
A contingent of young stars and star-forming gas clouds is sticking out of one of the Milky Way's spiral arms like a splinter protruding from a plank of wood. Stretching some 3,000 light-years, this is the first major structure identified with such a dramatically different orientation relative to the arm. The background image shows the location of the splinter in the Milky Way. The yellow region in the center of the image is the galaxy's bright and crowded center. The galaxy's arms spiral around the center, and are full of stars and star-forming clouds of gas and dust. A key property of spiral arms is how tightly they wind around a galaxy. This characteristic is measured by the arm's pitch angle. A circle has a pitch angle of 0 degrees; as the spiral becomes more open, the pitch angle increases. Most models of the Milky Way suggest that the Sagittarius Arm forms a spiral that has a pitch angle of about 12 degrees, but the protruding structure has a pitch angle of nearly 60 degrees. Similar structures – sometimes called spurs or feathers – are commonly found jutting out of the arms of other spiral galaxies. For decades scientists have wondered whether our Milky Way's spiral arms are also dotted with these structures or if they are relatively smooth. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24576

A new, dynamic portrait of our Milky Way galaxy shows a frenzy of gas, charged particles and dust as seen by the European Space Agency Planck mission.

Images of the Milky Way and the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) are overlaid on a map of the surrounding area, our galaxy's galactic halo. Dark blue represents a low concentration of stars; lighter blues indicate increasing stellar density. The map spans from about 200,000 light-years to 325,000 light-years from the galactic center and provides the first clear view of the major features in this region. The LMC is orbiting the Milky Way and will eventually merge with it. The high concentration in the lower half is a wake created by the LMC as it sails through the galactic halo. In the upper half of the image, astronomers observed an apparent excess of stars compared to the southern hemisphere. This is evidence that the Large Magellanic Cloud has pulled the Milky Way disk significantly off-center. The galactic halo can be thought of as a bubble surrounding the disk. The number of stars per area is highest near the center of the bubble, and drops off moving away from the center. If the Milky Way were in the center of the halo, astronomers would see an approximately equal number of stars in both hemispheres. But because the Milky Way has been pulled away from the center, when astronomers look into the northern hemisphere, they see more of the central, highly populated area. Comparing these two views, there is an apparent excess of stars in the northern hemisphere. The image of the Milky Way used here is from the ESA (European Space Agency) Gaia mission: https://www.eso.org/public/images/eso1908e/. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24571

This composite image comes from the ESA Planck shows a festive portrait of our Milky Way galaxy shows a mishmash of gas, charged particles and several types of dust.

In visible light, the bulk of our Milky Way galaxy stars are eclipsed behind thick clouds of galactic dust and gas. But to the infrared eyes of NASA Spitzer Space Telescope, distant stars and dust clouds shine with unparalleled clarity and color.
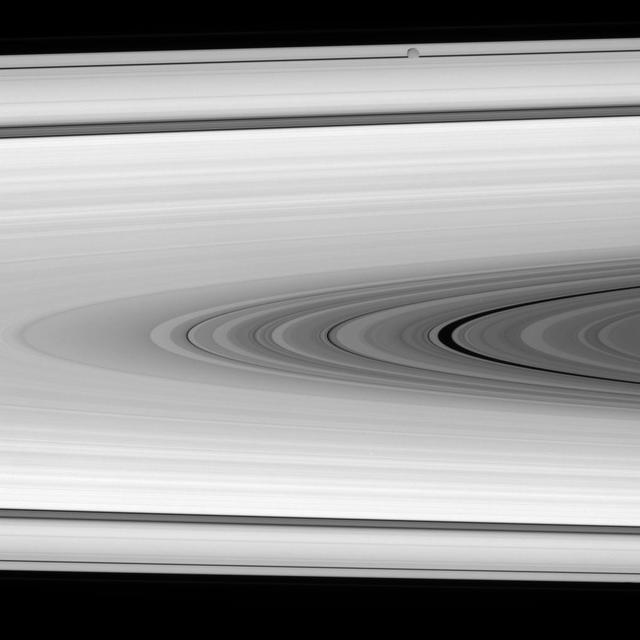

Epimetheus in the Way

Our Milky Way is a dusty place. So dusty that we cannot see the center of the galaxy in visible light. Thanks to NASA Spitzer Space Telescope excellent resolution, the dusty features within the galactic center are seen in unprecedented detail.

More than 800,000 frames from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope were stitched together to create this infrared portrait of dust and stars radiating in the inner Milky Way.

More than 444,580 frames from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope were stitched together to create this portrait of the raging star-formation occurring in the inner Milky Way.

Our Milky Way galaxy is ablaze with dust in this new all-sky map from Planck, a European Space Agency mission with important NASA contributions. The towers of fiery colors are actually dust in the galaxy and beyond that has been polarized.

This artist concept illustrates the new view of the Milky Way. The galaxy two major arms can be seen attached to the ends of a thick central bar, while the two now-demoted minor arms are less distinct and located between the major arms.
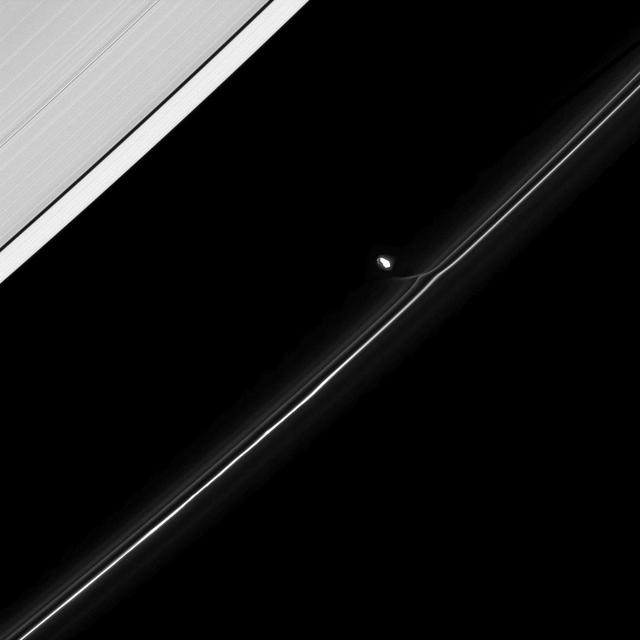

On His Merry Way

Saturn Gets in the Way
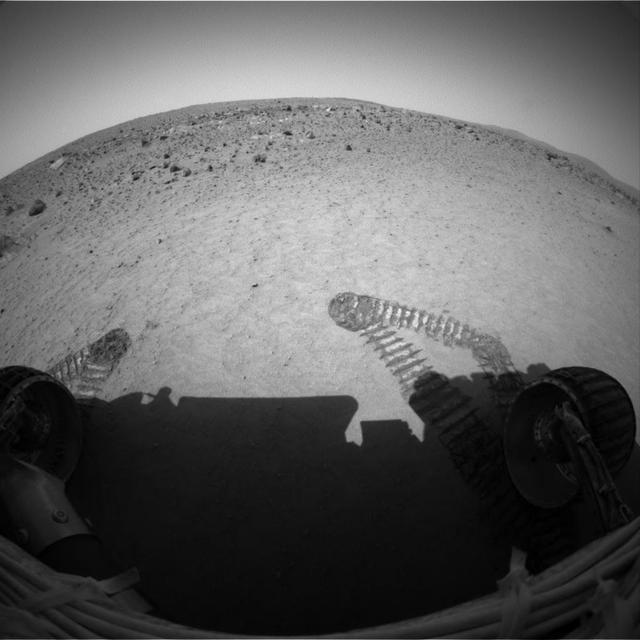

Wiggling Its Way to Discovery

Way to Go Spirit!

Wiggling Its Way to Discovery

A Long Way From Home
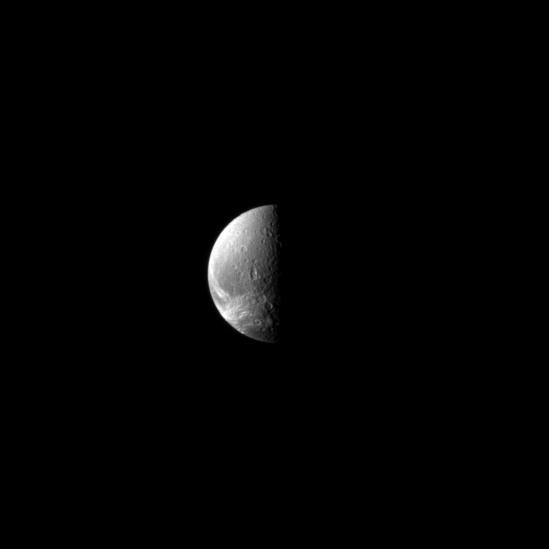

Down Dione Way
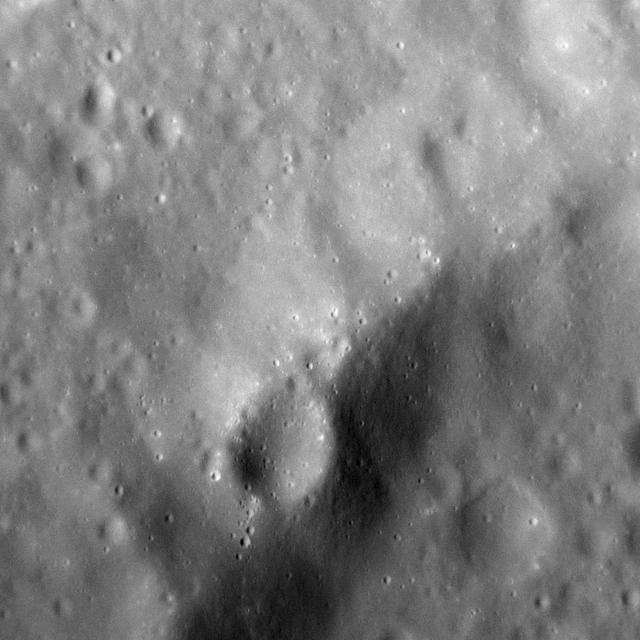

It Craters All the Way Down
Which Way to the Top?
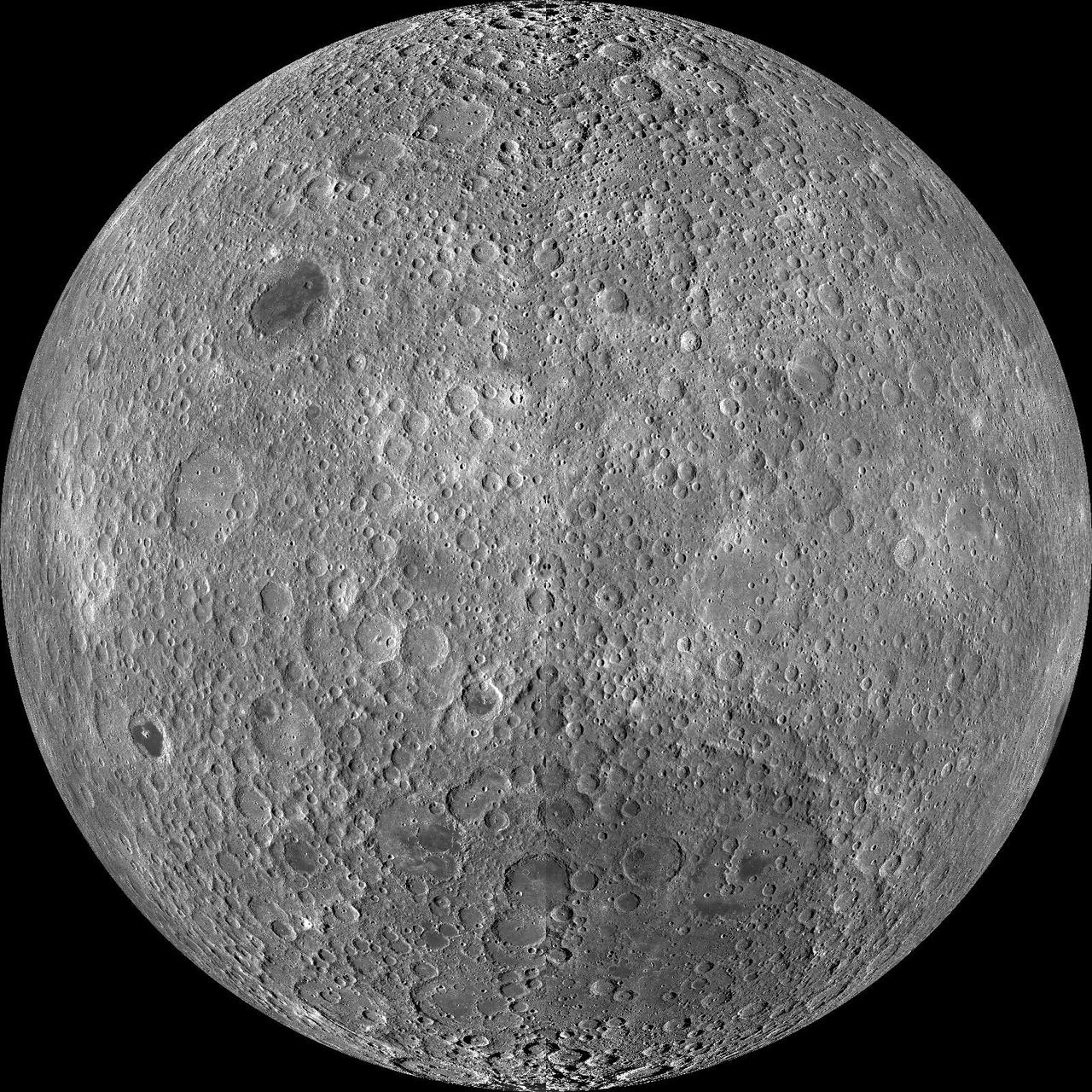

Farside! And All the Way Around

A "Hidden Figures Way" street sign is seen at the corner of 4th and E Street SW across from the NASA Headquarters building following a dedication ceremony, Wednesday, June 12, 2019 in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

A D.C. Department of Transportation employee removes a paper cover from the "Hidden Figures Way" street sign at the corner of 3rd and E Street SW during a dedication ceremony, Wednesday, June 12, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
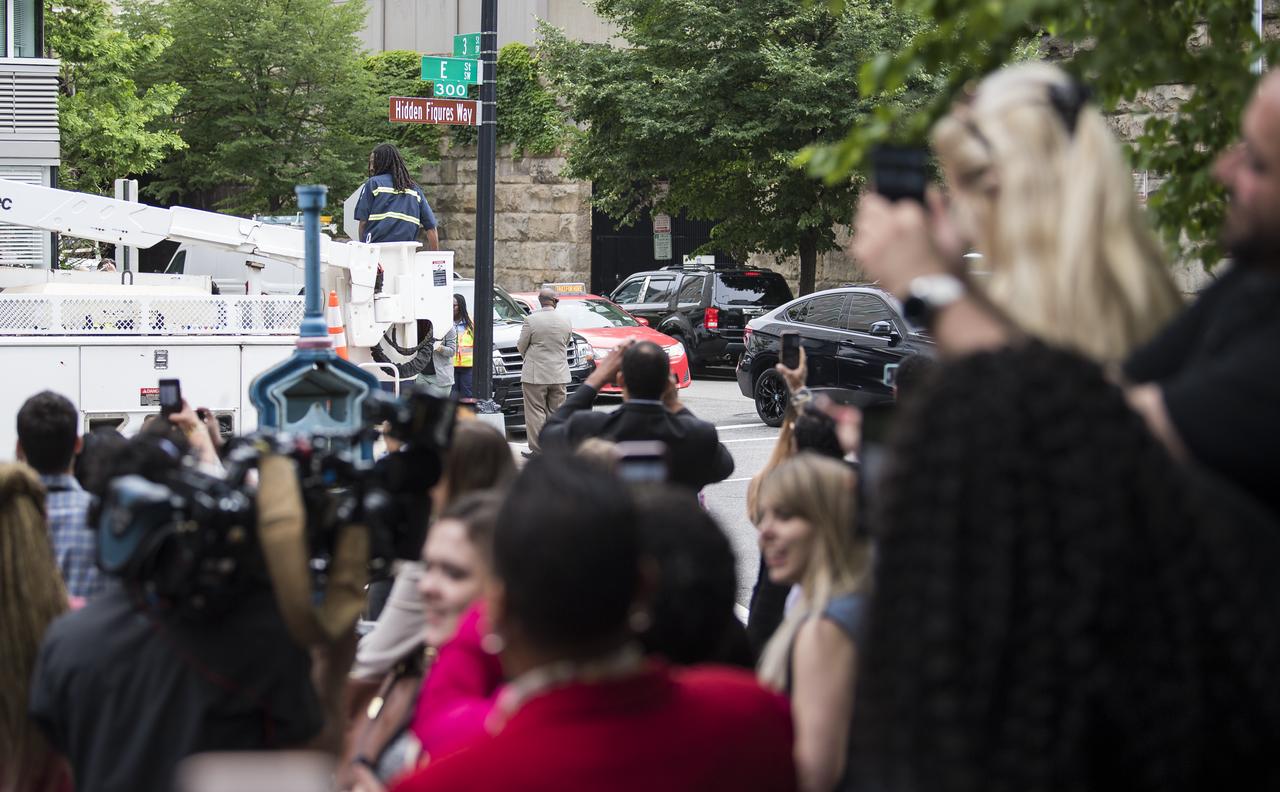

Attendees of the street dedication ceremony take pictures of the "Hidden Figures Way" street sign at the corner of 3rd and E Street SW following its unveiling, Wednesday, June 12, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

This image shows the star-studded center of the Milky Way towards the constellation of Sagittarius. The crowded center of our galaxy contains numerous complex and mysterious objects that are usually hidden at optical wavelengths by clouds of dust — but many are visible here in these infrared observations from Hubble. However, the most famous cosmic object in this image still remains invisible: the monster at our galaxy’s heart called Sagittarius A*. Astronomers have observed stars spinning around this supermassive black hole (located right in the center of the image), and the black hole consuming clouds of dust as it affects its environment with its enormous gravitational pull. Infrared observations can pierce through thick obscuring material to reveal information that is usually hidden to the optical observer. This is the best infrared image of this region ever taken with Hubble, and uses infrared archive data from Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3, taken in September 2011. Credit: NASA, ESA, and G. Brammer <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
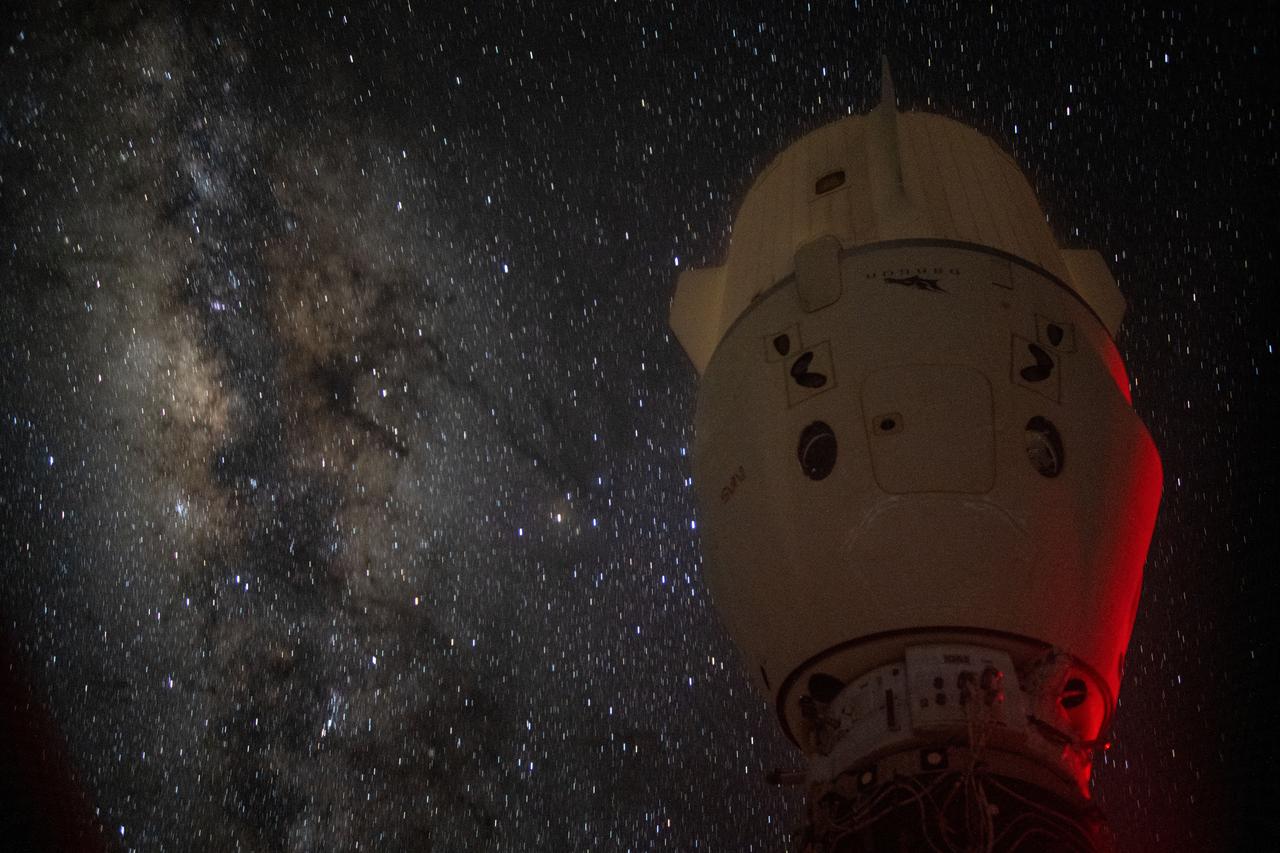

iss071e256593 (July 1, 2024) --- The Milky Way appears in the vastness of space behind the dimly lit SpaceX Dragon Endeavour spacecraft docked to the Harmony module's space-facing port on the International Space Station.
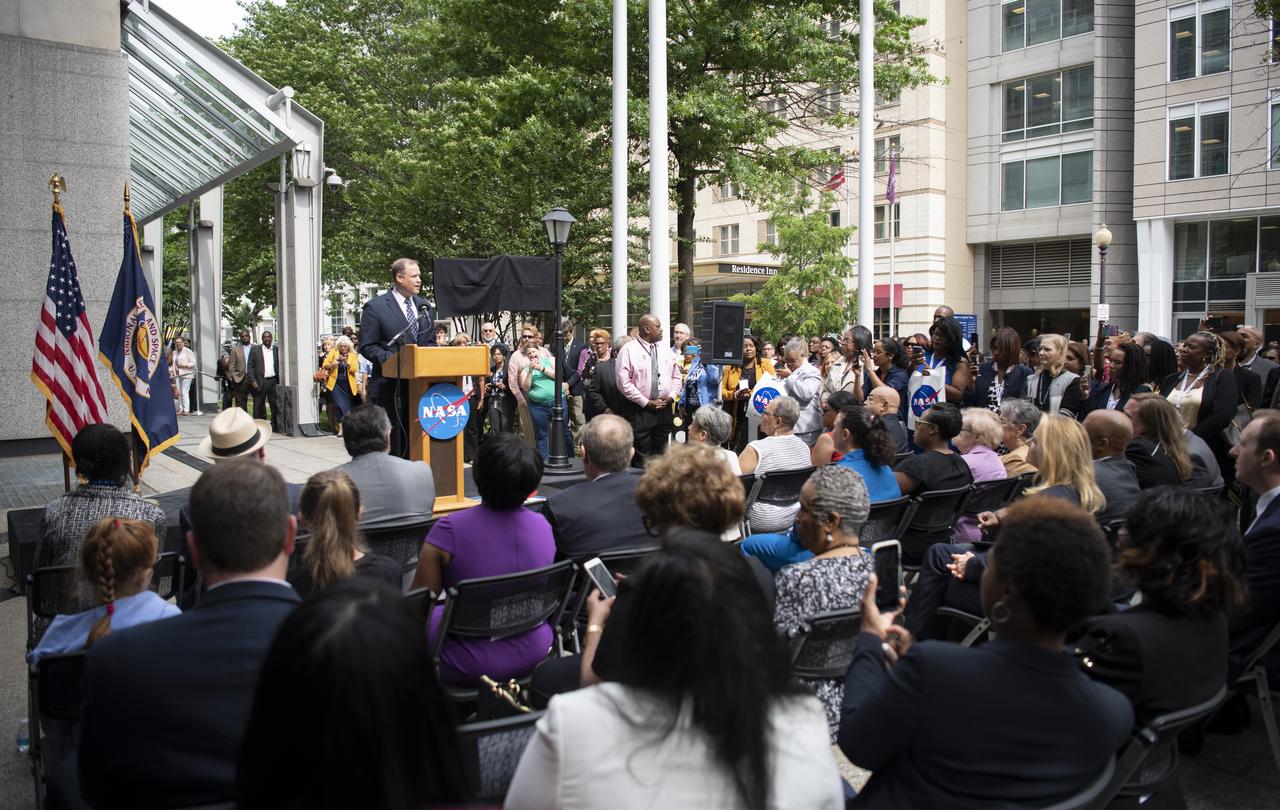

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine delivers remarks during the dedication ceremony for "Hidden Figures Way," Wednesday, June 12, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorthy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)4
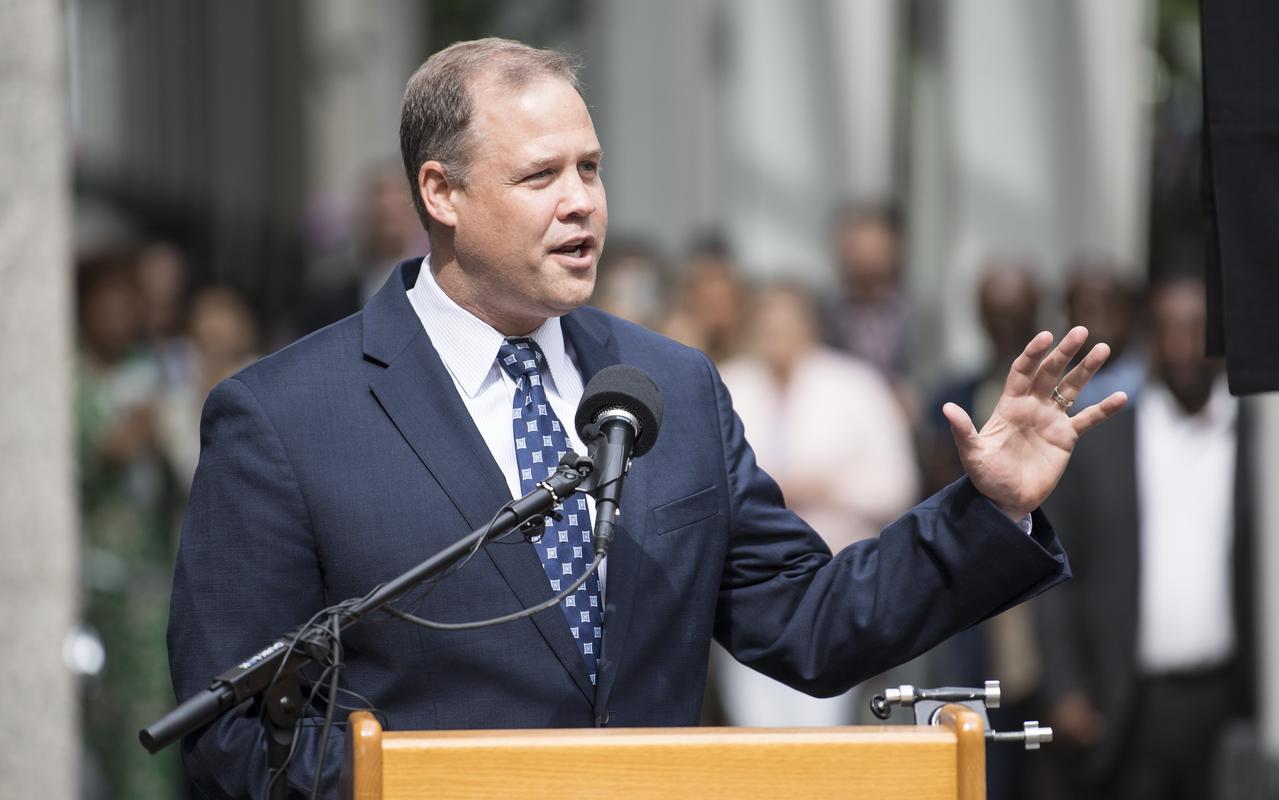

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine delivers remarks during the dedication ceremony for "Hidden Figures Way," Wednesday, June 12, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

D.C. Council Chairman Phil Mendelson delivers remarks during the dedication ceremony for "Hidden Figures Way," Wednesday, June 12, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine delivers remarks during the dedication ceremony for "Hidden Figures Way," Wednesday, June 12, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

U.S. Senator Ted Cruz, R-Texas, delivers remarks during the dedication ceremony for "Hidden Figures Way," Wednesday, June 12, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Margot Lee Shetterly, author of the book "Hidden Figures," delivers remarks during the dedication ceremony for "Hidden Figures Way," Wednesday, June 12, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

D.C. Council Chairman Phil Mendelson delivers remarks during the dedication ceremony for "Hidden Figures Way," Wednesday, June 12, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Margot Lee Shetterly, author of the book "Hidden Figures," delivers remarks during the dedication ceremony for "Hidden Figures Way," Wednesday, June 12, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

U.S. Senator Ted Cruz, R-Texas, delivers remarks during the dedication ceremony for "Hidden Figures Way," Wednesday, June 12, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
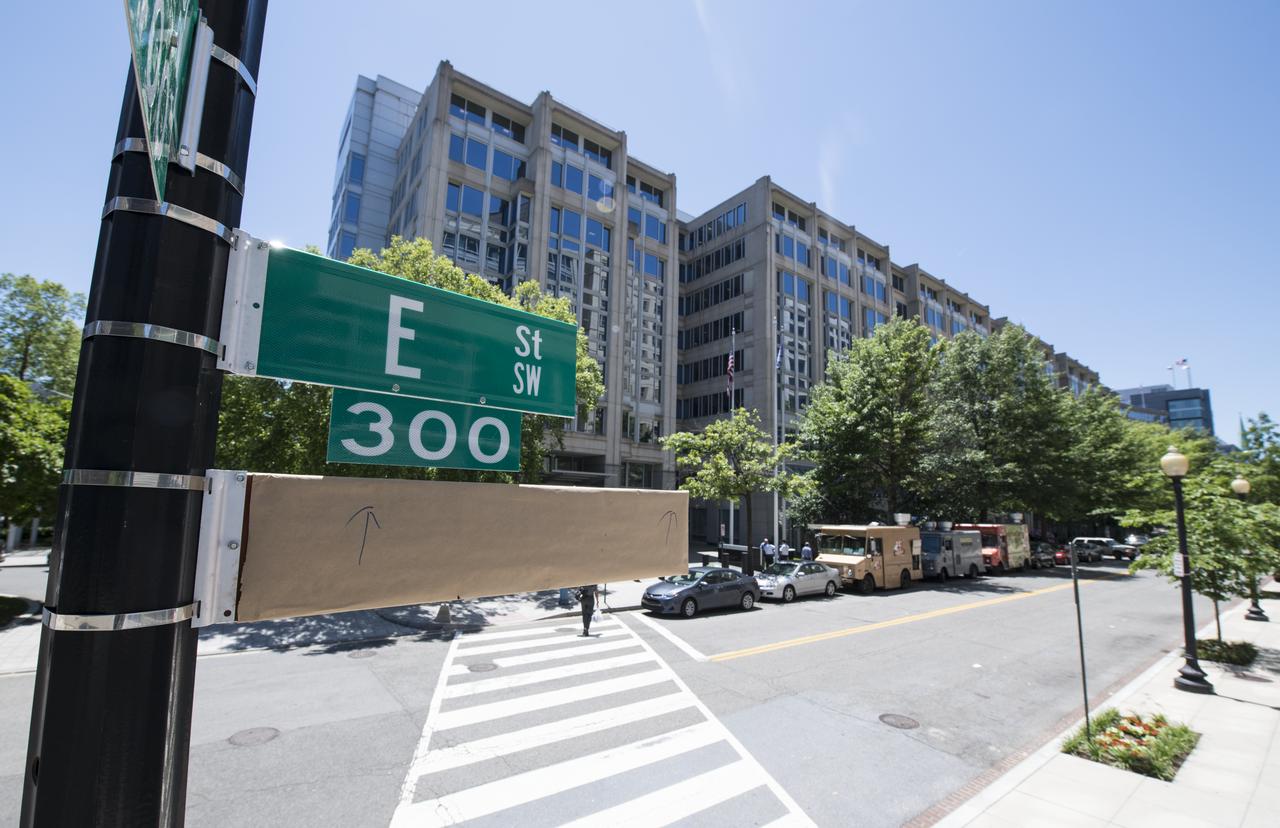

A covered street sign is seen outside of the NASA Headquarters building the day before a street renaming ceremony, Tuesday, June 11, 2019 in Washington, DC. On Wednesday, June 12, a ceremony was held to dedicate the 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
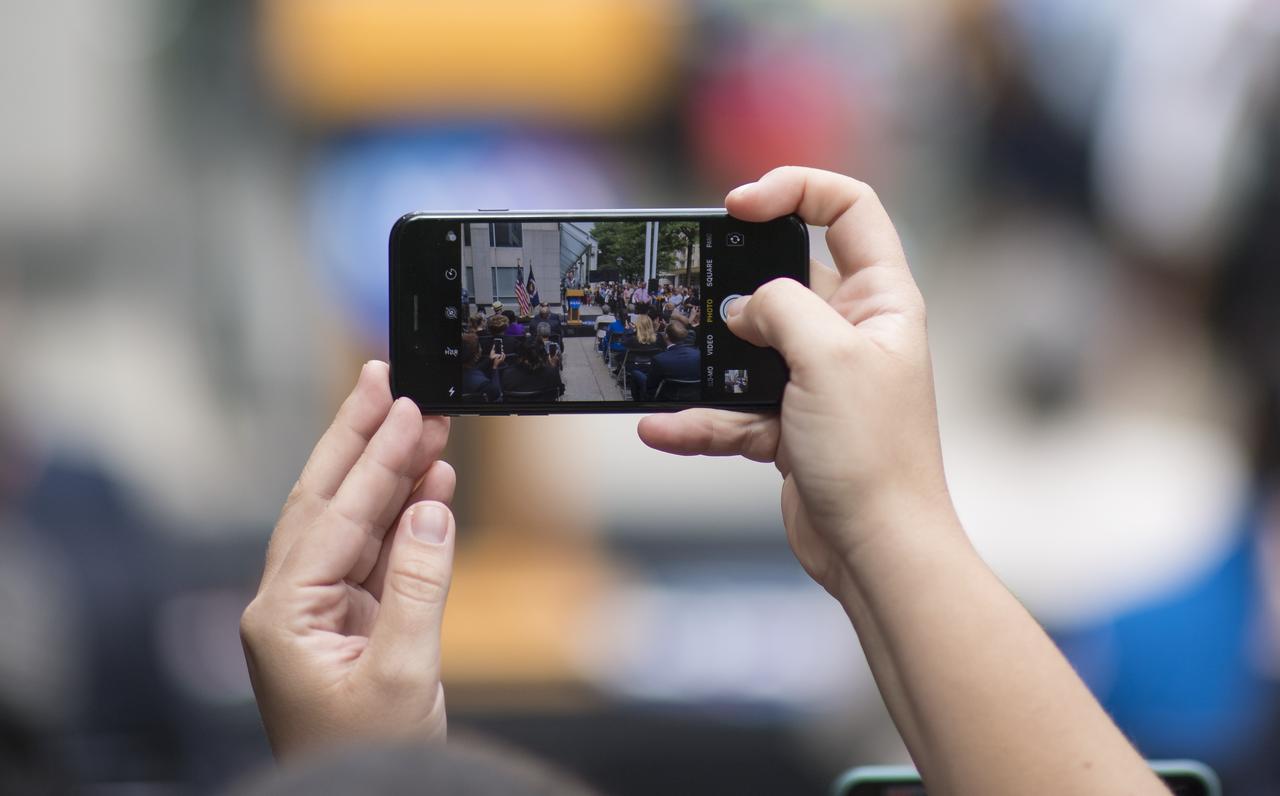

A member of the audience takes a picture with their cell phone as U.S. Senator Ted Cruz, R-Texas, delivers remarks during the dedication ceremony for "Hidden Figures Way," Wednesday, June 12, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Rays a Long Way from Home

Legacy Panorama on Spirit Way to Bonneville

Astronomers using data from NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, are helping to trace the shape of our Milky Way galaxy's spiral arms. This illustration shows where WISE data revealed clusters of young stars shrouded in dust, called embedded clusters, which are known to reside in spiral arms. The bars represent uncertainties in the data. The nearly 100 clusters shown here were found in the arms called Perseus, Sagittarius-Carina, and Outer -- three of the galaxy's four proposed primary arms. Our sun resides in a spur to an arm, or a minor arm, called Orion Cygnus. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19341
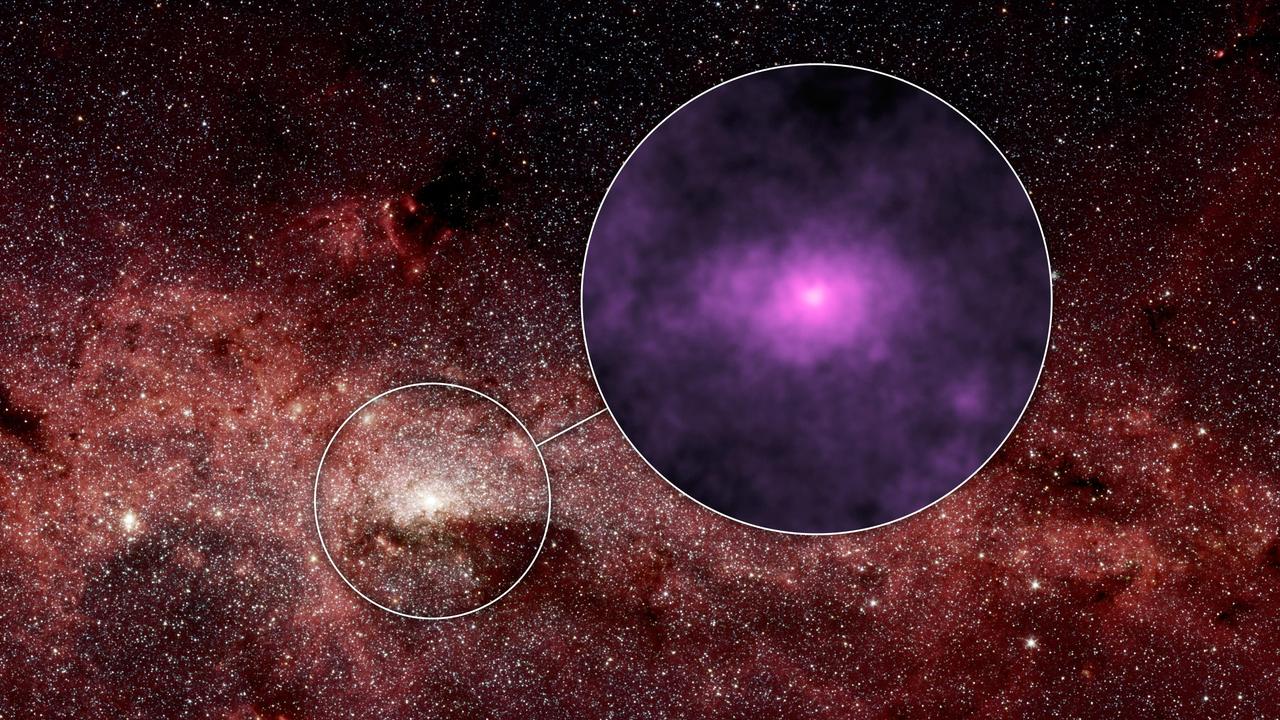
NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, has captured a new high-energy X-ray view (magenta, Figure 1) of the bustling center of our Milky Way galaxy. The smaller circle shows the area where the NuSTAR image was taken -- the very center of our galaxy, where a giant black hole resides. That region is enlarged to the right, in the larger circle, to show the NuSTAR data. The NuSTAR picture is one of the most detailed ever taken of the center of our galaxy in high-energy X-rays. The X-ray light, normally invisible to our eyes, has been assigned the color magenta. The brightest point of light near the center of the X-ray picture is coming from a spinning dead star, known as a pulsar, which is near the giant black hole. While the pulsar's X-ray emissions were known before, scientists were surprised to find more high-energy X-rays than predicted in the surrounding regions, seen here as the elliptical haze. Astronomers aren't sure what the sources of the extra X-rays are, but one possibility is a population of dead stars. The background picture was captured in infrared light by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. The NuSTAR image has an X-ray energy range of 20 to 40 kiloelectron volts. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19334
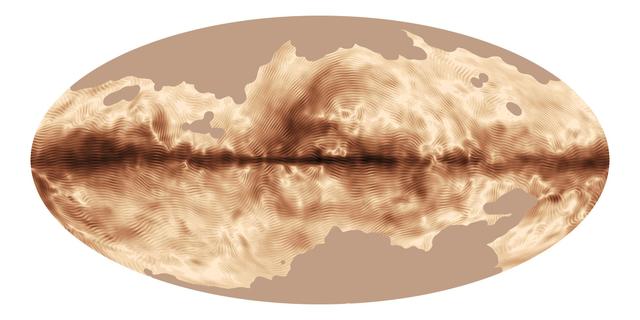
The magnetic field of our Milky Way galaxy as seen by ESA Planck satellite. This image was compiled from the first all-sky observations of polarized light emitted by interstellar dust in the Milky Way.

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, left, U.S. Senator Ted Cruz, R-Texas, second from left, D.C. Council Chairman Phil Mendelson, third from left, and Margot Lee Shetterly, author of the book "Hidden Figures," right, unveil the "Hidden Figures Way" street sign at a dedication ceremony, Wednesday, June 12, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, left, U.S. Senator Ted Cruz, R-Texas, second from left, D.C. Council Chairman Phil Mendelson, third from left, and Margot Lee Shetterly, author of the book "Hidden Figures," right, unveil the "Hidden Figures Way" street sign at a dedication ceremony, Wednesday, June 12, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, left, U.S. Senator Ted Cruz, R-Texas, second from left, D.C. Council Chairman Phil Mendelson, third from left, and Margot Lee Shetterly, author of the book "Hidden Figures," right, unveil the "Hidden Figures Way" street sign at a dedication ceremony, Wednesday, June 12, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

This dazzling infrared image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope shows hundreds of thousands of stars crowded into the swirling core of our spiral Milky Way galaxy.
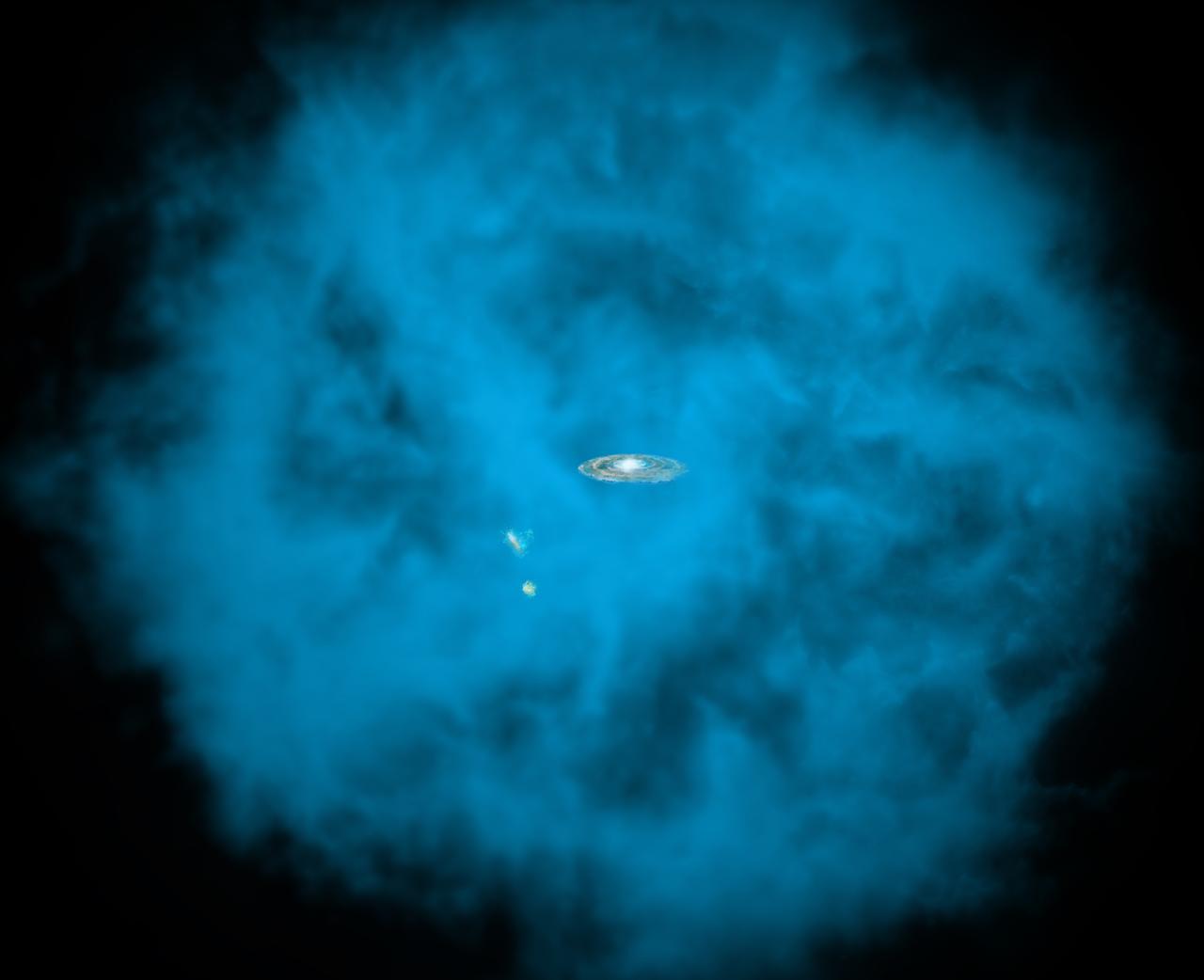

Our Milky Way galaxy and its small companions are surrounded by a giant halo of million-degree gas (seen in blue in this artists' rendition) that is only visible to X-ray telescopes in space. University of Michigan astronomers discovered that this massive hot halo spins in the same direction as the Milky Way disk and at a comparable speed. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/29VgLdK" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/29VgLdK</a> Credit: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss/Ohio State/A Gupta et al <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
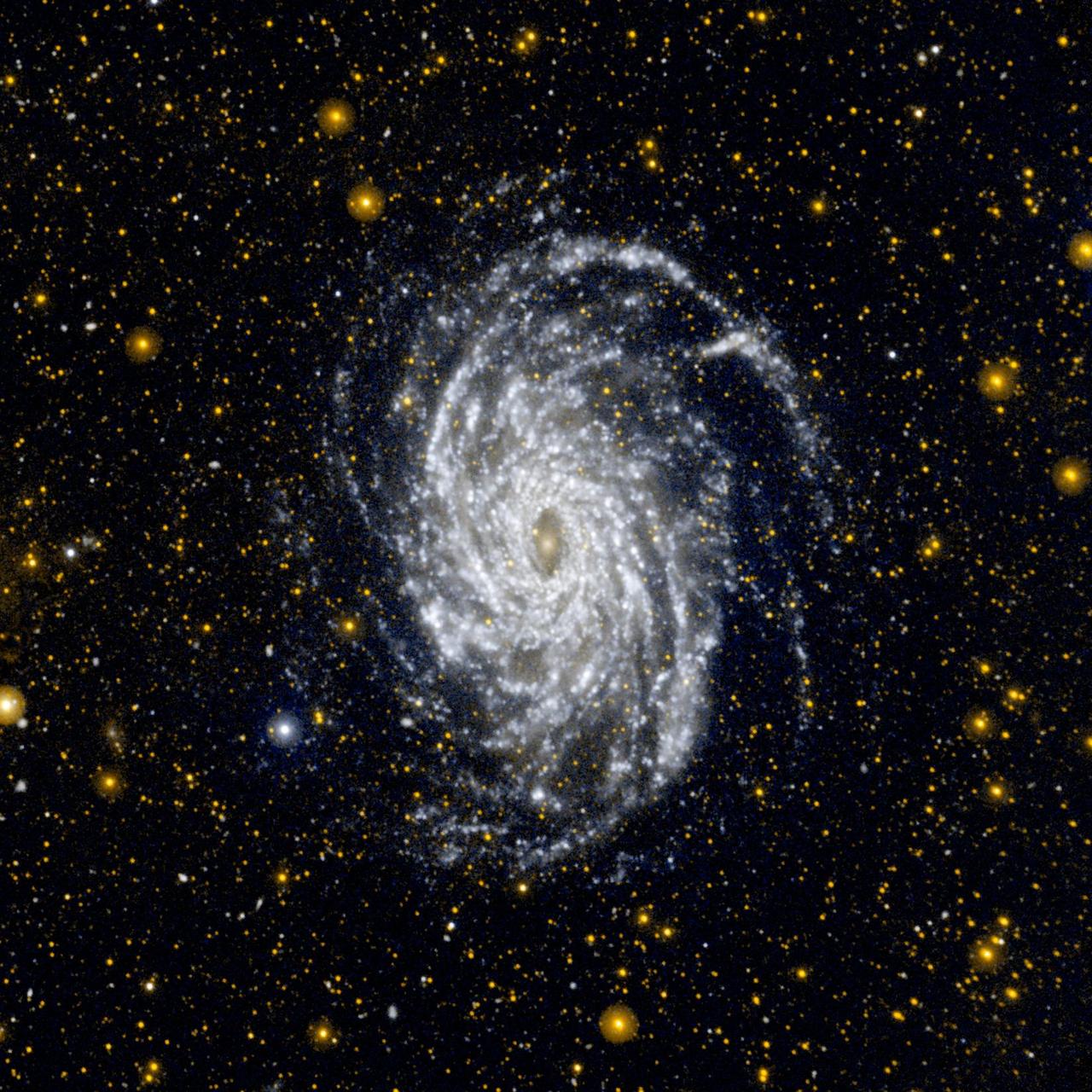

This image from NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer shows NGC 6744, one of the galaxies most similar to our Milky Way in the local universe.

NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope captured two festive-looking nebulas, situated so as to appear as one. They reside in the Small Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy that is a satellite of our Milky Way galaxy. Intense radiation from the brilliant central stars is heating hydrogen in each of the nebulas, causing them to glow red. The nebulas, together, are called NGC 248. They were discovered in 1834 by the astronomer Sir John Herschel. NGC 248 is about 60 light-years long and 20 light-years wide. It is among a number of glowing hydrogen nebulas in the dwarf satellite galaxy, which is located approximately 200,000 light-years away in the southern constellation Tucana. The image is part of a study called Small Magellanic Cloud Investigation of Dust and Gas Evolution (SMIDGE). Astronomers are using Hubble to probe the Milky Way satellite to understand how dust is different in galaxies that have a far lower supply of heavy elements needed to create dust. The Small Magellanic Cloud has between a fifth and a tenth of the amount of heavy elements that the Milky Way does. Because it is so close, astronomers can study its dust in great detail, and learn about what dust was like earlier in the history of the universe. “It is important for understanding the history of our own galaxy, too,” explained the study’s principal investigator, Dr. Karin Sandstrom of the University of California, San Diego. Most of the star formation happened earlier in the universe, at a time where there was a much lower percentage of heavy elements than there is now. “Dust is a really critical part of how a galaxy works, how it forms stars,” said Sandstrom. Credit: NASA, ESA, STScI, K. Sandstrom (University of California, San Diego), and the SMIDGE team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
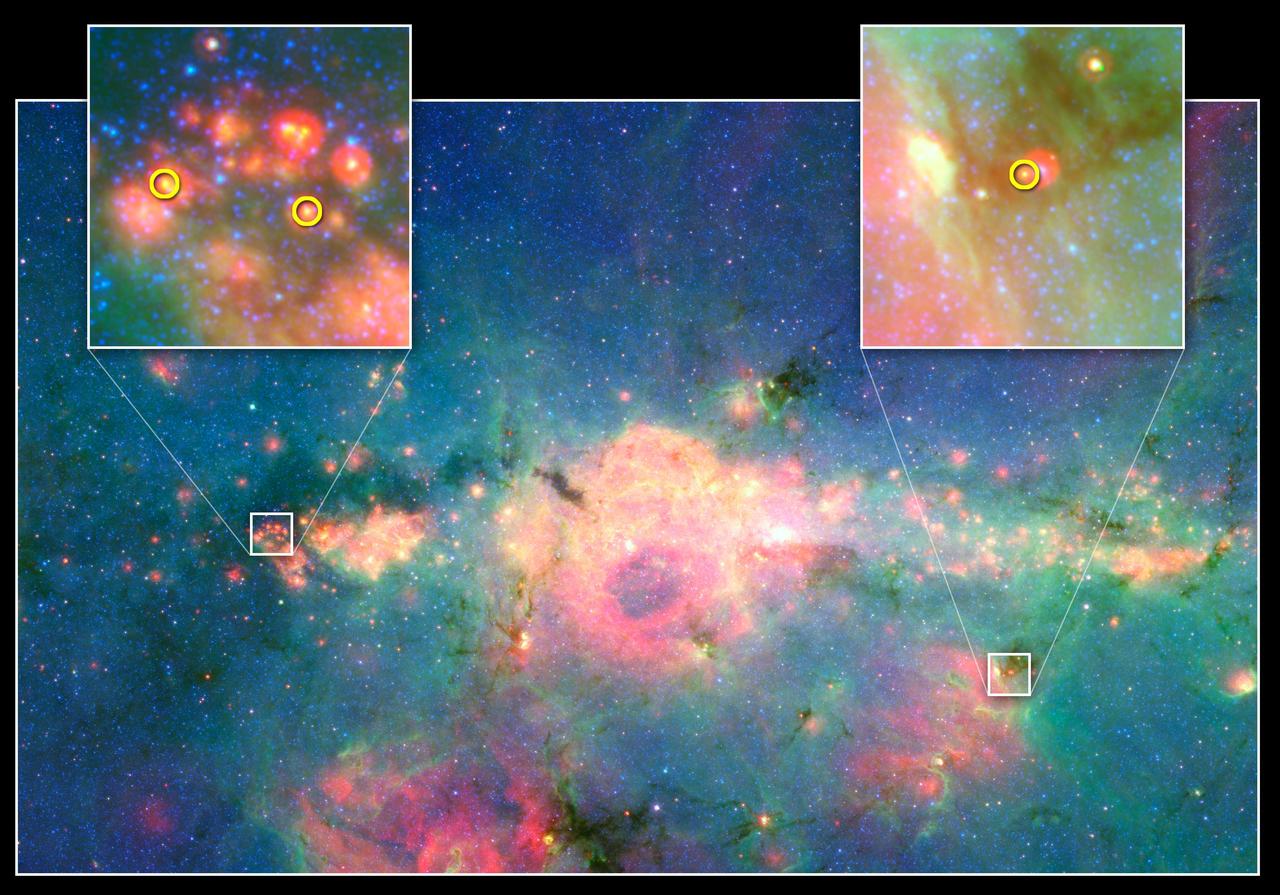

This infrared image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope shows three baby stars in the bustling center of our Milky Way galaxy. The three stars are the first to be discovered in the region.
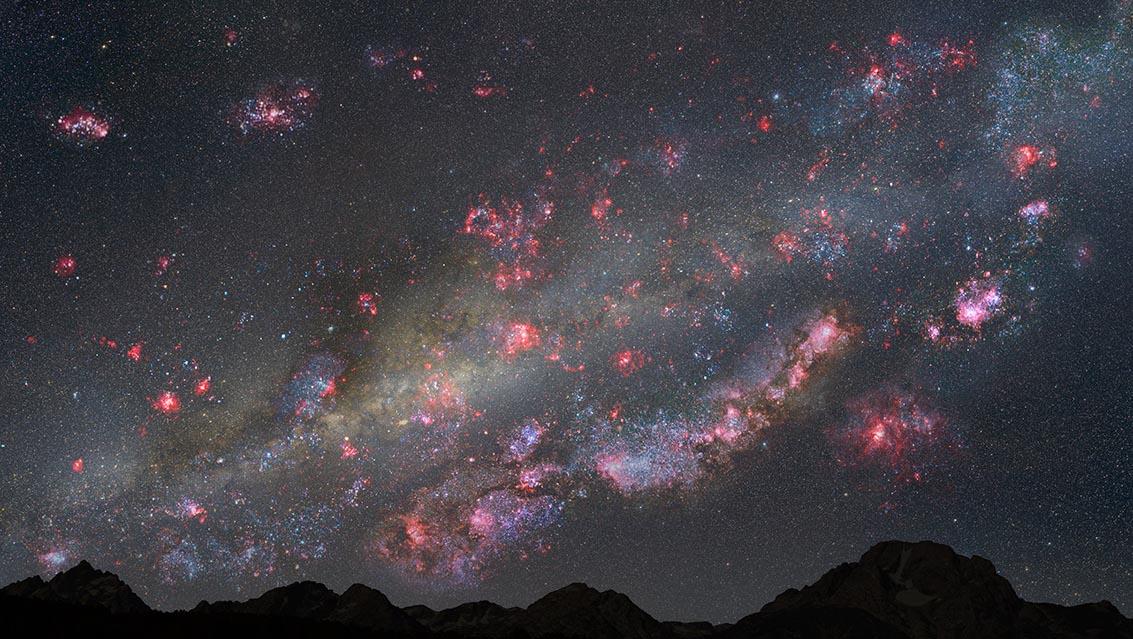

Caption: Artist's view of night sky from a hypothetical planet within a young Milky Way-like galaxy 10 billion years ago, the sky are ablaze with star birth. Pink clouds of gas harbor newborn stars, and bluish-white, young star clusters litter the landscape. Image Credit: NASA/ESA/Z. Levay (STScI) More info: In one of the most comprehensive multi-observatory galaxy surveys yet, astronomers find that galaxies like our Milky Way underwent a stellar “baby boom,” churning out stars at a prodigious rate, about 30 times faster than today. Our sun, however, is a late “boomer.” The Milky Way’s star-birthing frenzy peaked 10 billion years ago, but our sun was late for the party, not forming until roughly 5 billion years ago. By that time the star formation rate in our galaxy had plunged to a trickle. Missing the party, however, may not have been so bad. The sun’s late appearance may actually have fostered the growth of our solar system’s planets. Elements heavier than hydrogen and helium were more abundant later in the star-forming boom as more massive stars ended their lives early and enriched the galaxy with material that served as the building blocks of planets and even life on Earth. Astronomers don’t have baby pictures of our Milky Way’s formative years to trace the history of stellar growth so they studied galaxies similar in mass to our Milky Way, found in deep surveys of the universe. The farther into the universe astronomers look, the further back in time they are seeing, because starlight from long ago is just arriving at Earth now. From those surveys, stretching back in time more than 10 billion years, researchers assembled an album of images containing nearly 2,000 snapshots of Milky Way-like galaxies. The new census provides the most complete picture yet of how galaxies like the Milky Way grew over the past 10 billion years into today’s majestic spiral galaxies. The multi-wavelength study spans ultraviolet to far-infrared light, combining observations from NASA’s Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes, the European Space Agency’s Herschel Space Observatory, and ground-based telescopes, including the Magellan Baade Telescope at the Las Campanas Observatory in Chile. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/our-sun-came-late-to-the-milky-way-s-star-birth-party/" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/our-sun-came-late-to-the-mil...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
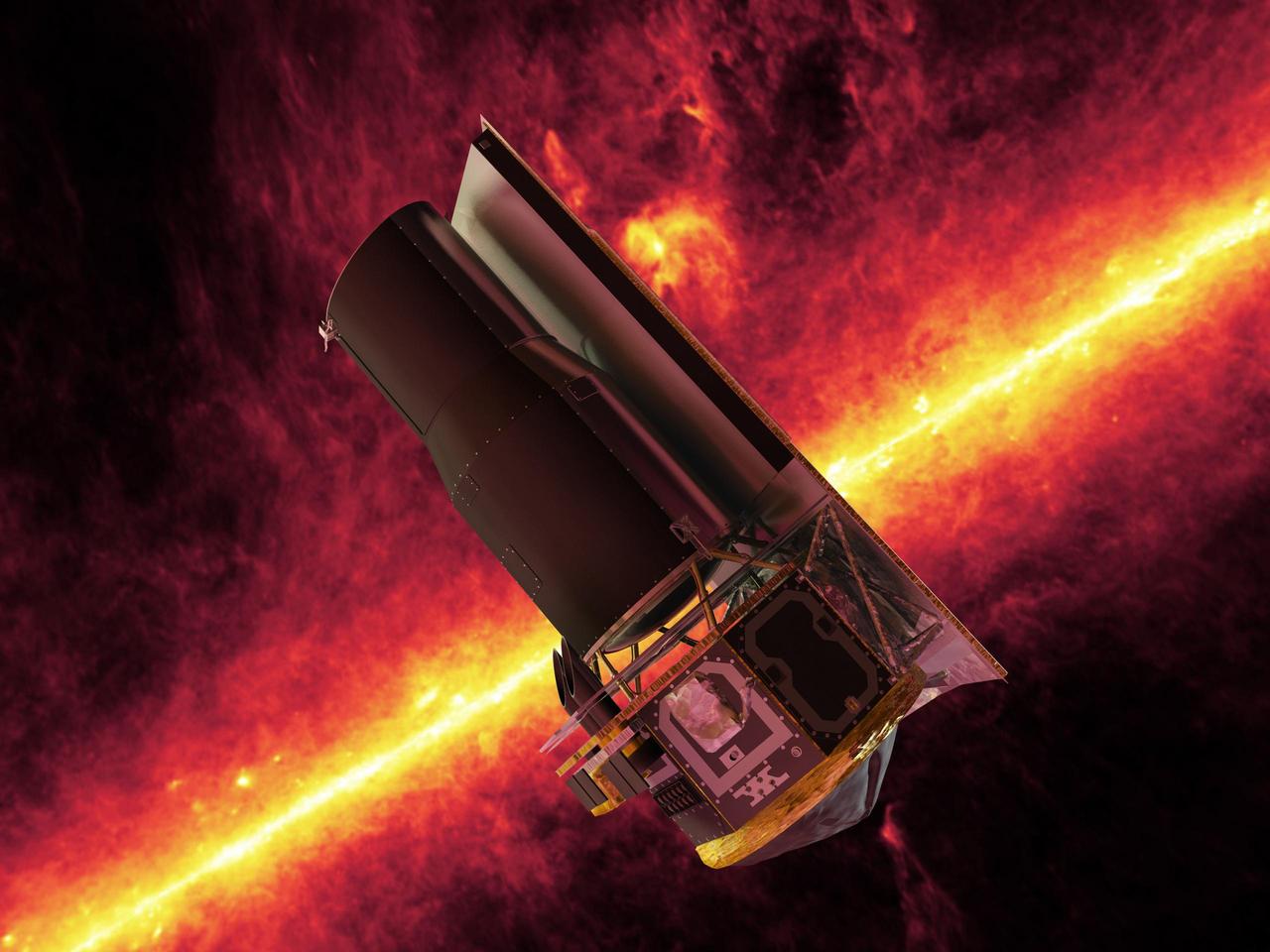

NASA Spitzer Space Telescope whizzes in front of a brilliant, infrared view of the Milky Way galaxy plane in this artistic depiction.

This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image presents the Arches Cluster, the densest known star cluster in the Milky Way. It is located about 25,000 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Sagittarius (The Archer), close to the heart of our galaxy, the Milky Way. It is, like its neighbor the Quintuplet Cluster, a fairly young astronomical object at between two and four million years old. The Arches cluster is so dense that in a region with a radius equal to the distance between the sun and its nearest star there would be over 100,000 stars! At least 150 stars within the cluster are among the brightest ever discovered in the Milky Way. These stars are so bright and massive that they will burn their fuel within a short time (on a cosmological scale that means just a few million years). Then they will die in spectacular supernova explosions. Due to the short lifetime of the stars in the cluster the gas between the stars contains an unusually high amount of heavier elements, which were produced by earlier generations of stars. Despite its brightness the Arches Cluster cannot be seen with the naked eye. The visible light from the cluster is completely obscured by gigantic clouds of dust in this region. To make the cluster visible astronomers have to use detectors which can collect light from the X-ray, infrared, and radio bands, as these wavelengths can pass through the dust clouds. This observation shows the Arches Cluster in the infrared and demonstrates the leap in Hubble’s performance since its 1999 image of same object. Credit: NASA/ESA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA image release Thursday, May 31, 2012 <b>To view a video from this Hubble release go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/7309212940">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/7309212940</a> </b> Caption: This illustration shows a stage in the predicted merger between our Milky Way galaxy and the neighboring Andromeda galaxy, as it will unfold over the next several billion years. In this image, representing Earth's night sky in 3.75 billion years, Andromeda (left) fills the field of view and begins to distort the Milky Way with tidal pull. Credit: NASA; ESA; Z. Levay and R. van der Marel, STScI; T. Hallas; and A. Mellinger To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/milky-way-collide.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/milky-way-colli...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
![In celebration of the International Year of Astronomy 2009, NASA's Great Observatories -- the Hubble Space Telescope, the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Chandra X-ray Observatory -- have produced a matched trio of images of the central region of our Milky Way galaxy. Each image shows the telescope's different wavelength view of the galactic center region, illustrating the unique science each observatory conducts. In this spectacular image, observations using infrared light and X-ray light see through the obscuring dust and reveal the intense activity near the galactic core. Note that the center of the galaxy is located within the bright white region to the right of and just below the middle of the image. The entire image width covers about one-half a degree, about the same angular width as the full moon. Spitzer's infrared-light observations provide a detailed and spectacular view of the galactic center region [Figure 1 (top frame of poster)]. The swirling core of our galaxy harbors hundreds of thousands of stars that cannot be seen in visible light. These stars heat the nearby gas and dust. These dusty clouds glow in infrared light and reveal their often dramatic shapes. Some of these clouds harbor stellar nurseries that are forming new generations of stars. Like the downtown of a large city, the center of our galaxy is a crowded, active, and vibrant place. Although best known for its visible-light images, Hubble also observes over a limited range of infrared light [Figure 2 (middle frame of poster)]. The galactic center is marked by the bright patch in the lower right. Along the left side are large arcs of warm gas that have been heated by clusters of bright massive stars. In addition, Hubble uncovered many more massive stars across the region. Winds and radiation from these stars create the complex structures seen in the gas throughout the image.This sweeping panorama is one of the sharpest infrared pictures ever made of the galactic center region. X-rays detected by Chandra expose a wealth of exotic objects and high-energy features [Figure 3 (bottom frame of poster)]. In this image, pink represents lower energy X-rays and blue indicates higher energy. Hundreds of small dots show emission from material around black holes and other dense stellar objects. A supermassive black hole -- some four million times more massive than the Sun -- resides within the bright region in the lower right. The diffuse X-ray light comes from gas heated to millions of degrees by outflows from the supermassive black hole, winds from giant stars, and stellar explosions. This central region is the most energetic place in our galaxy. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA12348](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA12348/PIA12348~medium.jpg)
In celebration of the International Year of Astronomy 2009, NASA's Great Observatories -- the Hubble Space Telescope, the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Chandra X-ray Observatory -- have produced a matched trio of images of the central region of our Milky Way galaxy. Each image shows the telescope's different wavelength view of the galactic center region, illustrating the unique science each observatory conducts. In this spectacular image, observations using infrared light and X-ray light see through the obscuring dust and reveal the intense activity near the galactic core. Note that the center of the galaxy is located within the bright white region to the right of and just below the middle of the image. The entire image width covers about one-half a degree, about the same angular width as the full moon. Spitzer's infrared-light observations provide a detailed and spectacular view of the galactic center region [Figure 1 (top frame of poster)]. The swirling core of our galaxy harbors hundreds of thousands of stars that cannot be seen in visible light. These stars heat the nearby gas and dust. These dusty clouds glow in infrared light and reveal their often dramatic shapes. Some of these clouds harbor stellar nurseries that are forming new generations of stars. Like the downtown of a large city, the center of our galaxy is a crowded, active, and vibrant place. Although best known for its visible-light images, Hubble also observes over a limited range of infrared light [Figure 2 (middle frame of poster)]. The galactic center is marked by the bright patch in the lower right. Along the left side are large arcs of warm gas that have been heated by clusters of bright massive stars. In addition, Hubble uncovered many more massive stars across the region. Winds and radiation from these stars create the complex structures seen in the gas throughout the image.This sweeping panorama is one of the sharpest infrared pictures ever made of the galactic center region. X-rays detected by Chandra expose a wealth of exotic objects and high-energy features [Figure 3 (bottom frame of poster)]. In this image, pink represents lower energy X-rays and blue indicates higher energy. Hundreds of small dots show emission from material around black holes and other dense stellar objects. A supermassive black hole -- some four million times more massive than the Sun -- resides within the bright region in the lower right. The diffuse X-ray light comes from gas heated to millions of degrees by outflows from the supermassive black hole, winds from giant stars, and stellar explosions. This central region is the most energetic place in our galaxy. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA12348
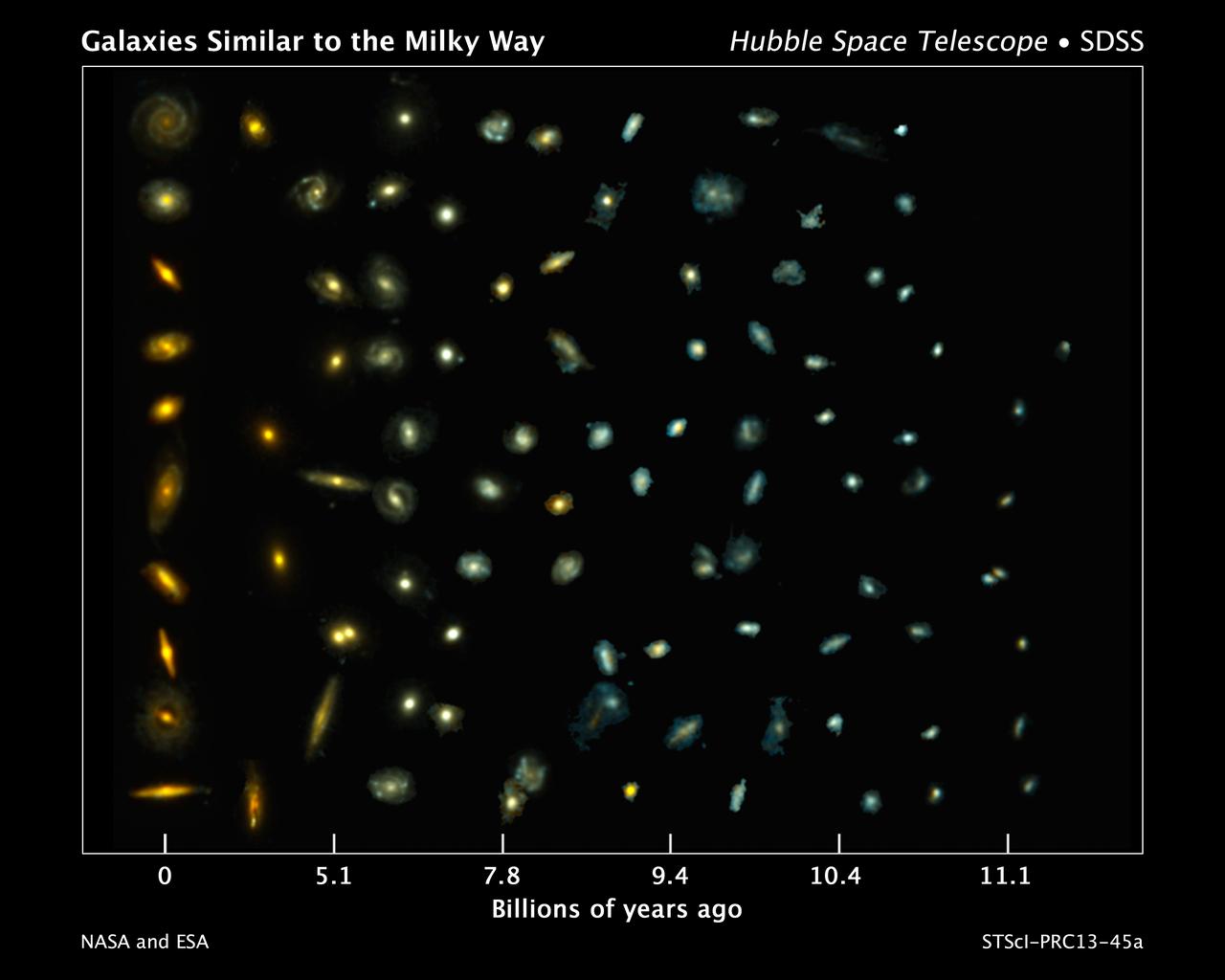
This composite image shows examples of galaxies similar to our Milky Way at various stages of construction over a time span of 11 billion years. The galaxies are arranged according to time. Those on the left reside nearby; those at far right existed when the cosmos was about 2 billion years old. The bluish glow from young stars dominates the color of the galaxies on the right. The galaxies at left are redder from the glow of older stellar populations. Astronomers found the distant galaxies in two Hubble Space Telescope surveys: 3D-HST and the Cosmic Assembly Near-infrared Deep Extragalactic Legacy Survey, or CANDELS. The observations were made in visible and near-infrared light by Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 and Advanced Camera for Surveys. The nearby galaxies were taken from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. This image traces Milky Way-like galaxies over most of cosmic history, revealing how they evolve over time. Hubble's sharp vision resolved the galaxies' shapes, showing that their bulges and disks grew simultaneously. Credit: NASA, ESA, P. van Dokkum (Yale University), S. Patel (Leiden University), and the 3D-HST Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
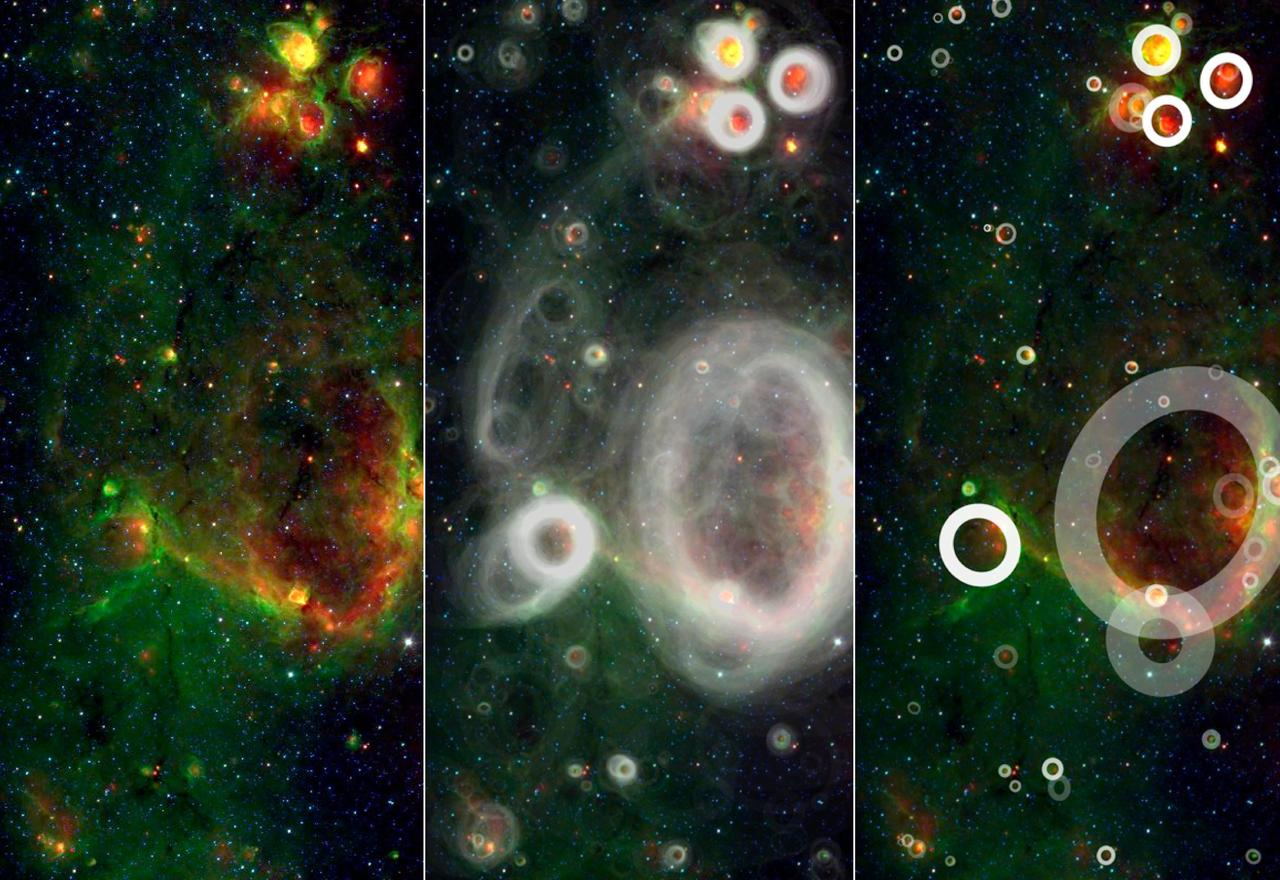

A team of volunteers from the general public has pored over observations from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope and discovered more than 5,000 bubbles in the disk of our Milky Way galaxy.
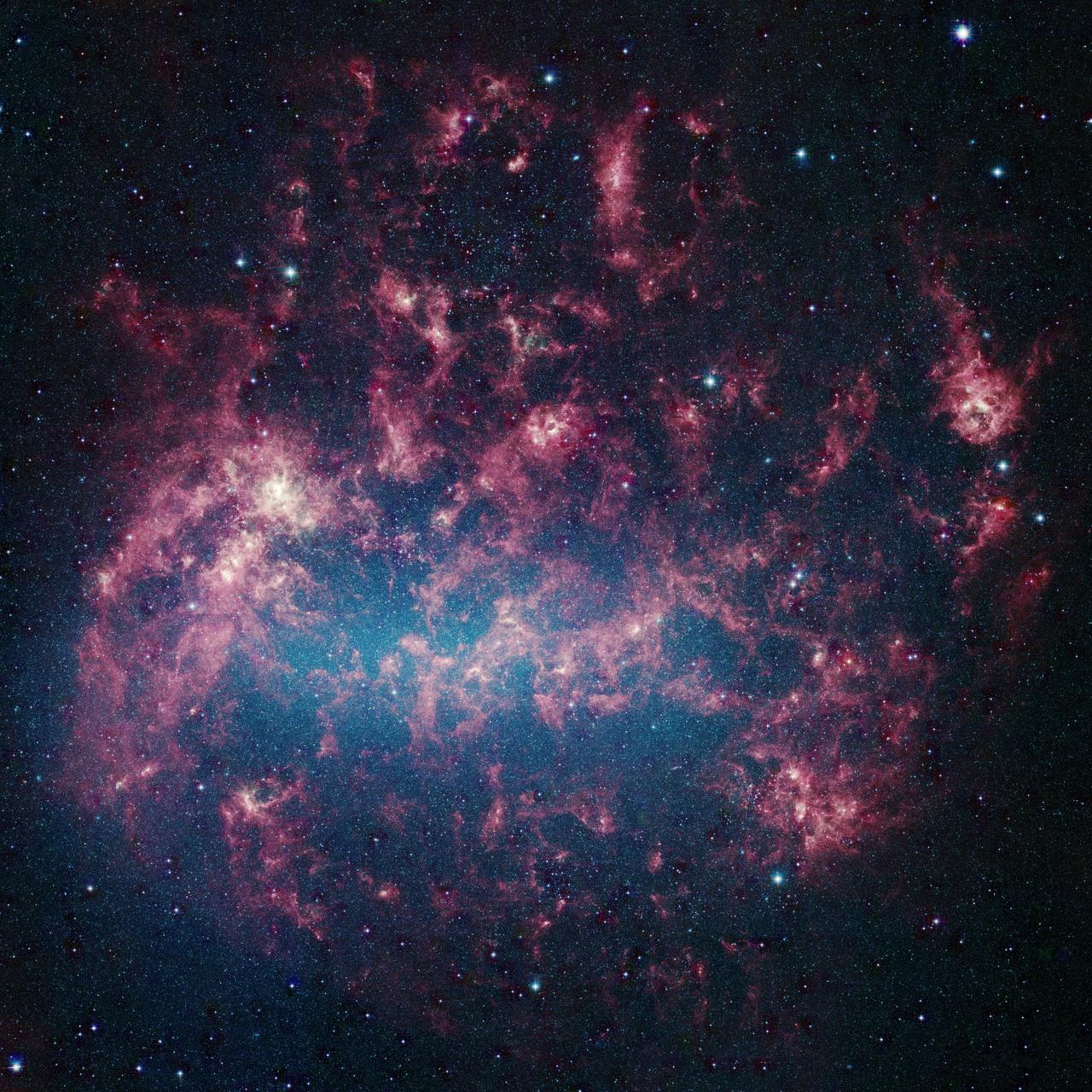

This vibrant image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy to our own Milky Way galaxy. The infrared image, a mosaic of more than 100,000 individual tiles, offers astronomers a unique chance to study the lifecycle of stars and dust in a single galaxy. Nearly one million objects are revealed for the first time in this Spitzer view, which represents about a 1,000-fold improvement in sensitivity over previous space-based missions. Most of the new objects are dusty stars of various ages populating the Large Magellanic Cloud; the rest are thought to be background galaxies. The blue color in the picture, seen most prominently in the central bar, represents starlight from older stars. The chaotic, bright regions outside this bar are filled with hot, massive stars buried in thick blankets of dust. The red clouds contain cooler interstellar gas and molecular-sized dust grains illuminated by ambient starlight. The Large Magellanic Cloud, located 160,000 light-years from Earth, is one of a handful of dwarf galaxies that orbit our own Milky Way. It is approximately one-third as wide as the Milky Way, and, if it could be seen in its entirety, would cover the same amount of sky as a grid of about 480 full moons. About one-third of the whole galaxy can be seen in the Spitzer image. This picture is a composite of infrared light captured by Spitzer's infrared array camera. Light with wavelengths of 8 and 5.8 microns is red and orange: 4.5-micron light is green; and 3.6-micron light is blue. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA07136
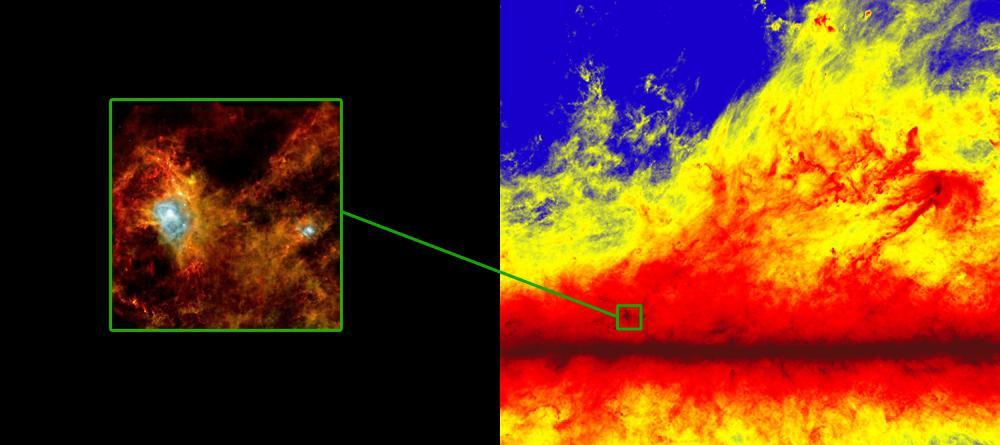
Filamentary structures in our Milky Way galaxy are apparent at large scales, as shown in this ESA image from Planck image, on the right, and small scales as seen the Herschel image on the left.

This artist concept illustrates the frenzied activity at the core of our Milky Way galaxy. The galactic center hosts a supermassive black hole in the region known as Sagittarius A*, or Sgr A*, with a mass of about four million times that of our sun.

A view from the bustling center of our galactic metropolis. NASA Spitzer Space Telescope offers a fresh, infrared view of the frenzied scene at the center of our Milky Way, revealing what lies behind the dust.

This mosaic reveals a panorama of the Milky Way from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. This picture covers only about three percent of the sky, but includes more than half of the galaxy stars and the majority of its star formation activity.
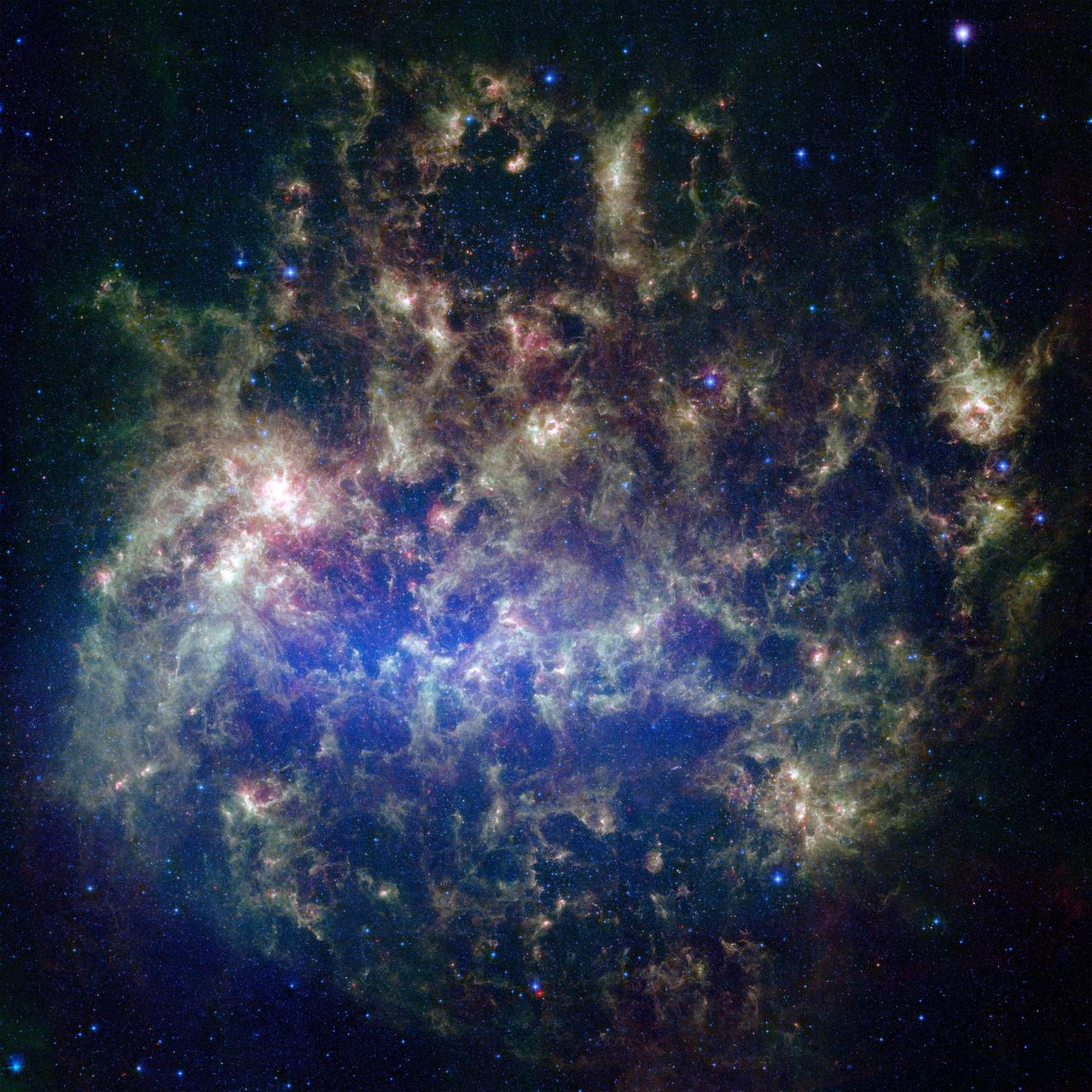

This vibrant image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy to our own Milky Way galaxy. The infrared image, a mosaic of 300,000 individual tiles, offers astronomers a unique chance to study the lifecycle of stars and dust in a single galaxy. Nearly one million objects are revealed for the first time in this Spitzer view, which represents about a 1,000-fold improvement in sensitivity over previous space-based missions. Most of the new objects are dusty stars of various ages populating the Large Magellanic Cloud; the rest are thought to be background galaxies. The blue color in the picture, seen most prominently in the central bar, represents starlight from older stars. The chaotic, bright regions outside this bar are filled with hot, massive stars buried in thick blankets of dust. The red color around these bright regions is from dust heated by stars, while the red dots scattered throughout the picture are either dusty, old stars or more distant galaxies. The greenish clouds contain cooler interstellar gas and molecular-sized dust grains illuminated by ambient starlight. Astronomers say this image allows them to quantify the process by which space dust -- the same stuff that makes up planets and even people -- is recycled in a galaxy. The picture shows dust at its three main cosmic hangouts: around the young stars, where it is being consumed (red-tinted, bright clouds); scattered about in the space between stars (greenish clouds); and in expelled shells of material from old stars (randomly-spaced red dots). The Large Magellanic Cloud, located 160,000 light-years from Earth, is one of a handful of dwarf galaxies that orbit our own Milky Way. It is approximately one-third as wide as the Milky Way, and, if it could be seen in its entirety, would cover the same amount of sky as a grid of about 480 full moons. About one-third of the entire galaxy can be seen in the Spitzer image. This picture is a composite of infrared light captured by Spitzer. Light with wavelengths of 3.6 (blue) and 8 (green) microns was captured by the telescope's infrared array camera; 24-micron light (red) was detected by the multiband imaging photometer. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA07137

Intertank STA on way to Pegasus Barge
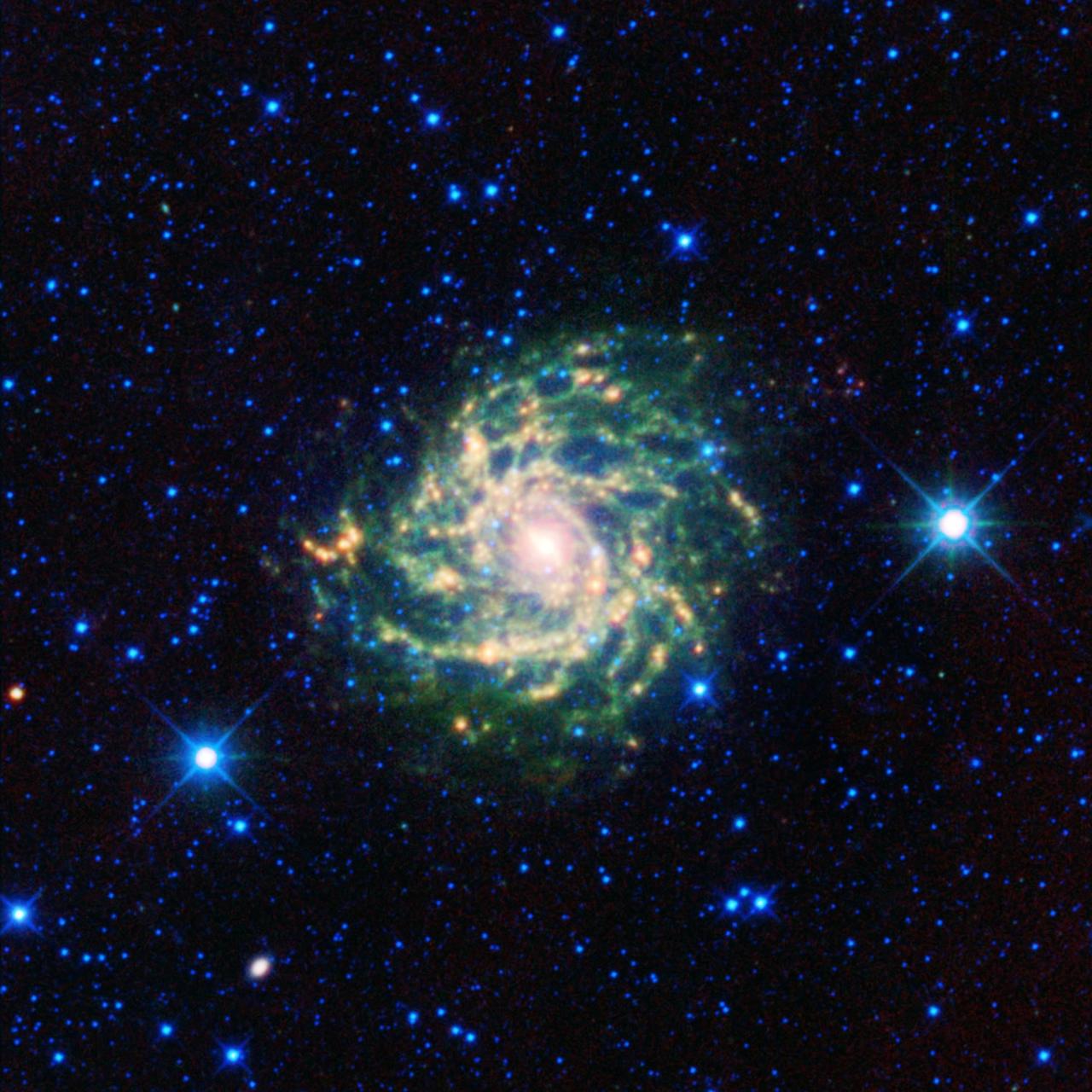

A leggy cosmic creature comes out of hiding in this new infrared view from NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer. The spiral beauty, called IC 342 and sometimes the hidden galaxy, is shrouded behind our own galaxy, the Milky Way.

This stellar object is called Spitzer 073425.3-465409, as seen by NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer; the cloud CG4 might be imagined as a cosmic alligator eating its way across the sky.
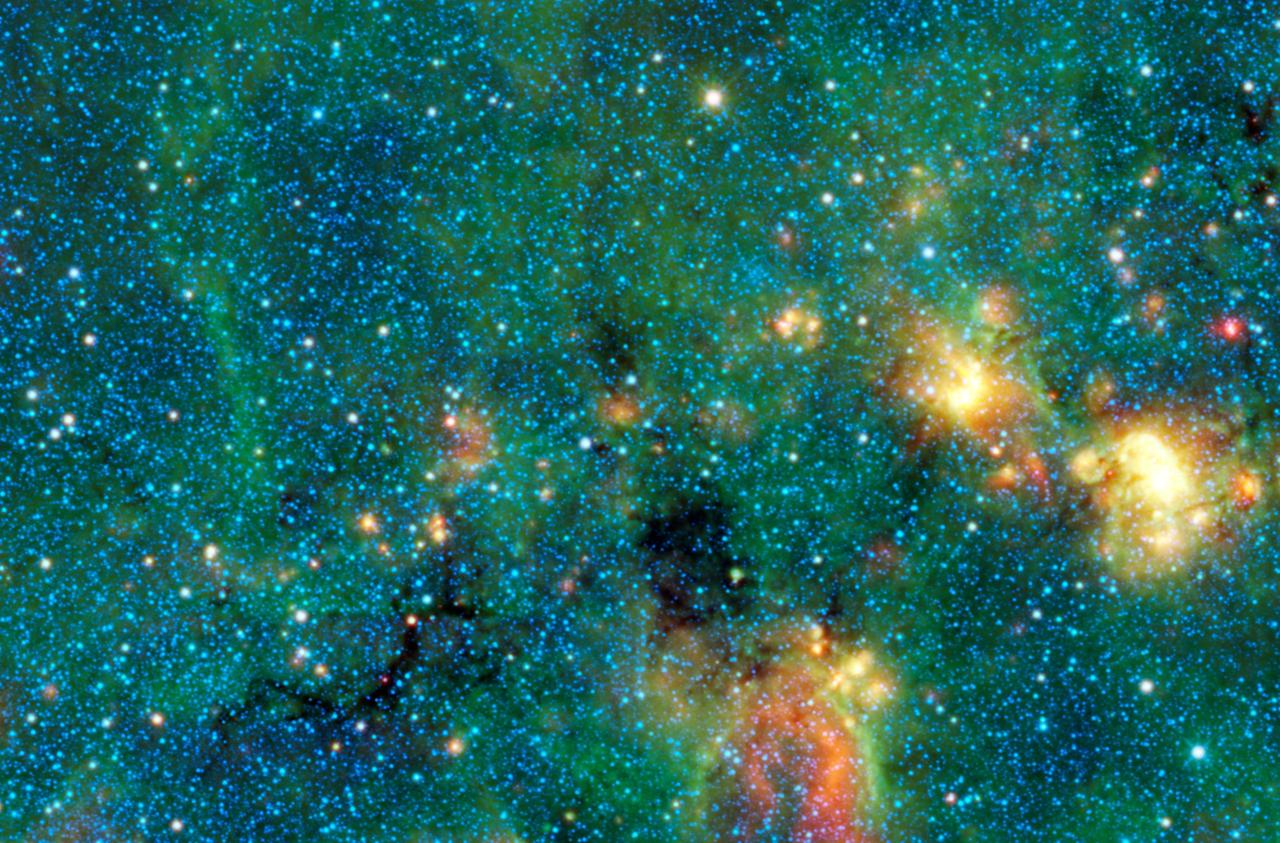

This infrared image from NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer shows exceptionally cold, dense cloud cores seen in silhouette against the bright diffuse infrared glow of the plane of the Milky Way galaxy.

NASA image release March 11, 2011 Caption: The lunar farside as never seen before! LROC WAC orthographic projection centered at 180° longitude, 0° latitude. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Arizona State University. Because the moon is tidally locked (meaning the same side always faces Earth), it was not until 1959 that the farside was first imaged by the Soviet Luna 3 spacecraft (hence the Russian names for prominent farside features, such as Mare Moscoviense). And what a surprise - unlike the widespread maria on the nearside, basaltic volcanism was restricted to a relatively few, smaller regions on the farside, and the battered highlands crust dominated. A different world from what we saw from Earth. Of course, the cause of the farside/nearside asymmetry is an interesting scientific question. Past studies have shown that the crust on the farside is thicker, likely making it more difficult for magmas to erupt on the surface, limiting the amount of farside mare basalts. Why is the farside crust thicker? That is still up for debate, and in fact several presentations at this week's Lunar and Planetary Science Conference attempt to answer this question. The Clementine mission obtained beautiful mosaics with the sun high in the sky (low phase angles), but did not have the opportunity to observe the farside at sun angles favorable for seeing surface topography. This WAC mosaic provides the most complete look at the morphology of the farside to date, and will provide a valuable resource for the scientific community. And it's simply a spectacular sight! The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera (LROC) Wide Angle Camera (WAC) is a push-frame camera that captures seven color bands (321, 360, 415, 566, 604, 643, and 689 nm) with a 57-km swath (105-km swath in monochrome mode) from a 50 km orbit. One of the primary objectives of LROC is to provide a global 100 m/pixel monochrome (643 nm) base map with incidence angles between 55°-70° at the equator, lighting that is favorable for morphological interpretations. Each month, the WAC provides nearly complete coverage of the Moon under unique lighting. As an added bonus, the orbit-to-orbit image overlap provides stereo coverage. Reducing all these stereo images into a global topographic map is a big job, and is being led by LROC Team Members from the German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt; DLR). Several preliminary WAC topographic products have appeared in LROC featured images over the past year (Orientale basin, Sinus Iridum). For a sneak preview of the WAC global DEM with the WAC global mosaic, view a rotating composite moon (70 MB video from ASU's LROC website). The WAC topographic dataset will be completed and released later this year. The global mosaic released today is comprised of over 15,000 WAC images acquired between November 2009 and February 2011. The non-polar images were map projected onto the GLD100 shape model (WAC derived 100 m/pixel DTM), while polar images were map projected on the LOLA shape model. In addition, the LOLA derived crossover corrected ephemeris, and an improved camera pointing, provide accurate positioning (better than 100 m) of each WAC image. As part of the March 2011 PDS release, the LROC team posted the global map in ten regional tiles. Eight of the tiles are equirectangular projections that encompass 60° latitude by 90° longitude. In addition, two polar stereographic projections are available for each pole from ±60° to the pole. These reduced data records (RDR) products will be available for download on March 15, 2011. As the mission progresses, and our knowledge of the lunar photometric function increases, improved and new mosaics will be released! Work your way around the moon with these six orthographic projections constructed from WAC mosaics. The nearside view linked below is different from that released on 21 February. To read more con't here: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/LRO/news/lro-farside.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/LRO/news/lro-farside.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
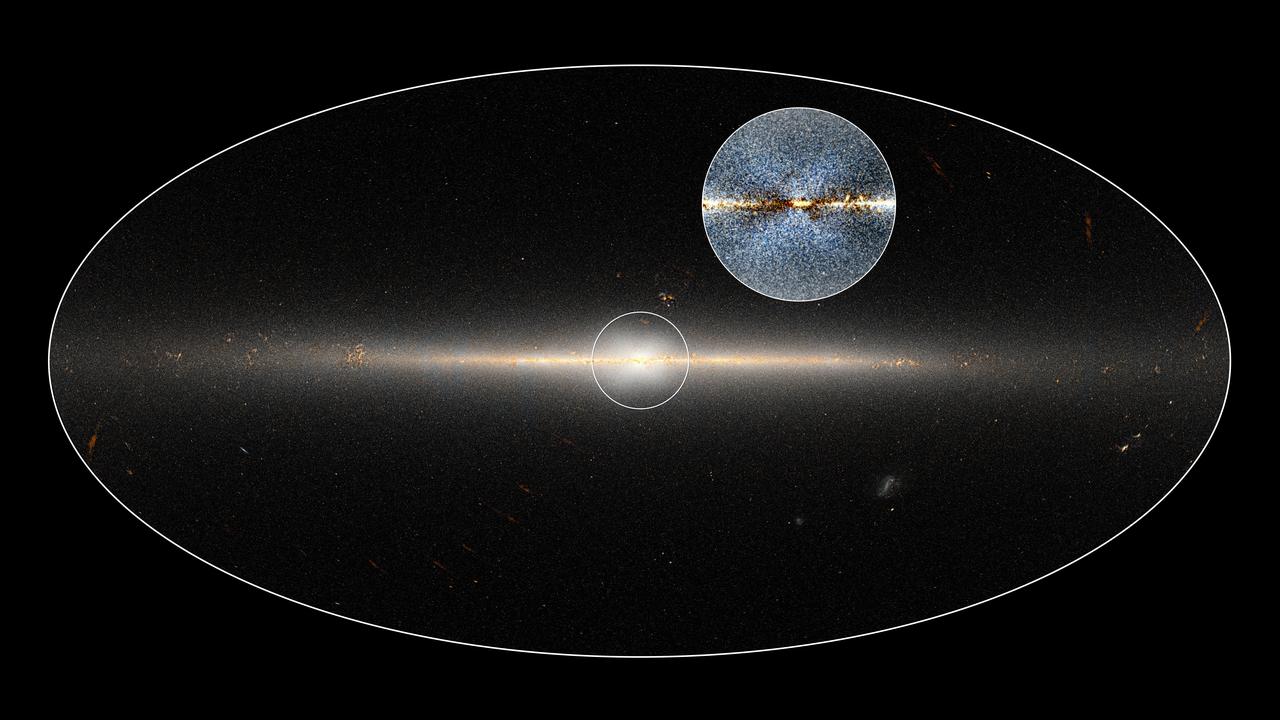
In 2010, NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) mission observed the entire sky twice. Astronomers used these data to point out the X-shaped structure in the bulge of the Milky Way, contained in the small circle at center, as well as the inset image. The circled central portion covers roughly the area of sky that would be blocked by a basketball when held out at arm's length. Dustin Lang, an astronomer at the Dunlap Institute of the University of Toronto, used these data to make this map, which shows the full 360-degree panorama of the sky as seen by WISE. Lang collaborated with Melissa Ness, postdoctoral researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Germany, http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20699

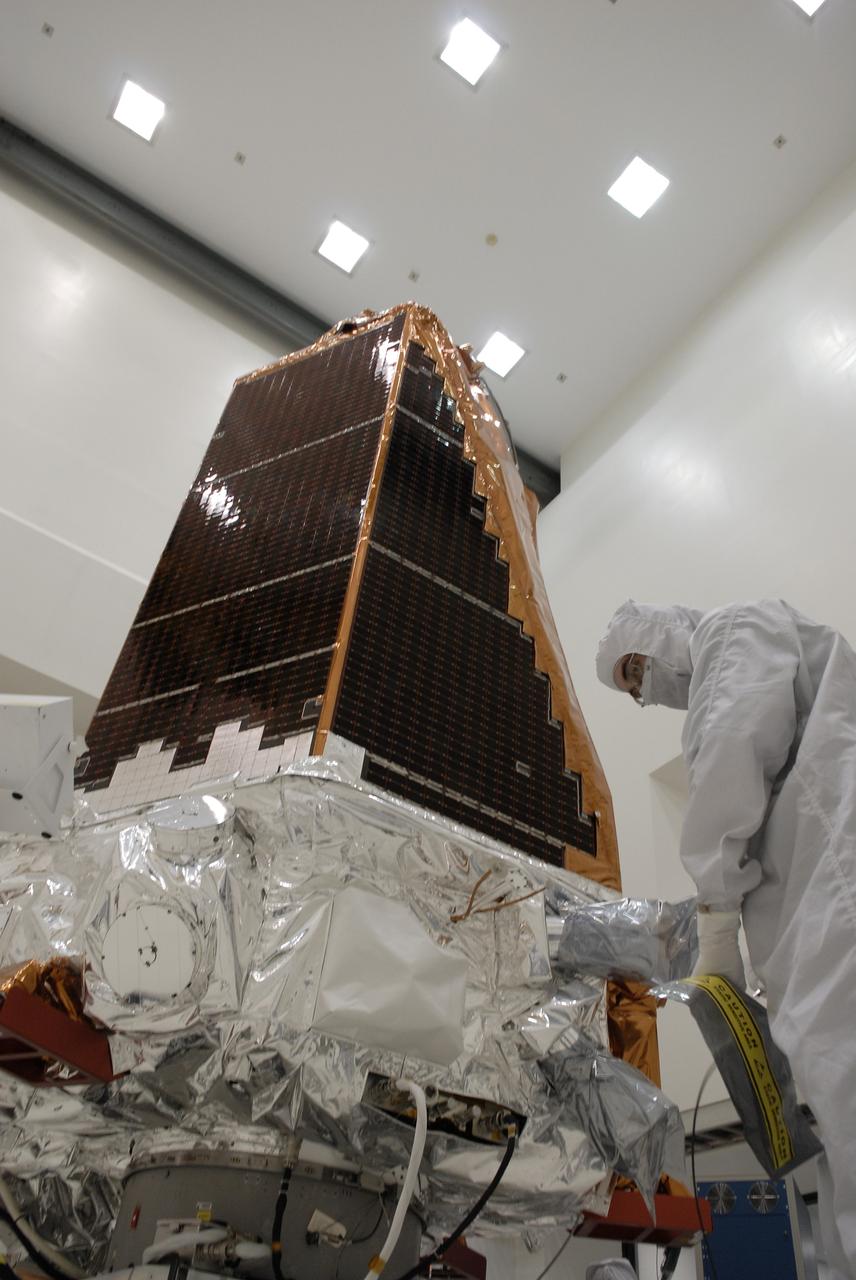
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lights are reflected on the solar array panels of NASA's Kepler spacecraft during illumination testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Kepler will hunt for planets using a specialized one-meter diameter telescope called a photometer to measure the small changes in brightness caused by the transits. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Ball Aerospace and Technology workers conduct a light test on the solar array panels of NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Kepler will hunt for planets using a specialized one-meter diameter telescope called a photometer to measure the small changes in brightness caused by the transits. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Ball Aerospace and Technology workers conduct a light test on the solar array panels of NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Kepler will hunt for planets using a specialized one-meter diameter telescope called a photometer to measure the small changes in brightness caused by the transits. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Ball Aerospace and Technology workers conduct a light test on the solar array panels of NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Kepler will hunt for planets using a specialized one-meter diameter telescope called a photometer to measure the small changes in brightness caused by the transits. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Ball Aerospace and Technology worker conducts a light sensor test on NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Kepler will hunt for planets using a specialized one-meter diameter telescope called a photometer to measure the small changes in brightness caused by the transits. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Ball Aerospace and Technology workers conduct a light test on the solar array panels of NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Kepler will hunt for planets using a specialized one-meter diameter telescope called a photometer to measure the small changes in brightness caused by the transits. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

NASA image release November 9, 2010 To view a video about this story go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5162413062">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5162413062</a> Using data from NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, scientists have recently discovered a gigantic, mysterious structure in our galaxy. This never-before-seen feature looks like a pair of bubbles extending above and below our galaxy's center. But these enormous gamma-ray emitting lobes aren't immediately visible in the Fermi all-sky map. However, by processing the data, a group of scientists was able to bring these unexpected structures into sharp relief. Each lobe is 25,000 light-years tall and the whole structure may be only a few million years old. Within the bubbles, extremely energetic electrons are interacting with lower-energy light to create gamma rays, but right now, no one knows the source of these electrons. Are the bubbles remnants of a massive burst of star formation? Leftovers from an eruption by the supermassive black hole at our galaxy's center? Or or did these forces work in tandem to produce them? Scientists aren't sure yet, but the more they learn about this amazing structure, the better we'll understand the Milky Way. To learn more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/new-structure.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/new-structure.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> Credit: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio</a>
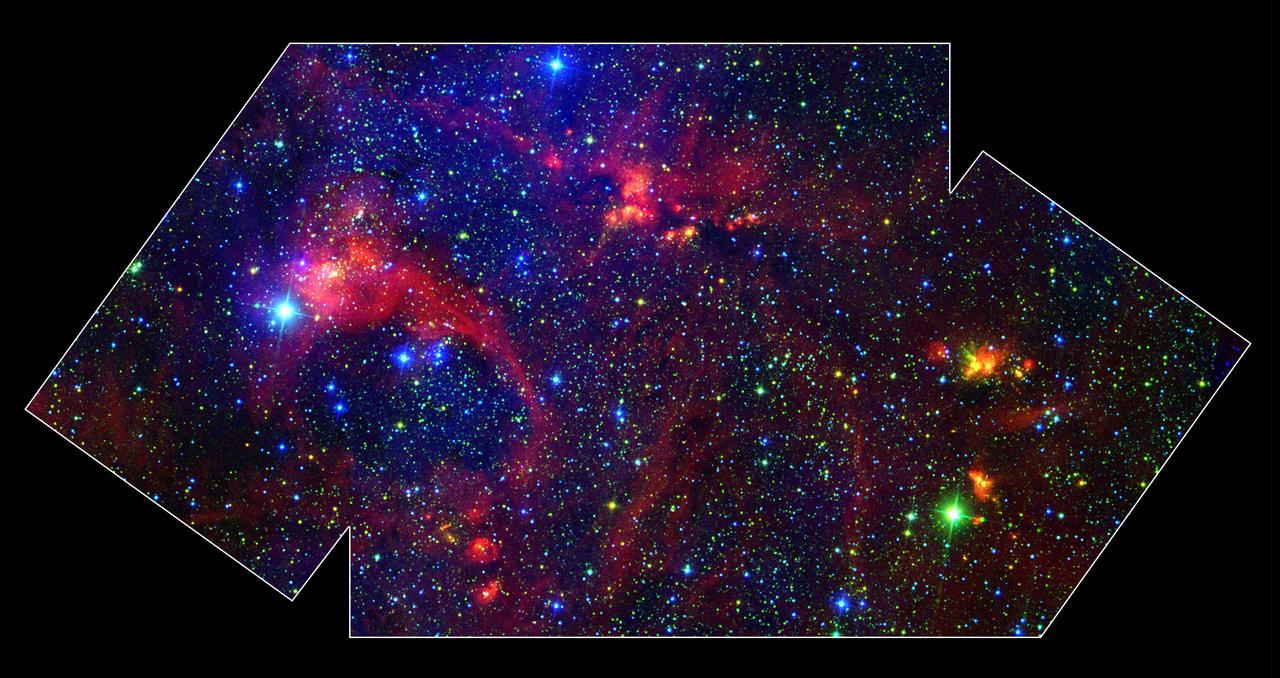

Hidden behind a shroud of dust in the constellation Cygnus is a stellar nursery called DR21, which is giving birth to some of the most massive stars in our galaxy. Visible light images reveal no trace of this interstellar cauldron because of heavy dust obscuration. In fact, visible light is attenuated in DR21 by a factor of more than 10,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 (ten thousand trillion heptillion). New images from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope allow us to peek behind the cosmic veil and pinpoint one of the most massive natal stars yet seen in our Milky Way galaxy. The never-before-seen star is 100,000 times as bright as the Sun. Also revealed for the first time is a powerful outflow of hot gas emanating from this star and bursting through a giant molecular cloud. The colorful image is a large-scale composite mosaic assembled from data collected at a variety of different wavelengths. Views at visible wavelengths appear blue, near-infrared light is depicted as green, and mid-infrared data from the InfraRed Array Camera (IRAC) aboard NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope is portrayed as red. The result is a contrast between structures seen in visible light (blue) and those observed in the infrared (yellow and red). A quick glance shows that most of the action in this image is revealed to the unique eyes of Spitzer. The image covers an area about two times that of a full moon. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05734
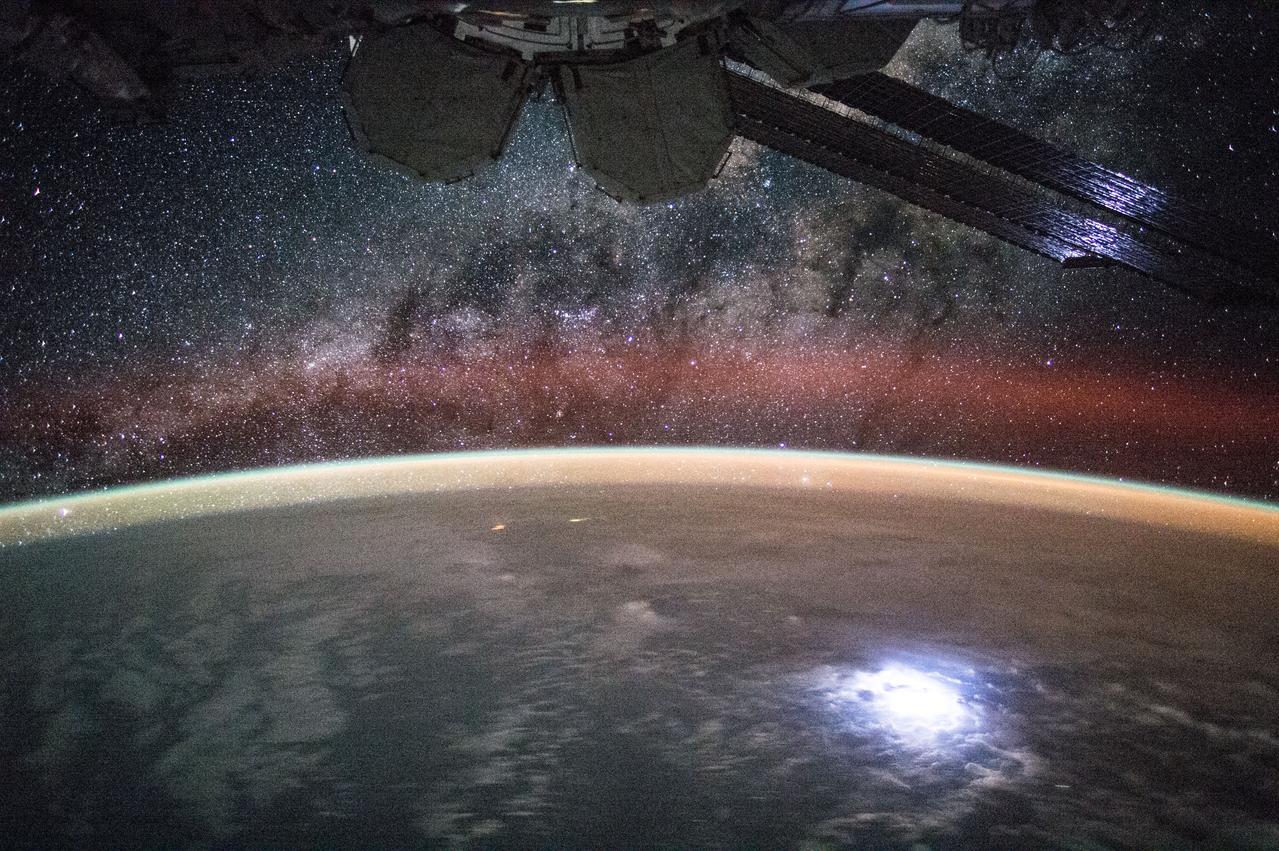

iss044e045215 (08/09/2015)-- View (part of a time lapse sequence) of stars in the Milky Way Galaxy visible over an Earth limb as seen by the Expedition 44 crew. Astronaut Kjell Lindgren captured a lightning strike from space so bright that it lights up the space station’s solar panels. He posted this on Twitter and Instagram on Sept. 2 saying "Large lightning strike on Earth lights up or solar panels."

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Ball Aerospace and Technology workers adjust the light cast on solar array panels during illumination testing of NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Kepler will hunt for planets using a specialized one-meter diameter telescope called a photometer to measure the small changes in brightness caused by the transits. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

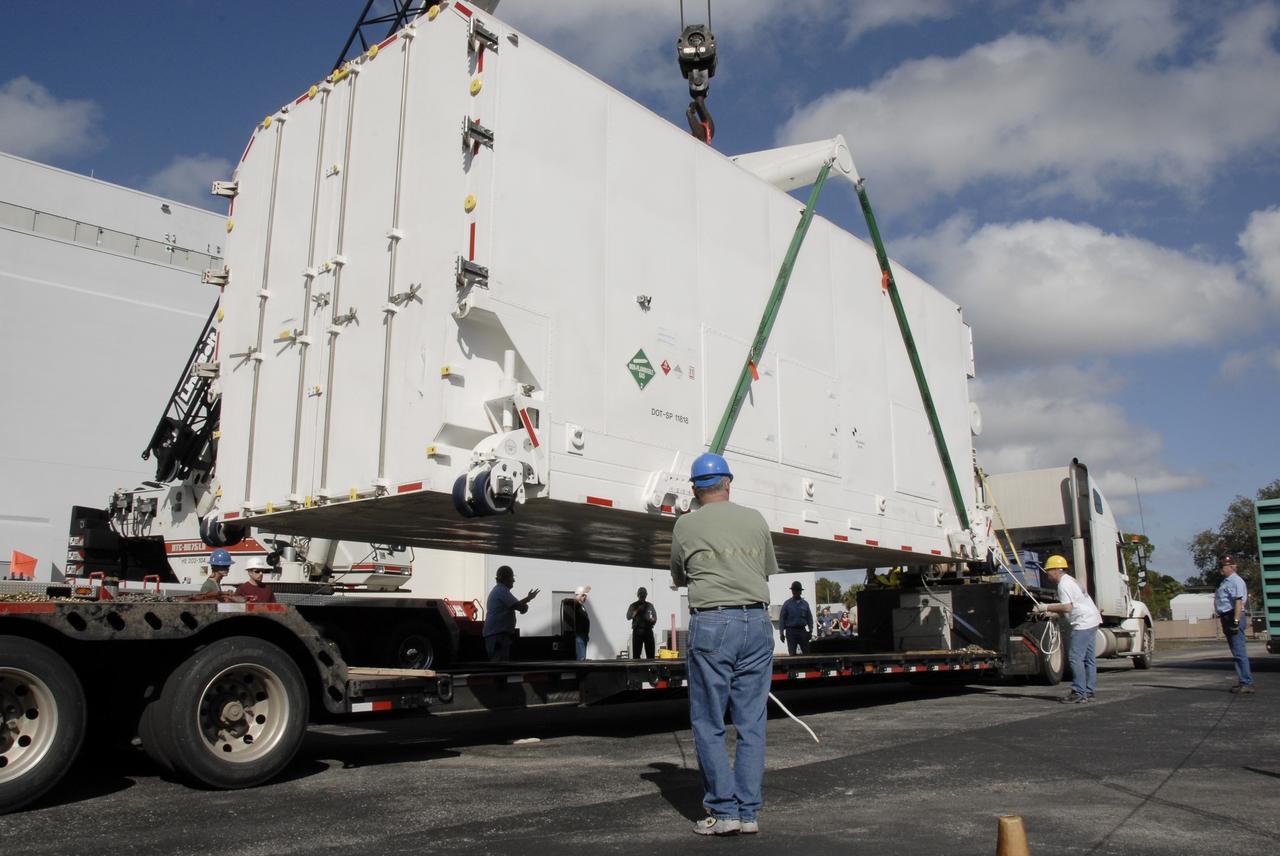
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The shipping container holding the Kepler spacecraft is placed on the tarmac outside Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., before being moved inside. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. The spacecraft will be processed at Astrotech before being carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009, atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
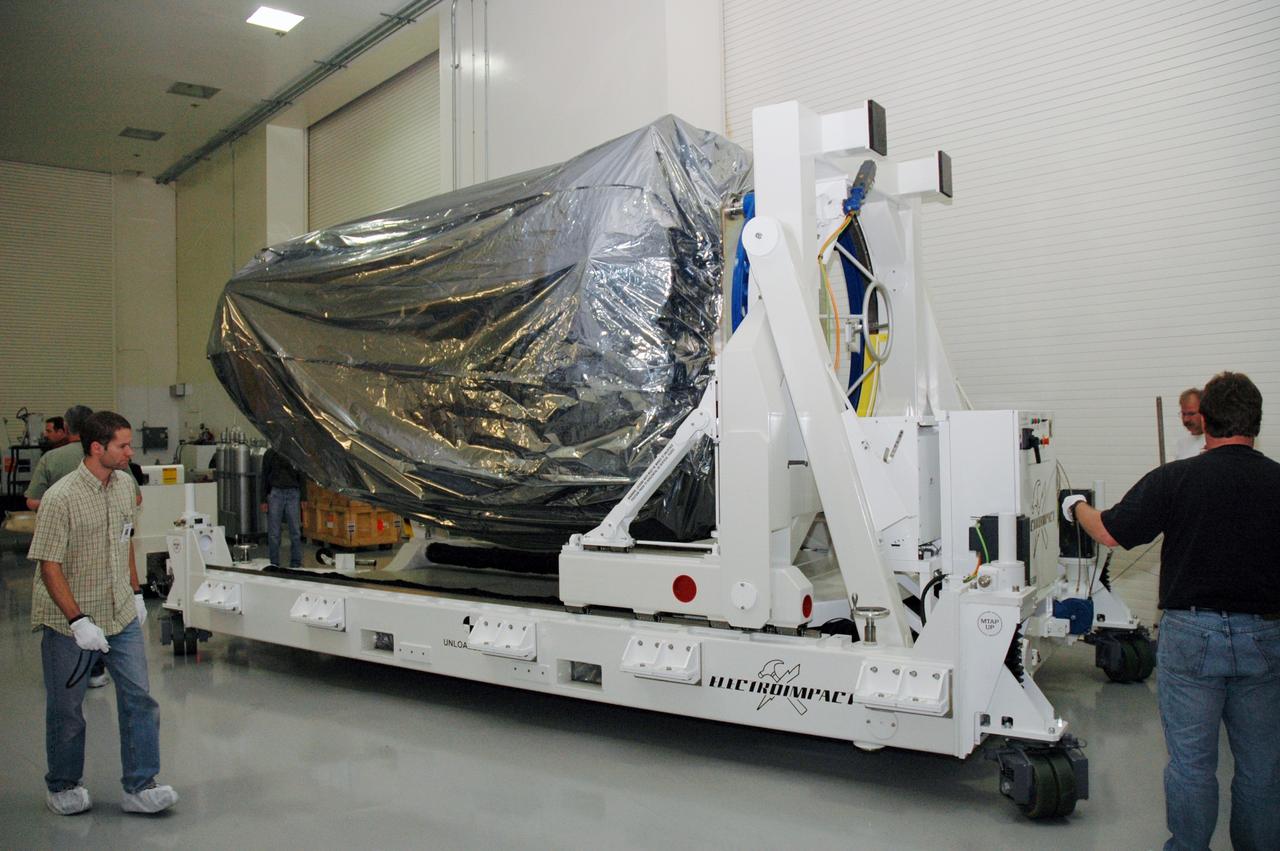

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is rolled into a clean room. The spacecraft will be rotated to vertical, uncovered and prepared for initial testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Rhodes

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. technician Phil Mislinski checks data from the light sensor test conducted on NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Ball Aerospace was responsible for the flight segment design and fabrication. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The shipping container holding the Kepler spacecraft is lifted off the trailer outside Astrotech in Titusville, Fla. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. The spacecraft will be processed at Astrotech before being carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009, atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. worker conducts a light sensor test on NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
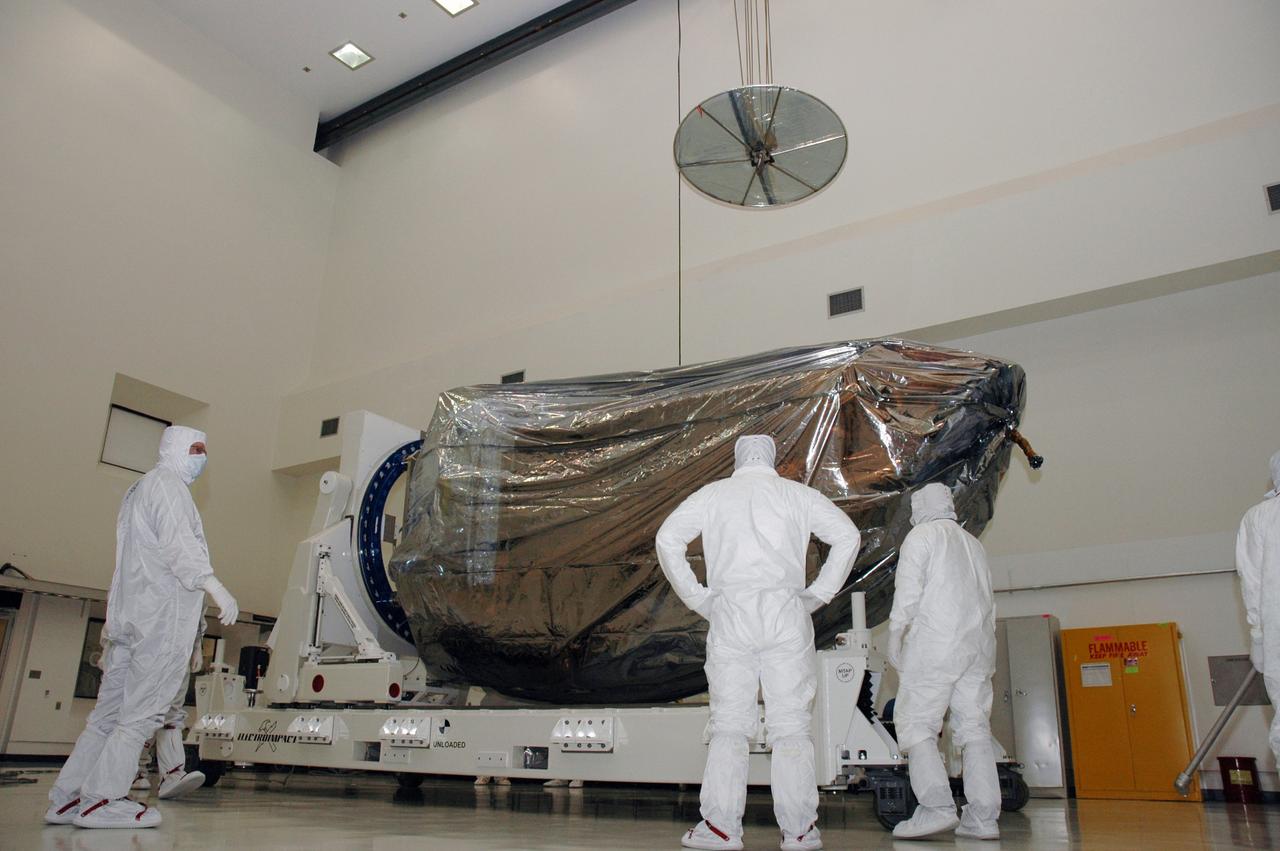

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In a clean room at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., workers prepare to rotate NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler will then be uncovered and prepared for initial testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Rhodes
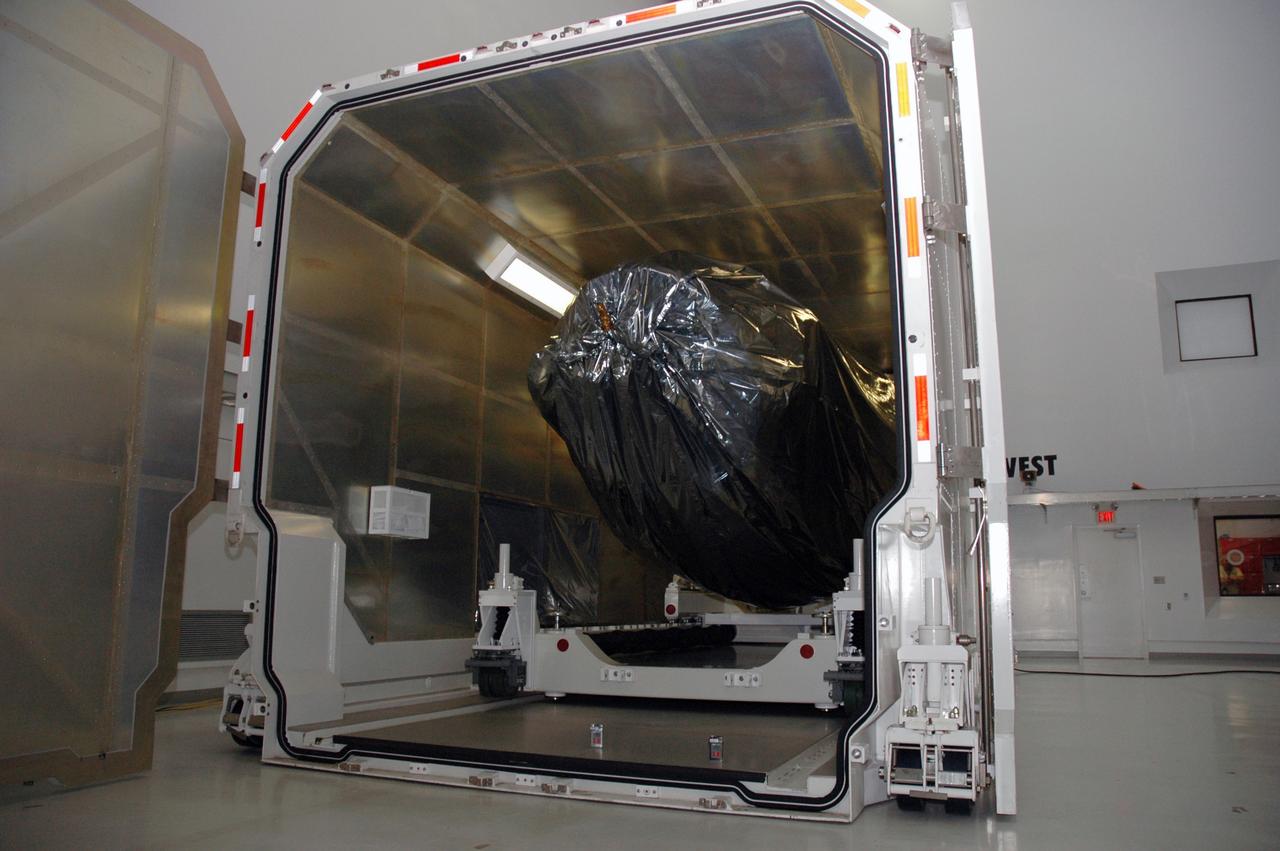

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., the open doors of the shipping container reveal NASA's Kepler spacecraft. After removal from the container, the spacecraft will be rotated to vertical, uncovered and prepared for initial testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Rhodes
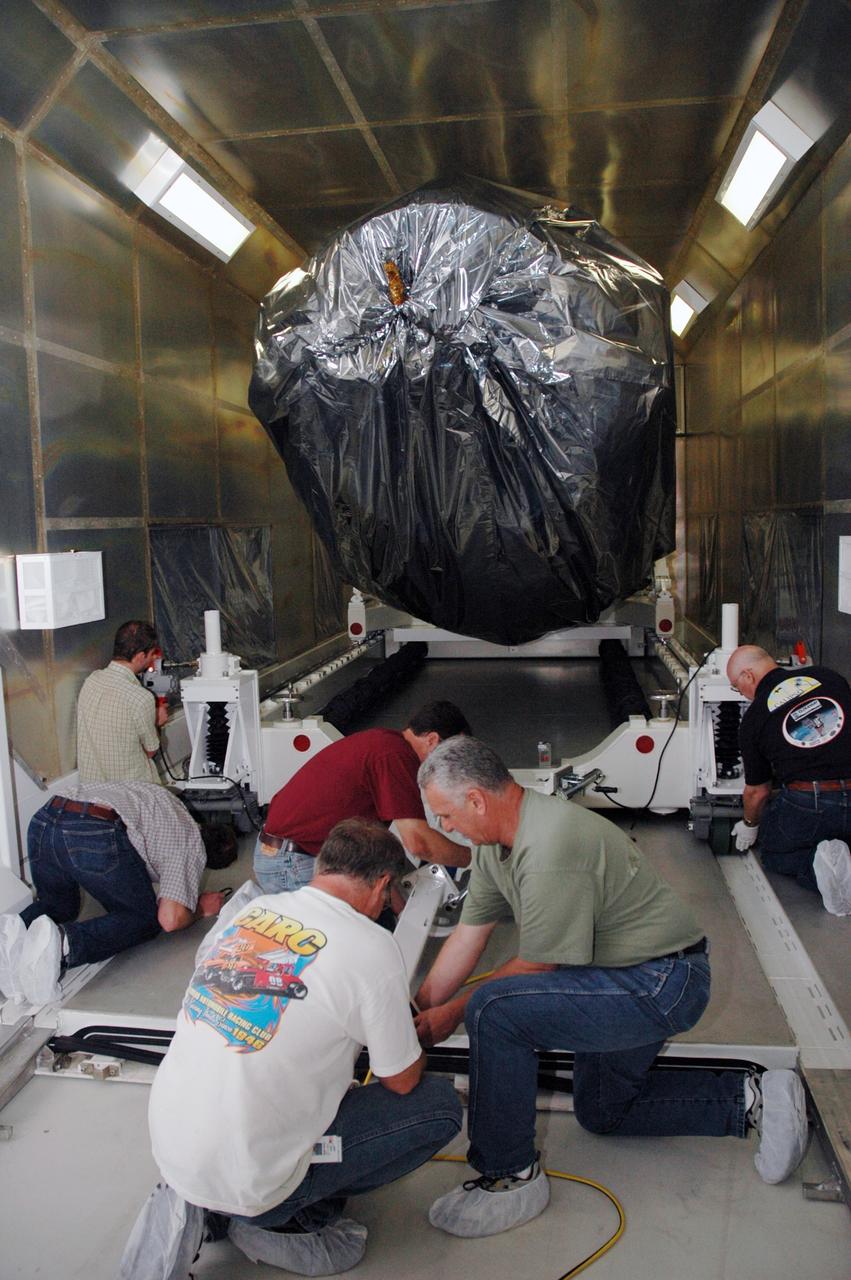

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., workers prepare the mobile stand for removal of NASA's Kepler spacecraft from its shipping container. After its removal, the spacecraft will be rotated to vertical, uncovered and prepared for initial testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Rhodes
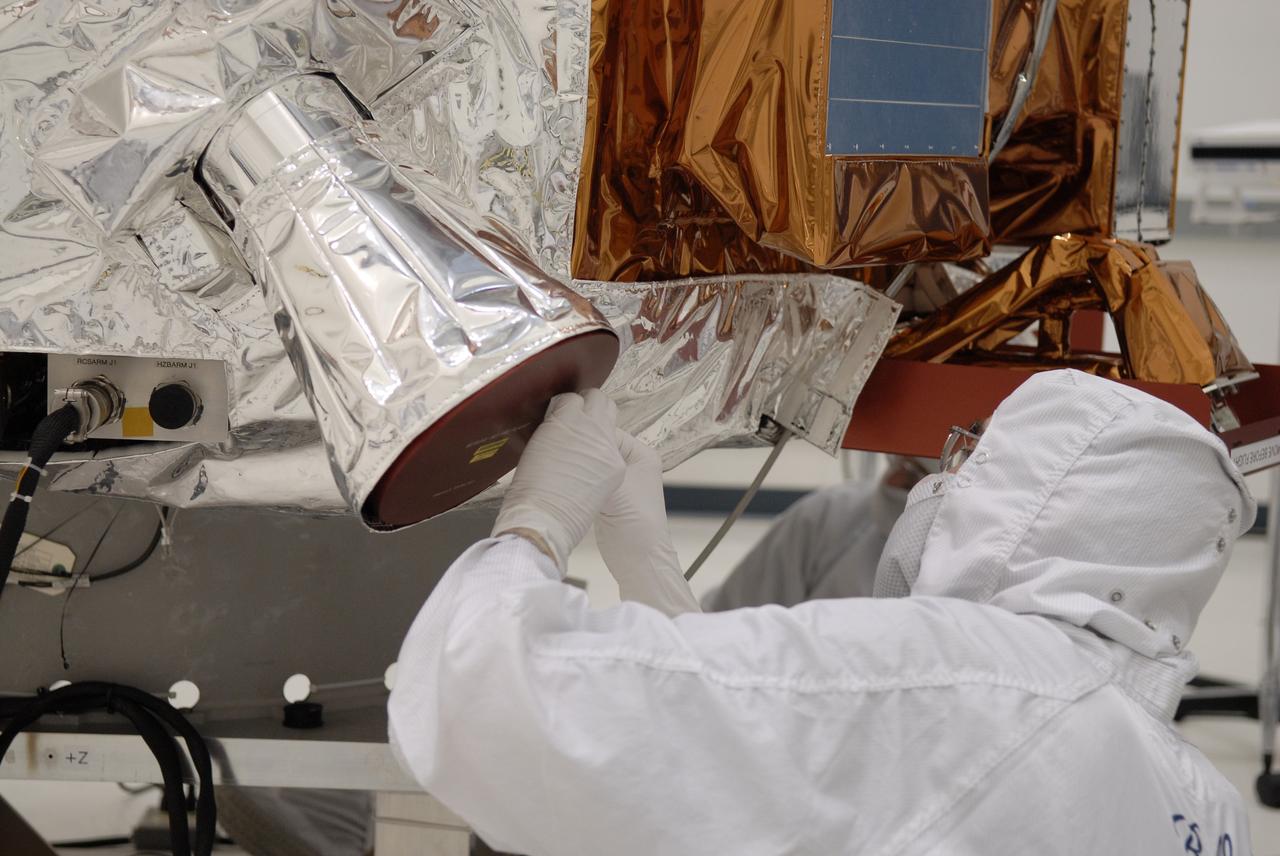

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is prepared for testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
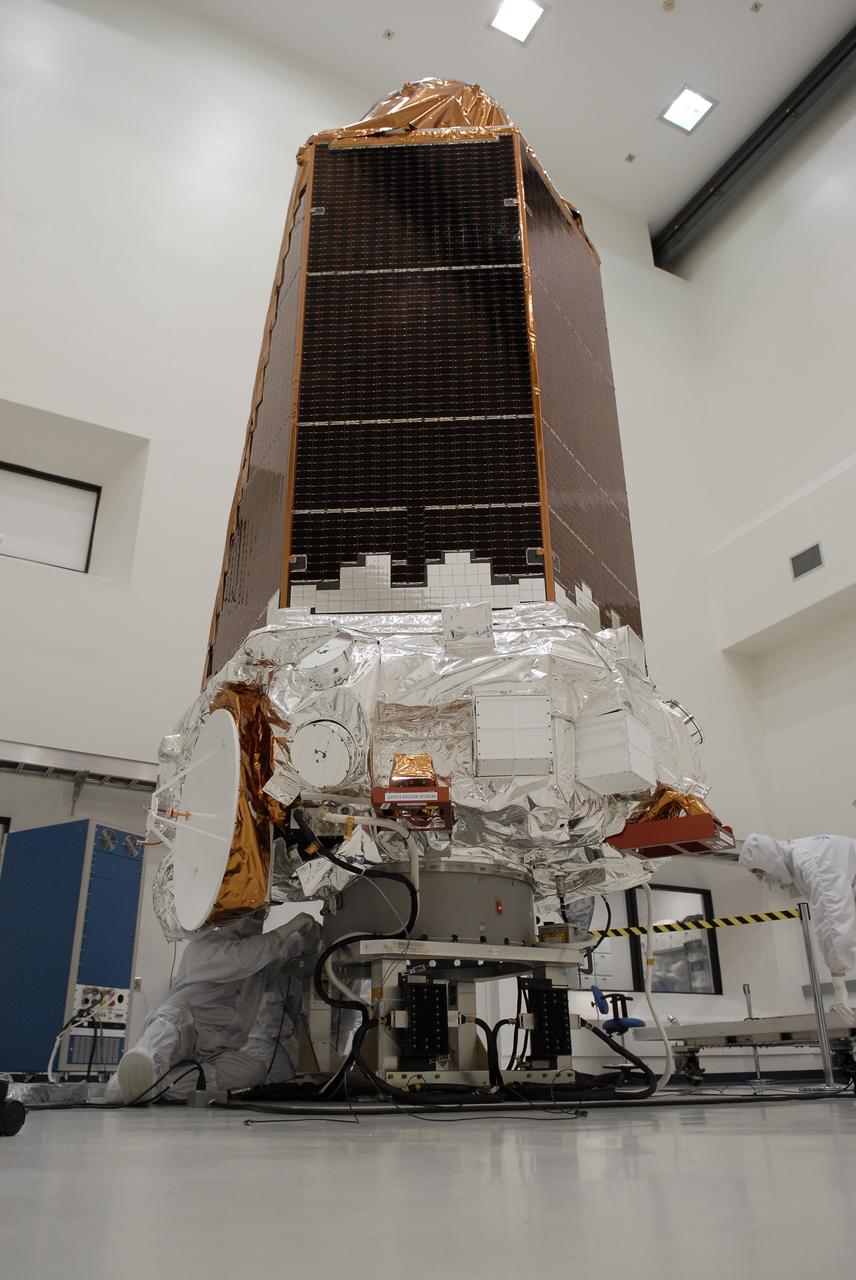

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is prepared for testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
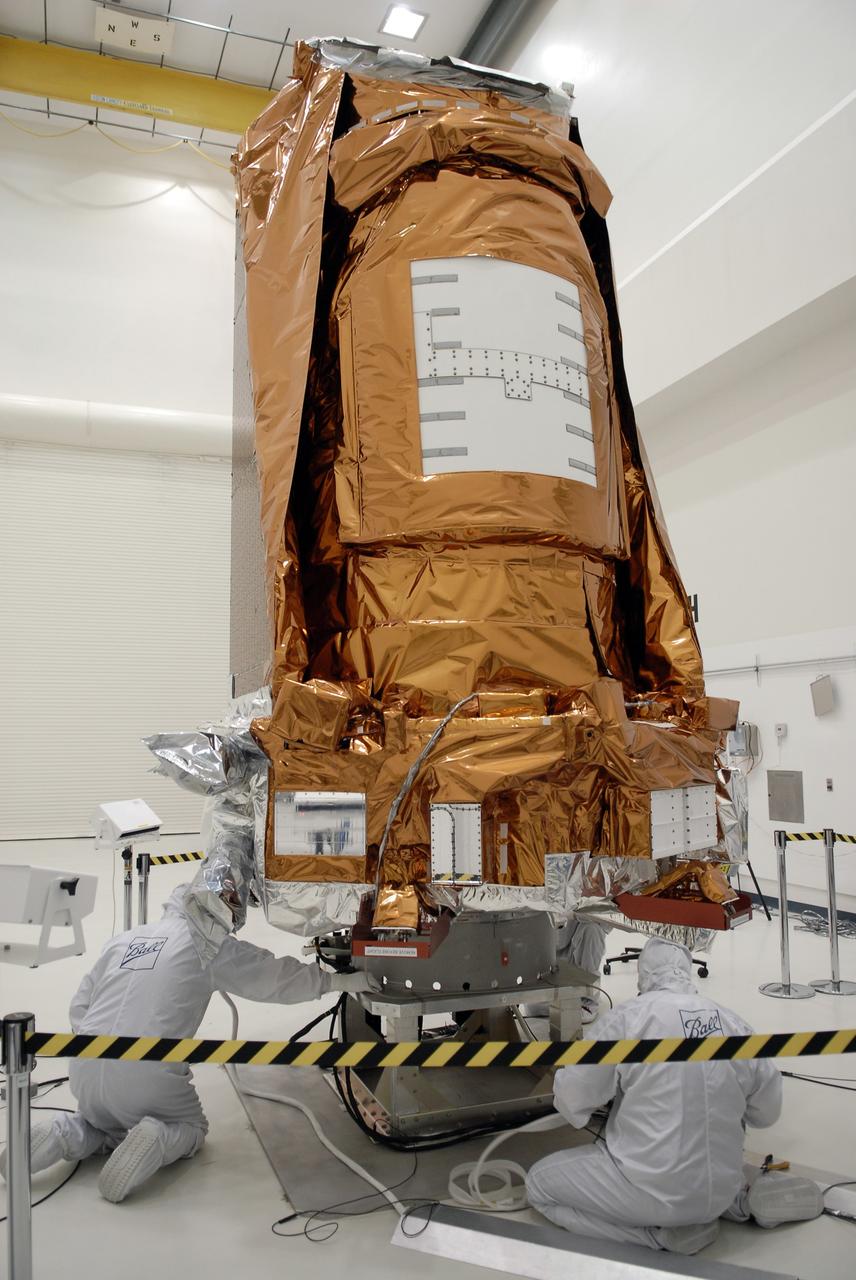

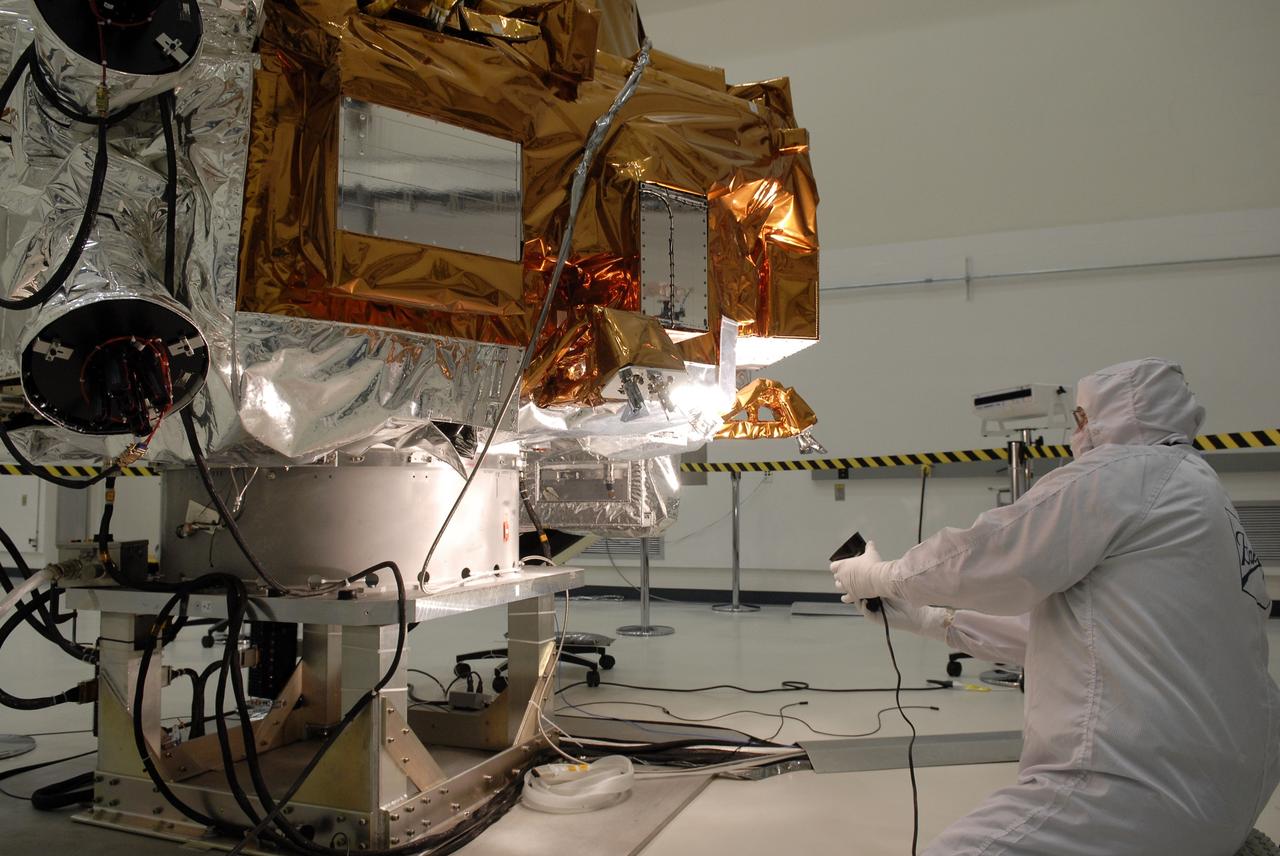
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., workers from Ball Aerospace check the Star Trackers on NASA's Kepler spacecraft before testing. Star Trackers are small aperture, space-qualified optical products which assure a spacecraft’s accurate navigation in space. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
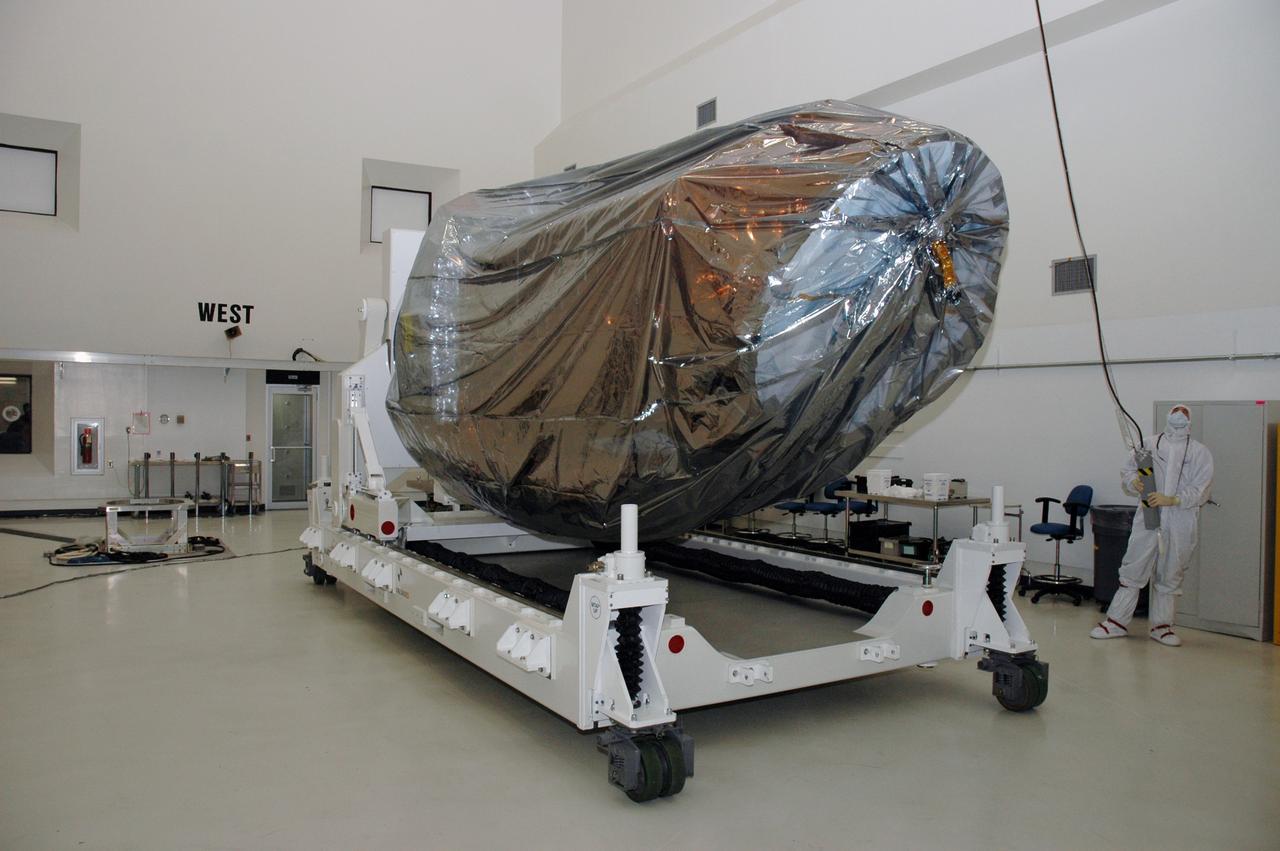

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In a clean room at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., workers prepare to rotate NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler will then be uncovered and prepared for initial testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Rhodes
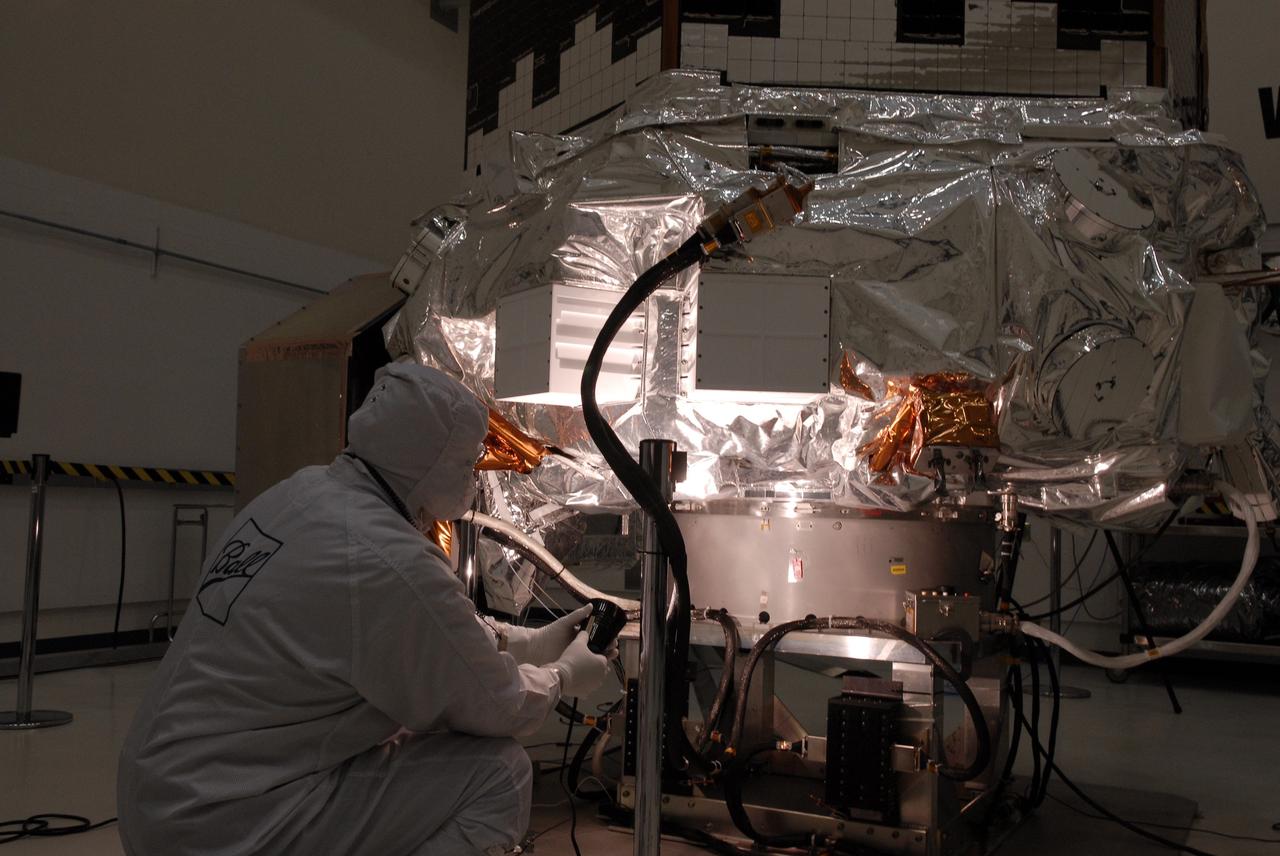

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. worker conducts a light sensor test on NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
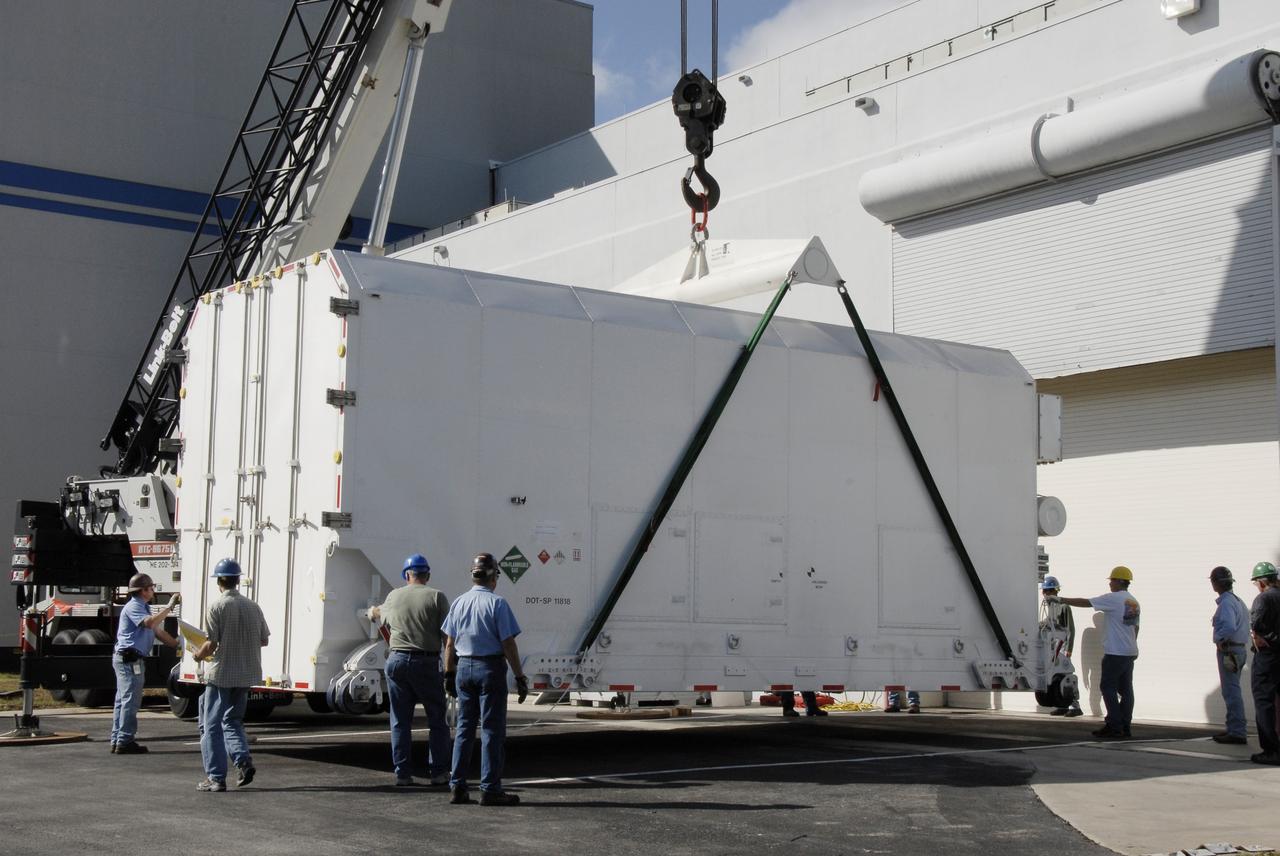

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The shipping container holding the Kepler spacecraft is placed on the tarmac outside Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., before being moved inside. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. The spacecraft will be processed at Astrotech before being carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009, atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

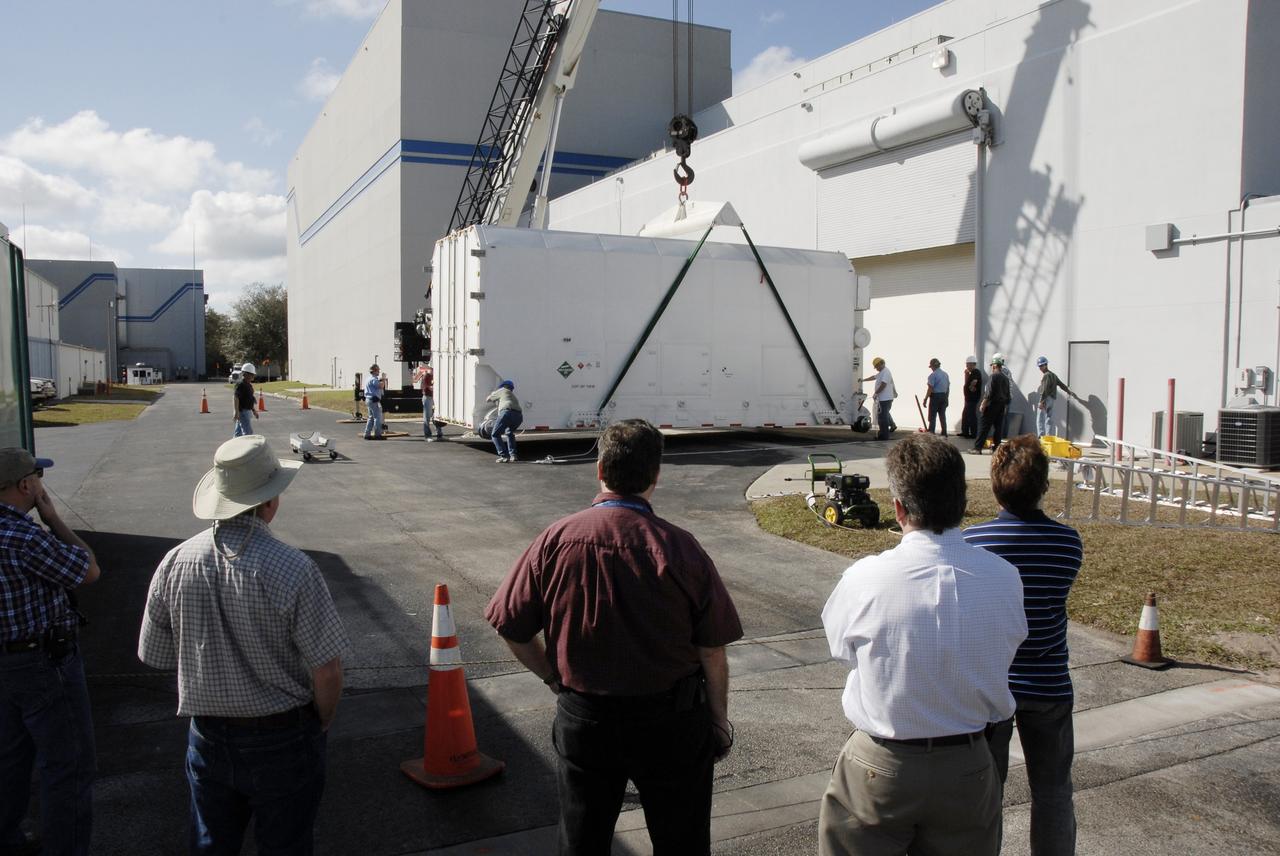
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is prepared for testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The shipping container holding the Kepler spacecraft is placed on the tarmac outside Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., before being moved inside. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. The spacecraft will be processed at Astrotech before being carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009, atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
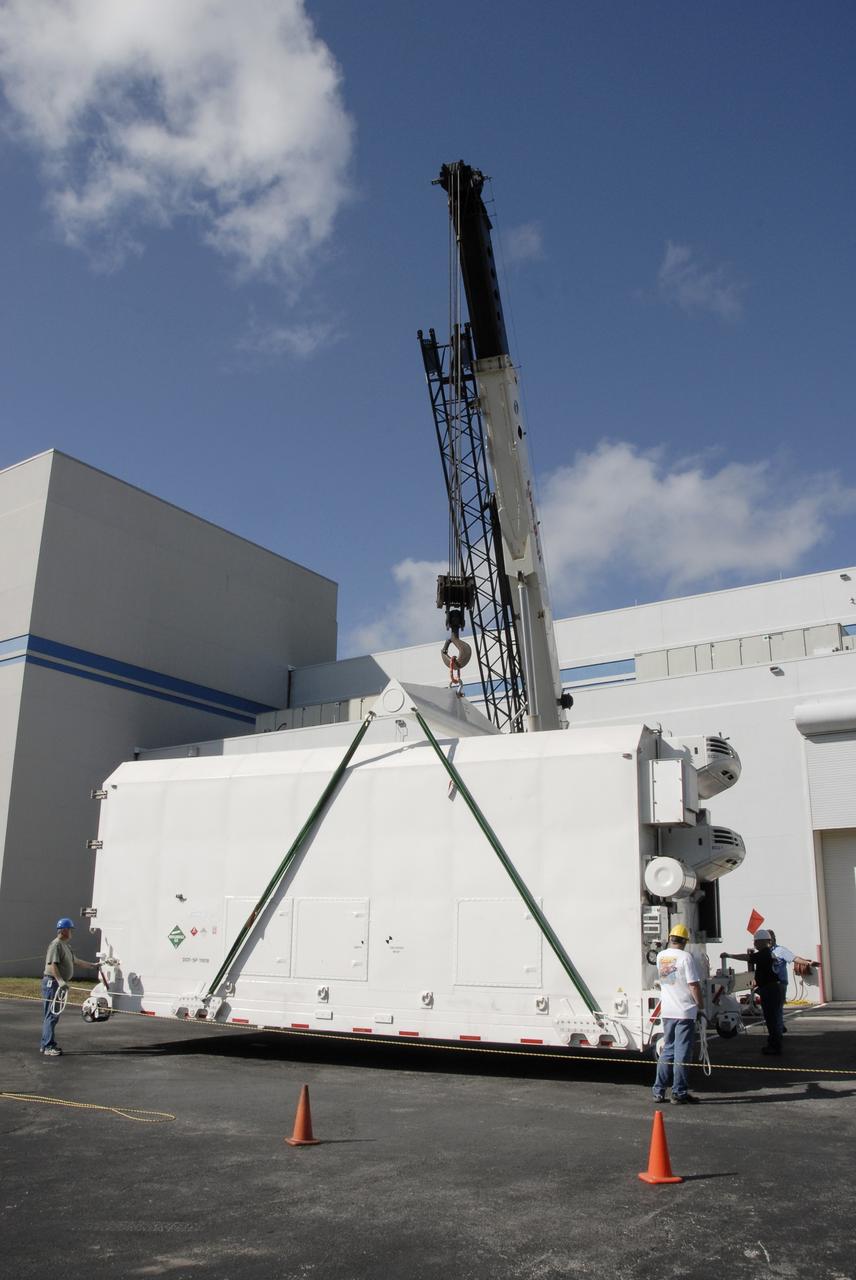

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The shipping container holding the Kepler spacecraft is placed on the tarmac outside Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., before being moved inside. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. The spacecraft will be processed at Astrotech before being carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009, atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
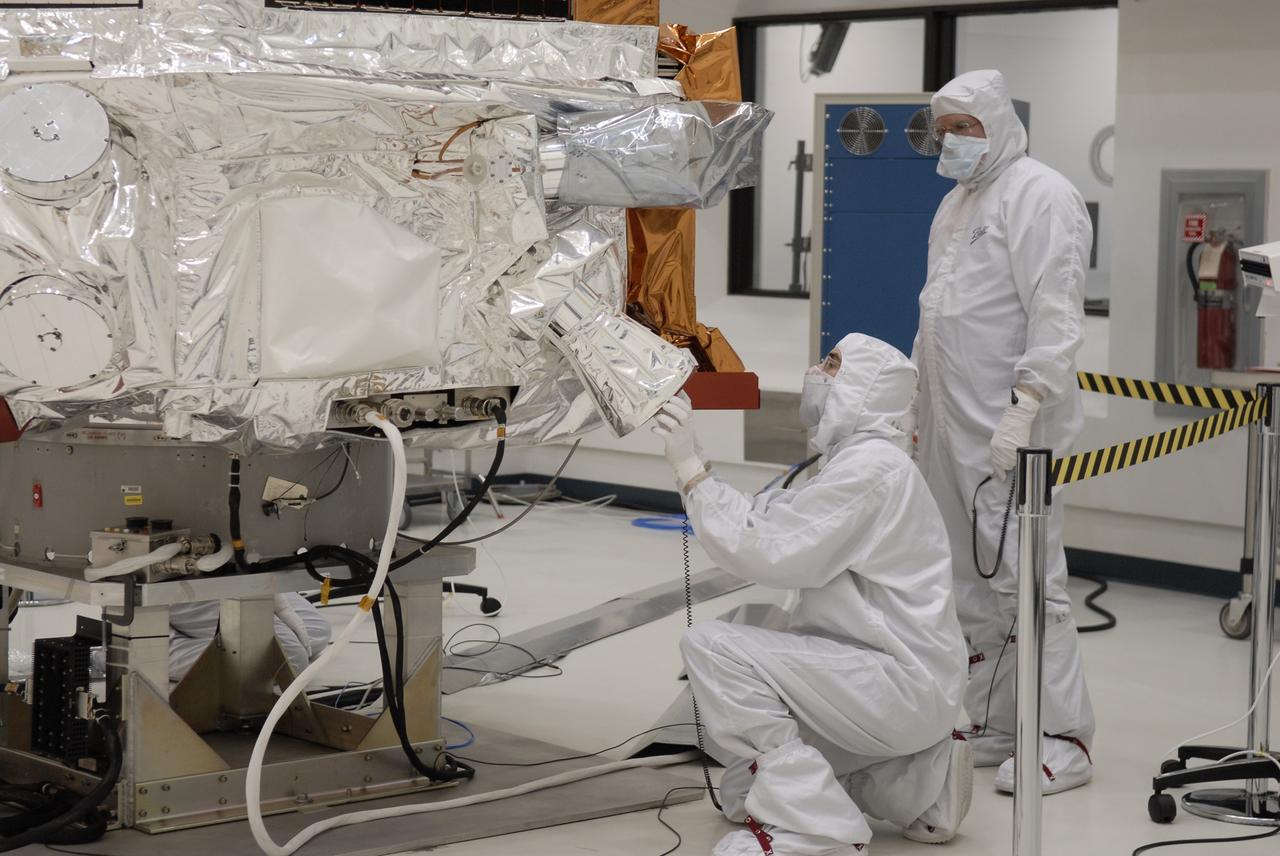

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is prepared for testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
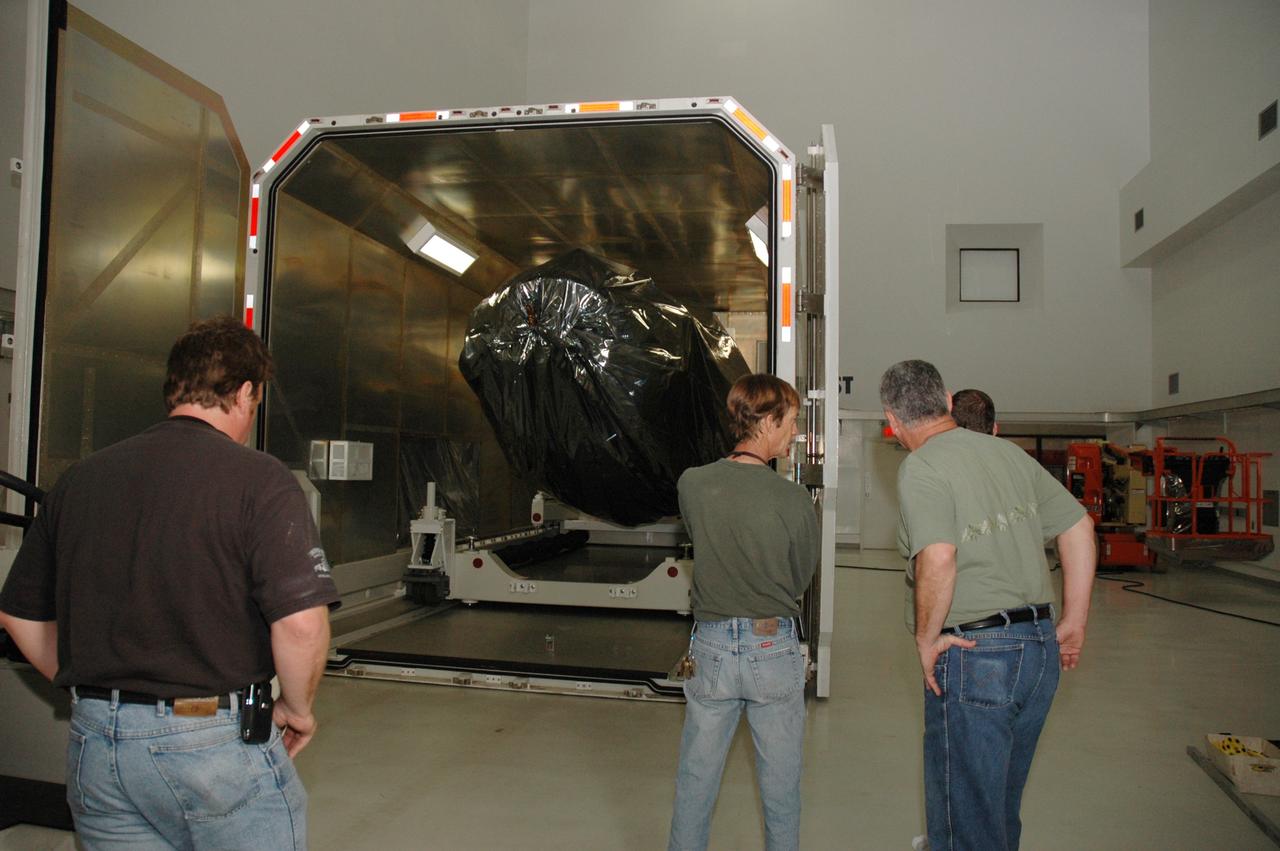

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., doors are opened on the shipping container holding NASA's Kepler spacecraft. After removal from the container, the spacecraft will be rotated to vertical, uncovered and prepared for initial testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Rhodes
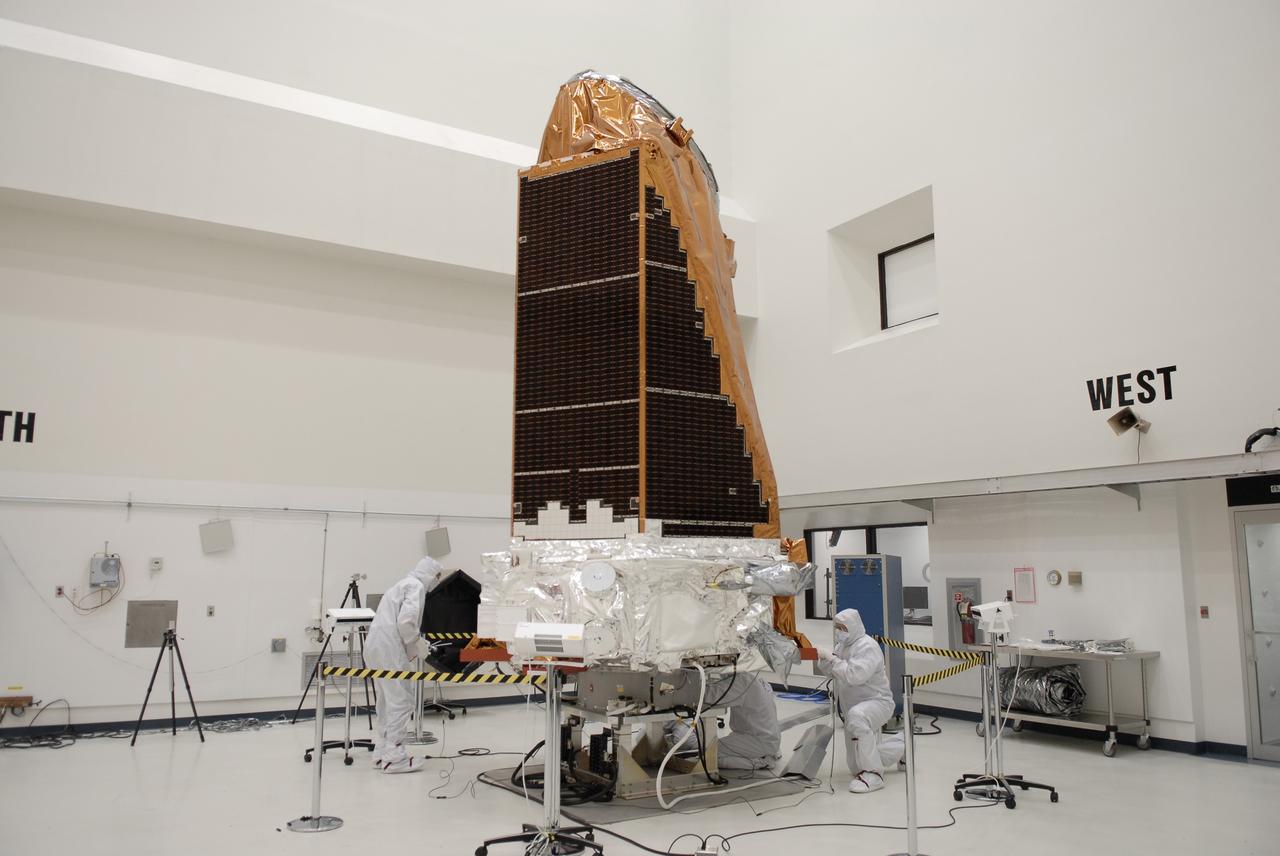

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., workers from Ball Aerospace check the star trackers on NASA's Kepler spacecraft before testing. Star Trackers are small aperture, space-qualified optical products which assure a spacecraft’s accurate navigation in space. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
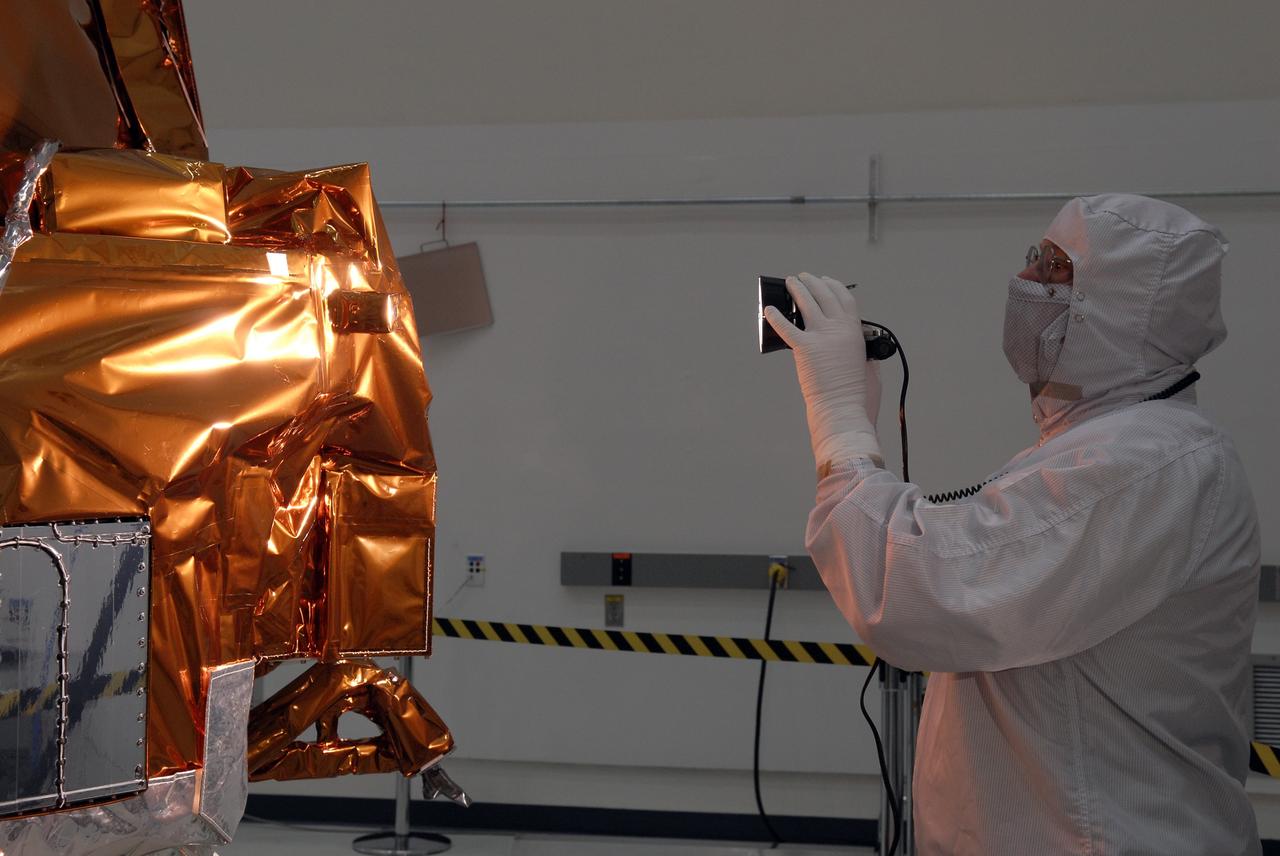

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. worker conducts a light sensor test on NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett