
On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
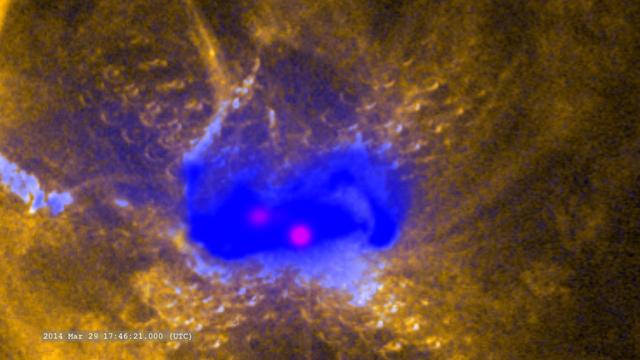
Zoom in on the flare in ultraviolet (SDO/AIA), X-rays (Hinode) and gamma-rays (RHESSI) -- On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

The March 29, 2014, X-class flare appears as a bright light on the upper right in this image from SDO, showing light in the 304 Angstrom wavelength. This wavelength shows material on the sun in what's called the transition region, where the chromosphere transitions into the upper solar atmosphere, the corona. Some light of the flare is clearly visible, but the flare appears brighter in other images that show hotter temperature material. Credit: NASA/SDO/AIA -- On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
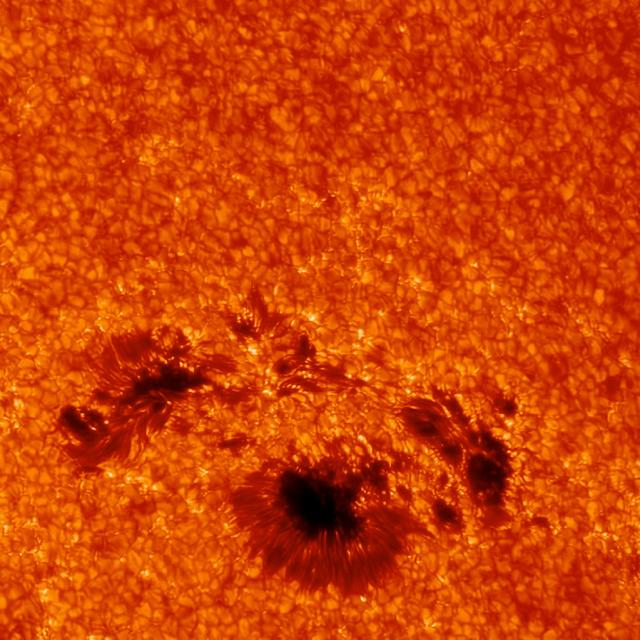

This close-up of the sunspot underneath the March 29, 2014, flare shows incredible detail. The image was captured by the G-band camera at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. This instrument can focus on only a small area at once, but provide very high resolution. Ground-based telescope data can be hindered by Earth's atmosphere, which blocks much of the sun's ultraviolet and X-ray light, and causes twinkling even in the light it does allow through. As it happens, the March 29 flare occurred at a time of day in New Mexico that often results in the best viewing times from the ground. Credit: Kevin Reardon (National Solar Observatory), Lucia Kleint (BAER Institute) -- On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

The sun emitted a significant solar flare, peaking at 1:01 a.m. EDT on Oct. 19, 2014. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which is always observing the sun, captured an image of the event. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel. To see how this event may affect Earth, please visit NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center at <a href="http://spaceweather.gov" rel="nofollow">spaceweather.gov</a>, the U.S. government's official source for space weather forecasts, alerts, watches and warnings. This flare is classified as an X1.1-class flare. X-class denotes the most intense flares, while the number provides more information about its strength. An X2 is twice as intense as an X1, an X3 is three times as intense, etc. Credit: NASA/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
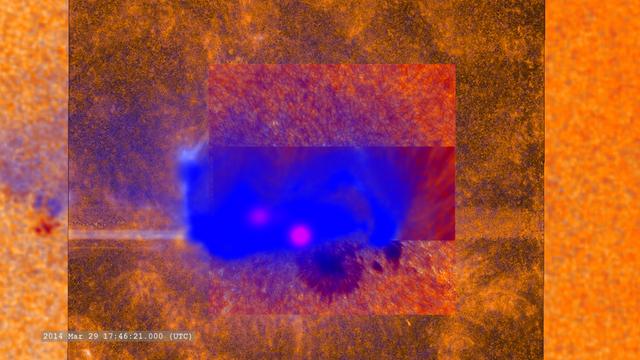
A combination of many (but not all) of the datasets which observed this flare. -- On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
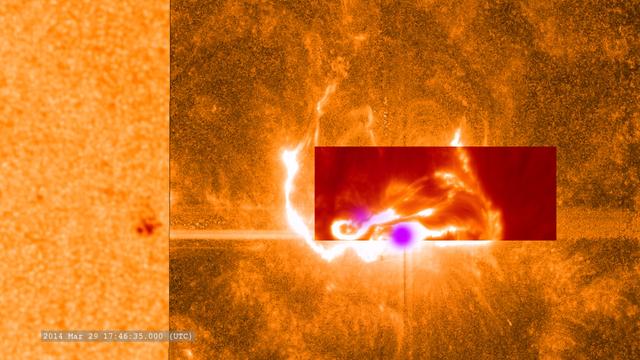
This combined image shows the March 29, 2014, X-class flare as seen through the eyes of different observatories. SDO is on the bottom/left, which helps show the position of the flare on the sun. The darker orange square is IRIS data. The red rectangular inset is from Sacramento Peak. The violet spots show the flare's footpoints from RHESSI. -- On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
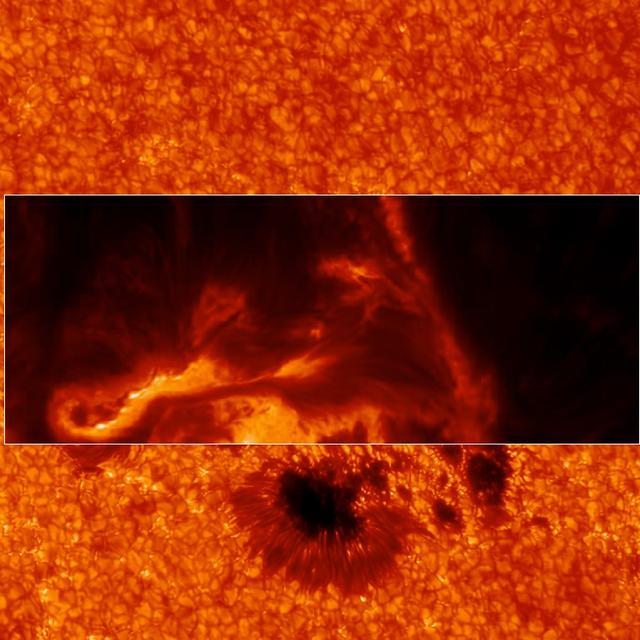

IBIS can focus in on different wavelengths of light, and so reveal different layers at different heights in the sun's lower atmosphere, the chromosphere. This image shows a region slightly higher than the former one. Credit: Lucia Kleint (BAER Institute), Paul Higgins (Trinity College Dublin, Ireland) -- On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
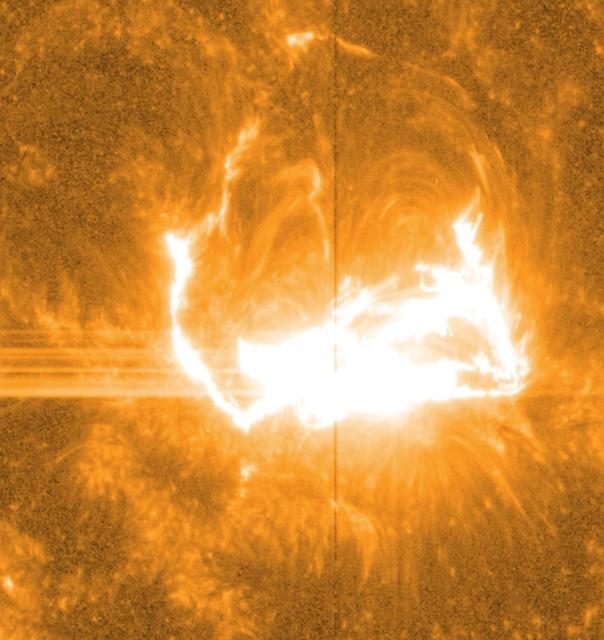
Like almost all solar observatories, NASA's IRIS can provide images of different layers of the sun's atmosphere, which together create a whole picture of what's happening. This image shows light at a wavelength of 1400 Angstrom, which highlights material some 650 miles above the sun's surface. The vertical line in the middle shows the slit for IRIS's spectrograph, which can separate light into its many wavelengths to provide even more information about the temperature and velocity of material during a flare. Credit: NASA/IRIS/Goddard Space Flight Center -- On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>