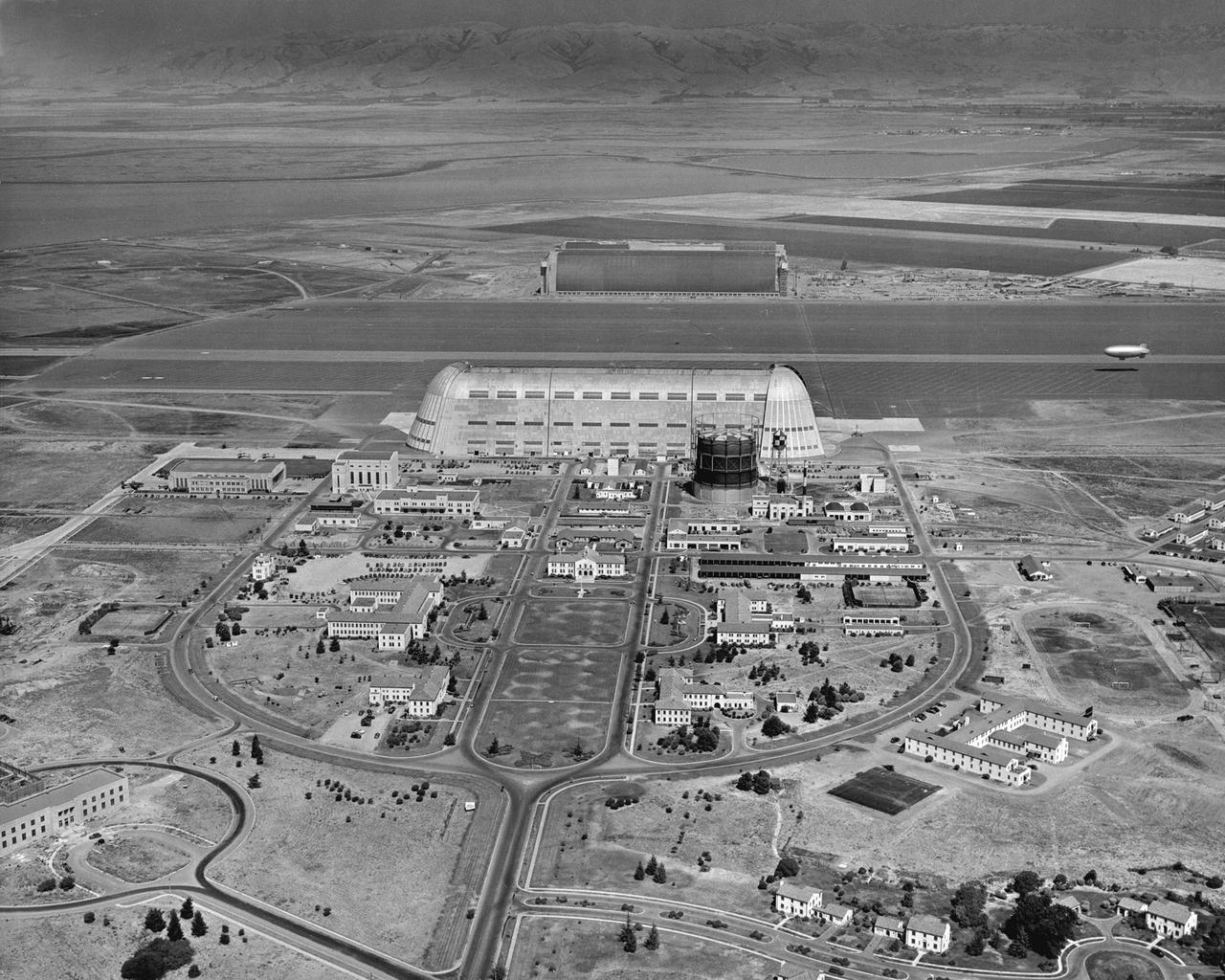

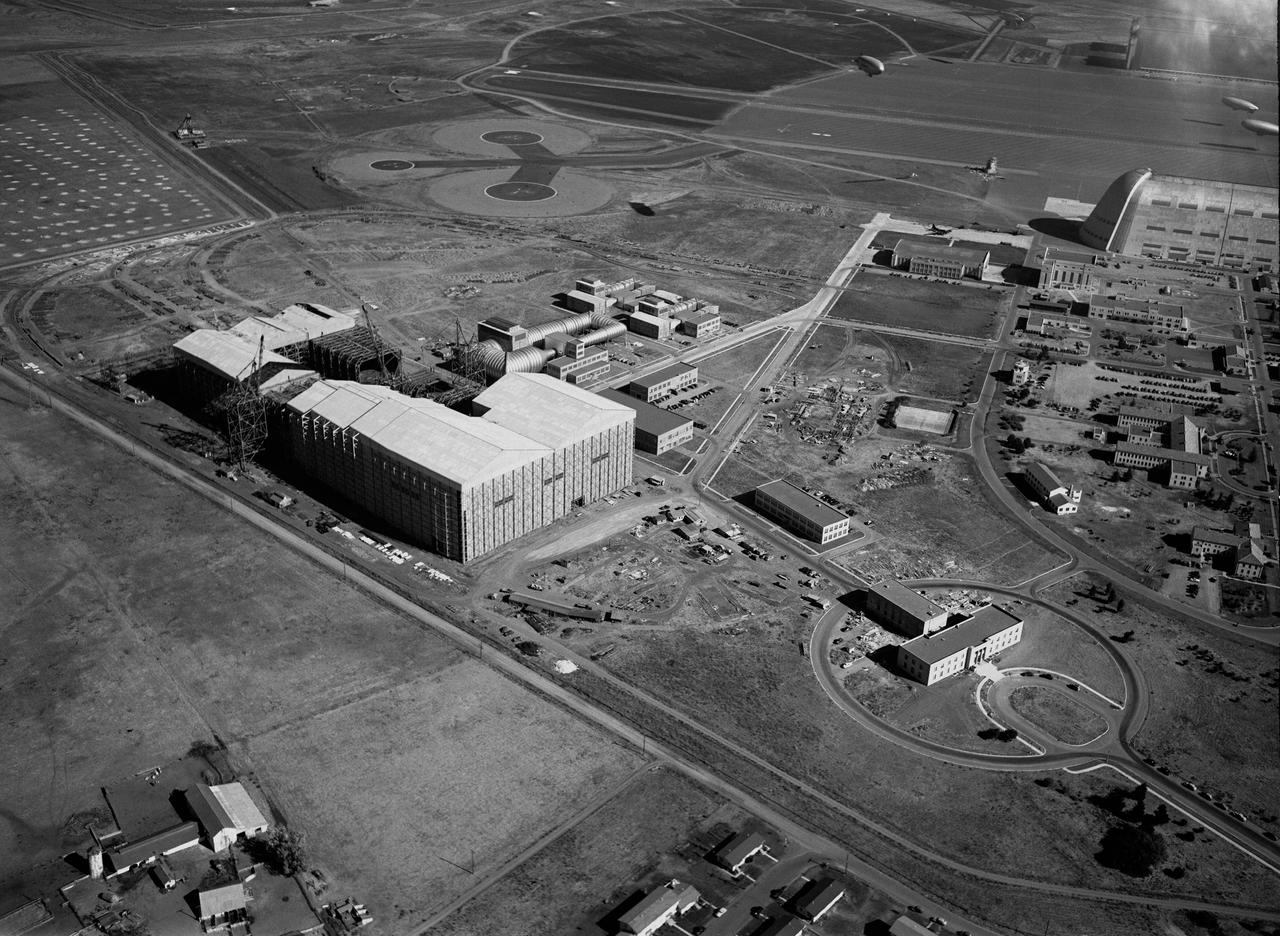
Navy NAS Sunnyvale, Moffett Field, Cat Altitude 1500ft E.S. East from front gate toward Shenandoah Plaza and Hangar One
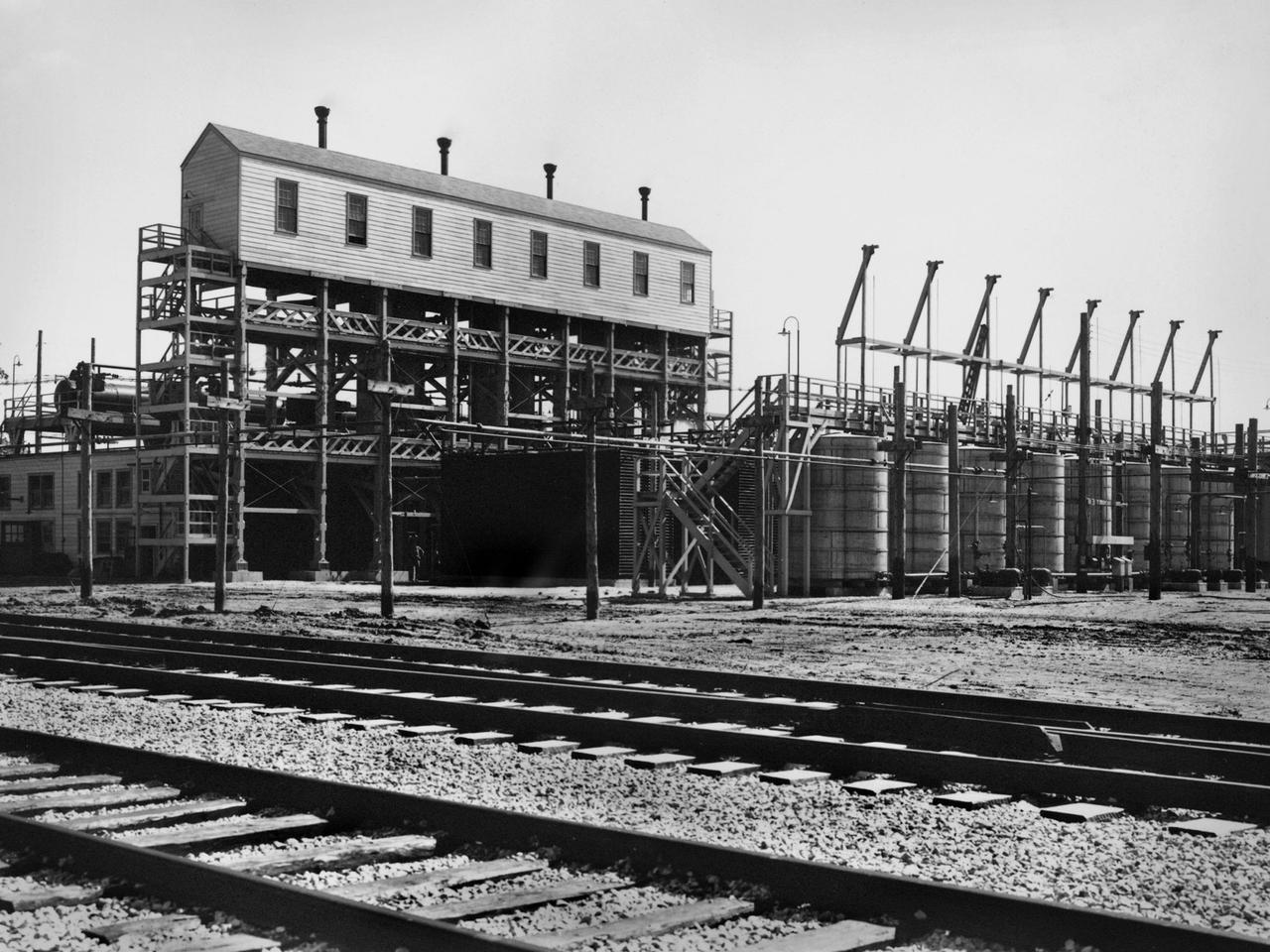

An ammonia oxidation plant at the Plum Brook Ordnance Works near Sandusky, Ohio, which later became the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station. During World War II the ordnance works produced trinitroluene (TNT), dinitrotoluene (DNT), and pentolite which were crated and shipped to an arsenal in Ravenna, Ohio. There, the explosives were packed into shells and sent to Allied forces overseas. Plum Brook was the third largest producer of TNT during World War II. Toluene, sulfuric acid, and nitric acid were used to manufacture the TNT. Nitric Acid is made by oxidizing ammonia, adding water, and concentrating it. The facility in this photograph was used for this oxidation. The structure included air compressors, filters, aftercoolers, power recovery systems, air receivers, heaters, ammonia gasifiers, gas mixers, cooler condensers, absorption columns, and bleaching columns. The Plum Brook Ordnance Works was shut down immediately after the war and remained vacant for the next ten years. NASA’s predecessor, the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), acquired the 500 acres of the site in 1955 to build a nuclear test reactor. By 1963, the agency had acquired the entire 9000 acres from the Army. Almost all of the military facilities were removed in the early 1960s. Plum Brook Station contained over 30 test facilities at its peak in the late 1960s. Today there are four major facilities in operation.

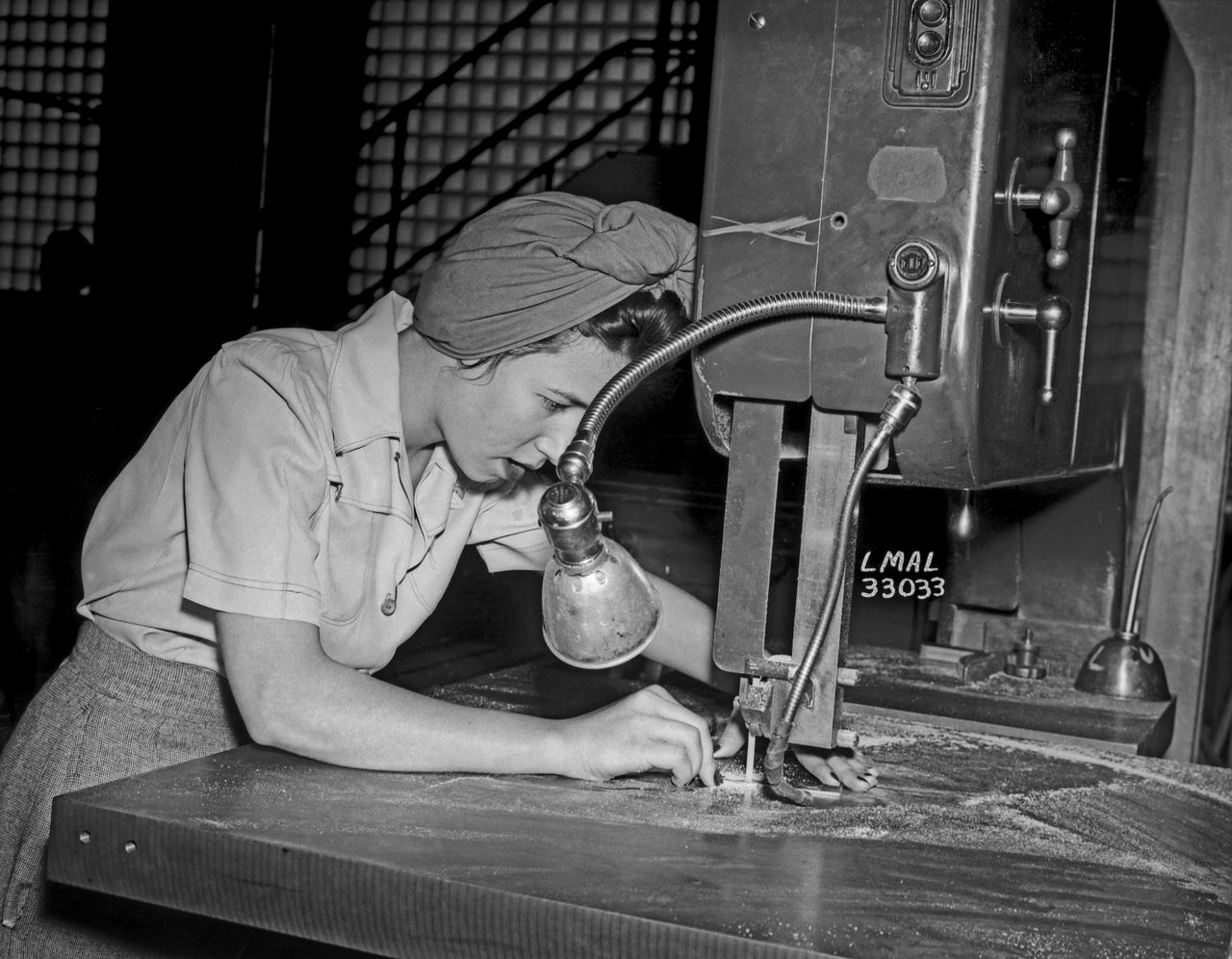
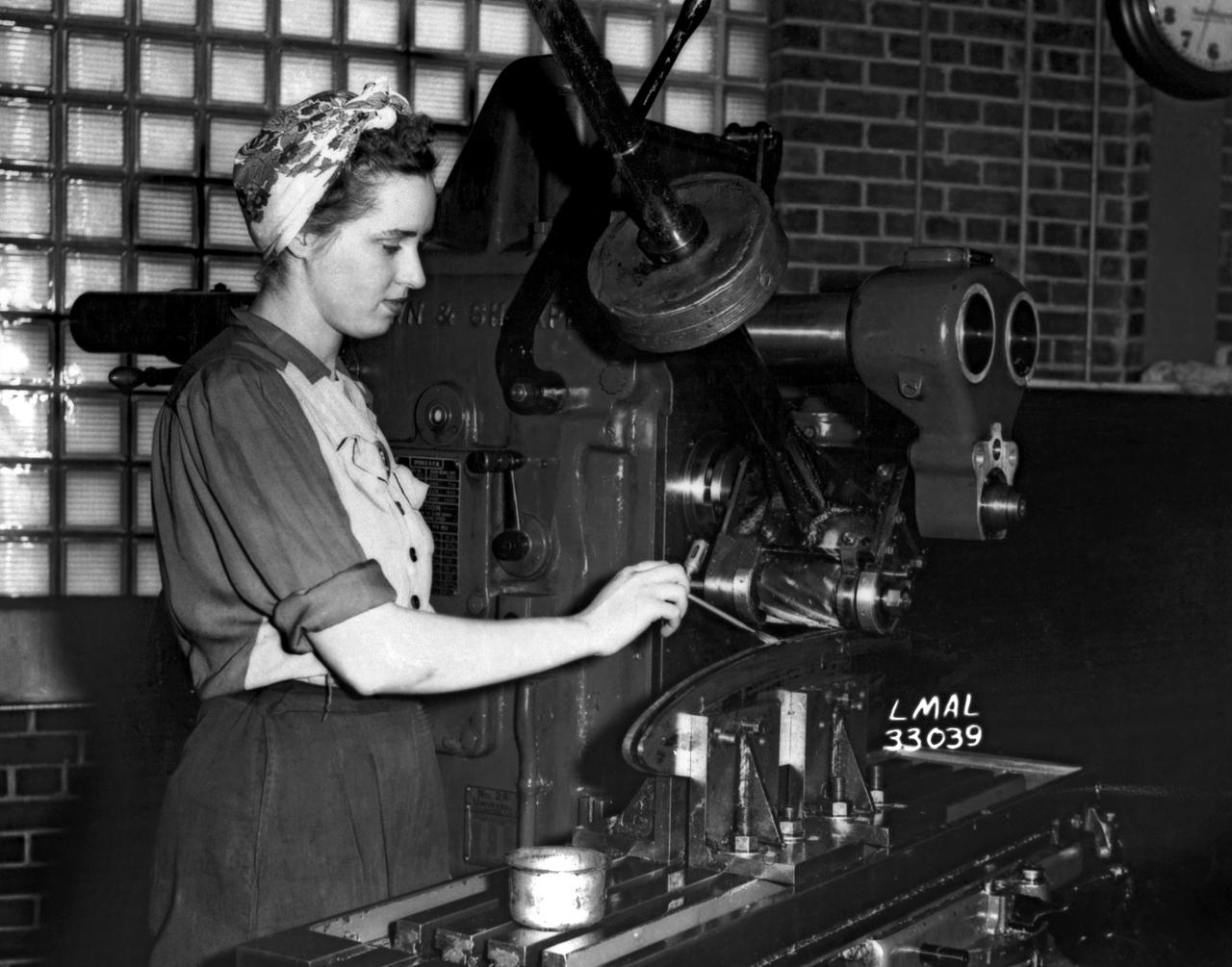
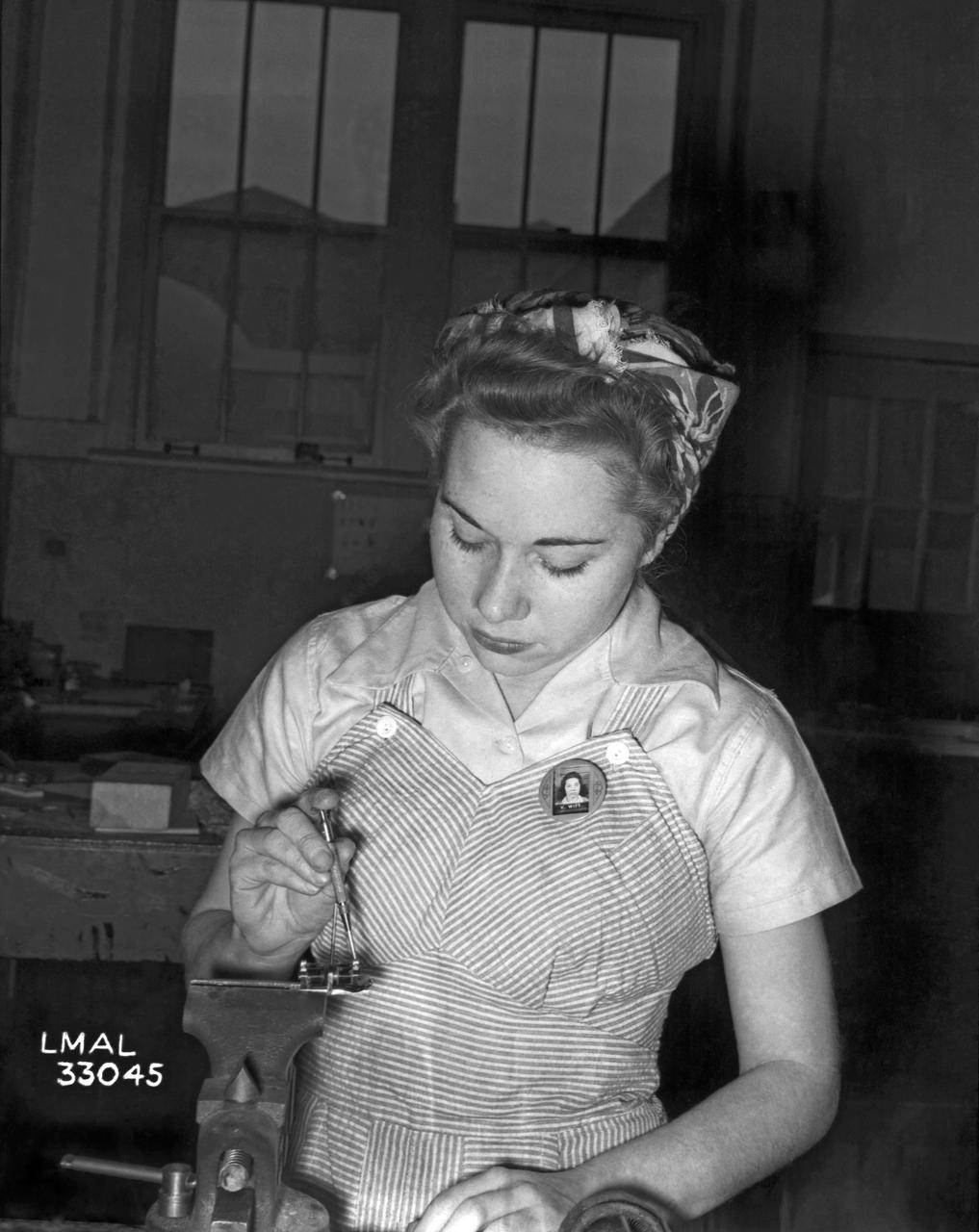
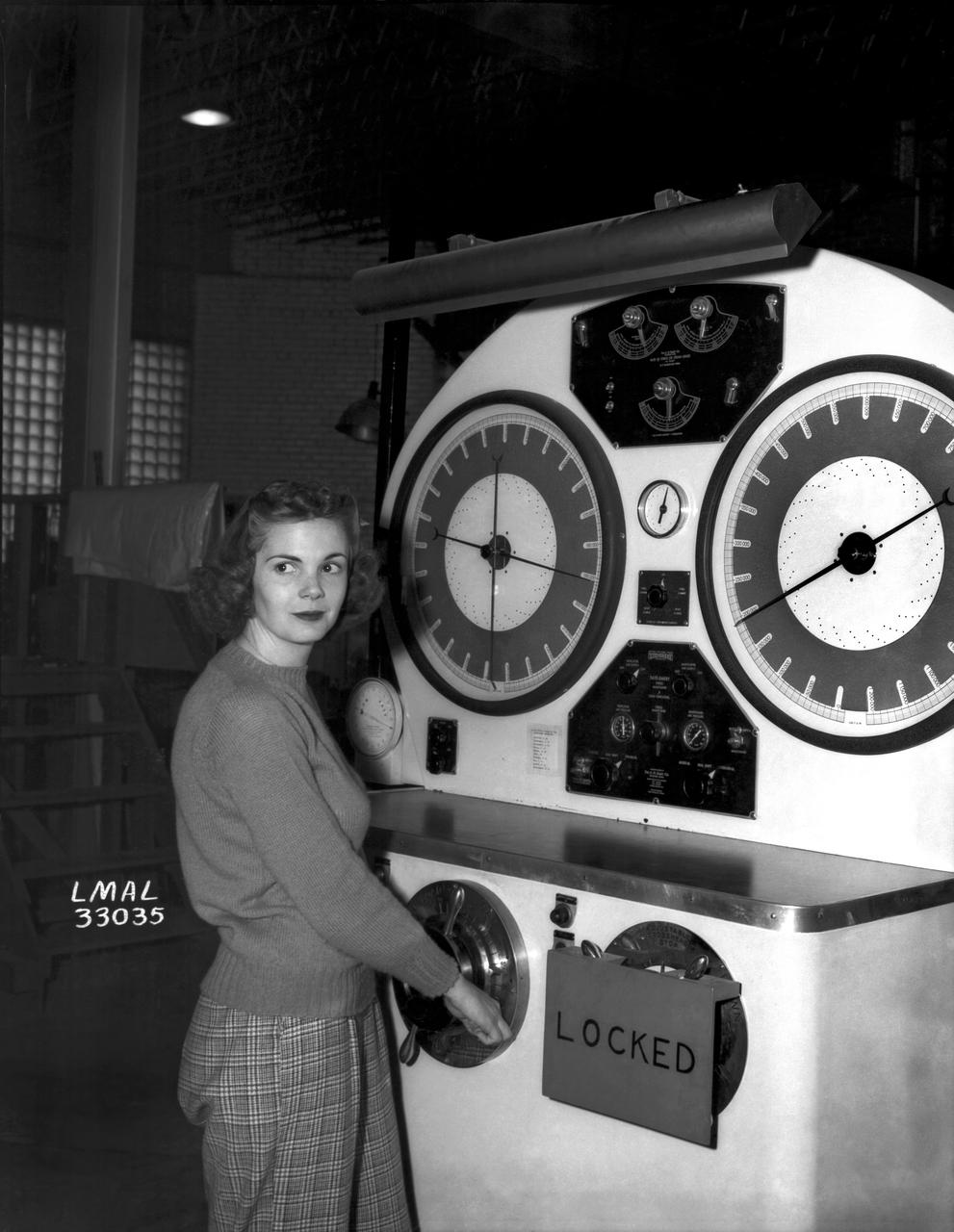
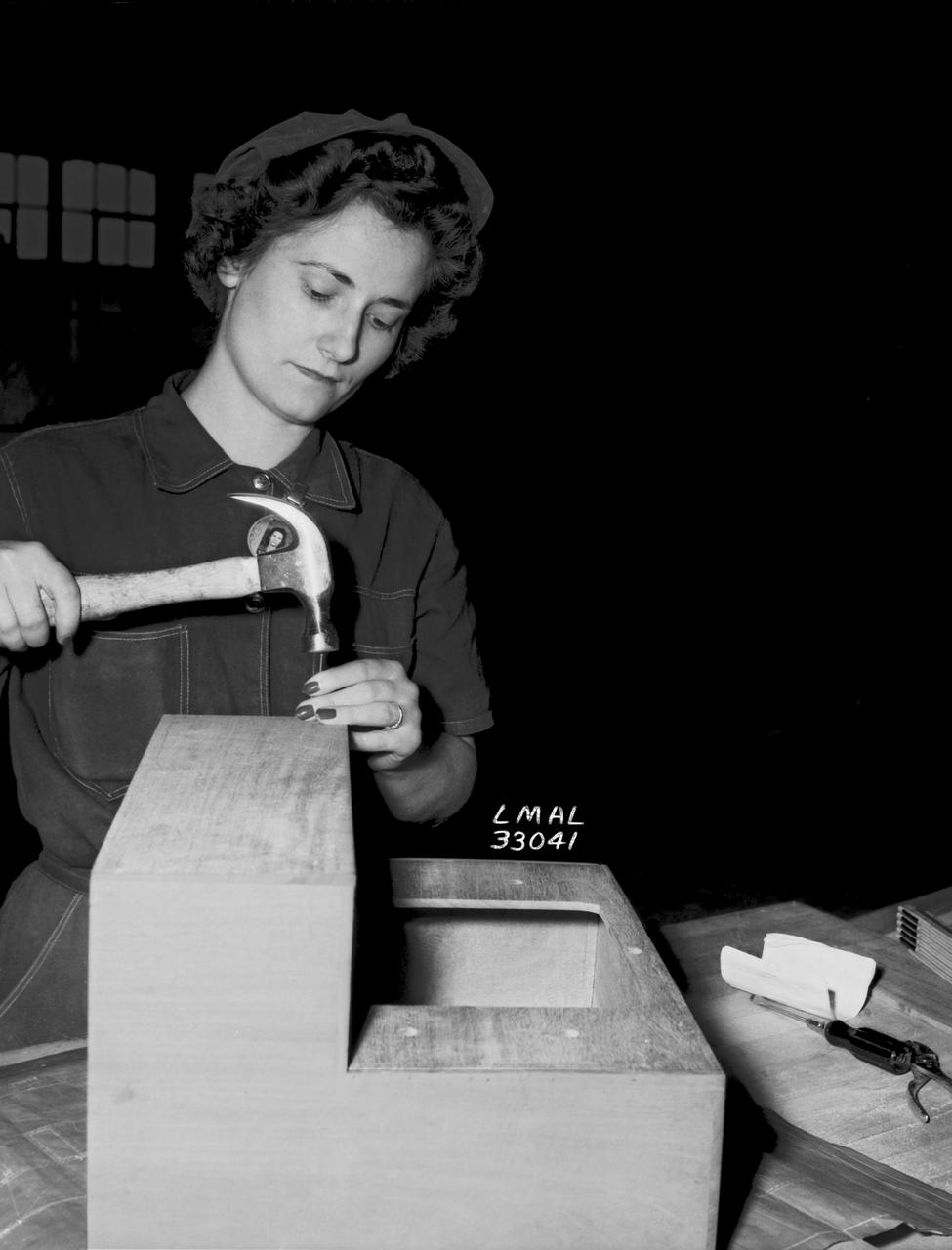
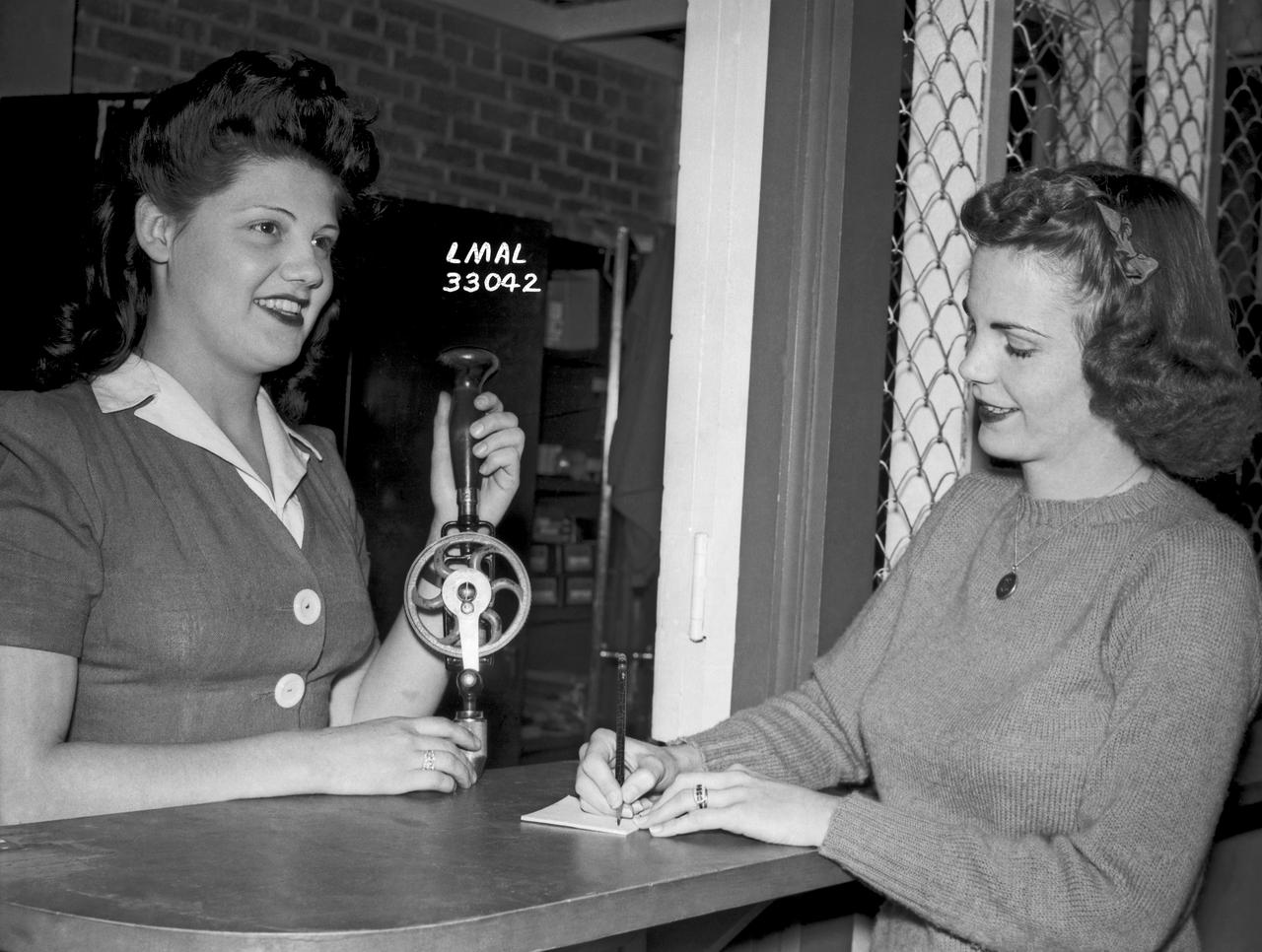
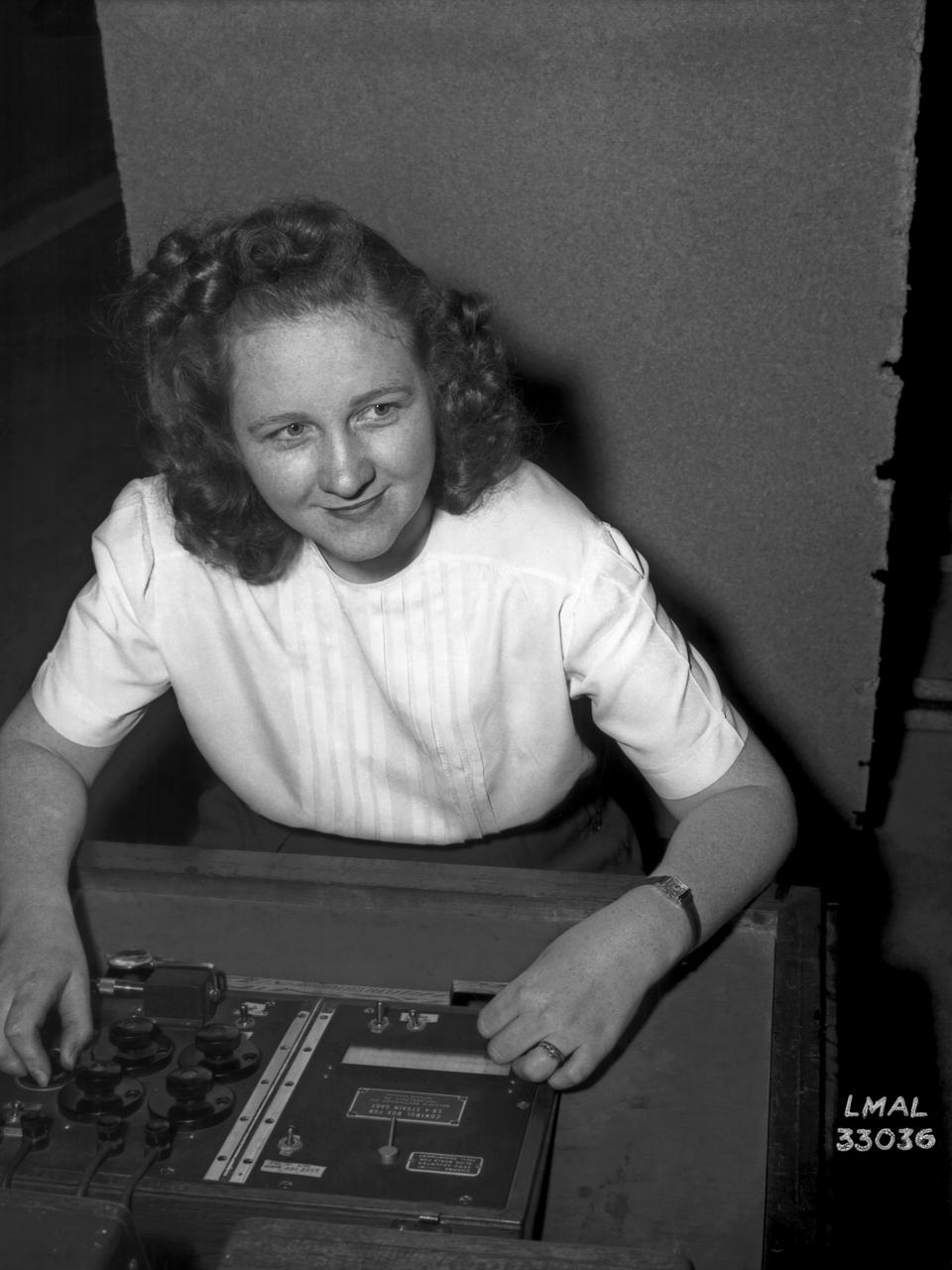
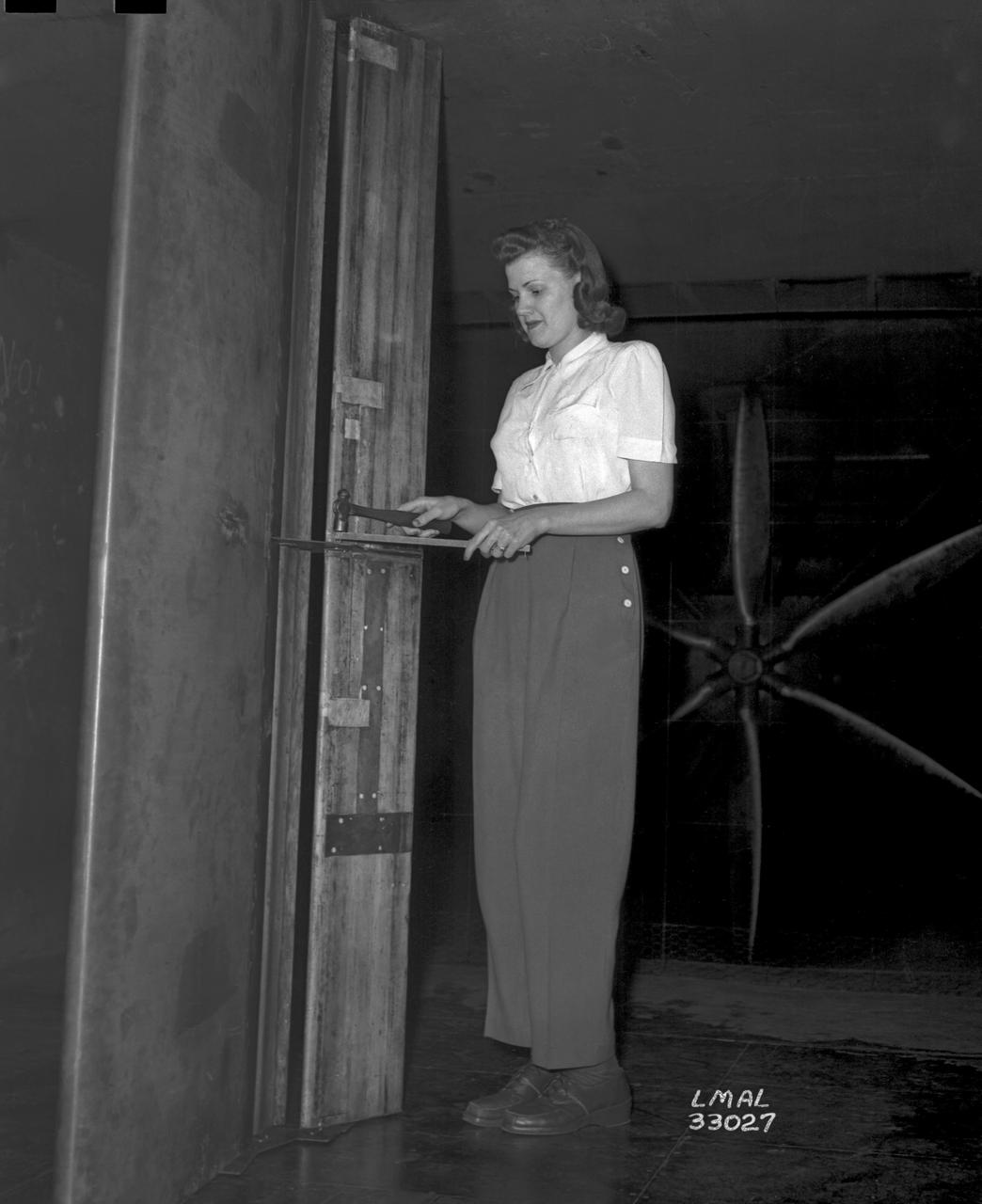
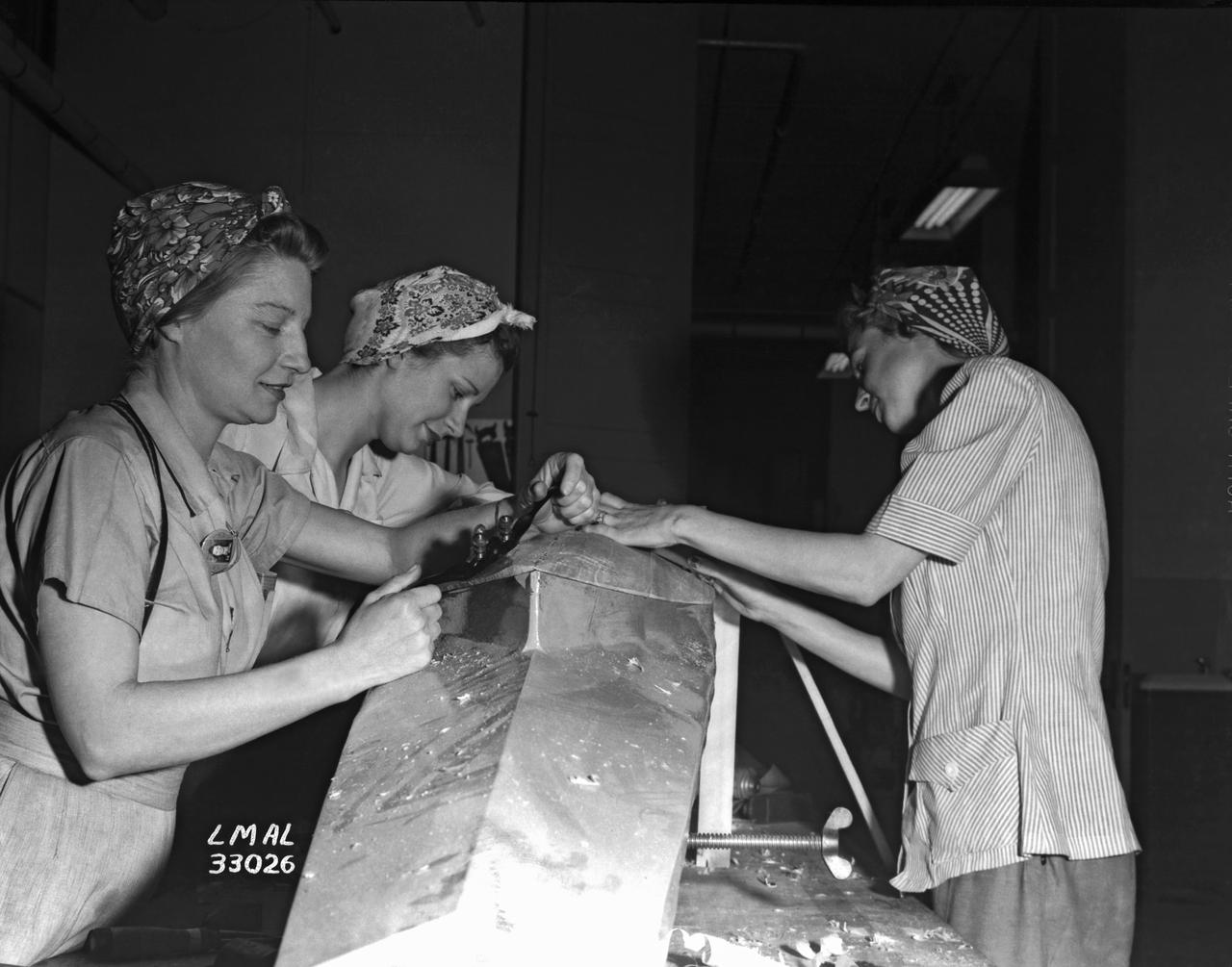
Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
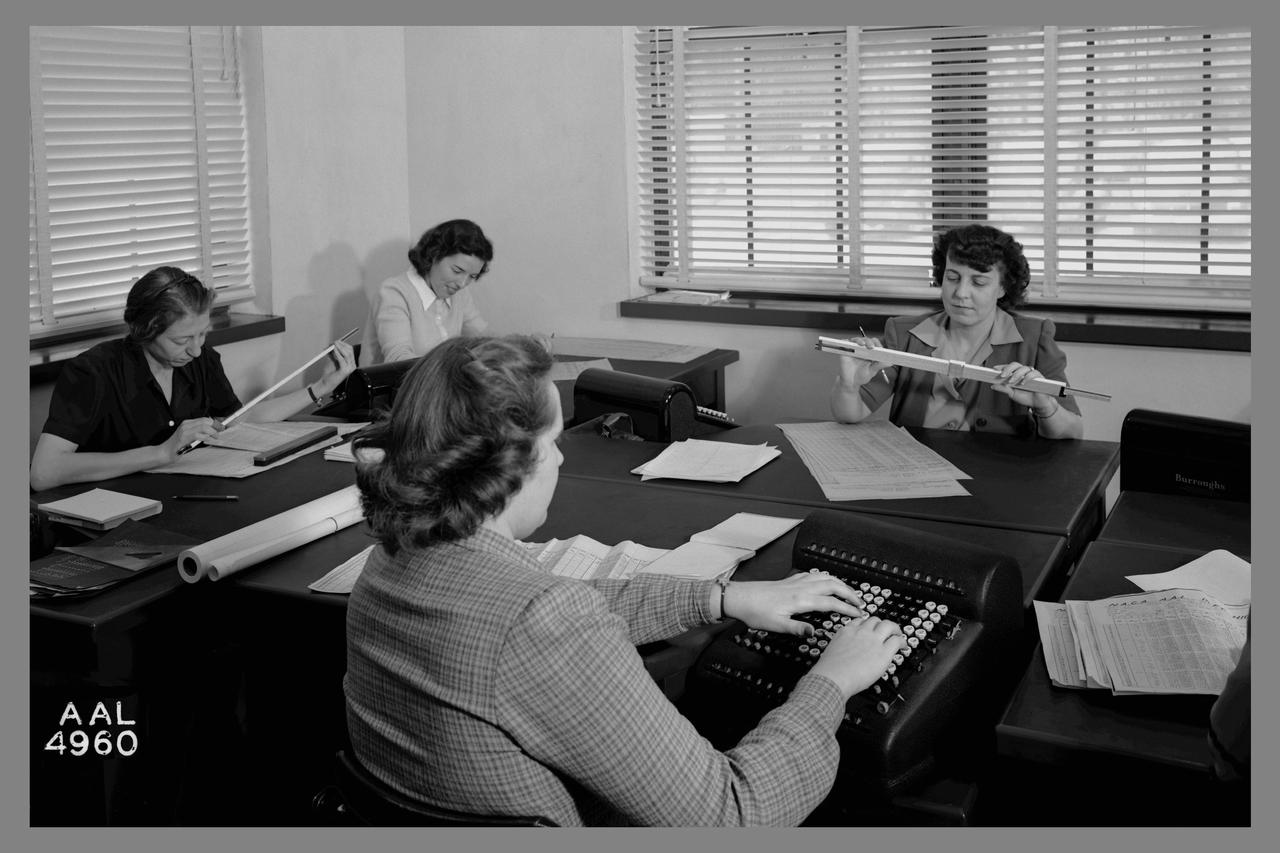

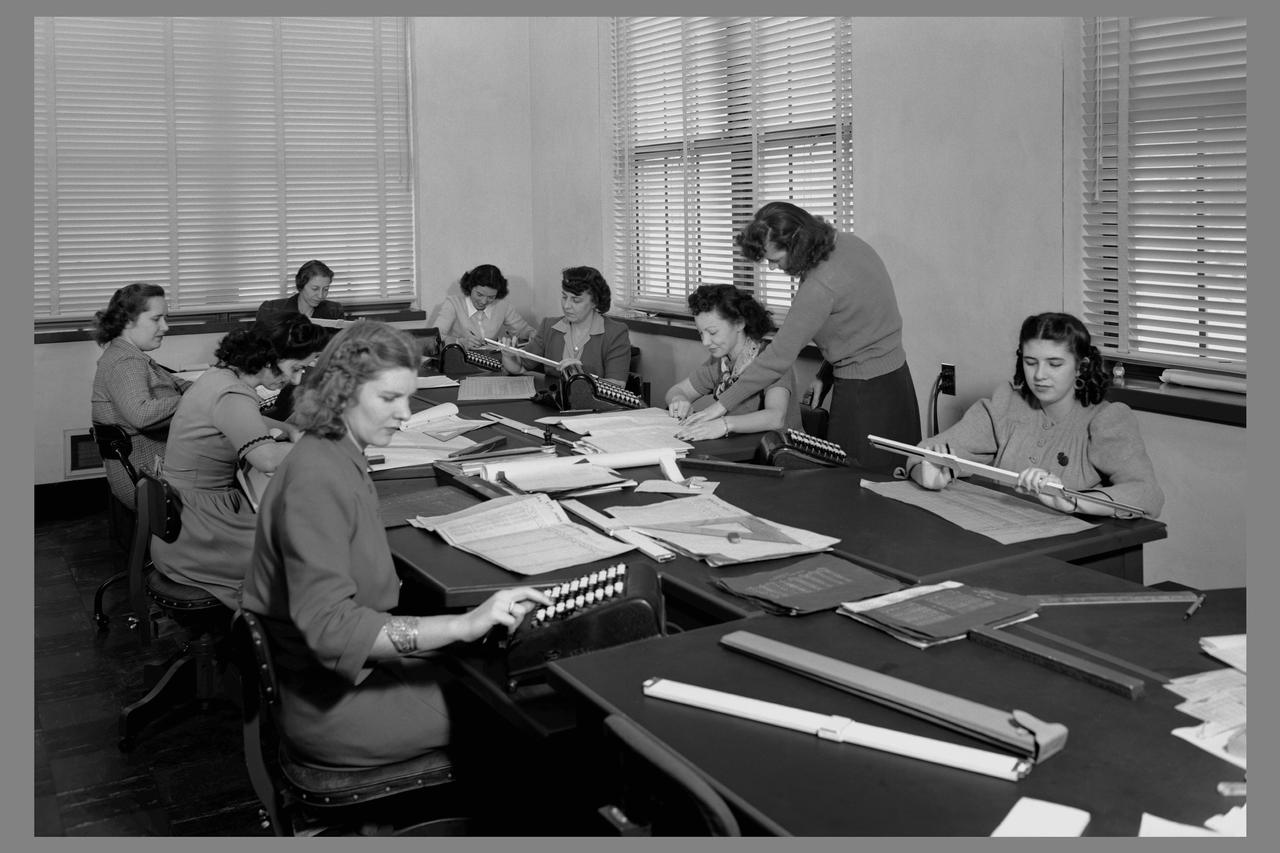
Computers' at work in 16ft wind tunnel - calculating test data
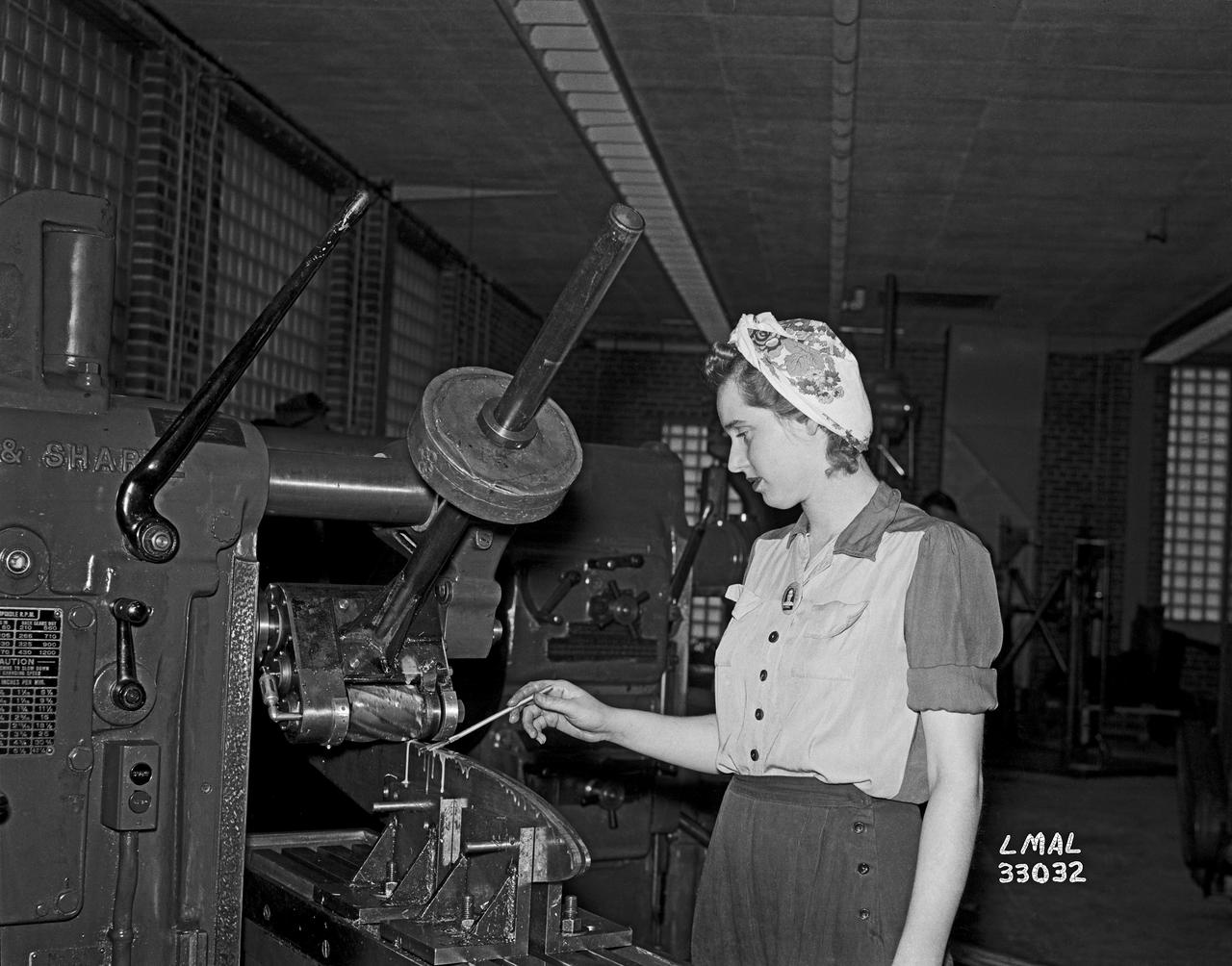

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
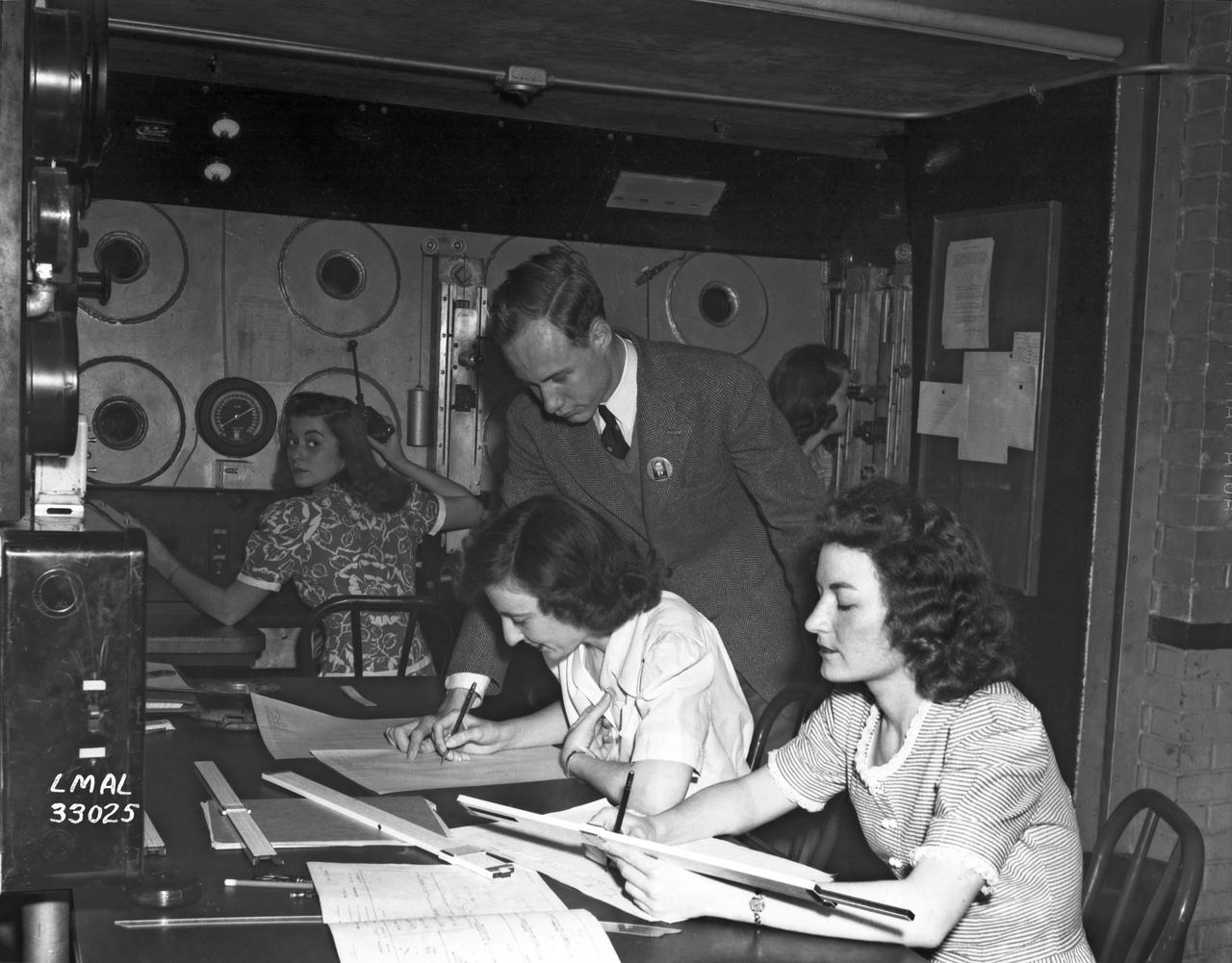

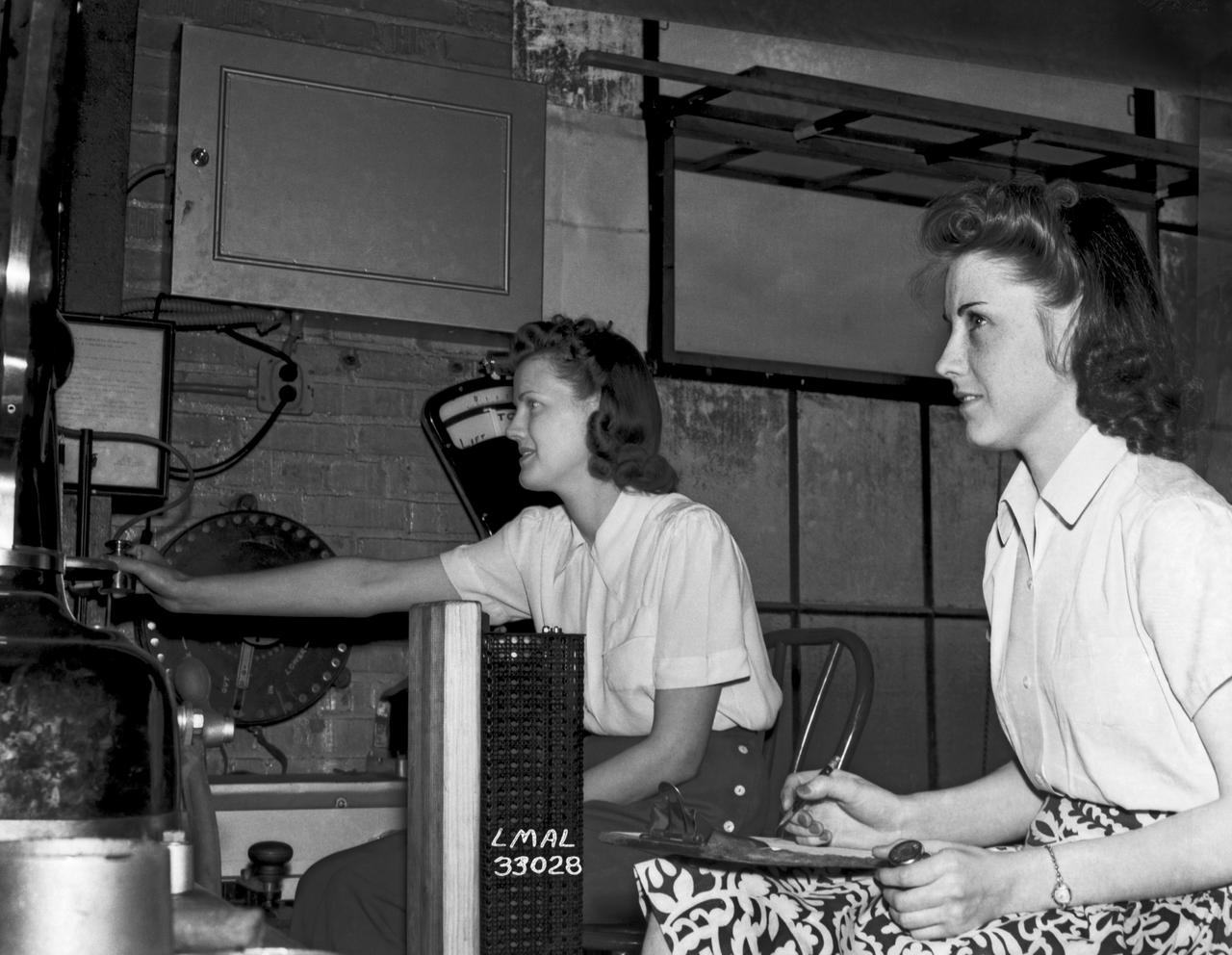
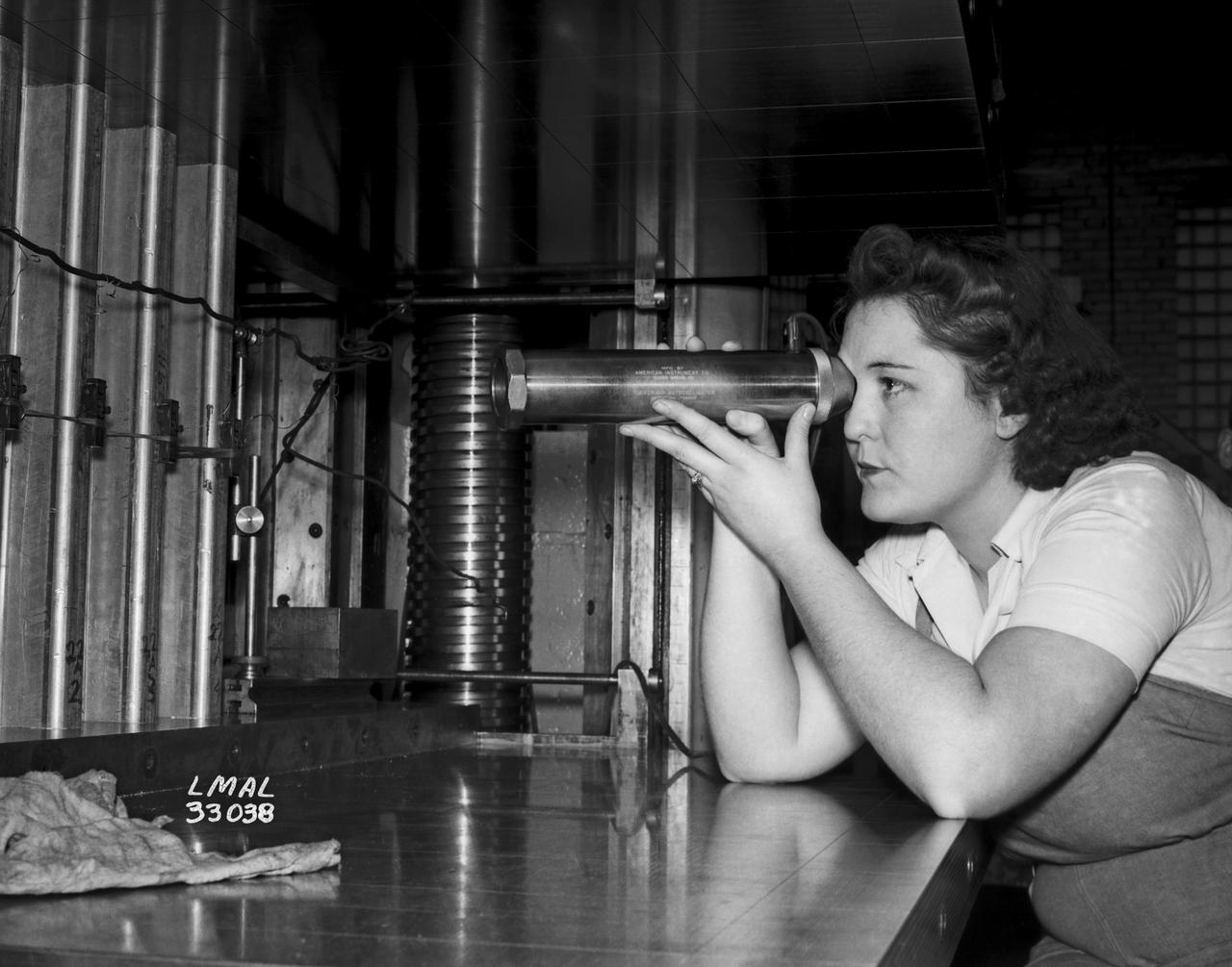
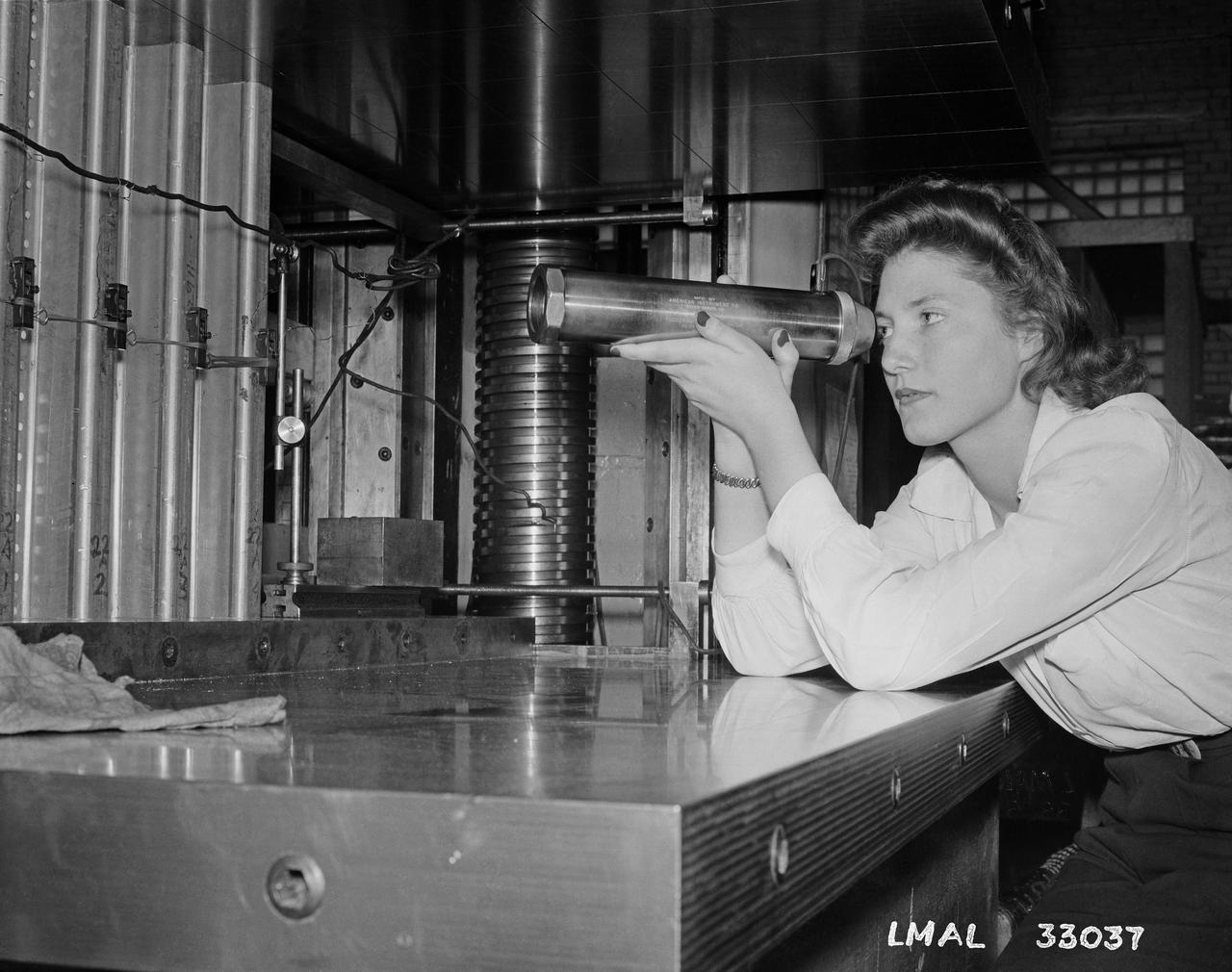
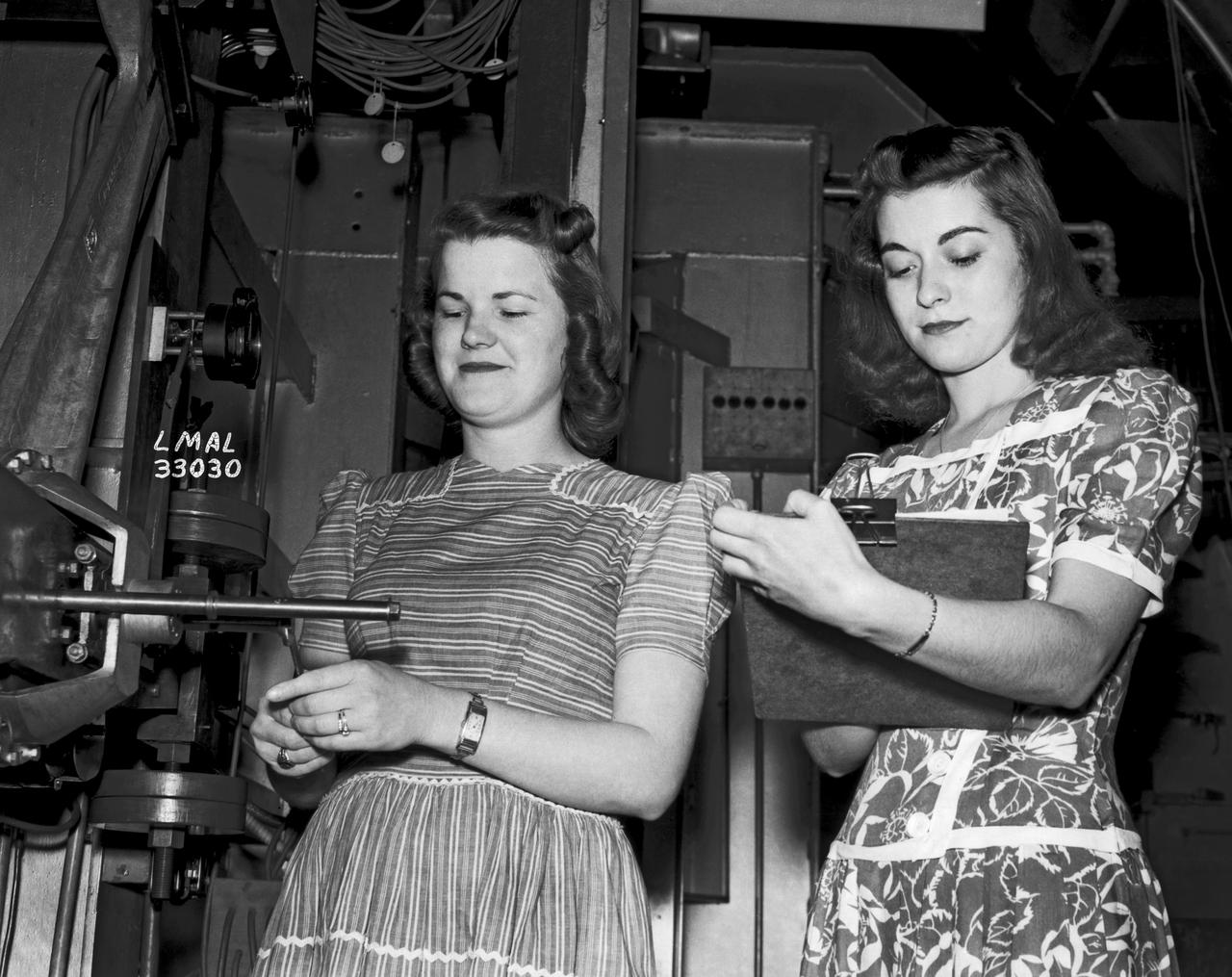
In the picture are F.F. Fullmer, aeronautical engineer, supervise a group of women who are helping operate the research equipment in the two-dimensional wind tunnel. Miss Elizabeth Patterson, left foreground, and Miss Katherine Thomason, right foreground obtains aerodynamic data, while Miss Lenore Woodland left background and Mrs. Blanche White help operate the tunnel. By Lee Dickinson 1943

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.

Navy NAS Air station Moffett Field, Hangar 2 from North West Corner Naval Air Station Moffett Field Public works Serial 1514 - Contract NOy-5604, Earl W. Heple & J.H. Pomeroy contractors
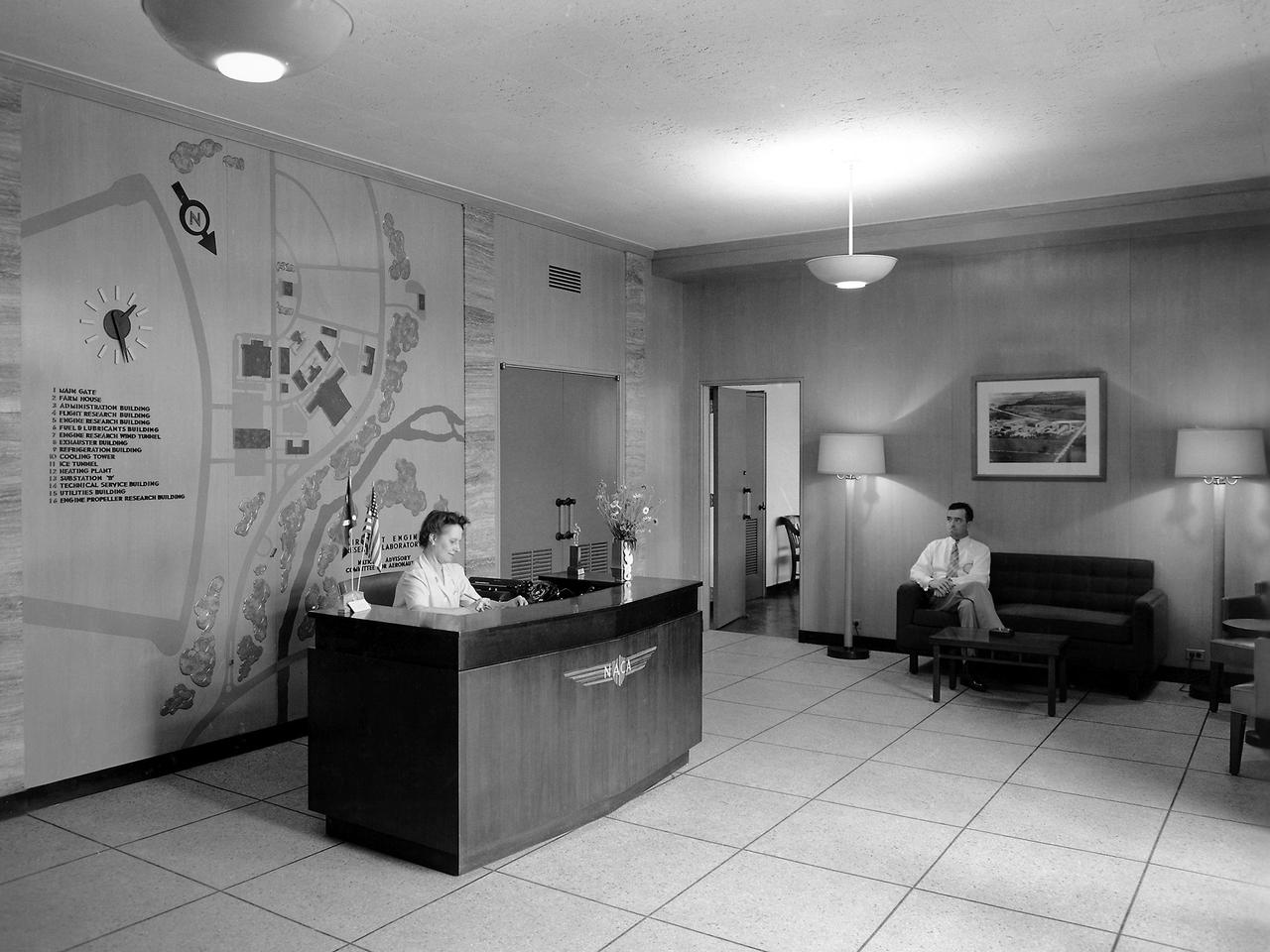

Receptionist Mary Louise Gosney enjoys the new Administration Building at the NACA’s Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory. The Administration Building, which was located near the front entrance to the laboratory, opened in December 1942. The staff, which had spent the previous year working in temporary offices inside the hangar, quickly occupied the new building. Lab director Raymond Sharp, the upper management team, and administrative staff had offices in the Administration Building. The structure also contained the lab’s library and auditorium. Gosney was a Chicago native who started at the lab in November 1941. Gosney’s services included welcoming visitors, arranging tours, and arranging interviews with staff members. Gosney’s “Lobby Lines” column in the lab’s newsletter Wing Tips noted the coming and goings of notable visitors and staff members. In addition to her role as receptionist, Gosney also served as the clearance officer. She would later head the entire Administrative Services Division.
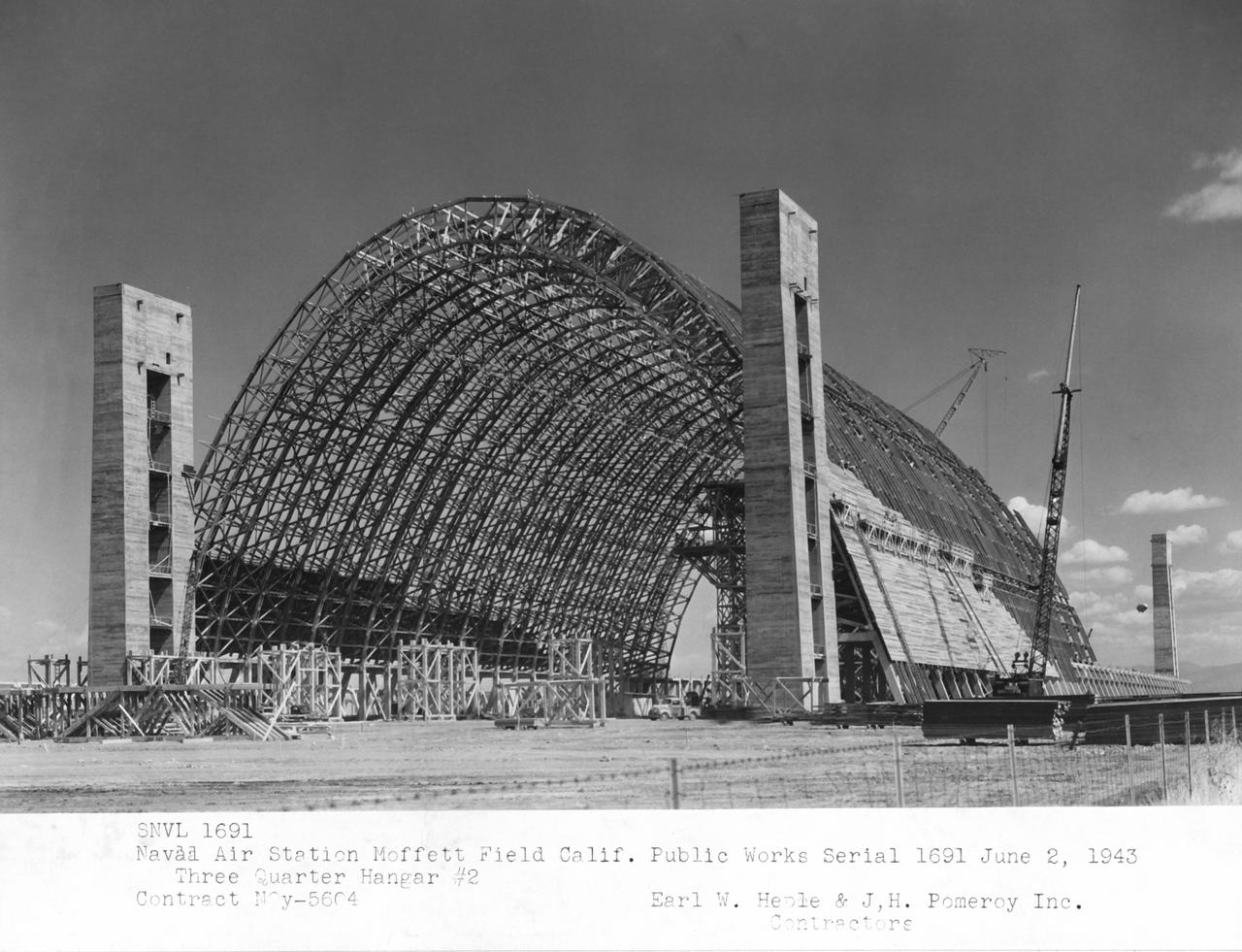

Navy Naval Air Station Moffett Field Public works Serial 1514 - Contract NOy-5604, Earl W. Heple & J.H. Pomeroy contractors NAS Air station Moffett Field, three quarter view of Hangar 2 from North West Corner
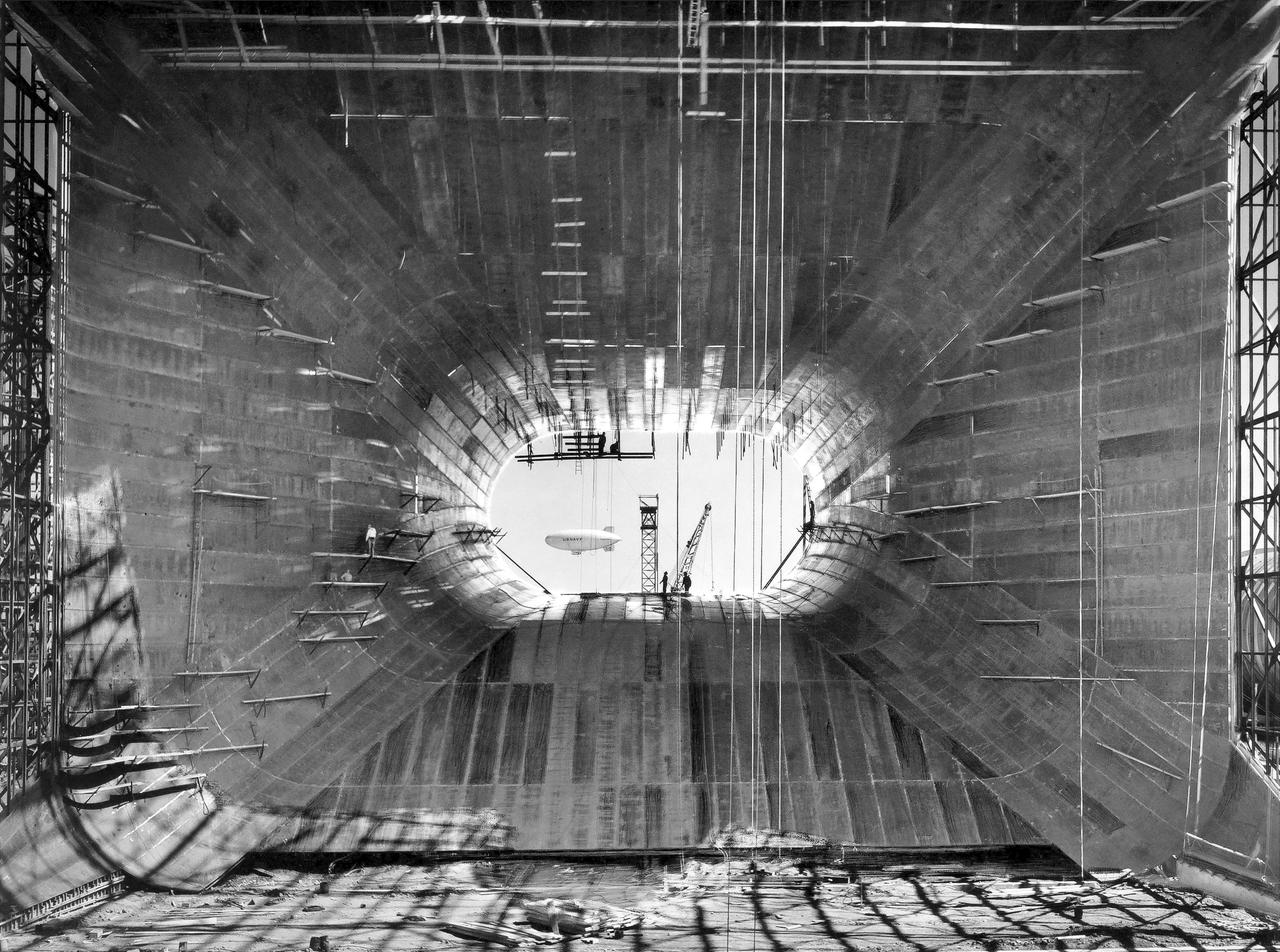
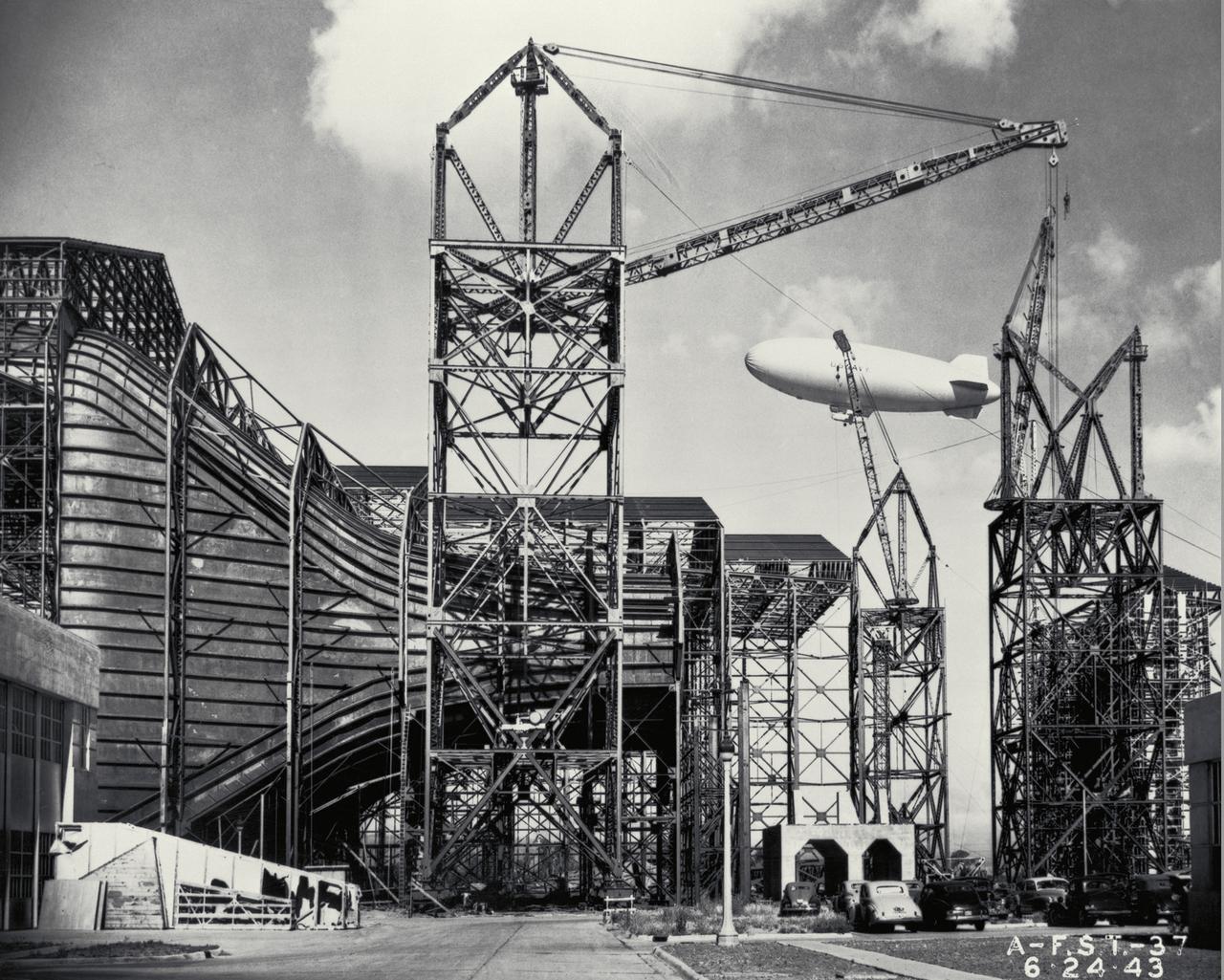
(07/07/1943) Construction view from inside the contraction framing of the 40x80 foot wind tunnel with a blimp flying in the background.
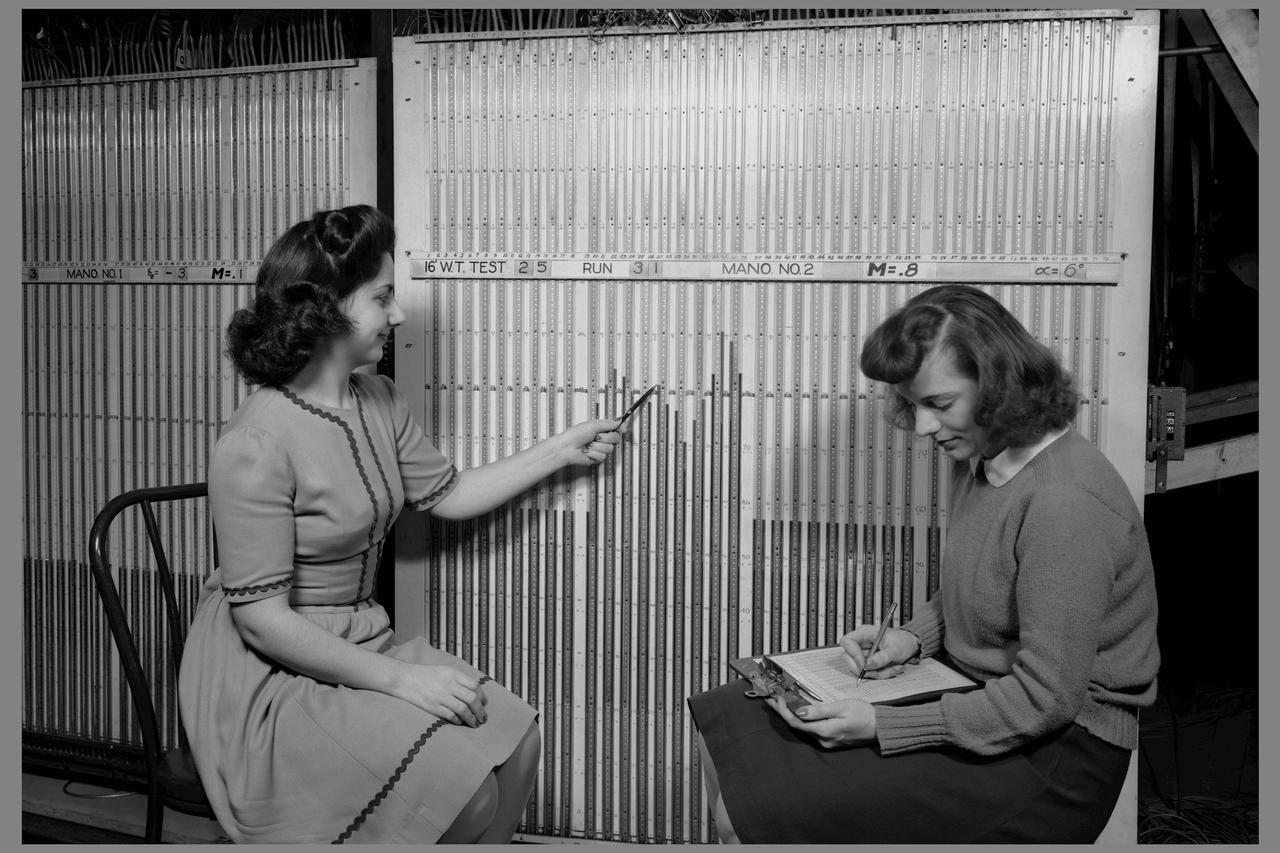

Computers' at work in 16ft wind tunnel - calculating test data - reading manometer board
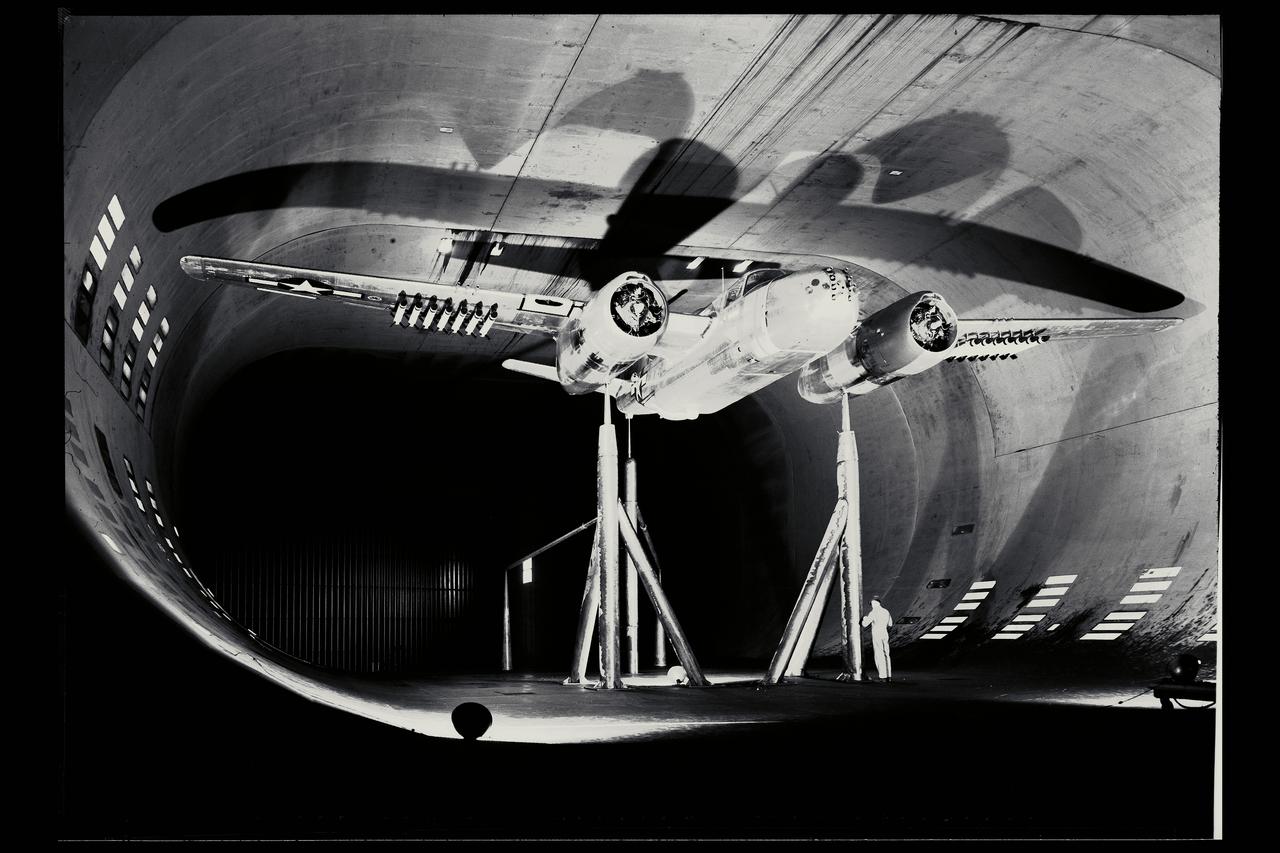

40x80ft wind tunnel testing of a modification to a Douglas A-26B Invader airplane (rockets, bomb and wing)
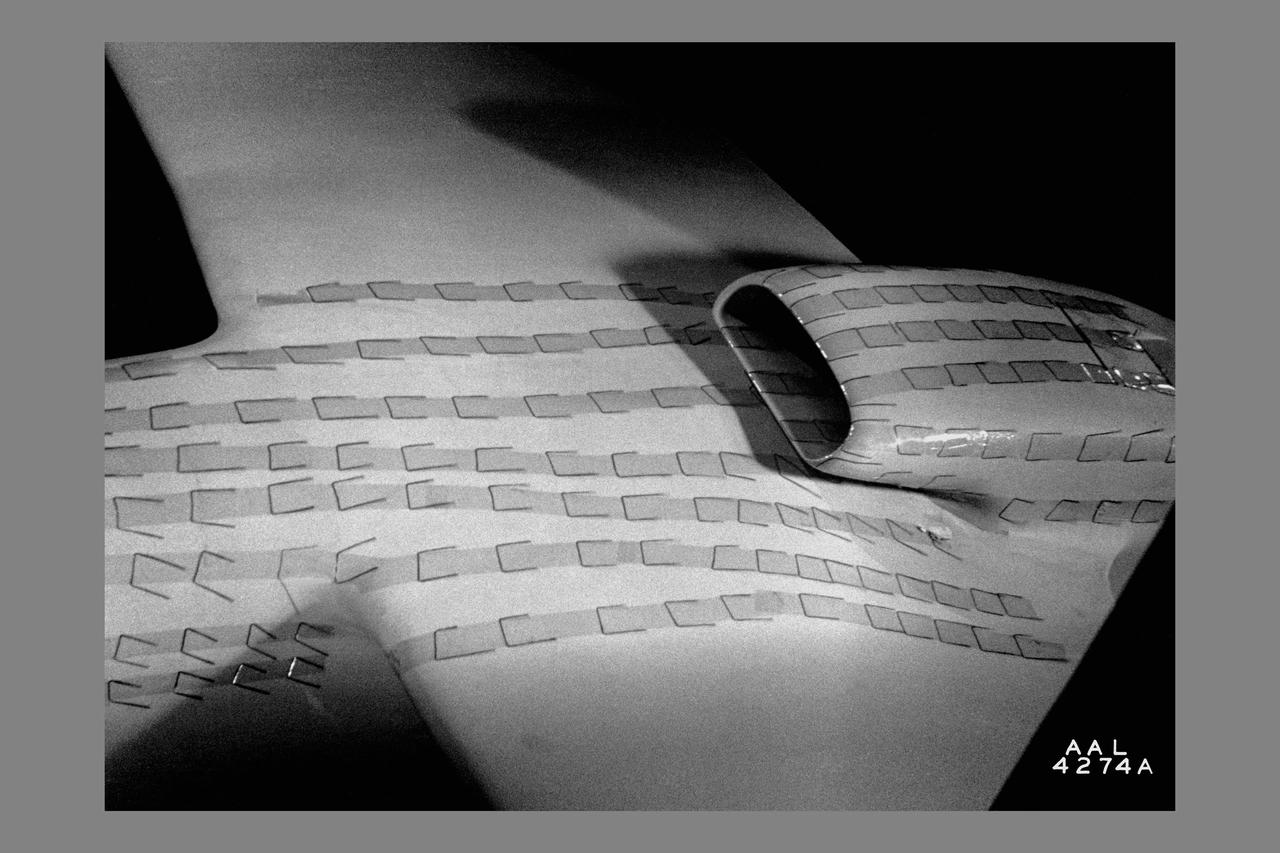
North American P-51B tuft studies done in the NACA Ames Research center 16ft Transonic Wind Tunnel Radiator air scoop with oil and prestone cooler exit flaps in flush position.

Navy (Contract NOy-5604 SNVL 1691) NAS Air station Moffett Field, overhead view of Hangar 2 and 3 from North West Corner Moffett Field Public Works Serial 1621 - Earl W. Heple & J. H. Pomeroy Contractors
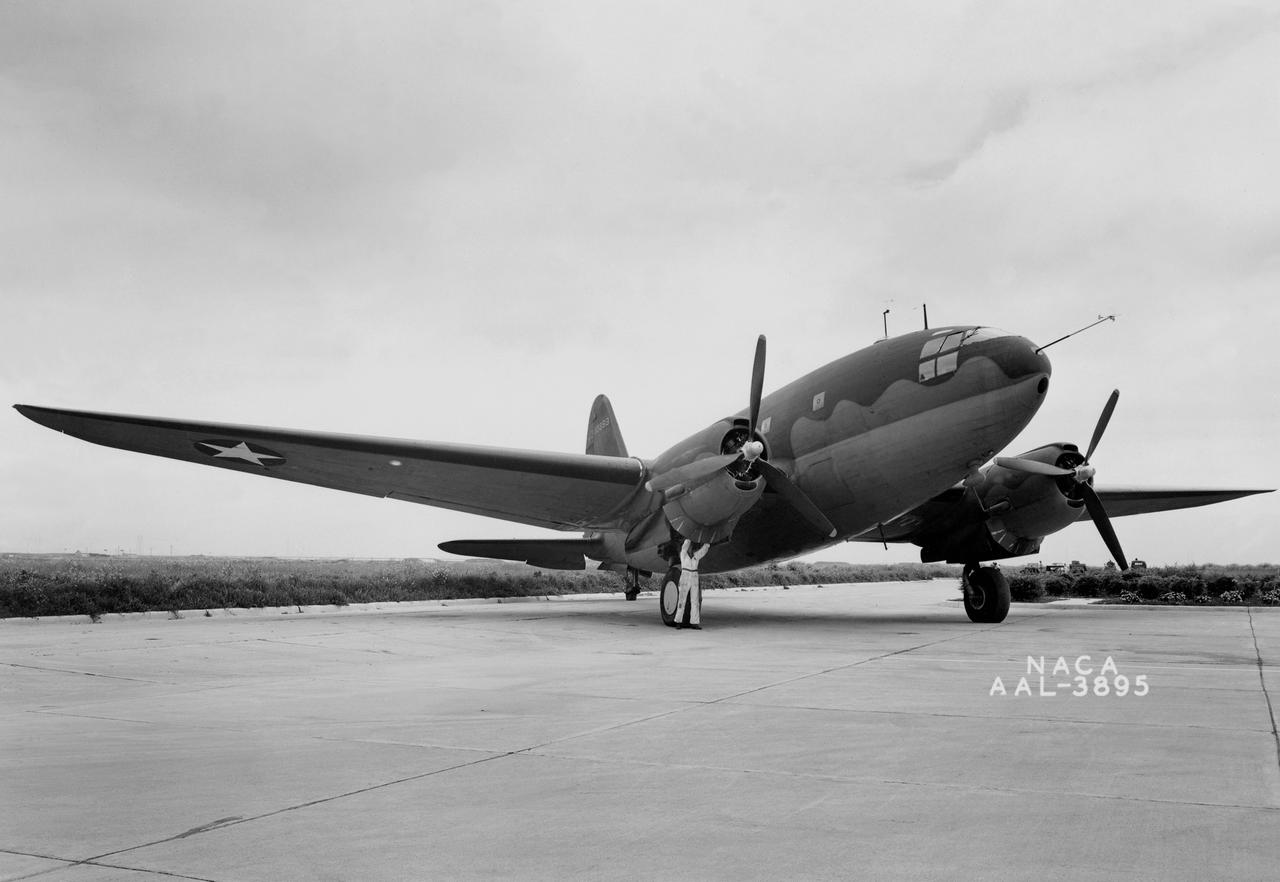

NACA Photographer 3/4 front view Curtiss C-46 airplane in which the thermal ice-prevention equipment was installed
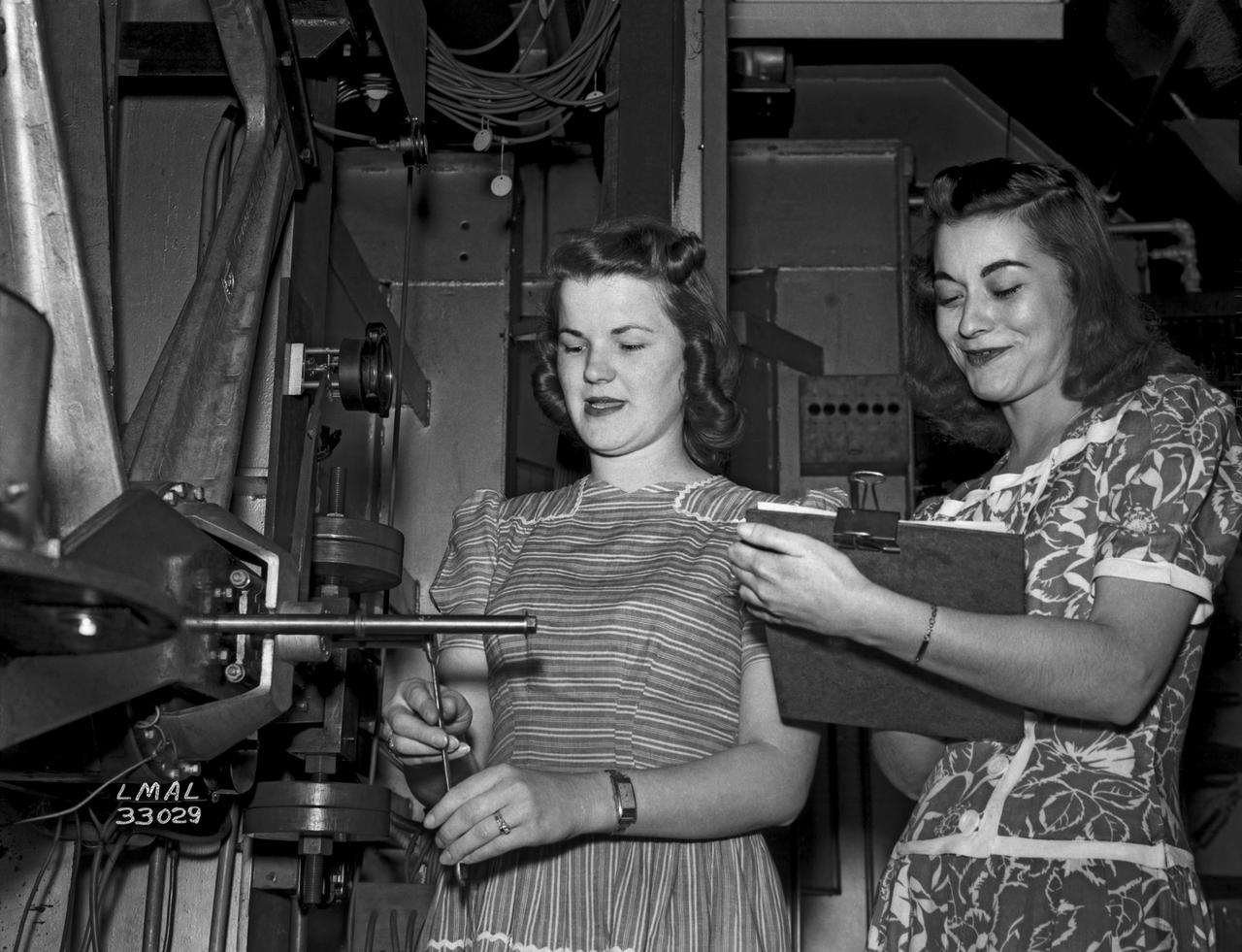

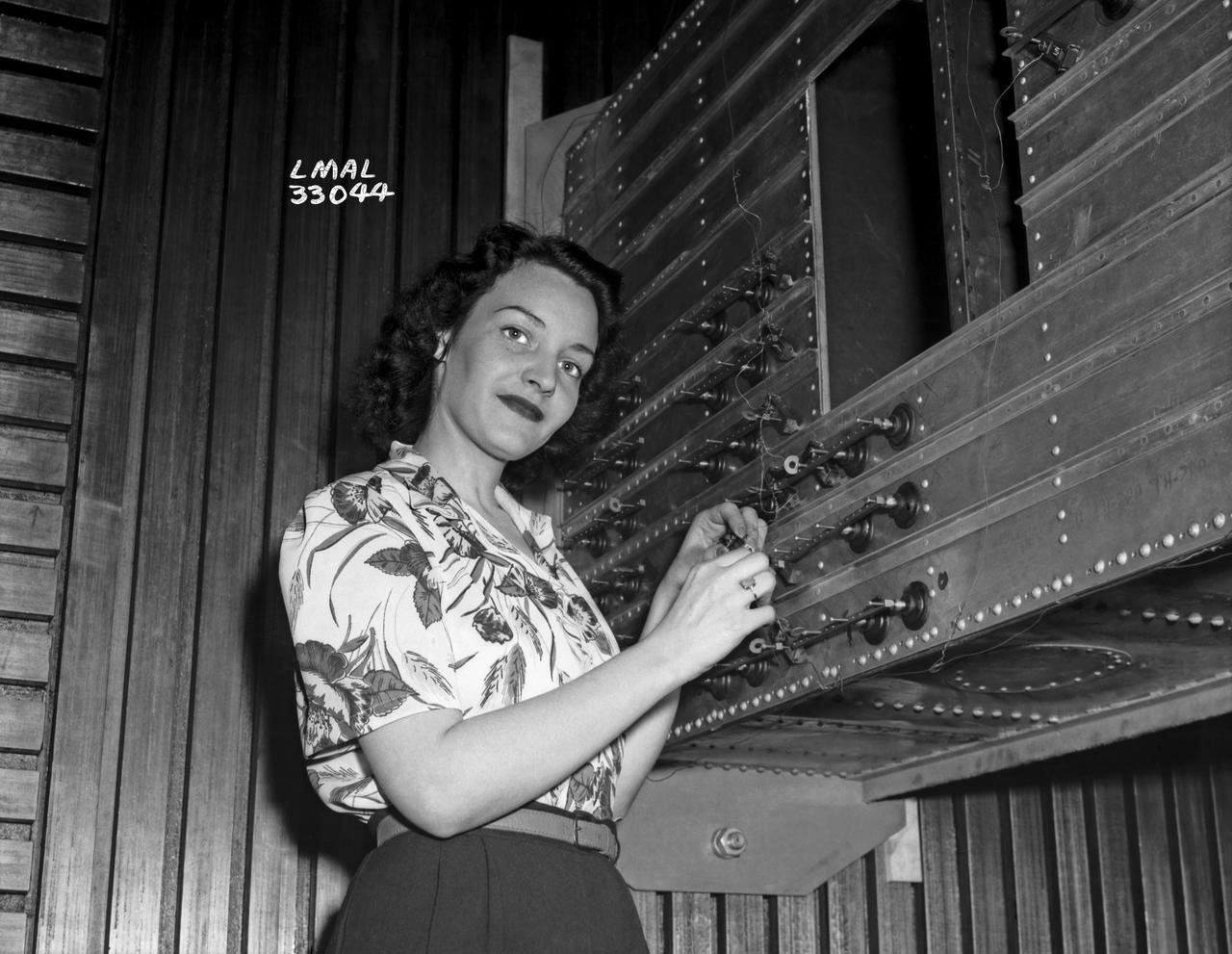
Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.

Navy (Contract NOY-5604 SNVL 1689) NAS Airstation Moffett Field, broadside view of Hangar 2 from middle of landing mat. Moffett Field Public Works Serial 1621 - Earl W. Heple & J. H. Pomeroy Contractors
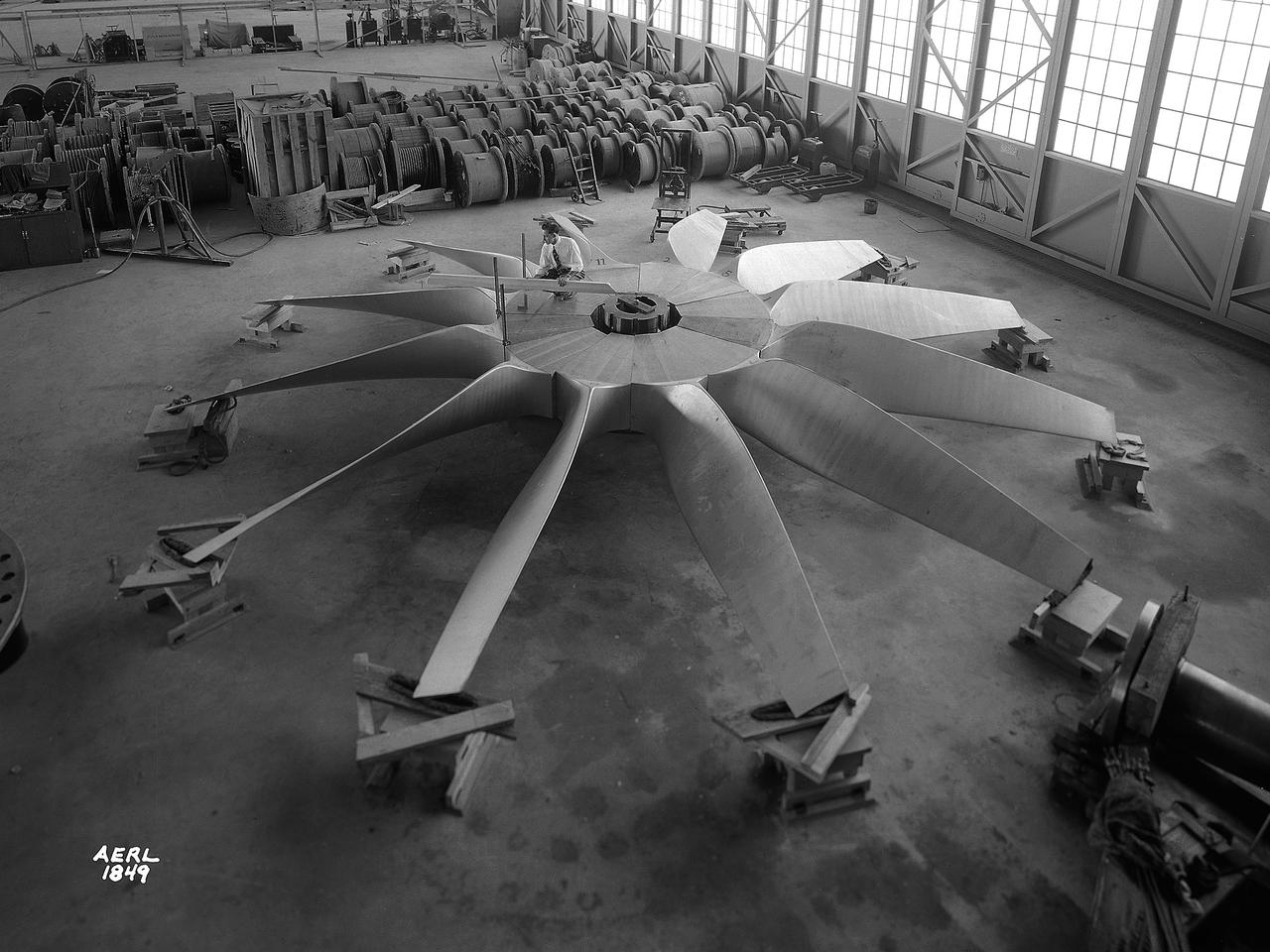

National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) engineers assembled the Altitude Wind Tunnel’s (AWT) large wooden drive fan inside the hangar at the Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory. When it was built at the in the early 1940s the AWT was among the most complex test facilities ever designed. It was the first wind tunnel capable of operating full-scale engines under realistic flight conditions. This simulation included the reduction of air temperature, a decrease in air pressure, and the creation of an airstream velocity of up to 500 miles per hour. The AWT was constructed in 1942 and 1943. This photograph shows NACA engineers Lou Hermann and Jack Aust assembling the tunnel’s drive fan inside the hangar. The 12-bladed, 31-foot-diameter spruce wood fan would soon be installed inside the wind tunnel to create the high-speed airflow. This massive propeller was designed and constructed by the engine lab's design team at Langley Field. John Breisch, a Langley technician with several years of wind tunnel installation experience, arrived in Cleveland at the time of this photograph to supervise the fan assembly inside the hangar. He would return several weeks later to oversee the actual installation in the tunnel. The fan was driven at 410 revolutions per minute by an 18,000-horsepower General Electric induction motor that was located in the rear corner of the Exhauster Building. An extension shaft connected the motor to the fan. A bronze screen protected the fan against damage from failed engine parts sailing through the tunnel. Despite this screen the blades did become worn or cracked over time and had to be replaced. An entire new fan was installed in 1951.

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.

XA-39 model mounted for testing in the 7x120ft w.t. at Ames Research Center, California, props spinning.
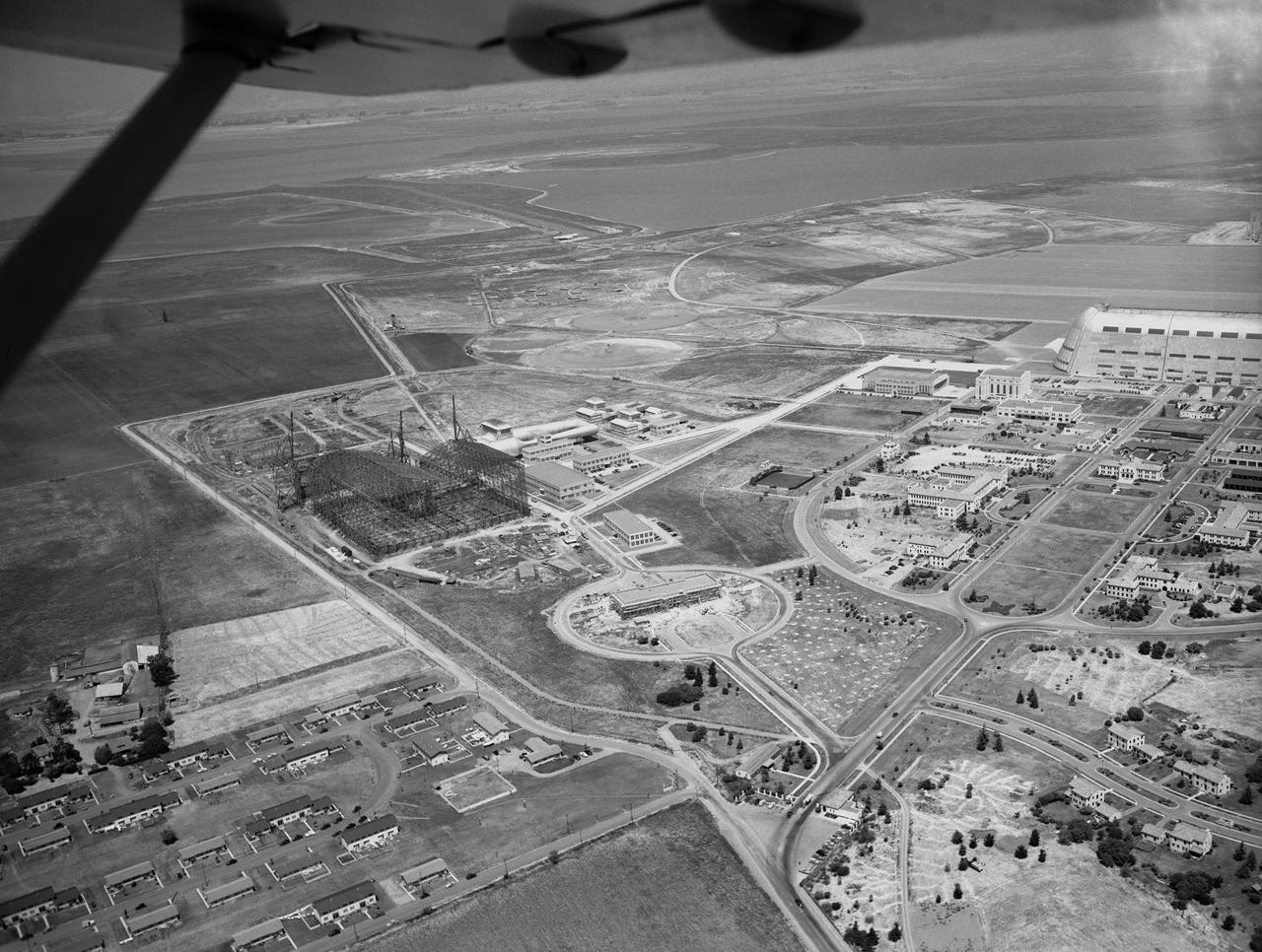

Early aerial of the NASA Ames Aeronautical Laboratory
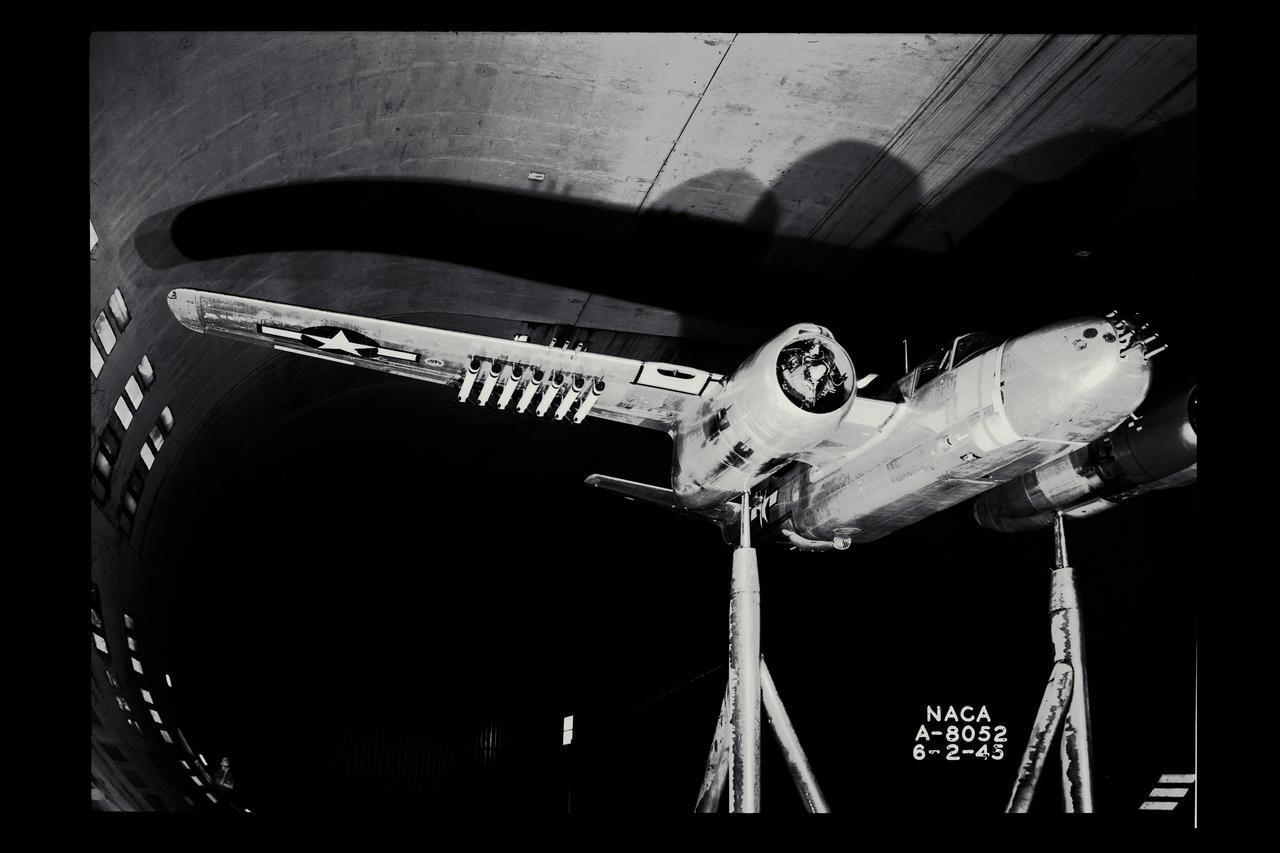
40x80ft wind tunnel testing of a modification to a A-26B airplane (rockets, bomb and wing)
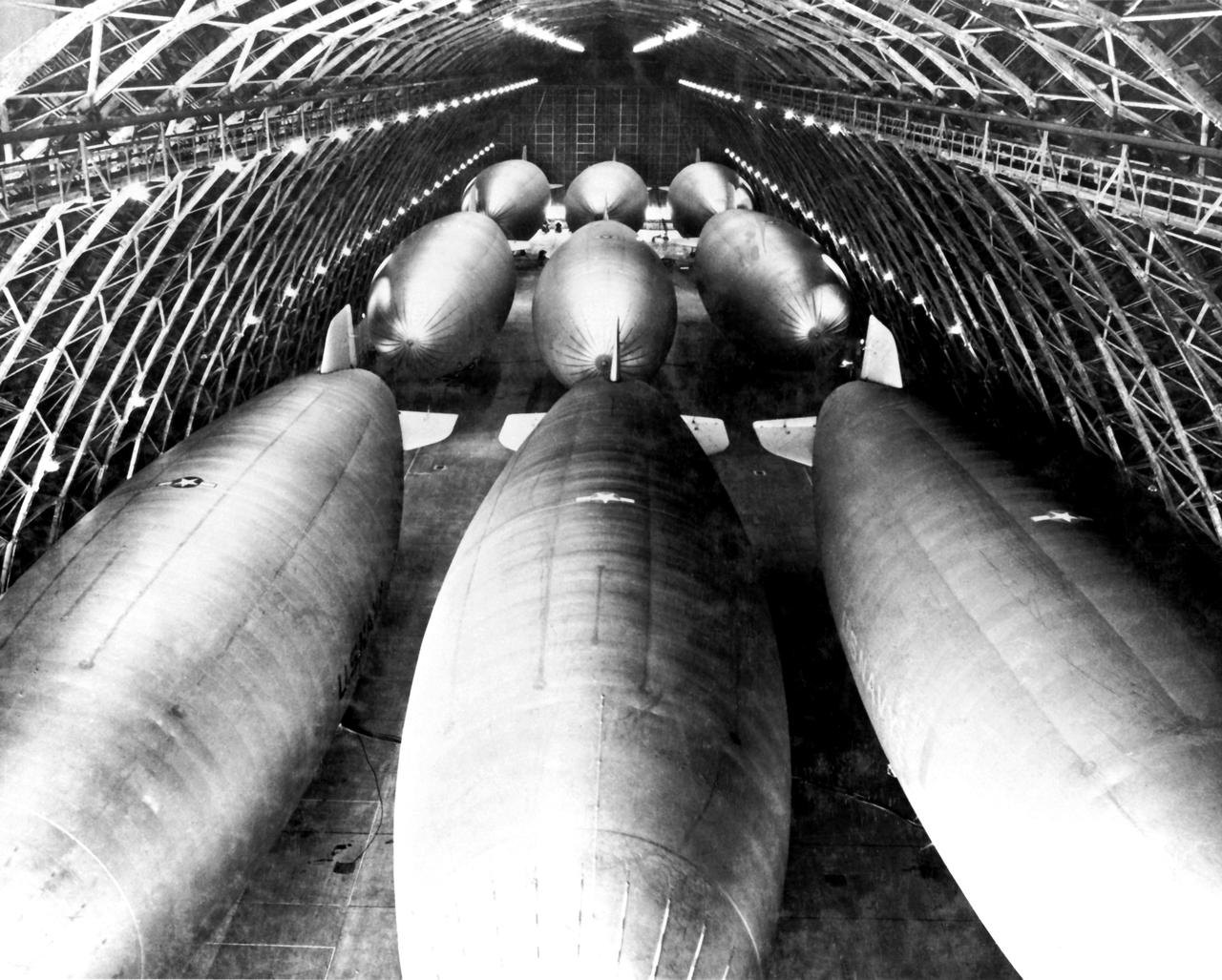

Navy Nine Blimps inflated in Hangar, NAS Sunnyvale, CA

The Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory’s first aircraft, a Martin B–26B Marauder, parked in front of the Flight Research Building in September 1943. The military loaned the B–26B to the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to augment the lab’s studies of the Wright Aeronautical R–2800 engines. The military wanted to improve the engine cooling in order to increase the bomber’s performance. On March 17, 1943, the B–26B performed the very first research flight at the NACA’s new engine laboratory. The B–26B received its “Widowmaker” nickname during the rushed effort to transition the new aircraft from design to production and into the sky. During World War II, however, the B–26B proved itself to be a capable war machine. The U.S. lost fewer Marauders than any other type of bomber employed in the war. The B–26B was originally utilized at low altitudes in the Pacific but had its most success at high altitudes over Europe. The B–26B’s flight tests in Cleveland during 1943 mapped the R-2800 engine’s behavior at different altitudes and speeds. The researchers were then able to correlate engine performance in ground facilities to expected performance at different altitudes. They found that air speed, cowl flap position, angle of attack, propeller thrust, and propeller speed influenced inlet pressure recovery and exhaust distribution. The flight testing proceeded quickly, and the B–26B was transferred elsewhere in October 1943.
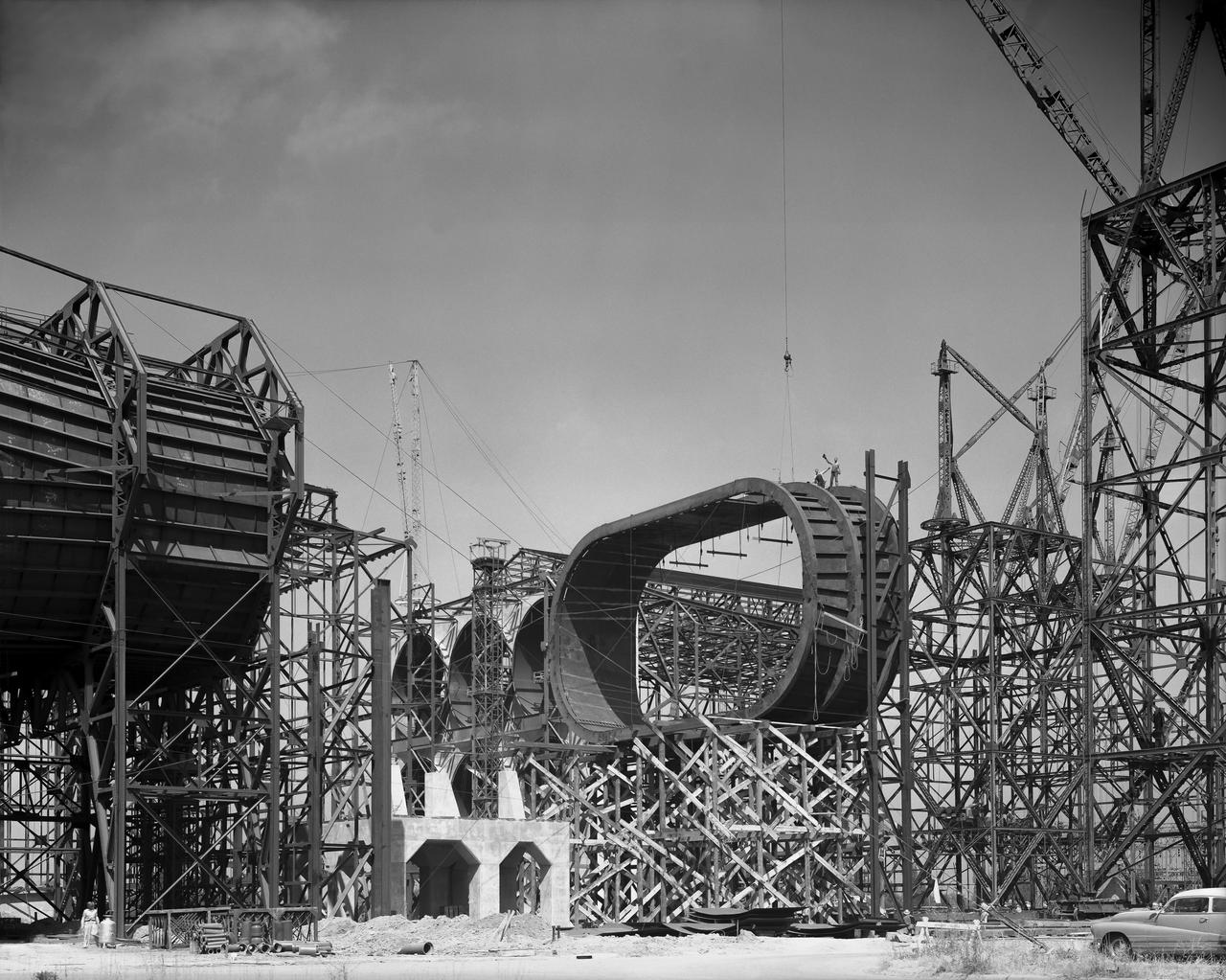

Looking West at three test section bents in place for the Ames 40 x 80 foot wind tunnel. Concrete model scale support visible in the middle.
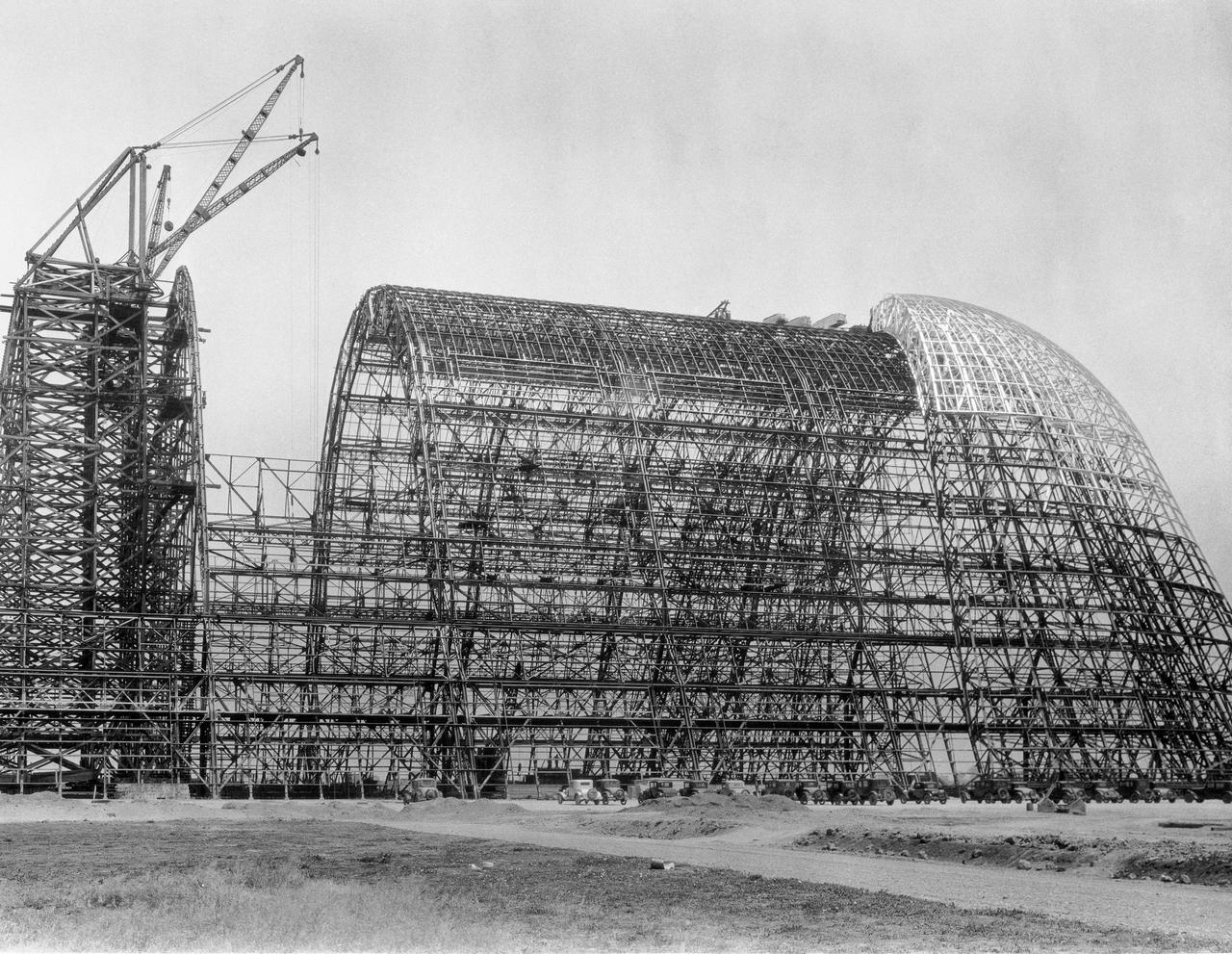
Navy Naval Air Station Moffett Field Public works Serial 1514 - Contract NOy-5604, Earl W. Heple & J.H. Pomeroy contractors Hangar 2 'Contruction of Arch'

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
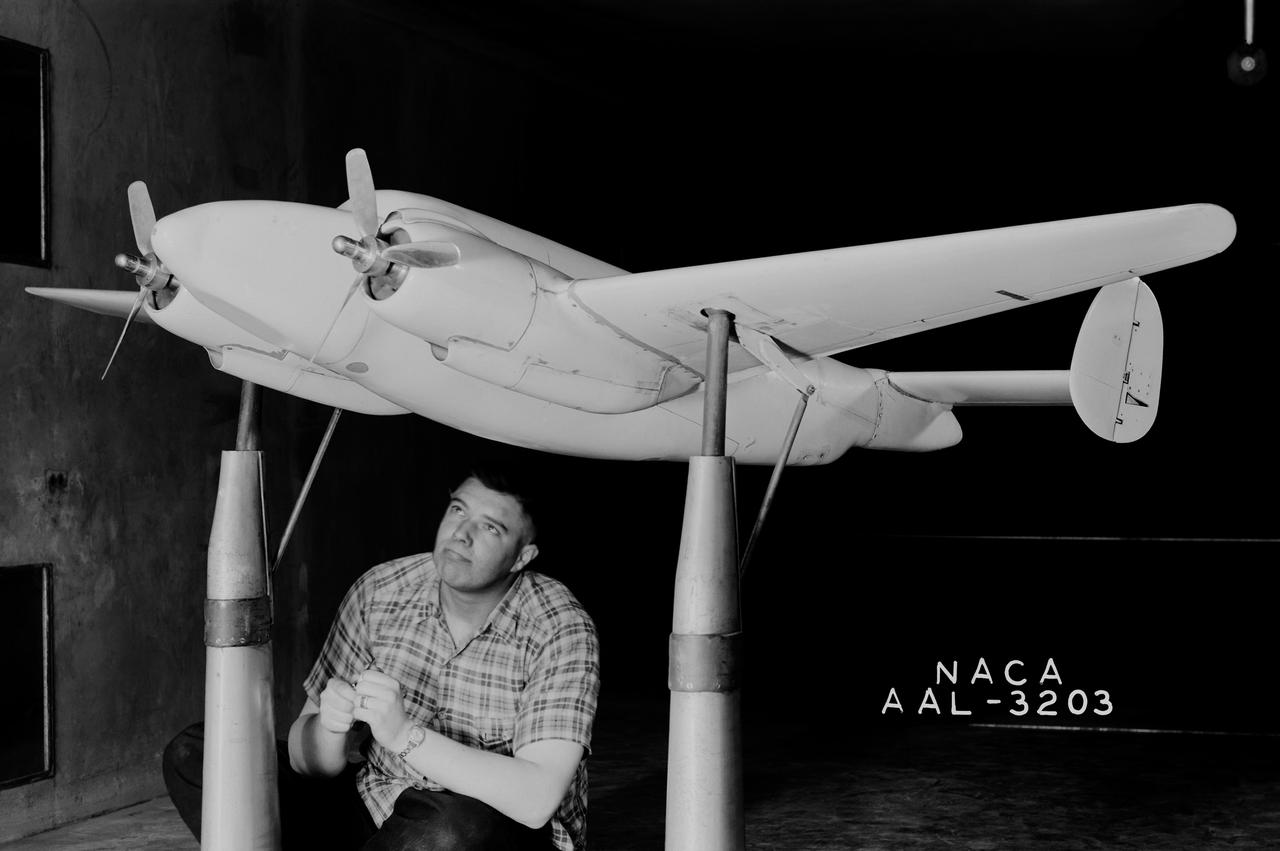

Vega XPV-2 complete model testing in the 7x10ft w.t. @ Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, CA
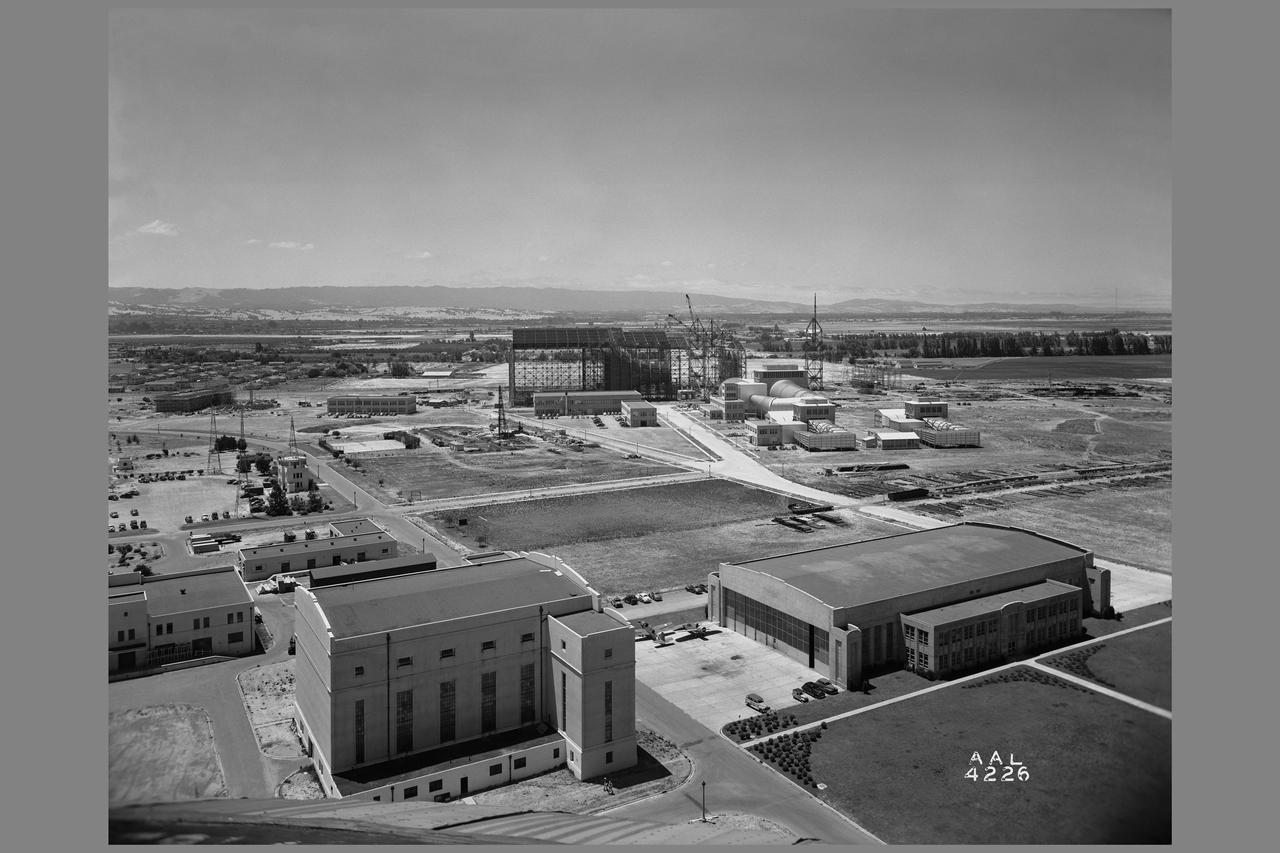

Panarama from Navy air ship dock showing NACA Ames grounds
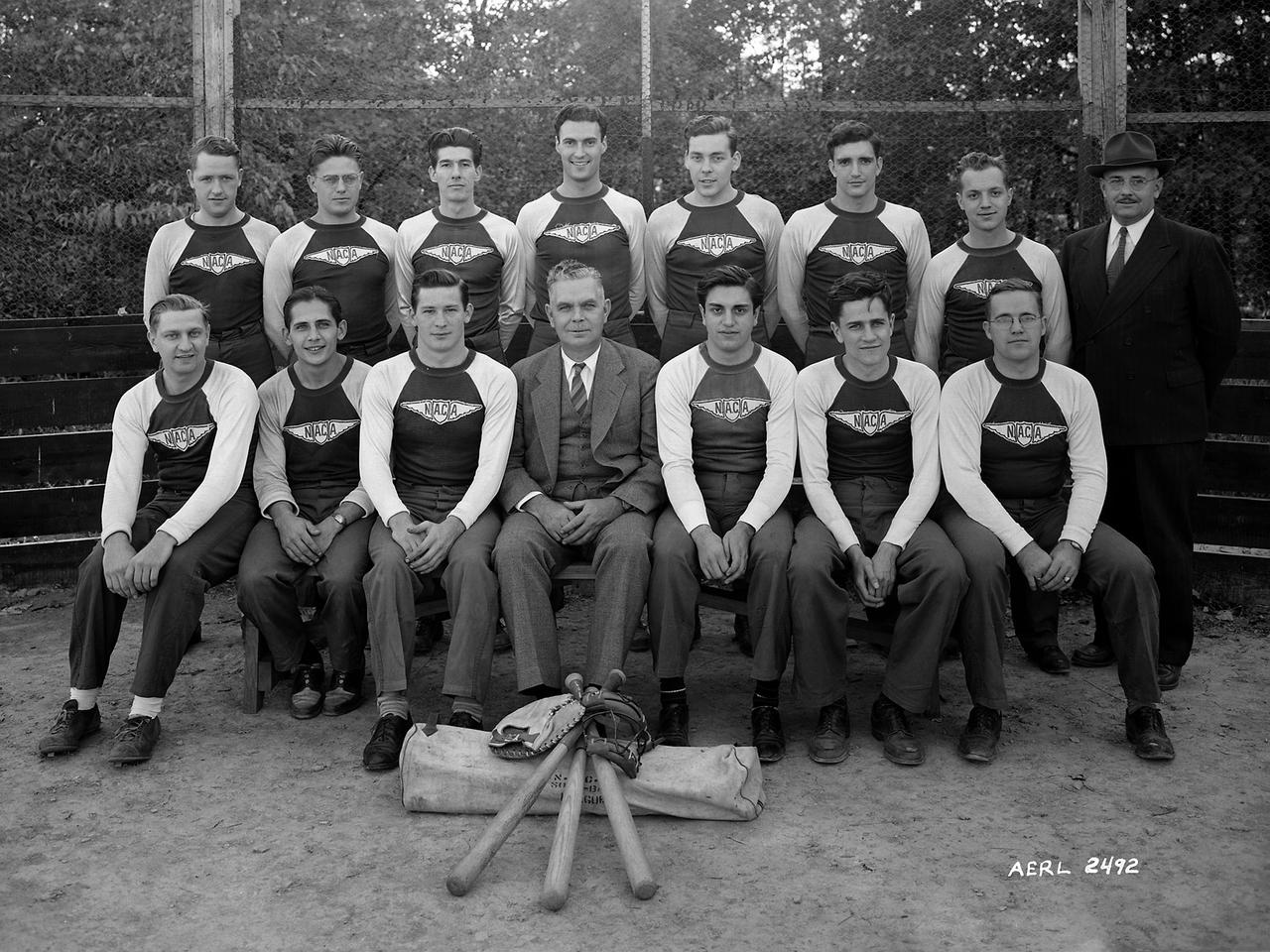

The NACA’s Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory’s baseball team photographed with director Raymond Sharp. The Exchange, which operated the non-profit cafeteria, sponsored several sports teams that participated in local leagues. The laboratory also had several intramural sports leagues. The baseball team, seen here in 1943, was suspended shortly thereafter as many of its members entered the military during World War II. The team was reconstituted after the war and became somewhat successful in the Class A Westlake League. After winning the championship in 1949 and 1950, the team was placed in the more advanced Middleberg League where they struggled.

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
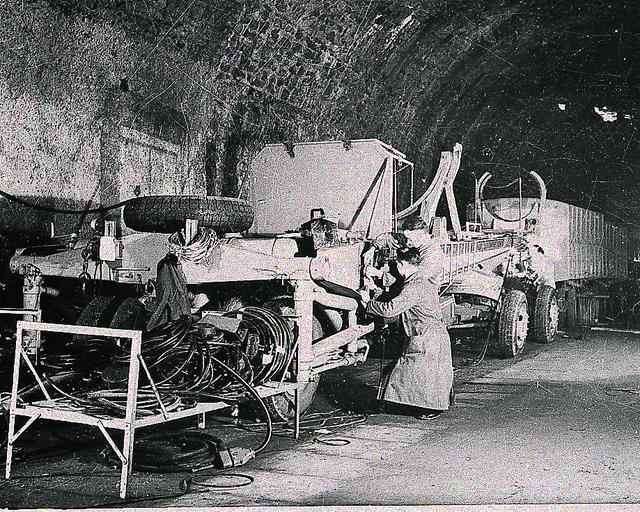
In this photograph from the fall of 1943, German technicians wire vehicles for mobile V-2 batteries in an abandoned railroad turnel in the Rhineland. The team of German engineers and scientists who developed the V-2 came to the United States at the end of World War II and worked for the U. S. Army at Fort Bliss, Texas, and Redstone Arsenal in Huntsville, Alabama.
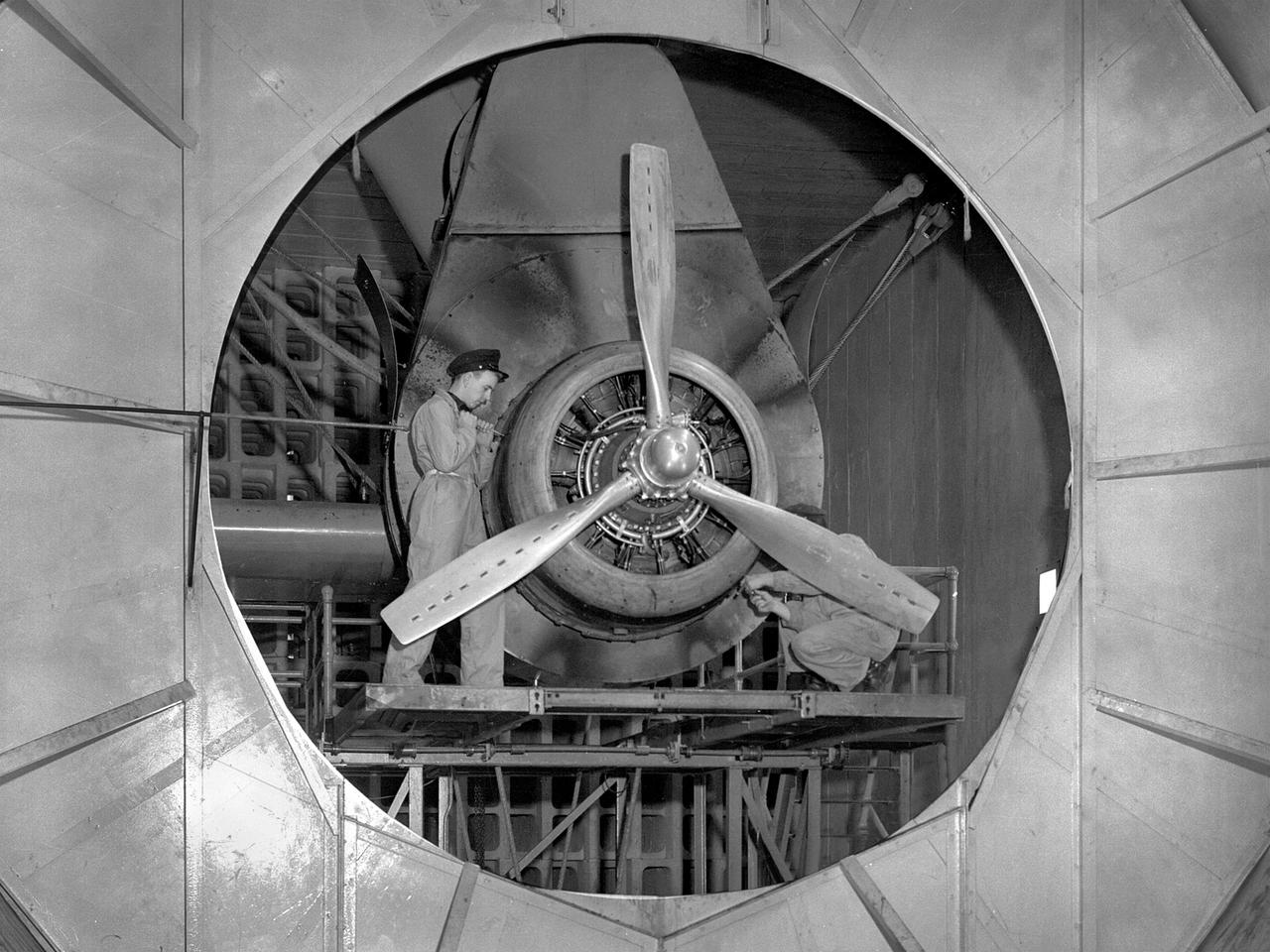

A Wright Aeronautical R–2600 Cyclone piston engine installed in the Engine Propeller Research Building, or Prop House, at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory. The R–2600 was among the most powerful engines that emerged during World War II. The engine, which was developed for commercial applications in 1939, was used to power the North American B–25 bomber and several other midsize military aircraft. The higher altitudes required by the military caused problems with the engine's cooling and fuel systems. The military requested that the Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory analyze the performance of the R–2600, improve its cooling system, and reduce engine knock. The NACA researchers subjected the engine to numerous tests in its Prop House. The R–2600 was the subject of the laboratory's first technical report, which was written by members of the Fuels and Lubricants Division. The Prop House contained soundproof test cells in which piston engines and propellers were mounted and operated at high powers. Electrically driven fans drew air through ducts to create a stream of cooling air over the engines. Researchers tested the performance of fuels, turbochargers, water-injection and cooling systems here during World War II. The facility was also investigated a captured German V–I buzz bomb during the war.

Aerial view of Ames Aeronautical Laboratory (with blimps in flight over Moffett runway)

Construction of the Ames Full-Scale 40x80ft Wind tunnel. - side view of entrance cone, blimp in background
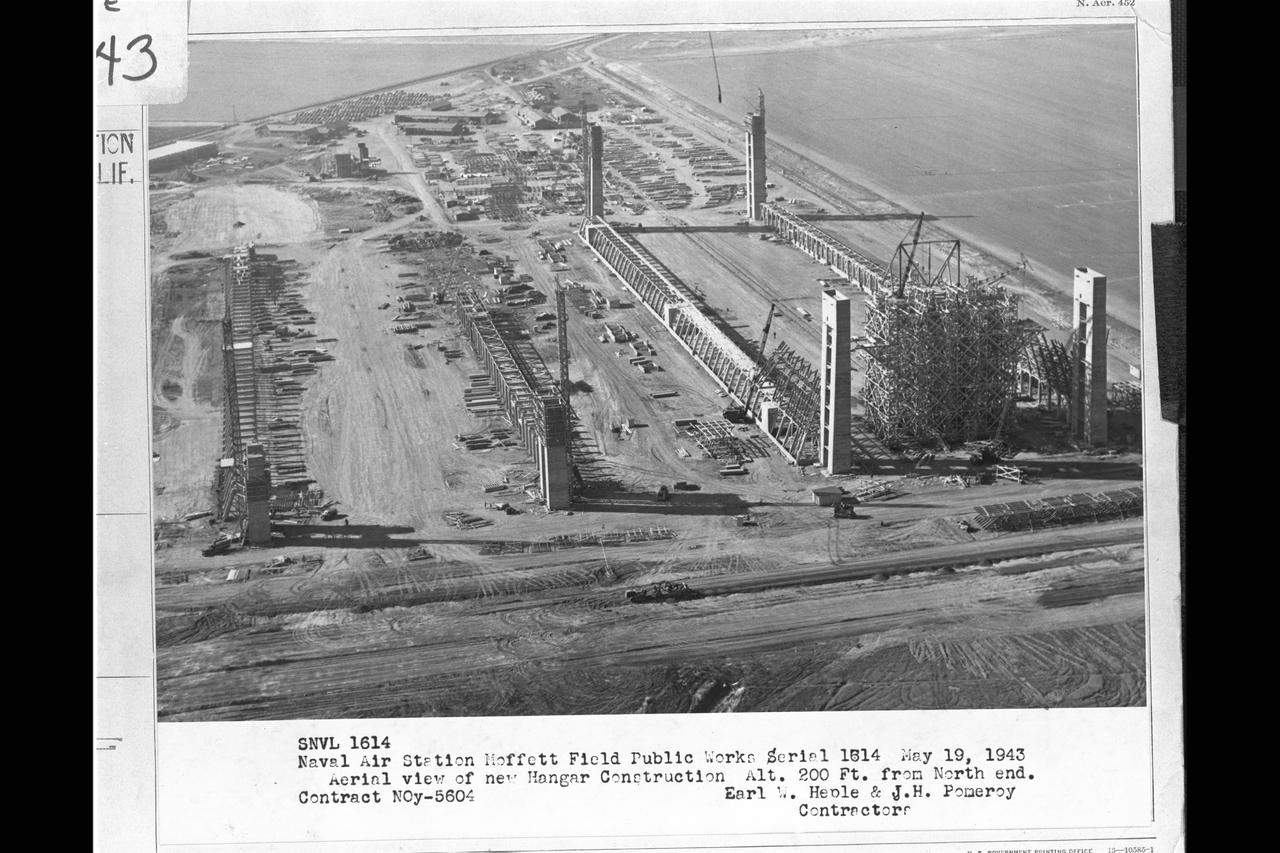

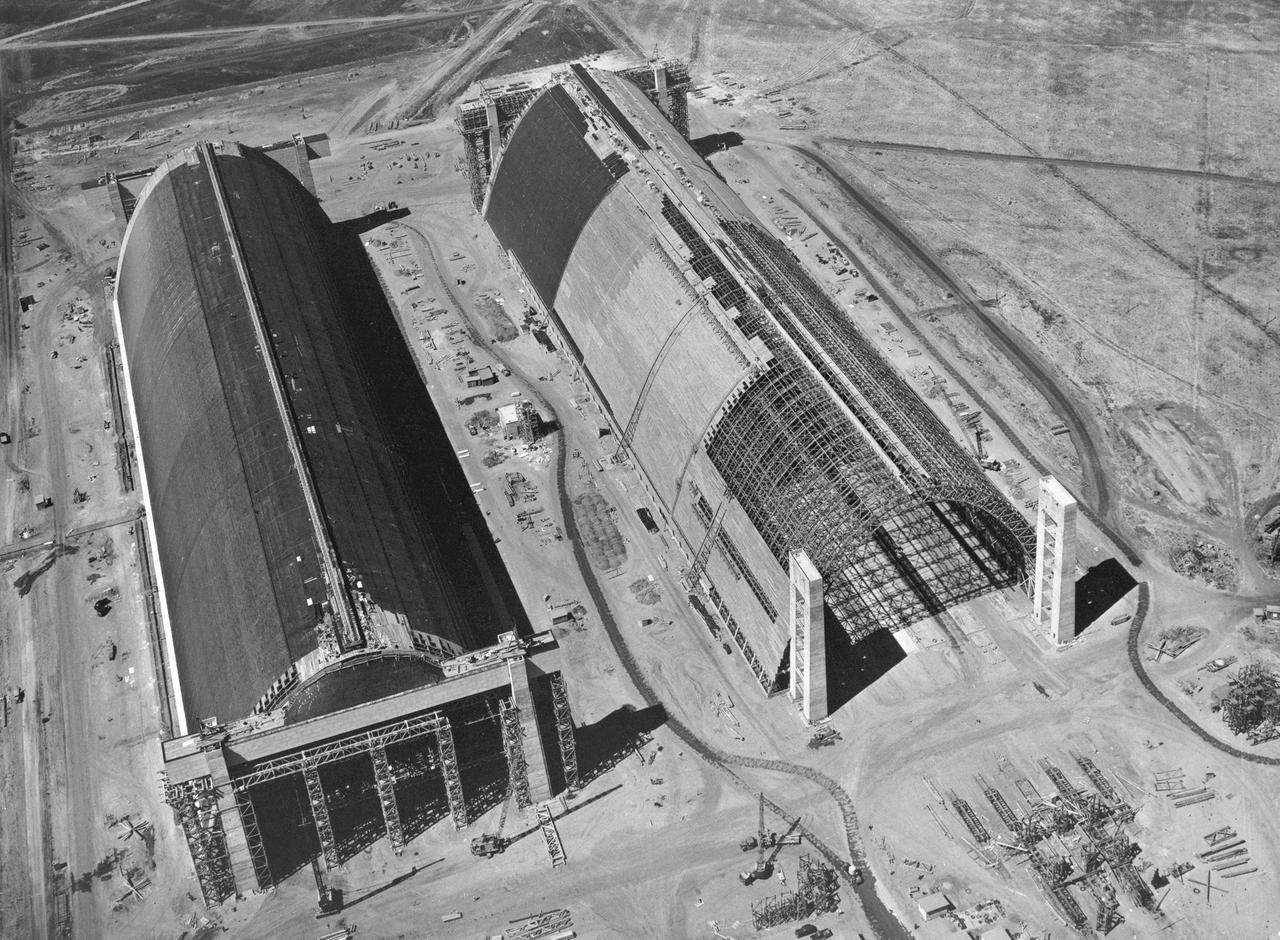
Navy Naval Air Station Moffett Field Public works Serial 1514 - Contract NOy-5604, Earl W. Heple & J.H. Pomeroy contractors NAS Moffett Field: Aerial view of new Hangar2 & Hangar 3 construction at alt 200 ft from north end.
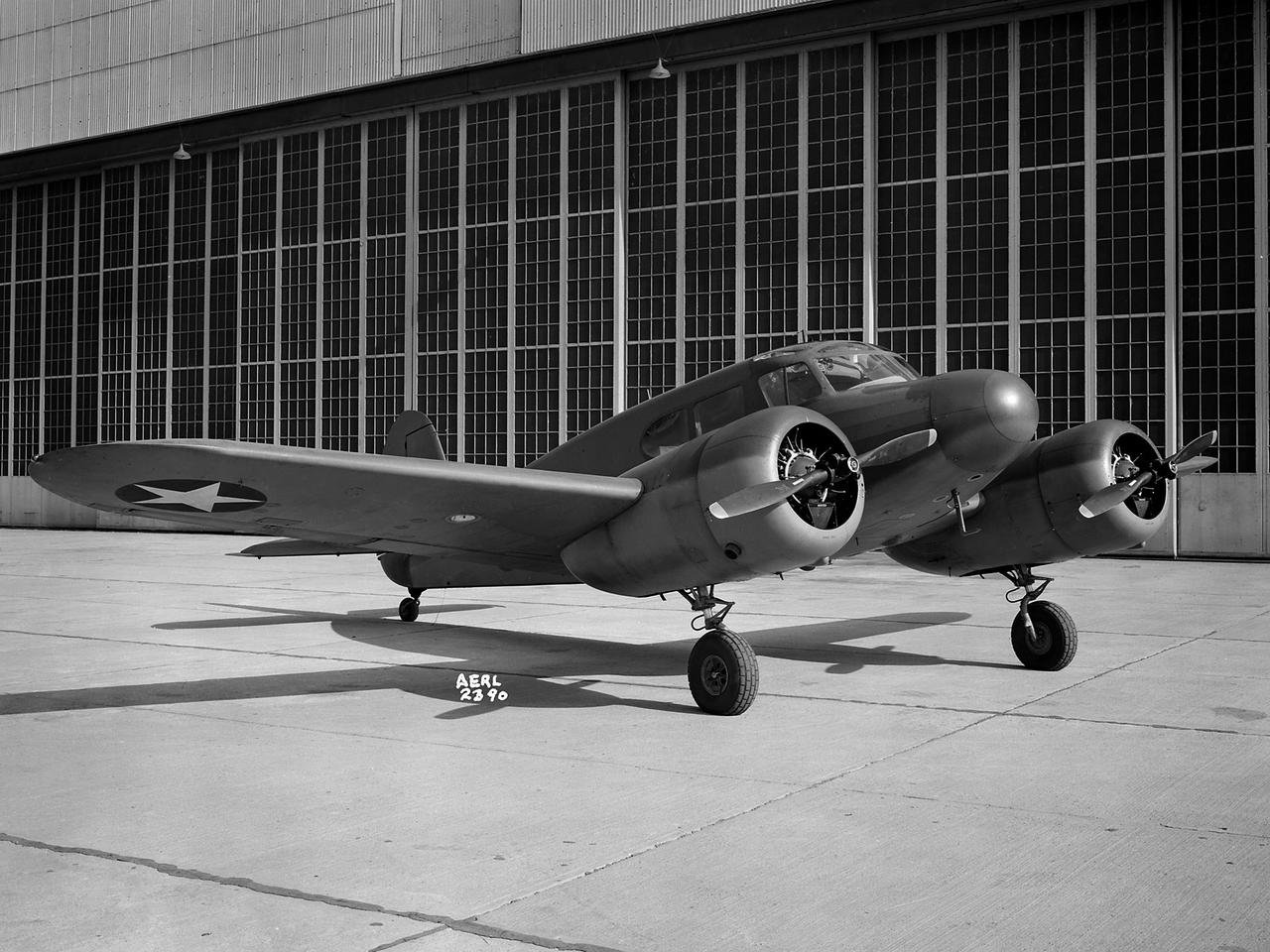

The Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory acquired the five-seat Cessna UC–78 in March 1943 to maintain the proficiency of its pilots. The UC–78 was referred to as the “Bamboo Bomber” because of its wooden wings and tail and its fabric-covered steel body. The aircraft was produced in 1939 for civilian use, but the military soon began ordering them as training aircraft. The military also began using the aircraft for personnel transport. Cessna produced over 4600 of the aircraft for the military during World War II. The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics’ (NACA) pilot Howard Lilly flew the UC–78 extensively during its residency in Cleveland. The aircraft was used for ferrying staff members to nearby locations and helping the pilots keep their flying hours up. The UC–78 was transferred in October 1945.

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
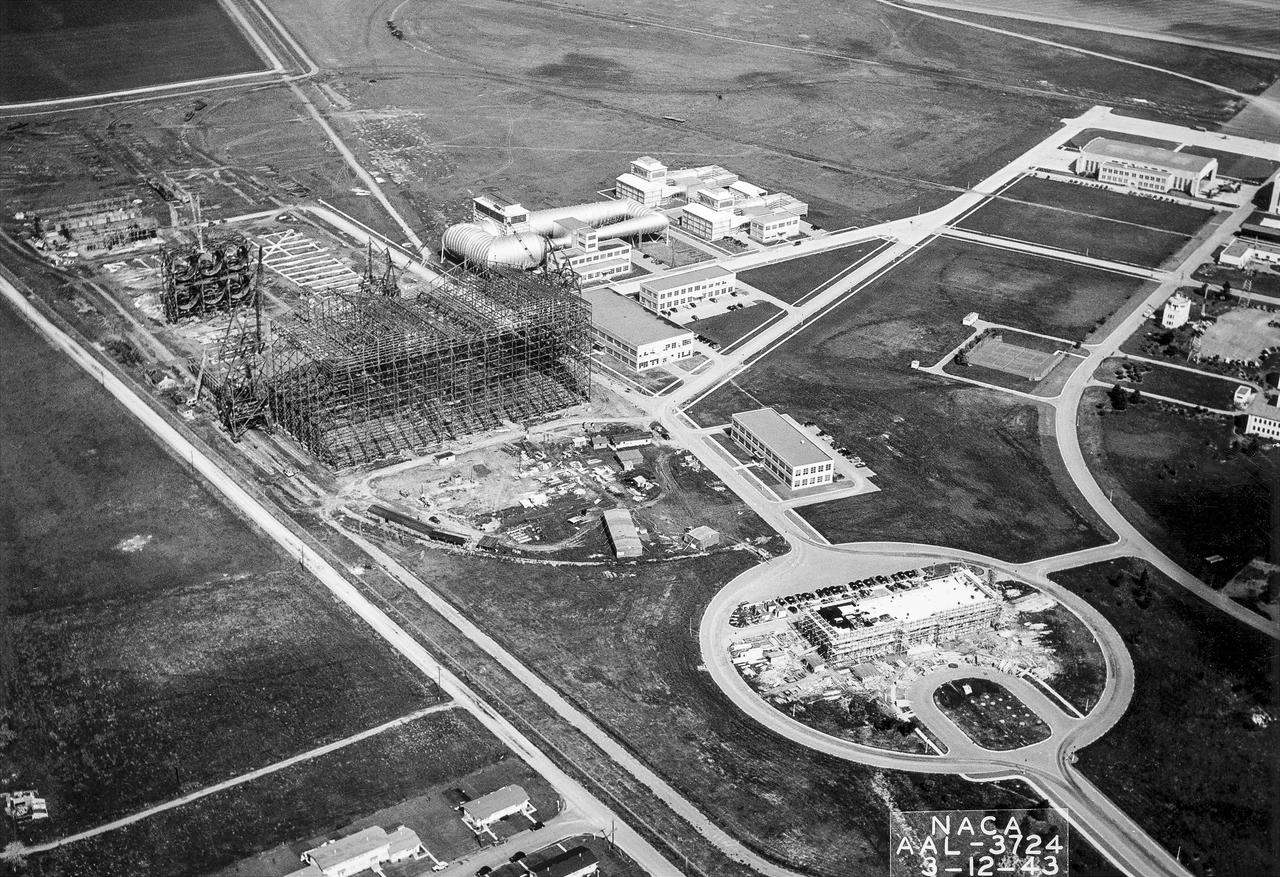

(03/12/1943) Aerial view of the site from the 40x80 wind tunnel At NASA Ames Research Center. Site includes the 16 foot and 7x10 wind tunnels in the background. Building 200 also under construction. Framing for the drive fans of the 40x80 in scene.

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.

Computers' at work in 16ft wind tunnel - calculating test data
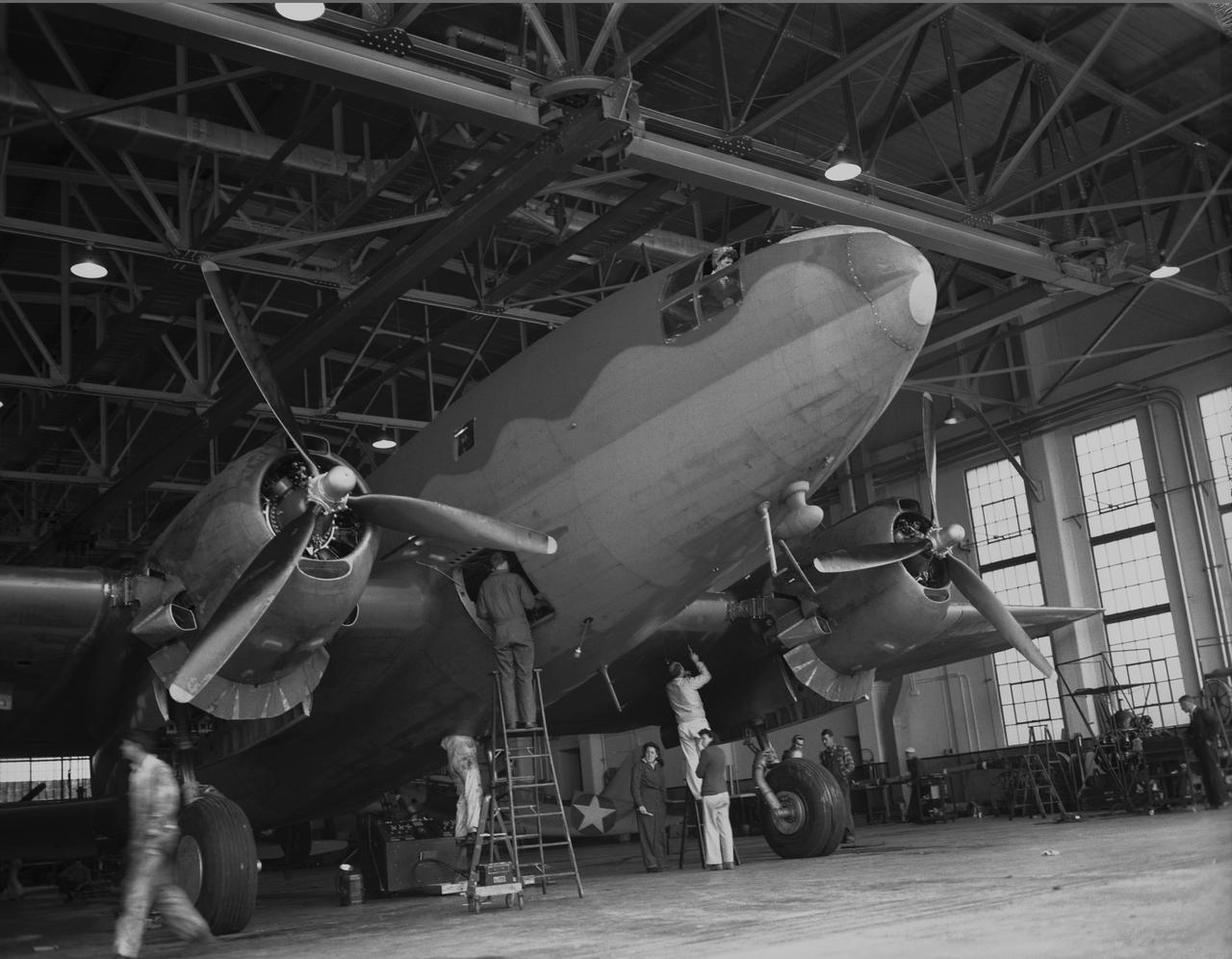

Ames mechanics working on C-46 airplane in front of hangar

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
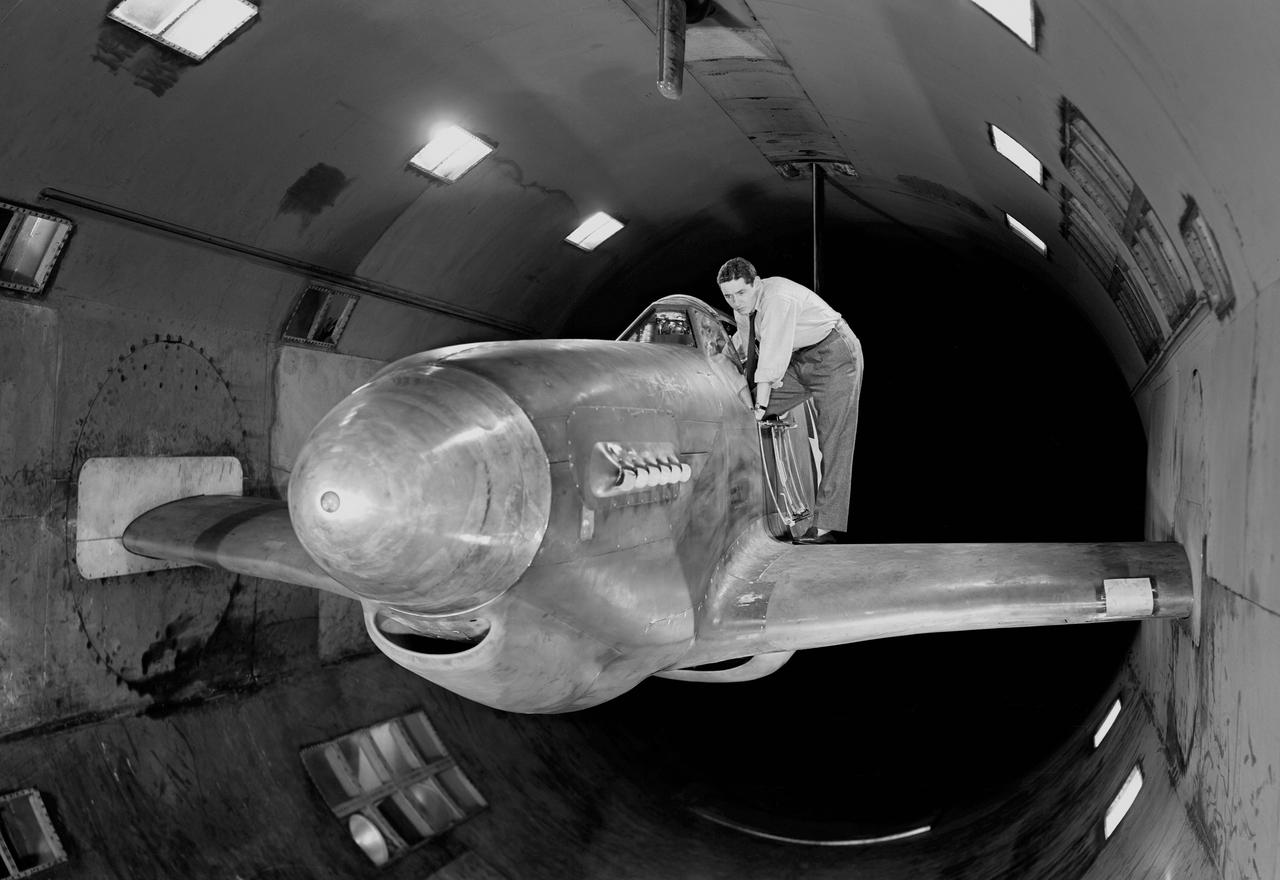

NACA Photographer - North American XP-51B Airplane with outer wing panels removed and ready for testing in Ames 16 foot wind tunnel.

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
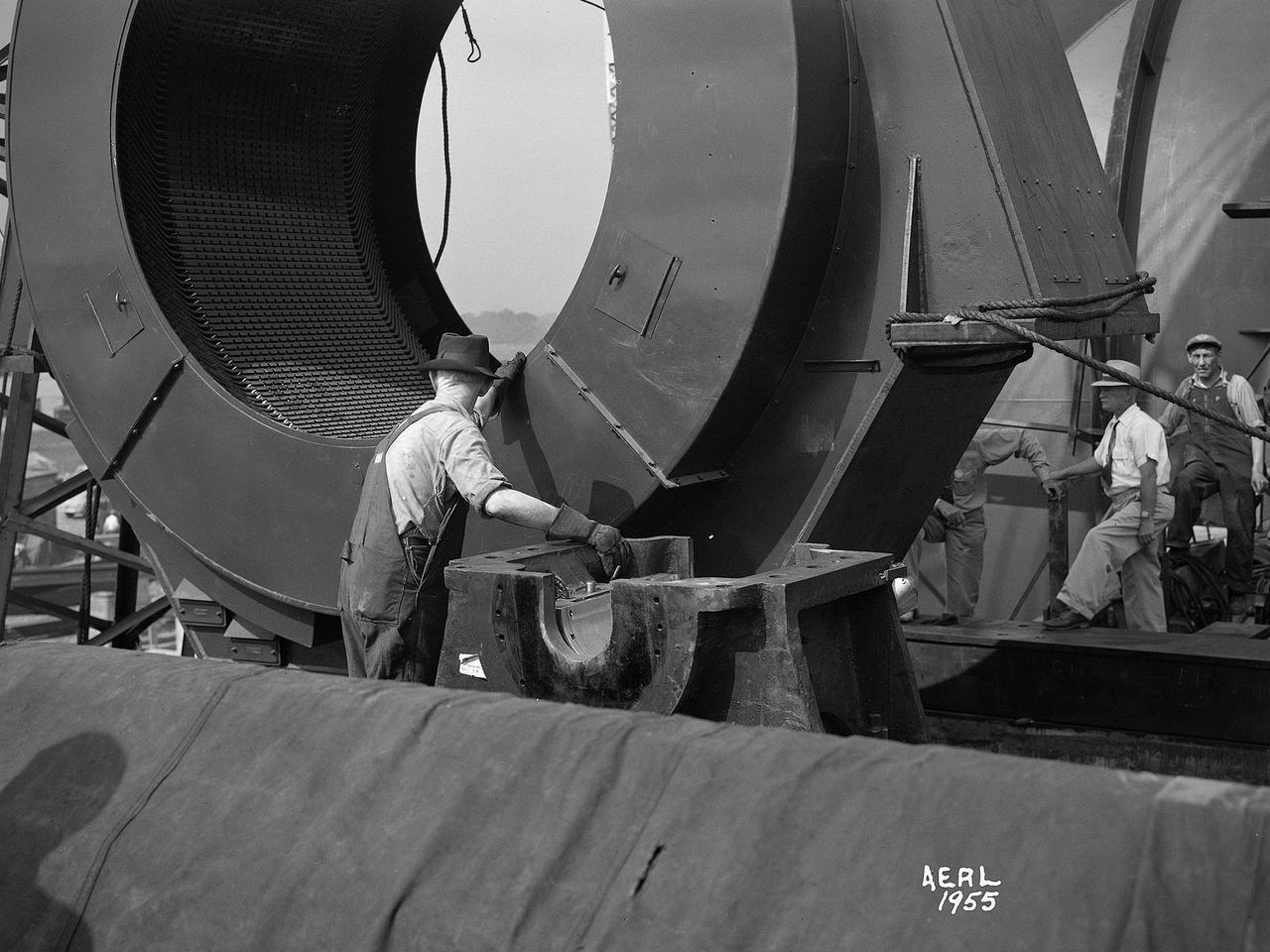

Construction workers install the drive motor for the Altitude Wind Tunnel (AWT) in the Exhauster Building at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory. The AWT was capable of operating full-scale engines in air density, speed, and temperature similar to that found at high altitudes. The tunnel could produce wind speeds up to 500 miles per hour through a 20-foot-diameter test section at the standard operating altitude of 30,000 feet. The airflow was created by a large wooden fan near the tunnel’s southeast corner. This photograph shows the installation of the 18,000-horsepower drive motor inside the adjoining Exhauster Building in July 1943. The General Electric motor, whose support frame is seen in this photograph, connected to a drive shaft that extended from the building, through the tunnel shell, and into a 12-bladed, 31-foot-diameter spruce wood fan. Flexible couplings on the shaft allowed for the movement of the shell. The corner of the Exhauster Building was built around the motor after its installation. The General Electric induction motor could produce 10 to 410 revolutions per minute and create wind speeds up to 500 miles per hour, or Mach 0.63, at 30,000 feet. The AWT became operational in January 1944 and tested piston, turbojet and ramjet engines for nearly 20 years.
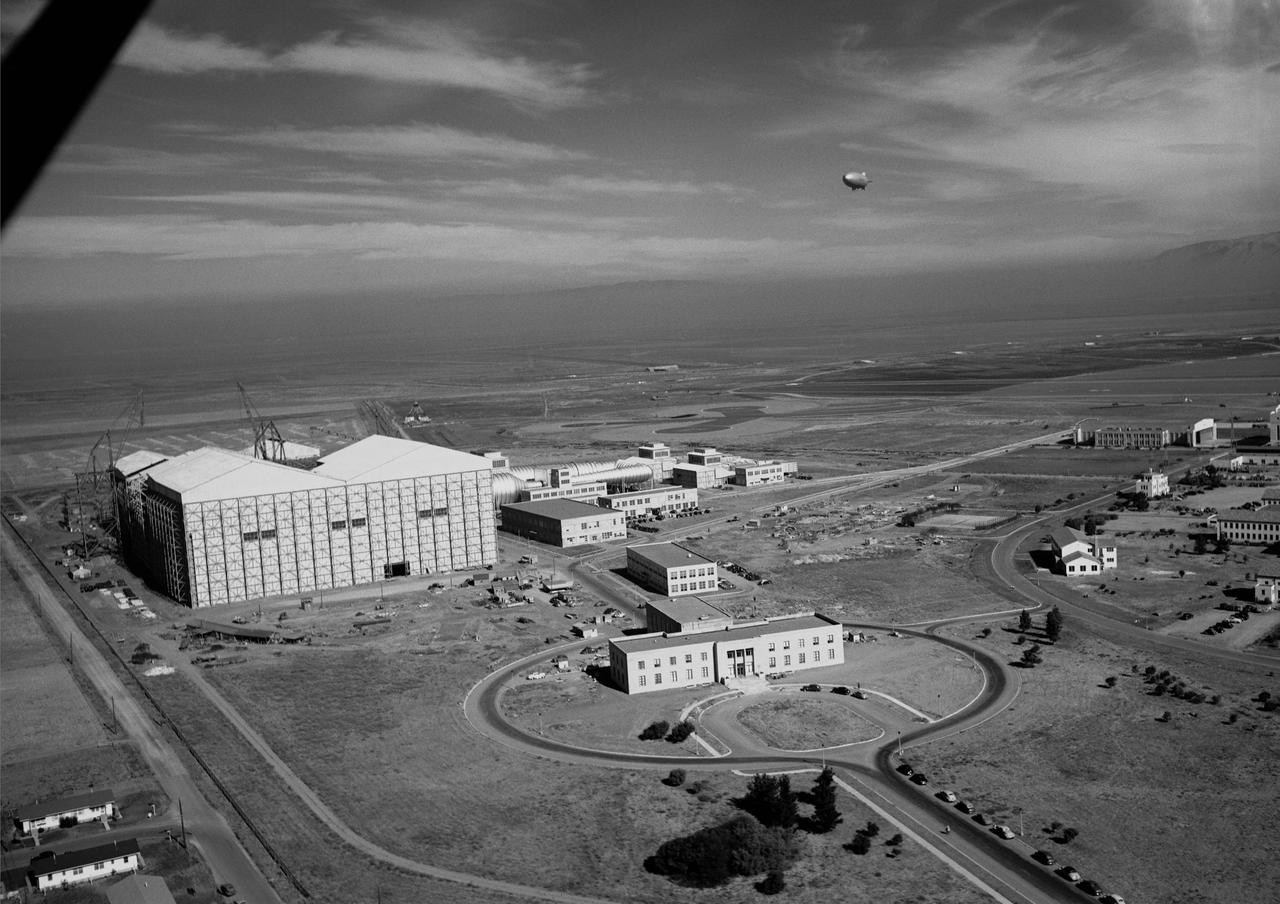

Ames aerial view of Ames Aeronautical Laboratory plot looking northeast with blimp in flight over Moffett Naval airstation.
![A researcher at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory studies the fuel ignition process. Improved fuels and lubrication was an area of particular emphasis at the laboratory during World War II. The military sought to use existing types of piston engines in order to get large numbers of aircraft into the air as quickly as possible. To accomplish its goals, however, the military needed to increase the performance of these engines without having to wait for new models or extensive redesigns. The Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory was called on to lead this effort. The use of superchargers successfully enhanced engine performance, but the resulting heat increased engine knock [fuel detonation] and structural wear. These effects could be offset with improved cooling, lubrication, and fuel mixtures. The NACA researchers in the Fuels and Lubrication Division concentrated on new synthetic fuels, higher octane fuels, and fuel-injection systems. The laboratory studied 16 different types of fuel blends during the war, including extensive investigations of triptane and xylidine.](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/GRC-1943-C-02124/GRC-1943-C-02124~medium.jpg)
A researcher at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory studies the fuel ignition process. Improved fuels and lubrication was an area of particular emphasis at the laboratory during World War II. The military sought to use existing types of piston engines in order to get large numbers of aircraft into the air as quickly as possible. To accomplish its goals, however, the military needed to increase the performance of these engines without having to wait for new models or extensive redesigns. The Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory was called on to lead this effort. The use of superchargers successfully enhanced engine performance, but the resulting heat increased engine knock [fuel detonation] and structural wear. These effects could be offset with improved cooling, lubrication, and fuel mixtures. The NACA researchers in the Fuels and Lubrication Division concentrated on new synthetic fuels, higher octane fuels, and fuel-injection systems. The laboratory studied 16 different types of fuel blends during the war, including extensive investigations of triptane and xylidine.
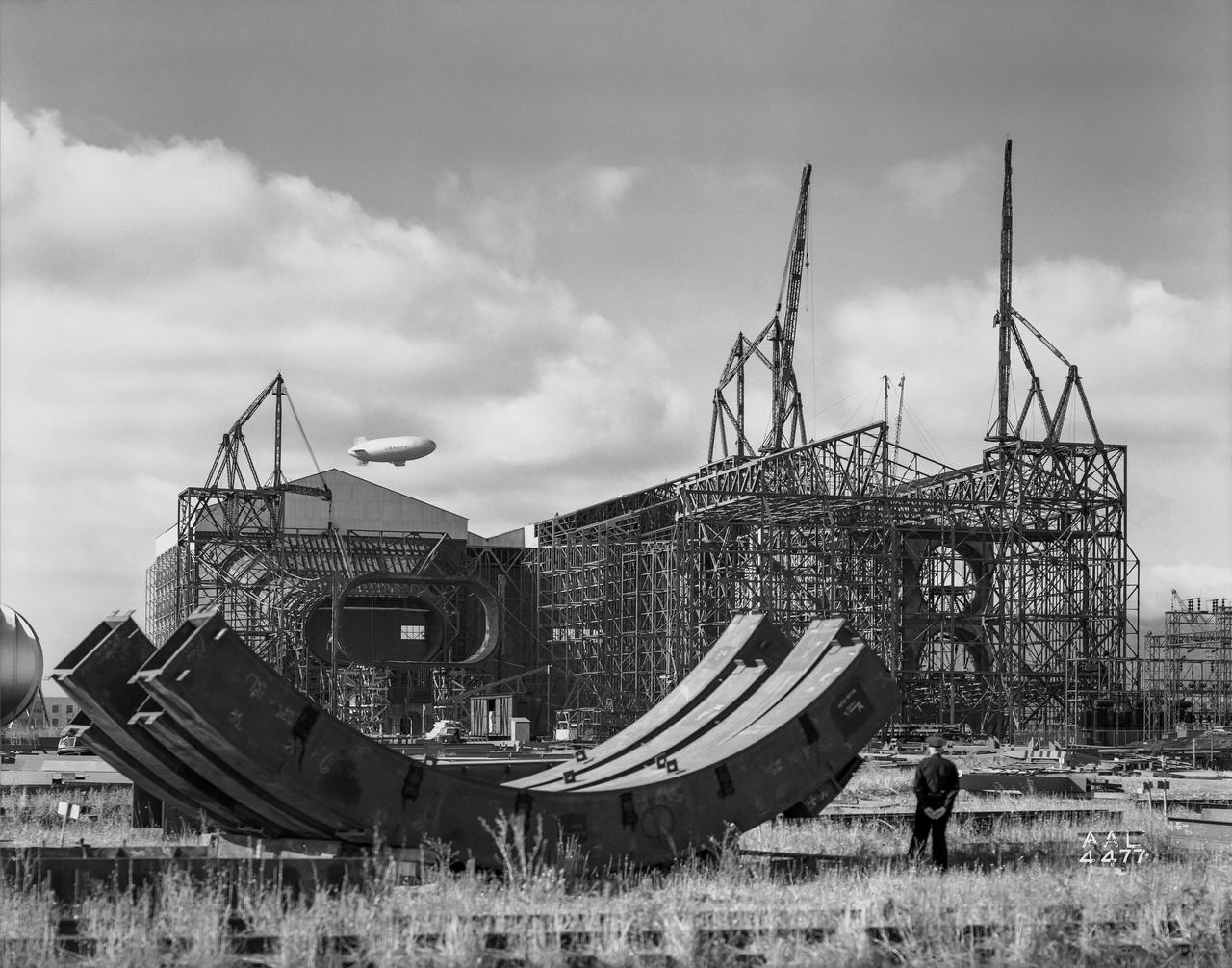

Looking south at the construction of the test section of the 40 x 80 foot wind tunnel. 4 parts of a test section bent seen in the foreground. Airship rising in the background.

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
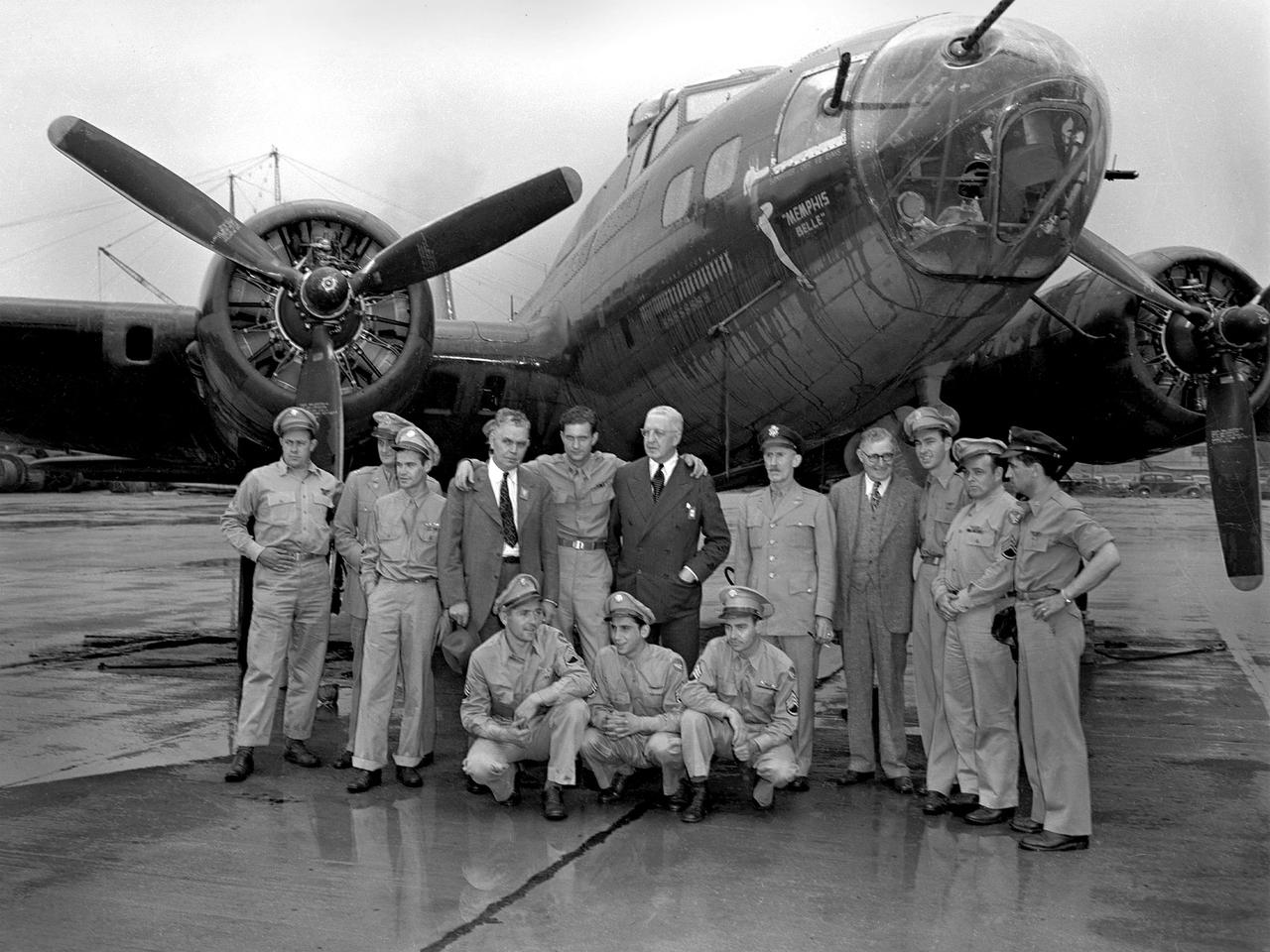

Captain Robert Morgan and the rest of the Memphis Belle crew arrive in Cleveland on a rainy July 7, 1943, for three-day publicity visit. This B–17 Flying Fortress had recently become the first U.S. bomber to complete 25 missions over Germany and France. The lack of long distance escort fighters made the feat even more remarkable. The Memphis Belle and its crew returned to the United States in June and were immediately thrown into a three-month-long war bond tour. While in Cleveland the crew toured the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory, the Cleveland Bomber Plant, and Thompson Products. In the evenings they were feted downtown by the Chamber of Commerce at the Hotel Cleveland. A local company brought Morgan’s family and his fiancé—the Memphis Belle’s inspiration—to Cleveland to participate in the activities. The bomber was on display to the public near the airport’s fenceline and stored in the NACA’s hangar overnight. Pictured in this photograph from left to right: Robert Hanson, Vincent Evans, Charles Leighton, NACA Manager Raymond Sharp, Robert Morgan, William Holliday of the Chamber of Commerce, Army Liaison Officer Colonel Edwin Page, Airport Commissioner Jack Berry, Cecil Scott, John Quinlan and James Verinis. Kneeling are Harold Loch, Casimer Nastal and Charles Wichell.
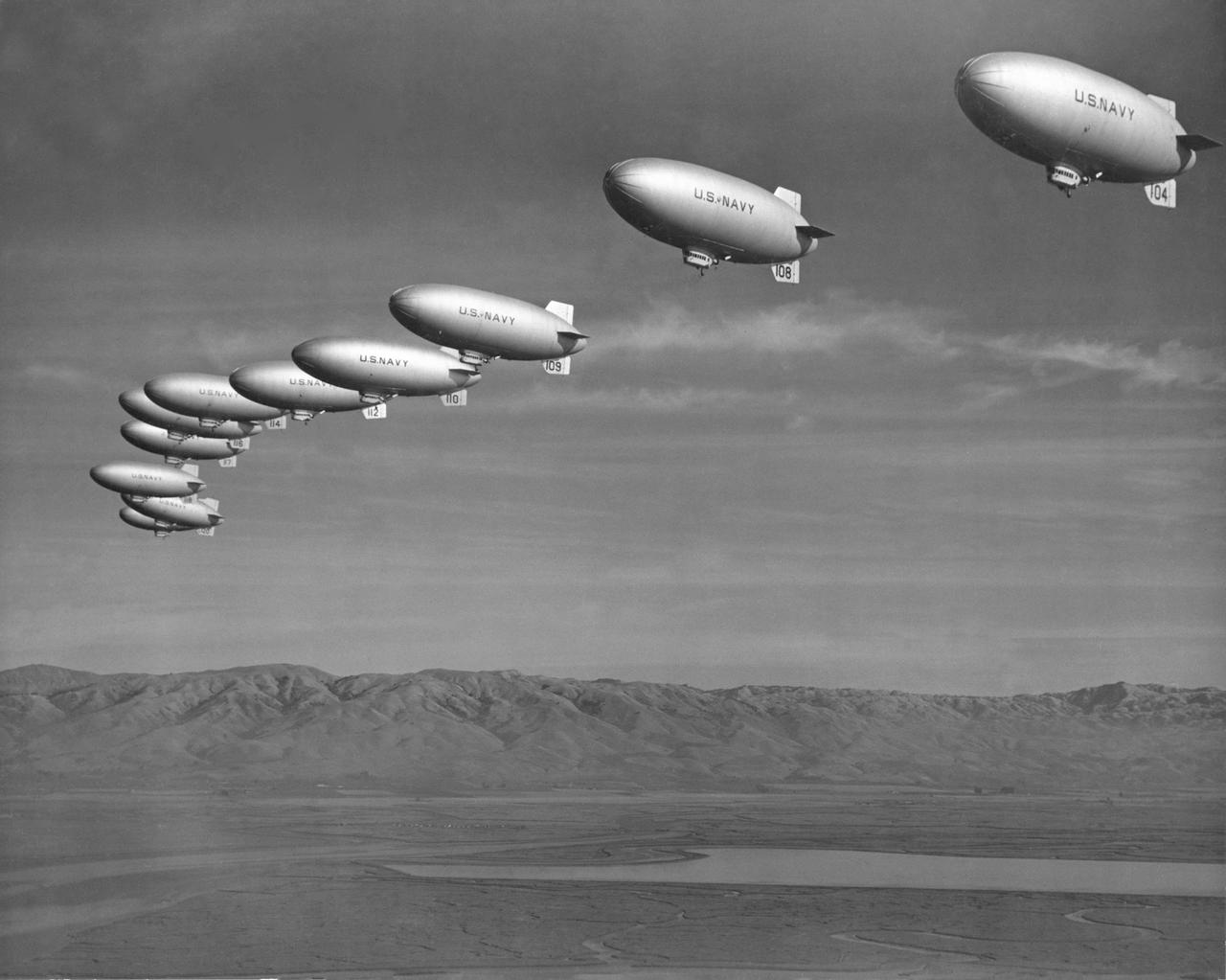

Navy L-Ships in formation (Alt. 600) heading south east lower San Francisco Bay

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.

Concrete frame enclosing the fan drive bents of the 40x80 foot wind tunnel at ames. Once installed, six 40-foot-diameter fans, each powered by a 6000-horsepower electric motor maintained airflow at 230 mph or less (these are still tornado velocities).
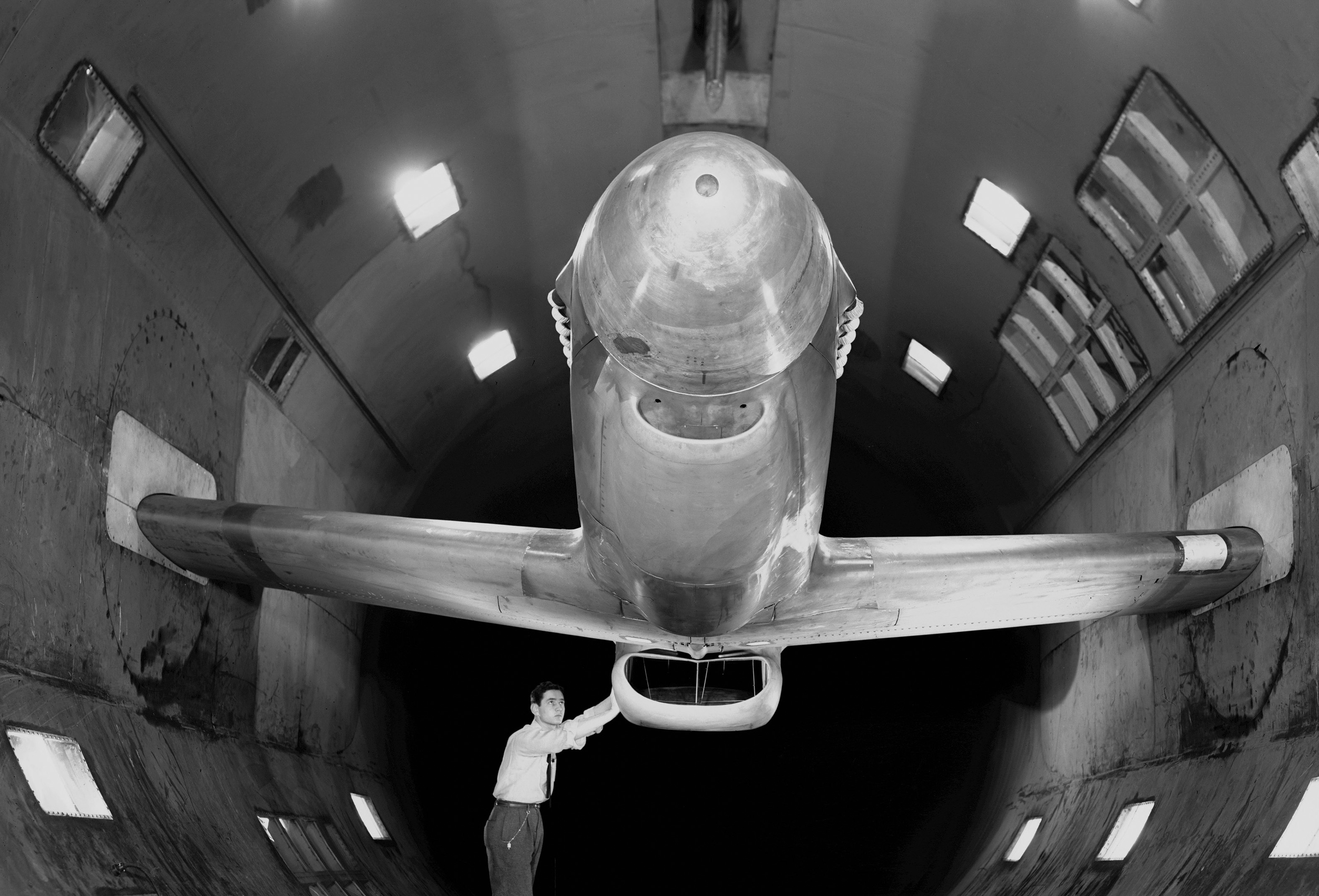

XP-51B airplane in 16ft wind tunnel with test engineer

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
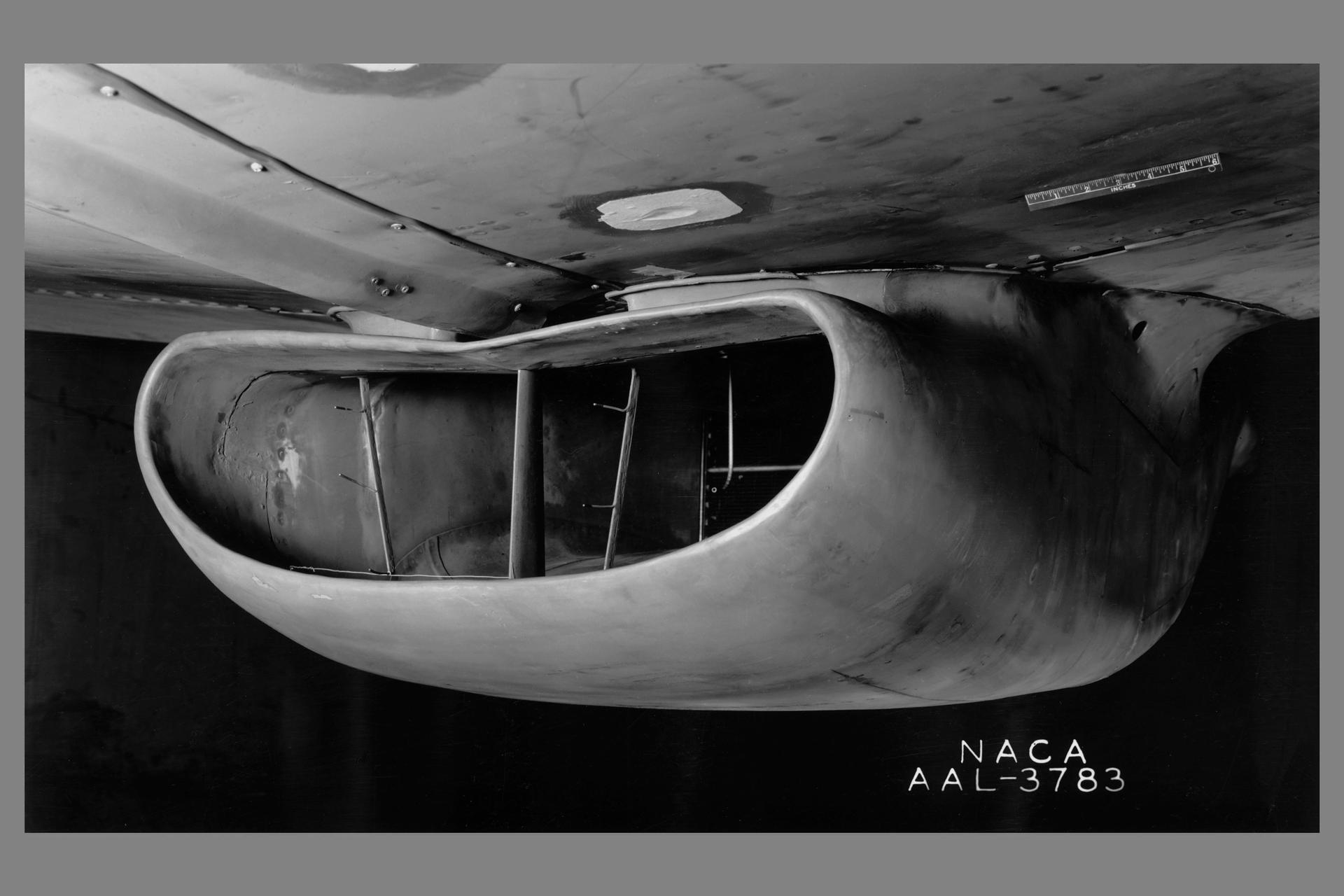

A portion of the North American P-51B airplane was tested in the 16-foot wind tunnel to devise a means of eliminating a rumble which occurred in the radiator duct system. The actual fuselage and center portion of the airplane was installed in the tunnel for this purpose as is shown. A change in the form of the duct was made and tested, which eliminated the rumble. The entrance to the original radiator duct is indicated in this photograph, and the revised form of the duct entrance in photographer AAL-3926.
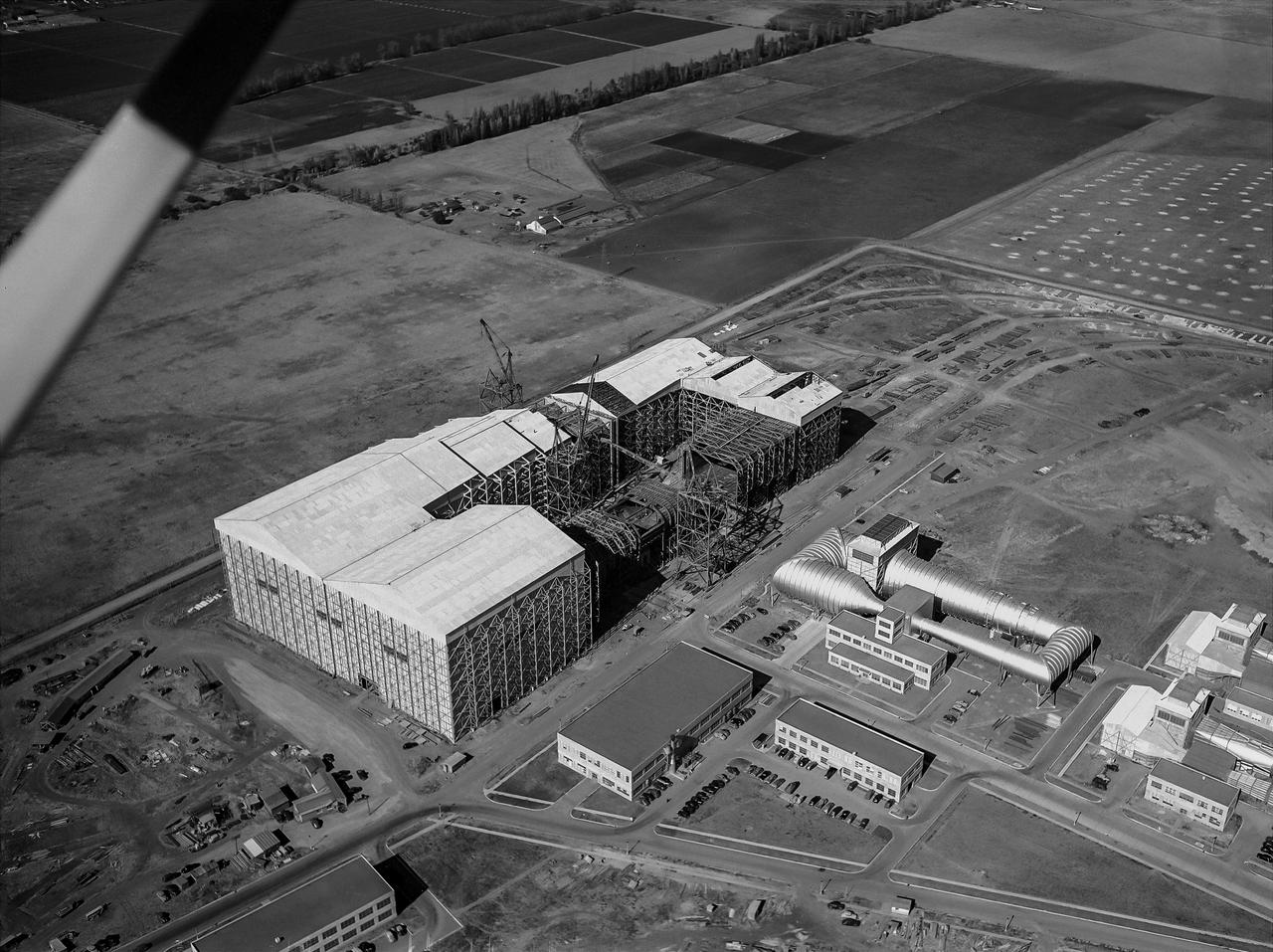

Aerial view looking North West of the nearly completed 40 x 80 foot wind tunnel. Drive and test section exposed. The facility covered 8 acres, and the air circuit was just over 1/2 mile long (2700 feet).

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
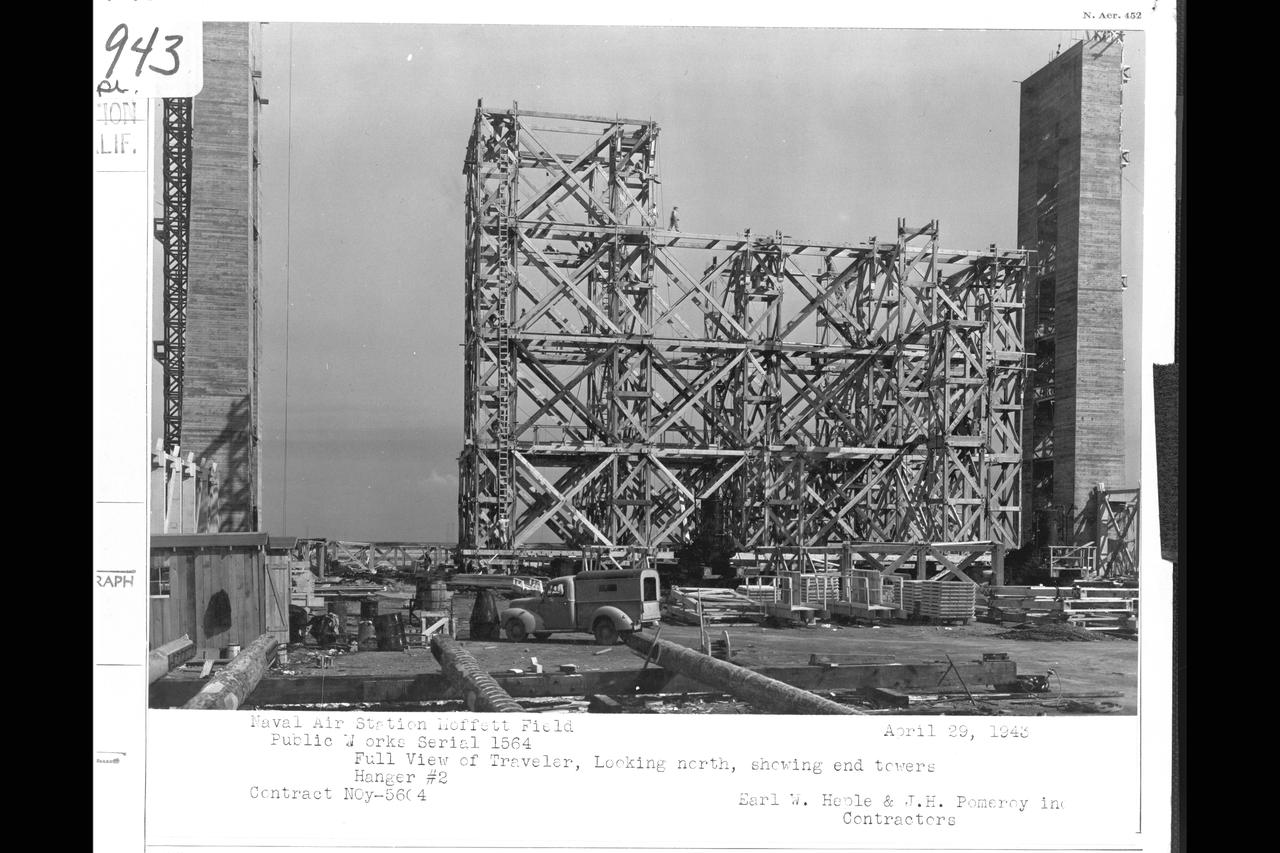

Navy Naval Air Station Moffett Field Public works Serial 1514 - Contract NOy-5604, Earl W. Heple & J.H. Pomeroy contractors NAS Moffett Field: full view of Traveler, looking north, showing end towers Hangar 2

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
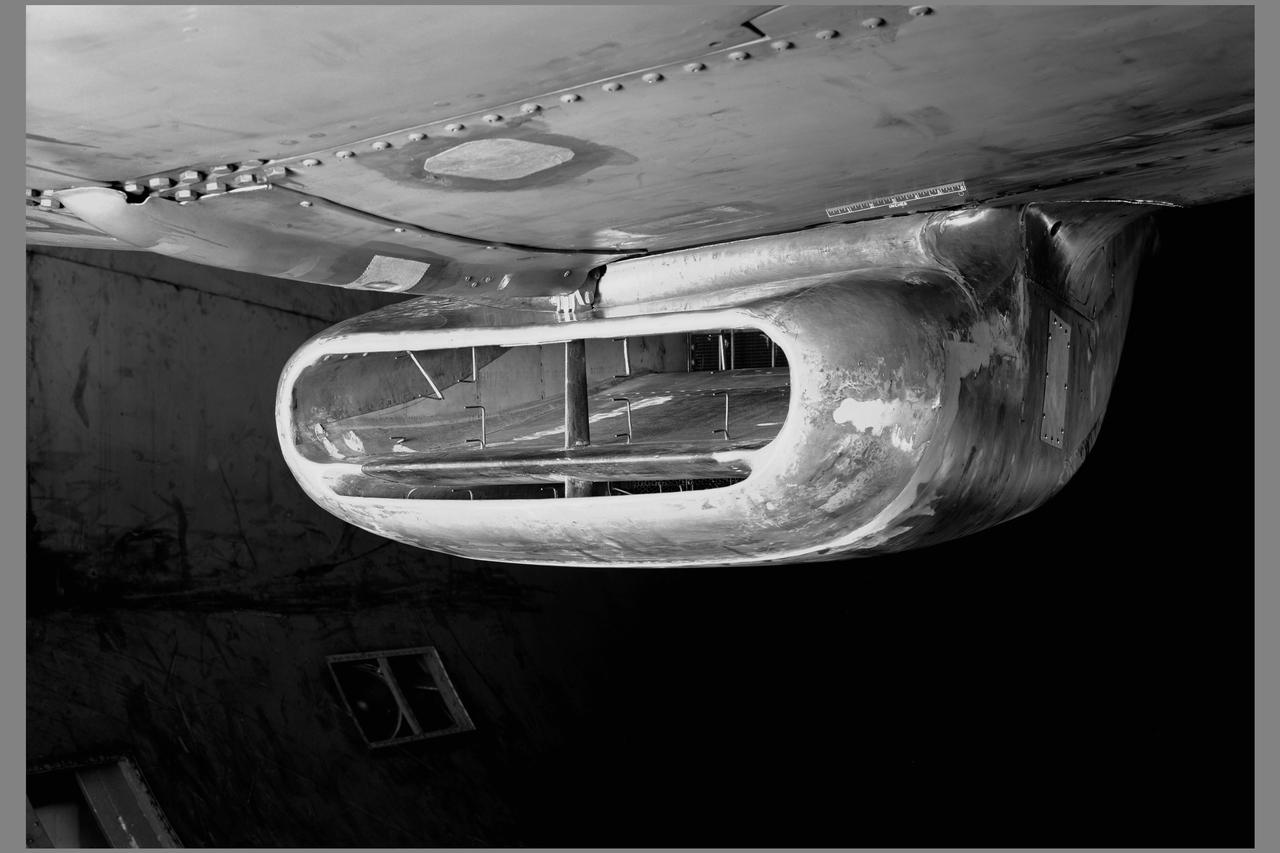

3/4 front view of modified production scoop on XP-51B airplane mounted in the 16ft w.t. (Ames contribution to the solution of the duct-rumble problem)
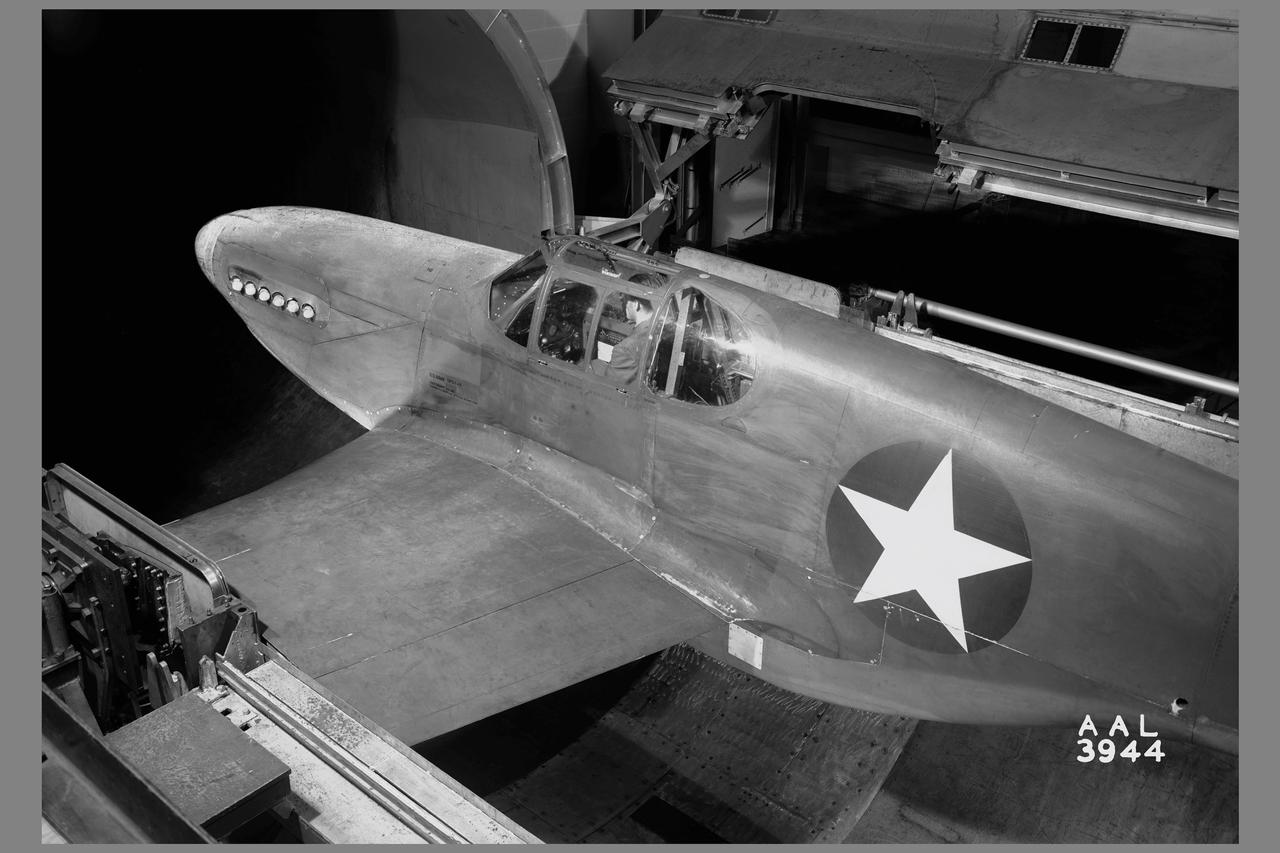

3/4 rear view of a XP-51B airplane mounted in the 16ft w.t. (Ames contribution to the solution of the duct-rumble problem)
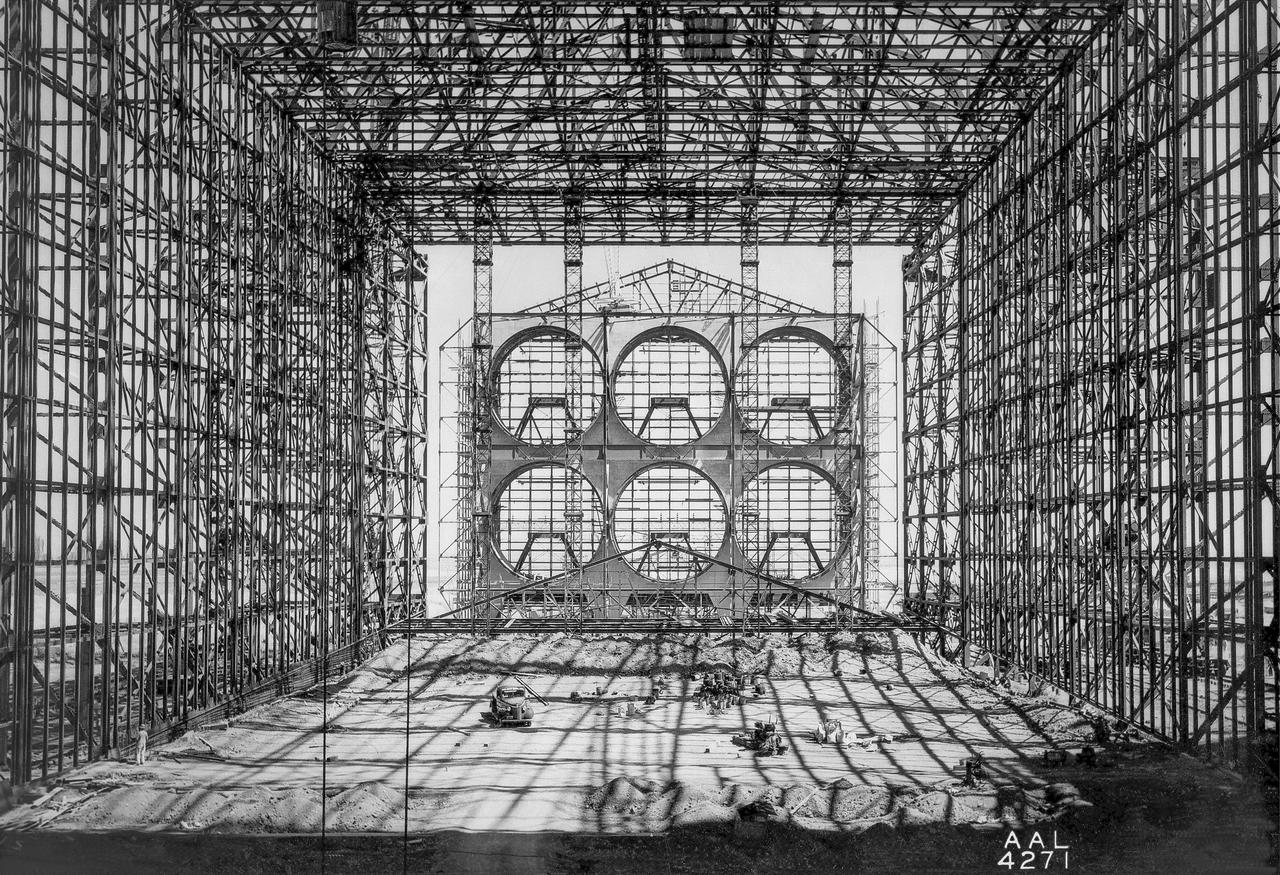
Looking South from inside the diffuser of the 40x80 foot wind tunnel at NACA's Ames Research Center. Construction began in late 1941, the mammoth construction task sorely taxing the resources of the new center. Two and a half years later, in dune 1944, the 40 x 80-foot full-scale tunnel went into operation.
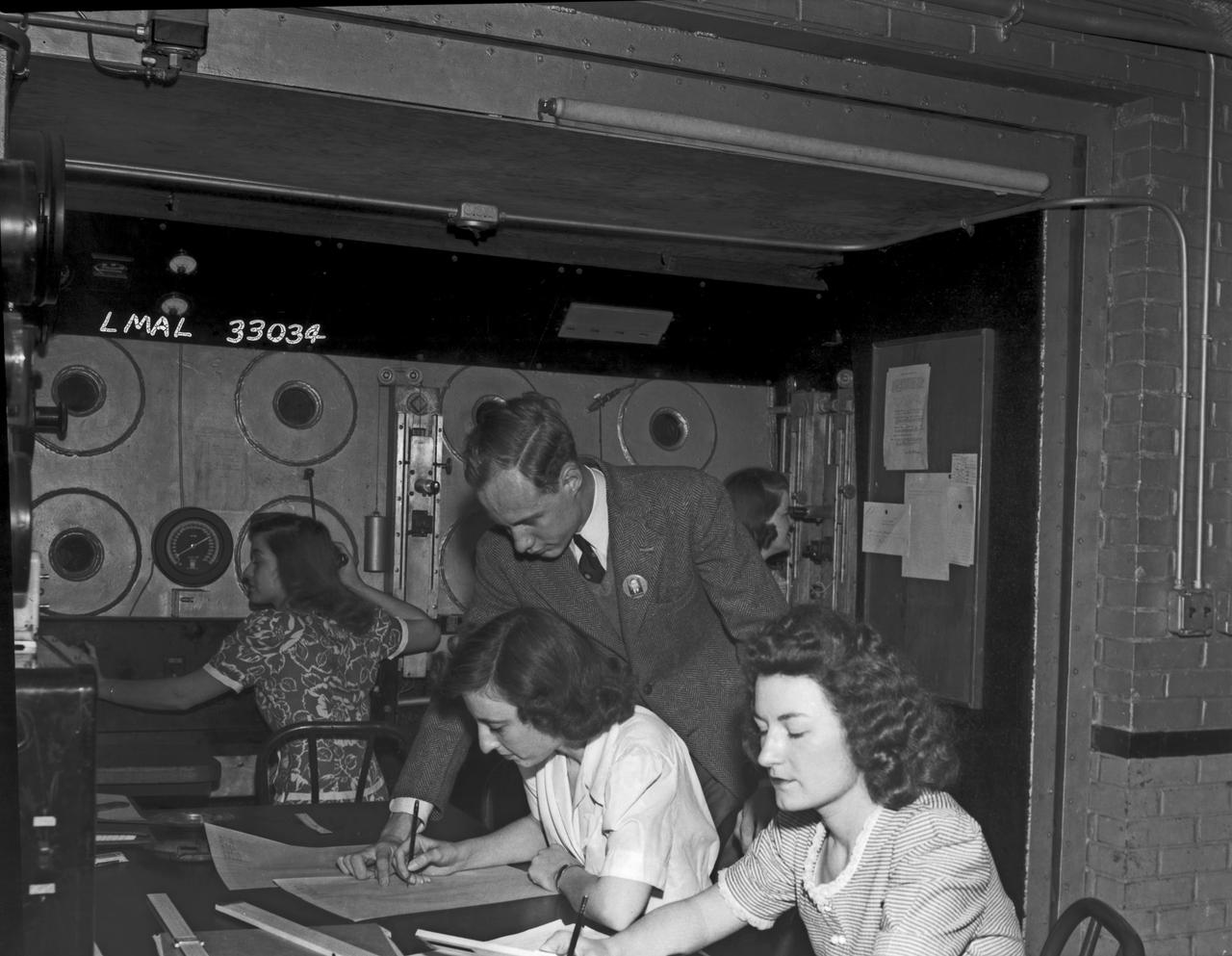

Women Adequately Filling Posts In NACA Laboratory: In the picture are F.F. Fullmer, aeronautical engineer, supervise a group of women who are helping operate the research equipment in the two-dimensional wind tunnel. Miss Elizabeth Patterson, left foreground, and Miss Katherine Thomason, right foreground obtains aerodynamic data, while Miss Lenore Woodland left background and Mrs. Blanche White help operate the tunnel. By Lee Dickinson 1943

Ames Aeronautical Laboratory skyline from Akron Road
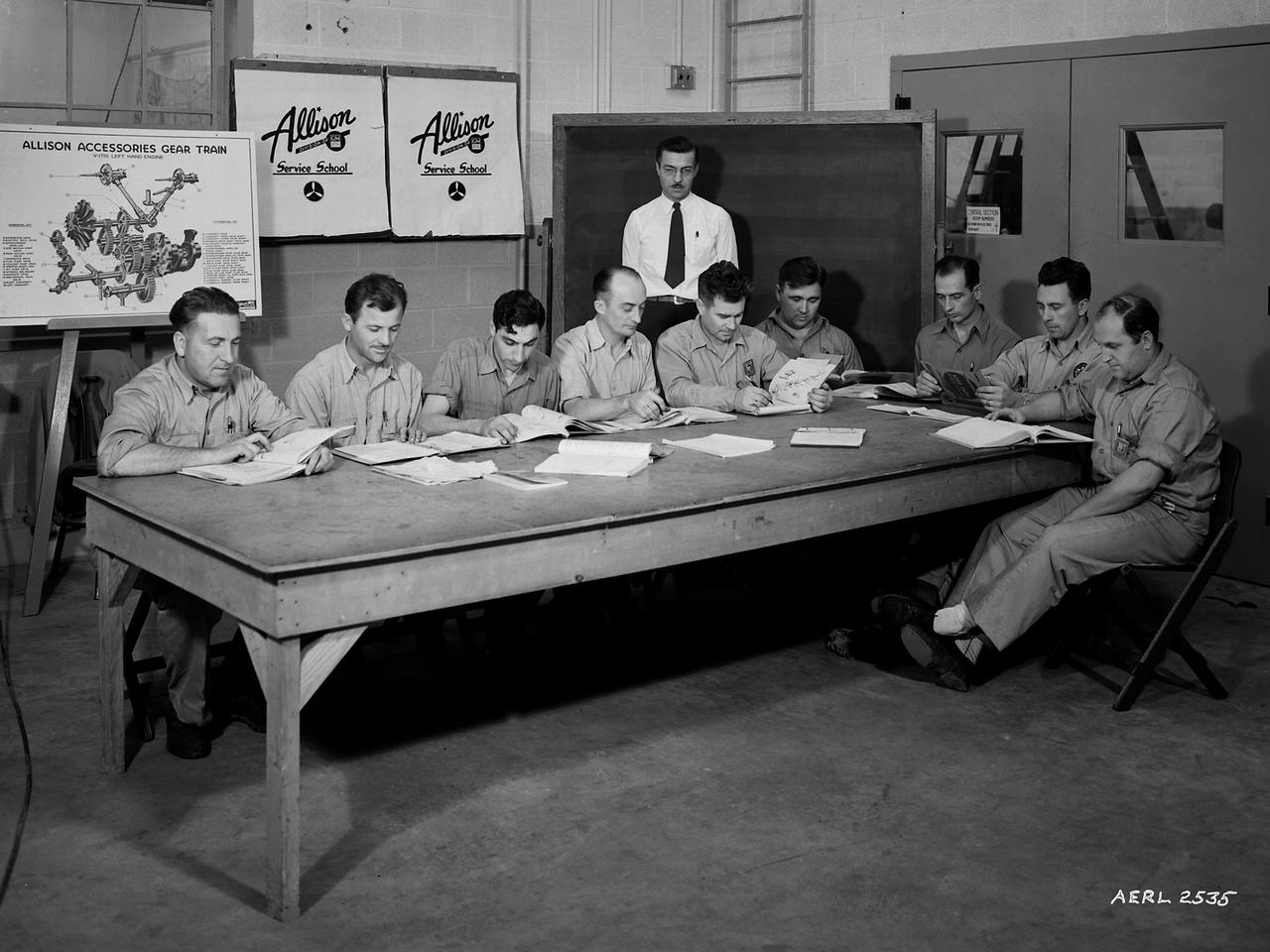

The Allison Engine Company's A.G. Covell instructs mechanics from various divisions at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory on the operation of the Allison Basic Engine. The military had asked that the laboratory undertake an extensive program to improve the performance of the Allison V–1710 engine. The V–1710 was the only liquid-cooled engine used during World War II, and the military counted on it to power several types of fighter aircraft. The NACA instituted an Apprentice Program during the war to educate future mechanics, technicians, and electricians. The program was suspended for a number of years due to the increasing rates of military service by its participants. The laboratory continued its in-house education during the war, however, by offering a number of classes to its employees and lectures for the research staff. The classes and lectures were usually taught by fellow members of the staff, but occasionally external experts were brought in. The students in the Allison class in the Engine Research Building were taught how to completely disassemble and reassemble the engine components and systems. From left to right are Don Vining, Ed Cudlin, Gus DiNovo, George Larsen, Charles Diggs, Martin Lipes, Harley Roberts, Martin Berwaldt and John Dempsey. A.G. Covell is standing.

Minneapolis Ice research project: Ice formation on left wing of the Lockheed 12-A during flight after shutting off heat. The wind was completely cleared within 2 minutes after the application of heat.
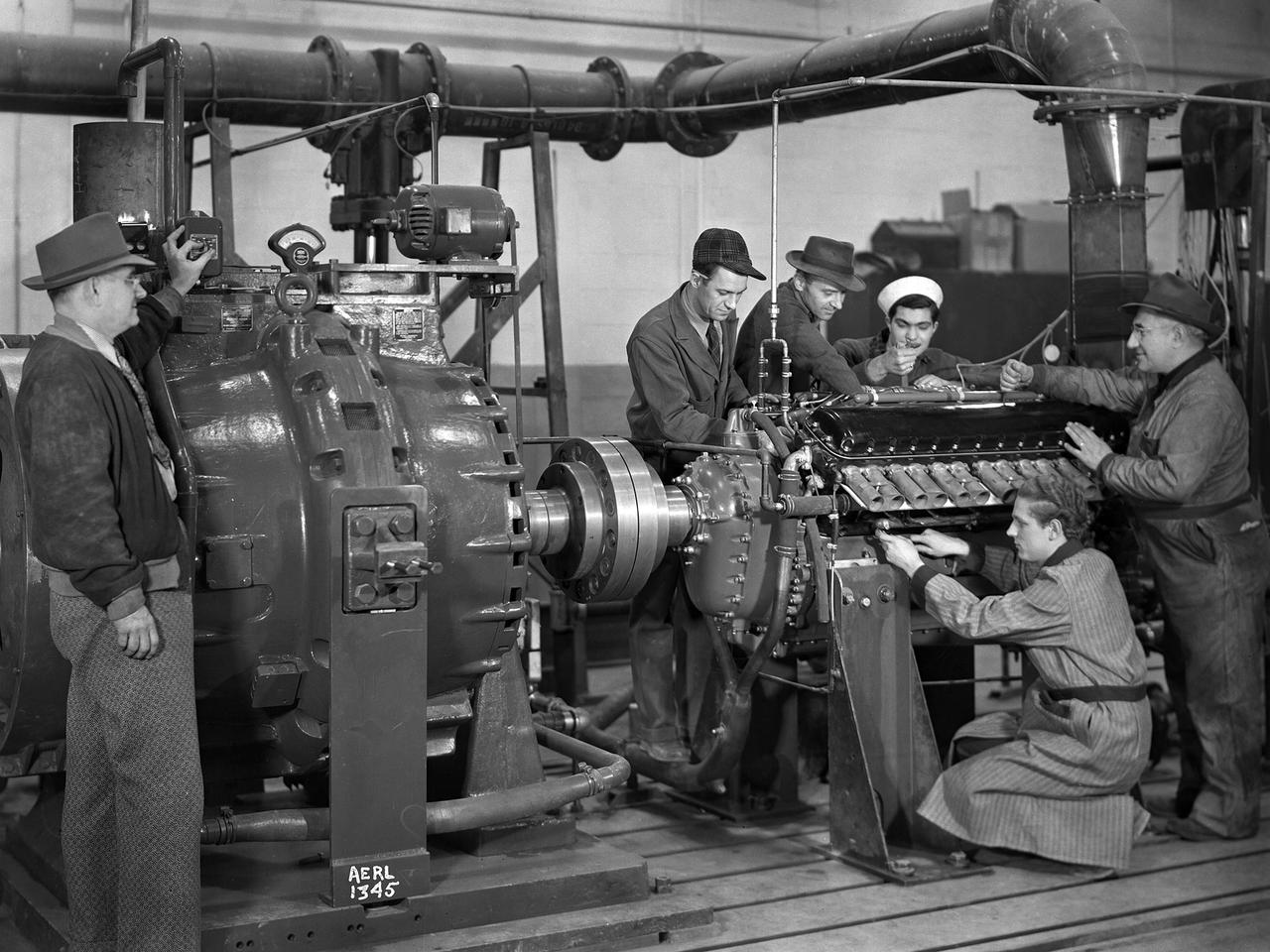
The first research assignment specifically created for the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics’ (NACA) new Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory was the integration of a supercharger into the Allison V–1710 engine. The military was relying on the liquid-cooled V–1710 to power several types of World War II fighter aircraft and wanted to improve the engine's speed and altitude performance. Superchargers forced additional airflow into the combustion chamber, which increased the engine’s performance resulting in greater altitudes and speeds. They also generated excess heat that affected the engine cylinders, oil, and fuel. In 1943 the military tasked the new Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory to integrate the supercharger, improve the cooling system, and remedy associated engine knock. Three Allison engines were provided to the laboratory’s research divisions. One group was tasked with improving the supercharger performance, another analyzed the effect of the increased heat on knock in the fuel, one was responsible for improving the cooling system, and another would install the new components on the engine with minimal drag penalties. The modified engines were installed on this 2000-horsepower dynamotor stand in a test cell within the Engine Research Building. The researchers could run the engine at different temperatures, fuel-air ratios, and speeds. When the modifications were complete, the improved V–1710 was flight tested on a P–63A Kingcobra loaned to the NACA for this project.