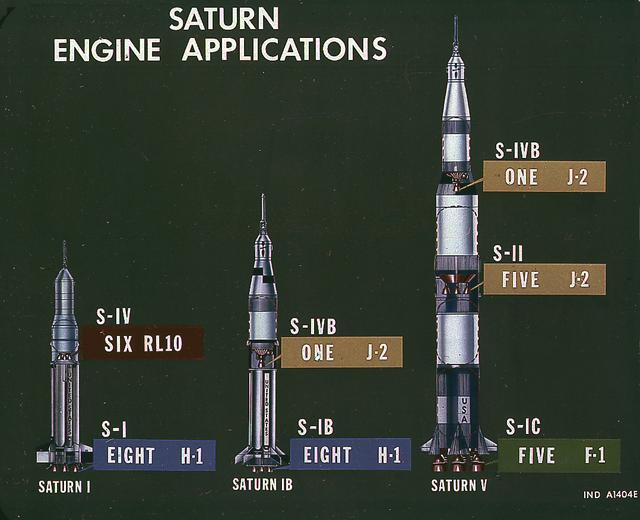
This image illustrates the basic differences between the three Saturn launch vehicles developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The Saturn I, consisted of two stages, the S-I (eight H-1 engines) and the S-IV (six RL-10 engines). The Saturn IB (center) also consisted of two stages, the S-IB (eight H-1 engines) and the S-IVB (one J-2 engine). The Saturn V consisted of three stages, the S-IC (five F-1 engines), the S-II (five J-2 engines), and the S-IVB (one J-2 engine).

ARCAS Rocket #E1-235 Image taken at Wallops Island

Tilt wing propeller model. 3/4 front view. 4 prop tilt wing nose down variable struts on ground board. Leo Holl, NASA Ames Engineer.

The Saturn I liquid-oxygen (LOX) tank for the Saturn I S-I stage being aligned with the end spider beam in the fabrication and engineering laboratory, building 4705, at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).

Collins Aerodyne vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft investigations. Ground plane support system. 3/4 front view. Dave Koening (from Collins Aerodyne) in photo. Mounted on variable height struts, ground board system, zero degree angle of attack. 01/11/1960
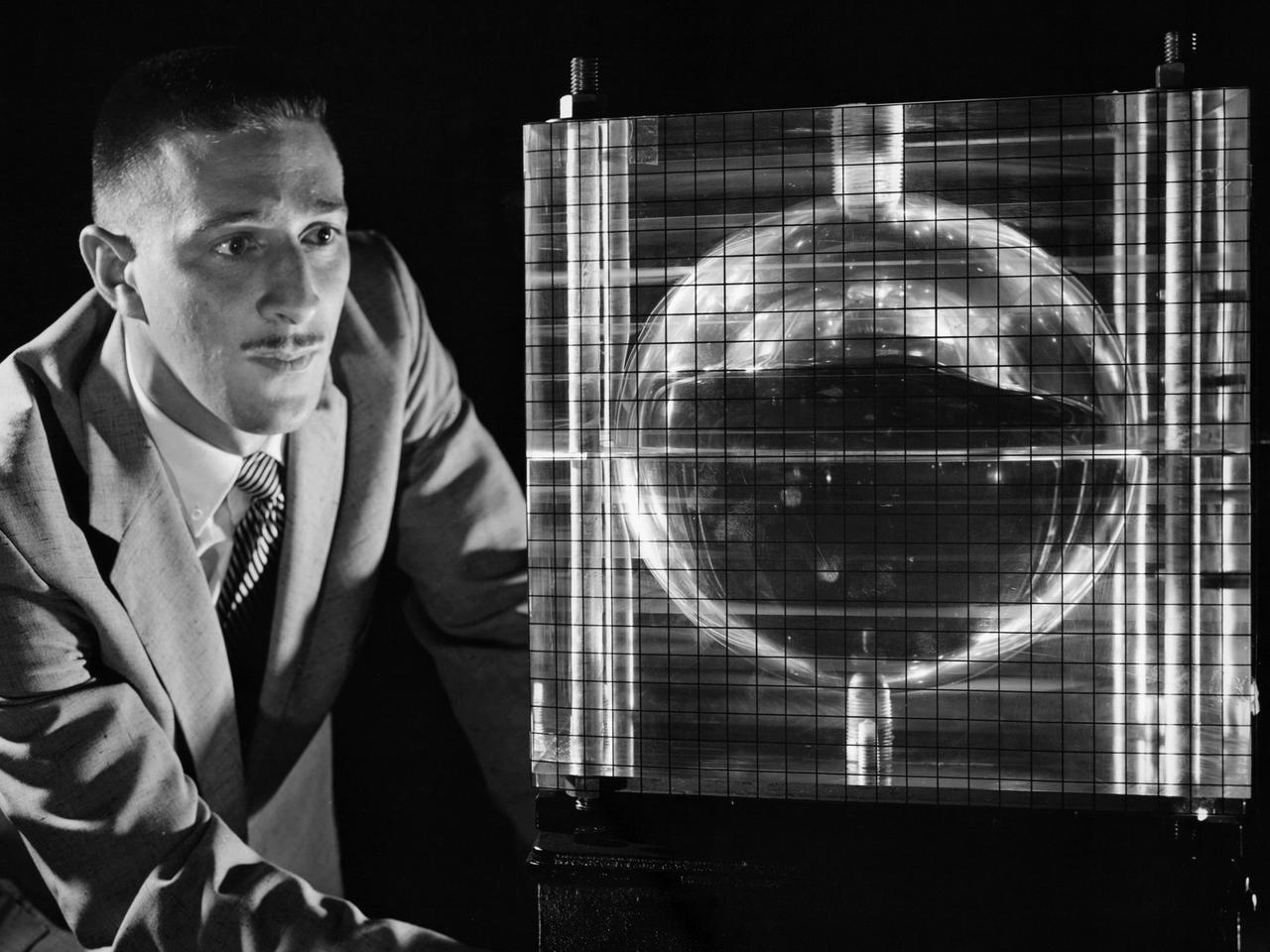

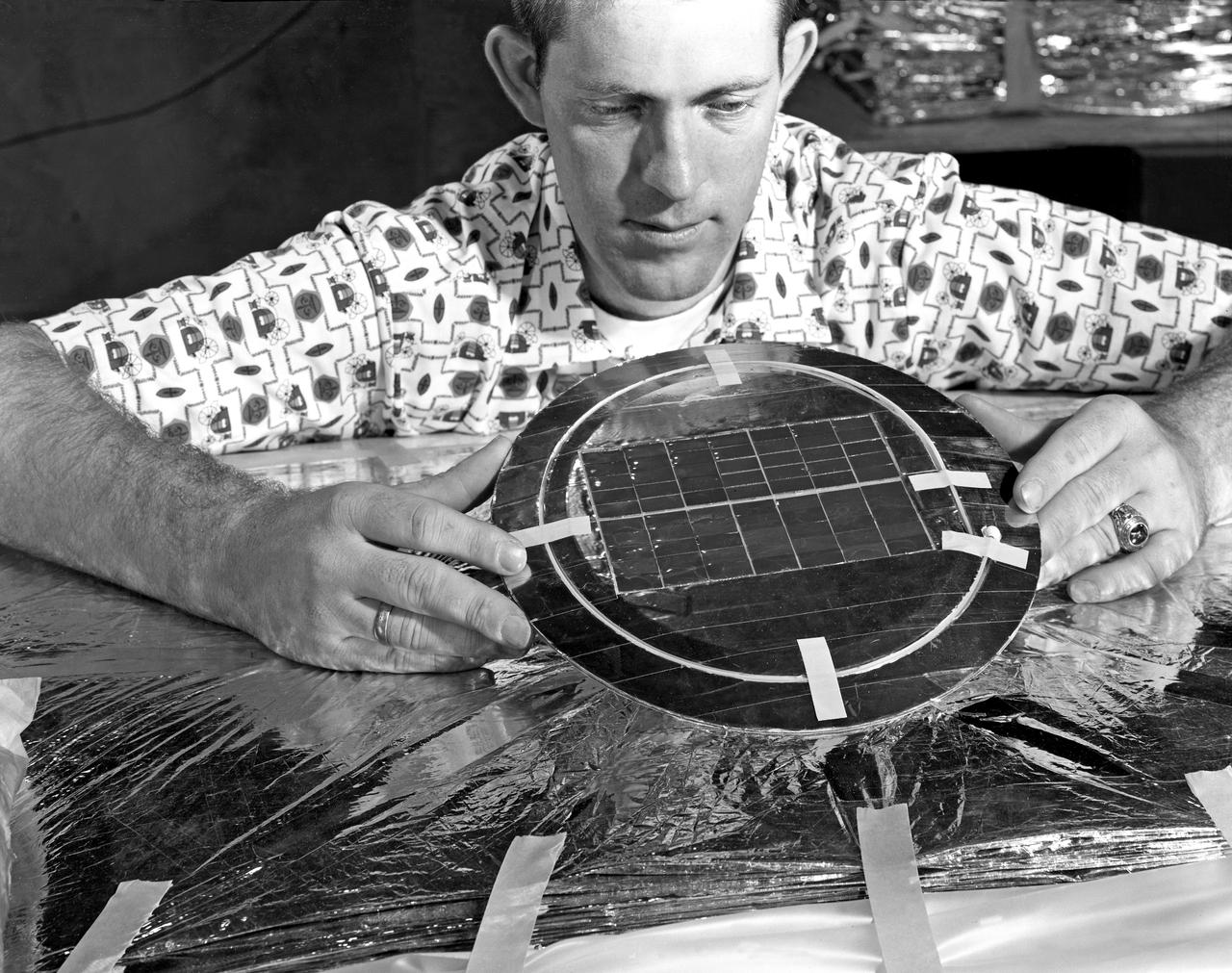
Andy Stofan views a small-scale tank built to study the sloshing characteristics of liquid hydrogen at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Stofan was tasked with the study of propellant motion, or sloshing, in space vehicle propellant tanks. At the time, there was little knowledge of the behavior of fluids in microgravity or the effects of the launch on the propellant’s motion. Sloshing in the tank could alter a spacecraft’s trajectory or move the propellant away from the turbopump. Stofan became an expert and authored numerous technical reports on the subject. Stofan was assigned to the original Centaur Project Office in 1962 as a member of the Propellant Systems Section. Stofan was instrumental in solving a dynamic instability problem on the Centaur vehicle and served as the systems engineer for the development of the Centaur propellant utilization system. The solution was also applied to the upper-stages of Saturn. In 1966, Stofan was named Head of the Propellant Systems Section. Stofan continued rising through the managerial ranks at Lewis. In 1967 he became Project Manager of a test program that successfully demonstrated the use of a pressurization system for the Centaur vehicle; in 1969 the Assistant Project Manager on the Improved Centaur project; in 1970 Manager of the Titan/Centaur Project Office; in 1974 Director of the Launch Vehicles Division. In 1978, Stofan was appointed Deputy Associate Administrator for the Headquarters Office of Space Science. In 1982, he was named Director of Lewis Research Center.

100' Satellite Packaging of Echo
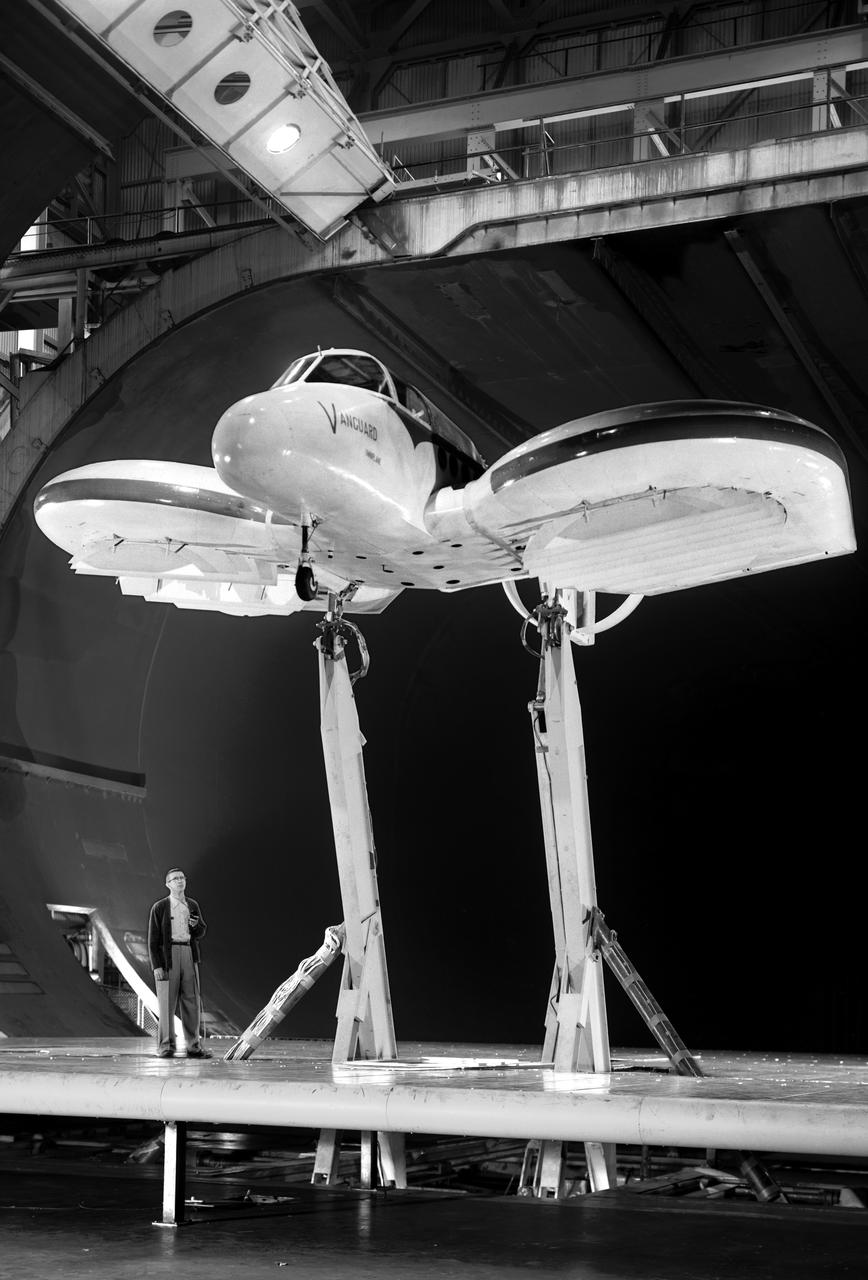

Vanguard 2C vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) airplane, wind tunnel test. Front view from below, model 14 1/2 feet high disk off. Nasa Ames engineer Ralph Maki in photo. Variable height struts and ground plane, low pressure ratio, fan in wing. 02/01/1960.

This photograph shows the Saturn V assembled LOX (Liquid Oxygen) and fuel tanks ready for transport from the Manufacturing Engineering Laboratory at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The tanks were then shipped to the launch site at Kennedy Space Center for a flight. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.

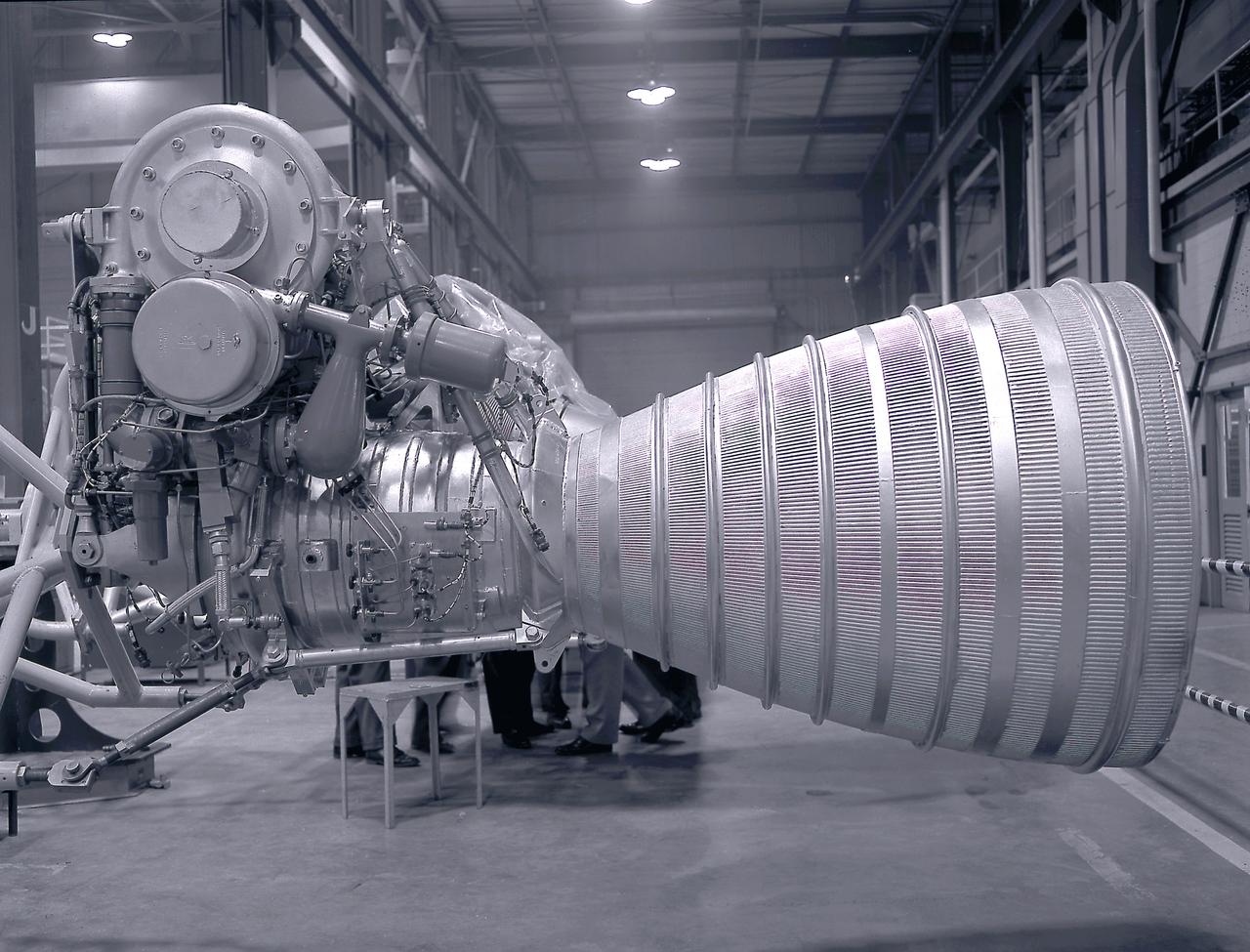
RL-10 engine characteristics. The RL-10 engine was developed under the management of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) to power the Saturn I upper stage (S-IV stage). The six RL-10 engines, which used liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen as propellants, were arranged in a circle on the aft end of the S-IV stage.

This photograph shows a test firing of a Saturn V second stage (S-II) on the S-IC test stand at the Propulsion Test Facility near New Orleans, Louisiana. This second stage component was used in the unmarned test flight of Apollo 4.
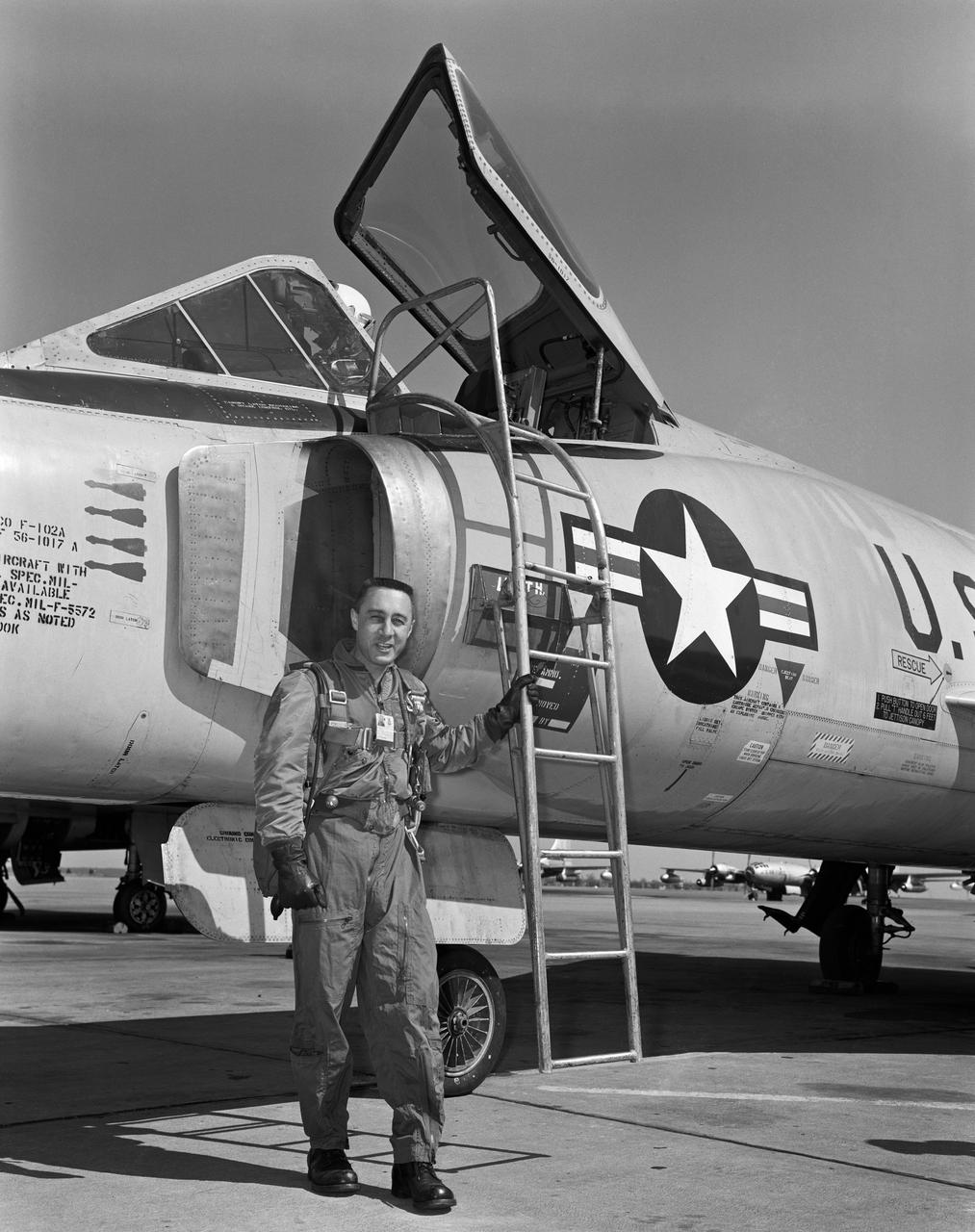

B60-00708 (1960) --- Astronaut Virgil I (Gus) Grissom pictured standing beside a F-102 on the flight line. Photo credit: NASA

3/4 Low front view of fuselage and fan. Showing jet engine hanging below. Lift fan powered by jet exhaust. General Aerodynamic Characteristics of a Research Model with High Disk Loading Direct Lifting Fan Mounted in Fuselage

100' Satellite Packaging of Echo

Doak VTOL Aircraft

Test Setup For Model Landing Investigation of a Winged Space Vehicle Image used in NASA Document TN-D-1496 1960-L-04633.01 is Figure 9a for NASA Document L-2064 Photograph of model on launcher and landing on runway.
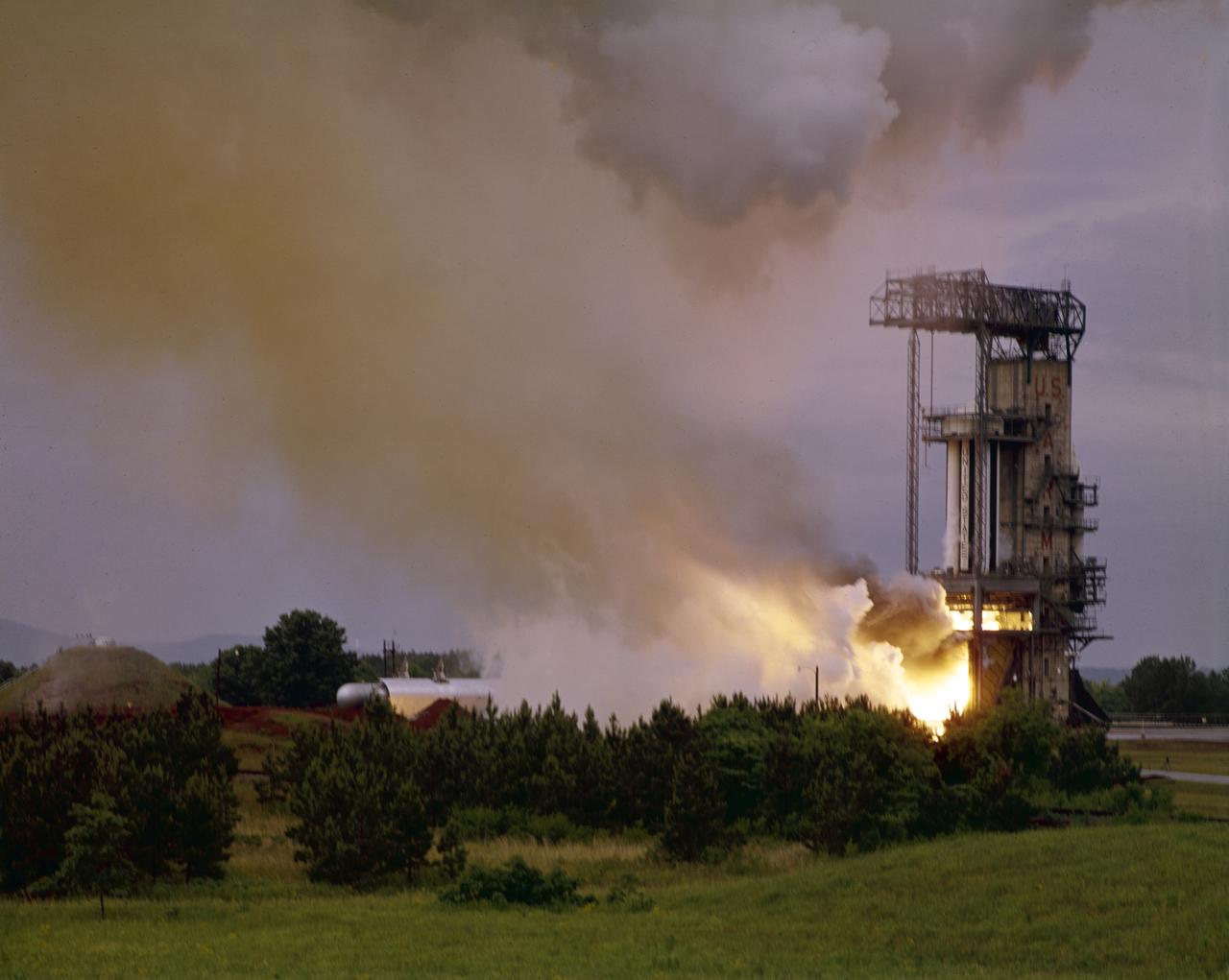

Pictured is one of the earliest testing of the Saturn I S-I (first) stage, with a cluster of eight H-1 engines, at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). It was a part of the test program to prove out the clustered-booster concept. MSFC was responsible for designing and development the Saturn launch vehicles.
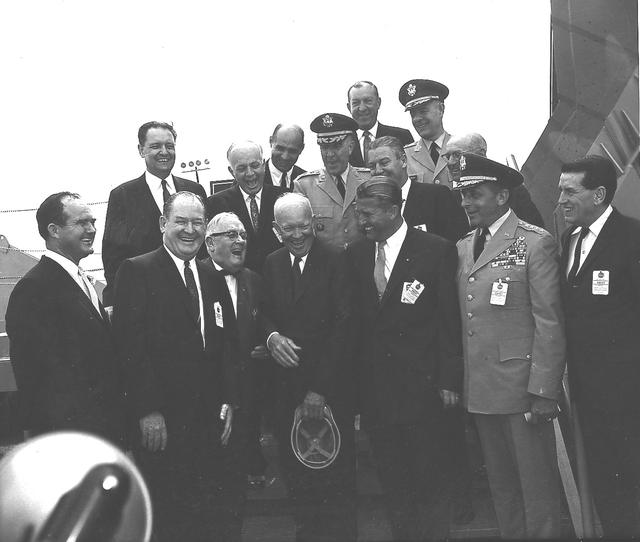

President Dwight D. Eisenhower and MSFC Director Dr. Wernher von Braun share a joke as other dignitaries look on. Eisenhower was visiting Marshall to participate in the September 8, 1960 dedication ceremony.

L1-422 Nike Smoke Rocket and Launcher in Firing Position. Image taken at Wallops Island.
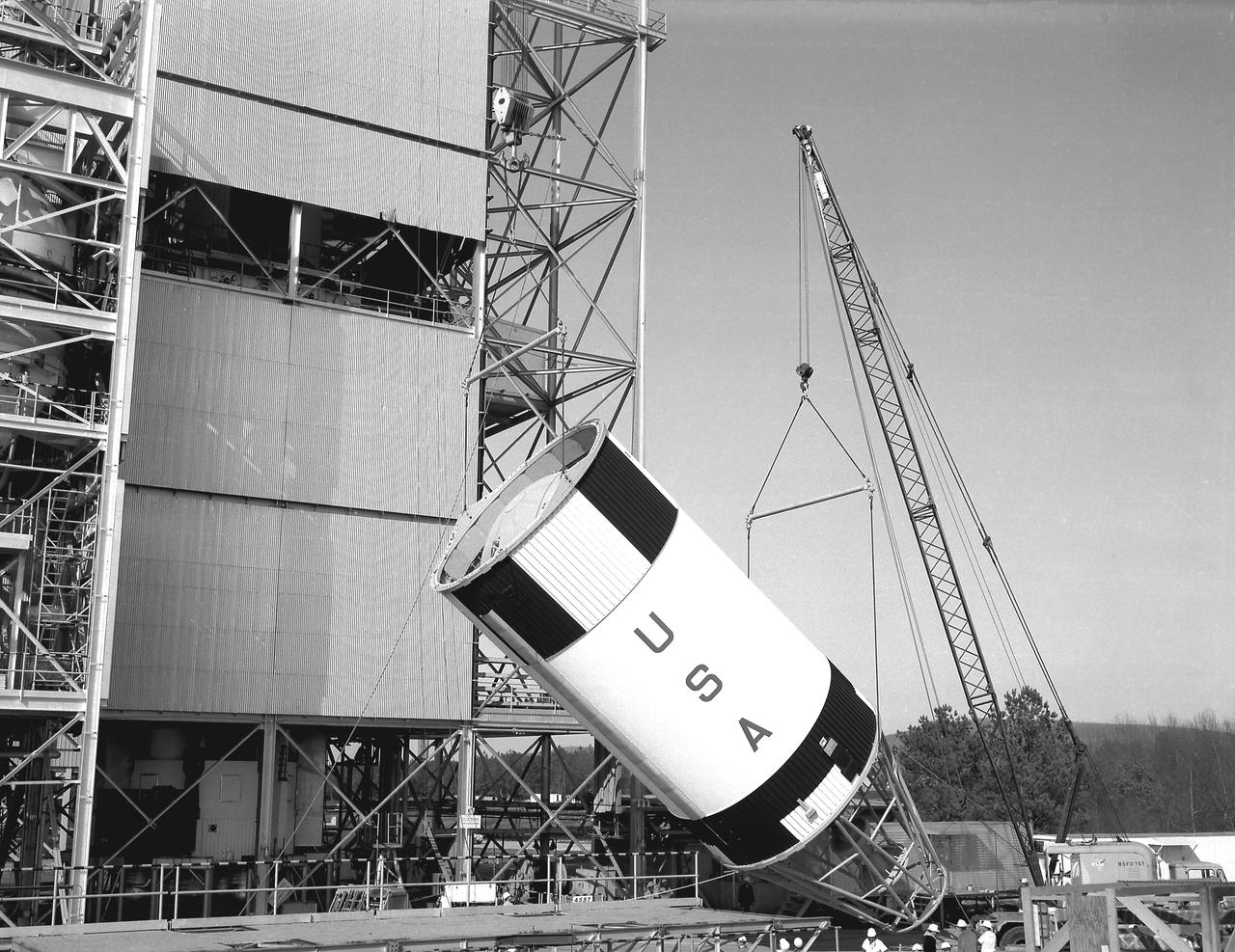

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) workers hoist a dynamic test version of the S-IVB stage, the Saturn IB launch vehicle's second stage, into the Center's Dynamic Test Stand on January 18, 1965. MSFC Test Laboratory persornel assembled a complete Saturn IB to test the launch vehicle's structural soundness. Developed by the MSFC as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine the larger boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.
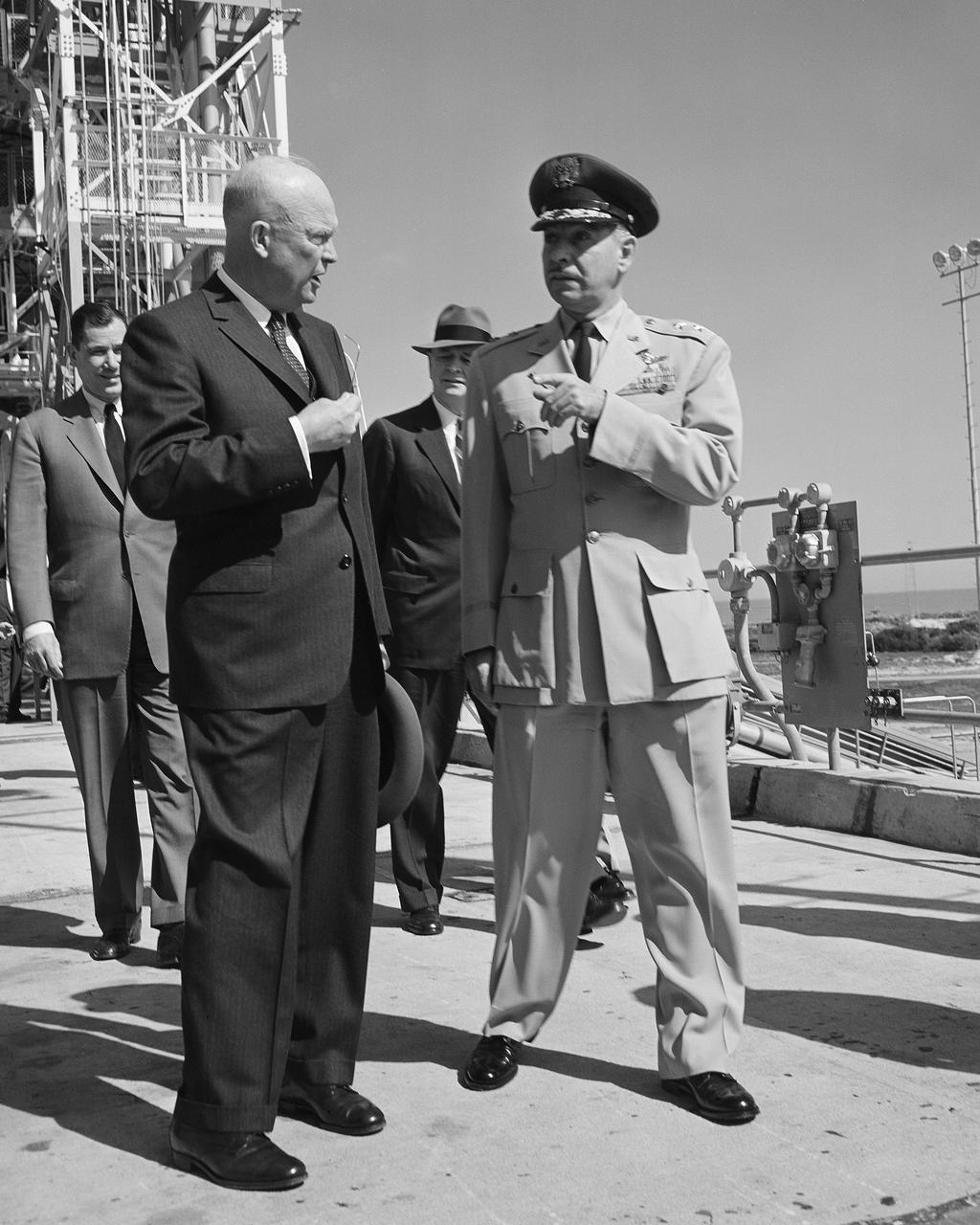

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- President Dwight D Eisenhower is briefed on operations at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: NASA
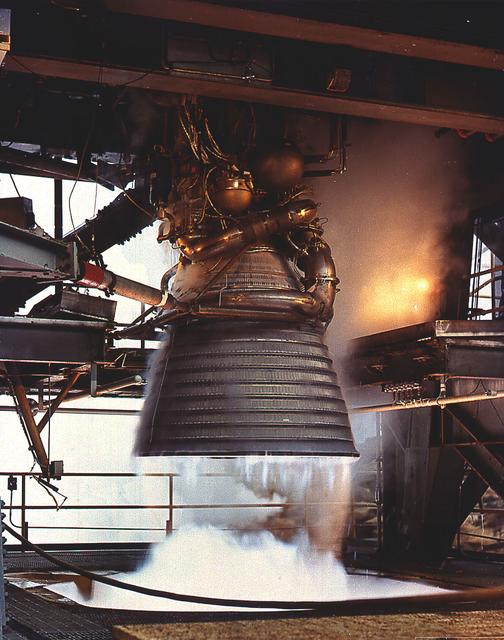
A J-2 engine undergoes static firing. The J-2, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, was propelled by liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. A single J-2 was utilized in the S-IVB stage (the second stage for the Saturn IB and third stage for the Saturn V) and in a cluster of five for the second stage (S-II) of the Saturn V. Initially rated at 200,000 pounds of thrust, the engine was later uprated in the Saturn V program to 230,000 pounds.

A Mercury capsule is mounted inside the Altitude Wind Tunnel for a test of its escape tower rockets at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. In October 1959 NASA’s Space Task Group allocated several Project Mercury assignments to Lewis. The Altitude Wind Tunnel was quickly modified so that its 51-foot diameter western leg could be used as a test chamber. The final round of tests in the Altitude Wind Tunnel sought to determine if the smoke plume from the capsule’s escape tower rockets would shroud or compromise the spacecraft. The escape tower, a 10-foot steel rig with three small rockets, was attached to the nose of the Mercury capsule. It could be used to jettison the astronaut and capsule to safety in the event of a launch vehicle malfunction on the pad or at any point prior to separation from the booster. Once actuated, the escape rockets would fire, and the capsule would be ejected away from the booster. After the capsule reached its apex of about 2,500 feet, the tower, heatshield, retropackage, and antenna would be ejected and a drogue parachute would be released. Flight tests of the escape system were performed at Wallops Island as part of the series of Little Joe launches. Although the escape rockets fired prematurely on Little Joe’s first attempt in August 1959, the January 1960 follow-up was successful.
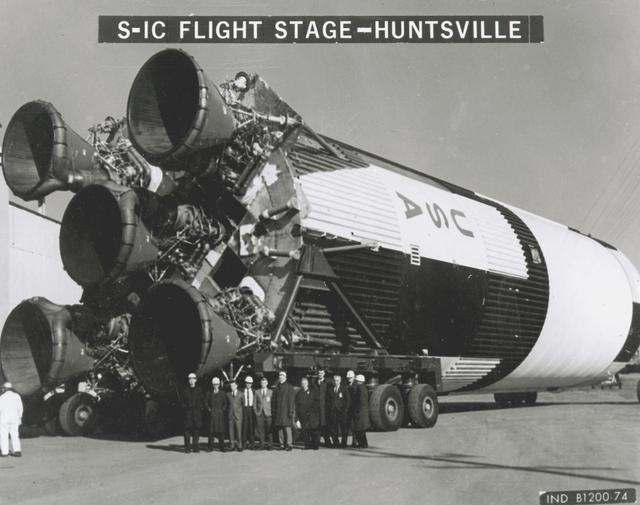

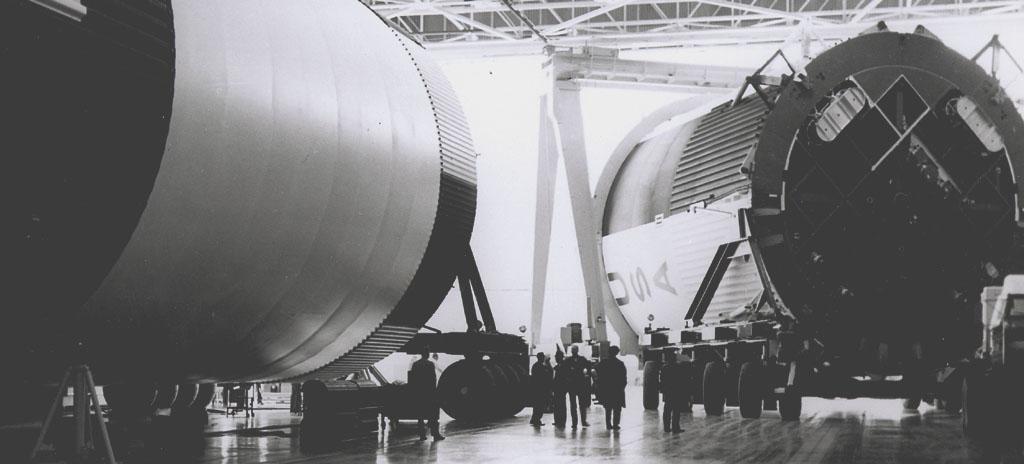
This small group of unidentified officials is dwarfed by the gigantic size of the Saturn V first stage (S-1C) at the shipping area of the Manufacturing Engineering Laboratory at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
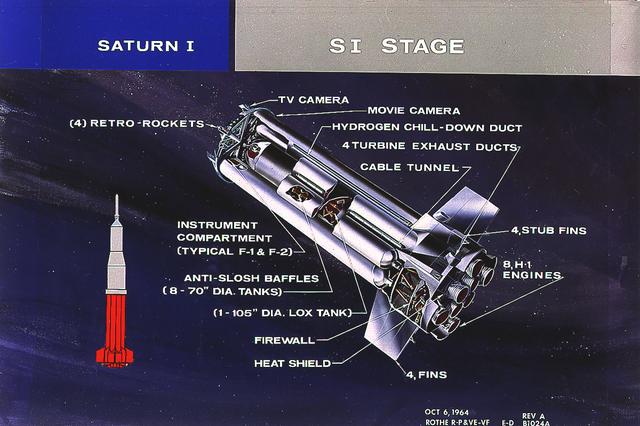
This cutaway illustrates the S-I stage, the first stage of the Saturn I vehicle developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The stage was propelled by a cluster of eight H-1 engines, capable of producing 1,500,000 pounds of thrust.
Images take for NASA Document L-1220

Model being tested with helicopter.
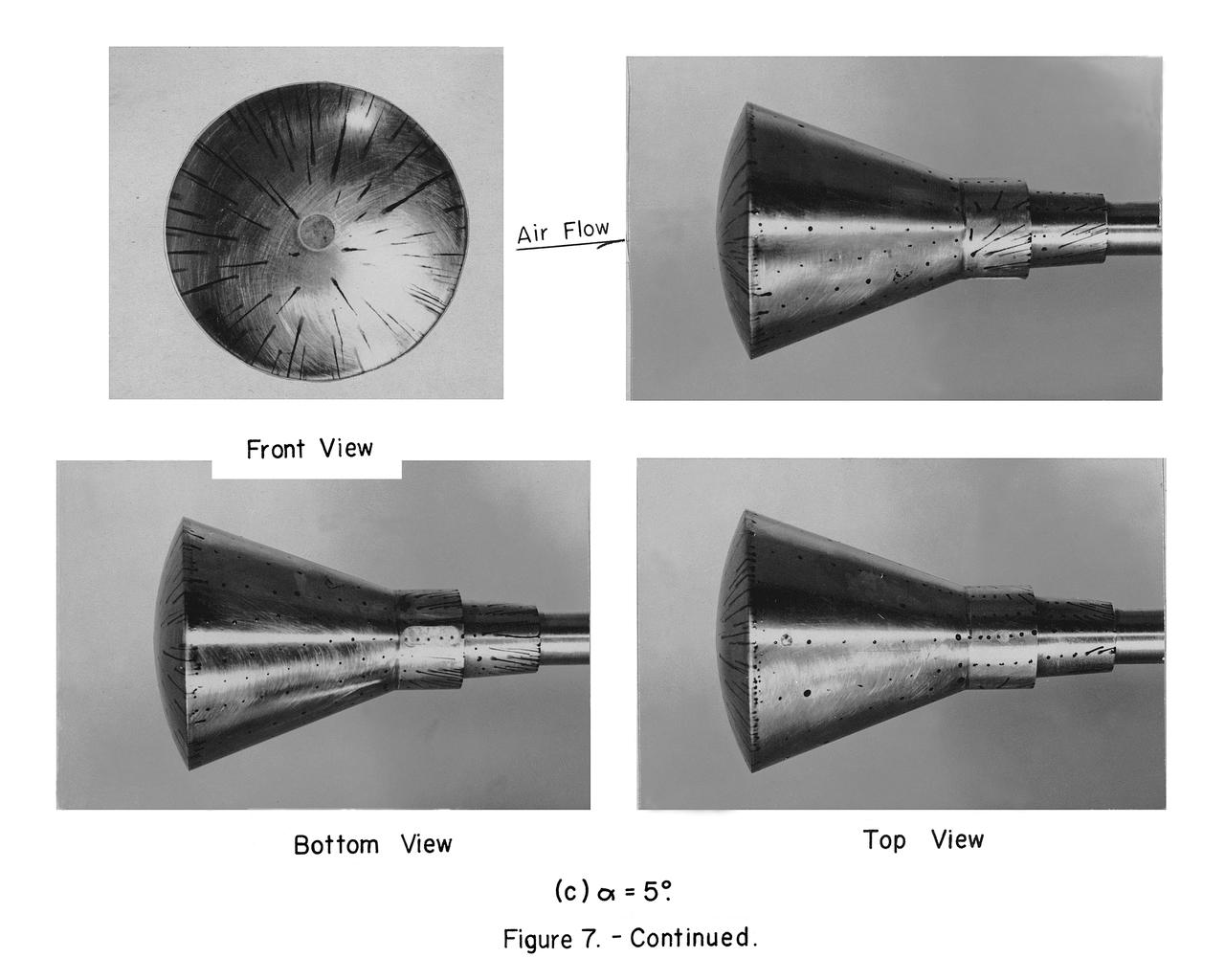
Images take for NASA Document L-1220
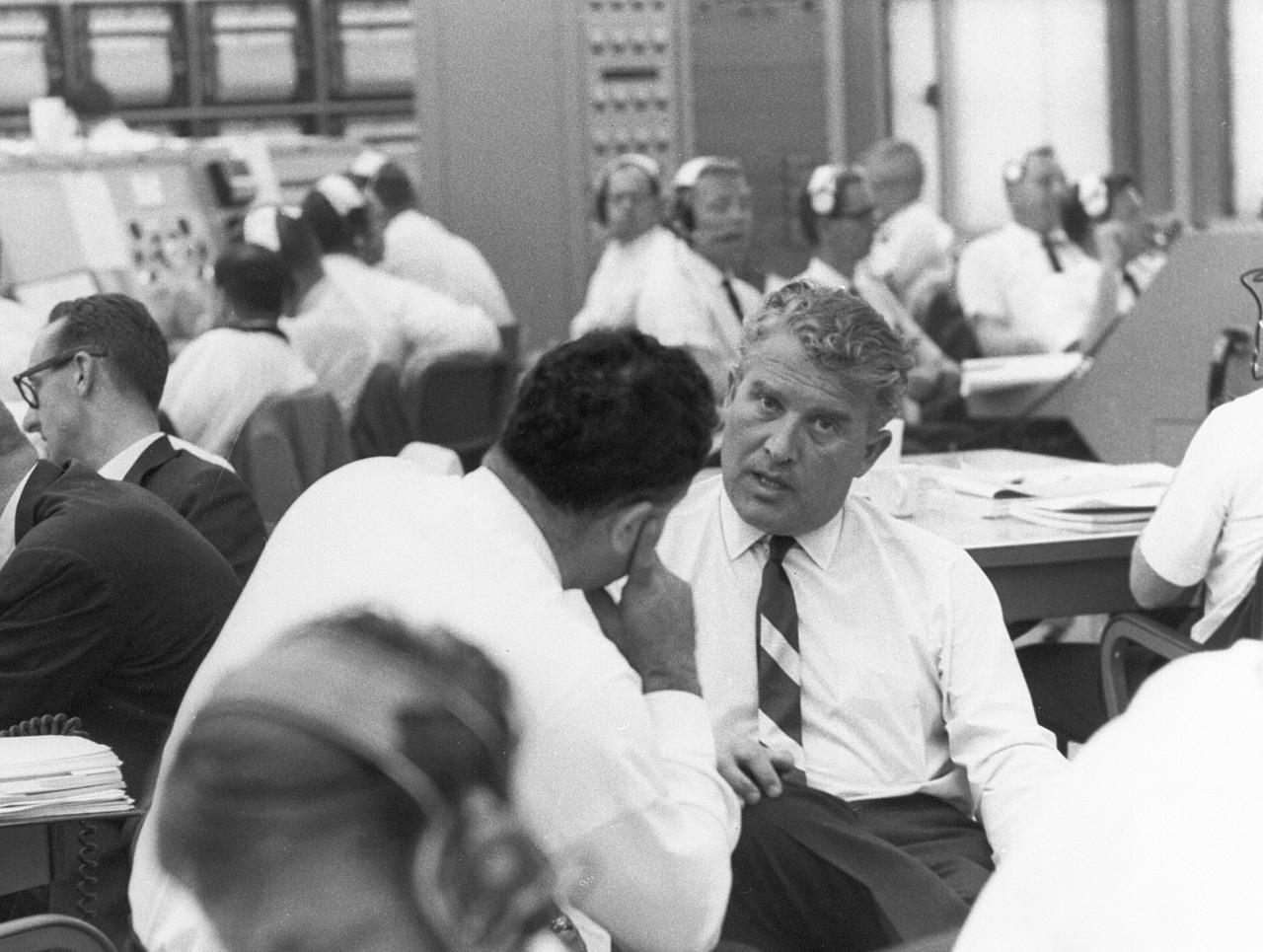

This photograph is not dated. It was probably taken in the late 1960s. Dr. von Braun appears to be in the launch control facilities at the Kennedy Space Center.
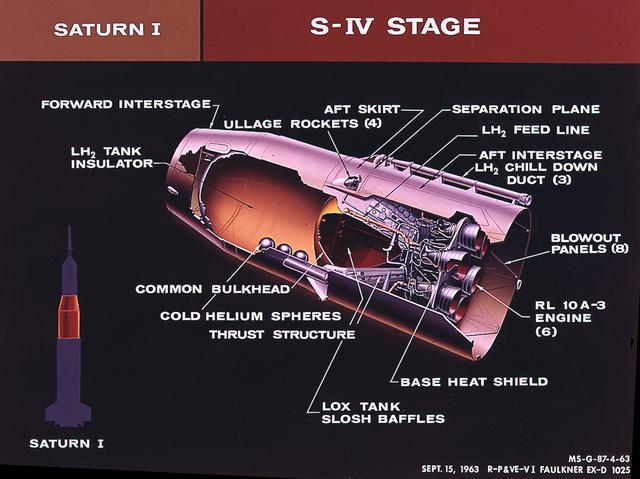
This cutaway of the Saturn I S-IV stage (second stage) illustrates the booster's components. Powered by six RL-10 engines, the S-IV stage was capable of producing 90,000 pounds of thrust. Development of the Saturn S-IV stage by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) contributed many technological breakthroughs vital to the success of the Apollo lunar program, including the use of liquid hydrogen as a propellant.
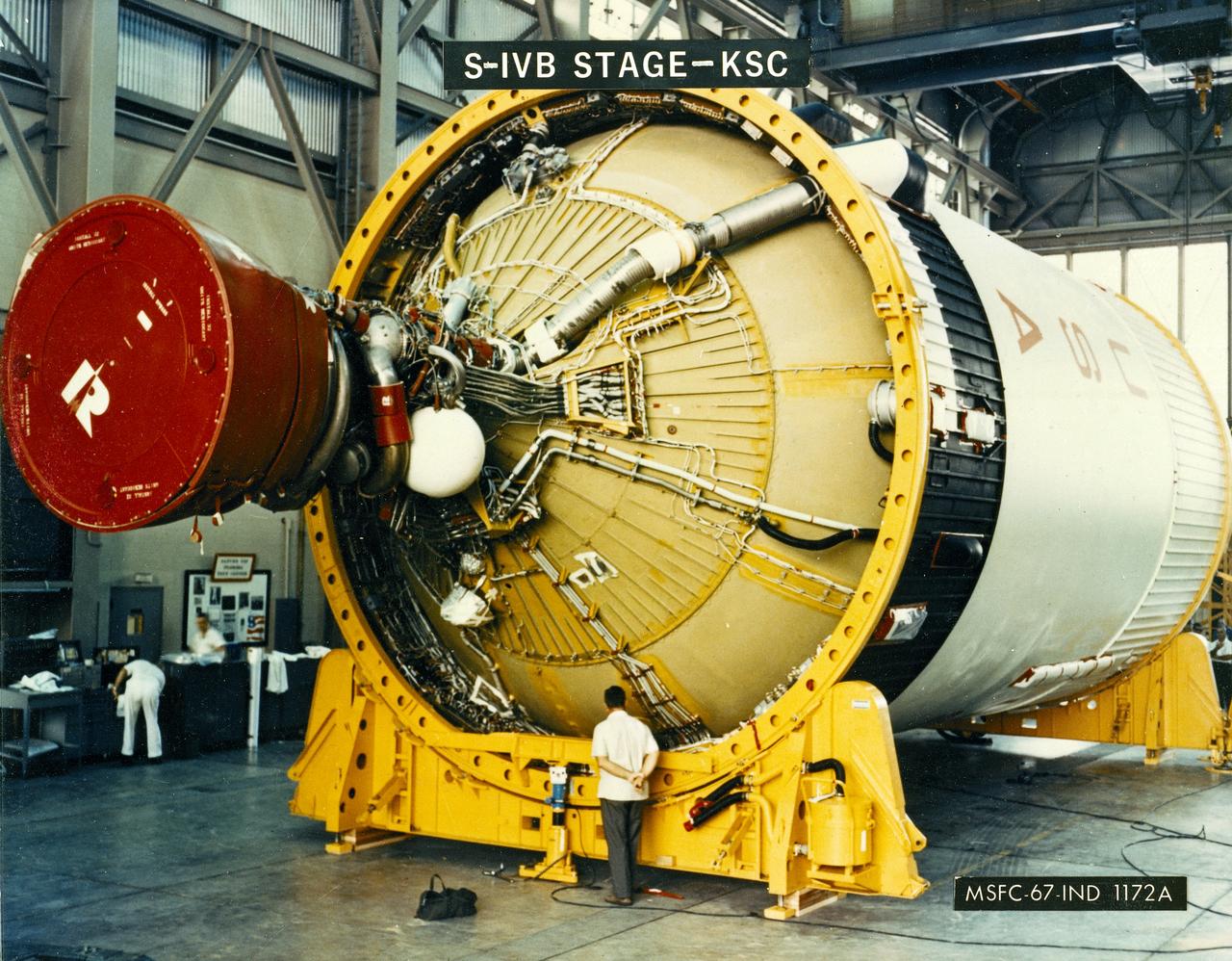
A NASA technician is dwarfed by the gigantic Third Stage (S-IVB) as it rests on supports in a facility at KSC. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
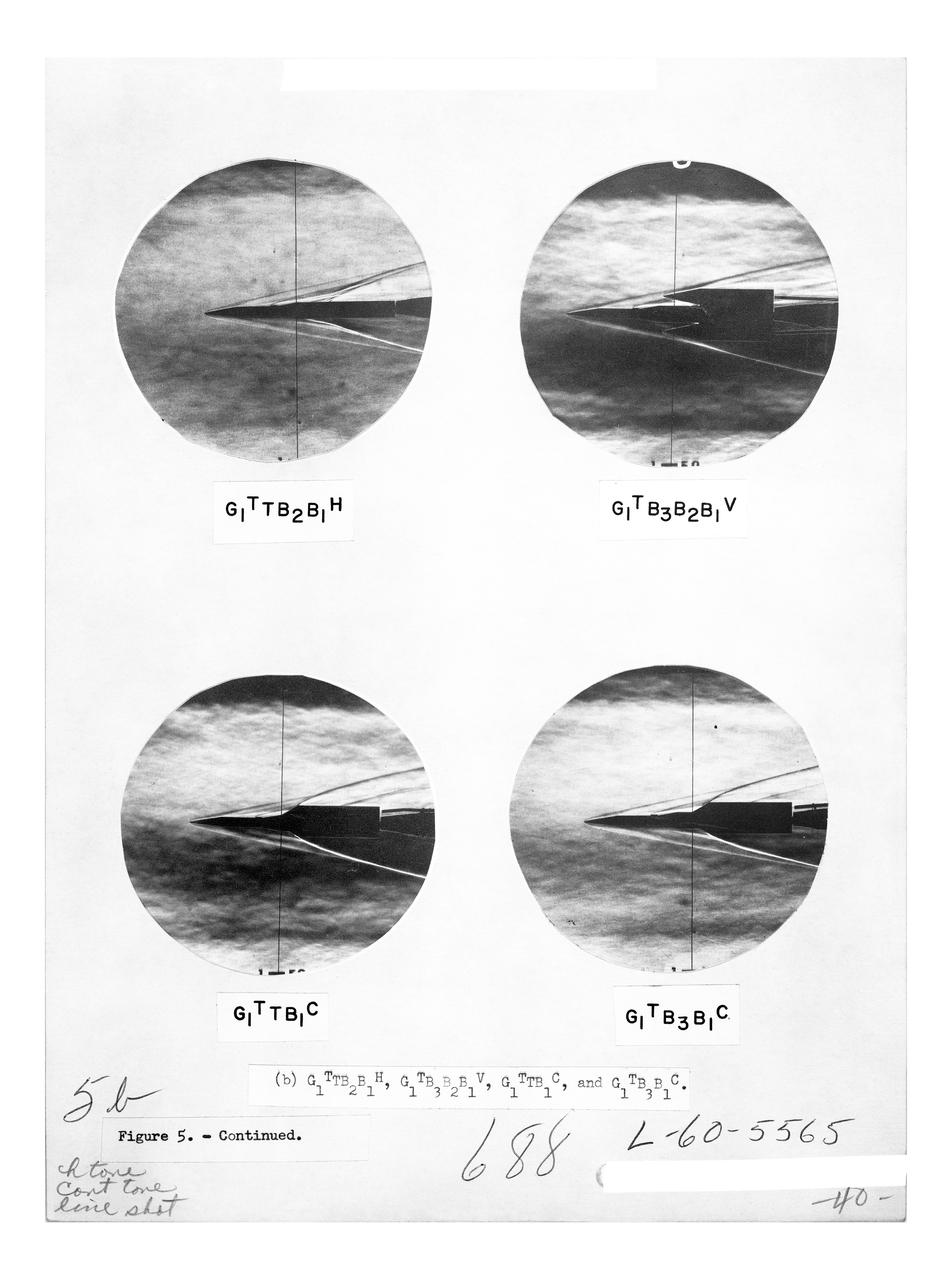
Figure 3-5 for NASA Document TM-X-356
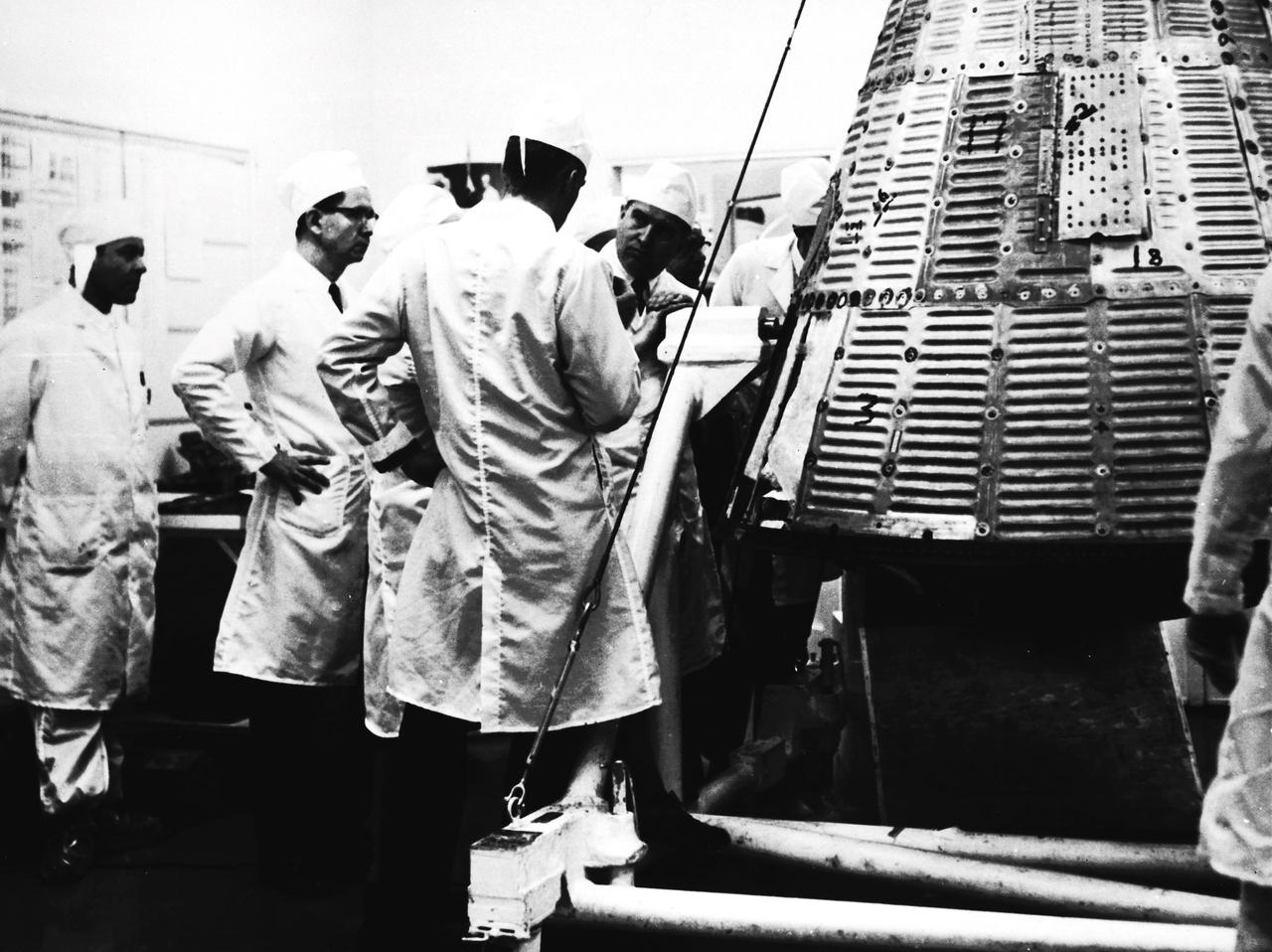

In this undated photograph, Dr. von Braun is shown during a visit to McDonnell Aircraft to inspect Mercury spacecraft manufacturing.

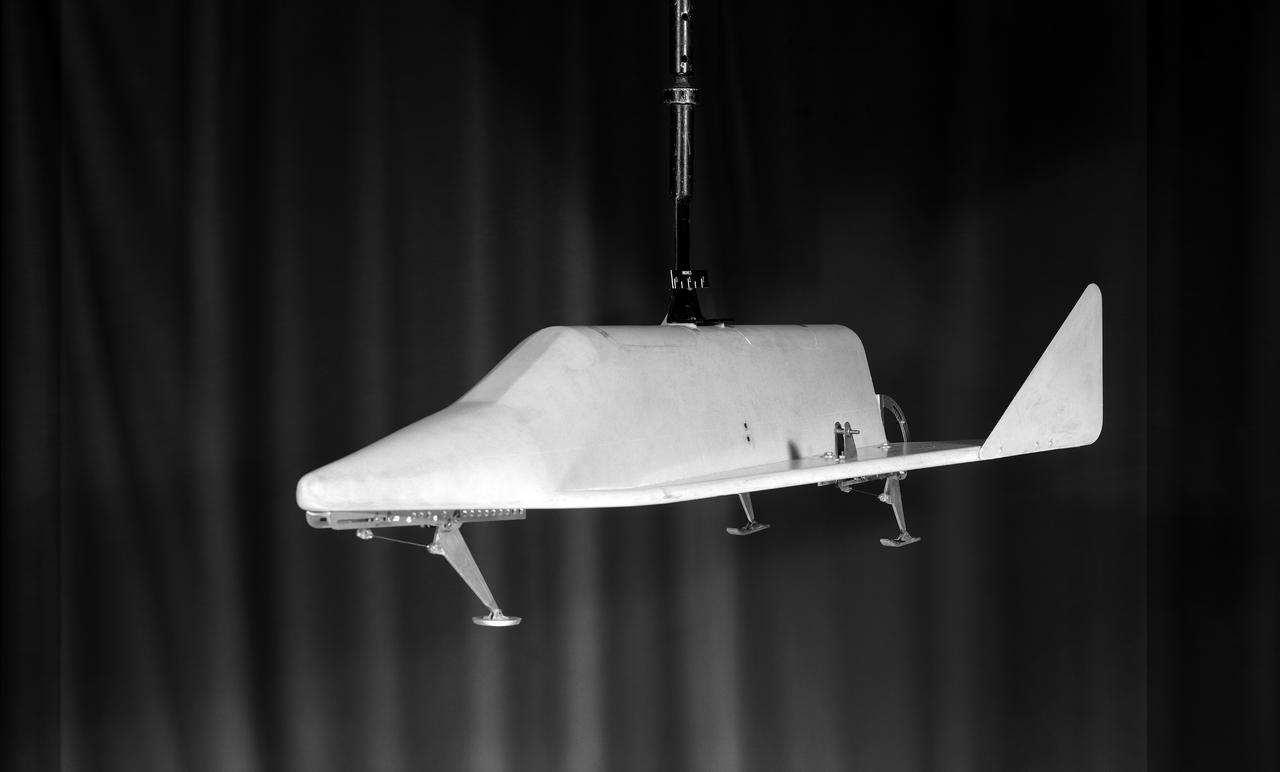
Model of Winged Space Vehicle
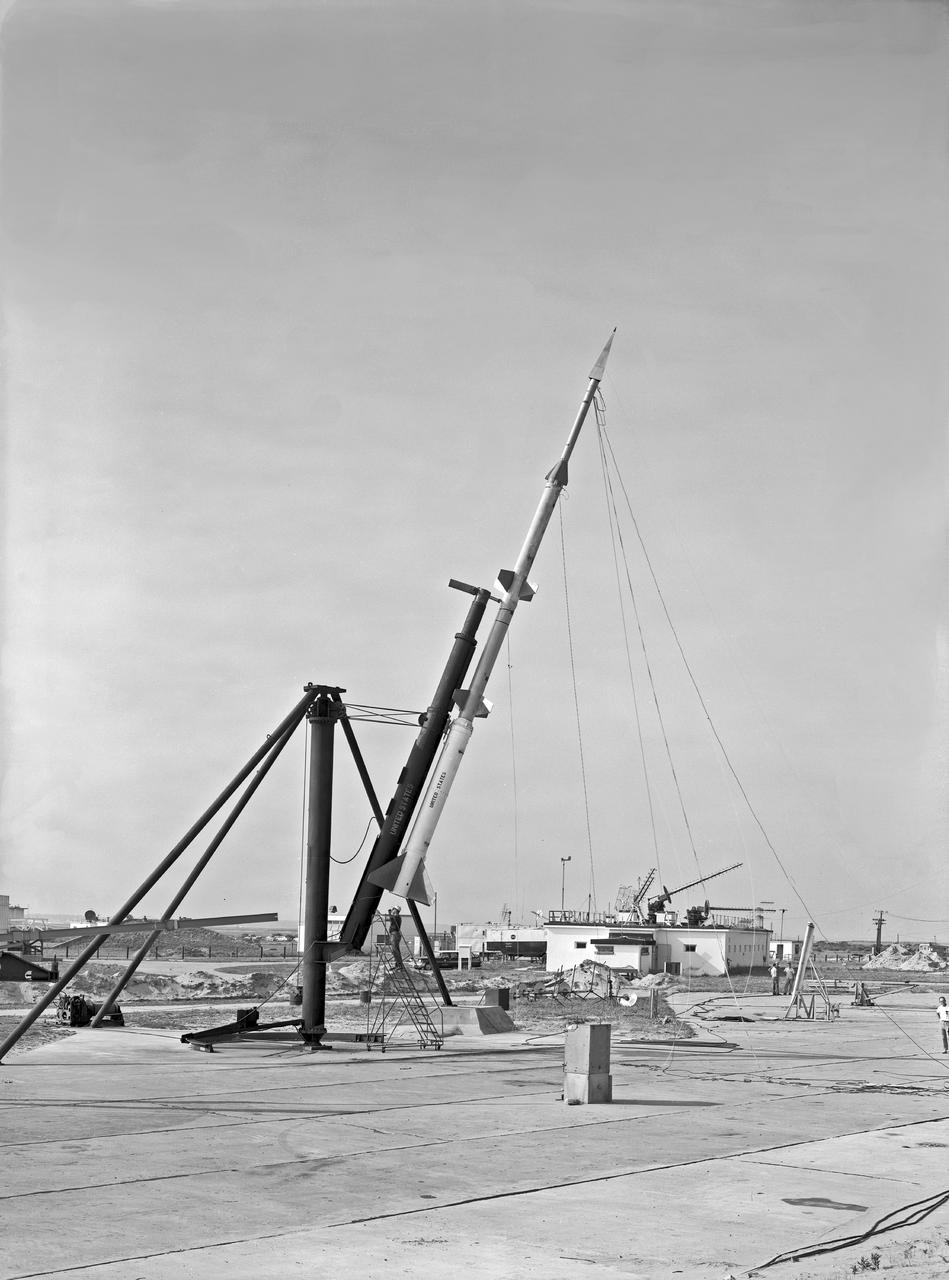

L5-19 (F40-2752) Model in Launch Position
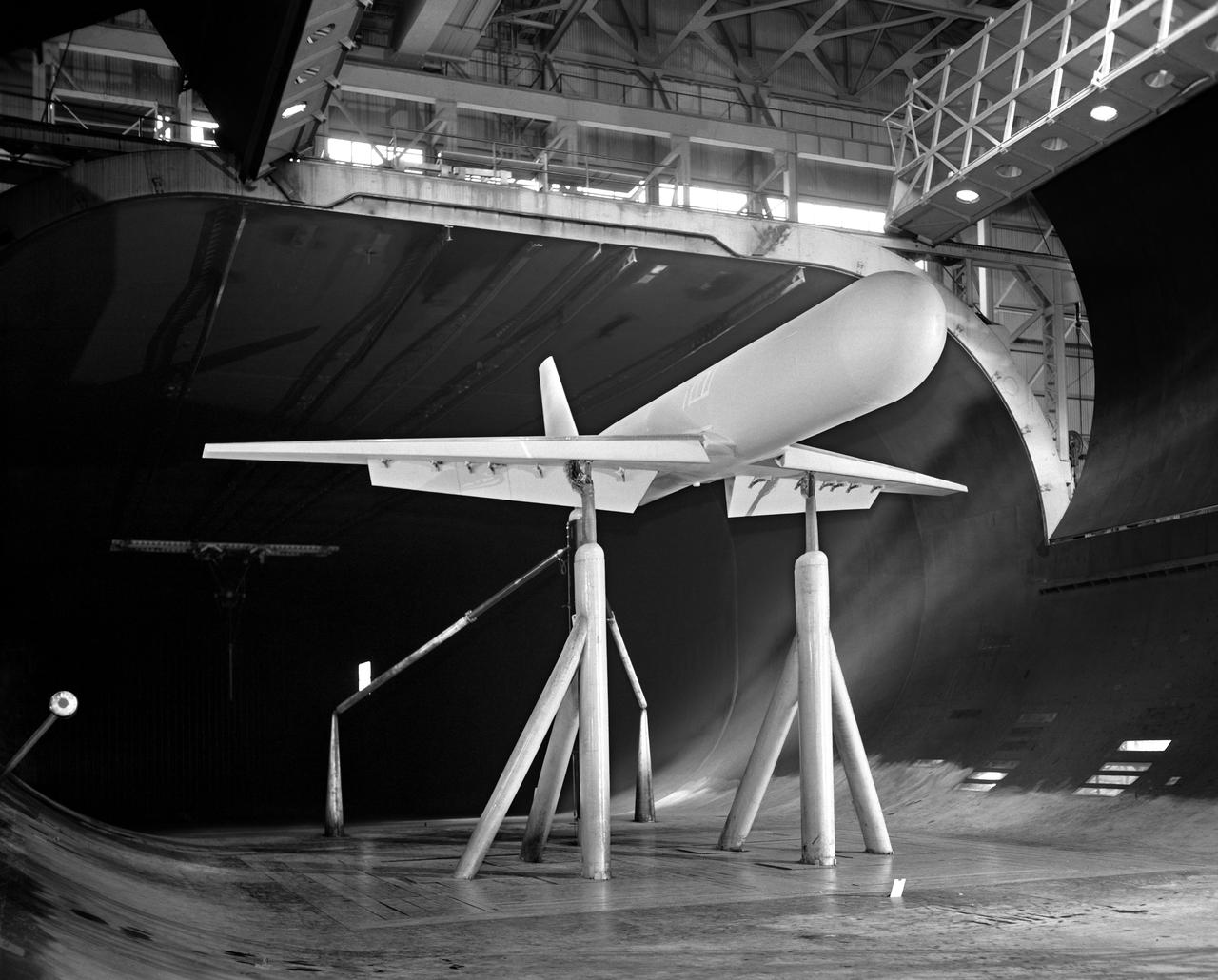

3/4 front view of model without nacelles on regular struts. Generalized Subsonic Jet Transport model with leading edge and trailing edge blowing BLC in the 40x80 foot wind tunnel at NASA Ames.
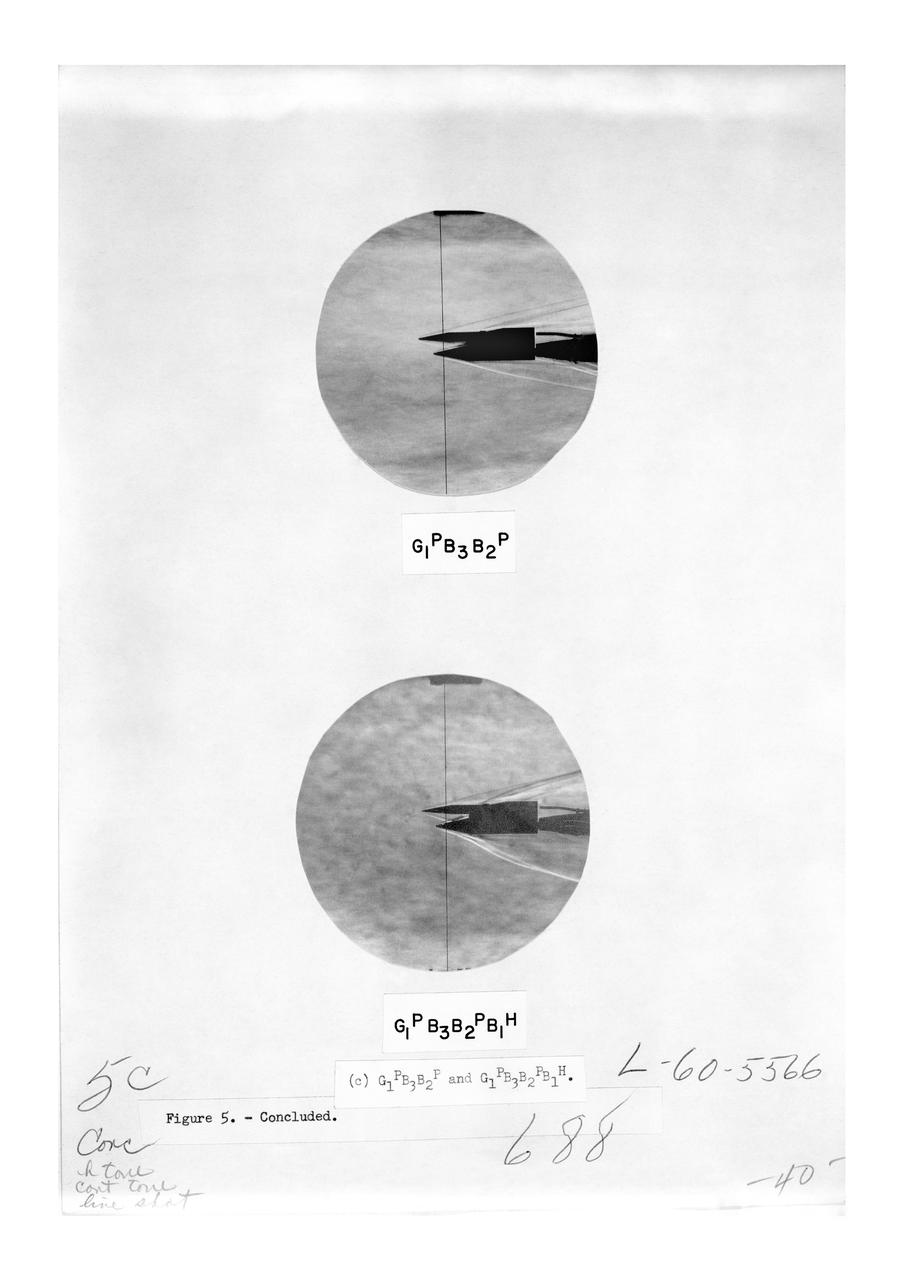
Figure 3-5 for NASA Document TM-X-356
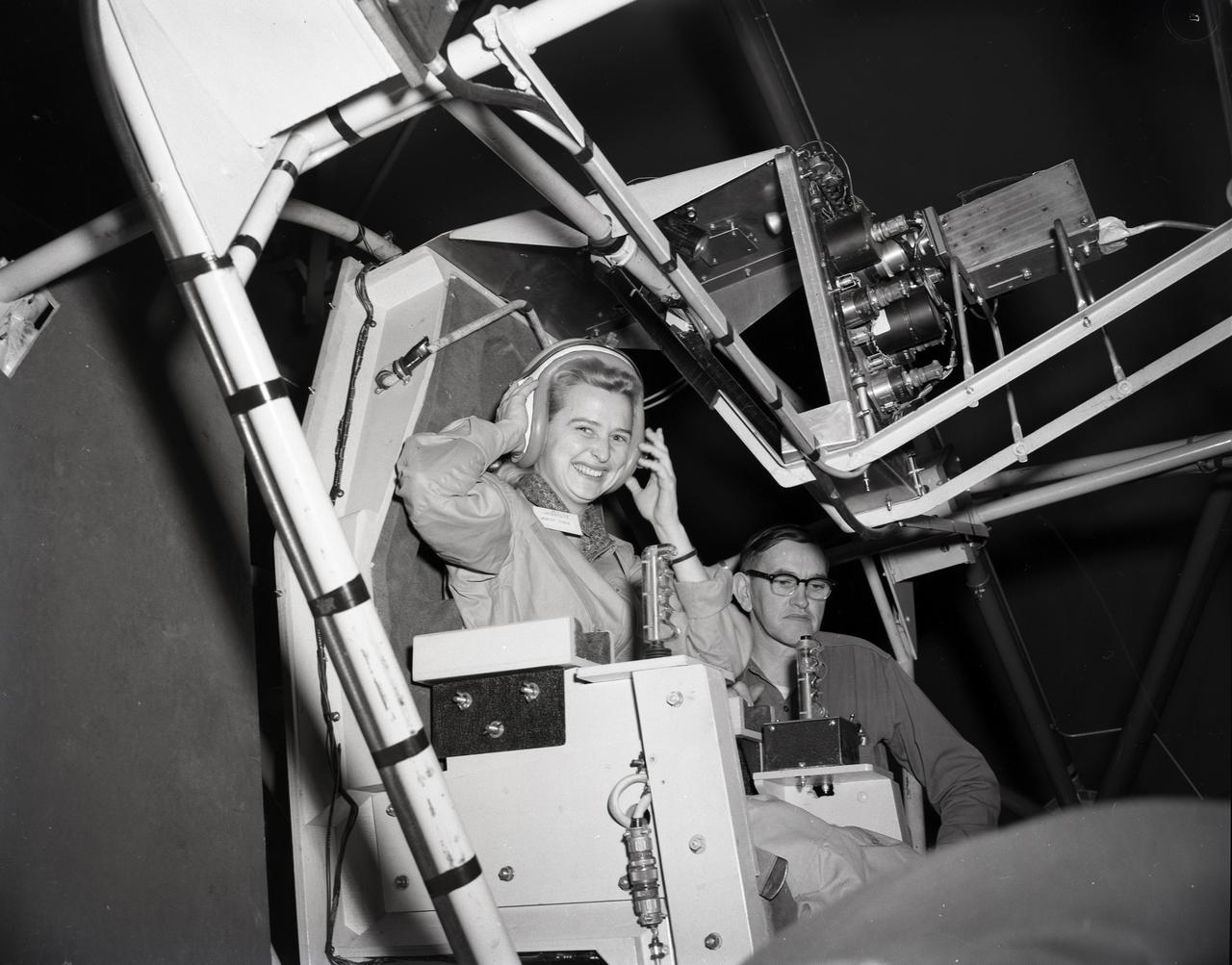

JERRIE COBB - PILOT - TESTING GIMBAL RIG IN THE ALTITUDE WIND TUNNEL, AWT
A Cluster of eight H-1 engines were used to thrust the first stage of Saturn I (S-I stage) and Saturn IB (S-IB stage). The engines were arranged in a double pattern. Four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern and each outer engine was gimbaled. The H-1 engine, fueled with liquid oxygen (LOX) and kerosene (RP-1), had a thrust of 188,000 pound each for a combined thrust of over 1,500,000 pounds. Each H-1 engine was developed under the direction of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
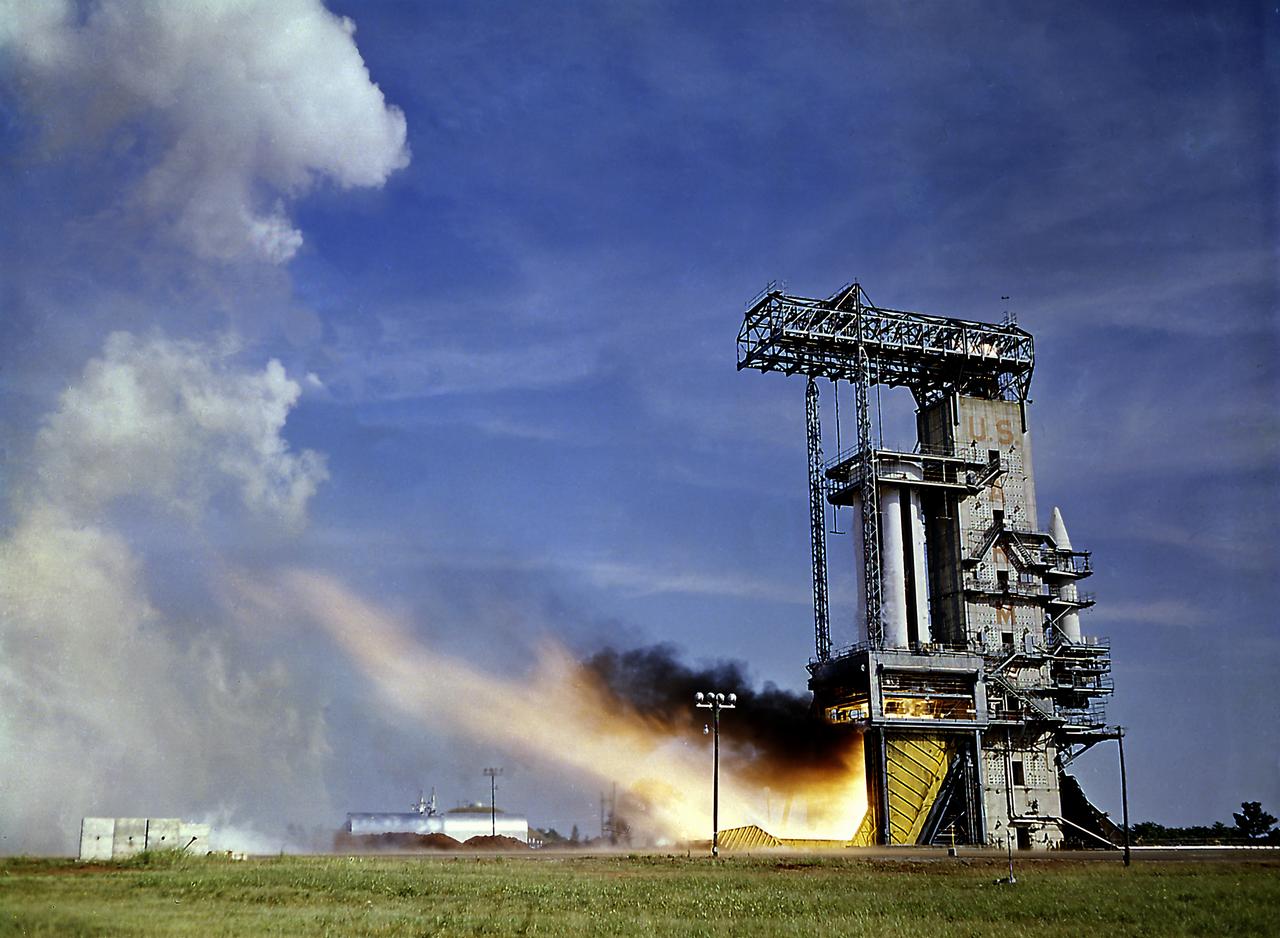

The Saturn Project was approved on January 18, 1960 as a program of the highest national priority. The formal test program to prove out the clustered-booster concept was well underway. A series of static tests of the Saturn I booster (S-I stage) began June 3, 1960 at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). This photograph depicts the Saturn I S-I stage equipped with eight H-1 engines, being successfully test-fired for the duration of 121 seconds on June 15, 1960.
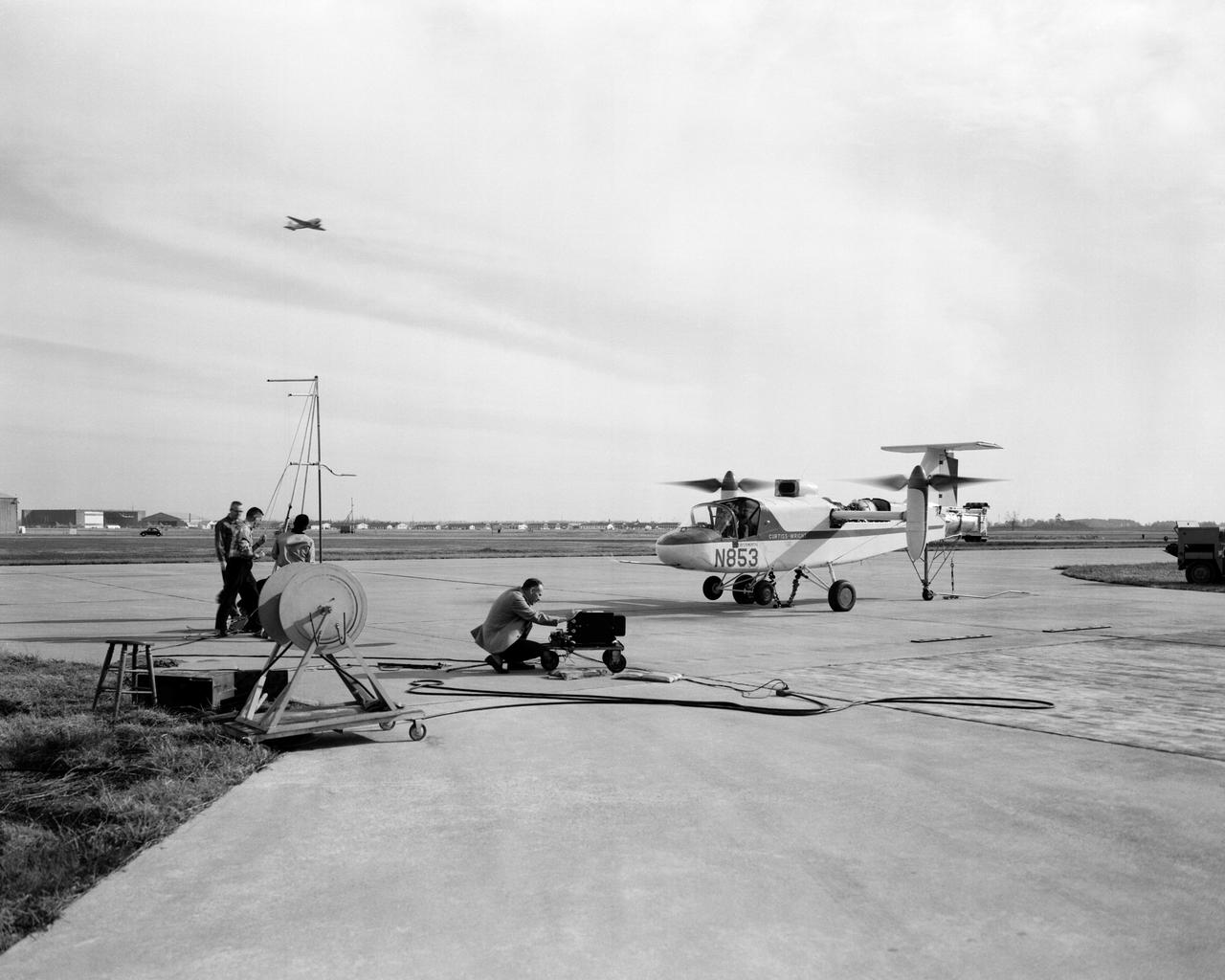

Curtiss-Wright X-100 (VTOL) Vertical Take-Off Transport.

100' Satellite Packaging of Echo
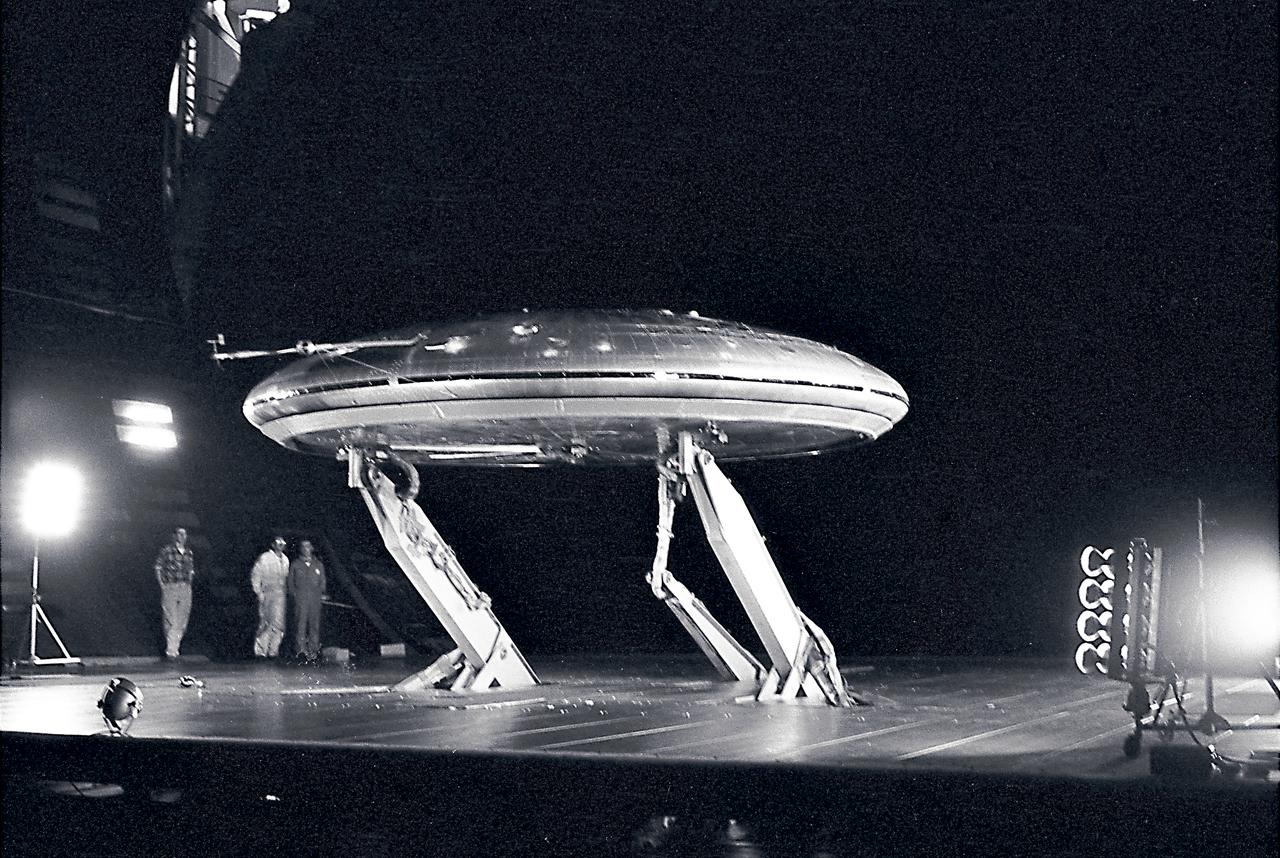

Front 3/4 view of the Avrocar mounted on variable height struts in the Ames 40x80 foot wind tunnel, without tail.
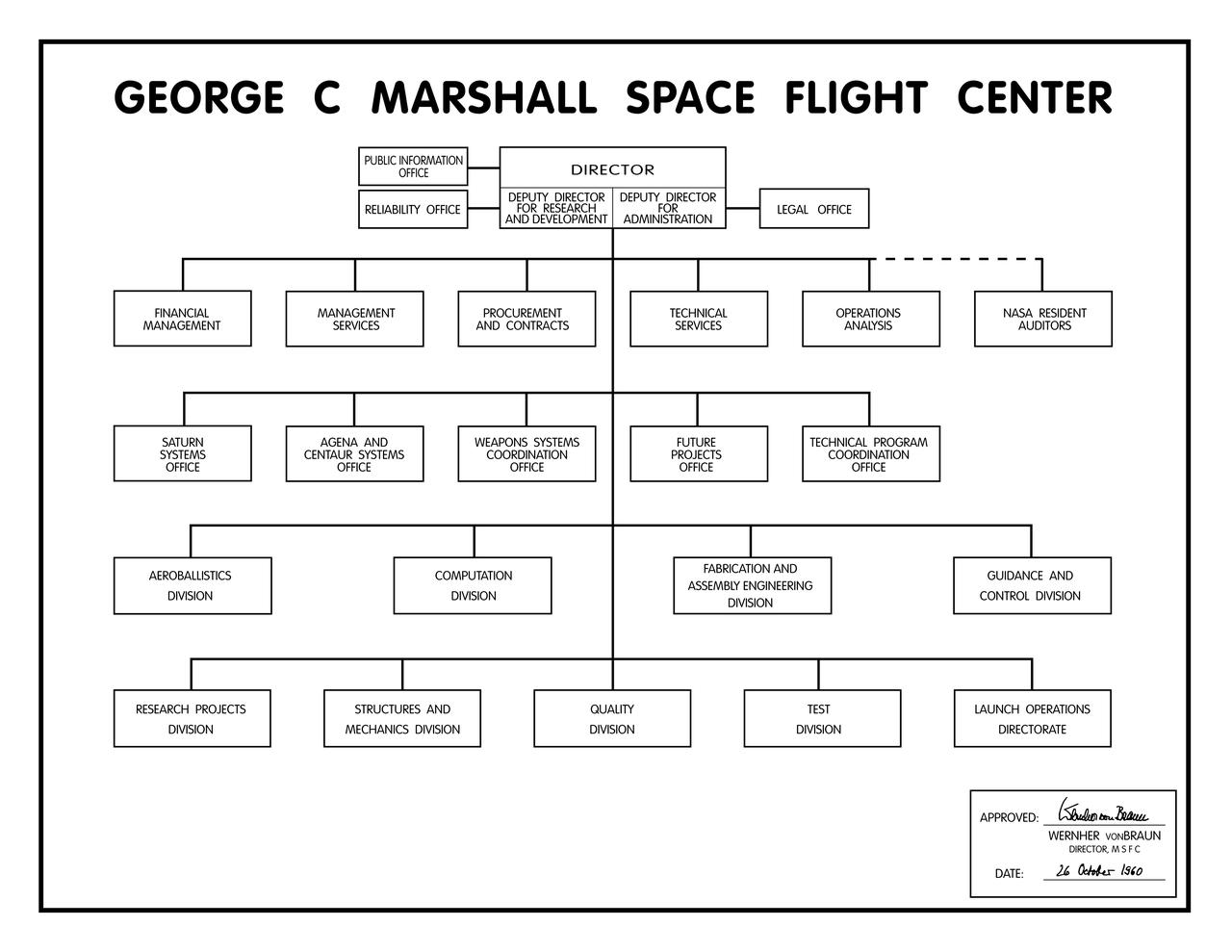
The first organizational chart of the George C. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) which was approved and signed by Dr. Wernher von Braun, Director, MSFC, on 26 October 1960.
Images take for NASA Document L-1220
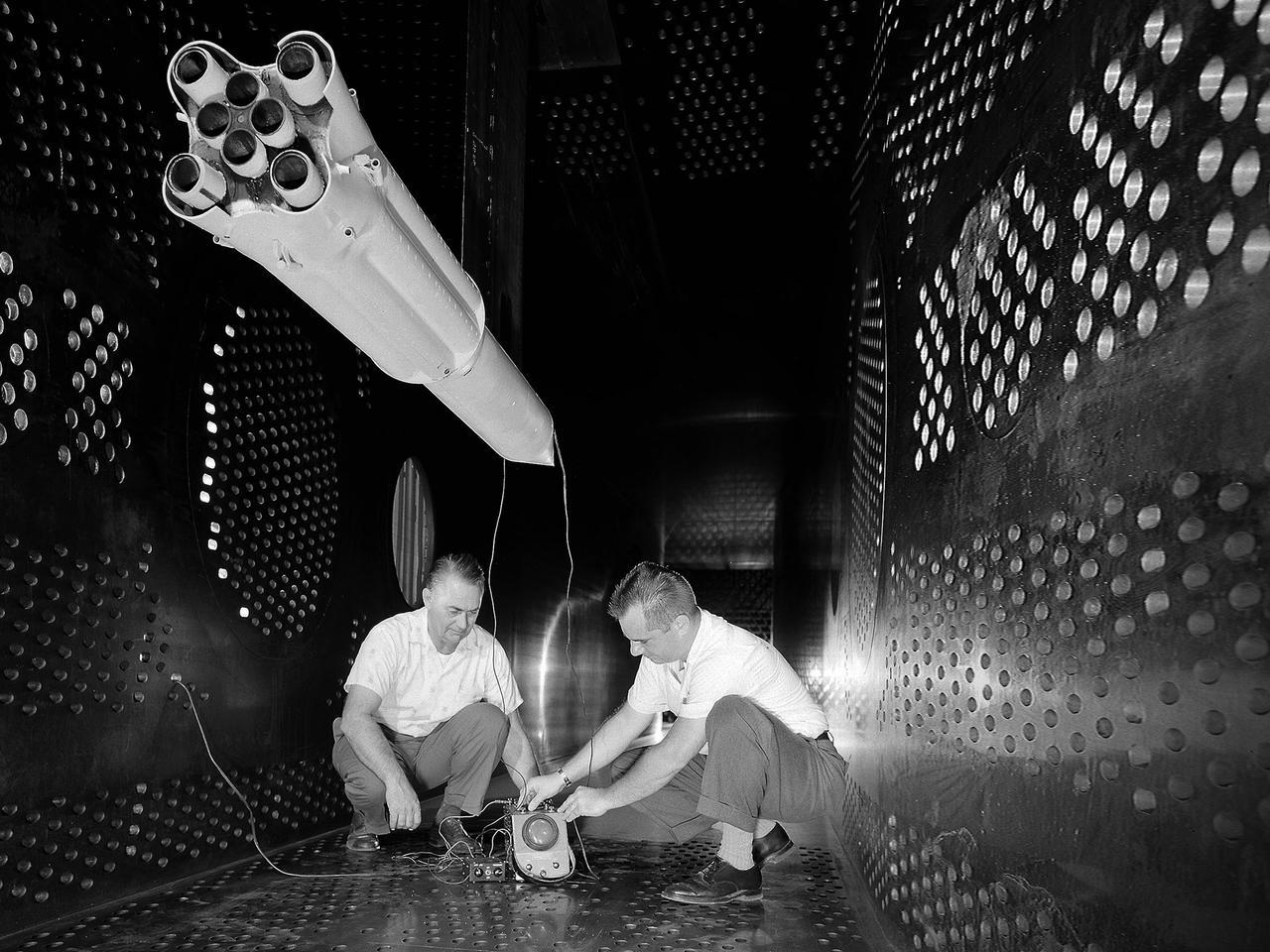

National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) researchers set up instrumentation on a 0.037- scale model of a Saturn booster in the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the NASA Lewis Research Center. In October 1960 Lewis researchers John Allen and Robert Wasko began a 14-month investigation of the eight-engine booster’s base heating in the tunnel. The model resembled the Saturn C-1, but only the afterbody totally mimicked the C-1. The over-heating of the lower end, or base, of the booster can cause the engines to fail or introduce aerodynamic concerns. Base heating results from the rocket engines’ exhaust heat, the recirculation of that heat into the base, and the burning of combustibles. Large boosters, like the Saturn, employed clusters of rocket engines that add to the complexity of the base heating problem. The 8- by 6-foot tunnel investigations studied the Saturn at speeds from Mach 1.0 to 2.0 using liquid oxygen and JP-4 as propellants. Researchers found that the use of cooling air scoops and external flow deflectors produced significant decreases in base heating.
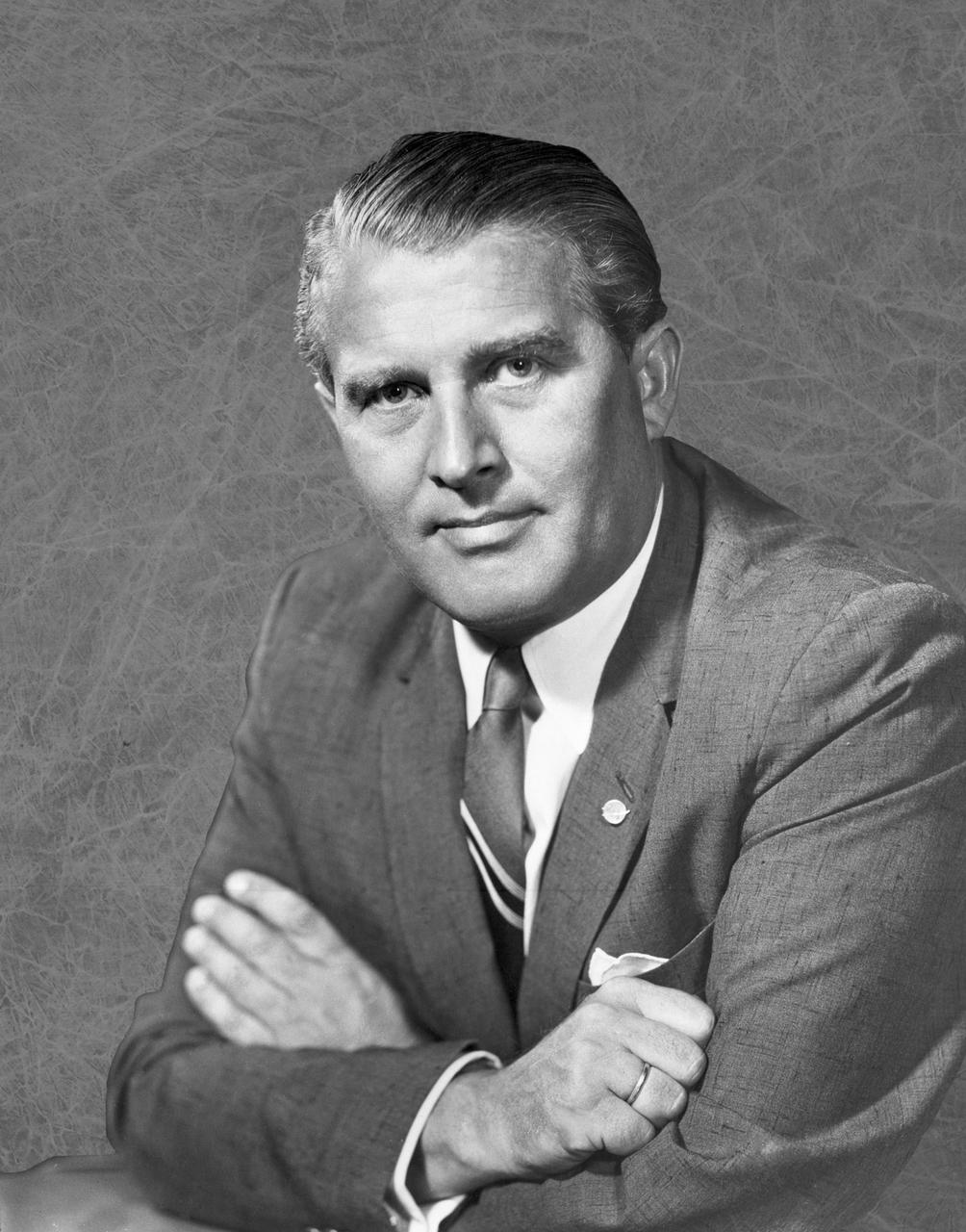

Dr. Wernher von Braun served as Marshall Space Flight Center's first director from July 1, 1960 until January 27, 1970, when he was appointed NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Plarning. Following World War II, Dr. von Braun and his German colleagues arrived in the United States under Project Paperclip to continue their rocket development work. In 1950, von Braun and his rocket team were transferred from Ft. Bliss, Texas to Huntsville, Alabama to work for the Army's rocket program at Redstone Arsenal and later, NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. Under von Braun's leadership, Marshall developed the Saturn V launch vehicle which took Apollo astronauts to the moon.

Project: Wing Sweep Range Series TAC Variable Sweep Model configure 8 A. Taken at 8 foot tunnels building 641. L60-3412 through 3416 Model of proposed military supersonic attack airplane shows wing sweep range. TAC Models taken at the 8 Foot Tunnel. Photograph published in Sixty Years of Aeronautical Research 1917-1977 By David A. Anderton. A NASA publication. Page 53.

The first Scout prepared for launch at Wallops Island July 1, 1960, and launched the evening of the same day. -- Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication (page 73), by James Schultz.
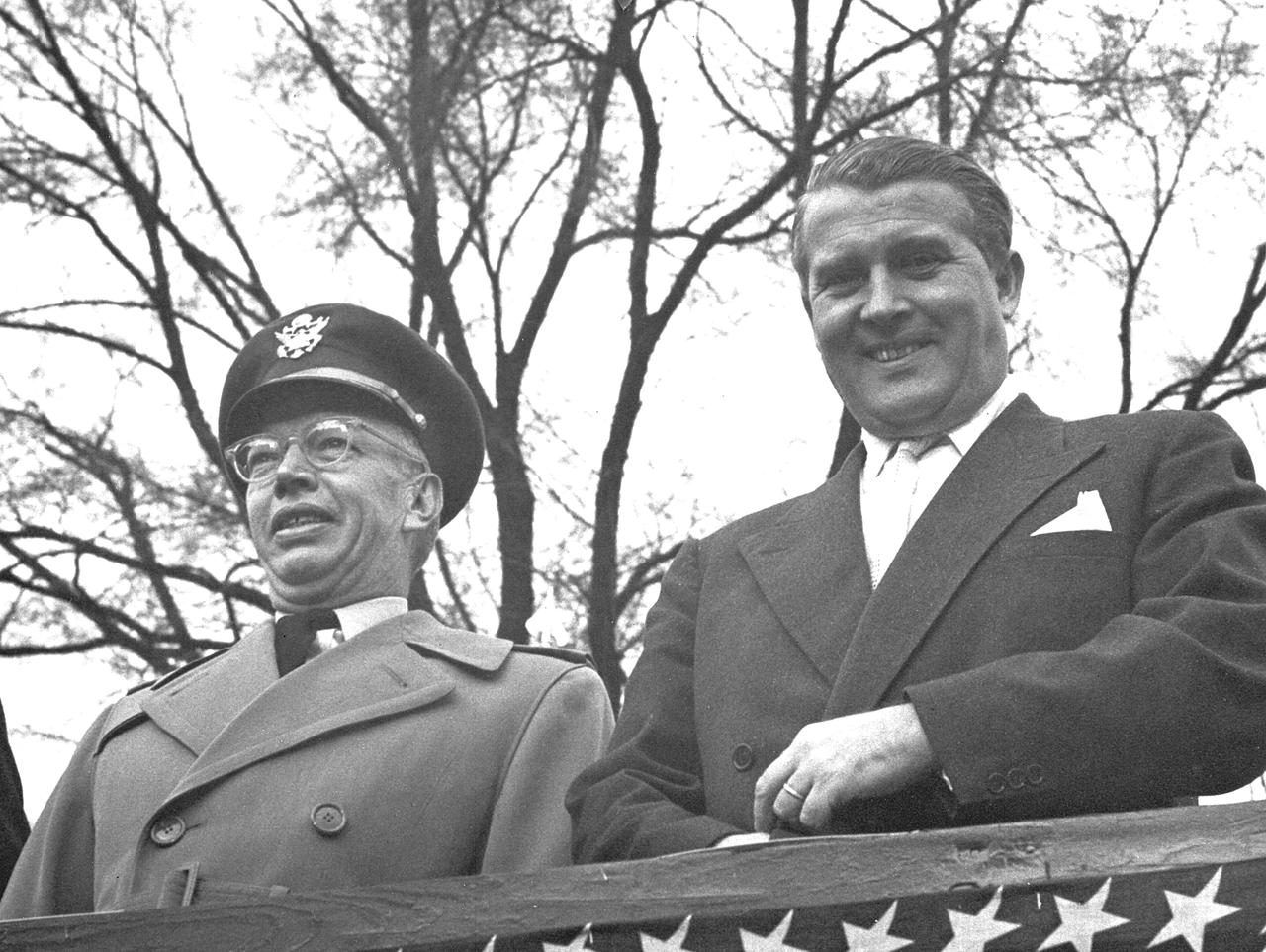

This photograph was taken about 1960 and shows Dr. von Braun viewing a parade with Major General John Barclay.

Model at building 193
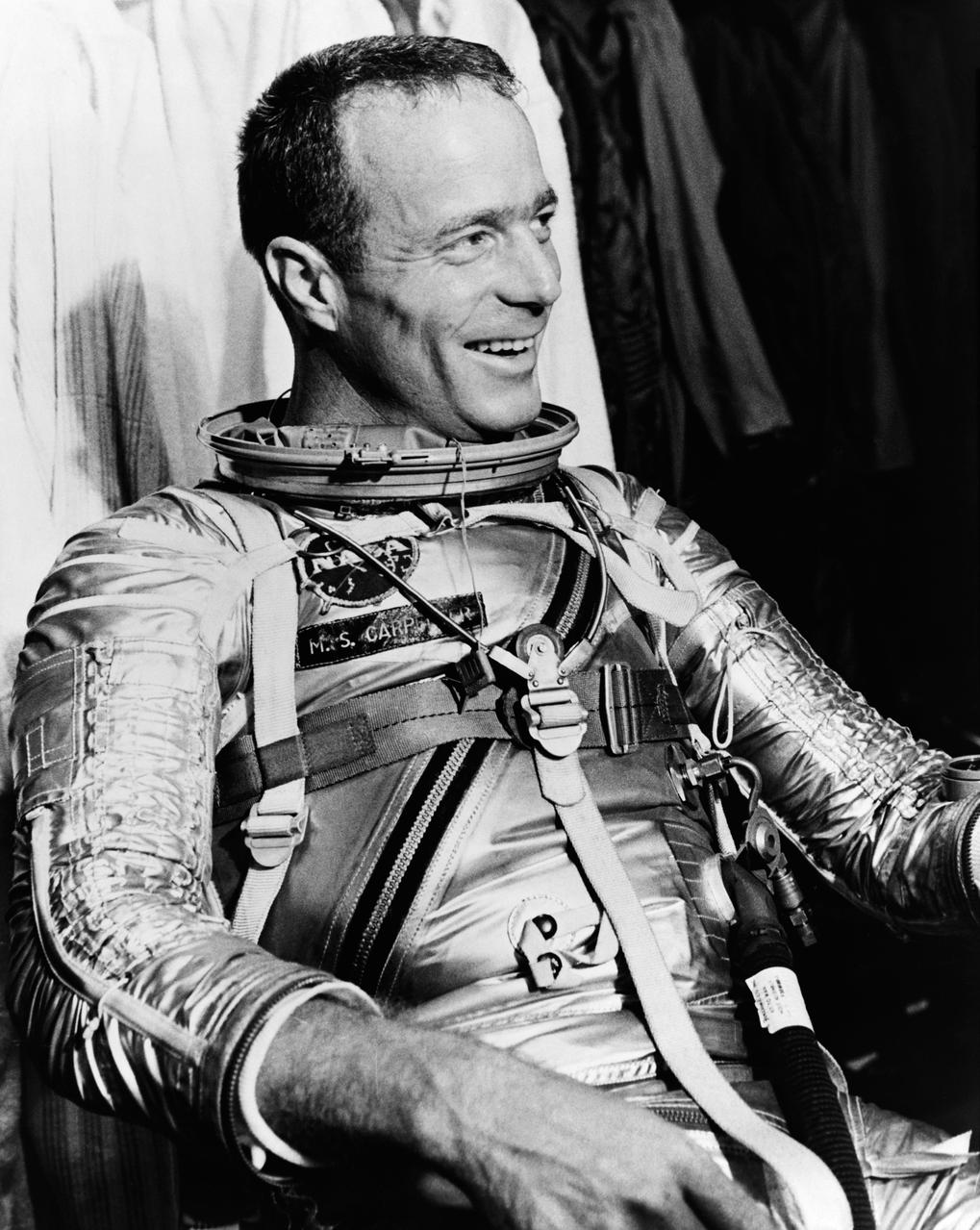

S61-03510 (1961) --- Project Mercury astronaut M. Scott Carpenter smiles, in his pressure suit, prior to participating in a simulated mission run at Cape Canaveral, Florida. Astronaut Carpenter has been selected as the prime pilot on the United States second attempt to put a man into orbit around Earth. Photo credit: NASA

Kite model flying in Full Scale Tunnel (FST)
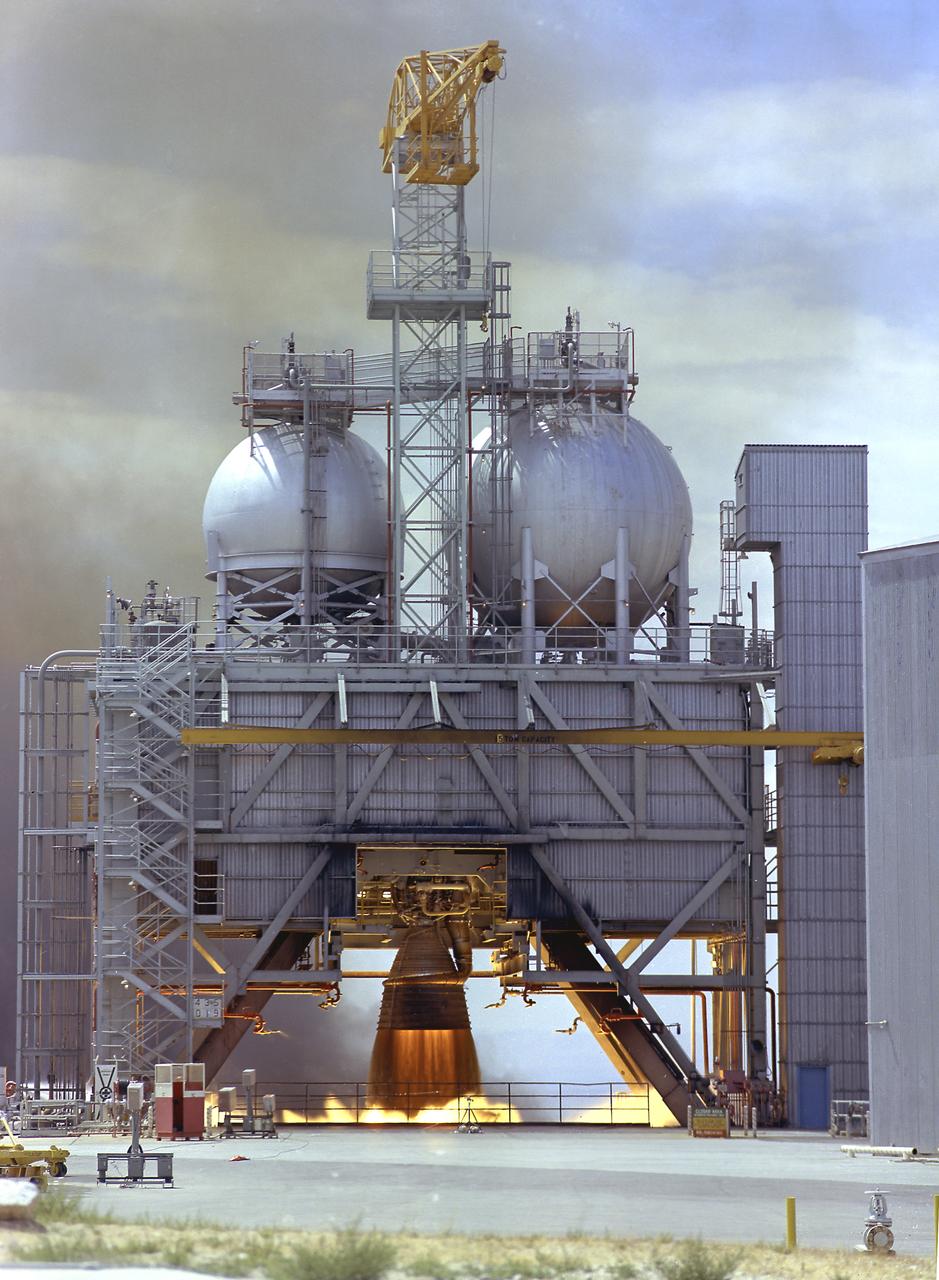

The F-1 engine was developed and built by Rocketdyne under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center. It measured 19 feet tall by 12.5 feet at the nozzle exit, and produced a 1,500,000-pound thrust using liquid oxygen and kerosene as the propellant. The image shows an F-1 engine being test fired at the Test Stand 1-C at the Edwards Air Force Base in California.
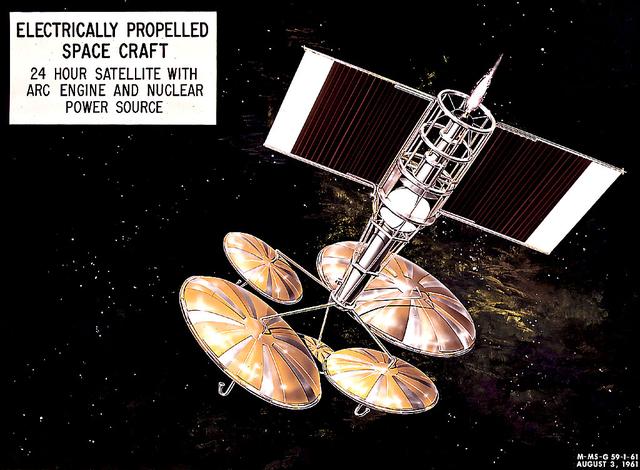
This 1960 artist's concept shows a 24-hour communication satellite design incorporating an arc engine with a nuclear power source. The concept was one of many missions proposed by the Marshall Space Flight Center for electrically-propelled spacecraft.
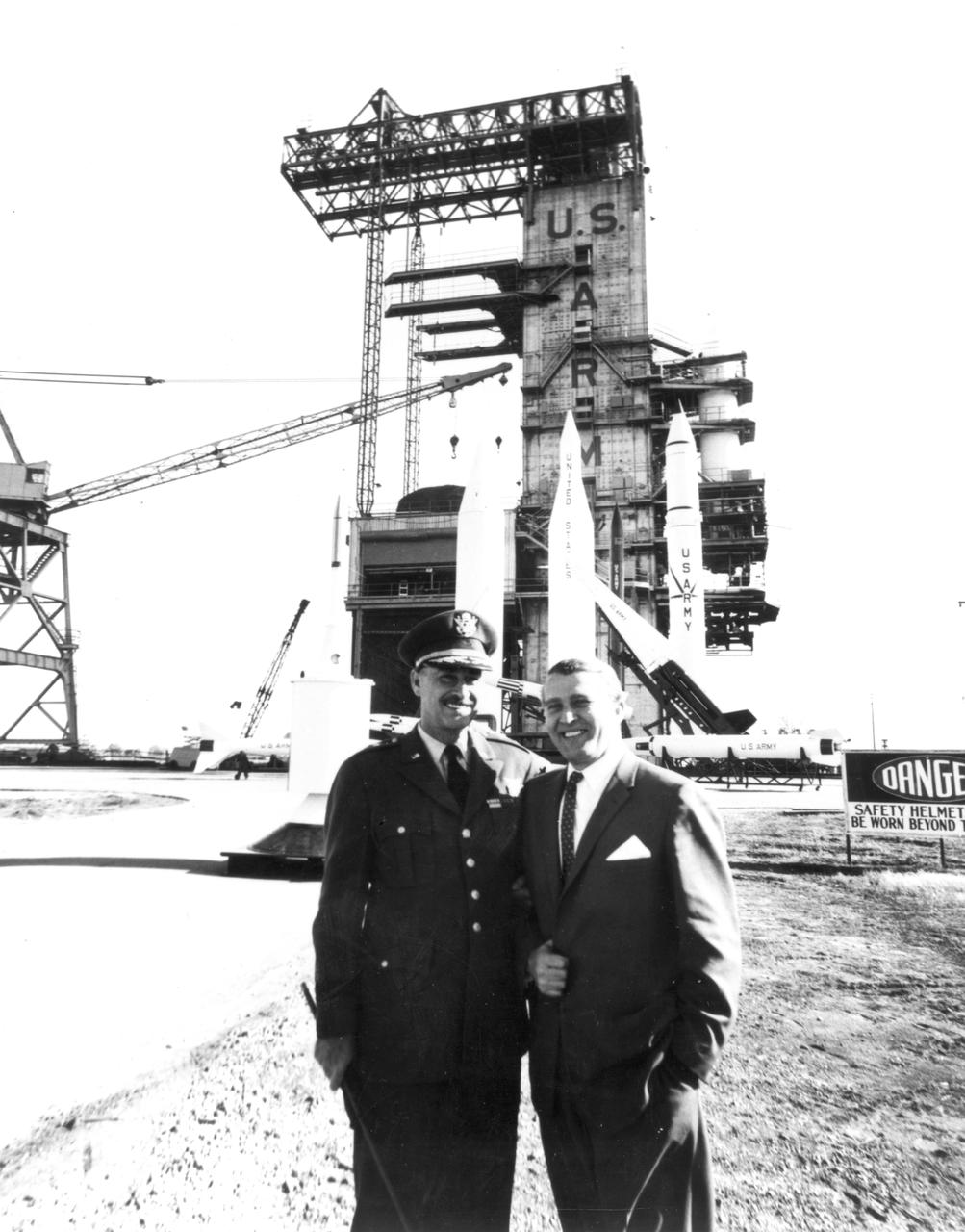

Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC) Director, Dr. Wernher von Braun, is pictured here with Army Ballistic Missile Agency’s (ABMA) Commanding General, J.B. Medaris, before a display of Army missles at the ABMA test lab.

100' Satellite Packaging of Echo
Hi-Speed impact test simulating space debris hitting an orbiting capsule. A blunt nose 20 millimeter model built of polyethylene hitting a aluminum target at 19,500 feet per second, in a pressure simulated as 100,000 feet altitude.

Adolf Busemann, the German aerodynamicist who first expressed the advantages of wing sweep in a 1935 theoretical paper, came to work at Langley in May 1947 as a result of Operation Paperclip. Photograph published in Engineer in Charge: A History of the Langley Aeronautical Laboratory, 1917-1958 by James R. Hansen. Page 283.
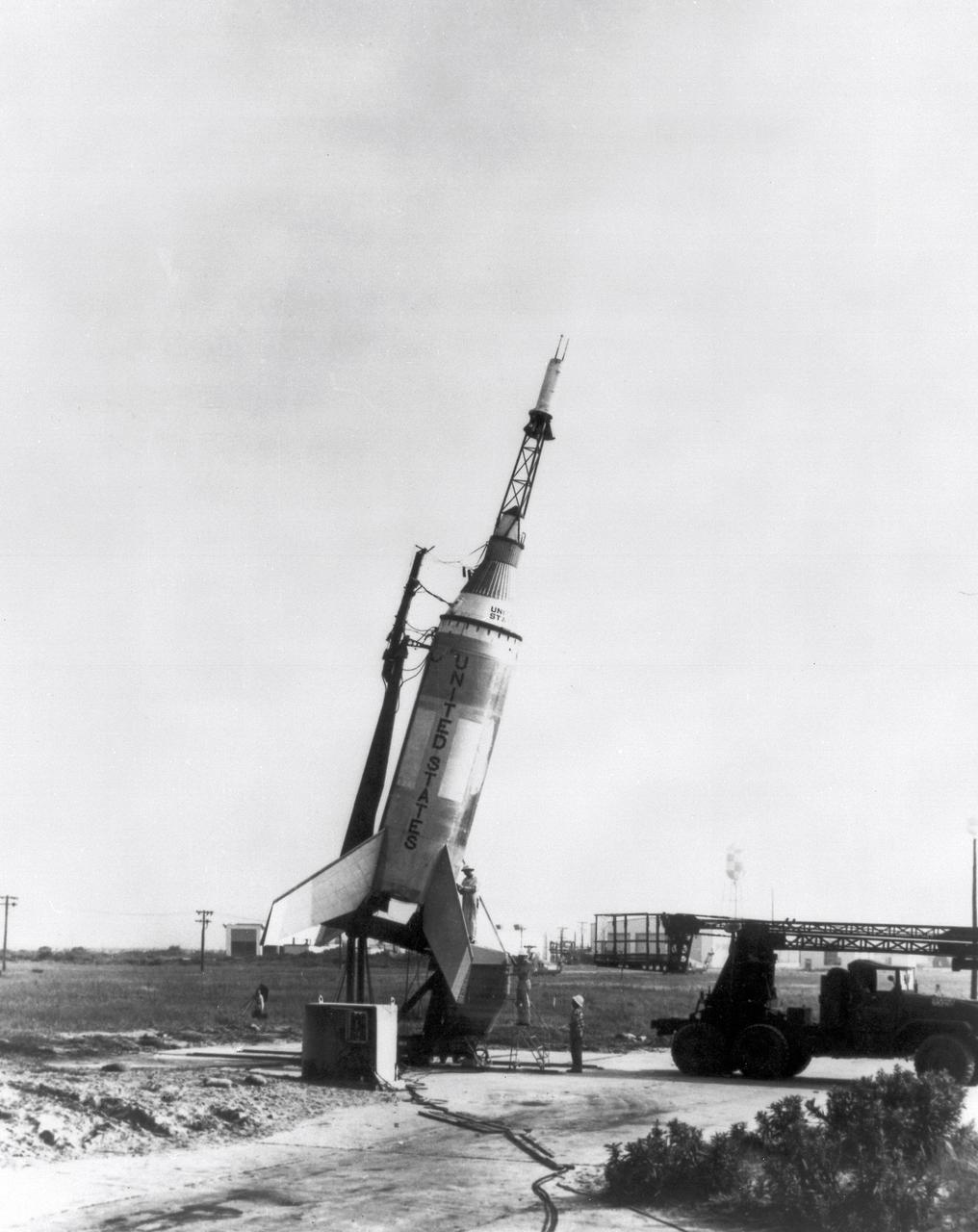

The Little Joe launch vehicle for the LJ1 mission on the launch pad at the wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Virginia, on January 21, 1960. This mission achieved the suborbital Mercury cupsule test, testing of the escape system, and biomedical tests by using a monkey, named Miss Sam.

Launch Phase of ARCAS E1-239 Image taken at Wallops Island

Model being tested with helicopter.
Images take for NASA Document L-1220
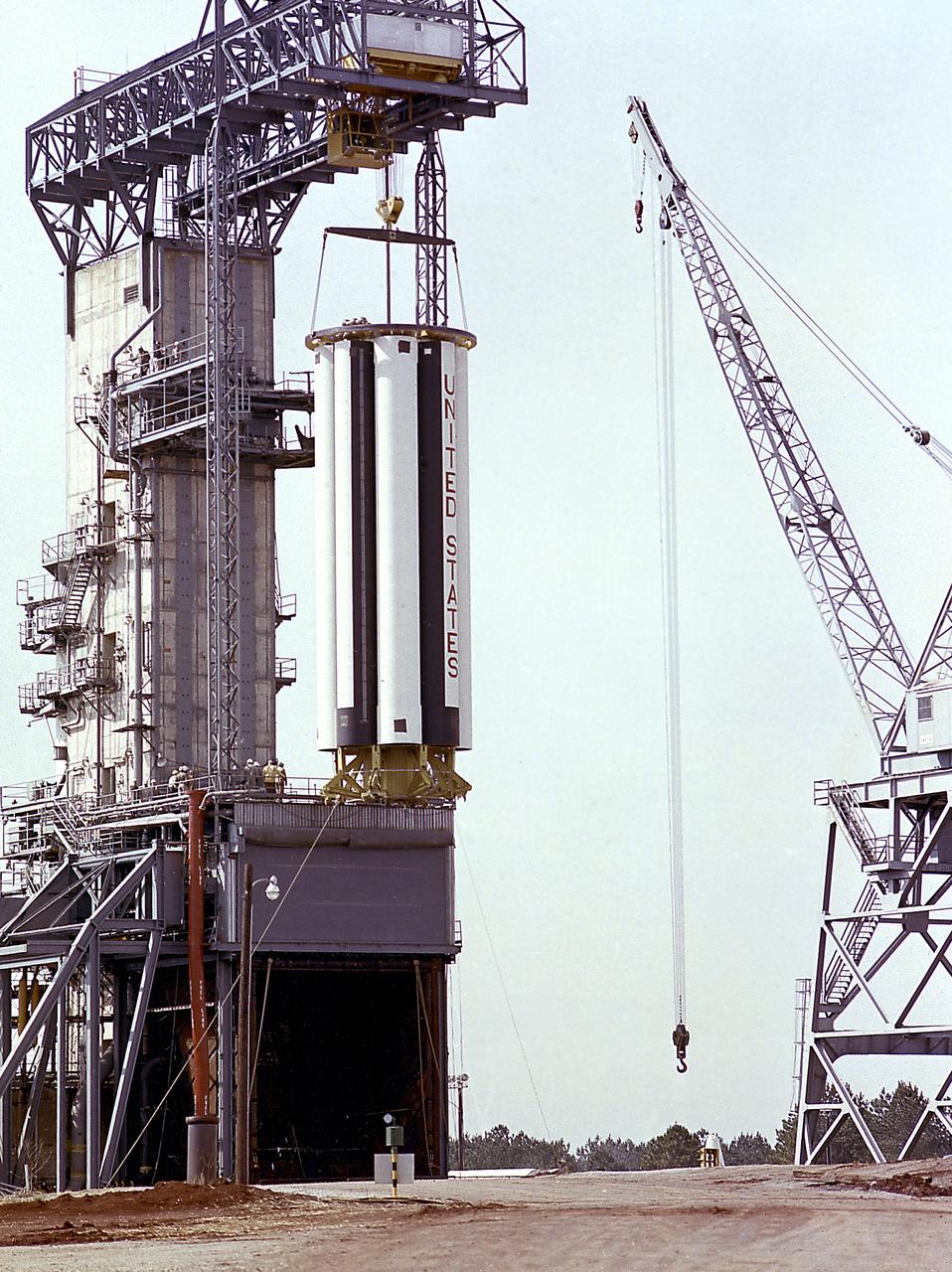

The Saturn Project was approved on January 18, 1960, as a program of the highest national priority. The formal test program to prove out the clustered-booster concept was well underway at Redstone Arsenal. This photograph depicts a mockup of the Saturn booster (S-I stage) being installed in the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) test stand, on January 19, 1960, to check mating of the booster and stand and servicing methods.

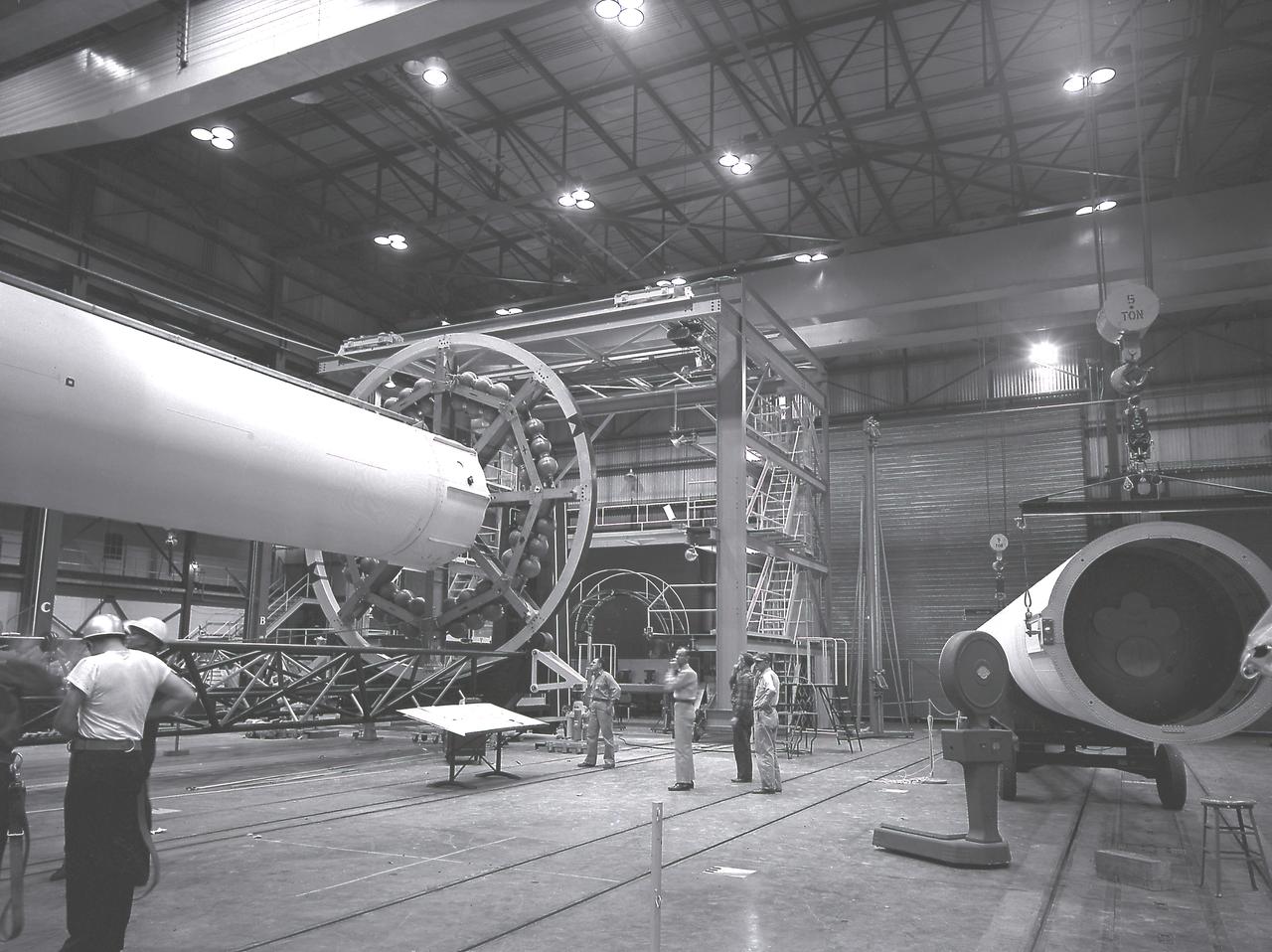
A spider beam for cornecting the Saturn I fuel tanks is being positioned in the fabrication and engineering laboratory of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
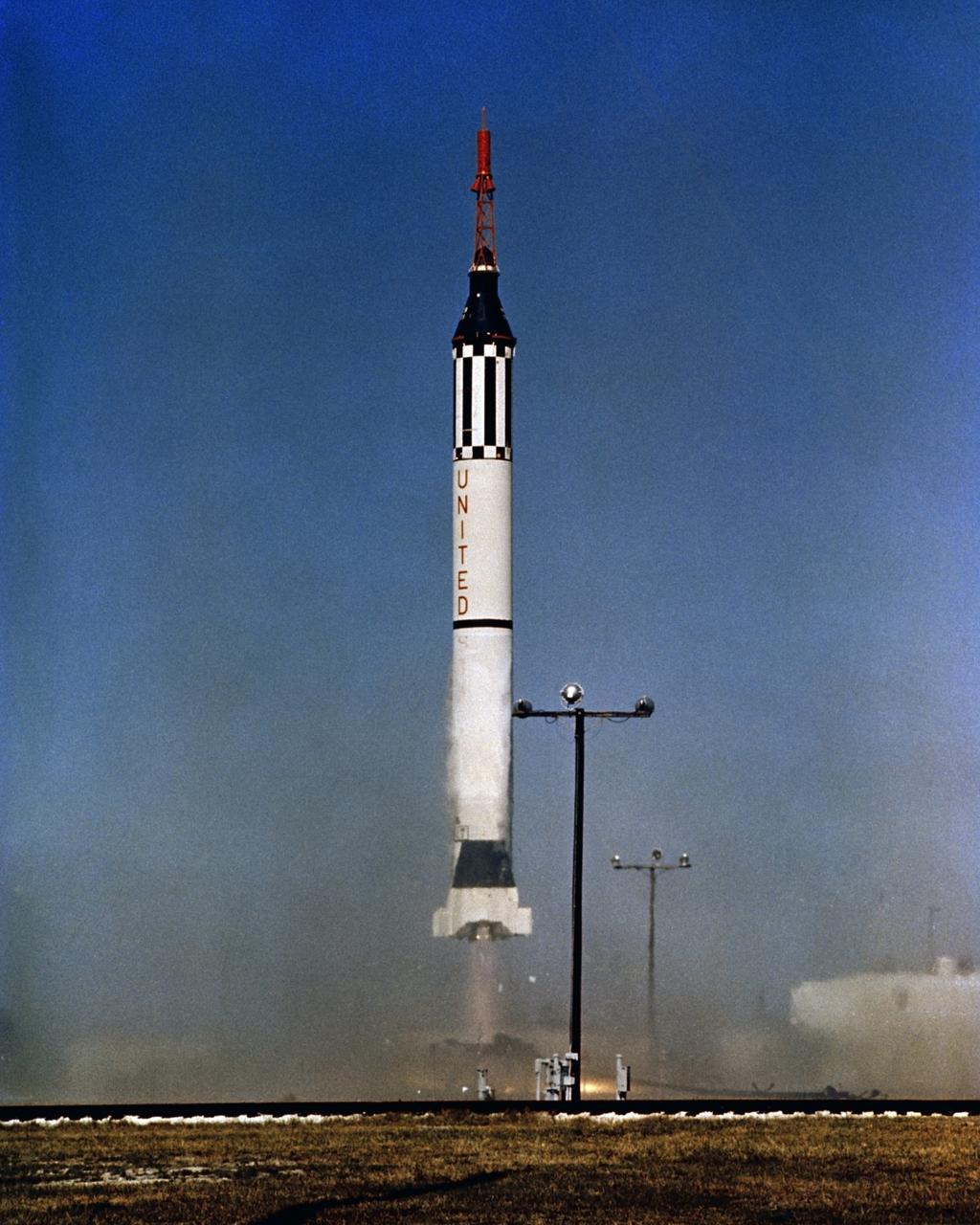

Test 5111 Missile MR1-A at liftoff. Reference PL-60-83896. Item 1.2-23.
Figure 3-5 for NASA Document TM-X-356

100' Satellite Packaging of Echo
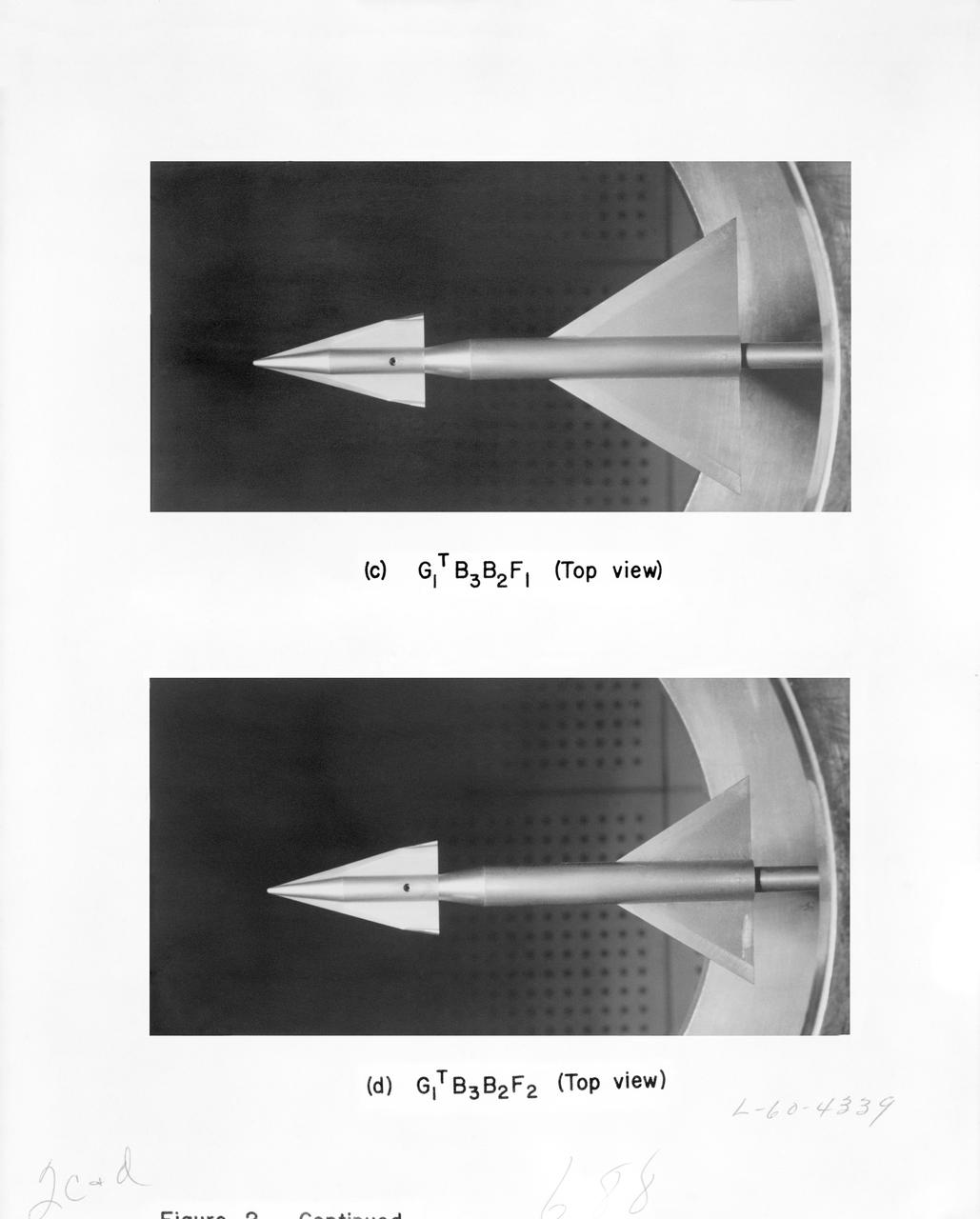
Photos of the eleven booster configurations
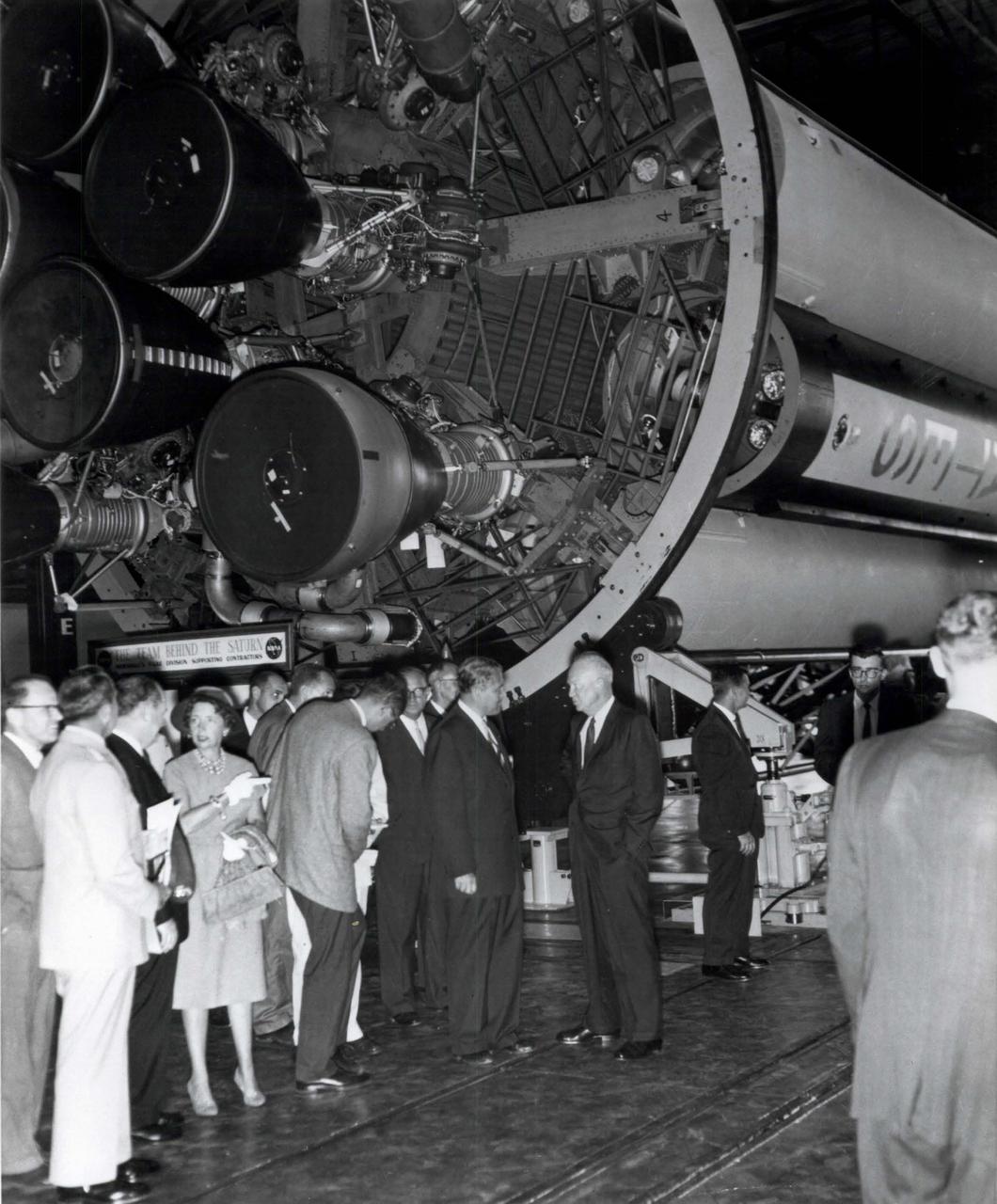
On September 8, 1960 President Dwight D. Eisenhower visited Huntsville, Alabama to dedicate a new NASA field center in honor of General George C. Marshall, Eisenhower's wartime colleague and the founder of the famous Marshall Plan for European recover after World War II. The new George C. Marshall Space Flight Center was placed under the control of Dr. Wernher Von Braun shown here talking with President Eisenhower. As parto f his remarks dedicating the center, President Eisenhowe refereed to General Marshall as a "man of yar, yet a builder of peace". the Marshall Center's first major assignment including building the huge Saturn V rocket that launched human beings on their first journey to the surface of the moon in 1969.
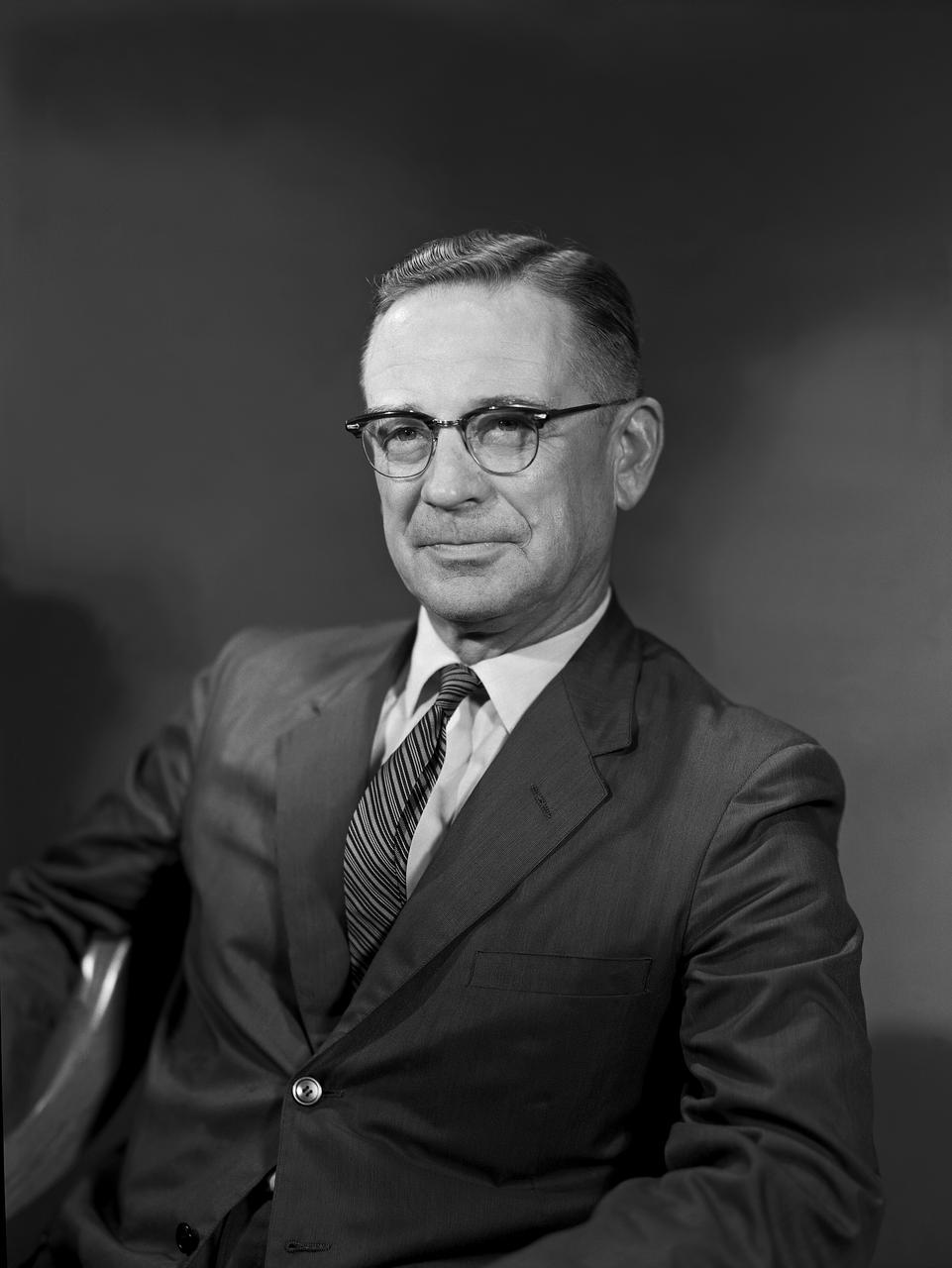

Portrait of Charles H. Zimmerman Associate Chief, Aero-Space Mechanics Division
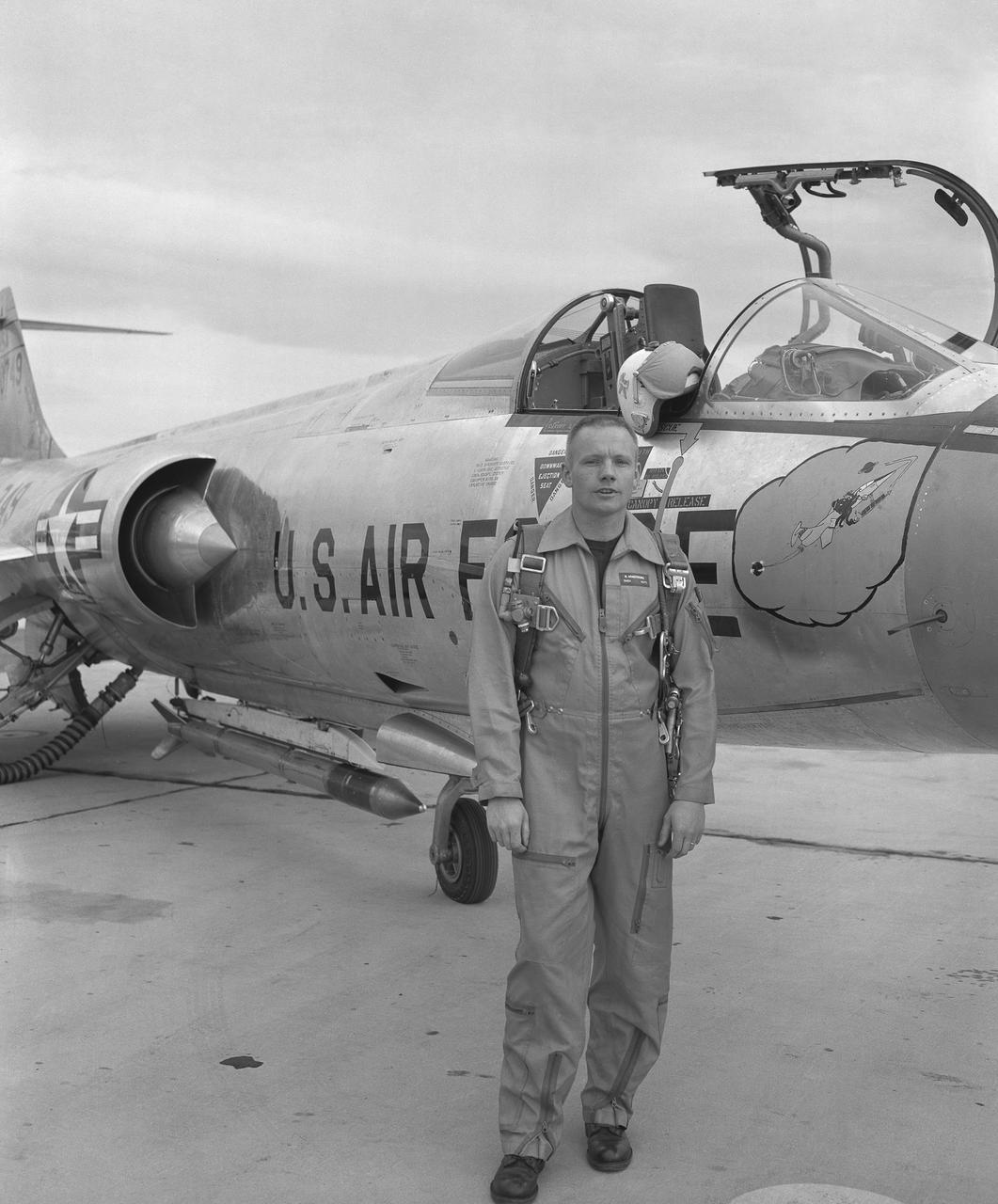

Famed astronaut Neil A. Armstrong – the first person to set foot on the Moon during the historic Apollo 11 mission in July 1969 – spent seven years as a research pilot at the NACA-NASA High-Speed Flight Station, now NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, before joining the space program. During his time there, he served as a project pilot on the F-100A, F-100C, F-101, and F-104A (pictured here).

From the program’s inception, Neil Armstrong was actively engaged in both the piloting and engineering aspects of the X-15. He flew the first mission using a new flow-direction sensor (ball nose) and the first flight with a self-adaptive flight control system. Collaborating closely with designers and engineers on the system’s development, he made seven flights in the X-15 between December 1960 and July 1962. During these missions, he reached a peak altitude of 207,500 feet in the X-15-3 and a top speed of 3,989 mph (Mach 5.74) in the X-15-1.
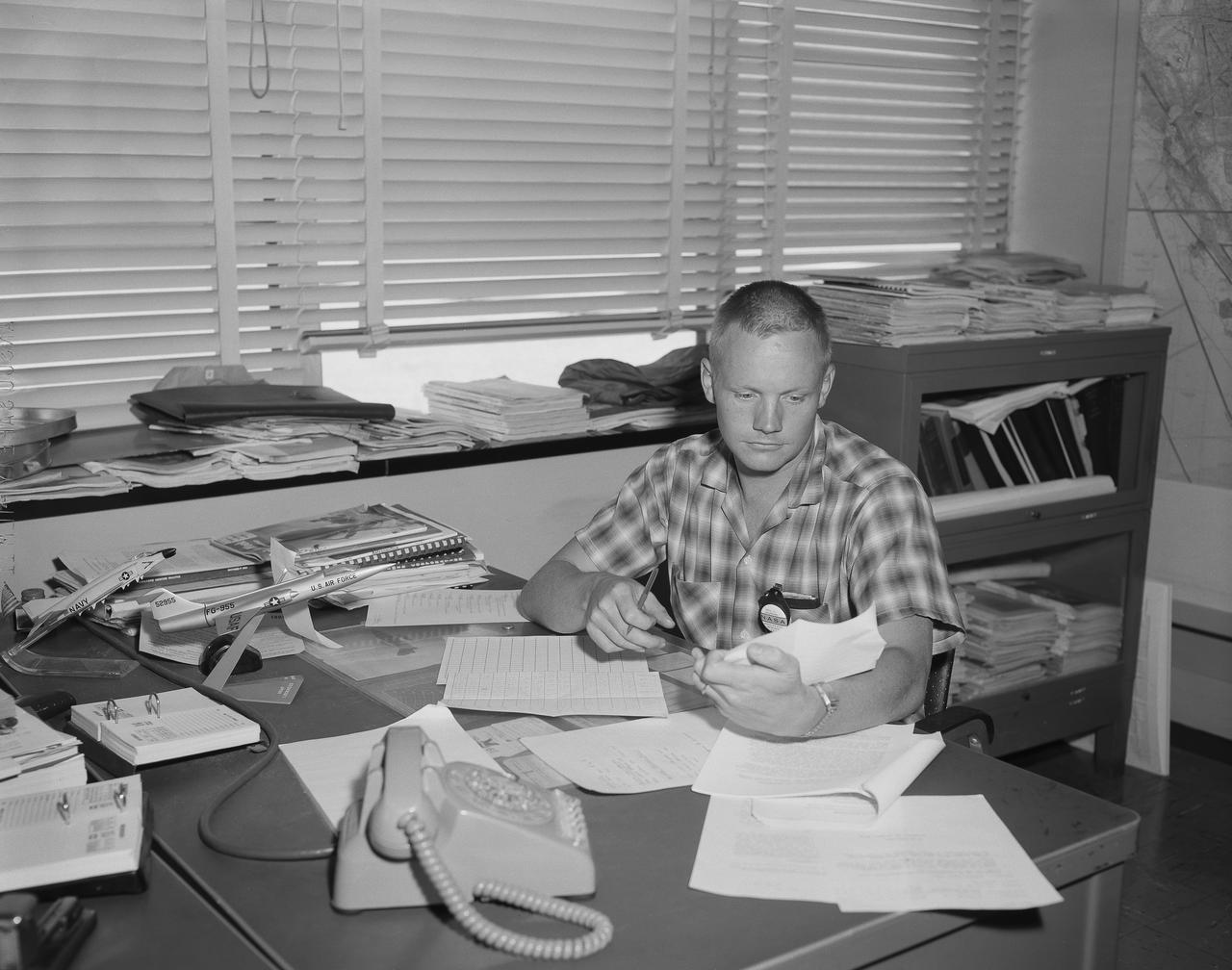

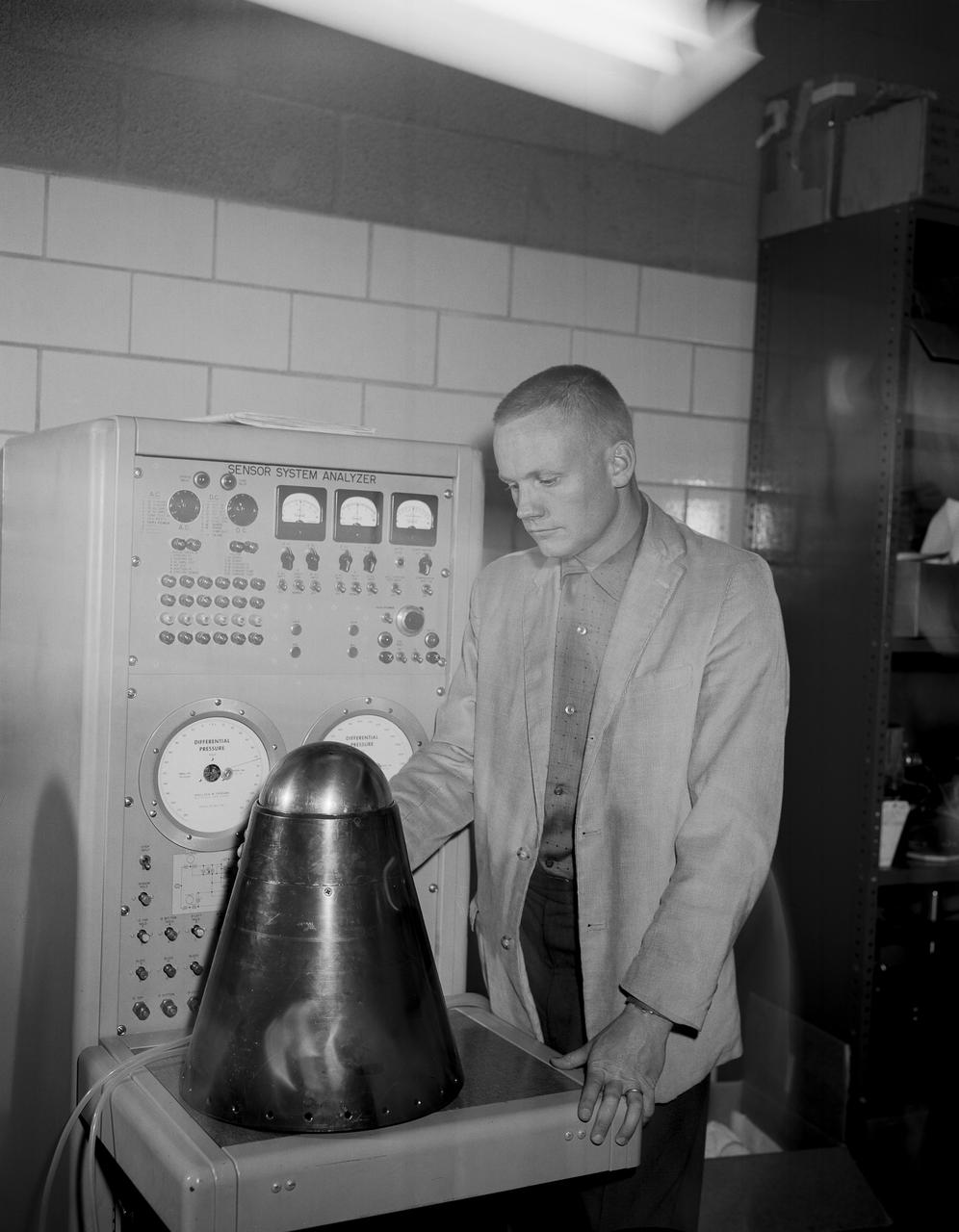
Famed astronaut Neil A. Armstrong – the first person to set foot on the Moon during the historic Apollo 11 mission in July 1969 – spent seven years as a research pilot at the NACA-NASA High-Speed Flight Station, now NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, before joining the space program. During his tenure, Armstrong was actively engaged in both the piloting and engineering aspects of numerous NASA programs and projects.
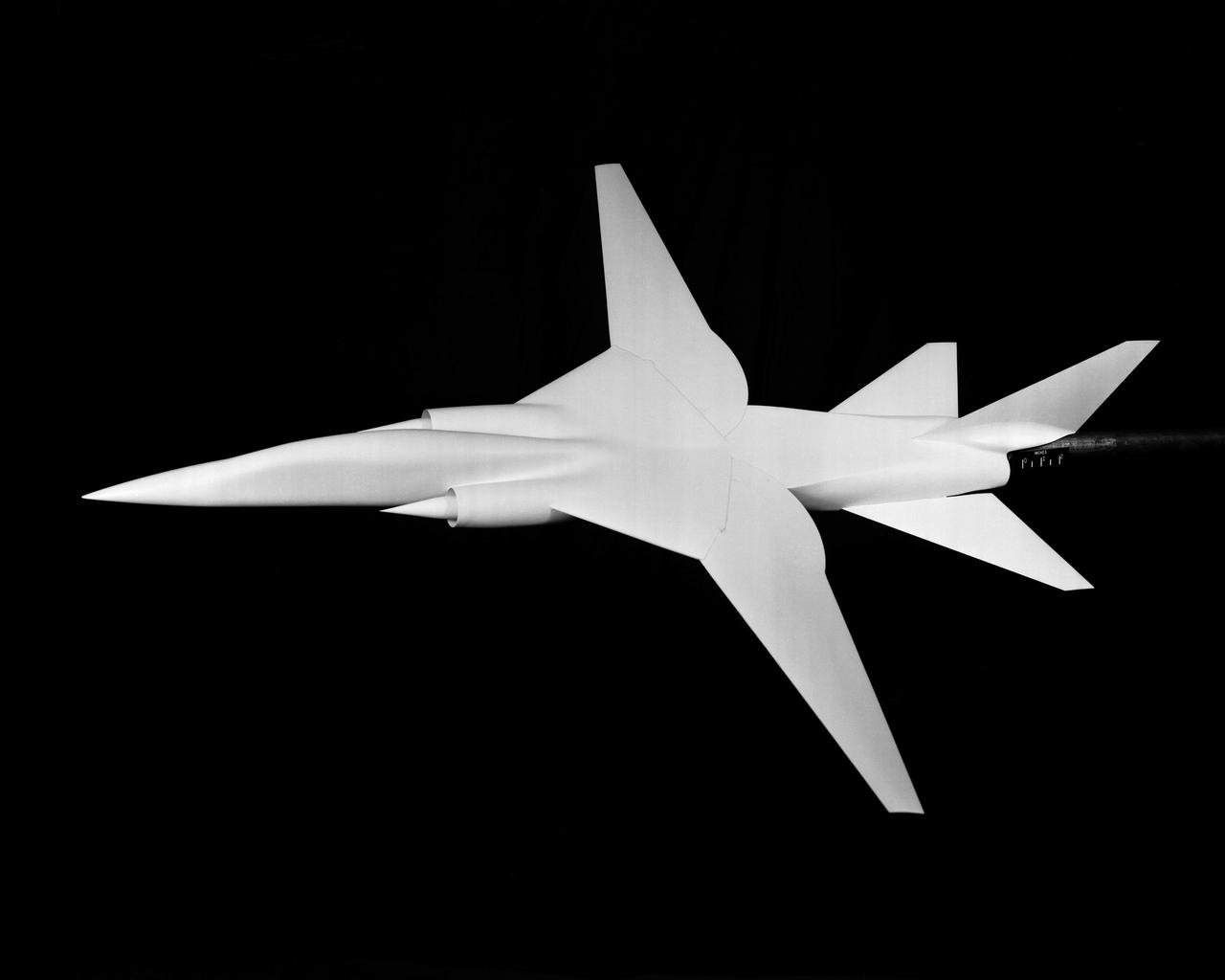

Project: Wing Sweep Range Series TAC Variable Sweep Model configure 8 A. Taken at 8 foot tunnels building 641. L60-3412 through 3416 Model of proposed military supersonic attack airplane shows wing sweep range. TAC Models taken at the 8 Foot Tunnel. Photograph published in Sixty Years of Aeronautical Research 1917-1977 By David A. Anderton. A NASA publication. Page 53.
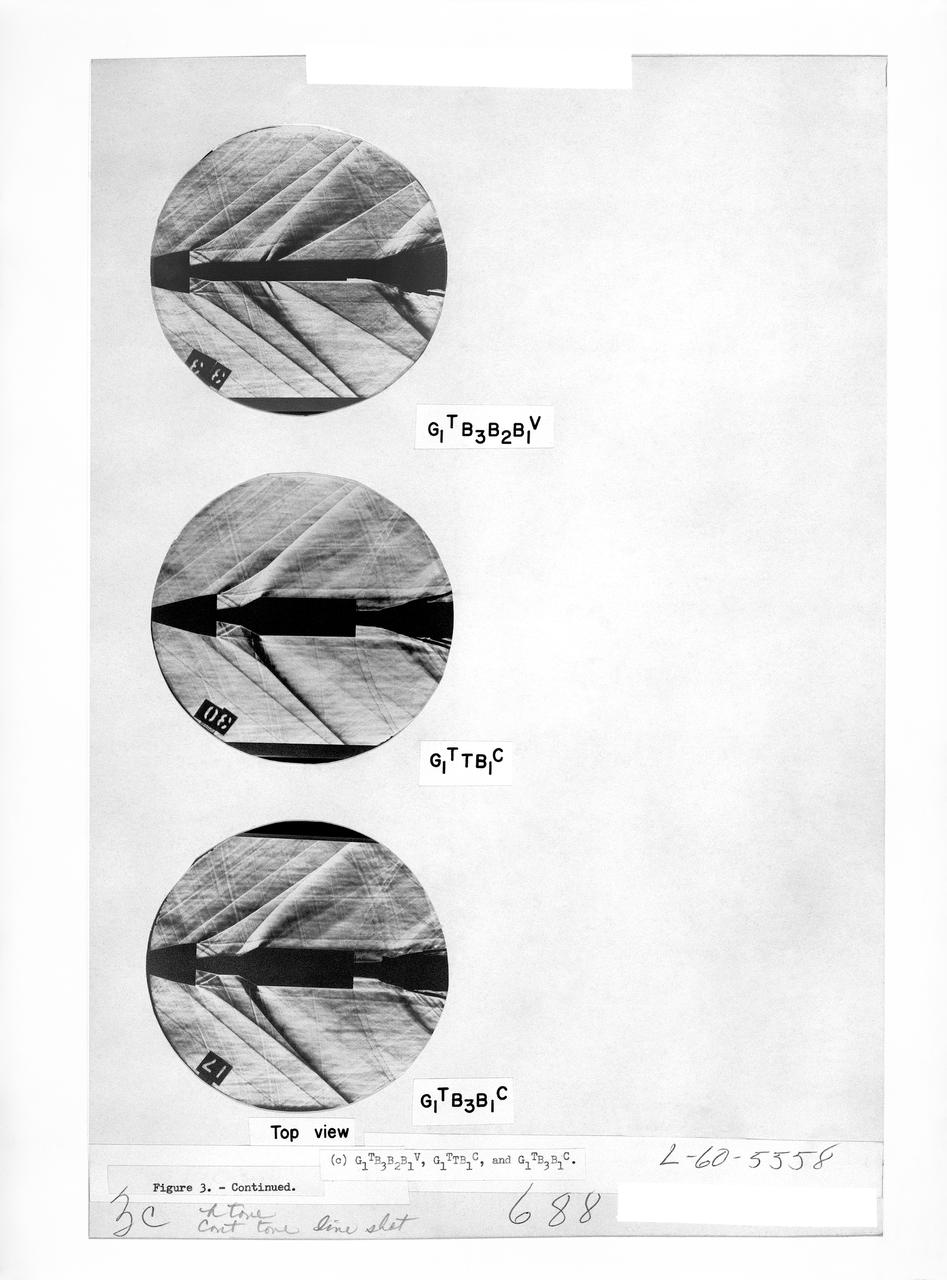
Figure 3-5 for NASA Document TM-X-356
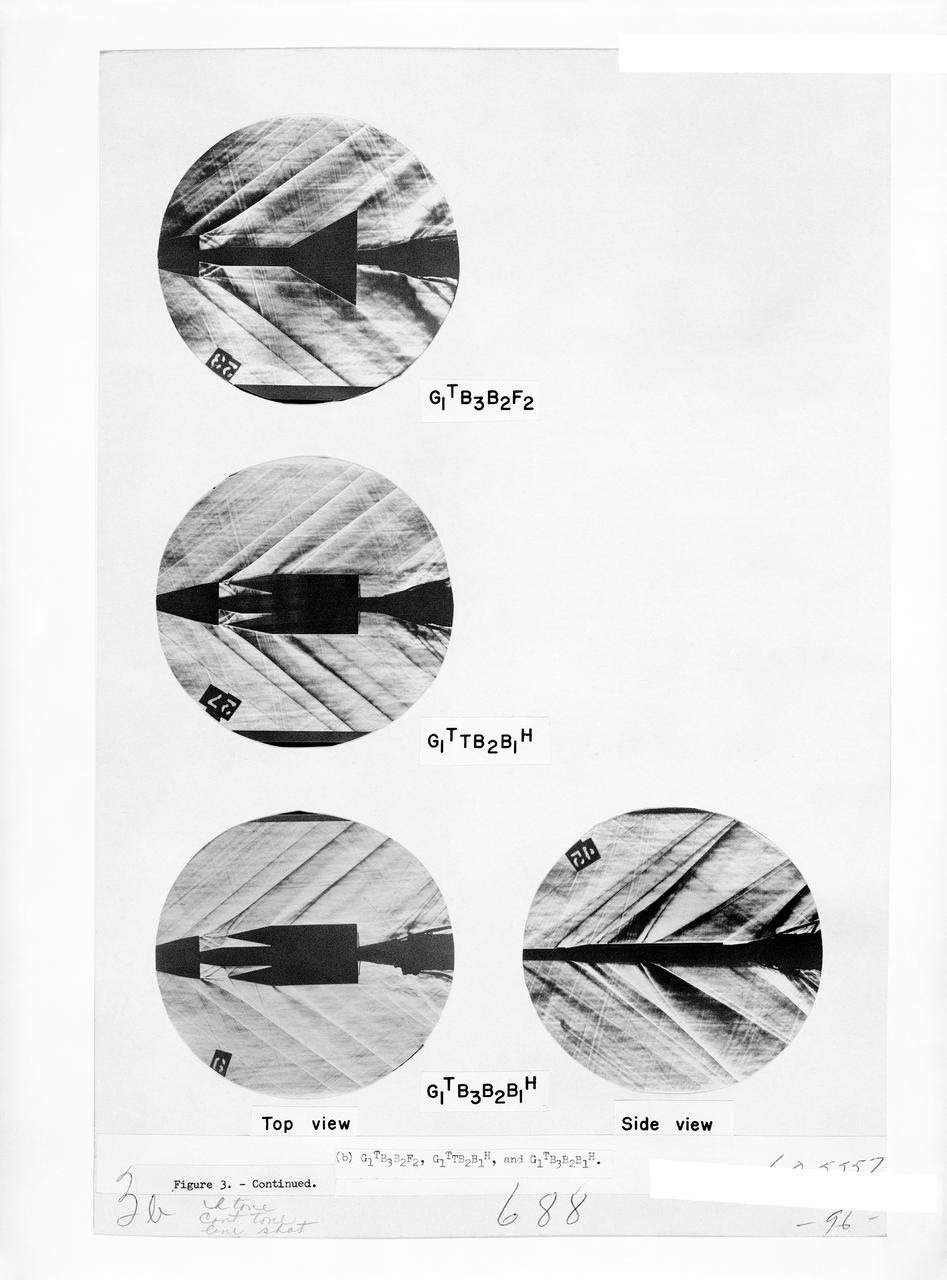
Figure 3-5 for NASA Document TM-X-356

100' Satellite Packaging of Echo

Model of Winged Space Vehicle

Edward O. Buckbee, the first Director of the Alabama Space Science Center (left), and Dr. Wernher von Braun (right) view a demonstration of a simulated spacecraft which uses an actual hybrid rocket engine for liftoff, hover, and landing. The display was presented to the Alabama Space Science Center, later renamed the U.S. Space and Rocket Center, by United Technology Center, a division of United Aircraft.

Model of Mercury capsule used for wind tunnel testing.
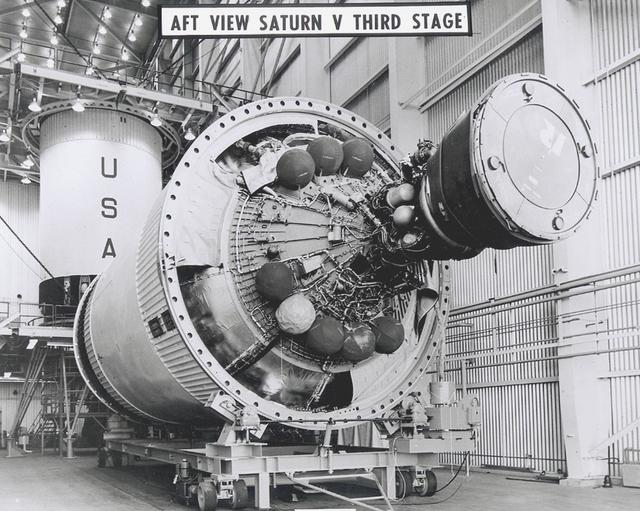
The powerful J-2 engine is prominent in this photograph of a Saturn V Third Stage (S-IVB) resting on a transporter in the Manufacturing Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
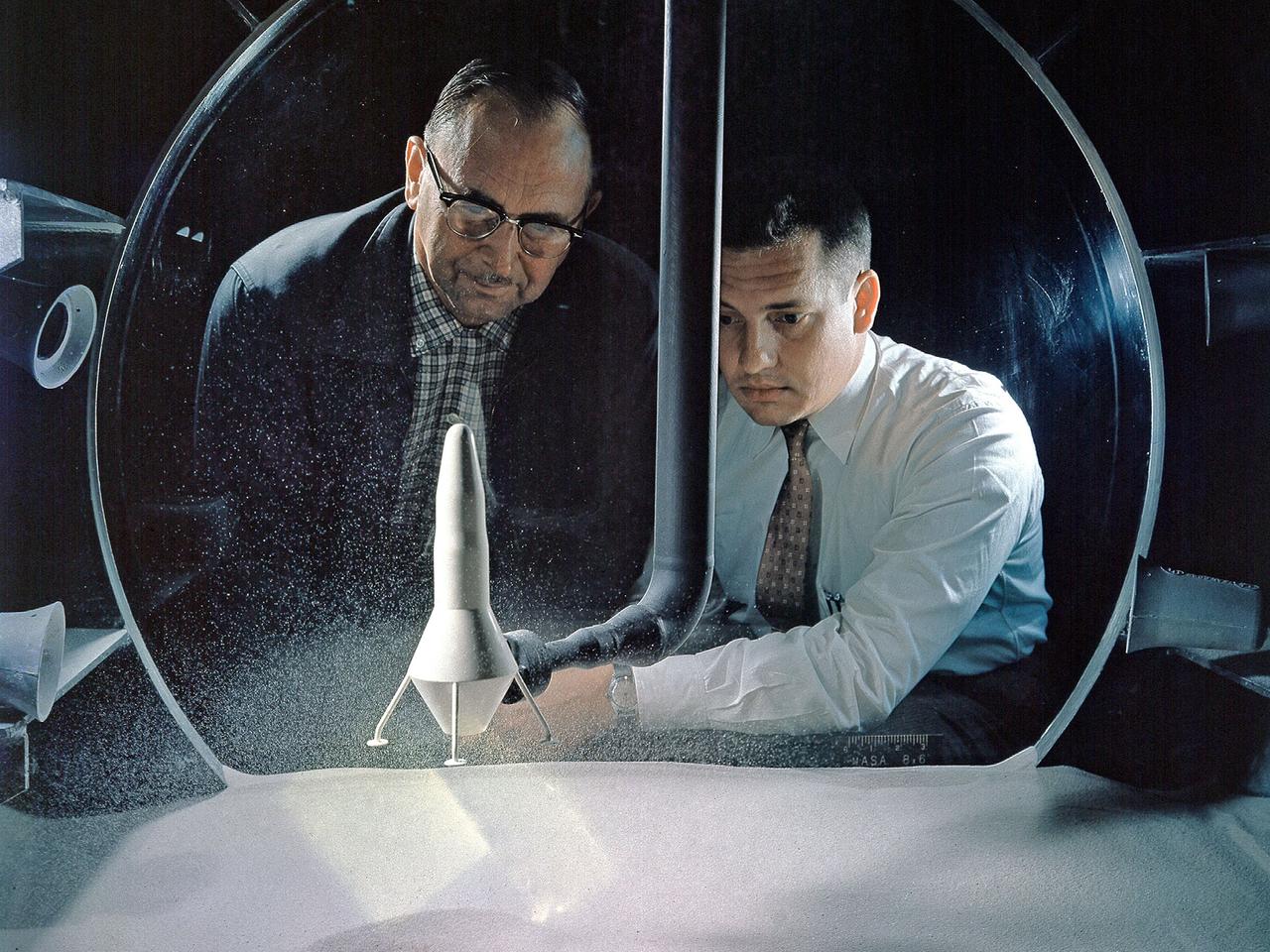

NASA Researchers view a demonstration of the moon dust simulator in the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel facility at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The researchers were studying the effect of the lunar lander’s retrorockets on the loose dust on the lunar surface. There was some concern that the retrorockets would kick up so much dust that the crew would lose the ability to see. They also did not know how the dust’s behavior would be affected by the space atmosphere. This small vacuum tank was built for very preliminary investigations into this matter. The pipe entering the top of the tank supplied the airflow to the lander model, which was affixed to the pipe. The researchers altered the vacuum levels and speed of the airflow.
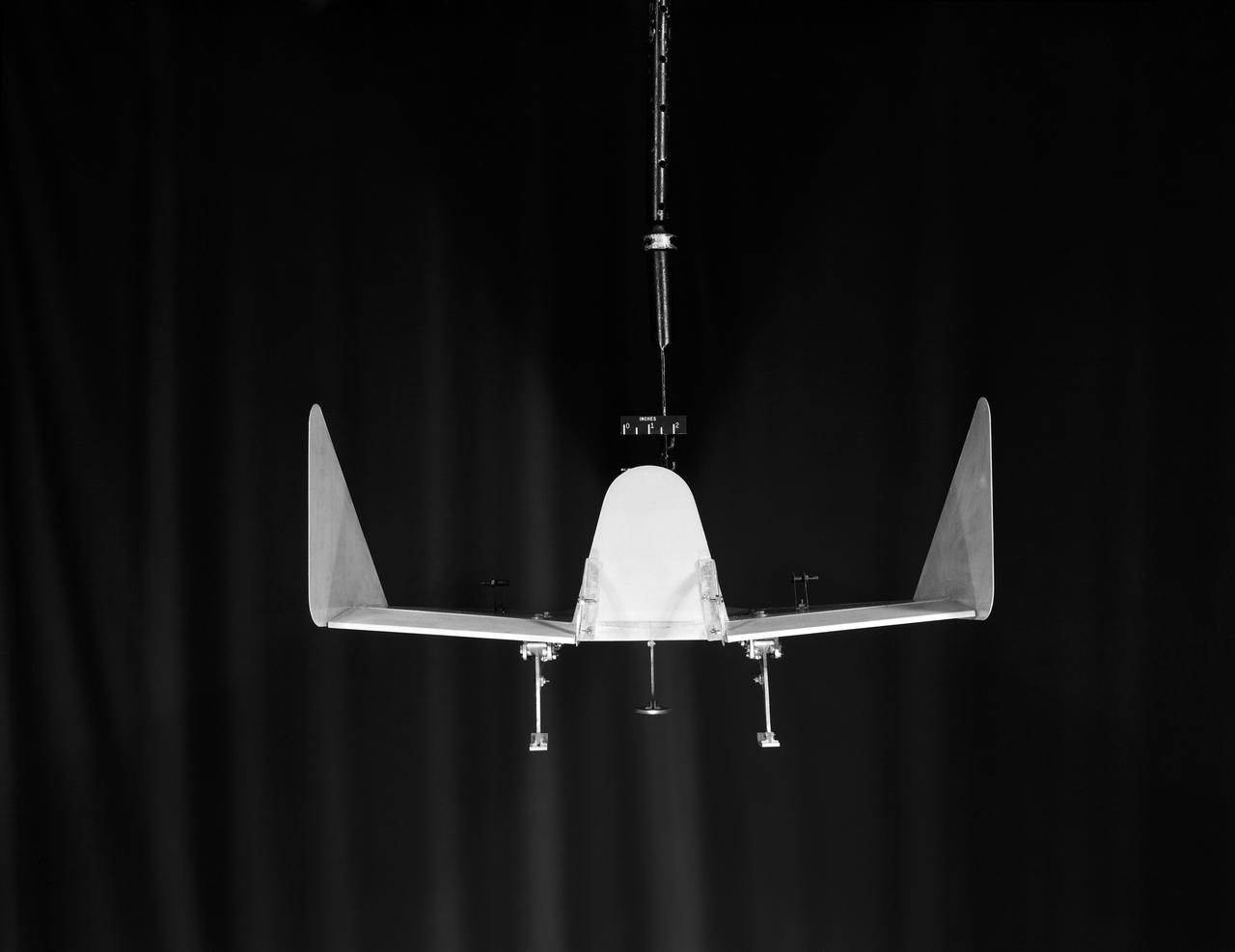

Model of Winged Space Vehicle

Mercury astronaut John Glenn prepares for a test in the Multi-Axis Space Test Inertia Facility (MASTIF) inside the Altitude Wind Tunnel at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The MASTIF was a three-axis test rig with a pilot’s chair mounted in the center. The device was designed to train Project Mercury pilots to bring a spinning spacecraft under control. An astronaut was secured in a foam couch in the center of the rig. The rig was then spun on three axes from 2 to 50 rotations per minute. Small nitrogen gas thrusters were used by the astronauts to bring the MASTIF under control. In February and March 1960, the seven Project Mercury astronauts traveled to Cleveland to train on the MASTIF. Warren North and a team of air force physicians were on hand to monitor their health. After being briefed by Lewis pilot Joe Algranti and researcher James Useller, the rider would climb into the rig and be secured in the chair, as seen in this photograph. A Lewis engineer would then slowly set the MASTIF in motion. It was the astronaut’s job to bring it under control. Each individual was required to accumulate 4.5 to 5 hours of MASTIF time. Glenn became the first American to orbit the earth on February 20, 1962 in the Friendship 7 Mercury capsule. In March 1999, the Lewis Research Center was renamed the John H. Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field.

G60-02737 (May 1960) --- Astronaut M. Scott Carpenter. Photo credit: NASA
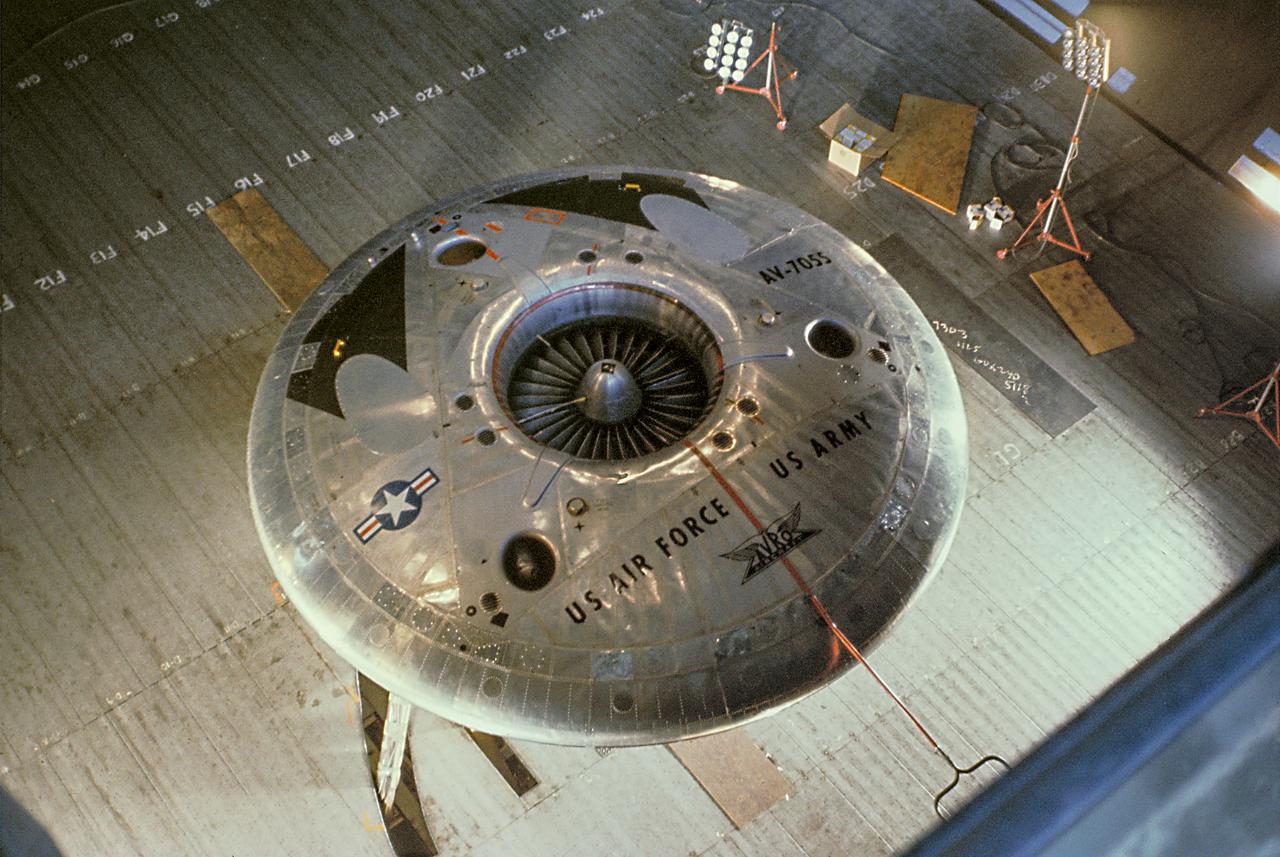
Color view of the Avrocar from overhead in the 40x80 wind tunnel, without A1:H73 mounted on variable height struts.
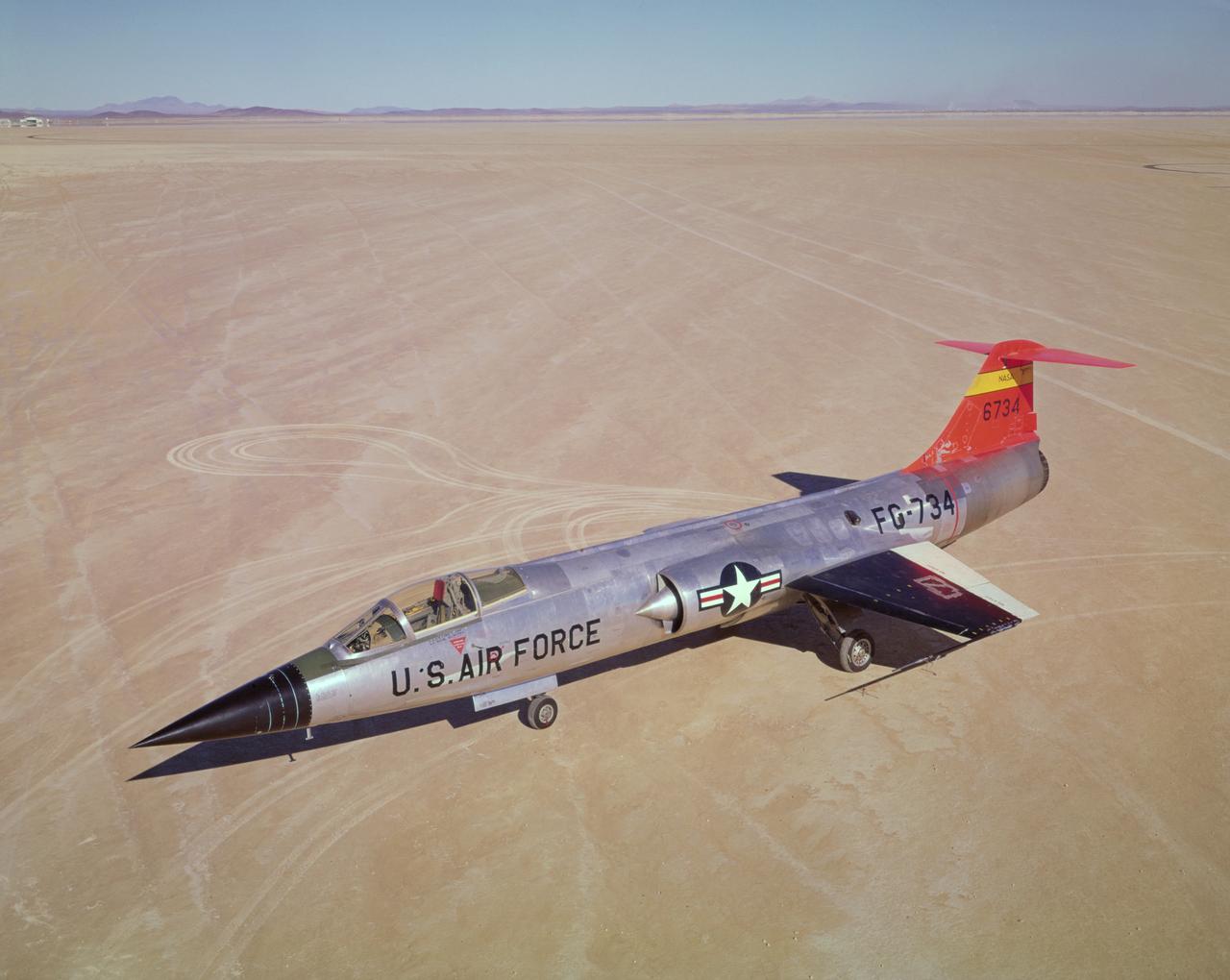

F-104A #734 on lakebed. 11/16/60
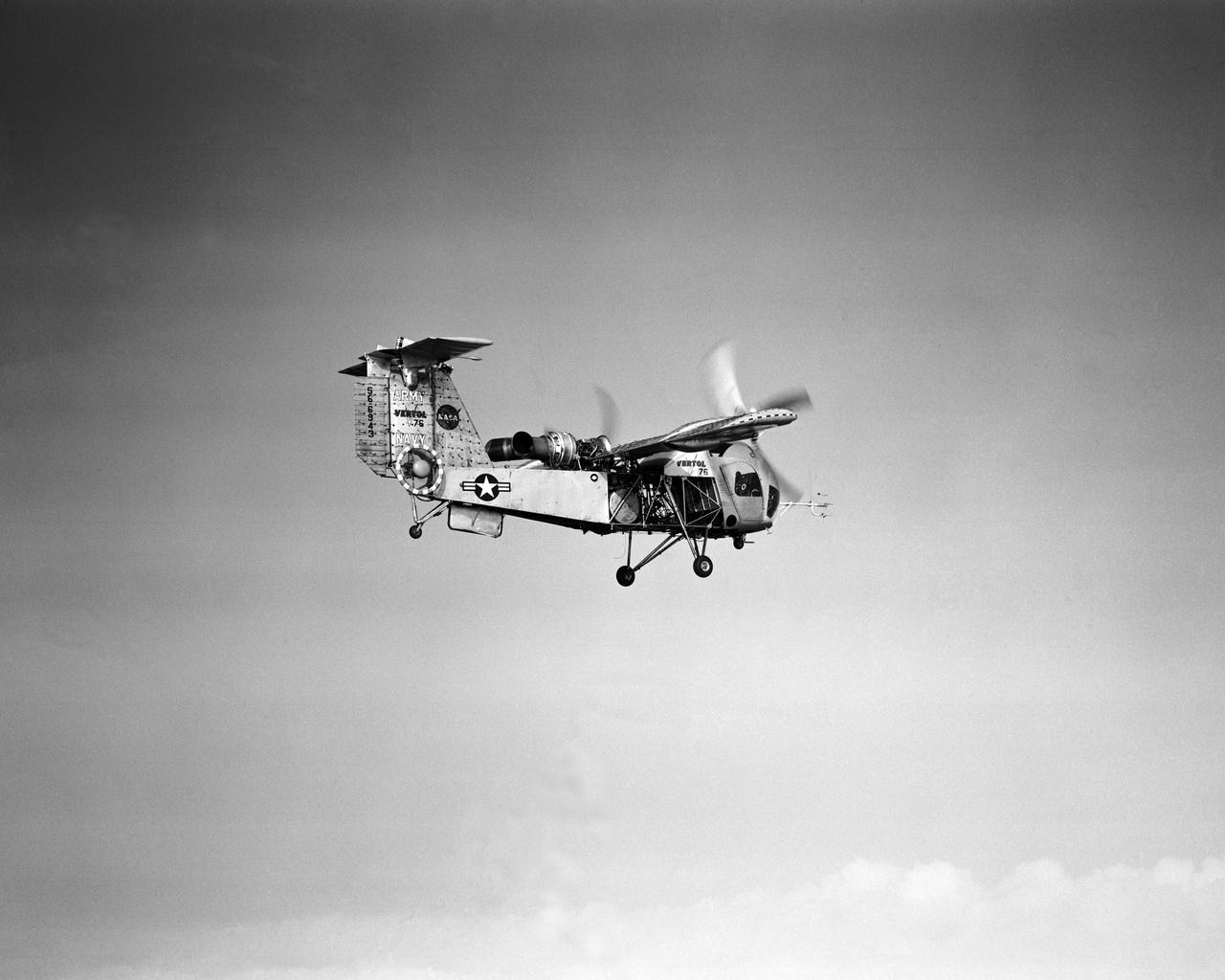

Vertol 76 Tilt Wing VTOL. Photographed 9/13/1960. Photograph published in Sixty Years of Aeronautical Research 1917-1977 By David A. Anderton, A NASA publication, Page 62.
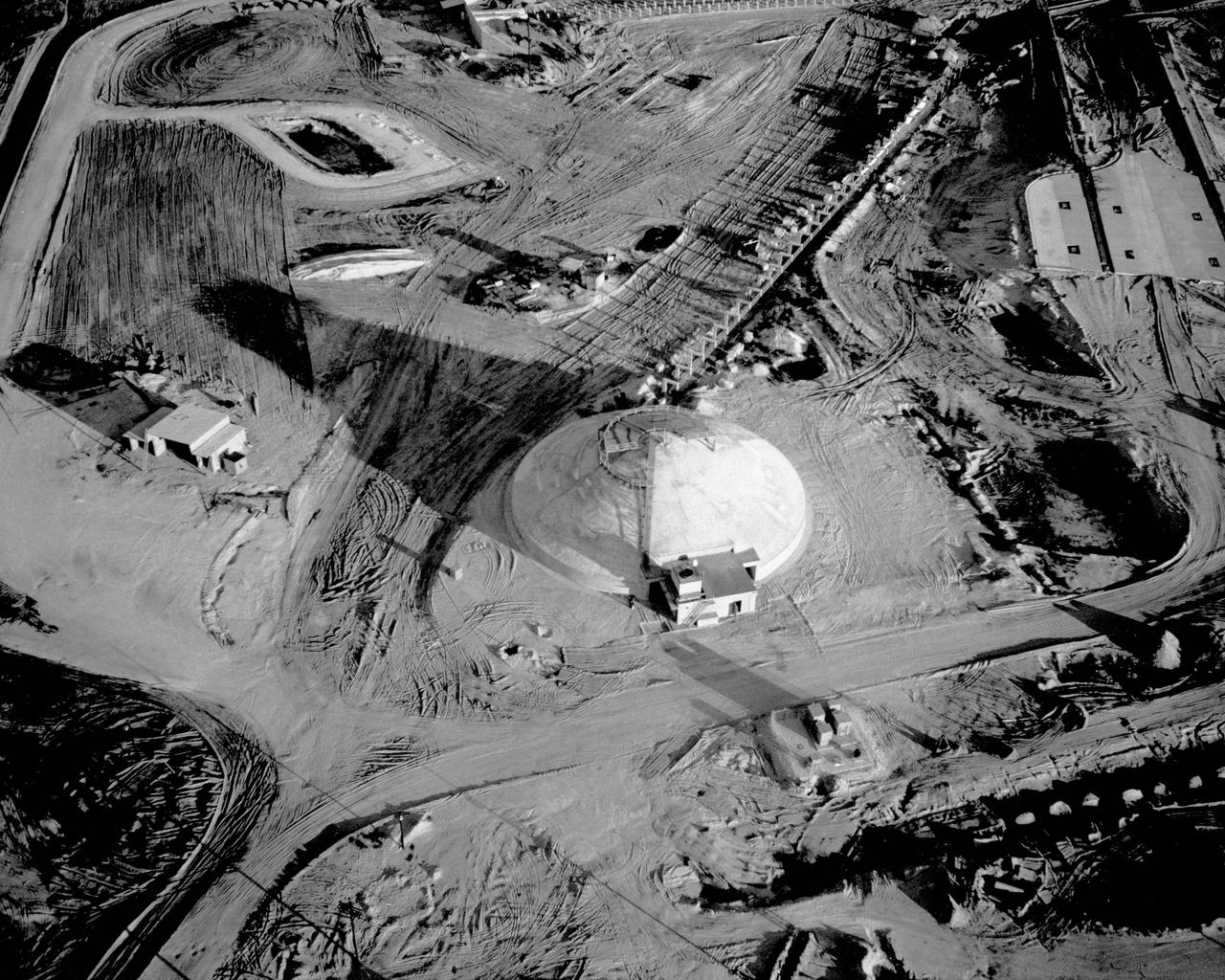

AERIAL VIEW PAD 34 BLOCKHOUSE CONSTRUCTION PROGRESS
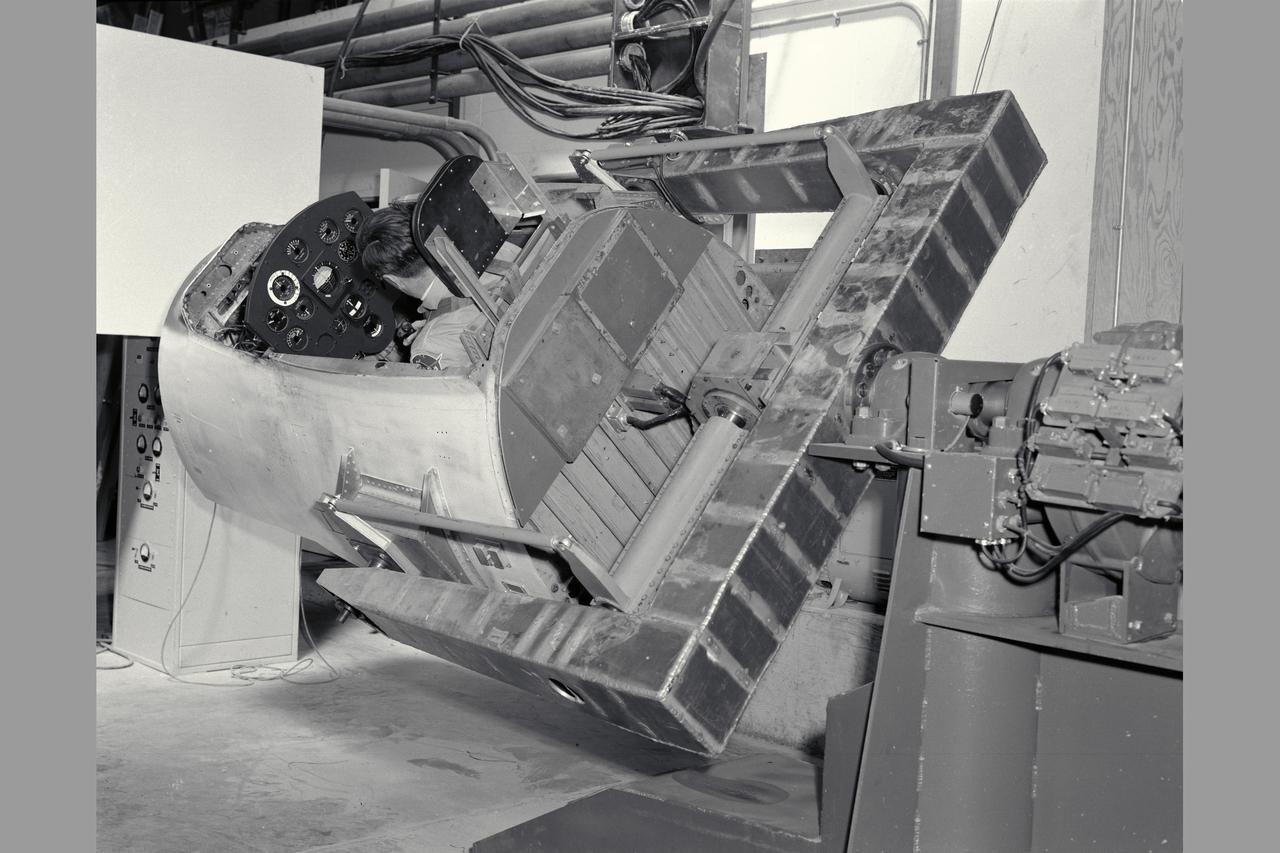

3/4 rear view with pilot Merriweather - 60 degrees bank angle. NE-2 degree of freedom simulator set-up for pitch and roll motion.
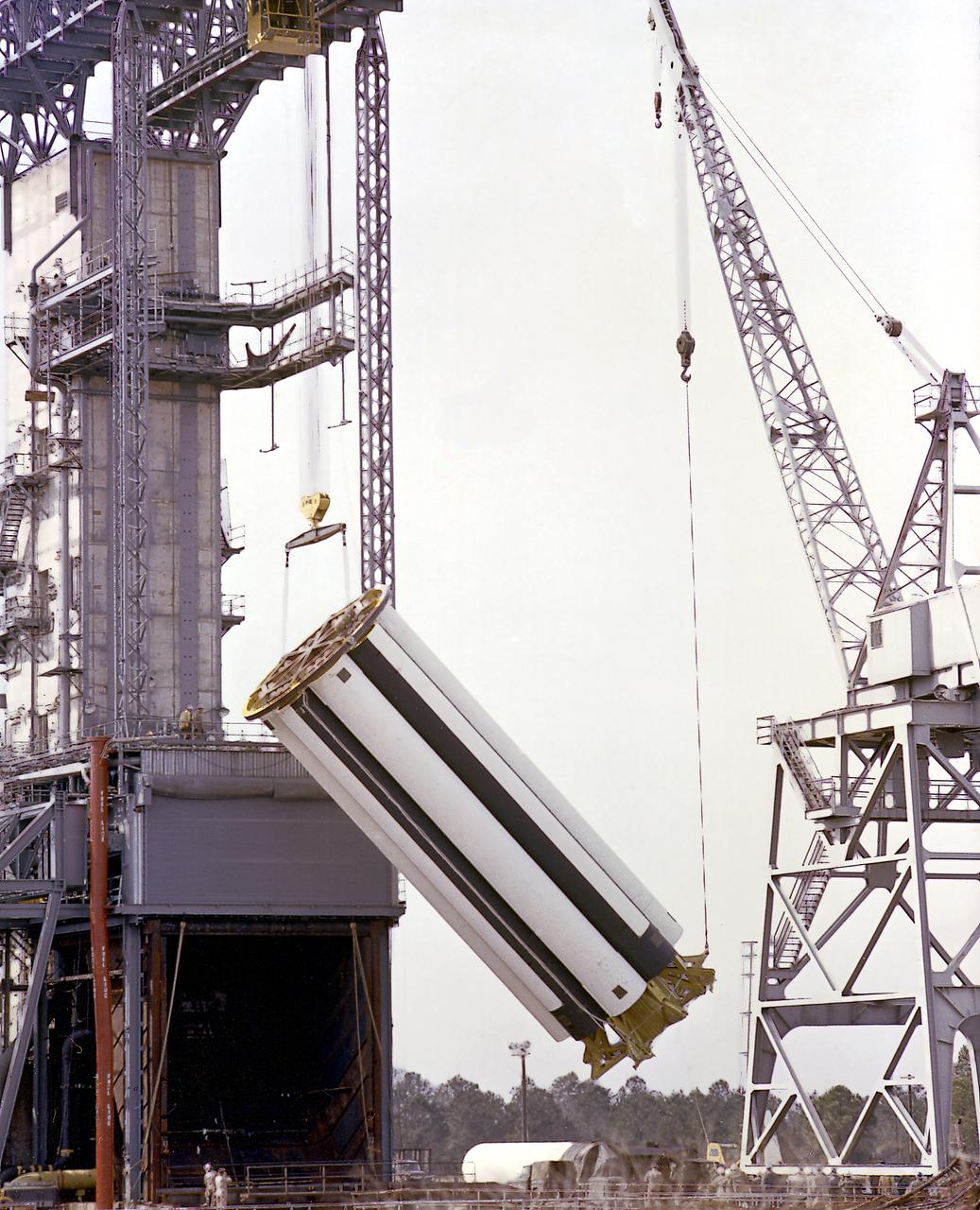

The Saturn Project was approved on January 18, 1960 as a program of the highest national priority. The formal test program, to prove out the clustered-booster concept, was well underway at Redstone Arsenal. This photograph depicts a mockup of the Saturn booster (S-I stage) being installed in the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) test stand, on January 19, 1960, to check mating of the booster and stand and servicing methods.
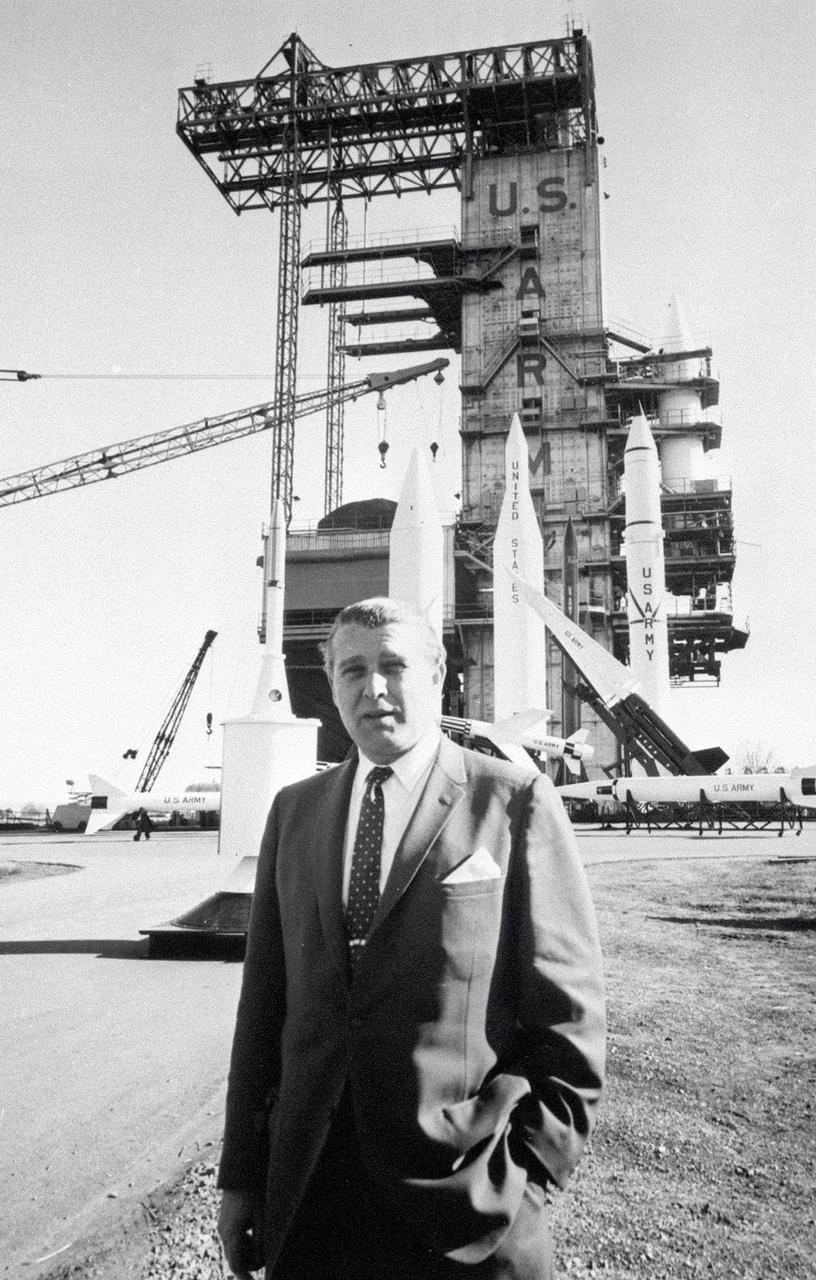

In this photo, Director of the US Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) Development Operations Division, Dr. Wernher von Braun, is standing before a display of Army missiles celebrating ABMA's Fourth Open House. The missiles in the background include (left to right) a satellite on a Juno II shroud with a Nike Ajax pointing left in front of a Jupiter missile. The Lacrosse is in front of the Juno II. The Nike Hercules points skyward in front of the Juno II and the Redstone.
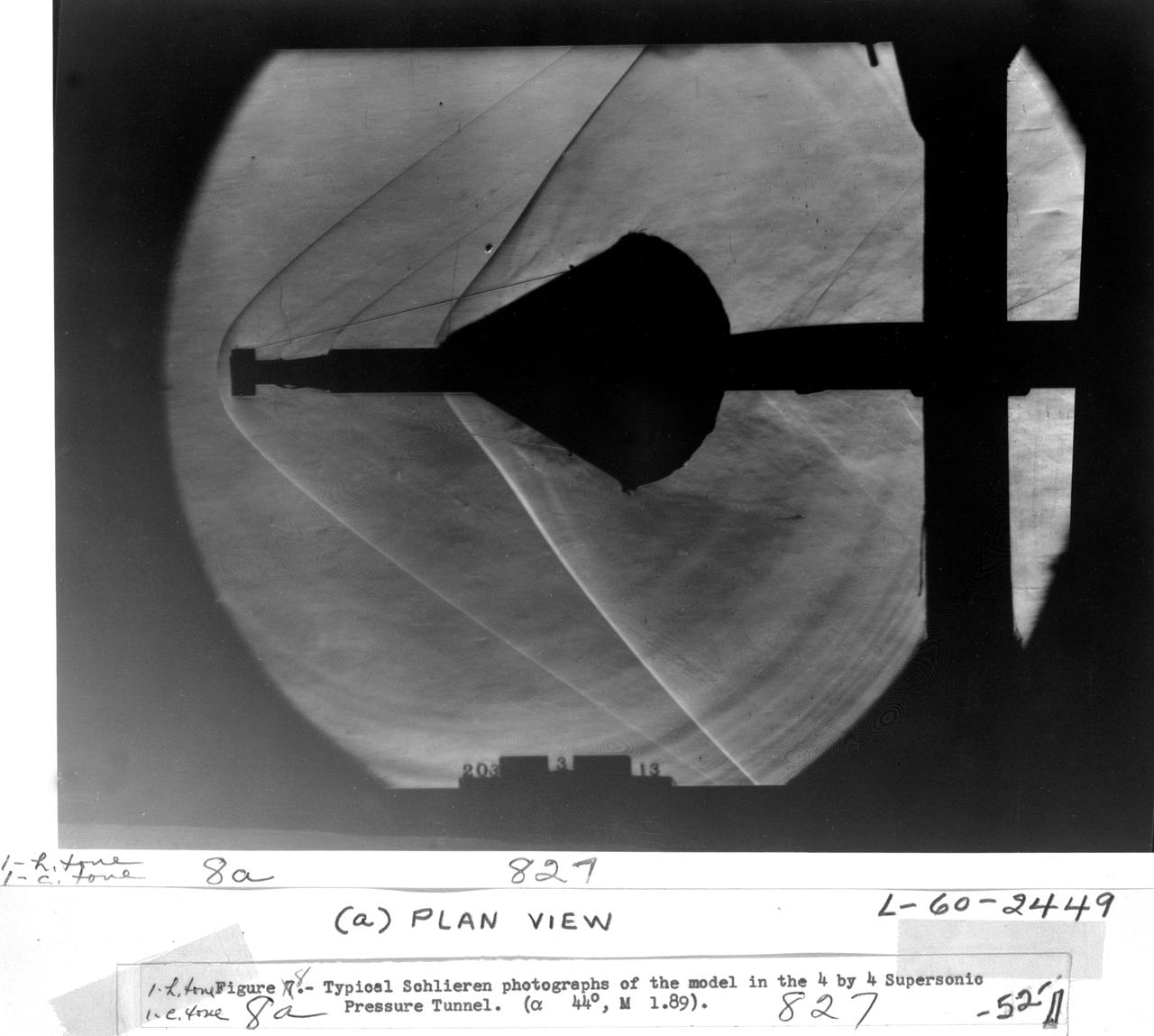
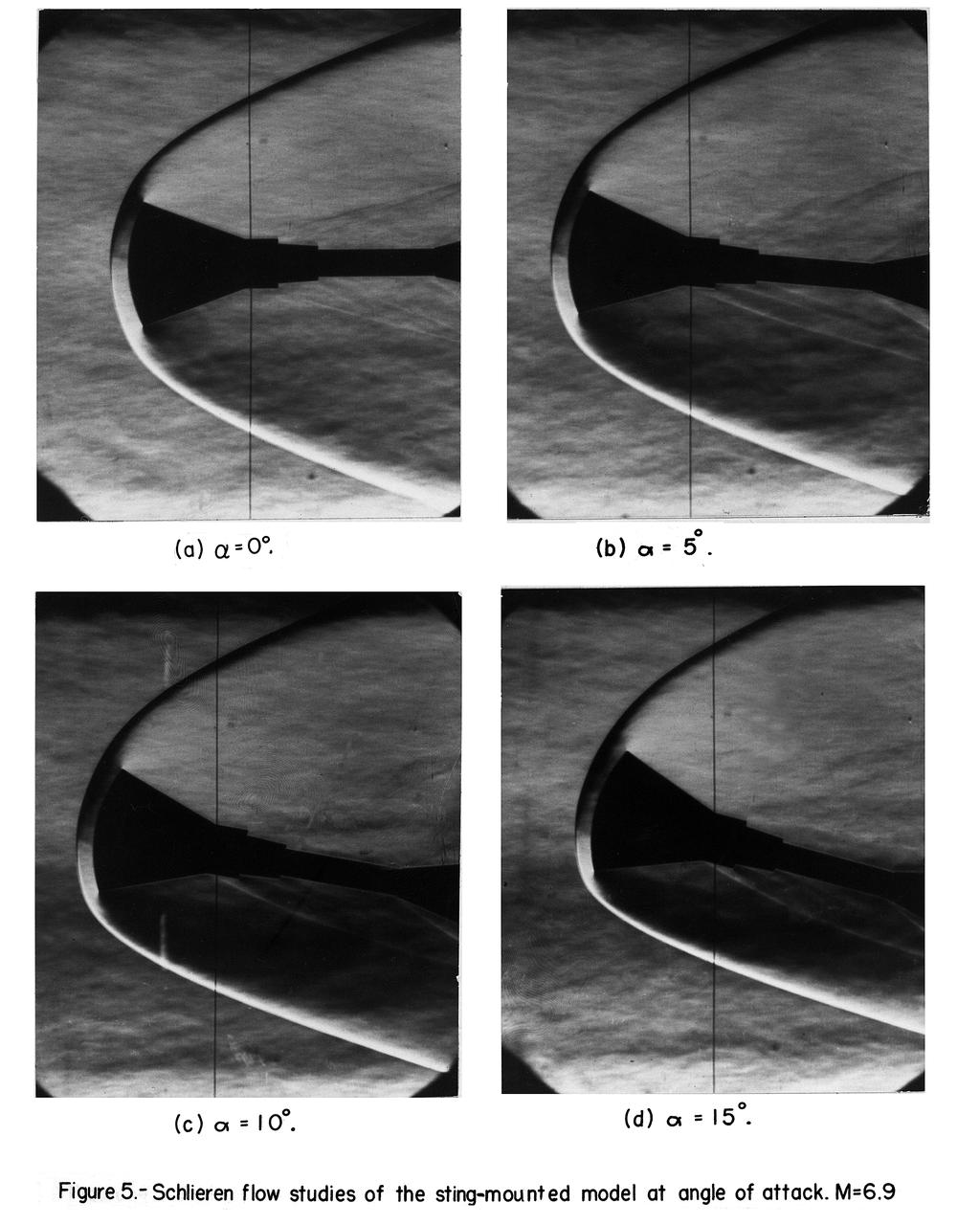
Schlieren photographs of the model in 4 x 4 Foot supersonic pressure tunnel
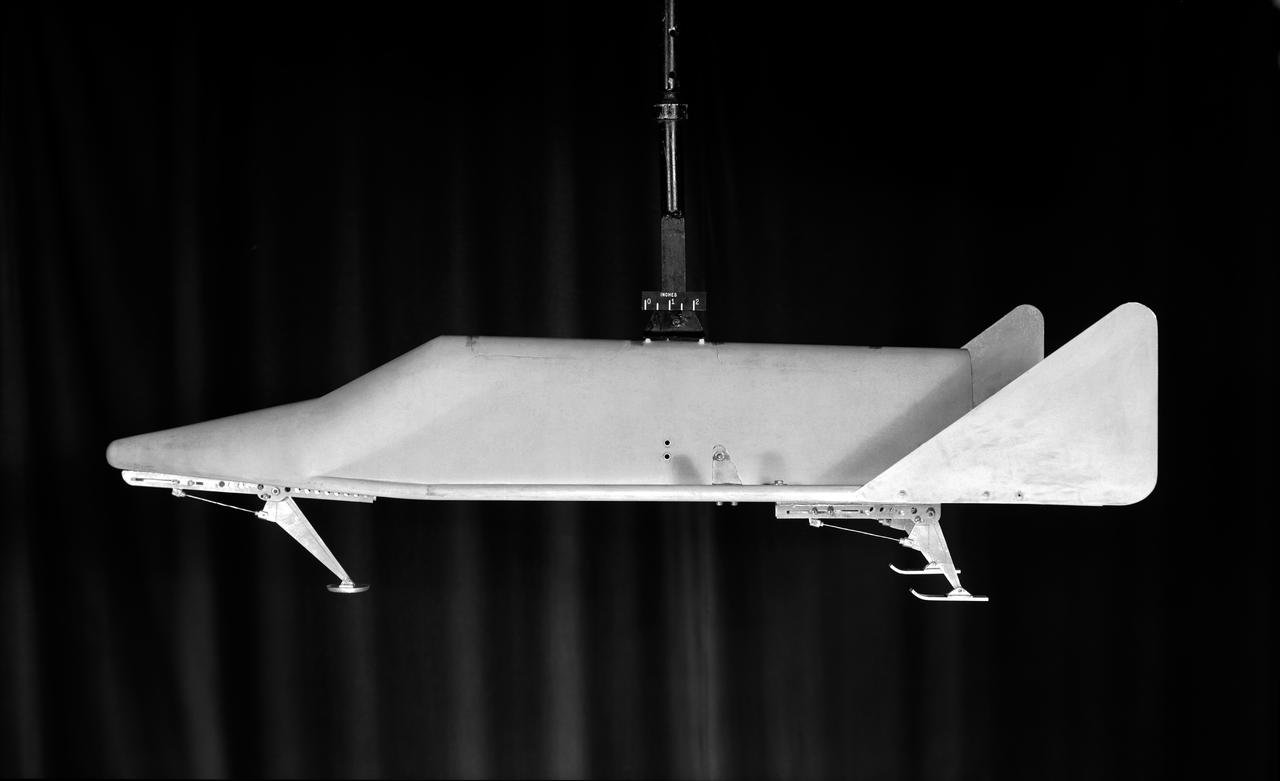

Model of Winged Space Vehicle
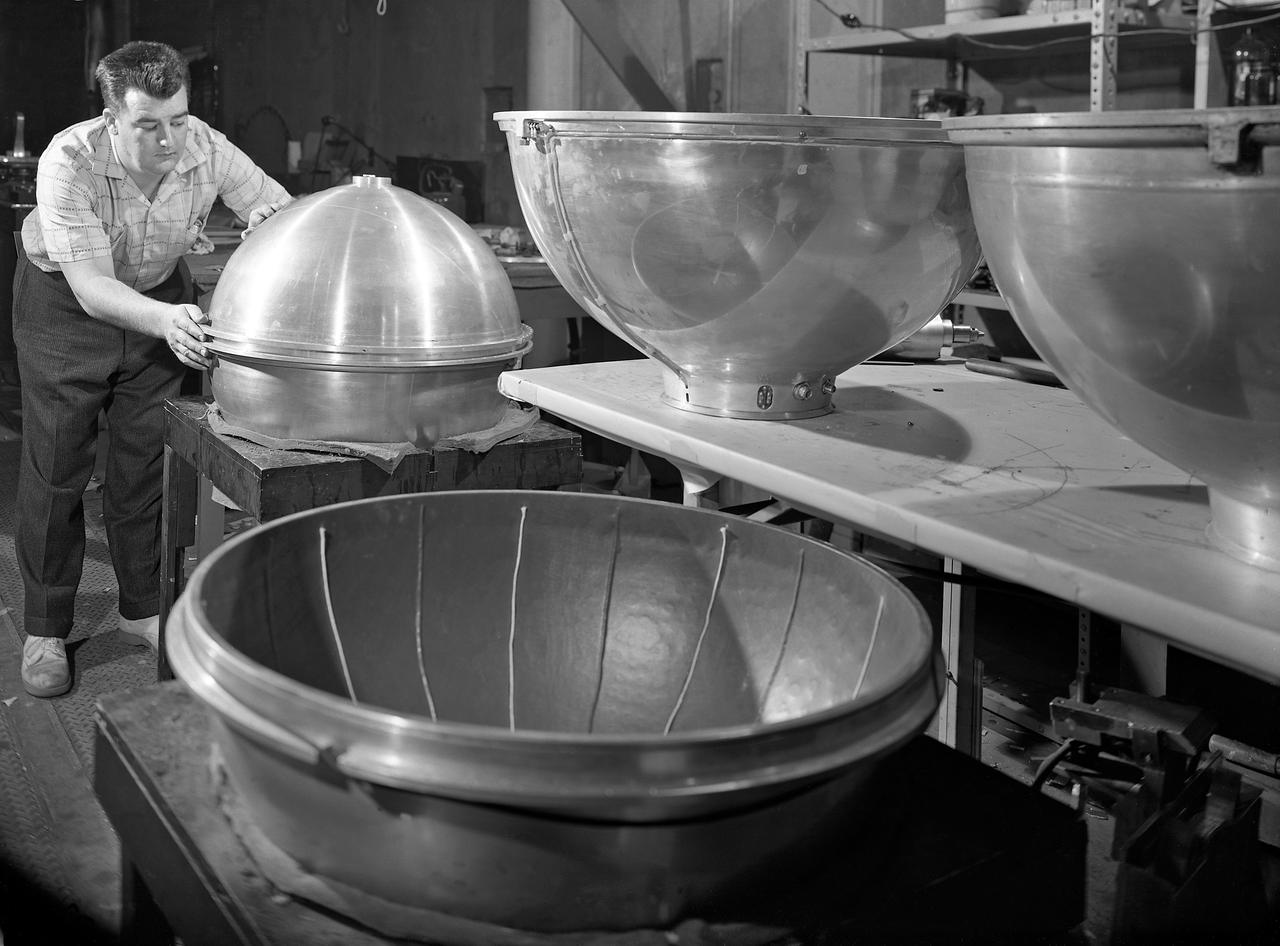

100' Satellite Packaging of Echo
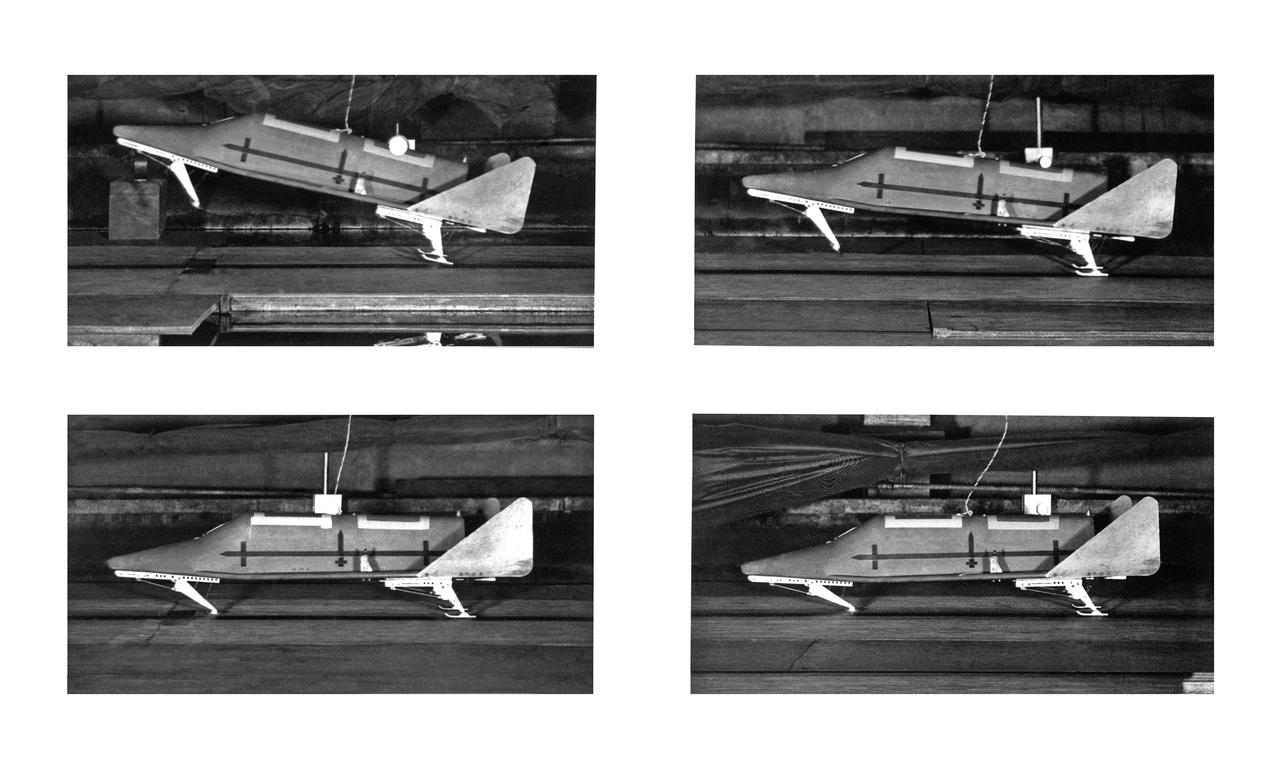
Copy Negative of Sequence Photo Shuttle Model
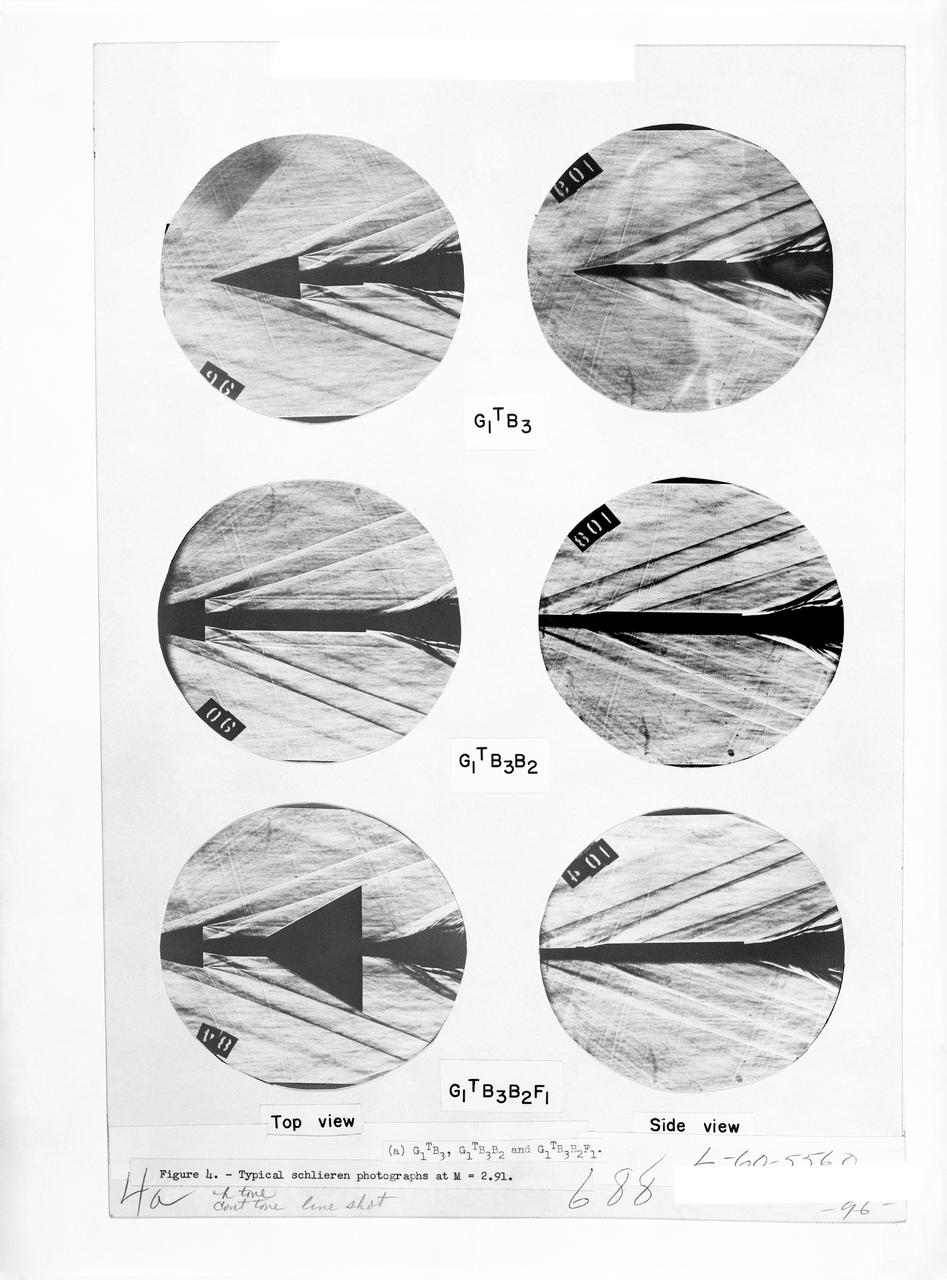

Figure 3-5 for NASA Document TM-X-356
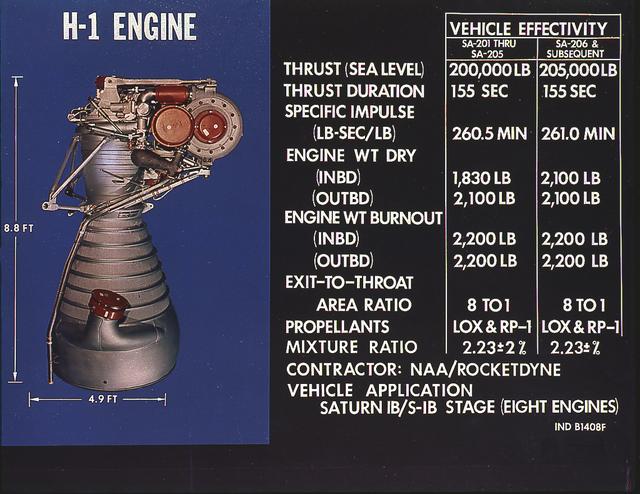
H-1 engine characteristics: The H-1 engine was developed under the management of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The cluster of eight H-1 engines was used to power the first stage of the Saturn I (S-I stage) and Saturn IB (S-IVB stage) launch vehicles, and produced 188,00 pounds of thrust, a combined thrust of 1,500,000 pounds, later uprated to 205,000 pounds of thrust and a combined total thrust of 1,650,000 pounds for the Saturn IB program.
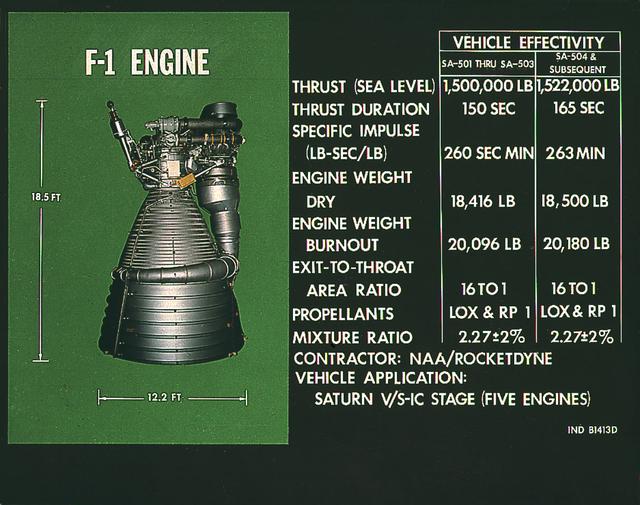
This chart provides the vital statistics for the F-1 rocket engine. Developed by Rocketdyne, under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the F-1 engine was utilized in a cluster of five engines to propel the Saturn V's first stage, the S-IC. Liquid oxygen and kerosene were used as its propellant. Initially rated at 1,500,000 pounds of thrust, the engine was later uprated to 1,522,000 pounds of thrust after the third Saturn V launch (Apollo 8, the first marned Saturn V mission) in December 1968. The cluster of five F-1 engines burned over 15 tons of propellant per second, during its two and one-half minutes of operation, to take the vehicle to a height of about 36 miles and to a speed of about 6,000 miles per hour.