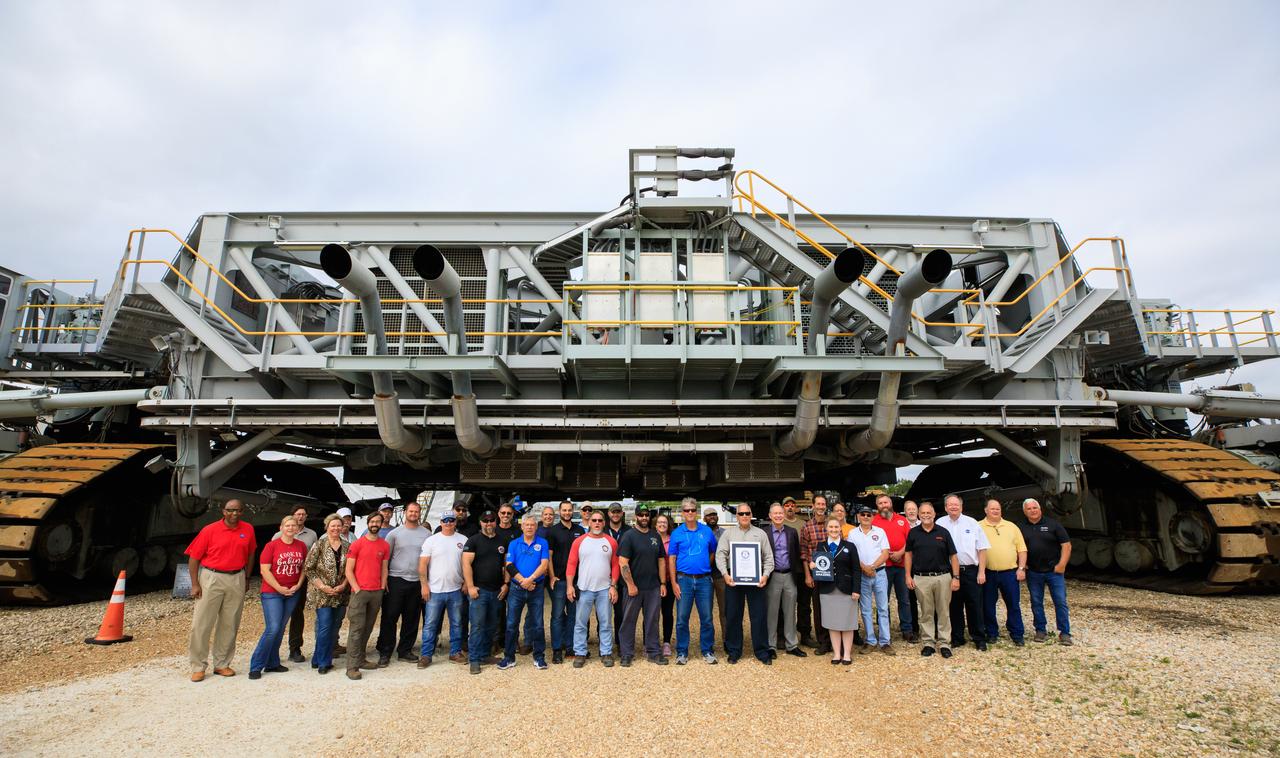

Guinness World Records officially designated NASA’s Crawler Transporter 2 as the heaviest self-powered vehicle, weighing approximately 6.65 million pounds. During a March 29, 2023, ceremony at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Guinness World Records presented a certificate to teams with the Exploration Ground Systems Program and Kennedy leadership. The crawler is responsible for carrying the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for the Artemis missions to and from the launch pad.
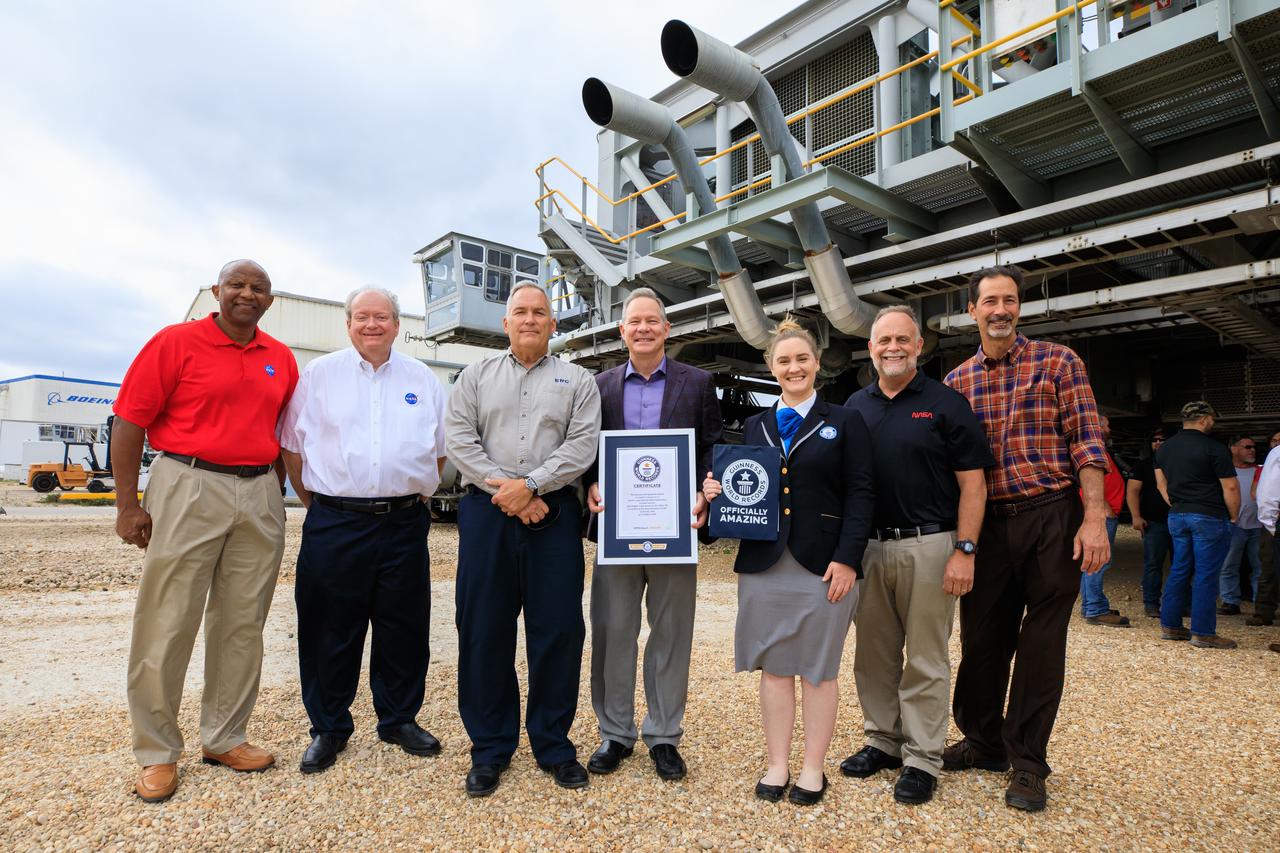

Guinness World Records officially designated NASA’s Crawler Transporter 2 as the heaviest self-powered vehicle, weighing approximately 6.65 million pounds. During a March 29, 2023, ceremony at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Guinness World Records presented a certificate to teams with the Exploration Ground Systems Program and Kennedy leadership. Pictured, from left, are: Kelvin Manning, Kennedy deputy director; Burt Summerfield, Kennedy associate director, management; Brett Raulerson, Jacobs TOSC Crawlers, Transporters and Structures group manager; Gary Casteel, Jacobs director, Ground Systems Support; Hannah Ortman, Guinness World Records adjudicator; Shawn Quinn, NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems manager; and John Giles, NASA’s Crawler Element Operations manager.
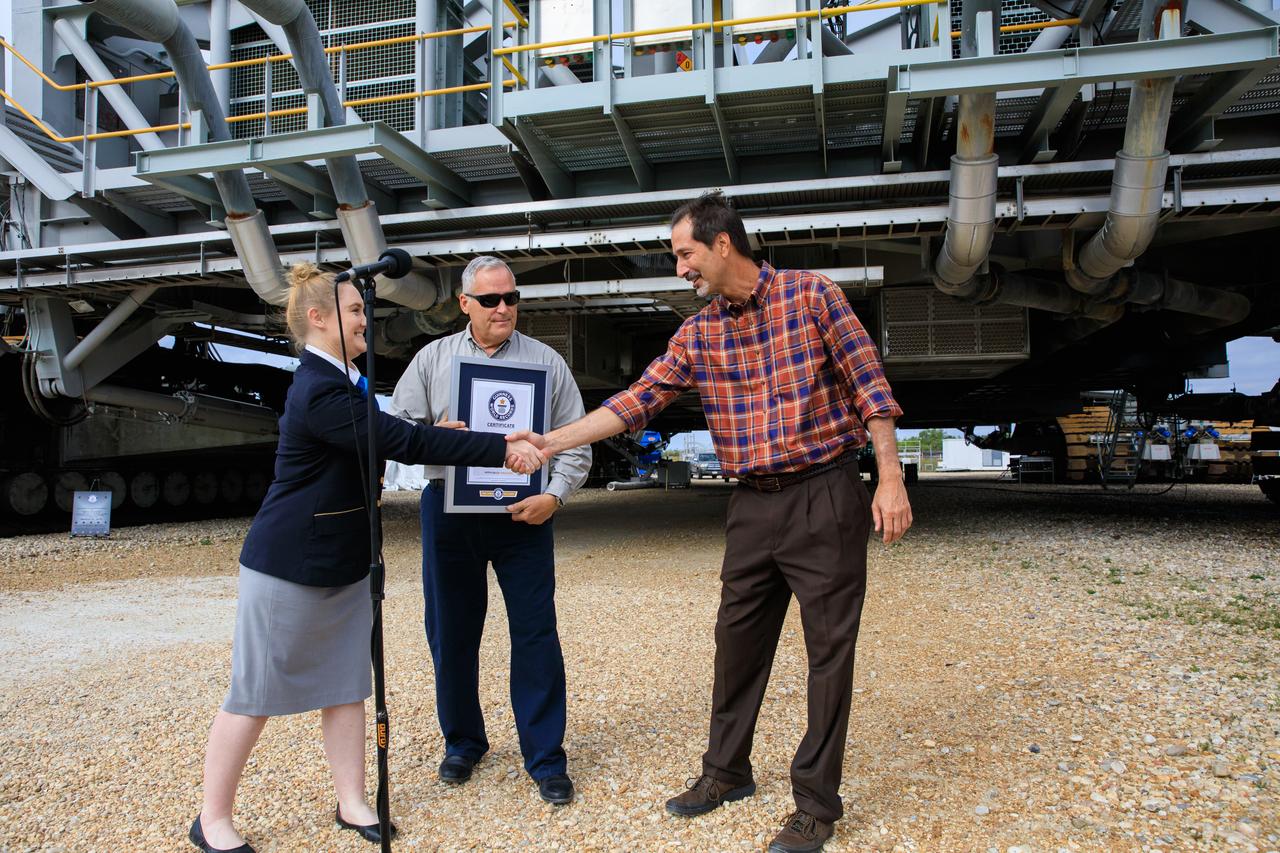

Guinness World Records adjudicator Hannah Ortman shakes hands NASA’s Crawler Element Operations Manager John Giles during a ceremony on March 29, 2023, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Also in the photo is Brett Raulerson, Jacobs TOSC Crawlers, Transporters and Structures group manager. Guinness World Records officially designated NASA’s Crawler Transporter 2 as the heaviest self-powered vehicle, weighing approximately 6.65 million pounds. The crawler is responsible for carrying the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for the Artemis missions to and from the launch pad.

Guinness World Records adjudicator Hannah Ortman shakes hands with Brett Raulerson, Jacobs TOSC Crawlers, Transporters and Structures group manager, left, and John Giles, NASA’s Crawler Element Operations manager, during a ceremony on March 29, 2023, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Guinness World Records officially designated NASA’s Crawler Transporter 2 as the heaviest self-powered vehicle, weighing approximately 6.65 million pounds. The crawler is responsible for carrying the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for the Artemis missions to and from the launch pad.

The Voyager aircraft circles before landing at Edwards Air Force Base, Edwards, California, to complete its record breaking, nonstop unfueled flight around the world.

ER-2 tail number 809, is one of two Airborne Science ER-2s used as science platforms by Dryden. The aircraft are platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They are also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation. The ER-2s are capable of carrying a maximum payload of 2,600 pounds of experiments in a nose bay, the main equipment bay behind the cockpit, two wing-mounted superpods and small underbody and trailing edges. Most ER-2 missions last about six hours with ranges of about 2,200 nautical miles. The aircraft typically fly at altitudes above 65,000 feet. On November 19, 1998, the ER-2 set a world record for medium weight aircraft reaching an altitude of 68,700 feet. The aircraft is 63 feet long, with a wingspan of 104 feet. The top of the vertical tail is 16 feet above ground when the aircraft is on the bicycle-type landing gear. Cruising speeds are 410 knots, or 467 miles per hour, at altitude. A single General Electric F118 turbofan engine rated at 17,000 pounds thrust powers the ER-2.
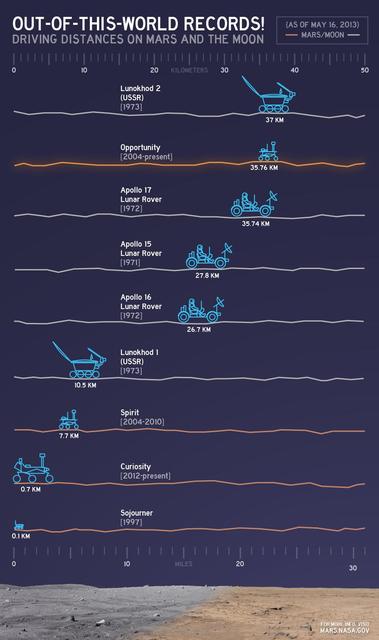
This chart illustrates comparisons among the distances driven by various wheeled vehicles on the surface of Earth moon and Mars. Of the vehicles shown, the NASA Mars rovers Opportunity and Curiosity are still active.
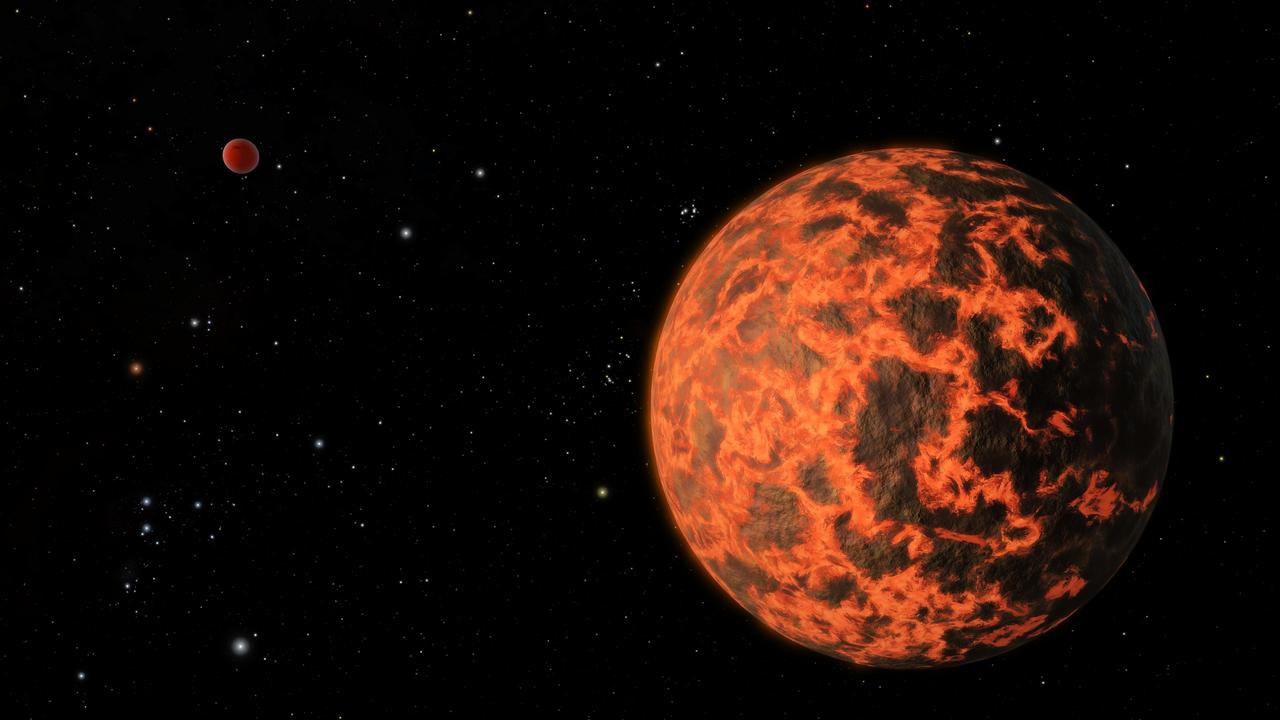

Astronomers using NASA Spitzer Space Telescope have detected what they believe is an alien world just two-thirds the size of Earth -- one of the smallest on record.
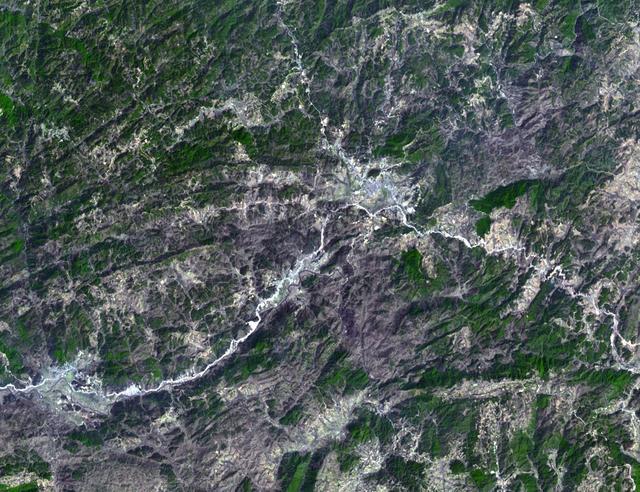

This image from NASA Terra spacecraft shows a cluster of villages known as Mawsynram in India, which is the current world record holder for the wettest place on earth.
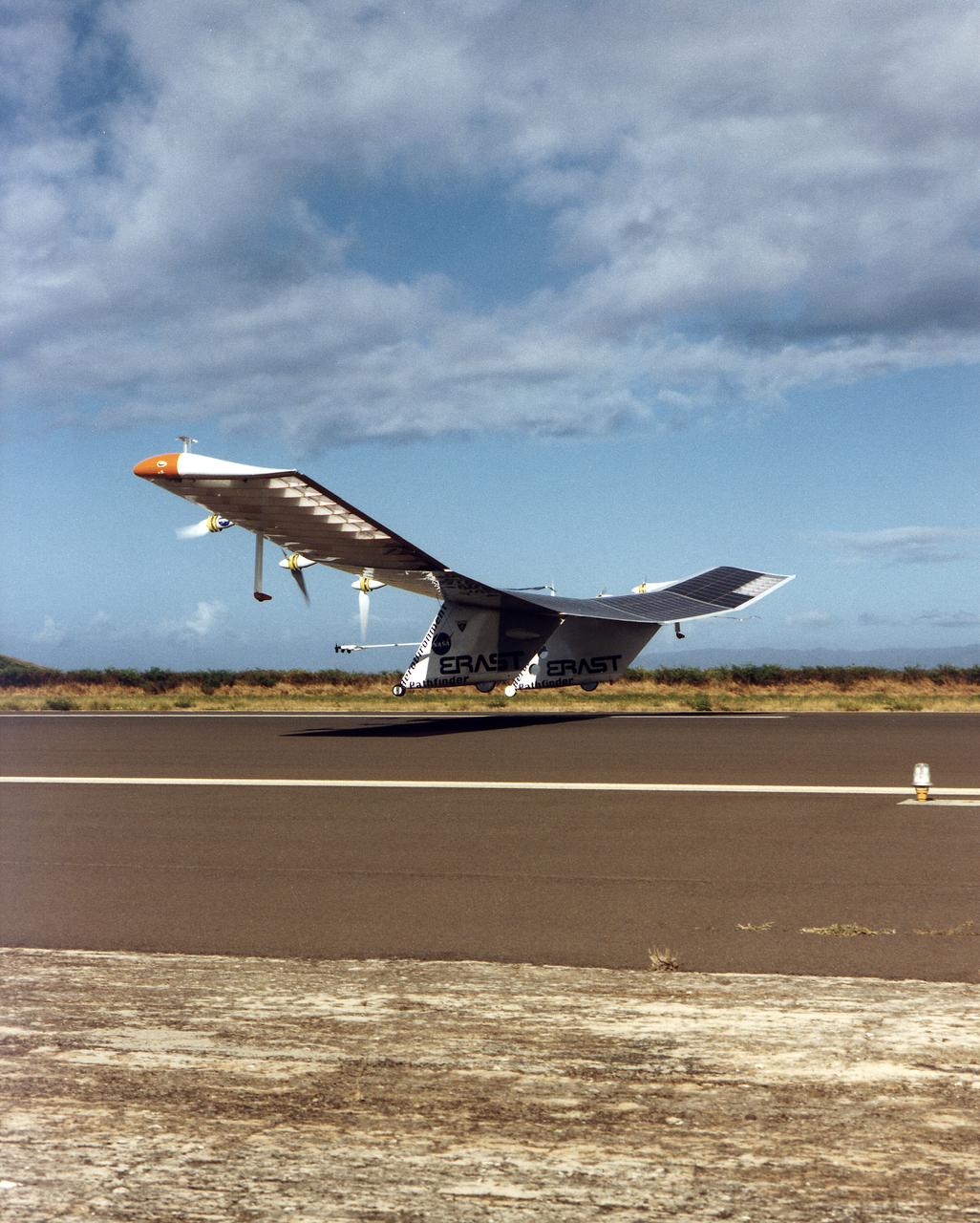

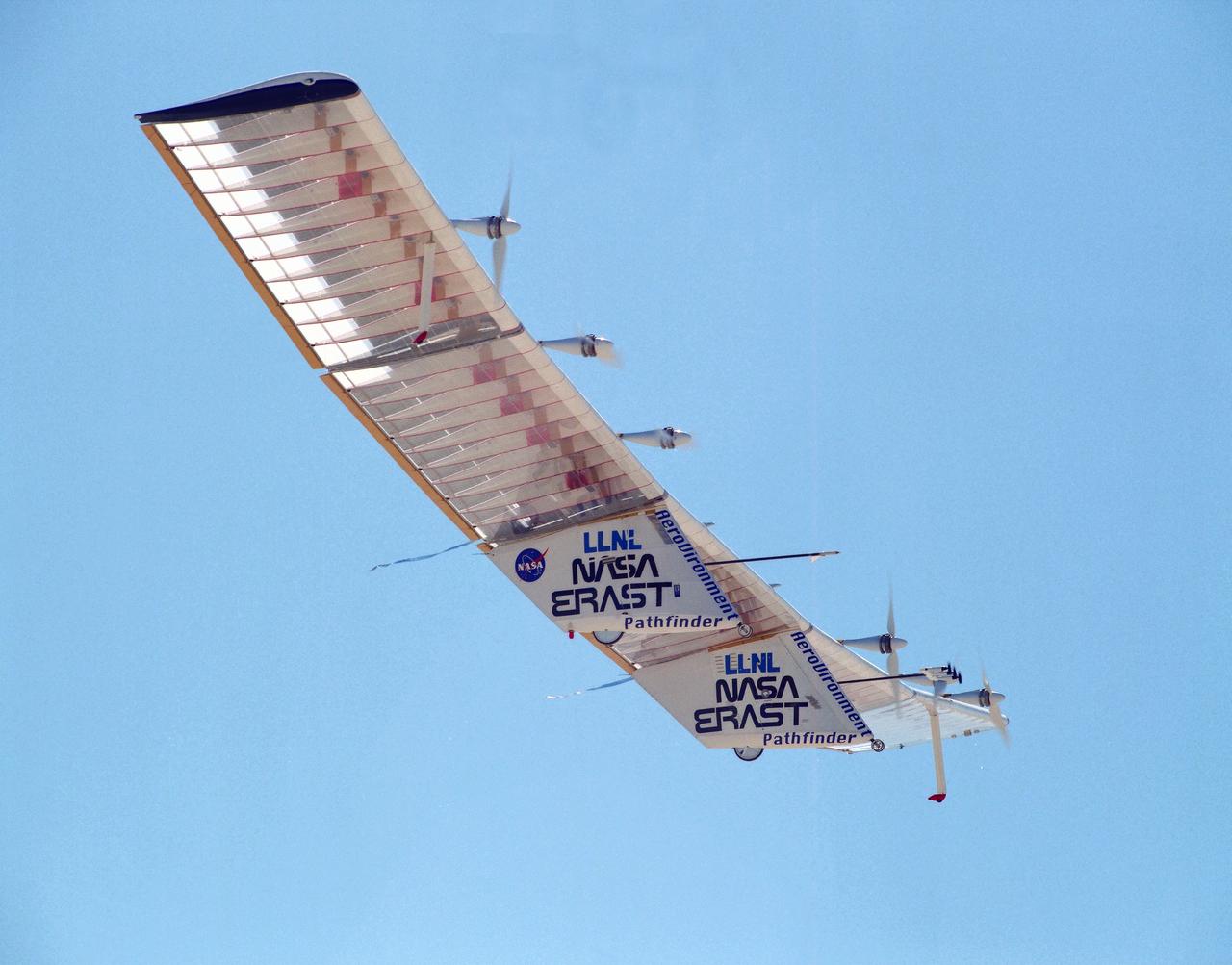
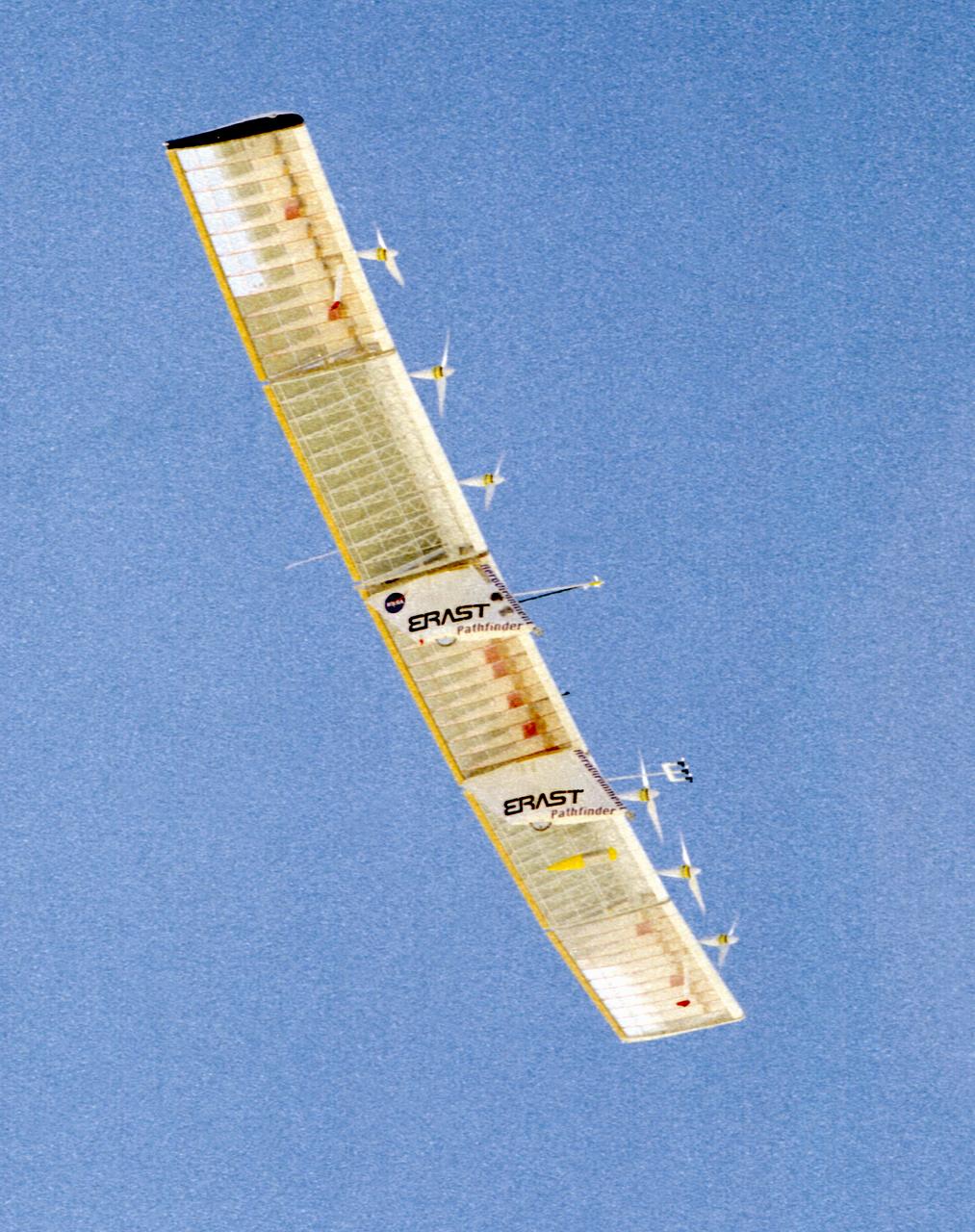
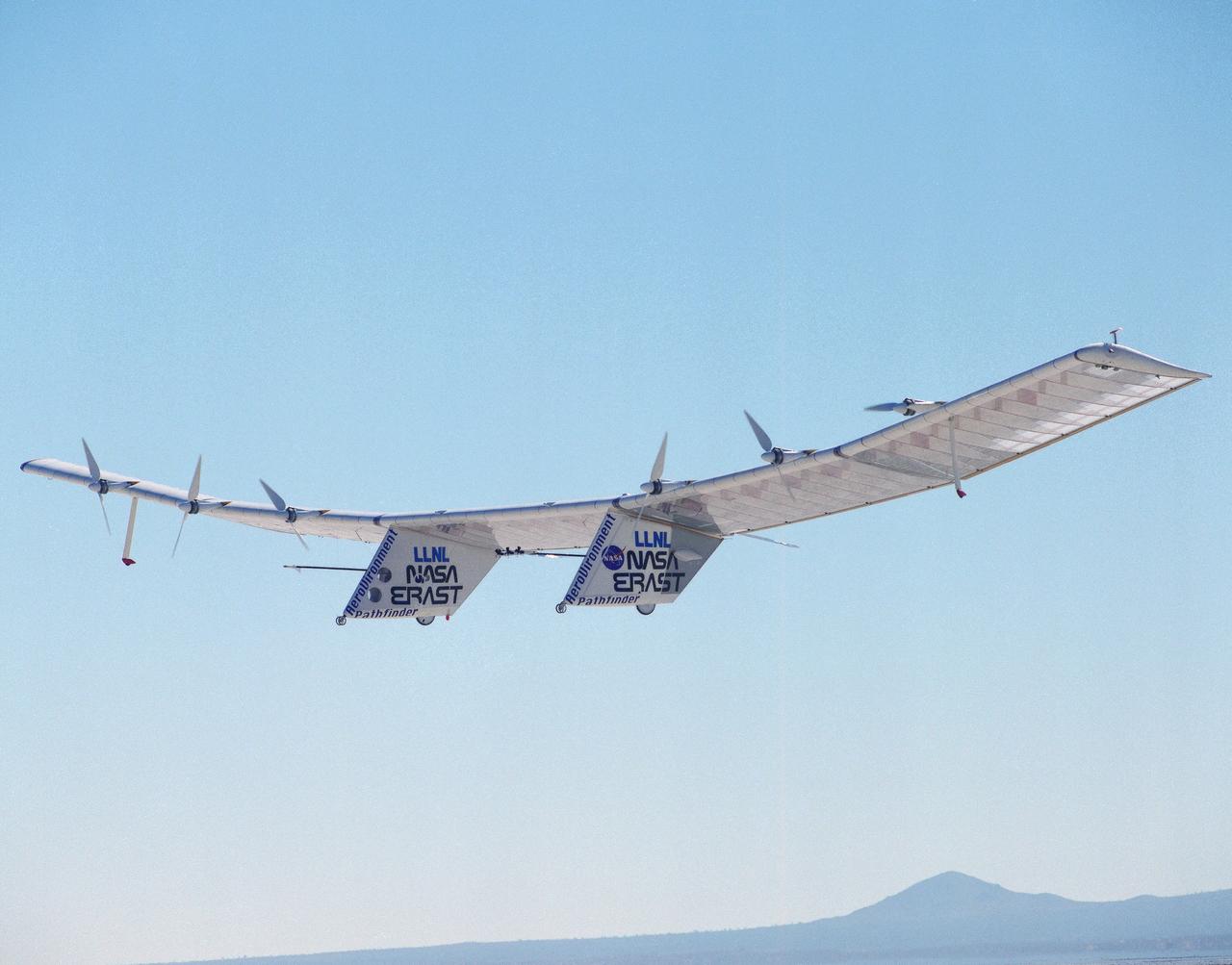
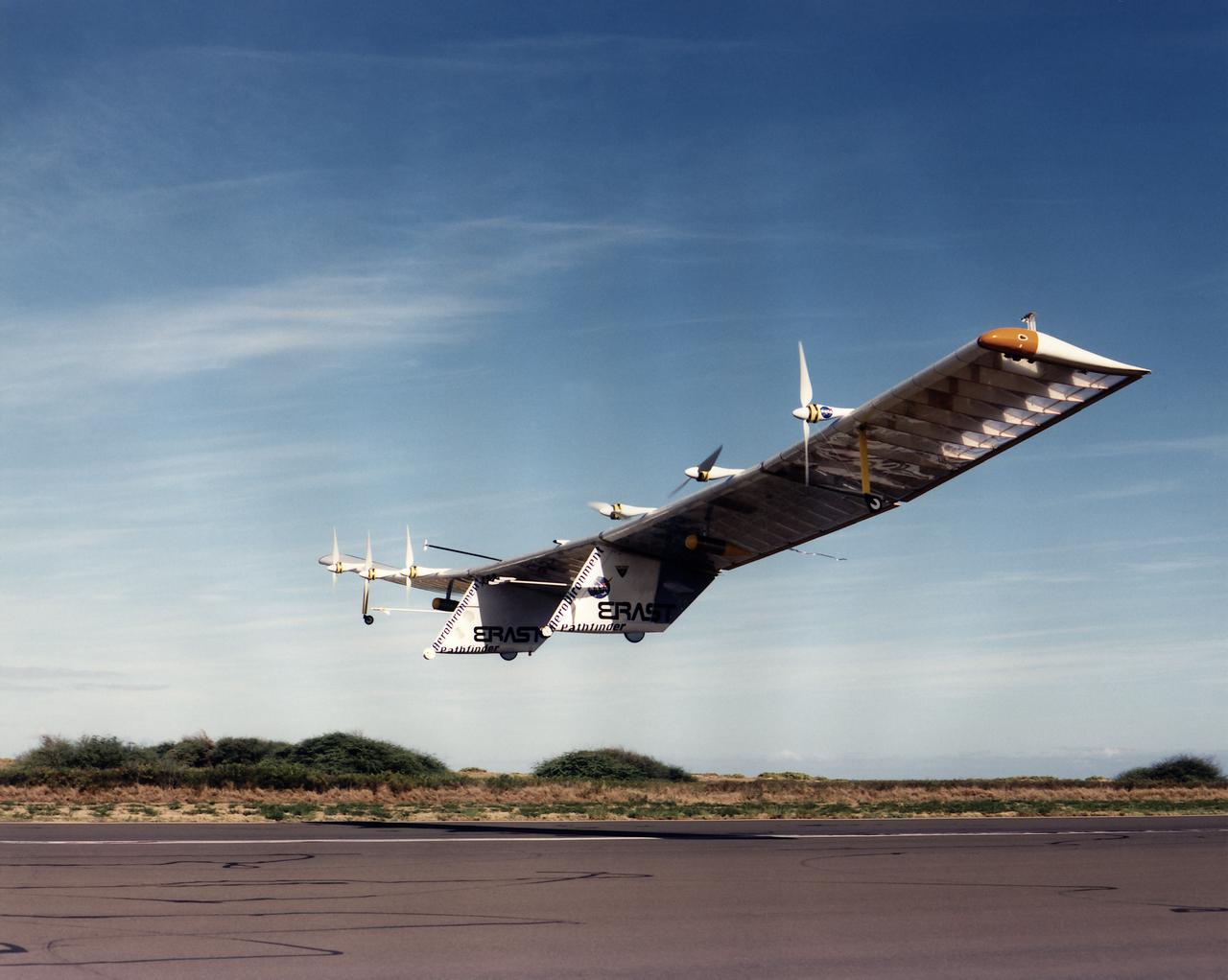
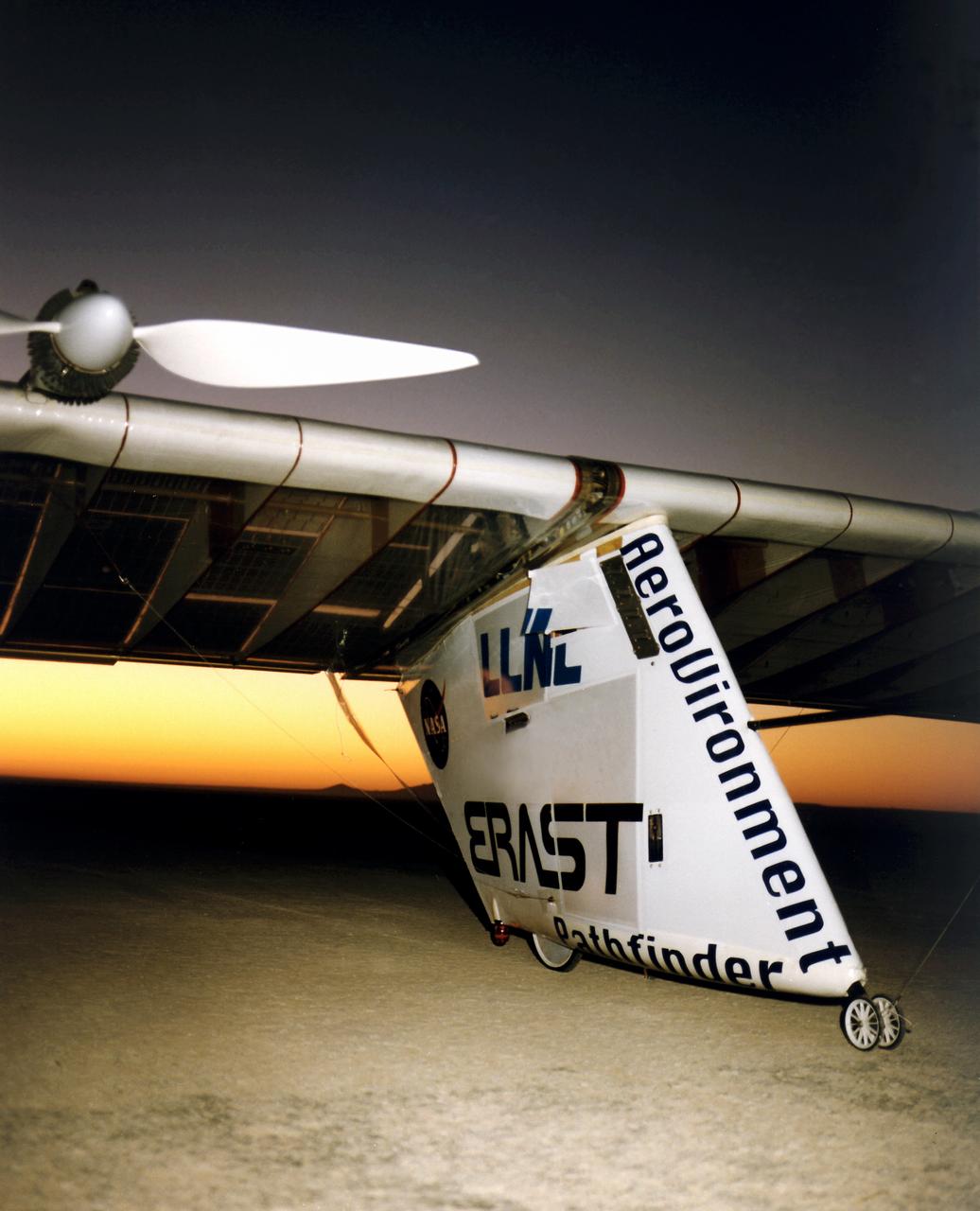
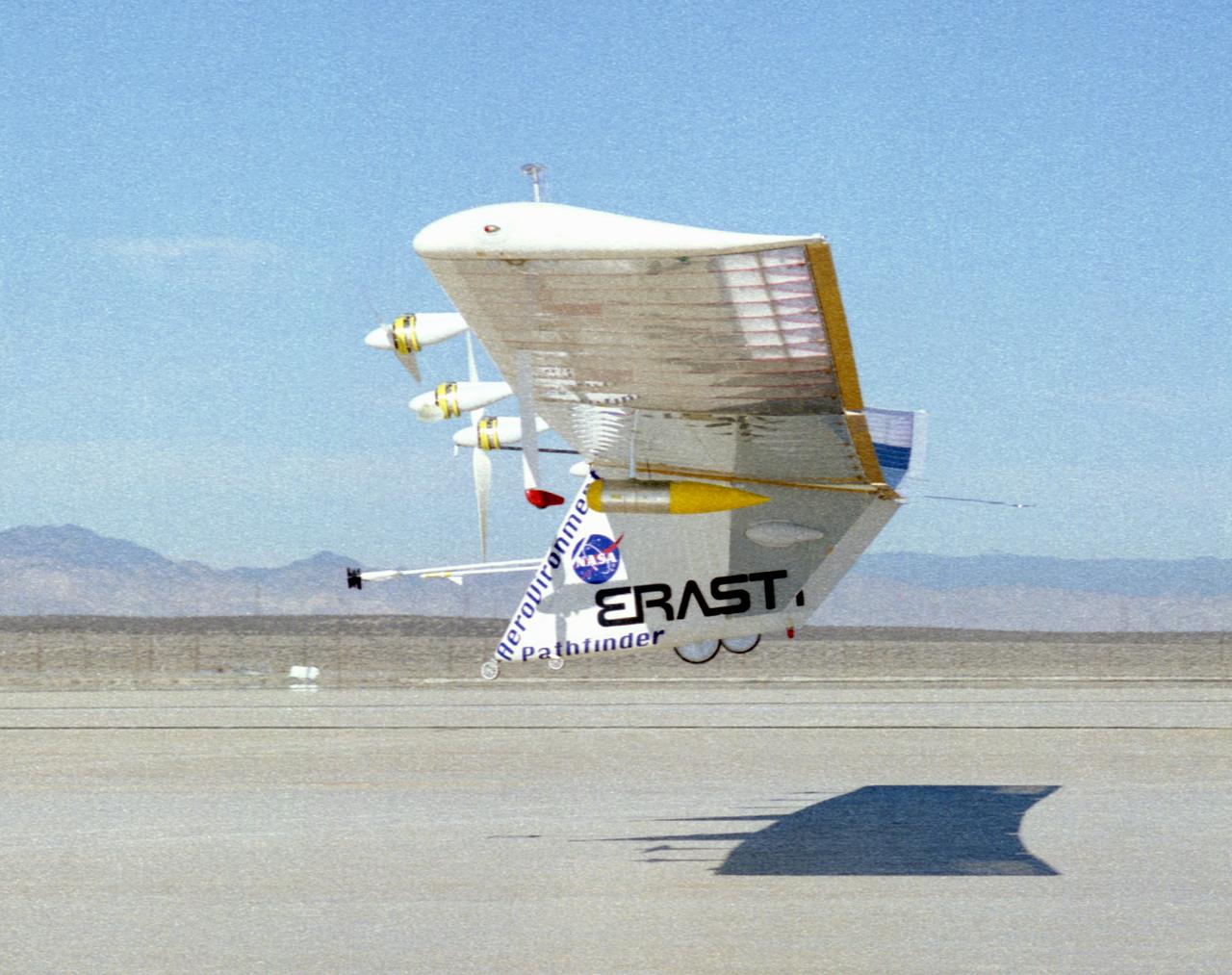
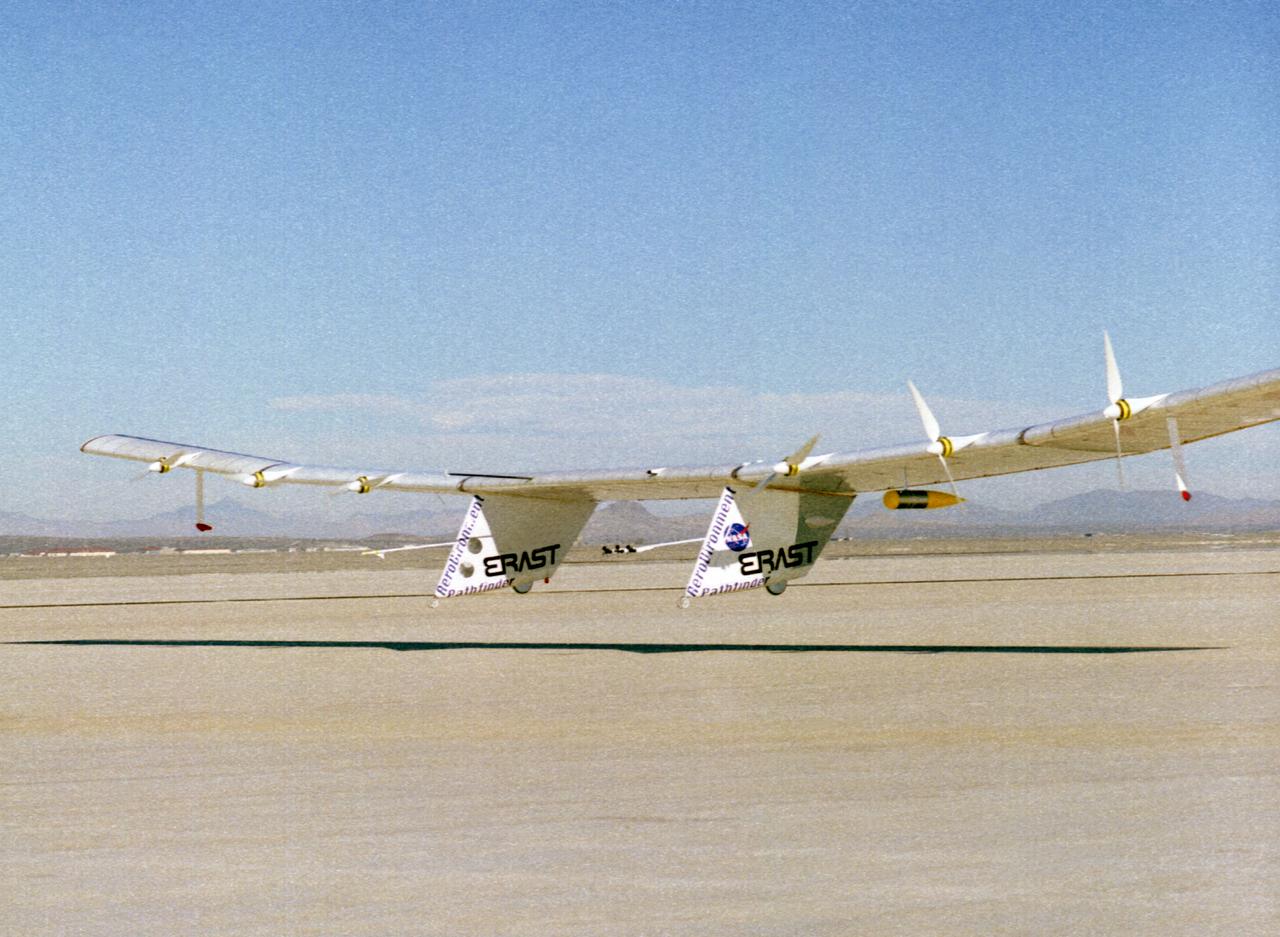
The Pathfinder aircraft has set a new unofficial world record for high-altitude flight of over 71,500 feet for solar-powered aircraft at the U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility, Kauai, Hawaii. Pathfinder was designed and manufactured by AeroVironment, Inc, of Simi Valley, California, and was operated by the firm under a jointly sponsored research agreement with NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. Pathfinder's record-breaking flight occurred July 7, 1997. The aircraft took off at 11:34 a.m. PDT, passed its previous record altitude of 67,350 feet at about 5:45 p.m. and then reached its new record altitude at 7 p.m. The mission ended with a perfect nighttime landing at 2:05 a.m. PDT July 8. The new record is the highest altitude ever attained by a propellor-driven aircraft. Before Pathfinder, the altitude record for propellor-driven aircraft was 67,028 feet, set by the experimental Boeing Condor remotely piloted aircraft.
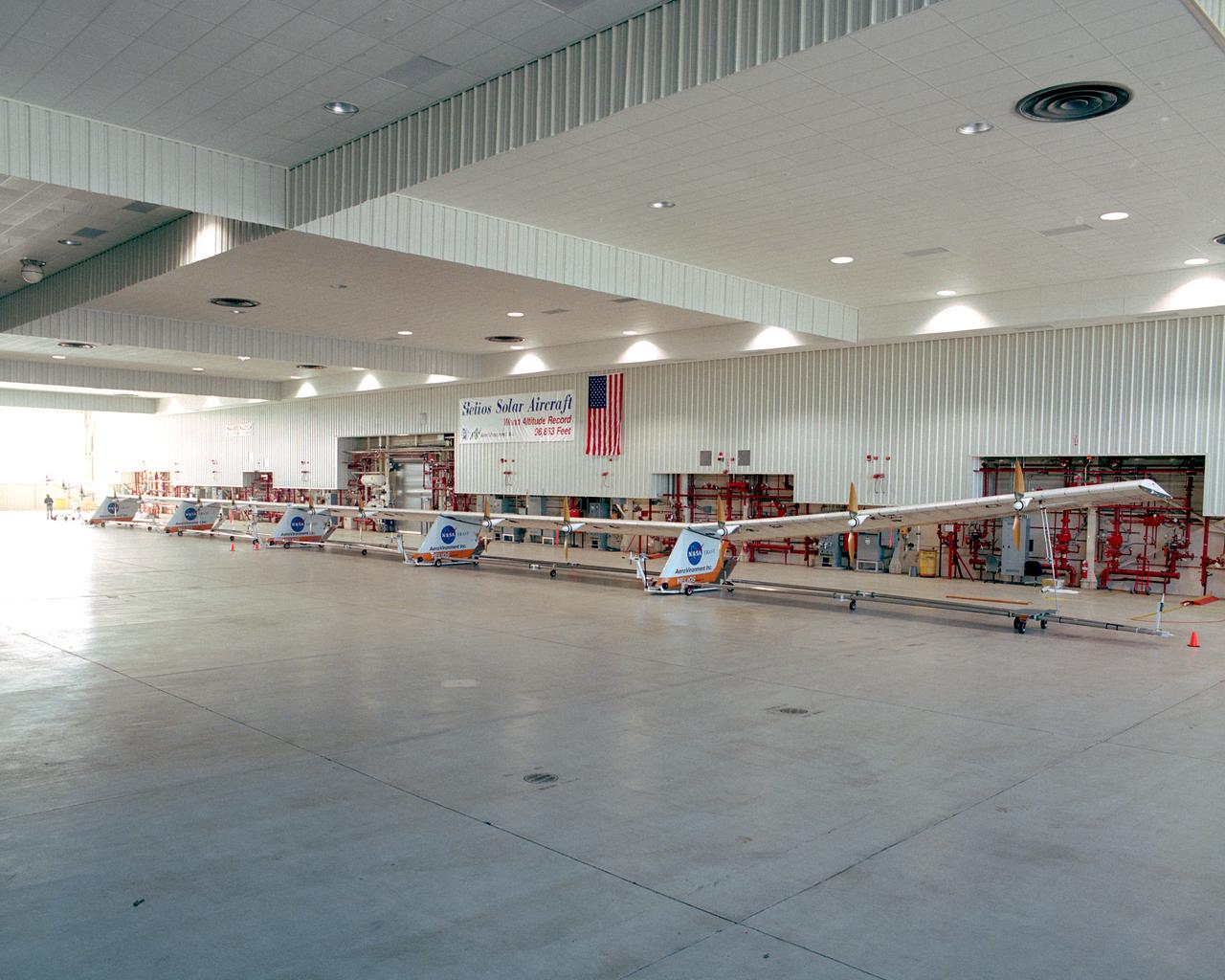

The Helios Prototype flying wing stretches almost the full length of the 300-foot-long hangar at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The 247-foot span solar-powered aircraft, resting on its ground maneuvering dolly, was on display for a visit of NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe and other NASA officials on January 31, 2002. The unique solar-electric flying wing reached an altitude of 96,863 feet during an almost 17-hour flight near Hawaii on August 13, 2001, a world record for sustained horizontal flight by a non-rocket powered aircraft. Developed by AeroVironment, Inc., under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) project, the Helios Prototype is the forerunner of a planned fleet of slow-flying, long duration, high-altitude uninhabited aerial vehicles (UAV) which can serve as "atmospheric satellites," performing Earth science missions or functioning as telecommunications relay platforms in the stratosphere.
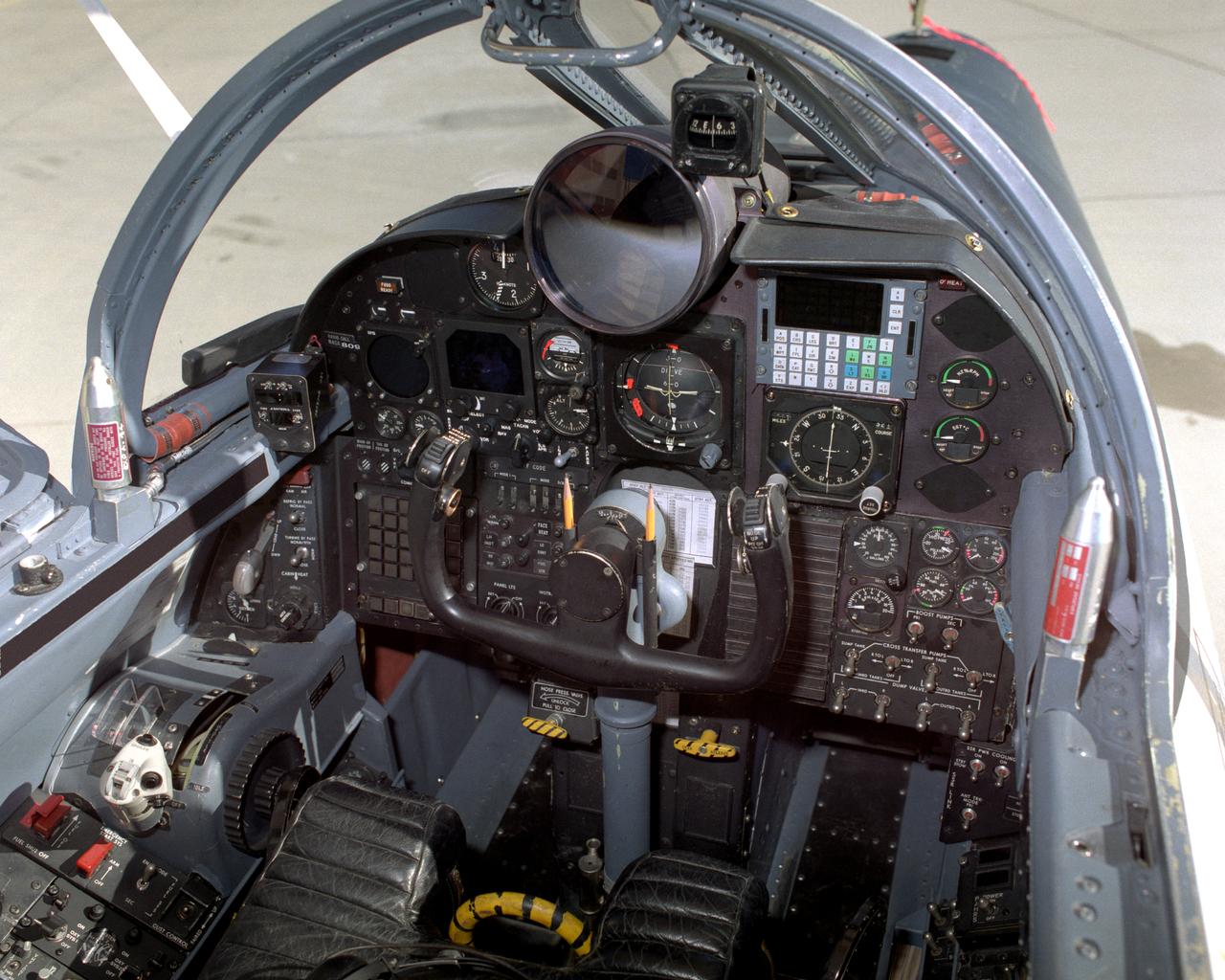

Lockheed ER-2 #809 cockpit
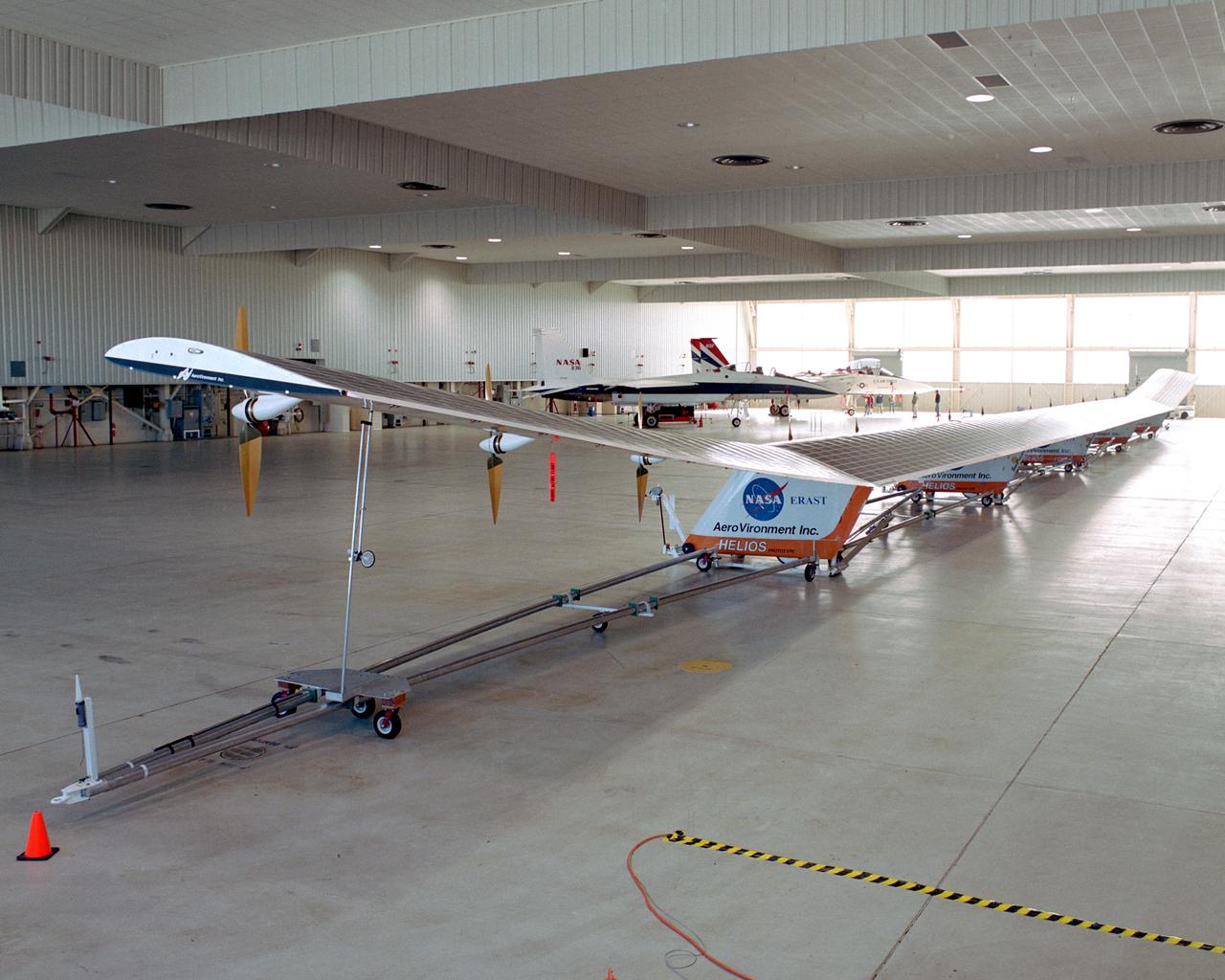

The solar-powered Helios Prototype flying wing frames two modified F-15 research aircraft in a hangar at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The elongated 247-foot span lightweight aircraft, resting on its ground maneuvering dolly, stretched almost the full length of the 300-foot long hangar while on display during a visit of NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe and other NASA officials on Jan. 31, 2002. The unique solar-electric flying wing reached an altitude of 96,863 feet during an almost 17-hour flight near Hawaii on Aug. 13, 2001, a world record for sustained horizontal flight by a non-rocket powered aircraft. Developed by AeroVironment, Inc., under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) project, the Helios Prototype is the forerunner of a planned fleet of slow-flying, long duration, high-altitude uninhabited aerial vehicles (UAV) which can serve as "atmospheric satellites," performing Earth science missions or functioning as telecommunications relay platforms in the stratosphere.

U.S. Secretary of Agriculture Tom Vilsack gives remarks via a previously recorded message, during an event at the U.S Department of State where it was announced that Cynthia Rosenzweig, a senior research scientist and head of the Climate Impacts Group at NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) in New York City, was awarded the 2022 World Food Prize from the World Food Prize Foundation, Thursday, May 5, 2022, at the Harry S. Truman Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
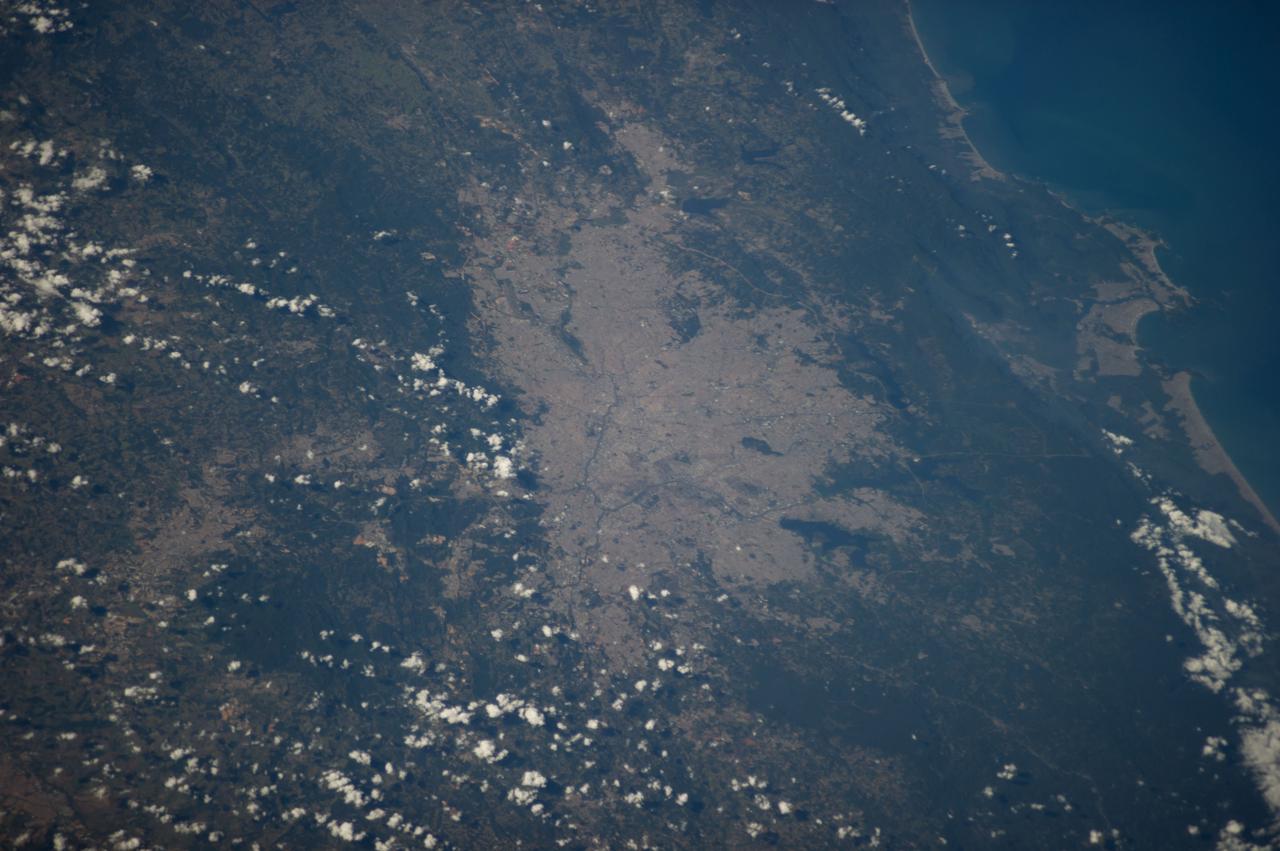

ISS040-E-010803 (12 June 2014) --- One of the Expedition 40 crew members aboard the International Space Station photographed this image featuring Sao Paulo, one of the host cities in Brazil for the 2014 World Cup. A 200mm focal length was used to record the photograph on June 12.
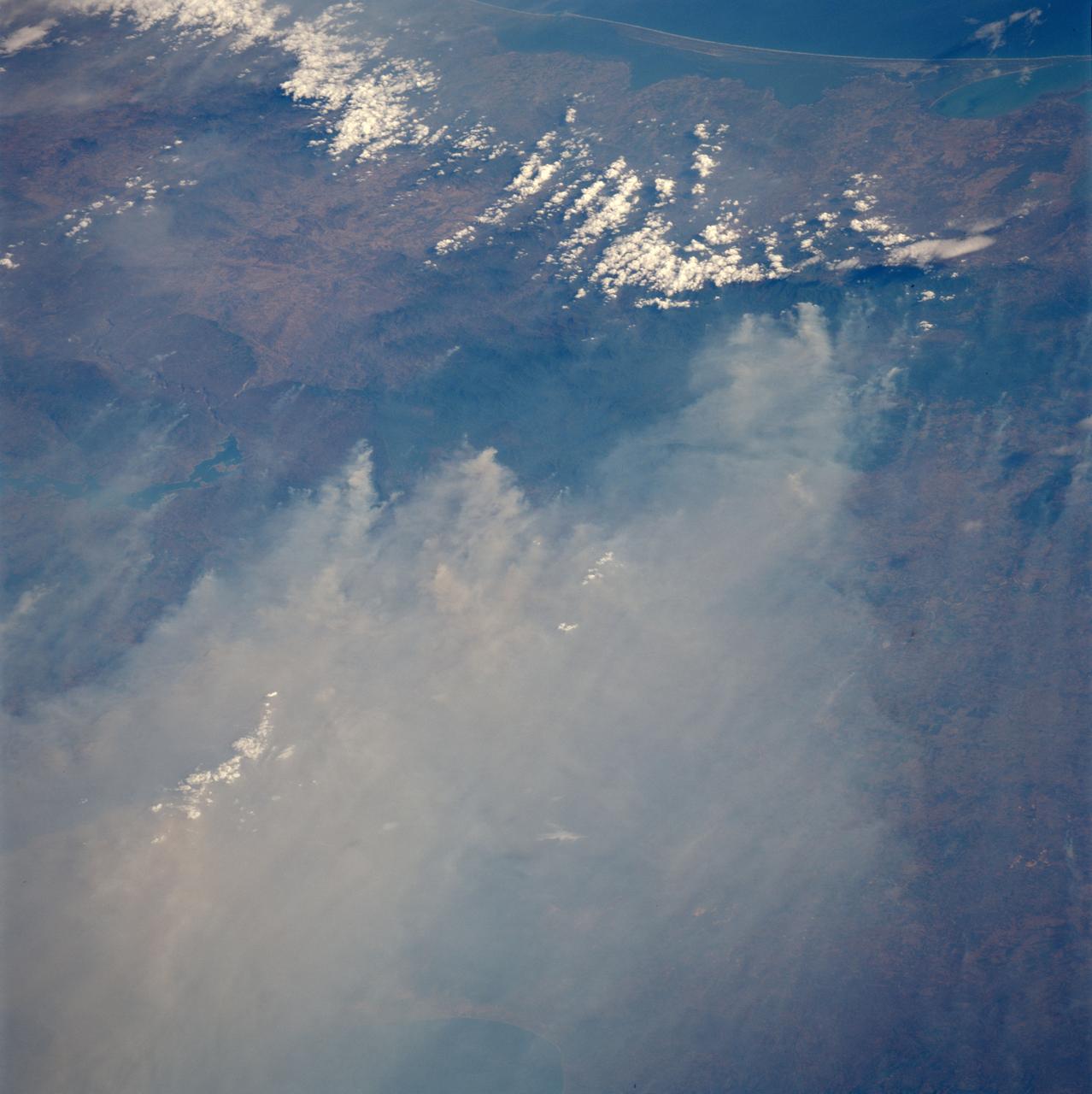

STS091-701-075 (2-12 June 1998) --- Fires across Mexico and Central America which created heavy smoke plumes for a few weeks in May and June, 1998, were recorded on 70mm film by the crewmembers of STS-91. The smoke circulated around a high pressure system over the Gulf of Mexico and brought thick smoke and soot to the south central United States. Scientists are looking at burning regions like this around the world to study the smokes affect on the albedo or the reflectance of the sun's rays and how it may influence the world's climate. This view captures the area from the Gulf of Tehuantepec, on the south side, to the Bay of Campeche to the north in early June 1998.
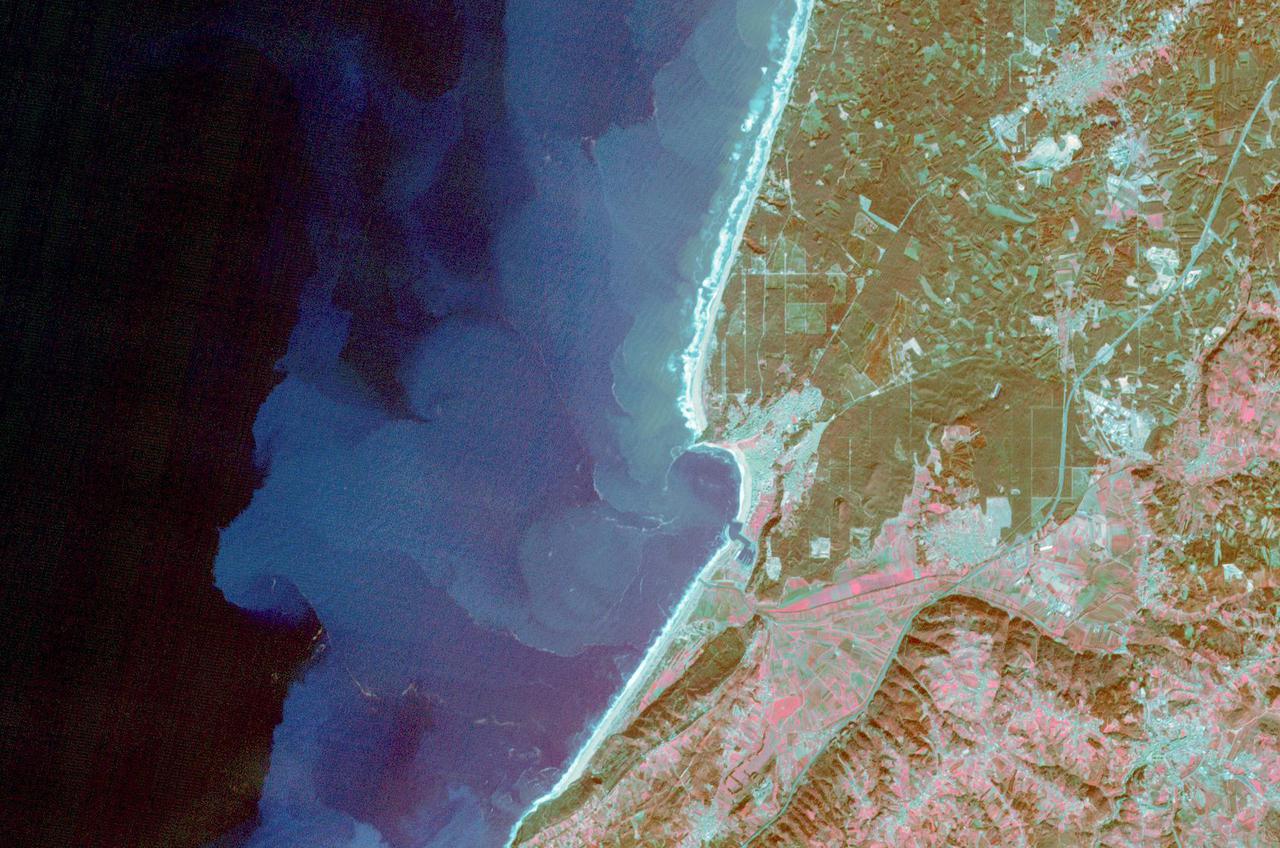

The fishing and tourist village of Nazare, Portugal was practically unknown, until 2000, when surfers first braved its monstrous winter waves. Since then, world records for surviving surfing the 30m+ high waves have fallen, and movies have been made, celebrating the brave (crazy?) surfers willing to risk their lives to challenge the world's tallest waves. Sediment highlights off-shore current patterns in the image. The image was acquired November 24, 2009, covers an area of 18 by 25.7 km, and is located at 39.6 degrees north, 9.1 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25121
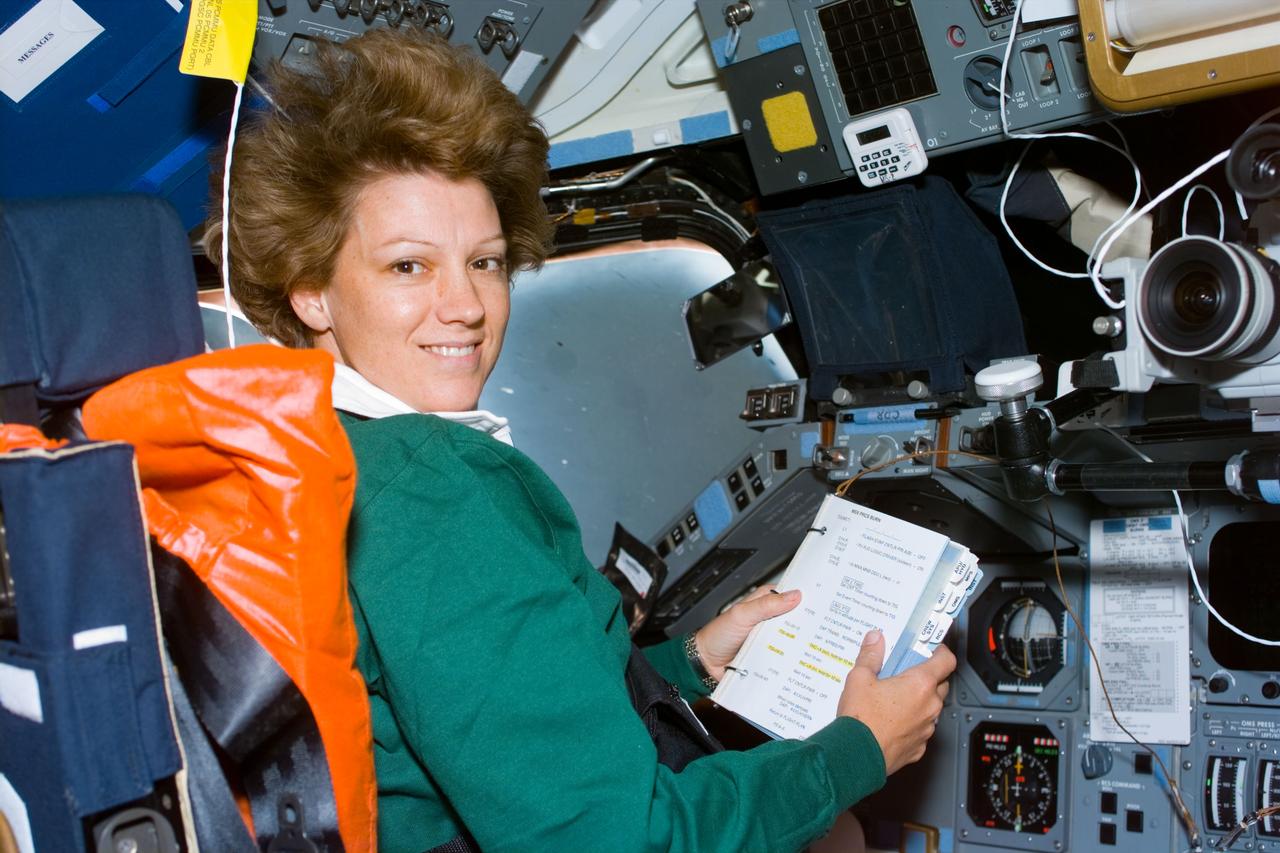

S93-E-5033 (23 July 1999) --- Astronaut Eileen M. Collins, mission commander, looks over a procedures checklist at the commander's station on the forward flight deck of the Space Shuttle Columbia on Flight Day 1. The most important event of this day was the deployment of the Chandra X-Ray Observatory, the world's most powerful X-Ray telescope. The photo was recorded with an electronic still camera (ESC).

STS093-706-035 (23 July 1999)--- This 70mm frame shows the Chandra X-Ray observatory backdropped against the darkness of space not long after its release from Columbia's payload bay. The primary duty of the STS-93 crew was to deploy the world's most powerful X-Ray telescope. It was also one of the first actions of the crew, occurring just a few hours following the shuttle's arrival in Earth orbit. This scene is one of a series of still photos recorded by the crew before and during the deployment of the 50,162 pound observatory.
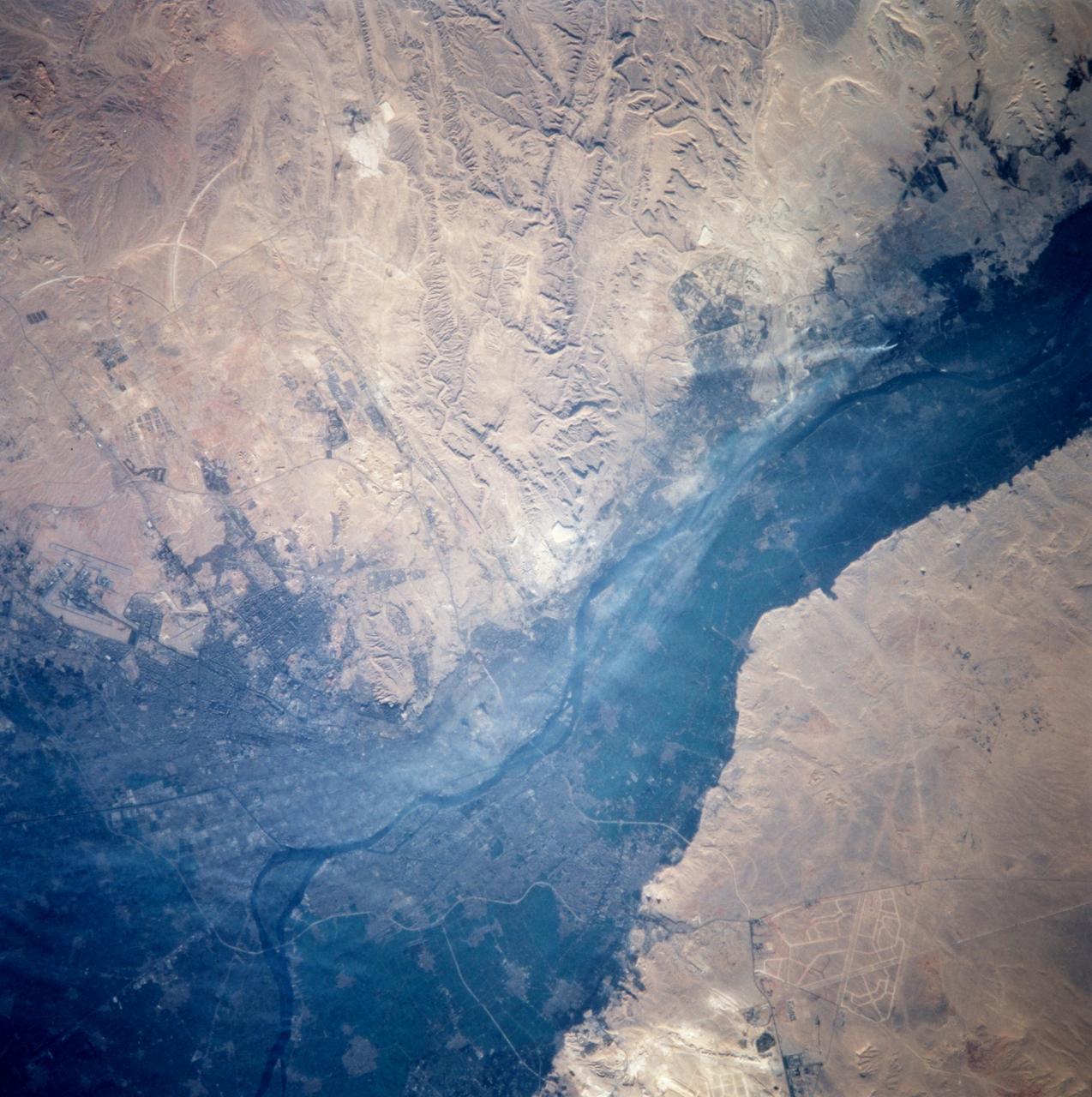

STS099-714-060 (11-22 February 2000) ---One of the STS-99 astronauts aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour recorded this 70mm image of Cairo, one of the fastest growing cities in the world. The city is moving outside the dark-colored Nile valley into the surrounding desert. New developments are side by side with ancient monuments. The pyramids at Giza are highlighted by their shadows and the new development in the desert to the South is outlined by lighter-colored roads. Further south of the Giza pyramids on the west side of the Nile River are the Step and Bent Pyramids, respectively.

STS093-705-020 (23 July 1999)--- This 70mm frame shows the Chandra X-Ray observatory just before it was tilted upward for its release from Columbia's payload bay. The primary duty of the STS-93 crew was to deploy the world's most powerful X-Ray telescope. It was also one of the first actions of the astronauts, occurring just a few hours following the shuttle's arrival in Earth orbit. This scene is one of a series of still photos recorded by the crew before and during the deployment of the 50,162 pound observatory.
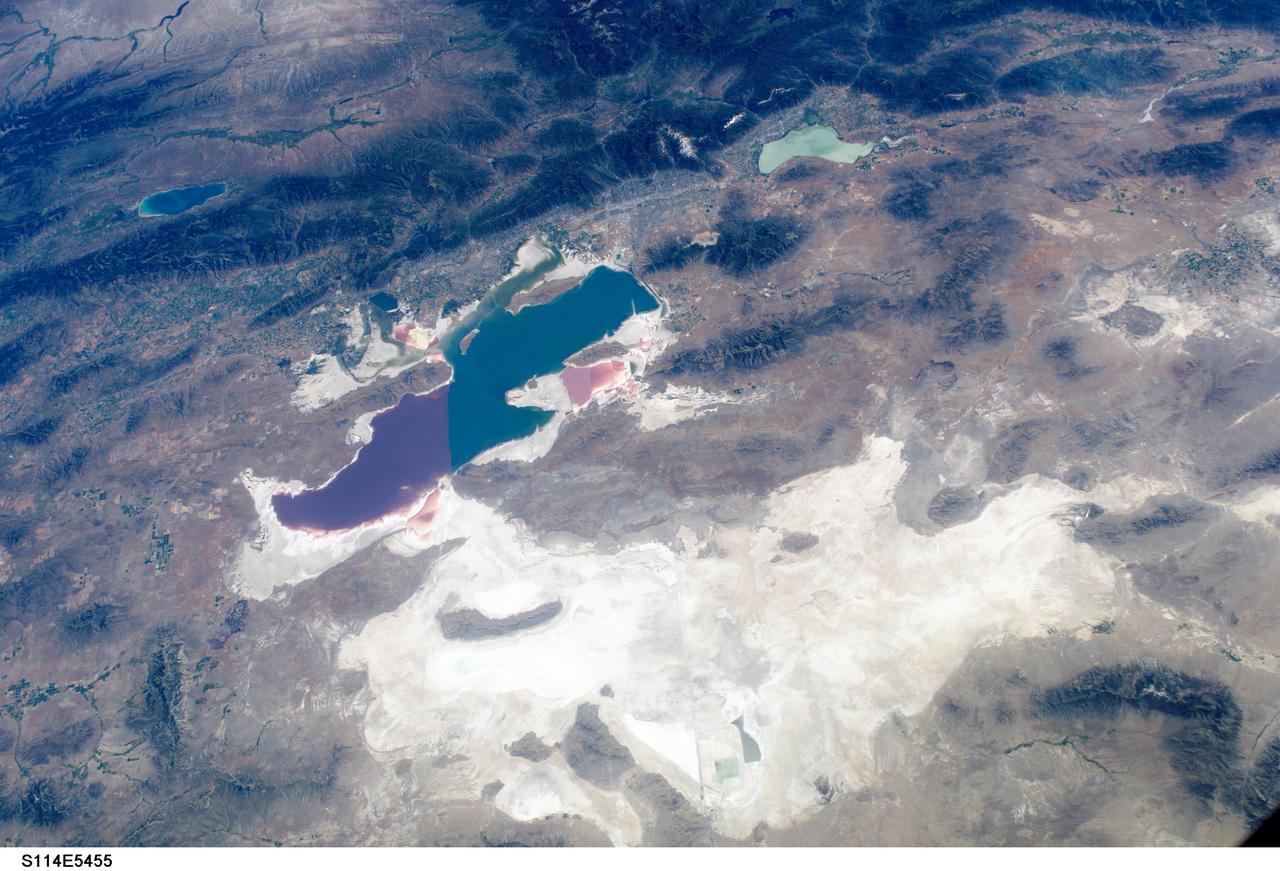

S114-E-5455 (27 July 2005) --- This digital still camera frame, showing the Great Salt Lake and Salt Lake City, is one of a series of photos of both domestic and world-wide targets of opportunity captured by the STS-114 astronauts. Salt Lake City is in the upper half of the photo between the Great Salt Lake and the smaller Lake Utah. A 28 mm lens was used to record the image.
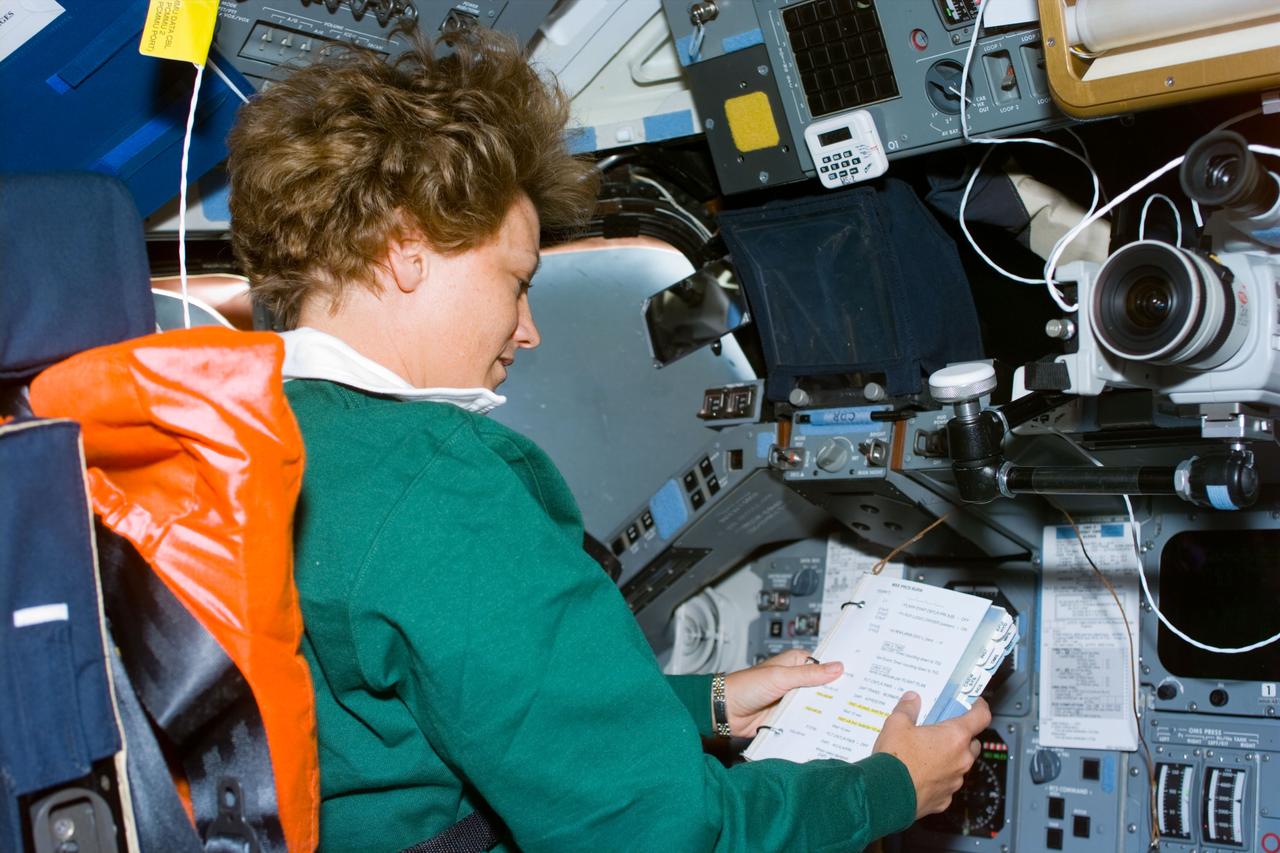

S93-E-5031 (23 July 1999) --- Astronaut Eileen M. Collins, mission commander, looks over a procedures checklist at the commander's station on the forward flight deck of the Space Shuttle Columbia on Flight Day 1. The most important event of this day was the deployment of the Chandra X-Ray Observatory, the world's most powerful X-Ray telescope. The photo was recorded with an electronic still camera (ESC).
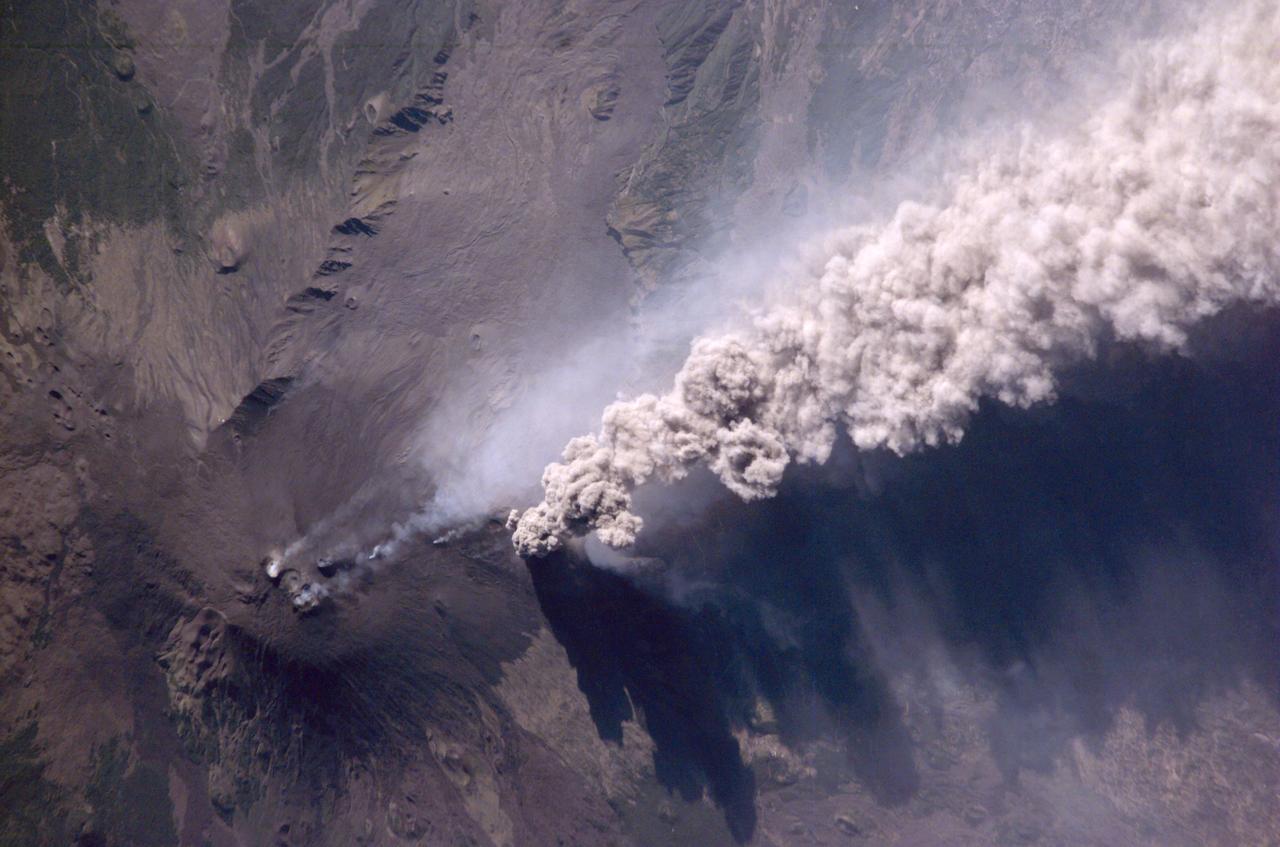

An Expedition Two crewmember aboard the International Space Station (ISS) captured this overhead look at the smoke and ash regurgitated from the erupting volcano Mt. Etna on the island of Sicily, Italy. At an elevation of 10,990 feet (3,350 m), the summit of the Mt. Etna volcano, one of the most active and most studied volcanoes in the world, has been active for a half-million years and has erupted hundreds of times in recorded history.
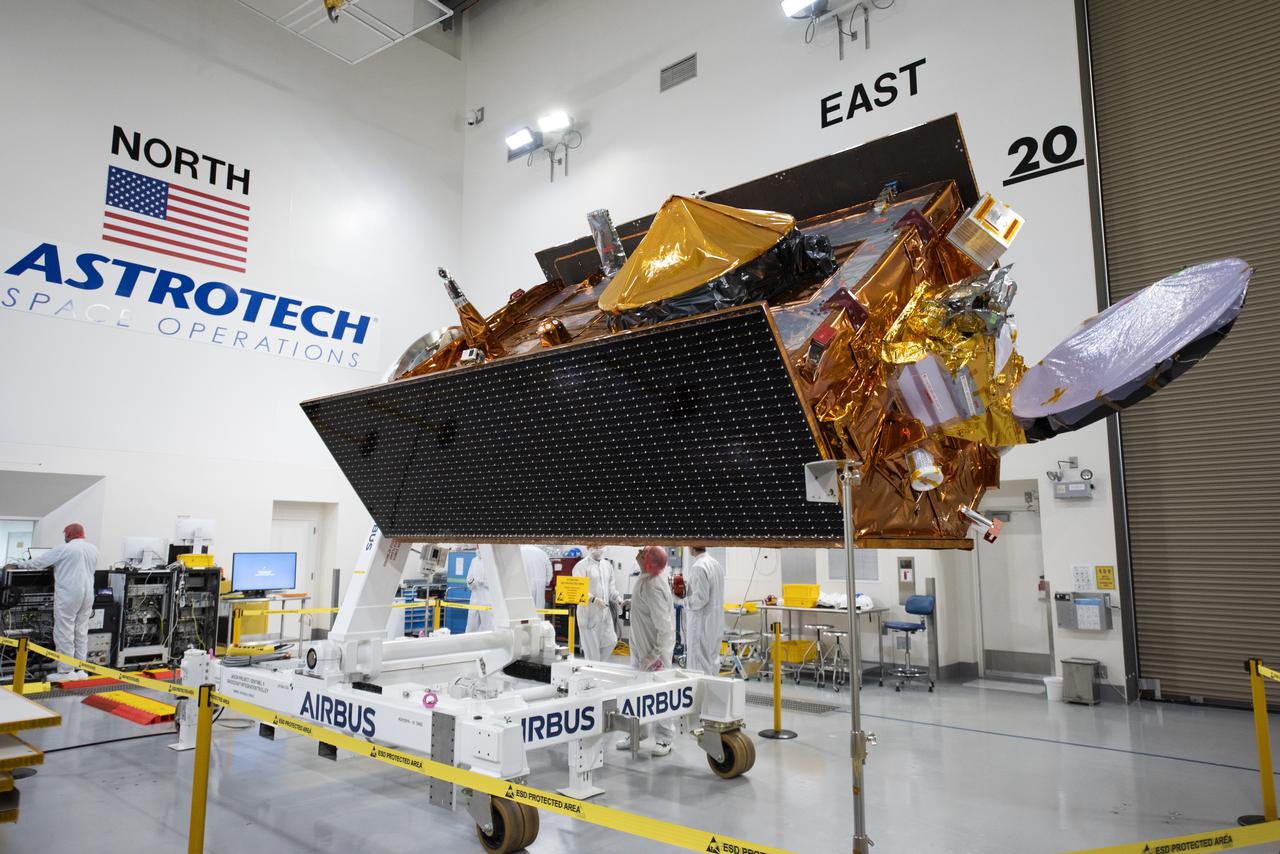

Technicians transfer the Sentinel-6B spacecraft from the NASA hangar to the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. The spacecraft is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. Sentinel-6B also will extend the record of atmospheric temperatures, begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich, out to a decade.
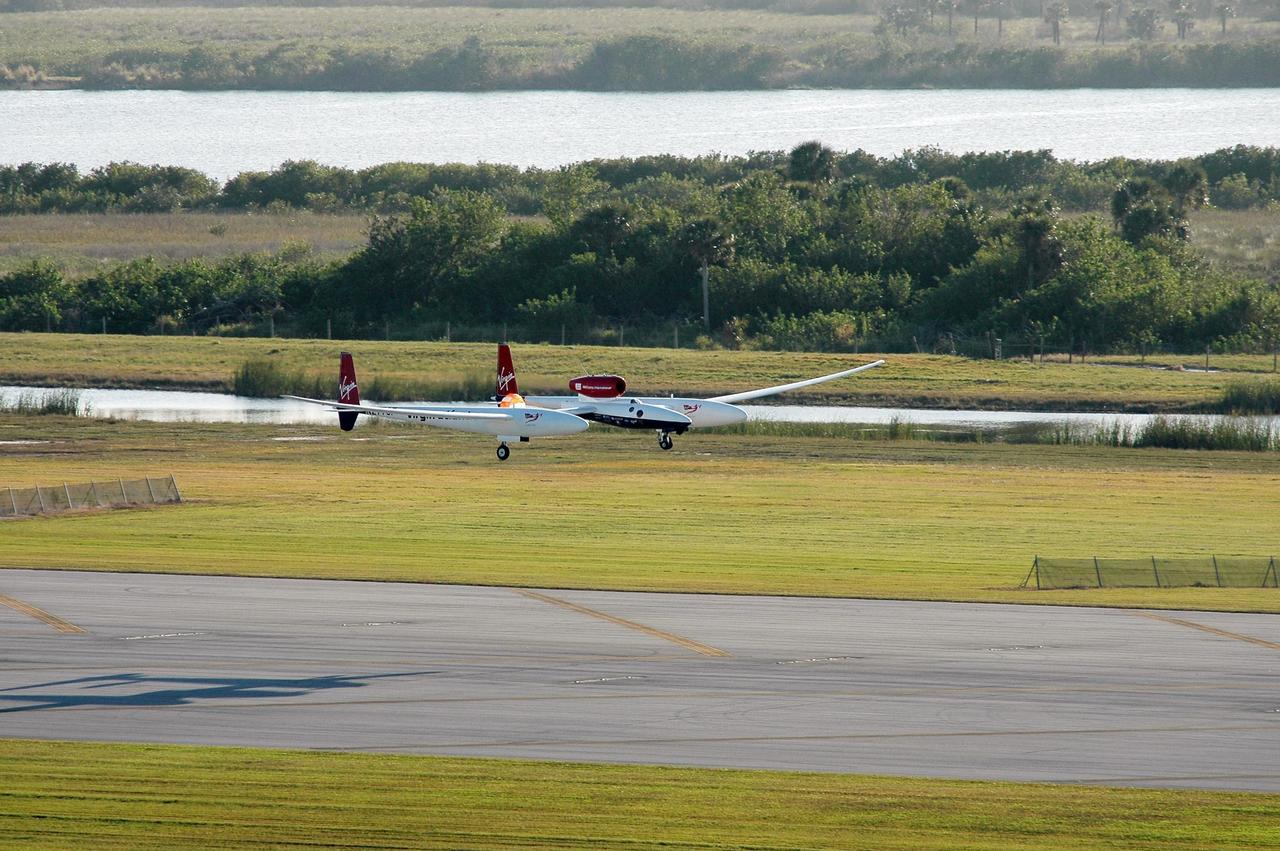

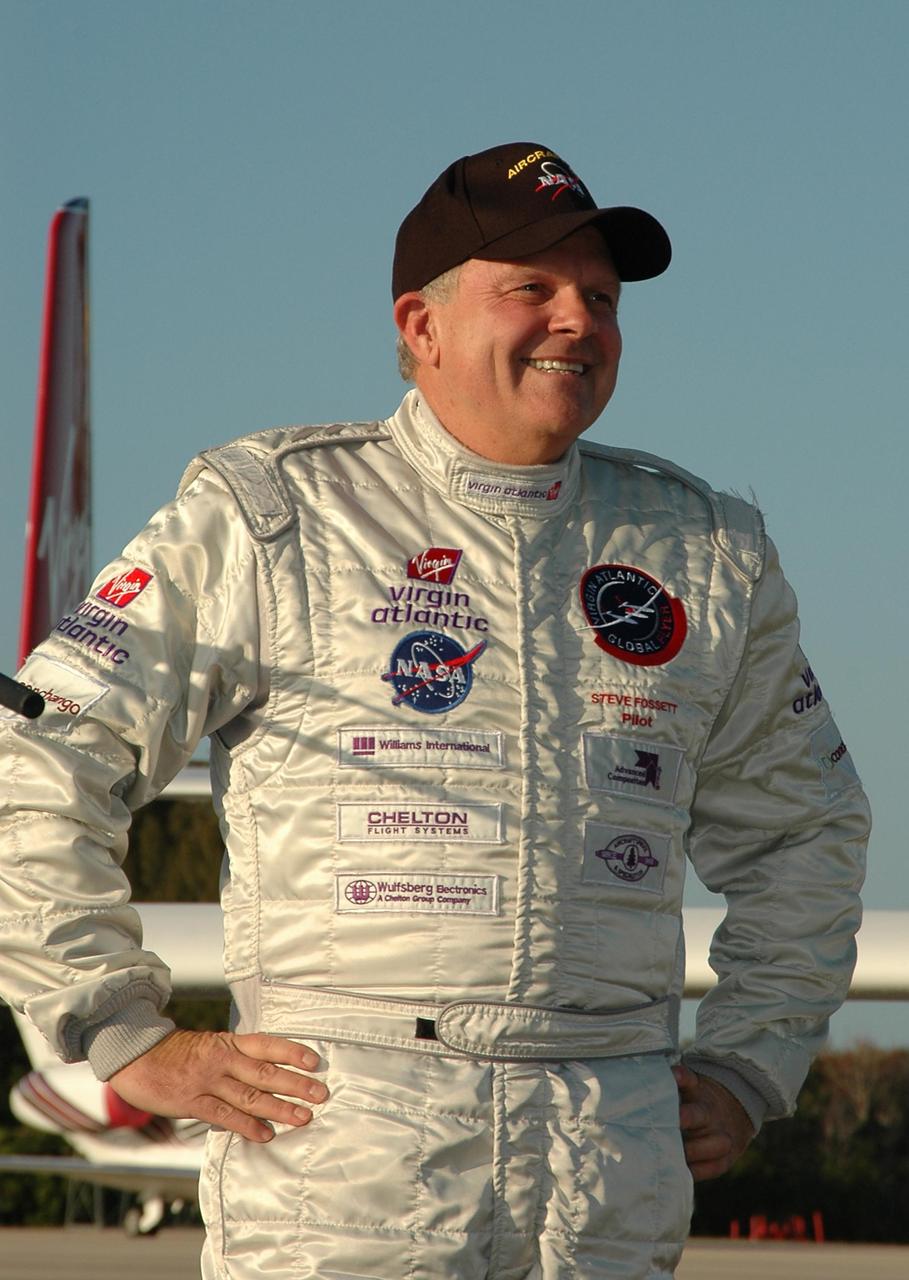
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Virgin Atlantic Airways GlobalFlyer aircraft approaches NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility for a landing. The aircraft, piloted by Steve Fossett, is being relocated from Salina, Kan., to the Shuttle Landing Facility to begin preparations for an attempt to set a new world record for the longest flight made by any aircraft. An exact takeoff date for the record-setting flight has not been determined and is contingent on weather and jet-stream conditions. The window for the attempt opens in mid-January, making the flight possible anytime between then and the end of February. NASA agreed to let Virgin Atlantic Airways use Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility as a takeoff site. The facility use is part of a pilot program to expand runway access for non-NASA activities.
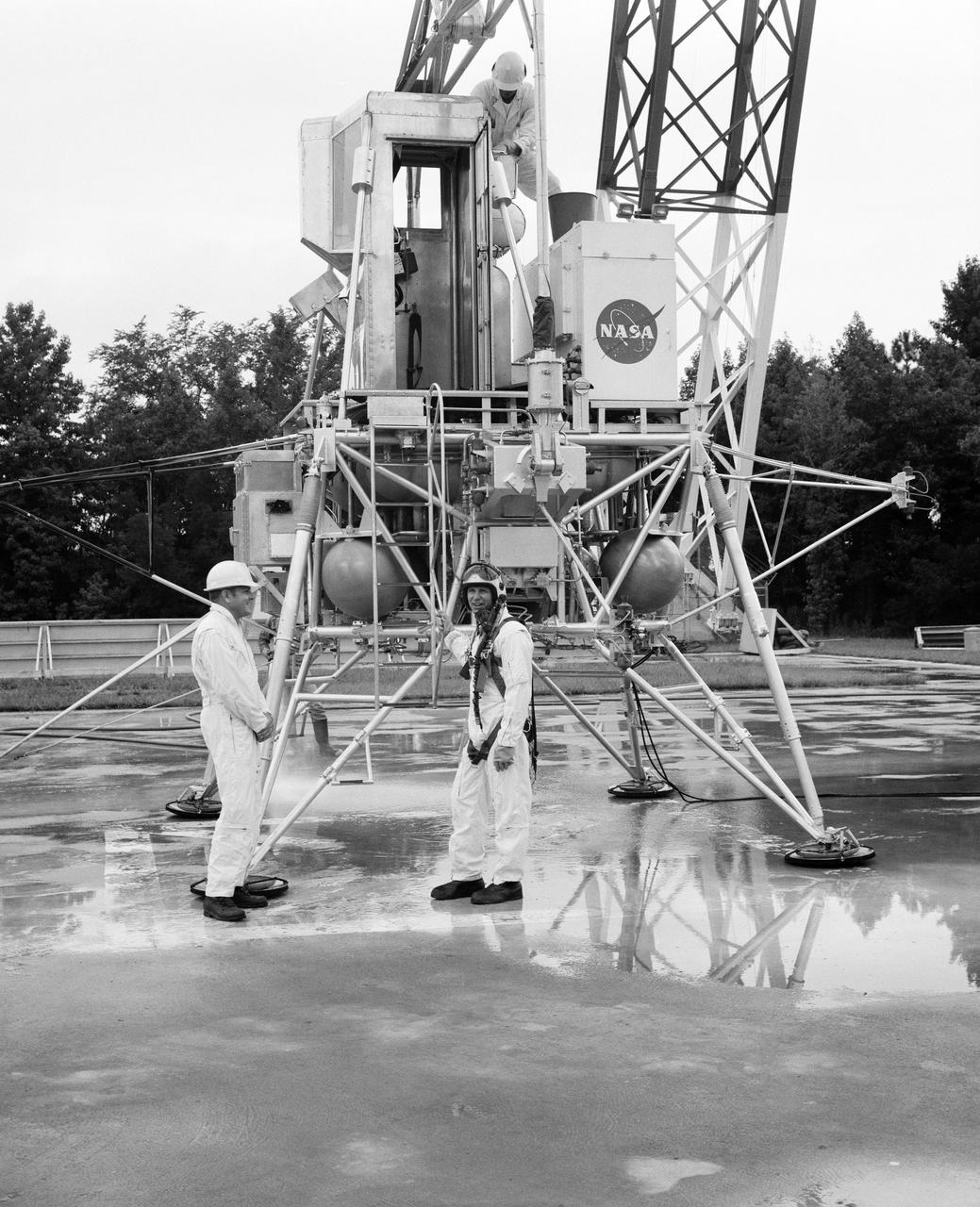

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
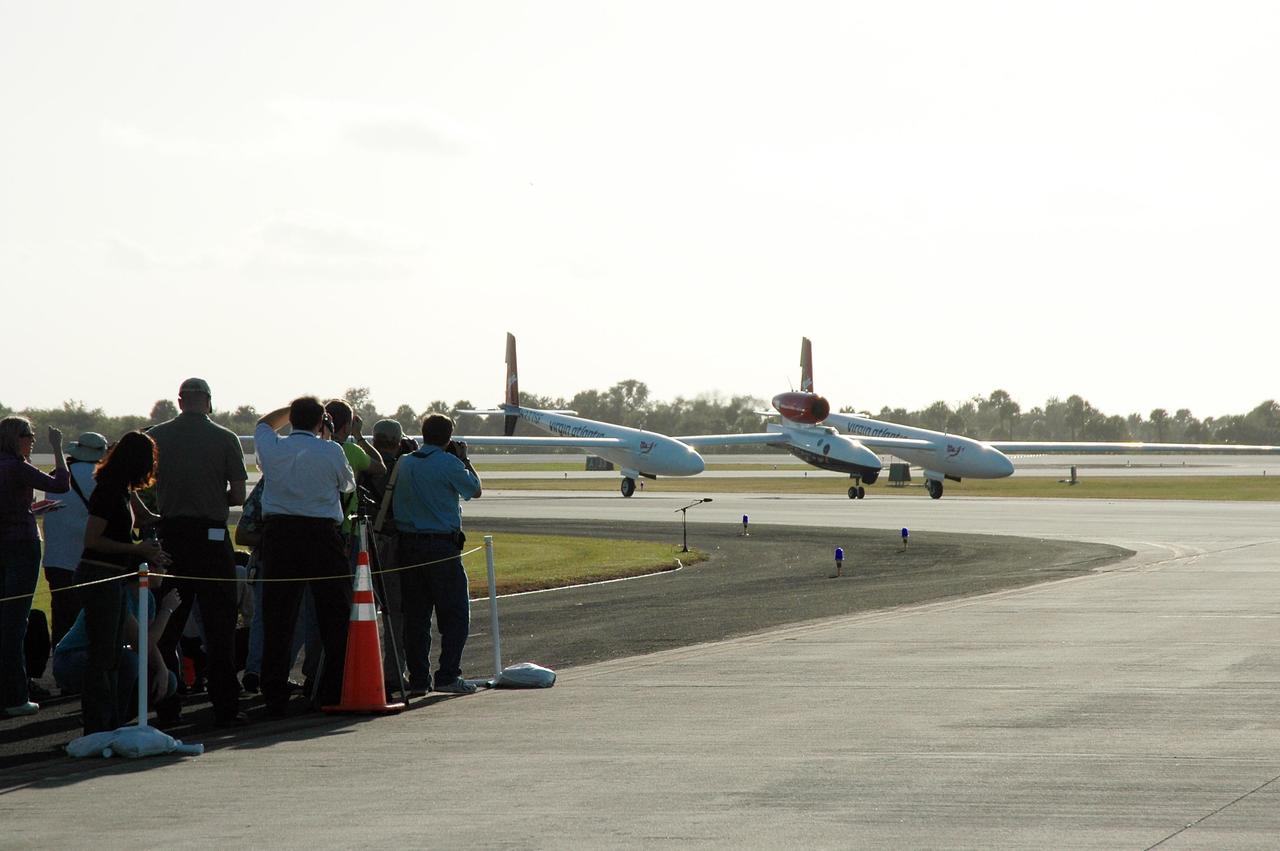

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The media (left) capture the landing of the Virgin Atlantic Airways GlobalFlyer aircraft at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. The aircraft, piloted by Steve Fossett, is being relocated from Salina, Kan., to the Shuttle Landing Facility to begin preparations for an attempt to set a new world record for the longest flight made by any aircraft. An exact takeoff date for the record-setting flight has not been determined and is contingent on weather and jet-stream conditions. The window for the attempt opens in mid-January, making the flight possible anytime between then and the end of February. NASA agreed to let Virgin Atlantic Airways use Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility as a takeoff site. The facility use is part of a pilot program to expand runway access for non-NASA activities.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Pilot Steve Fossett has landed the Virgin Atlantic Airways GlobalFlyer aircraft at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. The aircraft is being relocated from Salina, Kan., to the Shuttle Landing Facility to begin preparations for an attempt to set a new world record for the longest flight made by any aircraft. An exact takeoff date for the record-setting flight has not been determined and is contingent on weather and jet-stream conditions. The window for the attempt opens in mid-January, making the flight possible anytime between then and the end of February. NASA agreed to let Virgin Atlantic Airways use Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility as a takeoff site. The facility use is part of a pilot program to expand runway access for non-NASA activities.
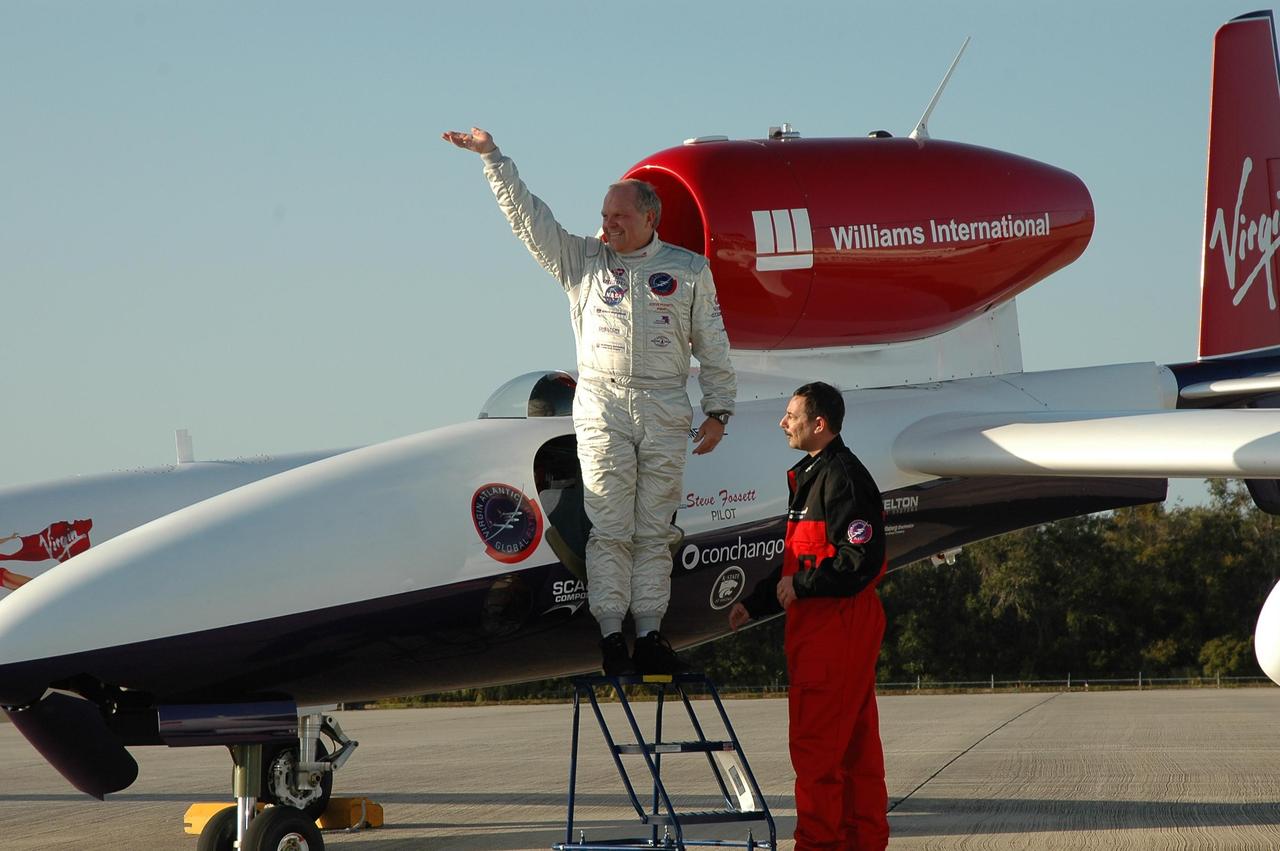

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Pilot Steve Fossett waves as he leaves the cockpit of the Virgin Atlantic Airways GlobalFlyer aircraft, which he landed at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. The aircraft is being relocated from Salina, Kan., to the Shuttle Landing Facility to begin preparations for an attempt to set a new world record for the longest flight made by any aircraft. An exact takeoff date for the record-setting flight has not been determined and is contingent on weather and jet-stream conditions. The window for the attempt opens in mid-January, making the flight possible anytime between then and the end of February. NASA agreed to let Virgin Atlantic Airways use Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility as a takeoff site. The facility use is part of a pilot program to expand runway access for non-NASA activities.
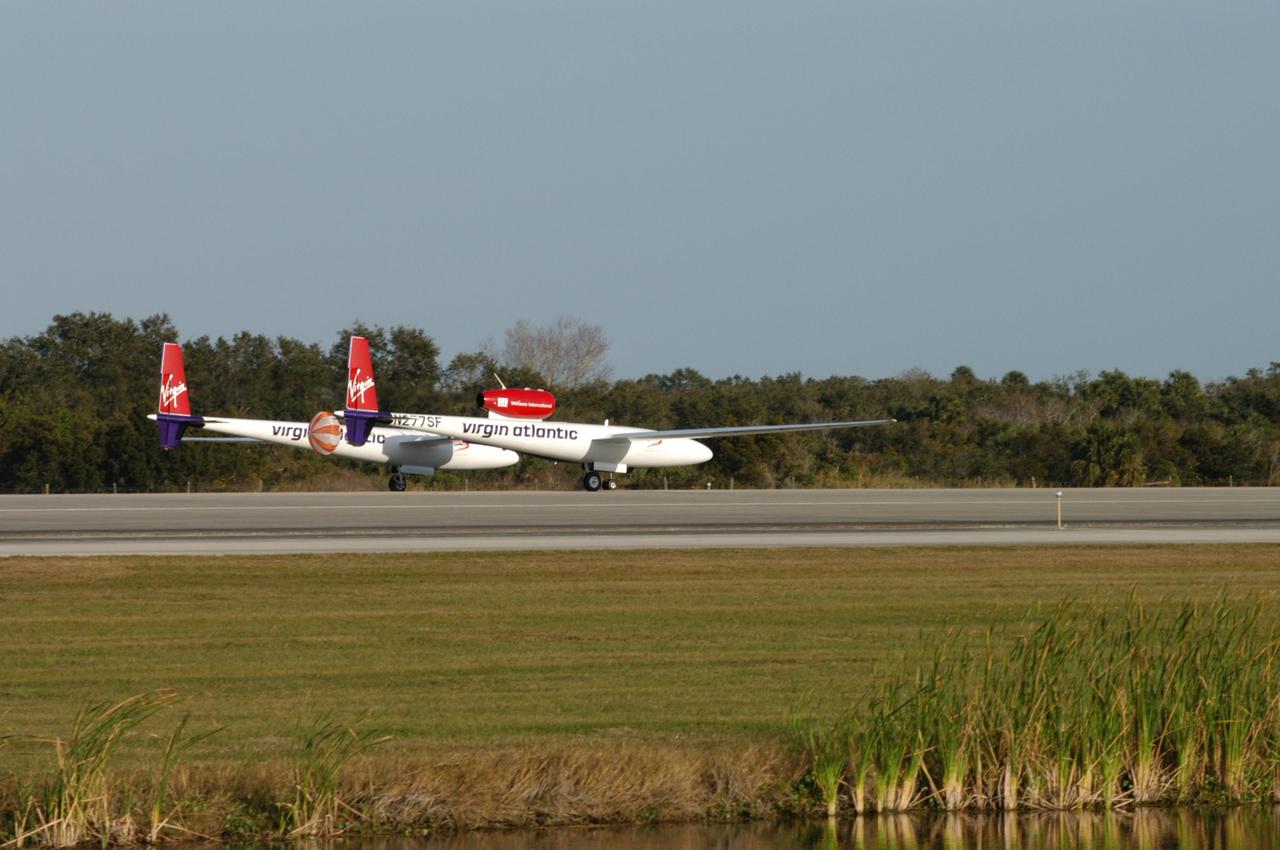

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Virgin Atlantic Airways GlobalFlyer aircraft touches down on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. The aircraft, piloted by Steve Fossett, is being relocated from Salina, Kan., to the Shuttle Landing Facility to begin preparations for an attempt to set a new world record for the longest flight made by any aircraft. An exact takeoff date for the record-setting flight has not been determined and is contingent on weather and jet-stream conditions. The window for the attempt opens in mid-January, making the flight possible anytime between then and the end of February. NASA agreed to let Virgin Atlantic Airways use Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility as a takeoff site. The facility use is part of a pilot program to expand runway access for non-NASA activities.
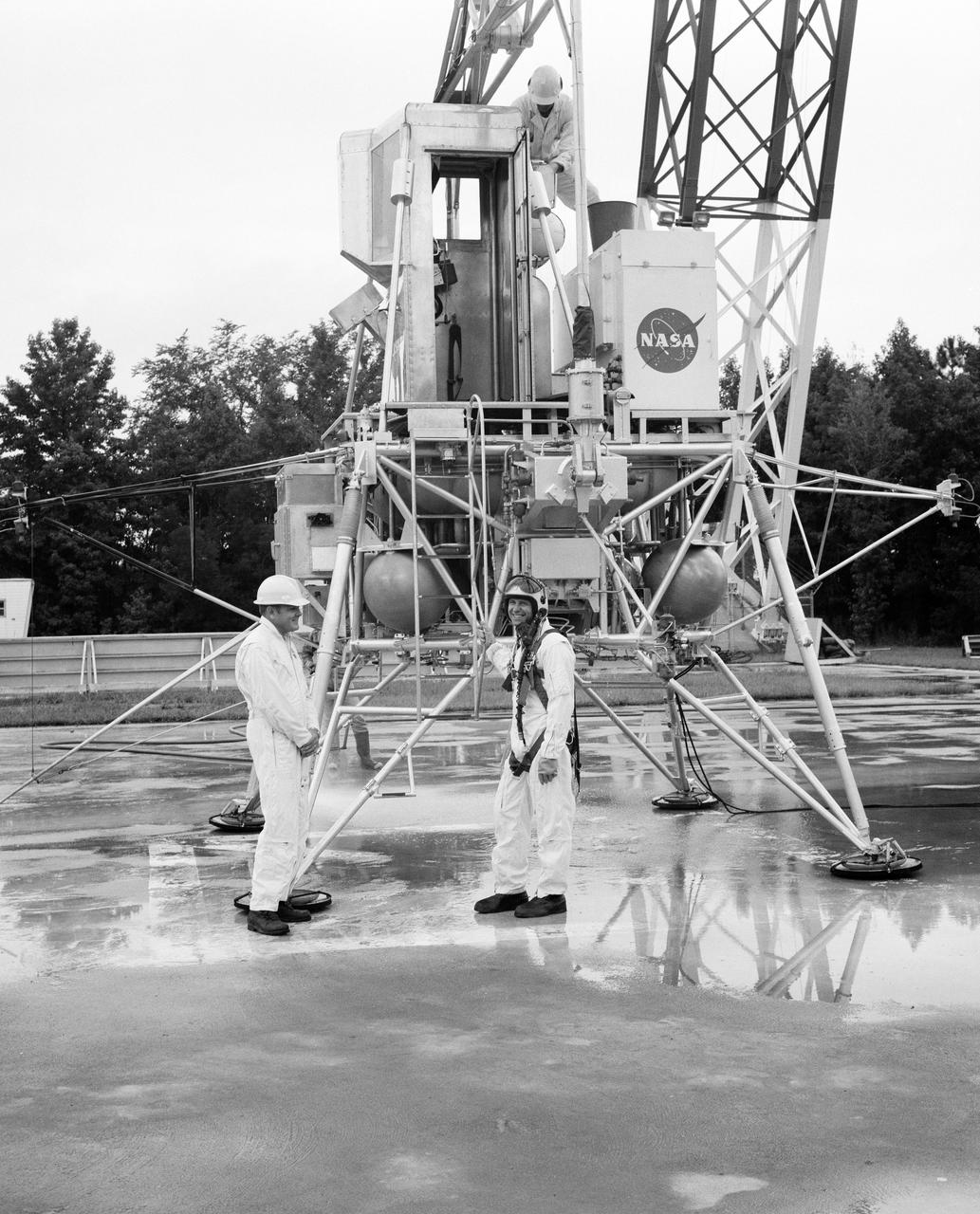

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
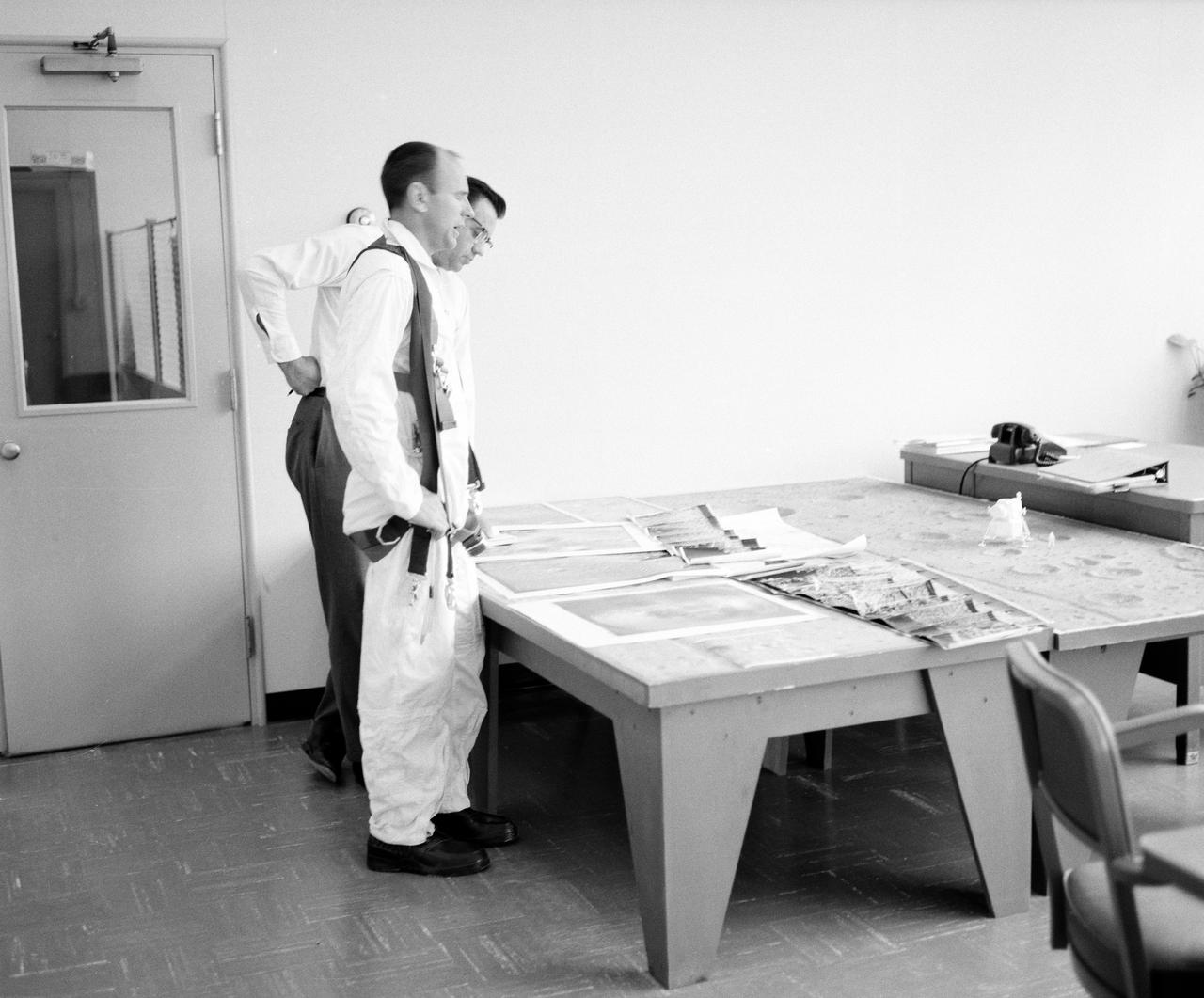

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
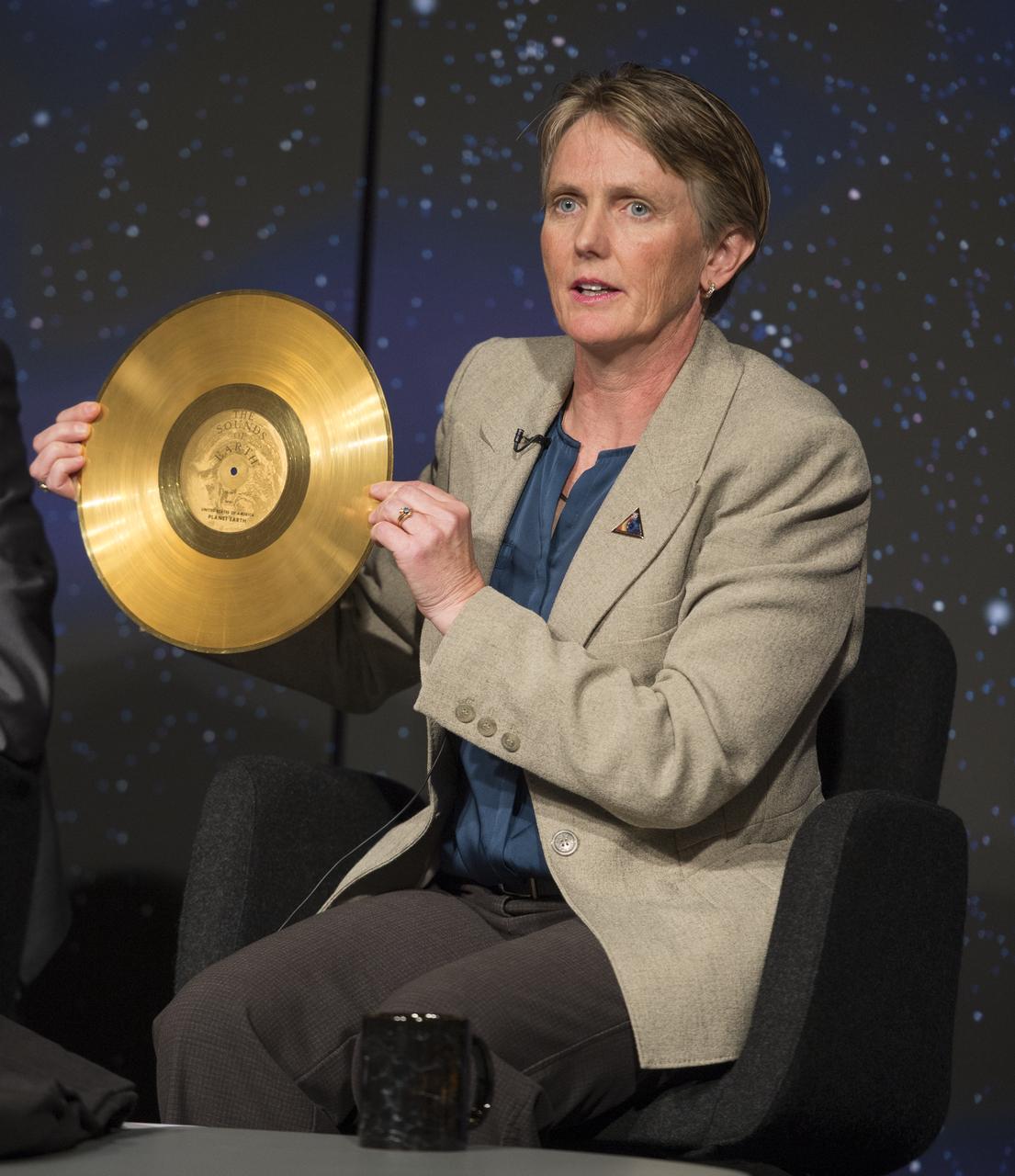

Suzanne Dodd, Voyager project manager, NASA's Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL) holds a replica of the golden record carried on Voyager at a news conference on NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft, Thursday, Sept. 12, 2013 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The Golden Record was intended to communicate a story of our world to extraterrestrials. NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft officially is the first human-made object to venture into interstellar space. The 36-year-old probe is about 12 billion miles (19 billion kilometers) from our sun. New and unexpected data indicate Voyager 1 has been traveling for about one year through plasma, or ionized gas, present in the space between stars. A report on the analysis of this new data is published in Thursday's edition of the journal Science. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
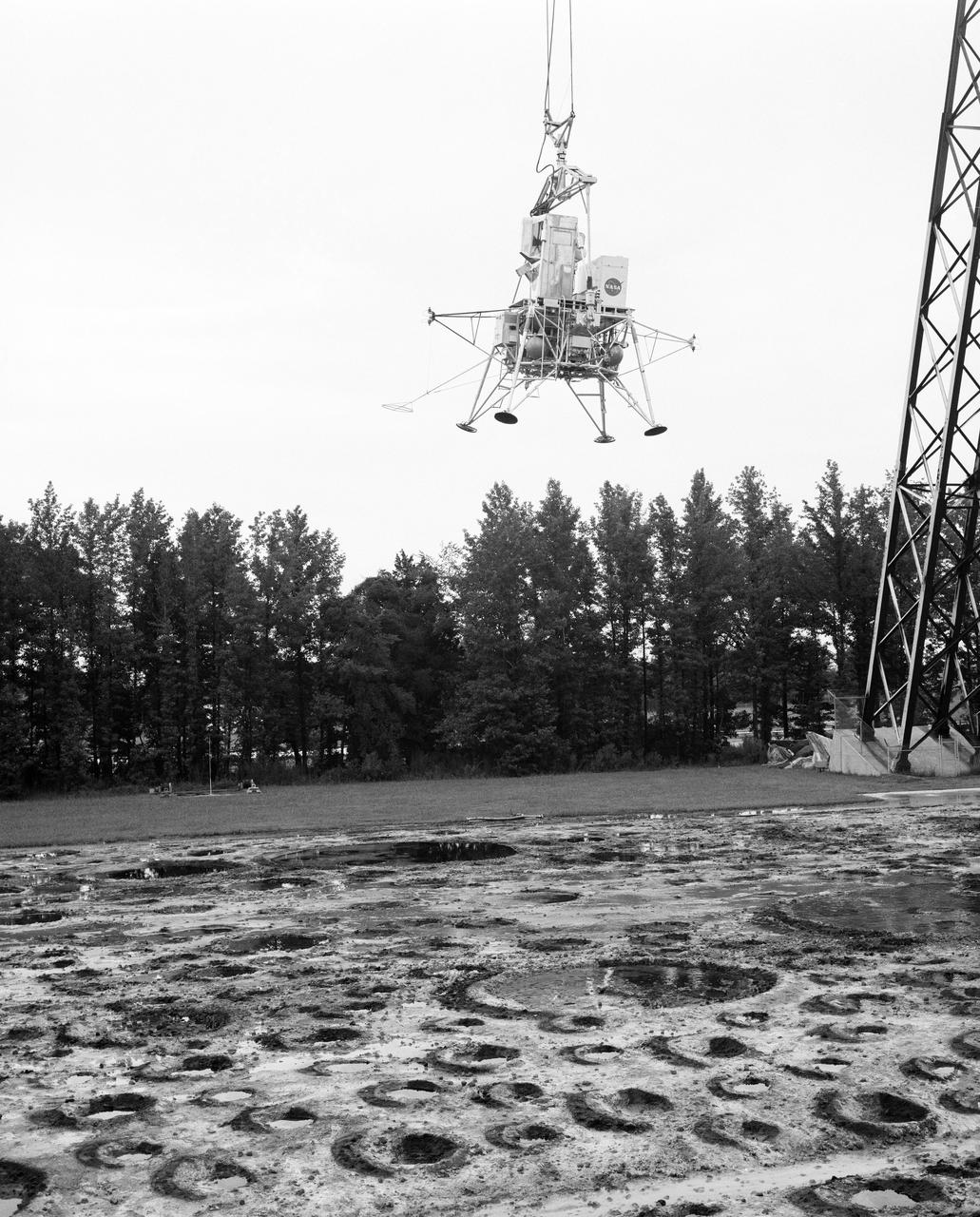

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.

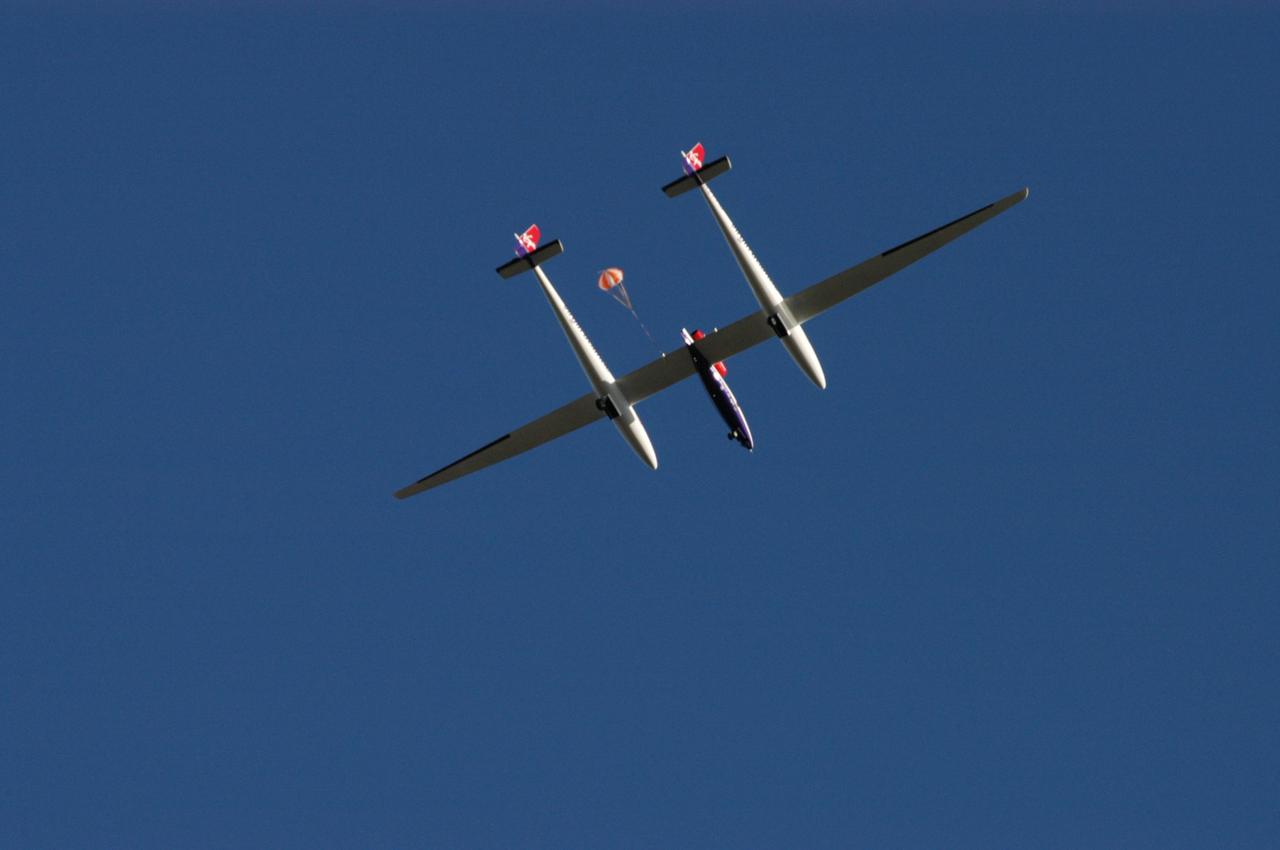
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Virgin Atlantic Airways GlobalFlyer aircraft approaches NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility for a landing. The aircraft, piloted by Steve Fossett, is being relocated from Salina, Kan., to the Shuttle Landing Facility to begin preparations for an attempt to set a new world record for the longest flight made by any aircraft. An exact takeoff date for the record-setting flight has not been determined and is contingent on weather and jet-stream conditions. The window for the attempt opens in mid-January, making the flight possible anytime between then and the end of February. NASA agreed to let Virgin Atlantic Airways use Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility as a takeoff site. The facility use is part of a pilot program to expand runway access for non-NASA activities.
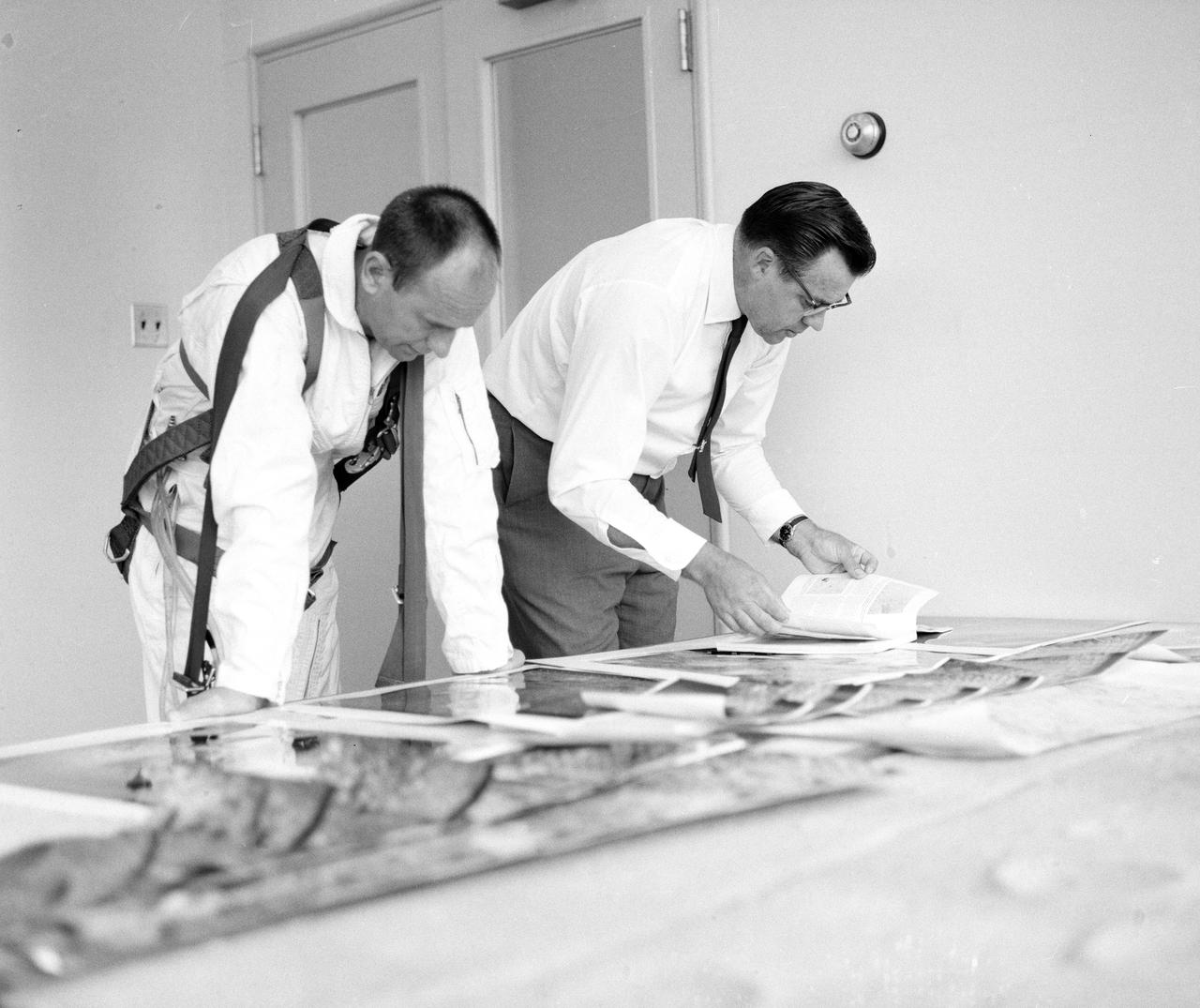

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.

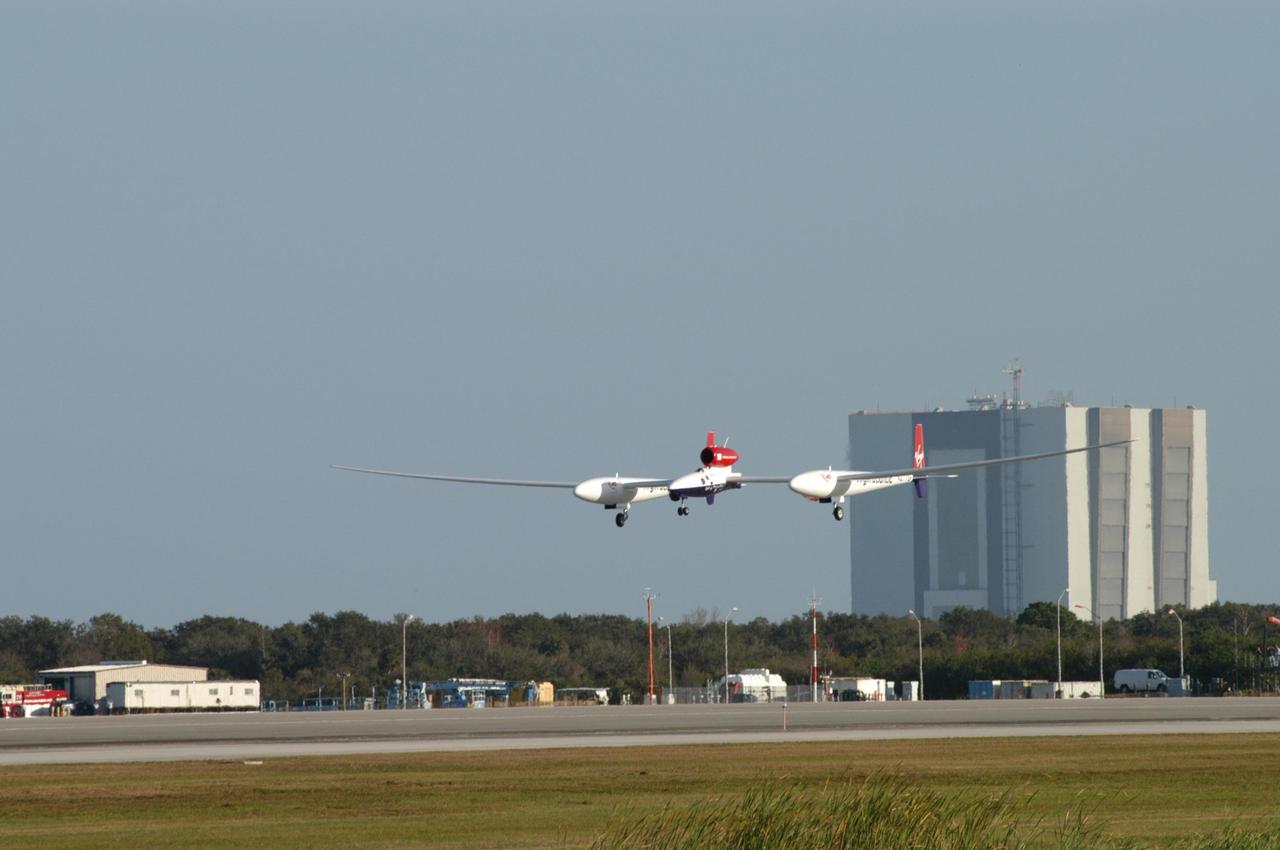
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Virgin Atlantic Airways GlobalFlyer aircraft sails across the sky near NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. The aircraft, piloted by Steve Fossett, is being relocated from Salina, Kan., to the Shuttle Landing Facility to begin preparations for an attempt to set a new world record for the longest flight made by any aircraft. An exact takeoff date for the record-setting flight has not been determined and is contingent on weather and jet-stream conditions. The window for the attempt opens in mid-January, making the flight possible anytime between then and the end of February. NASA agreed to let Virgin Atlantic Airways use Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility as a takeoff site. The facility use is part of a pilot program to expand runway access for non-NASA activities.
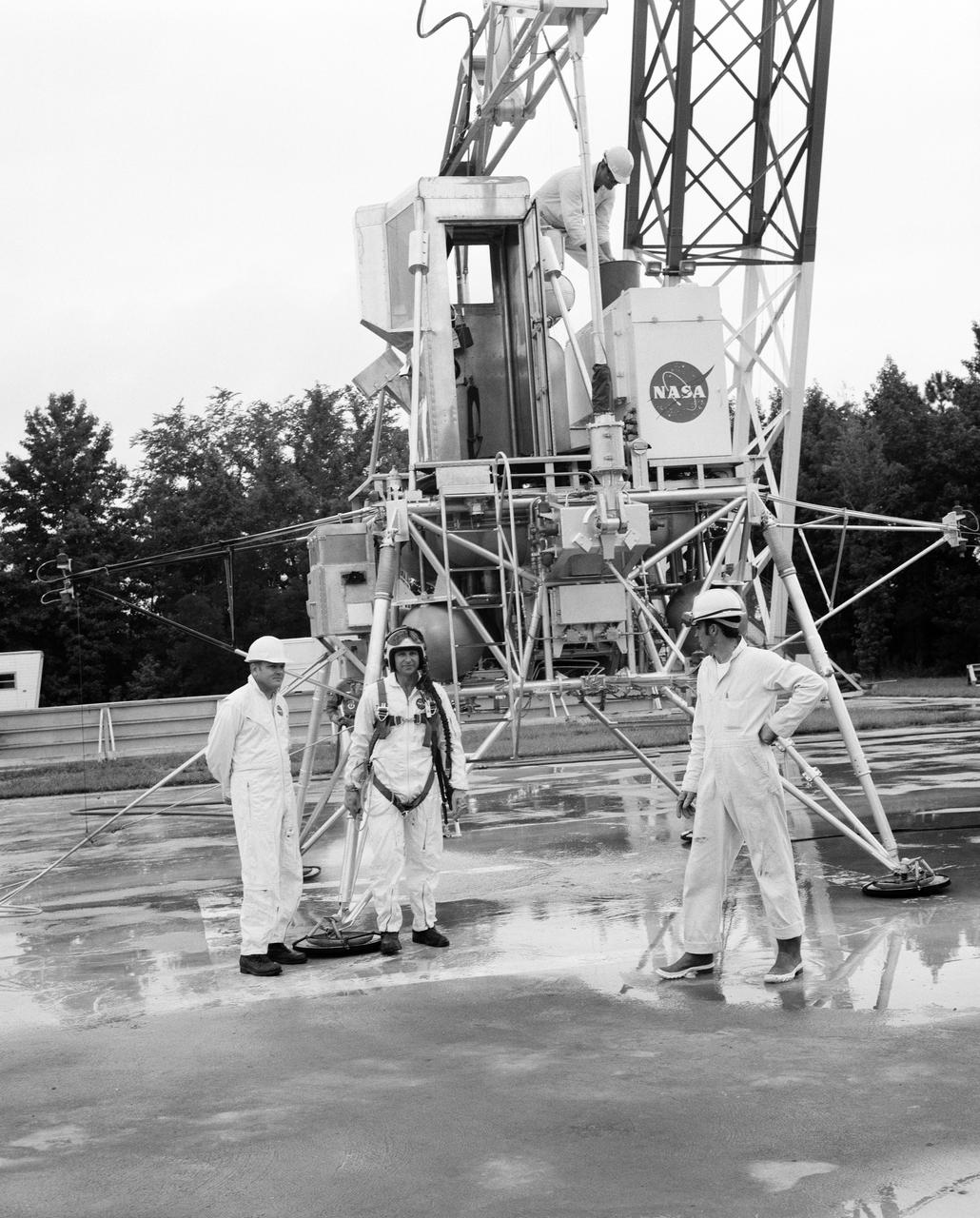

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
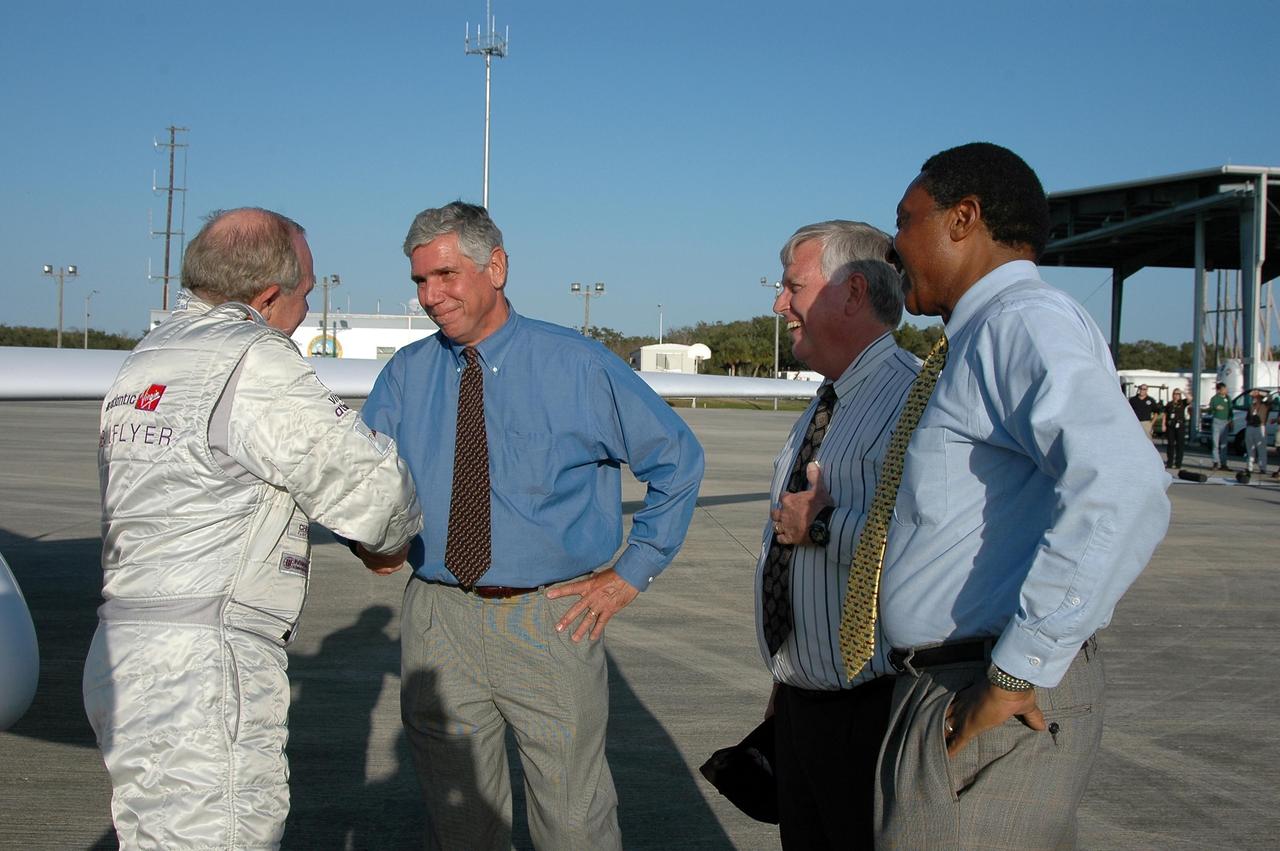

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After landing the Virgin Atlantic Airways GlobalFlyer aircraft at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, pilot Steve Fossett is welcomed (left to right) by KSC Spaceport Development Manager Jim Ball, Center Director James Kennedy and Executive Director of Florida Space Authority Winston Scott. The aircraft is being relocated from Salina, Kan., to the Shuttle Landing Facility to begin preparations for an attempt to set a new world record for the longest flight made by any aircraft. An exact takeoff date for the record-setting flight has not been determined and is contingent on weather and jet-stream conditions. The window for the attempt opens in mid-January, making the flight possible anytime between then and the end of February. NASA agreed to let Virgin Atlantic Airways use Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility as a takeoff site. The facility use is part of a pilot program to expand runway access for non-NASA activities.
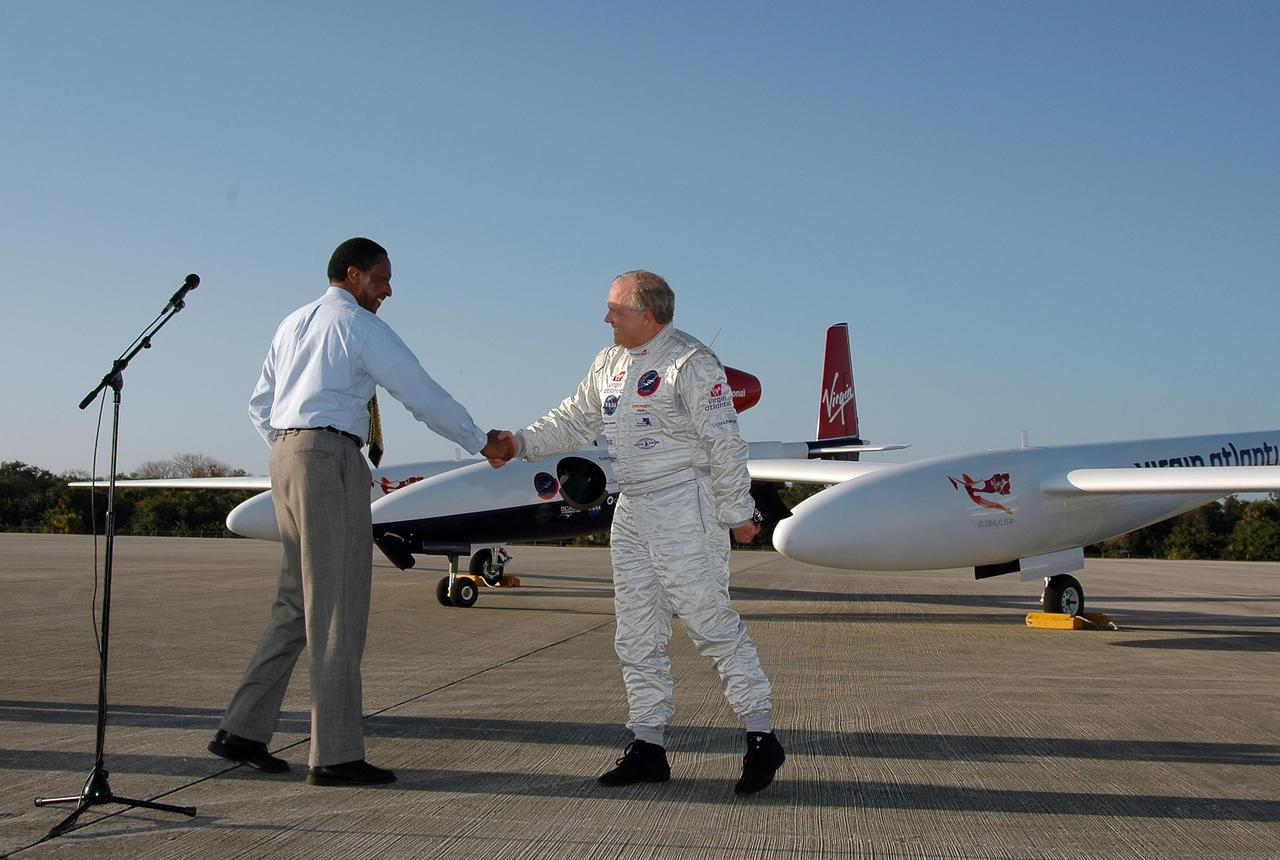

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After the landing of the Virgin Atlantic Airways GlobalFlyer aircraft at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Winston Scott (left), executive director of Florida Space Authority, brings pilot Steve Fossett to the microphone for a few words to the media. The aircraft is being relocated from Salina, Kan., to the Shuttle Landing Facility to begin preparations for an attempt to set a new world record for the longest flight made by any aircraft. An exact takeoff date for the record-setting flight has not been determined and is contingent on weather and jet-stream conditions. The window for the attempt opens in mid-January, making the flight possible anytime between then and the end of February. NASA agreed to let Virgin Atlantic Airways use Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility as a takeoff site. The facility use is part of a pilot program to expand runway access for non-NASA activities.
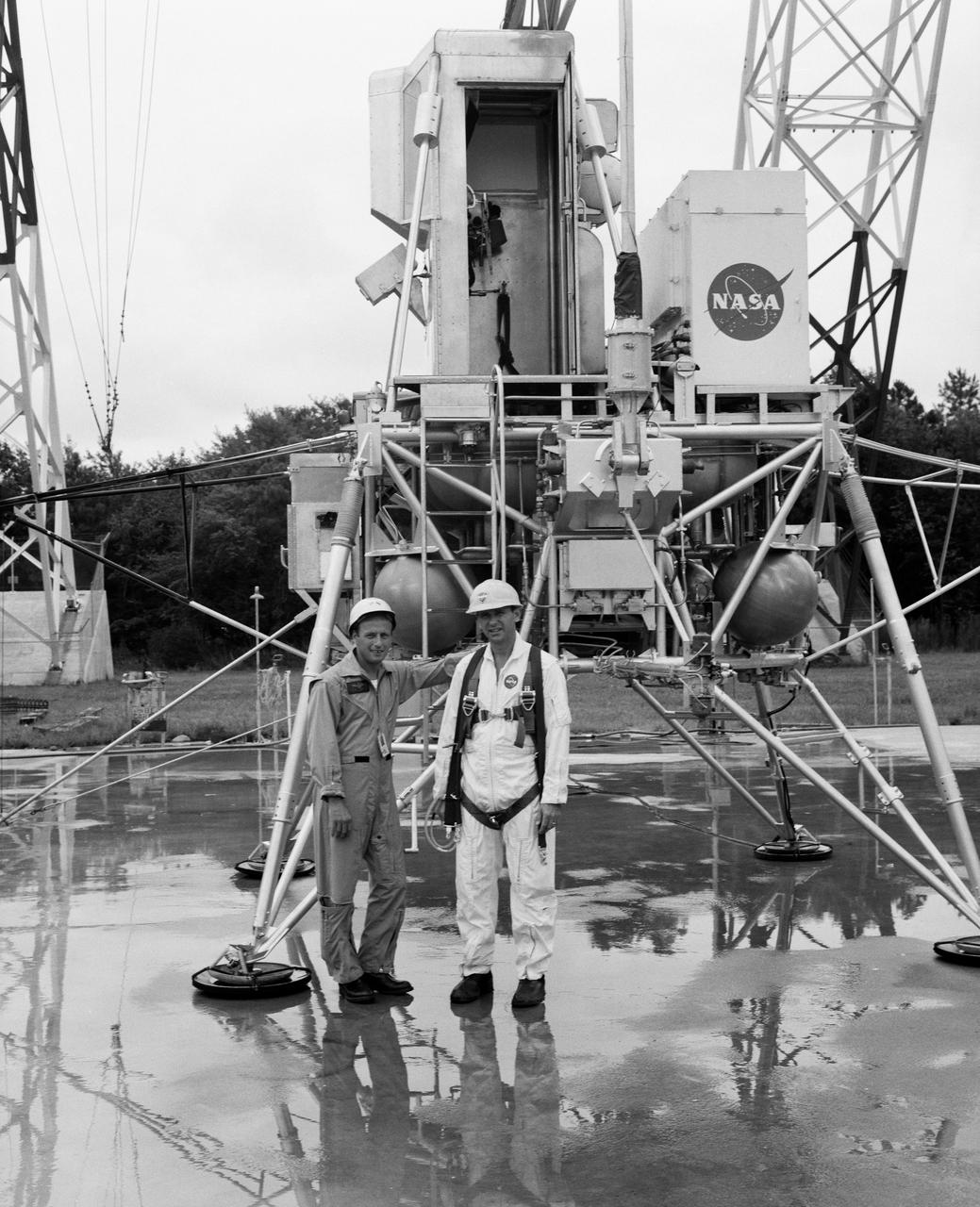

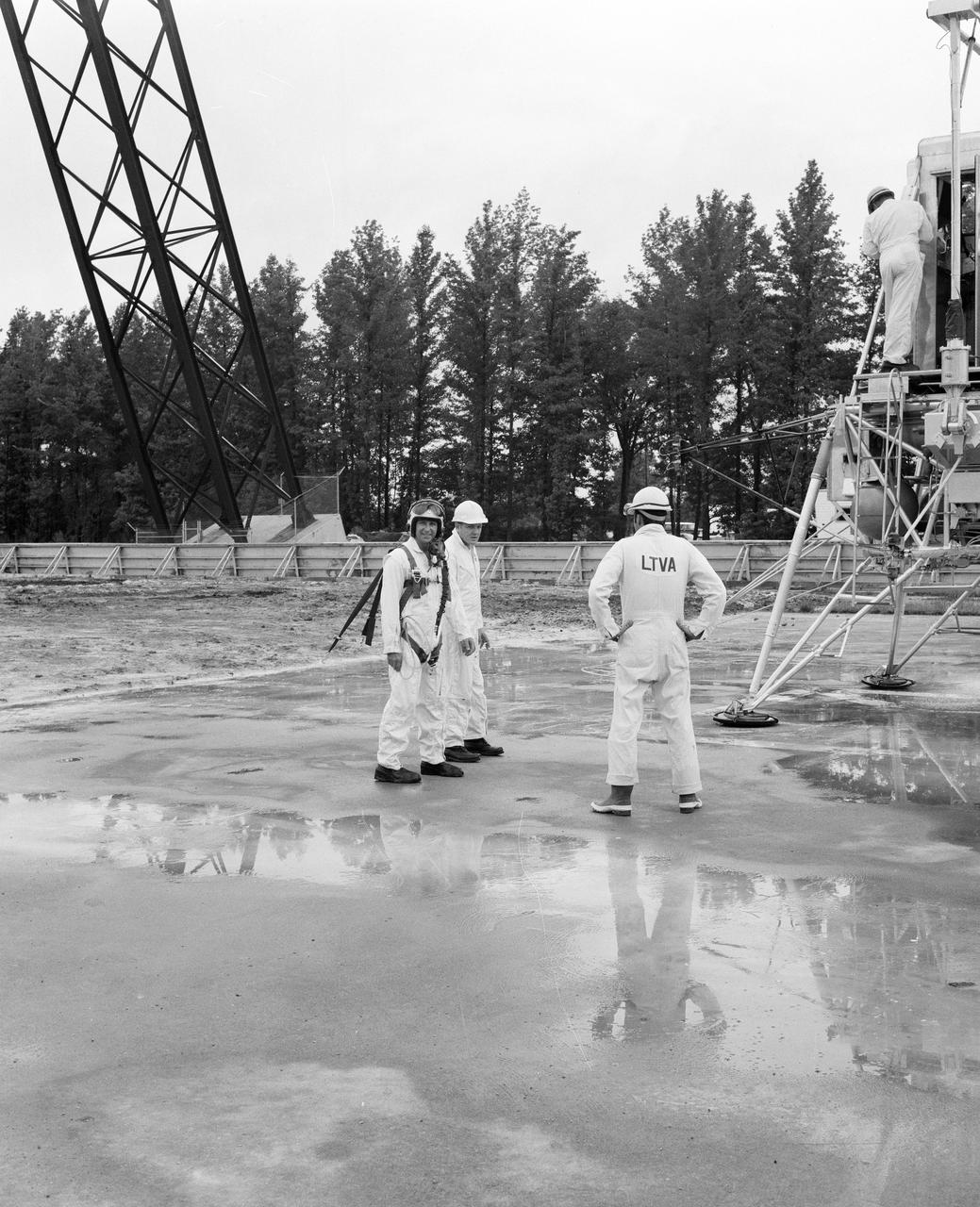
Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
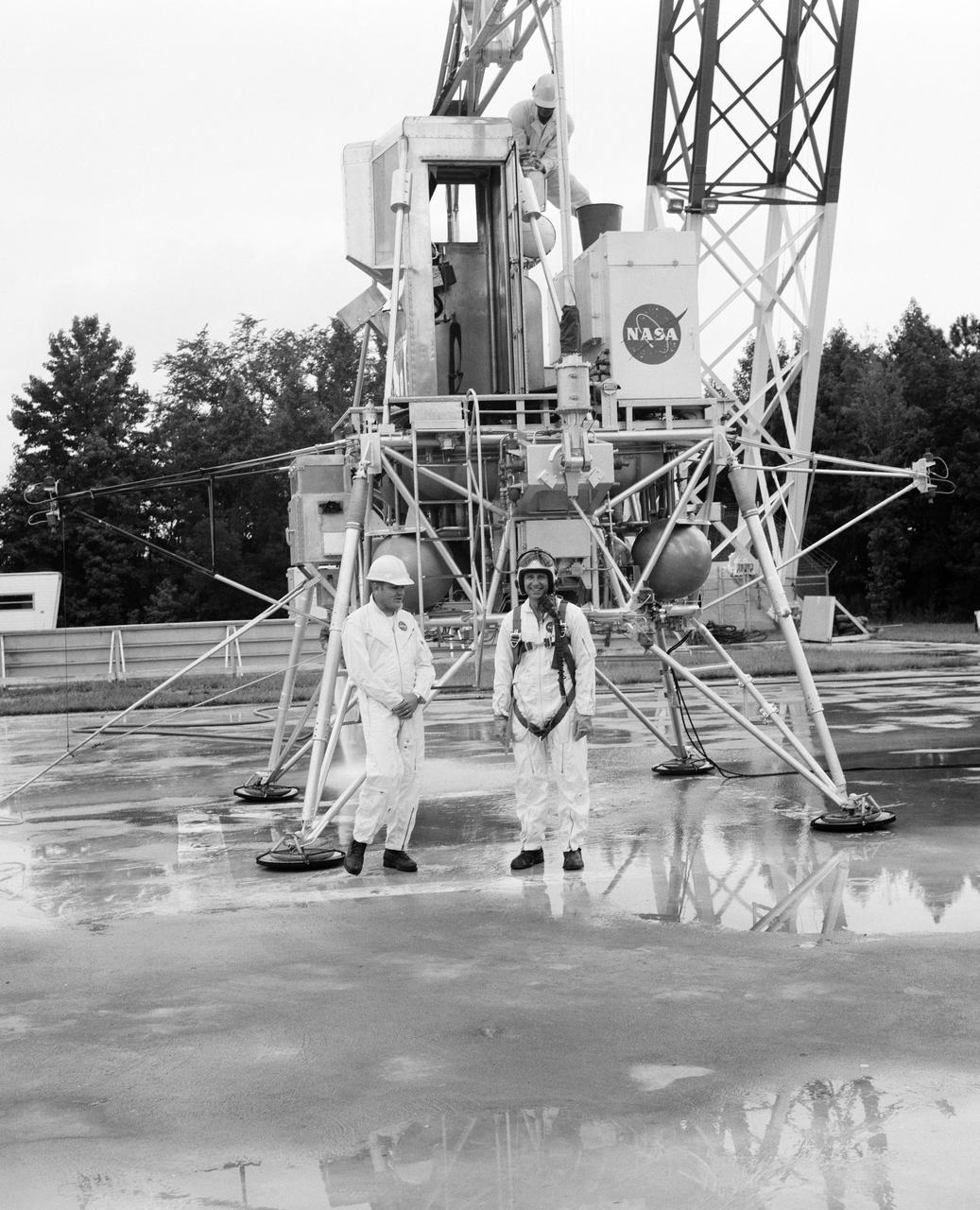

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
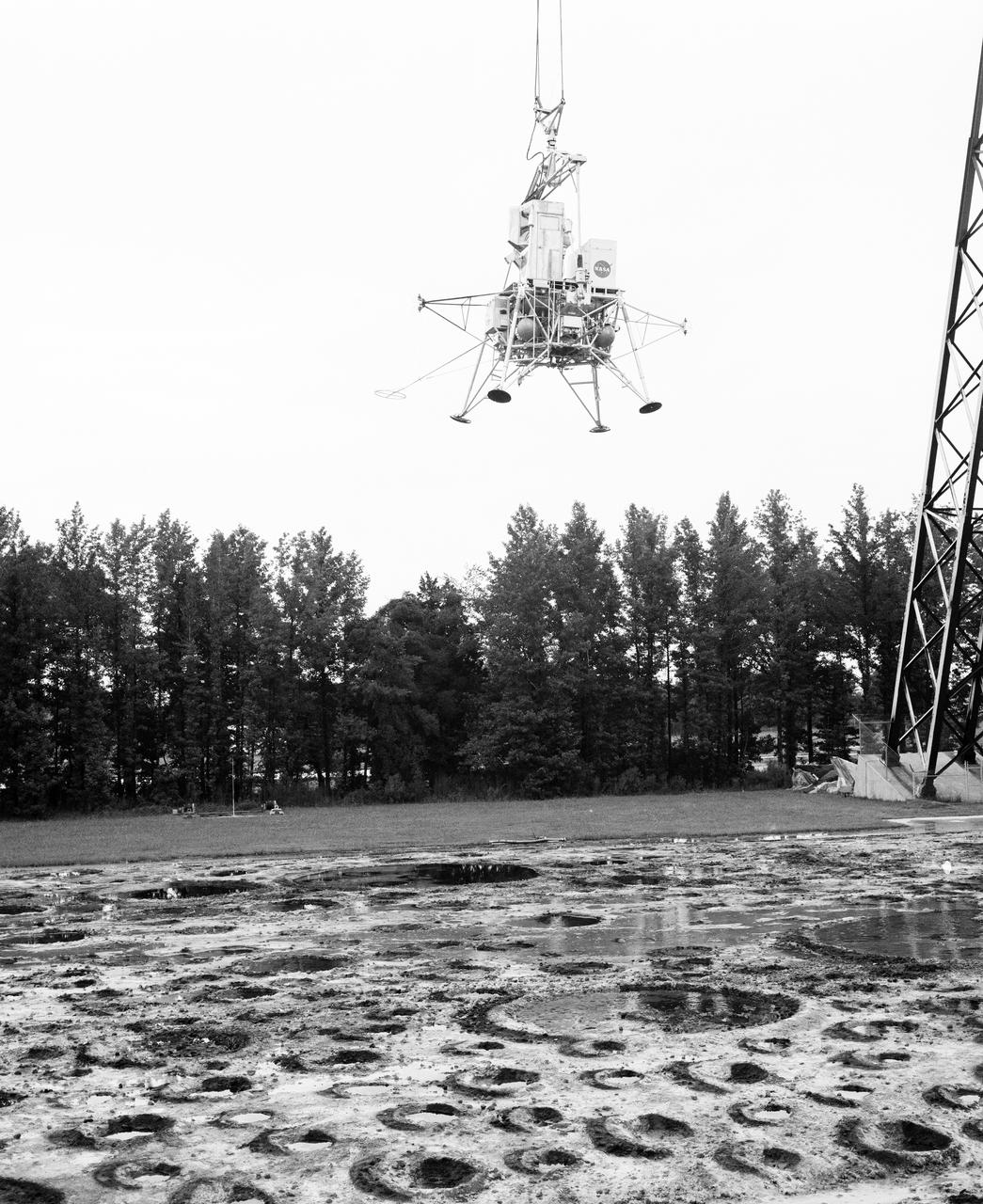

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
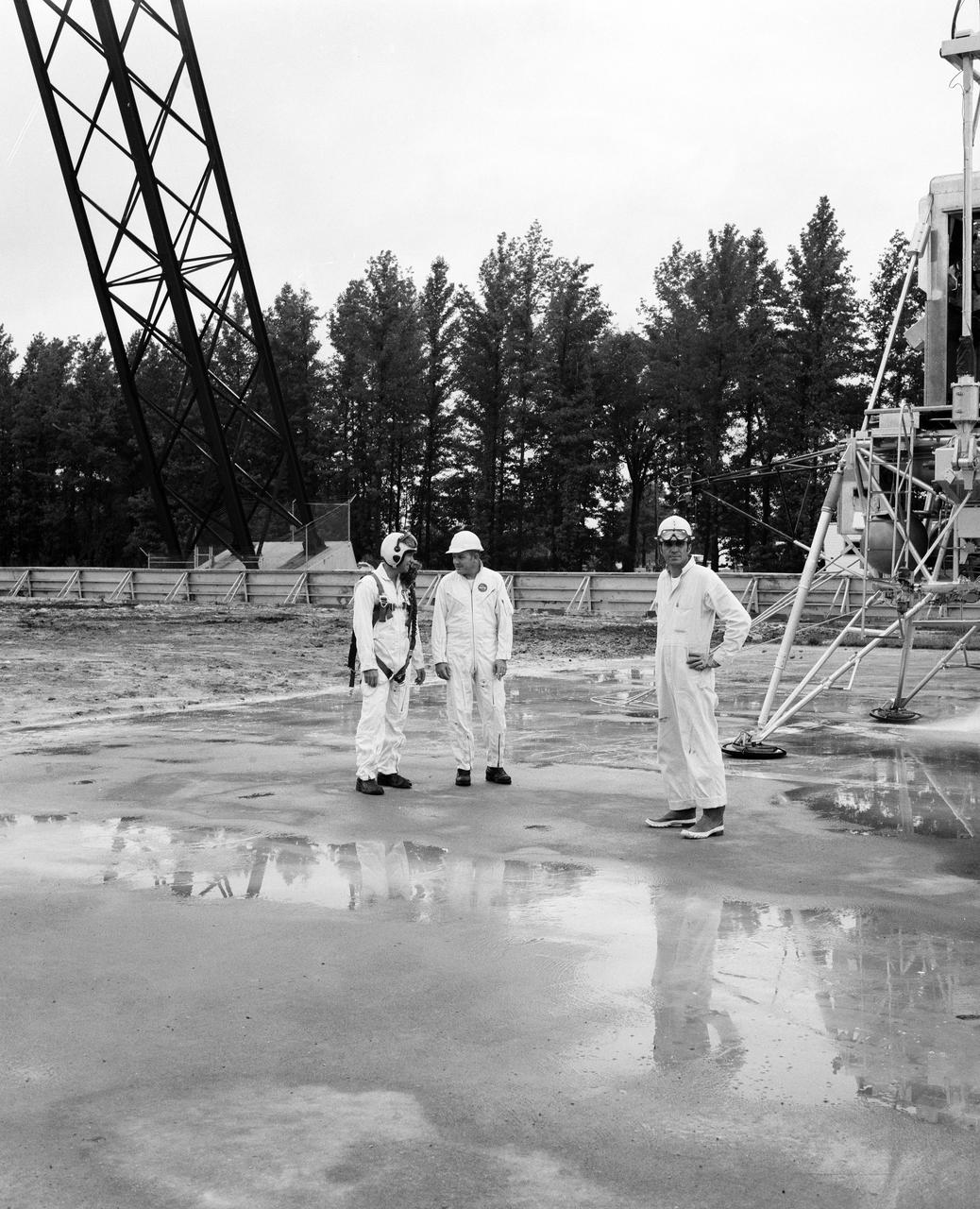

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After landing the Virgin Atlantic Airways GlobalFlyer aircraft at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, pilot Steve Fossett is greeted by Center Director James Kennedy (center) and Executive Director of Florida Space Authority Winston Scott. At far right is Jim Ball, KSC Spaceport Development manager. The aircraft is being relocated from Salina, Kan., to the Shuttle Landing Facility to begin preparations for an attempt to set a new world record for the longest flight made by any aircraft. An exact takeoff date for the record-setting flight has not been determined and is contingent on weather and jet-stream conditions. The window for the attempt opens in mid-January, making the flight possible anytime between then and the end of February. NASA agreed to let Virgin Atlantic Airways use Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility as a takeoff site. The facility use is part of a pilot program to expand runway access for non-NASA activities.
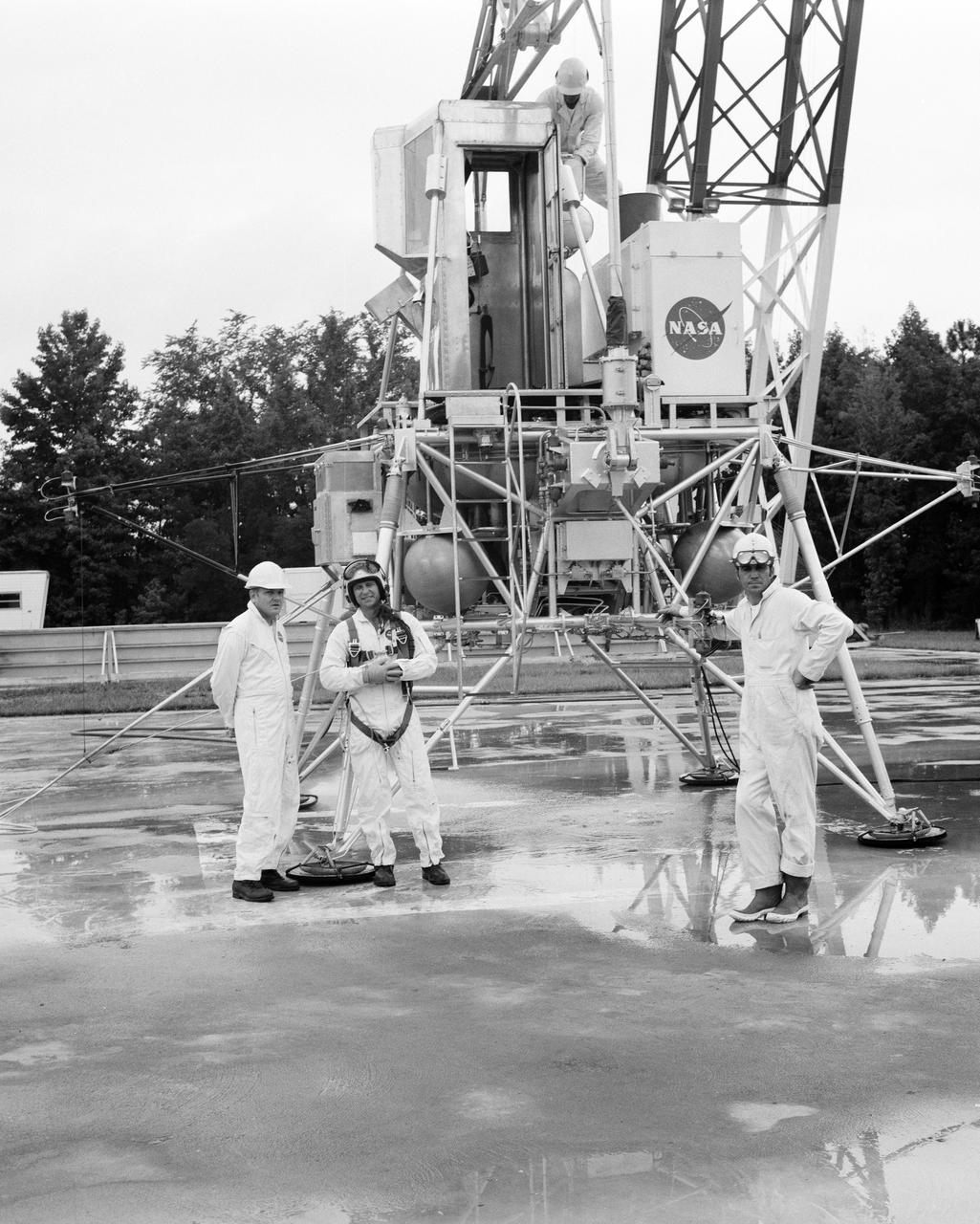

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
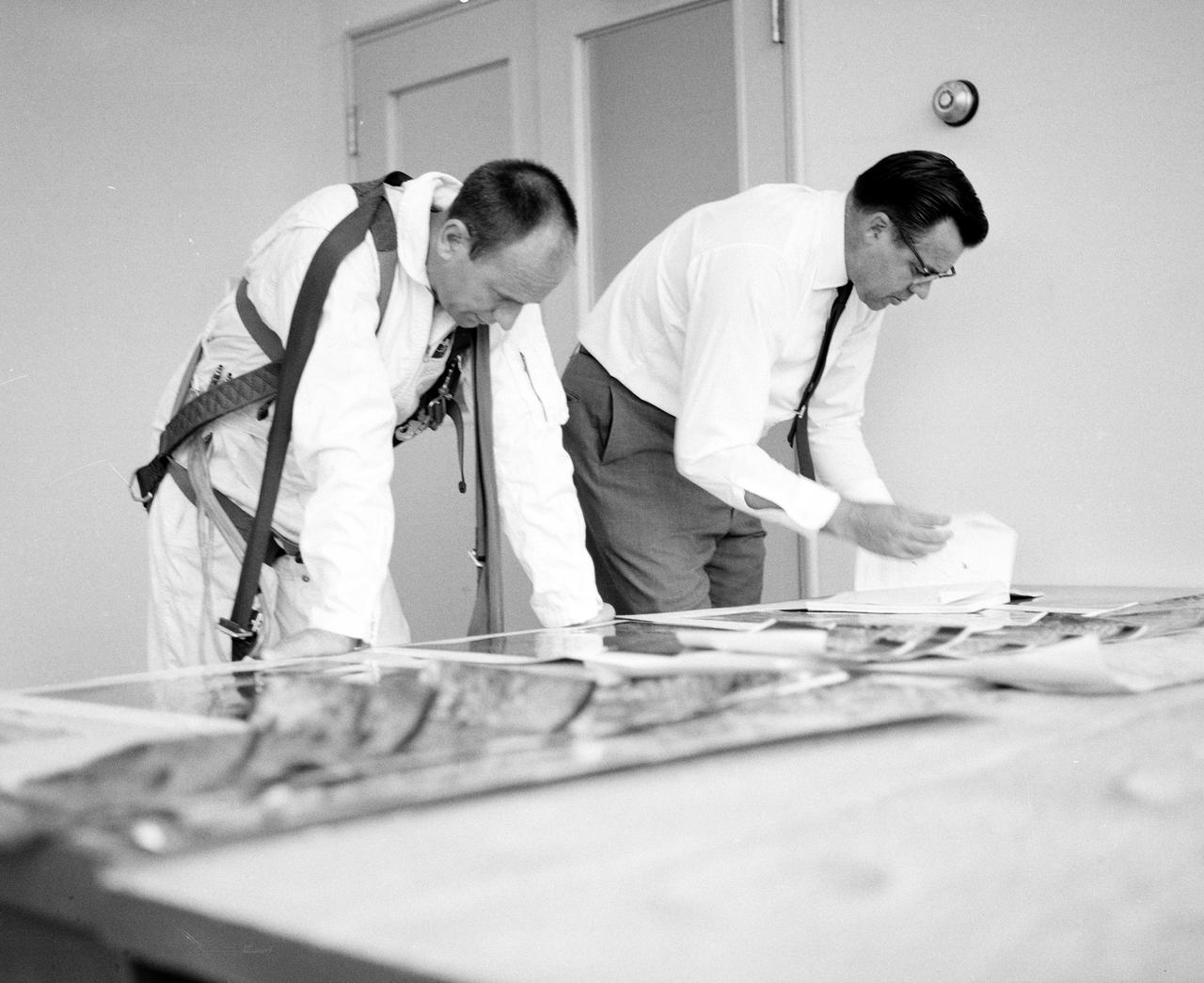

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
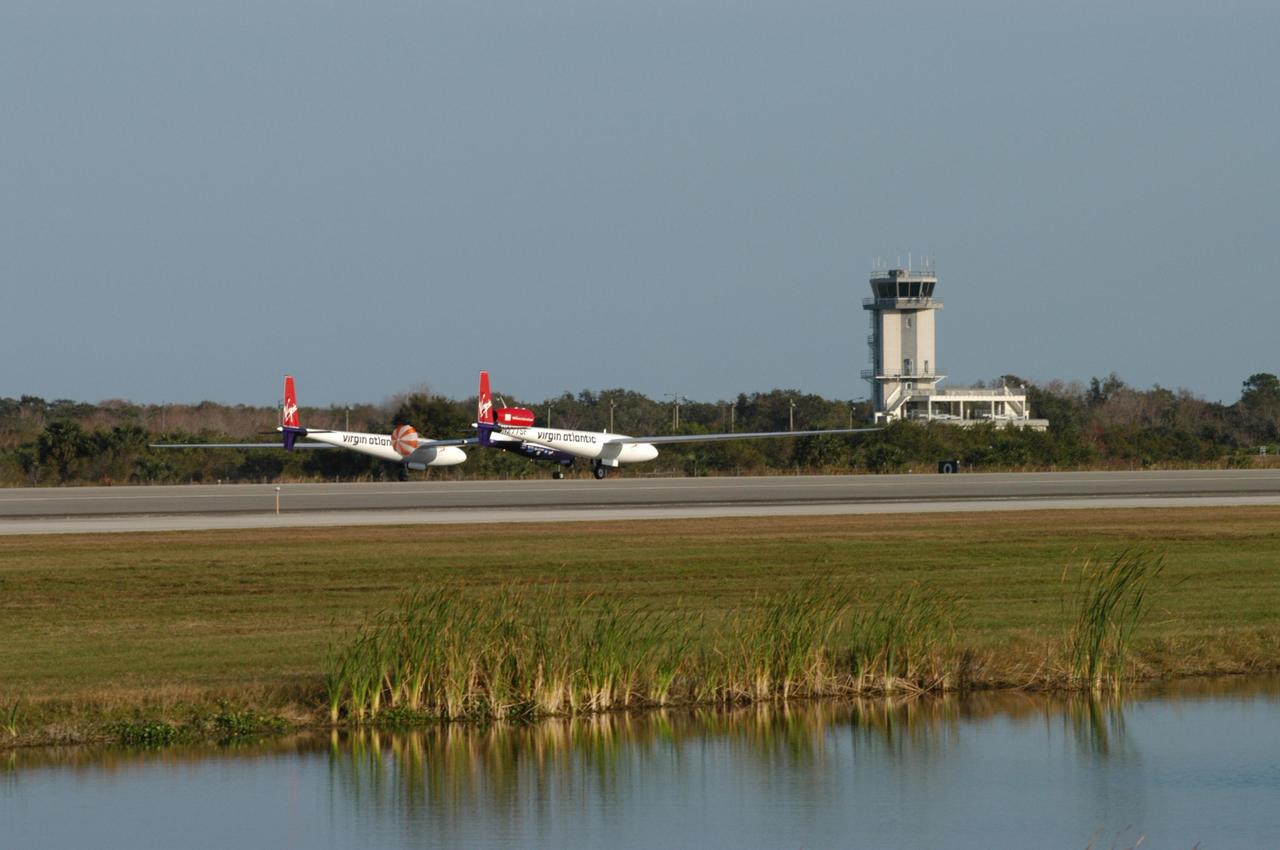

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Virgin Atlantic Airways GlobalFlyer aircraft lands on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. The aircraft, piloted by Steve Fossett, is being relocated from Salina, Kan., to the Shuttle Landing Facility to begin preparations for an attempt to set a new world record for the longest flight made by any aircraft. An exact takeoff date for the record-setting flight has not been determined and is contingent on weather and jet-stream conditions. The window for the attempt opens in mid-January, making the flight possible anytime between then and the end of February. NASA agreed to let Virgin Atlantic Airways use Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility as a takeoff site. The facility use is part of a pilot program to expand runway access for non-NASA activities.
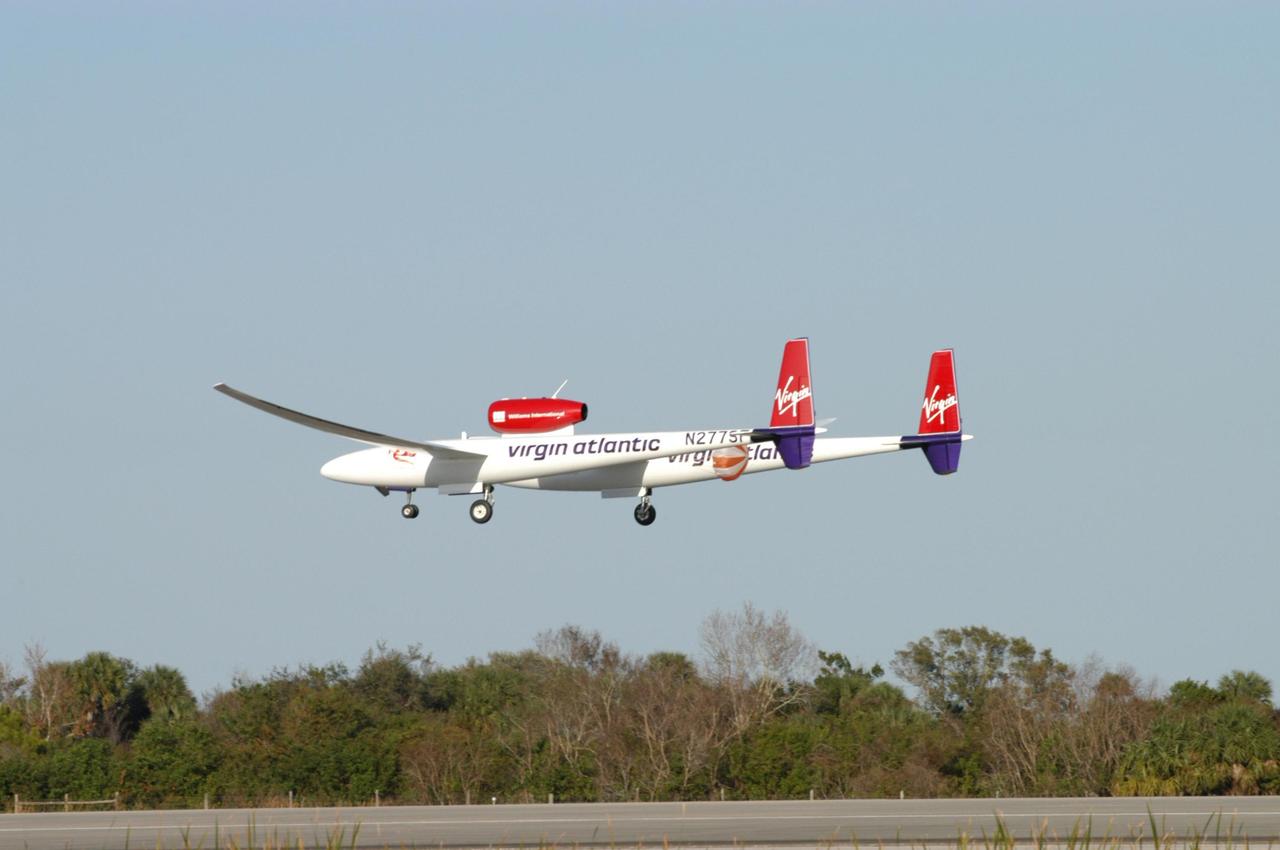

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Virgin Atlantic Airways GlobalFlyer aircraft approaches NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility for a landing. The aircraft, piloted by Steve Fossett, is being relocated from Salina, Kan., to the Shuttle Landing Facility to begin preparations for an attempt to set a new world record for the longest flight made by any aircraft. An exact takeoff date for the record-setting flight has not been determined and is contingent on weather and jet-stream conditions. The window for the attempt opens in mid-January, making the flight possible anytime between then and the end of February. NASA agreed to let Virgin Atlantic Airways use Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility as a takeoff site. The facility use is part of a pilot program to expand runway access for non-NASA activities.
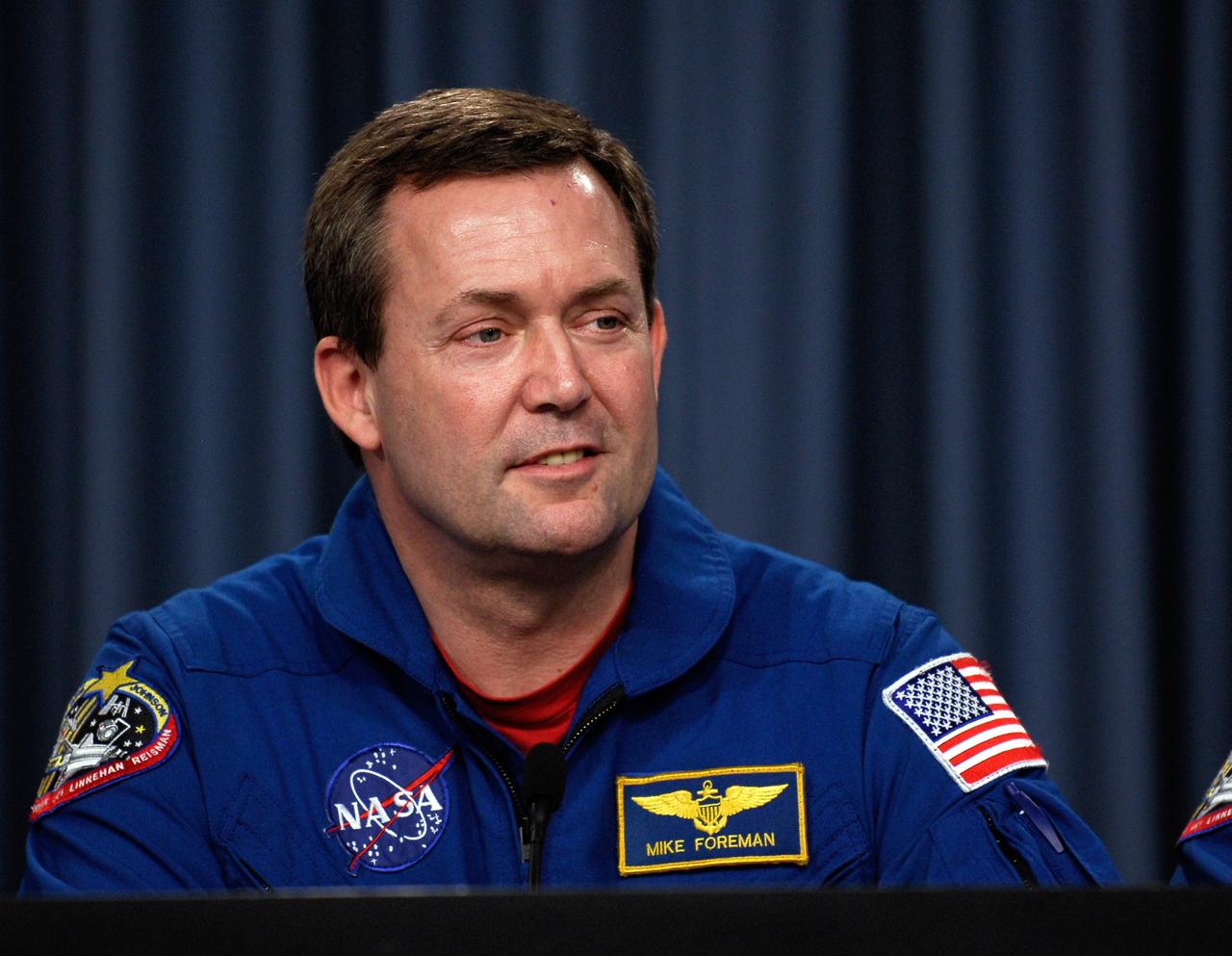

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. --- STS-123 Mission Specialist Mike Foreman talks to the media about his experiences on the mission to the International Space Station. The crew landed at Kennedy aboard space shuttle Endeavour at 8:39 p.m. EDT March 26. Endeavour's 16-day flight was the longest shuttle mission to the International Space Station and included a record five spacewalks. The shuttle's seven astronauts worked with the three-member station crew and ground teams around the world to install the first section of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory and the Canadian Space Agency's two-armed robotic system, known as Dextre. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
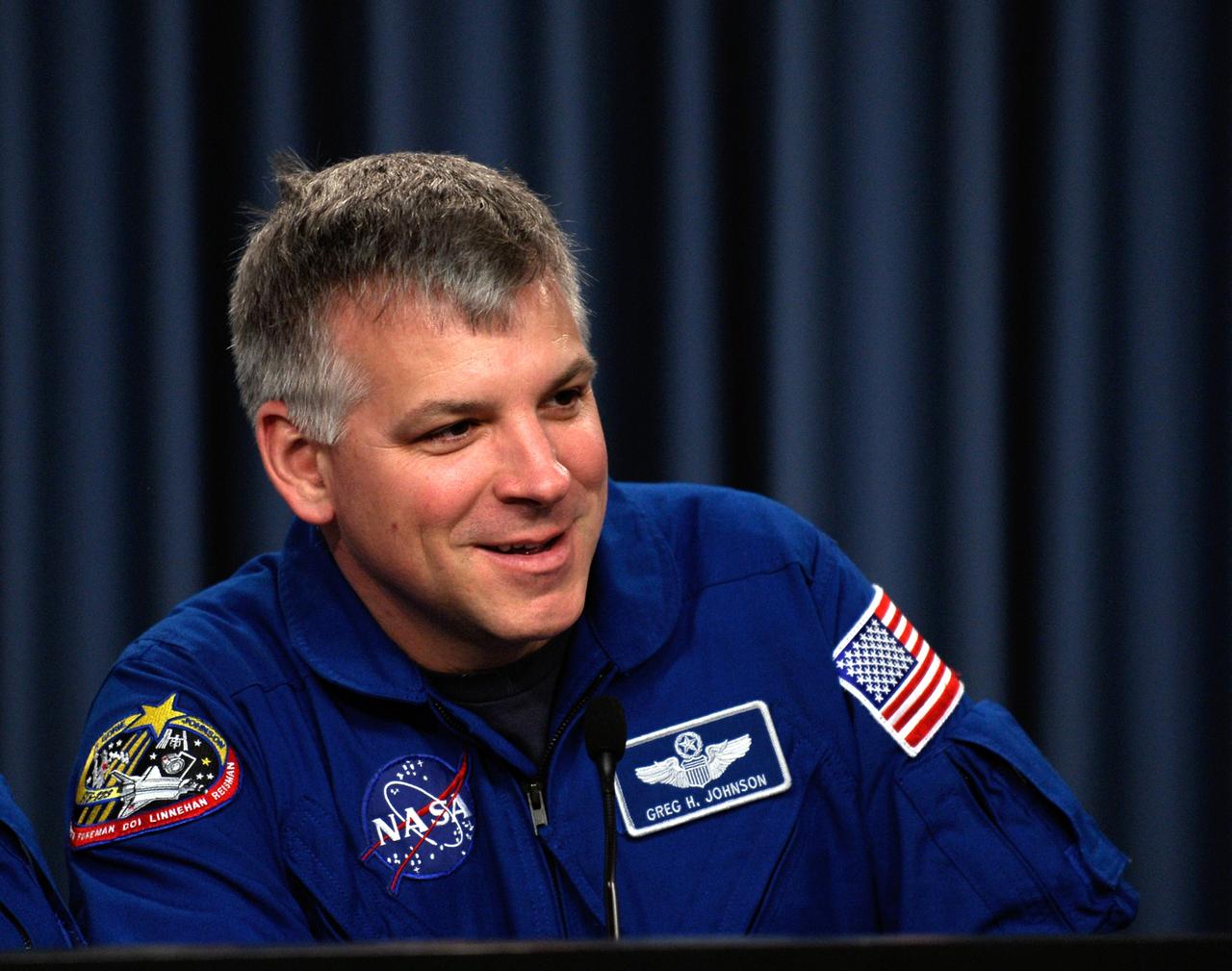

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. --- STS-123 Pilot Gregory H. Johnson talks to the media about his experiences on the mission to the International Space Station. The crew landed at Kennedy aboard space shuttle Endeavour at 8:39 p.m. EDT March 26. Endeavour's 16-day flight was the longest shuttle mission to the International Space Station and included a record five spacewalks. The shuttle's seven astronauts worked with the three-member station crew and ground teams around the world to install the first section of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory and the Canadian Space Agency's two-armed robotic system, known as Dextre. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
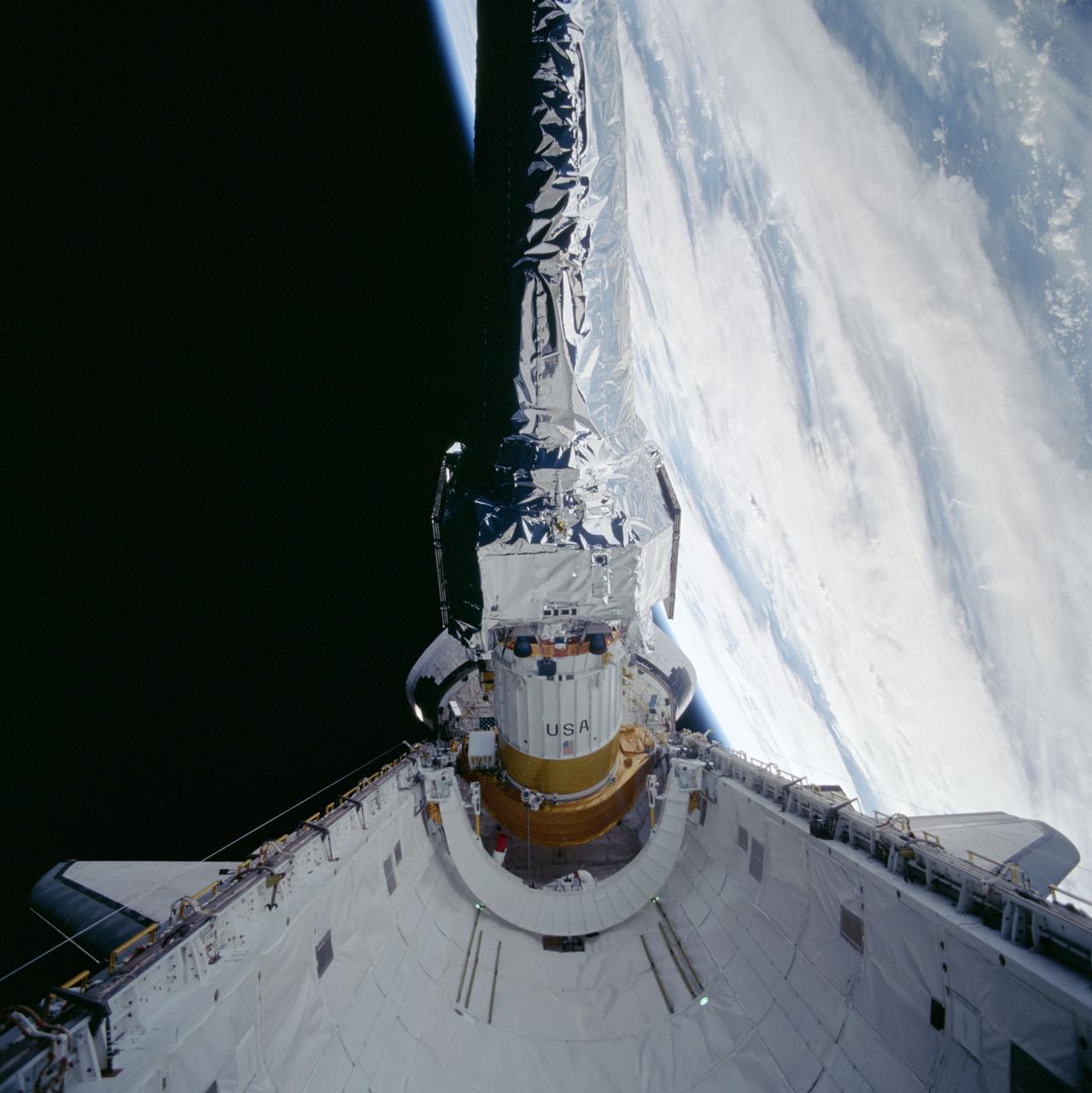

STS093-703-011 (22-27 July 1999) --- This 70mm frame shows the Chandra X-Ray observatory during its deployment from the Space Shuttle Columbia’s payload bay. The primary duty of the STS-93 crew was to deploy the world’s most powerful X-Ray telescope. It was also one of the first actions of the astronauts, occurring just a few hours following the shuttle’s arrival in Earth orbit. This scene is one of a series of still photos recorded by the crew before and during the deployment of the 50,162-pound observatory.
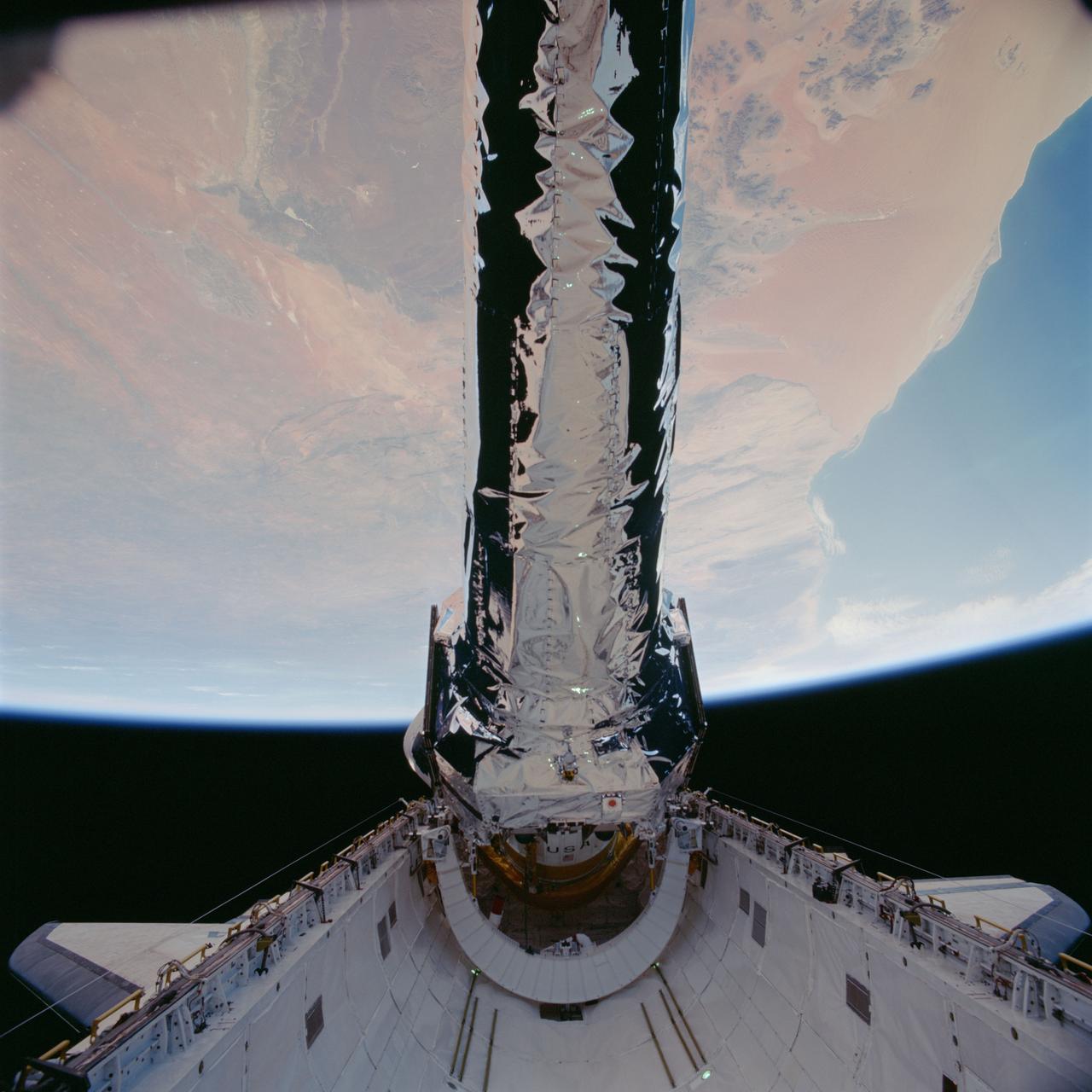

STS093-702-048 (23 July 1999)--- This 70mm frame shows the Chandra X-Ray observatory, backdropped against a desert area in Namibia, just before its release from Columbia's payload bay. The primary duty of the STS-93 crew was to deploy the world's most powerful X-Ray telescope. It was also one of the first actions of the astronauts, occurring just a few hours following the shuttle's arrival in Earth orbit. This scene is one of a series of still photos recorded by the crew before and during the deployment of the 50,162 pound observatory.
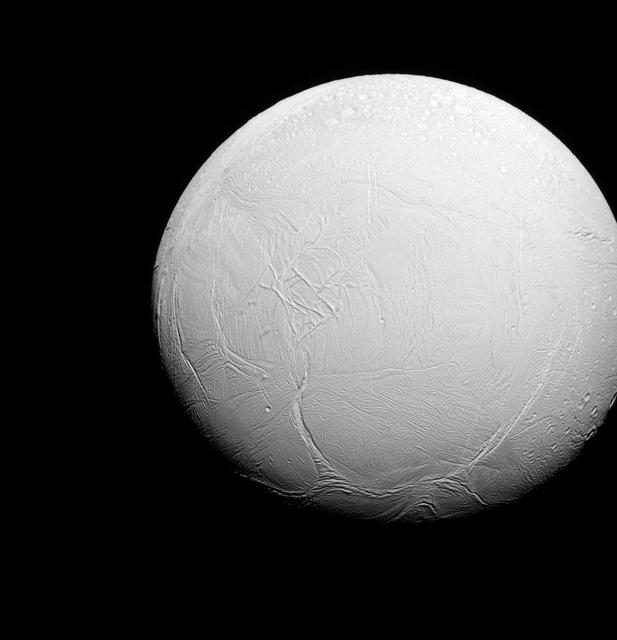

Enceladus is a world divided. To the north, the terrain is covered in impact craters, much like other icy moons. But to the south, the record of impact cratering is much more sparse, and instead the land is covered in fractures, ropy or hummocky terrain and long, linear features. Lit terrain seen here is on the trailing side of Enceladus. North on Enceladus is up. The image was taken in visible green light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on July 27, 2015. The view was obtained at a distance of approximately 70,000 miles (112,000 kilometers) from Enceladus and at a Sun-Enceladus-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 25 degrees. Image scale is 0.4 miles (0.7 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18340
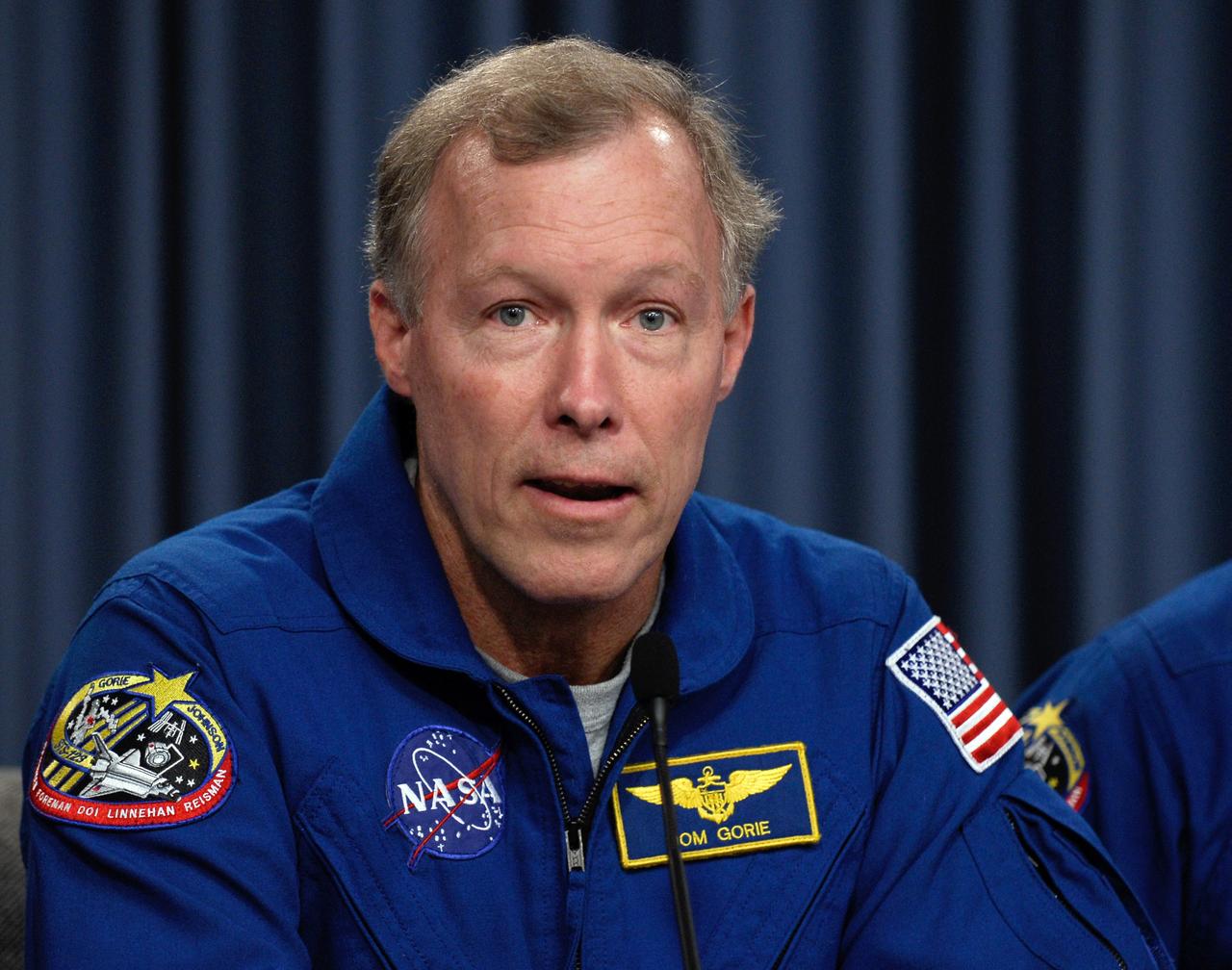

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. --- STS-123 Commander Dominic Gorie talks to the media about his experiences on the mission to the International Space Station. The crew landed at Kennedy aboard space shuttle Endeavour at 8:39 p.m. EDT March 26. Endeavour's 16-day flight was the longest shuttle mission to the International Space Station and included a record five spacewalks. The shuttle's seven astronauts worked with the three-member station crew and ground teams around the world to install the first section of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory and the Canadian Space Agency's two-armed robotic system, known as Dextre. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
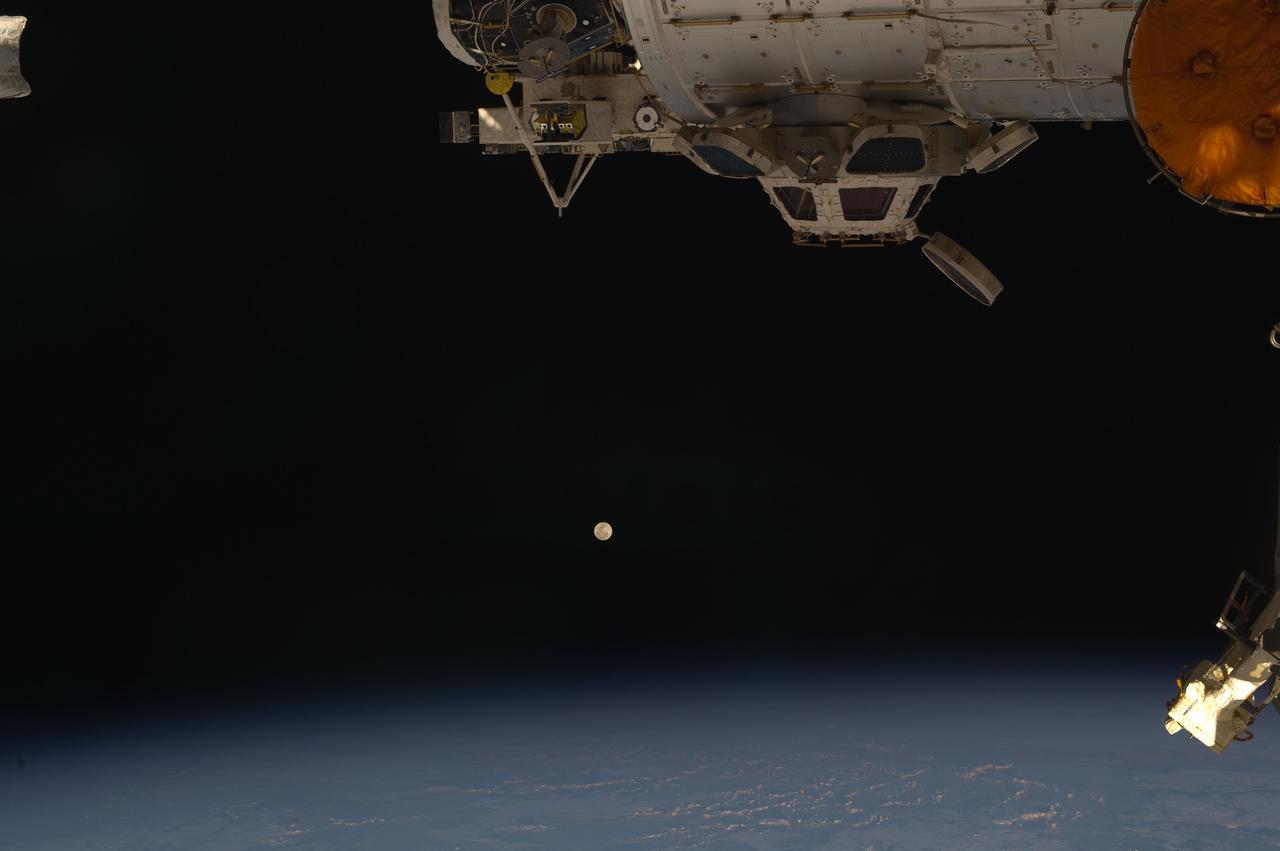

ISS031-E-018154 (6 May 2012) --- While most of the world's population had no trouble at all finding the full moon on the weekend of May 5-6, one has to look closely to recognize Earth's satellite just below center frame in the space traveler's eye-view aboard the International Space Station, some 240 miles above Earth. The station's cupola can be seen in upper portion of the image. While the photo was recorded around midnight on May 5 in the central daylight time zone, it was already early May 6 GMT. Three Expedition 31 crew members await the arrival of three additional crewmates in a little more than a week.
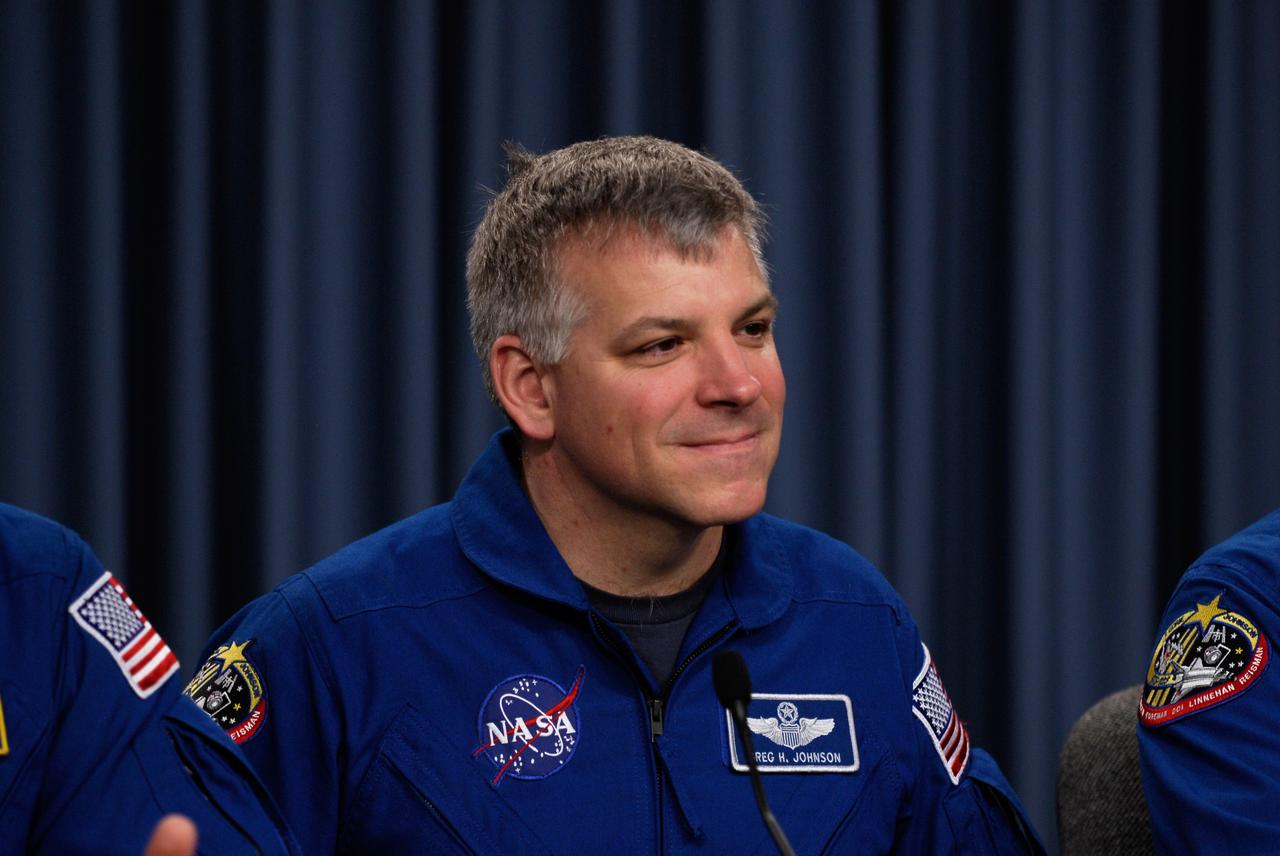

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. --- STS-123 Pilot Gregory H. Johnson talks to the media about his experiences on the mission to the International Space Station. The crew landed at Kennedy aboard space shuttle Endeavour at 8:39 p.m. EDT March 26. Endeavour's 16-day flight was the longest shuttle mission to the International Space Station and included a record five spacewalks. The shuttle's seven astronauts worked with the three-member station crew and ground teams around the world to install the first section of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory and the Canadian Space Agency's two-armed robotic system, known as Dextre. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

STS093-706-039 (23 July 1999)--- This 70mm frame shows the Chandra X-Ray observatory backdropped against the darkness of space not long after its release from Columbia's payload bay. The primary duty of the STS-93 crew was to deploy the world's most powerful X-Ray telescope. It was also one of the first actions of the crew, occurring just a few hours following the shuttle's arrival in Earth orbit. This scene is one of a series of still photos recorded by the crew before, during and after the deployment of the 50,162 pound observatory.
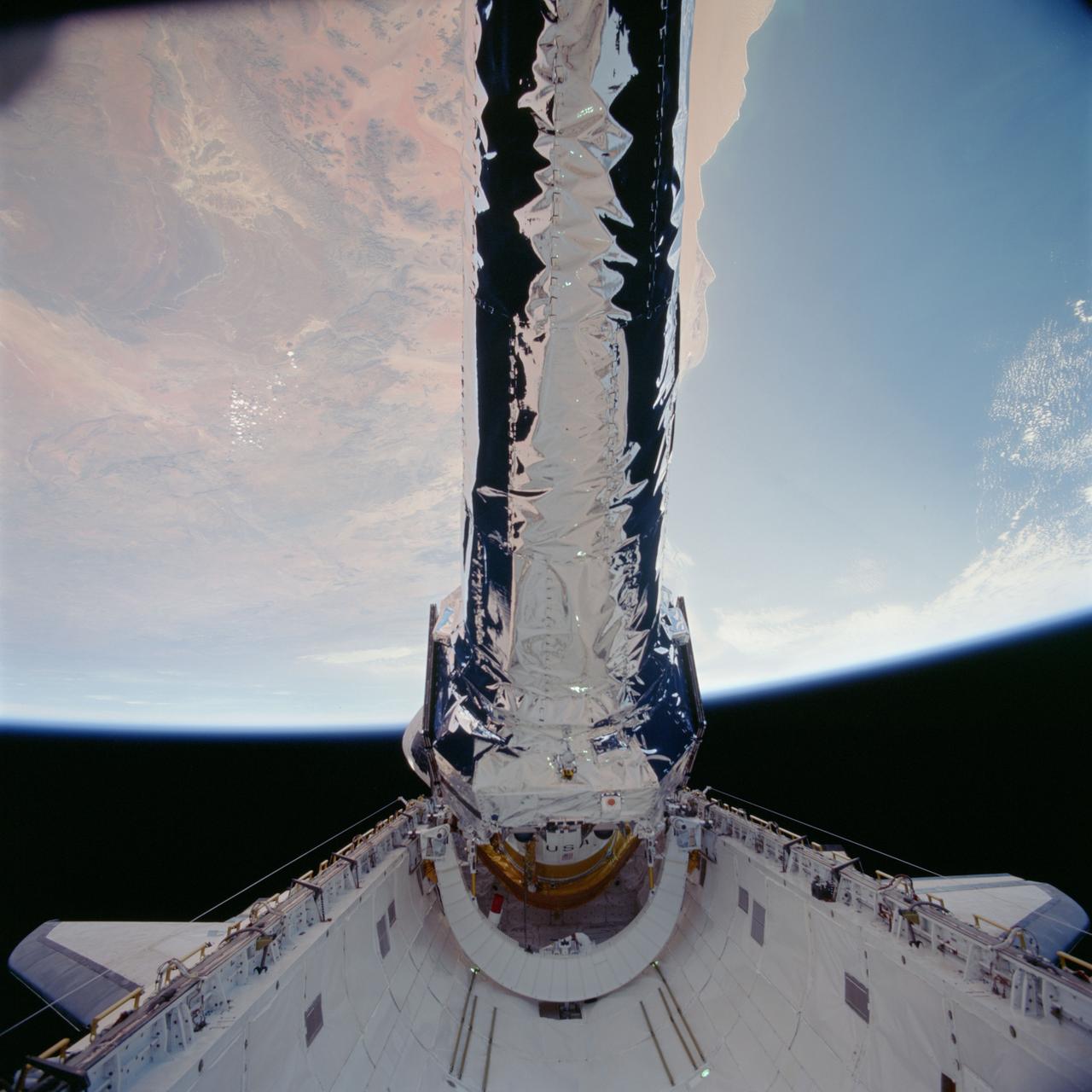

STS093-702-041 (23 July 1999)--- This 70mm frame shows the Chandra X-Ray observatory, backdropped against a desert area in Namibia, just before its release from Columbia's payload bay. The primary duty of the STS-93 crew was to deploy the world's most powerful X-Ray telescope. It was also one of the first actions of the astronauts, occurring just a few hours following the shuttle's arrival in Earth orbit. This scene is one of a series of still photos recorded by the crew before and during the deployment of the 50,162 pound observatory.

Technicians install protective solar array covers for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Sept. 26, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians install protective solar array covers for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Sept. 26, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.
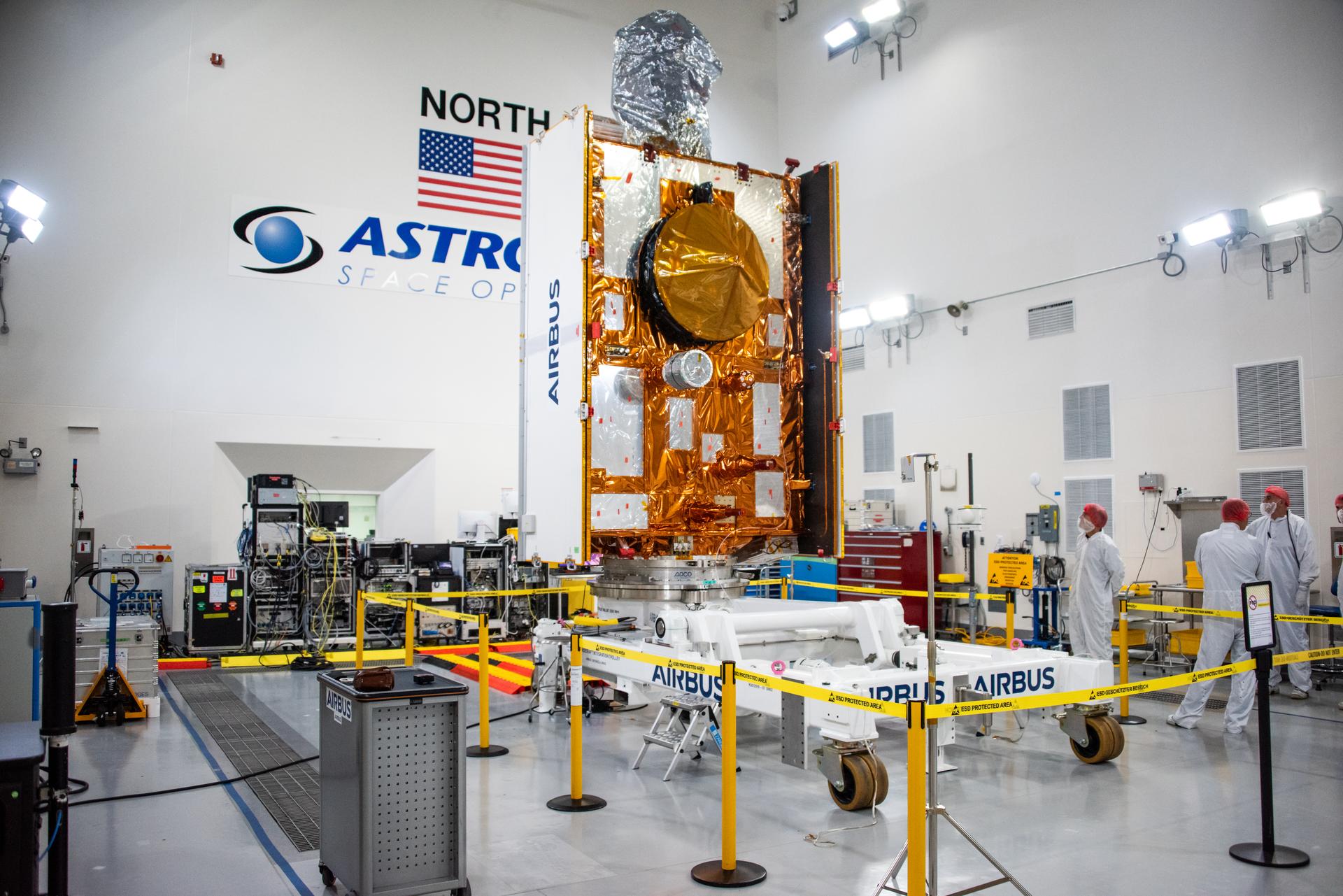

Technicians install protective solar array covers for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Sept. 26, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians install protective solar array covers for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Sept. 26, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.
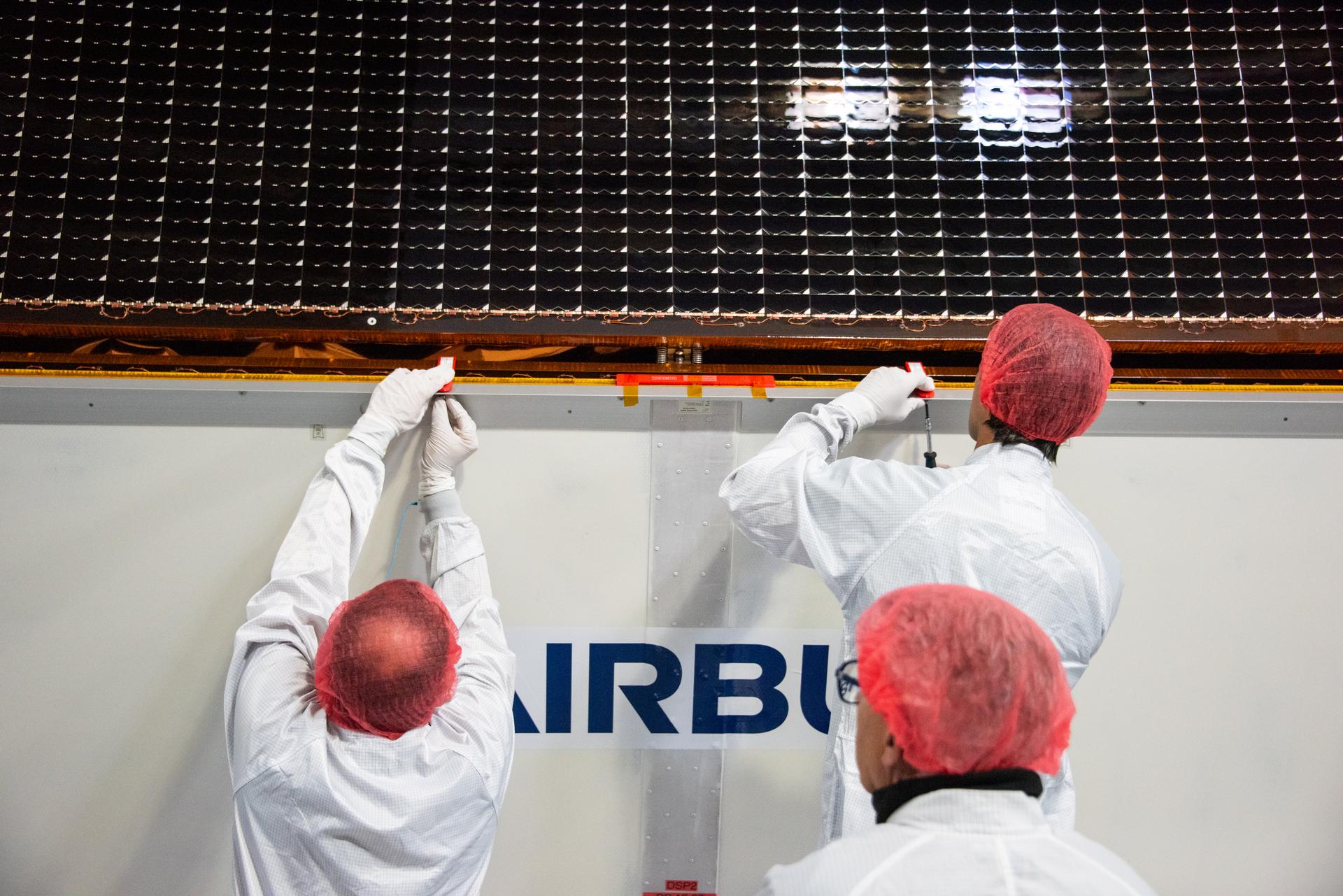

Technicians install protective solar array covers for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Sept. 26, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.
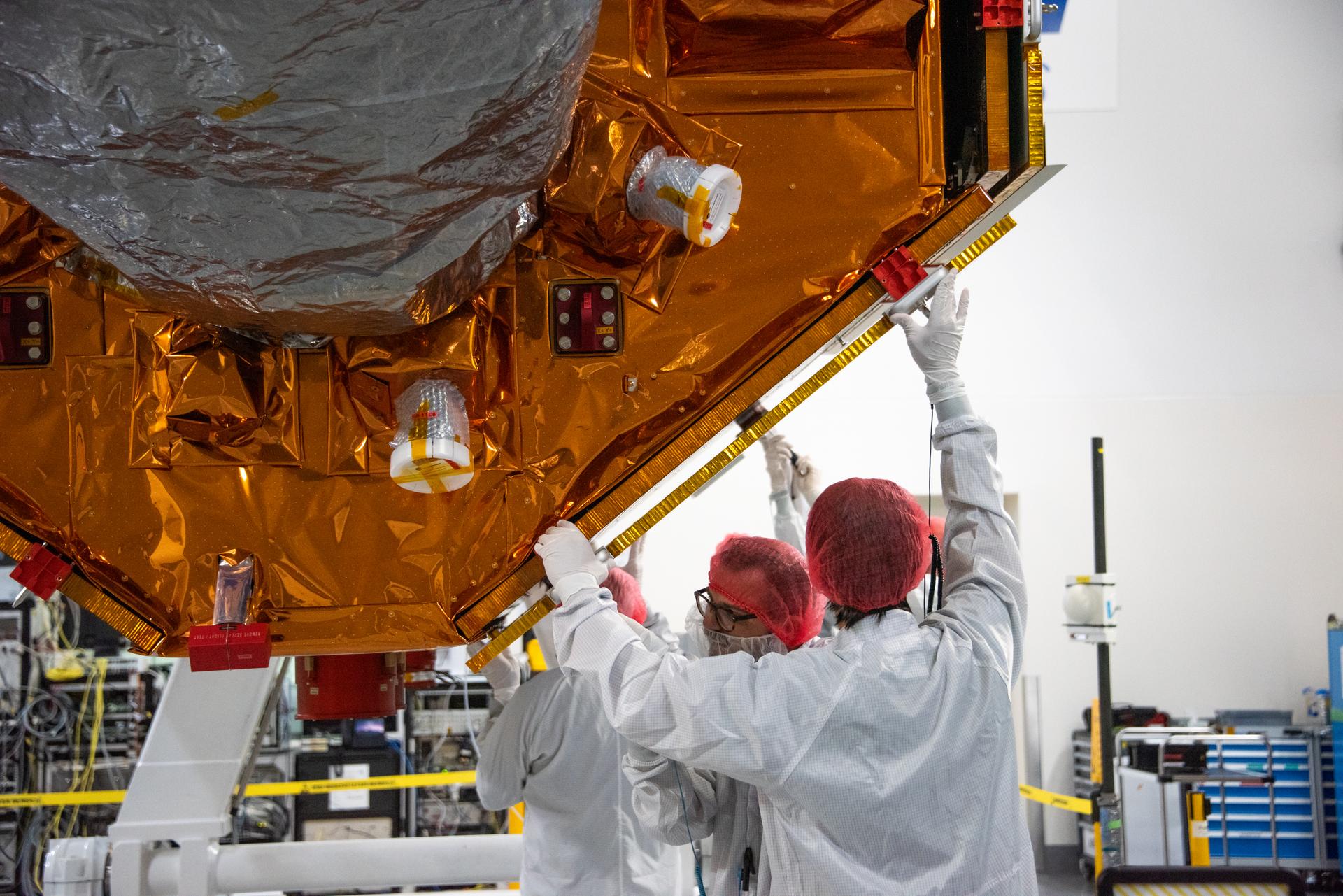

Technicians install protective solar array covers for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Sept. 26, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians install protective solar array covers for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Sept. 26, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.
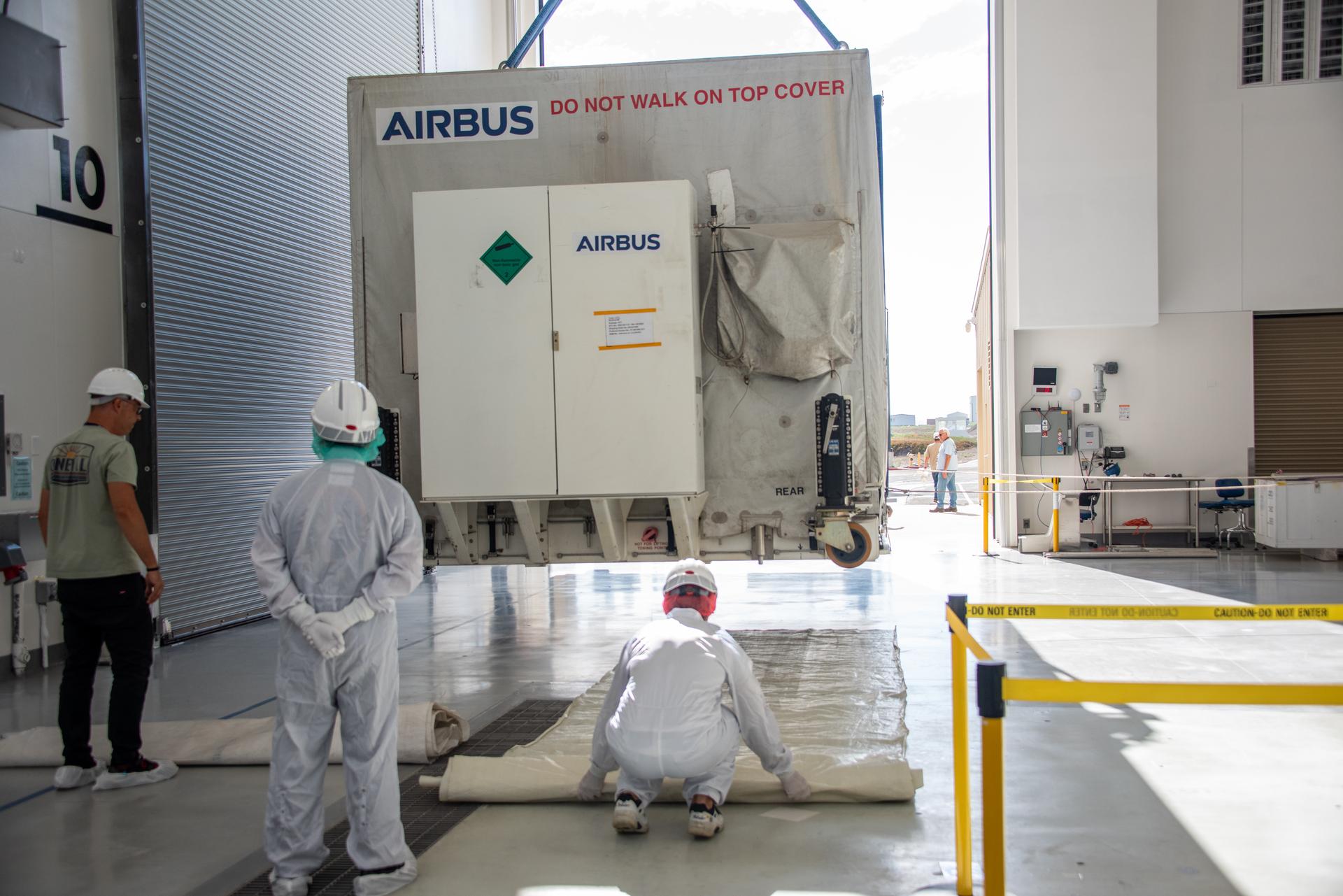

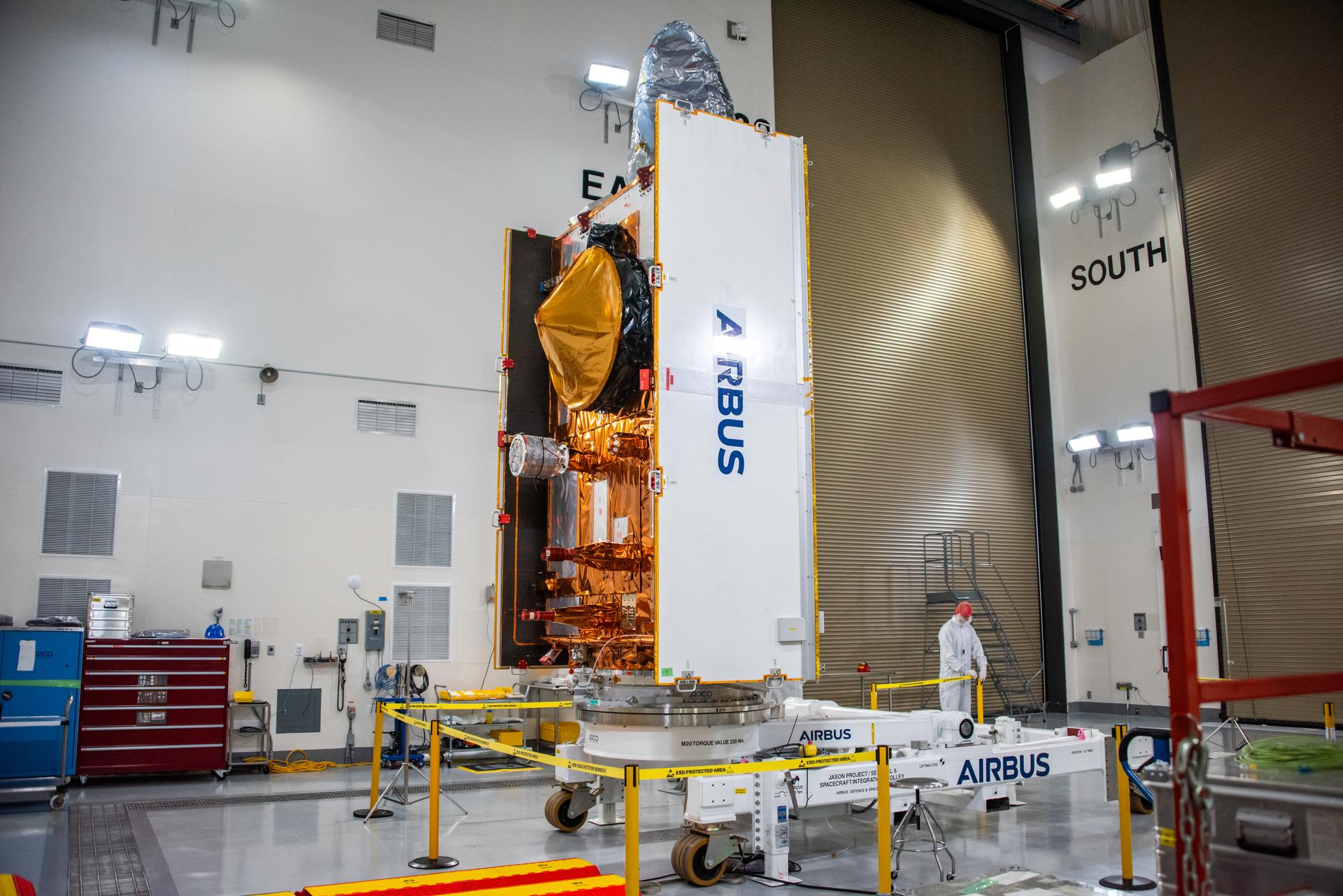
Technicians transfer the Sentinel-6B spacecraft from the NASA hangar to the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians transfer the Sentinel-6B spacecraft from the NASA hangar to the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.
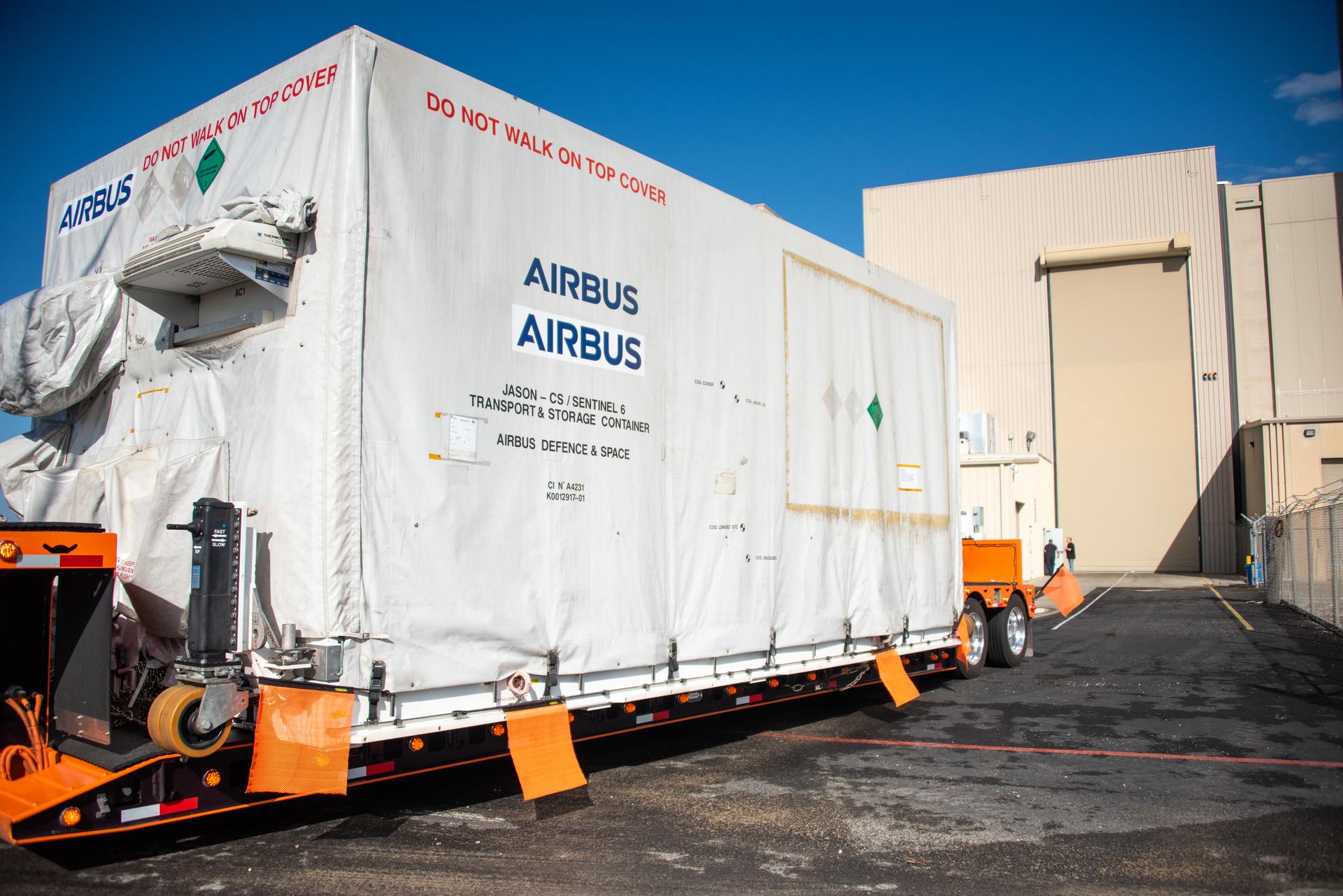

Technicians transfer the Sentinel-6B spacecraft from the NASA hangar to the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.
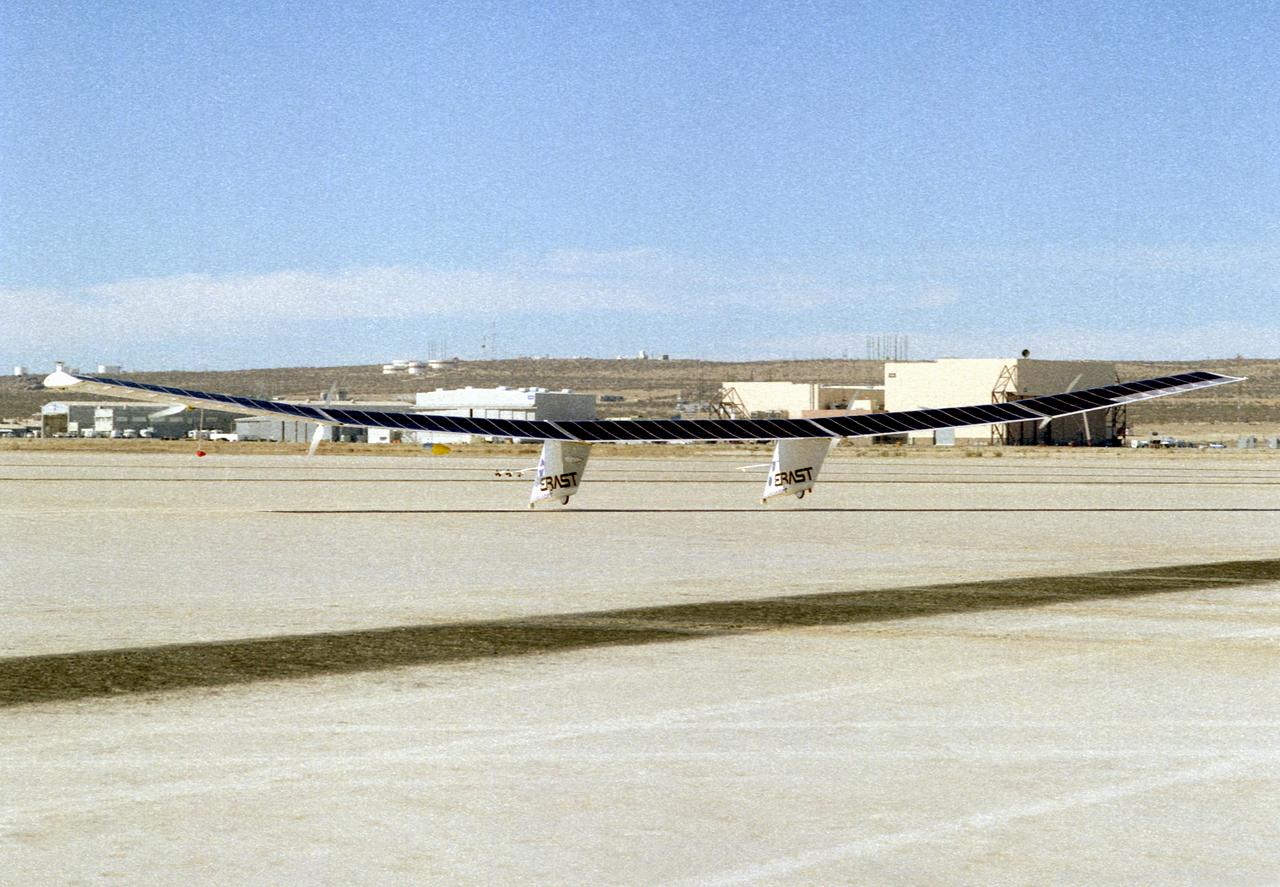

The Pathfinder research aircraft's solar cell arrays are prominently displayed as it touches down on the bed of Rogers Dry Lake at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, following a test flight. The solar arrays covered more than 75 percent of Pathfinder's upper wing surface, and provided electricity to power its six electric motors, flight controls, communications links and a host of scientific sensors.
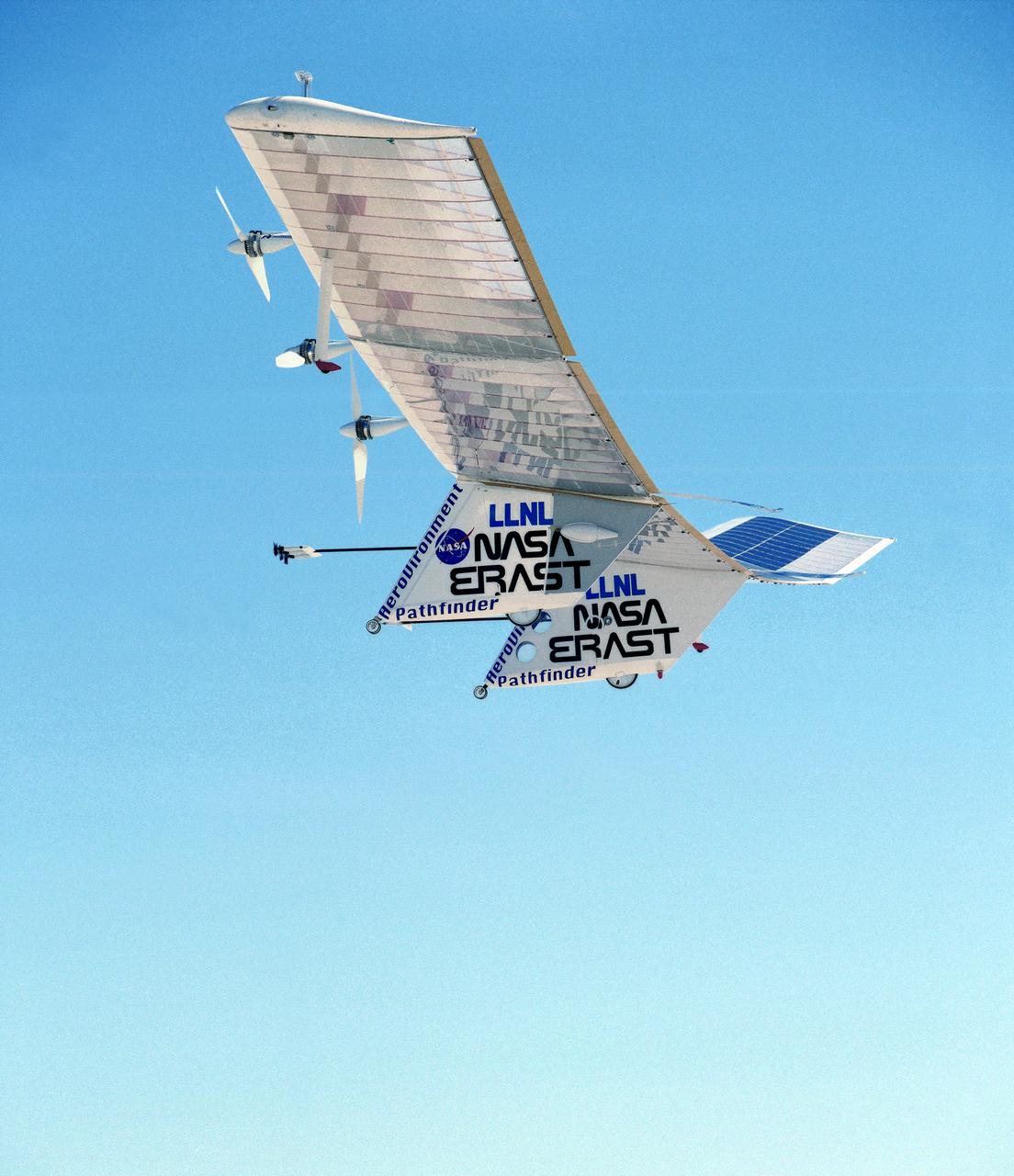

The Pathfinder solar-powered remotely piloted aircraft climbs to a record-setting altitude of 50,567 feet during a flight Sept. 11, 1995, at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California.

The Pathfinder research aircraft's wing structure was clearly defined as it soared under a clear blue sky during a test flight July 27, 1995, from Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The center section and outer wing panels of the aircraft had ribs constructed of thin plastic foam, while the ribs in the inner wing panels are fabricated from lightweight composite material. Developed by AeroVironment, Inc., the Pathfinder was one of several unmanned aircraft being evaluated under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program.

The Pathfinder research aircraft's wing structure is clearly defined as it soars under a clear blue sky during a test flight from Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, in November of 1996.
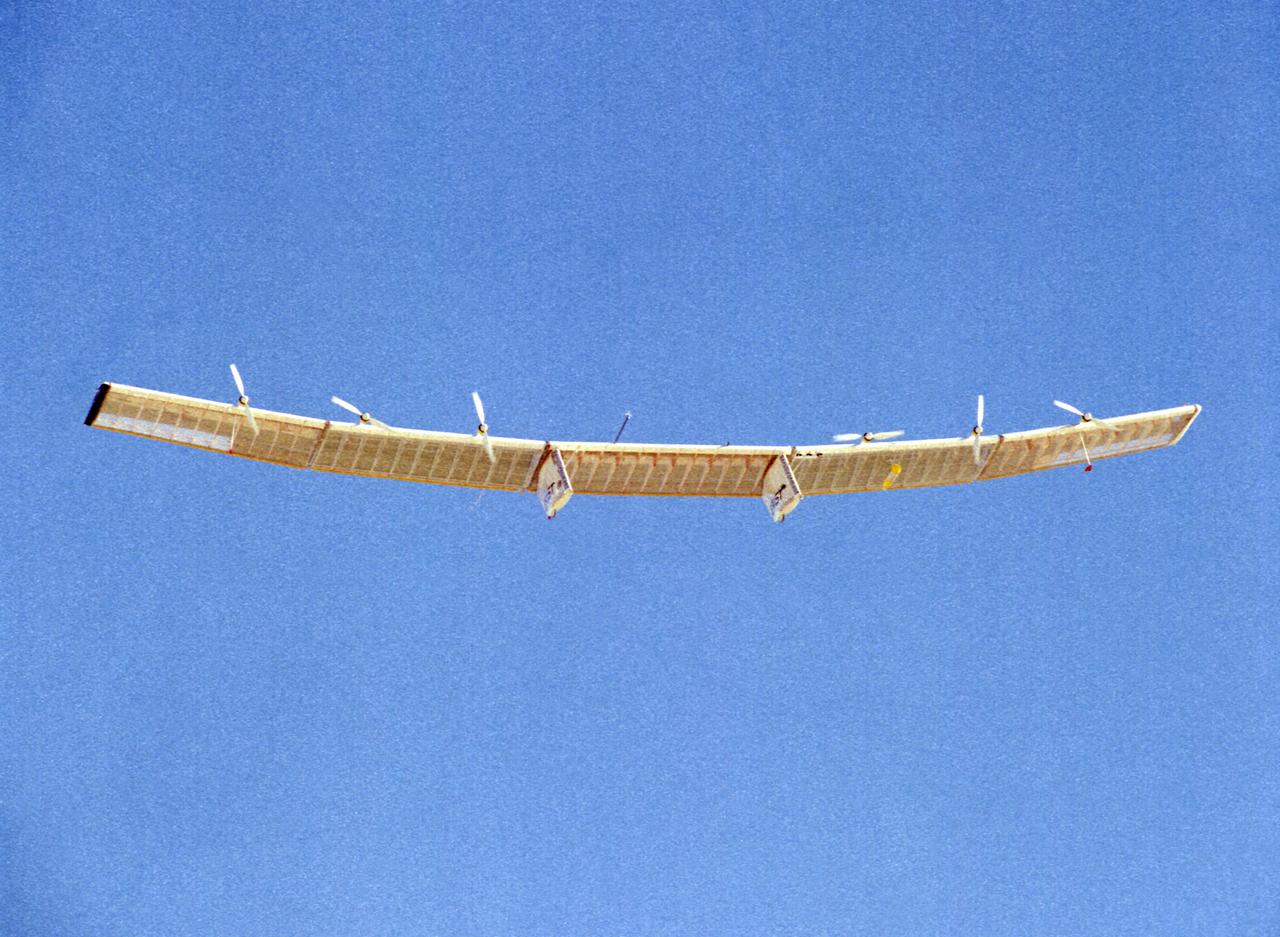
The Pathfinder solar-powered research aircraft is silhouetted against a clear blue sky as it soars aloft during a checkout flight from the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, November, 1996.

The Pathfinder solar-powered remotely piloted aircraft climbs to a record-setting altitude of 50,567 feet during a flight Sept. 11, 1995, at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The flight was part of the NASA ERAST (Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology) program. The Pathfinder was designed and built by AeroVironment Inc., Monrovia, California. Solar arrays cover nearly all of the upper wing surface and produce electricity to power the aircraft's six motors.

Pathfinder, NASA's solar-powered, remotely-piloted aircraft is shown while it was conducting a series of science flights to highlight the aircraft's science capabilities while collecting imagery of forest and coastal zone ecosystems on Kauai, Hawaii. The flights also tested two new scientific instruments, a high-spectral-resolution Digital Array Scanned Interferometer (DASI) and a high-spatial-resolution Airborne Real-Time Imaging System (ARTIS). The remote sensor payloads were designed by NASA's Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California, to support NASA's Mission to Planet Earth science programs.

The Pathfinder solar-powered aircraft sits on Rogers Dry Lake at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, before a research flight.

The Pathfinder solar-powered research aircraft heads for landing on the bed of Rogers Dry Lake at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, after a successful test flight Nov. 19, 1996.

The Pathfinder solar-powered research aircraft settles in for landing on the bed of Rogers Dry Lake at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, after a successful test flight Nov. 19, 1996. The ultra-light craft flew a racetrack pattern at low altitudes over the flight test area for two hours while project engineers checked out various systems and sensors on the uninhabited aircraft. The Pathfinder was controlled by two pilots, one in a mobile control unit which followed the craft, the other in a stationary control station. Pathfinder, developed by AeroVironment, Inc., is one of several designs being evaluated under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program.
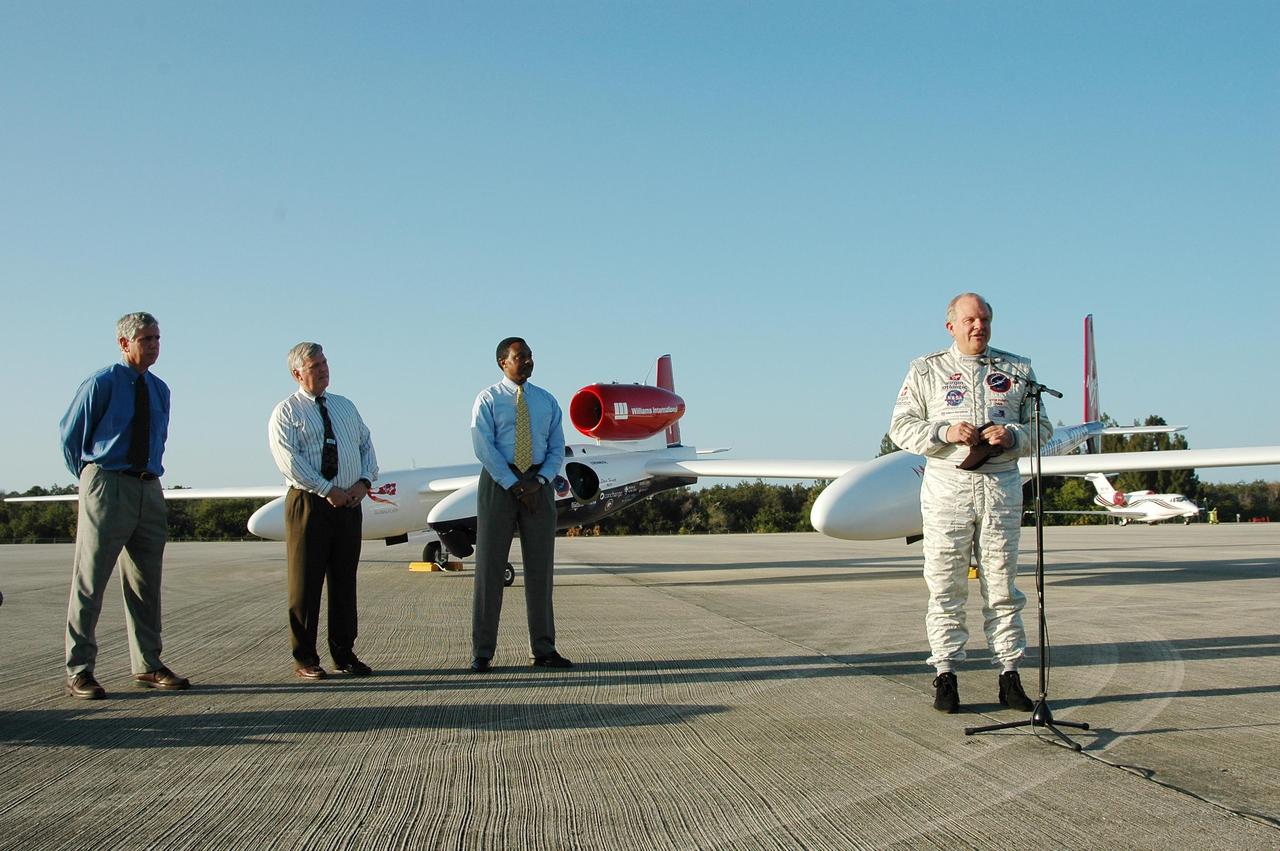

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Pilot Steve Fossett talks to the media after his landing of the Virgin Atlantic Airways GlobalFlyer aircraft at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Standing at left are KSC Spaceport Development Manager Jim Ball, Center Director James Kennedy and Executive Director of Florida Space Authority Winston Scott. The aircraft is being relocated from Salina, Kan., to the Shuttle Landing Facility to begin preparations for an attempt to set a new world record for the longest flight made by any aircraft. An exact takeoff date for the record-setting flight has not been determined and is contingent on weather and jet-stream conditions. The window for the attempt opens in mid-January, making the flight possible anytime between then and the end of February. NASA agreed to let Virgin Atlantic Airways use Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility as a takeoff site. The facility use is part of a pilot program to expand runway access for non-NASA activities.
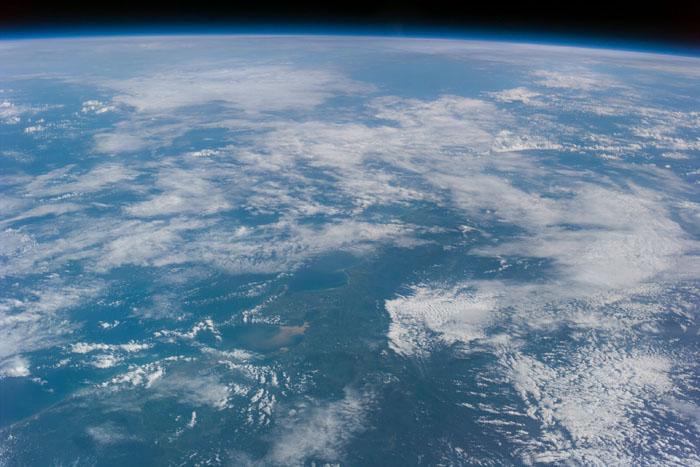

S99-E-5555 (17 February 2000) --- As photographed from the Space Shuttle Endeavour, this oblique electronic still image of Earth's horizon reveals a great deal of cloud cover. In the case of the electronic still camera (ESC), as well as film-bearing instruments, clouds naturally obscure views of recognizable land masses. Much of Earth is heavily cloud covered during the current mission and meteorlogists and oceanographers are interested in studying that aspect. However, the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission's other sensing equipment, X-SAR and C-band antennae, are able to penetrate cloud cover and record important topographic data for mapmakers and scientists of other disciplines. In addition to the sensing equipment mentioned above, this mission is supporting the EarthKAM project which utilizes the services of another electronic still camera mounted in Endeavour's windows. Unlike this oblique view, EarthKAM records strictly vertical or nadir imagery of points all over the world. Students across the United States and in France, Germany and Japan are taking photos throughout the STS-99 mission. And they are using these new photos, plus all the images already available in the EarthKAM system, to enhance their classroom learning in Earth and space science, social studies, geography, mathematics and more.
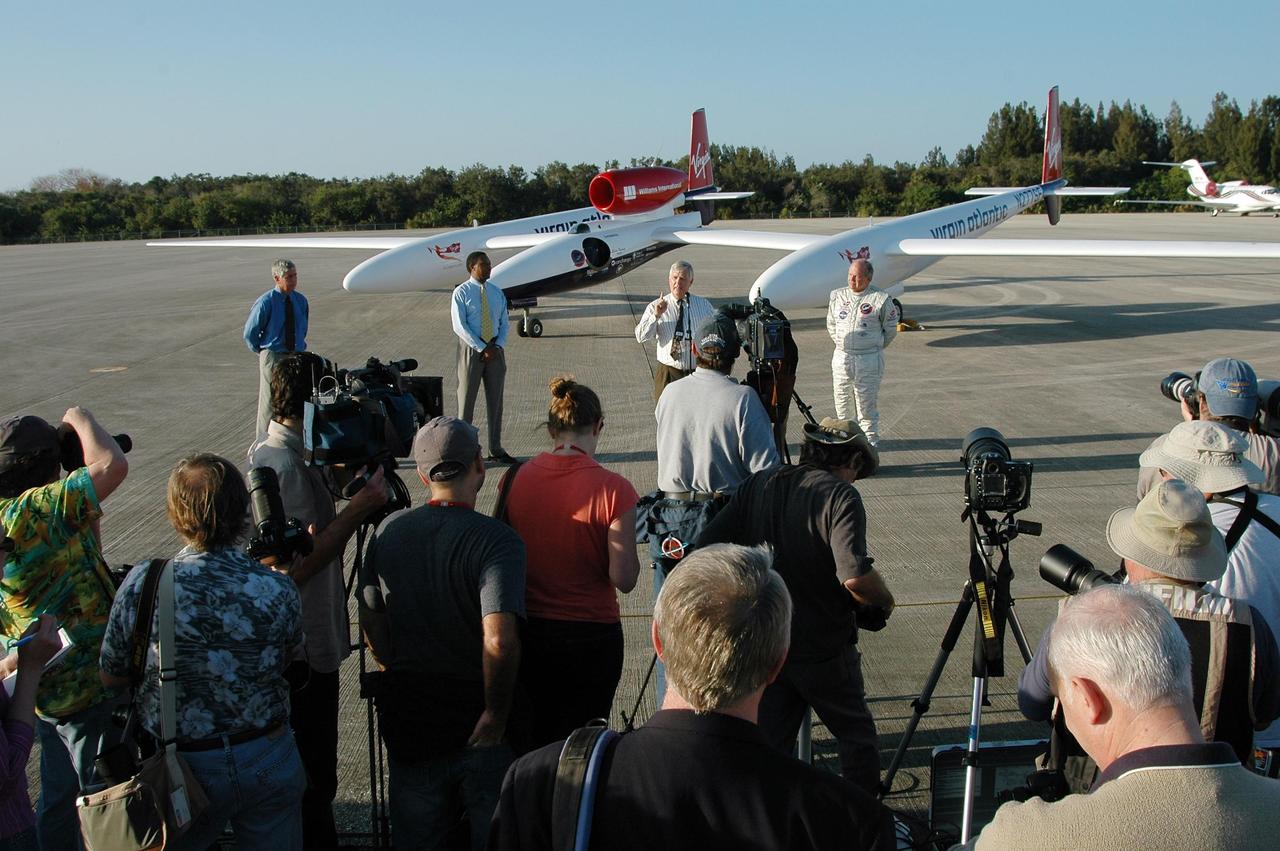

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After the landing of the Virgin Atlantic Airways GlobalFlyer aircraft at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Center Director James Kennedy (center, in front of the plane) addresses the media. At right is the pilot, Steve Fossett. At left are Jim Ball, KSC Spaceport Development manager, and Winston Scott, executive director of Florida Space Authority. The aircraft is being relocated from Salina, Kan., to the Shuttle Landing Facility to begin preparations for an attempt to set a new world record for the longest flight made by any aircraft. An exact takeoff date for the record-setting flight has not been determined and is contingent on weather and jet-stream conditions. The window for the attempt opens in mid-January, making the flight possible anytime between then and the end of February. NASA agreed to let Virgin Atlantic Airways use Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility as a takeoff site. The facility use is part of a pilot program to expand runway access for non-NASA activities.
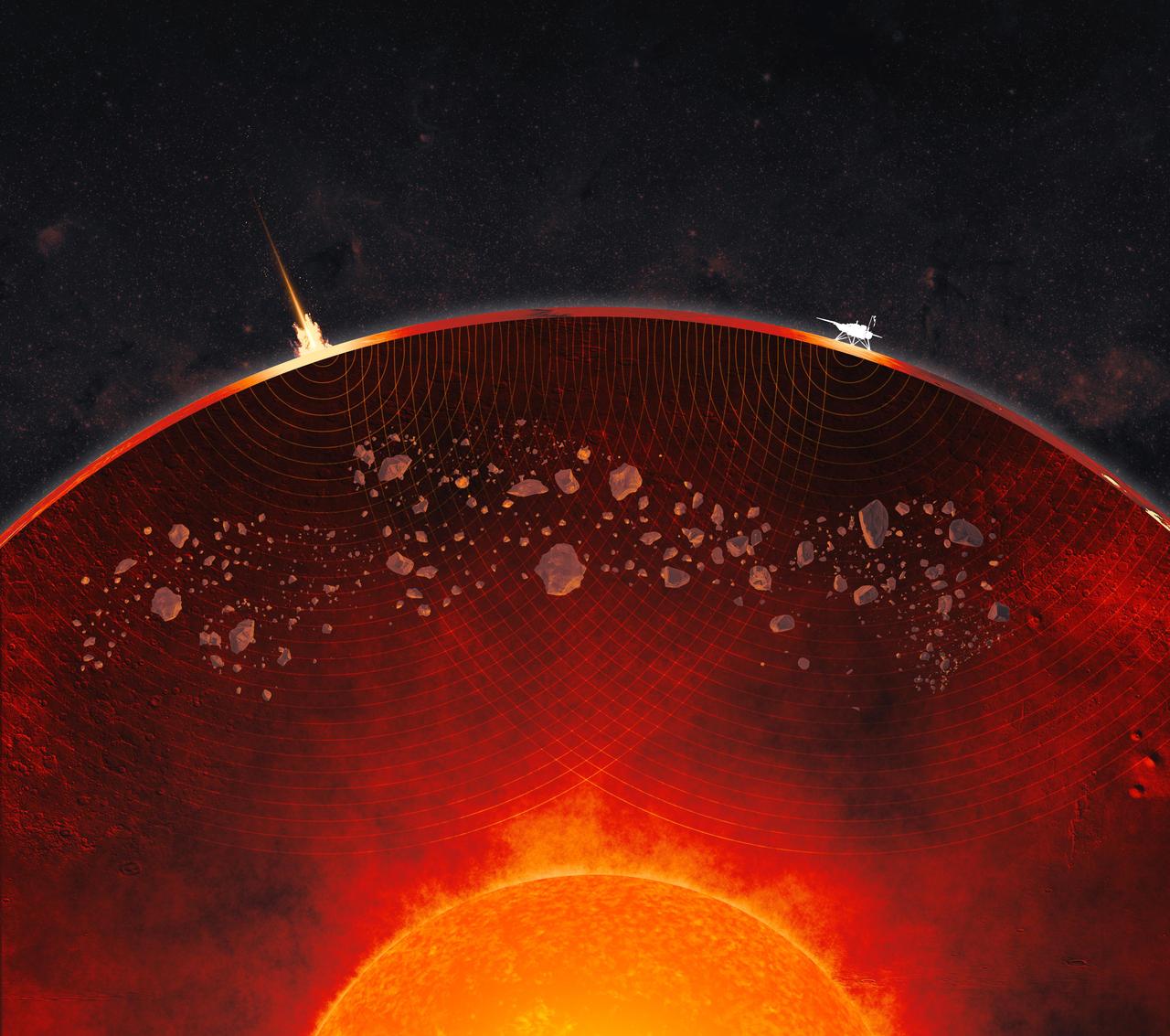

This not-to-scale artist's concept depicts a cutaway view of Mars' interior, revealing the crust, mantle, and core. Debris from ancient impacts lies scattered in the mantle in the form of lumps that are as large as 2.5 miles (4 kilometers) across, data from NASA's InSight Mars lander shows. On the Martian surface at left, a meteoroid impact sends seismic signals (shown as curving concentric lines) through the planet; InSight is depicted at right. InSight placed the first seismometer on Mars' surface in 2018. The extremely sensitive instrument recorded 1,319 marsquakes before the lander ran out of power in 2022, the result of dust caked on its solar panels. Quakes produce seismic waves that change as they pass through different kinds of material, providing scientists with a way to study the interior of a planetary body. To date, the InSight team has measured the size, depth, and composition of Mars' crust, mantle, and core. The impact debris in the Martian mantle offers a geologic record that could be preserved only on worlds like Mars, whose lack of tectonic plates has kept its interior from being churned up the way Earth's is through a process known as convection. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26636
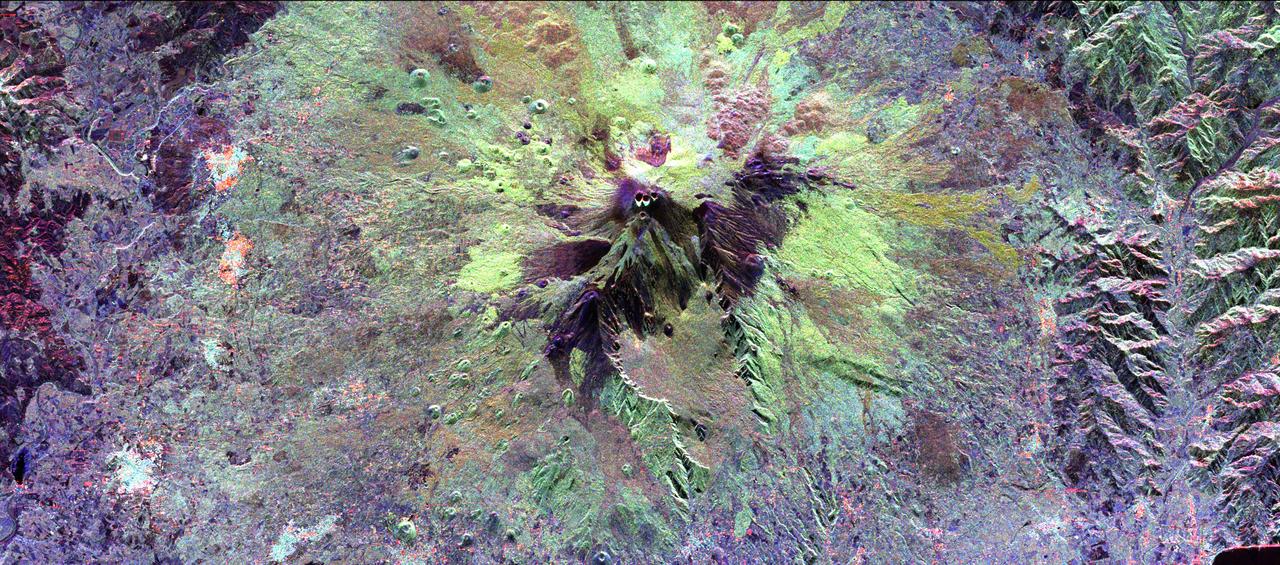

The summit of the Mount Etna volcano on the island of Sicily, Italy, one of the most active volcanoes in the world, is shown near the center of this radar image. Lava flows of different ages and surface roughness appear in shades of purple, green, yellow and pink surrounding the four small craters at the summit. Etna is one of the best-studied volcanoes in the world and scientists are using this radar image to identify and distinguish a variety of volcanic features. Etna has erupted hundreds of times in recorded history, with the most recent significant eruption in 1991-1993. Scientists are studying Etna as part of the international "Decade Volcanoes" project, because of its high level of activity and potential threat to local populations. This image was acquired on October 11, 1994 by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the space shuttle Endeavour. SIR-C/X-SAR, a joint mission of the German, Italian and the United States space agencies, is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth. The image is centered at 37.8 degrees North latitude and 15.1 degrees East longitude and covers an area of 51.2 kilometers by 22.6 kilometers (31.7 miles by 14.0 miles). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01776

ER-2 tail number 806, is one of two Airborne Science ER-2s used as science platforms by Dryden. The aircraft are platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They are also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation. The ER-2s are capable of carrying a maximum payload of 2,600 pounds of experiments in a nose bay, the main equipment bay behind the cockpit, two wing-mounted superpods and small underbody and trailing edges. Most ER-2 missions last about six hours with ranges of about 2,200 nautical miles. The aircraft typically fly at altitudes above 65,000 feet. On November 19, 1998, the ER-2 set a world record for medium weight aircraft reaching an altitude of 68,700 feet. The aircraft is 63 feet long, with a wingspan of 104 feet. The top of the vertical tail is 16 feet above ground when the aircraft is on the bicycle-type landing gear. Cruising speeds are 410 knots, or 467 miles per hour, at altitude. A single General Electric F-118 turbofan engine rated at 17,000 pounds thrust powers the ER-2.
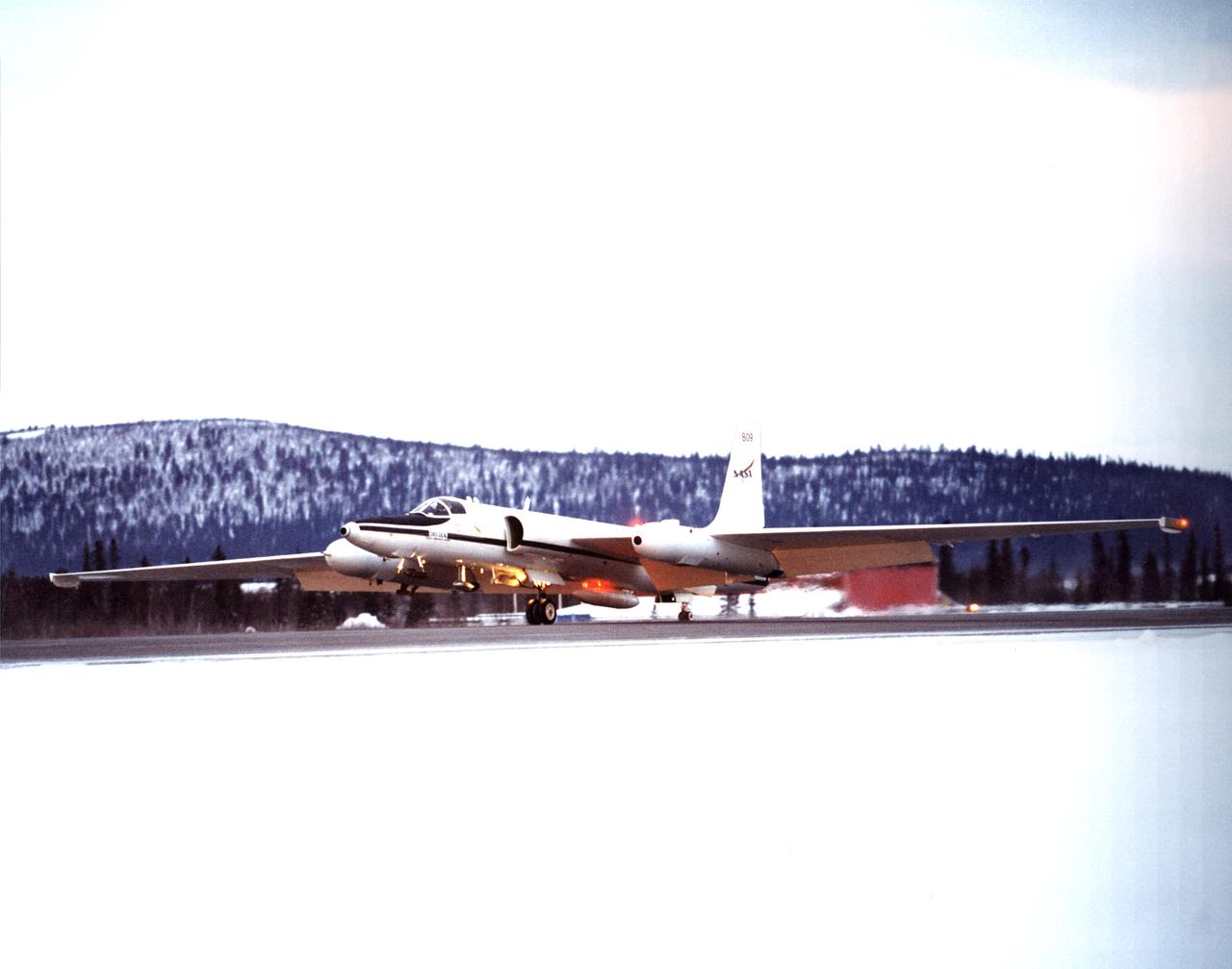

ER-2s bearing tail numbers 806 and 809 are used as airborne science platforms by NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The aircraft are platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They are also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation. The ER-2s are capable of carrying a maximum payload of 2,600 pounds of experiments in a nose bay, the main equipment bay behind the cockpit, two wing-mounted superpods and small underbody and trailing edges. Most ER-2 missions last about six hours with ranges of about 2,200 nautical miles. The aircraft typically fly at altitudes above 65,000 feet. On November 19, 1998, an ER-2 set a world record for medium weight aircraft reaching an altitude of 68,700 feet. The aircraft is 63 feet long, with a wingspan of 104 feet. The top of the vertical tail is 16 feet above ground when the aircraft is on the bicycle-type landing gear. Cruising speeds are 410 knots, or 467 miles per hour, at altitude. A single General Electric F-118 turbofan engine rated at 17,000 pounds thrust powers the ER-2.
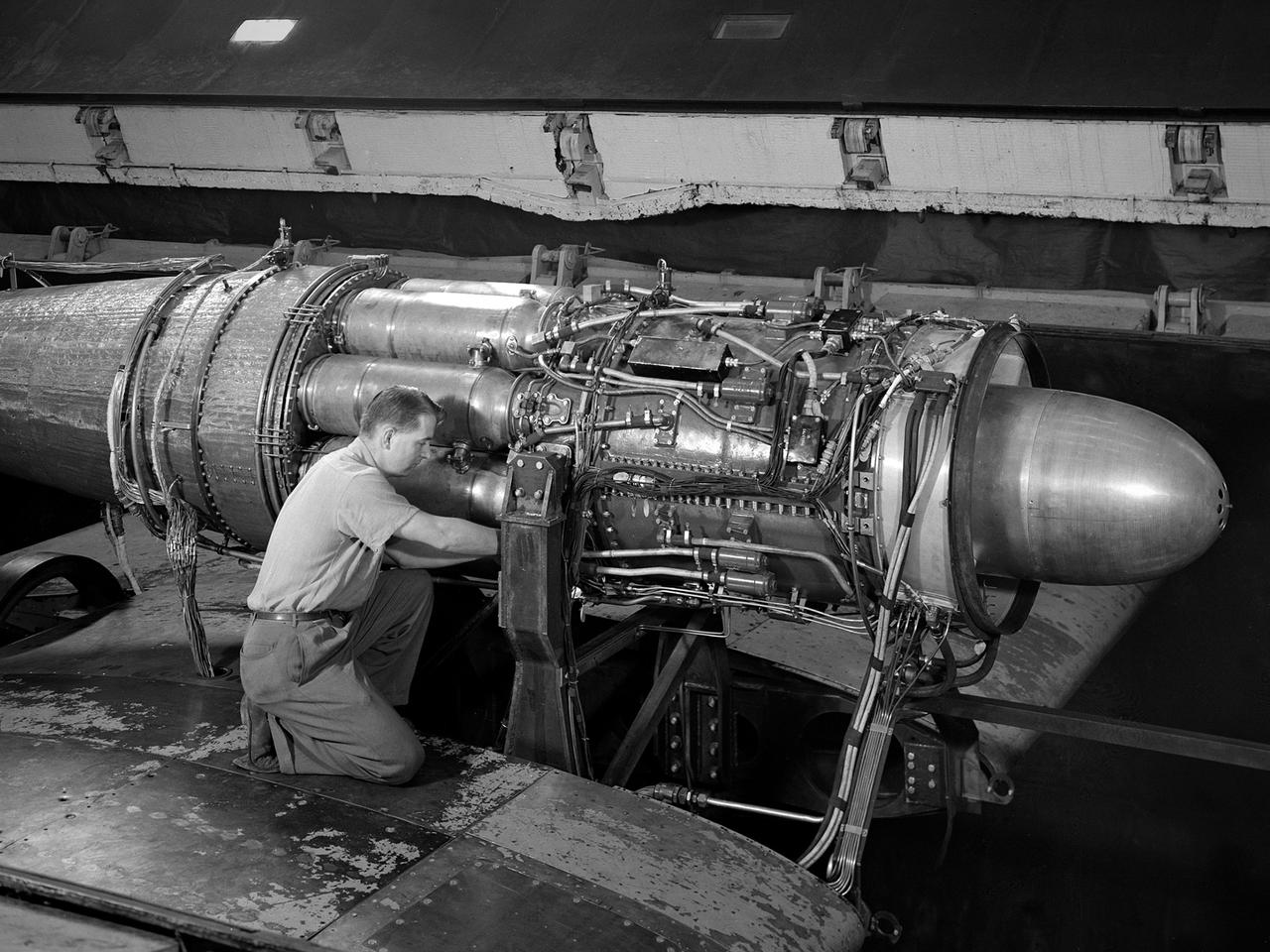

A General Electric TG-180 turbojet installed in the Altitude Wind Tunnel at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. In 1943 the military asked General Electric to develop an axial-flow jet engine which became the TG-180. The military understood that the TG-180 would not be ready during World War II but recognized the axial-flow compressor’s long-term potential. Although the engine was bench tested in April 1944, it was not flight tested until February 1946. The TG-180 was brought to the Altitude Wind Tunnel in 1945 for a series of investigations. The studies, which continued intermittently into 1948, analyzed an array of performance issues. NACA modifications steadily improved the TG-180’s performance, including the first successful use of an afterburner. The Lewis researchers studied a 29-inch diameter afterburner over a range of altitude conditions using several different types of flameholders and fuel systems. Lewis researchers concluded that a three-stage flameholder with its largest stage upstream was the best burner configuration. Although the TG-180 (also known as the J35) was not the breakthrough engine that the military had hoped for, it did power the Douglas D-558-I Skystreak to a world speed record on August 20, 1947. The engines were also used on the Republic F-84 Thunderjet and the Northrup F-89 Scorpion.

ER-2 tail number 806, is one of two Airborne Science ER-2s used as science platforms by Dryden. The aircraft are platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They are also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation. The ER-2s are capable of carrying a maximum payload of 2,600 pounds of experiments in a nose bay, the main equipment bay behind the cockpit, two wing-mounted superpods and small underbody and trailing edges. Most ER-2 missions last about six hours with ranges of about 2,200 nautical miles. The aircraft typically fly at altitudes above 65,000 feet. On November 19, 1998, the ER-2 set a world record for medium weight aircraft reaching an altitude of 68,700 feet. The aircraft is 63 feet long, with a wingspan of 104 feet. The top of the vertical tail is 16 feet above ground when the aircraft is on the bicycle-type landing gear. Cruising speeds are 410 knots, or 467 miles per hour, at altitude. A single General Electric F-118 turbofan engine rated at 17,000 pounds thrust powers the ER-2.

ER-2 tail number 806, is one of two Airborne Science ER-2s used as science platforms by Dryden. The aircraft are platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They are also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation. The ER-2s are capable of carrying a maximum payload of 2,600 pounds of experiments in a nose bay, the main equipment bay behind the cockpit, two wing-mounted superpods and small underbody and trailing edges. Most ER-2 missions last about six hours with ranges of about 2,200 nautical miles. The aircraft typically fly at altitudes above 65,000 feet. On November 19, 1998, the ER-2 set a world record for medium weight aircraft reaching an altitude of 68,700 feet. The aircraft is 63 feet long, with a wingspan of 104 feet. The top of the vertical tail is 16 feet above ground when the aircraft is on the bicycle-type landing gear. Cruising speeds are 410 knots, or 467 miles per hour, at altitude. A single General Electric F-118 turbofan engine rated at 17,000 pounds thrust powers the ER-2.
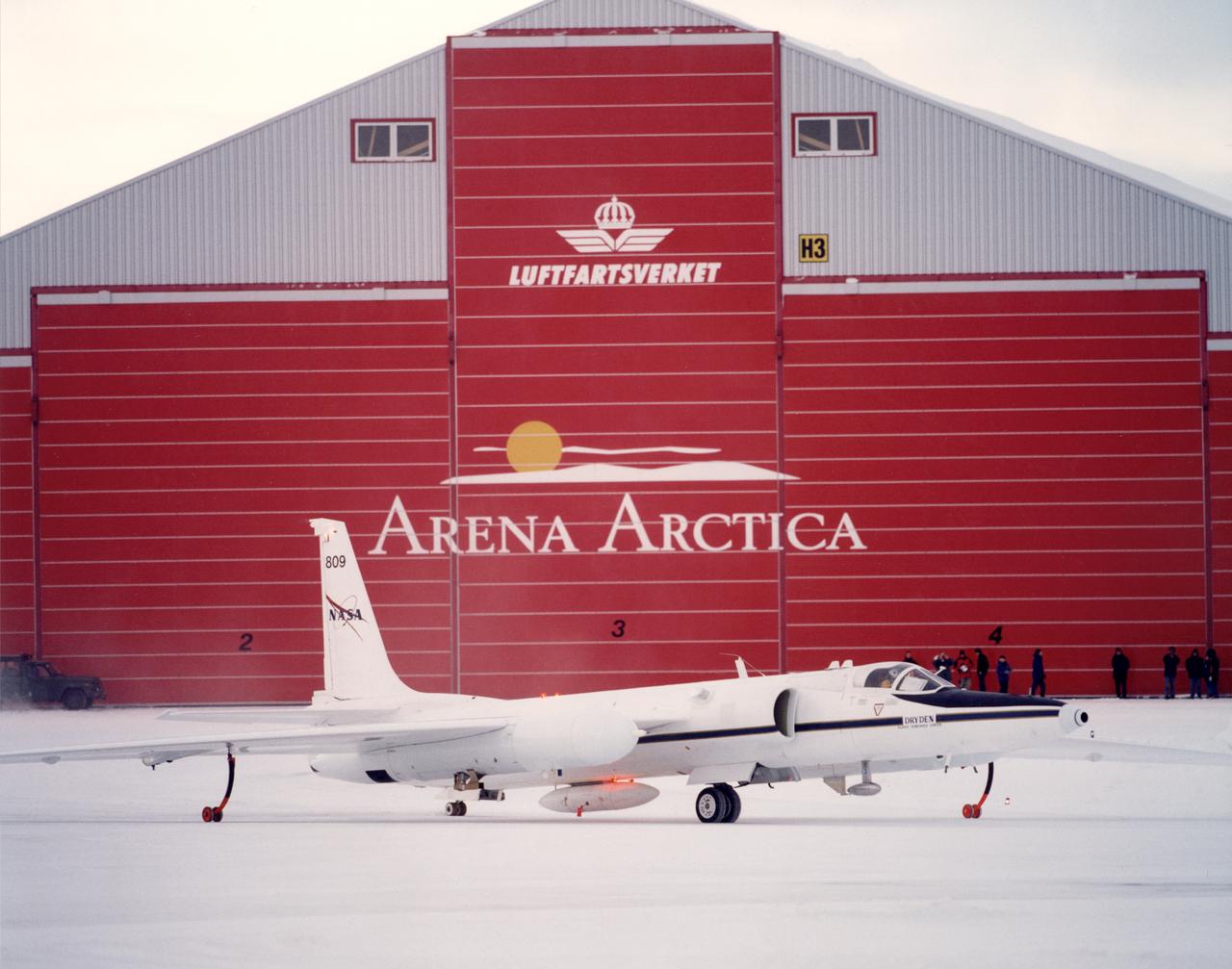

ER-2s bearing tail numbers 806 and 809 are used as airborne science platforms by NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The aircraft are platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They are also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation. The ER-2s are capable of carrying a maximum payload of 2,600 pounds of experiments in a nose bay, the main equipment bay behind the cockpit, two wing-mounted superpods and small underbody and trailing edges. Most ER-2 missions last about six hours with ranges of about 2,200 nautical miles. The aircraft typically fly at altitudes above 65,000 feet. On November 19, 1998, an ER-2 set a world record for medium weight aircraft reaching an altitude of 68,700 feet. The aircraft is 63 feet long, with a wingspan of 104 feet. The top of the vertical tail is 16 feet above ground when the aircraft is on the bicycle-type landing gear. Cruising speeds are 410 knots, or 467 miles per hour, at altitude. A single General Electric F-118 turbofan engine rated at 17,000 pounds thrust powers the ER-2.

ER-2s bearing tail numbers 806 and 809 are used as airborne science platforms by NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The aircraft are platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They are also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation. The ER-2s are capable of carrying a maximum payload of 2,600 pounds of experiments in a nose bay, the main equipment bay behind the cockpit, two wing-mounted superpods and small underbody and trailing edges. Most ER-2 missions last about six hours with ranges of about 2,200 nautical miles. The aircraft typically fly at altitudes above 65,000 feet. On November 19, 1998, an ER-2 set a world record for medium weight aircraft reaching an altitude of 68,700 feet. The aircraft is 63 feet long, with a wingspan of 104 feet. The top of the vertical tail is 16 feet above ground when the aircraft is on the bicycle-type landing gear. Cruising speeds are 410 knots, or 467 miles per hour, at altitude. A single General Electric F-118 turbofan engine rated at 17,000 pounds thrust powers the ER-2.
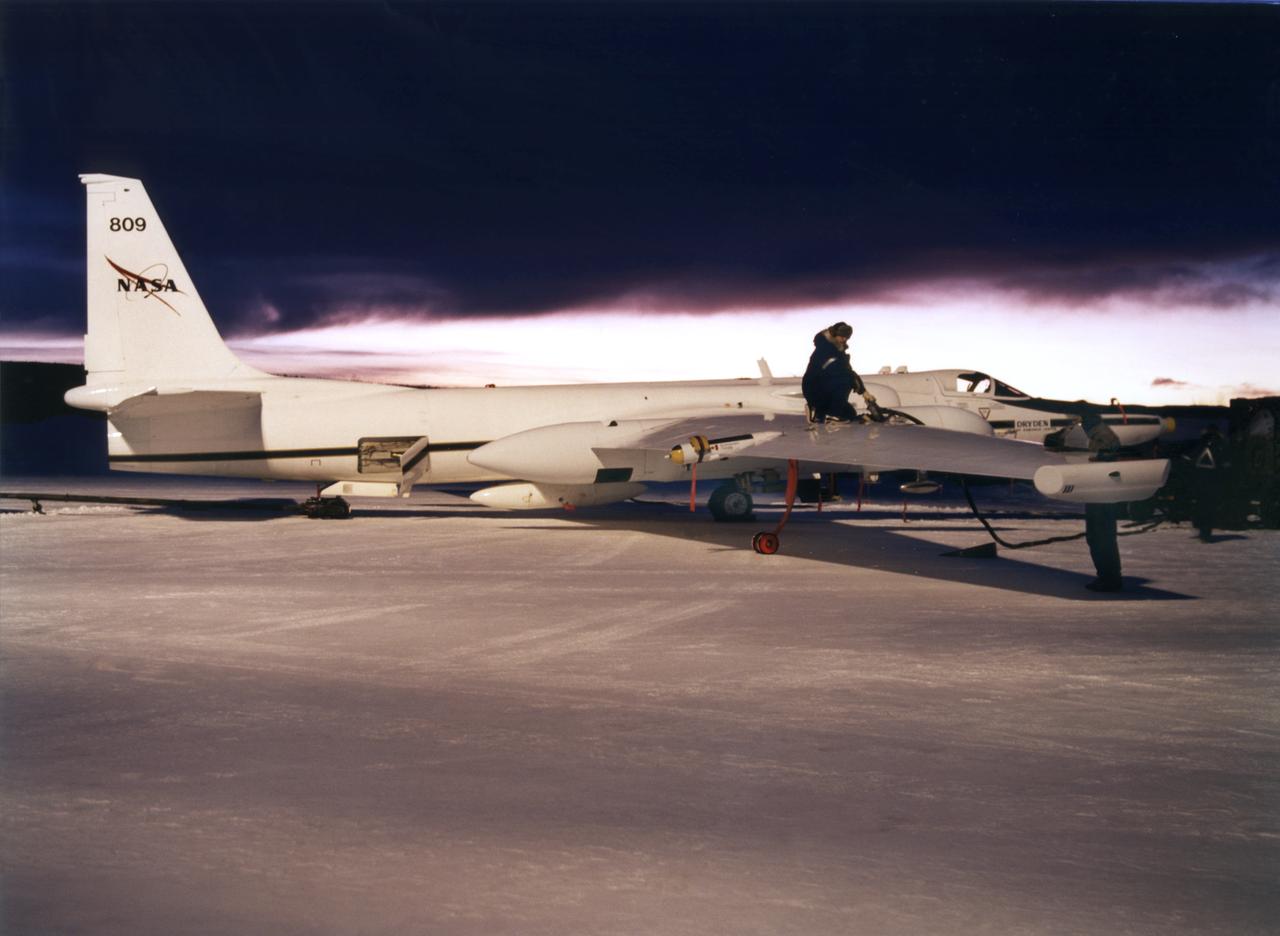

ER-2s bearing tail numbers 806 and 809 are used as airborne science platforms by NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The aircraft are platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They are also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation. The ER-2s are capable of carrying a maximum payload of 2,600 pounds of experiments in a nose bay, the main equipment bay behind the cockpit, two wing-mounted superpods and small underbody and trailing edges. Most ER-2 missions last about six hours with ranges of about 2,200 nautical miles. The aircraft typically fly at altitudes above 65,000 feet. On November 19, 1998, an ER-2 set a world record for medium weight aircraft reaching an altitude of 68,700 feet. The aircraft is 63 feet long, with a wingspan of 104 feet. The top of the vertical tail is 16 feet above ground when the aircraft is on the bicycle-type landing gear. Cruising speeds are 410 knots, or 467 miles per hour, at altitude. A single General Electric F-118 turbofan engine rated at 17,000 pounds thrust powers the ER-2.
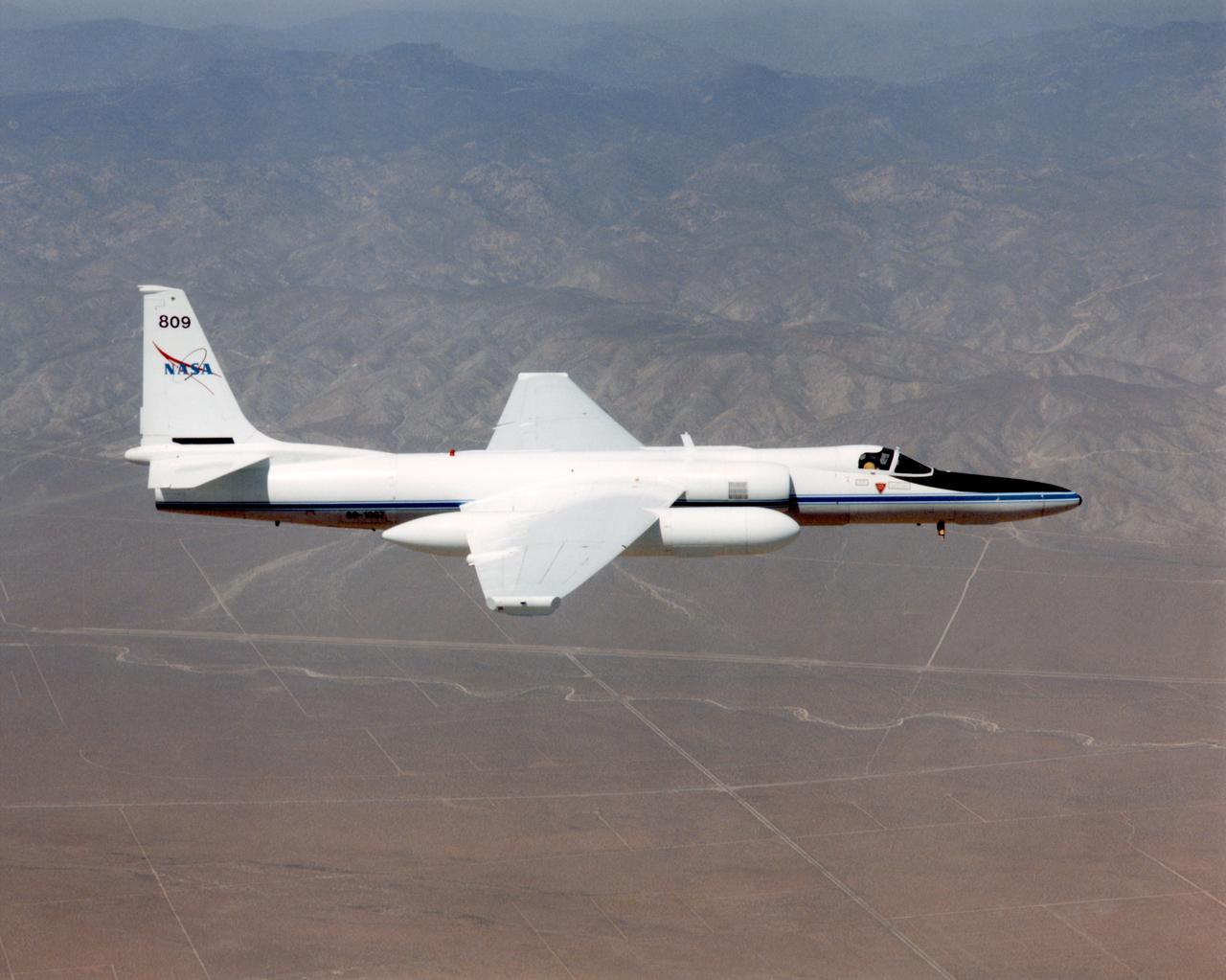

ER-2C tail number 809, was one of two Airborne Science ER-2Cs used as science platforms by Dryden. The aircraft were platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They were also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation. The ER-2Cs were capable of carrying a maximum payload of 2,600 pounds of experiments in a nose bay, the main equipment bay behind the cockpit, two wing-mounted superpods and small underbody and trailing edges. Most ER-2C missions lasted about six hours with ranges of about 2,200 nautical miles. The aircraft typically flew at altitudes above 65,000 feet. On November 19, 1998, the ER-2C set a world record for medium weight aircraft reaching an altitude of 68,700 feet. The aircraft was 63 feet long, with a wingspan of 104 feet. The top of the vertical tail was 16 feet above ground when the aircraft was on the bicycle-type landing gear. Cruising speeds were 410 knots, or 467 miles per hour, at altitude. A single General Electric F-118 turbofan engine rated at 17,000 pounds thrust powers the ER-2C.
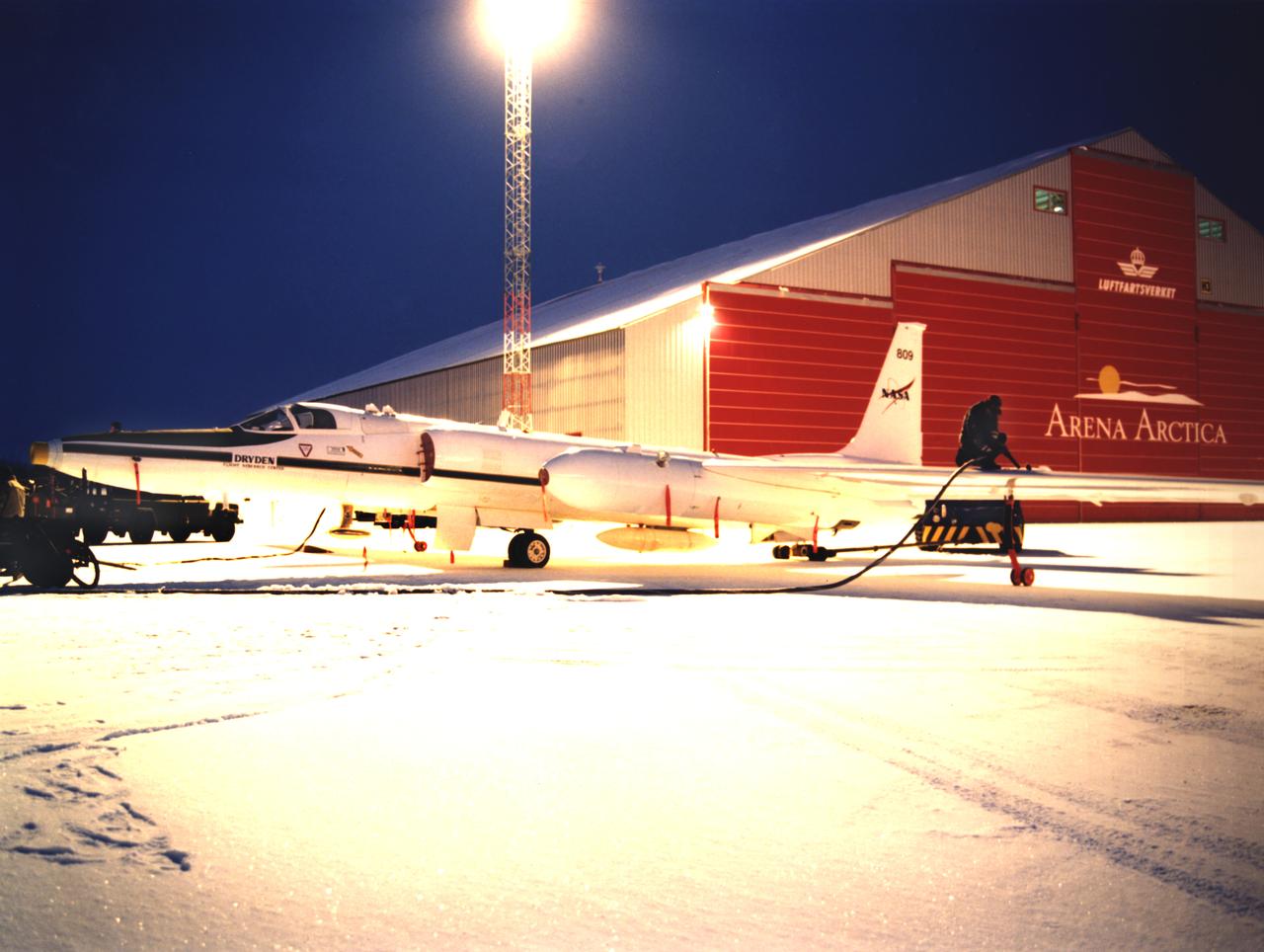

ER-2s bearing tail numbers 806 and 809 are used as airborne science platforms by NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The aircraft are platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They are also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation. The ER-2s are capable of carrying a maximum payload of 2,600 pounds of experiments in a nose bay, the main equipment bay behind the cockpit, two wing-mounted superpods and small underbody and trailing edges. Most ER-2 missions last about six hours with ranges of about 2,200 nautical miles. The aircraft typically fly at altitudes above 65,000 feet. On November 19, 1998, an ER-2 set a world record for medium weight aircraft reaching an altitude of 68,700 feet. The aircraft is 63 feet long, with a wingspan of 104 feet. The top of the vertical tail is 16 feet above ground when the aircraft is on the bicycle-type landing gear. Cruising speeds are 410 knots, or 467 miles per hour, at altitude. A single General Electric F-118 turbofan engine rated at 17,000 pounds thrust powers the ER-2.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. --- STS-123 Mission Specialist Takao Doi talks to the media about his experiences on the mission to the International Space Station. Doi represents the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. The crew landed at Kennedy aboard space shuttle Endeavour at 8:39 p.m. EDT March 26. Endeavour's 16-day flight was the longest shuttle mission to the International Space Station and included a record five spacewalks. The shuttle's seven astronauts worked with the three-member station crew and ground teams around the world to install the first section of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory and the Canadian Space Agency's two-armed robotic system, known as Dextre. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

ISS022-E-035426 (22 Jan. 2010) --- Photographed from the International Space Station orbiting Earth at an altitude of 211 statute miles, this image of the Port au Prince area of Haiti from Jan. 22 is centered on the area that was heavily damaged by a magnitude 7.0 earthquake on Jan. 12. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Earthquake Center, a number of tremors of varying magnitudes up to 6.0 were recorded in ensuing days. Ships can be easily delineated in the harbor. The single runway of the airport, heavily damaged by the quake, is seen near center of the frame. The airport?s control tower was destroyed and has since been rebuilt and is now in service, thanks to part of the huge world-wide aid offered to the nation
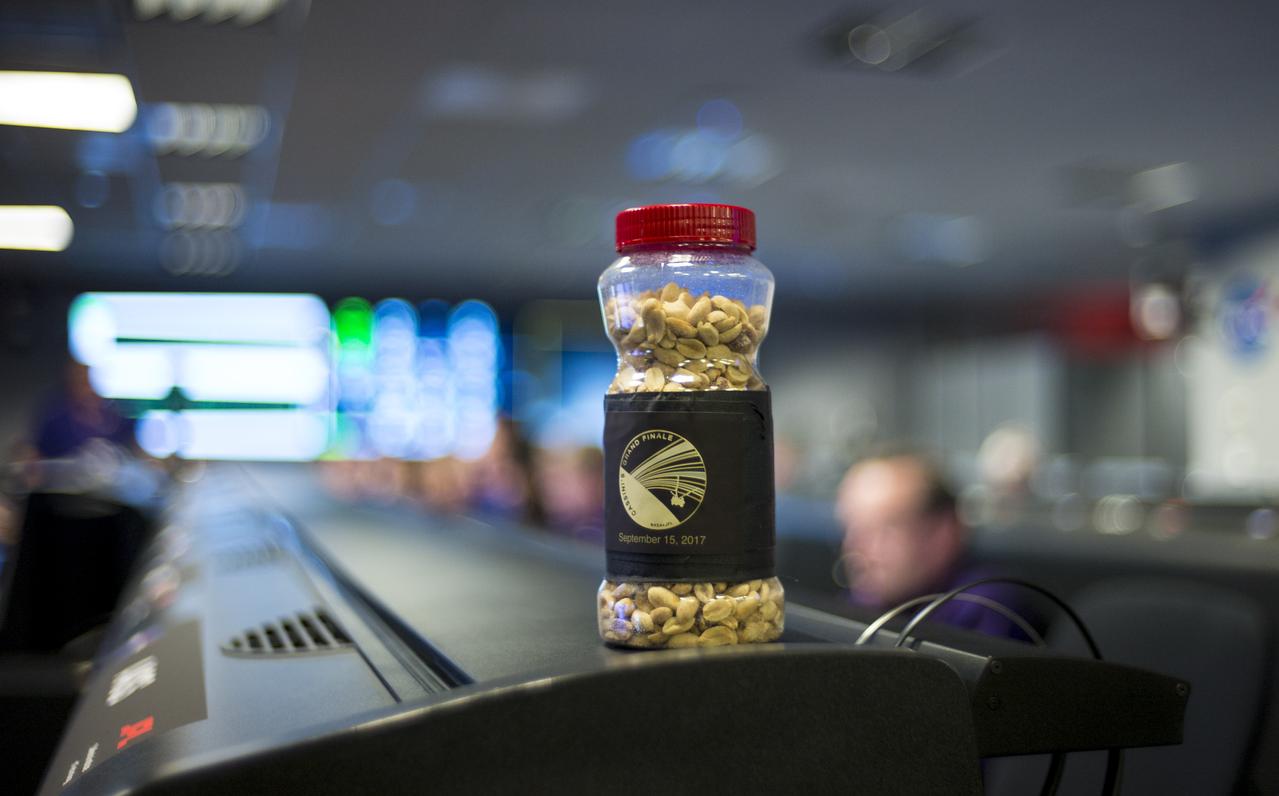

A jar of peanuts is seen sitting on a console in mission control of the Space Flight Operations Center as the Cassini mission team await the final downlink of the spacecraft's data recorder, Thursday, Sept. 14, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
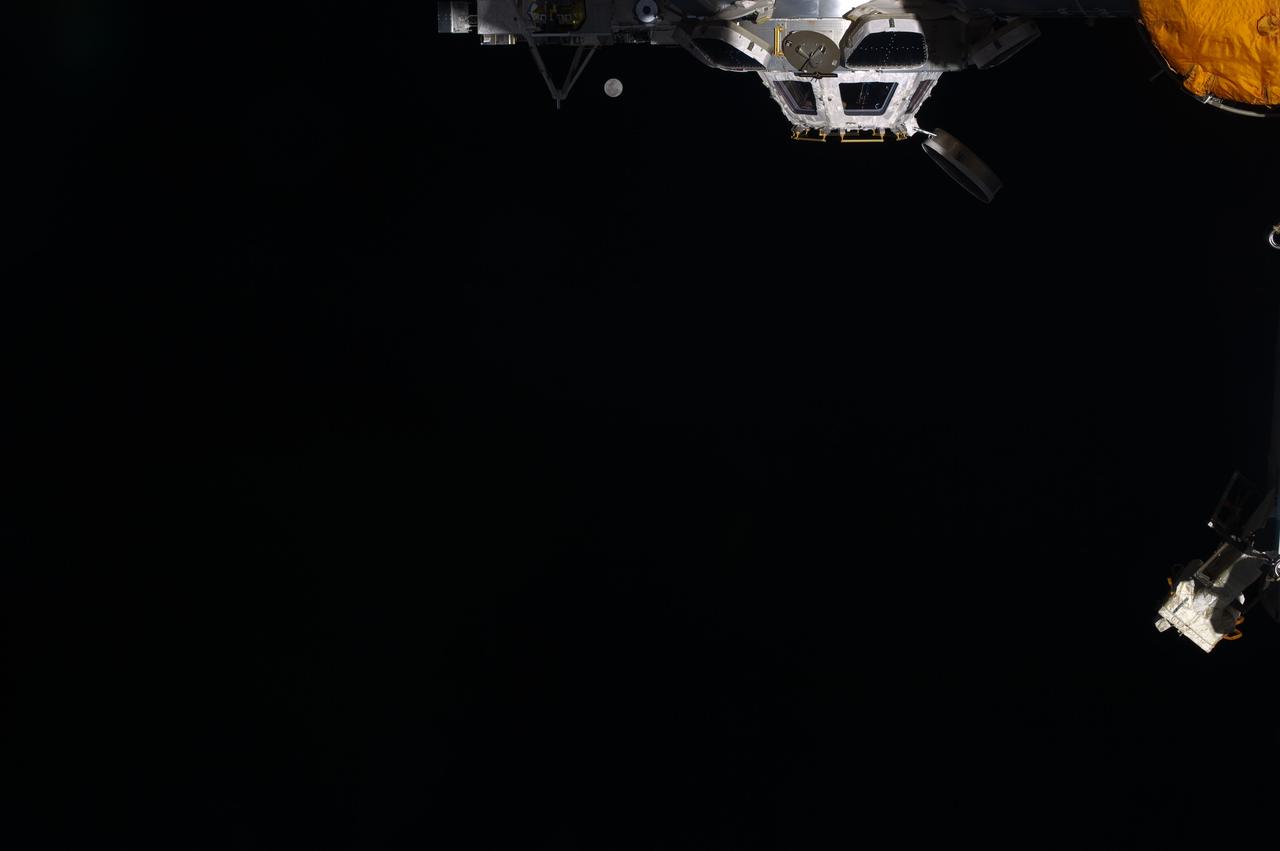

ISS031-E-018530 (6 May 2012) --- While most of the world's population had no trouble at all finding the full moon on the weekend of May 5-6, one has to look really closely to spot Earth's satellite in the space traveler's eye-view aboard the International Space Station, some 240 miles above Earth. The moon can be seen just to the left of the station's Cupola and just to the right of one of its solar array panels. While the photo was recorded around midnight on May 5 in the central daylight time zone, it was already early May 6 GMT. Three Expedition 31 crew members await the arrival of three additional crewmates in a little more than a week.