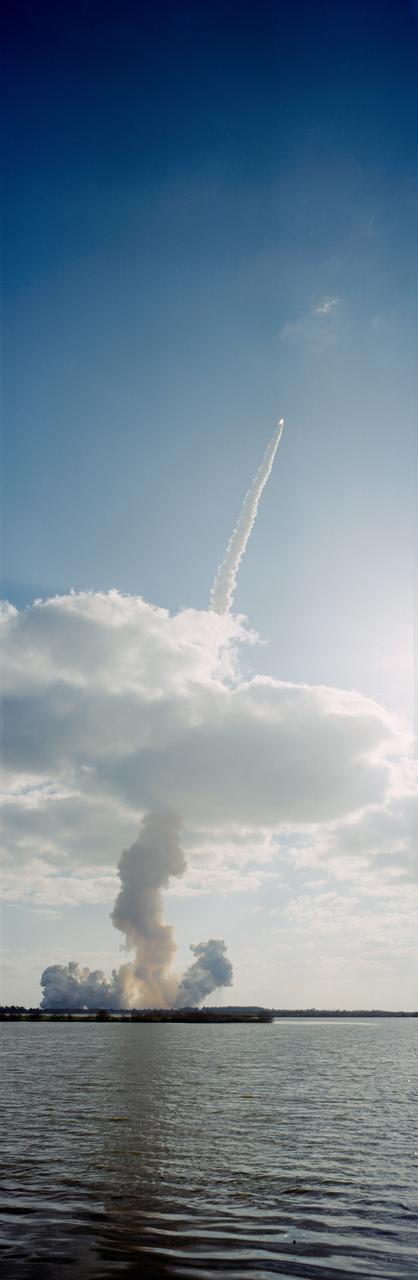

STS-31 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, rides above the firey glow of the solid rocket boosters (SRBs) and space shuttle main engines (SSMEs) and a long trail of exhaust as it heads toward Earth orbit. Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39B is covered in an exhaust cloud moments after the liftoff of OV-103 at 8:33:51.0492 am (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)). The exhaust plume pierces the low-lying clouds as OV-103 soars into the clear skies above. A nearby waterway appears in the foreground.
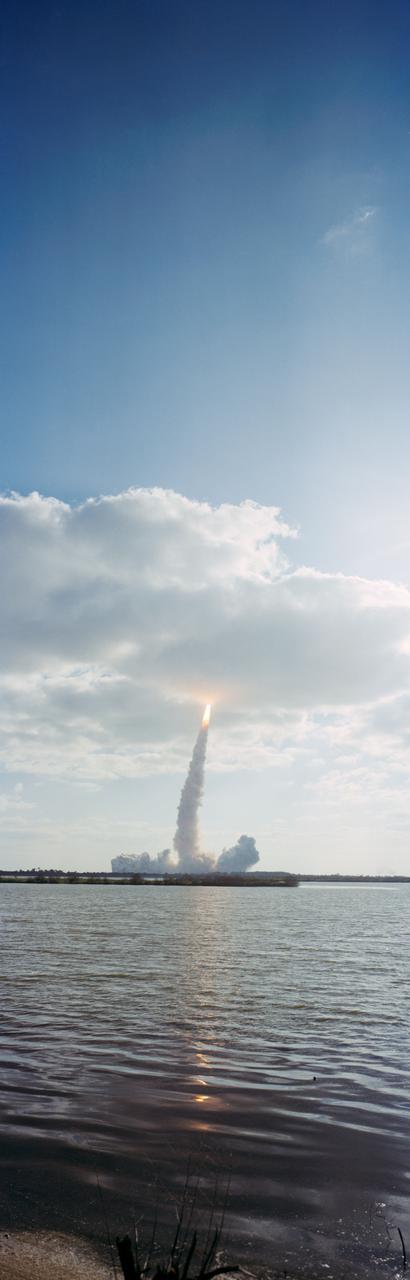

STS-31 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is hidden in low-lying cloud cover as it rises above Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39B just after its liftoff at 8:33:51.0492 am (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)). The glow of the solid rocket booster (SRB) and the space shuttle main engine (SSME) firings appears just below the cloud cover and is reflected in the nearby waterway (foreground). An exhaust plume trails from OV-103 and its SRBs and covers the launch pad area.
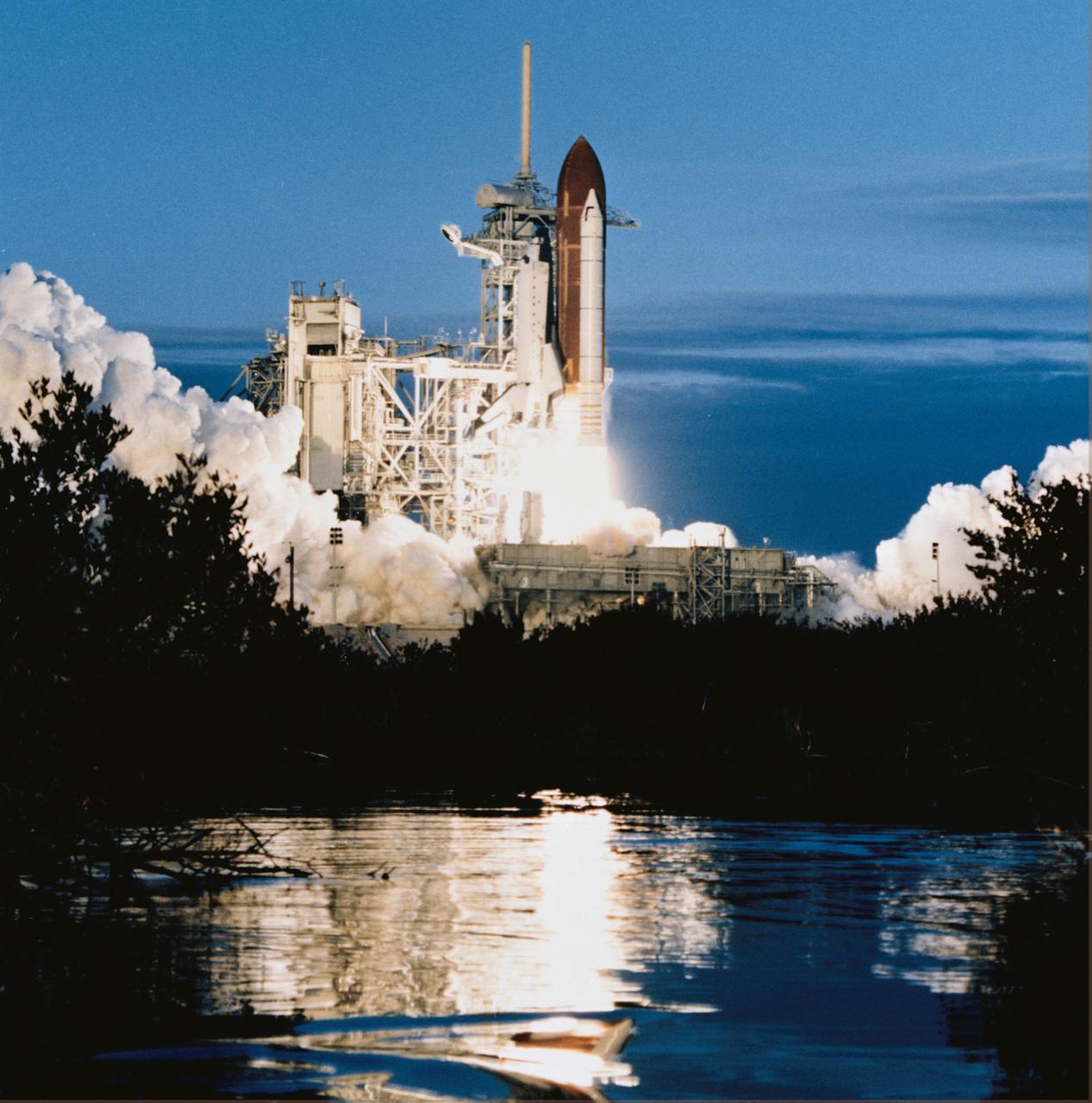

STS032-S-069 (9 Jan. 1990) --- The space shuttle Columbia, with a five member crew aboard, lifts off for the ninth time as STS-32 begins a 10-day mission in Earth orbit. Leaving from Launch Pad 39A at 7:34:59:98 a.m. EST, in this horizontal (cropped 70mm) frame, Columbia is seen reflected in nearby marsh waters some 24 hours after dubious weather at the return-to-launch site (RTLS) had cancelled a scheduled launch. Onboard the spacecraft were astronauts Daniel C. Brandenstein, James D. Wetherbee, Bonnie J. Dunbar, G. David Low and Marsha S. Ivins. Photo credit: NASA
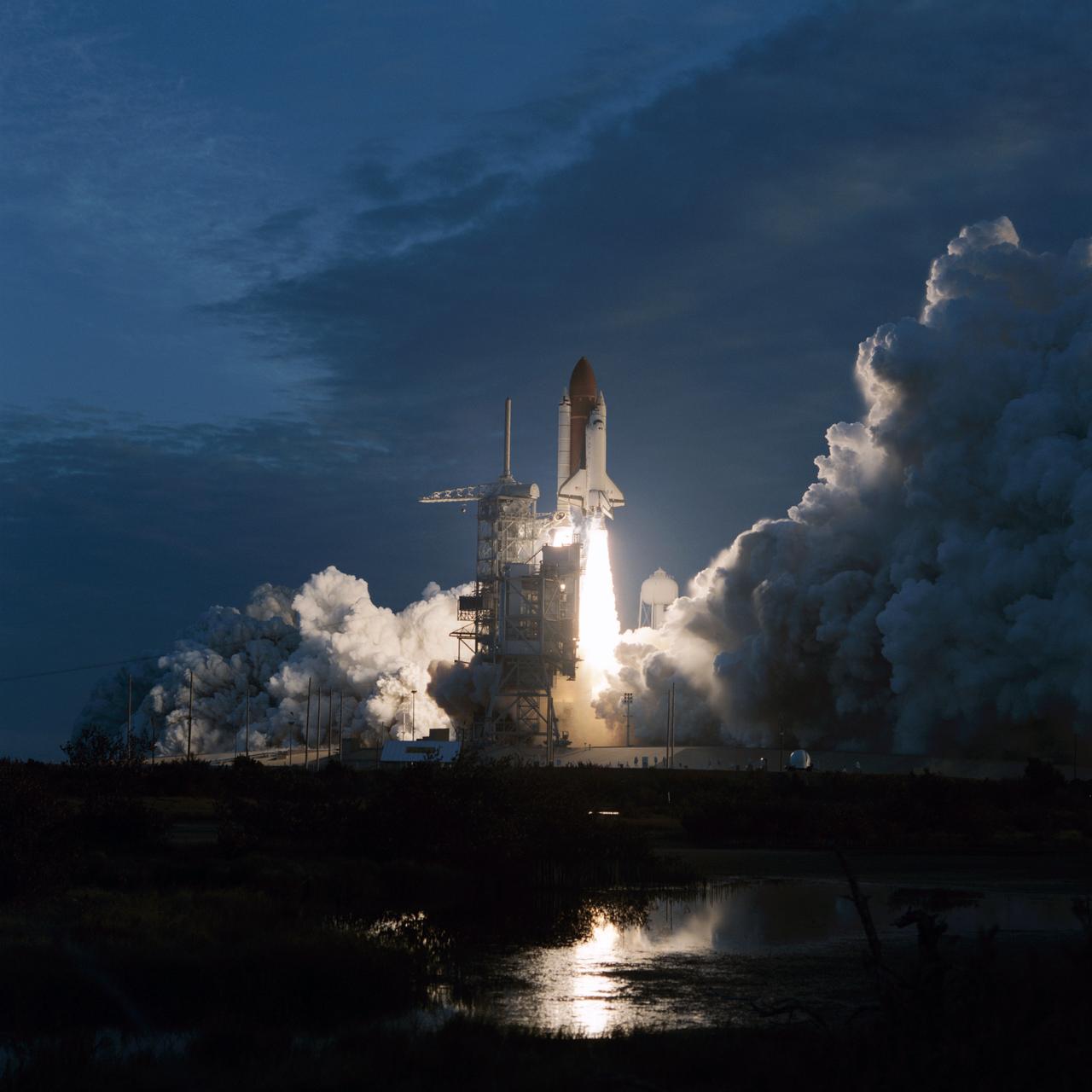

STS-32 Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, its external tank (ET), and solid rocket boosters (SRBs) rise above the mobile launcher platform and begin to clear fixed service structure (FSS) tower (with rotating service structure (RSS) retracted) at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39A. Liftoff occurred at 7:34:59:98 am Eastern Standard Time (EST) some 24 hours after dubious weather at the return-to-landing site (RTLS) had cancelled a scheduled launch. An exhaust cloud covers the launch pad. The firing SRBs and space shuttle main engines (SSMEs) are reflected in a nearby waterway. OV-102's launch is highlighted against the early morning darkness.
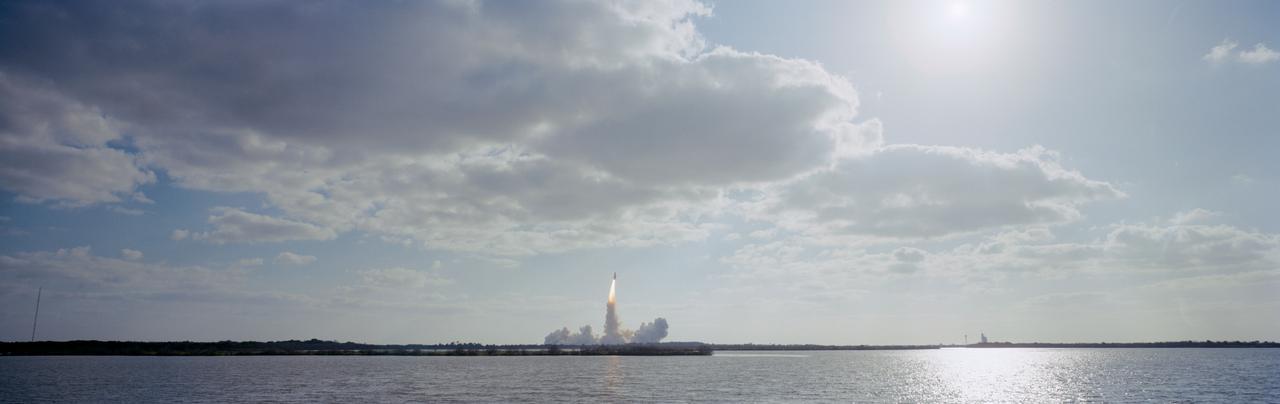

In this distant view, STS-31 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is seen as it heads skyward after liftoff from Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39B at 8:33:51.0492 am (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)). OV-103's silhouette atop the external tank (ET) appears above the glow of the solid rocket booster (SRB) and space shuttle main engine (SSME) firings. An exhaust plume trails behind and covers the launch pad area below the orbiter. A nearby waterway reflects the SRB/SSME glow in the foreground. At the far right and barely discernible is KSC LC Pad 39A and the Sound Supression Water System tower. Columbia, OV-102, is on LC Pad 39A which is separated by a distance of 1.6 miles. This was the first time since January 1986 that there was a shuttle on each pad.
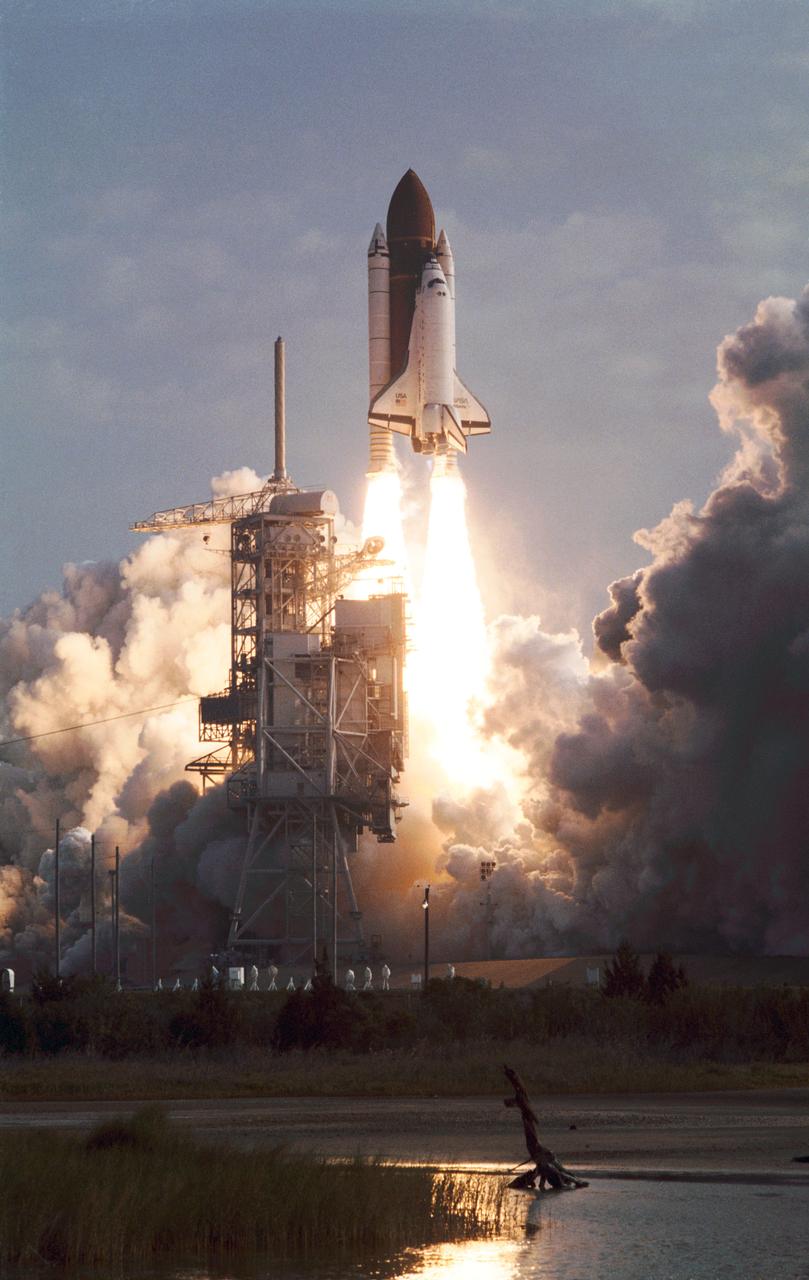

STS-45 Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, lifts off from a Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad at 8:13:40:048 am (Eastern Standard Time (EST)). Exhaust billows out the solid rocket boosters (SRBs) as OV-104 atop its external tank (ET) soars above the mobile launcher platform and is nearly clear of the fixed service structure (FSS) tower. The diamond shock effect produced by the space shuttle main engines (SSMEs) is visible. The glow of the SRB/SSME firings is reflected in a nearby waterway. An exhaust cloud covers the launch pad area.
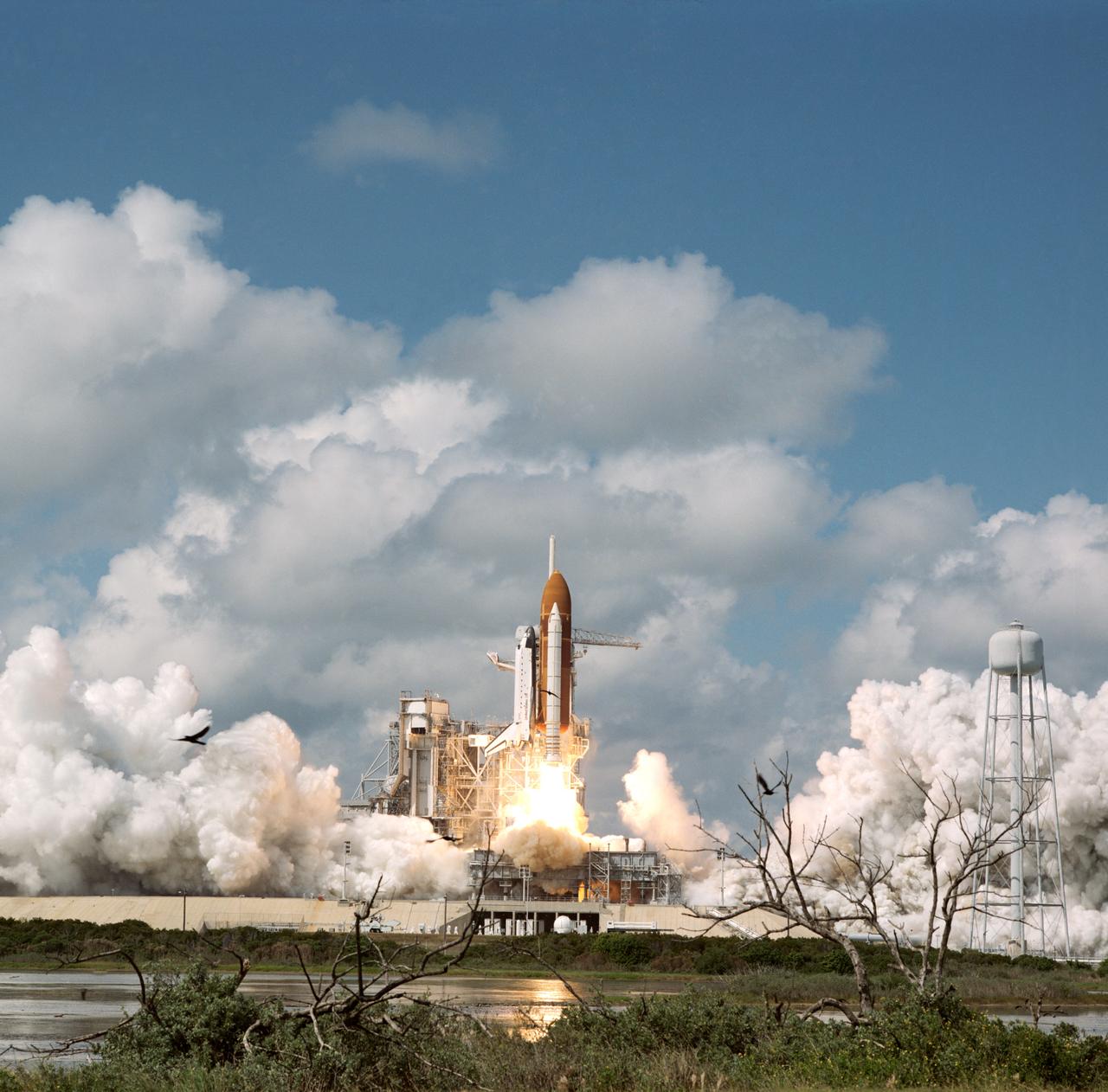

STS-26 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, lifts off from mobile launcher platform at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) pad 39B. Riding atop the orange external tank (ET), OV-103 heads for Earth orbit as the exhaust plumes from the two solid rocket boosters (SRBs) cover the mobile launcher platform and the area surrounding the launch pad. SRB firings are reflected in a nearby waterway. In the foreground are trees and several birds in flight. STS-26 marks OV-103's first flight since September 1985 and NASA's first manned mission since the 51L Challenger accident, 01-28-86.
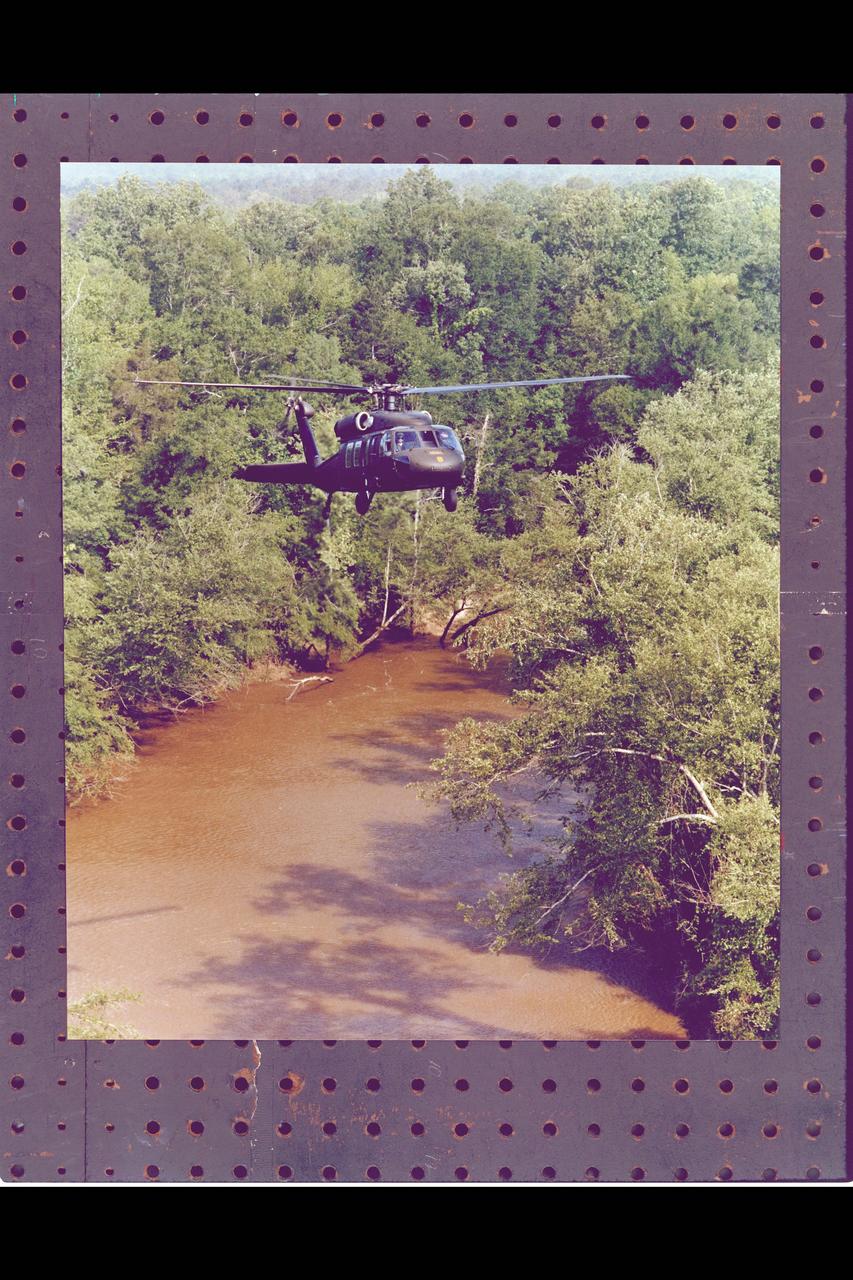

Army UH-60 Blackhawk helicopter flying Nap of the Earth in waterway of heavely wooded terrain.
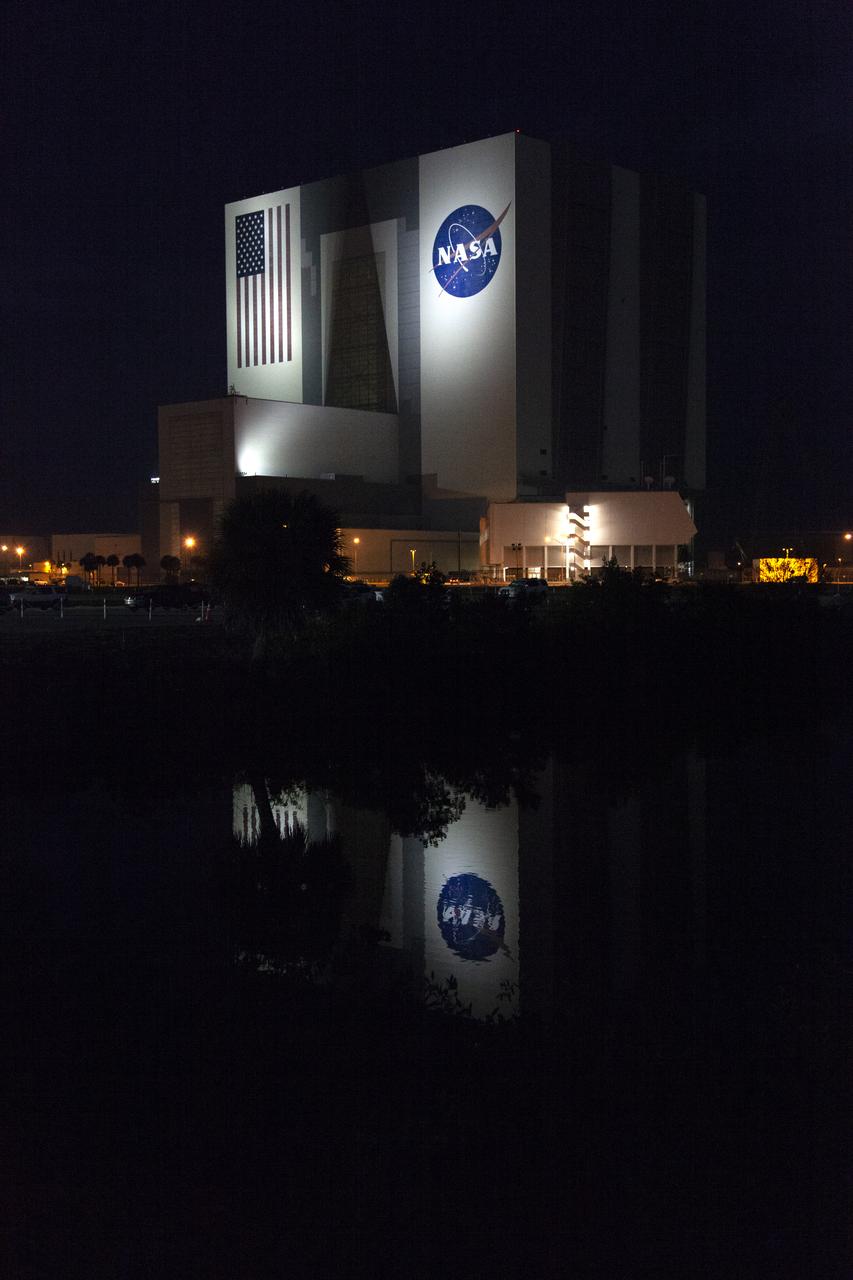

The iconic Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) and Launch Control Center cast reflections on the surface of a nearby waterway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The lights illuminating the VAB provided a splendid nighttime view.
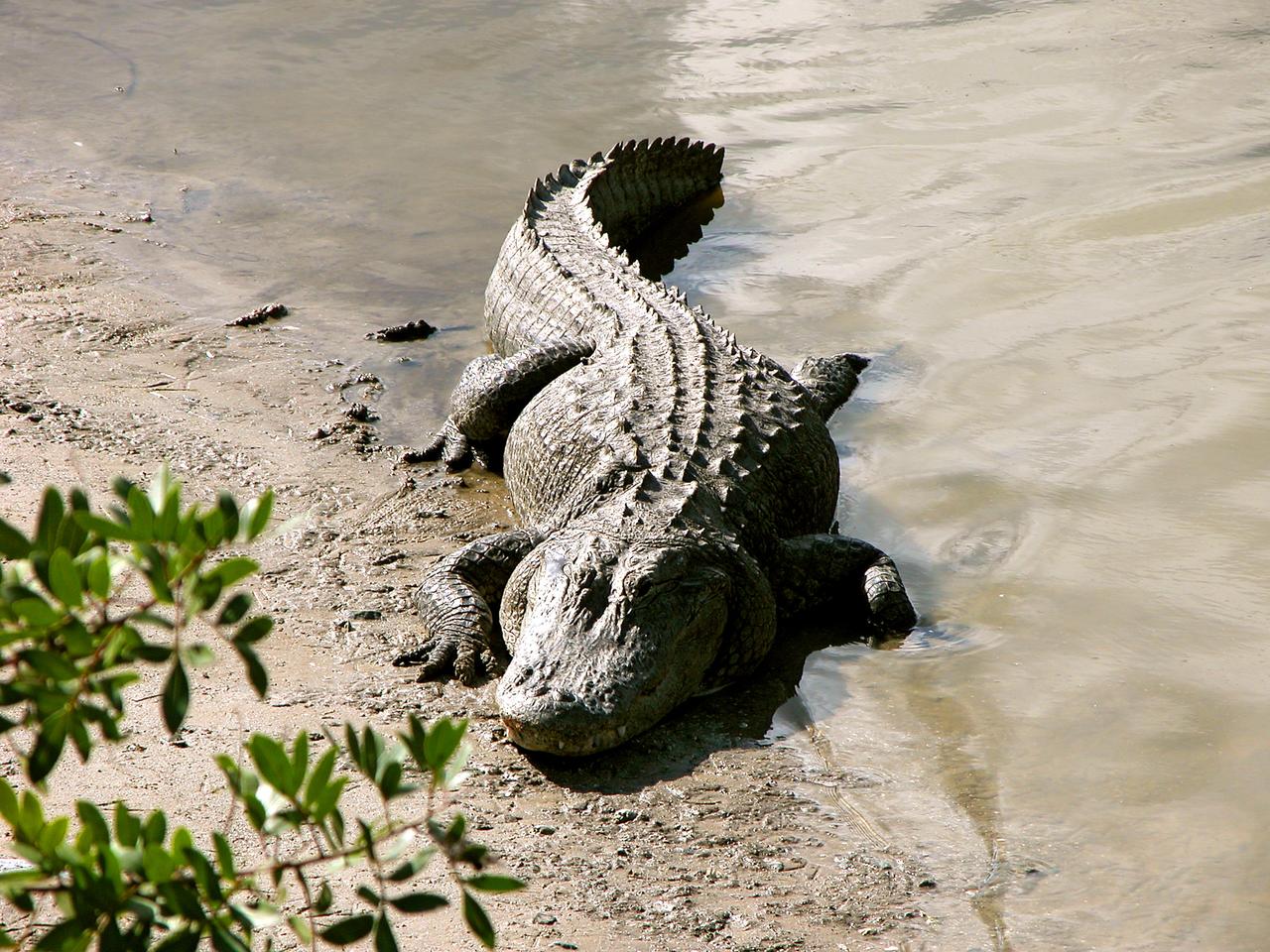

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- An alligator is spotted sunning on the muddy bank of a canal in KSC. Nearly 5,000 alligators can be found in canals, ponds, and waterways throughout the Center and the surrounding Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. American alligators feed and rest in the water, and lay their eggs in dens they dig into the banks. The young alligators spend their first several weeks in these dens. The Wildlife Refuge encompasses 92,000 acres that are a habitat for more than 331 species of birds, 31 mammals, 117 fishes, and 65 amphibians and reptiles.
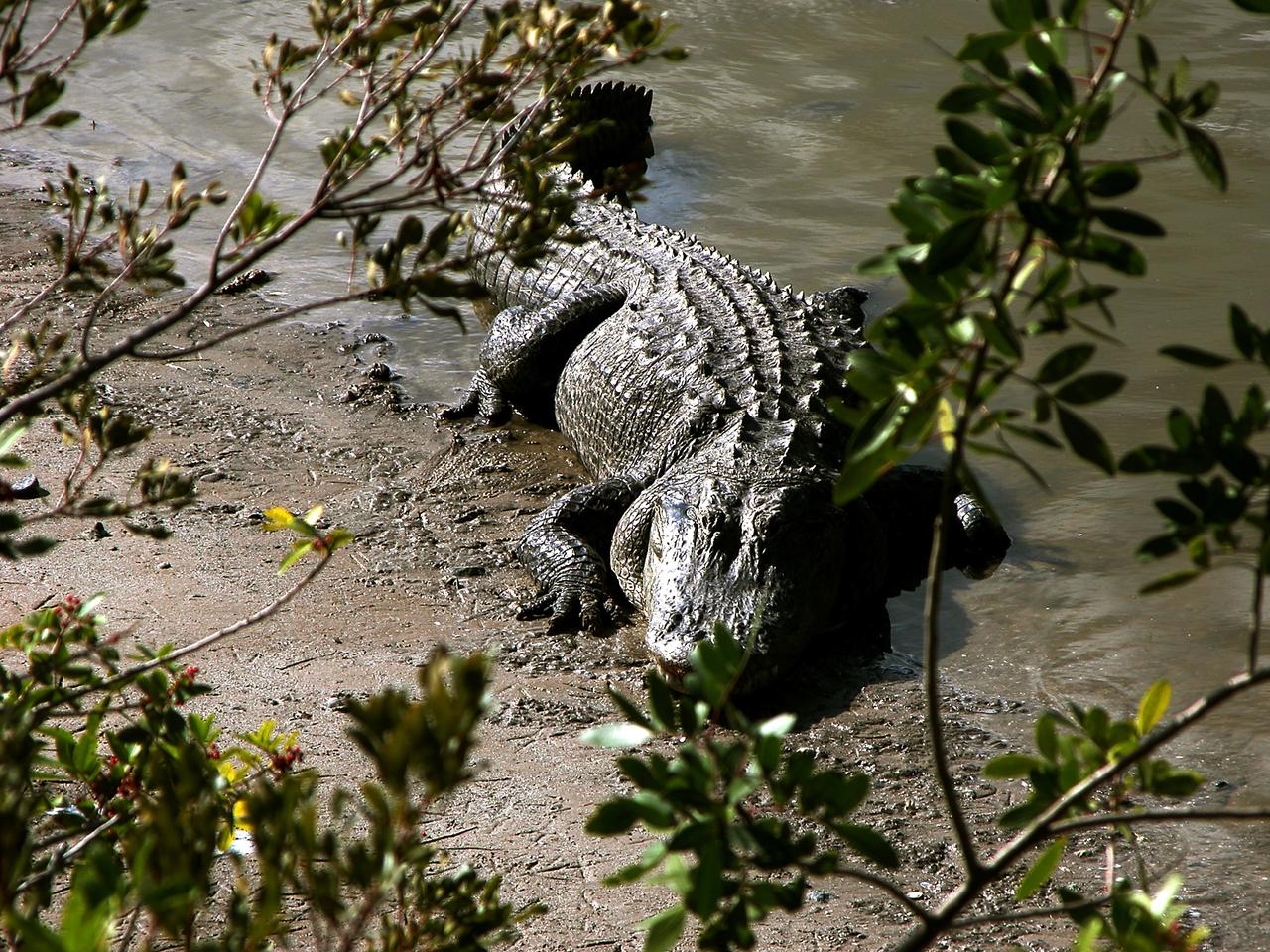

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- An alligator is spotted sunning on the muddy bank of a canal in KSC. Nearly 5,000 alligators can be found in canals, ponds, and waterways throughout the Center and the surrounding Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. American alligators feed and rest in the water, and lay their eggs in dens they dig into the banks. The young alligators spend their first several weeks in these dens. The Wildlife Refuge encompasses 92,000 acres that are a habitat for more than 331 species of birds, 31 mammals, 117 fishes, and 65 amphibians and reptiles.
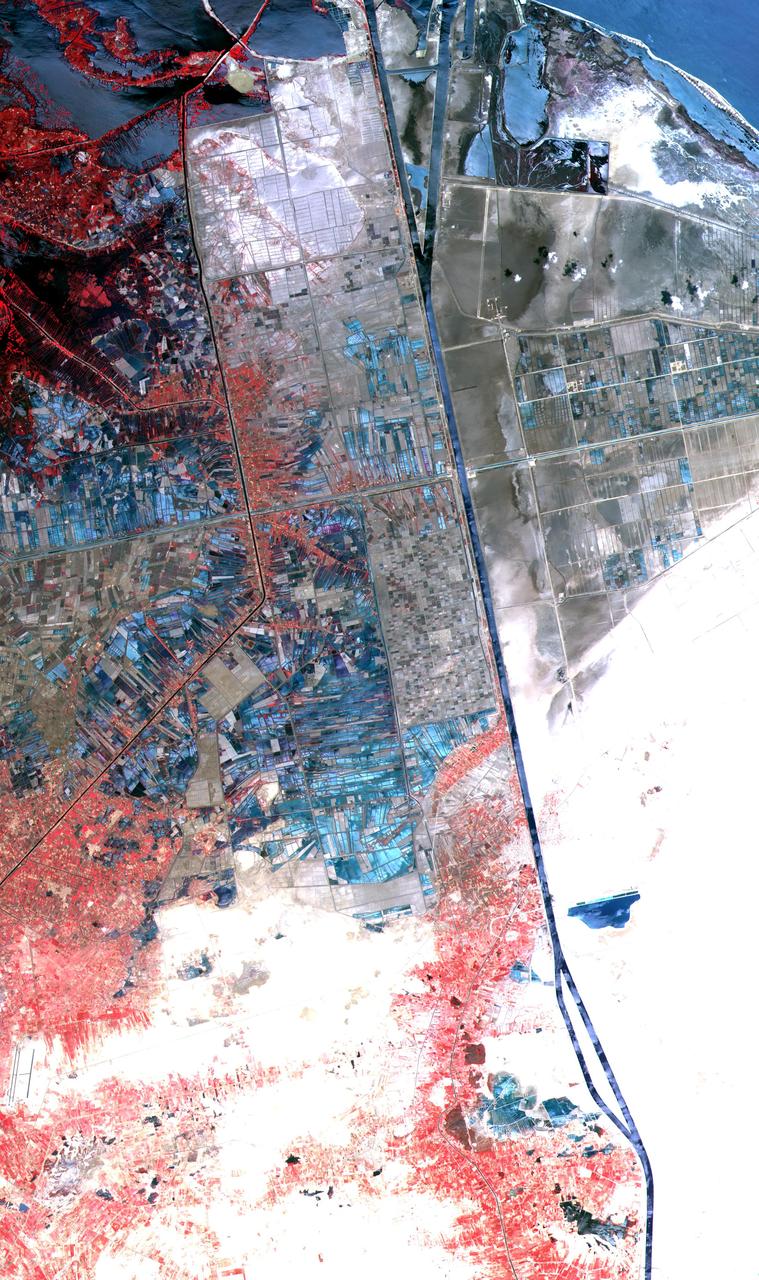

One of the most important waterways in the world, the Suez Canal runs north to south across the Isthmus of Suez in northeastern Egypt. This image of the canal covers an area 36 kilometers (22 miles) wide and 60 kilometers (47 miles) long in three bands of the reflected visible and infrared wavelength region. It shows the northern part of the canal, with the Mediterranean Sea just visible in the upper right corner. The Suez Canal connects the Mediterranean Sea with the Gulf of Suez, an arm of the Red Sea. The artificial canal provides an important shortcut for ships operating between both European and American ports and ports located in southern Asia, eastern Africa, and Oceania. With a length of about 195 kilometers (121 miles) and a minimum channel width of 60 meters (197 feet), the Suez Canal is able to accommodate ships as large as 150,000 tons fully loaded. Because no locks interrupt traffic on this sea level waterway, the transit time only averages about 15 hours. ASTER acquired this scene on May 19, 2000. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02661
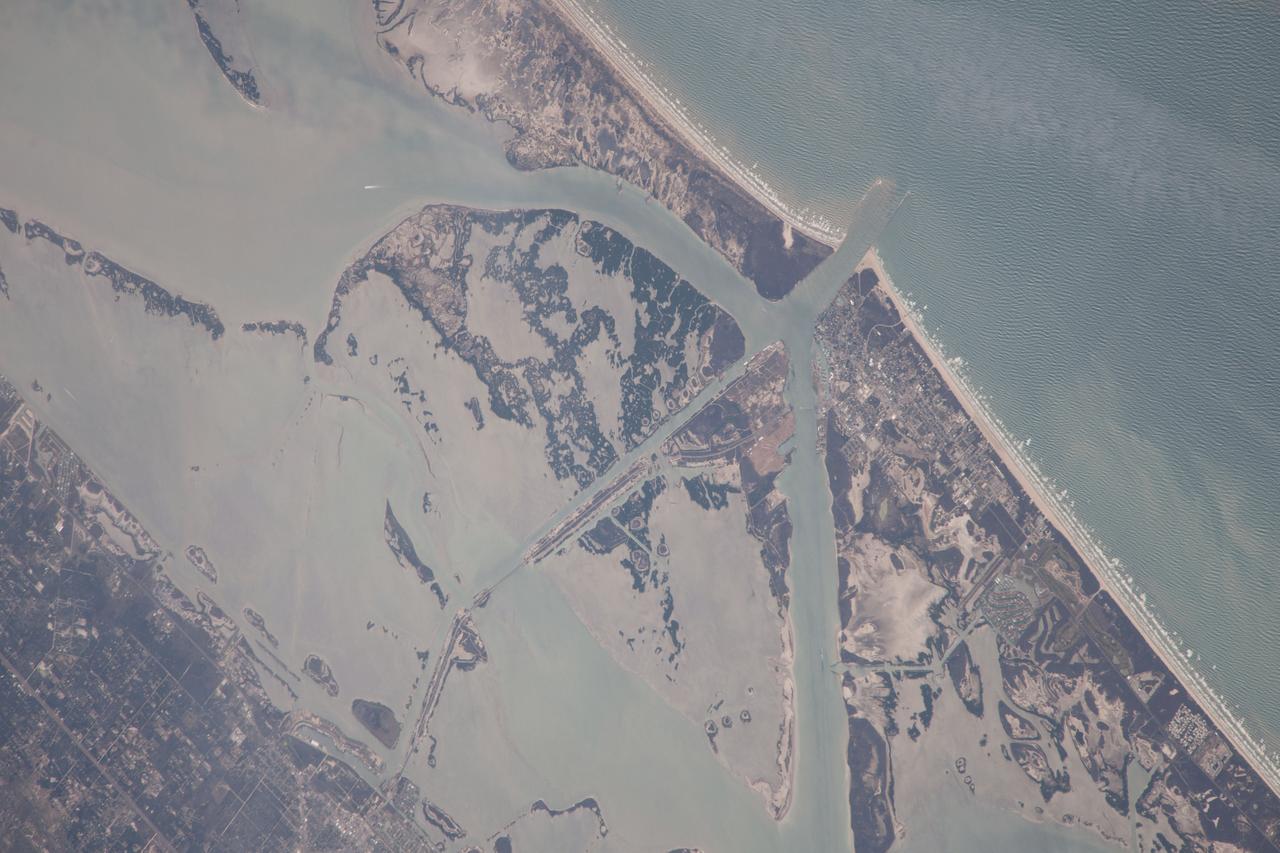

ISS038-E-57806 (21 Feb. 2014) --- One of the Expedition 38 crew members aboard the International Space Station photographed this image of the Gulf of Mexico's Intracoastal Waterway in southern Texas. Represented in the photo are 18 kilometers (11.2 miles) of the overall 4800 kilometers-long (3000 miles) barge channel that lies on the protected inshore of the coastal islands of the southern and eastern USA, including coastal Texas. The small city of Port Aransas lies on a barrier island fully 18 kilometers (11.2 miles) seaward of the mainland and its sister city, Aransas Pass (lower left). This image shows parts of the waterway that are artificial, as in the straight sector leading into Corpus Christi Bay. Corpus Christi lies outside the lower margin of the image. Other sectors of the waterway are natural bays such as Aransas Bay. Jetties protect the inlet into the Gulf of Mexico (top right). Inlets at many points cut through the barrier islands to give shipping access to the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean.
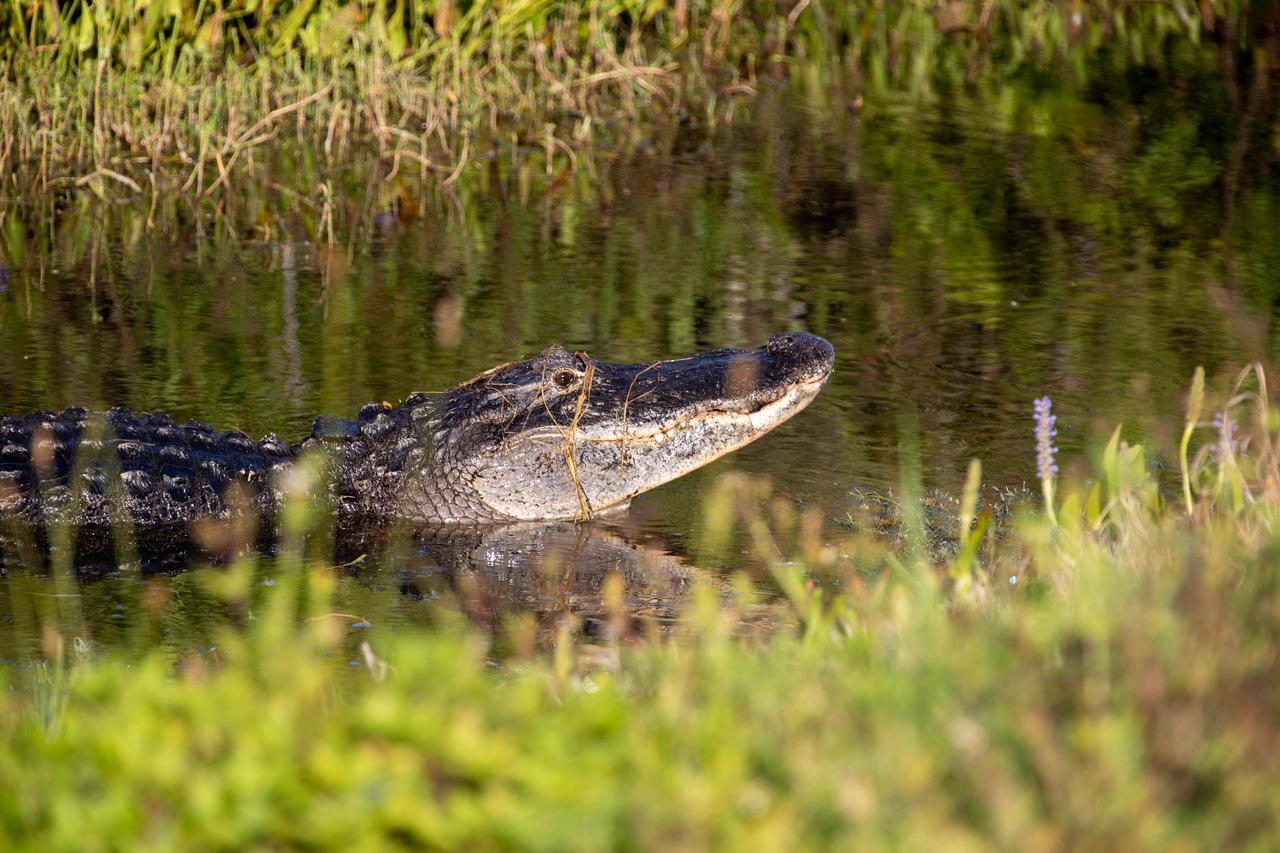

An alligator is in view in a waterway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 16, 2022. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island Wildlife Refuge. More than 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.

An alligator moves through a brackish waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
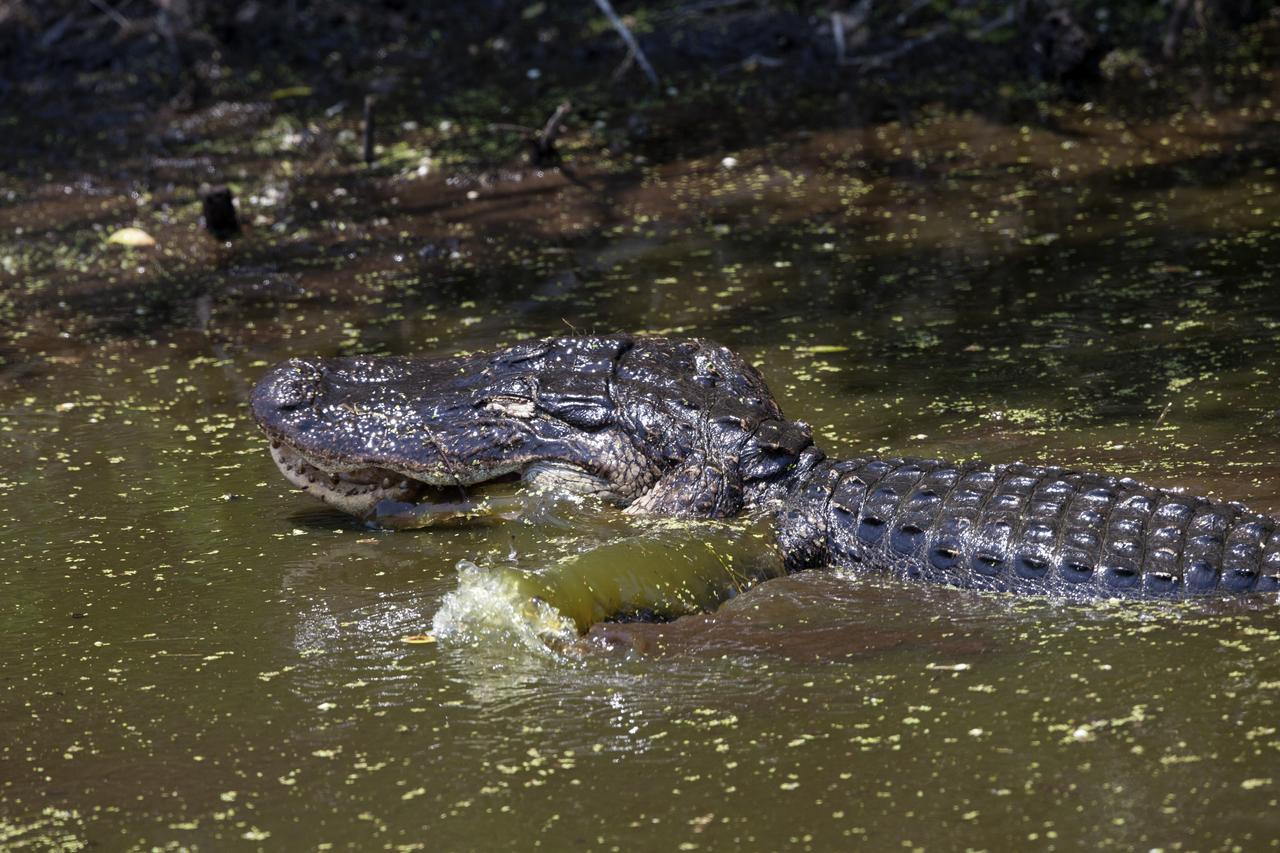

An alligator moves through a brackish waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
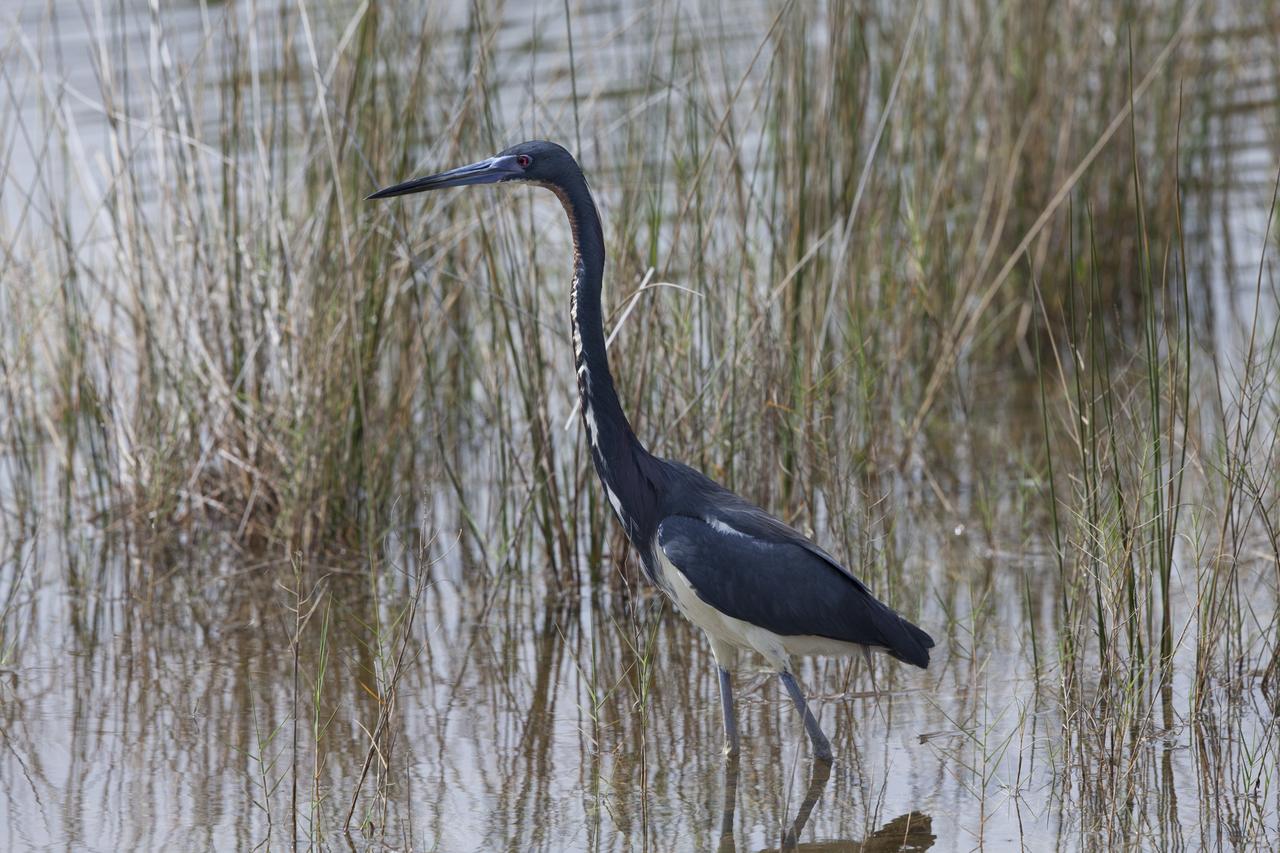

A tricolored heron wades in a shallow waterway at Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge in Florida. NASA’s Kennedy Space Center shares boundaries with the refuge, which is home to more than 330 native and migratory bird species, along with 25 mammal, 117 fish, and 65 amphibian and reptile species.
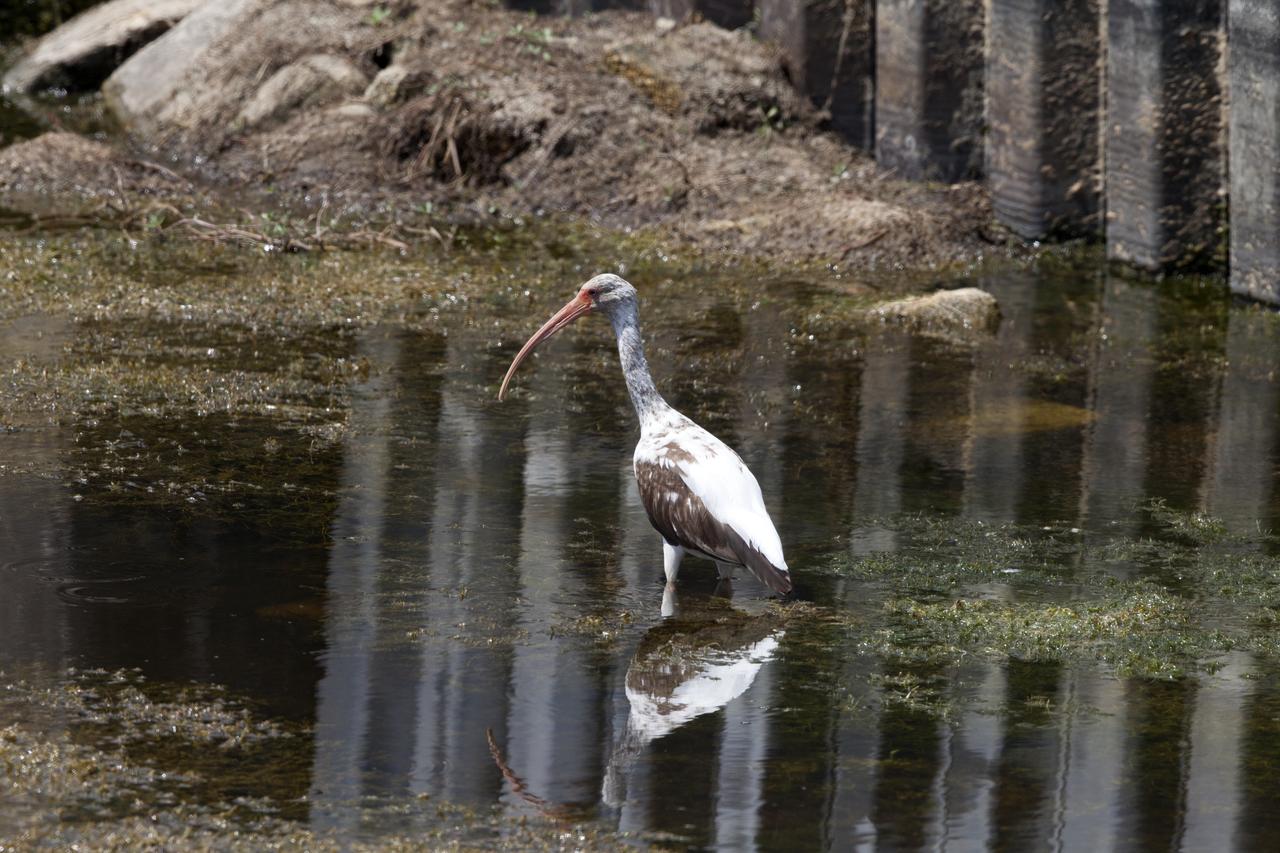

A juvenile white ibis stands in a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
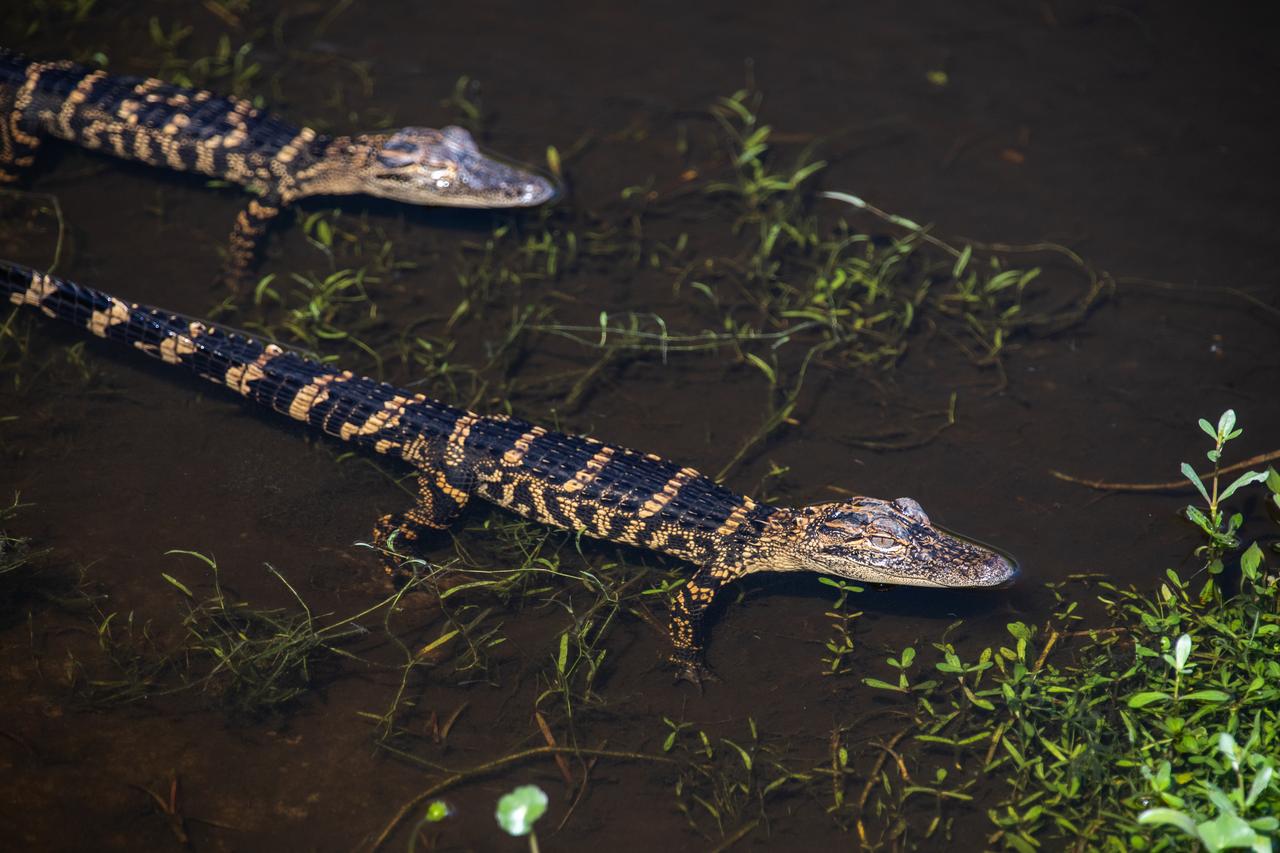

Two baby alligators are in view in a waterway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 9, 2023. The center shares a boundary with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. The refuge is home to more than 65 amphibian and reptile species, along with 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal and 117 fish species.
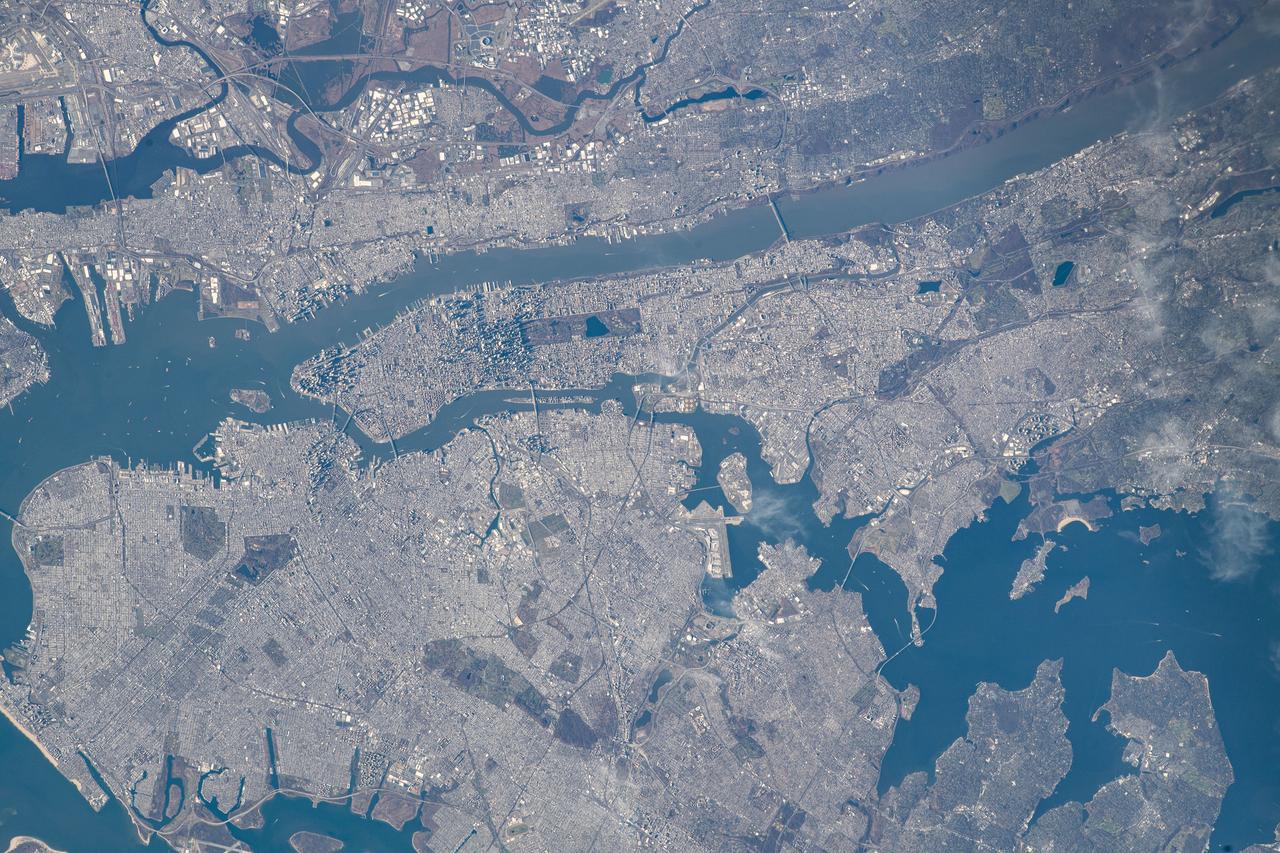

iss070e034497 (Nov. 30, 2023) --- The New York Metroolitan Area, including four of five New York city boroughs, portions of New Jersey, and numeorus waterways, is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 261 miles above.
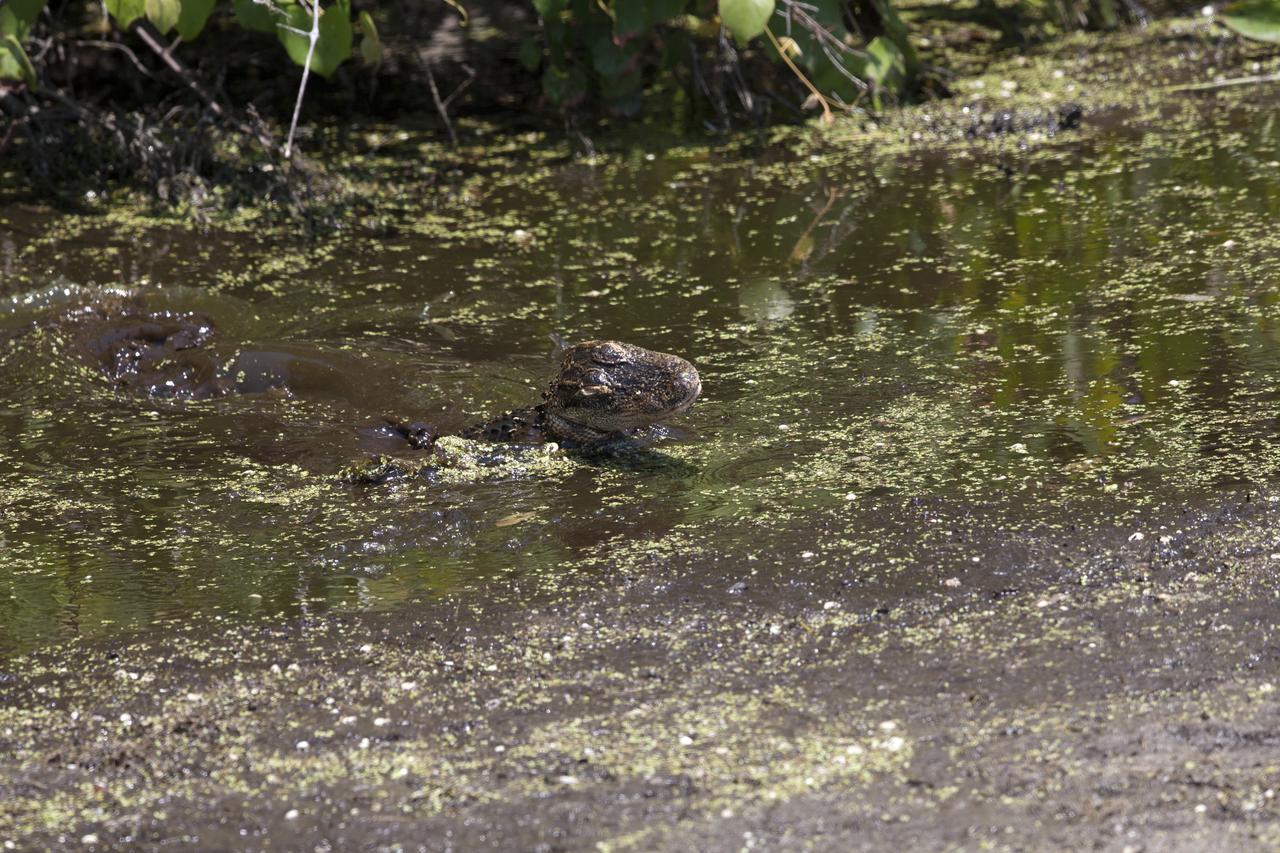

An alligator lurks in a brackish waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
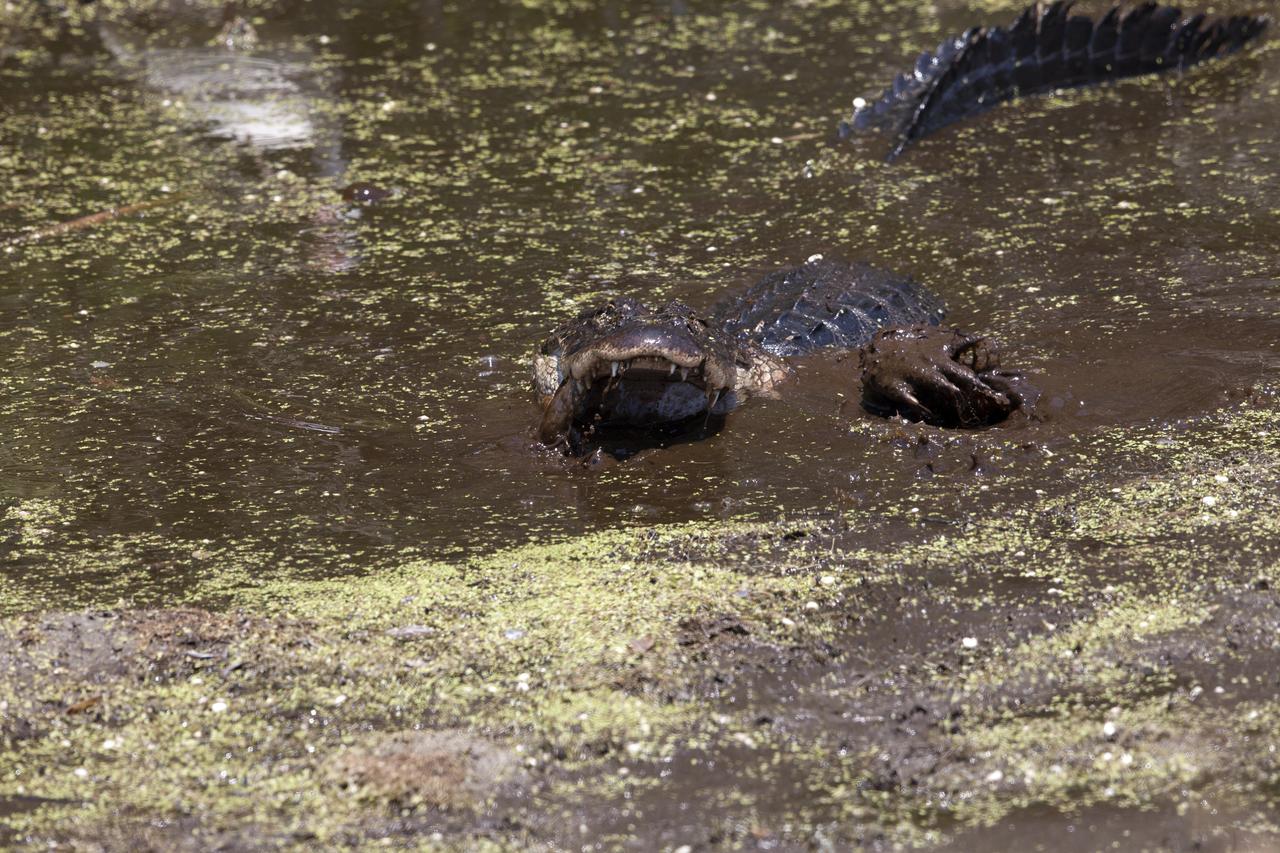

An alligator moves through a brackish waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
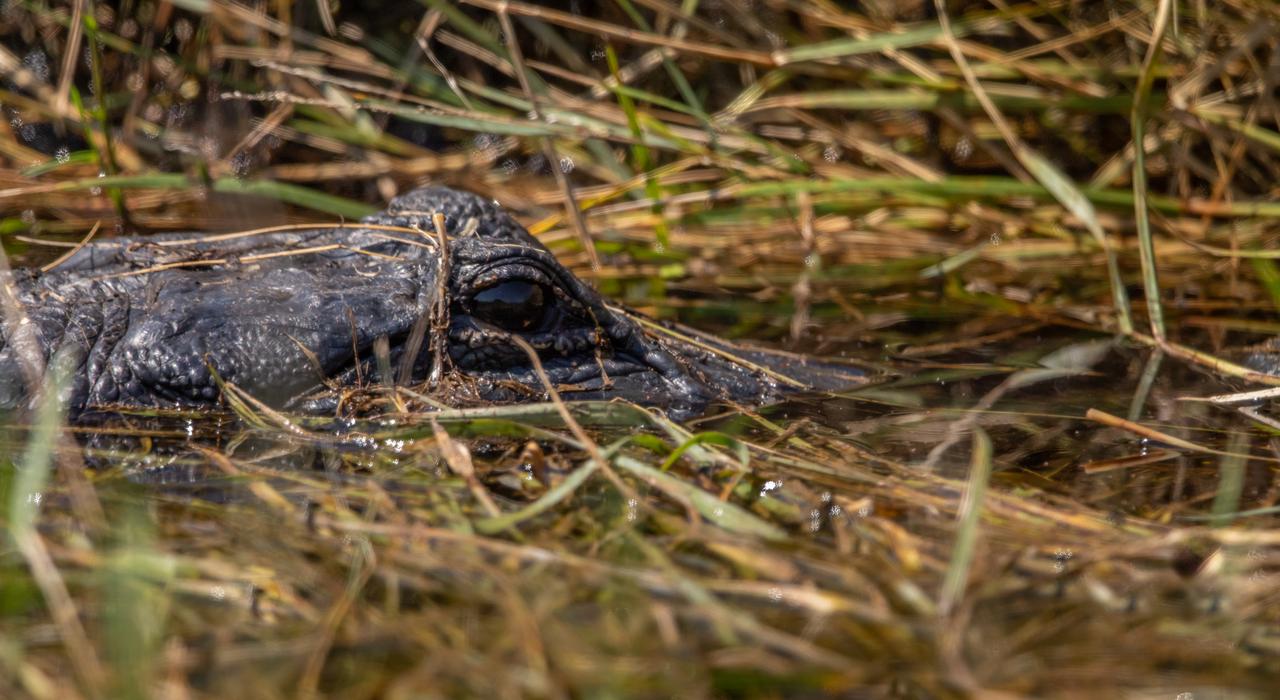

An alligator lurks in a marshy waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
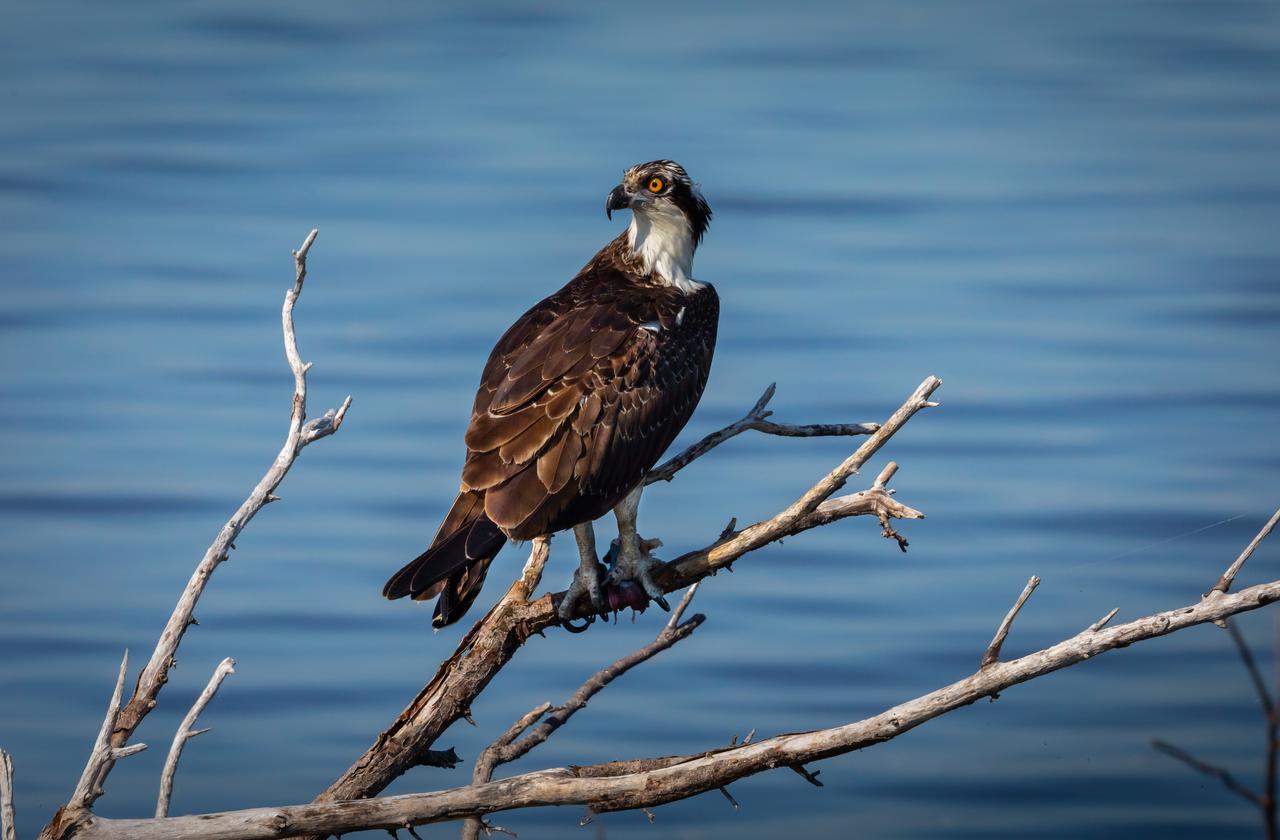

An osprey sits on a branch near a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
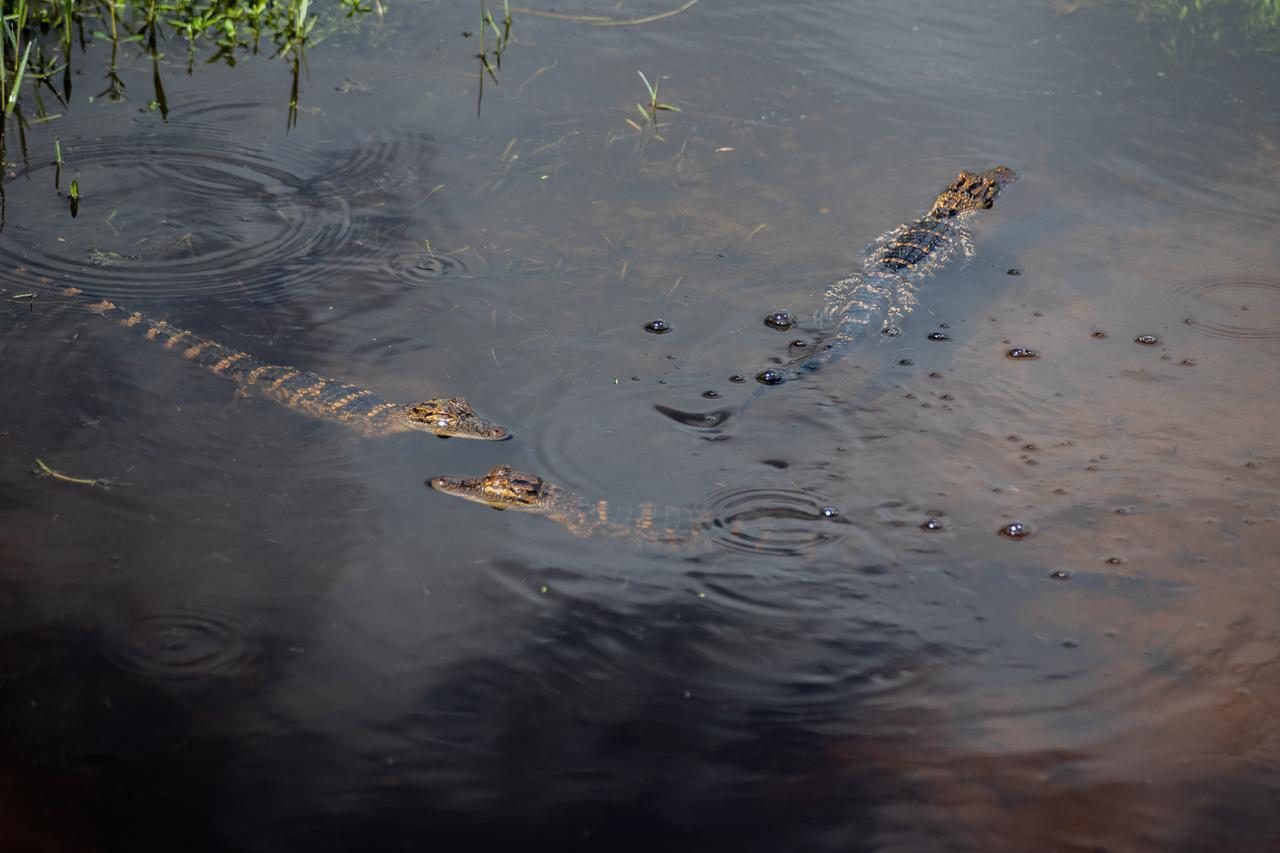

Three baby alligators are in view in a waterway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 9, 2023. The center shares a boundary with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. The refuge is home to more than 65 amphibian and reptile species, along with 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal and 117 fish species.
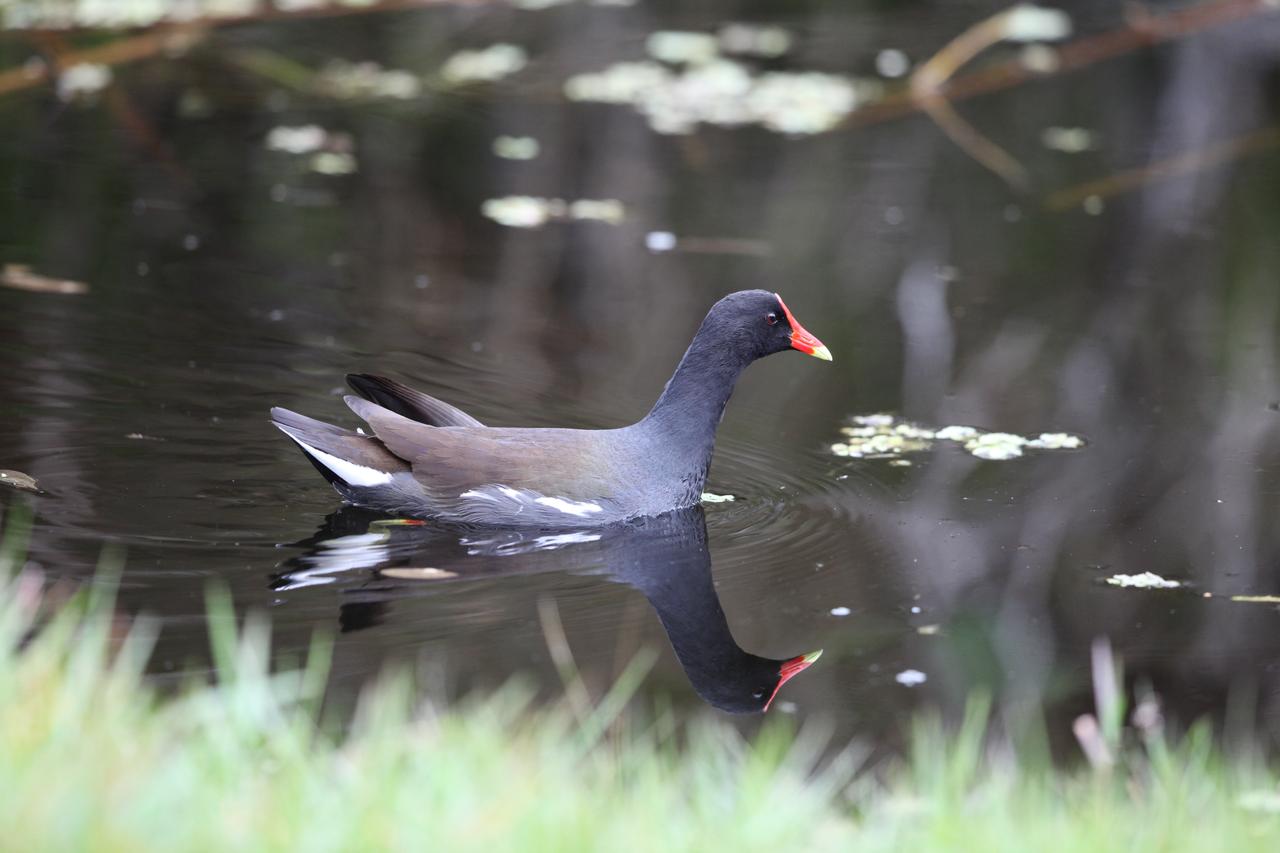

A common gallinule swims in a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
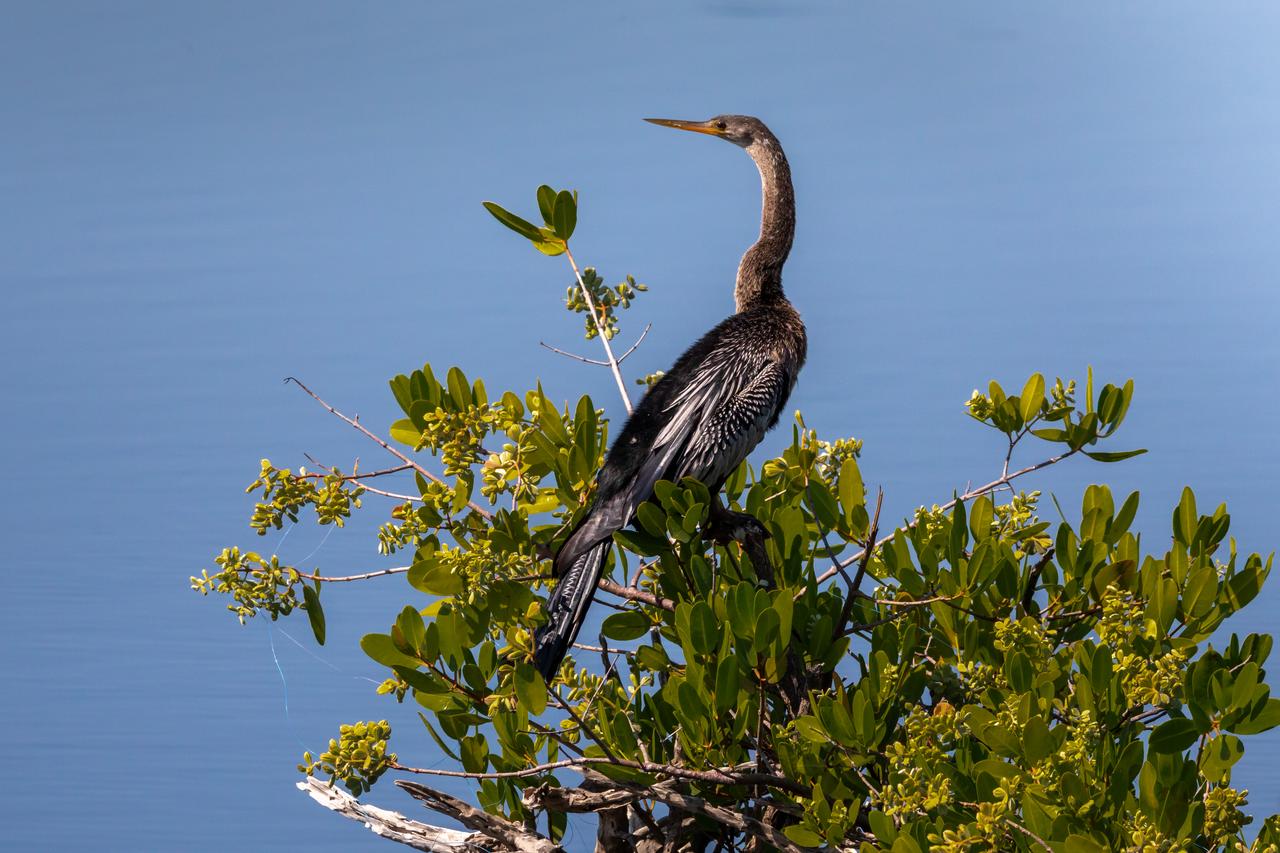

A Reddish Egret perches in a tree near a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
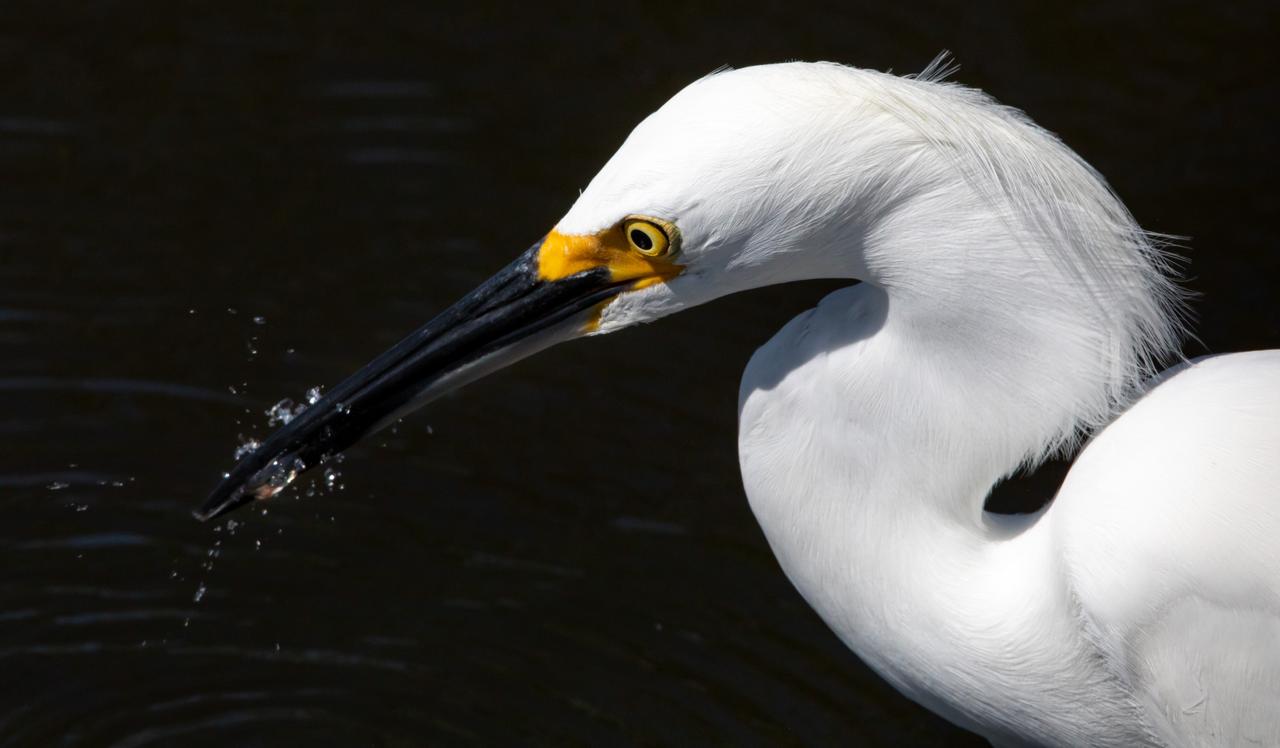

A Great Egret catches a small fish in a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
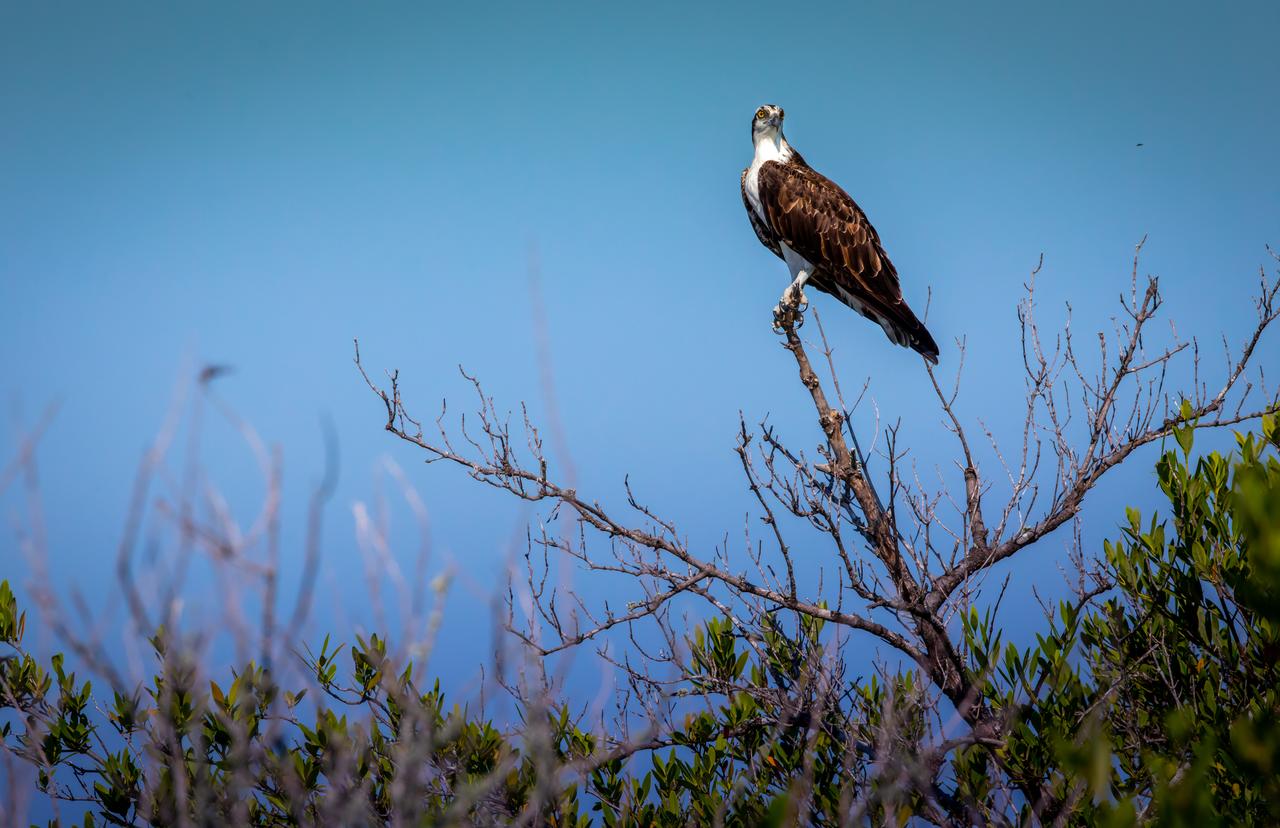

An osprey sits on a branch near a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
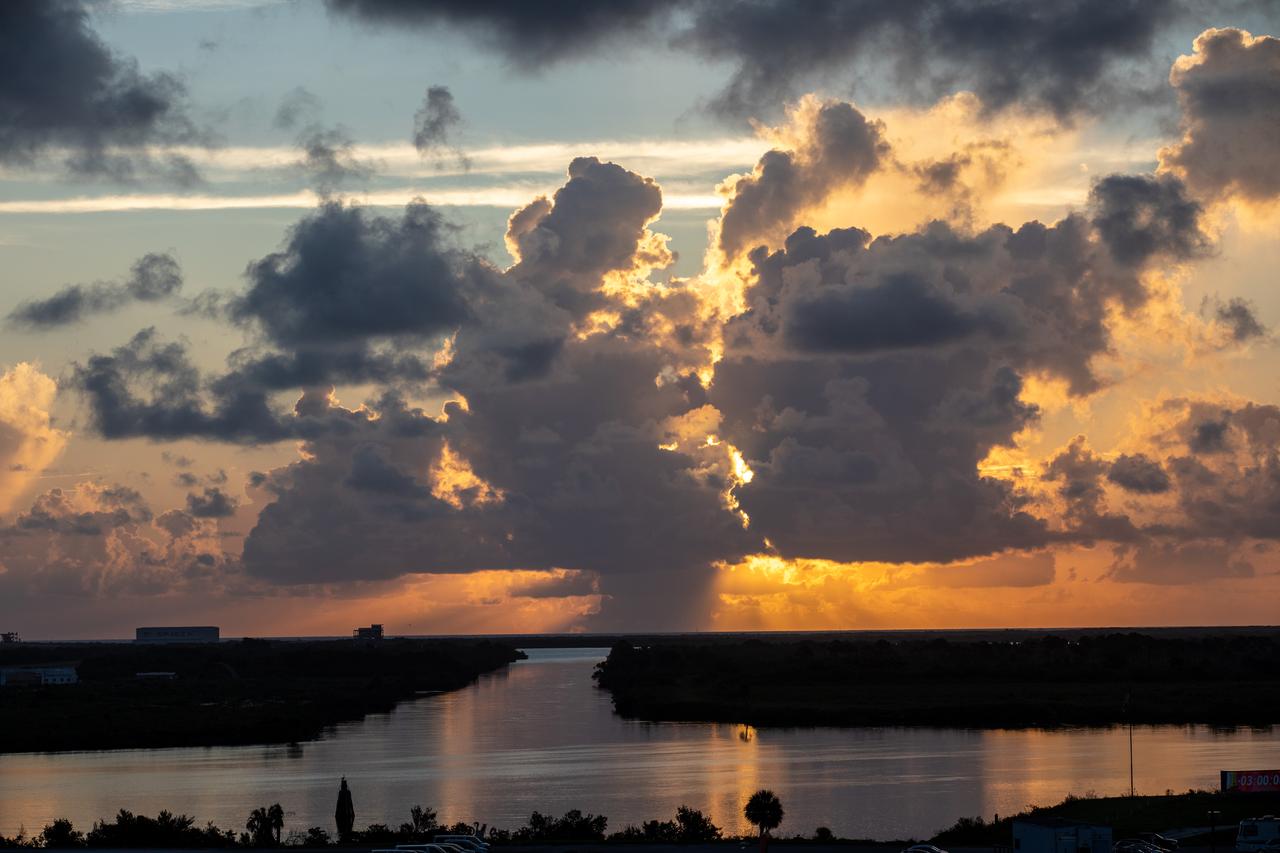

An early sunrise view of a waterway surrounding Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 25, 2020. NASA’s Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft will lift off from Launch Complex 39B on Artemis I, an uncrewed mission around the Moon.
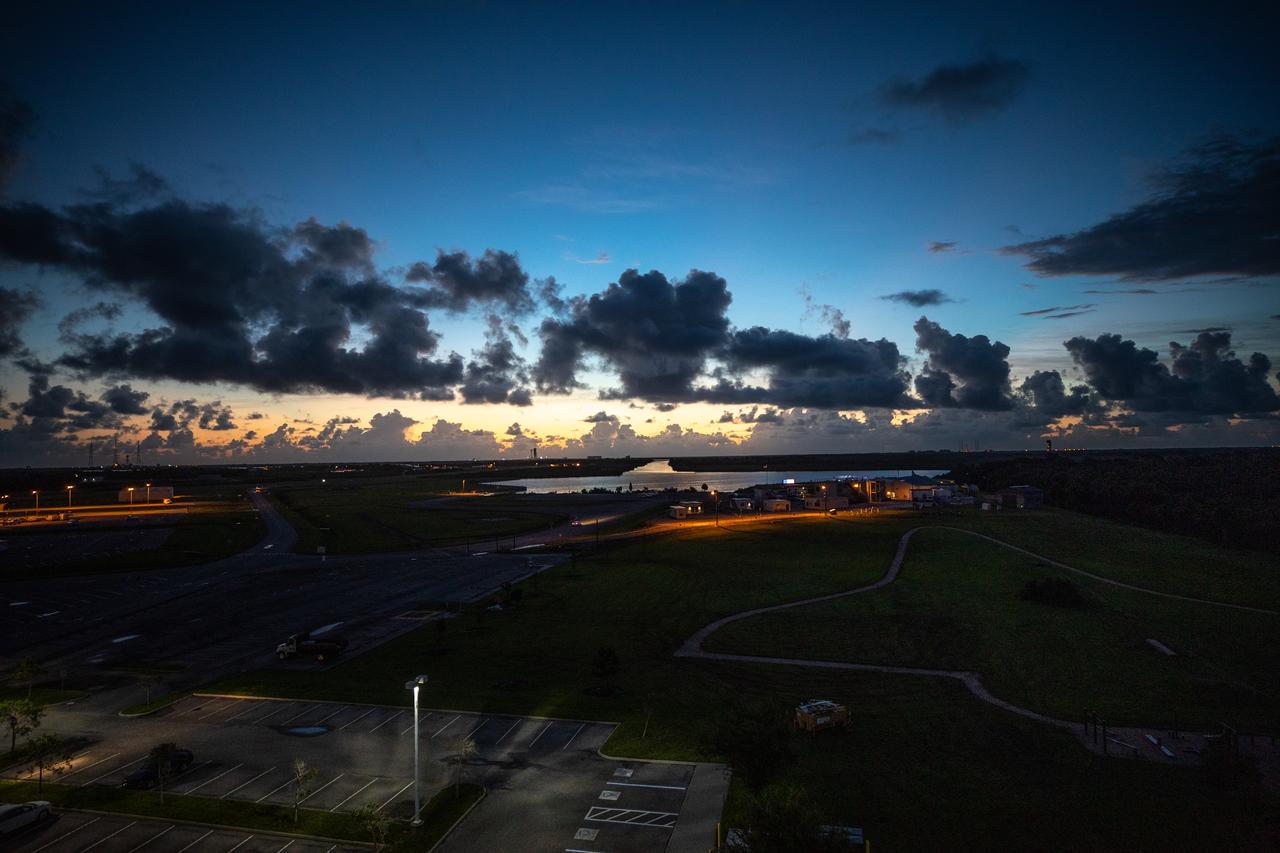

An early sunrise view of a waterway surrounding Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 25, 2020. NASA’s Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft will lift off from Launch Complex 39B on Artemis I, an uncrewed mission around the Moon.
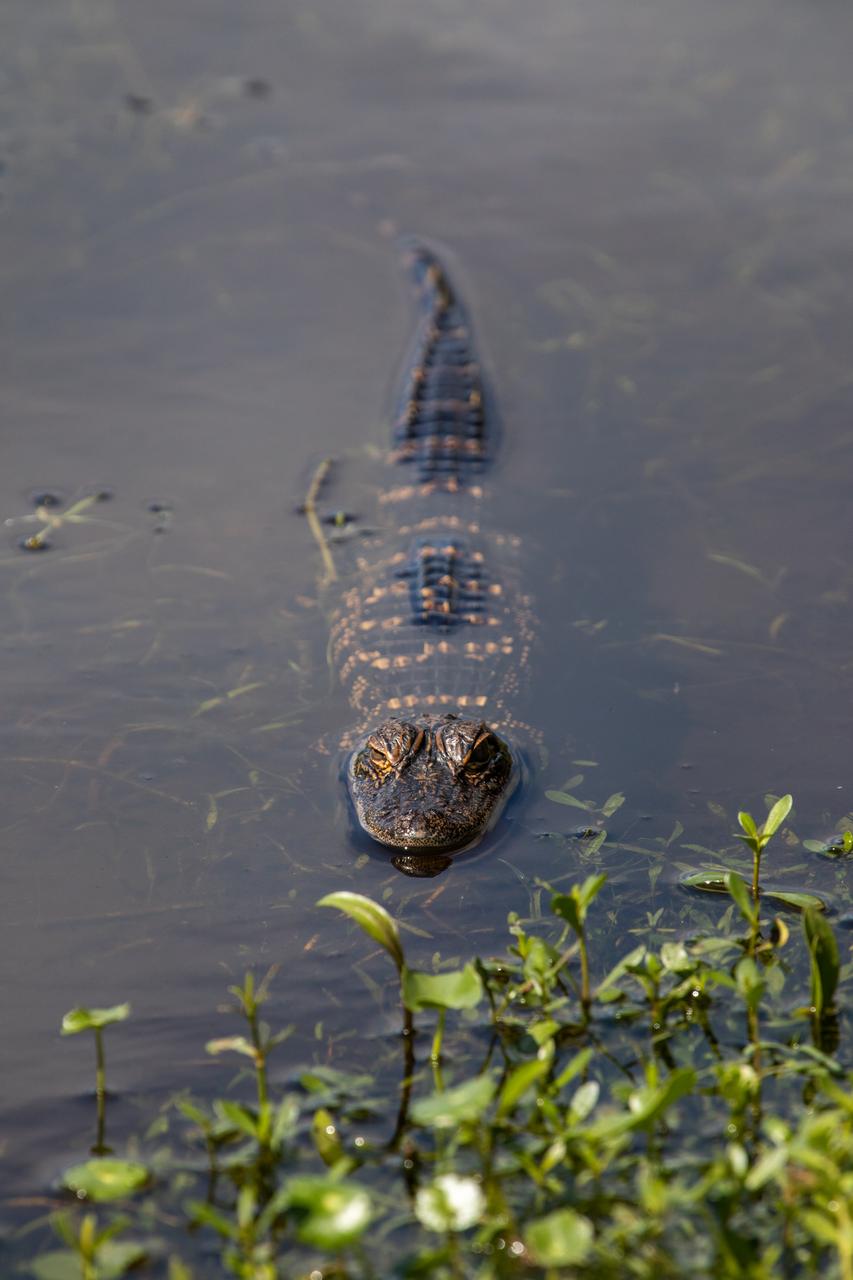

A baby alligator is in view in a waterway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 9, 2023. The center shares a boundary with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. The refuge is home to more than 65 amphibian and reptile species, along with 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal and 117 fish species.
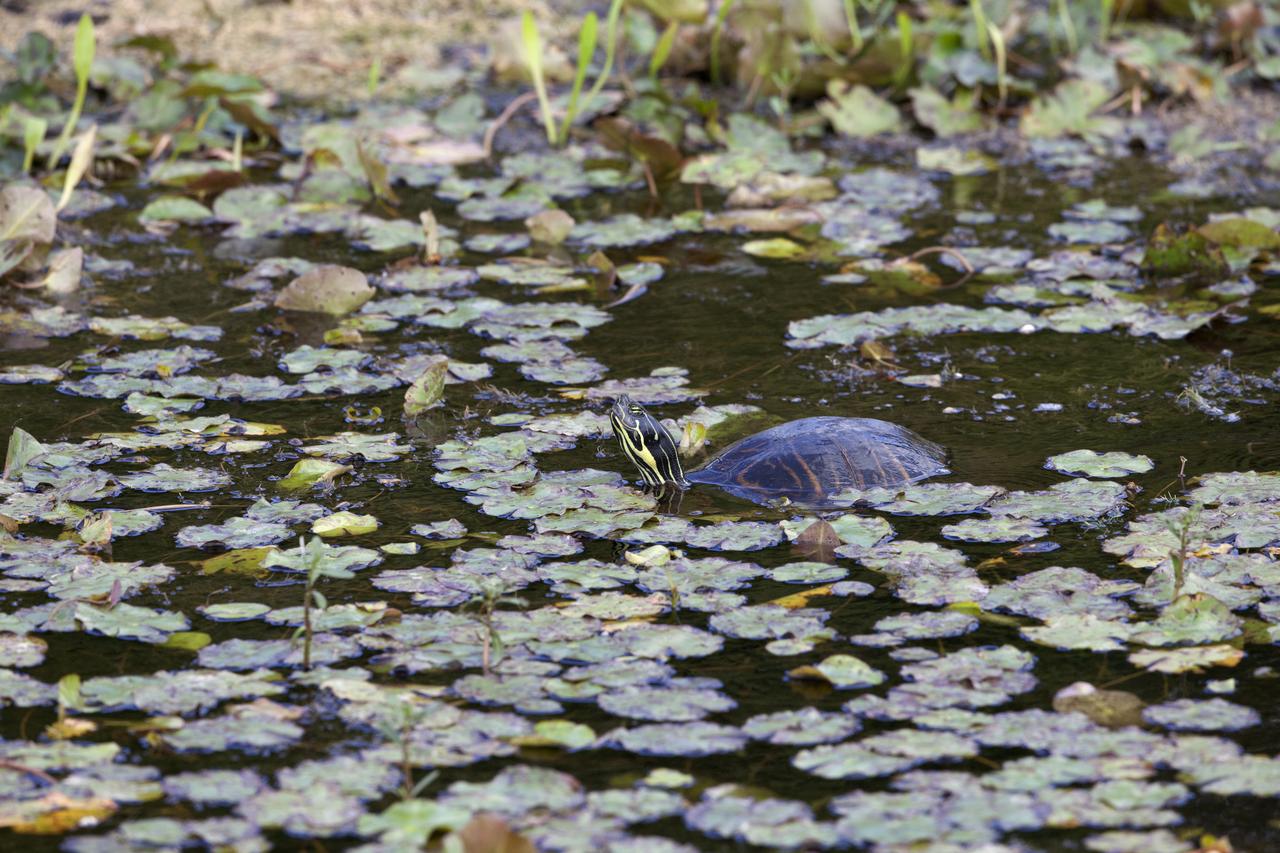

A turtle moves through a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
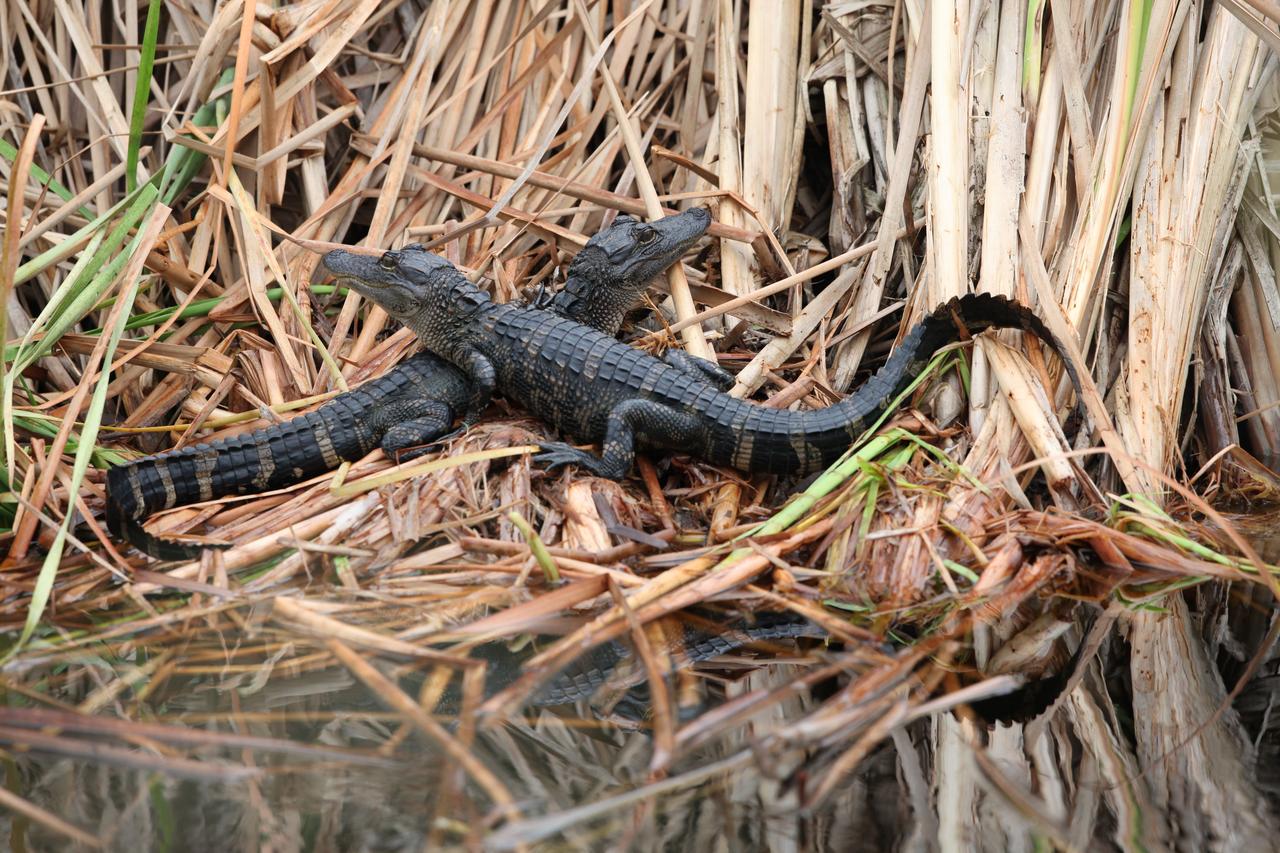

Juvenile alligators sit at the shoreline of a marshy waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
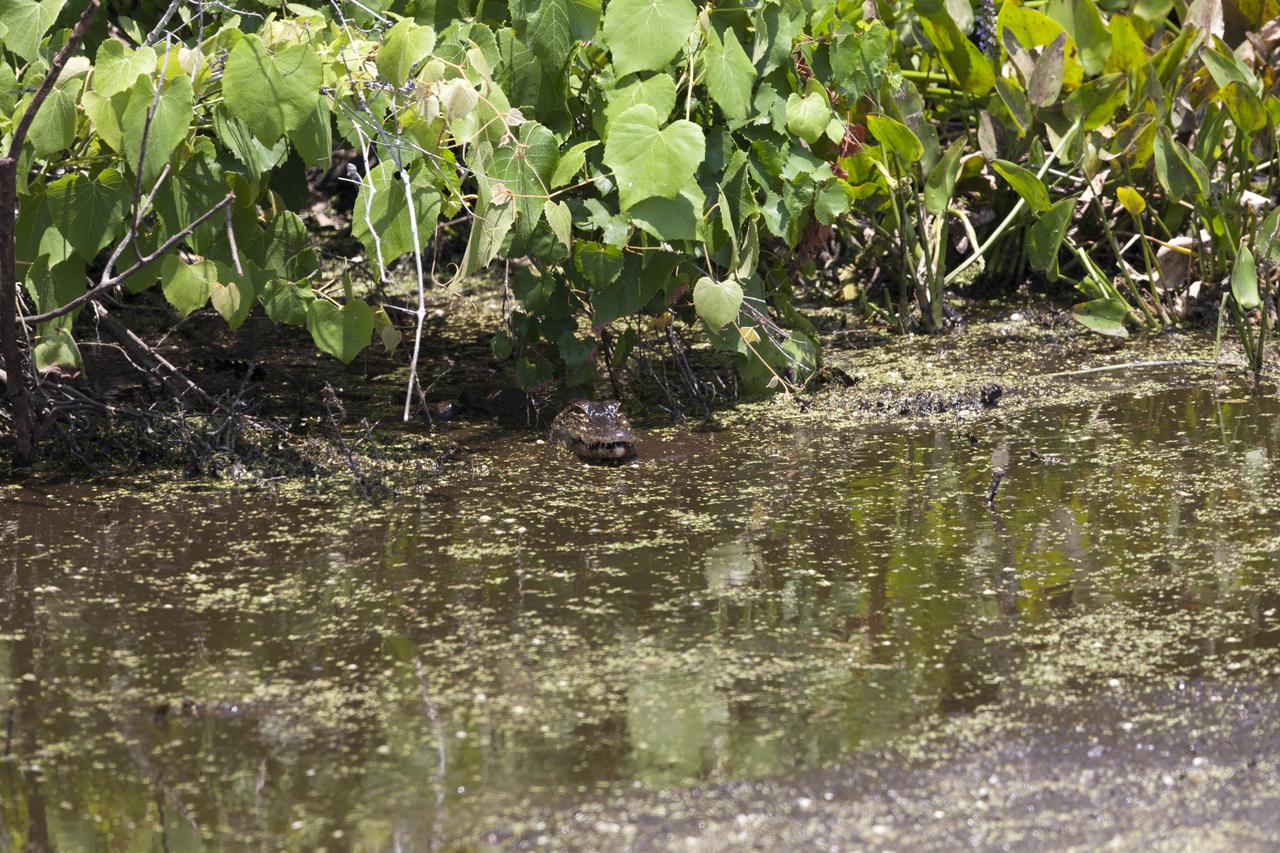

An alligator lurks in a brackish waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.

Two juvenile roseate spoonbills pause near a waterway at Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge in Florida. NASA’s Kennedy Space Center shares boundaries with the refuge, which is home to more than 330 native and migratory bird species, along with 25 mammal, 117 fish, and 65 amphibian and reptile species.
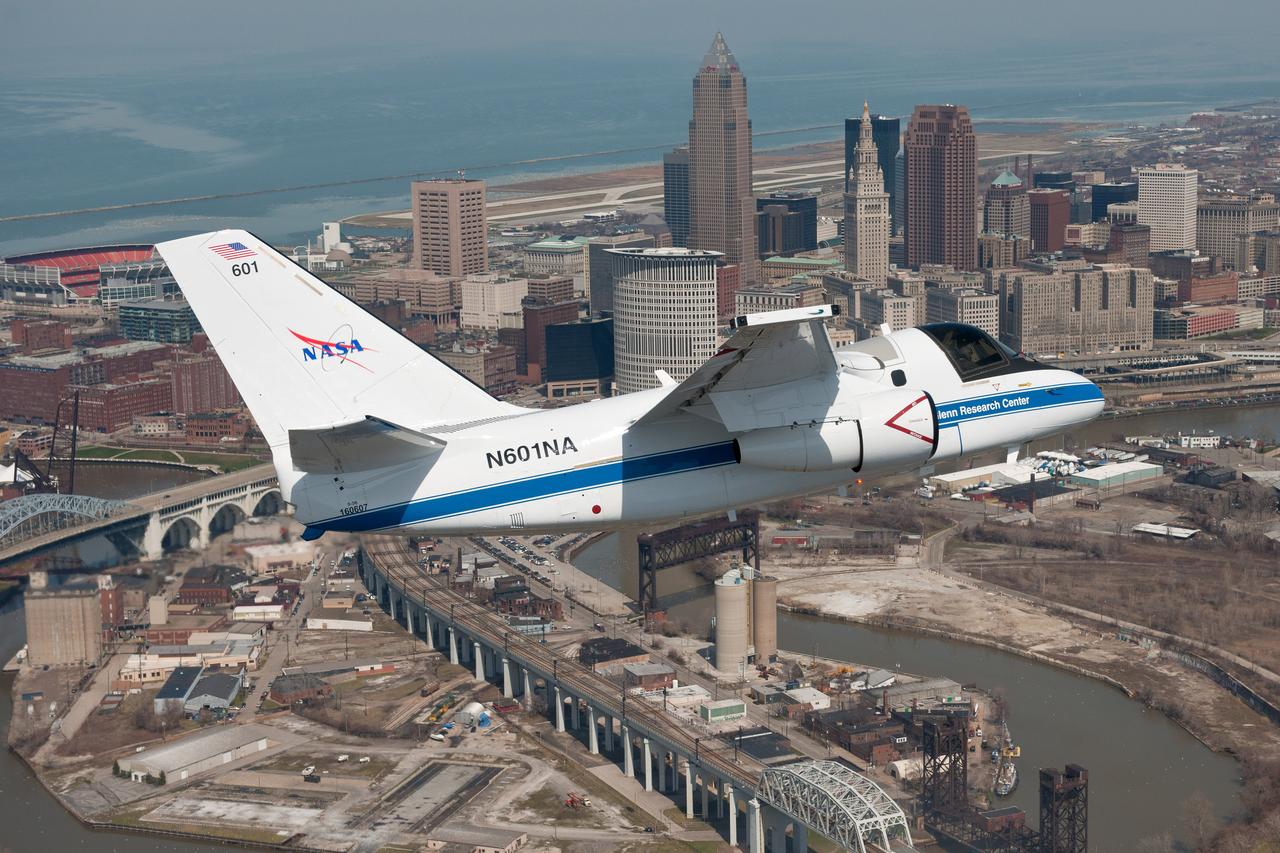

This photo shows NASA Glenn’s S-3 Viking Aircraft flying over downtown Cleveland, Ohio. The S-3 continues to conduct important research including regular flights over Lake Erie and other waterways to image algal blooms that have plagued the area’s waters.
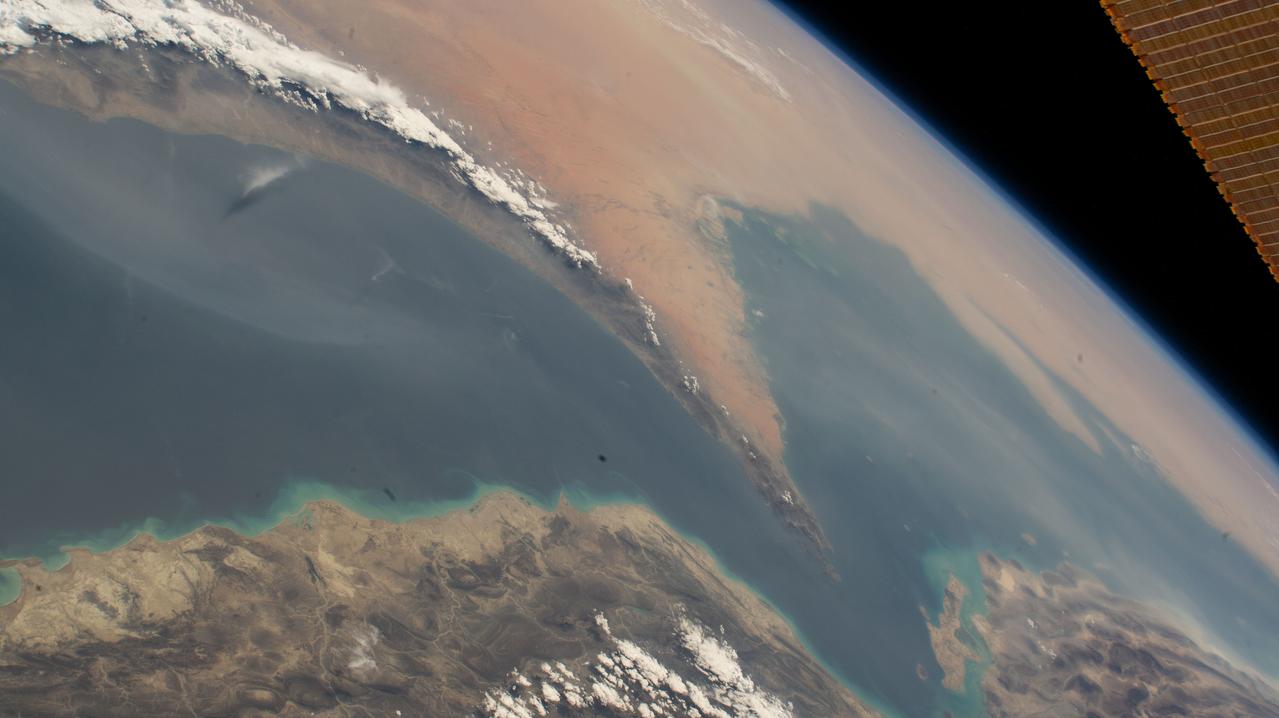

iss067e270600 (Aug. 18, 2022) --- The Strait of Hormuz connects the Gulf of Oman (left) with the Persian Gulf (right). The waterway also separates the Middle Eastern nation of Iran (bottom) from the Arabian Peninsula nations of Oman, United Arab Emirates, and Qatar (top left to right).
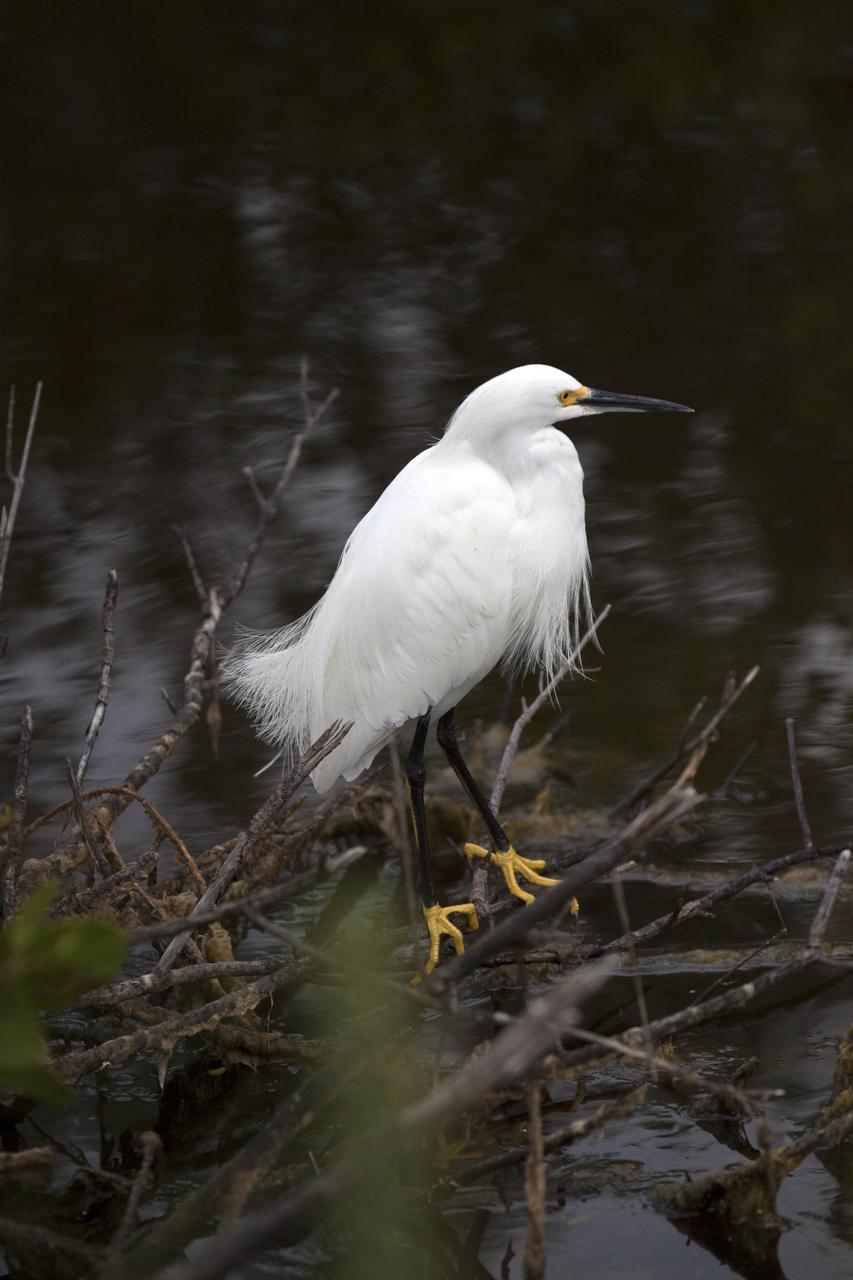

A snowy egret perches on a branch near a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. The bird is one of more than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles that call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
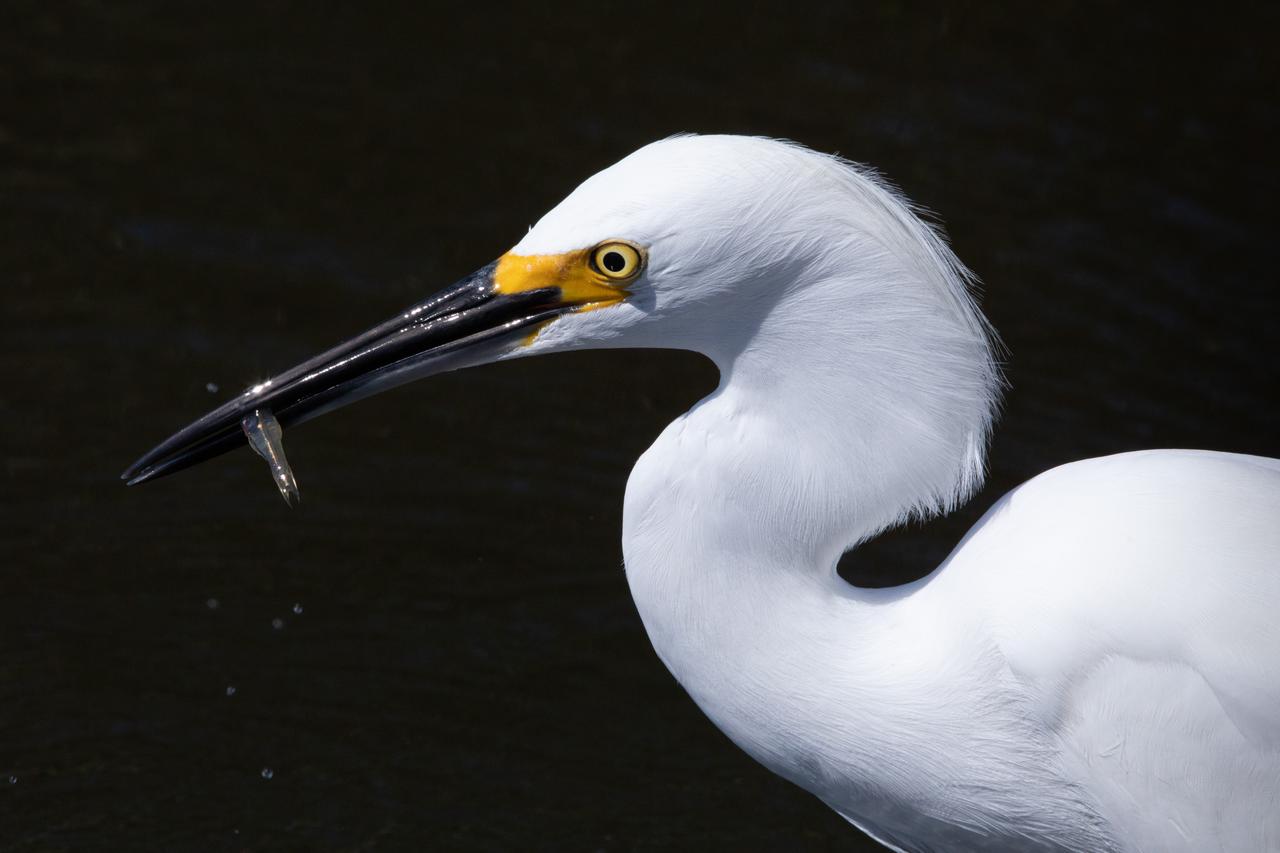

A Great Egret catches a small fish in a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
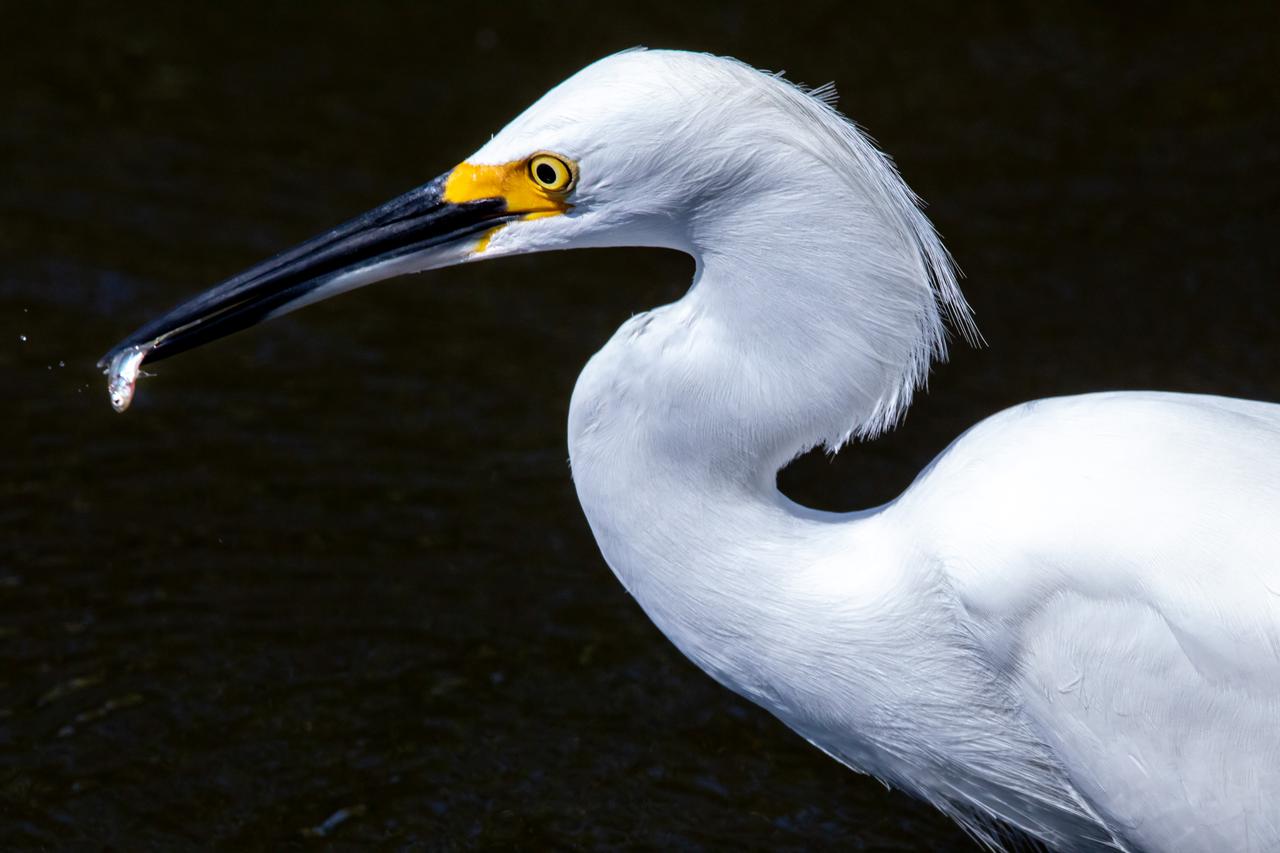

A Great Egret catches a small fish in a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
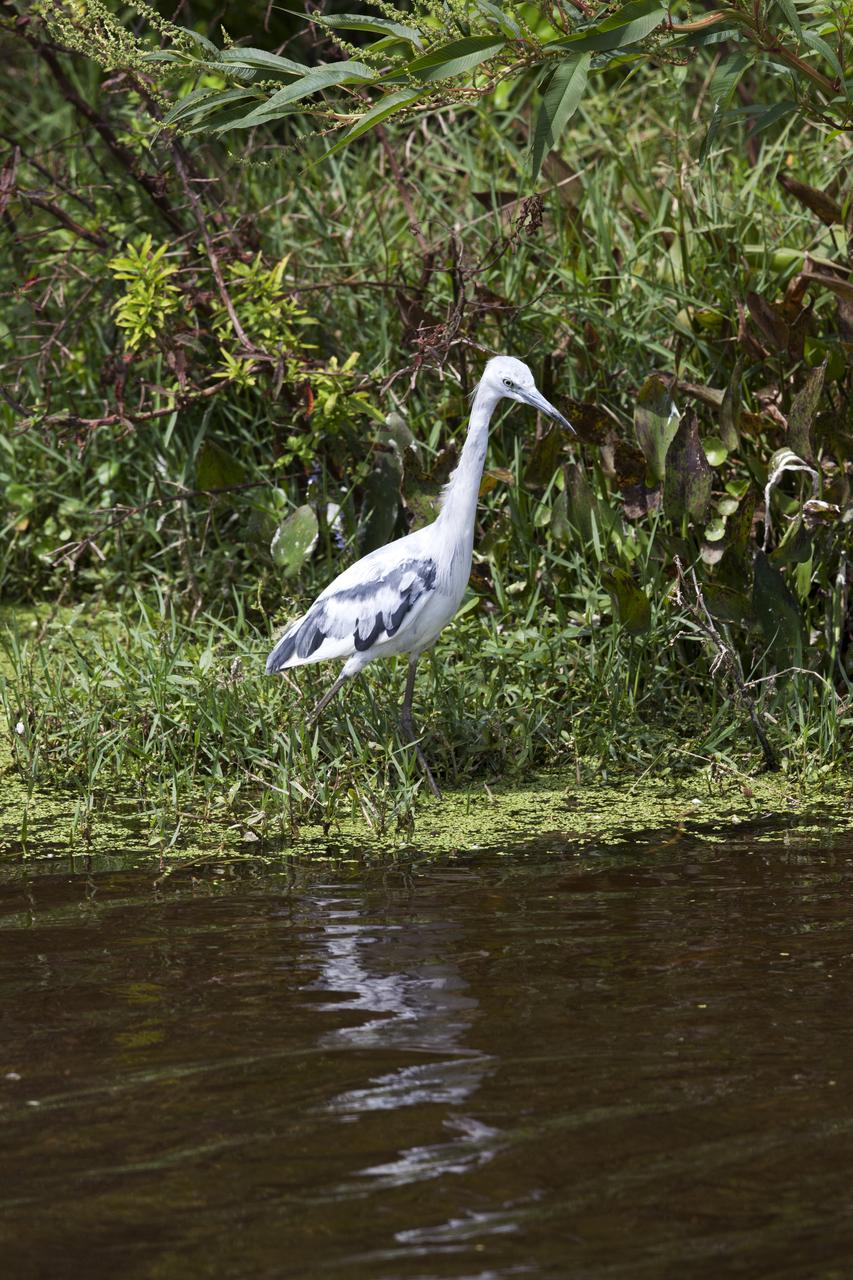

A juvenile heron wades in a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
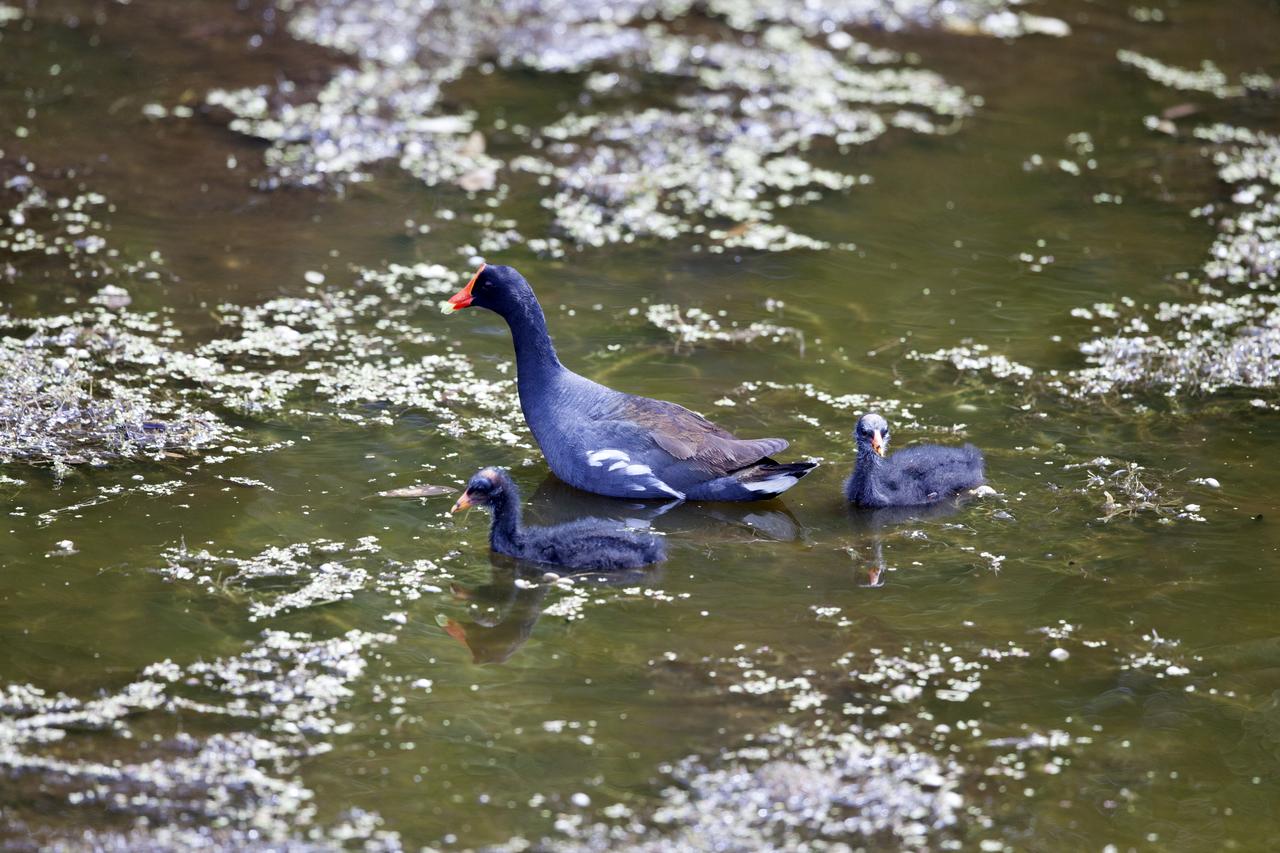

Common gallinules swim in a shallow waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
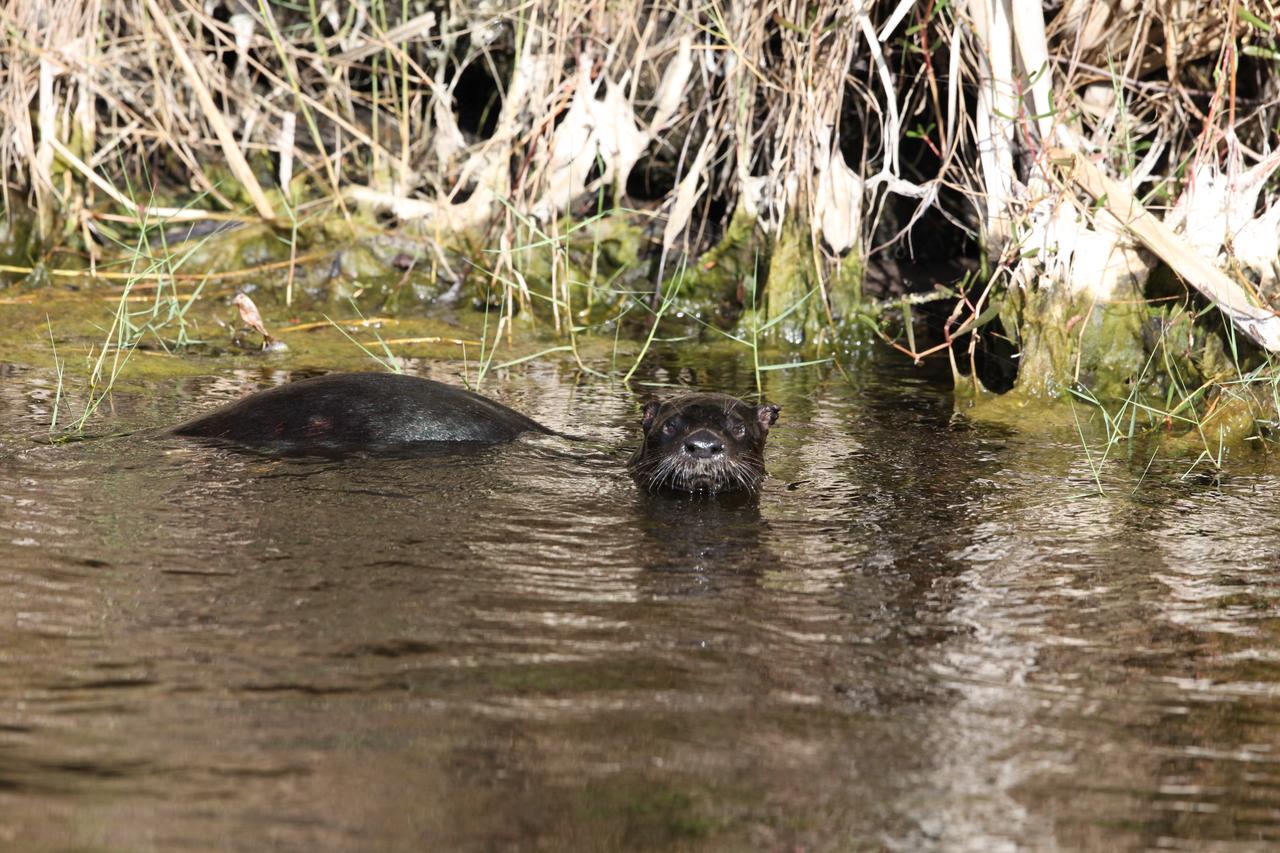

An otter swims through a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
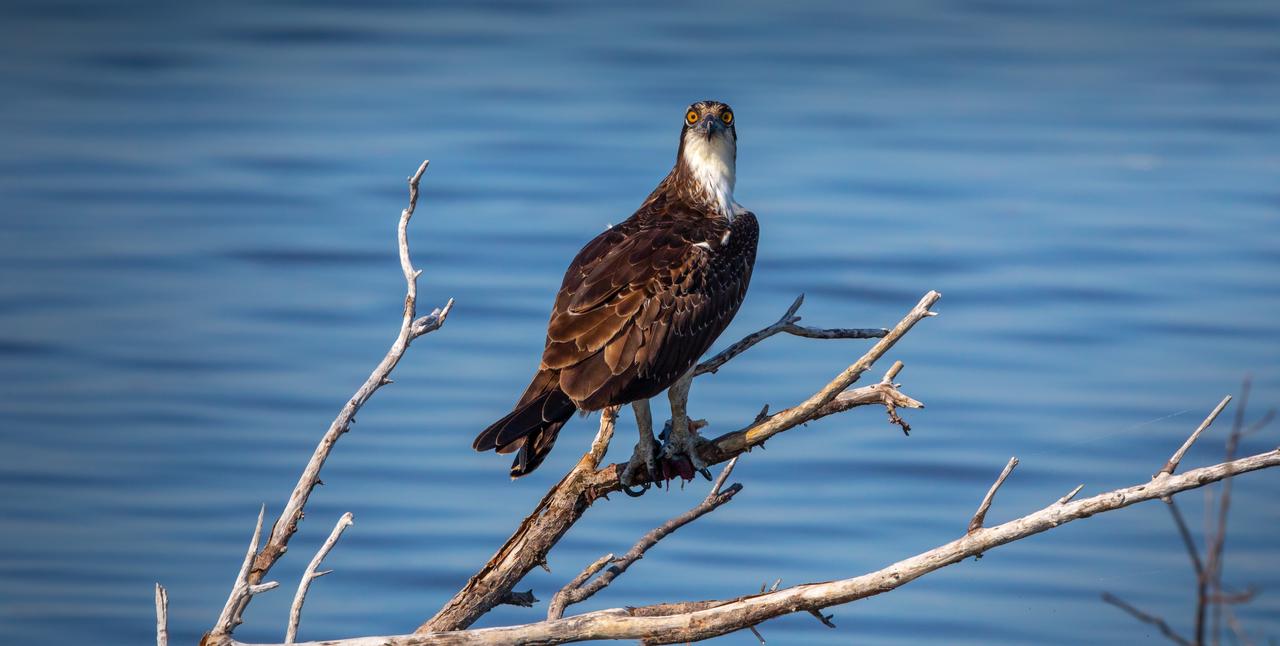

An osprey sits on a branch near a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
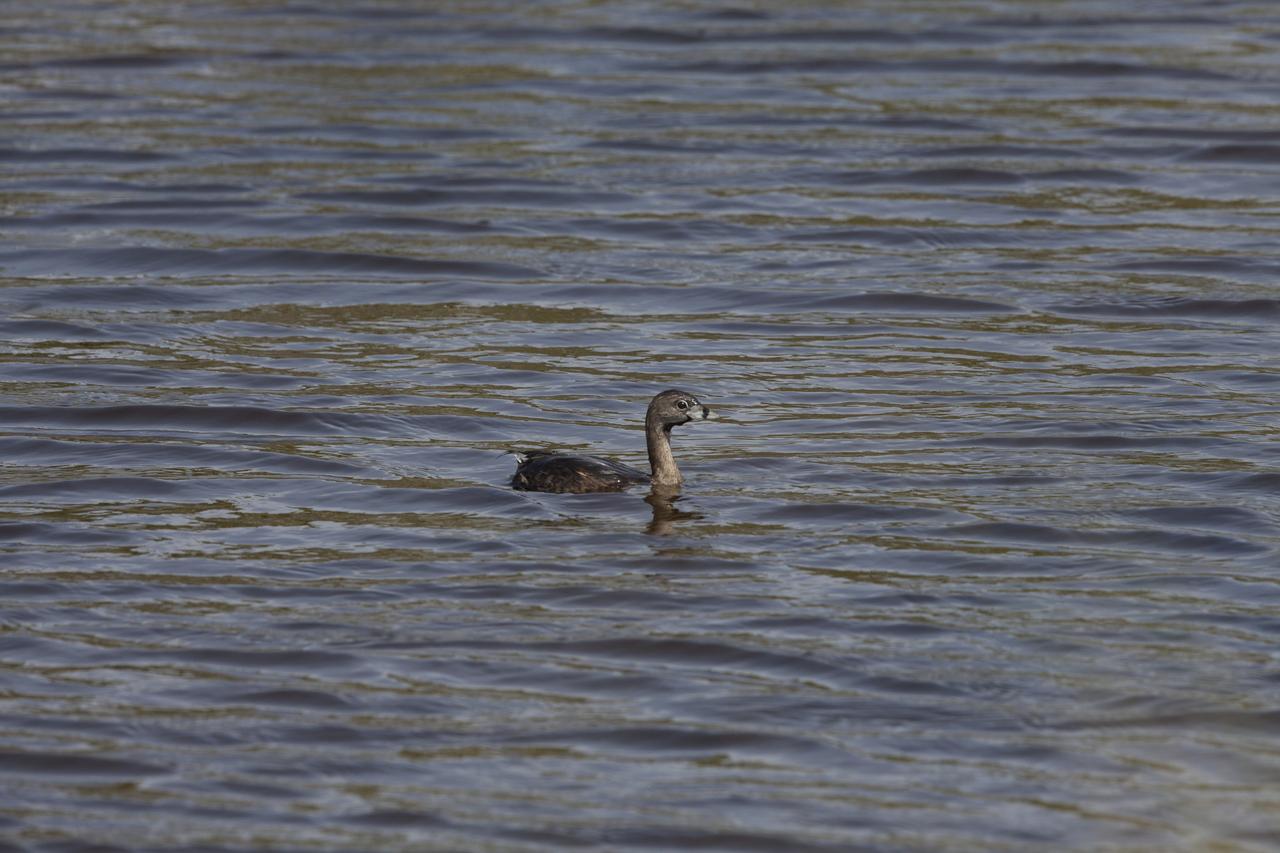

A pied-billed grebe paddles in one of the many waterways at Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge in Florida. NASA’s Kennedy Space Center shares boundaries with the refuge, which is home to more than 330 native and migratory bird species, along with 25 mammal, 117 fish, and 65 amphibian and reptile species.
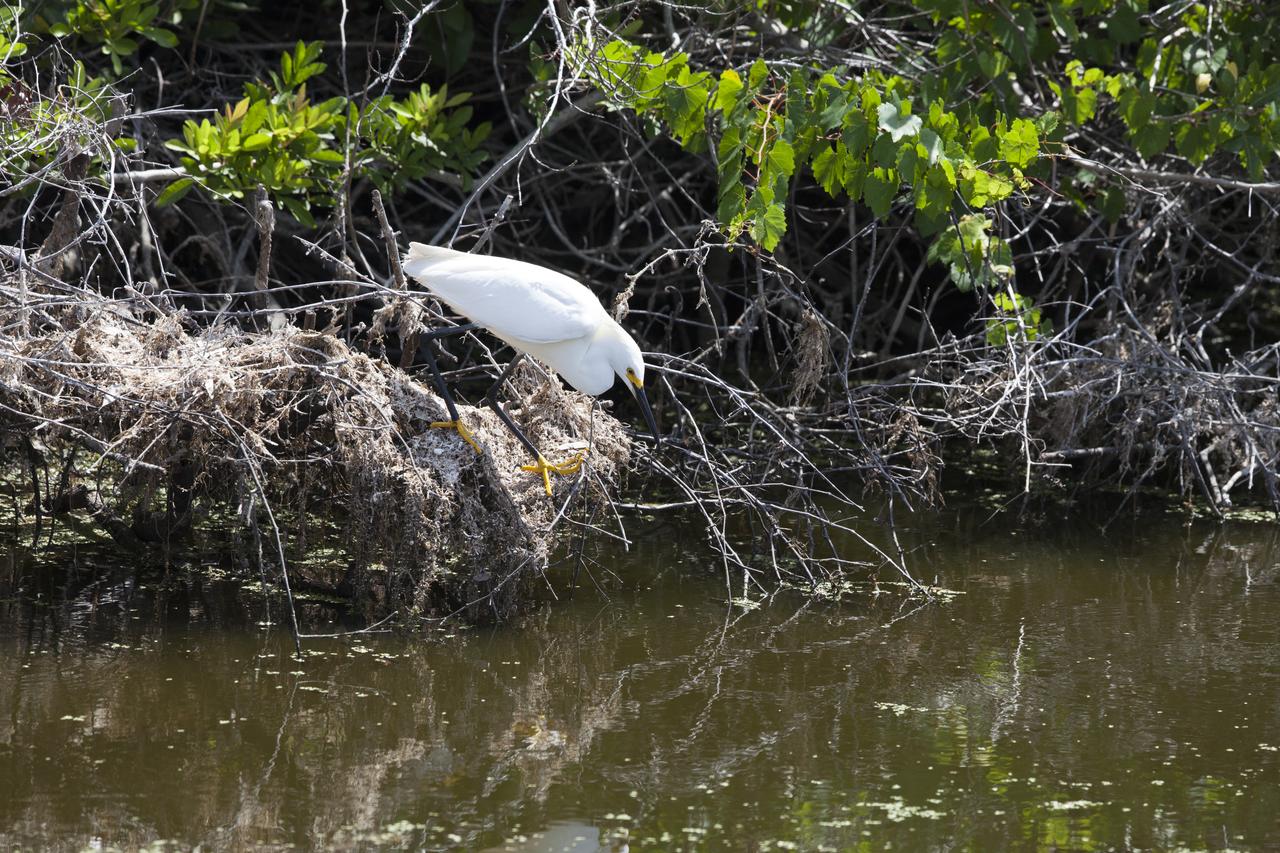

A snowy egret perches on a branch at the shoreline of a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
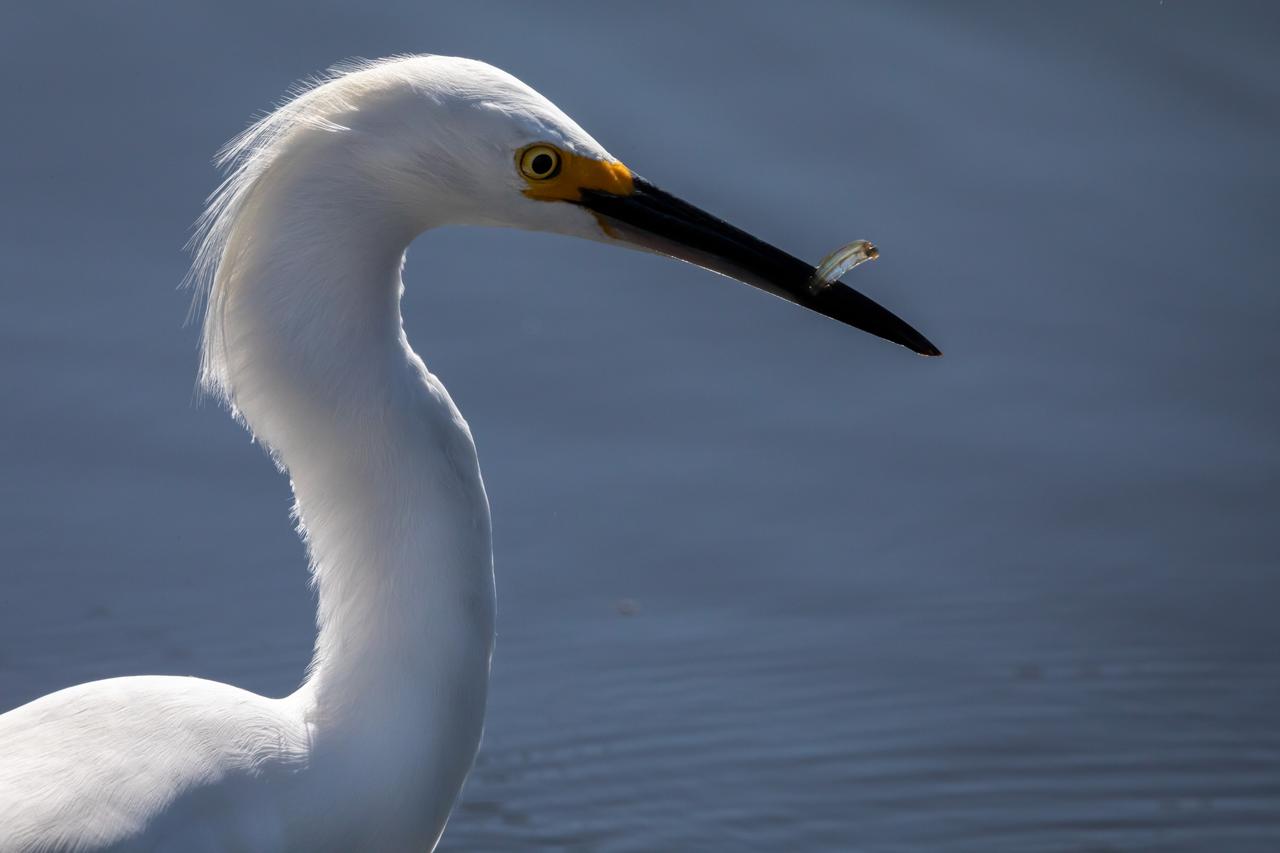

A Great Egret catches a small fish in a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
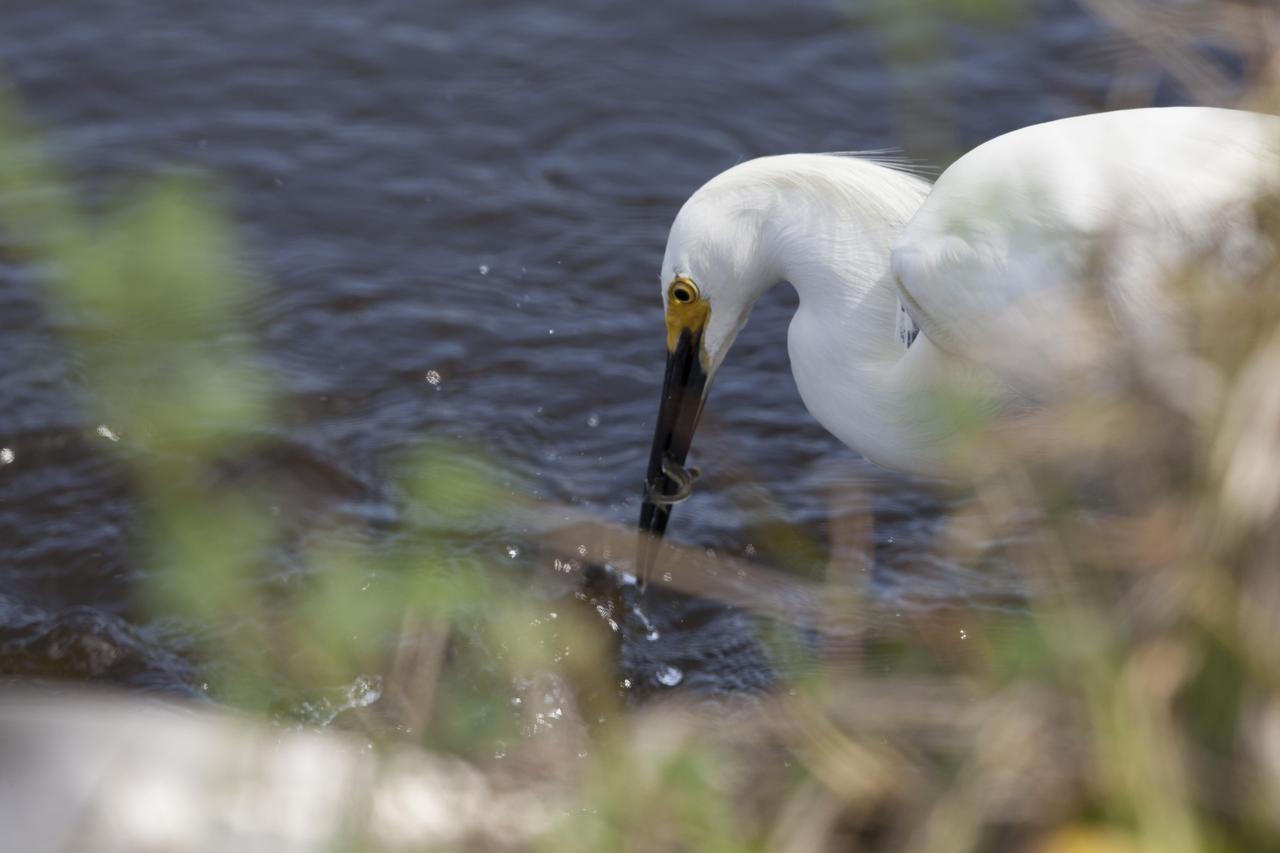

A snowy egret successfully catches a small fish in a shallow waterway at Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge in Florida. NASA’s Kennedy Space Center shares boundaries with the refuge, which is home to more than 330 native and migratory bird species, along with 25 mammal, 117 fish, and 65 amphibian and reptile species.
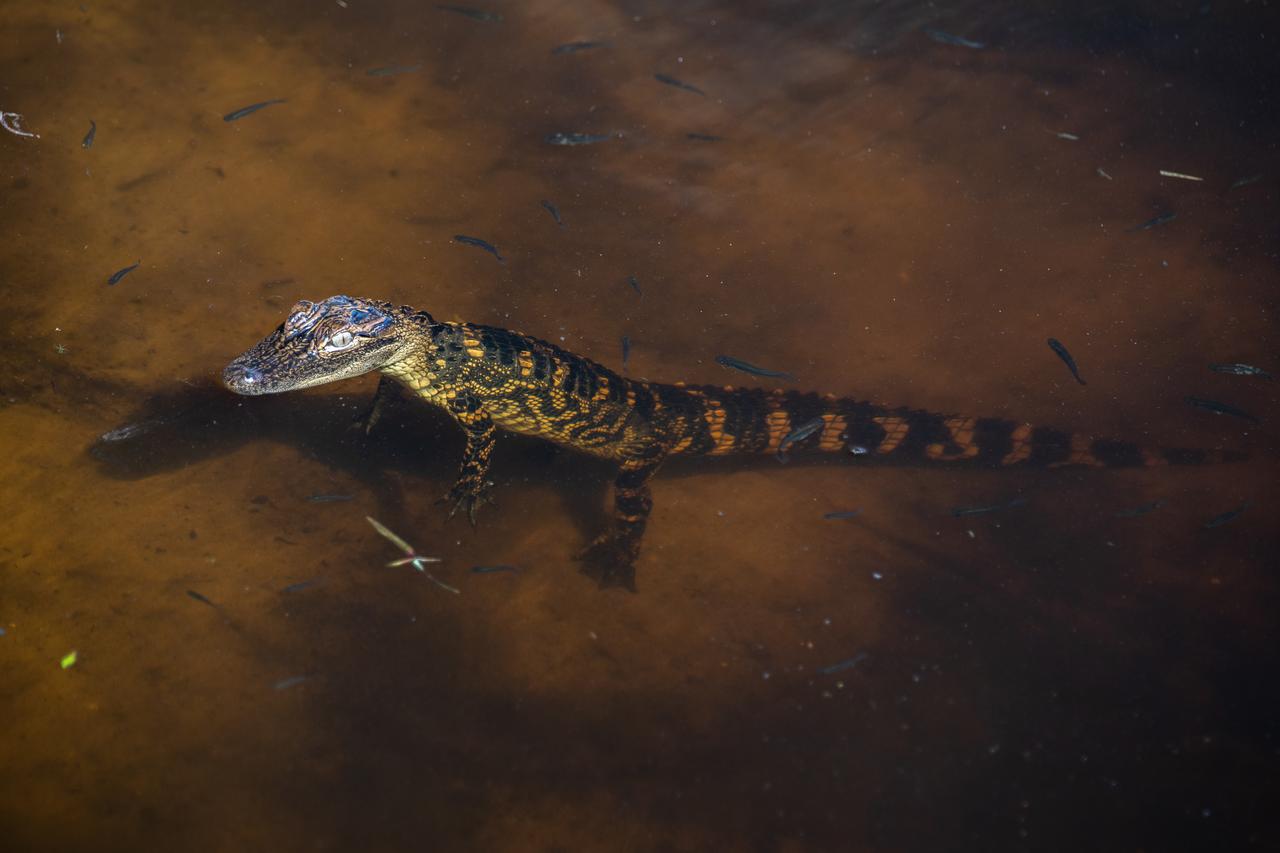

A baby alligator is in view in a waterway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 9, 2023. The center shares a boundary with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. The refuge is home to more than 65 amphibian and reptile species, along with 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal and 117 fish species.
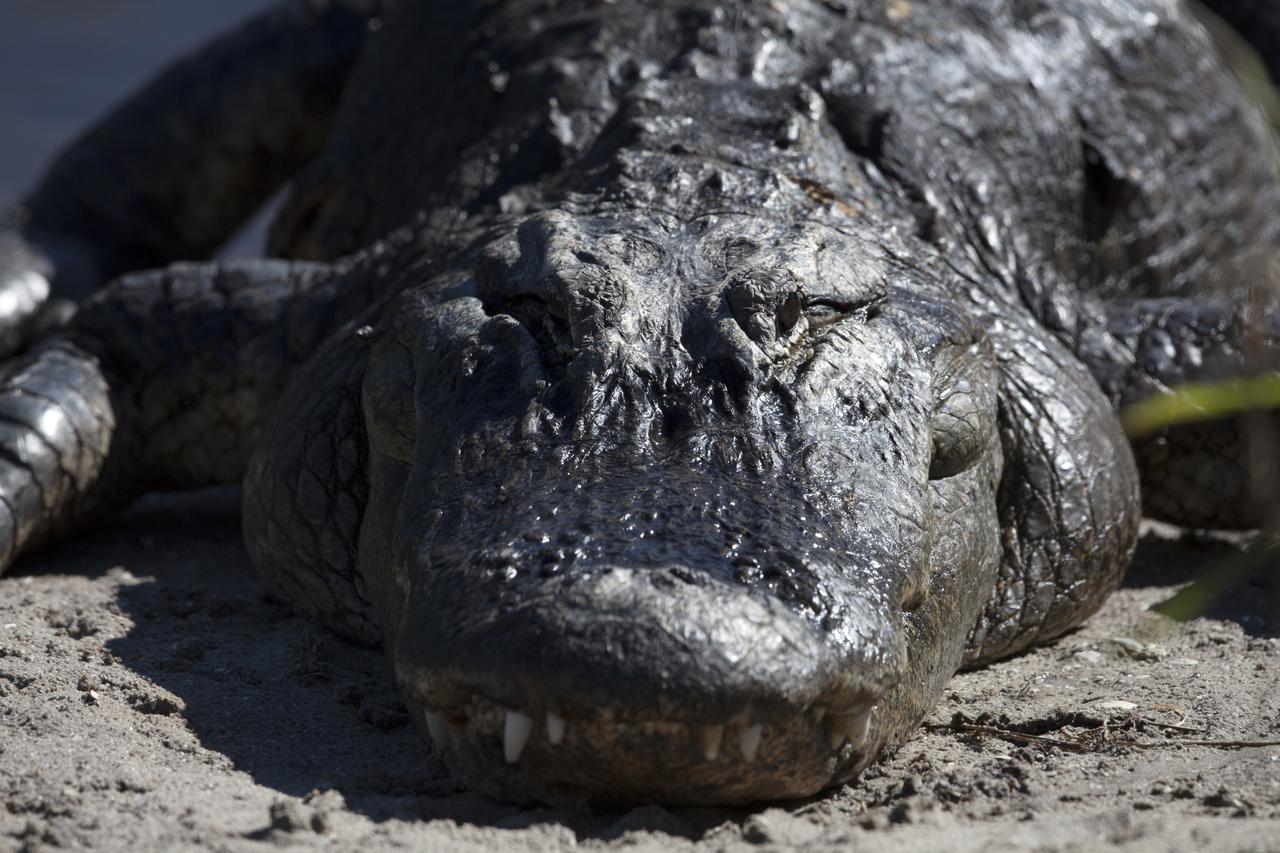

An adult alligator suns himself along the shoreline of a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
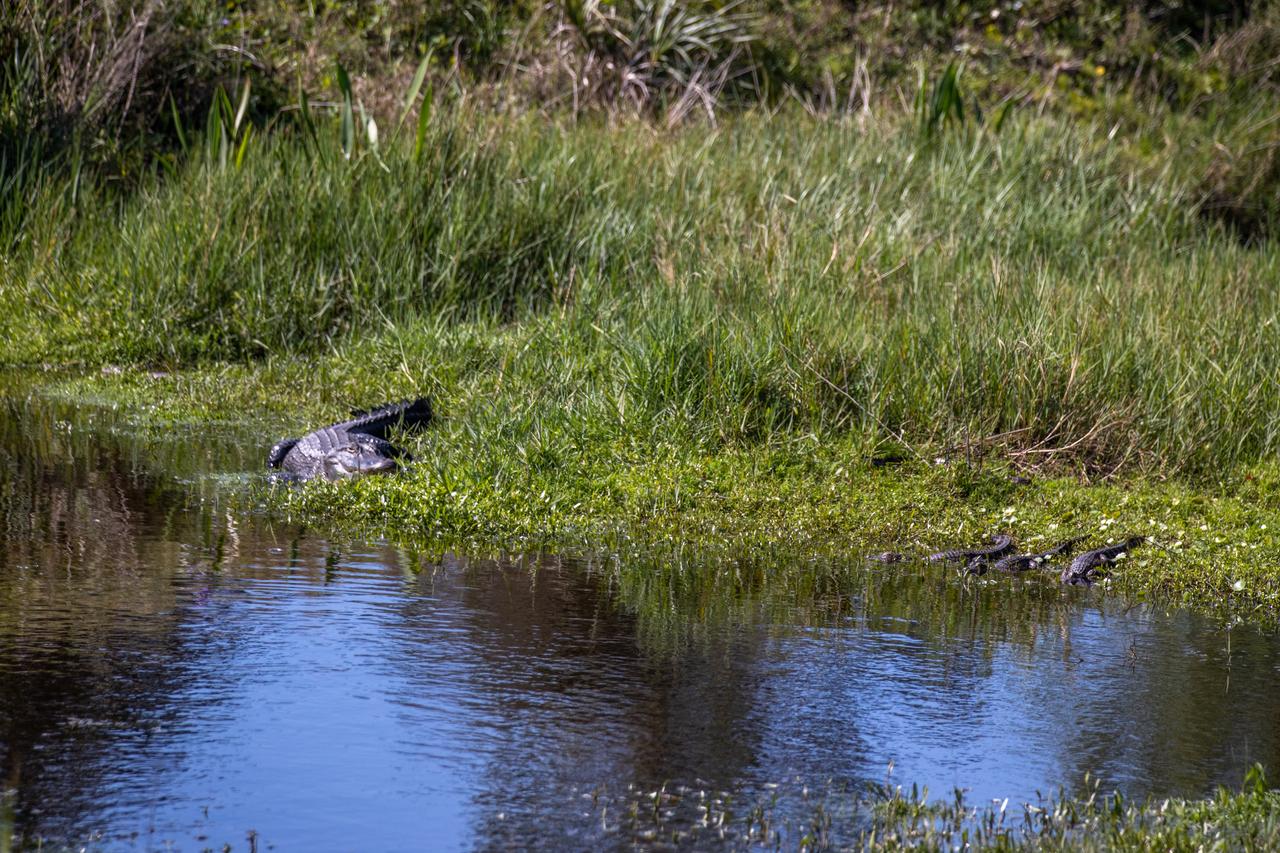

A large alligator is in view in a waterway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 9, 2023. The center shares a boundary with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. The refuge is home to more than 65 amphibian and reptile species, along with 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal and 117 fish species.
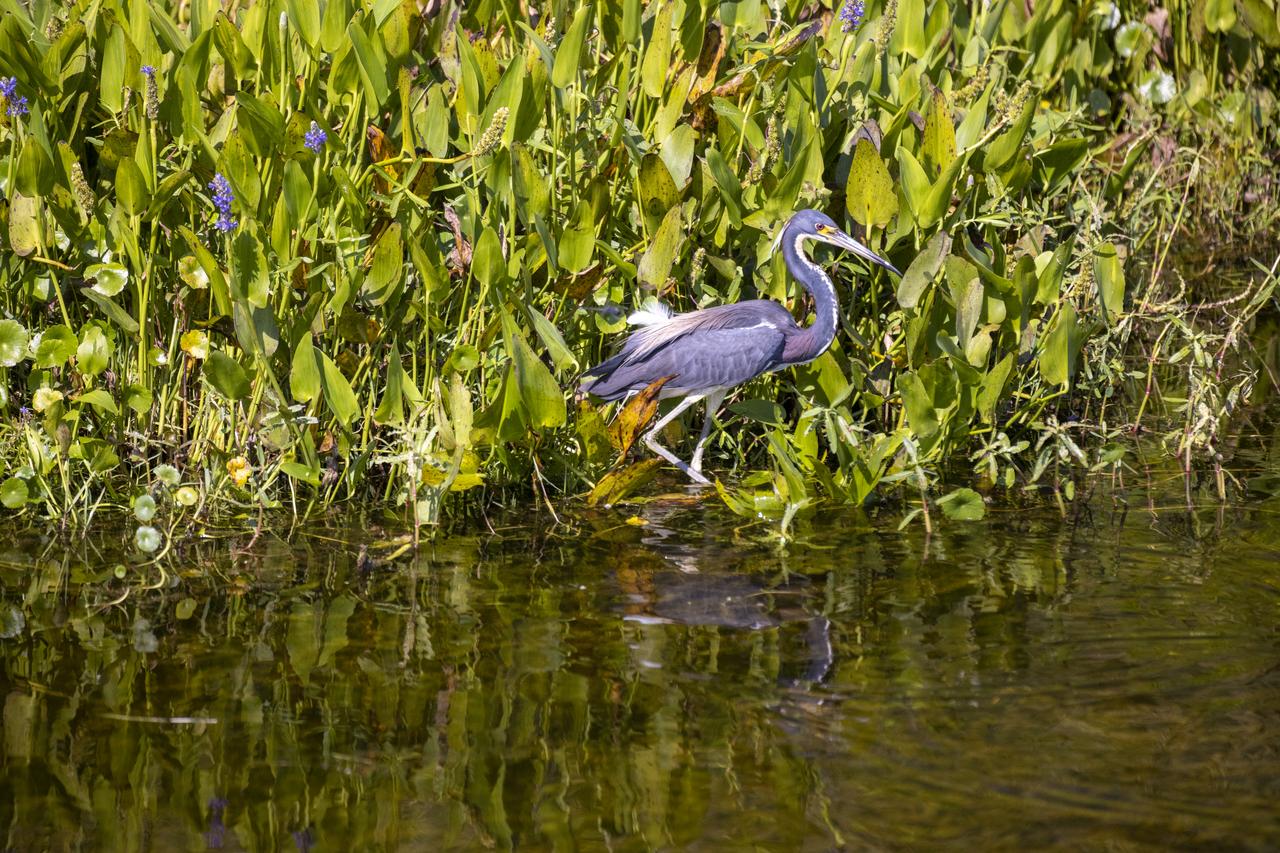

Framed by wildflowers, a tricolored heron wades in a waterway at NASA’s John F. Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 19, 2023. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.

Juvenile alligators gather at the shoreline of a marshy waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
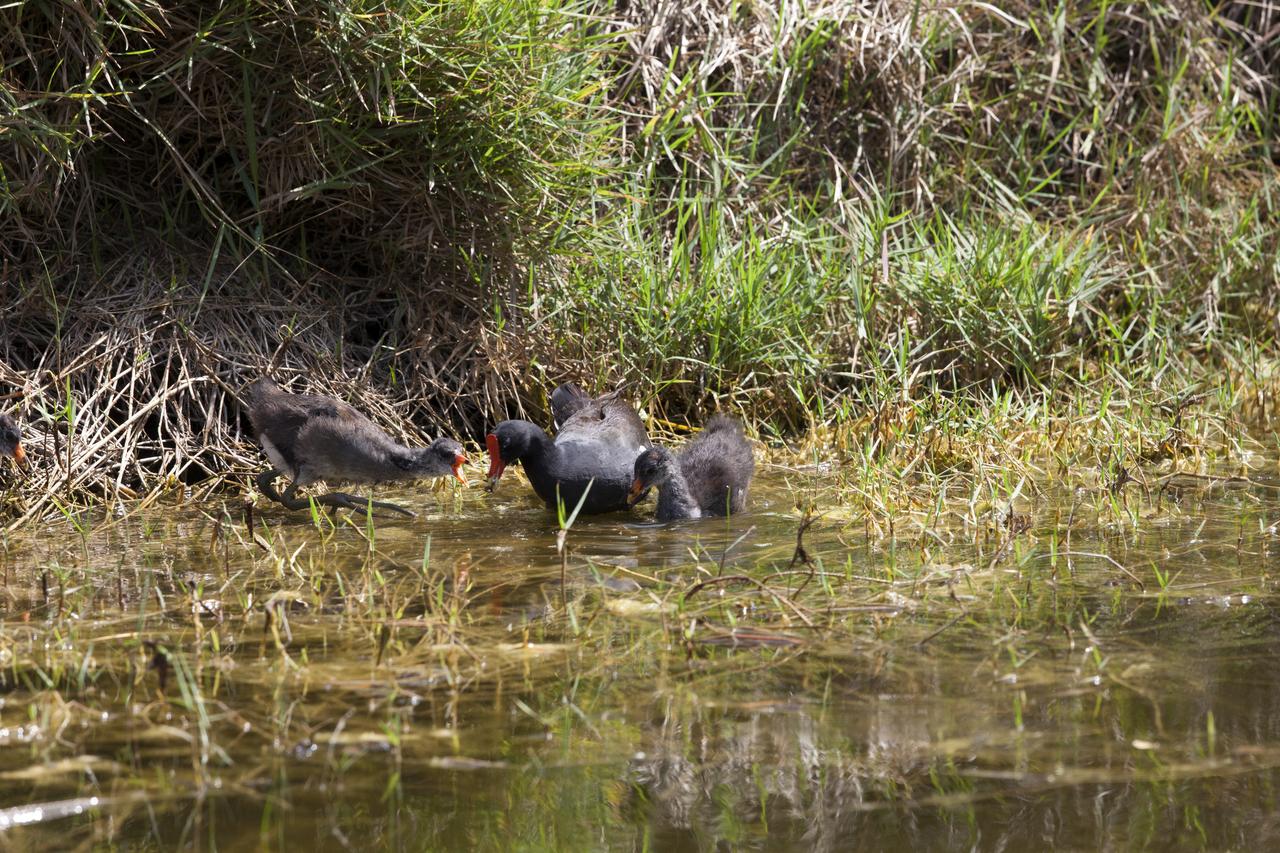

Common gallinules search for food in a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
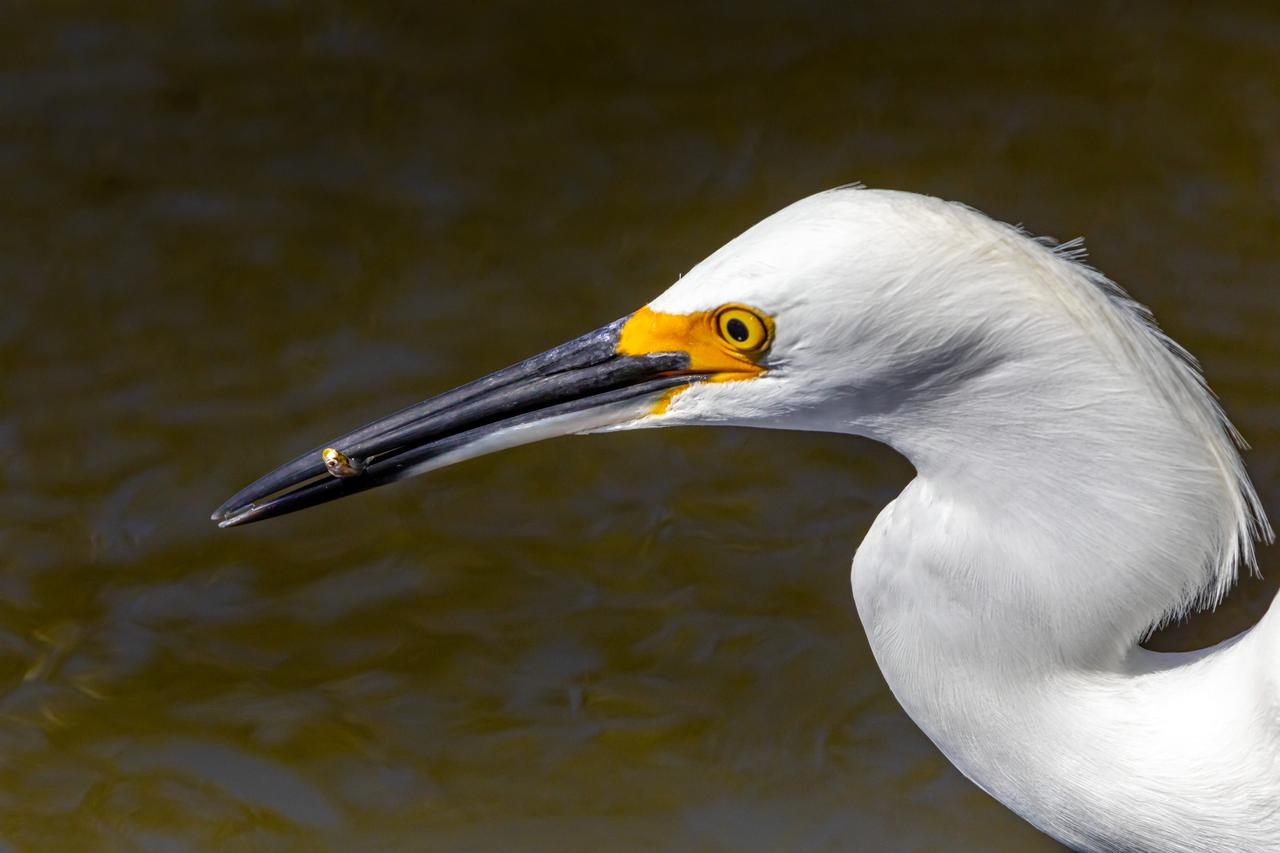

A Great Egret is in a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
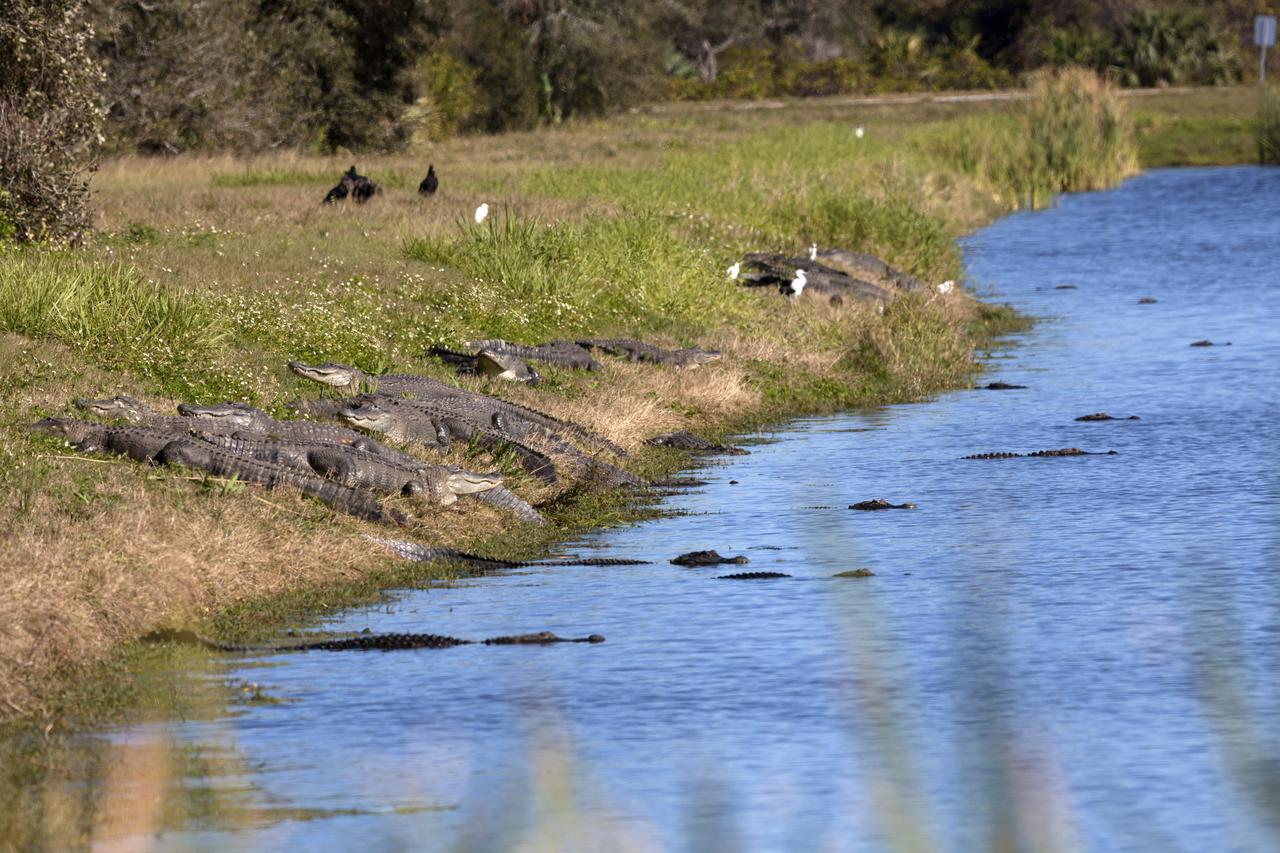

Alligators sun themselves along the shoreline of waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
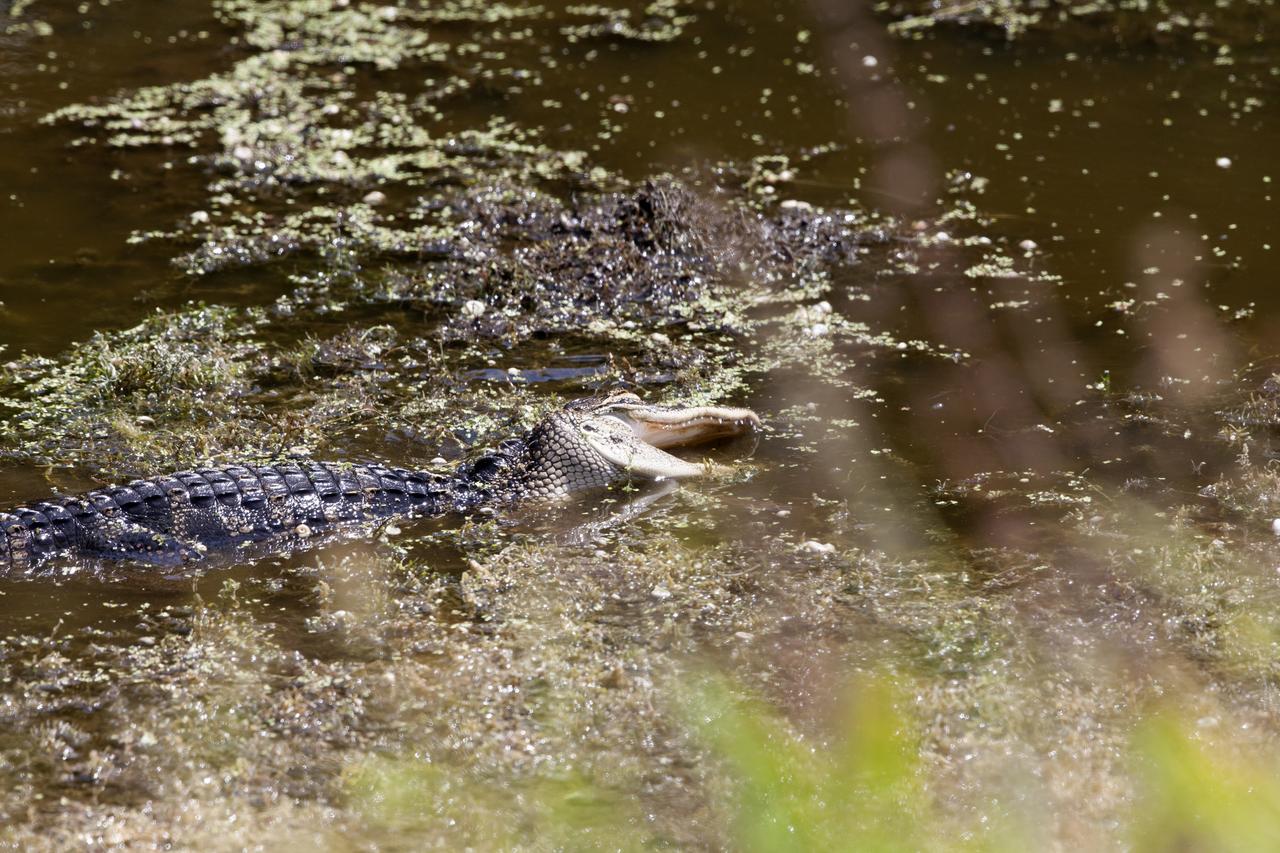

An alligator swims in a brackish waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
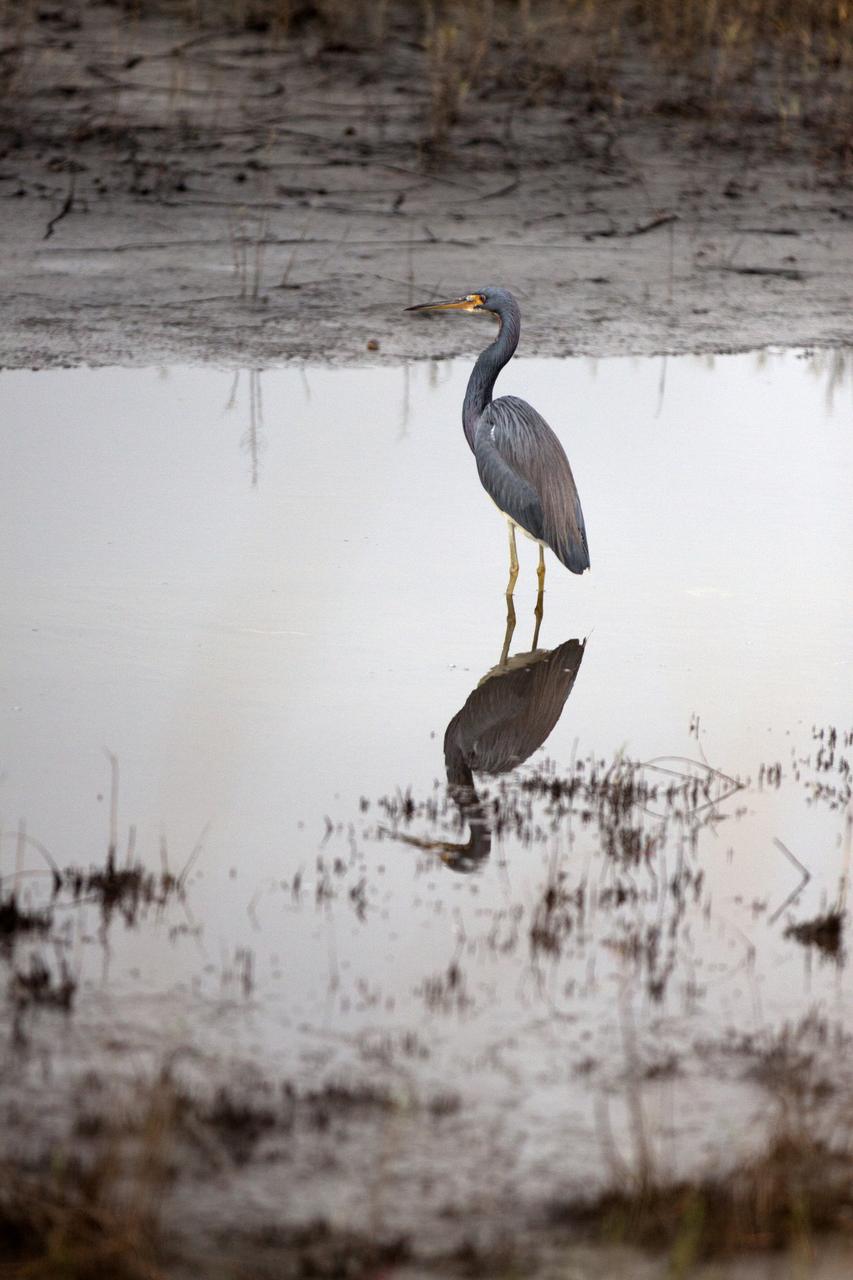

A Great Blue Heron wades in a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. The bird is one of more than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles that call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
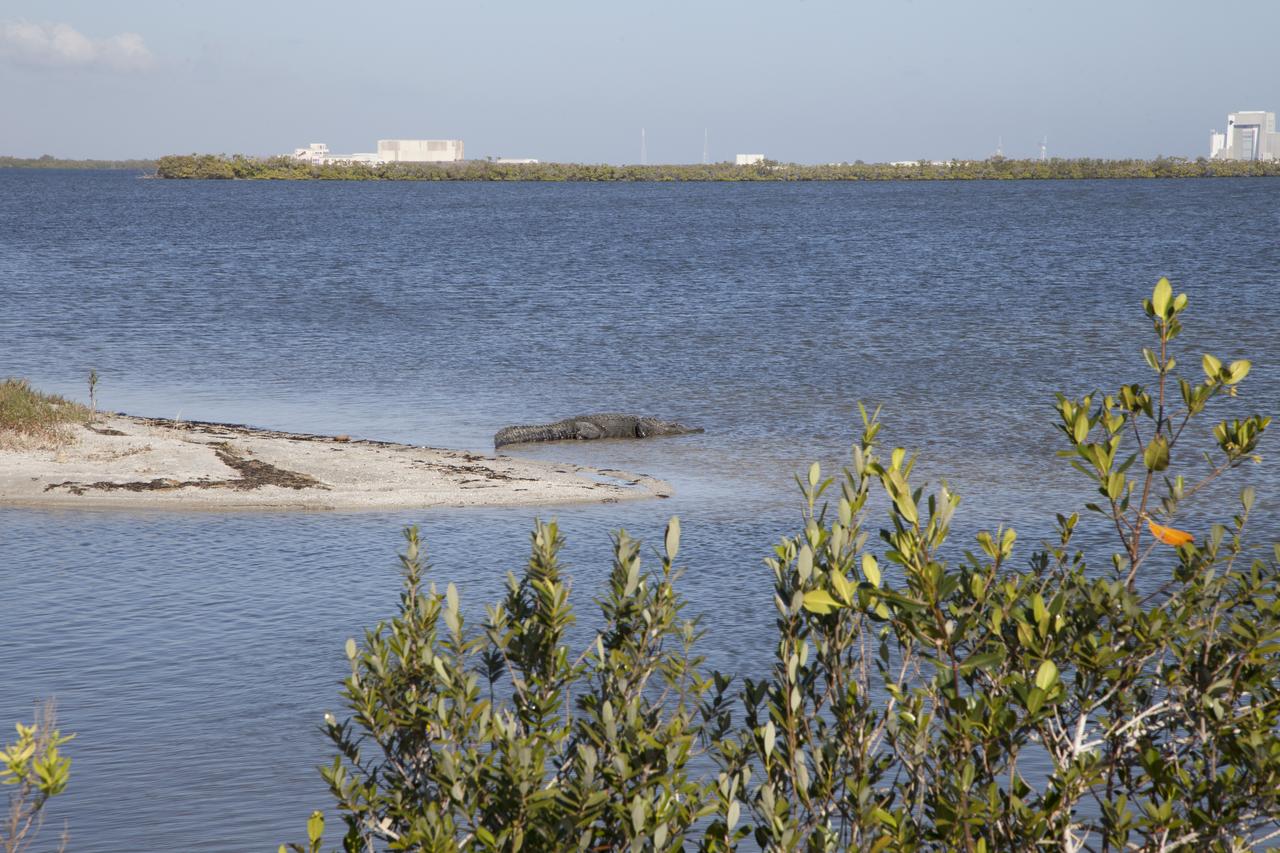

A large alligator basks in the intercoastal waterway near the NASA Causeway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a boundary with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. The refuge is home to more than 65 amphibian and reptile species, along with 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal and 117 fish species.
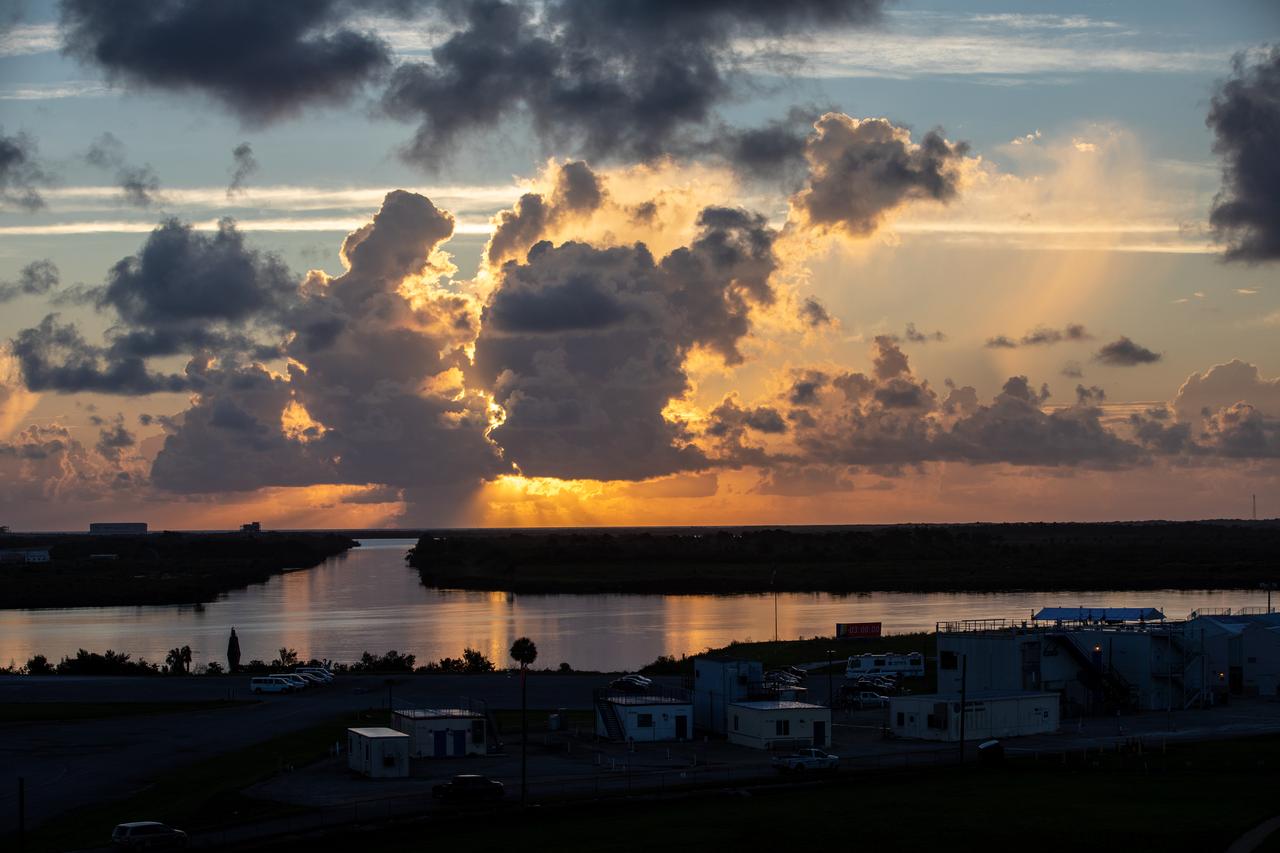

An early sunrise view of a waterway surrounding Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 25, 2020. NASA’s Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft will lift off from Launch Complex 39B on Artemis I, an uncrewed mission around the Moon.
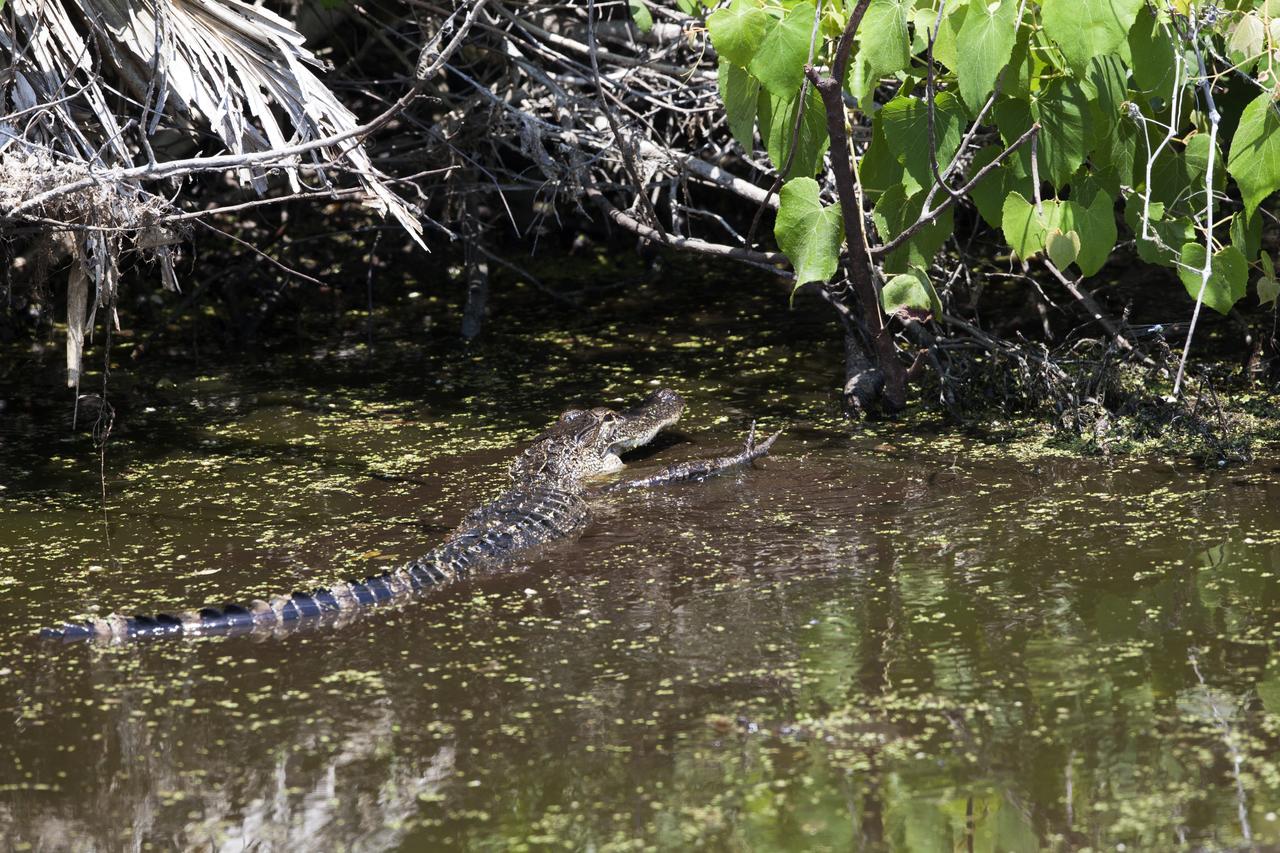

An alligator moves through a brackish waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.

A large alligator is in view in a waterway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 9, 2023. The center shares a boundary with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. The refuge is home to more than 65 amphibian and reptile species, along with 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal and 117 fish species.
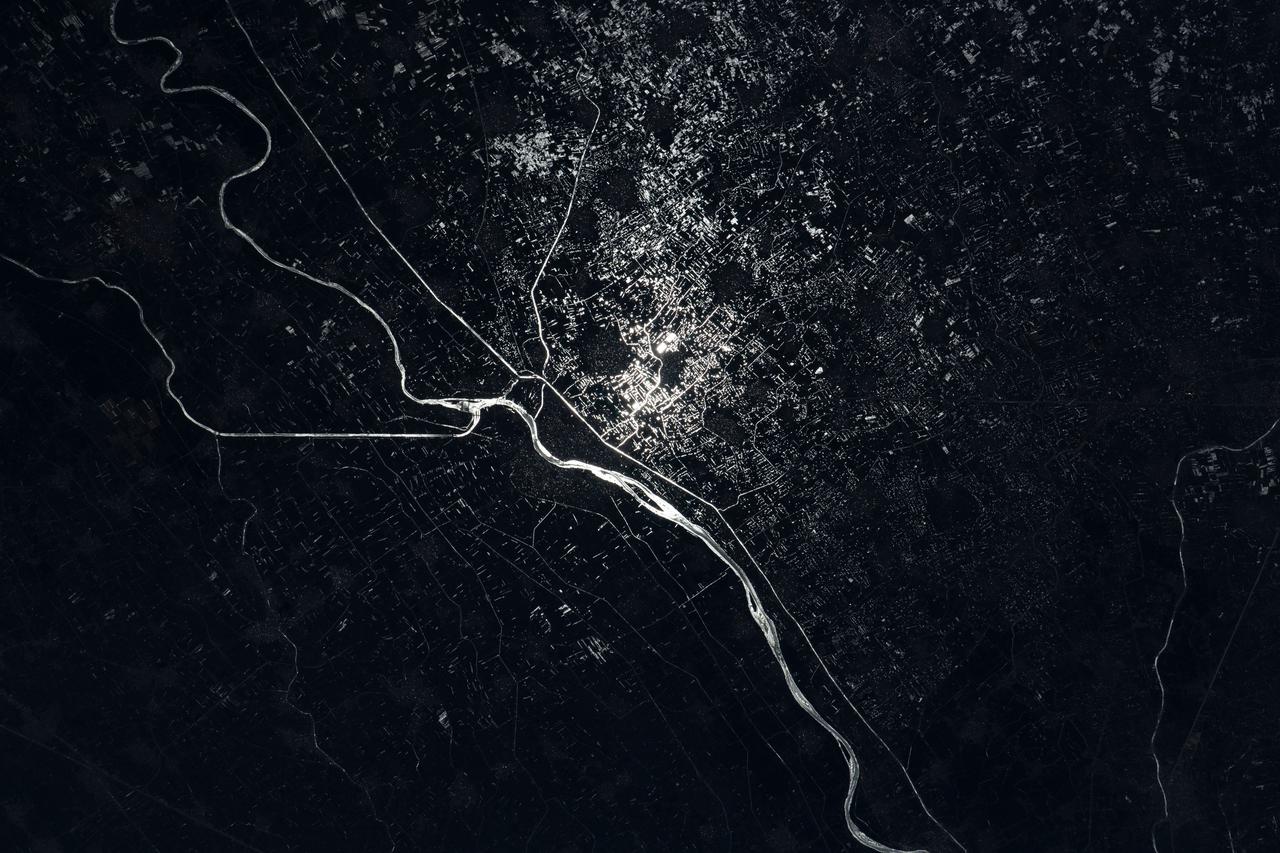
iss067e089285 (May 29, 2022) --- The Damietta Branch of the Nile River splits into canals in the central portion of the Nile Delta in Egypt. Lights from several cities surrounding the Egyptian waterways are pictured in this nighttime photograph from the International Space Station as it orbited 262 miles above the Mediterranean Sea off the coast of the Sinai Peninsula.
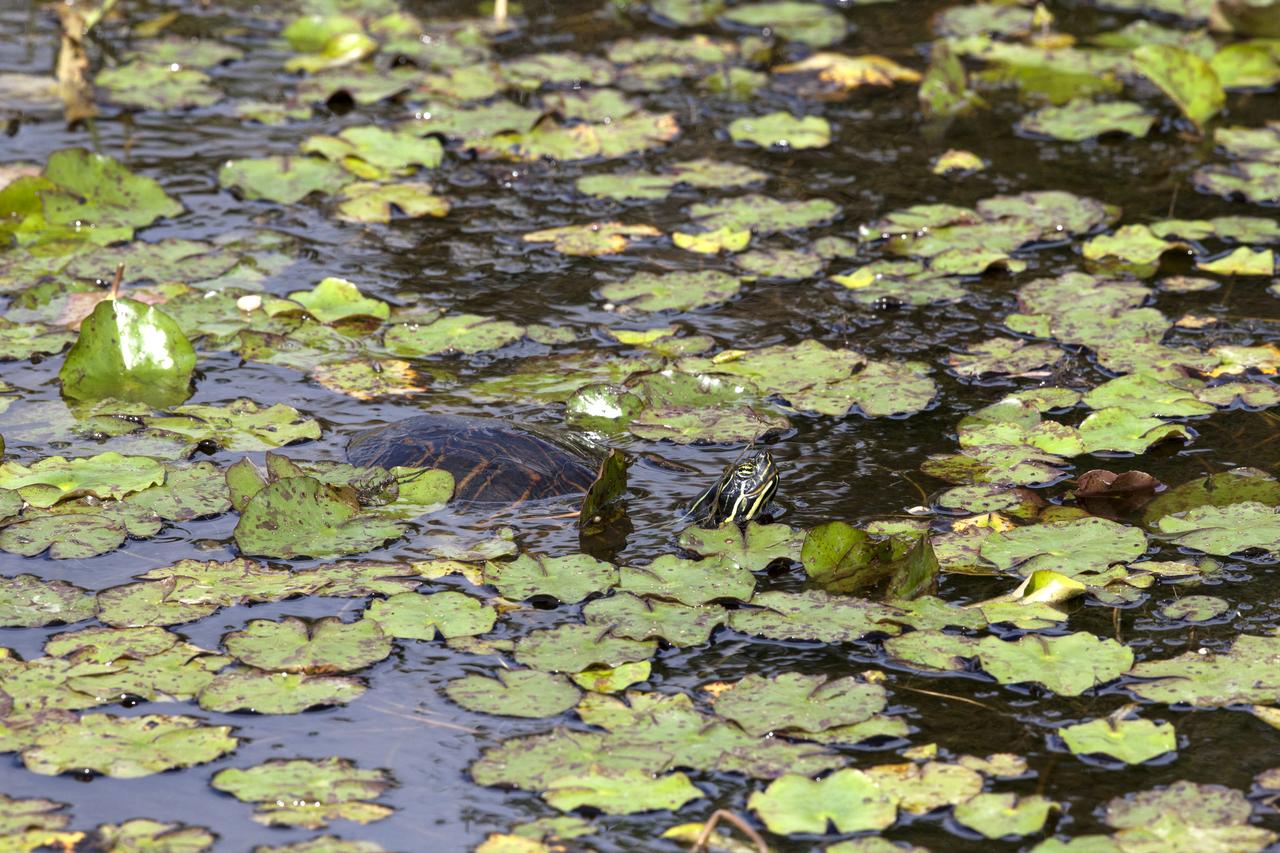

A turtle moves through a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
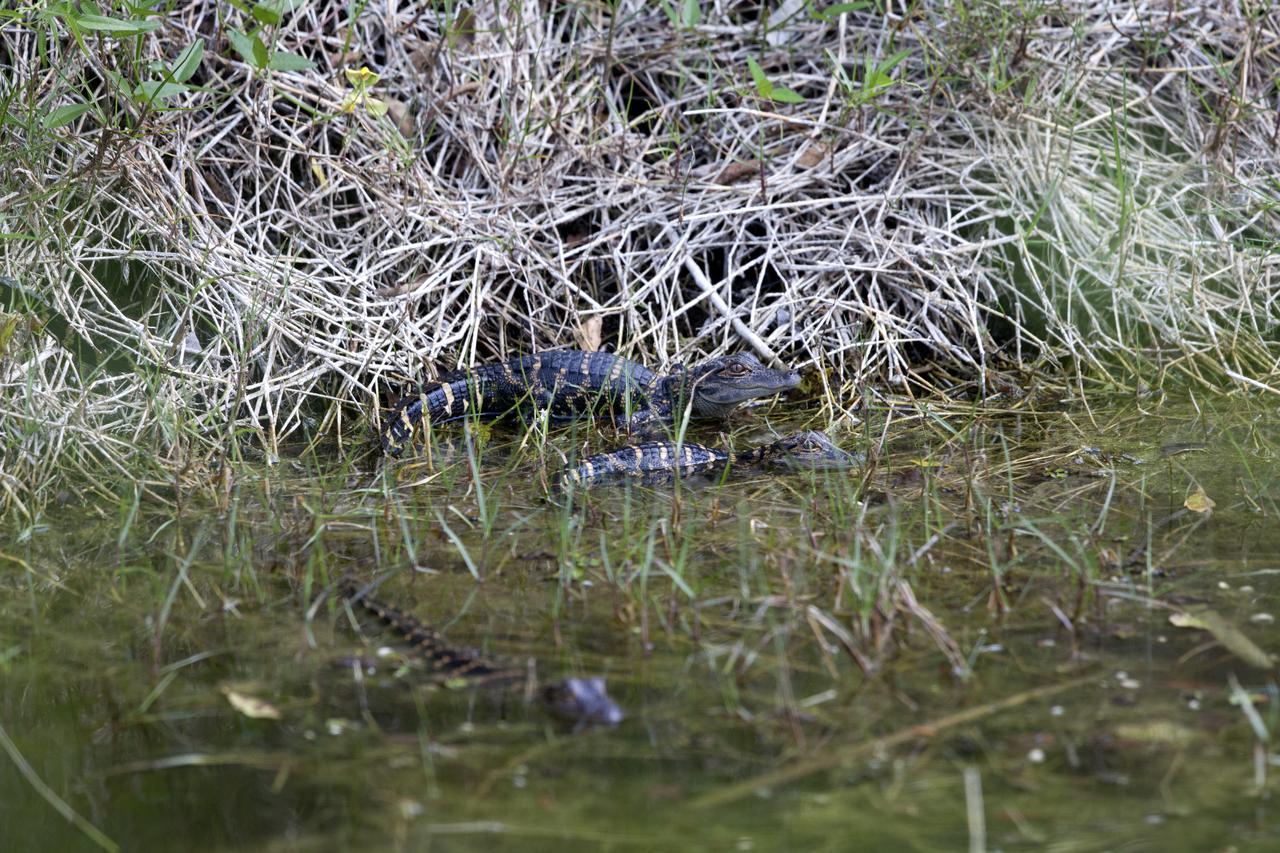

Baby alligators gather in a shallow waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
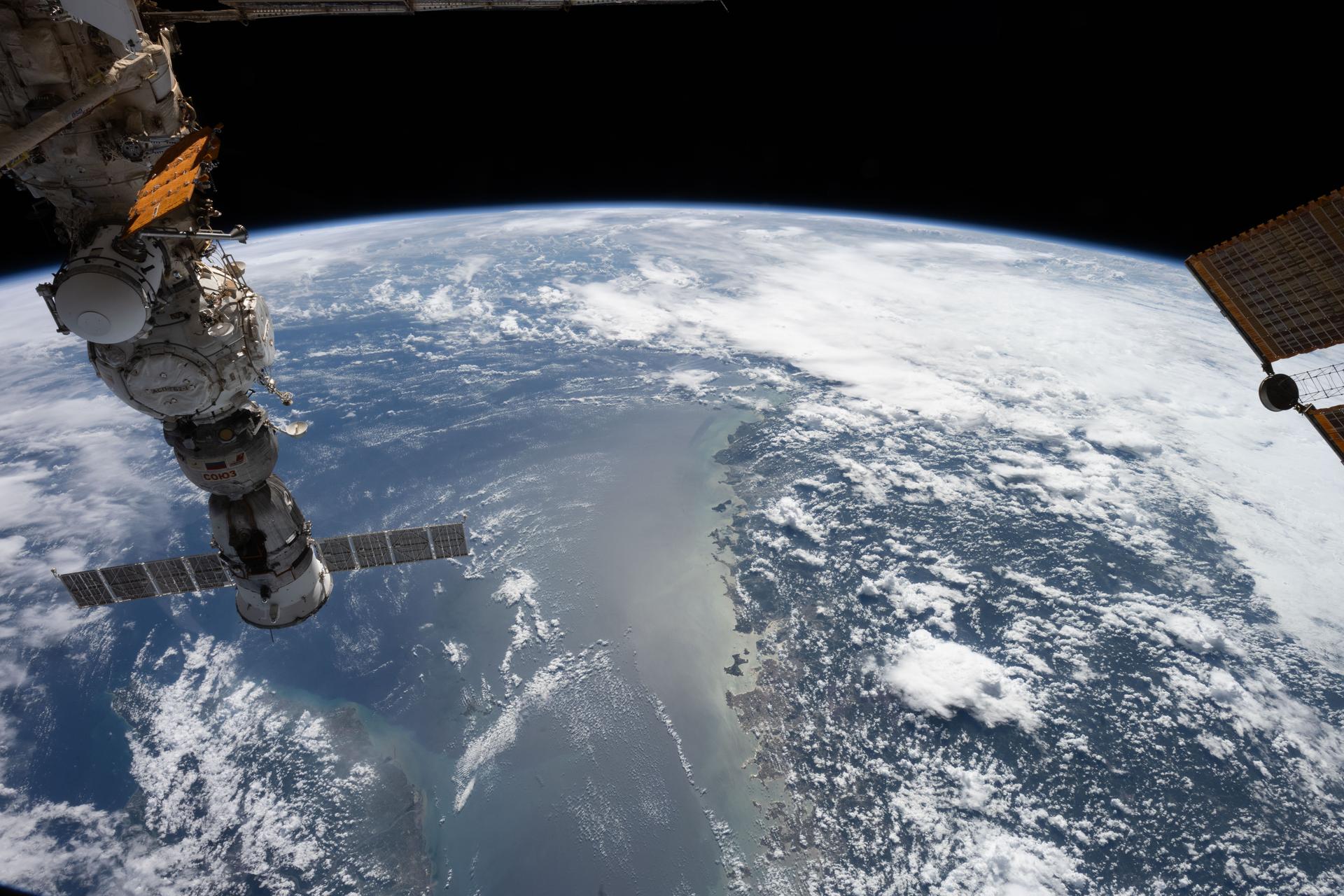

iss073e0983013 (Oct. 21, 2025) --- The Taiwan Strait separates the eastern coast of China’s Fujian Province (right) from the island nation of Taiwan (lower left) in this photograph taken from the International Space Station as it orbited 257 miles above Earth. The strait is a vital waterway in East Asia, supporting the fishing, shipping, and communications industries.
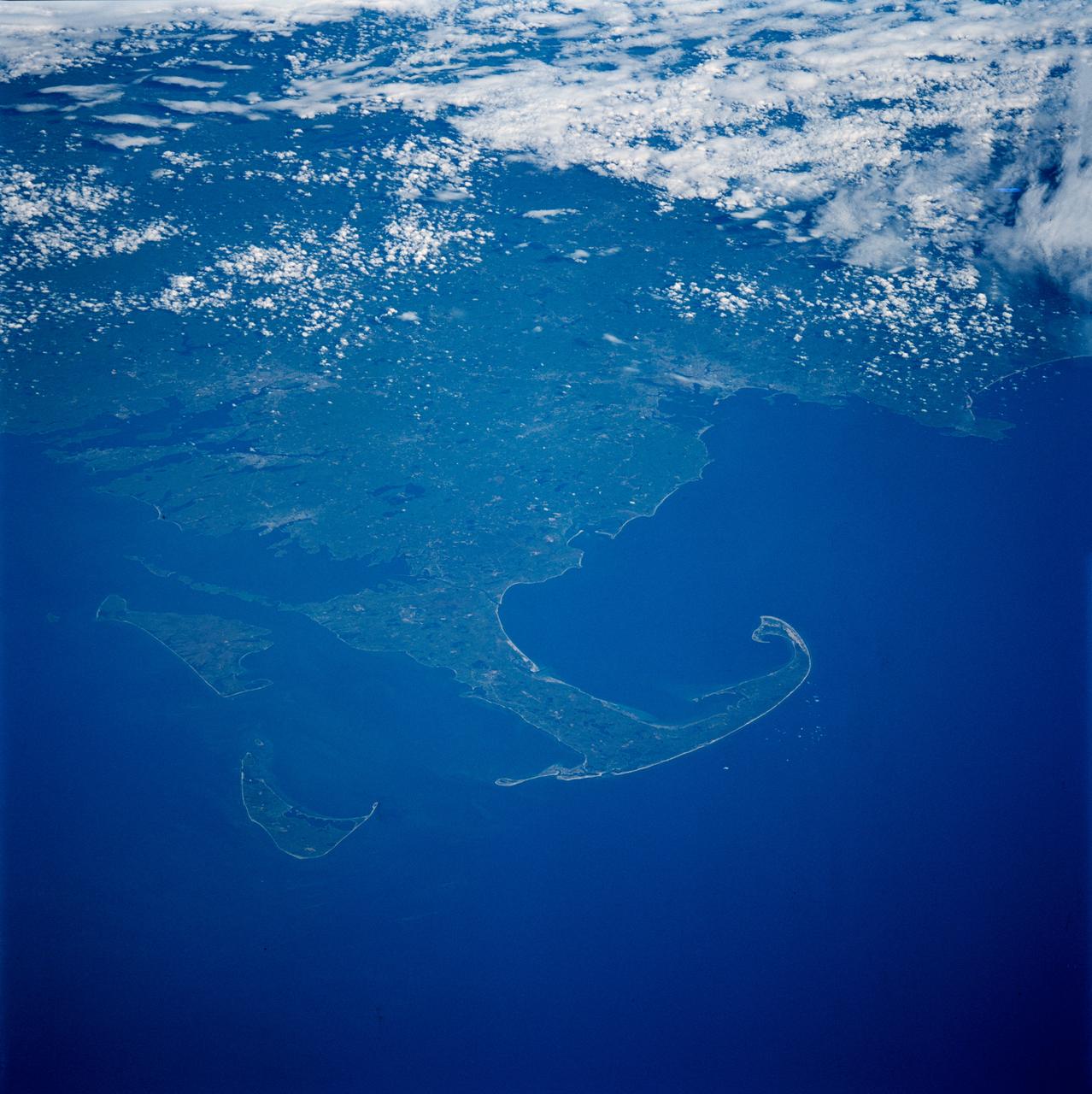

STS084-703-003 (15-24 May 1997) --- Cape Cod extends 105 kilometers (65 miles) into the Atlantic Ocean. To the south of Cape Cod are the islands of Martha's Vineyard (west) and Nantucket (east). The city of Boston can be seen surrounding the bay above the "hook" on Cape Cod. To the south are the cities of New Bedford on Buzzards Bay, and Providence, Rhode Island. The Cape Cod Canal is an artificial waterway that connects Buzzards Bay and Cape Cod Bay. The waterway is 28 kilometers (17.5 miles) and does not contains locks. The canal was built to shorten the distance over water between New York City and Boston. In 1620 the Pilgrims landed at Provincetown, on the upper tip of Cape Cod, before they proceeded to Plymouth.
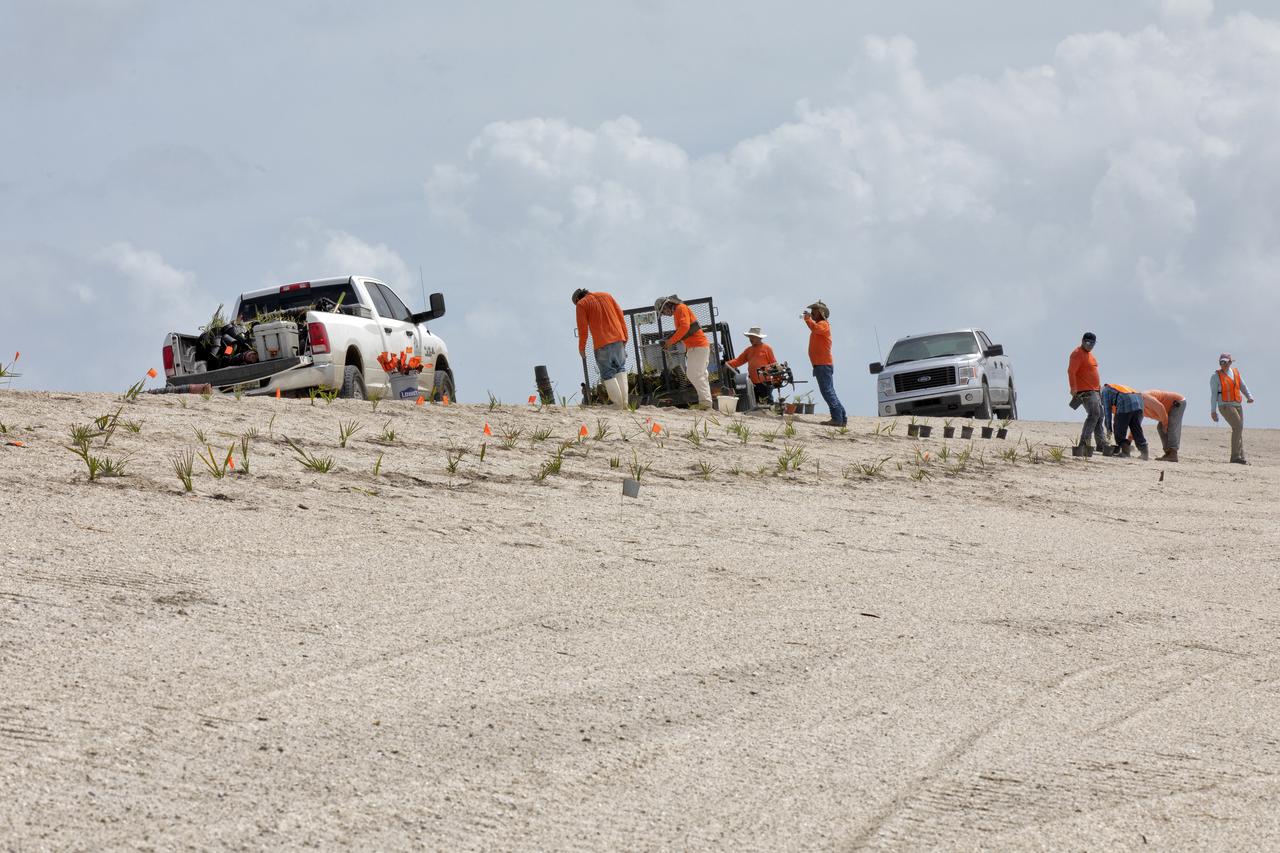

Native vegetation is being planted in a portion of the restored dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 8, 2018. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, is being transported to the space center’s beaches. One the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coast wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and is targeted to be completed by April 2019.
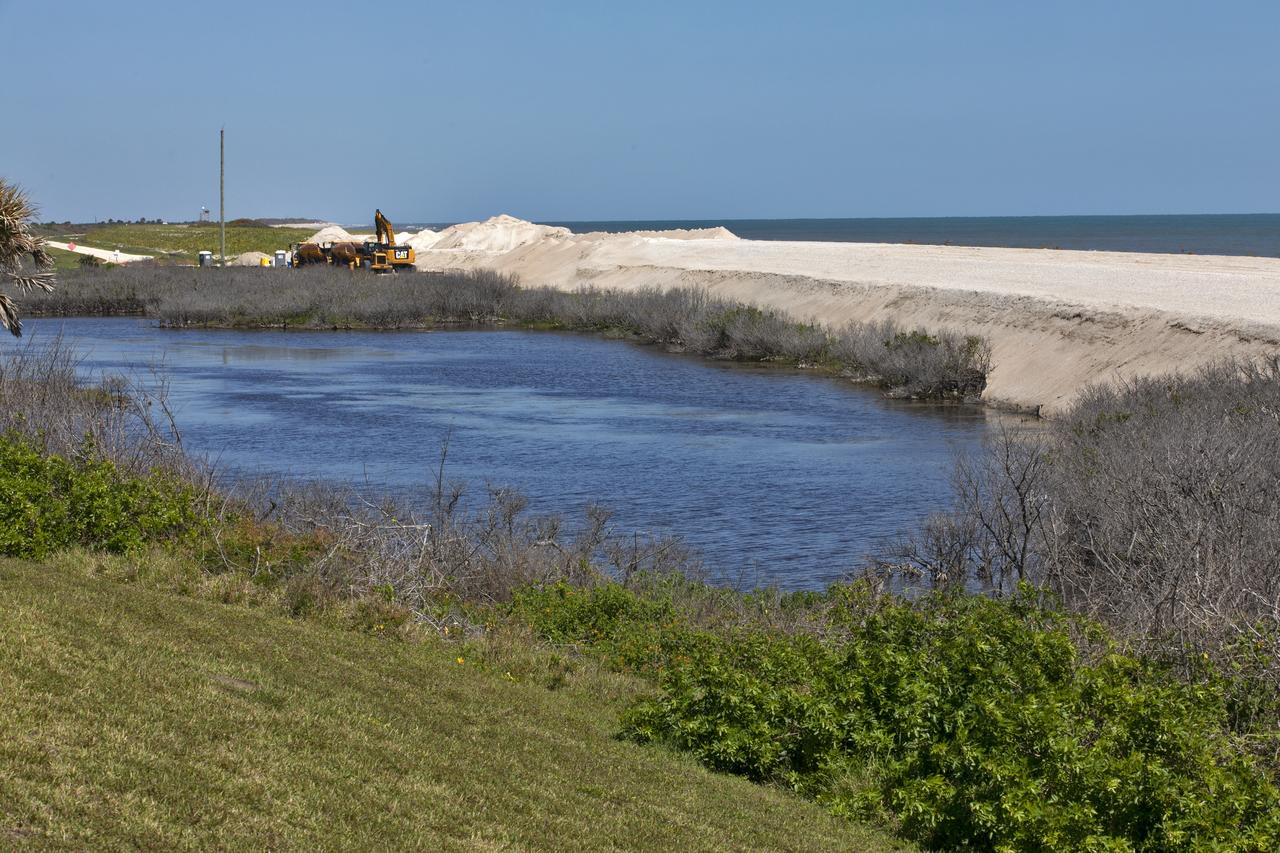

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. Once the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coastal wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. After the dune was built up, native coastal vegetation was replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coast wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. After the dune was built up, native coastal vegetation was replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coast wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.
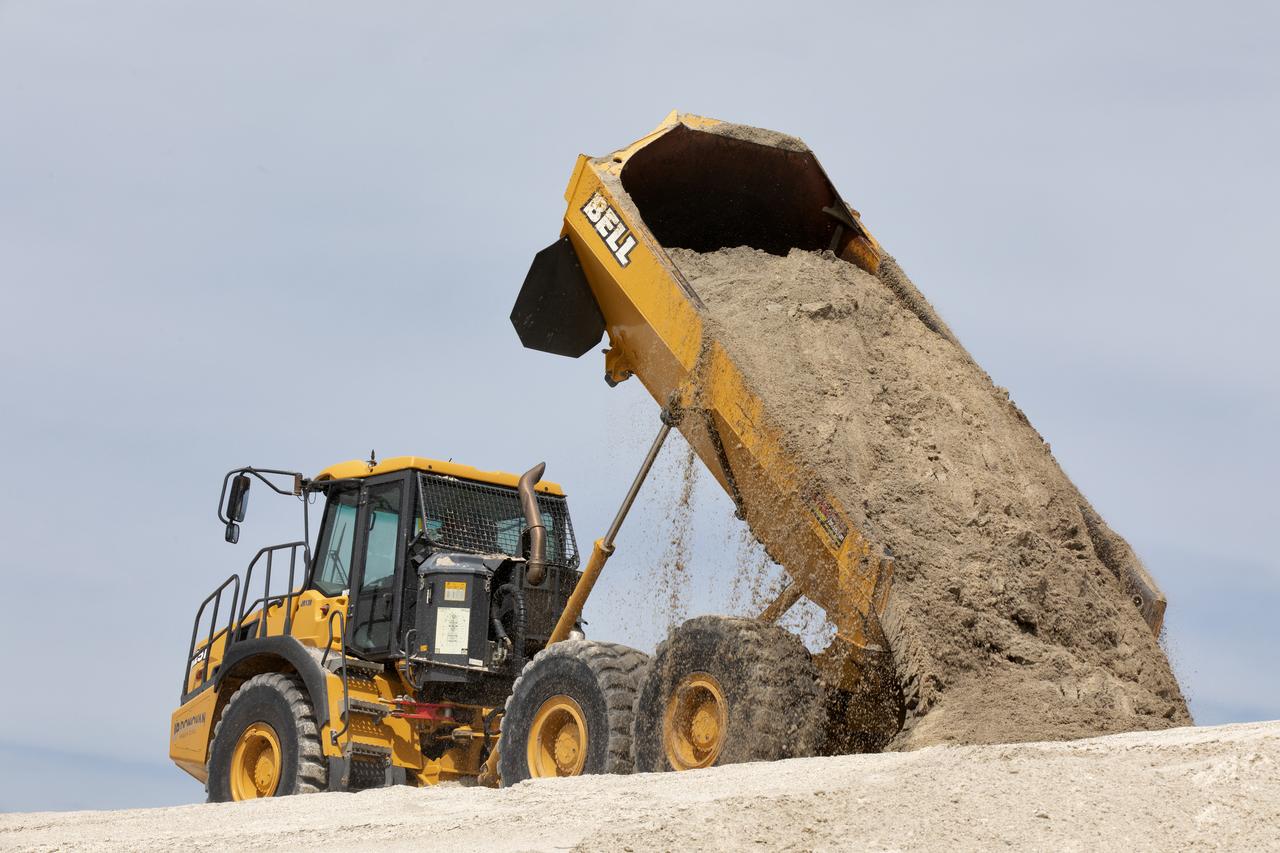

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 8, 2018. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, is being transported to the space center’s beaches. One the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coast wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and is targeted to be completed by April 2019.
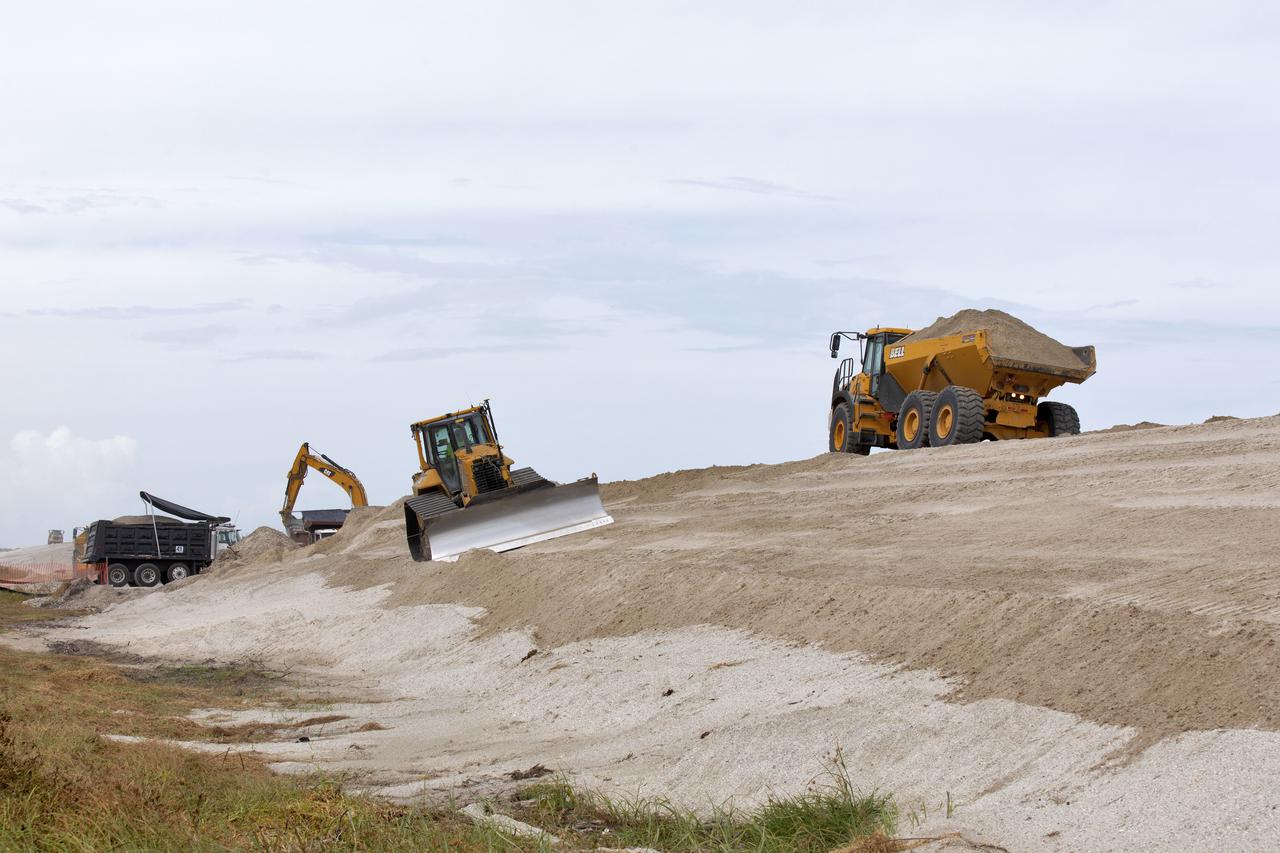

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 8, 2018. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, is being transported to the space center’s beaches. One the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coast wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and is targeted to be completed by April 2019.
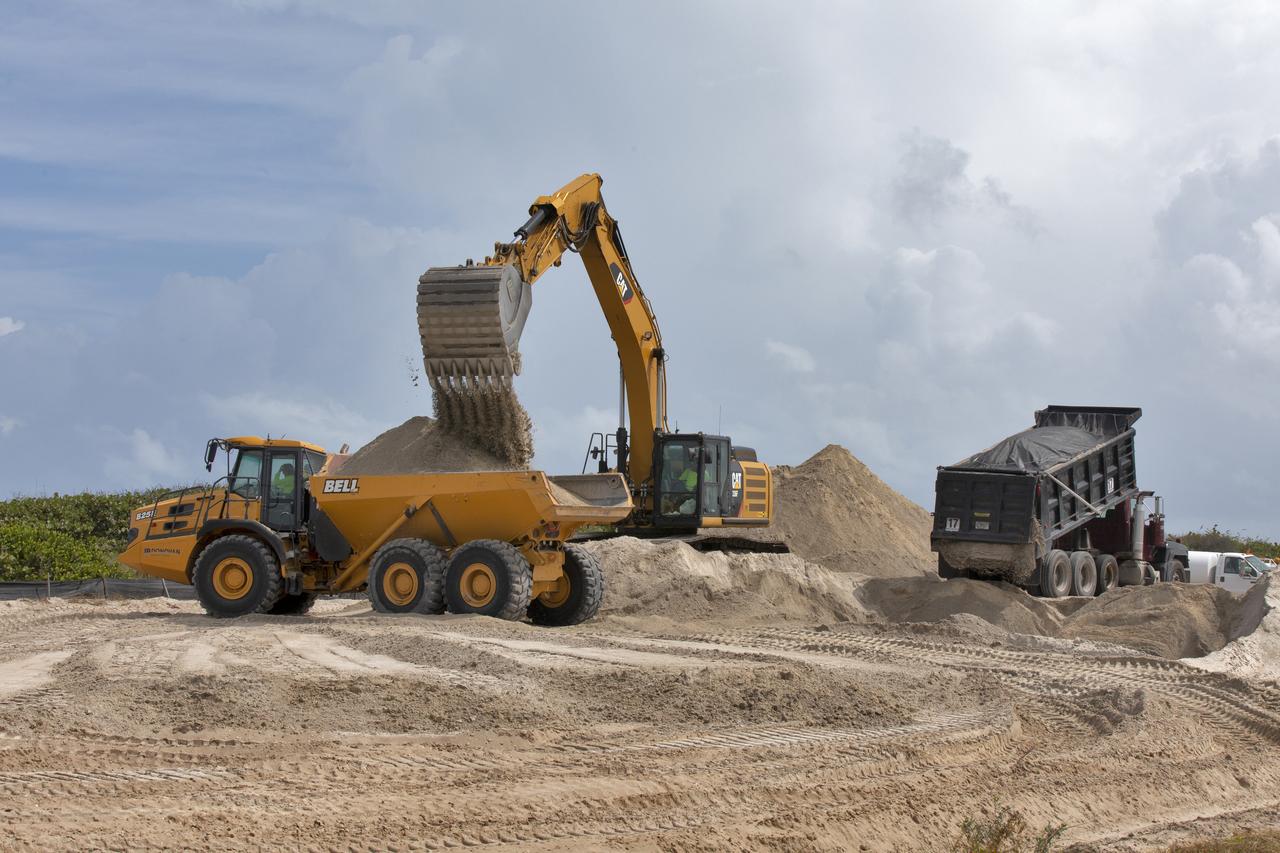

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 8, 2018. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, is being transported to the space center’s beaches. One the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coast wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and is targeted to be completed by April 2019.
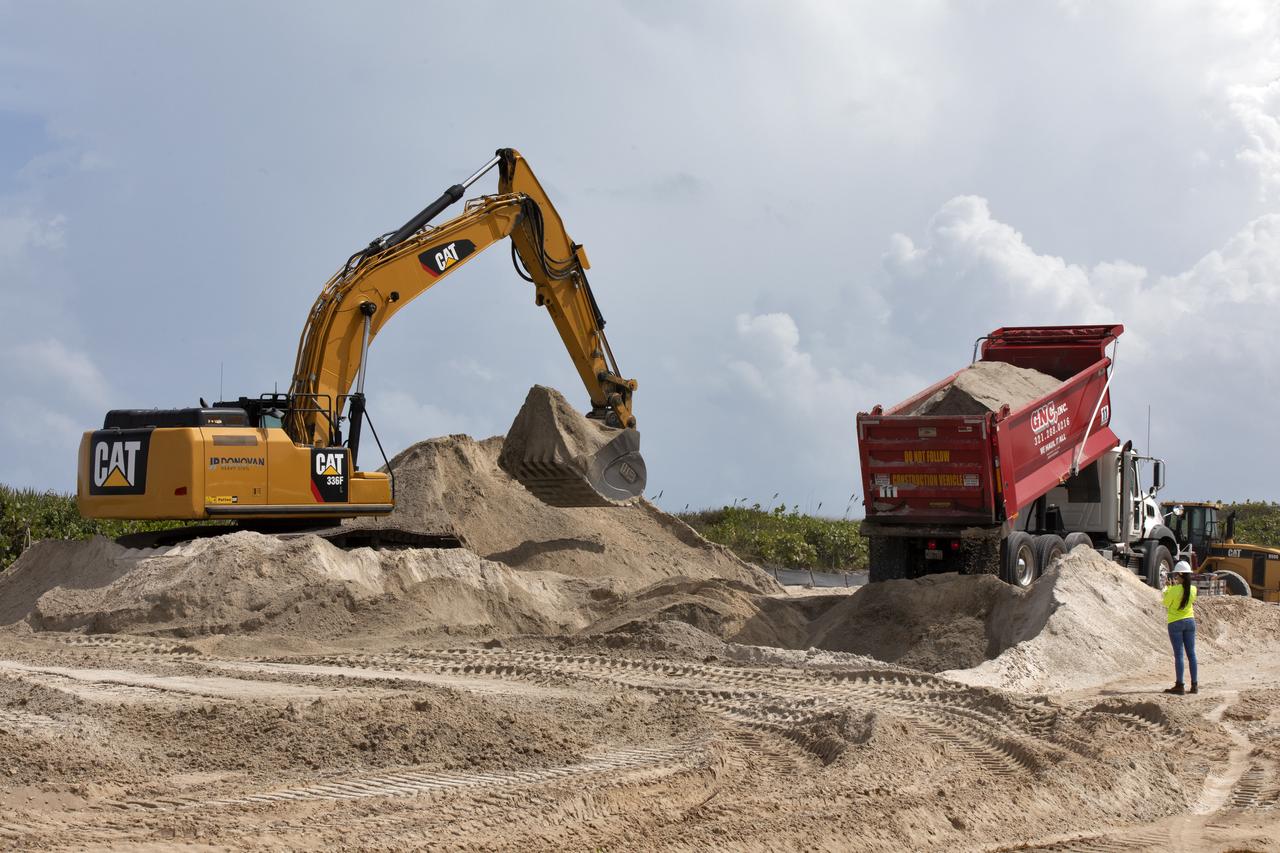

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 8, 2018. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, is being transported to the space center’s beaches. One the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coast wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and is targeted to be completed by April 2019.
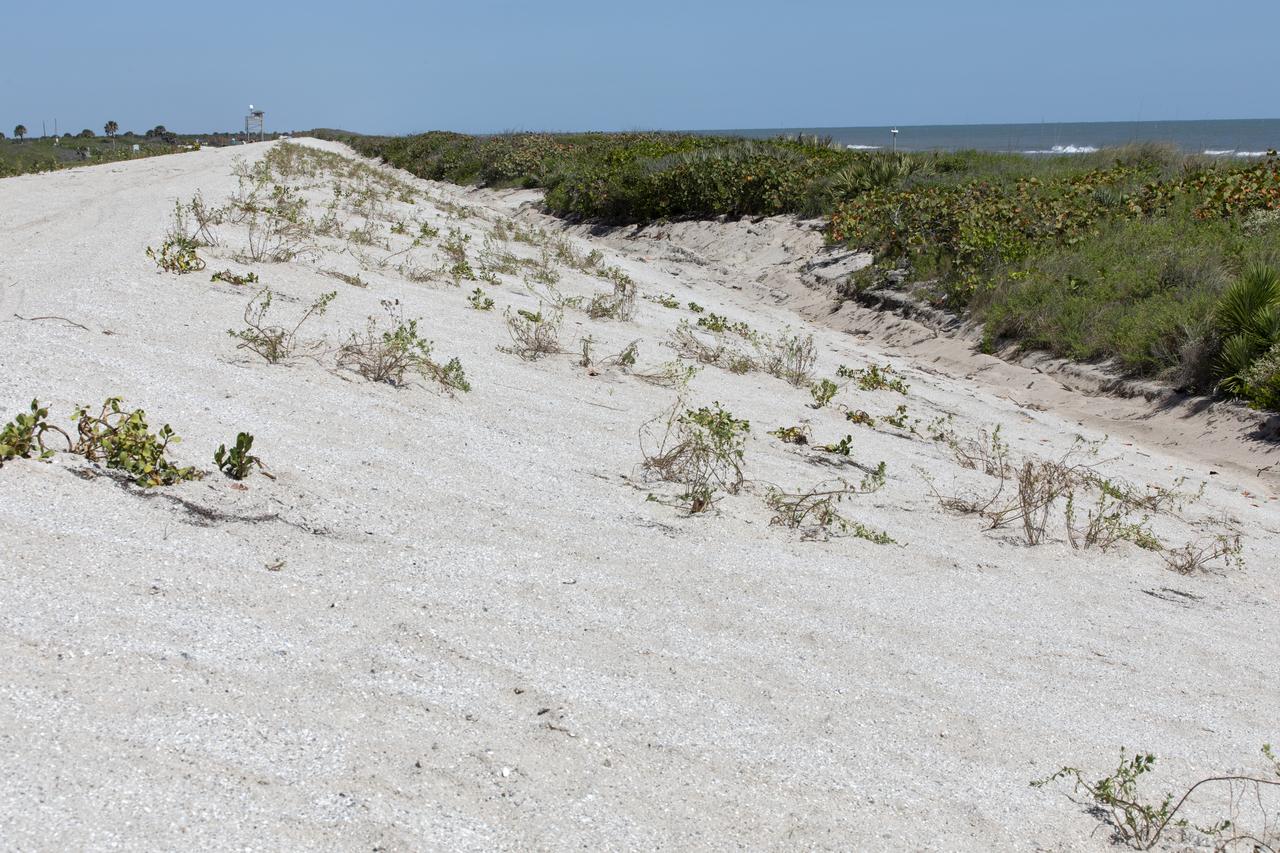

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. After the dune was built up, native coastal vegetation was replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coastal wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.
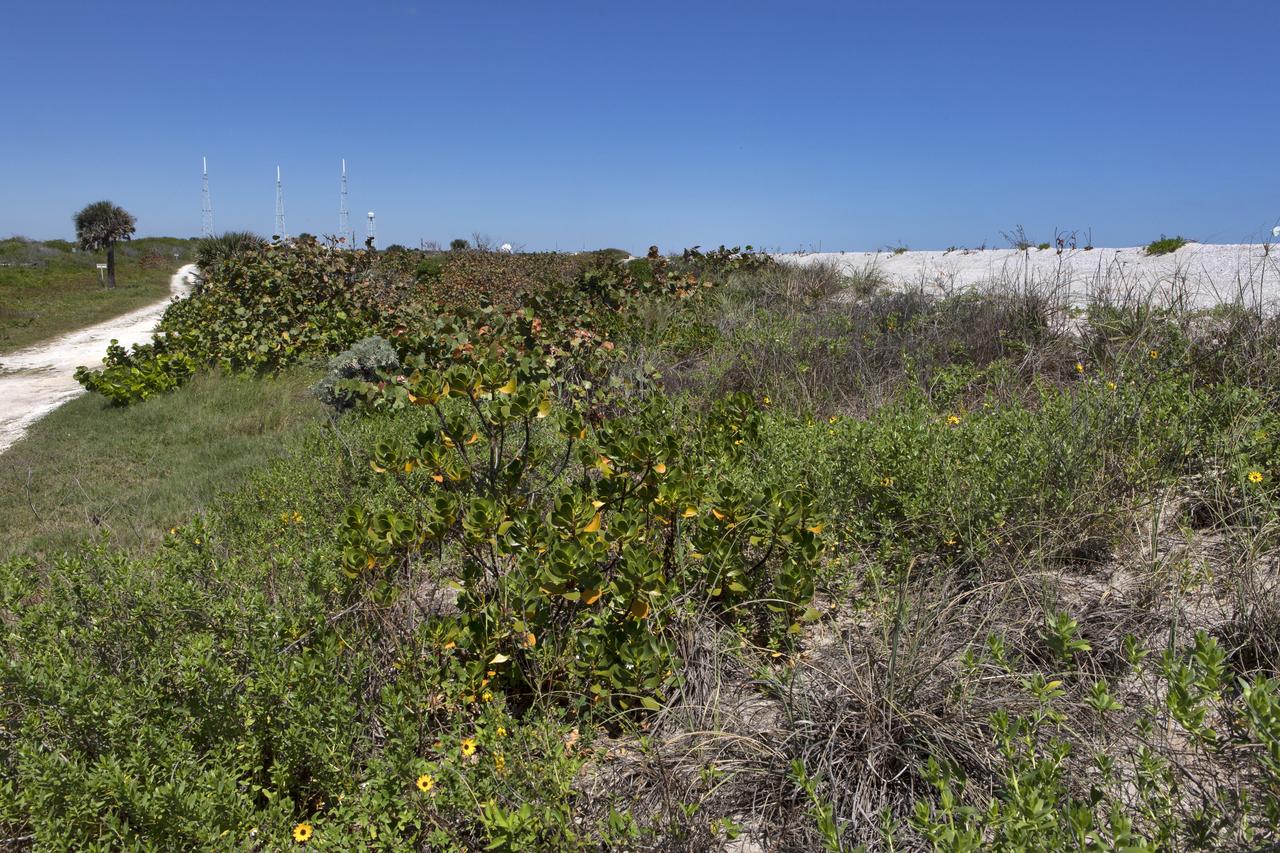

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. The existing dunes in the foreground are a contrast to a small portion of the dune restoration in view at far right. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. Once the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coast wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.
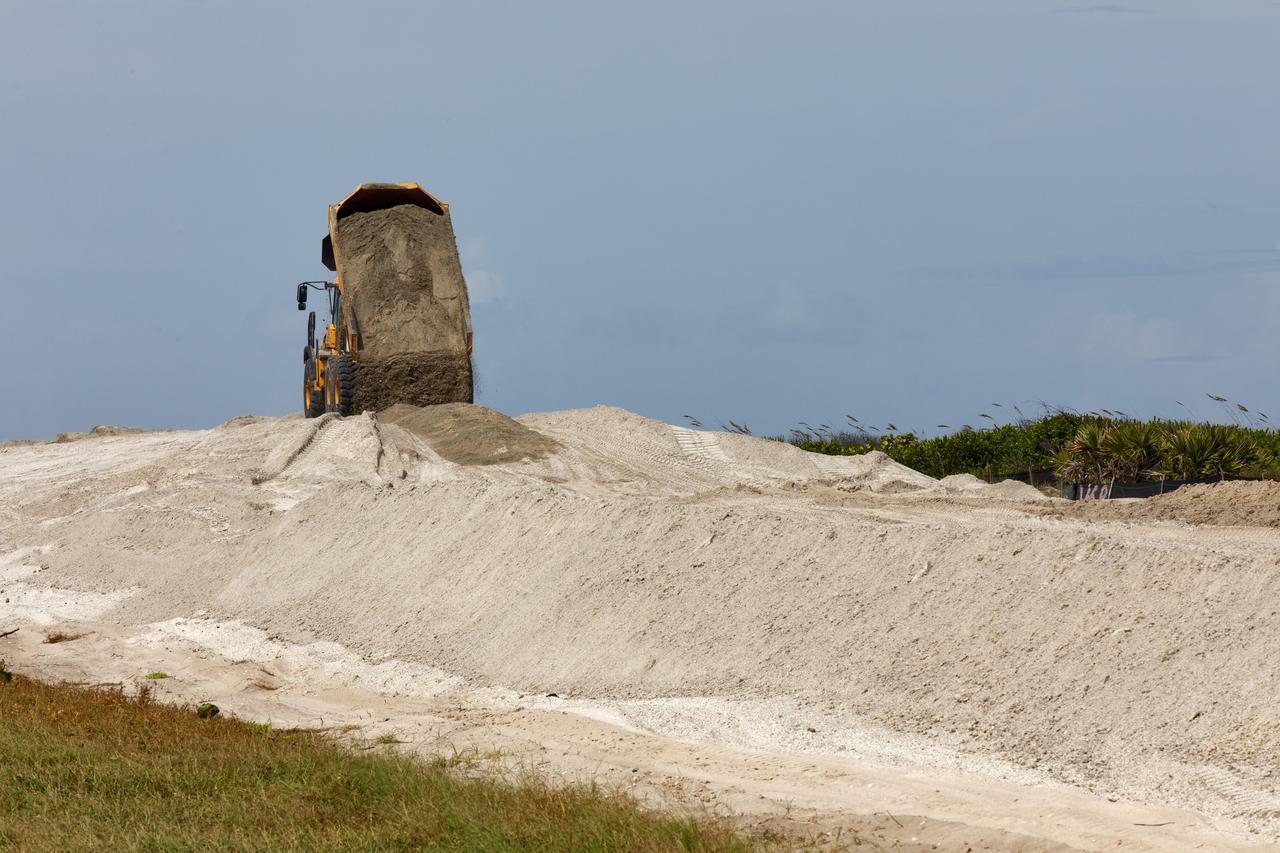

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 8, 2018. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, is being transported to the space center’s beaches. One the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coast wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and is targeted to be completed by April 2019.
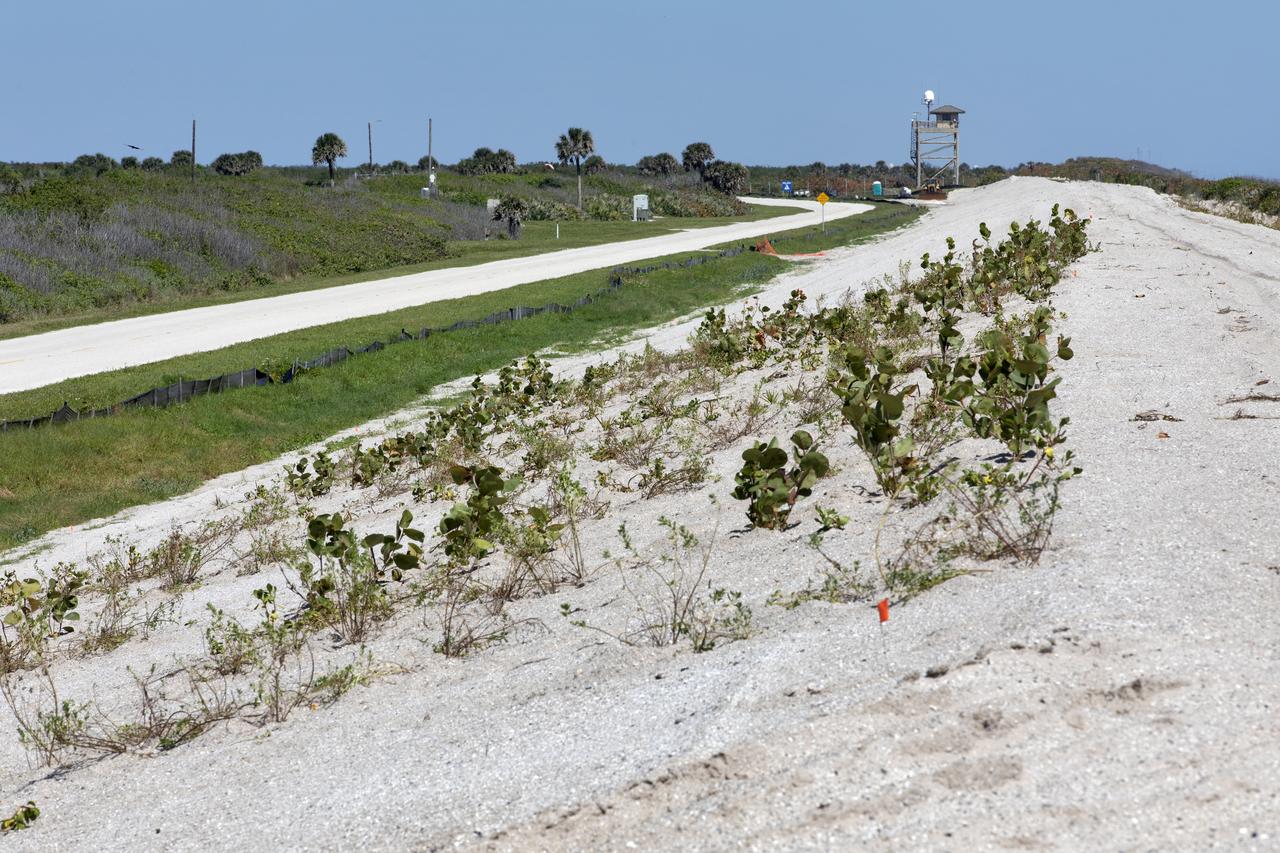

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. After the dune was built up, native coastal vegetation was replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coastal wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.
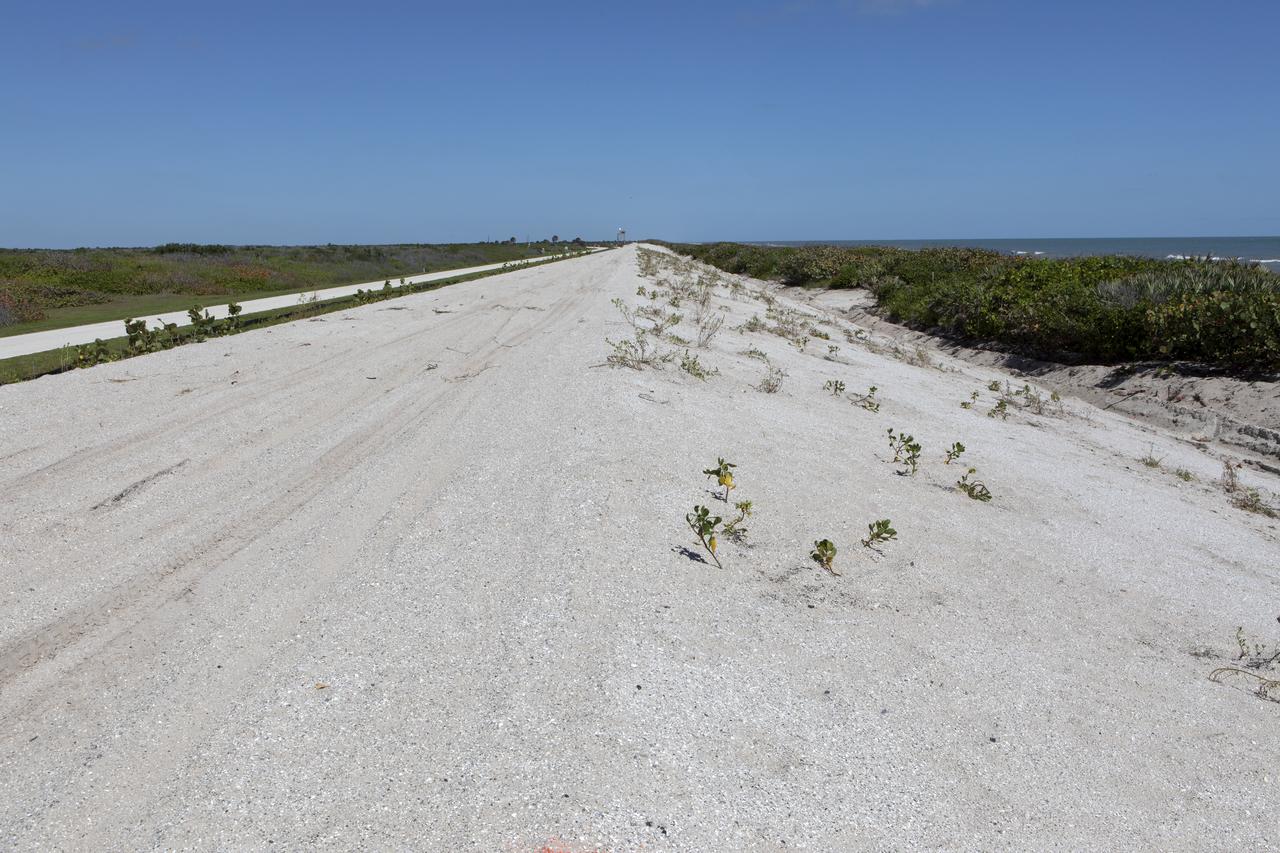

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. Once the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coastal wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.
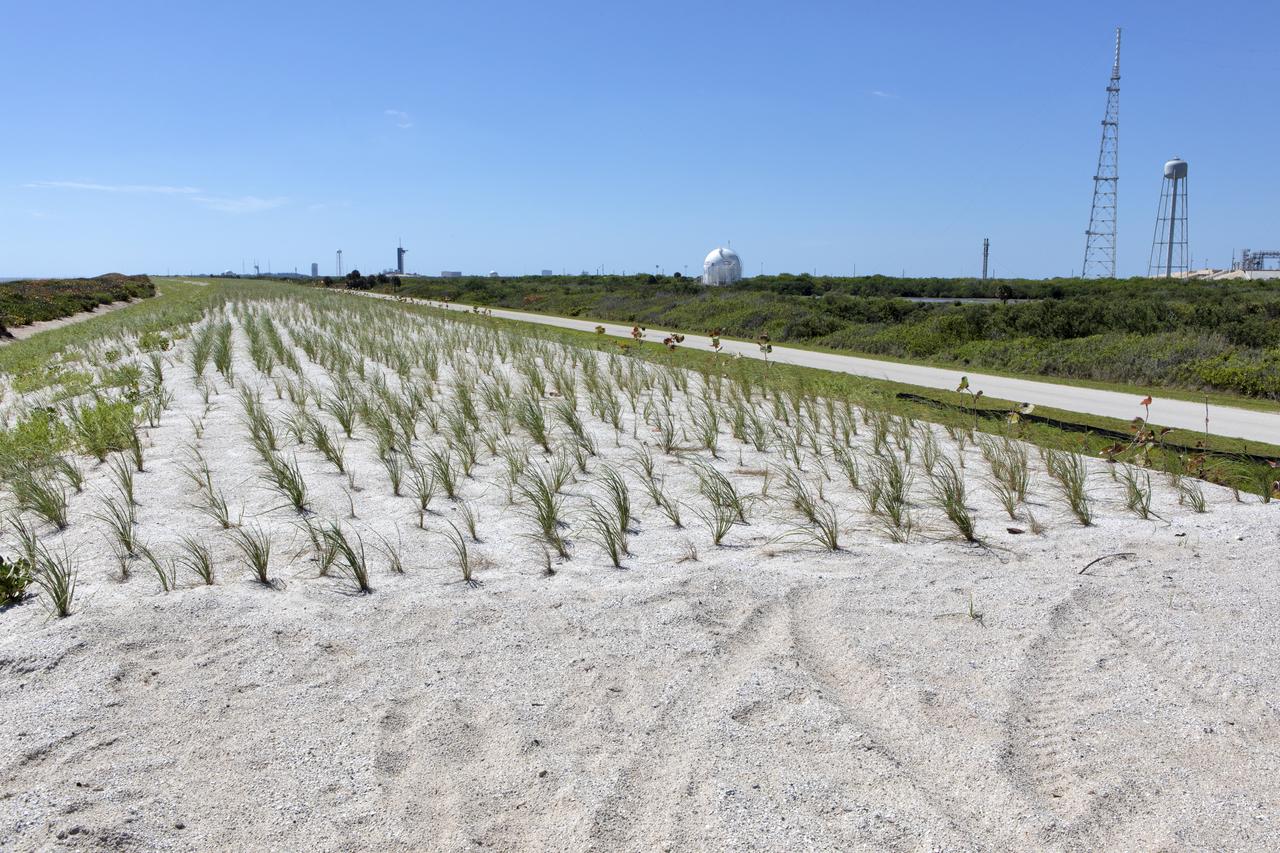

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. After the dune was built up, native coastal vegetation was replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coastal wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.
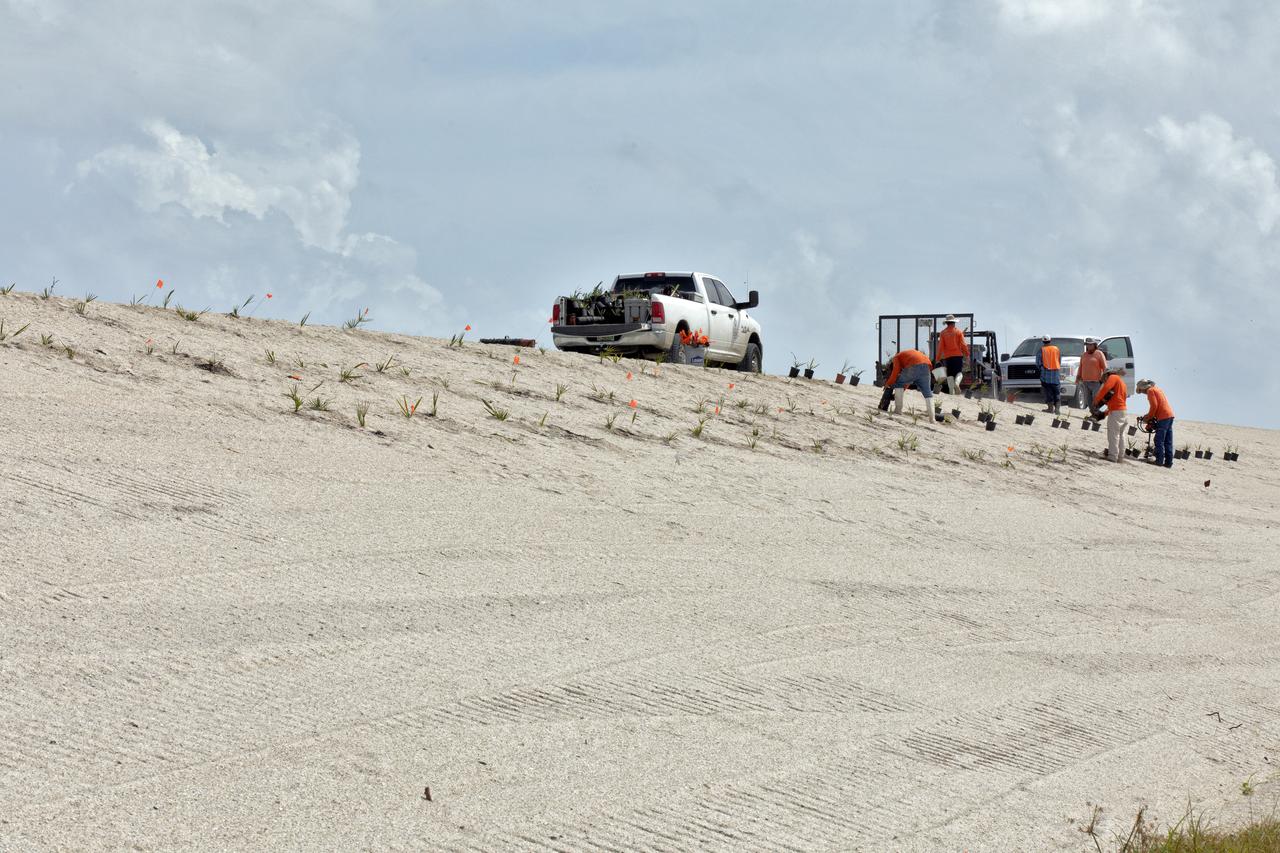

Native vegetation is being planted in a portion of the restored dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 8, 2018. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, is being transported to the space center’s beaches. Once the dune is built up, native vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coast wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and is targeted to be completed by April 2019.
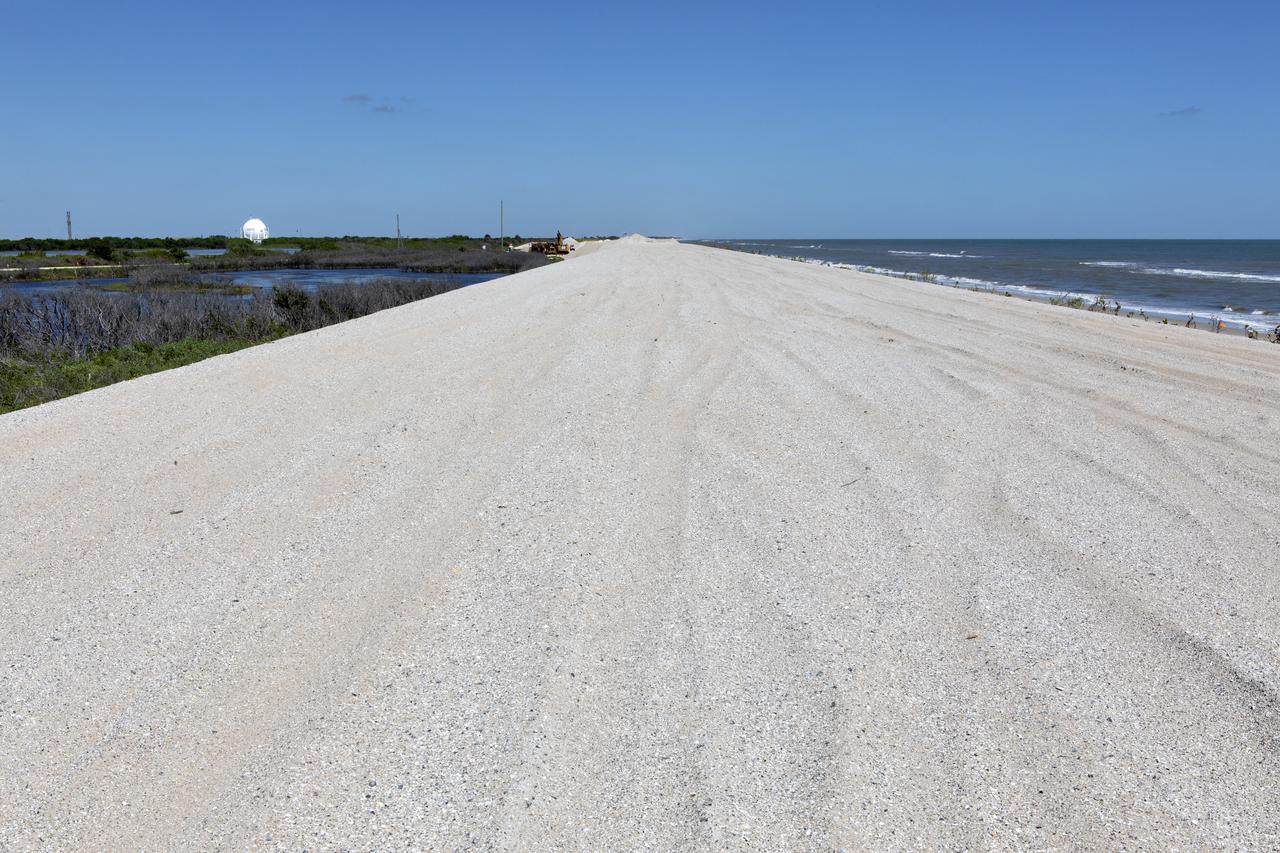

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. Once the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coastal wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.
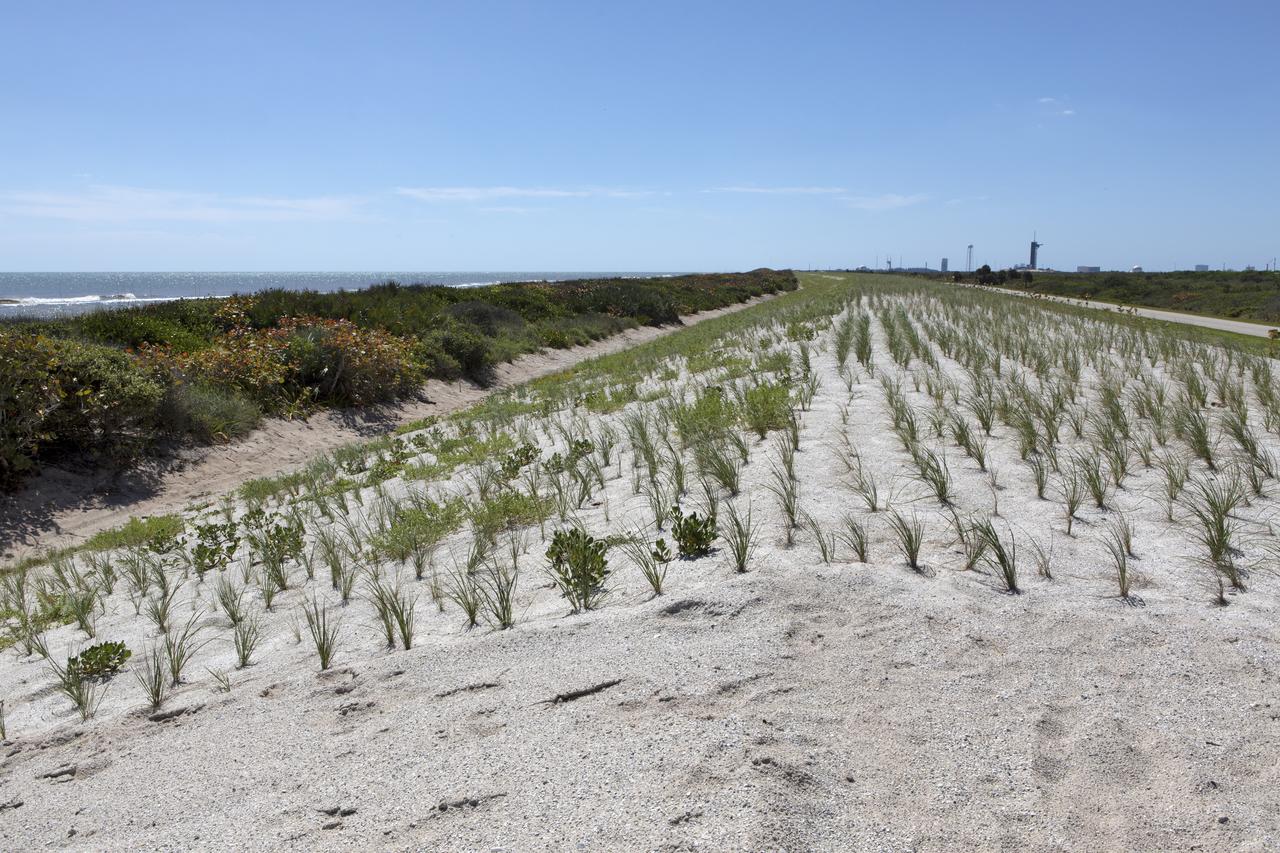

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. After the dune was built up, native coastal vegetation was replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coastal wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.
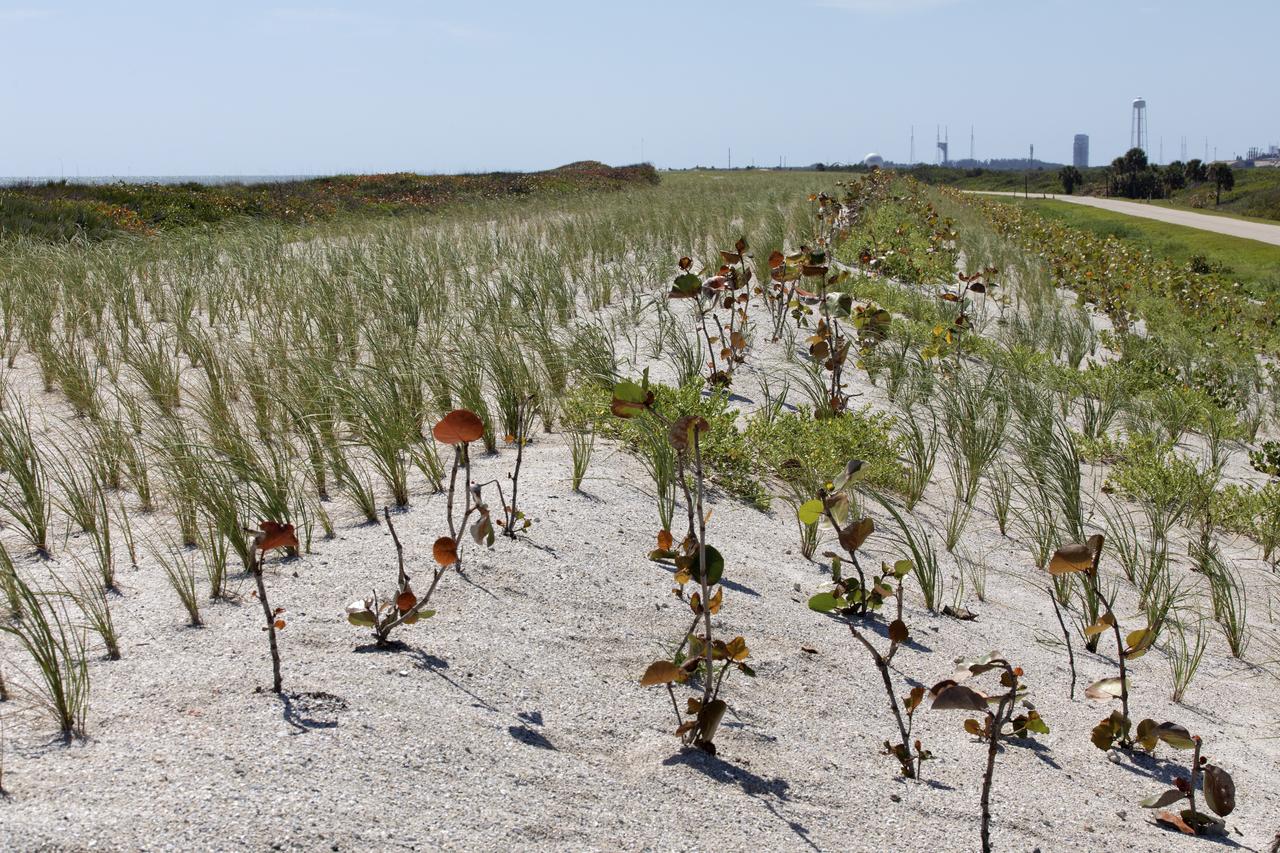

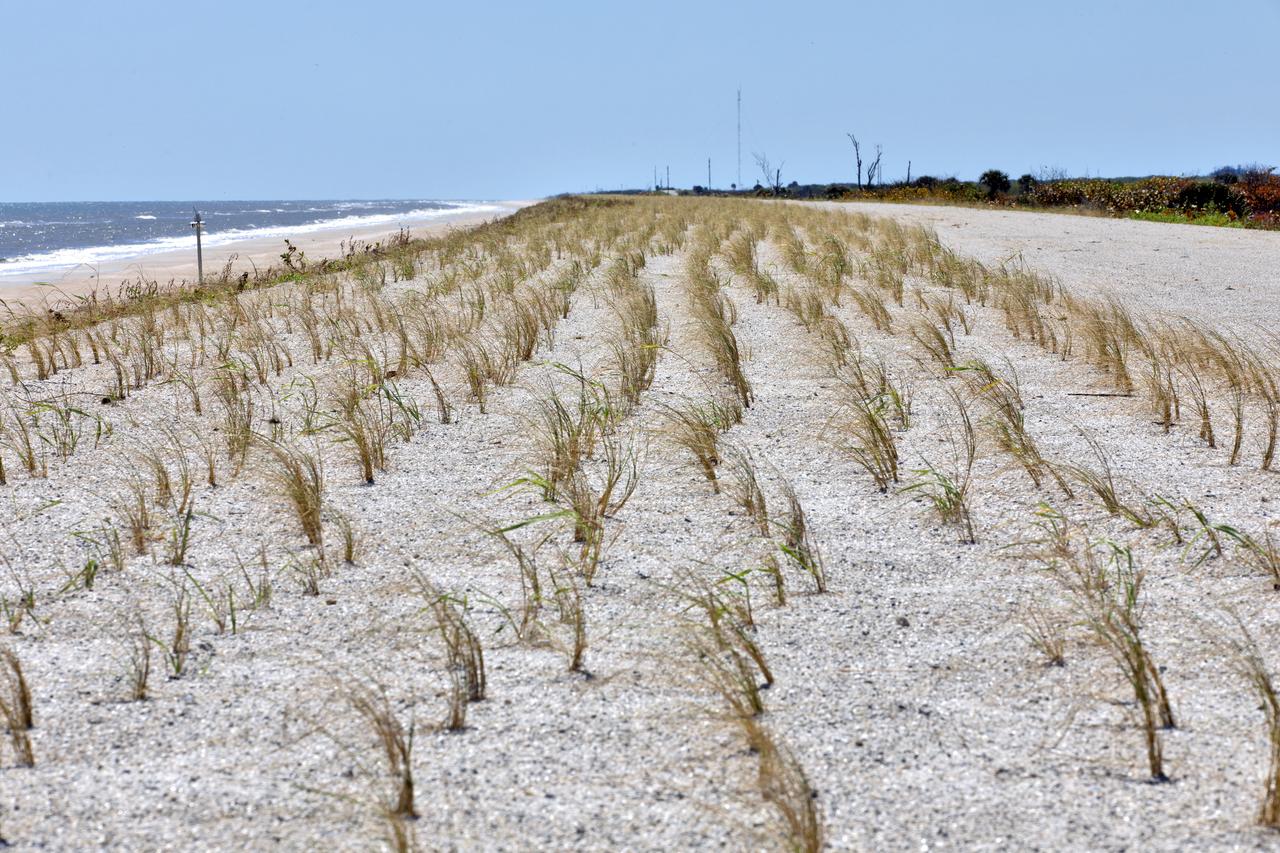
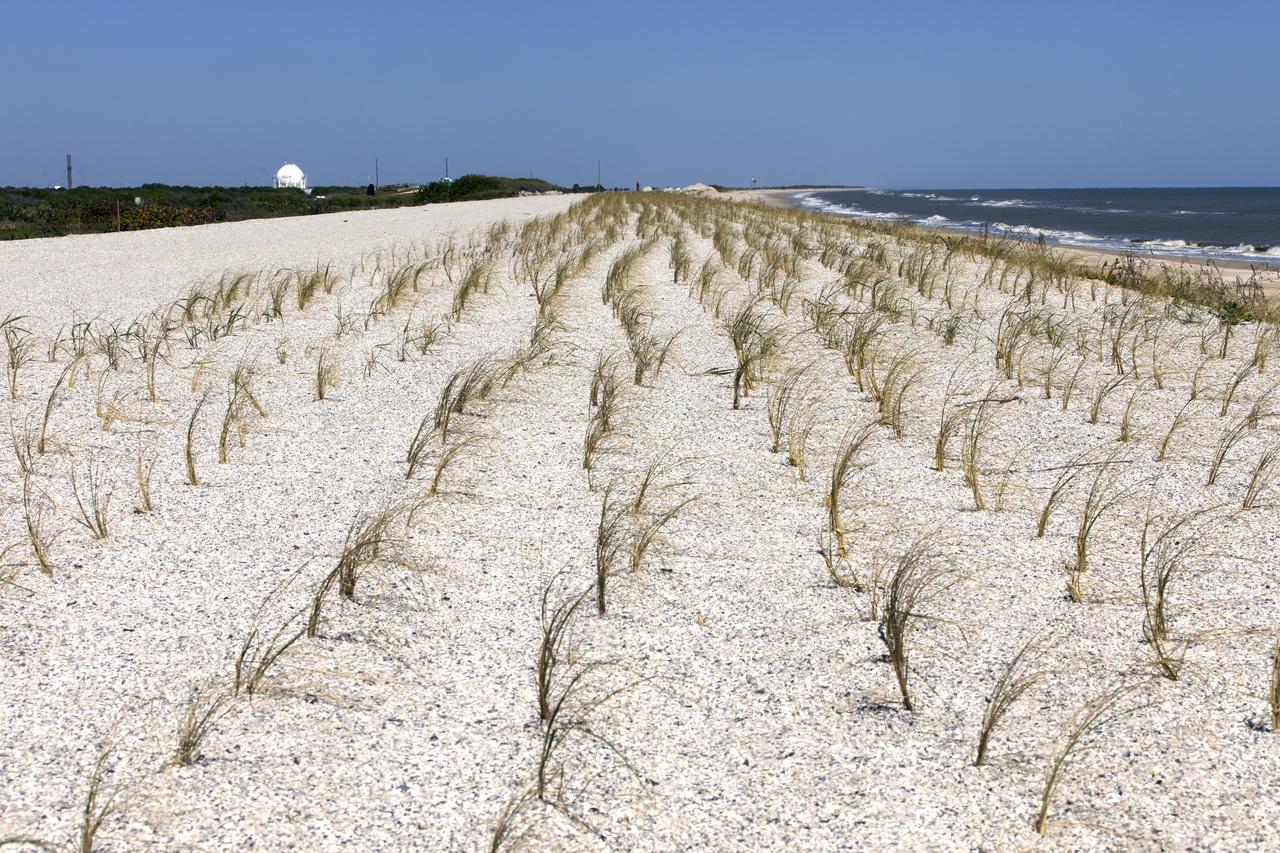
Native vegetation has been planted in the restored dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. After the dune was built up, native vegetation was replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coastal wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.
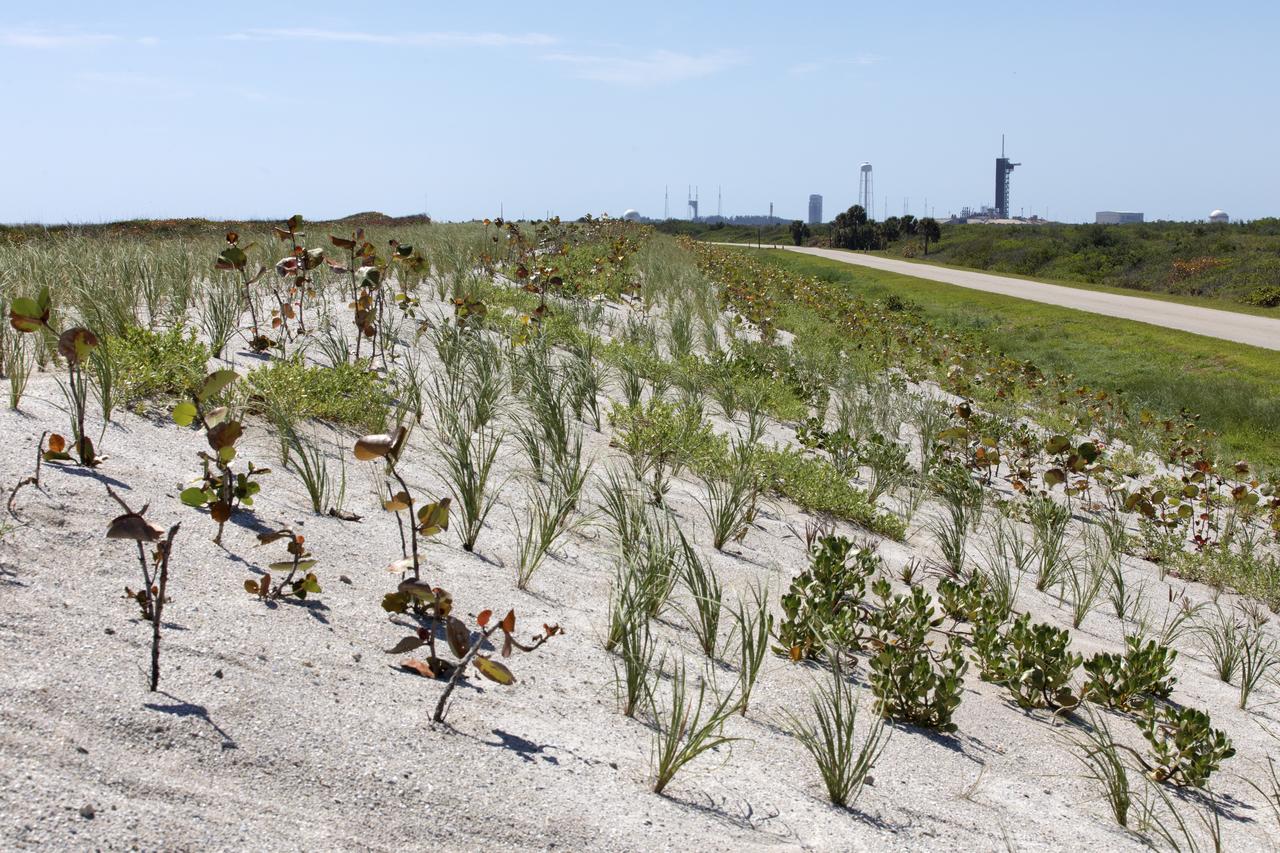

Native vegetation has been planted in the restored dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. After the dune was built up, native vegetation was replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coastal wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.
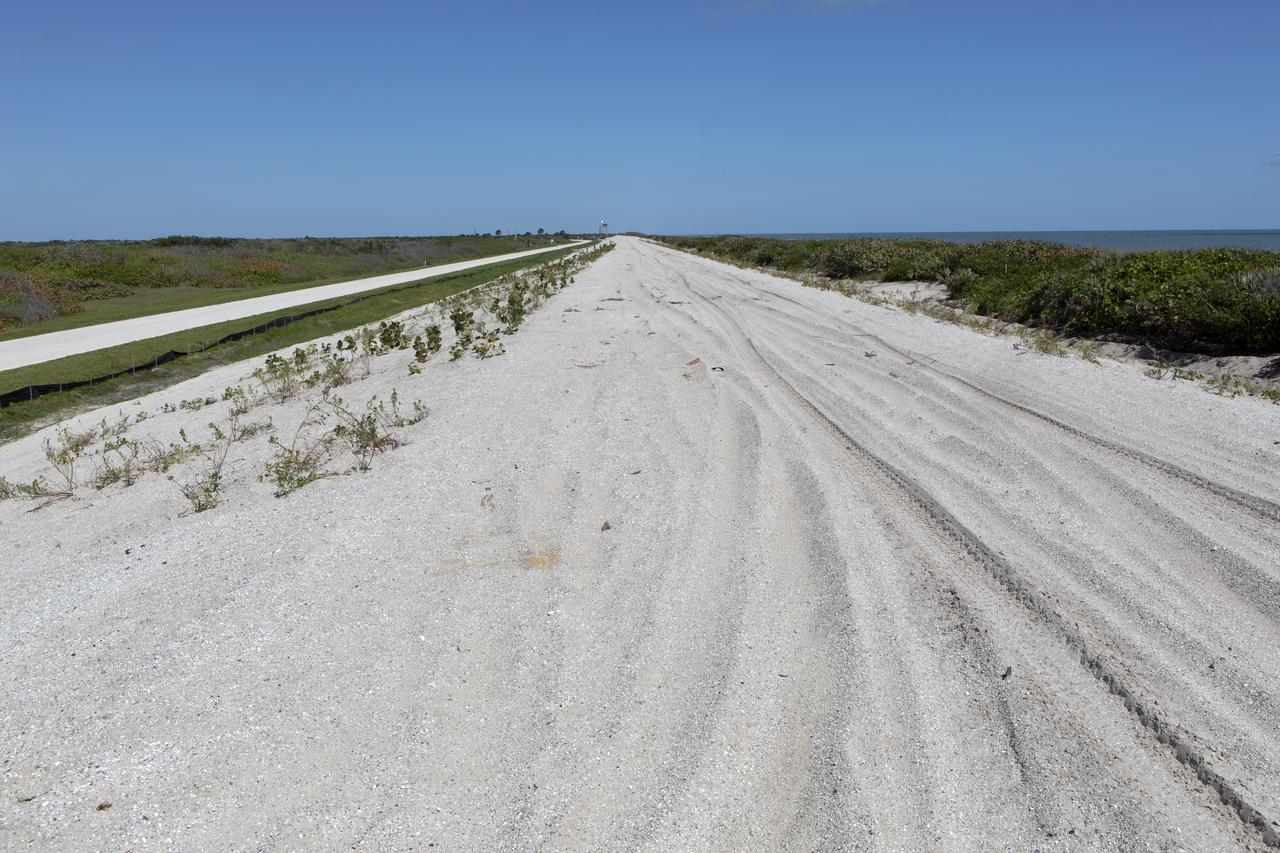

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. Once the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coastal wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.
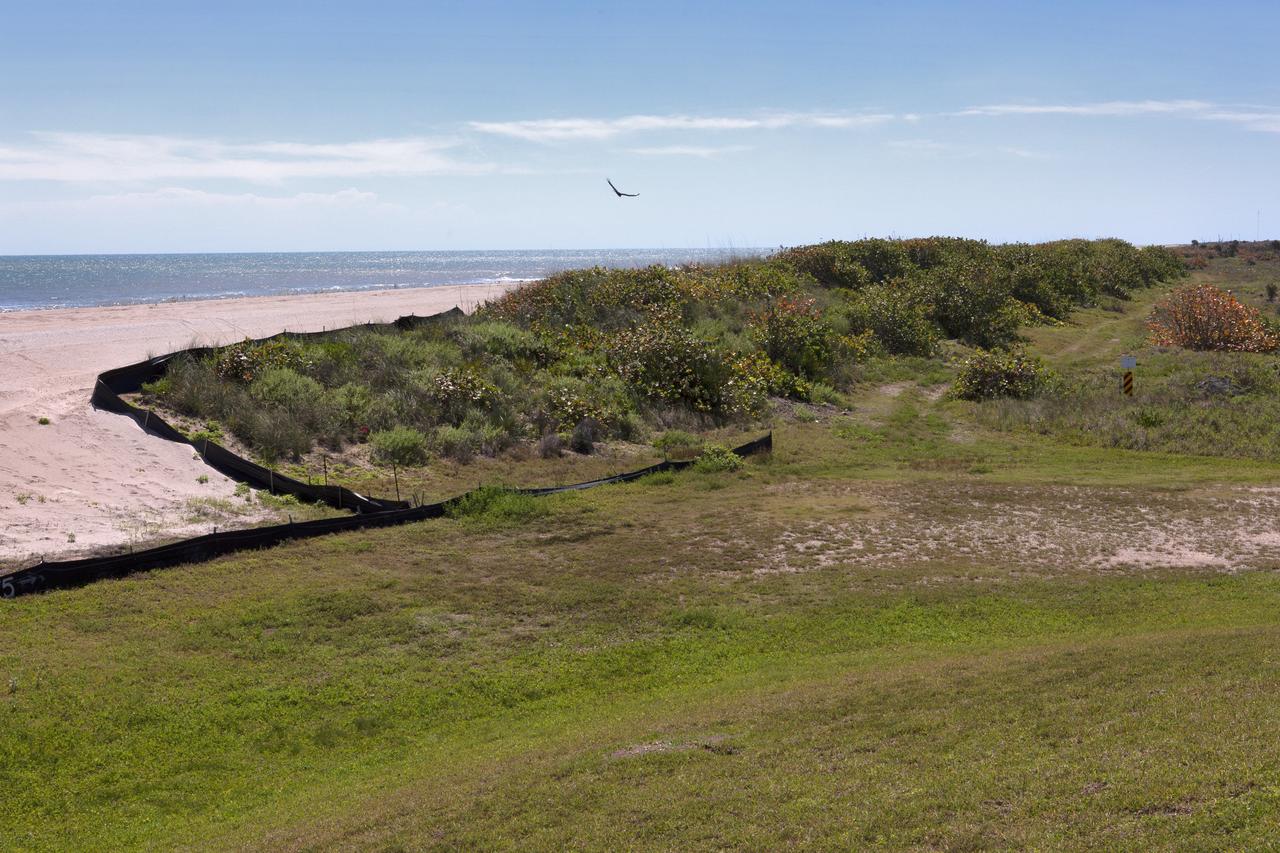

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. The existing dunes with the Atlantic Ocean in the background are a contrast to a small portion of the dune restoration in view. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. Once the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coastal wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.
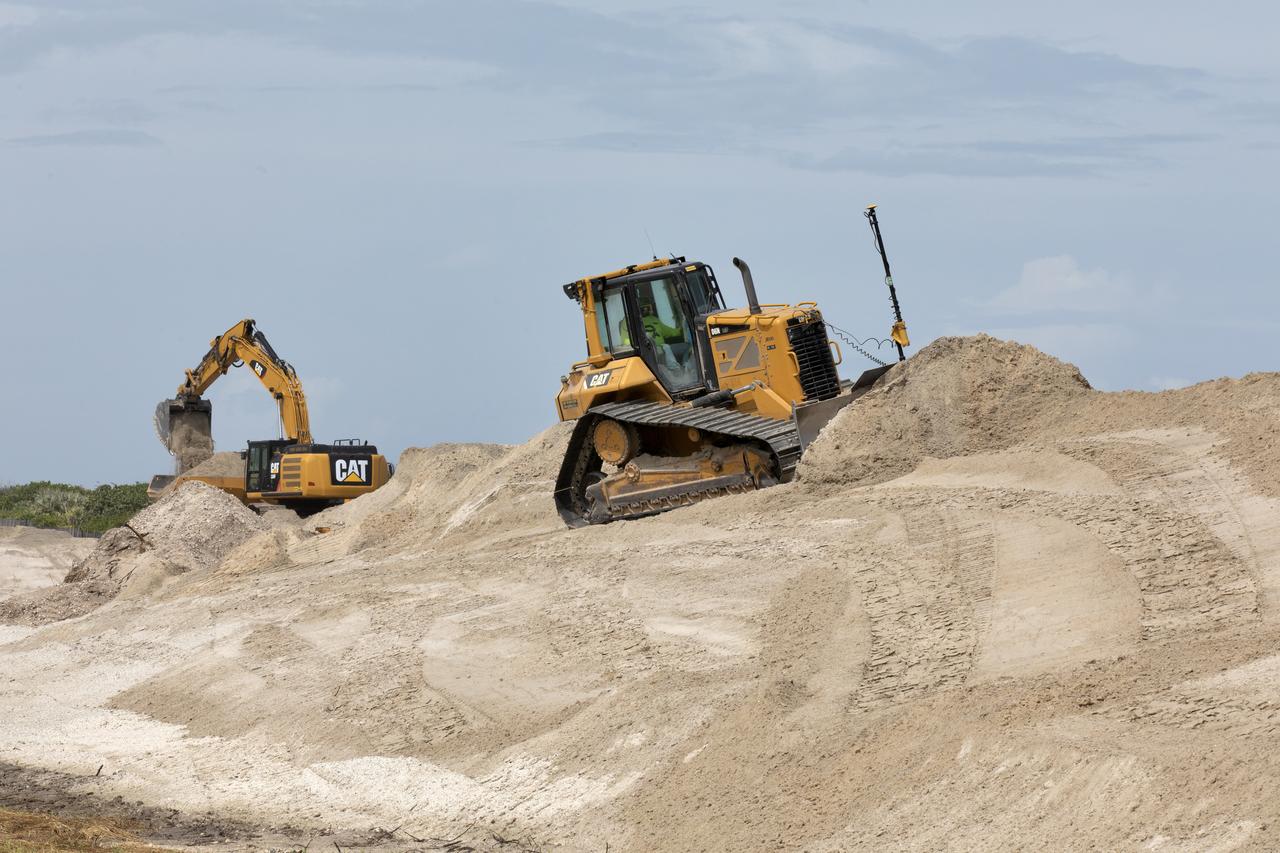

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 8, 2018. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, is being transported to the space center’s beaches. One the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coast wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and is targeted to be completed by April 2019.

Native vegetation has been planted in the restored dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. After the dune was built up, native vegetation was replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coastal wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.
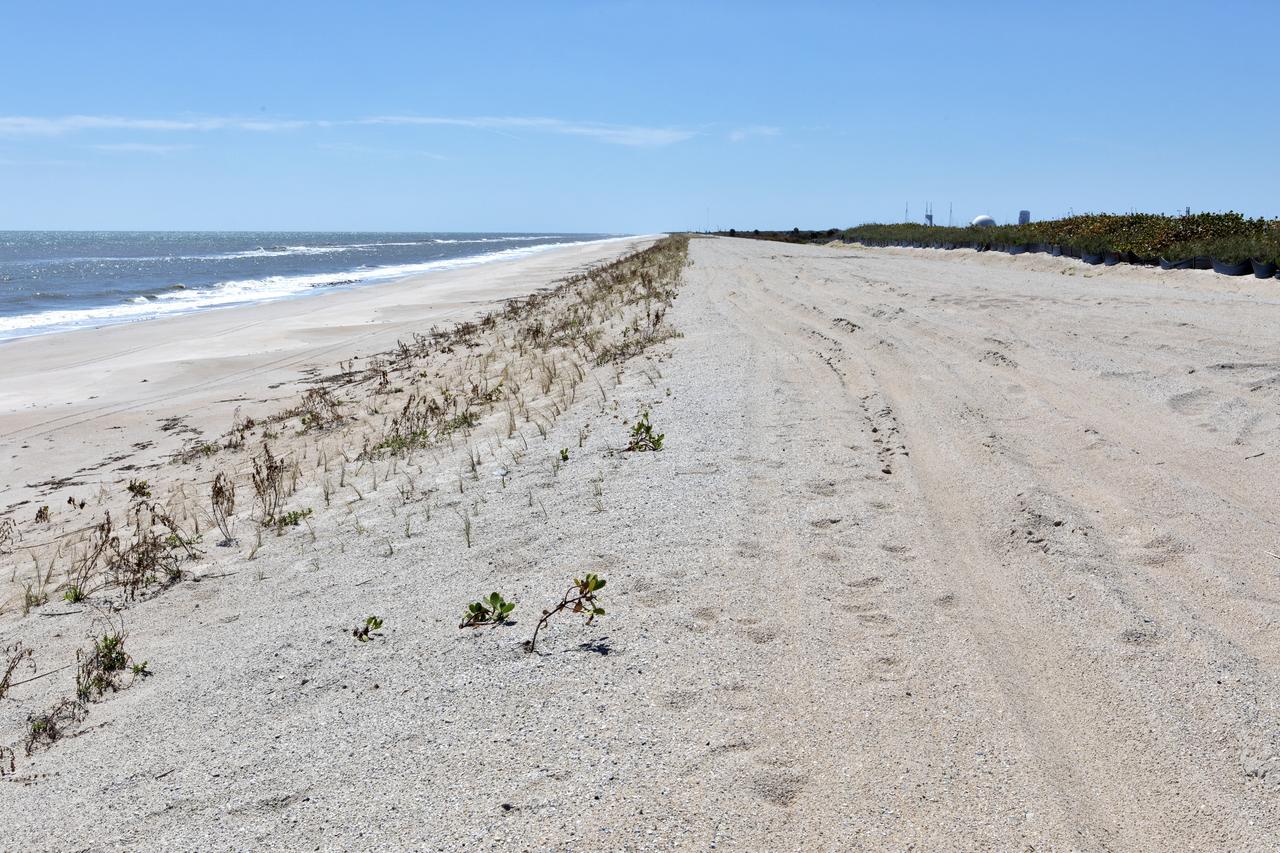

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. After the dune was built up, native coastal vegetation was replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coast wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.
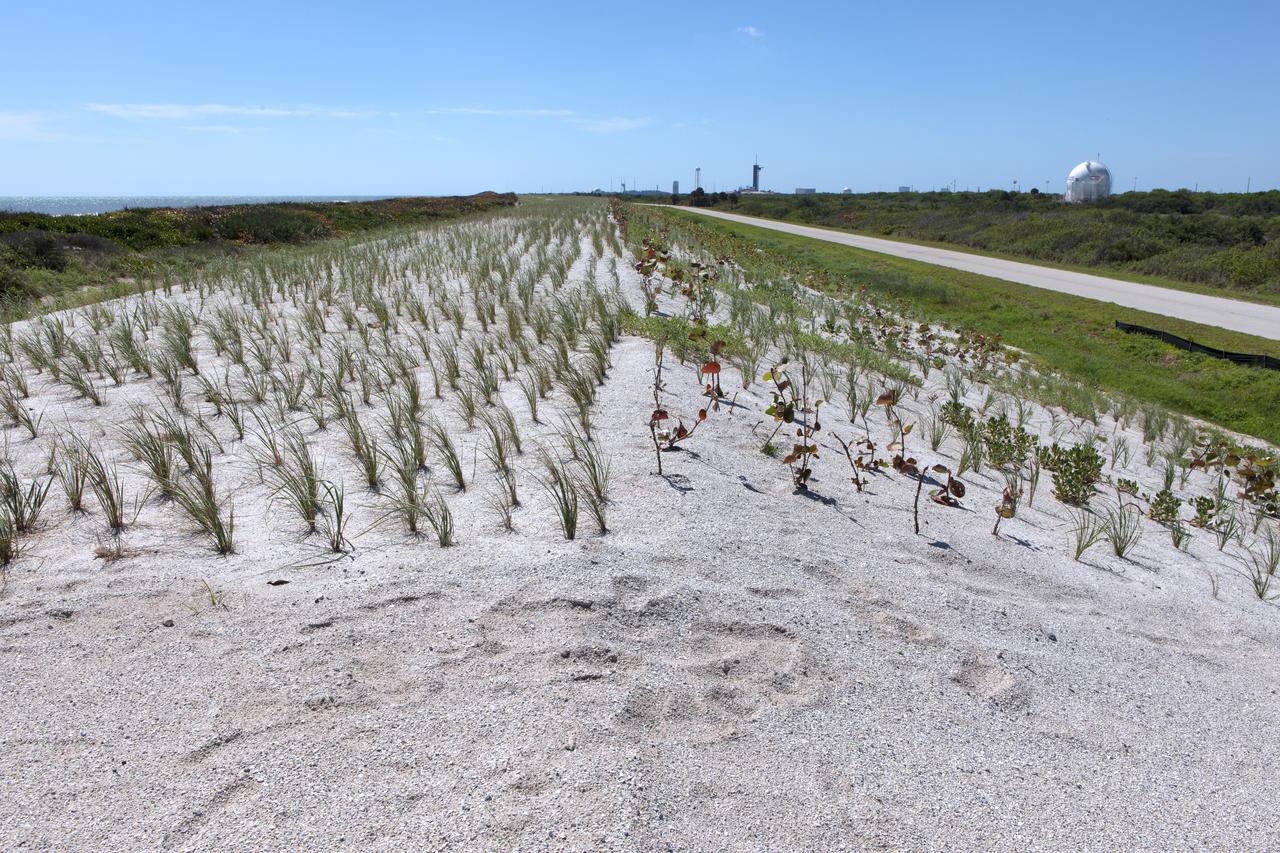

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. After the dune was built up, native coastal vegetation was replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coastal wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. Once the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coastal wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.
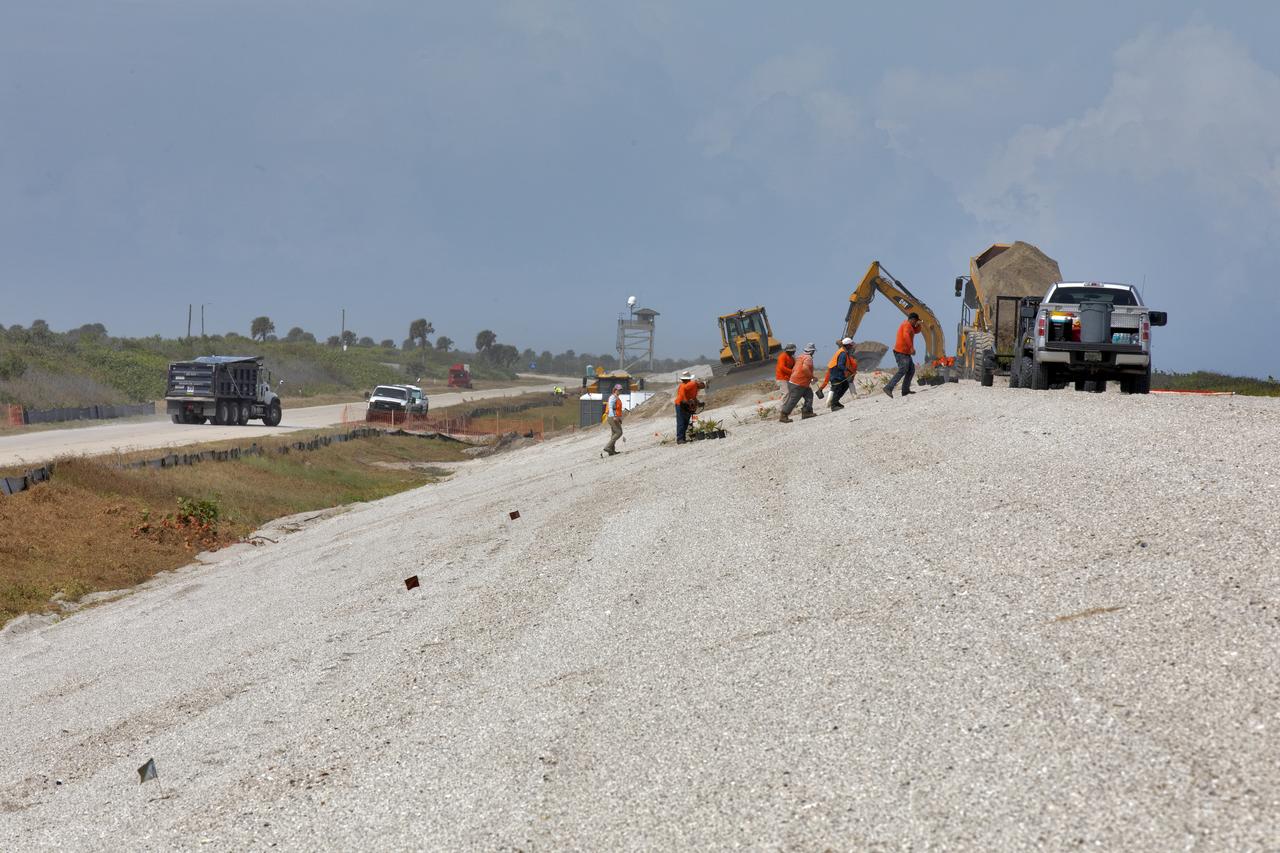

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 8, 2018. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, is being transported to the space center’s beaches. Once the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coast wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and is targeted to be completed by April 2019.
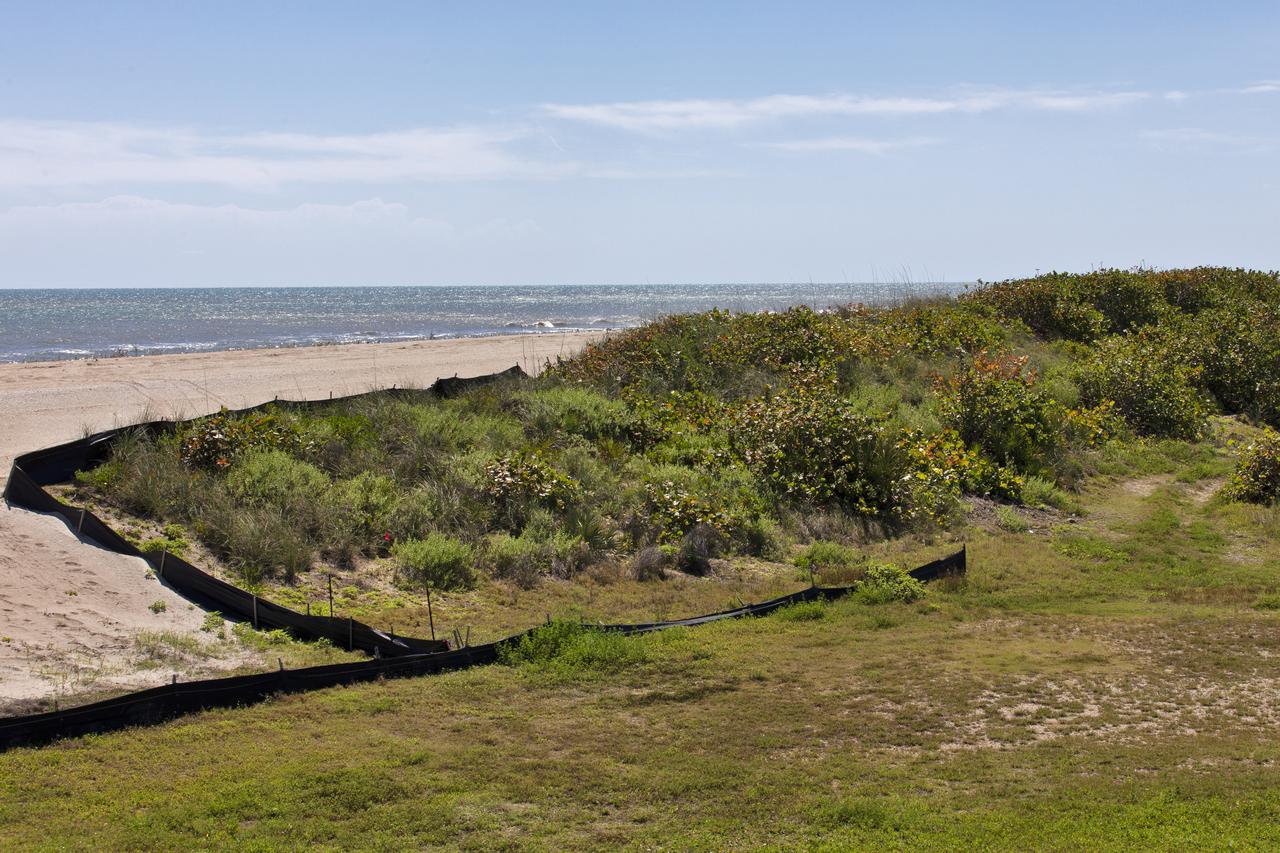

Restoration efforts are underway to the dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this view on April 15, 2019. The existing dunes with the Atlantic Ocean in the background are a contrast to a small portion of the dune restoration in view. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, was transported to the space center’s beaches. Once the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coastal wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and was targeted to be completed by April 2019.