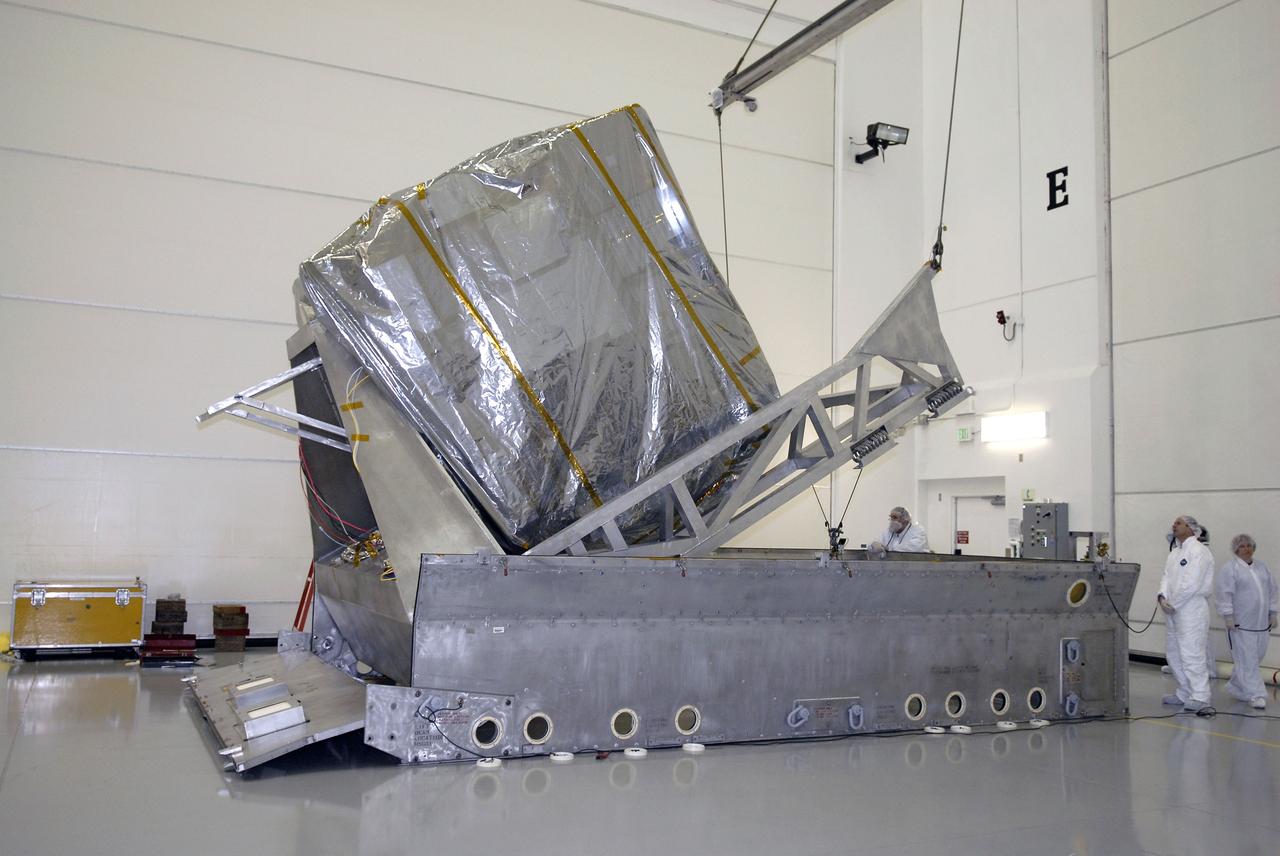

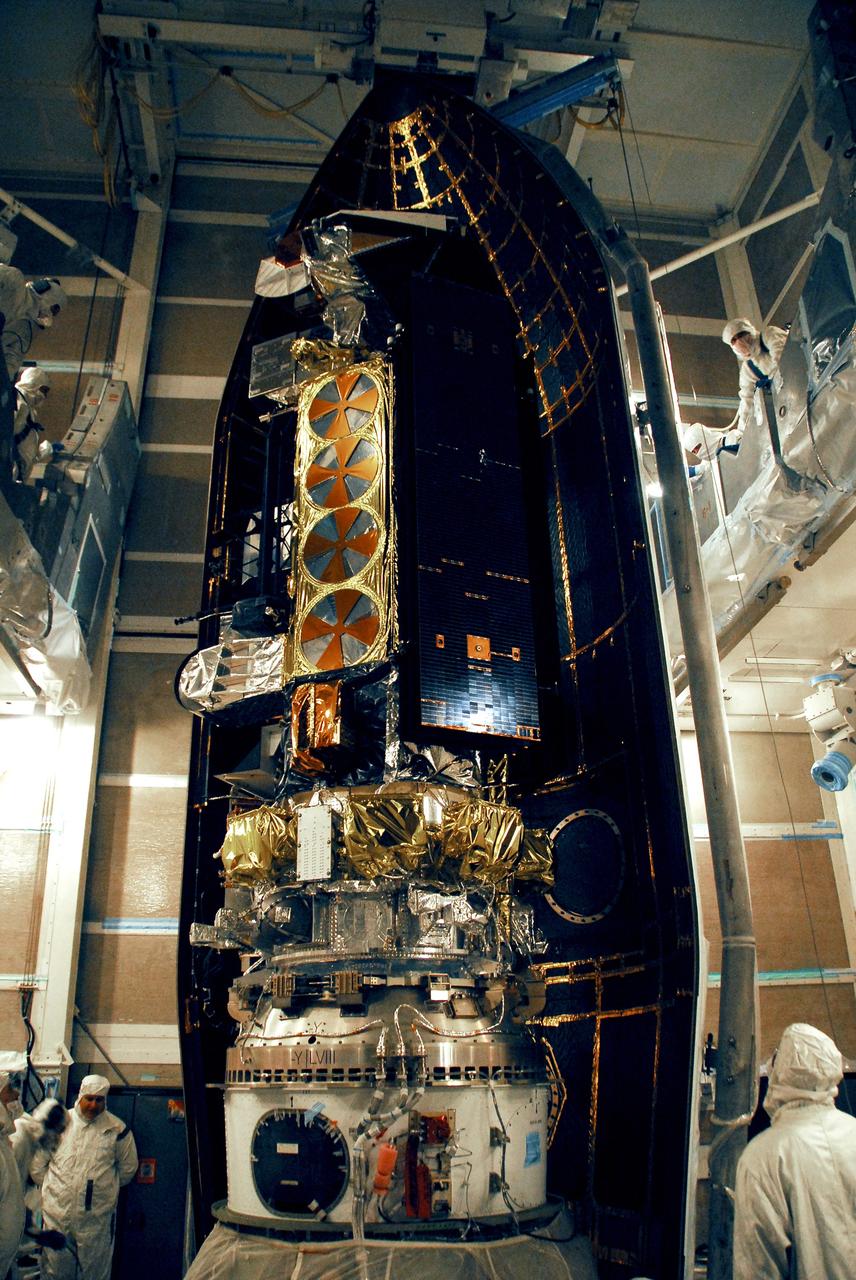
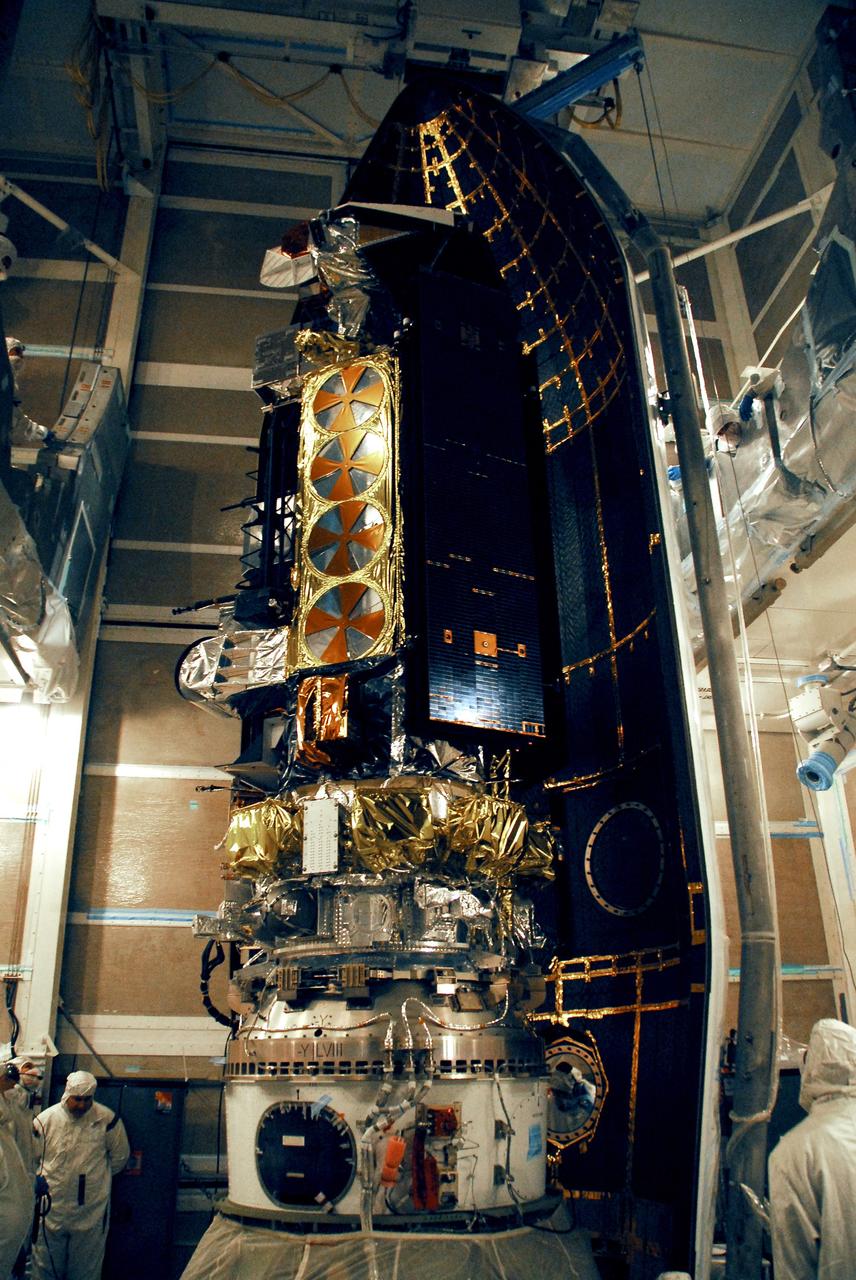
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., the GOES-O satellite is lifted out of its shipping container. It will be placed on a stand for final testing of the imaging system, instrumentation, communications and power systems. The latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, GOES-O was developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. The GOES-O satellite is targeted to launch April 28 onboard a United Launch Alliance Delta IV expendable launch vehicle. Once in orbit, GOES-O will be designated GOES-14, and NASA will provide on-orbit checkout and then transfer operational responsibility to NOAA. GOES-O will be placed in on-orbit storage as a replacement for an older GOES satellite. GOES-O carries an advanced attitude control system using star trackers with spacecraft optical bench Imager and Sounder mountings that provide enhanced instrument pointing performance for improved image navigation and registration to better locate severe storms and other events important to the NOAA National Weather Service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
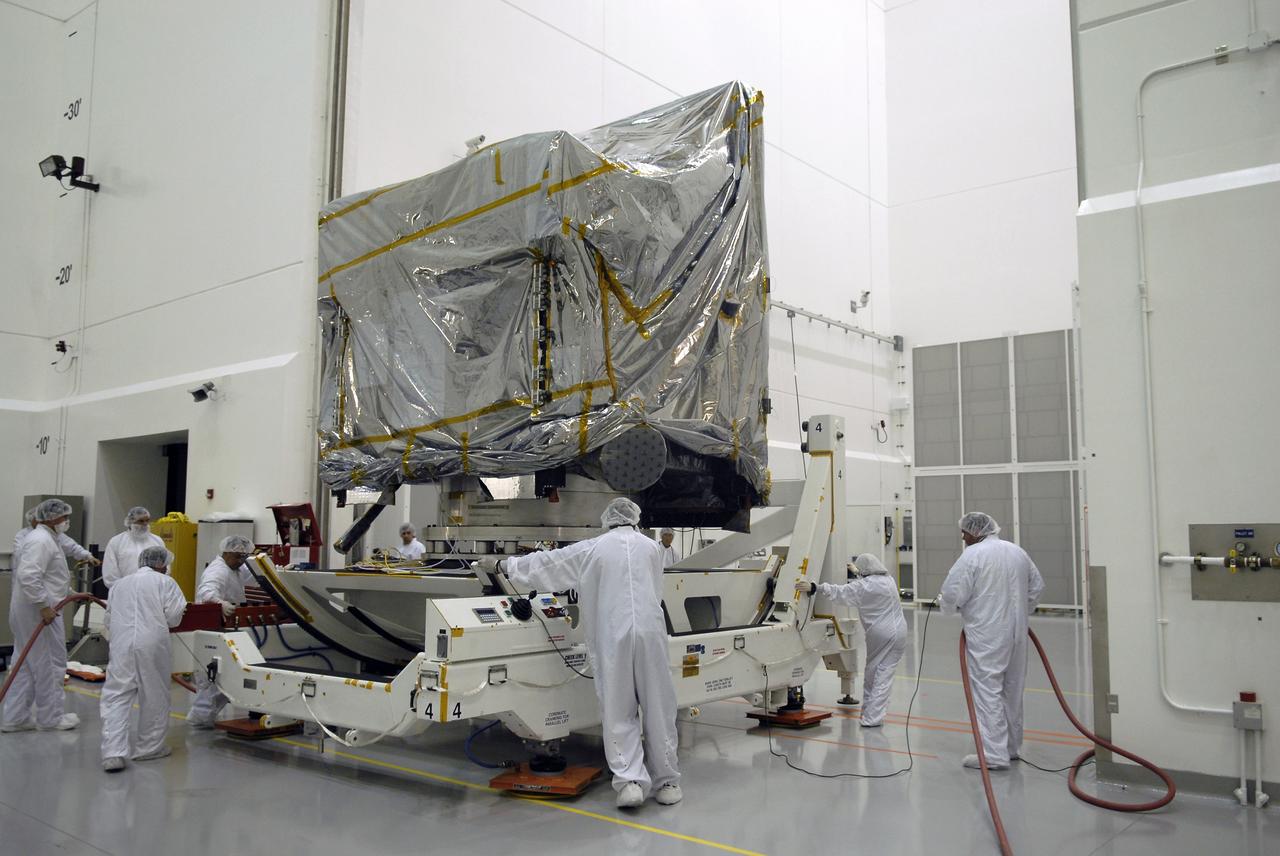

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., technicians move the test stand with the GOES-O satellite. The satellite will undergo final testing of the imaging system, instrumentation, communications and power systems. The latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, GOES-O was developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. The GOES-O satellite is targeted to launch April 28 onboard a United Launch Alliance Delta IV expendable launch vehicle. Once in orbit, GOES-O will be designated GOES-14, and NASA will provide on-orbit checkout and then transfer operational responsibility to NOAA. GOES-O will be placed in on-orbit storage as a replacement for an older GOES satellite. GOES-O carries an advanced attitude control system using star trackers with spacecraft optical bench Imager and Sounder mountings that provide enhanced instrument pointing performance for improved image navigation and registration to better locate severe storms and other events important to the NOAA National Weather Service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
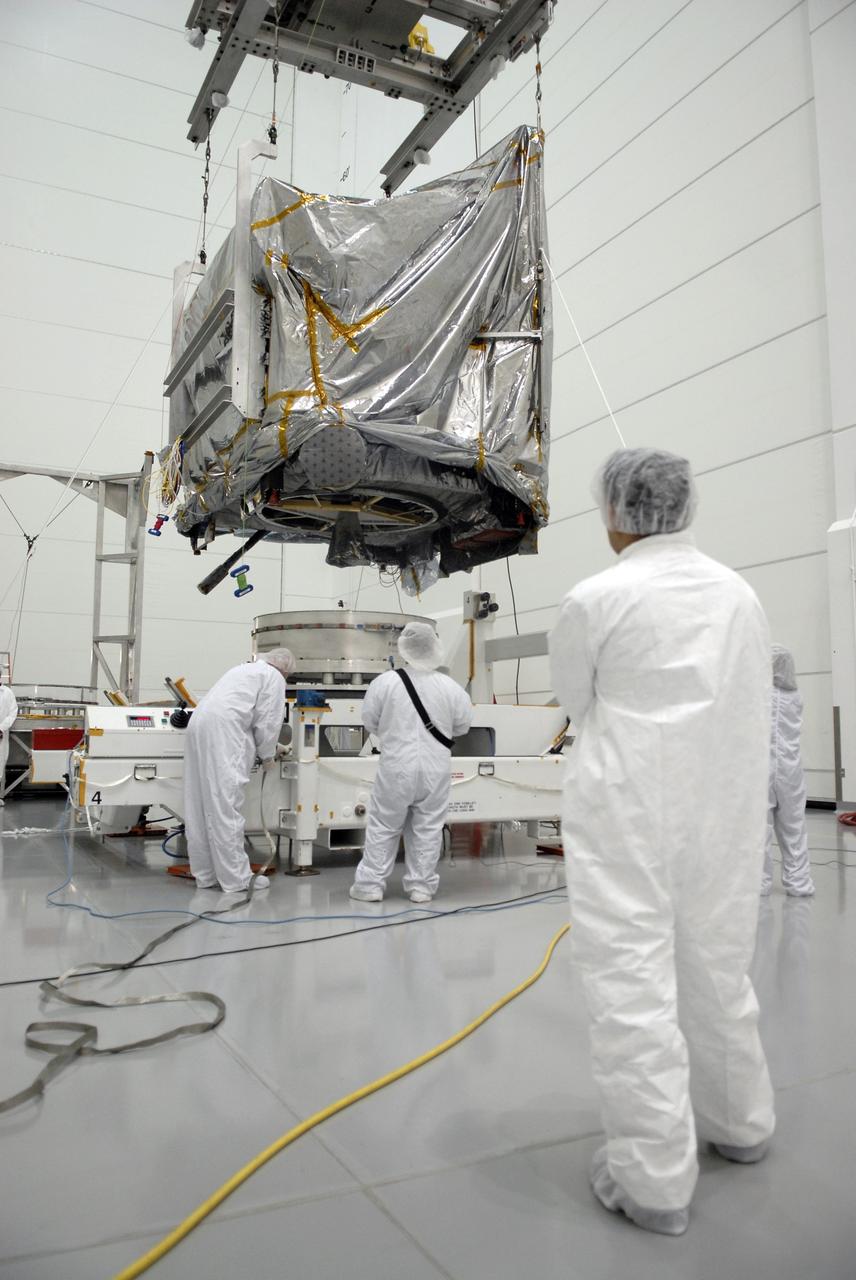

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., the GOES-O satellite is lowered toward a stand. The satellite will undergo final testing of the imaging system, instrumentation, communications and power systems. The latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, GOES-O was developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. The GOES-O satellite is targeted to launch April 28 onboard a United Launch Alliance Delta IV expendable launch vehicle. Once in orbit, GOES-O will be designated GOES-14, and NASA will provide on-orbit checkout and then transfer operational responsibility to NOAA. GOES-O will be placed in on-orbit storage as a replacement for an older GOES satellite. GOES-O carries an advanced attitude control system using star trackers with spacecraft optical bench Imager and Sounder mountings that provide enhanced instrument pointing performance for improved image navigation and registration to better locate severe storms and other events important to the NOAA National Weather Service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
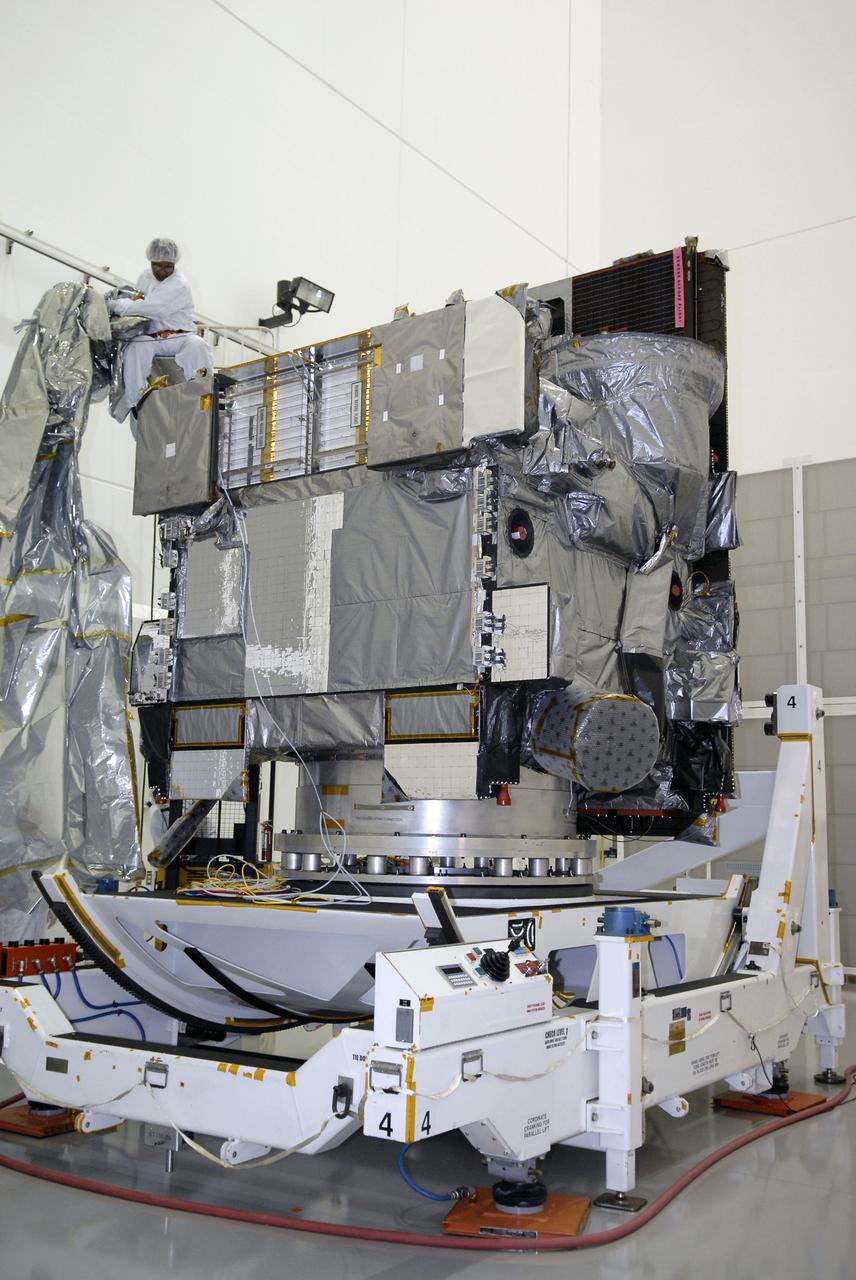

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., technicians remove the protective cover wrapped around the GOES-O satellite. The satellite will undergo final testing of the imaging system, instrumentation, communications and power systems. The latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, GOES-O was developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. The GOES-O satellite is targeted to launch April 28 onboard a United Launch Alliance Delta IV expendable launch vehicle. Once in orbit, GOES-O will be designated GOES-14, and NASA will provide on-orbit checkout and then transfer operational responsibility to NOAA. GOES-O will be placed in on-orbit storage as a replacement for an older GOES satellite. GOES-O carries an advanced attitude control system using star trackers with spacecraft optical bench Imager and Sounder mountings that provide enhanced instrument pointing performance for improved image navigation and registration to better locate severe storms and other events important to the NOAA National Weather Service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
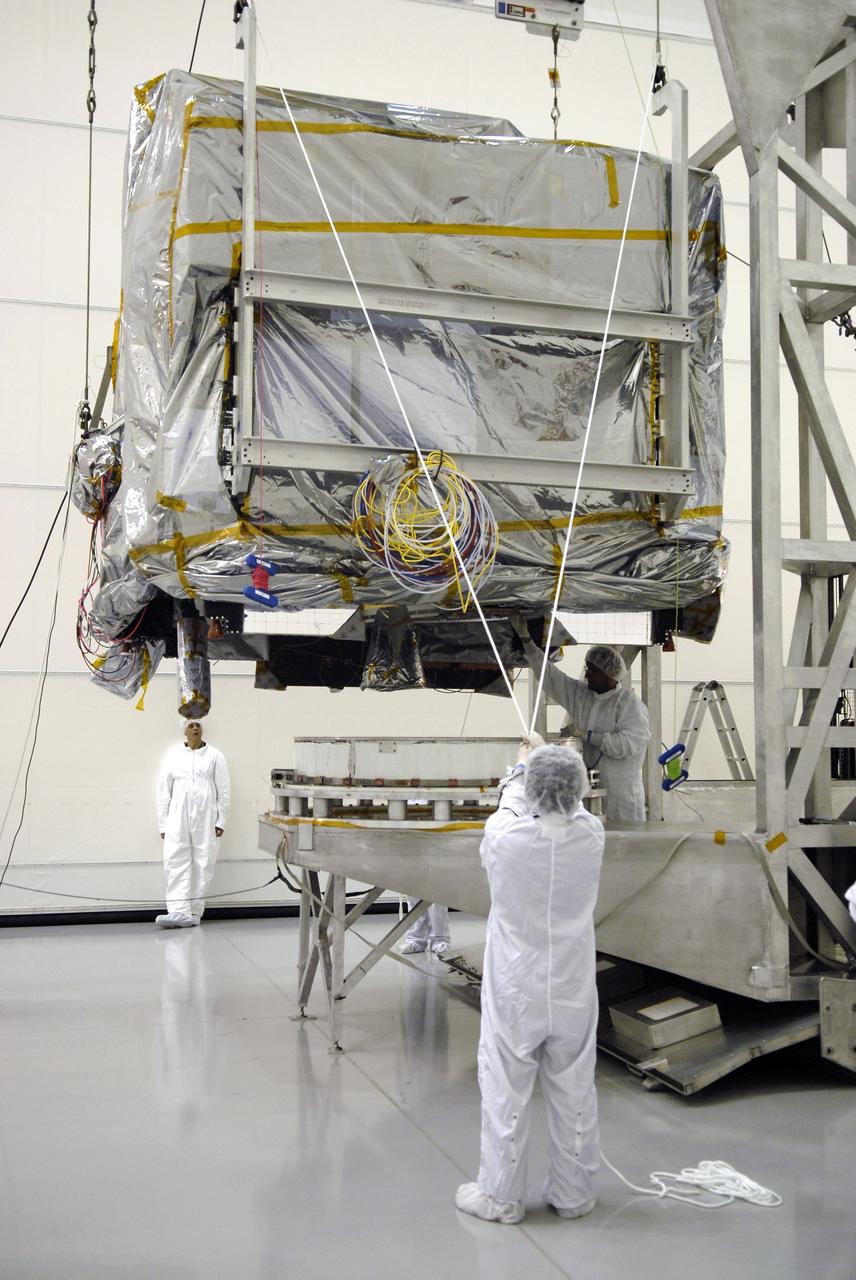

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., technicians help guide the cables lifting the GOES-O satellite away from its shipping container. The satellite will be placed on a stand for final testing of the imaging system, instrumentation, communications and power systems. The latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, GOES-O was developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. The GOES-O satellite is targeted to launch April 28 onboard a United Launch Alliance Delta IV expendable launch vehicle. Once in orbit, GOES-O will be designated GOES-14, and NASA will provide on-orbit checkout and then transfer operational responsibility to NOAA. GOES-O will be placed in on-orbit storage as a replacement for an older GOES satellite. GOES-O carries an advanced attitude control system using star trackers with spacecraft optical bench Imager and Sounder mountings that provide enhanced instrument pointing performance for improved image navigation and registration to better locate severe storms and other events important to the NOAA National Weather Service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
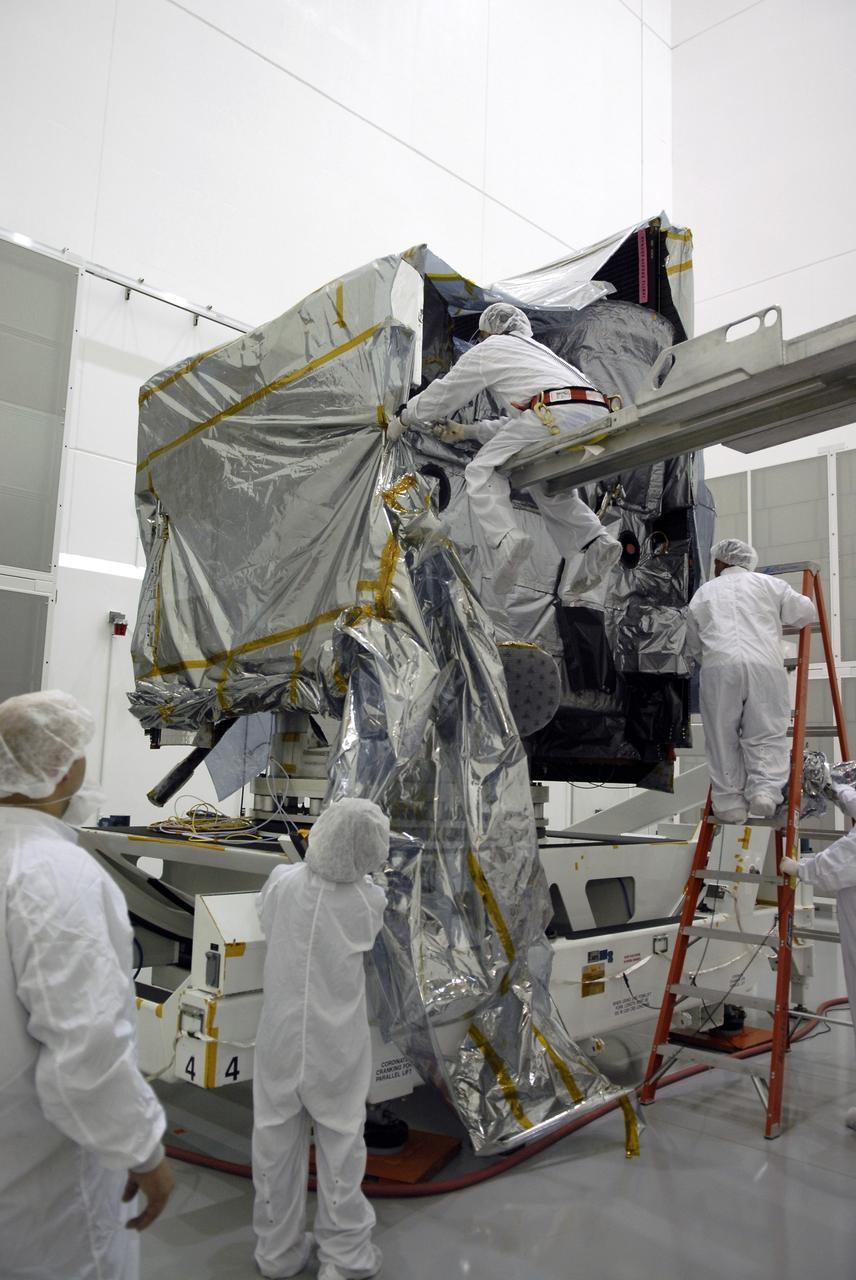

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., technicians remove the protective cover wrapped around the GOES-O satellite. The satellite will undergo final testing of the imaging system, instrumentation, communications and power systems. The latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, GOES-O was developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. The GOES-O satellite is targeted to launch April 28 onboard a United Launch Alliance Delta IV expendable launch vehicle. Once in orbit, GOES-O will be designated GOES-14, and NASA will provide on-orbit checkout and then transfer operational responsibility to NOAA. GOES-O will be placed in on-orbit storage as a replacement for an older GOES satellite. GOES-O carries an advanced attitude control system using star trackers with spacecraft optical bench Imager and Sounder mountings that provide enhanced instrument pointing performance for improved image navigation and registration to better locate severe storms and other events important to the NOAA National Weather Service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
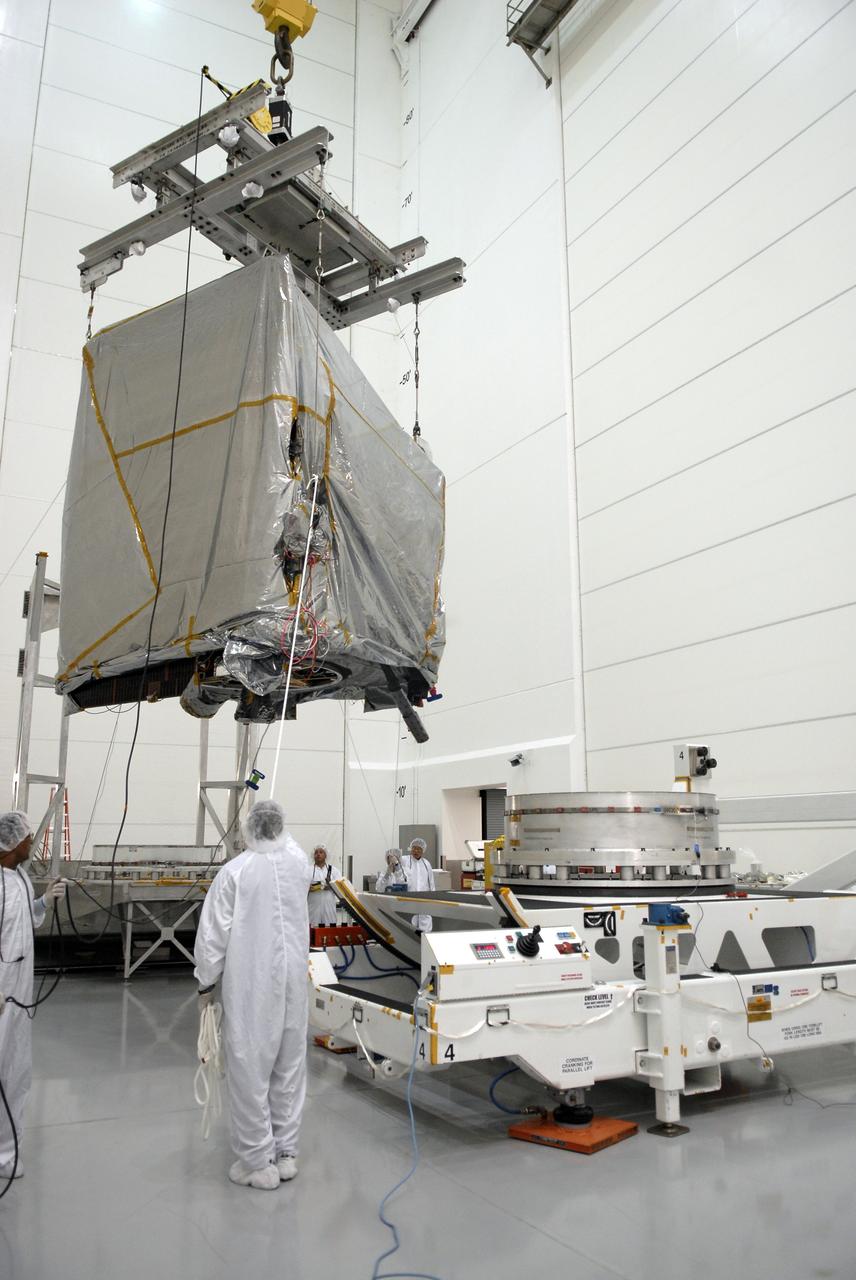

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., technicians help guide the cables lifting the GOES-O satellite toward the stand at right. The satellite will undergo final testing of the imaging system, instrumentation, communications and power systems. The latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, GOES-O was developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. The GOES-O satellite is targeted to launch April 28 onboard a United Launch Alliance Delta IV expendable launch vehicle. Once in orbit, GOES-O will be designated GOES-14, and NASA will provide on-orbit checkout and then transfer operational responsibility to NOAA. GOES-O will be placed in on-orbit storage as a replacement for an older GOES satellite. GOES-O carries an advanced attitude control system using star trackers with spacecraft optical bench Imager and Sounder mountings that provide enhanced instrument pointing performance for improved image navigation and registration to better locate severe storms and other events important to the NOAA National Weather Service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
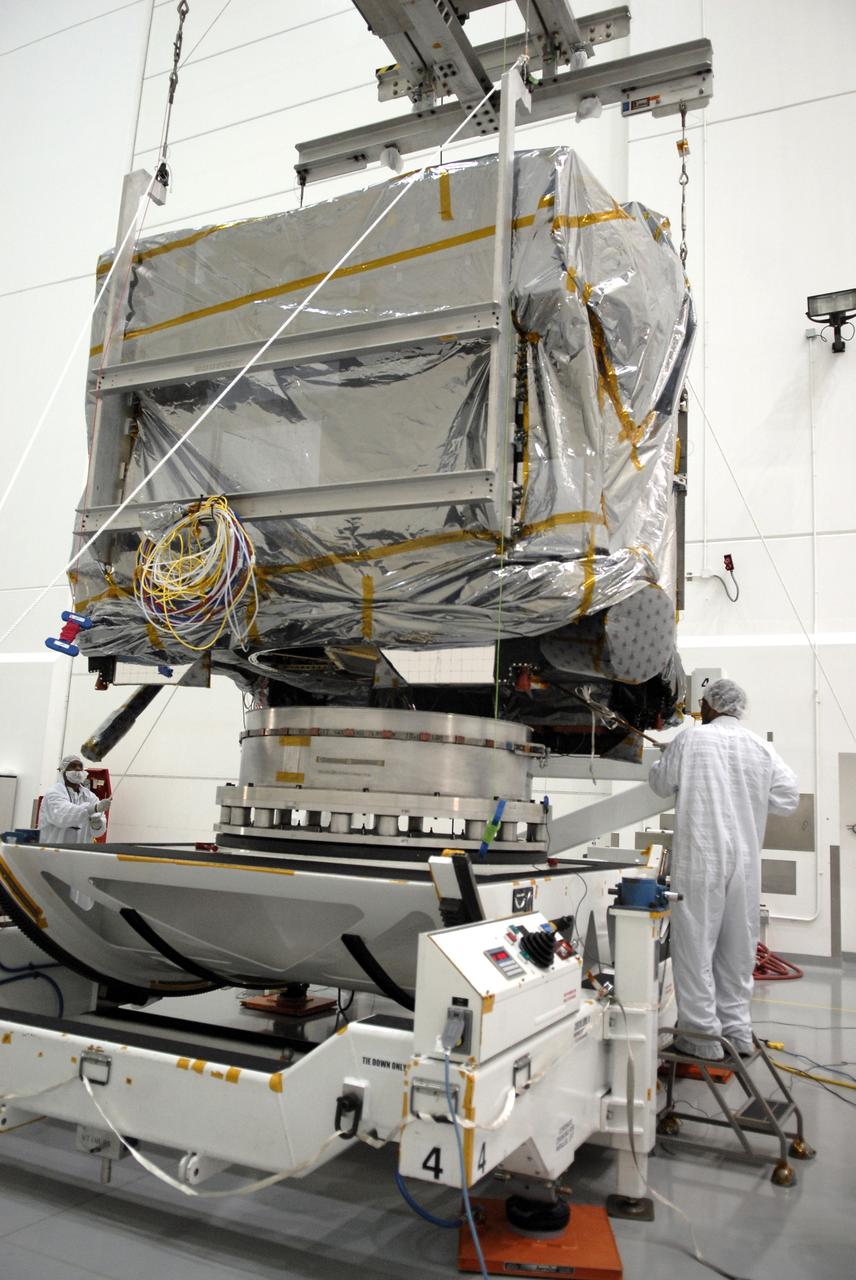

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., the GOES-O satellite is lowered toward a test stand. The satellite will undergo final testing of the imaging system, instrumentation, communications and power systems. The latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, GOES-O was developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. The GOES-O satellite is targeted to launch April 28 onboard a United Launch Alliance Delta IV expendable launch vehicle. Once in orbit, GOES-O will be designated GOES-14, and NASA will provide on-orbit checkout and then transfer operational responsibility to NOAA. GOES-O will be placed in on-orbit storage as a replacement for an older GOES satellite. GOES-O carries an advanced attitude control system using star trackers with spacecraft optical bench Imager and Sounder mountings that provide enhanced instrument pointing performance for improved image navigation and registration to better locate severe storms and other events important to the NOAA National Weather Service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
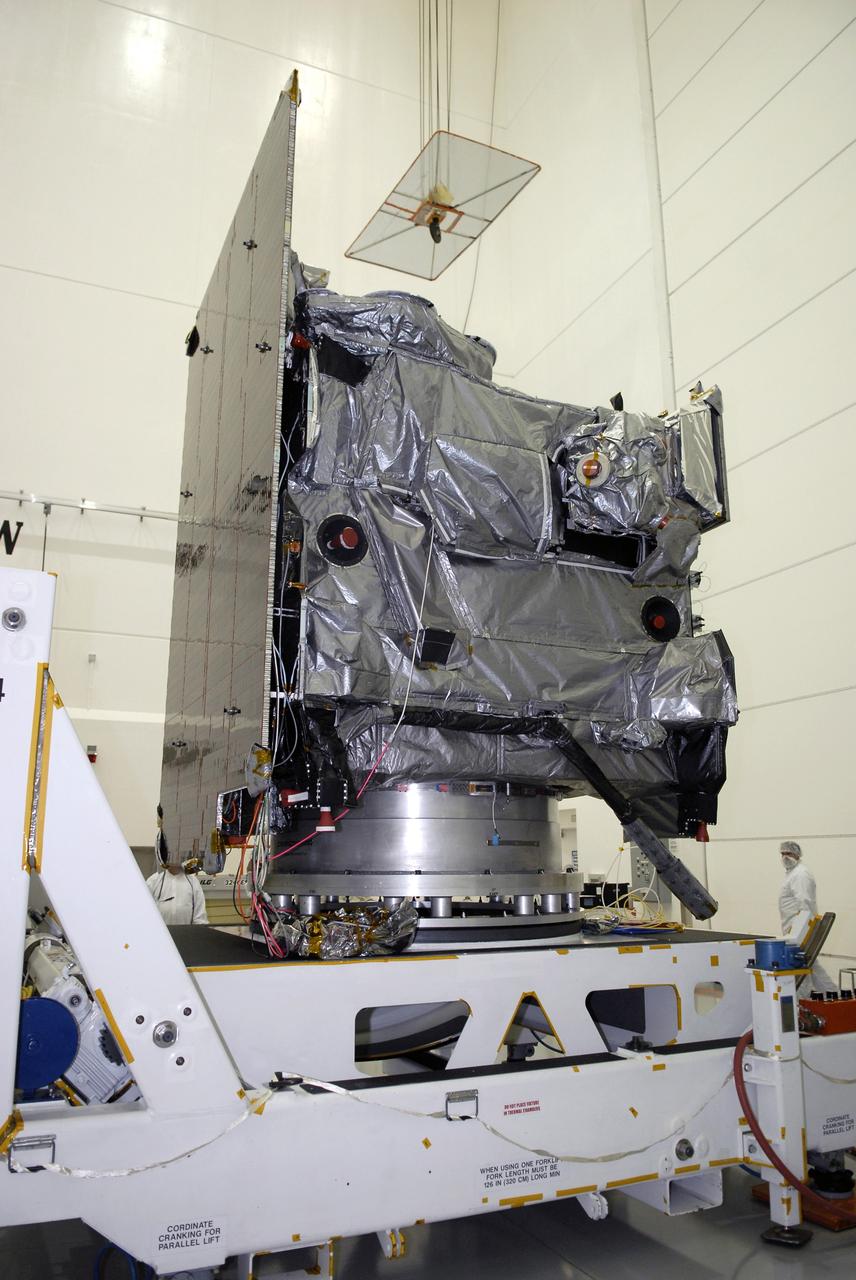

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., the solar arrays on the GOES-O satellite are revealed. GOES-O will undergo final testing of the imaging system, instrumentation, communications and power systems. The latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, GOES-O was developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. The GOES-O satellite is targeted to launch April 28 onboard a United Launch Alliance Delta IV expendable launch vehicle. Once in orbit, GOES-O will be designated GOES-14, and NASA will provide on-orbit checkout and then transfer operational responsibility to NOAA. GOES-O will be placed in on-orbit storage as a replacement for an older GOES satellite. GOES-O carries an advanced attitude control system using star trackers with spacecraft optical bench Imager and Sounder mountings that provide enhanced instrument pointing performance for improved image navigation and registration to better locate severe storms and other events important to the NOAA National Weather Service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

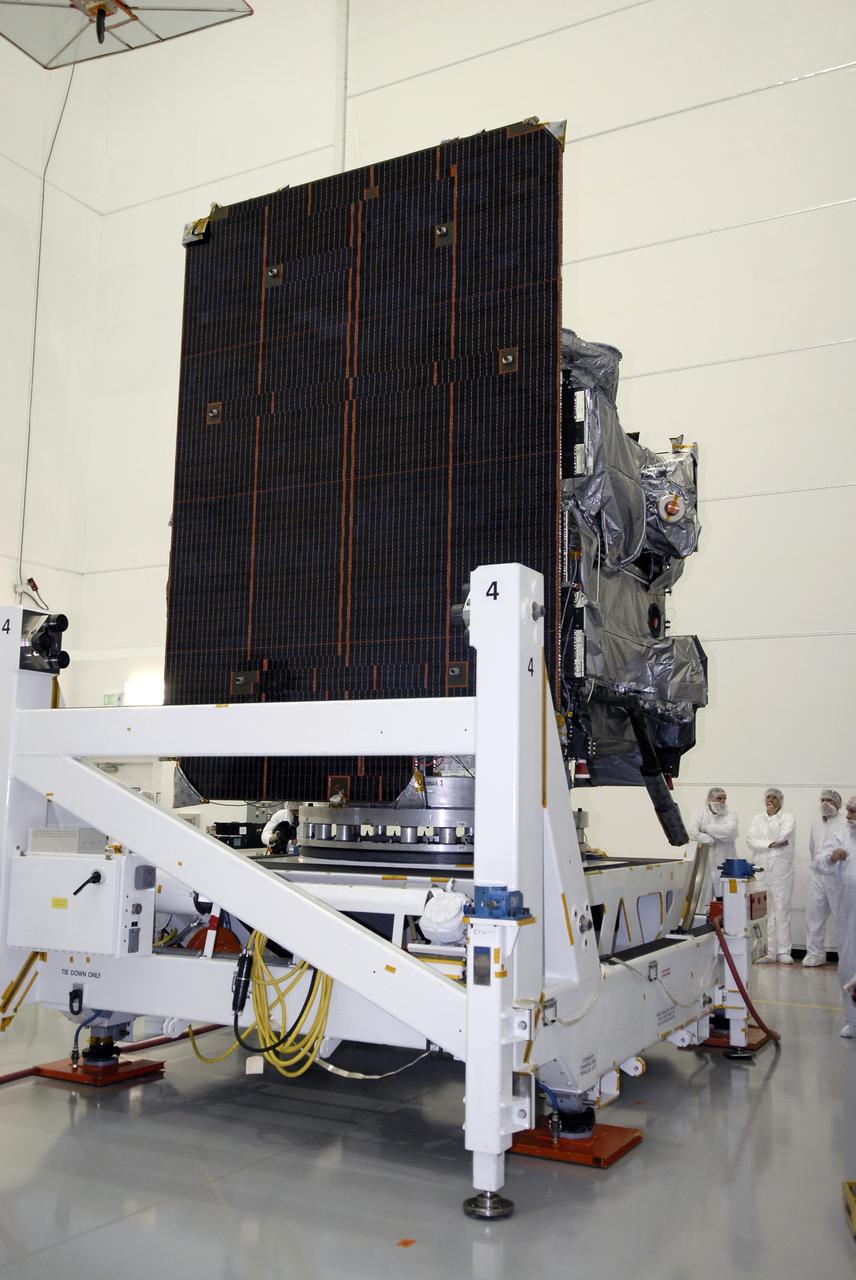
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., the GOES-O satellite is lifted out of its shipping container to a vertical position. It will be placed on a stand for final testing of the imaging system, instrumentation, communications and power systems. The latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, GOES-O was developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. The GOES-O satellite is targeted to launch April 28 onboard a United Launch Alliance Delta IV expendable launch vehicle. Once in orbit, GOES-O will be designated GOES-14, and NASA will provide on-orbit checkout and then transfer operational responsibility to NOAA. GOES-O will be placed in on-orbit storage as a replacement for an older GOES satellite. GOES-O carries an advanced attitude control system using star trackers with spacecraft optical bench Imager and Sounder mountings that provide enhanced instrument pointing performance for improved image navigation and registration to better locate severe storms and other events important to the NOAA National Weather Service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

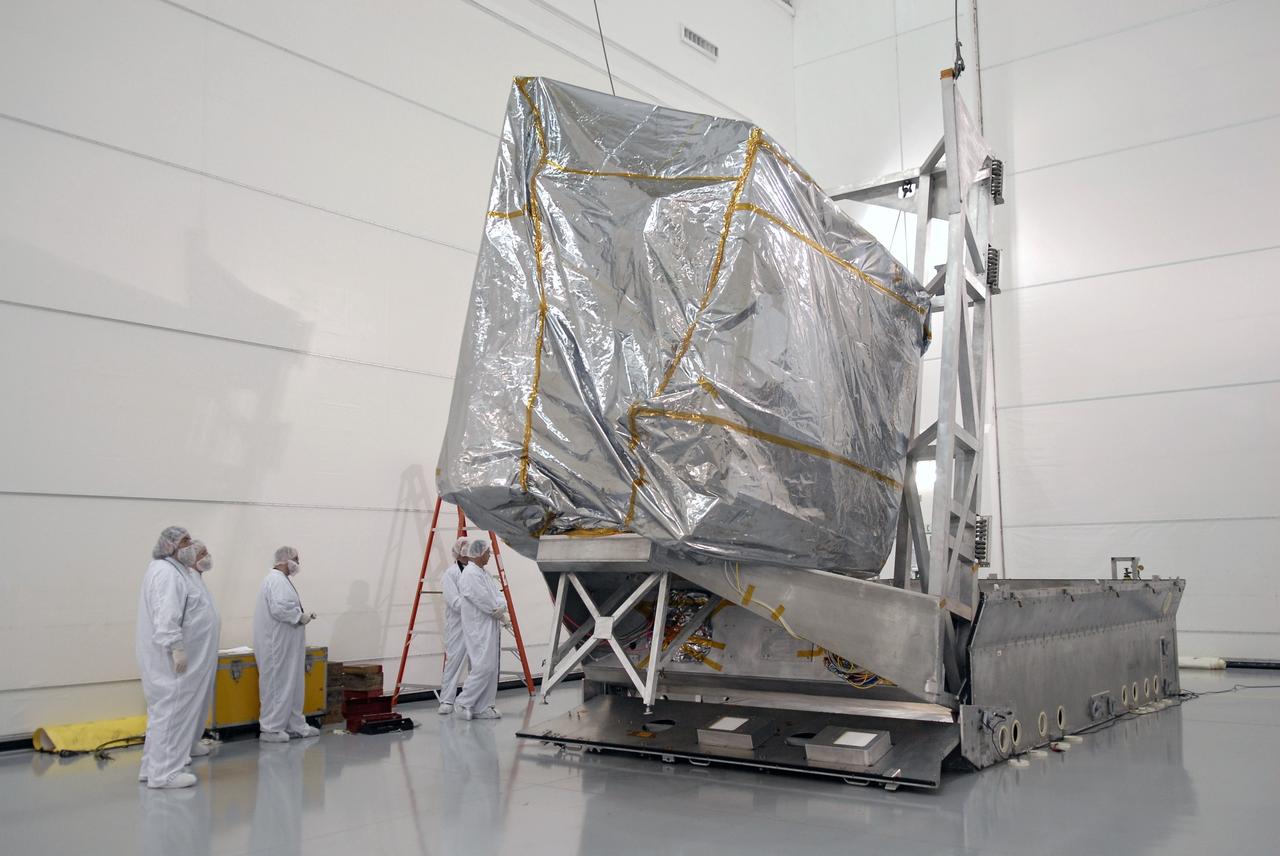
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., the protective shipping cover has been removed from the GOES-O satellite. GOES-O will undergo final testing of the imaging system, instrumentation, communications and power systems. The latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, GOES-O was developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. The GOES-O satellite is targeted to launch April 28 onboard a United Launch Alliance Delta IV expendable launch vehicle. Once in orbit, GOES-O will be designated GOES-14, and NASA will provide on-orbit checkout and then transfer operational responsibility to NOAA. GOES-O will be placed in on-orbit storage as a replacement for an older GOES satellite. GOES-O carries an advanced attitude control system using star trackers with spacecraft optical bench Imager and Sounder mountings that provide enhanced instrument pointing performance for improved image navigation and registration to better locate severe storms and other events important to the NOAA National Weather Service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

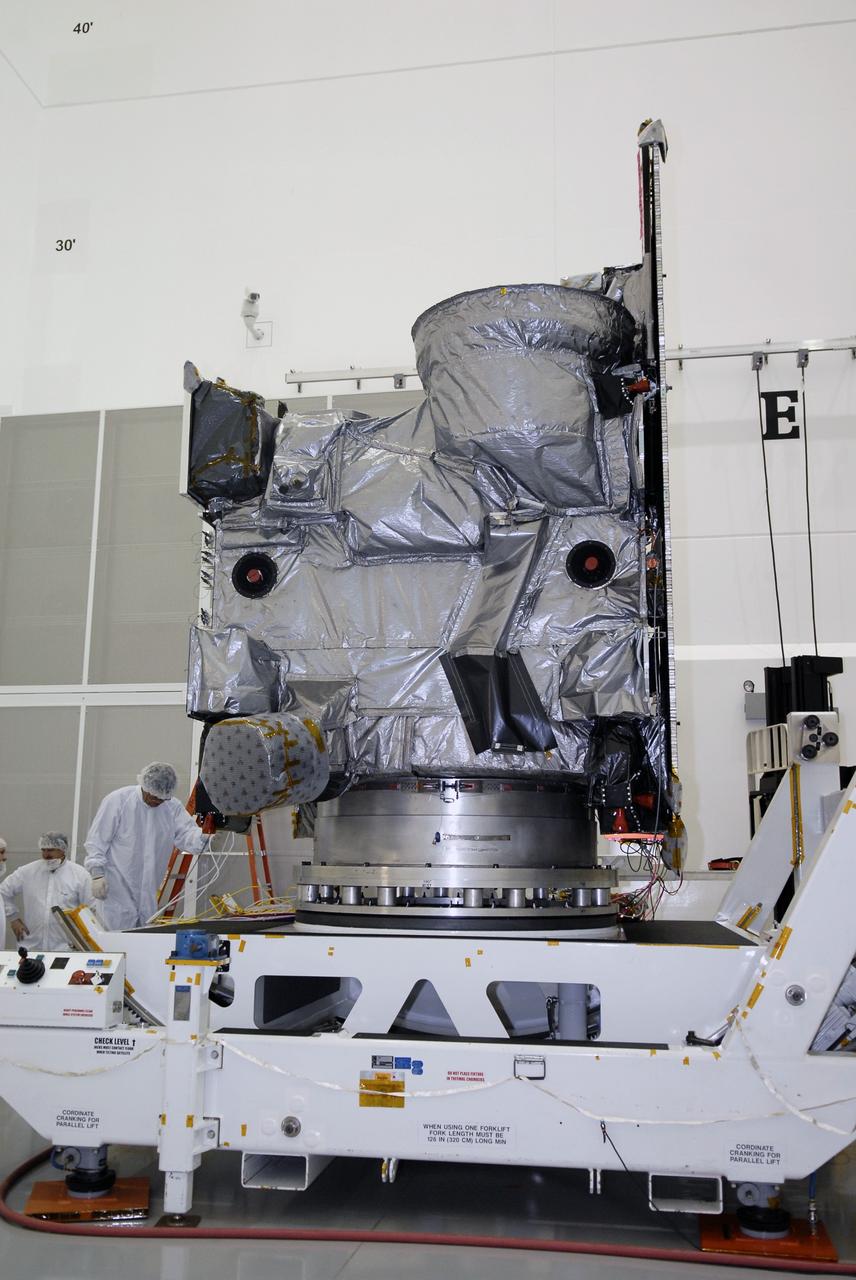
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., the GOES-O satellite will undergo final testing of the imaging system, instrumentation, communications and power systems. The latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, GOES-O was developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. The GOES-O satellite is targeted to launch April 28 onboard a United Launch Alliance Delta IV expendable launch vehicle. Once in orbit, GOES-O will be designated GOES-14, and NASA will provide on-orbit checkout and then transfer operational responsibility to NOAA. GOES-O will be placed in on-orbit storage as a replacement for an older GOES satellite. GOES-O carries an advanced attitude control system using star trackers with spacecraft optical bench Imager and Sounder mountings that provide enhanced instrument pointing performance for improved image navigation and registration to better locate severe storms and other events important to the NOAA National Weather Service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The first half of the fairing is moved into place around the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft in the launch service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the rocket and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. It is built by Lockheed Martin and similar to NOAA-N that was launched on May 20, 2005. Launch of NOAA-N Prime aboard a Delta II rocket is scheduled for Feb. 4. Photo credit: NASA

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The first half of the fairing is moved into place around the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft in the launch service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the rocket and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. It is built by Lockheed Martin and similar to NOAA-N that was launched on May 20, 2005. Launch of NOAA-N Prime aboard a Delta II rocket is scheduled for Feb. 4. Photo credit: NASA
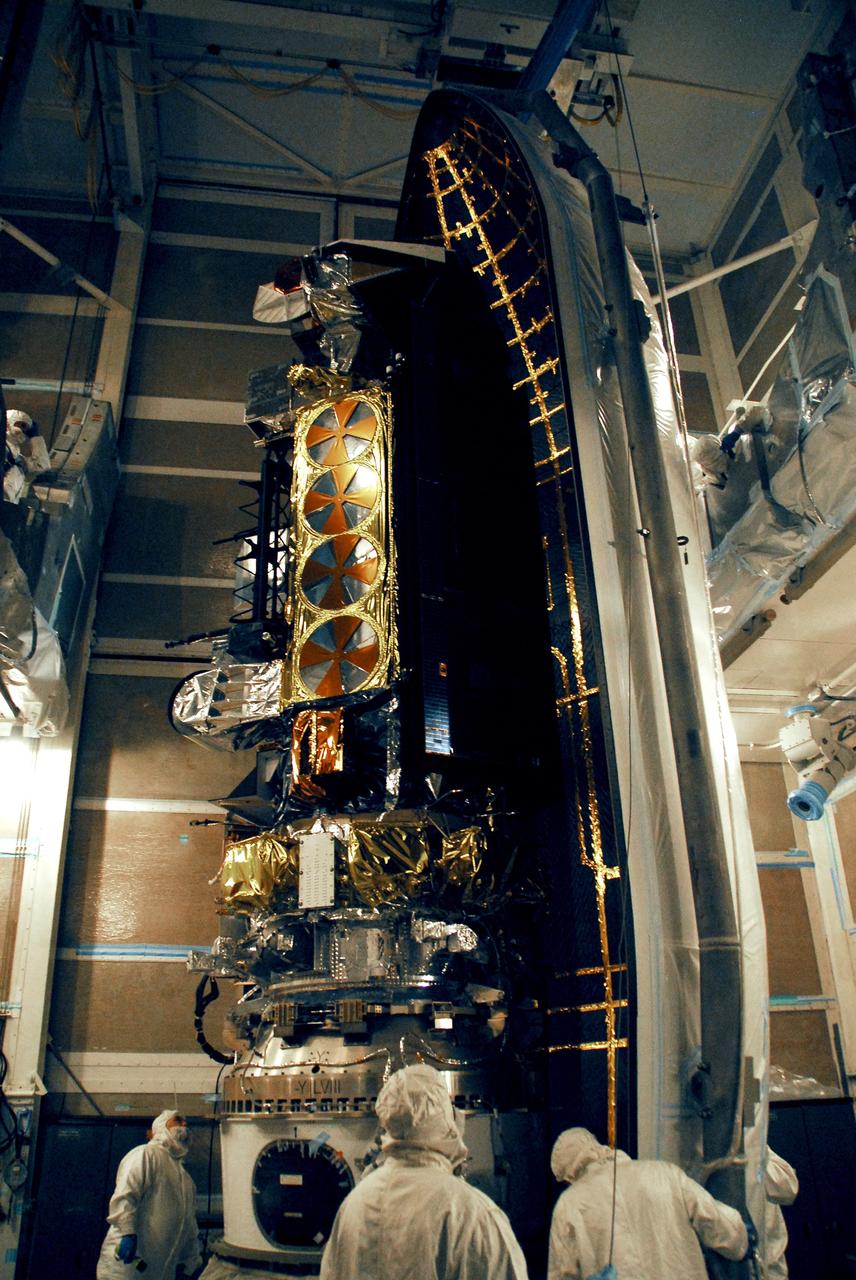
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The first half of the fairing is moved into place around the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft in the launch service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the rocket and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. It is built by Lockheed Martin and similar to NOAA-N that was launched on May 20, 2005. Launch of NOAA-N Prime aboard a Delta II rocket is scheduled for Feb. 4. Photo credit: NASA

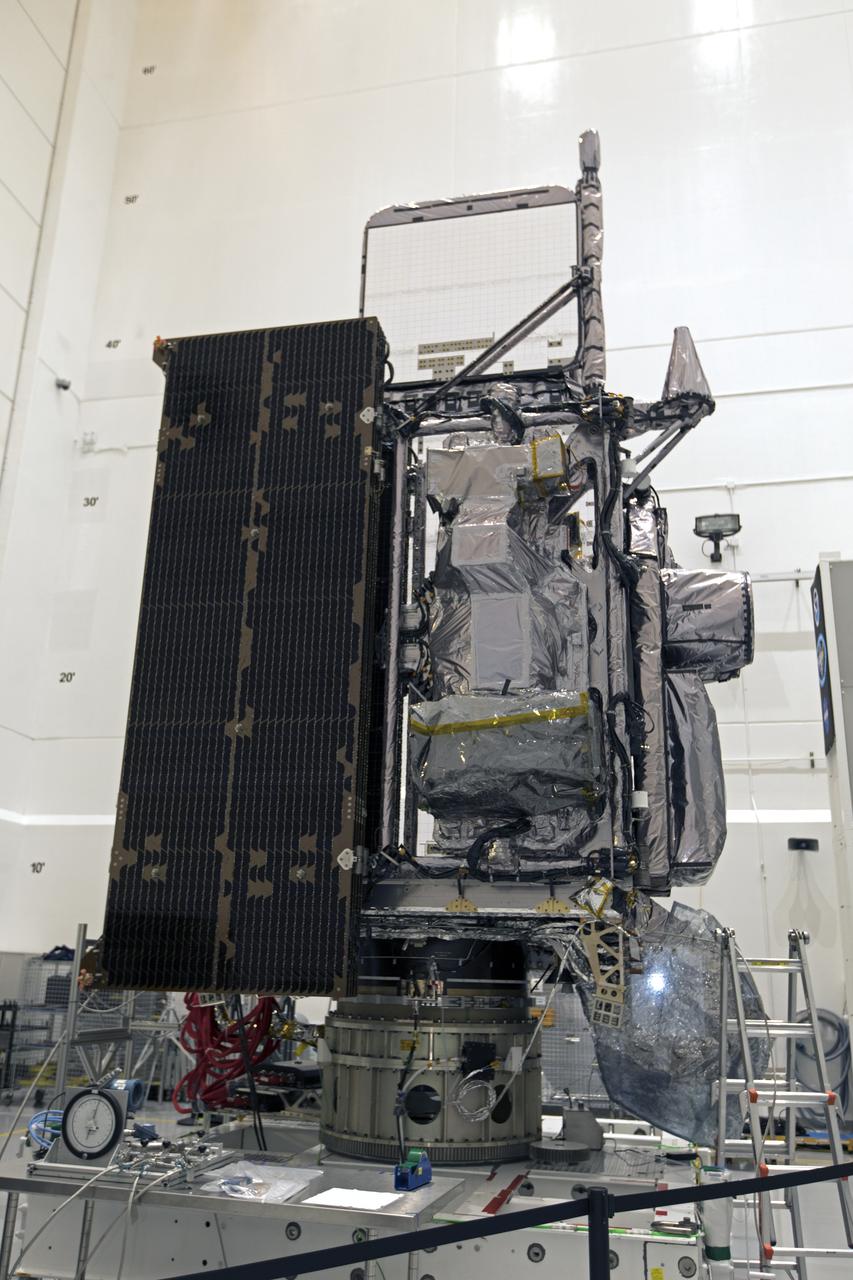
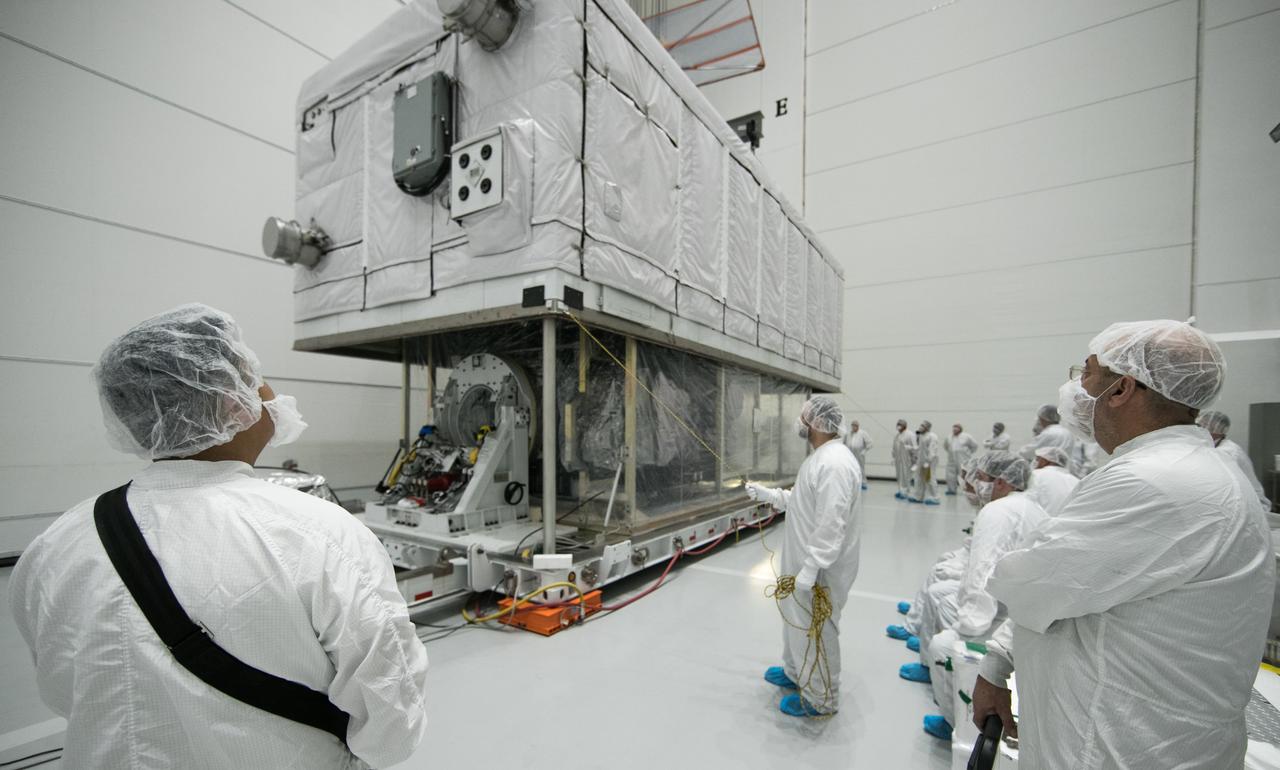
In a clean room at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, is being prepared for encapsulation in it payload fairing. After encapsulation, the weather satellite will be moved to Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
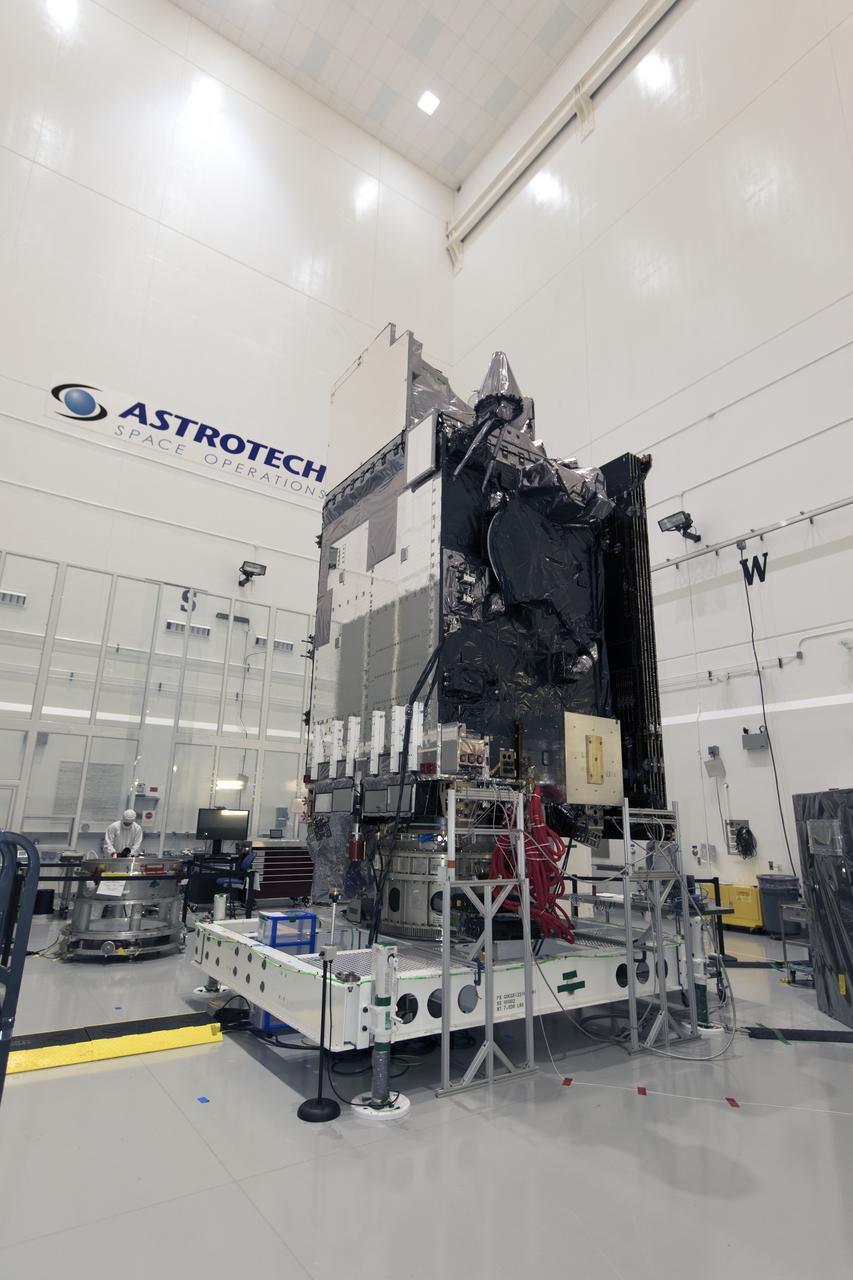

In a clean room at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, is being prepared for encapsulation in it payload fairing. After encapsulation, the weather satellite will be moved to Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
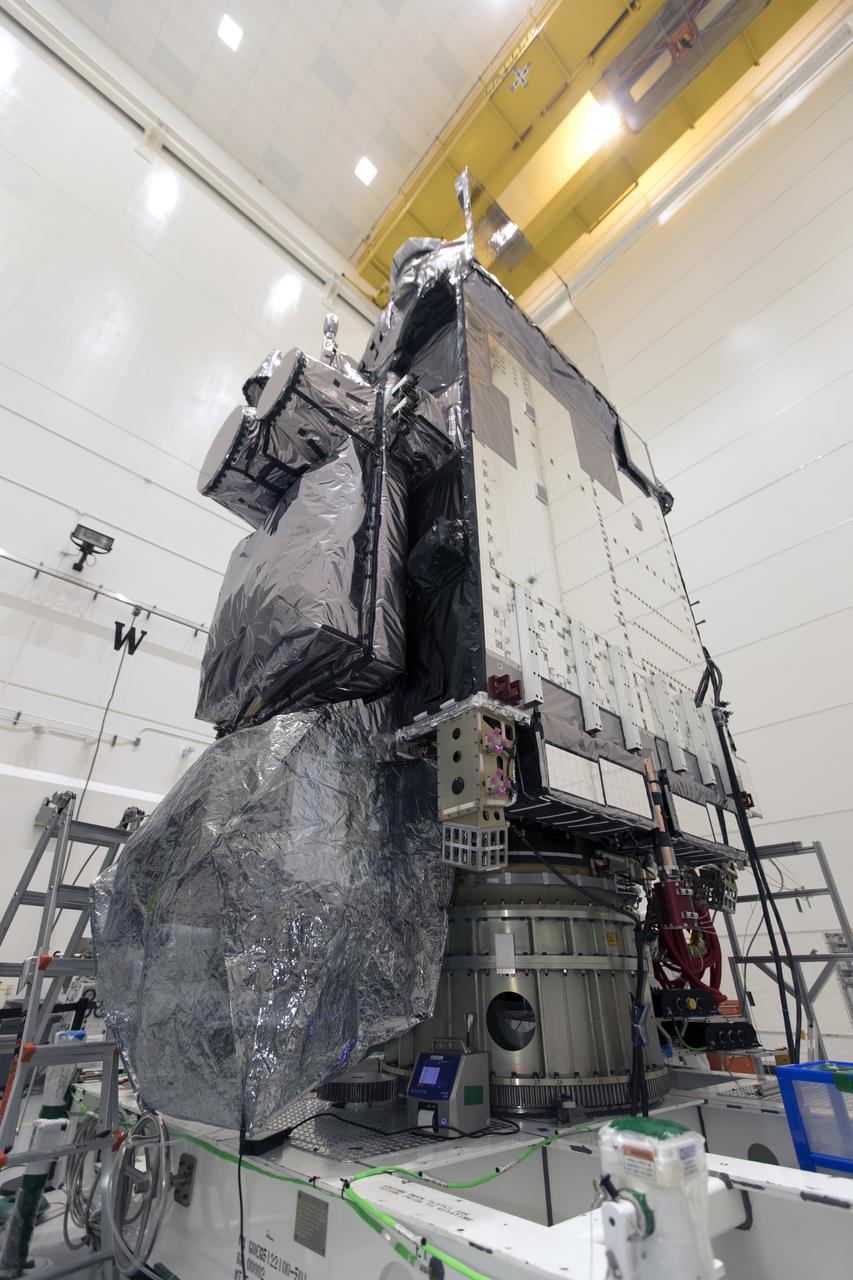

In a clean room at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, is being prepared for encapsulation in it payload fairing. After encapsulation, the weather satellite will be moved to Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
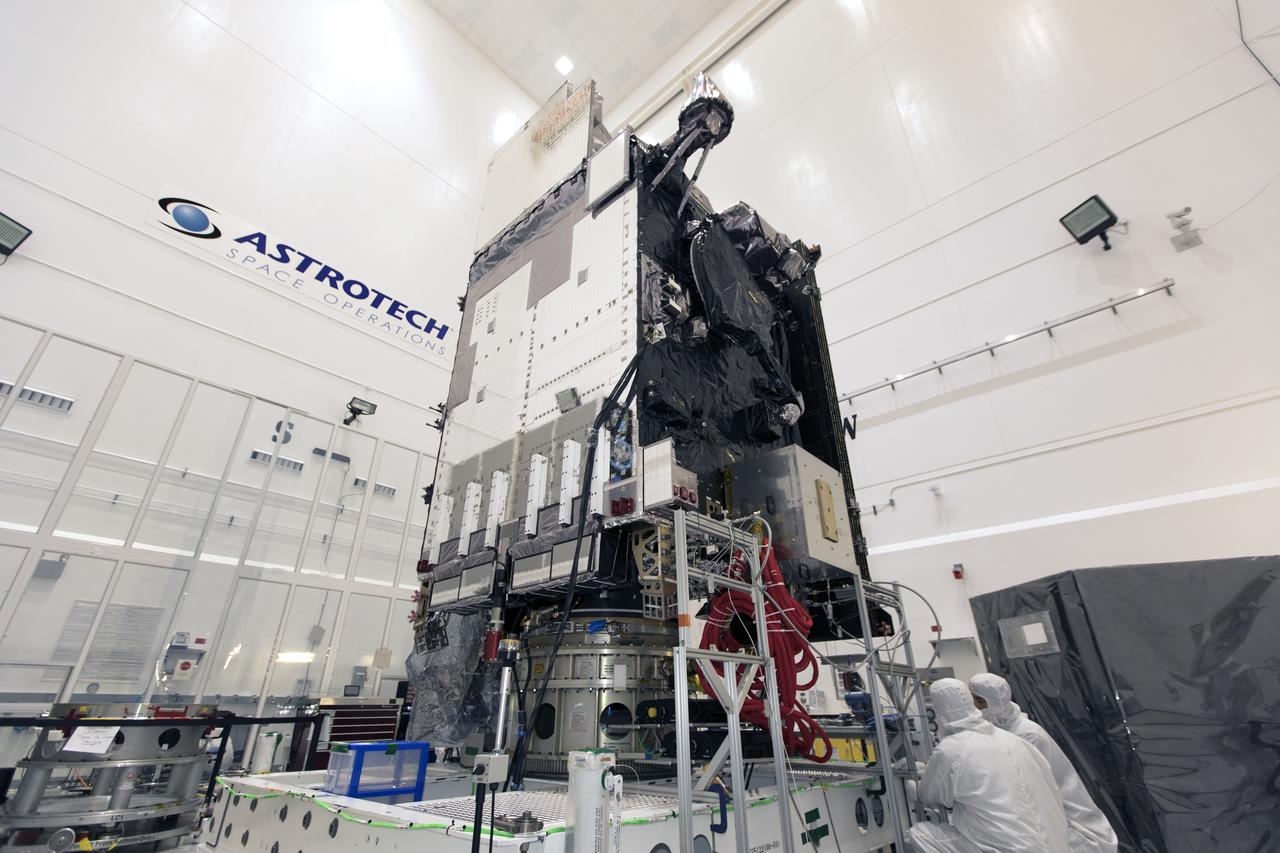

In a clean room at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers are preparing NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, for encapsulation in it payload fairing. After encapsulation, the weather satellite will be moved to Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
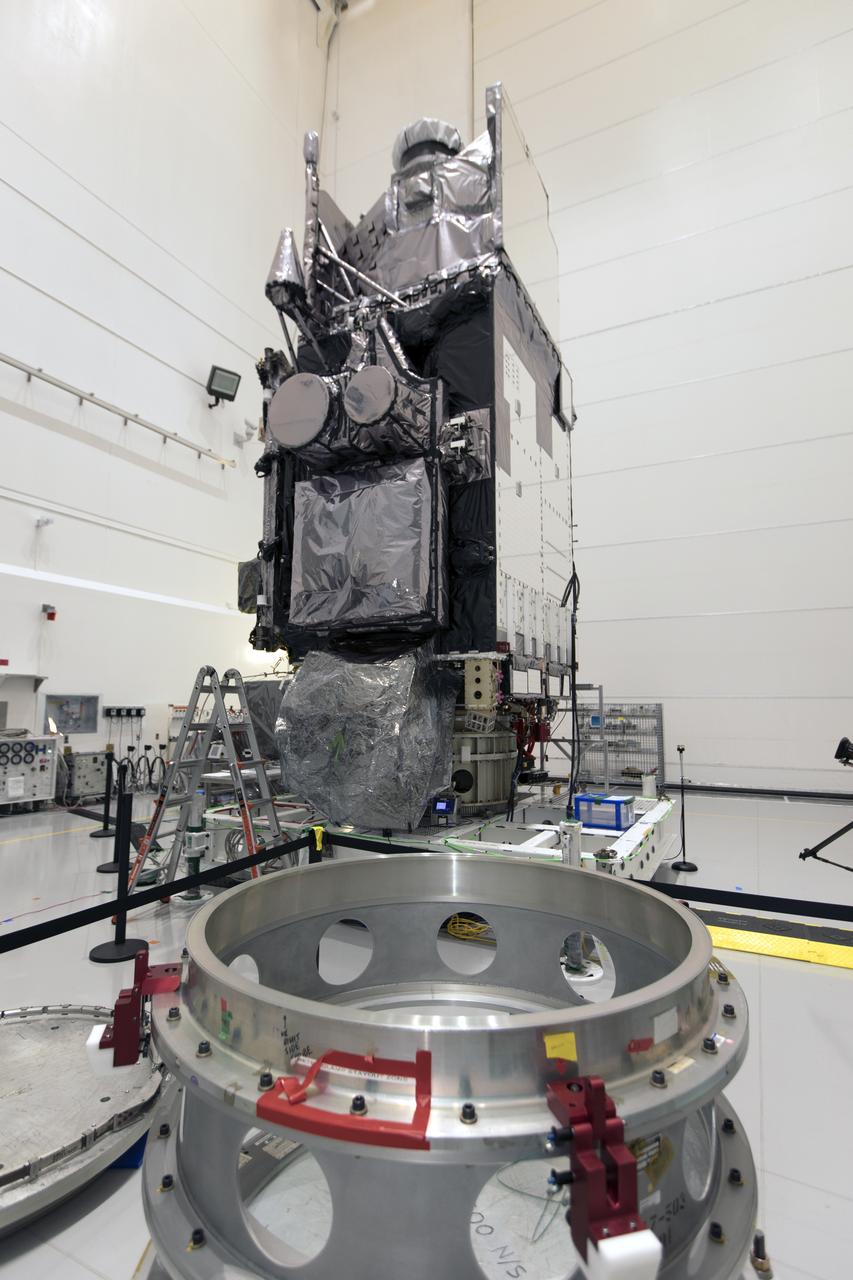

In a clean room at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, is being prepared for encapsulation in it payload fairing. After encapsulation, the weather satellite will be moved to Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
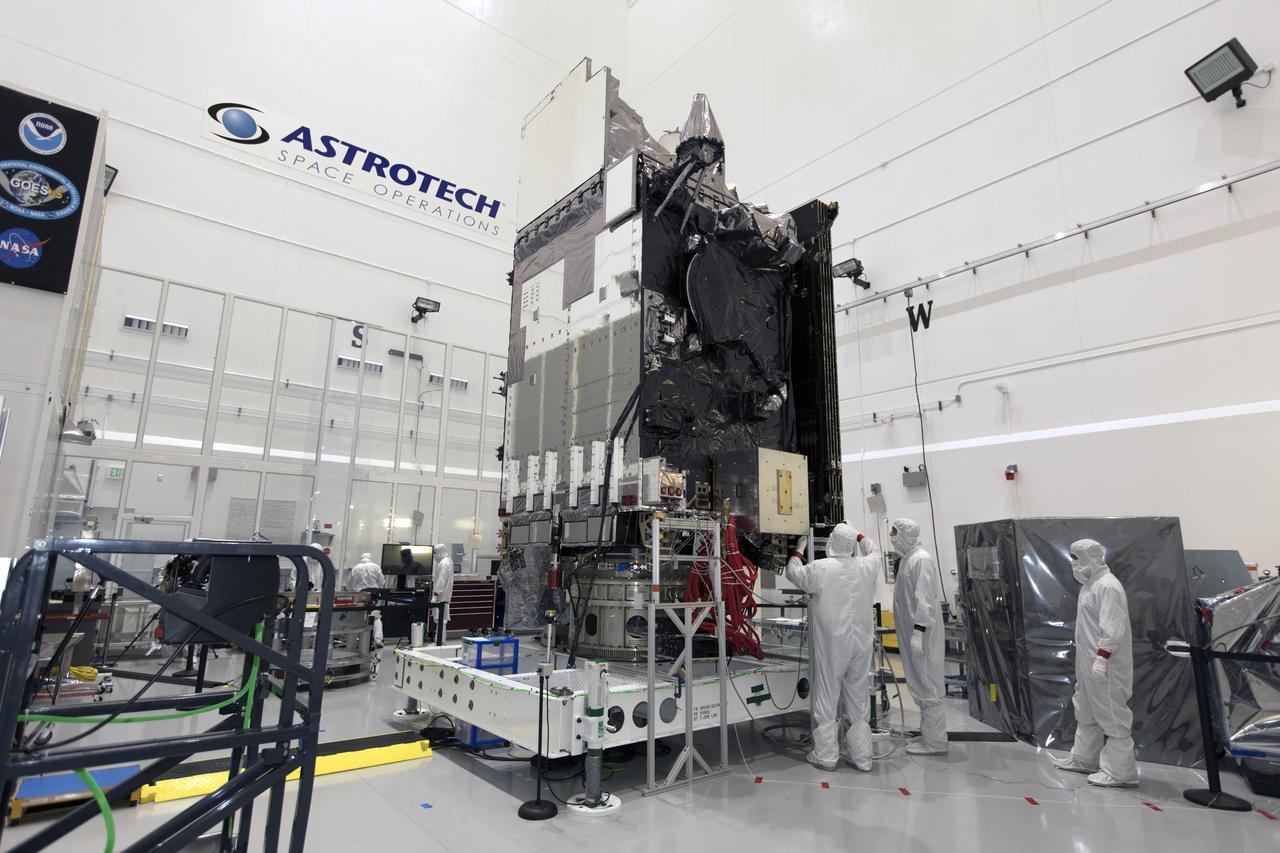

In a clean room at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers are preparing NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, for encapsulation in it payload fairing. After encapsulation, the weather satellite will be moved to Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.

In a clean room at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, is being prepared for encapsulation in it payload fairing. After encapsulation, the weather satellite will be moved to Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.

In a clean room at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, is being prepared for encapsulation in it payload fairing. After encapsulation, the weather satellite will be moved to Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
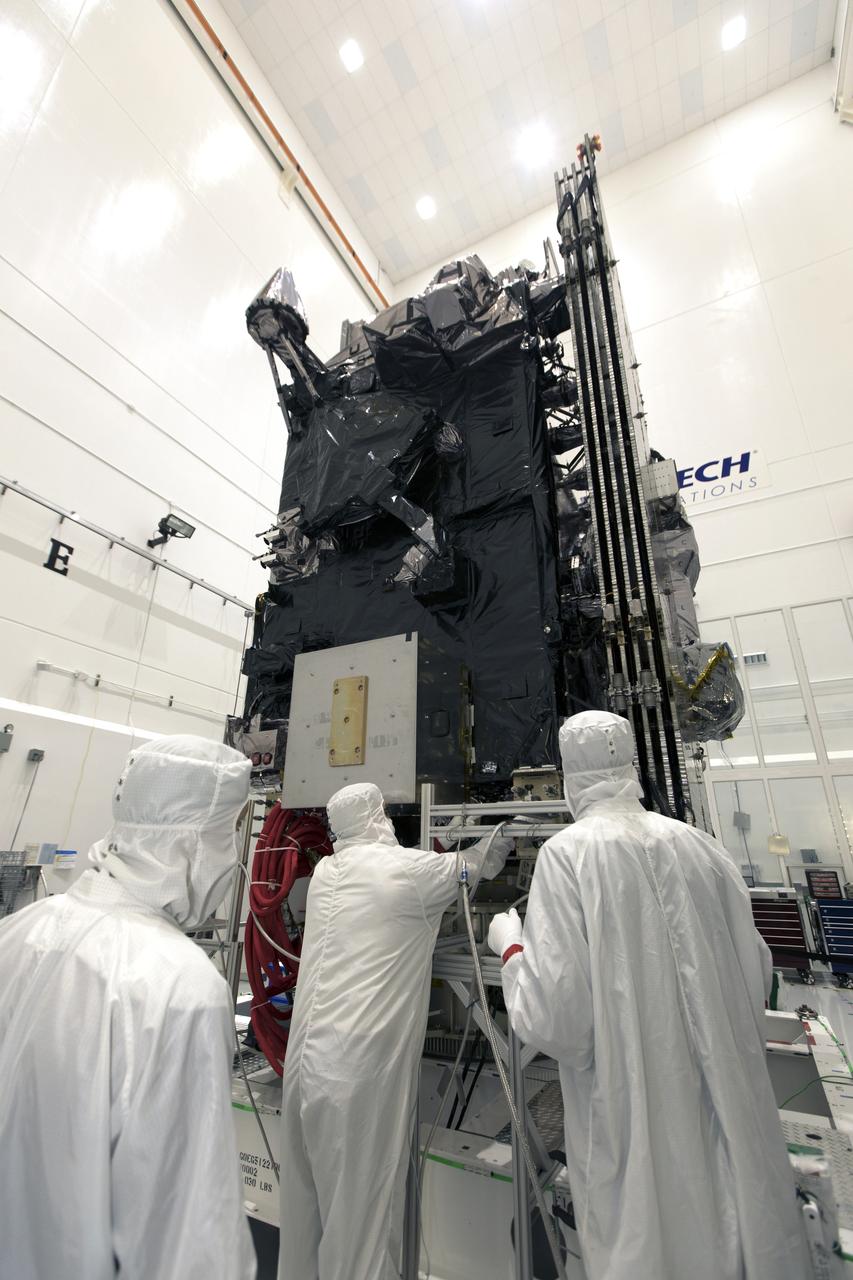

In a clean room at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers are preparing NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, for encapsulation in it payload fairing. After encapsulation, the weather satellite will be moved to Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
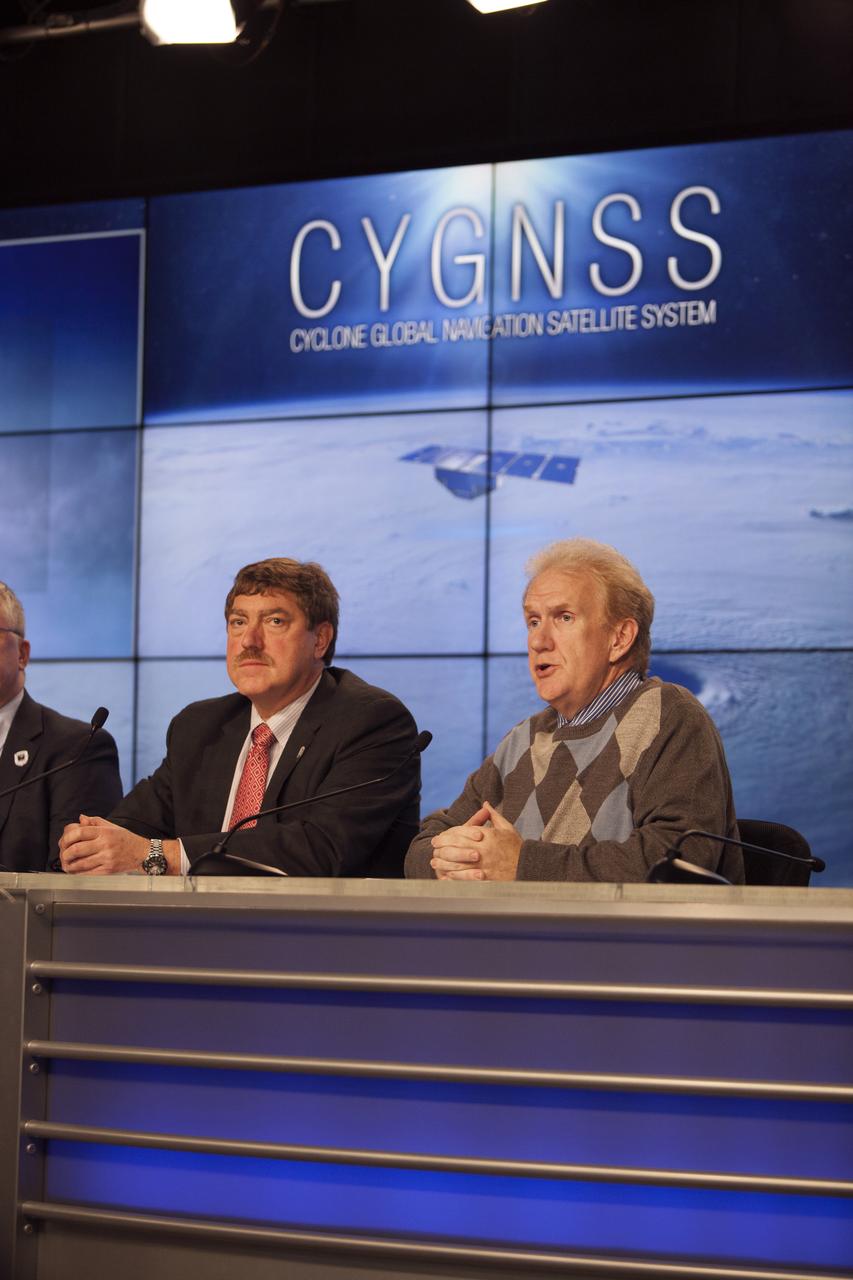

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, NASA and industry leaders speak to members of the media during a prelaunch news conference for the agency’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft. From left are: John Scherrer, CYGNSS project manager for the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio, Texas; and Mike Rehbein, launch weather officer for the 45th Weather Squadron at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. The eight CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data will help scientists probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a crucial role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
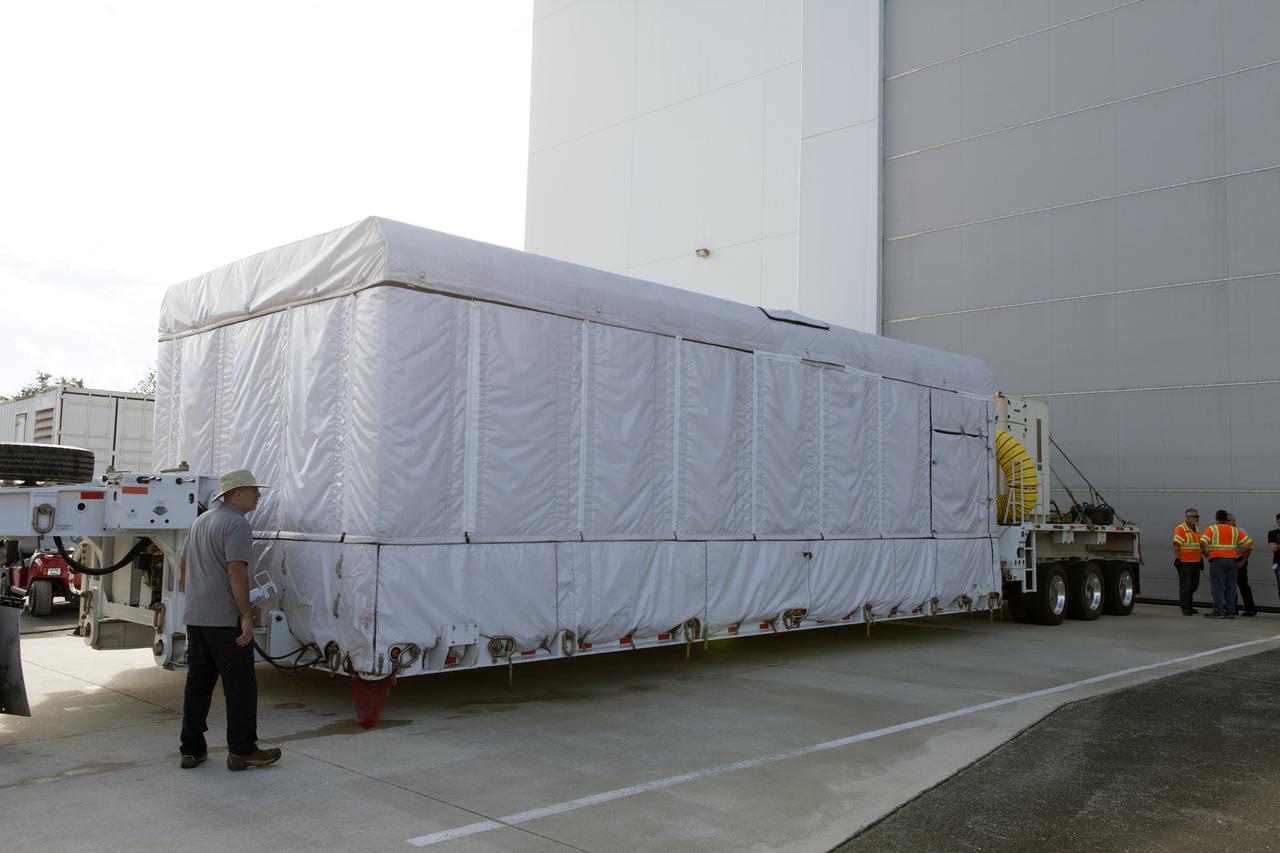

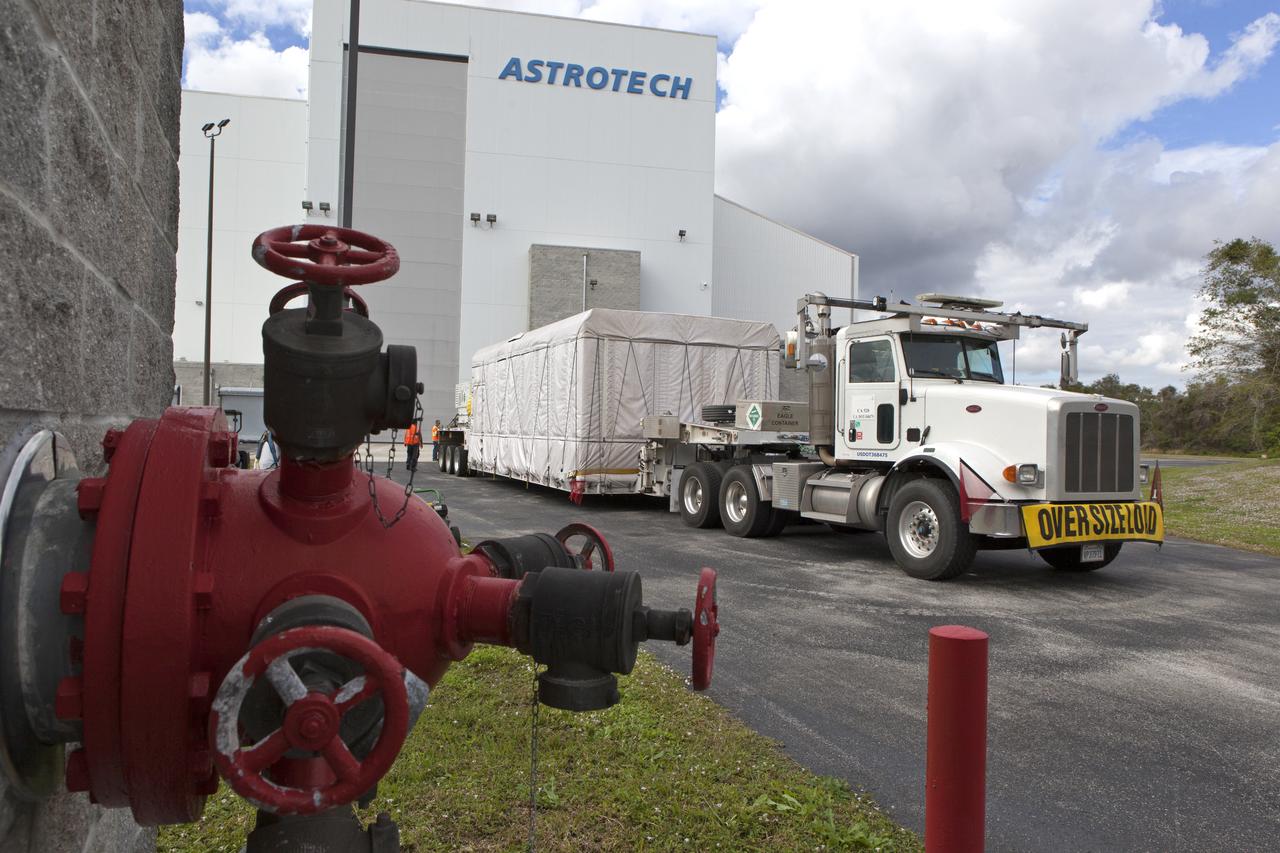
NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
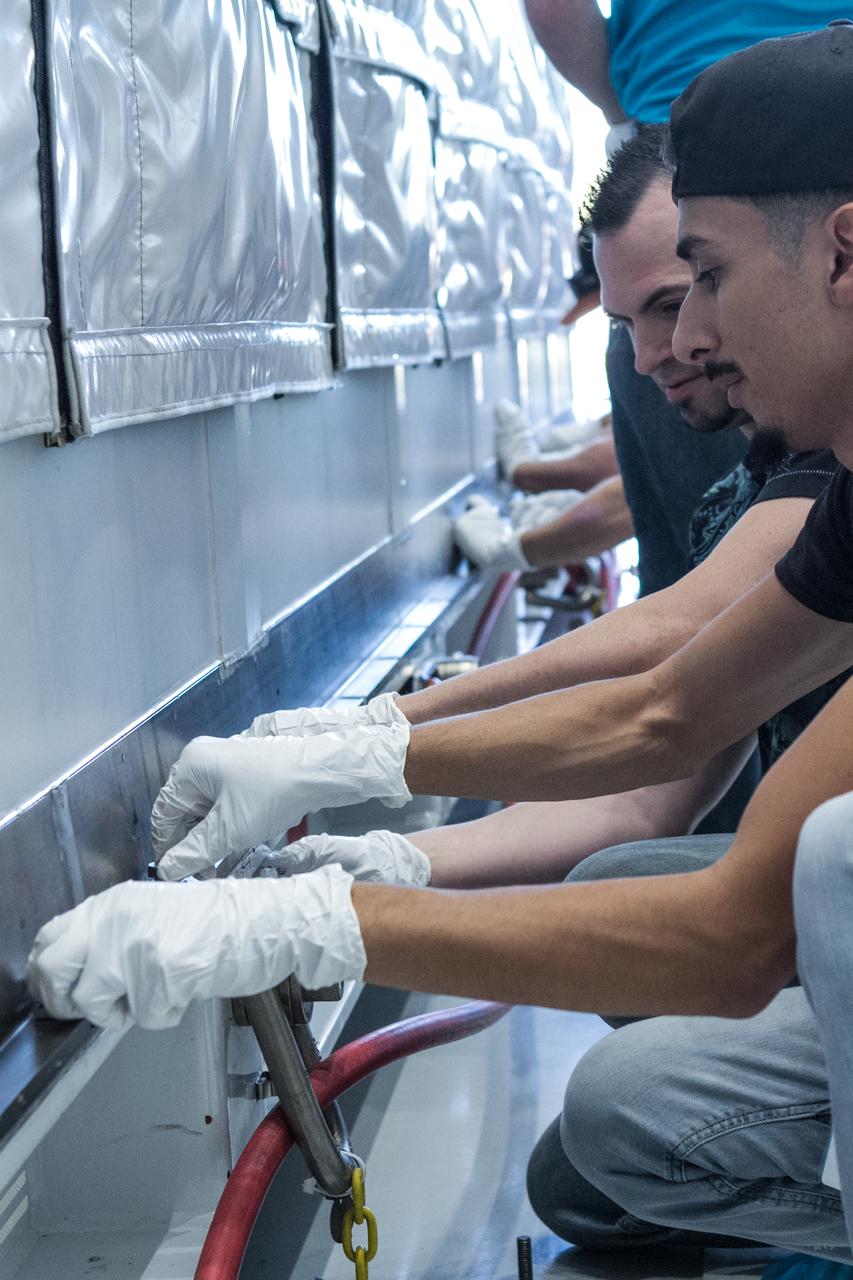

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers prepare to remove NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) from its shipping container. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers remove NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) from its shipping container. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
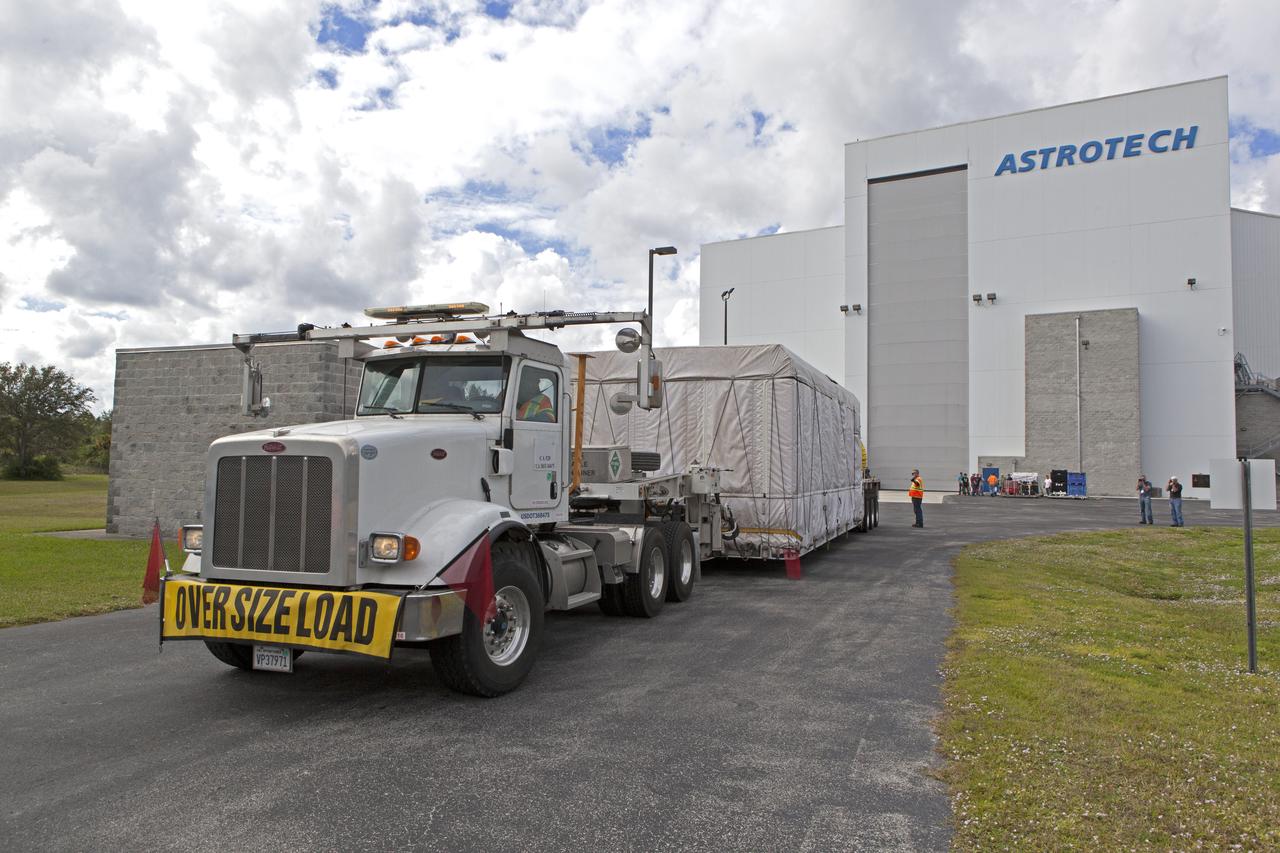

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
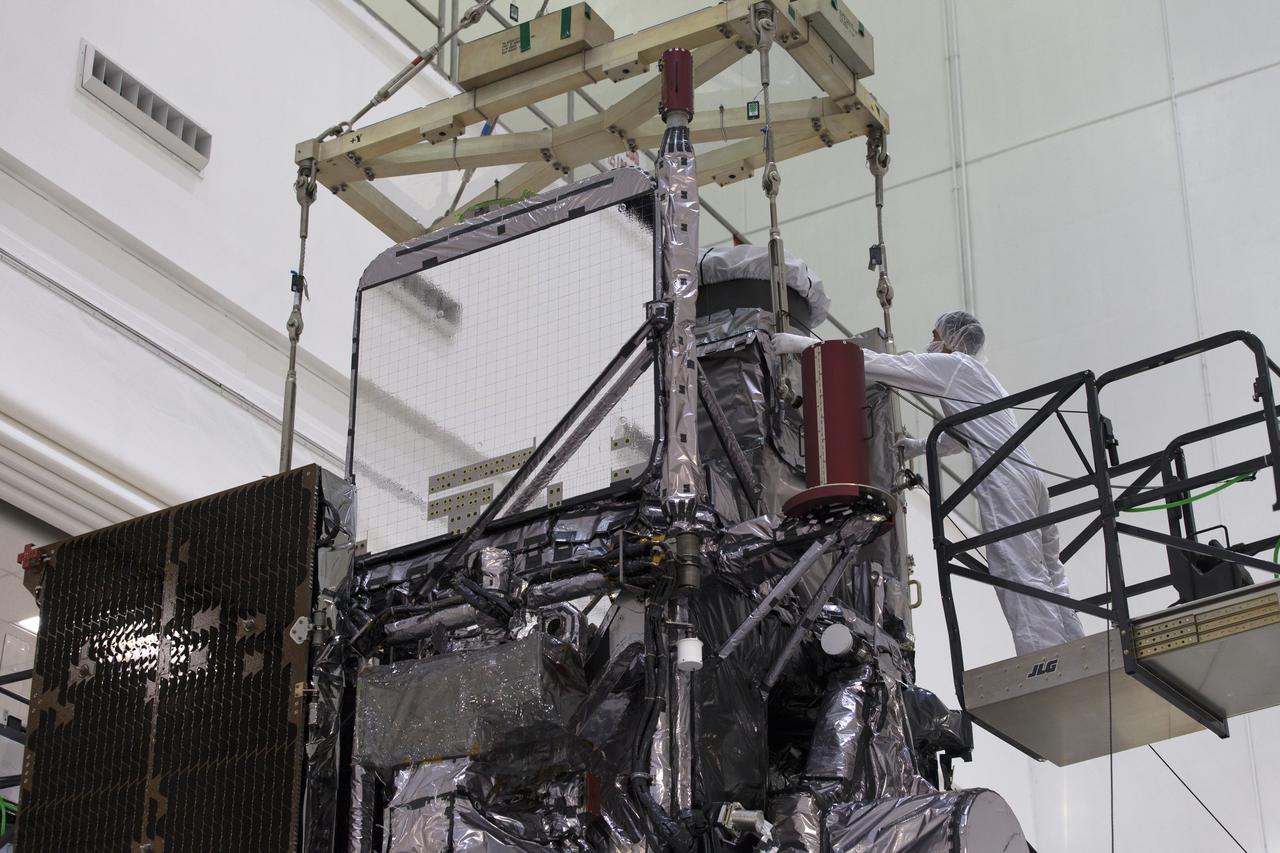

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, a technician inspects NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S). The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
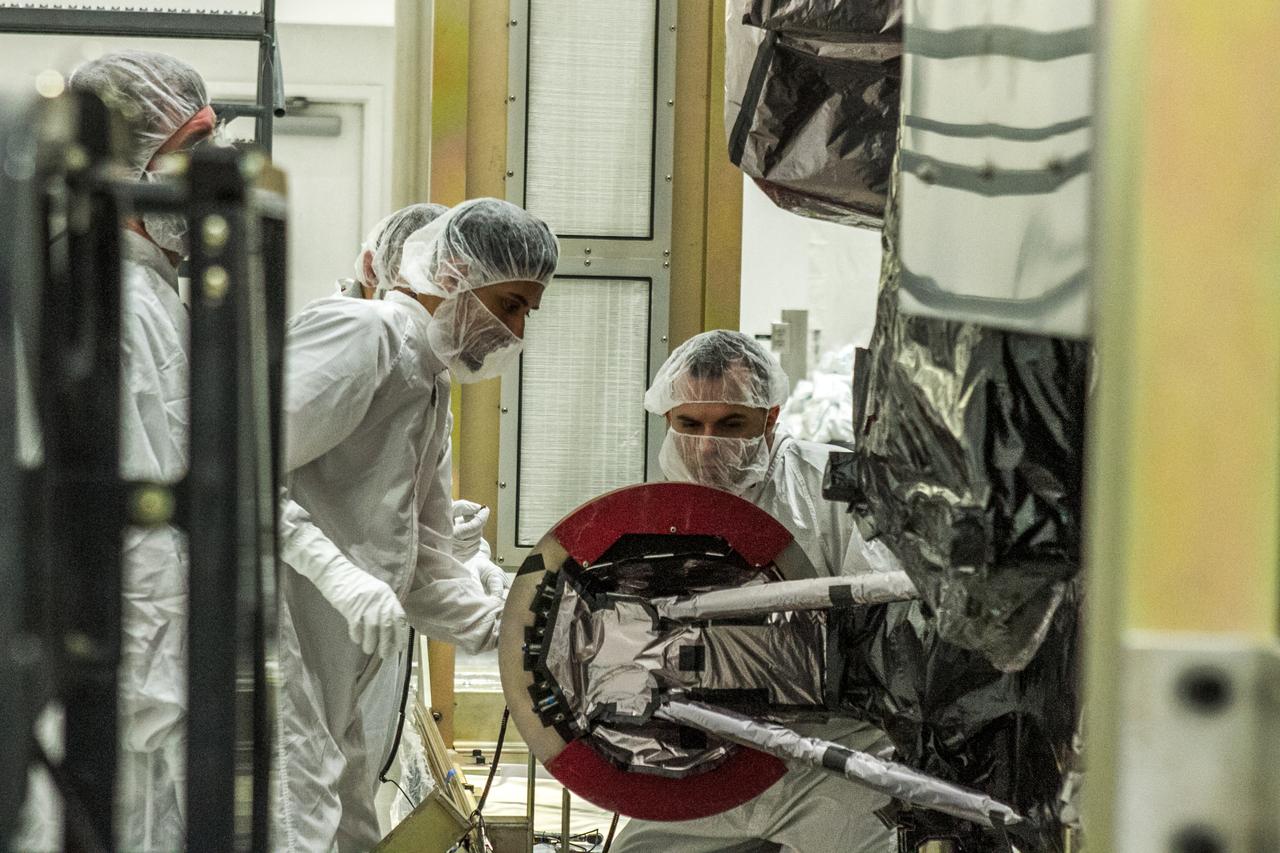

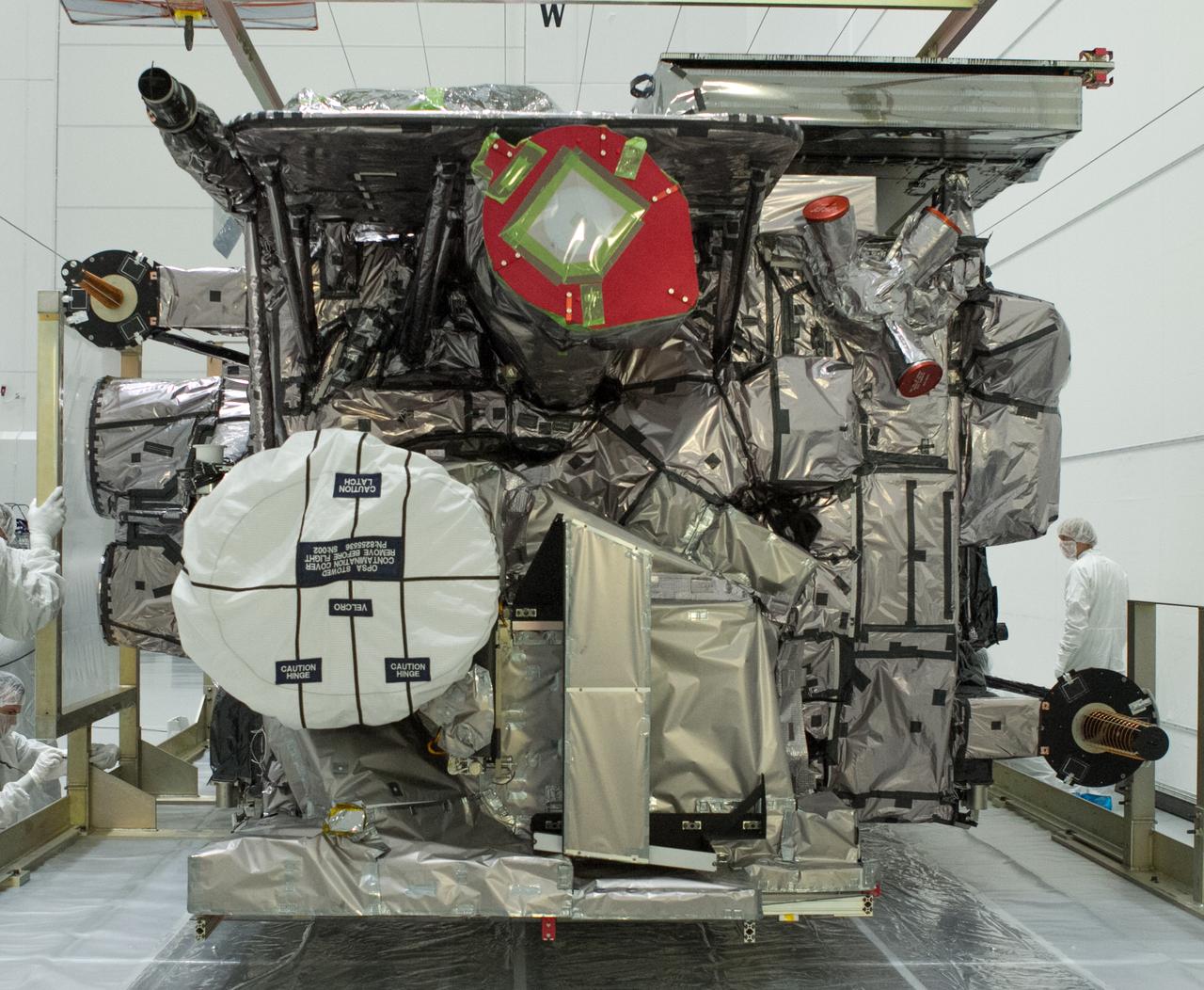
At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after removal from its shipping container. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S). The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
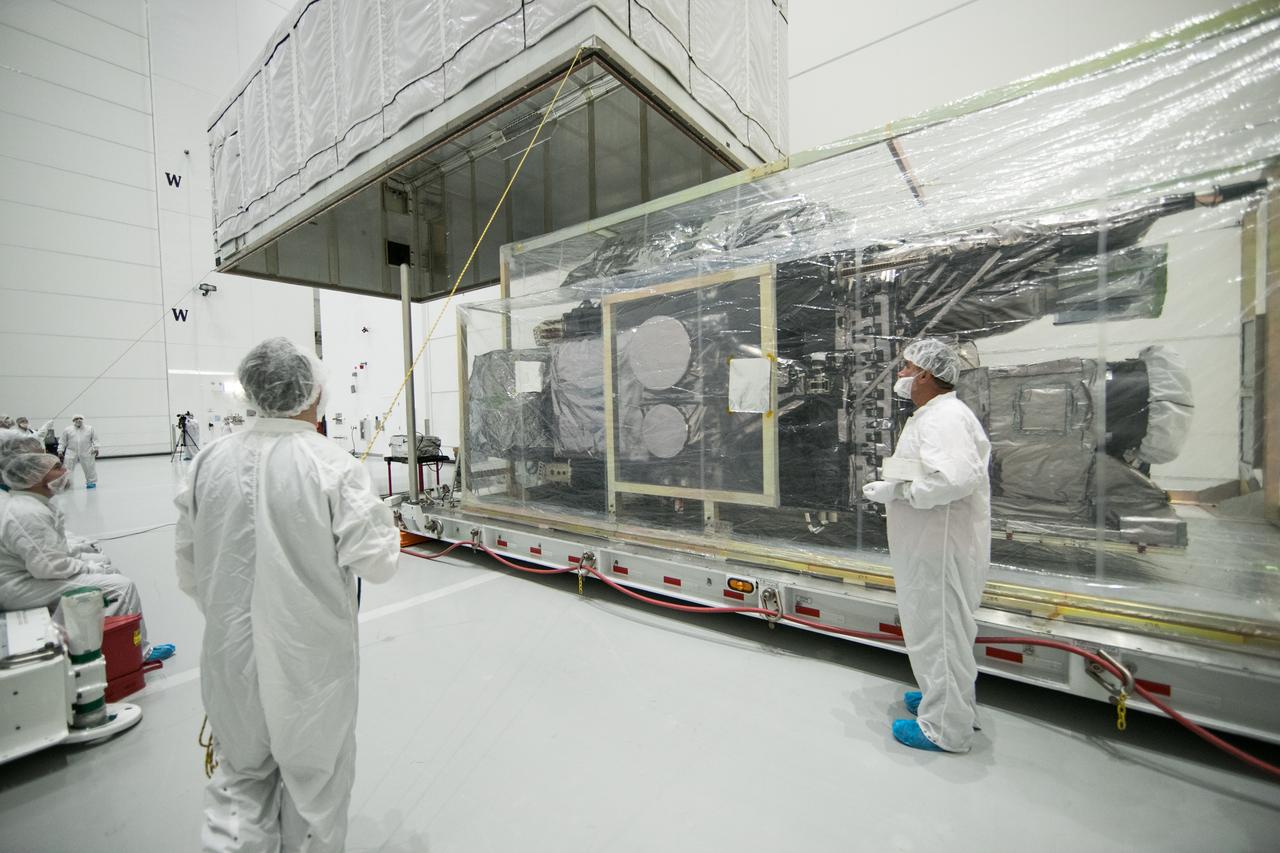

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers remove NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) from its shipping container. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
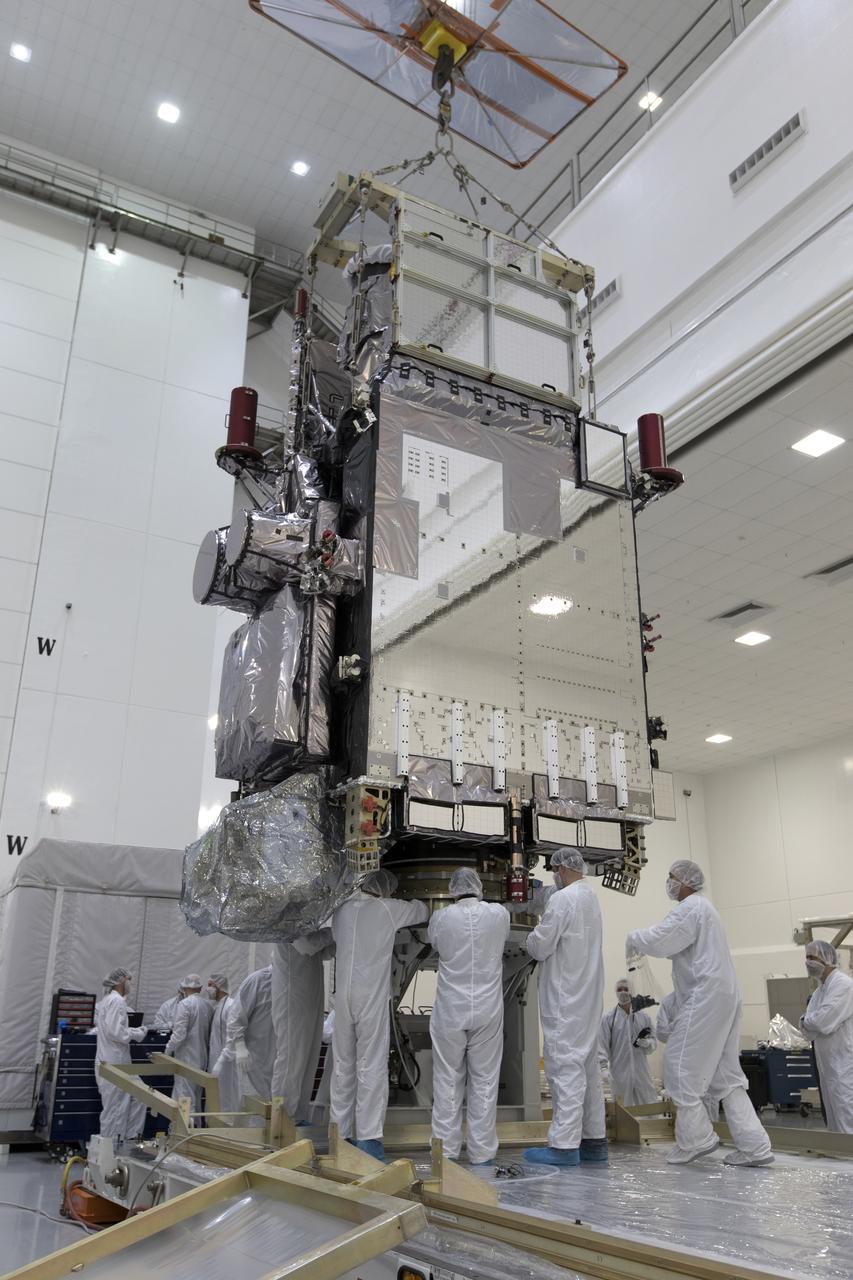

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S). The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

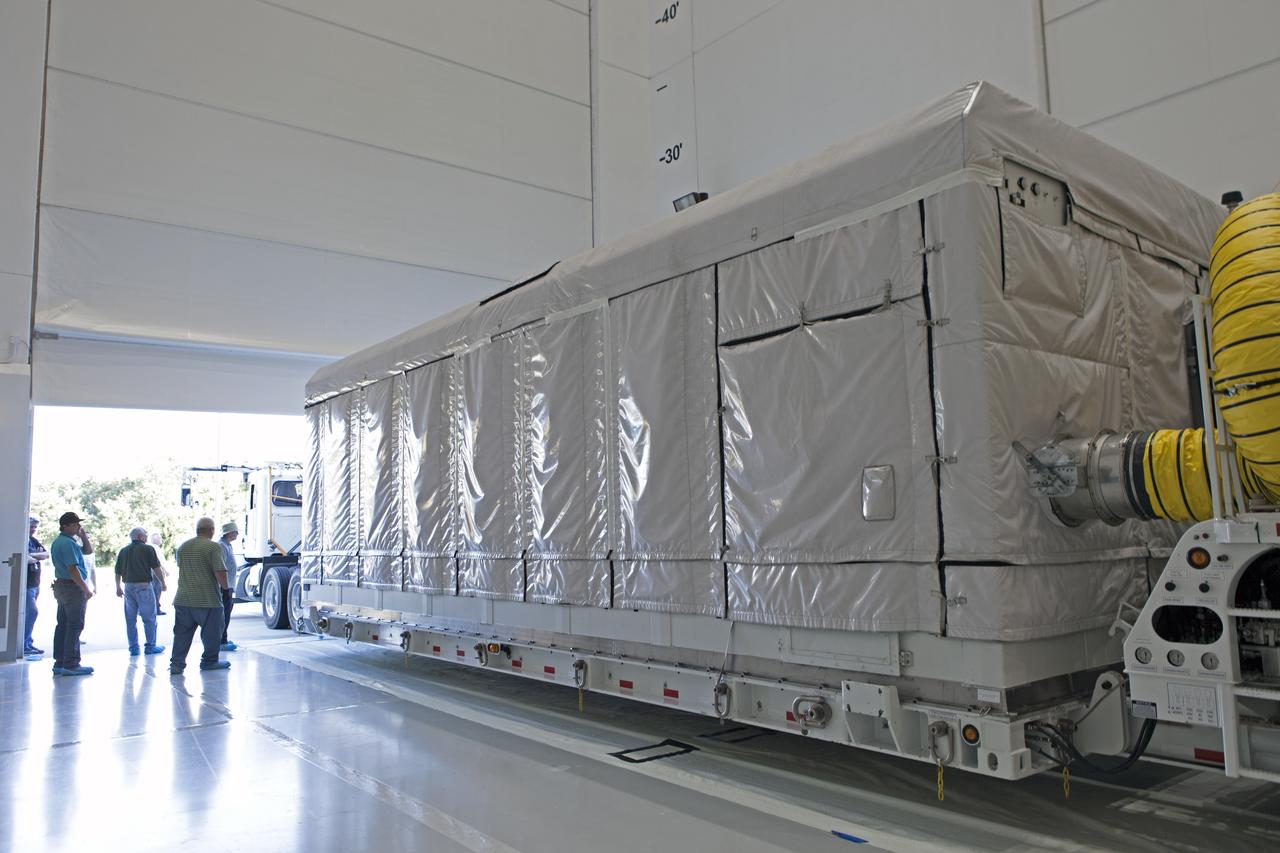
At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been removed from its shipping container. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
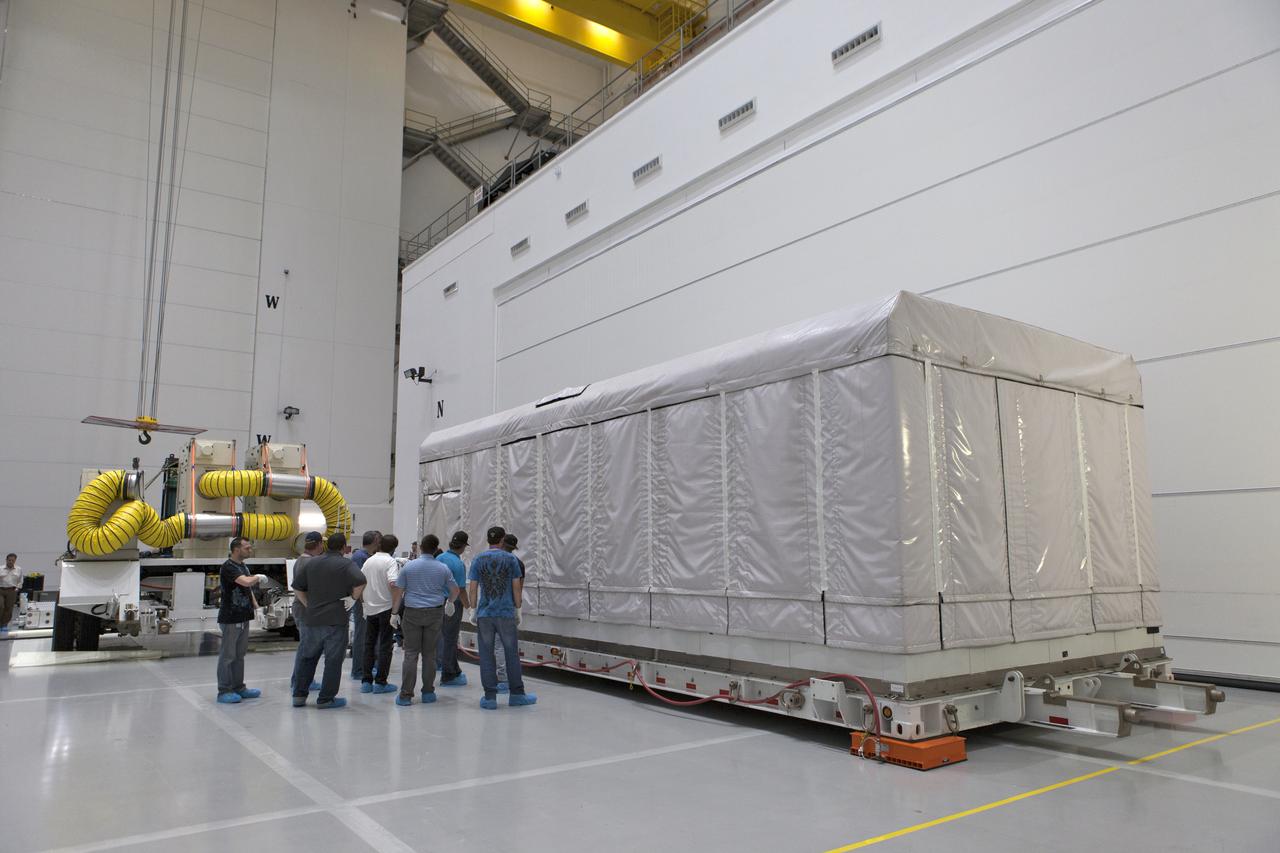

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives inside Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
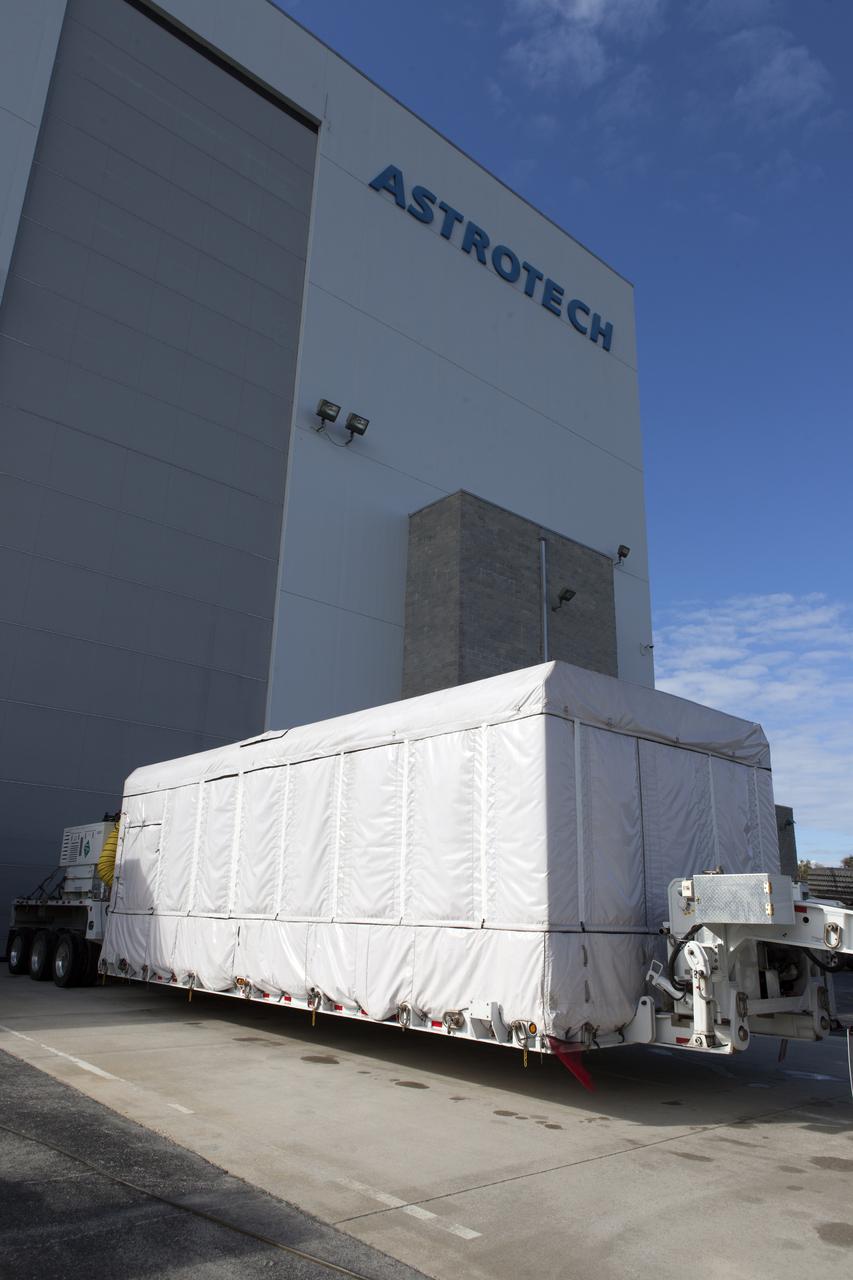

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
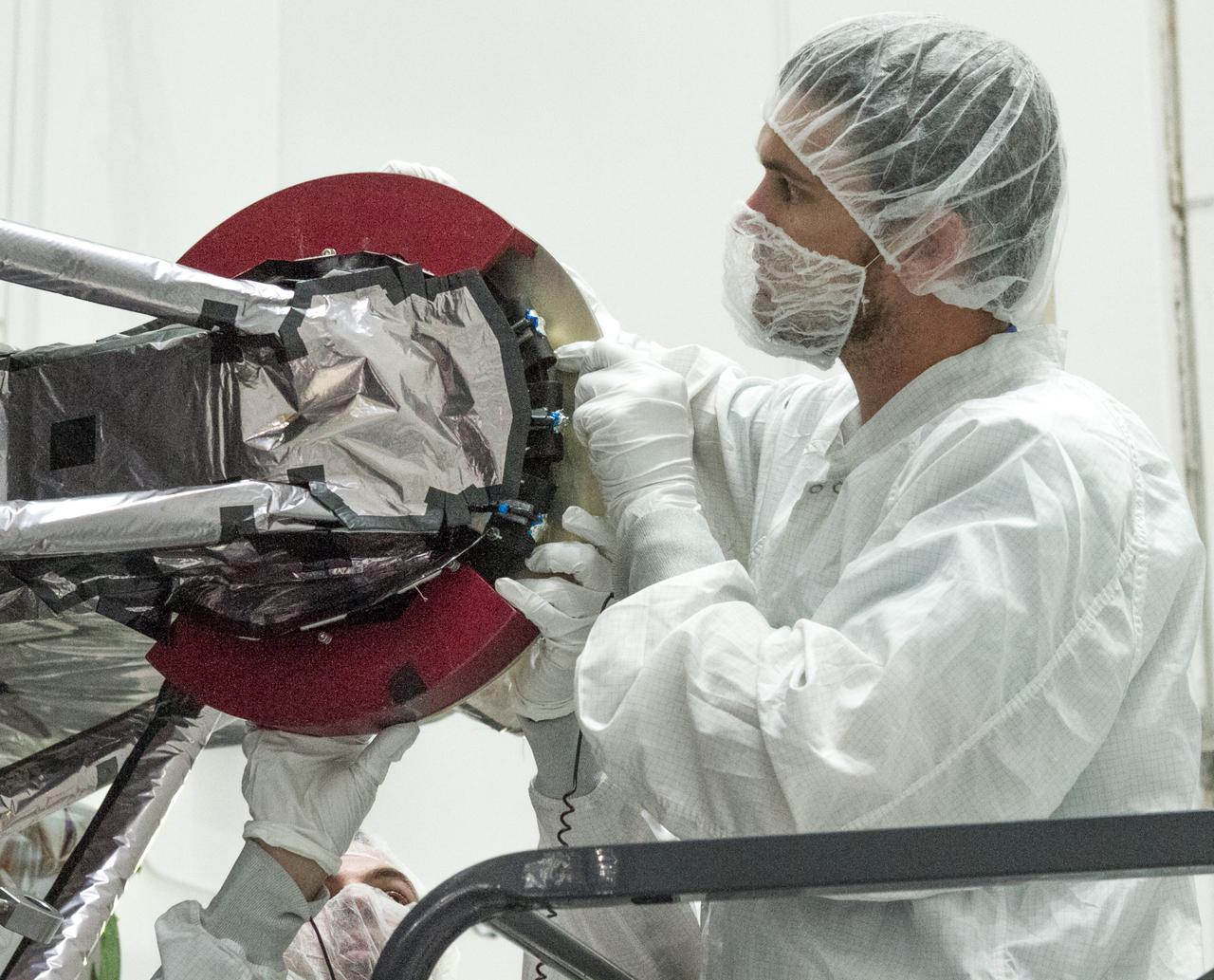

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after removal from its shipping container. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
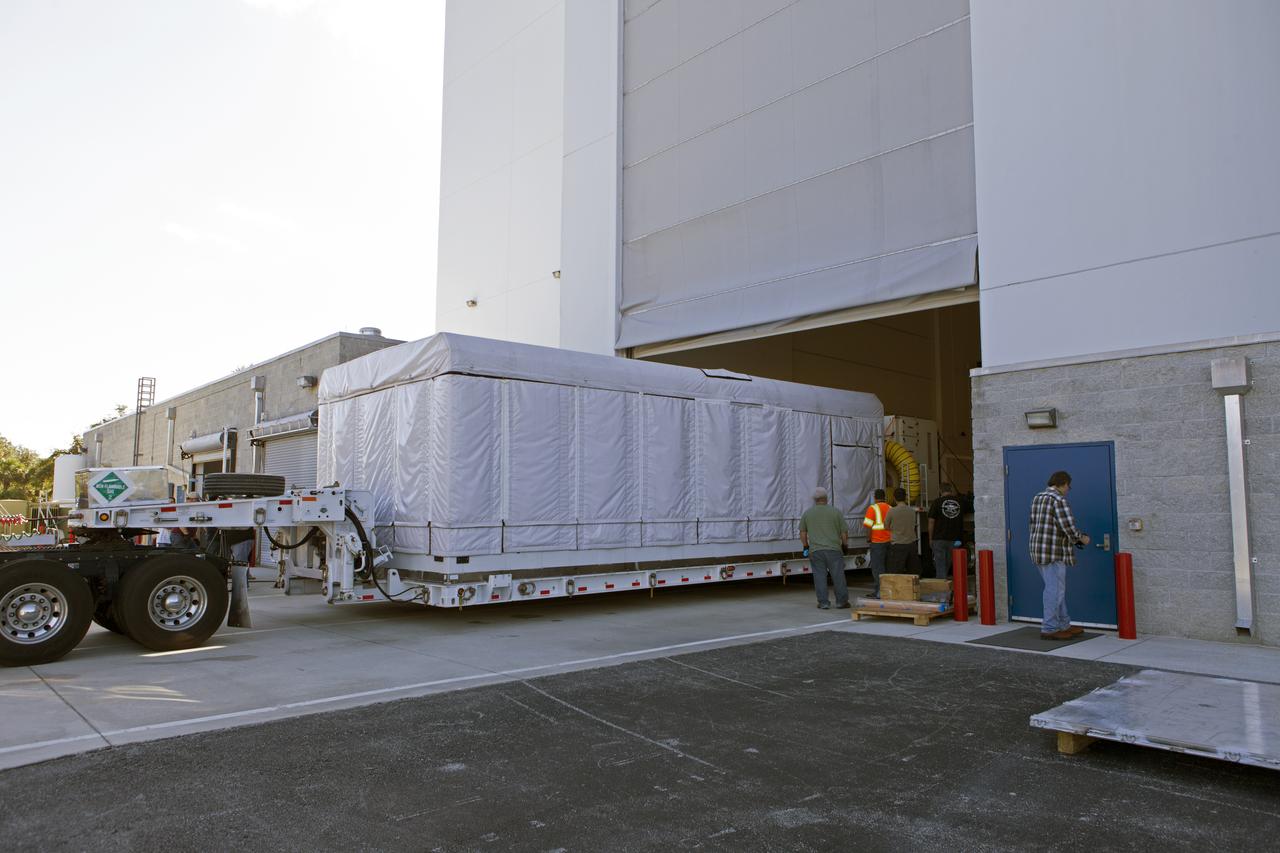

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after removal from its shipping container. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
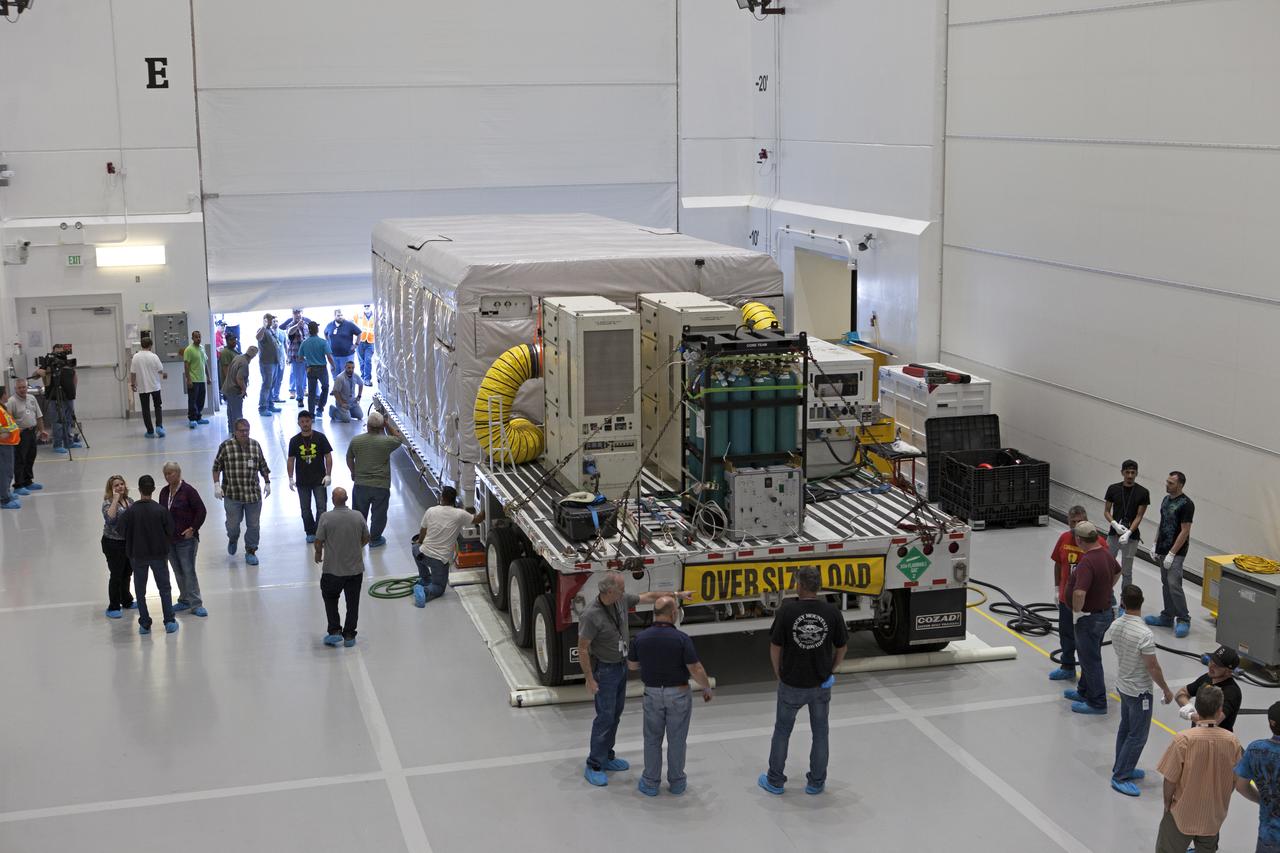

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives inside Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
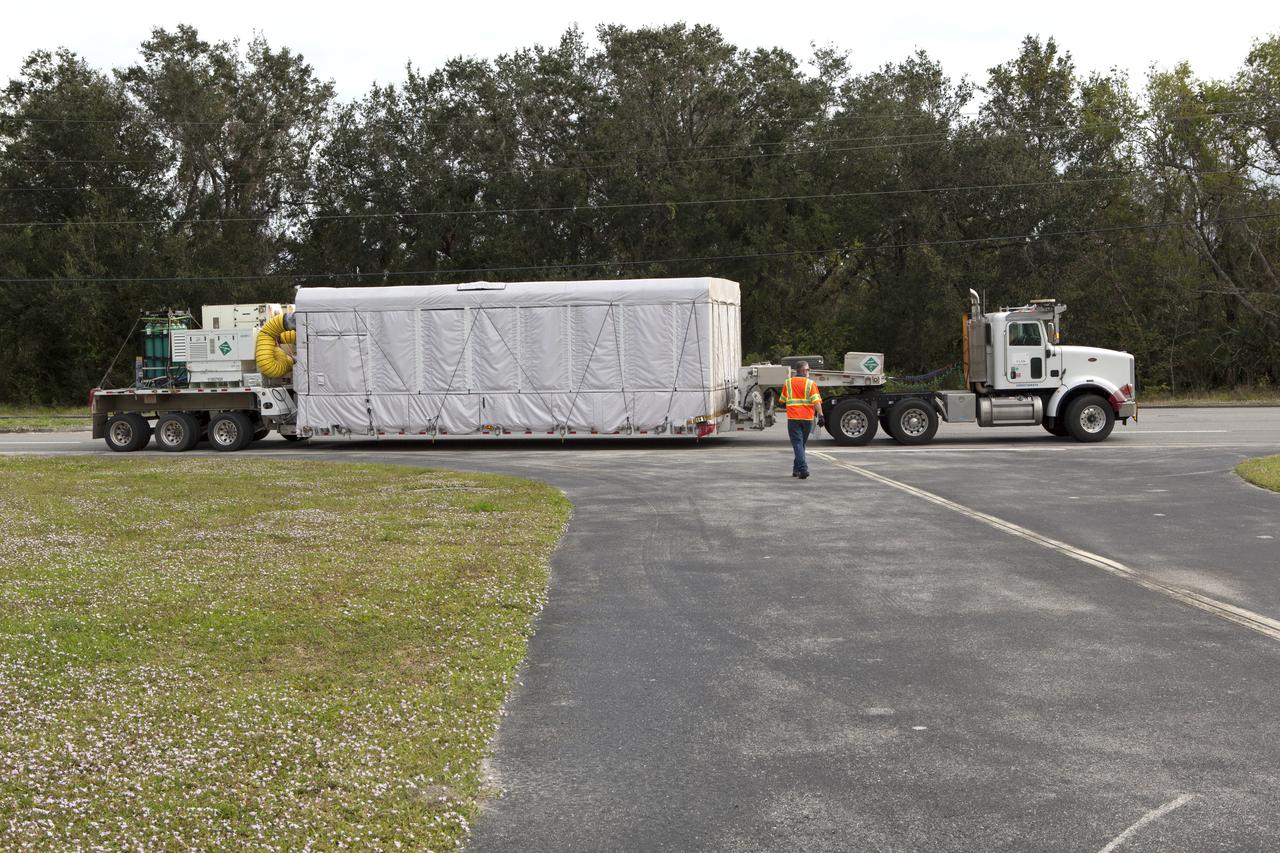

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
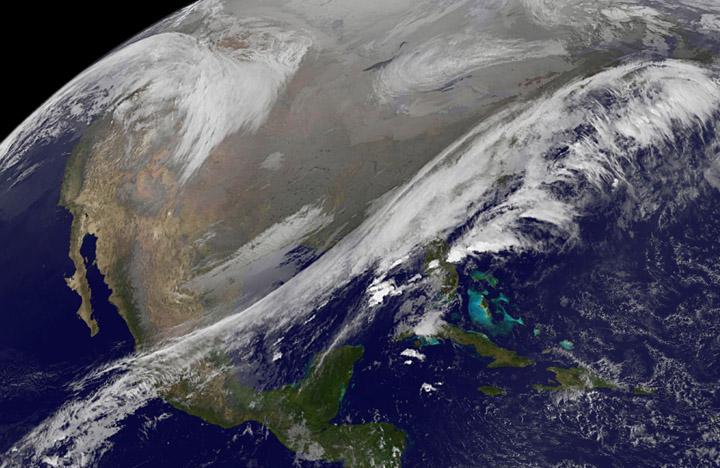

This NOAA's GOES satellite infrared image taken on Nov. 25 at 11:45 UTC (6:45 a.m. EST) shows two main weather systems over the U.S. Credit: NASA/NOAA GOES Project As the U.S. Thanksgiving holiday approaches this Thursday, November 27, NOAA's GOES-East and GOES-West satellites are keeping a weather eye out for storms that may affect early travelers. In an image from Nov. 25, the satellites show an active weather pattern is in place for travelers across the central and eastern U.S. NOAA's GOES-East satellite provides visible and infrared images over the eastern U.S. and the Atlantic Ocean, while NOAA's GOES-West satellite covers the western U.S. and Pacific Ocean from its fixed orbit in space. Data from both satellites were combined at NASA's GOES Project to create a full view of the U.S. on Nov. 25 at 11:45 UTC (6:45 a.m. EST). The image shows clouds associated with cold front stretching from the Gulf of Mexico over northern Florida and along the U.S. East coast to eastern Canada. Clouds associated with another area of low pressure are in the northern Rockies and northwestern U.S. To create the image, NASA/NOAA's GOES Project takes the cloud data from NOAA's GOES-East satellite and overlays it on a true-color image of land and ocean created by data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS, instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites. Together, those data created the entire picture of the storm and show its movement. After the storm system passes, the snow on the ground becomes visible. NOAA's National Weather Service Weather Prediction Center said "a storm system will develop off the coast of the Carolinas early Wednesday (Nov. 25) and strengthen as it moves rapidly up the East Coast Wednesday into early Thursday (Nov. 26). Heavy snow is likely to begin in the central Appalachians early Wednesday morning, spreading northeast through the interior Mid-Atlantic into New England by Wednesday night. Winter Storm Watches are in effect for these areas." For travelers in the western U.S., the Northern Rocky Mountains are expected to receive more snow from the north side of a stationary frontal boundary. South of the boundary rain showers will affect the lower valley. The National Weather Service calls for cold weather to continue in the northern Plains and Upper Midwest as a Canadian surface high pressure rules the weather. The U.S. Southwest will experience nice weather for mid-week. In the Pacific Northwest, the National Weather Service noted that a warm front will bring rain, heavy at times, to the Cascades today and tonight. There will be a break in the heavier rains on Wednesday, then another period of heavy rain for the Cascades Wednesday night through Friday morning as a cold front slowly drags through the area. NOAA's GOES satellites provide the kind of continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. Geostationary describes an orbit in which a satellite is always in the same position with respect to the rotating Earth. This allows GOES to hover continuously over one position on Earth's surface, appearing stationary. As a result, GOES provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric triggers for severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes.

The mission insignia of NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) mission is pictured in front of the satellite in a vertical position on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
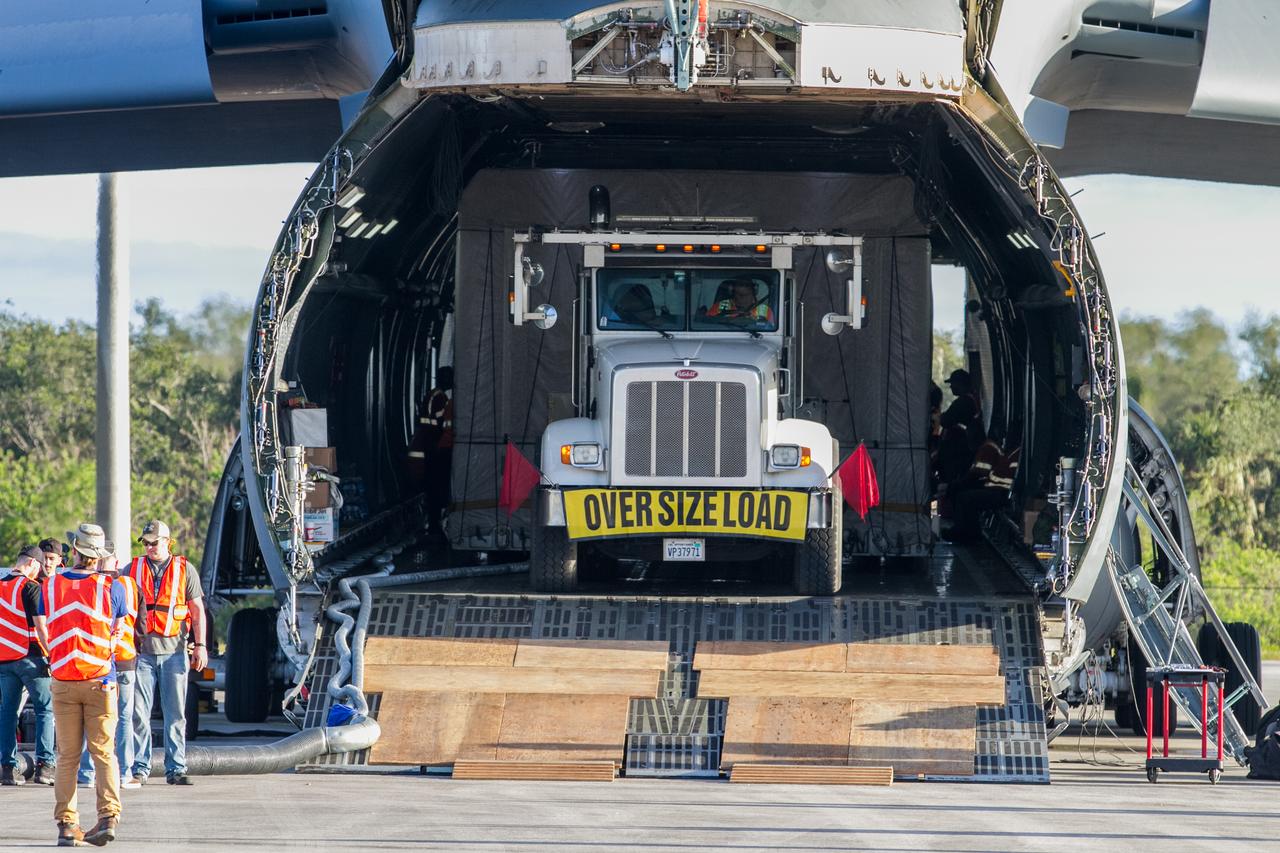

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
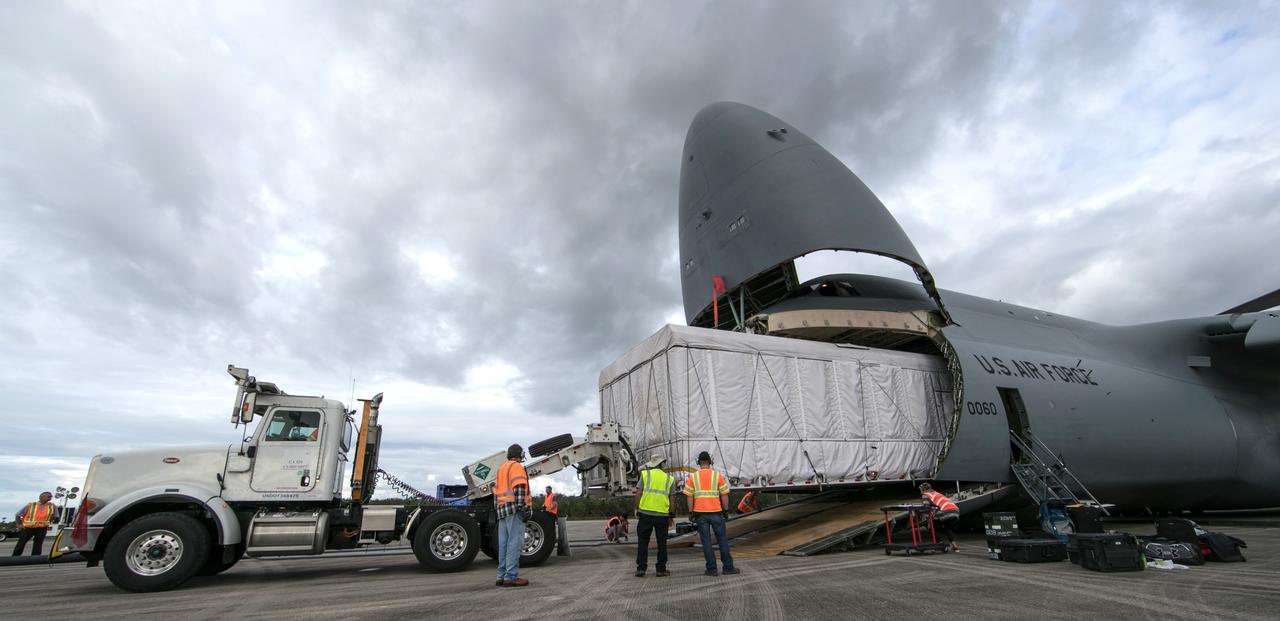

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
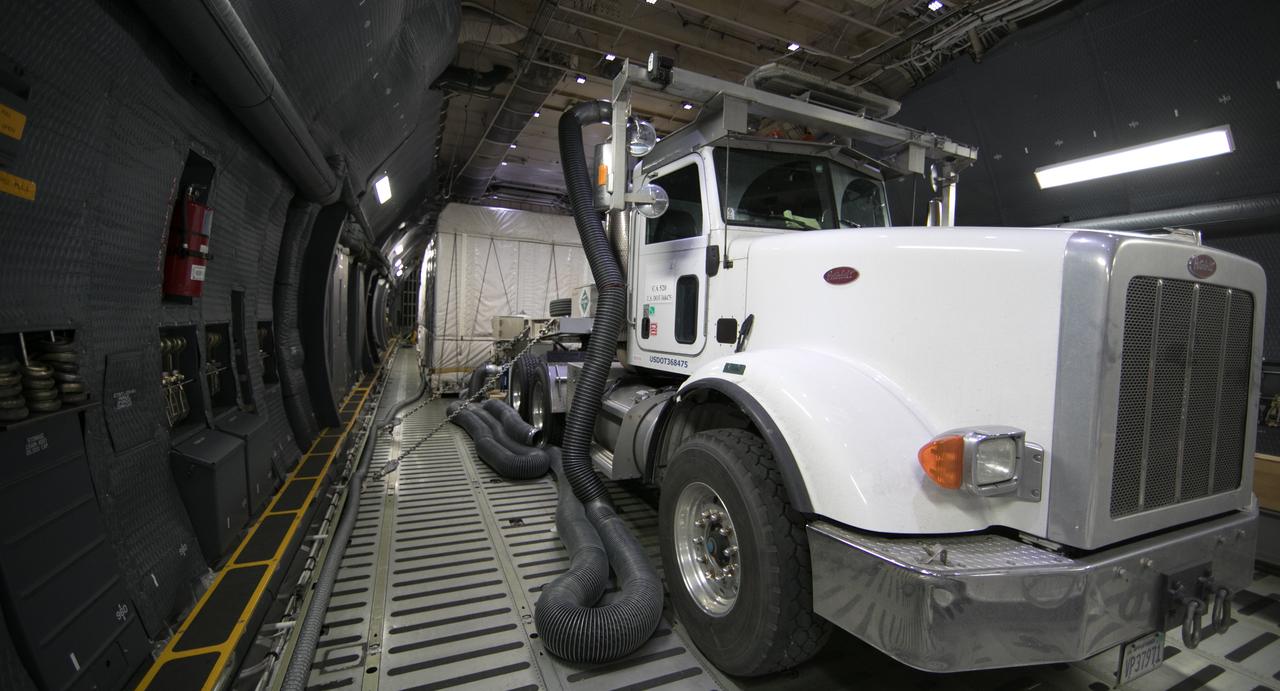

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
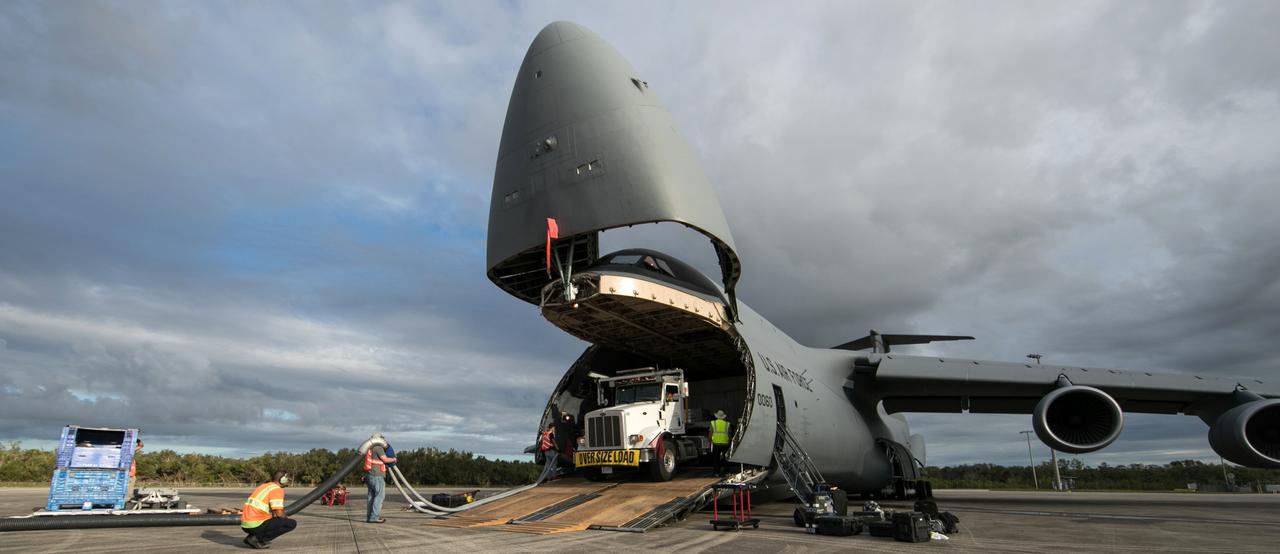

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
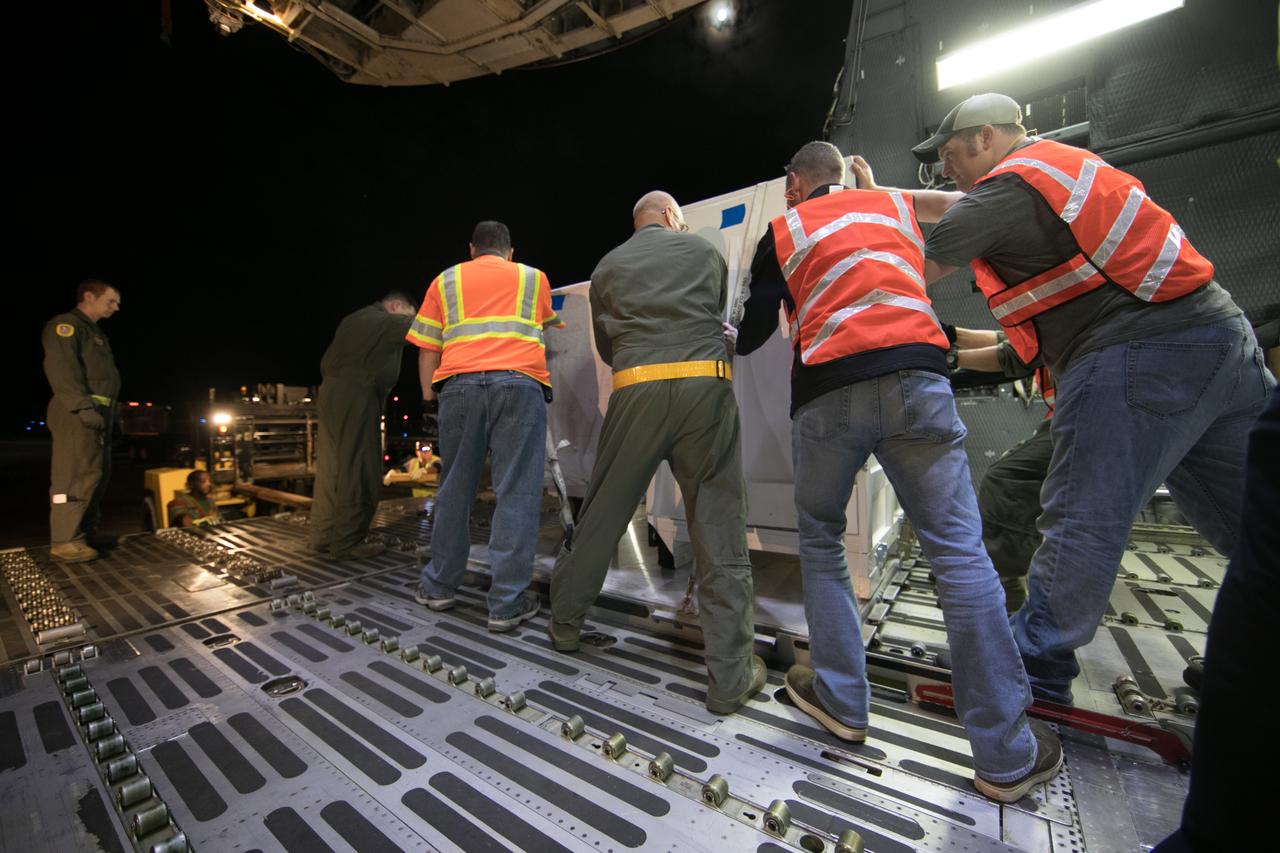

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
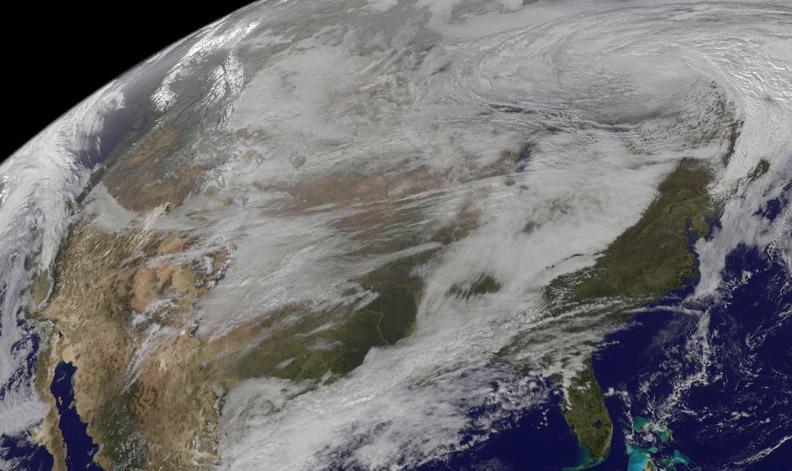

On Nov. 12, NOAA's GOES satellite showed the storm system that brought wintry weather entire U.S. centered near Ontario, Canada. Snow is visible in the U.S. and Canadian Rockies. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/new-satellite-movie-shows-us-pre-winter-wintry-outbreak/#.VGPP8t6FxgP" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/new-satellite-movie-shows-us...</a> Image Credit: NASA/NOAA GOES Project
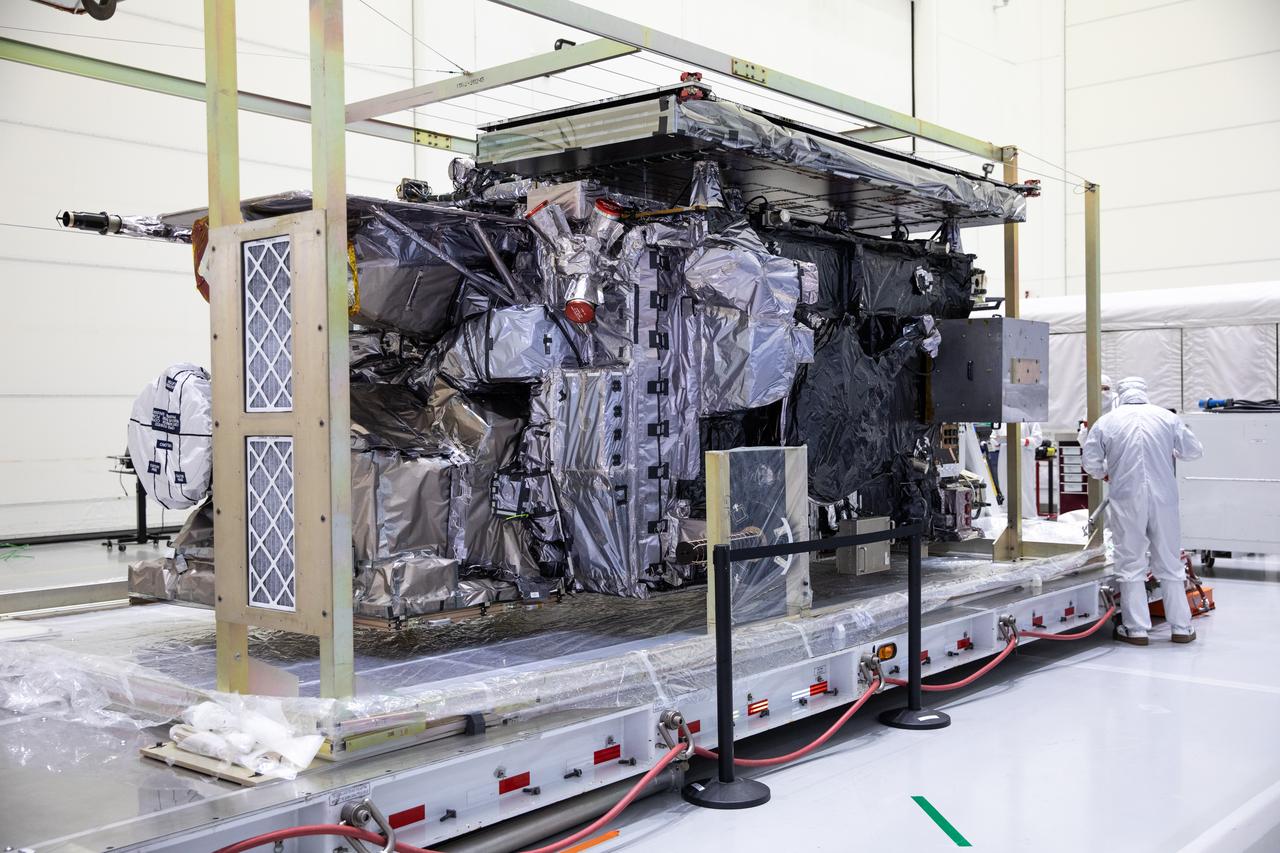

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is uncrated for prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the final in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
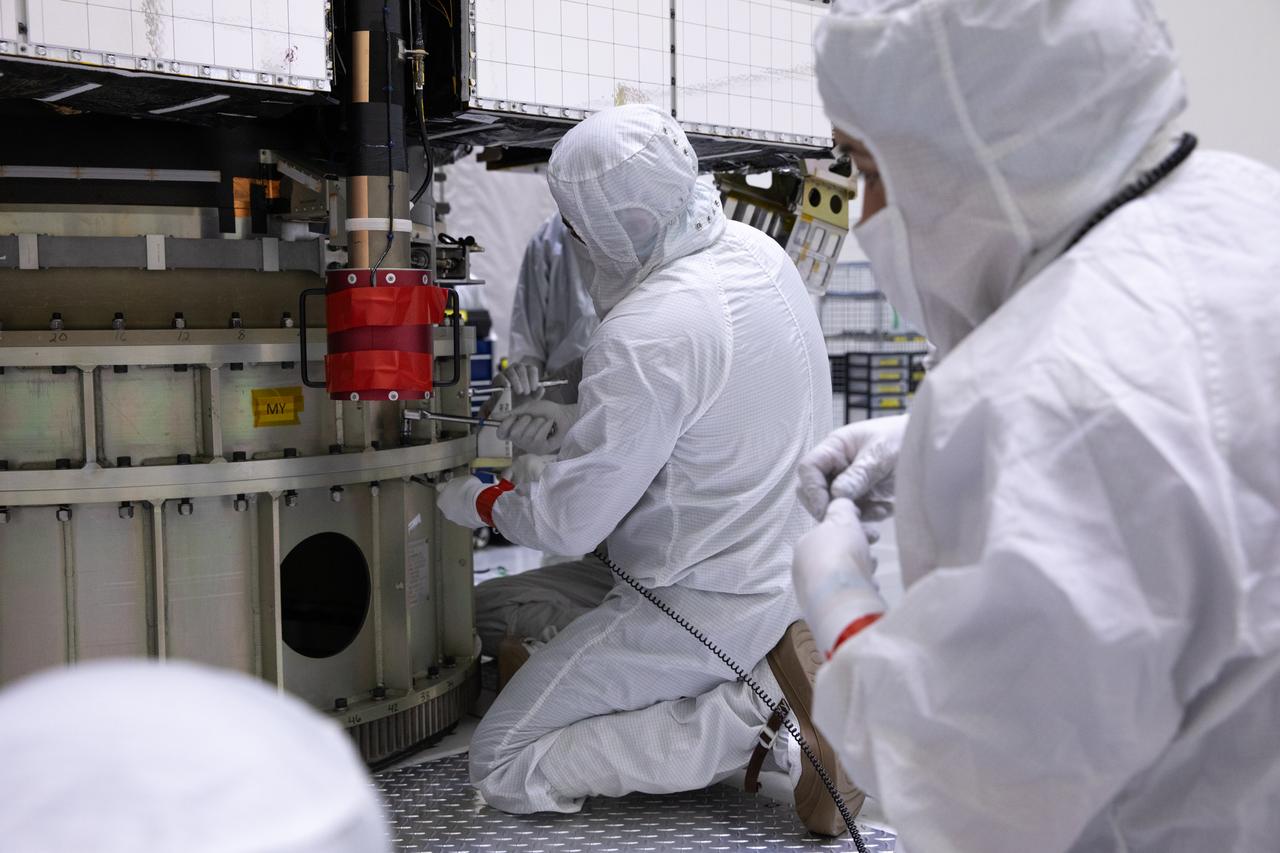

Technicians monitor movement and guide NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) as a crane hoists it on to a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
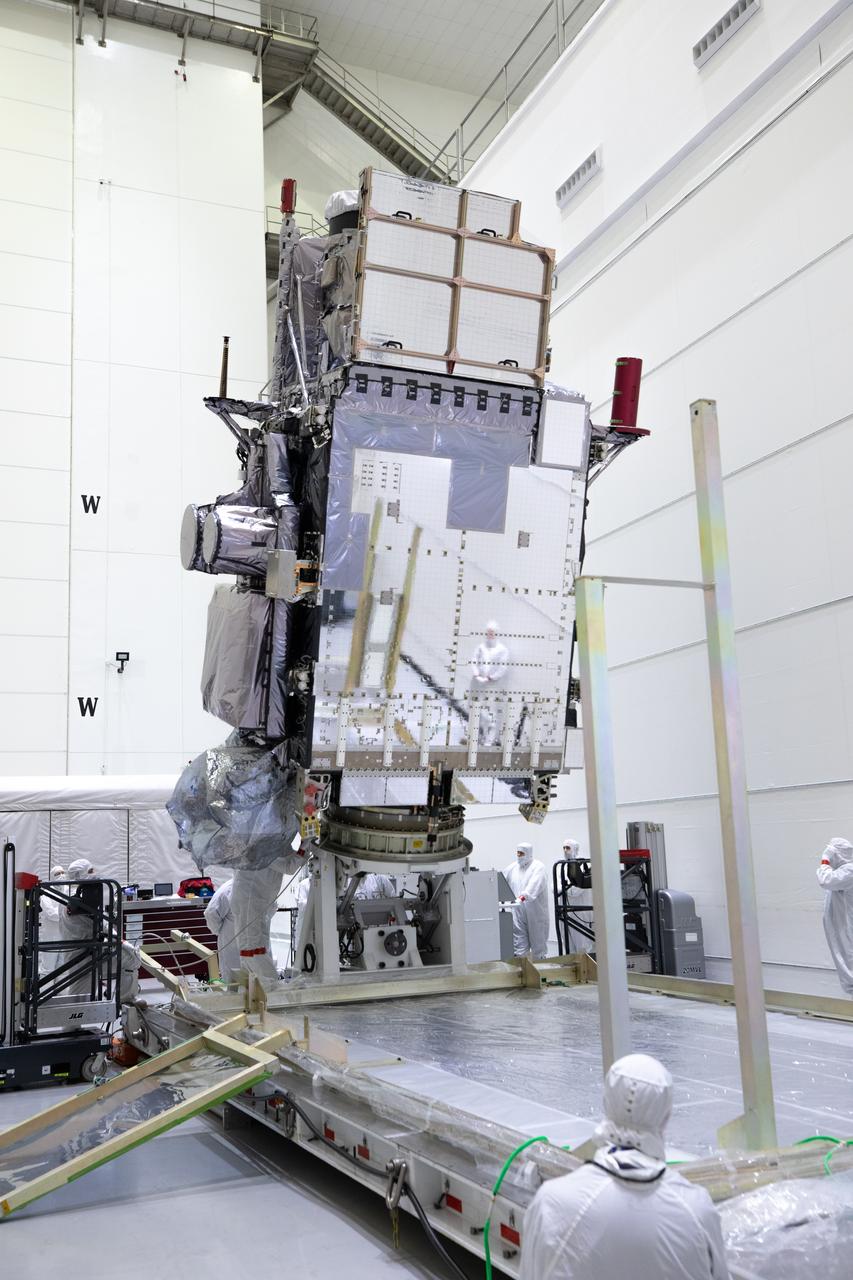

Technicians prepare to rotate NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) vertical after being uncrated on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
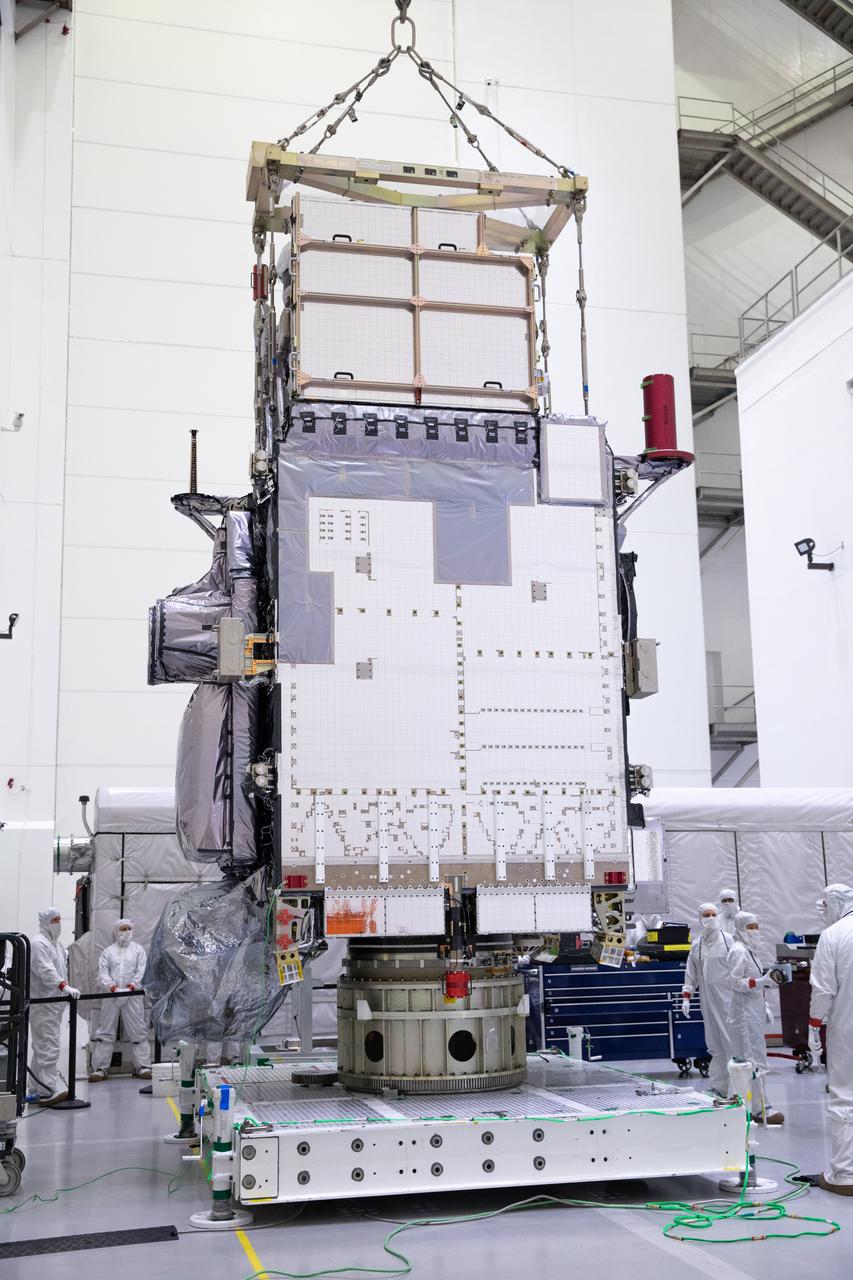
Technicians monitor movement and guide NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) as a crane hoists it on to a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
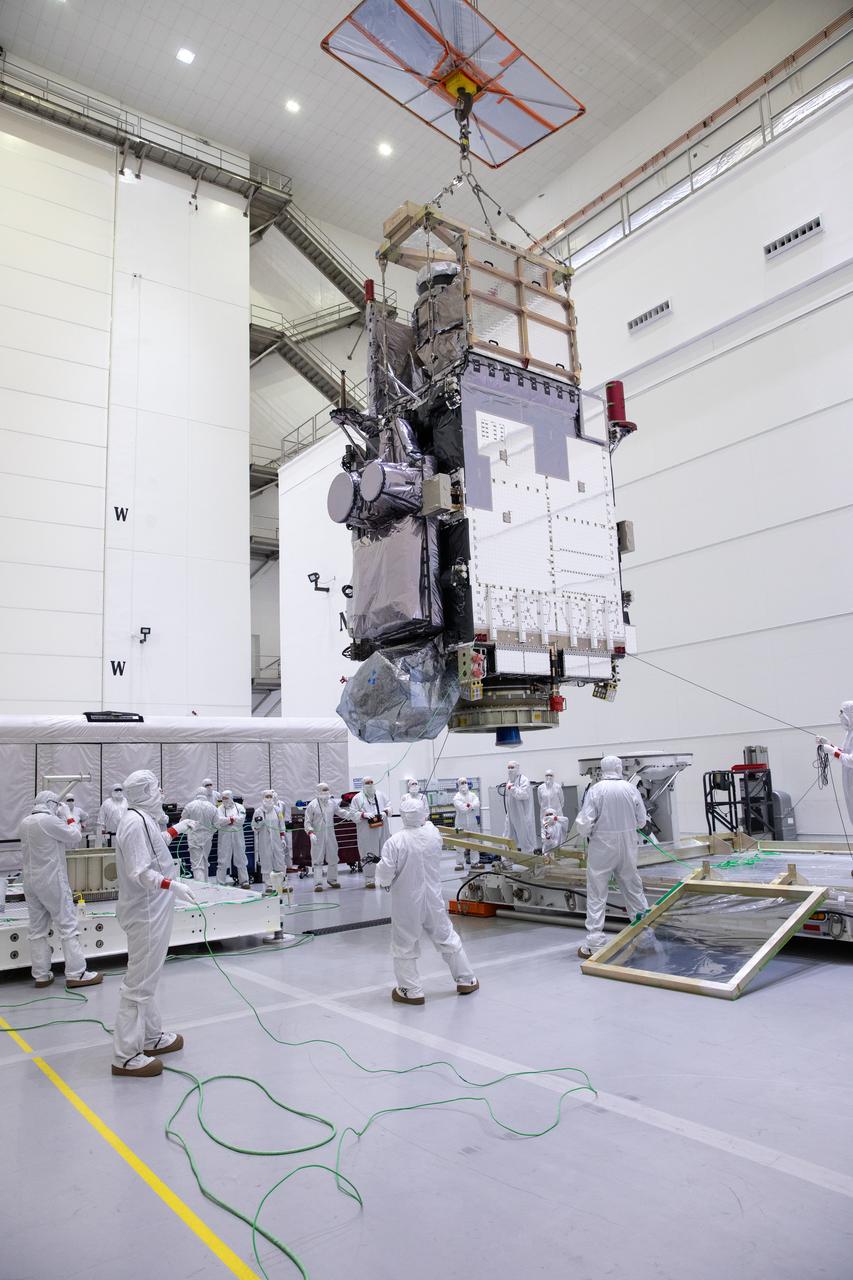

Technicians monitor movement as a crane hoists NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) after being uncrated and rotated into a vertical position on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
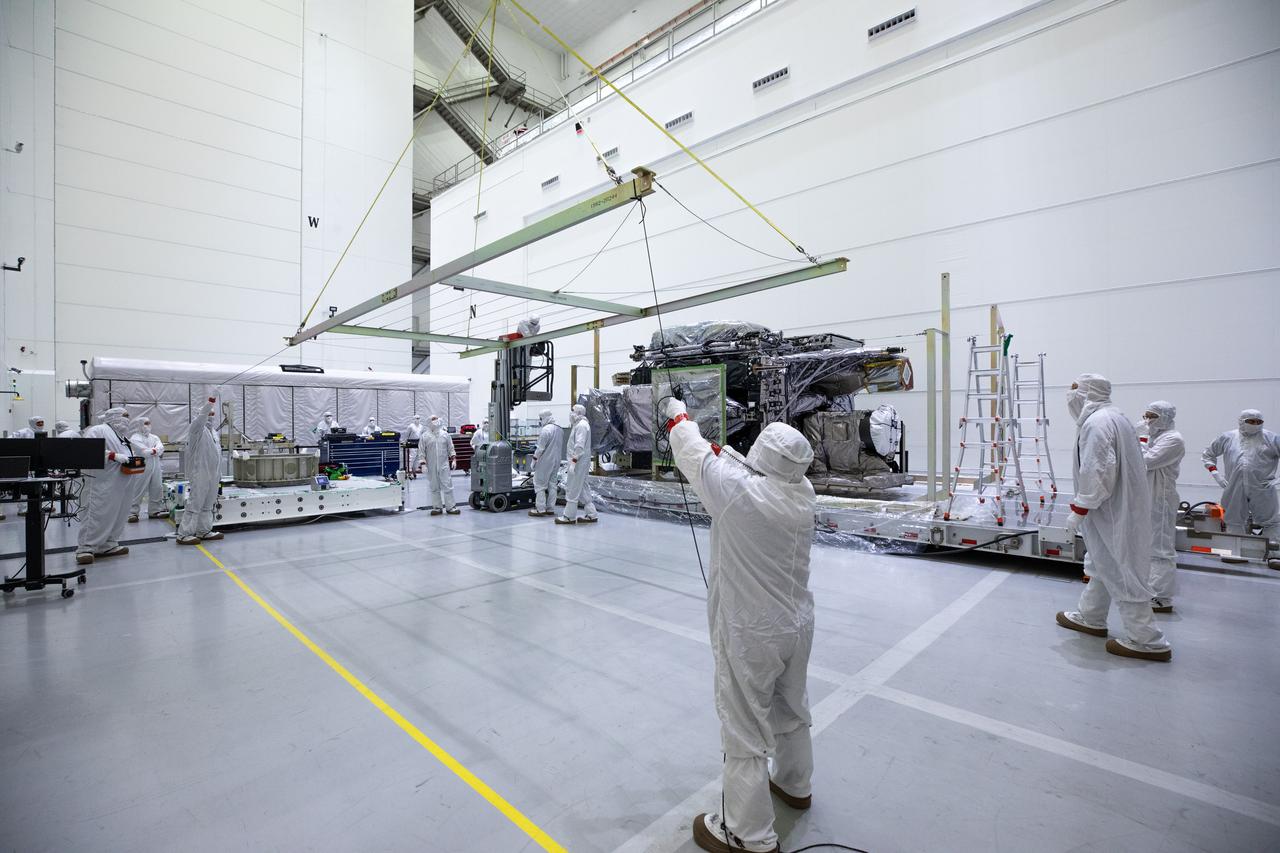

Technicians remove part of a protective enclosure as they prepare to rotate NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) vertical after being uncrated on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
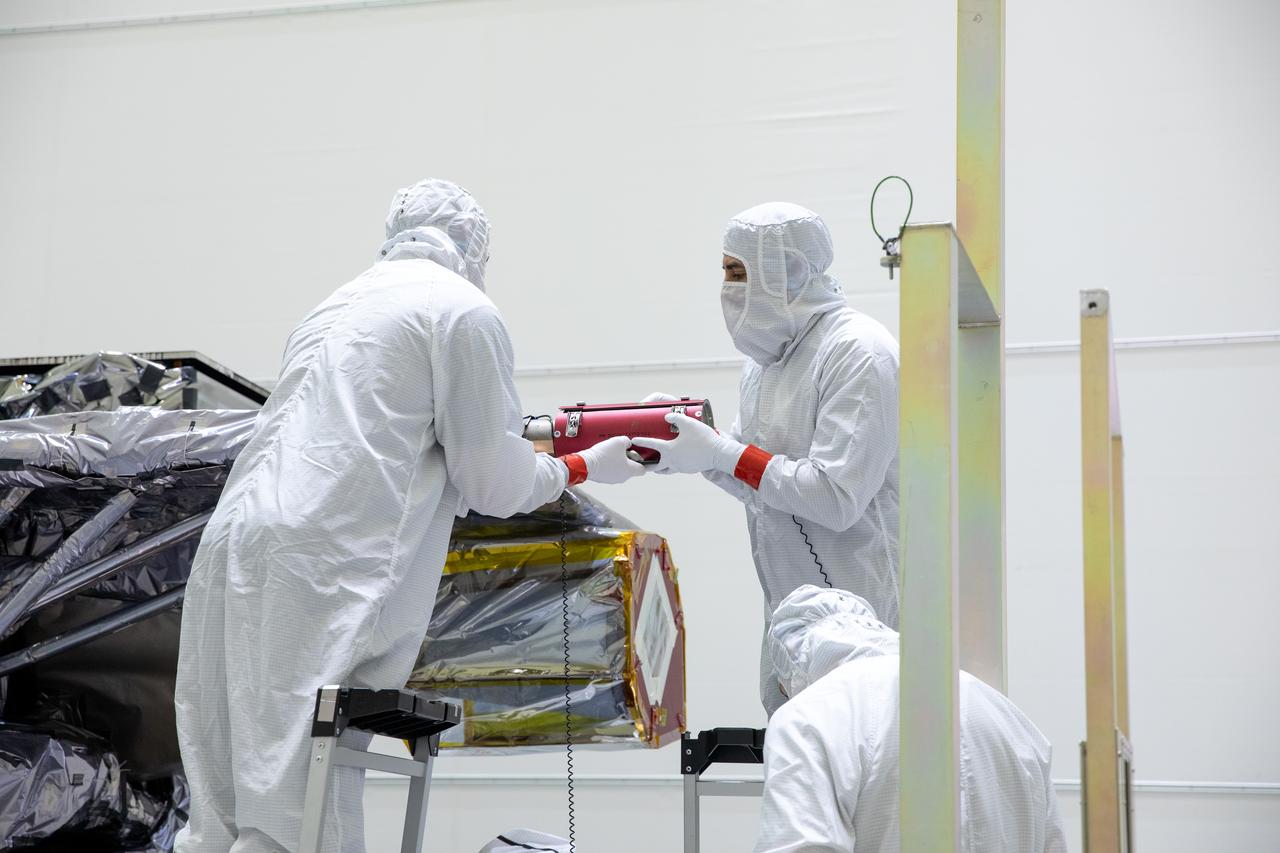

Technicians prepare to rotate NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) vertical after being uncrated on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

Technicians monitor movement and guide NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) as a crane hoists it on to a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
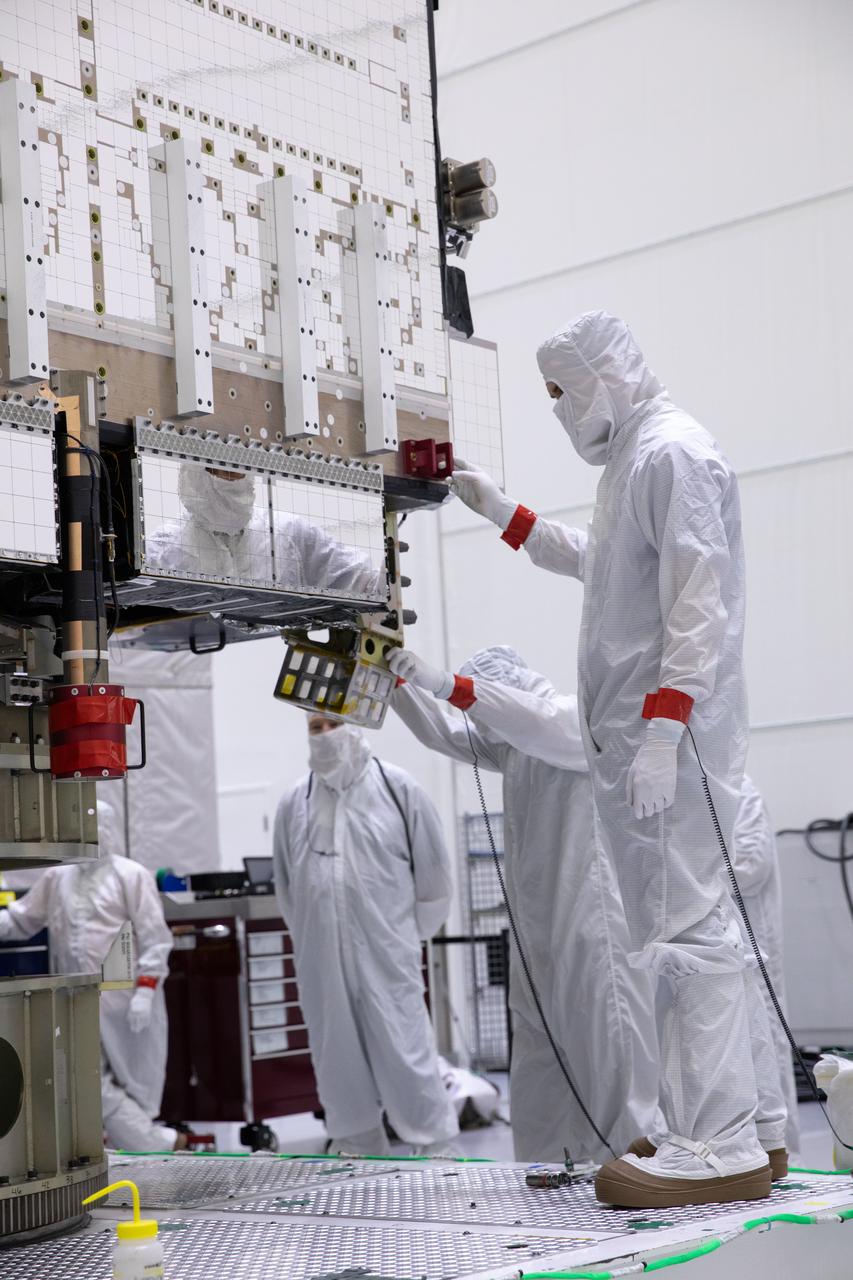

Technicians monitor movement and guide NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) as a crane hoists it on to a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
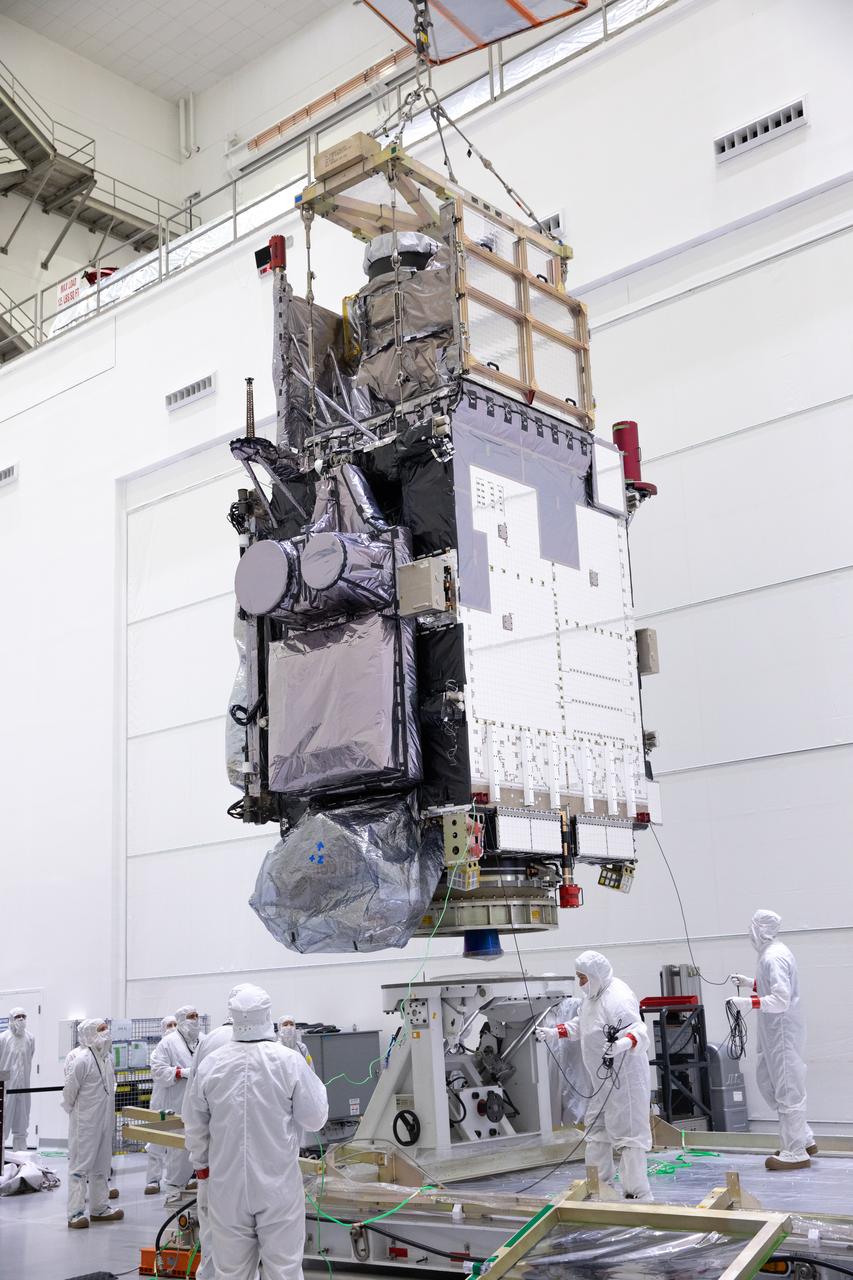

Technicians monitor movement as a crane hoists NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) after being uncrated and rotated into a vertical position on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, NASA and industry leaders speak to members of the media during a prelaunch news conference for the agency’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft. From left are: George Diller of NASA Communications; Christine Bonniksen, CYGNSS program executive in the Earth Science Division of the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington, D.C.; Tim Dunn, NASA launch director at Kennedy; Bryan Baldwin, Pegasus launch vehicle program manager for Orbital ATK, Dulles, Virginia; John Scherrer, CYGNSS project manager for the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio, Texas; and Mike Rehbein, launch weather officer for the 45th Weather Squadron at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. The eight CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data will help scientists probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a crucial role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, NASA and industry leaders speak to members of the media during a prelaunch news conference for the agency’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft. From left are: George Diller of NASA Communications; Christine Bonniksen, CYGNSS program executive in the Earth Science Division of the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington, D.C.; Tim Dunn, NASA launch director at Kennedy; Bryan Baldwin, Pegasus launch vehicle program manager for Orbital ATK, Dulles, Virginia; John Scherrer, CYGNSS project manager for the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio, Texas; and Mike Rehbein, launch weather officer for the 45th Weather Squadron at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. The eight CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data will help scientists probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a crucial role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
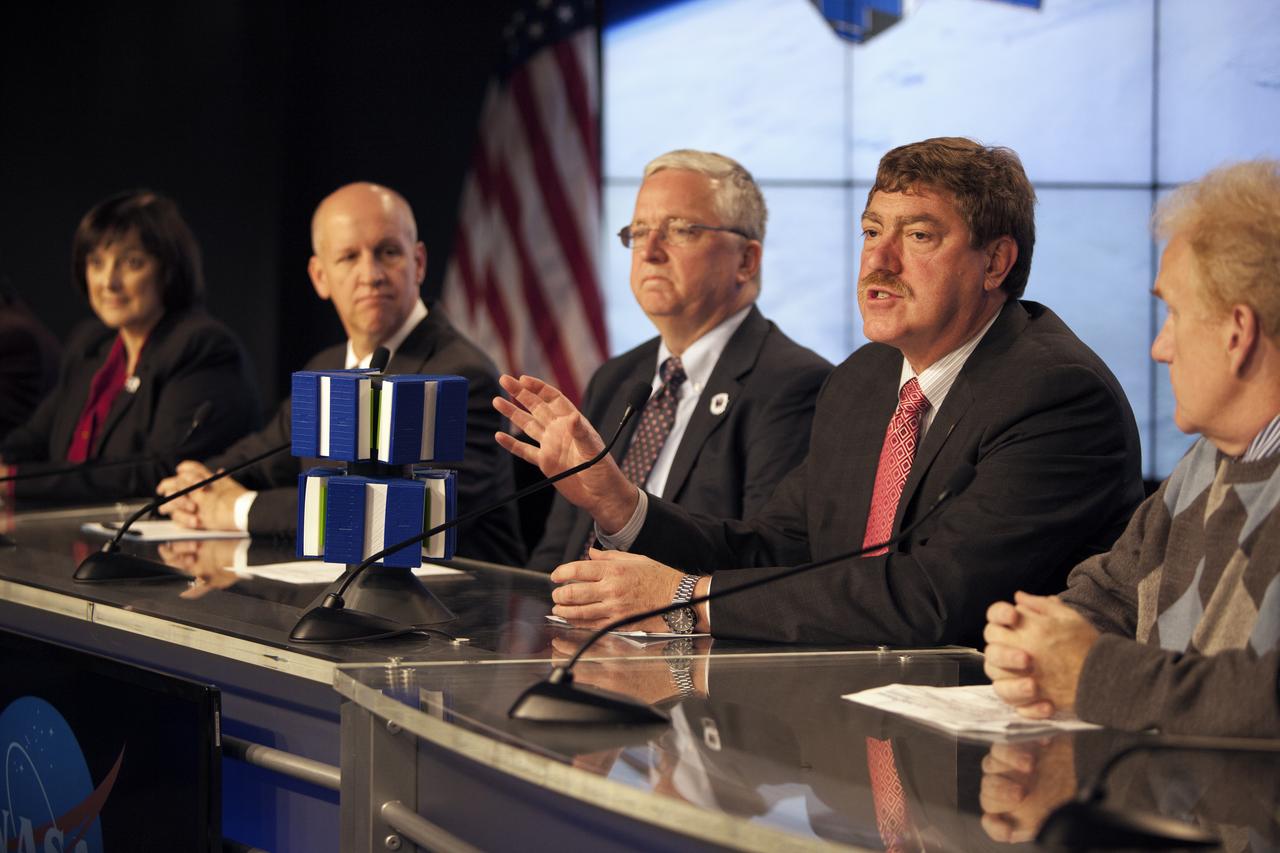

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, NASA and industry leaders speak to members of the media during a prelaunch news conference for the agency’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft. From left are: Christine Bonniksen, CYGNSS program executive in the Earth Science Division of the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington, D.C.; Tim Dunn, NASA launch director at Kennedy; Bryan Baldwin, Pegasus launch vehicle program manager for Orbital ATK, Dulles, Virginia; John Scherrer, CYGNSS project manager for the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio, Texas; and Mike Rehbein, launch weather officer for the 45th Weather Squadron at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. The eight CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data will help scientists probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a crucial role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
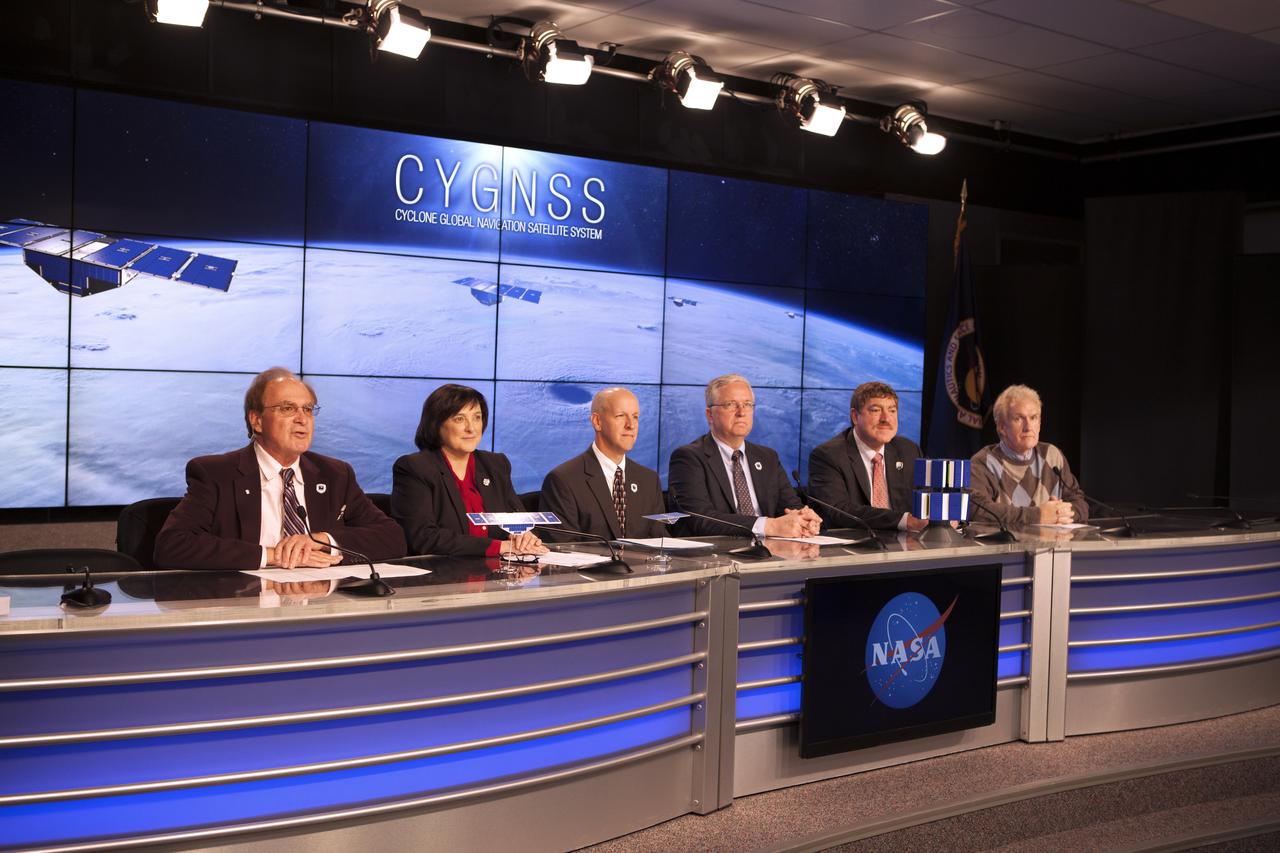

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, NASA and industry leaders speak to members of the media during a prelaunch news conference for the agency’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft. From left are: George Diller of NASA Communications; Christine Bonniksen, CYGNSS program executive in the Earth Science Division of the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington, D.C.; Tim Dunn, NASA launch director at Kennedy; Bryan Baldwin, Pegasus launch vehicle program manager for Orbital ATK, Dulles, Virginia; John Scherrer, CYGNSS project manager for the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio, Texas; and Mike Rehbein, launch weather officer for the 45th Weather Squadron at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. The eight CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data will help scientists probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a crucial role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
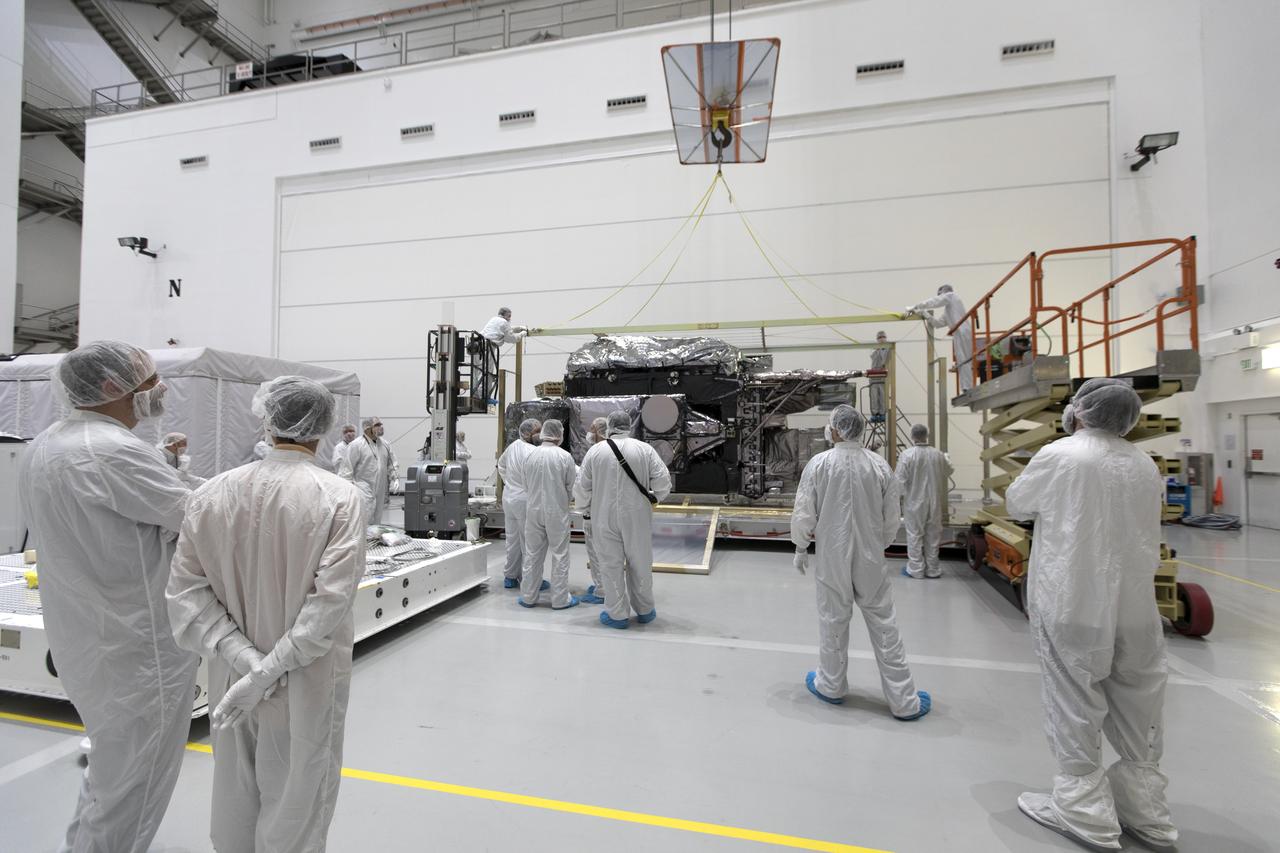

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technician and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers prepare to begin preflight processing of NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after removal from its shipping container. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
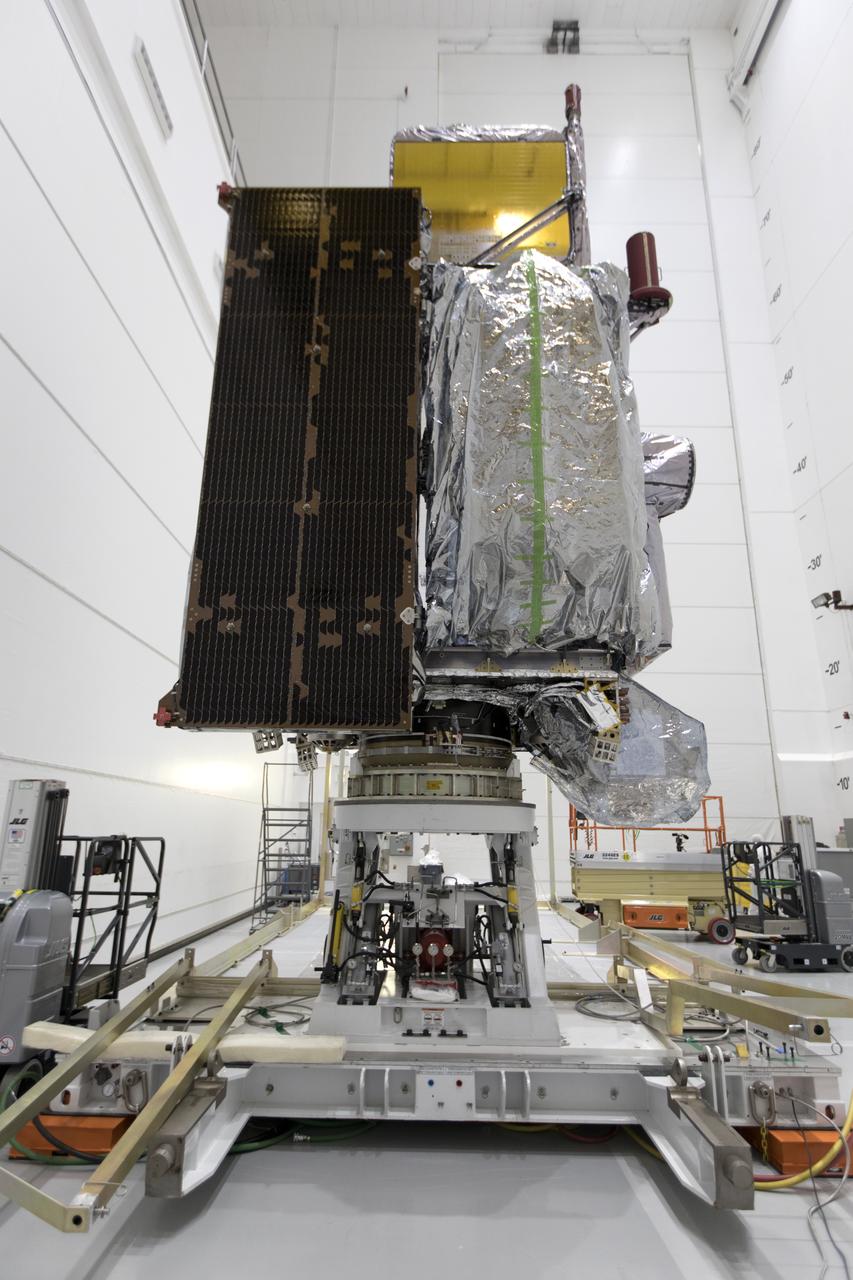

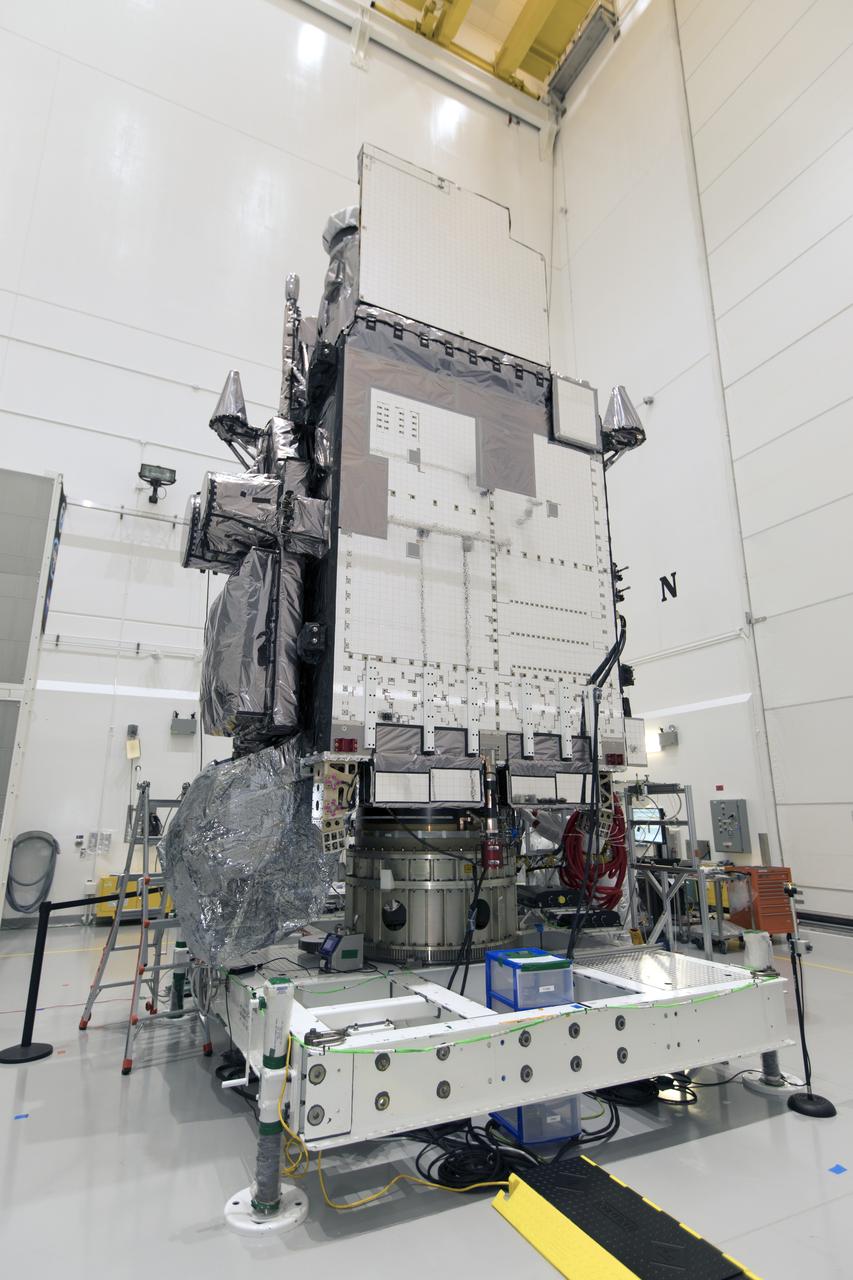
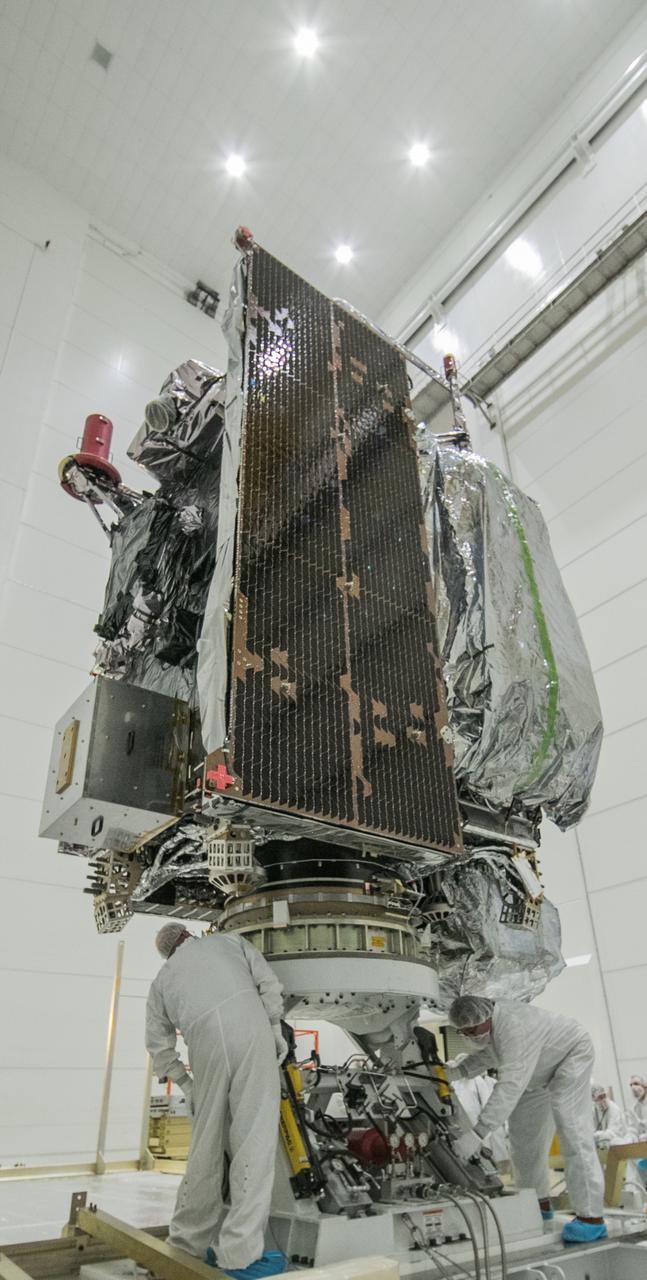
At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
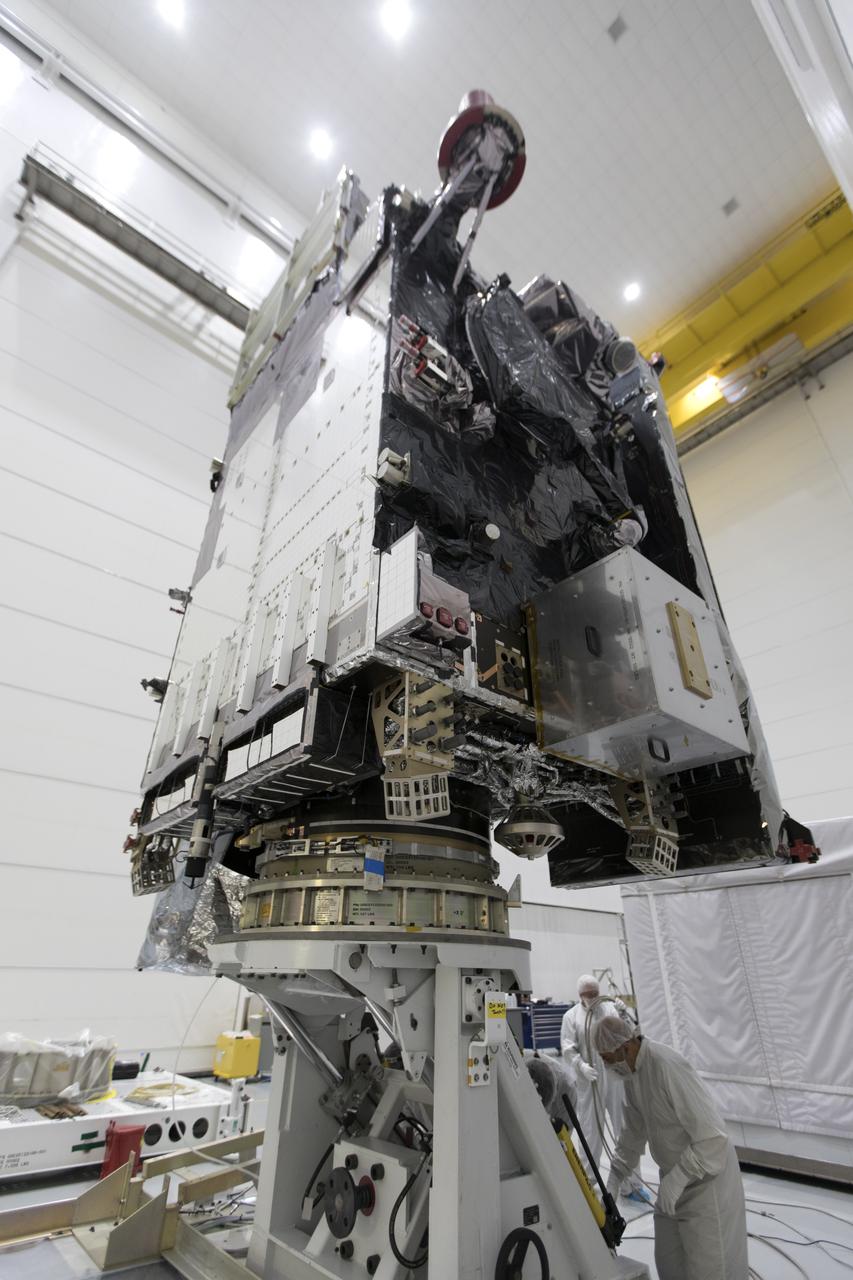

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
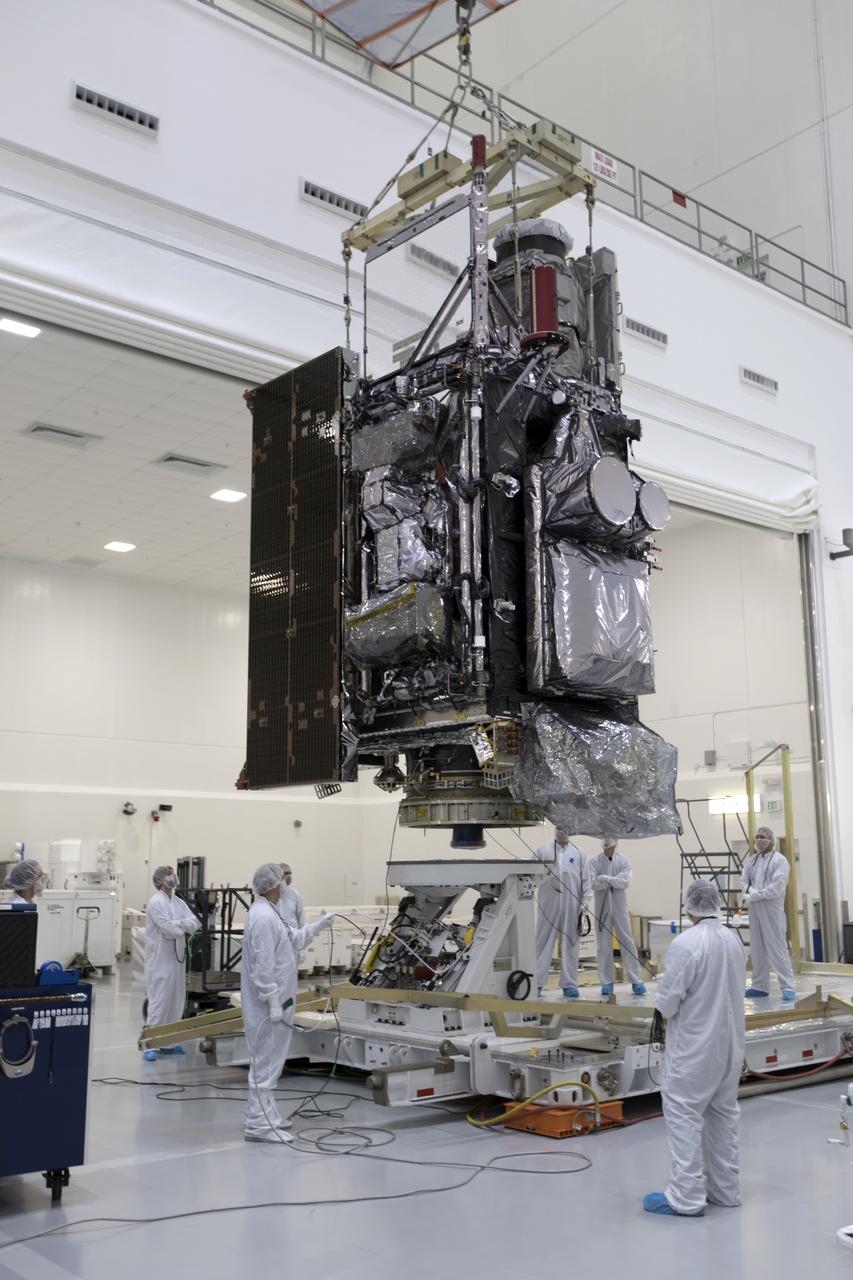

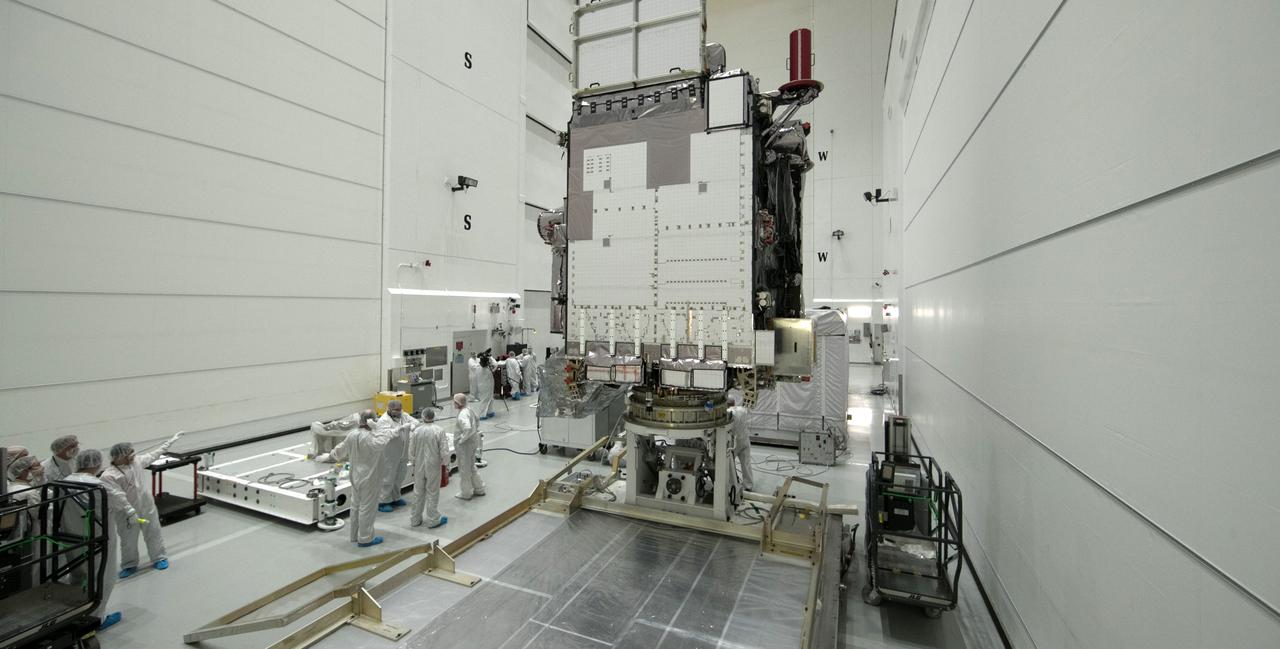
At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers keep a watchful eye on NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) as it is moved to a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
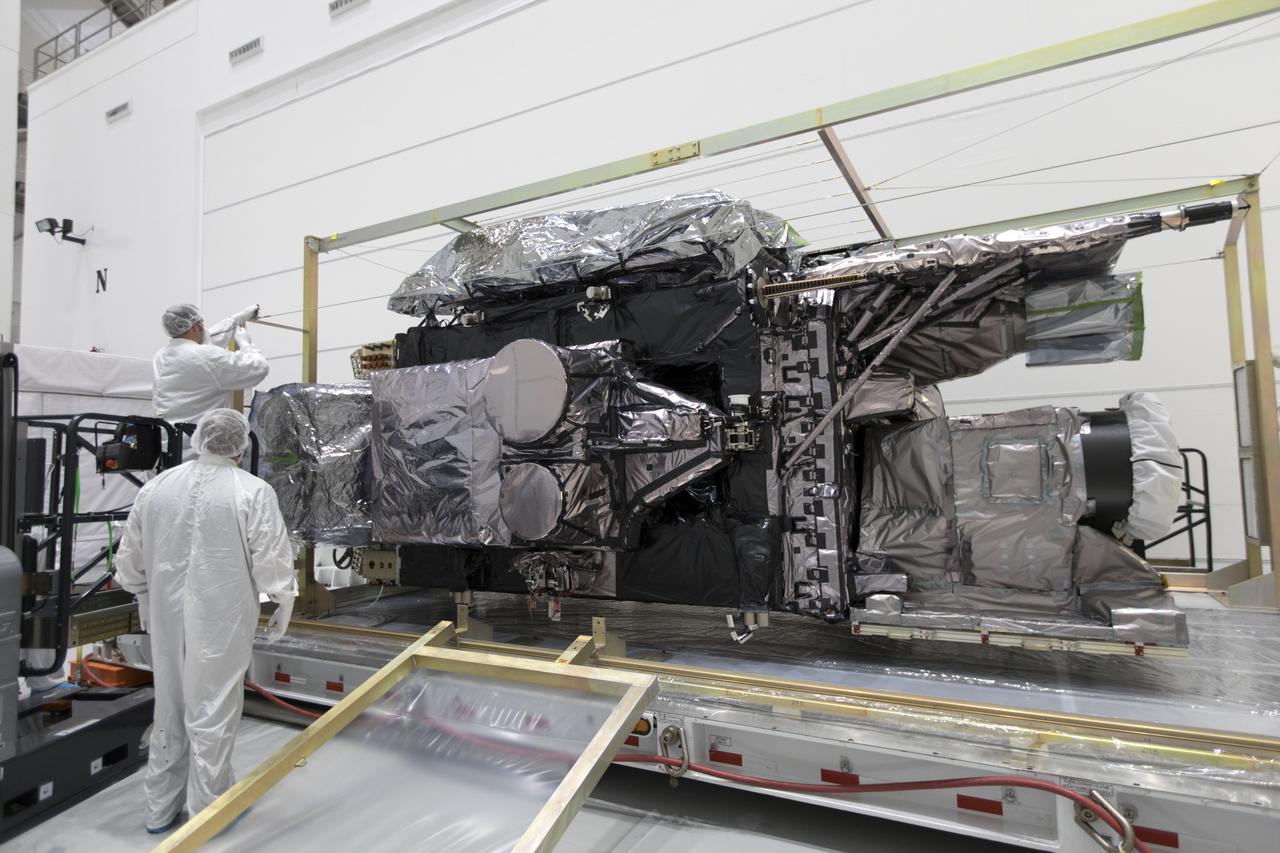

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, a technician inspects NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
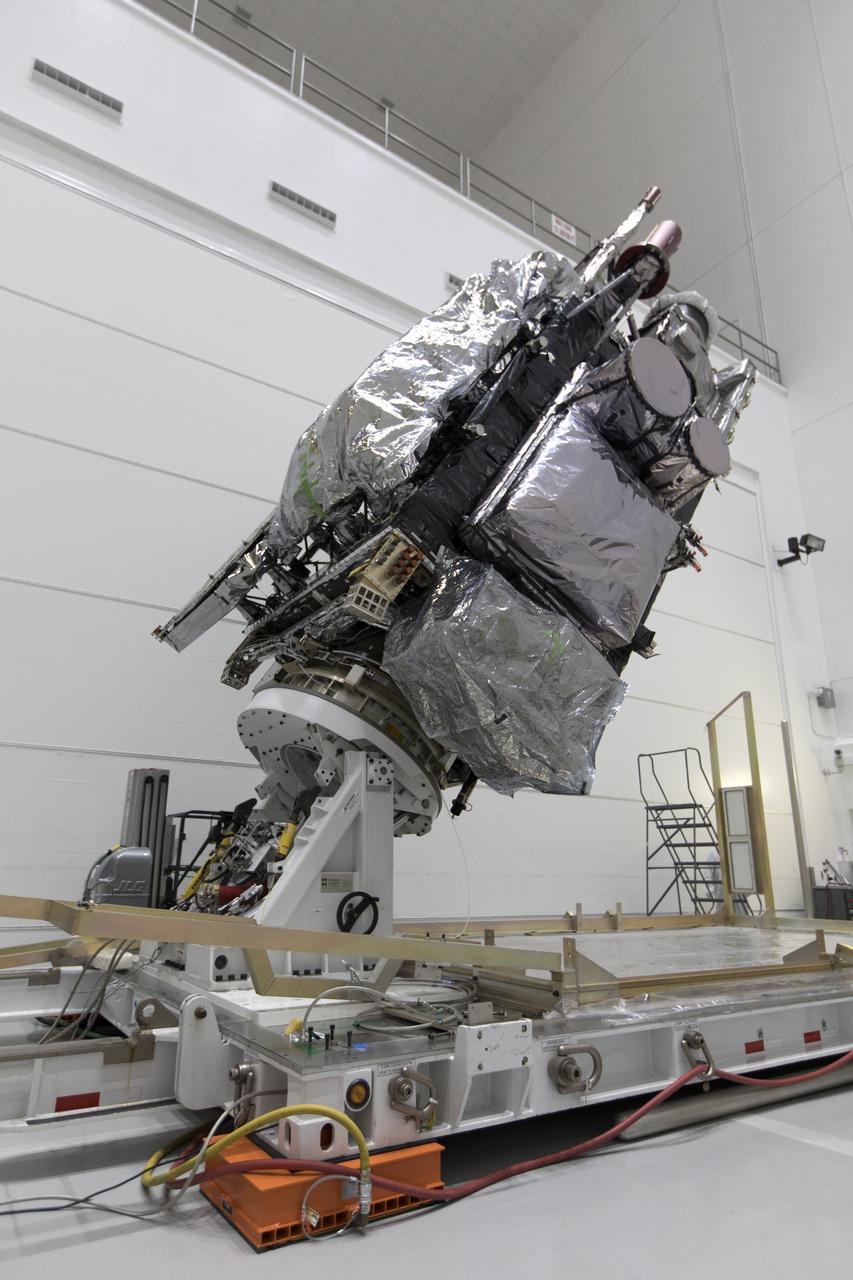

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
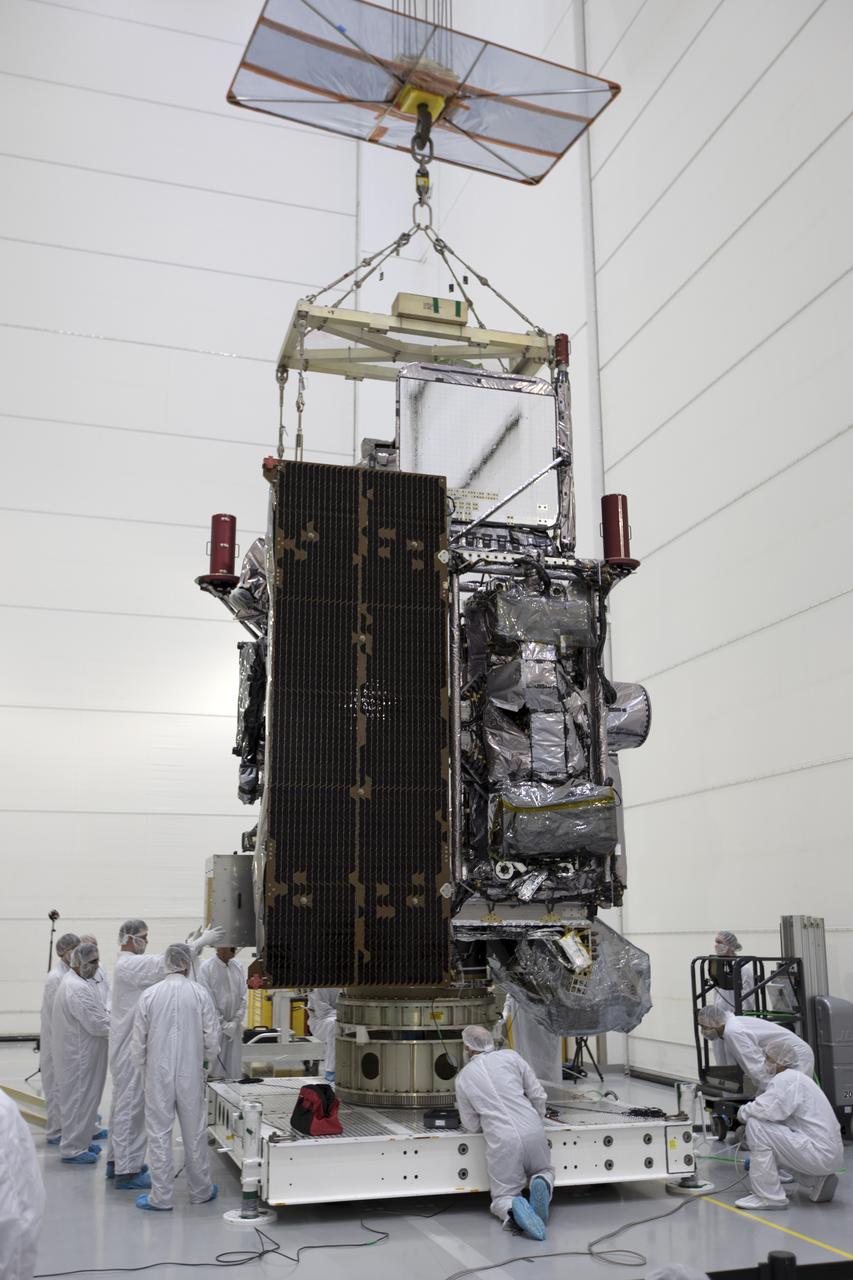

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers keep a watchful eye on NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) as it is positioned on a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
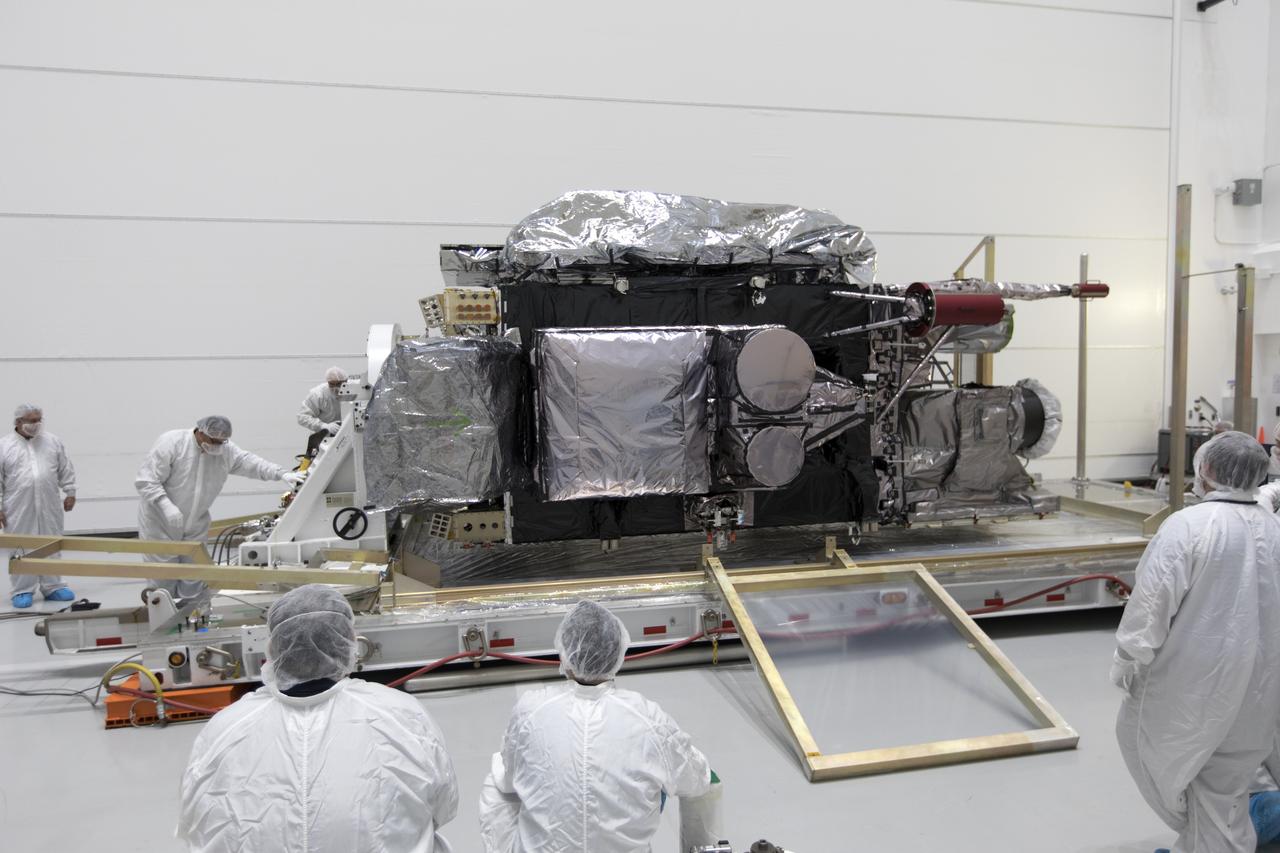

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technician and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
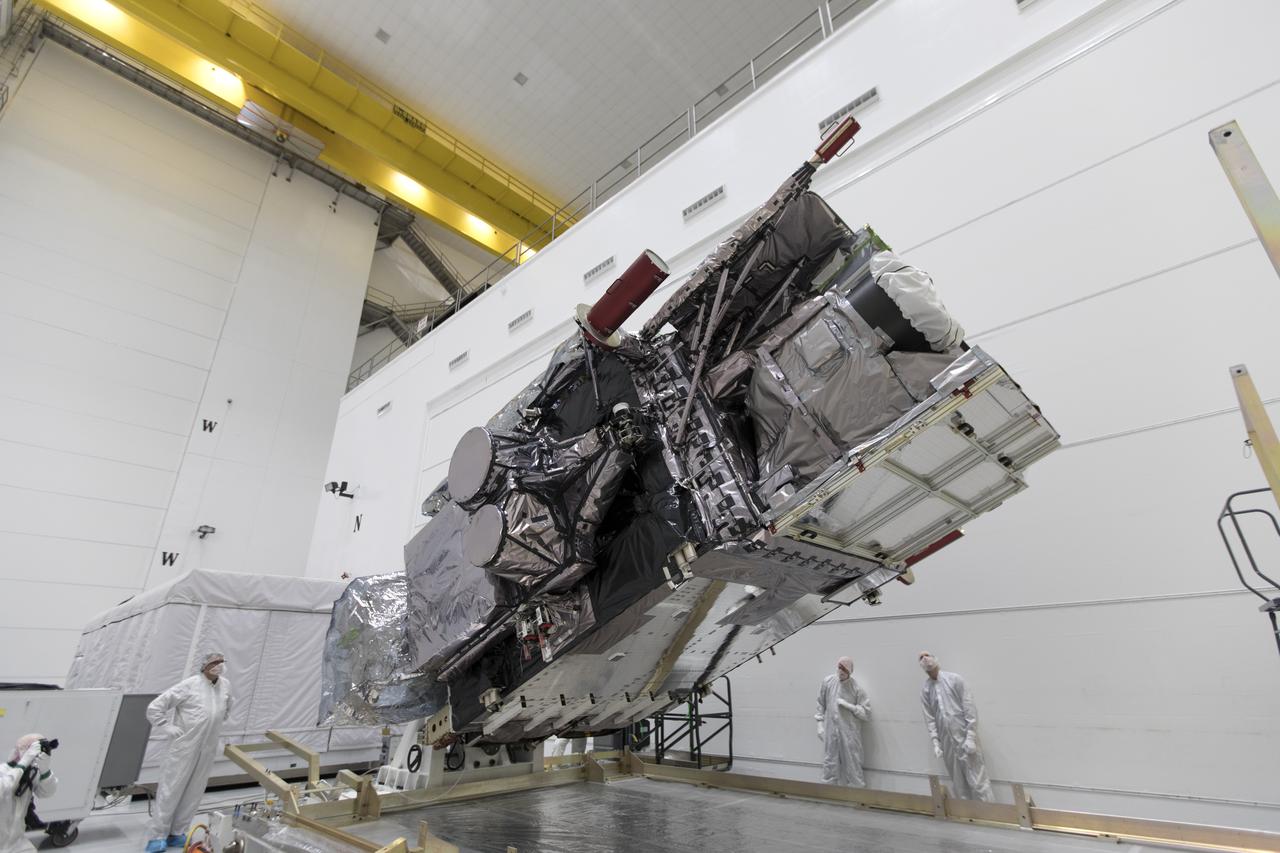

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
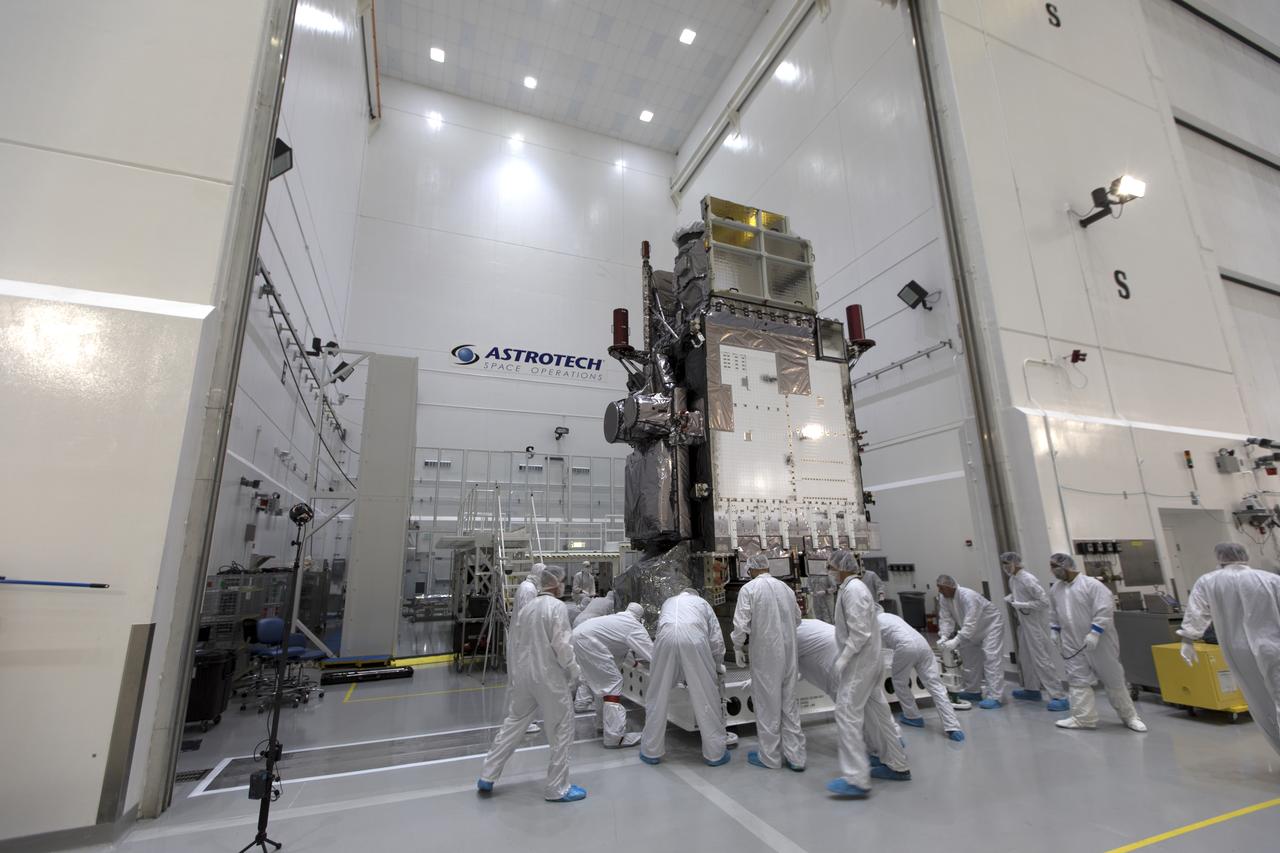

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers move NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) into a clean room for further processing. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
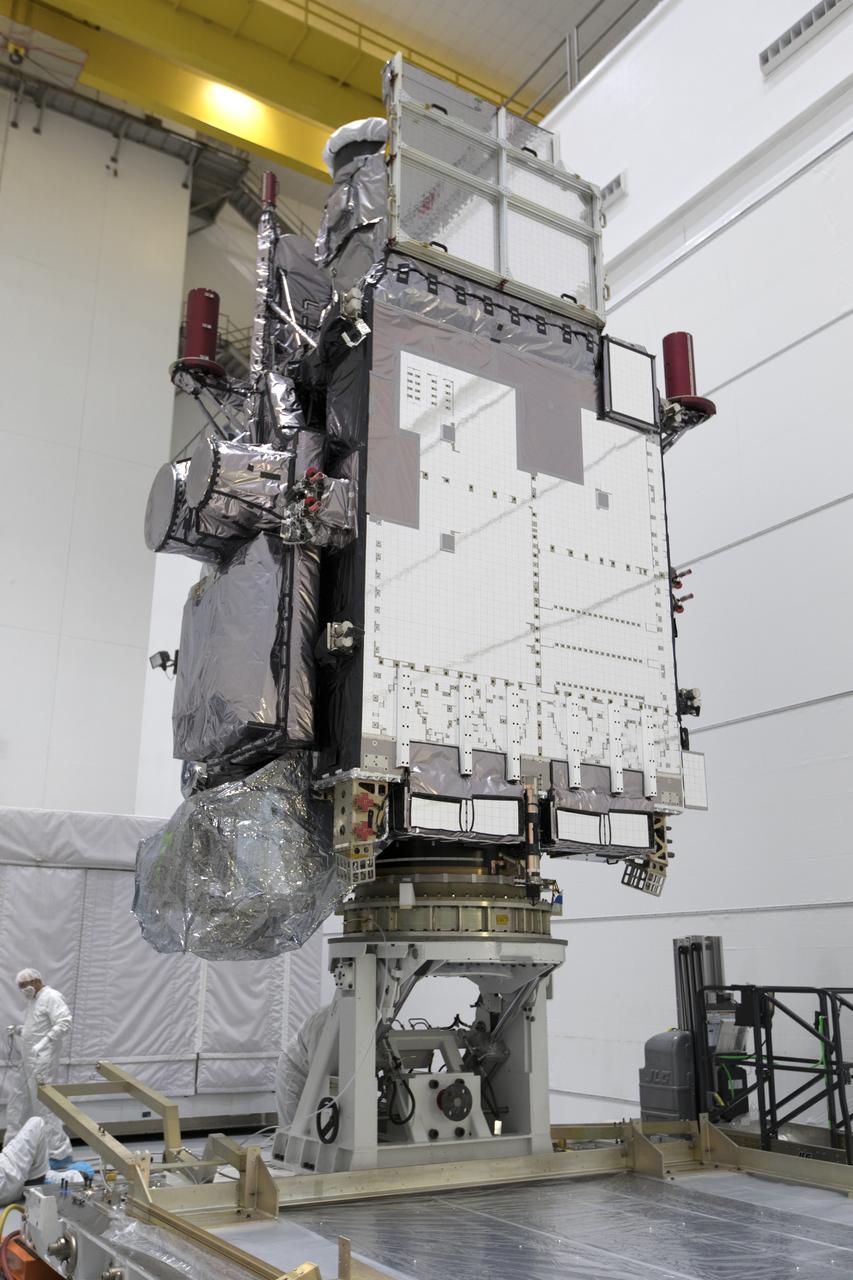

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
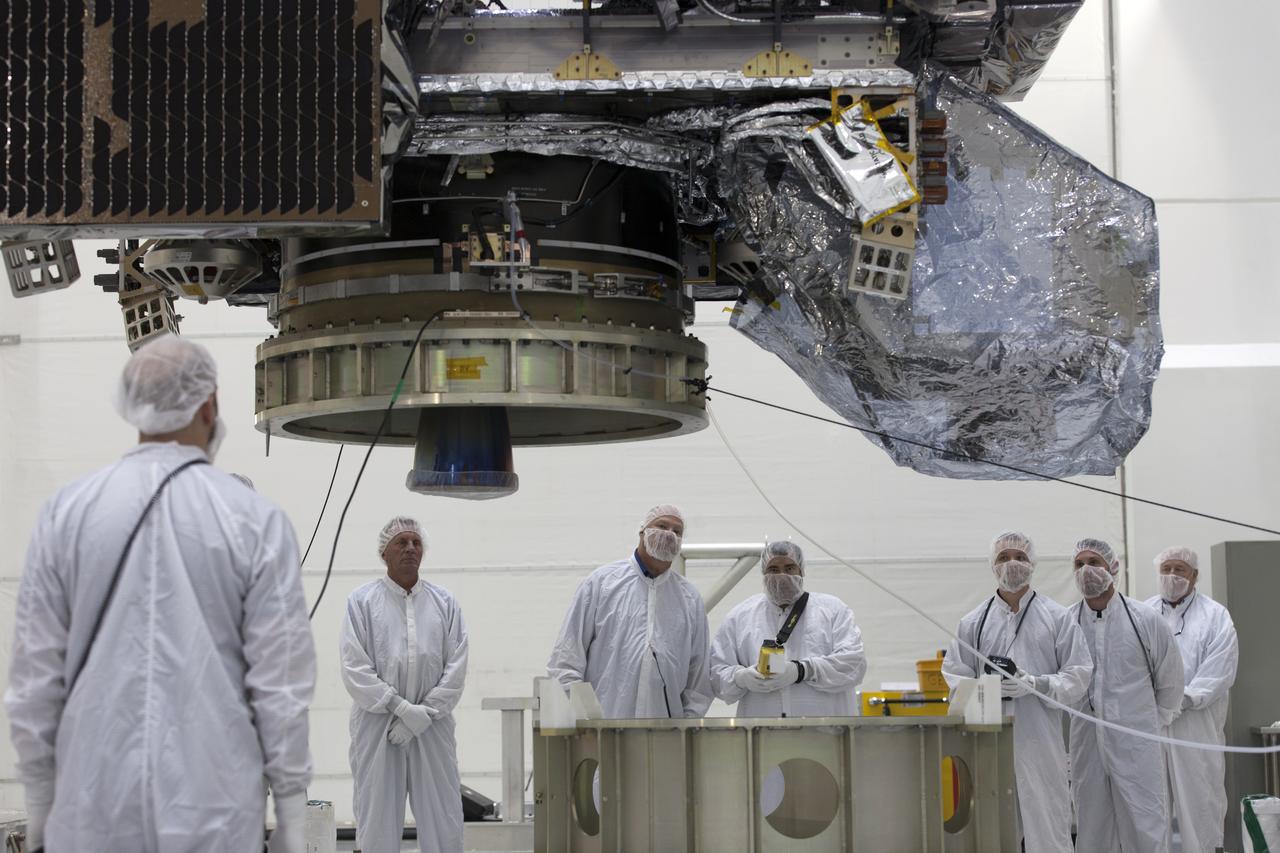

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers keep a watchful eye on NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) as it is moved to a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
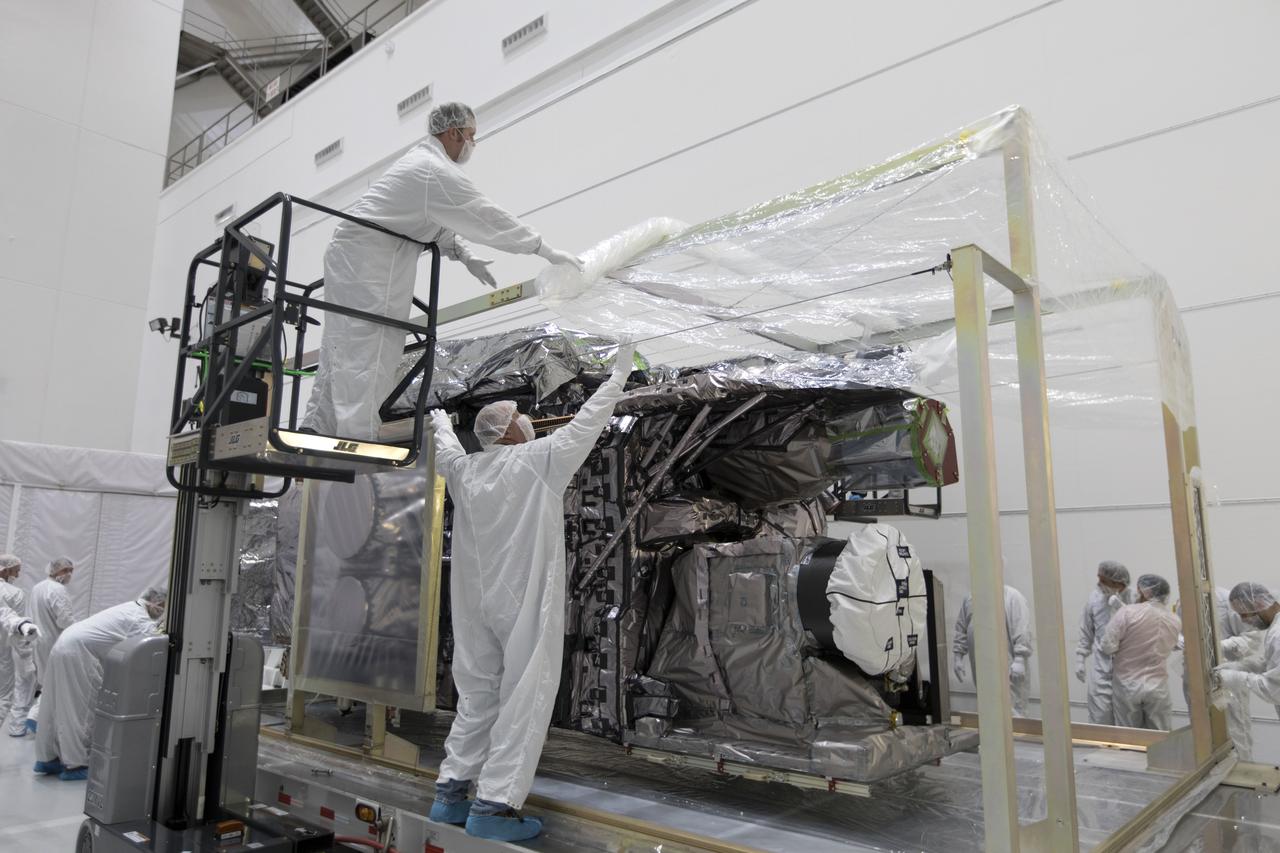

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technician and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
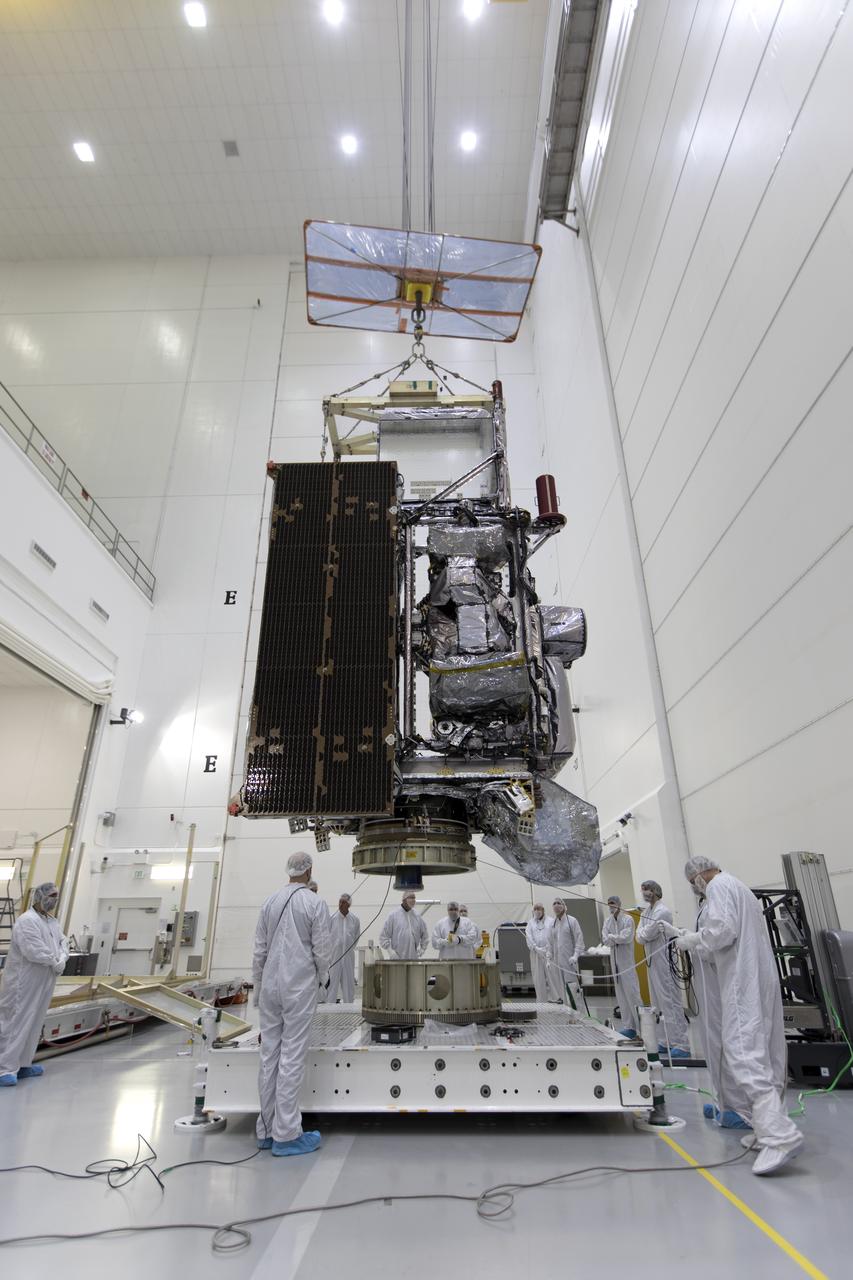

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers keep a watchful eye on NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) as it is positioned on a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
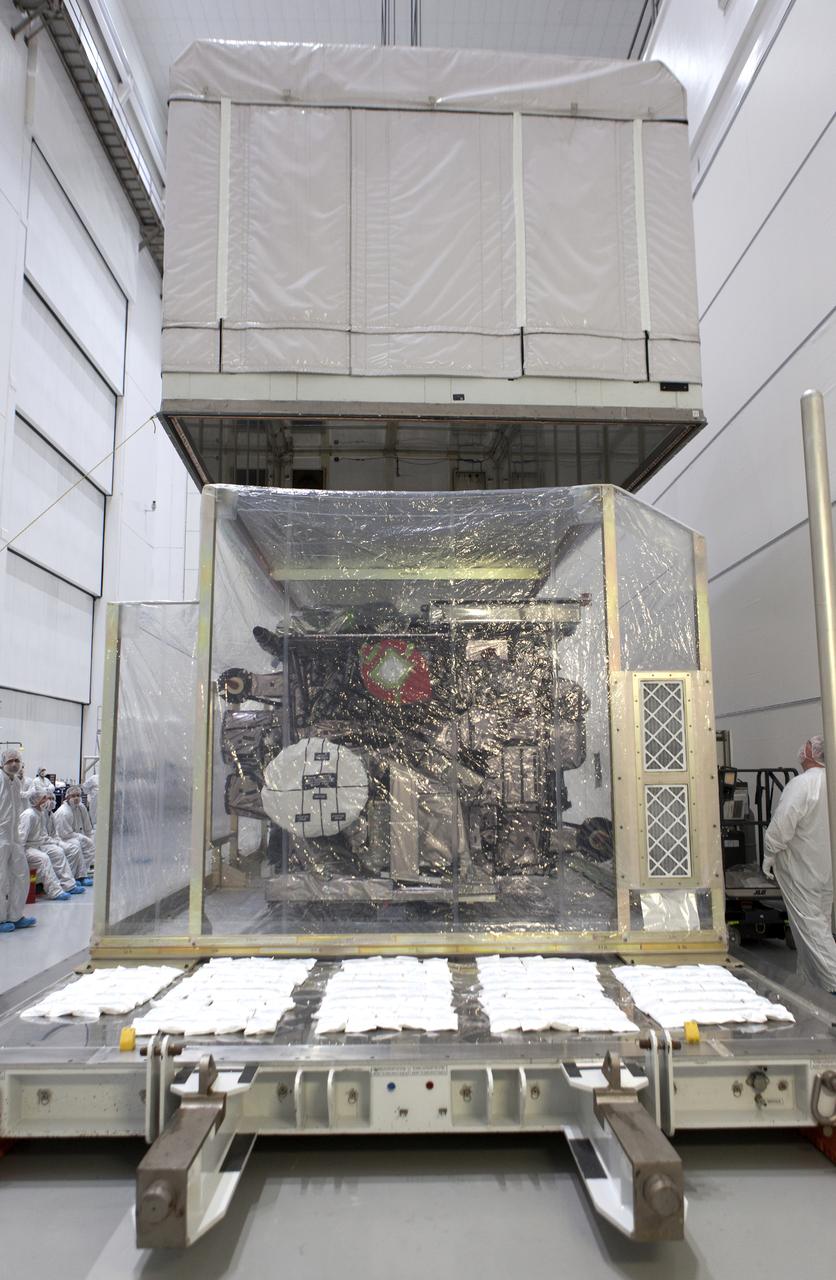

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
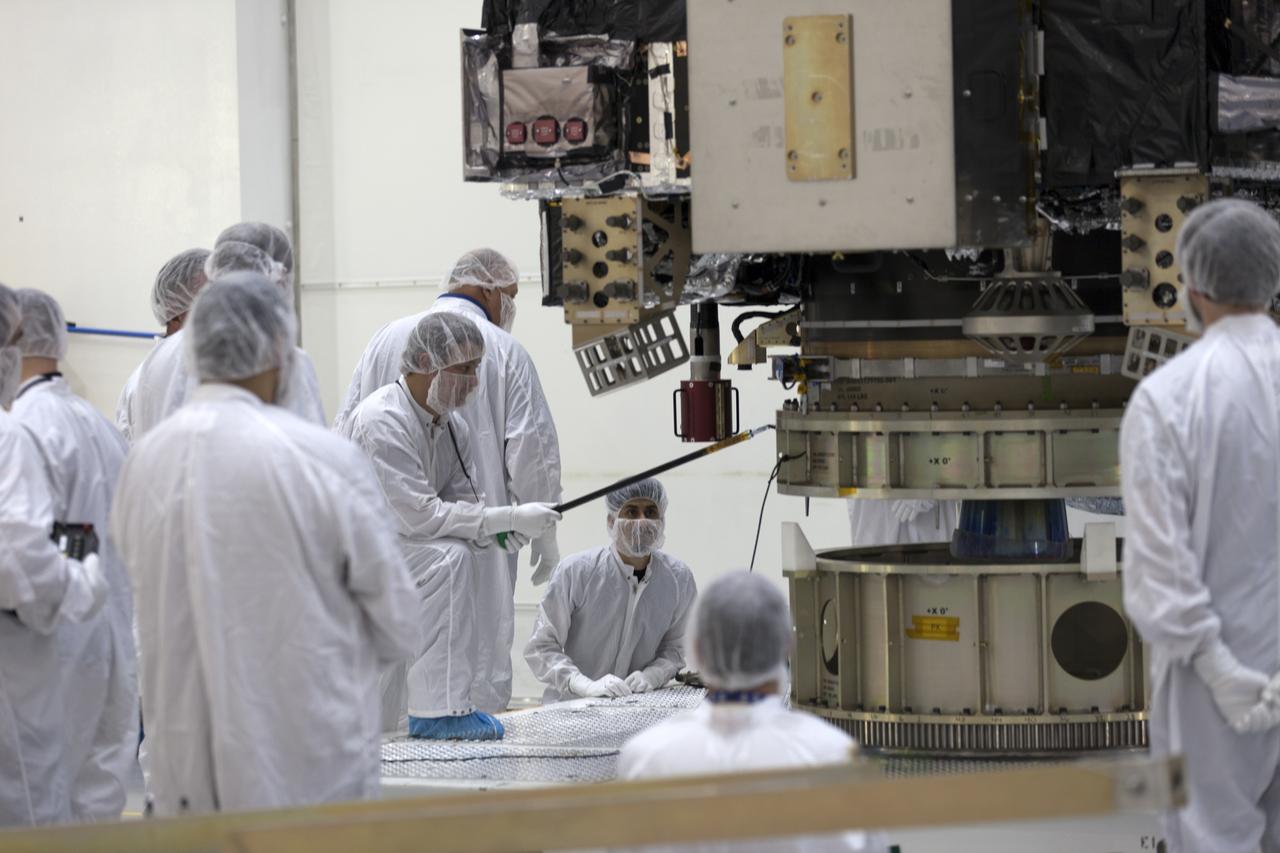

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers keep a watchful eye on NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) as it is positioned on a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been positioned on a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
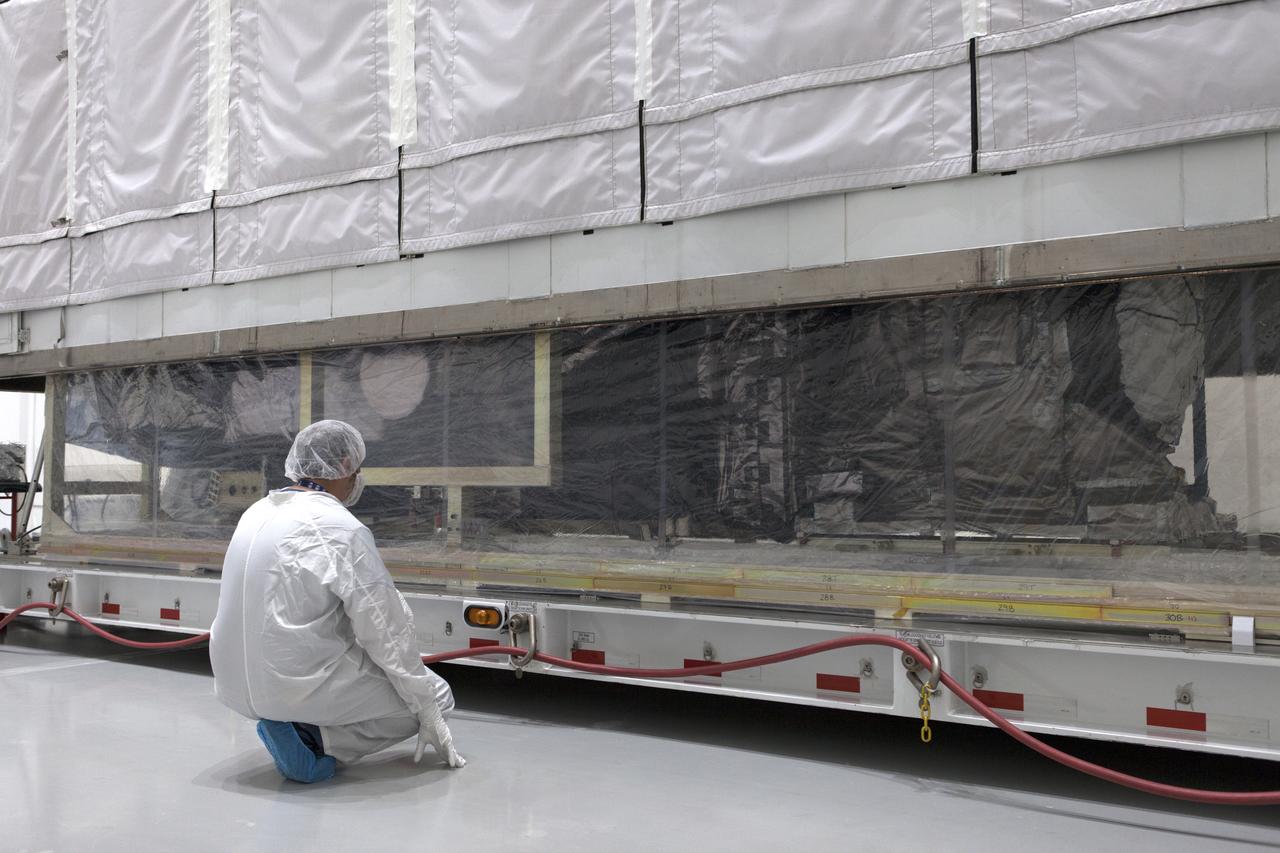

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, a technician watches as NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was positioned on a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
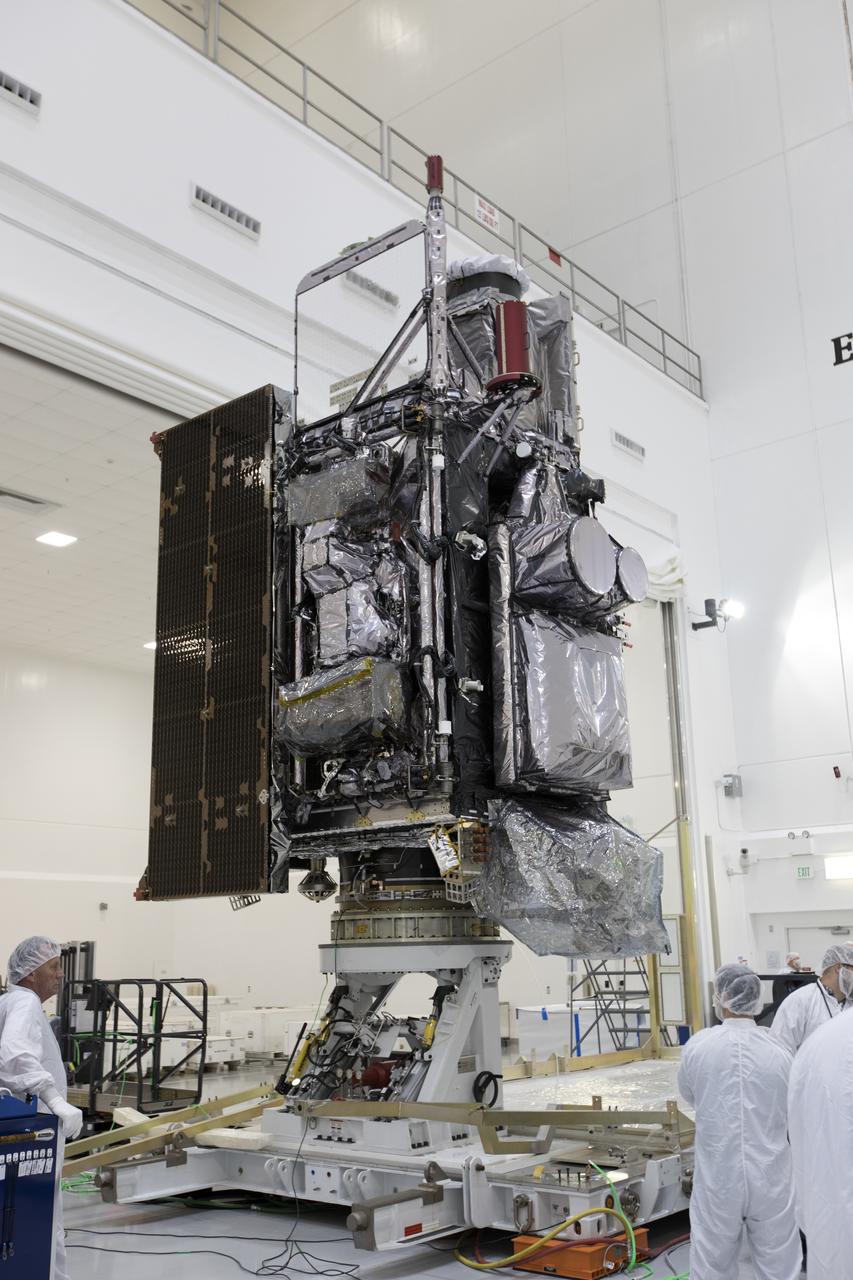

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
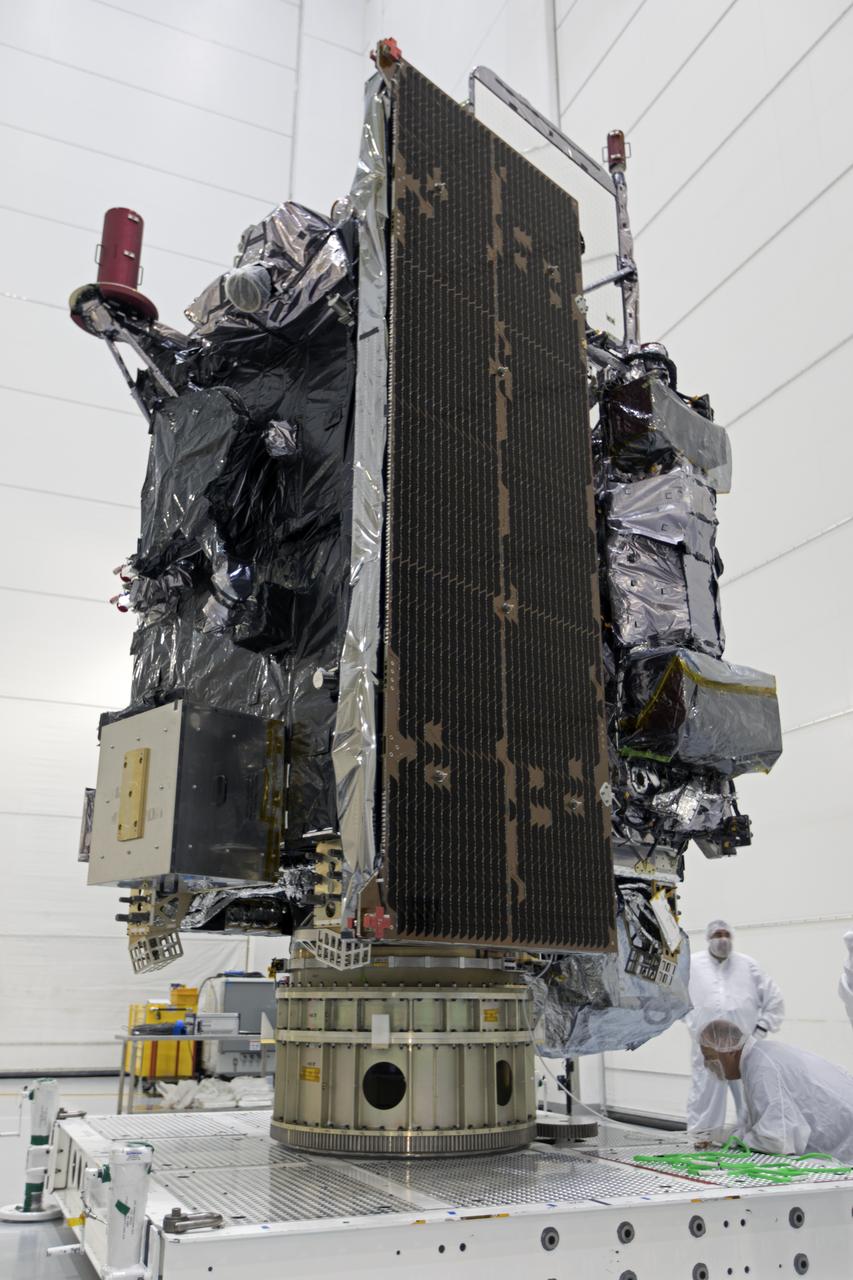

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was positioned on a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
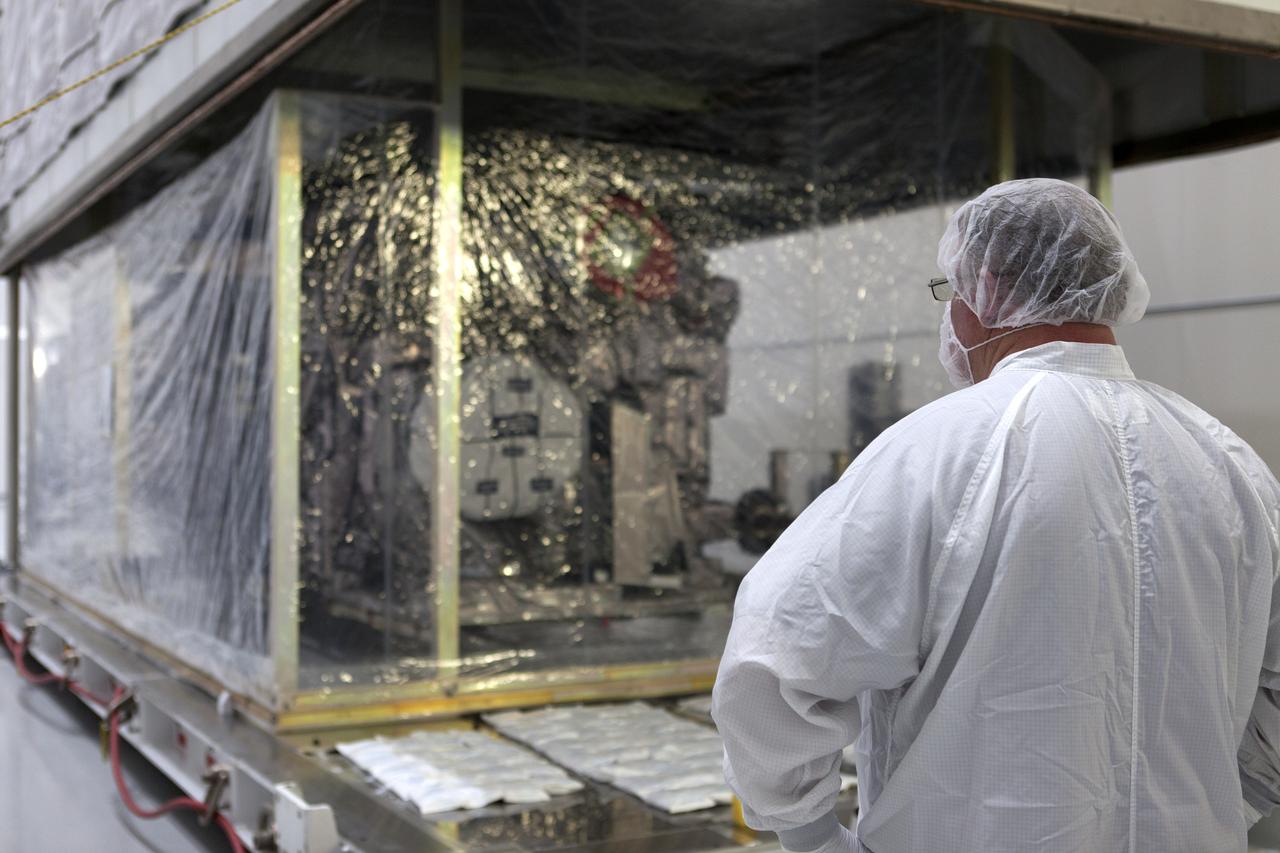

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, a technician watches as NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
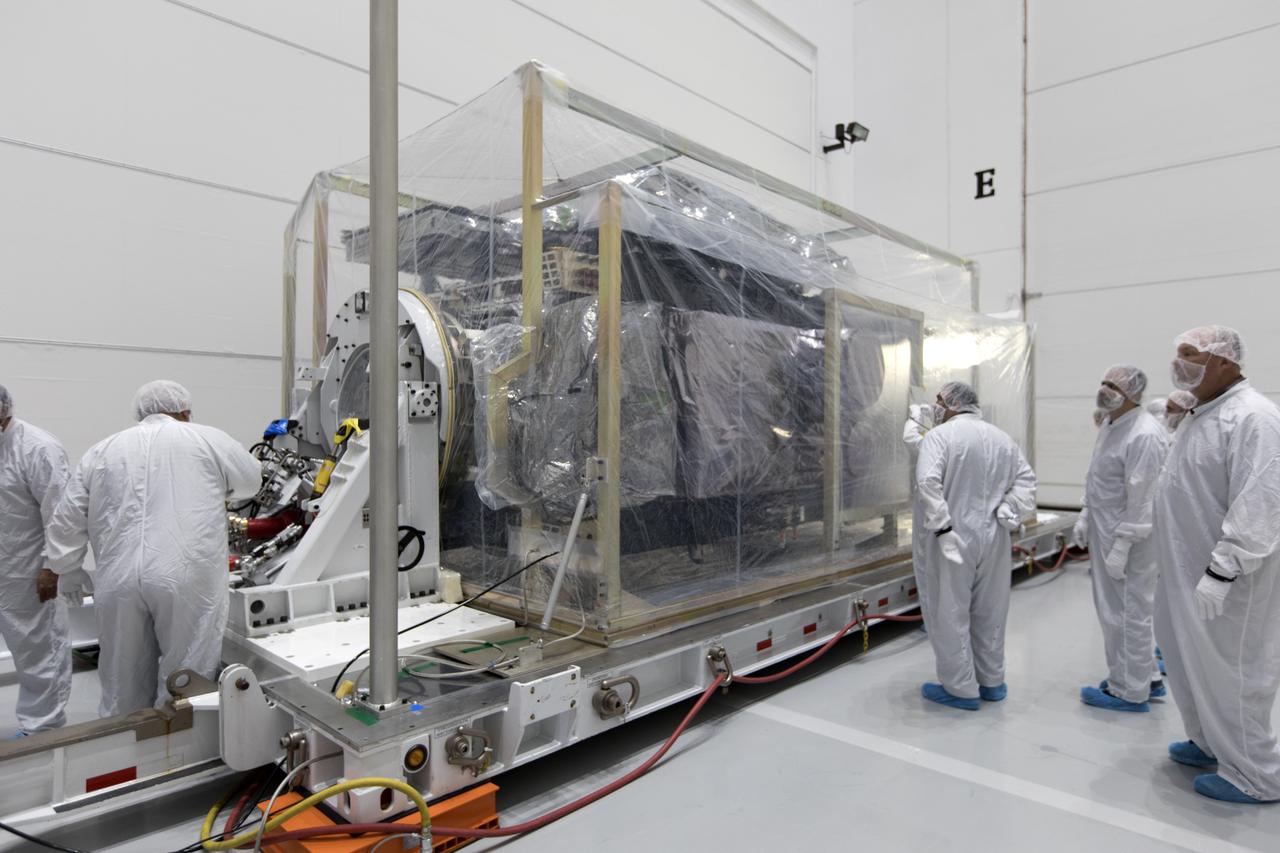

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technician and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
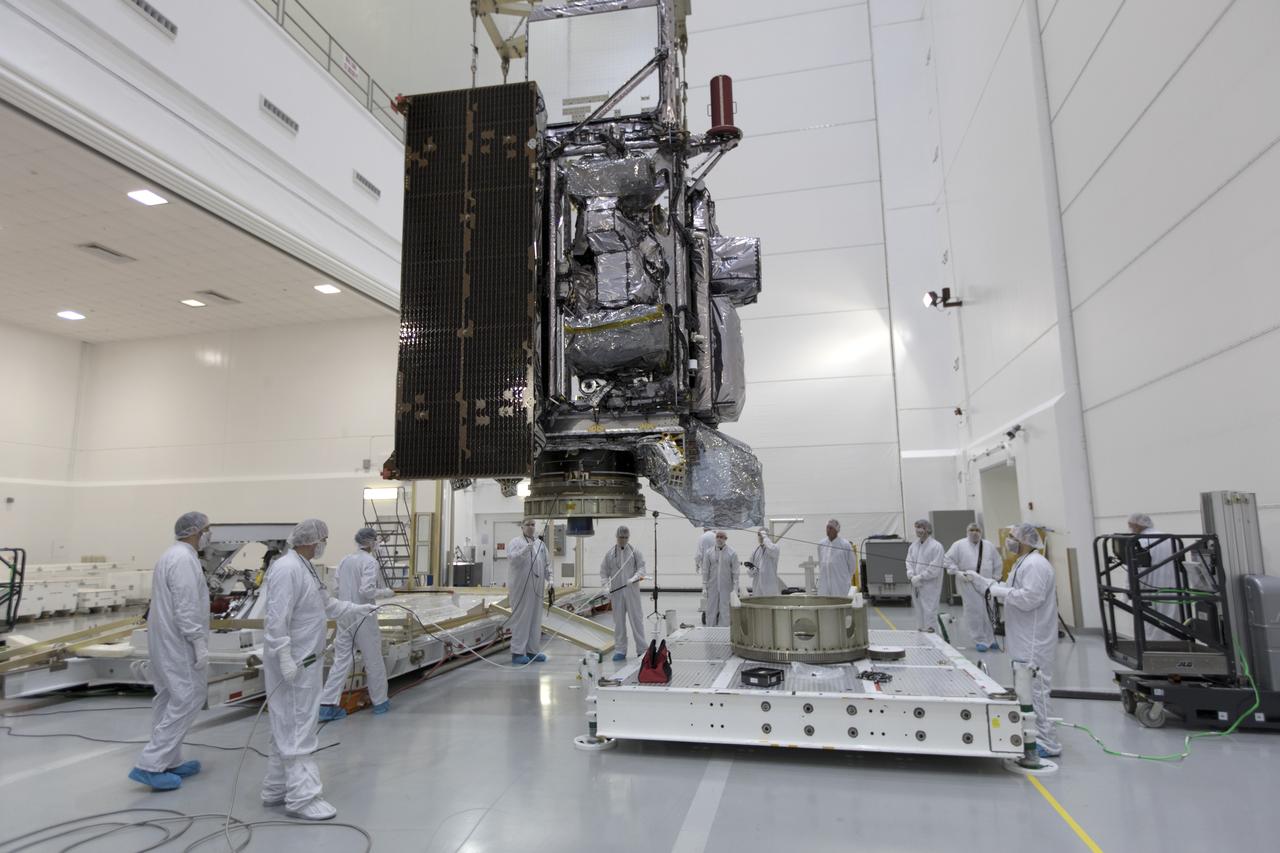

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers keep a watchful eye on NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) as it is moved to a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
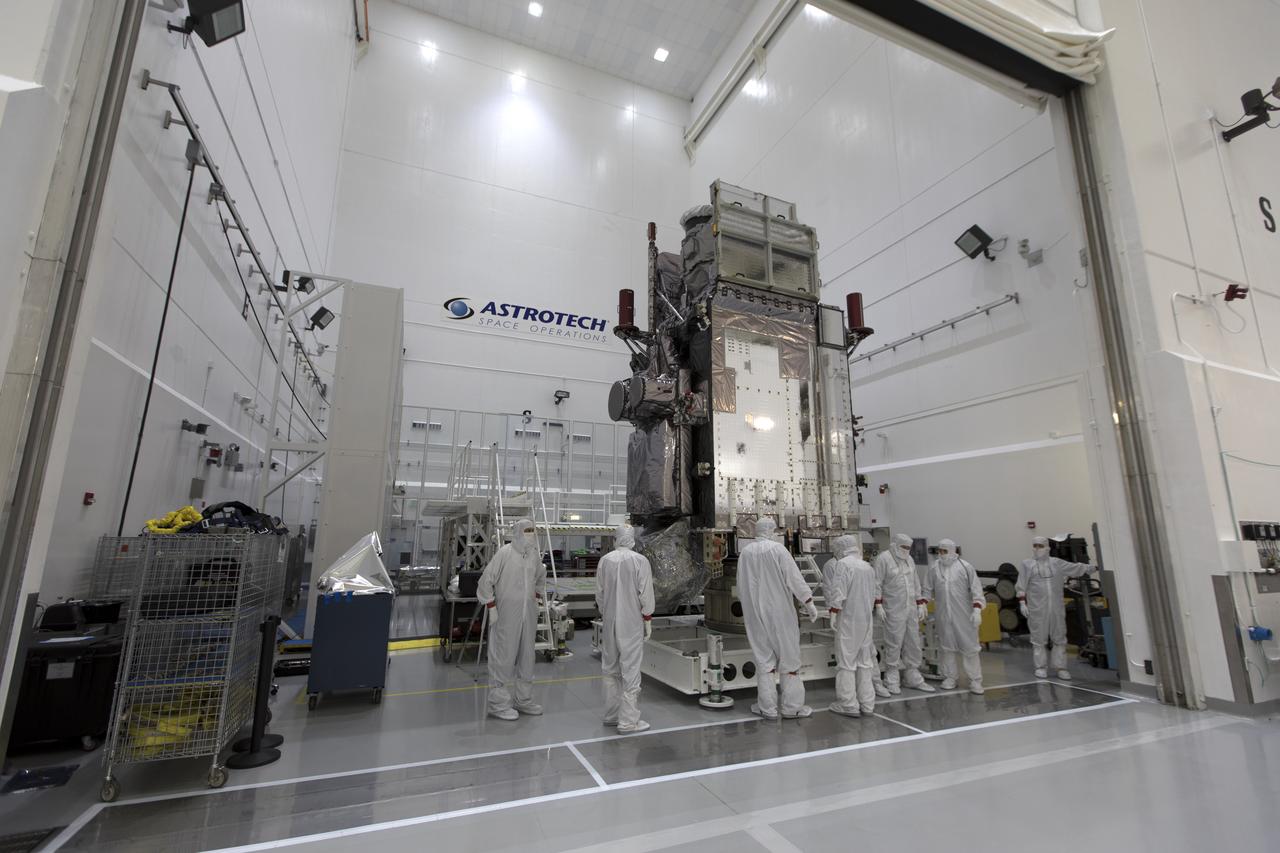

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers move NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) into a clean room for further processing. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
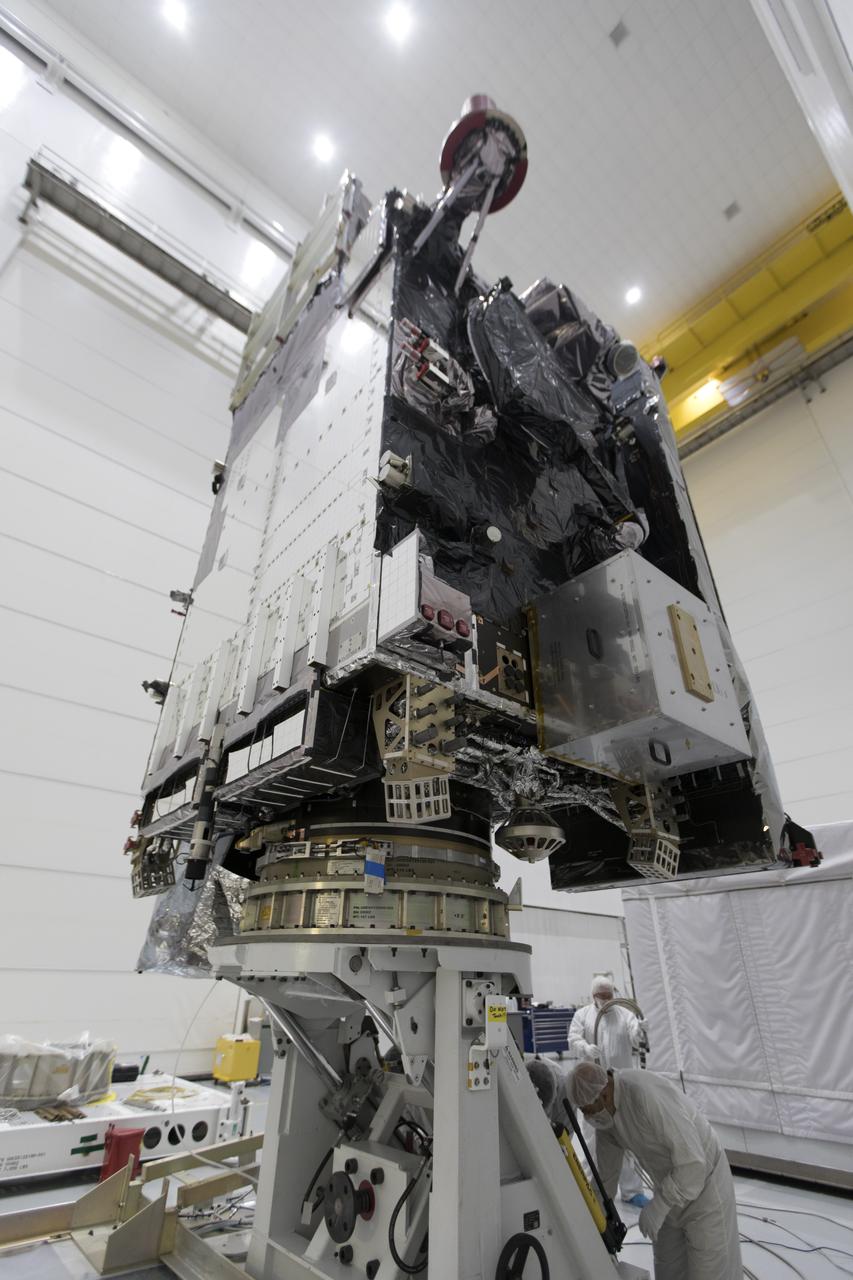

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
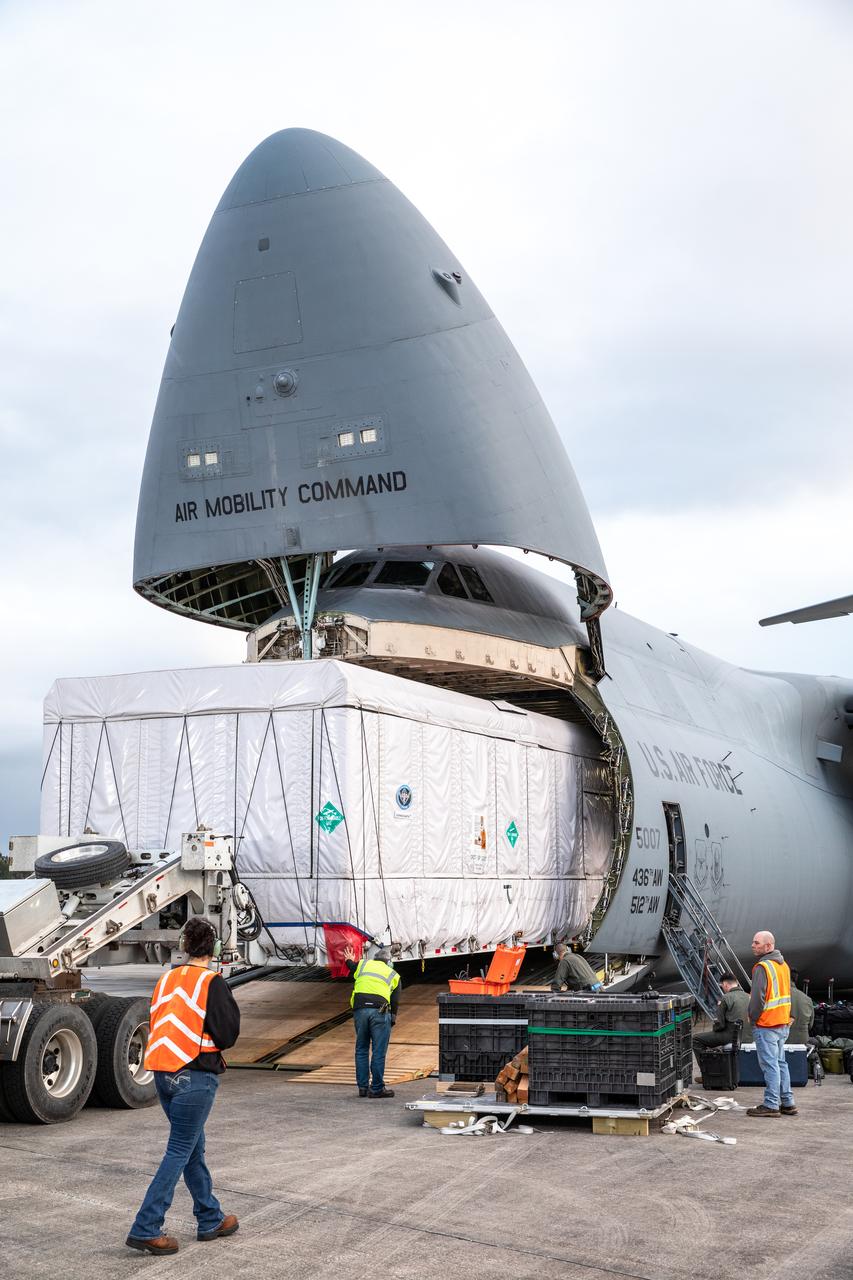

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
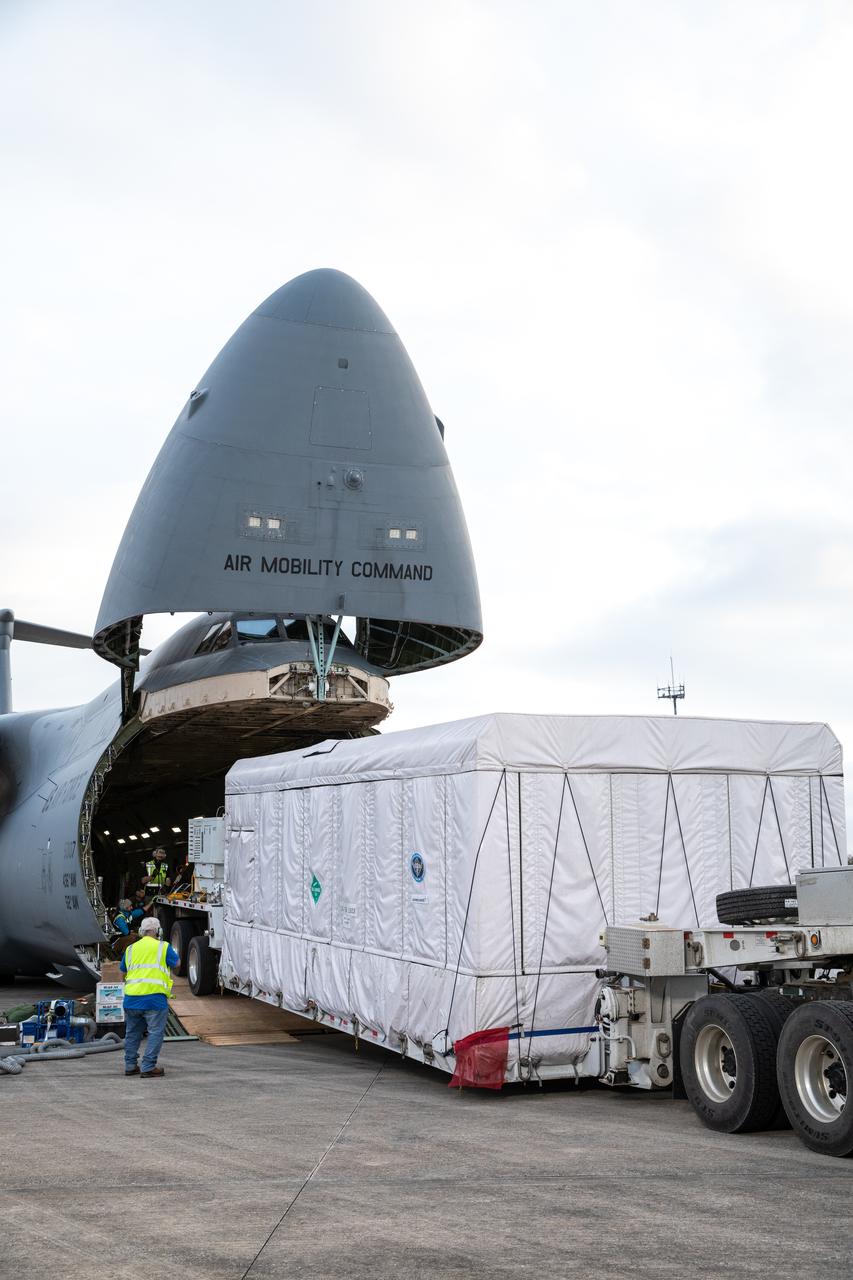

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.